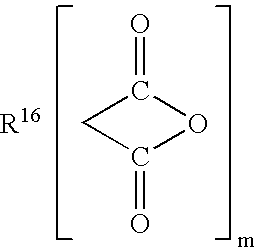
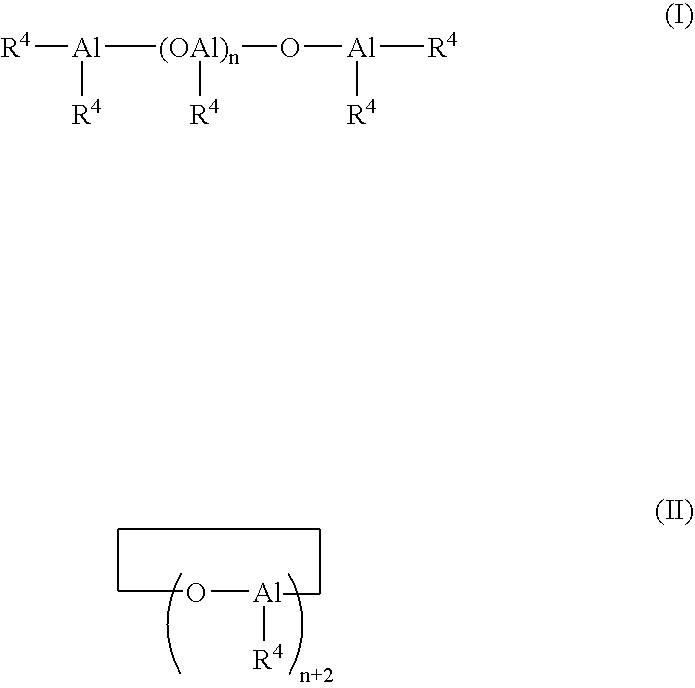
Patents
Literature
53775 results about "Hardness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hardness is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. Some materials (e.g. metals) are harder than others (e.g. plastics, wood). Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, there are different measurements of hardness: scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness.
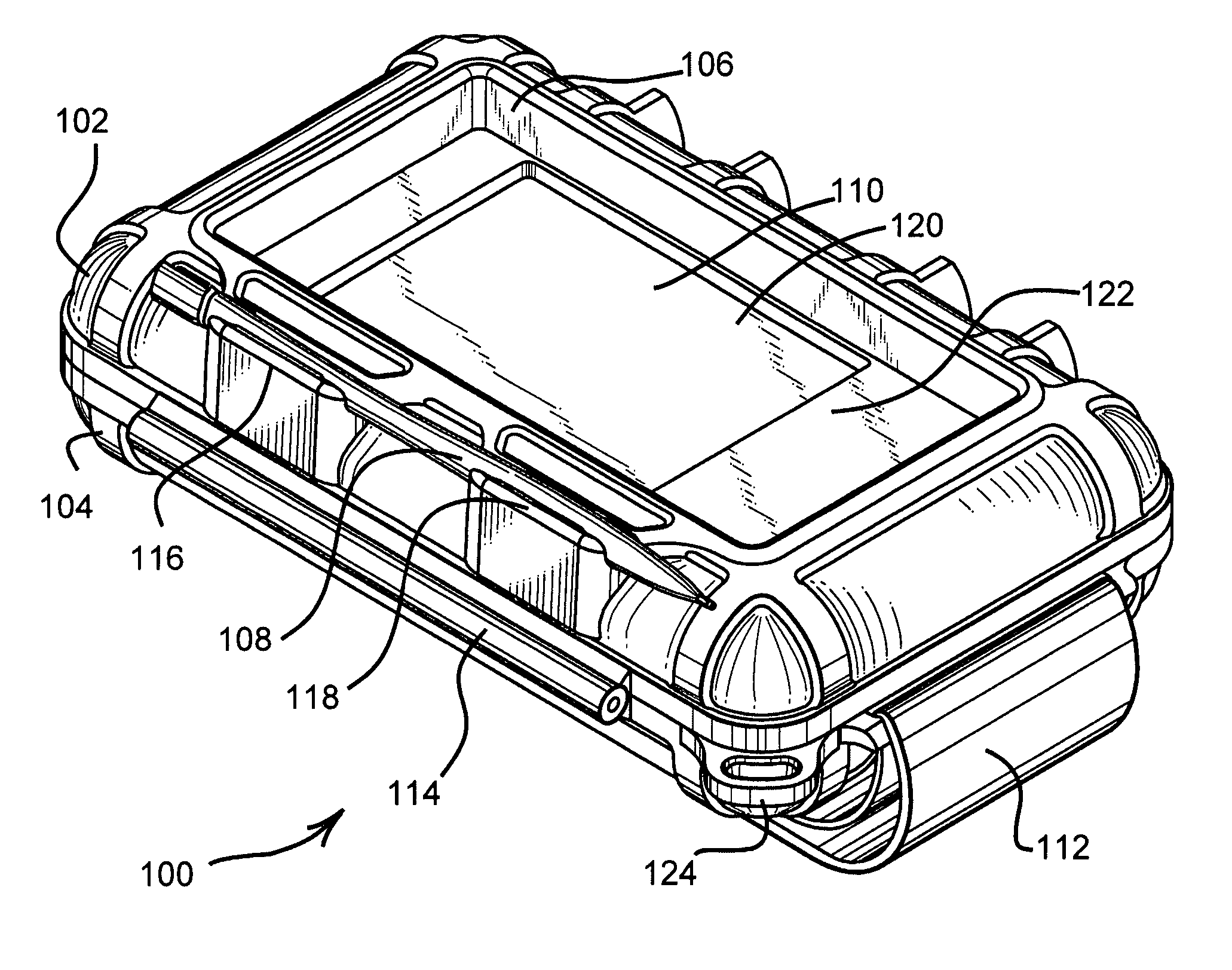
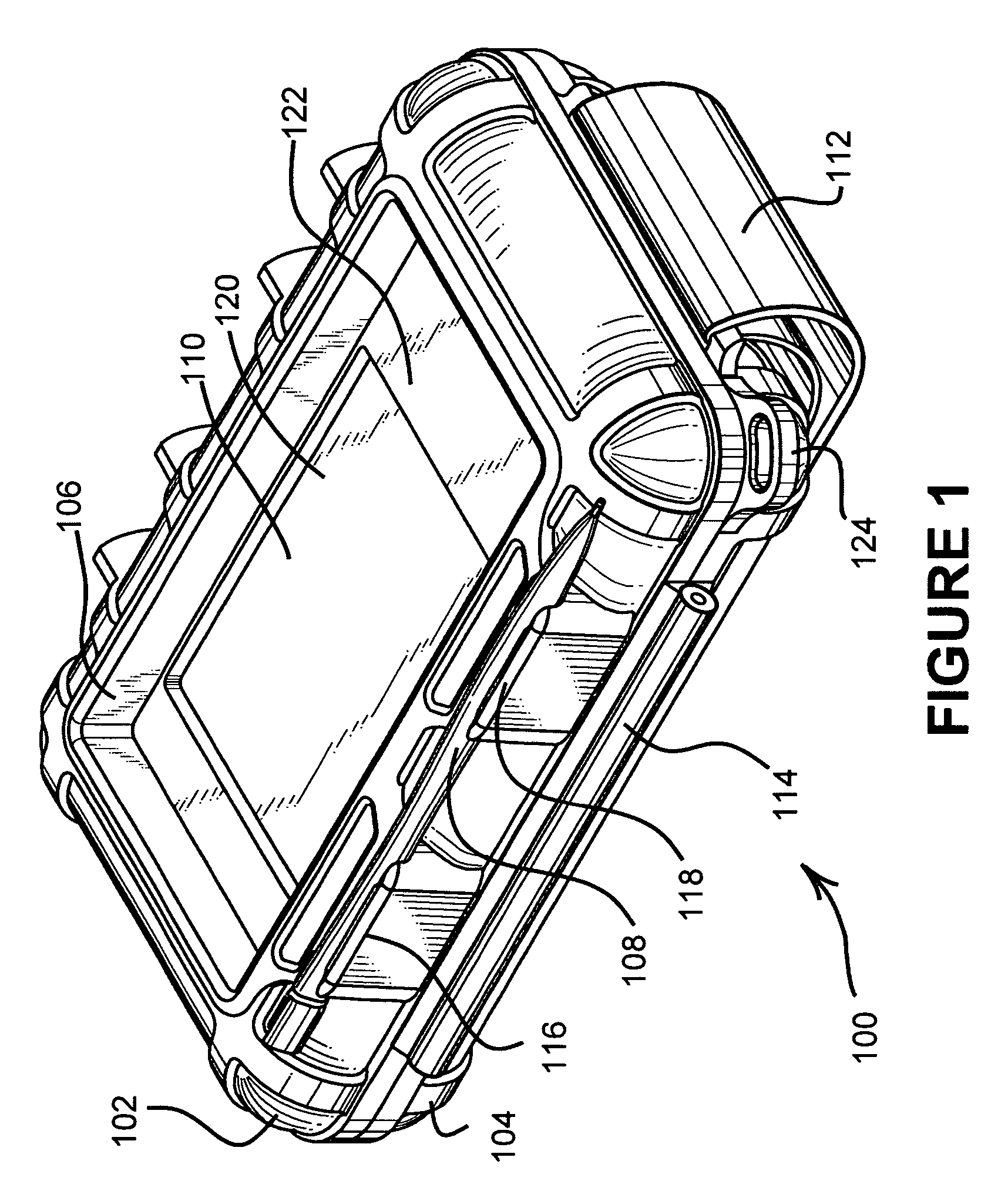
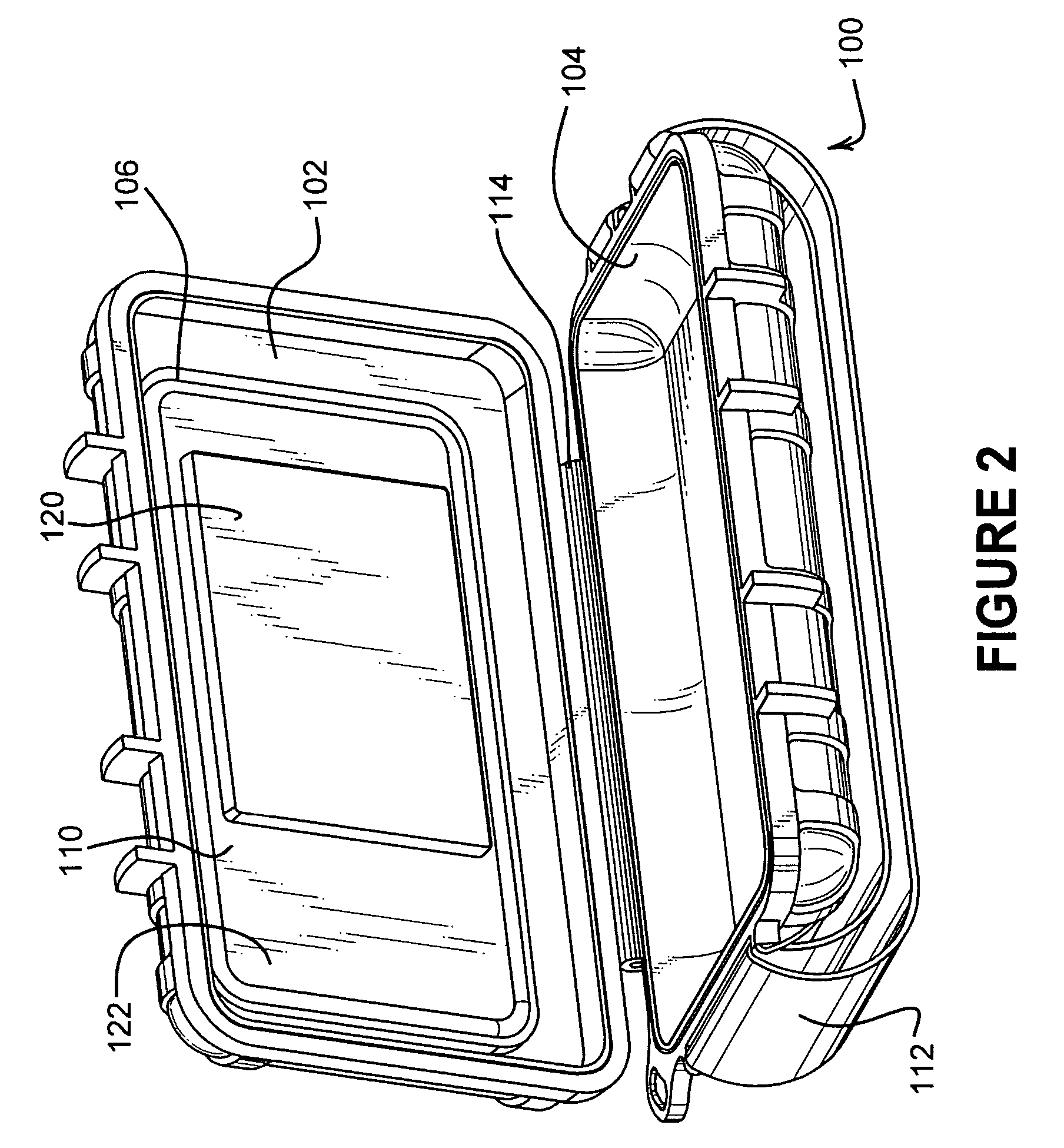
Protective enclosure for an interactive flat-panel controlled device
InactiveUS7158376B2Permits smooth and accurate interactive use of the flat-panel controlDigital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus contructional detailsTectorial membraneCapacitance
A protective enclosure is disclosed for an interactive flat-panel controlled device. The protective enclosure is watertight, crush-resistant, and impact-resistant. While providing protection, the protective enclosure simultaneously allows smooth and accurate interaction with the interactive flat-panel controlled device. The protective enclosure has a protective membrane that permits RF and touch screen stylus inputs, as well as capacitance, such as from a finger, to be transmitted accurately to the flat-panel control. The hardness and texture of the protective membrane allows a stylus or finger to glide smoothly along the surface of the membrane without catching or sticking. The protective enclosure is further adapted to allow infrared and other communication signals while the device is secured inside the case. Further, electrical connections can be made through the case without affecting the protection afforded the electronic device inside.
