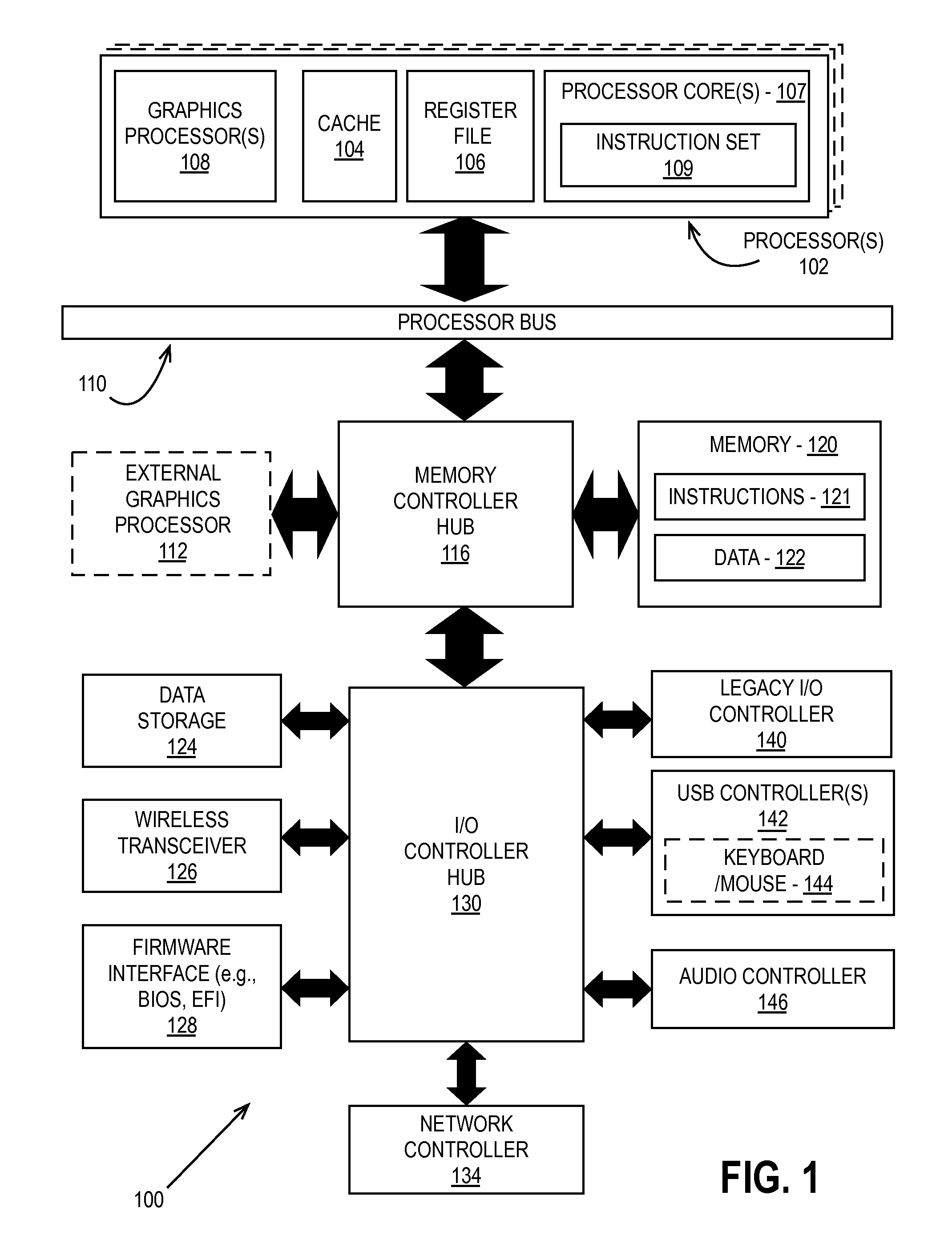
Patents
Literature
1295results about "Details involving image processing hardware" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
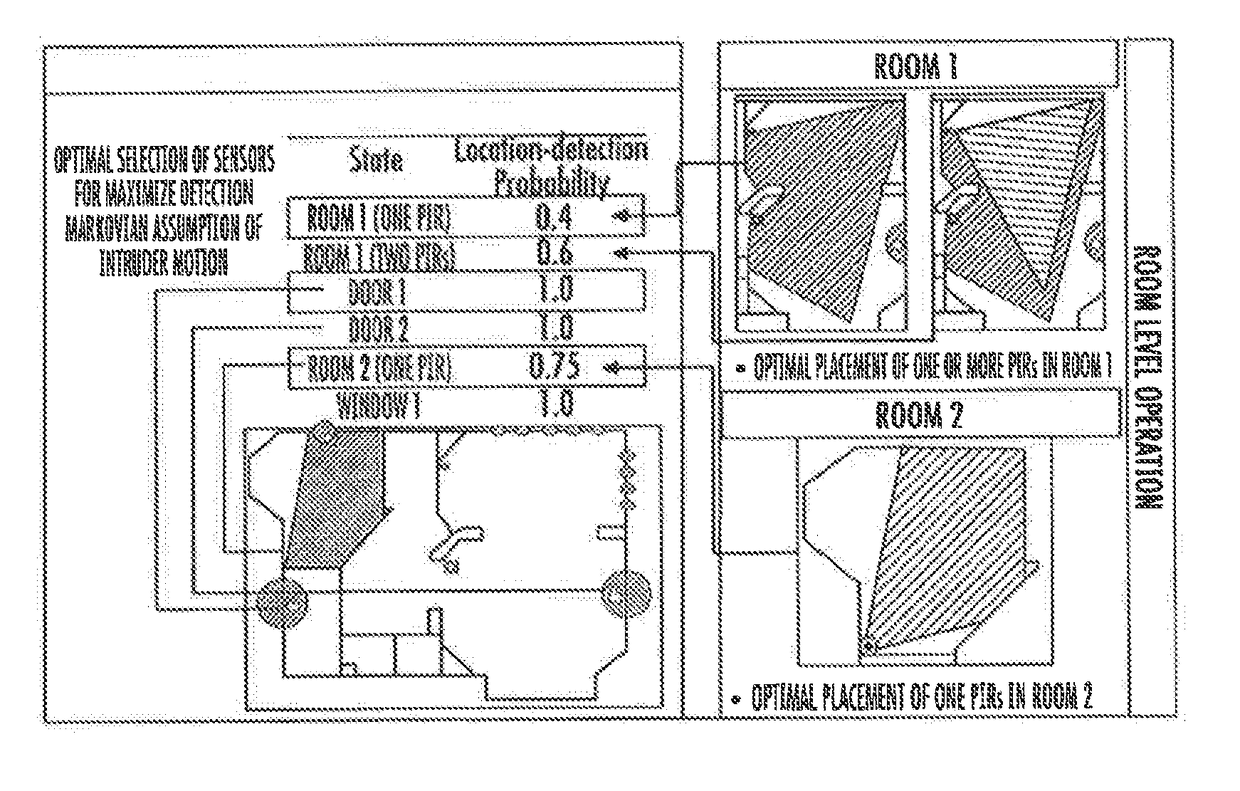
System and method for capturing and analyzing multidimensional building information
A method for capturing building information includes capturing dimensions of a 360 degree image at a first location within a room of a building using a mobile device equipped with at least direction sensor and at least one motion sensor. The step of capturing dimensions is repeated within at least one additional room. The mobile device receives user input to connect the rooms to create a floor plan of the building and align the floor plans over each other to create a multi-level building map.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
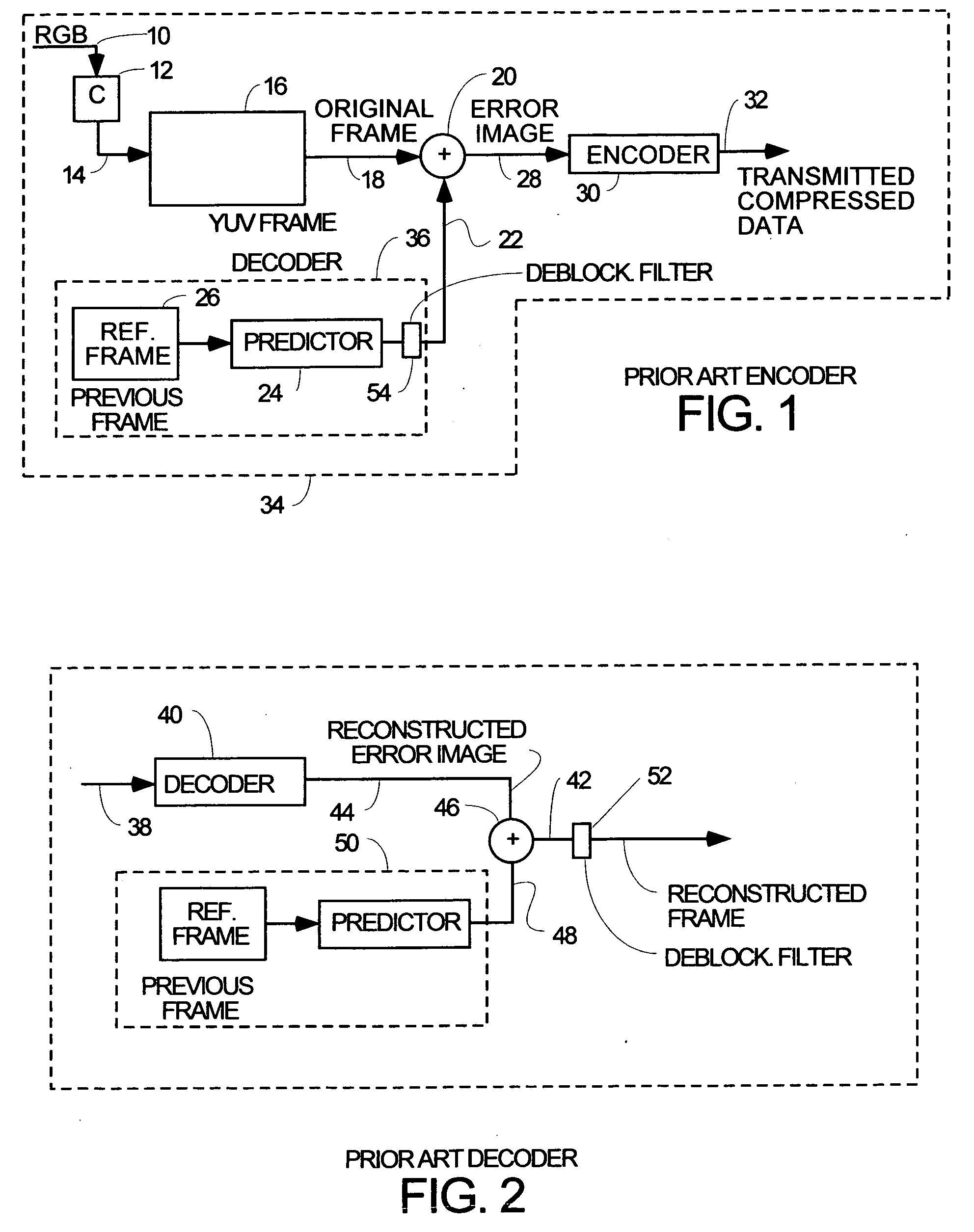
Parallel processing motion estimation for H.264 video codec
InactiveUS20080126278A1Low costMinimize the numberImage enhancementImage analysisMotion vectorMotion estimate
A genus of motion estimation processes is disclosed which is characterized by the following characteristics which all species in the genus will share 1) a process within this genus does not perform the motion estimation separately for each of the partitions and subpartitions defined in the H.264 standard; 2) a process within the genus computes for each motion vector in the search region the partial costs for all macroblock partitions and sub-partitions, compares them to the best partial costs found so far, and for partitions and sub-partitions having lower costs updates the corresponding best partial costs and records the current motion vectors as the one realizing them. 3) a process within the genus after finishing scanning the motion vectors in the search region, computes from the best partial costs the total costs for all possible macroblock partitioning modes and selects the one with the lowest total cost as the best macroblock partitioning mode, with the best motion vectors corresponding to each of the selected macroblock partitions and sub-partitions.
Owner:NOVAFORA
Generating a low-latency transparency effect
InactiveUS20150194128A1Efficiently display deviceTransparency effectImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDisplay deviceLatency (engineering)
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for generating a transparency effect for a computing device. The technique includes transmitting, to a camera, a synchronization signal associated with a refresh rate of a display. The technique further includes determining a line of sight of a user relative to the display, acquiring a first image based on the synchronization signal, and processing the first image based on the line of sight of the user to generate a first processed image. Finally, the technique includes compositing first visual information and the first processed image to generate a first composited image, and displaying the first composited image on the display.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
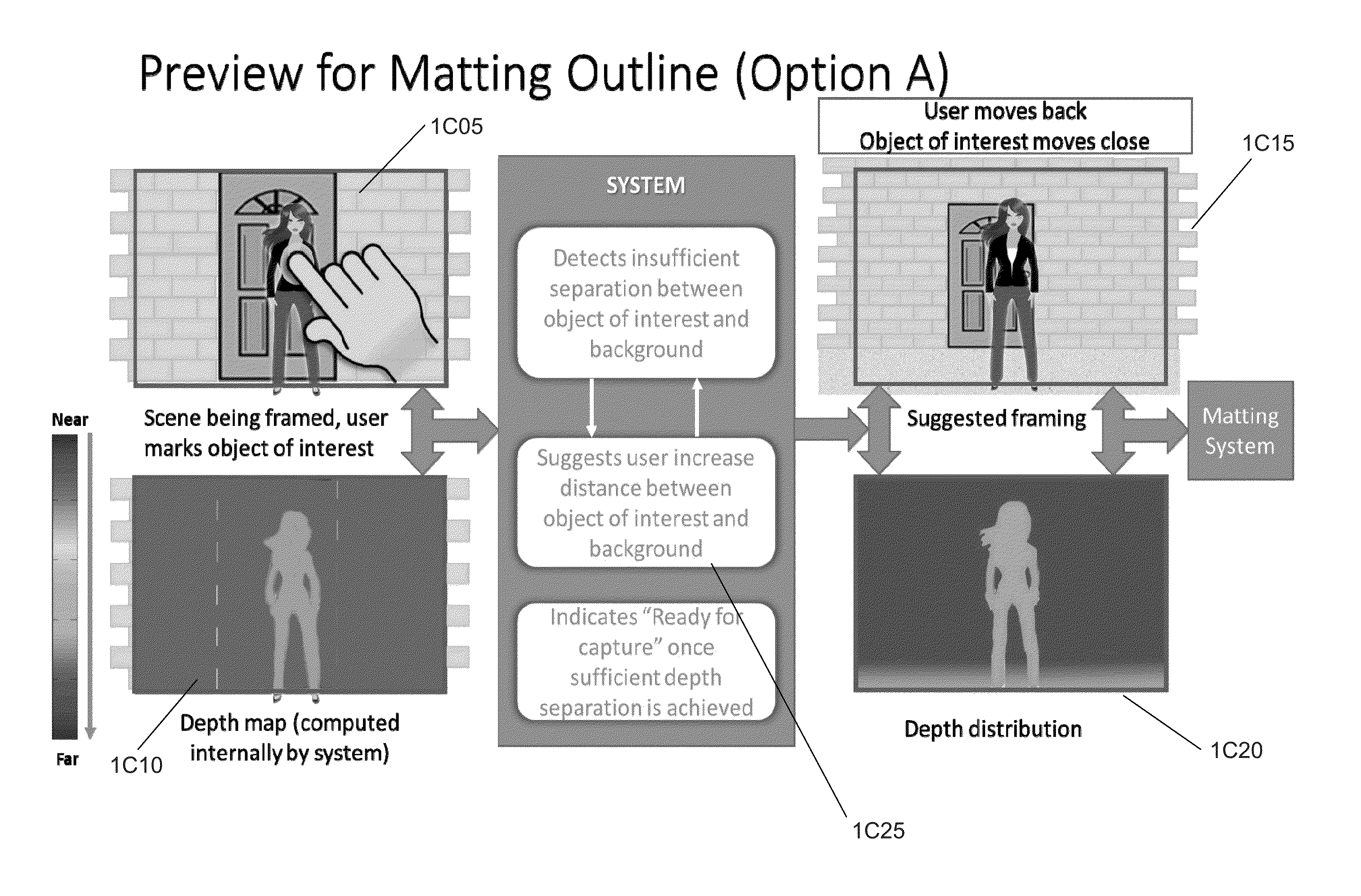
