Patents
Literature
91 results about "Observable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, an observable is a physical quantity that can be measured. Examples include position and momentum. In systems governed by classical mechanics, it is a real-valued "function" on the set of all possible system states. In quantum physics, it is an operator, or gauge, where the property of the quantum state can be determined by some sequence of operations. For example, these operations might involve submitting the system to various electromagnetic fields and eventually reading a value.
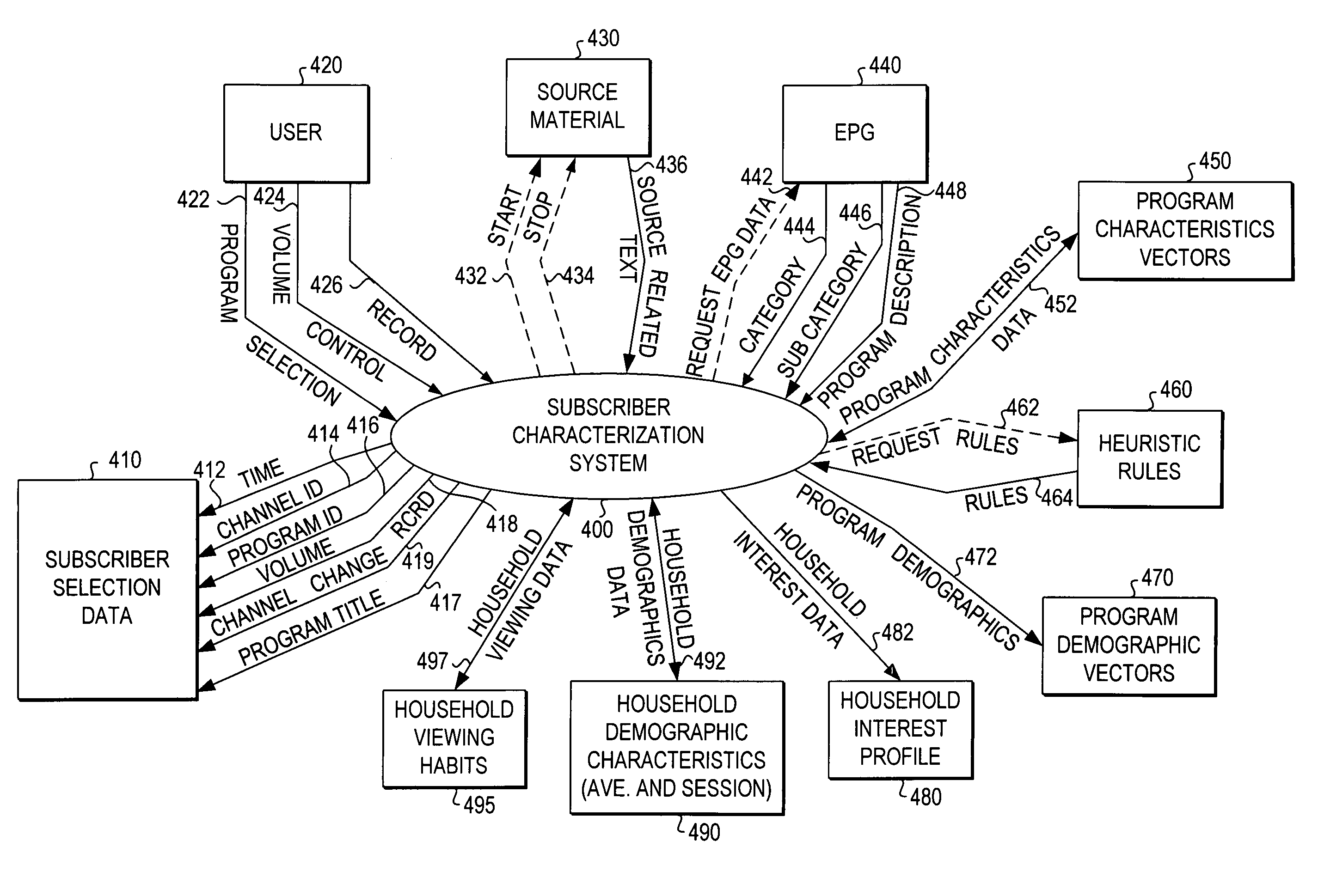
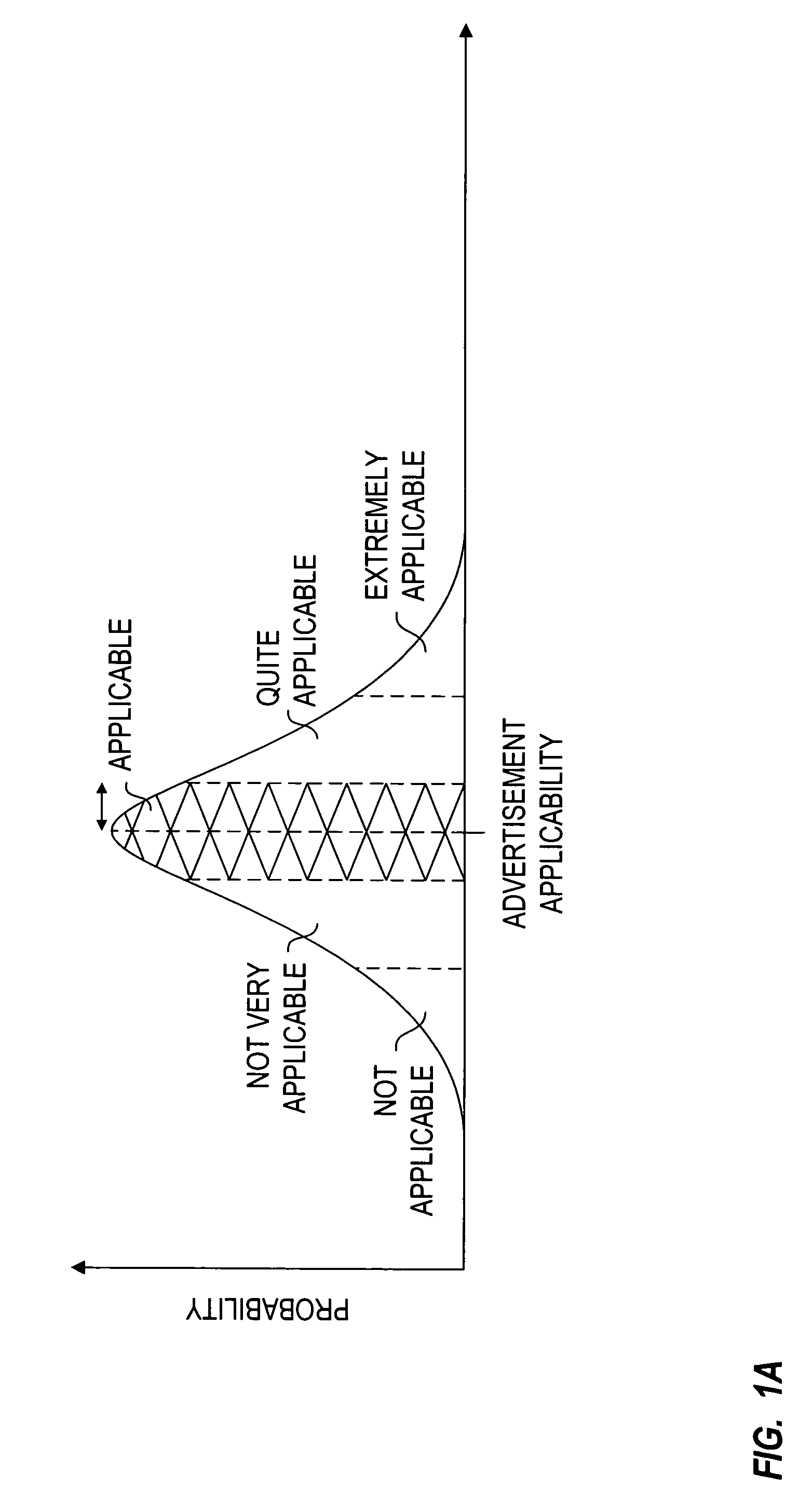
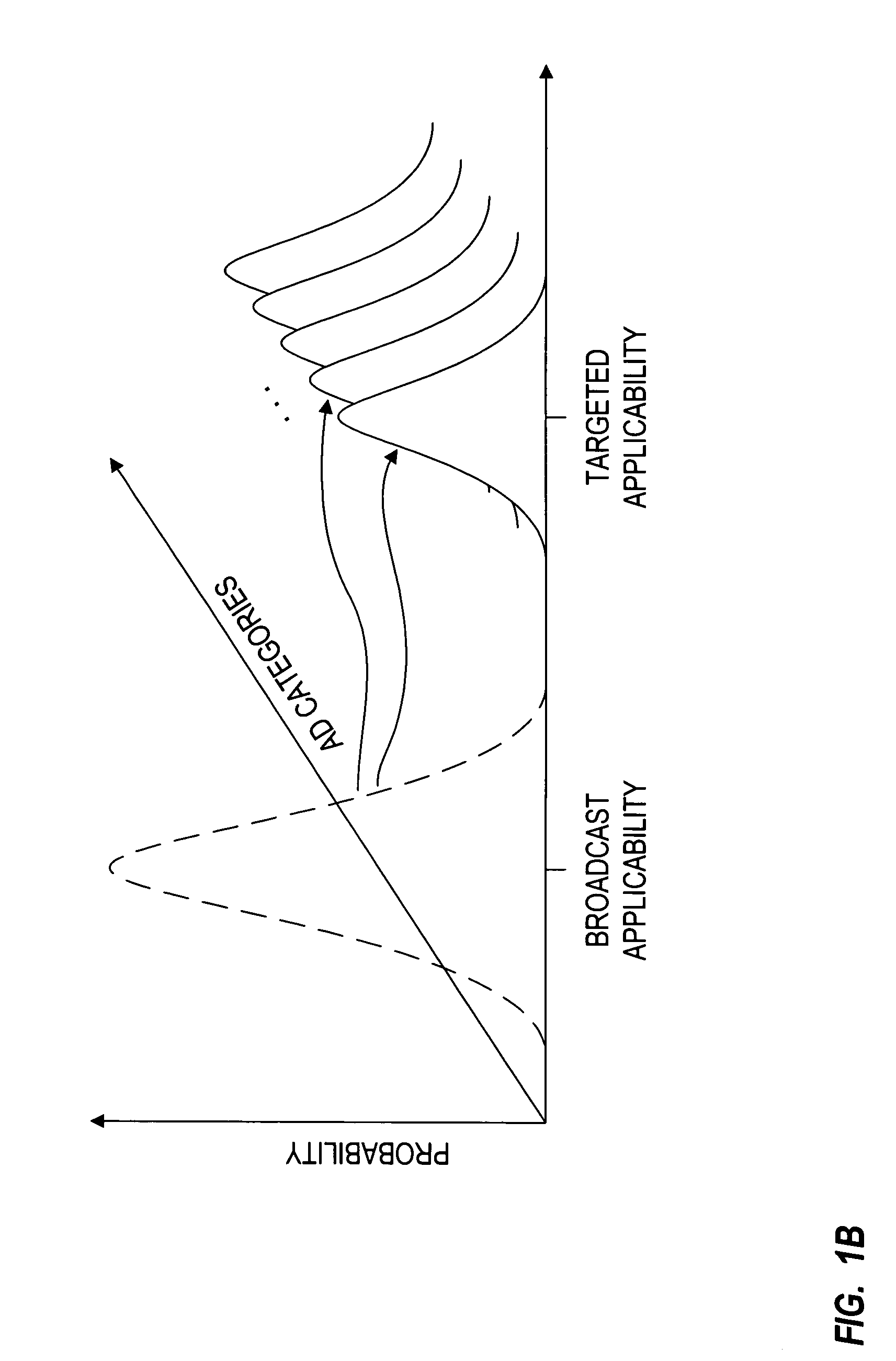
Privacy-protected advertising system
InactiveUS7949565B1Easy to usePermit targetingBroadcast-related systemsBroadcast information switching/replacementPrivacy protectionDemographic data
A database of consumer profiles is generated from multiple sources of information including demographic databases identifying demographic attributes of the consumers and transaction records for the consumers. The transaction records are processed to generate transaction attributes and interests of the consumer. The consumer profiles identify deterministic and probabilistic attributes about the consumer, but do not contain privacy violating information such as raw transaction records. The consumer profiles may be maintained in a plurality of distributed databases. Advertisers generate profiles that identify attributes of an intended target market of the advertisement. The advertisement profiles are in the form of operators that can be applied to the database of consumer profiles to determine applicability of advertisements to the subscribers. The operators may only be applied to or make measurements on certain “observables”. The operators will not be able to obtain private information from the database of consumer profiles.
Owner:PRIME RES ALLIANCE E LLC
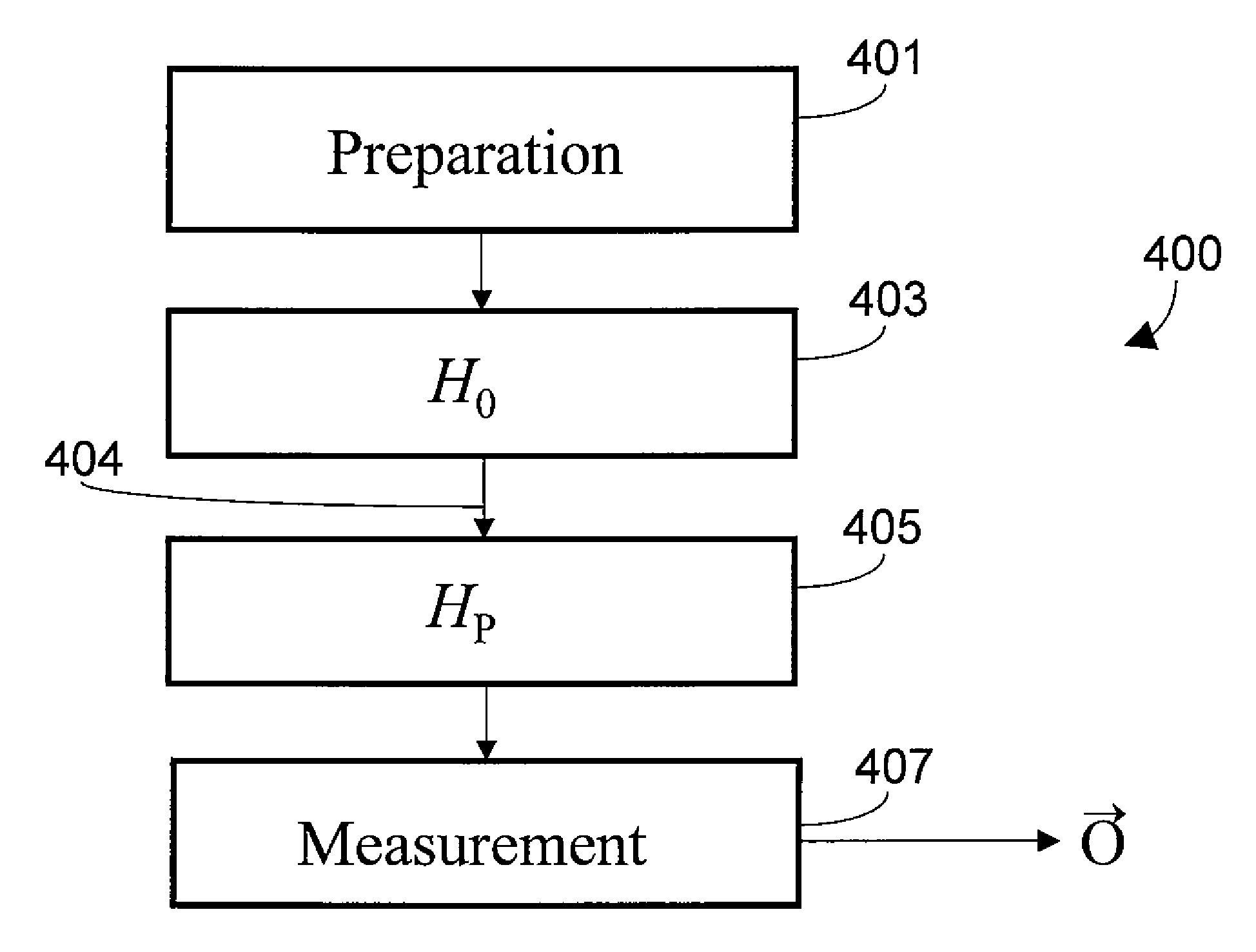
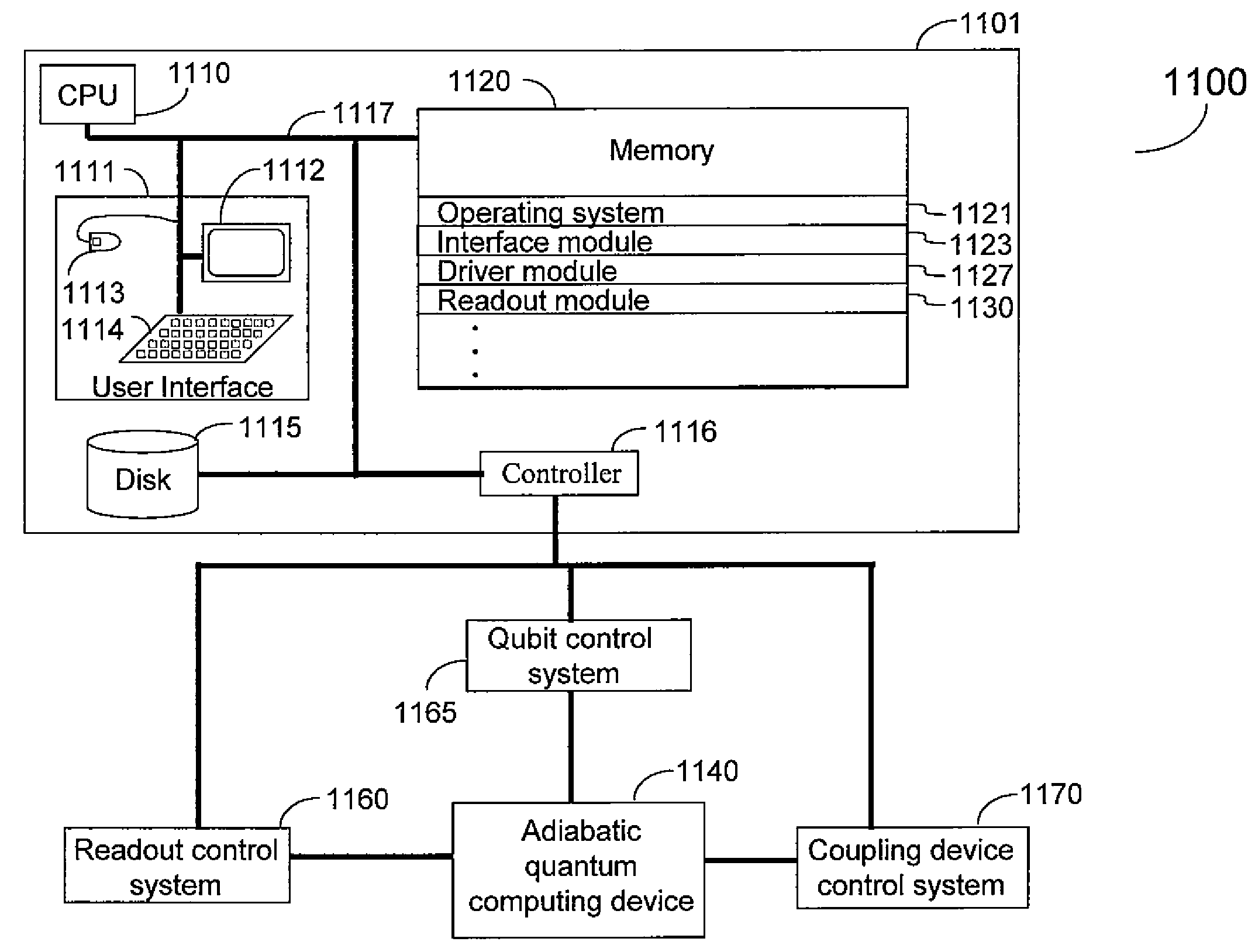
Methods of adiabatic quantum computation
ActiveUS20070180586A1Increasing effective charging energyIncrease the gap sizeQuantum computersDigital data processing detailsAdiabatic quantum computationComputational problem
A method for quantum computing using a quantum system comprising a plurality of qubits is provided. The system can be in any one of at least two configurations at any given time including one characterized by an initialization Hamiltonian H0 and one characterized by a problem Hamiltonian HP. The problem Hamiltonian HP has a final state. Each respective first qubit in the qubits is arranged with respect to a respective second qubit in the qubits such that they define a predetermined coupling strength. The predetermined coupling strengths between the qubits in the plurality of qubits collectively define a computational problem to be solved. In the method, the system is initialized to H0 and is then adiabatically changed until the system is described by the final state of the problem Hamiltonian HP. Then the state of the system is read out by probing an observable of the σX Pauli matrix operator.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
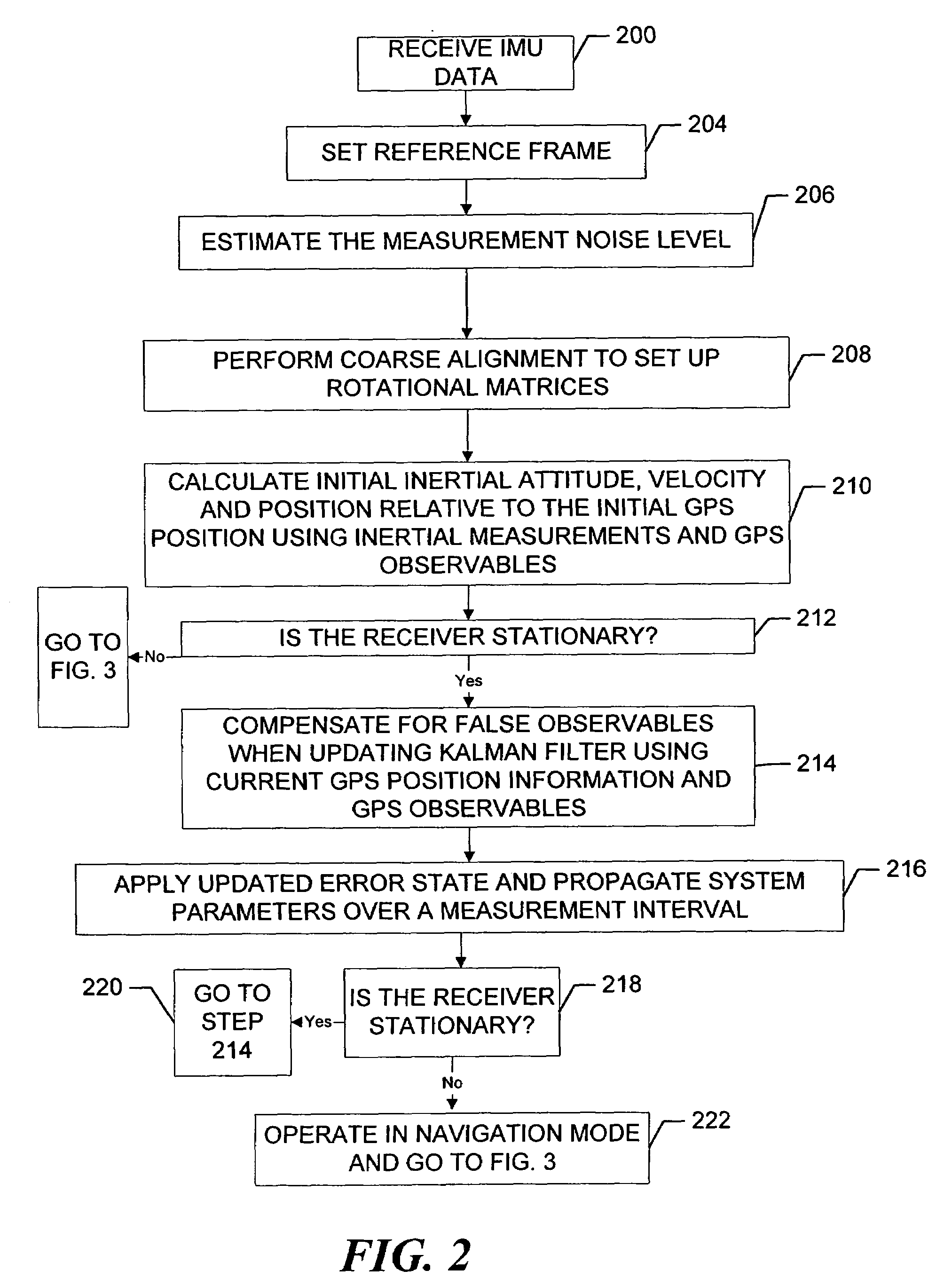
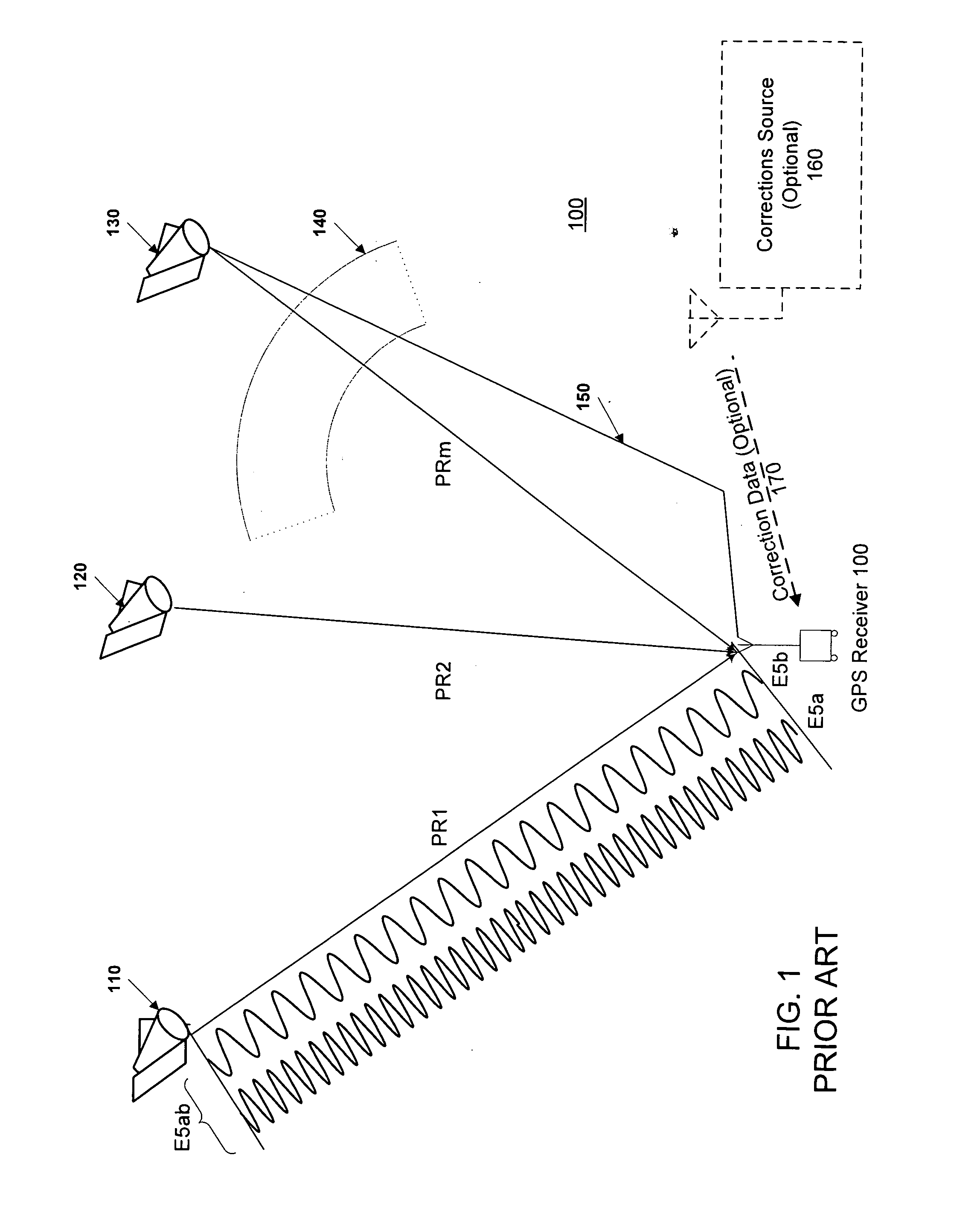
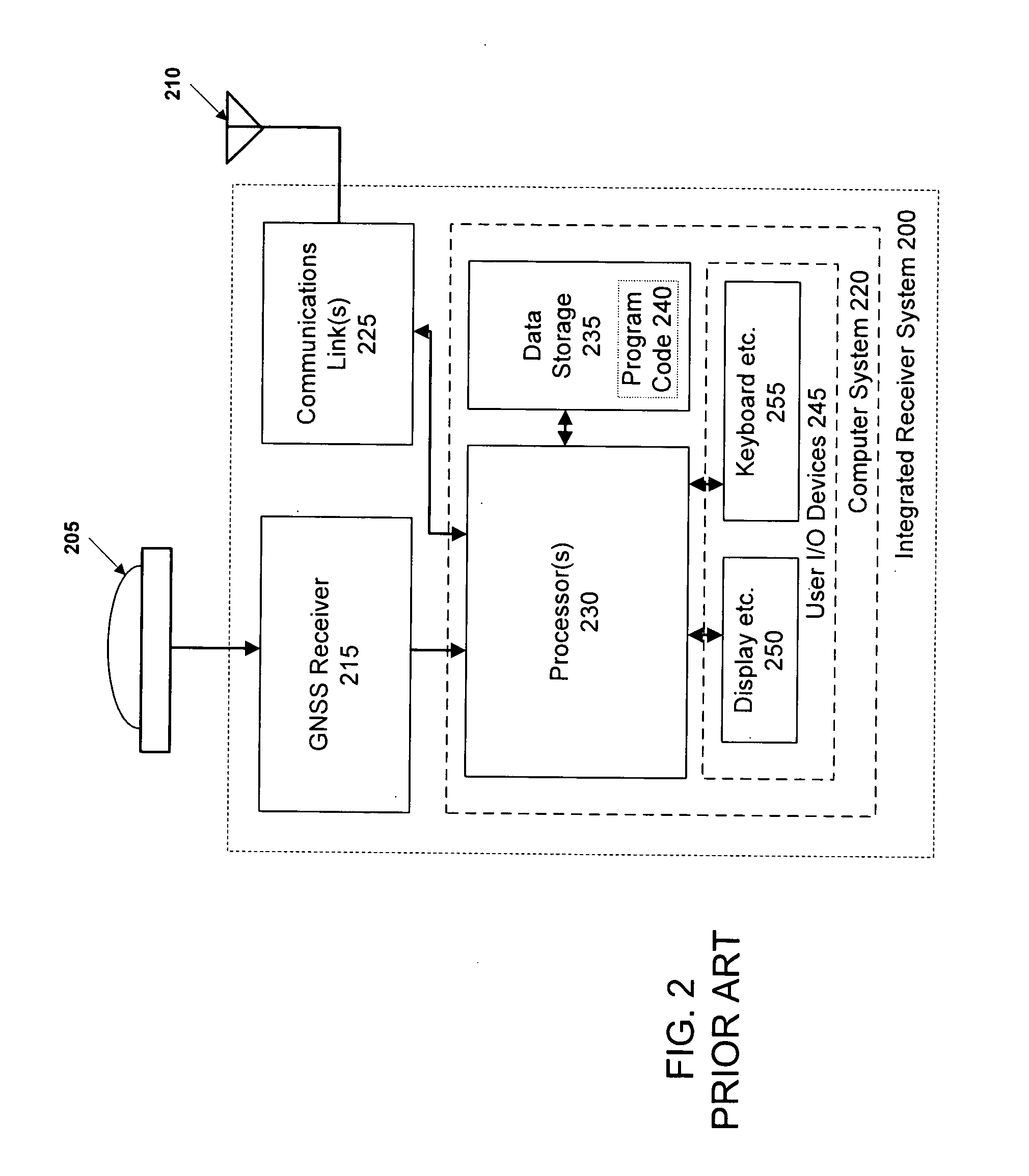
Inertial GPS navigation system with modified kalman filter
ActiveUS7193559B2Eliminate the effects ofShorten the timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPhase differenceDirect observation
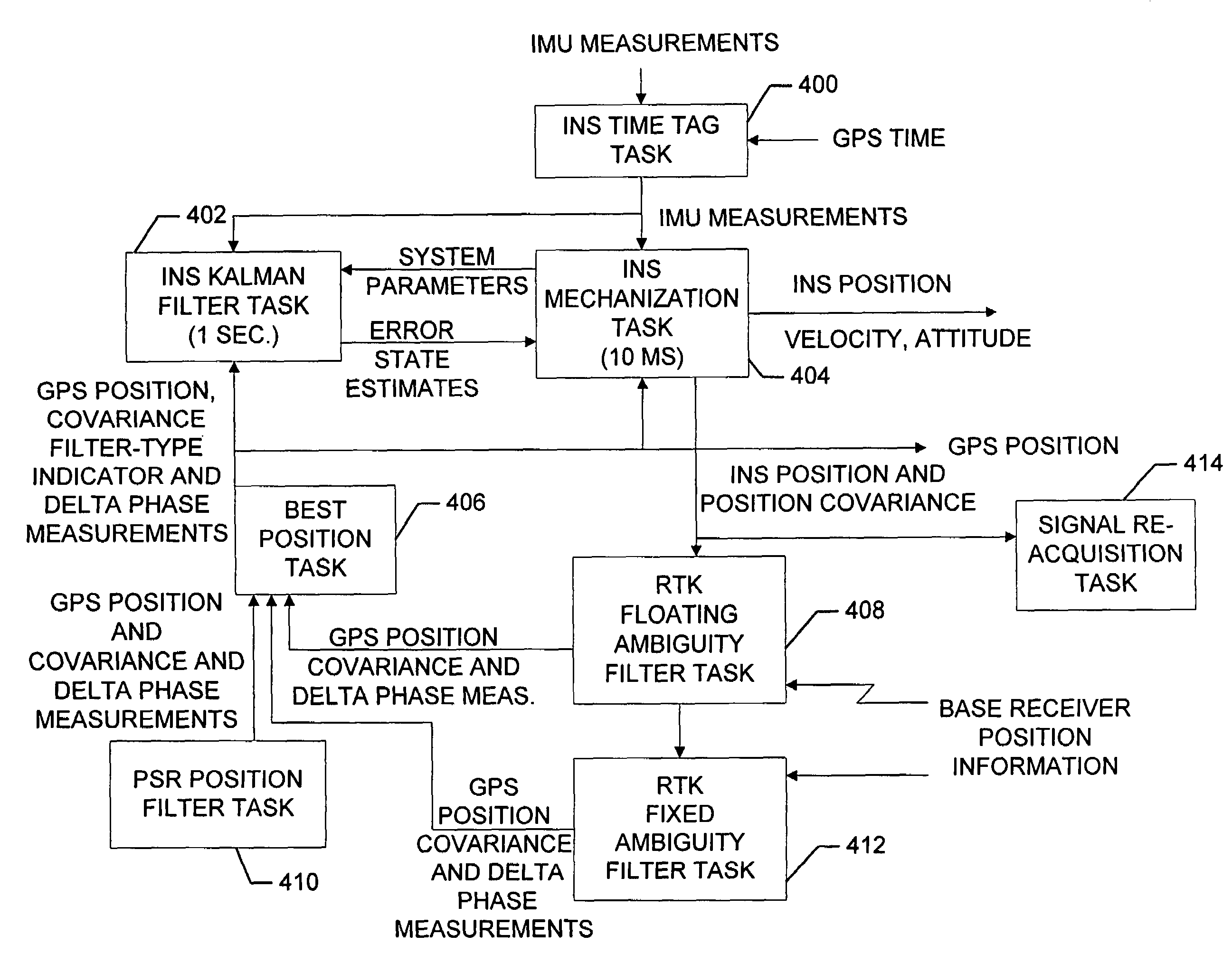
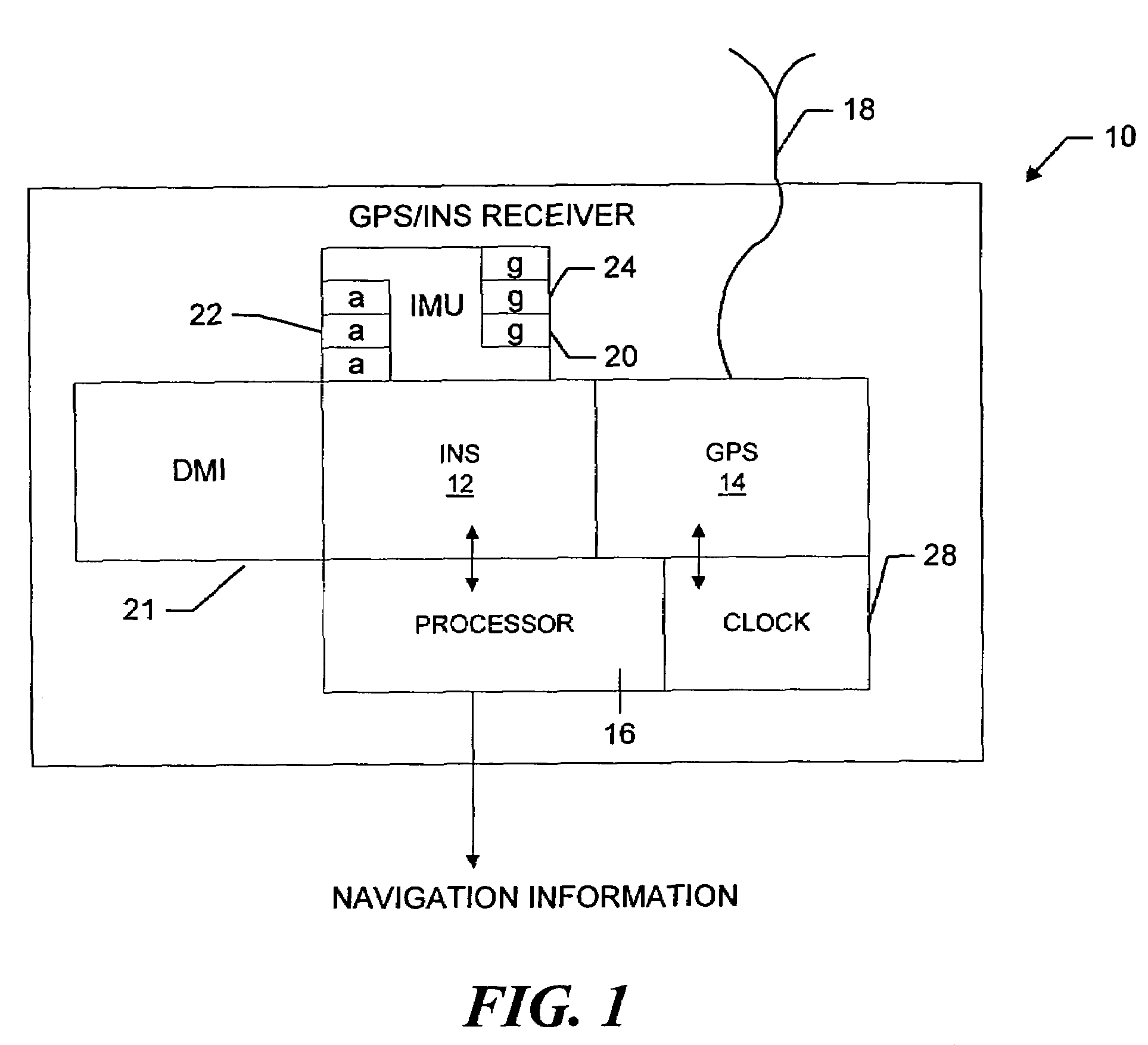
An inertial (“INS”) / GPS receiver includes an INS sub-system which incorporates, into a modified Kalman filter, GPS observables and / or other observables that span previous and current times. The INS filter utilizes the observables to update position information relating to both the current and the previous times, and to propagate the current position, velocity and attitude related information. The GPS observable may be delta phase measurements, and the other observables may be, for example, wheel pick-offs (or counts of wheel revolutions) that are used to calculate along track differences, and so forth. The inclusion of the measurements in the filter together with the current and the previous position related information essentially eliminates the effect of system dynamics from the system model. A position difference can thus be formed that is directly observable by the phase difference or along track difference measured between the previous and current time epochs. Further, the delta phase measurements can be incorporated in the INS filter without having to maintain GPS carrier ambiguity states. The INS sub-system and the GPS sub-system share GPS and INS position and covariance information. The receiver time tags the INS and any other non-GPS measurement data with GPS time, and then uses the INS and GPS filters to produce INS and GPS position information that is synchronized in time. The GPS / INS receiver utilizes GPS position and associated covariance information and the GPS and / or other observables in the updating of the INS filter. The INS filter, in turn, provides updated system error information that is used to propagate inertial current position, velocity and attitude information. Further, the receiver utilizes the inertial position, velocity and covariance information in the GPS filters to speed up GPS satellite signal re-acquisition and associated ambiguity resolution operations