Owner:OTTER PRODS
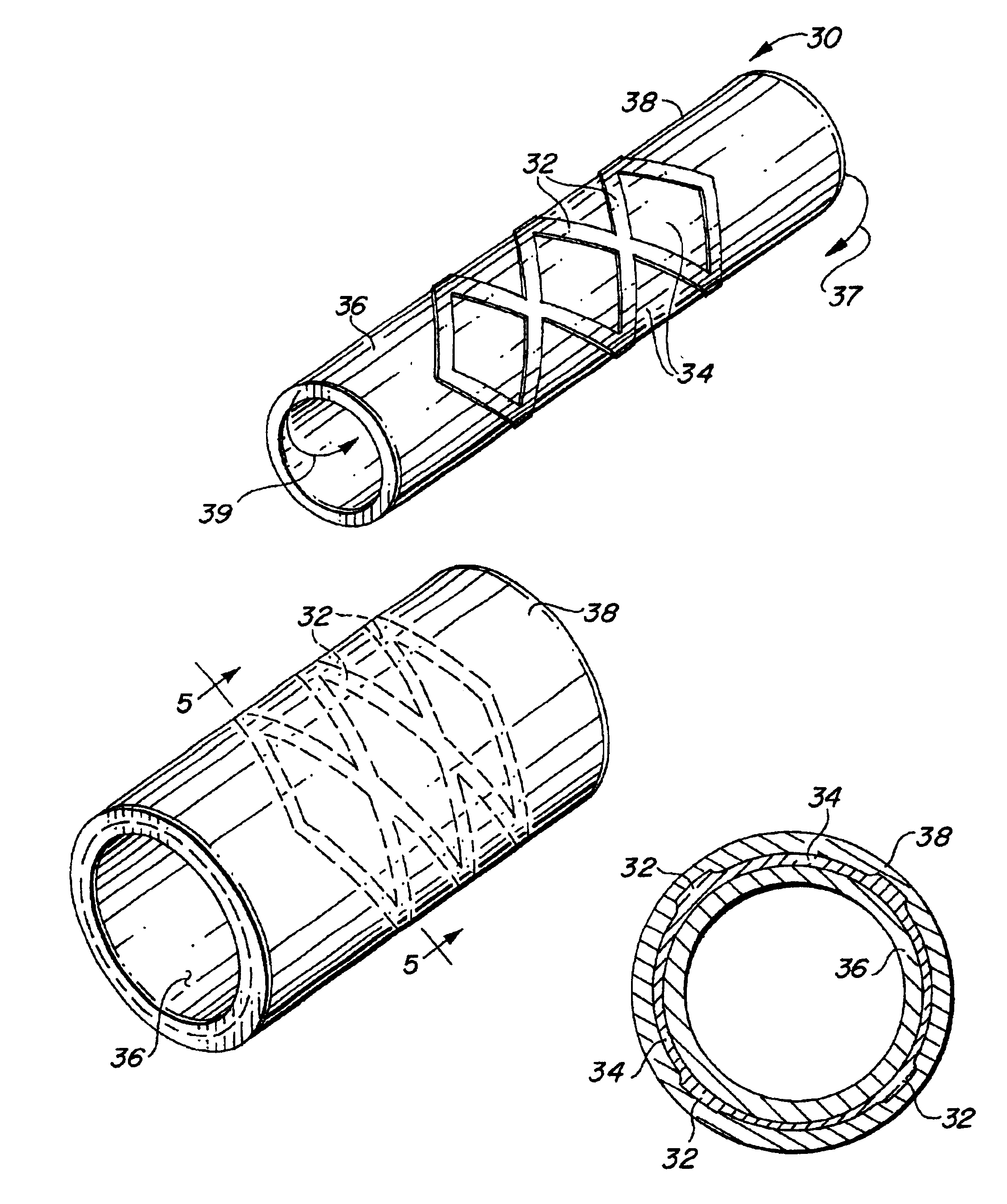
Self-supporting laminated films, structural materials and medical devices manufactured therefrom and methods of making same
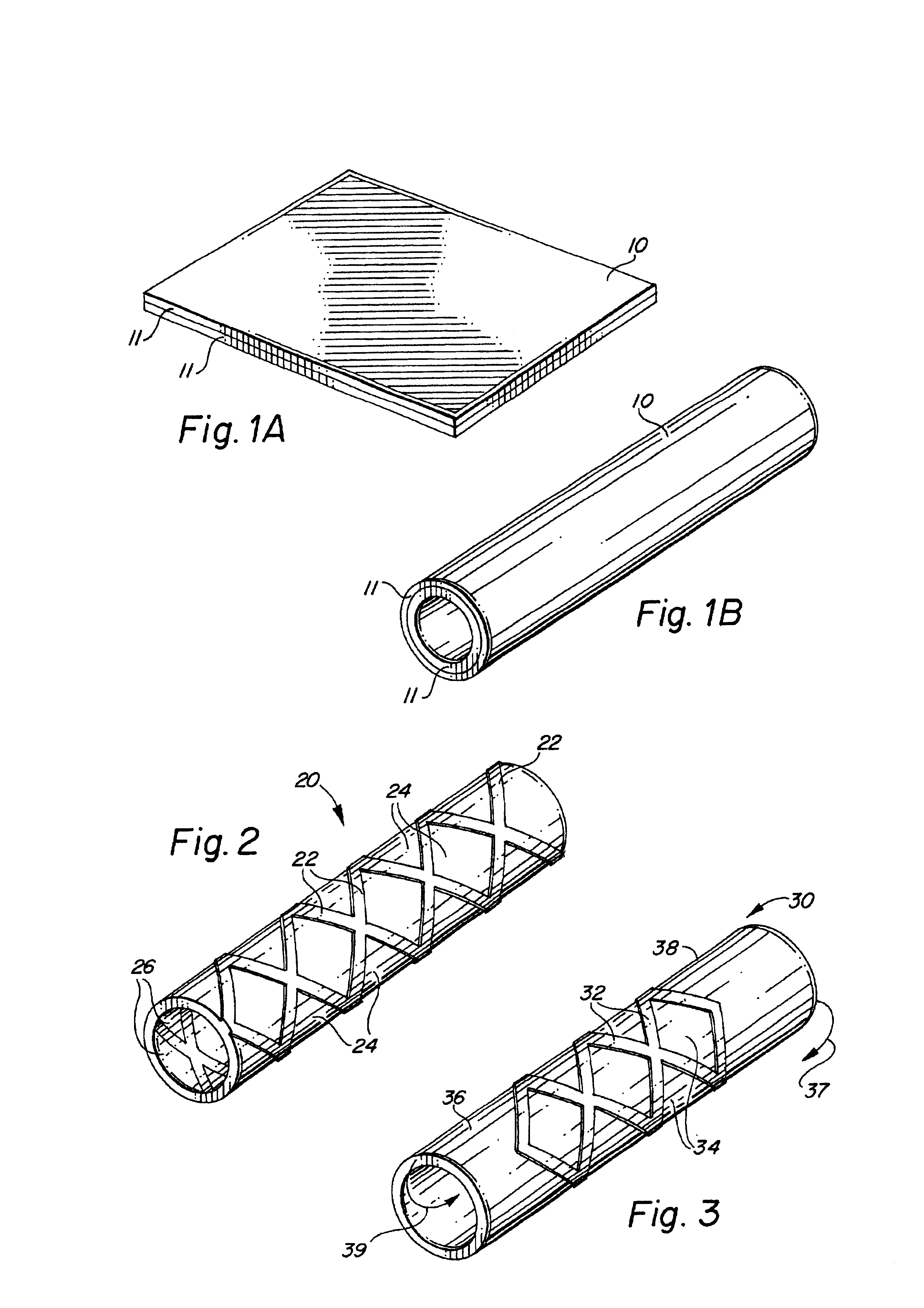
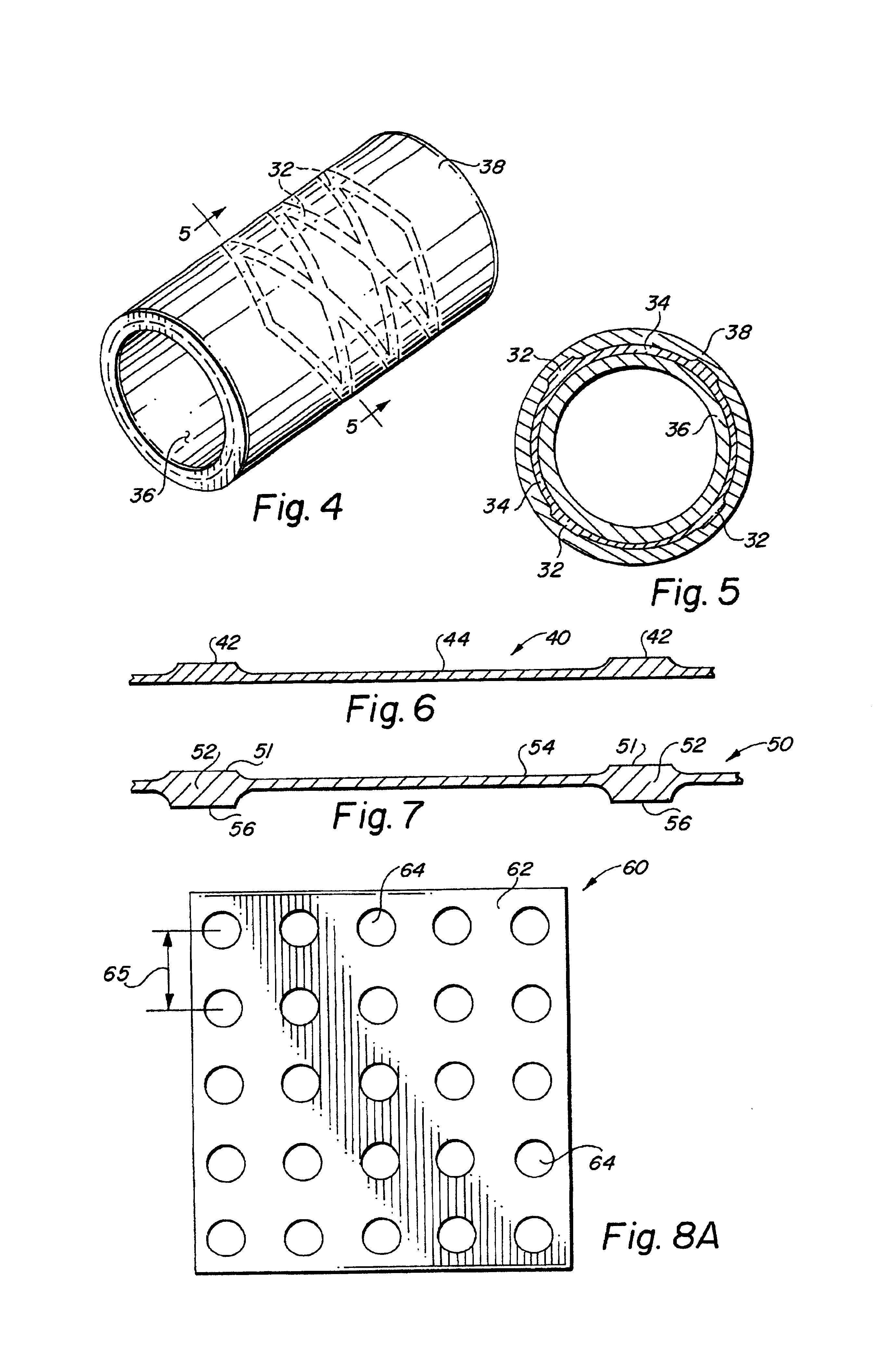
Metal foils, wires, and seamless tubes with increased mechanical strength are provided. As opposed to wrought materials that are made of a single metal or alloy, these materials are made of two or more layers forming a laminate structure. Laminate structures are known to increase mechanical strength of sheet materials such as wood and paper products and are used in the area of thin films to increase film hardness, as well as toughness. Laminate metal foils have not been used or developed because the standard metal forming technologies, such as rolling and extrusion, for example, do not lend themselves to the production of laminate structures. Vacuum deposition technologies can be developed to yield laminate metal structures with improved mechanical properties. In addition, laminate structures can be designed to provide special qualities by including layers that have special properties such as superelasticity, shape memory, radio-opacity, corrosion resistance etc. Examples of articles which may be made by the inventive laminate structures include implantable medical devices that are fabricated from the laminated deposited films and which present a blood or body fluid and tissue contact surface that has controlled heterogeneities in material constitution. An endoluminal stent-graft and web-stent that is made of a laminated film material deposited and etched into regions of structural members and web regions subtending interstitial regions between the structural members. An endoluminal graft is also provided which is made of a biocompatible metal or metal-like material. The endoluminal stent-graft is characterized by having controlled heterogeneities in the stent material along the blood flow surface of the stent and the method of fabricating the stent using vacuum deposition methods.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Plasma curing process for porous low-k materials
InactiveUS6913796B2Improving elastic modulusImproving material hardnessSilicaLayered productsHardnessMaterials science
Low dielectric constant porous materials with improved elastic modulus and hardness. The process of making such porous materials involves providing a porous dielectric material and plasma curing the porous dielectric material to produce a plasma cured porous dielectric material. Plasma curing of the porous dielectric material yields a material with improved modulus and hardness. The improvement in elastic modulus is typically greater than or about 50%, more typically greater than or about 100%, and more typically greater than or about 200%. The improvement in hardness is typically greater than or about 50%. The plasma cured porous dielectric material can optionally be post-plasma treated. The post-plasma treatment of the plasma cured porous dielectric material reduces the dielectric constant of the material while maintaining an improved elastic modulus and hardness as compared to the plasma cured porous dielectric material. The post-plasma treated, plasma cured porous dielectric material has a dielectric constant between about 1.1 and about 3.5 and an improved elastic modulus and hardness.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Chewable soft capsules and method for preparing same
ActiveCN101810336ADissolution stabilityRapid dissolutionFood shapingFood preparationFlavorPlasticizer
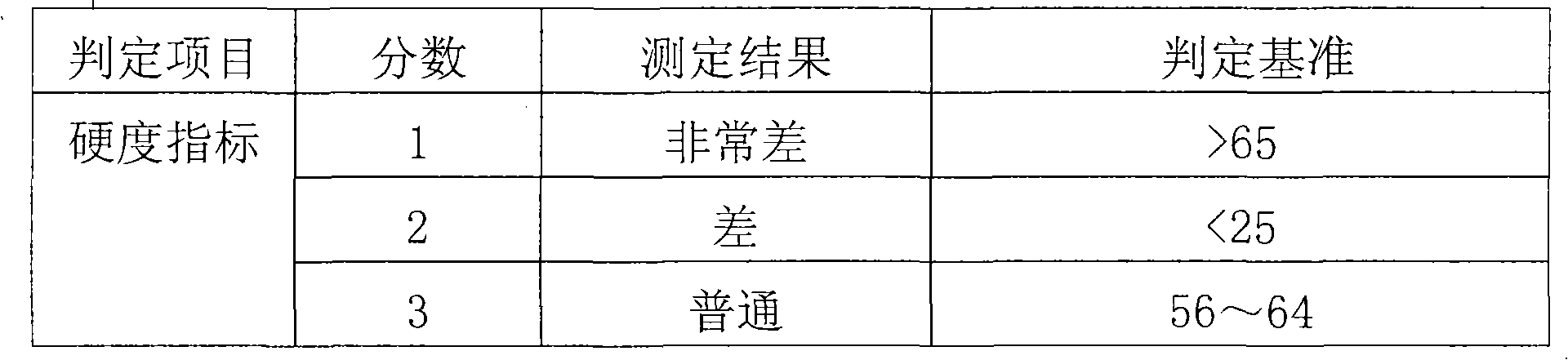
The invention discloses chewable soft capsules, which comprise capsule shells and contents sealed in the capsule shells. The chewable soft capsules are characterized by comprising the following raw materials in part by weight: 25 to 65 parts of glutin, 1 to 25 percent of thickening agent, 18 to 65 parts of plasticizer, 4 to 16 parts of water and a mixture containing one or more of 0.005 to 20 parts of sweetening agent, 0.005 to 2 parts of essence, 0.0001 to 10 parts of pigment and 0.0001 to 5 parts of acid additive. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the novel chewable soft capsules. The chewable soft capsules have the advantages of reasonable blending ratio, proper hardness, good temperature resistance, no adhesion, no deformation, stable storage, quick dissolution of effectively components and high chewiness; and when the chewing soft capsules are chewed, tastes of the capsule shells and the contents easily and uniformly spread in the mouth so as to cover up bad taste of raw materials.
Owner:SIRIO PHARMA CO LTD
Particles and device for displaying image
InactiveUS20050001810A1Improve stabilityEnhance the imageStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsBreaking strengthUltrasound attenuation
The present invention intends to provide particles for displaying images used in an image display device capable of displaying and eliminating repeatedly accompanied by flight and movement of particles utilizing Coulomb force, being superior in stability, particularly in repetition durability, memory characteristic stability, adaptability for temperature change, having capability of regulating charge amount, and accordingly, favorable images with sufficient contrast should be stably obtained. The present invention provides particles coated with a resin; specifying Span of particle diameter distribution, charge attenuation property, thermal change of the surface hardness, tensile break strength, Izod impact strength (with a notch), abrasion loss (Taber), tensile elastic modulus, flexural elastic modulus, or tear strength. The present invention also proposes about the structure of the particles.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
High molecular wegiht polymers, devices and method for making and using same
Anhydride polymers that release active or activatable agent(s) have pre-selected properties such as molecular weight, flexibility, hardness, adhesiveness, and other valuable properties. The polymers are suitable for use in compositions, formulations, coatings, devices, and the like that benefit from the controlled release of an agent(s) over a period of time. The polymers are prepared by a process involving various alternative and sequential steps that allow the design a priori of products with specific characteristics. The polymers are suitable as delivery systems, either by themselves, as compositions, formulations or devices.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Bulk enhanced paperboard and shaped products made therefrom
An improved paperboard has been bulk enhanced by retaining a substantial portion of bulk-enhanced additives including expandable microspheres in a suitable distribution within the paperboard. The cellulosic paperboard web has an overall fiber weight (w) of at least 40 lbs. / 3000 square feet and at a fiber density of 3, 4.5, 6.5, 7, 8.3, and 9 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch respectively, has a GM Taber stiffness of at least about 0.00716 w2.63 grams-centimeter / fiber mat density1.63 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch, and a GM tensile stiffness of at least about 1890+24.2 w pounds per inch. The high retention of the bulk enhancing additives is believed to result from the incorporation of suitable retention aids. The resulting paperboard has better GM Taber stiffness values and GM tensile stiffness than prior art paperboards. The paperboard also has increased strain to failure and is able to be formed into suitable paperboard containers without loss of integrity. The resulting containers have increased hold times when they contain hot or cold food or drink.
Owner:DIXIE CONSUMER PROD
Method for making a nano-stamp and for forming, with the stamp, nano-size elements on a substrate
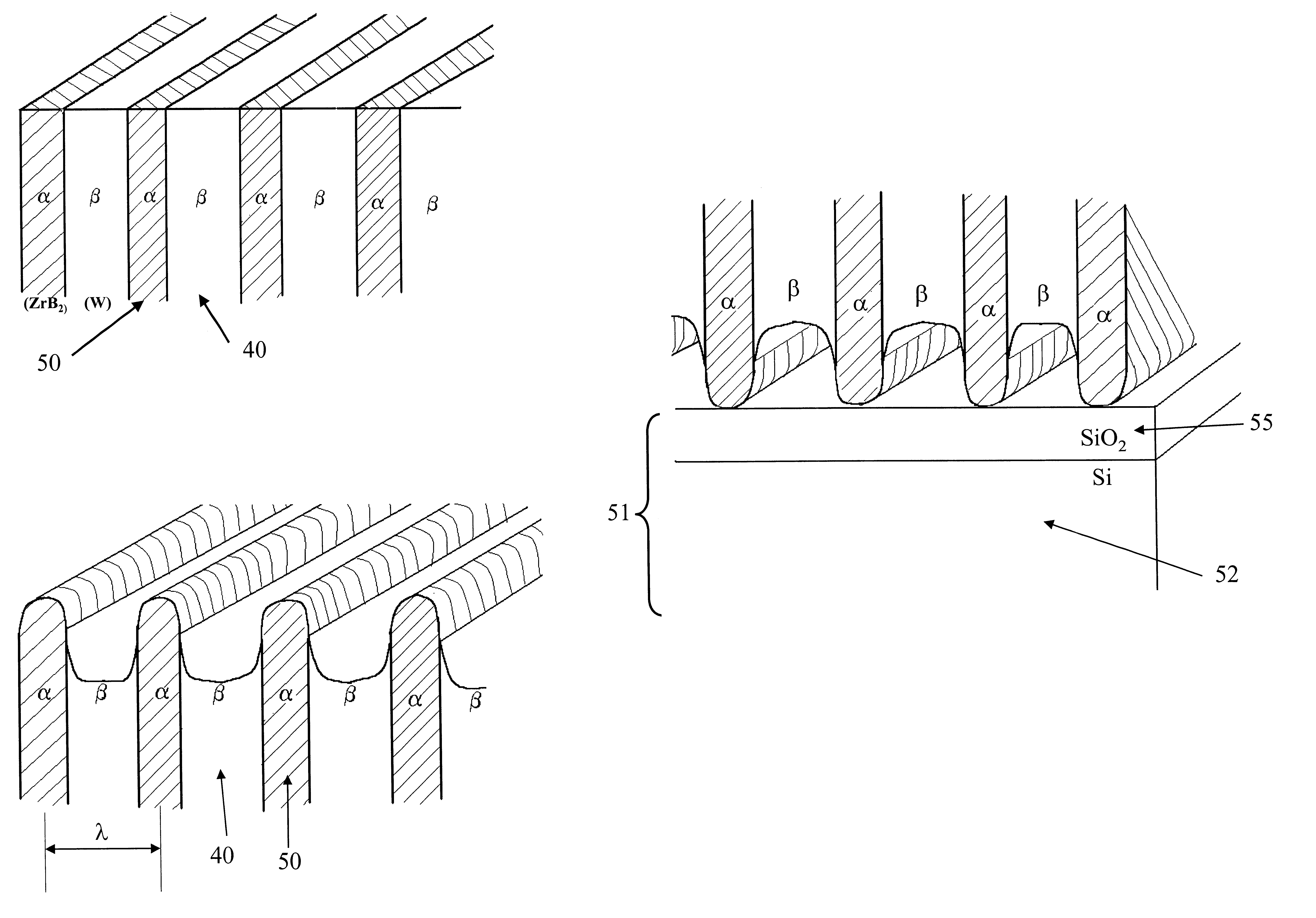
The stamping process and a method of fabrication of nano-stamps with characteristic dimensions below 1 nm and up to 100 nm intended for usage in making patterns of characteristic dimensions the same as those of the nano-stamp on surface of a substrate is provided. In the process a very hard stamp is fabricated by first depositing alternating layers of two materials, one of which has very high hardness, on some sacrificial substrate via PVD, CVD or any other deposition procedure that produces alternating layers of selected thickness, from sub 1 nm to above 100 nm. The layered film is then polished to an atomically smooth finish perpendicular to the plane of the layers and etched to produce dips in the softer layers. These steps produce a grid of parallel elevations and valleys on the etched surface, which now can be used as a stamp to stamp out patterns on a substrate of lower hardness than the hardness of the elevated layers. If the substrate is stamped twice with a turning of the stamp 90 degrees between first and second stampings, a square pattern of elevations or hills and valleys is formed, which can be used for magnetic memory storage by subsequently sputtering magnetic material on the tops of the elevations or hills.
