Patents
Literature
337 results about "GLONASS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
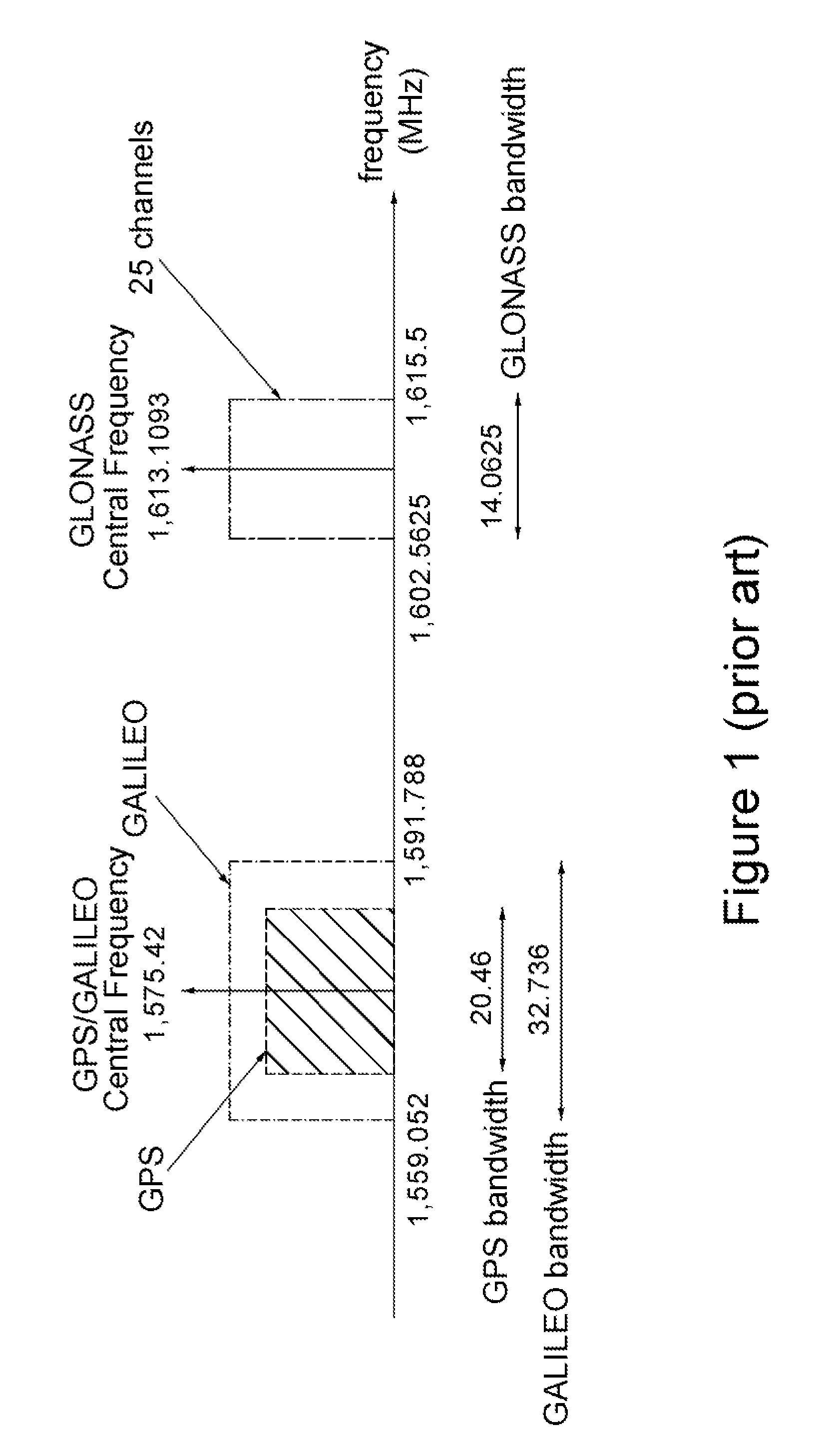
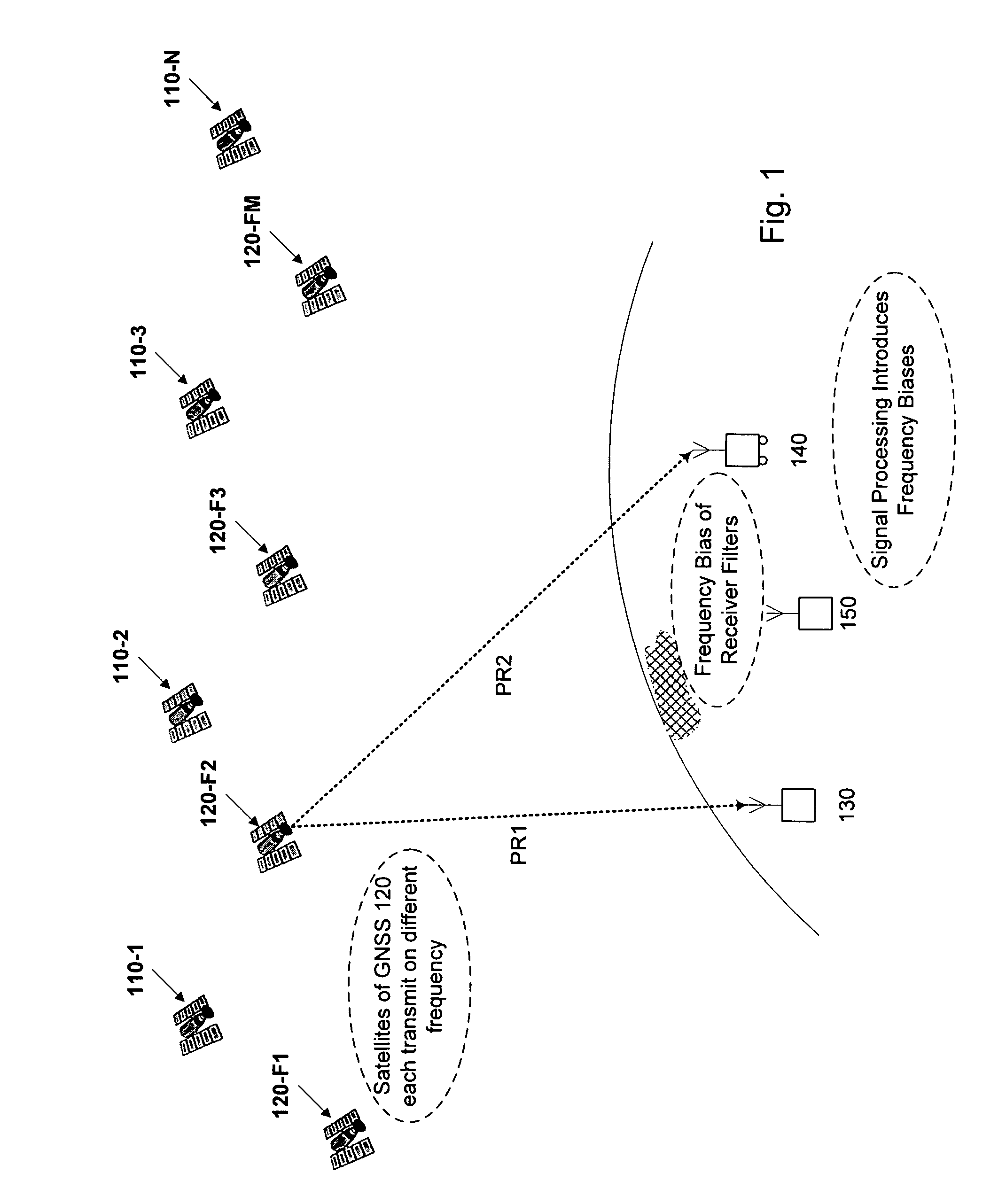
GLONASS (Russian: ГЛОНАСС, IPA: [ɡɫɐˈnas]; Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, transliteration: Globalnaya navigatsionnaya sputnikovaya sistema), or "GLObal NAvigation Satellite System", is a space-based satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to GPS and is the second navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision.
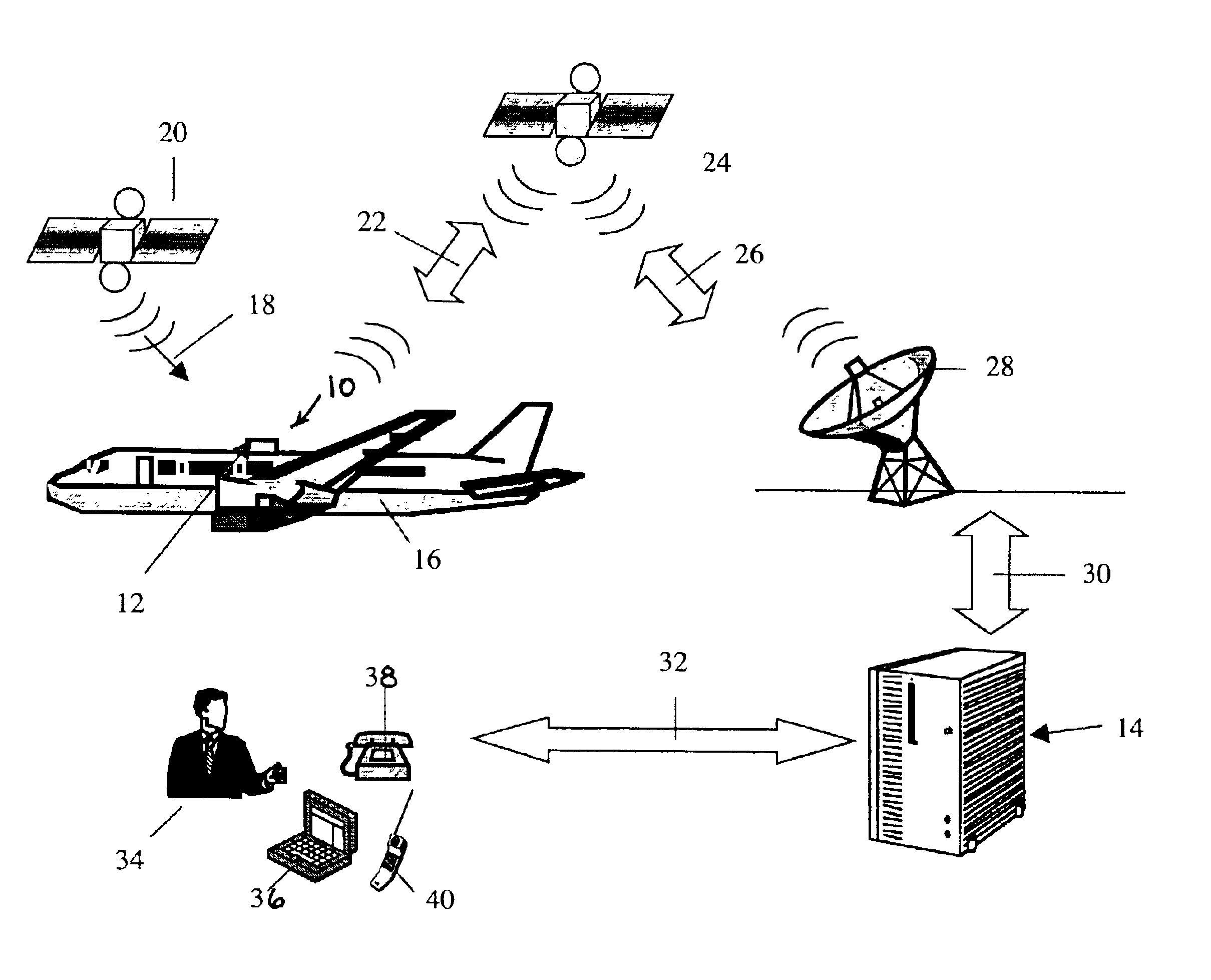
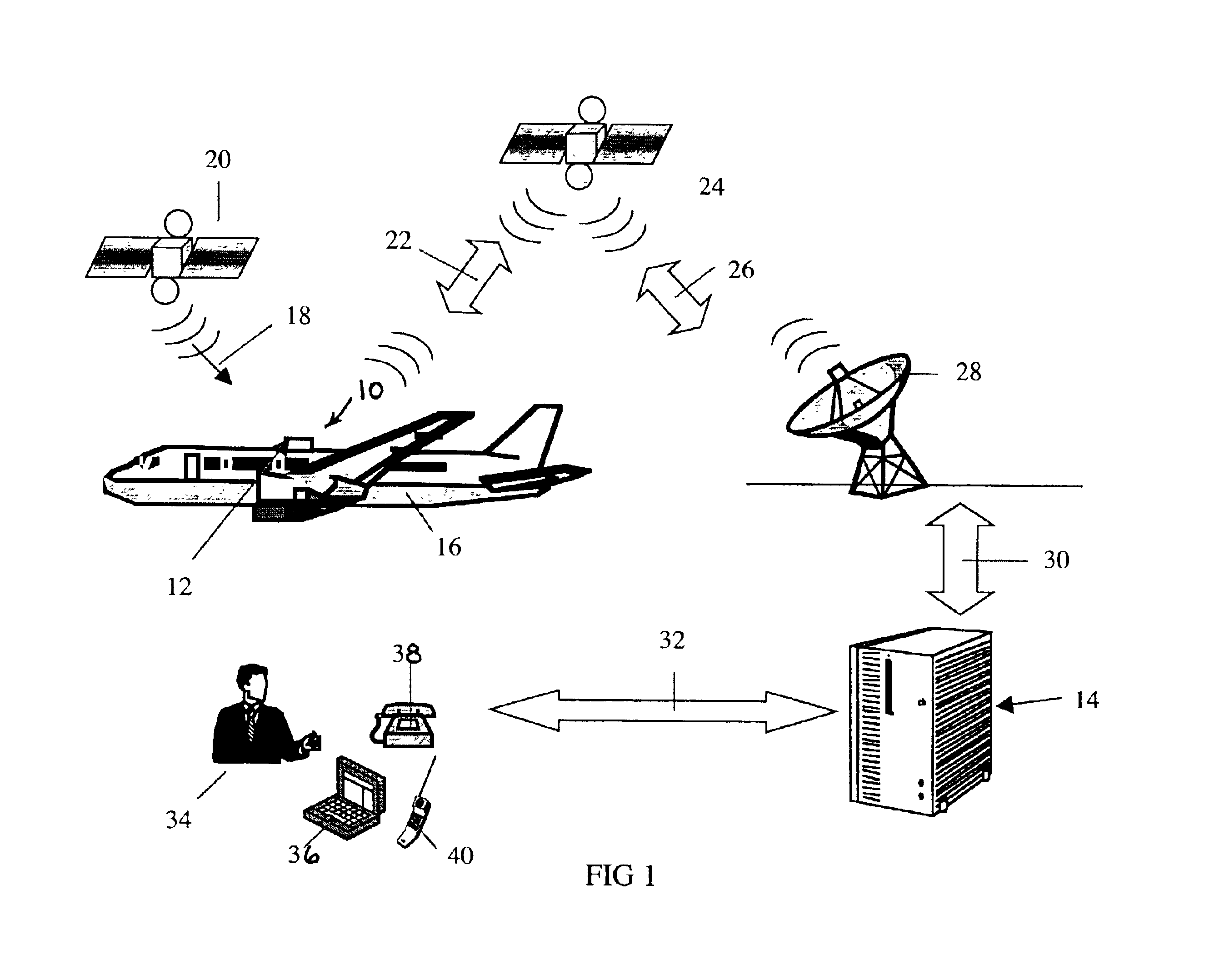
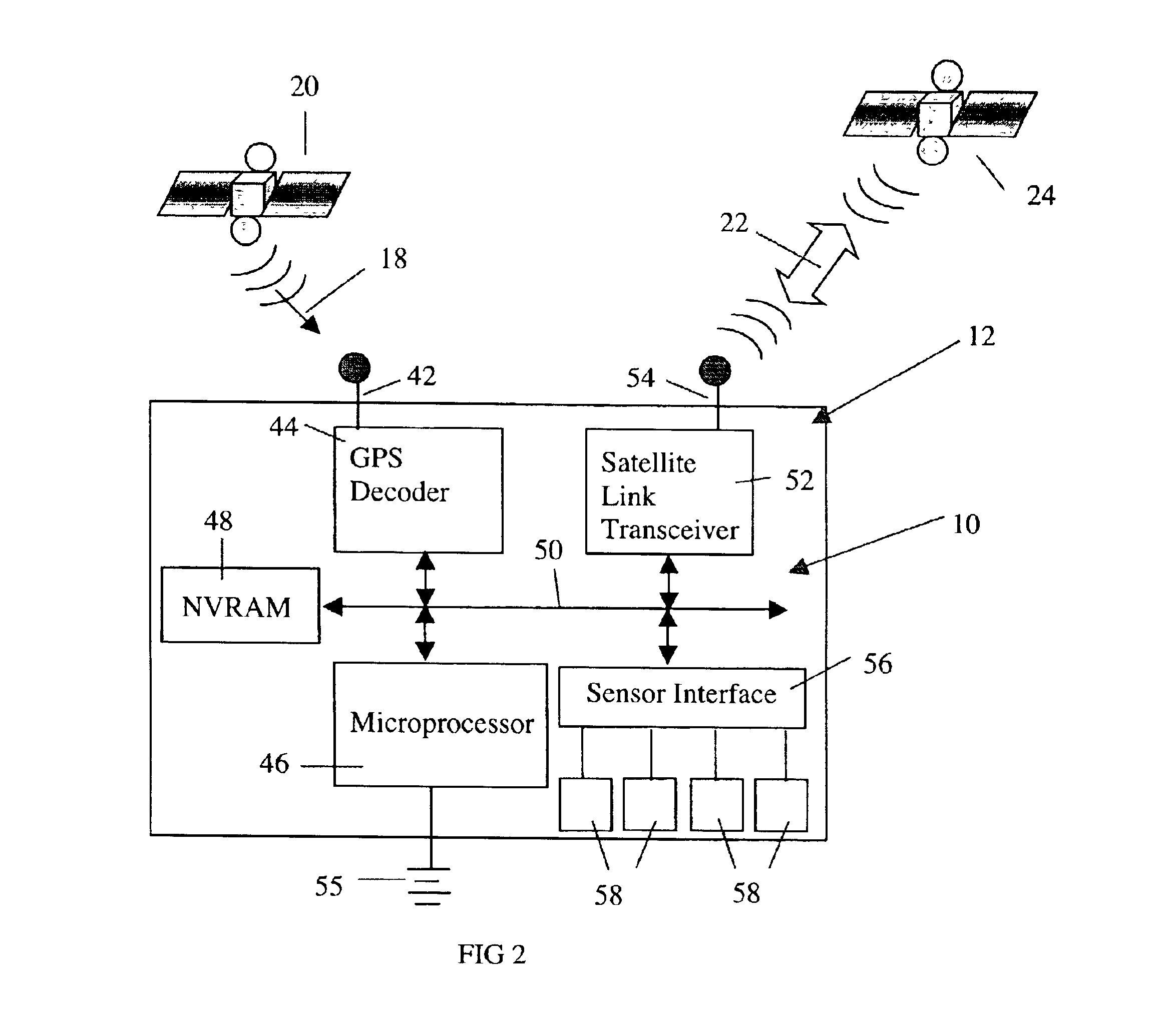
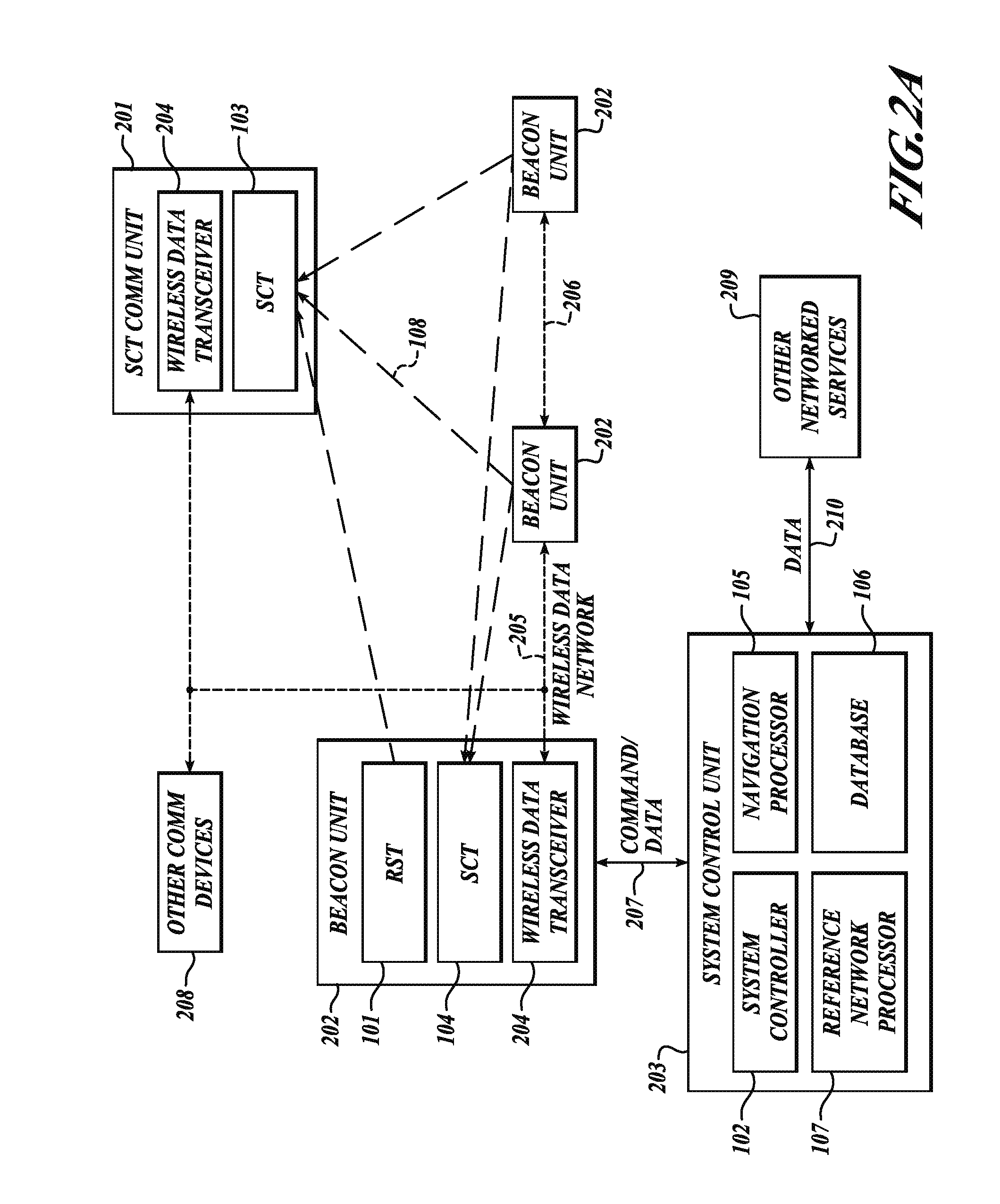
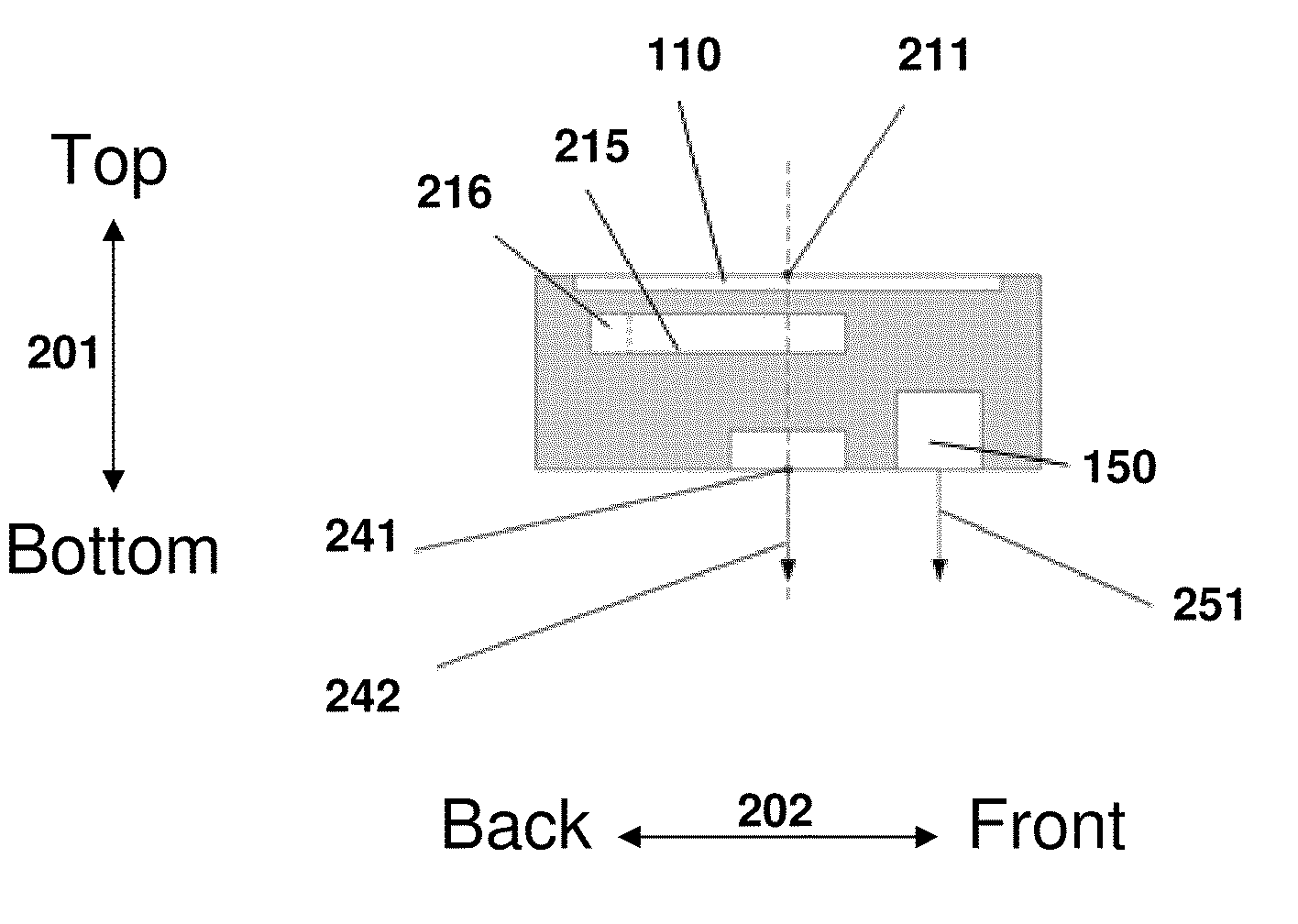
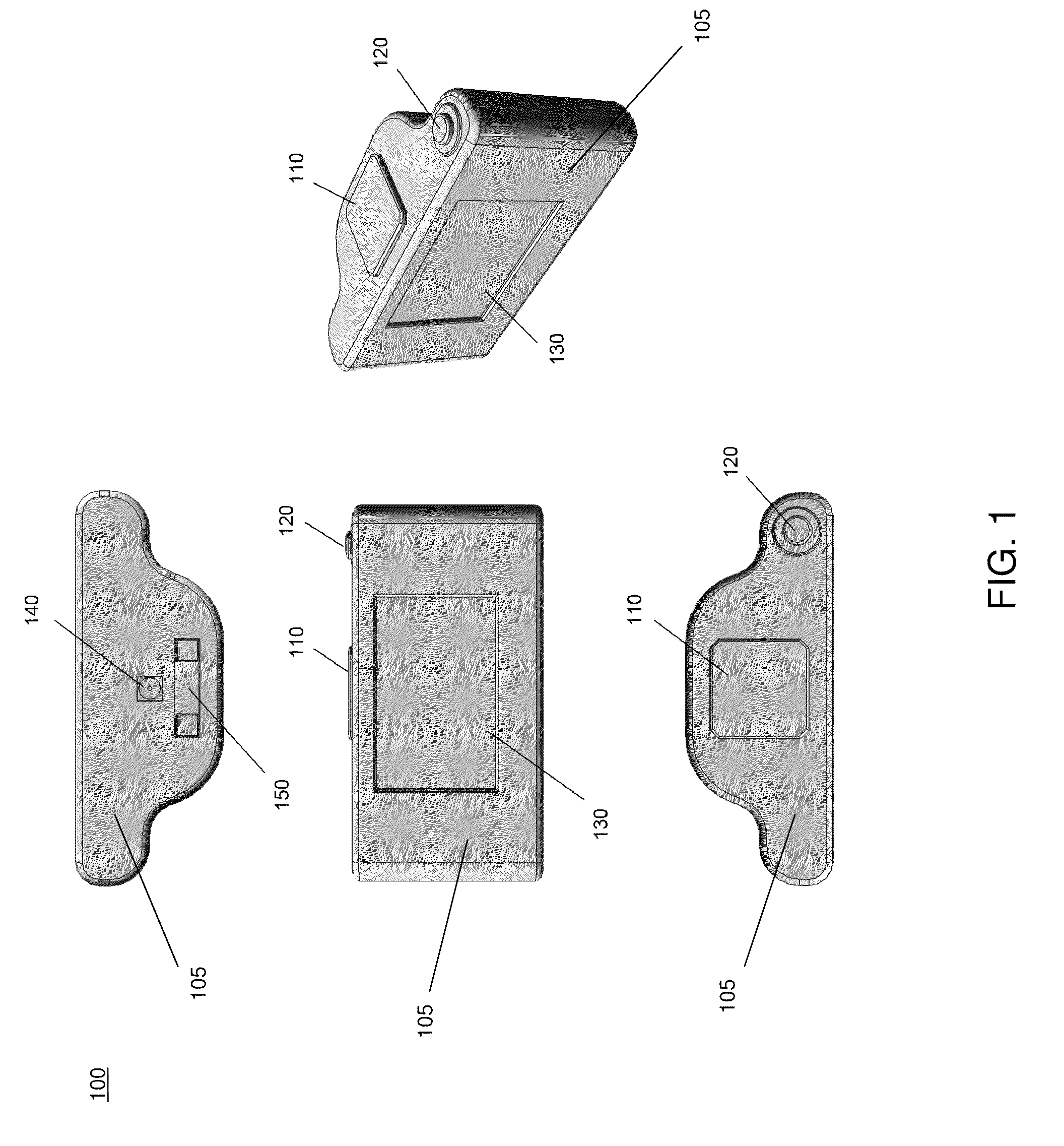
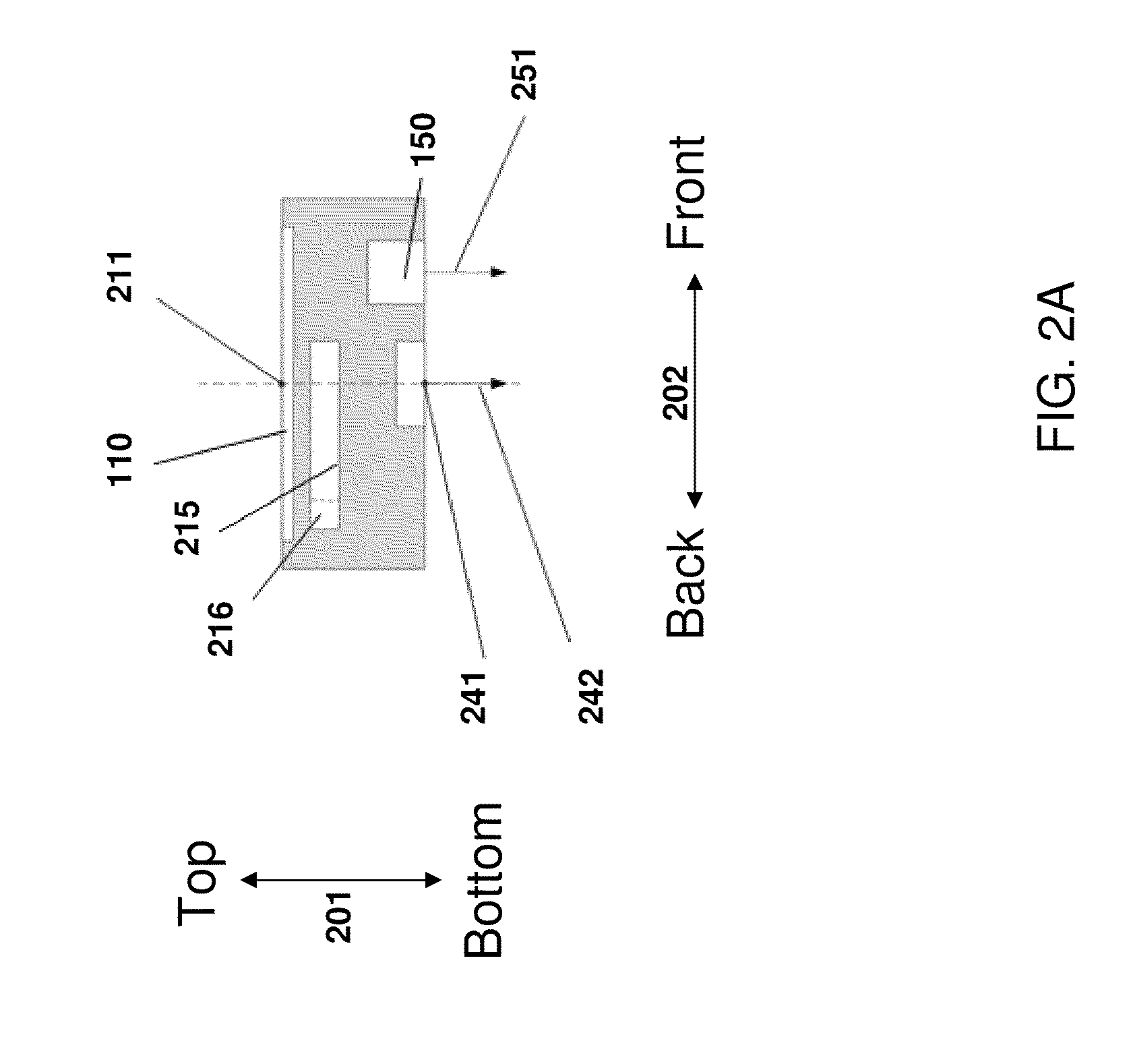
Aircraft location monitoring system and method of operation
InactiveUS6799094B1Easy to adaptDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationTransceiverMonitoring system
An aircraft monitoring system adapted for mounting in an aircraft and at a location independent of the aircraft for providing information related to aircraft location and / or the current state of the operation of the aircraft. The monitoring system includes an aircraft-tracking device and a server computer adapted for communicating with an aircraft owner / operator. The device includes a signal receiving antenna for receiving signals from a satellite positioning system and a decoder connected to the antenna for decoding the location position coordinates (GPS or GLONASS). Further, the aircraft-tracking device includes a microprocessor connected to the decoder and a two-way satellite communication transceiver. The transceiver is connected to a two-way radio communication antenna. The radio communication antenna receives and sends two-way satellite communications between a satellite communication system. The satellite communication system communicates with a ground-based satellite communication service. The server computer is connected to the satellite communication service and is connected to a telecommunication system for alerting the owner / operator as to the aircraft's location and / or the current state of operation.
