Patents
Literature
8040results about "Analogue computers for vehicles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
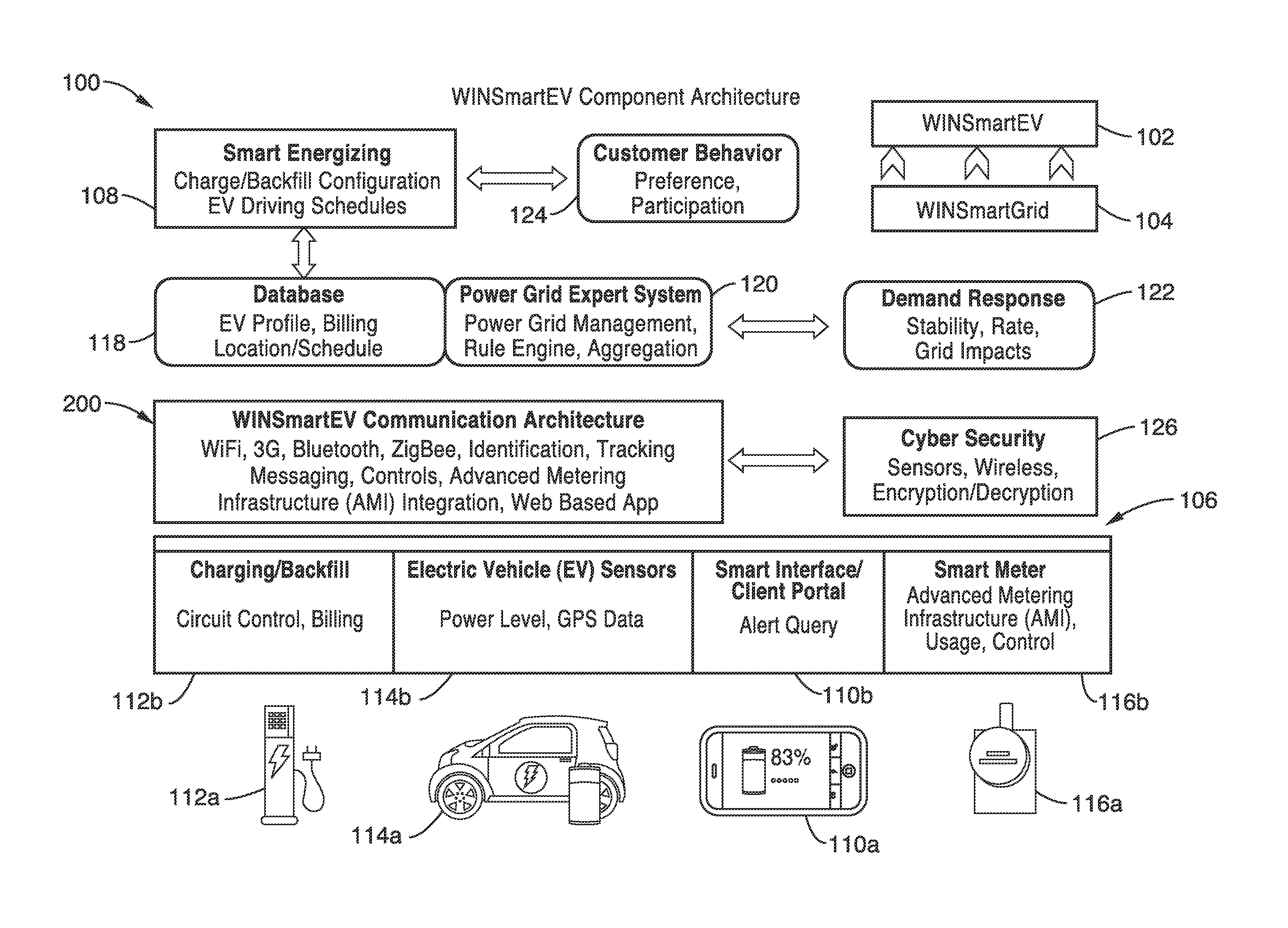
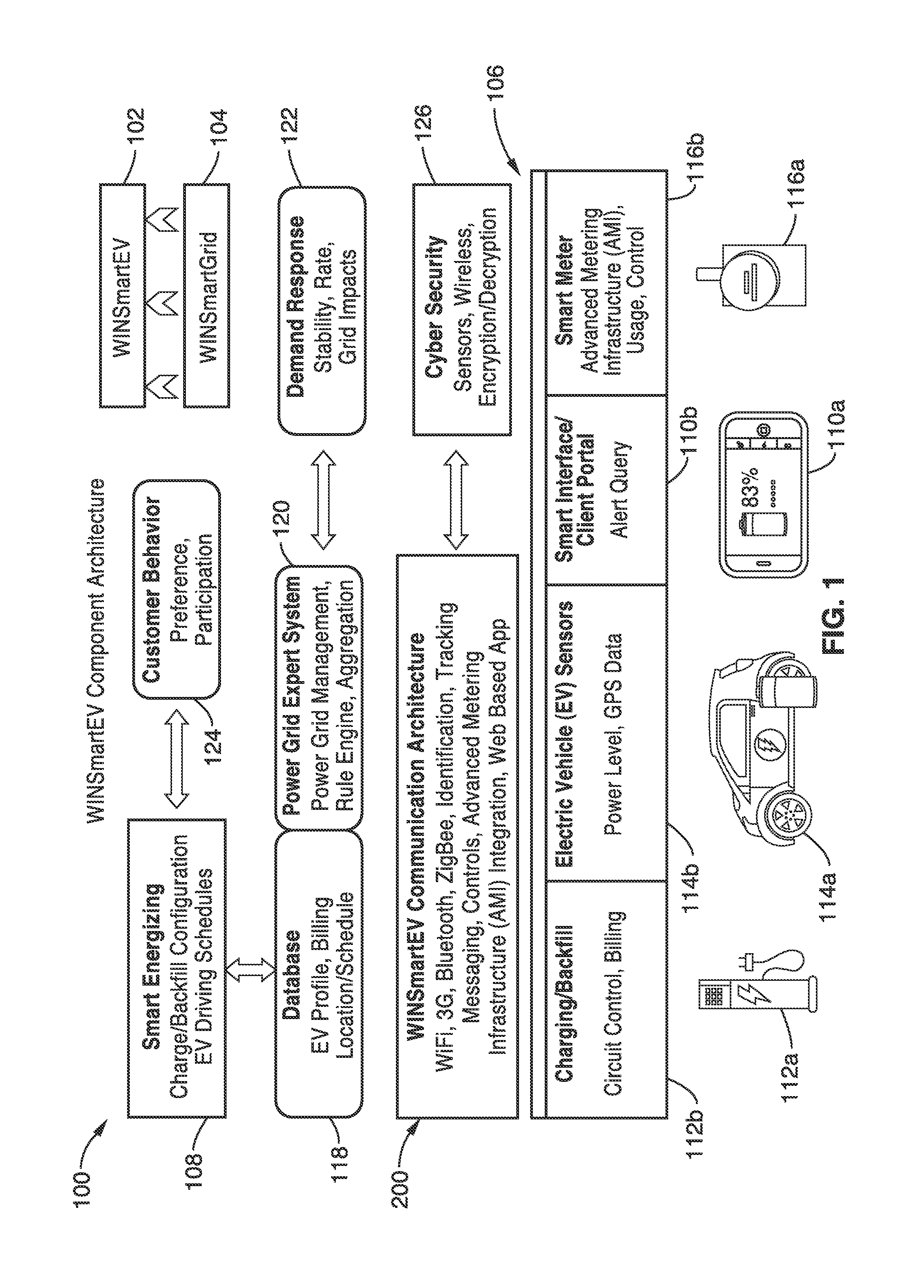
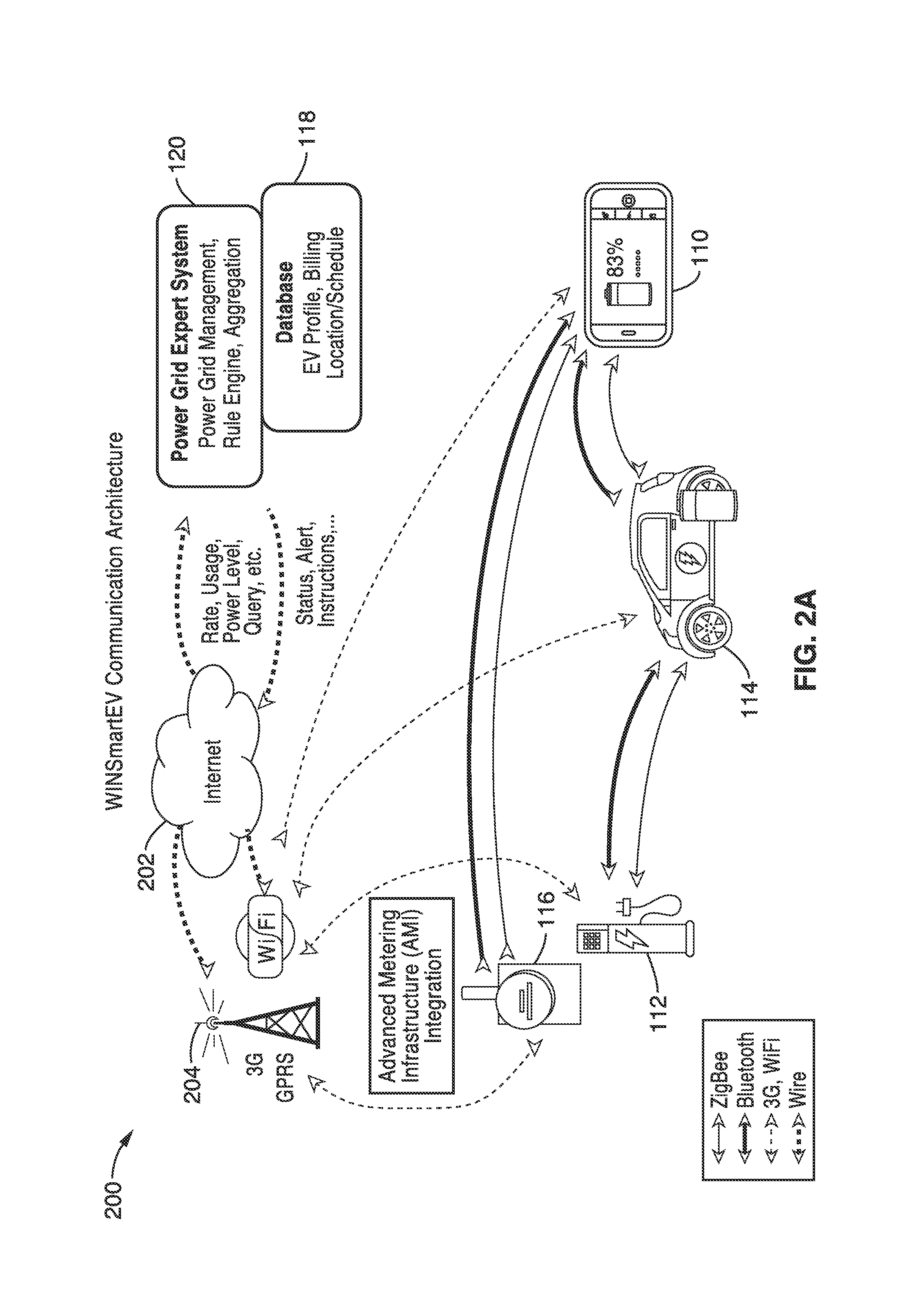
Smart electric vehicle (EV) charging and grid integration apparatus and methods
ActiveUS9026347B2Increase capacityAdding smartnessAnalogue computers for vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsGrid-tie inverterElectrical battery
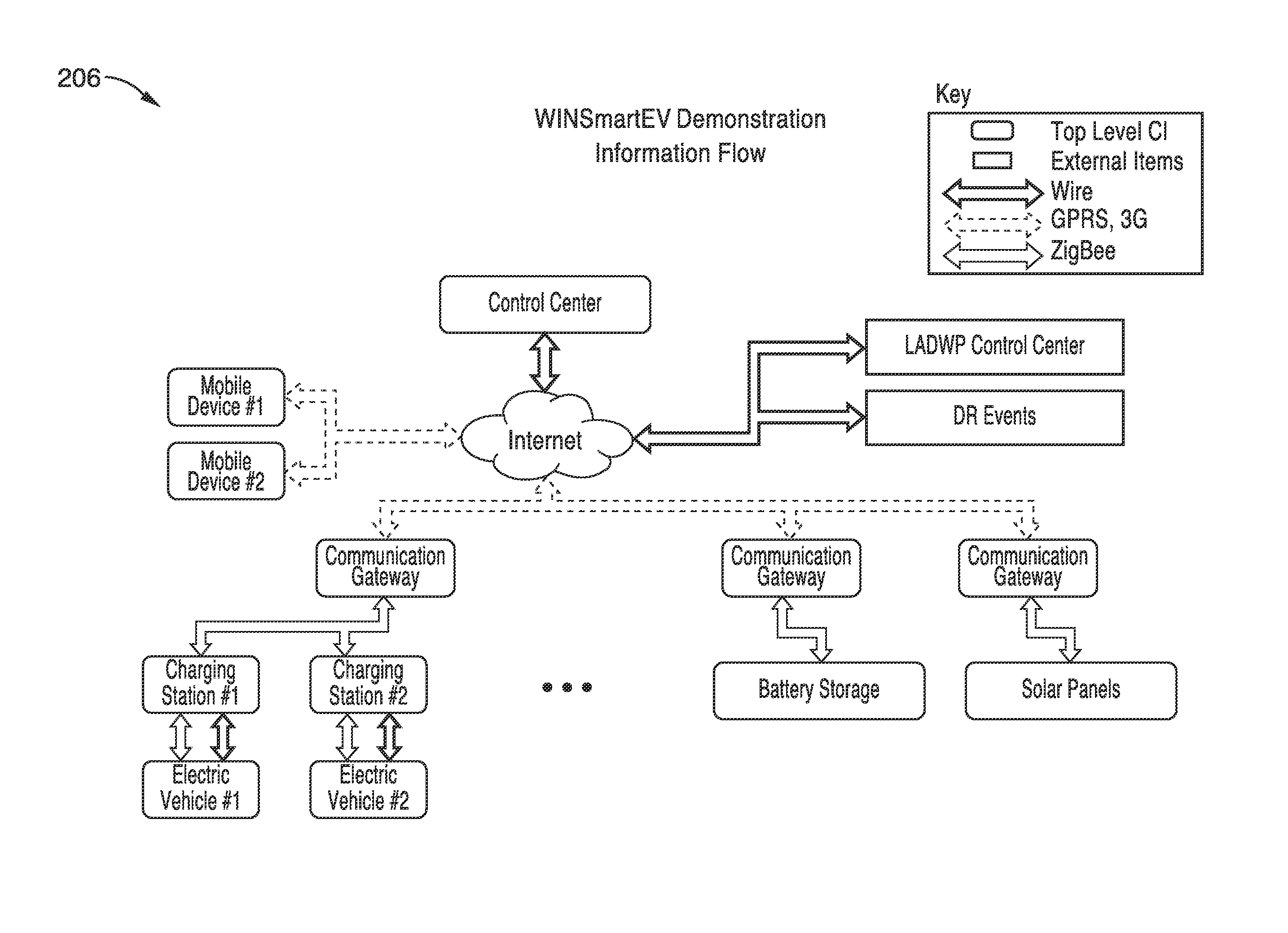
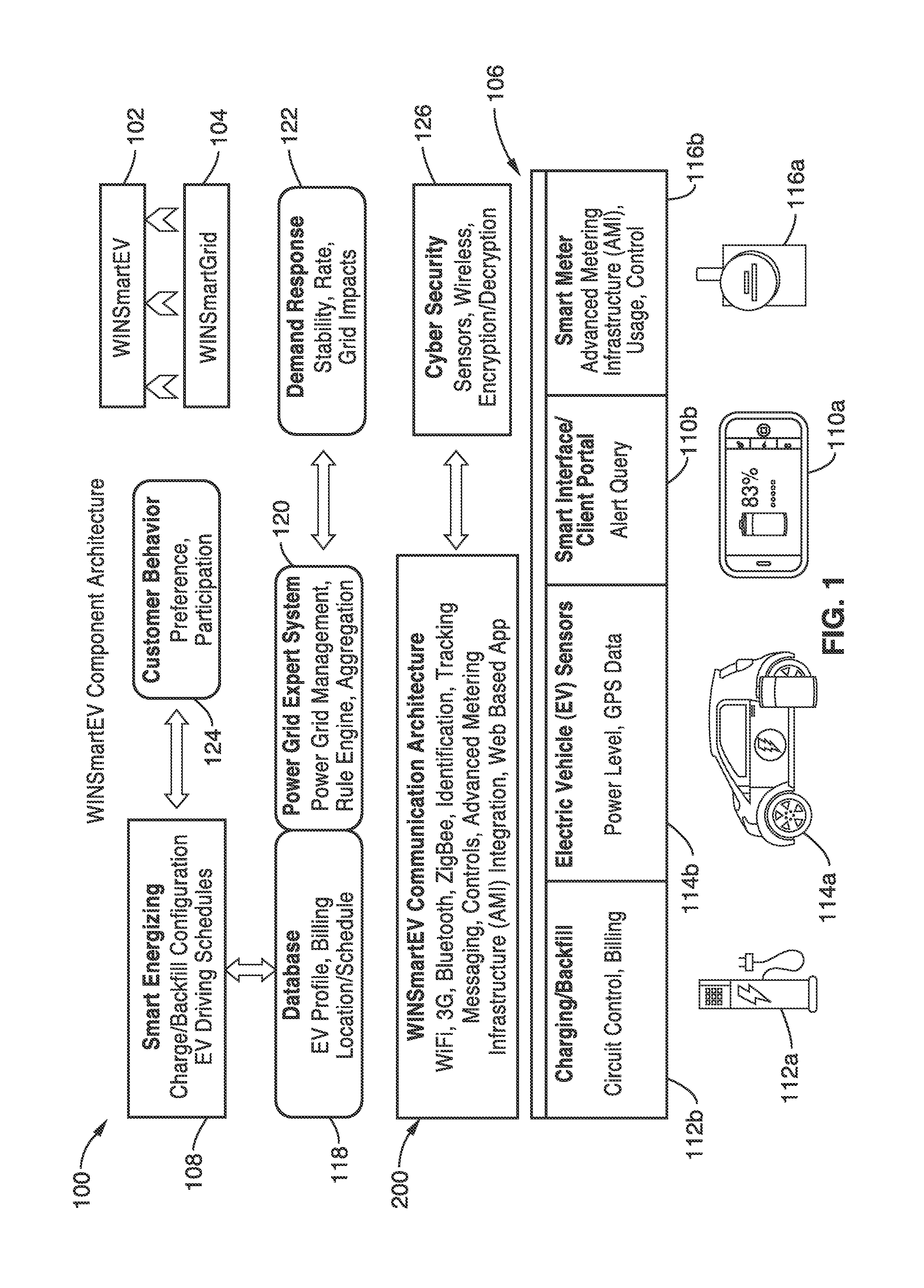
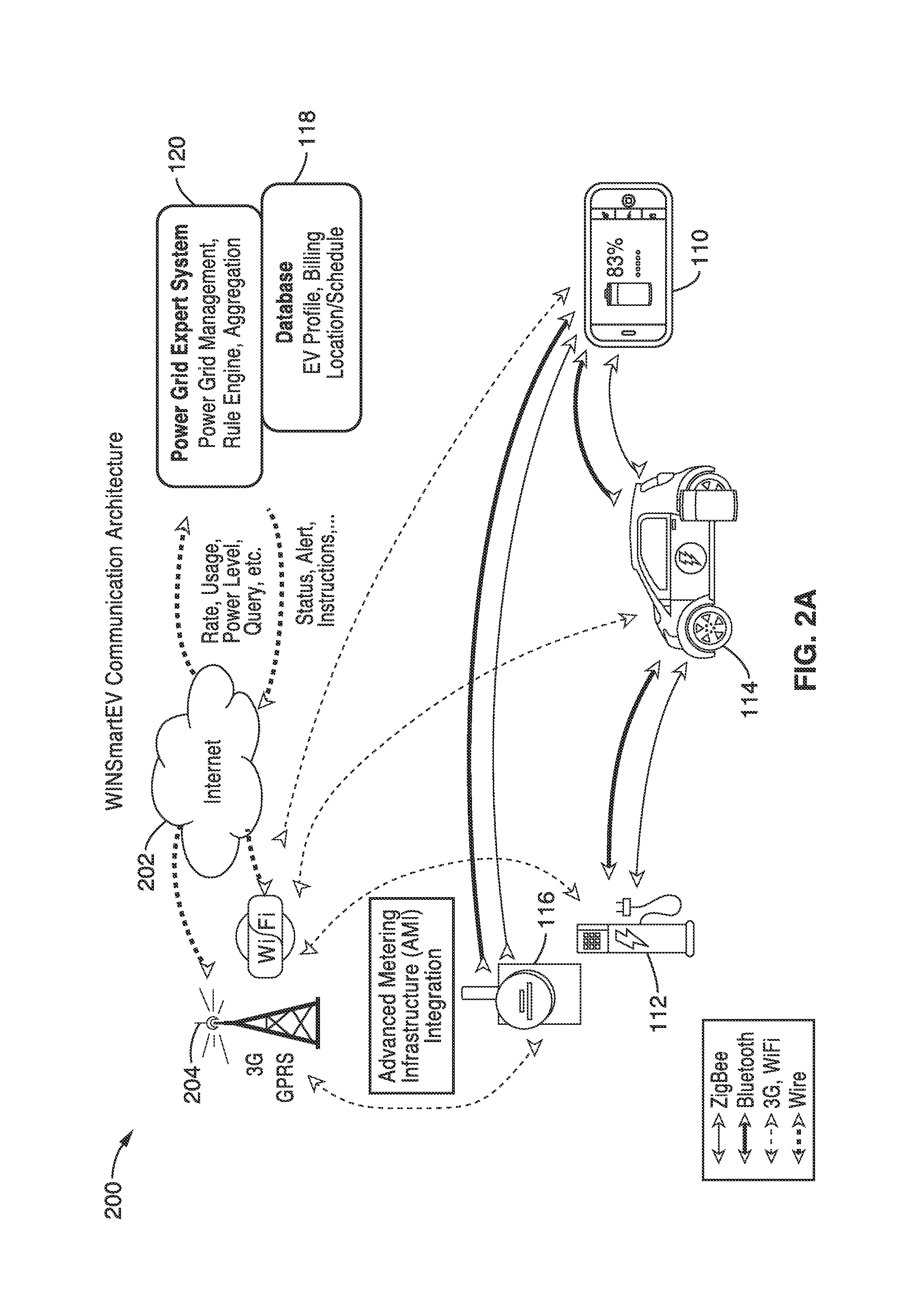
An expert system manages a power grid wherein charging stations are connected to the power grid, with electric vehicles connected to the charging stations, whereby the expert system selectively backfills power from connected electric vehicles to the power grid through a grid tie inverter (if present) within the charging stations. In more traditional usage, the expert system allows for electric vehicle charging, coupled with user preferences as to charge time, charge cost, and charging station capabilities, without exceeding the power grid capacity at any point. A robust yet accurate state of charge (SOC) calculation method is also presented, whereby initially an open circuit voltage (OCV) based on sampled battery voltages and currents is calculated, and then the SOC is obtained based on a mapping between a previously measured reference OCV (ROCV) and SOC. The OCV-SOC calculation method accommodates likely any battery type with any current profile.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
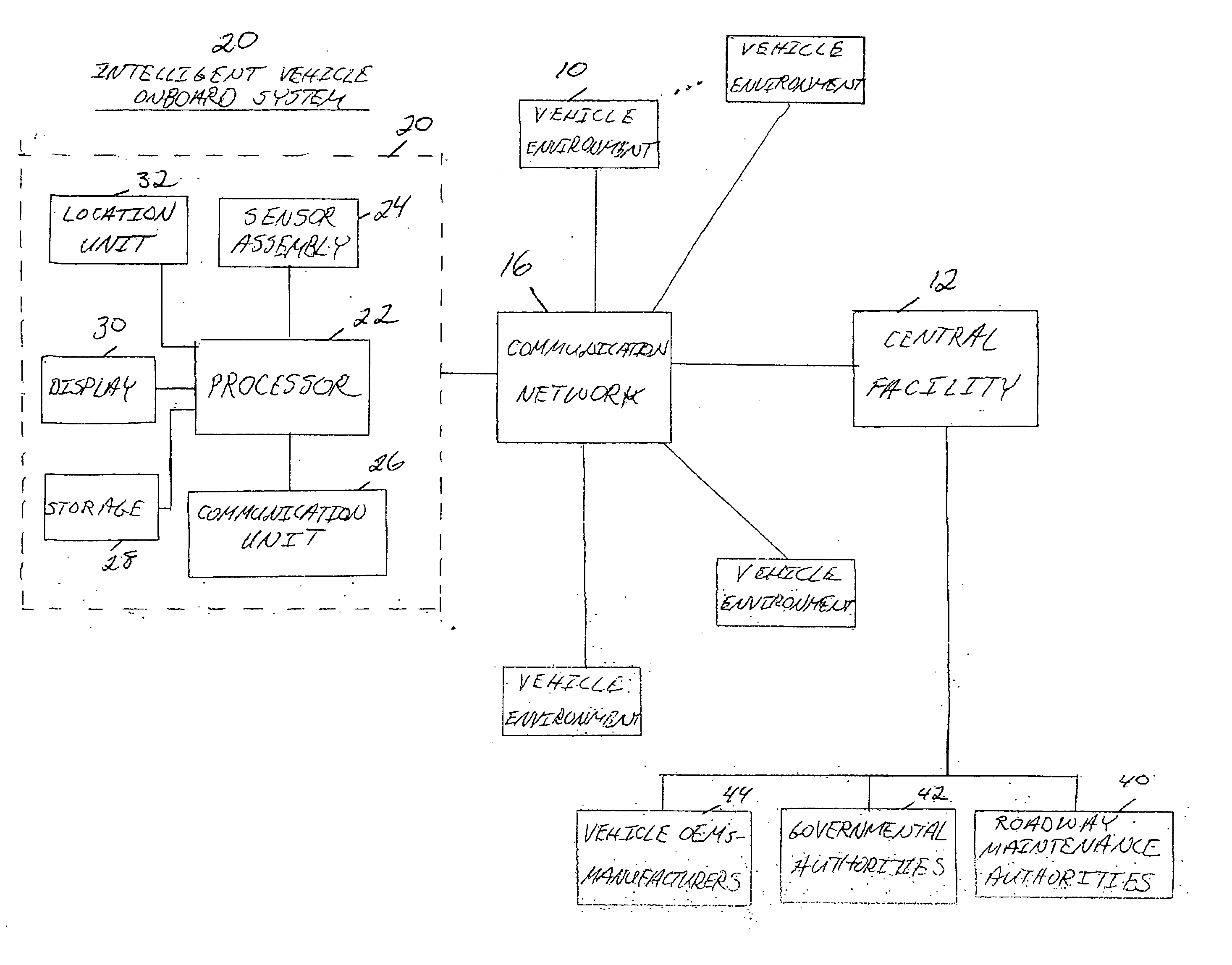