Owner:VIGIL THOMAS R +1
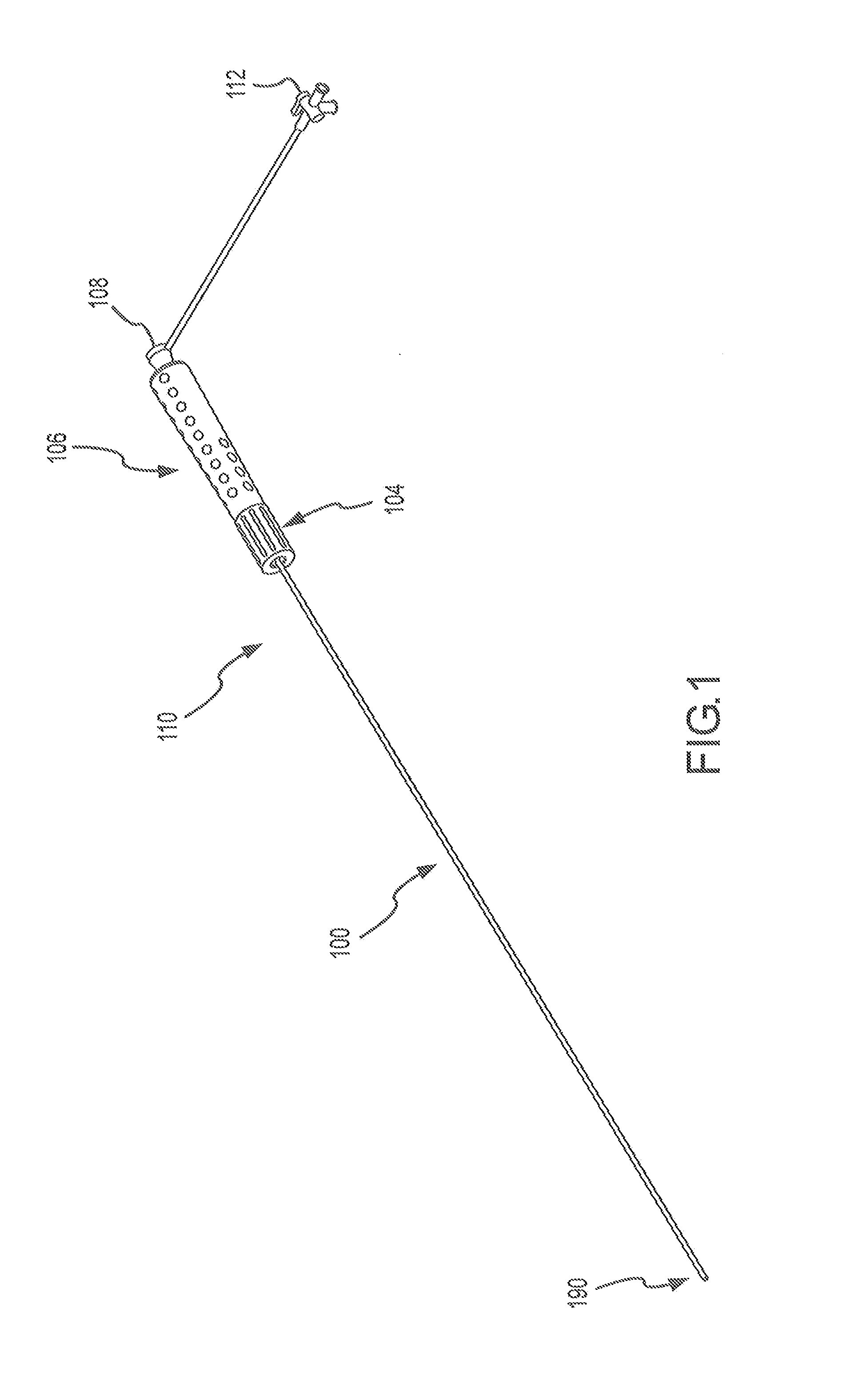
Steerable catheter using flat pull wires and having torque transfer layer made of braided flat wires
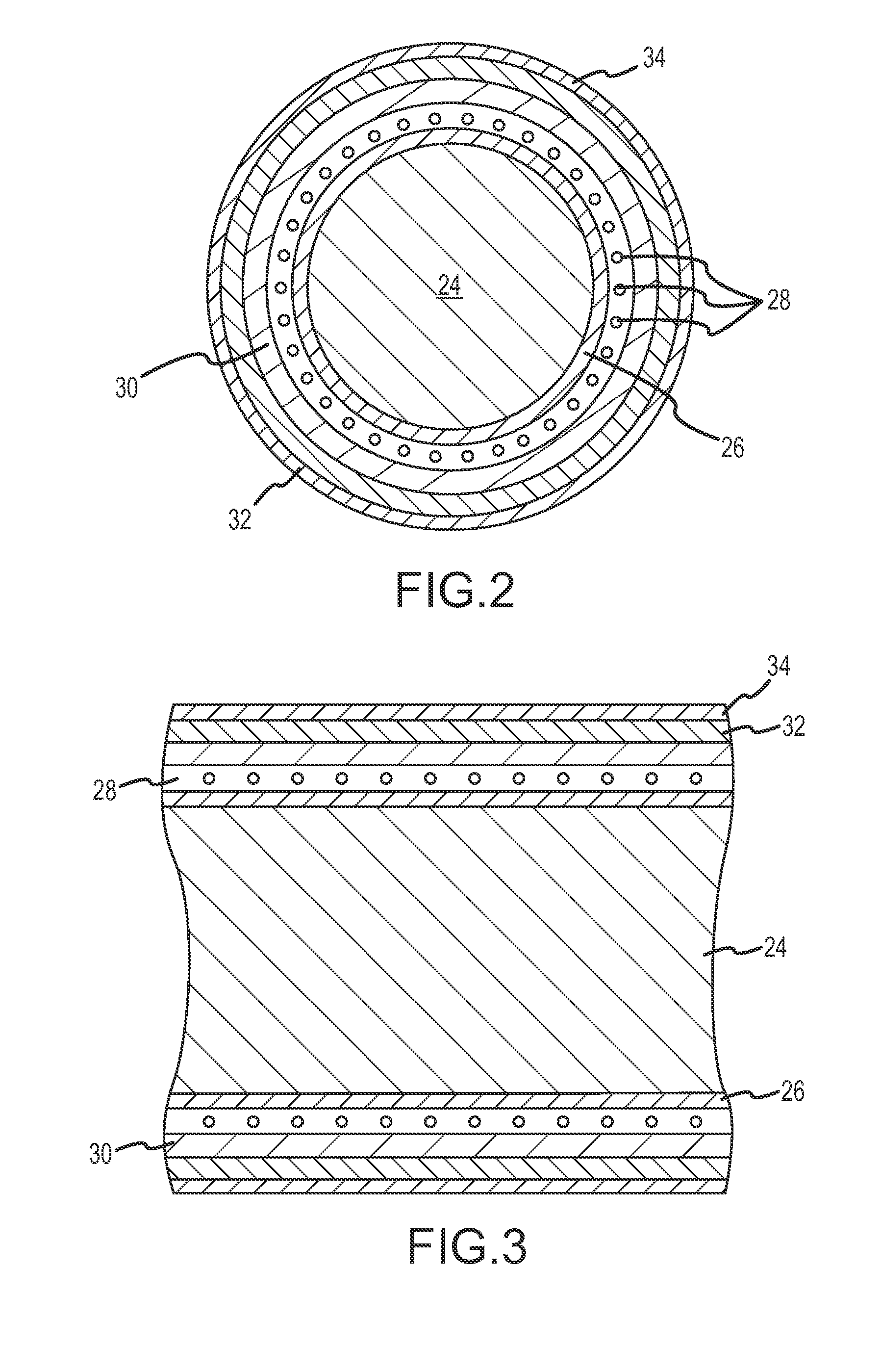
InactiveUS20080091169A1Overall cross-section of the catheter may be reducedGood flexibilityLaminationLamination apparatusEngineeringHardness
A catheter assembly includes an inner liner made of flexible material and an outer layer having a steering mechanism. The steering mechanism includes at least one flat wire and a corresponding lumen through which the flat wire may travel. The steering mechanism may also include at least one pull ring to which the flat wires are attached. A layer of heat shrink material may encompass the outer layer. A braided wire assembly may also be provided in the outer layer, and may be formed by braiding a plurality of flat wires into a wire mesh. The overall cross-section of the catheter assembly is preferably substantially circular. A catheter shaft may include a plurality of segments of differing hardness characteristics. The outer layer typically comprises a melt processing polymer such that the catheter assembly may be laminated using heat.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Golf ball
InactiveUS6921345B2Solid comfortable feelGood rebound characteristicsGolf ballsSolid ballsPolymer scienceAntioxidant
A golf ball includes a hot-molded product of a rubber composition comprising a base rubber composed of (a) 20-100 wt % of a polybutadiene having a high cis-1,4 content, a minimal 1,2 vinyl content, and a viscosity η of up to 600 mPa·s at 25° C. as a 5 wt % toluene solution, and satisfying a certain relationship between Mooney viscosity and polydispersity index Mw / Mn, in combination with (b) 0-80 wt % of another diene rubber, (c) an unsaturated carboxylic acid, (d) an organosulfur compound, (e) an inorganic filler, (f) an organic peroxide, and optionally, (g) an antioxidant. The hot-molded product has a difference in JIS-C hardness between the center and surface thereof of up to 15 units. The composition and hardness characteristics of the hot-molded product provide the golf ball with a solid comfortable feel upon impact and an excellent rebound.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Insulating sheathing with tough three-ply facers
InactiveUS6093481AImprove insulation performanceHighly controllableSynthetic resin layered productsHeat proofingPuncture resistanceHardness
A method for continuously manufacturing an insulation board by facing a foam-forming composition with one or two facing sheets to form a singly or doubly faced composite, at least one sheet comprising either a tough polymeric layer or a laminate of a tough polymeric layer with at least one other facing material, the tough polymeric layer of at least one sheet facing to the outside of the composite, and foaming and curing the faced foam-forming mixture to produce an insulation board having an exceptional hardness and puncture resistance.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
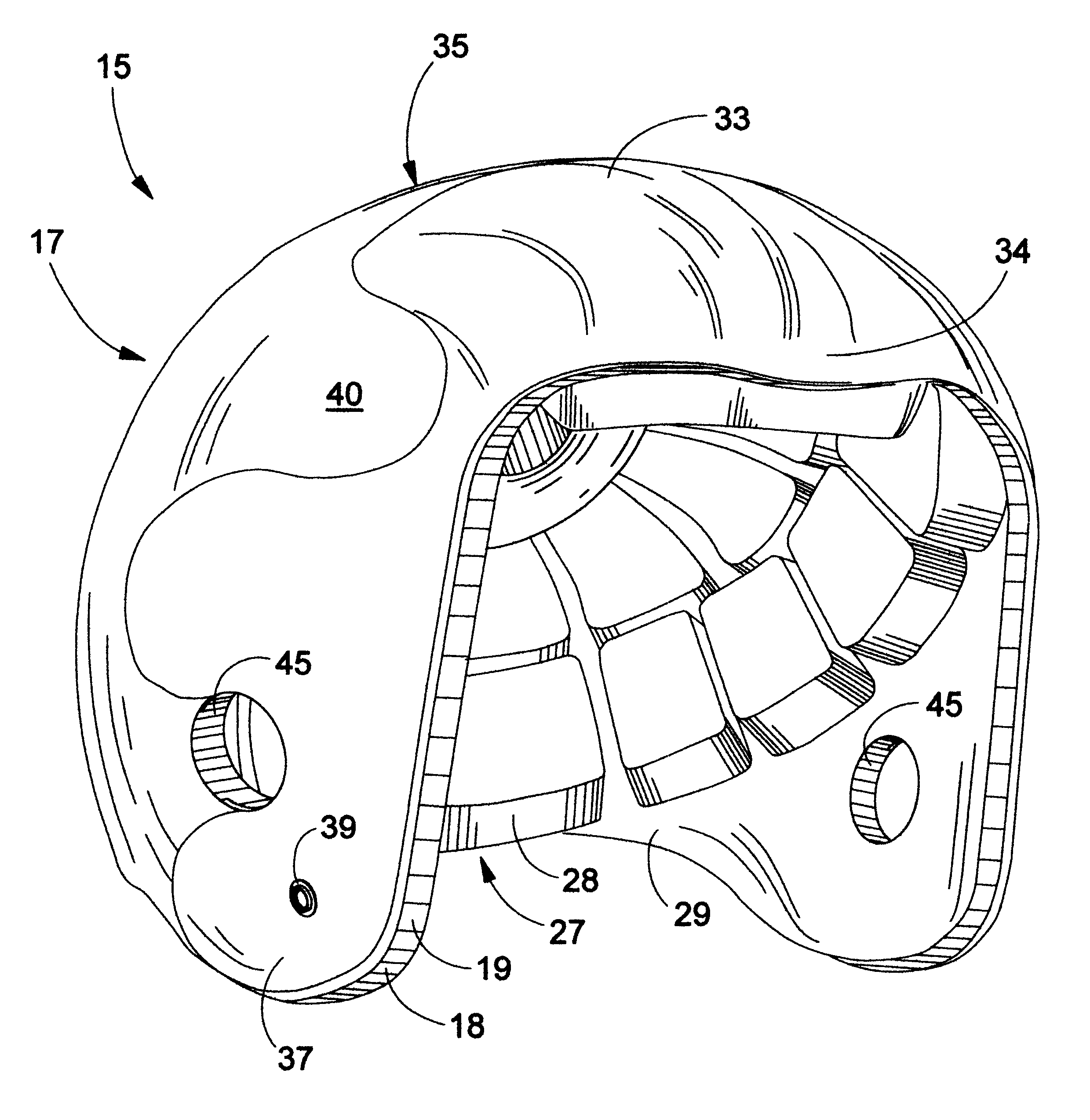
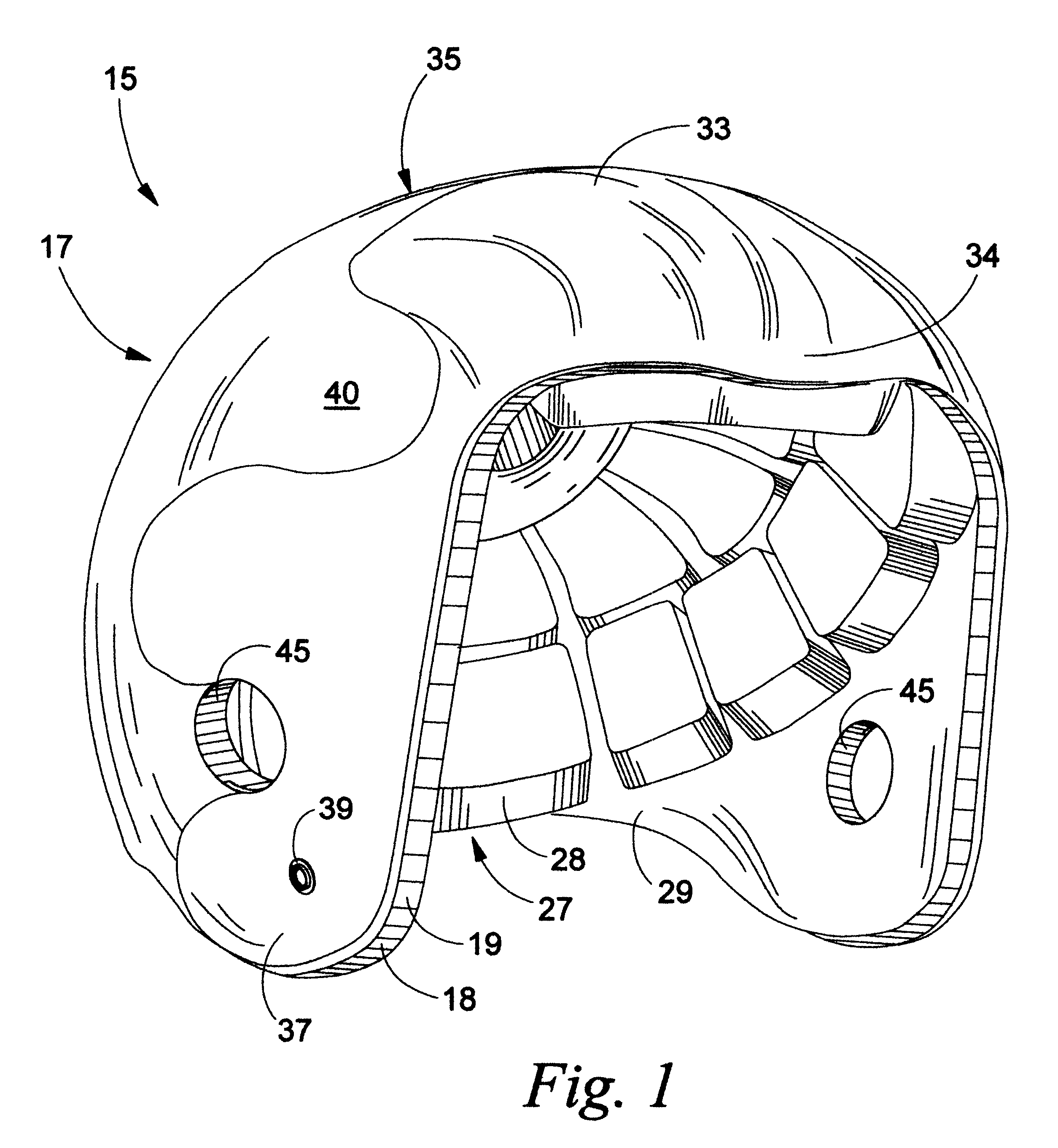
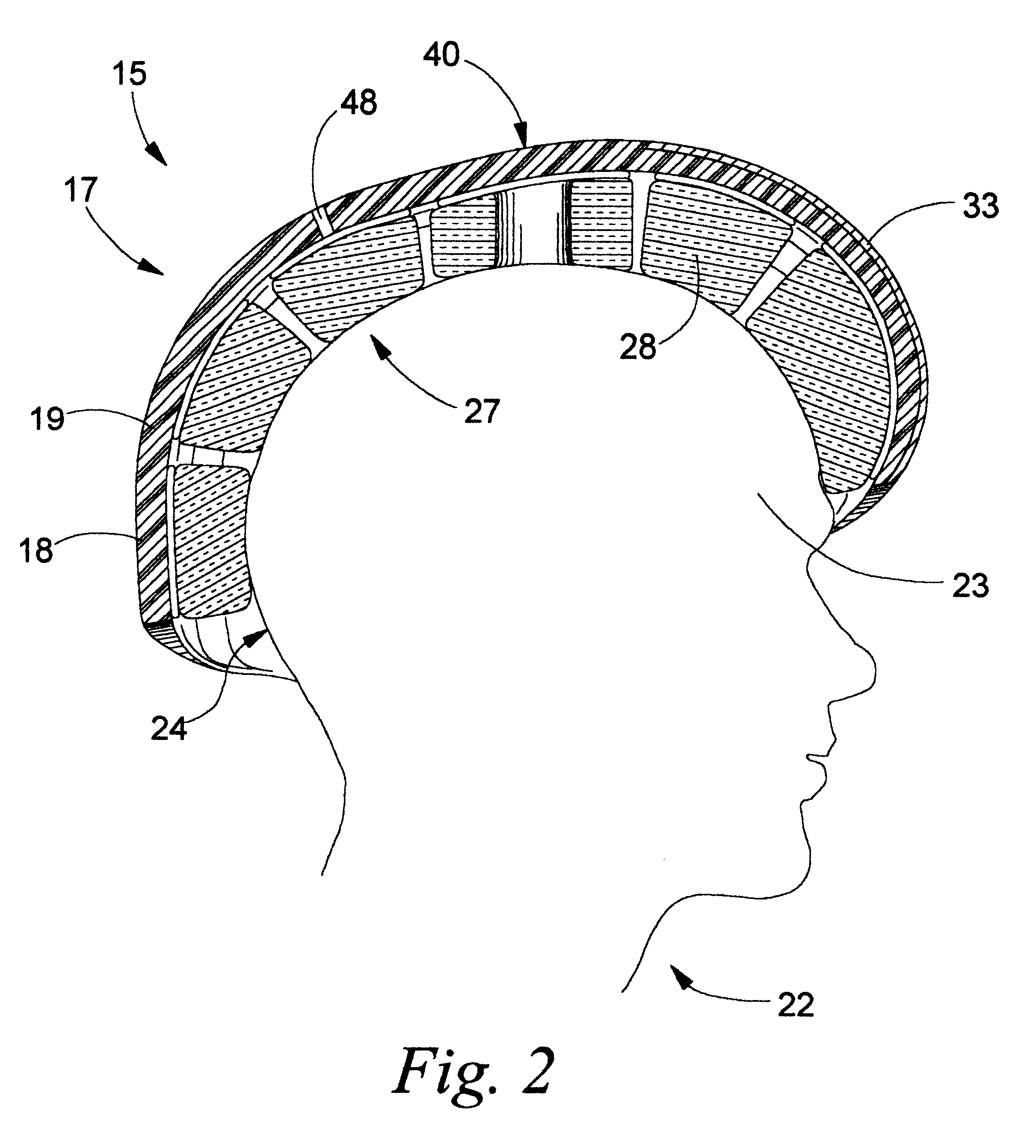
Soft foam sport helmet
A protective sports helmet that is molded from a shock absorbing foam. The helmet is preferably an single, homogenous piece of injection molded foam. An insert plate can be positioned near the user's forehead at the top and forward portion of the helmet. The purpose of the insert plate is to simulate the hardness of the user's head for heading a ball. The helmet can head the ball without the injury to the head and the brain as potentially encountered without protection. The soft-shell also minimizes injuries on other parts of the body that are struck by the helmet. The helmet can be utilized for football and other contact sports. Additional external components such as metal or plastic inserts can be inset molded into the foam. The purpose of these inserts is to improve stability and allow for attachment of face guards and chin straps.
