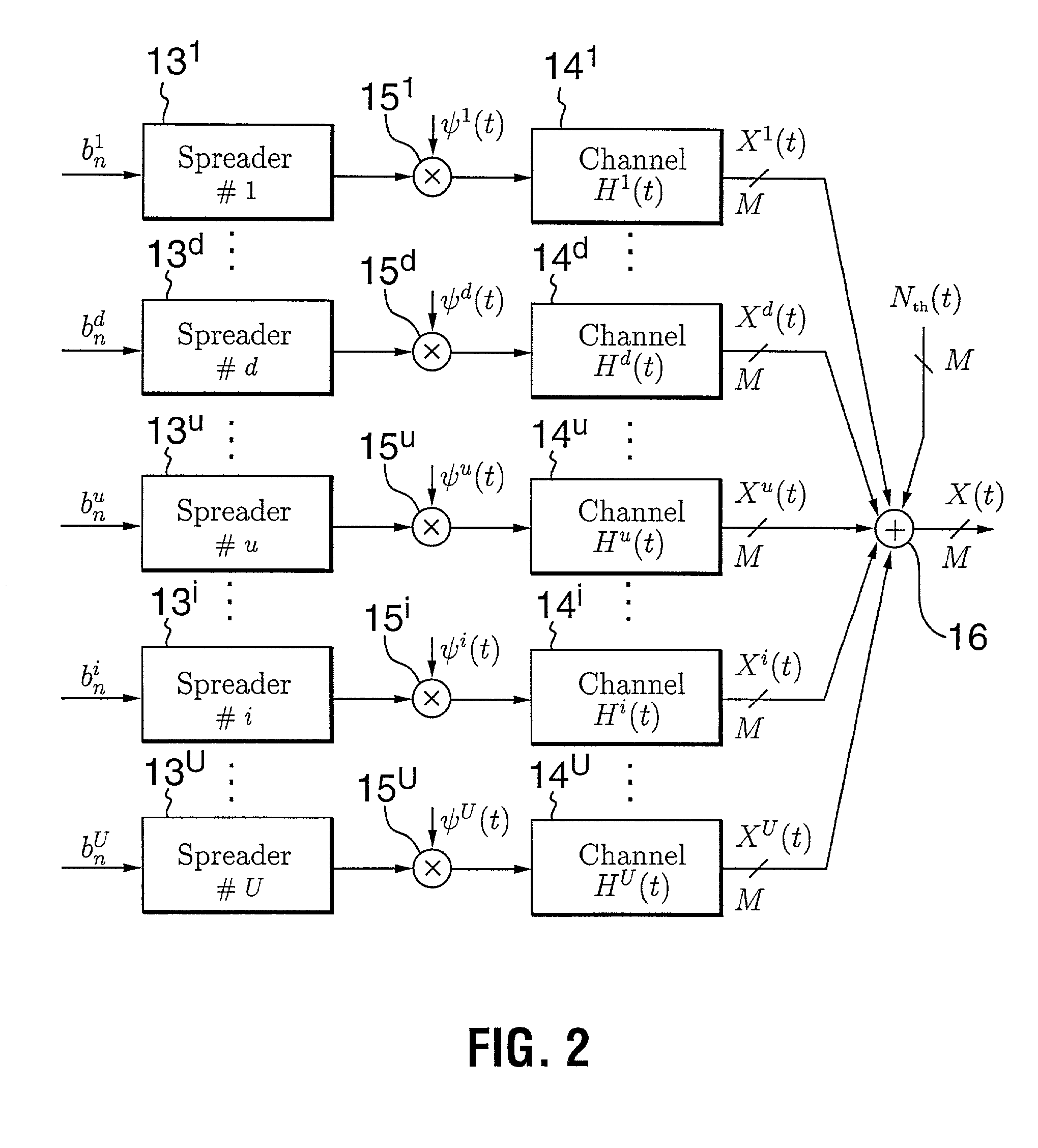
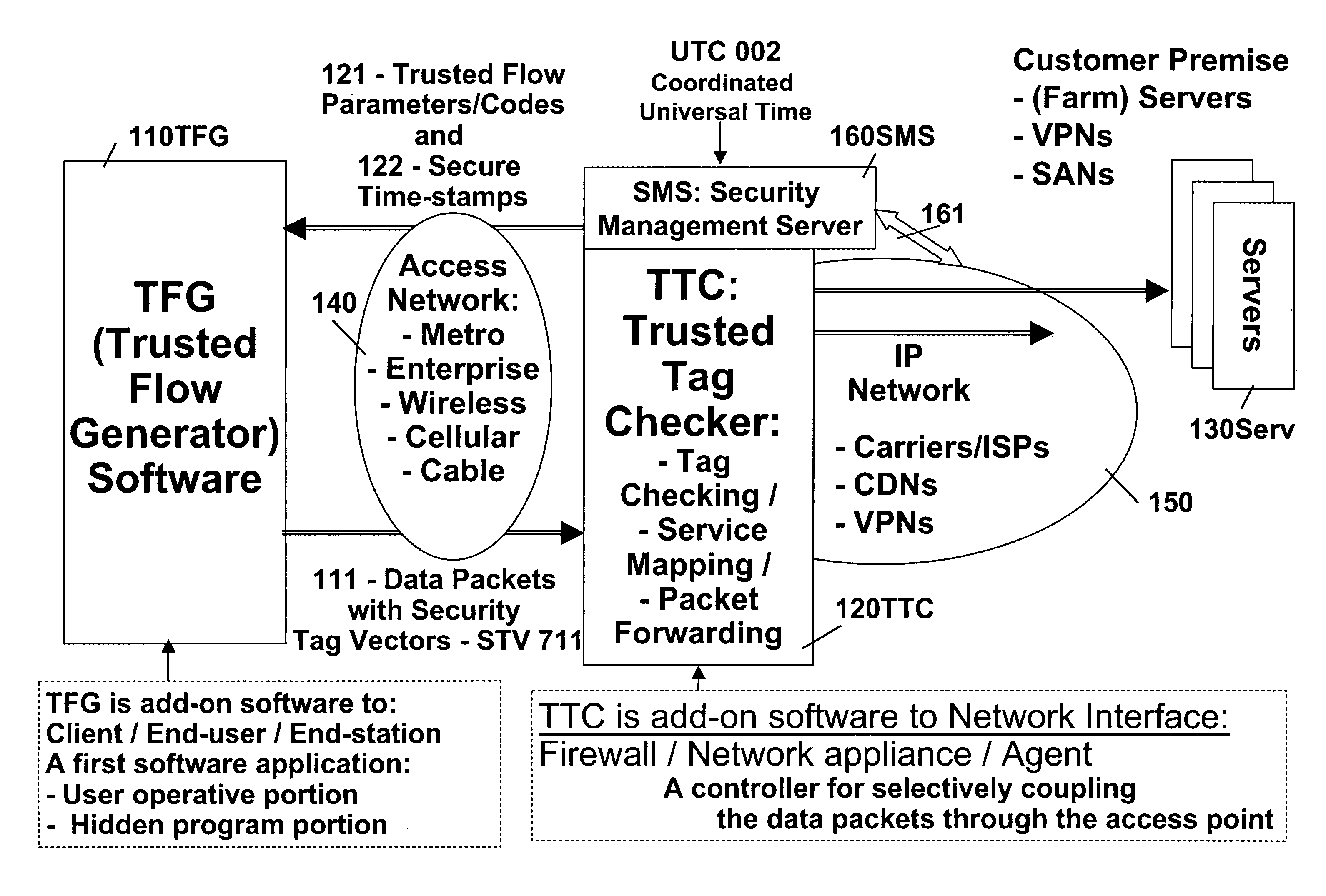
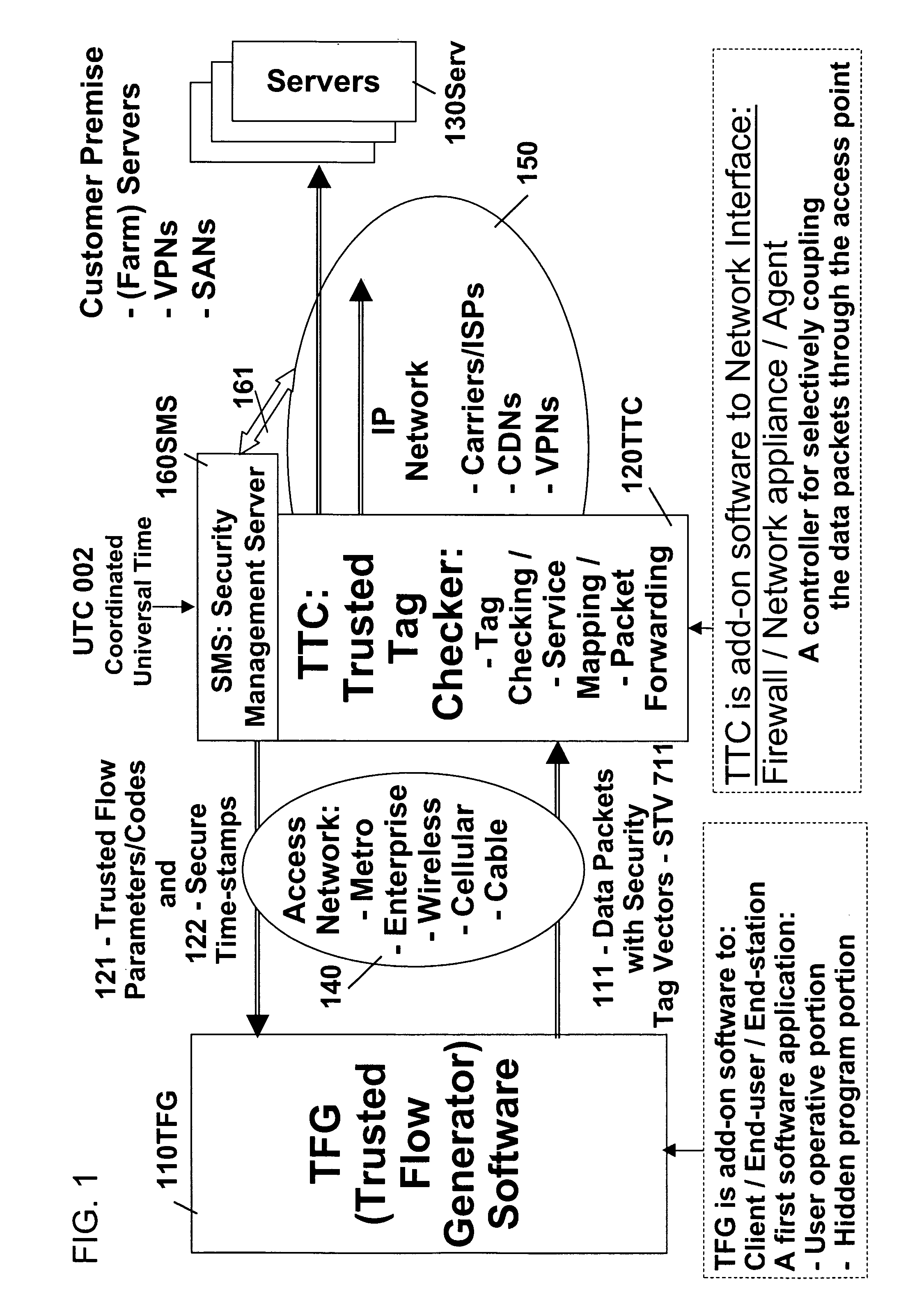
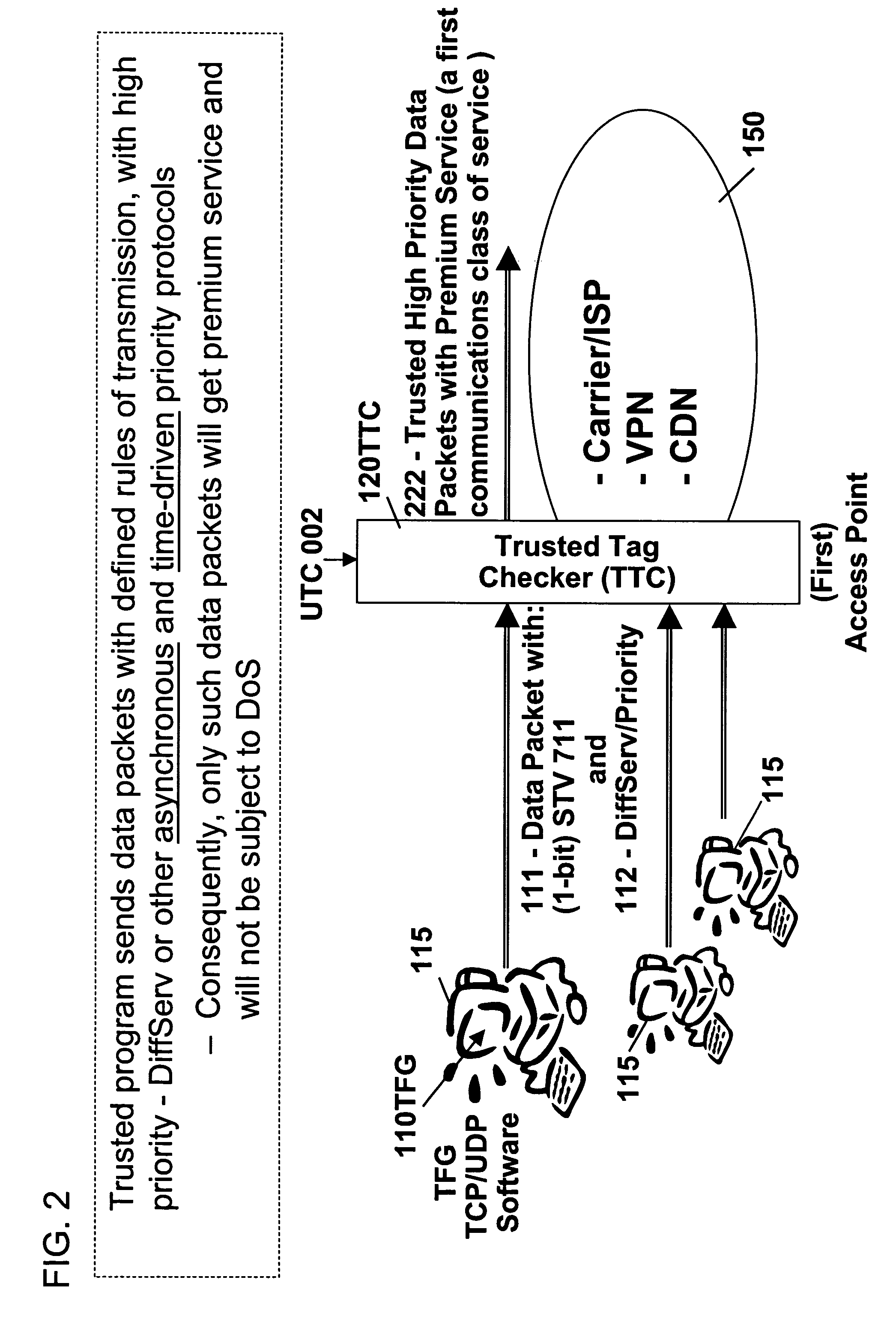
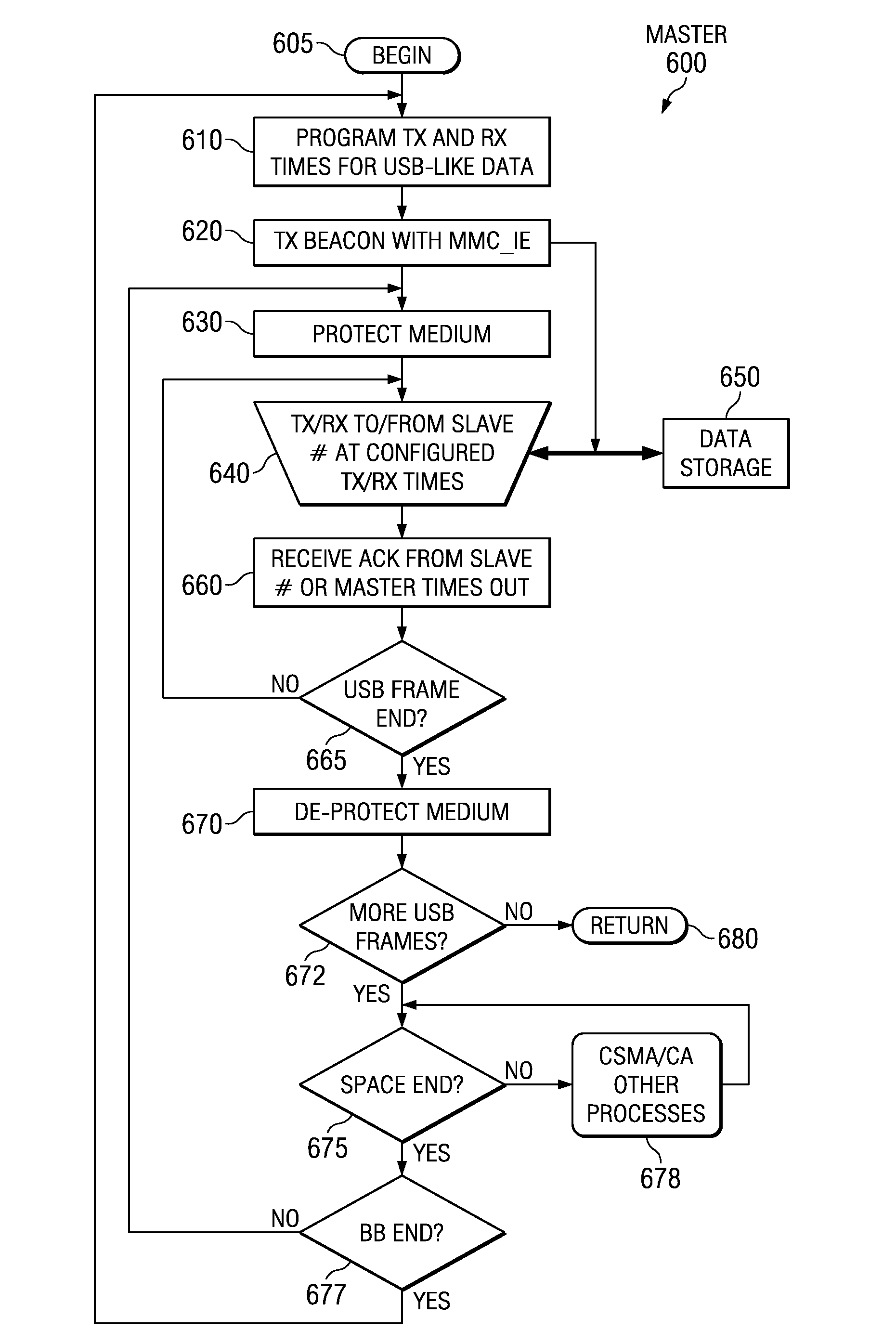
Patents
Literature
6275 results about "Station" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
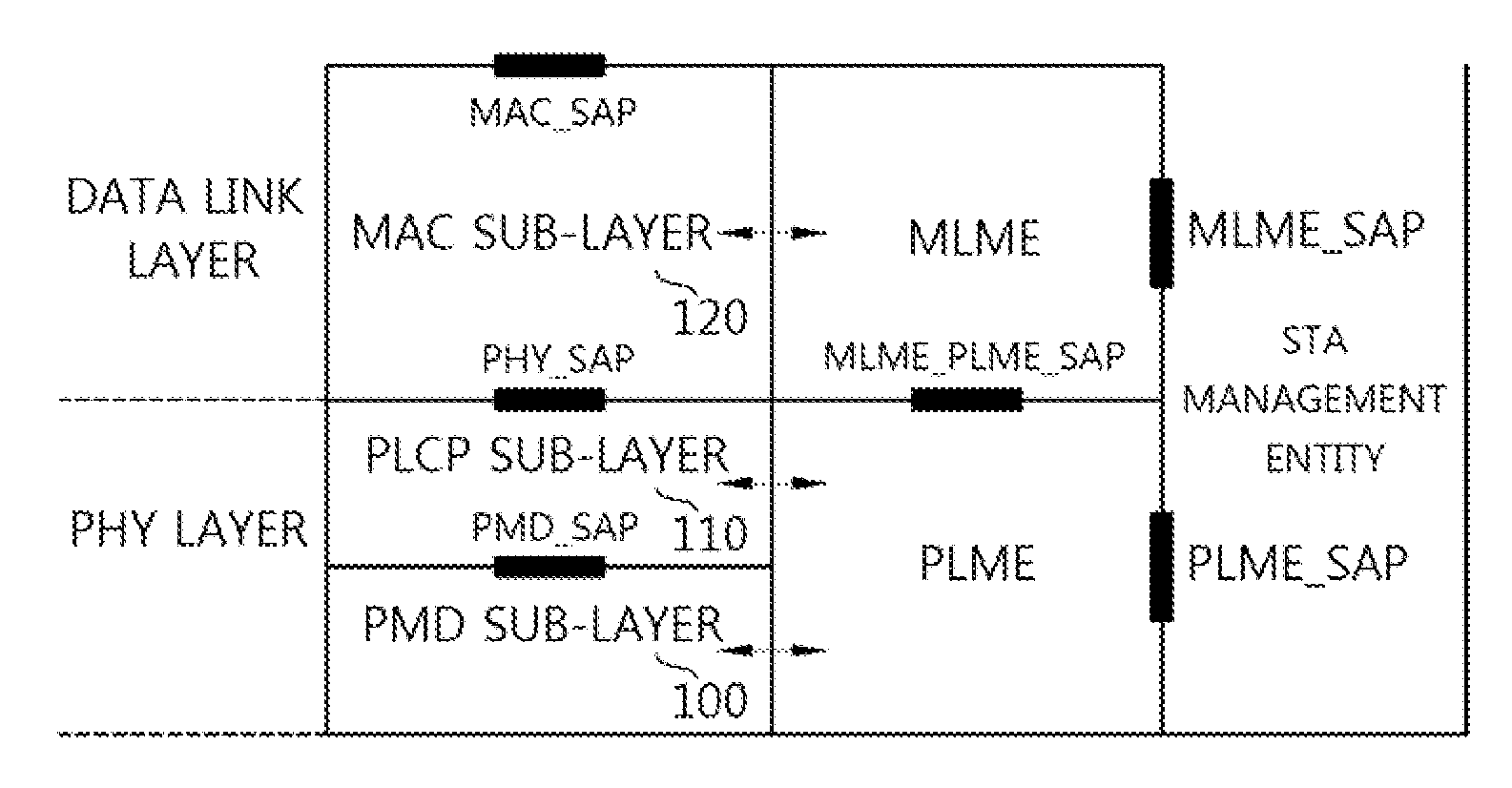
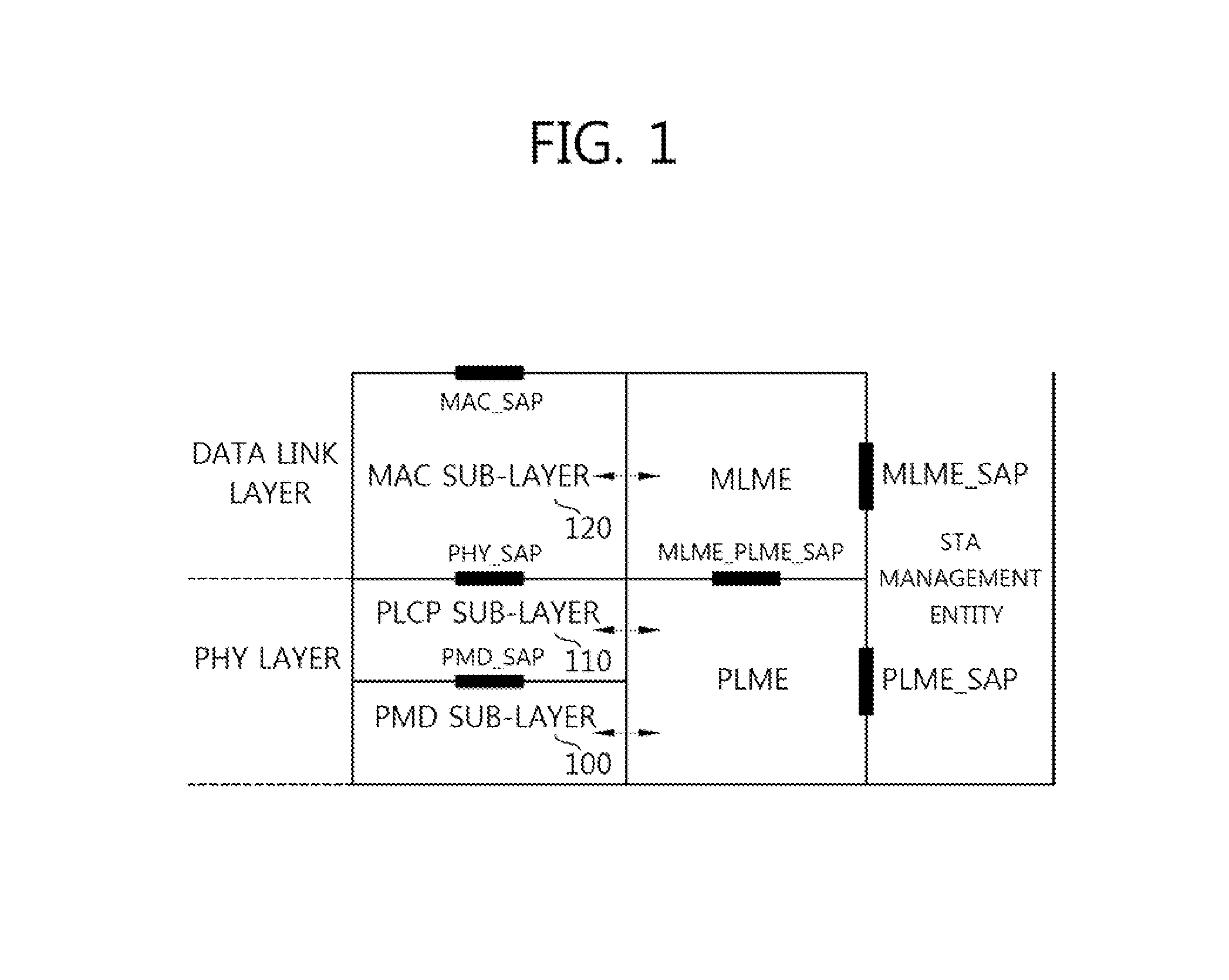
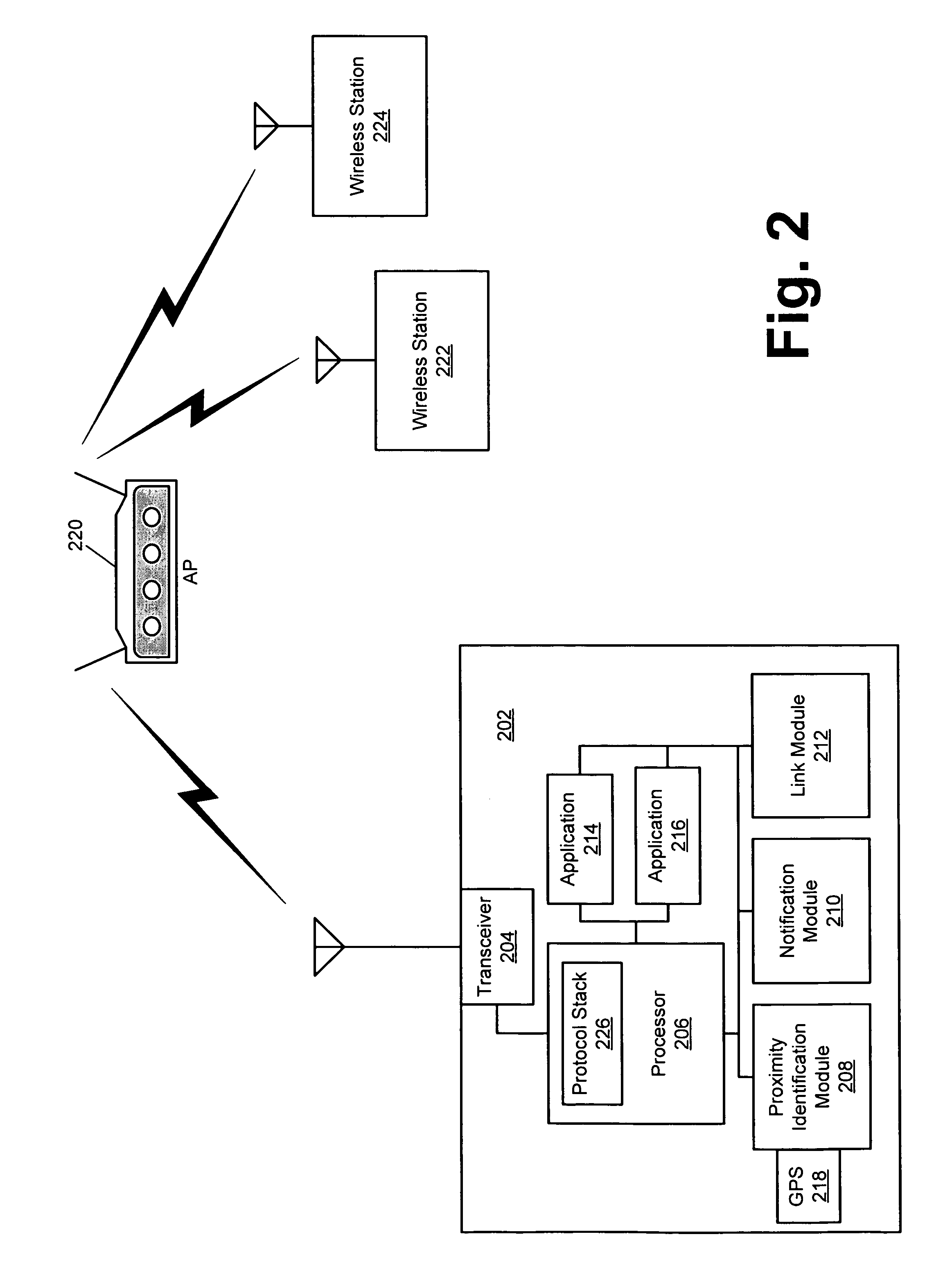
In IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) terminology, a station (abbreviated as STA) is a device that has the capability to use the 802.11 protocol. For example, a station may be a laptop, a desktop PC, PDA, access point or Wi-Fi phone. An STA may be fixed, mobile or portable. Generally in wireless networking terminology, a station, wireless client and node are often used interchangeably, with no strict distinction existing between these terms. A station may also be referred to as a transmitter or receiver based on its transmission characteristics. IEEE 802.11-2007 formally defines station as: Any device that contains an IEEE 802.11-conformant media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) interface to the wireless medium (WM).