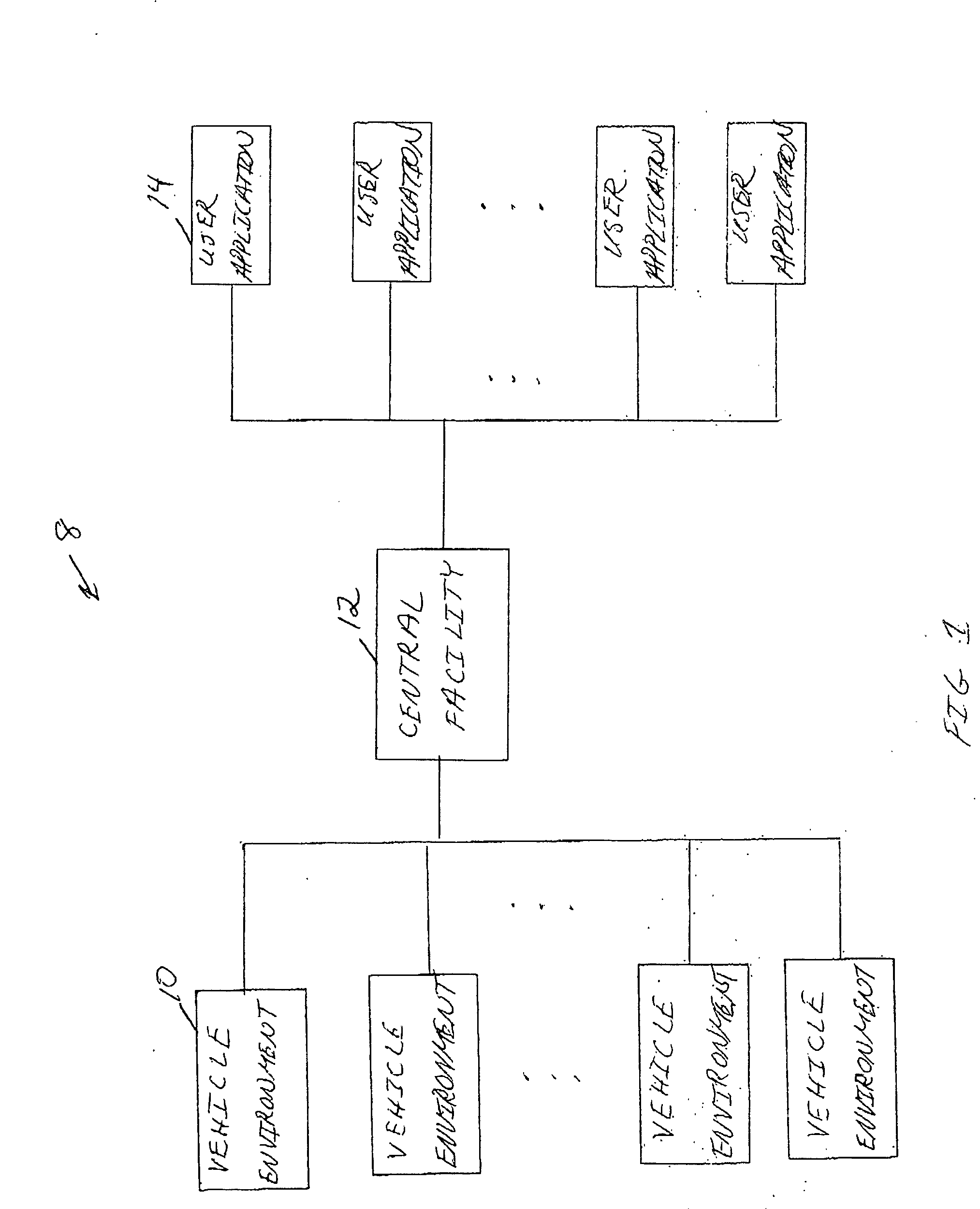
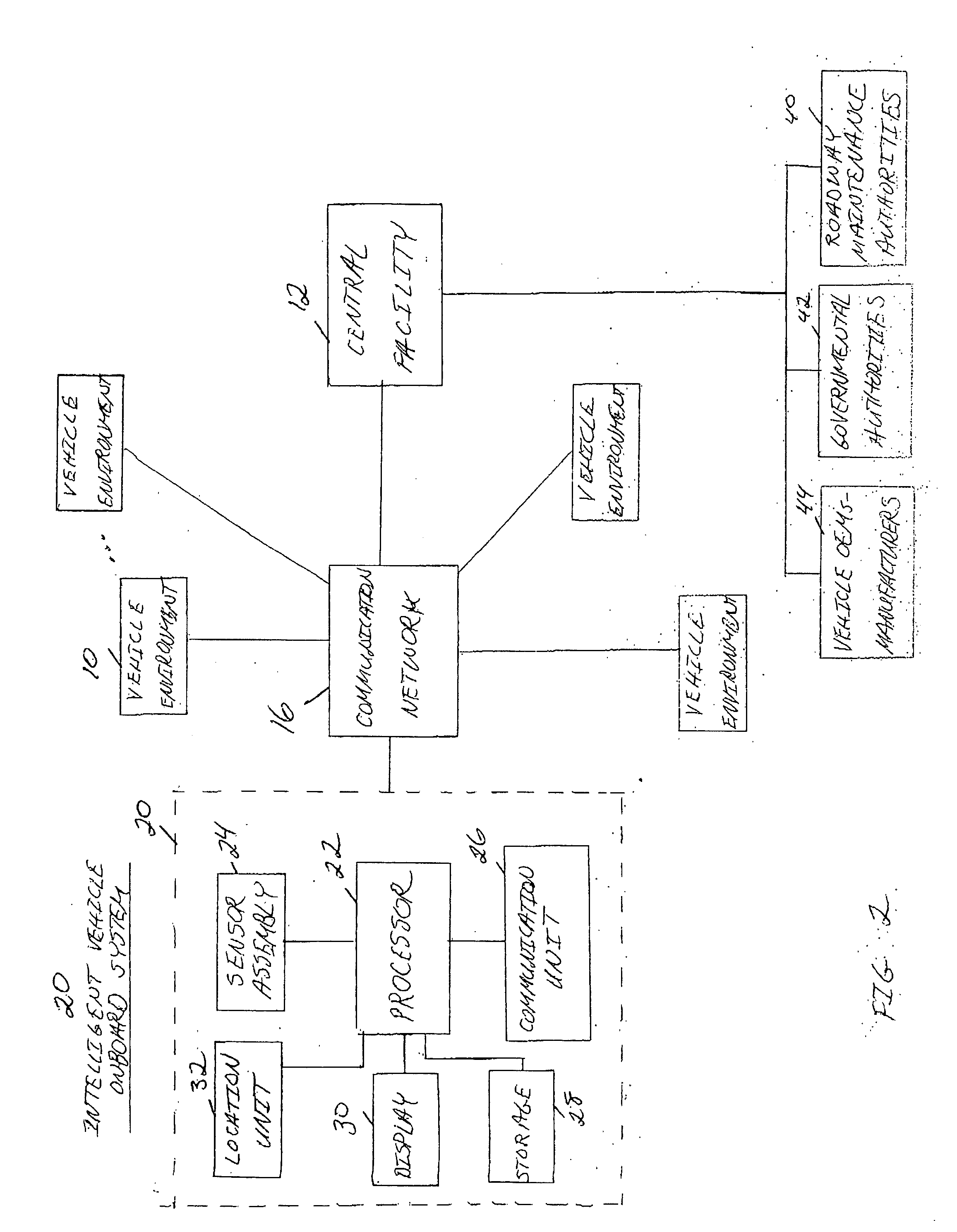
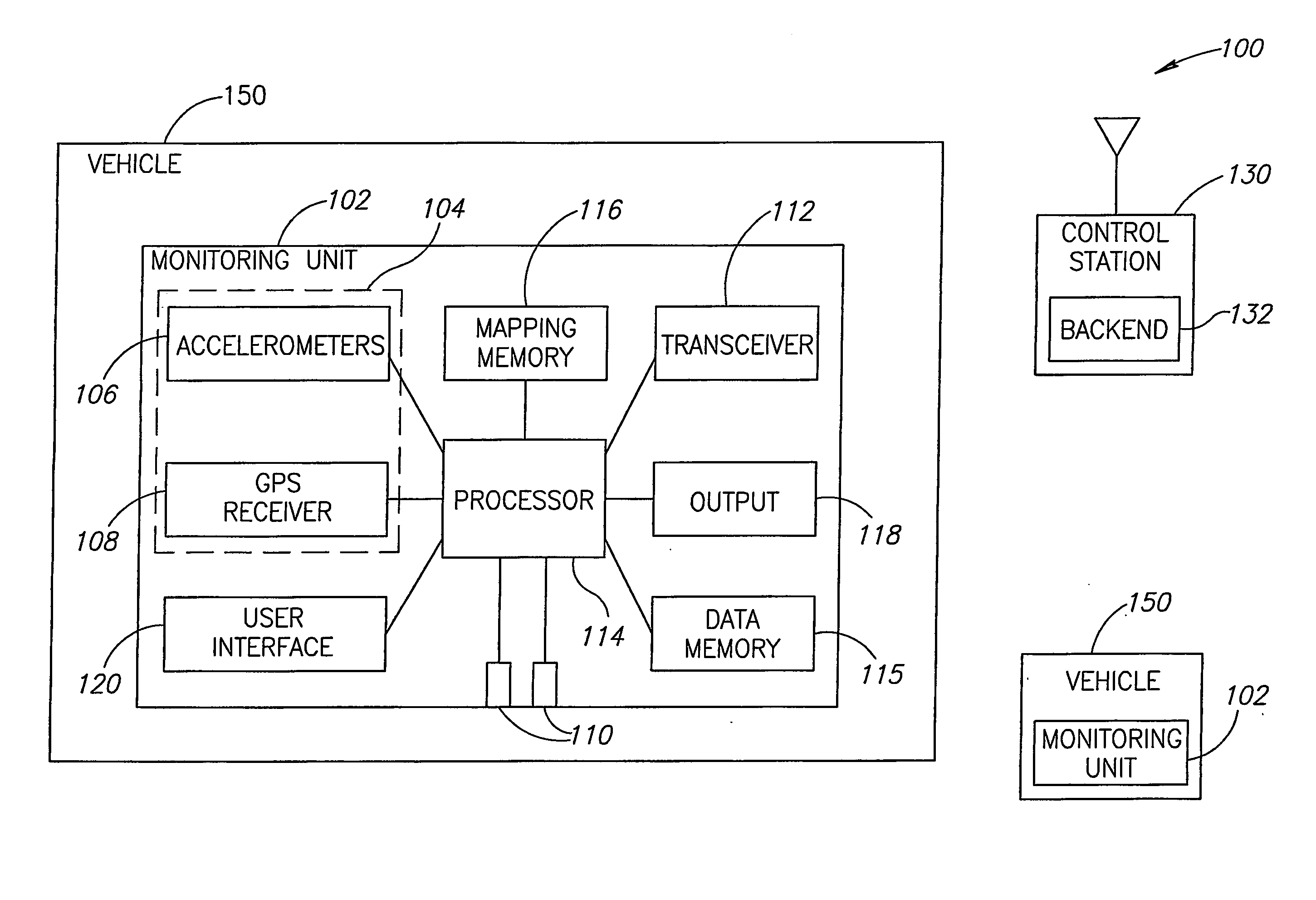
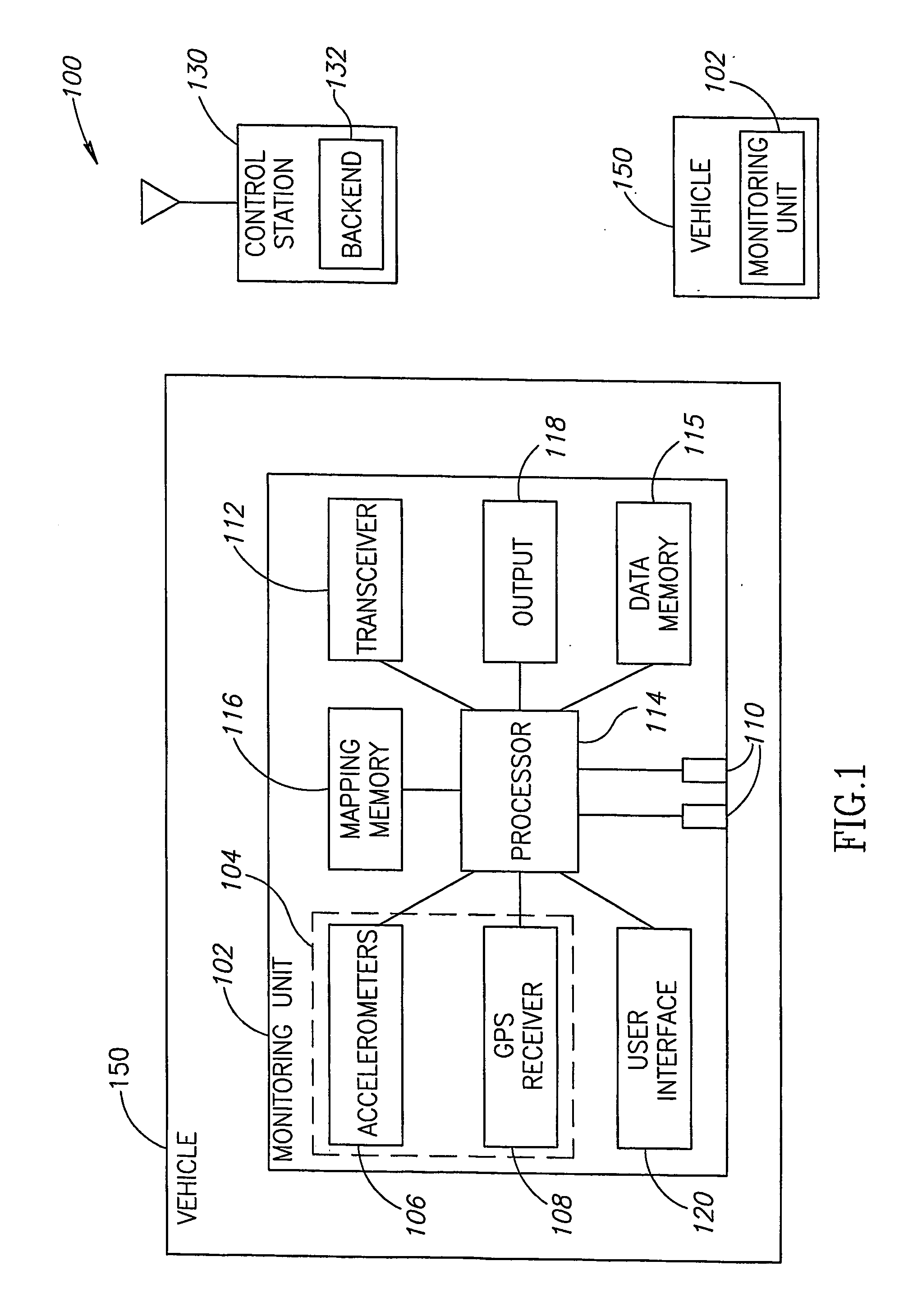
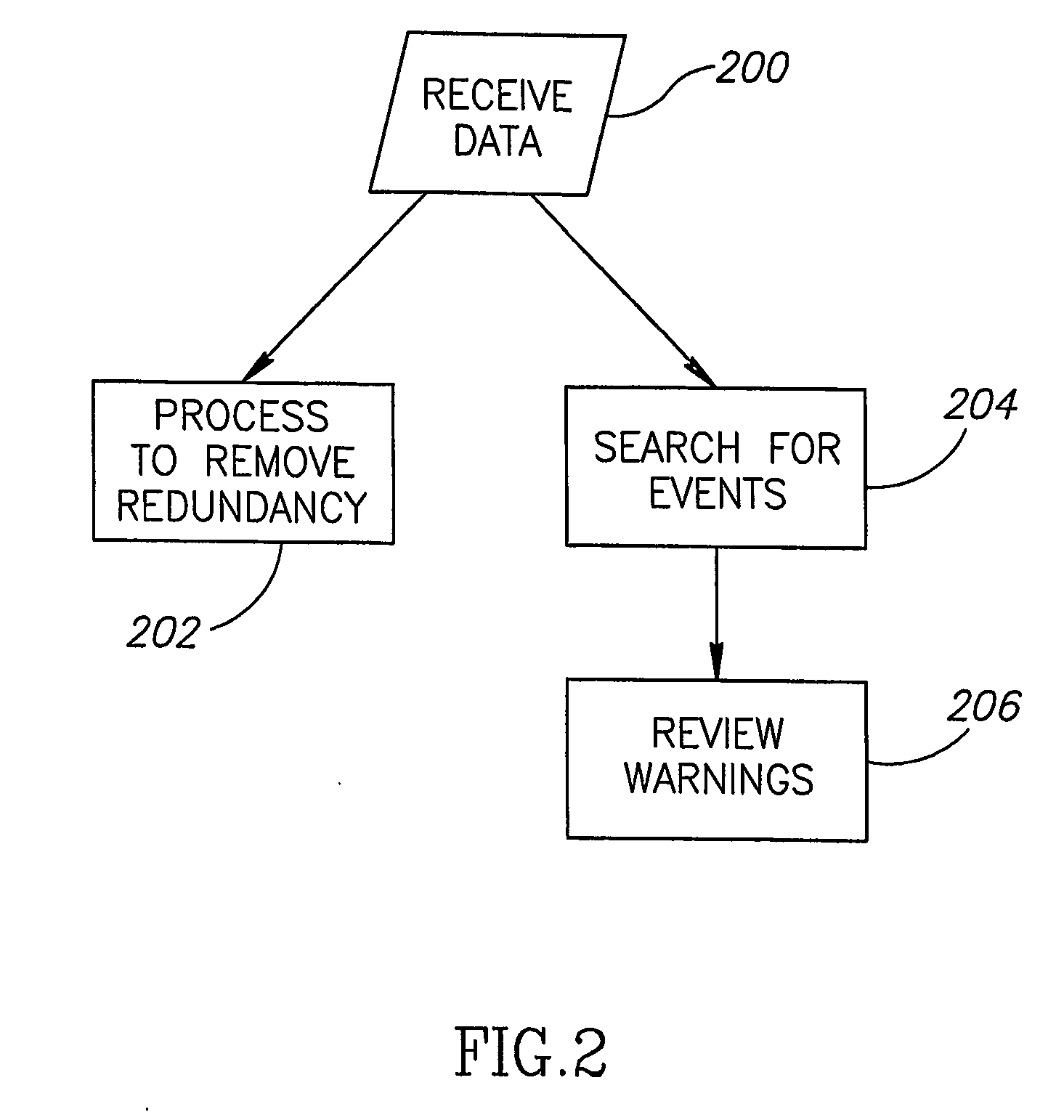
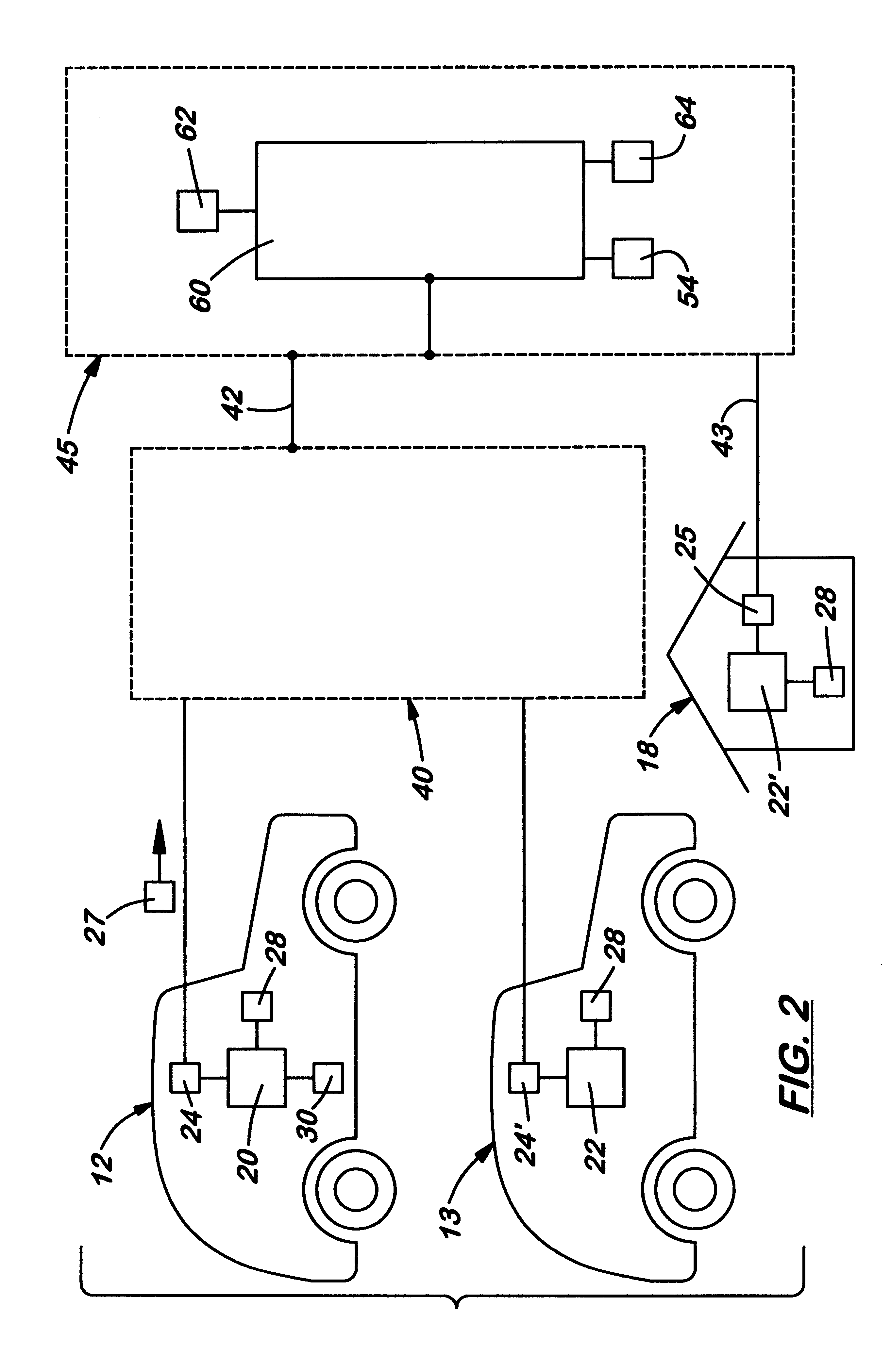
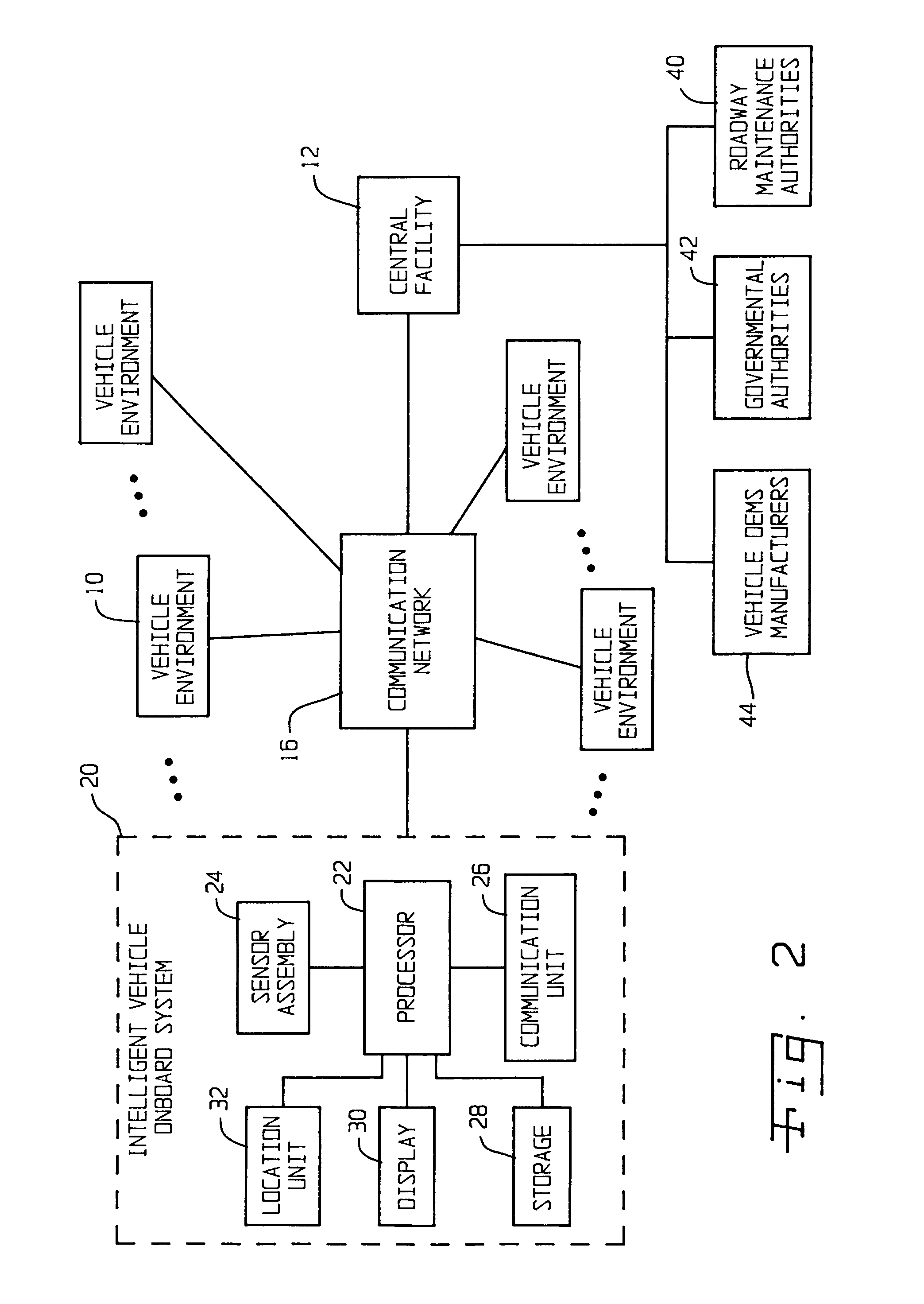
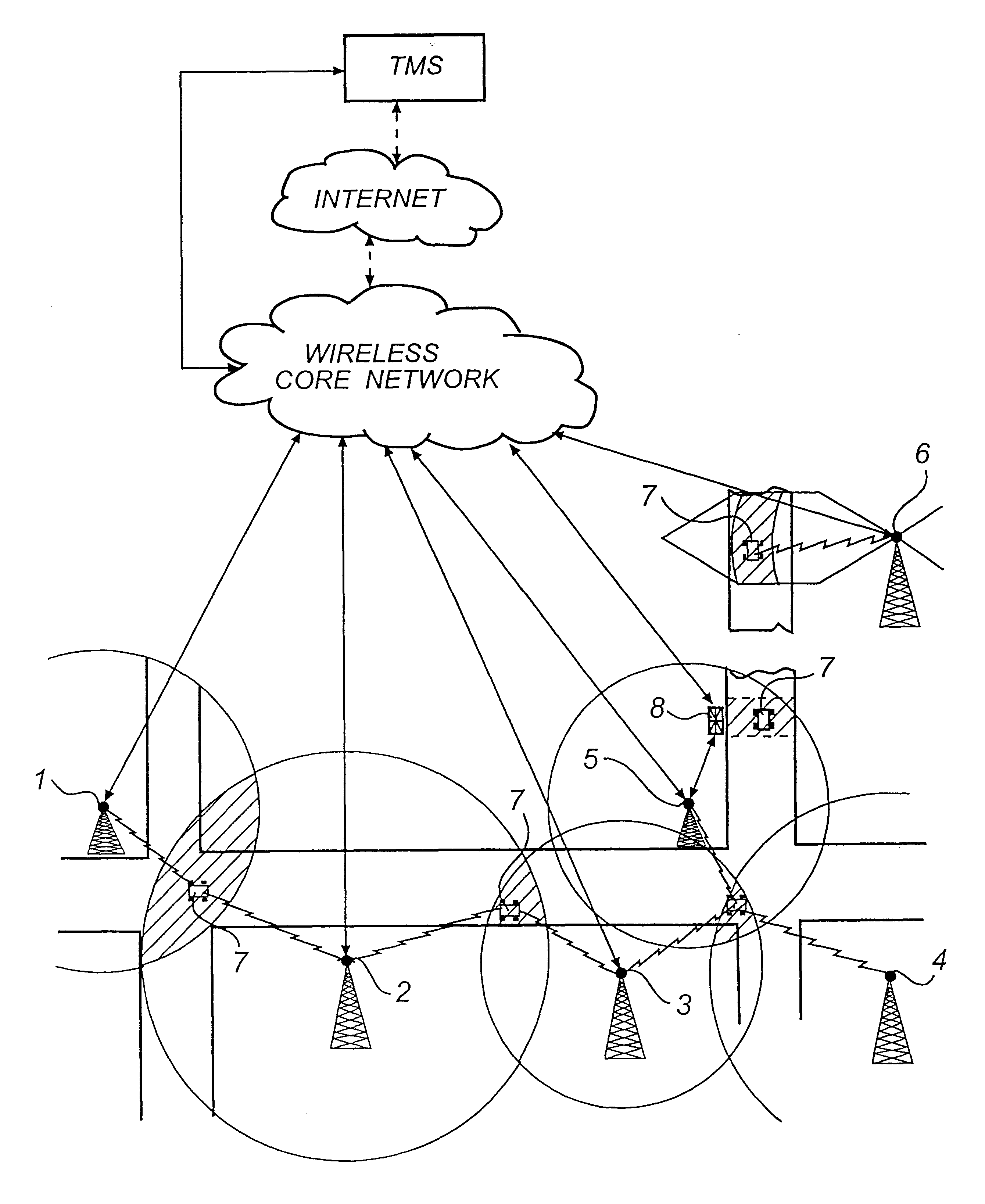
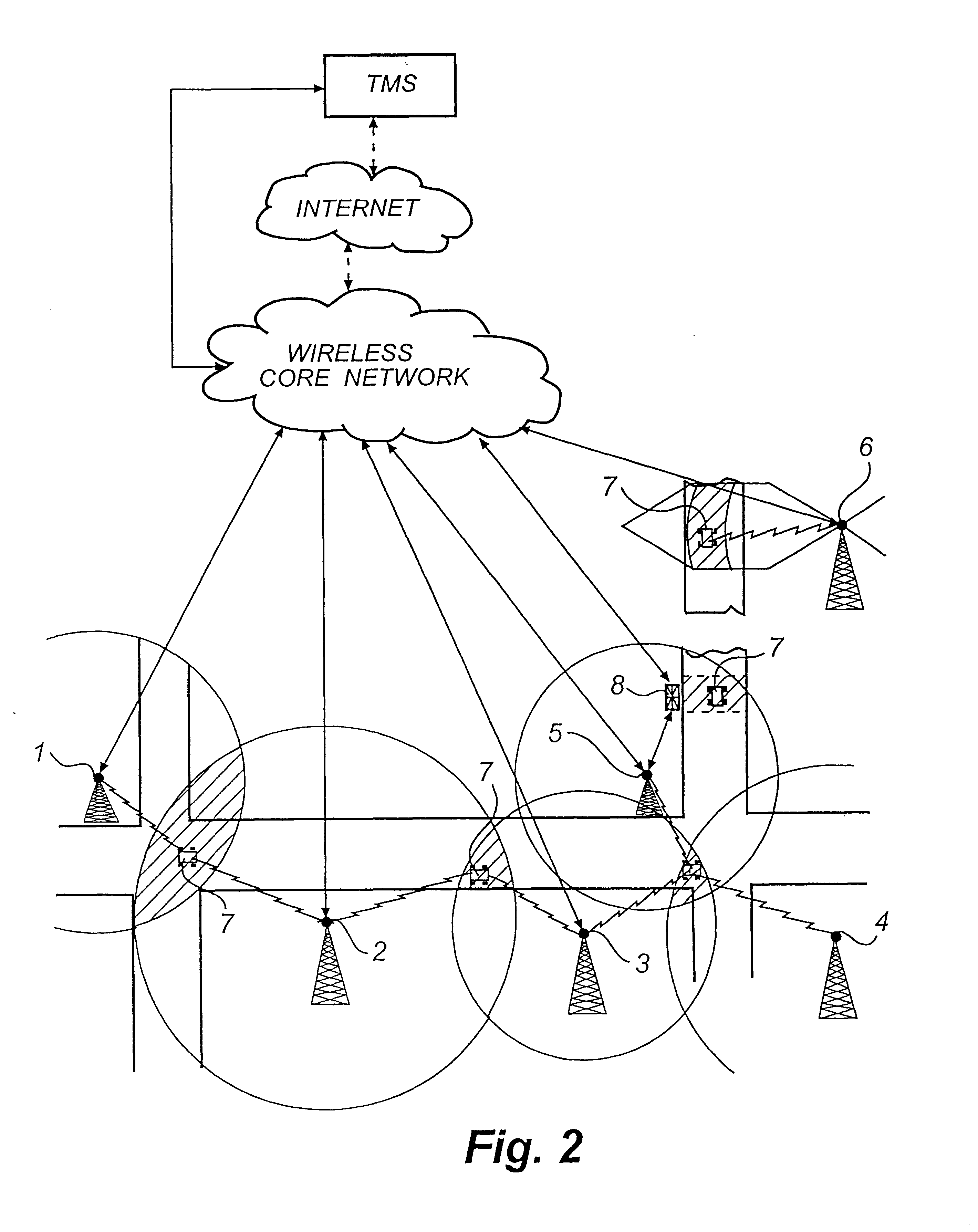
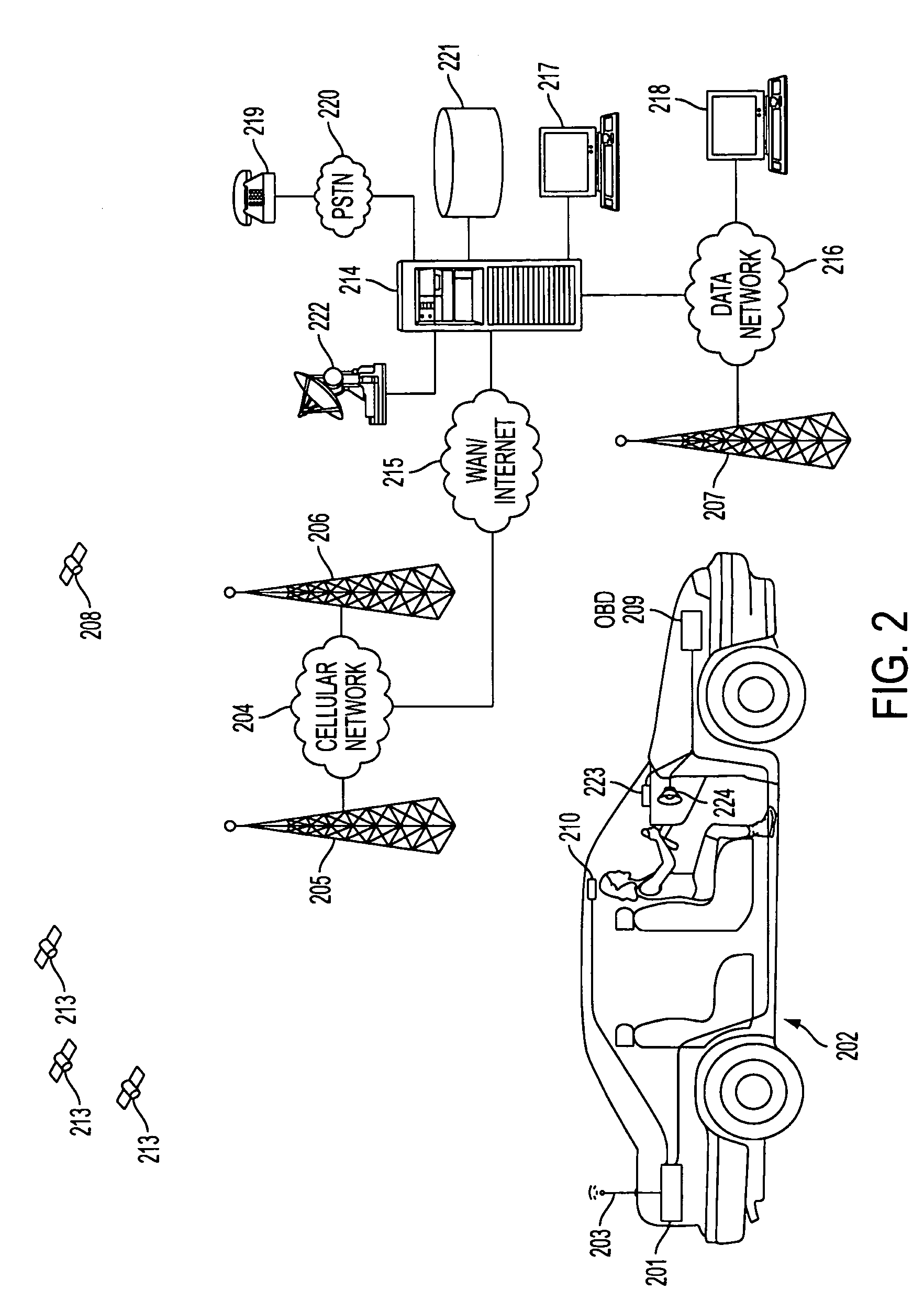
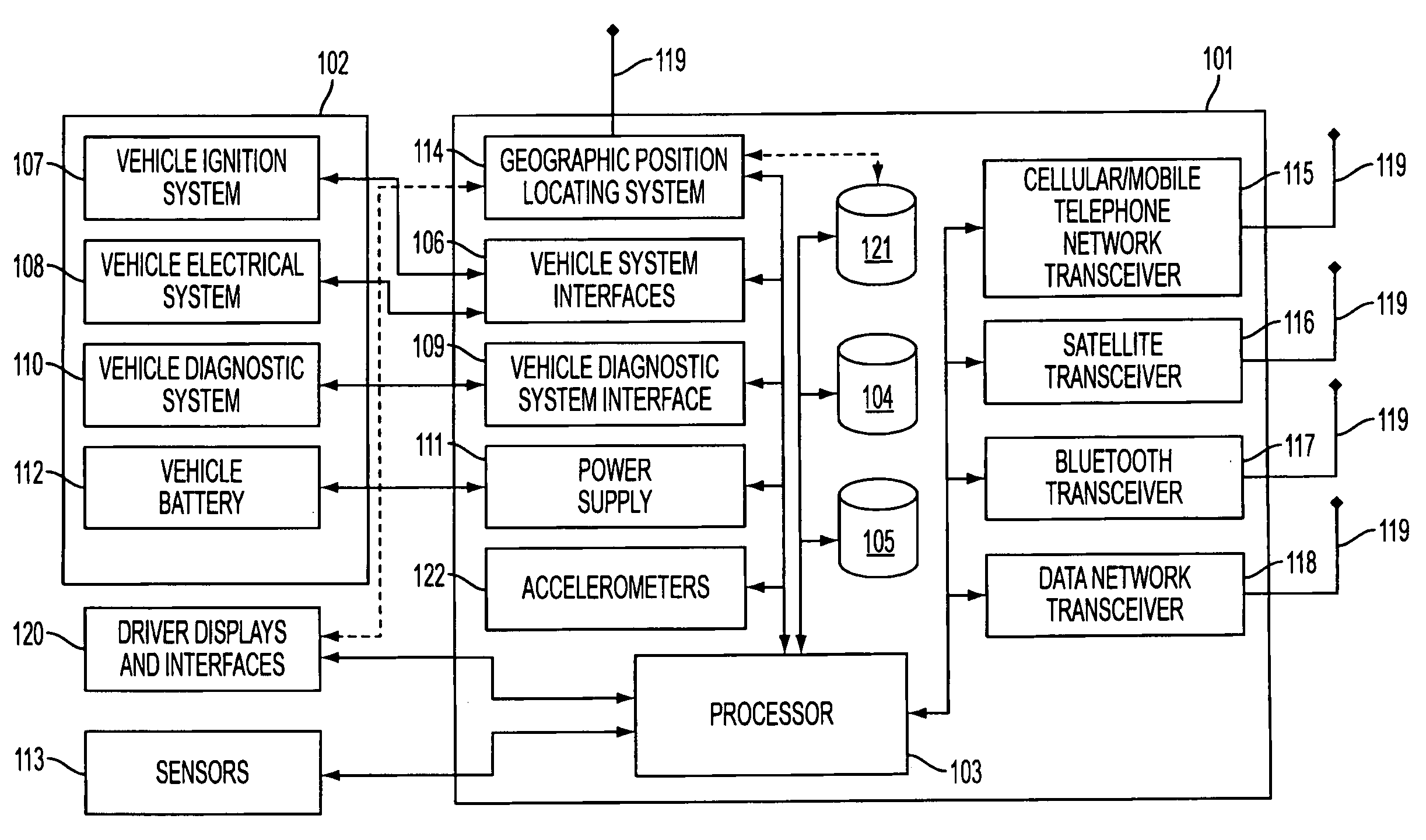
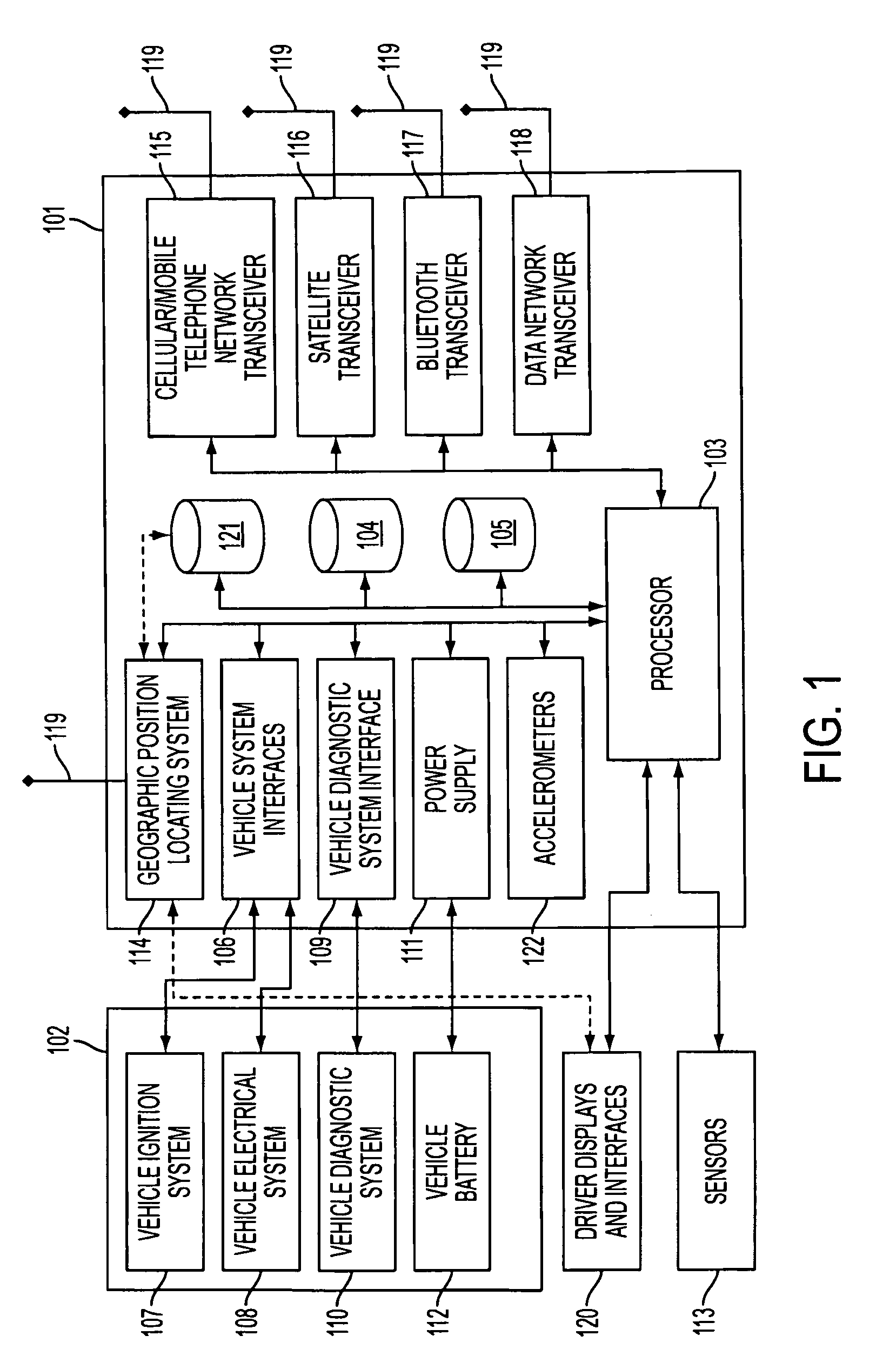
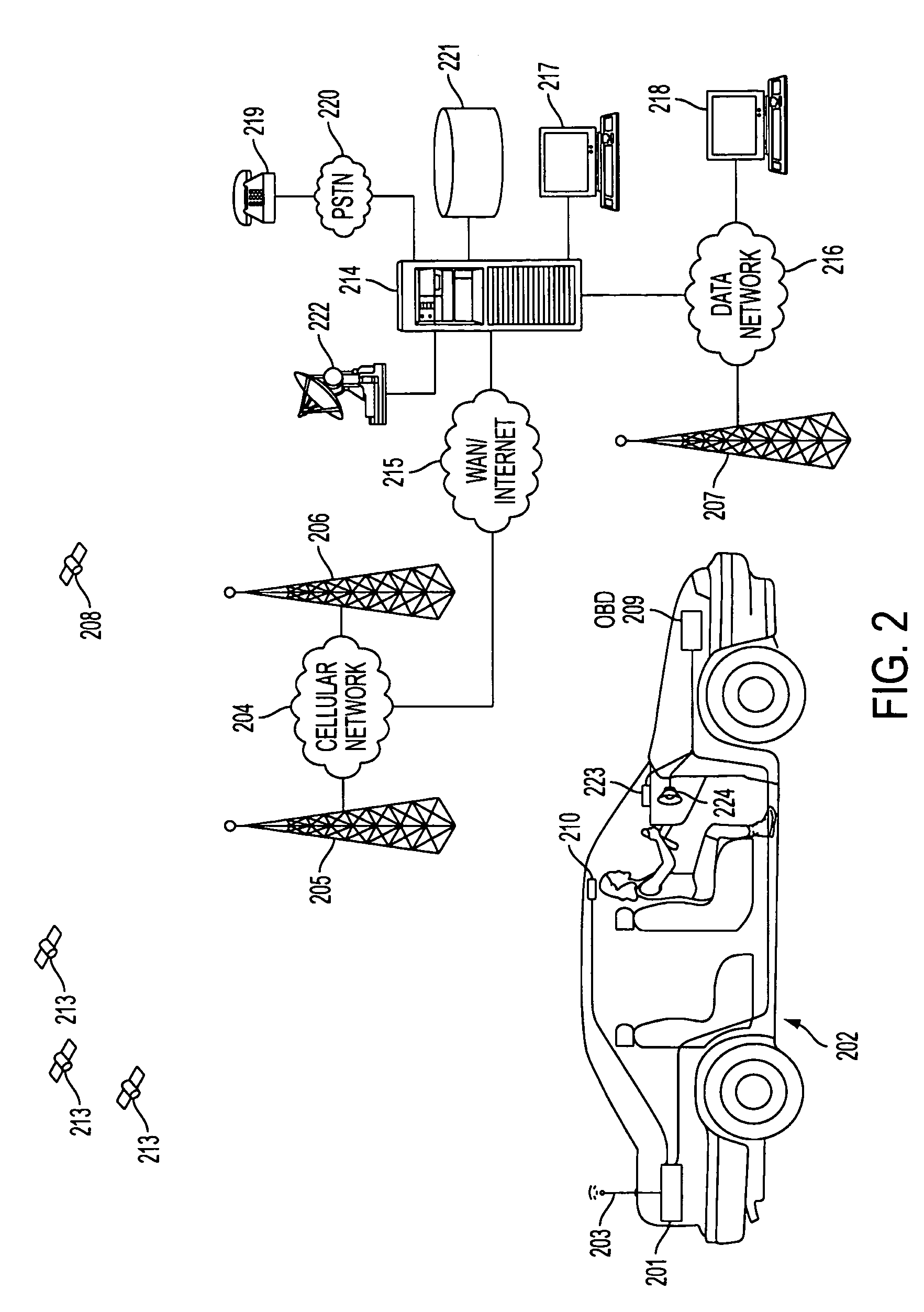
Centralized facility and intelligent on-board vehicle platform for collecting, analyzing and distributing information relating to transportation infrastructure and conditions
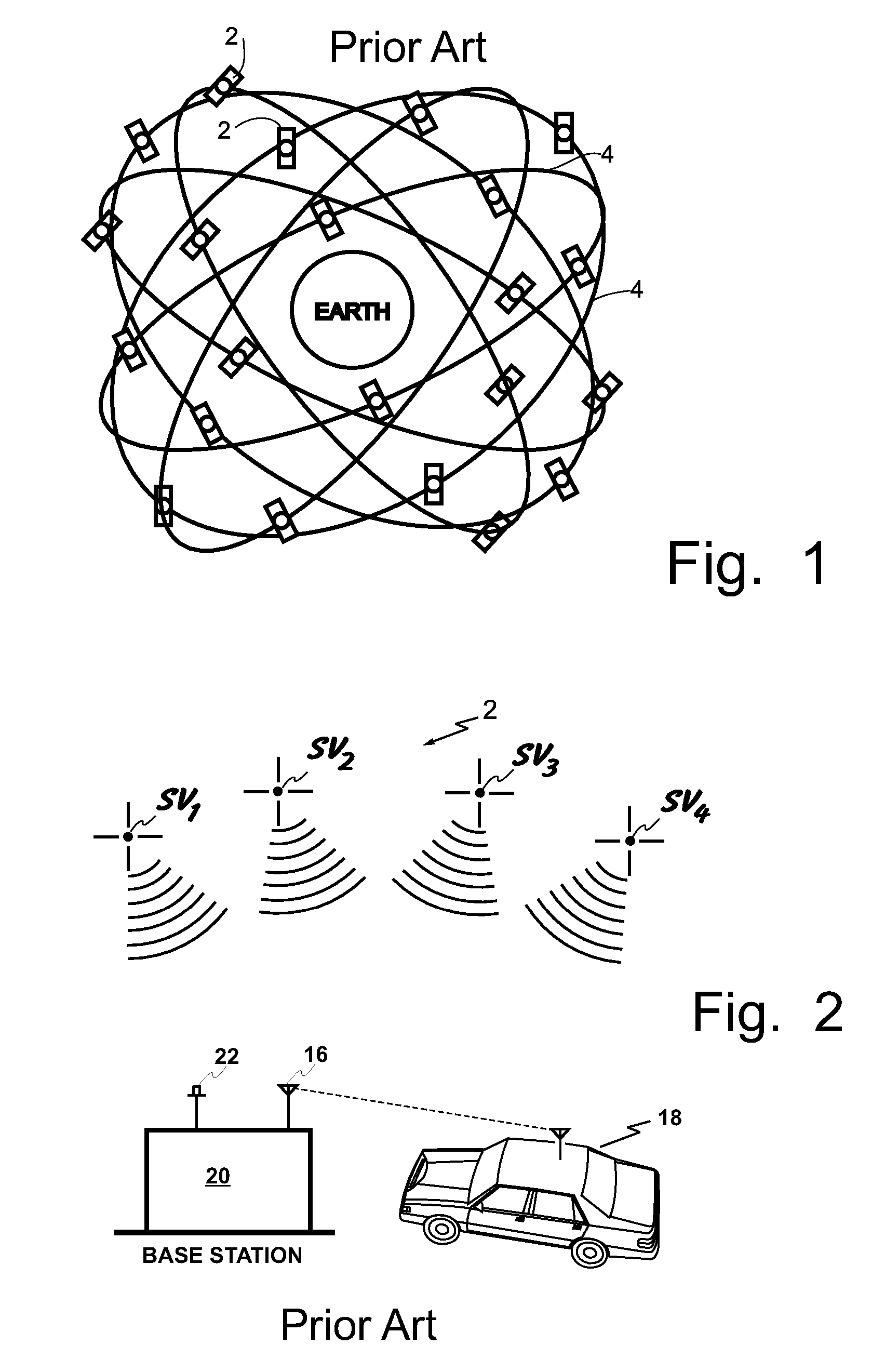
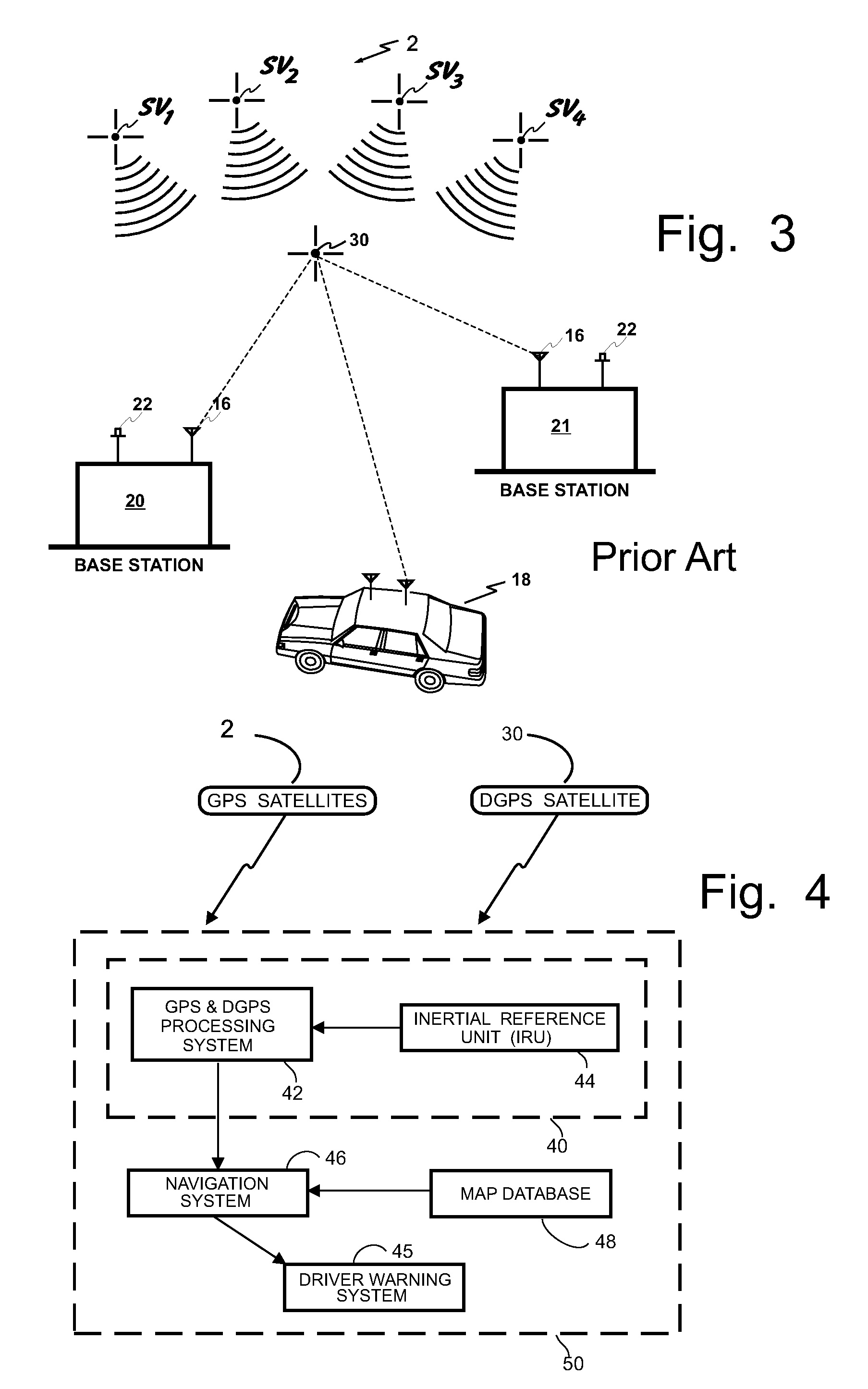
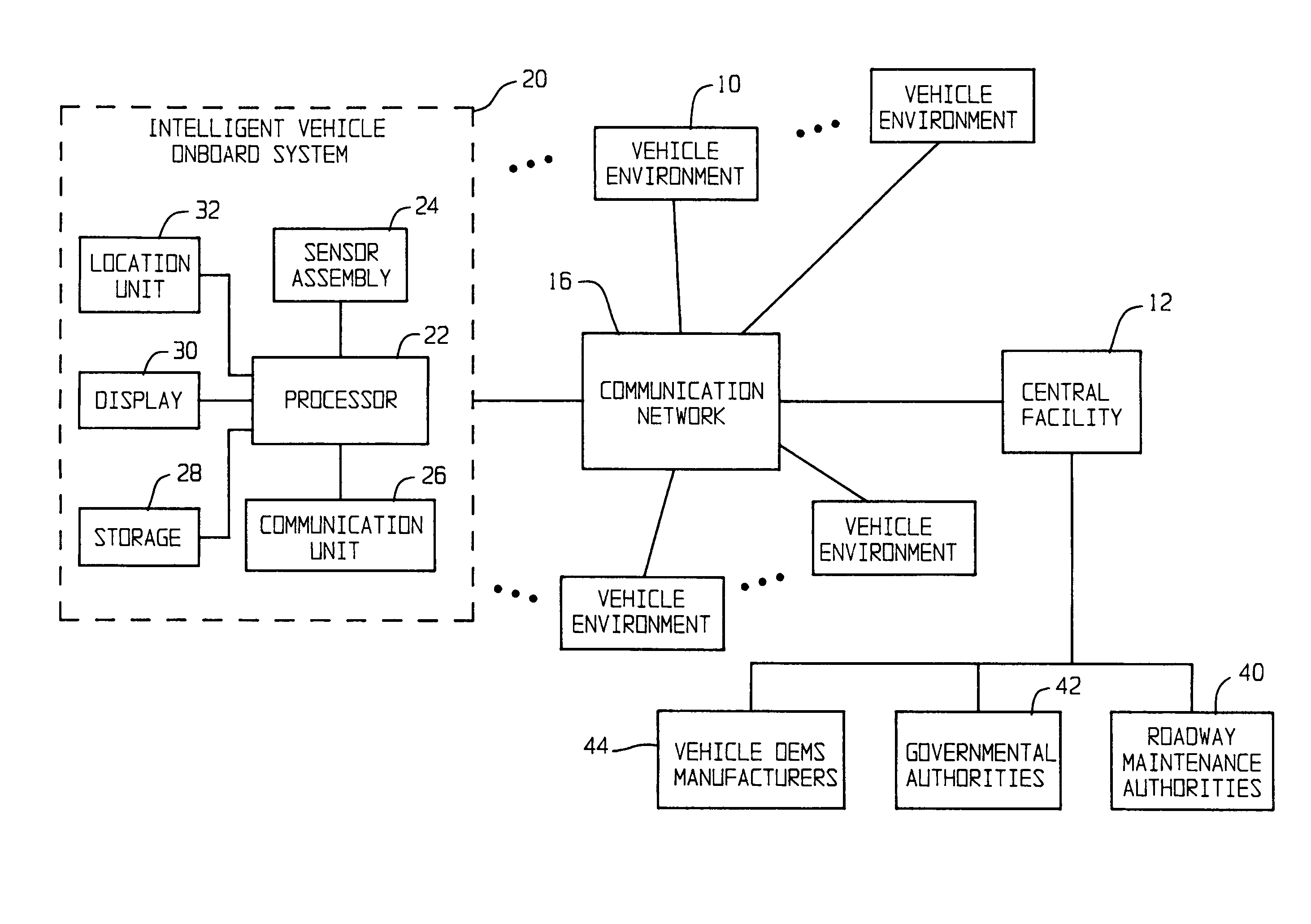
ActiveUS20050065711A1Effectively conditionEfficient designAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTransportation infrastructureIn vehicle
An on-board intelligent vehicle system includes a sensor assembly to collect data and a processor to process the data to determine the occurrence of at least one event. The data may be collected from existing standard equipment such as the vehicle communication bus or add-on sensors. The data may be indicative of conditions relating to the vehicle, roadway infrastructure, and roadway utilization, such as vehicle performance, roadway design, roadway conditions, and traffic levels. The detection of an event may signify abnormal, substandard, or unacceptable conditions prevailing in the roadway, vehicle, or traffic. The vehicle transmits an event indicator and correlated vehicle location data to a central facility for