Owner:WOOD JAMES C
Multi-layer core golf ball
InactiveUS7255656B2Extended service lifeGolf ballsDomestic articlesMoisture vapor transmission rateEngineering
The present invention is directed to an improved golf ball displaying the desired spin profile and having a generally rigid, thermoset polybutadiene outer core surrounding a relatively soft, low compression inner core. In general, this golf ball has an inner core and at least one outer core layer surrounding the inner core. The inner core has a hardness less than a hardness of the outer core and a specific gravity less than or equal to the outer core specific gravity. Overall the inner core compression and outer core are formulated to provide a combined overall core compression of greater than about 50, preferably greater than about 70. A cover layer is provided to surround and to cover the outer core layer. A moisture barrier layer is provided between the outer core layer and the cover layer to protect the inner and outer cores from degradation due to exposure to water. The moisture vapor transmission rate of the moisture barrier layer is selected to be less than the moisture vapor transmission rate of the cover layer.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Multiple segment catheter and method of fabrication
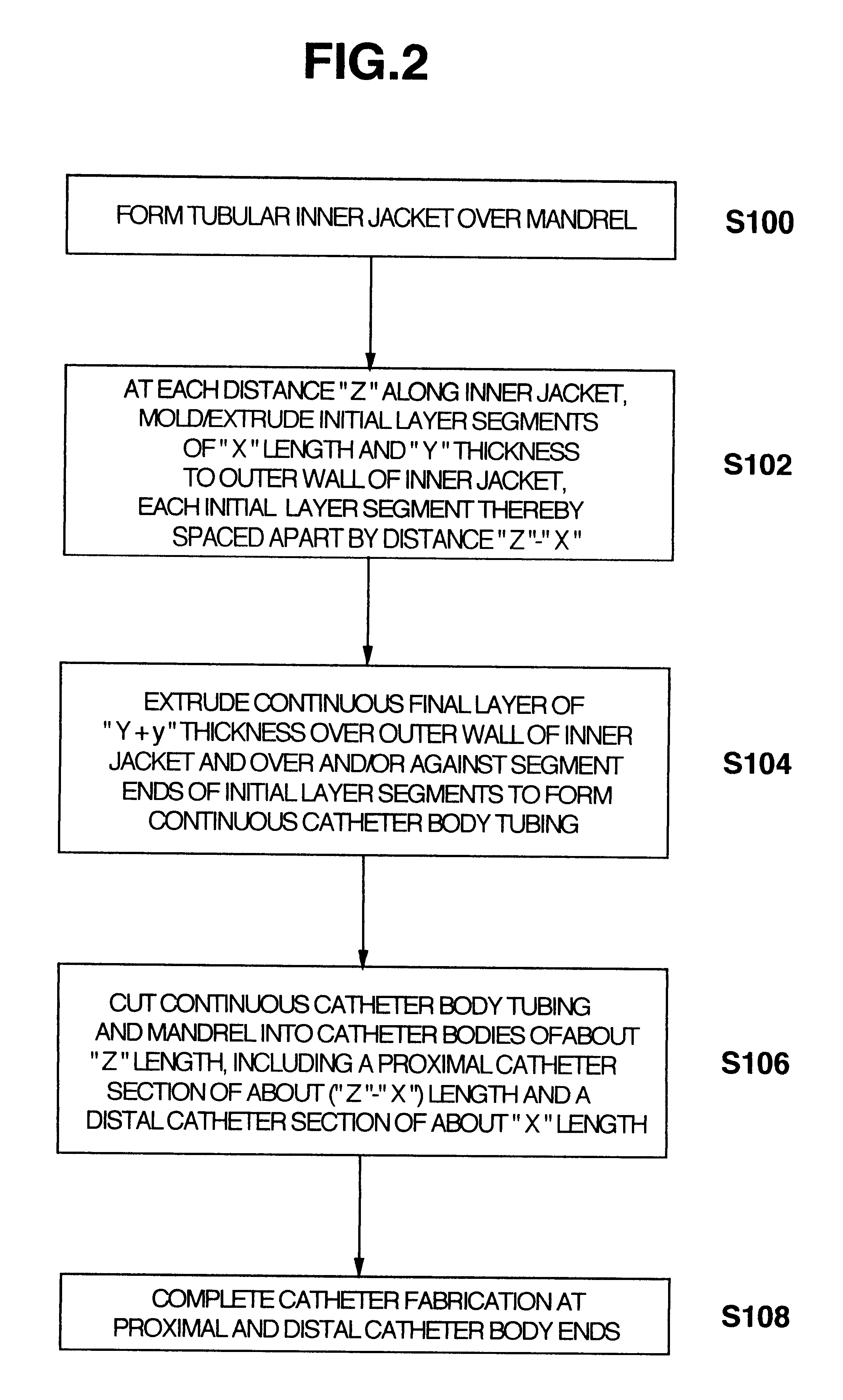
Methods of fabricating medical vascular catheters adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel from an incision through the skin of a patient for introducing other devices or fluids for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes and particularly methods for fabricating such catheters with catheter bodies having catheter sections of differing flexibility are disclosed. Such catheter bodies having a proximal catheter body end and a distal catheter body end and formed of a proximal section and at least one distal section that have differing flexibilities are formed in a process comprising the steps of: (1) forming a continuous tubular inner jacket preferably of an inner liner and a reinforcement layer; (2) forming initial layer segments having an initial layer thickness along the length of the inner jacket from a material of first durometer hardness, whereby each initial layer segment is separated by a separation distance: (3) forming a final layer of a material of second durometer hardness with a second layer thickness over the tubular inner jacket along the separation distances and over and / or against the proximal and distal initial layer ends of the initial layer segments to form a continuous catheter body tubing; (4) severing the continuous catheter body tubing into catheter body lengths including a proximal catheter section formed of the material of second hardness and a distal catheter section of the material of first hardness; and (5) completing the catheter fabrication at the proximal catheter body end and the distal catheter body end. Centerless grinding of the catheter body or body tubing, formation of Intermediate catheter body sections, distal soft tips, and discontinuities in the reinforcement layer formed prior to step (2) are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Tissue cutter with differential hardness
Disclosed is a tubular cutting element for axial reciprocal movement within an outer tubular sleeve. The cutting element has an elongate tubular body, having a proximal end, a distal end and a cutting tip. The tubular body is formed in a drawing operation and the cutting tip is formed in a milling operation. The tubular body may have a Rockwell C hardness of no more than about 40, and the cutting tip may have a Rockwell C hardness of at least about 50.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Friction plunge riveting
InactiveUS20020125297A1Welding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesFriction weldingHardness
A method of joining a pair of metal components with a rivet having a hardness that is substantially similar to at least one of the metal components. The metal components are stack upon each other and the rivet is rotated and simultaneously plunged in the metal components under pressure to friction weld and metallurgically bond the rivet to the metal components.
Owner:ARCONIC INC
Brightness enhancement film having a reinforcing structure
InactiveUS7269327B2Degree of improvementPrevent warpage and abrasionPrismsCoupling light guidesOptoelectronicsHardness
A brightness enhancement film includes a light-refracting microstructure layer, a substrate and a reinforcing layer. The substrate has a first surface and a second surface opposite thereto. The light-refracting microstructure layer is arranged on the first surface of the substrate and is so configured to vary in curvatures for refracting light. The reinforcing layer is arranged on the second surface of the substrate and is so configured to form a relatively high degree of hardness. Accordingly, the reinforcing layer can prevent warpage and abrasion of the brightness enhancement film.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINHUI OPTOELECTRONIC MATERIAL CO LTD
Wheat and casein dog chew with modifiable texture
InactiveUS6110521ANutritional diversityEasily digested by dogsDough treatmentBaking mixturesHardnessDog owners
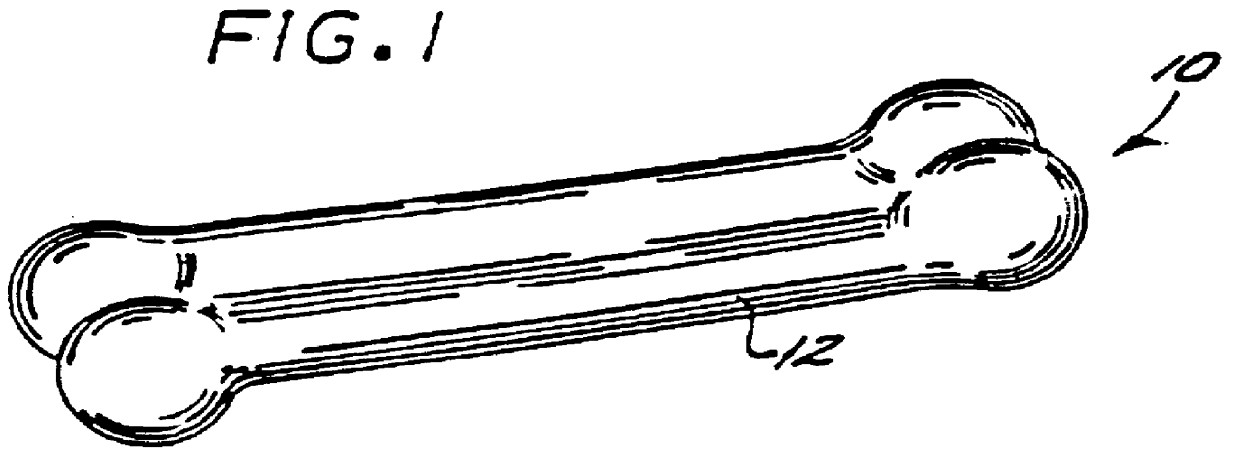
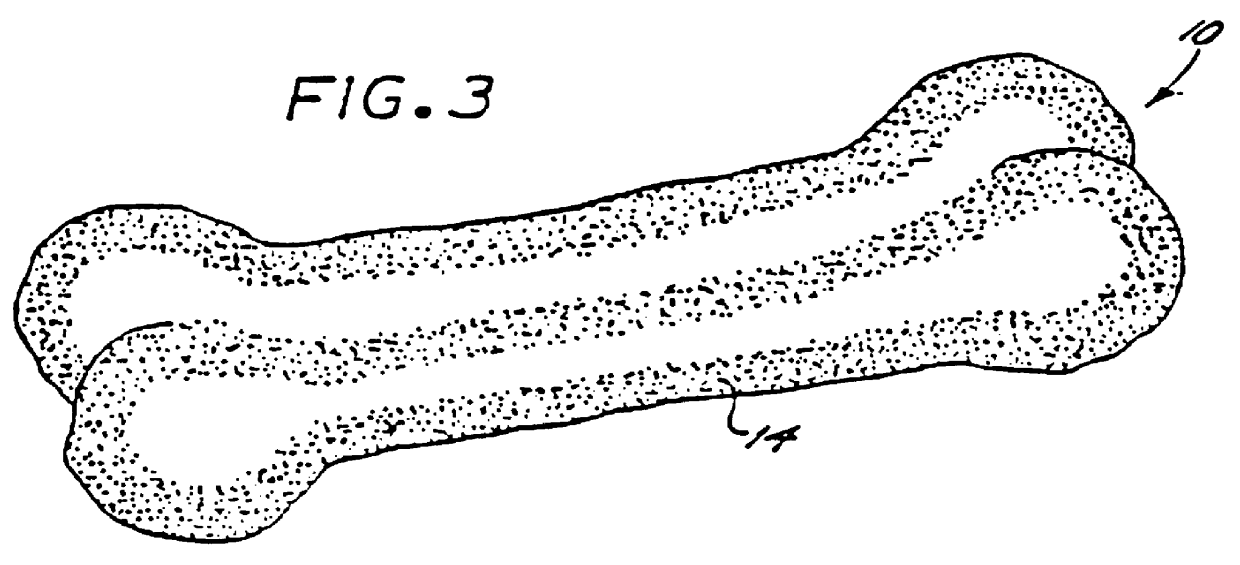
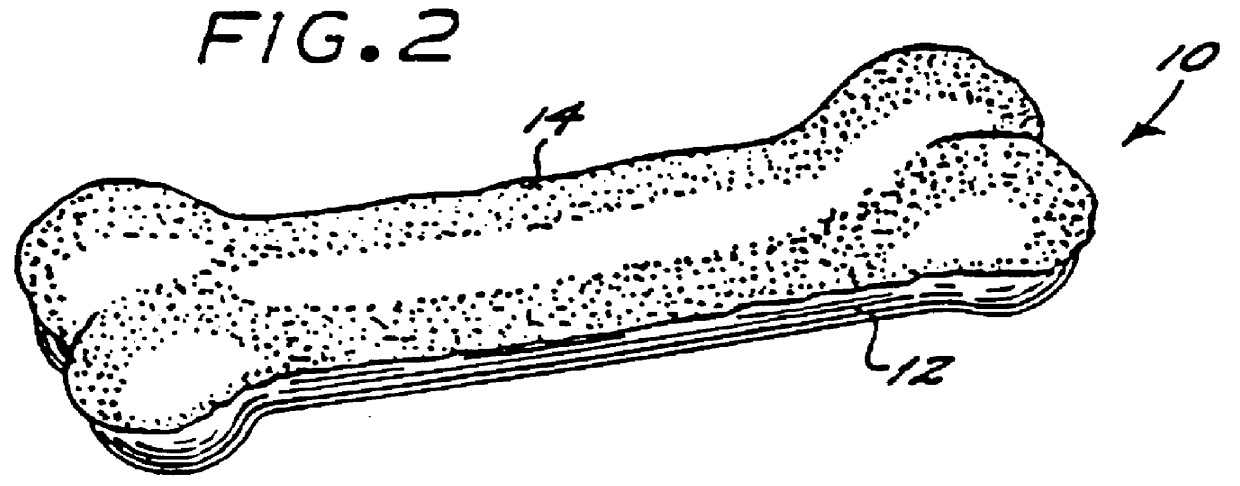
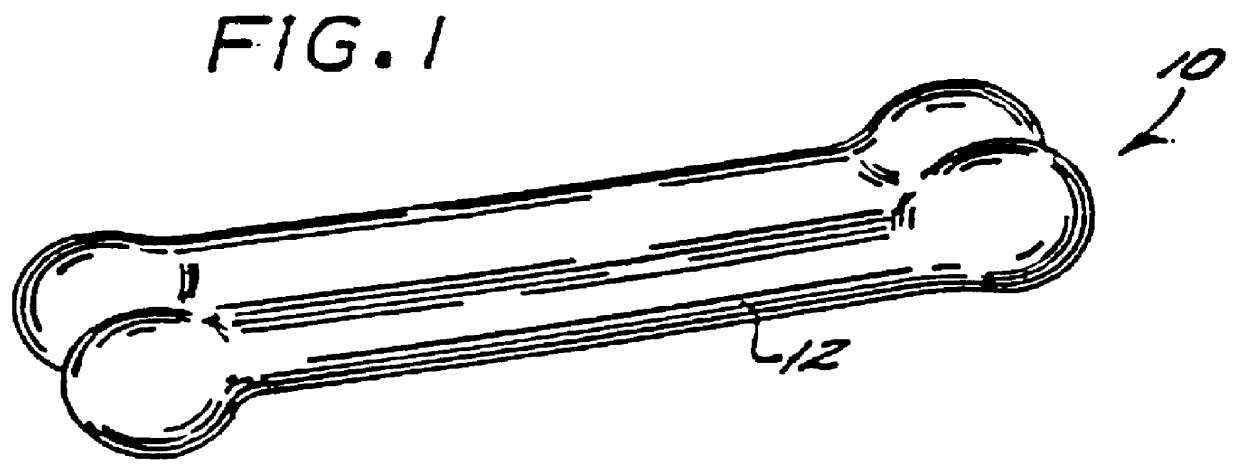
A completely digestible highly nutritious dog chew formulated primarily of wheat flour, casein and starch carbohydrate, the texture of hardness of which is easily modified to suit a particular dog by the dog owner. By irradiating the chew in a microwave oven, the chew is caused to expand and is thereby rendered more easily chewable.
