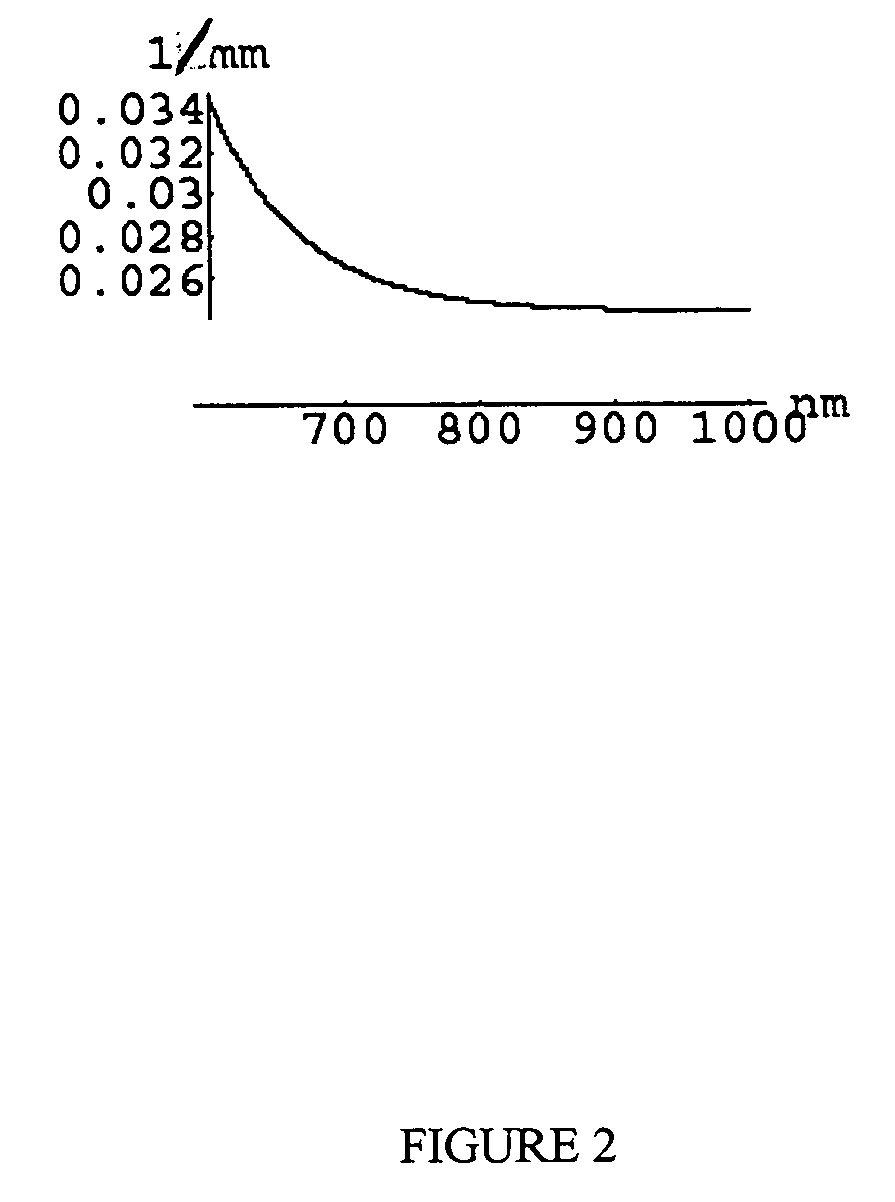Patents
Literature
4080 results about "Layers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
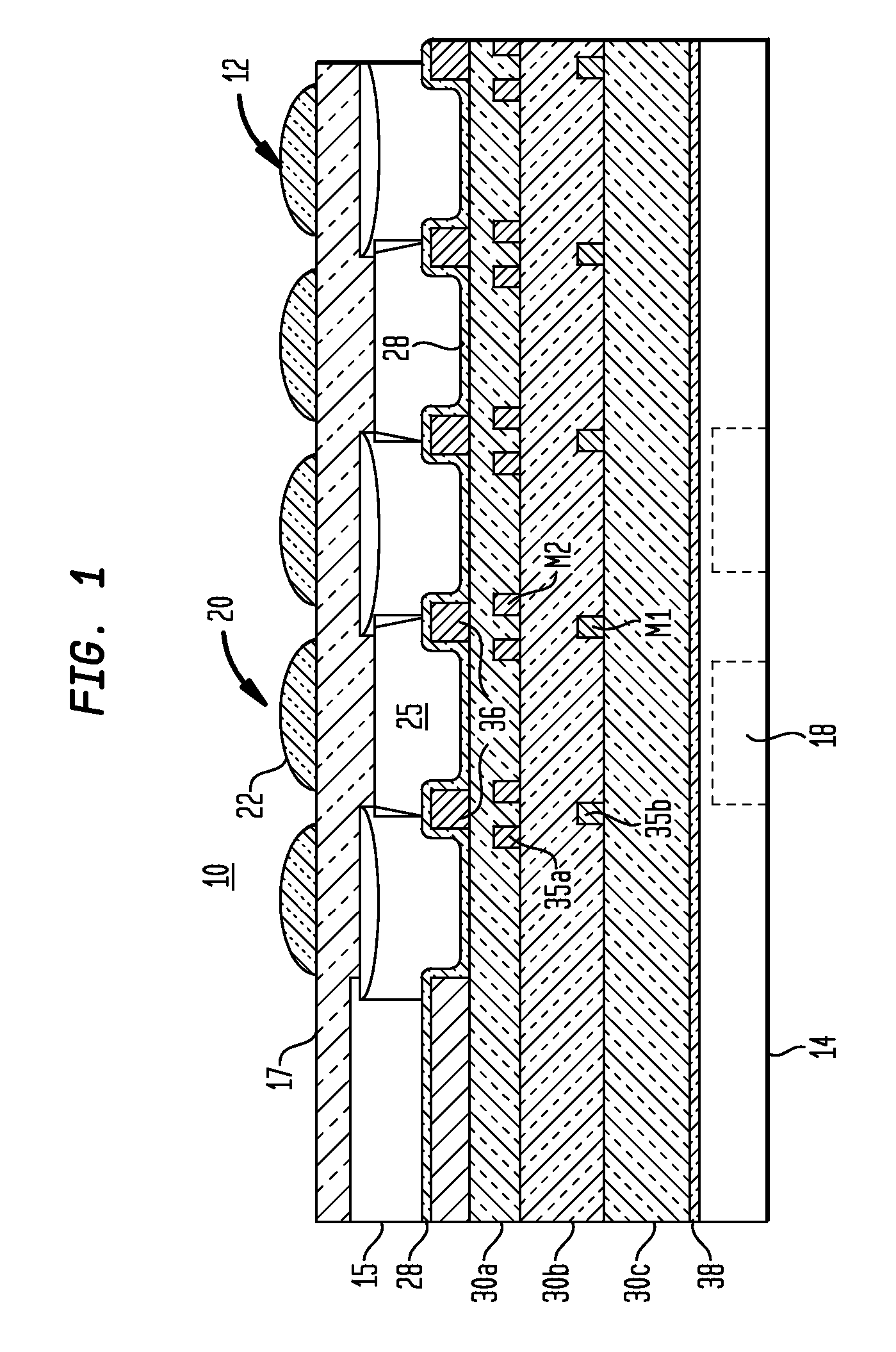
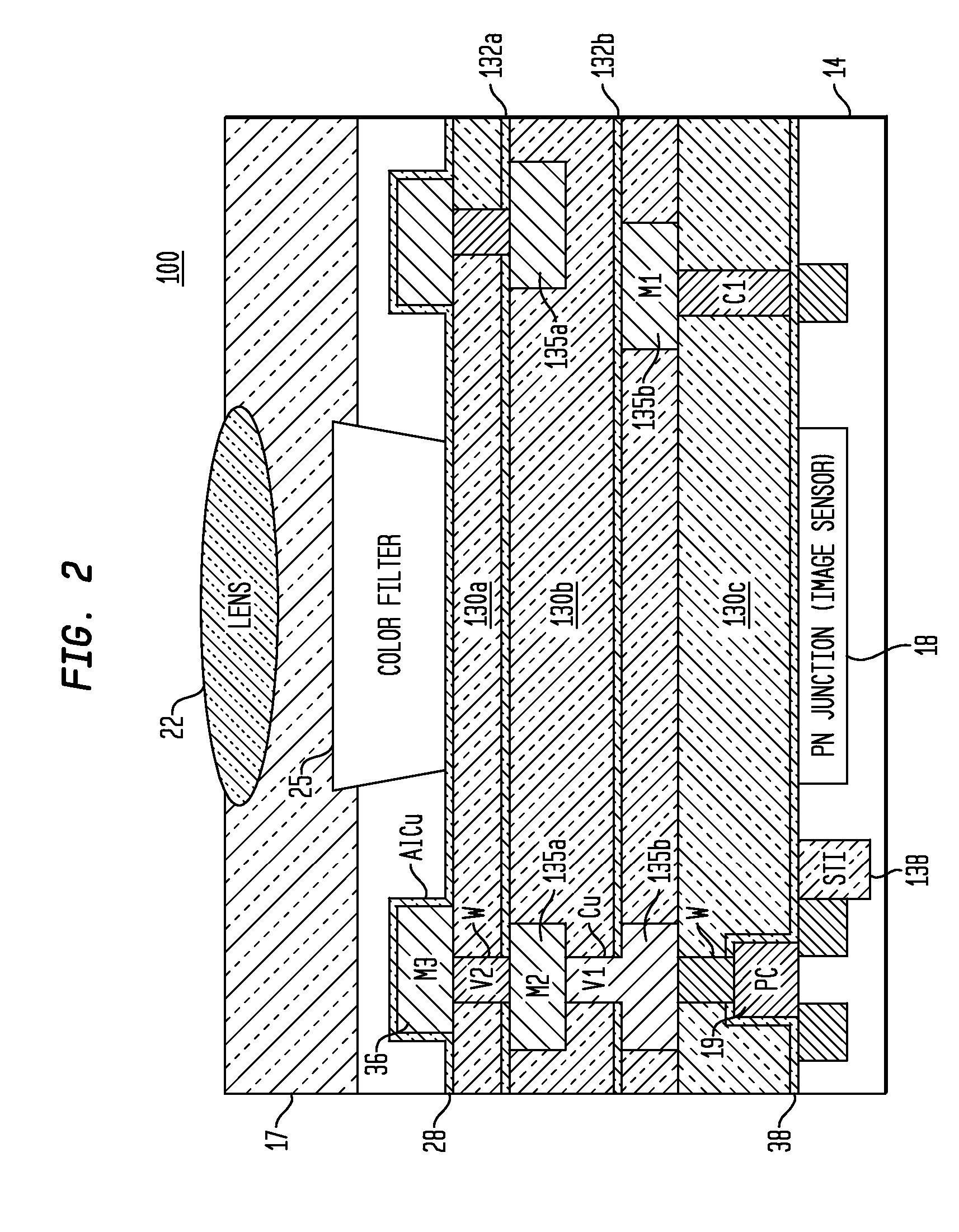
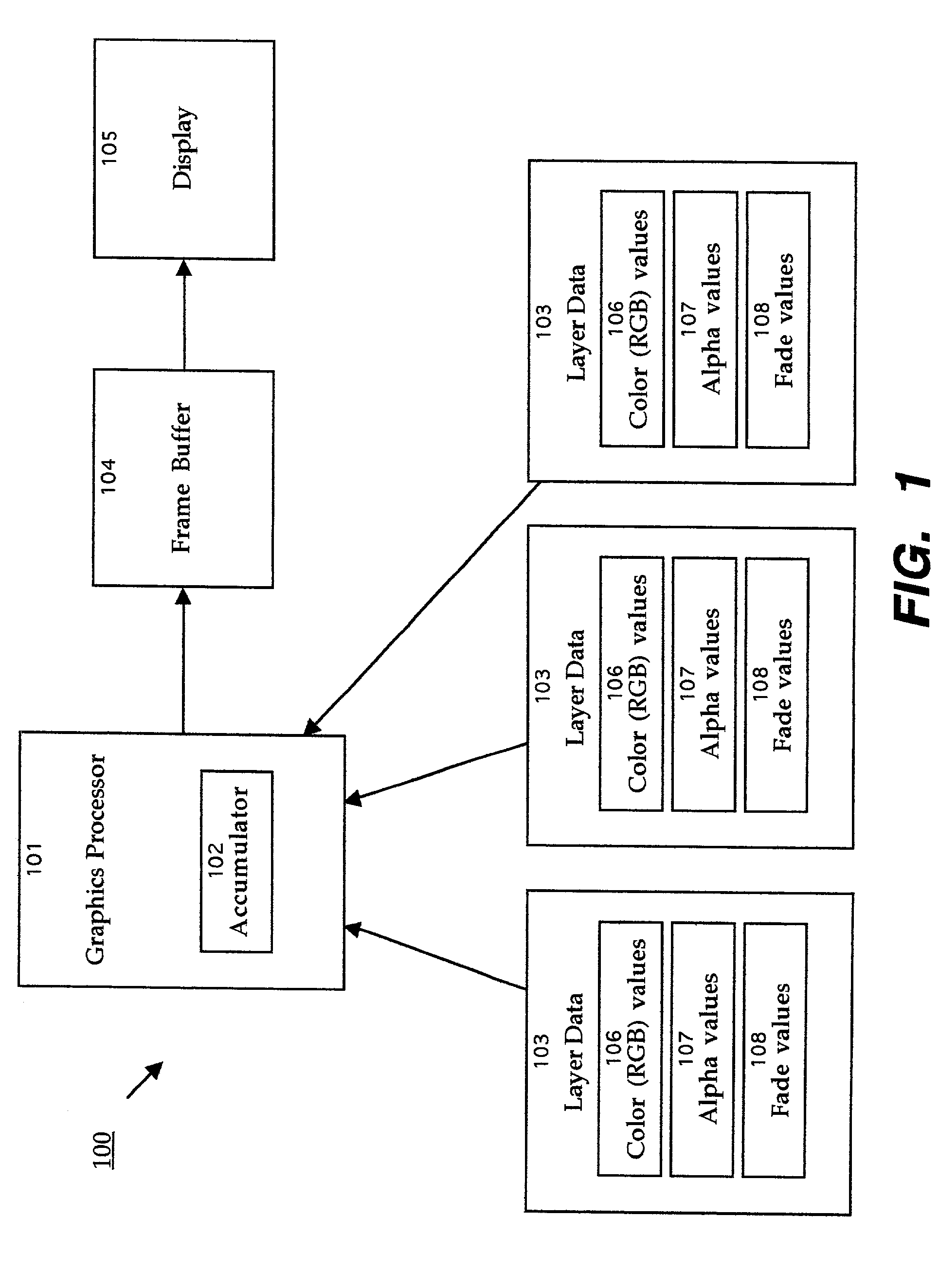
Layers are used in digital image editing to separate different elements of an image. A layer can be compared to a transparency on which imaging effects or images are applied and placed over or under an image. Today they are an integral feature of image editors.
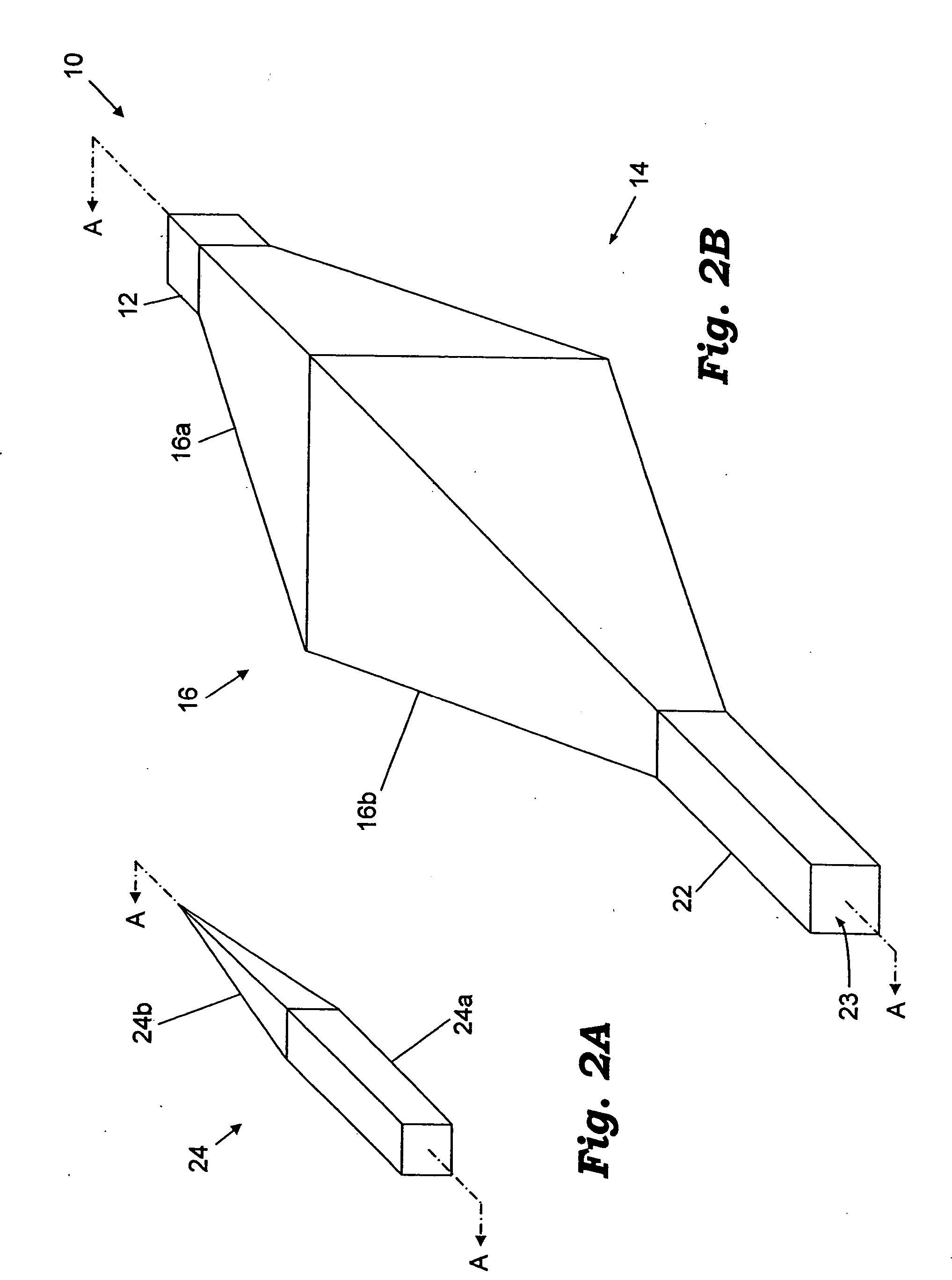
Systems for and methods of three dimensional viewing
InactiveUS7190518B1Low costGreat easeColor television detailsSteroscopic systemsParallaxDisplay device
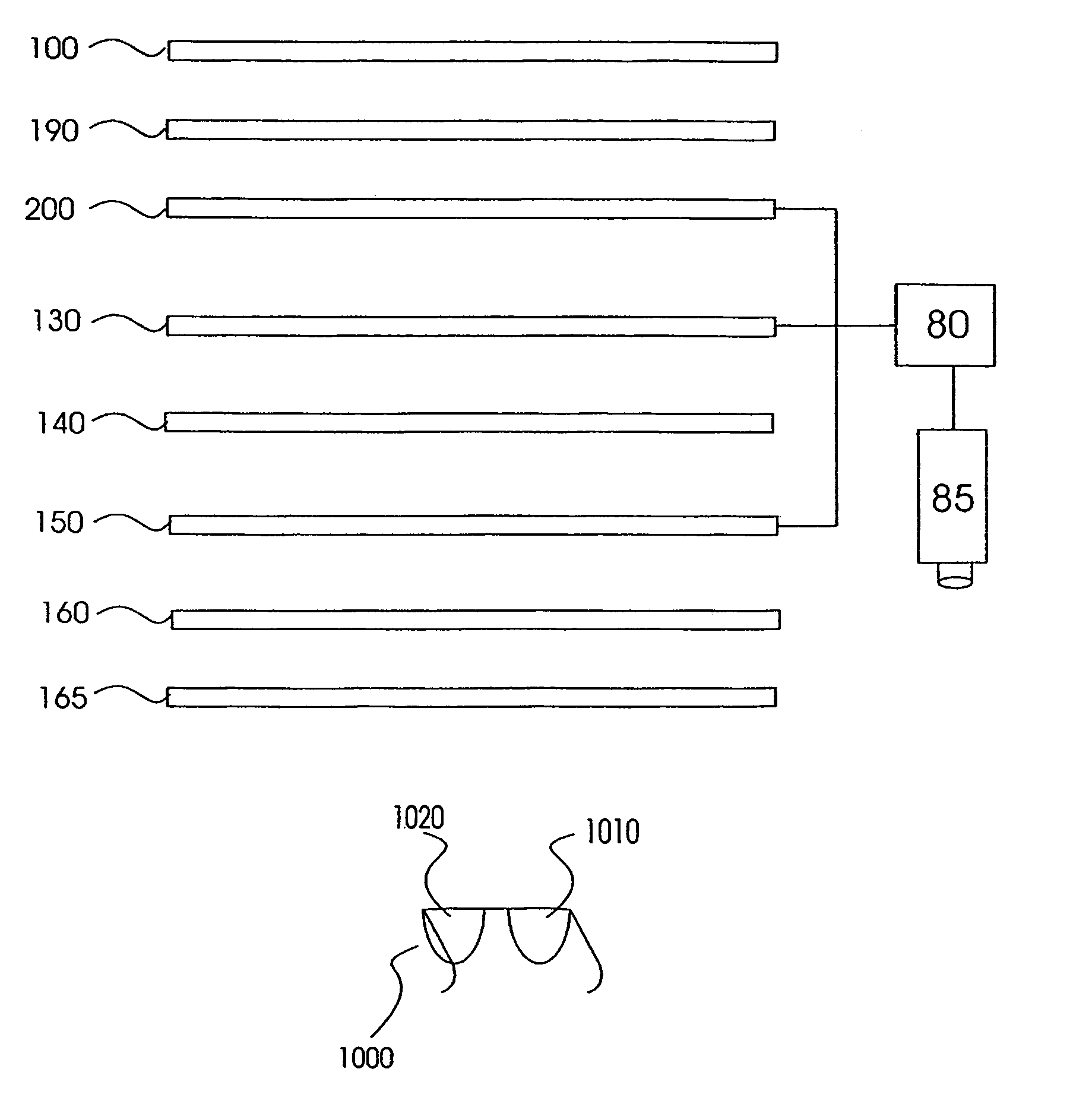
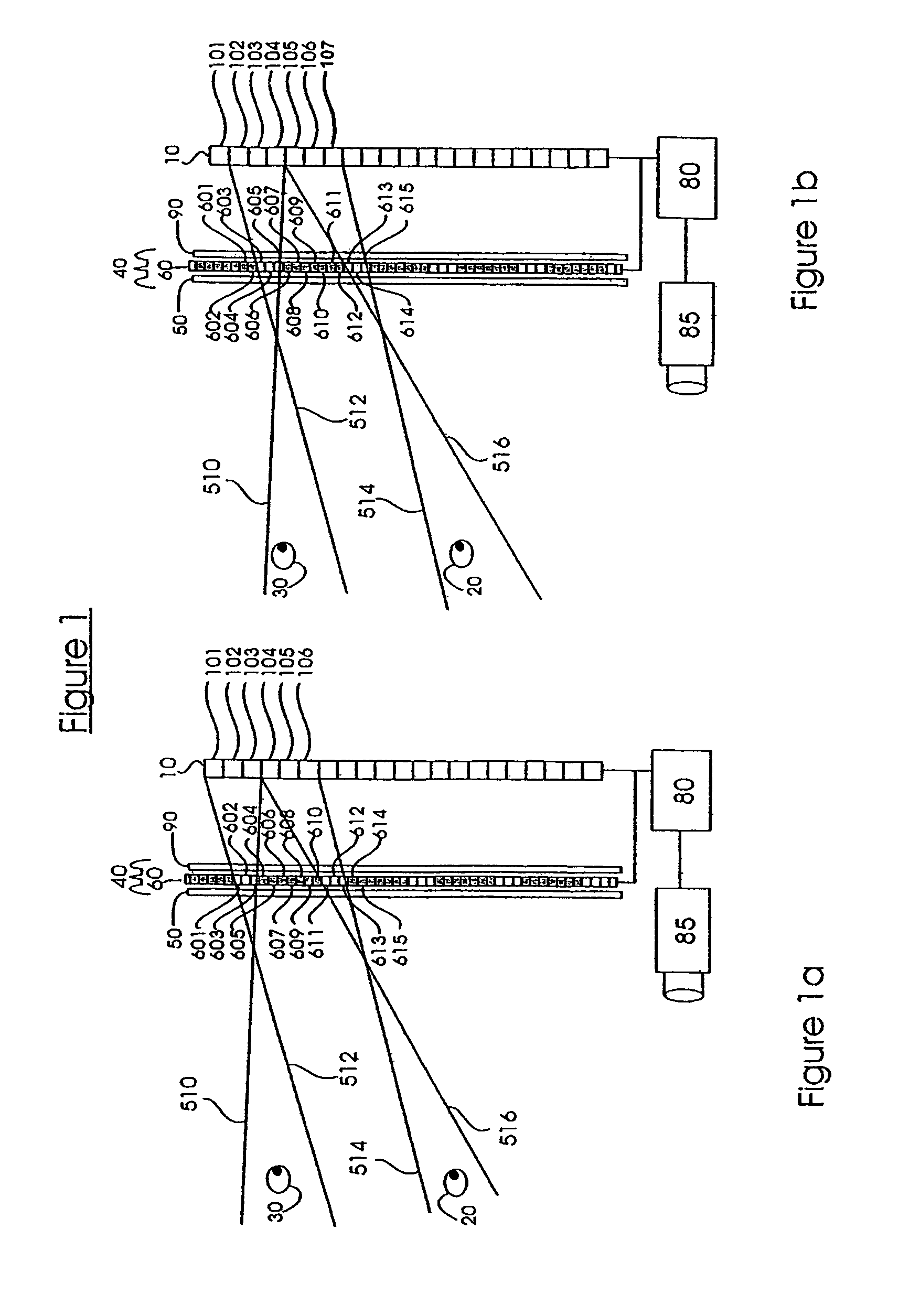
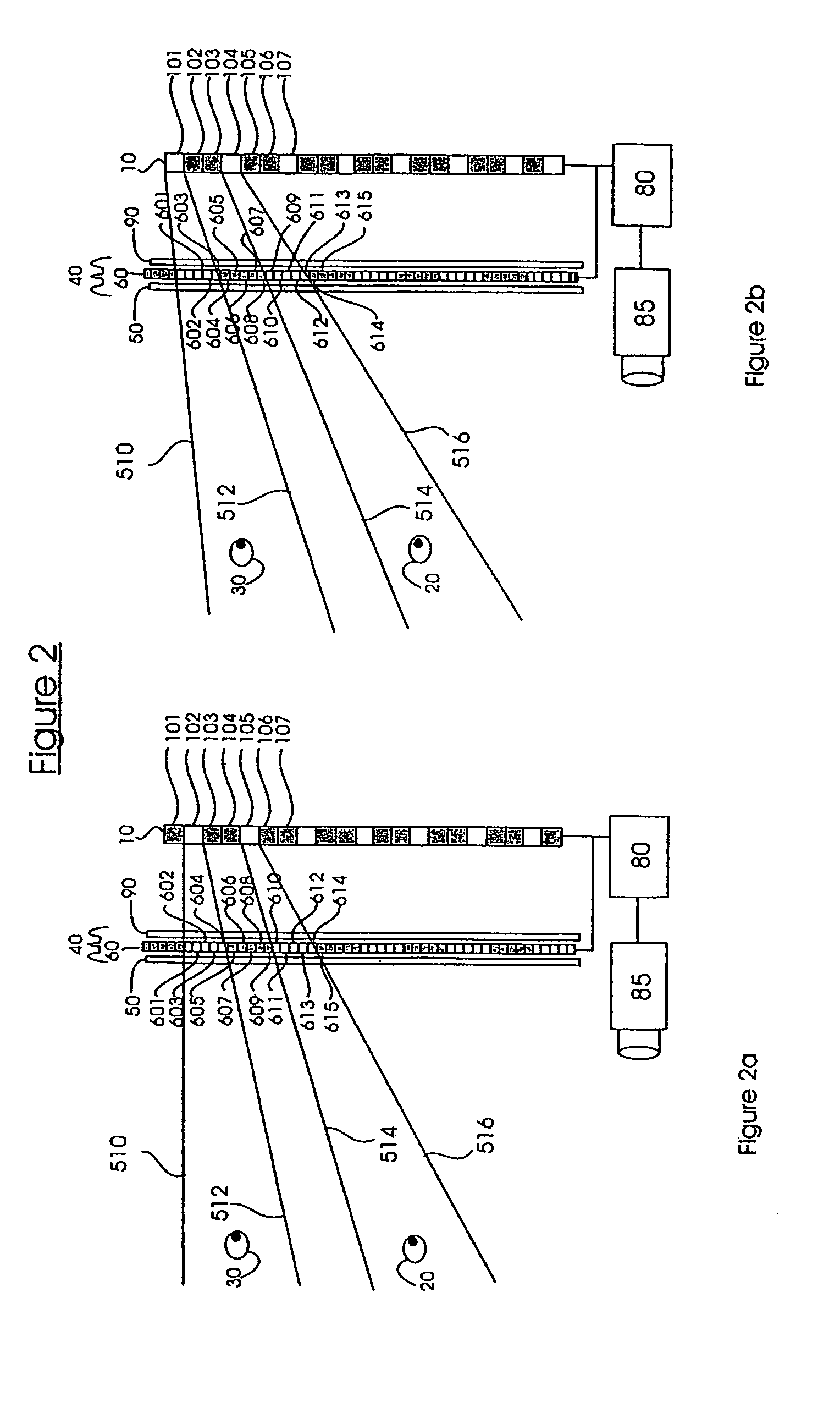
The present invention relates in general to systems for and methods of three-dimensional viewing of displays and projections. One embodiment two layers (50, 90) are uniform polarizing filters and a birefringent layer with individually switchable elements (60) is sandwiched between them. Together these layers (50, 60, 90) constitute a parallax layer (40). This parallax layer (40) is located at a certain distance from a display (10). This placement, and the existence of opaque areas on the parallax layer (40) which permits to a viewer see a three-dimensional image. The individual elements (601–615) of the birefringent layer (60) are controlled by a control element (80), which is in communication with a head-tracking sensor (85). This allows the individual elements (601–615) of the birefringent layer (60) to be selectively turned on and off according to the position of the viewer's head.
Owner:DISPLAY VECTORS LLC +1
Apparatus and method for production of three-dimensional models by spatial light modulator
InactiveUS6051179AFacilitate cross-linkingHigh mechanical strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnalogue computers for control systemsSpatial light modulatorWide beam
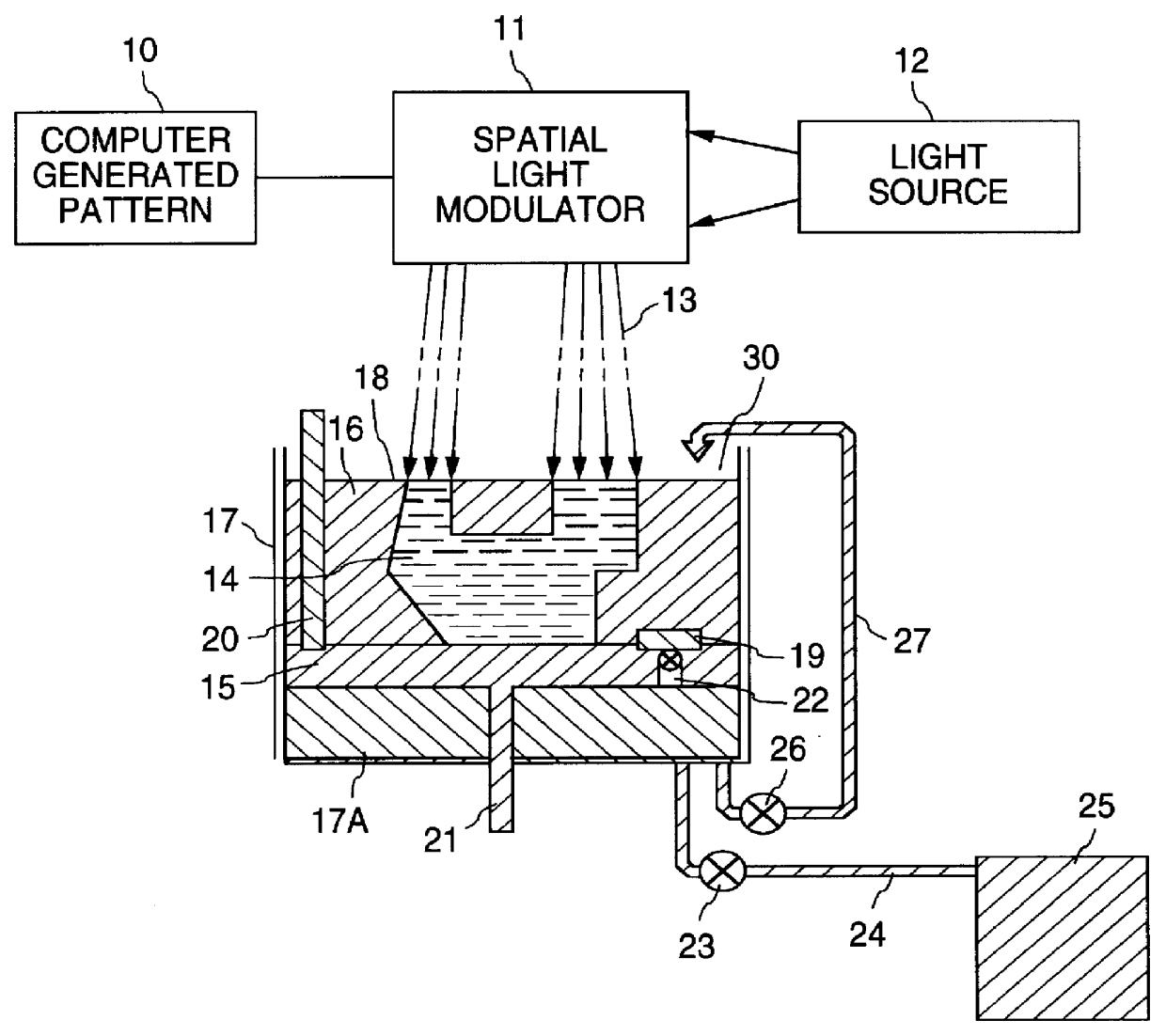