Owner:NOVATEL INC
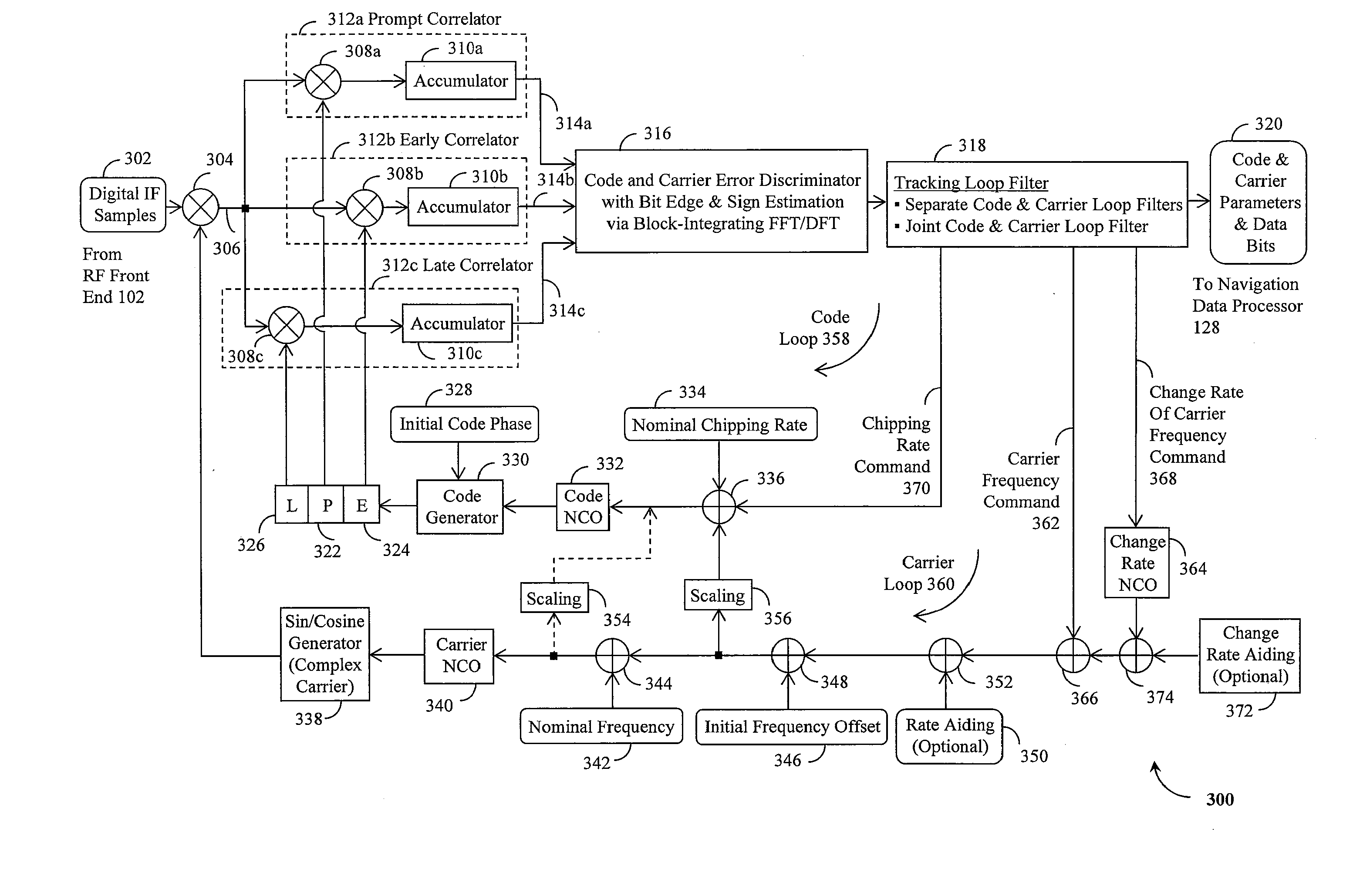
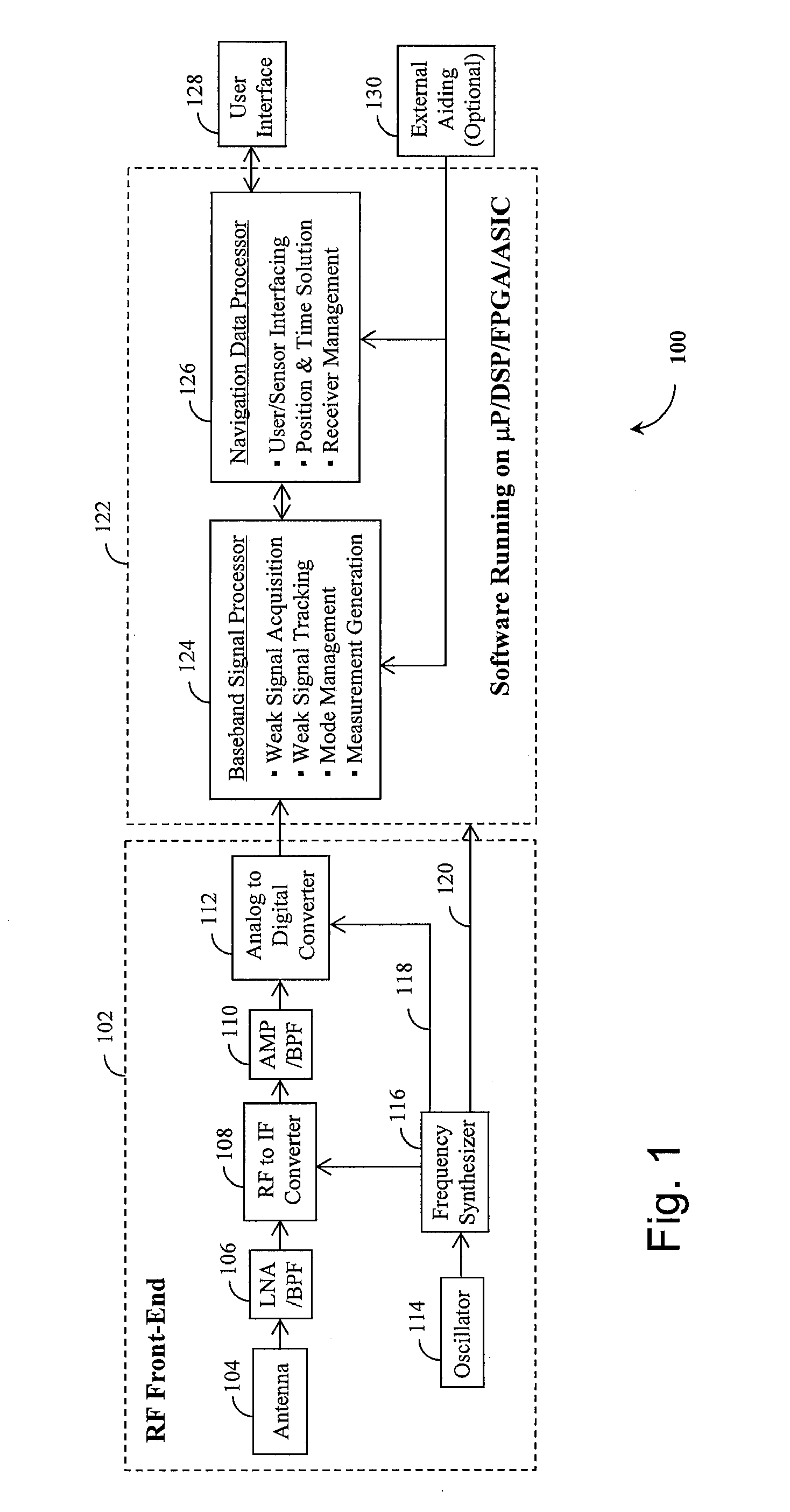
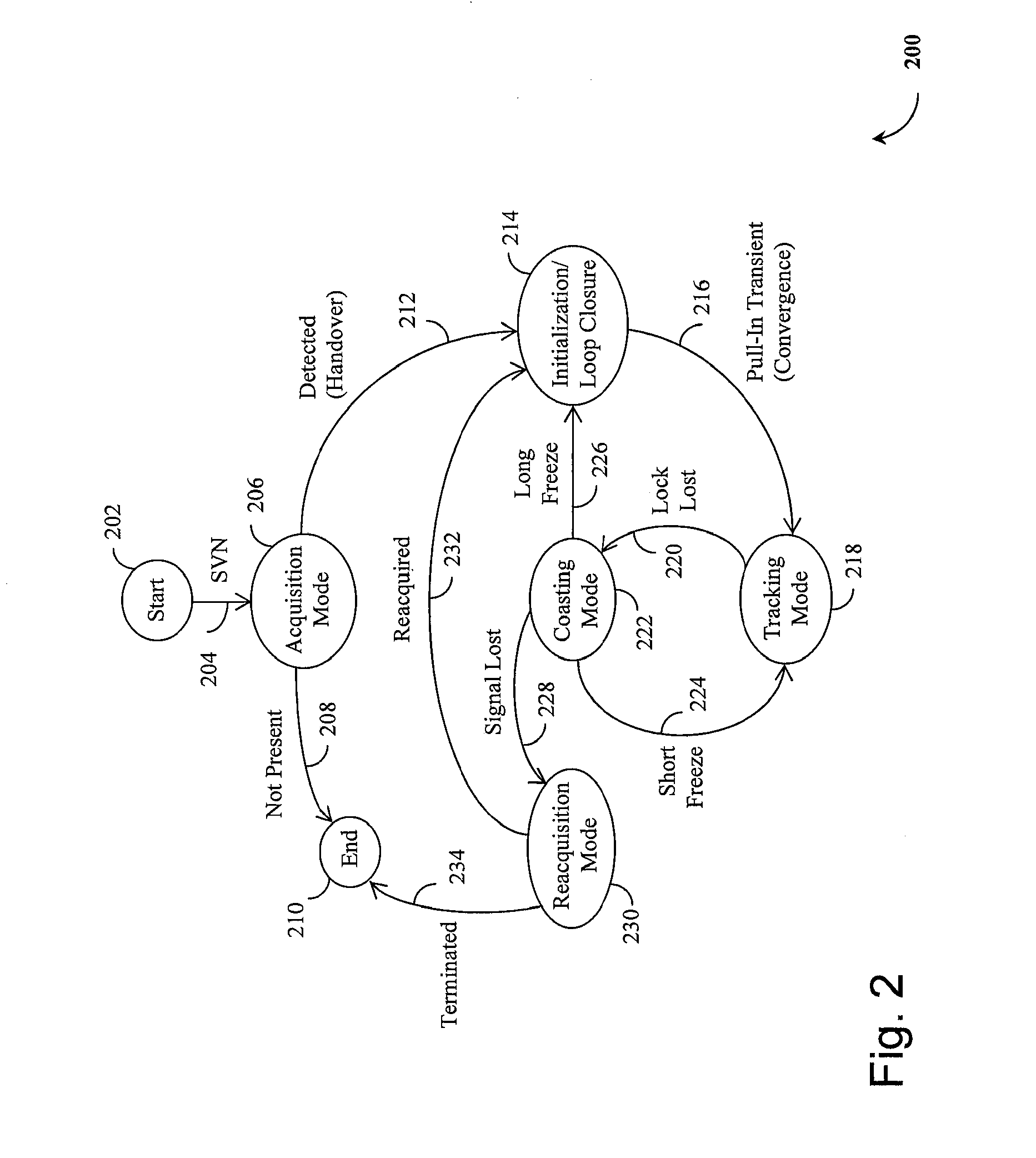
Method and device for tracking weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
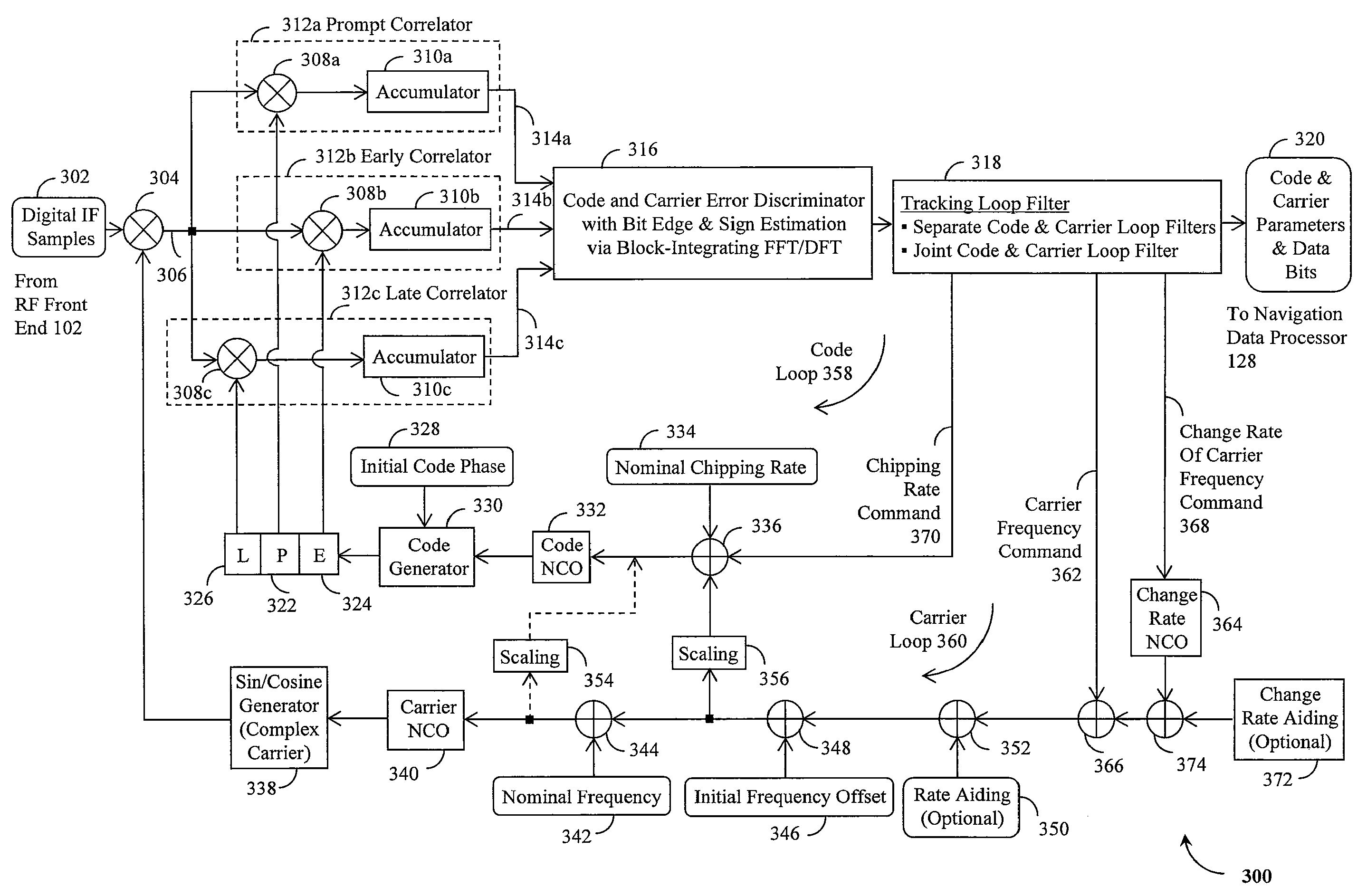
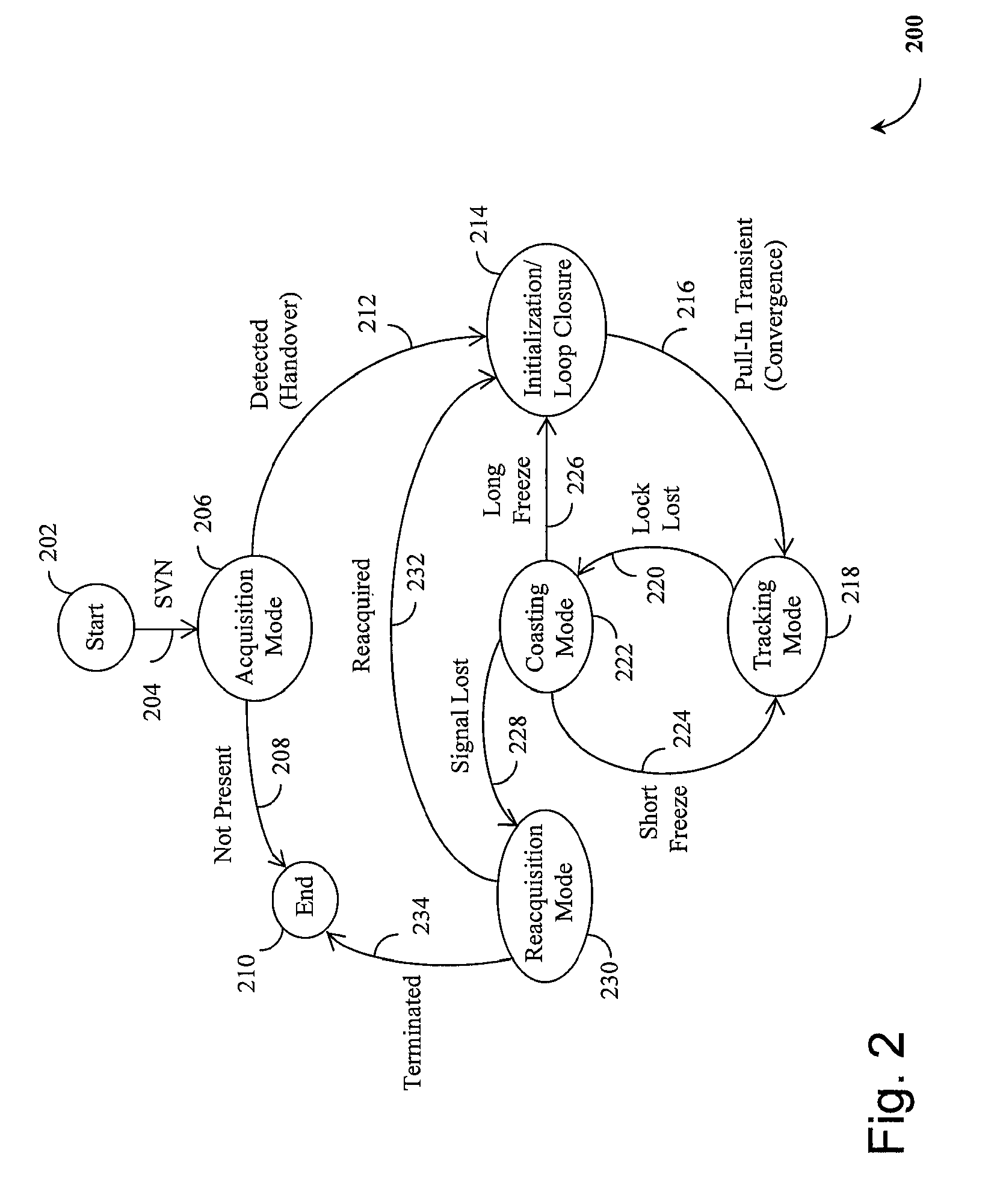
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of tracking weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites. In a preferred embodiment, code and carrier tracking loops are initially closed around the code phase, carrier frequency, and data bit edge estimates handed over from an acquisition mode. In subsequent tracking, early, prompt, and late copies of the code replica are correlated with the incoming signal. The prompt correlations are coherently integrated over an extended updating interval for data bit edge and sign estimation as well as for carrier phase and frequency error discrimination whereas the early and late correlations are used for code error discrimination. Code delay and carrier phase and frequency errors are used to update the code and carrier tracking loop filters. Together with data bits, they form observables of a GNSS signal's time and frequency parameters for timing and position fixing.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
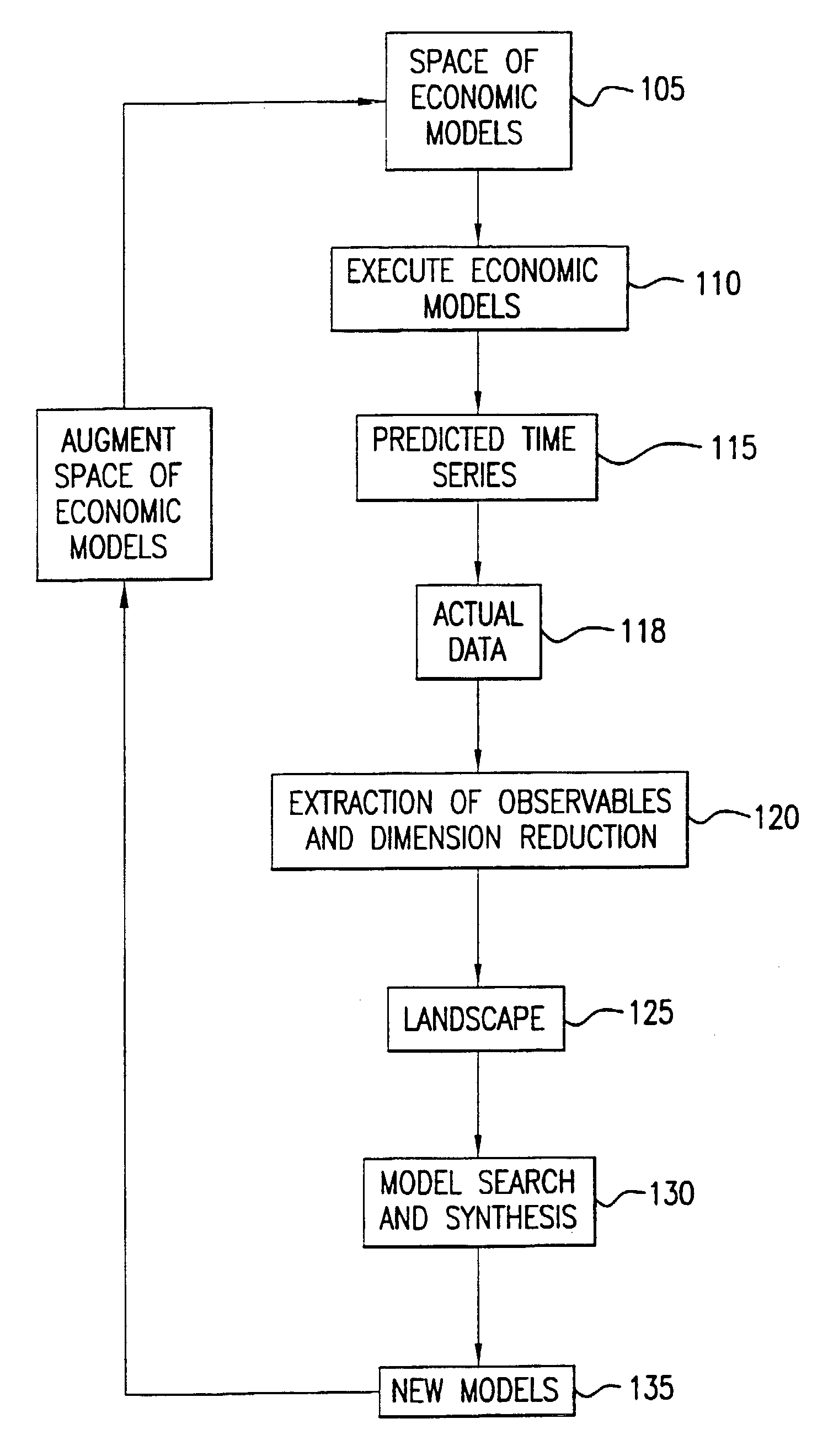
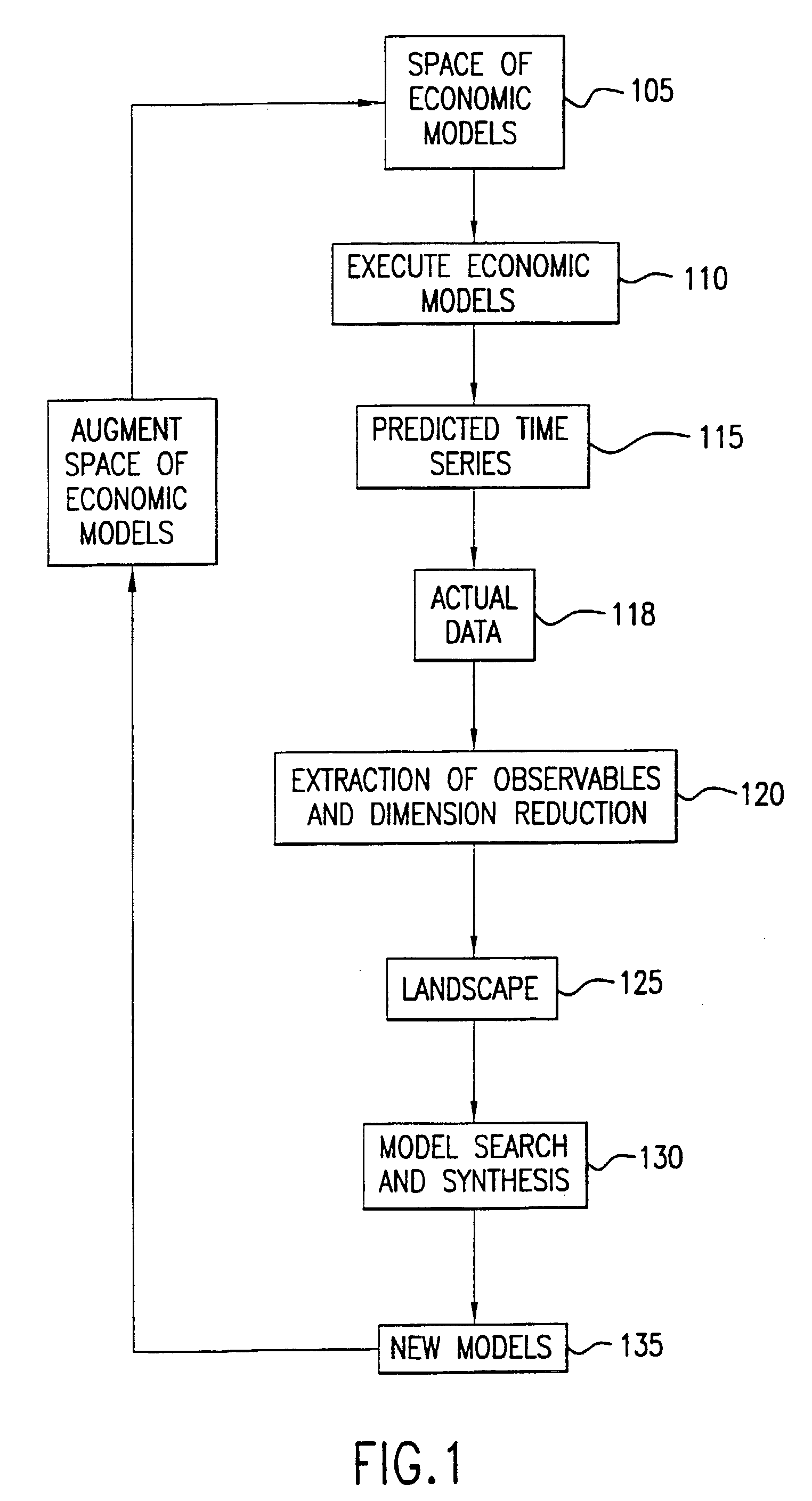
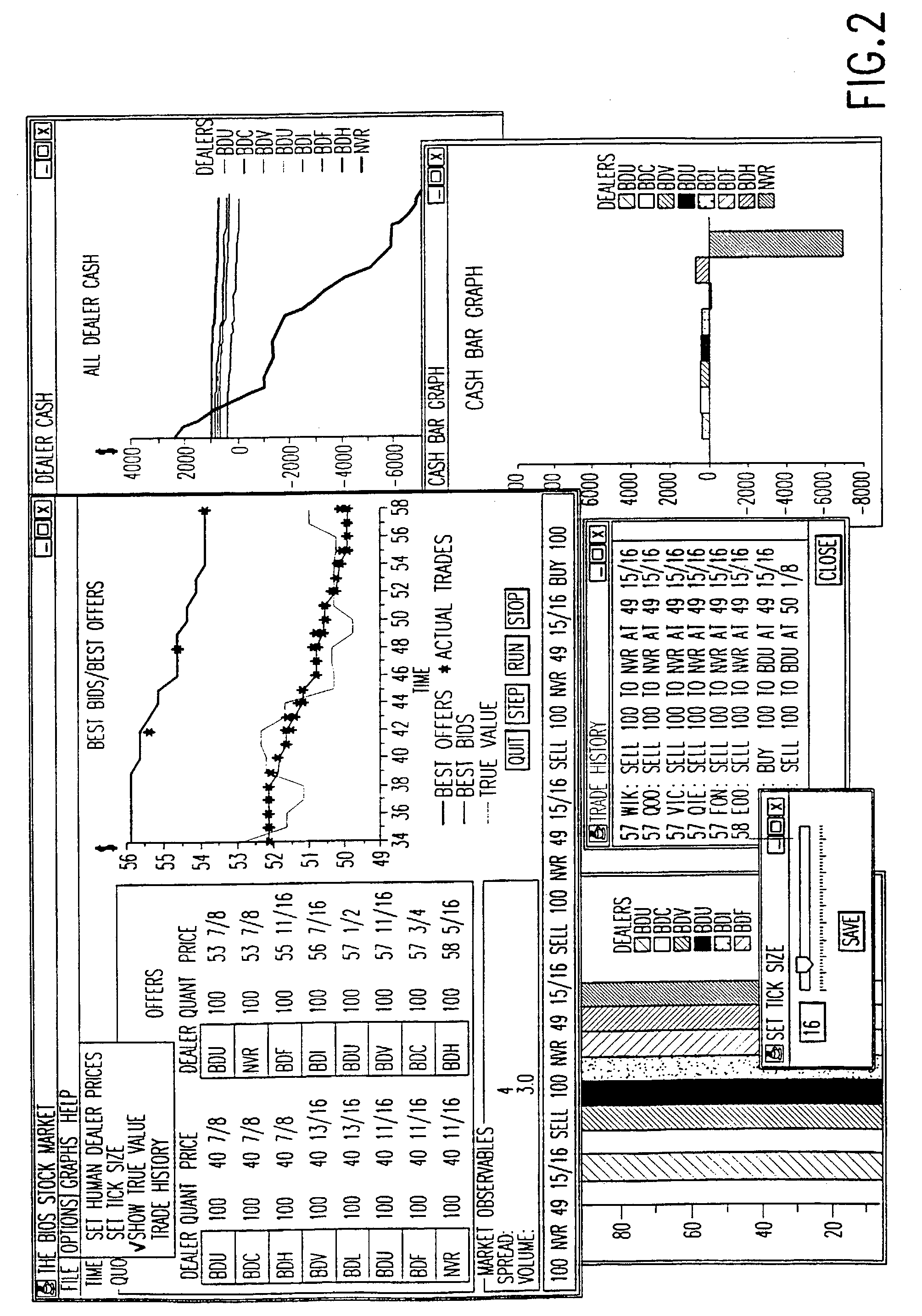
System and method for the analysis and prediction of economic markets
A system and method are provided which dynamically adapts to a changing economic environment by selecting or synthesizing an economic model from a set of economic models based on the selected model's ability to make accurate predictions about an actual economic market. The method and system each forms a space of different economic models, forms a behavioral landscape by extracting observables from executions of the economic models, and performs model selection and composite model synthesis through optimization over the behavioral landscape.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
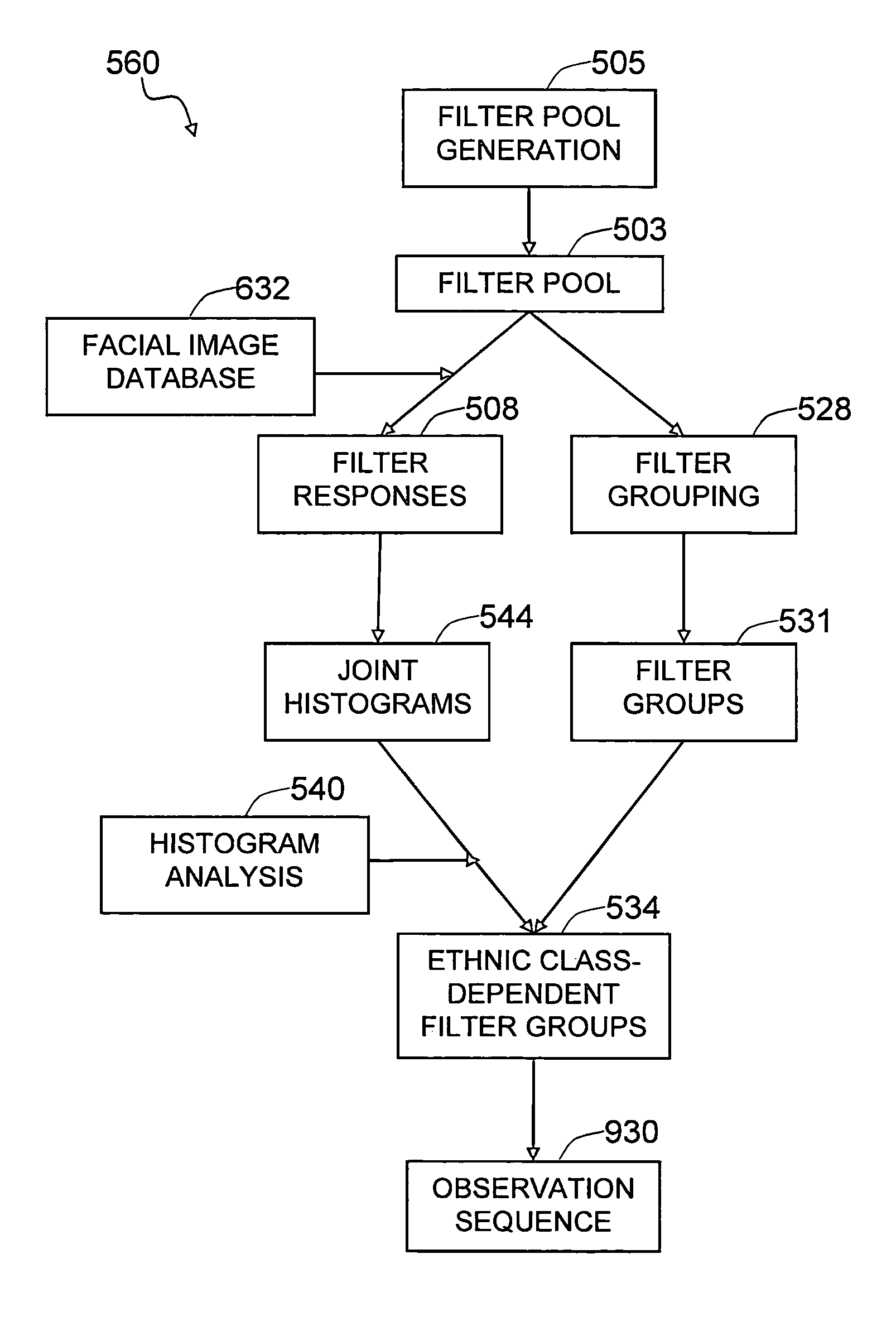
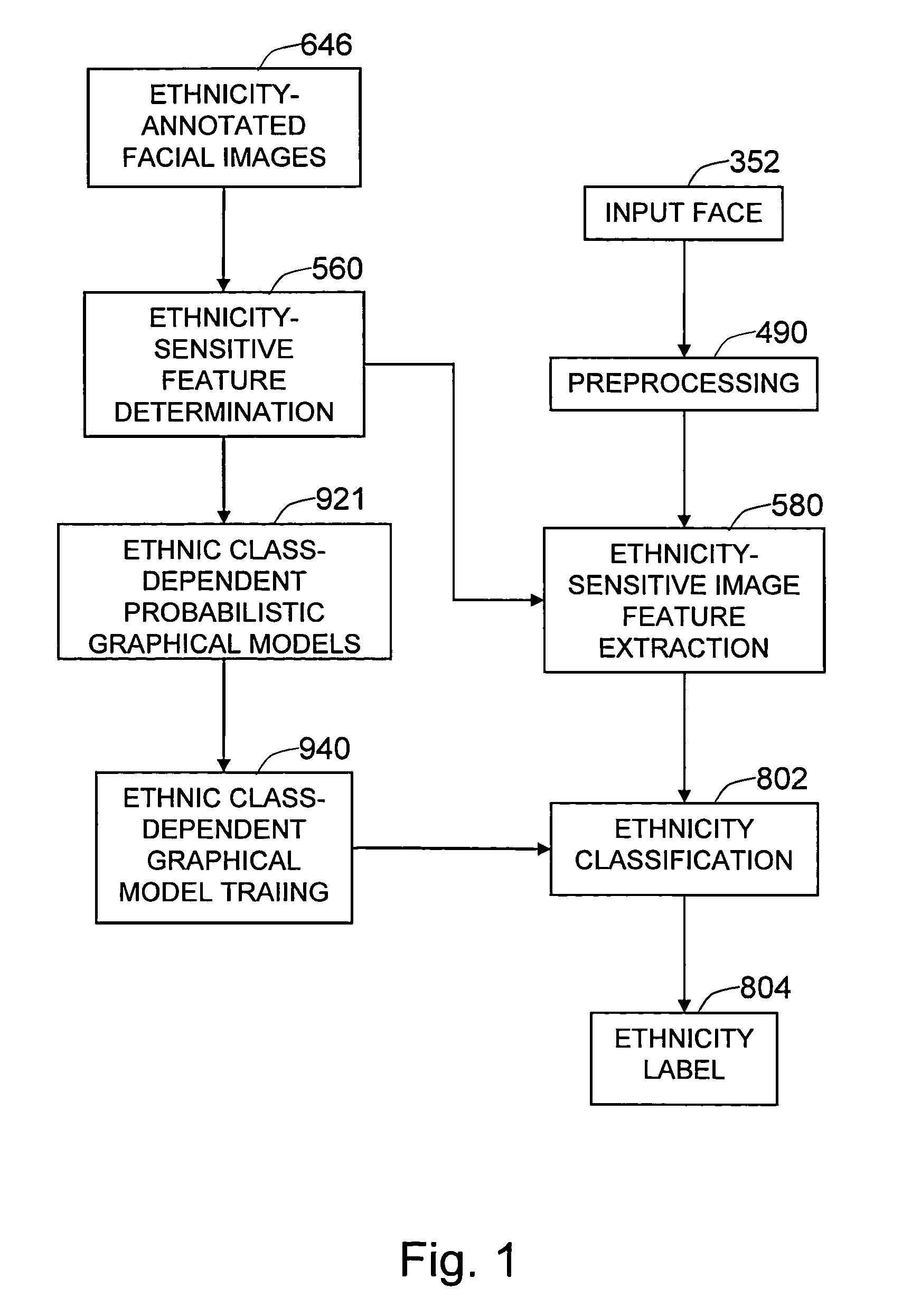
Method and system for robust human ethnicity recognition using image feature-based probabilistic graphical models
ActiveUS8379937B1High likelihood scoreLow likelihood scoreCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsSkin complexion
The present invention is a method and system to provide a face-based automatic ethnicity recognition system that utilizes ethnicity-sensitive image features and probabilistic graphical models to represent ethnic classes. The ethnicity-sensitive image features are derived from groups of image features so that each grouping of the image features contributes to more accurate recognition of the ethnic class. The ethnicity-sensitive image features can be derived from image filters that are matched to different colors, sizes, and shapes of facial features—such as eyes, mouth, or complexion. The ethnicity-sensitive image features serve as observable quantities in the ethnic class-dependent probabilistic graphical models, where each probabilistic graphical model represents one ethnic class. A given input facial image is corrected for pose and lighting, and ethnicity-sensitive image features are extracted. The extracted image features are fed to the ethnicity-dependent probabilistic graphical models to determine the ethnic class of the input facial image.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
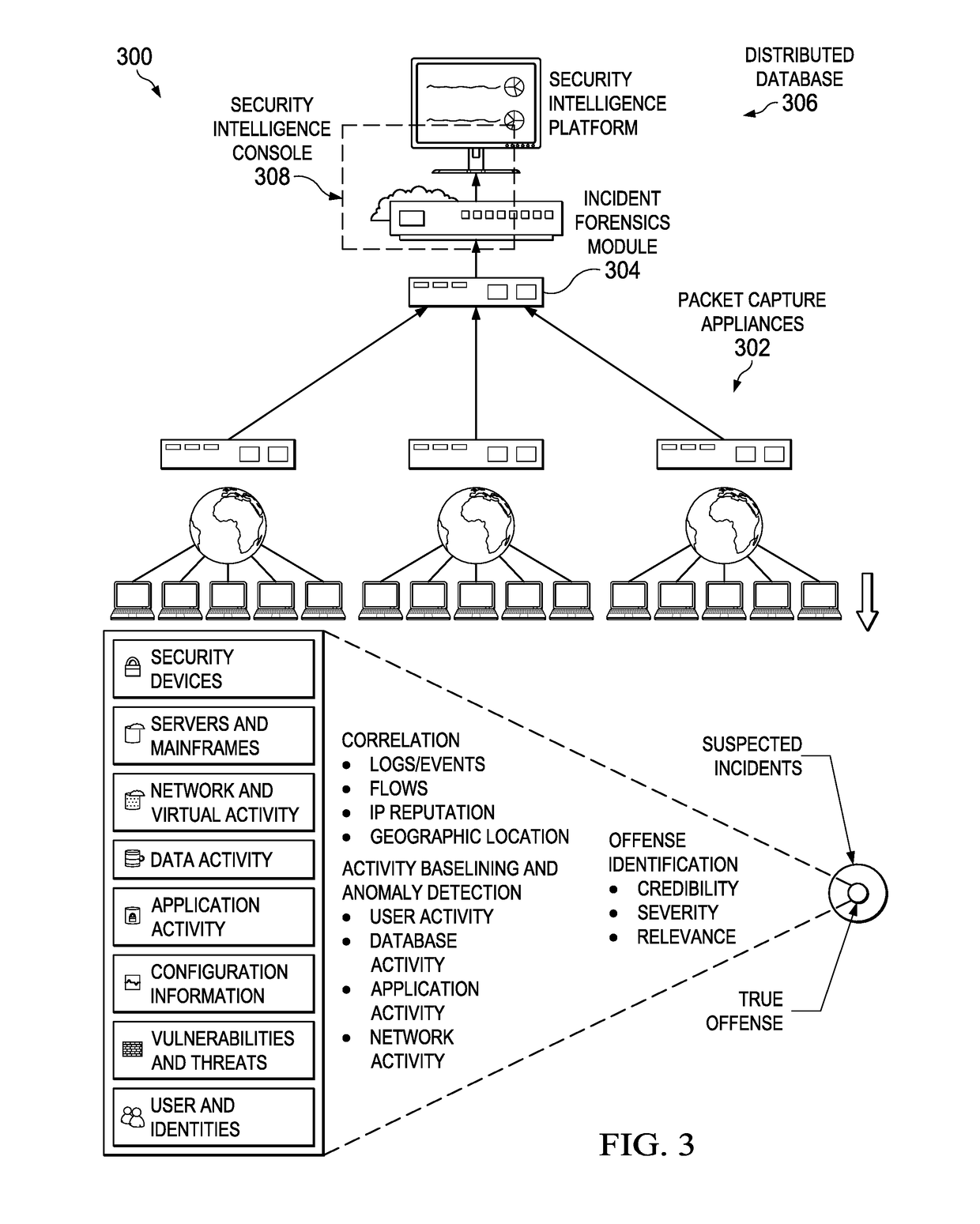
Cognitive offense analysis using contextual data and knowledge graphs
ActiveUS20180048661A1Simplifies further analysisSimplifies corrective taskDigital data information retrievalPlatform integrity maintainanceGraph spectraData source
An automated method for processing security events in association with a cybersecurity knowledge graph. The method begins upon receipt of information from a security system representing an offense. An initial offense context graph is built based in part on context data about the offense. The graph also activity nodes connected to a root node; at least one activity node includes an observable. The root node and its one or more activity nodes represent a context for the offense. The knowledge graph, and potentially other data sources, are then explored to further refine the initial graph to generate a refined graph that is then provided to an analyst for further review and analysis. Knowledge graph exploration involves locating the observables and their connections in the knowledge graph, determining that they are associated with known malicious entities, and then building subgraphs that are then merged into the initial graph.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for adiabatic quantum computing comprising of Hamiltonian scaling