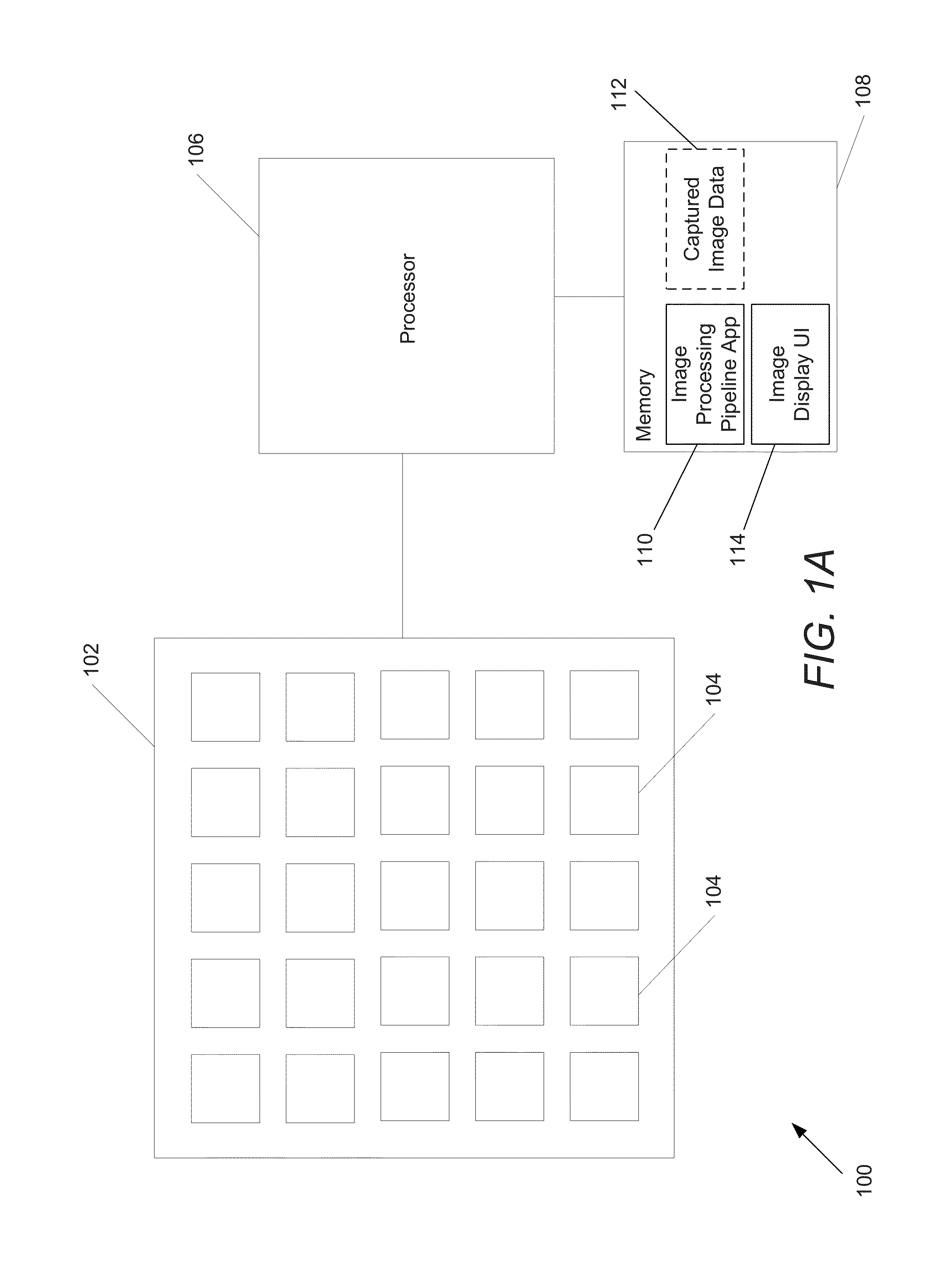
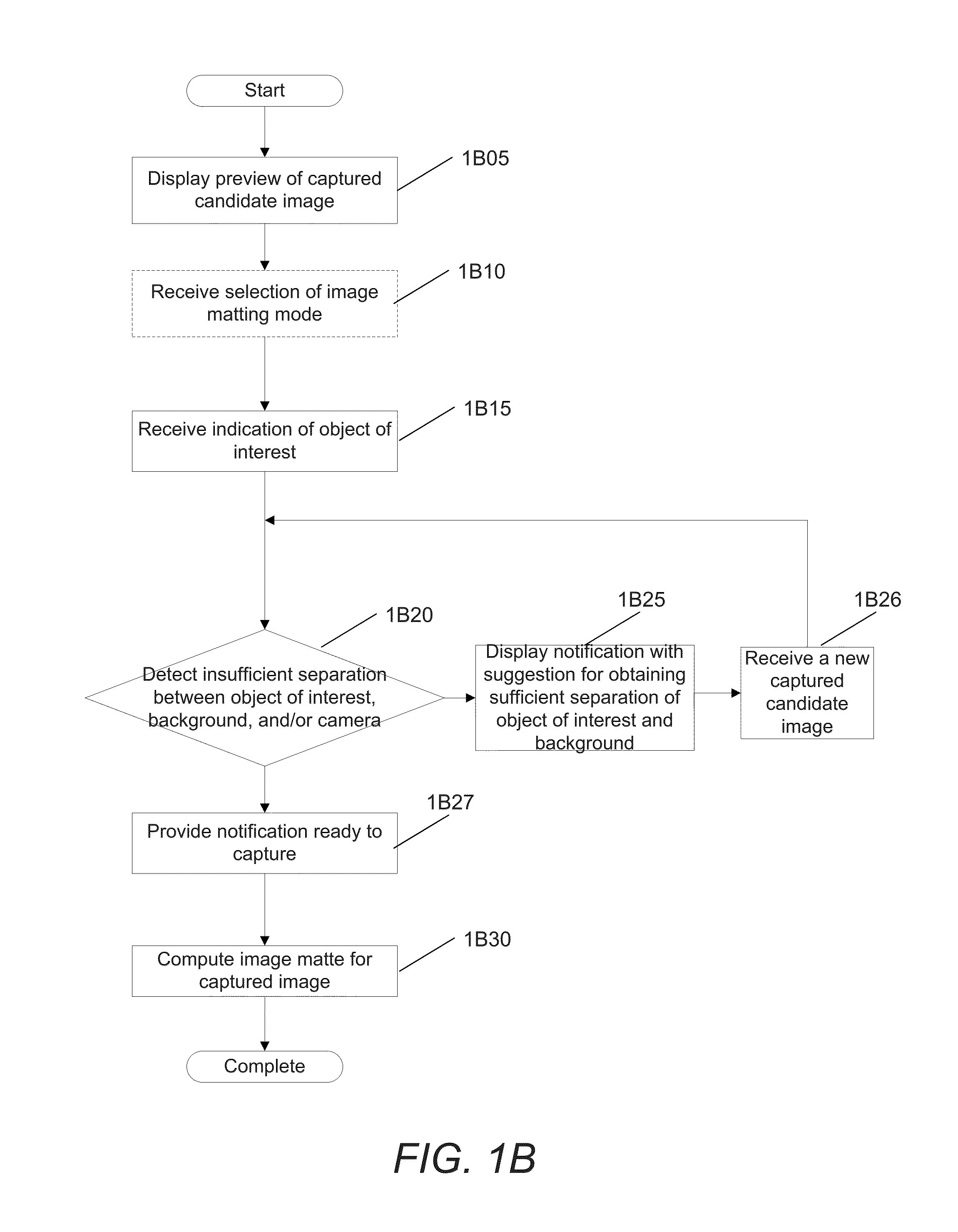
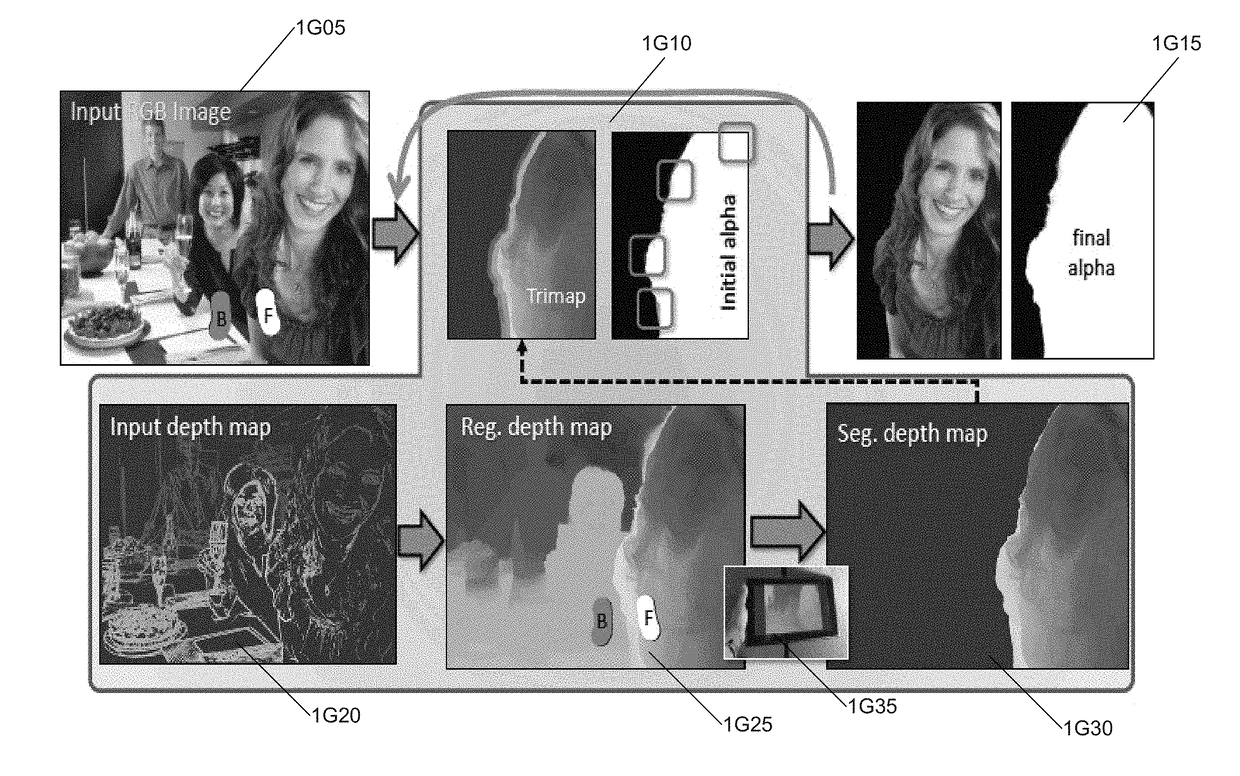
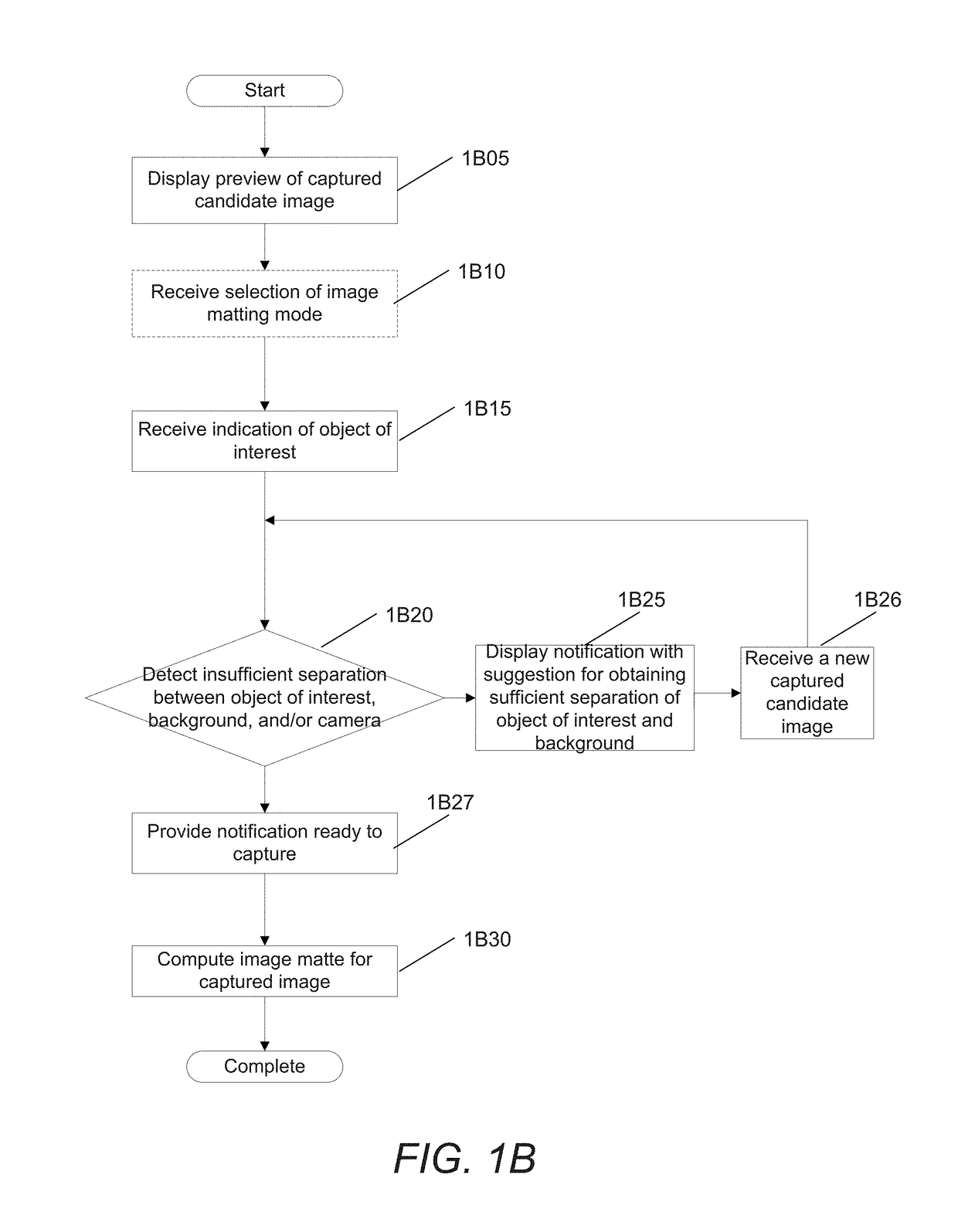
System and methods for depth regularization and semiautomatic interactive matting using rgb-d images
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of this invention perform depth regularization and semiautomatic interactive matting using images. In an embodiment of the invention, the image processing pipeline application directs a processor to receive (i) an image (ii) an initial depth map corresponding to the depths of pixels within the image, regularize the initial depth map into a dense depth map using depth values of known pixels to compute depth values of unknown pixels, determine an object of interest to be extracted from the image, generate an initial trimap using the dense depth map and the object of interest to be extracted from the image, and apply color image matting to unknown regions of the initial trimap to generate a matte for image matting.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
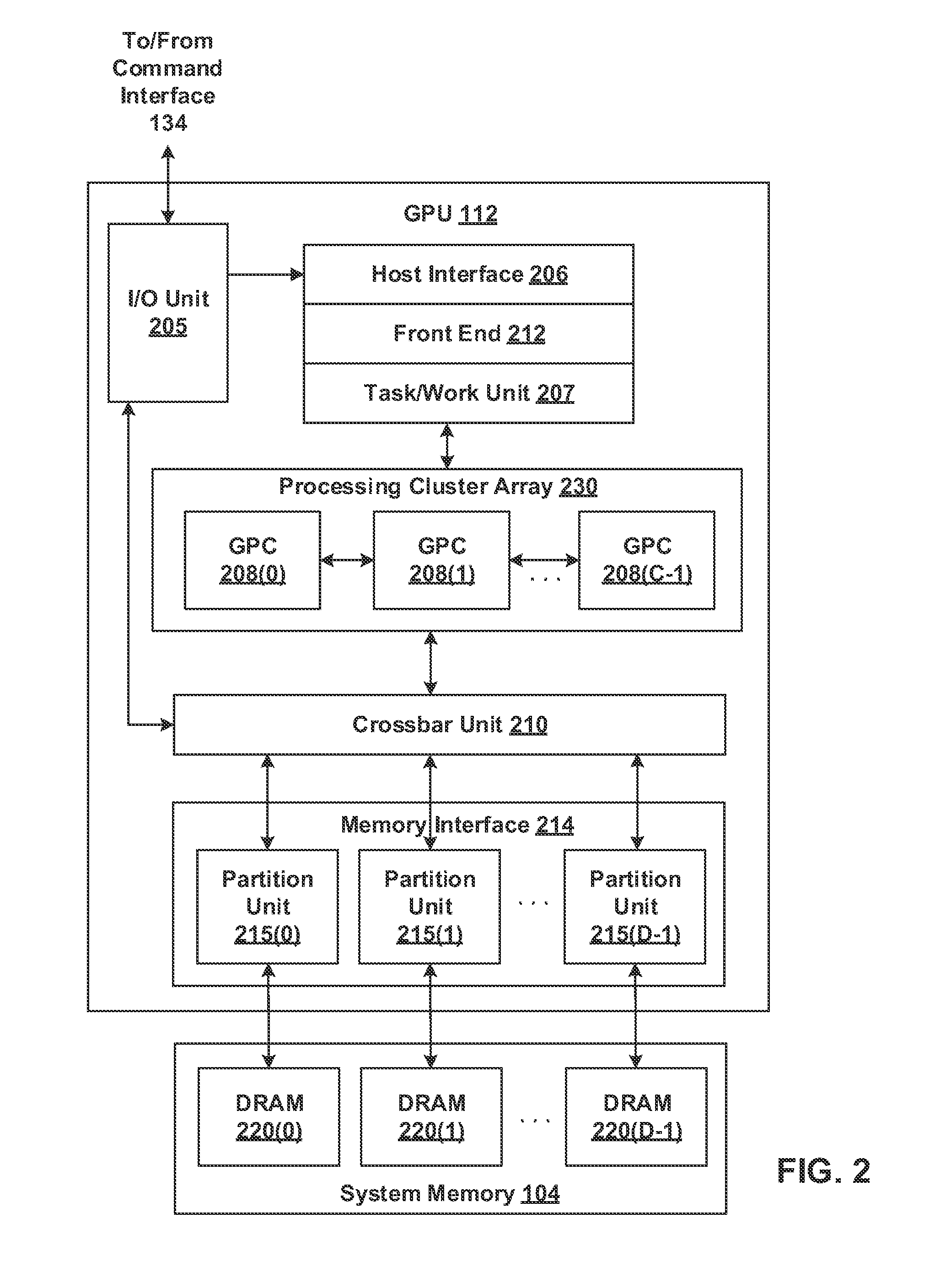
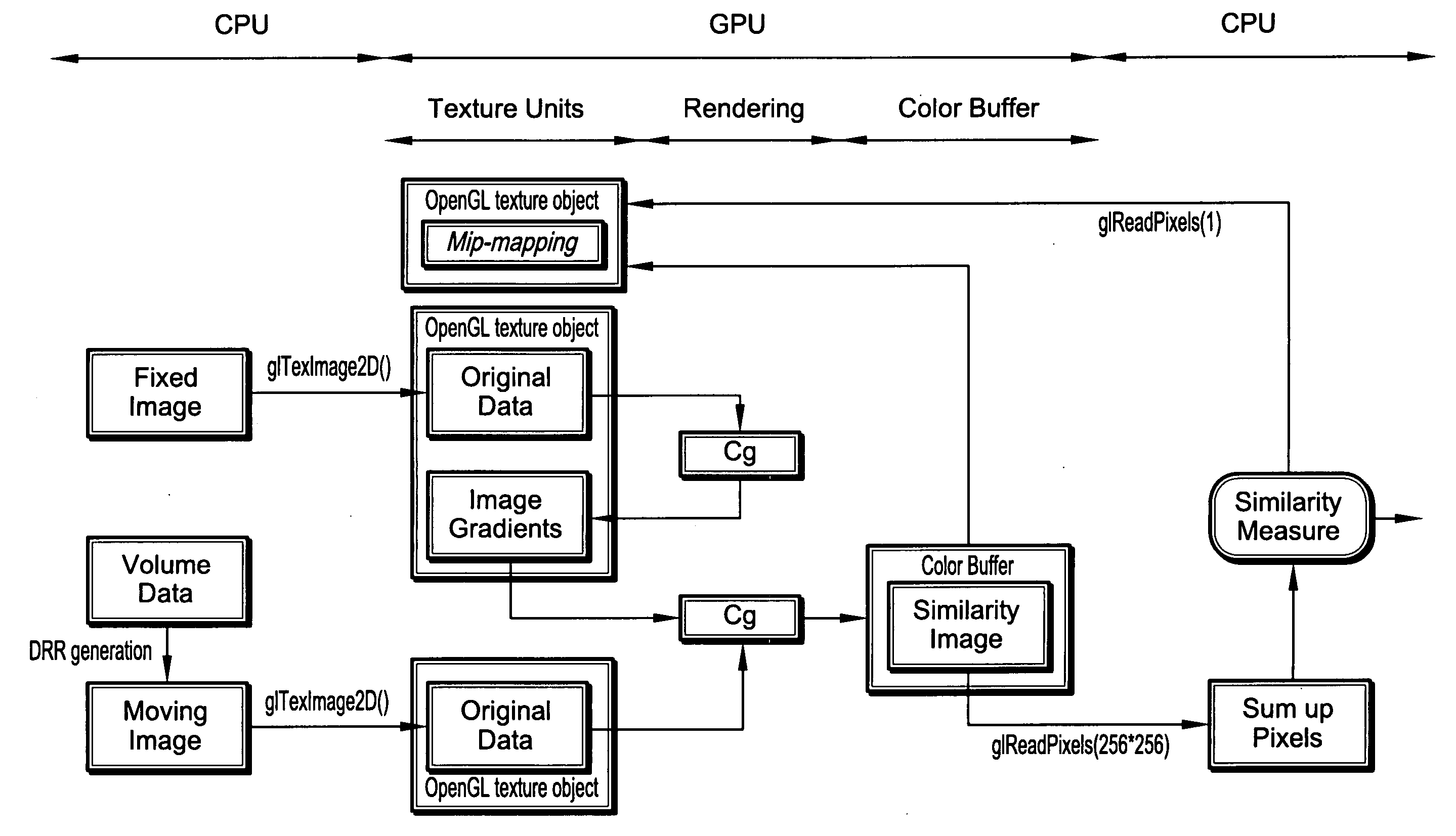
GPU-based image manipulation method for registration applications
Exemplary systems and methods for performing registration applications are provided. An exemplary system includes a central processing unit (CPU) for transferring a plurality of images to a graphics processing unit (GPU); wherein the GPU performs a registration application on the plurality of images to produce a registration result, and wherein the GPU returns the registration result to the CPU. An exemplary method includes the steps of transferring a plurality of images from a central processing unit (CPU) to a graphics processing unit (GPU); performing a registration application on the plurality of images using the GPU; transferring the result of the step of performing from the GPU to CPU.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
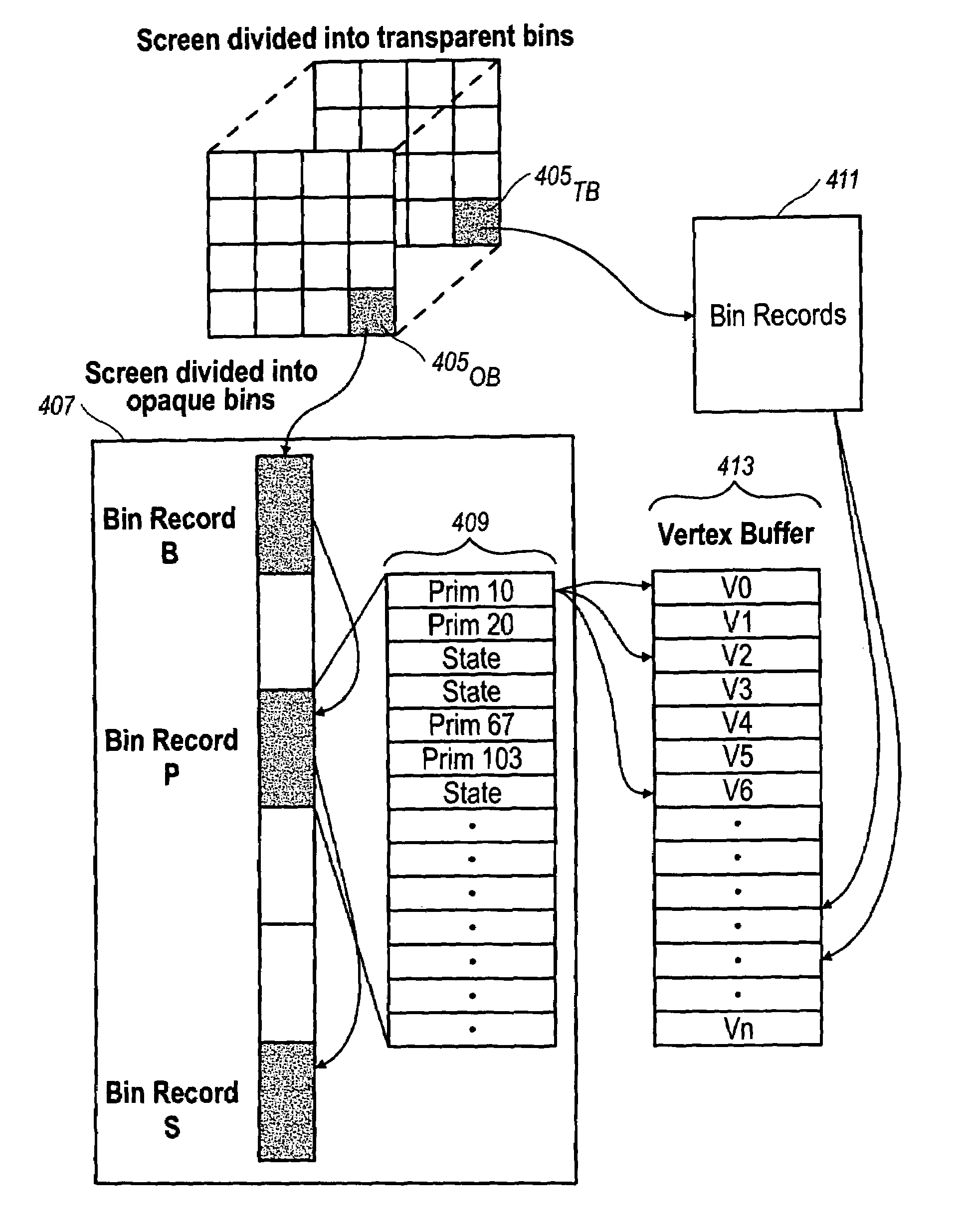
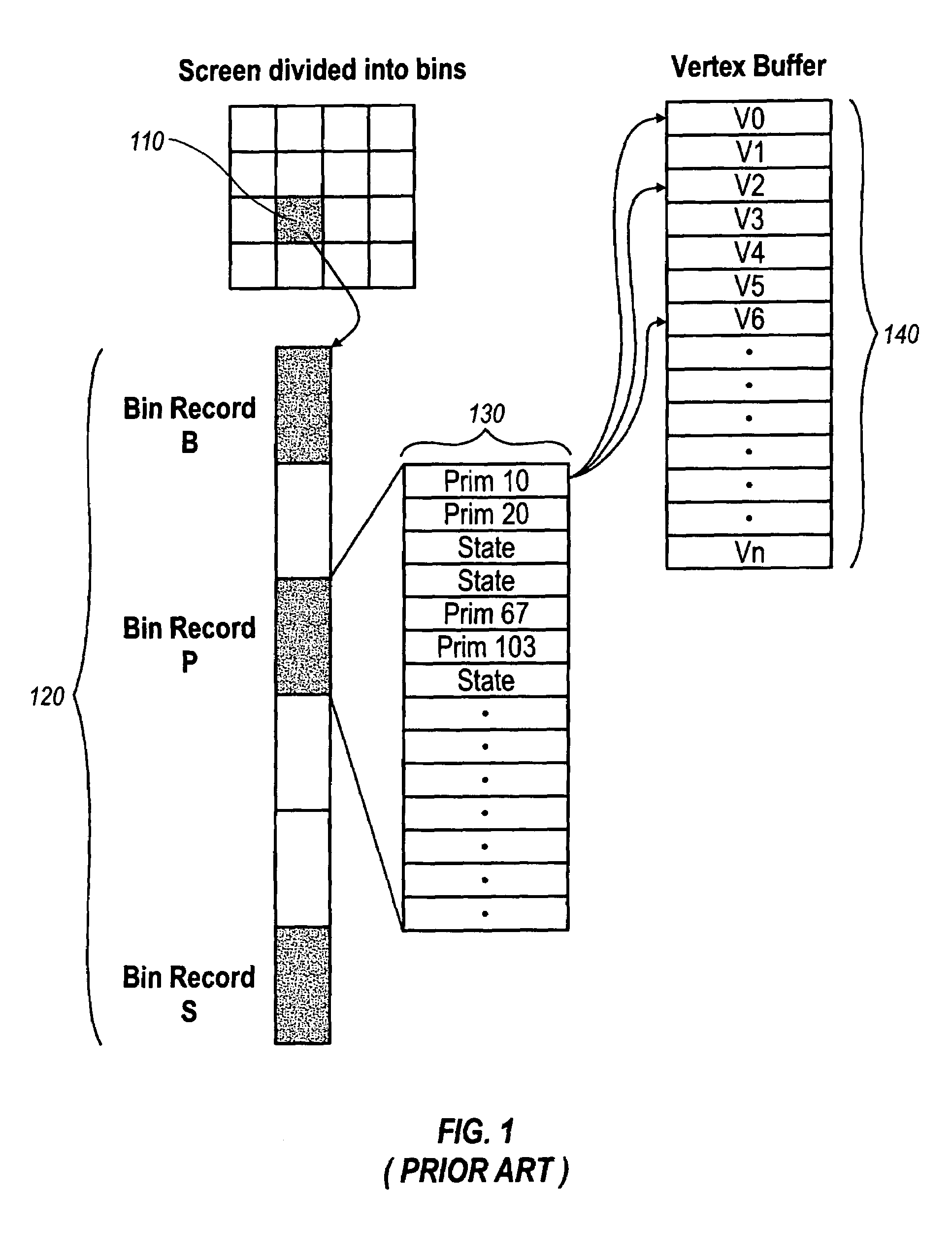
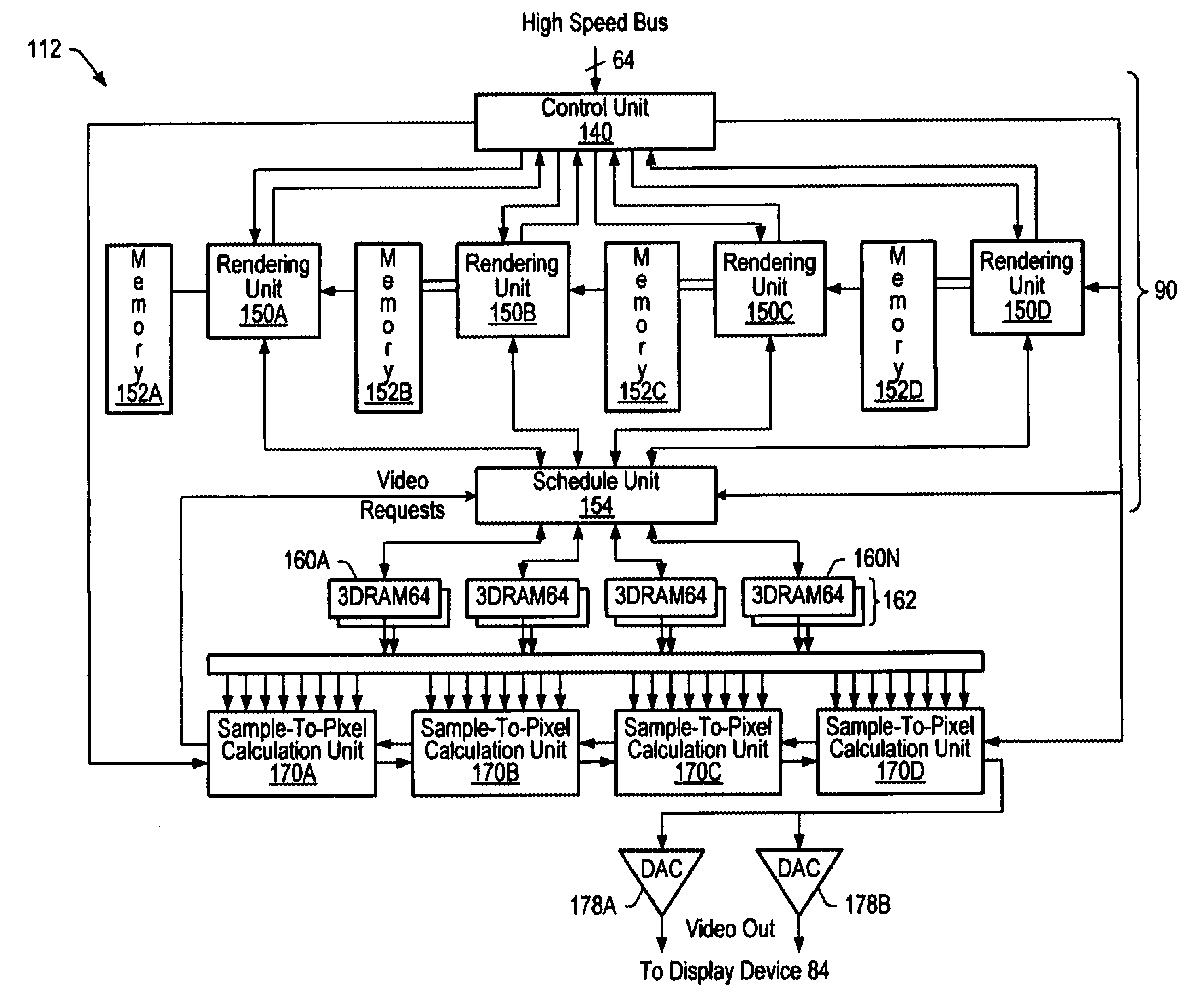
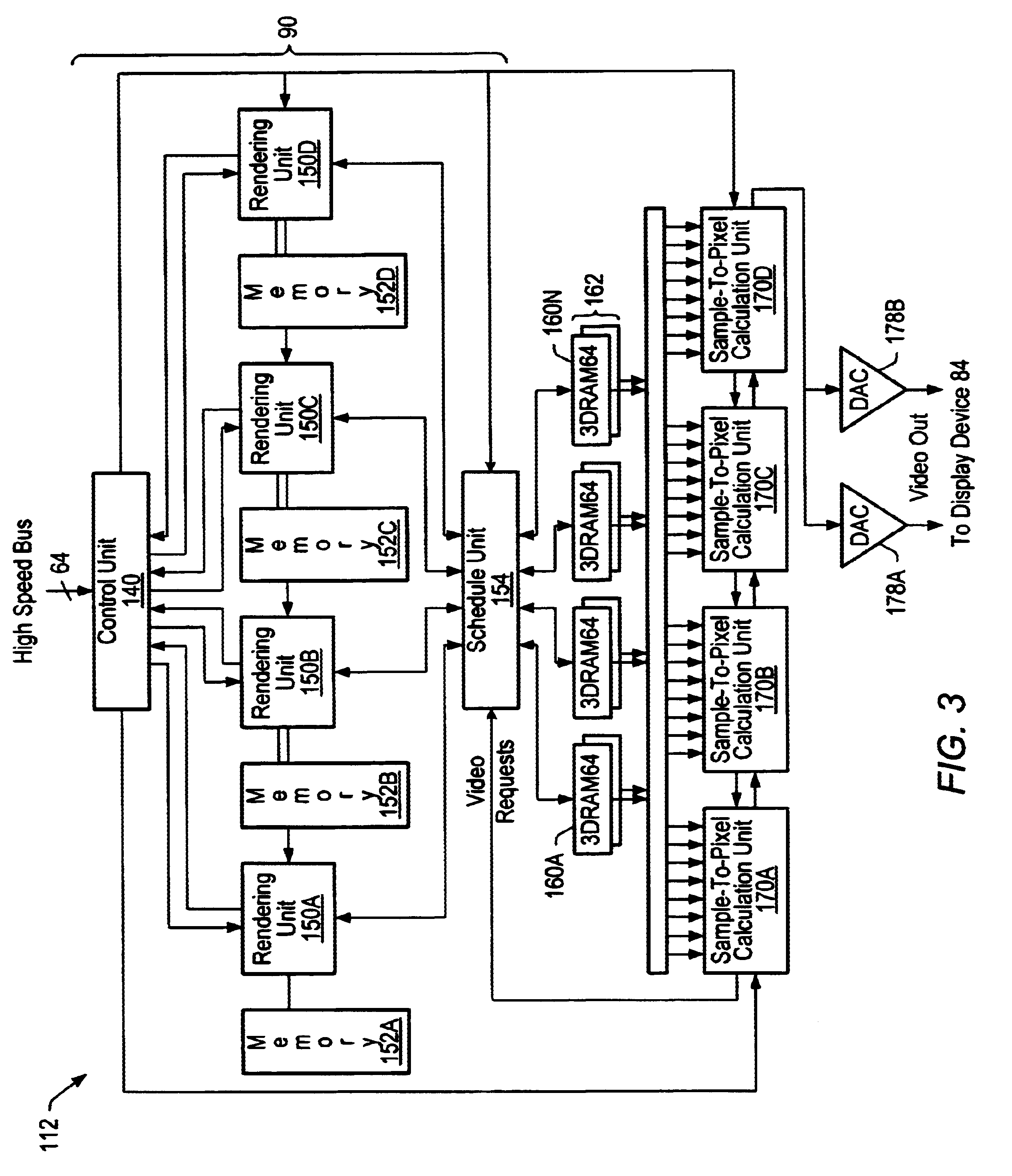
Order-independent 3D graphics binning architecture
ActiveUS7505036B1Increased complexityIncrease frame rateDetails involving image processing hardwareElectric digital data processingGraphicsDepth peeling
A binning architecture that allows opaque and transparent primitives to be segregated automatically into pairs of bins covering the same bin rectangle on the screen. When the frame is complete, the opaque bin will be rendered first and then the transparent bin will be rendered repeatedly using the depth peeling algorithm until all the layers have been resolved. This will happen automatically without requiring the application to isolate and store the transparent primitives until all of the opaque primitives have been rendered or submit the transparent primitives repeated until all of the transparent layers have been resolved.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
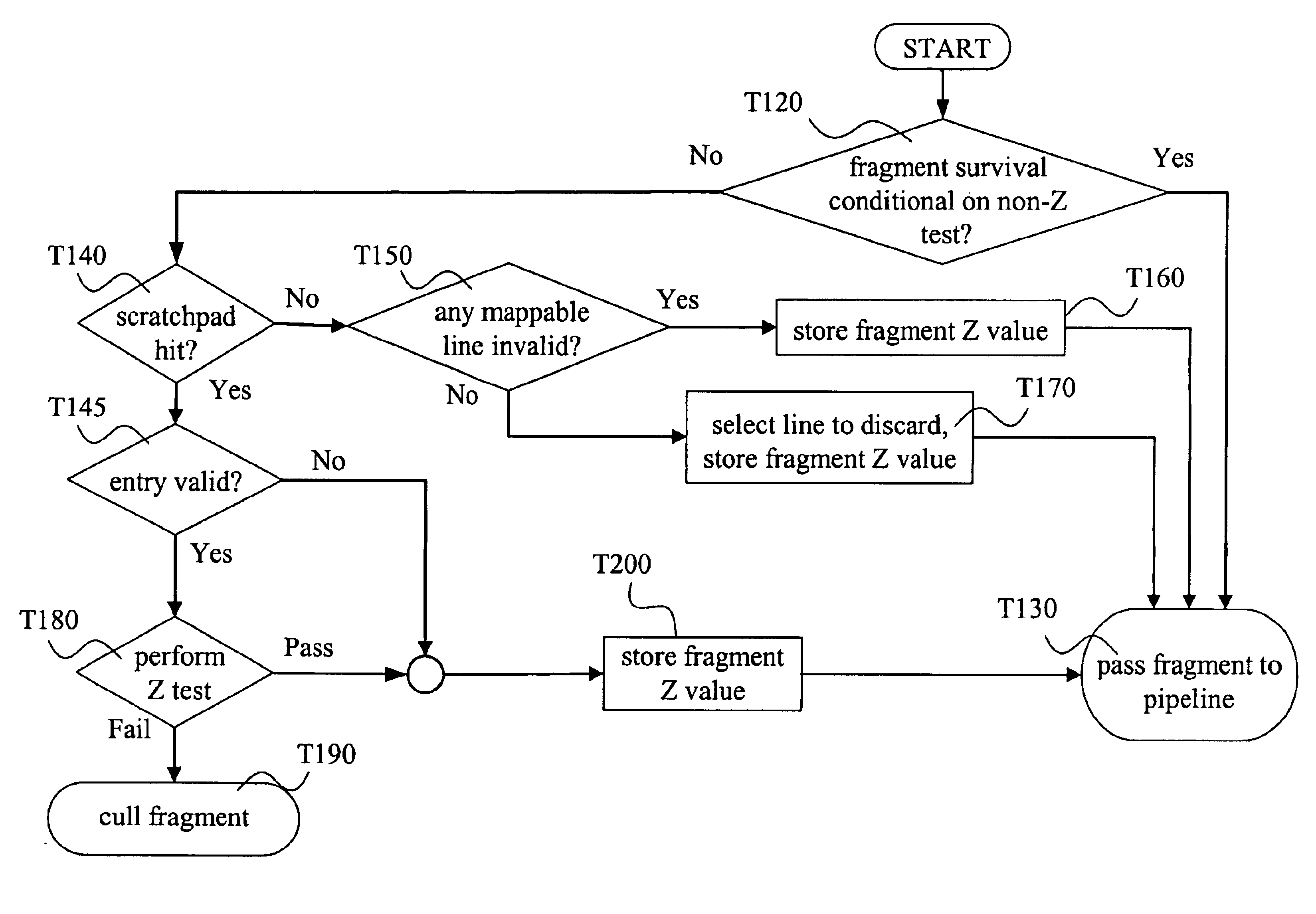