further management of the information. The central facility sends communications reflecting event occurrence to various relevant or interested users. The user population can include other vehicle subscribers (e.g., to provide rerouting data based on location-relevant roadway or traffic events), roadway maintenance crews, vehicle manufacturers, and governmental agencies (e.g., transportation authorities, law enforcement, and legislative bodies).
Owner:ZOOM INFORMATION SYST
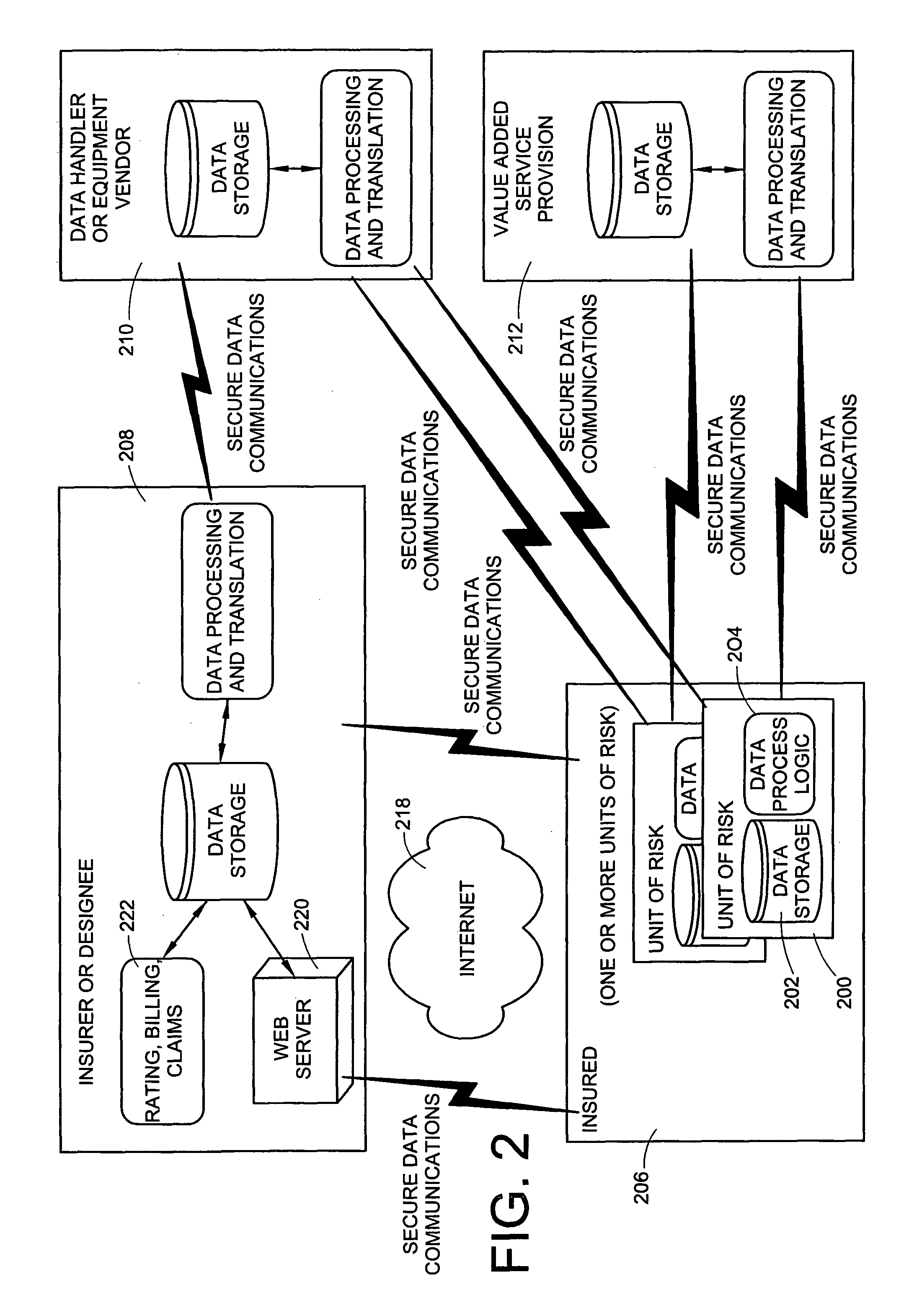
Monitoring system for determining and communicating a cost of insurance
InactiveUS8090598B2Easy to analyzeAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficWeb siteMonitoring system
Means are provided for recording, storing, calculating, communicating and reviewing one or more operational aspects of a machine. Insurance costs are based, in part, on activities of the machine operator. A discount may be provided in exchange for recording the operational aspects and providing the recorded information to the insurer. The party may review information and decide whether to provide it to the insurer. The means for reviewing may present comparative information. Information that causes insurance costs to vary may be highlighted. Provided data may be used to verify insurance application information, generate actuarial information or determine insurance rates. Operating data may be reviewed on a computer, a Web site or other display medium so a party can observe how his operating behavior compares to that of other operators of similar machines and may be manipulated so a party can understand how changes in operating behavior can affect his insurance rates.
