Patents
Literature
333 results about "Differential GPS" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
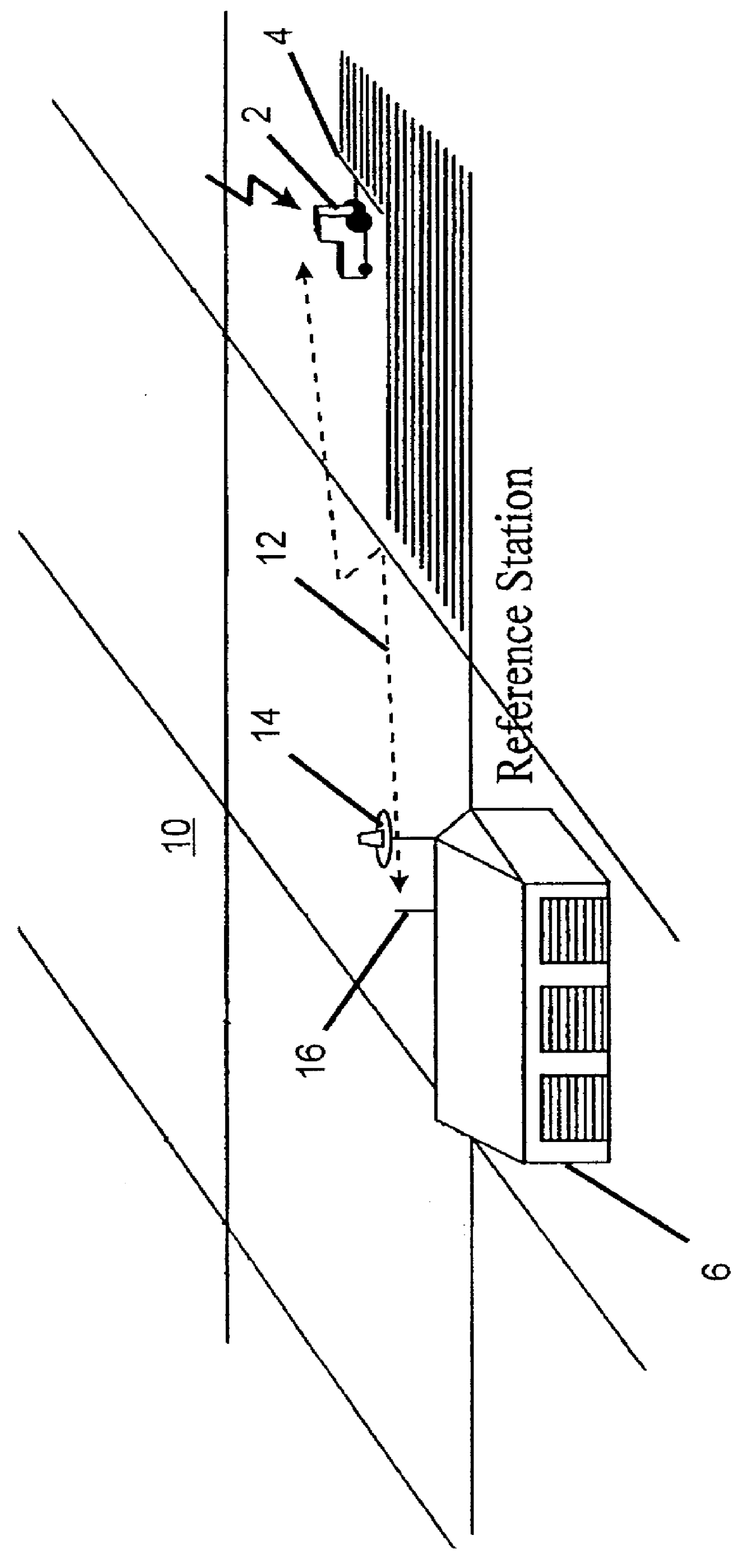
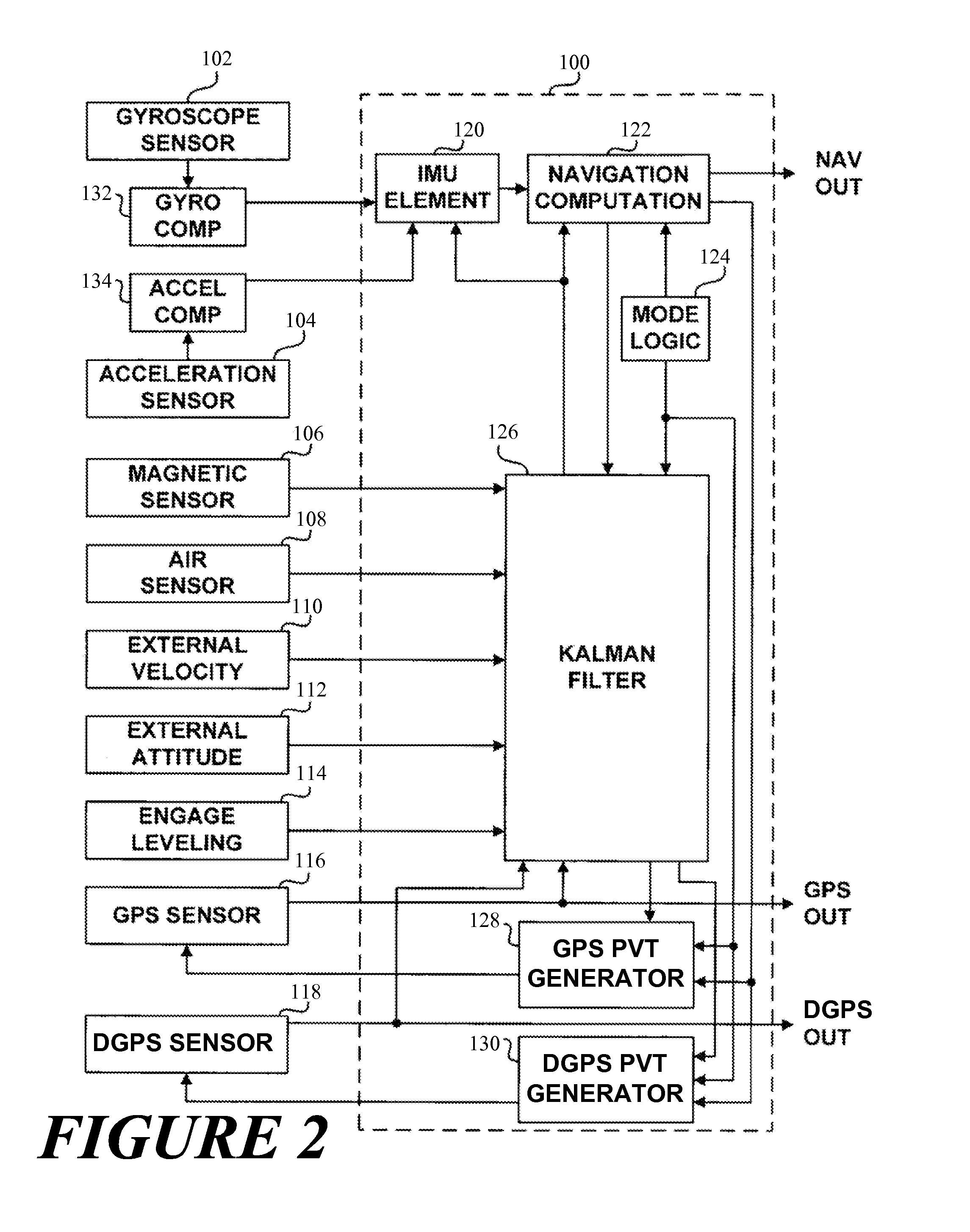
A Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) is an enhancement to the Global Positioning System (GPS) which provides improved location accuracy, in the range of operations of each system, from the 15-meter nominal GPS accuracy to about 1-3 cm in case of the best implementations.
Method and system for automatic control of vehicles based on carrier phase differential GPS
InactiveUS6052647AImprove system stabilitySimple processDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationAutomatic train controlAutomatic control
Described is an automatic control system for land (and possible marine) vehicles based on carrier phase differential GPS (CPGPS). The system relies on CPGPS to determine vehicle position and attitude very precisely (position to within 1 cm and attitude to within 0.1 DEG ). A system incorporates a technique to calculate and compensate for antenna motion due to vehicle roll and pitch. One aspect of the system utilizes an intelligent vehicle controller that recognizes and adapts to changing conditions, such as vehicle speed, implements towed by the vehicle, soil conditions, and disturbance level. The system provides the capability to control the vehicle on various paths, including straight lines and arbitrary curves. Also described is a technique for initialization and vehicle control using only a single pseudolite.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Fully-coupled vehicle positioning method and system thereof
InactiveUS6424914B1Improve performanceImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesFully coupledNavigation system
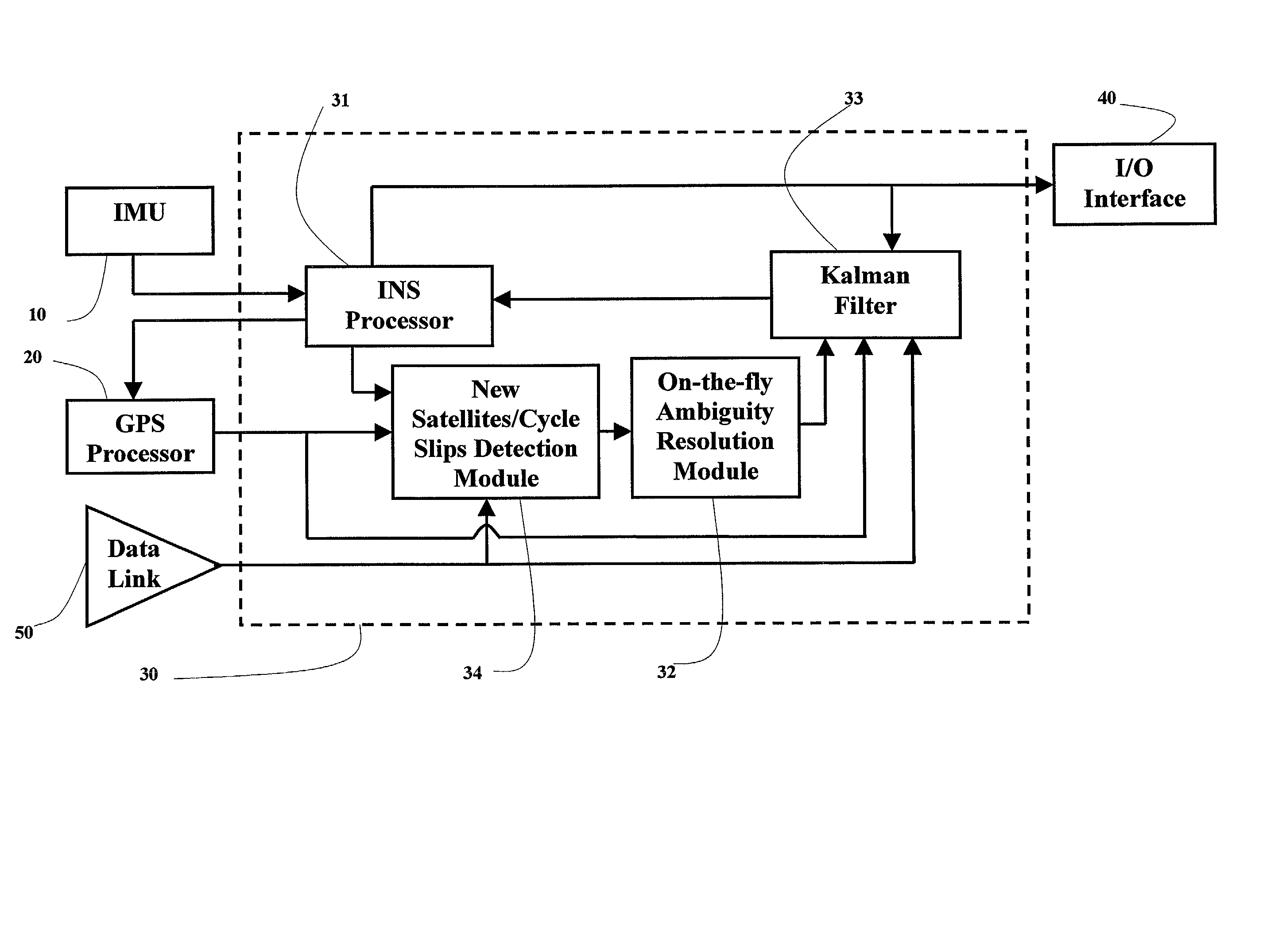
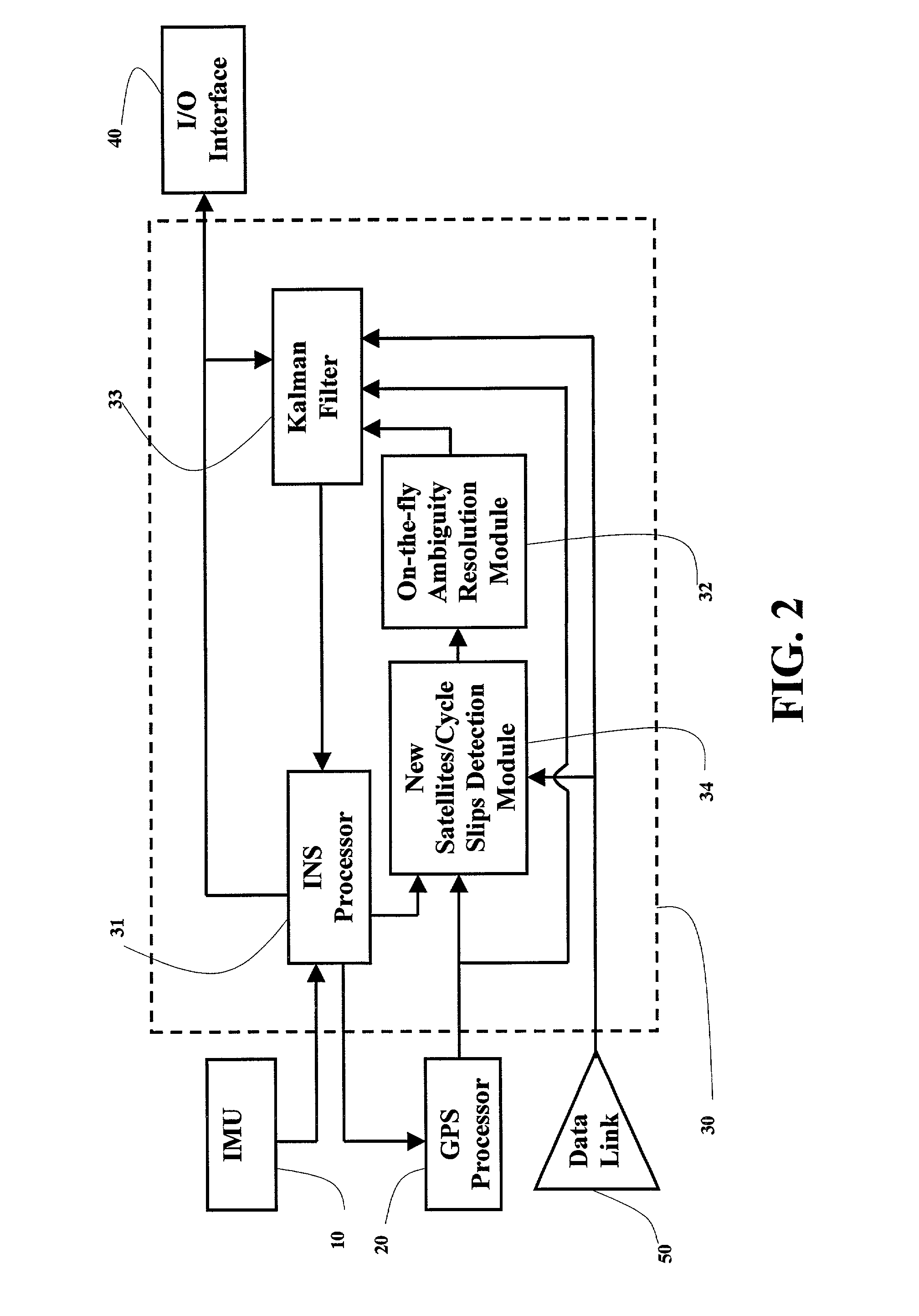
A fully-coupled vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS substantially solves problems encountered in either the global positioning system-only or the inertial novigation system-only, such as loss of global positioning satellite signal, sensitivity to jamming and spoofing, and an inertial solution's drift over time, in which the velocity and acceleration from an inertial navigation processor of the integrated GPS / INS system are used to aid the code and carrier phase tracking of the global positioning system satellite signals, so as to enhance the performance of the global positioning and inertial integration system, even in heavy jamming and high dynamic environments. To improve the accuracy of the integrated GPS / INS navigation system, phase measurements are used and the idea of the differential GPS is employed. A master-slave relative positioning scheme is invented and is effective for high accuracy formation driving and flight.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS