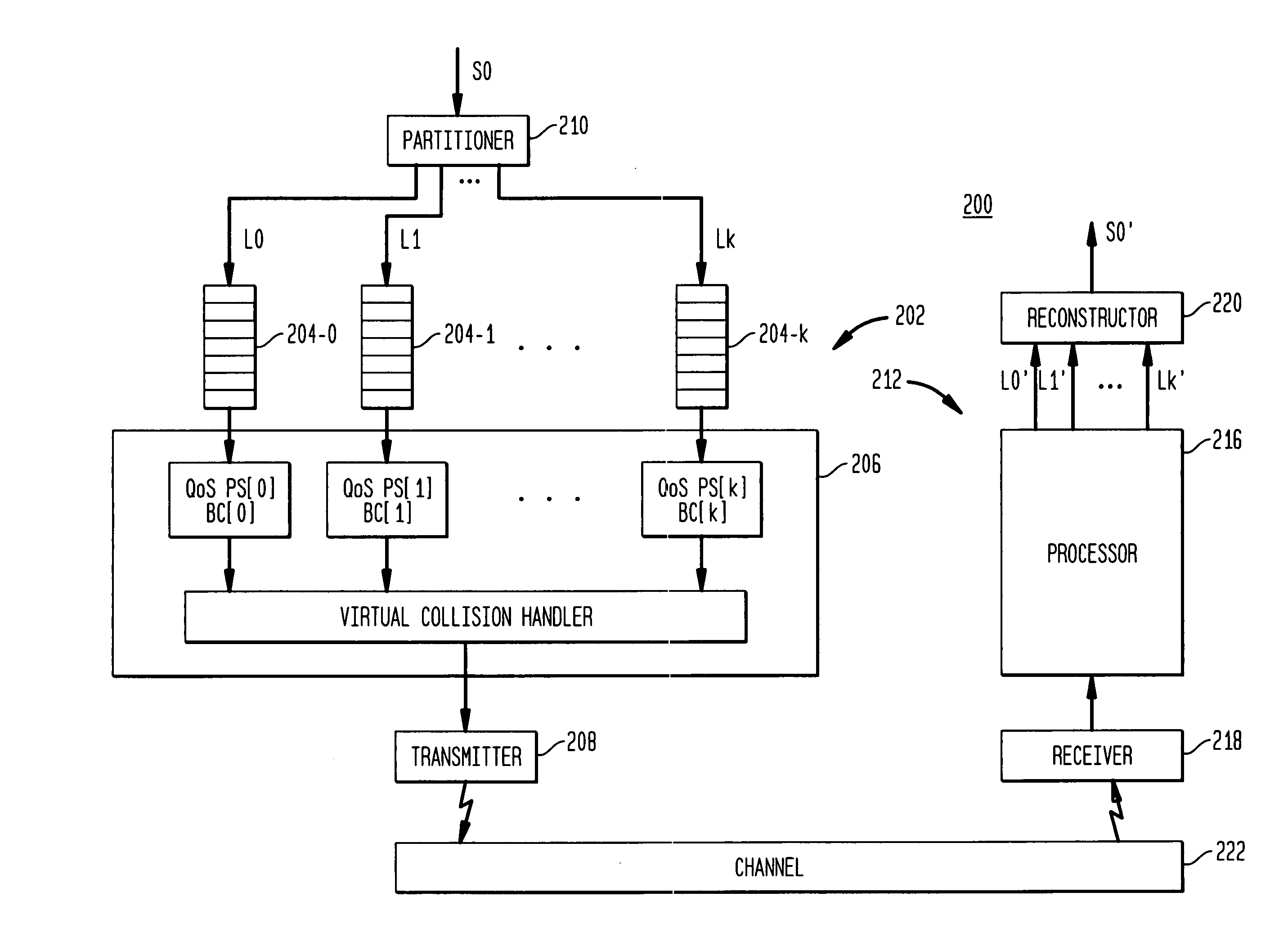
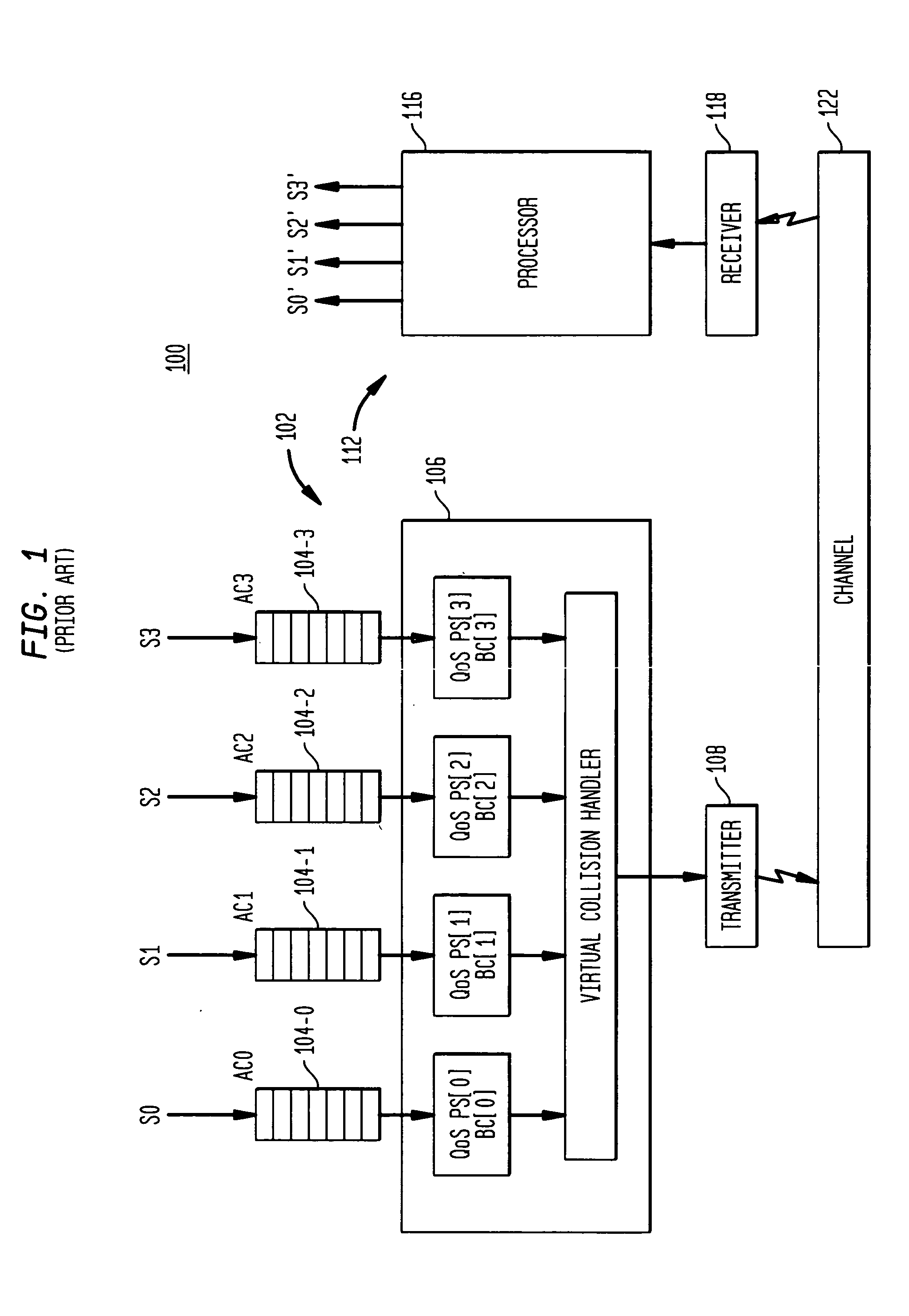
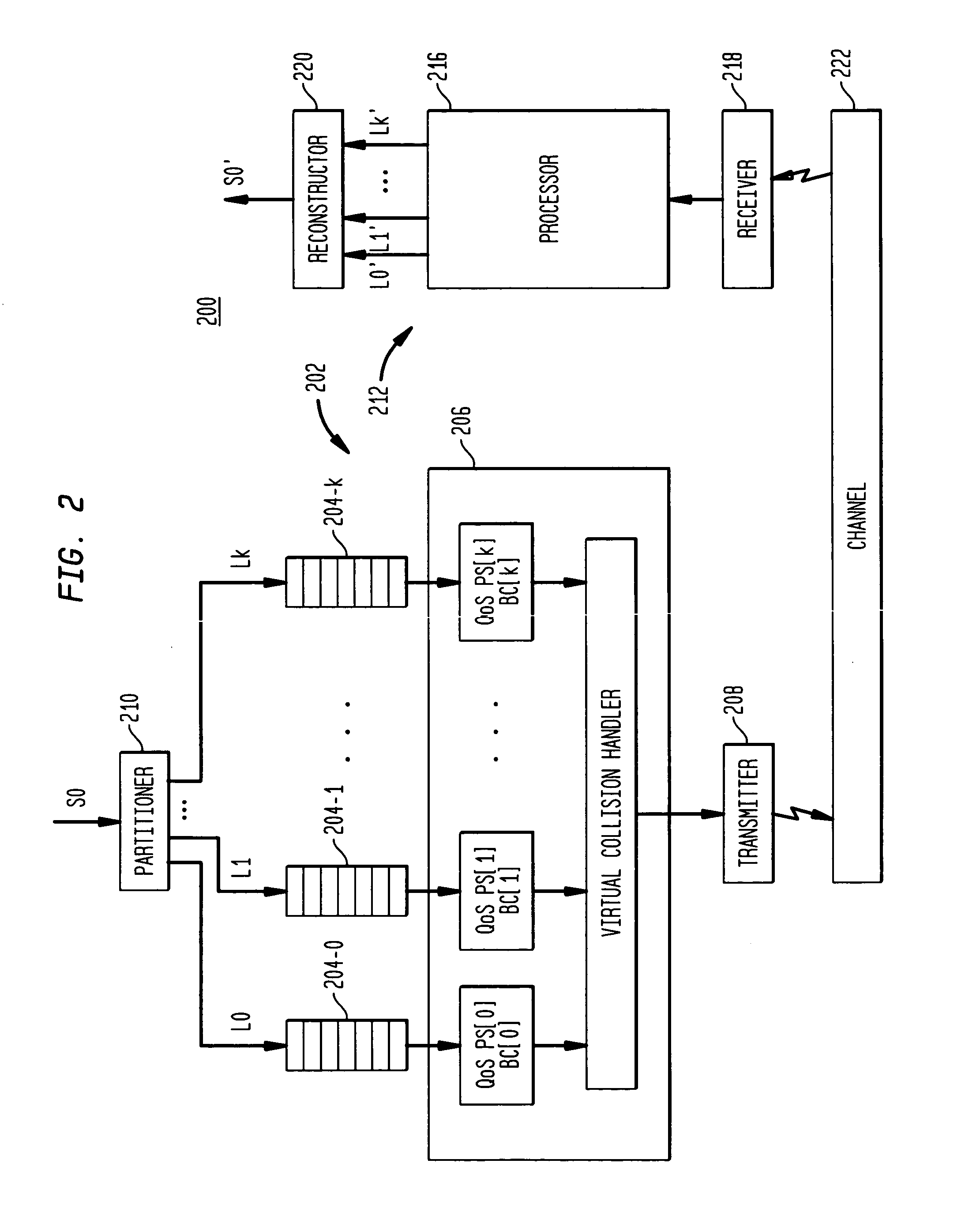
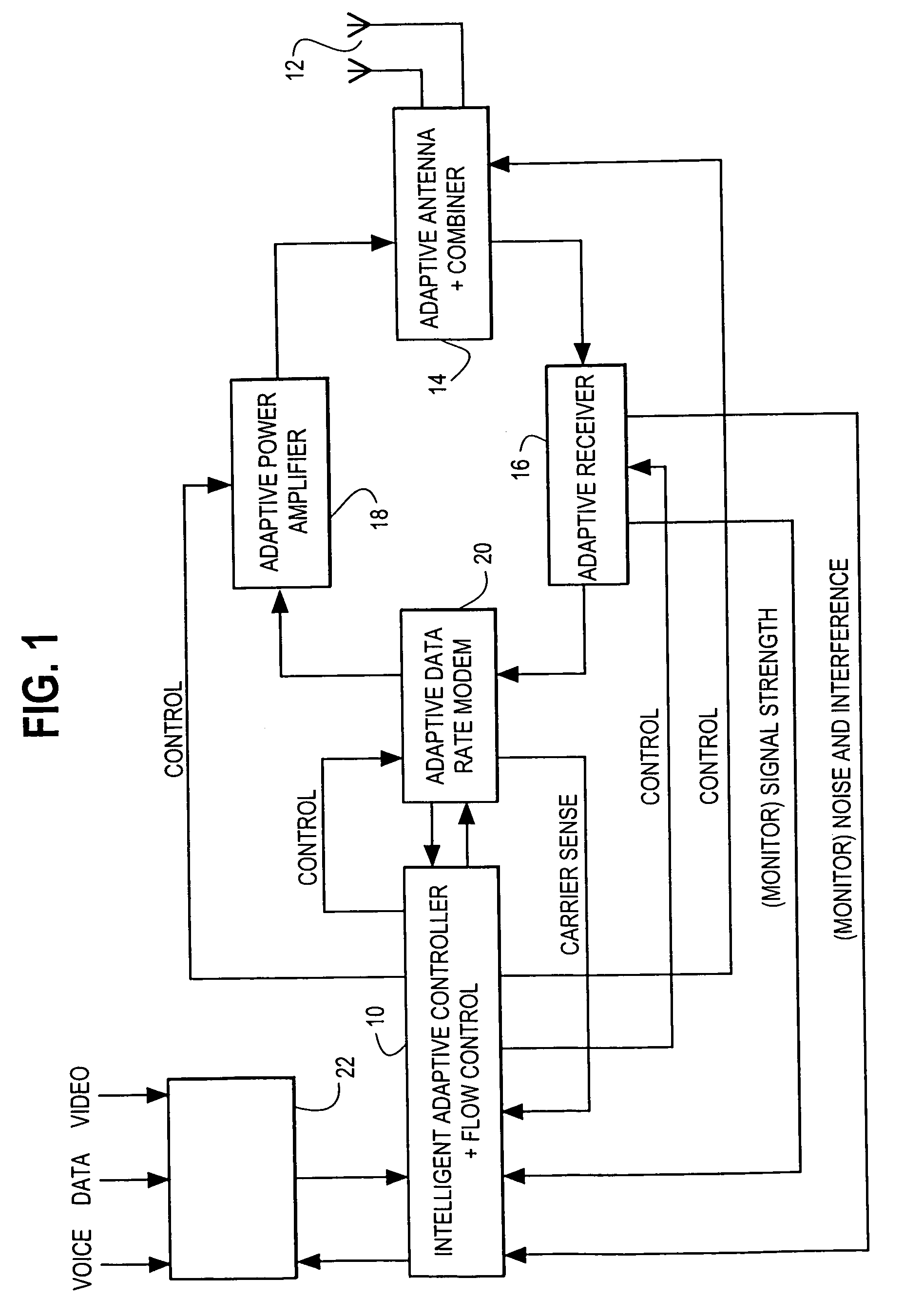
Media delivery using quality of service differentiation within a media stream
ActiveUS20050100022A1Equal qualityError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementQos quality of serviceStation
A WLAN system adapted to apply QoS differentiation to a media stream to be transmitted from a transmitting station (STA) to a receiving STA of that system. The transmitting STA processes the media stream to generate a base sub-stream and one or more enhancement sub-streams for subsequent transmission over a wireless communication channel and assigns different priorities to different sub-streams. Depending on the channel conditions, the transmitting STA may select to discard, without transmission, portions of data from enhancement sub-streams. The selection process is based on the assigned priority and operates to preserve as much of relatively high-priority data as possible. The receiving STA then processes the received data to generate a reconstructed media stream, which provides signal quality equal to or better than the signal quality supported by the base sub-stream. Advantageously, a WLAN system of the invention is adapted to change signal quality dynamically and incrementally in a manner commensurate with current channel conditions without the need for communication between the higher and lower network layers. In addition, it provides gradual and graceful degradation of signal quality when channel conditions deteriorate as opposed to abrupt degradation inherent in analogous prior art systems.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
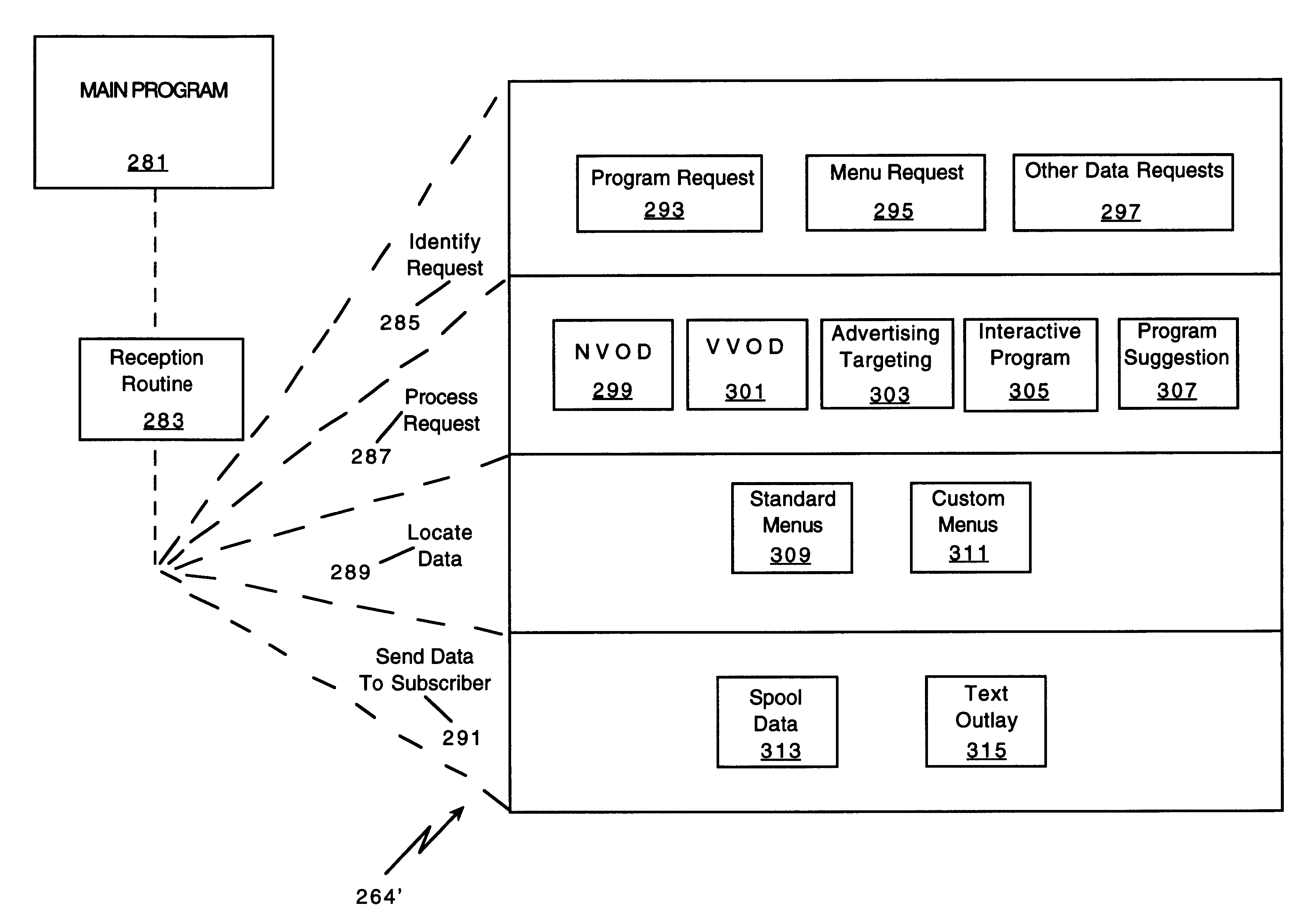
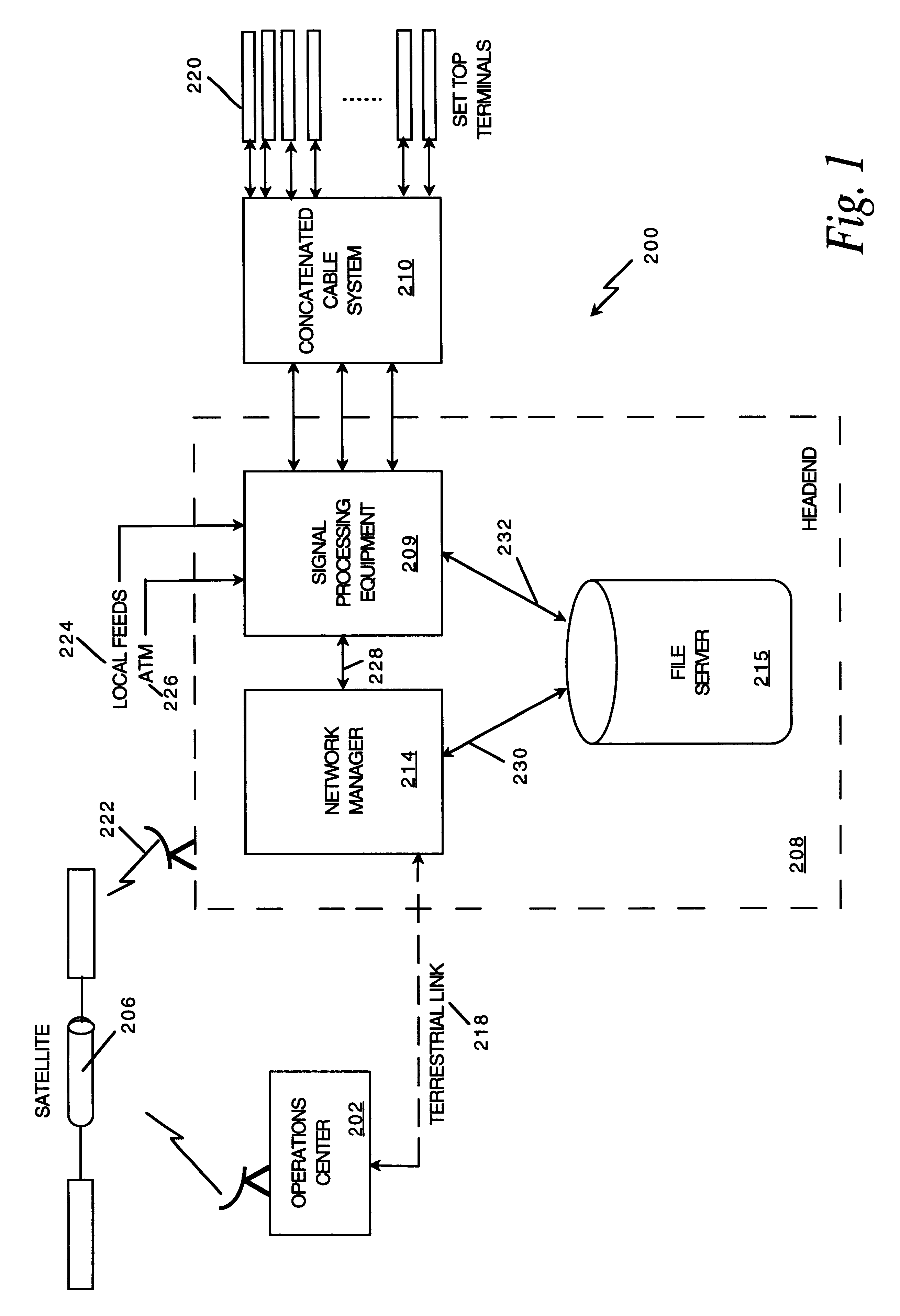
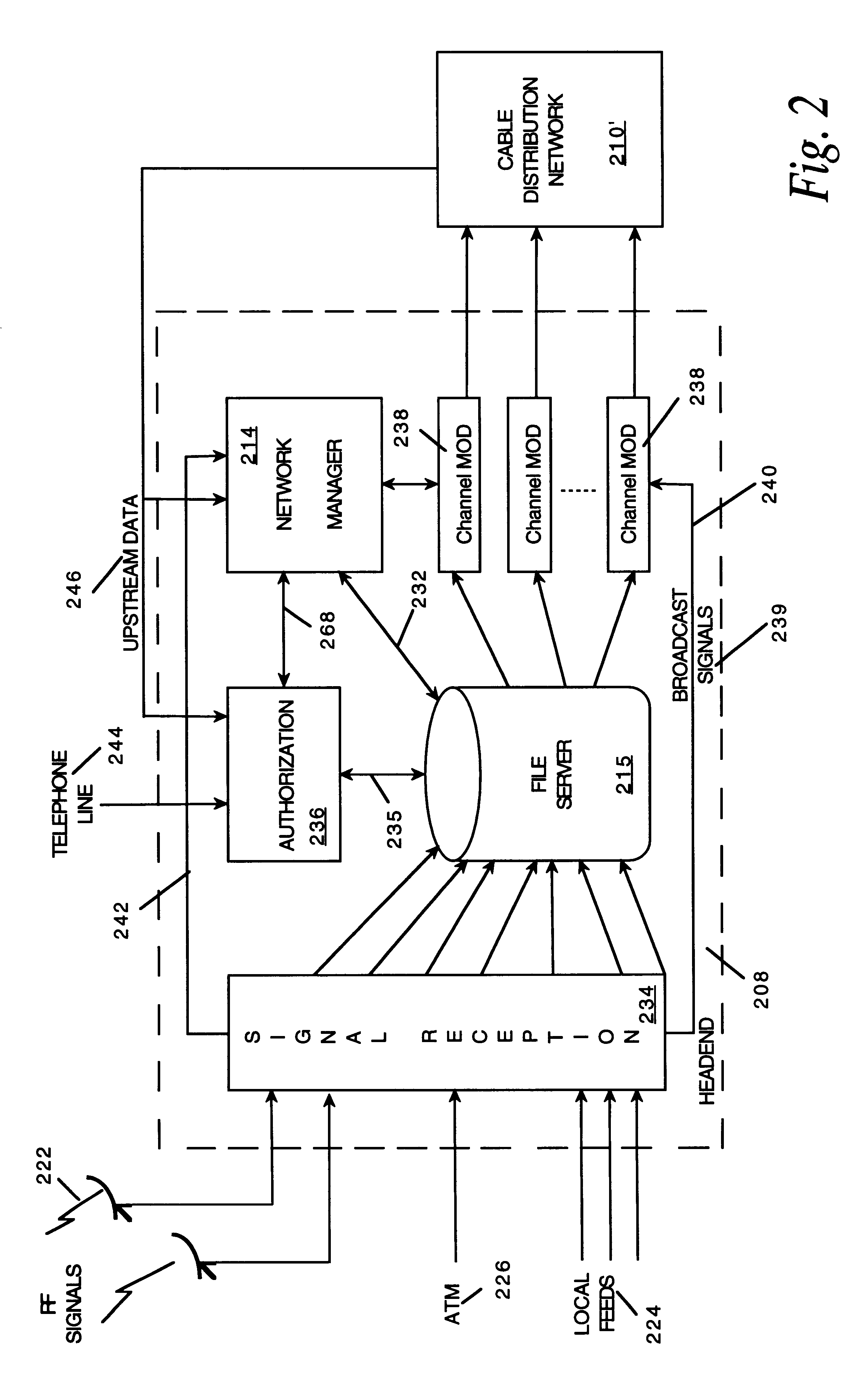
Network manager for cable television system headends
InactiveUS6201536B1Increase flexibilityImprove rendering capabilitiesTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionInformation processingInstruction memory
A novel network manager for use with a cable television system headend capable of monitoring and managing headend components and set top terminals in a television delivery system is described. The invention relates to methods and apparatus that manage and coordinate the reception of various programming and control signals at a headend. The invention manages and coordinates the storage of such signals for intelligent selection and distribution to set top terminals. The invention makes use of a receiver or set of receivers, a work station, a program control information processing component, a network management CPU, databases, control software and an instruction memory. The invention uses these components to manage and monitor certain headend components, such as signal reception equipment, an authorization component, a file server, MPEG decoders, a digital buffer with frame repeat and channel modulators. The invention is particularly useful in processing and responding to upstream information and subscriber communications received from set top terminals. In so doing, the invention accommodates various system services, including (1) near video on demand (NVOD), (2) virtual video on demand (VVOD), (3) video on demand (VOD), (4) interactive program services, (5) program suggestion features, (6) advertisement targeting, (7) generation of standard and custom menus, and (8) data spooling and text overlaying.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
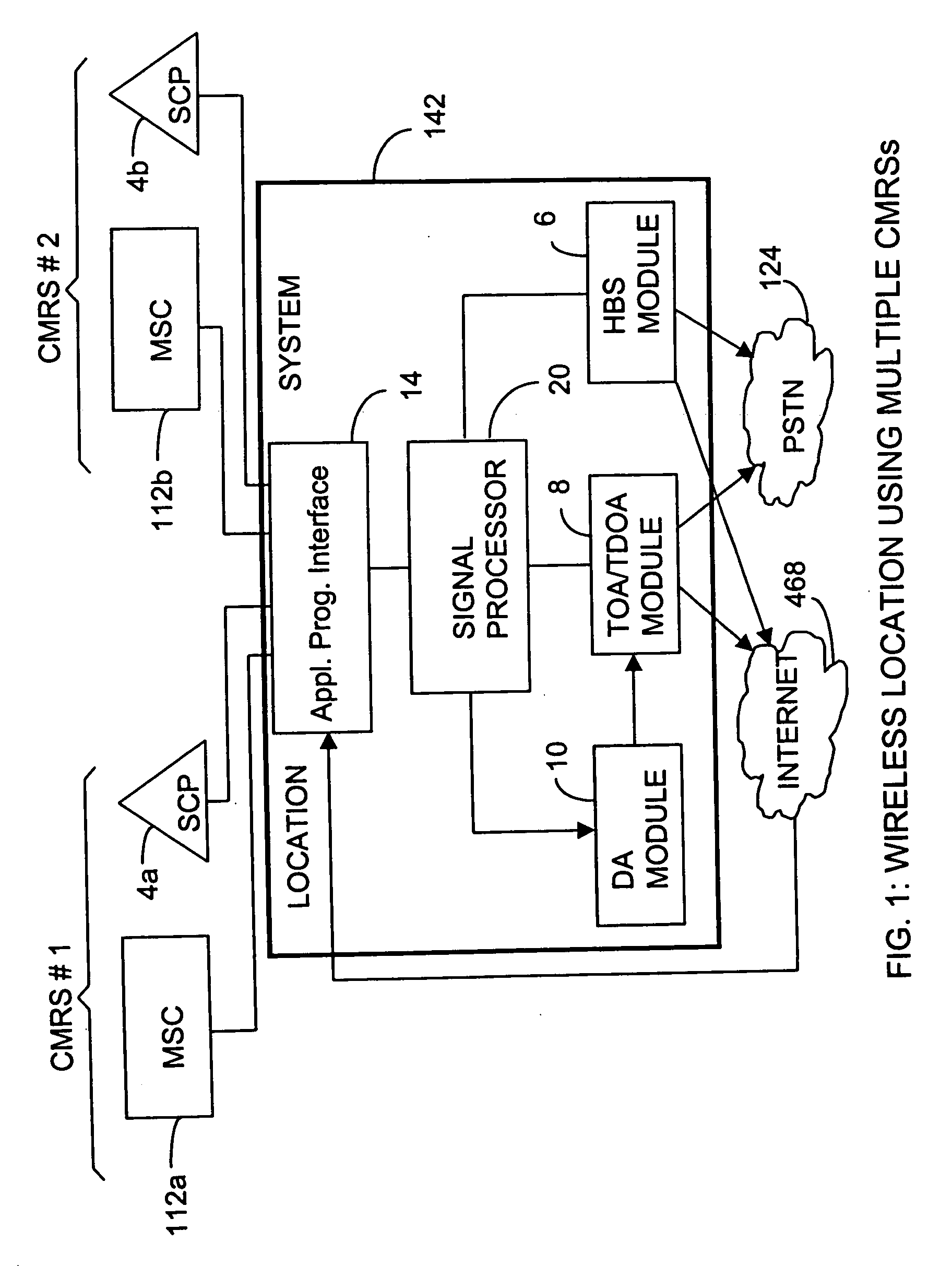
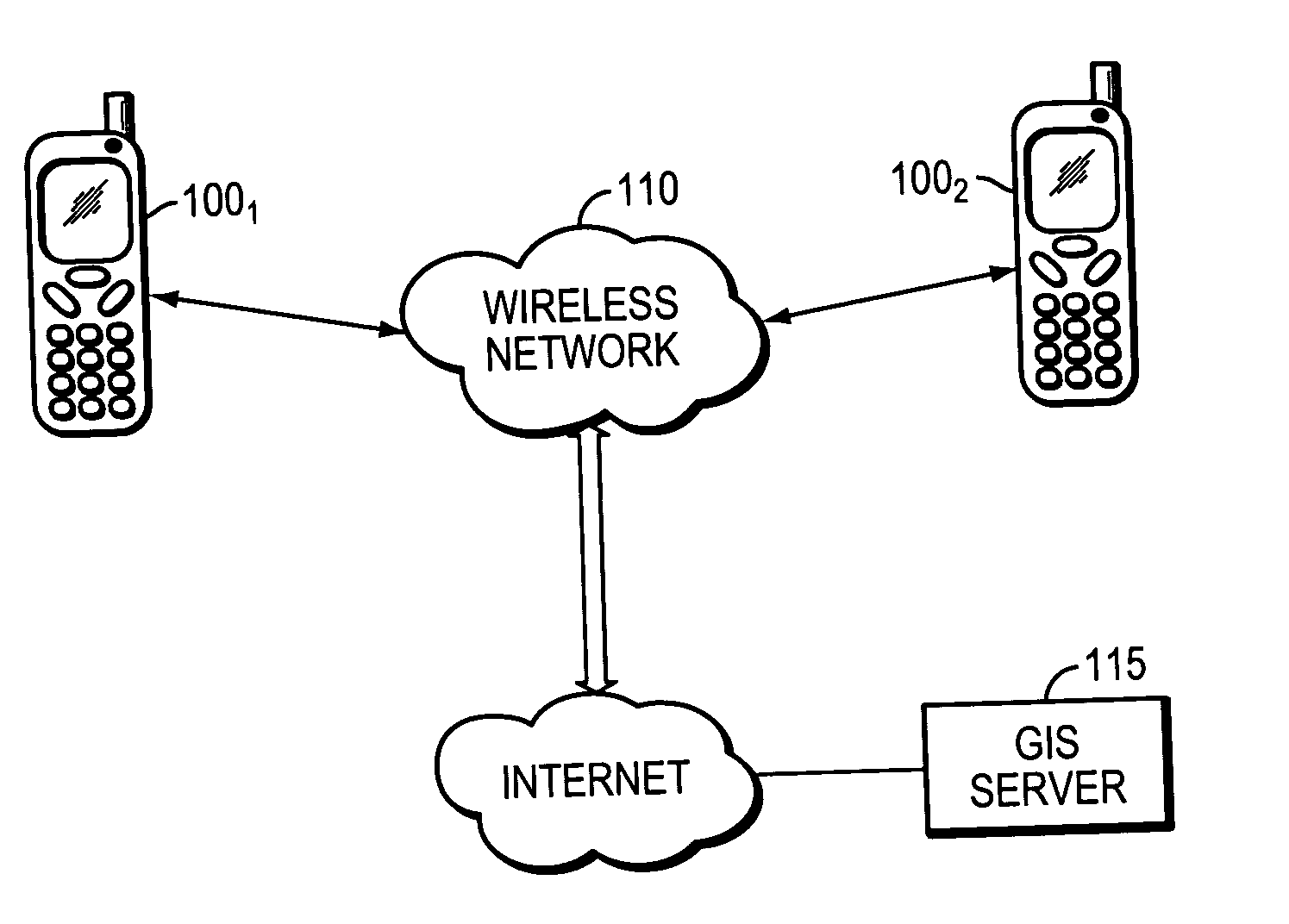
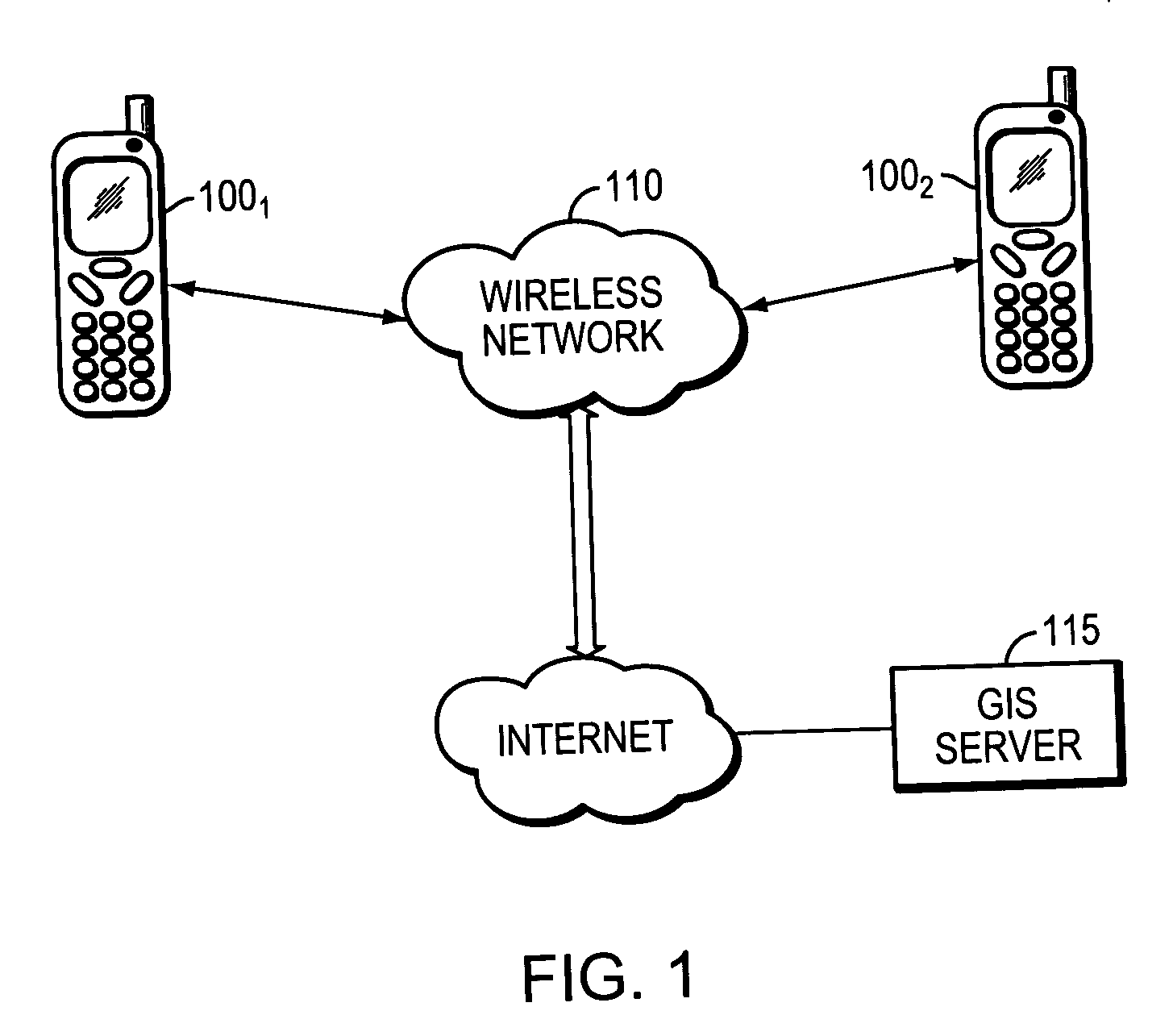
Locating a mobile station and applications therefor
InactiveUS20060025158A1Accurate locationEmergency connection handlingNetwork traffic/resource managementInternet communicationModularity
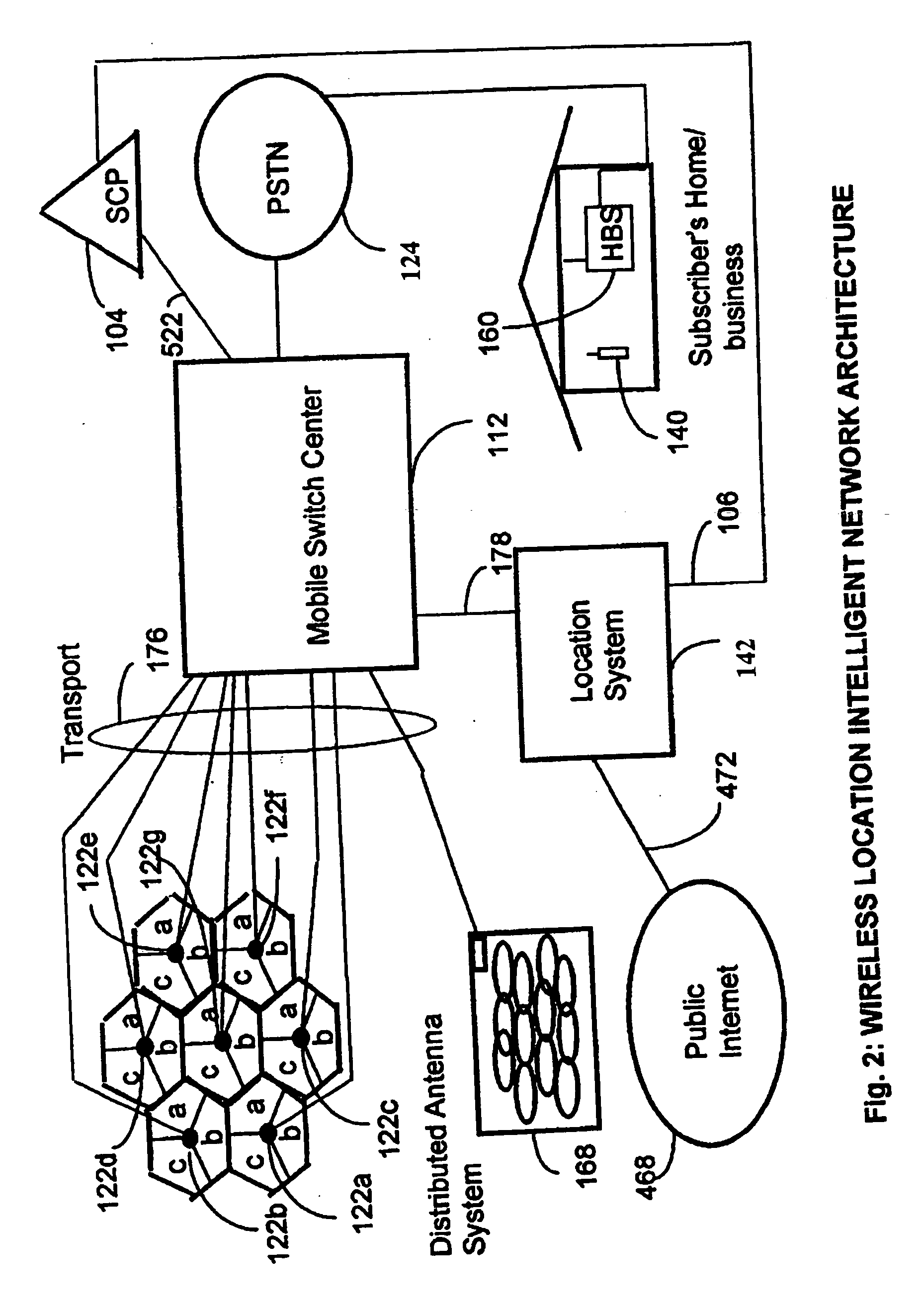
A location system is disclosed for wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location systems for outputting requested locations of hand sets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., AMPS, NAMPS, CDMA or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local mobile station location requests and more global mobile station location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location systems. The system uses a plurality of mobile station locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) home base stations and (3) distributed antenna provisioning. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. The system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:FINETRAK LLC
MAC extensions for smart antenna support
ActiveUS20030169769A1Reduce reception errorsLess bitError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityTelecommunicationsStation
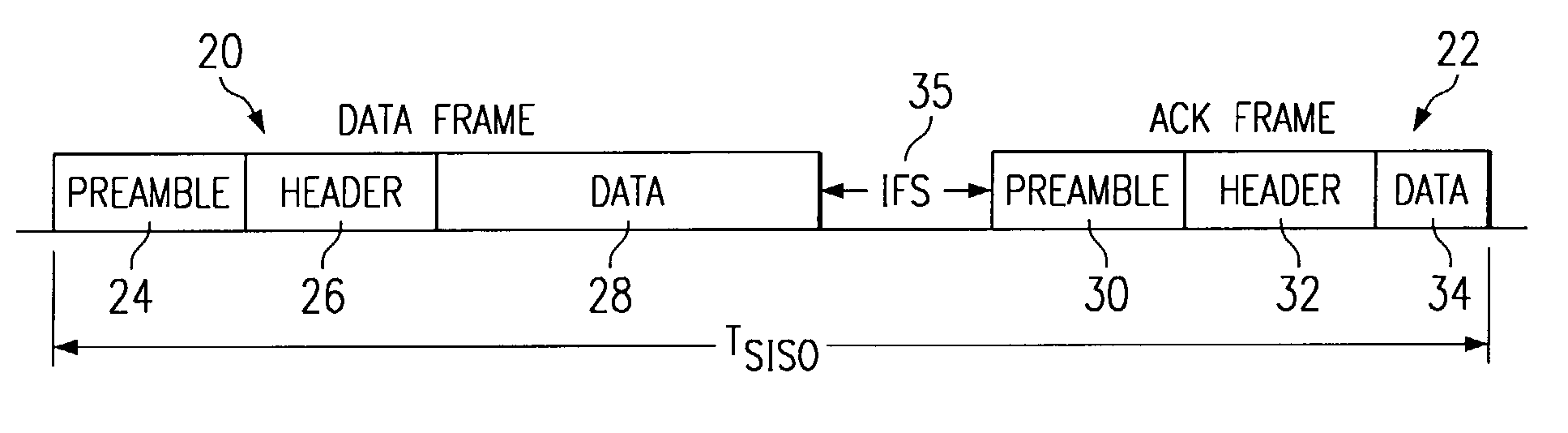
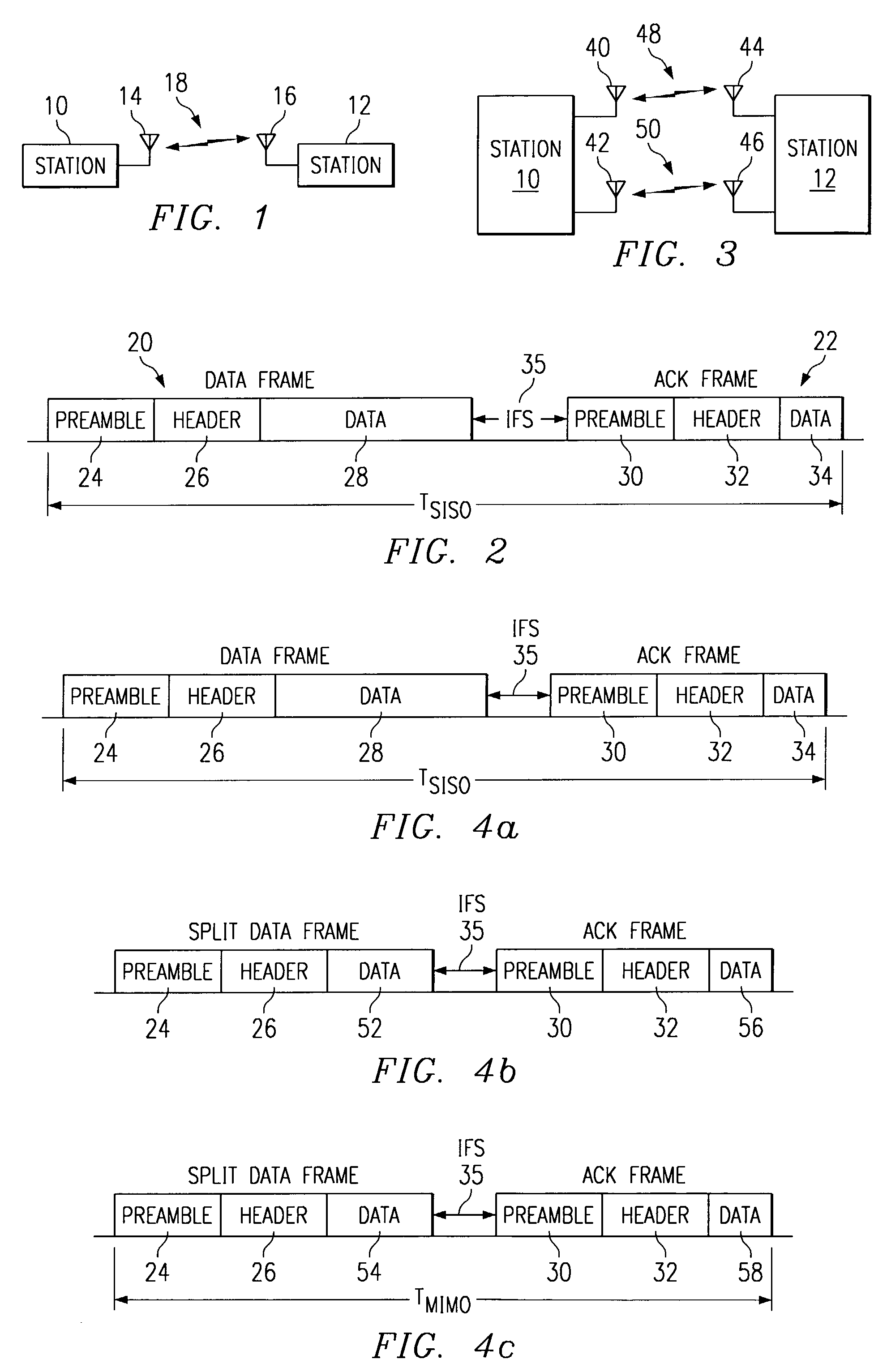
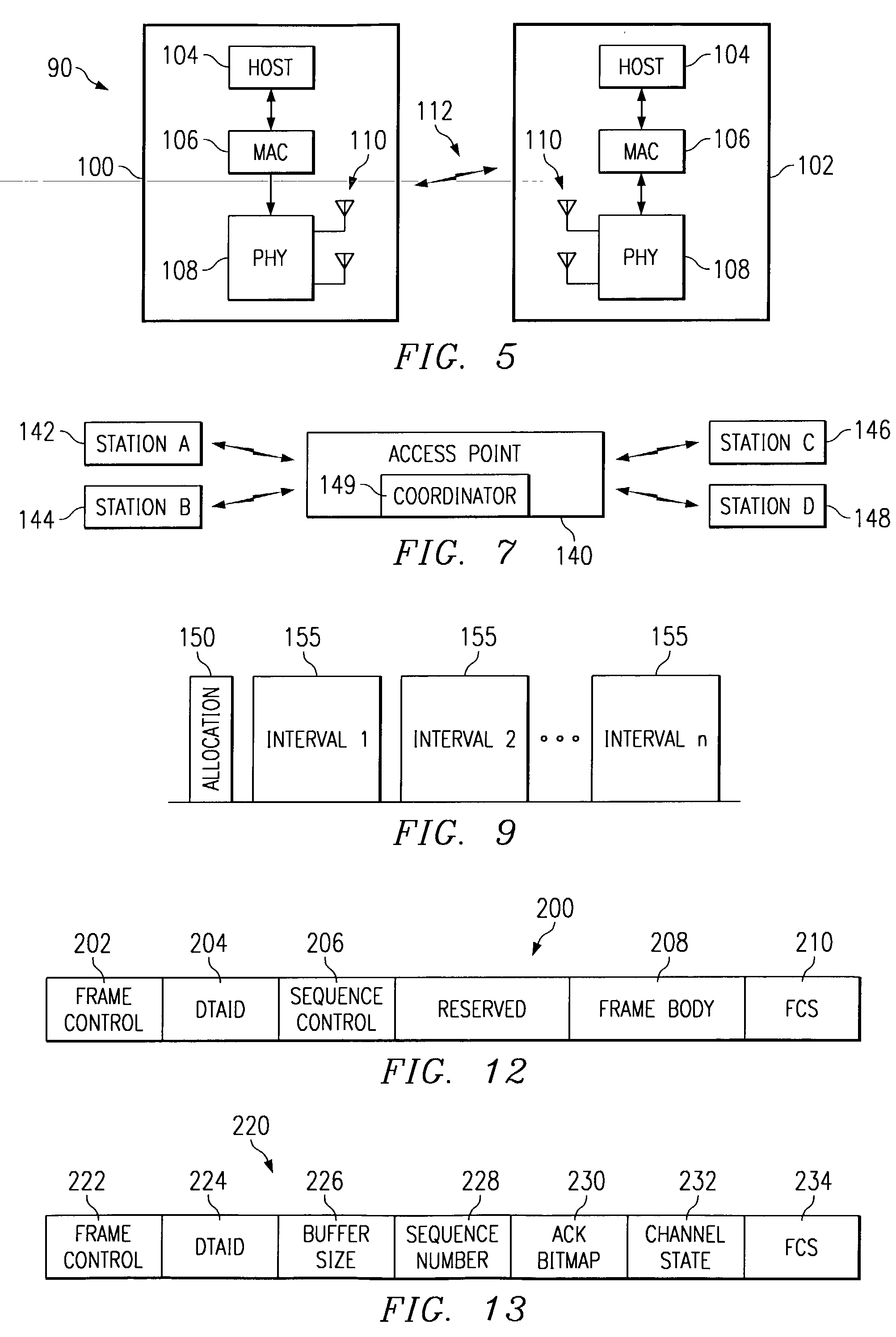