An apparatus and the method of its operation for rapid prototyping of a three-dimensional object which includes a radiant energy source of a wide beam of radiant energy of suitable intensity and wavelength for curing a layer of photo-curable resin contained in an open vat, a spatial light modulator (SLM) having an array of pixel elements which are individually digitally controllable by a computer, for modulating the radiant energy beam projected from the radiant energy source on a pixel by pixel basis, to form a series of time sequential images of the cross-sectional laminae of the object, an optical system for focusing each image formed by the SLM, one at a time, onto successive layers of photo-curable resin for predetermined exposure times to thereby form stacked laminae of cured resin, each lamina of cured resin being in the shape of a different one of the cross-sectional laminae, and a piston support for lowering each lamina of cured resin after it is formed by the SLM and for depositing a layer of resin corresponding to the thickness of one cross sectional lamina of the three-dimensional object before the step of projecting a new image by the SLM. The SLM, the piston support for lowering, and the optical system operate repeatedly and sequentially until a complete copy of the object is thereby produced.
Owner:GLOBAL FILTRATION SYST
Projection of subsurface structure onto an object's surface
InactiveUS20060122515A1Increase awarenessTelevision system detailsDiagnostics using lightVisibilityVideo image
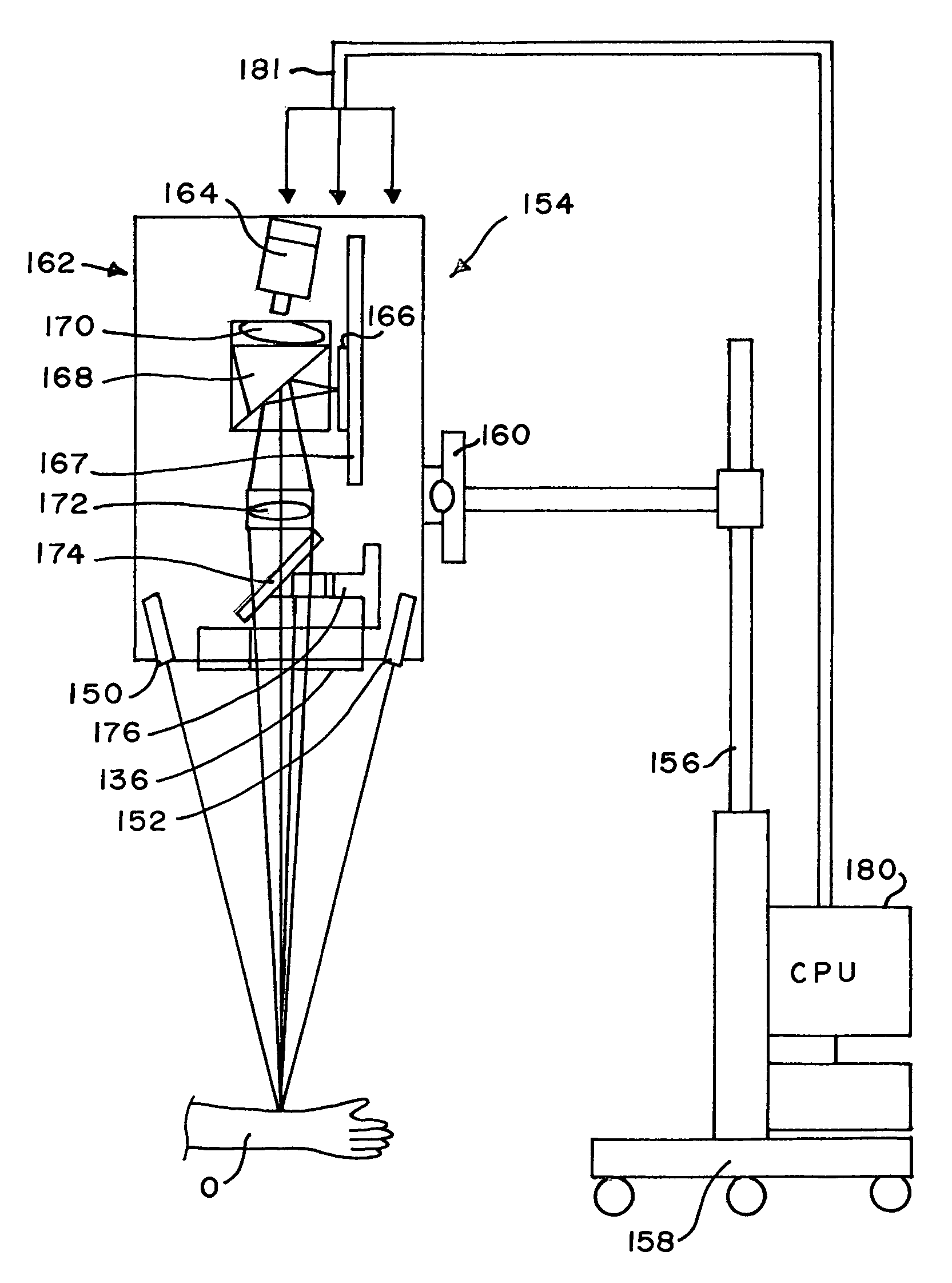
An imaging system illuminates an object with infrared light to enhance visibility of buried structure beneath the surface of the object, and projects a visible light image of the buried structure onto the surface of the object. The system may include an infrared light source for generating the infrared light and a structure for diffusing the infrared light. The diffusing structure may include one or more layers of diffusing material for diffusing the light. The system further includes a video imaging device for receiving the infrared light reflected from the object and for generating a video image of the buried structure based on the reflected infrared light. The buried structure may be a subcutaneous blood vessel. A calibration procedure is described as well as embodiments for ensuring that the object is maintained in focus at the correct distance.