InactiveUS6496778B1Improve performanceLow costPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceFully coupled
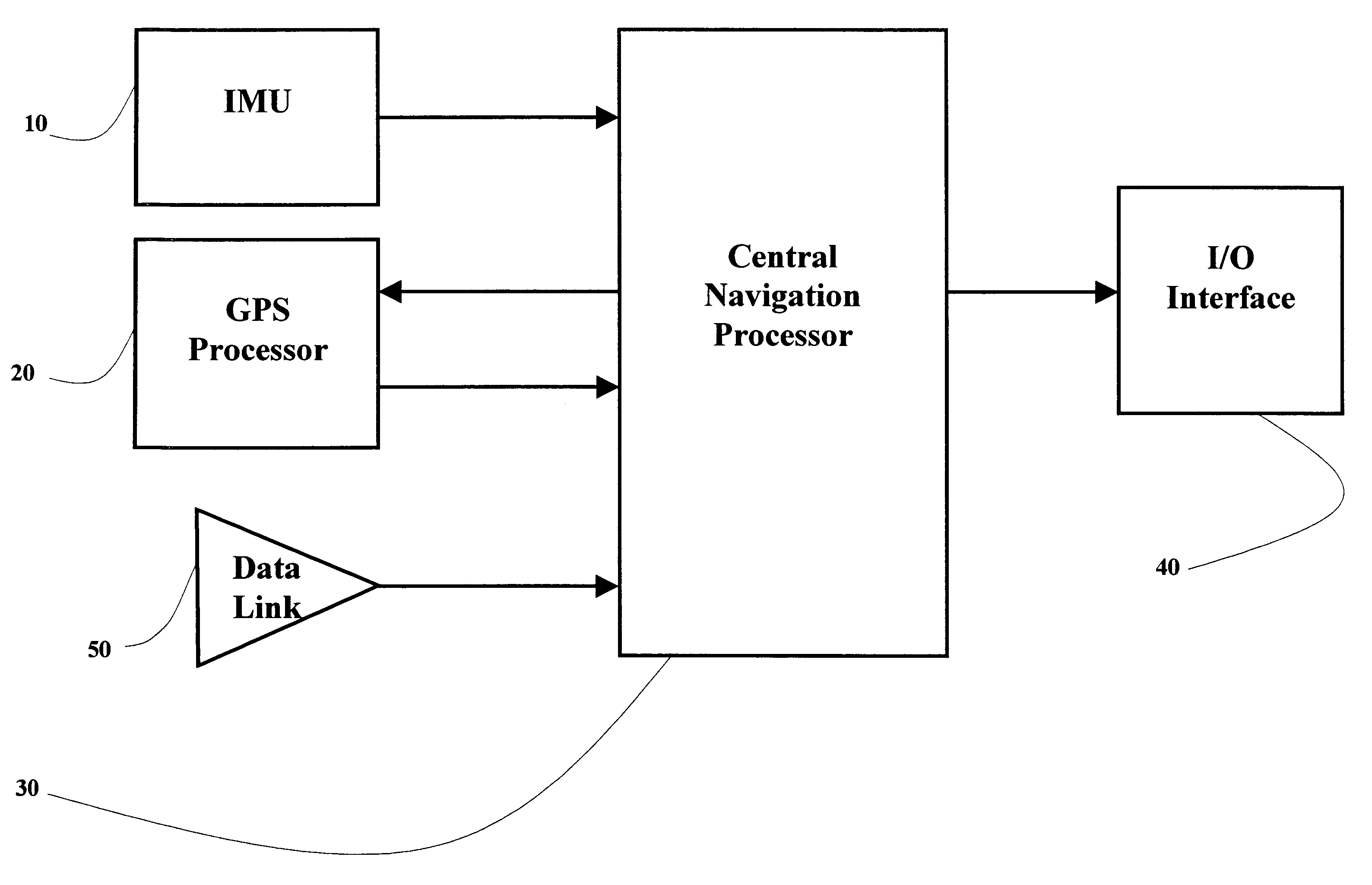
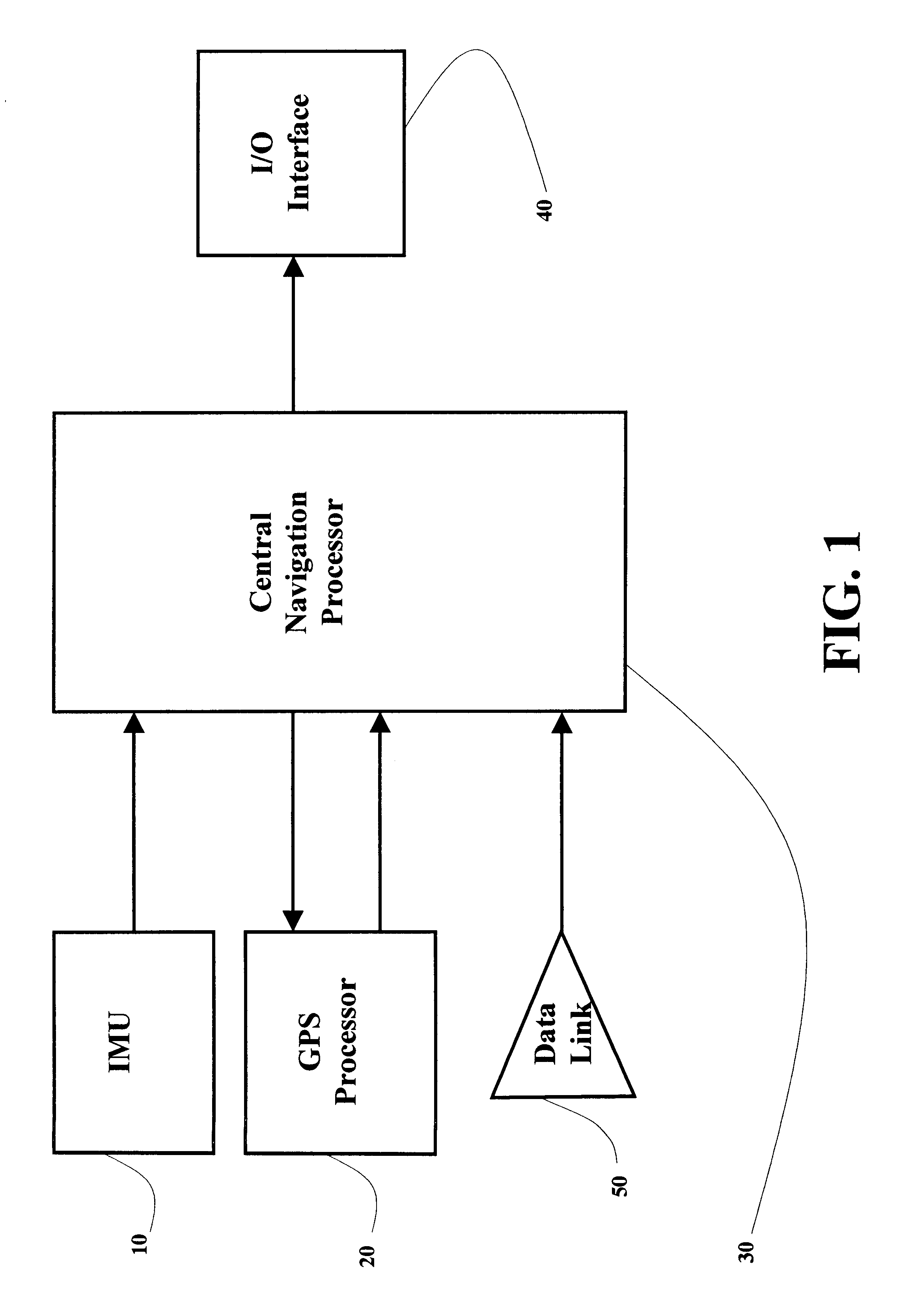
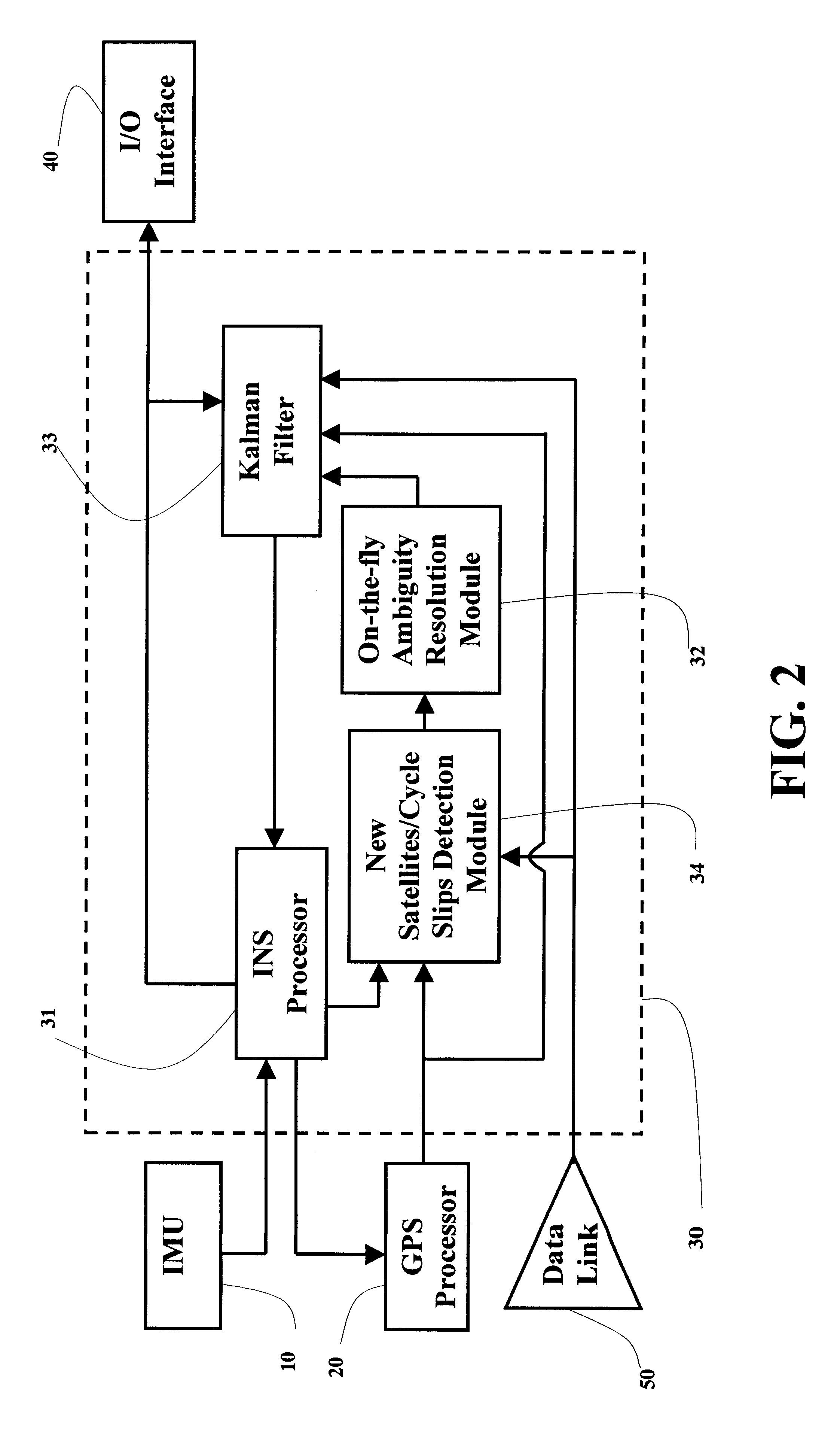
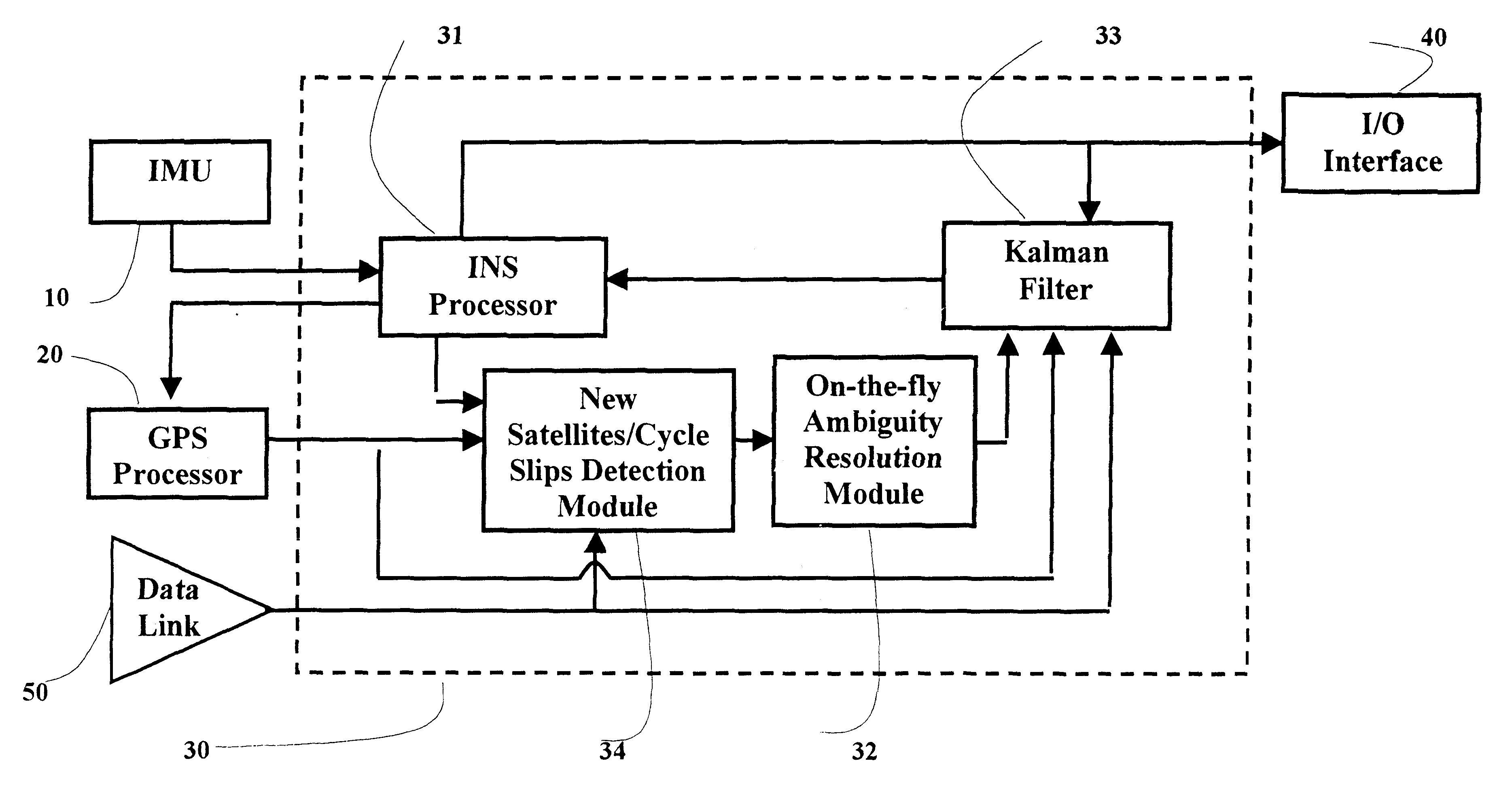
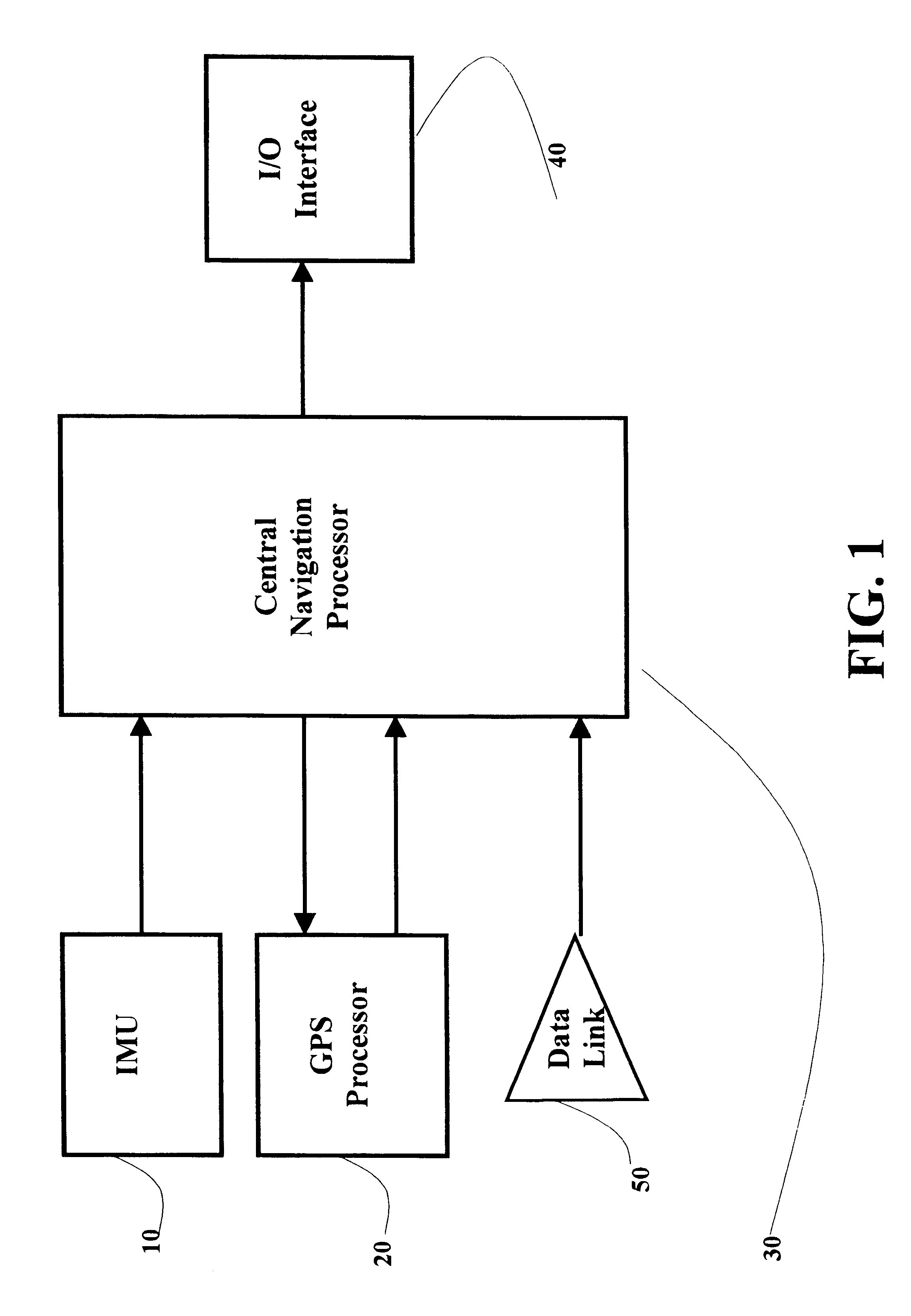
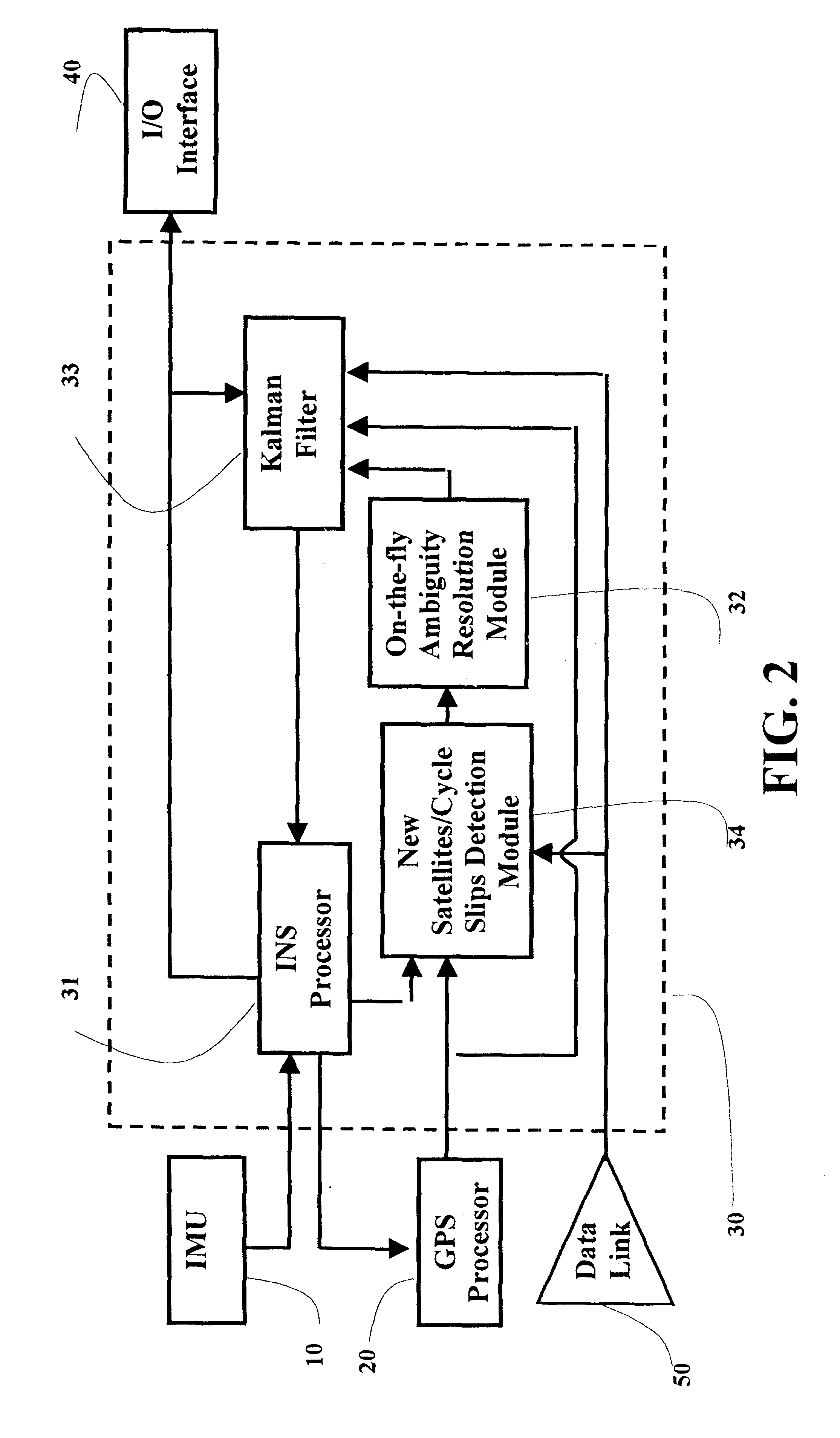
A real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS can substantially solve the problems encountered in either the global positioning system-only or the inertial navigation system-only, such as loss of global positioning satellite signal, sensitivity to jamming and spoofing, and an inertial solution's drift over time. In the present invention, the velocity and acceleration from an inertial navigation processor of the integrated GPS / INS system are used to aid the code and carrier phase tracking of the global positioning system satellite signals, so as to enhance the performance of the global positioning and inertial integration system, even in heavy jamming and high dynamic environments. To improve the accuracy of the integrated GPS / INS navigation system, phase measurements are used and the idea of the differential GPS is employed. However, integer ambiguities have to be resolved for high accuracy positioning. Therefore, in the present invention a new on-the-fly ambiguity resolution technique is disclosed to resolve double difference integer ambiguities. The real-time fully-coupled GPS / IMU vehicle positioning system includes an IMU (inertial measurement unit), a GPS processor, and a data link which are connected to a central navigation processor to produce a navigation solution that is output to an I / O (input / output) interface.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Railroad surveying and monitoring system
InactiveUS20100026551A1Easy to adaptOptimizationPosition fixationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTerrainLandform
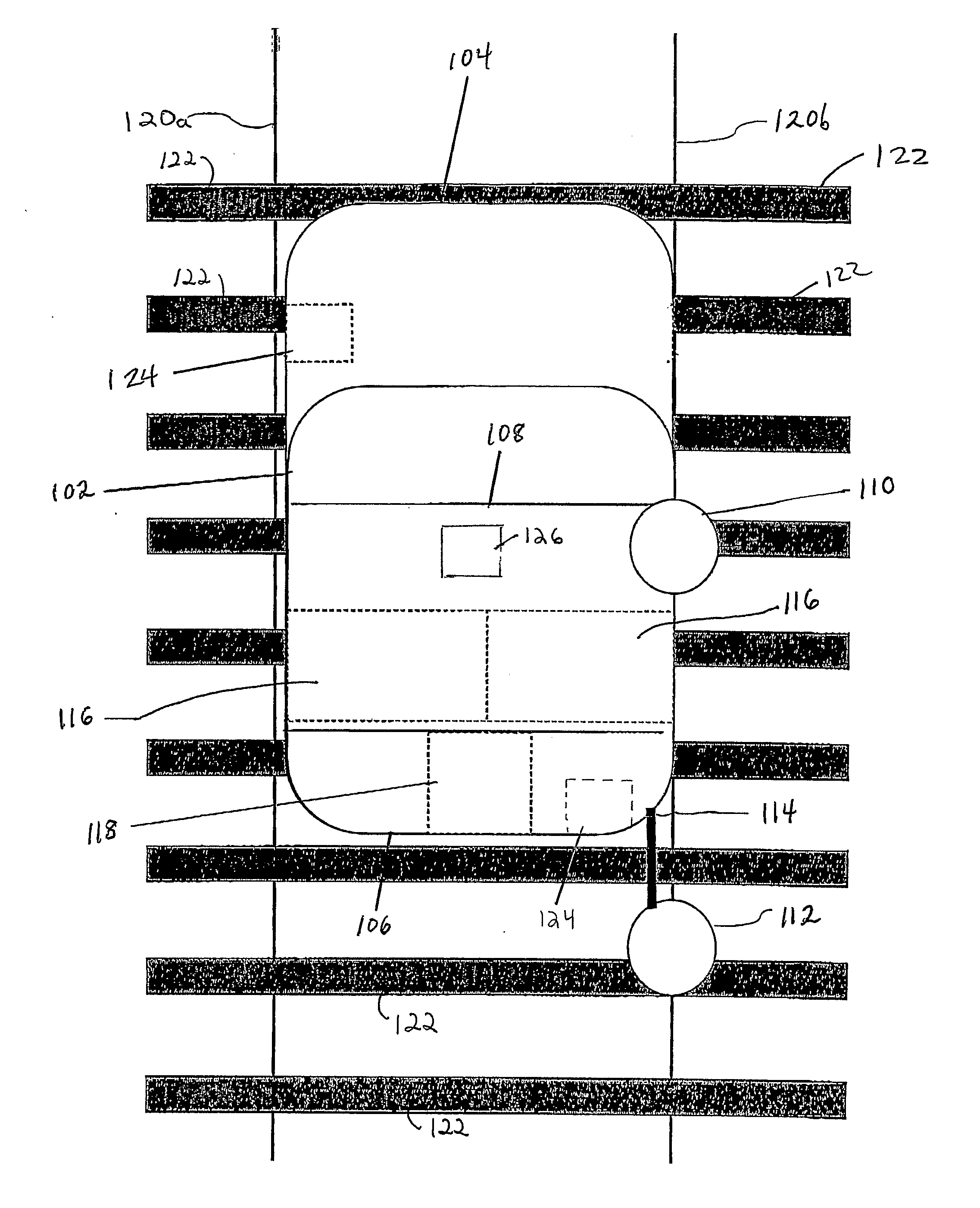
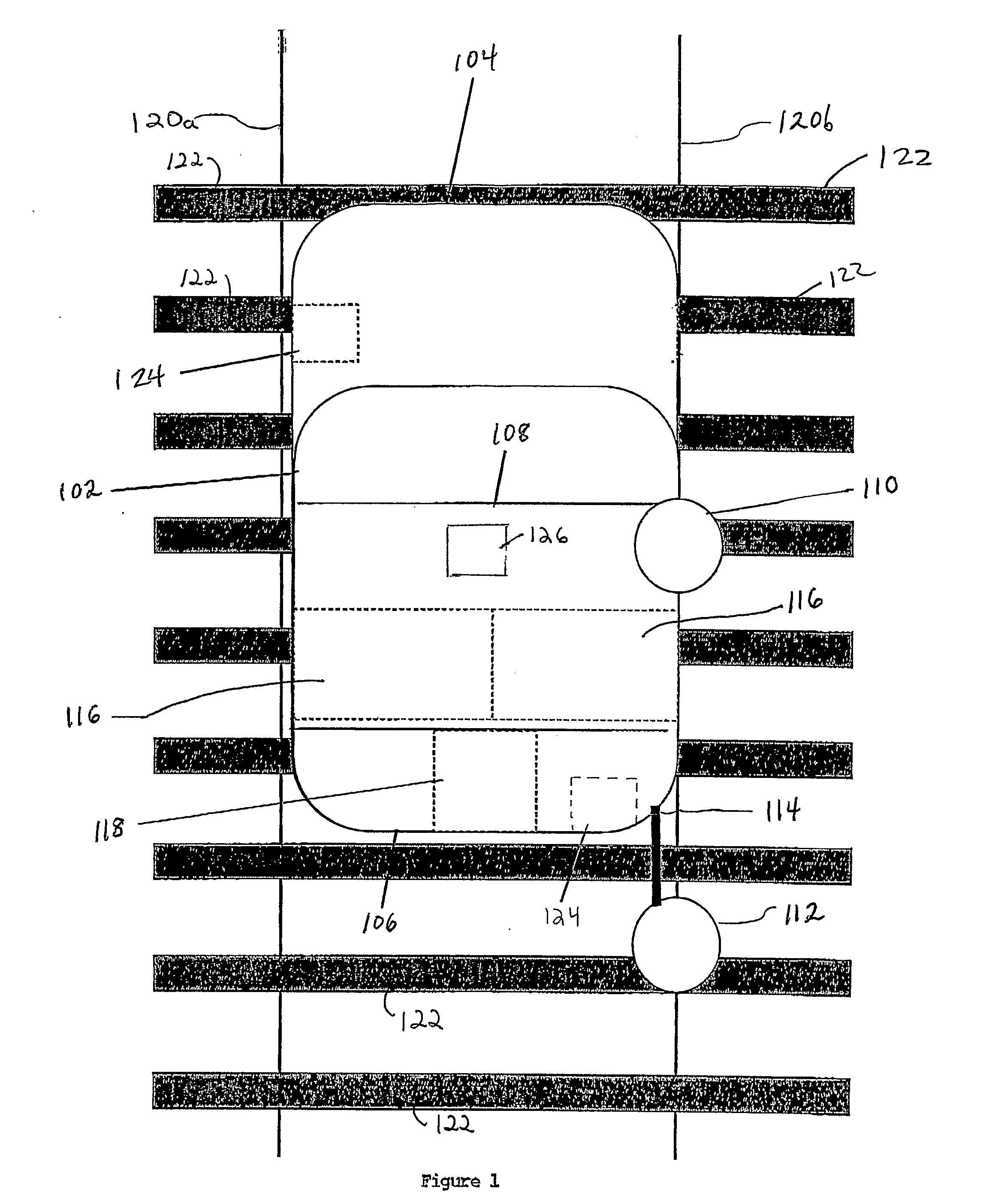
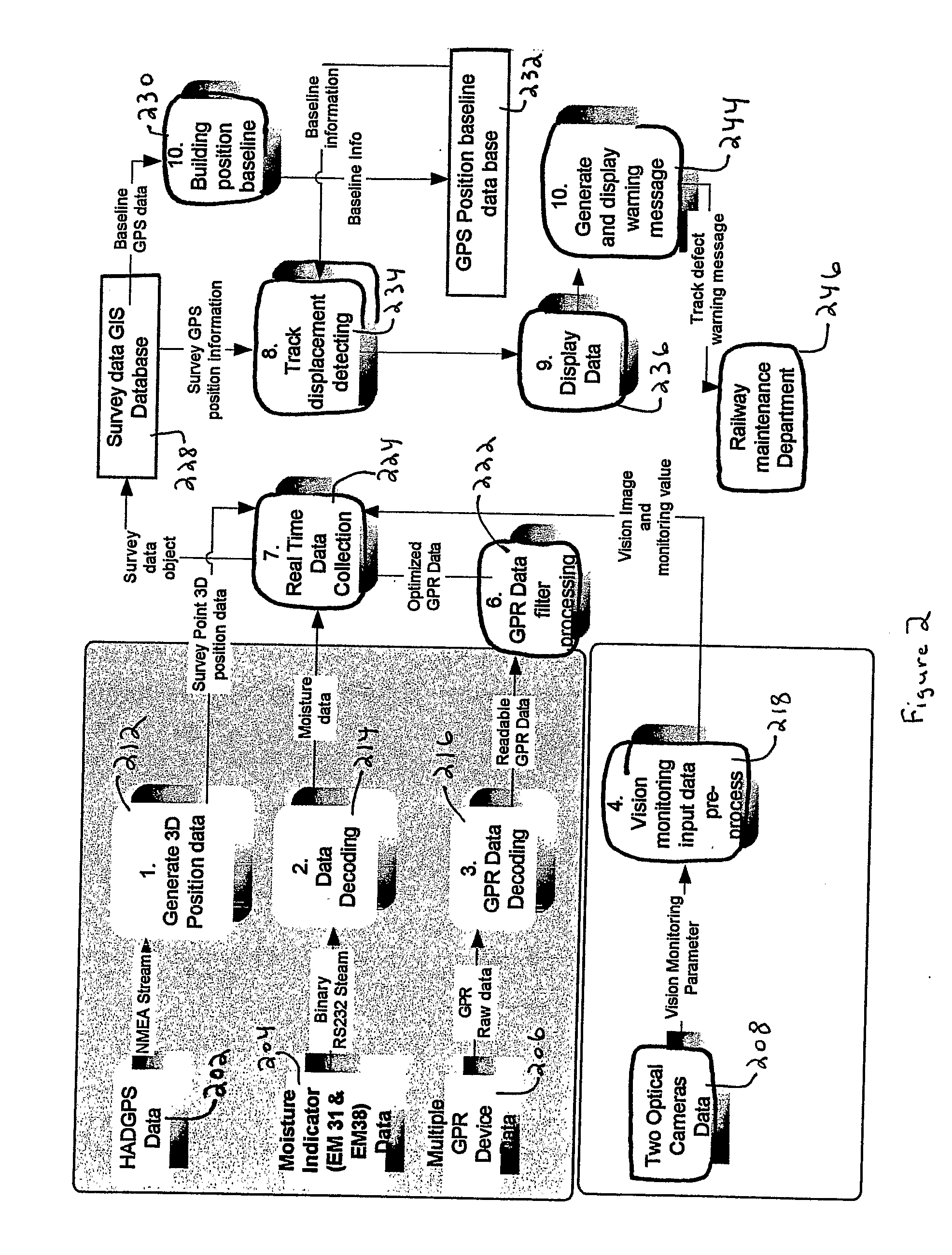
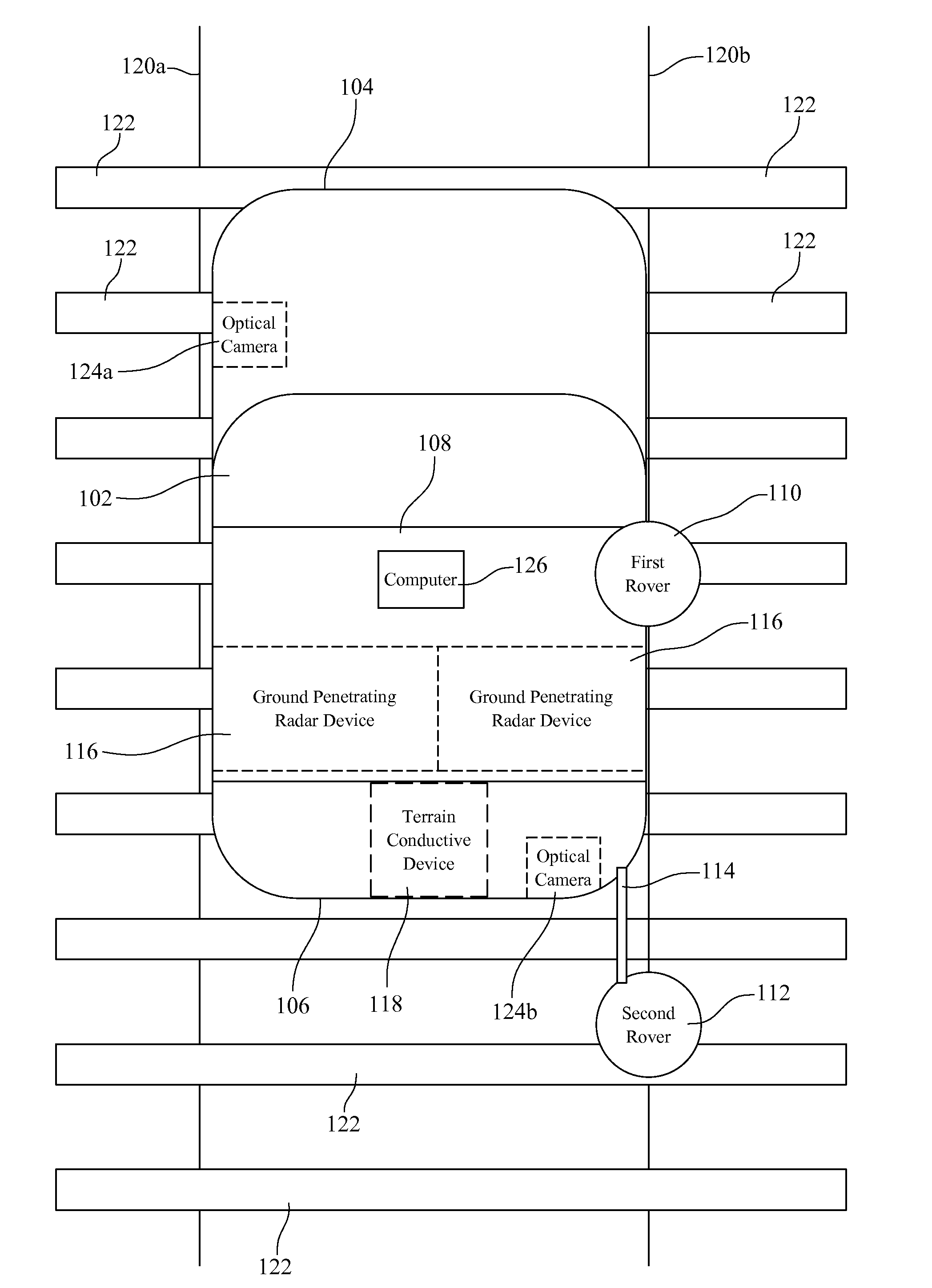
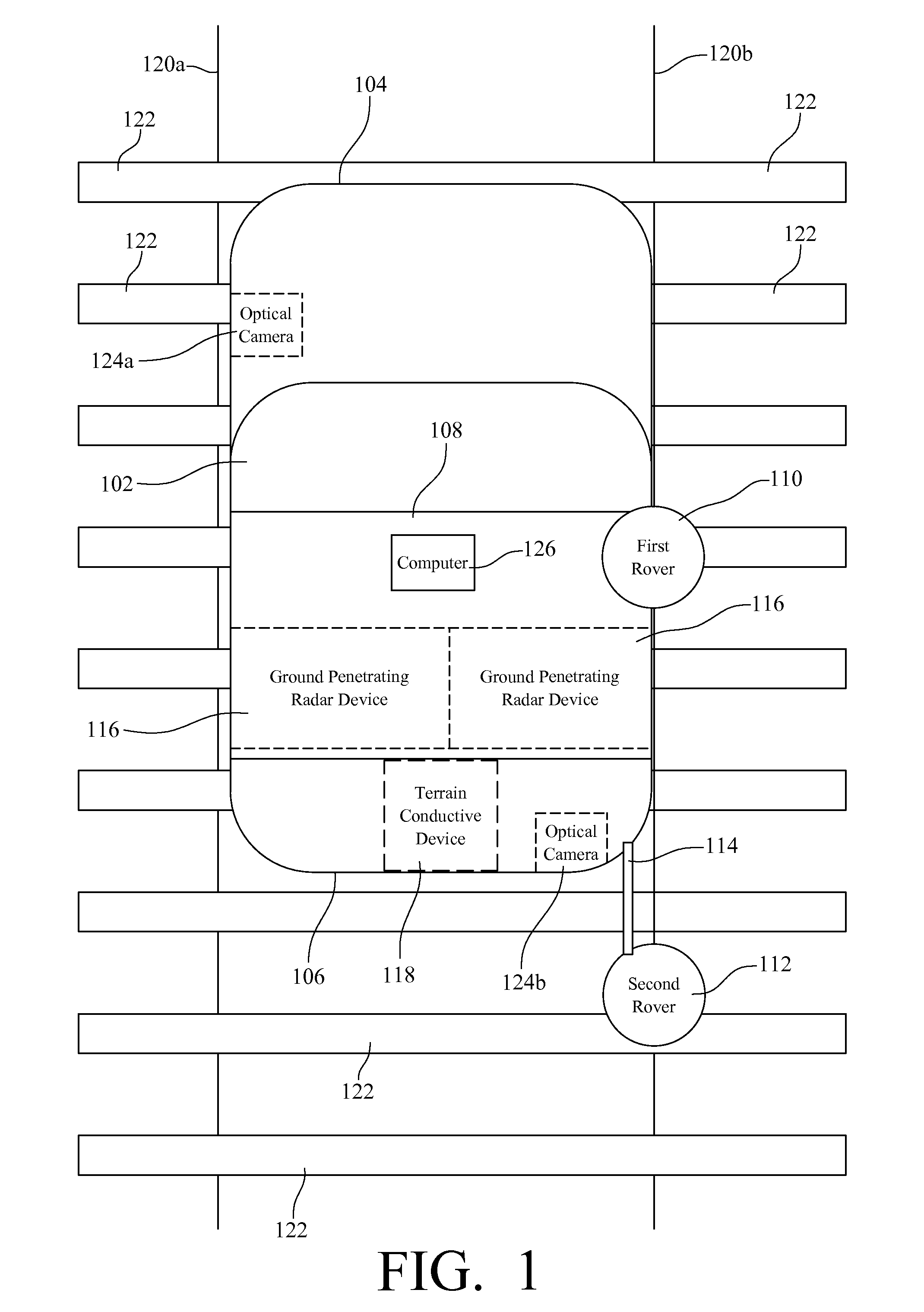
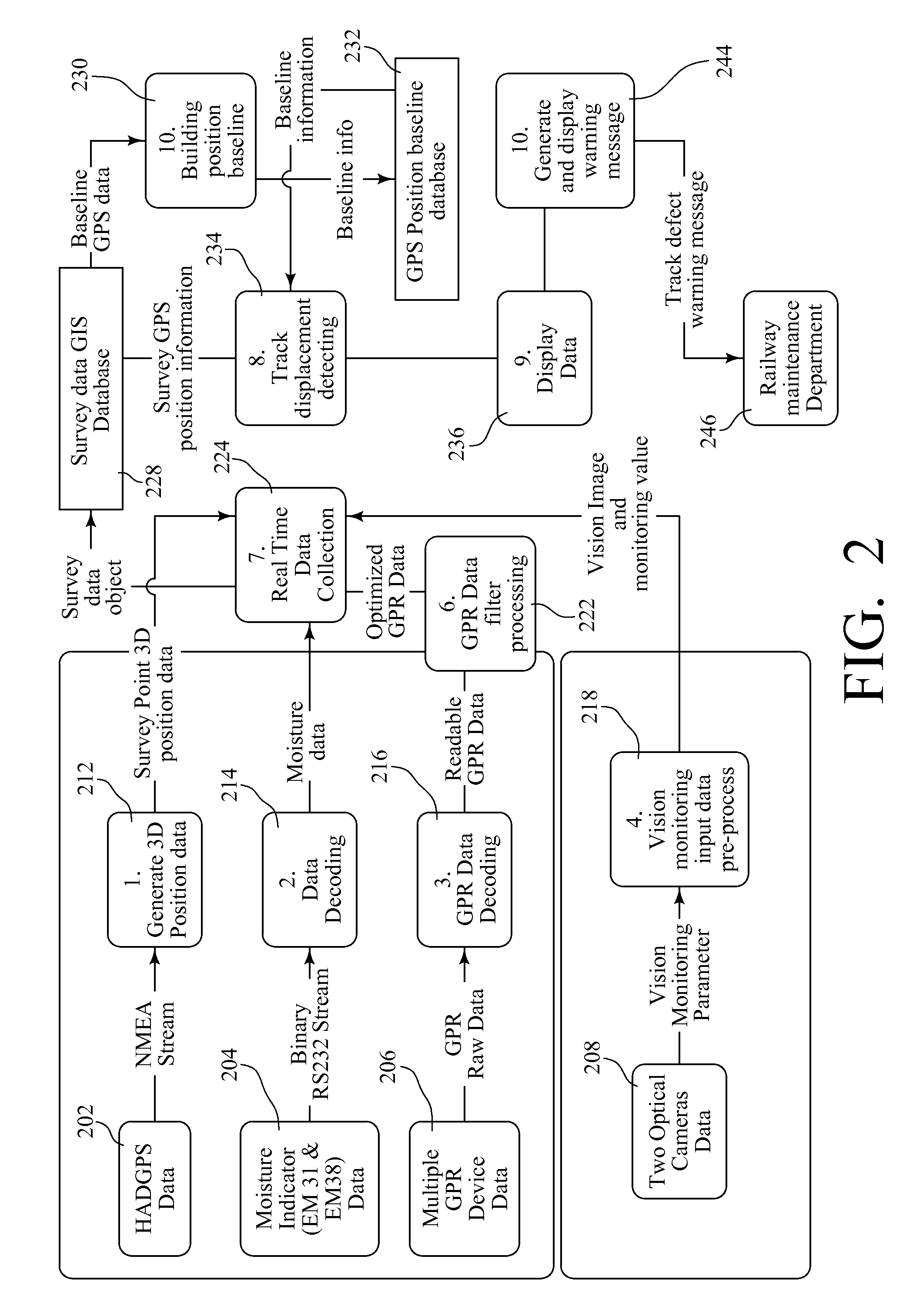
A Railroad Surveying and Monitoring System configured on a mobile platform for surveying, monitoring, and analyzing rail position and superstructure and terrain substructure of railroad tracks (20a,b) or other structures. The system employs two or more High Accuracy Differential Global Positioning System devices (110,112), ground penetrating radar devices (116), terrain conductivity instruments (118), optical cameras (124), and data receivers and processors (126), which in turn process, display, and store the data in a usable database. Precise coordinate data generated from a High Accuracy Global Positioning System provides both location data for subsurface sensors and surface sensors and rail position coordinates to monitor track displacements during track inspection in real time.