Owner:NORTHSTAR SYST LLC
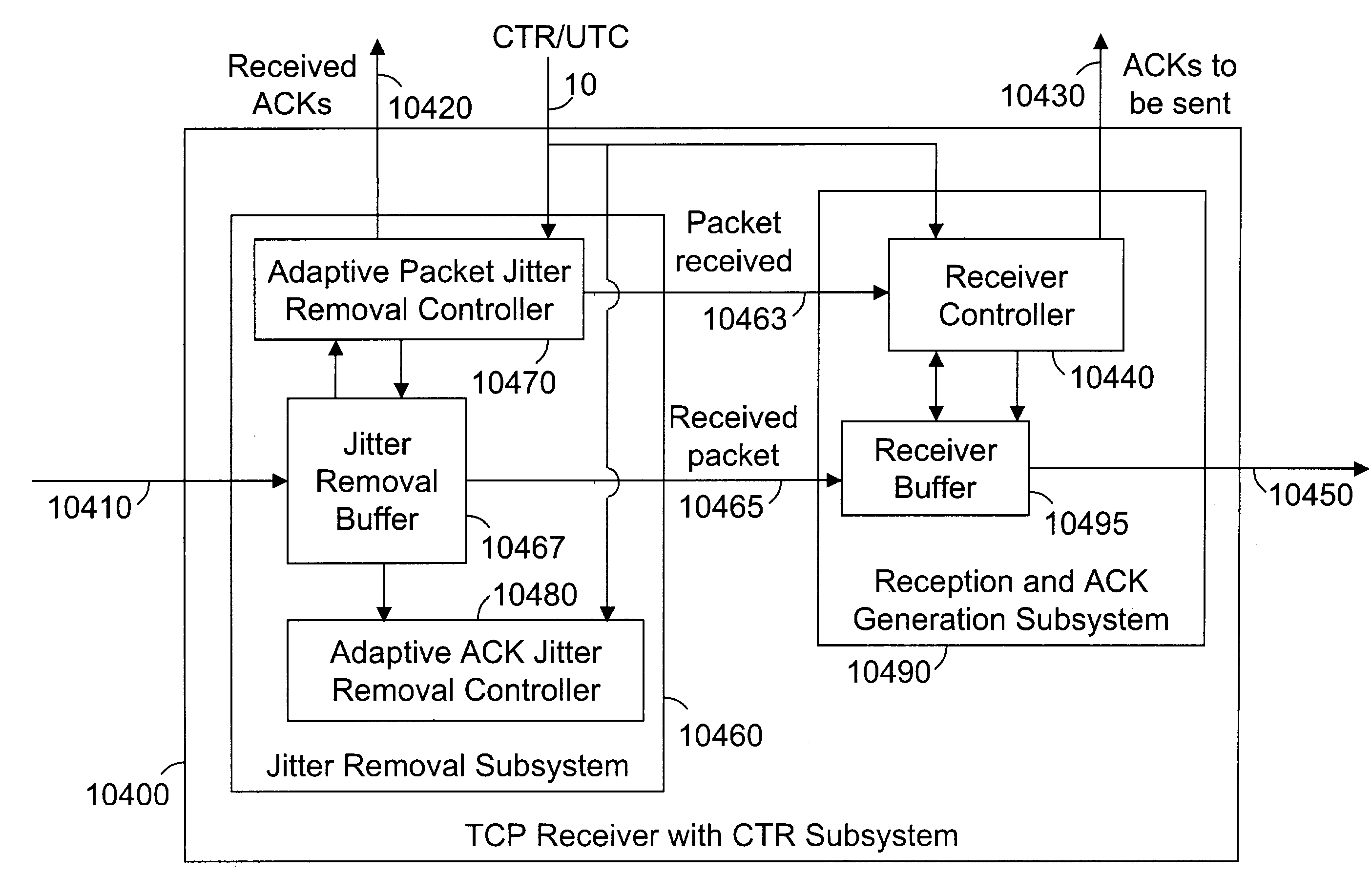
Window flow control with common time reference
ActiveUS7307989B2Restrict levelData processing applicationsTime-division multiplexSlide windowData transmission
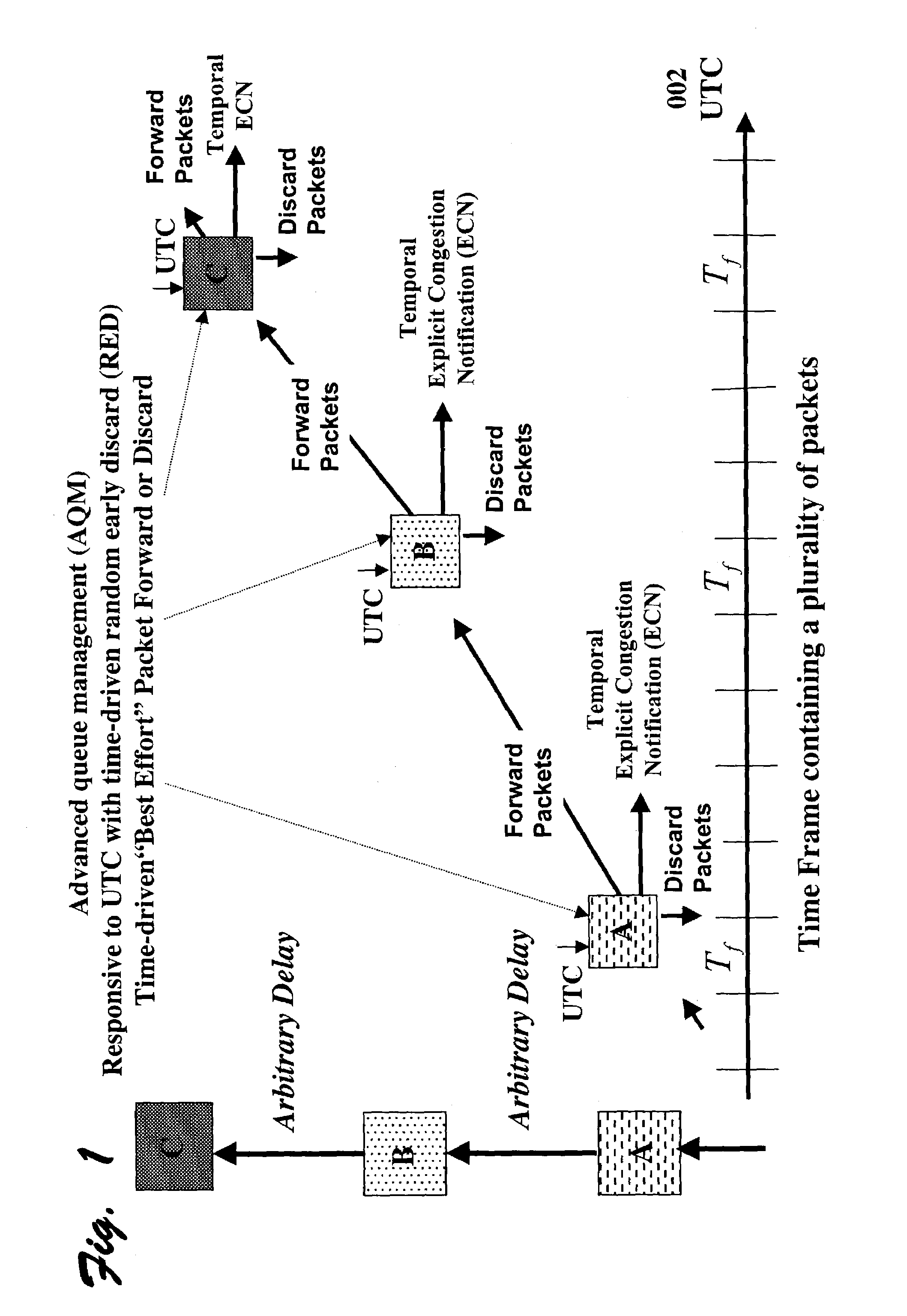
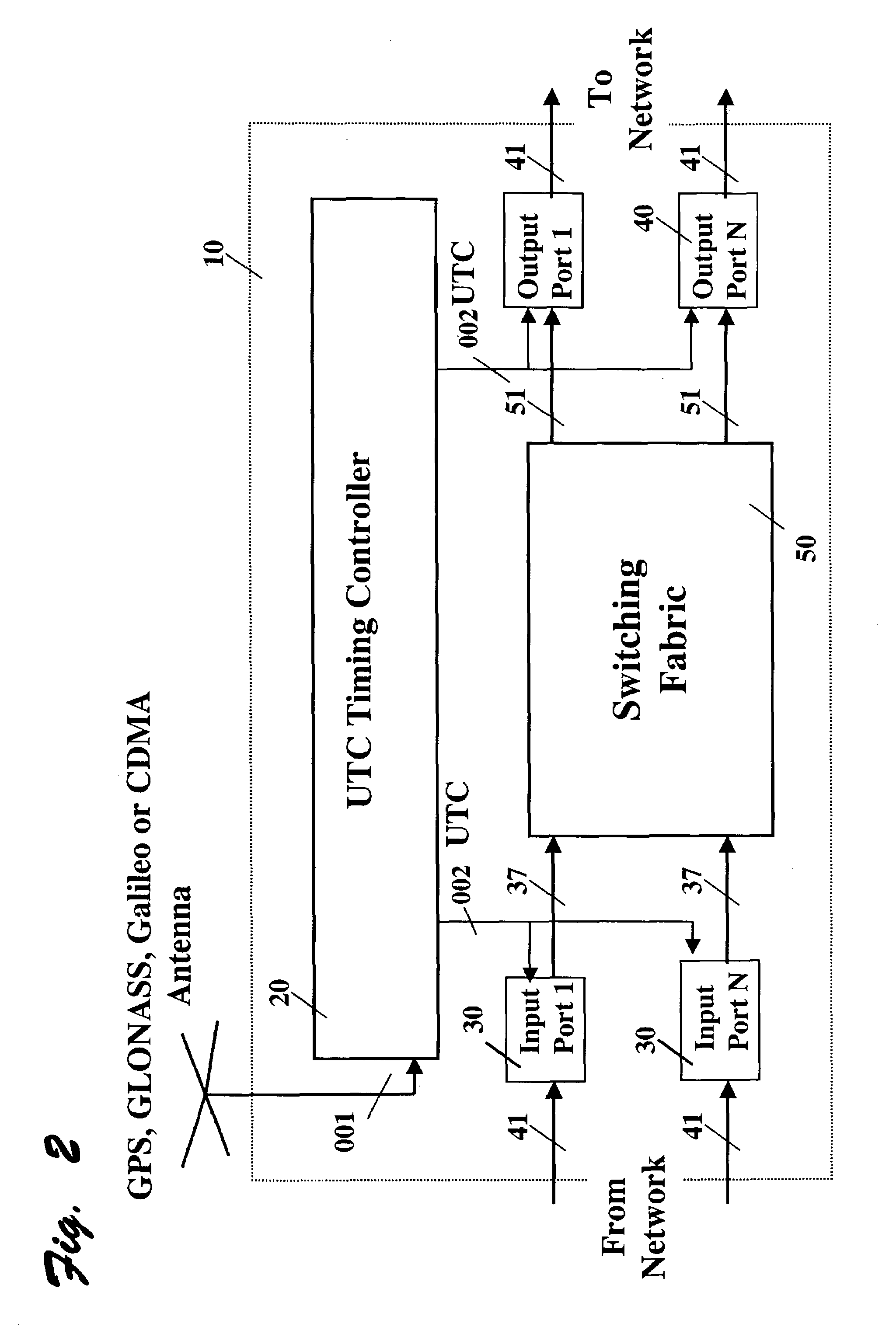
This invention relates generally to a method and apparatus for timely forwarding, discarding, and delivering data packets over the network and to their destination nodes and the optimization of data transfer throughput through the network. The timely forwarding and discarding are possible thanks to the standard global common time reference (CTR) that is known as UTC (Coordinated Universal Time). UTC is available from GPS (Global Positioning System), Galileo, and GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System). Data transfer throughput optimization is pursued by taking advantage of the timely forwarding and discarding properties to improve the data packets transfer flow control mechanisms, such as the sliding window re-sizing algorithm implemented by the widely deployed Transmission Control Protocol (TCP).
Owner:ATTESTWAVE LLC
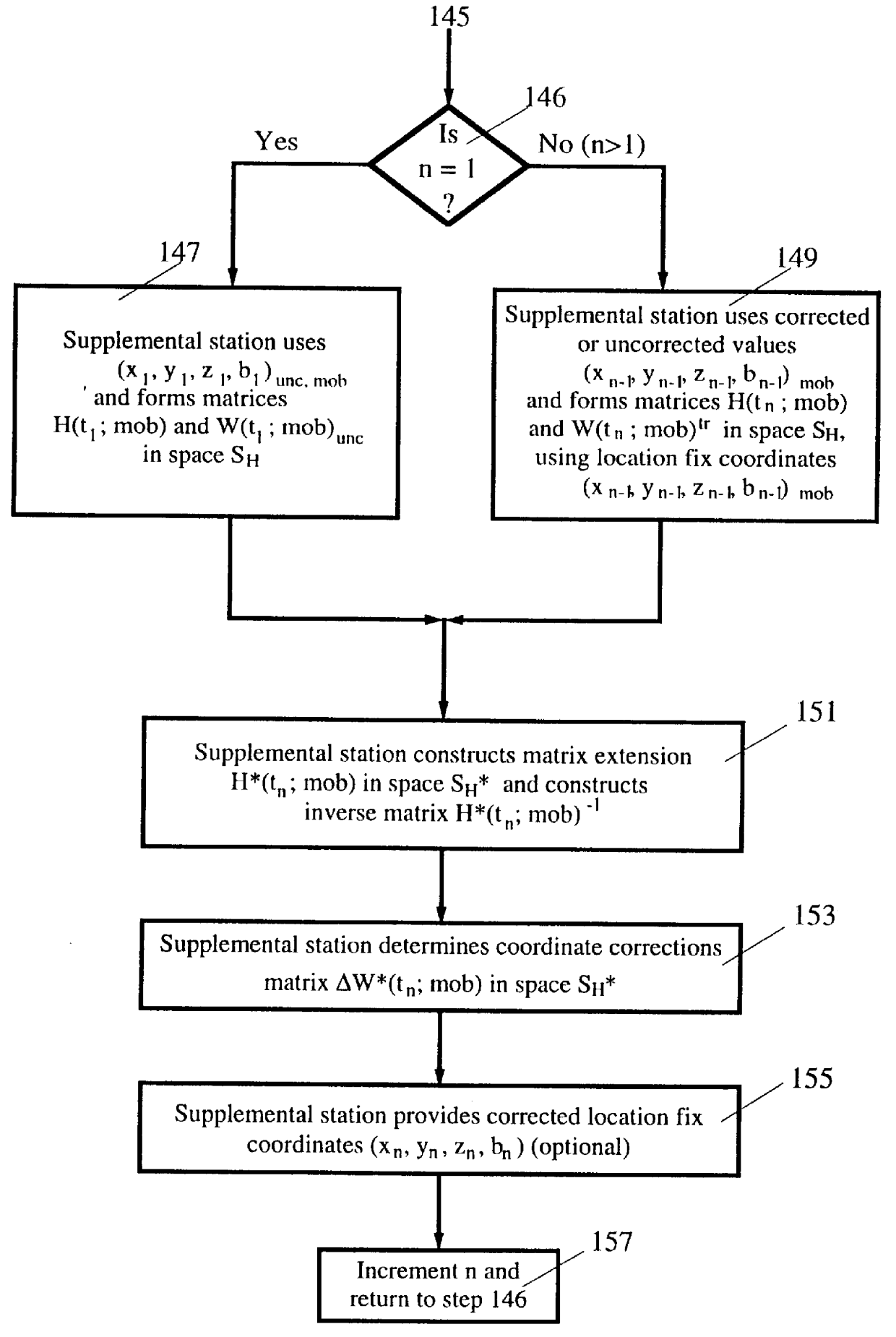
Post-processing of inverse DGPS corrections
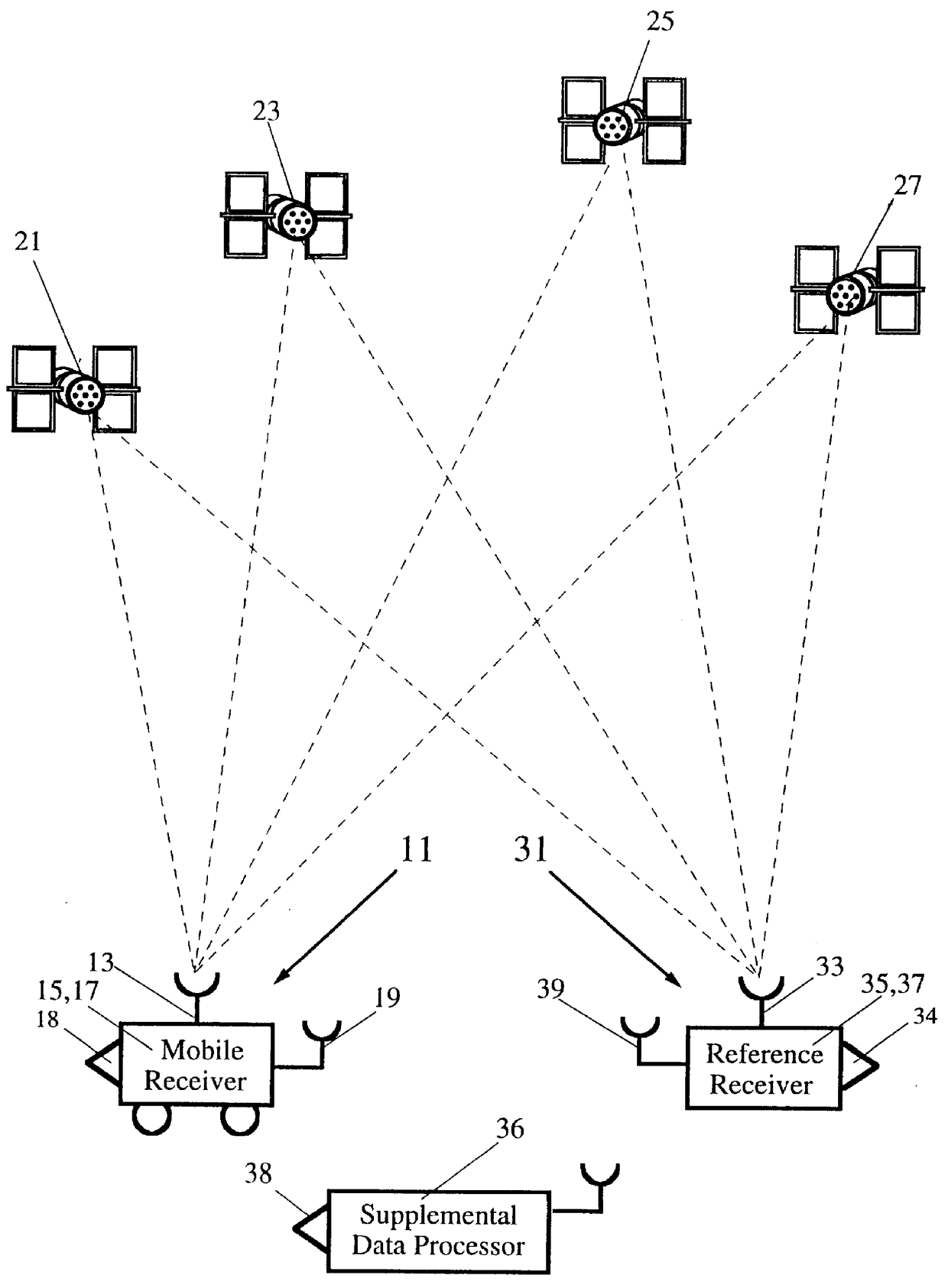
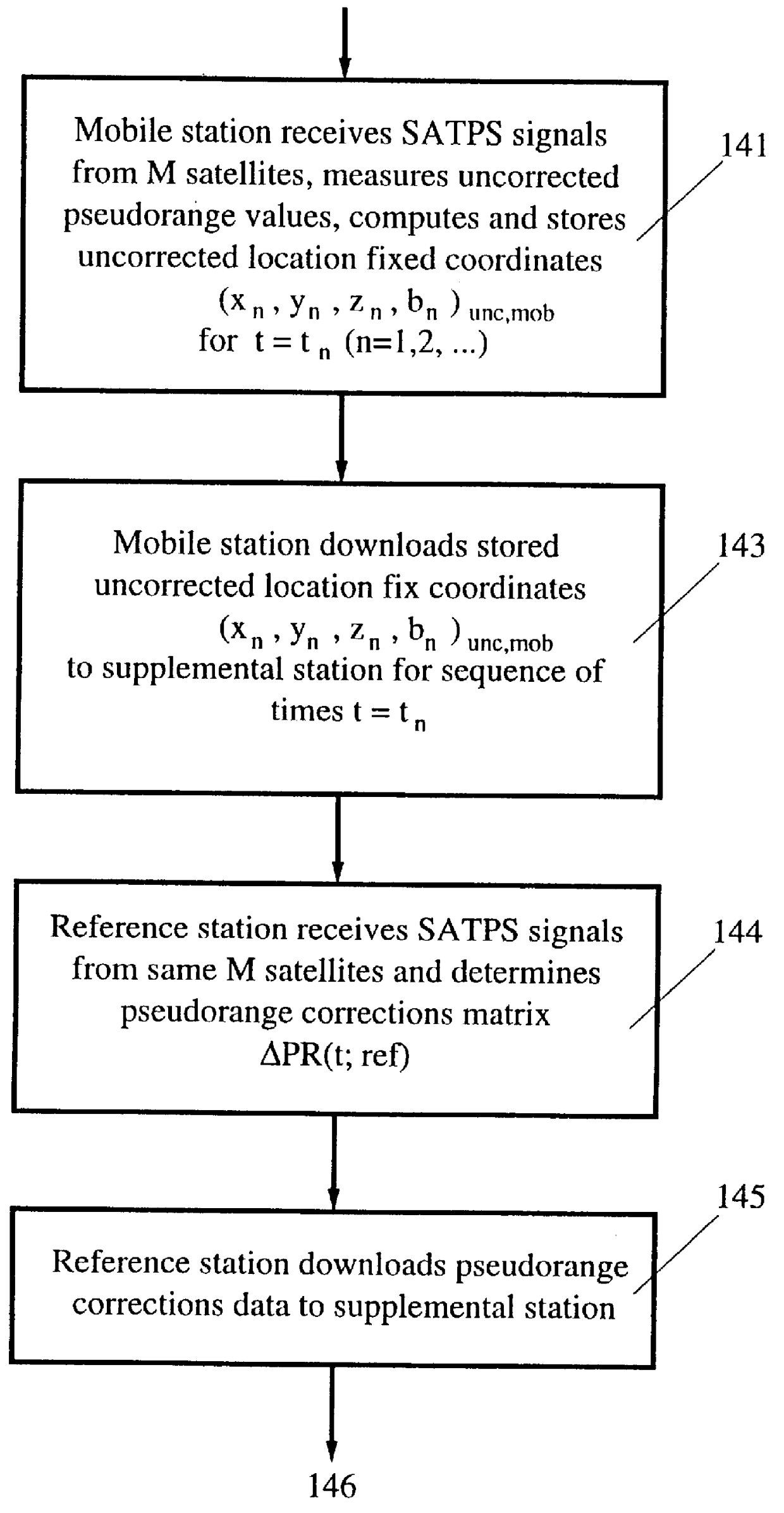
A method for enhancing the accuracy of location coordinates and / or clock bias computed for a mobile user station that is part of a Satellite Positioning System (SATPS), such as GPS or GLONASS. A data processing station is provided with pseudorange corrections PRC(t;j;ref) for an SATPS reference station for each of M SATPS satellites (j=1, . . . , M; M> / =3) and with uncorrected location fix coordinates x'(tf), y'(tf)', z'(tf)' and / or b'(tf) for the mobile station for a selected location fix time tf. A matrix equation H(tf;mob) DELTA W(tf;mob)=PRC(tf;ref) relates a matrix DELTA W of location fix coordinate corrections for the mobile station to a matrix PRC(t;ref) of the pseudorange correction values, where H(tf;mob) is an MxN matrix (M< / =N; N=3 or 4) with known entries computed from mobile station data. An inverse or pseudo-inverse matrix H(tf;mob)(-1) is formed satisfying the relation H(tf;mob)(-1)H(tf;mob)=the identity matrix I, and the matrix DELTA W(tf;mob)=H(tf;mob)(-1)PRC(tf;ref) is computed. The entries of the matrix DELTA W(tf) are interpreted as additive corrections for the location fix coordinates x'(tf), y'(tf)', z'(tf)' and / or b'(tf) for the mobile station. Post-processing can be performed to apply the pseudorange corrections to the mobile station data.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
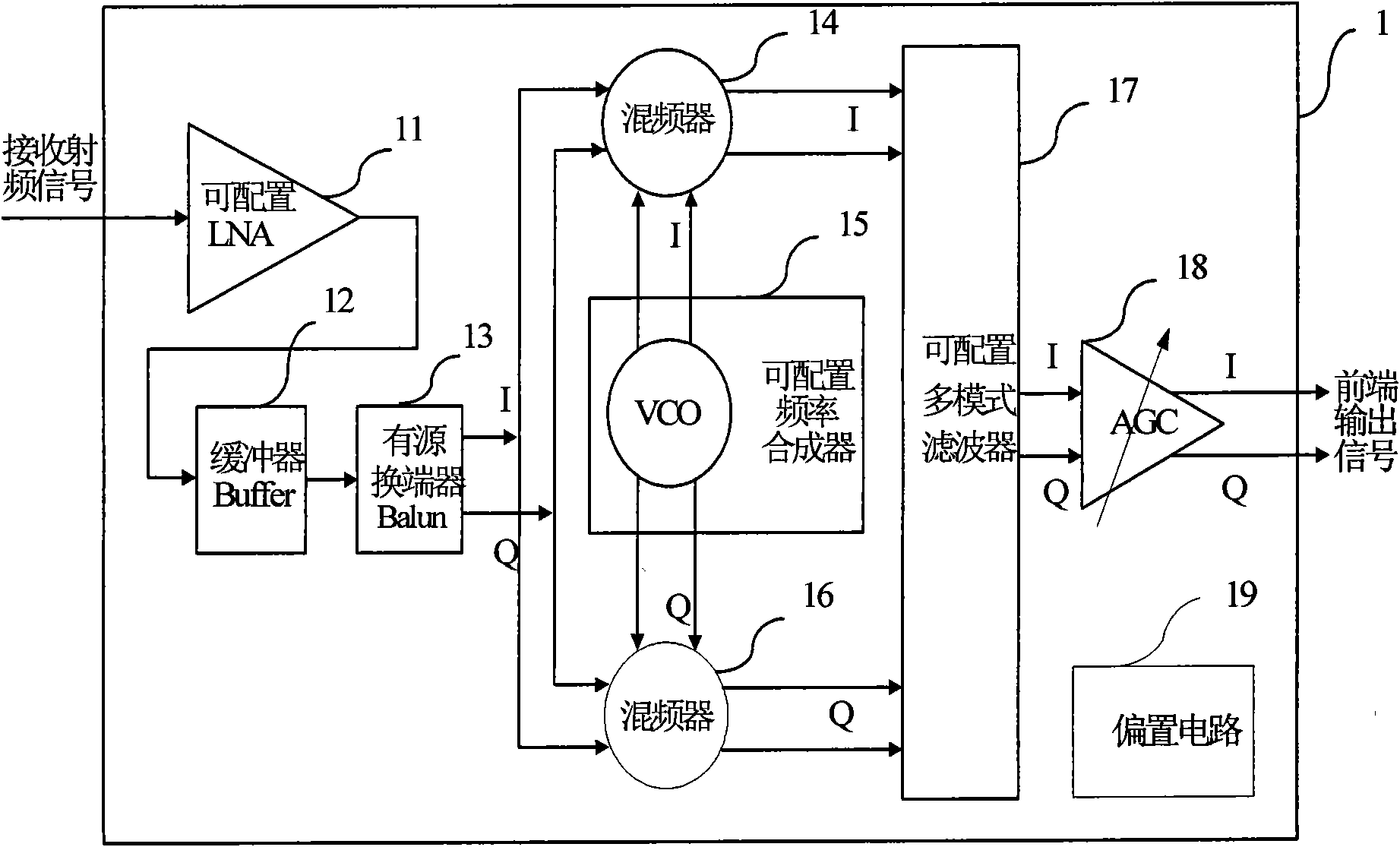
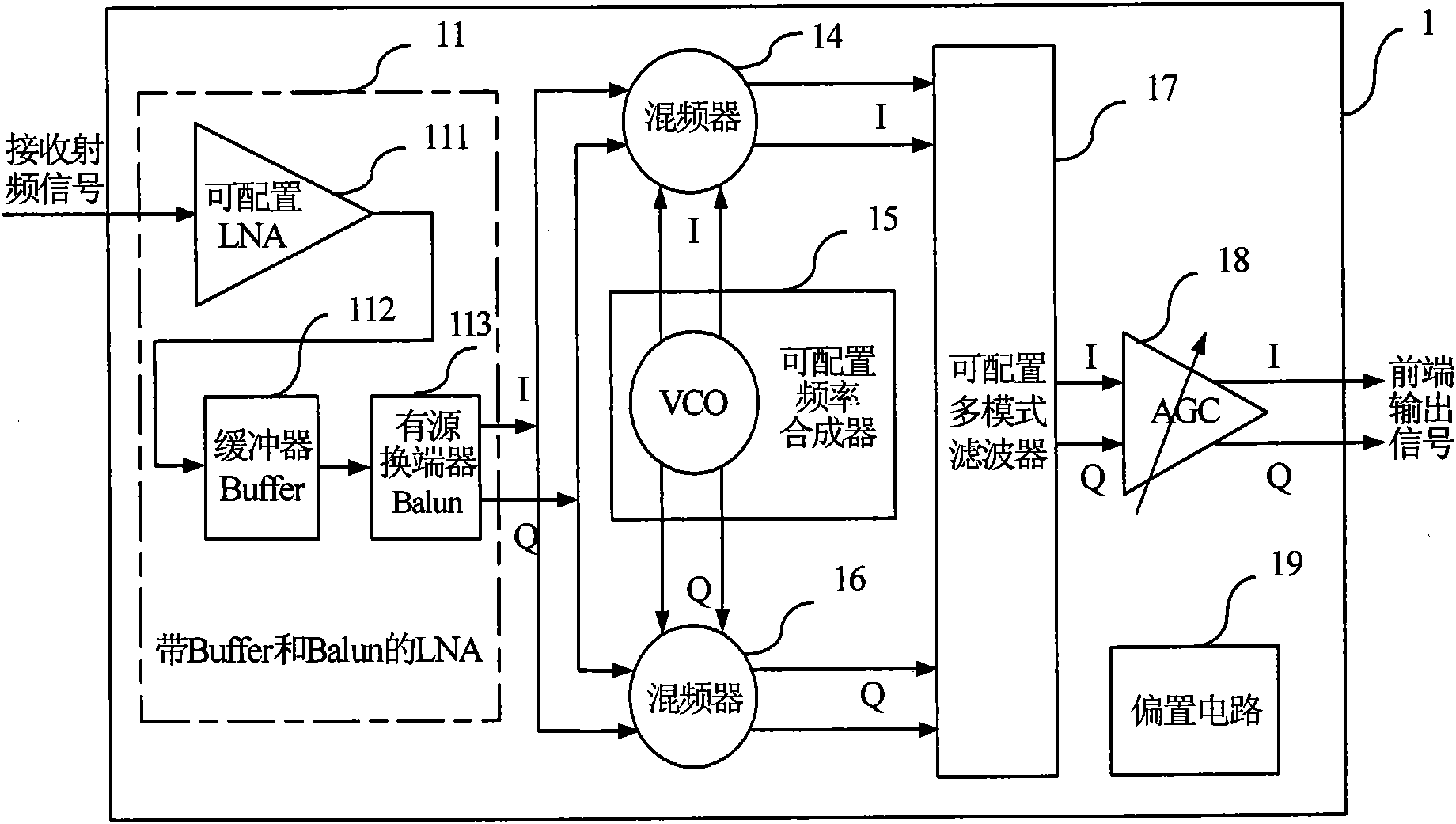
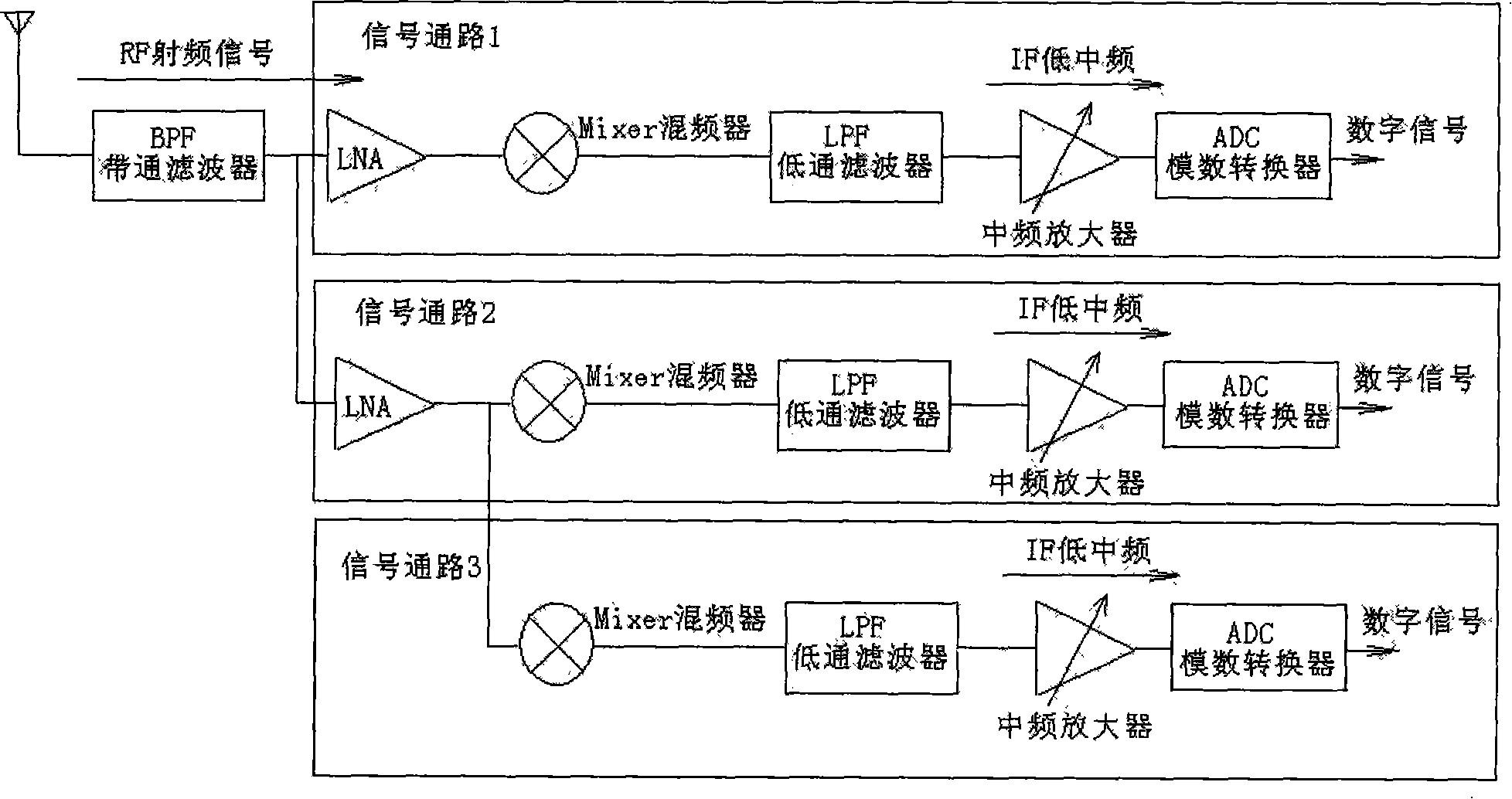
Method for constructing radio frequency front end of multi-mode multi-band satellite navigation receiver and module thereof
InactiveCN102096079ASimple and reliable compositionReduce common mode noiseBeacon systems using radio wavesSatellite radio beaconingMulti bandDifferential signaling
The invention discloses a configurable multi-mode multi-band satellite navigation receiving method and a radio frequency front end module constructed by the method. The front end module can receive signals of satellite navigation and positioning systems such as a global positioning system (GPS), the Big Dipper, a Galileo positioning system and a global navigation satellite system (Glonass), and comprises a configurable low-noise amplifier (LNA) with a buffer and an active balun, a folding passive mixer with a configurable frequency synthesizer, a configurable multi-mode filter, an automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier, a direct-current bias circuit, and a multi-mode multi-band program controlled and coded on-off control word from a receiving system. The radio frequency front end module can meet the requirement of multi-band multi-mode work through the control word programmed by the receiving system, has a simple and reliable structure, does not need complicated time division multiplexing control system and off-chip module, has low cost and high flexibility, and improves the noise performance of the radio frequency front end of the whole receiver and multi-mode multi-band signal processing capacity; and a one-channel signal is input into the module, and the module outputs a two-channel differential signal. The receiver can be used for receiving and processing multi-mode satellite navigation signals asynchronously, and receiving and processing satellite navigation signals with the required mode in different time intervals according to the requirement.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Processing Multi-GNSS data from mixed-type receivers
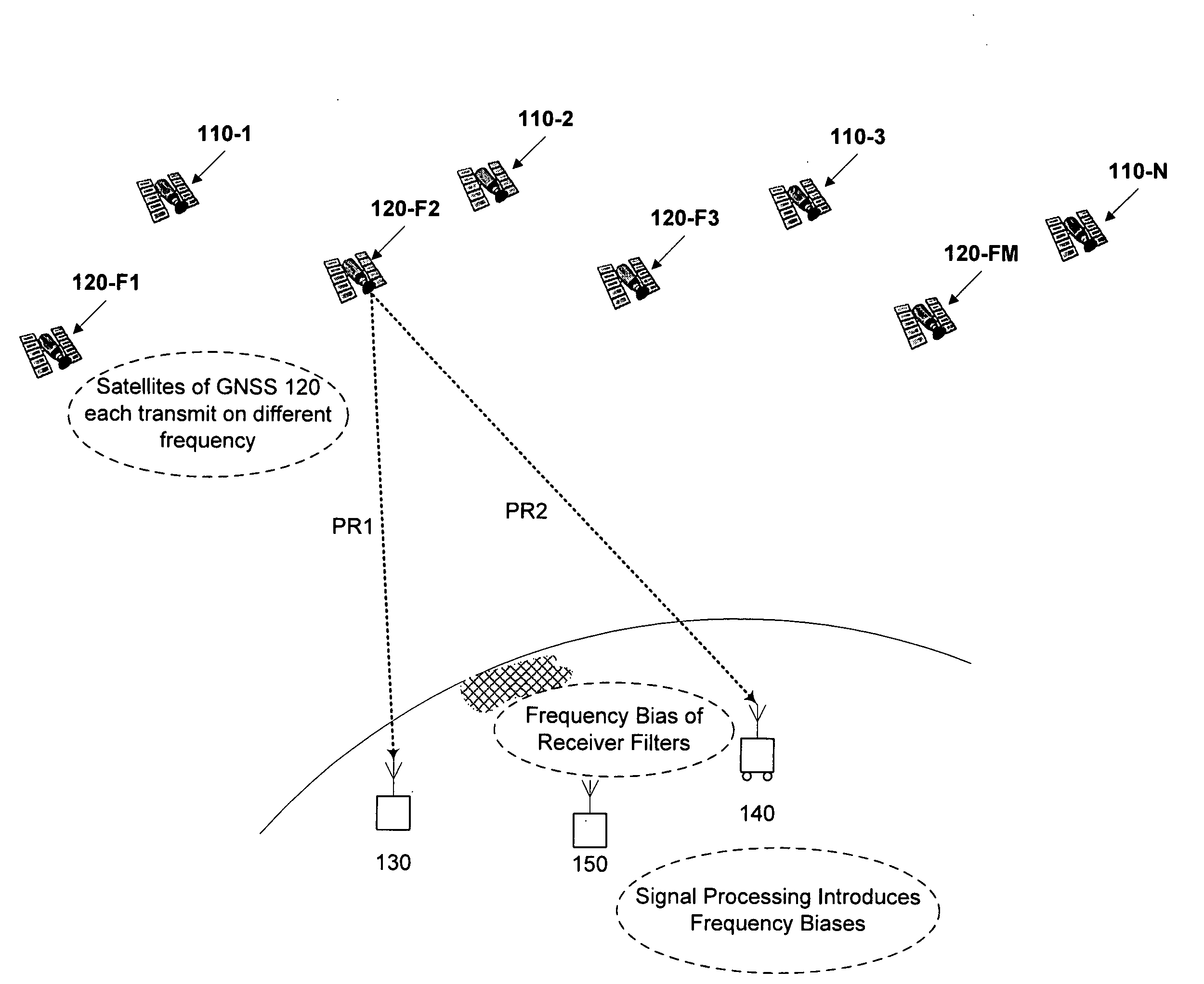
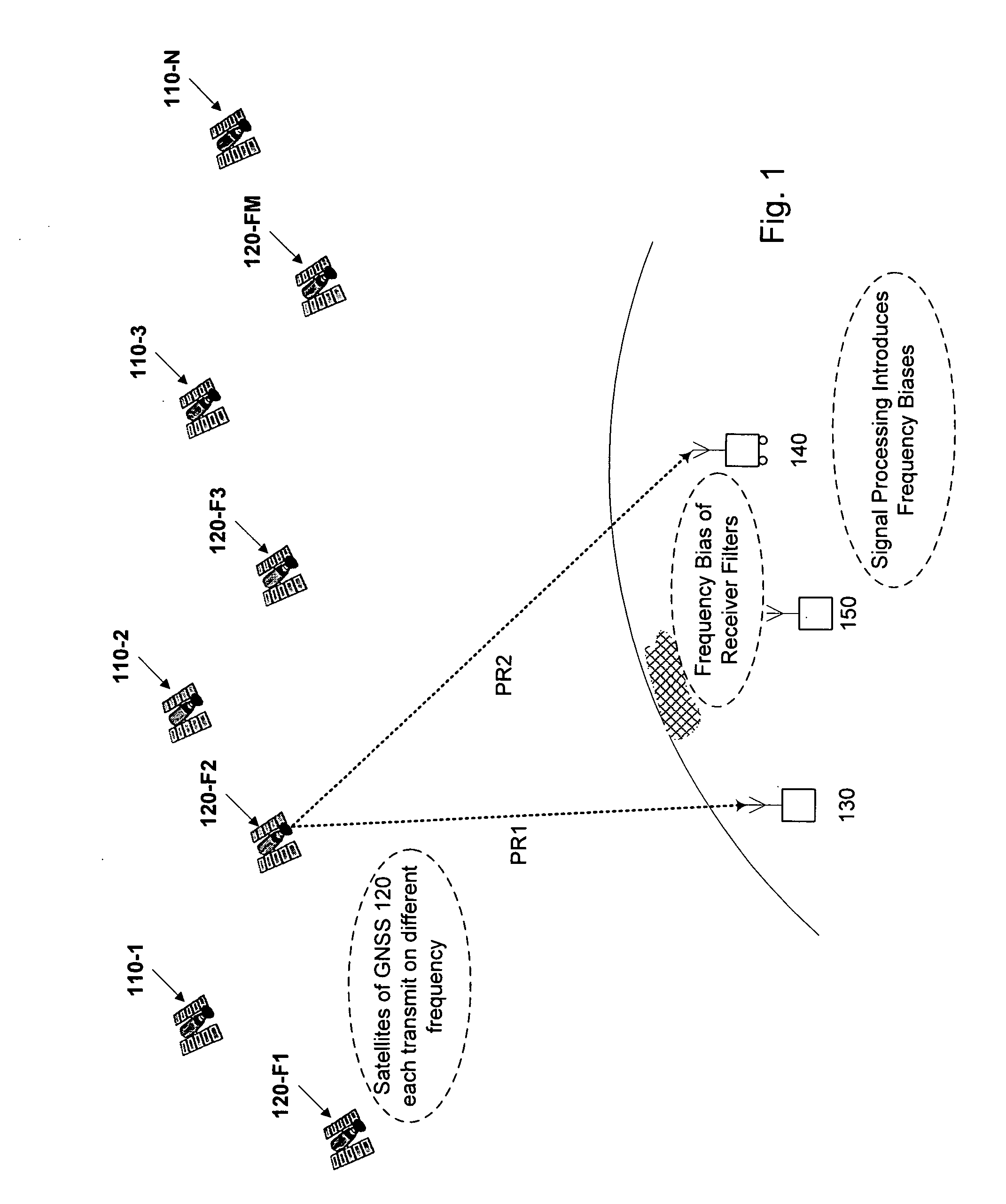
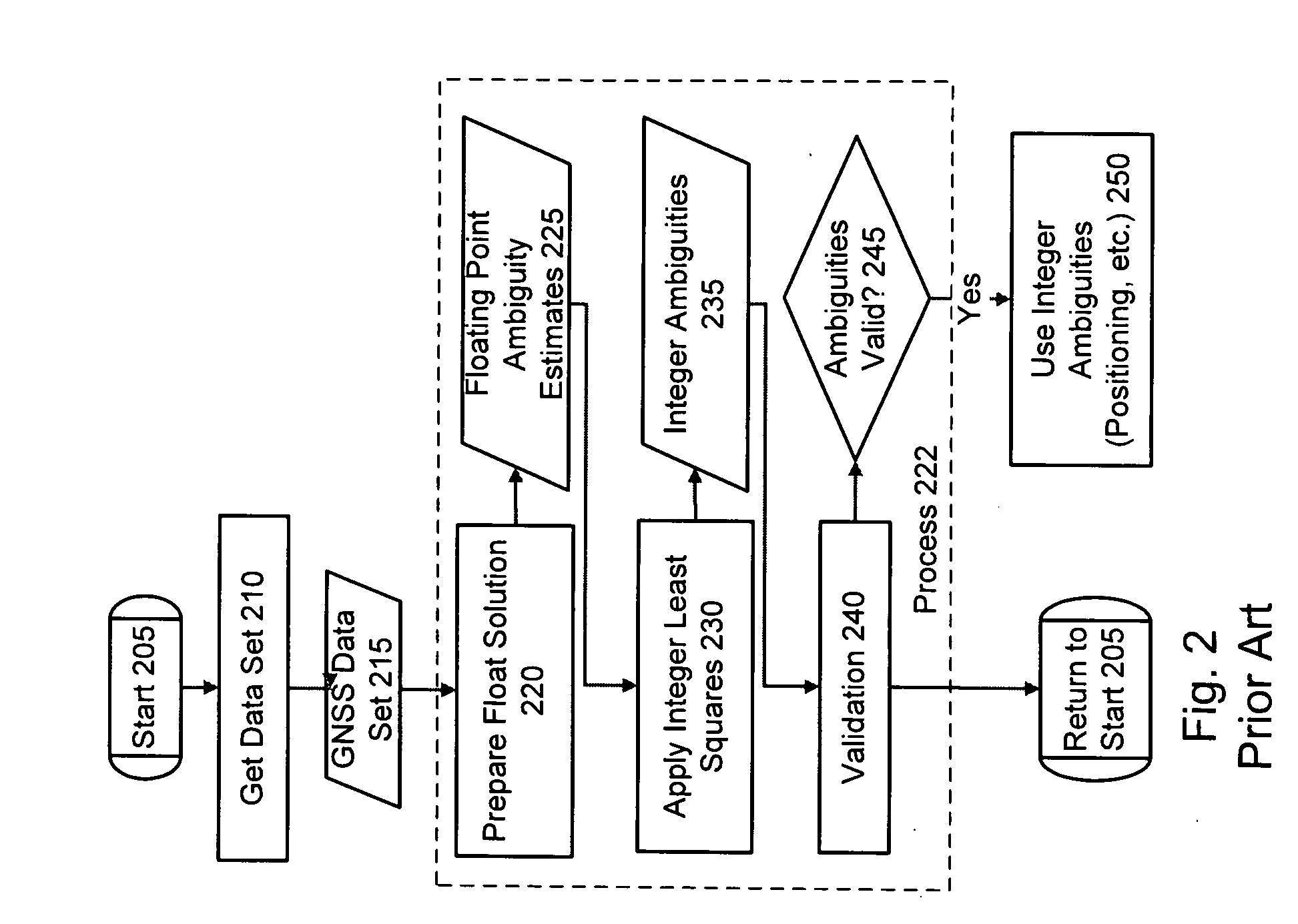
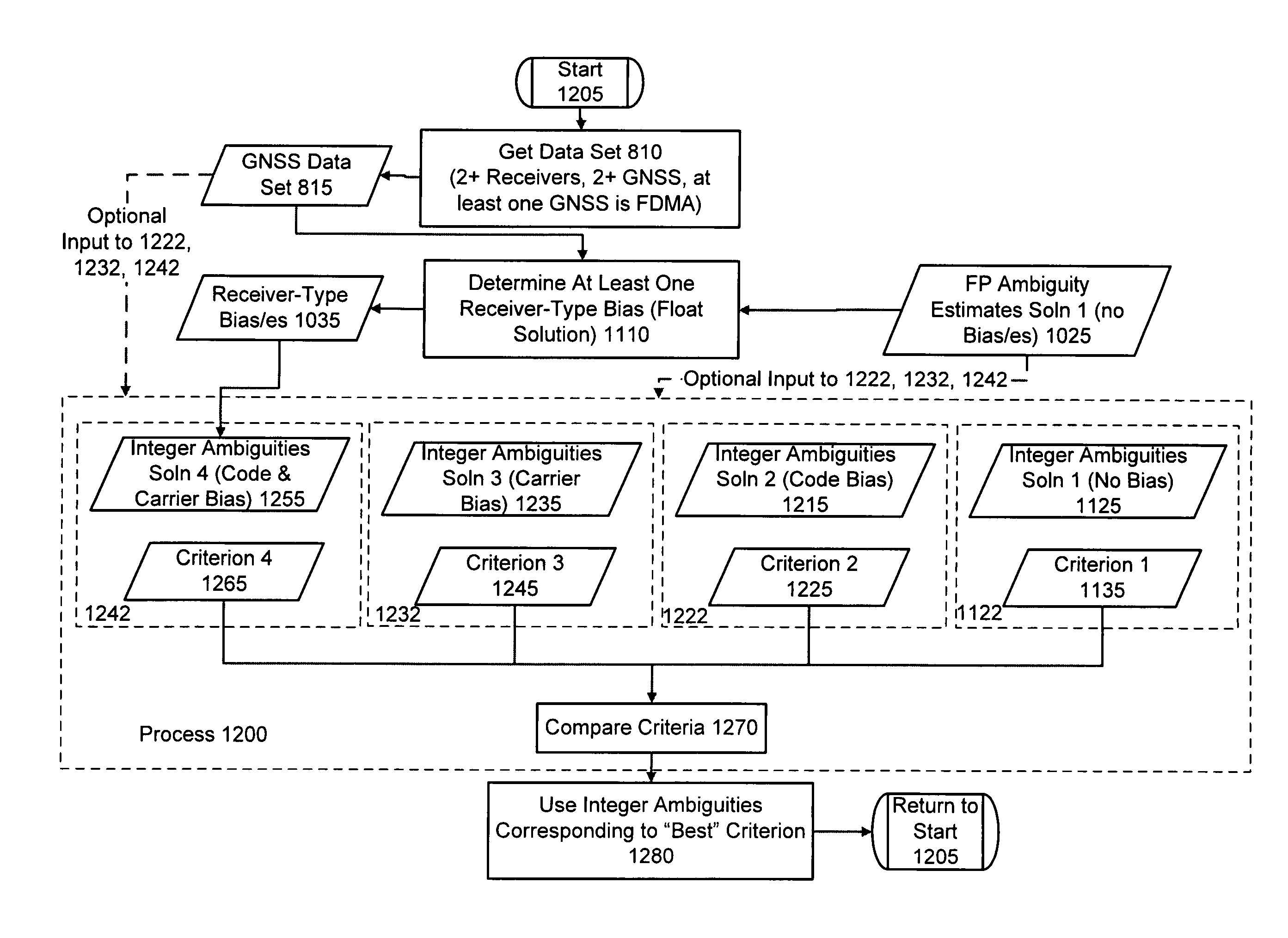
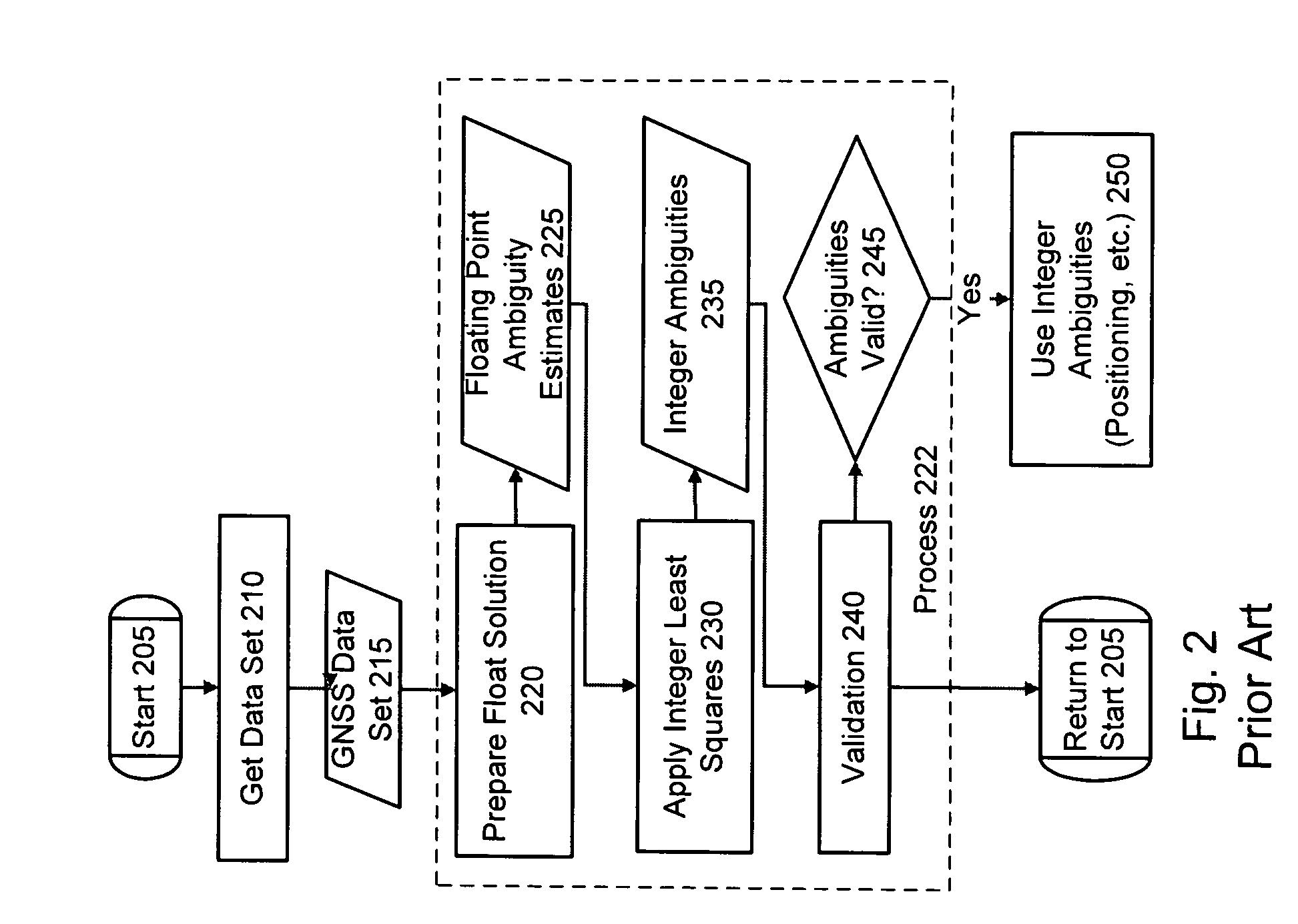