Owner:CHRISTIE MEDICAL HLDG
Image capture and integrated display apparatus
InactiveUS20080165267A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging lensElectronic component
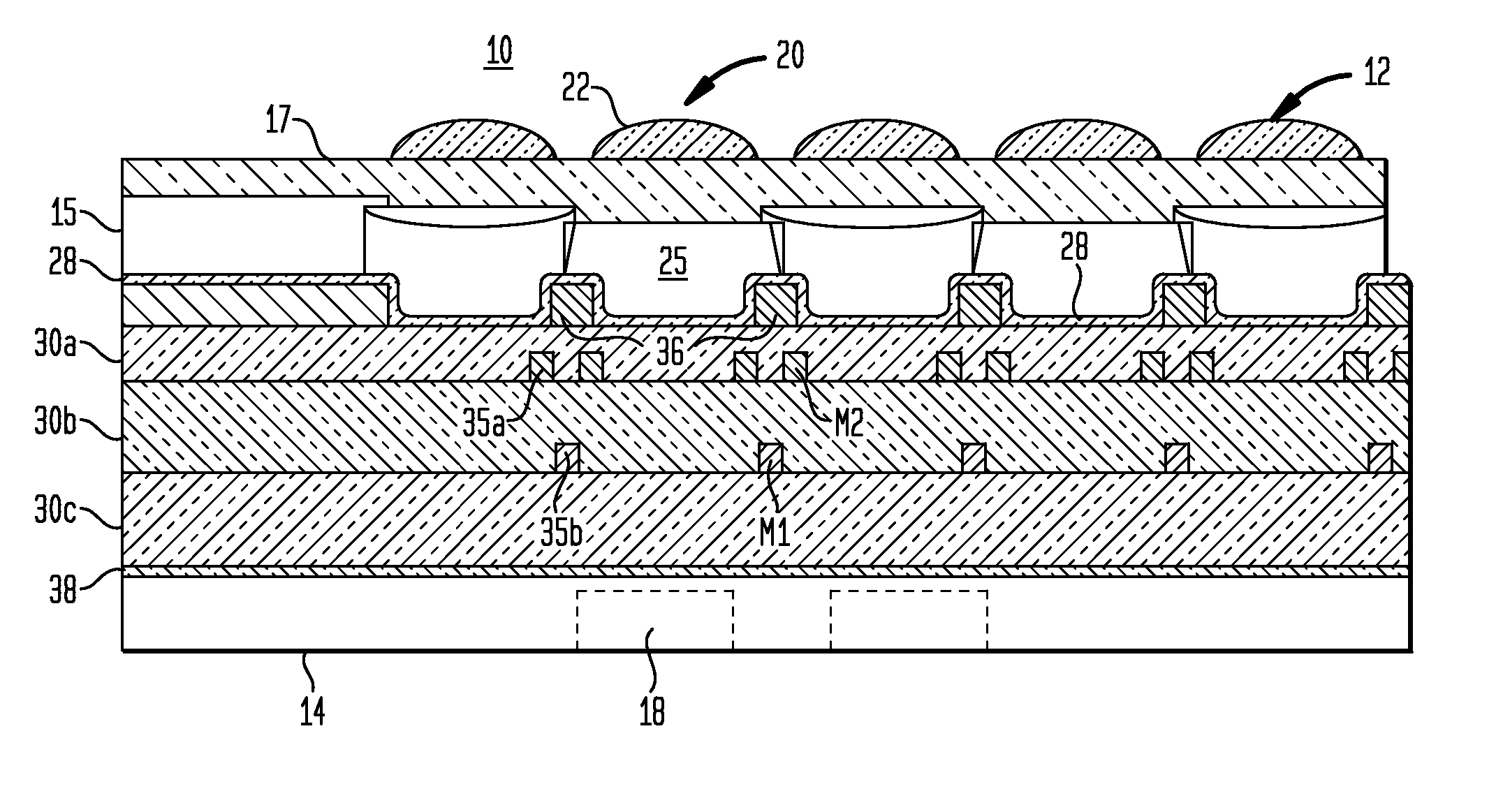
An integrated imaging apparatus is disclosed for displaying images of a scene, including an electronic display having a display pixel that is used to display image content, the display pixel having a substrate, one-or-more electronic component(s) formed over a distinct portion of the substrate, a first electrode connected to the electronic component(s) having a first transparent portion formed over the substrate but not over the electronic component(s) and a second reflective portion formed over the electronic component(s), a light-emitting layer(s) formed over the first electrode, and a second transparent electrode formed over the light-emitting layers; and at least one image capture device which captures an image, wherein the image capture device has at least an imaging lens and an image sensor array; and wherein the image capture device receives light through the transparent portion of the first electrode, and wherein the display pixel also provides light to display image content.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
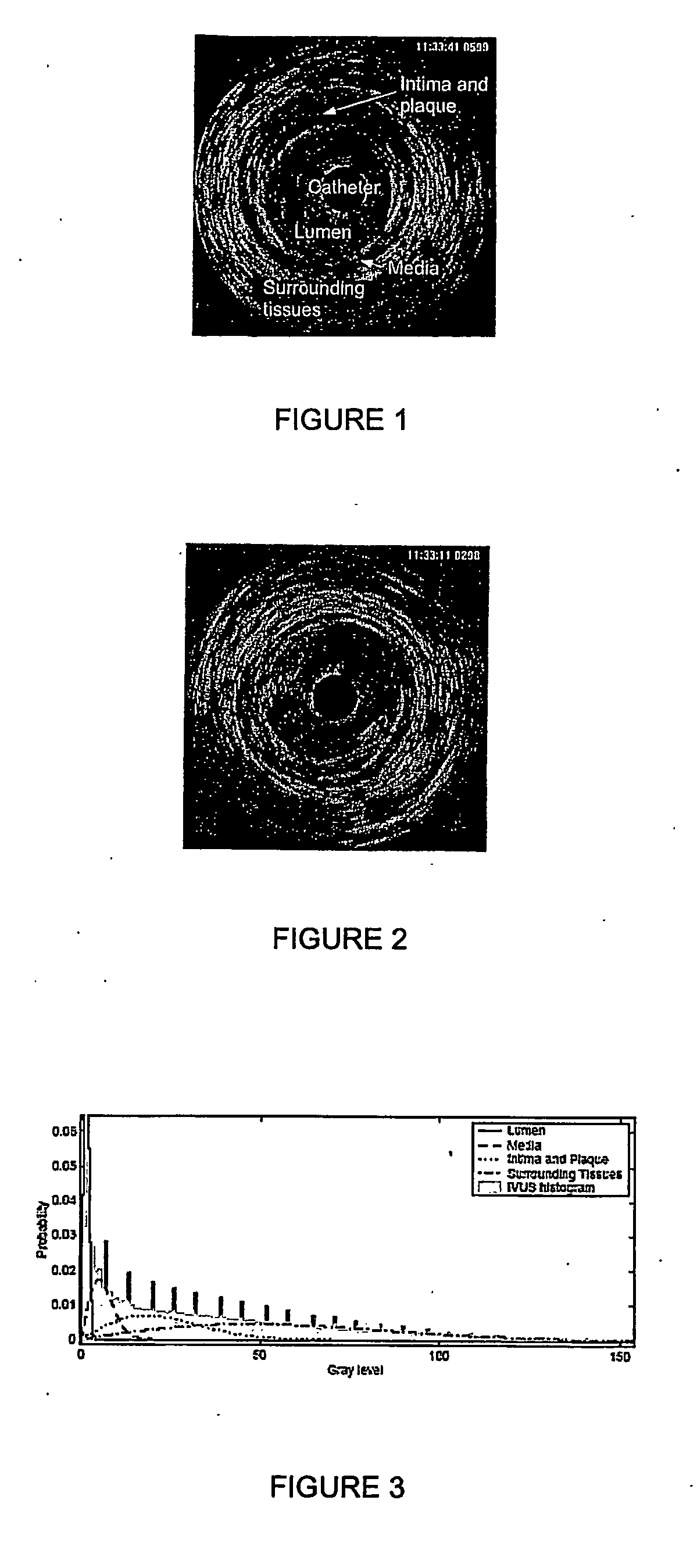
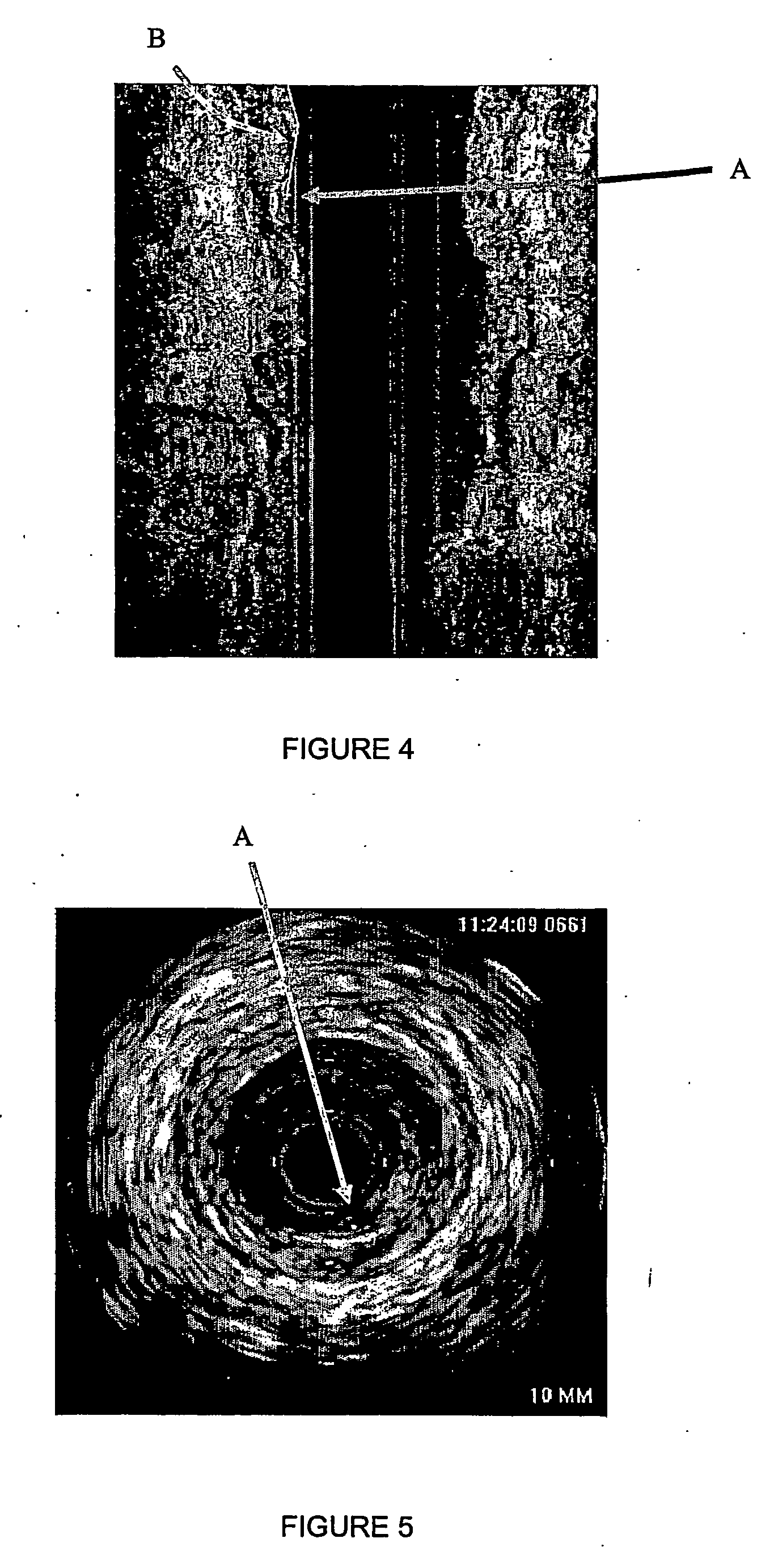
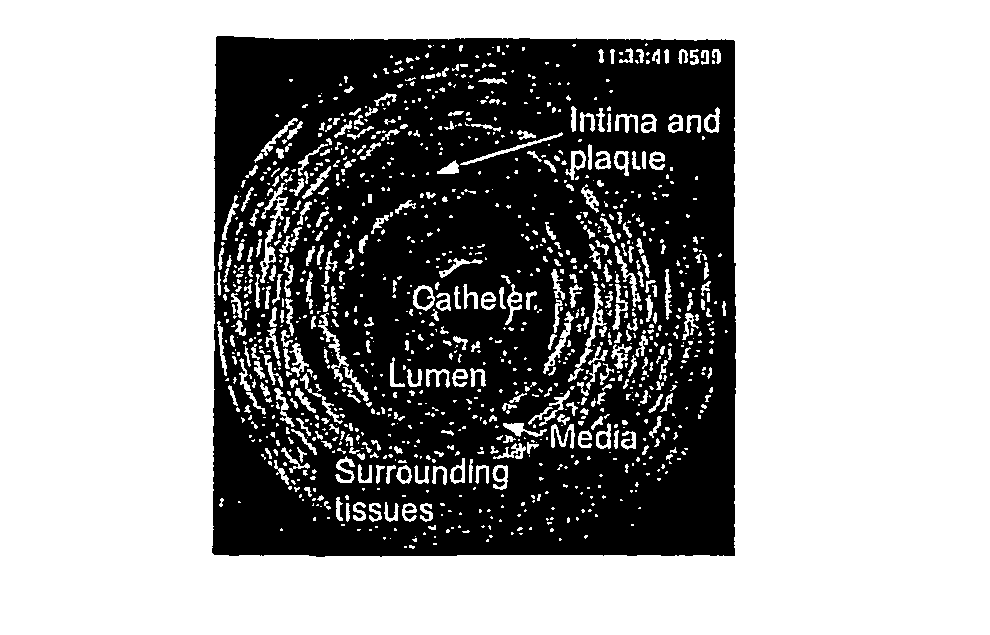
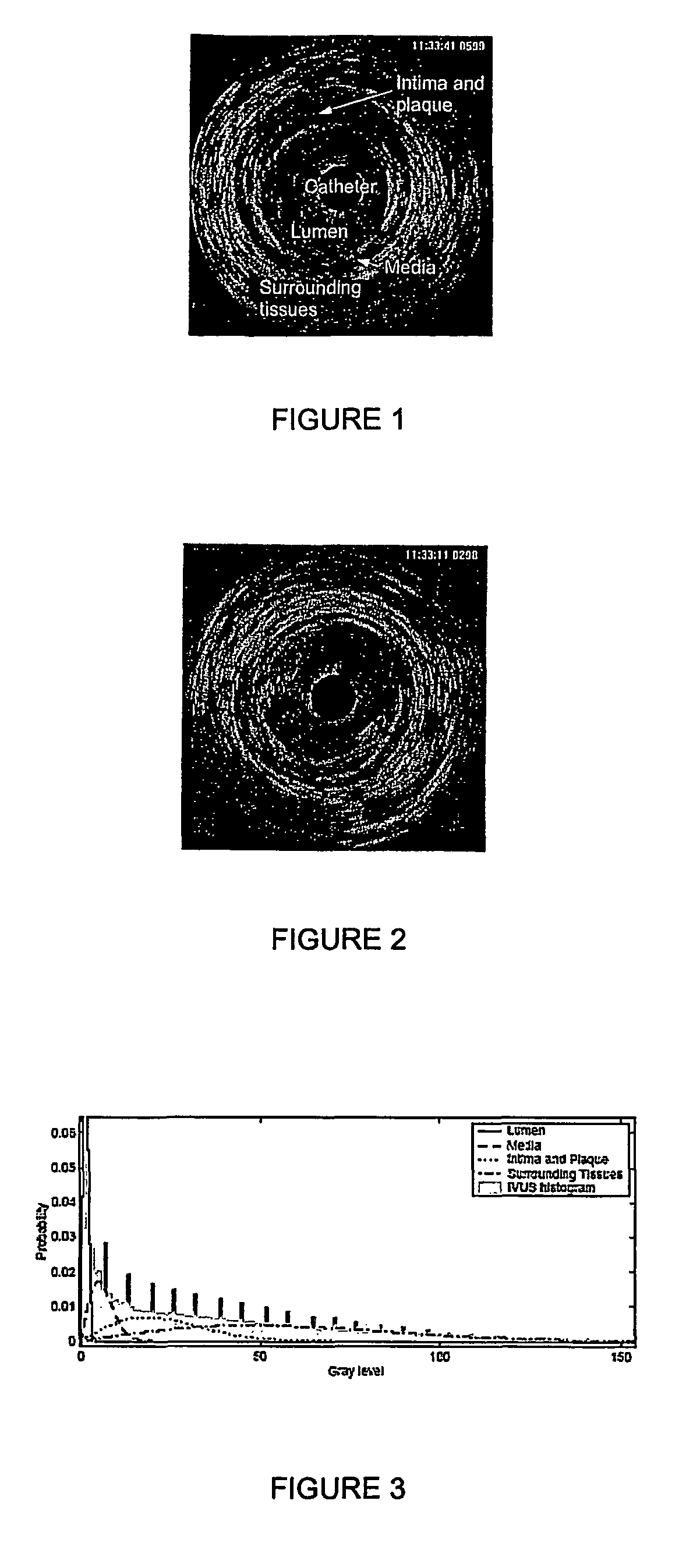
Automatic multi-dimensional intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method
The present invention generally relates to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) image segmentation methods, and is more specifically concerned with an intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method for characterizing blood vessel vascular layers. The proposed image segmentation method for estimating boundaries of layers in a multi-layered vessel provides image data which represent a plurality of image elements of the multi-layered vessel. The method also determines a plurality of initial interfaces corresponding to regions of the image data to segment and further concurrently propagates the initial interfaces corresponding to the regions to segment. The method thereby allows to estimate the boundaries of the layers of the multi-layered vessel by propagating the initial interfaces using a fast marching model based on a probability function which describes at least one characteristic of the image elements.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP +1
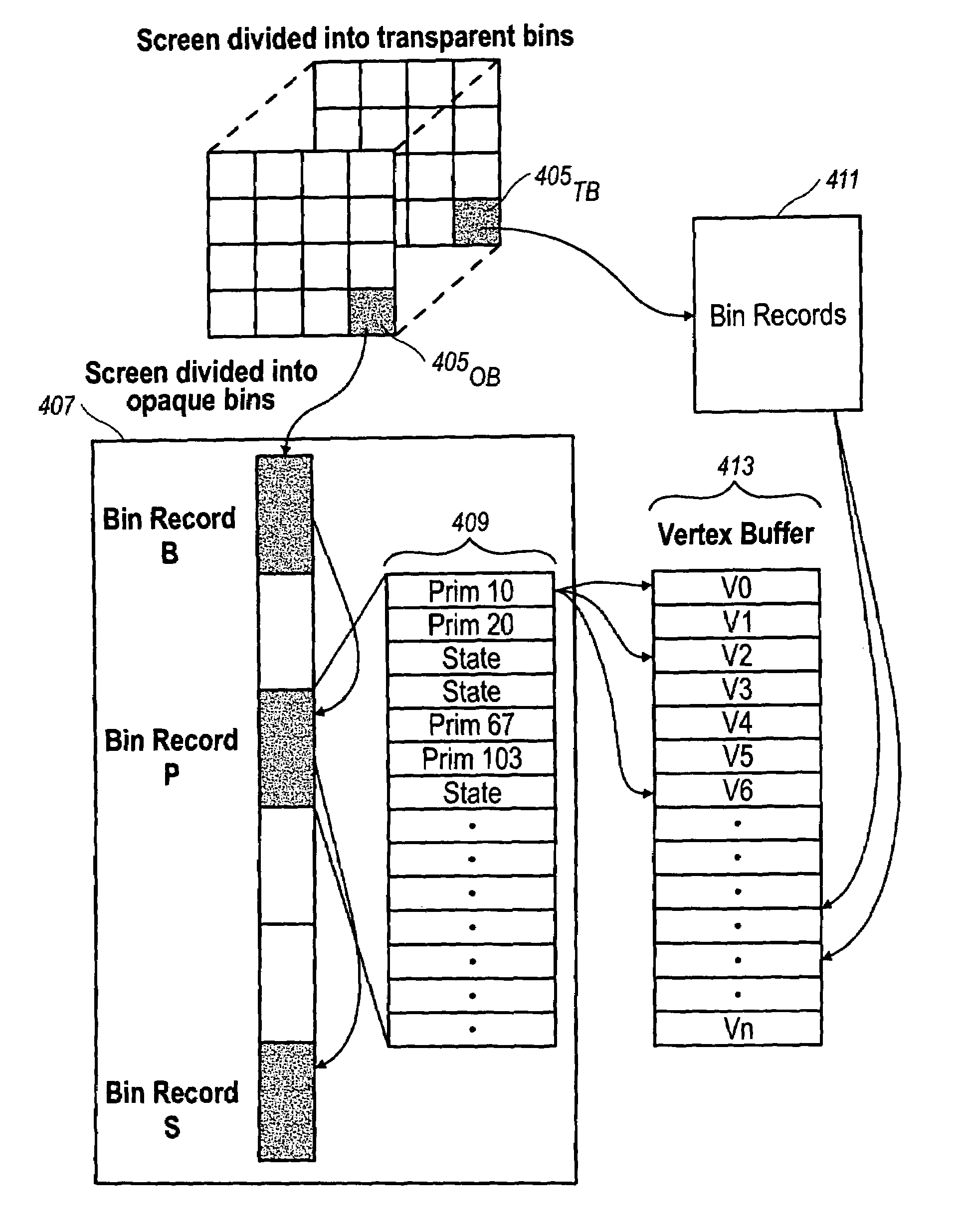
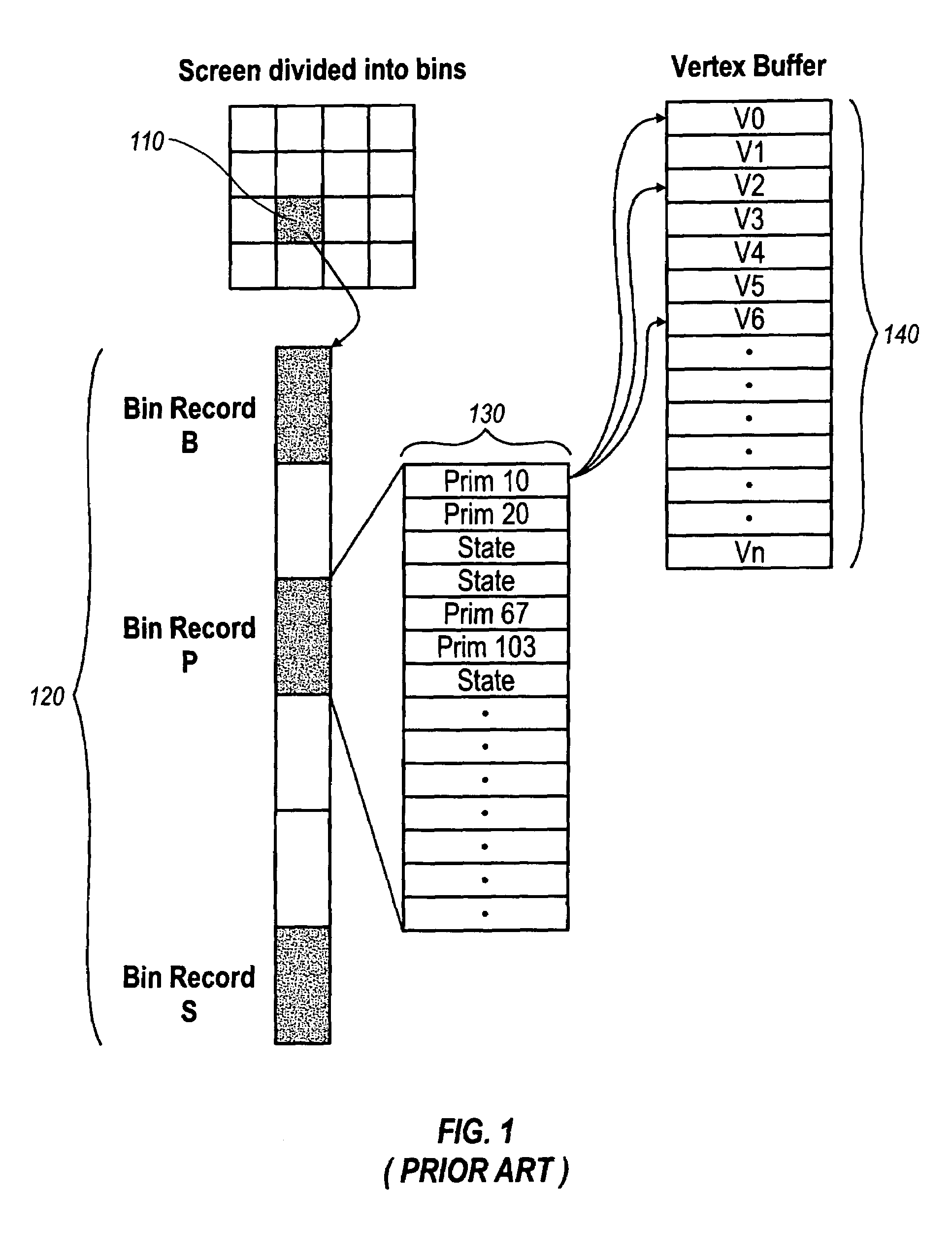
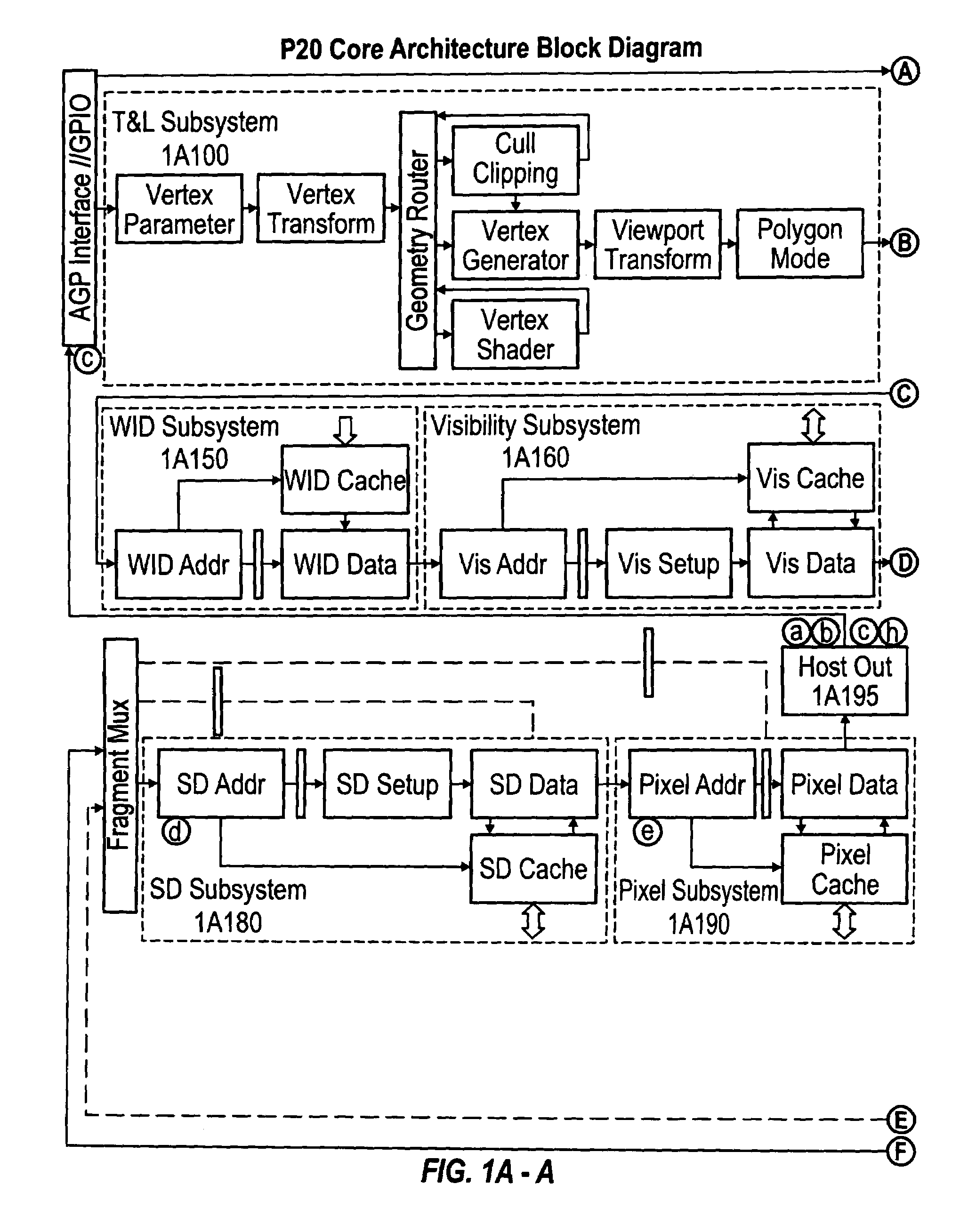
Order-independent 3D graphics binning architecture
ActiveUS7505036B1Increased complexityIncrease frame rateDetails involving image processing hardwareElectric digital data processingGraphicsDepth peeling
A binning architecture that allows opaque and transparent primitives to be segregated automatically into pairs of bins covering the same bin rectangle on the screen. When the frame is complete, the opaque bin will be rendered first and then the transparent bin will be rendered repeatedly using the depth peeling algorithm until all the layers have been resolved. This will happen automatically without requiring the application to isolate and store the transparent primitives until all of the opaque primitives have been rendered or submit the transparent primitives repeated until all of the transparent layers have been resolved.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Lecture method and device in virtual lecture room
InactiveUS20130314421A1Improve concentrationCost lotTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsGraphicsTablet computer
Disclosed in a lecture method in which a presentation content of various inputs (cameras, notebook computer, motion pictures) is combined with a virtual lecture room using a Chromakey or TOF technique, so displaying a lecture and a presentation content on one screen with a beautiful background studio screen. The lecture method of the present invention comprises (1) a virtual lecture room editing and storing step in which a plurality of 3D background layers are provided, edited and designed, the lecturer and the presentation content are arranged in the virtual lecture room and are displayed on various screens, (2) a step in which the image of the lecture of the lecturer is taken using a single or a plurality of cameras, (3) a step in which the image of only a lecturer is extracted from the taken lecture images using a Chromakey technique in a form of a lecturer layer, (4) a step in which a lecture material layer and the lecturer layer are combined with the virtual lecture room graphic background layer, with the lecture material layer indicating at least one lecture material, and (5) a step in which the final image is combined and outputted to the display apparatus when the lecturer writes using the tablet.