Owner:MARSHALL UNIV RES
Fully-coupled vehicle positioning method and system thereof
InactiveUS20020120400A1Improve performanceImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationFully coupledNavigation system
An improved fully-coupled vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS can substantially solve the problems encountered in either the global positioning system-only or the inertial navigation system-only, such as loss of global positioning satellite signal, sensitivity to jamming and spoofing, and an inertial solution's drift over time. In the present invention, the velocity and acceleration from an inertial navigation processor of the integrated GPS / INS system are used to aid the code and carrier phase tracking of the global positioning system satellite signals, so as to enhance the performance of the global positioning and inertial integration system, even in heavy jamming and high dynamic environments. To improve the accuracy of the integrated GPS / INS navigation system, phase measurements are used and the idea of the differential GPS is employed. A master-slave relative positioning scheme is invented and is effective for high accuracy formation driving and flight.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Auto-steering apparatus and method
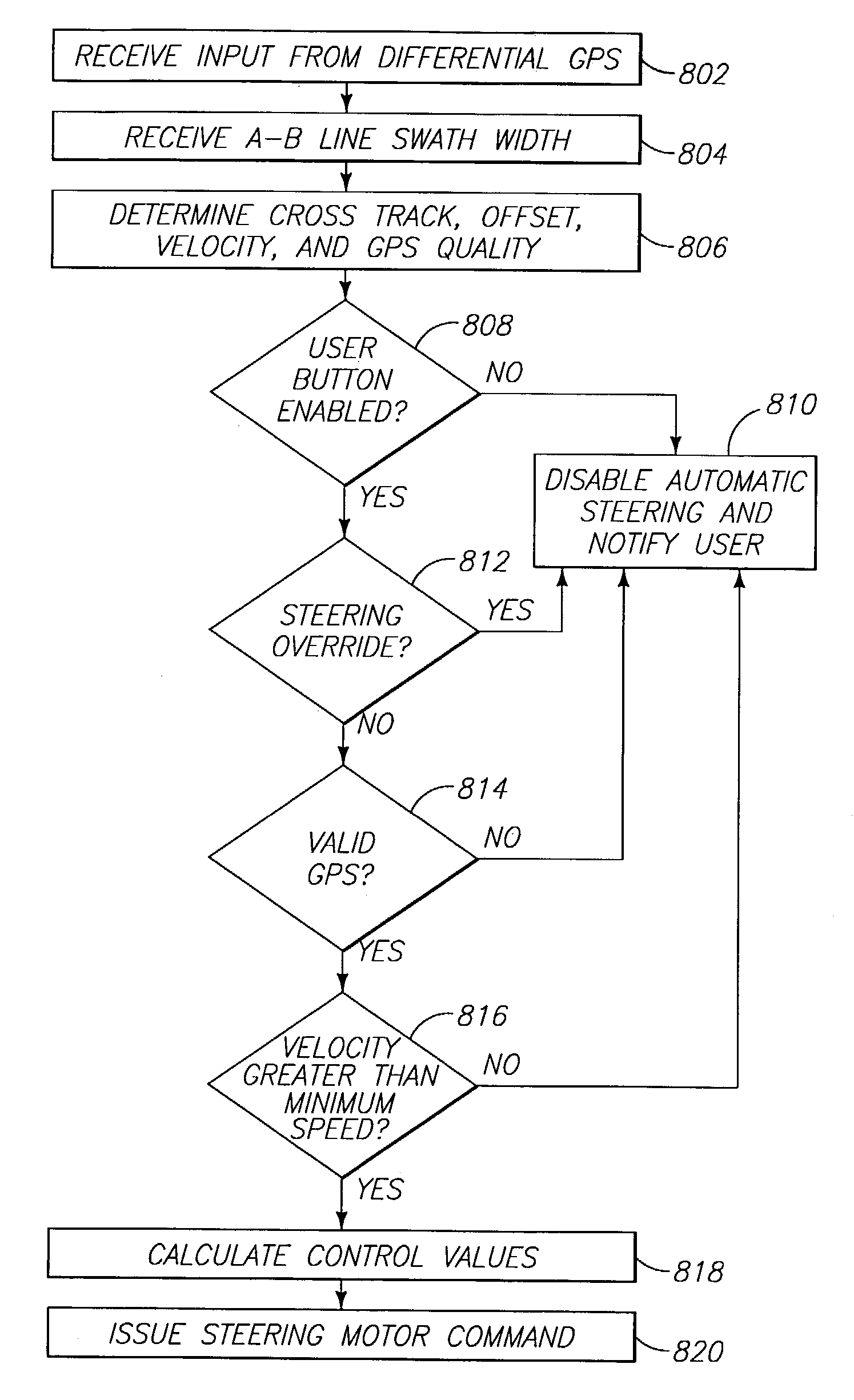
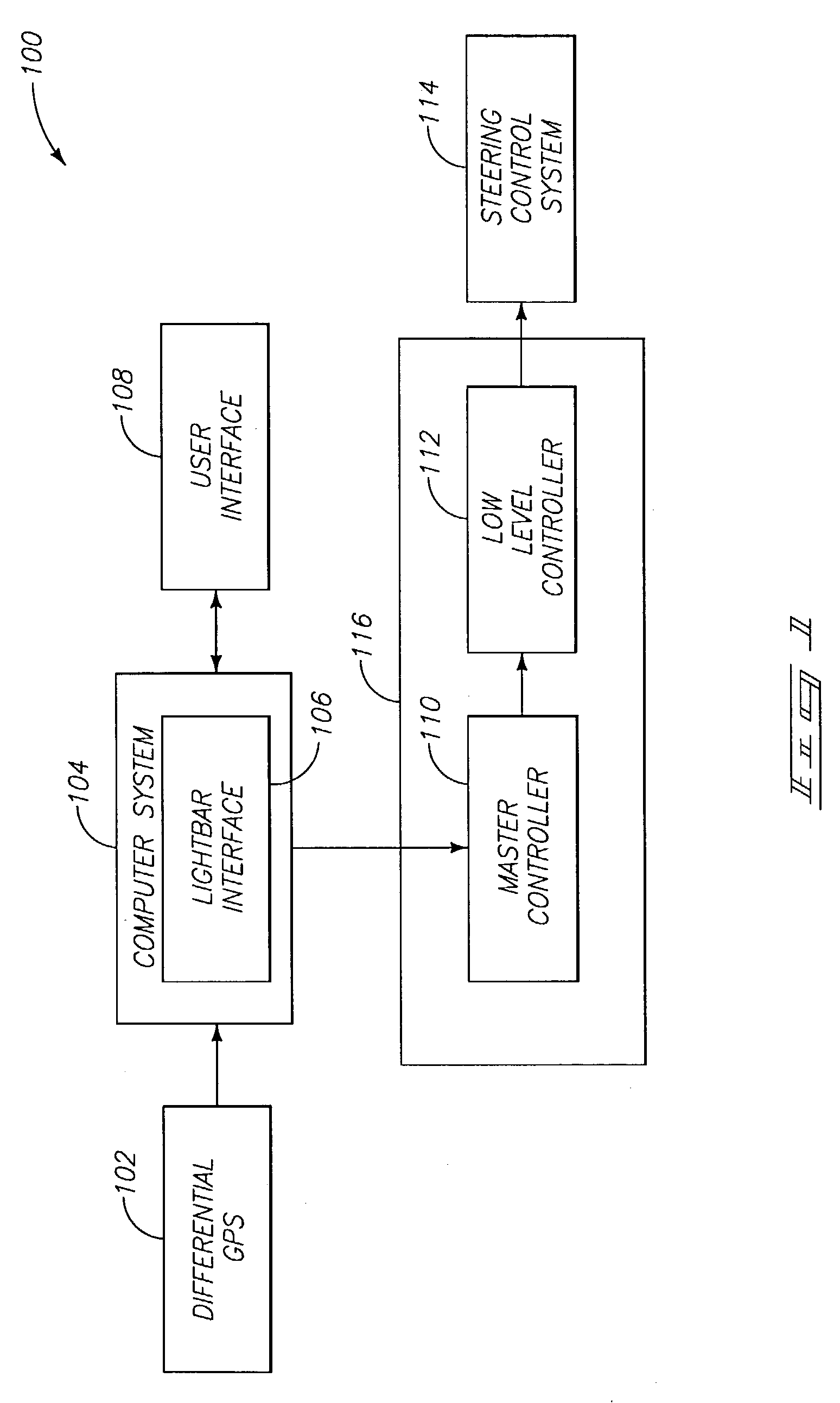
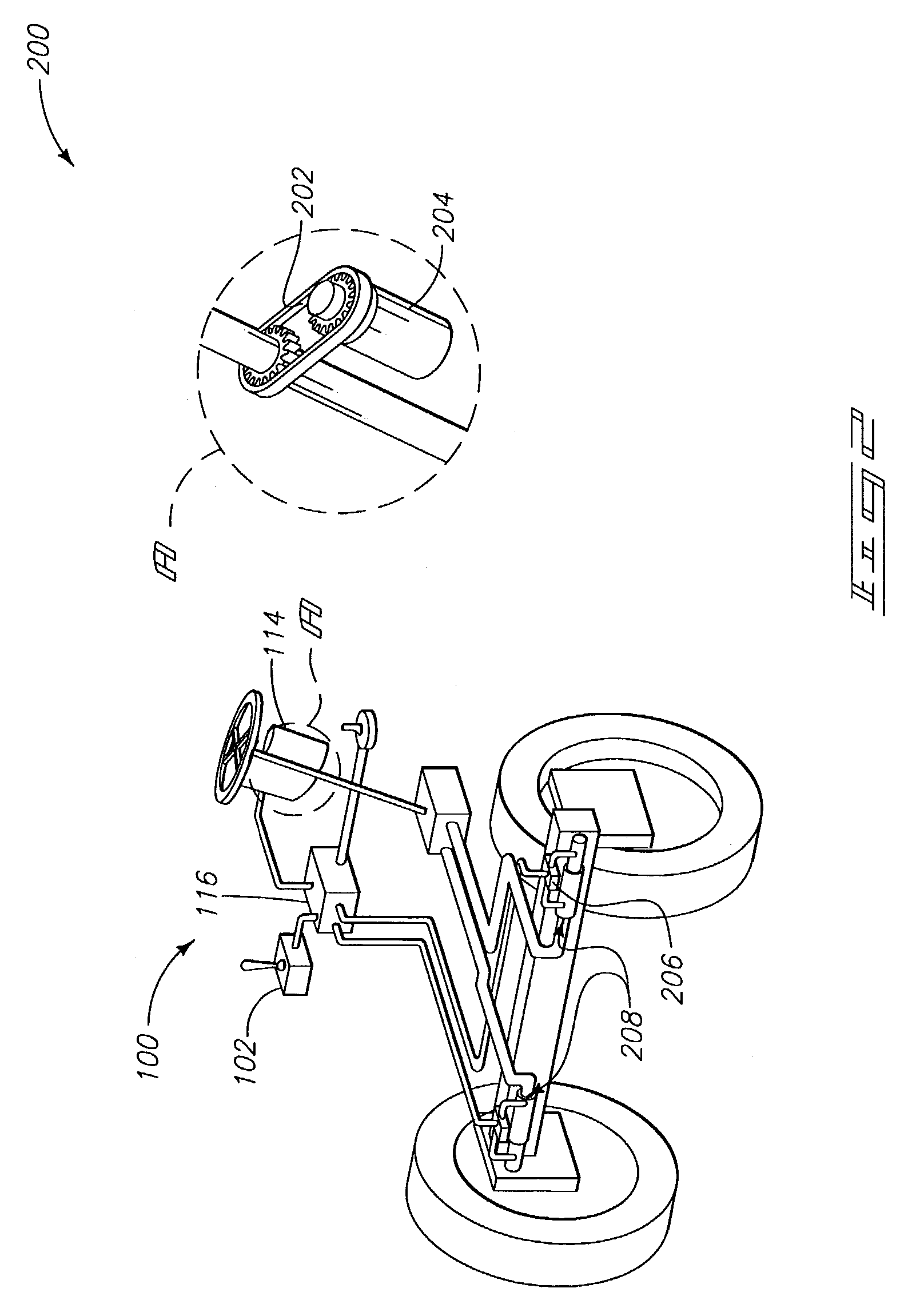
A vehicular guidance method involves providing a user interface using which data can be input to establish a contour for a vehicle to follow, the user interface further configured to receive information from a differential global positioning system (DGPS), determining cross track and offset data using information received from the DGPS, generating control values, using at least vehicular kinematics, the cross track, and the offset data, and providing an output to control steering of the vehicle, using the control values, in a direction to follow the established contour while attempting to minimize the cross track and the offset data.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
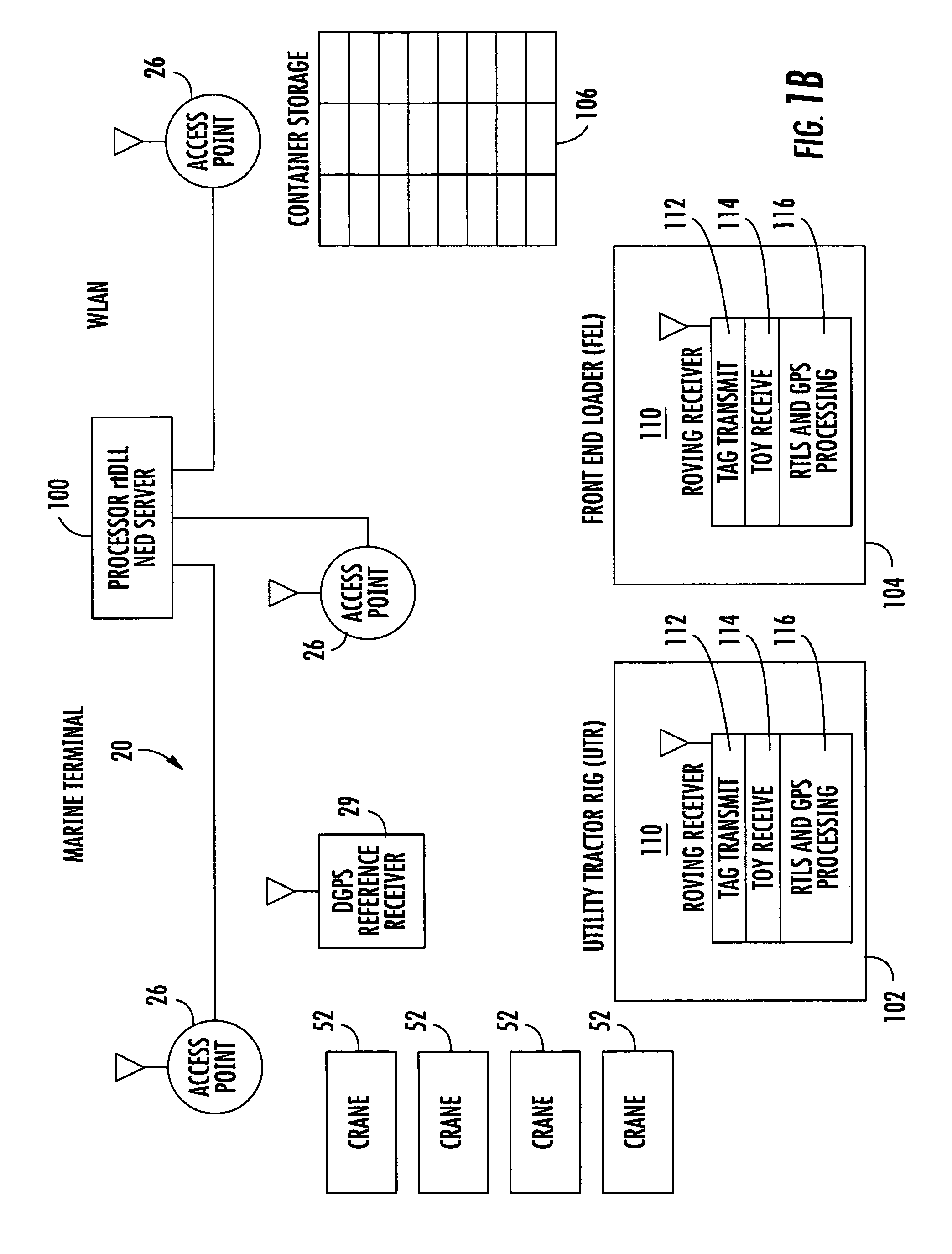
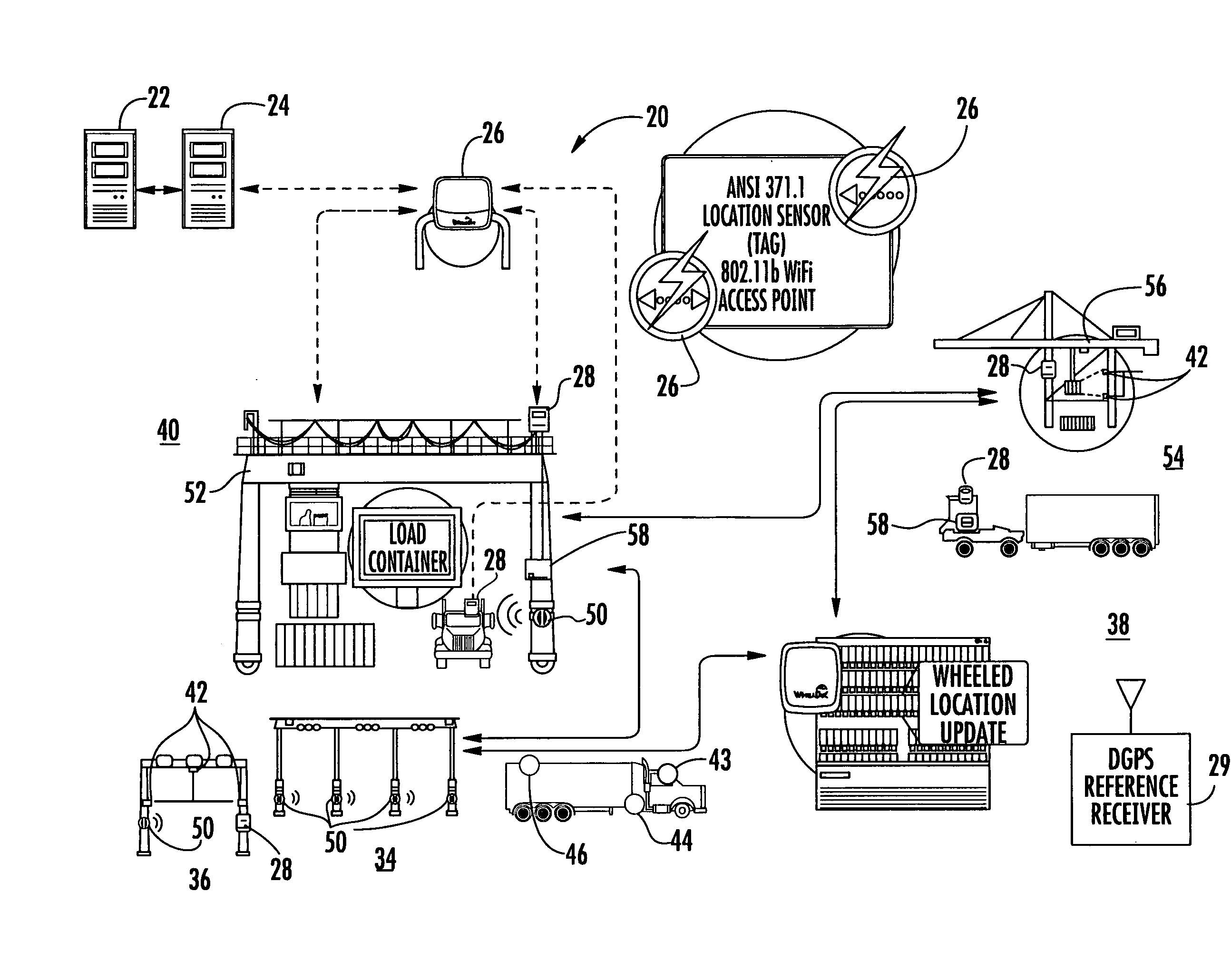
System and method for tracking vehicles and containers
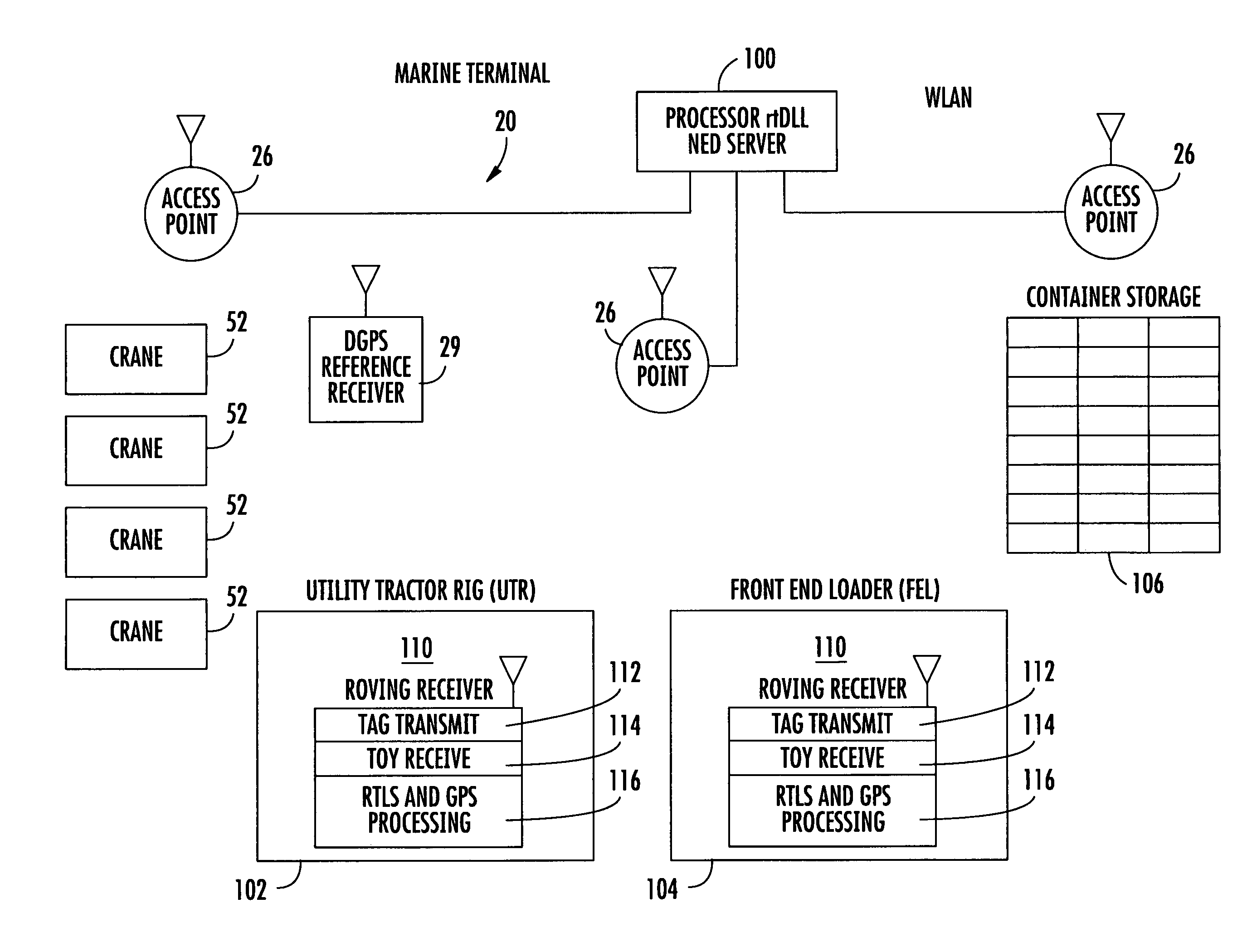
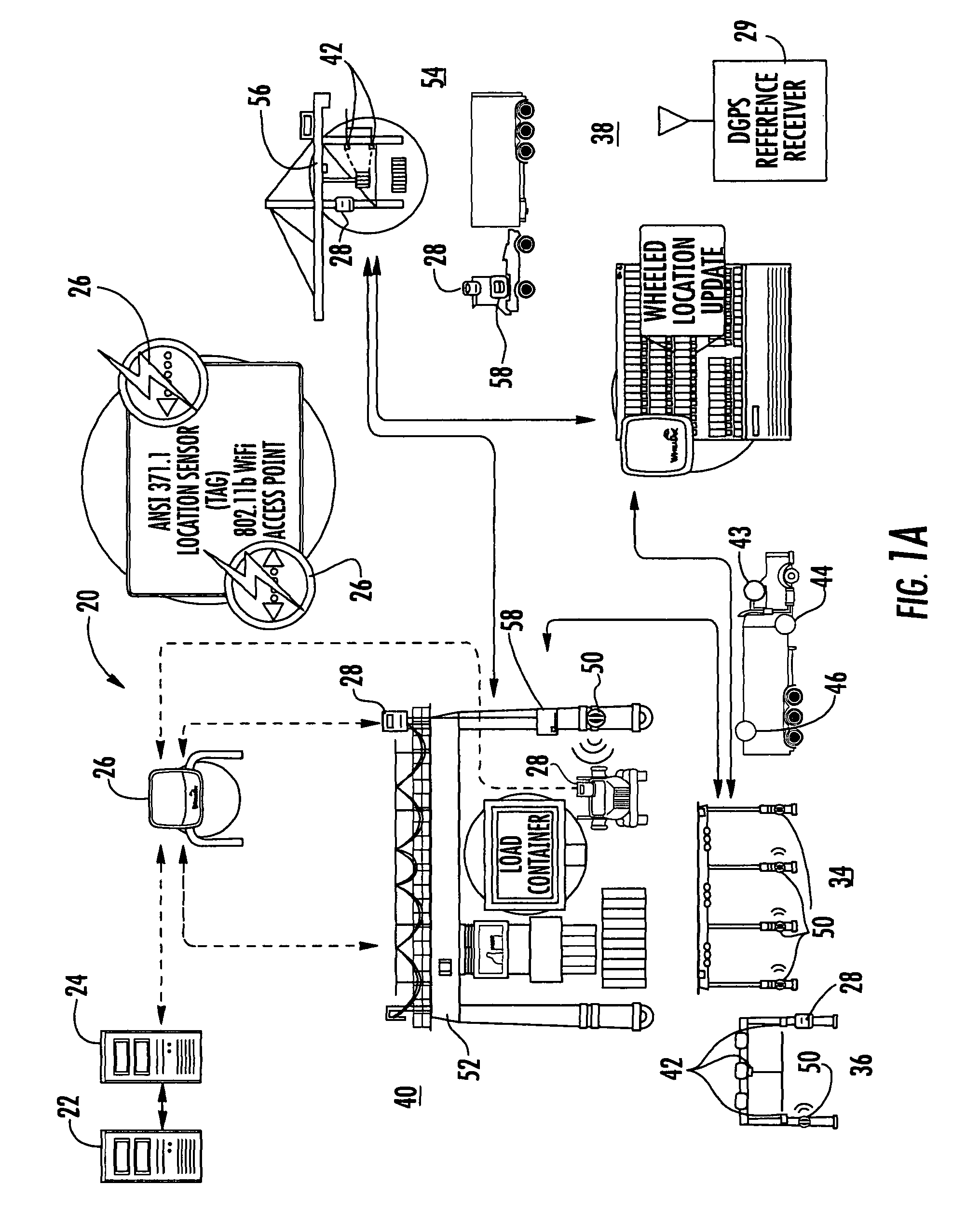
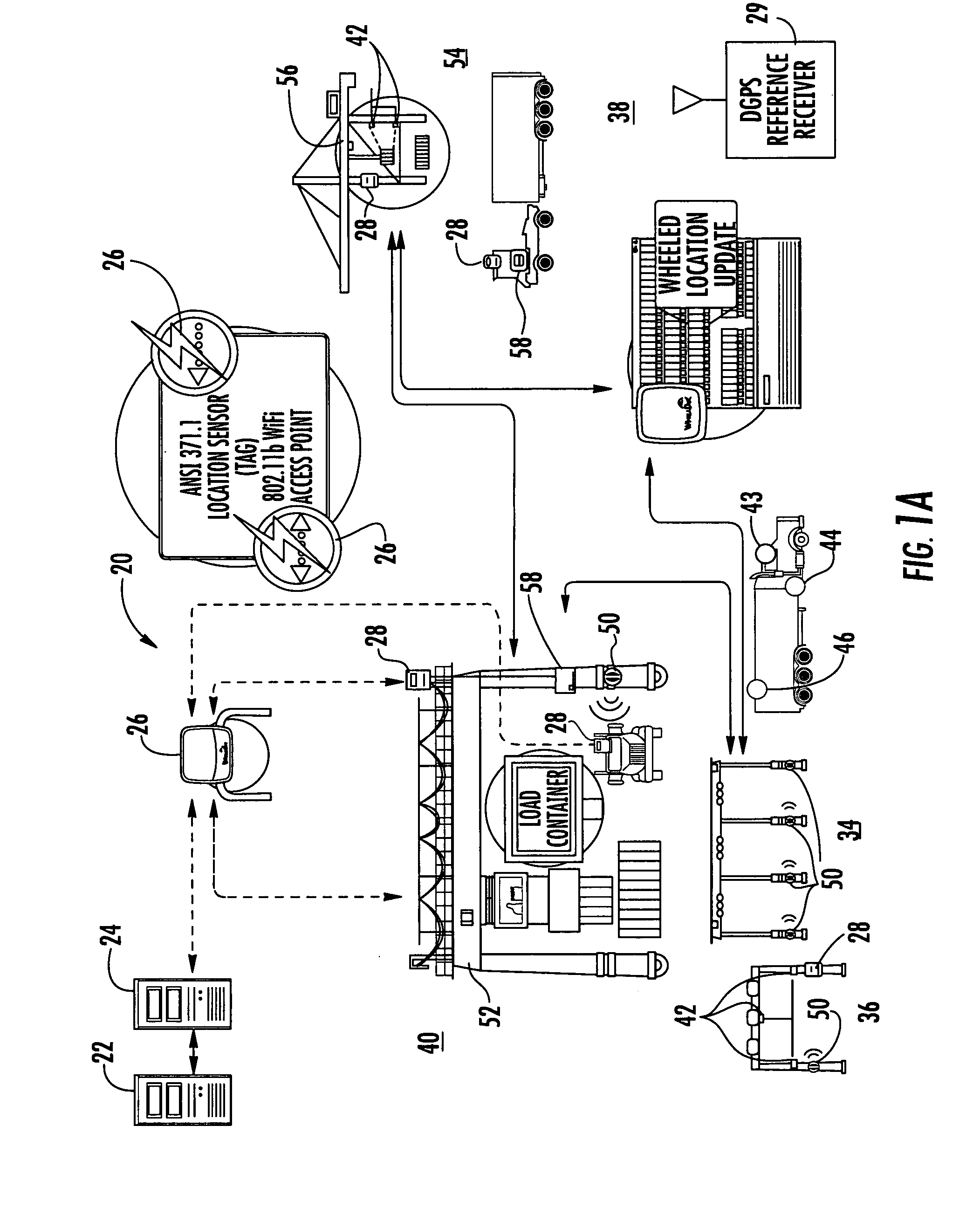
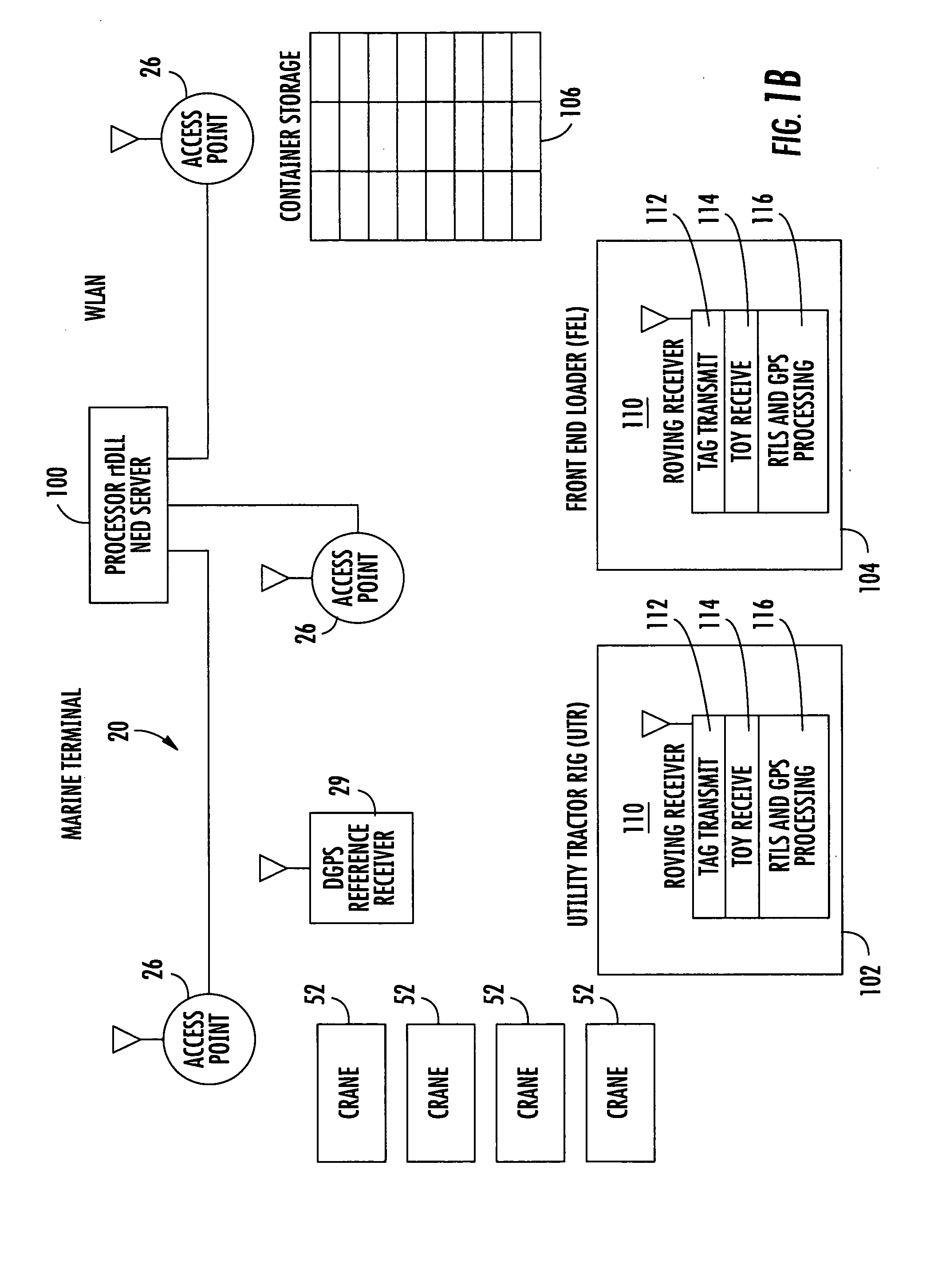
A location system for tracking assets within a terminal includes a Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) reference receiver within the terminal that receives GPS signals and generates DGPS correction data. In one aspect, a roving receiver unit is carried by an asset to be tracked within the terminal. It includes a GPS receiver that receives GPS signals and the DGPS correction data from the DGPS reference receiver. A tag transmitter transmits a wireless RF signal containing GPS location data based on received GPS signals and DGPS correction data. At least one access point is positioned within the terminal for receiving the wireless RF signal from the tag transmitter. A processor is operatively connected to the at least one access point for receiving GPS location data and determining a location of the asset to be tracked.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
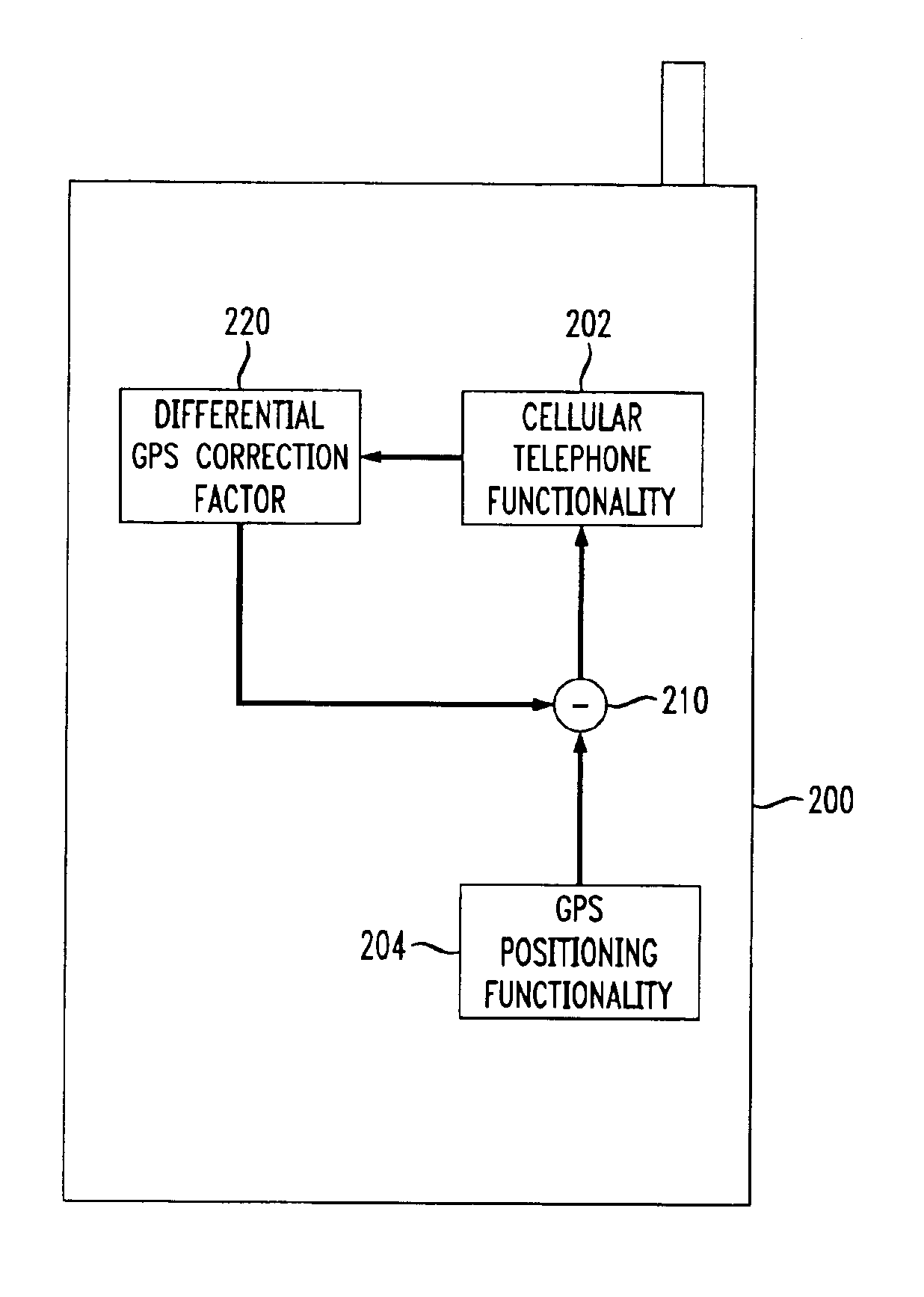
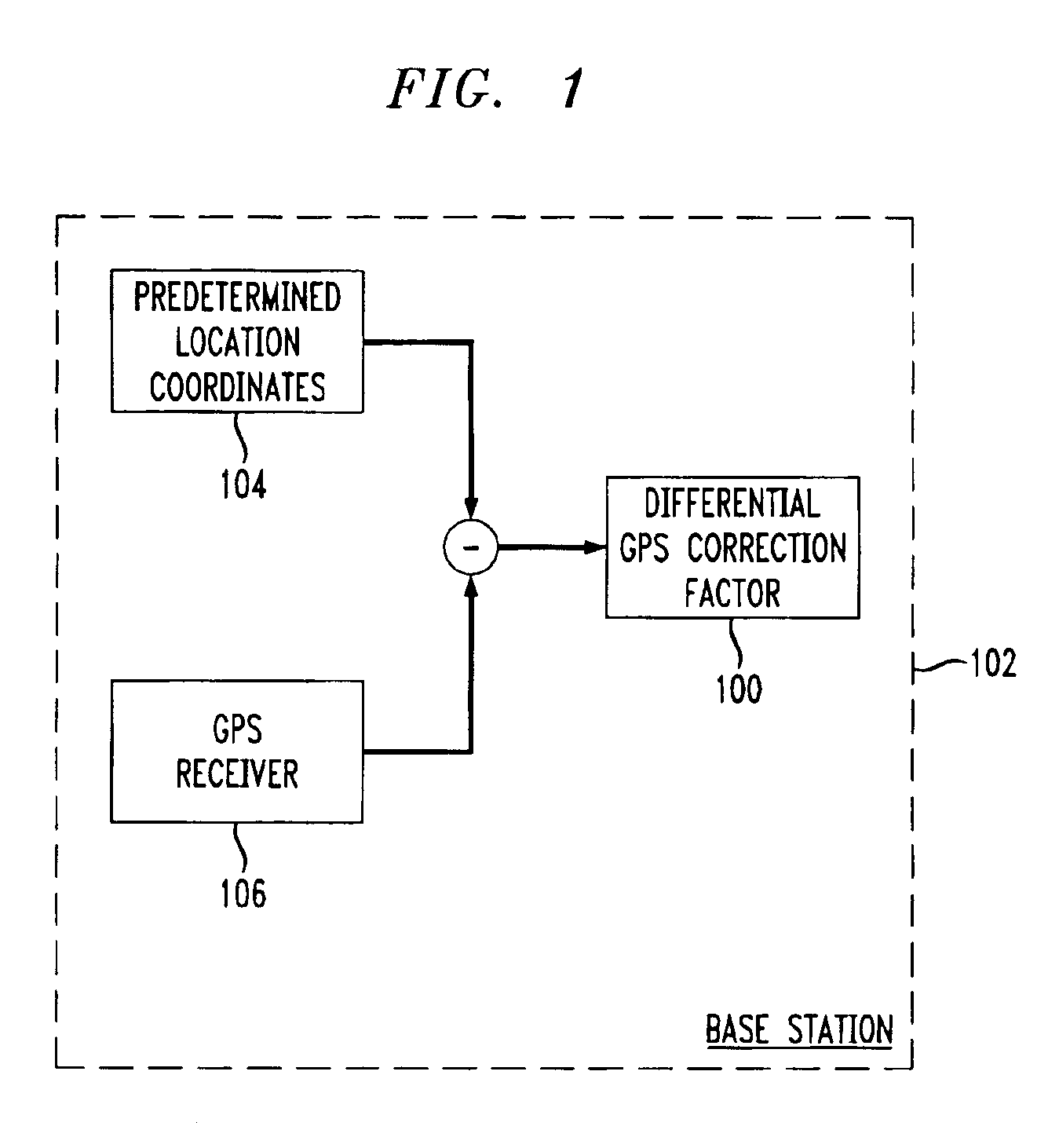
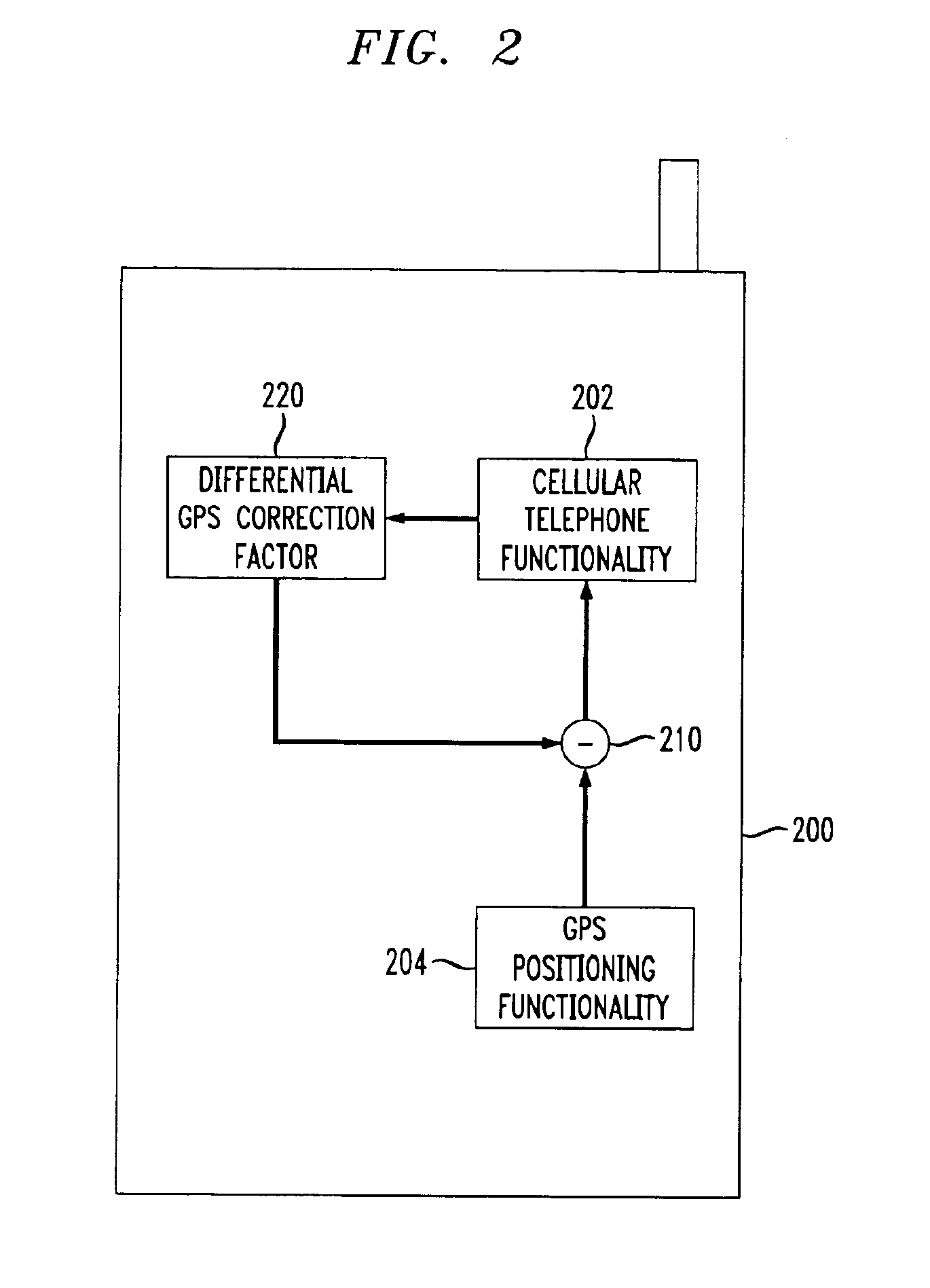
Differential GPS and/or glonass with wireless communications capability
InactiveUS6901260B1Improve reception accuracyHighly accurate location informationTelephonic communicationPosition fixationGps receiverCellular telephone
A differential GPS or GLONASS system (collectively referred to herein as a ‘GPS system’) is implemented for use by a base station of a wireless telephone system (e.g., by a cellular telephone base station). Using the differential GPS system, a differential location ‘correction’ factor is determined based on a difference between a received GPS location signal and a known fixed location of a GPS system receiver for the base station. A differential GPS correction signal containing the correction factor is transmitted to any or all cellular telephone users of that base station to allow the cellular telephones to improve the accuracy of location information independently measured by GPS receivers located in each of the cellular telephones. The differential GPS signal may be used to increase the accuracy of the GPS system, whatever the current accuracy of the GPS system, allowing practical implementation of an emergency telephone system such as a 911 system using a wireless system such as a cellular telephone system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Electric control system for automatic driving electric automobile
ActiveCN106774291AReduce in quantityImprove compatibilityNon-mechanical steering controlVehicle position/course/altitude controlExecution controlEngineering
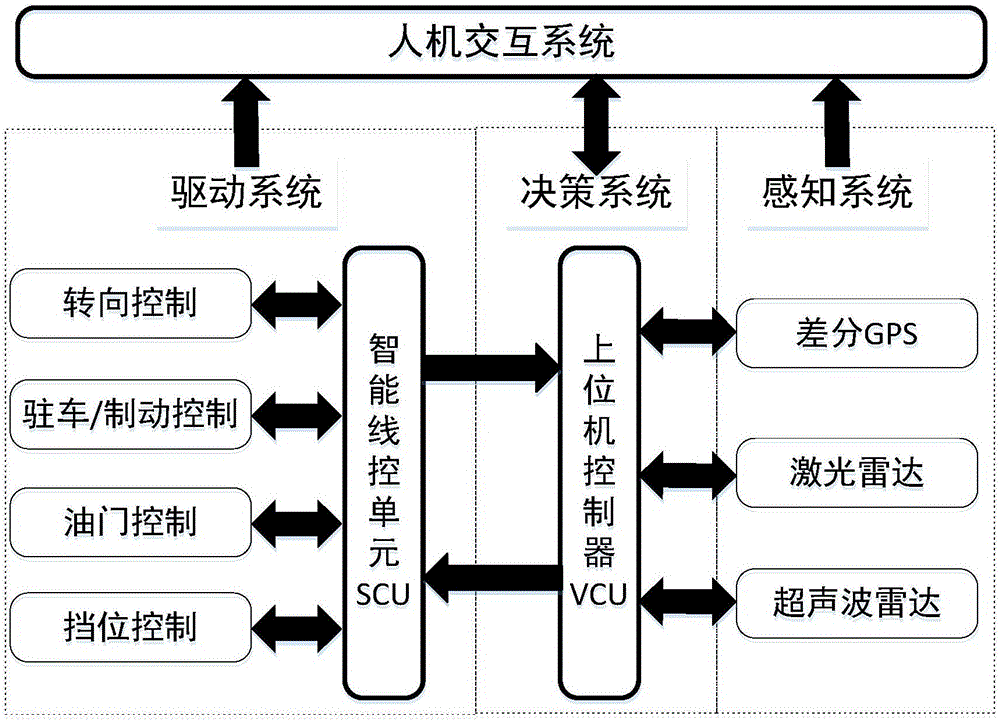
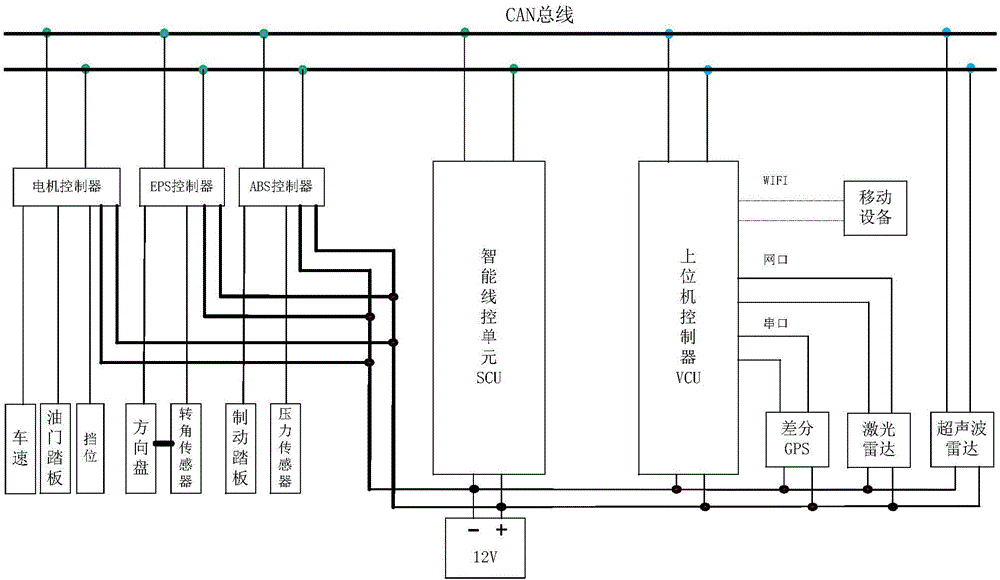
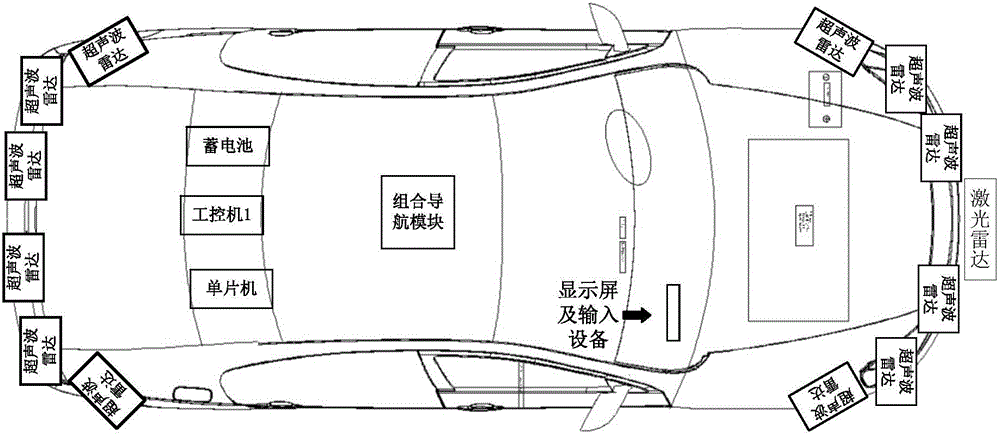
The invention discloses a forward safety monitoring and warning device for an automobile. The forward safety monitoring and warning device comprises a decision-making system, a perception system, a laser radar module, an ultrasonic radar module, a driving system, an intelligent remote control unit, and a man-machine interactive system, wherein the decision-making system syncretises data collected by perception system and processes it according to the decision algorithm, and acquires decision-making data to control the vehicle and control the vehicle to execute the control task; the perception system connected with the decision-making system comprises a differential GPS module used to provide vehicle position information and heading attitude; the laser radar module is used for acquiring barrier information of the front of the automobile; the ultrasonic radar module is used for sensing environmental information around the automobile; the driving system is connected to the decision-making system through an intelligent remote control unit and the intelligent remote control unit is also connected with an actuating mechanism in the bottom of the automobile for controlling the automobile and switching automatic driving mode and traditional mode; the man-machine interactive system is used to display vehicle status, command information, conduct performance and geographic information. The adoption of drive-by-wire chassis and modular design reduces the cost of debugging, improves the efficiency of developing and facilitates expansion.