Computer-implemented methods and apparatus are presented for processing data collected by at least two receivers from multiple satellites of multiple GNSS, where at least one GNSS is FDMA. Data sets are obtained which comprise a first data set from a first receiver and a second data set from a second receiver. The first data set comprises a first FDMA data set and the second data set comprises a second FDMA data set. At least one of a code bias and a phase bias may exist between the first FDMA data set and the second FDMA data set. At least one receiver-type bias is determined, to be applied when the data sets are obtained from receivers of different types. The data sets are processed, based on the at least one receiver-type bias, to estimate carrier floating-point ambiguities. Carrier integer ambiguities are determined from the floating-point ambiguities. The scheme enables GLONASS carrier phase ambiguities to be resolved and used in a combined FDMA / CDMA (e.g., GLONASS / GPS) centimeter-level solution. It is applicable to real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning, high-precision post-processing of positions and network RTK positioning.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
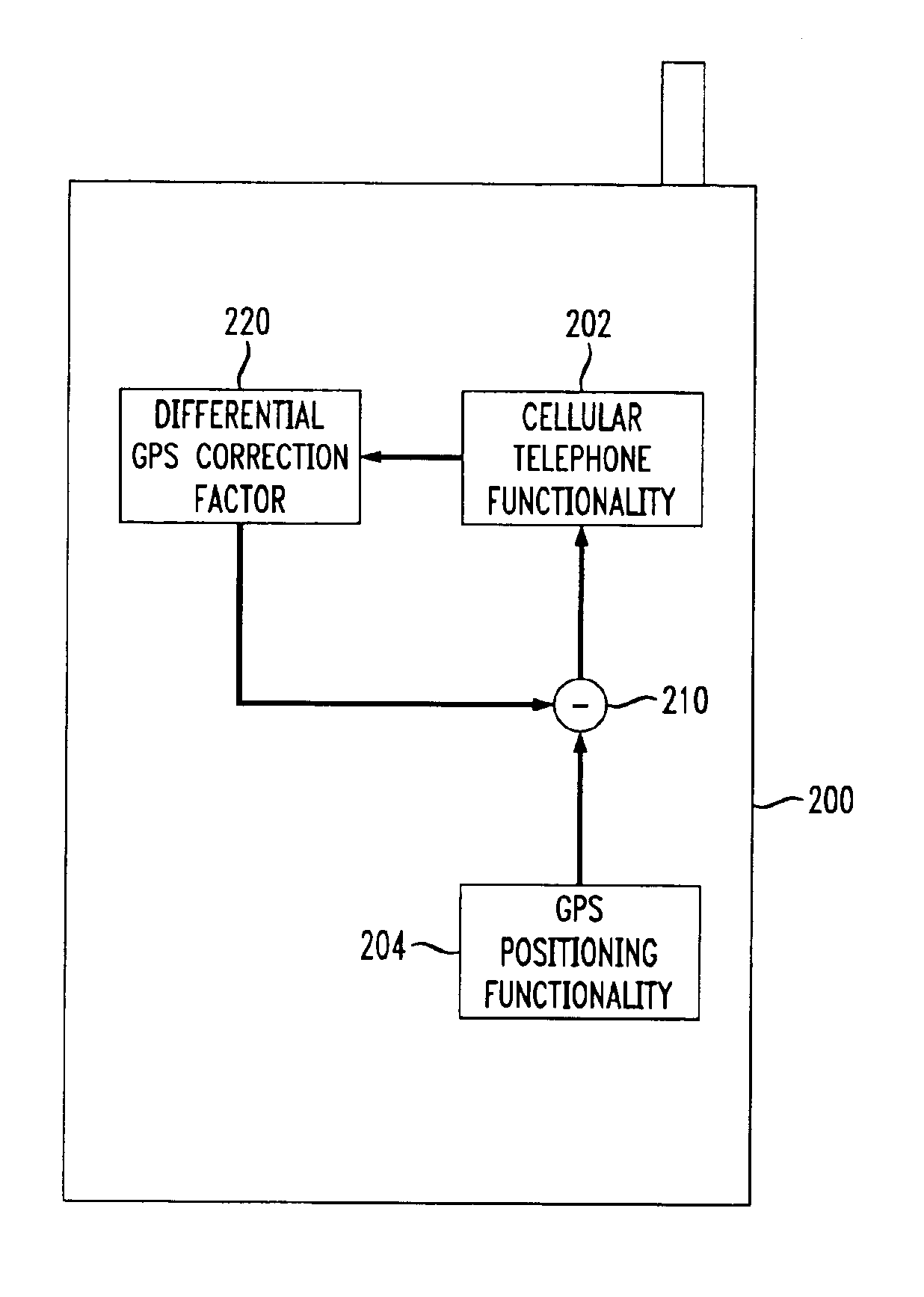
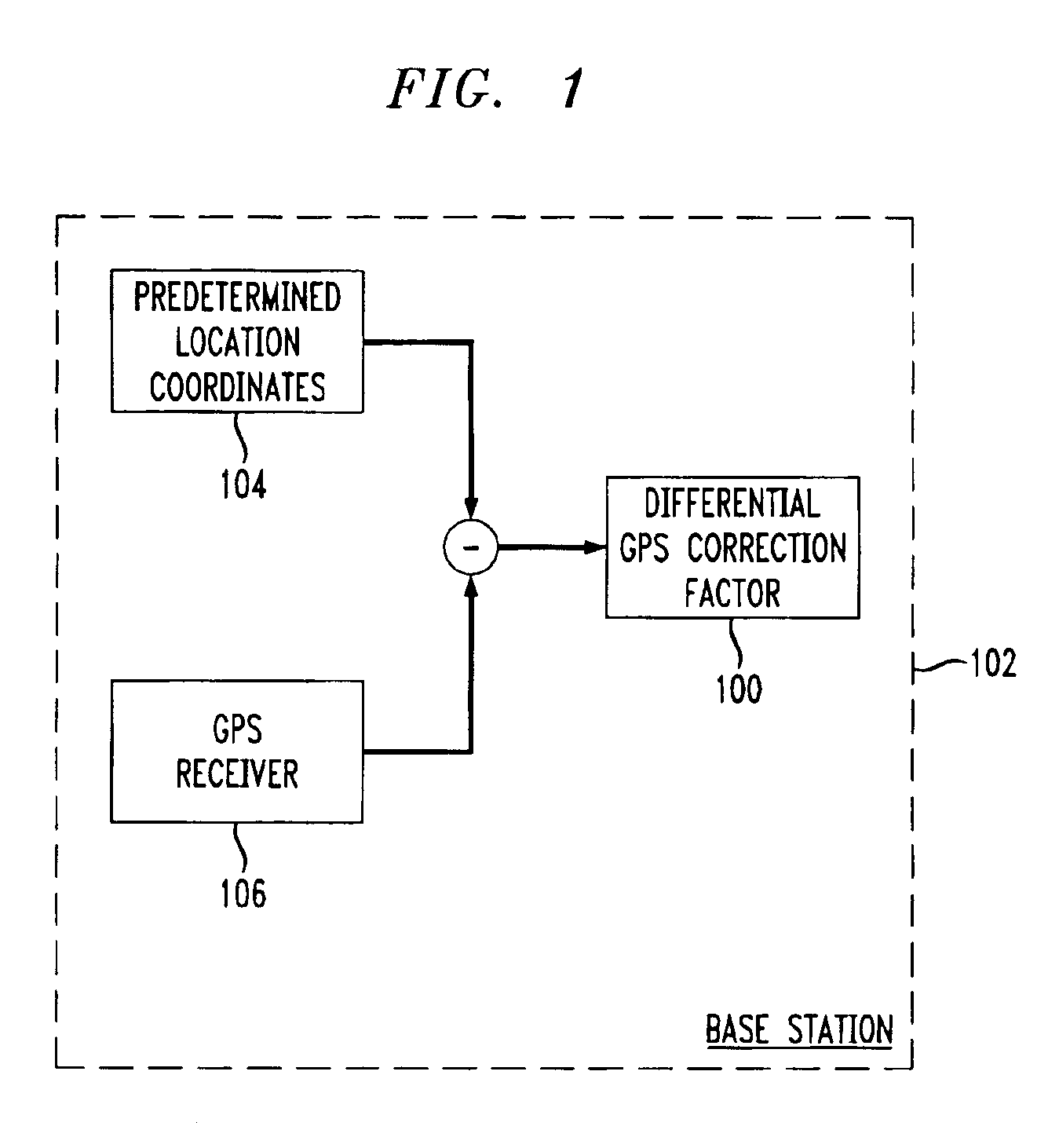
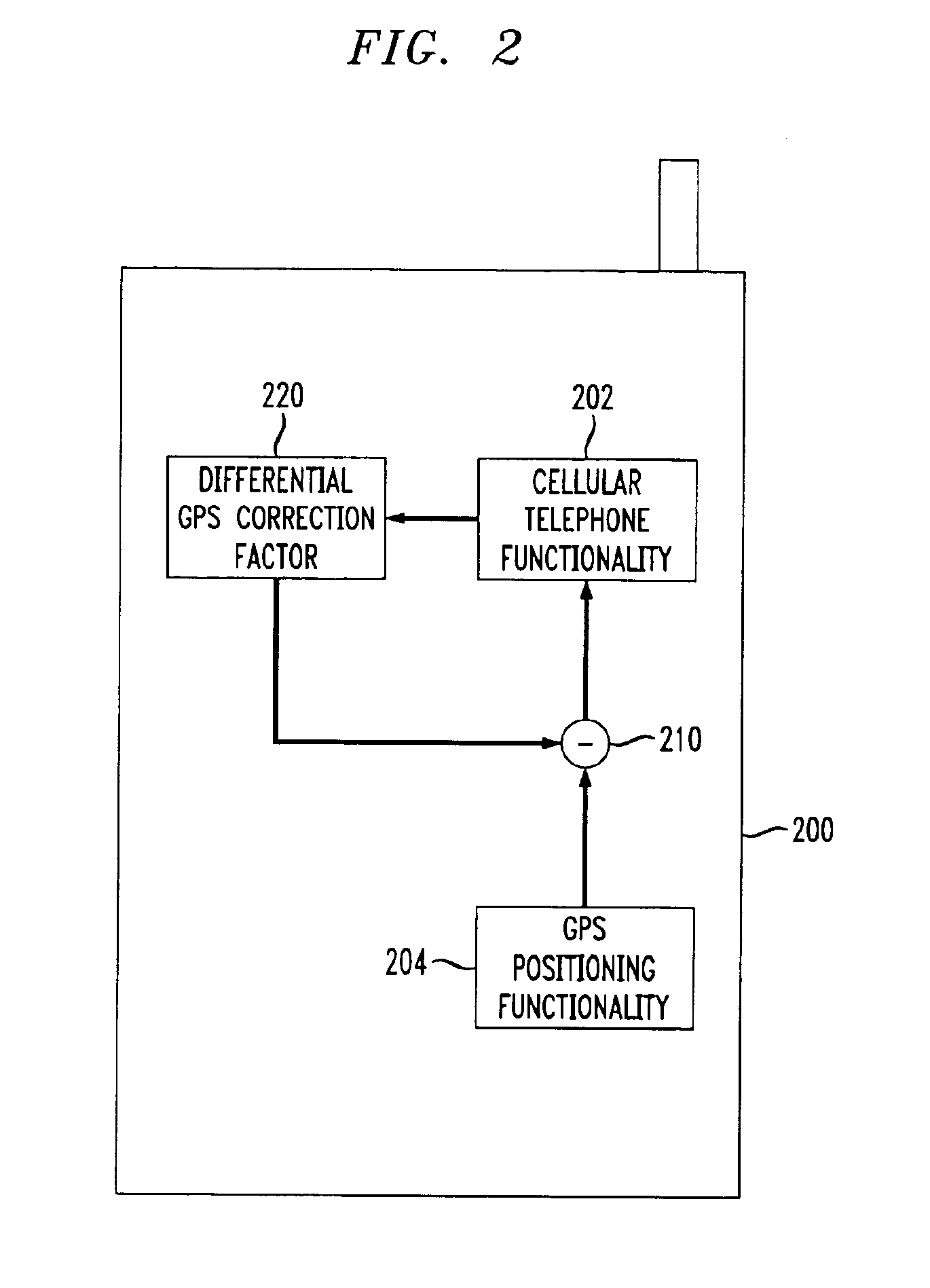
Differential GPS and/or glonass with wireless communications capability
InactiveUS6901260B1Improve reception accuracyHighly accurate location informationTelephonic communicationPosition fixationGps receiverCellular telephone
A differential GPS or GLONASS system (collectively referred to herein as a ‘GPS system’) is implemented for use by a base station of a wireless telephone system (e.g., by a cellular telephone base station). Using the differential GPS system, a differential location ‘correction’ factor is determined based on a difference between a received GPS location signal and a known fixed location of a GPS system receiver for the base station. A differential GPS correction signal containing the correction factor is transmitted to any or all cellular telephone users of that base station to allow the cellular telephones to improve the accuracy of location information independently measured by GPS receivers located in each of the cellular telephones. The differential GPS signal may be used to increase the accuracy of the GPS system, whatever the current accuracy of the GPS system, allowing practical implementation of an emergency telephone system such as a 911 system using a wireless system such as a cellular telephone system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
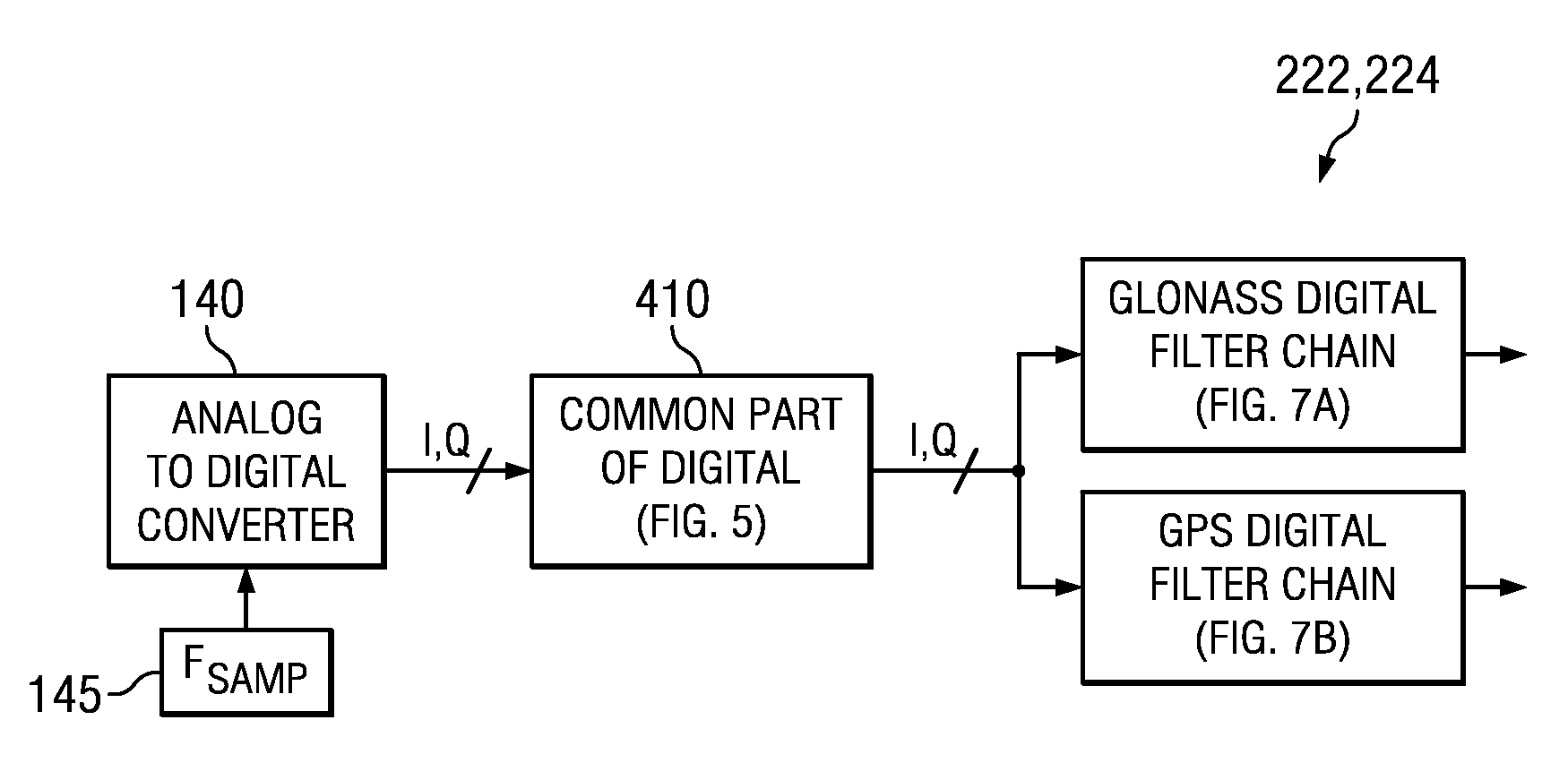
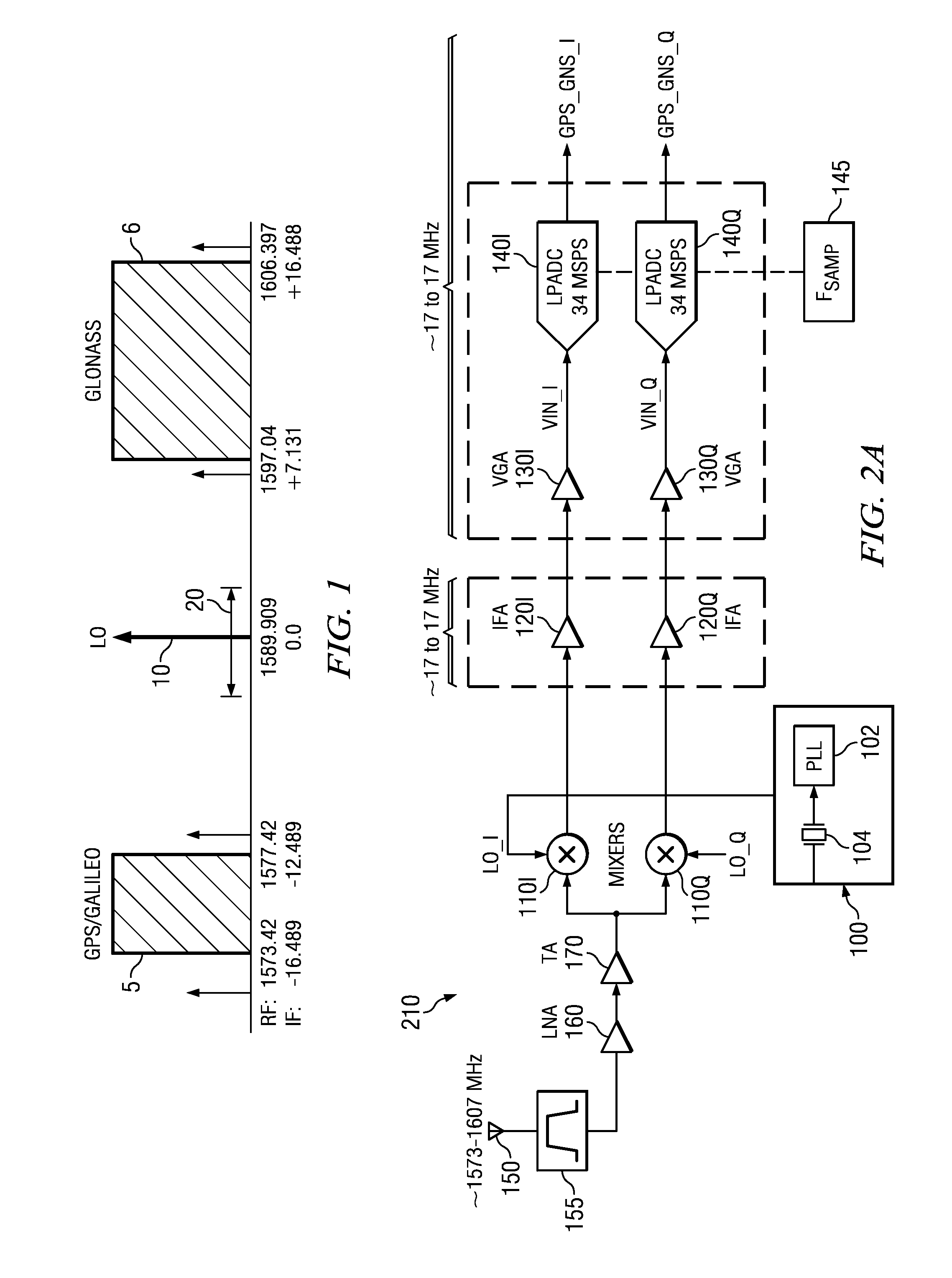
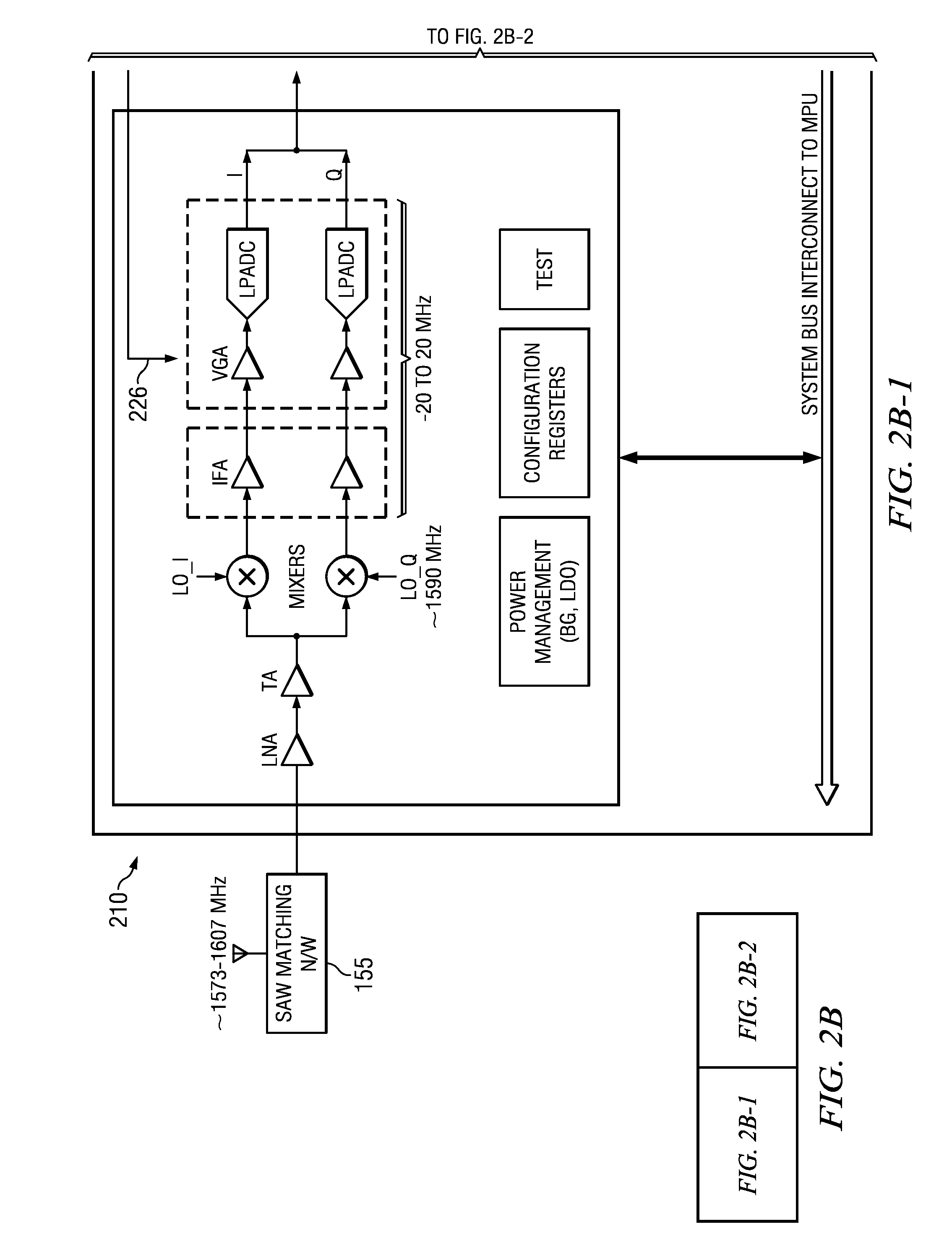
Single RF receiver chain architecture for gps, galileo and glonass navigation systems, and other circuits, systems and processes
ActiveUS20120026039A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingMulti bandIntermediate frequency
A wireless receiver for multiple frequency bands reception includes a single receive radio frequency (RF) circuit (160, 170) having an RF bandpass substantially confined to encompass at least two non-overlapped such frequency bands at RF, a single in-phase and quadrature (approximately I, Q) pair of intermediate frequency (IF) sections (120I, 120Q) having an IF passband, and a mixer circuit (110) including an in-phase and quadrature (I,Q) pair of mixers (110I, 110Q) fed by said RF circuit (160, 170) and having a local oscillator (100) with in-phase and quadrature outputs coupled to said mixers (110I, 110Q) respectively, said mixer circuit (110) operable to inject and substantially overlap the at least two non-overlapped frequency bands with each other into the IQ IF sections (120I, 120Q) in the IF passband, the IF passband substantially confined to a bandwidth encompassing the thereby-overlapped frequency bands. Other receivers, circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
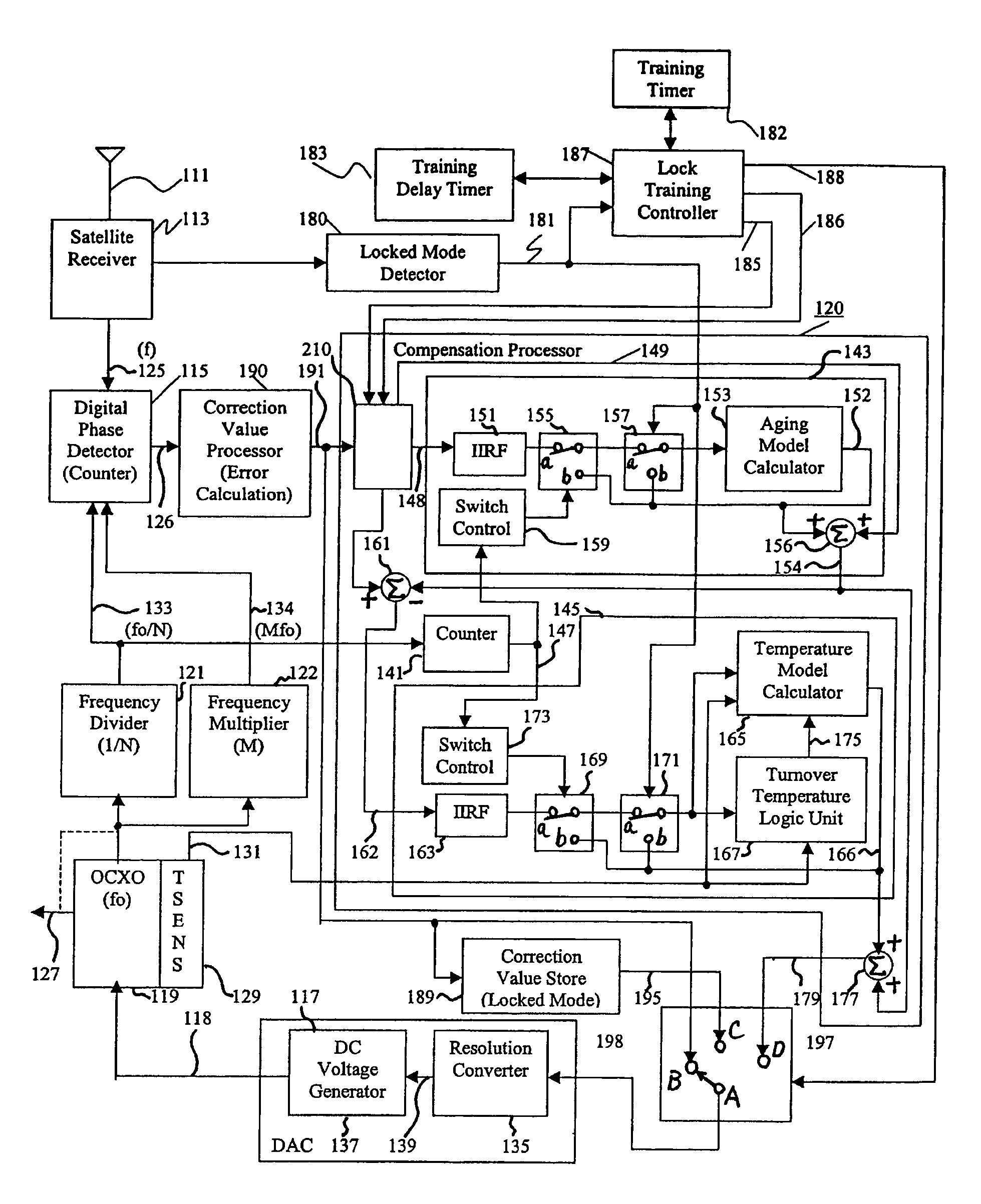
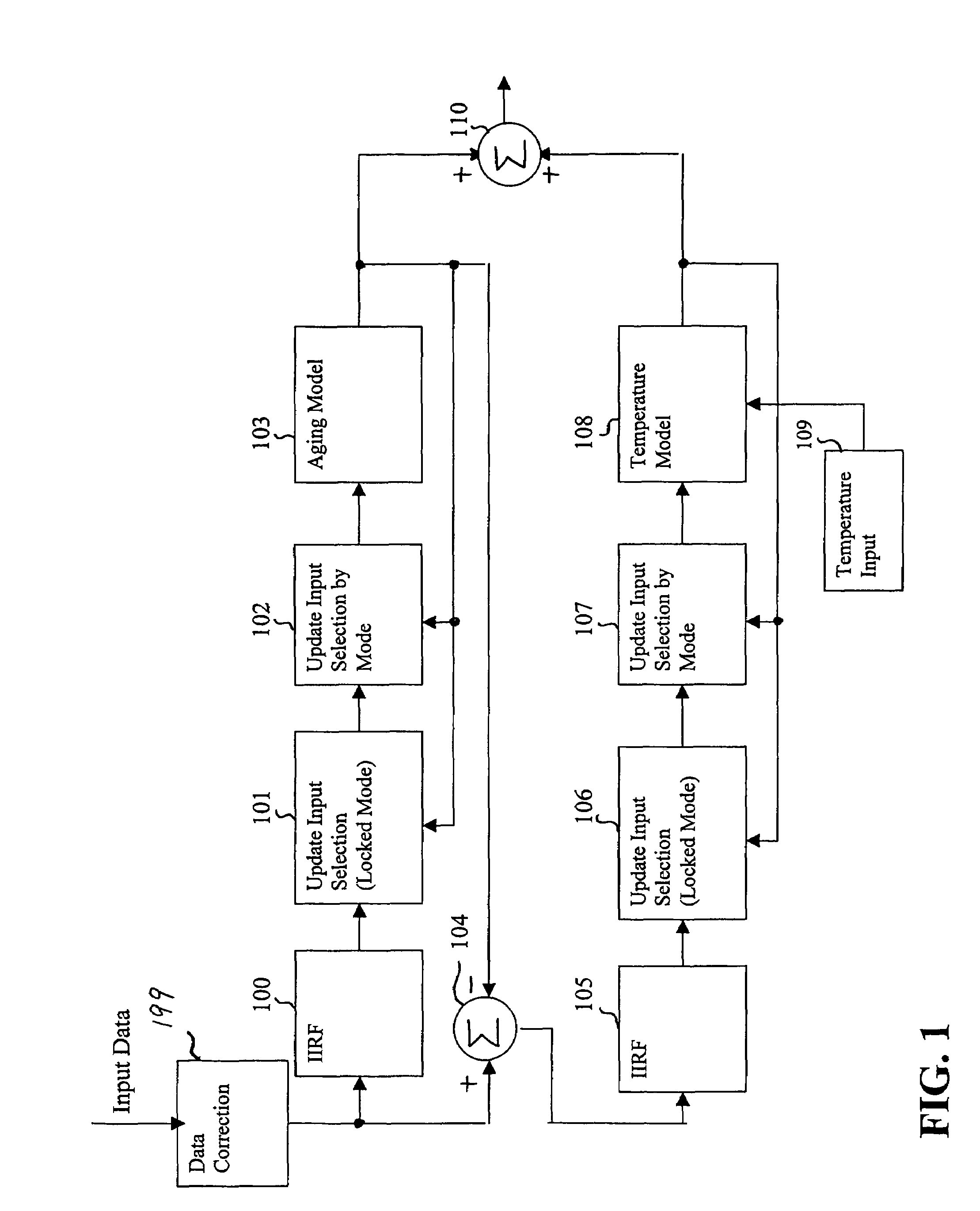
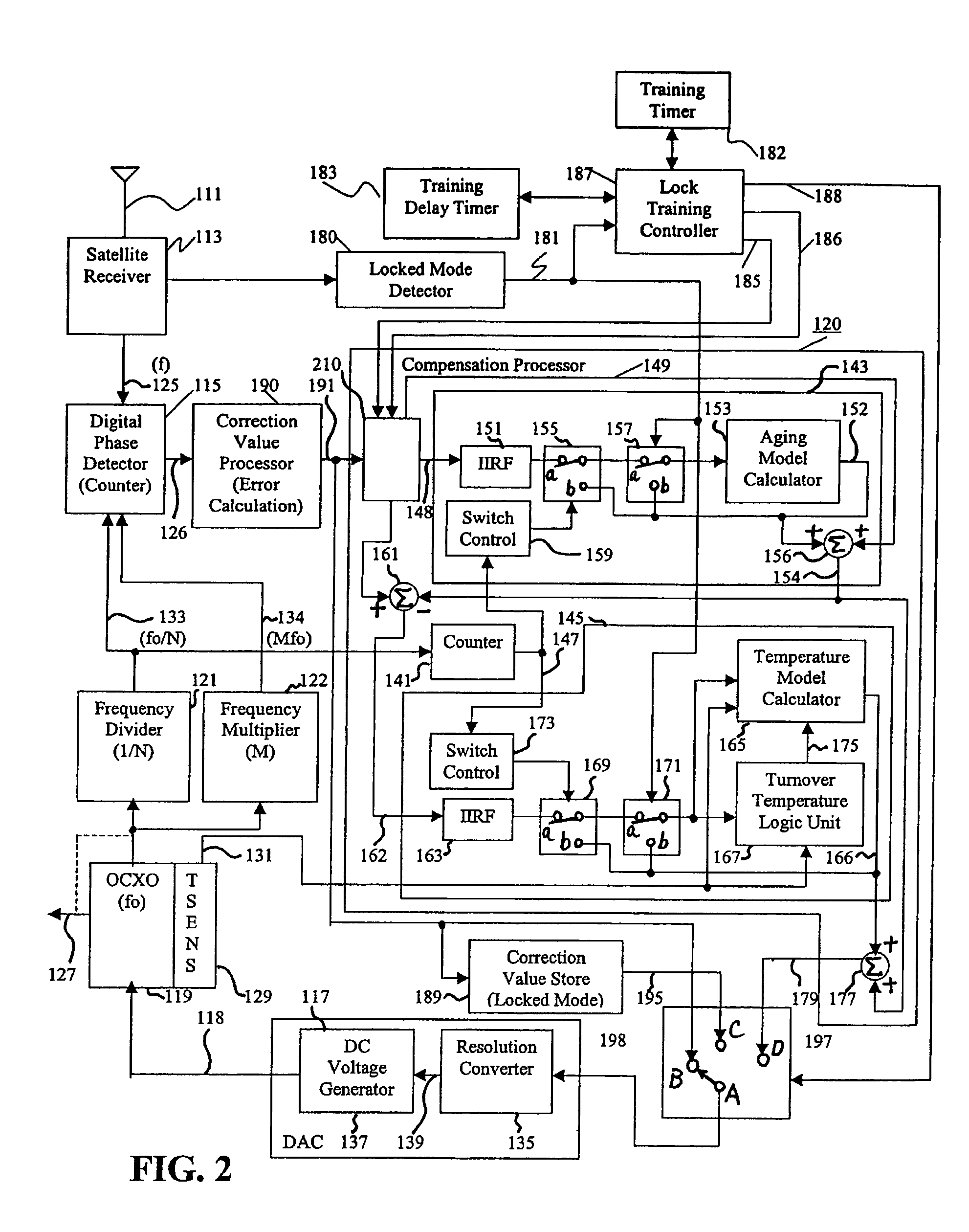
Reference timing signal apparatus and method
ActiveUS7015762B1Increase currentGood compensationRadiation pyrometryPulse automatic controlTraining periodAdaptive filter
A reference timing signal apparatus with a phase-locked loop (PLL) has a computer algorithm which adaptively models the multiple frequencies of an oscillator following a training period. The oscillator is part of a PLL and the oscillation frequency thereof is controlled in response to the phase detector output. The computer algorithm processes the control signal applied to the oscillator. The computer algorithm updates the characteristics of the model relating to the aging and temperature of the oscillator, using for example, a Kalman filter as an adaptive filter, in accordance with a cumulative phase error in the PLL calculated during a given time interval. By the algorithm, the subsequent model predicts the future frequency state of the oscillator on which it was trained. The predicted frequency of the model functions as a reference to correct the frequency of the oscillator in the event that no input reference timing signal is available. Also, the calculated phase error is stored and is used while no input reference timing signal or accurate predicted frequency value is available. With the model updating algorithm, oscillators of low stability performance may be used as cellular base station reference oscillator, which is based on satellite systems, for example, GPS, GLONASS or Galileo systems.