Owner:KIM E E
MOS type image sensor
A MOS type image sensor has an image area that consists of a matrix of pixels and a peripheral circuitry area that drives the image area. To make the MOS type image sensor finer, each of the pixels consists of a second p-well region having a lower impurity concentration than a first p-well region disposed in the peripheral circuitry area; a photodiode having a first main electrode region made of the second p-well region and a second main electrode region formed as a first n-diffusion layer disposed at the surface of the second p-well region; a read transistor having a first main electrode region made of the first n-diffusion layer, a second main electrode region formed as a second n-diffusion layer disposed at the surface of the second p-well region, a gate insulation film disposed on the surface of the second p-well region between the first and second n-diffusion layers, and a gate electrode disposed on the gate insulation film and connected to a read signal line; and an amplification transistor disposed in a third p-well region, having a gate electrode connected to the second main electrode region of the read transistor, a first main electrode region connected to an output signal line, and a second main electrode region. Since the impurity concentration of the second p-well region is low, scaled design rules are employable without causing "white pixels", sensitivity deterioration, signal read voltage increase, or short-channel effect.
Owner:NORTH PLATE SEMICON LLC
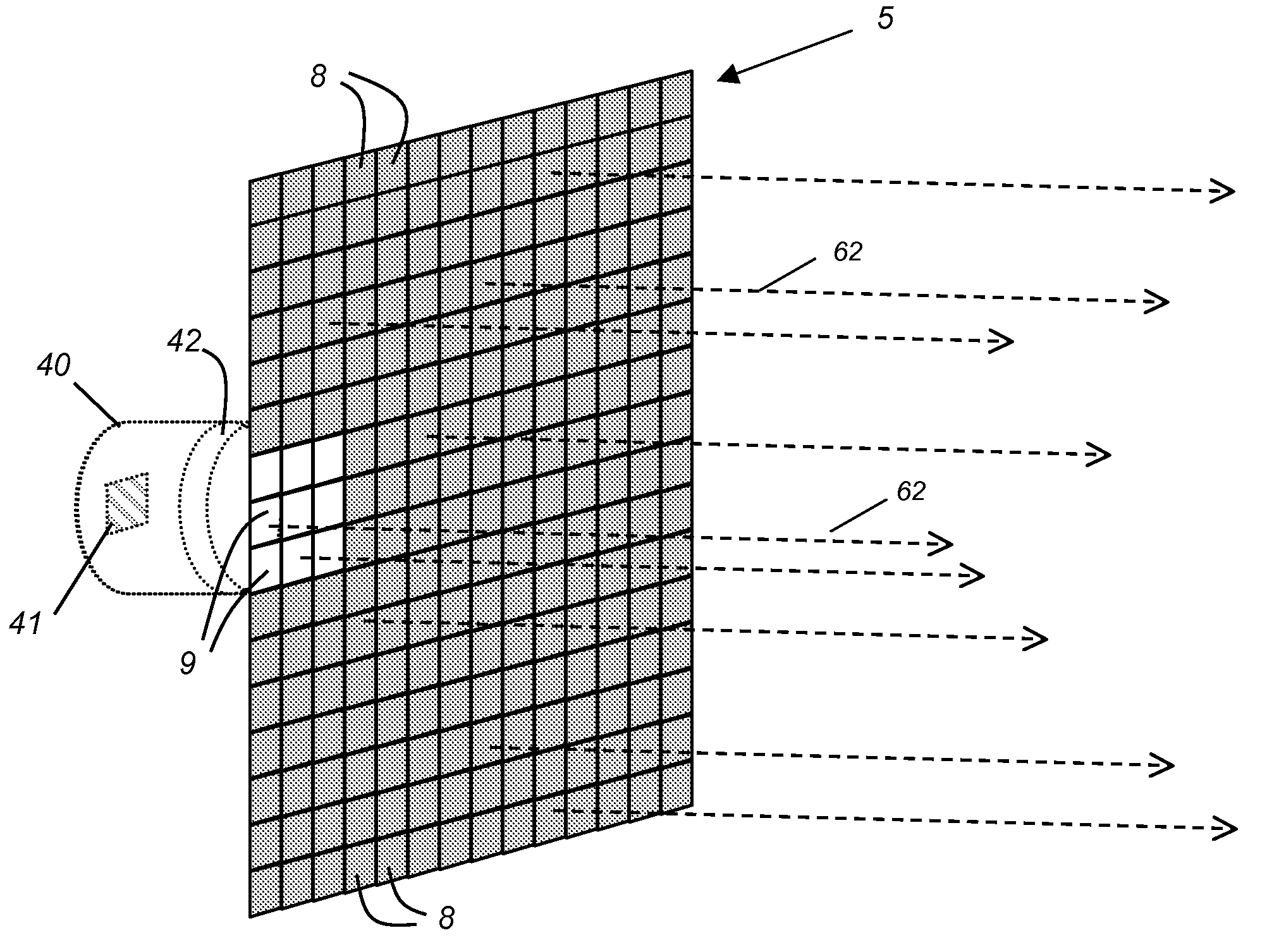
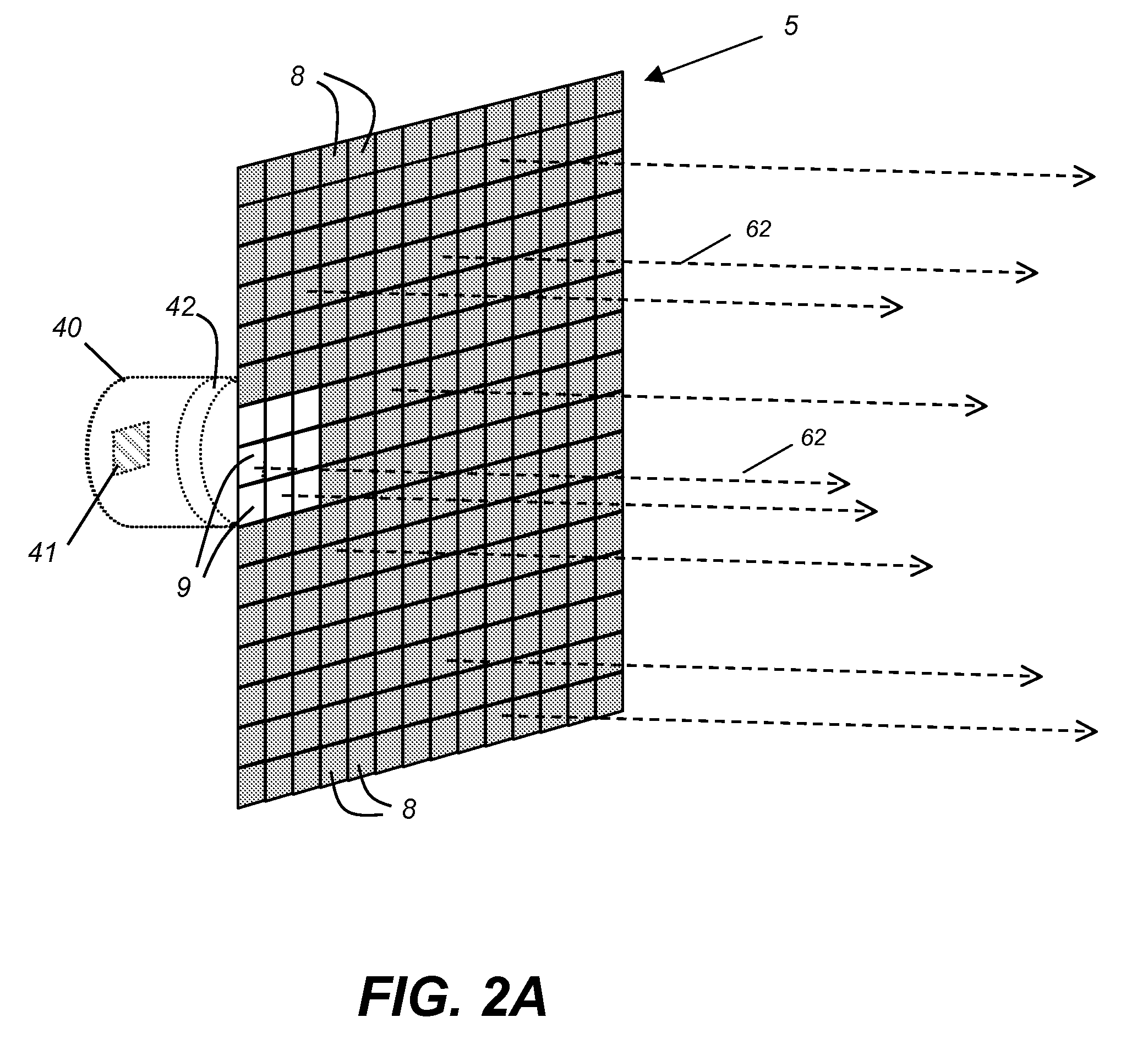
Multispectral imaging for quantitative contrast of functional and structural features of layers inside optically dense media such as tissue
InactiveUS20050273011A1Easy to measureImprove analysisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTelevision system detailsCalorescenceWavelength
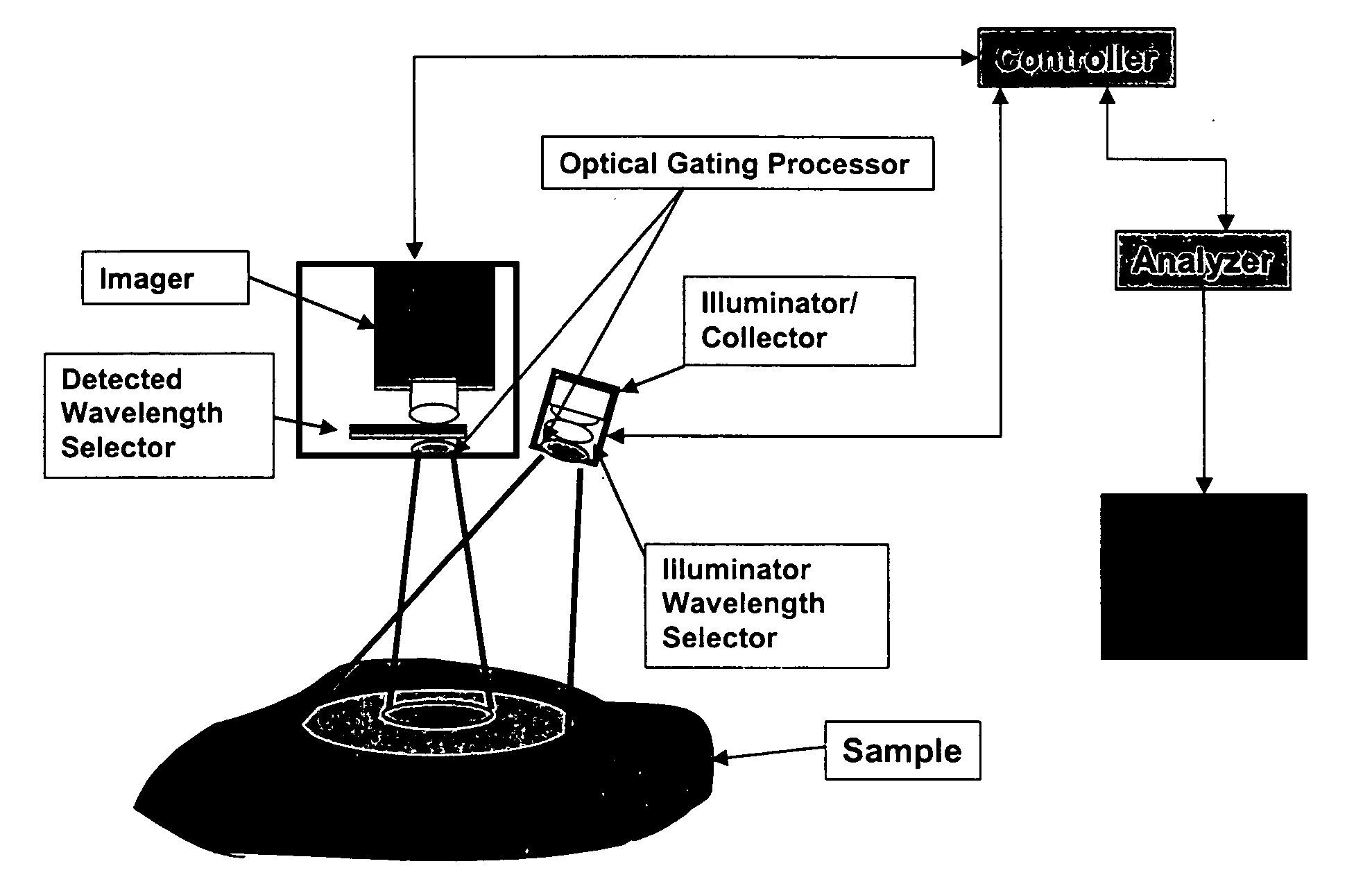
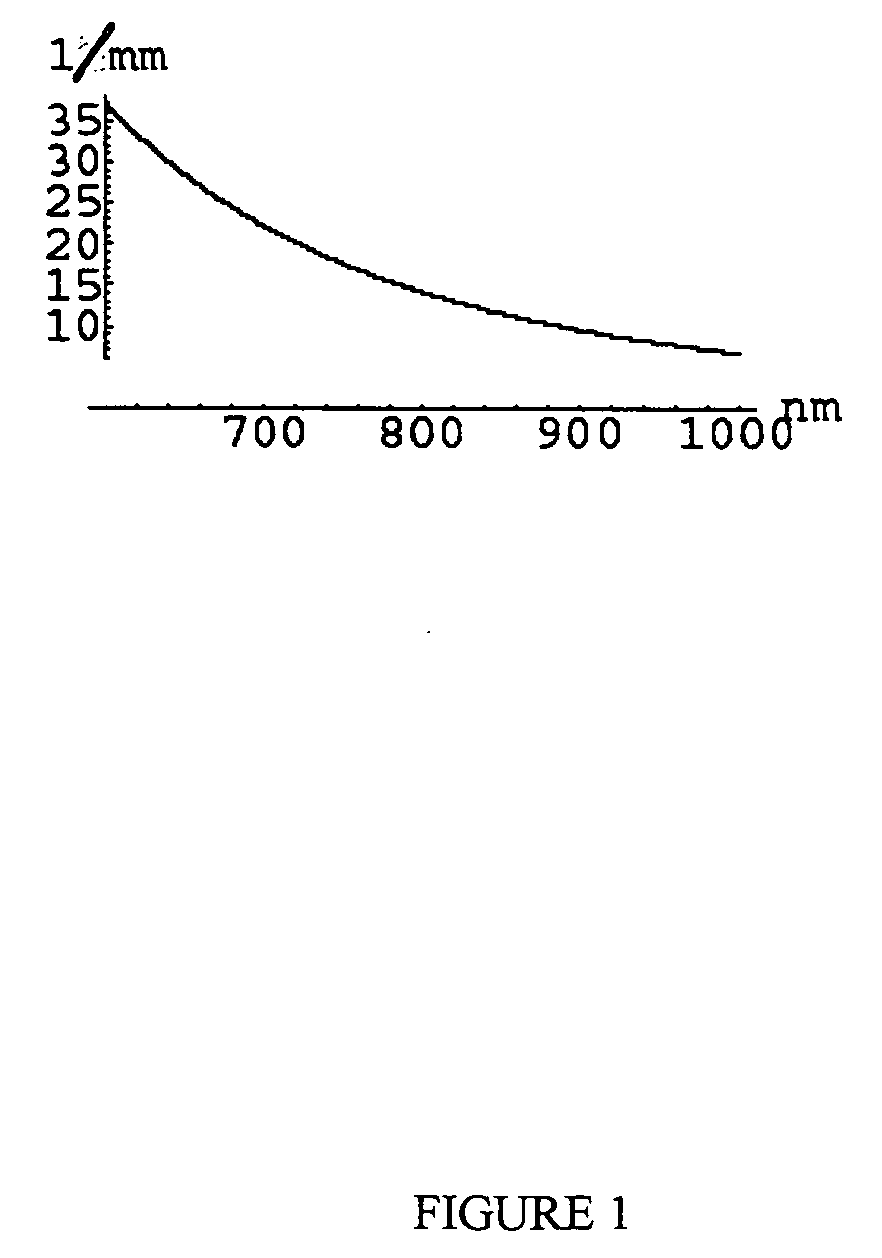
A method for the evaluation of target media parameters in the visible and near infrared is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a light source, an illuminator / collector, optional illumination wavelength selector, an optional light gating processor, an imager, detected wavelength selector, controller, analyzer and a display unit. The apparatus illuminates an in situ sample of the target media in the visible through near infrared spectral region using multiple wavelengths and gated light. The sample absorbs some of the light while a large portion of the light is diffusely scattered within the sample. Scattering disperses the light in all directions. A fraction of the deeply penetrating scattered light exits the sample and may be detected in an imaging fashion using wavelength selection and an optical imaging system. The method extends the dynamic range of the optical imager by extracting additional information from the detected light that is used to provide reconstructed contrast of smaller concentrations of chromophores. The light detected from tissue contains unique spectral information related to various components of the tissue. Using a reiterative calibration method, the acquired spectra and images are analyzed and displayed in near real time in such a manner as to characterize functional and structural information of the target tissue.
Owner:APOGEE BIODIMENSIONS
Method and apparatus for high-speed thickness mapping of patterned thin films
InactiveUS20020030826A1Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMechanical engineeringImaging spectrometer
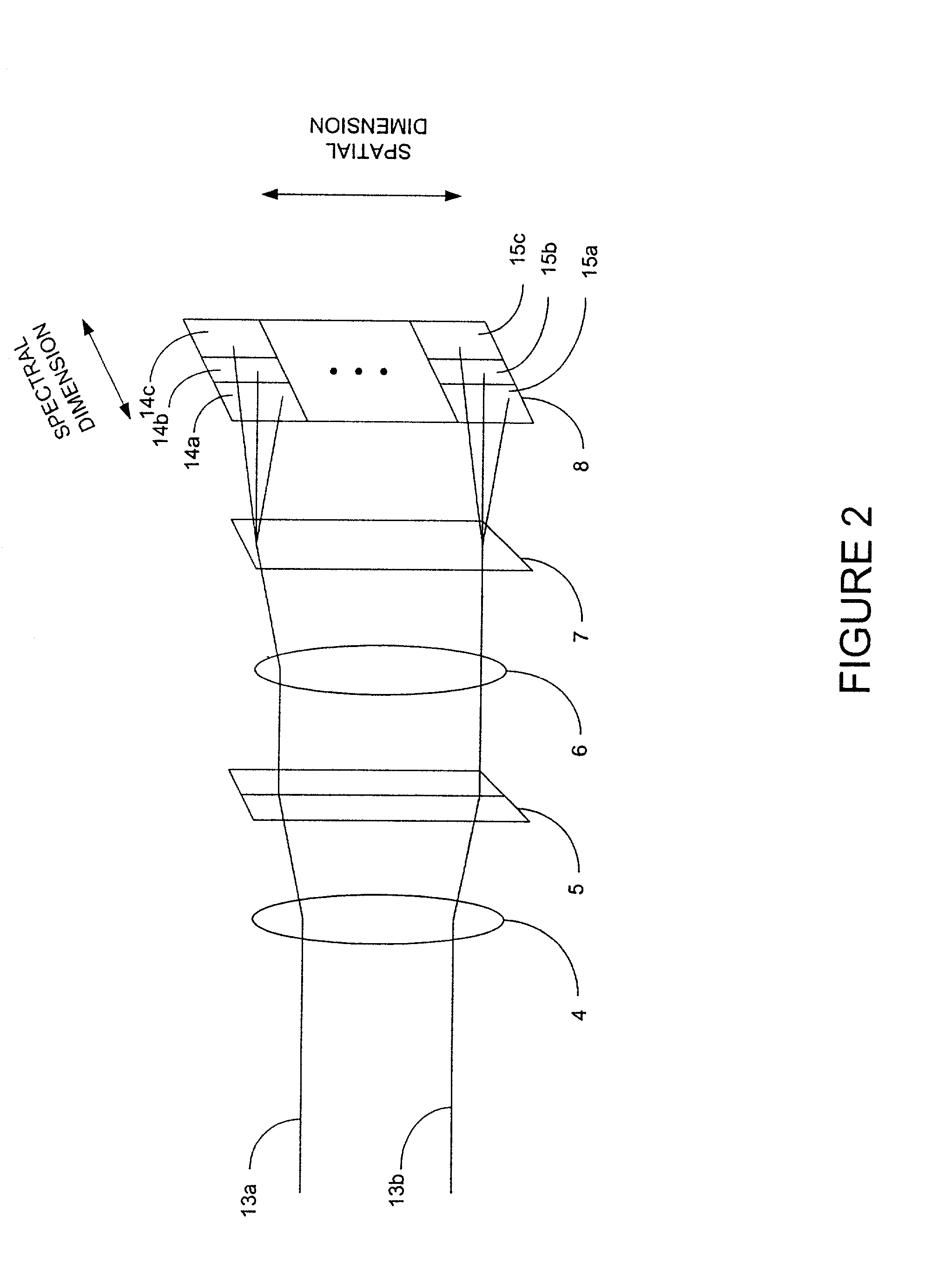
A system is described that permits high-speed, high-resolution mapping of thicknesses (or other properties) of layers on patterned semiconductor wafers. The system comprises one or more spectrometers that each simultaneously image a plurality of spatial locations. In one example, the spectrometer comprises a two-dimensional CCD imager with one axis of the imager measuring spectral data and the other axis measuring spatial data. Spectral reflectance or transmission of the patterned wafer under test is obtained by passing the wafer under (or over) the imaging spectrometer(s) and taking sequential reflectance or transmission images for successive pluralities of spatial locations. The resulting spectral reflectance or transmission map can then be analyzed at discrete locations to determine the thicknesses or other properties of the layers at those locations.