Owner:清华大学苏州汽车研究院(吴江)
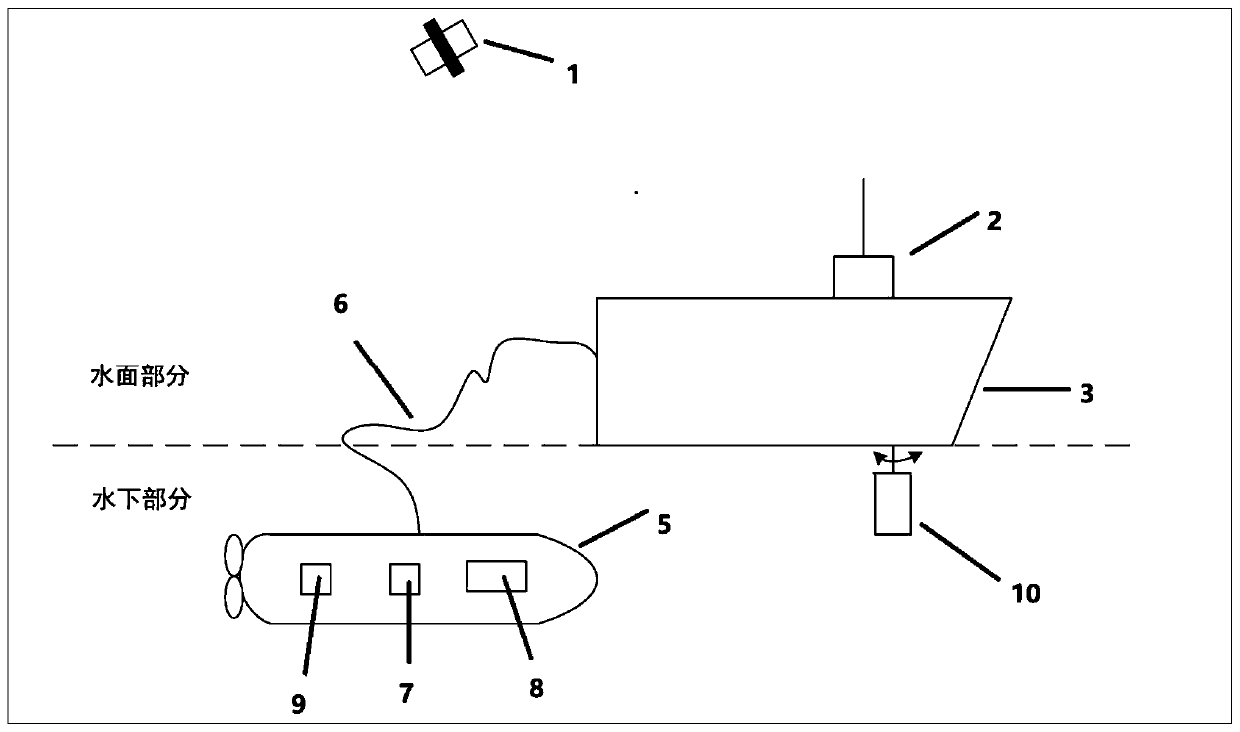
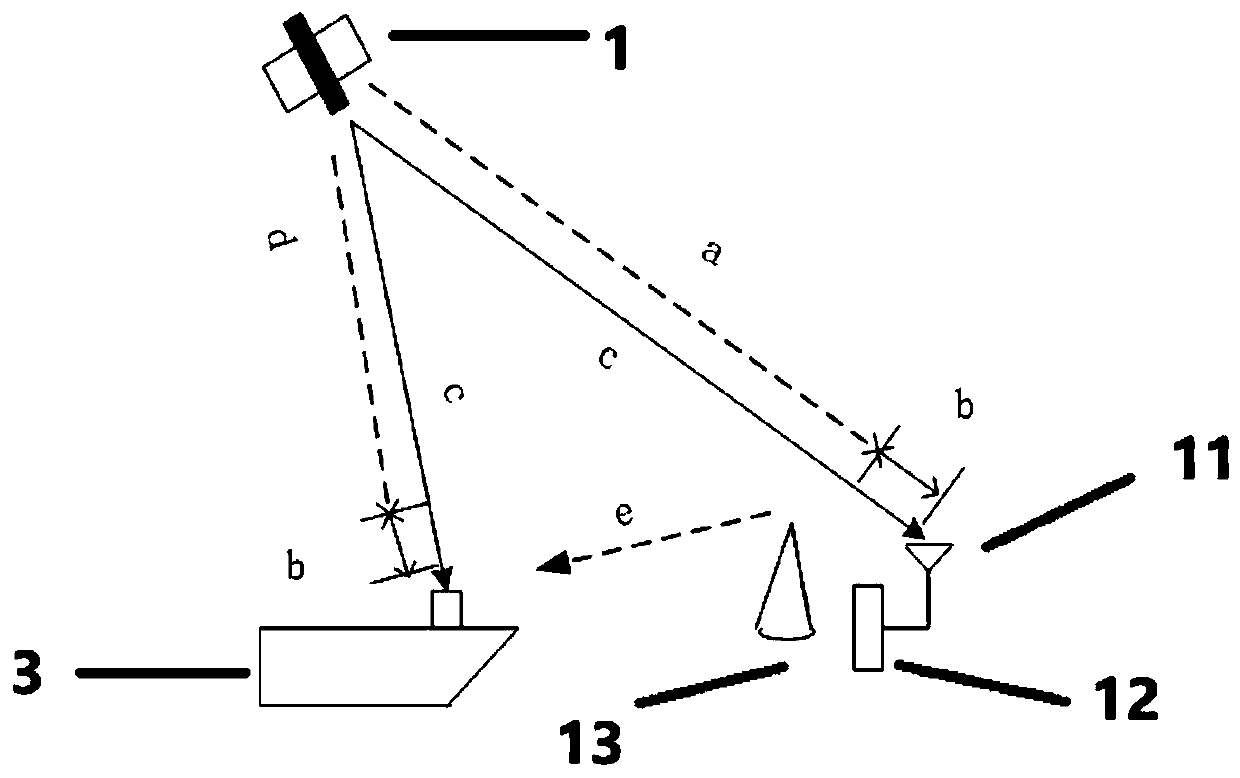
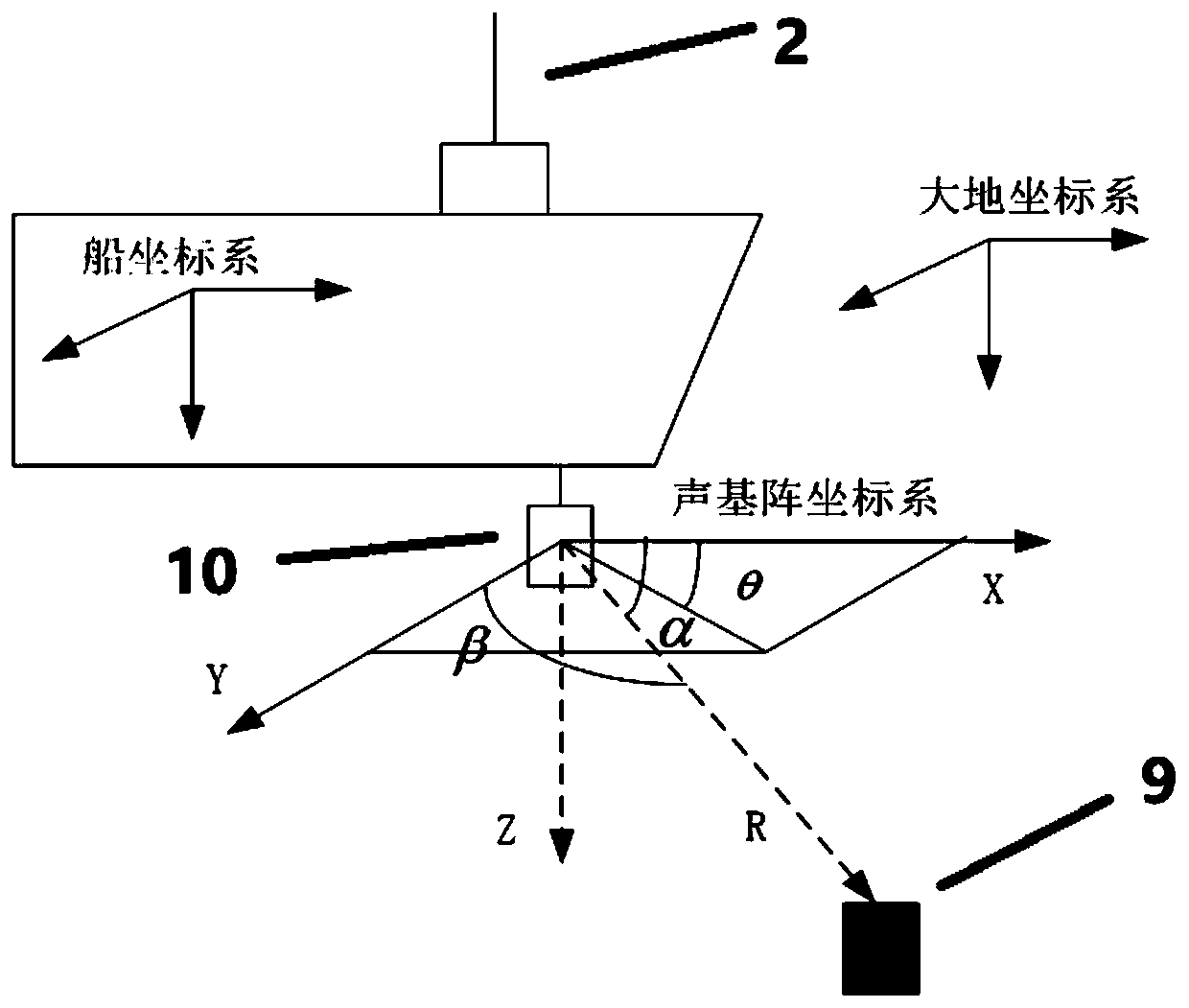
Underwater object precision positioning system and method
InactiveCN102495420AOvercome limitationsRealize real-time positioningSatellite radio beaconingAcoustic wave reradiationTransceiverGps positioning system
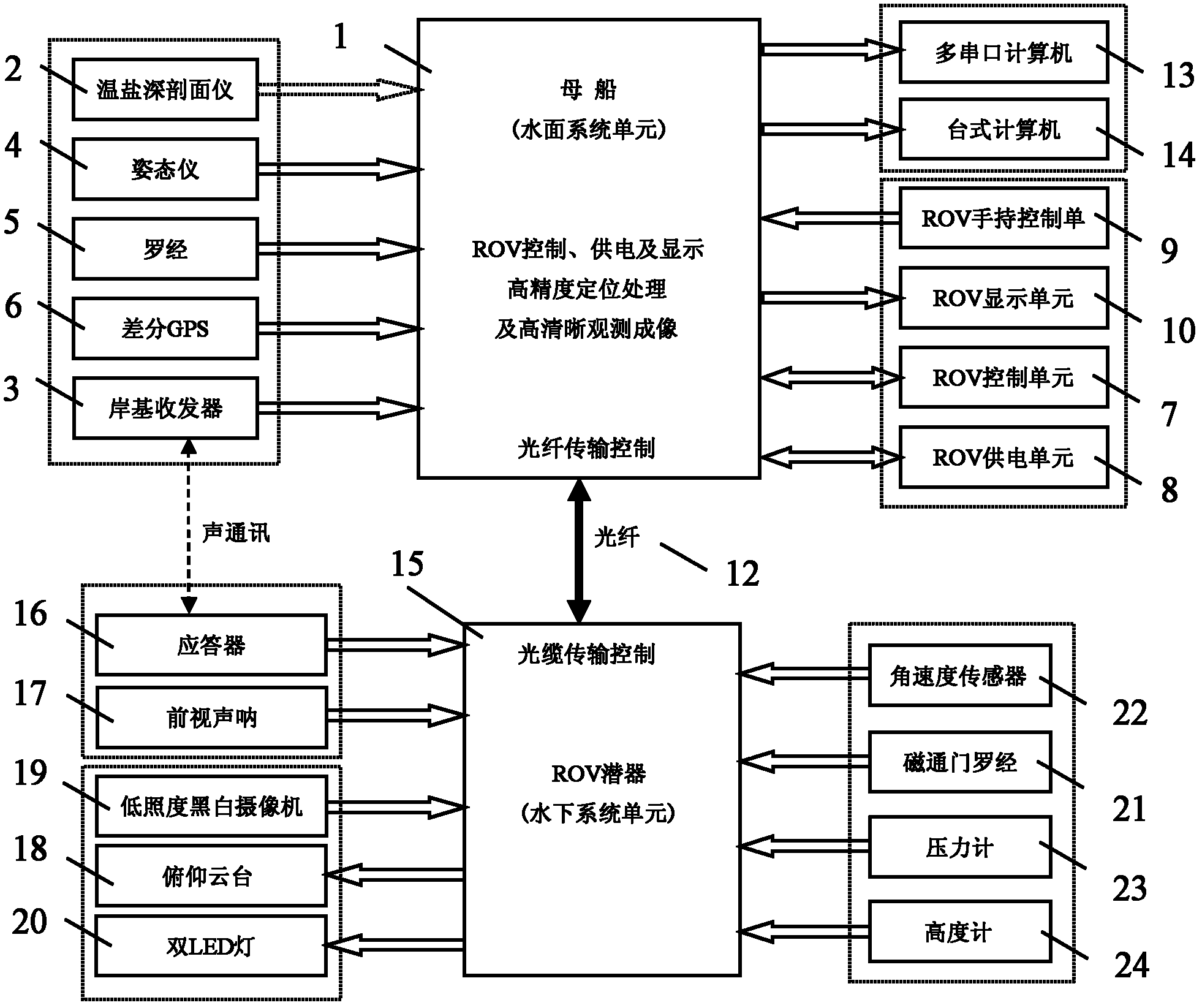
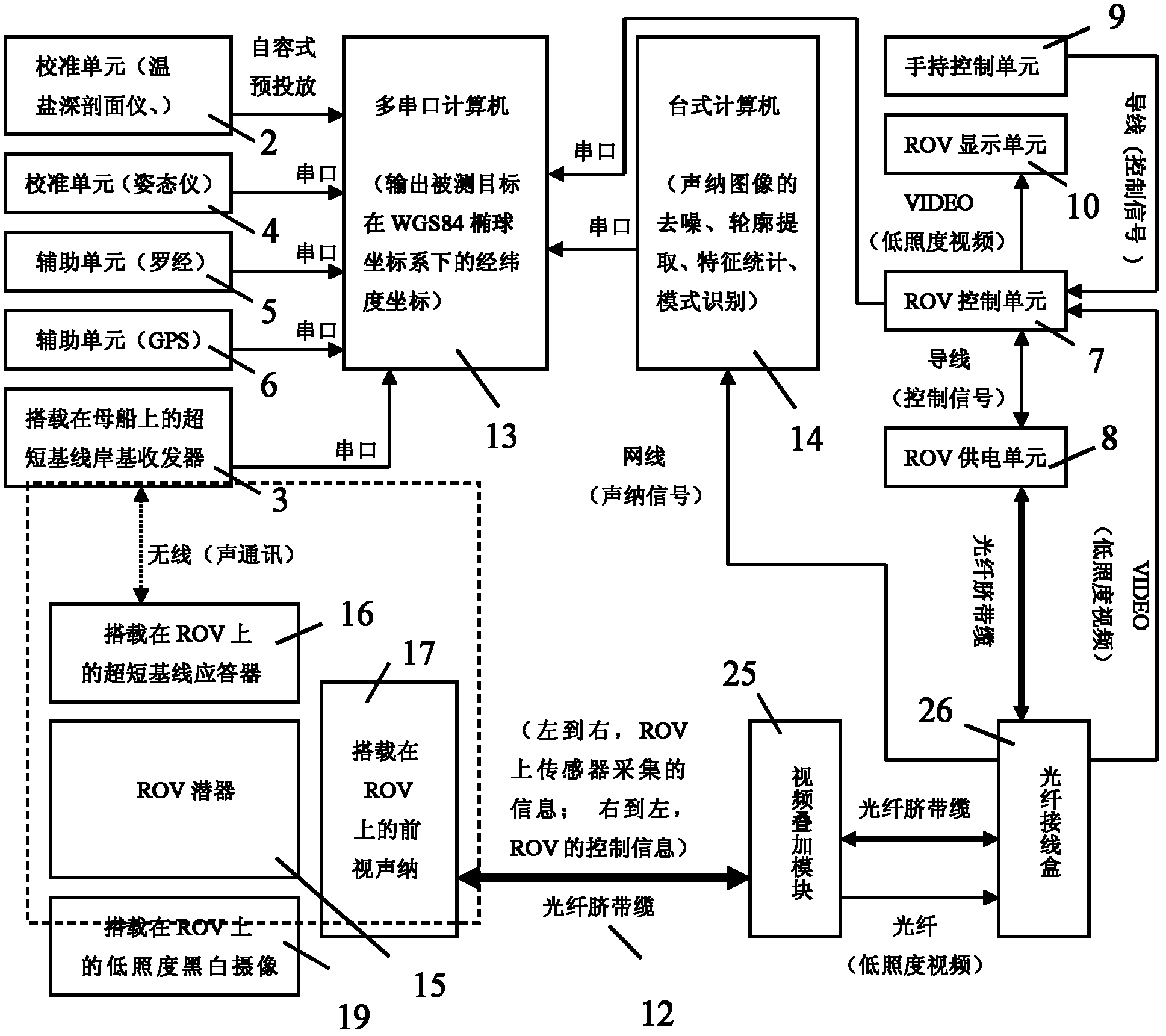
The invention discloses an underwater object precision positioning system and a method. The system comprises a mother ship, a computer with a plurality of serial ports, a desk computer, an ultra short base line positioning system, a differential GPS (global positioning system), a compass, an ROV (remote-operated vehicle) system, a forward-looking sonar camera, a low-illuminance black and white video camera, an attitude indicator and a temperature-salinity depth profiling instrument. A shore-based transceiver, an ROV water surface system unit and the like of the ultra-short base line positioning system are carried by the mother ship, and underwater system units such as a transponder of the ultra-short base line positioning system, the forward-looking sonar camera and the like are carried by an ROV submersible vehicle, so that the underwater object precision positioning system is formed. By the aid of acoustic positioning between the shore-based transceiver and the transponder of the ultra-short base line positioning system and acoustic positioning of forward-looking sonar, the shortcoming that an existing underwater GPS positioning system only can position an object carried with anacoustic response device in a water area is overcome, and longitude and latitude coordinates of an optional unknown object in an optional water area can be positioned in a WGS (world geodetic system)84 ellipsoidal coordinate system in real time.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Integrity of differential GPS corrections in navigation devices using military type GPS receivers
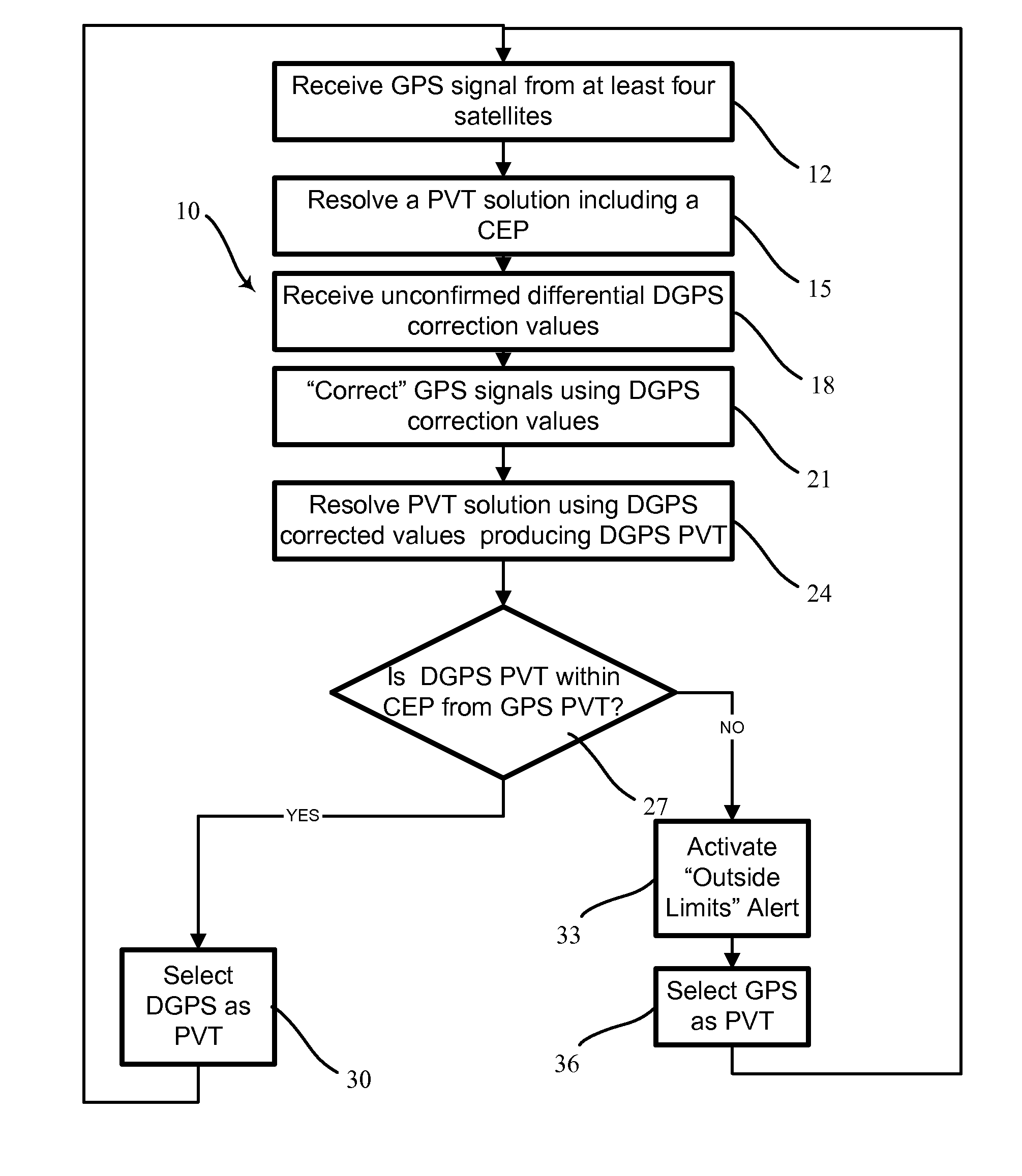
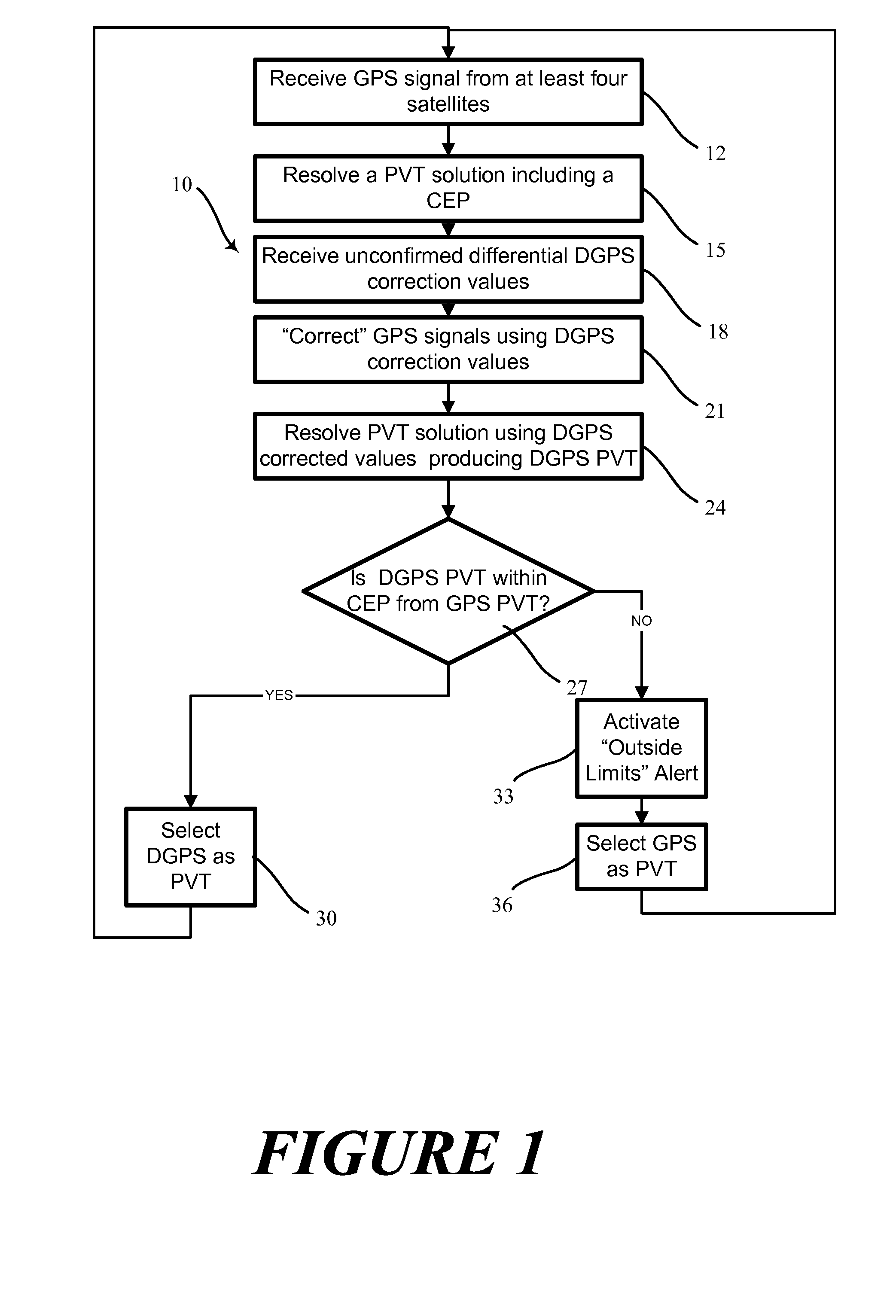
A method and apparatus for calculating corrections to a navigation solution based on differential GPS data includes receiving GPS ephemeris from at least three GPS satellites. A PVT solution is resolved from the GPS ephemeris. The PVT solution includes a Circular Error Probable (CEP). Differential GPS data for calculating the corrections to the PVT solution is received. A corrected PVT solution is then based upon the differential GPS data. The corrected PVT solution is compared to an area defined by the CEP. Where the corrected PVT solution is not within the area, the corrected PVT solution is rejected in favor of the PVT solution for determining an accurate navigational solution.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
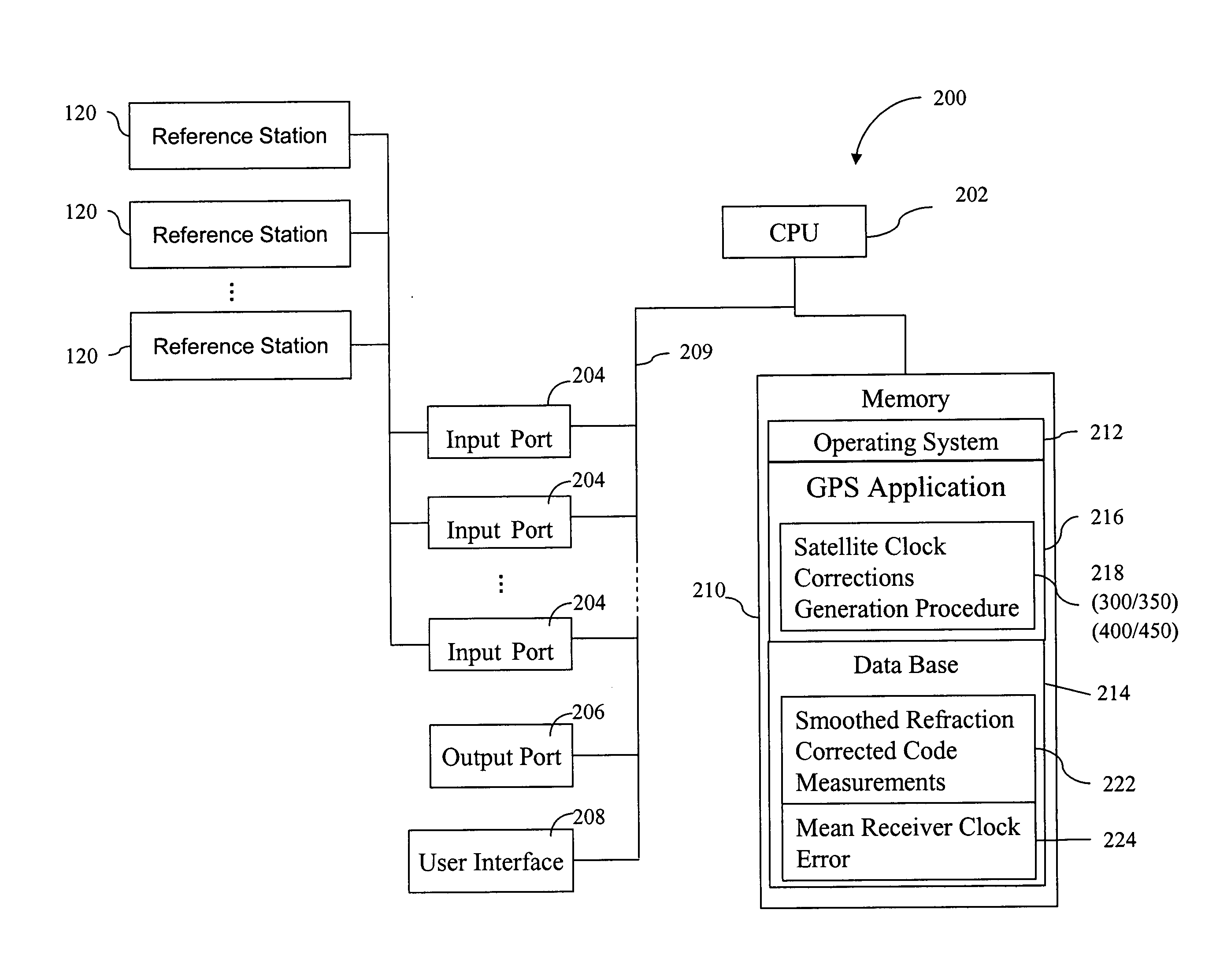
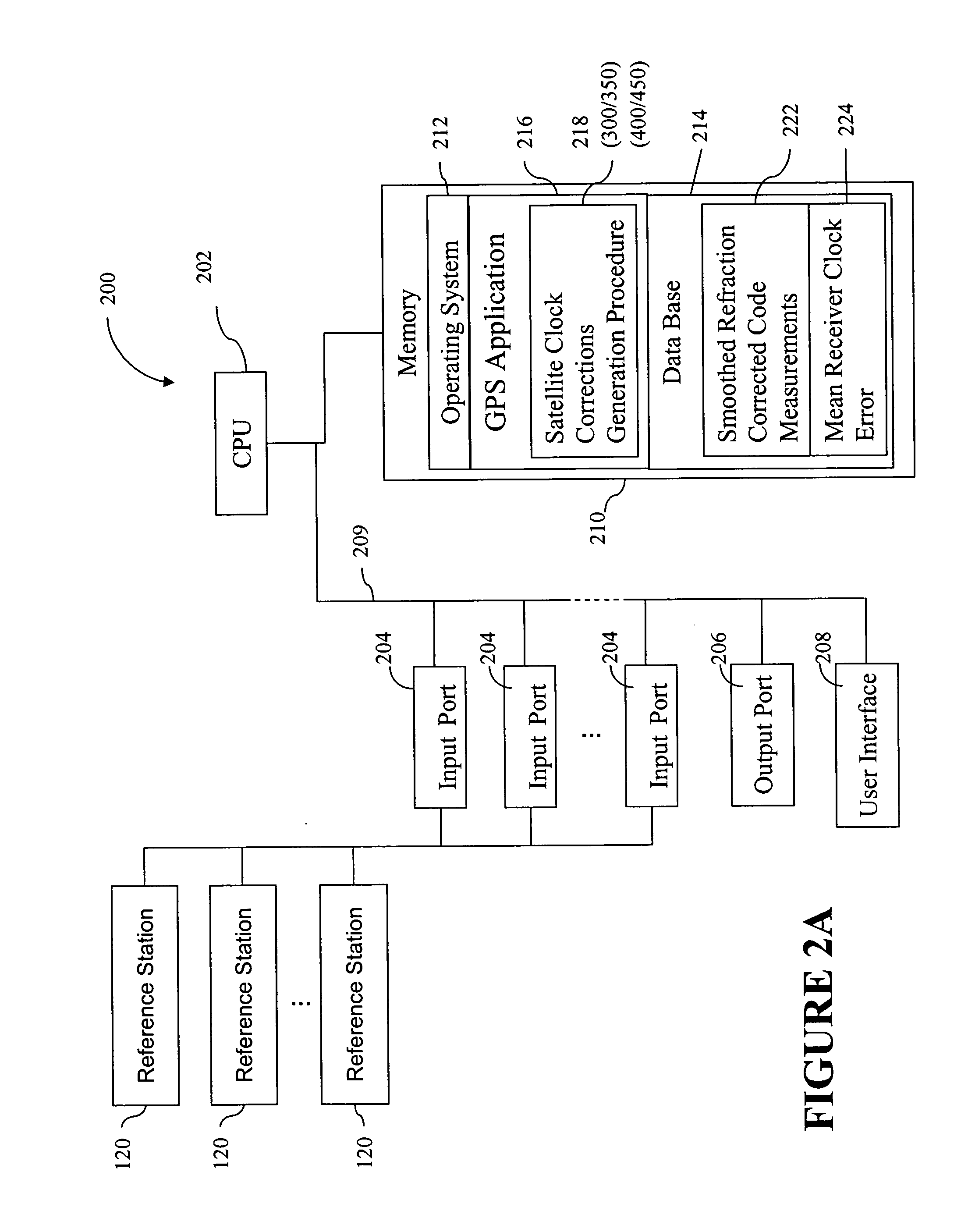
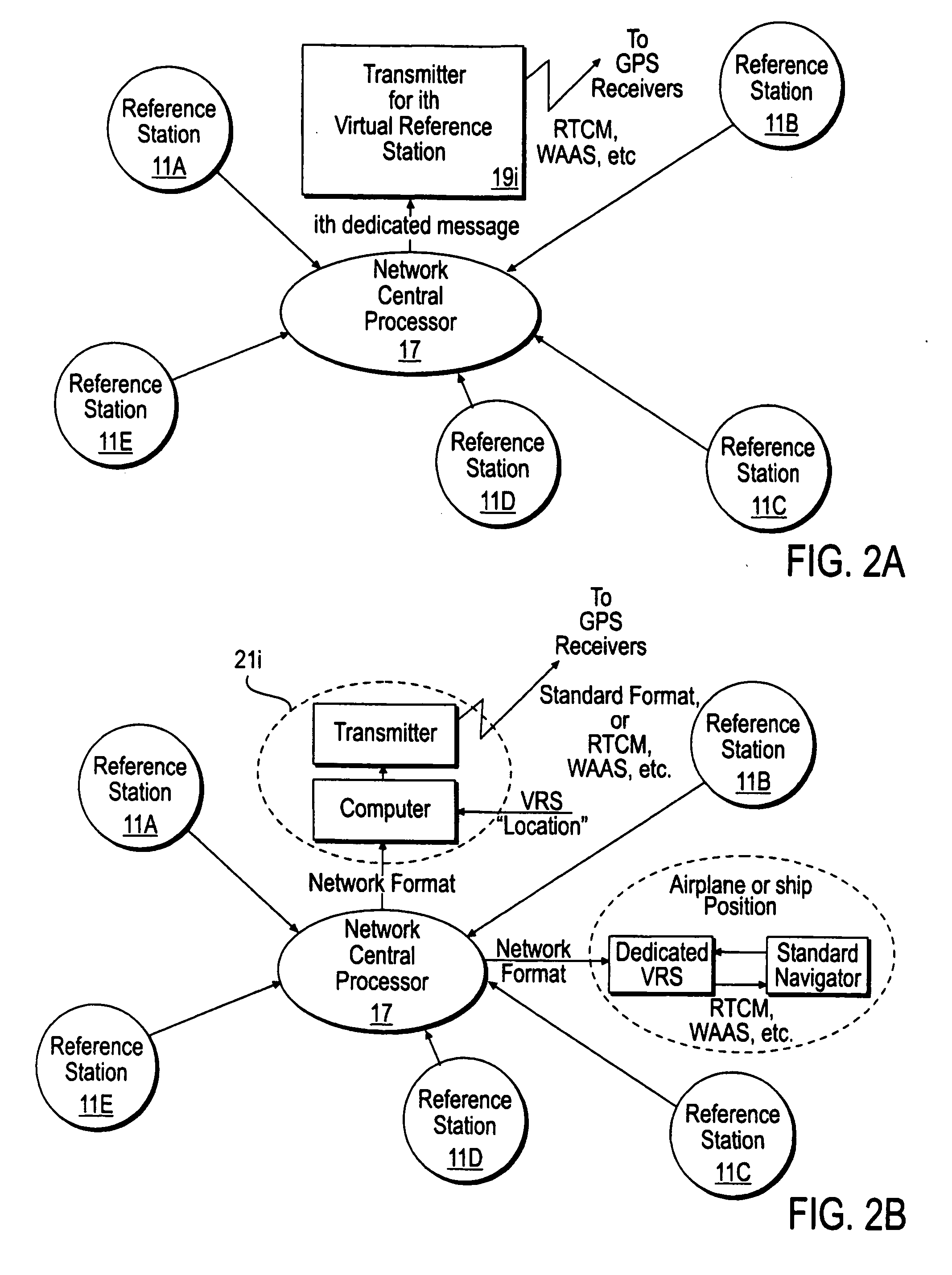
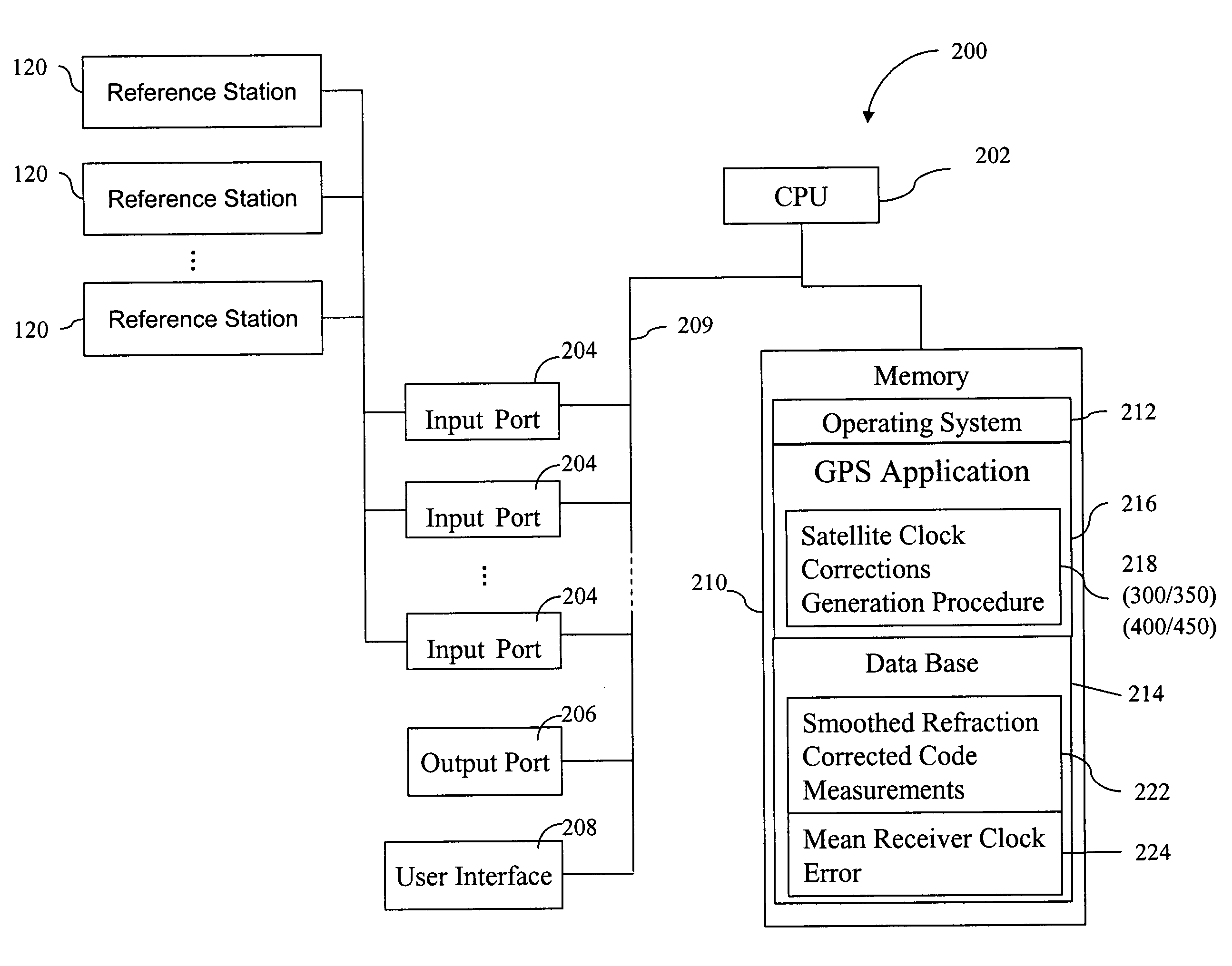
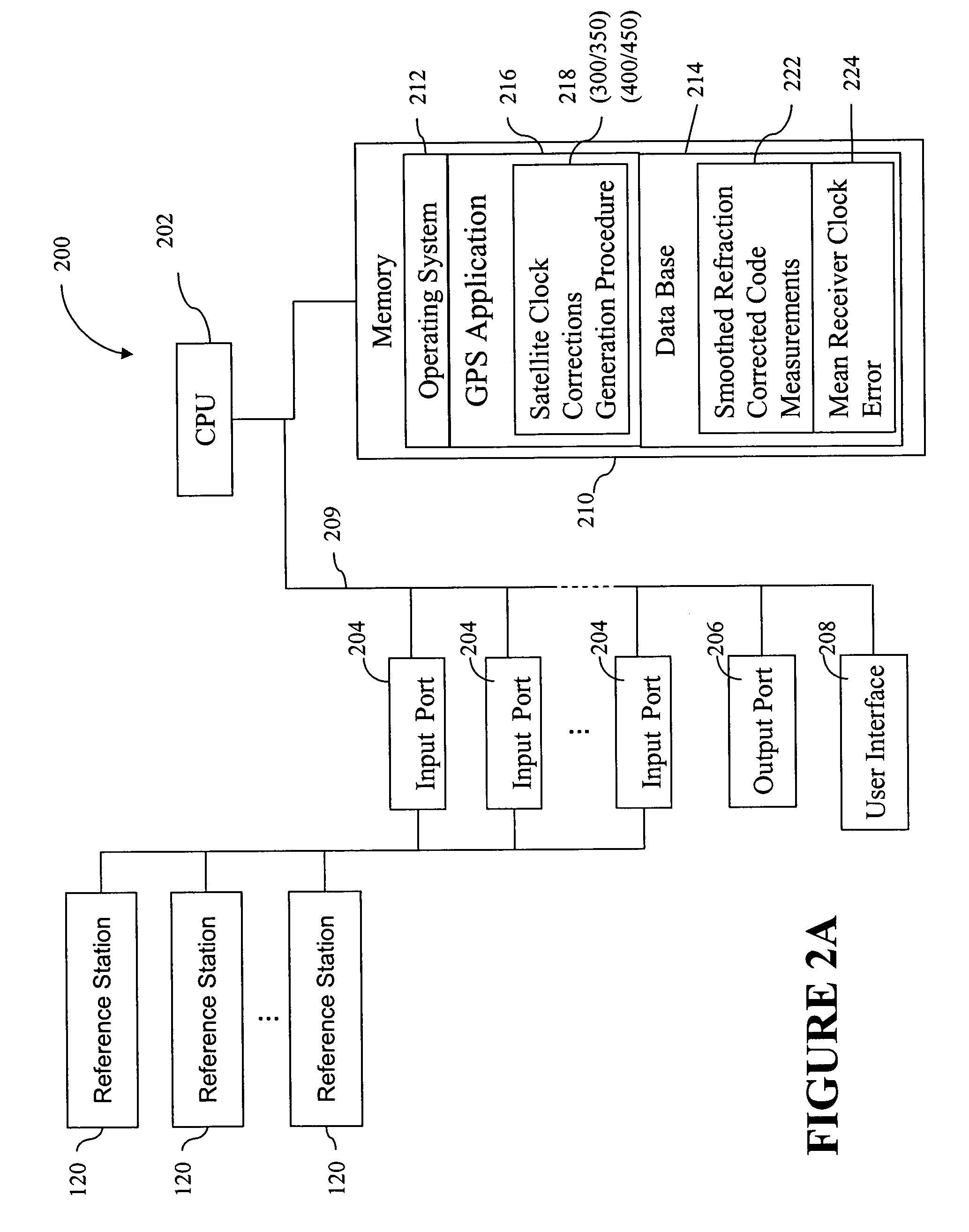
Method for generating clock corrections for a wide-area or global differential GPS system
InactiveUS20050024263A1Easy accessCancel noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyGps measurement
A method for generating satellite clock corrections for a WADGPS network computers satellite clock corrections after removing other substantial error components. Errors caused by the ionosphere refraction effects are removed from GPS measurements taken at reference stations using dual-frequency GPS measurements. The multipath noise are removed by smoothing of GPS pseudorange code measurements with carrier-phase measurements. The tropospheric refraction effect can be largely removed by modeling, and if desired, can be improved by the use of small stochastic adjustments included in the computation of the clock correction. After removing the above error factors, satellite clock corrections are computed for individual reference stations, and an average clock correction is formed for each of a plurality of satellites by taking an average or weighted average of the satellite clock corrections over reference stations to which the satellite is visible.