Owner:APPLE INC
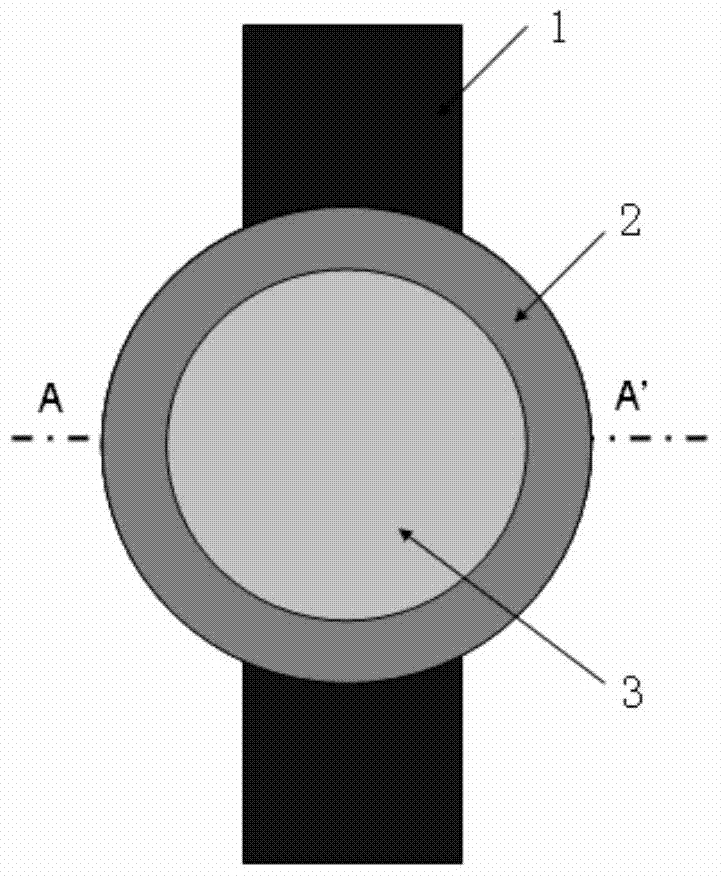
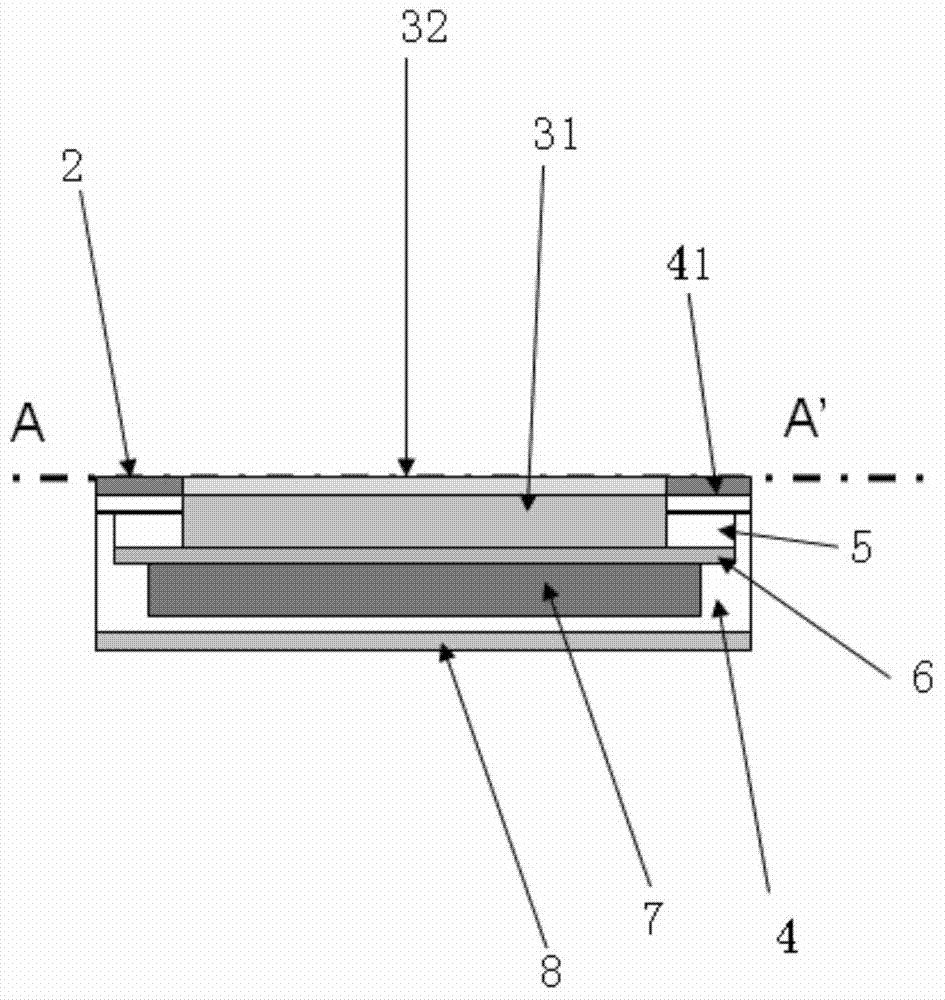
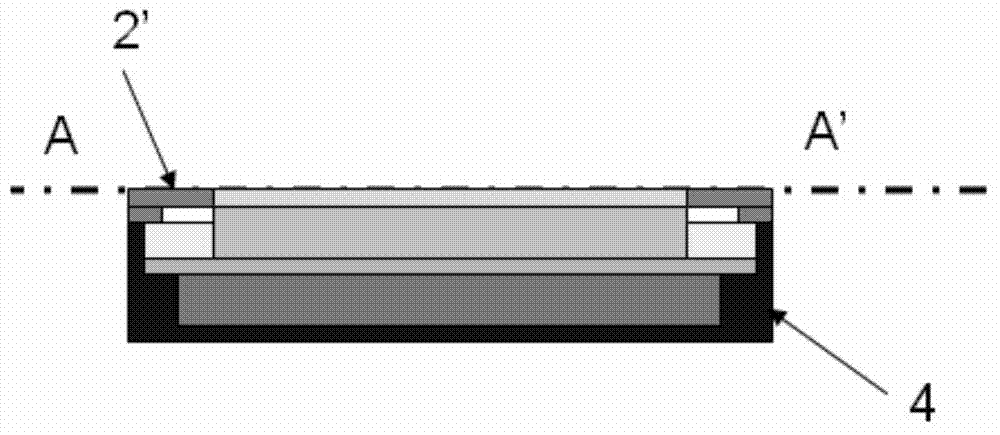
Watch antenna and watch with watch antenna
ActiveCN103943945AExcellent GPSExcellent GlonassAntenna arraysAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesEngineeringAntenna radiation
Disclosed are a watch antenna and a watch with the watch antenna. The invention discloses a watch antenna which can be used for communication of GPS / Glonass and BT / WiFi / WLAN. The watch antenna includes antenna parts arranged in the watch. A metal ring / frame is arranged above the antenna parts of the watch. The antenna parts are electrically coupled with the metal ring / frame. The metal ring / frame is used as a main antenna radiation body and arranged at the periphery of the watch. The invention also discloses the watch which uses the antenna. The watch antenna uses the electrically coupled (feed) antenna structure and the metal ring / frame which is electrically coupled with the antenna parts is arranged above the antenna parts in the watch and the metal ring / frame is used as the antenna radiation body so that the antenna achieves an excellent performance in communication of the GPS / Glonass and the BT / WiFi / WLAN.
Owner:SHANGHAI AMPHENOL AIRWAVE COMM ELECTRONICS CO LTD
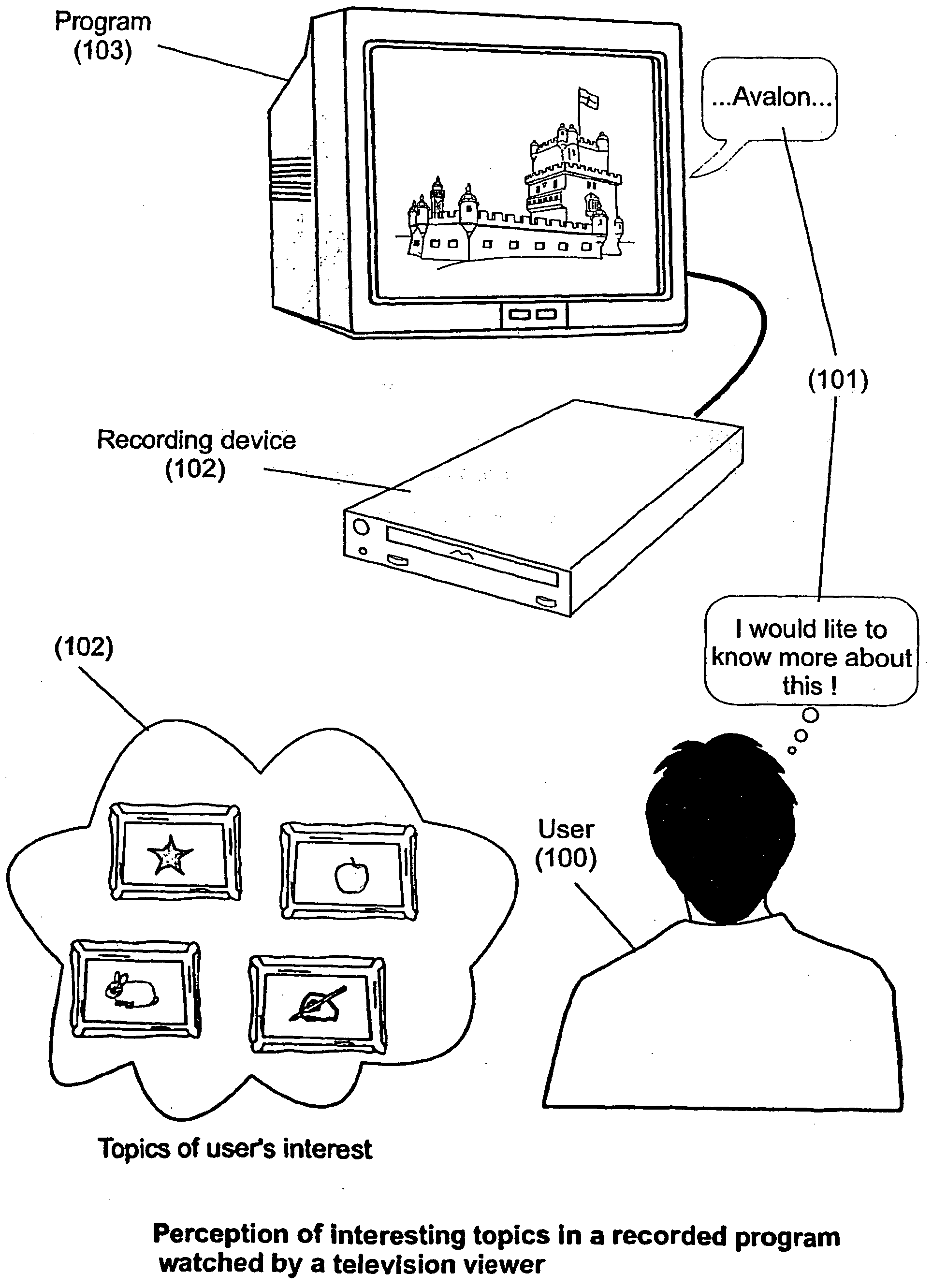
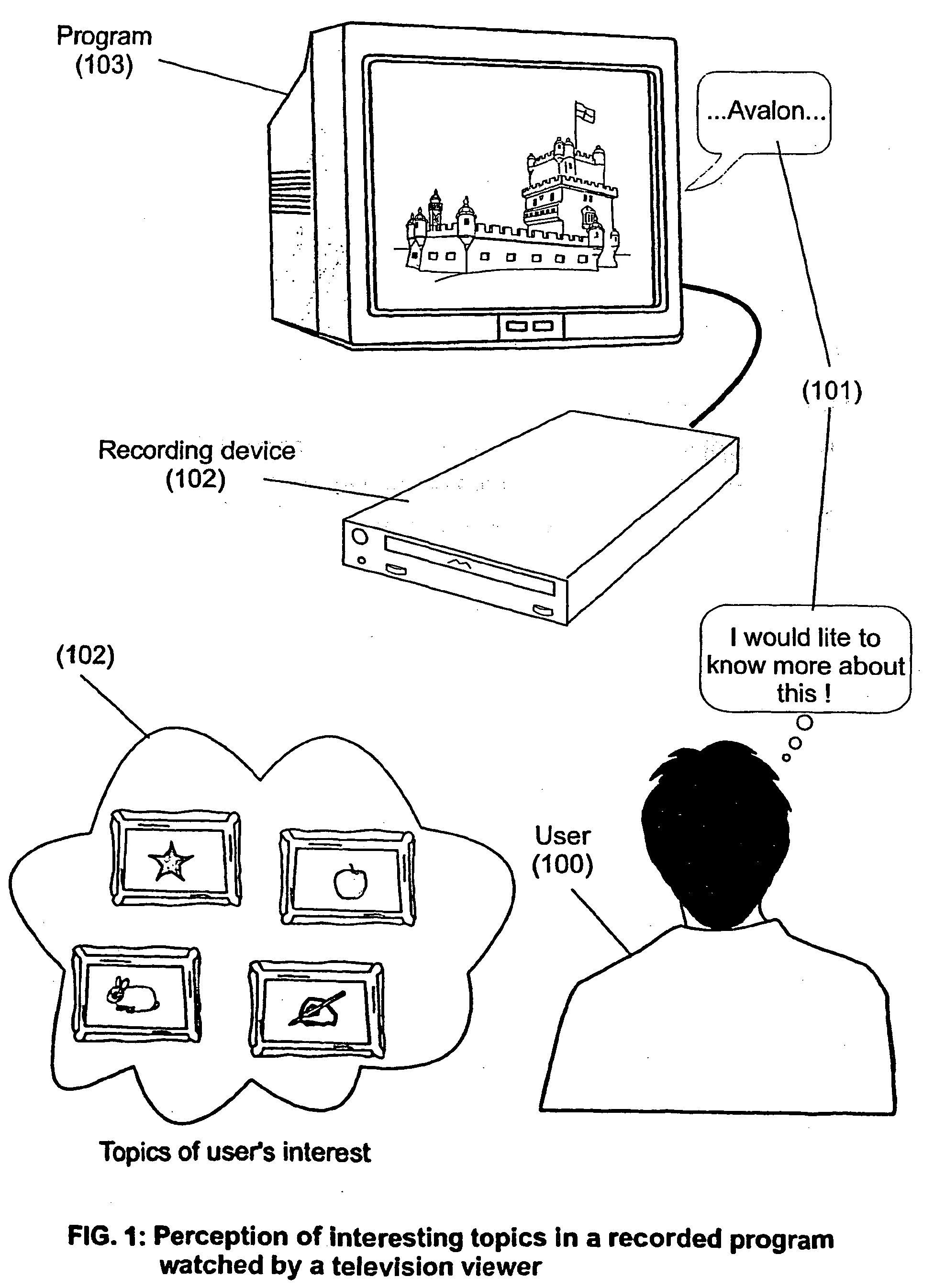
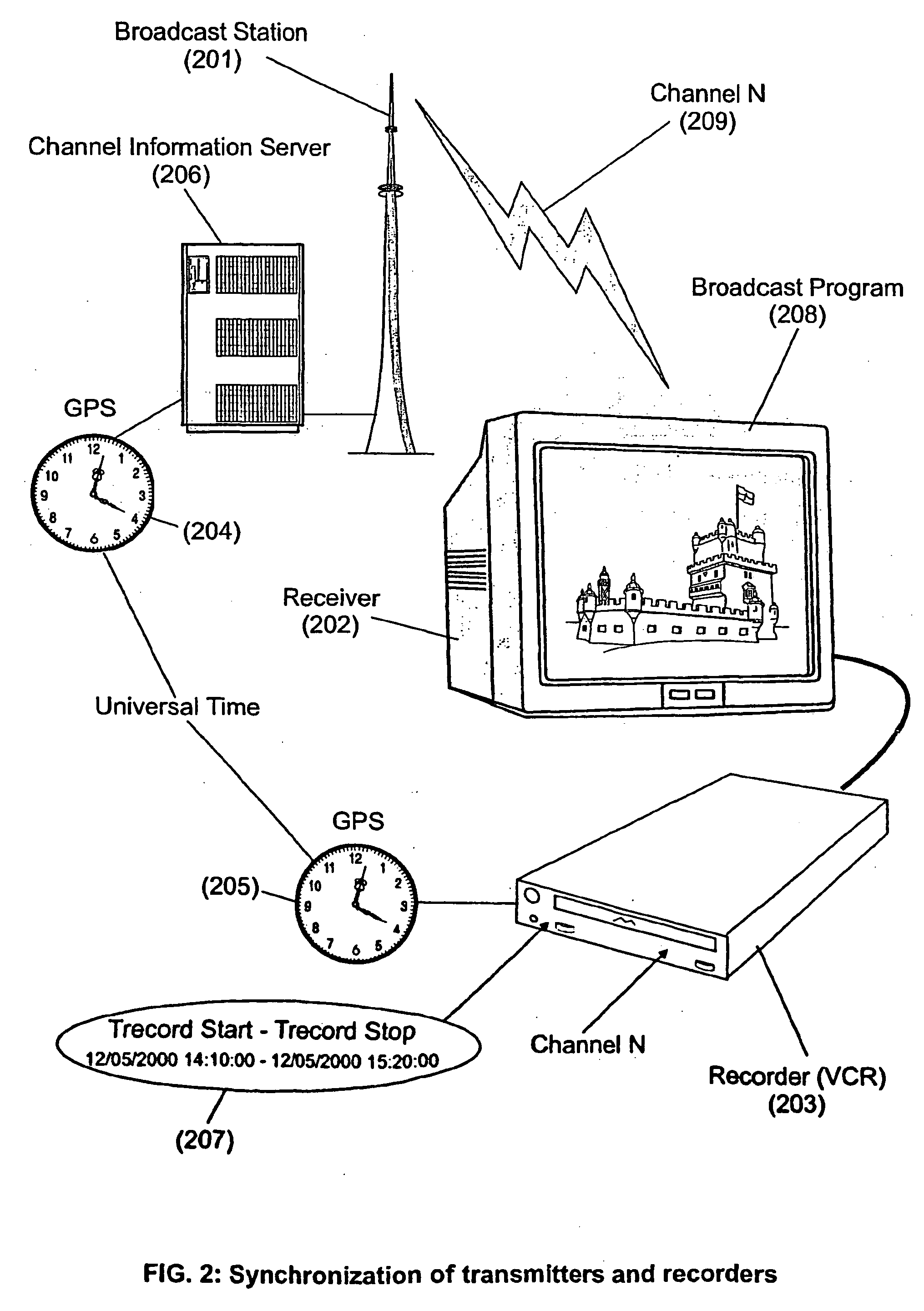
System and method for enhancing recorded radio or television programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS20040133919A1Enhanced informationEasy access to informationTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionHyperlinkBroadcasting
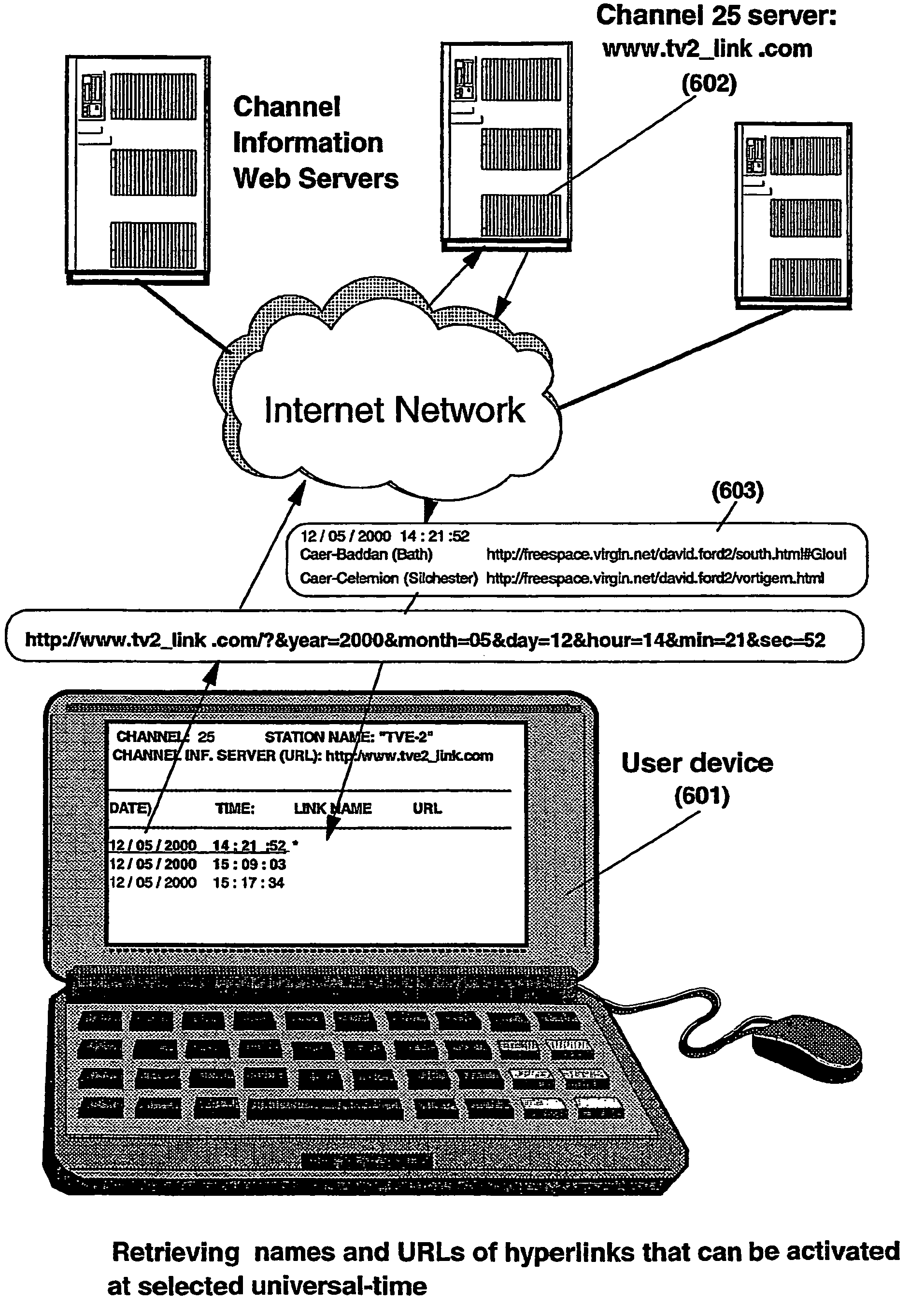
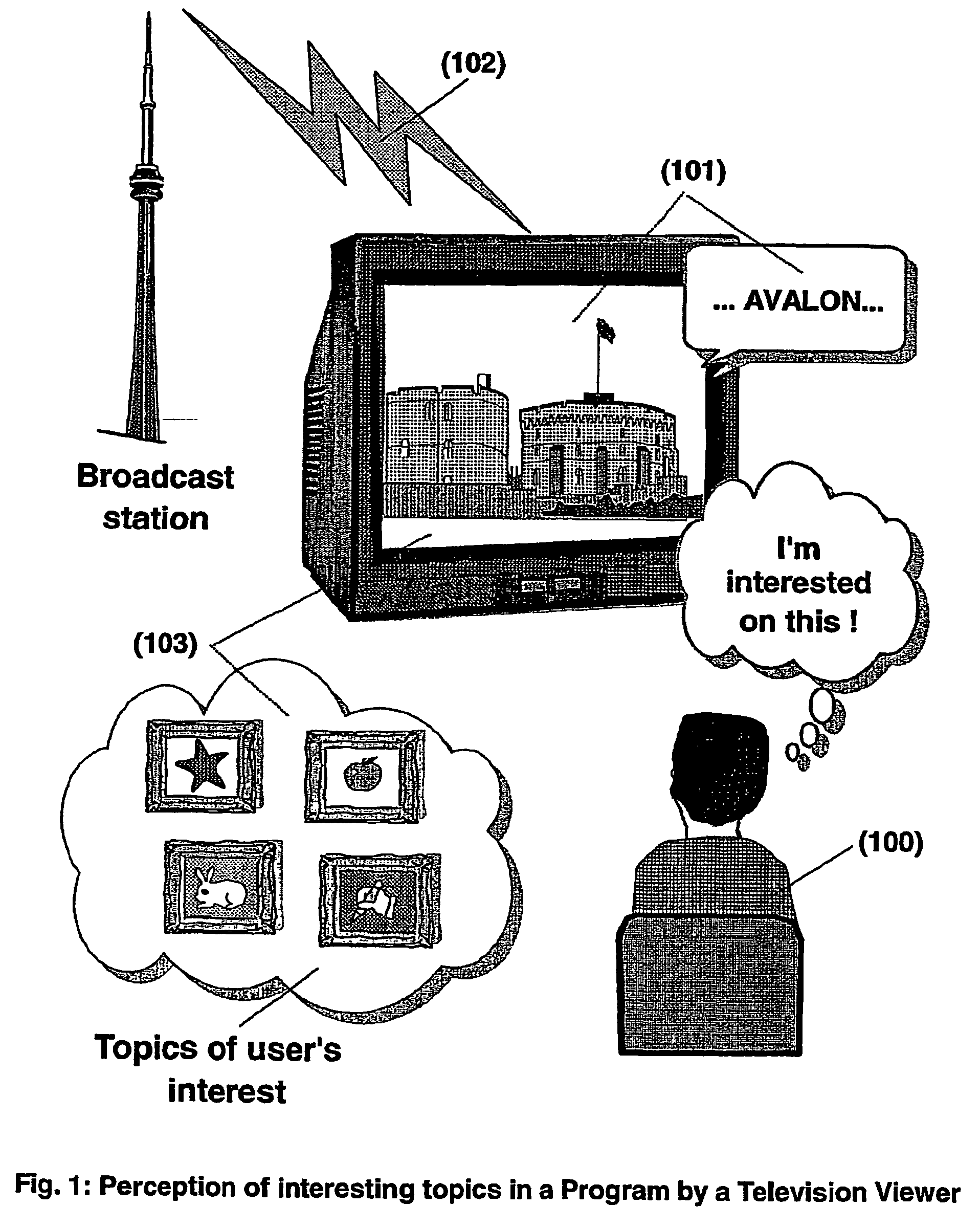
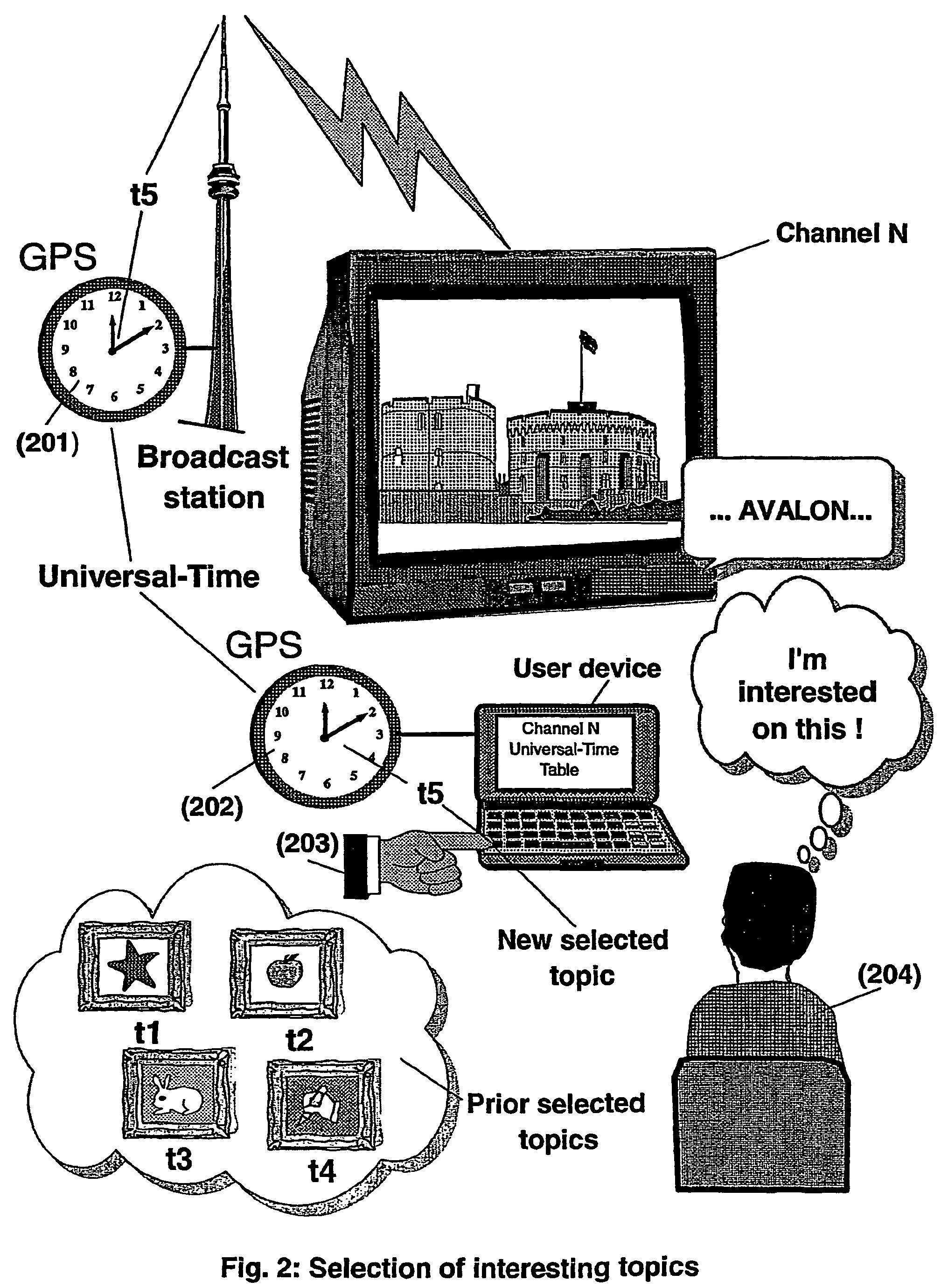
The present invention is directed to a system, method and computer program for enabling a user (100) (an auditor or a viewer) to access complementary information related to one or a plurality of sequences or topics of interest (102) in a recorded program (103) previously broadcast on the radio or television and played back on a device, such as an audio or video tape or disk recorder / player (104). The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) listening to or watching a recorded program (103), to select one or a plurality of topics (101) (102) drawing his or her attention and for immediately receiving further information related to these topics from the World Wide Web. The system is based on the synchronization of local times (204) (205) of transmitters (201) and recorders (203). The flow of information transmitted, received and recorded is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of recorders and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an absolute or universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are integrated or connected to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to the audio or video recorders. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined during the production and recording of the broadcast program, for given sequences corresponding to particular intervals of time synchronized with the universal (absolute) time. The hyperlinks are associated wit the information that is broadcast in the program. They can be selected by users during the playback of the recorded program during predefined intervals of time and activated to access additional information and services.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
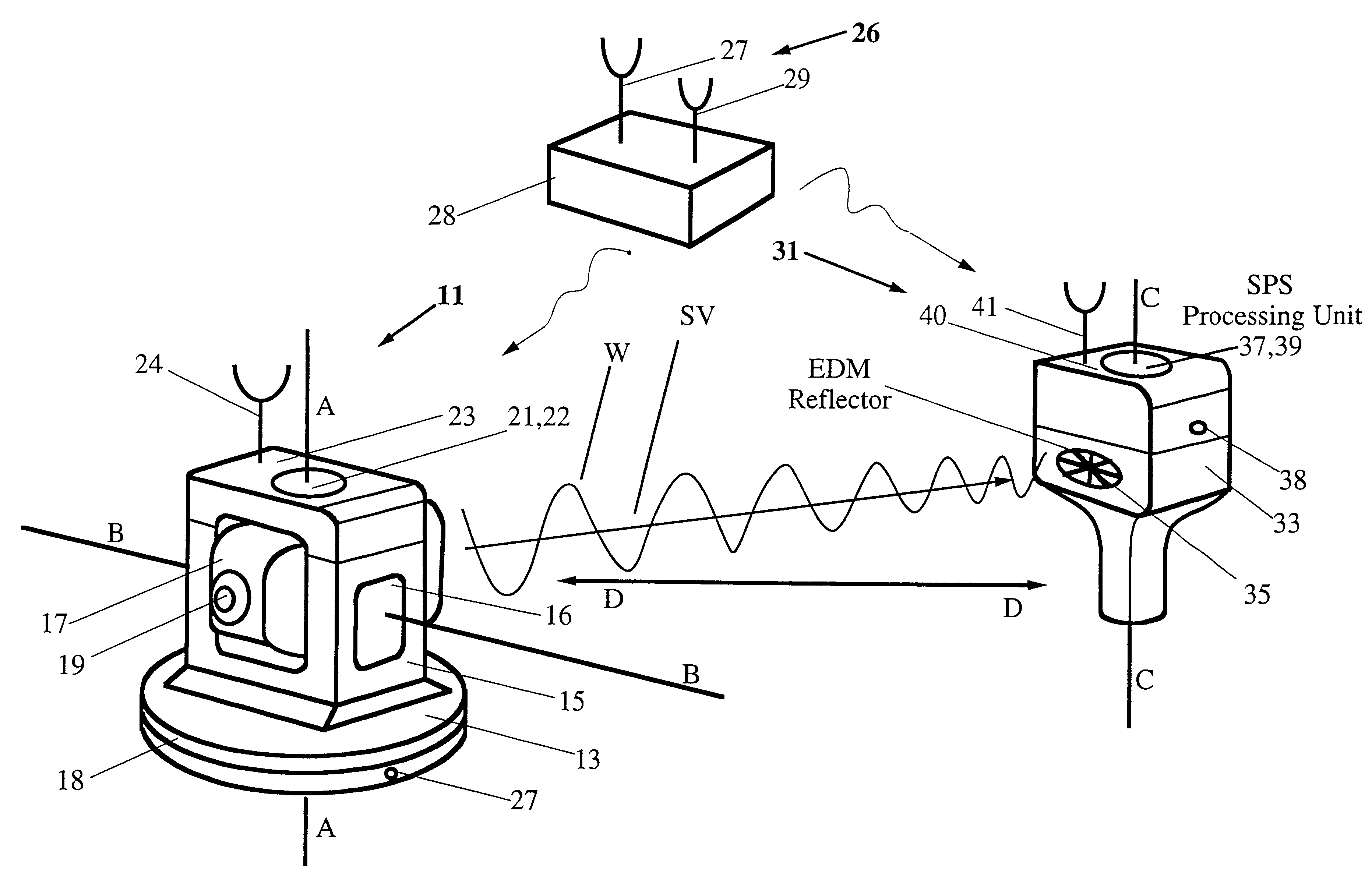
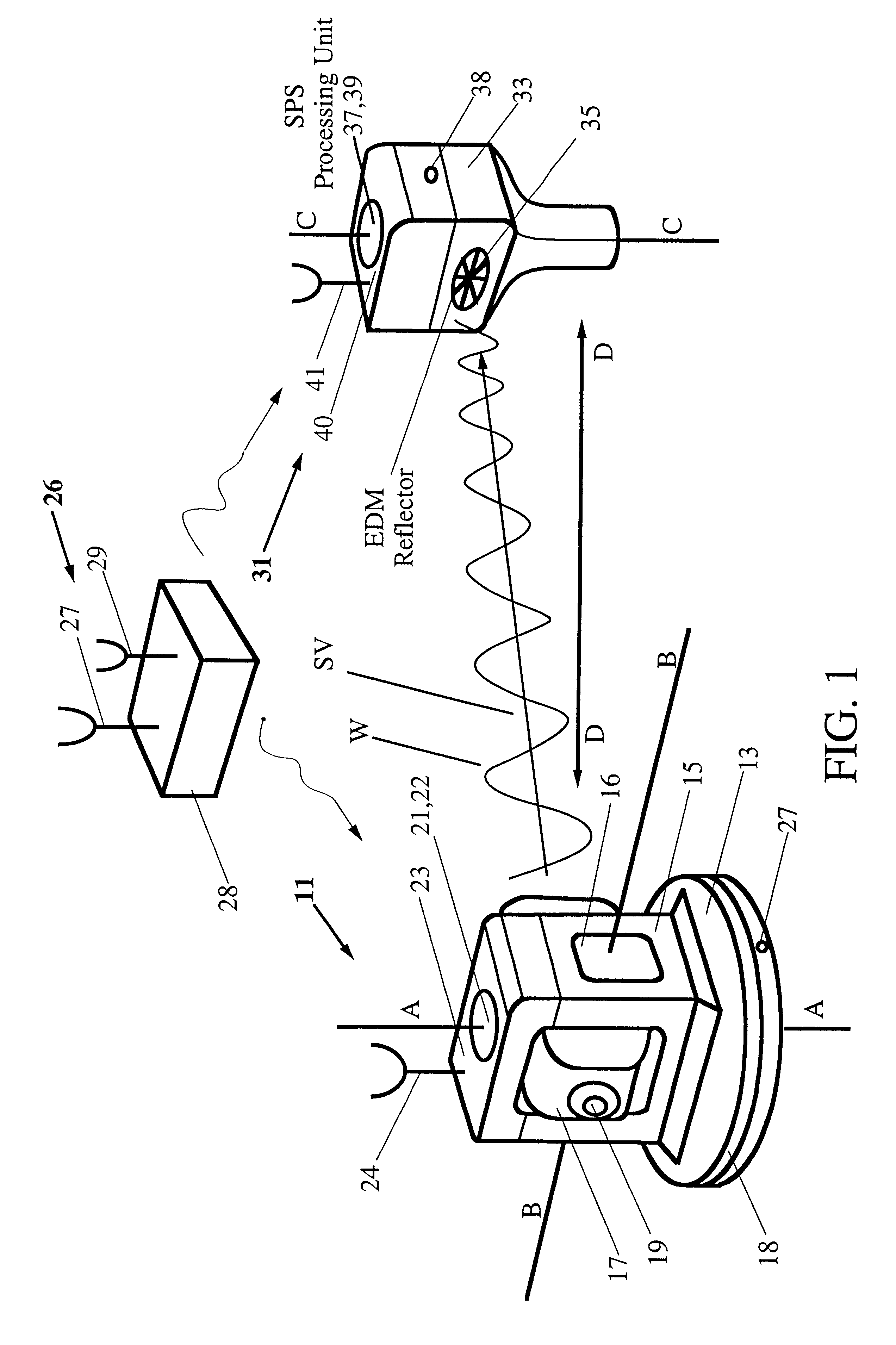
Integrated SATPS total survey station
Apparatus for measuring surveying parameters, such as distances and angular displacements between an instrument survey station and a mobile survey station, with improved accuracy. The invention combines a differential satellite positioning system (DSATPS), available with positioning systems such as GPS and GLONASS, with electromagnetic measurements of distances and optically encoded angles by a conventional electro-optical survey instrument to provide survey measurements that can be accurate to within a few millimeters in favorable situations. The DSATPS relies upon pseudorange measurements or upon carrier phase measurements, after removal of certain phase integer ambiguities associated with carrier phase SATPS signals. The SATPS may be retrofitted within the housing of the conventional electro-optical instrument. In a first approach, a remote station provides DSATPS corrections for the mobile station and / or for the instrument station. In a second approach, the mobile station provides DSATPS corrections for itself and for the instrument station. In a third approach, the instrument station provides DSATPS corrections for itself and for the mobile station.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