System, method, and apparatus for early culling
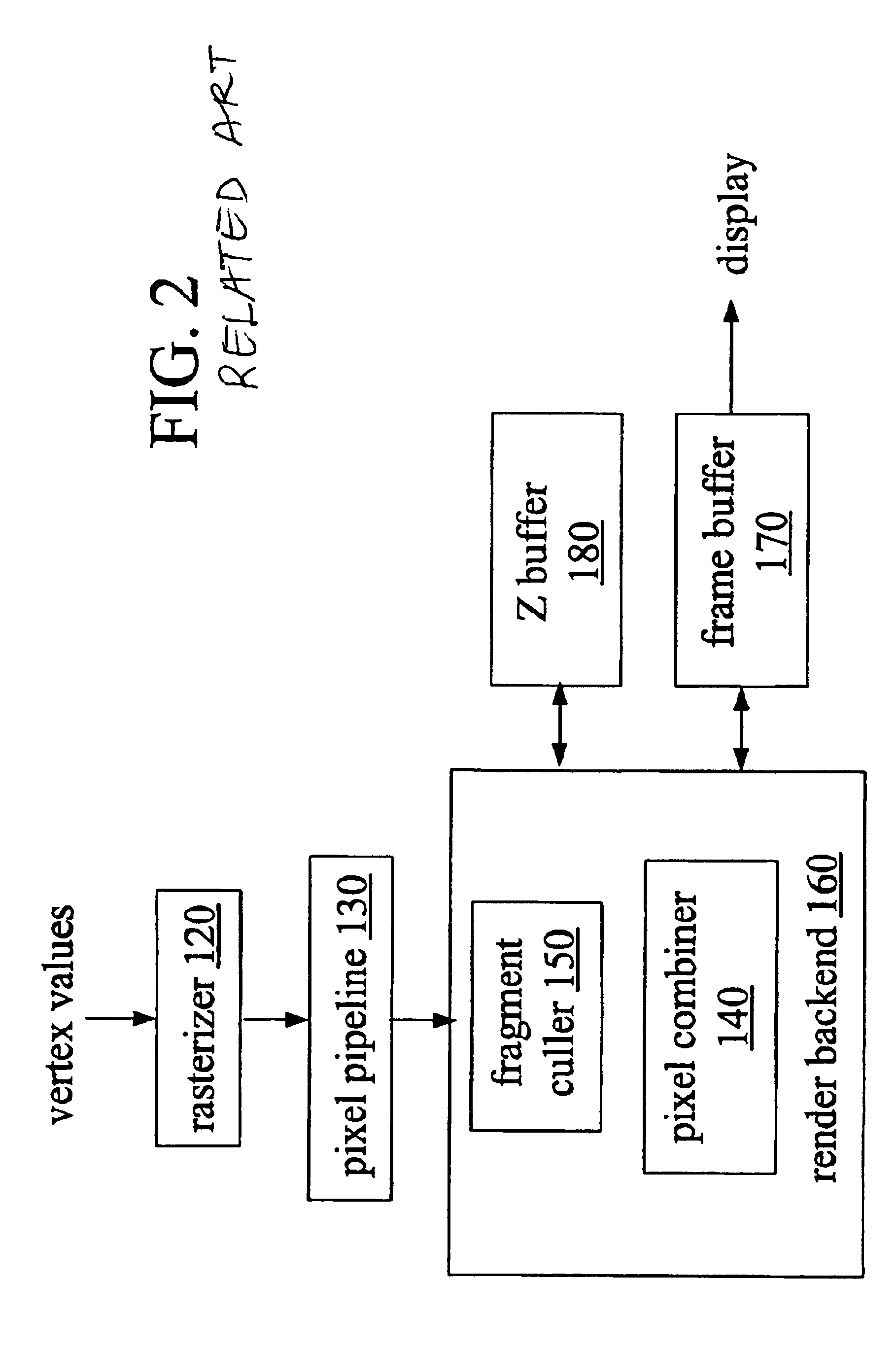
InactiveUS6999076B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails involving image processing hardwareComputational scienceGraphics
A method of graphics processing includes determining a non-depth conditional status and an occlusion status of a fragment. Such a method may be used in culling occluded fragments before expending resources such as processing cycles and memory bus usage. In one example, a scratchpad stores depth values of robust fragments and is used for occlusion testing. Graphics architectures, and methods that include use of representative Z values, are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
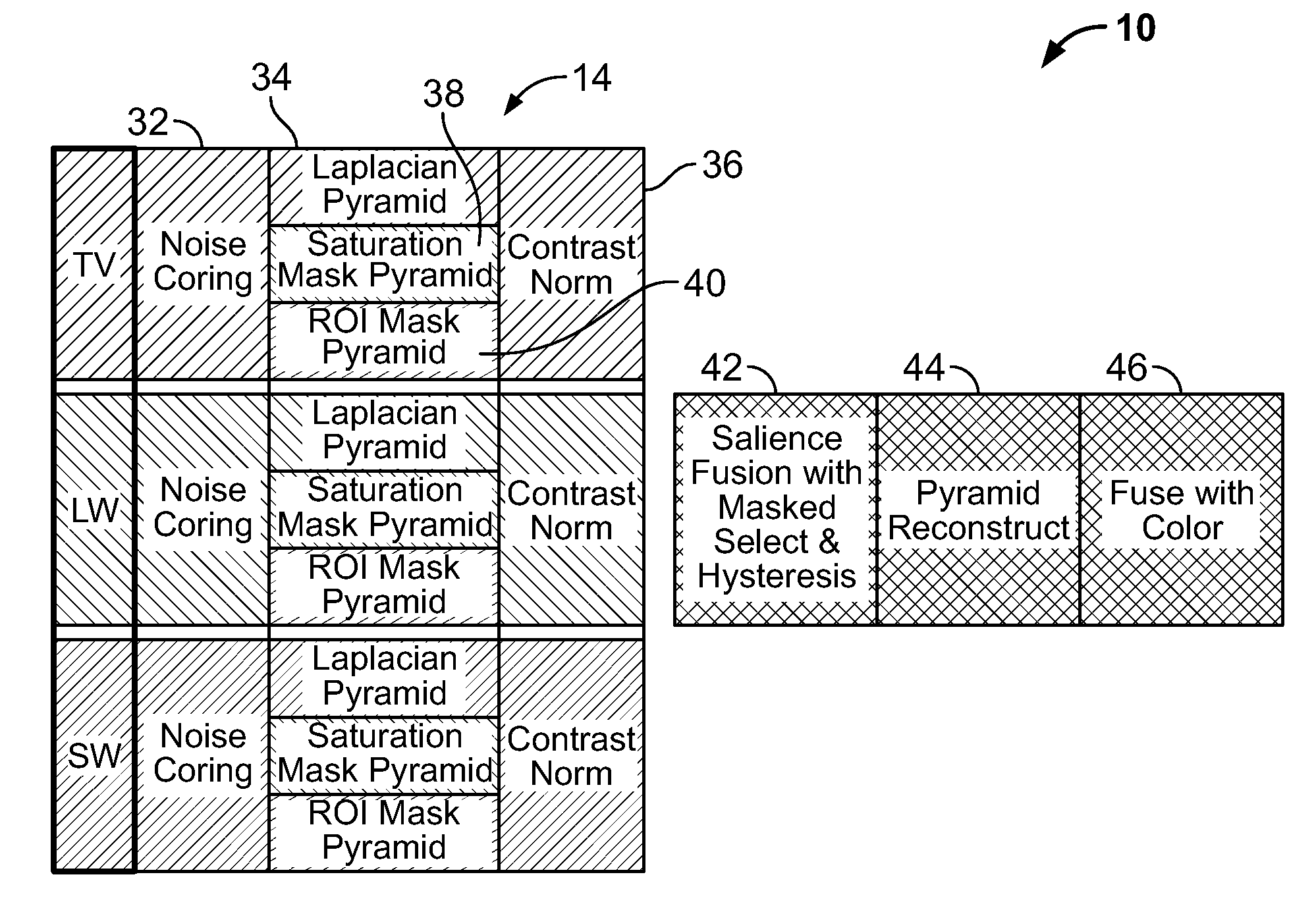
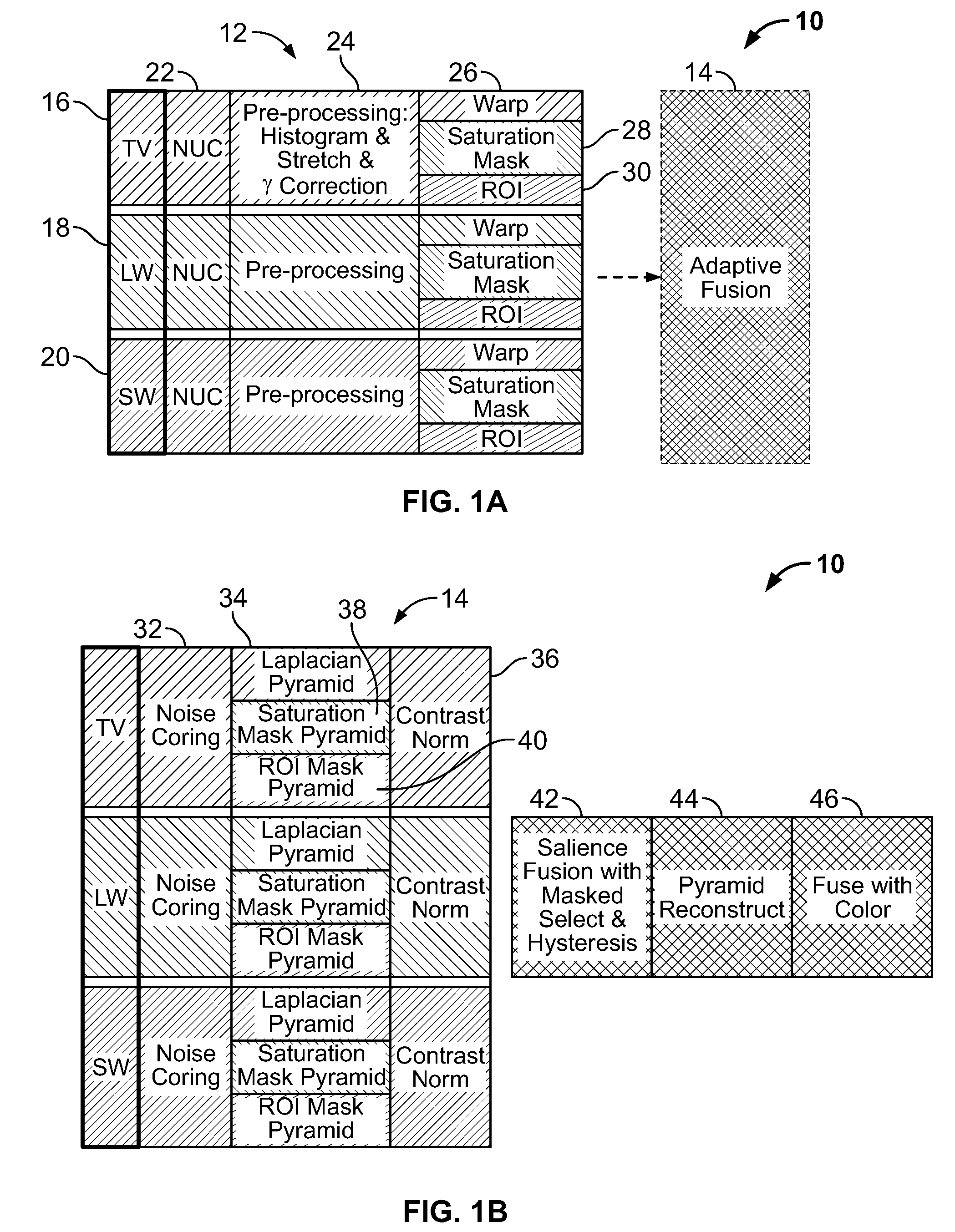
Multi-scale multi-camera adaptive fusion with contrast normalization
ActiveUS20090169102A1Reduce flickering artifactReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementMulti cameraEnergy based
A computer implemented method for fusing images taken by a plurality of cameras is disclosed, comprising the steps of: receiving a plurality of images of the same scene taken by the plurality of cameras; generating Laplacian pyramid images for each source image of the plurality of images; applying contrast normalization to the Laplacian pyramids images; performing pixel-level fusion on the Laplacian pyramid images based on a local salience measure that reduces aliasing artifacts to produce one salience-selected Laplacian pyramid image for each pyramid level; and combining the salience-selected Laplacian pyramid images into a fused image. Applying contrast normalization further comprises, for each Laplacian image at a given level: obtaining an energy image from the Laplacian image; determining a gain factor that is based on at least the energy image and a target contrast; and multiplying the Laplacian image by a gain factor to produce a normalized Laplacian image.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
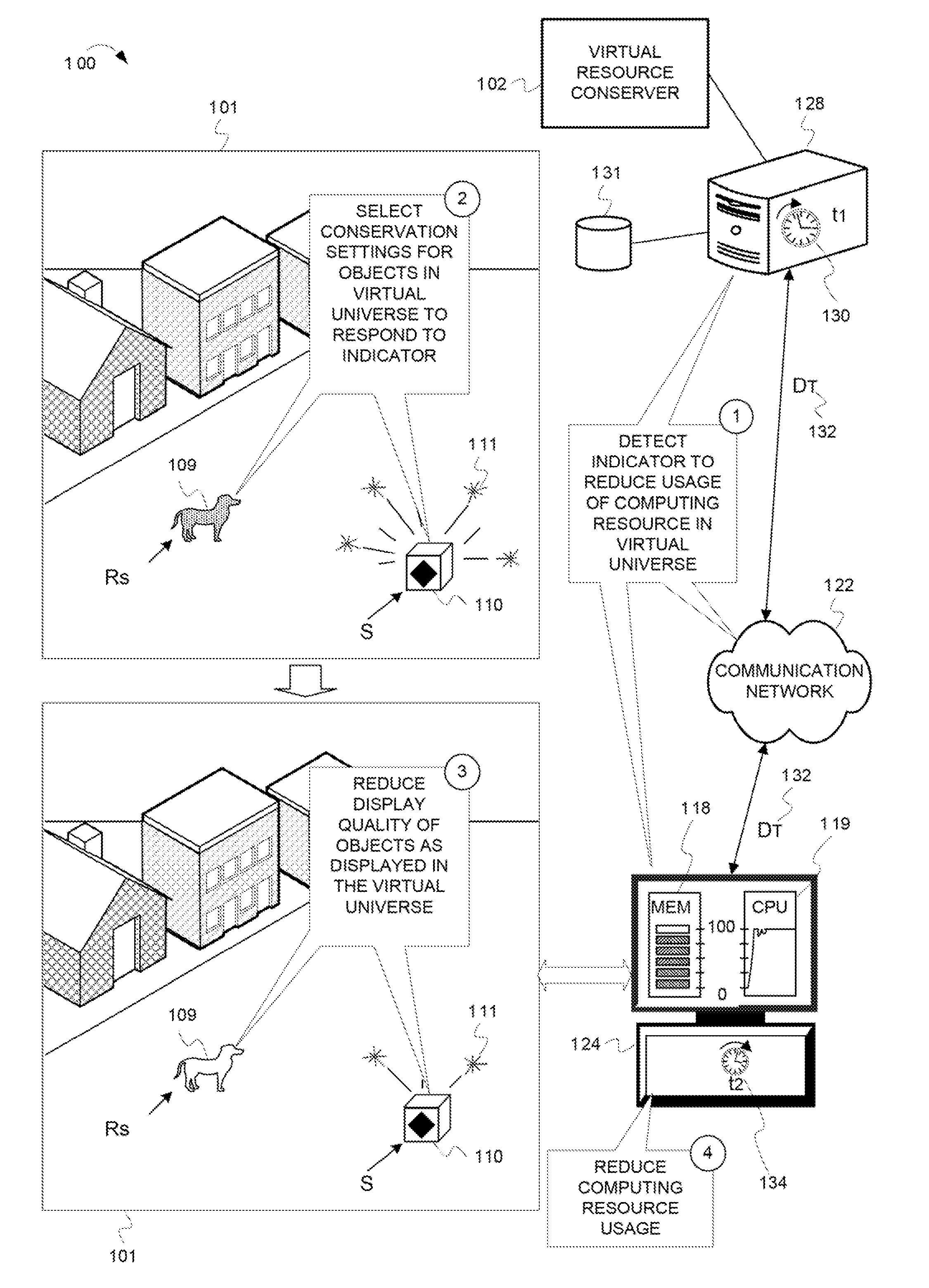
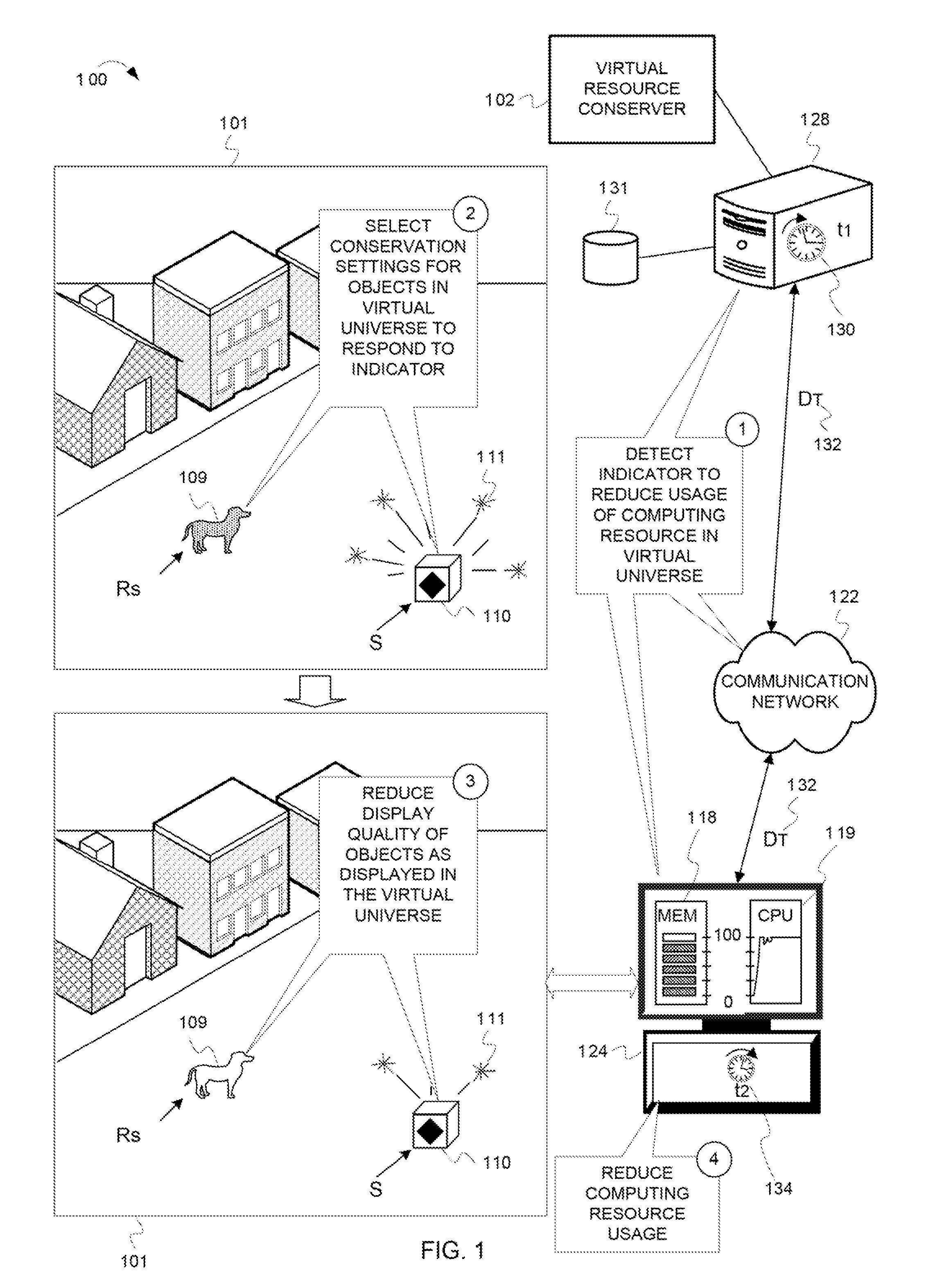
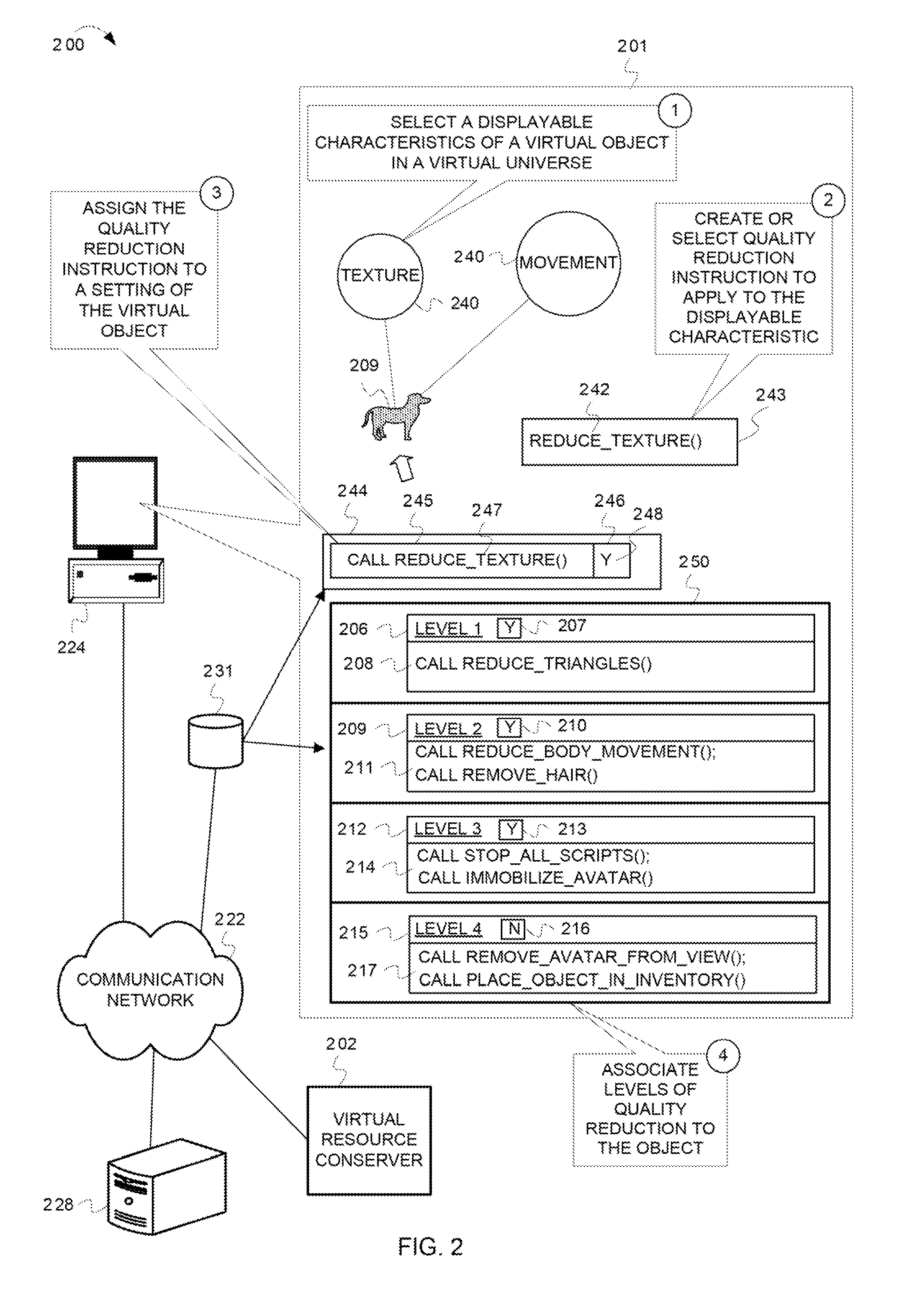
Reducing a display quality of an area in a virtual universe to conserve computing resources
ActiveUS8013861B2Quality improvementReduce displayAnimationVideo gamesHuman–computer interactionVirtual universe
Described herein are processes and devices that reduce a display quality of an area of a virtual universe to conserve computing resources. One of the devices described is a virtual resource conserver. The virtual resource conserver determines, or selects, an area in the virtual universe. A computing resource processes data for presenting the area in the virtual universe. The virtual resource conserver evaluates significance factors about the area to determine a significance of how the area is being used, or an extent to which an area is being viewed by an avatar. The virtual resource conserver reduces a display quality of the area based on the significance of how the area is being used or viewed. The virtual resource conserver thus reduces usage of the computing resource.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