Owner:FILMETRICS
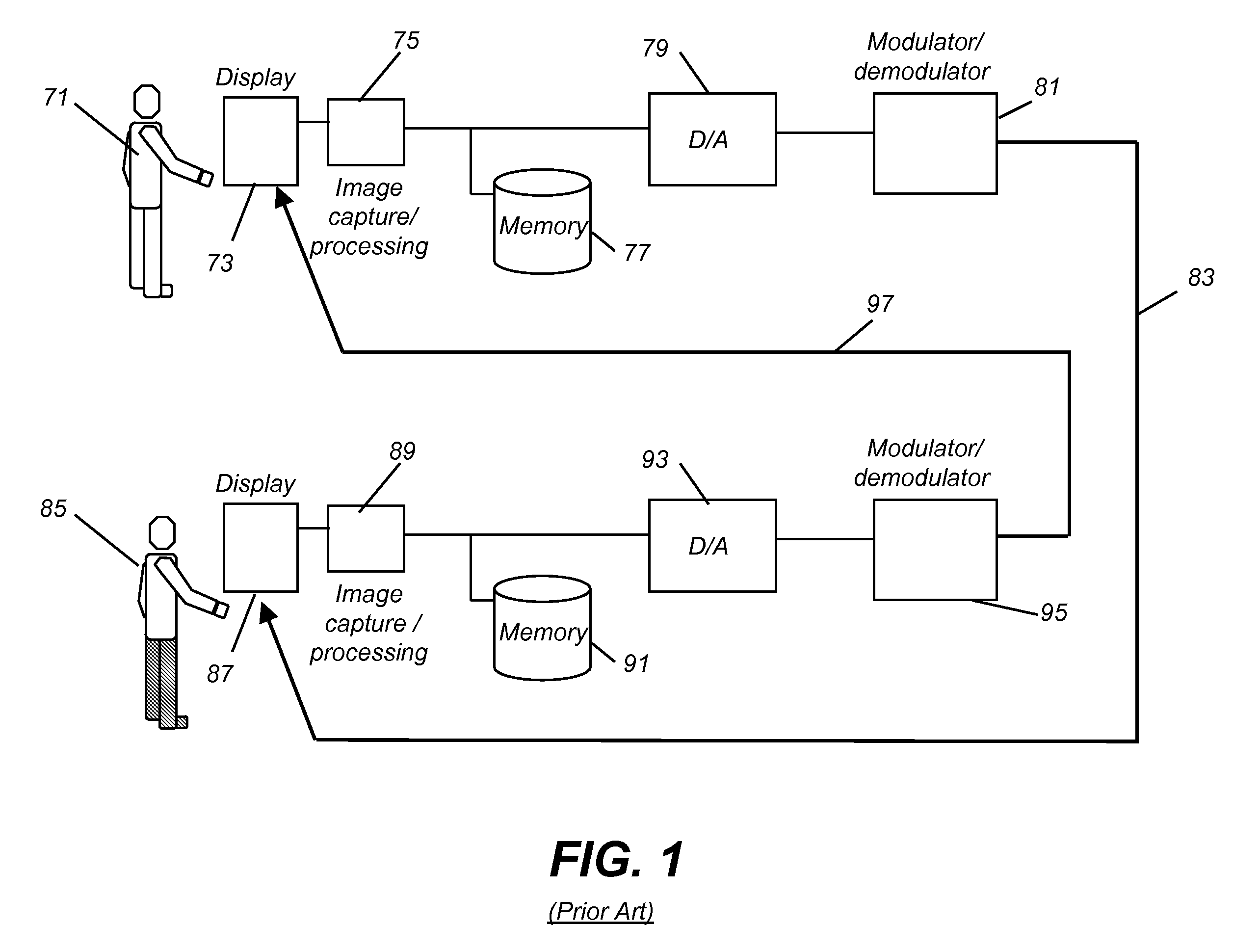
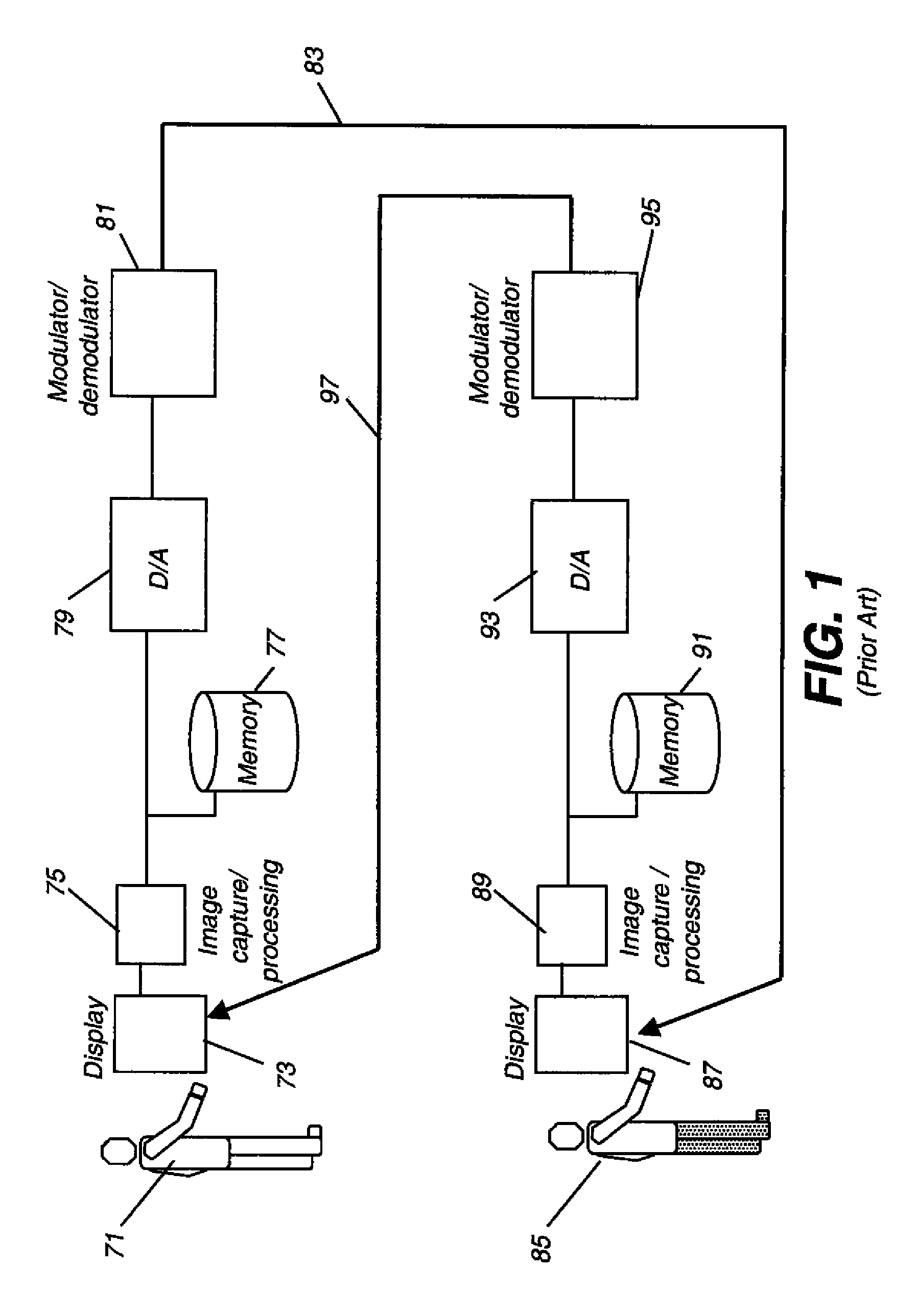
Digital imaging system for evidentiary use
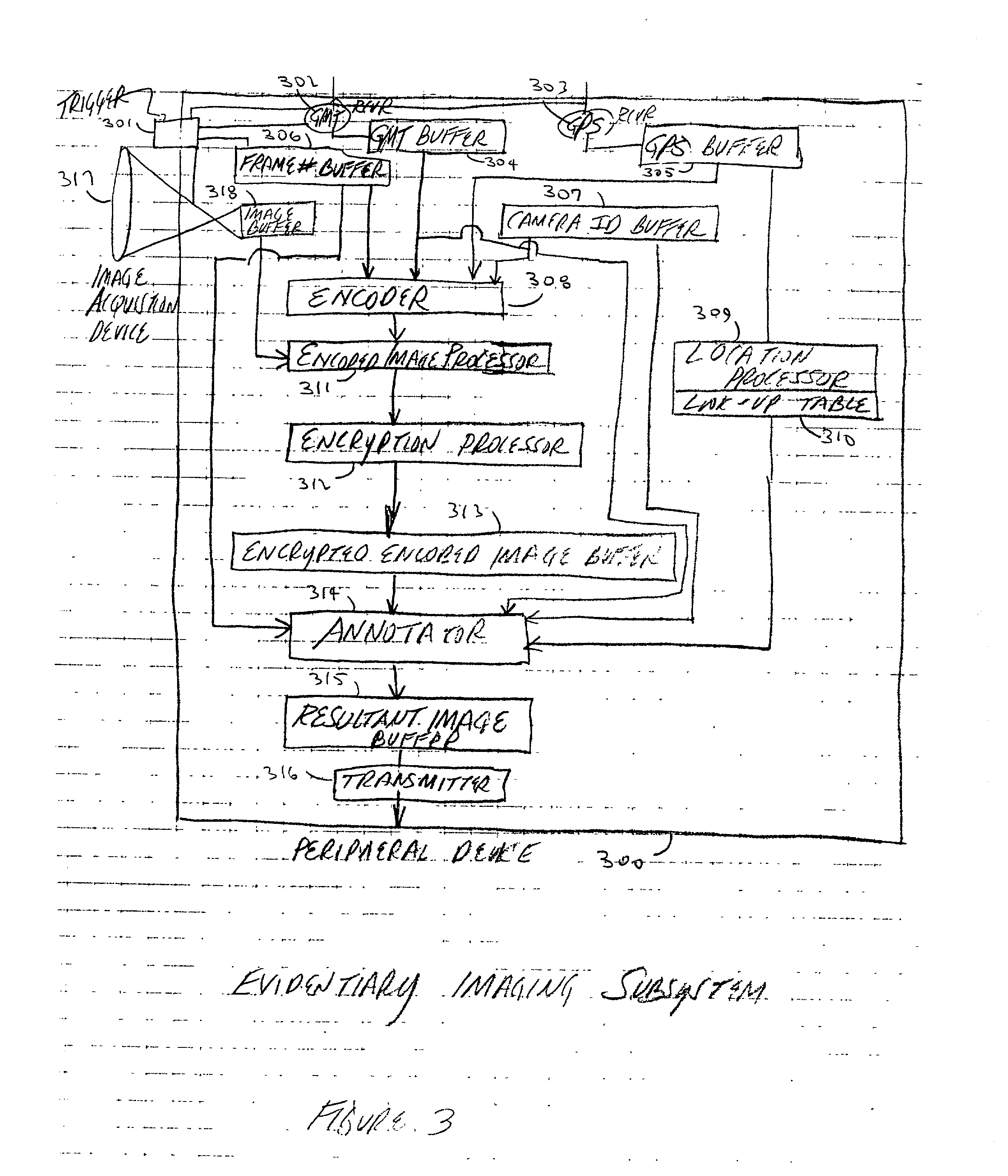
InactiveUS20010033661A1Separate controlImprove securityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareDigital imaging
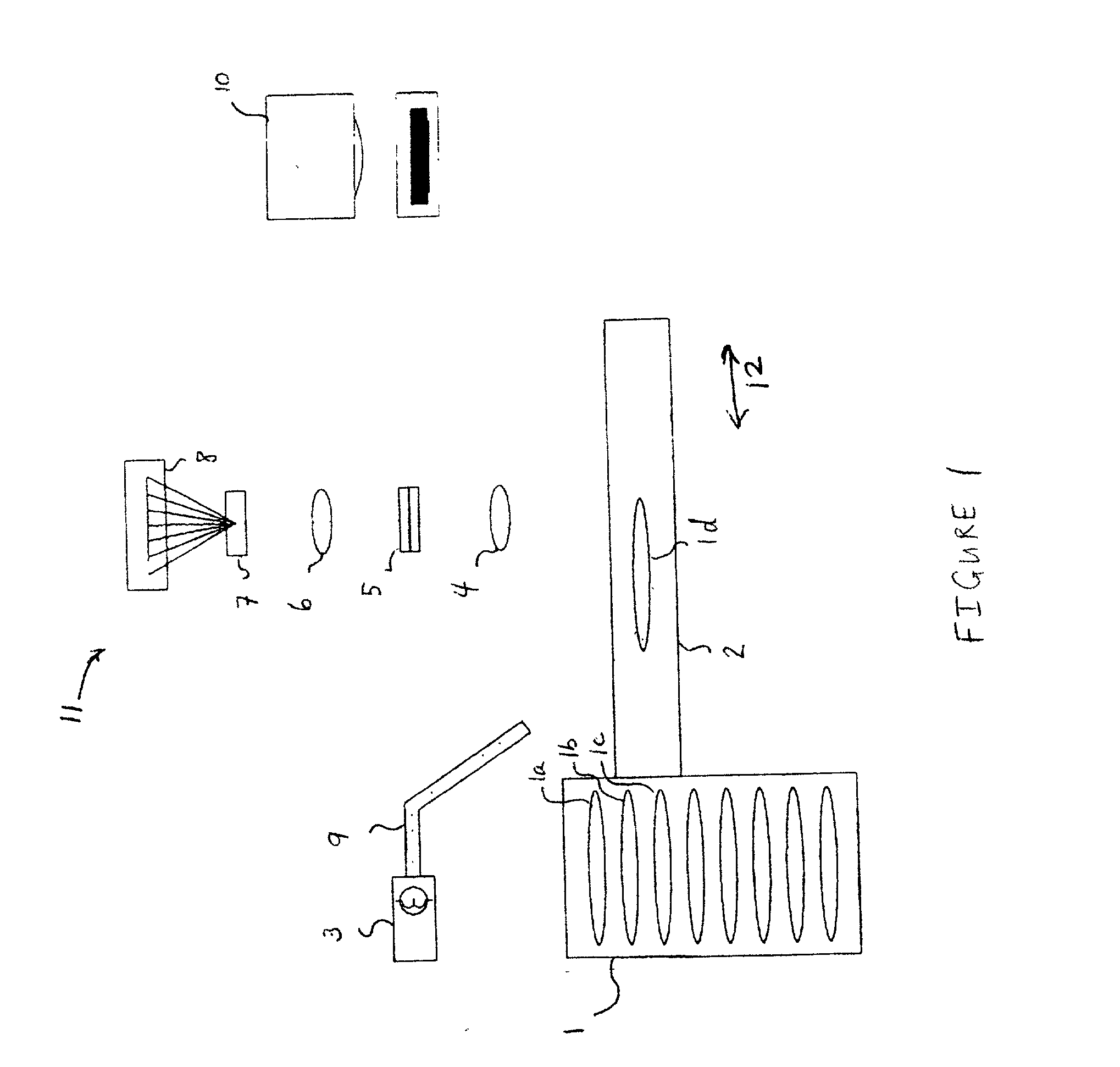
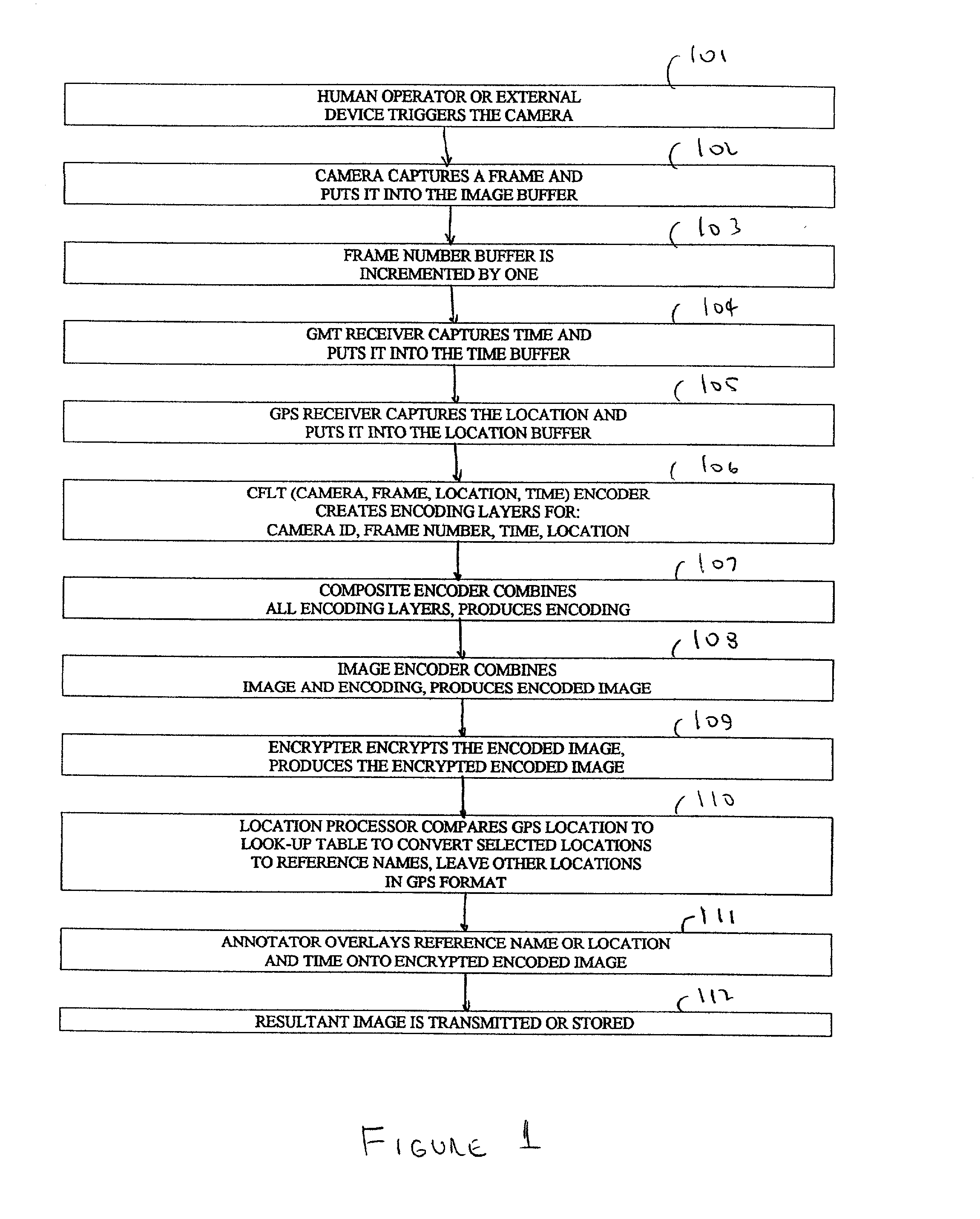
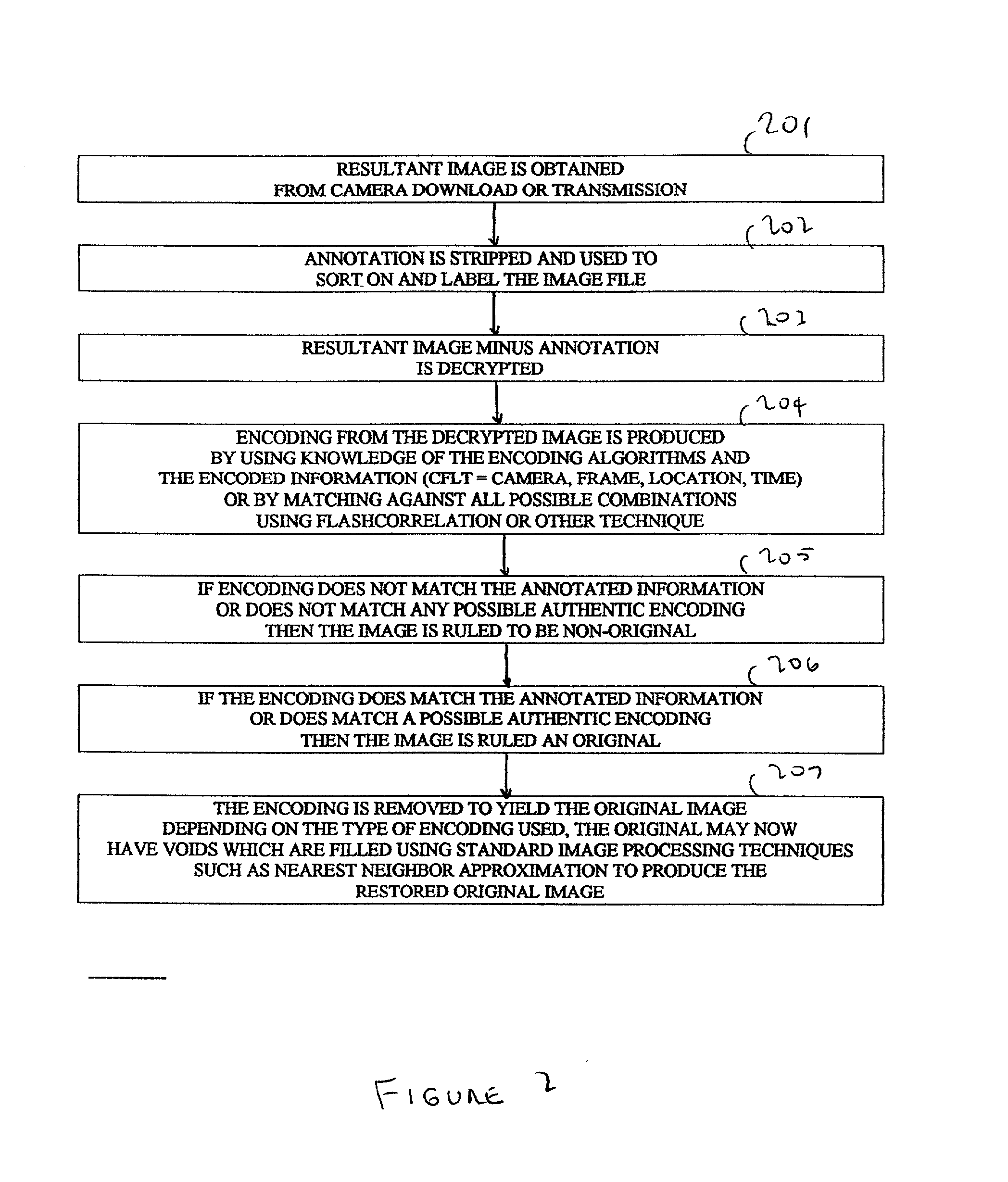
The Evidentiary Imaging System (EIS) provides secure storage or transmission of a digital image into which is encoded the date, time, and location at which the image was taken, along with the camera ID and frame number. The encoding is dispersed throughout the image so that the image cannot be modified without distorting the encoding. The image may be encrypted for additional security. Annotation can be superimposed on the encoded or encoded and encrypted image to classify or identify the image to human or automated scanning systems. The annotation can also be used to key the decoding and decryption tasks. The EIS produces imagery which may be authenticated as to originality, time and location of imaging. The imagery may be stored, duplicated, and transmitted while retaining its authenticity. However, any modifications to the image, including any local changes, are readily detected because the encoding will not decode correctly. The EIS is designed to provide imagery which may be used for evidentiary proof of authenticity, ownership, originality, date and time, and location of imaged events. Certain users of EIS systems, such as police forensics labs, may have a central depository for the decoding and decryption keys used with their cameras. Other users may rely upon authentication services provided by the EIS manufacturer or an independent expert in the EIS technique. While many different schemes for encoding and encryption may be used, FlashCorrelation(R) provides a computationally simple and rapid method for encoding each item of information; allowing for separate or total encoding and readout of encoding layers representing: date, time, location, camera ID, and frame number. As covered in the issued FlashCorrelation(R) U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,583,950 and 5,982,932, readout and authentication can be done by one party authorized to have the decoding and decryption schemes, or readout and authentication may require two or more parties.
Owner:MIKOS
Thermal imaging system
A multicolor imaging system is described wherein at least two, and preferably three, different image-fonning layers of a thermal imaging member are addressed at least partially independently by a thermal printhead or printheads from the same surface of the imaging member by controlling the temperature of the thermal printhead(s) and the time thermal energy is applied to the image-forming layers. Each color of the thermal imaging member can be printed alone or in selectable proportion to the other color(s). Novel thermal imaging members are also described.
Owner:ZINK IMAGING
Process for building three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS20120231175A1Deformation MinimizationLiquid surface applicatorsElectrographic process apparatusObject basedEngineering
A process for building three-dimensional objects based on electrophotographic printing is disclosed, comprising the steps of depositing a first layer of powdered base material on a substrate, operating an imaging member, a charging device, an image generating device and an image developing device, in that order, to deliver and deposit filler material onto the layer of powdered base material in an image-wise manner to produce a layer of bonded base material that correspond to the first cross-section of the three-dimensional object being built, repeating all the above steps for as many times as required to form successive layers that constitute the three-dimensional object, said filler material further causing adjacent layers to be bonded with one another; and removing unbonded material to cause the three-dimensional object to appear.