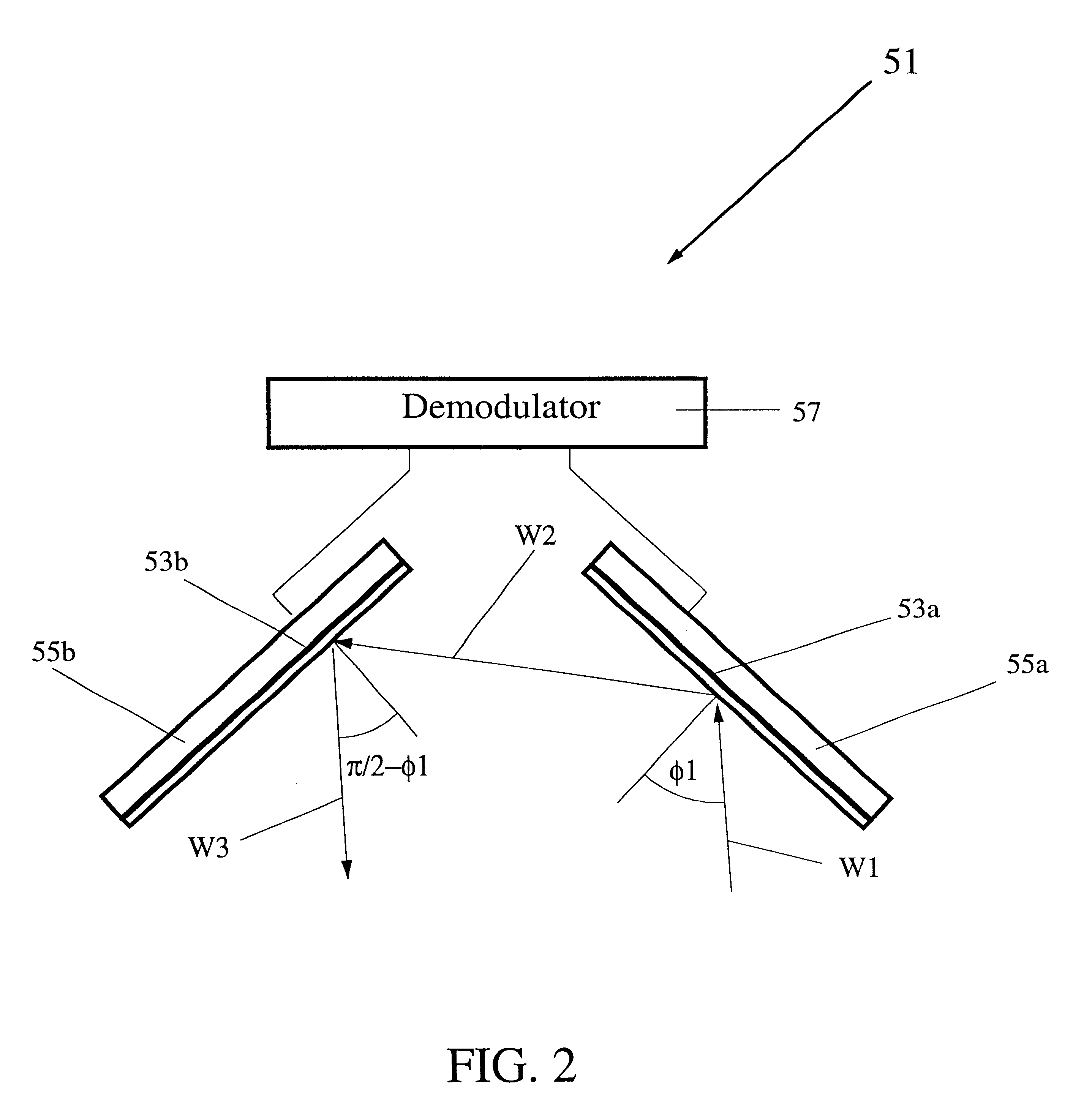
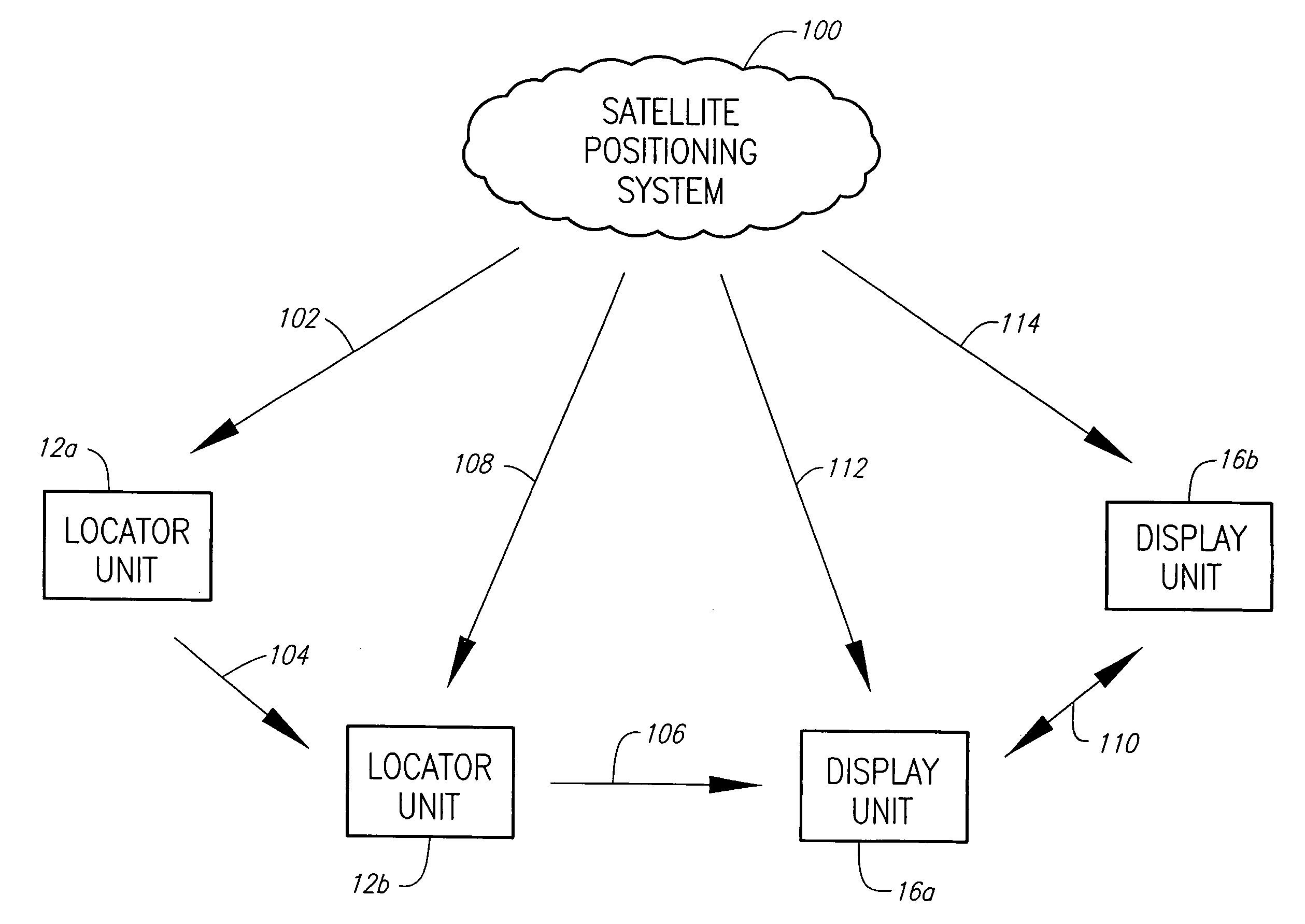
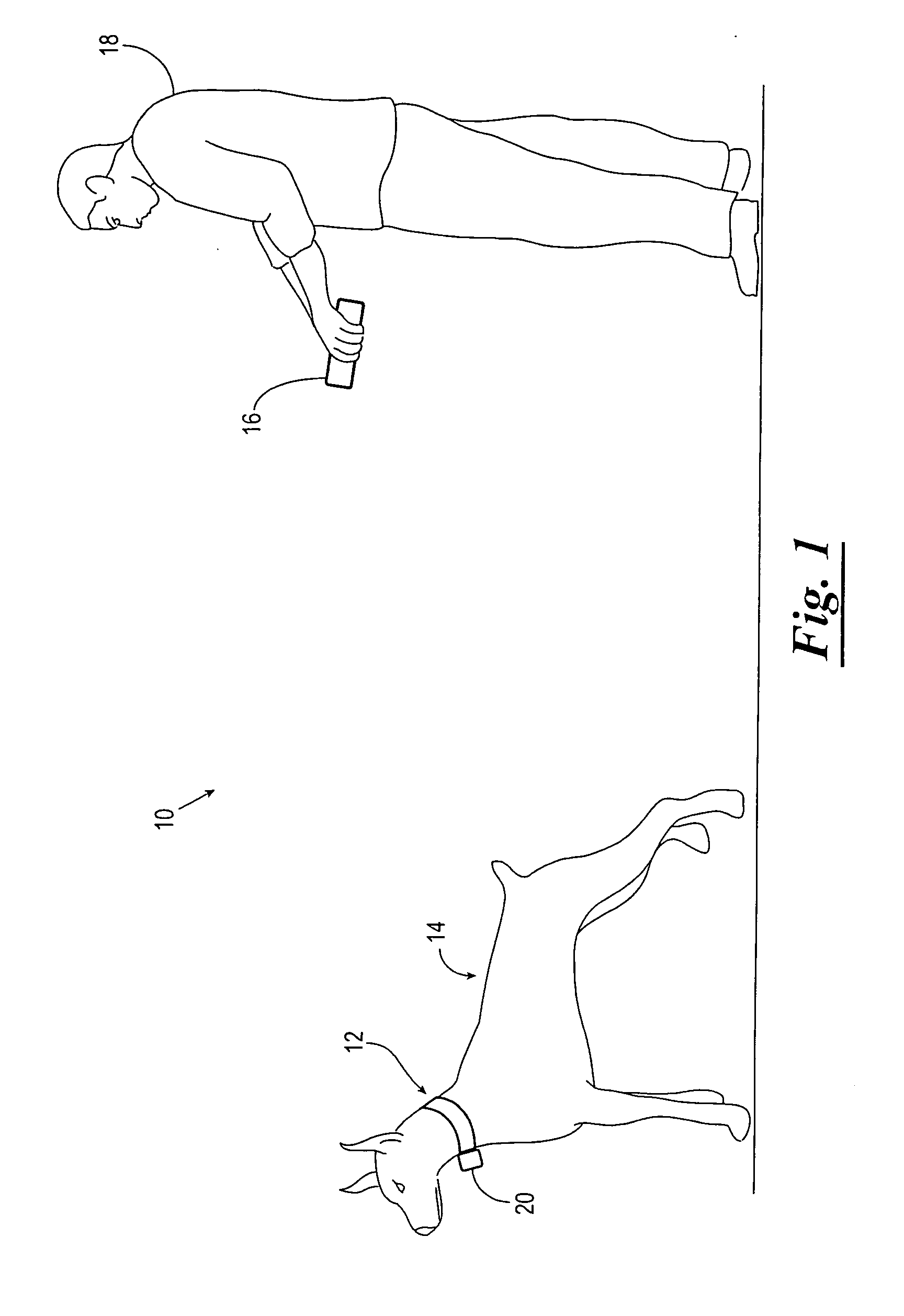
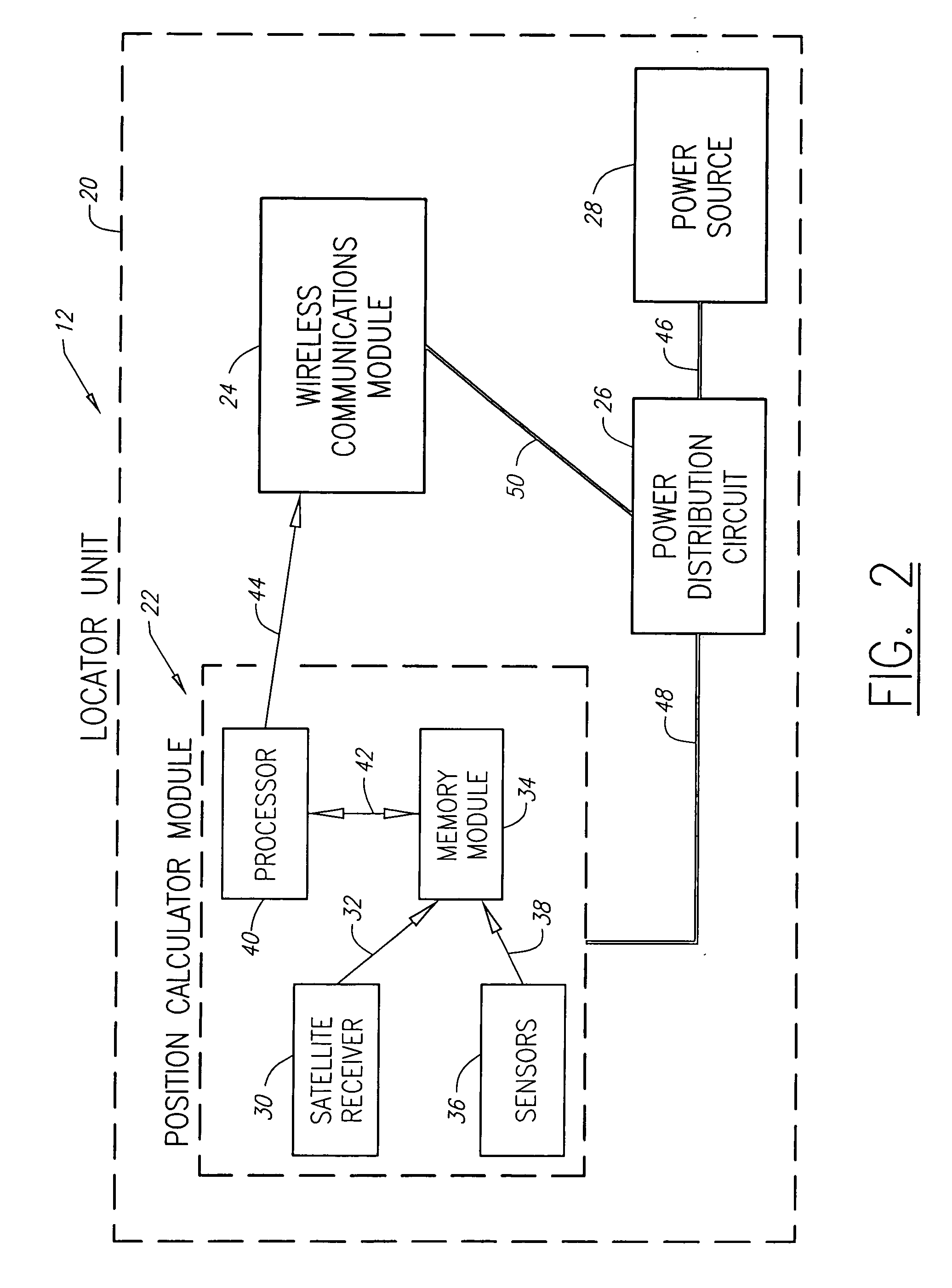
Object identity and location tracking system
A system and method for tracking the identity and position of an object. The system includes at least one locator unit that is attached to the object to be tracked. The system also includes at least one display unit carried by or with a user. The locator unit obtains its satellite position data from a satellite positioning system such as GPS, GLONASS, LORAN, GALILEO, or the like. The locator unit then measures local position data with one or more sensors such as accelerometers and compasses and augments the satellite position data with the local position data. The locator unit transmits the augmented position data to a display unit. The display unit calculates its own position in the same way and outputs the augmented position of the locator unit relative to the augmented position of the display unit via a user interface.
Owner:PINPOINT PRODIONS L L C AN OKLAHOMA LIMITED LIABILITY
Multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device
ActiveCN103117767AEasy to changeEasy to adjustSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionLow noiseSignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device. The device comprises a low-noise amplifier, a power divider, and multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits, wherein the low-noise amplifier, the power divider, and the multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits are connected in sequence. Each radio-frequency signal processing circuit comprises a first radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency filter bank, a second radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency amplifying module, a lower frequency mixing module, an intermediate frequency filter module, an intermediate frequency amplifying module, and an automatic gain control unit, wherein the first radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency filter bank, the second radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency amplifying module, the lower frequency mixing device, the intermediate frequency filter module, the intermediate frequency amplifying module, and the automatic gain control unit are connected in sequence. The lower frequency mixing module comprises a lower frequency mixing device and a local oscillating generating module which are connected with each other. A control unit is connected with the first radio-frequency switch and the second radio-frequency switch of each radio-frequency signal processing circuit and the local oscillating generating module of the lower frequency mixing module. The device can flexibly select intermediate frequency inputting from various combination frequency ranges of a quad-mode 11 frequency range, and therefore functions of collecting in the same module and processing navigation system intermediate frequency signals of four system satellites are realized, namely a global position system (GPS), Glonass, Galileo, and Big Dipper.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Navigational satellite signal receiving module and information processing method applied to same
InactiveCN101950027AReduce processingSave occupancySatellite radio beaconingInformation processingBeiDou Navigation Satellite System
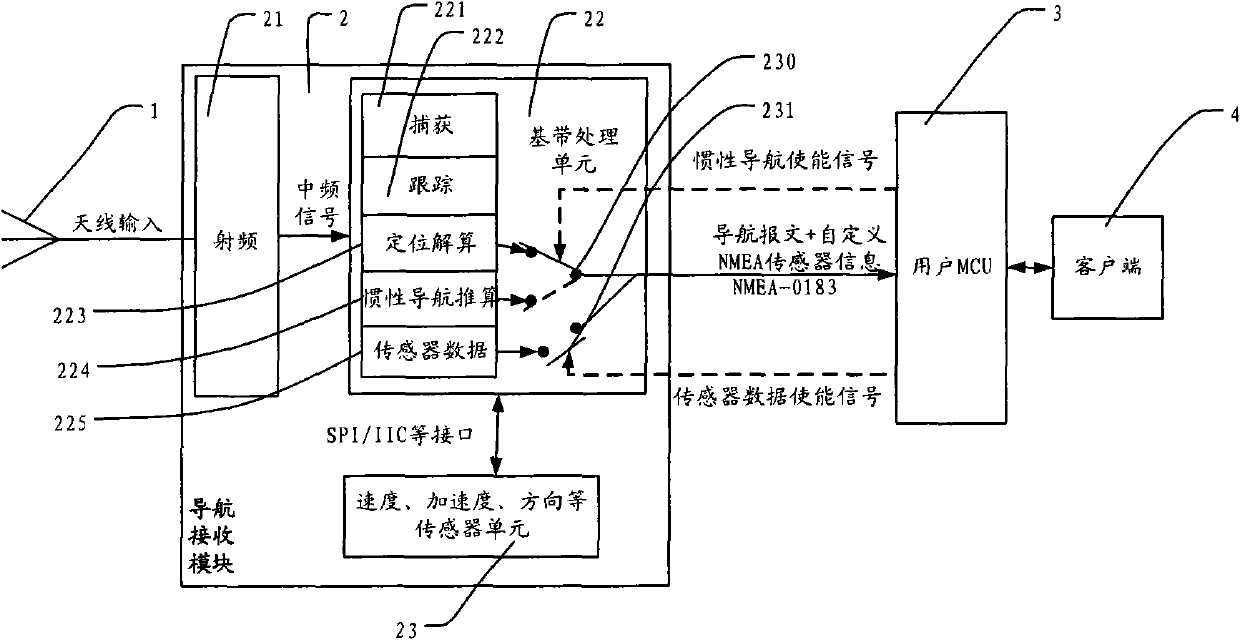
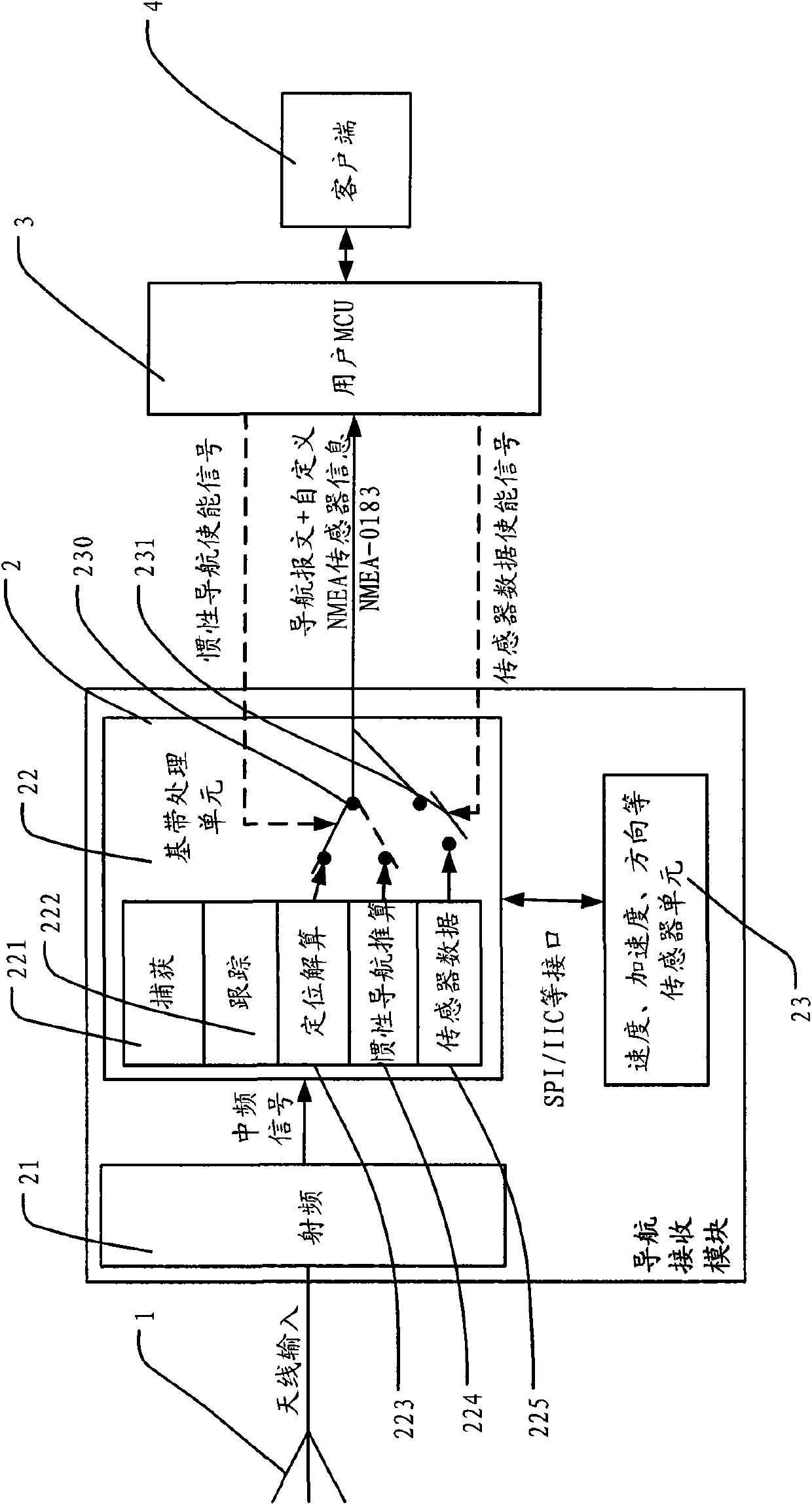
The invention relates to a navigational satellite signal receiving module, comprising a radio frequency input unit, a base band processing unit, a sensor unit and a information output unit; wherein the radio frequency input unit is used for receiving a navigational satellite signal and outputting a digital intermediate frequency signal, the base band processing unit is used for acquiring satellite navigation information and positioning and resolving the current position of the receiving module, the sensor unit is used for acquiring the speed, acceleration or directional information of the current receiving module and outputting the speed, acceleration or directional information to the base band processing unit, and the information output unit is used for outputting the current position of the receiving module in NMEA format. By adopting the technical scheme of the invention, processing on sensor information of a user MCU can be eliminated, only a UART interface reported by a navigation message is processed, and navigation positioning information of NMEA-0183 and sensor information can be simultaneously acquired and reported. Thus, user demand can be met flexibly, not only accuracy of positioning is improved, but also port occupancy rate and processing overhead of the user MCU are reduced. The invention can be applicable to navigational satellite positioning systems such as GPS, Beidou navigation satellite system, GLONASS and Galileo navigation satellite system.