Owner:DEERE & CO
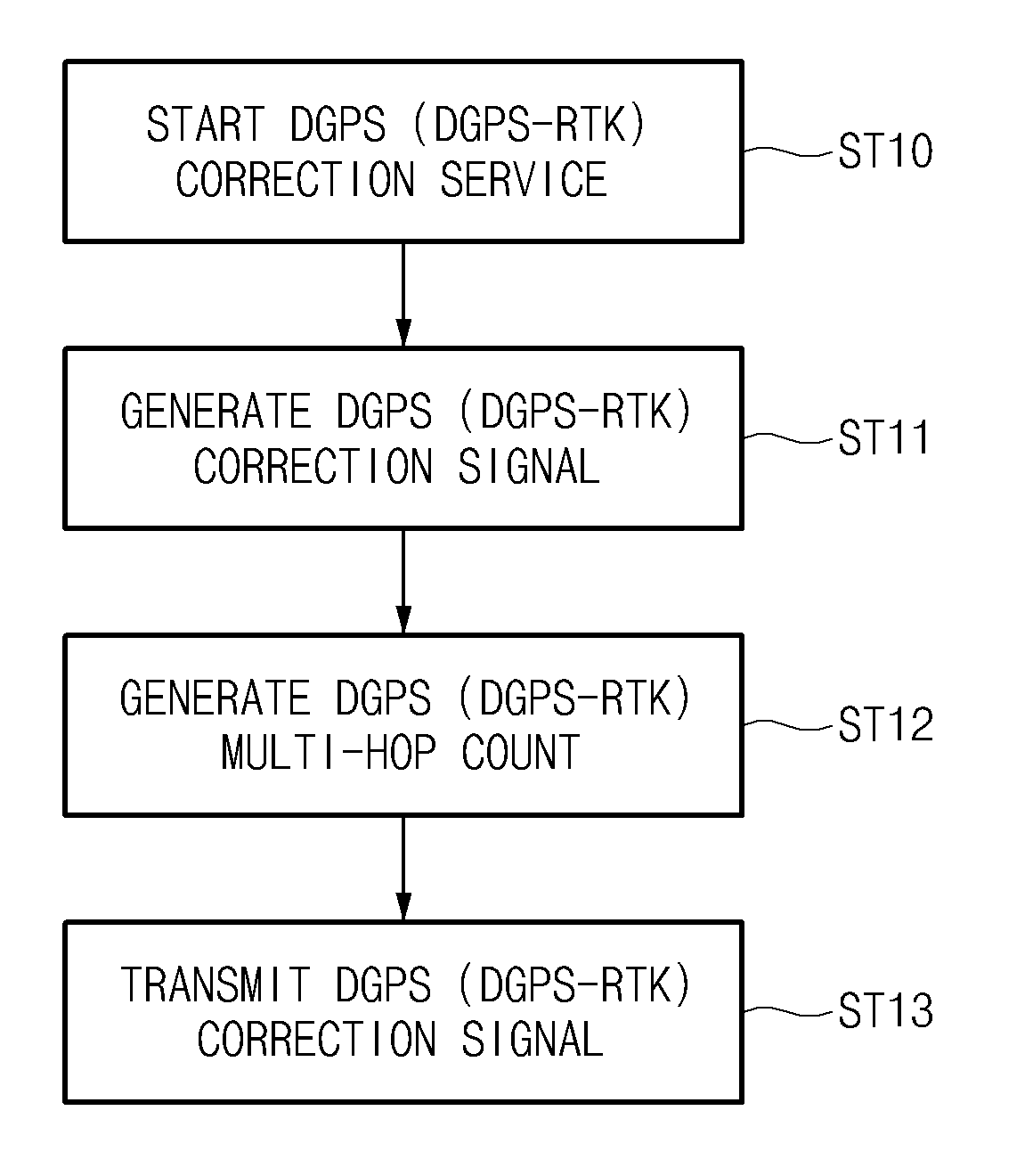
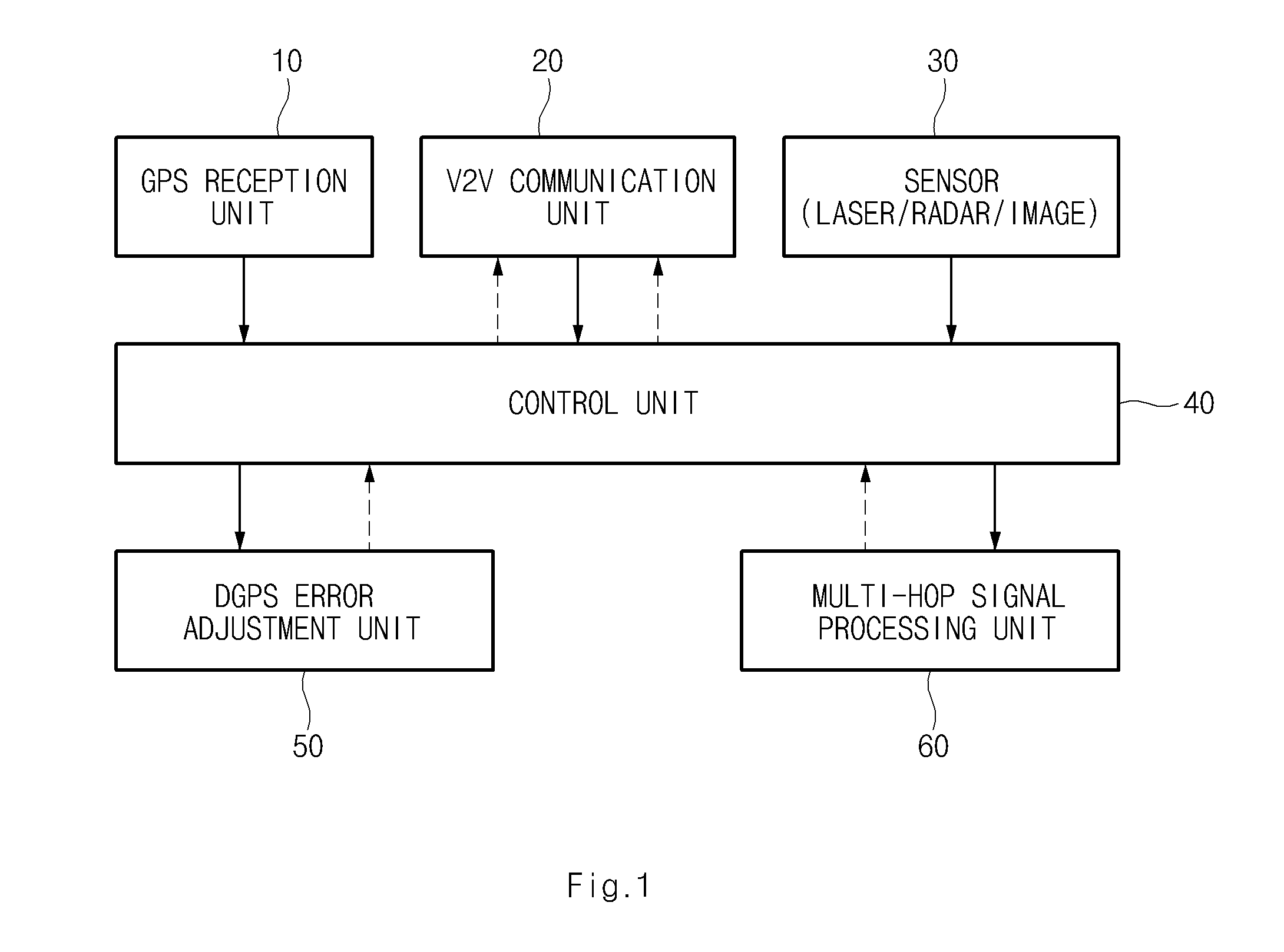
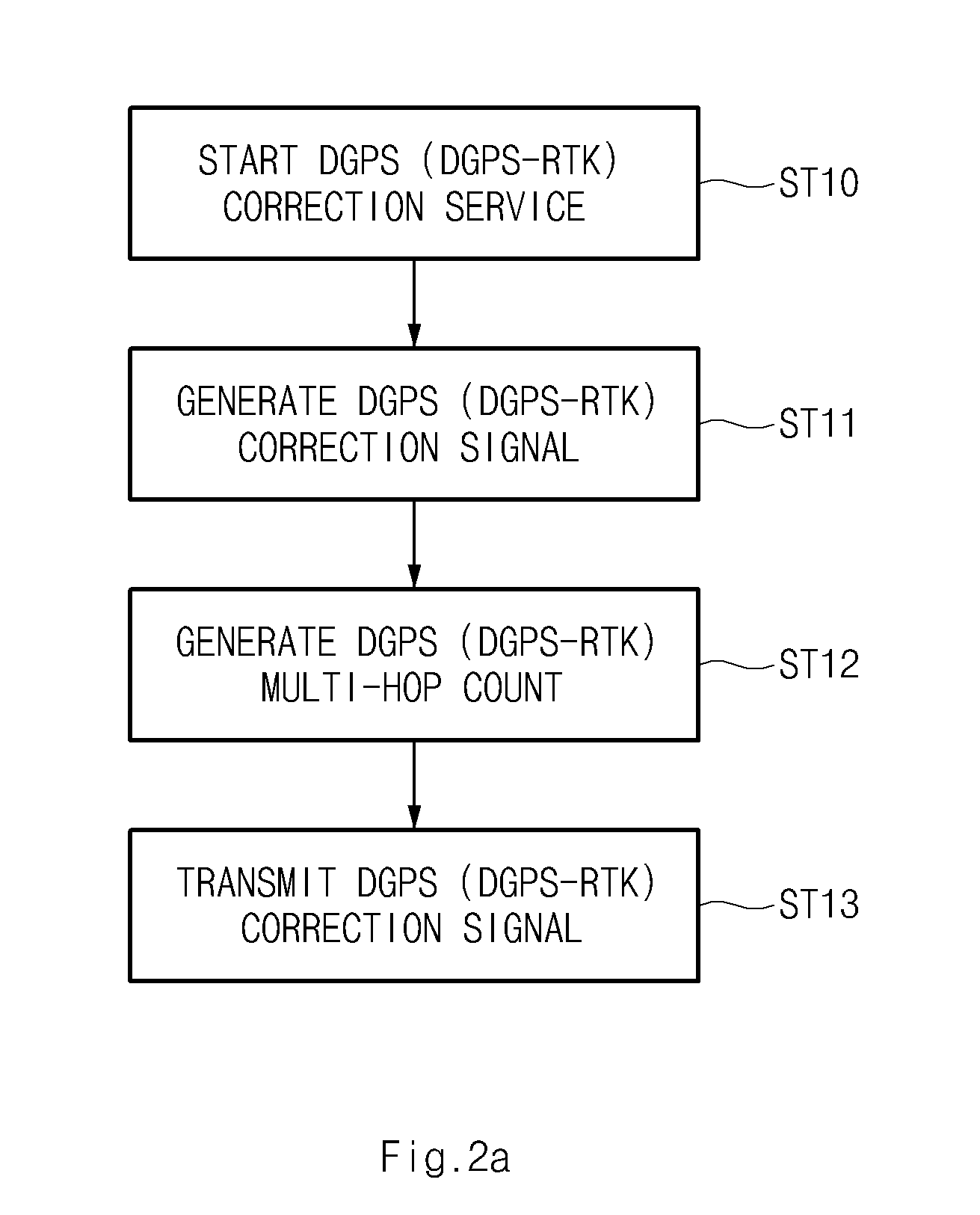
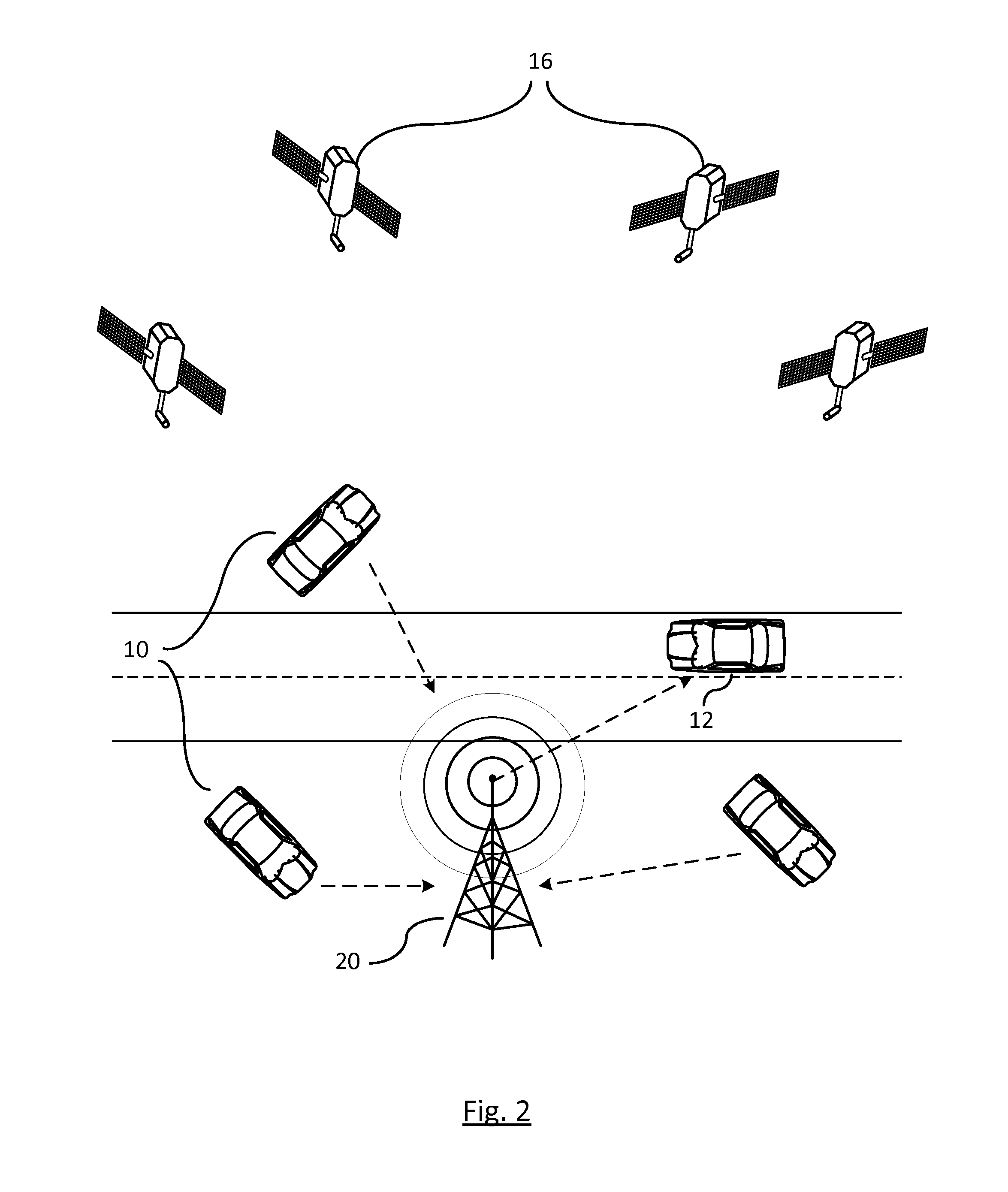
Method and system for improving accuracy of position correction data in differential global positioning system using vehicle to vehicle communication
InactiveUS20130093618A1High positioning accuracyImprove errorRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationDifferential GPSReal-time computing
A method and system for improving accuracy of a position correction data in a differential global positioning system (DGPS) using vehicle to vehicle (V2V) communication, capable of correcting a DGPS data received from a road side unit (RSU) into information calculated by a sensor, and providing neighbouring vehicles with the corrected value as the DGPS data using the V2V communication, are provided.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for using corrected signals from a global positioning system to perform precision survey
InactiveUS7110762B1Comfortable to useEasy to integrateSurveyor's staffsMovable markersTransceiverElectrical connection
In a differential global positioning system that includes one or more base stations and rover units, a system and method for including a radio modem transceiver in the rover units, and packaging several components, including the transceiver and a radio antenna in a single package, and possibly including re-chargeable batteries, a GPS receiver, and a GPS antenna in the package, to reduce the number of external electrical connections. Several of the components may be packaged into a survey range pole. GPS satellite correction information is transmitted from a base station in response to a request transmitted from the rover unit by means of the radio modem transceiver. Automatic channel selection is performed by the base stations to select a channel having low communication traffic. The rover units scan the available channels for valid GPS correction information and, in the event that more than one such channel is located, select the channel with the strongest signal.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
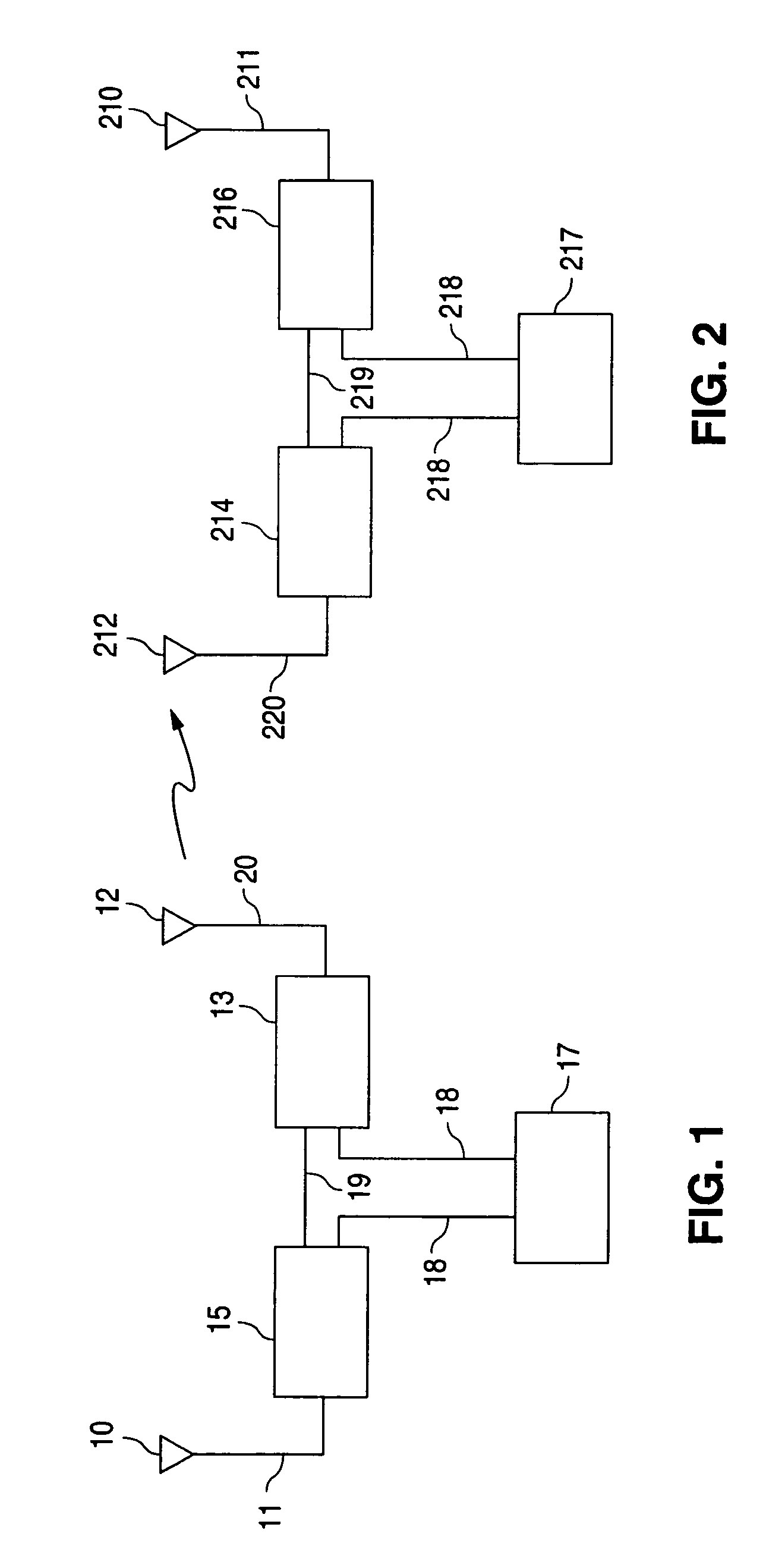
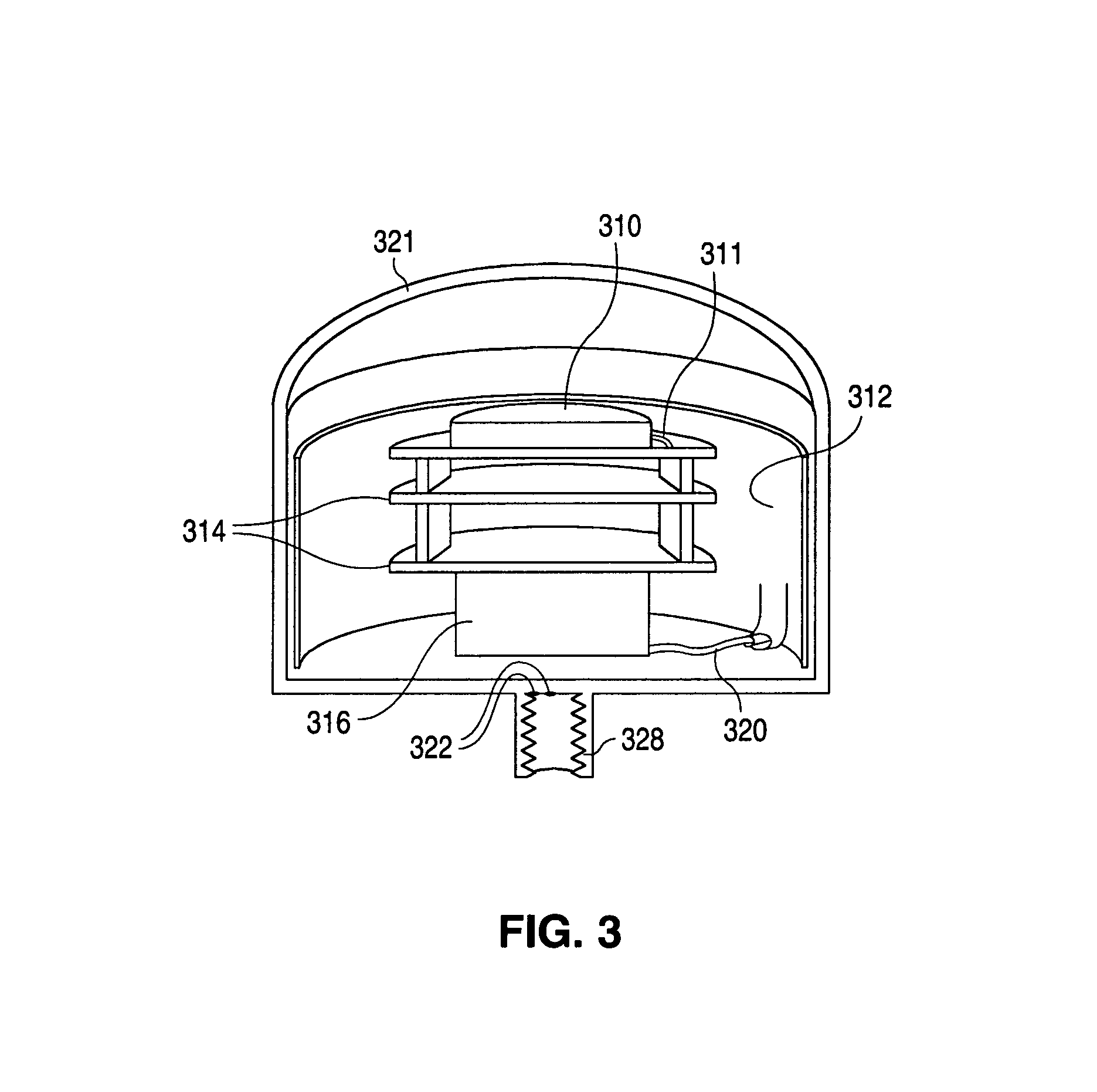
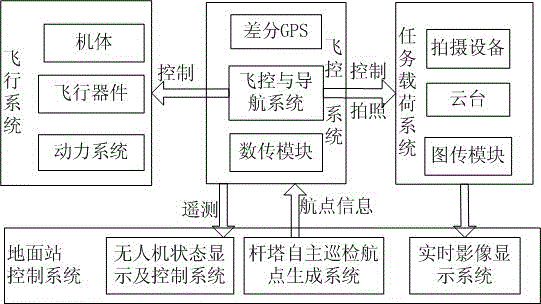
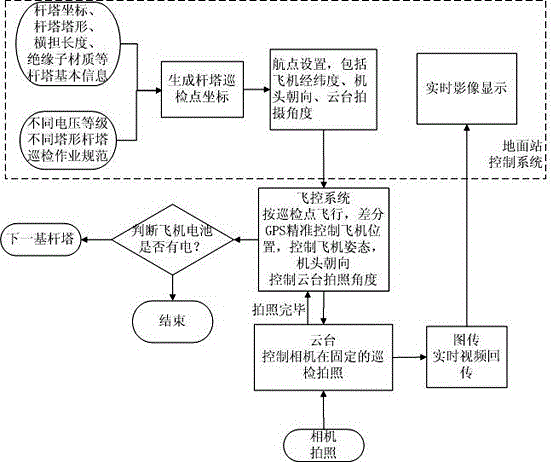
Differential-GPS-based unmanned-aerial-vehicle autonomous routing inspection system and method for power transmission line
InactiveCN105790155ASolve the problem of self-blockingAvoid damageApparatus for overhead lines/cablesLongitudeGround station
The invention discloses a differential-GPS-based unmanned-aerial-vehicle autonomous routing inspection system for a power transmission line. The system comprises an unmanned aerial vehicle and a ground station control system. A flight control system of the unmanned aerial vehicle receives waypoint information generated by a tower autonomous routing inspection waypoint generation system of the ground station control system; and according to the waypoint information, the flight control system is controlled to carry out flight, wherein the waypoint information consists of the flight latitude and longitude, the altitude, the plane head orientation, and the cloud platform angle orientation of the unmanned aerial vehicle. According to the invention, the power transmission tower can be identified precisely by using the geographic information technology; the unmanned aerial vehicle platform can be localized precisely during flight by using the differential GPS positioning technology; the routing inspection point can be solidified by using the power transmission tower routing inspection technology; and the cloud platform angle displacement can be controlled precisely by using the control technology. Therefore, unmanned-aerial-vehicle autonomous routing inspection system and routing inspection method of the power transmission line can be realized.