Owner:TAN YU EN
Method of making a microelectronic and/or optoelectronic circuitry sheet
InactiveUS7259106B2Printed electric component incorporationSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsThin membrane
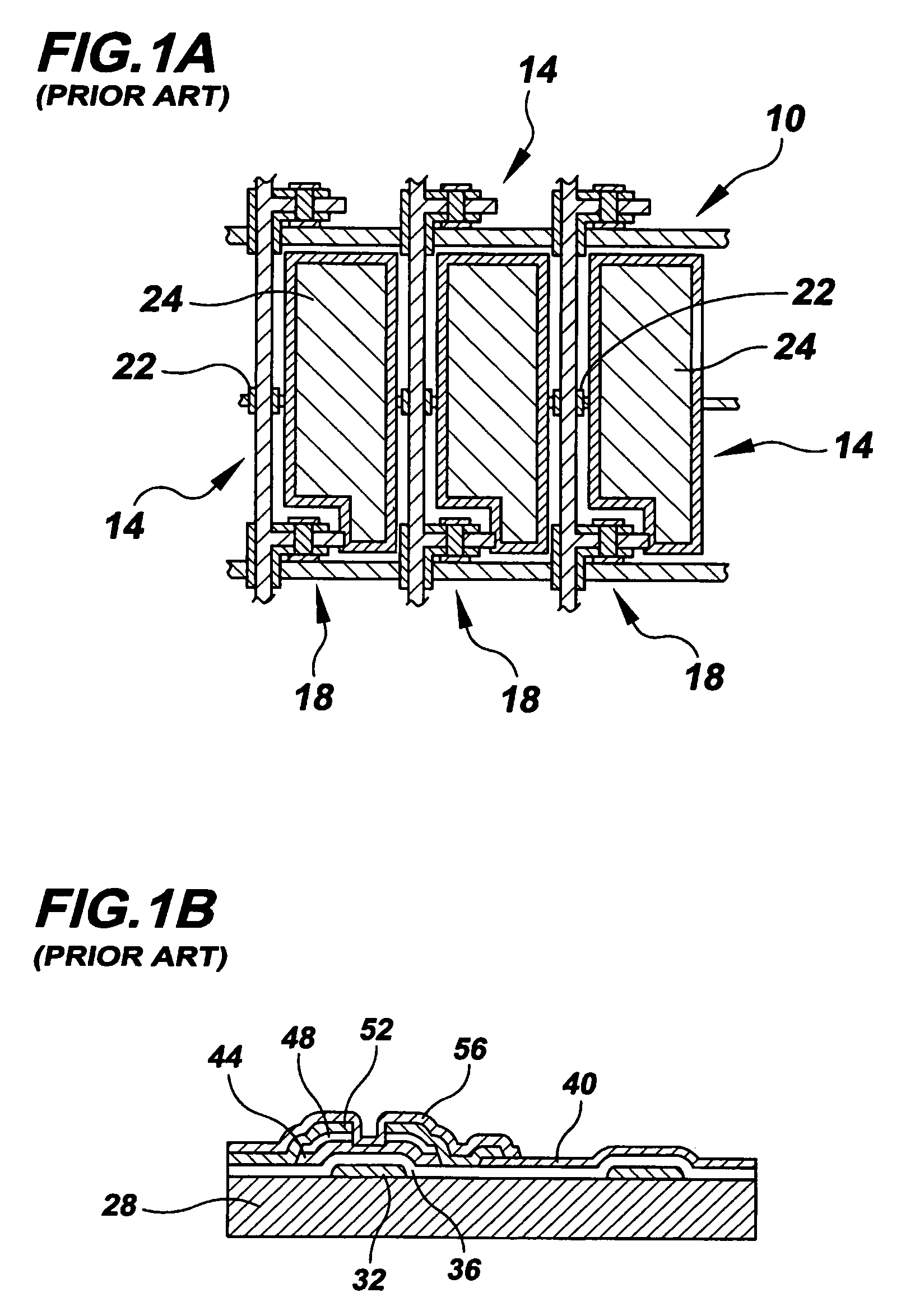
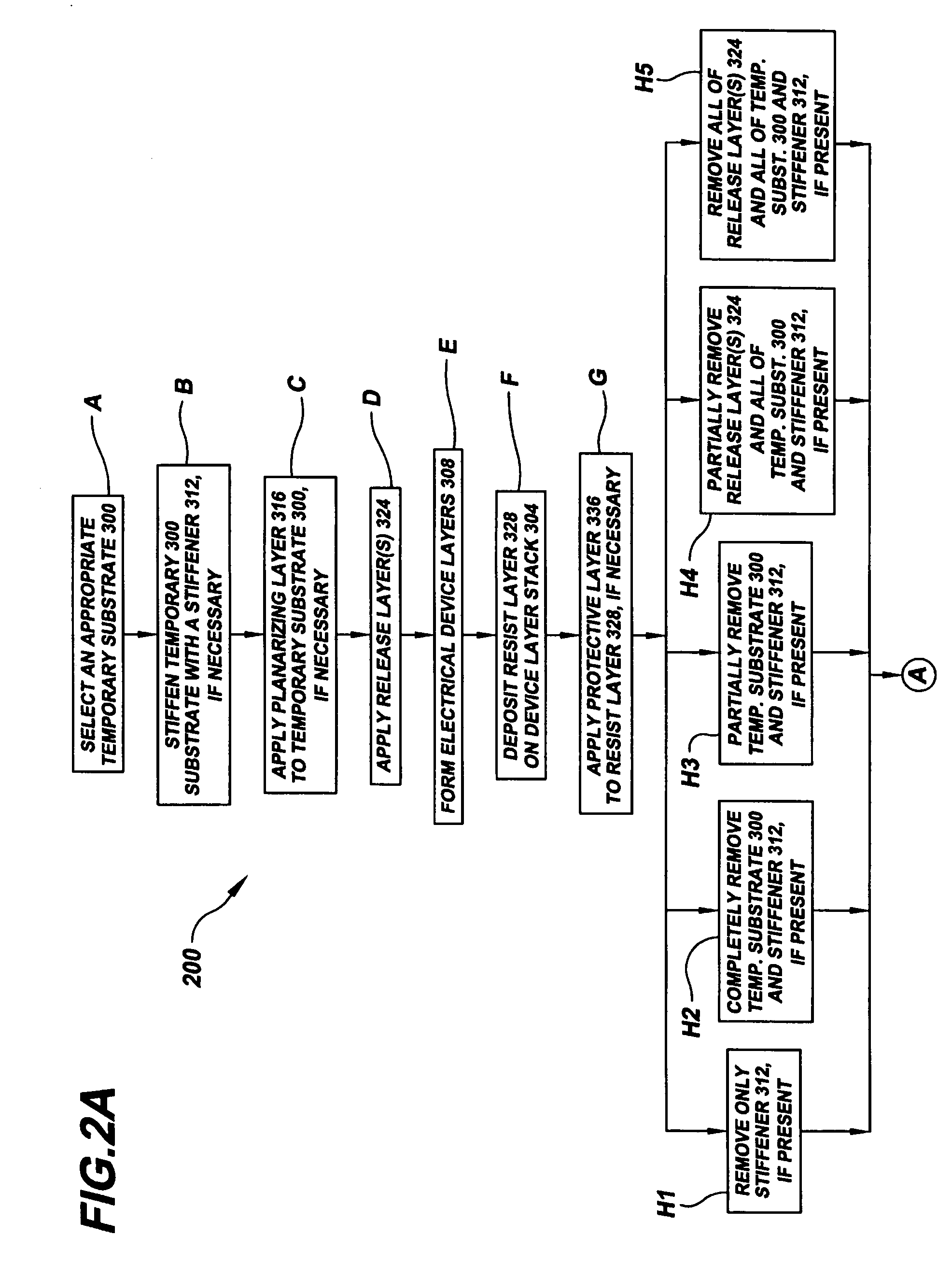
A circuitry sheet (322) comprising an electronic device layer stack (304) containing electronic devices, e.g., thin-film transistors, or portions thereof, formed by removing material from both sides of the device layer stack. The circuitry sheet may be made by an electronic / optoelectronic device manufacturing method (200) that includes the steps of forming the device layer stack on a temporary substrate (300), removing material from both sides of the device layer stack, and then attaching a permanent substrate (348) to the device layer stack. The method uses one or more resist layers (600) that may be activated simultaneously and independently to impart distinct circuit pattern images (603, 608, 612) into each of a plurality of image levels (612, 616, 620) within each resist layer, thereby obviating repetitive sequential exposure, registration and alignment steps.
Owner:VERSATILIS
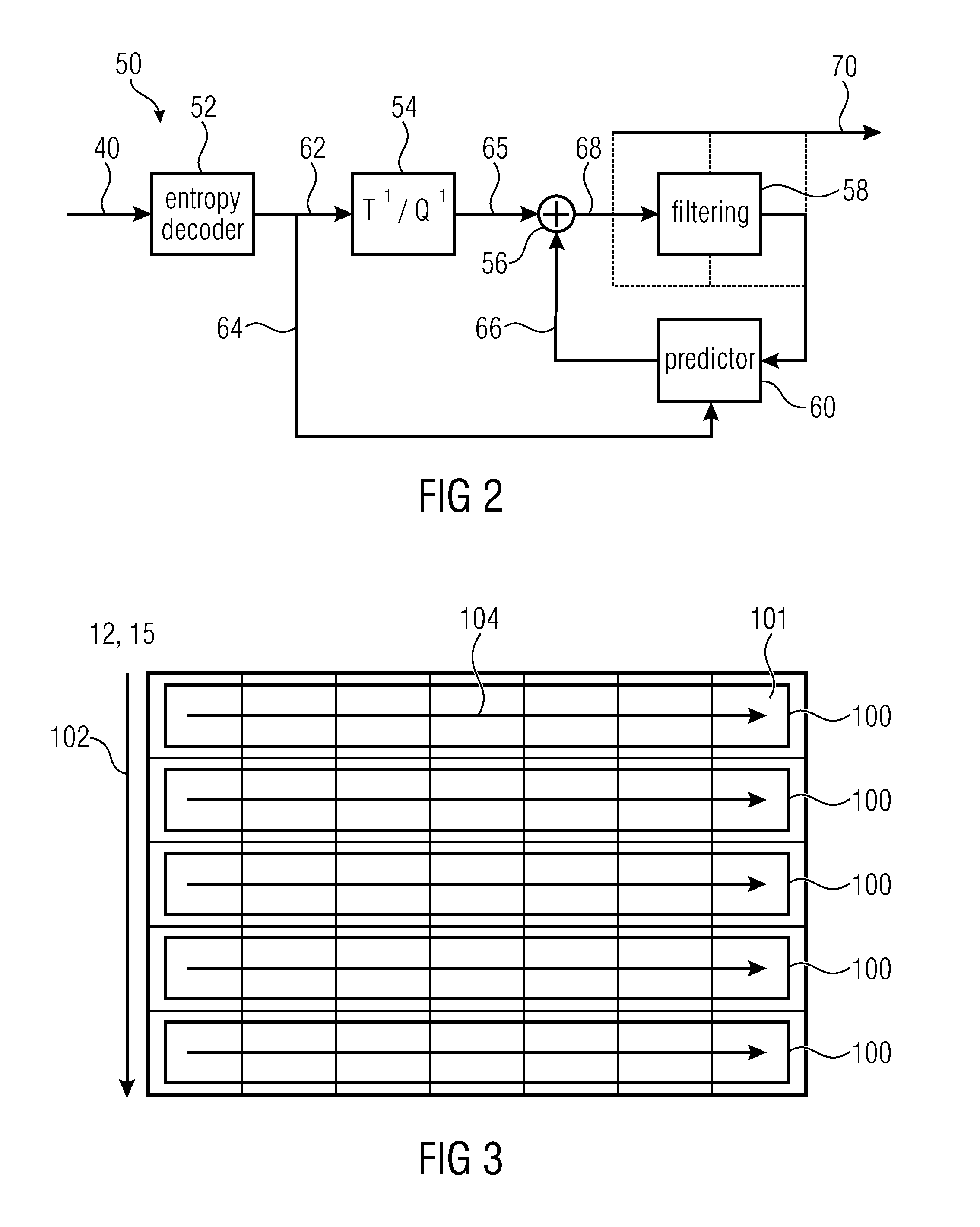
Efficient scalable coding concept
ActiveUS20150304667A1Alleviate decoder 's burdenReduce the numberColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionOverlayData stream
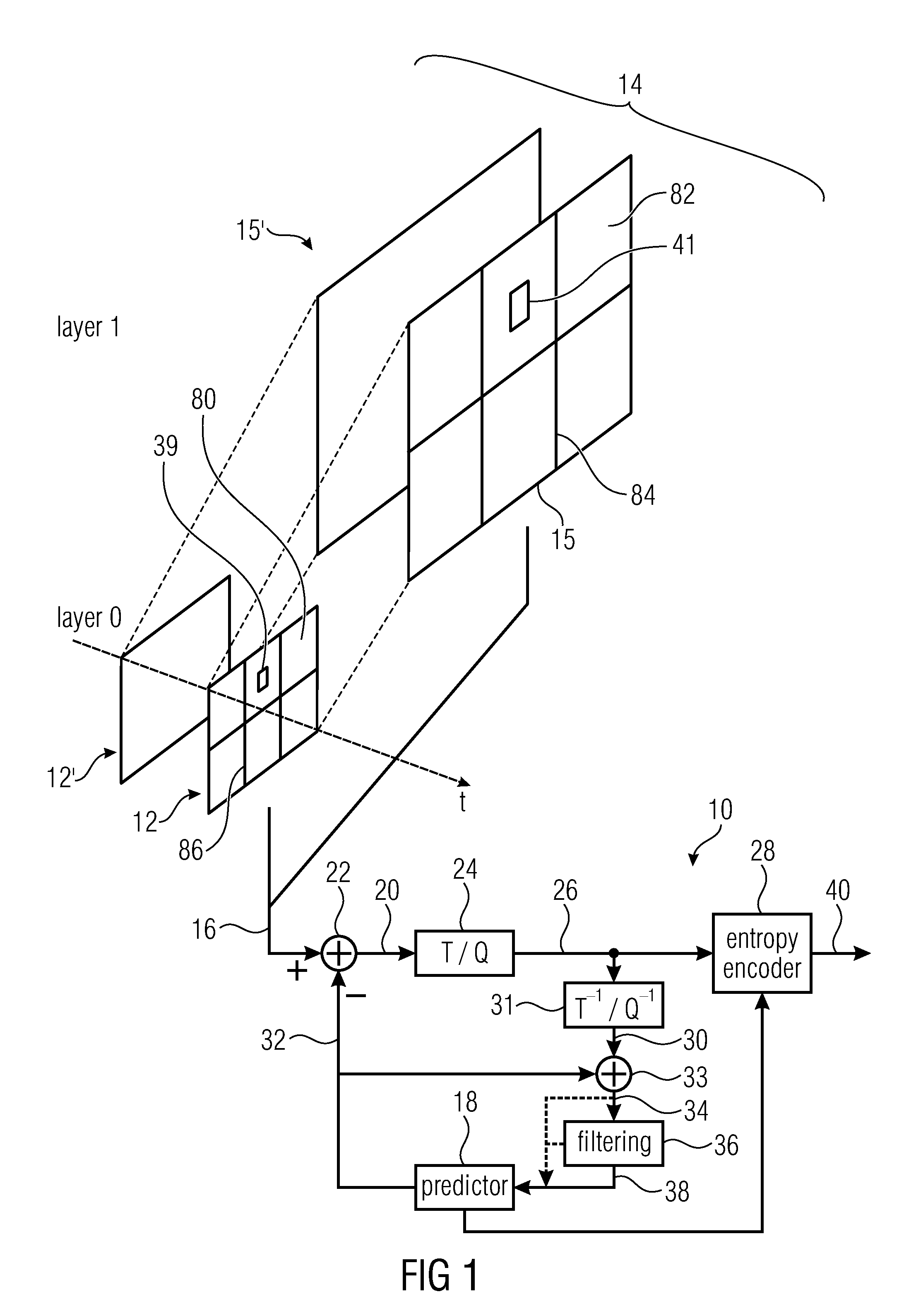
Scalable coding concepts are described. One aspect improves parallel decoding of inter-dependent layers of a multi-layer video data stream by introducing a long-term syntax element structure for guaranteeing that during a predetermined time period the pictures of the dependent layer are subdivided so that borders of the spatial segments of the pictures of the second layer and the spatial segments of the first layer overlay. Another aspect concerns upsampling from base layer to enhancement layer. Another aspect introduces a long-term syntax element structure allowing the decoder to determine the inter-layer offset for a predetermined time period. Another aspect introduces a type indicator field changing a way a layer indicator field within the NAL unit headers is to be interpreted. Another aspect allows different codecs / standards to be used for the different layers. Another aspect concerns a syntax element structure which indicates the inter-layer offset in units of the base layer blocks.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Lenticular card and processes for making
InactiveUS6900944B2Improve propertiesImproved indestructibilityDecorative surface effectsLayered productsAdhesiveEngineering
A process for making a lenticular card including: providing an imaged transparent sheet having a first smooth side and a second side with a lenticulated region, the transparent sheet optionally having at least one printed image area on the first smooth side and a moisture cure adhesive layer over the printed image areas and non-image areas of the first smooth side, and the moisture cure adhesive layer being applied with a screen press through a screen; and combining the imaged transparent sheet on the adhesive layer side of the transparent sheet with a backing sheet by nipping the paired sheets with a nip roller. The invention also provides processes useful for preparing a lenticular card including an optional core sheet, or optional primer layers.
Owner:TRAVEL TAGS
Projection of subsurface structure onto an object's surface
InactiveUS8078263B2Increase awarenessTelevision system detailsDiagnostics using lightVideo imageImaging equipment
An imaging system illuminates an object with infrared light to enhance visibility of buried structure beneath the surface of the object, and projects a visible light image of the buried structure onto the surface of the object. The system may include an infrared light source for generating the infrared light and a structure for diffusing the infrared light. The diffusing structure may include one or more layers of diffusing material for diffusing the light. The system further includes a video imaging device for receiving the infrared light reflected from the object and for generating a video image of the buried structure based on the reflected infrared light. The buried structure may be a subcutaneous blood vessel. A calibration procedure is described as well as embodiments for ensuring that the object is maintained in focus at the correct distance.
Owner:CHRISTIE MEDICAL HLDG
Damascene copper wiring optical image sensor
ActiveUS20070114622A1Eliminate contaminationHigh light sensitivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricCopper-wiring
A CMOS image sensor array and method of fabrication wherein the sensor includes Copper (Cu) metallization levels allowing for incorporation of a inner interlevel dielectric stack with improved thickness uniformity to result in a pixel array exhibiting increased light sensitivity. In the sensor array, each Cu metallization level includes a Cu metal wire structure formed at locations between each array pixel and, a barrier material layer is formed on top each Cu metal wire structure that traverses the pixel optical path. By implementing a single mask or self-aligned mask methodology, a single etch is conducted to completely remove the interlevel dielectric and barrier layers that traverse the optical path. The etched opening is then refilled with dielectric material. Prior to depositing the refill dielectric, a layer of either reflective or absorptive material is formed along the sidewalls of the etched opening to improve sensitivity of the pixels by either reflecting light to the underlying photodiode or by eliminating light reflections.
Owner:SMARTSENS TECH (HK) CO LTD
Image capture and integrated display apparatus
InactiveUS7808540B2Television system detailsColor television detailsMedicineComputer graphics (images)
An integrated imaging apparatus is disclosed for displaying images of a scene, including an electronic display having a display pixel that is used to display image content, the display pixel having a substrate, one-or-more electronic component(s) formed over a distinct portion of the substrate, a first electrode connected to the electronic component(s) having a first transparent portion formed over the substrate but not over the electronic component(s) and a second reflective portion formed over the electronic component(s), a light-emitting layer(s) formed over the first electrode, and a second transparent electrode formed over the light-emitting layers; and at least one image capture device which captures an image, wherein the image capture device has at least an imaging lens and an image sensor array; and wherein the image capture device receives light through the transparent portion of the first electrode, and wherein the display pixel also provides light to display image content.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Method for manufacturing three-dimensional object, three-dimensional object, and print medium
InactiveUS20070146734A1Easy to manufactureEasy to createDigitally marking record carriersAdditive manufacturing apparatusPrint mediaEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for manufacturing a three-dimensional object which method is able to easily manufacture a three-dimensional object using a low-cost apparatus. The present invention thus manufactures a three-dimensional object containing a three-dimensional image by printing a two-dimensional image on print media each having at least an ink receiving layer and a bonding layer, on the basis of an ink jet scheme, and stacking the print media on which the two-dimensional image is printed so that the print media are bonded together via the bonding layers.
Owner:CANON KK
Three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of GPU technology
InactiveCN105336003ATroubleshoot preprocessing issuesEliminate noise3D modellingVideo memoryEngineering
The invention provides a three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of a GPU technology, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The objective of the invention is to provide the three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of the GPU technology so that cache reuse in multiple times of drawing can be realized based on the current popular programmable GPU technology with a global digital elevation model acting as a data source, and load of computation space is effectively reduced. The method comprises the steps of construction of a multi-resolution pyramid model, elimination of image noise points, filtering of images, partitioning of planar projection of the earth according to equal latitude and longitude, and construction of different hierarchical levels of pyramid layers according to a mode from the top to the bottom. Acceleration and enhancement of terrain rendering are realized based on the programmable GPU technology, i.e. all phases of a graphical drawing pipeline are controlled by using shader languages, two and textures are respectively generated by vertex information and index information of elevation data to be stored in video memory for scheduling of whole terrain drawing; and vertex interpolation and migration are performed in the geometric phase by utilizing a curved surface subdivision and fractal technology so that procedural details are generated and the phenomenon of edges and corners of the terrain mesh when resolution is insufficient can be compensated.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE AVIATION UNIVERSITY
Method and system to enhance robust identification of abnormal regions in radiographs
InactiveUS6067372AImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionPotentially abnormal
A method and apparatus for detecting abnormal regions in living tissue depicted in a digital radiograph includes identifying suspected abnormal regions depicted in the radiograph and then, for each identified suspected abnormal region, extracting multiple topographic layers of the region from the digital radiograph; determining features of the region in each of the layers; and applying inter-layer multivariate non-linear criteria to the features to determine whether the suspected abnormal region is to be classified as an abnormal region. The distribution of digital values in the digitized radiograph is modified and a probabalistic determination is made as to whether suspected abnormal regions are actually abnormal from multiple analyses. An image is processed using at least two partially correlated detection schemes to produce at least two corresponding result sets of potentially abnormal regions; and the results of the detection schemes are combined using logical "AND" or logical "OR" combining rules to detect abnormal regions in the radiograph.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
Photoconductor on active pixel image sensor
InactiveUS20040036010A1Low costMass productionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSemiconductor materialsSpectral response
A MOS or CMOS based photoconductor on active pixel image sensor. Thin layers of semi-conductor material, doped to PIN or NIP photoconducting layers, located above MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits produce an array of layered photodiodes. Positive and negative charges produced in the layered photodiodes are collected and stored as electrical charges in the MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits. The present invention also provides additional MOS or CMOS circuits for reading out the charges and for converting the charges into images. With the layered photodiode of each pixel fabricated as continuous layers of charge generating material on top of the MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits, extremely small pixels are possible with almost 100 percent packing factors. MOS and CMOS fabrication techniques permit sensor fabrication at very low costs. In preferred embodiments all of the sensor circuits are incorporated on or in a single crystalline substrate along with the sensor pixel circuits. Techniques are disclosed for tailoring the spectral response of the sensor for particular applications.