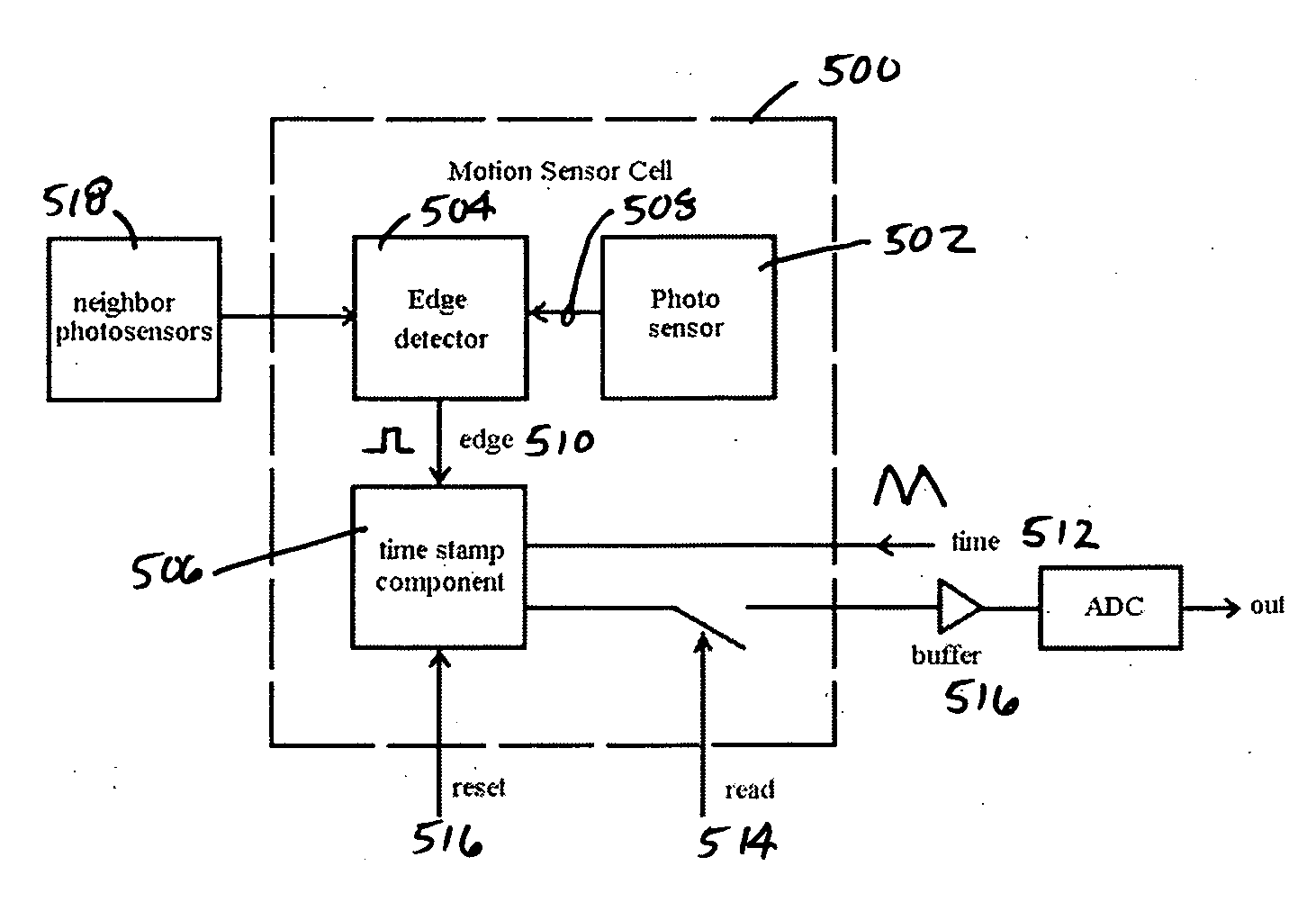
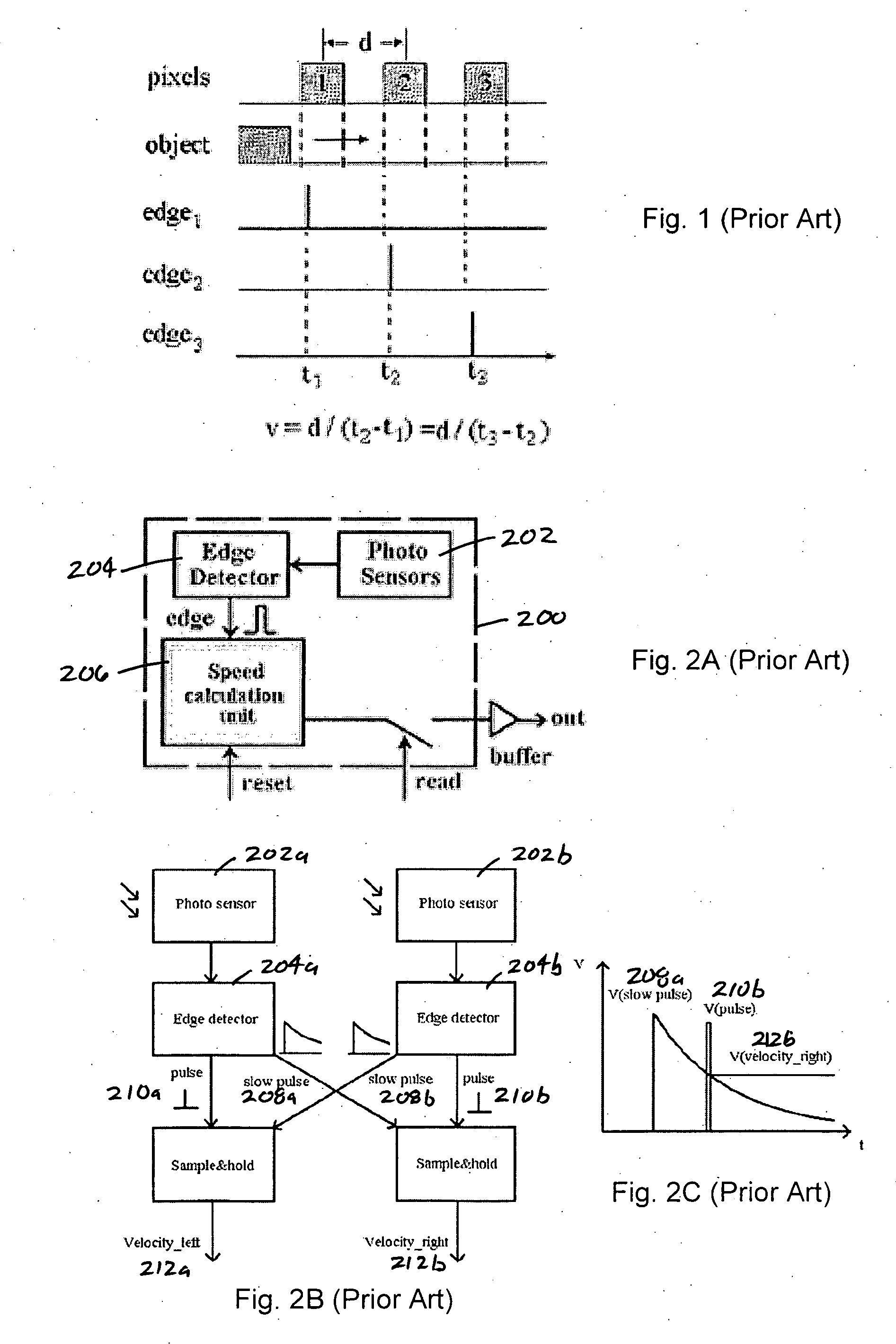
Method, system and apparatus for a time stamped visual motion sensor
InactiveUS20060197664A1Improve accuracyHigh detectionImage analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementData transmissionComputer science
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for a time stamped visual motion sensor that provides a compact pixel size, higher speed motion detection and accuracy in velocity computation, high resolution, low power integration and reduces the data transfer and computation load of the following digital processor. The present invention provides a visual motion sensor cell that includes a photosensor, an edge detector connected to the photosensor and a time stamp component connected to the edge detector. The edge detector receives inputs from the photosensor and generates a pulse when a moving edge is detected. The time stamp component tracks a time signal and samples a time voltage when the moving edge is detected. The sampled time voltage can be stored until the sampled time voltage is read. In addition, the edge detector can be connected to one or more neighboring photosensors to improve sensitivity and robustness.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
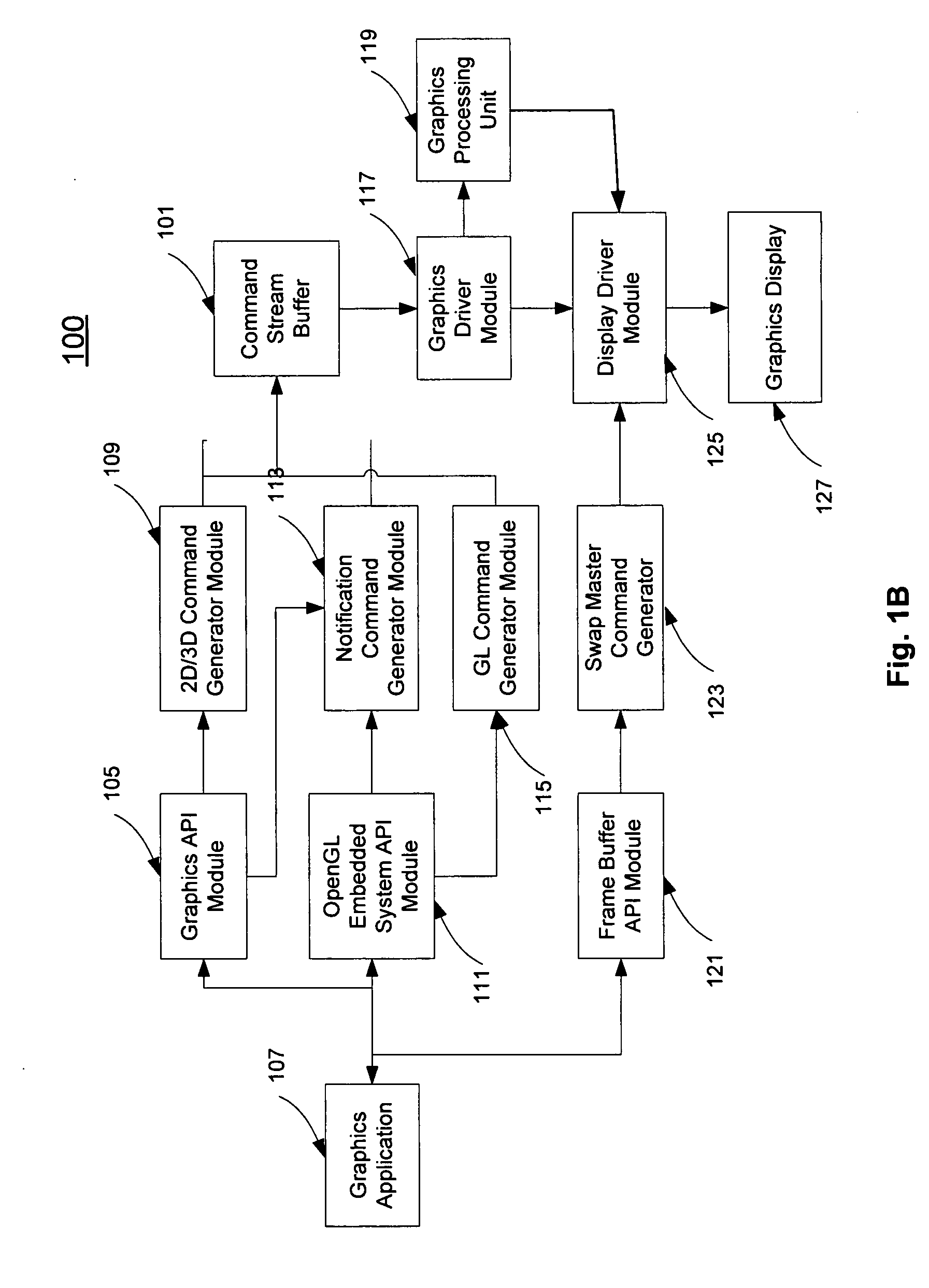
Asnchronous notifications for concurrent graphics operations
ActiveUS20080303833A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsGraphics processing unit
A method and an apparatus for notifying a display driver to update a display with a graphics frame including multiple graphics data rendered separately by multiple graphics processing units (GPUs) substantially concurrently are described. Graphics commands may be received to dispatch to each GPU for rendering corresponding graphics data. The display driver may be notified when each graphics data has been completely rendered respectively by the corresponding GPU.
Owner:APPLE INC
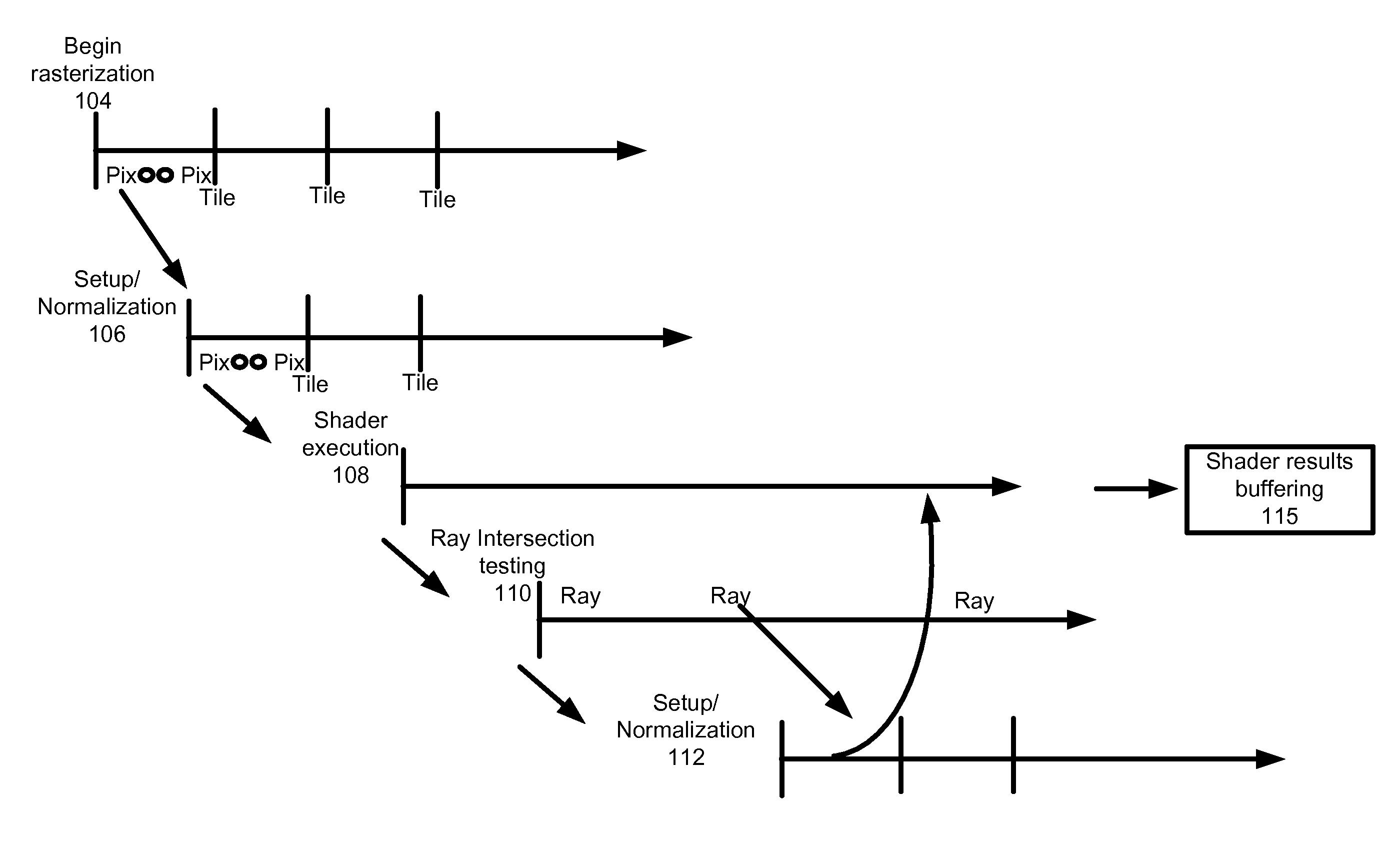
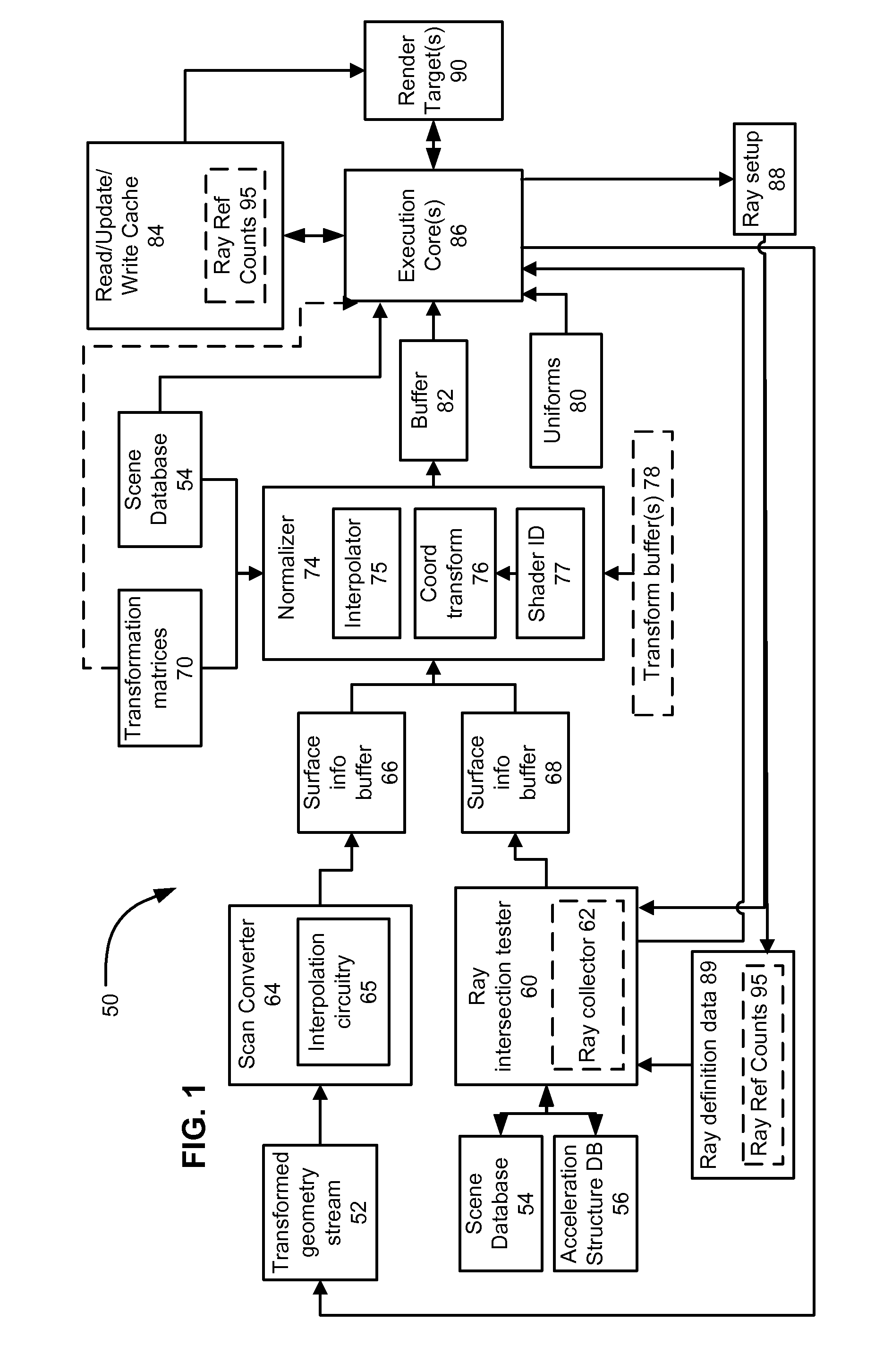
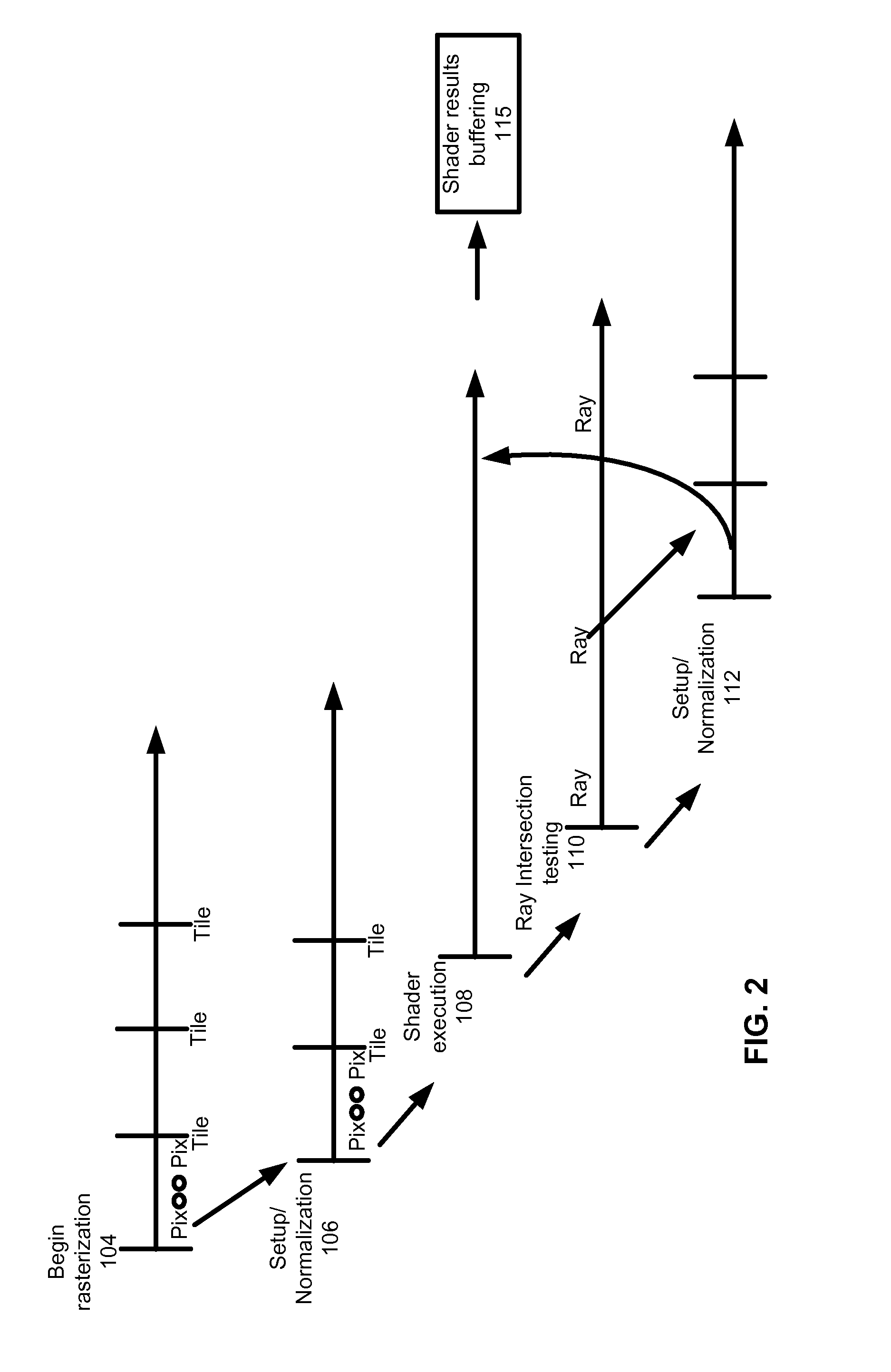
Unified rasterization and ray tracing rendering environments
A graphics processor architecture provides for scan conversion and ray tracing approaches to visible surface determination as concurrent and separate processes. Surfaces can be identified for shading by scan conversion and ray tracing. Data produced by each can be normalized, so that instances of shaders, being executed on a unified shading computation resource, can shade surfaces originating from both ray tracing and rasterization. Such resource also may execute geometry shaders. The shaders can emit rays to be tested for intersection by the ray tracing process. Such shaders can complete, without waiting for those emitted rays to complete. Where scan conversion operates on tiles of 2-D screen pixels, the ray tracing can be tile aware, and controlled to prioritize testing of rays based on scan conversion status. Ray population can be controlled by feedback to any of scan conversion, and shading.