Apparatus and methods implement aggregation frames and allocation frames. The aggregation frames include a plurality of MSDUs or fragments thereof aggregated or otherwise combined together. An aggregation frame makes more efficient use of the wireless communication resources. The allocation frame defines a plurality of time intervals. The allocation frame specifies a pair of stations that are permitted to communicate with each other during each time interval as well as the antenna configuration to be used for the communication. This permits stations to know ahead of time when they are to communicate, with which other stations and the antenna configuration that should be used. A buffered traffic field can also be added to the frames to specify how much data remains to be transmitted following the current frame. This enables network traffic to be scheduled more effectively.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
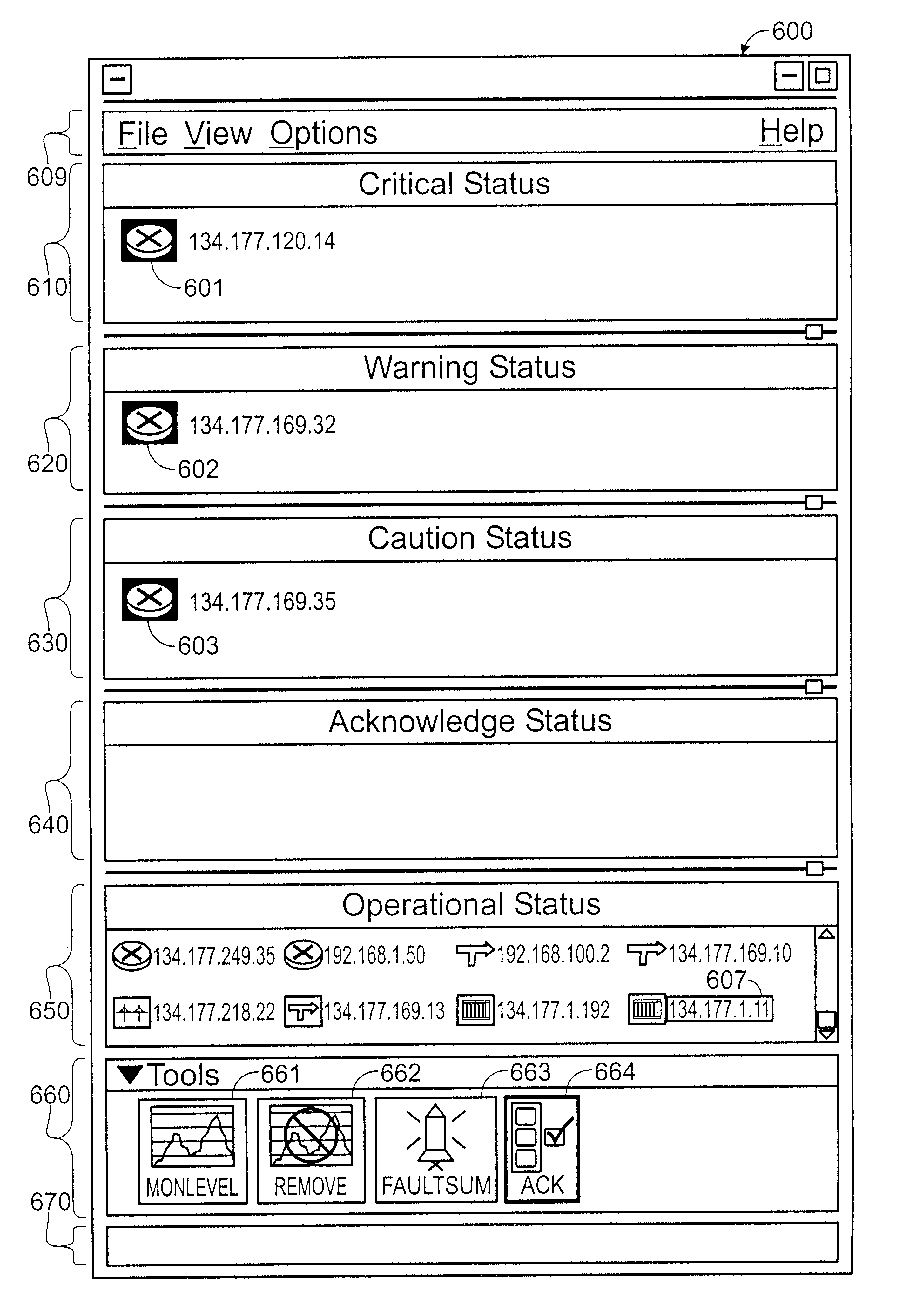
Method and apparatus for displaying health status of network devices
A method and apparatus for concurrently displaying from a single window on a network management station the health status of all network devices and objects of a computer network. The network devices may be categorized according to state or device type, as determined by the network manager. The method and apparatus provides a network manager with the ability to determine the current state of network devices and objects within an enterprise network and invoke further actions such as configuration, performance, fault, and security management tasks. The network manager can drag and drop icons from one network management system application window to another network management system application window to obtain fault information about network devices and objects, thus allowing multiple network management system applications to run concurrently on the same network management station. The network manager is further able to add new network devices and objects by dragging site, folder or device icons from one network management system application window to a second network management system application window for displaying the health status of the new devices. The dragged-in devices are added to the appropriate status panes within the second window according to the method of the present invention.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
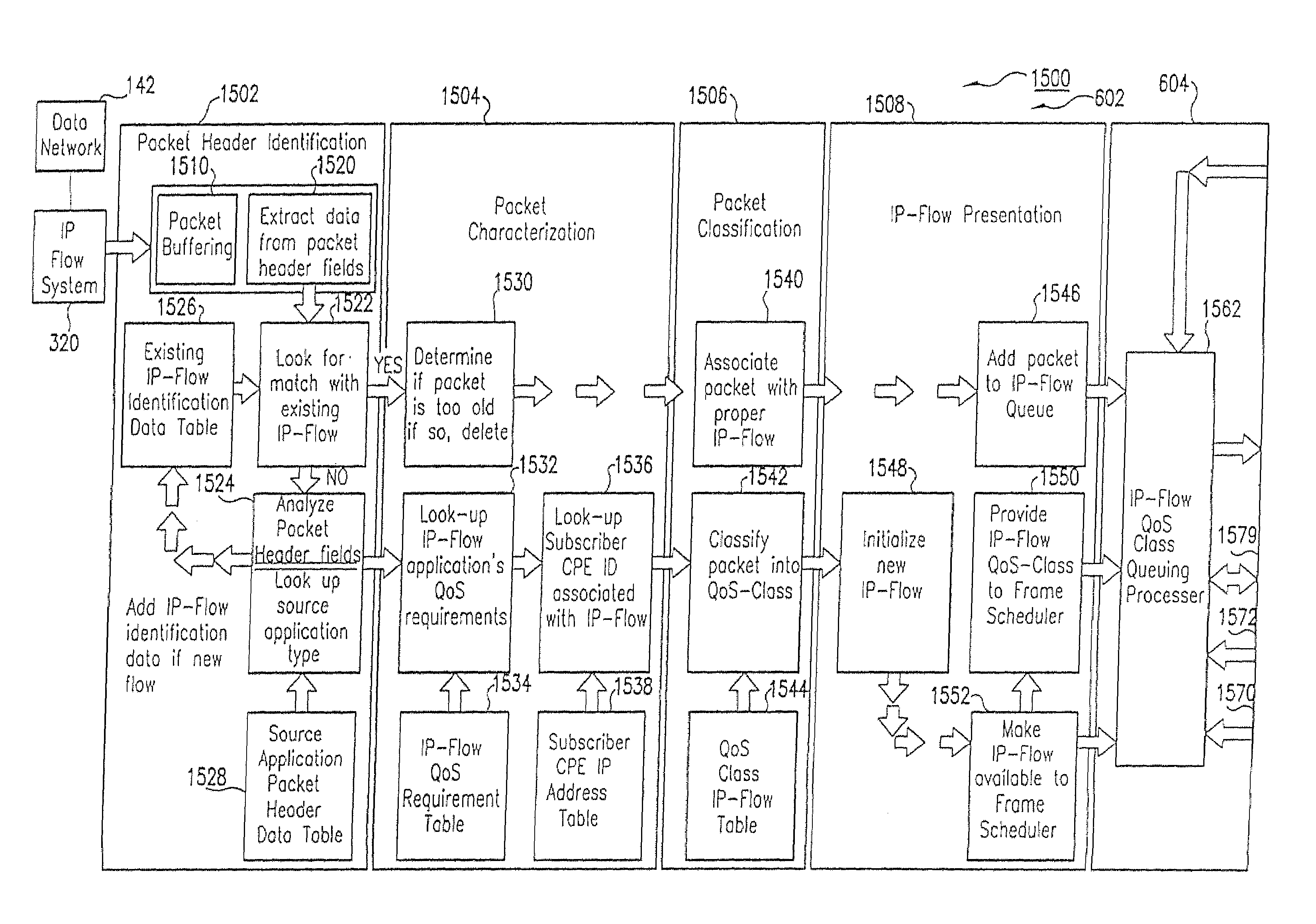
Method and computer program product for internet protocol (IP)-flow classification in a wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system
InactiveUS7251218B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceWireless access point
A system and method for Internet Protocol (IP) flow classification group IP flows in a packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system is disclosed. The method comprises analyzing an IP flow in a packet-centric manner, classifying the IP flow, scheduling the IP flow for transmission over a shared wireless bandwidth between a wireless base station and at least one subscriber customer premises equipment (CPE) station, allocating the shared wireless bandwidth to a communication of the IP flow between the wireless base station and a subscriber CPE station so as to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS) associated with the IP flow.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Interference suppression in CDMA systems
ActiveUS20020051433A1Improved interference suppressionSuppresses any sensitivitySpatial transmit diversityInterference (communication)Communications system
A receiver of the present invention addresses the need for improved interference suppression without the number of transmissions by the power control system being increased, and, to this end, provides a receiver for a CDMA communications system which employs interference subspace rejection to tune a substantially null response to interference components from selected signals of other user stations. Preferably, the receiver also tunes a substantially unity response for a propagation channel via which a corresponding user's signal was received. The receiver may be used in a base station or in a user / mobile station.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
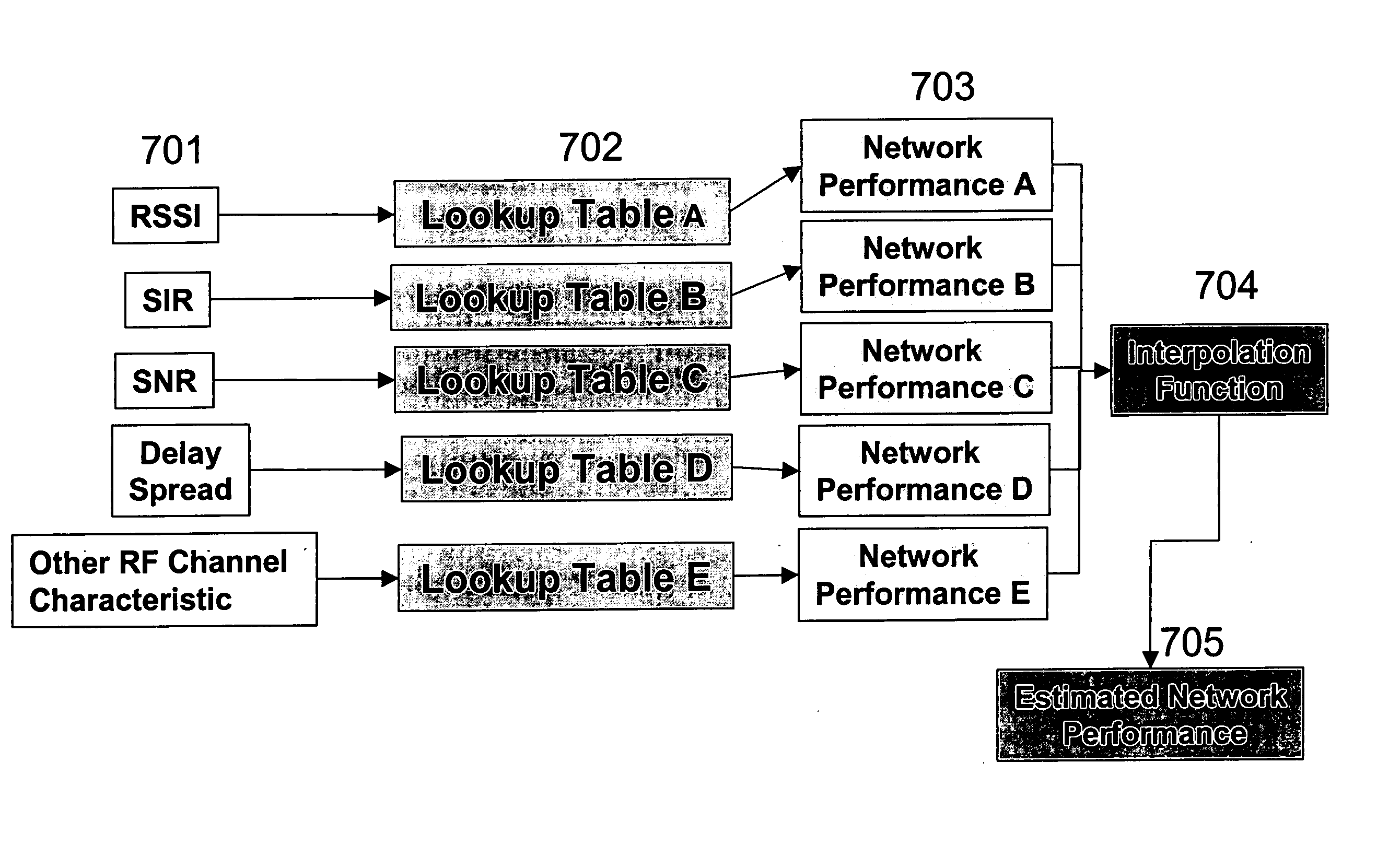
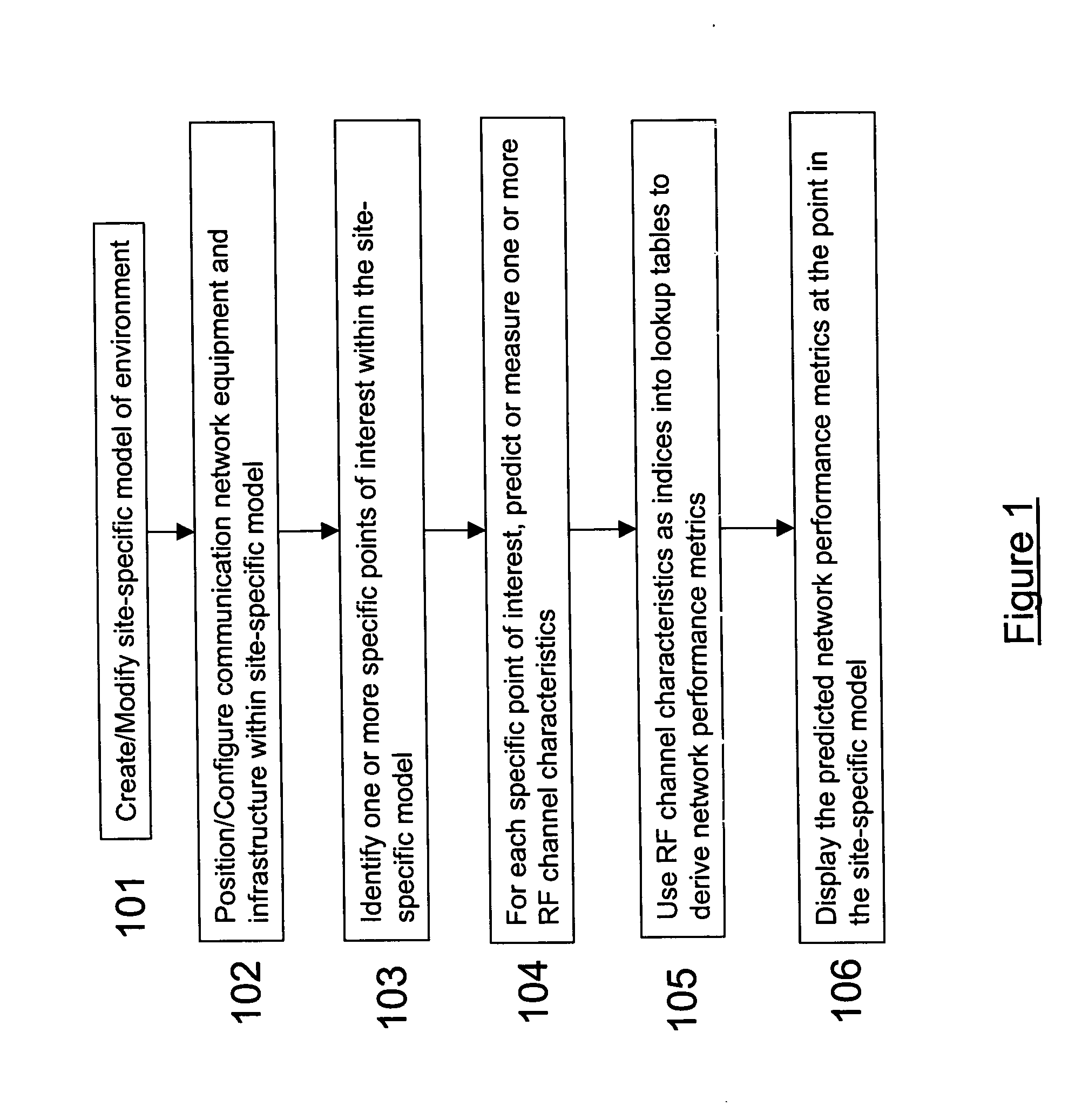
System and method for predicting network performance and position location using multiple table lookups
InactiveUS20040259555A1Quick estimateEasy to handleRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionChannel dataNetwork performance
This invention provides a system and method for the design, prediction, and control of wireless communication networks by combining RF channel data from multiple lookup tables, each of which correlates an RF channel characteristic to some higher order network performance metric. Network performance predictions, and resulting network control instructions, are produced from look-up tables of measured or predicted data relating one or more RF channel characteristics to one or more network performance metrics. These lookup tables are uniquely constructed by site-specific location, technology, wireless standard, or equipment types.