Owner:SICHUAN SUNLIGHT INTELLIGENT ELECTRIC EQUIP CO LTD
Railroad surveying and monitoring system
InactiveUS8180590B2Avoid large vibrationsPosition fixationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTrackwayMonitoring system
A Railroad Surveying and Monitoring System configured on a mobile platform for surveying, monitoring, and analyzing rail position and superstructure and terrain substructure of railroad tracks (20a,b) or other structures. The system employs two or more High Accuracy Differential Global Positioning System devices (110,112), ground penetrating radar devices (116), terrain conductivity instruments (118), optical cameras (124), and data receivers and processors (126), which in turn process, display, and store the data in a usable database. Precise coordinate data generated from a High Accuracy Global Positioning System provides both location data for subsurface sensors and surface sensors and rail position coordinates to monitor track displacements during track inspection in real time.
Owner:MARSHALL UNIV RES
Data fusion system and method of differential GPS (Global Position System) and inertial navigation in intelligent vehicle
InactiveCN103207634AEffective controlAchieve precisionInstruments for road network navigationSatellite radio beaconingData transmissionDifferential GPS
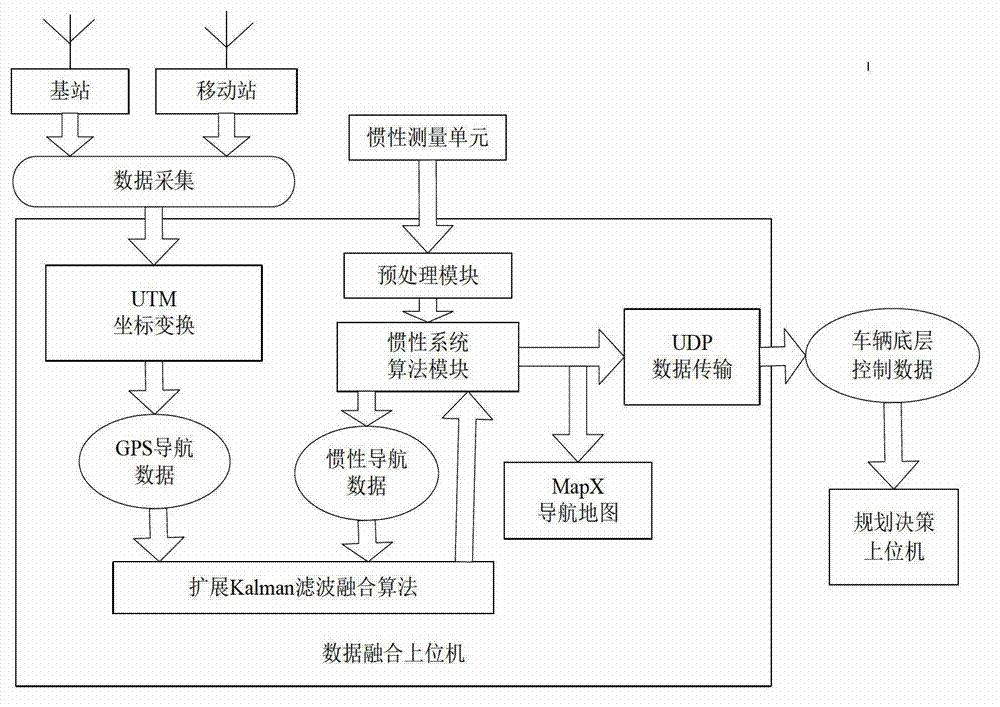
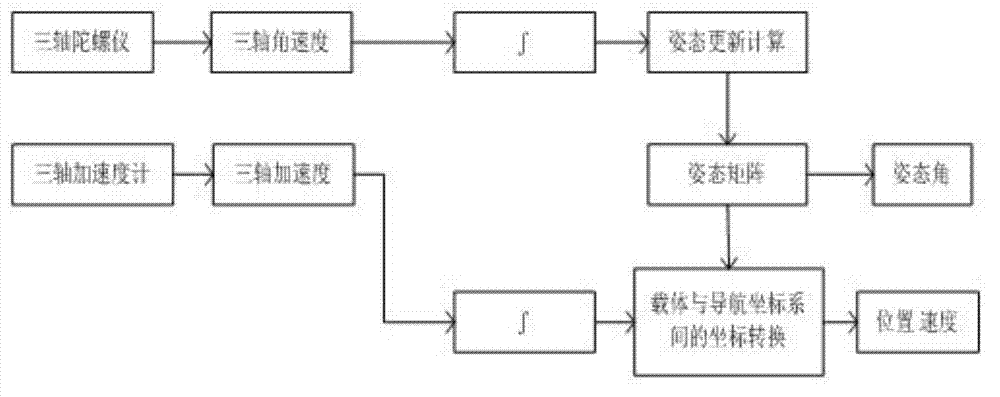
The invention relates to a data fusion system and method of a differential GPS and an inertial navigation in an intelligent vehicle. The data fusion method of the differential GPS and the inertial navigation in the intelligent vehicle includes utilizing the differential GPS arranged at the top of the vehicle to obtain information provided by a space satellite and utilizing an upper computer which is to perform data fusion to extract GPS data according to the NEMA-0183 protocol to obtain information such as heading, speed and position; utilizing an inertial navigation system arranged in the middle of the inside of the vehicle body to collect data of a heading changing rate and x-axis and y-axis accelerations during vehicle operating, and transmitting the data to the upper computer which is to perform data fusion to obtain a heading angle and the speed and the displacement of the x-axis and the y-axis; and through algorithm integration, finally obtaining accurate navigational positioning information and utilizing the inertial system to provide RI (Related Information) under the condition that the GPS signals are lost. Besides, the method further includes displaying the navigational positioning data in a map and transmitting the packed data to a planning decision-making upper computer through an LAN (Local Area Network) created through a router, and controlling the intelligent vehicle according to analyzed information and actual travelling conditions.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Driving vehicles in convoy
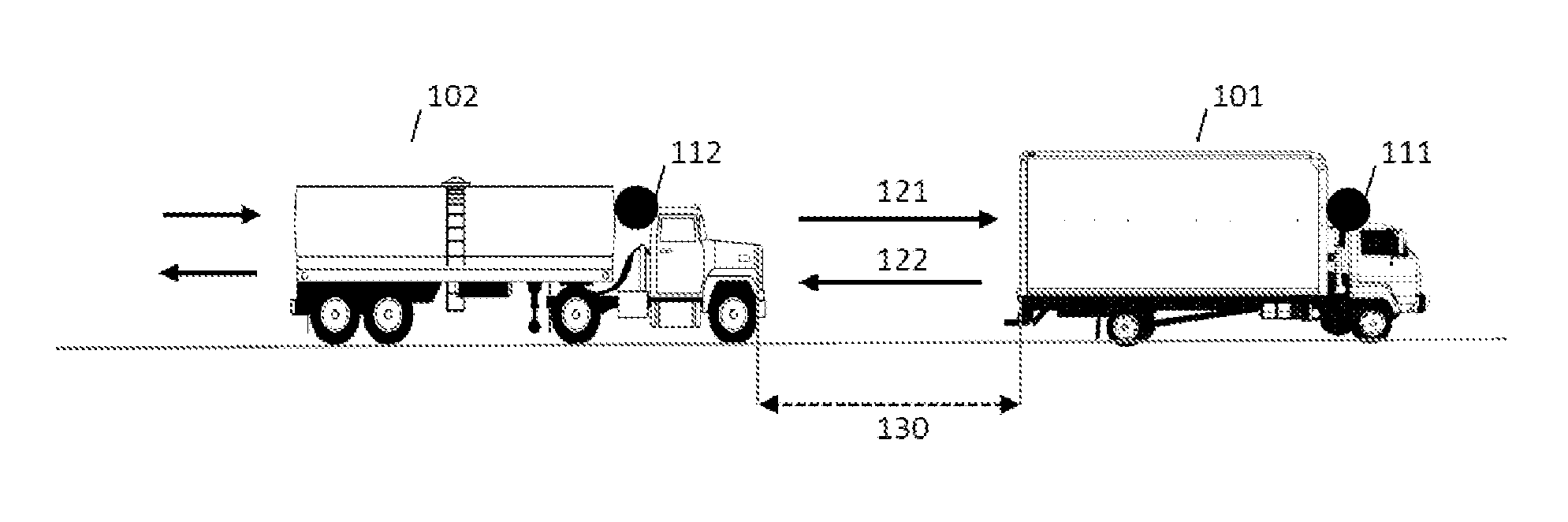
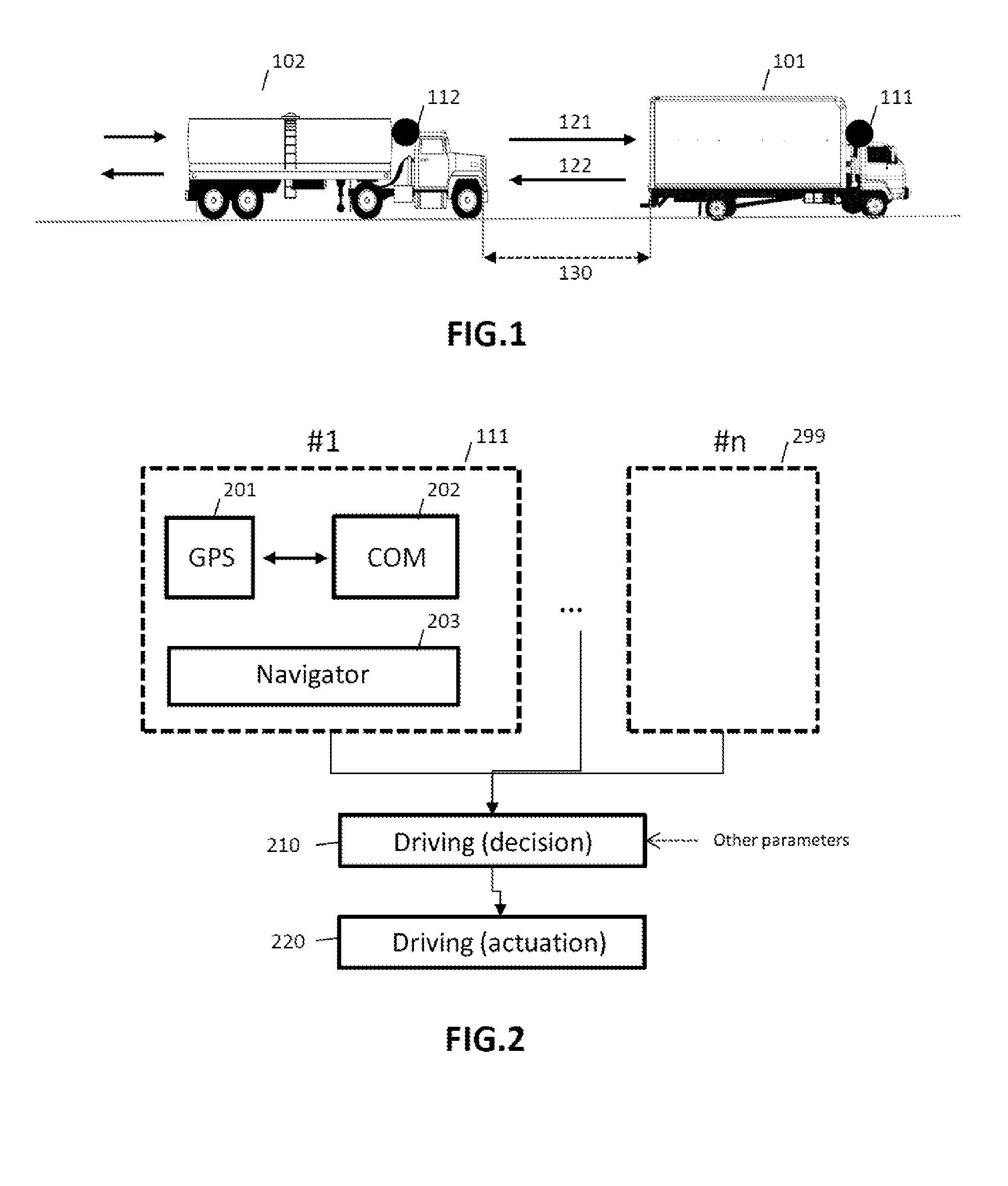
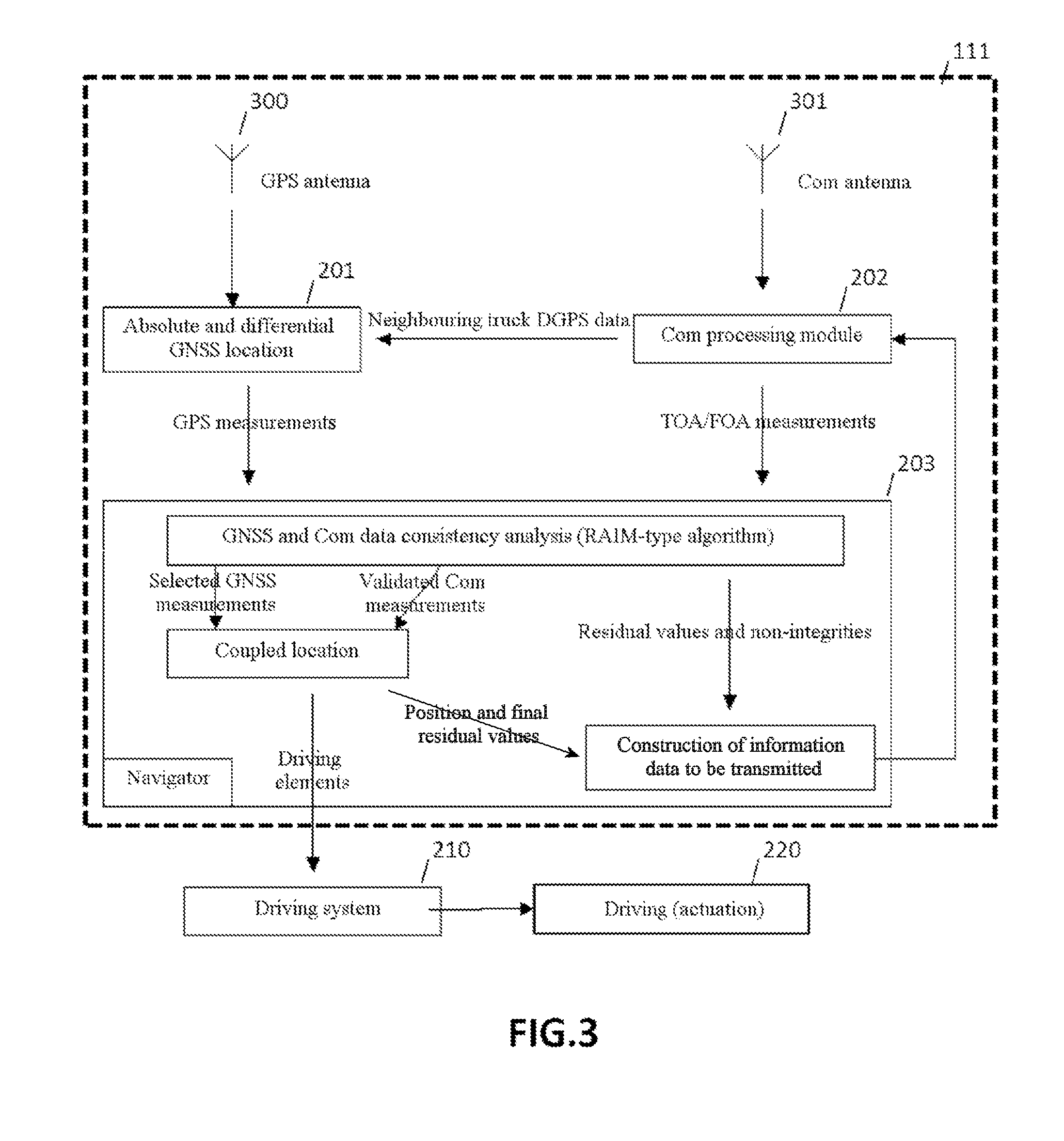
ActiveUS20150269845A1Good propagation time measurement qualityExternal condition input parametersSatellite radio beaconingEngineeringSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A method is implemented by computer for the management of a convoy comprising at least two vehicles, each of the at least two vehicles comprising satellite positioning means and vehicle-to-vehicle communication means, the method comprising the determination of the relative positioning of the vehicles, the determination comprising the measurement of the propagation time of a signal between vehicles by the communication means, the clocks associated with the communication means being synchronized via satellite positioning means at a reference clock time. Developments comprise the communication between the vehicles of various data (e.g. measurement uncertainties, signal-to-noise ratios, residual values), the determination of absolute locations, the use of an SBAS-type system, the use of differential GPS, the use of Doppler measurements for the turns or even the exclusion of a failing satellite. A computer program product and associated systems are described.
Owner:THALES SA
High-precision autonomous obstacle-avoiding flying method for unmanned plane
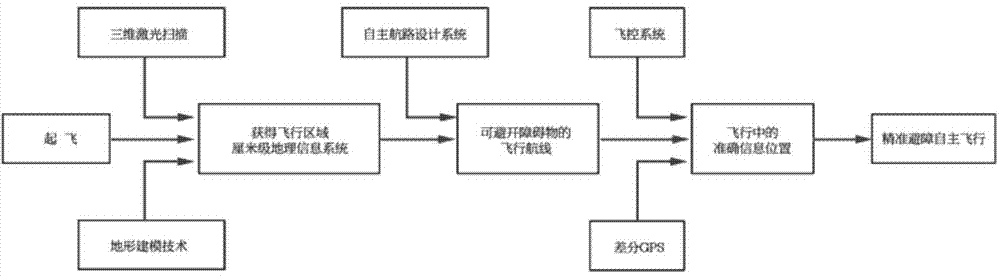
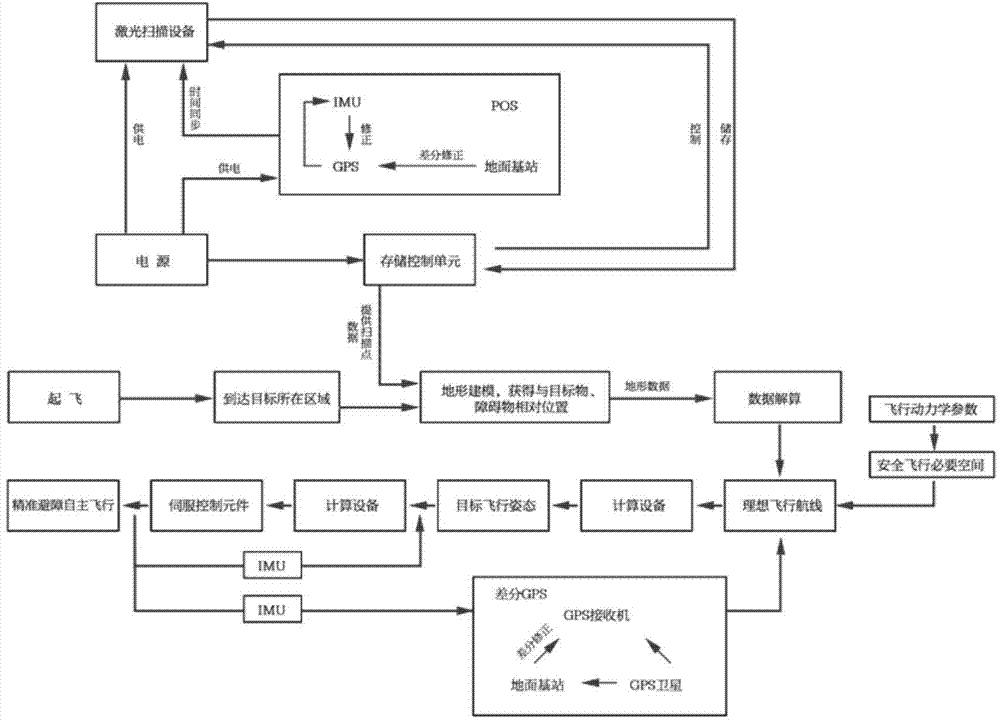
ActiveCN104850134AHigh positioning accuracySpatial location is accuratePosition/course control in three dimensionsAircraft navigation/guiding aidsTerrainControl signal
The invention relates to a high-precision autonomous obstacle-avoiding flying method for an unmanned plane, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) building a high-precision map model; (2) planning flight control for a three-dimensional airline; (3) transmitting a flight control signal at step (2) to a steering engine of an unmanned plane servo mechanism, thereby achieving the control purpose through the changing of the position of the steering engine. The advantages of the method lie in that the space coordinates of the terrain environment of a region through the combination of the technology of laser scanning and the technology of differential GPS, thereby providing support for the autonomous obstacle-avoiding line planning; the position control error of the whole flight process is controlled at a centimeter level, thereby guaranteeing that the unmanned plane can fly along a planned path, achieving an effect of automatically avoiding obstacles, and finally enabling the unmanned plane to arrive at a destination for operation.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGFEIAIWEI AERO SCI & TECH
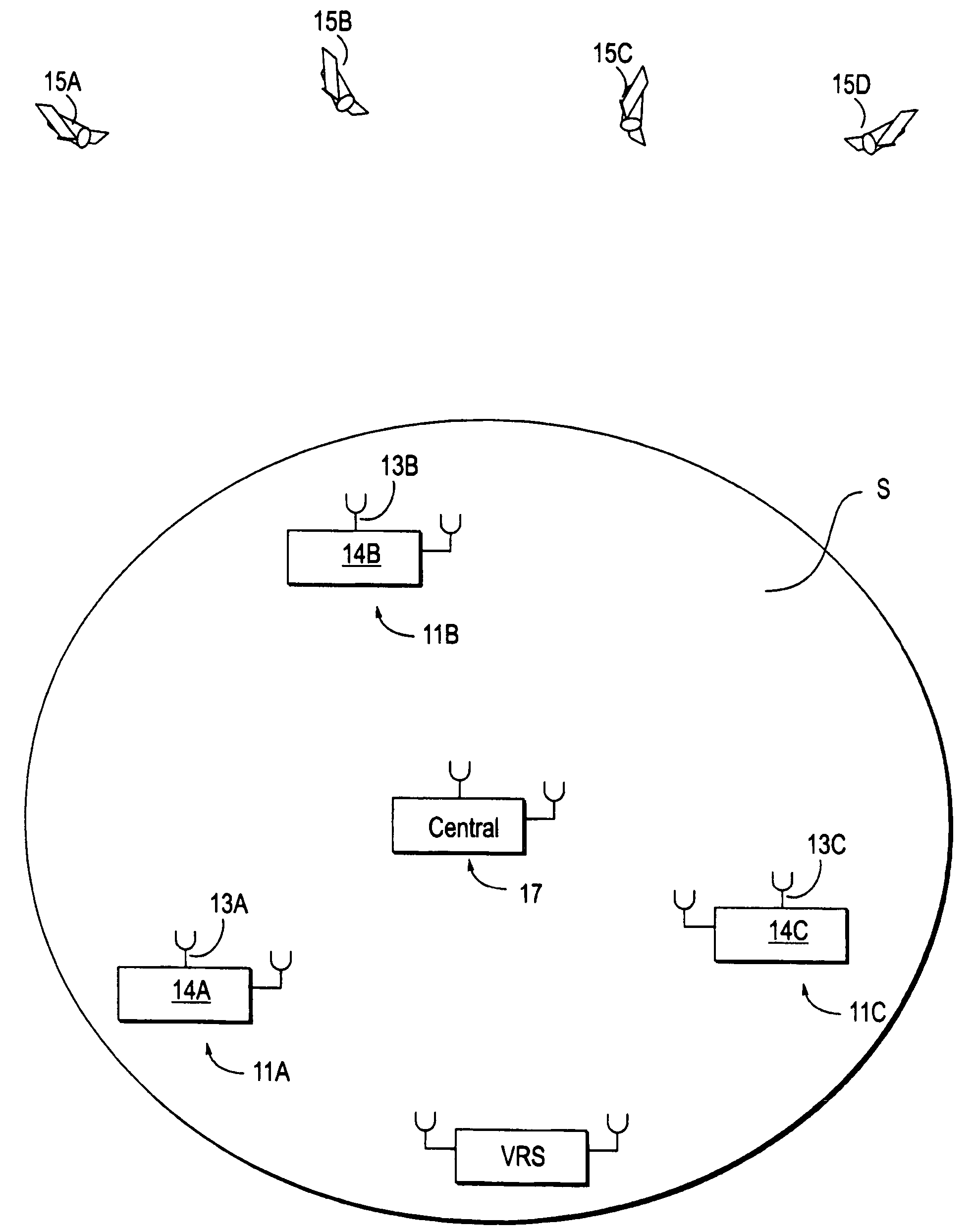
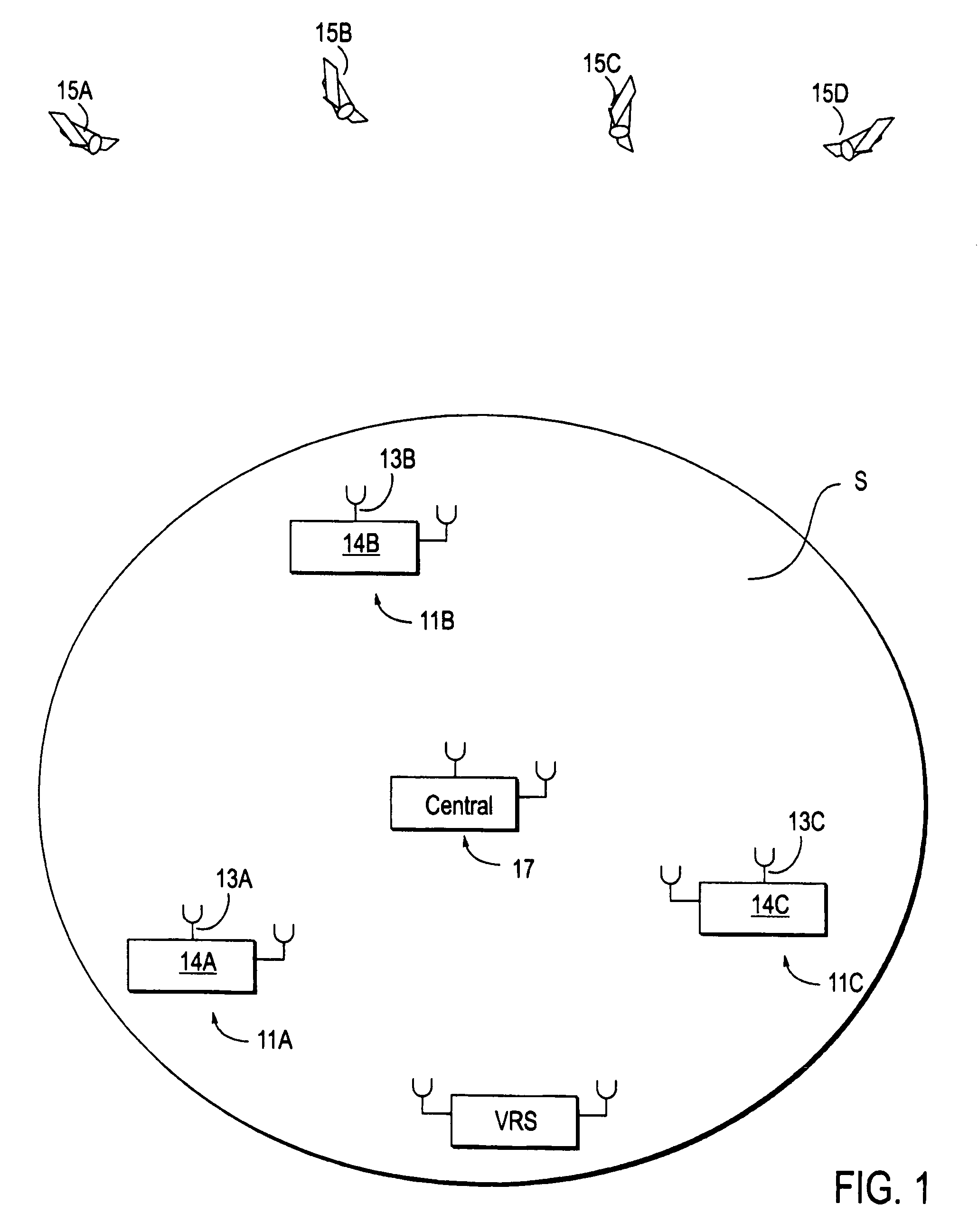
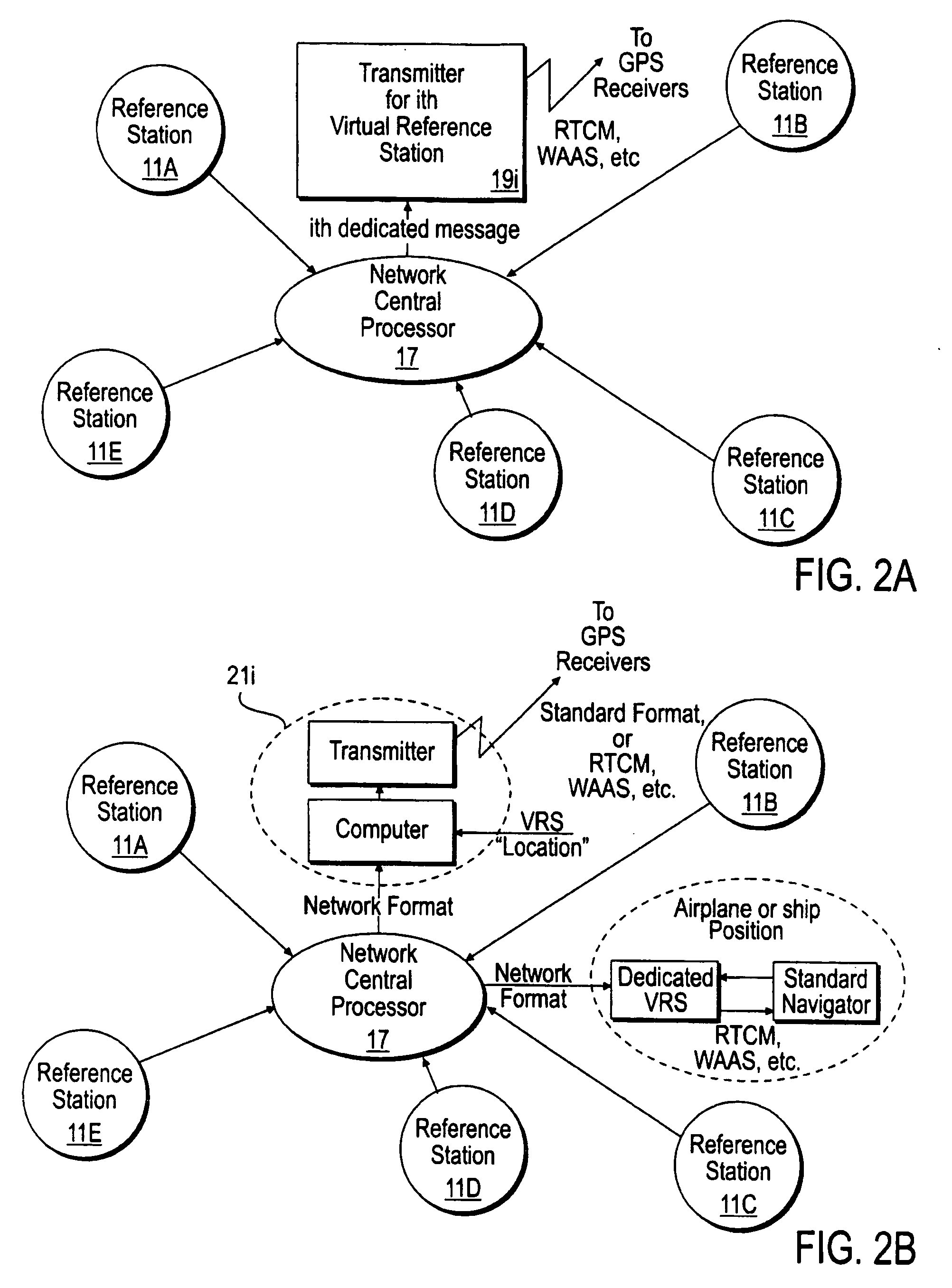
Differential GPS corrections using virtual stations
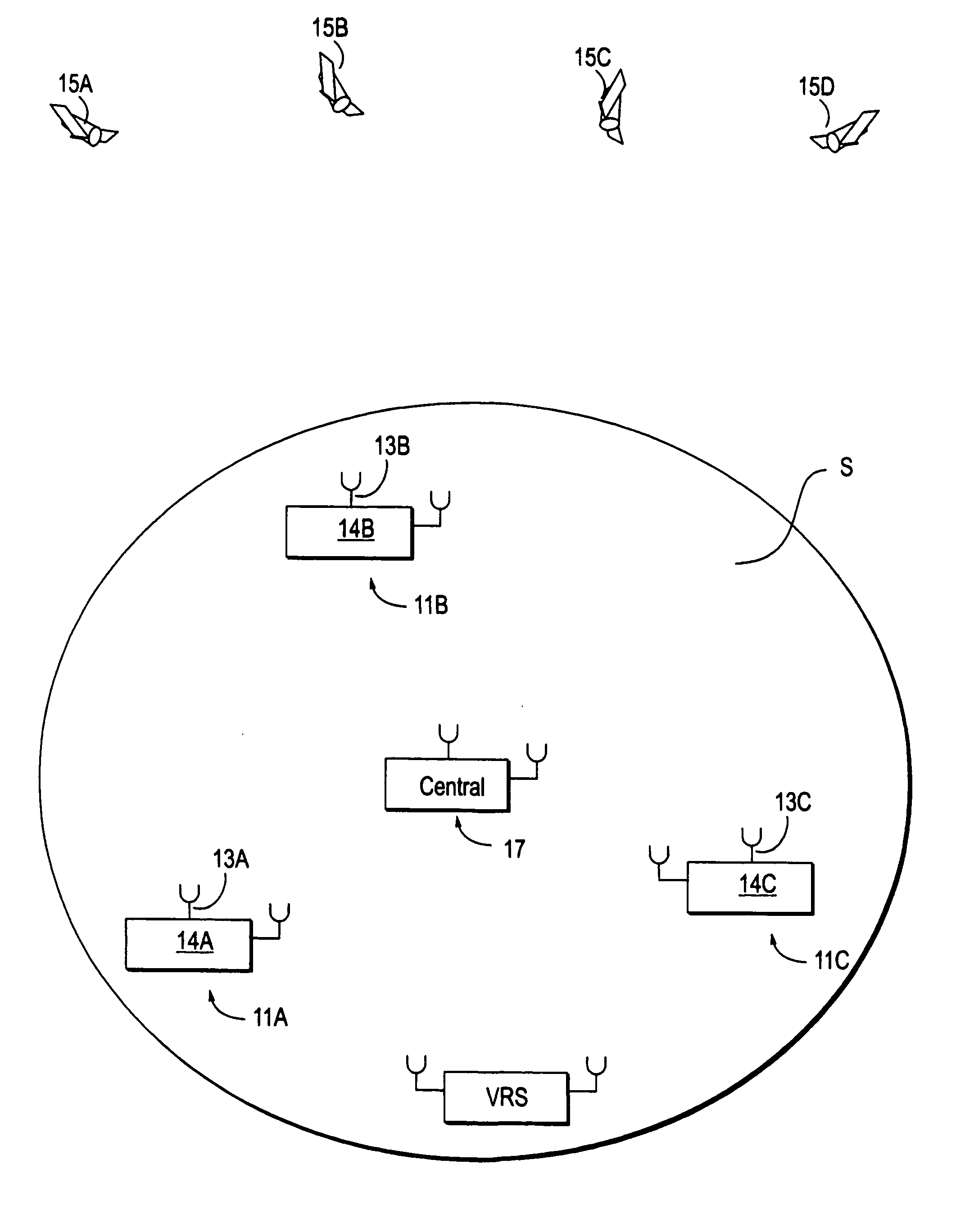
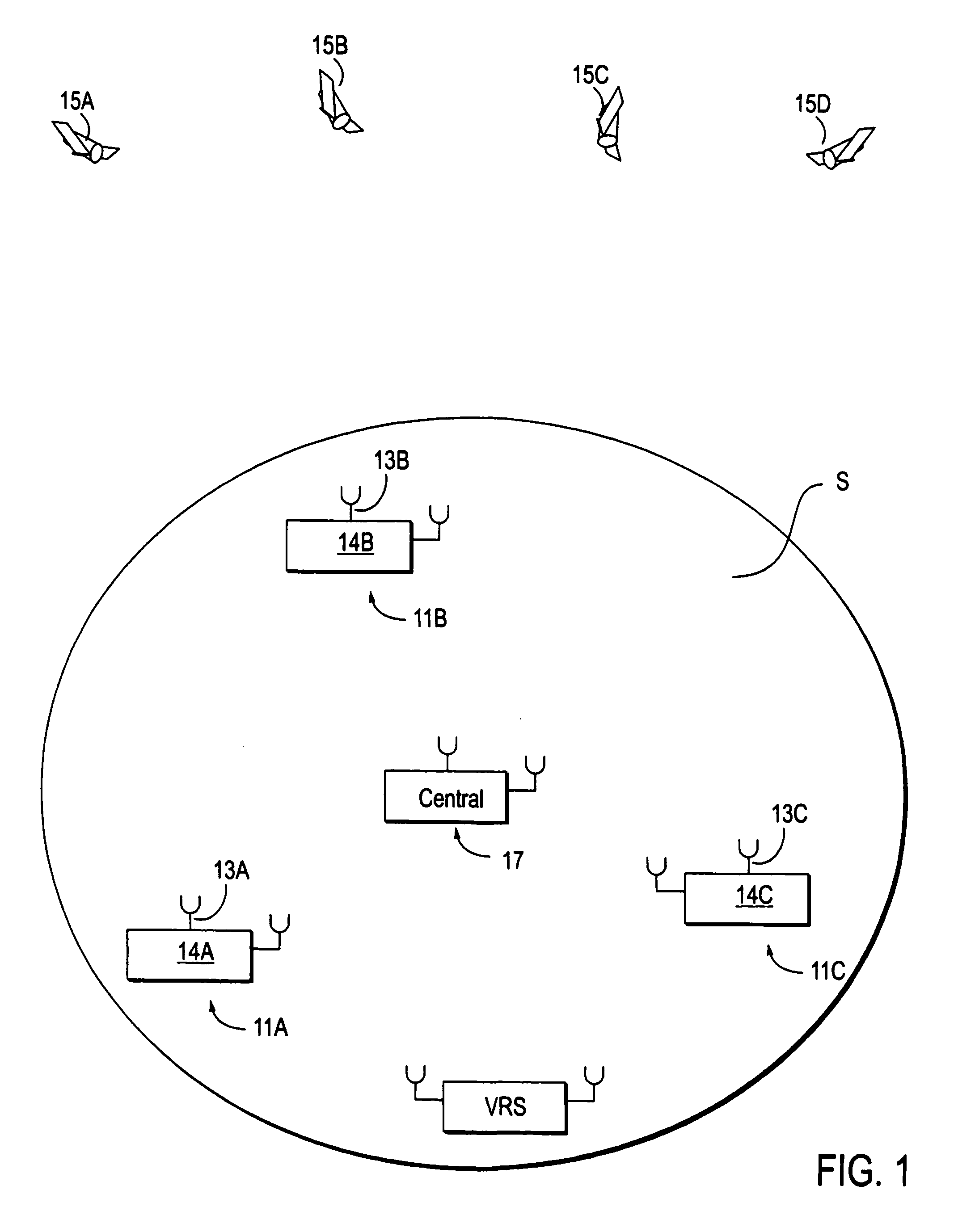
InactiveUS20060064244A1Small sizeEasy to useInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationGeographic regionsCarrier signal
