Differential GPS corrections using virtual stations
a virtual station and gps technology, applied in the field of networked global positioning system stations, can solve the problems of increasing the total location error of a dgps calculation to tens of meters or larger, and the differential gps corrections for location and/or time determination are usually limited, so as to reduce the size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
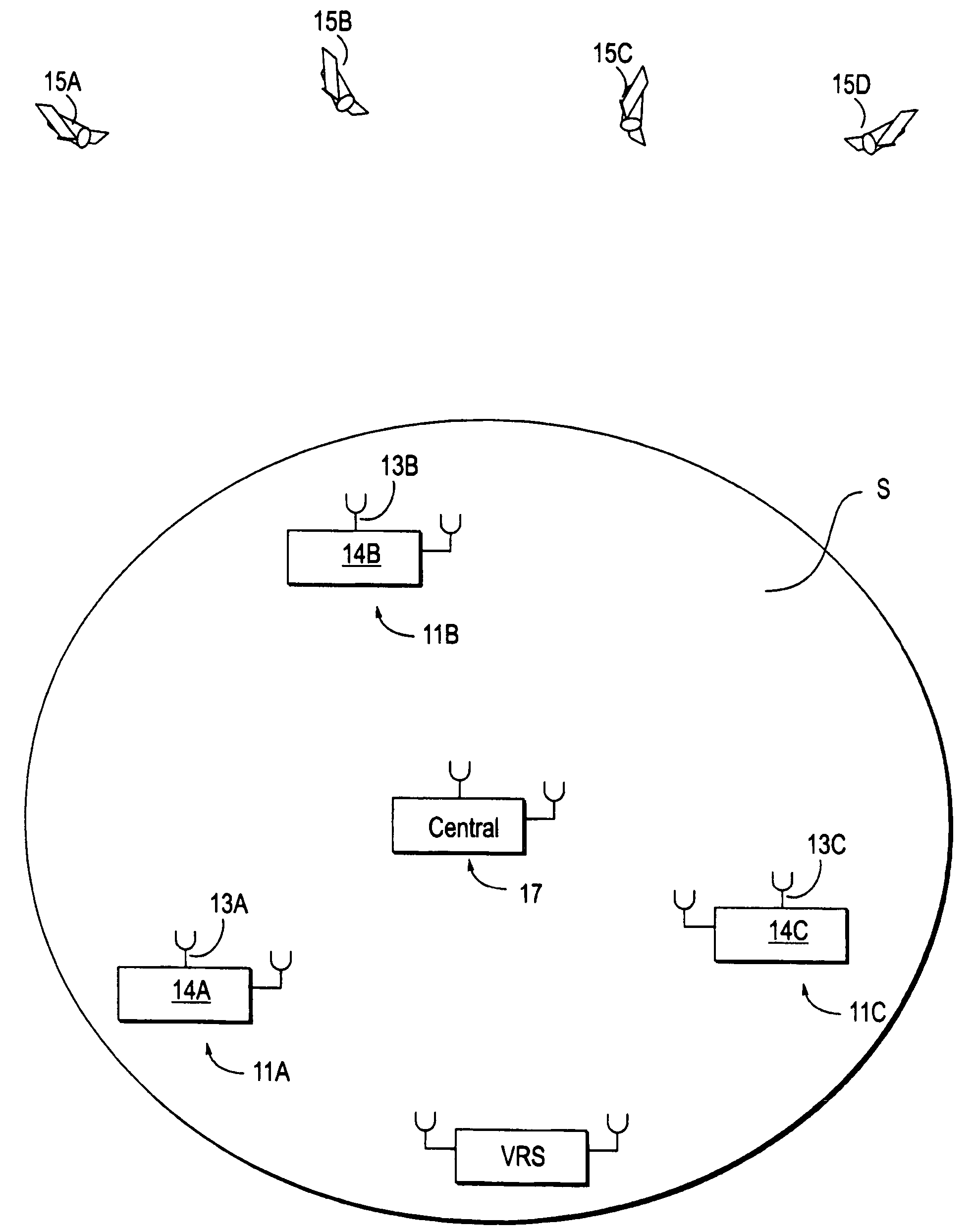
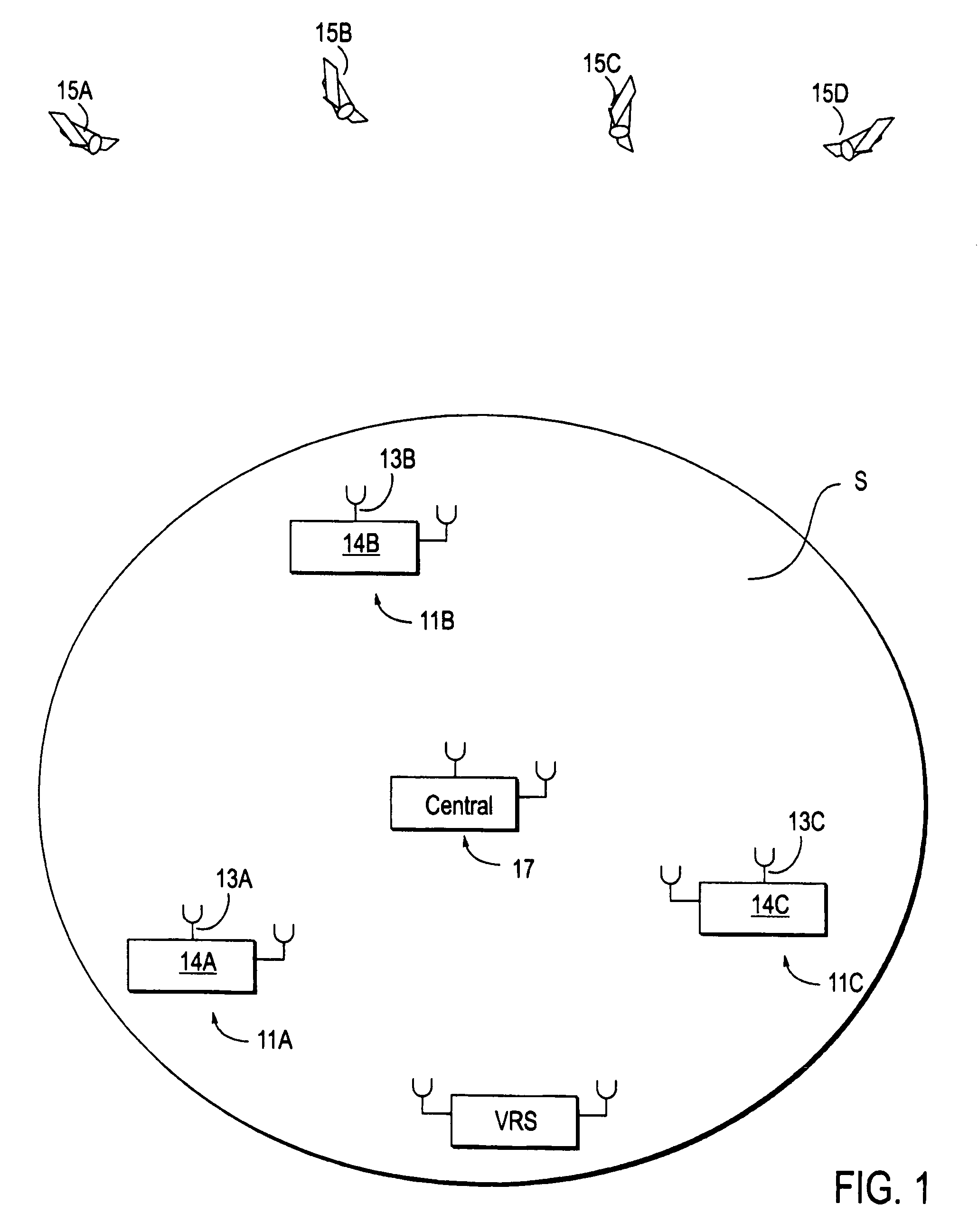