Owner:WIRELESS VALLEY COMM
Uniform power save method for 802.11e stations
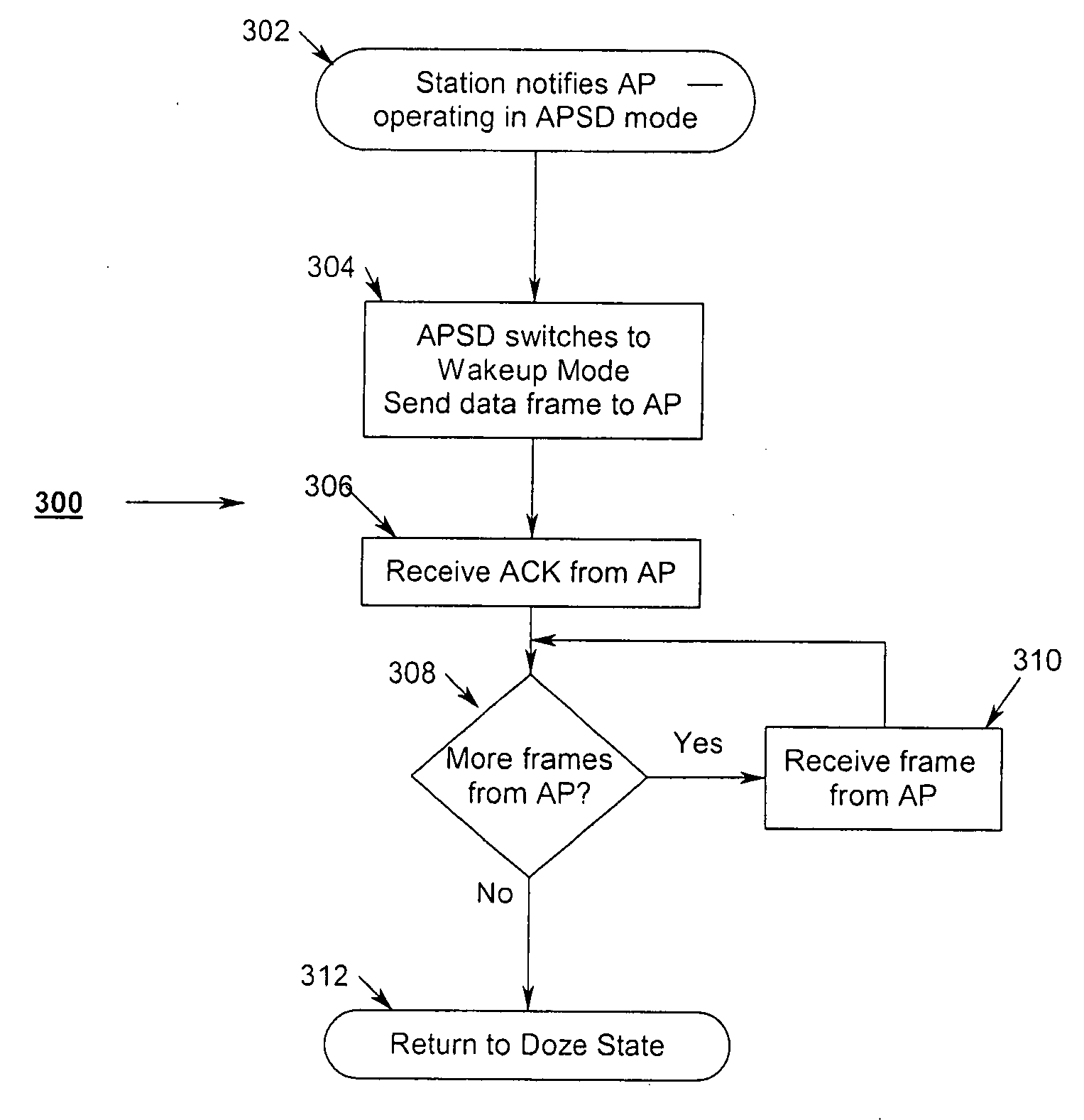
ActiveUS20050018624A1Delay minimizationFast sampling rateEnergy efficient ICTPower managementAccess methodClient-side
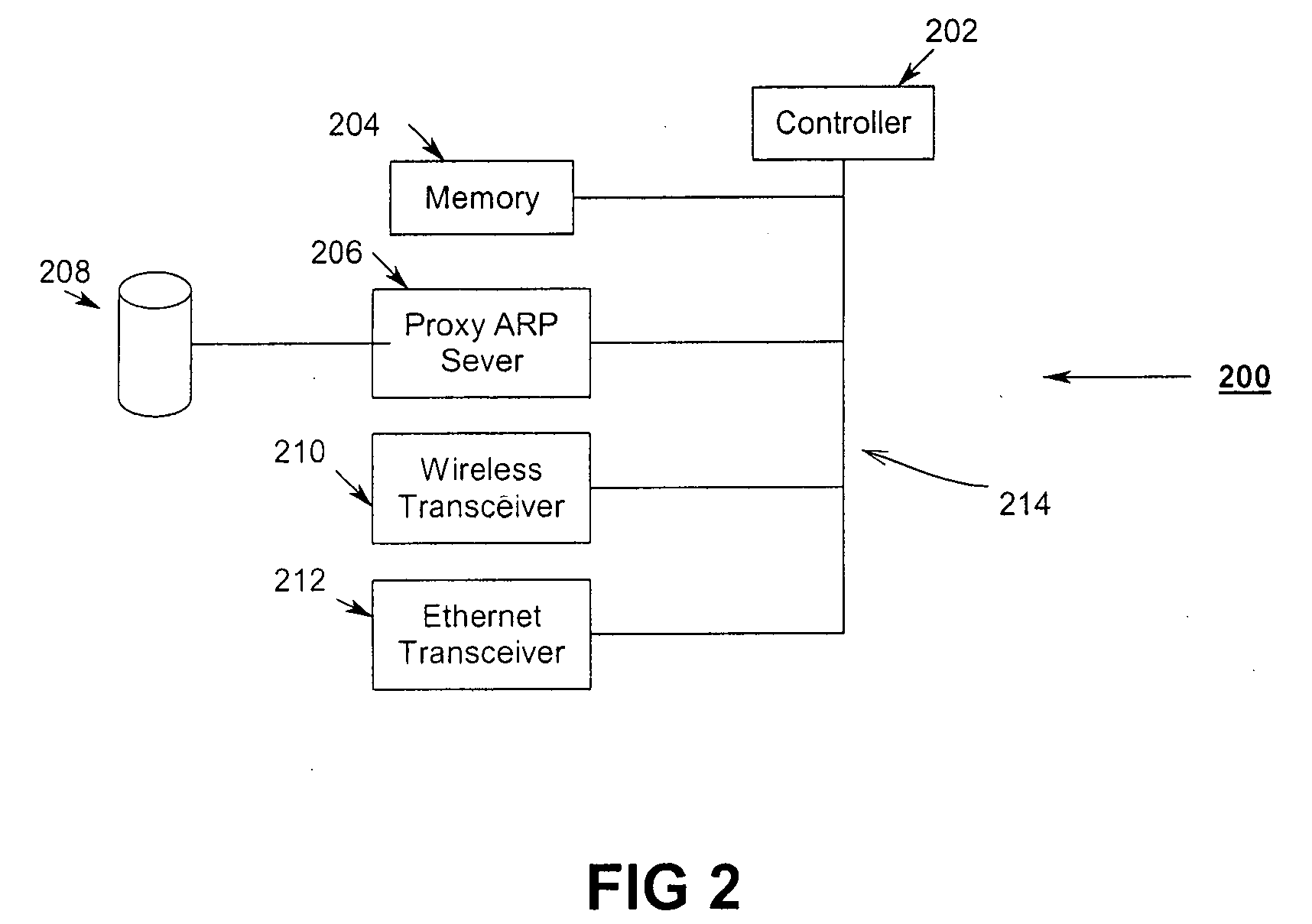
A power-save QSTA notifies an Access Point (AP) that its operating in a automatic power-save delivery (APSD) mode and negotiates a periodic wakeup schedule and a scheduled startup time with the AP. Wakeup times are synchronized with the 802.11 Timer Synchronization Function (TSF). The AP automatically sends frames to the QSTA when it determines the QSTA is in an awake state, otherwise downlink frames are buffered. The AP uses a combination poll+EDCF access method wherein at the start of each wakeup period the AP sends a poll to the QSTA, the poll having a flag that indicates to the QSTA if the AP has a downlink fame buffered for the QSTA. In addition, a Proxy ARP Server in an AP maintains IP / MAC bindings for associated clients so that when the AP receives a proxy ARP request for a client, the AP may respond for the client.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
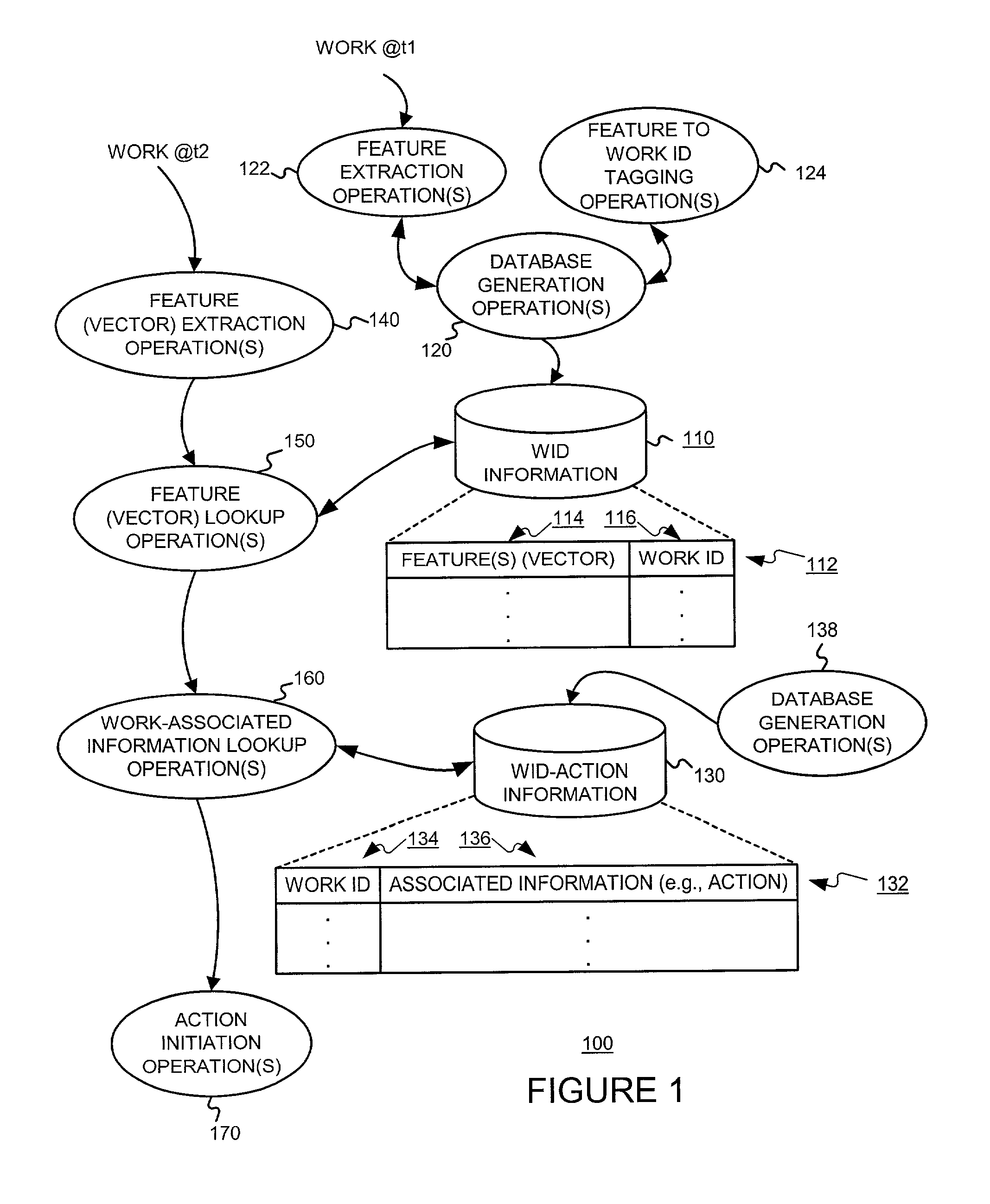
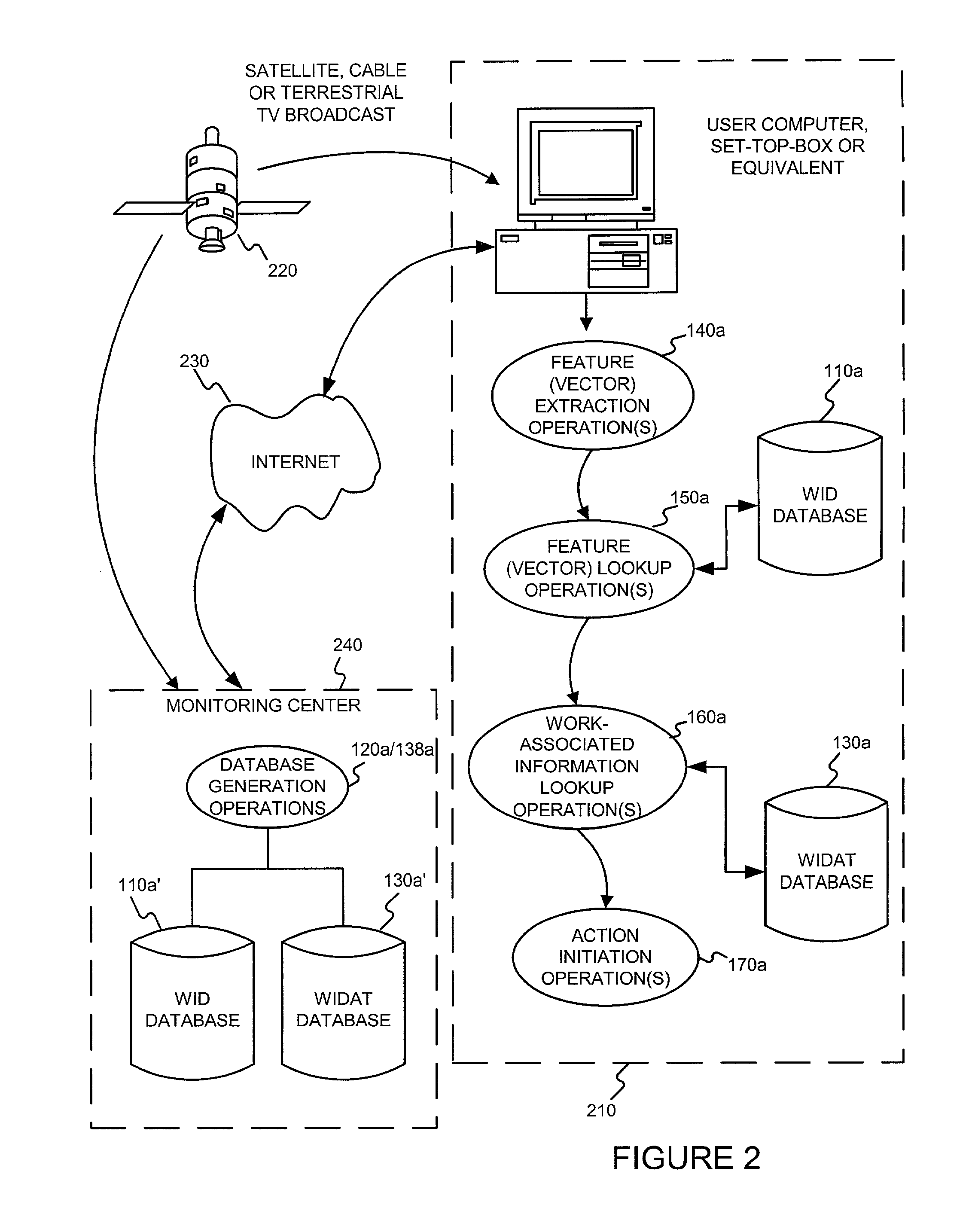
Identifying works for initiating a work-based action, such as an action on the internet
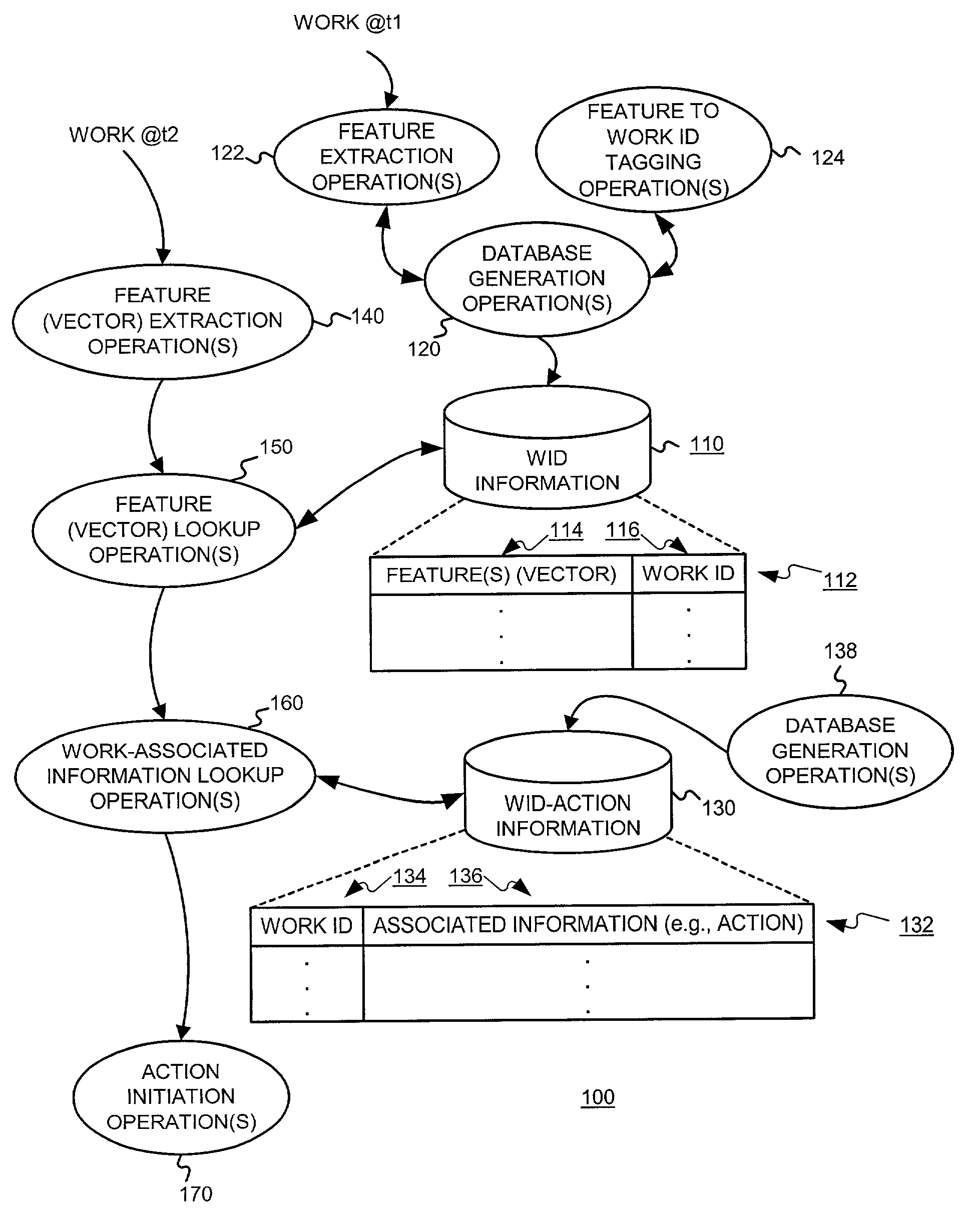
A system is described for linking traditional media works, such as print and broadcast media for example, to a more interactive media conduit, such as the Internet. The system avoids the need to modify the media work in anyway. Instead, it employs a passive recognition system that uniquely identifies the specific work, such as a particular television or radio broadcast or printed commercial. The identification may be based in intra-work and / or extra-work information. Several different embodiments / environments are described. The best embodiment may depend, at least in part, on costs of hardware and communication. These costs can change over time. In one embodiment, all of the databases and computation are performed at the user's premises. In another embodiment, all of the databases and computation occur at remote sites that user premise equipment can query using uniquely identifying extra-work information, such as the time, place and station on which the work was broadcast. This second embodiment is most suitable for content that is published, e.g. magazines, newspapers, etc., or broadcasted, e.g. cable, satellite and terrestrial television and radio. Alternative embodiments, in which various operations are performed at both the user's premises and remote locations are also possible.
Owner:NETWORK 1 TECH
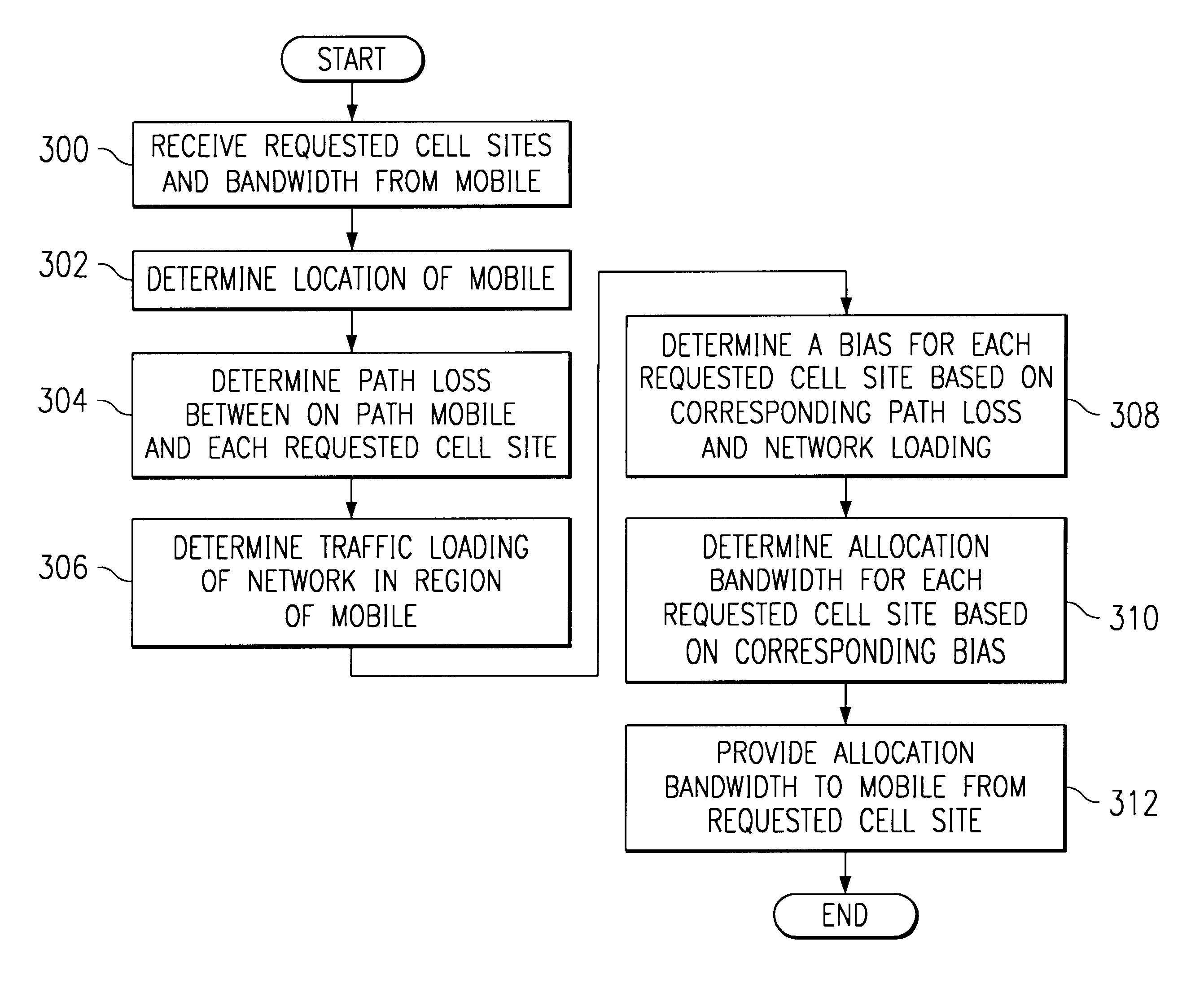
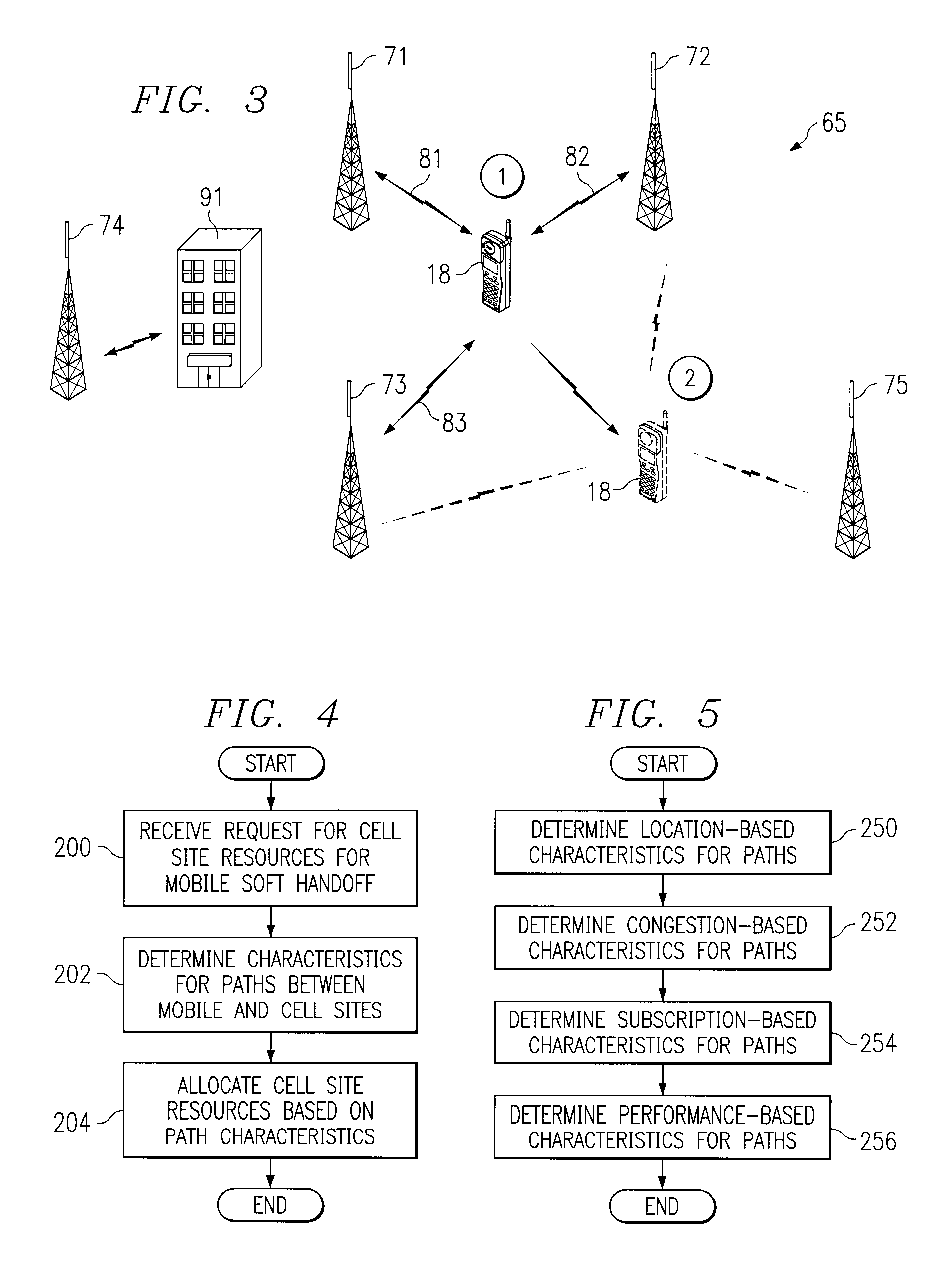
Method and system for dynamic soft handoff resource allocation in a wireless network
InactiveUS6907243B1Resource allocatedMinimize air-link congestionPower managementAccounting/billing servicesTelecommunicationsMobile device
A method and system for dynamic soft handoff resource allocation in a wireless communications network includes determining a wireless path characteristic individually for each path of a macro diversity connection between a mobile device and a plurality of wireless sites. Wireless resources are allocated for the macro diversity connection between the mobile device and the wireless sites based on the wireless path characteristic. The wireless path characteristic includes a location-based characteristic, a congestion-based characteristic, a subscriber-based characteristic and / or a performance-based characteristic.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
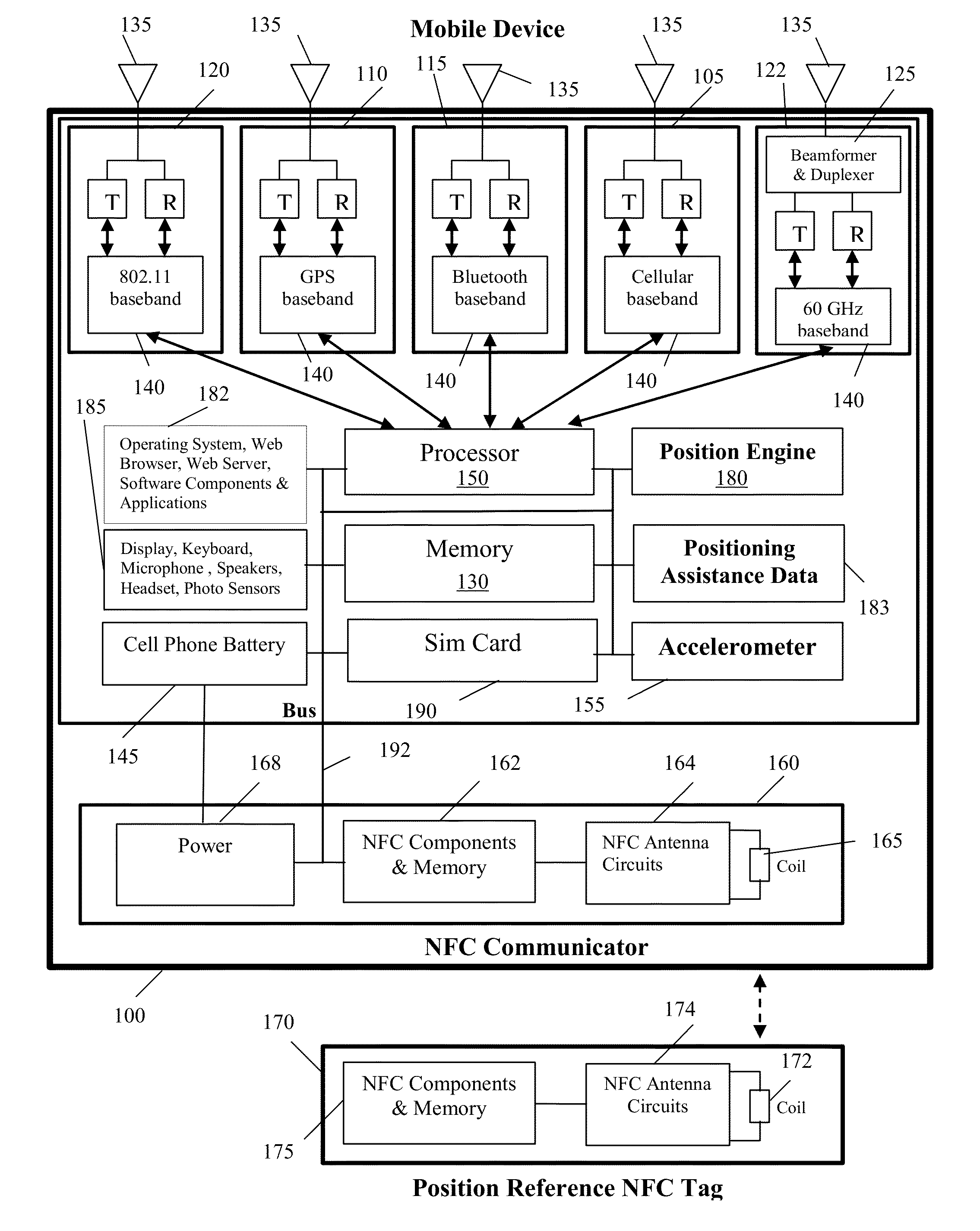
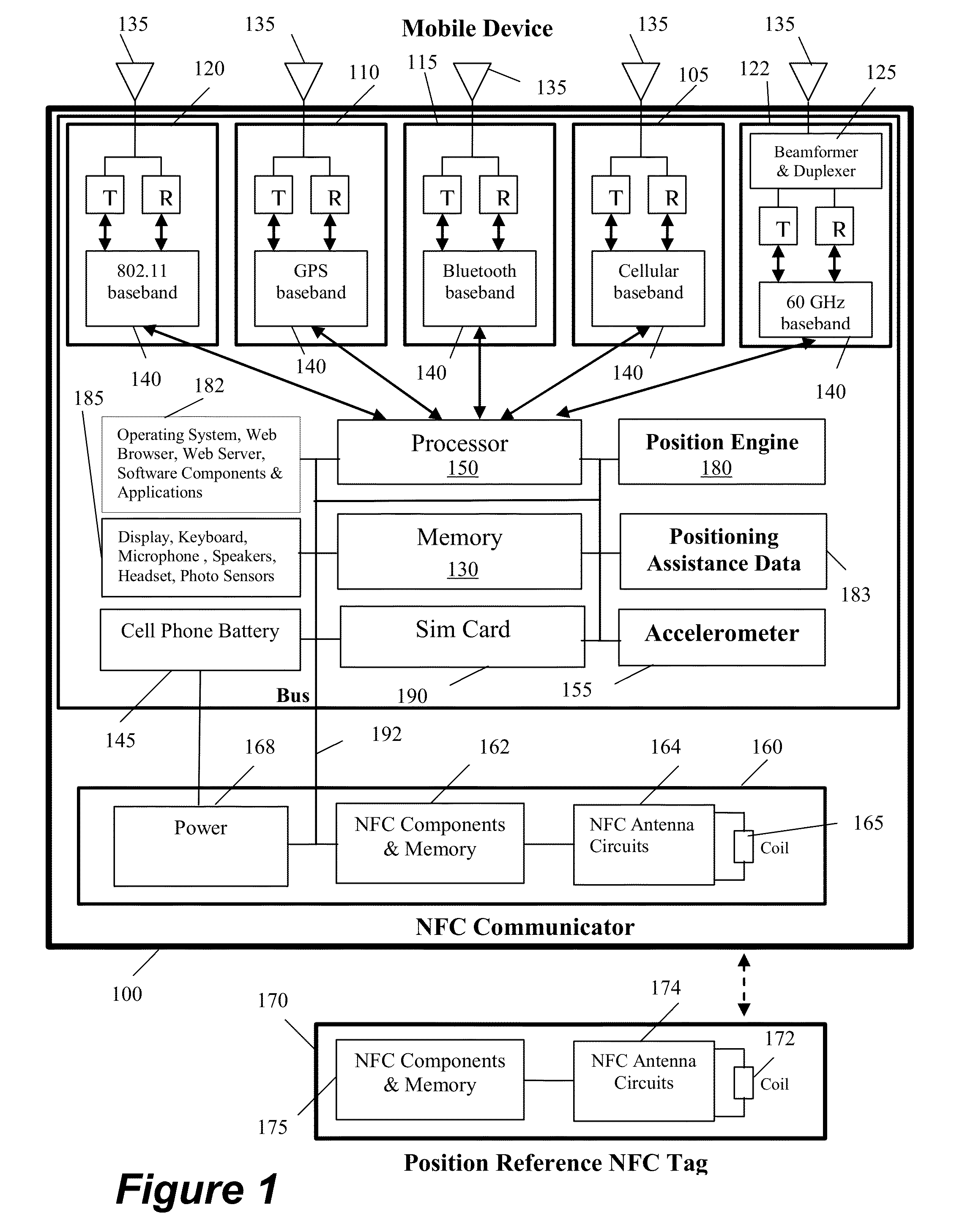
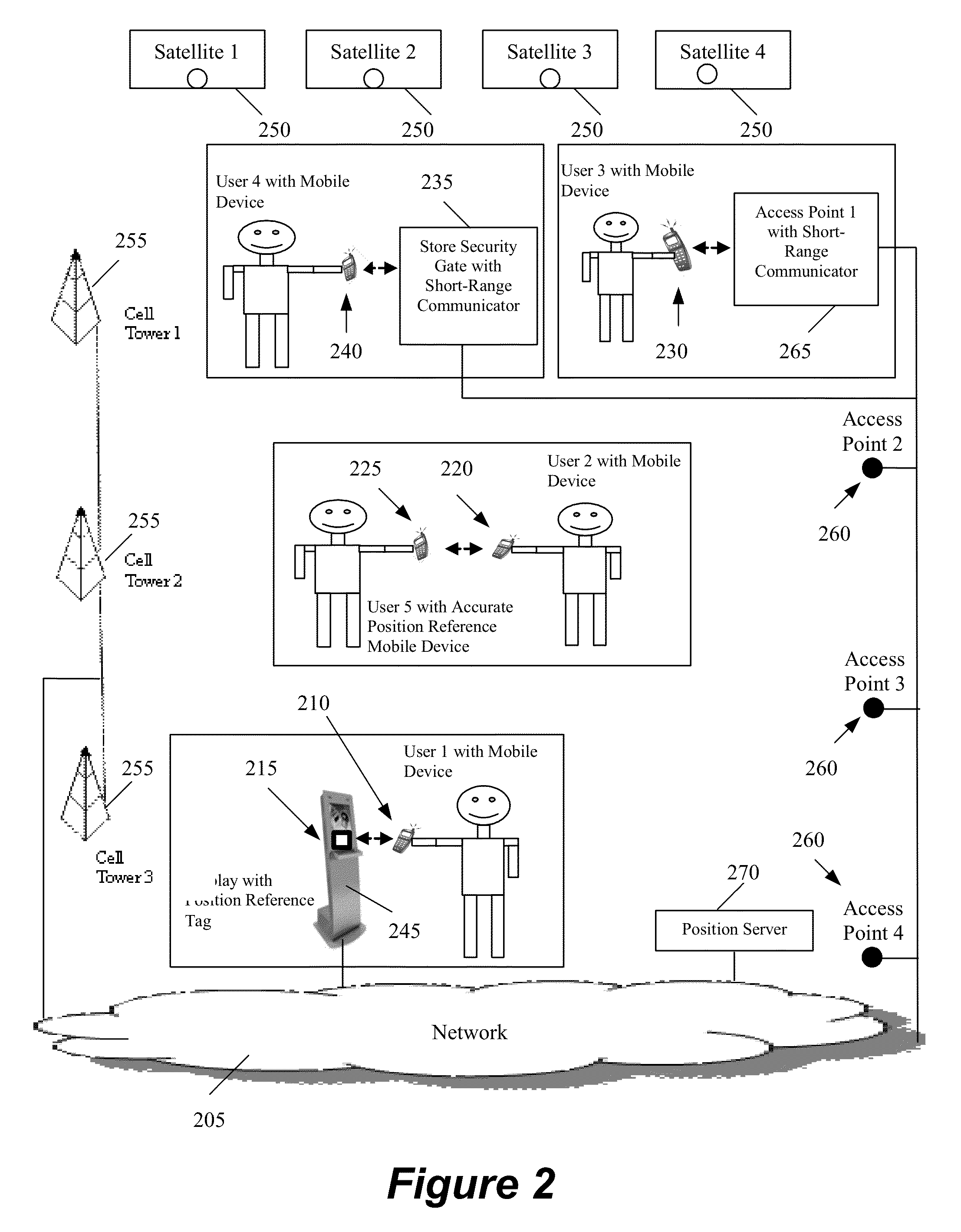
Distributed method and system for determining the position of a mobile device using long-range signals and calibrating the position using short-range signals
InactiveUS20130029685A1Energy efficient ICTNear-field transmissionWireless communication protocolTraffic signal
A method and system is described where a plurality of position reference devices use short-range wireless communication protocols to transmit positioning assistance data to nearby mobile devices, and the mobile devices use the assistance data to model errors and re-calibrate their positioning systems. The short-range communication methods include NFC, RFID, Bluetooth®, short-range 802.11, Wi-Fi Direct, and high frequency focused beams such as 60 GHz. The position reference devices are passive or active NFC tags, passive or active RFID tags, other devices that include such tags as their components, Bluetooth®-enabled devices, 60 GHz-enabled devices, and 802.11 access points that can lower their transmit power. The reference devices are located at various indoor and outdoor locations such as smart posters, kiosks, ATM machines, malls, store checkout counters, store security gates, wireless access points, cellular base-stations, tollbooths, traffic lights, and street lamp posts.