Owner:IMAGINATION TECH LTD
Graphics system configured to interpolate pixel values
InactiveUS6664955B1Geometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsImage resolution
A method and computer graphics system capable of super-sampling and performing real-time convolution are disclosed. In one embodiment, the computer graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to generate a plurality of samples. The sample buffer, which is coupled to the graphics processor, may be configured to store the samples. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is programmable to generate a first subset of pixels by filtering using the rendered samples and a second subset of the output pixels by interpolating using the first subset of pixels and / or the rendered samples. By interpolating a subset of the output pixels, the graphics system may be able to operate at higher resolutions and / or refresh rates since filtering of the samples is computationally intensive. Any ratio of the number of first subset of pixels to the number of the second subset of pixels may be used, and furthermore, a different ratio may be used for different regions of the display screen. A higher ratio of the number of first subset of pixels to the number of second subset of pixels may be used for regions of the screen where a higher quality image is desired and a lower ration may be used for regions where a lower quality image may be sufficient. For example, a higher quality image may be desired close to and around the foveation point where the eye of an observer is focused.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
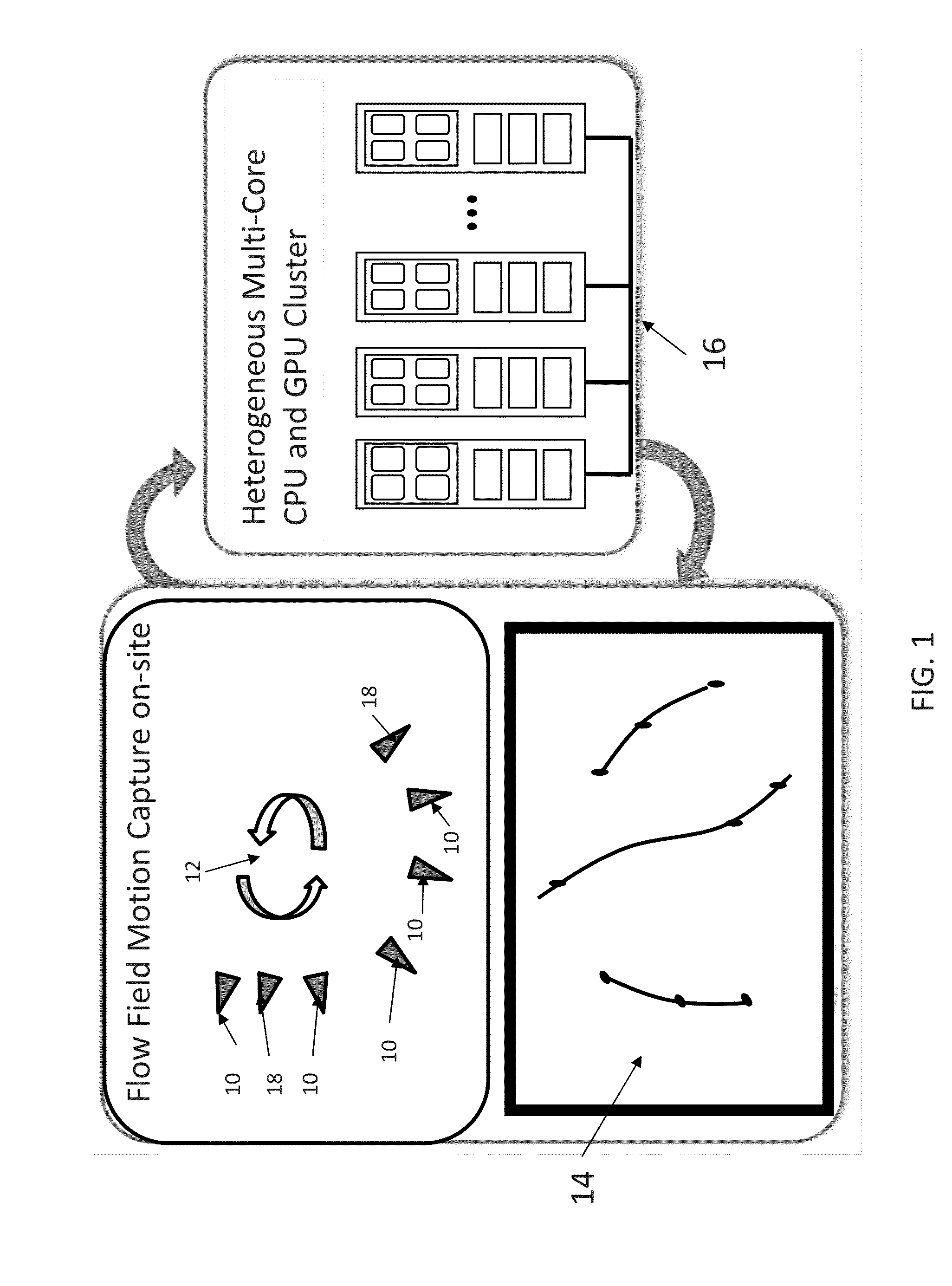
Particle tracking system and method
InactiveUS20140002617A1Increasing observable volumeIncrease volumeImage enhancementImage analysisHigh frame rateStorage Problem
Preferred embodiment systems of the invention use a scalable number of cameras that can image a volume of interest from plurality of angles. The volume can be large and illuminated with general non-coherent illumination. Synchronized cameras process data in real time to addresses particle overlap issues while also increasing observable volumes. Systems of the invention also use higher frame rate cameras to increase the amount of particle travel in each frame. Approaches of the invention alleviate the concerns with additional data accumulation by conducting image processing and segmentation at the time of acquisition prior to transfer from a camera to eliminate a data transfer bottleneck between camera and computer and eliminate a data storage problem. A heterogeneous CPU / GPU processor cluster processes data sent from the plurality of programmable, synchronized cameras and conducting multi-camera correspondence, 3D reconstruction, tracking and result visualization in real time by spreading processing over multiple CPUs and GPUs. Systems of the invention be scaled to hundreds of cameras and fully characterize fluid flows extending to room size and larger.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
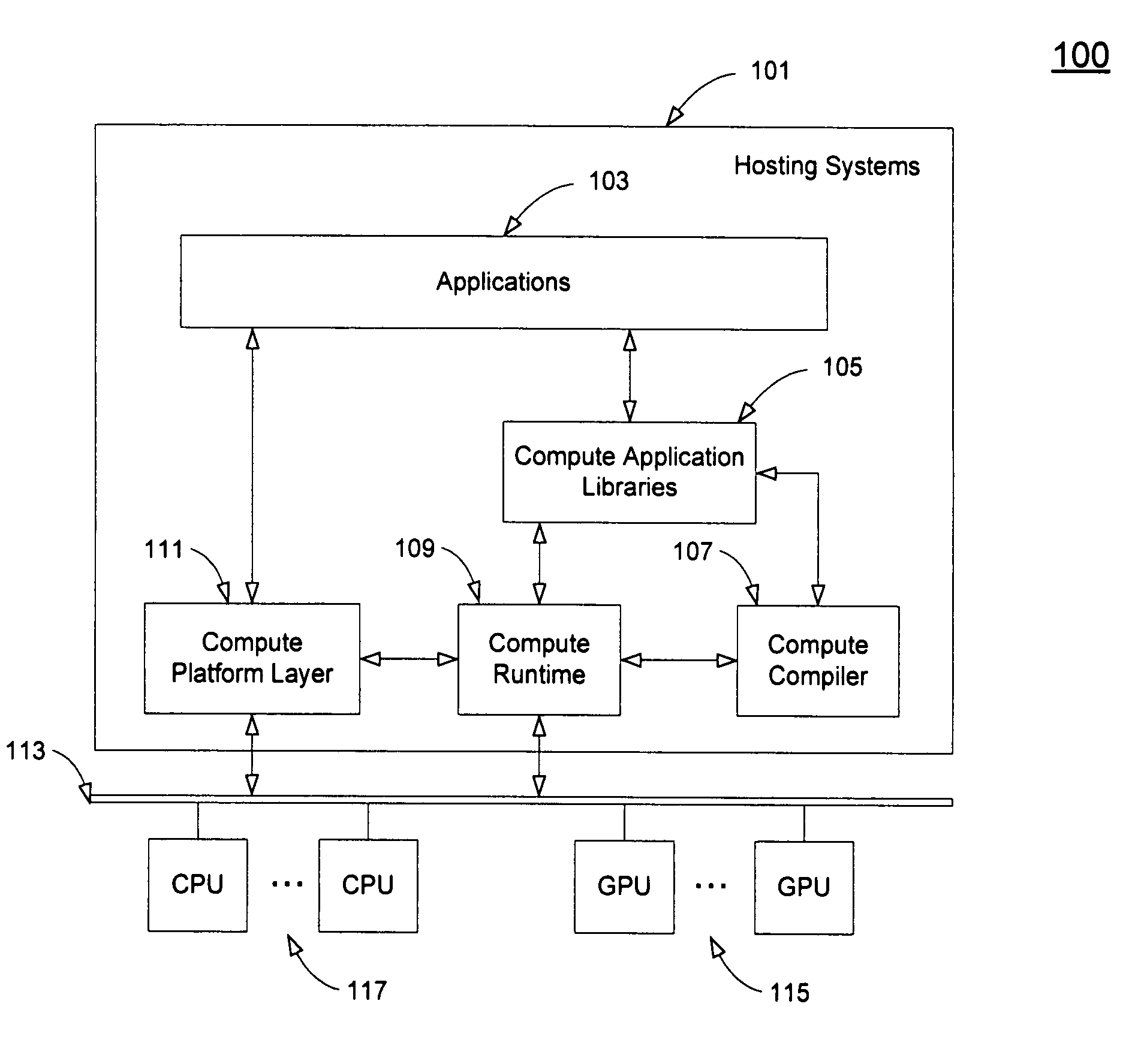
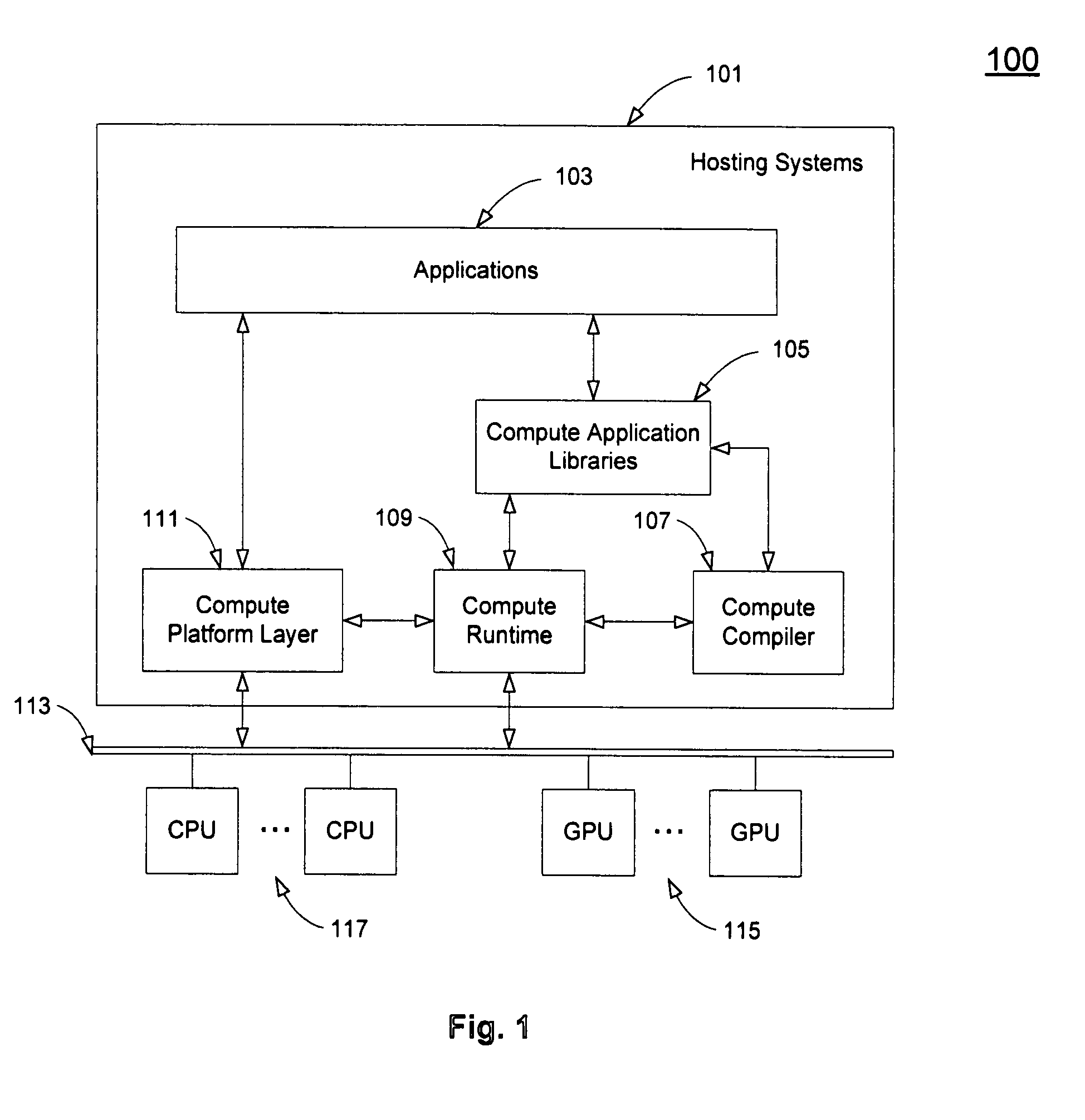
Application interface on multiple processors
ActiveUS20080276220A1Processor architectures/configurationSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsMulti processor
A method and an apparatus that execute a parallel computing program in a programming language for a parallel computing architecture are described. The parallel computing program is stored in memory in a system with parallel processors. The system includes a host processor, a graphics processing unit (GPU) coupled to the host processor and a memory coupled to at least one of the host processor and the GPU. The parallel computing program is stored in the memory to allocate threads between the host processor and the GPU. The programming language includes an API to allow an application to make calls using the API to allocate execution of the threads between the host processor and the GPU. The programming language includes host function data tokens for host functions performed in the host processor and kernel function data tokens for compute kernel functions performed in one or more compute processors, e.g. GPUs or CPUs, separate from the host processor. Standard data tokens in the programming language schedule a plurality of threads for execution on a plurality of processors, such as CPUs or GPUs in parallel. Extended data tokens in the programming language implement executables for the plurality of threads according to the schedules from the standard data tokens.
Owner:APPLE INC
Parallel model processing method and device based on multiple graphics processing units
ActiveCN104036451AImprove processing efficiencyImprove the efficiency of storage accessProcessor architectures/configurationProgram controlGraphicsVideo memory
The invention relates to a parallel model processing method based on multiple graphics processing units (GPUs). The method includes the steps: creating multiple Workers used for respectively controlling multiple Worker Groups in a central processing unit (CPU), wherein each Worker Group comprises the GPUs; binding each Worker with one corresponding GPU; loading one Batch of training data from a nonvolatile memory into a GPU video memory corresponding to one Worker Group; transmitting data, needed by the GPUs for data processing, among the GPUs corresponding to one Worker Group in a Peer to Peer manner; controlling the GPUs to perform data processing in parallel through the Workers. By the method, efficiency of parallel data processing of the GPUs can be improved. Besides, the invention further provides a parallel data processing device.
Owner:SHENZHEN TENCENT COMP SYST CO LTD
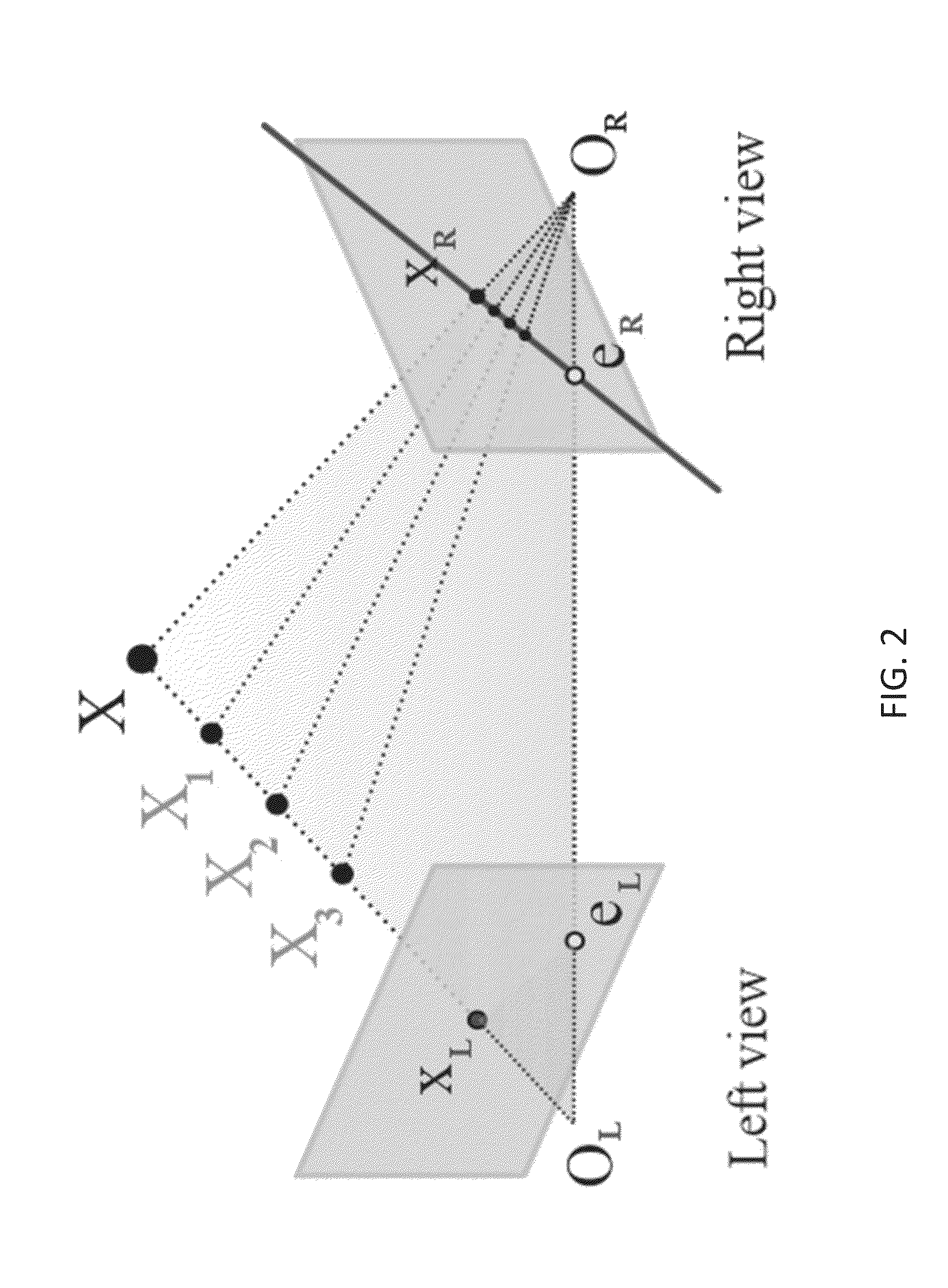
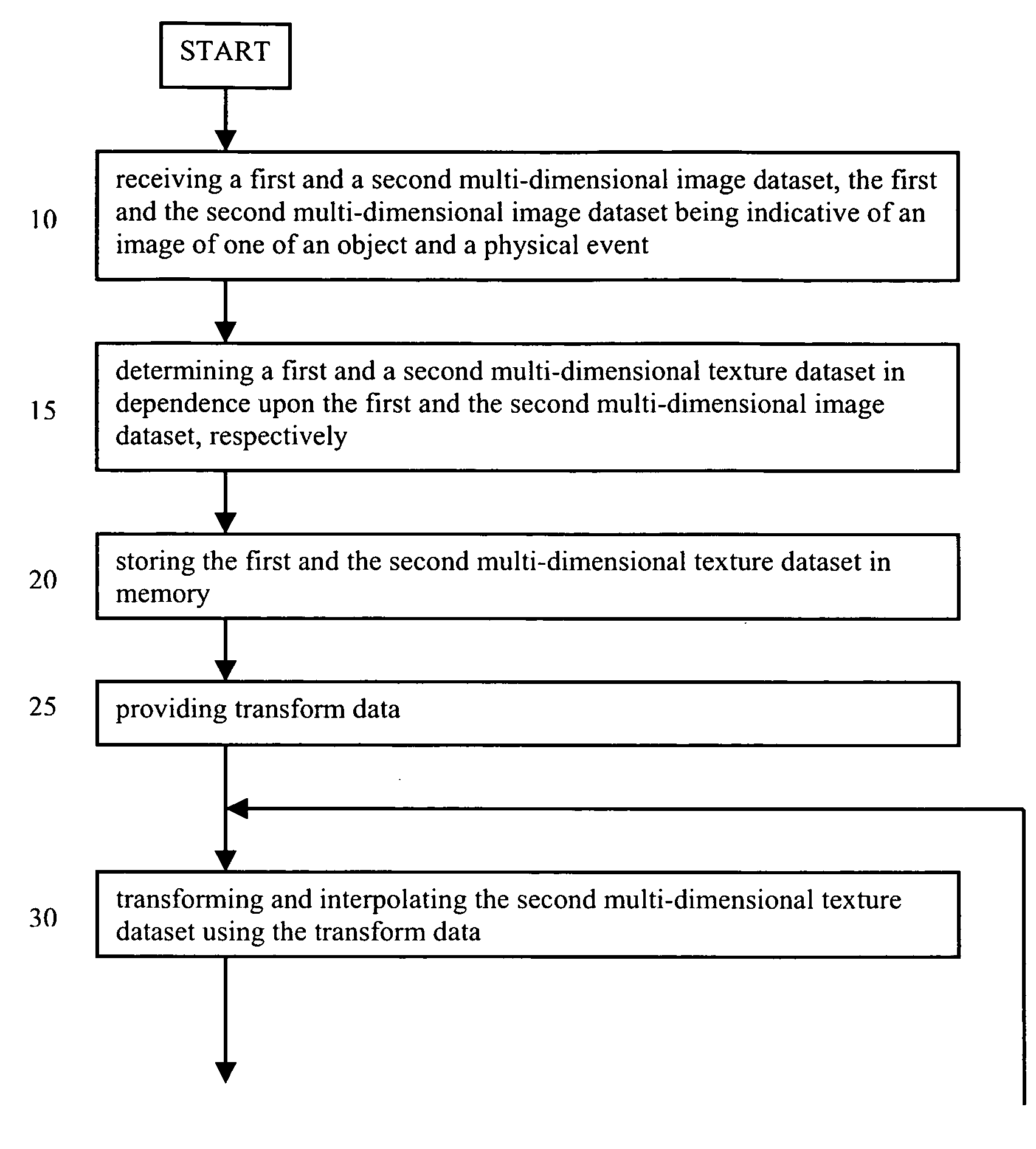
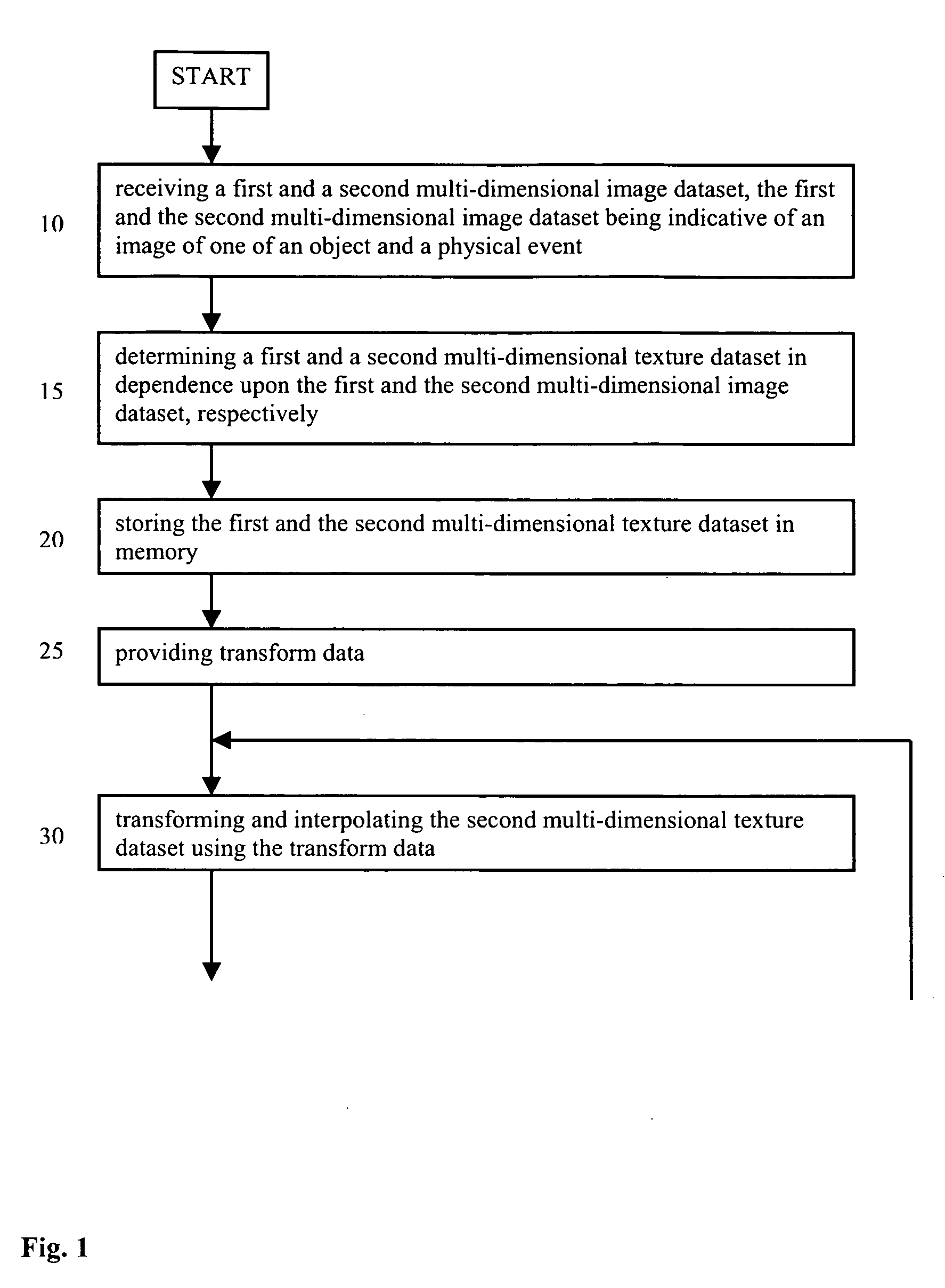
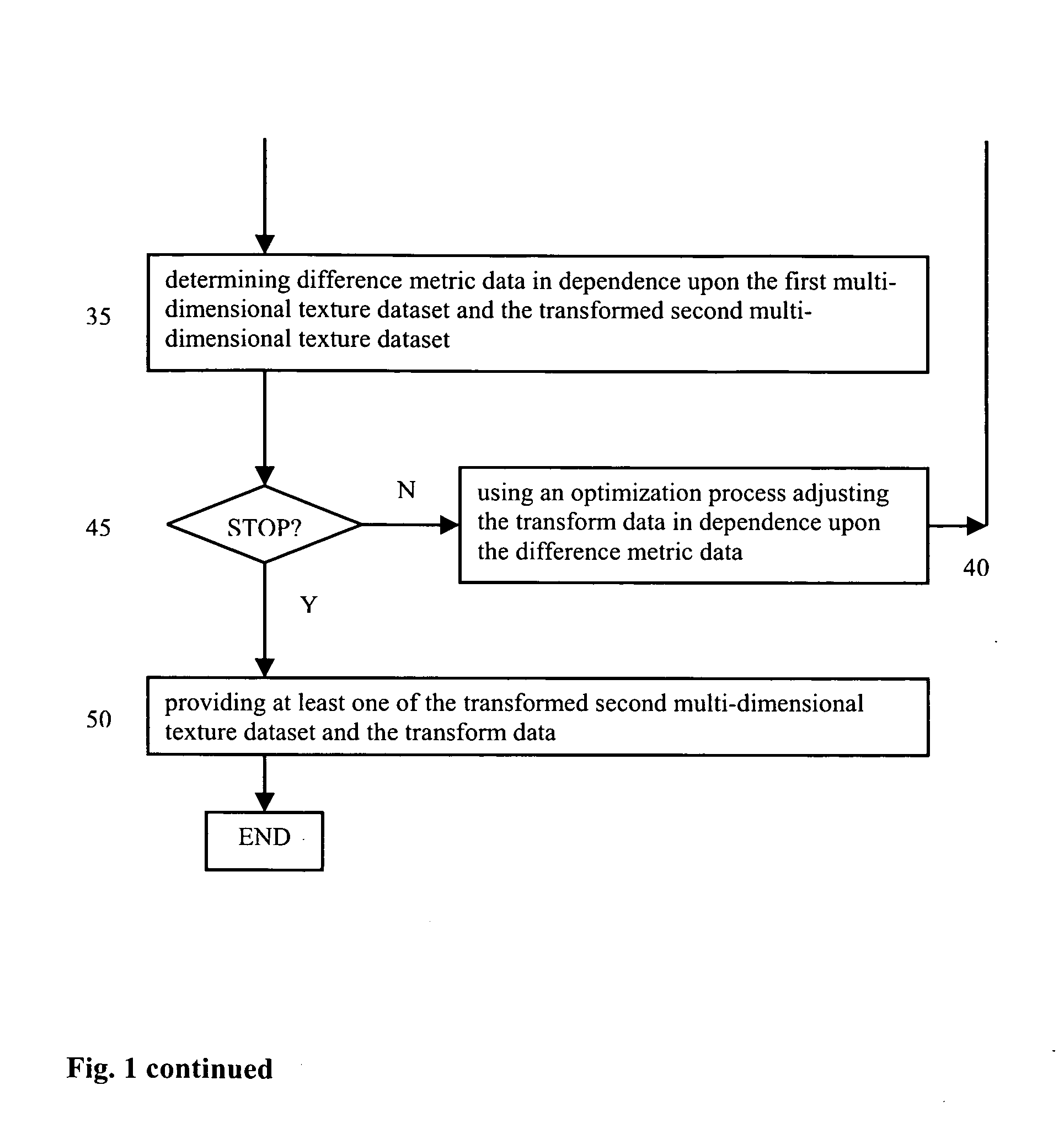
Texture-based multi-dimensional medical image registration
The present invention relates to a method for registering multi-dimensional image data. First and second multi-dimensional texture datasets are determined in dependence upon received first and second multi-dimensional image datasets, respectively. Initial transform data are then provided. The second multi-dimensional texture dataset is then transformed and interpolated using the transform data. Difference metric data are determined in dependence upon the first multi-dimensional texture dataset and the transformed second multi-dimensional texture dataset. Using an improvement process the transform data are adjusted. The transformation and adjustment of the transform data is iterated until a stopping criterion is satisfied. Use of texture data allows employment of a texture unit of a graphics processor for the transformation, the interpolation and the determination of the difference metric data.