ActiveUS7788192B2Increase the gap sizeControl rateQuantum computersDigital data processing detailsComputational problemQuantum system
A method for quantum computing using a quantum system comprising a plurality of qubits is provided. The system can be in any one of at least two configurations at any given time including one characterized by an initialization Hamiltonian HO and one characterized by a problem Hamiltonian HP. The problem Hamiltonian HP has a final state. Each respective first qubit in the qubits is arranged with respect to a respective second qubit in the qubits such that they define a predetermined coupling strength. The predetermined coupling strengths between the qubits in the plurality of qubits collectively define a computational problem to be solved. In the method, the system is initialized to HO and is then adiabatically changed until the system is described by the final state of the problem Hamiltonian HP. Then the state of the system is read out by probing an observable of the σX Pauli matrix operator.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Systems and Methods for Satellite Image Processing to Estimate Crop Yield
Systems and methods for generating a crop yield estimate for an area as small as an individual field from images captured by a satellite are disclosed. The system generates simulations of crop yields in a region that includes the area by applying combinations of different parameters to a crop yield models. Observable quantities for simulated yields are determined from the simulations. The simulations and the observable properties are used to train a statistic model for the region that has two or more variables. Images captured by a satellite that include at least a portion of the area are obtained. Crop information is then determined from the images and weather information associated with the dates that the images where captured is obtained. The statistical model is then applied to the crop information and the weather information to determine a crop yield estimate.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System and method for positioning using hybrid spectral compression and cross correlation signal processing
InactiveUS20120169542A1Easy to implementRapidly deployableDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency spectrumCode division multiple access
The present invention relates to a system and method for positioning and navigation using hybrid spectral compression and cross correlation signal processing of signals of opportunity, which may include Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) as well as other wideband energy emissions in GNSS obstructed environments. Examples of these signals of opportunity include but are not limited to GPS, GLONASS, cellular Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) communications signals, and 802.11 Wi-Fi. Combining spectral compression with spread spectrum cross correlation enables extraction of code and carrier observables without the need to implement the tracking loops (e.g. Costas tracking loop) commonly used in conventional GNSS receivers. For applications where dynamics and transmission medium may make it difficult to continuously track carrier phase, the hybrid approach of the present invention has significant utility.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
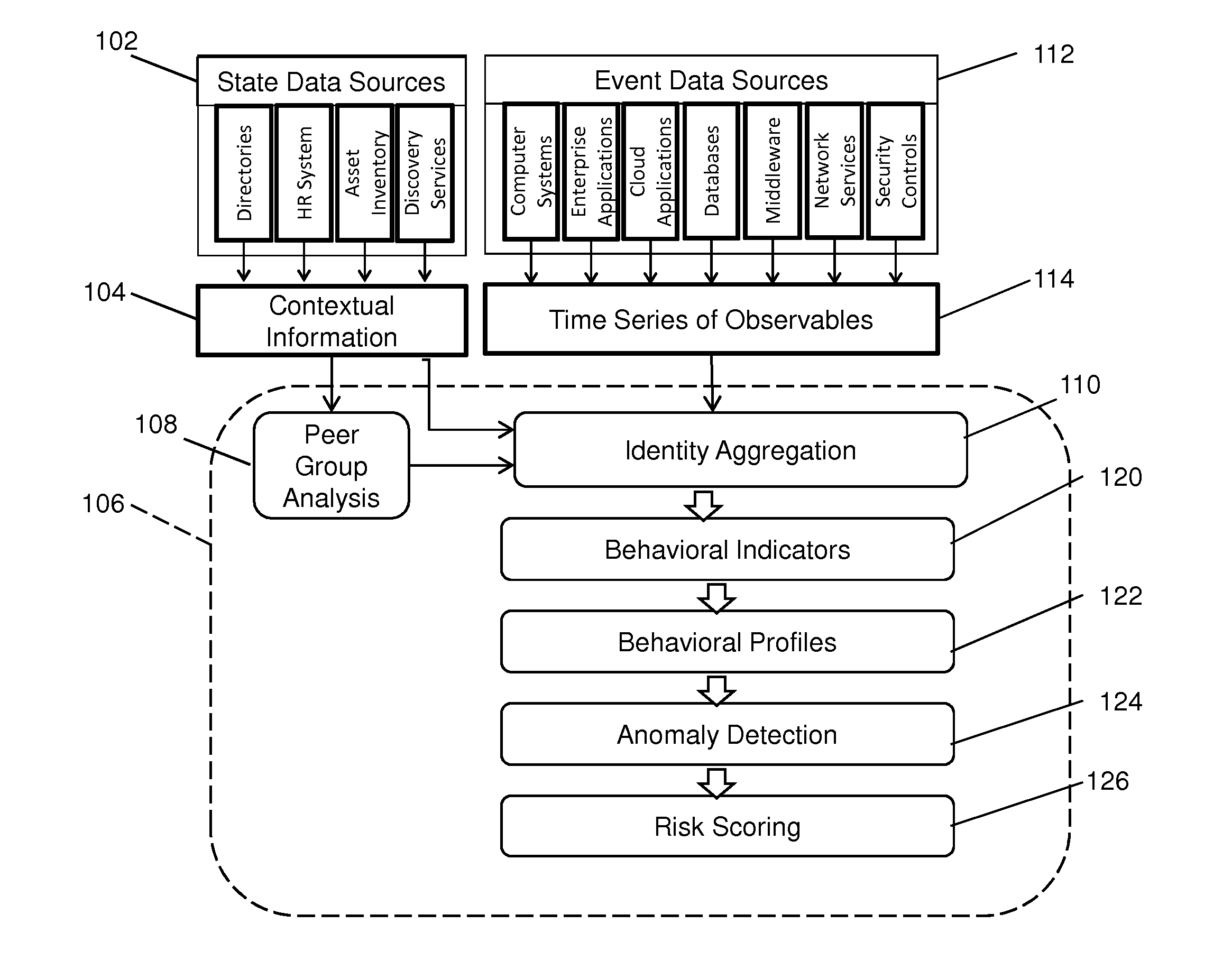
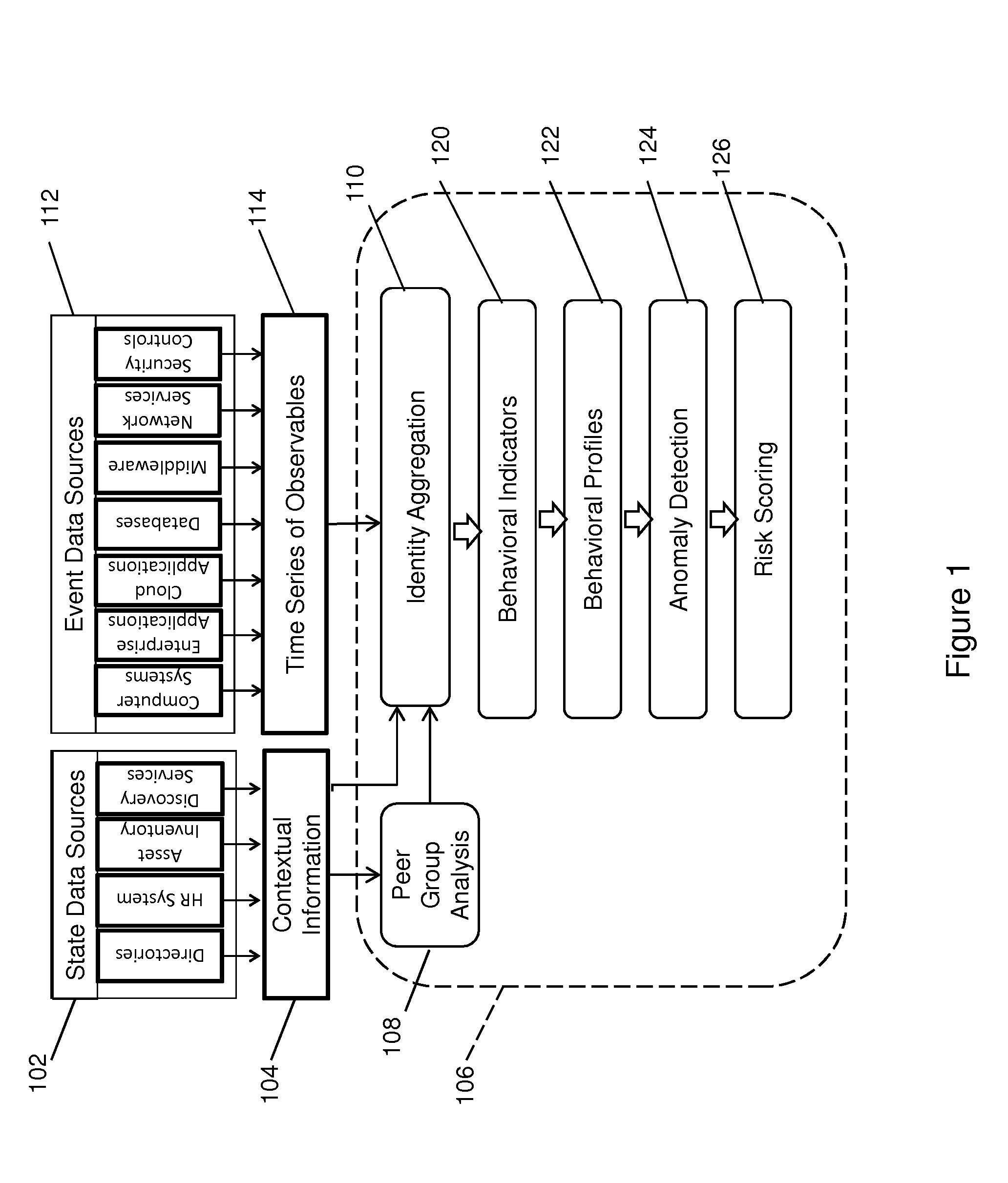
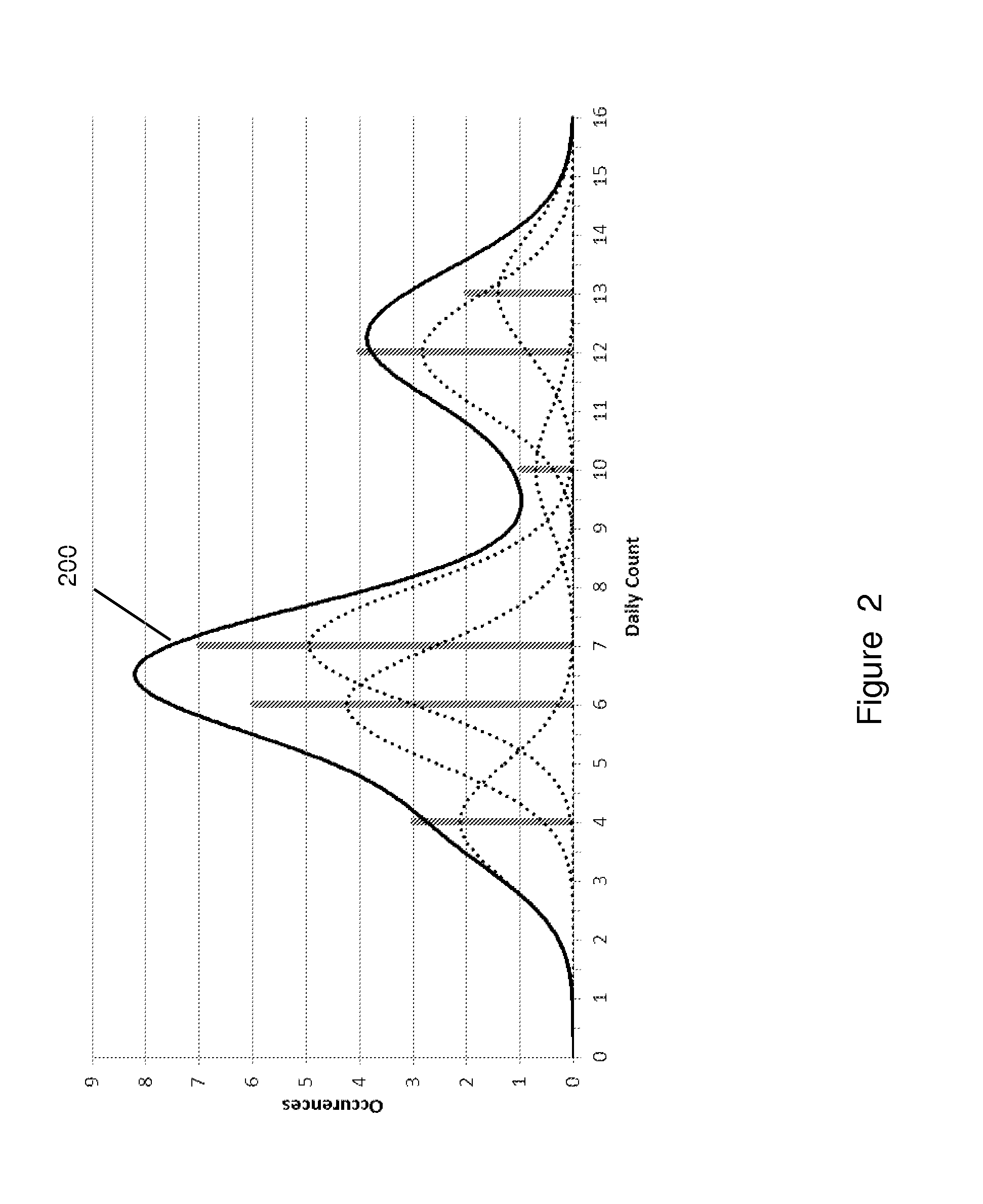
Anomaly Detection Using Adaptive Behavioral Profiles
Anomalous activities in a computer network are detected using adaptive behavioral profiles that are created by measuring at a plurality of points and over a period of time observables corresponding to behavioral indicators related to an activity. Normal kernel distributions are created about each point, and the behavioral profiles are created automatically by combining the distributions using the measured values and a Gaussian kernel density estimation process that estimates values between measurement points. Behavioral profiles are adapted periodically using data aging to de-emphasize older data in favor of current data. The process creates behavioral profiles without regard to the data distribution. An anomaly probability profile is created as a normalized inverse of the behavioral profile, and is used to determine the probability that a behavior indicator is indicative of a threat. The anomaly detection process has a low false positive rate.