Owner:GOLBA LLC
Remotely authenticated operation method
InactiveUS7509687B2Improvement effortsEfficient use ofDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrusted ComputingMedia server
The objective of this invention is to provide continuous remote authenticated operations for ensuring proper content processing and management in remote untrusted computing environment. The method is based on using a program that was hidden within the content protection program at the remote untrusted computing environment, e.g., an end station. The hidden program can be updated dynamically and it includes an inseparable and interlocked functionality for generating a pseudo random sequence of security signals. Only the media server that sends the content knows how the pseudo-random sequence of security signals were generated; therefore, the media server is able to check the validity of the security signals, and thereby, verify the authenticity of the programs used to process content at the remote untrusted computing environment. If the verification operation fails, the media server will stop the transmission of content to the remote untrusted computing environment.
Owner:ATTESTWAVE LLC
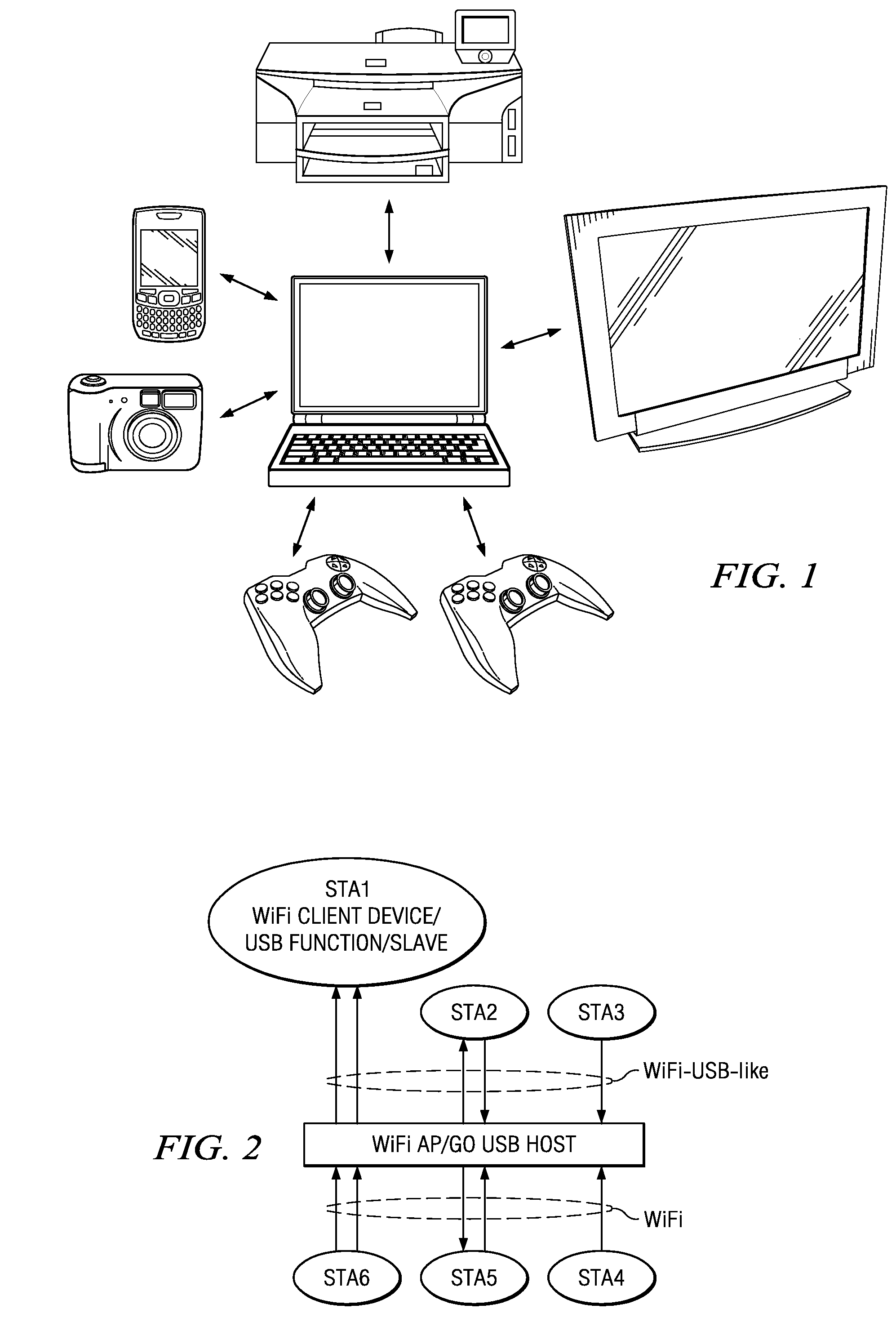
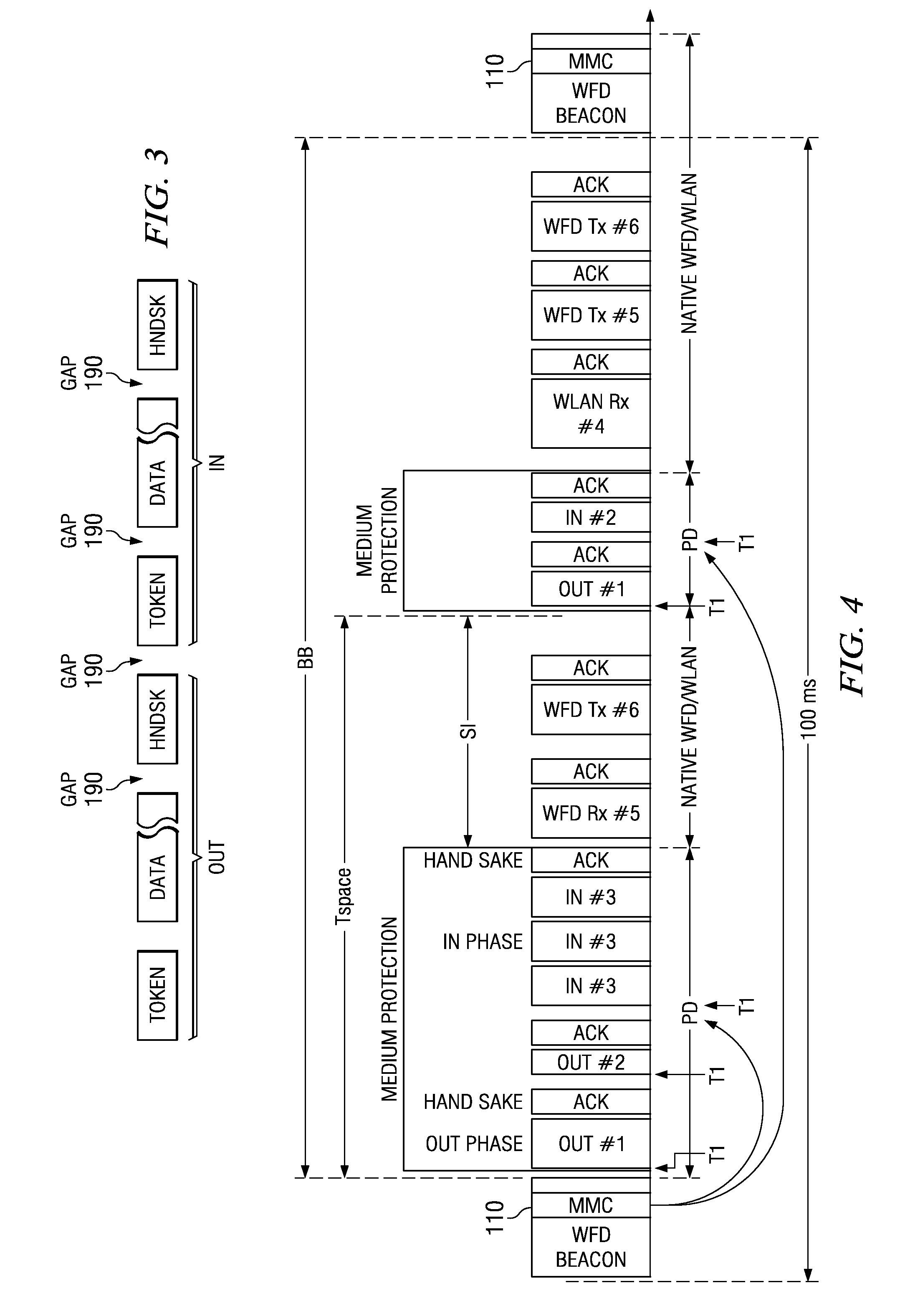
INTERRELATED WiFi AND USB PROTOCOLS AND OTHER APPLICATION FRAMEWORK PROCESSES, CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS
ActiveUS20110188391A1Avoid collisionEnergy efficient ICTError preventionModem deviceData transmission
A master electronic circuit (300) includes a storage (324) representing a wireless collision avoidance networking process (332) involving collision avoidance overhead and combined with a schedulable process (345) including a serial data transfer process and a scheduler, a wireless modem (350) operable to transmit and receive wireless signals for the networking process (332), and a processor (320) coupled with the storage (324) and with the wireless modem (350) and operable to execute the scheduler to establish and transmit a schedule (110) for plural serial data transfers involving the processor (320) and distinct station identifications, and to execute the serial data transfers inside the wireless networking process and according to the schedule so as to avoid at least some of the collision avoidance overhead. Other electronic circuits, processes of making and using, and systems are disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
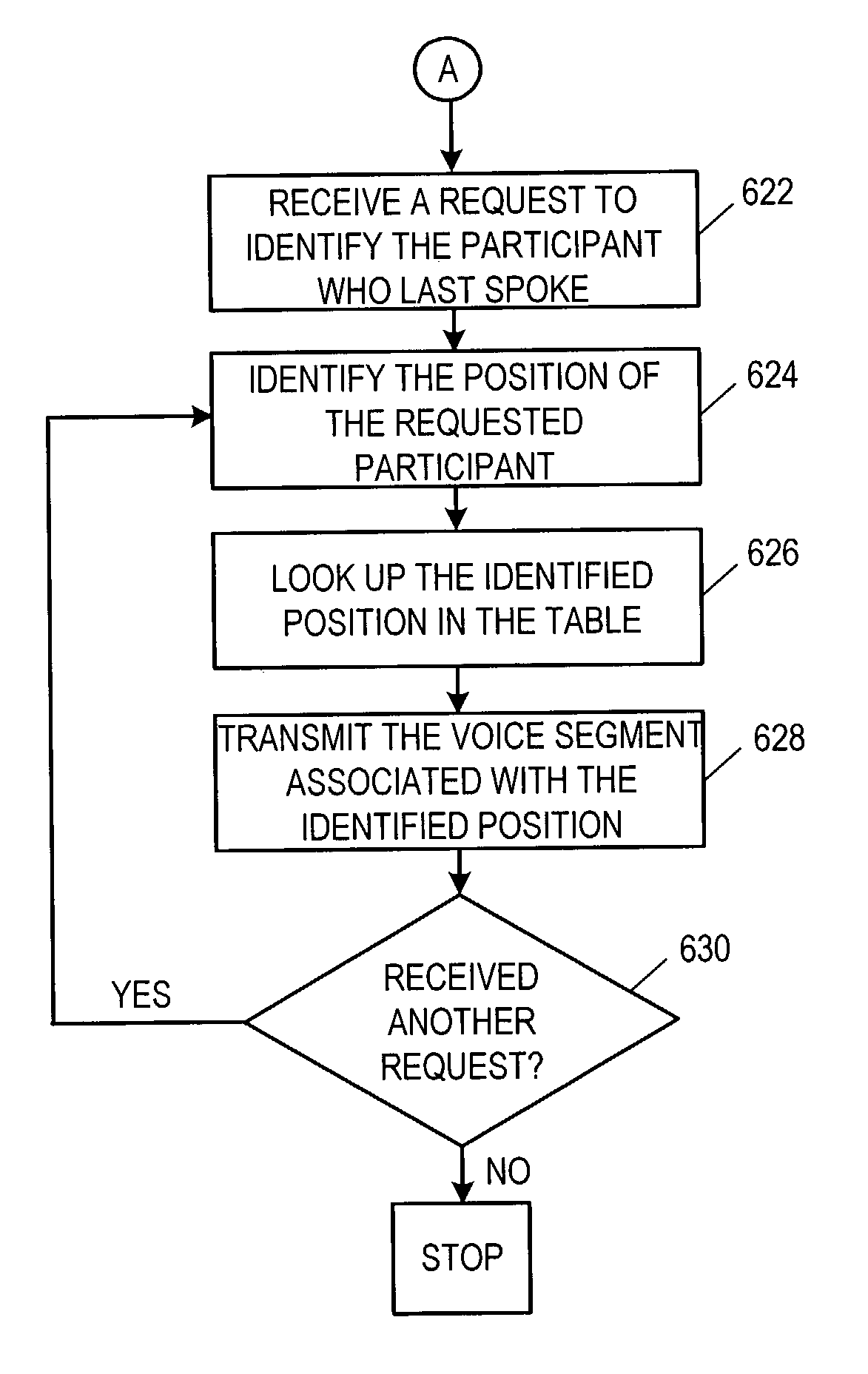
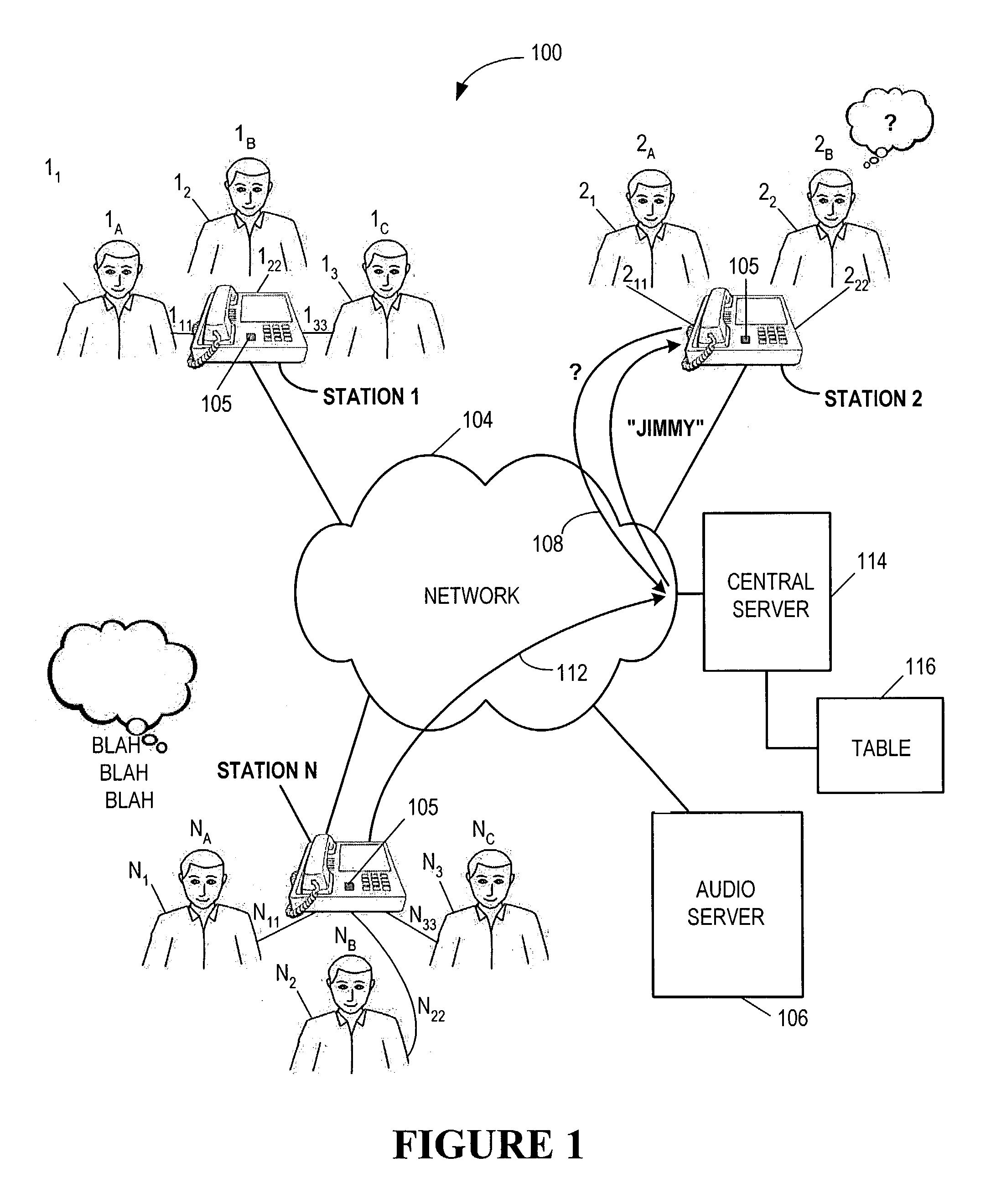
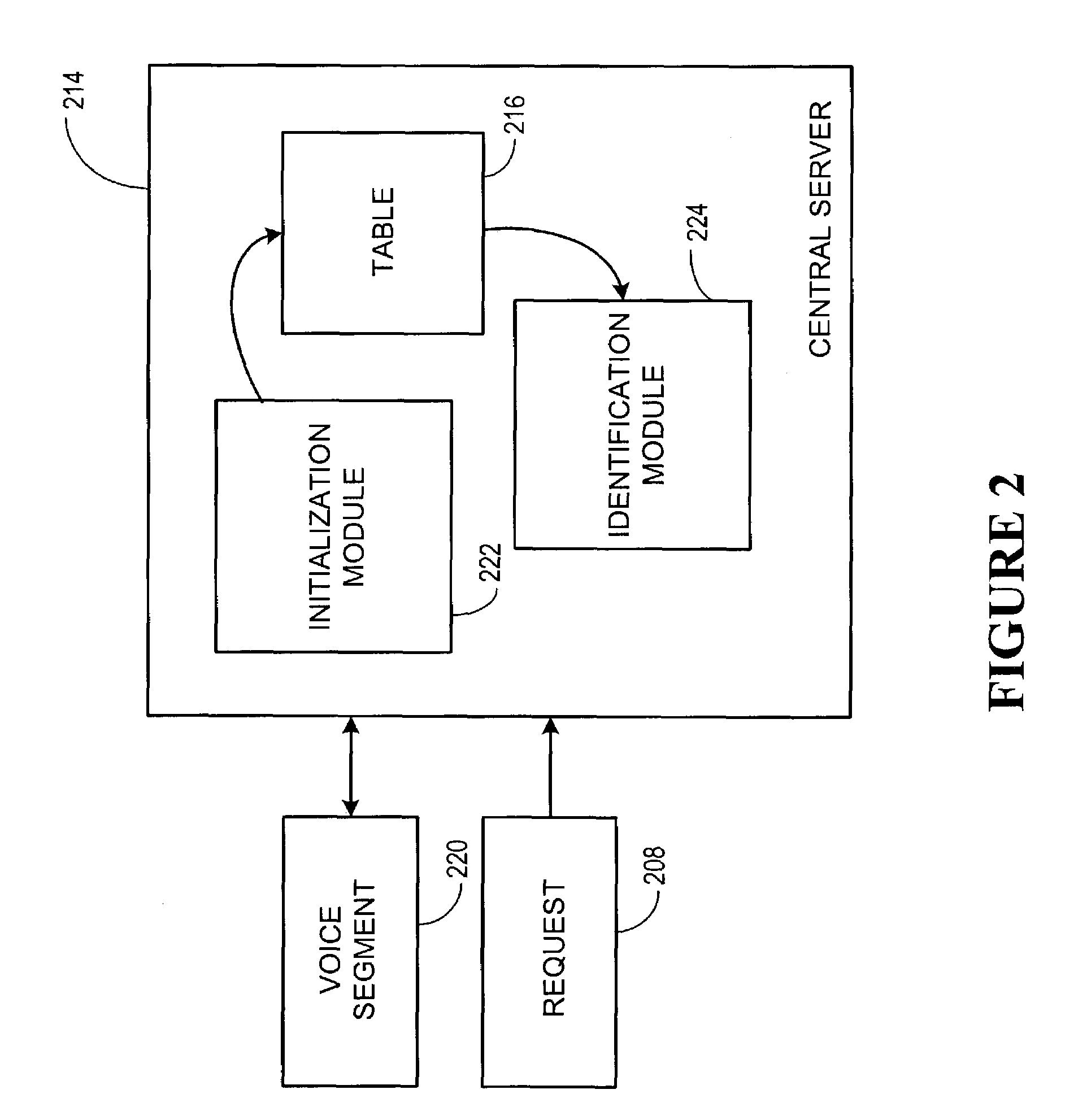
Who said that? teleconference speaker identification apparatus and method
InactiveUS7266189B1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionSpecial service for subscribersIdentification deviceTeleconference
The invention relates to an apparatus and method for identifying teleconference participants. More particularly, the invention relates to a conference system that includes an initialization means for initializing a call between participants located in at least two remote stations and an identification means for identifying one of the participants in one remote station responsive to a request from another of the participants in another remote station. The initialization means comprises table means for creating a table associating each of the participants to a position in a particular remote station and including a recorded voice segment of each of the participants. The identification means uses the table to identify the participant last to speak by looking up the position of the last speaker on the table and playing back the recorded voice segment of the participant associated with that position.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
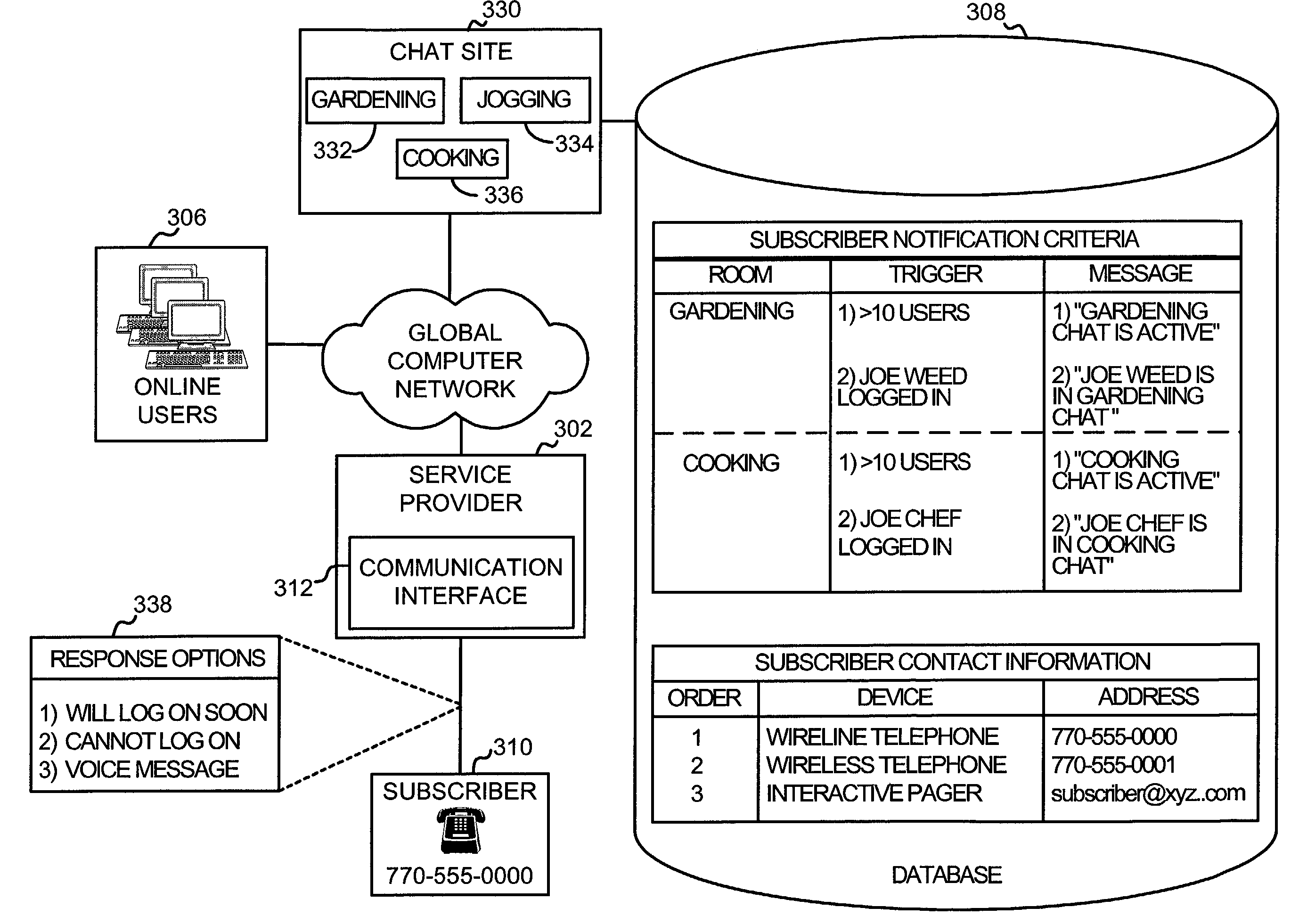
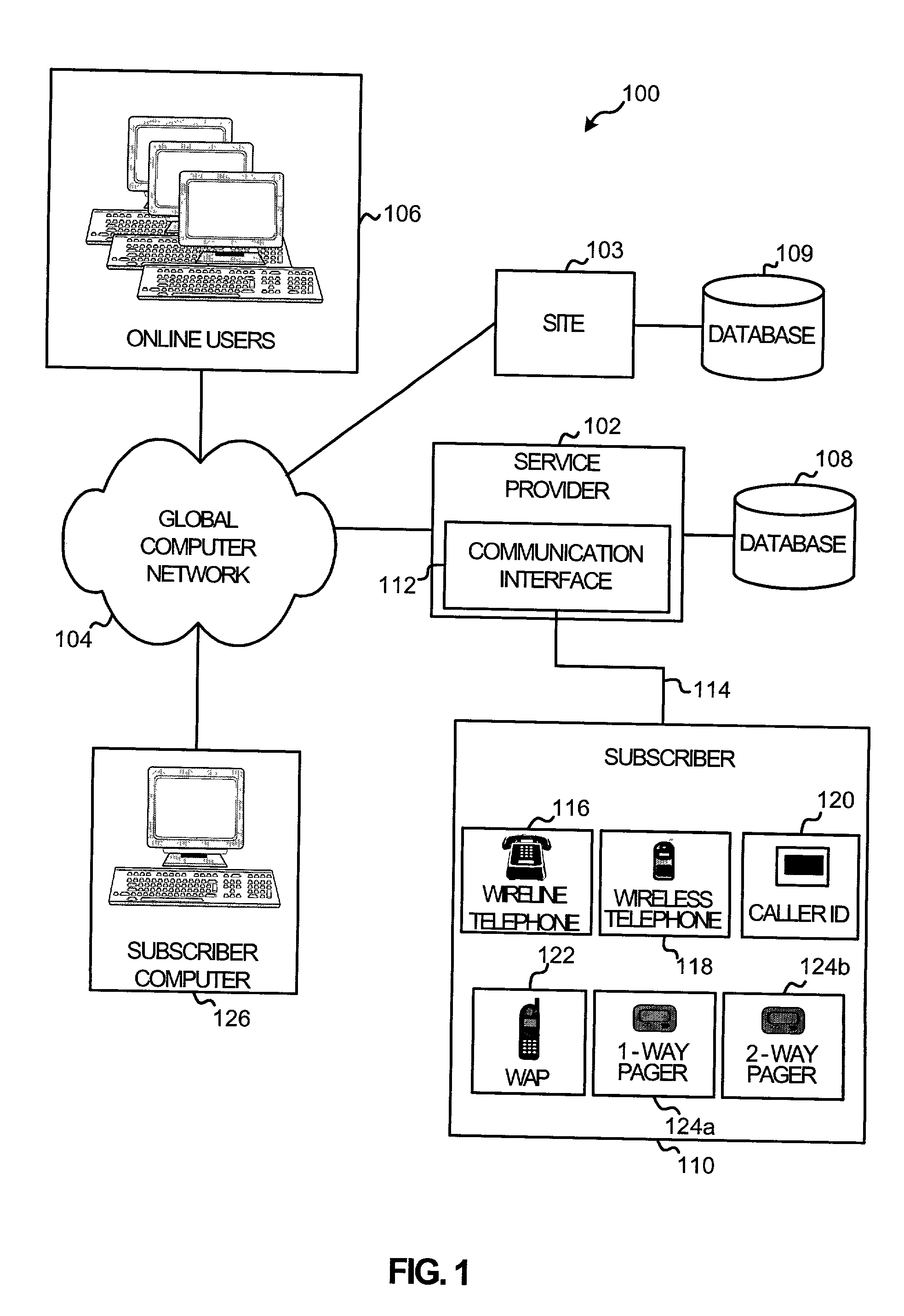
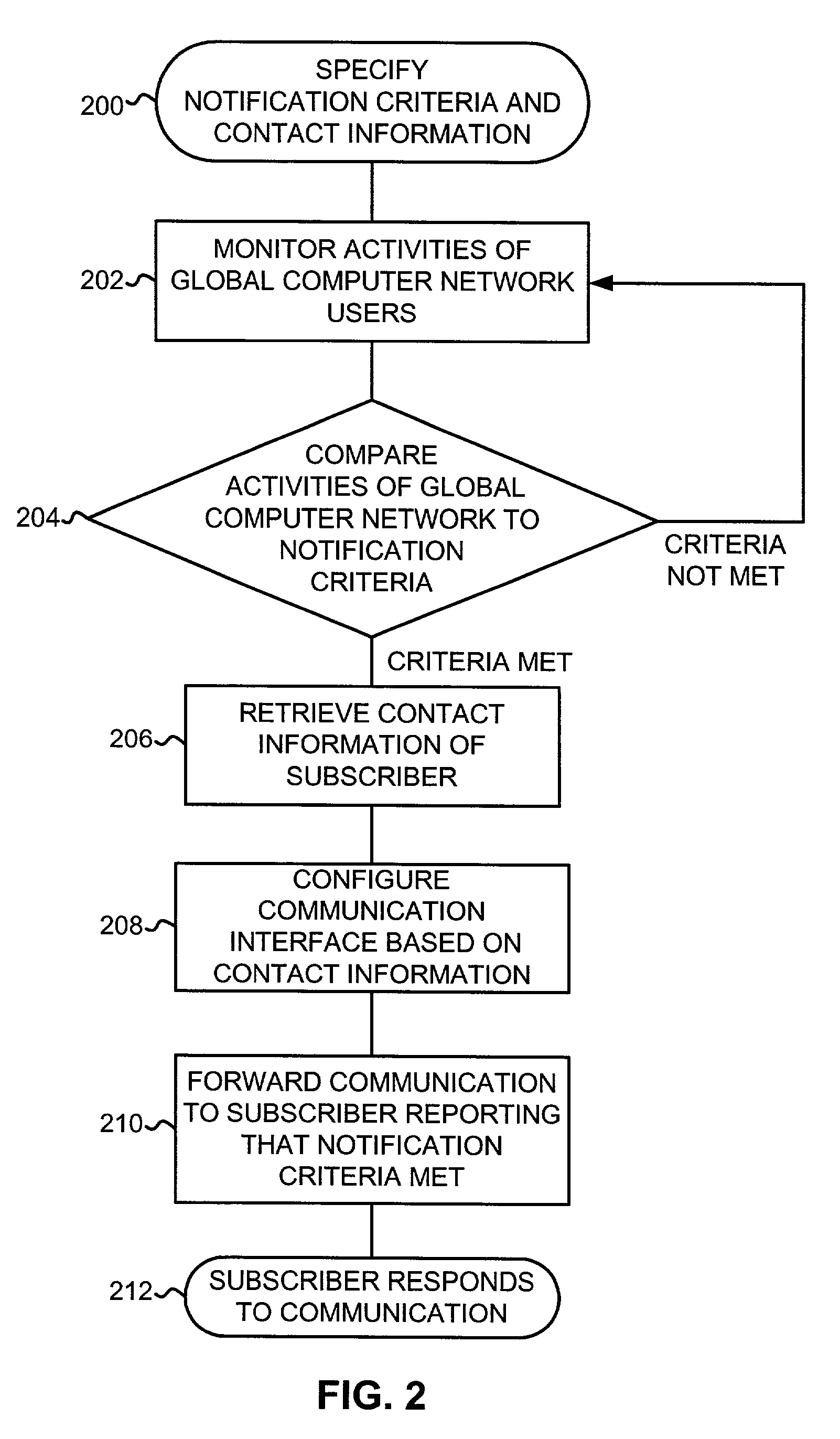
System and method for notifying an offline global computer network user of an online interaction
InactiveUS20050004984A1Easy to placeAvoid difficultySpecial service provision for substationFinanceChat roomPager