Owner:T F H PUBLICATIONS
Heat modifiable peanut dog chew
A completely digestible highly nutritious dog chew formulated primarily of peanut flour, casein and a vegetable starch carbohydrate, the texture of hardness of which is easily modified to suit a particular dog by the dog owner. By irradiating the chew in a microwave oven, the chew is caused to expand and is thereby rendered more easily chewable.
Owner:T F H PUBLICATIONS
Multi-piece solid golf ball
InactiveUS6739986B2Stretching flight performanceExtended driving distancePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsGolf ballsLow speedHardness
In a multi-piece solid golf ball comprising a solid core and a cover of two inner and outer layers enclosing the solid core and formed on the surface with a plurality of dimples, the solid core in its entirety has a hardness distribution falling within the range of JIS-C hardness 50-85, the difference between maximum and minimum JIS-C hardnesses in the solid core falls within 5%, the cover inner layer has a JIS-C hardness of 70-90, the cover outer layer has a JIS-C hardness of 60-80, the sum of high-speed region dimple operative volumes HDOV of respective dimples is 170-310, the sum of low-speed region dimple operative volumes of respective dimples LDOV is 200-310, and the overall dimple volume is 260-360 mm<3>.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Catheter Shaft and Method of its Manufacture
ActiveUS20090166913A1Increase flexibilityIncrease resistanceMedical devicesLaminationHardnessCo extrusion
A method of manufacturing a catheter shaft includes the steps of forming an inner layer of a first polymeric material, forming a plait matrix layer including a second polymeric material about the inner layer, and forming an outer layer of a third polymeric material about the plait matrix layer. The plait matrix layer includes a braided wire mesh partially or fully embedded within the second polymeric material, which is different from at least one of the first polymeric material forming the inner layer and the third polymeric material forming the outer layer. The second polymeric material has a higher yield strain and / or a lower hardness than at least the first polymeric material, and preferably both the first and the third polymeric materials. The first polymeric material and the third polymeric material may be different or the same. The catheter shaft may be formed by stepwise extrusion, co-extrusion, and / or reflow processes.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
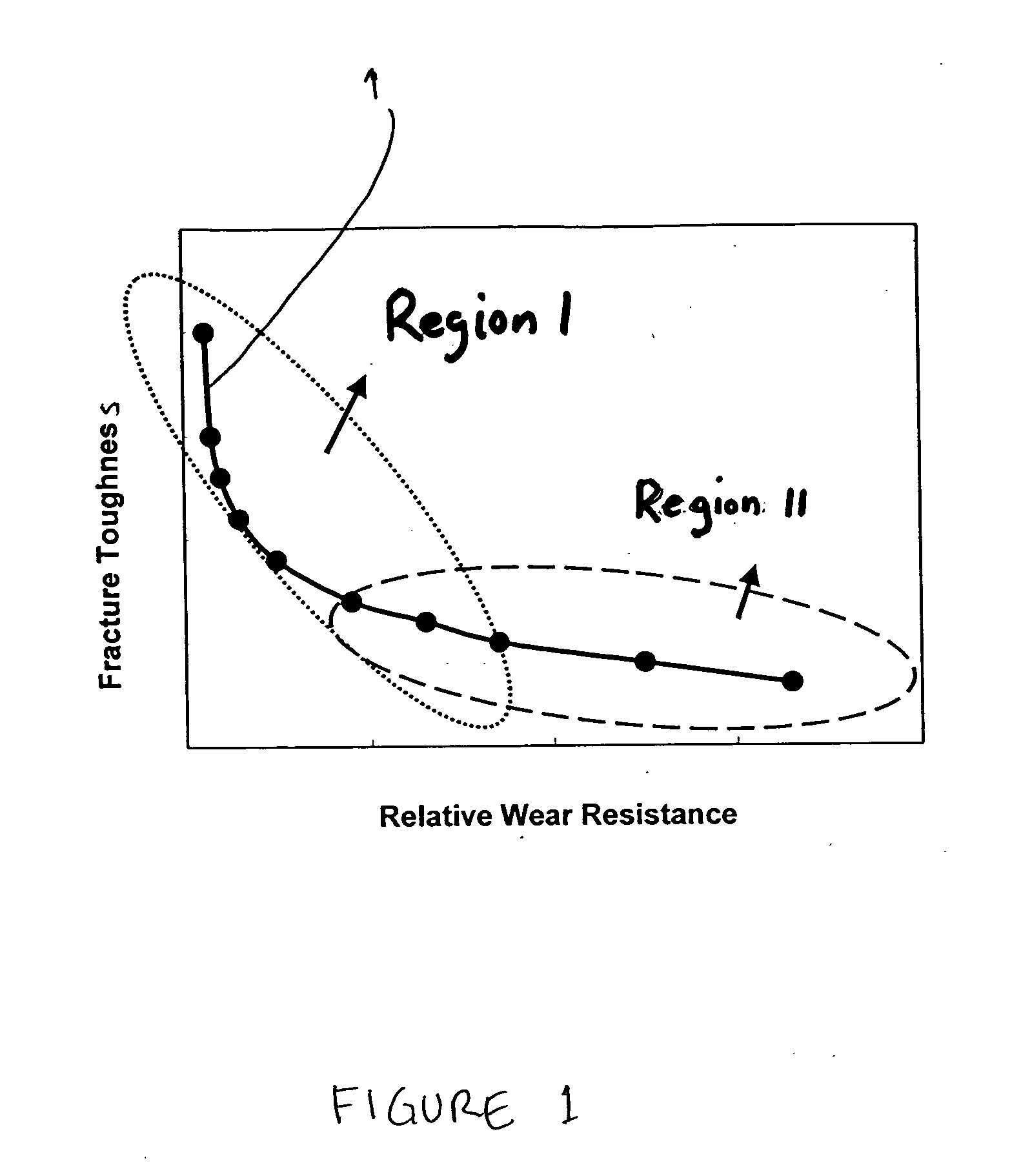
Hybrid cemented carbide composites
Embodiments of the present invention include hybrid composite materials comprising a cemented carbide dispersed phase and a cemented carbide continuous phase. The contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase of embodiments may be less than or equal to 0.48. The hybrid composite material may have a hardness of the dispersed phase that is greater than the hardness of the continuous phase. For example, in certain embodiments of the hybrid composite material, the hardness of the dispersed phase is greater than or equal to 88 HRA and less than or equal to 95 HRA and the hardness of the continuous phase is greater than or equal to 78 and less than or equal to 91 HRA. Additional embodiments may include hybrid composite materials comprising a first cemented carbide dispersed phase wherein the volume fraction of the dispersed phase is less than 50 volume percent and a second cemented carbide continuous phase, wherein the contiguity ratio of the dispersed phase is less than or equal to 1.5 times the volume fraction of the dispersed phase in the composite material. The present invention also includes a method of making a hybrid cemented carbide composite by blending partially and / or fully sintered granules of the dispersed cemented carbide grade with “green” and / or unsintered granules of the continuous cemented carbide grade to provide a blend. The blend may then be consolidated to form a compact. Finally, the compact may be sintered to form a hybrid cemented carbide.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Two-piece solid golf ball
InactiveUS6494793B1Excellent shot feelingImprove flight performanceGolf ballsSolid ballsHardnessGolf Ball
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
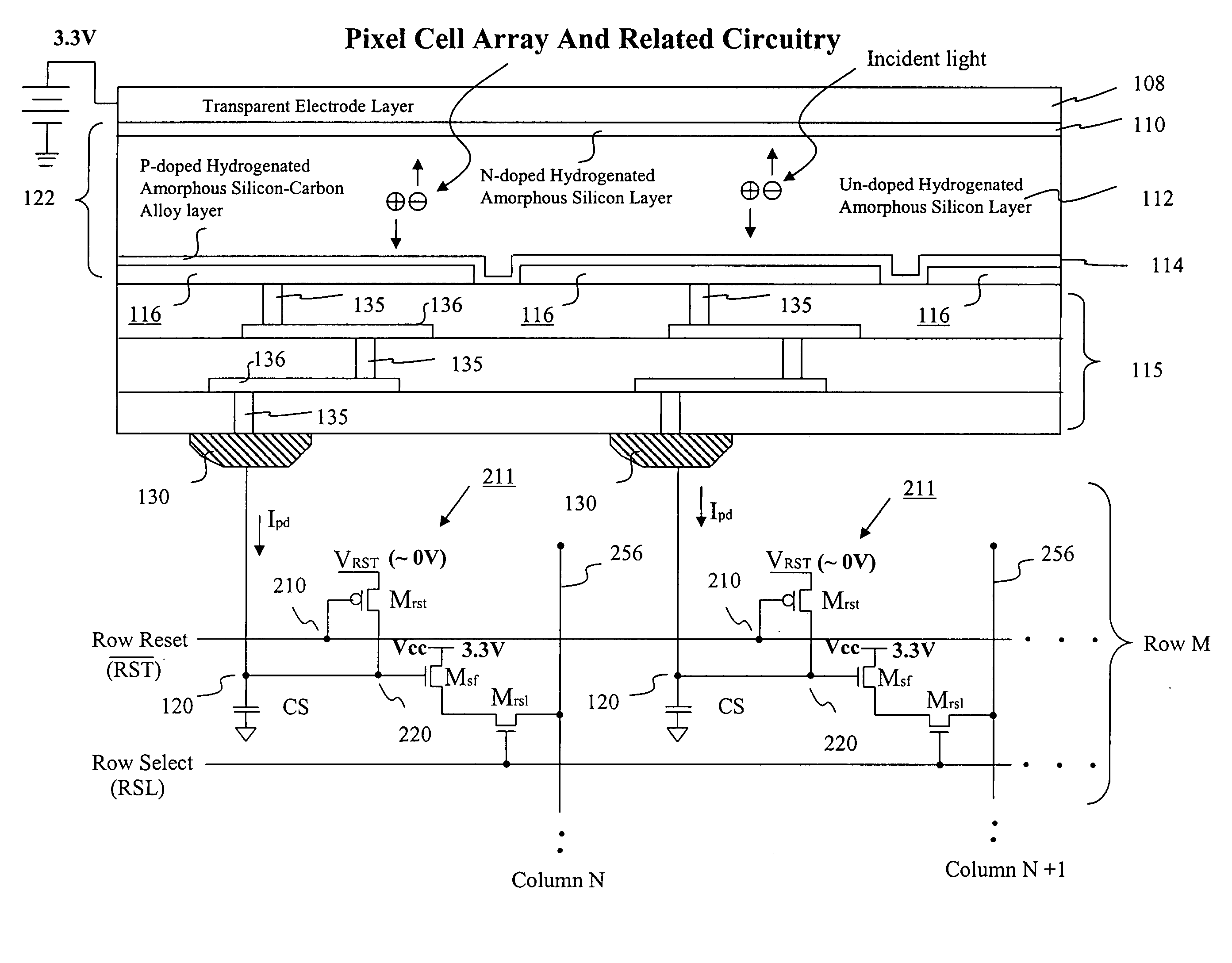
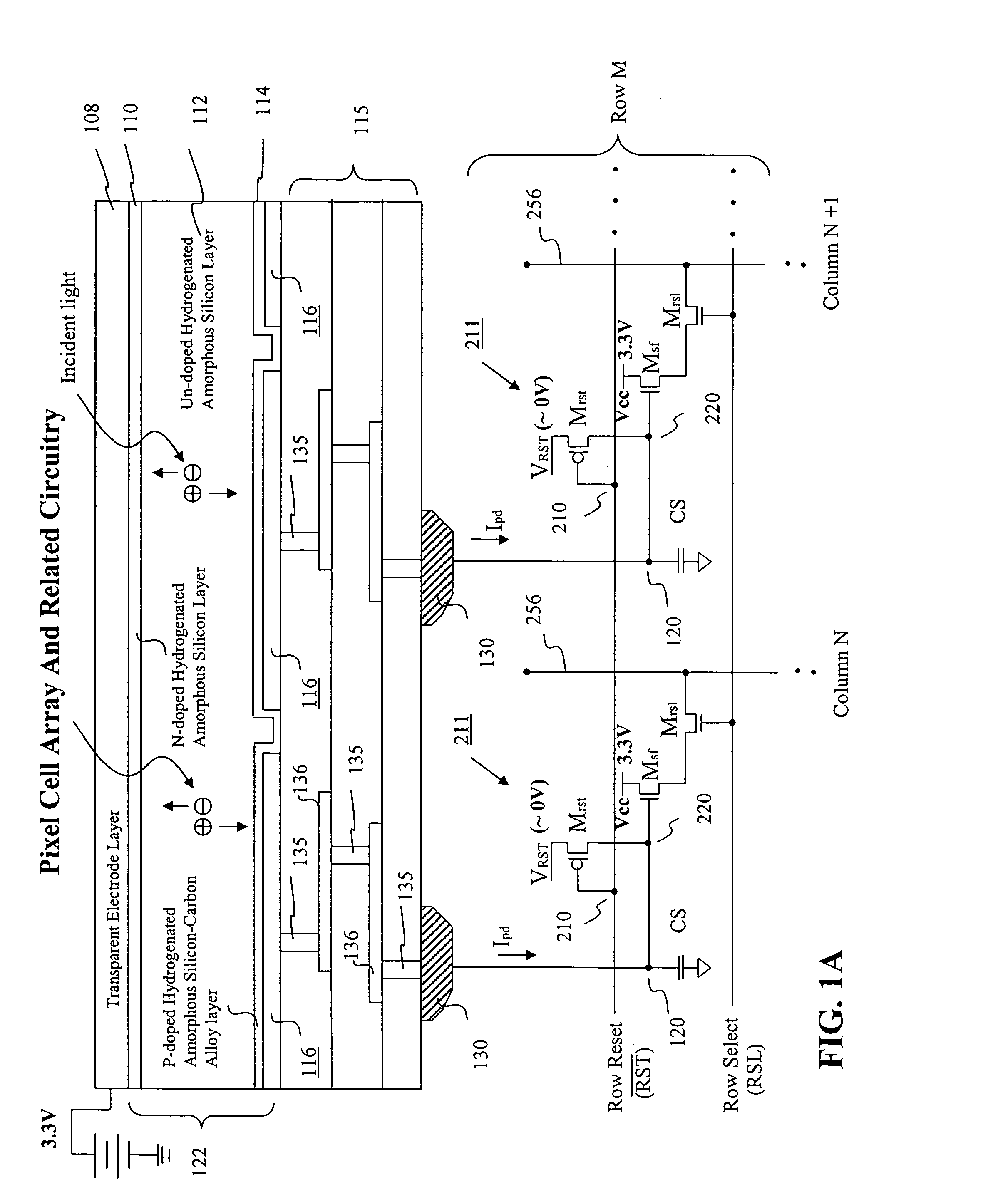
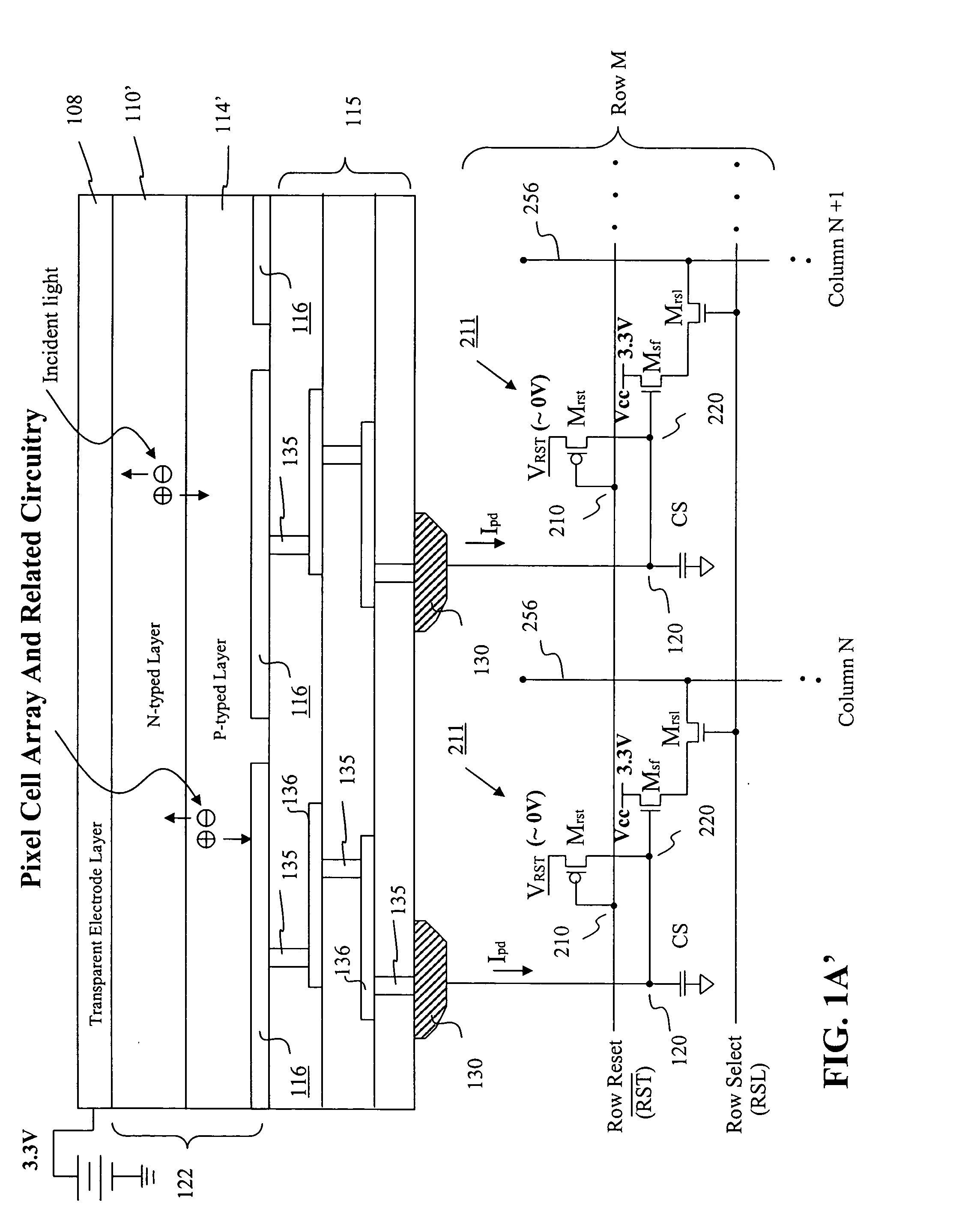
Visible/near infrared image sensor
InactiveUS20050104089A1Improve performanceHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow earth orbitBeam steering
A MOS or CMOS sensor for high performance imaging in broad spectral ranges including portions of the infrared spectral band. These broad spectral ranges may also include portions or all of the visible spectrum, therefore the sensor has both daylight and night vision capabilities. The sensor includes a continuous multi-layer photodiode structure on a many pixel MOS or CMOS readout array where the photodiode structure is chosen to include responses in the near infrared spectral ranges. A preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline copper indium diselenide / cadmium sulfide photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. An alternate preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline silicon germanium photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. Each of these embodiments provides night vision with image performance that greatly surpasses the GEN III night vision technology in terms of enhanced sensitivity, pixel size and pixel count. Further advantages of the invention include low electrical bias voltages, low power consumption, compact packaging, and radiation hardness. In special preferred embodiments CMOS stitching technology is used to provide multi-million pixel focal plane array sensors. One embodiments of the invention made without stitching is a two-million pixel sensor. Other preferred embodiments available using stitching techniques include sensors with 250 million (or more) pixels fabricated on a single wafer. A particular application of these very high pixel count sensors is as a focal plane array for a rapid beam steering telescope in a low earth orbit satellite useful for tracking over a 1500-meter wide track with a resolution of 0.3 meter.