Owner:TECHTOTOP MICROELECTRONICS
Efficient and flexible GPS receiver baseband architecture
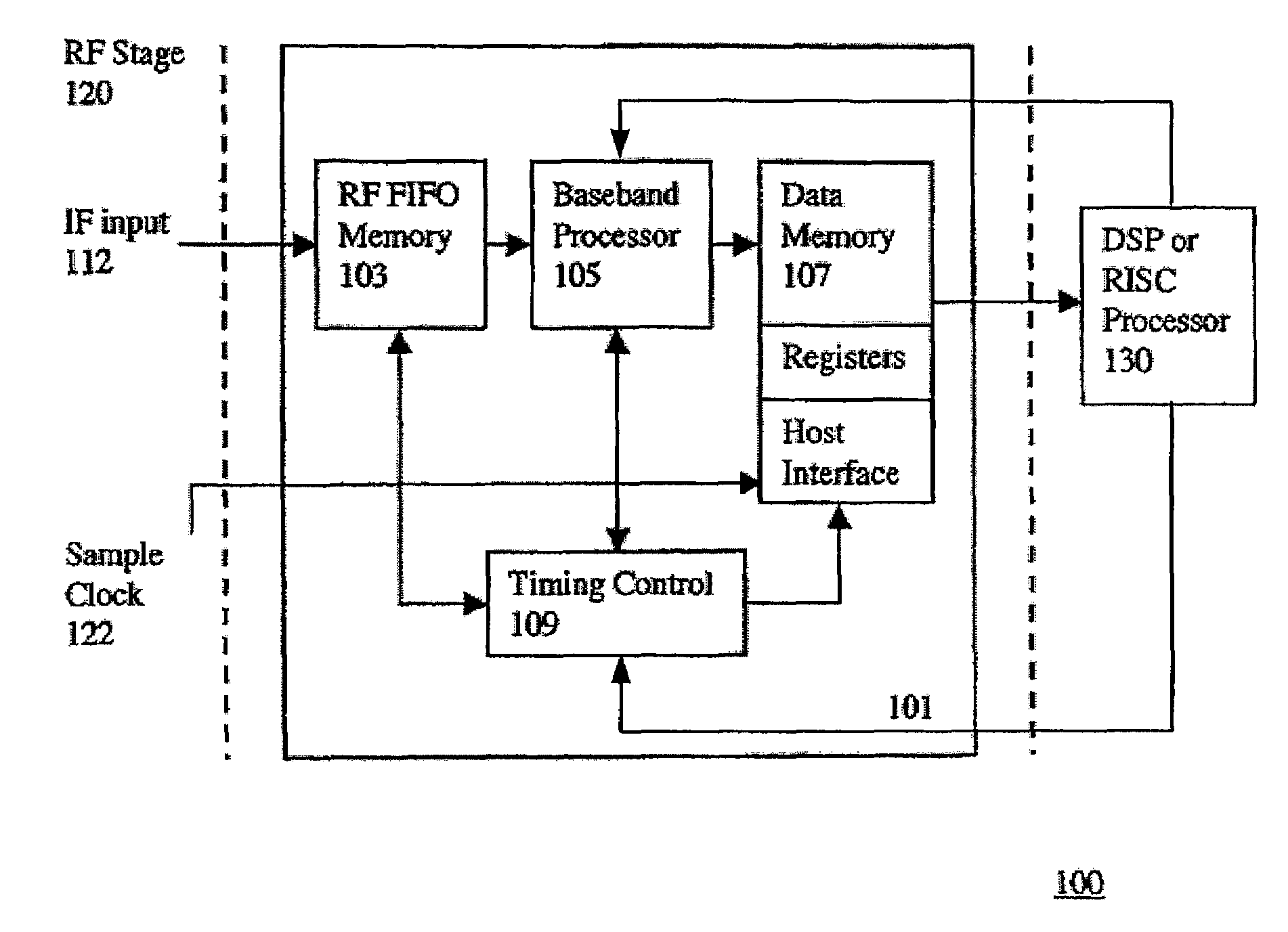
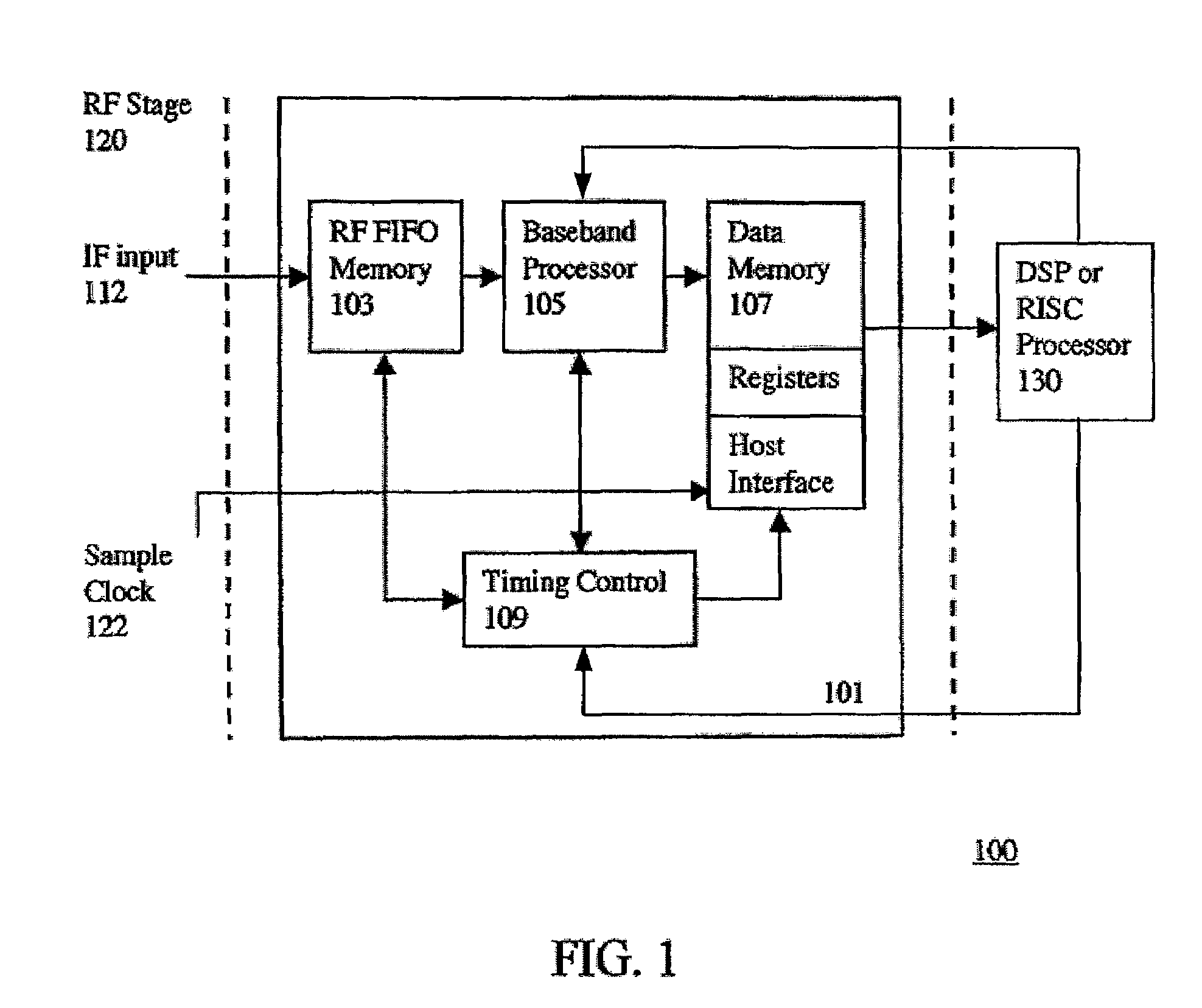
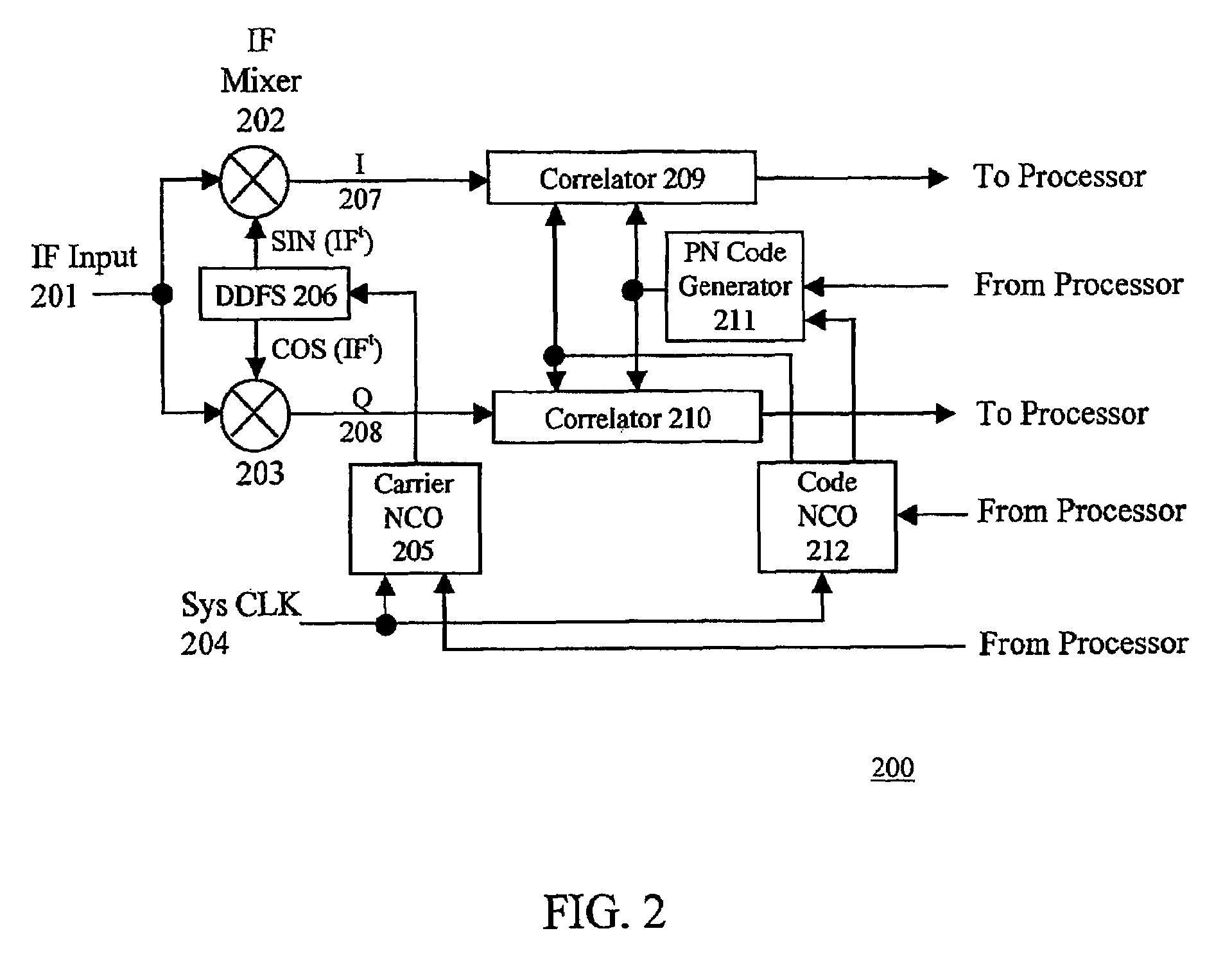
ActiveUS7428259B2Minimize the numberEfficient powerColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionNCOSNumerically controlled oscillator
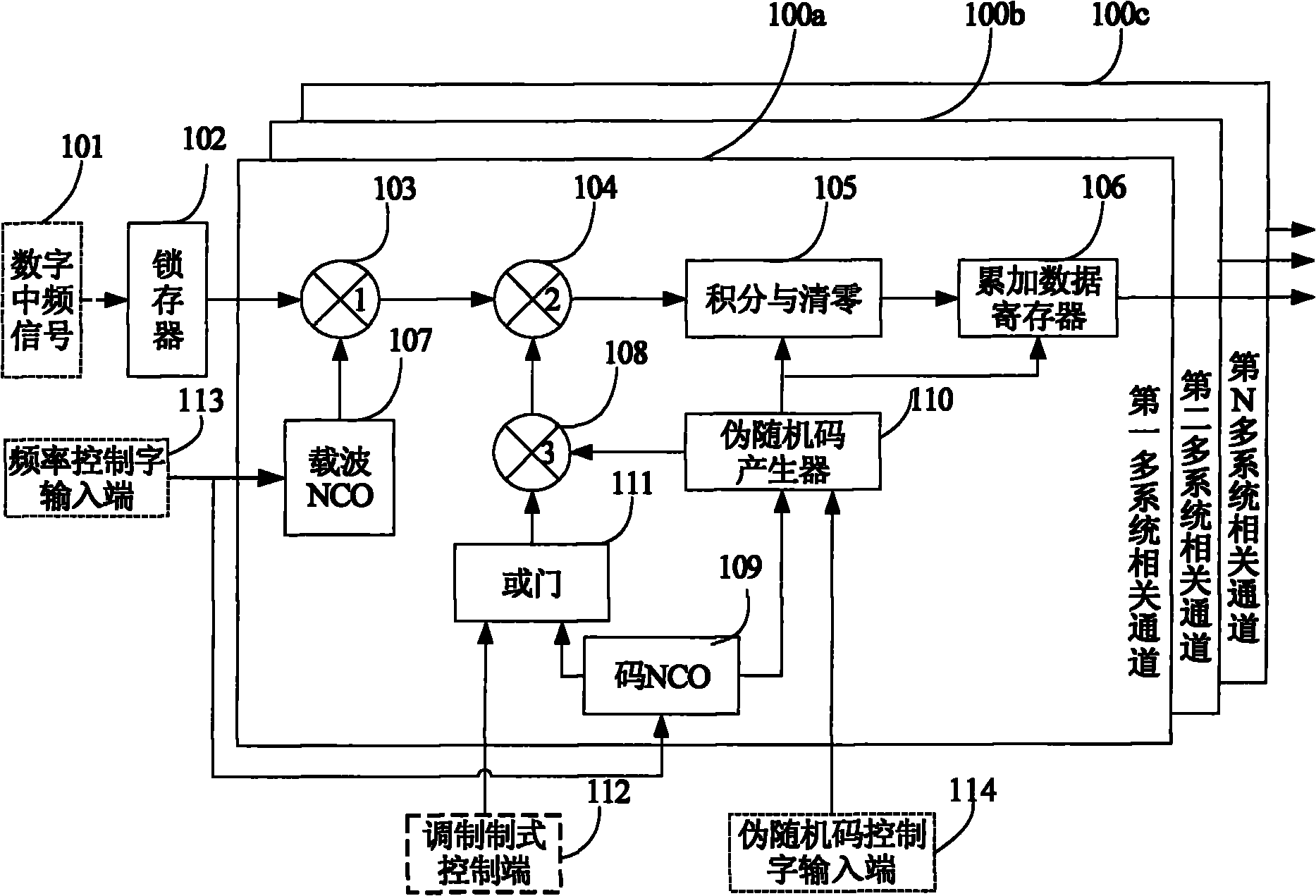
The present invention provides a new baseband integrated circuit (IC) architecture for direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communication receivers. The baseband IC has a single set of baseband correlators serving all channels in succession. No complex parallel channel hardware is required. A single on-chip code Numerically Controlled Oscillator (NCO) drives a pseudorandom number (PN) sequence generator, generates all code sampling frequencies, and is capable of self-correct through feedback from an off-chip processor. A carrier NCO generates corrected local frequencies. These on-chip NCOs generate all the necessary clocks. This architecture advantageously reduces the total hardware necessary for the receiver and the baseband IC thus can be realized with a minimal number of gate count. The invention can accommodate any number of channels in a navigational system such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), GLONASS, WAAS, LAAS, etc. The number of channels can be increased by increasing the circuit clock speed.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
Method to secure GNSS based locations in a device having GNSS receiver
A method to detect at a GNSS receiver whether the received GNSS signals and navigation messages are the product of an attack. If there is evidence, as provided by the method described here, that the received signals and messages originate from adversarial devices, then receiver equipped with an instantiation of the method notifies the user or the computing platform that integrates the GNSS receiver that the calculated via the GNSS functionality position and time correction are not trustworthy. In other words, our method enables any GNSS receiver, for example, GPS, GLONASS, or Galileo, or any other GNSS system, to detect if the received navigation messages are the legitimate ones (from the satellites) or not (e.g., from attacker devices that generate fake messages that overwrite the legitimate messages). Based on this detection, neither the user and nor any application running in the computing platform is misled to utilize erroneous position information.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
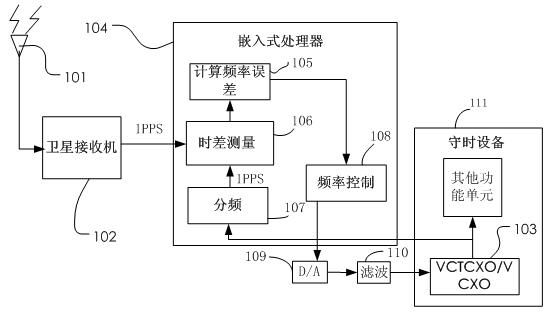
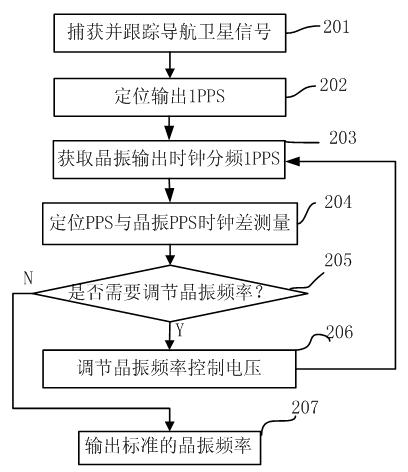
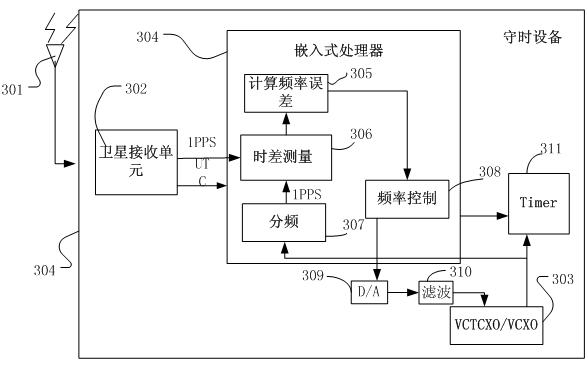
Method and corresponding device for taming crystal oscillation frequency of time-keeping device
InactiveCN102436174AReduce manufacturing costSmall device sizeSynchronous motors for clocksRadio-controlled time-piecesNavigation systemFirst generation
The invention discloses a method and corresponding device for taming crystal oscillation frequency of a time-keeping device, which comprises the following steps of: step 1, acquiring the standard time pulse A that is located and output by a navigation satellite; step 2, acquiring the standard time pulse B output by device crystal oscillation fractional frequency; step 3, measuring the clock difference between the standard time pulse A and the standard time pulse B; and step 4, if clock difference exists between A and B, adjusting the crystal oscillation frequency of the device to make the clock difference be in the allowed scope. For the time-keeping equipment with pressure control and temperature compensating crystal oscillation or pressure control crystal oscillation, the frequency deviation of the corrected crystal oscillation can be detected in real time by the method provided by the invention to eliminate the time-keeping error caused by crystal oscillation frequency deviation and avoid accumulation of error. Therefore, the invention is suitable for various satellite navigation systems, such as GPS, Beidou first generation navigation satellite, Beidou second generation navigation satellite, GLONASS, GALILEO and other satellite navigation systems.
Owner:TECHTOTOP MICROELECTRONICS
Method and device for implementing GNSS multi-module parallelism receiving at front end by using single path radio frequency
InactiveCN101198160ASimple structureHigh module reuse ratePosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPeriodic alternatingIntermediate frequency
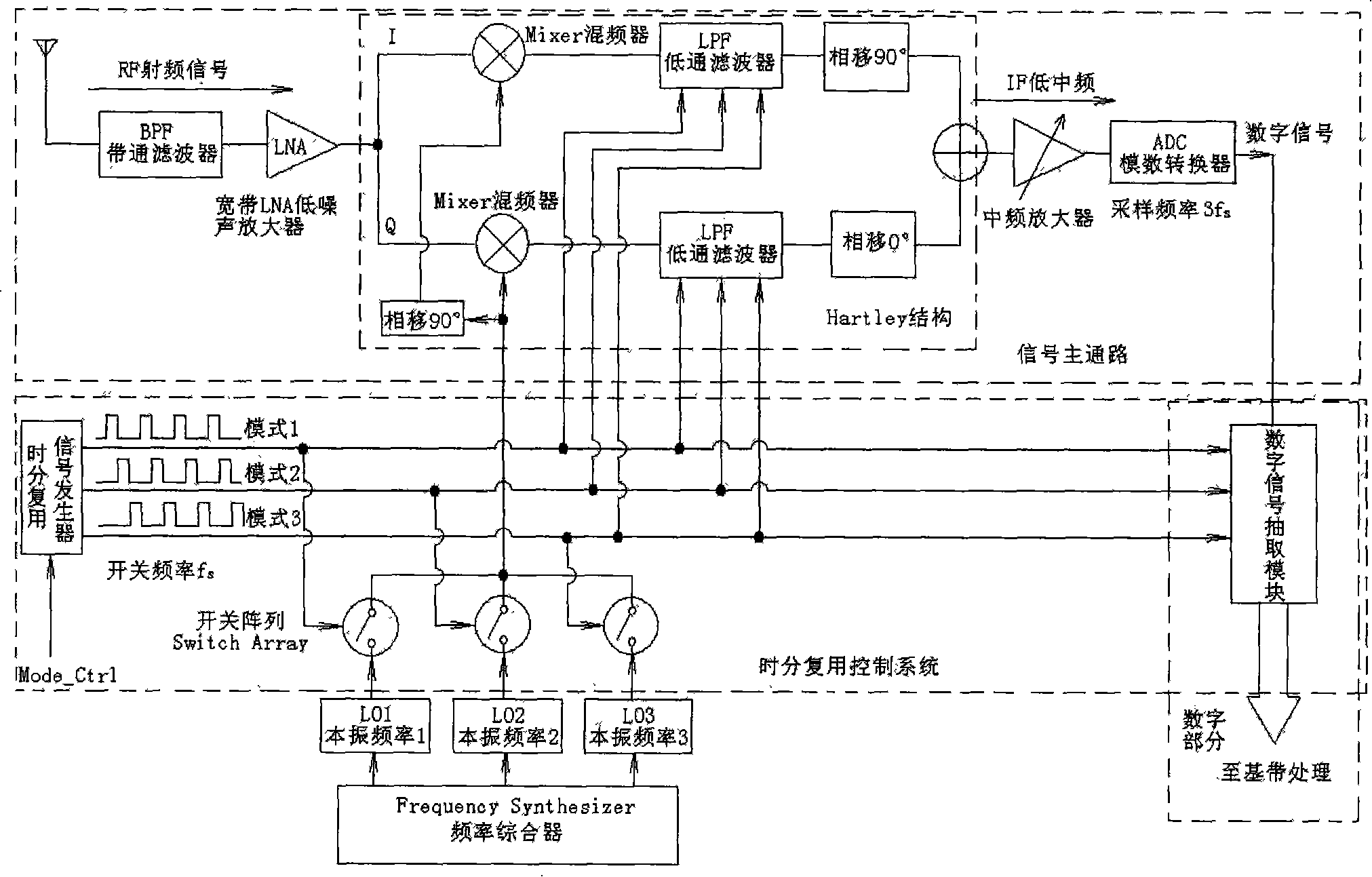
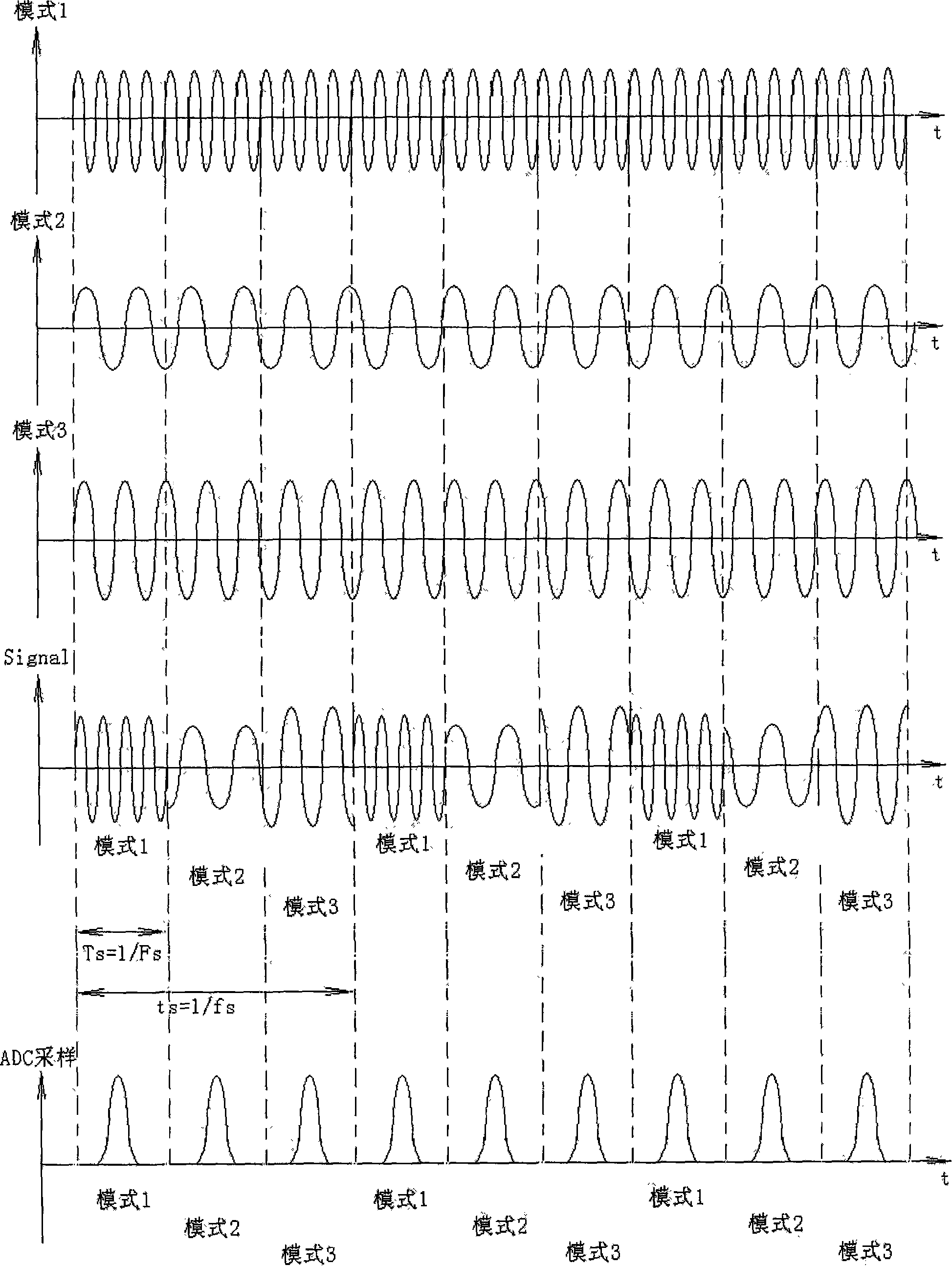
The invention provides a method and device of realizing parallel receiving of GNSS multimode by adopting a single-pass radio frequency front-end and belongs to the radio frequency communication technical field. The method comprises: after RF frequency signal received entering the single-pass radio frequency front-end, a sampling period of a signal pathway is divided into N short time segments according to the number N of the modes of receiving signals, the RF signals is down converted into IF signals by a Mixer and a LPF low pass filter controlled by a time division multiplexed signal to shift the time division multiplexed signal, the single-pass radio frequency front-end receives a mode of signal within every short time segment and realizes parallel receiving signals of N modes at the single-pass radio frequency front-end in such periodic alternating repetition. The invention can realize the parallel receiving of GNSS multiple modes (including BD-2, GPS, Galileo and GLONASS) with only a single-pass radio frequency front-end under the control of the time division multiplexed system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
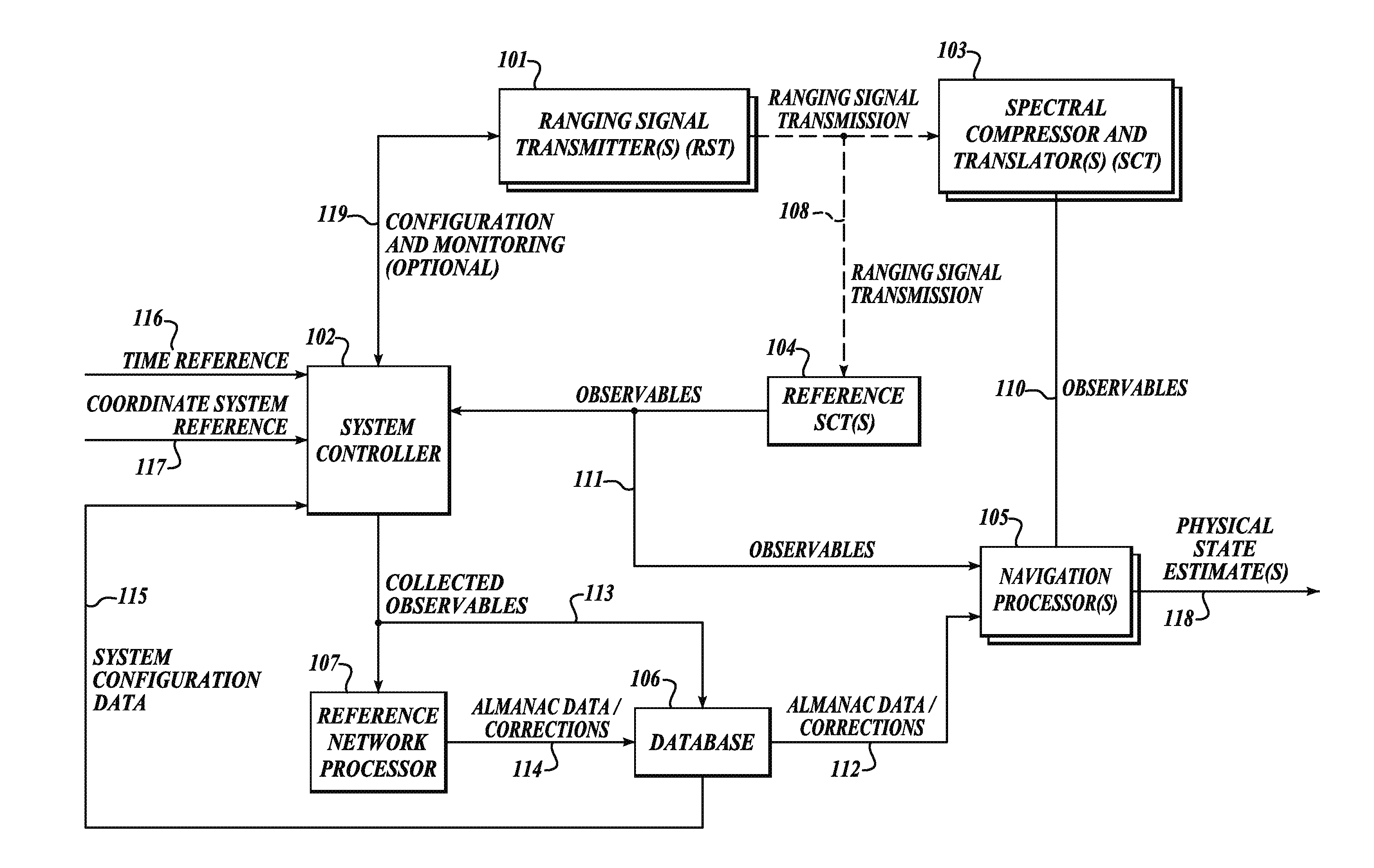
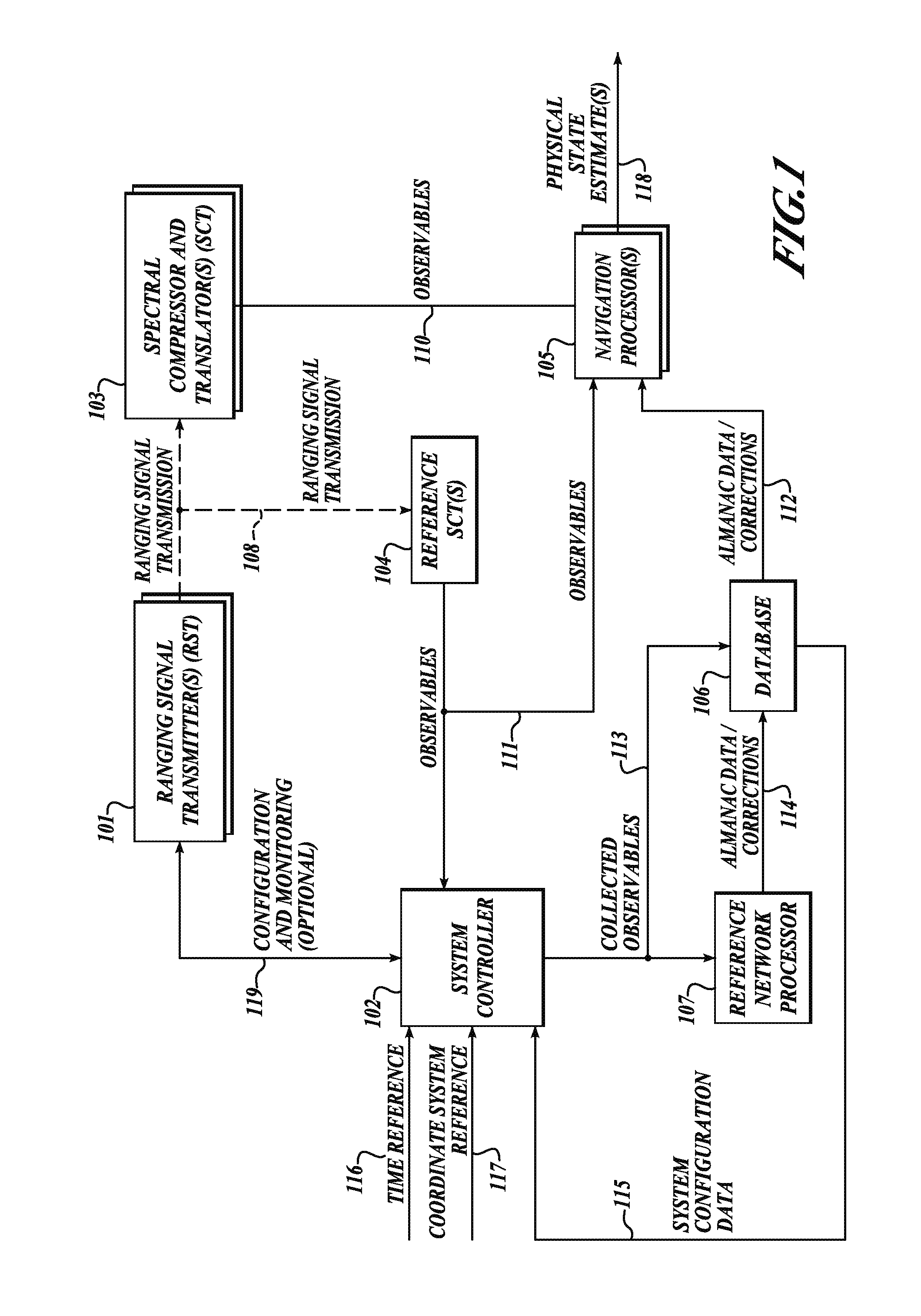
System and method for positioning using hybrid spectral compression and cross correlation signal processing
InactiveUS20120169542A1Easy to implementRapidly deployableDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency spectrumCode division multiple access
The present invention relates to a system and method for positioning and navigation using hybrid spectral compression and cross correlation signal processing of signals of opportunity, which may include Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) as well as other wideband energy emissions in GNSS obstructed environments. Examples of these signals of opportunity include but are not limited to GPS, GLONASS, cellular Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) communications signals, and 802.11 Wi-Fi. Combining spectral compression with spread spectrum cross correlation enables extraction of code and carrier observables without the need to implement the tracking loops (e.g. Costas tracking loop) commonly used in conventional GNSS receivers. For applications where dynamics and transmission medium may make it difficult to continuously track carrier phase, the hybrid approach of the present invention has significant utility.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