Owner:SECURONIX INC
GNSS Signal Processing Methods and Apparatus
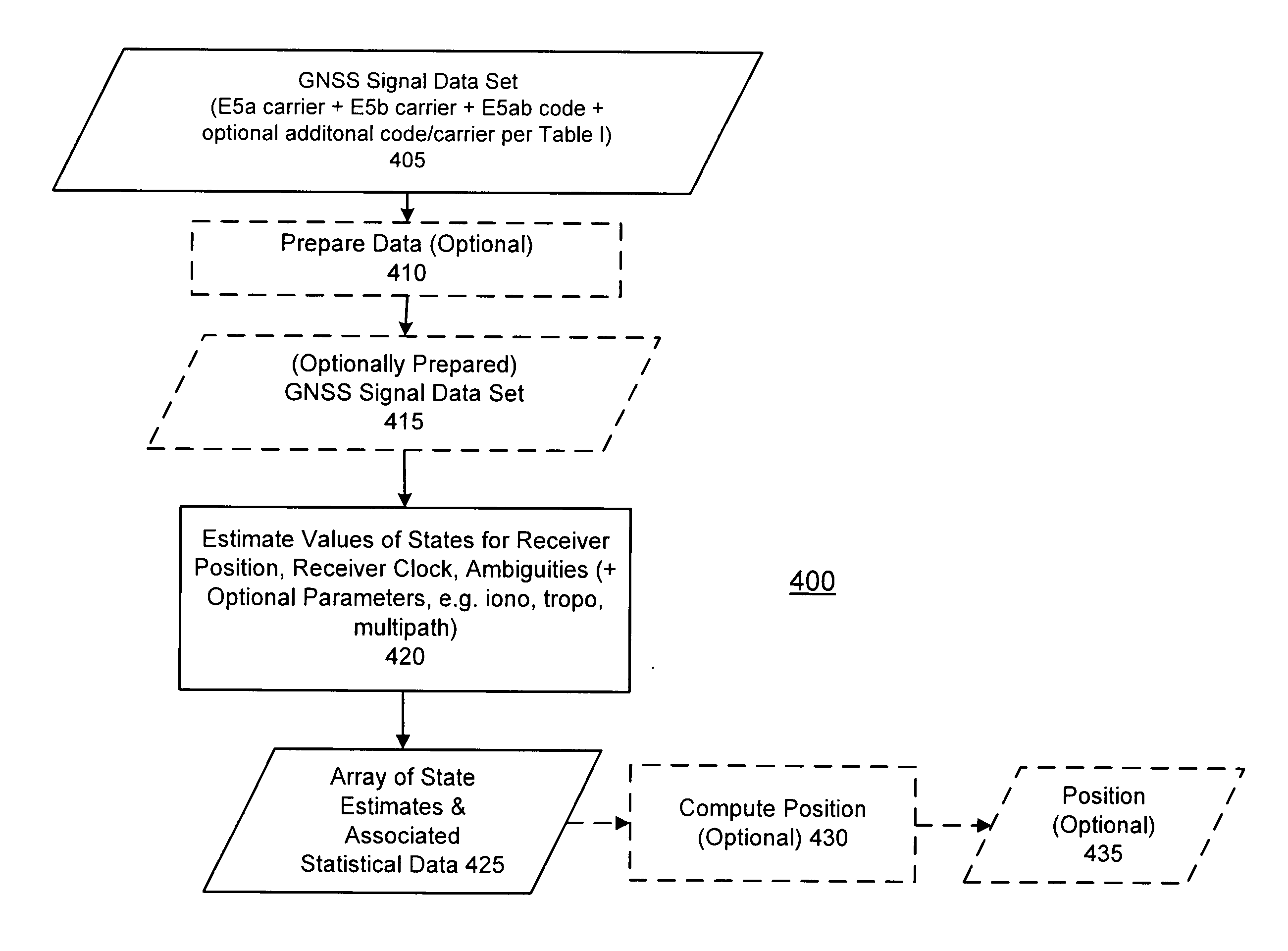
ActiveUS20120026038A1Speed up the processImproved ambiguity estimationSatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityWide band
Methods and apparatus are provided for processing a set of GNSS signal data derived from observations of GNSS signals of multiple transmitters over multiple epochs, the GNSS signals having a first signal and a second signal in a first band which can be tracked as a single wide-band signal and each of which can be tracked separately, comprising: obtaining carrier-phase observations of the first signal, obtaining carrier-phase observations of the second signal, obtaining code observations of the wide-band signal, and estimating from a set of observables comprising the carrier-phase observations of the first signal, the carrier-phase observations of the second signal and the code observations of the wide-band signal values for a set of parameters comprising: position of a receiver of the GNSS signals, clock error of a receiver of the GNSS signals, and an array of ambiguities comprising an ambiguity for each transmitter from which carrier-phase observations of the first signal are obtained and an ambiguity for each transmitter from which carrier-phase observations of the second signal are obtained.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
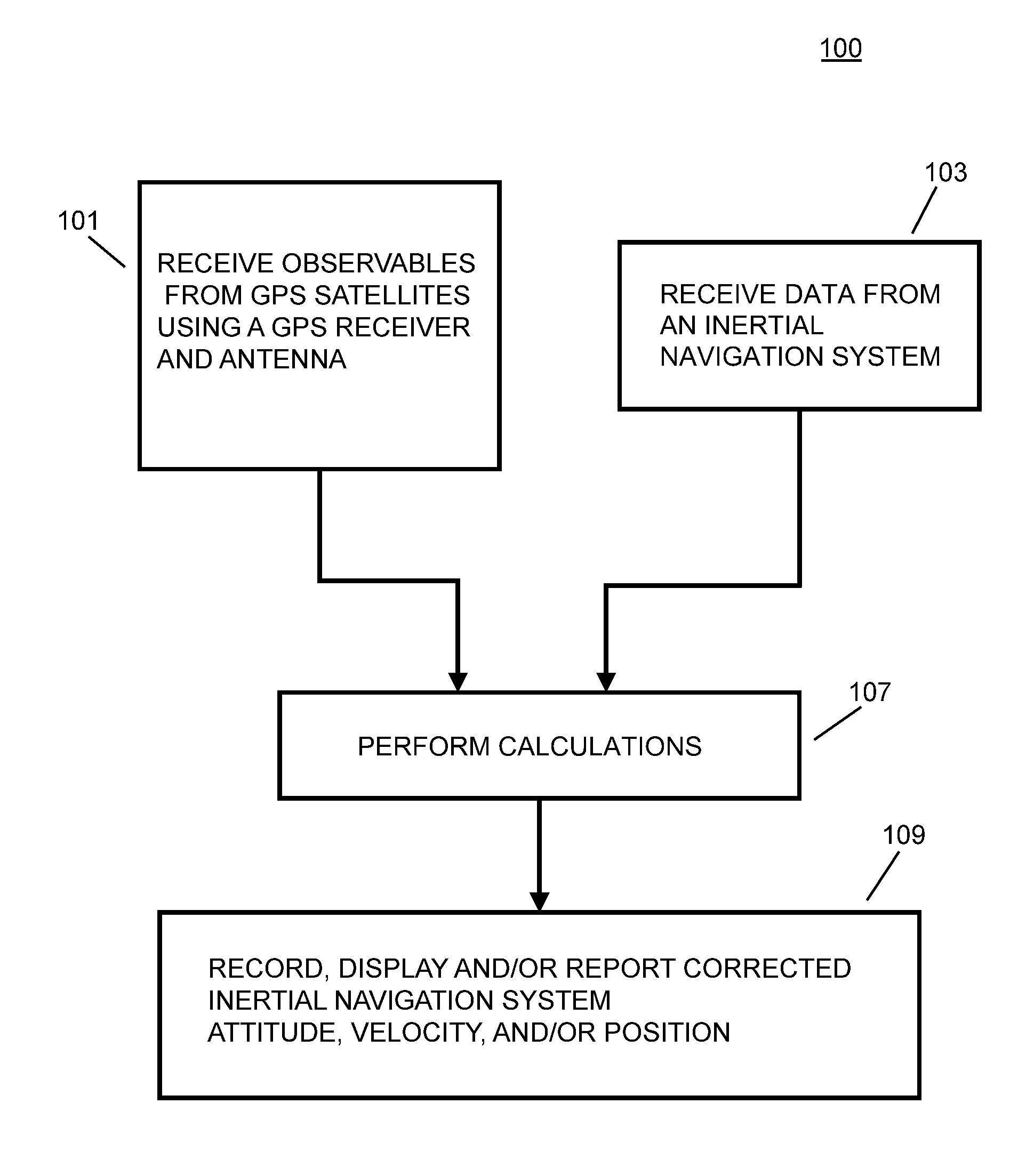
Gps/ins sensor fusion using GPS wind up model
InactiveUS20120065883A1Enhanced accuracy yaw angleImprove accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingGps receiverSensor fusion
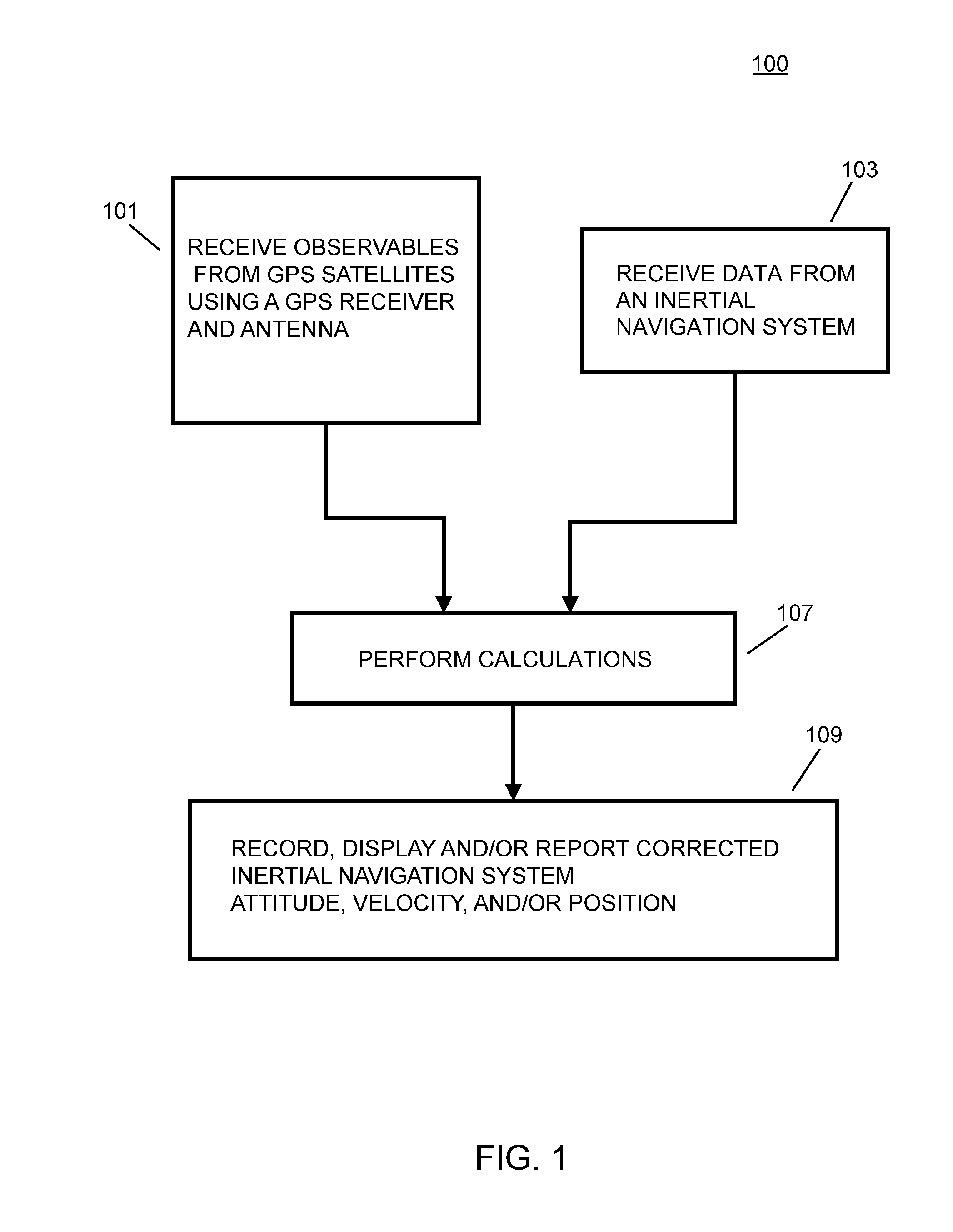
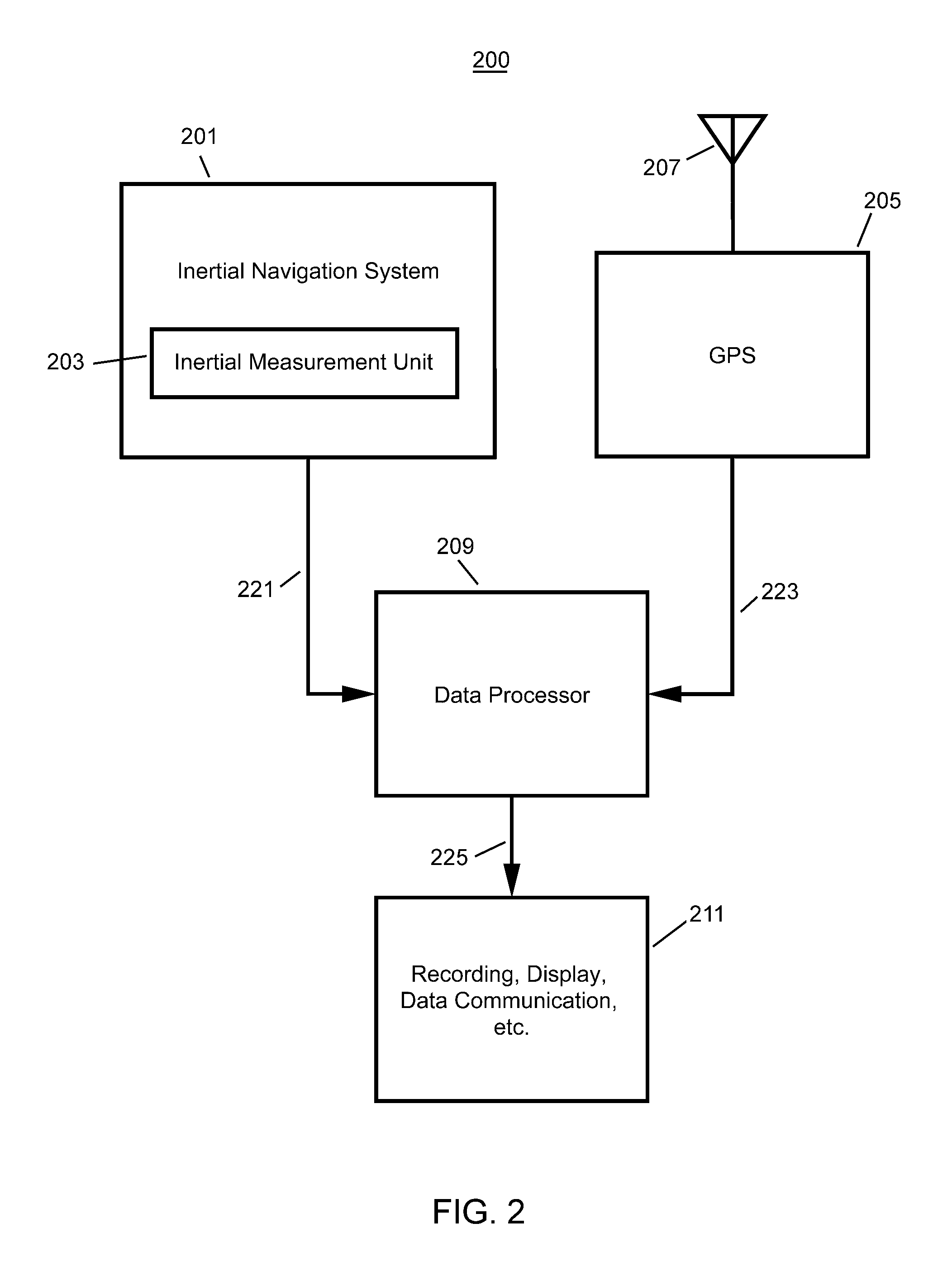
A method of stabilizing an inertial navigation system (INS), includes the steps of: receiving data from an inertial navigation system; and receiving a finite number of carrier phase observables using at least one GPS receiver from a plurality of GPS satellites; calculating a phase wind up correction; correcting at least one of the finite number of carrier phase observables using the phase wind up correction; and calculating a corrected IMU attitude or velocity or position using the corrected at least one of the finite number of carrier phase observables; and performing a step selected from the steps consisting of recording, reporting, or providing the corrected IMU attitude or velocity or position to another process that uses the corrected IMU attitude or velocity or position. A GPS stabilized inertial navigation system apparatus is also described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and device for tracking weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of tracking weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites. In a preferred embodiment, code and carrier tracking loops are initially closed around the code phase, carrier frequency, and data bit edge estimates handed over from an acquisition mode. In subsequent tracking, early, prompt, and late copies of the code replica are correlated with the incoming signal. The prompt correlations are coherently integrated over an extended updating interval for data bit edge and sign estimation as well as for carrier phase and frequency error discrimination whereas the early and late correlations are used for code error discrimination. Code delay and carrier phase and frequency errors are used to update the code and carrier tracking loop filters. Together with data bits, they form observables of a GNSS signal's time and frequency parameters for timing and position fixing.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
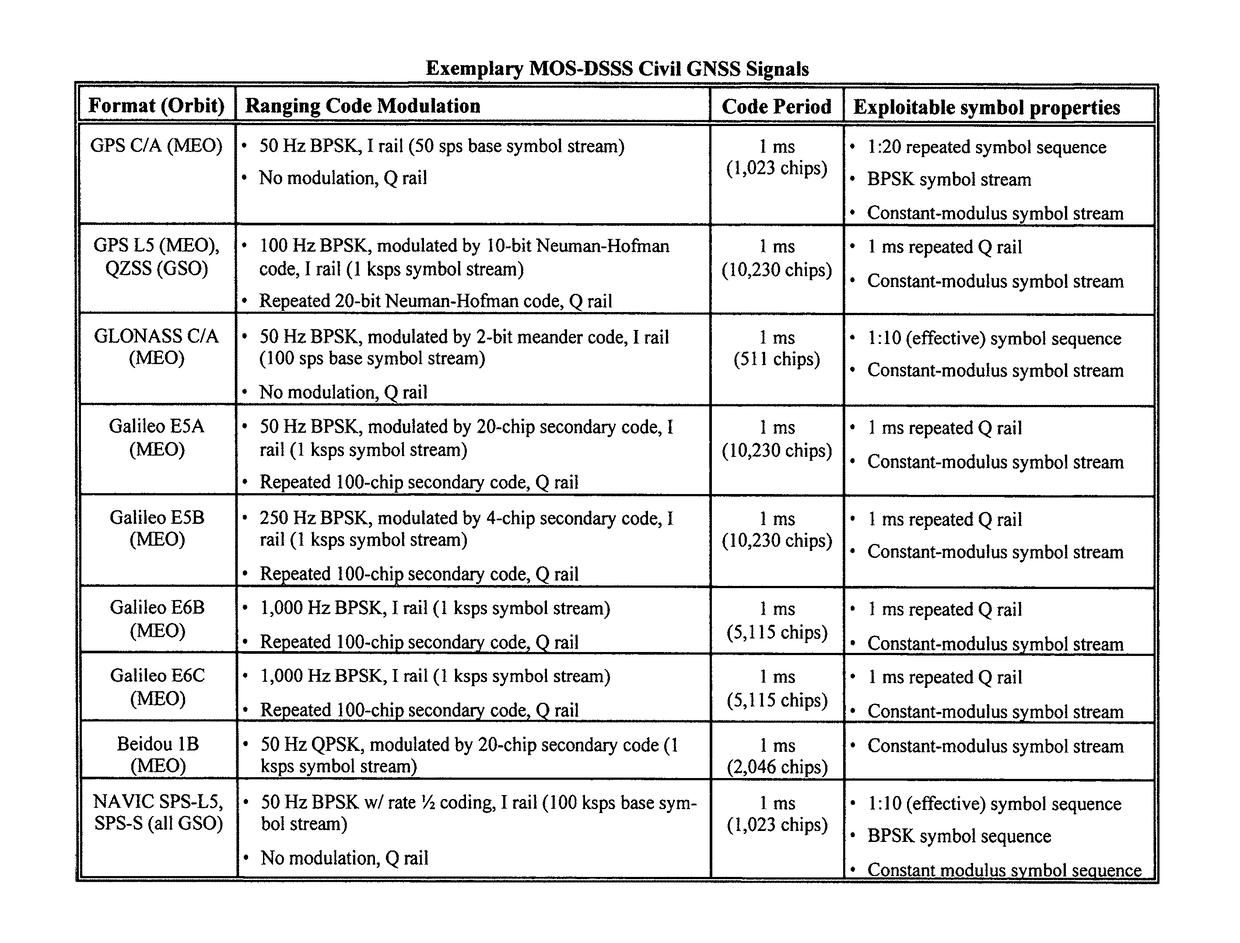
Blind despreading of civil GNSS signals for resilient PNT applications
ActiveUS20170350985A1Reduce computing loadLow costSatellite radio beaconingTime to first fixDiversity scheme
A method, system and apparatus are claimed for receiving, blindly despreading, and determining geo-observables, of true civil Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) navigation signals generated by any of the set of satellite vehicles and ground beacons, amongst false echoes and malicious GNSS signals from spoofers and repeaters; for identifying malicious GNSS signals, and preventing those signals from corrupting or capturing Pointing, Navigation, and Timing tracking operations; and for geolocating malicious GNSS signals. The invention also provides time-to-first-fix over much smaller time intervals than existing GNSS methods and can operate both in the presence of signals with much wider disparity in received power than existing techniques, and in the presence of arbitrary multipath. Further embodiments employing spatial / polarization diverse receivers that remove non-GNSS jammers received by the system, as well as targeted GNSS spoofers that can otherwise emulate GNSS signals received at victim receivers, are also claimed.