Owner:CALGARY SCIENTIFIC INC
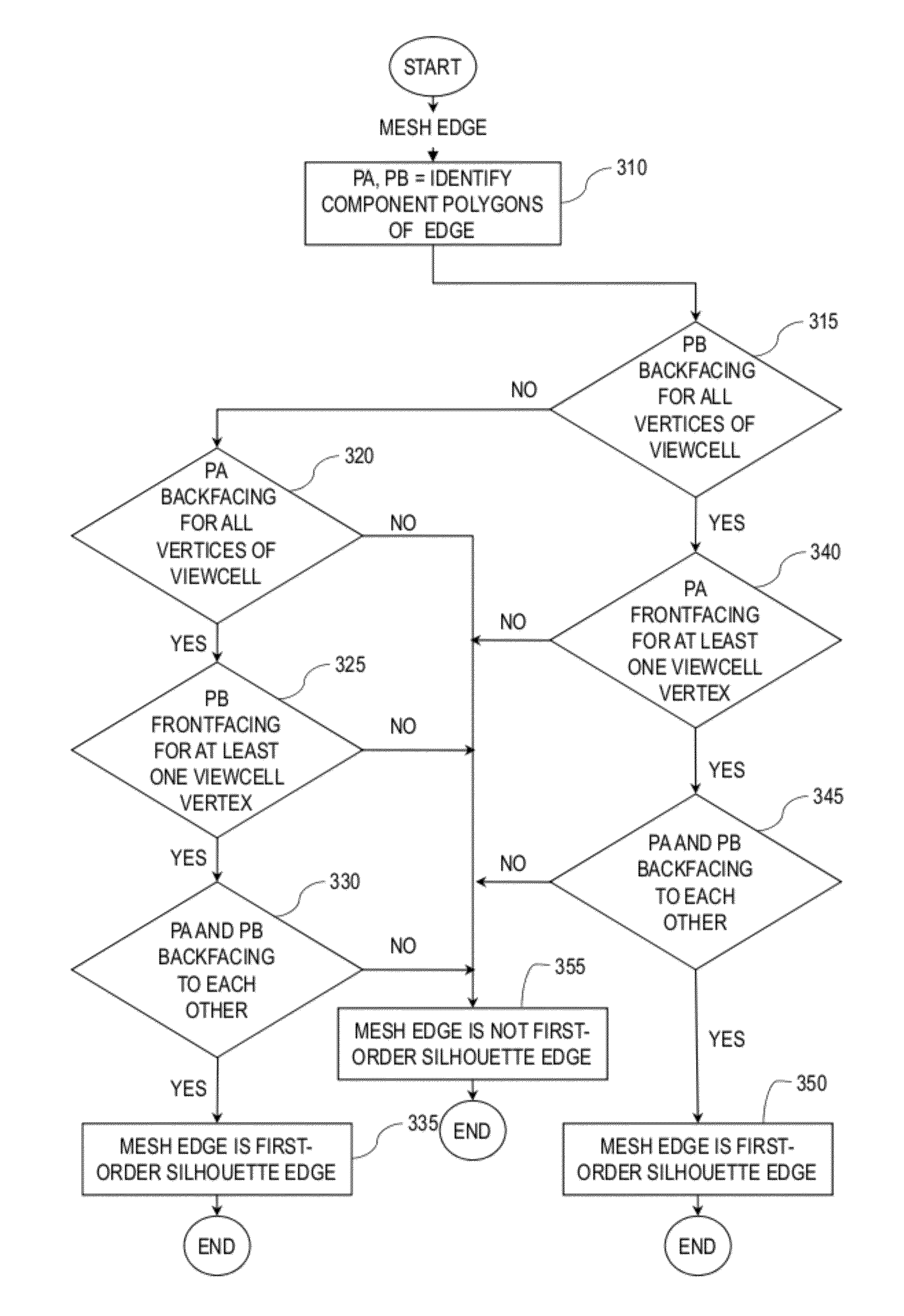
System and method of reducing transmission bandwidth required for visibility-event streaming of interactive and non-interactive content
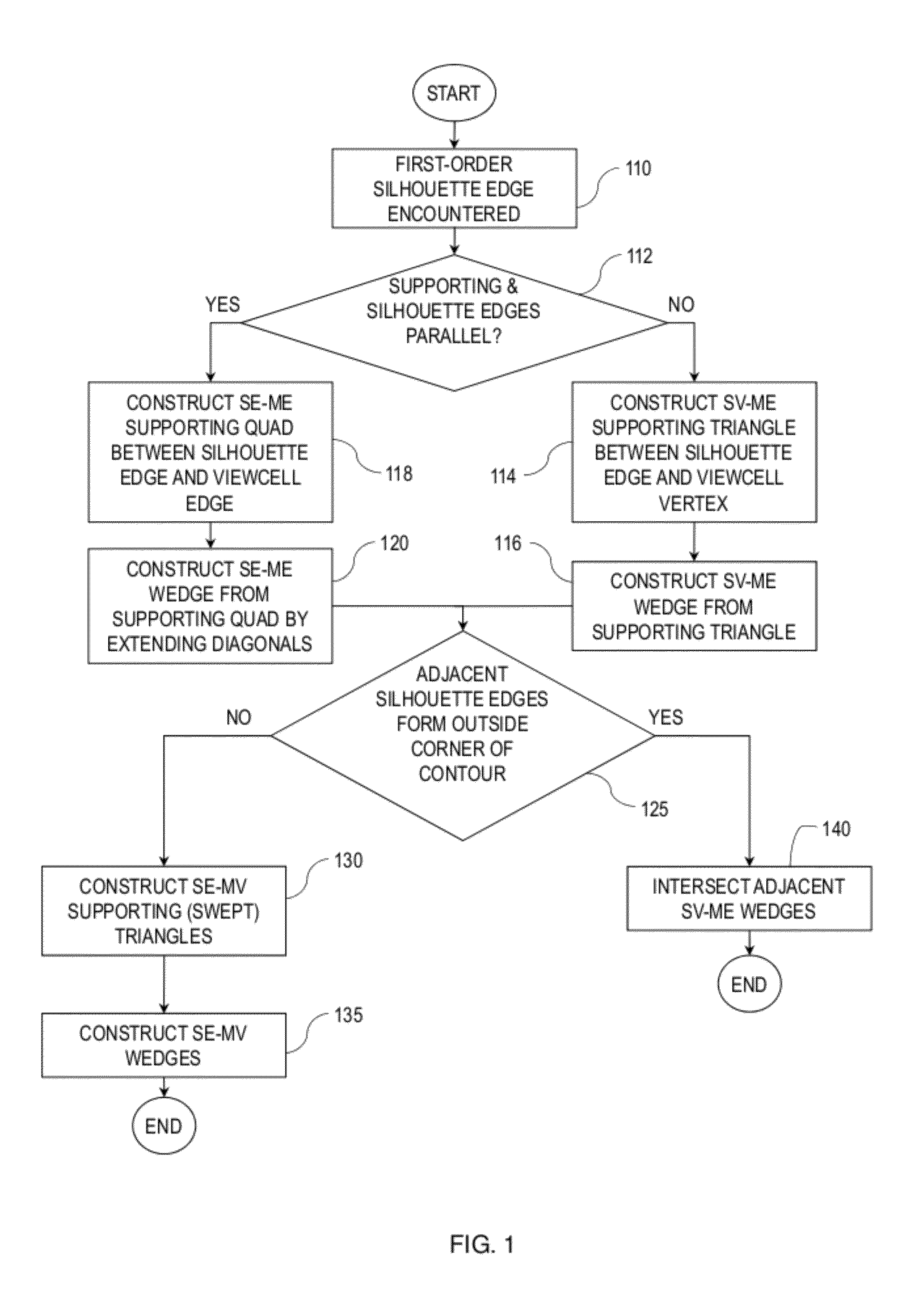
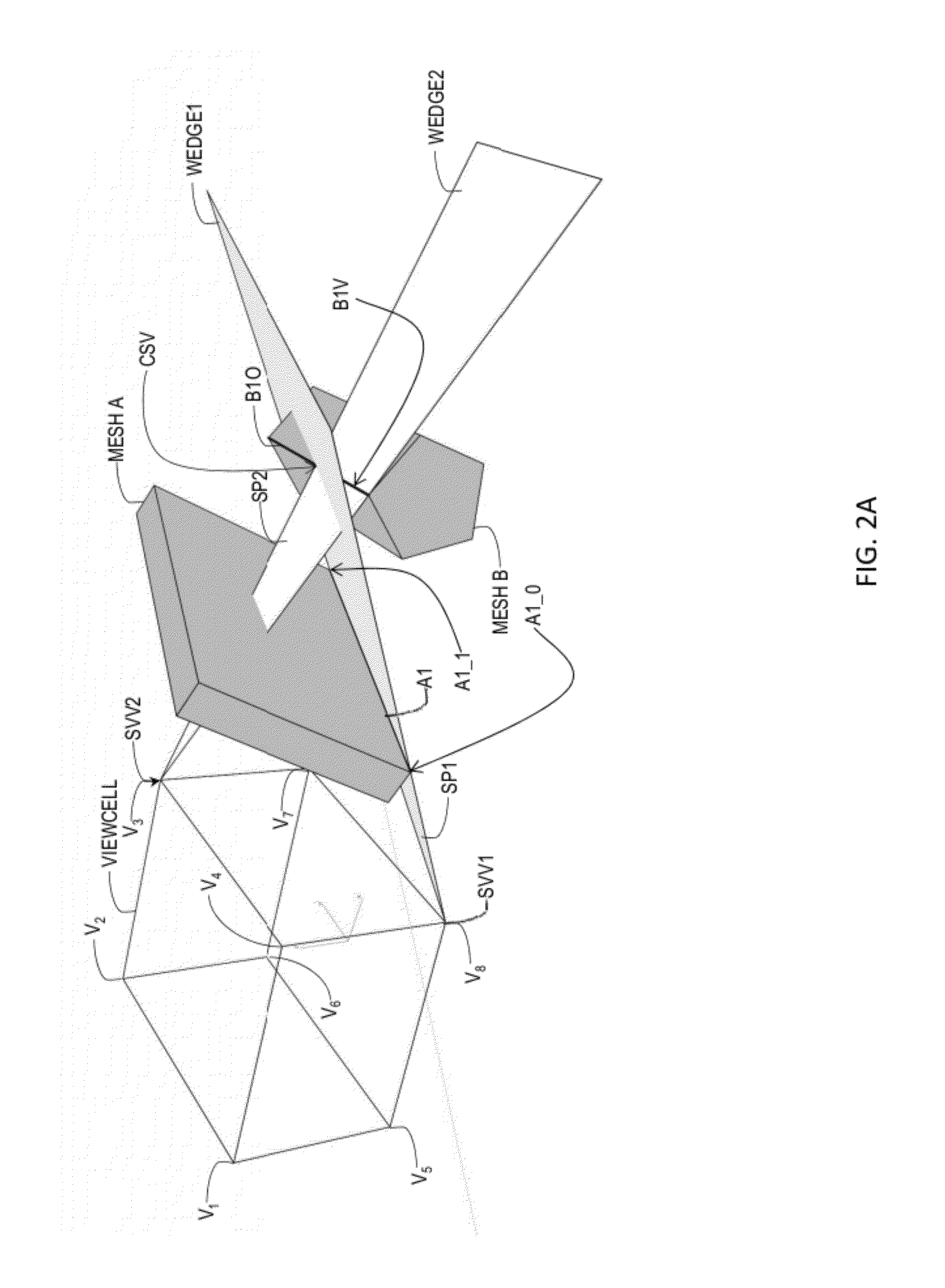
InactiveUS20120229445A1High precisionReduce computing costSpecial data processing applicationsDetails involving image processing hardwareVisibilityInteractive content
In an exemplary embodiment, a computer-implemented method determines a set of mesh polygons or fragments of the mesh polygons visible from a navigation cell. The method includes determining a composite view frustum containing predetermined view frusta and determining mesh polygons contained in the composite view frustum. The method includes determining at least one supporting polygon between the navigation cell and the contained mesh polygons. The method further includes constructing at least one wedge from the at least one supporting polygon, the at least one wedge extending away from the navigation cell beyond at least the contained mesh polygons. The method includes determining one or more intersections of the at least one wedge with the contained mesh polygons. The method also includes determining the set of the contained mesh polygons or fragments of the contained mesh polygons visible from the navigation cell using the determined one or more intersections.
Owner:JENKINS BARRY L
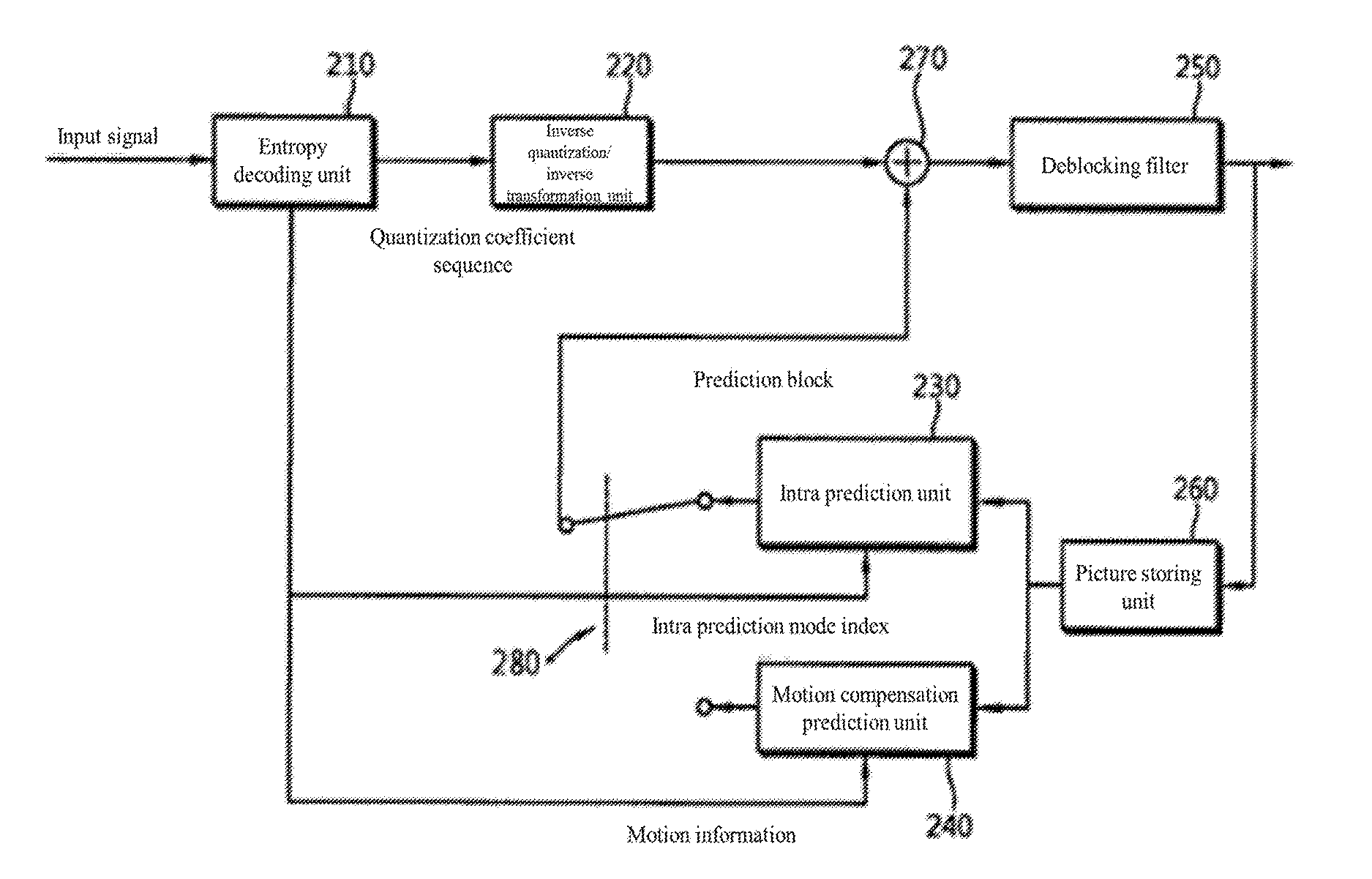
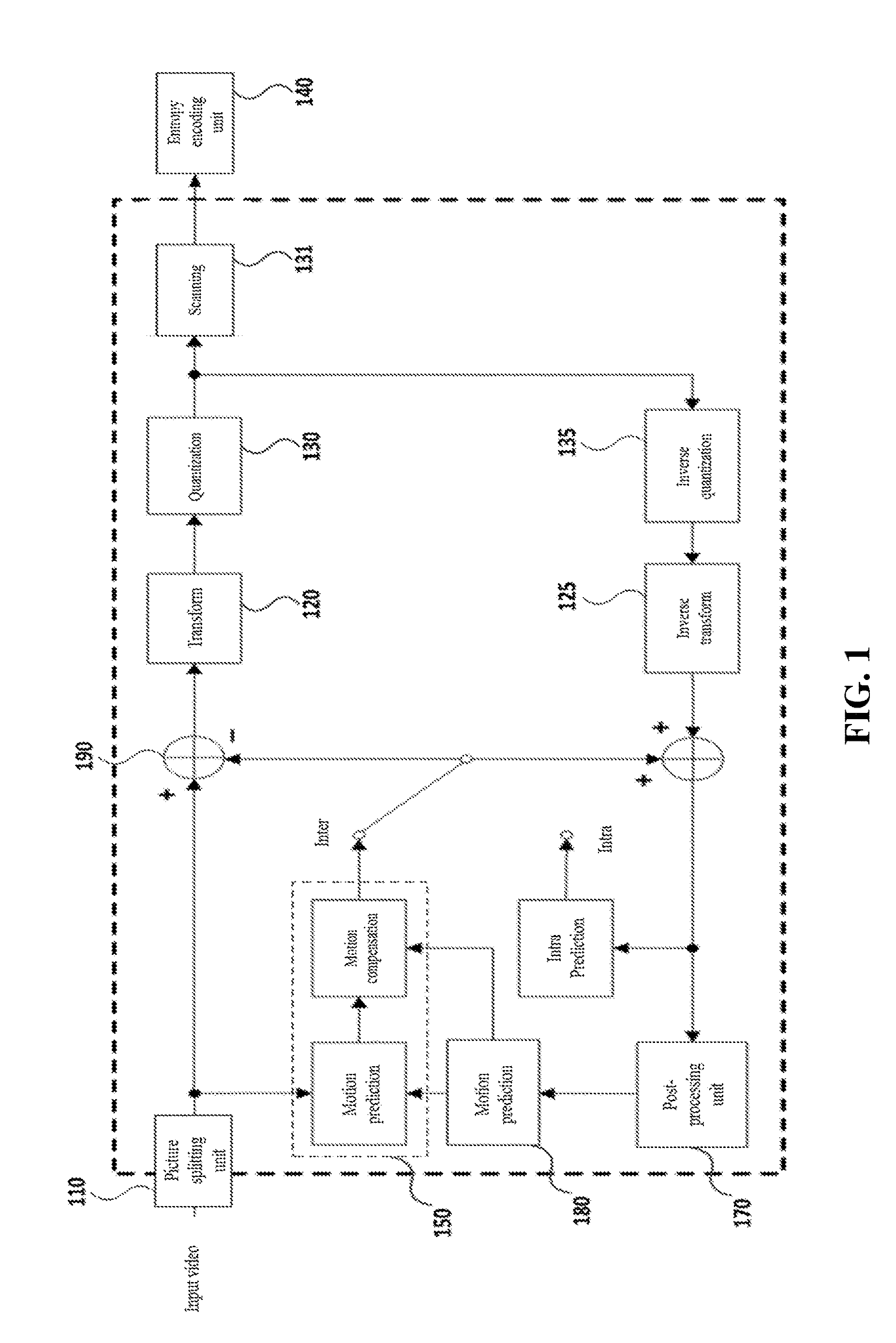
Method and apparatus for processing video
ActiveUS20170013269A1Inhibit decrease in bandwidth efficiencyEffective alignmentProcessor architectures/configurationDigital video signal modificationVideo bitstreamComputer graphics (images)
The present invention relates to a method for processing a video, comprising: a step in which a video central processing unit communicates with a host, receives a bitstream, parses header information, and generates a plurality of tasks for parallel processing; a step in which free scan information is generated by a free scan of a video bitstream inputted from the host according to the control of the video central processing unit; and a step in which a plurality of video processing units process the plurality of tasks on the basis of the free scan information and the parsed header information by receiving the control of the video central processing unit.
Owner:CHIPS&MEDIA
Depth calculation processor, data processing method and 3D image equipment
PendingCN107424187AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageDepth map
The invention discloses a depth calculation processor, a data processing method, and a 3D image device. The depth calculation processor includes at least two input ports for receiving first image data, the first image data including at least a structured light image collected under the projection of structured light; an input switch connected to the input ports and for the passage of all or part of the first image data from the input port; a data processing engine connected to the input switch and for calculation processing of the first image data output by the input switch so as to output second image data which at least comprise a depth map, wherein, the data processing engine at least comprises a depth processing engine for performing depth calculation processing on the structured light image to obtain the depth map; and at least one output port, directly or indirectly connected to the data processing engine, and for outputting the second image data to a host device.
Owner:SHENZHEN ORBBEC CO LTD
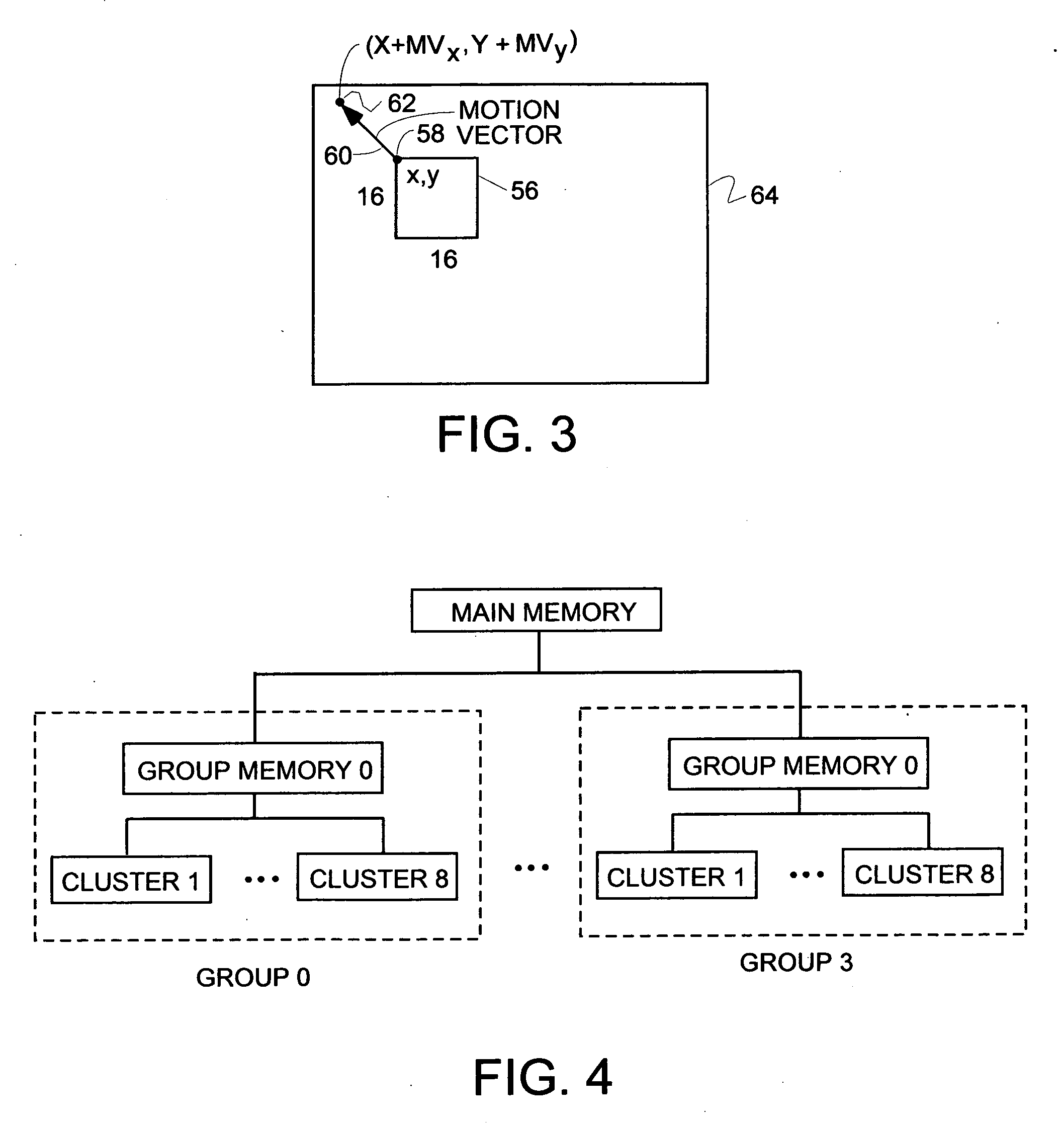
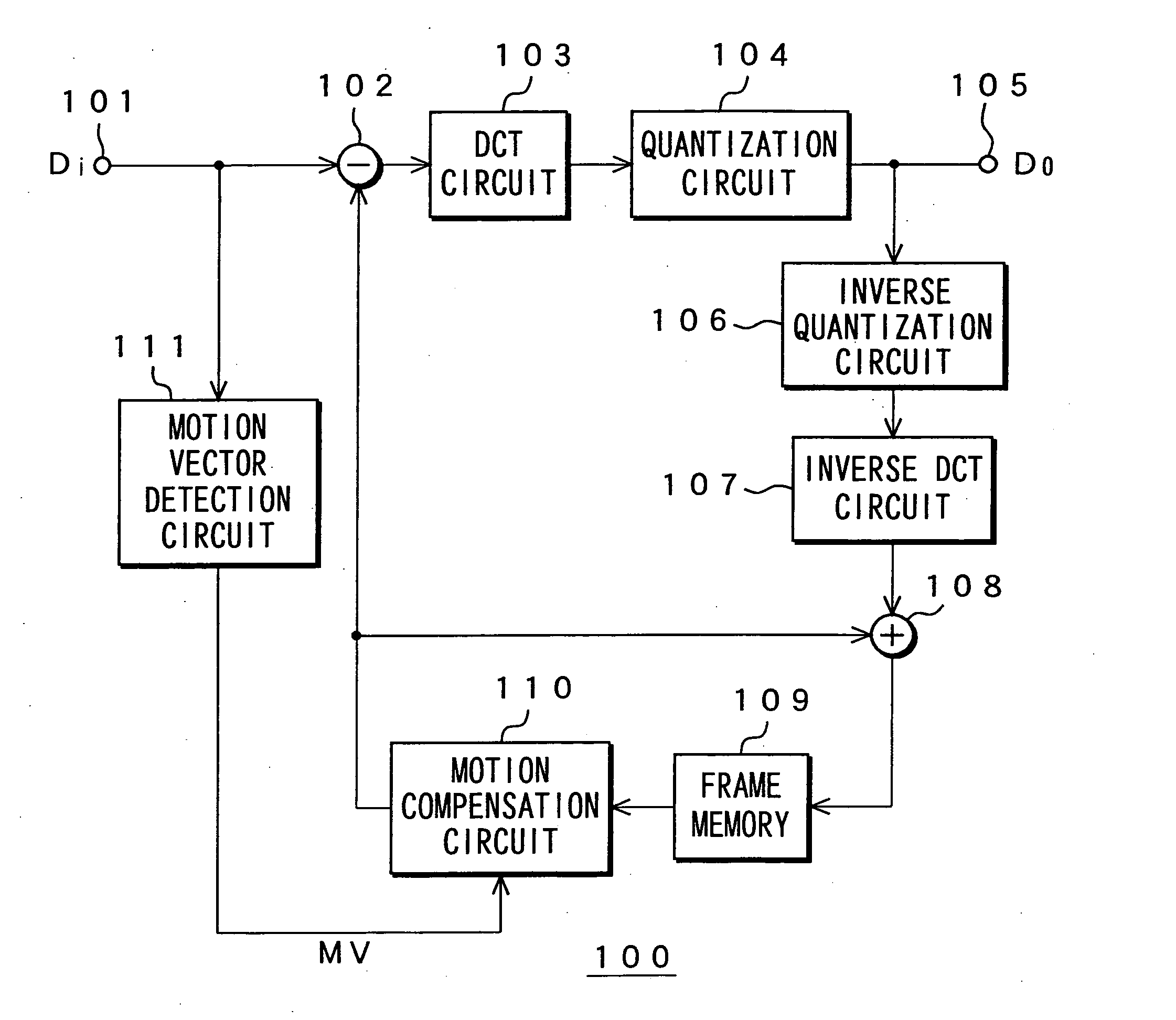
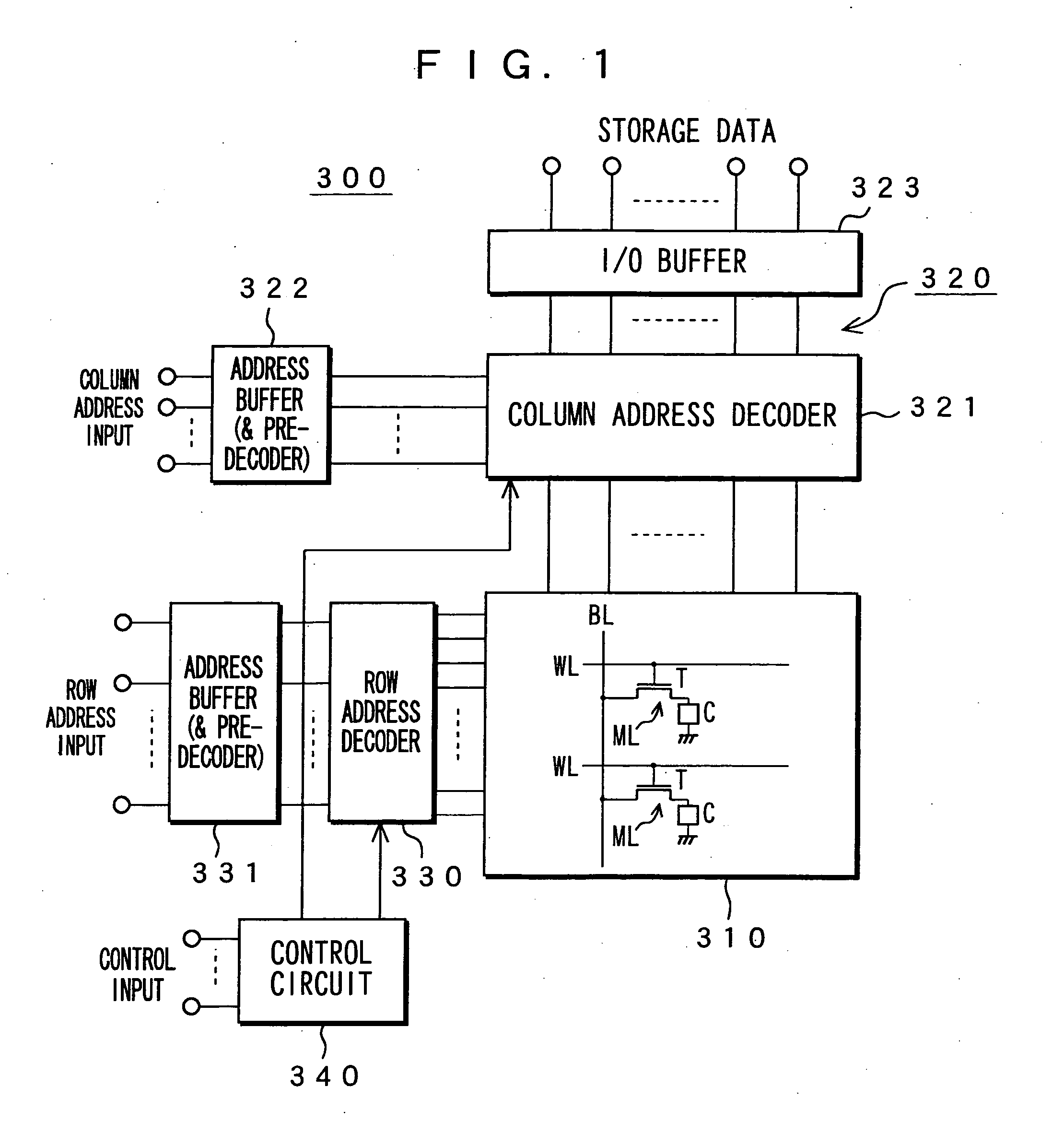
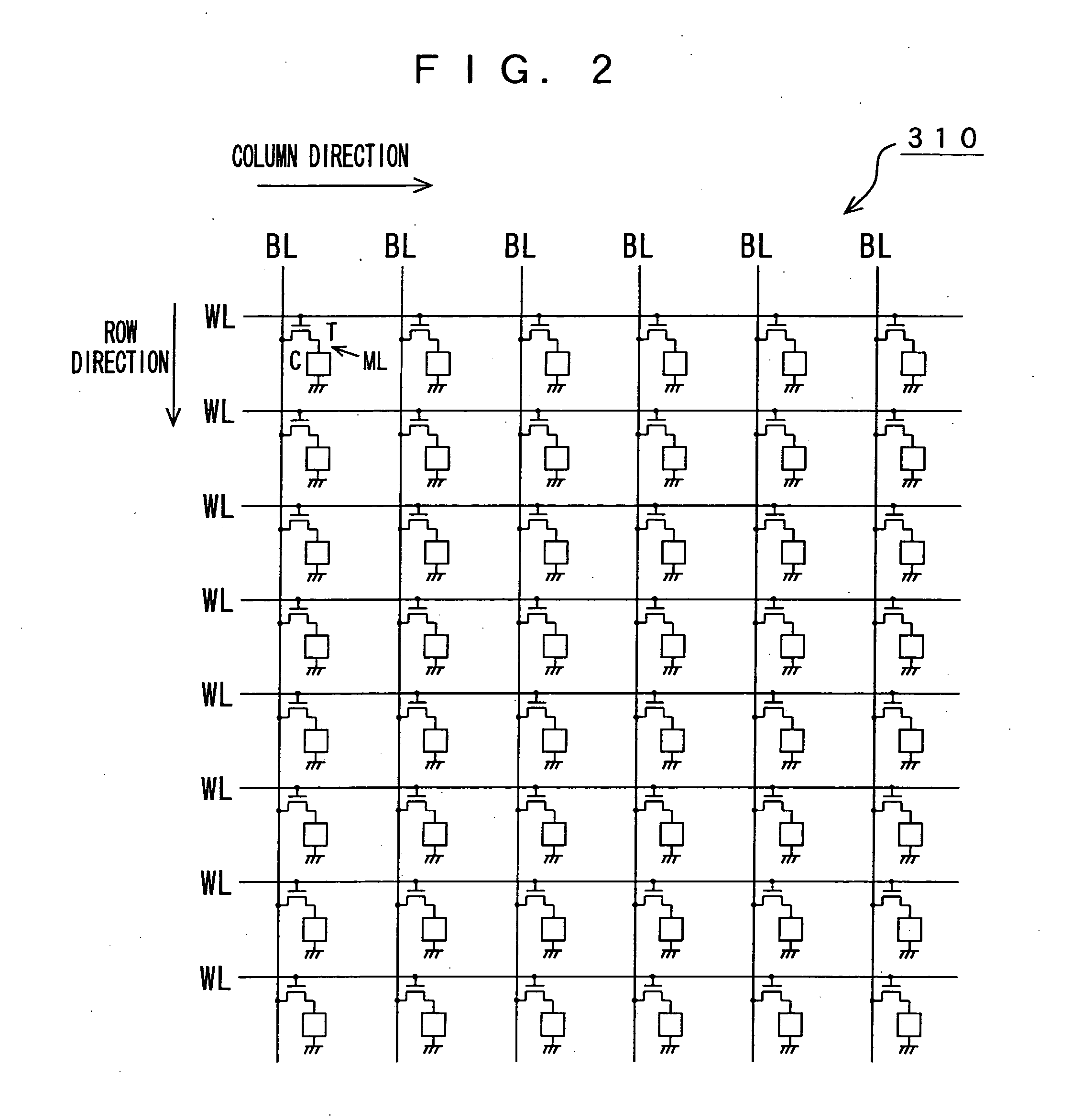
Memory device, motion vector detection device, and detection method
InactiveUS20060062483A1Increase computing speedLow costTelevision system detailsImage enhancementMotion vectorAbsolute difference
This invention relates to a memory device and the like that are preferably applied to a case where motion vector is detected using a block matching. Pixel data of a first frame (a reference frame) is stored in a unit A of memory cell array portion 20a in straight binary format. Pixel data of a second frame (a search frame) is stored in a unit B of memory cell array portion 20b in two's complement format. The units A and B have a plurality of memory cells, respectively. Word lines WL related to the pixel data of the first and second frames are simultaneously activated so that charges accumulated in capacitors of each of the memory cells can be combined along one bit line BL. A / D converter 53 outputs a digital signal (absolute difference value) having a value that corresponds to a total amount of charges. When reading the pixel data, a subtraction and a conversion into the absolute difference value are simultaneously performed.