Method and apparatus for providing GPS pseudorange correction and carrier phase correction information for navigation or surveying activities over a selected geographic region S of arbitrary size. In a navigation mode, a virtual reference station (VRS), positioned near a selected location L, receives differential GPS (DGPS) correction signals, translates these signals into a selected format, and broadcasts this DGPS information in this format for use by a local user. In a survey mode, the VRS receives corrected GPS information, translates this information into a selected format and broadcasts this translated and corrected GPS information and the VRS location, for use by a mobile station in forming a baseline vector from the GPS mobile station to the VRS location.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Method for generating clock corrections for a wide-area or global differential GPS system
InactiveUS7117417B2Easy accessCancel noiseInstruments for road network navigationError preventionWide areaDual frequency
Owner:DEERE & CO
Integrated navigation and positioning system and method for submarine oil-gas pipe detection robot
PendingCN110006433AExact effective positionAccurate and effective attitude informationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsOcean bottomTime course
The invention belongs to the technical field of navigation and provides an integrated navigation and positioning system and method for a submarine oil and gas pipe detection robot. The integrated navigation and positioning system mainly comprises a differential GPS system, an ultra-short baseline positioning system (USBL), a strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS), a Doppler log (DVL) and thelike. The differential GPS system accurately positions geographic position coordinates of a surface vessel; the ultra-short baseline positioning system determines a three-dimensional vector position of the underwater unmanned aerial vehicle relative to the water surface unmanned ship; the strapdown inertial navigation system detects the real-time course and attitude of the underwater unmanned vehicle; and the Doppler log detects the absolute running speed of the underwater unmanned vehicle. The SINS and the DVL are combined to realize short-time high-precision positioning of the underwater unmanned vehicle, and the differential GPS and the USBL are combined to realize absolute positioning of the underwater unmanned vehicle; the long-endurance and long-voyage high-precision positioning of the underwater unmanned vehicle is realized, and the accurate position information is provided. The invention further provides a combined positioning method of various navigation instruments, and a solution is provided for underwater high-precision combined navigation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
AD-HOC differential GPS referencing using parked vehicles
InactiveUS9020755B1Reduce positioningPrecise positioningInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesMobile vehicleComputer science
A method of determining a position of a moving vehicle. A global position is detected by a global positioning device of at least one parked vehicle in a vicinity of the moving vehicle. The global position is determined as a function of signals broadcast by a plurality of satellites. Errors associated with the broadcast signals are determined. A correction error that provides a solution for eliminating the errors associated with the broadcast signals is determined. The correction error is transmitted to the moving vehicle. The correction error is applied to a received global positioning signal received by the moving vehicle. A global position of the moving vehicle is determined as a function of the correction error. The determined global position of the moving vehicle is applied in a vehicle application.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
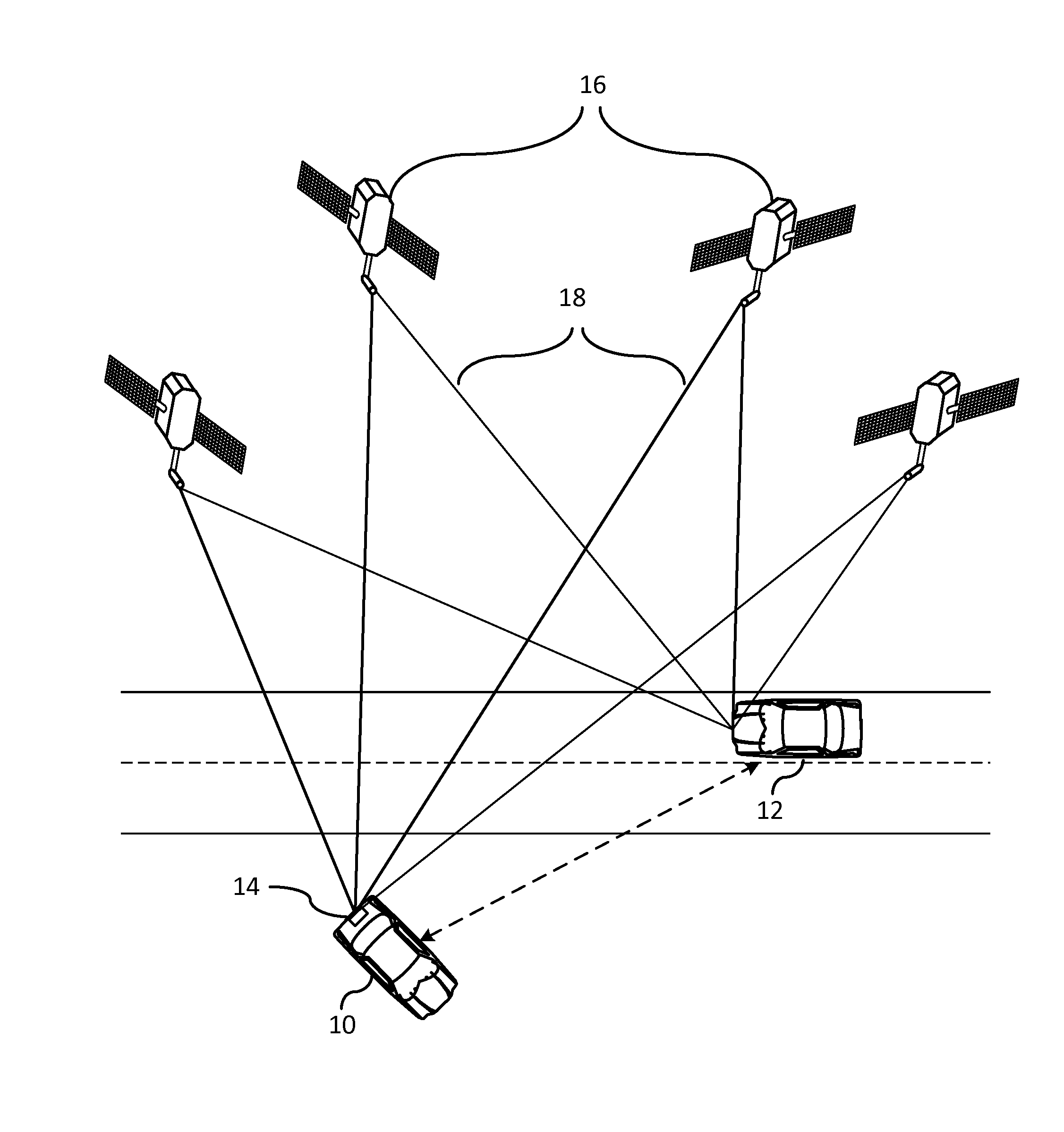
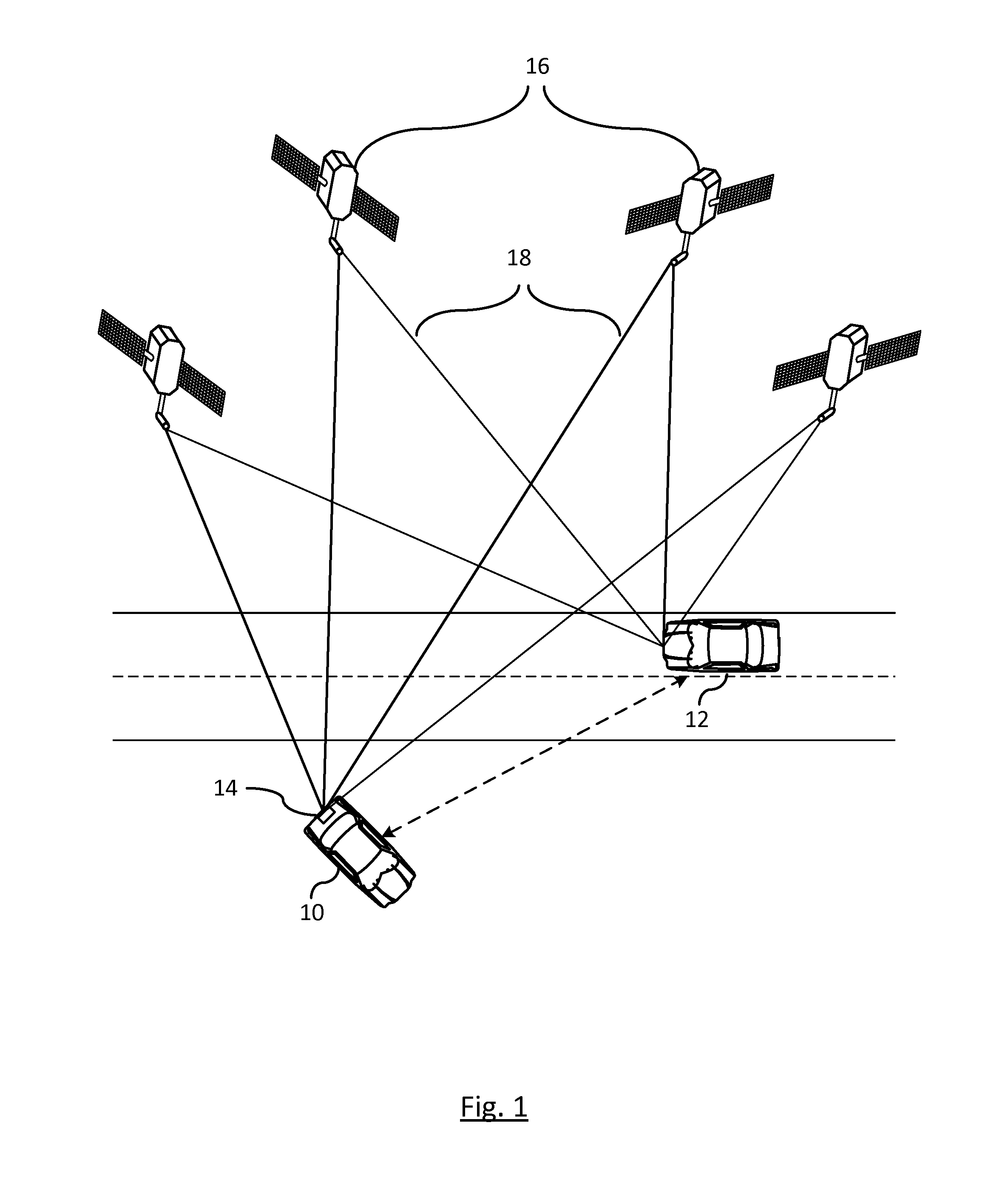
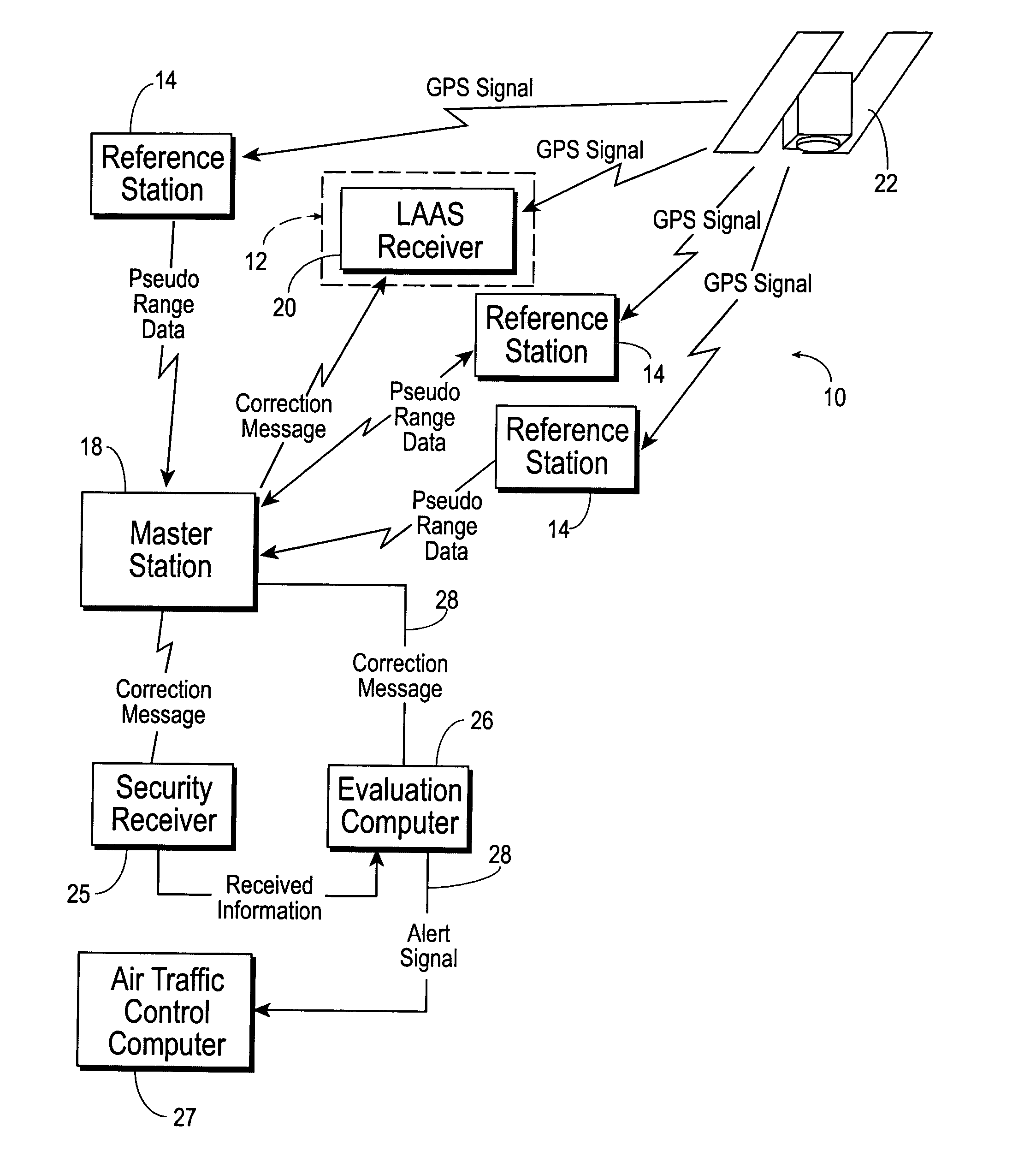
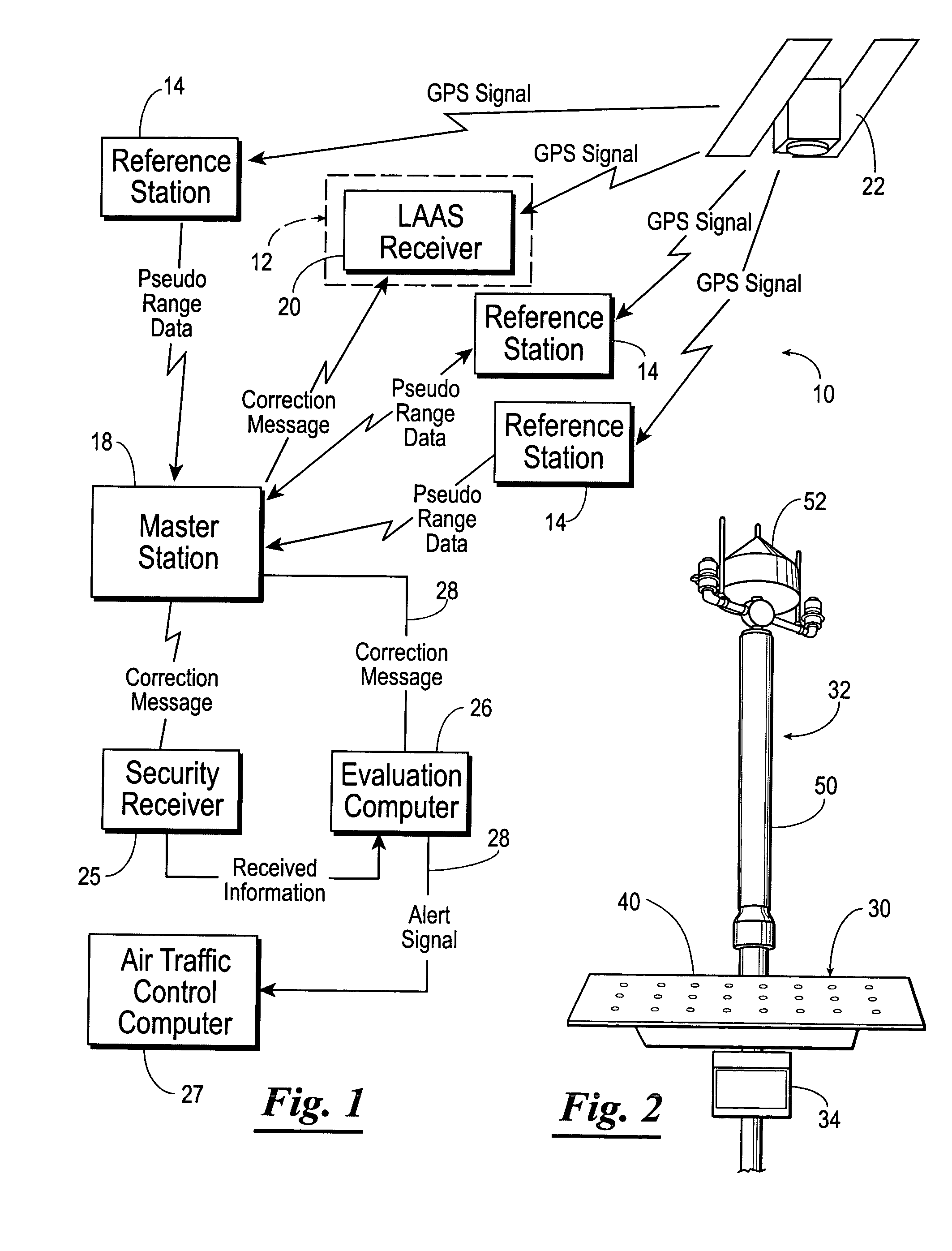
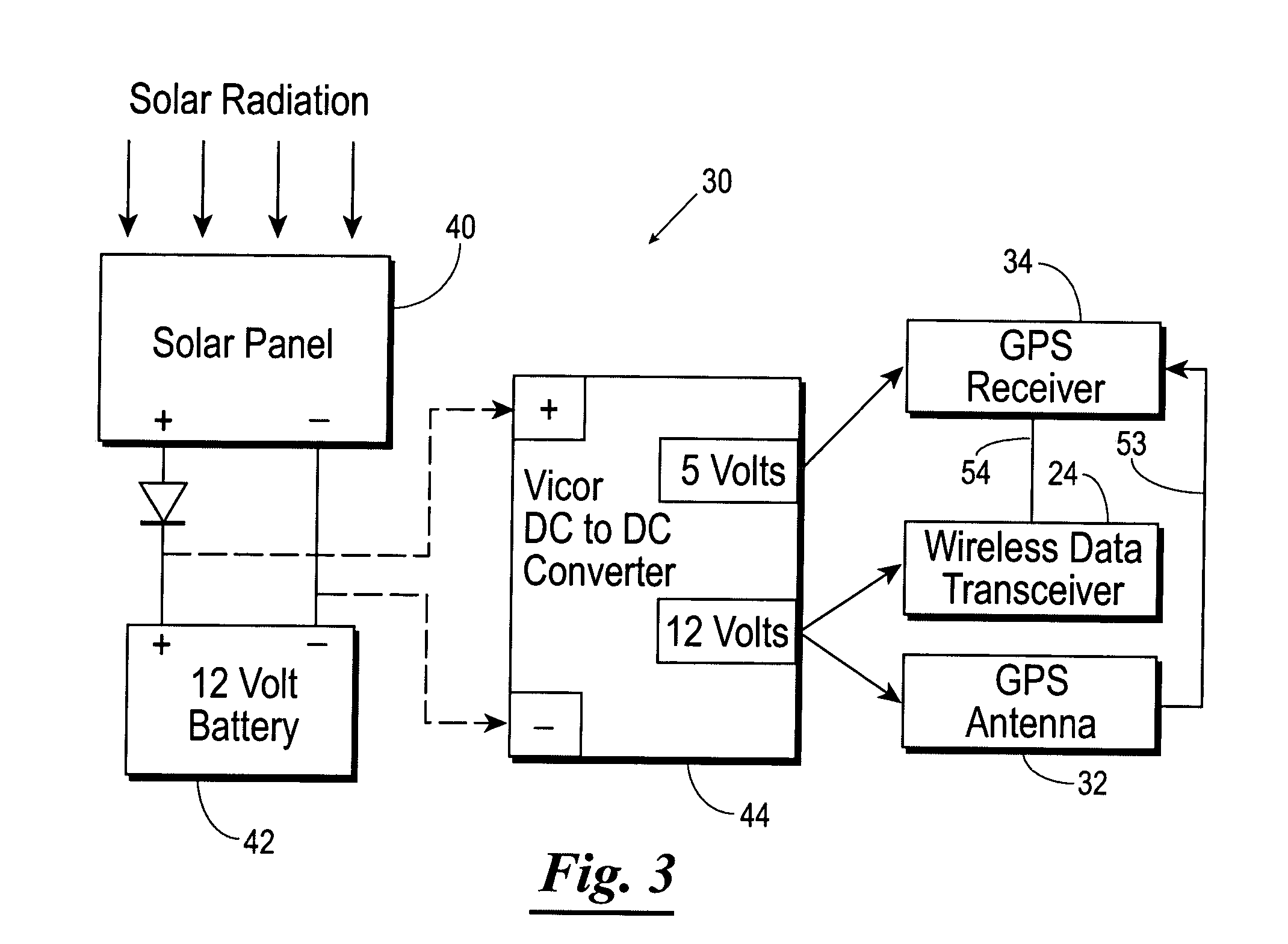
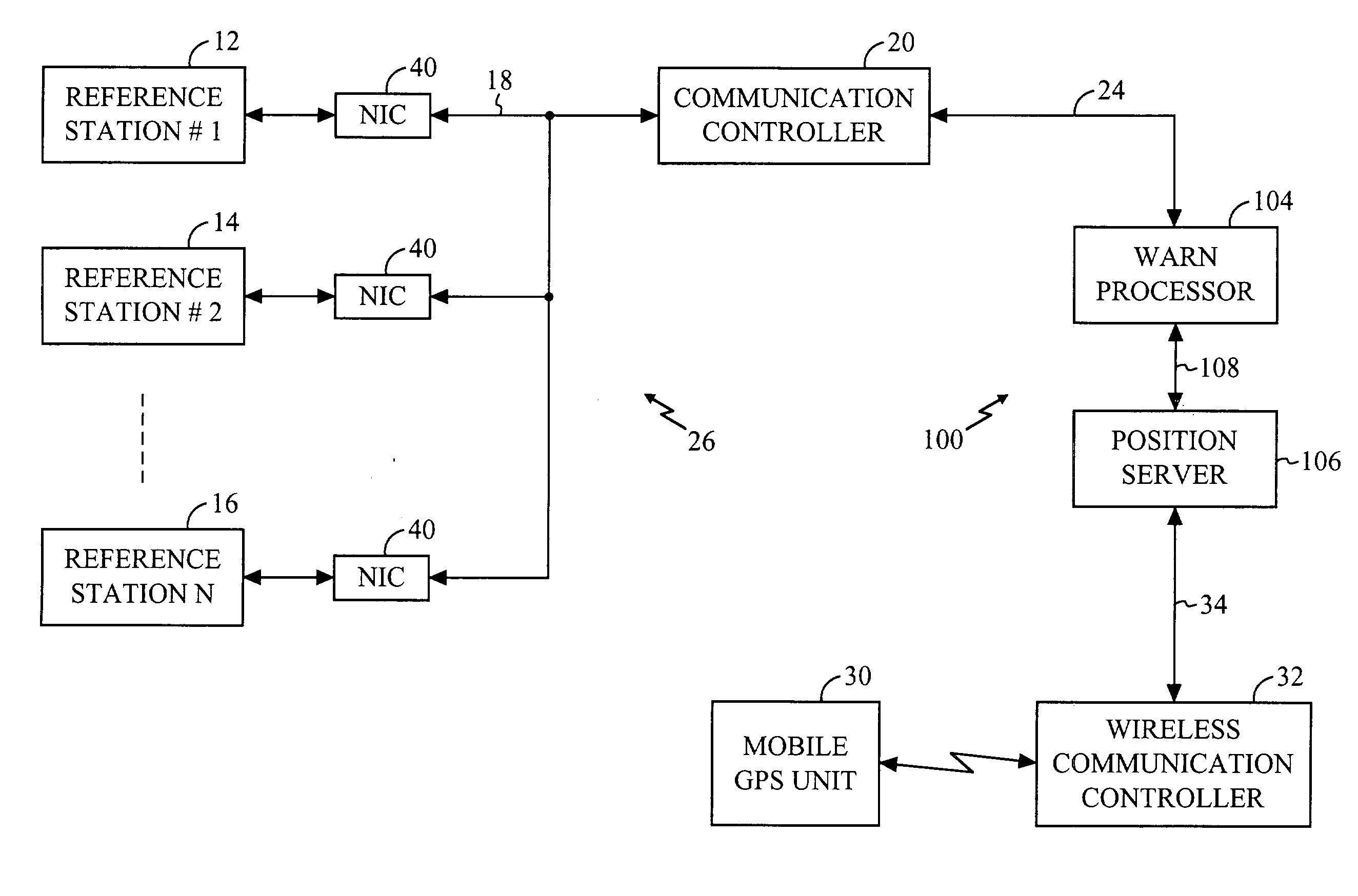
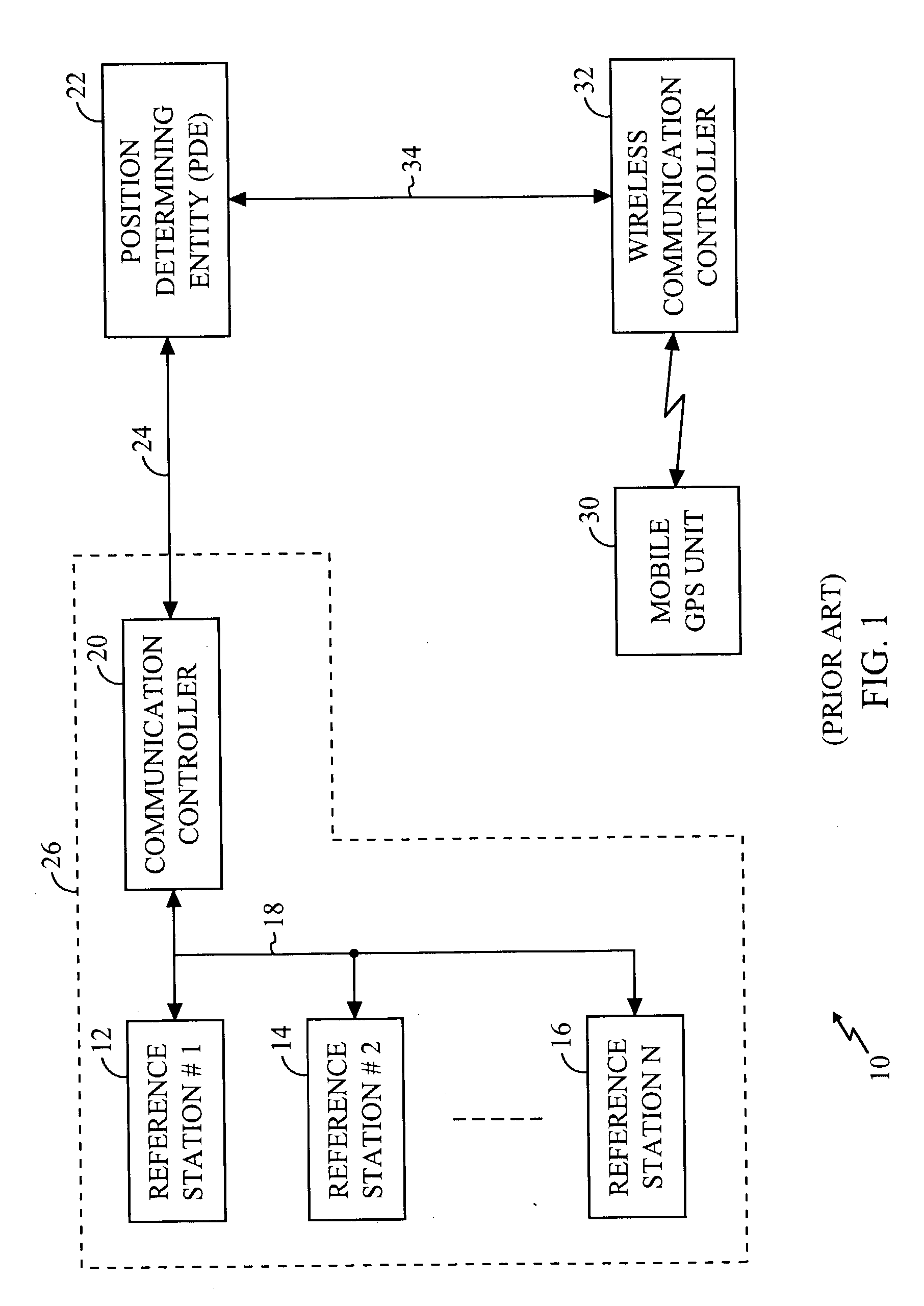
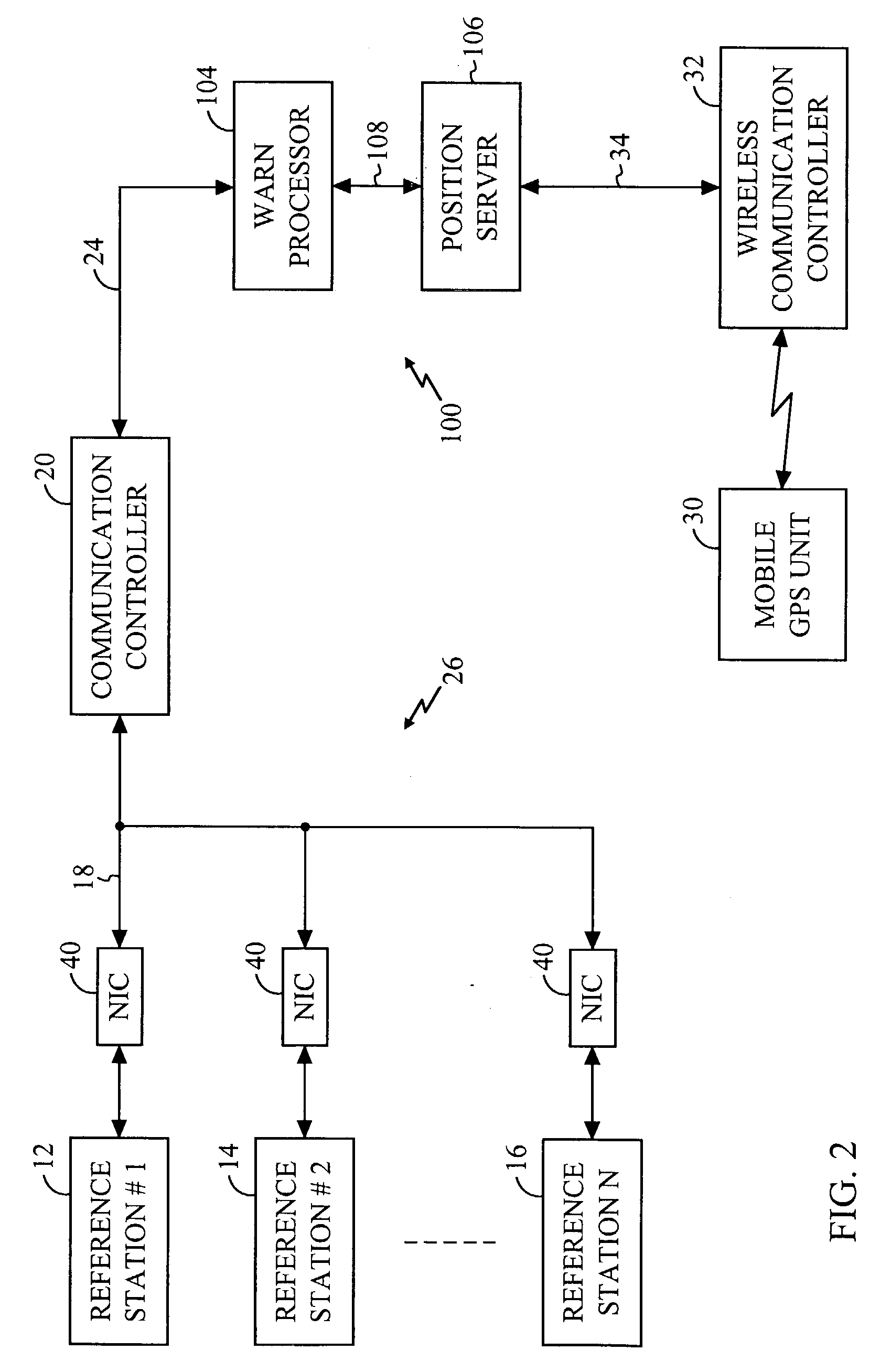
Navigation system using locally augmented GPS
InactiveUS20040119638A1Increase workloadSignificant economic and safety benefitPosition fixationBeacon systemsWireless transceiverTransceiver
A local area augmentation navigation system for determining the location of an object using differential GPS. The system does not require any significant power or communication infrastructure. The system includes at least three reference stations, a master station and a LAAS receiver. The at least three reference stations are located in close proximity to each other and at known locations. Each of the reference stations receive a GPS signal from a GPS constellation and collect and output via a wireless transceiver the pseudo-range data from the GPS signal. The master station is positioned in close proximity to the reference stations and receives the pseudo-range data from the reference stations. The master station forms a correction message from the pseudo-range data and the known locations of the reference stations. The master station broadcasts the correction message within a specified area. The LAAS receiver is positioned within the specified area and receives the correction message broadcast by the master station as well as a GPS signal from the GPS constellation. The LAAS receiver calculates the location of the LAAS receiver with the correction message and the GPS signal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
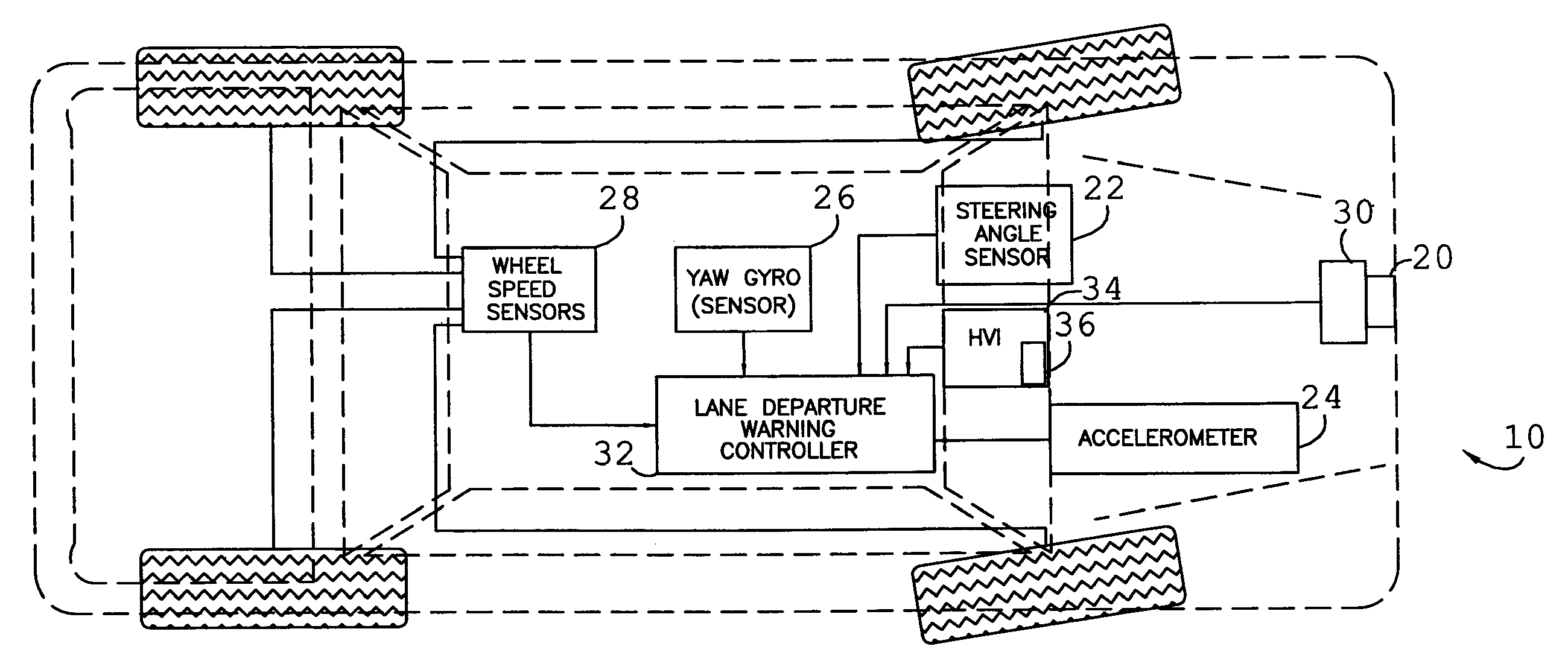
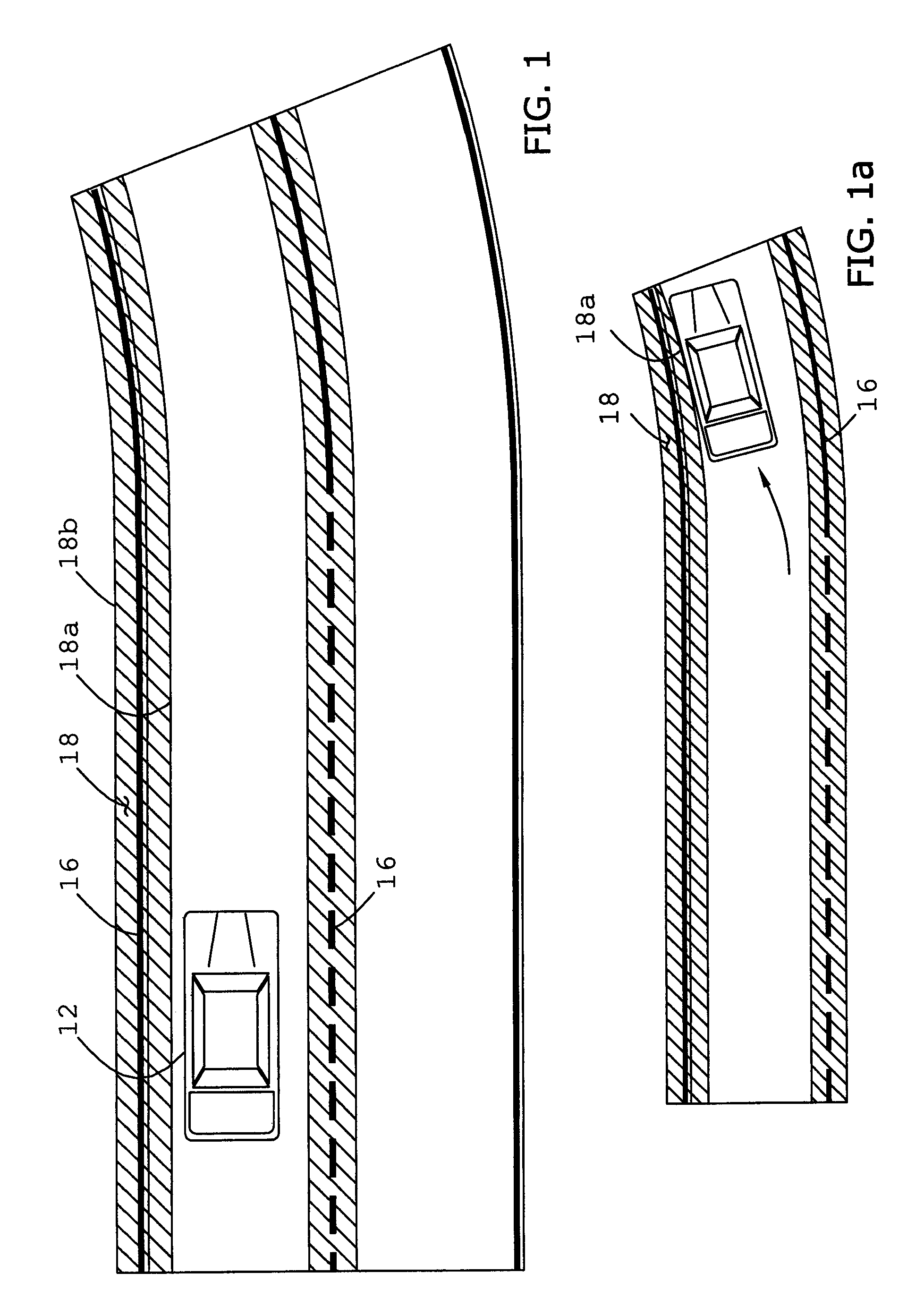
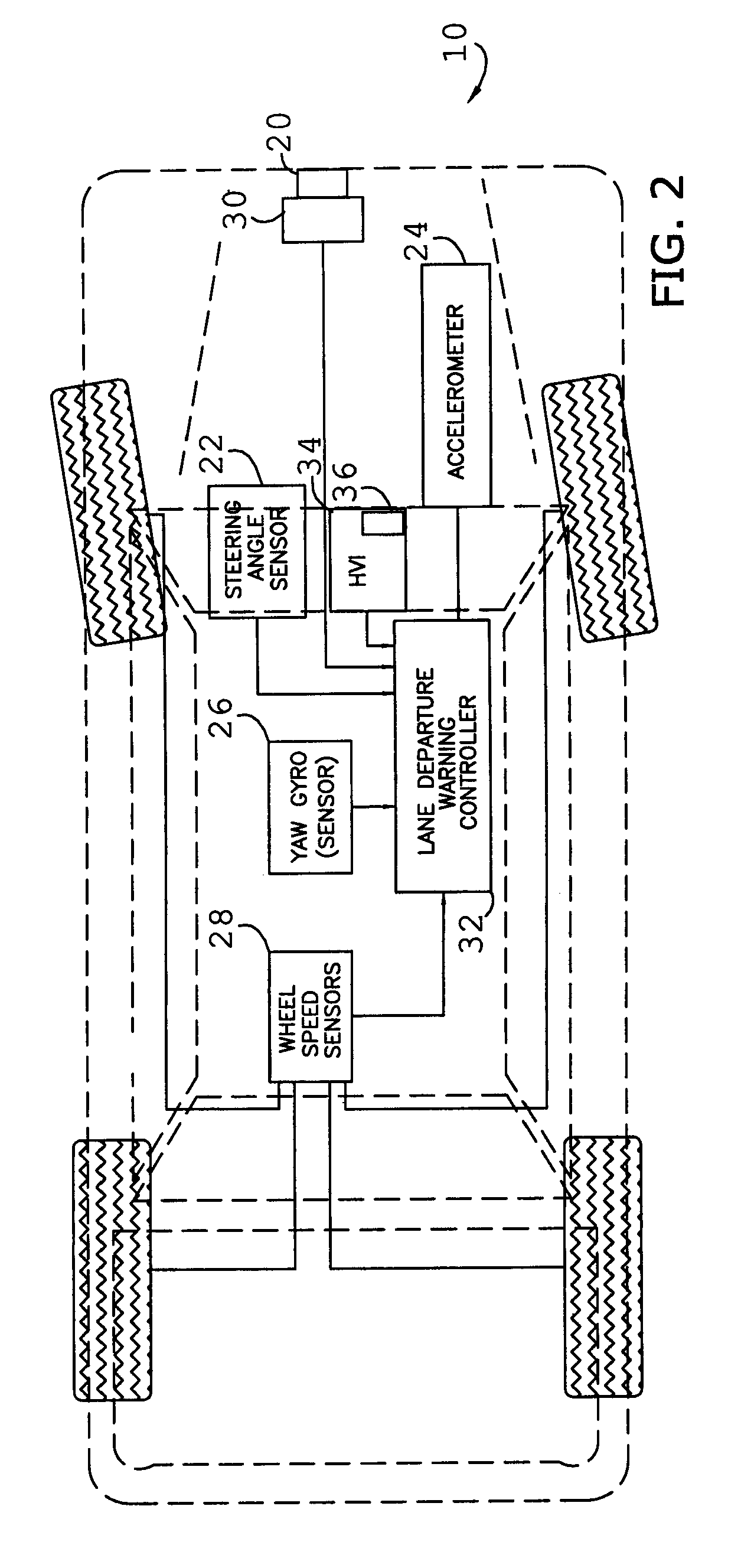
Selectable lane-departure warning system and method
InactiveUS7561032B2Reduce the possibilityEasy to detectSteering partsOptical signallingLane departure warning systemEngineering