Owner:C PHOCUS
Multi-piece solid golf ball
InactiveUS6855074B2Superior in flight distance and spin performance and shot feelGolf ballsSolid ballsHardnessEngineering
The present invention provides a multi-piece solid golf ball, which is superior in flight distance, spin performance and shot feel. The present invention relates to a multi-piece solid golf ball comprising a core consisting of a center, an intermediate layer formed on the center and an outer layer formed on the intermediate layer, and a cover covering the core, whereinthe center has a diameter of 10 to 20 mm and a central point hardness in JIS-A hardness of 30 to 85,the intermediate layer has a surface hardness in Shore D hardness of 30 to 55,the outer layer has a hardness in Shore D hardness of 55 to 70, andthe cover has a Shore D hardness of 35 to 55 and a thickness of 0.3 to 1.5 mm.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Electronic device and manufacturing method thereof
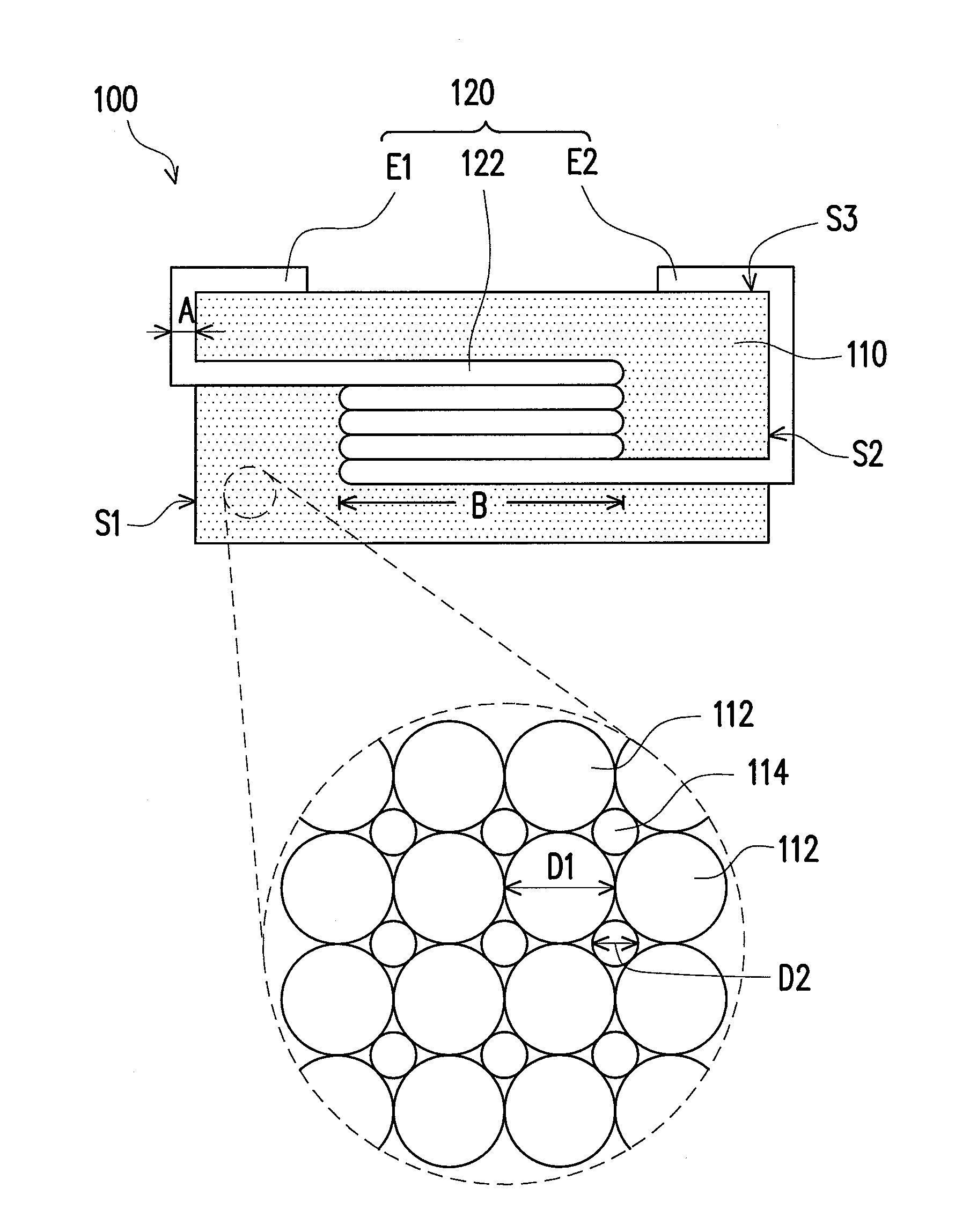
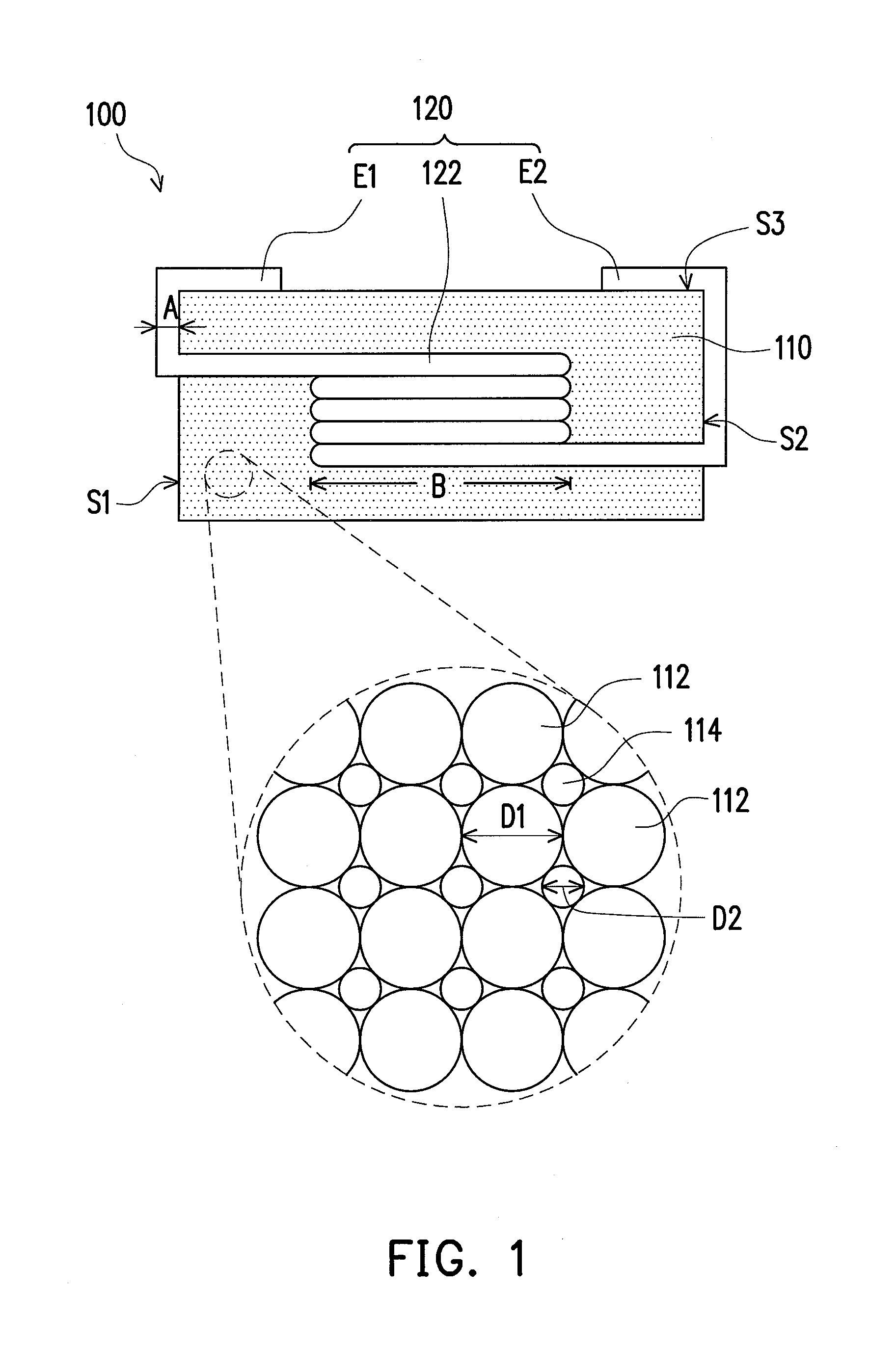
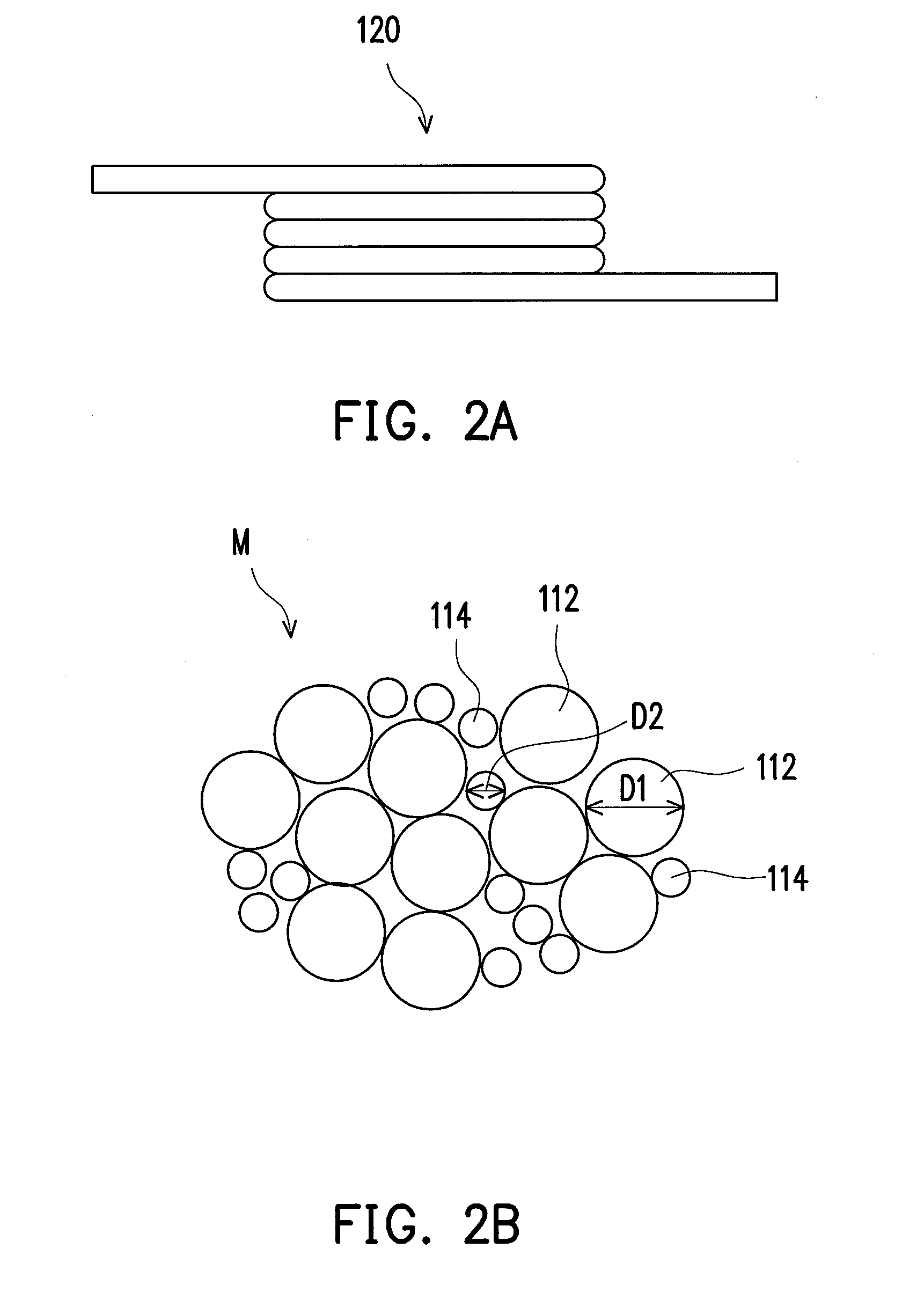
ActiveUS20100289609A1Improve breathabilityPrevent oxidationTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInorganic material magnetismMagnetic powderHardness
An electronic device including a magnetic body and a wire is provided. The magnetic body has a first magnetic powder and a second magnetic powder mixed with the first magnetic powder. The Vicker's Hardness of the first magnetic powder is greater than that of the second magnetic powder and the mean particle diameter of the first magnetic powder is greater than that of the second magnetic powder.