Owner:PROGRESSIVE CASUALTY INSURANCE
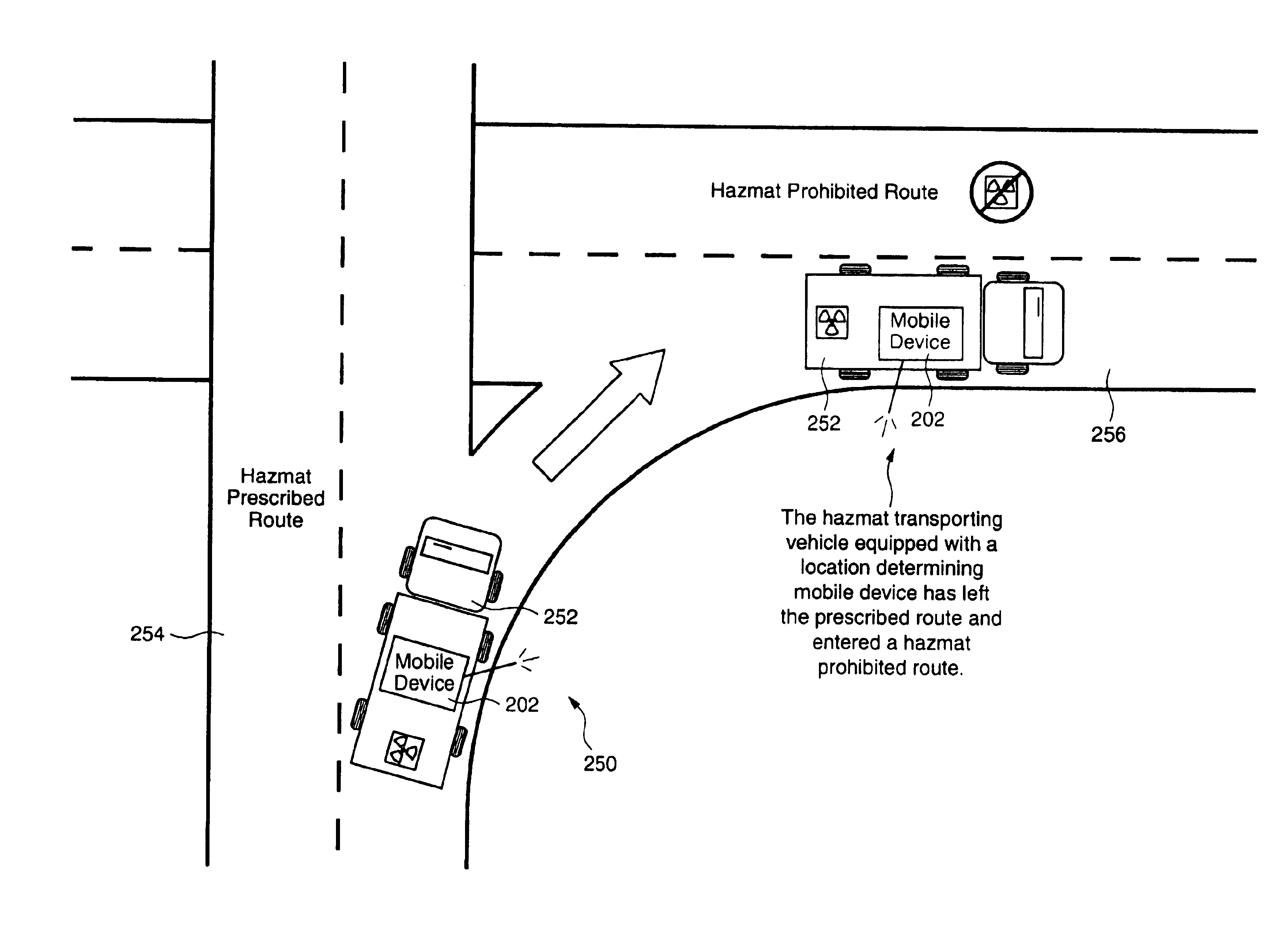
Using location data to determine traffic and route information
InactiveUS6862524B1Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTraffic conditionsSpeed limit
System and methods for determining and disseminating current traffic information and / or route information are presented. For example, in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, traffic condition information is collected from mobile units that provide their location or position information. The traffic condition may be determined, for example, based on the difference between the velocity of each mobile unit and the speed limit corresponding to their location. Furthermore, the fastest routes between two locations may be determined and provided based on historical and / or current conditions and provided to a mobile unit. In accordance with another embodiment of the present invention, route information may be utilized to determine whether a mobile unit (e.g., associated with a vehicle) is allowed or prohibited from traveling along a certain route.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Traffic information system
ActiveUS20070027583A1Minimize the numberAccurate insurance rateAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficEngineeringVehicle driving
Owner:INSURANCE SERVICES OFFICE INC
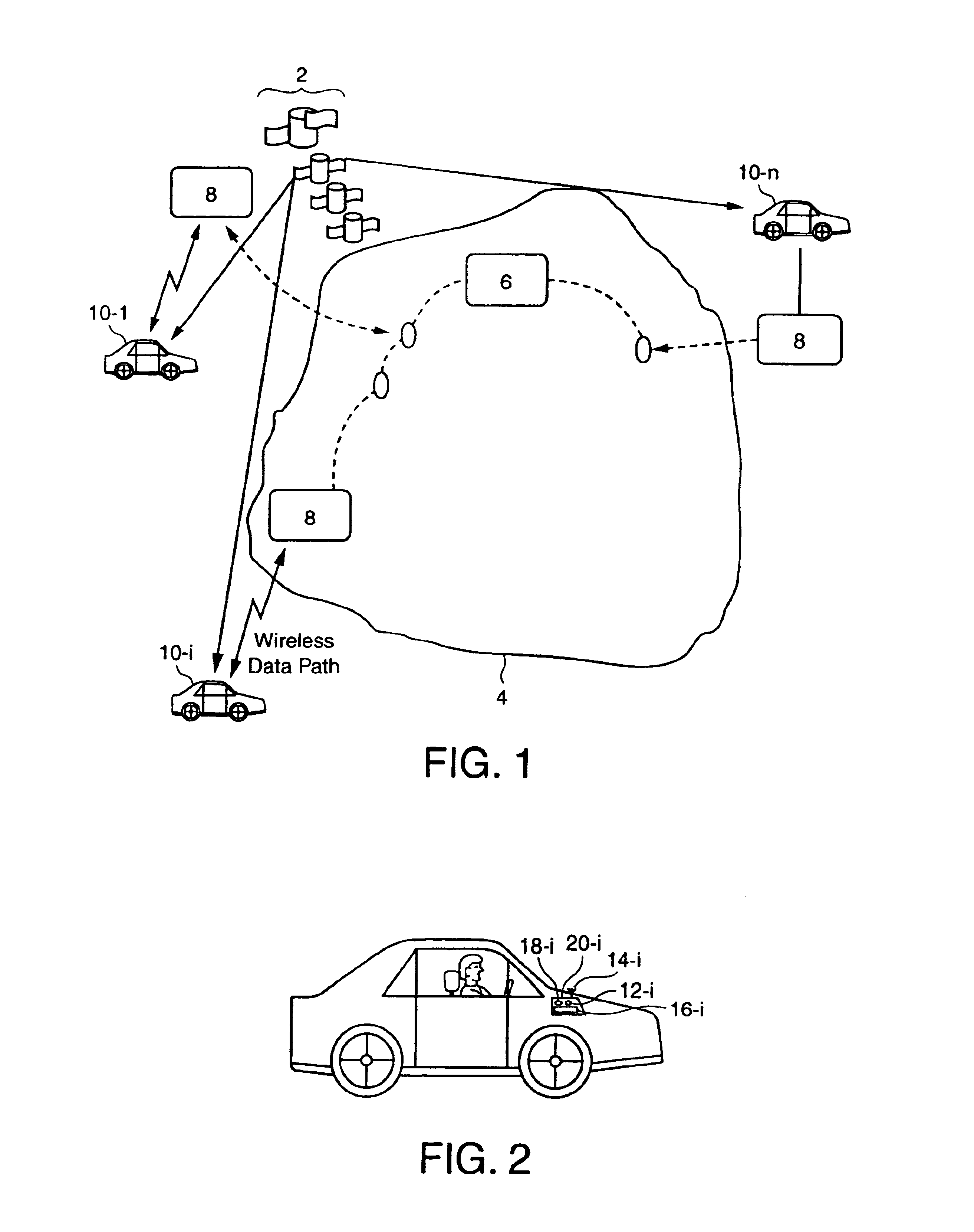
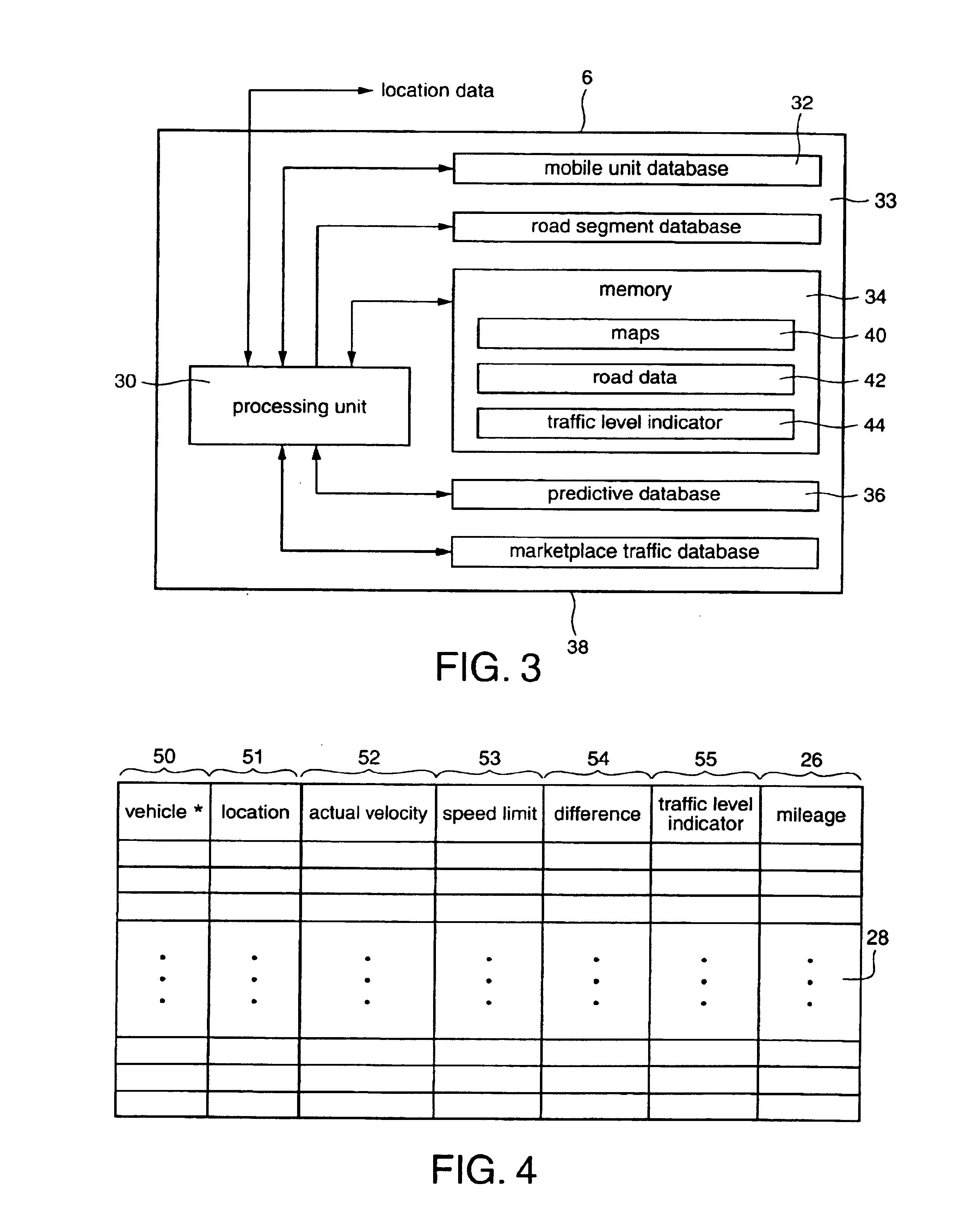
Automated traffic mapping
InactiveUS6150961AIncrease coverageOptimize dataAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTraffic capacityHighway system
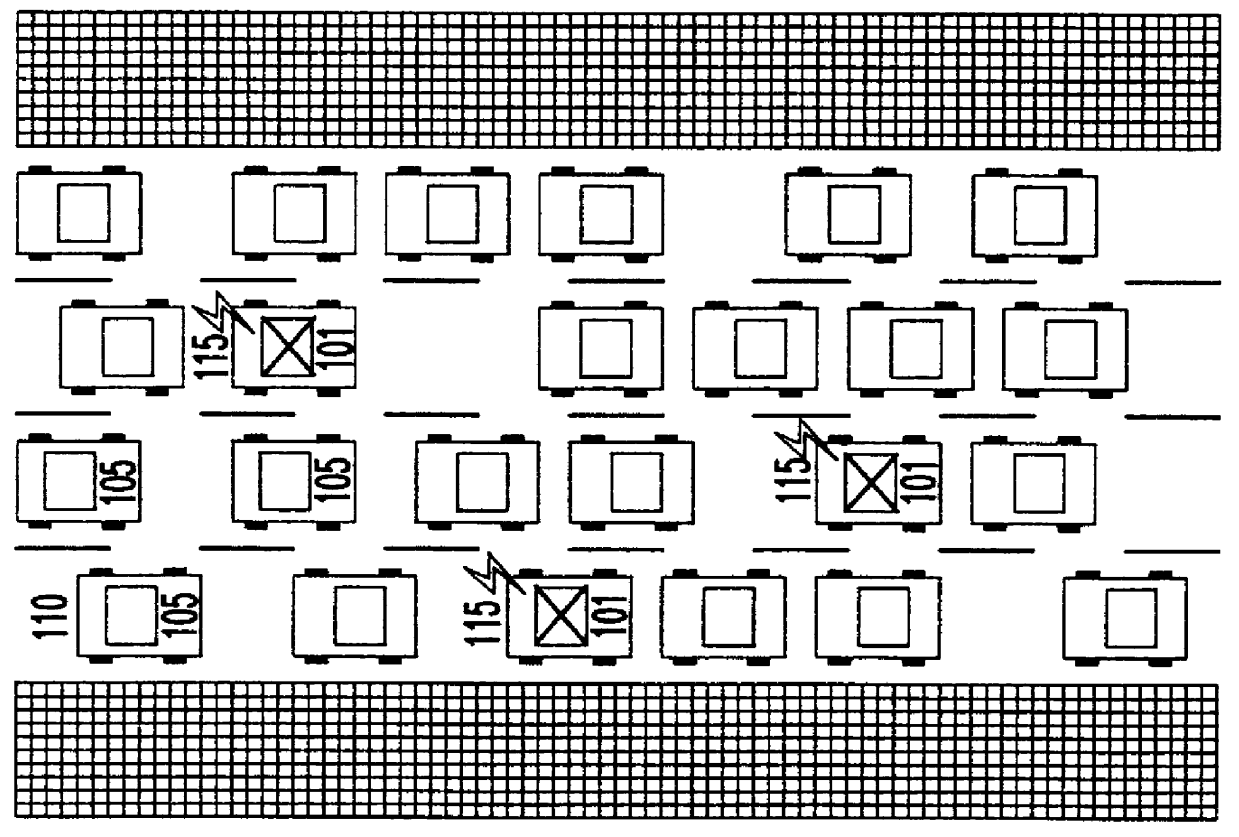
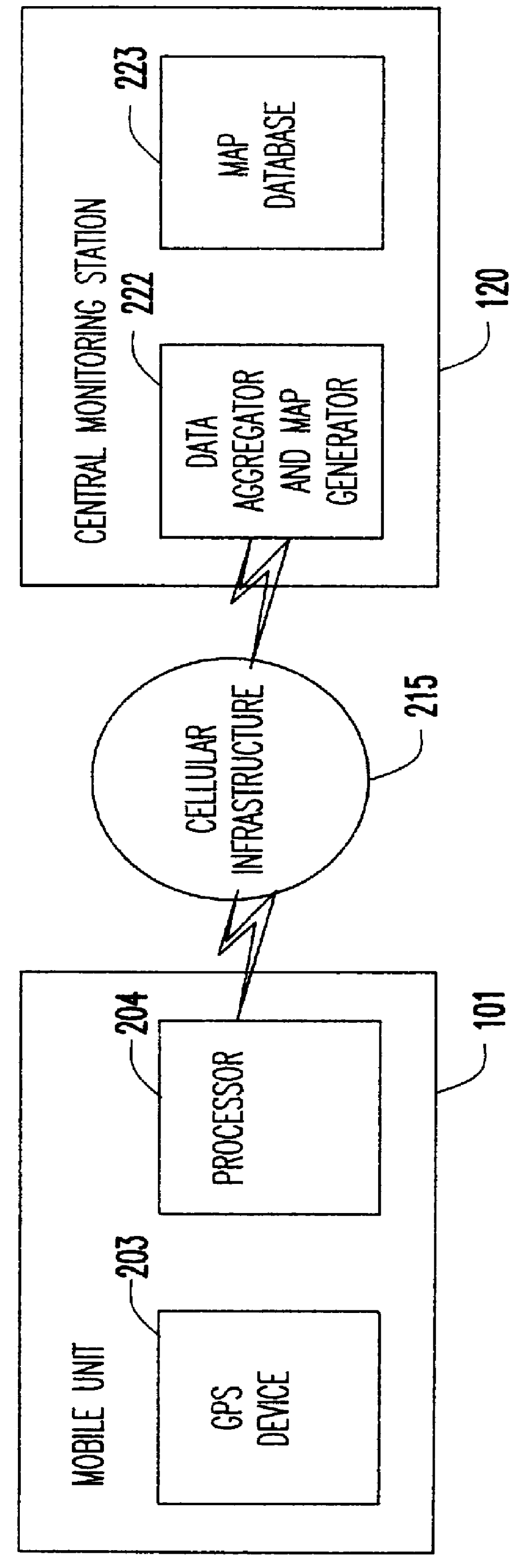
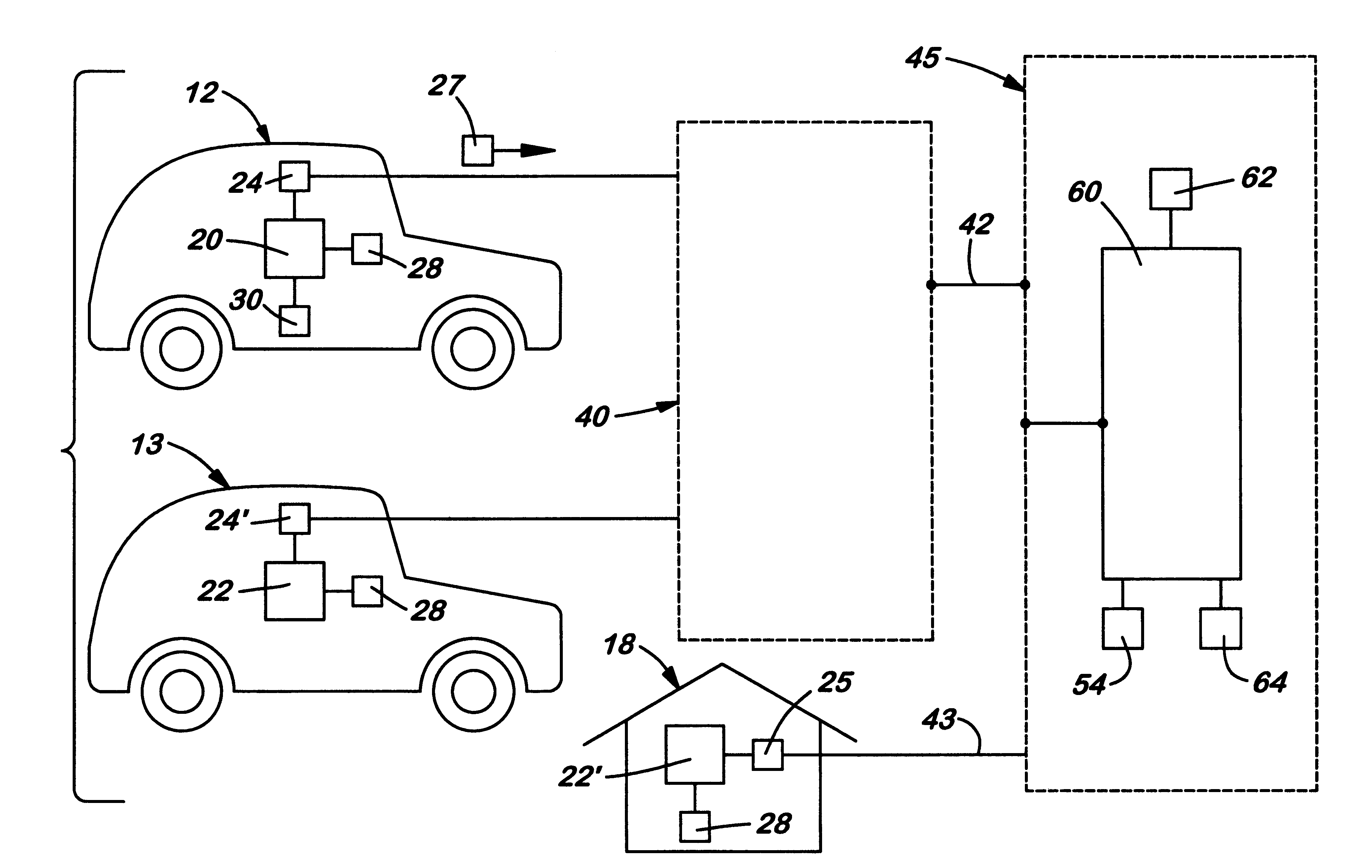
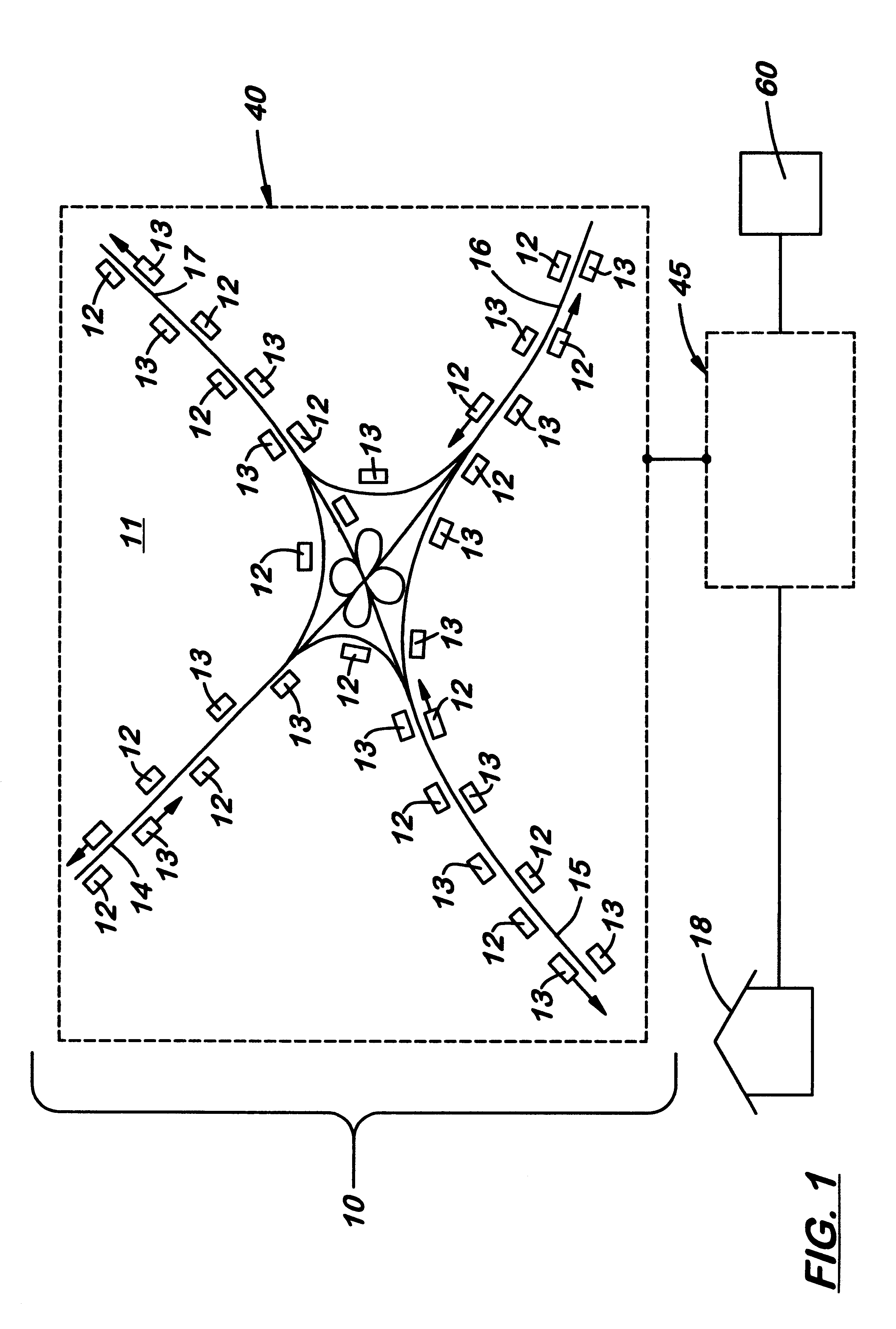
A system of mobile units are installed in multiple vehicles in traffic. These mobile units include both wireless communications devices and apparatus that determines the location of each vehicle. Monitoring a vehicle's position as a function of time also reveals the velocity of the vehicle. Position and speed information is periodically broadcast by the vehicles to a central monitoring station and to neighboring vehicles. At the central monitoring station, the collective input of a set of vehicles is processed to provide an instant chart of traffic conditions in the area. Warnings of delays or updates on traffic conditions on the road ahead are then automatically returned to subscribers of the information or are used as part of an Intelligent Vehicle Highway System (IVHS). Neighboring vehicles within a region communicating with one another form a network in which the broadcast information is processed locally on the respective vehicles to estimate possible problems ahead and consider computing an alternate road and / or checking with the central monitoring station for more information. If out of range of the central monitoring station, the vehicles in the network form a local area network for the exchange and update of information, and when any vehicle in the network is within range of the central monitoring station, the local area network data is uploaded to help update the overall traffic information.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
Instantaneous traffic monitoring system
InactiveUS6236933B1Less congestedControlling traffic signalsAnalogue computers for vehiclesModem deviceEngineering
A system for instantaneously monitoring traffic congestion including a plurality of monitoring electronic devices located in motor vehicles traveling on roadways in a selected region. Each monitoring electronic device is coupled to a GPS receiver that provides physical location to a wireless modem capable of connecting to a wireless communication network. The system also includes a central computer connected to a wide area network that is able of continuously downloading physical location information from a plurality of monitoring electronic devices also connected to the wide area network. The central computer uses a traffic monitoring software program and a mapping database containing roadway information for a region and the movement information from the monitoring electronic devices to create a continuously updated traffic congestion database. Authorized users of the system are able to log onto the central computer to a portion of the database that contains specific traffic flow and congestion information. Using the system, users are also able to obtain estimated times of arrival for a specific trip, and recommendations on alternative route information. The system can also take into consideration current or anticipated events that may affect traffic congestion.
Owner:INFOMOVE COM
Detecting anomalous road traffic conditions
InactiveUS20070208497A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficSimulationTraffic conditions
Techniques are described for automatically detecting anomalous road traffic conditions and for providing information about the detected anomalies, such as for use in facilitating travel on roads of interest. Anomalous road traffic conditions may be identified using target traffic conditions for a particular road segment at a particular selected time, such as target traffic conditions that reflect actual traffic conditions for a current or past selected time, and / or target traffic conditions that reflect predicted future traffic conditions for a future selected time. Target traffic conditions may be compared to distinct expected road traffic conditions for a road segment at a selected time, with the expected conditions reflecting road traffic conditions that are typical or normal for the road segment at the selected time. Anomalous conditions may be identified based on sufficiently large differences from the expected conditions, and information about the anomalous conditions may be provided in various ways.
Owner:INRIX
Smart electric vehicle (EV) charging and grid integration apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20130179061A1Increase capacityAdding smartnessAnalogue computers for vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsGrid-tie inverterState of charge
An expert system manages a power grid wherein charging stations are connected to the power grid, with electric vehicles connected to the charging stations, whereby the expert system selectively backfills power from connected electric vehicles to the power grid through a grid tie inverter (if present) within the charging stations. In more traditional usage, the expert system allows for electric vehicle charging, coupled with user preferences as to charge time, charge cost, and charging station capabilities, without exceeding the power grid capacity at any point. A robust yet accurate state of charge (SOC) calculation method is also presented, whereby initially an open circuit voltage (OCV) based on sampled battery voltages and currents is calculated, and then the SOC is obtained based on a mapping between a previously measured reference OCV (ROCV) and SOC. The OCV-SOC calculation method accommodates likely any battery type with any current profile.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Accident avoidance systems and methods
InactiveUS7295925B2Avoid accidentsAvoid and minimize effectVehicle seatsAnalogue computers for vehiclesCommunications systemEngineering
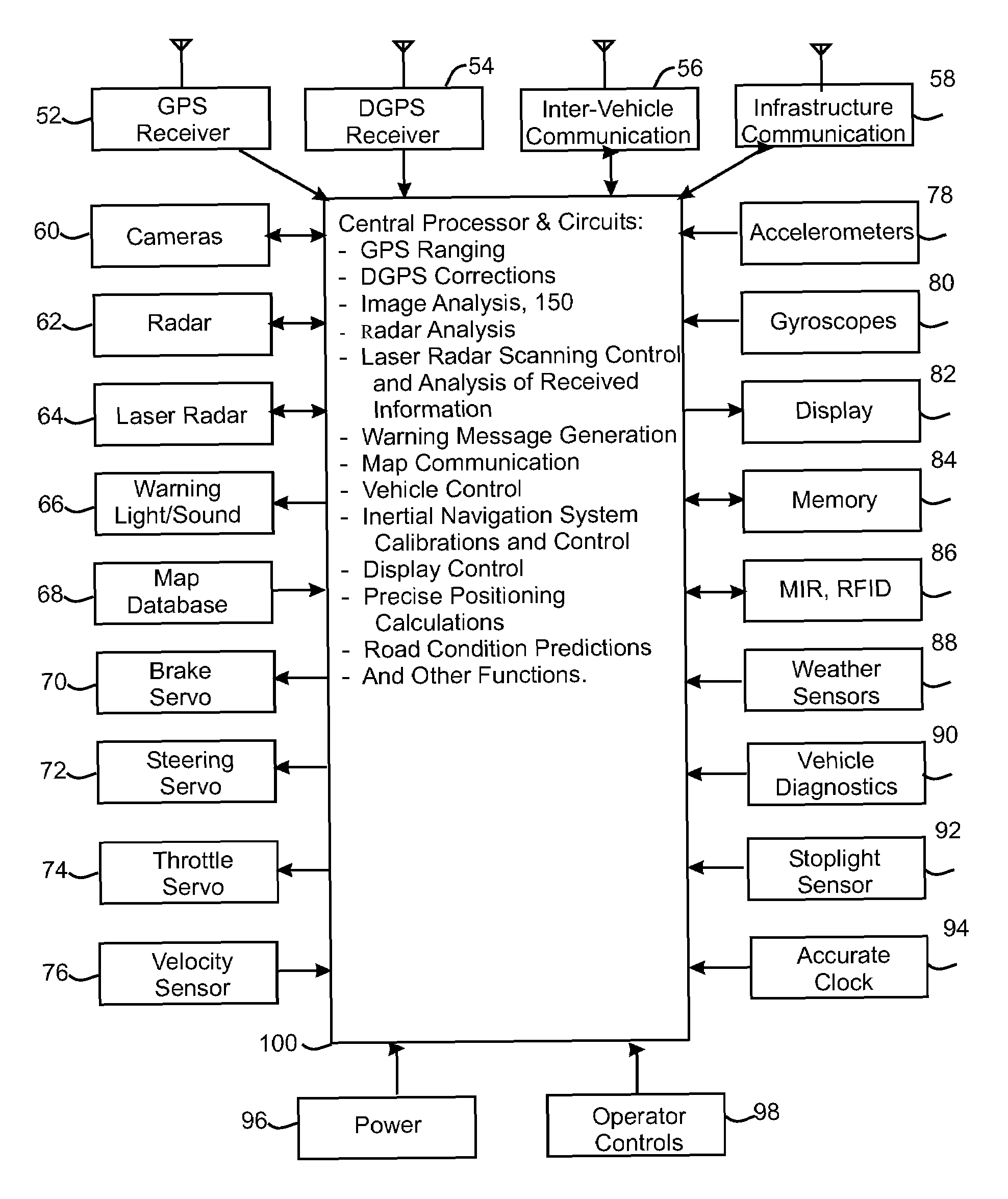
Method and system for preventing accidents between first and second vehicles includes a positioning system arranged in each vehicle for determining the absolute position thereof, a memory unit arranged in the first vehicle for storing data about travel lanes, a communication system for transmitting the position of the second vehicle to the first vehicle, a receiver system arranged in the first vehicle for receiving position information from the second vehicle, a processor coupled to the positioning system, the receiver system and the memory unit in the first vehicle for predicting a collision between the vehicles based on the position of the vehicles and travel lane data, and a reactive component arranged in the first vehicle and coupled to the processor. The reactive component is arranged to initiate an action or change its operation when a collision is predicted by the processor, e.g., sound or indicate an alarm.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Centralized facility and intelligent on-board vehicle platform for collecting, analyzing and distributing information relating to transportation infrastructure and conditions
ActiveUS7421334B2Efficient managementAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTransportation infrastructureIn vehicle
An on-board intelligent vehicle system includes a sensor assembly to collect data and a processor to process the data to determine the occurrence of at least one event. The data may be collected from existing standard equipment such as the vehicle communication bus or add-on sensors. The data may be indicative of conditions relating to the vehicle, roadway infrastructure, and roadway utilization, such as vehicle performance, roadway design, roadway conditions, and traffic levels. The detection of an event may signify abnormal, substandard, or unacceptable conditions prevailing in the roadway, vehicle, or traffic. The vehicle transmits an event indicator and correlated vehicle location data to a central facility for further management of the information. The central facility sends communications reflecting event occurrence to various relevant or interested users. The user population can include other vehicle subscribers (e.g., to provide rerouting data based on location-relevant roadway or traffic events), roadway maintenance crews, vehicle manufacturers, and governmental agencies (e.g., transportation authorities, law enforcement, and legislative bodies).