A selectable lane departure detection system (10) adapted for use by an operator, and with a vehicle (12) traveling upon a thoroughfare having lane-markings (16), and including at least one vehicle condition sensor (22 through 28), a tracking sensor (20) or differential global positioning system (38) configured to determine the location and configuration of the lane-markings (16), and a controller (32) communicatively coupled to the sensors (20 through 28), and configured to determine a spatial relationship between the vehicle (12) and lane-markings (16), determine a sporty driving maneuver by or preference of the operator, modify a predefined warning threshold when so determined, compare the relationship to the adjusted threshold, and issue a warning when the relationship does not exceed the threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for reference data processing in network assisted position determination
A system and method of preprocessing reference data in a reference assisted location technology are disclosed. A plurality of reference stations each provides reference data over a network to a preprocessing. The preprocessor analyzes the data from the multiple reference stations and eliminates multiples sets of redundant data. In addition, the preprocessor can perform quality assurance checks on the data as well as the status of the reference stations themselves. Non-redundant data may also be preprocessed to perform differential GPS calculations. The preprocessed data is transmitted to one or more position servers for additional processing and position determination.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
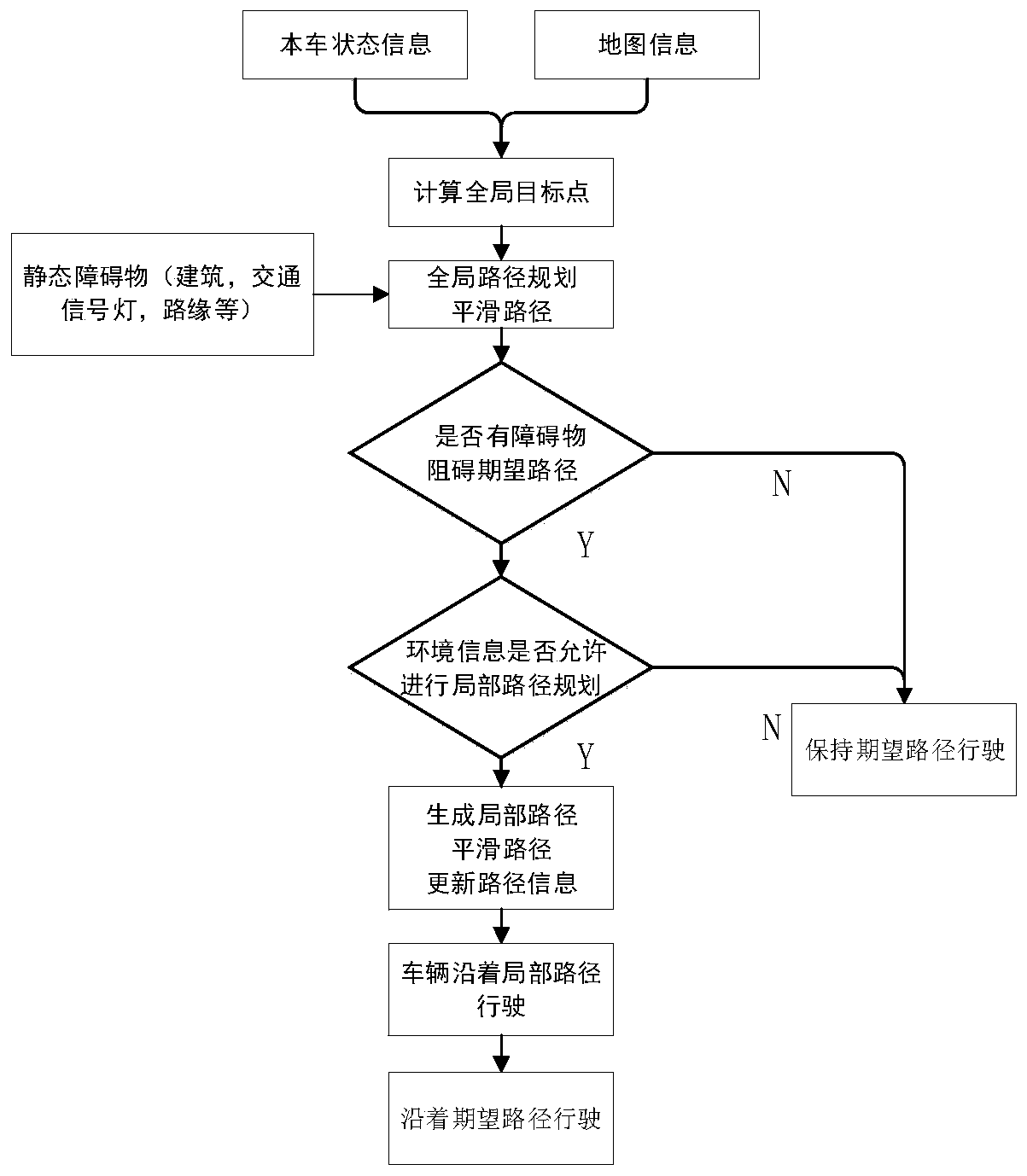
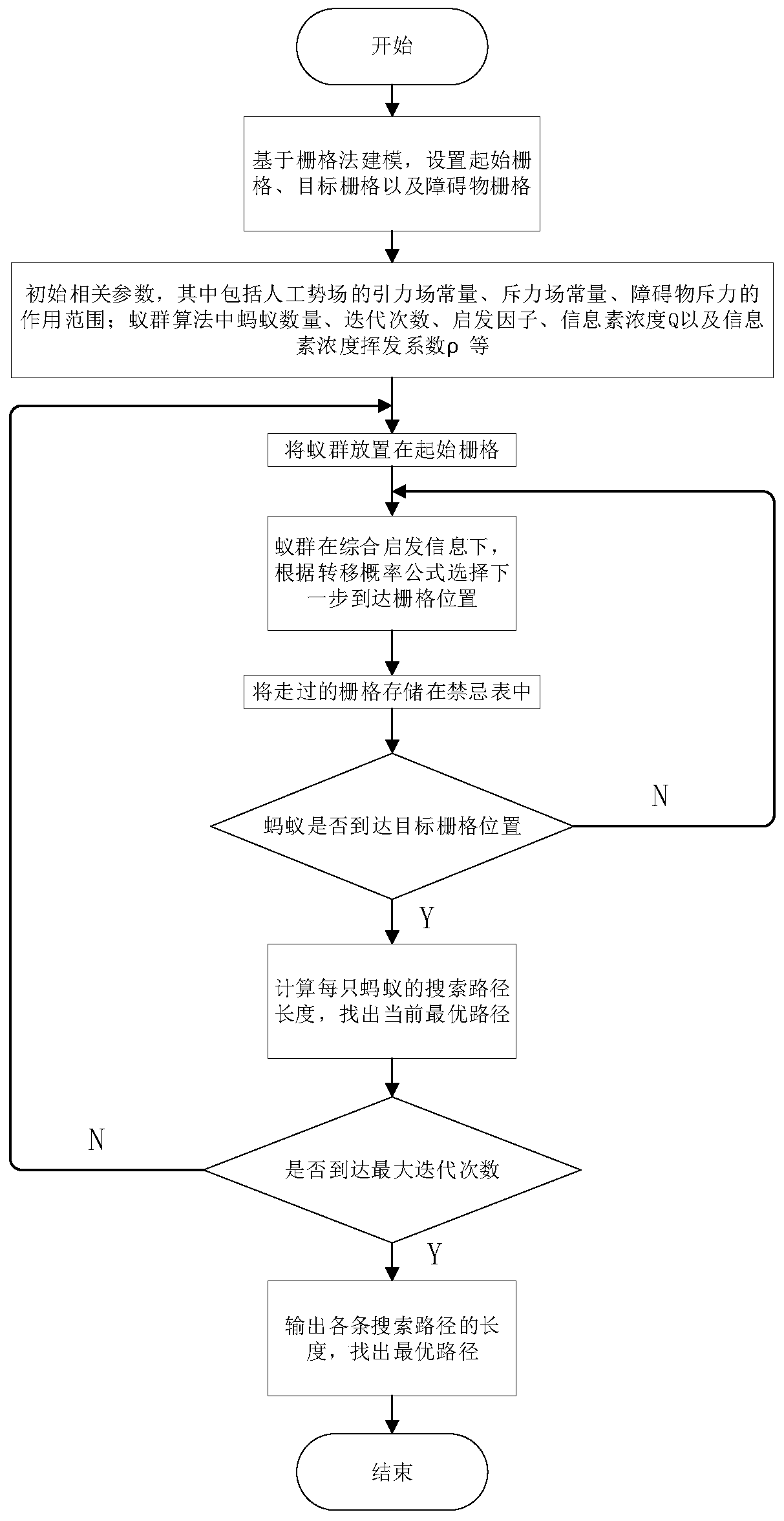
Driverless vehicle path planning method and device
ActiveCN110333714AEfficient and reasonable planningImprove operational efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPotential fieldPlanning approach
The invention discloses a driverless vehicle path planning method and device. The driverless vehicle path planning method comprises the following steps: S1, locating a current vehicle: obtaining the location of the current driverless vehicle as a starting point according to a differential GPS / INS system, then selecting a target point, loading the data of a global map, and reading the vehicle status information; S2, planning a global path: establishing a global raster map according to the coordinate information of the starting point and the target point, using a modified artificial potential field-ant colony algorithm to plan the global path, and generating a desired path; S3, driving and analyzing the current road condition by the vehicle, and analyzing and judging whether local path planning is needed or not according to the obtained sensor information; S4, selecting a local path planning strategy; and S5, sending the generated path information to a vehicle control layer. The invention improves the running efficiency of the program; and the vehicle can efficiently and reasonably plan a safe path in a complex and varied environment; therefore, the global optimality and local real-time performance of the path planning are ensured.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
System and method for tracking vehicles and containers
A location system for tracking assets within a terminal includes a Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) reference receiver within the terminal that receives GPS signals and generates DGPS correction data. In one aspect, a roving receiver unit is carried by an asset to be tracked within the terminal. It includes a GPS receiver that receives GPS signals and the DGPS correction data from the DGPS reference receiver. A tag transmitter transmits a wireless RF signal containing GPS location data based on received GPS signals and DGPS correction data. At least one access point is positioned within the terminal for receiving the wireless RF signal from the tag transmitter. A processor is operatively connected to the at least one access point for receiving GPS location data and determining a location of the asset to be tracked.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
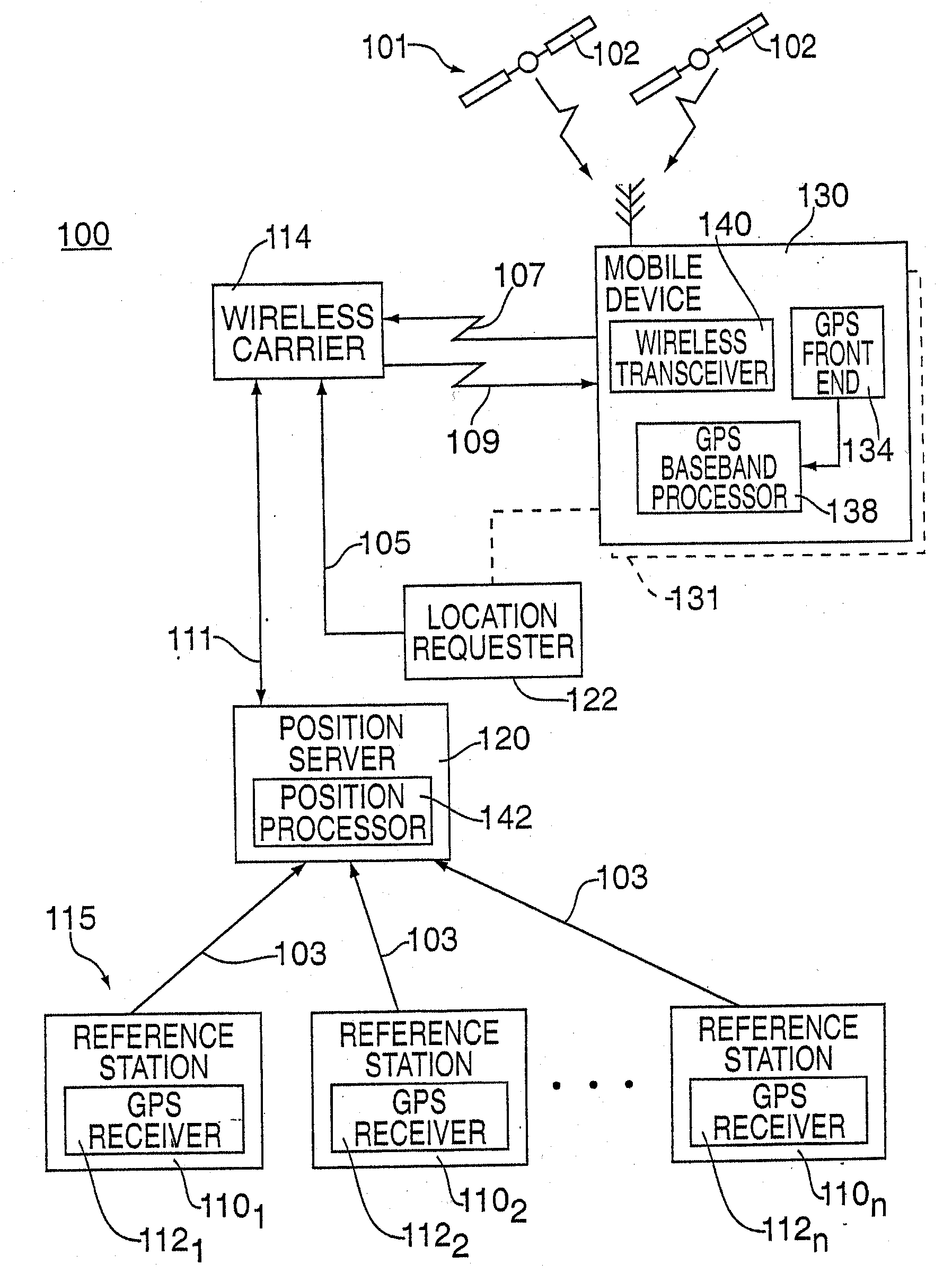
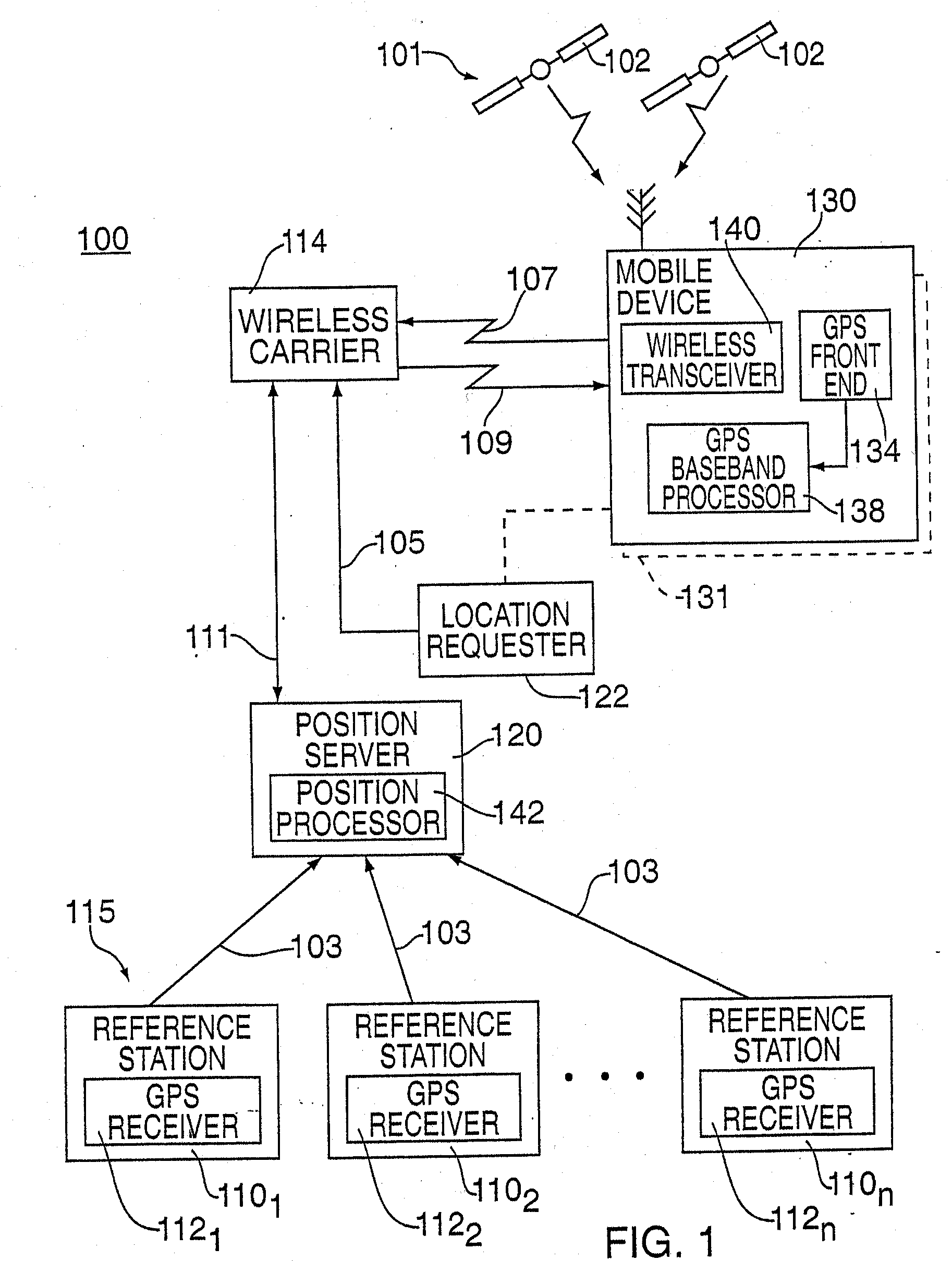
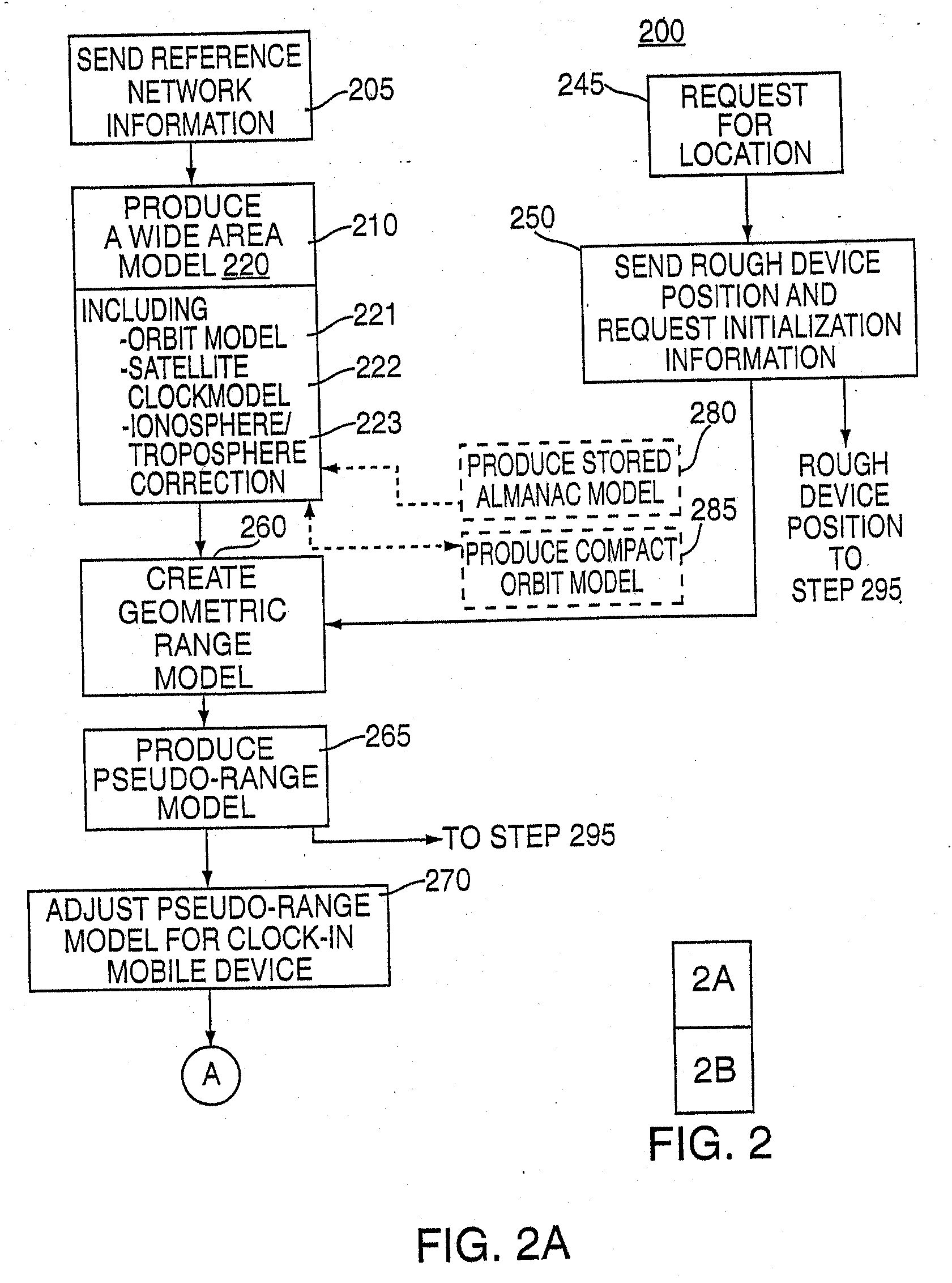
Wide area inverse differential GPS
InactiveUS20020072855A1Message being delayedKeep for a long timeInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationTelecommunications linkSignal on
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A method and apparatus for locatiredetermining the sets of millisecond integers until a set of millisecond integers solves for the position of the GPS device.ng mobile device over a broad coverage area using a wireless communications link that may have large and unknown latency. The apparatus comprises at least one mobile device, a reference network, a position server, a wireless carrier, and a location requester. The mobile device is in communication with the wireless carrier and receives global positioning system (GPS) signals from a plurality of satellites in the GPS satellite constellation. The reference network is coupled to the position server and provides GPS data. The mobile receiver receives GPS signals, performs rudimentary signal processing and transmits the processed signals to the wireless carrier. The wireless carrier passes the signals on to the position server. The position server processes the mobile receiver's GPS data and the reference network ephemeris data to identify the location of the mobile receiver. The location is sent to the location requester.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Differential GPS corrections using virtual stations
InactiveUS20060282216A1Instruments for road network navigationPosition fixationGeographic regionsCarrier signal
Method and apparatus for providing GPS pseudorange correction and carrier phase correction information for navigation or surveying activities over a selected geographic region S of arbitrary size. In a navigation mode, a virtual reference station (VRS), positioned near a selected location L, receives differential GPS (DGPS) correction signals, translates these signals into a selected format, and broadcasts this DGPS information in this format for use by a local user. In a survey mode, the VRS receives corrected GPS information, translates this information into a selected format and broadcasts this translated and corrected GPS information and the VRS location, for use by a mobile station in forming a baseline vector from the GPS mobile station to the VRS location.
Owner:ROBBINS JAMES E
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com