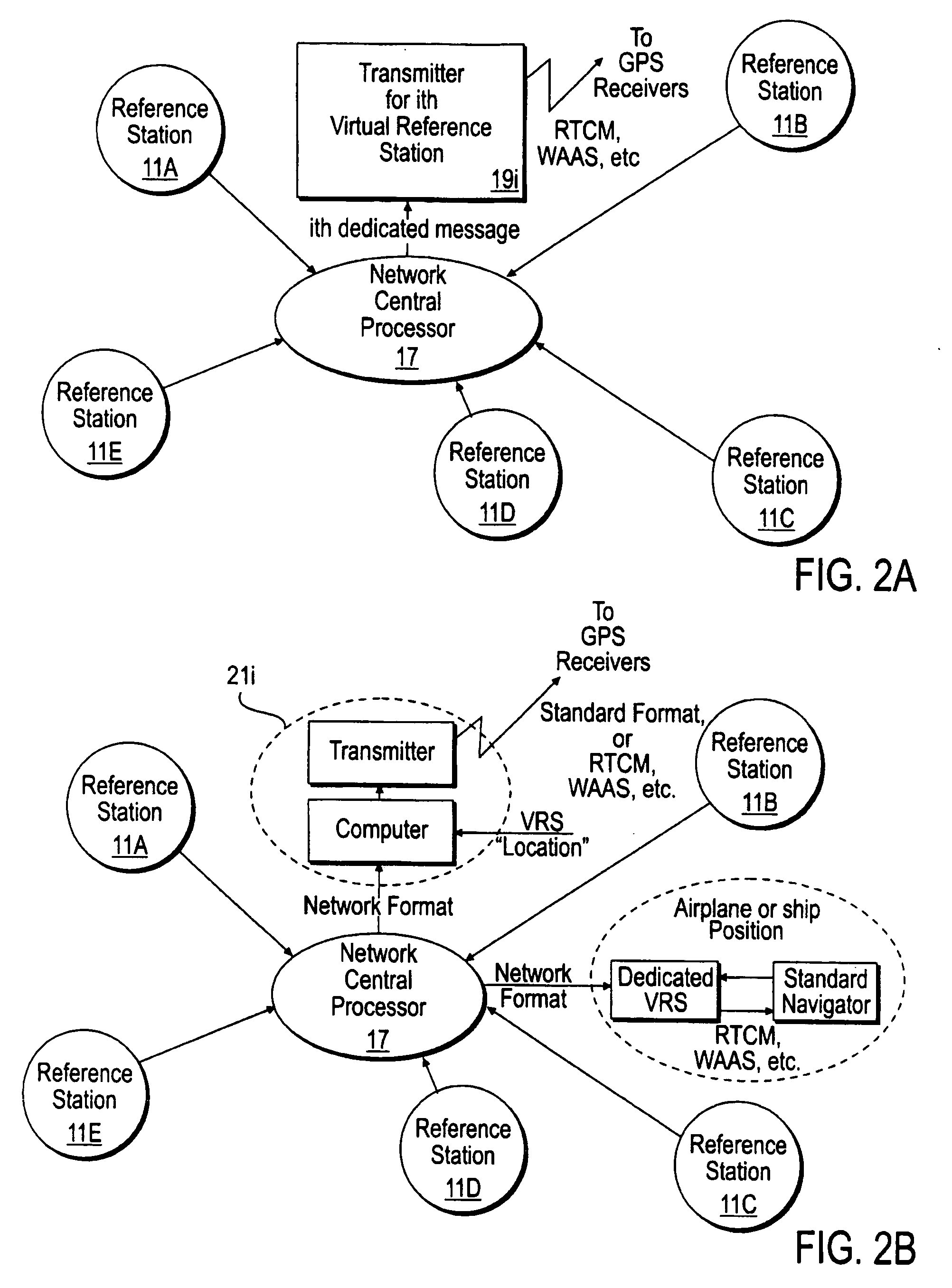
[0049]FIG. 1 illustrates use of the invention to cover a large region S, which may extend over the entire Earth or may have a smaller diameter. Each of three or more GPS reference stations 11A, 11B, 11C, with GPS signal antennas 13A, 13B, 13C, and receiver / processors 14A, 14B, 14C receives GPS signals, including pseudorange information, from several common-view GPS satellites 15A, 15B, 15C, 15D. A common-view” satellite is visible from the sites of at least three reference stations at the same observation times. The location coordinates of each of the reference stations 11A, etc. is known with high accuracy, either by use of a surveyor by some other means. As each reference station 11A, 11B, 11C, receives the GPS signals from each of the GPS satellites 15A, 15B, 15C, the GPS-determined pseudorange for the GPS antenna for that station and that satellite is compared with a calculated pseudorange for that station and that satellite, and GPS pseudorange corrections PRC(t;t0;m;n) are gen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com