Owner:AGEE BRIAN G
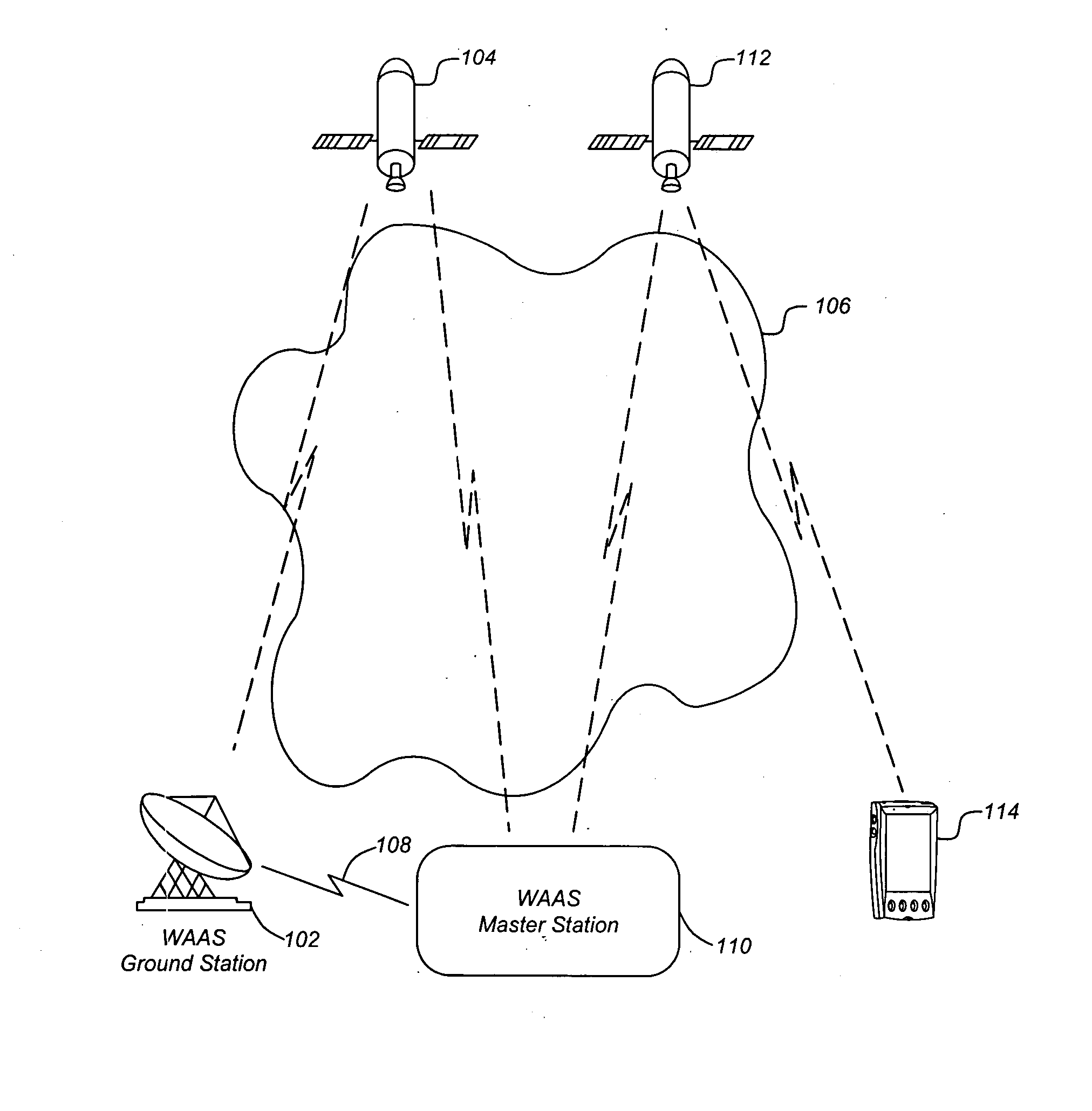
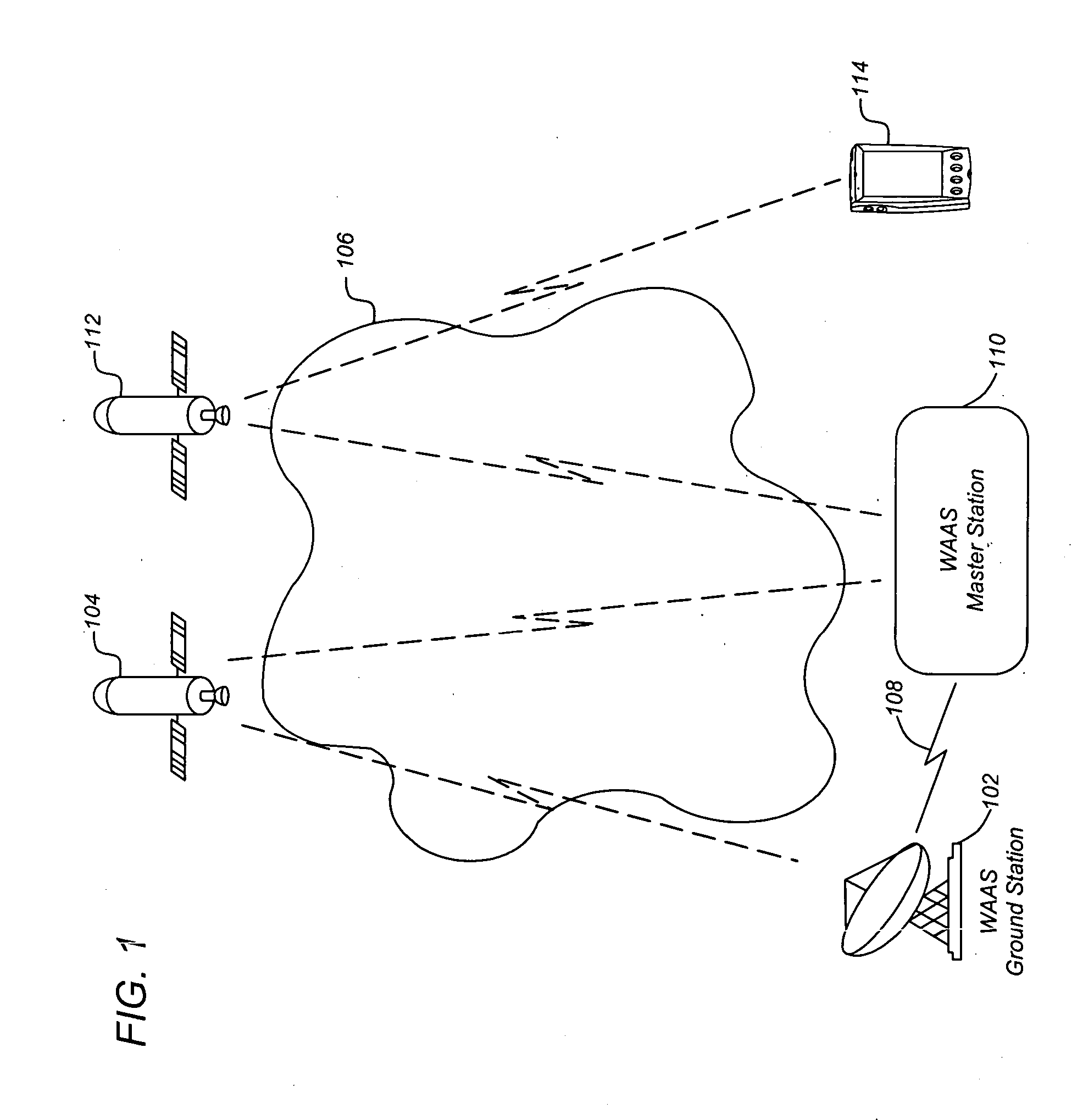
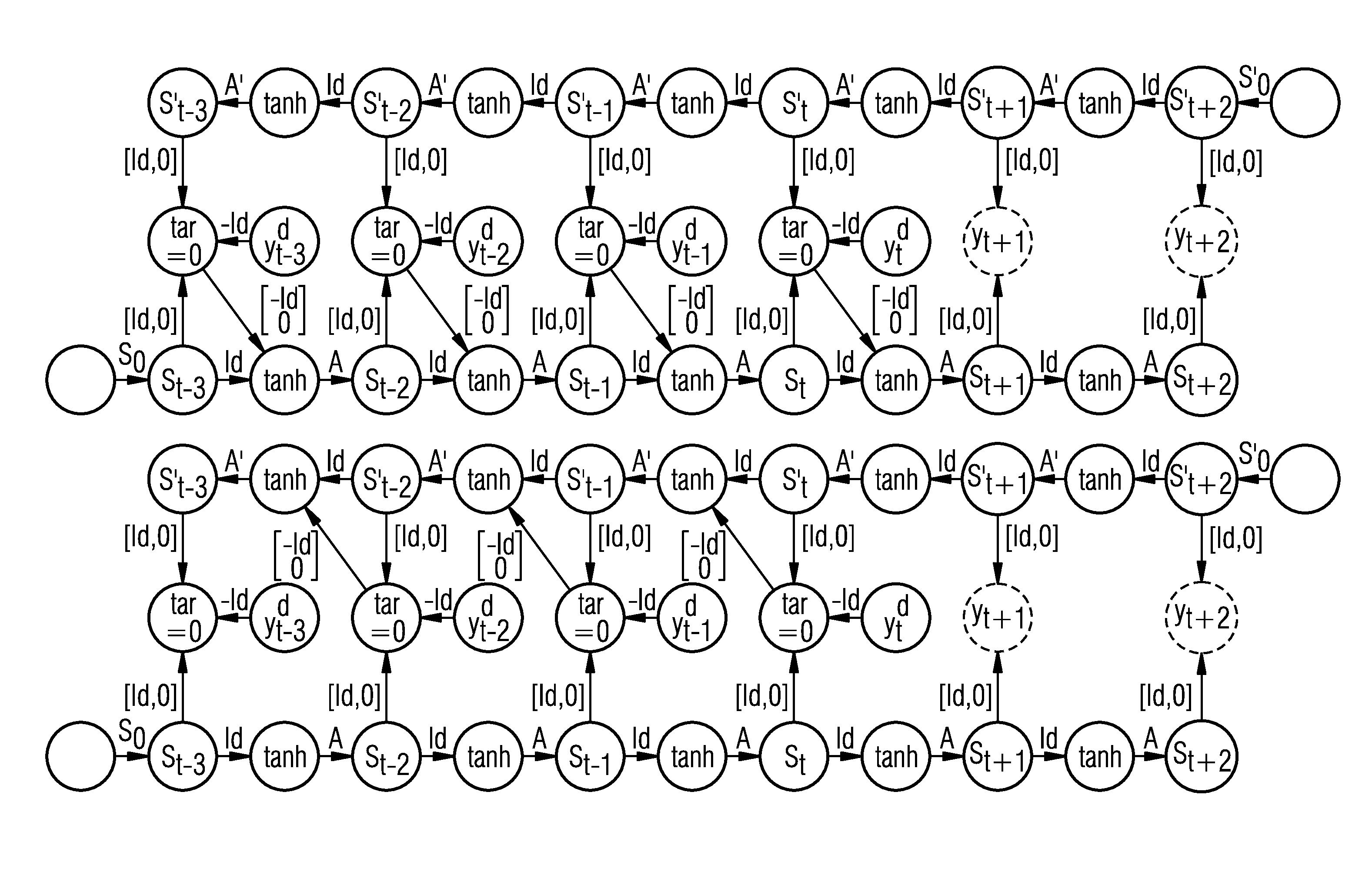
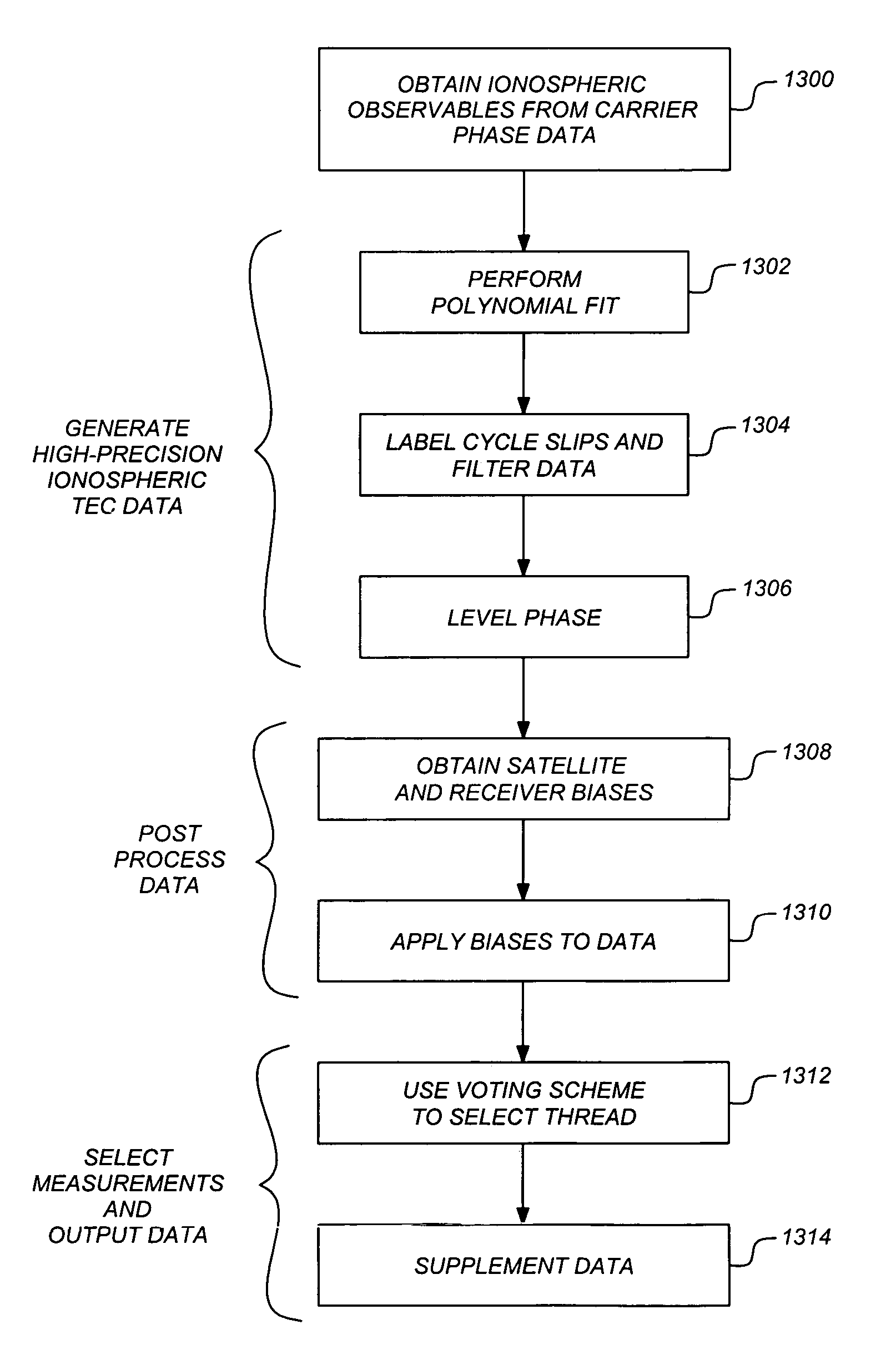
Generating high precision ionospheric ground-truth measurements
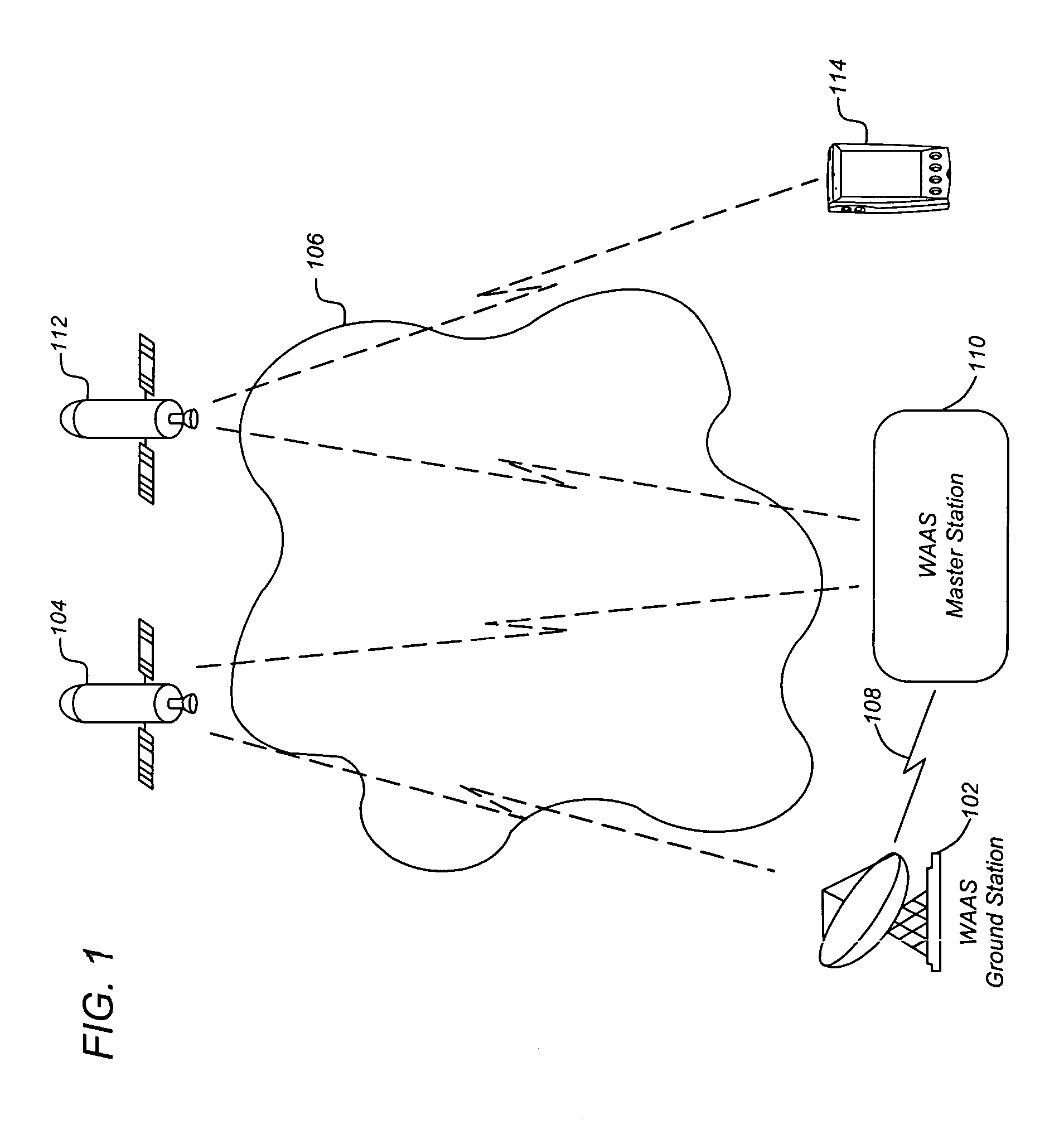
ActiveUS20060017610A1More data volumeEasy QAPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingGround truthWide area
A method, apparatus and article of manufacture provide ionospheric ground-truth measurements for use in a wide-area augmentation system (WAAS). Ionospheric pseudorange / code and carrier phase data as primary observables is received by a WAAS receiver. A polynomial fit is performed on the phase data that is examined to identify any cycle slips in the phase data. The phase data is then leveled. Satellite and receiver biases are obtained and applied to the leveled phase data to obtain unbiased phase-leveled ionospheric measurements that are used in a WAAS system. In addition, one of several measurements may be selected and data is output that provides information on the quality of the measurements that are used to determine corrective messages as part of the WAAS system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
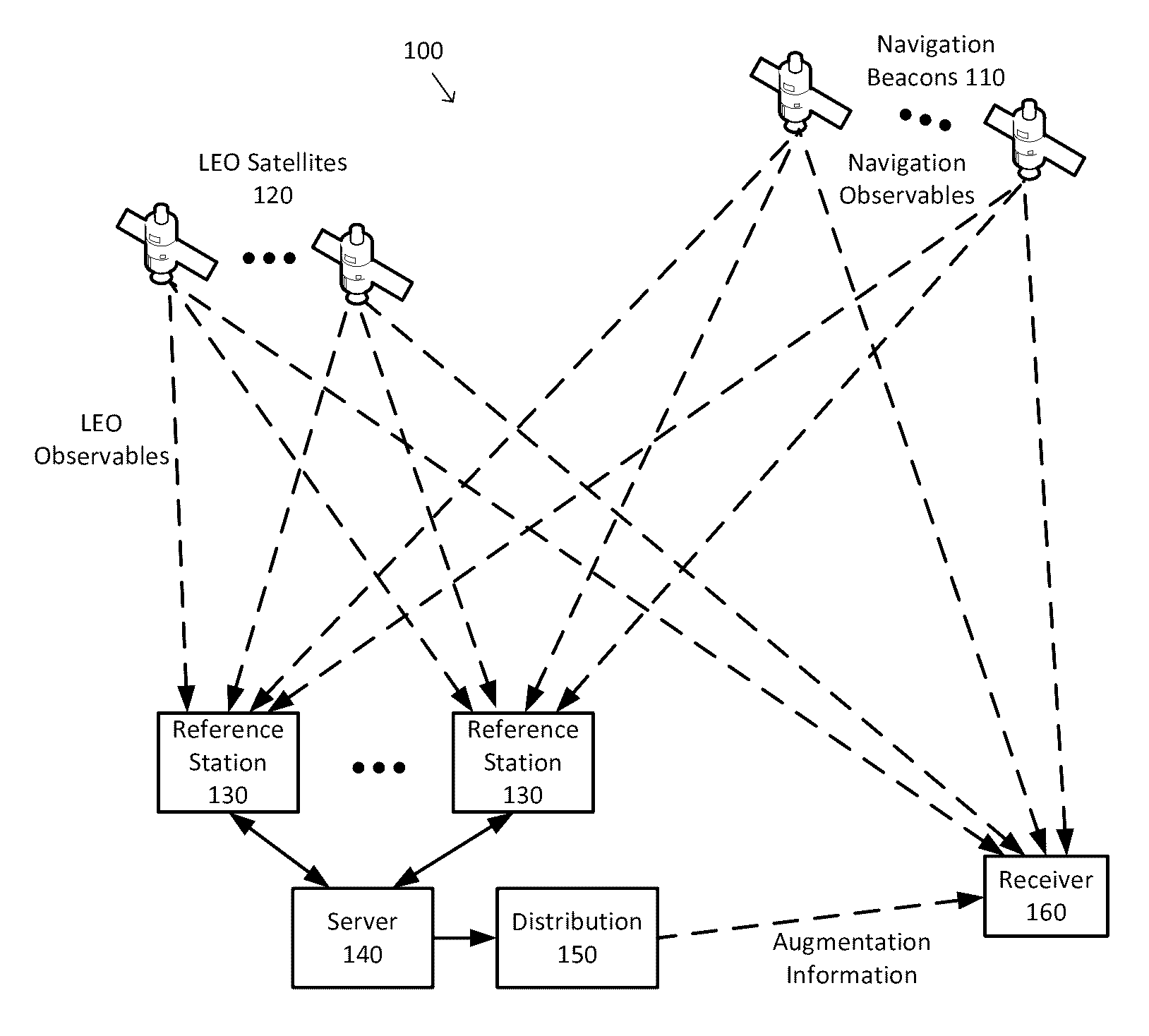
Systems, methods, devices and subassemblies for creating and delivering a GNSS augmentation service
InactiveUS9557422B1Extension of timeShorten convergence timeSatellite radio beaconingGPS enhancementComputational model
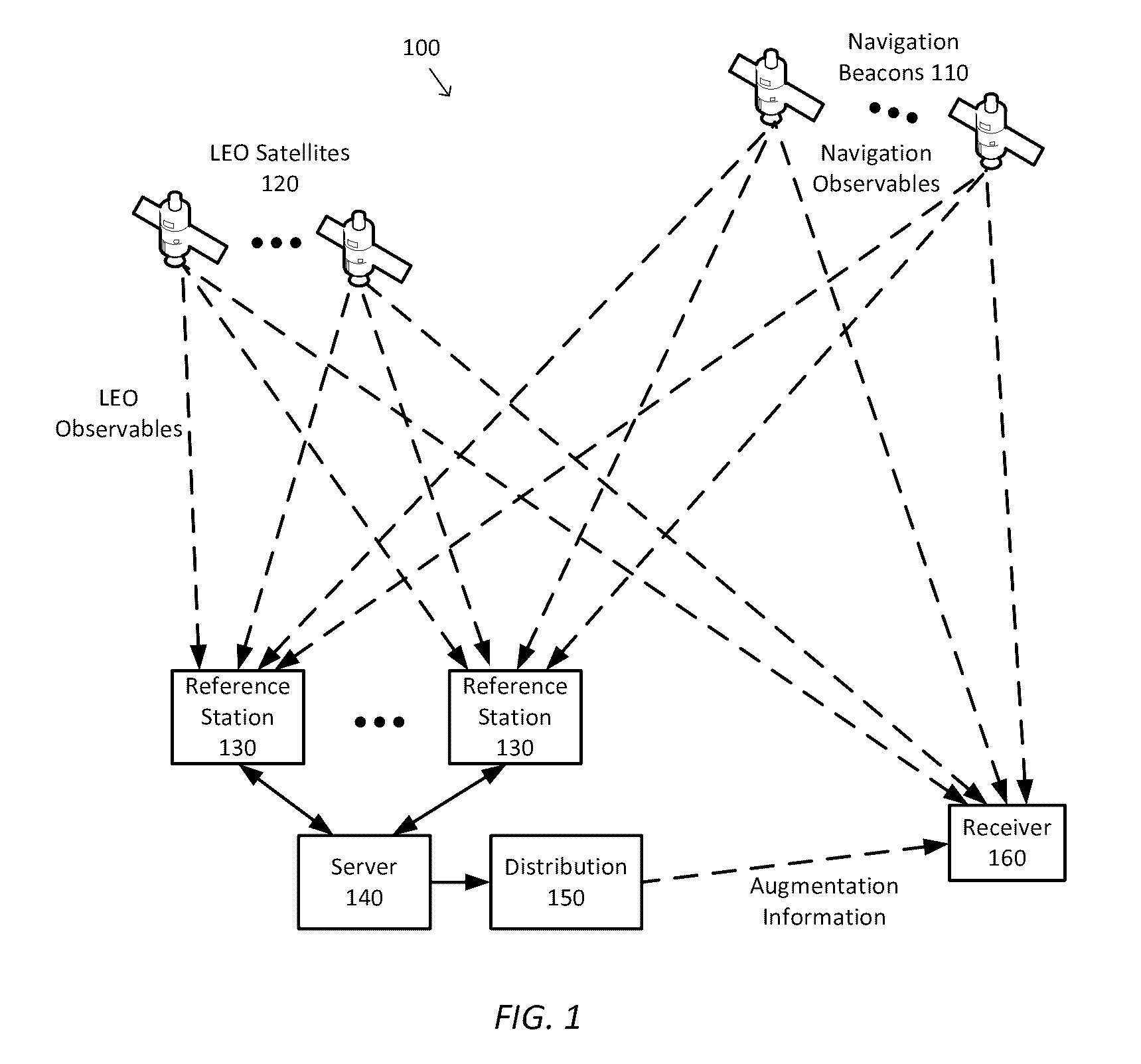
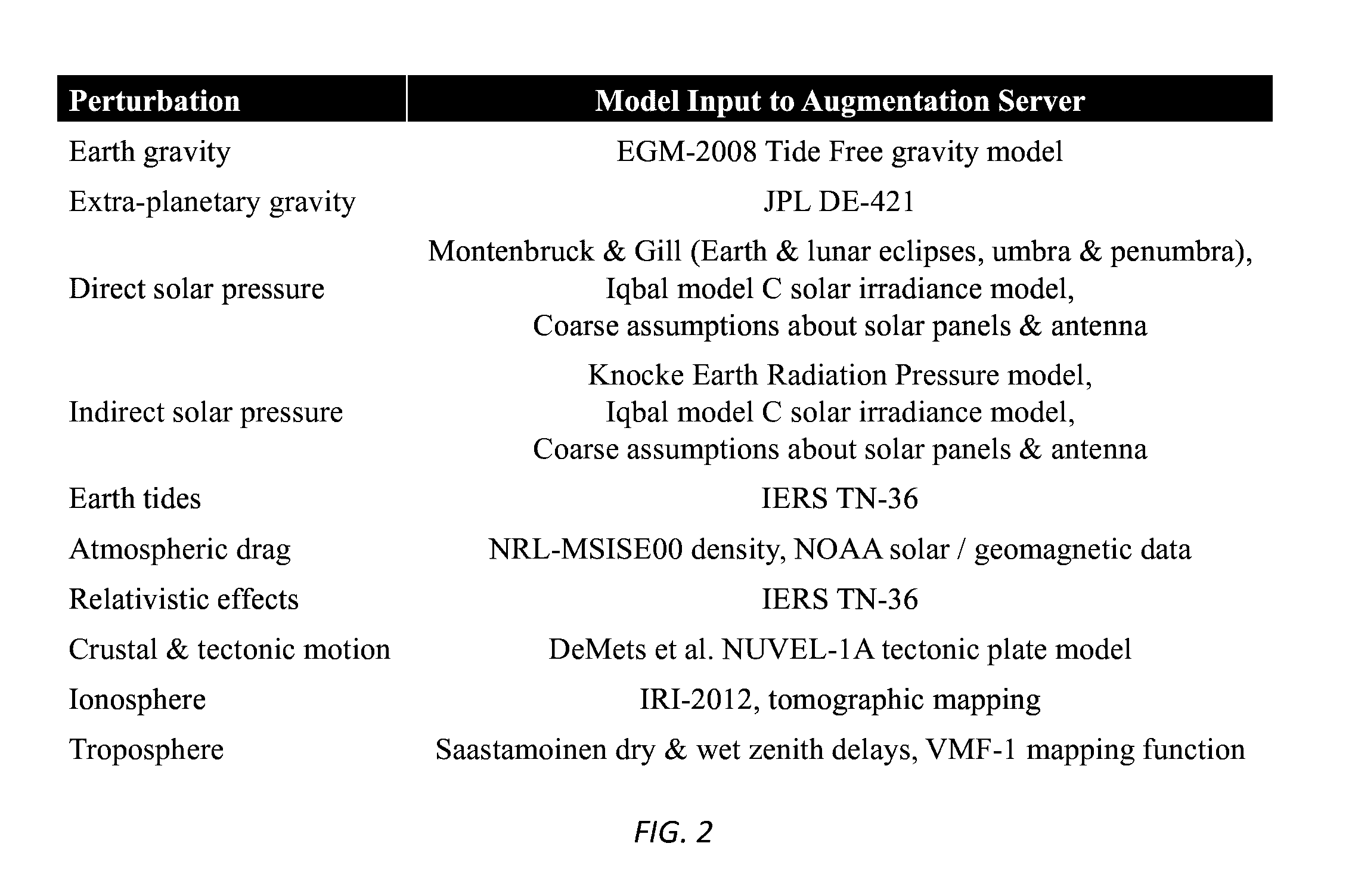
Systems, methods, devices and subassemblies for creating and delivering a GNSS augmentation service include one or more reference stations for receiving signals transmitted by navigation beacons and an augmentation server coupled to the reference stations. At least one of the reference stations is able to receive at least one of the signals from a low earth orbit satellite. Each of the reference stations determines first navigation observables based on the received signals and transmit information associated with the first navigation observables to the augmentation server. The augmentation server is configured to determine and distribute augmentation information to a receiver. The augmentation information is based on the received information associated with the first navigation observables, locations of the reference stations, and computational models. The distributed augmentation information is usable by the receiver to determine a high-precision position, velocity, and time solution for the receiver based on second navigation observables associated with the receiver.