Owner:SONY CORP
DATA DISTRIBUTION FABRIC IN SCALABLE GPUs
In on embodiment, a hybrid fabric interconnects multiple graphics processor cores within a processor. The hybrid fabric interconnect includes multiple data channels, including programmable virtual data channels. The virtual data channels carry multiple traffic classes of packet-based messages. The virtual data channels and multiple traffic classes may be assigned one of multiple priorities. The virtual data channels may be arbitrated independently. The hybrid fabric is scalable and can support multiple topologies, including multiple stacked integrated circuit topologies.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for real-time volume rendering on thin clients via render server
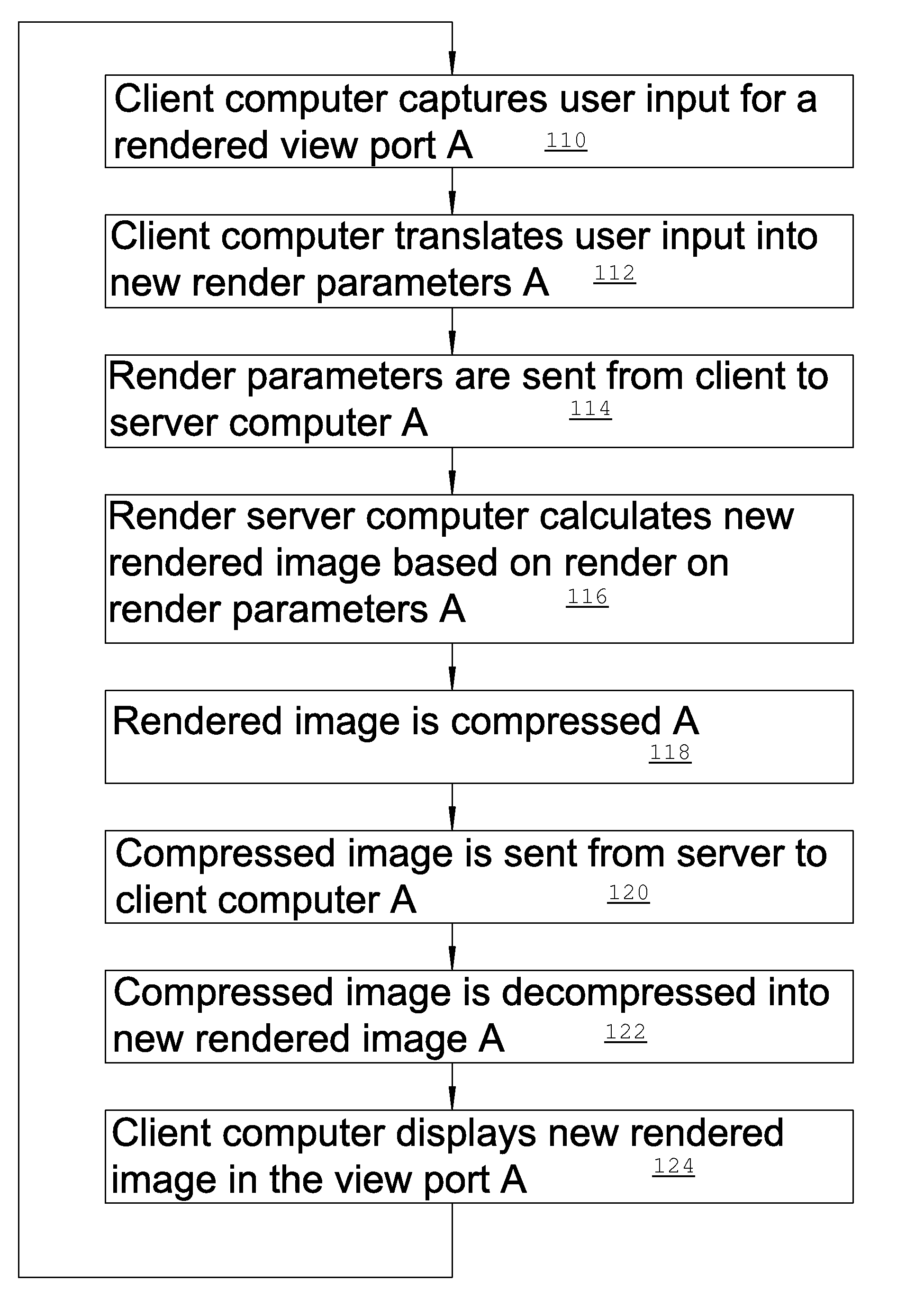
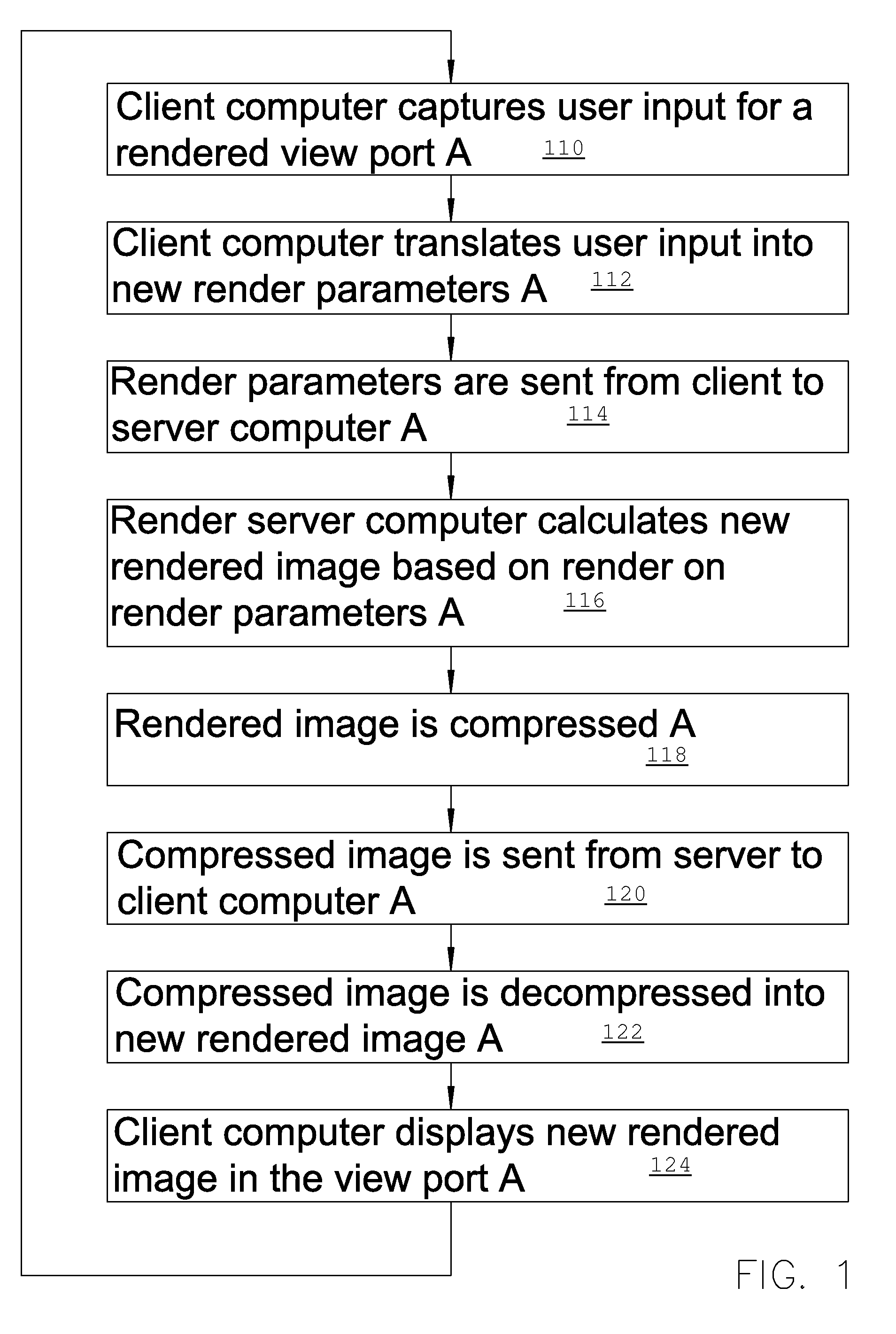
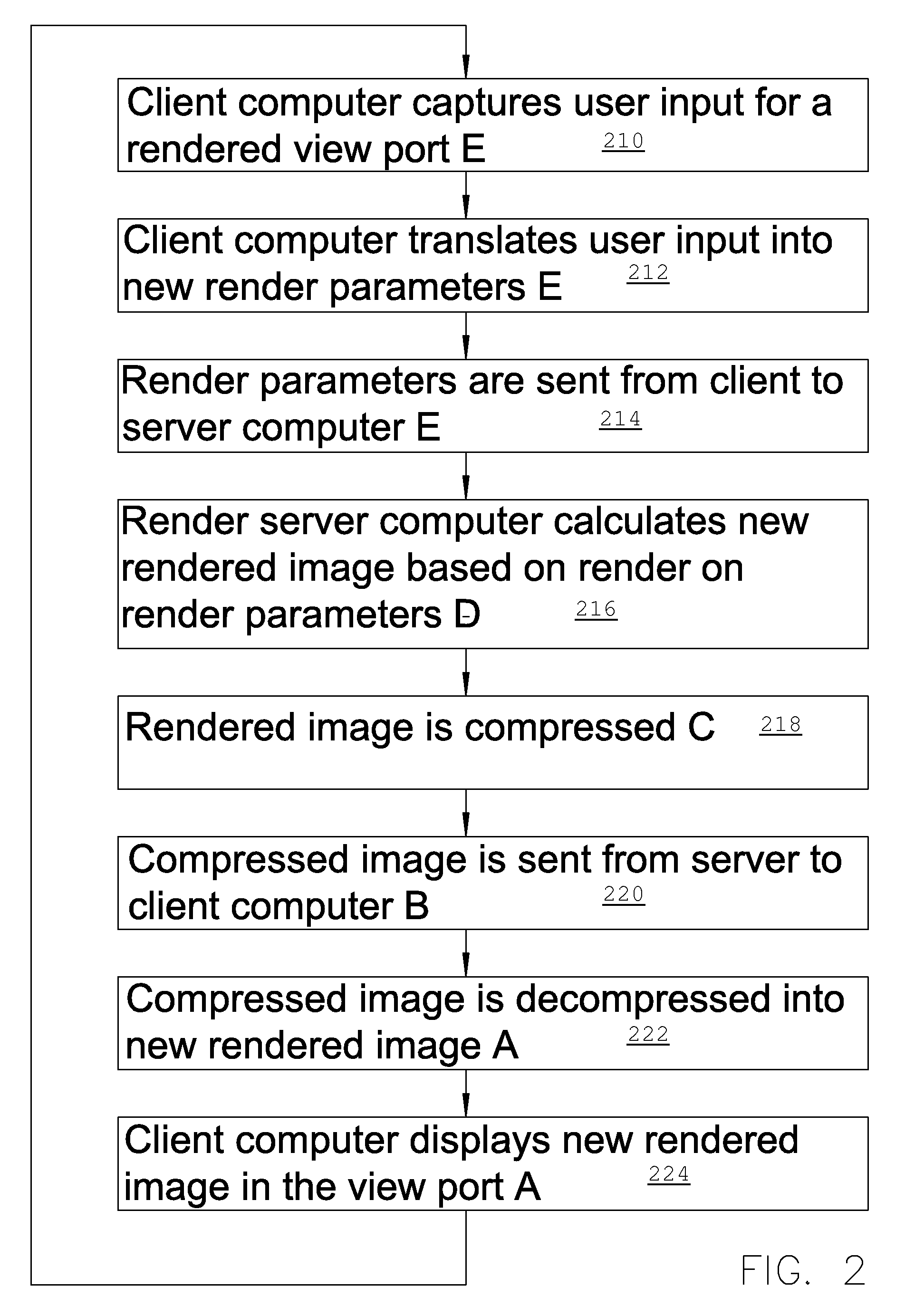
ActiveUS8508539B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer graphics (images)Client-side
A method of server site rendering 3D images on a server computer coupled to a client computer wherein the client computer instructs a server computer to load data for 3D rendering and sends a stream of rendering parameter sets to the server computer, each set of rendering parameters corresponding with an image to be rendered; next the render computer renders a stream of images corresponding to the stream of parameter sets and the stream of images is compressed with a video compression scheme and sent from the server computer to the client computer where the client computer decompresses the received compressed video stream and displays the result in a viewing port. The rendering and communication chain is subdivided in successive pipeline stages that work in parallel on successive rendered image information.
Owner:AGFA HEALTHCARE NV
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
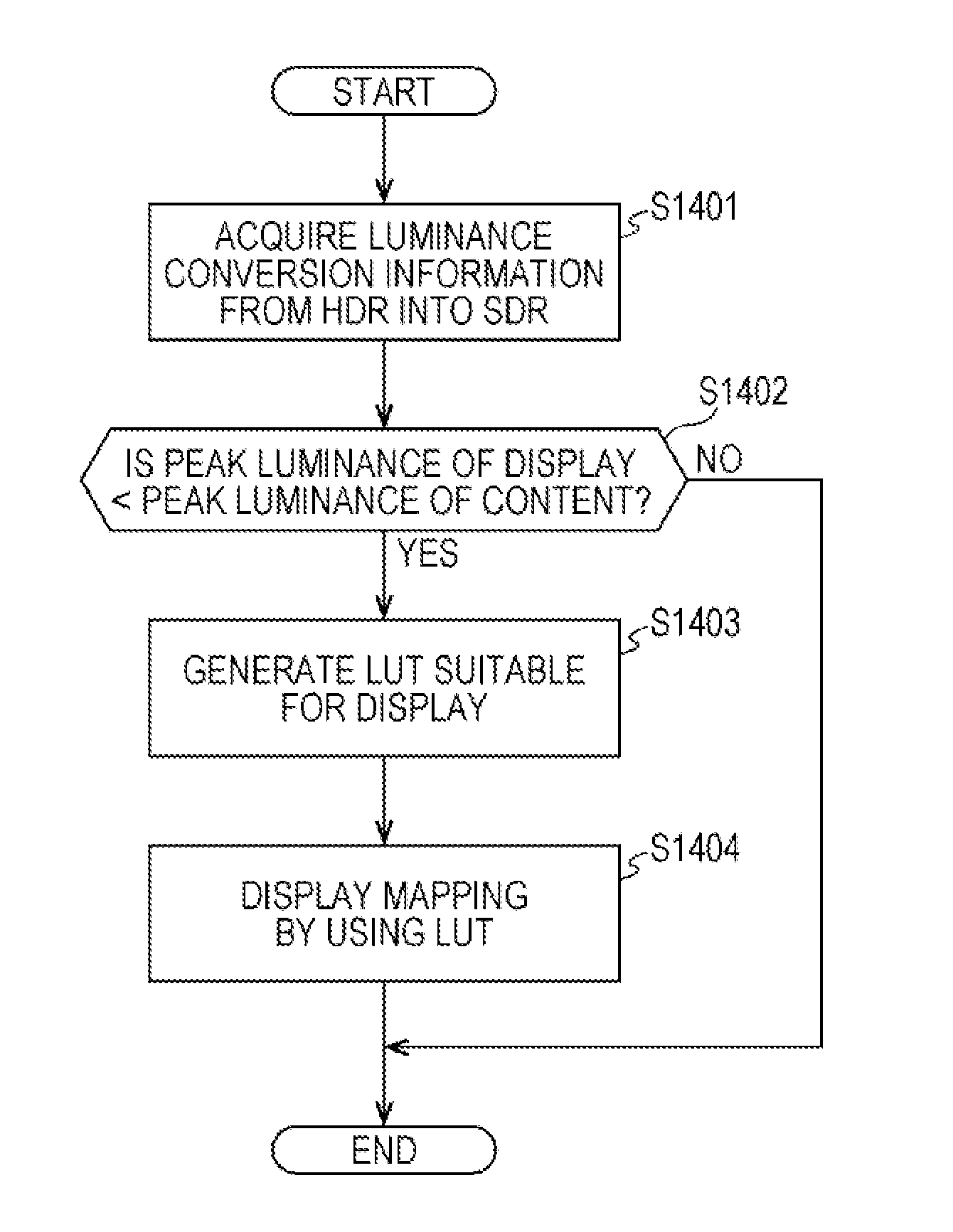
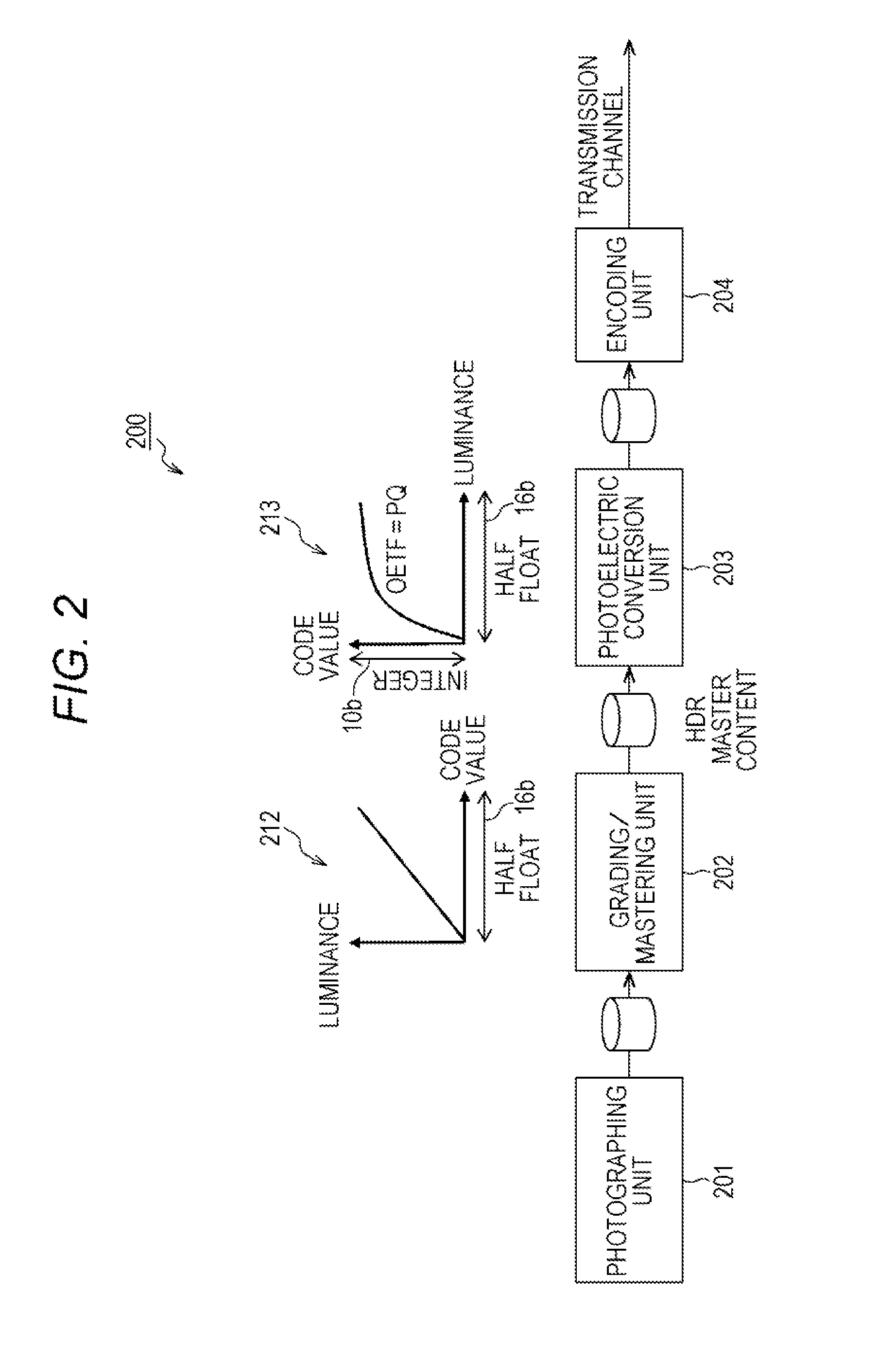
ActiveUS20160292834A1Suitable dynamic rangeEliminate the effects ofImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus and an image processing method which can transmit / receive or display a high-dynamic-range image suitably are provided. An image transmission apparatus transfers, as metadata of content, luminance conversion information, which is for conversion of HDR content (for example, with maximum luminance 2000 nit) into SDR content (having, for example, 100 nit), or differential information. Based on the metadata, an image reception apparatus generates luminance conversion information, in which received HDR content is adapted to a capability of a display (for example, with maximum luminance 500 nit or 1000 nit) in an output destination, and realizes display mapping which is not against an intention of a producer.