Owner:E PHOCUS
Practical Modeling and Acquisition of Layered Facial Reflectance
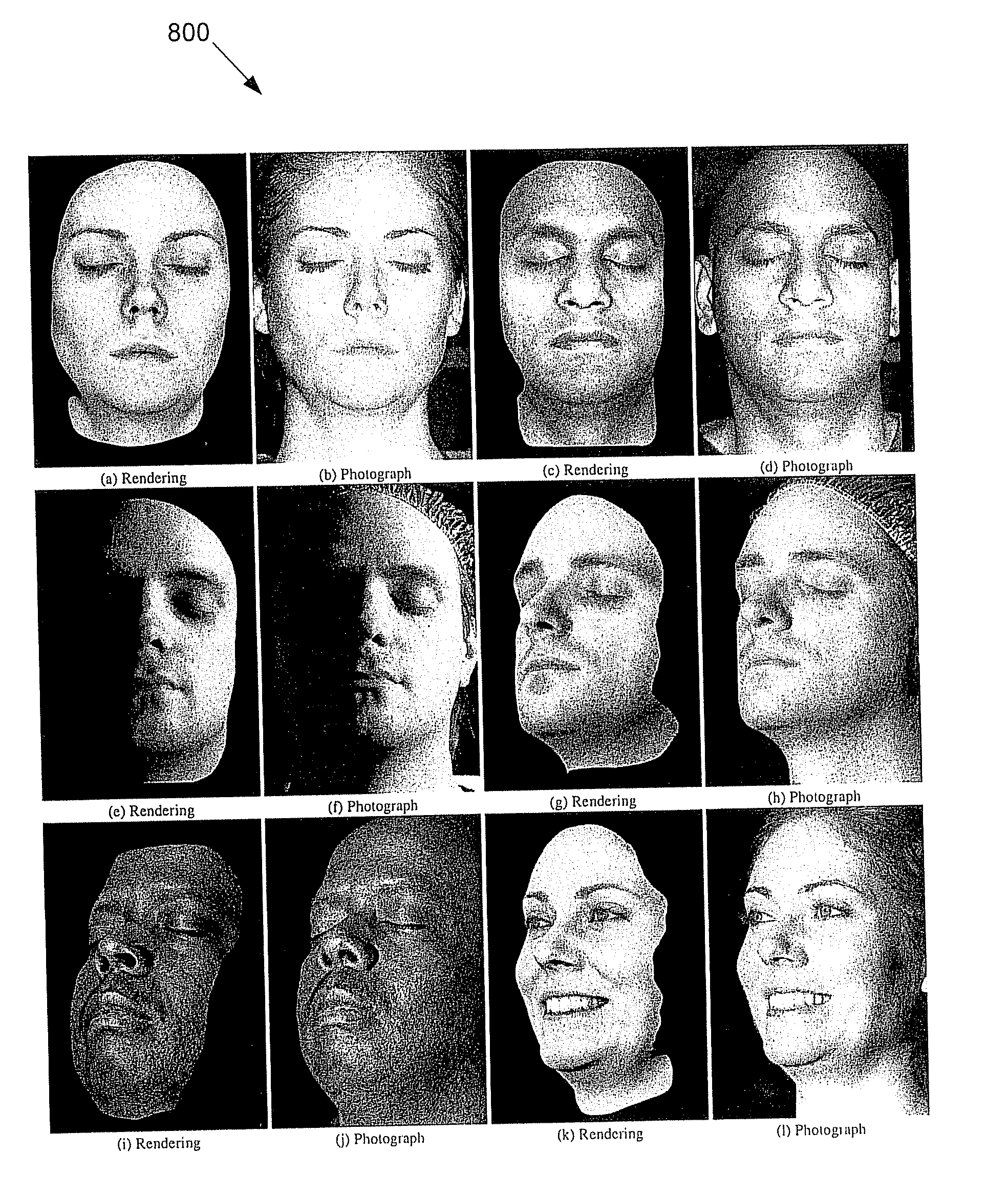
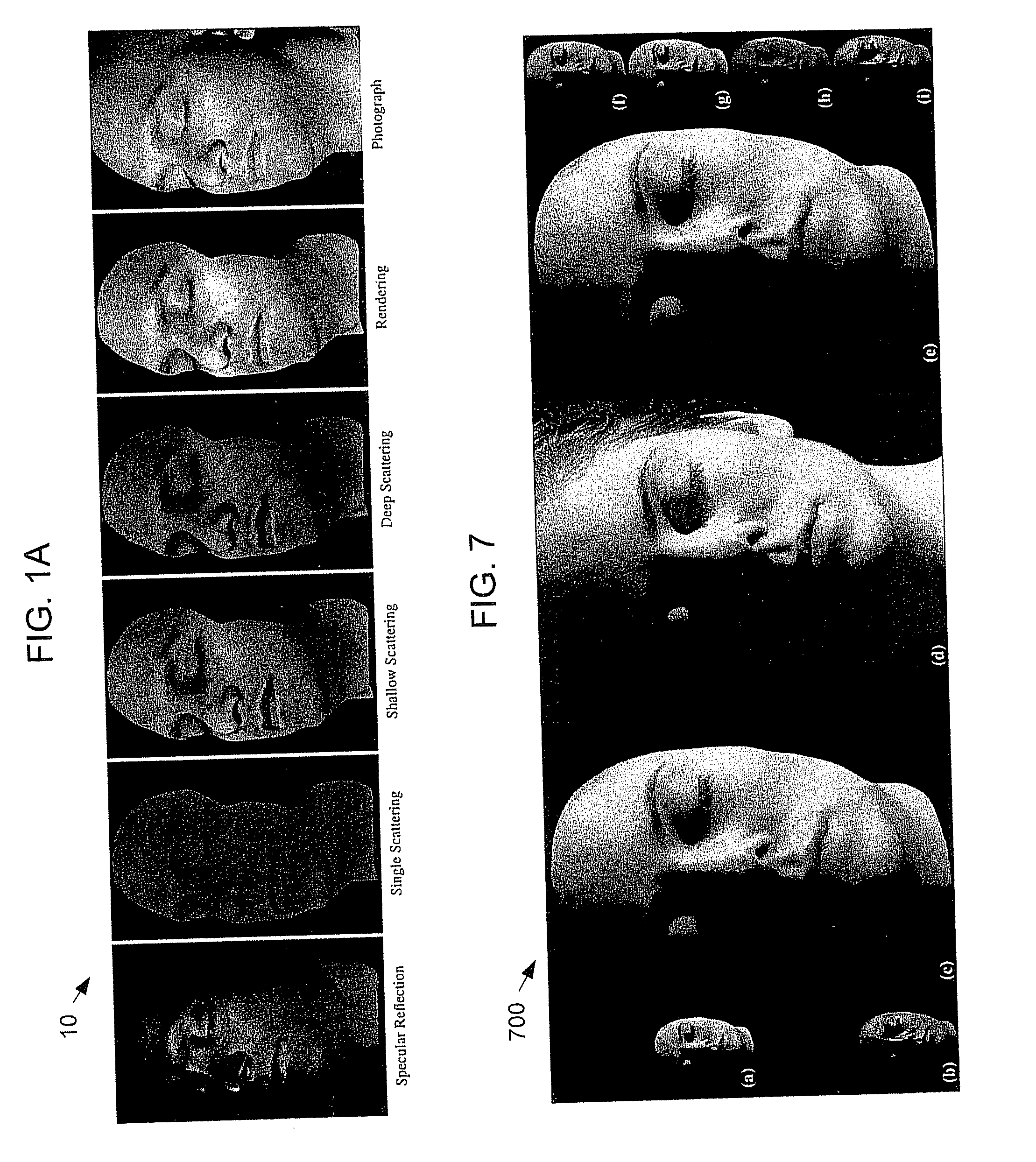
ActiveUS20090226049A1Easy to mergeConvenience to workCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsViewpointsDeep level
Techniques are described for modeling layered facial reflectance consisting of specular reflectance, single scattering, and shallow and deep subsurface scattering. Parameters of appropriate reflectance models can be estimated for each of these layers, e.g., from just 20 photographs recorded in a few seconds from a single view-point. Spatially-varying specular reflectance and single-scattering parameters can be extracted from polarization-difference images under spherical and point source illumination. Direct-indirect separation can be employed to decompose the remaining multiple scattering observed under cross-polarization into shallow and deep scattering components to model the light transport through multiple layers of skin. Appropriate diffusion models can be matched to the extracted shallow and deep scattering components for different regions on the face. The techniques were validated by comparing renderings of subjects to reference photographs recorded from novel viewpoints and under novel illumination conditions. Related geometry acquisition systems and software products are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
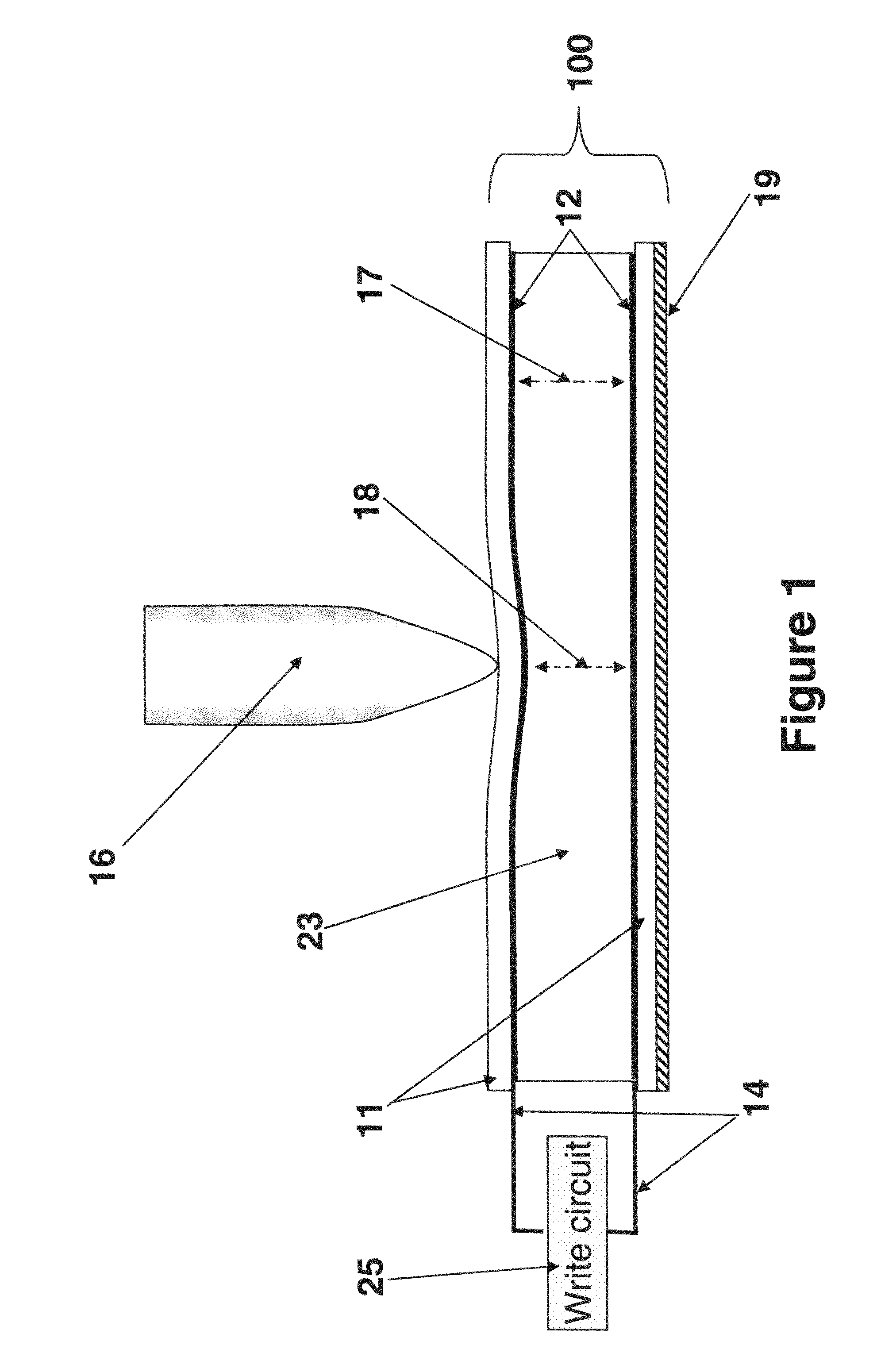
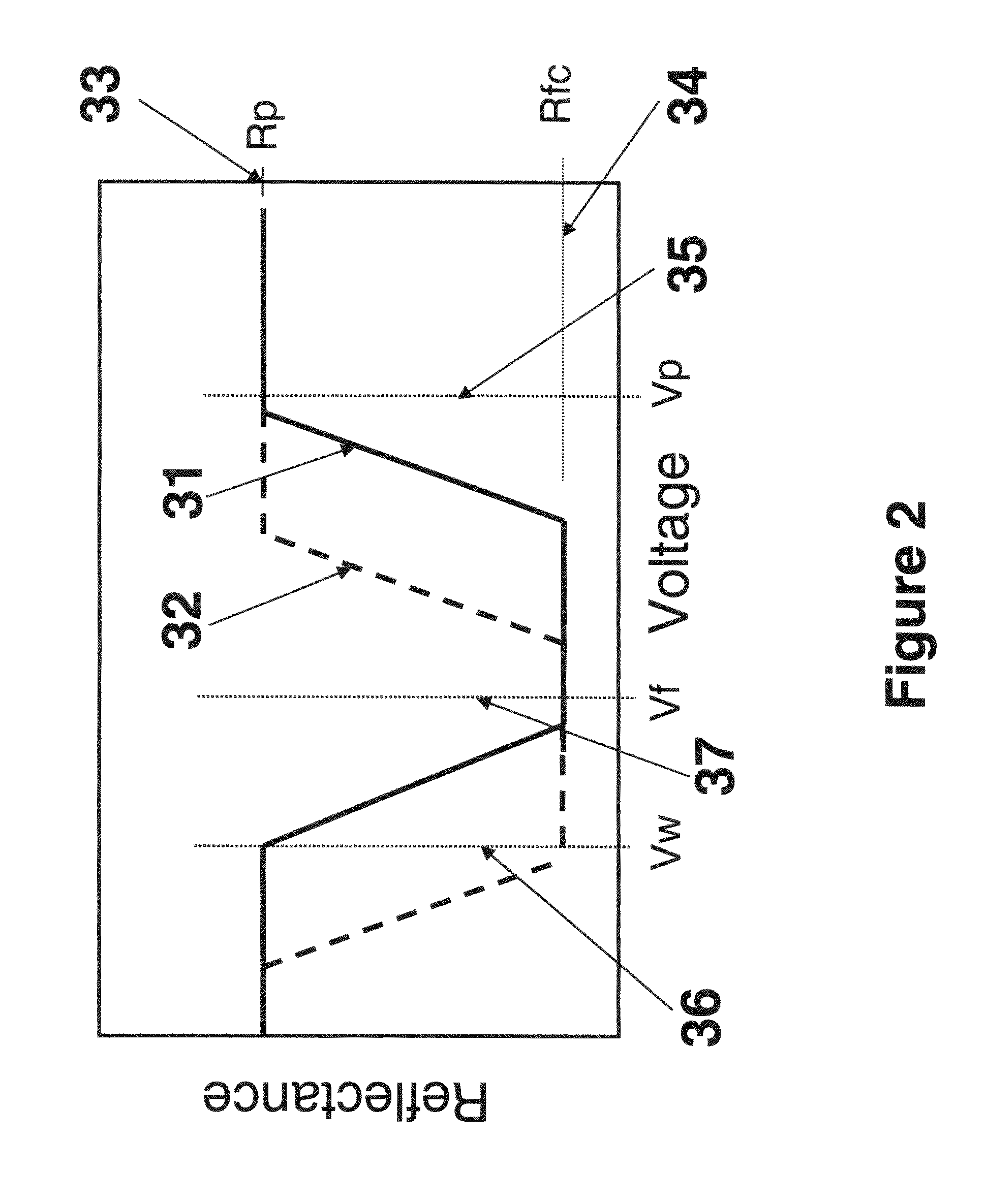
Multiple color writing tablet
One aspect of the invention is a bistable cholesteric writing tablet on which an image is formed by applying a suitable voltage while applying writing pressure, which results in a focal conic texture in a reduced gap region of the active layer while not changing the texture of the unreduced gap region of the active layer (e.g., a written portion being in a focal conic texture on a background in the planar texture). Another aspect of the invention is a multi-color stacked writing tablet in which a color of an image is selected by applying a suitable voltage while applying writing pressure using an instrument such as an untethered stylus on the surface of the tablet. The writing tablet includes at least two or three stacked layers of bistable cholesteric liquid crystal material. Selected colors can be additively mixed to achieve intermediate colors as desired. The image can be erased and new images written on the tablet. Gray scale achieved by varying the applied voltage during writing or the writing pressure in some cases, enables the writing tablet to produce a broad range of colors. The writing device is suitable for many applications such as a toy, sketch pad, erasable signage, tags or a large writing board without the mess of chalk or ink.
Owner:KENT DISPLAY SYST
Automatic multi-dimensional intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method
The present invention generally relates to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) image segmentation methods, and is more specifically concerned with an intravascular ultrasound image segmentation method for characterizing blood vessel vascular layers. The proposed image segmentation method for estimating boundaries of layers in a multi-layered vessel provides image data which represent a plurality of image elements of the multi-layered vessel. The method also determines a plurality of initial interfaces corresponding to regions of the image data to segment and further concurrently propagates the initial interfaces corresponding to the regions to segment. The method thereby allows to estimate the boundaries of the layers of the multi-layered vessel by propagating the initial interfaces using a fast marching model based on a probability function which describes at least one characteristic of the image elements.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP +1
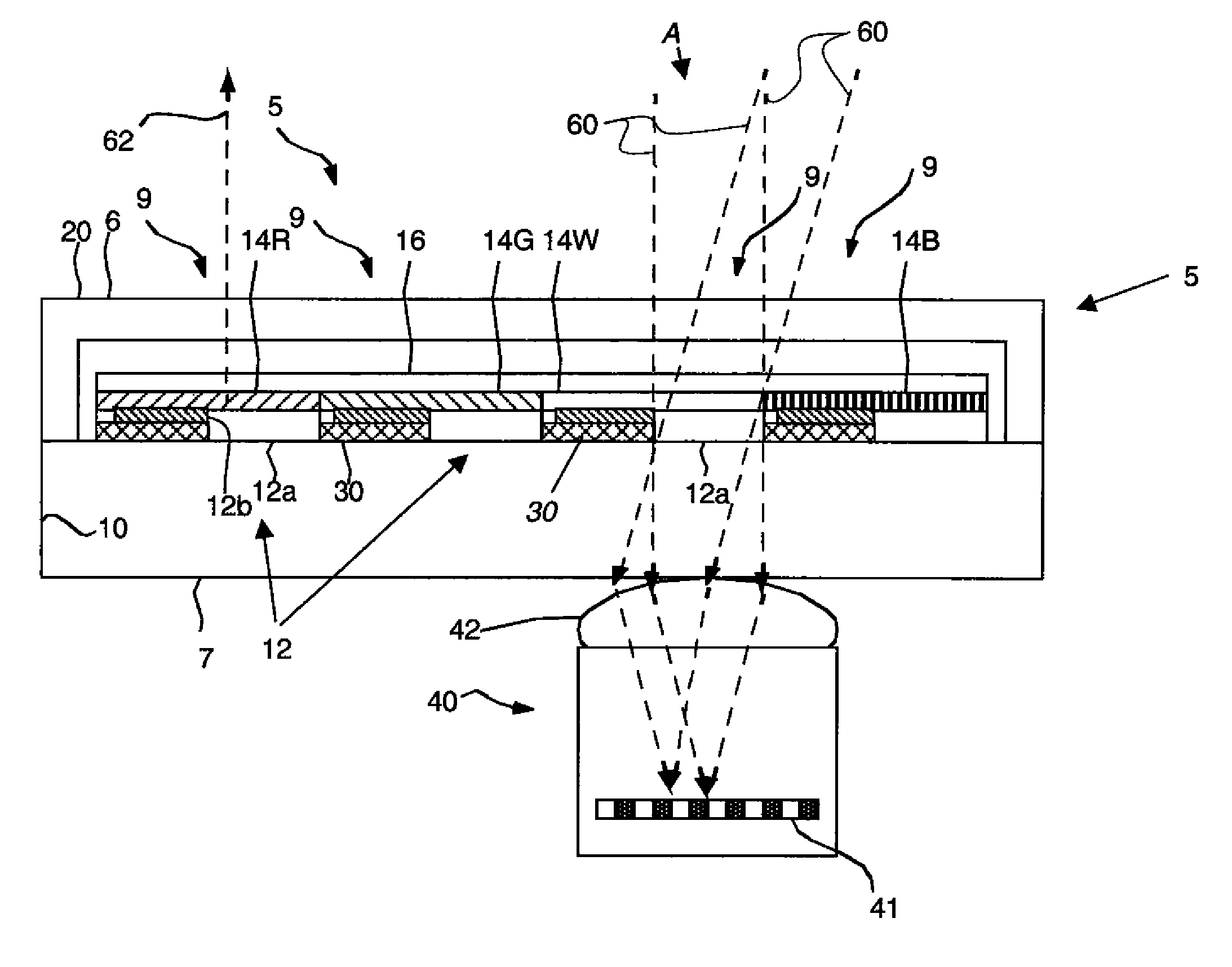
Miniature integrated multispectral/multipolarization digital camera
InactiveUS20090021598A1Increase in numberDecrease in numberTelevision system detailsPolarisation spectroscopyWave bandFrame rate
Several aspects of the invention respectively record one or more multispectral (MS) images using at least one sensor array, each array getting one respective image and simultaneously polarization state at the array points; and get and displays a MS, multipolarization (MP) movie, at MS / MP frame rates that suit a scene or the acquisition; and get an MS image, and a polarization-state image, so that the two are inherently in register; and provide a digital camera for plural-waveband imaging, including polarization data, using a chip with an optically sensitive layer continuously spanning a field of view—for each of at least two substantially distinct bands, and with stacked layers, some radiation penetrating plural layers to a corresponding sensitive layer, and with a polarization mosaic over the stack to define a superpixel array that differentiates polarization states, and with an electronic shutter actuating the layers. Another aspect makes a time sequence of registered MS / MP images; and yet another gets data for one or more MS images, including polarization state at most image points, via a single, common aperture.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Rendering translucent layers in a display system
InactiveUS7106275B2Improve performanceFlickering effect is reducedGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Display device
A system and method of rendering overlapping layers in a computer display, such as a windowing system, employs front-to-back assembly of the displayed image. An arbitrary number of overlapping elements, such as windows, can be presented, without requiring temporary storage space or additional off-screen buffers. The front-to-back assembly technique minimizes the number of memory transfers performed in connection with rendering an image, and avoids unnecessary reading and processing of pixels that will not contribute to the final image. Special effects such as semi-transparency, shadows, and irregular shapes can be accommodated and processed in an efficient manner.