Owner:APPLE INC
Remote Rotor Parameter Sensor for Electric Drives
ActiveUS20140042876A1Extended operating rangeExtend lifetimeAssociation with control/drive circuitsElectric devicesElectric driveHybrid vehicle
A rotor parameter sensor can be used for electric drives. A rotor of an electric engine or motor is monitored by a sensor sensing one or more physical observables or operation parameters. Furthermore, a method and system can be used for monitoring an electric engine or motor for use in electric or hybrid vehicles.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
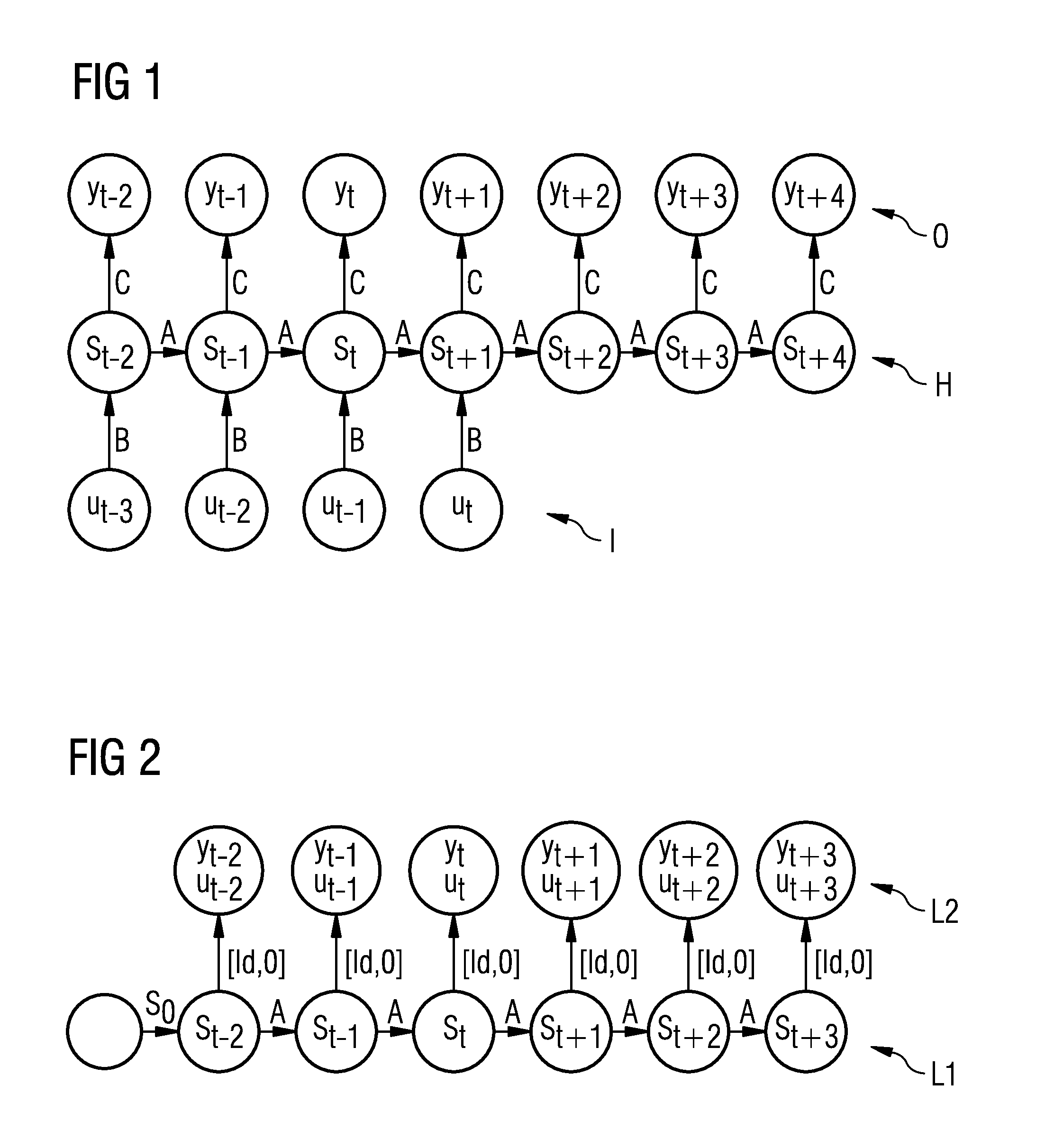
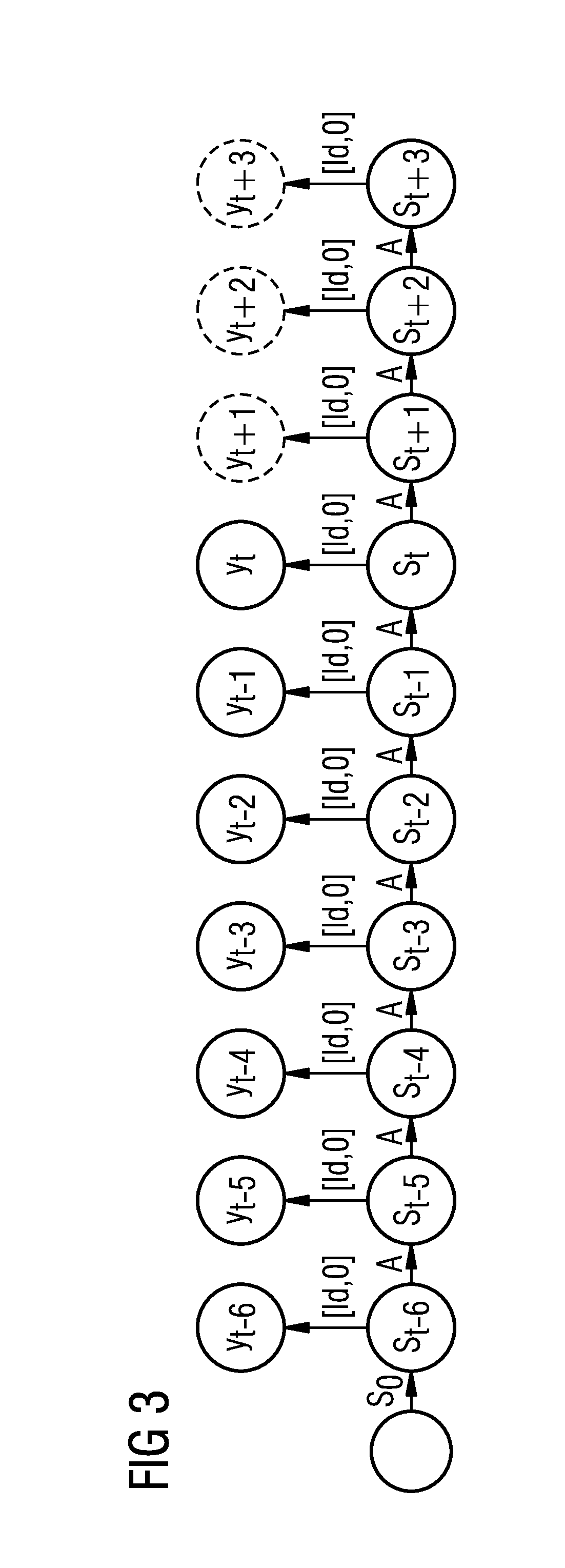
Method for the computer-aided learning of a recurrent neural network for modeling a dynamic system
ActiveUS20130204815A1Easy to shapeSimple and efficient learningDigital computer detailsDigital dataNerve networkLearning methods
A method for the computer-aided learning of a recurrent neural network for modeling a dynamic system which is characterized at respective times by an observable vector with one or more observables as entries is provided. The neural network includes both a causal network with a flow of information that is directed forwards in time and a retro-causal network with a flow of information which is directed backwards in time. The states of the dynamic system are characterized by first state vectors in the causal network and by second state vectors in the retro-causal network, wherein the state vectors each contain observables for the dynamic system and also hidden states of the dynamic system. Both networks are linked to one another by a combination of the observables from the relevant first and second state vectors and are learned on the basis of training date including known observables vectors.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Generating high precision ionospheric ground-truth measurements
A method, apparatus and article of manufacture provide ionospheric ground-truth measurements for use in a wide-area augmentation system (WAAS). Ionospheric pseudorange / code and carrier phase data as primary observables is received by a WAAS receiver. A polynomial fit is performed on the phase data that is examined to identify any cycle slips in the phase data. The phase data is then leveled. Satellite and receiver biases are obtained and applied to the leveled phase data to obtain unbiased phase-leveled ionospheric measurements that are used in a WAAS system. In addition, one of several measurements may be selected and data is output that provides information on the quality of the measurements that are used to determine corrective messages as part of the WAAS system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
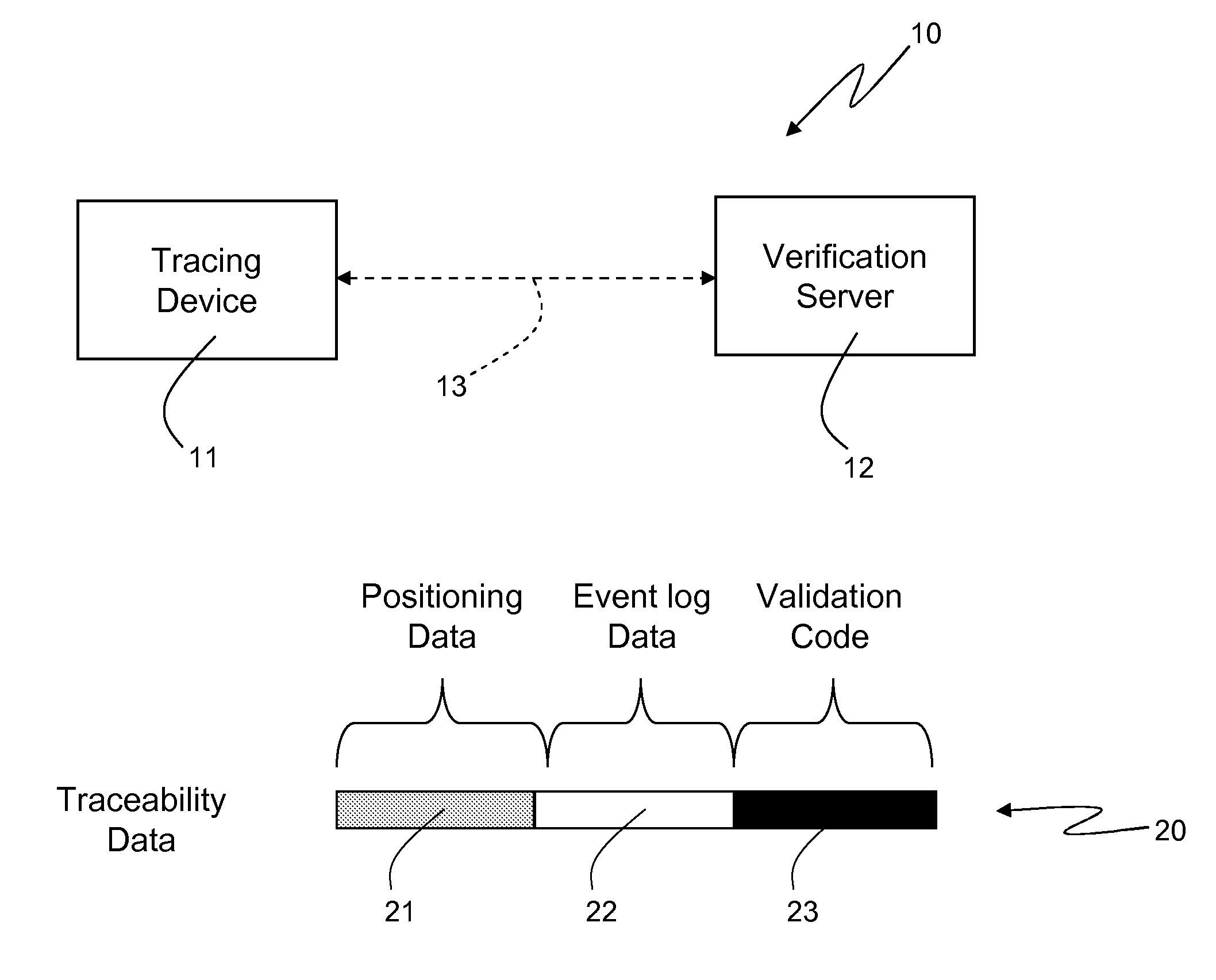
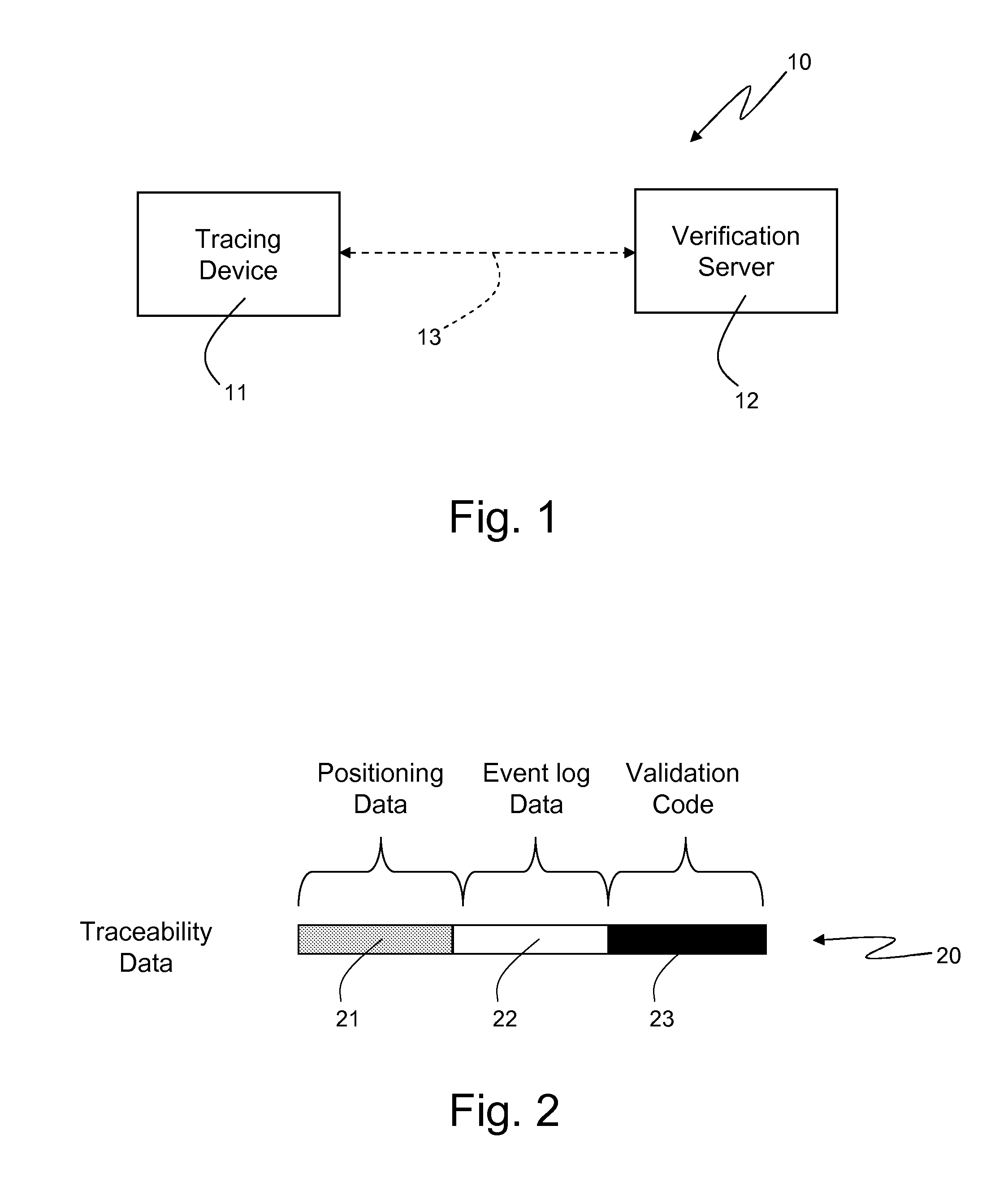
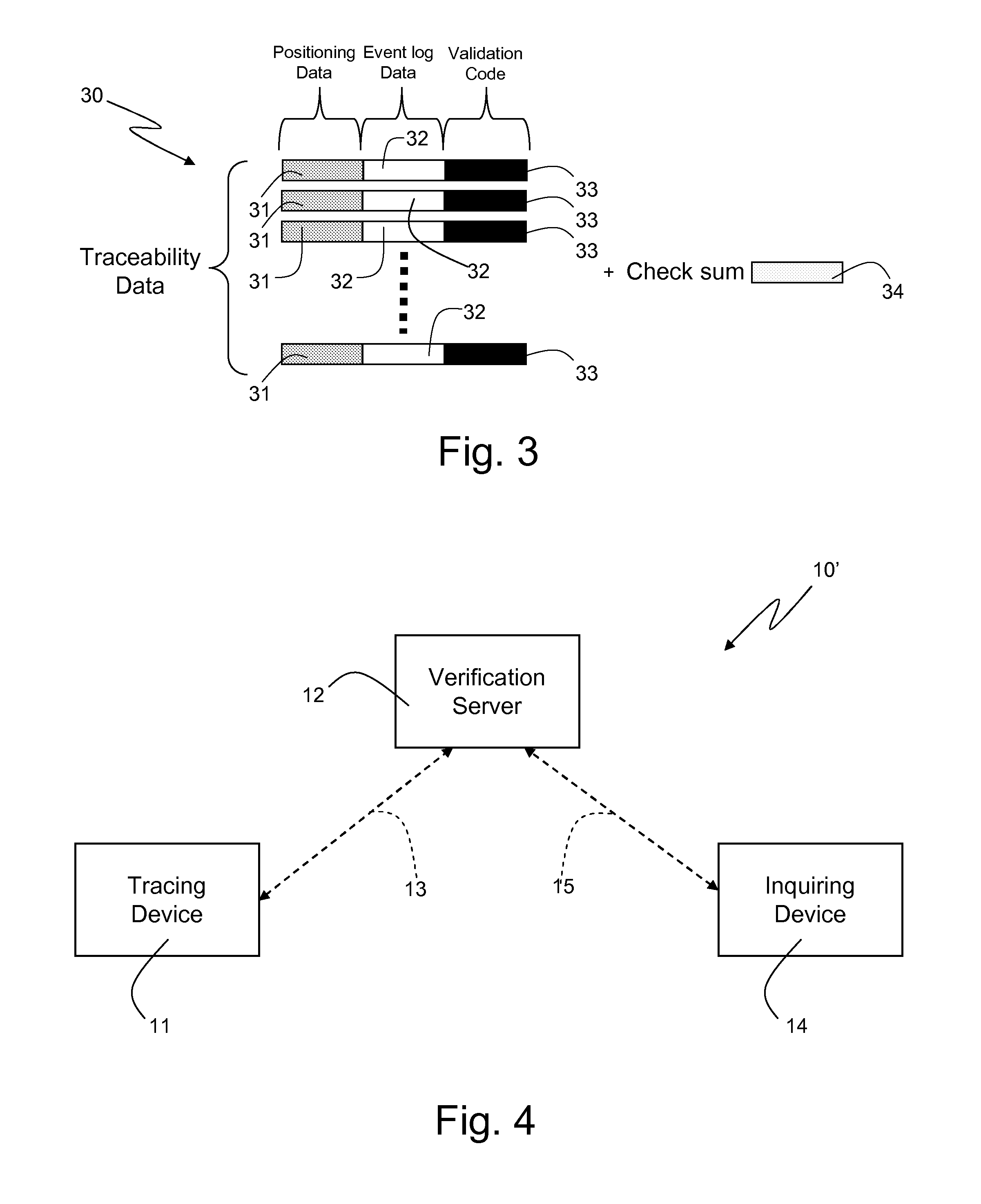
High-Reliability Product/Activity Tracking System
Disclosed herein is a tracking system configured to track a product and / or an activity. The tracking system comprises a tracing device and a verification server. The tracing device is coupled with the verification server by means of communication means configured to allow exchange of data between the tracing device and the verification server. The tracing device is coupled with a first satellite localization receiver which is configured to receive signals from a satellite localization system, process the received signals to obtain satellite localization observables, and compute locations based on the satellite localization observables. The tracing device is configured to acquire from the first satellite localization receiver positioning data. The positioning data comprise a location computed by the first satellite localization receiver, and a location time which represents time and data at which the location is computed by the first satellite localization receiver. The positioning data are related to a product and / or an activity to be tracked. The tracing device is further configured to select a satellite localization observable based on which location is computed by the first satellite localization receiver, and to acquire from the satellite localization receiver the selected satellite localization observable. The tracing device is further configured to provide the verification server with the positioning data and the satellite localization observable acquired from the satellite localization receiver. Moreover, the verification server, in turn, is configured to perform a location consistency check based on the location comprised in the positioning data provided by the tracing device, and on the satellite localization observable provided by the tracing device. The verification server is further configured to generate a validation code on the basis of an outcome of the location consistency check, and on the basis of the positioning data provided by the tracing device. The verification server is further configured to provide the tracing device with the generated validation code. Furthermore, the tracing device is configured to store the positioning data and the validation code provided by the verification server on tracking means associated with the product and / or the activity to be tracked.
Owner:TELESPAZIO SPA
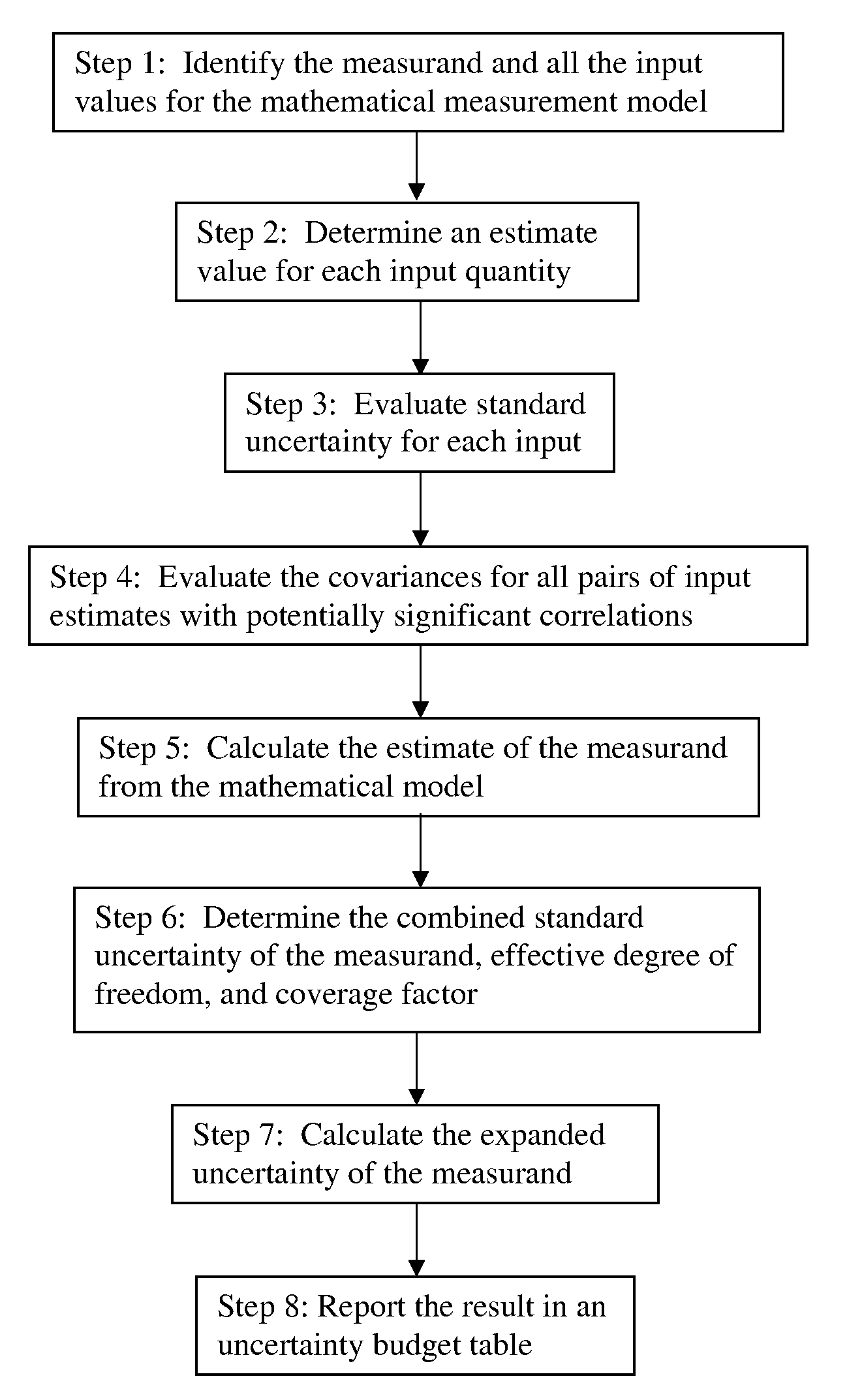
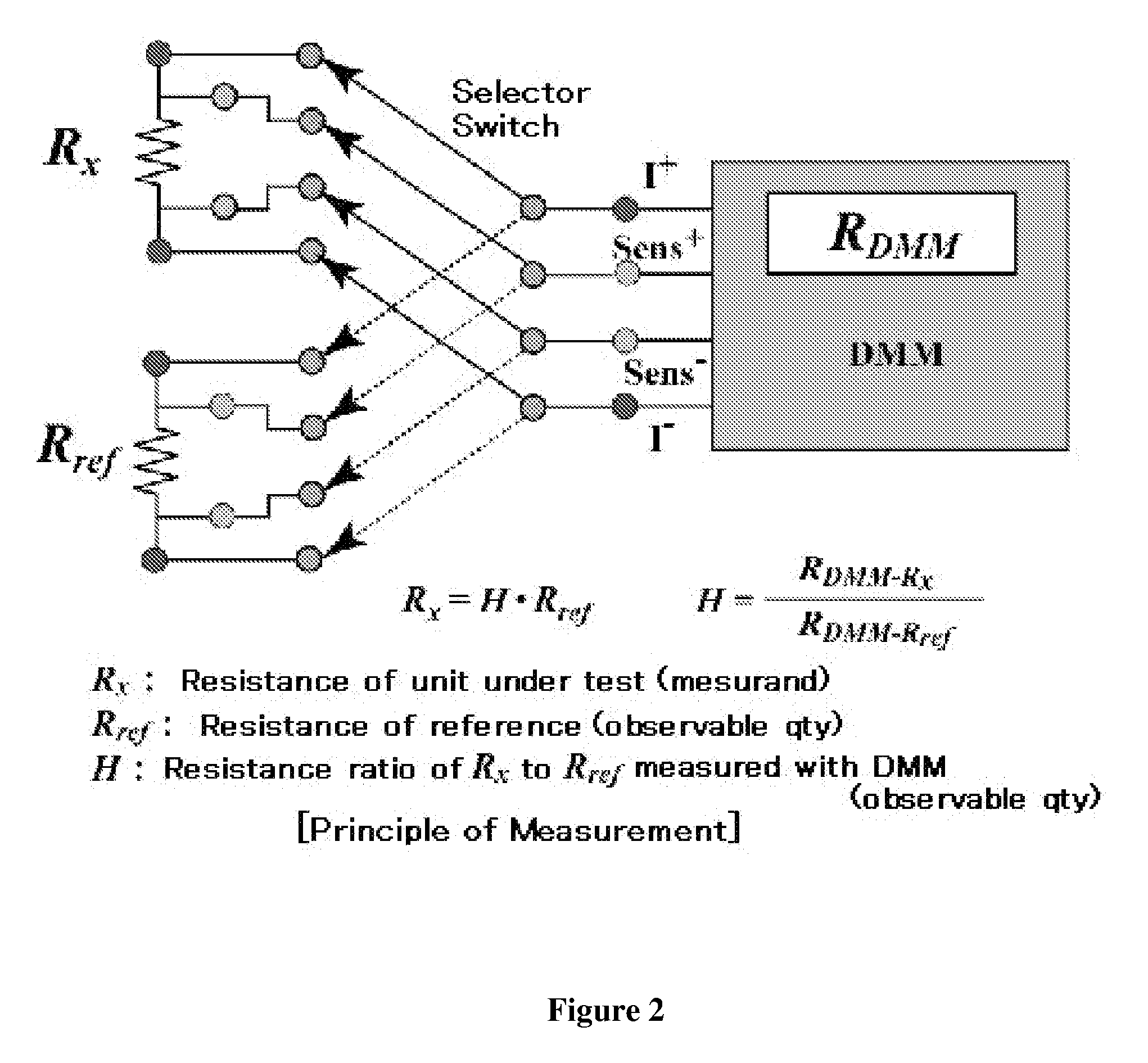
Method for the evaluation of measurement uncertainty, and a device and system thereof
InactiveUS20080125982A1Automated measurementSpecial tariff metersFlow propertiesMathematical modelReference device
A method of evaluating uncertainty associated with the value of a measurand derived from measurements of a device under test comprising providing a mathematical model wherein the measurand is expressed as a function of (i) at least one physically observable quantity, and (ii) the reference value of said physically observable quantity in a reference device; measuring the reference value of the reference device and the value of the measurand of the device under test; measuring the value of said at least one physically observable quantity; and determining at least one uncertainty value as a function of said physically observable quantity from said mathematical model, wherein the mathematical model takes into account the at least one source of uncertainty and the reference value of the reference device.
Owner:MTA JAPAN
Method and system for representing wells in modeling a physical fluid reservoir
InactiveUS20100286917A1Accurate modelingUnprecedented level of accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalReservoir modelingFeedback control
The disclosure is directed to a method of representing fluid flow response to imposed conditions in a physical fluid reservoir through wells. The invention utilizes techniques and formulas of unprecedented accuracy and speed for computations for a fundamental element in analysis of fluid movement through subterranean reservoirs—the calculation of Green's and Neumann functions in finite three-dimensional space. The method includes modeling of pressure and / or flow rate observables at wells in said reservoir using an easily computable, closed-form Green's or Neumann function for a linear well segment in arbitrary orientation within a three dimensional cell of spatially invariant but anisotropic permeability. The method further includes the modeling of fluid flow in the physical fluid reservoir with an assemblage of linear well segments operating in unison with uniform flux density to represent arbitrary well trajectory. The method further includes modeling reservoir flow through one or more linear well segments of non-uniform flux related by a constitutive expression linking pressure distribution and flow rate within the well. The method further includes generalization through integration of easily computable Green's or Neumann functions to represent fractures or fractured wells in modeling fluid flow in a physical reservoir. The system includes modeling fluid flow through a mesh representation of the physical fluid reservoir containing one or more wells represented by easily computable Green's or Neumann functions. The system further includes modeling of flow in the physical reservoir via a numerical method in which the values of pressure and flux assigned to the mesh are related to observables at the well using aforementioned easily computable Green's or Neumann functions. The system further includes the coupling of well and mesh values within the numerical solution method for well observation or feedback control. The system still further includes the localization of the well model to the properties assigned to only those mesh elements penetrated by the well using boundary integral equation methods. The invention also incorporates the addition of transients in fluid flow towards a steady or pseudo-steady state, and use thereof, in the above constructs.