Owner:ZOOM INFORMATION SYST
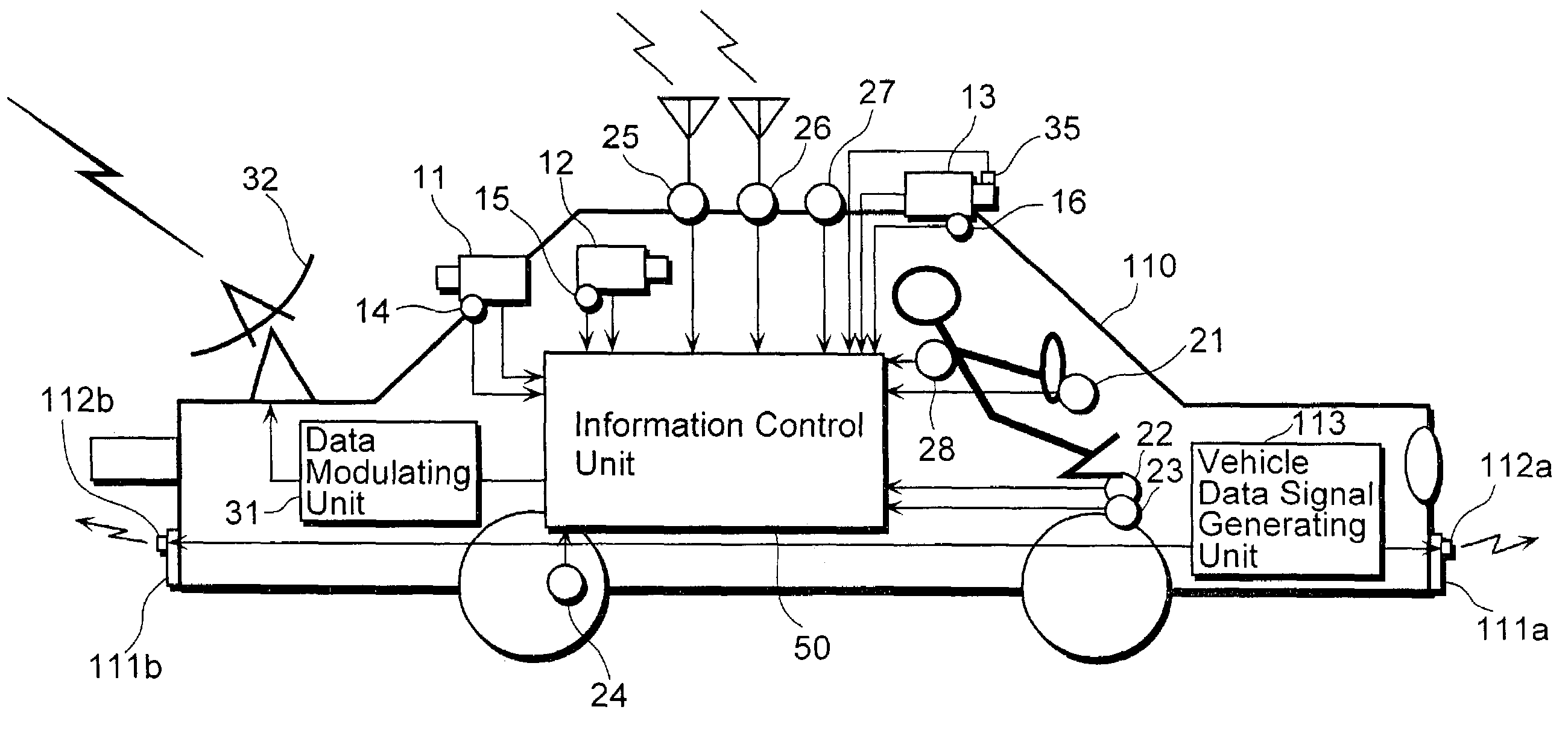
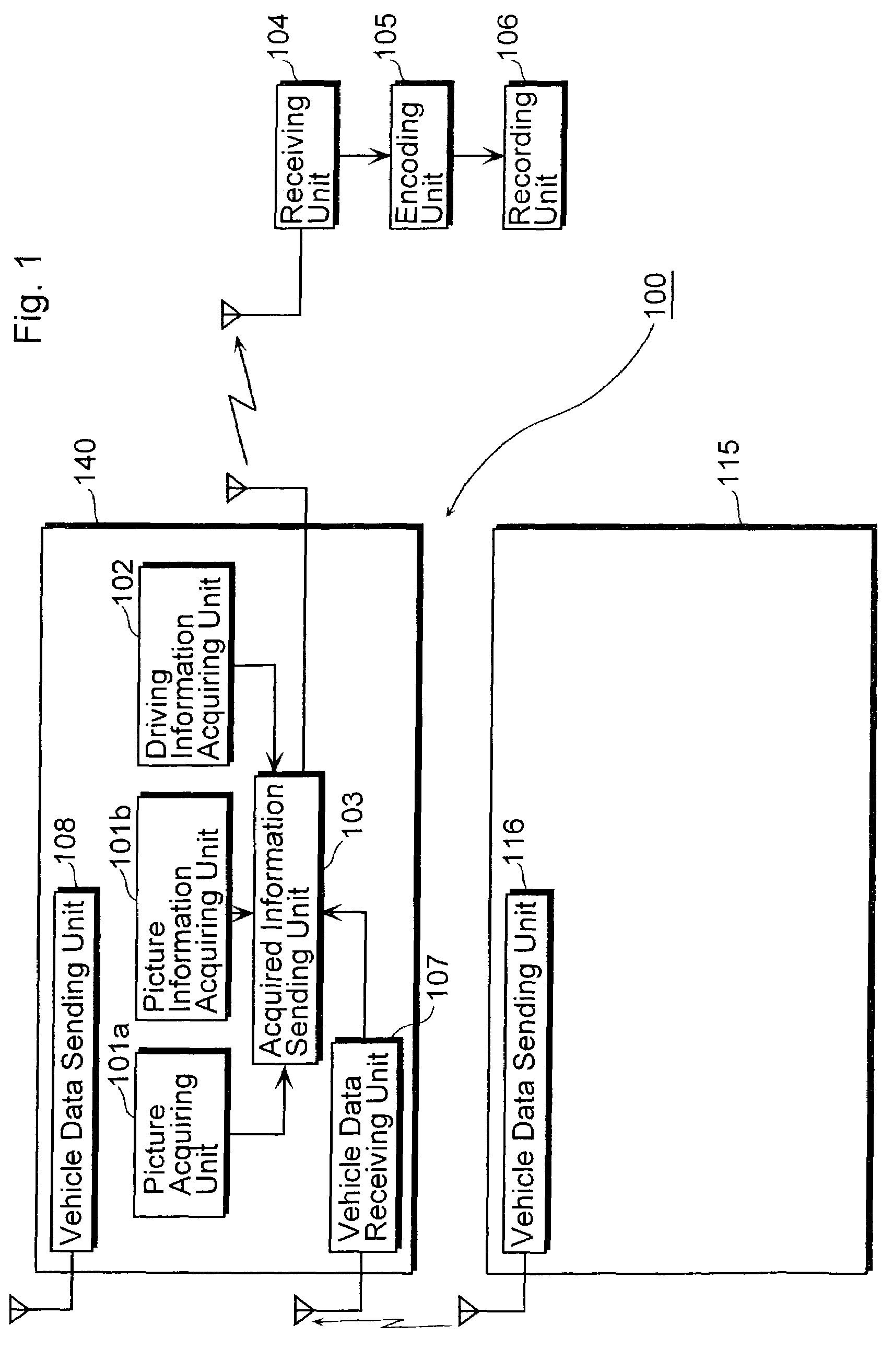
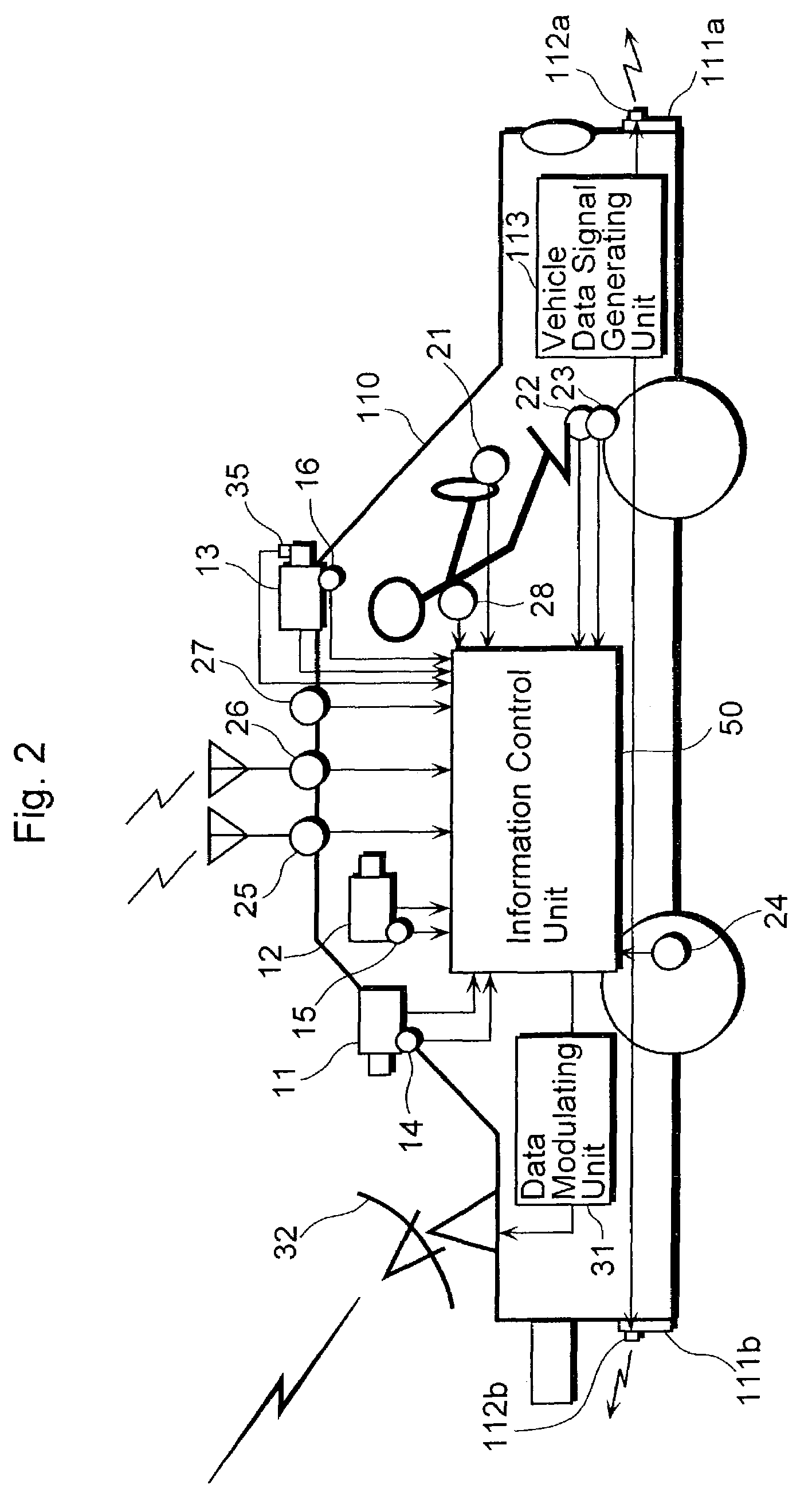
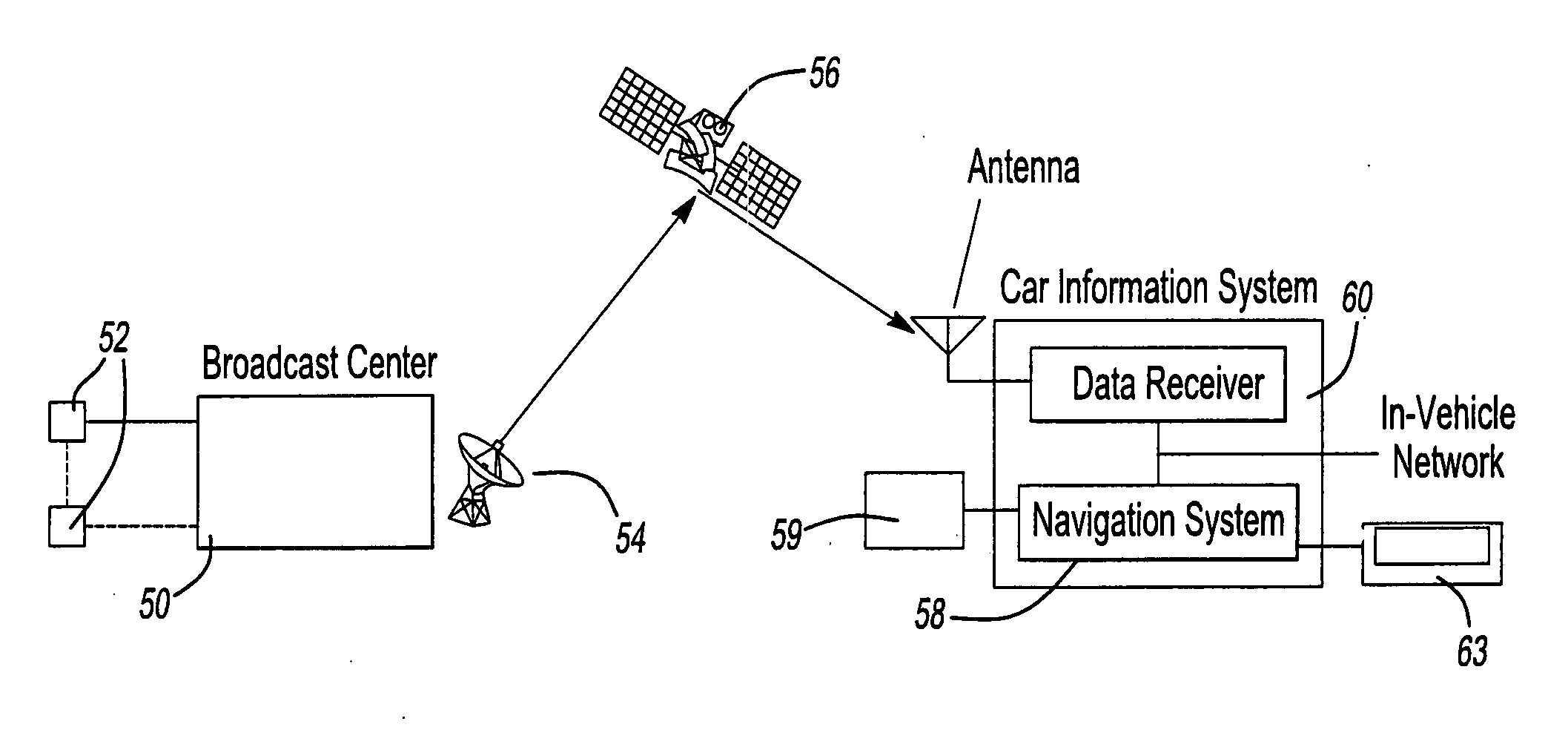
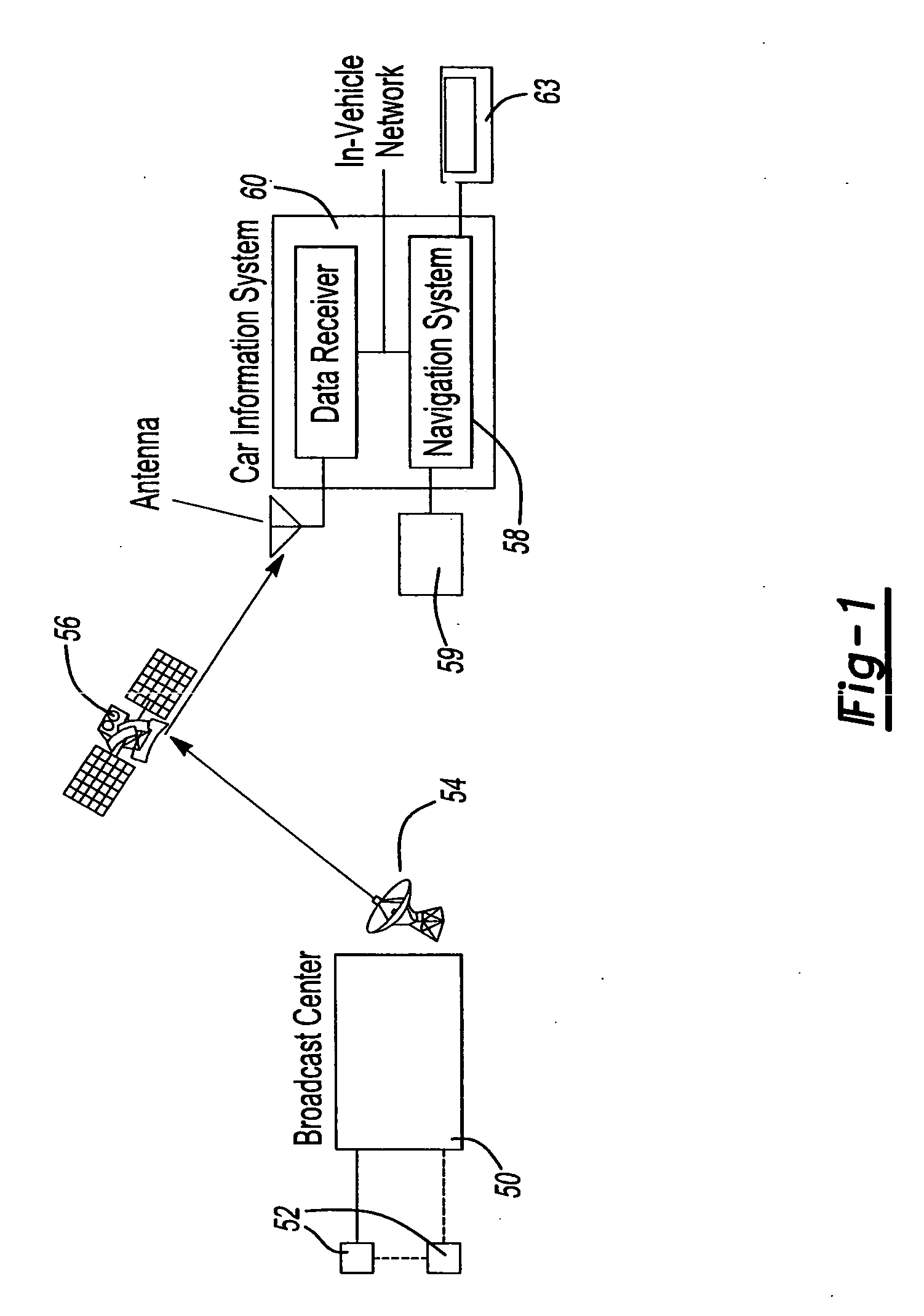
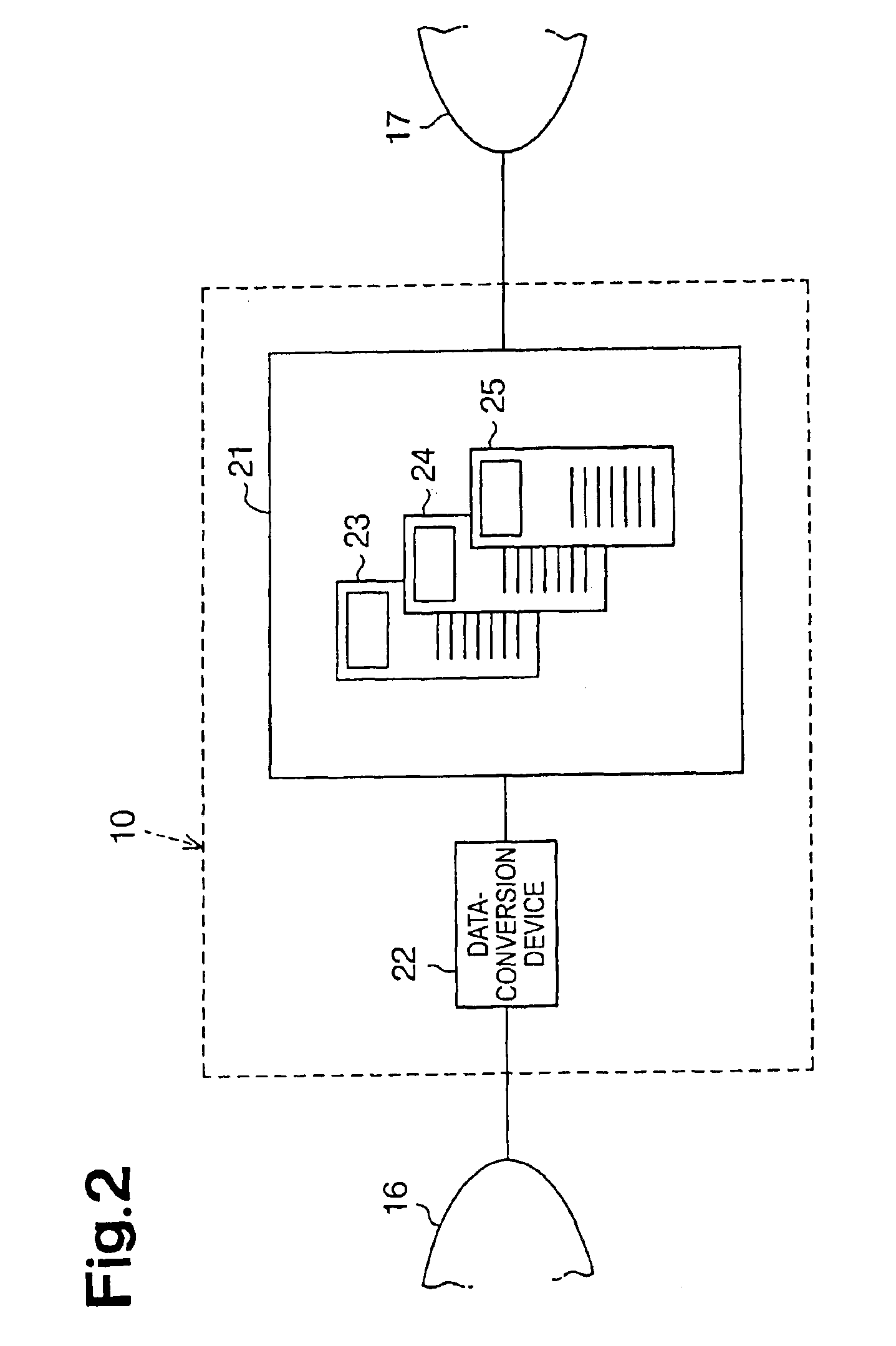
Vehicle information recording system
InactiveUS7254482B2Easy searchAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationReal-time computingRecording system
A vehicle information recording system 100 includes a picture acquiring unit 101a placed in a vehicle that takes a picture of surroundings and generates picture data showing the picture, a vehicle data receiving unit 107 placed in the vehicle that receives other vehicle data concerning another vehicle shown in the picture acquired by the picture acquiring unit 101a, an acquired information sending unit 103 placed in the vehicle that sends data including the picture data and the other vehicle data outside of the vehicle, a receiving unit 104 placed outside of the vehicle that receives the data sent by the acquired information sending unit 103, an encoding unit 105 placed outside of the vehicle that encodes the other vehicle data among the data received by the receiving unit 104 and adds the encoded data to the picture data as related data, and a recording unit 106 placed outside of the vehicle that records the picture data to which the other vehicle data is added by the encoding unit 105.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Traffic monitoring system and method
InactiveUS6505114B2High potential frequency reuseHigh densityAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationTraffic intensityTelecommunications network
A method and system for traffic monitoring and prediction of traffic intensity. The method comprises the steps of determining at least twice, within a specified time interval, geographical positions of a plurality of mobile devices in a mobile telecommunications network. This is done by means of measuring at least one property of signals transmitted between the mobile devices and base stations in the mobile telecommunications network. At least a subset of the geographical positions are compared with a route of a road provided in a route database in order to identify mobile devices having routes corresponding to at least a part of the road route. A velocity for the identified mobile devices based on the at least two positions, and the calculated velocity of at least one identified mobile device is compared with a reference velocity of the road in order to predict traffic intensity on the road. A system for short range monitoring is also provided.
Owner:STRATEGIC DESIGN FEDERATION W LLC
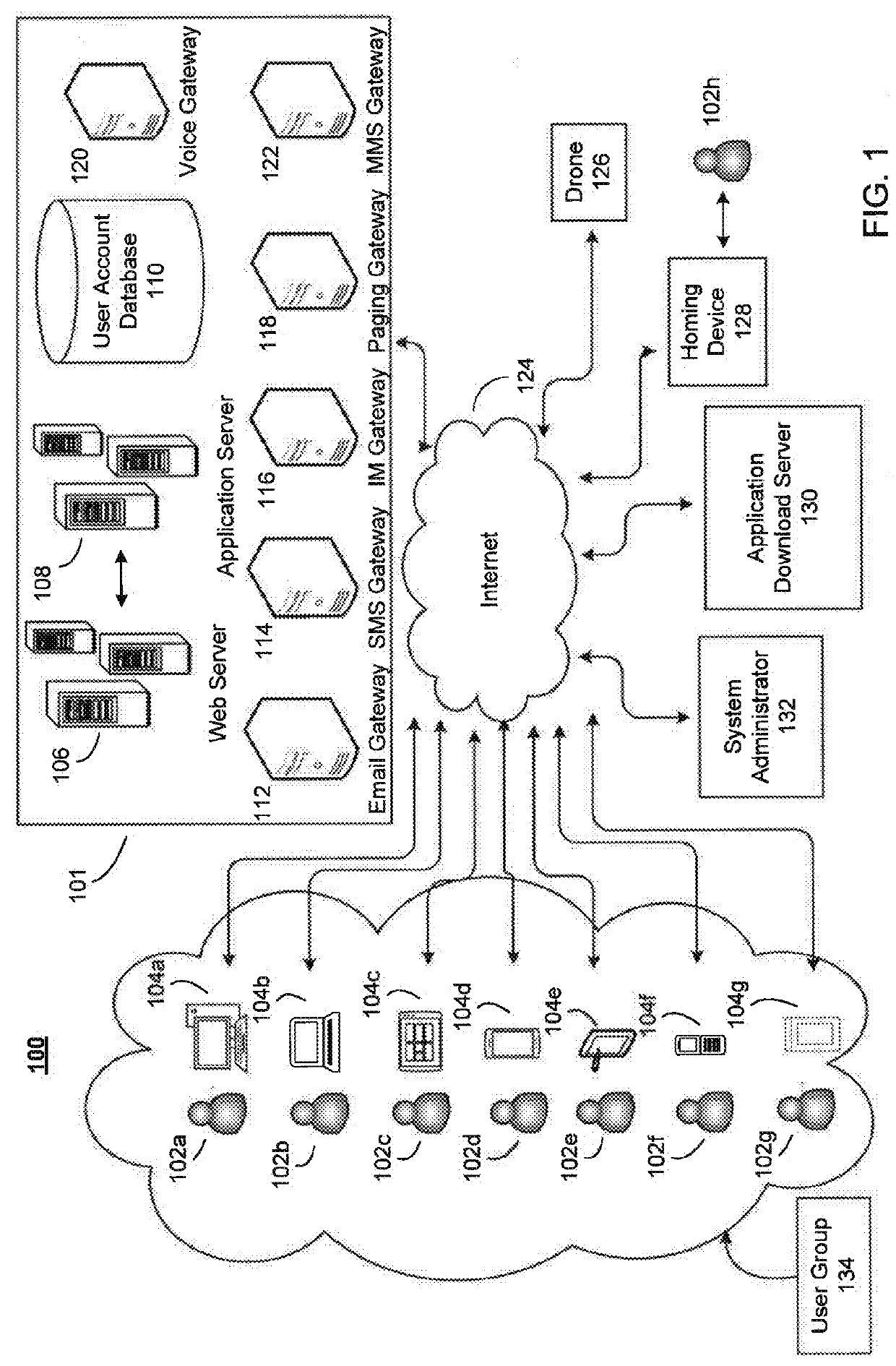
System and method for controlling drone delivery or pick up during a delivery or pick up phase of drone operation
ActiveUS20160033966A1Accurate and secure deliveryAnalogue computers for vehiclesData processing applicationsAirplaneFlight plan
A system including a landing location where a drone at least one of delivers and acquires a parcel, and a homing device to interact with the drone to guide the drone to the landing location independent of interaction from another source. The homing device guides the drone during the landing phase of a flight plan. A method is also disclosed.
Owner:FARRIS EMMETT +1
System and method for monitoring and updating speed-by-street data
ActiveUS20080252487A1Accurate trackingPrevent speedingAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsData systemIdentification error
System and method for identifying speeding violations, comprising determining a current speed and a current location of a vehicle, determining a posted speed limit for the current location from a speed-by-street database, comparing the current speed of the vehicle to the posted speed limit, and evaluating whether the current speed exceeds the posted speed limit. Errors are identified in the speed-by-street database by storing a plurality of speeding violation records, wherein the speeding violation records each include a speeding event location; analyzing the speeding violation records to identify one or more speeding event locations having multiple speeding violations; comparing a posted speed limit at the one or more speeding event locations having multiple speeding violations to corresponding speed limit data in the speed-by-street database; and identifying one or more speed limit entries in the speed-by-street database that do not match the posted speed limit.
Owner:IWI
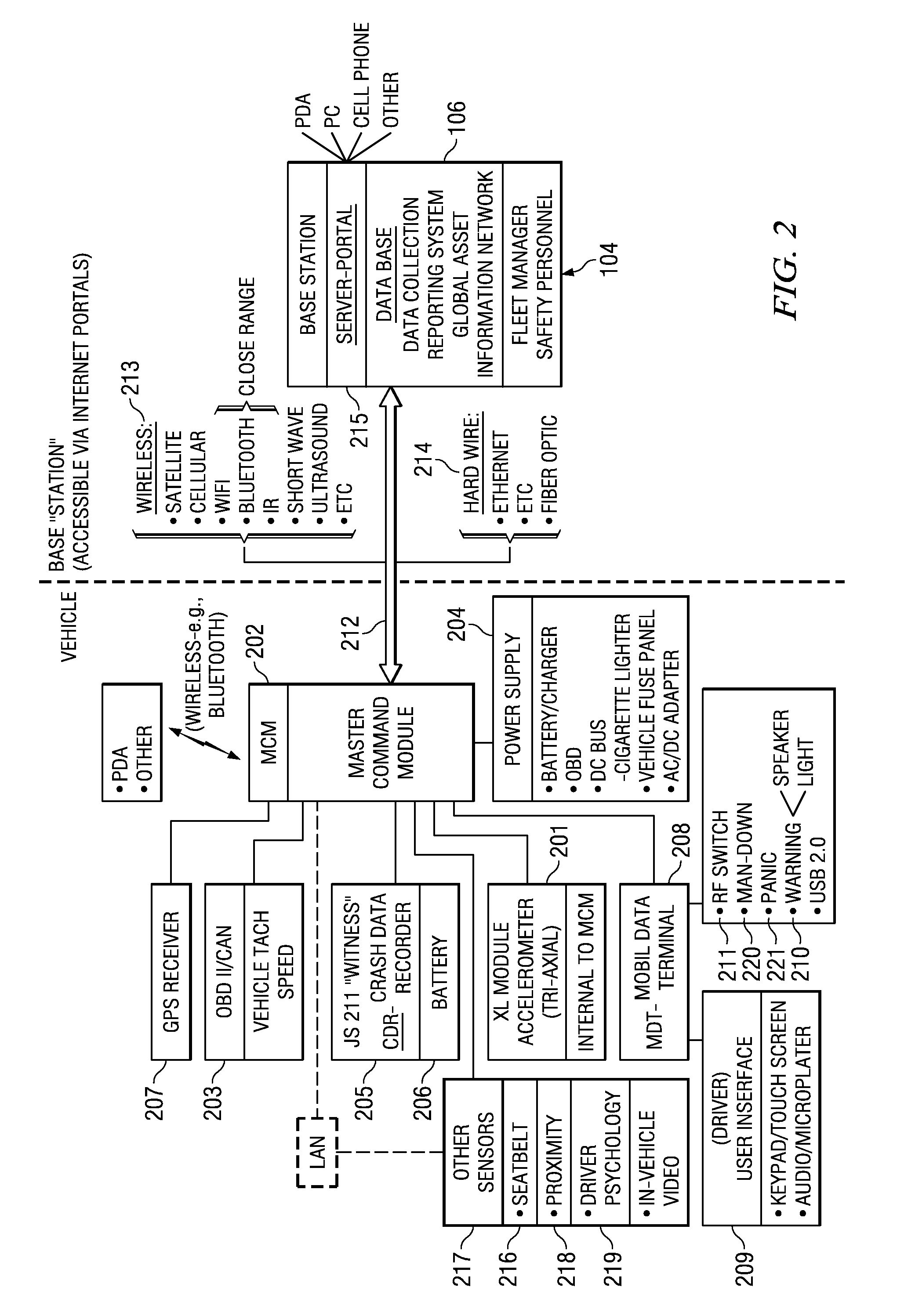
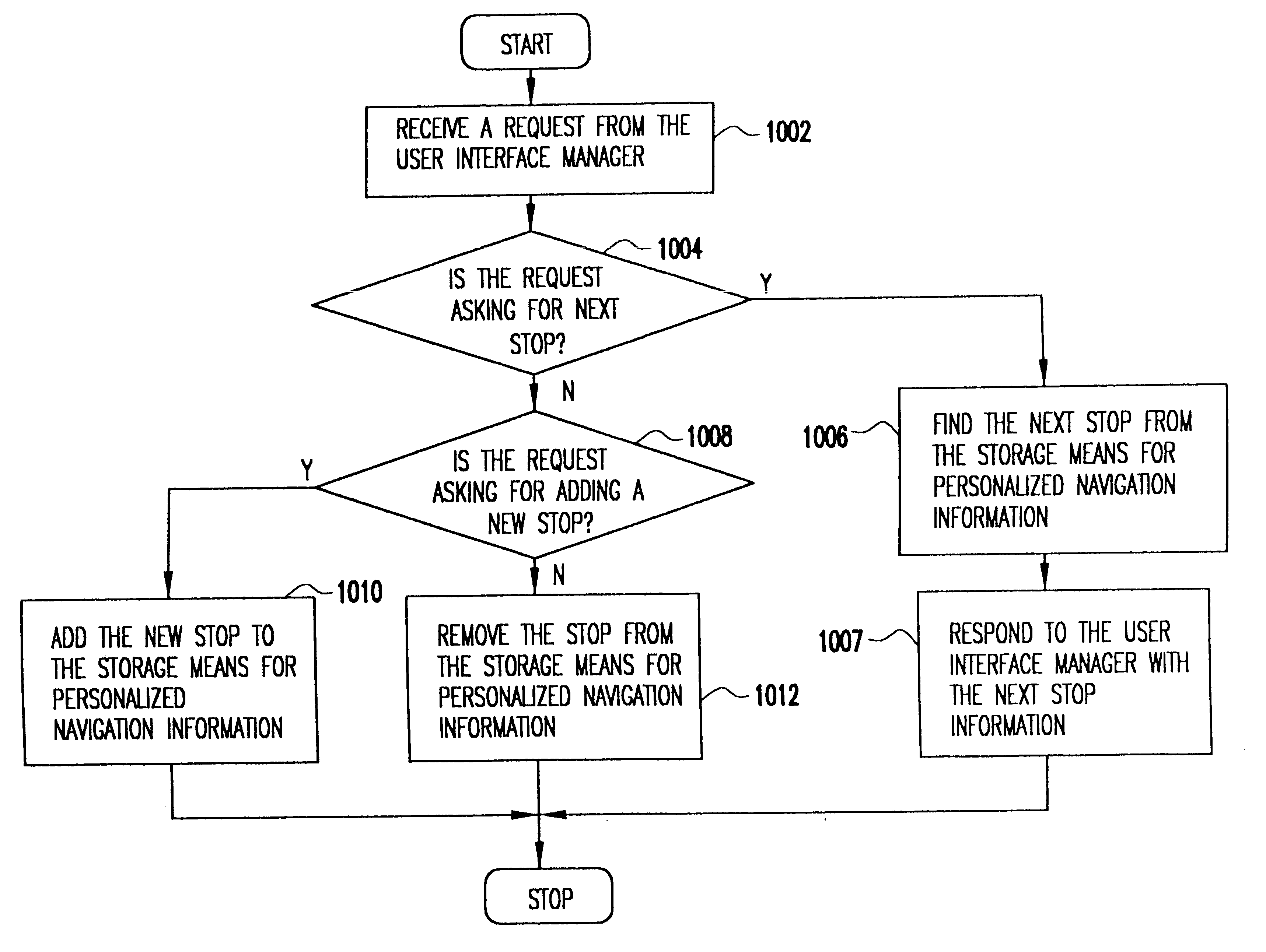
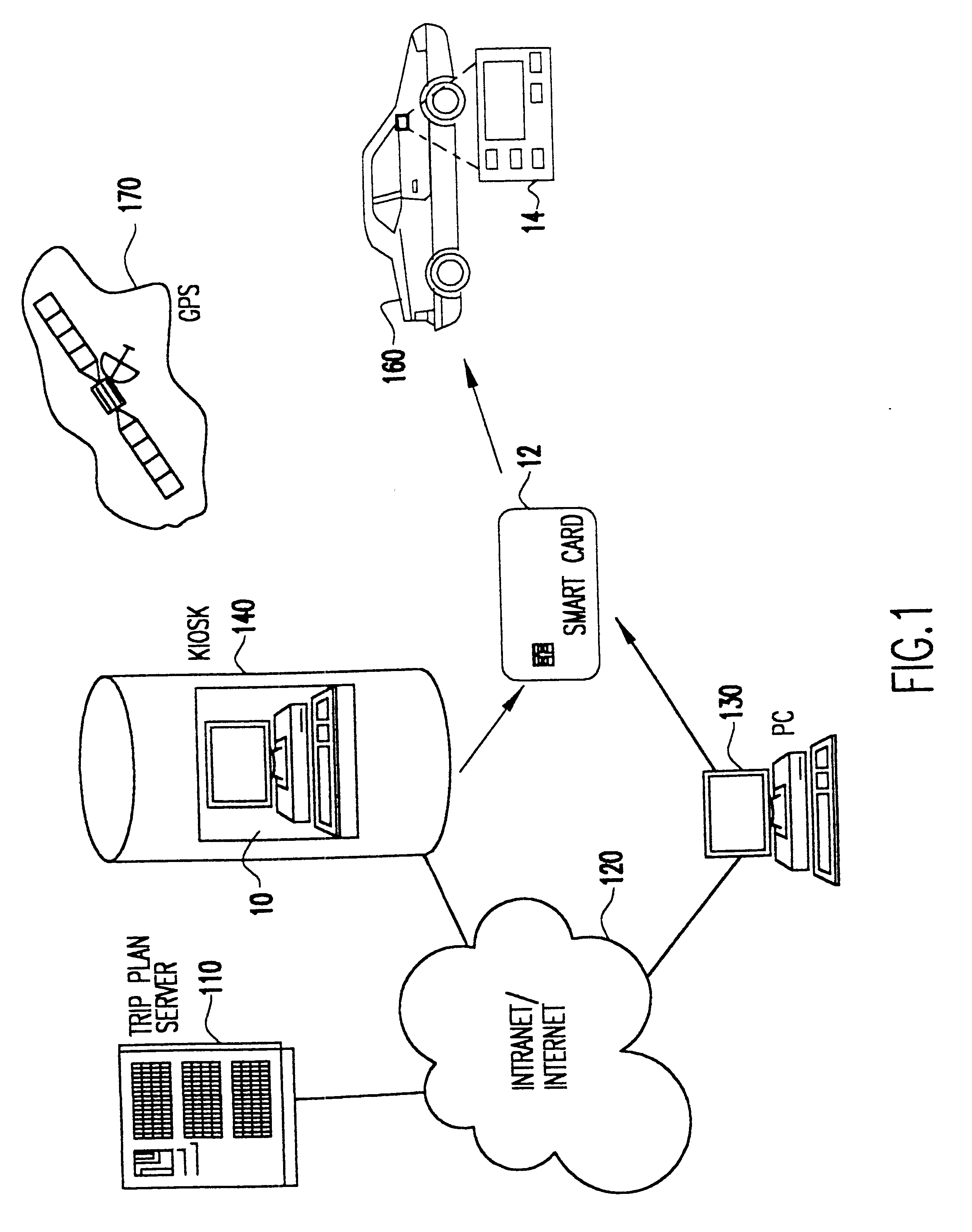
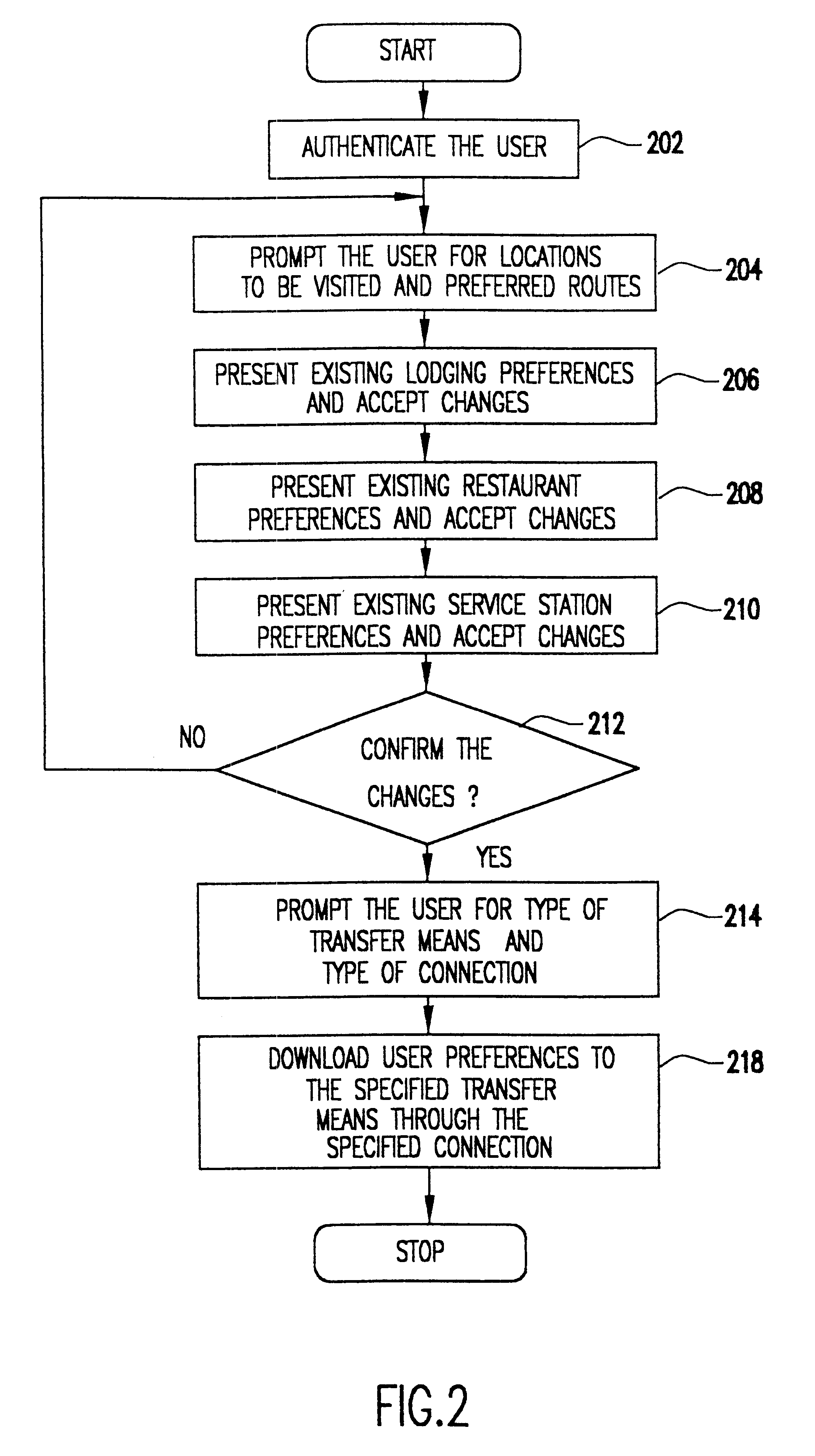
System for personalized mobile navigation information
InactiveUS6349257B1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectric signal transmission systemsPersonalizationMobile navigation
A mobile navigation system implemented as an embedded system in a vehicle is easy to use, does not detract the driver's attention from the road, and limits the number of choices presented to the user of the navigation system according to a predetermined set of preferences or personalized information. Choices are filtered according to a set of driver preferences, according to the vehicle's geographic position, direction of motion, and the driver's intended itinerary. The itinerary, including intermediate stops, is calculated on an external computing system. The information is downloaded from the computing system to a memory device such as, for example, a smart card. The information is then transferred from the smart card to the embedded vehicle navigation system. In one application of the invention, a kiosk located at a car rental agency may be used to create and store personalized navigation information onto a smart card which the customer then inserts into the vehicle navigation system that is installed in the rental car.