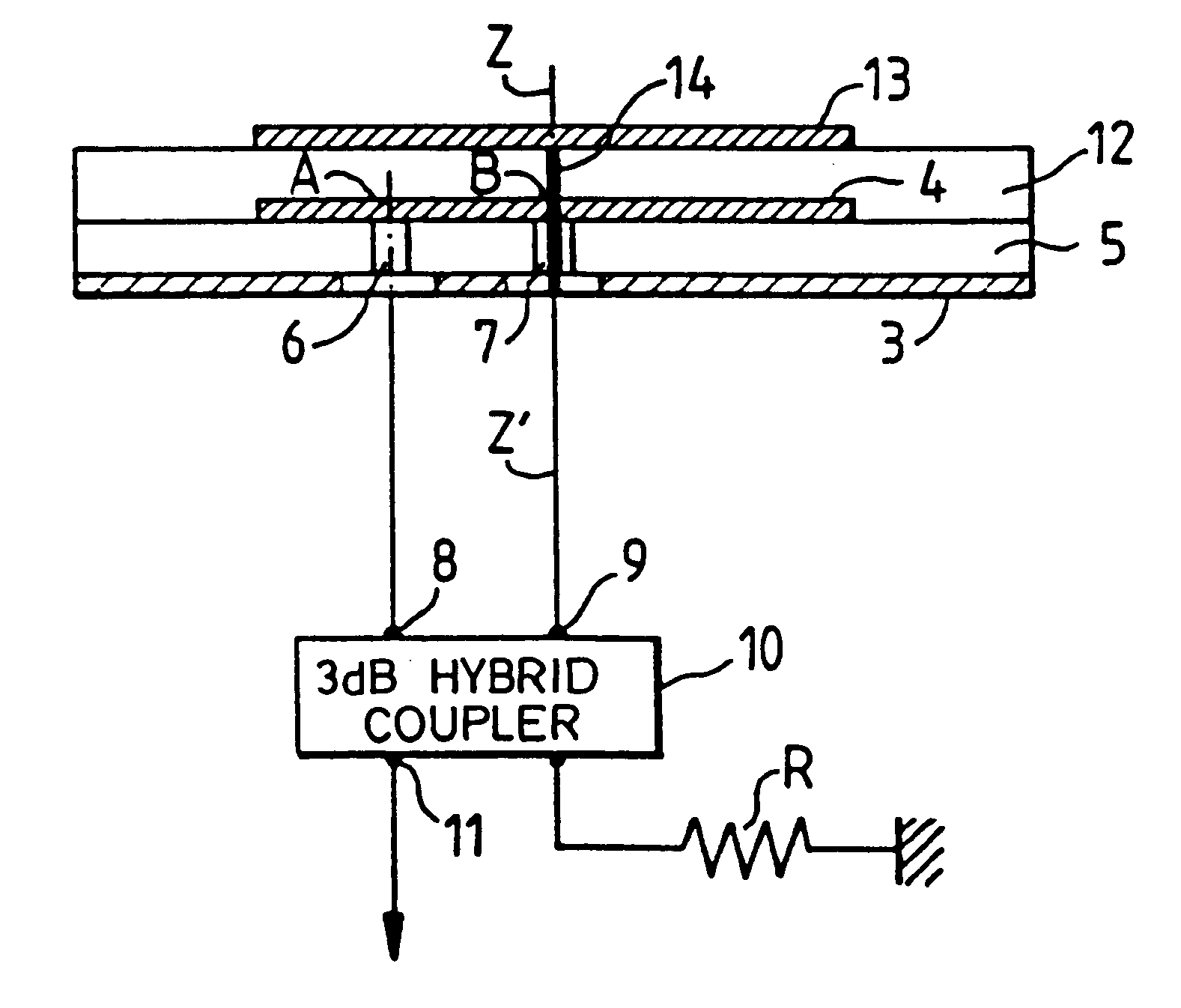
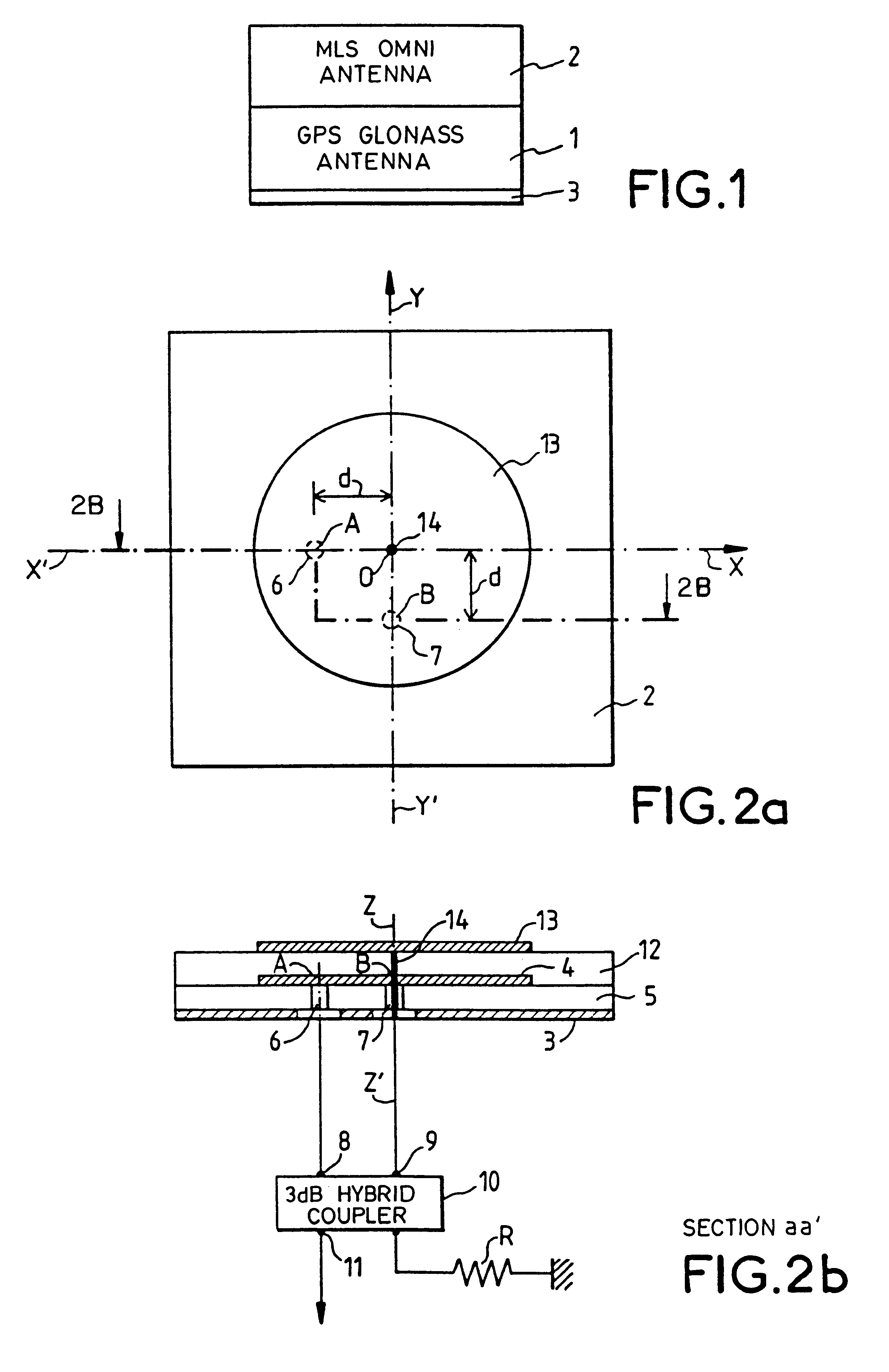
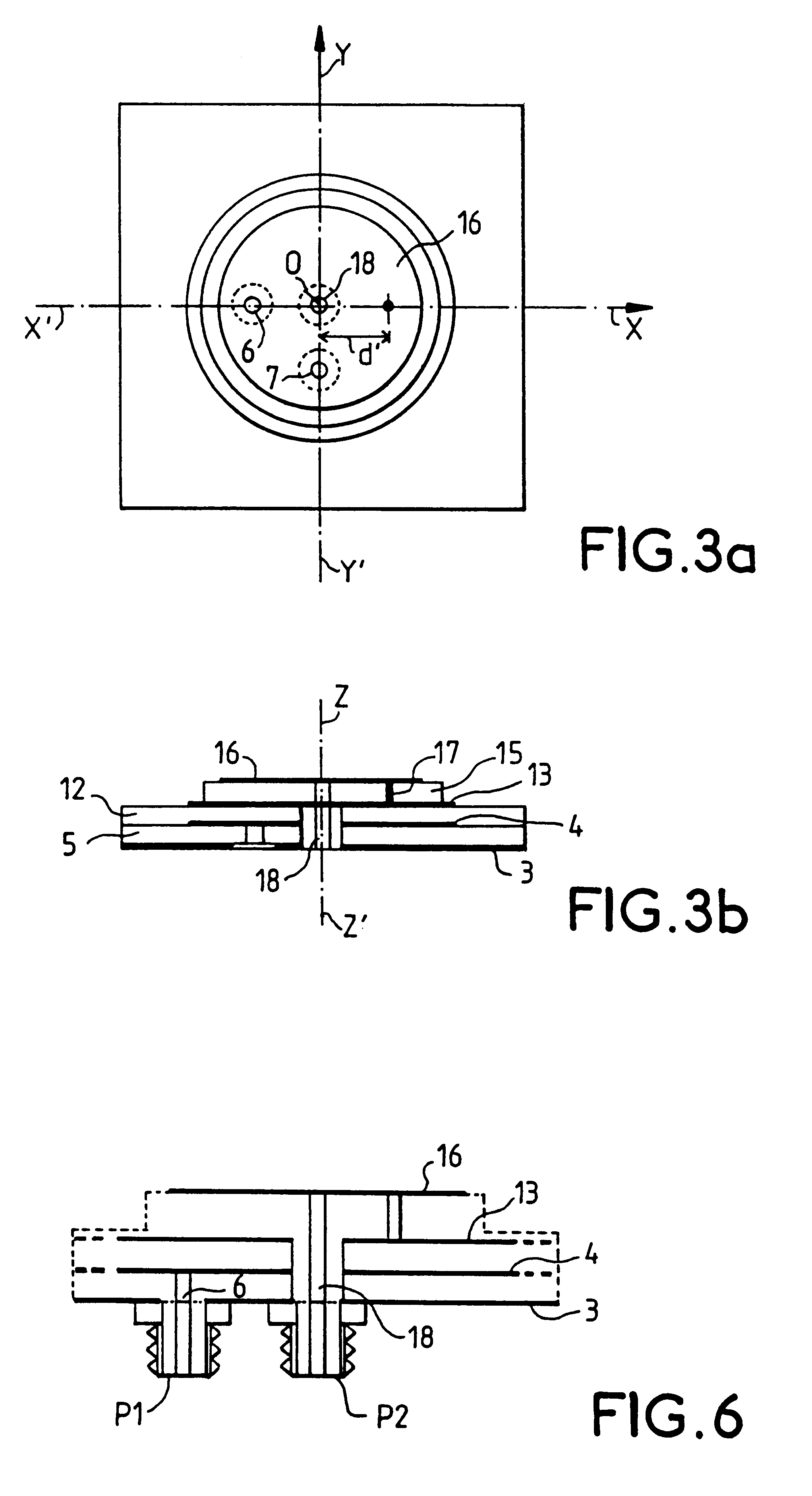
Multifunction printed-circuit antenna
InactiveUS6198439B1Efficient connectionSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDielectric substrateGround plane
The multifunction printed-circuit antenna is designed for the reception of radioelectric waves sent by the GPS, GLONASS and MLS radio navigation systems. It comprises first, second and third circular patches that are parallel to one another and superimposed in this order above one and the same ground plane that is parallel to them, the centers of the patches being aligned on one and the same axis z'z perpendicular to the plane of the three patches, the patches being separated from one another by thicknesses of a substrate-forming dielectric material for each of the patches. The first and second patches form, with the ground plane, the antenna structure for the reception of the GPS, GLONASS waves. The MLS antenna reception structure is formed by the third and second patches. The second patch also serves as a ground plane for the MLS antenna structure. The third patch of the MLS structure has a diameter smaller than that of the first and second patches of the GPS, GLONASS structure, and the surface dimensions of the dielectric substrate between the third and second patches are smaller than those of the first and second patches. Application to GPS / GLONASS, MLS antennas.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
Algorithm for implementing GNSS and WIFI system seamless vertical handoff
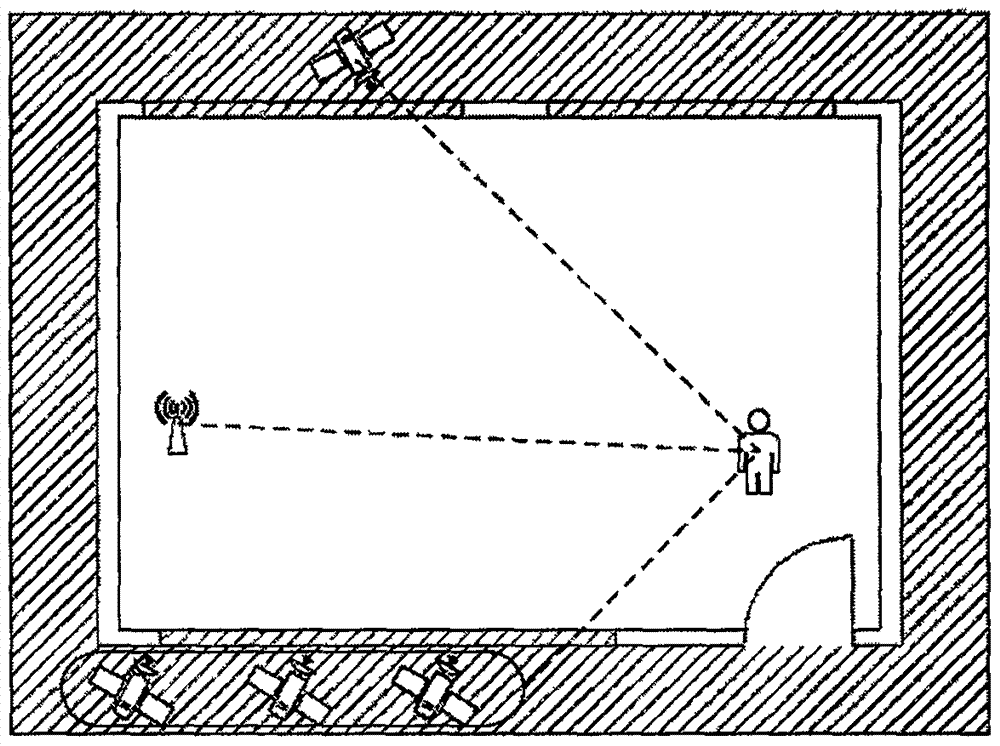
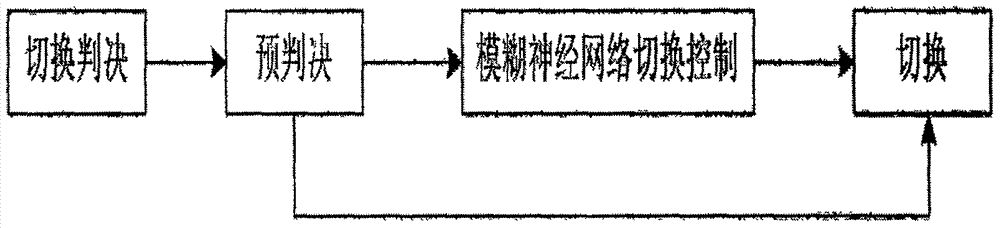
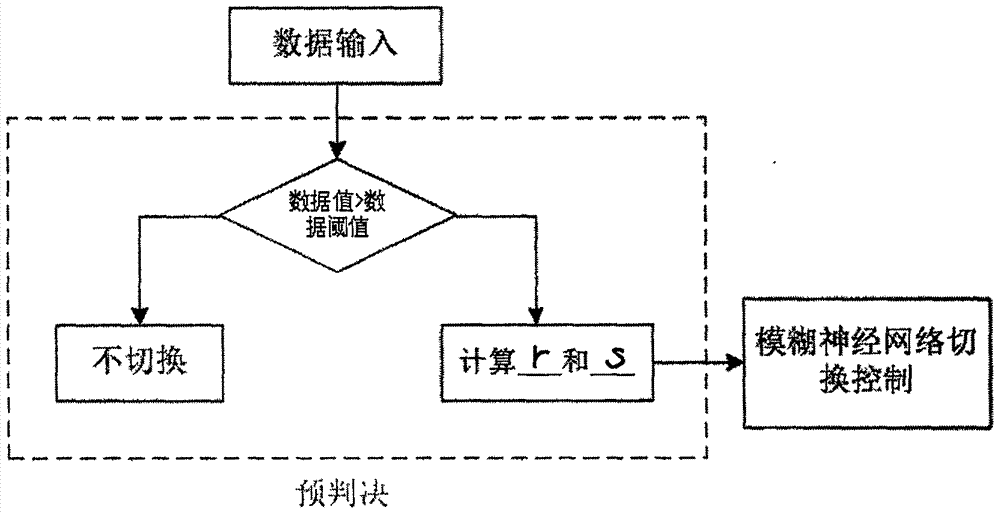
InactiveCN106993319AReduce the "ping-pong effect"Satellite radio beaconingWireless communicationNetwork controlEarth surface
The invention provides an algorithm for implementing global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and WIFI system seamless vertical handoff based on a fuzzy neural network algorithm in order to realize a purpose of fusing two different positioning systems mutually to implement seamless handoff of indoor and outdoor positioning and navigation. The algorithm comprises the following steps: acquisition of main positioning information, handoff triggering based on received signals, and handoff algorithm judgment based on fuzzy neural network control. The algorithm for implementing the GNSS and WIFI system seamless vertical handoff has the beneficial effect of overcoming a defect that WIFI position precision is reduced outdoor and GNSS signals have a possible of occurring interruption indoor so as to provide wrong positioning information for a user; America GPS, Russia Glonass, EU Galileo and China Beidou satellite have a large development on satellite positioning and navigation application technology positioning aspects indoor, outdoor, underground, on the earth surface and the like; and meanwhile, the algorithm provided by the invention has wide applications in the fields of national military applications, international counter terrorism, tunnel detection and the like.
Owner:吕皓
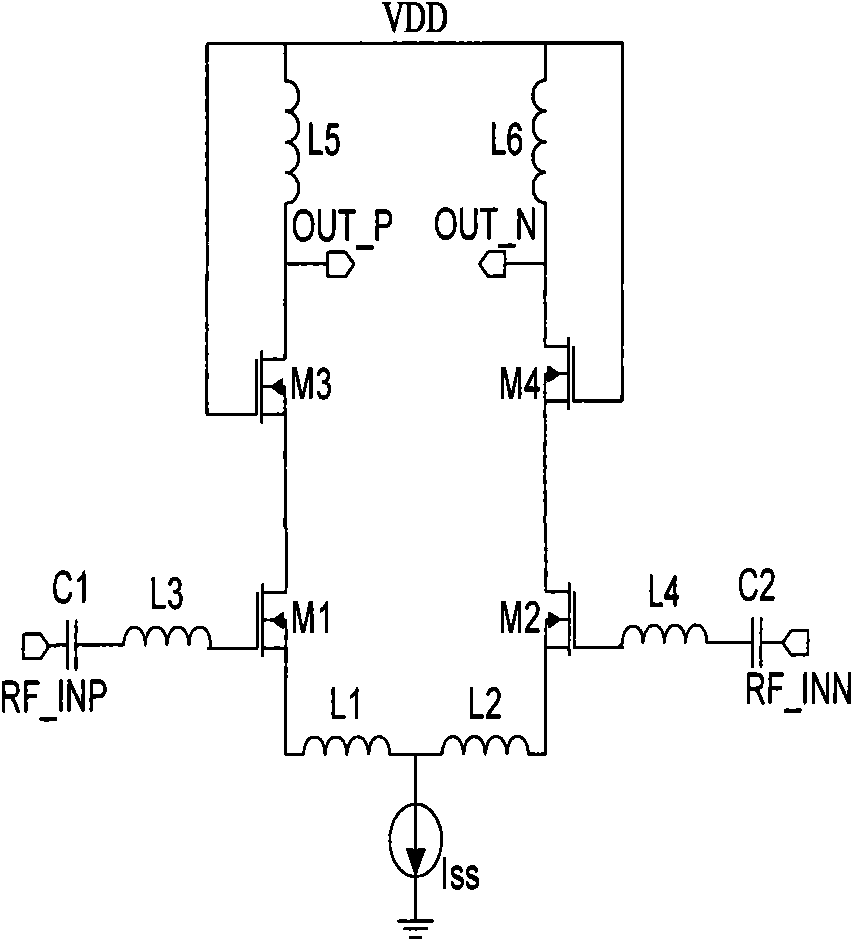
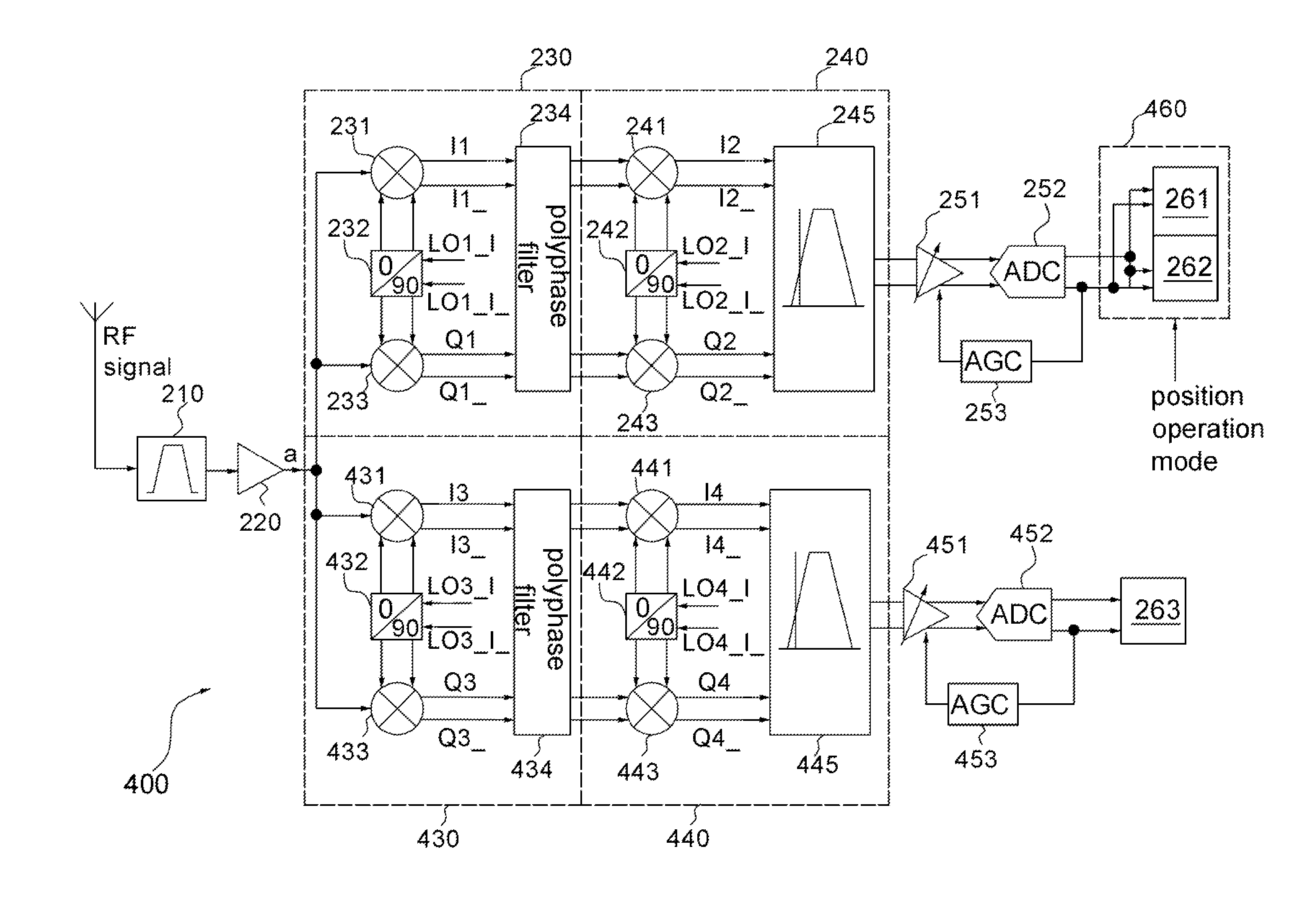
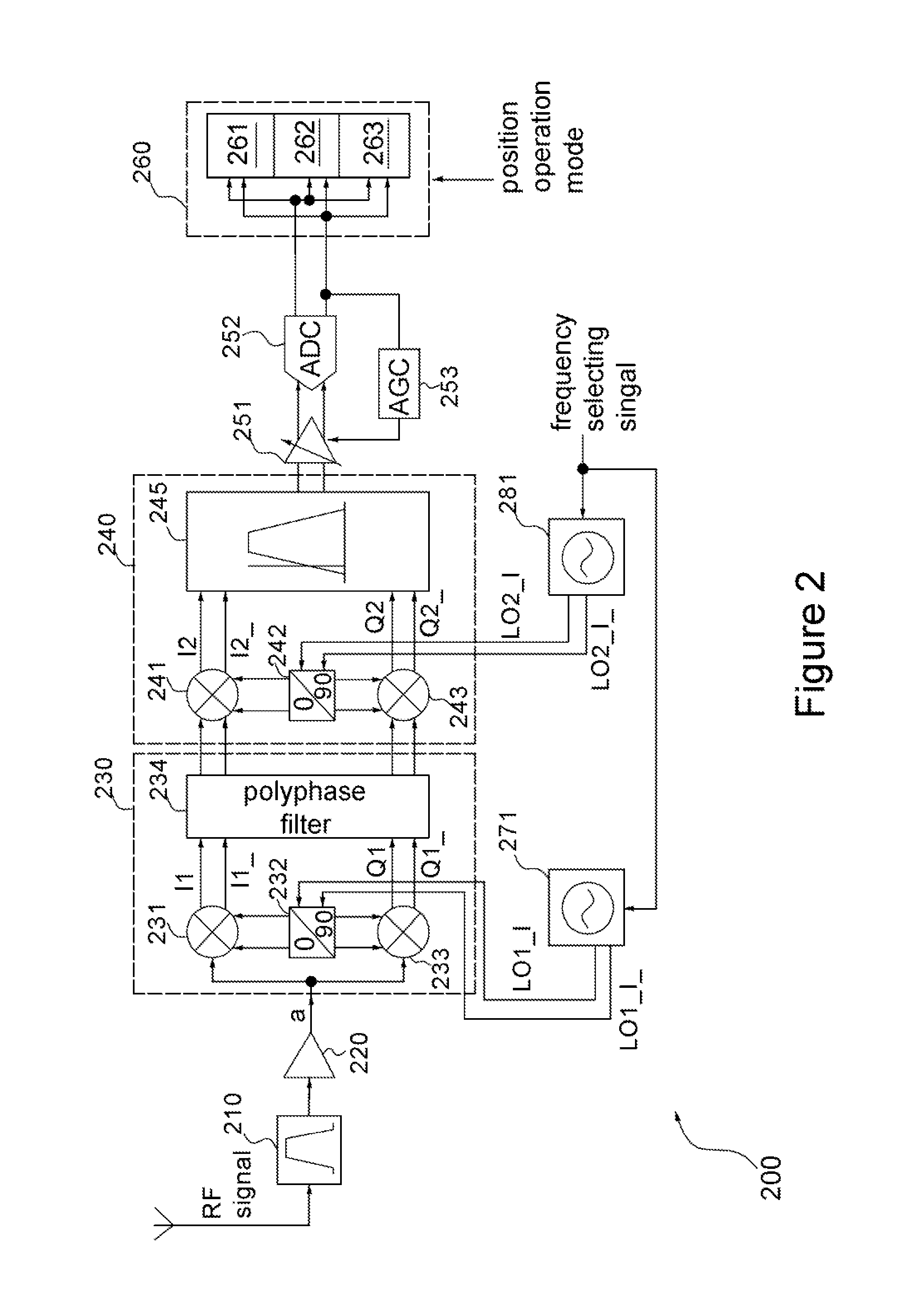
Signal Processing Apparatus for Multi-mode Satellite Positioning System and Method Thereof
A signal processing apparatus for a multi-mode satellite positioning system includes a band-pass filter, a local oscillator circuit, a first mixing circuit, a second mixing circuit, an analog-to-digital converter and a baseband circuit. By properly allocating a local frequency, radio frequency (RF) signals of a Global Positioning System (GPS), a Galileo positioning system and a Global Navigation System (GLONASS) are processed via a single signal path to save hardware cost.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
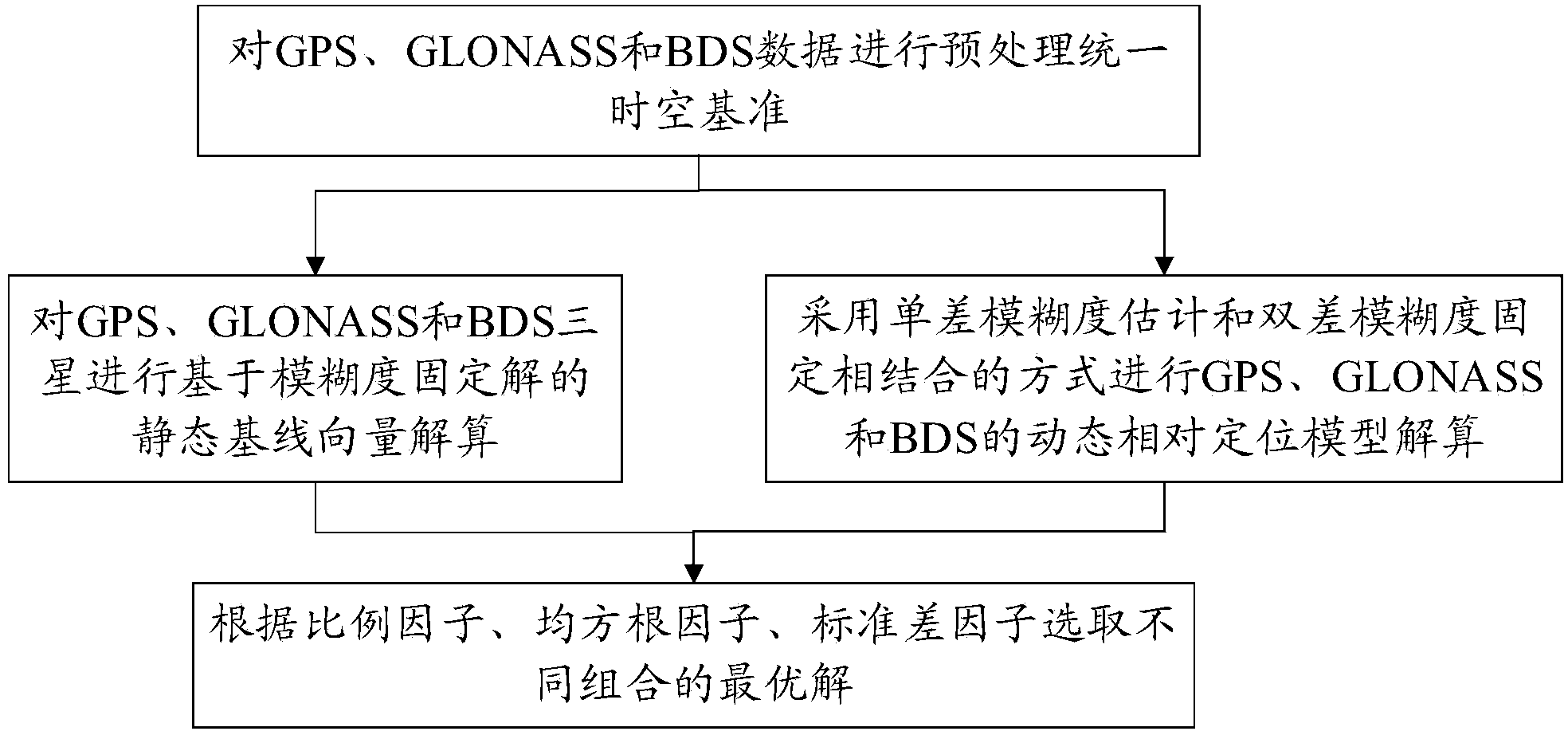
GPS, GLONASS and BDS unified solution positioning method
ActiveCN103941272AHigh positioning accuracyImprove positioning reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityComputer science
The invention relates to a GPS, GLONASS and BDS unified solution positioning method. The method includes the steps of conducting static relative positioning based on GPS, GLONASS and BDS three-satellite unified solution, and conducting dynamic relative positioning based on GPS, GLONASS and BDS three-satellite unified solution. By means of the GPS, GLONASS and BDS unified solution positioning method, solution is achieved through three-satellite unification, positioning accuracy and positioning reliability under the severe observation environment are improved, and initialization time is shortened; the partial ambiguity fixing strategies, namely, the partial ambiguity fixing method oriented to statistic relative positioning and based on the RMS and the partial ambiguity fixing method oriented to dynamic relative positioning and based on the coordinated factor matrix, are adopted, and therefore the success rate of ambiguity fixing can be increased, and accuracy and reliability of baseline solution can be improved; a unified observation model is set up, the method can be easily expanded and used, and the method has a wider application range.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUACE NAVIGATION TECH
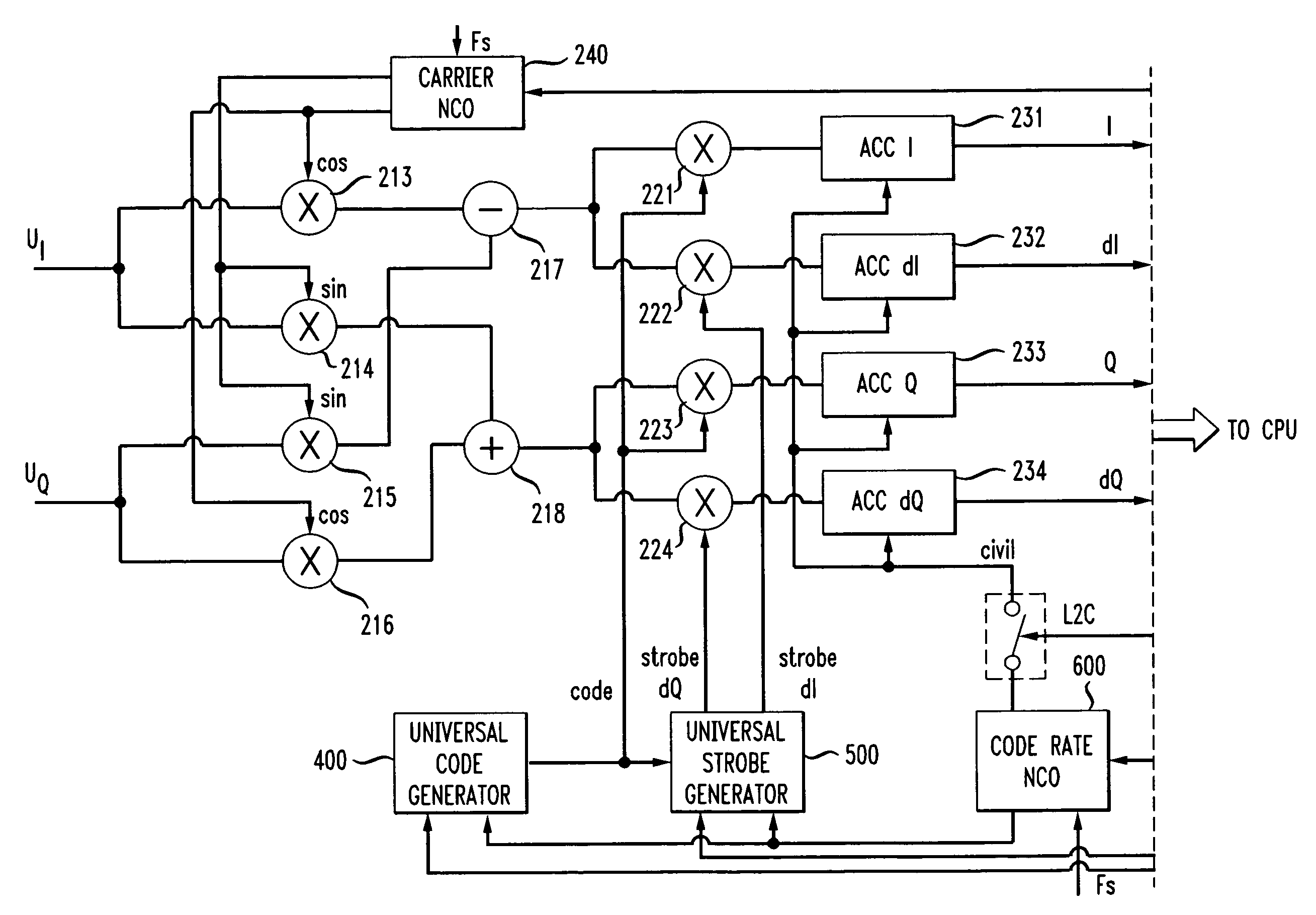
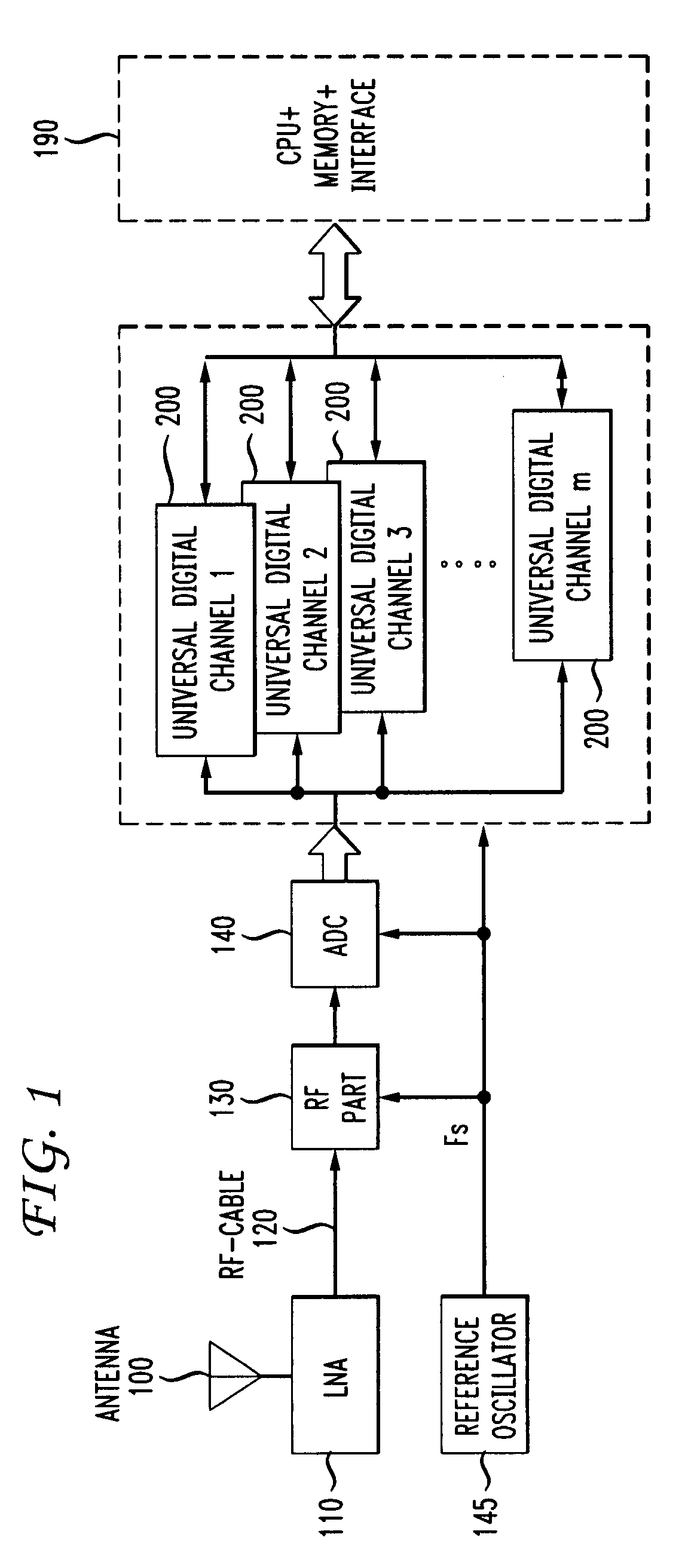
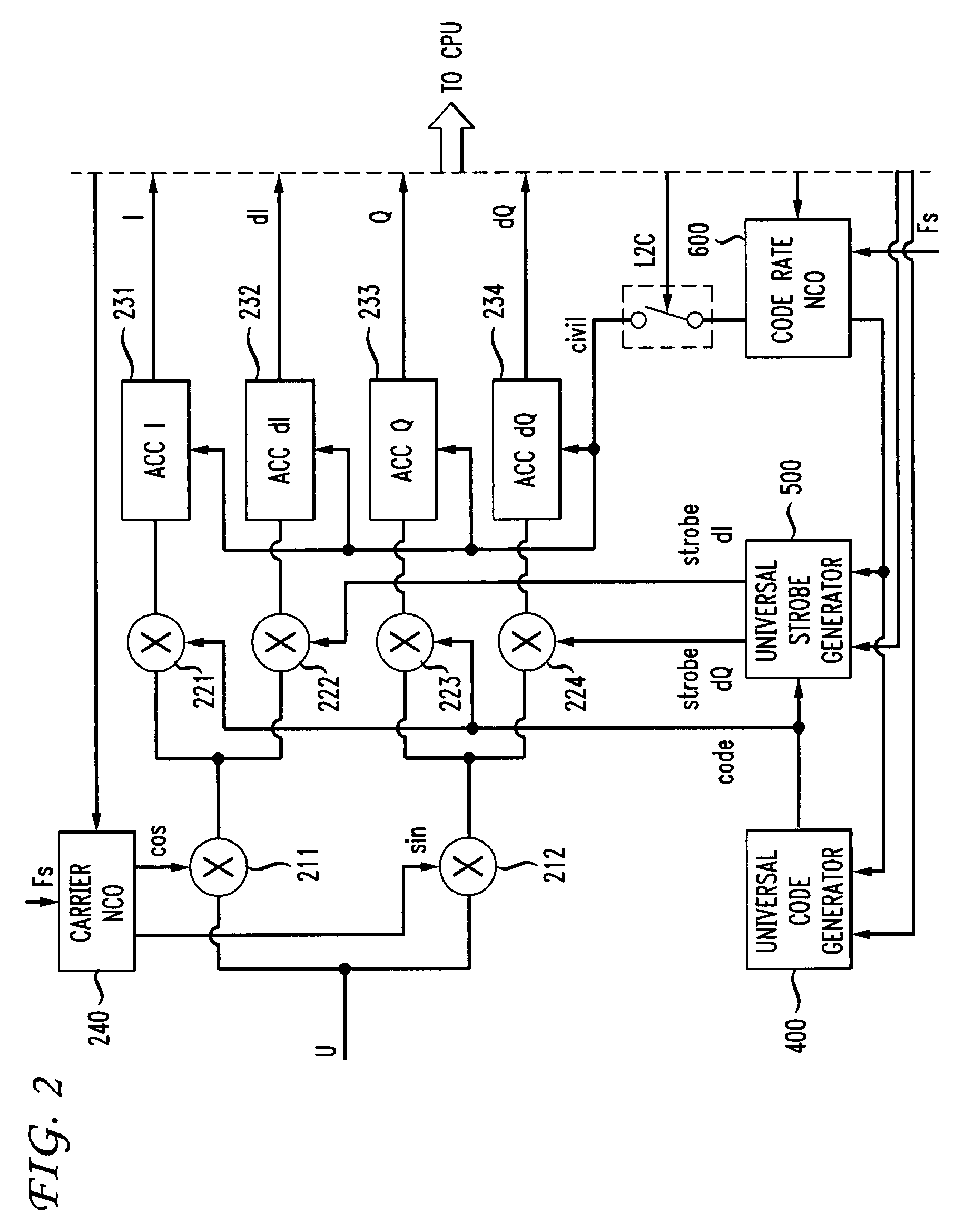
Universal digital channel for receiving signals of global navigation satellite systems
ActiveUS7764226B1Shorten the construction periodReduce errorsSatellite radio beaconingMarine navigationSatellite
Disclosed is a system and method for processing signals received from different global navigation satellite systems. The receiver includes a number of universal digital channels. The universal digital channel can be used to receive and process different code signals of each of the three navigation satellite systems GPS, GLONASS, and GALILEO. The universal digital channels have the same structure. Each of them can be tuned to receive different signals. The core of the universal digital channel is a code generator and a universal strobe generator.