Owner:HAZLETT RANDY DOYLE +1
Apparatus and method for carrier phase-based relative positioning
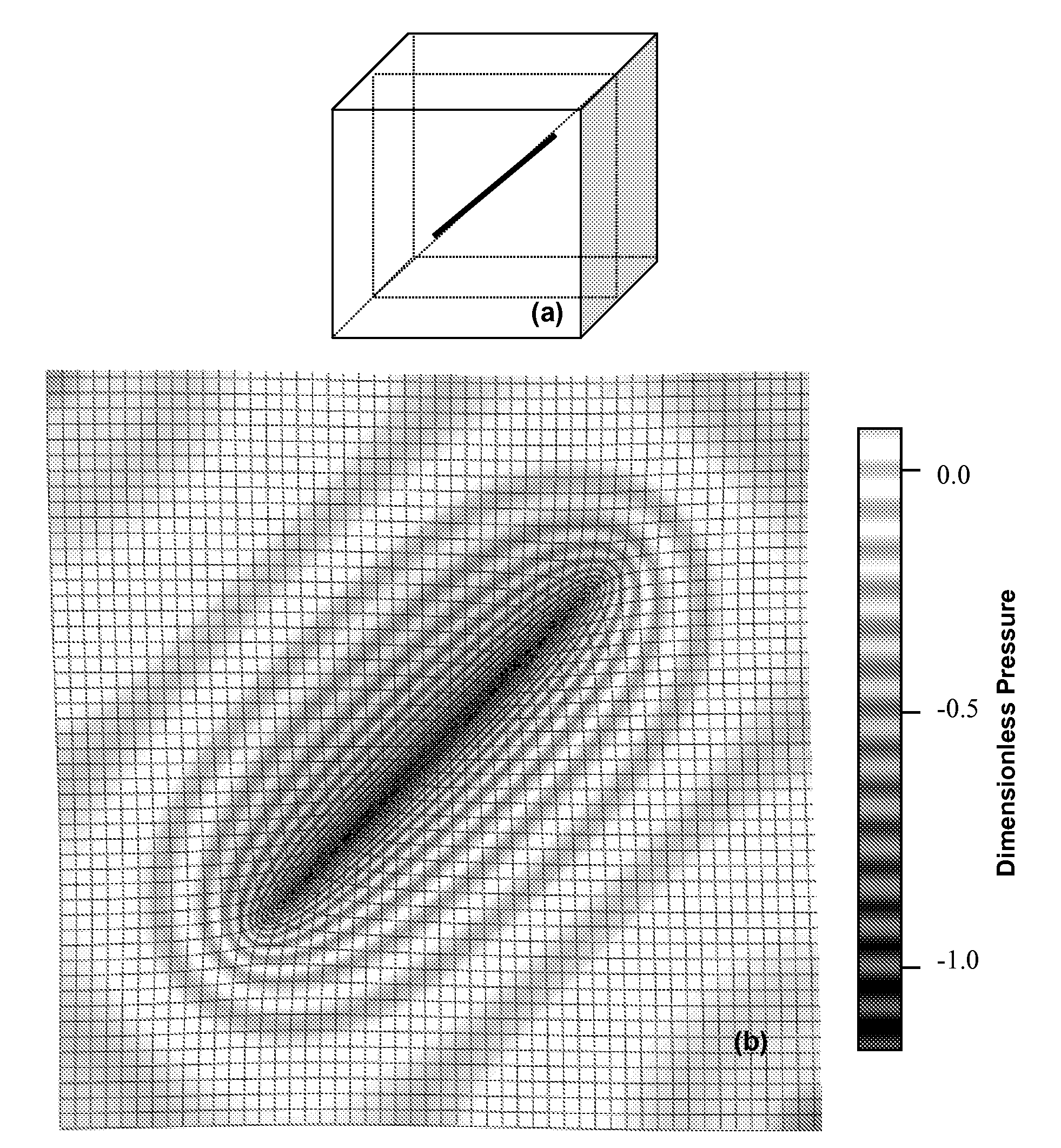
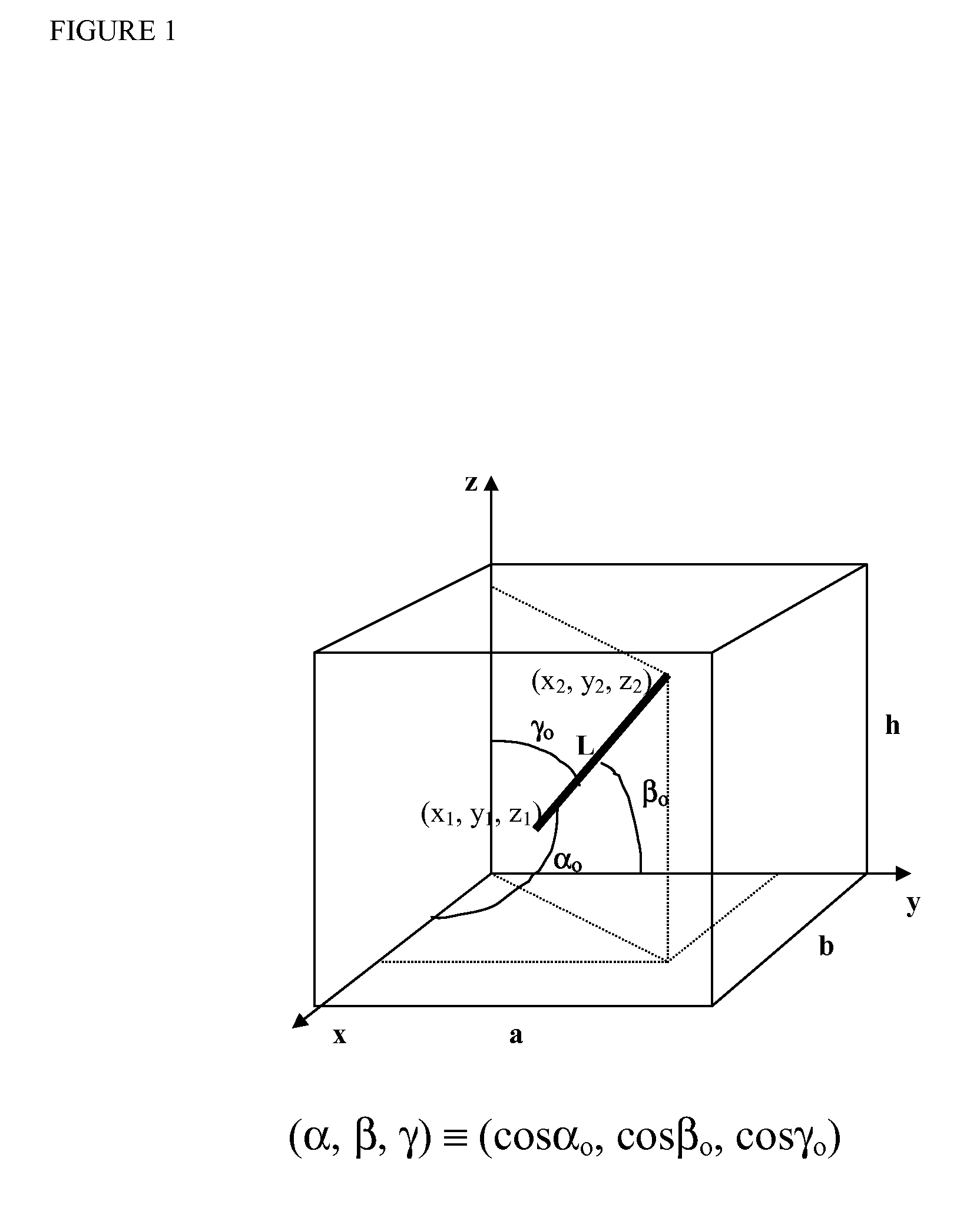
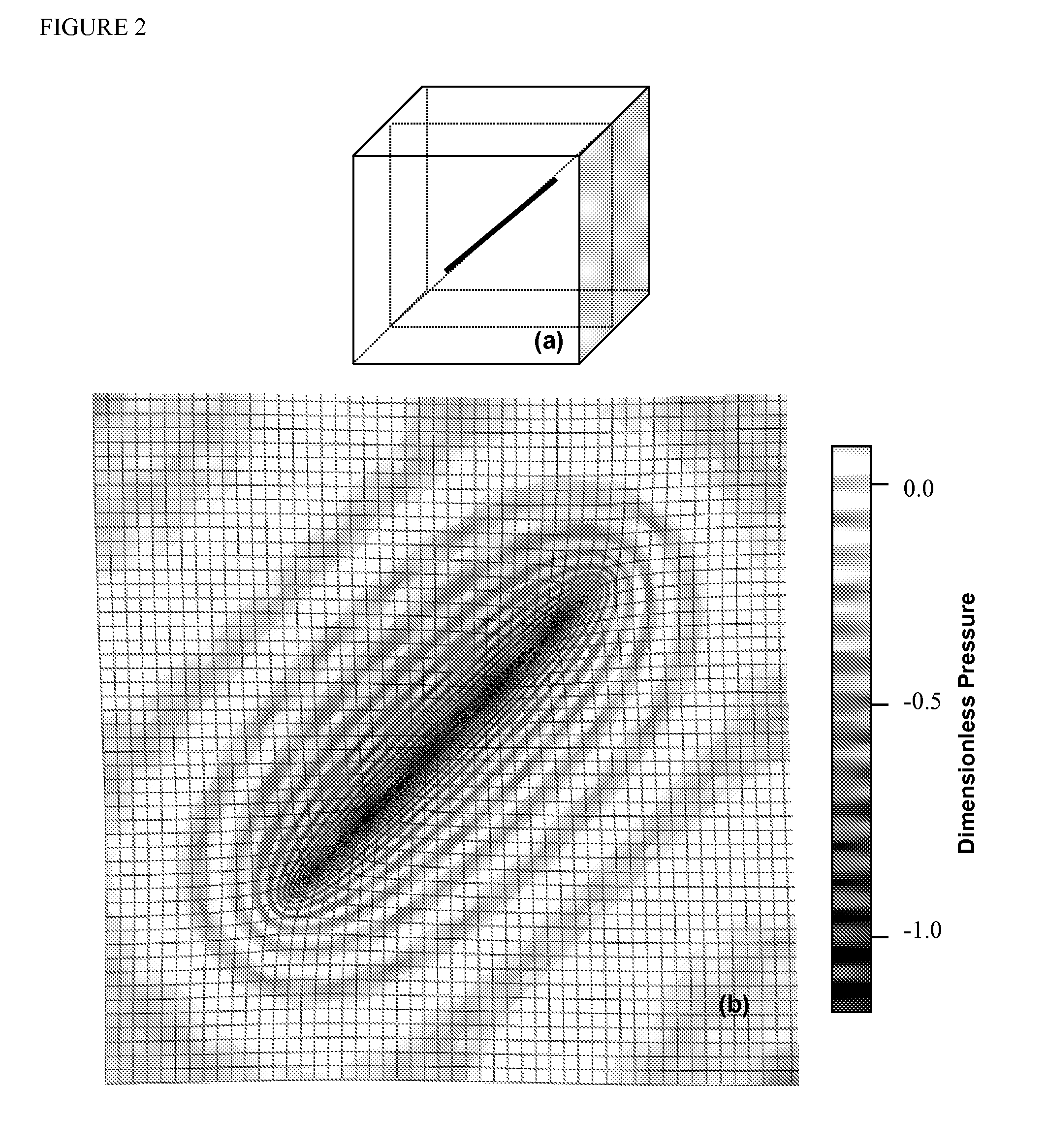
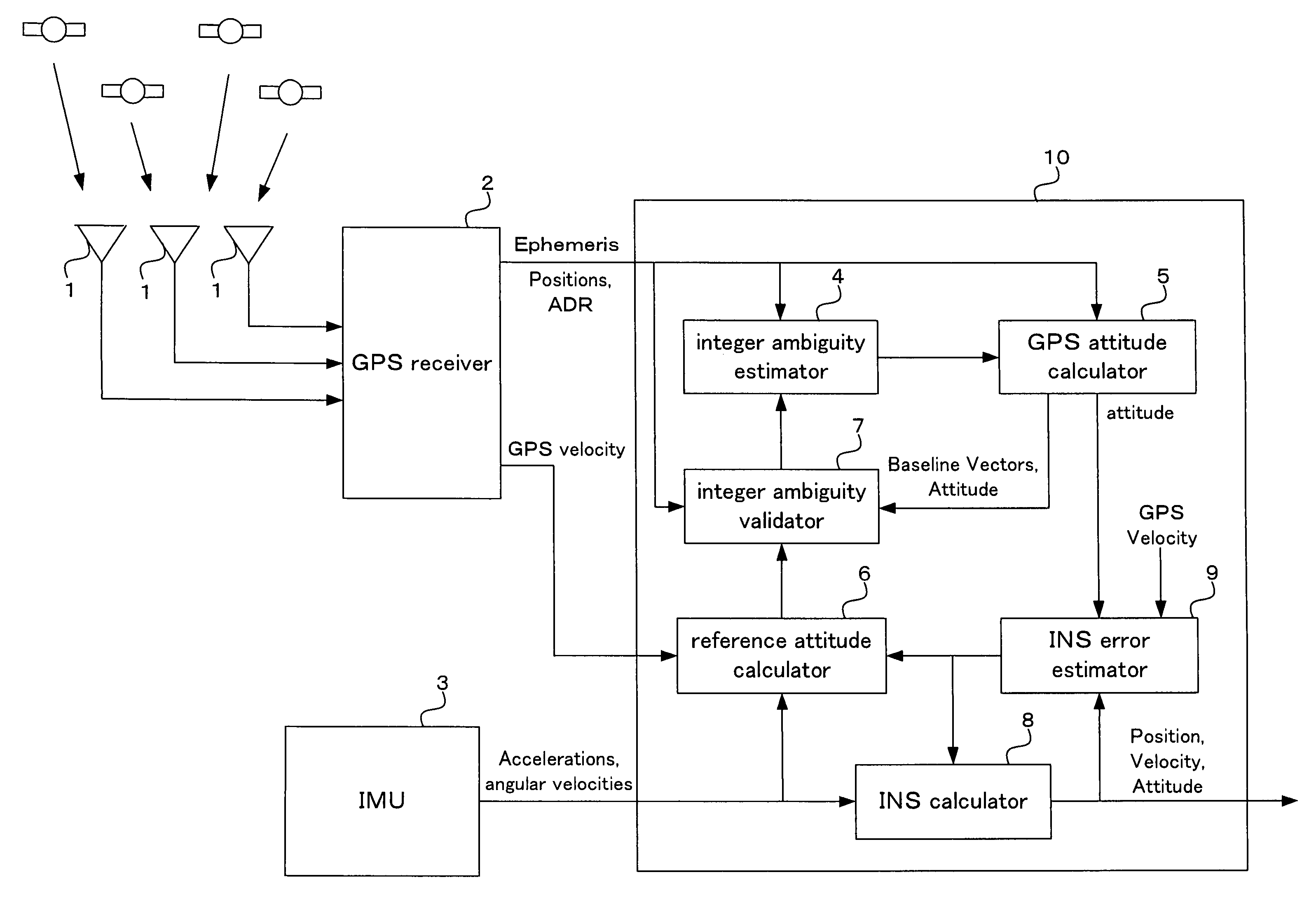
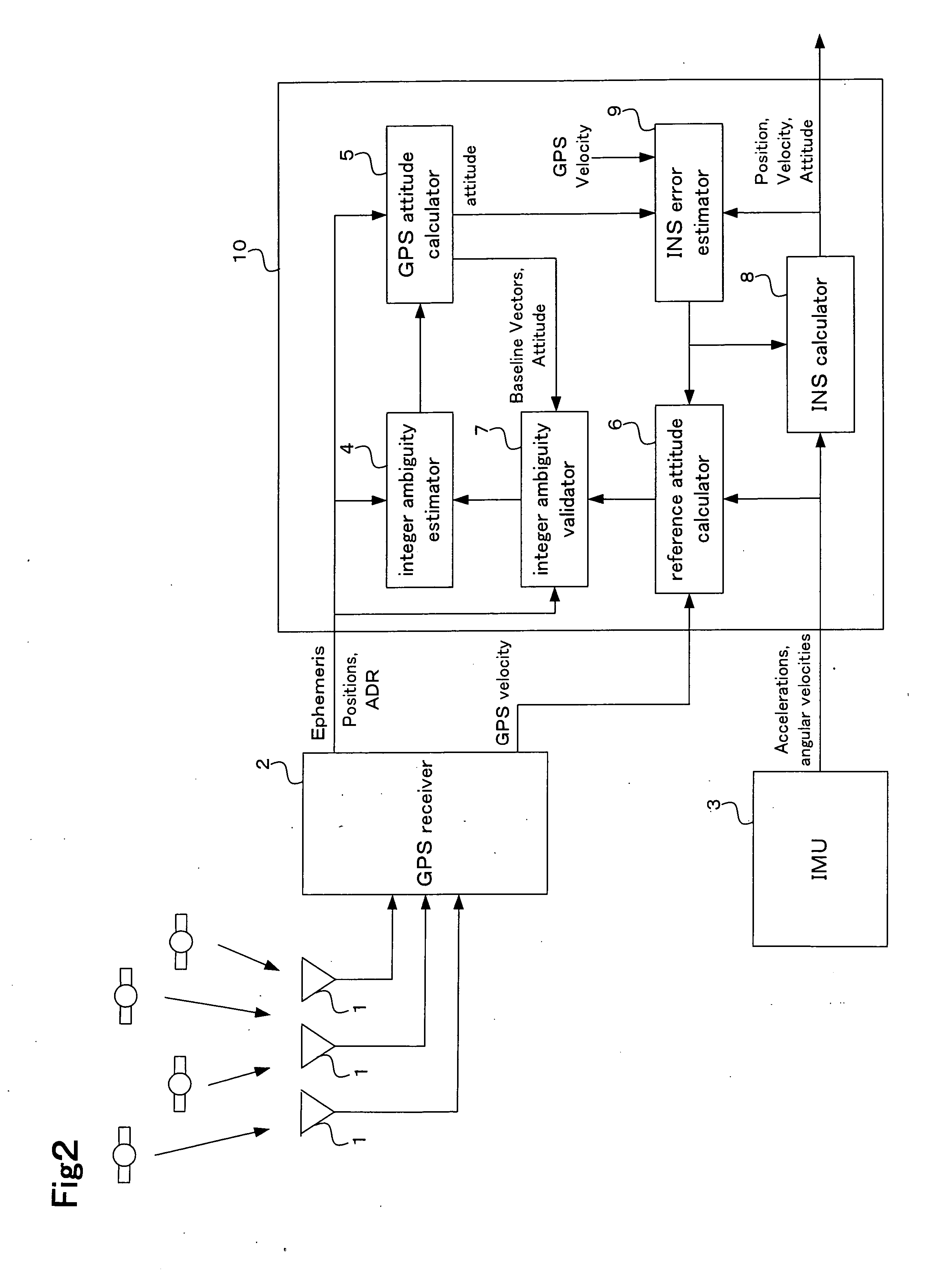
ActiveUS7355549B2High success rateReduction in size and costPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsAngular velocityInteger ambiguity
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Apparatus and method for carrier phase-based relative positioning
ActiveUS20070040737A1Improve accuracyHigh success ratePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsAngular velocityInteger ambiguity
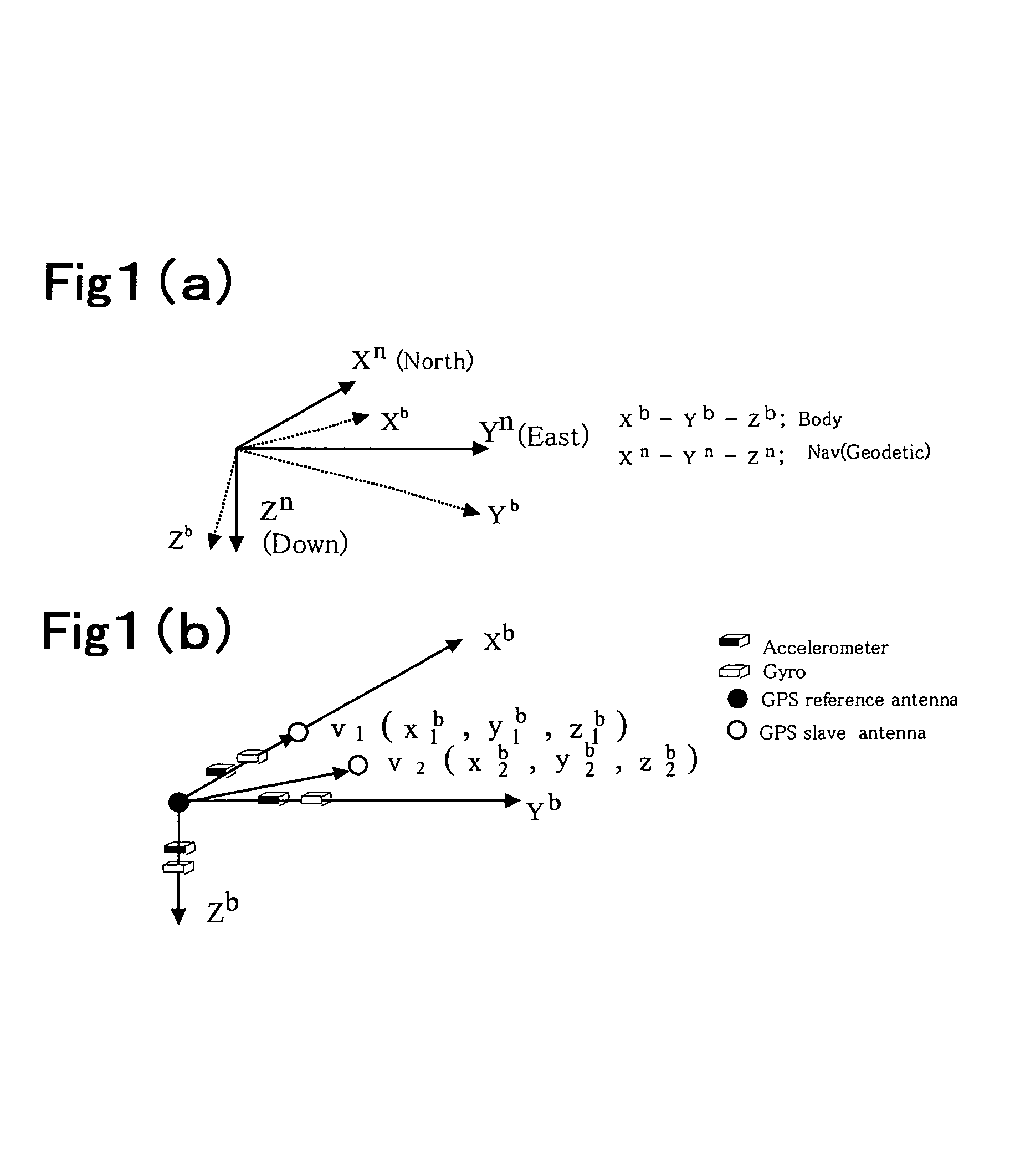
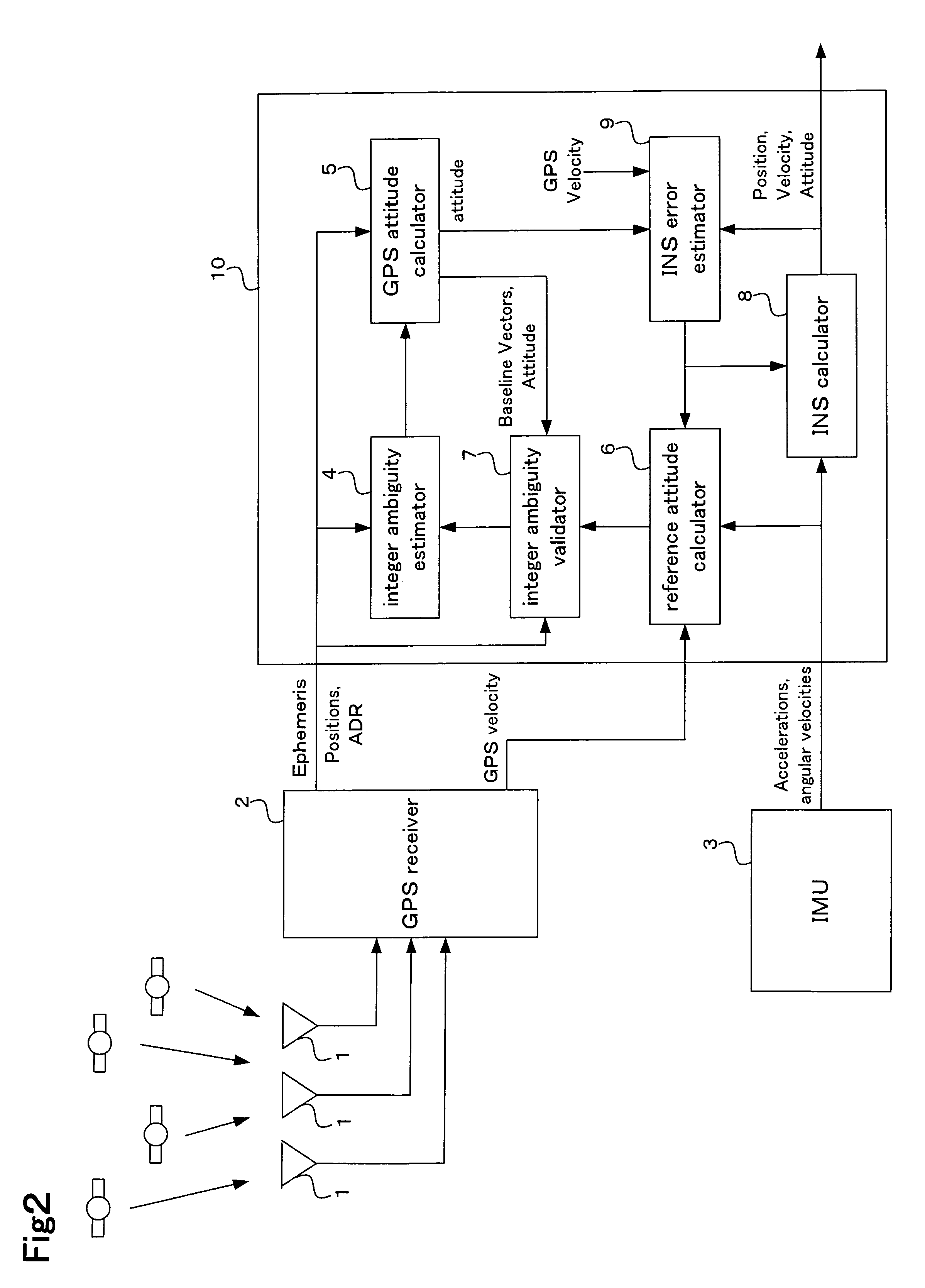
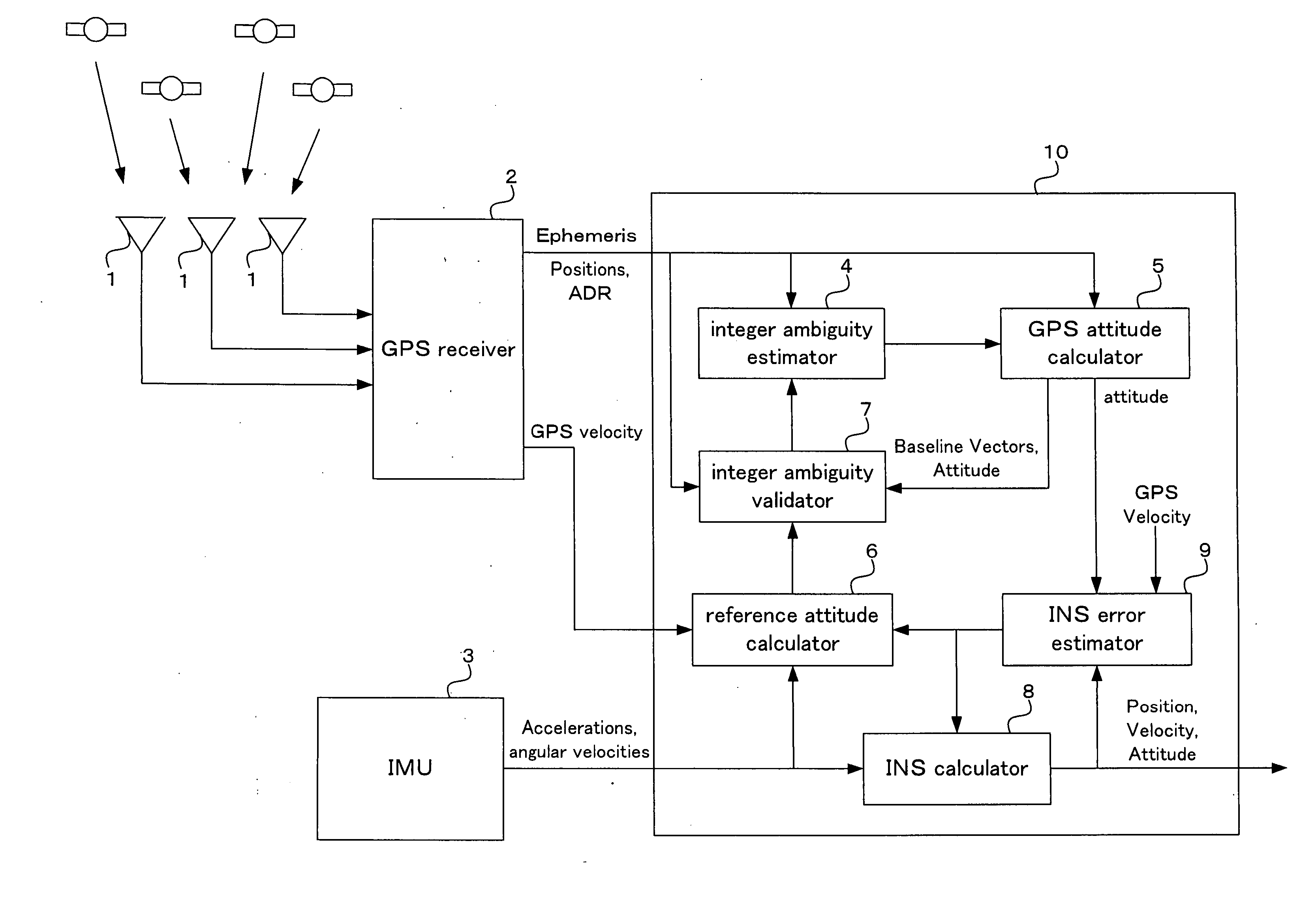
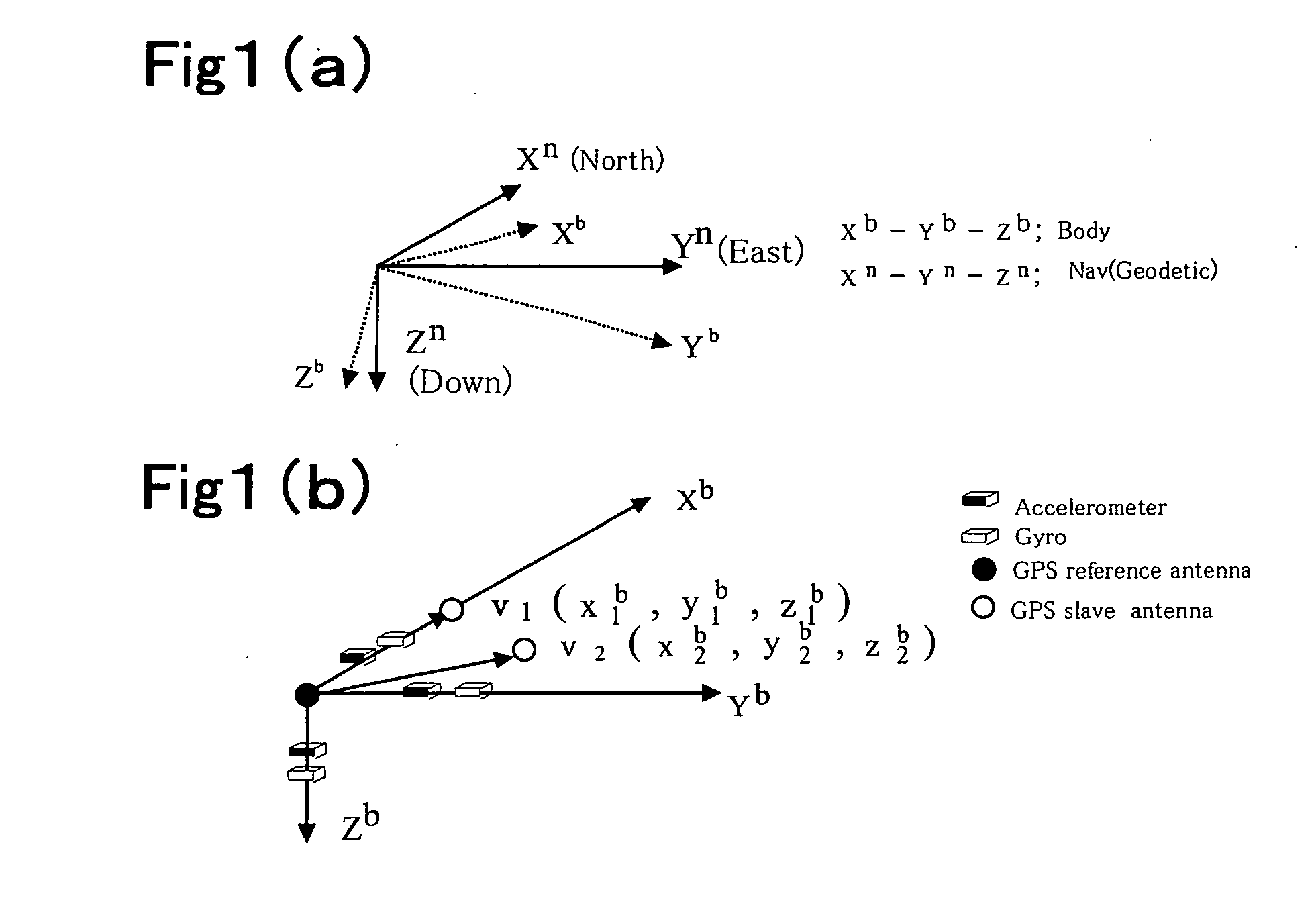
A carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus includes a plurality of antennas fixedly mounted on a moving body for receiving positioning signals from satellites, an inertial measurement unit (IMU) for measuring accelerations and angular velocities of the moving body, a reference attitude calculator for calculating attitude information about the attitude of the moving body from observables of the IMU at least before an integer ambiguity candidate is initially determined, an integer ambiguity estimator for estimating integer ambiguity candidates from the positioning signals received by the antennas, and an integer ambiguity validator for evaluating correctness of the integer ambiguity candidates estimated by the integer ambiguity estimator.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
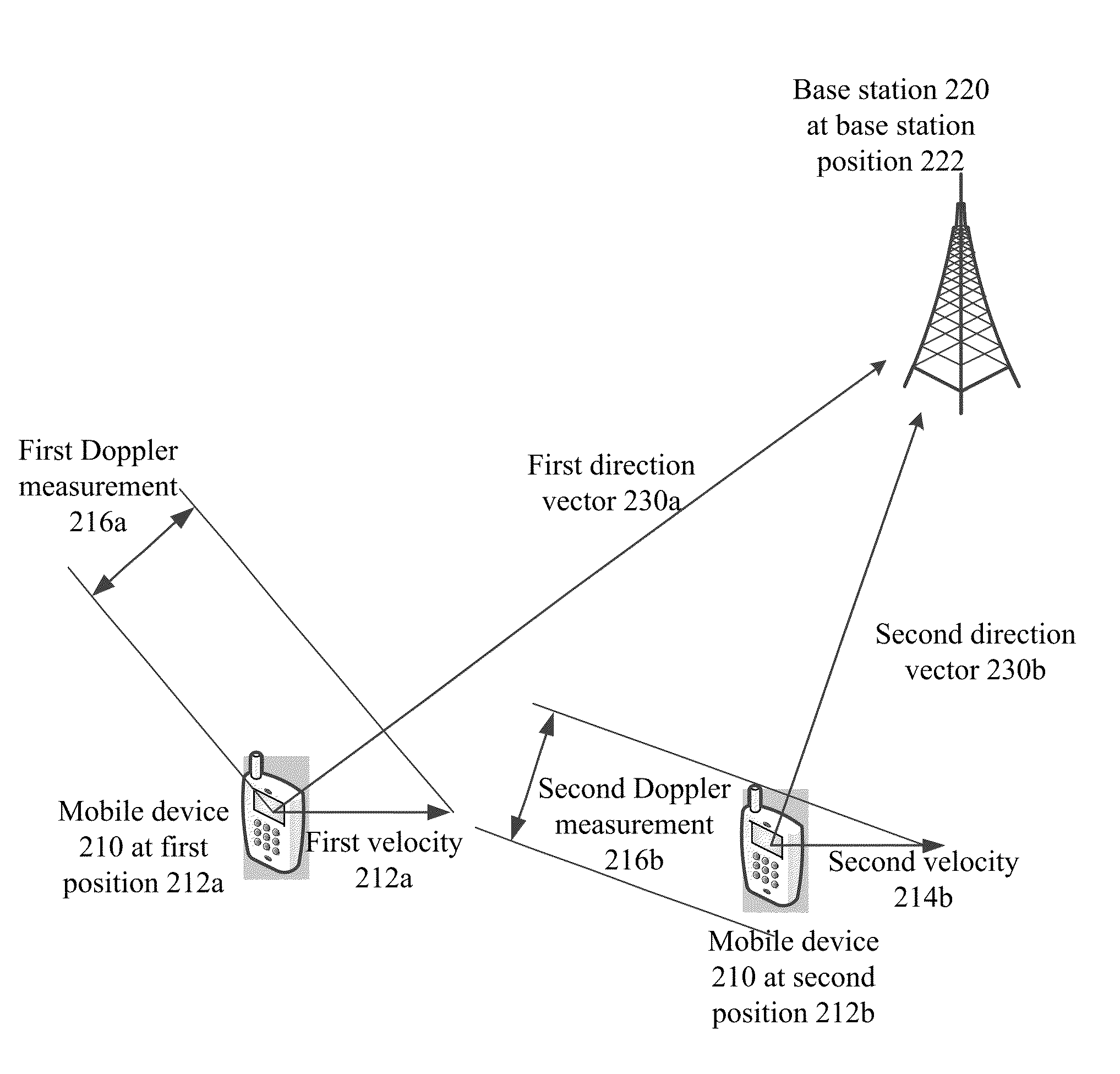
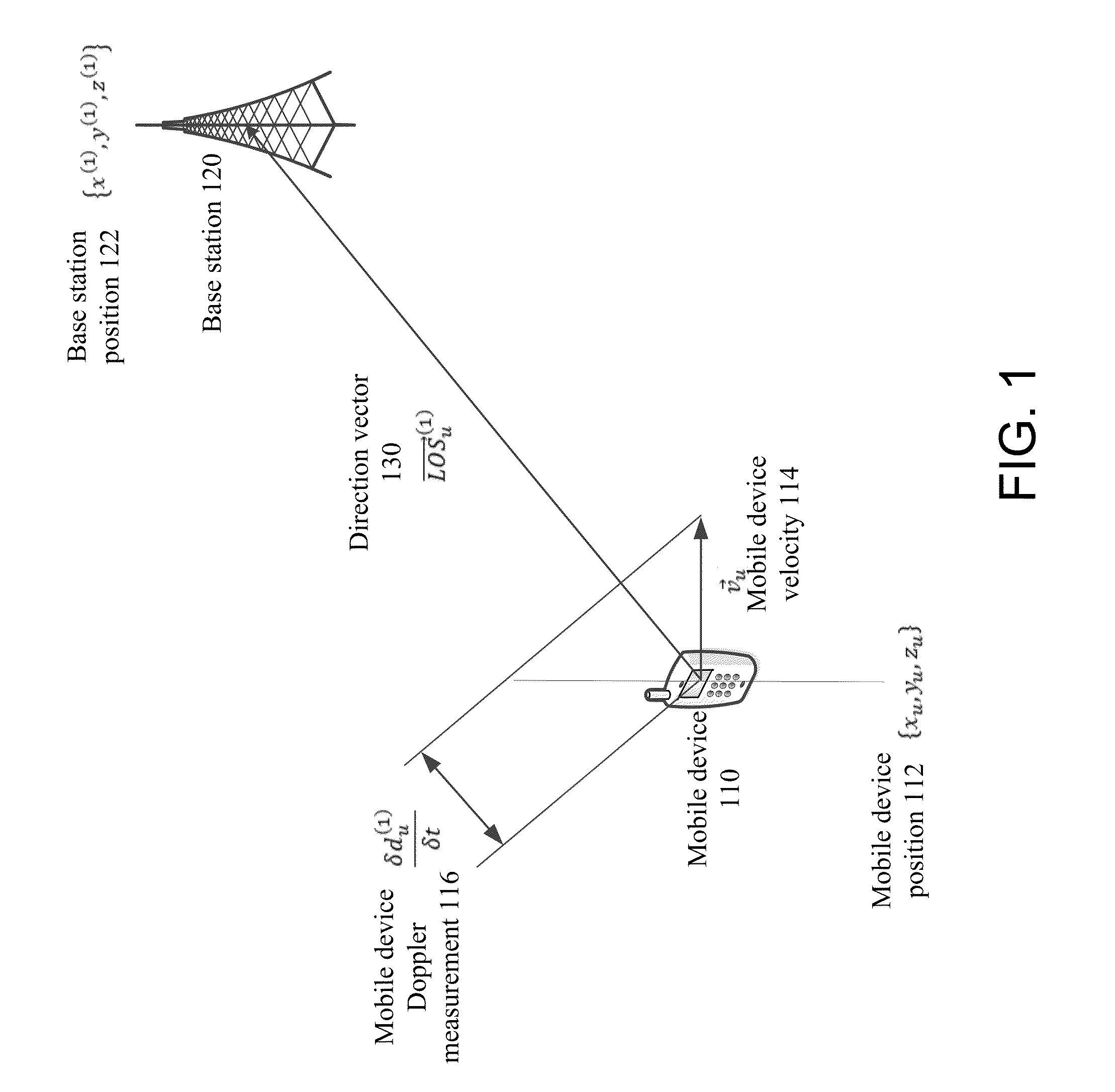
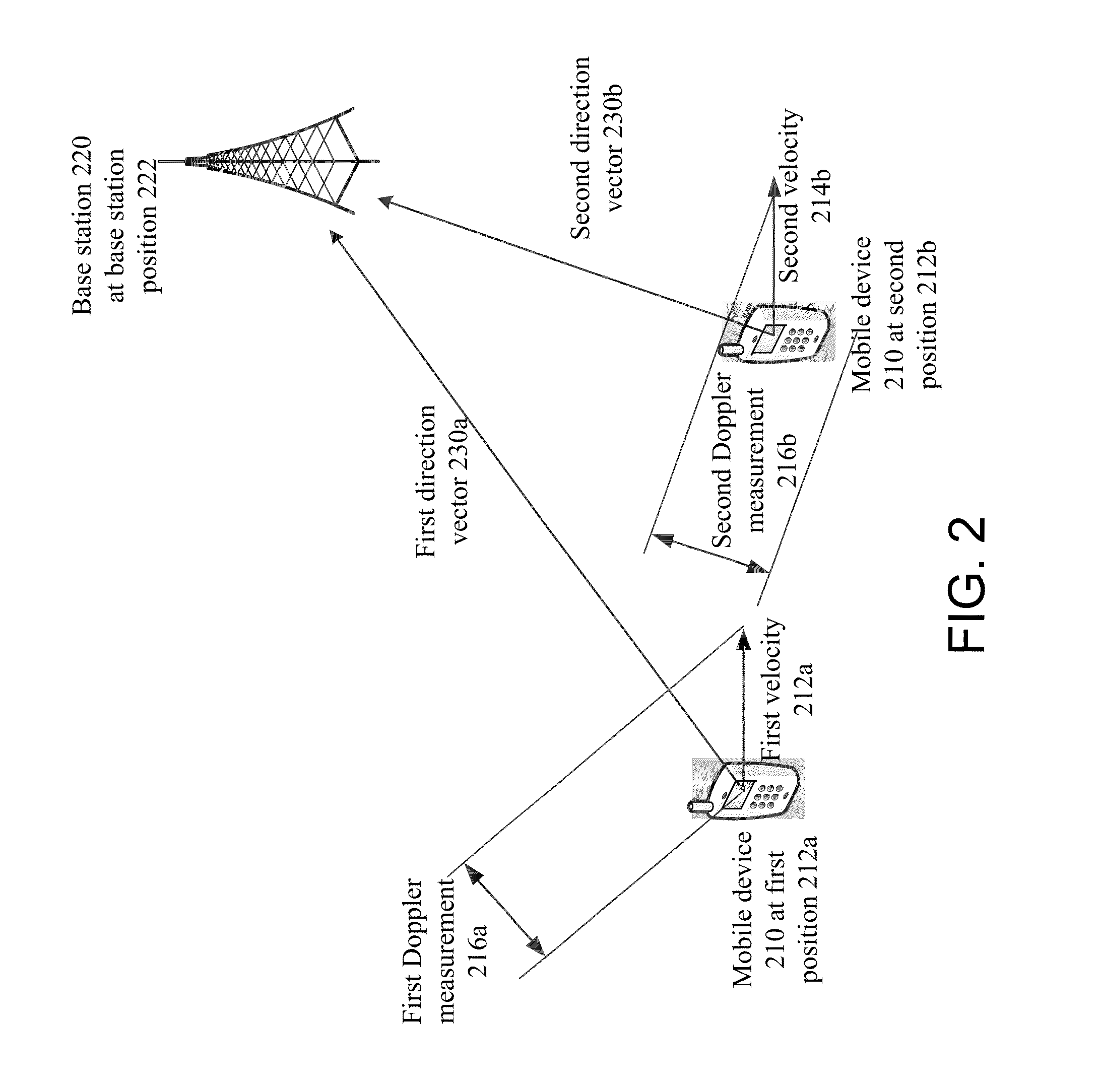
Base station positioning using doppler observables, position, and velocity
Methods, devices, and systems are described for using multiple measurements including Doppler measurements from a mobile device to identify the position of the base station. Repeated Doppler and velocity measurements from different locations, with measurement groups taken at the same time or within a certain time frame, may be used to identify the location of a base station with which the mobile device is communicating.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Moving base transfer alignment method based on measurement of misalignment angle
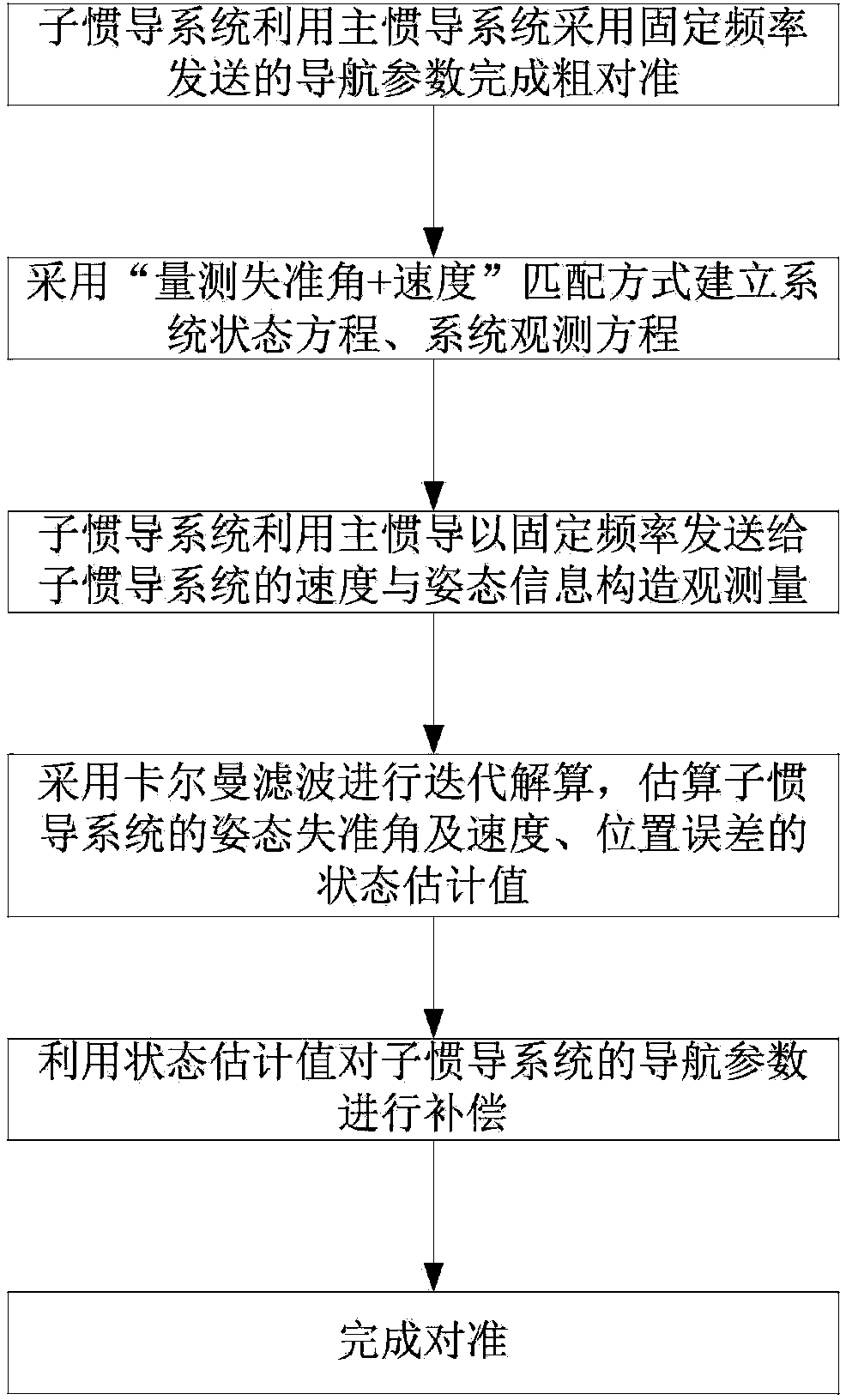
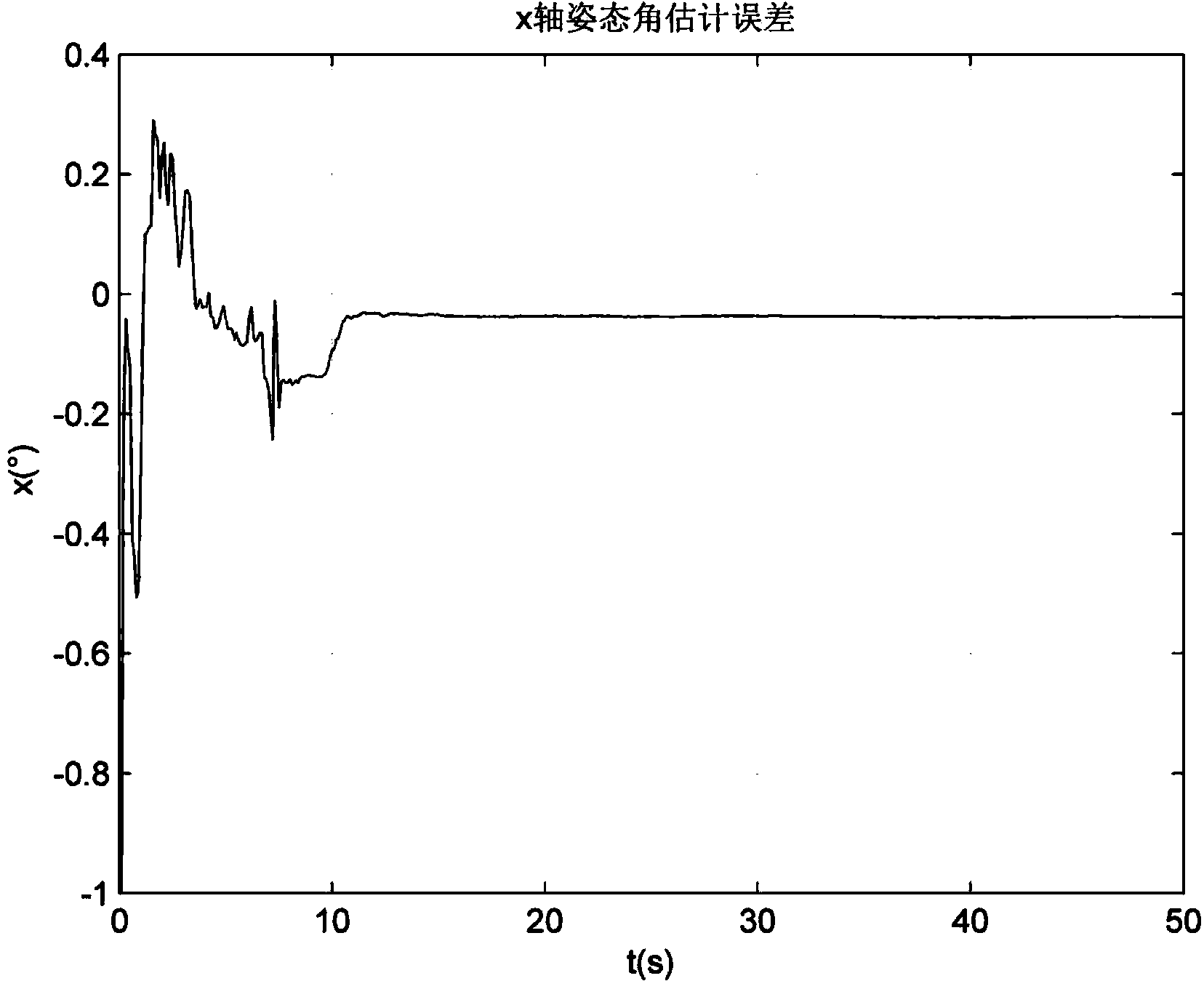
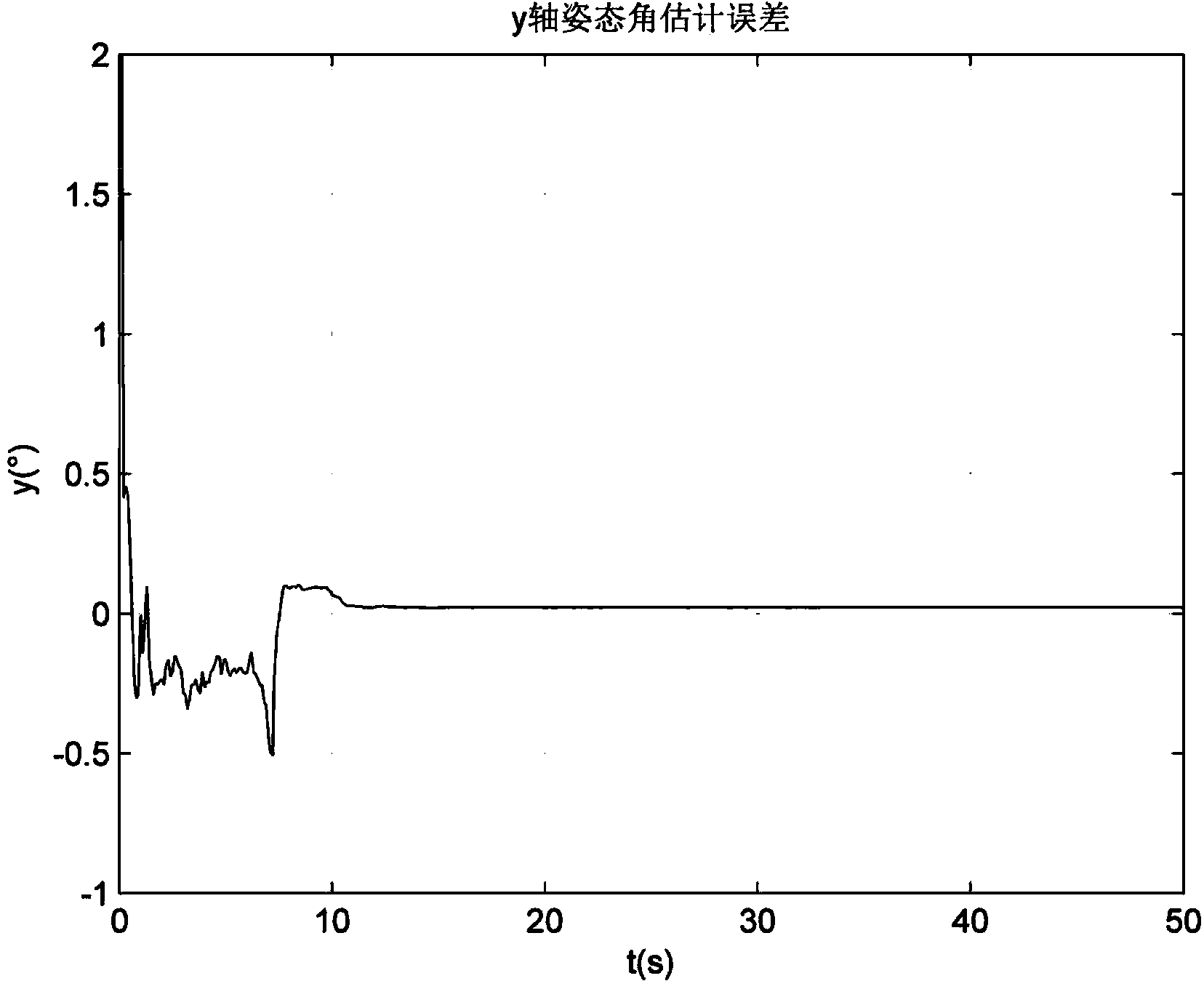
The invention provides a moving base transfer alignment method based on measurement of a misalignment angle. The moving base transfer alignment method comprises the following steps: step (1), completing coarse alignment by a sub-inertial navigation system by use of navigation parameters sent by a main inertial navigation system at fixed frequency, wherein the navigation parameters comprise speed, attitude and position information; step (2), establishing a system state equation and a system observation equation in a'measurement of misalignment angle and speed' matching way; step (3), constructing observables by the sub-inertial navigation system by used of the speed and posture information which is sent from the main inertial navigation system to the sub-inertial navigation system at fixed frequency; and step (4), performing iterative solution by virtue of Kalman filtration, estimating state estimated values of attitude misalignment angle, speed and position errors of the sub-inertial navigation system and correcting navigation information of the sub-inertial navigation system correspondingly so as to complete transfer alignment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
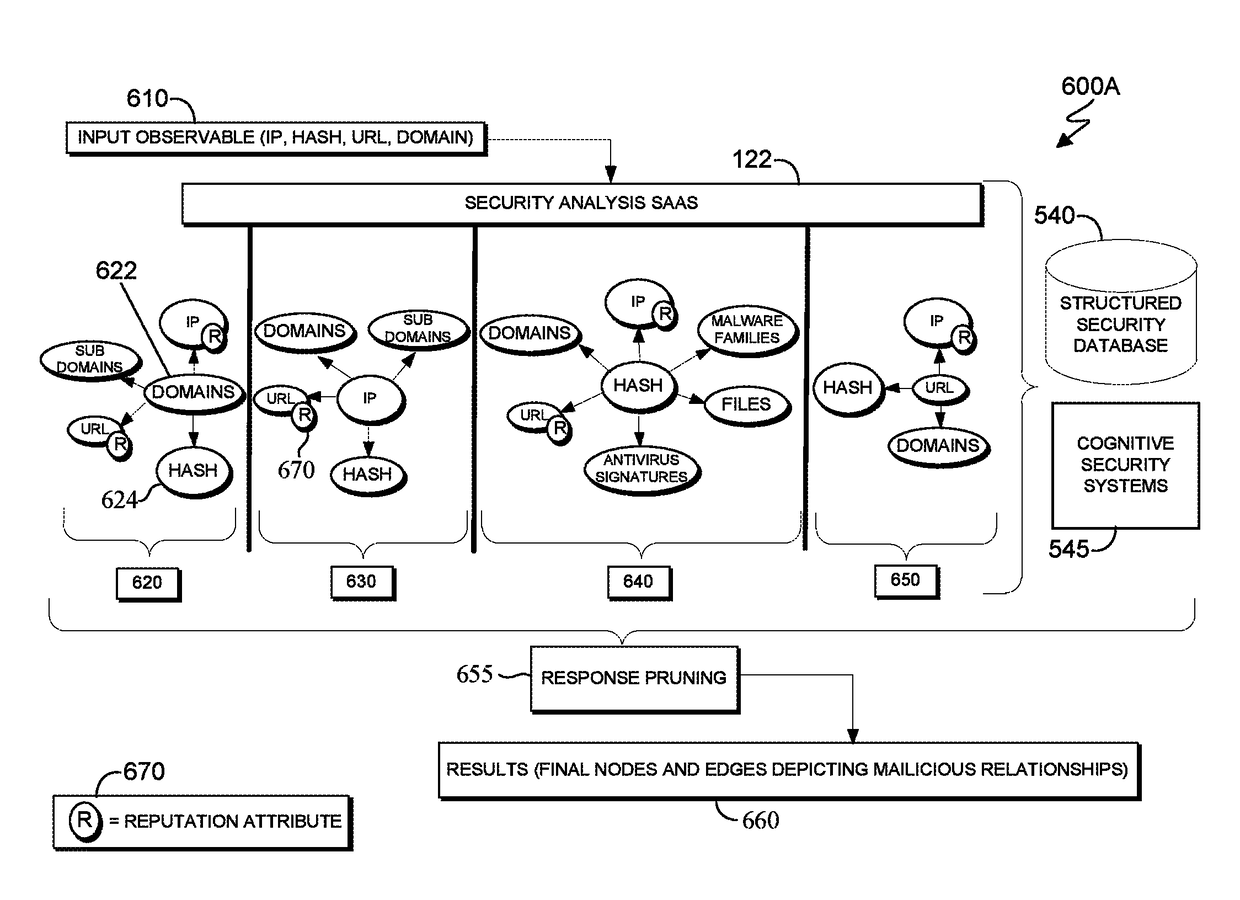
Optimizing security analyses in SaaS environment