Owner:IBM CORP
Aerial system and vehicle for continuous operation
ActiveUS20160137311A1Analogue computers for vehiclesArrester hooksContinuous operationSurveillance data
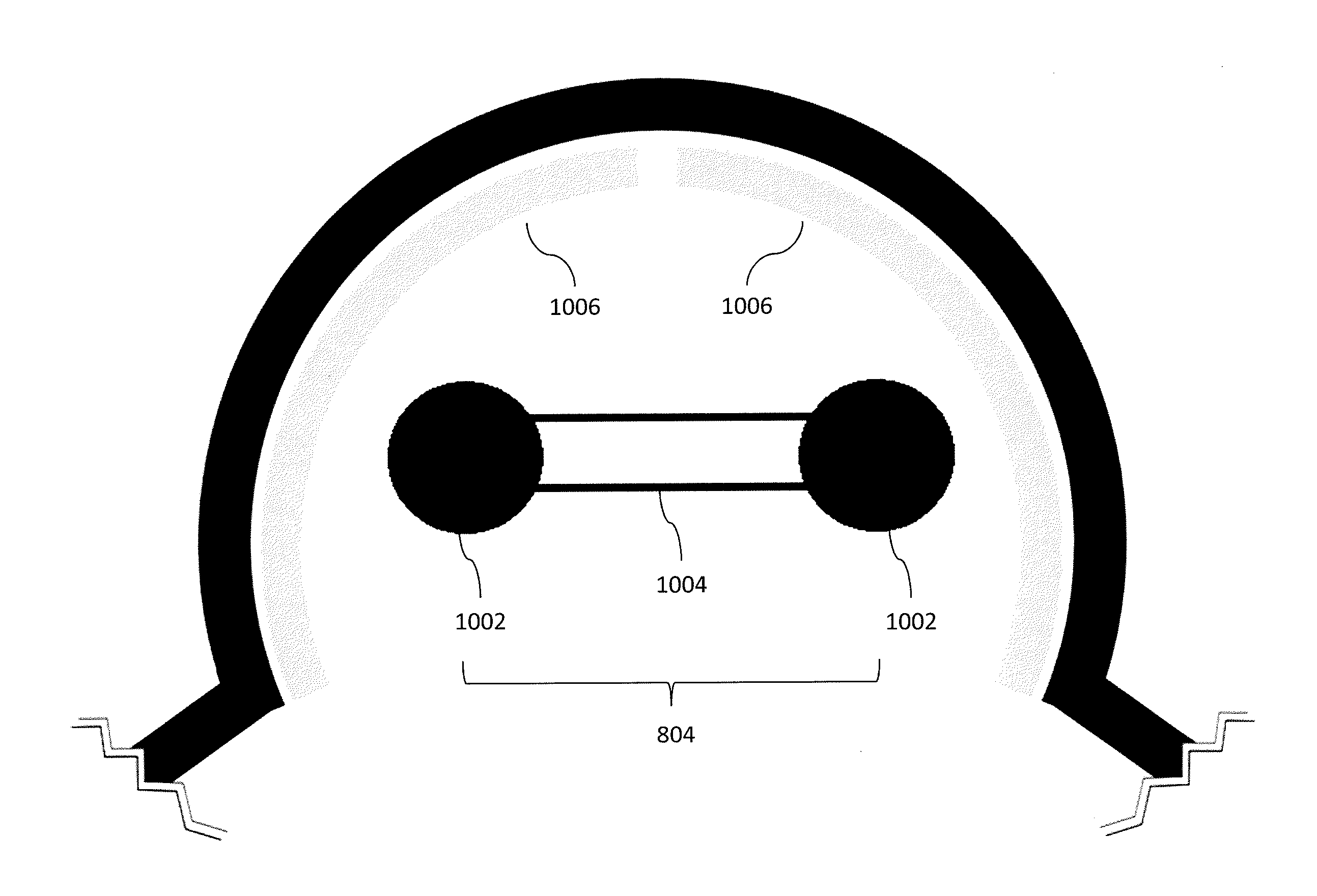
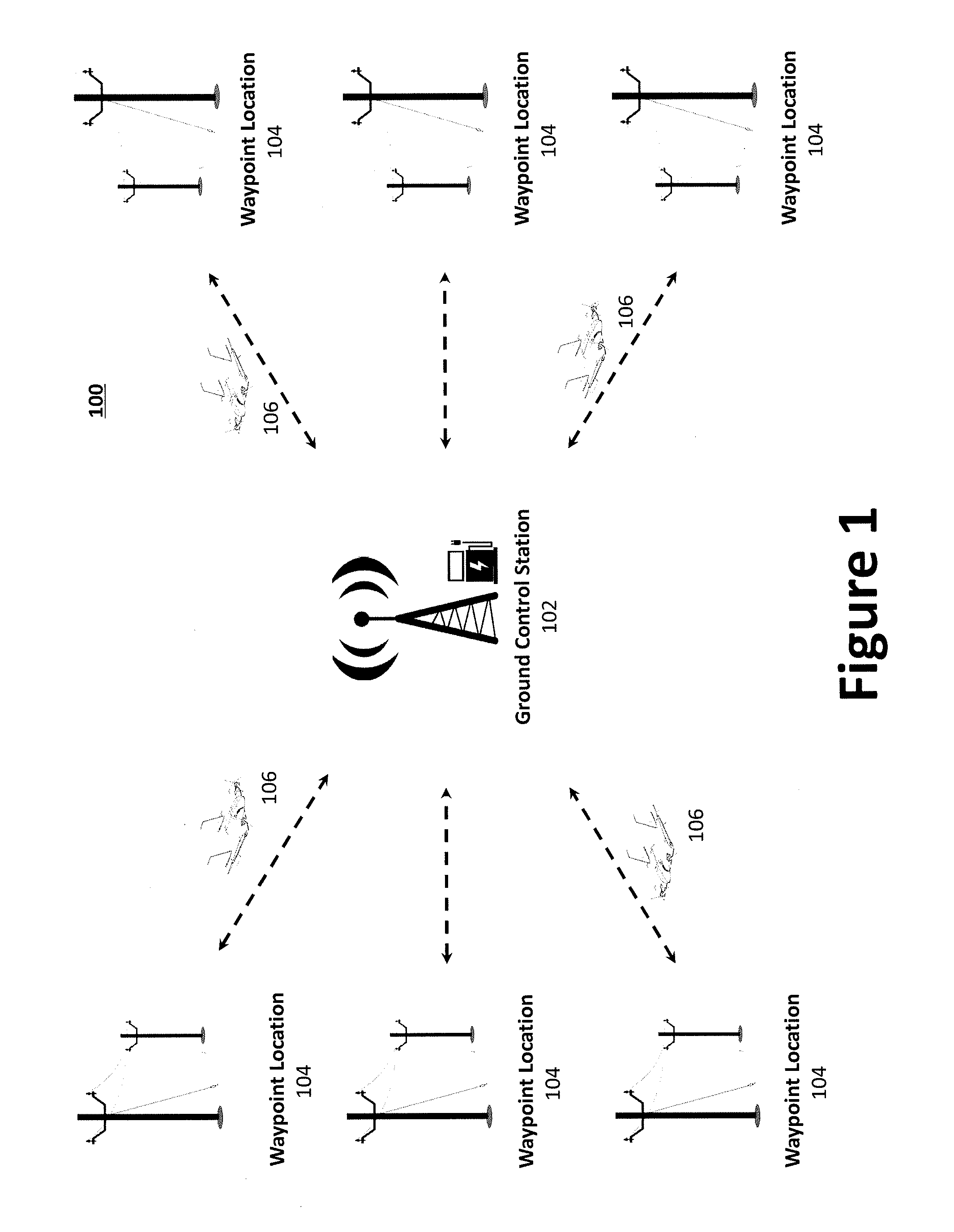
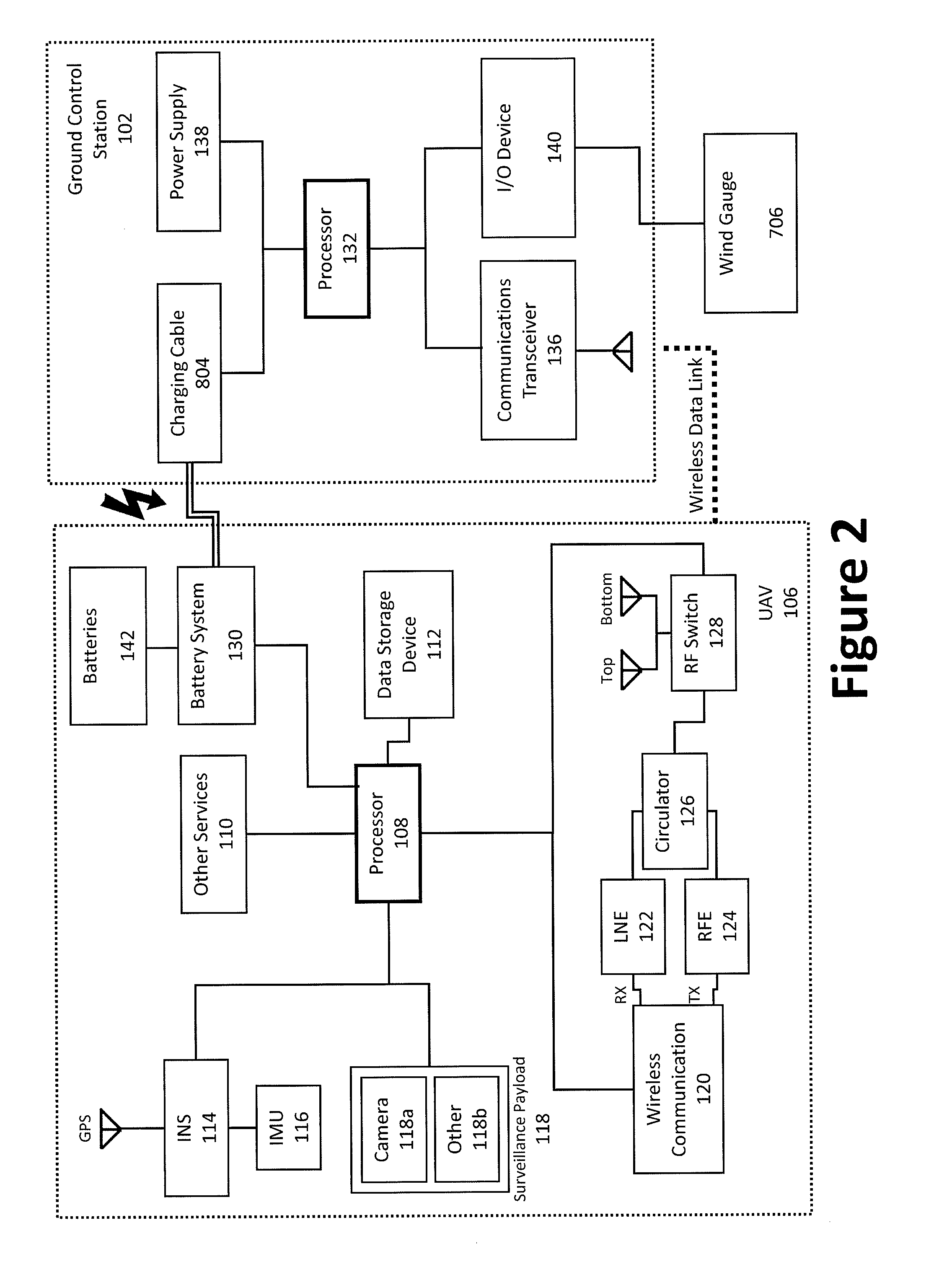
An aerial vehicle system for gathering data may comprise a Waypoint Location, wherein the Waypoint Location comprises an arresting cable; a Ground Control Station, wherein the Ground Control Station comprises a charging cable; and an aerial vehicle, wherein the aerial vehicle comprises an onboard battery, a capturing hook and a sensor payload for generating surveillance data. The aerial vehicle may be configured to autonomously travel between the Waypoint Location and the Ground Control Station. The aerial vehicle may be configured to couple with the arresting cable via the capturing hook. The aerial vehicle may be configured to electronically couple with the charging cable via the capturing hook to facilitate charging the aerial vehicle's onboard battery.
Owner:AURORA FLIGHT SCI CORP
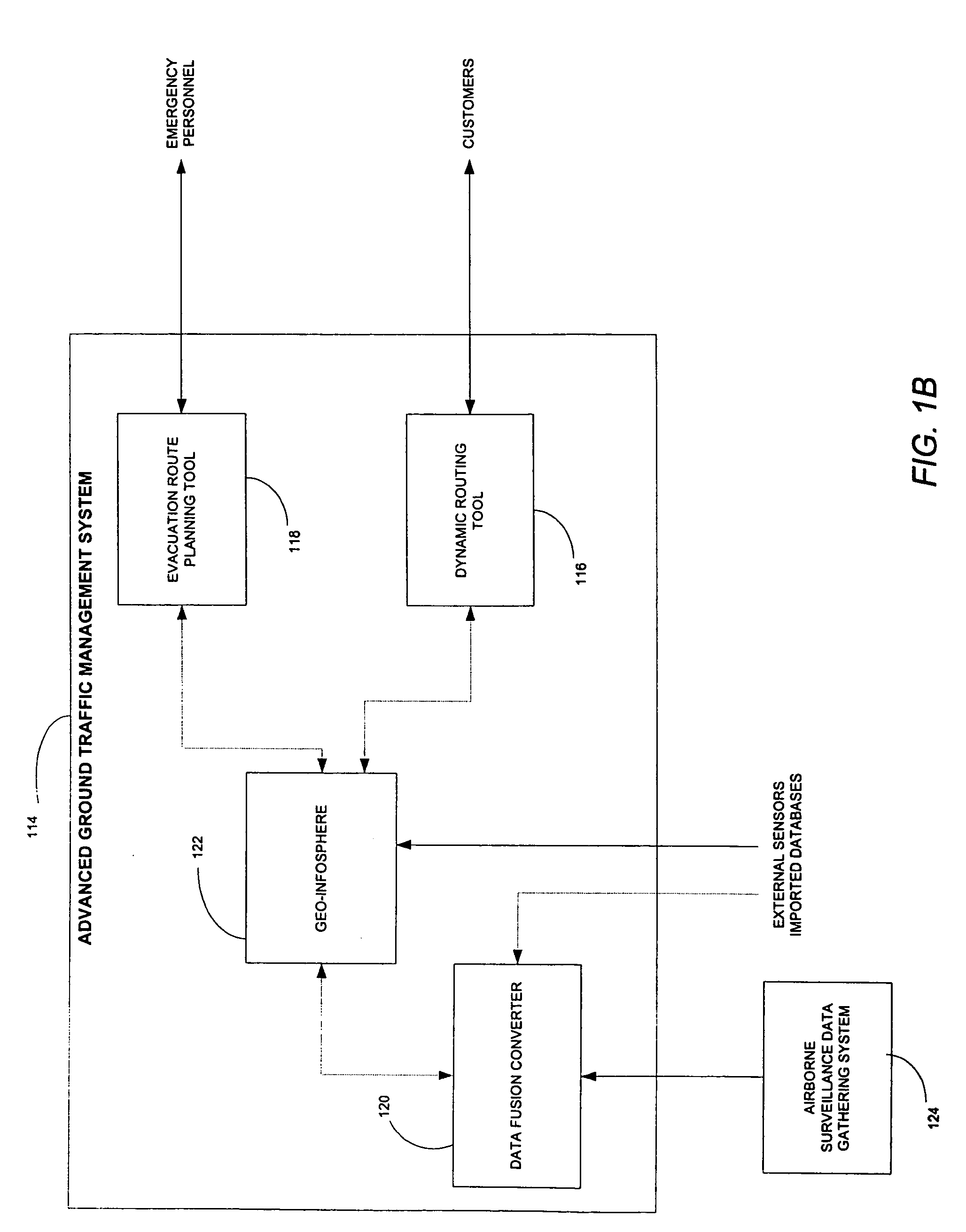
Evacuation route planning tool
InactiveUS7349768B2Maximizing traffic flowMinimize timeAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficEmergency encounterRoute planning
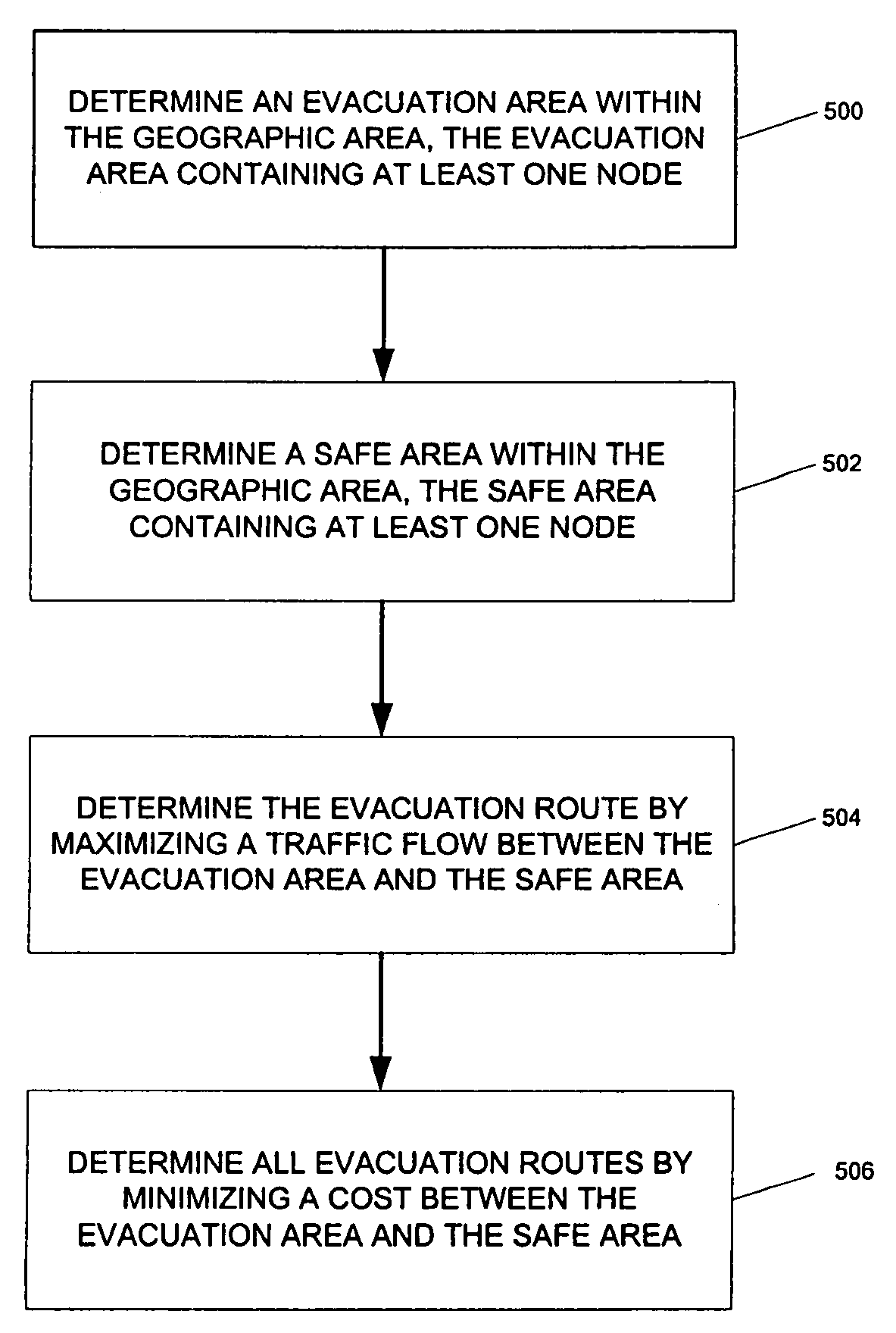
A GIS-based system that determines evacuation routes for specific areas requiring evacuation. Evacuation and safe areas are determined, and evacuation routes plotted, based on emergency-specific information as well as road flow and estimated time of travel for each section of road between the evacuation area and safe area. Routes, evacuation areas, and safe areas are dynamically calculated and recalculated based on additional data, either real-time, historical, or other data added to the system, to compute optimal initial routes and redirect evacuees if changes in the emergency situation occur.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
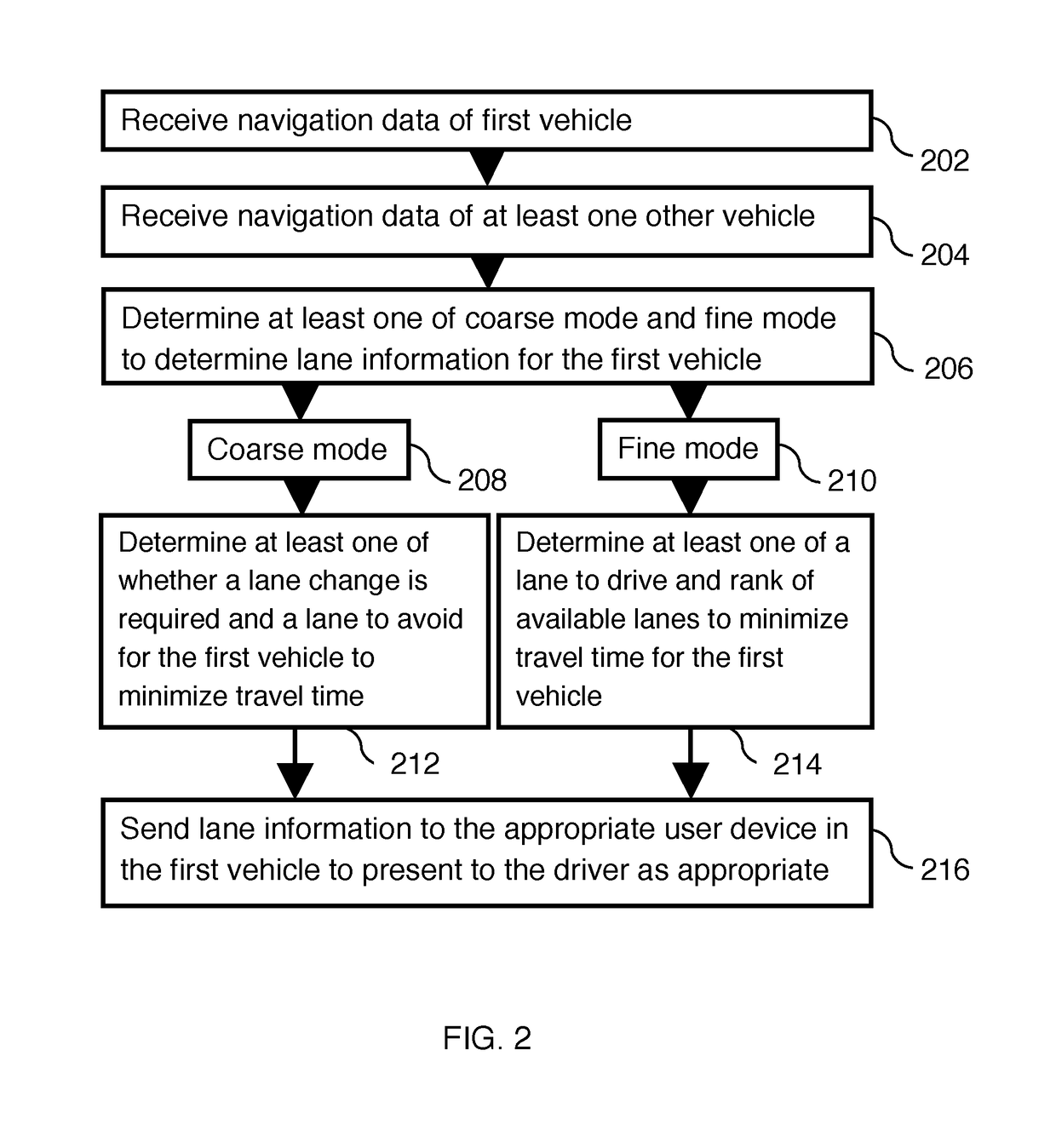
Traffic aware lane determination for human driver and autonomous vehicle driving system
ActiveUS9672734B1Minimize disruptionQuickly reachAnalogue computers for vehiclesParticular environment based servicesDriver/operatorUser device
A system, method, and computer program product for determining lane information in a road segment to drive a first vehicle to minimize travel time. According to an embodiment, navigation data of the first vehicle and at least one other vehicle in a road segment is sent to a computer server system via their respective clique leaders through a communication network. The lane information may include whether a change of lane is required, a lane to avoid, an optimum lane, and rank order of drivable lanes according to increasing order of travel time for the first vehicle to minimize travel time. The determined lane information is sent to the appropriate user device through its clique leader. The user device presents the lane information to a human driver and / or autonomous vehicle driving system of the first vehicle appropriately.
Owner:RATNASINGAM SIVALOGESWARAN
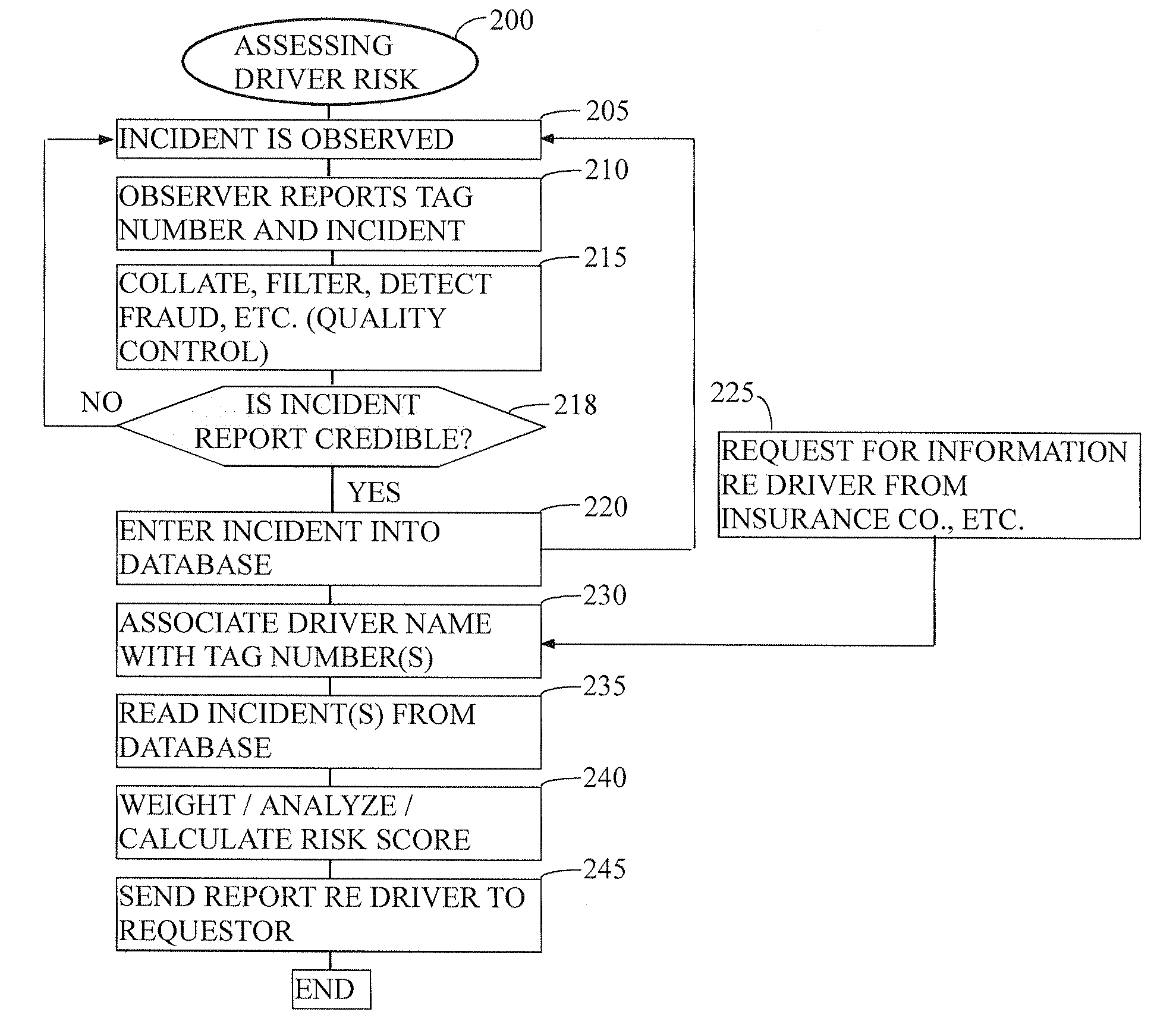
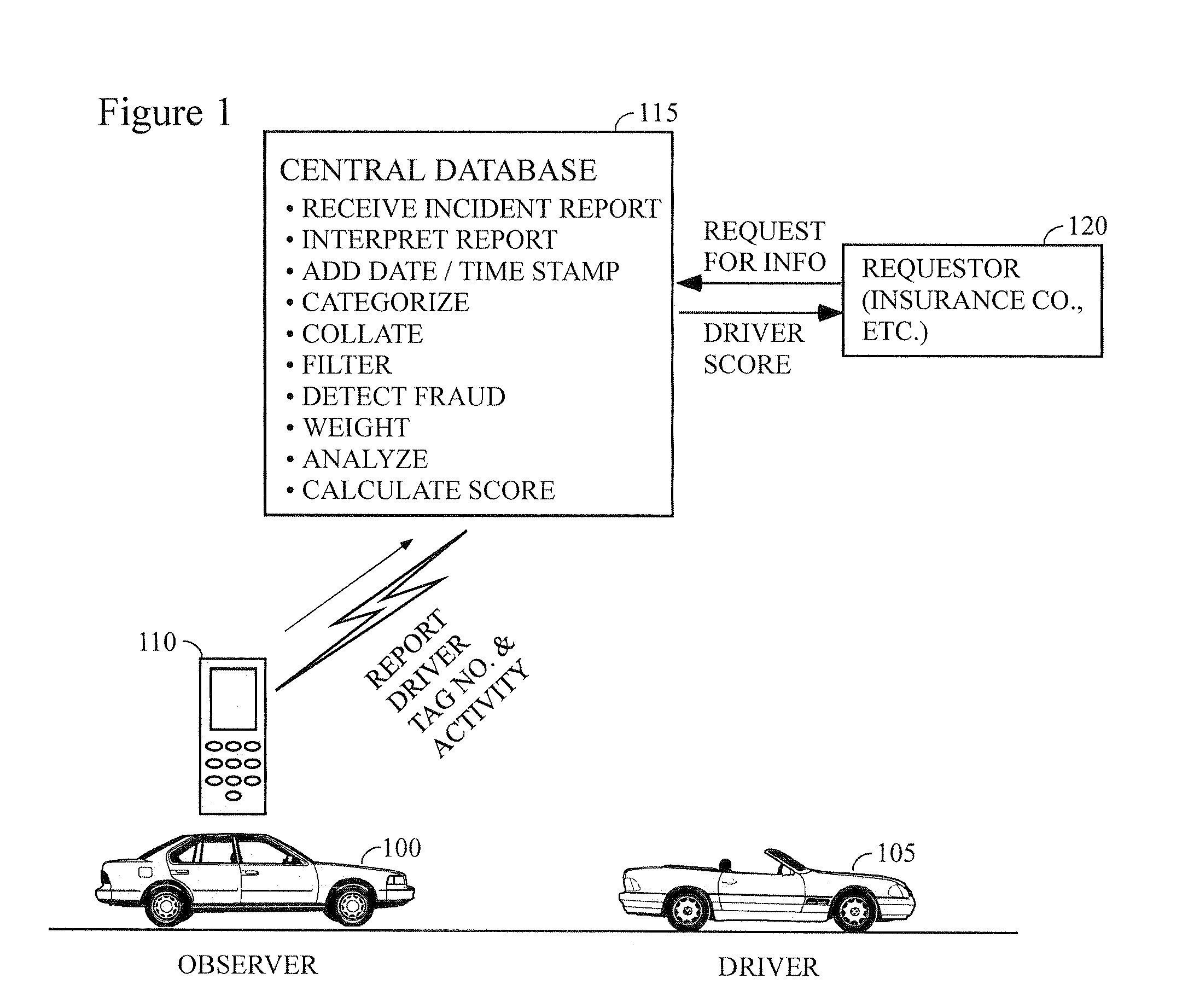
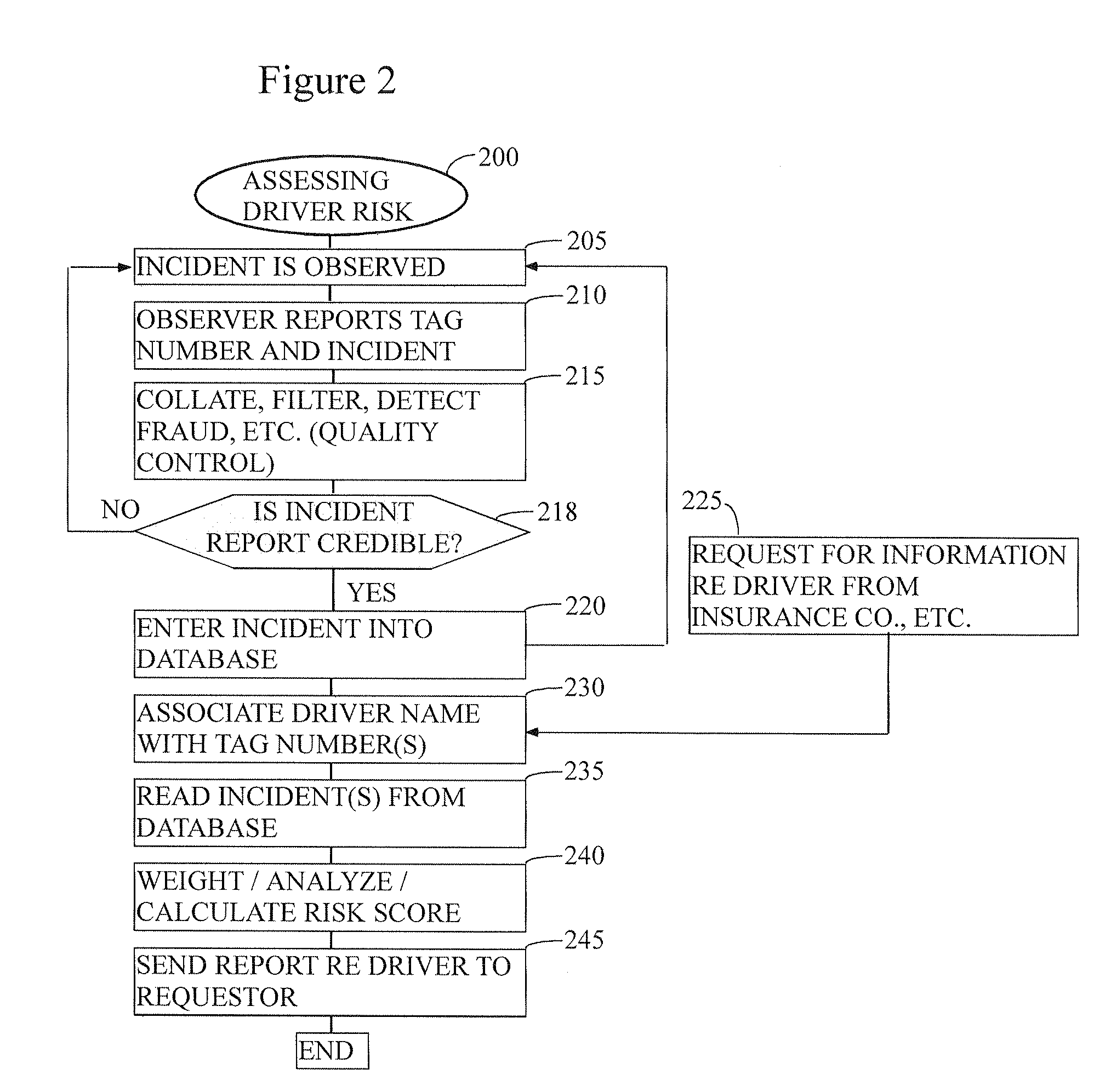
Method for ranking driver's relative risk based on reported driving incidents
InactiveUS20090132294A1Understand clearlyAnalogue computers for vehiclesFinanceDriver/operatorDriving risk
The present invention relates generally to the field of improvement in the driving risk assessment arts. More particularly, but not by way of limitation, the present invention generally relates to a method of rating the driving risks of individuals based on that driver's actual driving record as obtained from his or her fellow drivers.