A system and method for notifying an offline global computer network user of an online interaction in which the offline user could participate. The system and method specify notification criteria of the offline user, monitor activities occurring on the global computer network, compare the activities to the notification criteria, and, if the activities satisfy the notification criteria, forward an offline communication to the offline user, which notifies the offline user of the online interaction. Examples of the online interactions include chat rooms, game sites, instant messaging services, auctions, and calls made over the global computer network. Examples of the offline communication include calls to a wireline telephone, calls to a wireless telephone, messages to a caller identification device, messages to a wireless access protocol device, messages to a one-way pager, and messages to an interactive pager.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
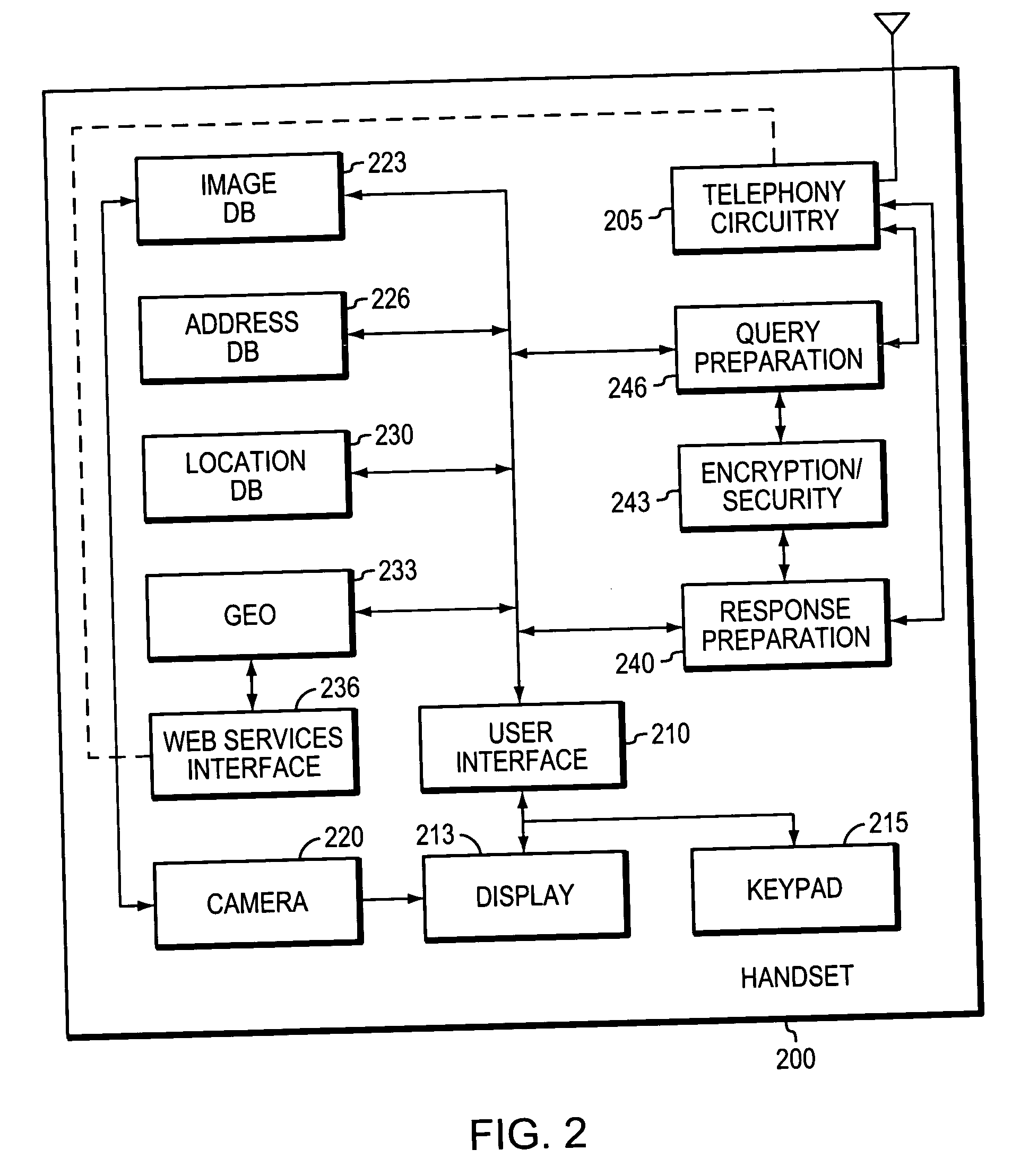
Implementation of serverless applications over wireless networks
InactiveUS20060030339A1Facilitates display of and selectionFacilitates associationPosition fixationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsHandsetTelephony
Owner:CELLITITUDE
Ppdu receiving method and apparatus based on the MIMO technique in a WLAN system
ActiveUS20120327915A1Improve throughputBottleneck phenomenon can be decreasedError preventionTransmission path divisionMulti inputTelecommunications
Provided is a method of receiving a physical layer convergence procedure (PLCP) protocol data unit (PPDU) by an access point (AP) in a wireless local area (LAN) system. The method includes: allocating a first transmission channel bandwidth to a first station (STA) which is multiple input multiple output (MIMO)-paired with the AP; allocating a second transmission channel bandwidth to a second STA which is MIMO-paired with the AP; transmitting to the first STA and the second STA a sync trigger for determining a time point at which the first STA transmits a first PPDU and a time point at which the second STA transmits a second PPDU; and receiving simultaneously the first PPDU and the second PPDU from the first STA and the second STA.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
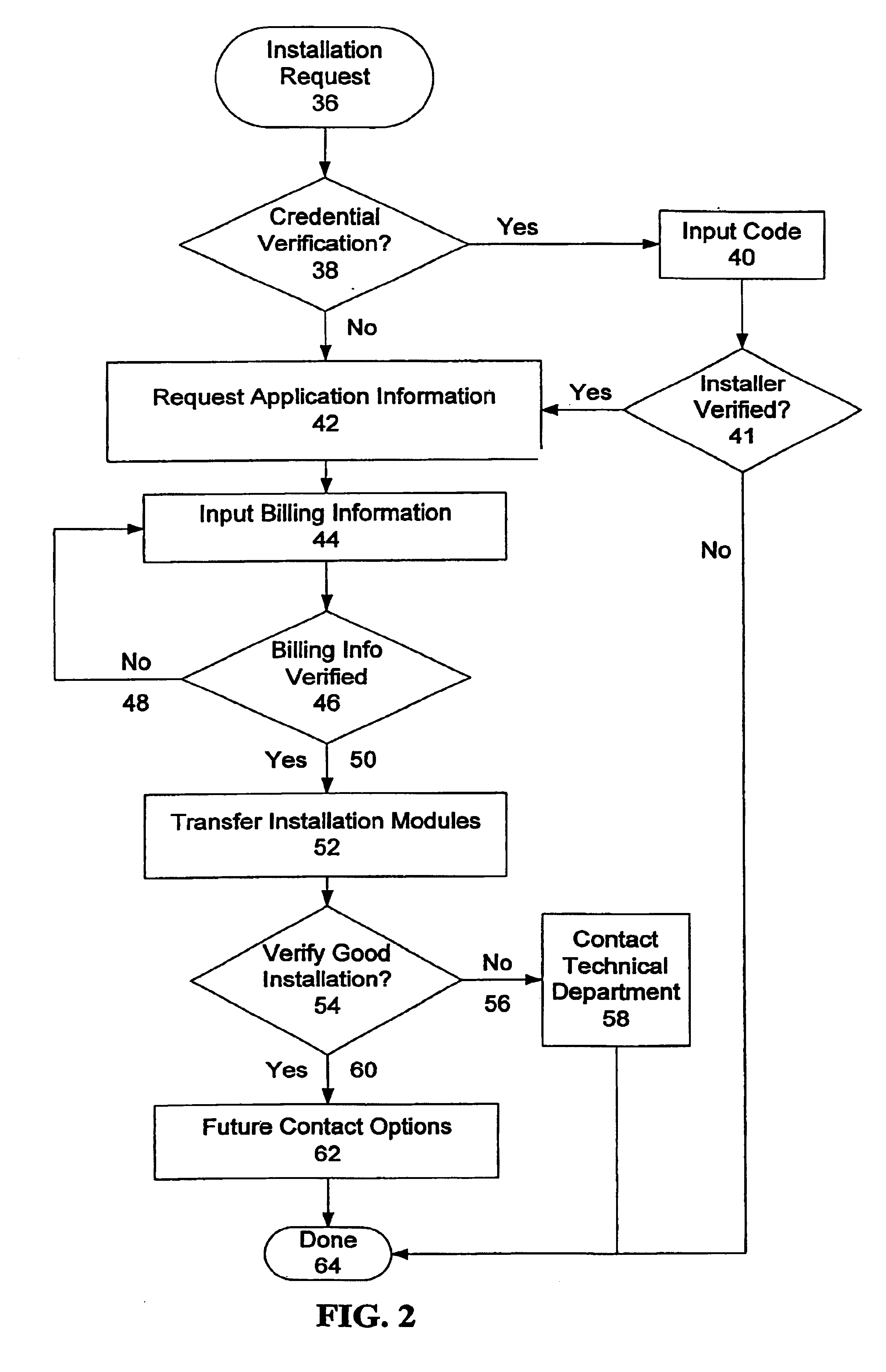
System and method for installing an auditable secure network
InactiveUS6918038B1Short timeImprove securityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionStationPassword
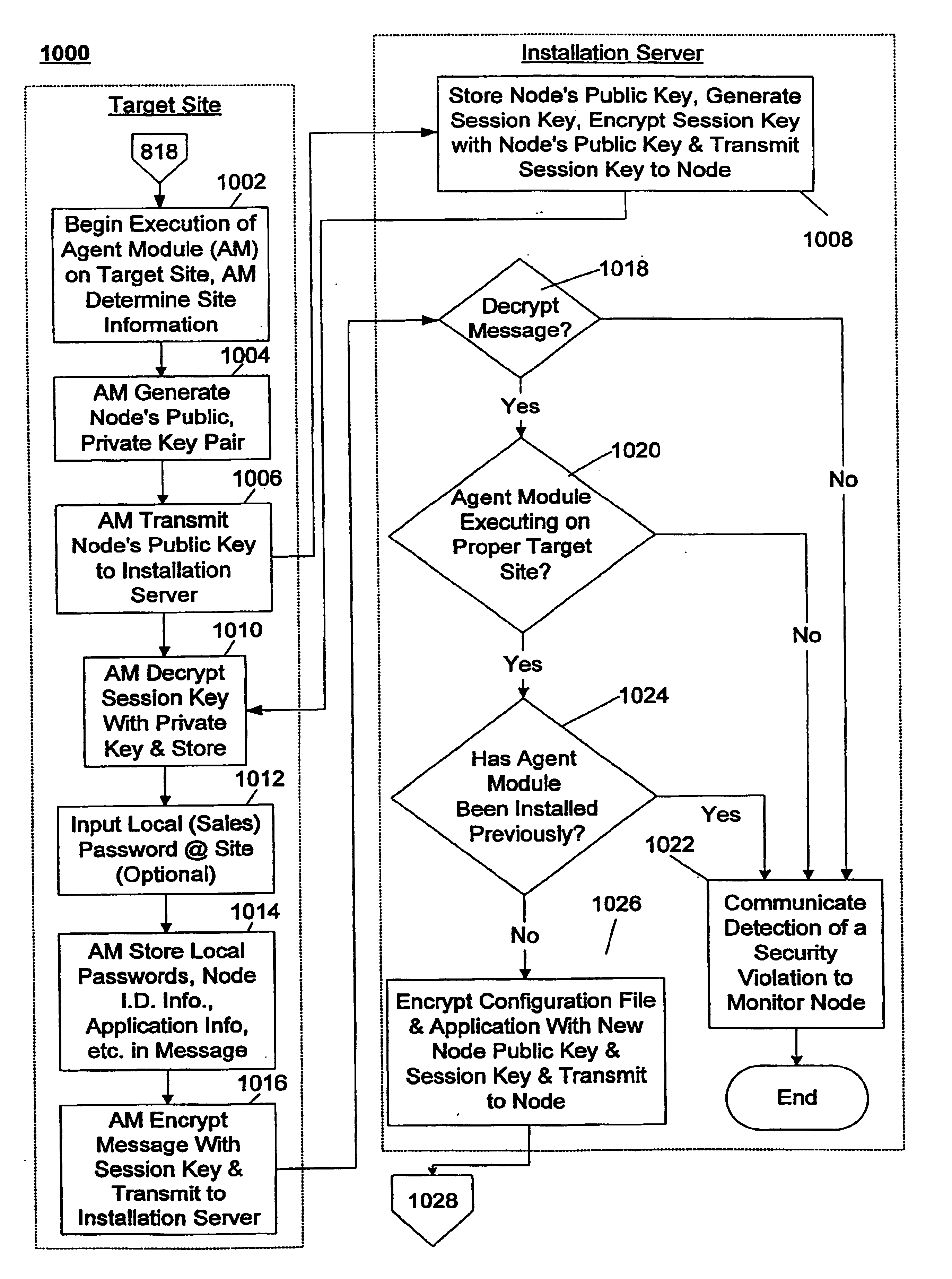
A system and method for generating and remotely installing a private secure and auditable network is provided. Node identification, link, and application information is input into a template. A generator generates components using the information in the template and the components are remotely installed using an installation server. The components include agent modules which are each installed at predetermined target site and establish communication with the installation server to facilitate the download of other components, including application software and configuration files. Each node can only be installed once and is specific to a predetermined target site. For each link, a unique pair of keys is generated in a form which is not human readable, each key corresponds to a different direction of communication over the link. Data transmitted between nodes is encrypted using public-private key pairs. At least one monitor node manages the security of the network, strobes keys, and may take nodes out of the network in the event of a security violation. In such a case, one or more nodes, or the entire network, may be regenerated and installed anew. Throughout the generation and installation a plurality of verifications, authorizations, and password entries may be required by independent groups to arrive at the network. Preferably, the installation is audited by several groups, and the overall operation may be audited by a second monitor node to detect the presence of an interposed “pirate” node.
Owner:ANGEL SECURE NETWORKS
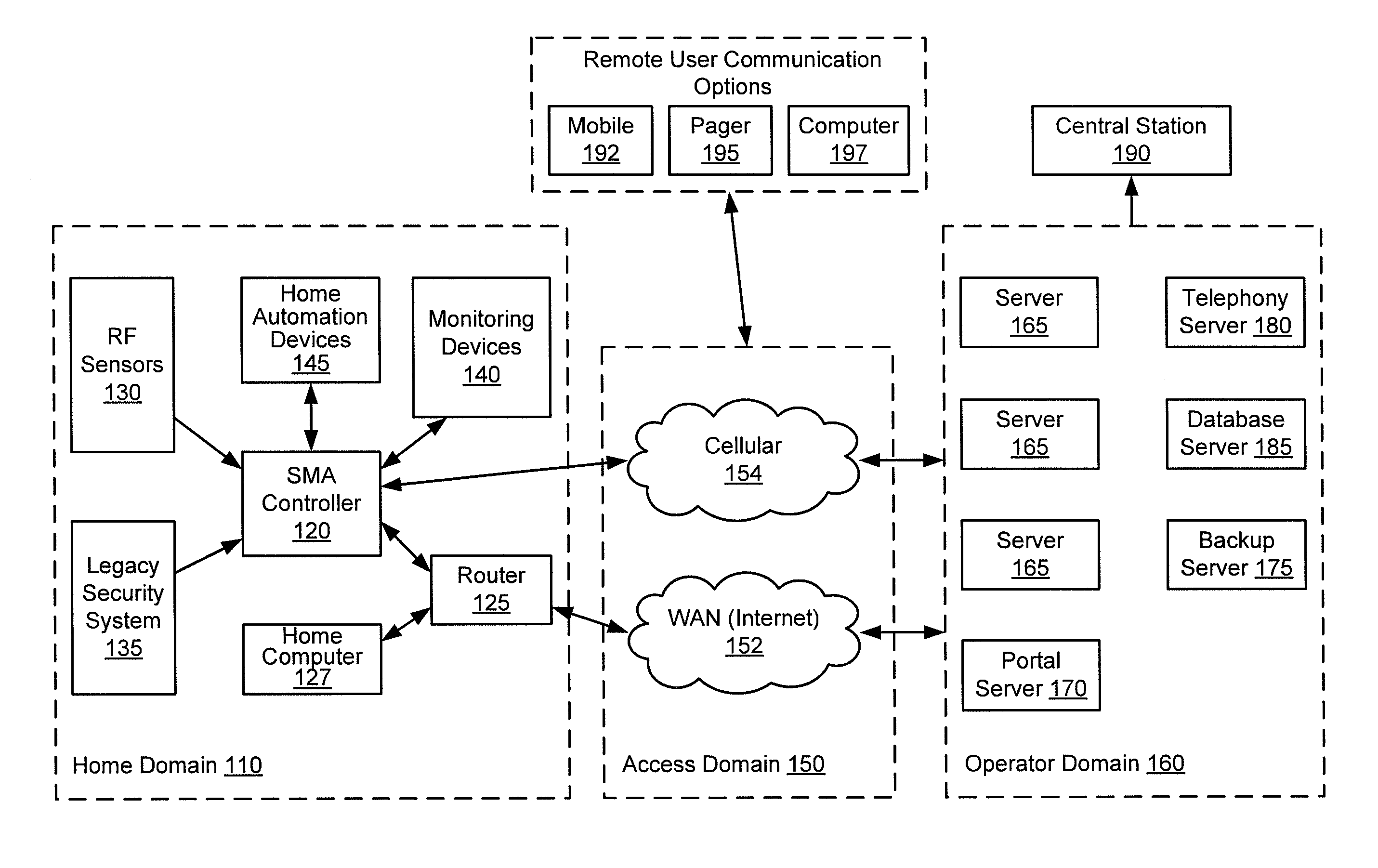
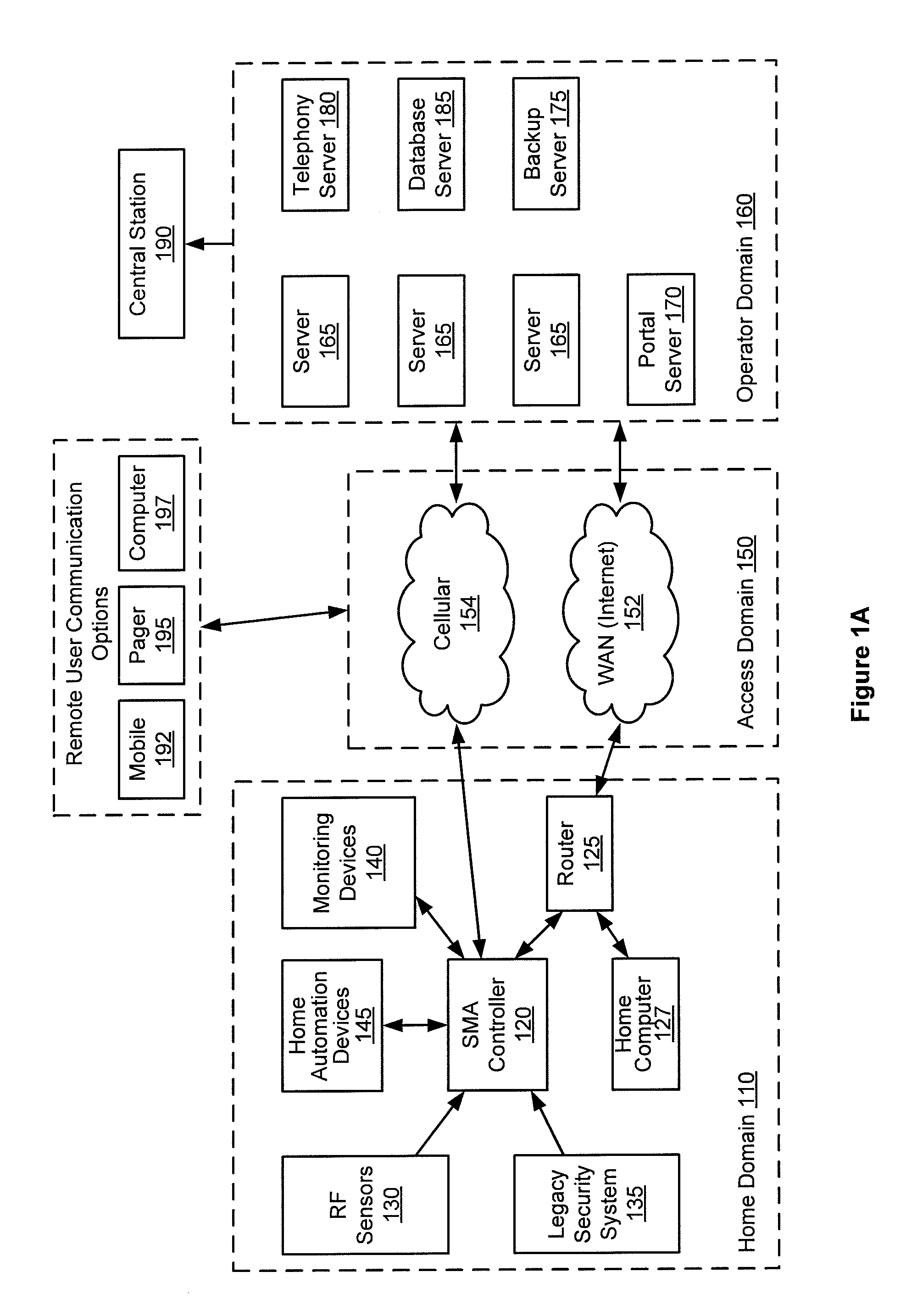
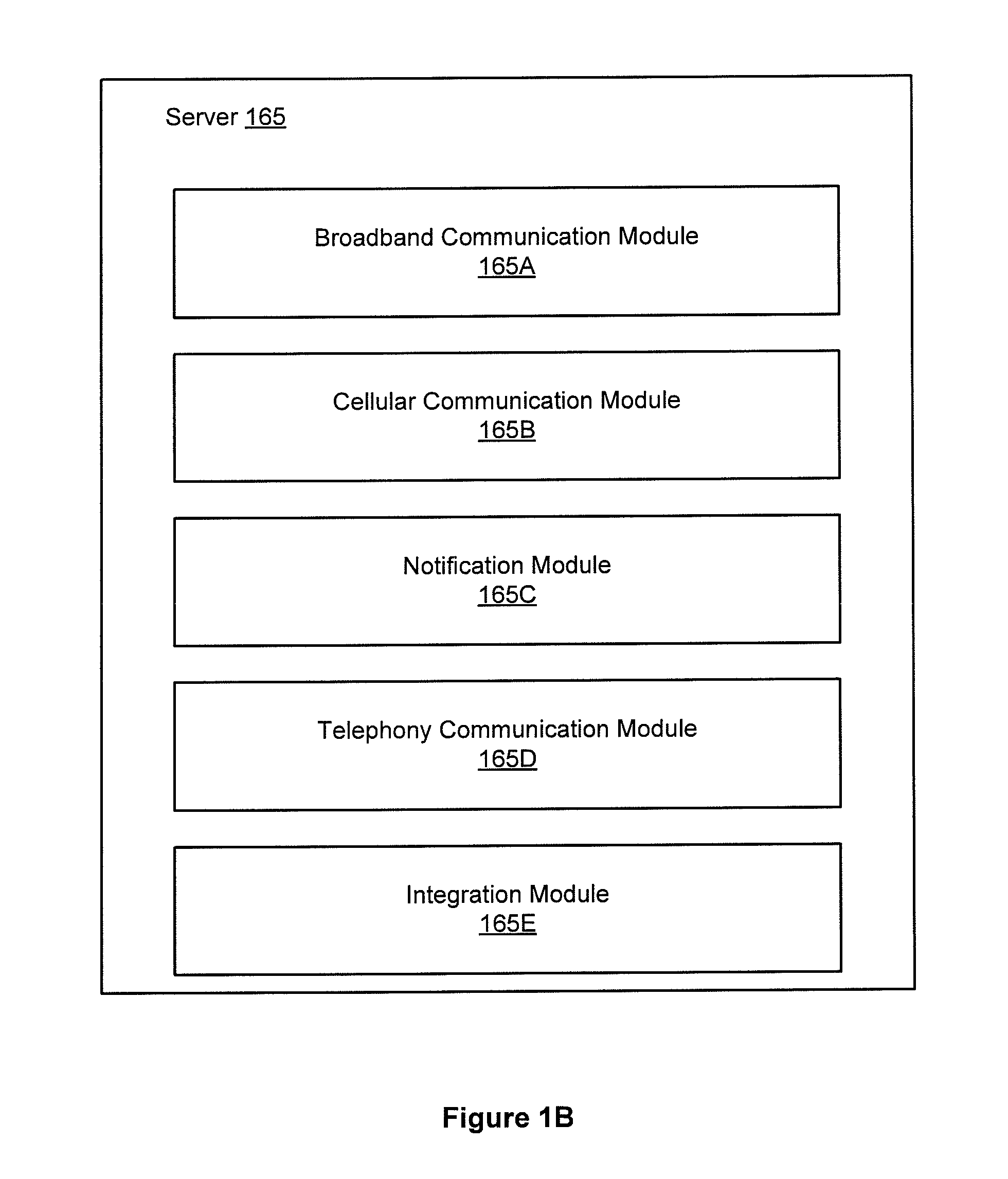
Server-based notification of alarm event subsequent to communication failure with armed security system
A server-based environment for reporting a status of a security, monitoring and automation controller is provided. Detecting cessation of an always-on persistent network connection between the SMA controller and the server is also provided. Reporting the cessation of the network connection to an end user and defined others is further provided. A further aspect provides for automatically reporting an alarm event to a central station, the end user, and others, in the event the cessation of the network connection occurs while the SMA controller is armed and after a zone fault event, and not receiving a disarm notification prior to expiration of a preset entry delay.