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for performing a security analysis on a set of observables by inferring malicious relationships. The method includes receiving a set of observables and structured and unstructured threat data. The method further includes analyzing the observables and the structured and unstructured threat data using cognitive computing, and creating and transferring a subgraph.
Owner:IBM CORP
Sampling method
InactiveUS20060242217A1Increase sampleReduce probabilityDigital computer detailsDigital function generatorsState spaceDistribution function
The present invention is an incremental umbrella sampling method to improve the performance of established sampling methods. It is sampling the state space by iteratively generating states xi,t and their weighting factors represented by Formula (a) by fitting the sampling distribution function ρj(x) of the next iteration to at least one weighted property of the already sampled states. This means that ρj(x) is fitted to the product represented by Formula (b), in which Formula (a) is the weighting factor and O(x,i) is a function respectively a property of the states xi,t. The number of states xi,t and the number of weighting factors (see Formula (a)) is incremented with each iteration. In order to have a consistent set of weighting factors (see Formula (a)), the weighting factors are recalculated in each iteration for all, respectively for a set of selected, states. By fitting ρj(x) in the state space it is possible to use all the information of Formula (a) and O(xi,t) for the states xi,t generated so far. The fitting step allows to use different fitting strategies. For example the fitting can bias the sampling away from areas where intensive sampling has been done in the preceding iterations, or the sampling can be directed along local gradients respectively towards local minima or maxima of one or several weighted properties. In each of the iterations, the sampling distribution function is fitted in a way to improve the overall sampling of the state space. The method supports multi-objective optimisations. State space integrals can be solved. It reduces the probability that the system is trapped. The invention is general. It can be used with different sampling methods, in particular with Monte Carlo sampling, Metropolis Monte Carlo sampling, or dynamic simulations. It can be combined with the concepts of simulated annealing and multicanonical sampling. It provides a general framework that can be adapted to the system and the observables of interest.
Owner:BARTELS CHRISTIAN
Method and device for generating second pulse of satellite navigation receiver
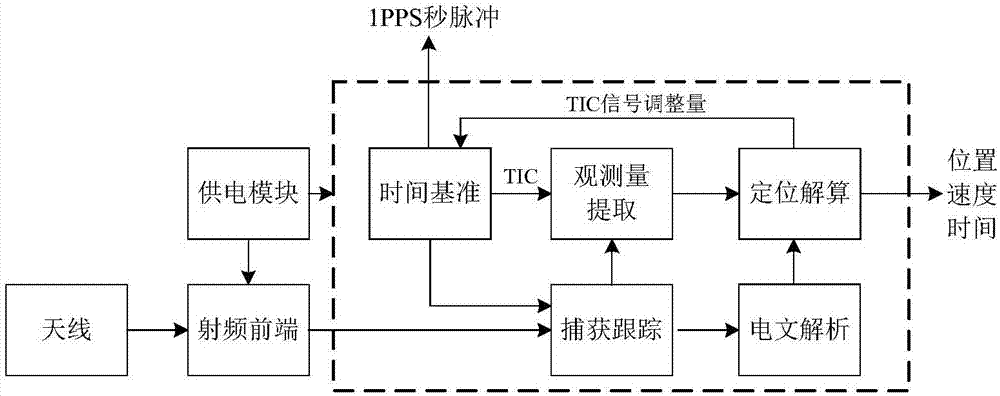
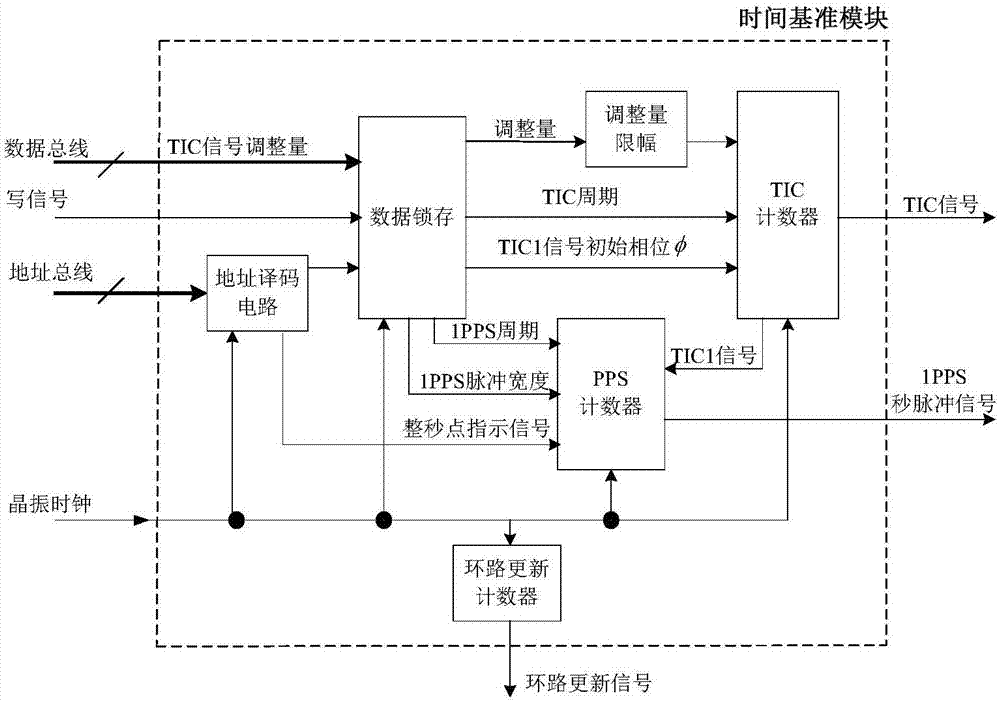
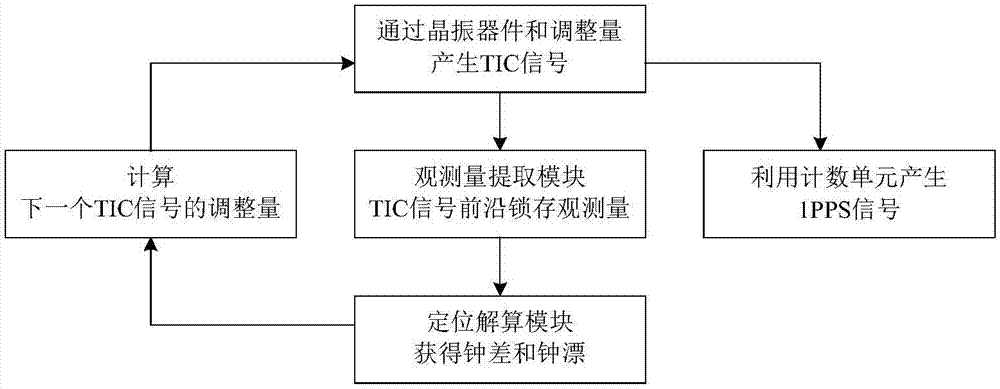
ActiveCN108008424AHigh time accuracyFlexible modificationSatellite radio beaconingClock driftDistance correction
The invention discloses a method and a device for generating a second pulse of a satellite navigation receiver. The method includes the following steps: generating a rough timing signal TIC through afrequency reference device such as a crystal oscillator; latching the pseudo code phase, carrier Doppler value and other observables of a satellite signal at the leading edge of the TIC signal; carrying out positioning calculation according to the satellite position, pseudo distance correction and other parameters in a navigation message to obtain the position, speed, clock difference and clock drift; calculating the adjustment amount of next TIC signal cycle by using the clock difference and the clock drift value; and finally, adjusting the TIC signal, and generating an accurate 1PPS second pulse signal. The problem that large deviation is caused as the existing satellite navigation receiver generates a second pulse according to the clock difference only is solved. The defect that the method for generating a second pulse under stable control of a phase locked loop needs a large amount of computation is overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACEFLIGHT INST OF TT&C & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com