Owner:SONY CORP
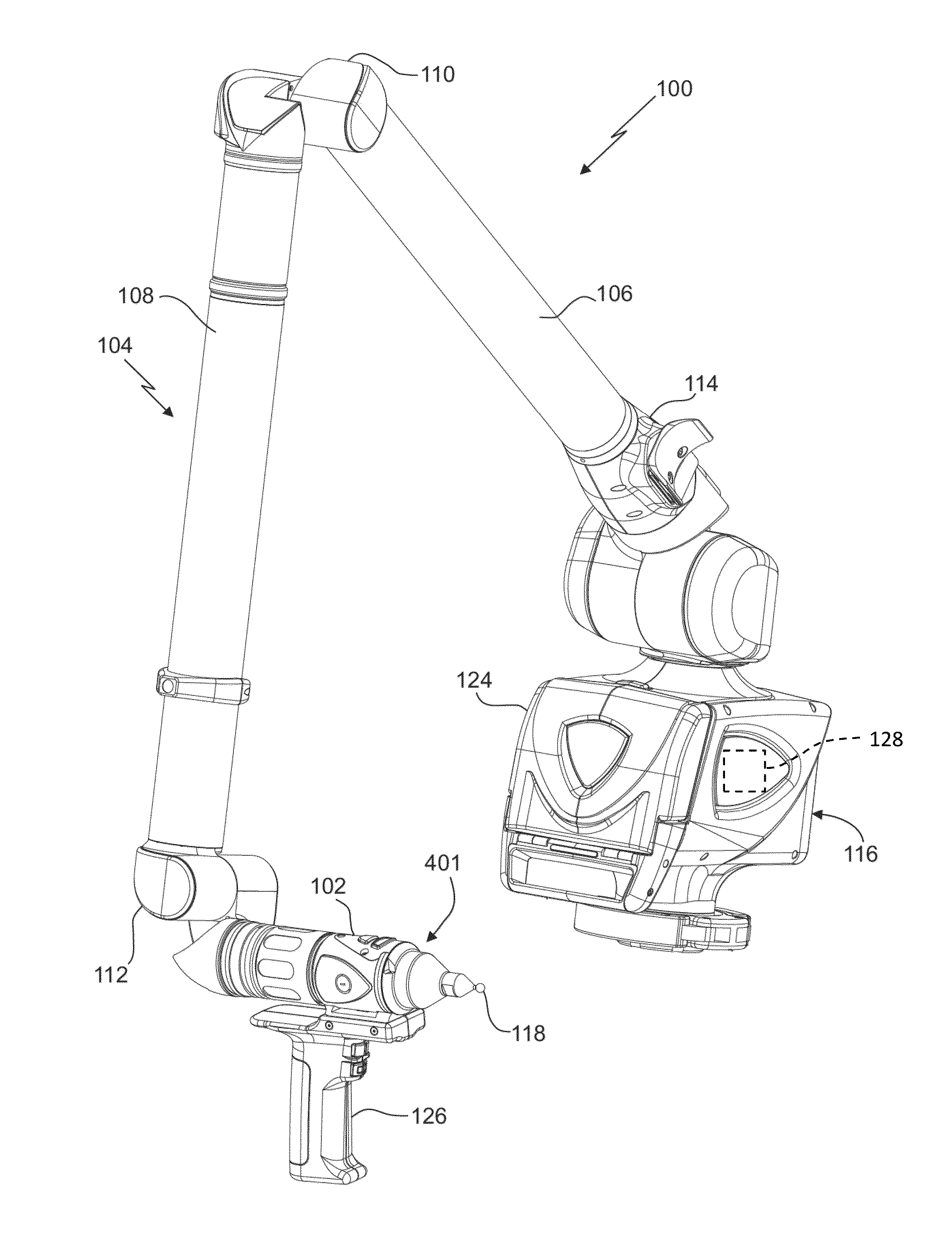
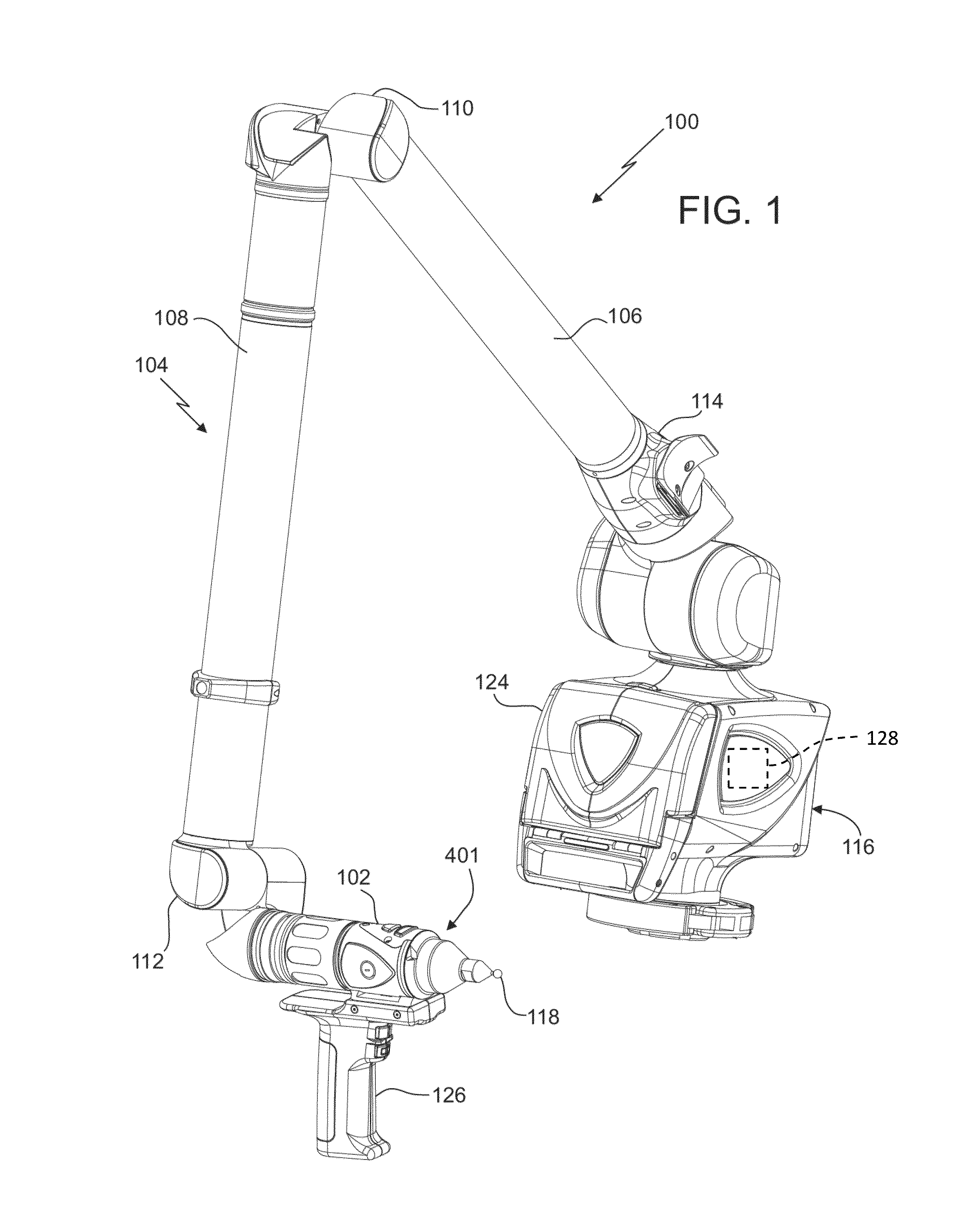
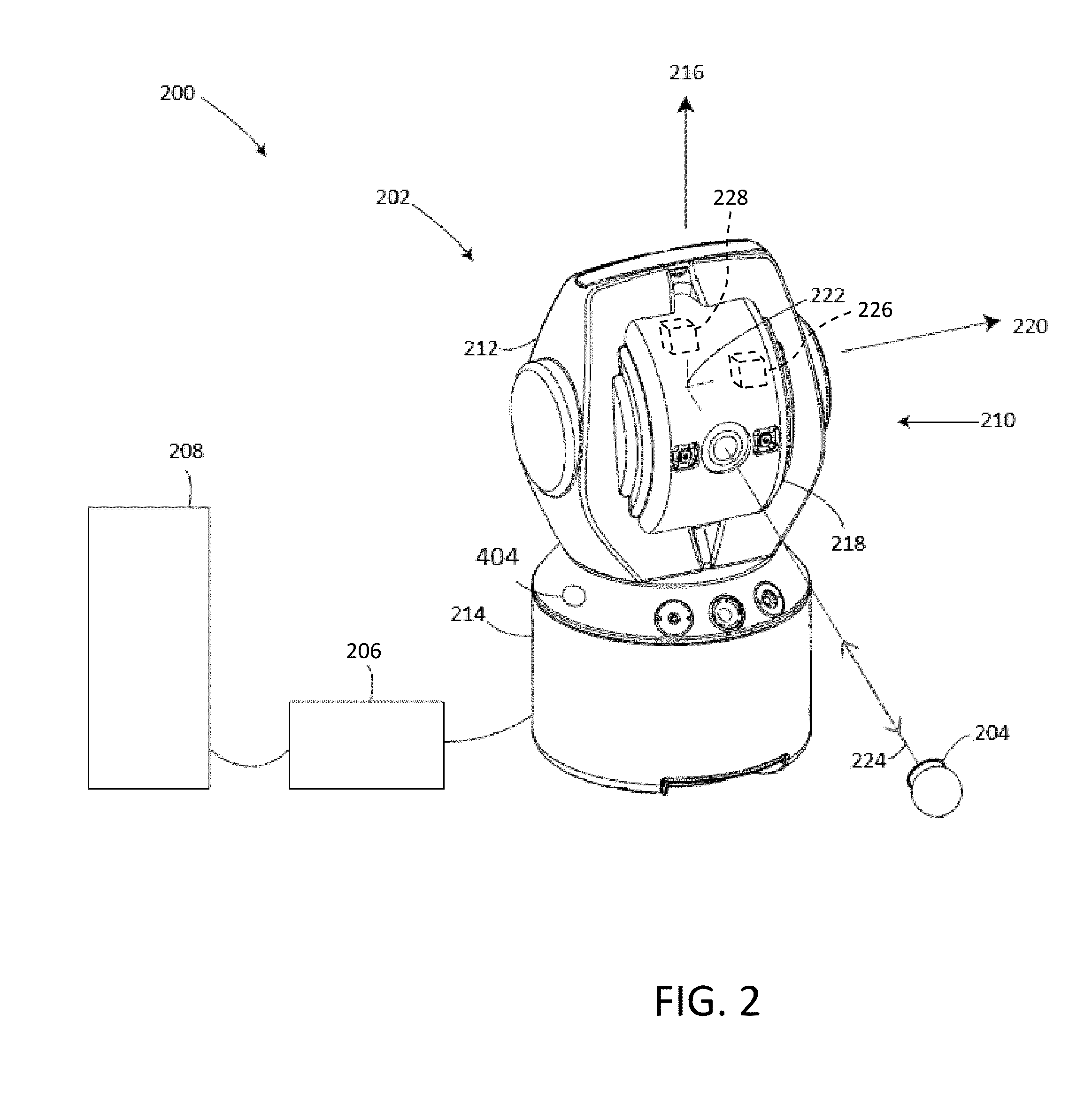
Augmented reality camera for use with 3D metrology equipment in forming 3D images from 2d camera images
Owner:FARO TECH INC
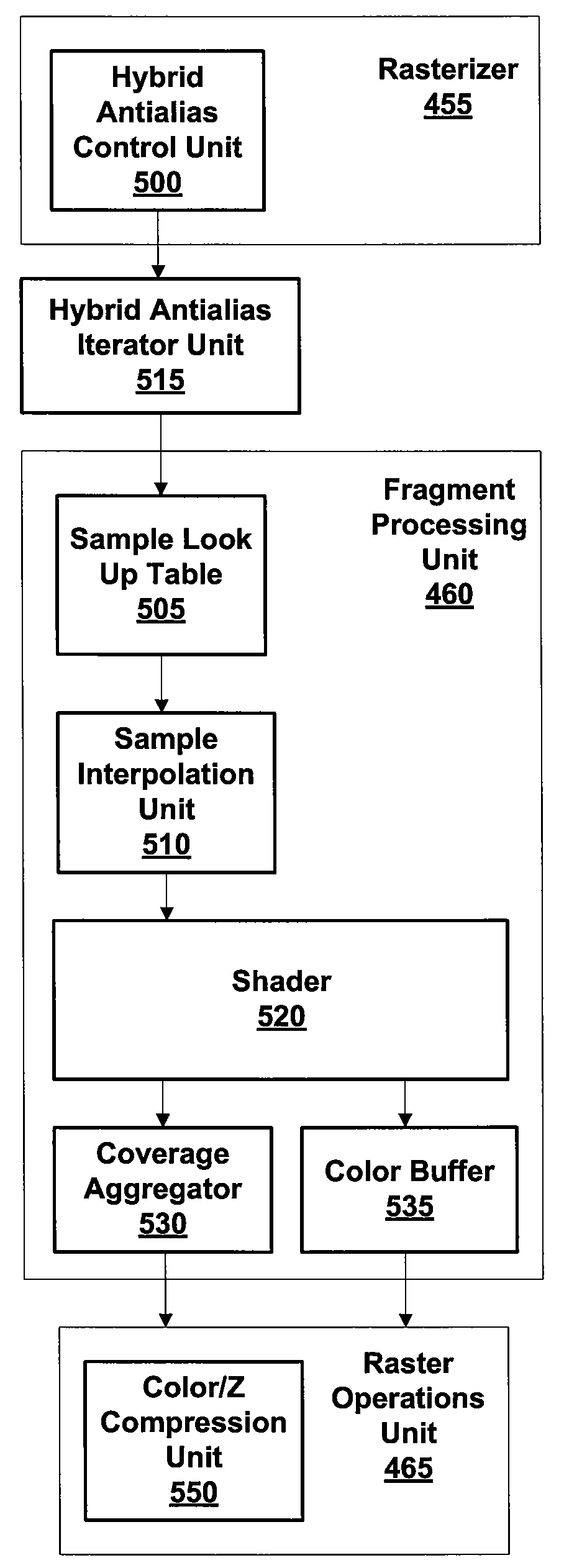
Hybrid Multisample/Supersample Antialiasing
ActiveUS20100002000A1Improve image qualityGood colorCathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails involving image processing hardwareImaging qualityComputer graphics (images)
A system and method for dynamically adjusting the pixel sampling rate during primitive shading can improve image quality or increase shading performance. Hybrid antialiasing is performed by selecting a number of shaded samples per pixel fragment. A combination of supersample and multisample antialiasing is used where a cluster of sub-pixel samples (multisamples) is processed for each pass through a fragment shader pipeline. The number of shader passes and multisamples in each cluster can be determined dynamically for each primitive based on rendering state.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System and methods for depth regularization and semiautomatic interactive matting using RGB-D images
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of this invention perform depth regularization and semiautomatic interactive matting using images. In an embodiment of the invention, the image processing pipeline application directs a processor to receive (i) an image (ii) an initial depth map corresponding to the depths of pixels within the image, regularize the initial depth map into a dense depth map using depth values of known pixels to compute depth values of unknown pixels, determine an object of interest to be extracted from the image, generate an initial trimap using the dense depth map and the object of interest to be extracted from the image, and apply color image matting to unknown regions of the initial trimap to generate a matte for image matting.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
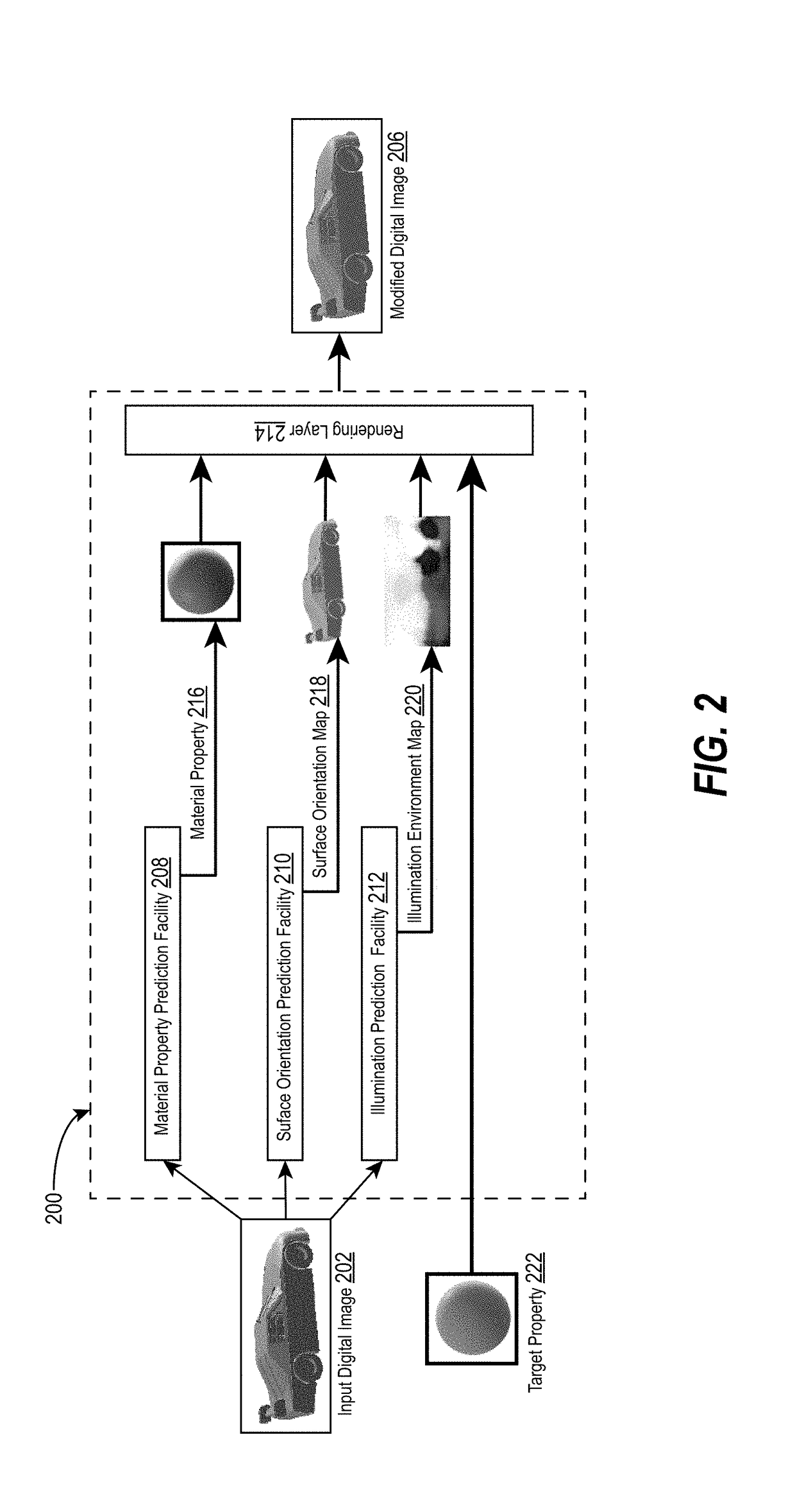
Editing digital images utilizing a neural network with an in-network rendering layer
ActiveUS20180253869A1Effective trainingMore appearanceTexturing/coloringDetails involving 3D image dataDigital imageComputer vision
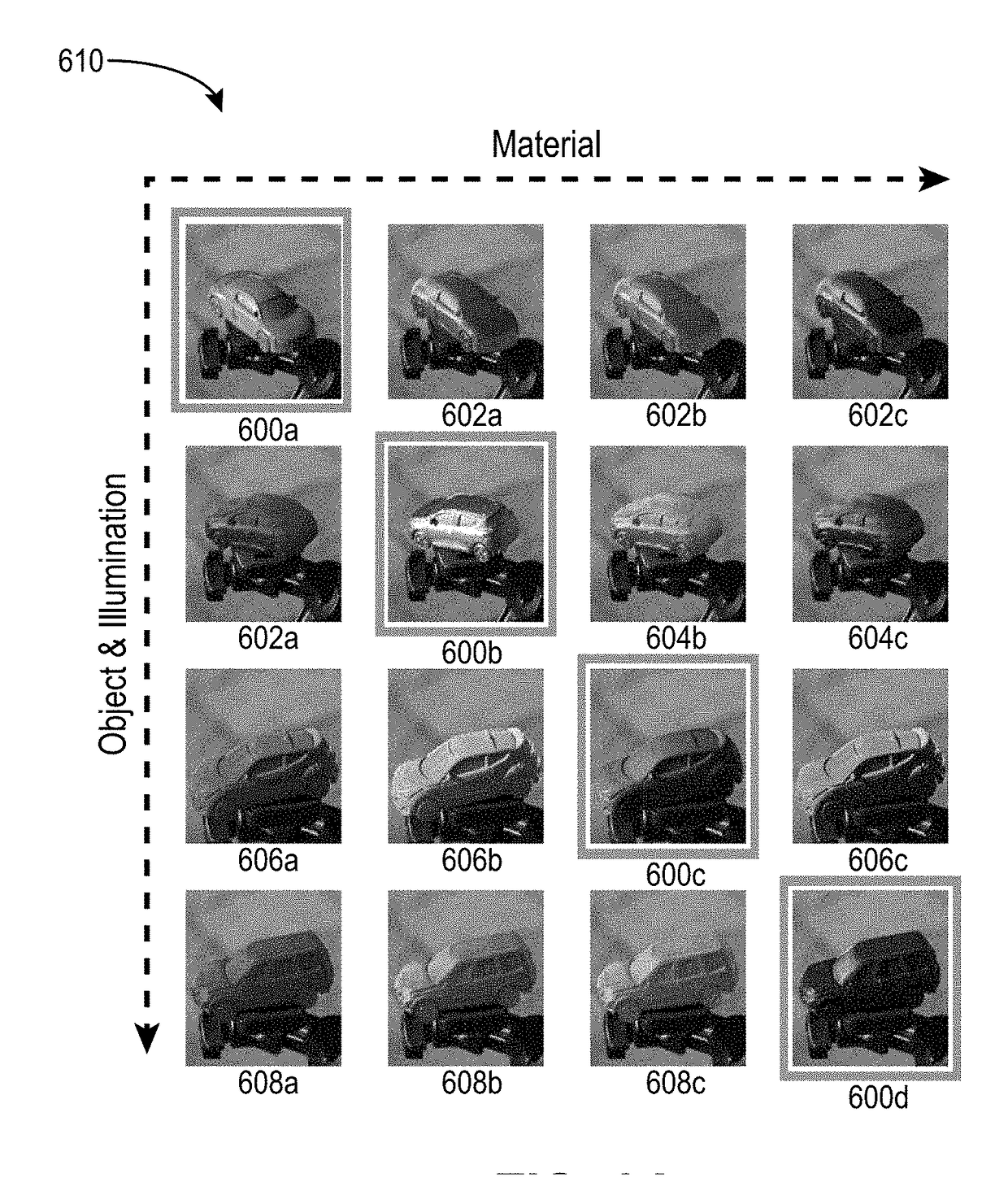
The present disclosure includes methods and systems for generating modified digital images utilizing a neural network that includes a rendering layer. In particular, the disclosed systems and methods can train a neural network to decompose an input digital image into intrinsic physical properties (e.g., such as material, illumination, and shape). Moreover, the systems and methods can substitute one of the intrinsic physical properties for a target property (e.g., a modified material, illumination, or shape). The systems and methods can utilize a rendering layer trained to synthesize a digital image to generate a modified digital image based on the target property and the remaining (unsubstituted) intrinsic physical properties. Systems and methods can increase the accuracy of modified digital images by generating modified digital images that realistically reflect a confluence of intrinsic physical properties of an input digital image and target (i.e., modified) properties.
Owner:ADOBE INC
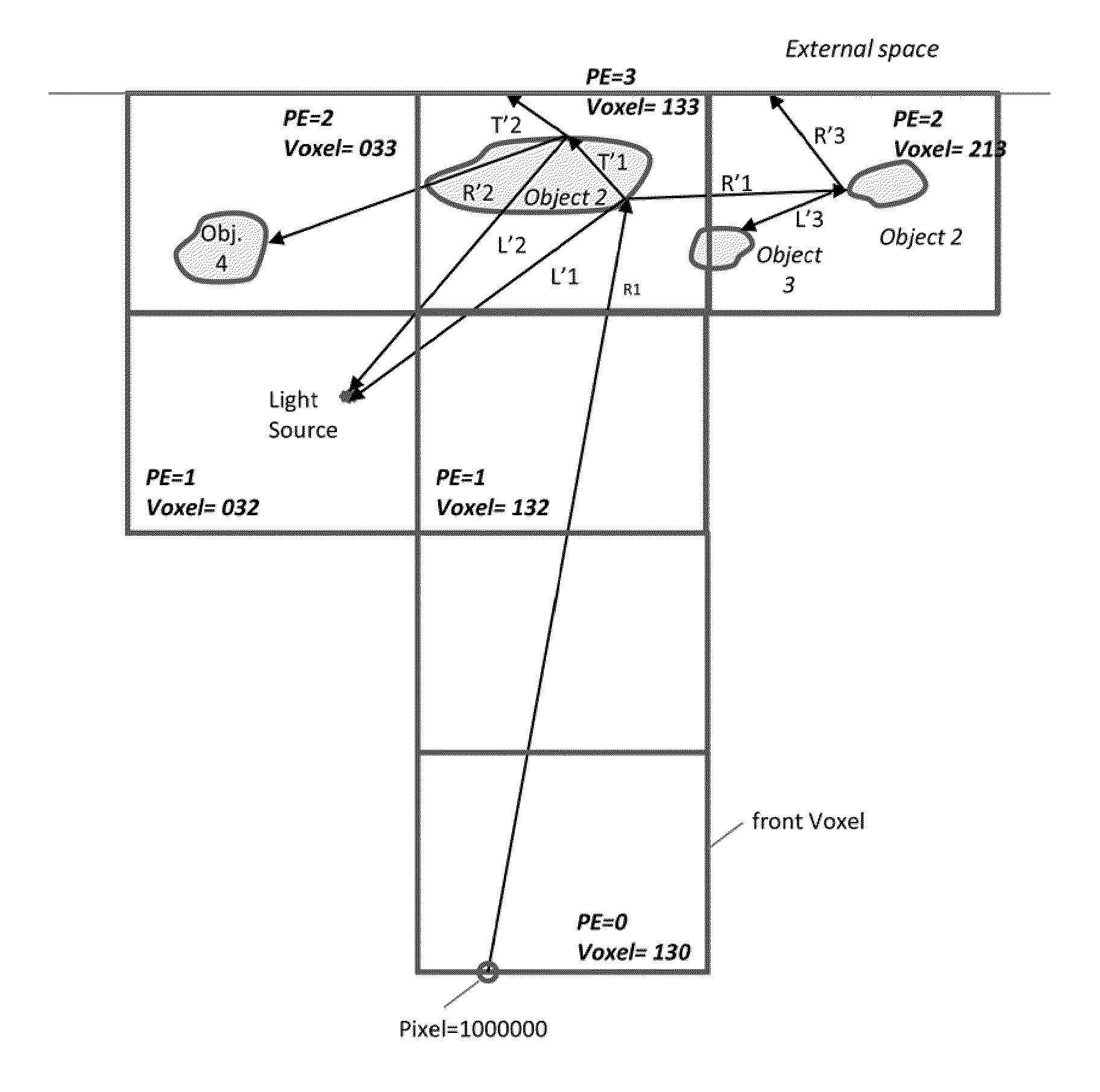
Method and apparatus for parallel ray-tracing employing modular space division
ActiveUS20110234583A1Efficient data exchangeIncrease profitDetails involving image processing hardwareElectric digital data processingModularityParallel computing
Novel method and system for distributed database ray-tracing is presented, based on modular mapping of scene-data among processors. Its inherent properties include scattering data among processors for improved load balancing, and matching between geographical proximity in the scene with communication proximity between processors. High utilization is enabled by unique mechanism of cache sharing. The resulting improved performance enables deep level of ray tracing for real time applications.
Owner:SNAP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com