Owner:HAINES SAMUEL H
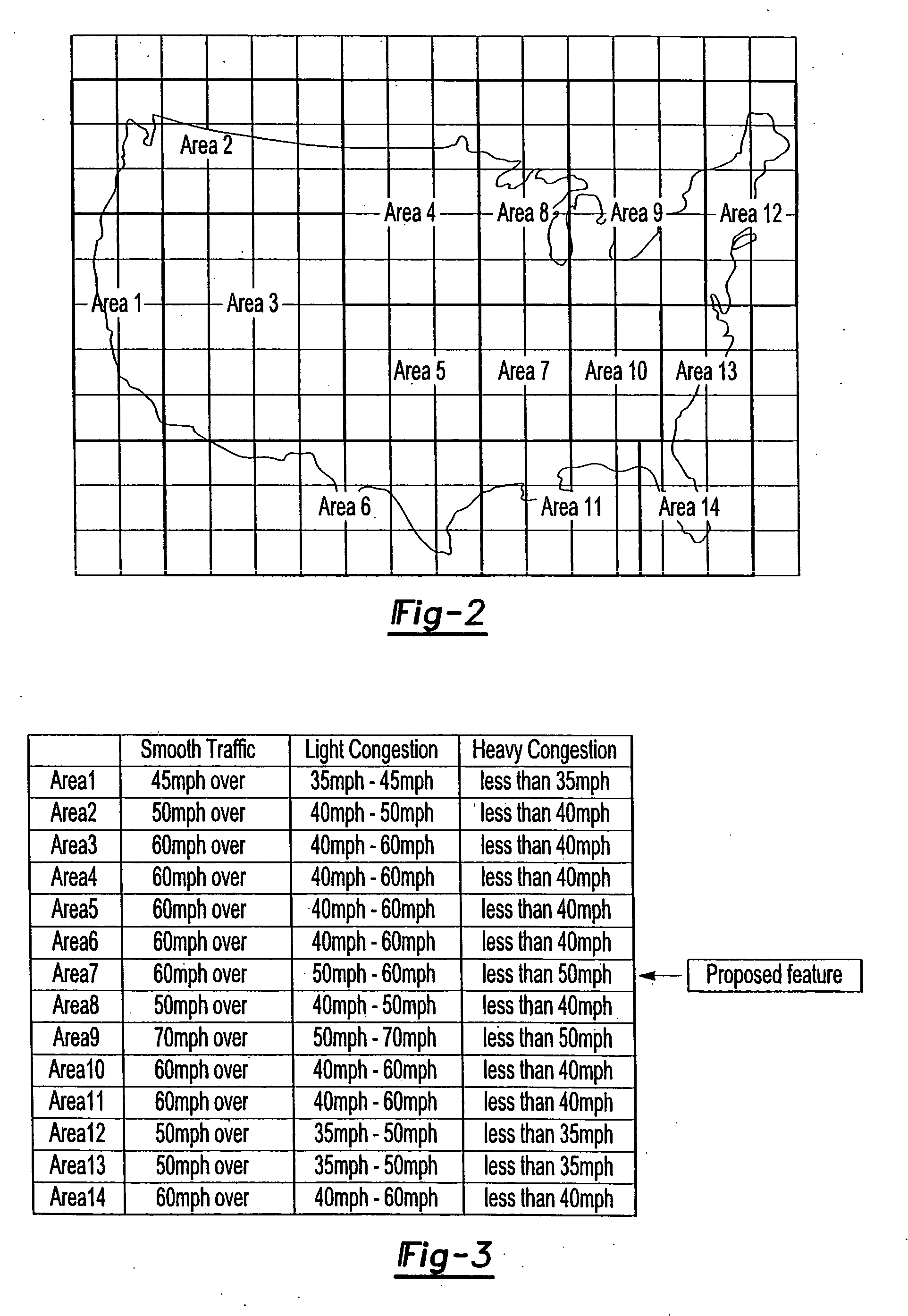
System and method for processing and displaying traffic information in an automotive navigation system
InactiveUS20060055565A1Analogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsDisplay deviceTraffic flow
A system and method for displaying traffic information in an automotive navigation system having a display, memory and a data receiver. The method includes the first step of storing in a traffic speed table in memory at least two speed threshold limits wherein each speed threshold limit represents a different traffic flow category. The receiver receives data representative of the vehicle speed on at least one road segment and compares that received vehicle speed data with the traffic speed table to determine the traffic flow category corresponding to the received speed data for the road segment. A visual indicator is then displayed on the display which corresponds to the traffic flow category for the road segment. The user is able to customize the speed threshold limits through a GUI. These speed threshold limits are further user modifiable as a function of weather, day of the week, road conditions, type of road, as well as other factors.
Owner:CLARION CO LTD
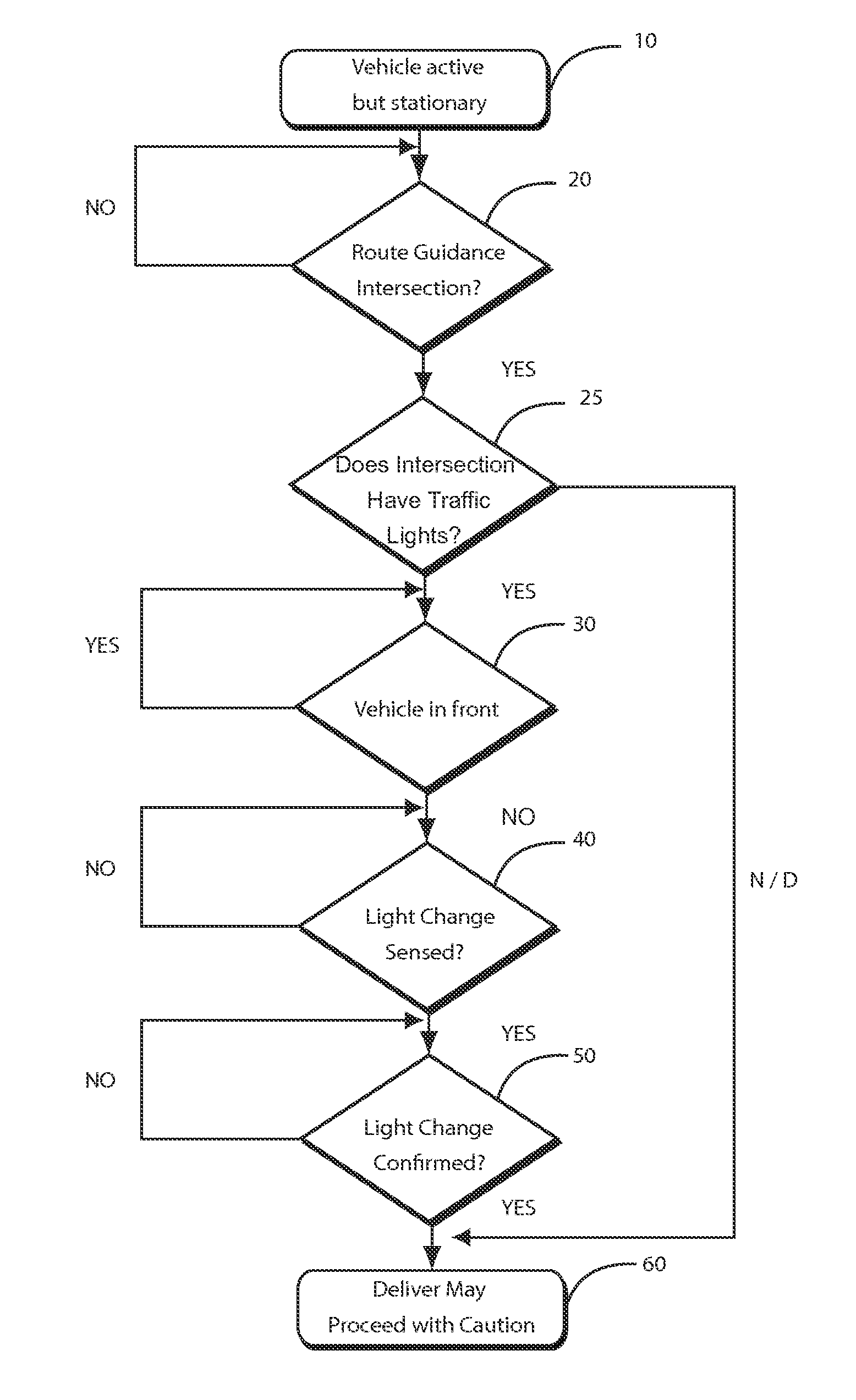
Method and apparatus to improve vehicle situational awareness at intersections
ActiveUS20090174573A1Improving vehicle situational awarenessEasy to seeAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsGuidance systemTraffic signal
The present invention includes a number of embodiments for improving vehicle situational awareness at intersections. A first embodiment may comprise a lens fitted at the top of the windshield or outside the vehicle, for refracting the light to the driver, so the driver may more easily see signals, signage and other features of an intersection, as well as other traffic. A second embodiment of the invention is used as an aid to prompt the driver that a light has changed. In a third embodiment, the light change sensor may be combined with other vehicle status information. As the car comes to a stop, the route guidance system may determine if the vehicle is at or in the vicinity of an intersection. Depending on the route guidance database, the system may also know whether or not there are traffic lights at the intersection. Using the vehicle's on board forward-looking radar sensor, the system may then determine if it is first in line at the intersection. In a fourth embodiment the system may be part of a portable after-market routing device. In a fifth embodiment the system, either portable or fixed, may be used to detect changes in the intensity of the brake lights of the vehicle ahead.
Owner:SMITH ALEXANDER E
System and method for alerting drivers to road conditions
System and method for warning drivers of changing road conditions is disclosed. In one embodiment road condition information is obtained for at least a portion of a route. The road condition information is analyzed to identify one or more significant features on the portion of the route. The driver is alerted to the one or more significant features.
Owner:IWI
System and method for alerting drivers to road conditions
System and method for warning drivers of changing road conditions is disclosed. In one embodiment road condition information is obtained for at least a portion of a route. The road condition information is analyzed to identify one or more significant features on the portion of the route. The driver is alerted to the one or more significant features.
Owner:IWI
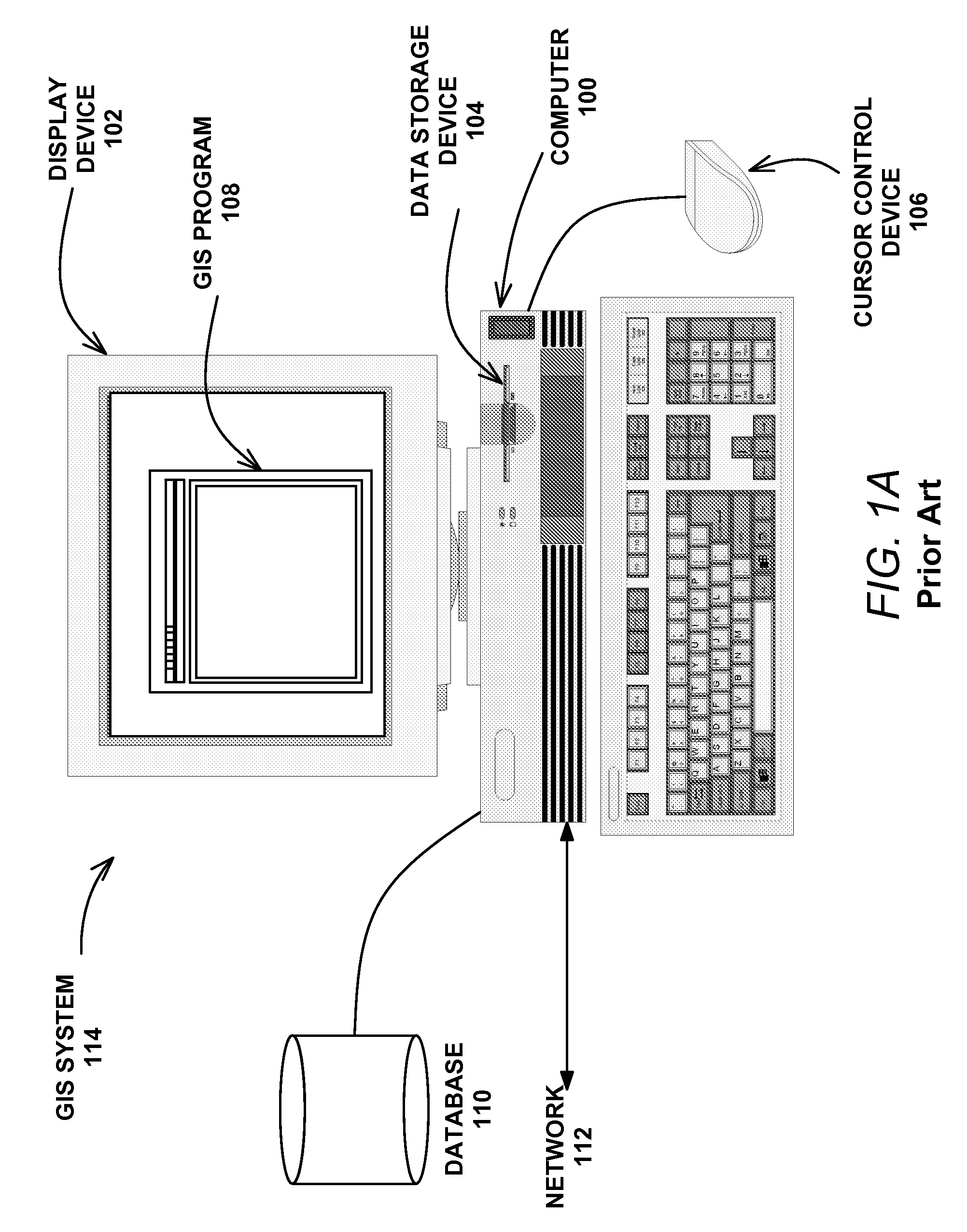
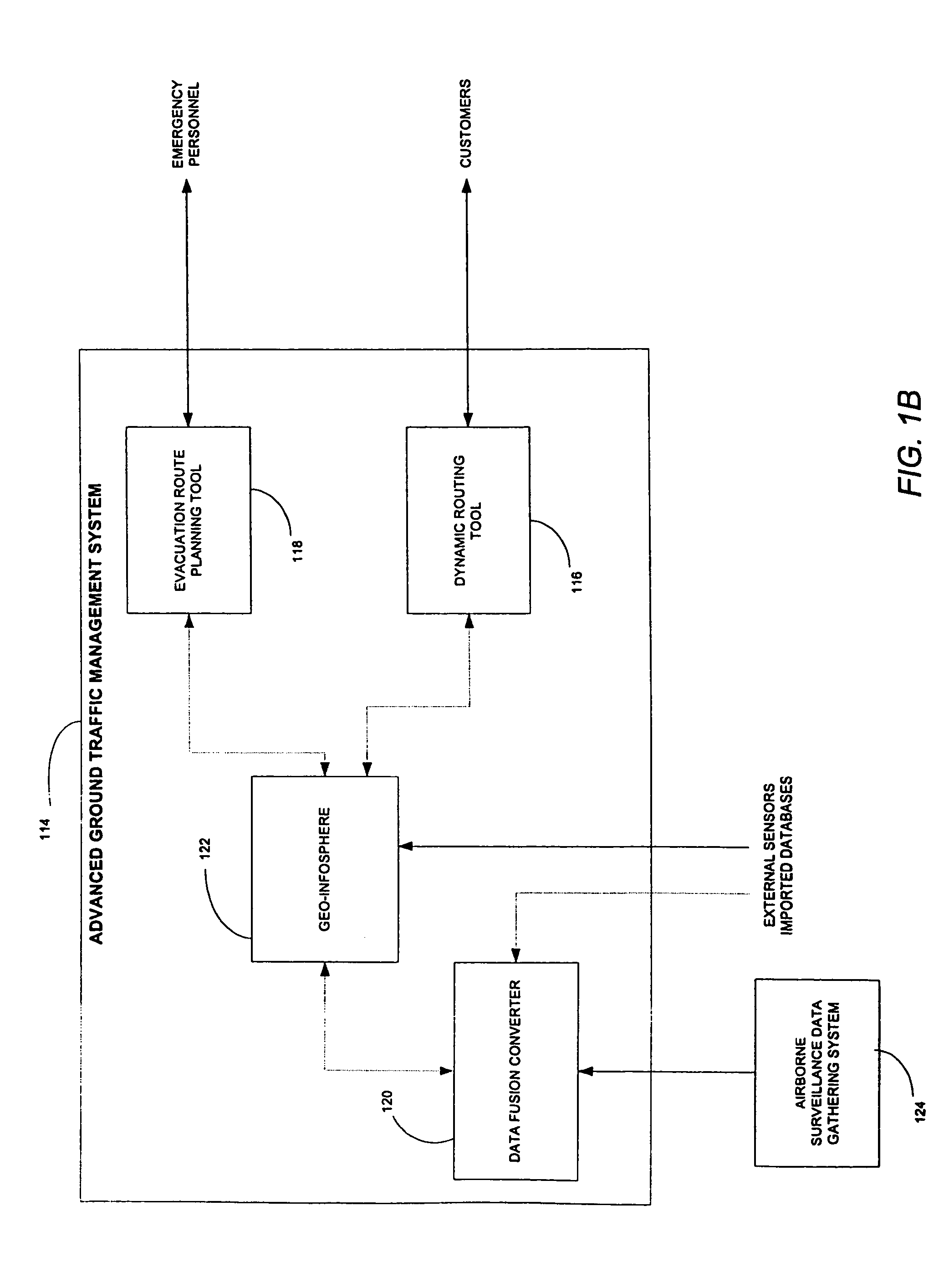
AGTM airborne surveillance
ActiveUS7650231B2Analogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationGeolocationAdaptive routing
Systems, methods and apparatuses for managing ground transportation in a geographical area are disclosed. A system for managing ground transportation in a geographical area in accordance with the present invention comprises at least one airborne surveillance platform, a graphical information systems (GIS) database, receiving information from the airborne surveillance platform, the GIS database storing data that represents the geographical area, the GIS database including at least one node representing at least one geographical location within the geographic area and at least one arc representing at least one street within the geographic area, and a routing tool, coupled to the GIS database, wherein the dynamic routing tool accepts data from the GIS database and determines a transportation route for at least one vehicle within the geographical area using at least the data from the GIS database and the information from the airborne surveillance platform.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
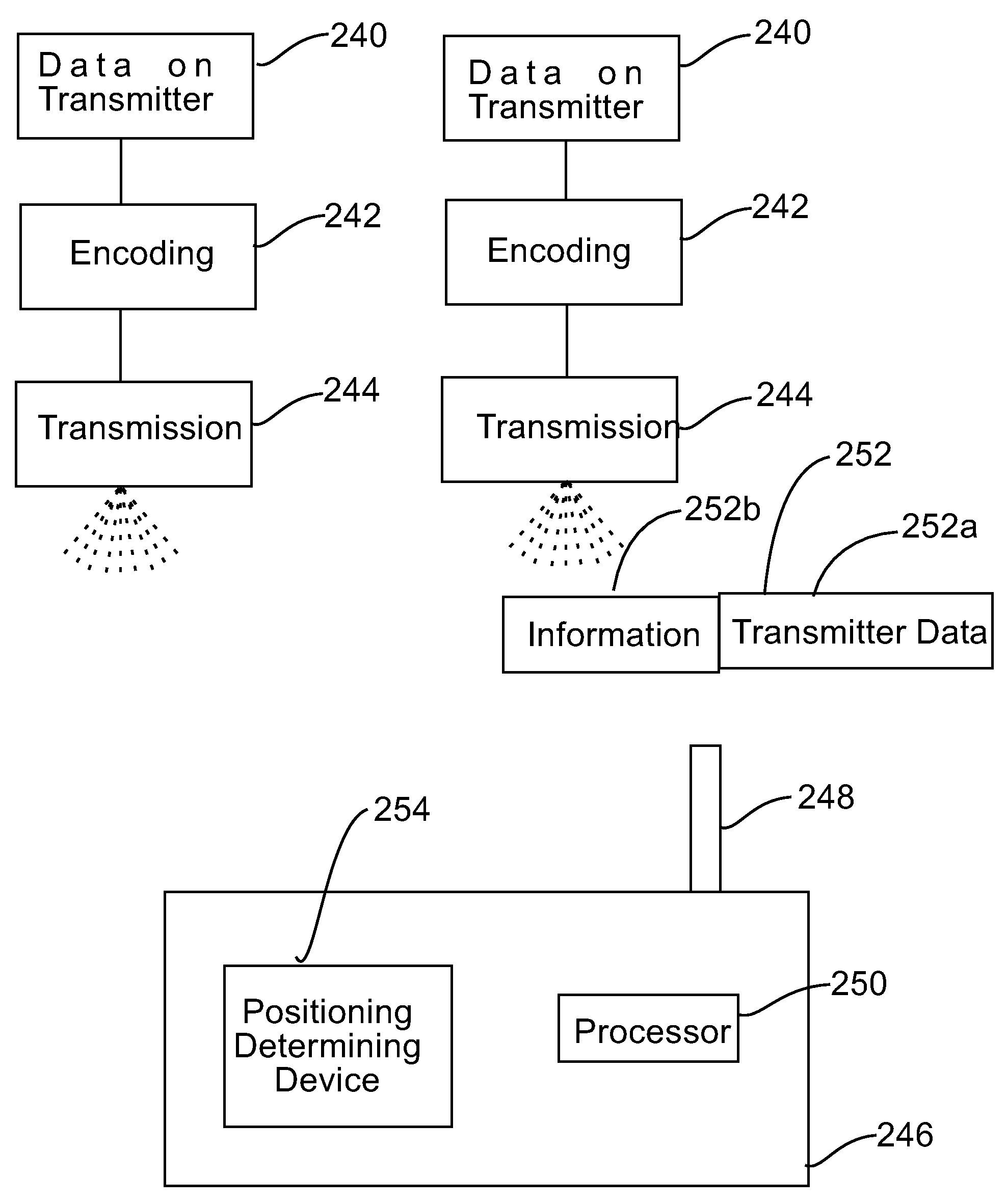
Collision avoidance methods and systems
InactiveUS7418346B2Avoid collisionAnalogue computers for vehiclesVehicle seatsEngineeringTransmitter
Method for avoiding collisions between a host vehicle and other vehicles in which the position of the vehicles is determined, the vehicles are equipped with a transmitter / receiver, and in the host vehicle, the possibility of a collision involving the host vehicle is assessed by receiving signals from the transmitter / receivers of each other vehicle, analyzing the received signals to extract positional information about the transmitter / receivers from each signal, and when a received signal contains additional information of interest about a possible collision involving the host vehicle, analyzing the extracted positional information to determine whether any signals contain additional information of interest about a possible collision involving the host vehicle. Additional information is extracted only from such signals and analyzed to ascertain whether a collision between the host vehicle and any other vehicles is likely to occur in order to enable action to be taken to prevent the collision, e.g., evasive action.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