Owner:ICONTROL NETWORKS
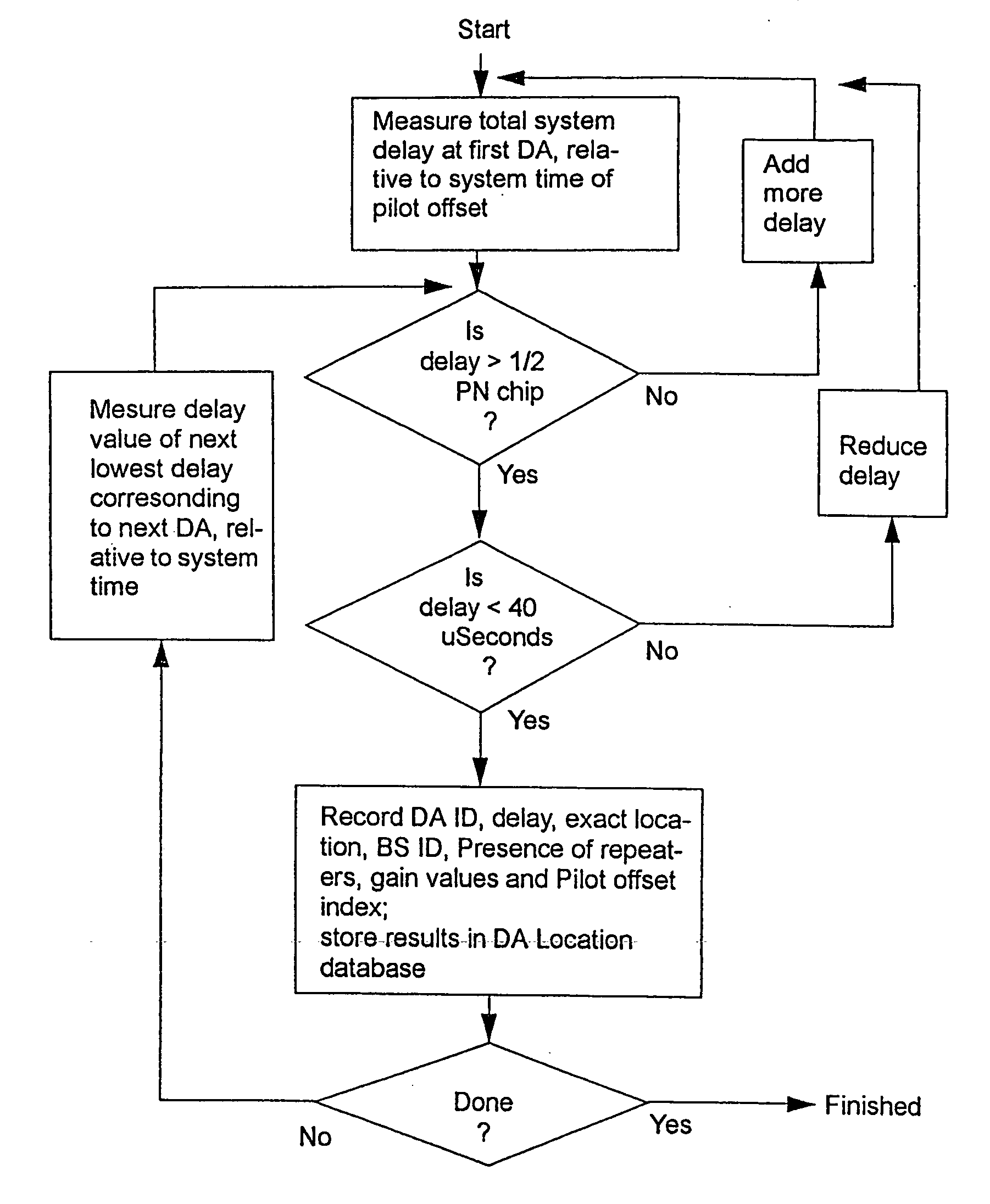
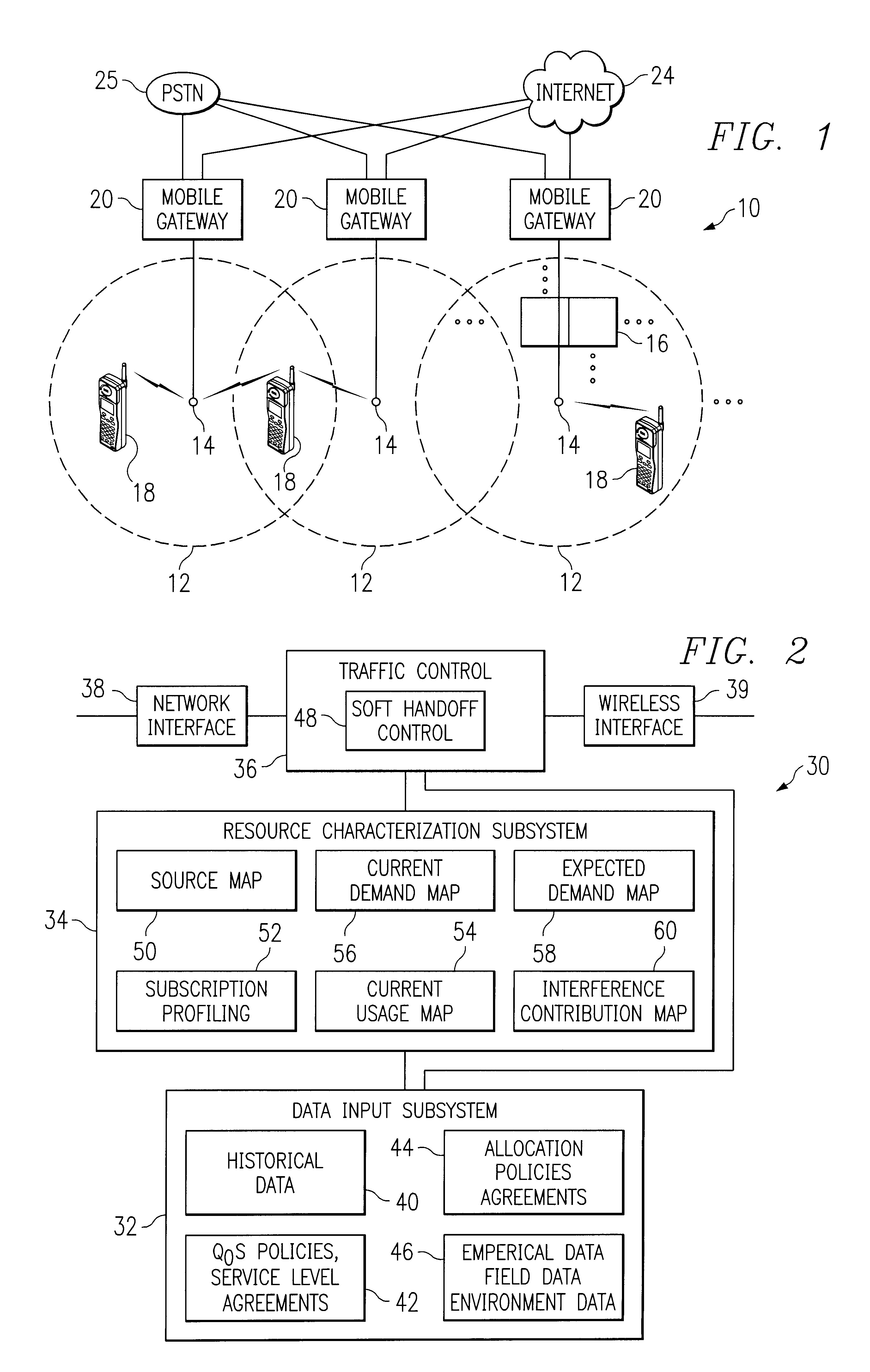
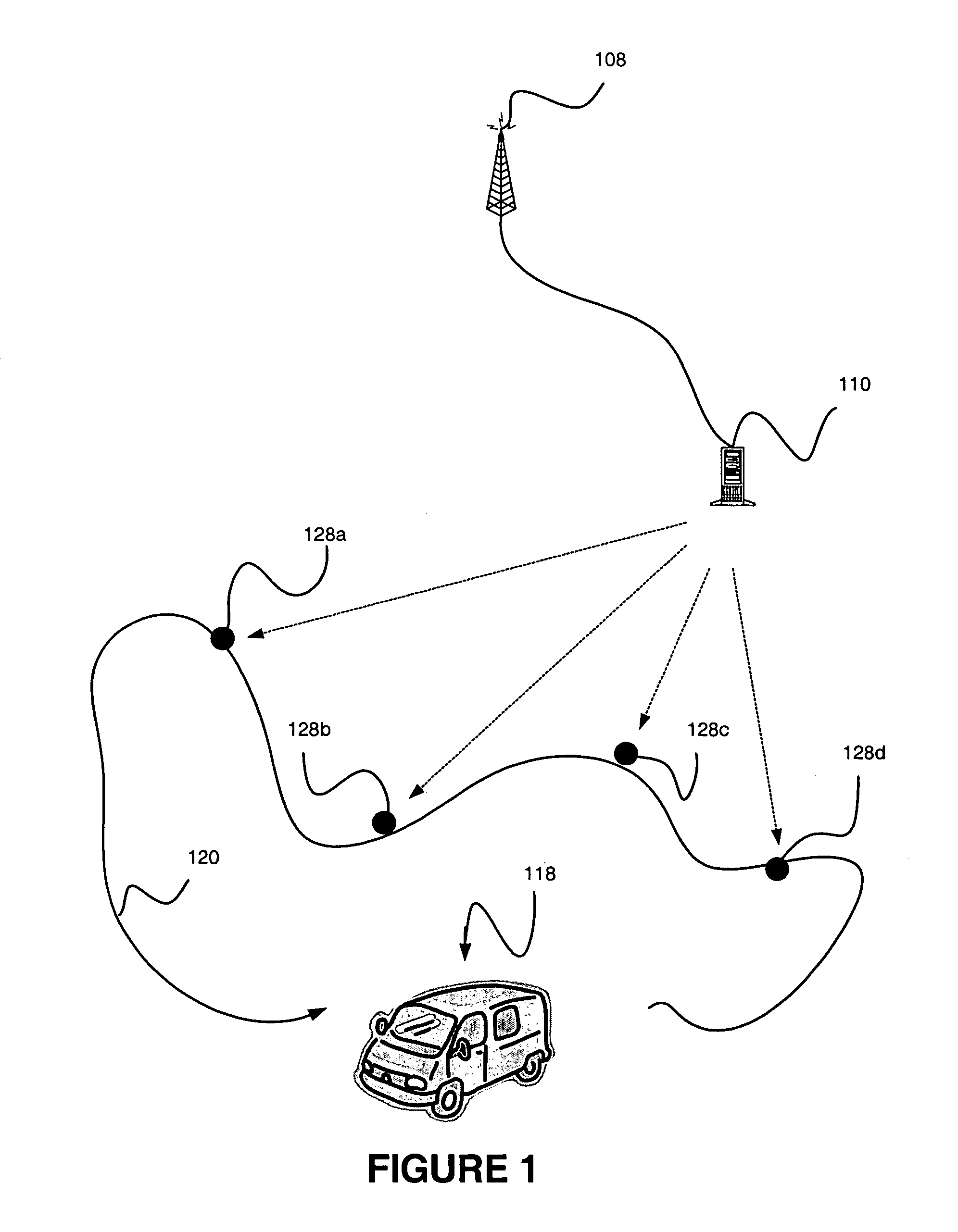
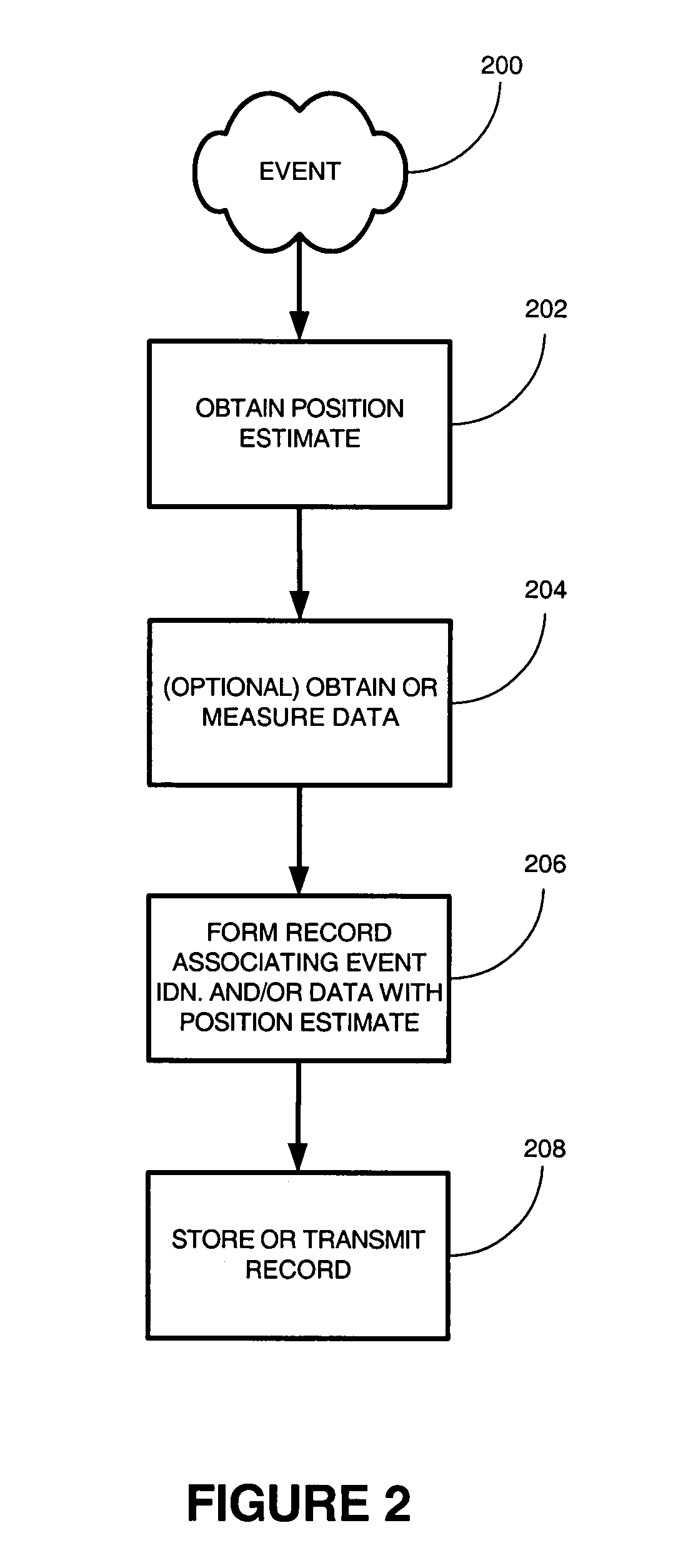
Event-triggered data collection
A method of obtaining data useful for one or more network applications is described. The method is performed responsive to a triggering event, such as a dropped call, a position fix, or even expiration of a timer. A position estimate for a subscriber station is obtained responsive to the event. A record is then formed associating the position estimate for the subscriber station with an identifier of the triggering event and / or data measured or obtained responsive to the event, such as the strength of one or more pilots visible to the subscriber station. The record is either stored locally or transmitted to a remote location. In one implementation, the record is transmitted to a remote location, and stored in a database holding like records relating to other subscriber stations.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
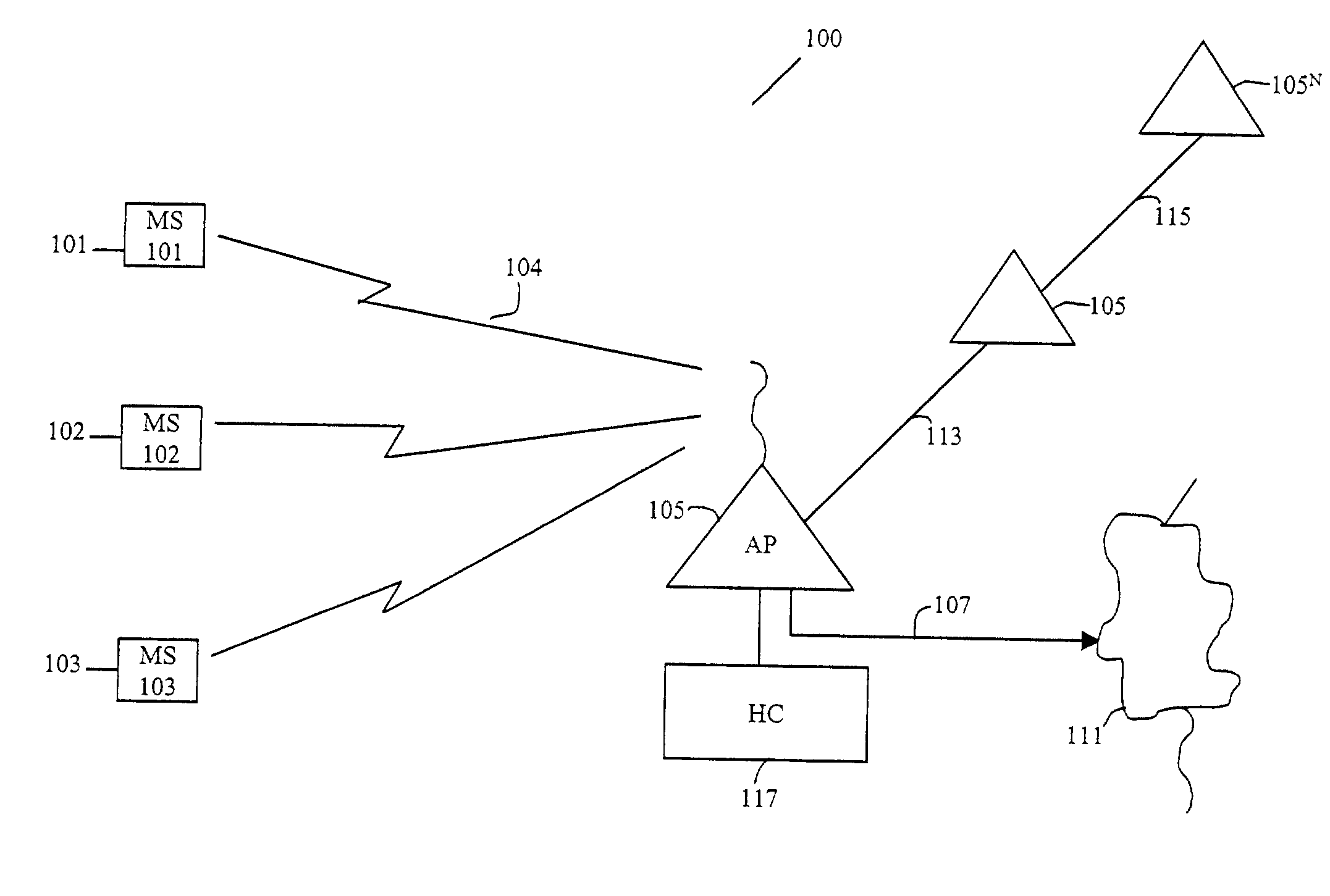
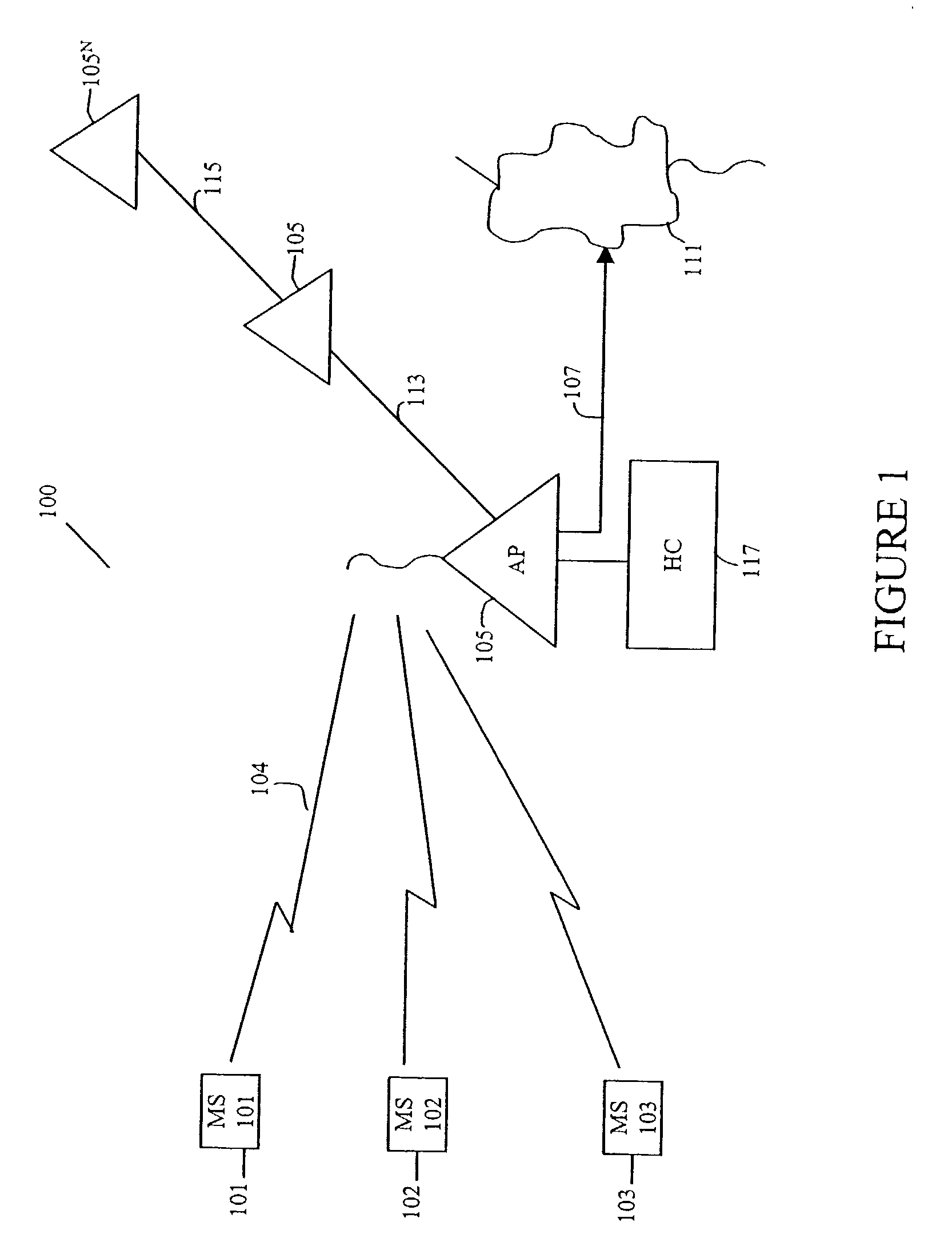
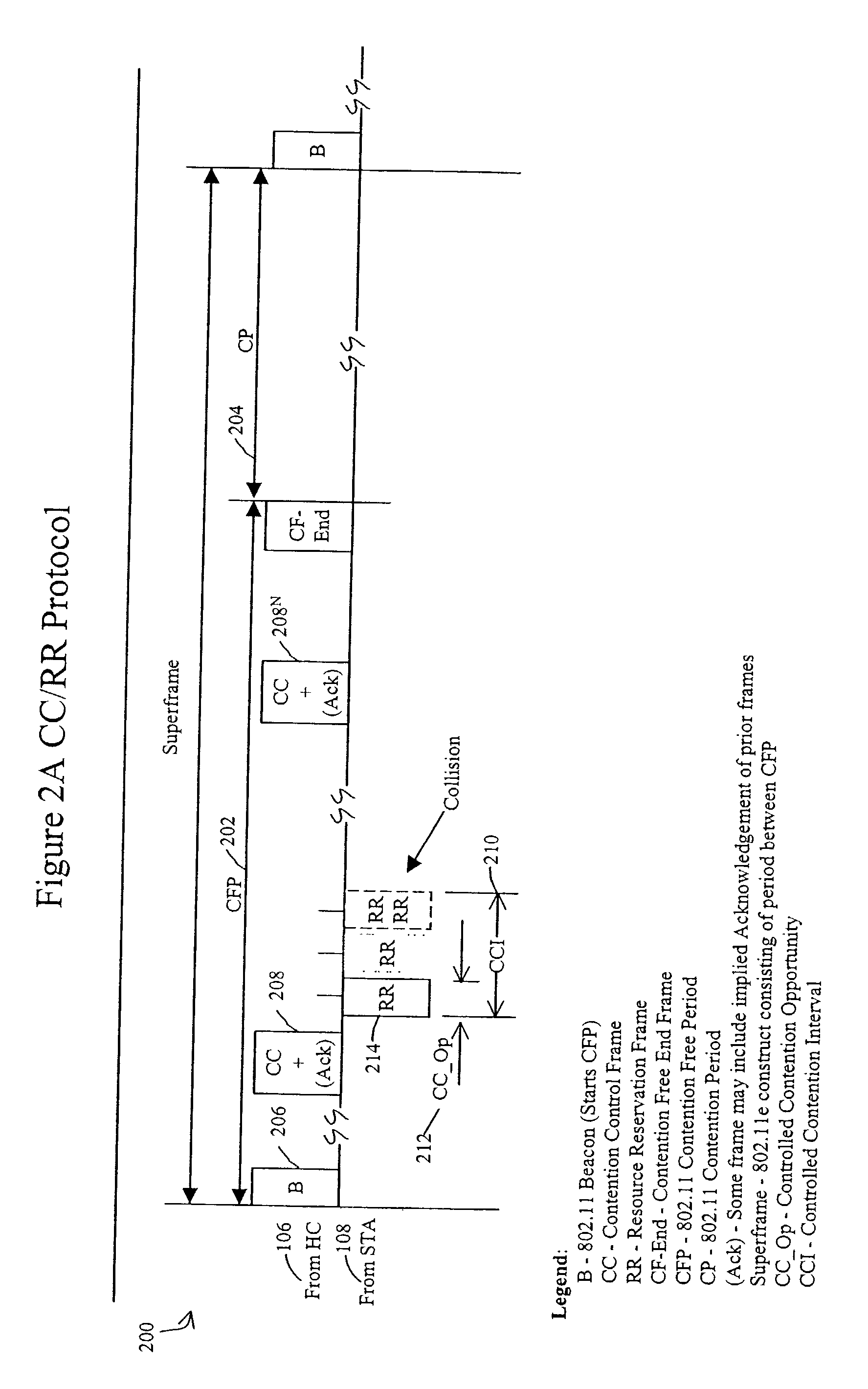
Method and system for optimally serving stations on wireless LANs using a controlled contention/resource reservation protocol of the IEEE 802.11e standard
ActiveUS20030161340A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesBasic serviceLocal area network
A method for optimally serving Stations (STA) on Wireless Local Area Network (LAN) using a Controlled Contention / Resource Reservation protocol of the IEEE 802.11e standard. The Wireless LAN includes multiple STAs, mobile or Stationary, airlinked to an access point as a Basic Service Set (BSS). A Hybrid Coordinator (HC) is co-located with the access point for allocating the bandwidth for the BSS using a Controlled Contention / Resource Reservation protocol defined in the IEEE Standard 802.11(e). The HC transmits Contention Control (CC) frames and initiates Controlled Contention Intervals (CCI) having a selected number of slotted intervals. HC receives Resource Reservations (RR) detailing bandwidth needs from STA contenders during a specified time interval called the Controlled Contention Interval (CCI.). Several parameters are installed in each CC for contention control purpose. The several parameters are controlled to optimize efficient use of the wireless medium and reduce access delays for RR frames contending for the wireless medium.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
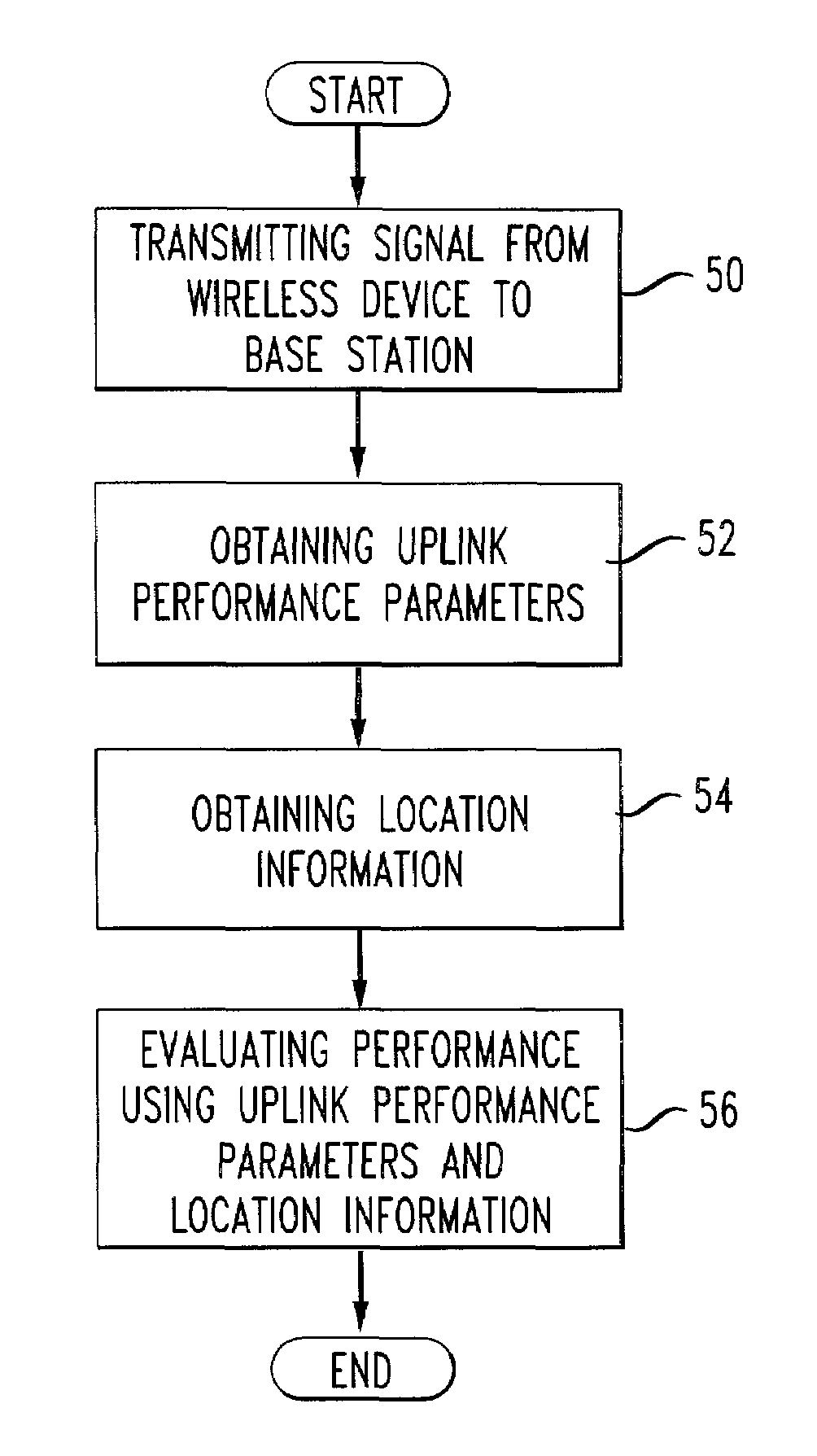
Monitoring network performance using individual cell phone location and performance information
A system and method of collecting call data from a Mobile Telephone Switching Office and combining this data with location information of a wireless device (or devices) to generate information reports concerning the electromagnetic coverage of a cell site. The collection of call data from a switch permits consideration of uplink information in the analysis of system performance. This information combined with location information obtained using a time difference of arrival (TDOA) technique allows the cell site to be evaluated and to remove transient effects associated with, for example, local terrain and other physical impairments.
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
Personnel location and monitoring system and method for enclosed facilities
InactiveUS20110227740A1Limit power usageMeet growth requirementsRegistering/indicating time of eventsPosition fixationMotion detectorMonitoring system
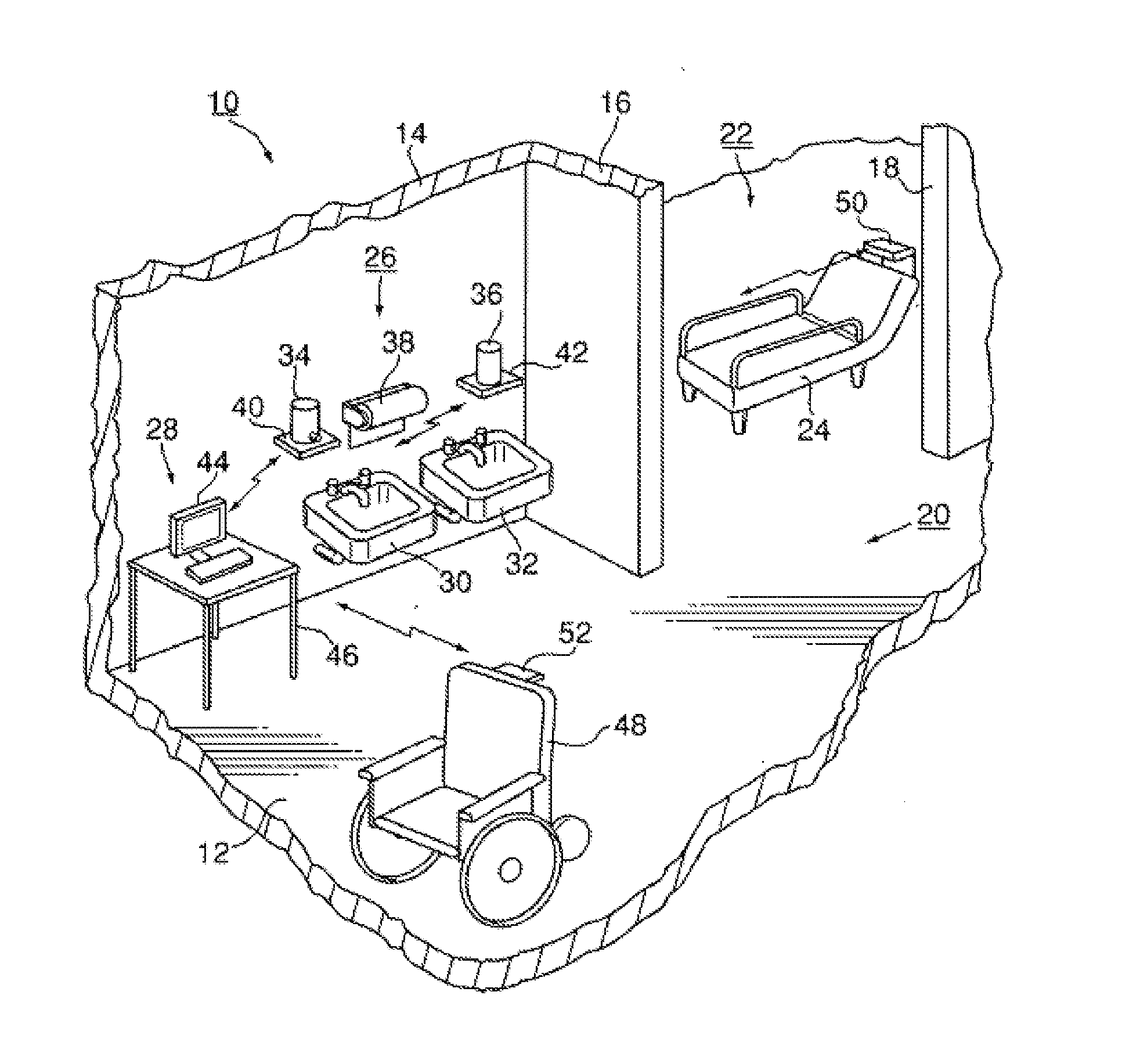
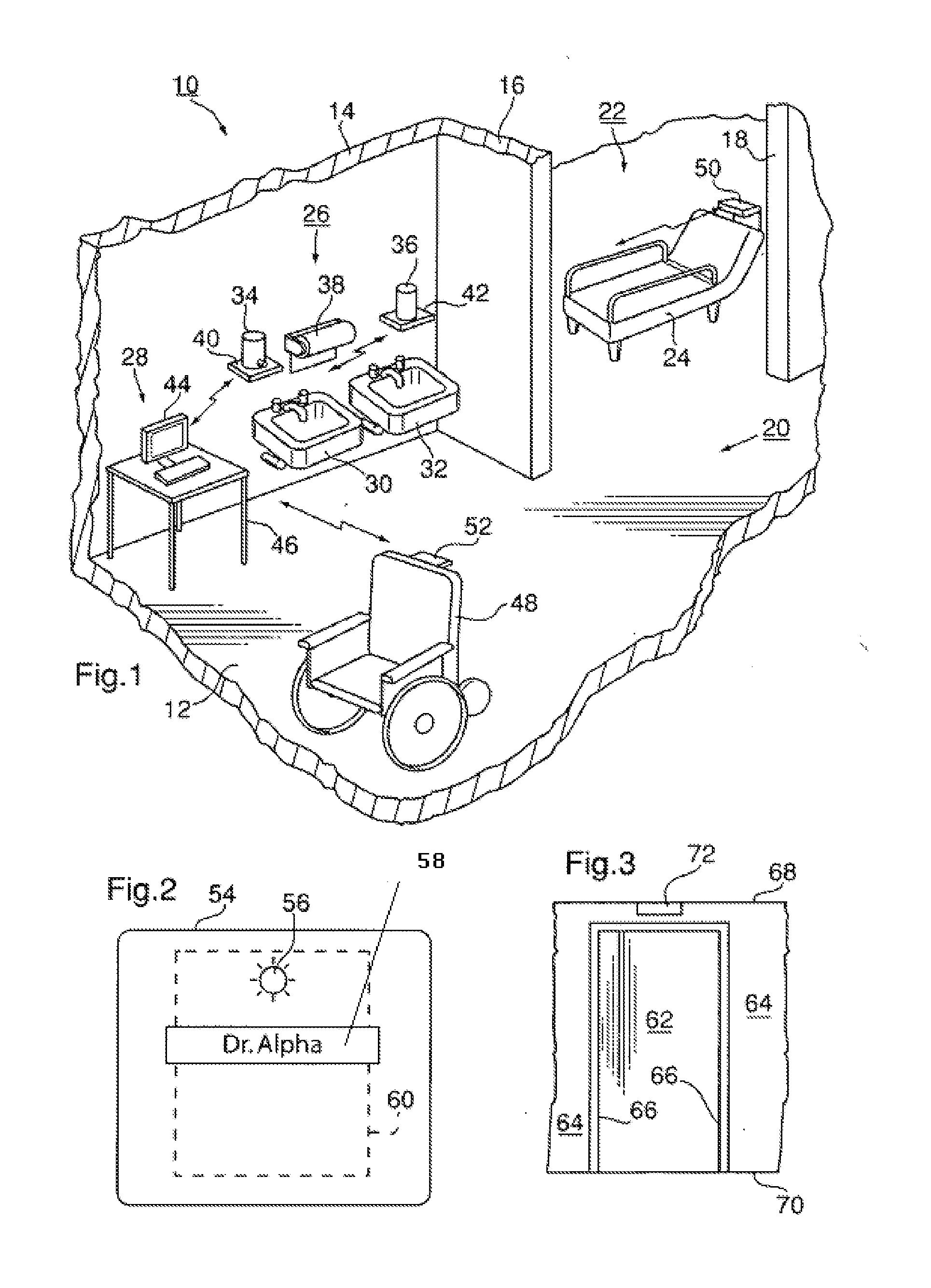
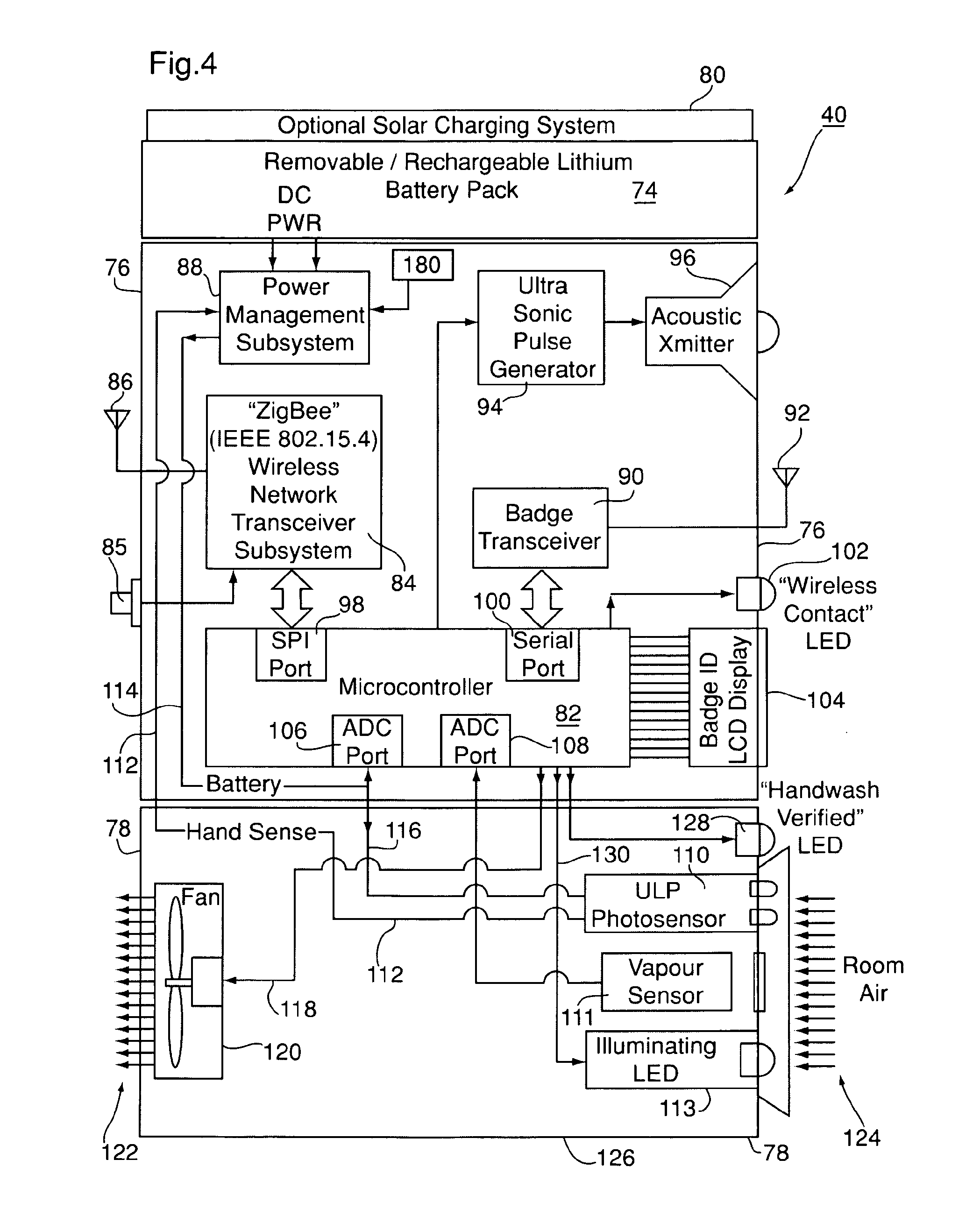
A wireless time-of-flight distance measurement device a motion detector is used at each of a plurality of stations in a wireless network in an enclosed facility to accurately locate a badge-wearing person near the station. The location, badge number and time of detection are transmitted through the network and stored in a computer memory. In a healthcare facility, hand washing detectors are located at some of the stations and caused to energize a hand wash status indicator light on the badge when the wearer has washed his or her hands. The light remains “on” for only a certain length of time, but will be extinguished sooner by a monitor device near each patient when the healthcare worker leaves the vicinity of the patient. These events also are transmitted and stored so that a timed record of each worker's hand washing and visits to patients is created.