Owner:TOPCON GPS
Graphics-aided remote position measurement with handheld geodesic device
A graphics-aided geodesic device is provided. The device may include a display, camera, distance meter, GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System, including GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo) receiver and antenna, and horizon sensors. Data from the camera and horizon sensors may be displayed to assist the user in positioning the device over a point of interest. In one example, the distance meter may be used to determine the position of the point of interest. In another example, images of the point of interest taken from multiple locations may be used to determine the position of the point of interest.
Owner:JAVAD GNSS
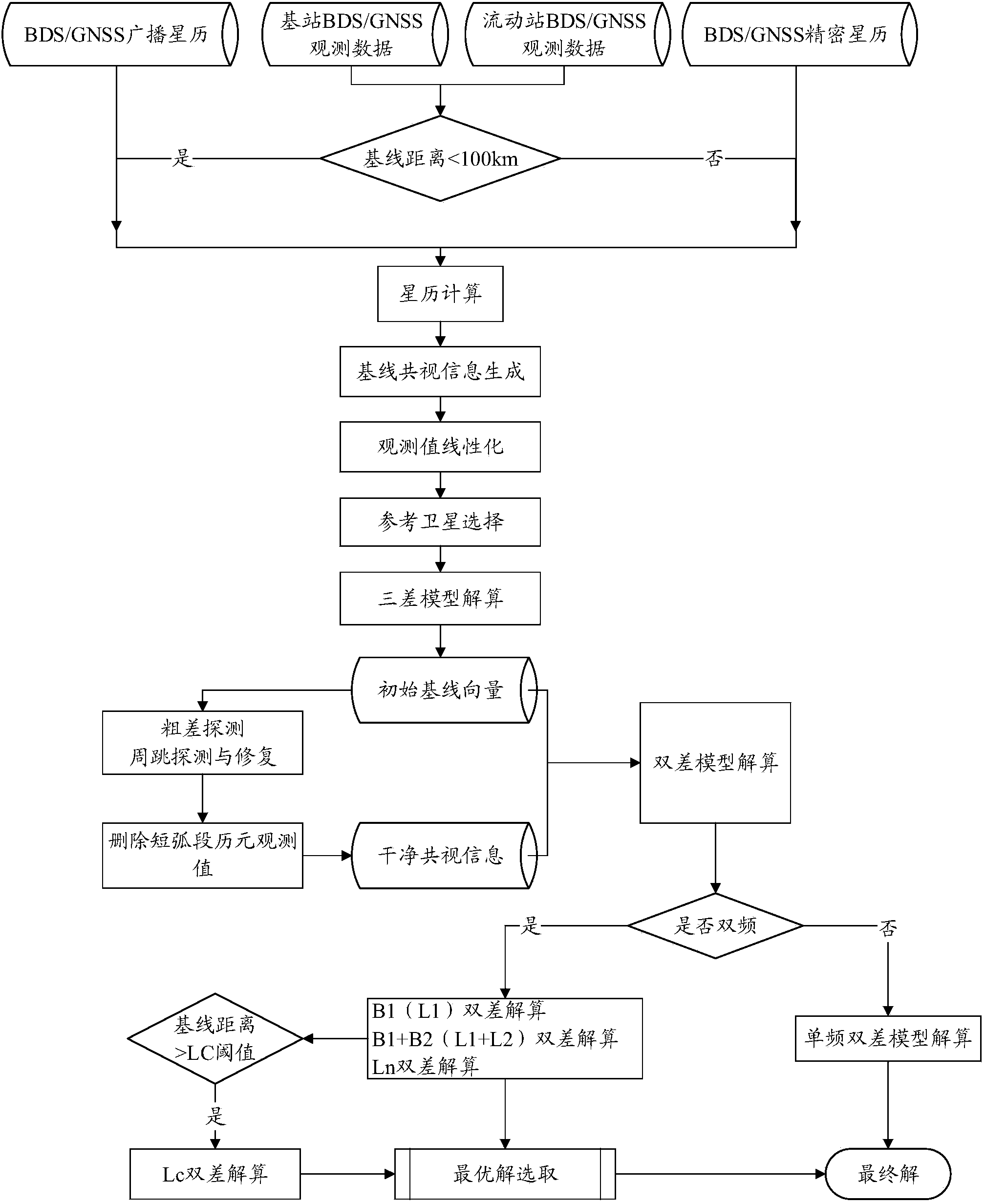
High-precision point positioning method and system for global navigation satellite system (GNSS)
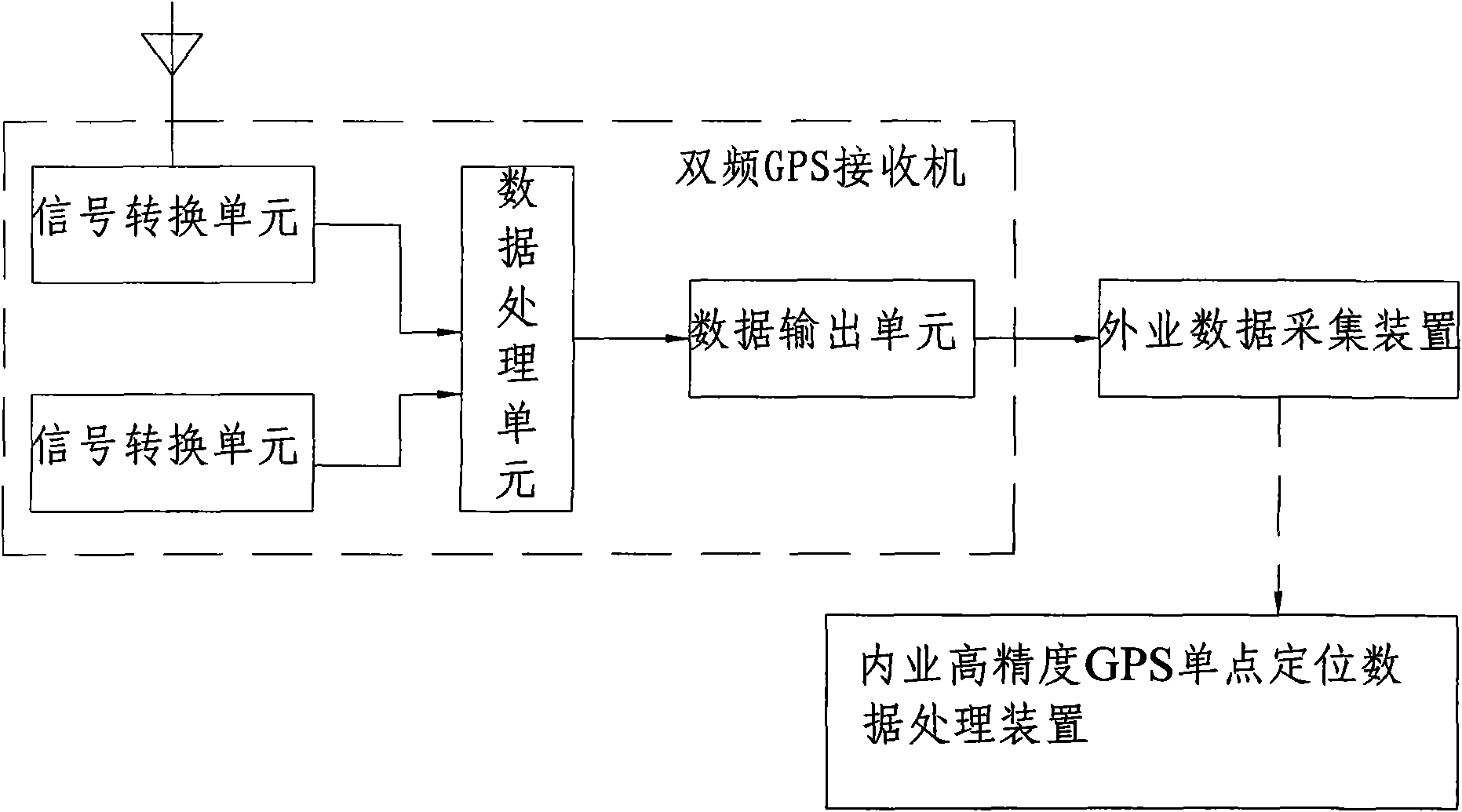
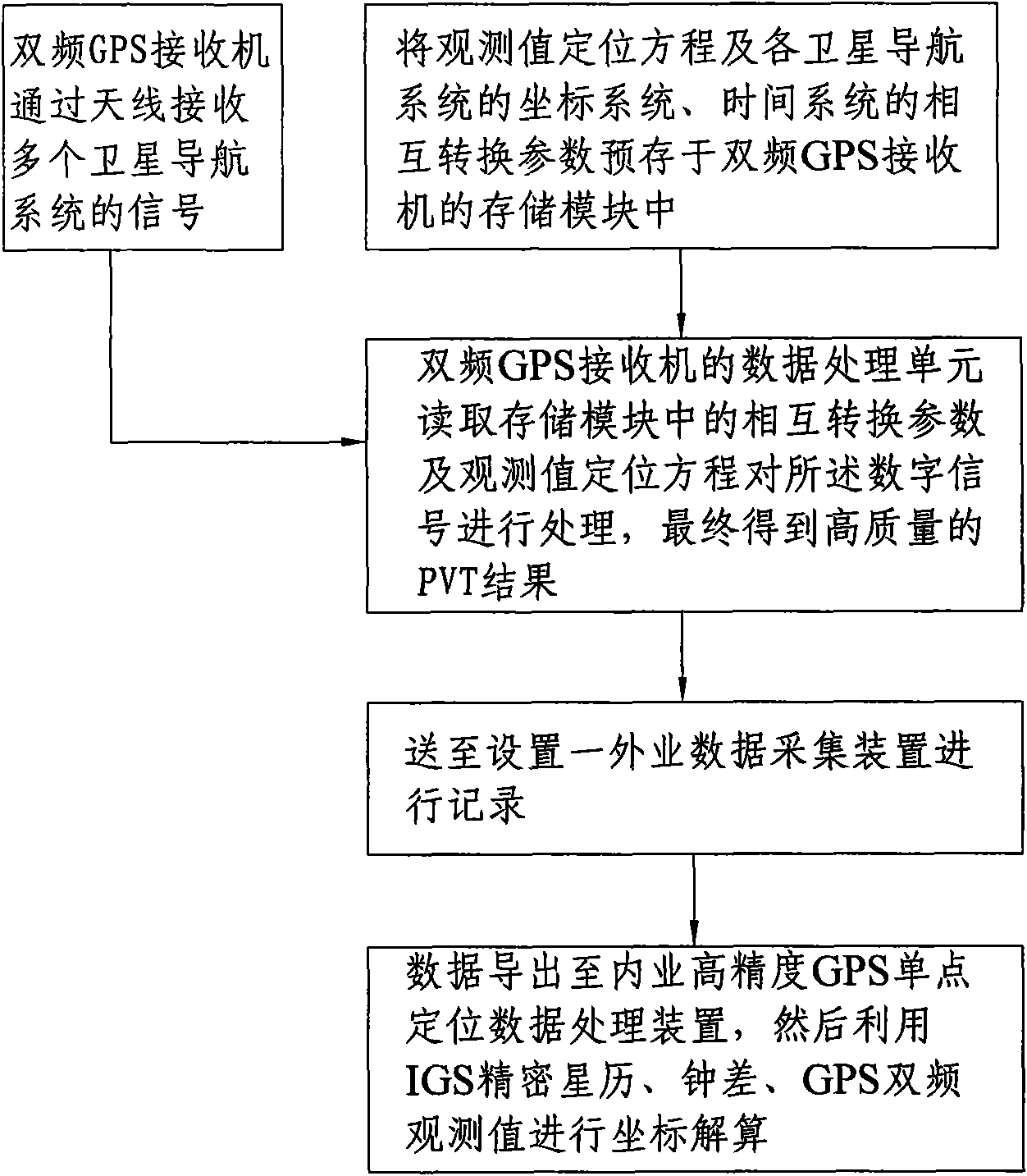
InactiveCN101581774AQuality improvementPrecise 3D positionBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationData acquisitionGalilean moons
The invention provides a high-precision point positioning method and a high-precision point positioning system for a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). The method comprises the following steps: prestoring an observed value positioning equation with commonality for a compass navigation satellite system, a GPS, a GLONASS and a Galileo satellite navigation system, and interconvertible parameters of coordinate systems and time systems of the various satellite navigation systems into a storage module of a double-frequency GPS receiver; receiving signals of the various satellite navigation systems by the double-frequency GPS receiver through an antenna, and converting the signals into digital signals by a signal converting unit; reading the interconvertible parameters in the storage module and the observed value positioning equation by a data processing unit to process the digital signals; finally obtaining a high-quality PVT result; realizing the combination use of observed quantities and ephemerides of the various satellite navigation systems; and sending the PVT result to a field data acquisition device for recording. The method and the system realize the compatible high-precision point positioning based on the compass navigation satellite system / the GPS / the GLONASS / the Galileo satellite navigation system, and can provide point positioning position information with higher quality.
Owner:CHINA ZHENGYUAN GEOMATICS CO LTD
Multiple-channel digital receiver for global positioning system
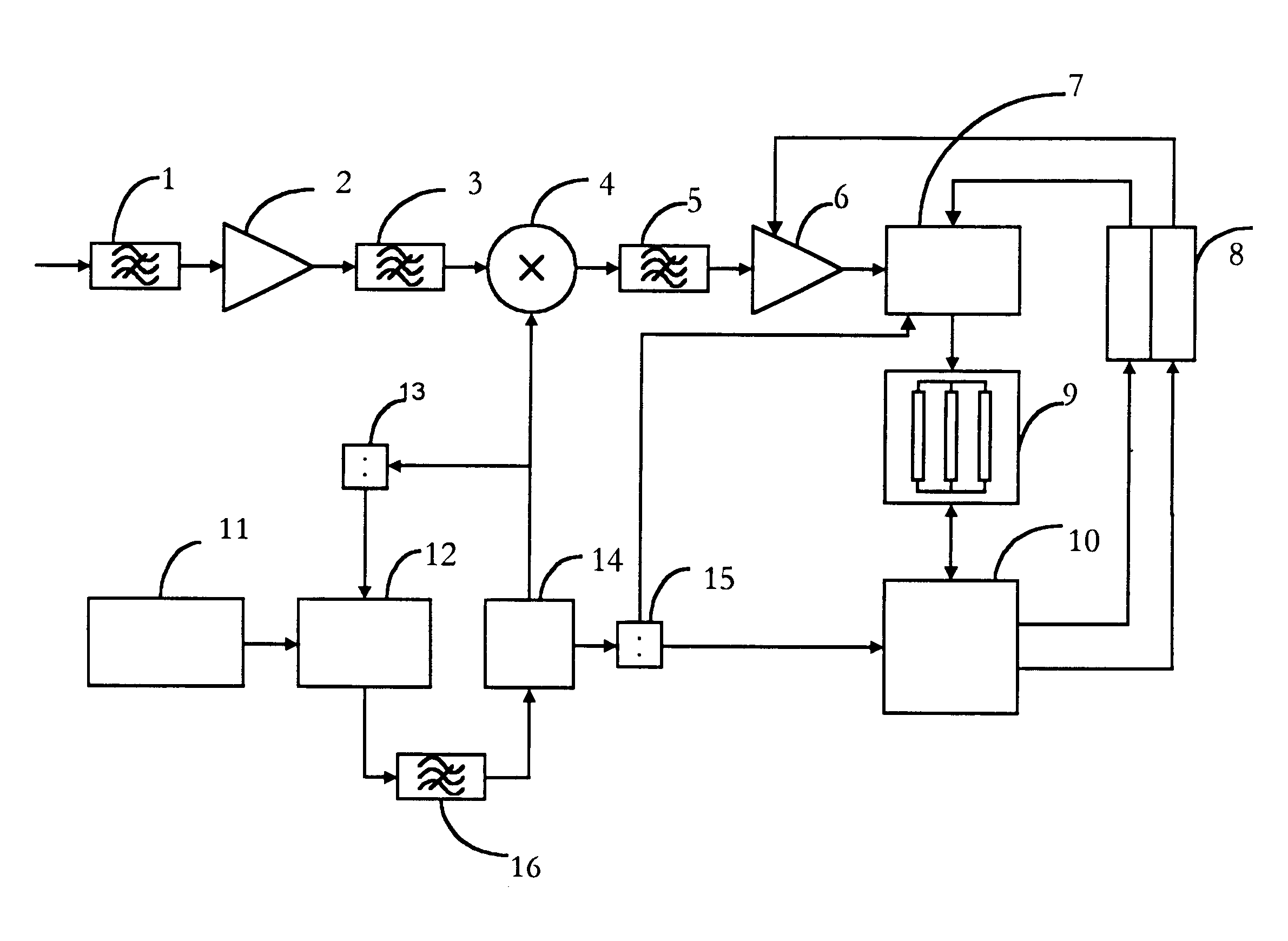
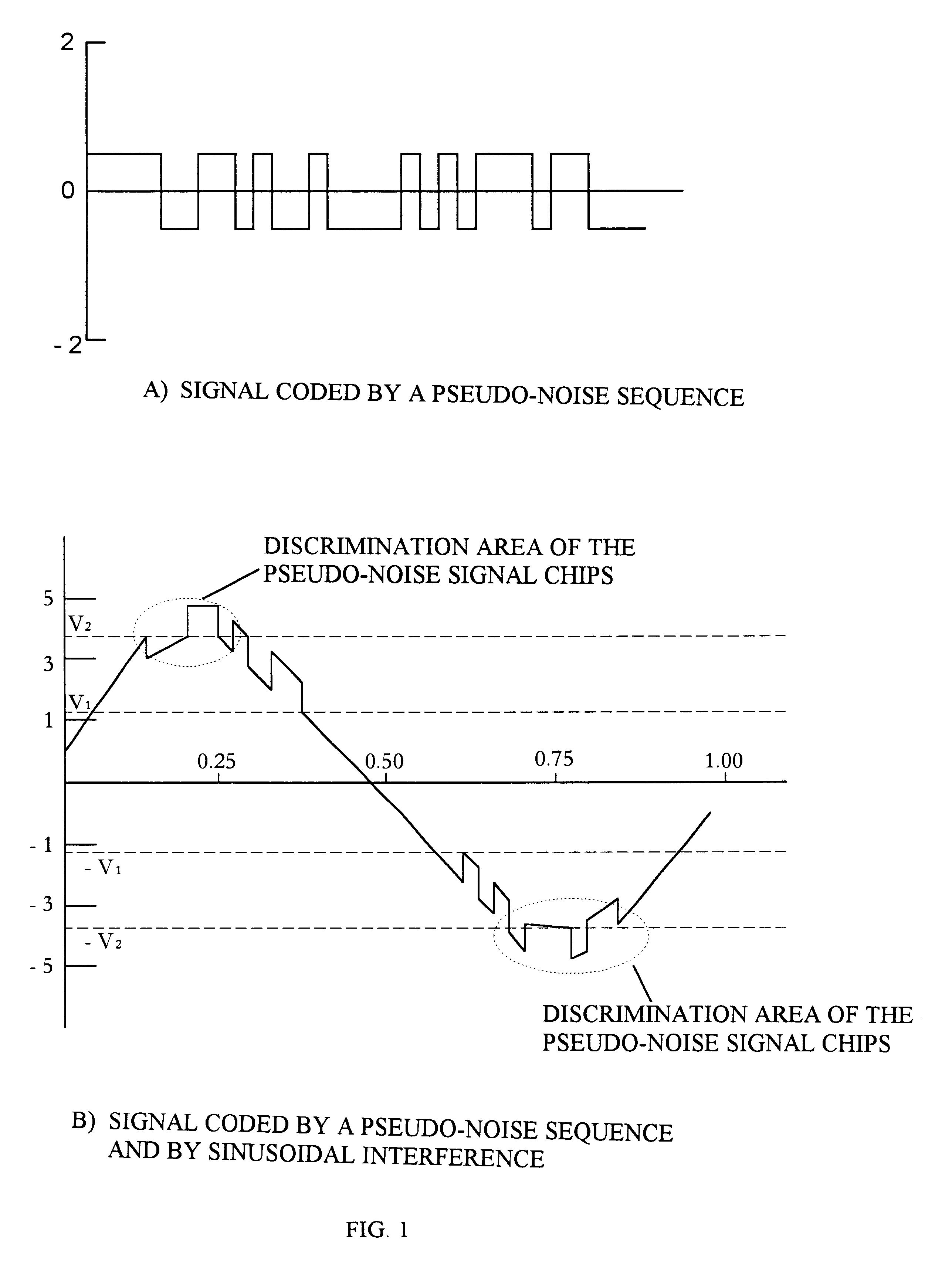
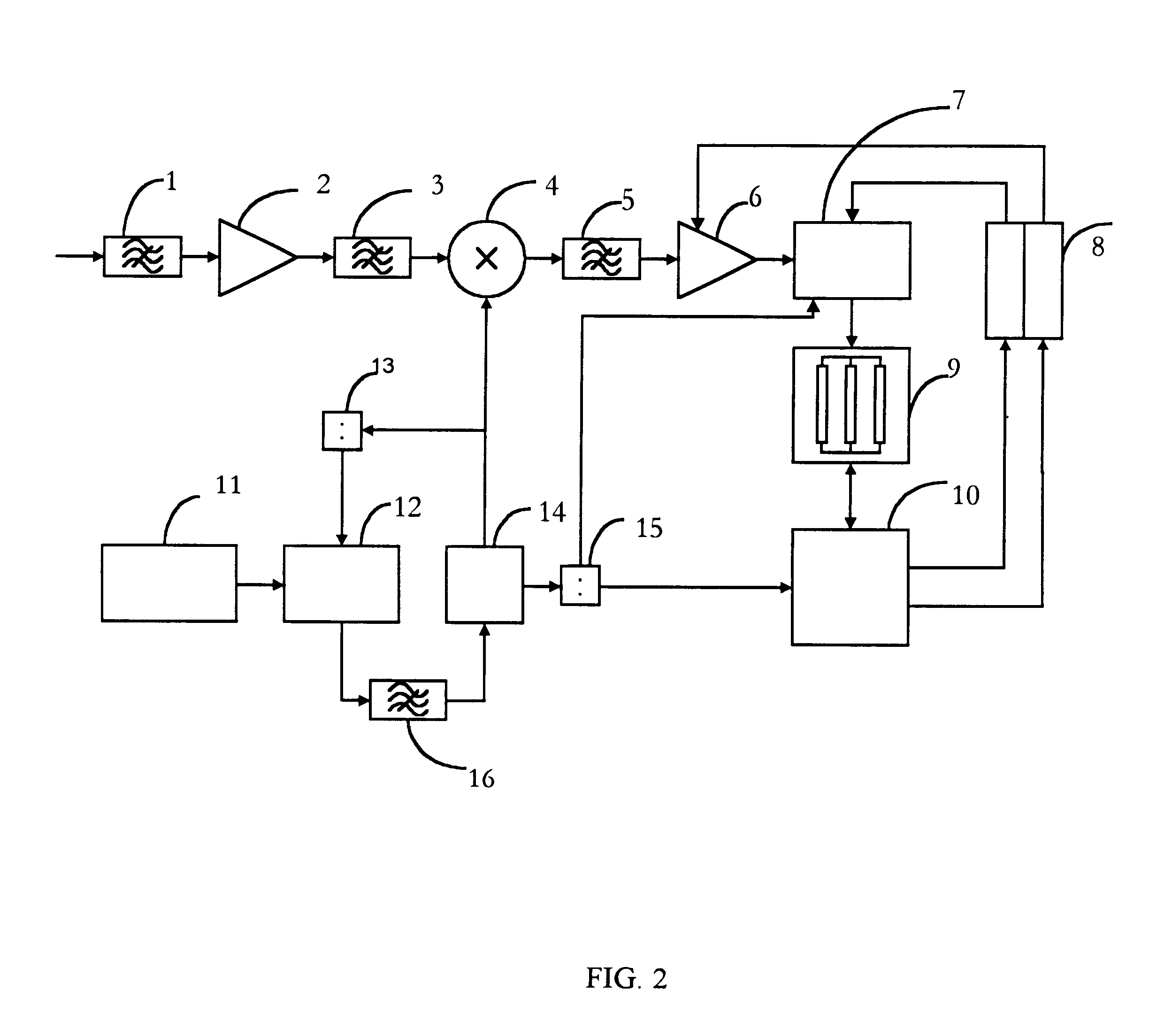
InactiveUS6816539B1Easy to quantifyInhibition is effectiveBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingControl signalCompensation effect
The invention relates to systems for receiving a digital radio signal and, more particularly, to receivers of radio signals, coded with a pseudo-noise sequence, which are used in global positioning system GPS (USA) and GLONASS (Russia), allowing a compensation effect for the narrow-band interference by using a device, controlled by the processor, with an automatic gain control, multilevel analog-to-digital converter, and additional correlation channel for detection of sinusoidal interference consisting of the digital generator having quadrature mixers and accumulators. Information from output of the of accumulators is read by a processor, in which is detected the presence (or absence) of interference, and the amplitude is evaluated. Therefore, the processor generates control signal directing amplification in the device using an automatic gain control.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signal receiving method and correlator thereof
ActiveCN102096078AFix compatibility issuesImprove continuitySatellite radio beaconingNumerical controlNatural satellite
The invention provides a multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) signal receiving method which supports the receiving of satellite signals of a GPS (Global Position System), a GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System), a Big Dipper navigation system and a Galileo satellite navigation system at present. The invention also discloses a multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS signal receiving correlator which comprises N multi-system correlated channels, wherein each multi-system correlated channel mainly comprises a carrier numerical controlled oscillator (NCO), a code NCO, a pseudo-random code generator and an integrating and zero clearing module; each code NCO is used for outputting a pulse sequence for triggering the pseudo-random code generator and also generating square signals with the same rate as subcarrier signals in a BOC (1, 1) signal demodulation mode; each pseudo-random code generator can generate 14 grades of pseudo-random codes at most; and each integrating and zero clearing module has an overflow protection function and improves the reliability. The multi-satellite navigation system compatible GNSS correlator can be compatible with four satellite systems, effectively improves the reliability and the continuity of navigation and positioning and obviously reduces the use risk of single-system navigation.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
Processing multi-GNSS data from mixed-type receivers
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
System and method for enhancing broadcast or recorded programs with information on the world wide web
ActiveUS7552193B2Easy access to informationEasy accessTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVideo playerTelevision receivers
The present invention is directed to a system, method or computer program, for enabling a radio auditor or a television viewer (100) to access complementary information (101) related to a broadcast program (102) received in real-time (or to a recorded program previously broadcast and played back on an audio or video player / recorder). The preferred embodiment of the invention relates to a system and method for enabling a person (100) receiving a broadcast program (102), (or listening or watching a recorded program), to select a plurality of topics or sequences drawing his or her attention (101, 103) and for immediately, or later on, accessing additional information related to these topics or sequences from the Word Wide Web. The system is based on a synchronization of the local times of receivers (or recorders) and transmitters according to a same universal-time (201, 202), so that the flow of information transmitted and received (or recorded) is always synchronized, independently of the relative positions of receivers (or recorders) and transmitters. The synchronization is done referring to an universal time such as the Global Positioning System Time (GPS-time), the Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System (GLONASS) time or another suitable universal time based on a satellite system. The GPS or GLONASS receivers are connected or integrated to the broadcasting stations. At the receiver side, GPS or GLONASS receivers may be integrated or connected to user devices e.g., Personal Computers, wearable computers, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), smart phones or onboard mobile computers (or to the audio or video recorders) that may be independent or separate from the radio or television receivers. The system is also based on a plurality of hyperlinks defined for given time intervals during the production of the broadcast program. These time intervals are synchronized with the universal Time. The hyperlinks are associated with the transmitted (and recorded) information. The hyperlinks can be retrieved, selected and activated by radio auditors or television viewers during the time intervals for which they have been defined, during the broadcast of the program (or during its playback).
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com