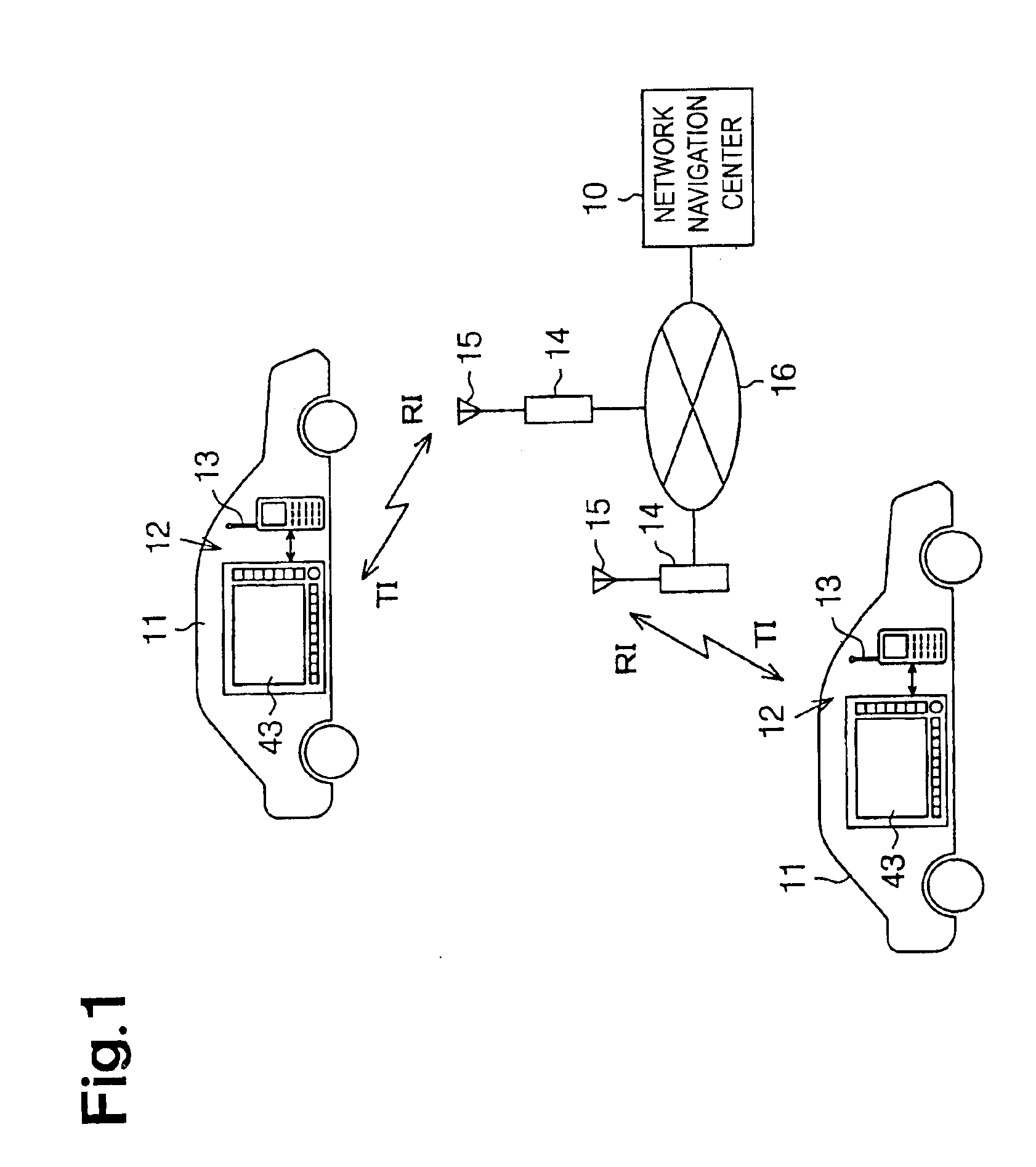
Traffic information retrieval method, traffic information retrieval system, mobile communication device, and network navigation center
InactiveUS6922629B2Easy to getAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationWeb navigationDisplay device
From a mobile communication device, road information about either a preliminarily registered point or an arbitrary point on a route from a present position to a destination is transmitted to and received in a network navigation center via a cellular phone base station and a general telephone network. Based on that road information, the network navigation center retrieves traffic information about the registered point or the arbitrary point on the route, and then transmits the retrieved traffic information to the mobile communication device via the general telephone network and the cellular phone base station. The traffic information includes traffic congestion area data about the registered point or the arbitrary point on the route, which is displayed on a display in the mobile communication device wherein the user is informed of future traffic information like traffic congestion.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
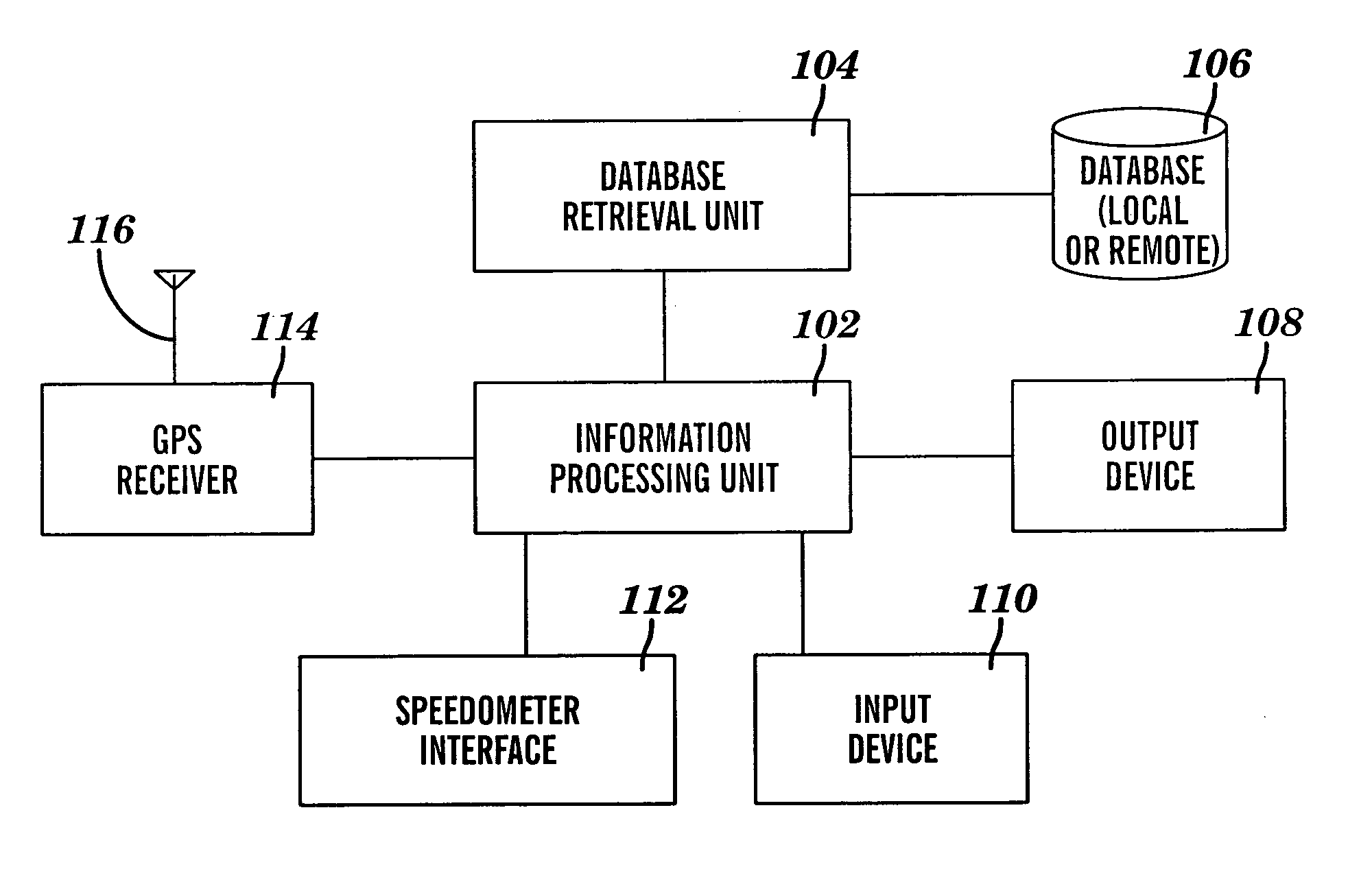
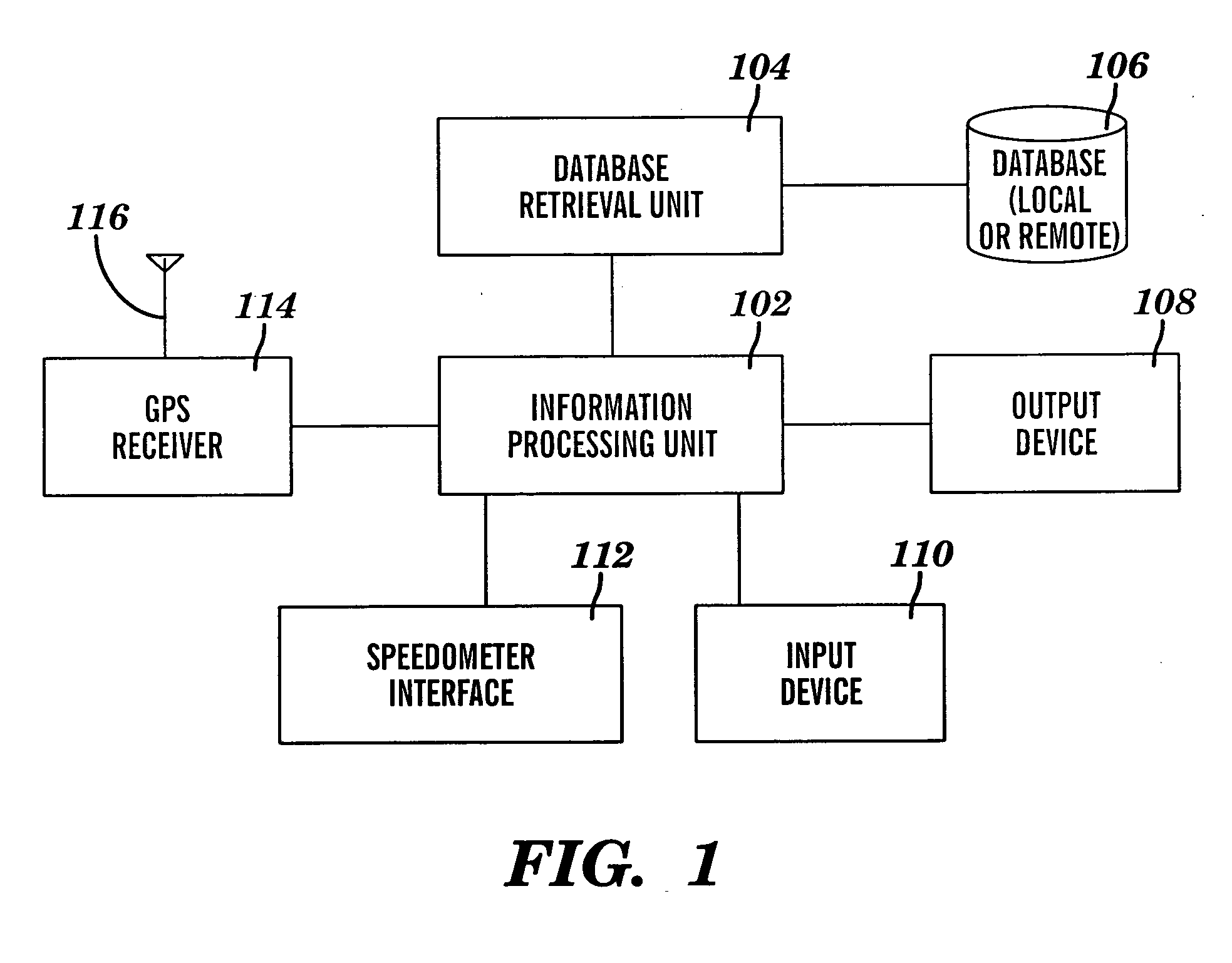
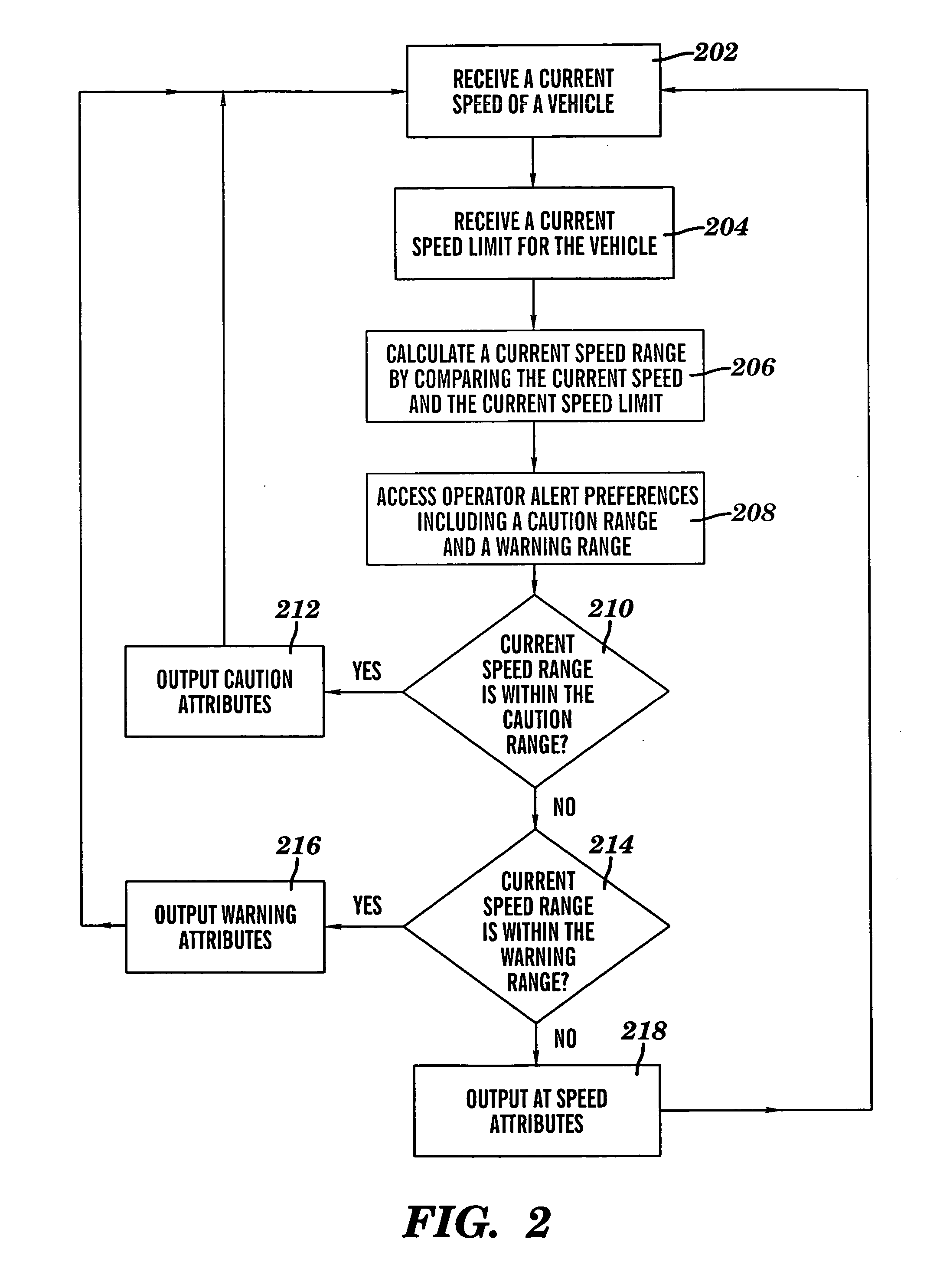
Vehicle speed monitoring system
A method for monitoring vehicle speed is provided. The method includes receiving a current speed of a vehicle and a current speed limit associated with a current location of the vehicle. A current speed range is calculated by comparing the current speed of the vehicle to the current speed limit. Operator alert preferences including a caution range and a warning range are accessed. An alert responsive to the current speed range and to the operator alert preferences is communicated to the operator of the vehicle. The alert includes one or more caution attributes when the current speed range of the vehicle is within the caution range. The alert includes one or more warning attributes when the current speed range of the vehicle is within the warning range. The alert includes one or more at speed attributes when the current speed range of the vehicle is not within the caution range or the warning range.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
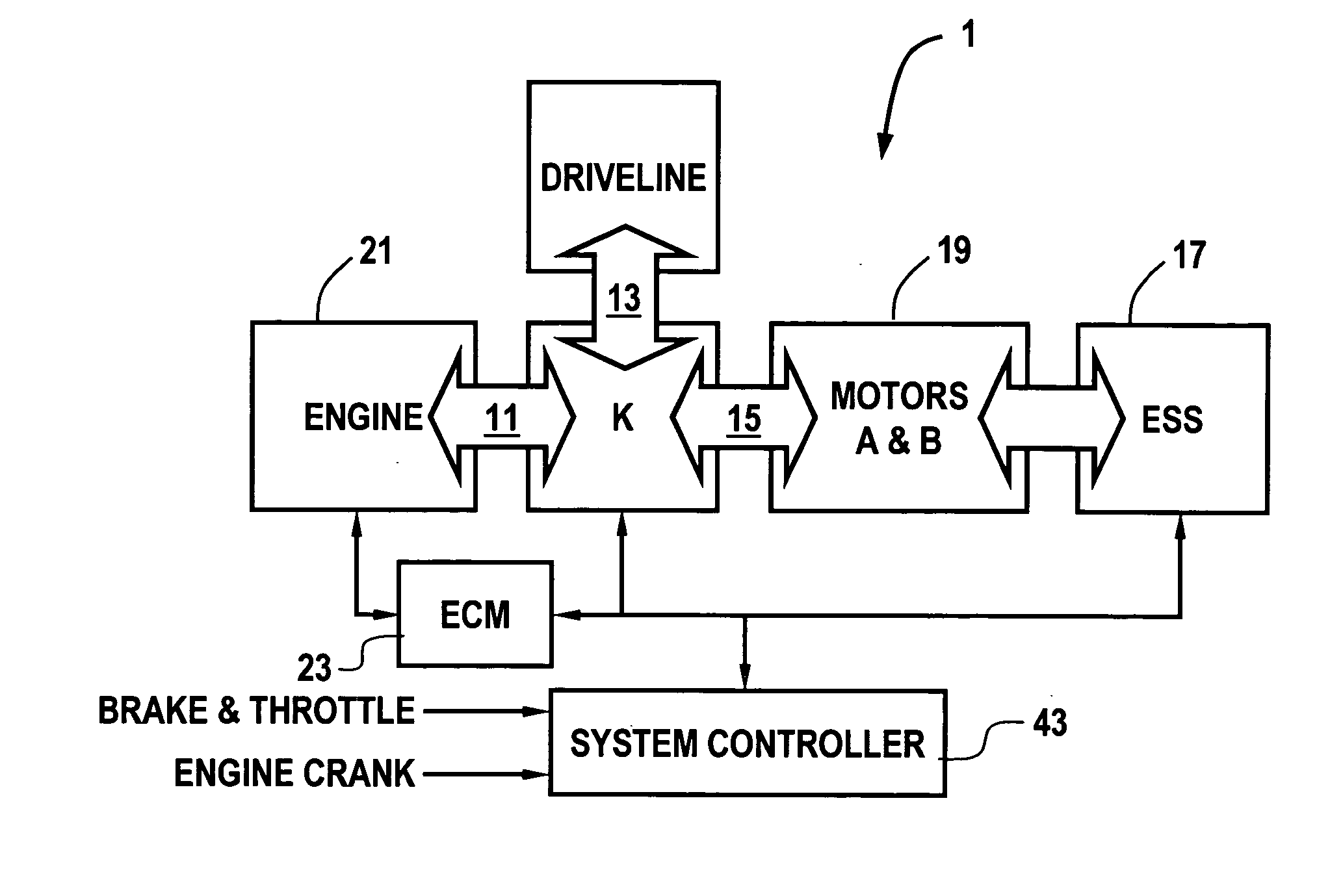
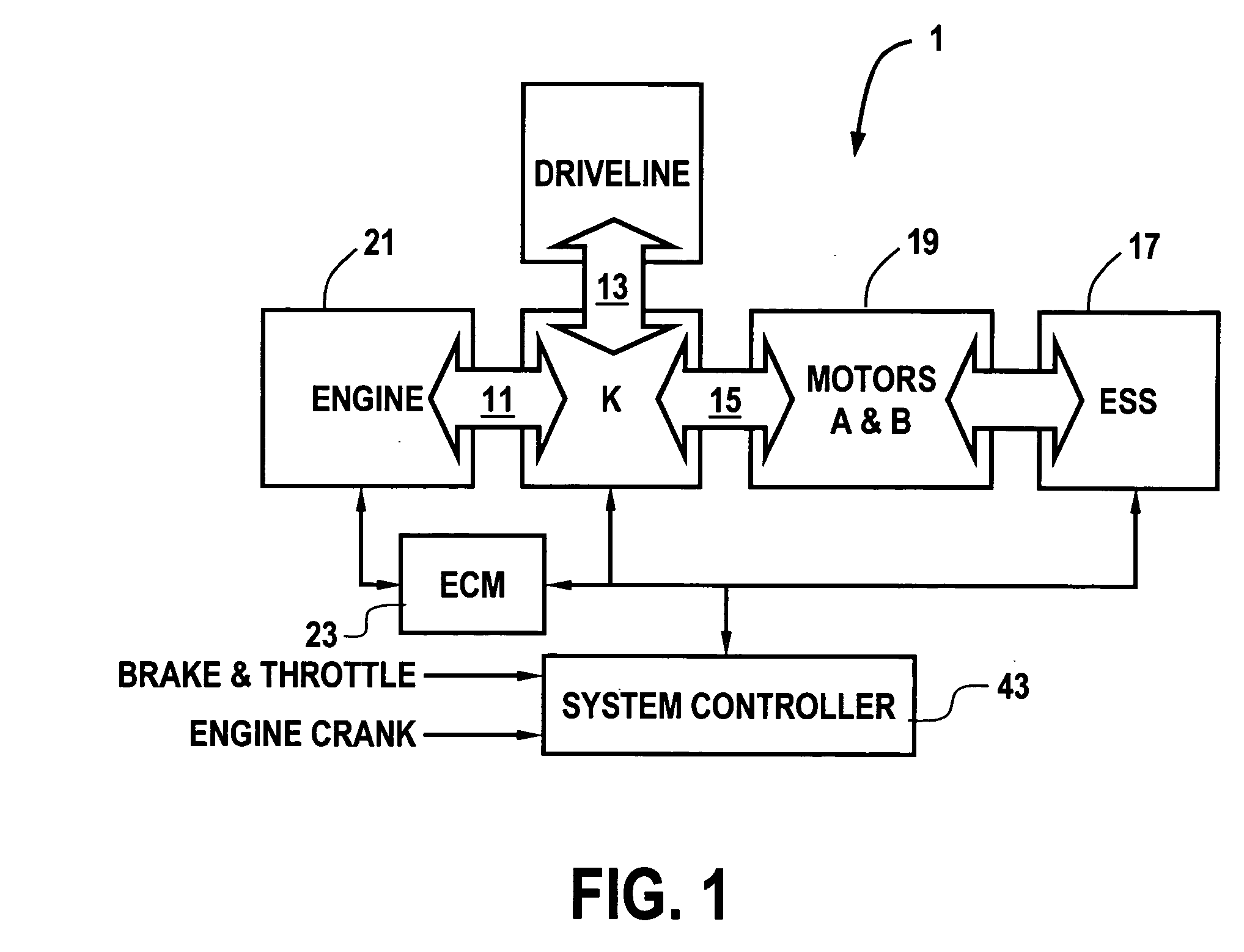
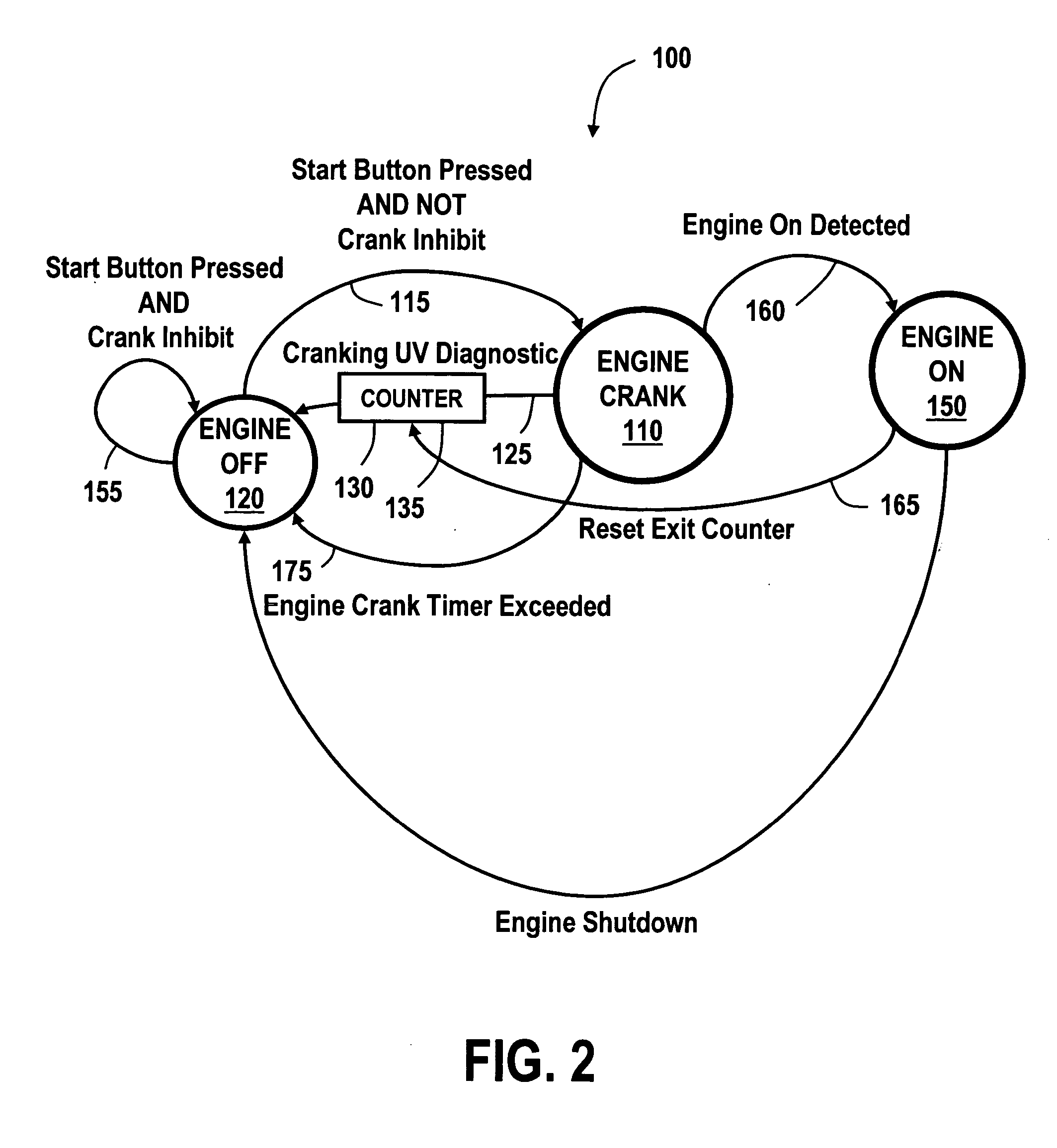
Method of undervoltage protection during engine cranking
ActiveUS20050256617A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove protectionHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectric machineEngineering
A method for controlling the cranking of an engine of a vehicle powertrain system having a rechargeable energy storage system that is adapted to provide electric power to an electric machine, wherein the system is adapted to exit from the engine crank state as a function of an output voltage of the energy storage system to the electric machine during the crank state, if the output voltage is less than a crank undervoltage threshold for a predetermined crank time. According to the method, the crank undervoltage threshold is a function of the number of failed start attempts, generally decreasing as a function of the number of failed start attempts. The predetermined crank time is a function of a magnitude of a difference between the output voltage and the crank undervoltage threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
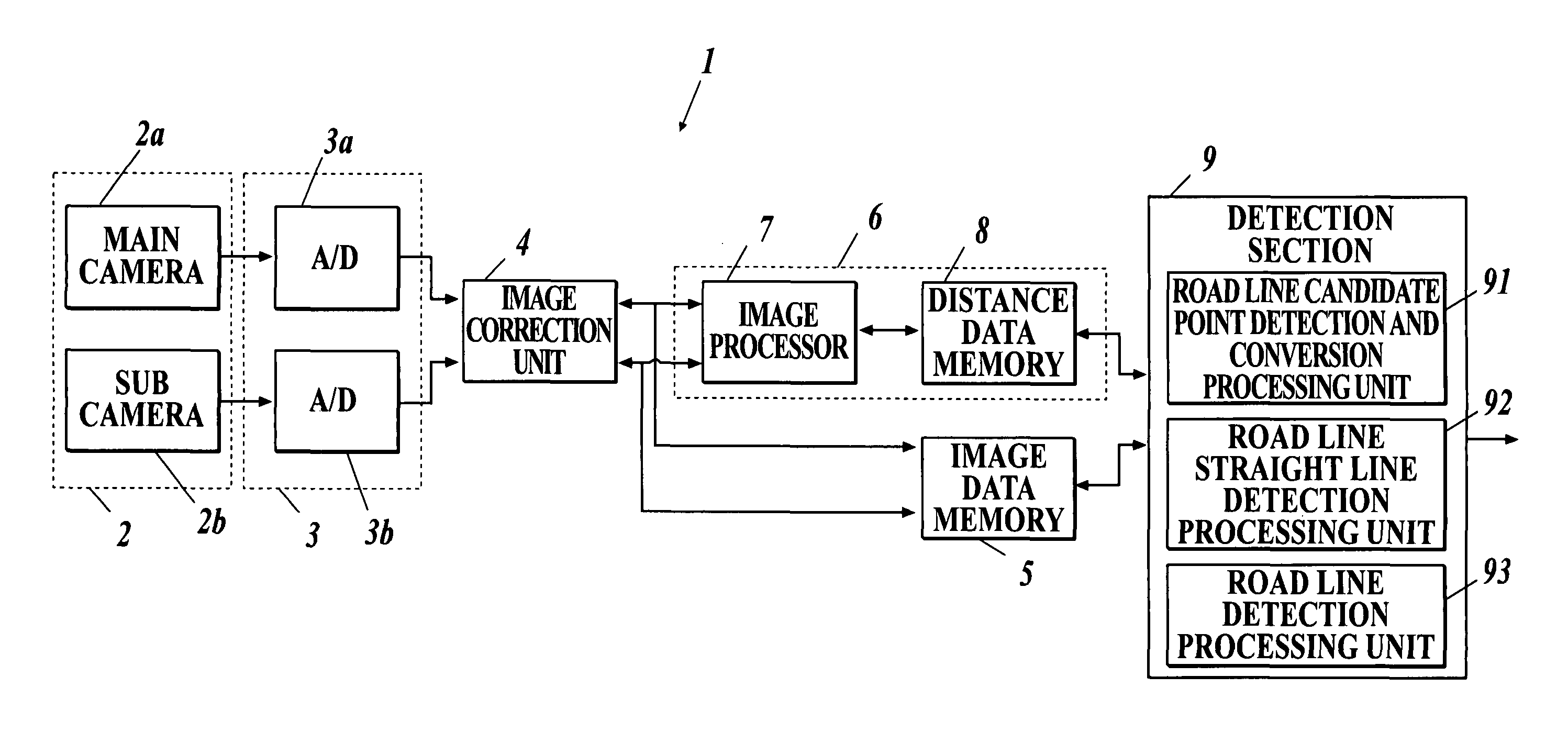
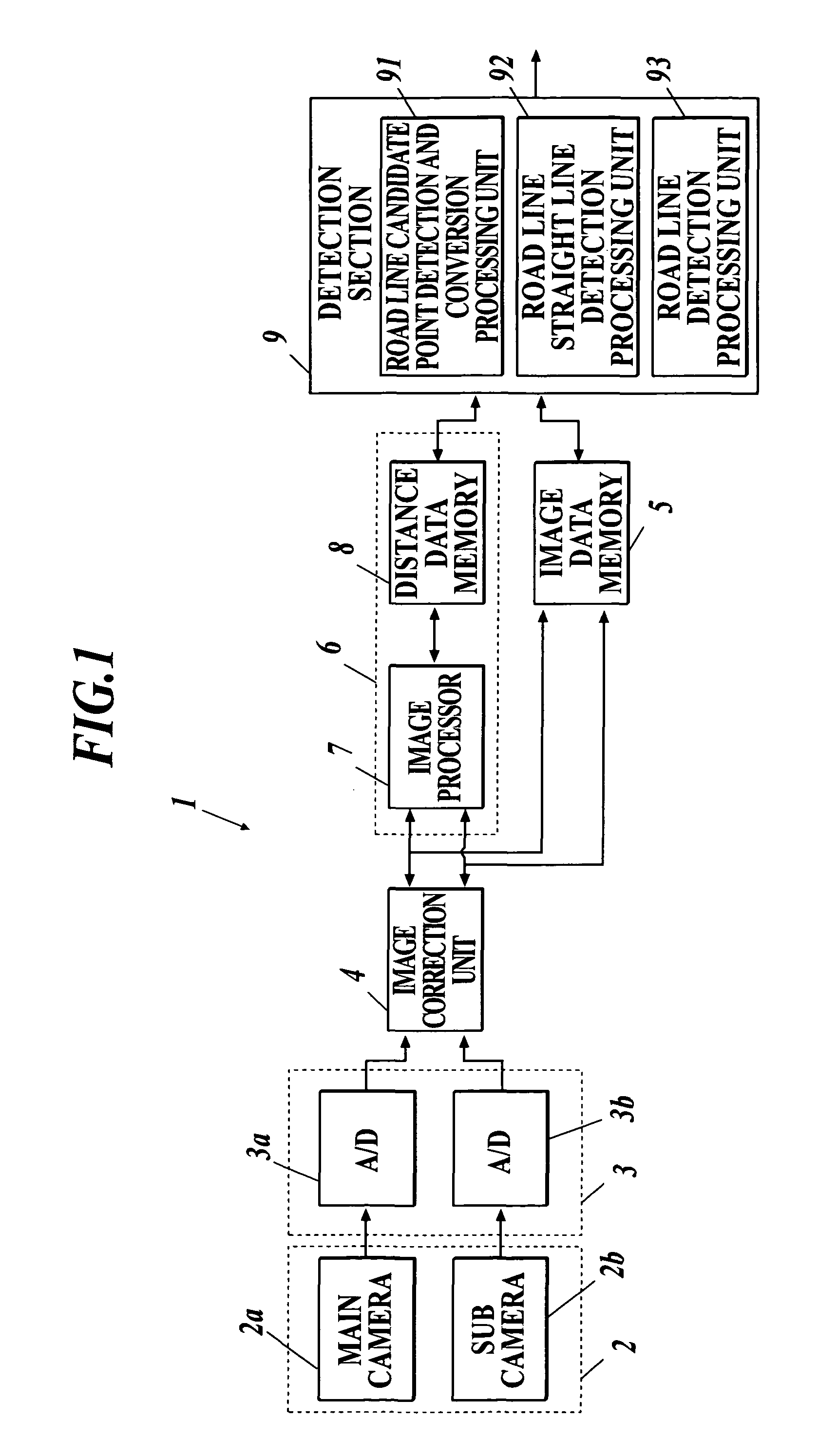
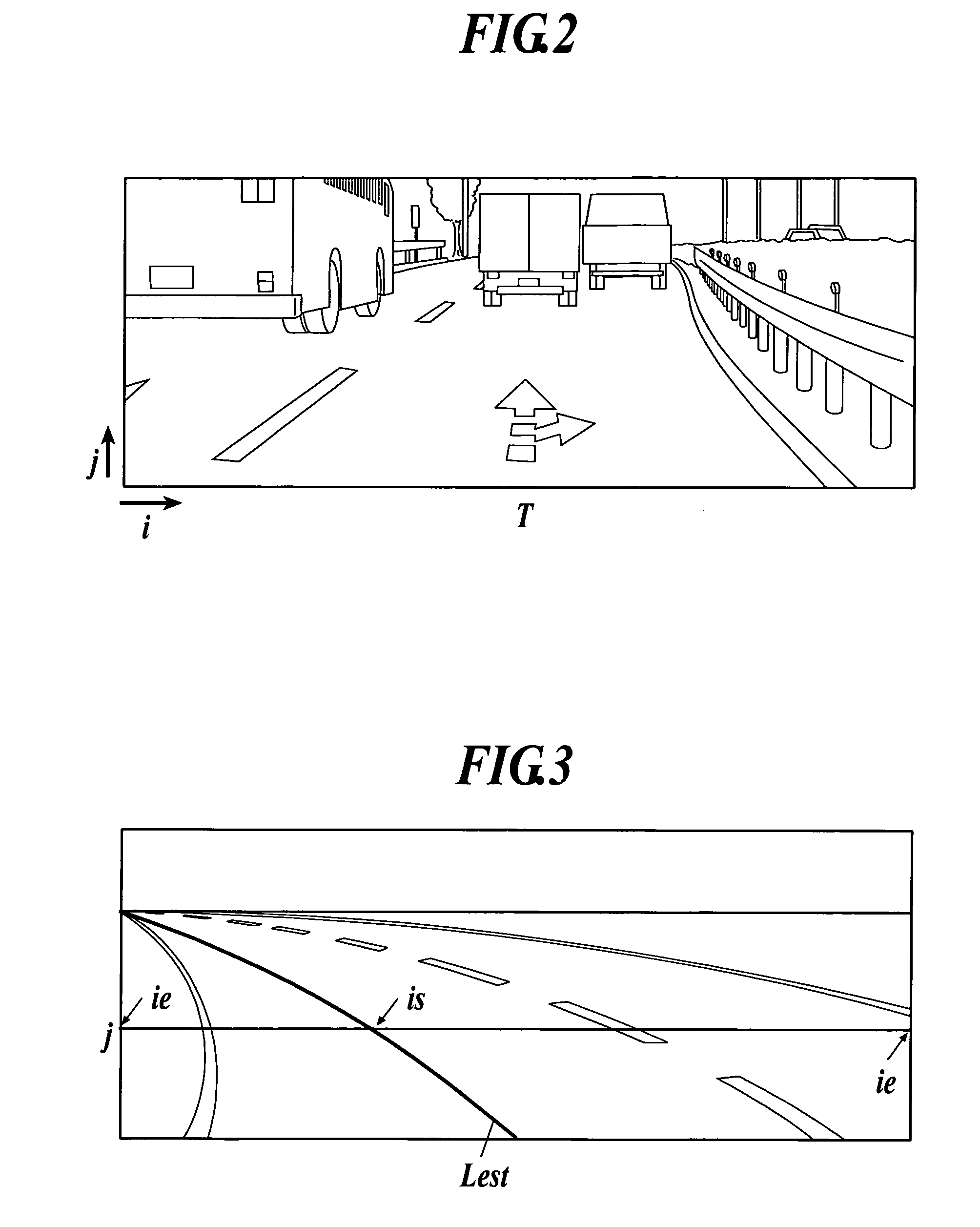
Road line recognition apparatus
ActiveUS8224031B2Stable detectionAccurate detectionAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficImaging processingRoad surface
A road line recognition apparatus, including: an imaging section imaging a progress path of a own vehicle including a road to output a couple of images; an image processing section calculating a distance in a real space in a set region of at least an image on one side based on the imaged couple of images; and a detection section detecting a road line; wherein the detection section includes: a road line candidate point detection and conversion processing unit detecting a pixel on a road surface as a road line candidate point based on luminance and the distance with regard to the image on one side, and performing Hough conversion of the road line candidate point; a road line straight line detection processing unit detecting one straight line proper to the road line on each of a right side and a left side of the own vehicle based on at least a position or a behavior of the own vehicle between straight lines obtained by the Hough conversion; and a road line detection processing unit detecting the road line of a shape of a straight line or a curved line by recording a road line position which is a road line candidate point indicating a road line among the road line candidate points based on the detected straight line.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com