Owner:APPLE INC
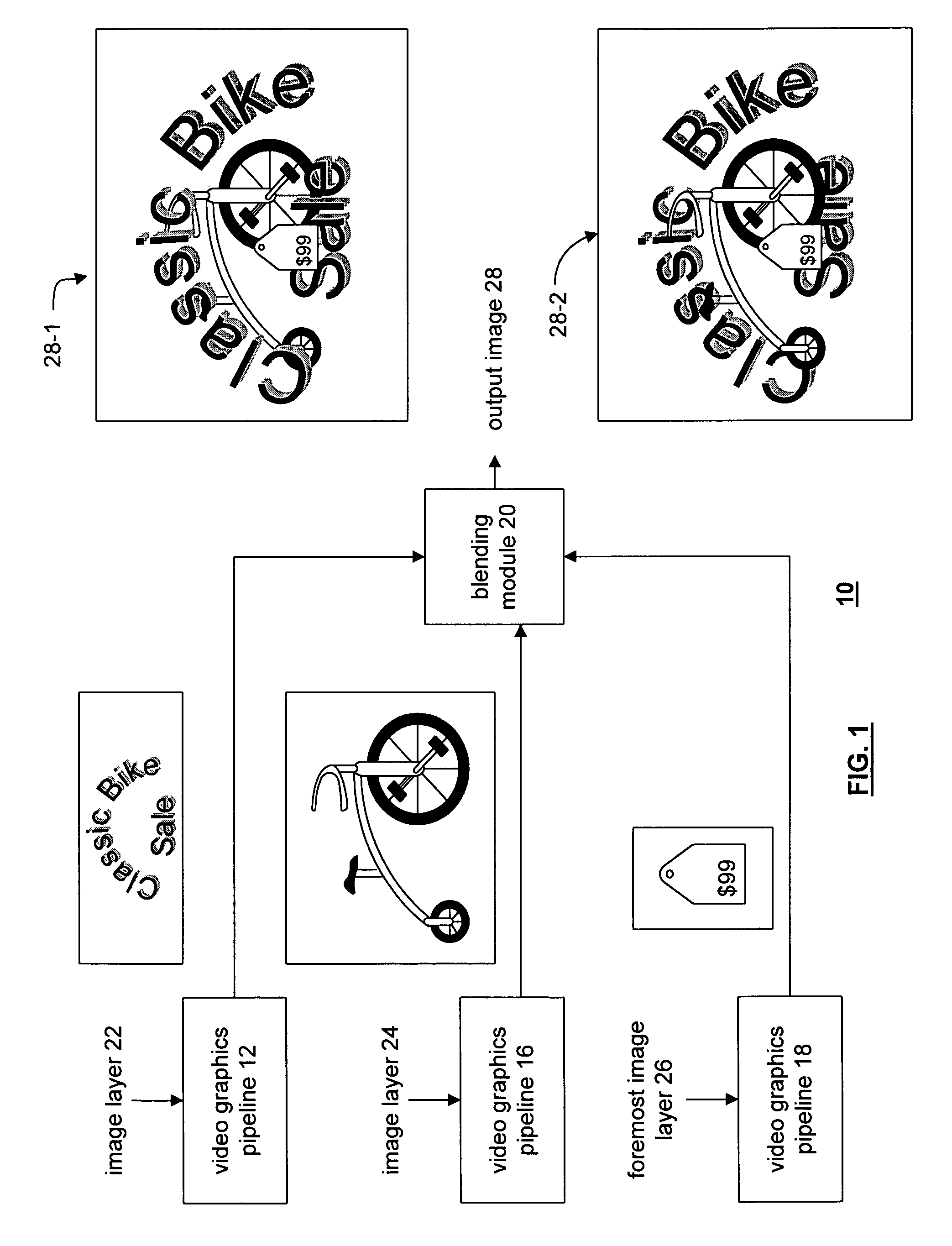
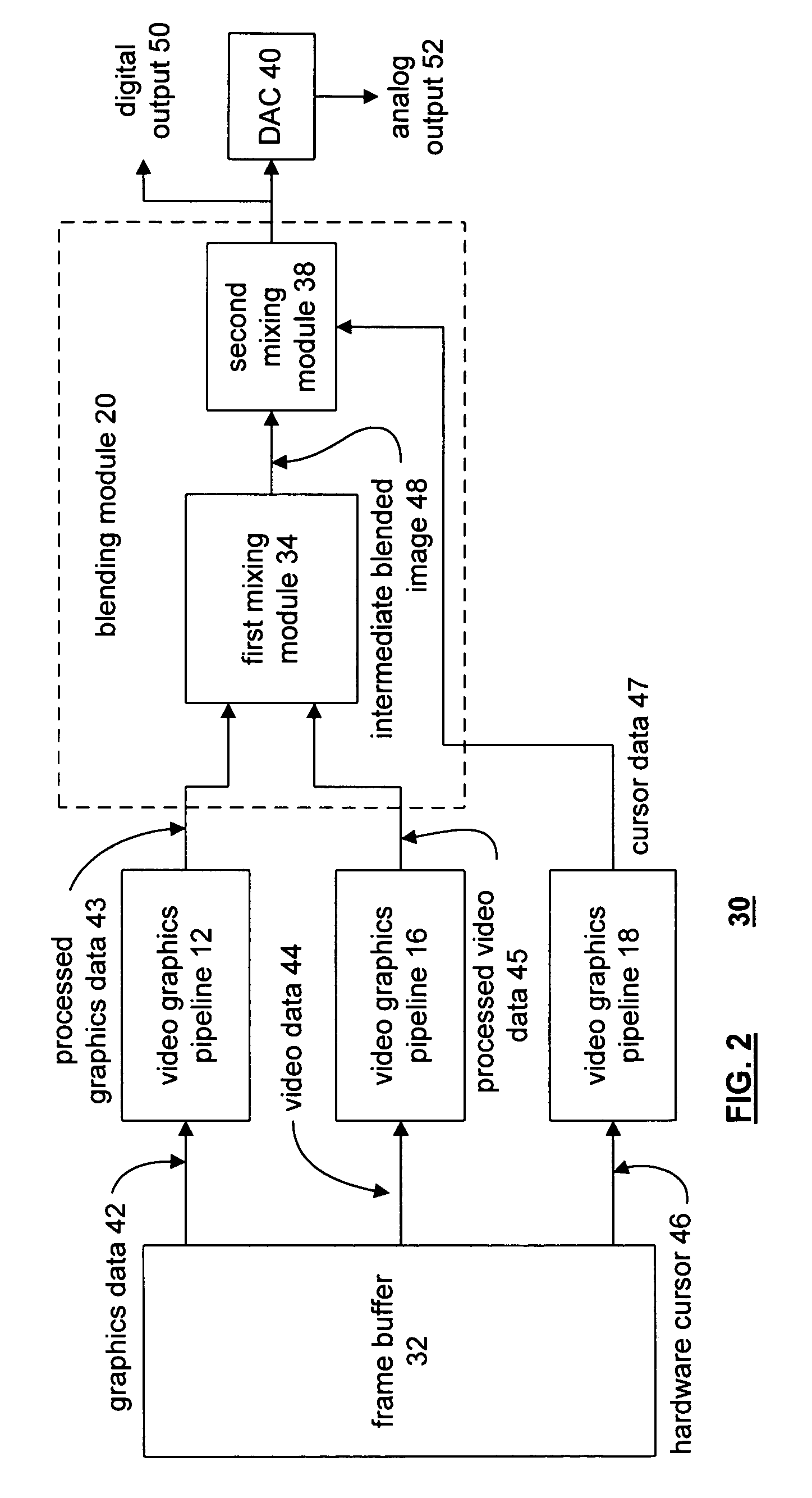
Video graphics module capable of blending multiple image layers
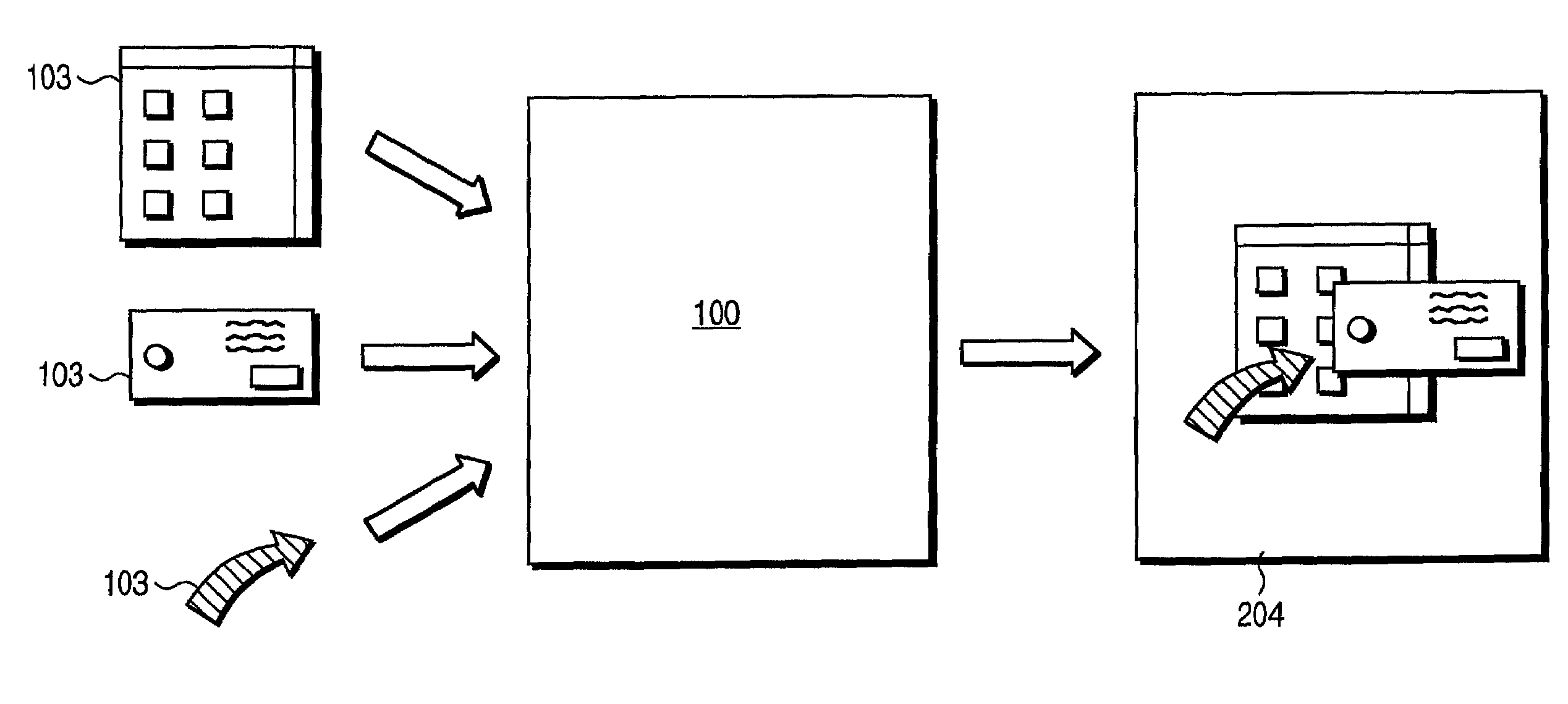
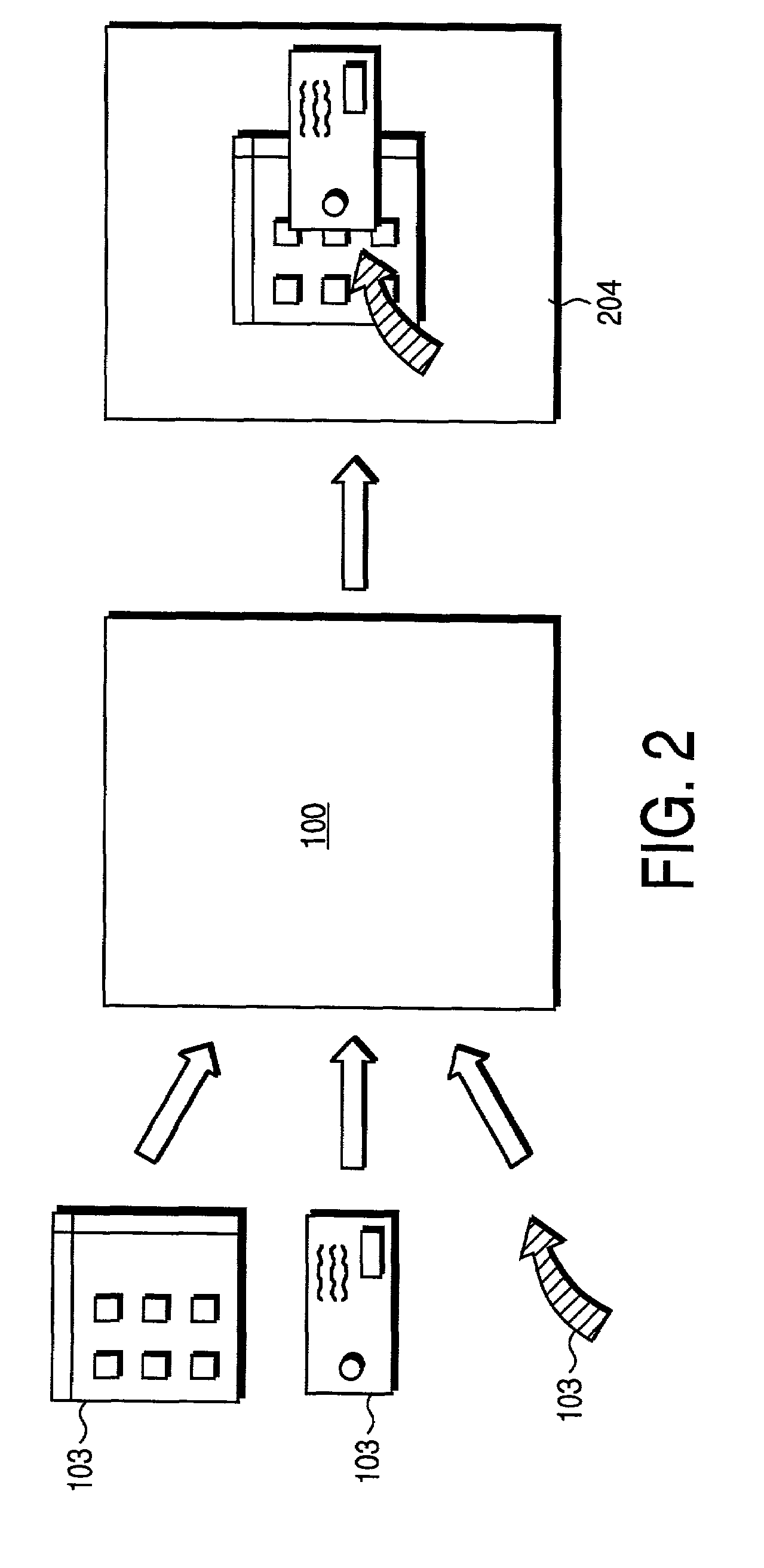
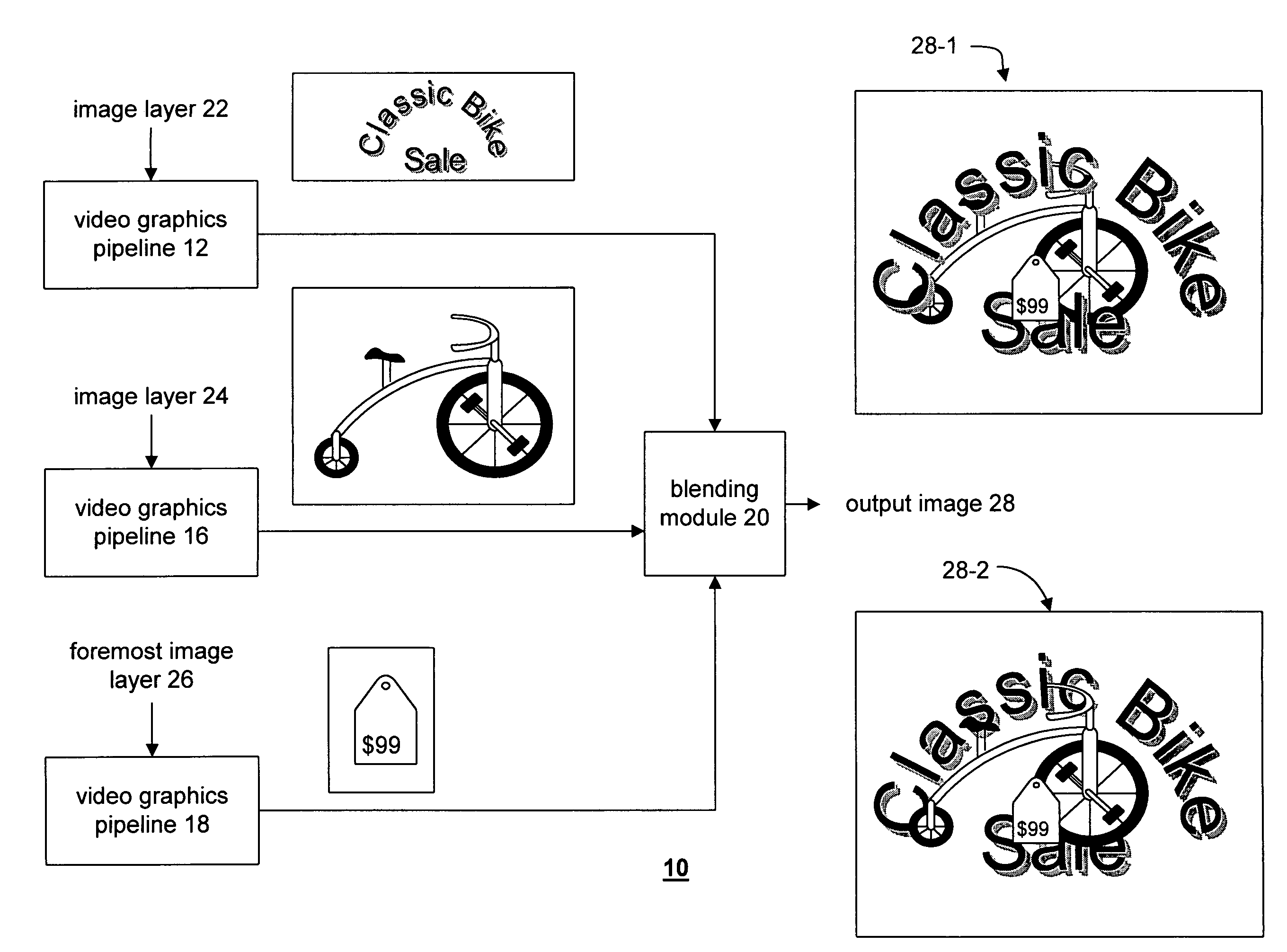
A video graphics module capable of blending multiple image layers includes a plurality of video graphic pipelines, each of which is operable to process a corresponding image layer. One of the video graphic pipelines processes a foremost image layer. For example, the foremost image layer may be a hardware cursor. The video graphics module also includes a blending module that is operably coupled to the plurality of video graphic pipelines. The blending module blends, in accordance with a blending convention (e.g., AND / Exclusive OR blending and / or alpha blending), the corresponding image layers of each pipeline in a predetermined blending order to produce an output image. The blending module blends the foremost image layer such that it appears in a foremost position with respect to the other image layers.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Surface position location system and method
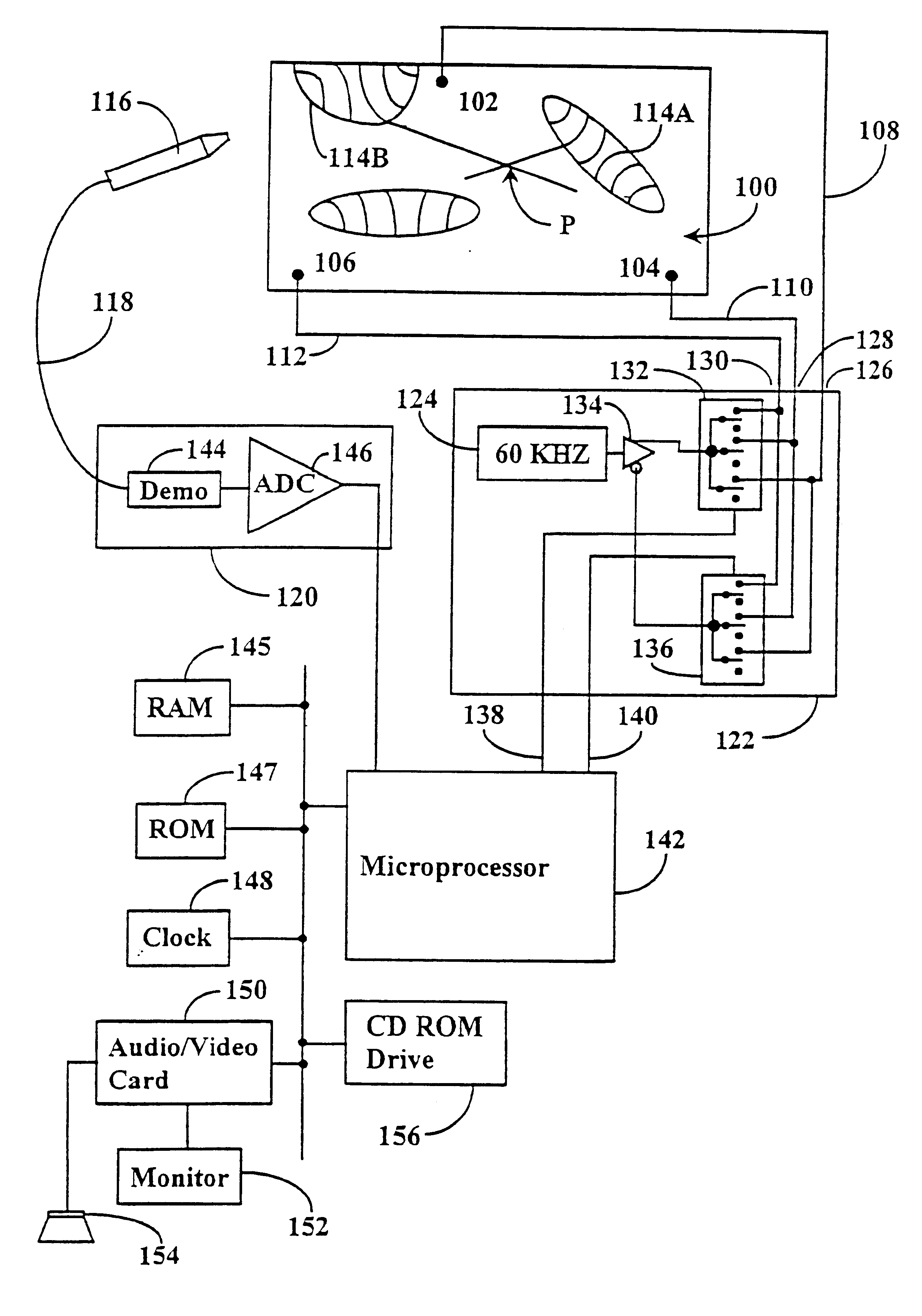
InactiveUSRE38286E1Maximize probabilityImprove comfortTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsEngineeringConductive materials
An electrographic sensor unit and method for determining the position of a user selected position thereon. The electrographic sensor unit includes a layer of a conductive material having an electrical resistivity and a surface, at least three spaced apart contact points electrically interconnected with a layer of conductive material, a processor connected to the spaced apart contacts and disposed to selectively apply a signal to each of the contact points, and a probe assembly, that includes either a stylus of a flexible conductive layer spaced apart from the layer, coupled to the processor with the stylus disposed to be positioned by a user in vicinity of a user selected position on the surface of the layer, or that position being selected with a user's finger on the flexible layer and to receive signals from the layer when the contact points have signals selectively applied thereto. The user selected position is determined by the processor from signals received from the stylus, or flexible layer, each in relation to a similar excitation of different pairs of the contact points under control of the processor. The conductive layer may be either two or three dimensional and may be a closed three dimensional shape. There may also be multiple layers with the processor being able to discern on which of those layers the user selected position is located. Further, provision is made to correct the calculated coordinates of the selected position for variations in contact resistance of each of the contact points individually. Additionally, a nonconductive skin having selected graphics printed thereon, such as a map, can be placed over the layer and the proces-sor further convert the calculated coordinates of the selected position to coordinates that relate to the graphical information printed in the skin, and even electro-nically (e.g., audio or visual) present information to the user relative to the graphical location selected as the selected position.
Owner:LEAPFROG ENTERPRISES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com