Owner:CYNTEC
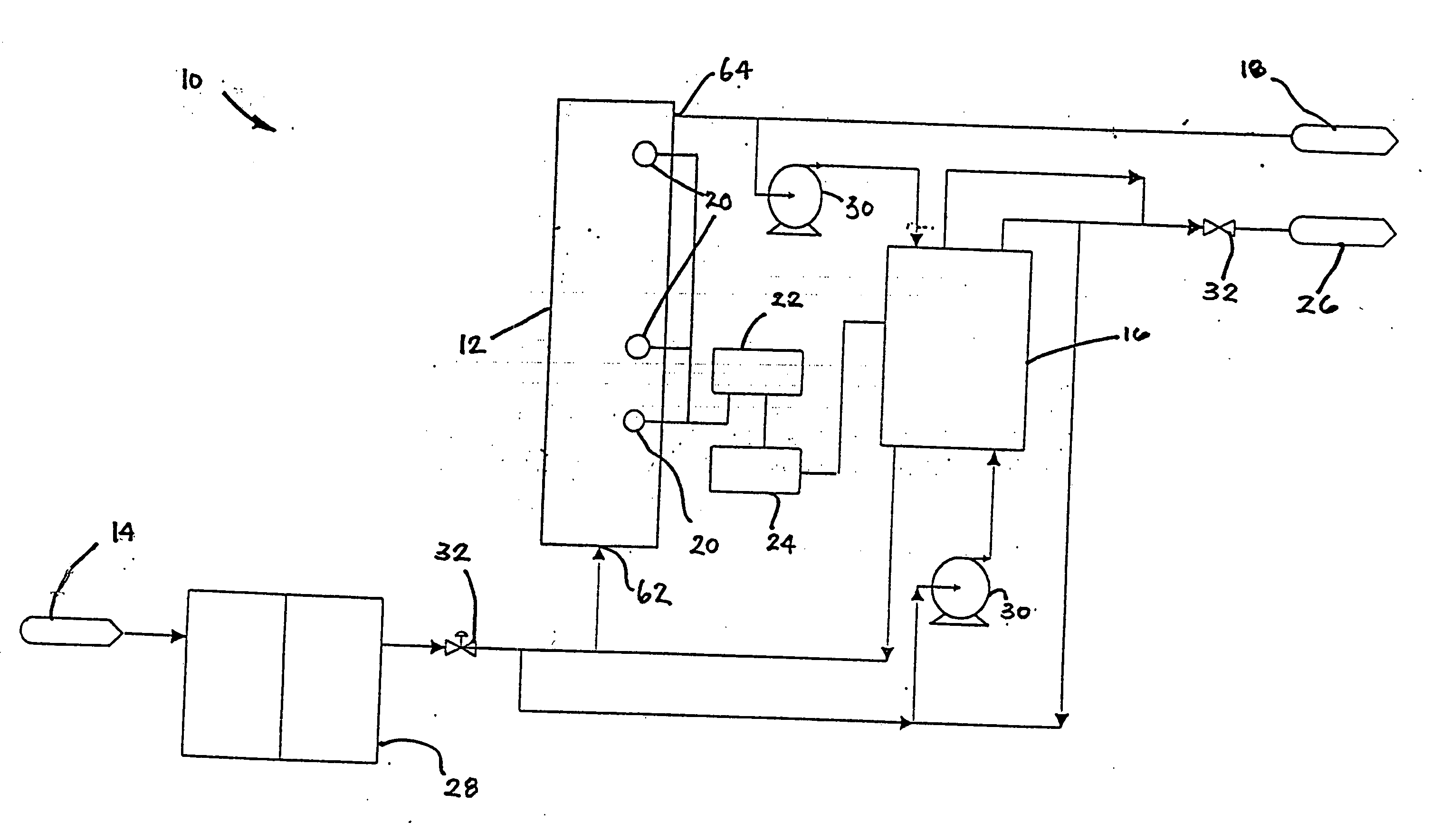
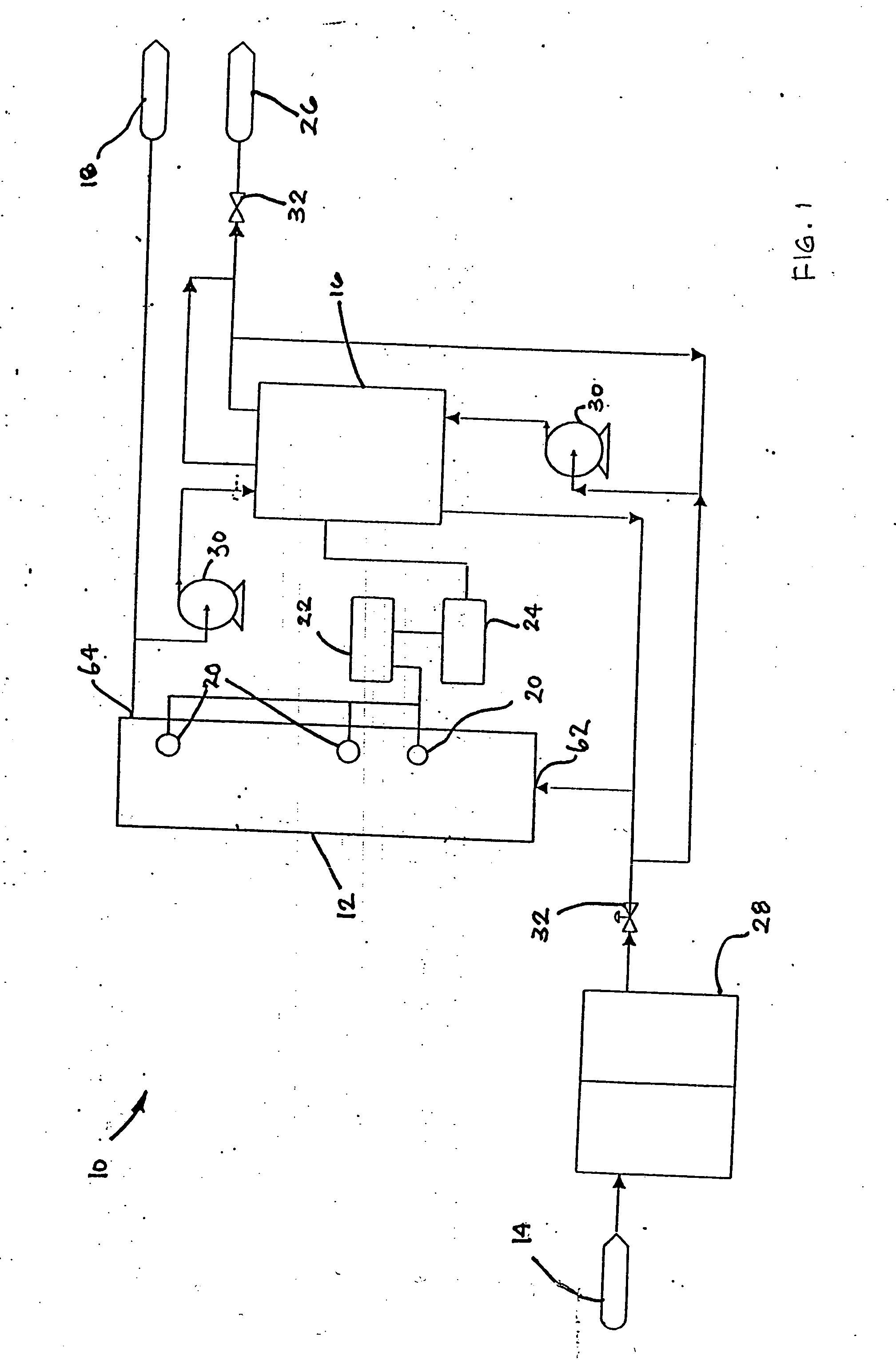
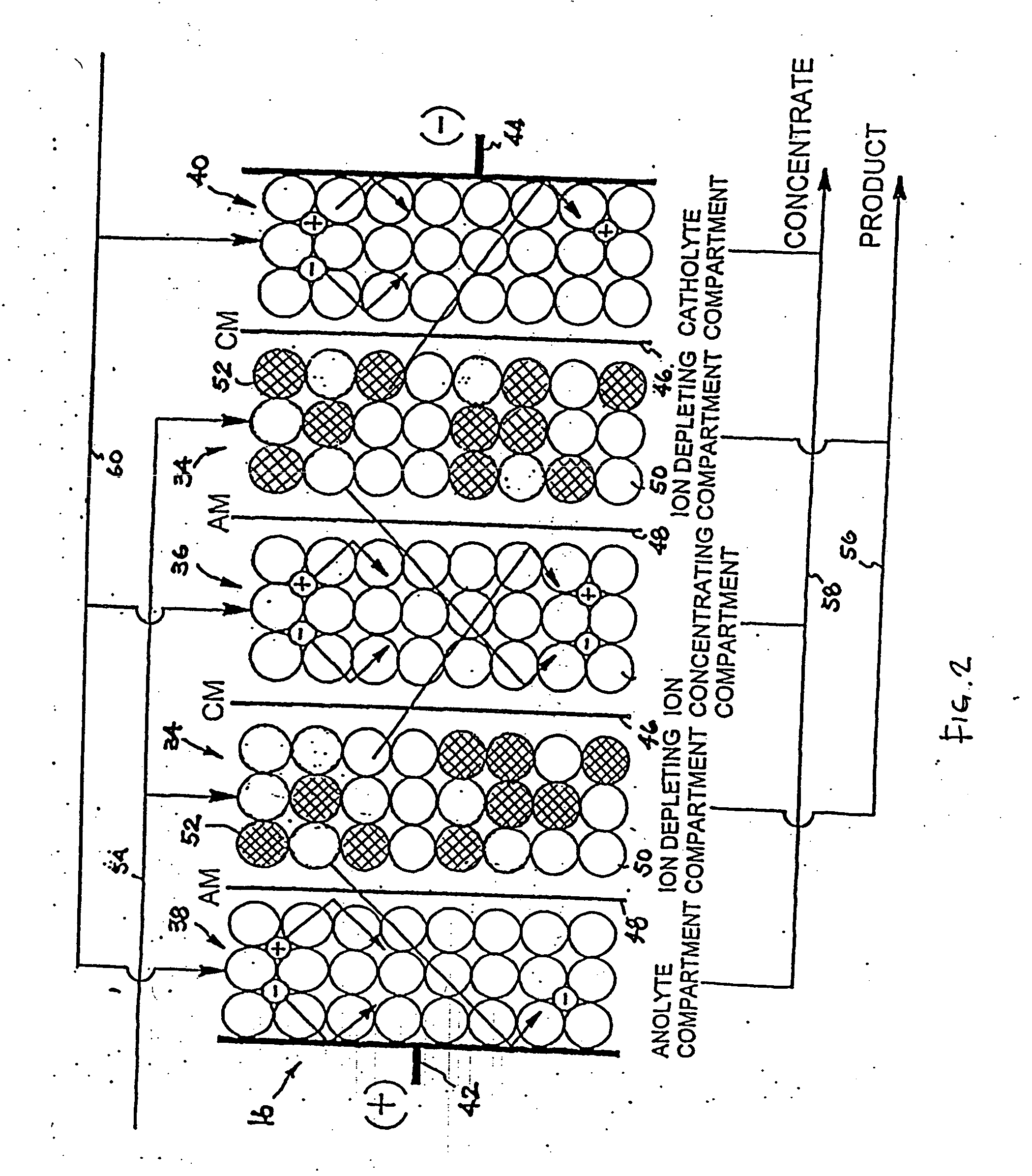
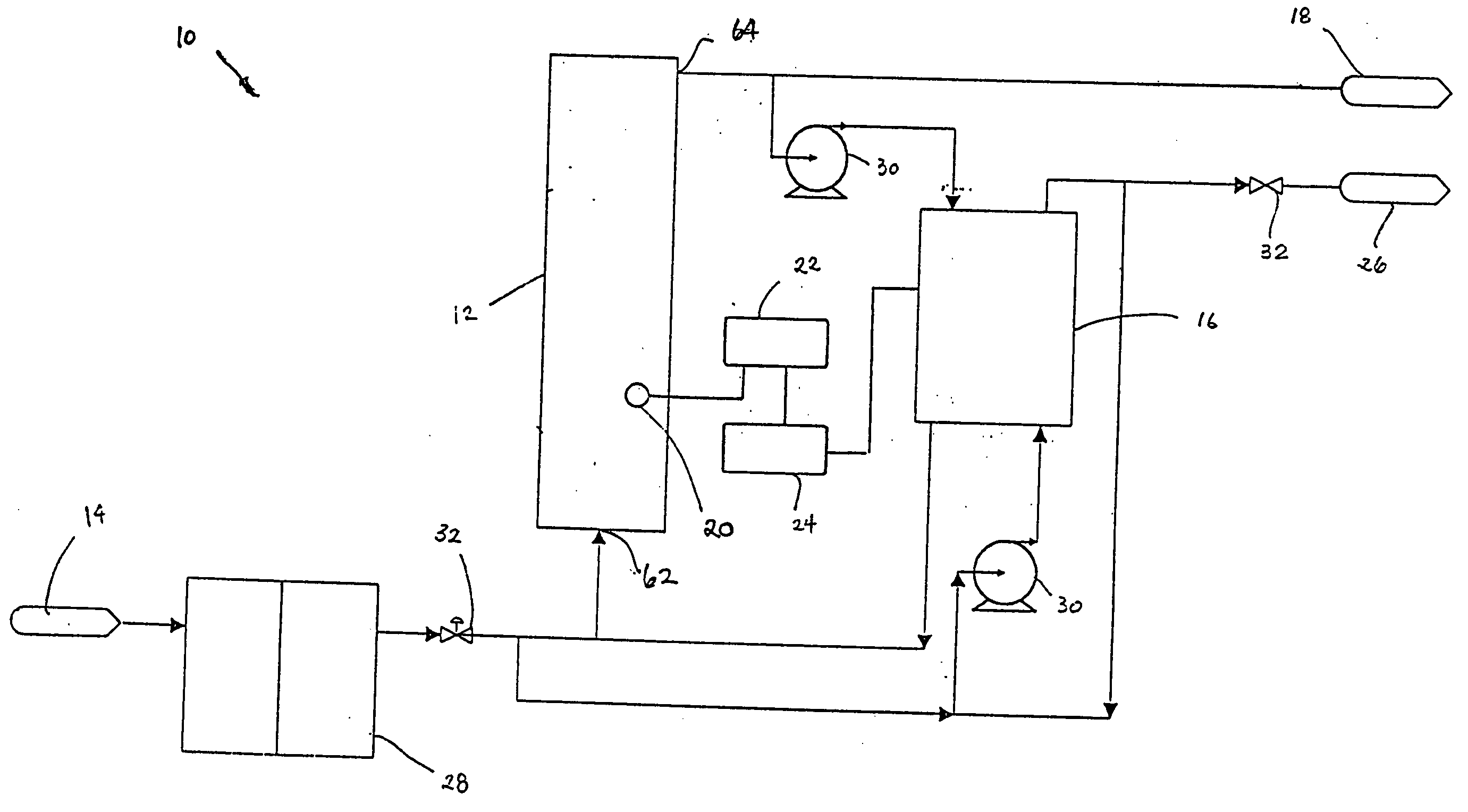
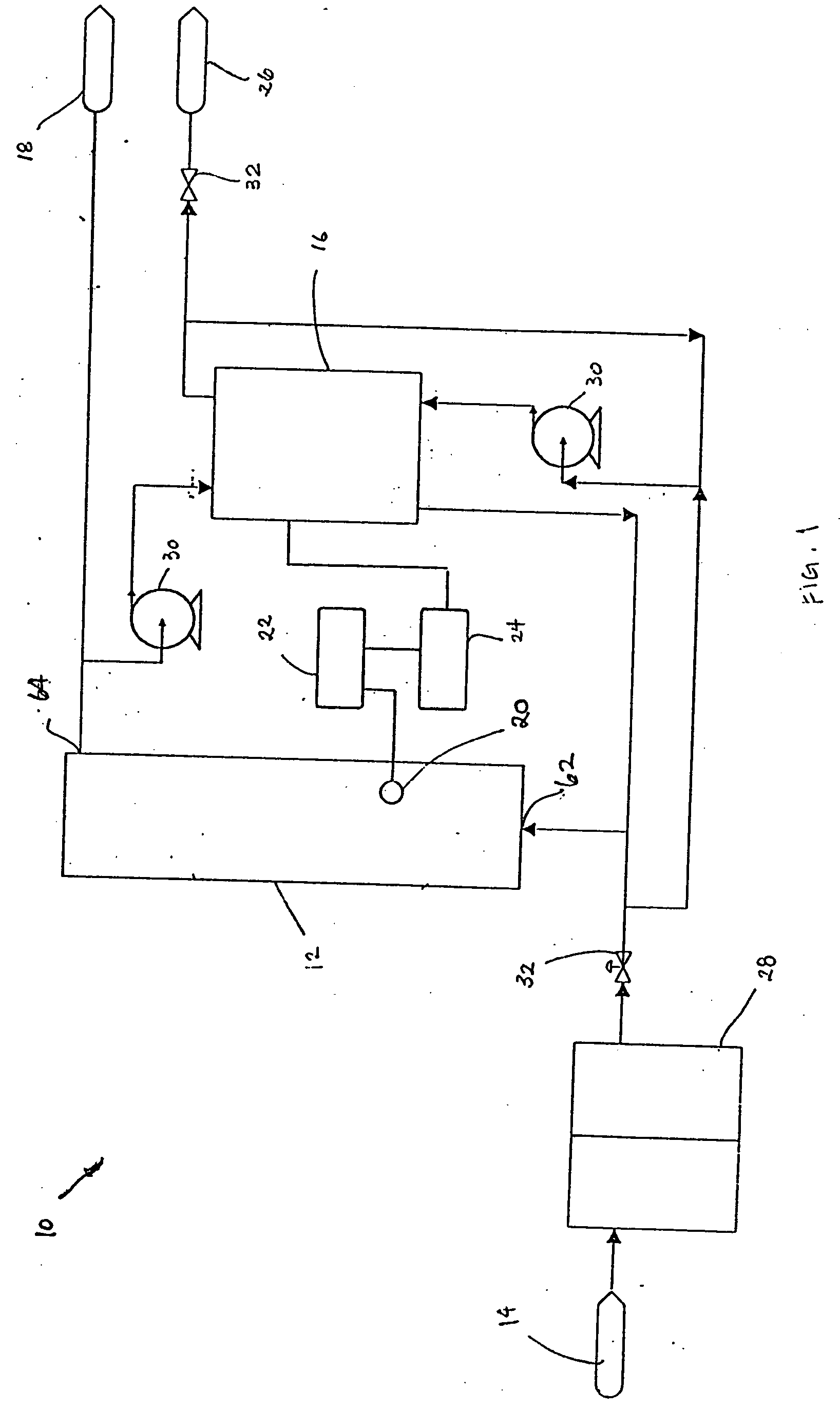
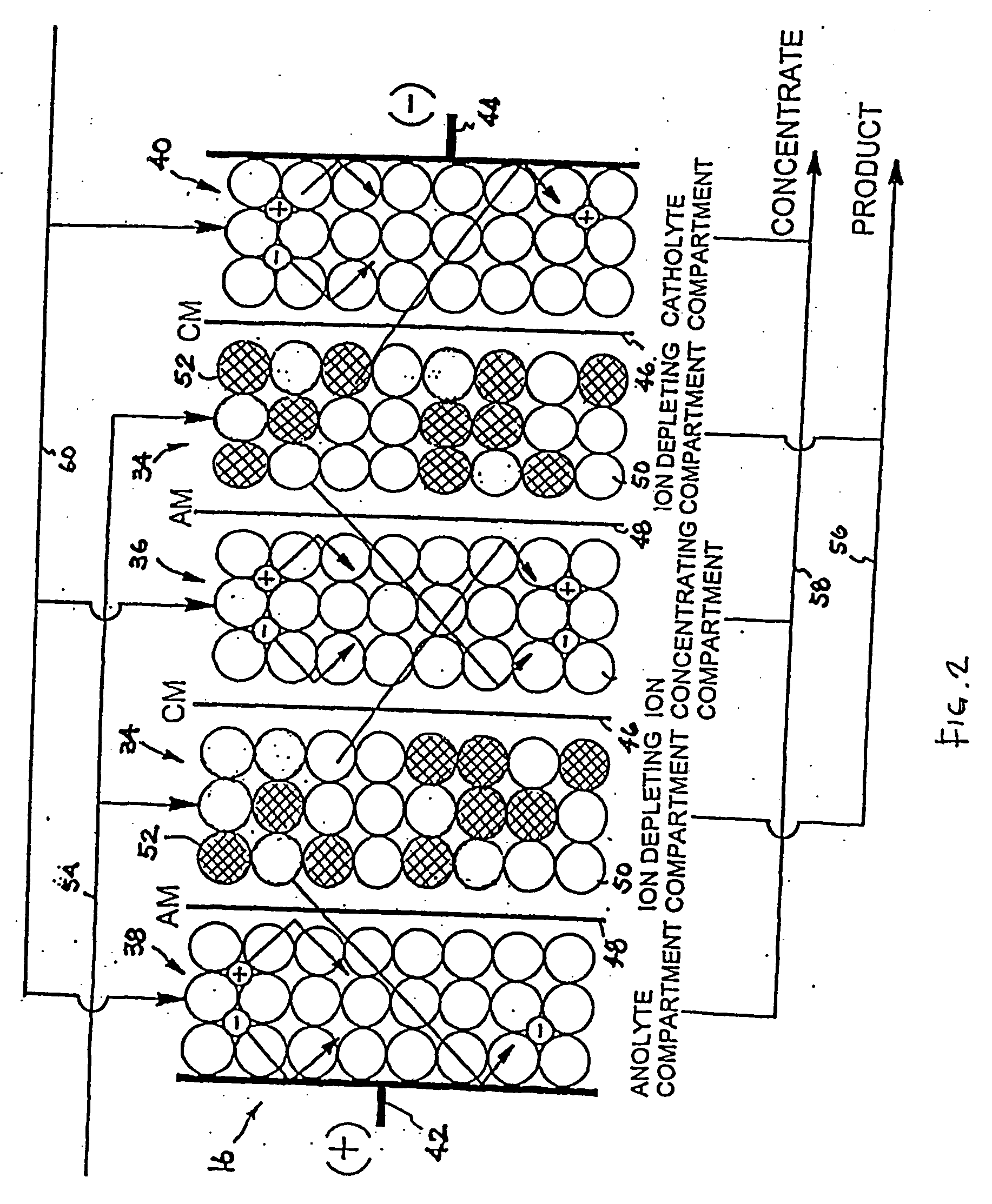
Water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20050103722A1Water treatment parameter controlIon-exchange column/bed processesWater treatment systemWater source
A water treatment system provides treated or softened water to a point of use by removing a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a point of entry coming from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically treats the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system has a sensor or a set of sensors for measuring at least one property of the water or an operating condition of the treatment system. The water treatment system also has a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system to optimize the operation and performance of the system or components of the system to supply water tailored to quality requirements.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
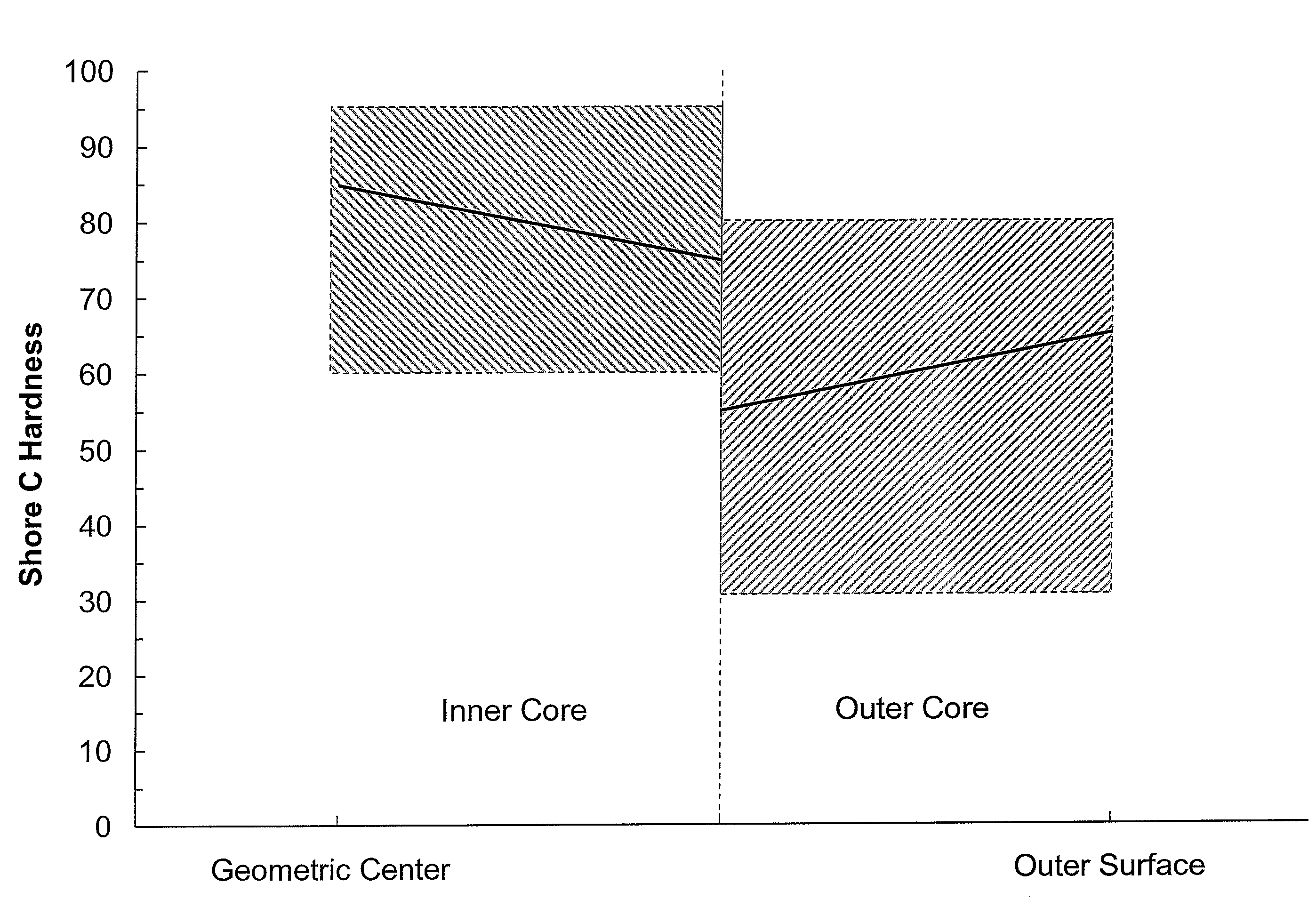
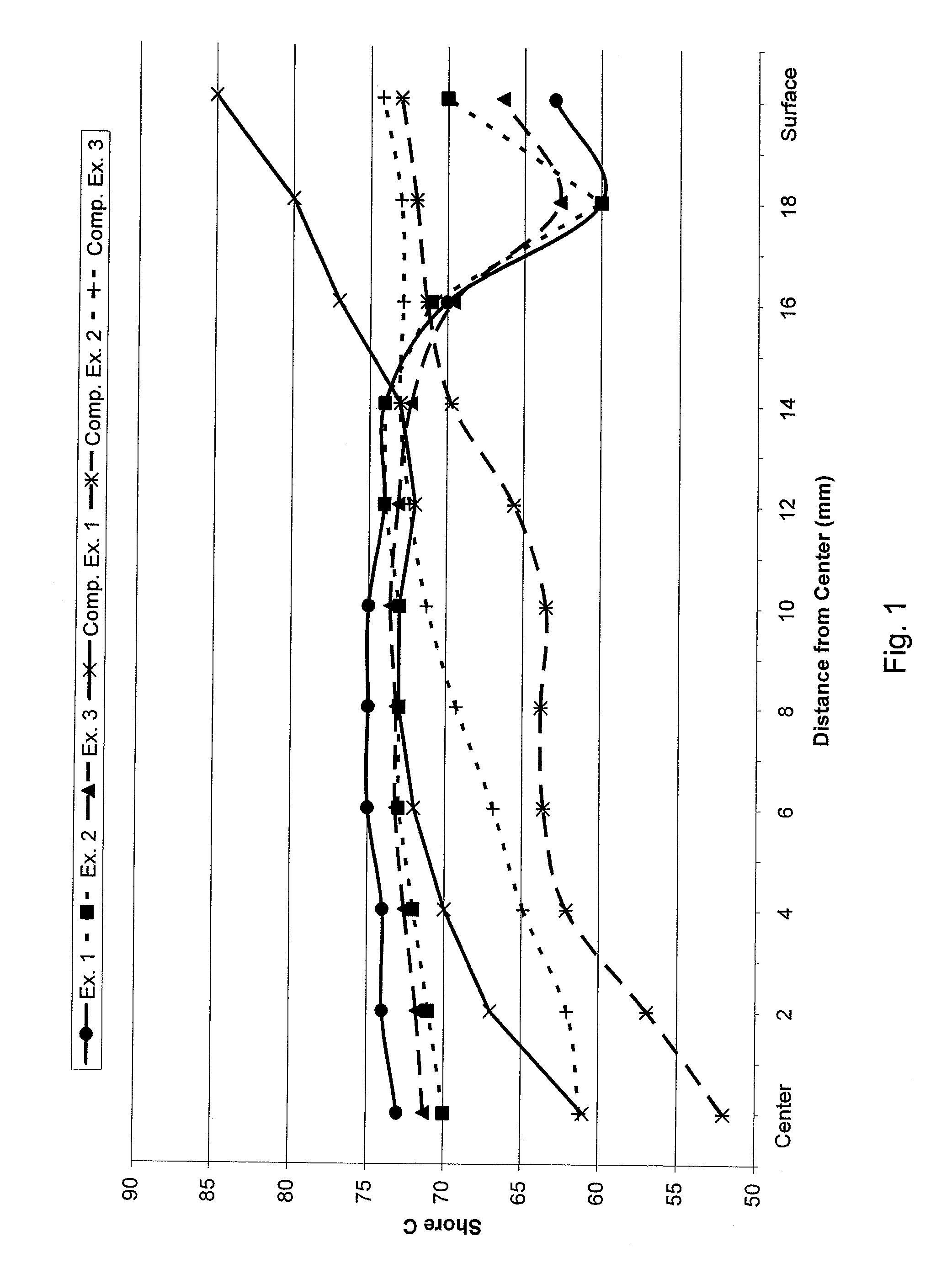
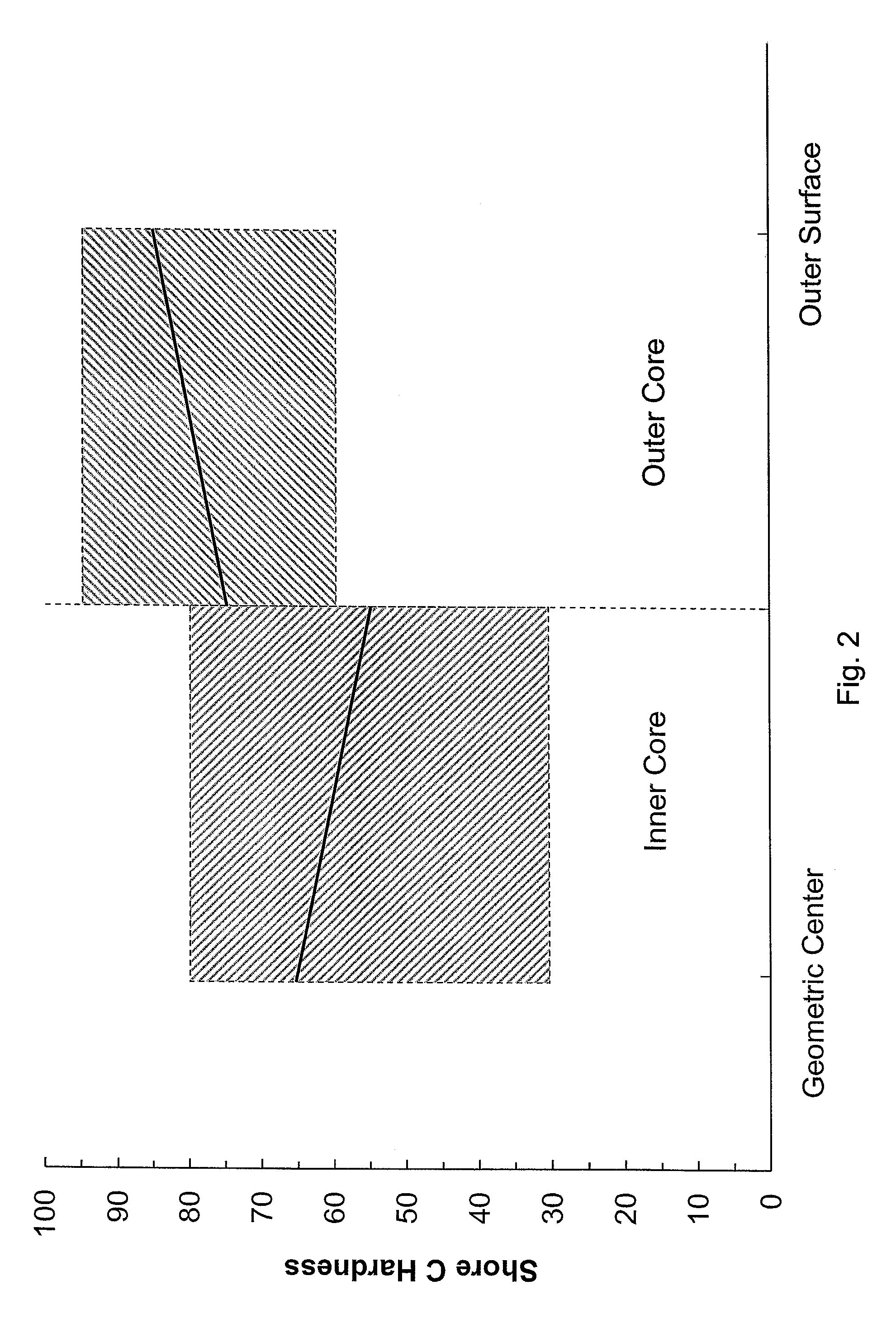
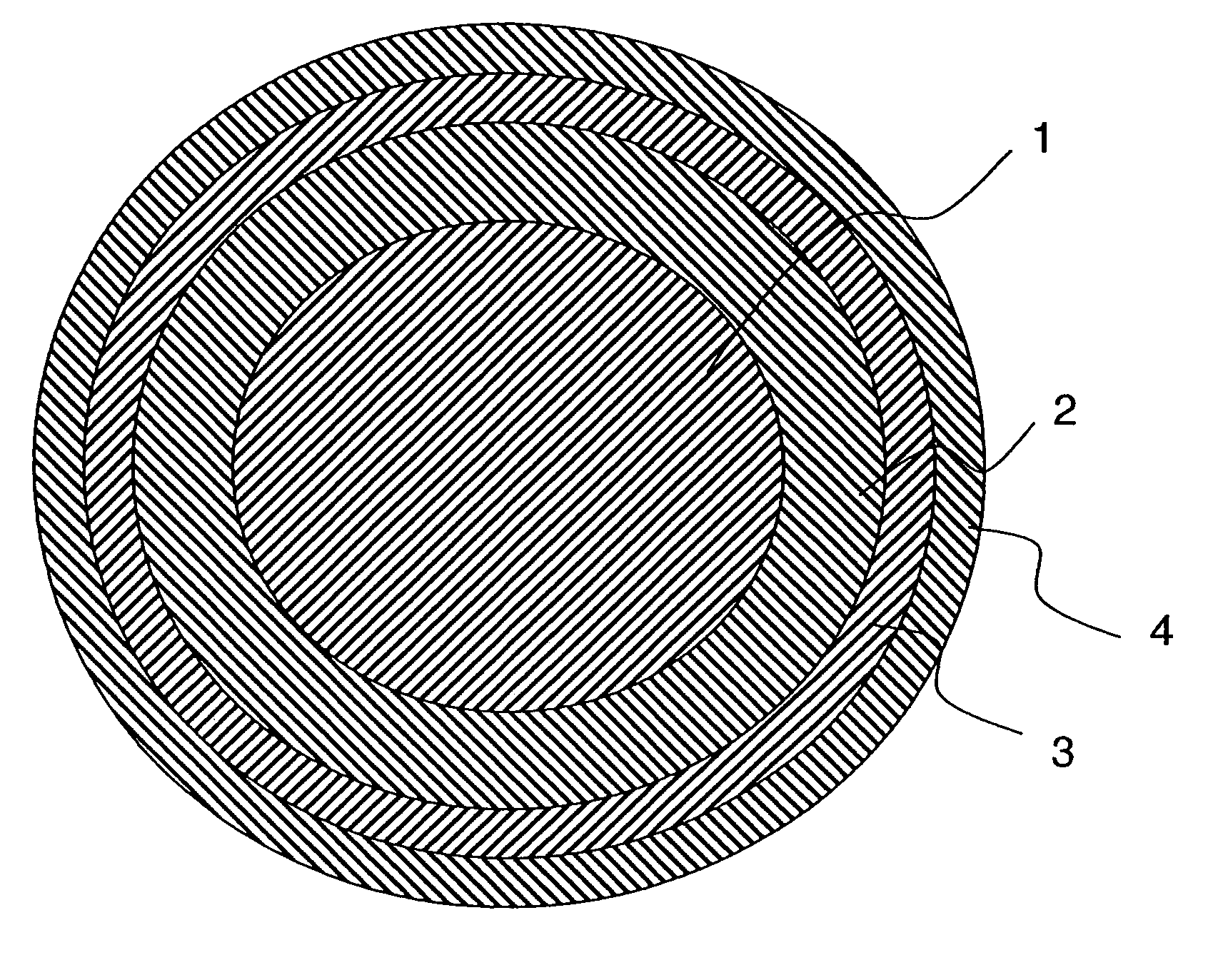
Negative hardness gradient inner core for dual core golf ball
A golf ball having an inner core having a first outer surface and a geometric center and being formed from a substantially homogenous formulation such that the inner core has a hardness of 45 Shore C to 65 Shore C; an outer core layer disposed about the inner core having a second outer surface and an inner surface and being formed from a substantially homogenous formulation such that the outer core layer has a hardness of 55 Shore C to 90 Shore C. A cover is disposed about the outer core layer. The hardness of the first outer surface is the same as or lower than the hardness of the geometric center to define a “negative hardness gradient” and the hardness of the second outer surface is greater than the hardness of the inner surface to define a “positive hardness gradient.”
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Multi-piece solid golf ball
InactiveUS7086969B2Improve spin performanceIncrease total distance traveledGolf ballsSolid ballsPtru catalystSulphur compound
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20050103717A1Water treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectricityWater treatment system
A water treatment system provides treated water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically receives water from the water source or a point of entry and purifies the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a pressurized reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system can have a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system.
Owner:SIEMENS WATER TECH HLDG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com