Owner:XHALE
Power management for wireless direct link
ActiveUS20050122927A1Improve economyTransparent operationPower managementTransmission systemsTiming Synchronization FunctionFast recovery
Disclosed herein are exemplary techniques for managing power in a direct wireless link between two wireless devices. The present invention provides at least three direct link power management techniques: Fast Resumption Mode (FRM) wherein the direct link is resumed automatically at a specified timing synchronization function (TSF); Slow Resumption Mode (SRM) wherein the direct link may be resumed by sending a Resume-Request via the access point; and Reverse Polling (RP), wherein one peer station of the direct link is continually awake and the other peer station uses reverse polling to start a service period. Thus, a method for power management of a direct wireless link between two wireless devices is disclosed. The method comprising the steps of establishing a direct wireless link between the first wireless device and the second wireless device; transmitting, from a first wireless device, a frame having a time value; receiving, at the second wireless device, the frame from the first wireless device; suspending the direct wireless link a duration determined based on the time value; and resuming the direct wireless link at a time determined based on the time value.
Owner:OZMO LICENSING LLC
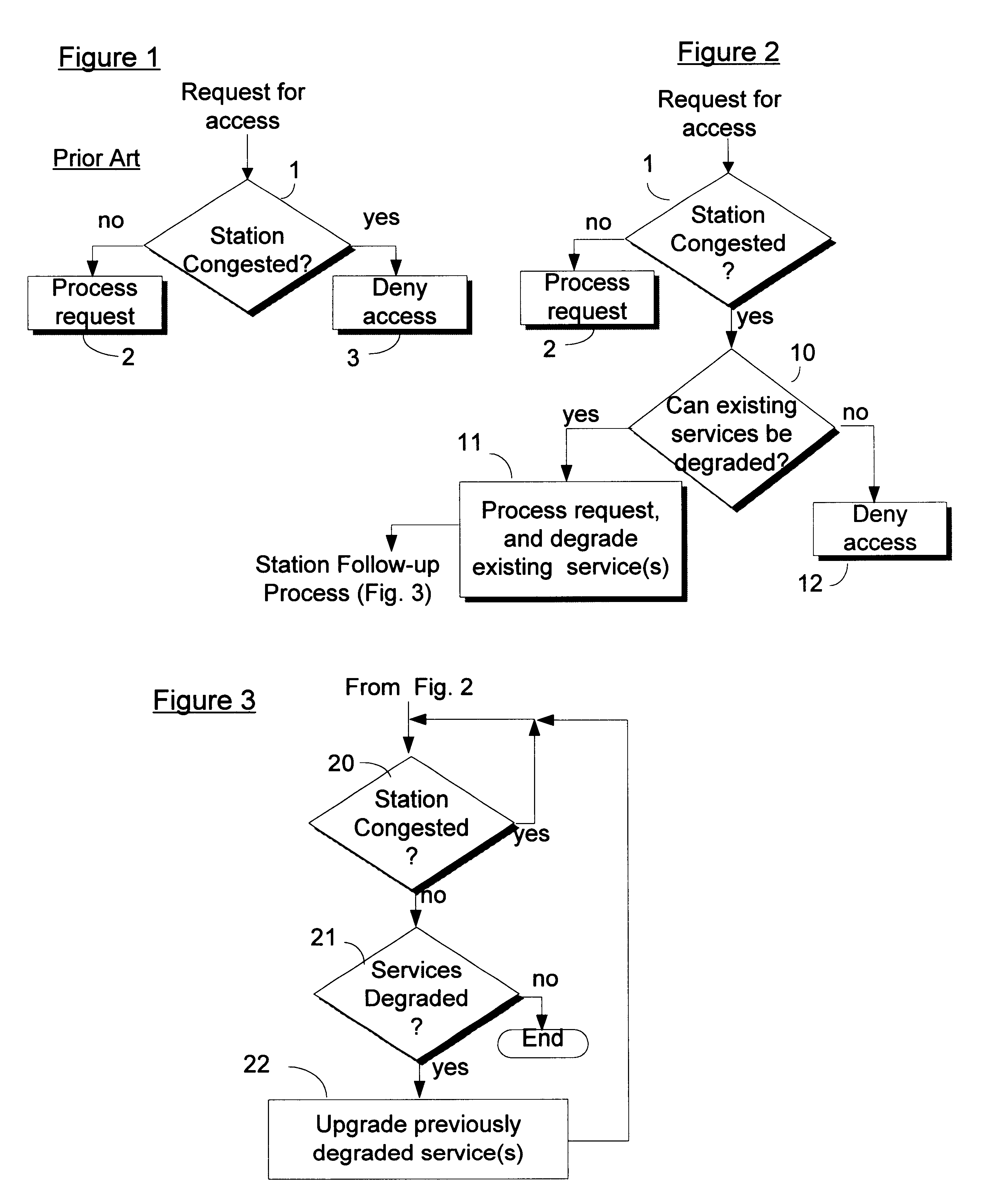
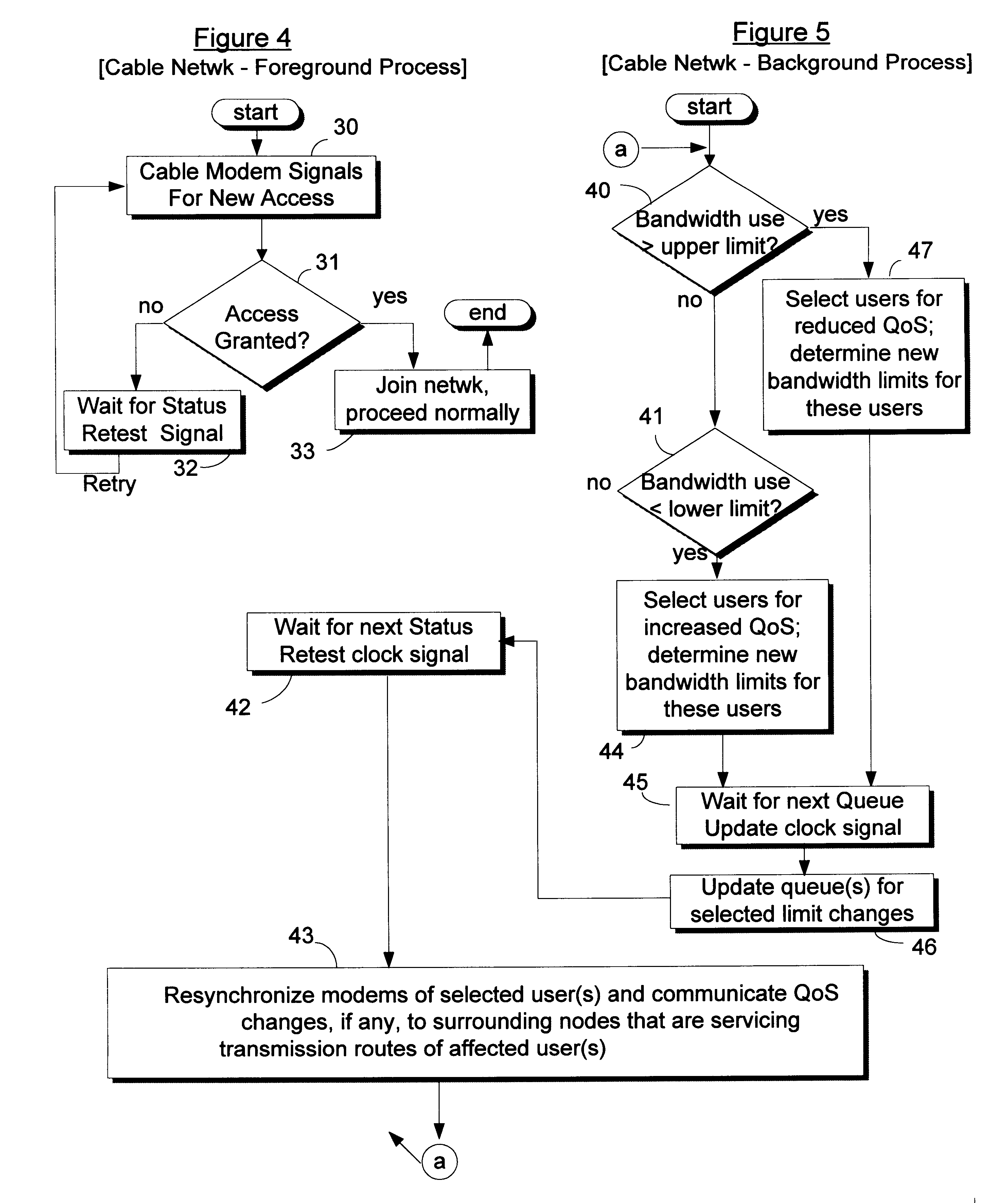
Improving access to congested networks
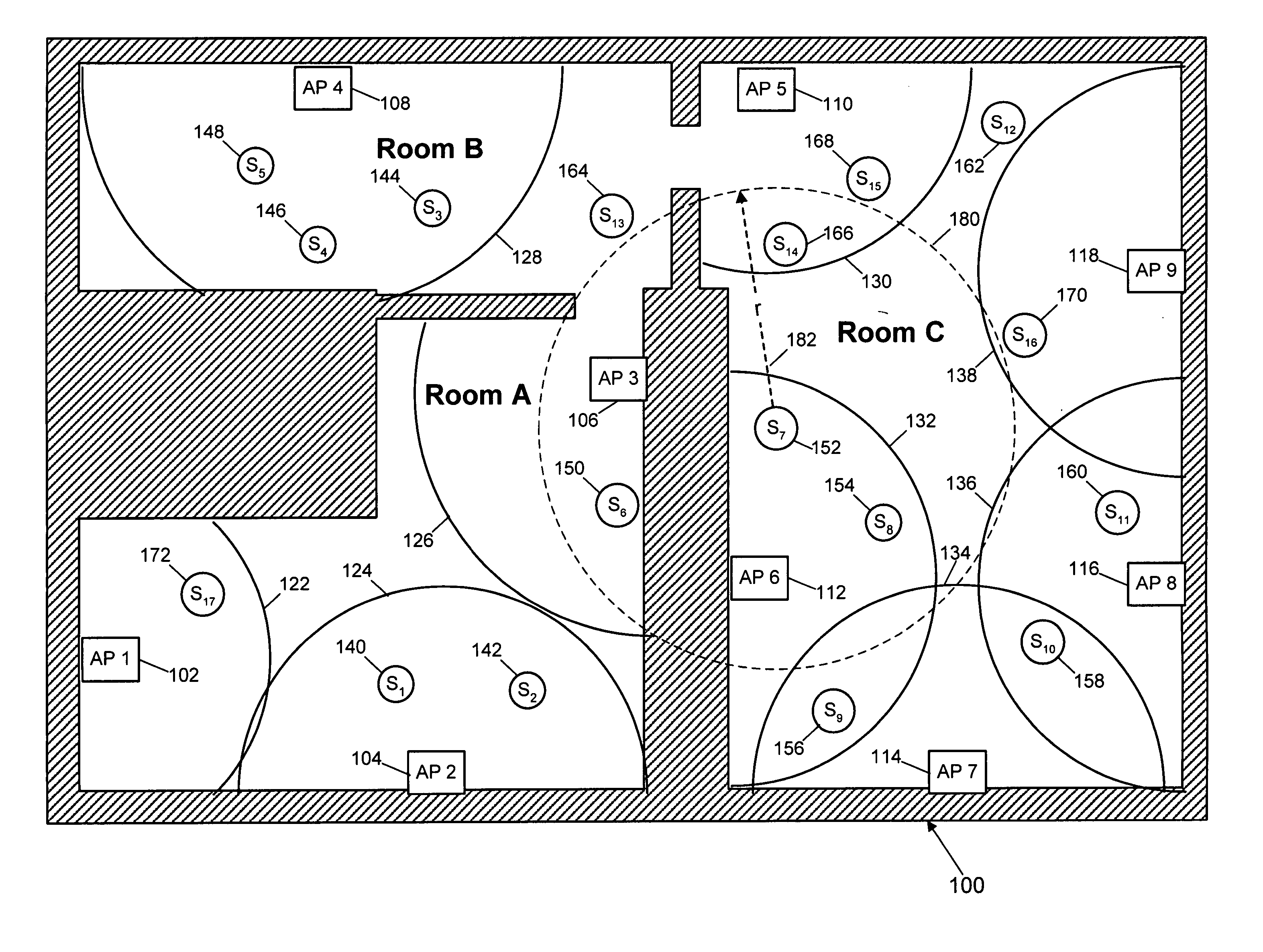
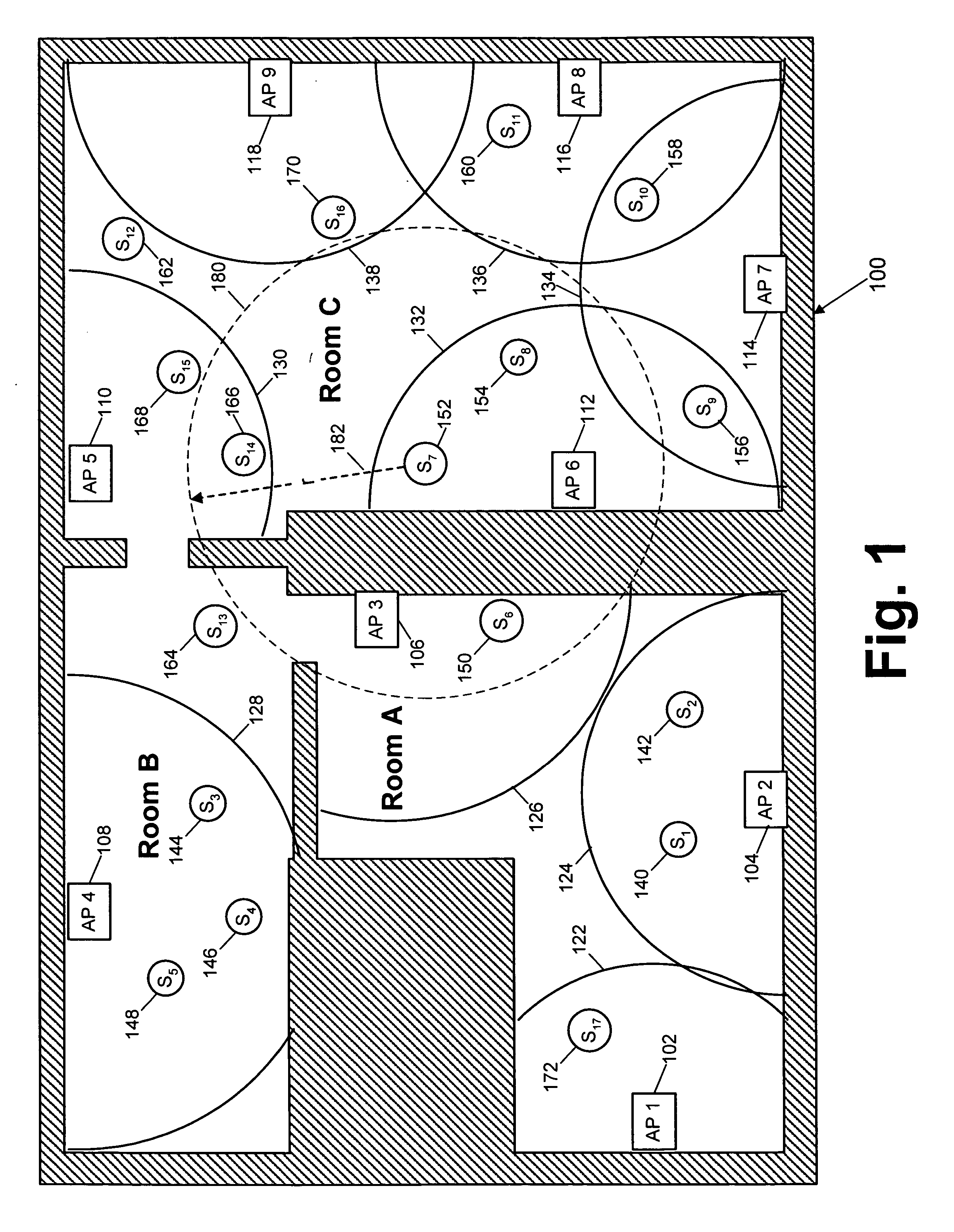
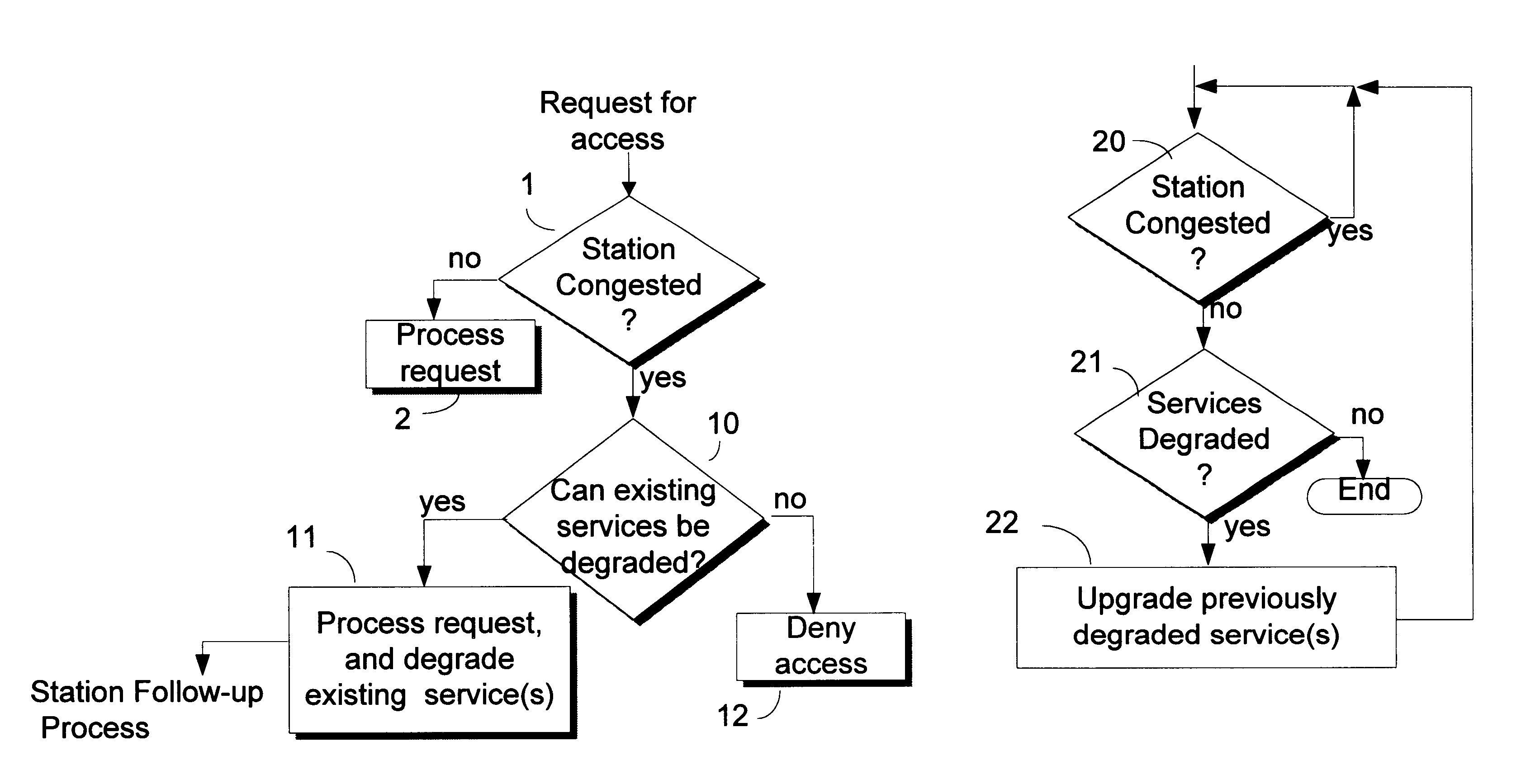
InactiveUS6345038B1Reduce usageError preventionTransmission systemsData transmissionQuality of service
For a station in a data communication network having a predefined limit of congestion for handling data immediately undergoing transmission through the station, a system for improving service given to network users requesting new access services to support new transmissions through the same station while the predefined congestion limit is exceeded. This system contains: a first element for determining when the predefined limit is exceeded by existing data transmissions through the station; and a second element, responsive to requests for new access services that are received while the predefined limit is being exceeded for: concurrently processing the request for new service and reducing the quality of service (QoS) to selected users. The reductions in QoS generally have the effects of reducing the speed / priority of handling of data being transmitted to or from the selected users, and of freeing up of sufficient bandwidth to accommodate the requested new access services. The system includes a third element for restoring / upgrading QoS, to users whose QoS has been reduced, when bandwidth usage subsides to a level allowing for such restoration. This latter level is sufficiently less than the congestion limit to provide a hysteresis effect that delays actions by the third element sufficiently to prevent successive actions of said second and third elements from producing unstable fluctuations in the operation of the station. Arrangements are disclosed for applying the invention in a cable television network environment and in private network environments serving a single business enterprise such as a banking institution.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for efficiently accessing affiliated network addresses from a wireless device
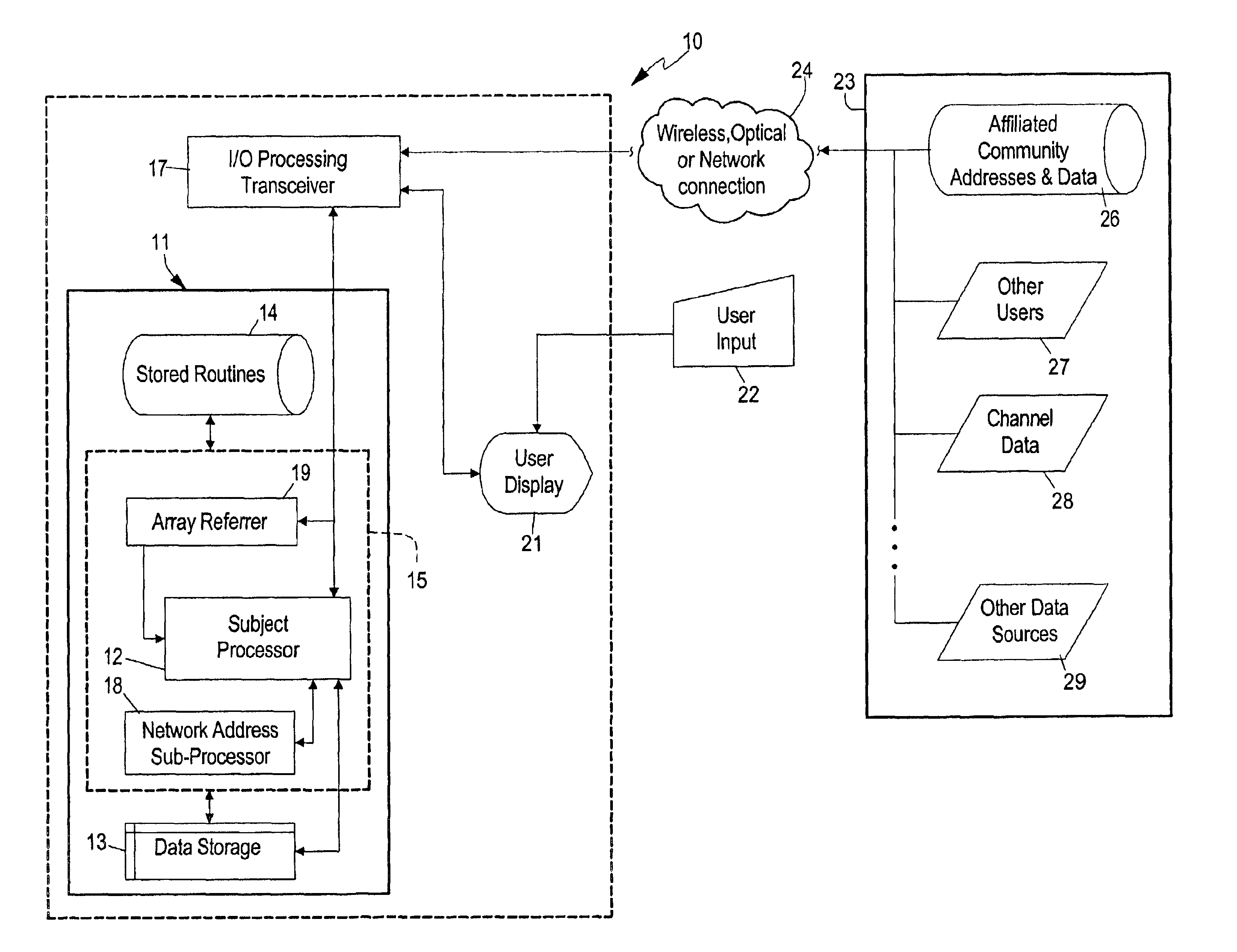
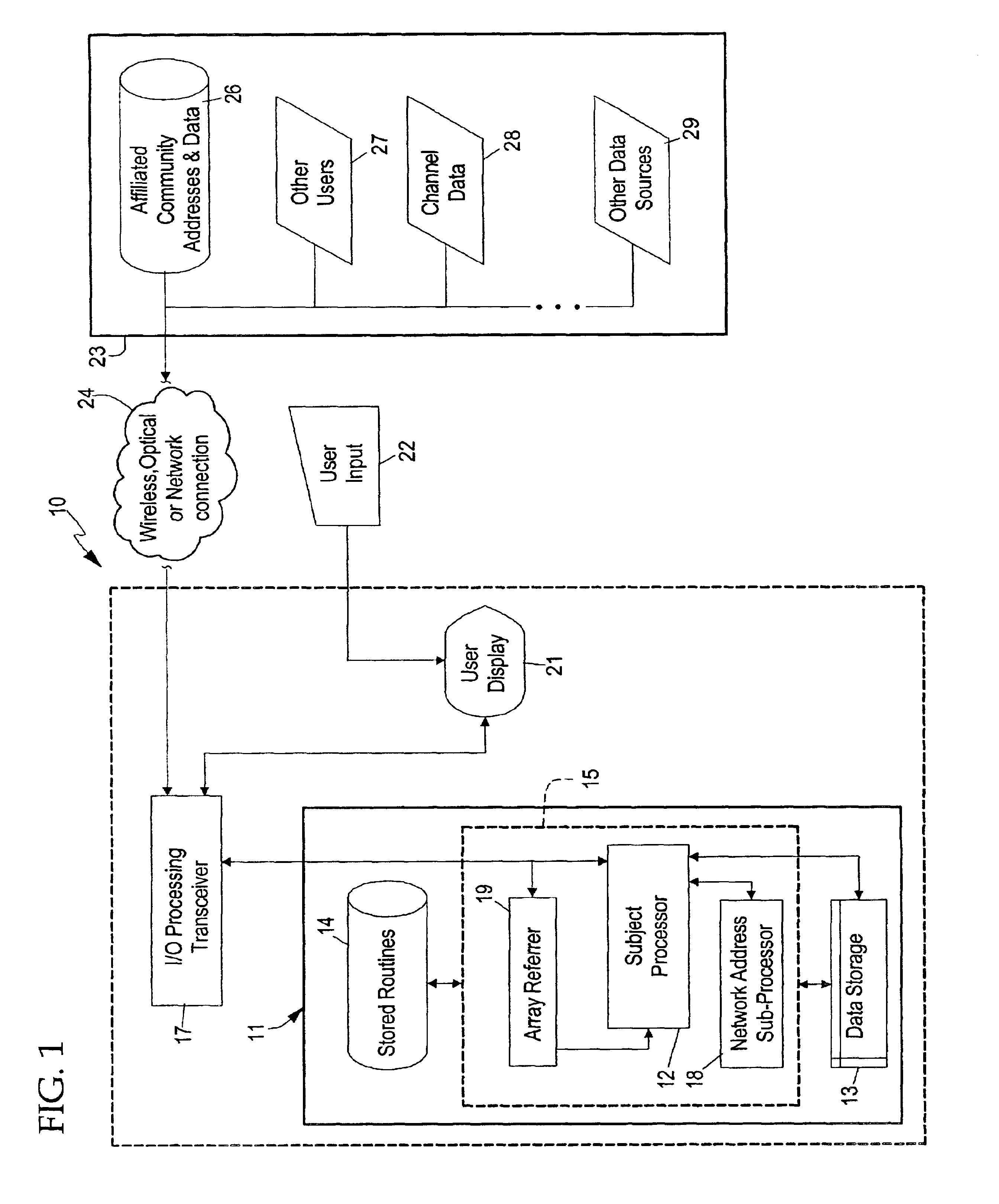
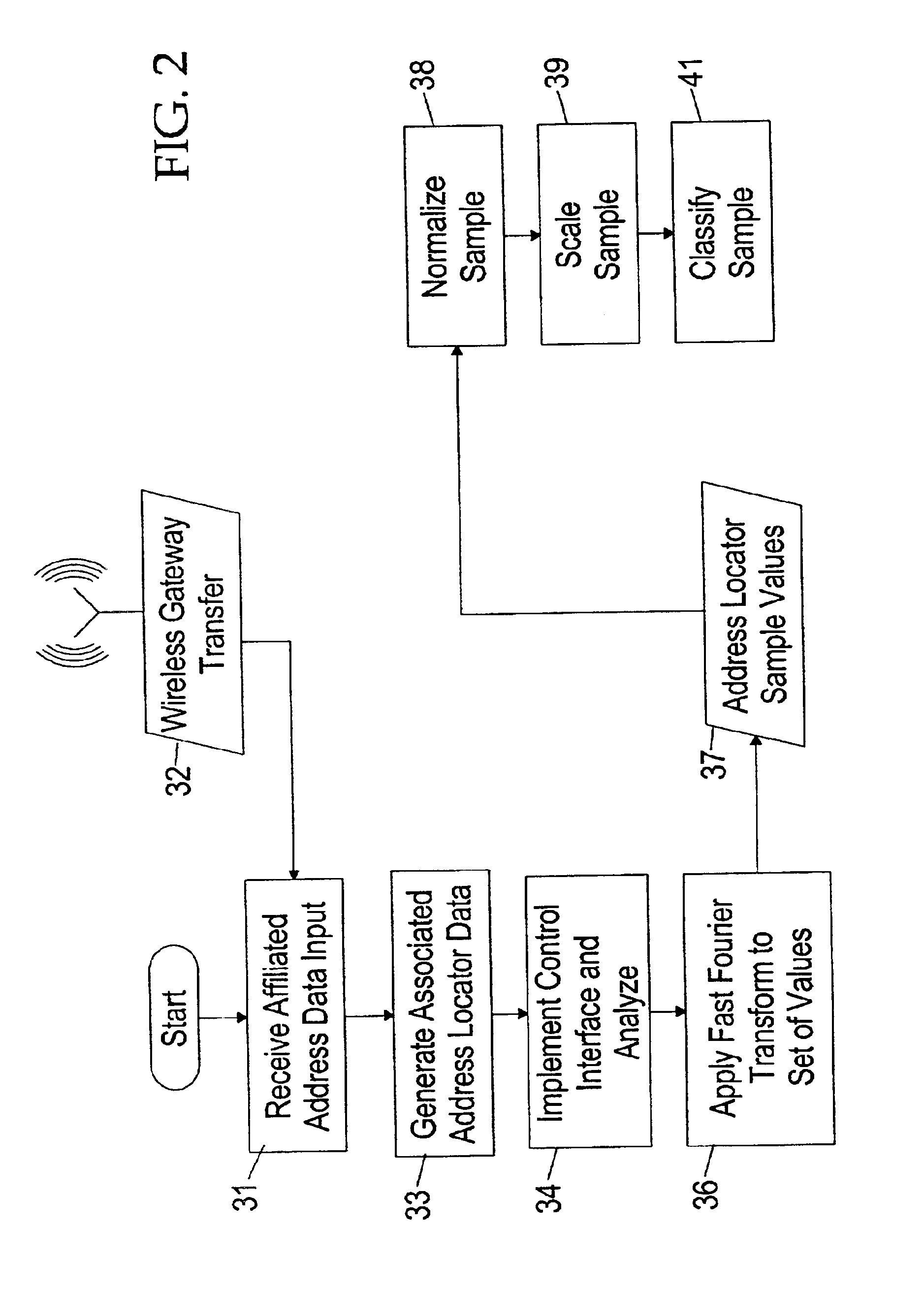
InactiveUS6873610B1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsHigh speed memoryNetwork addressing
A system and method for a wireless device to efficiently access affiliated addresses across linked topical communities, such as an Internet WebRing, through a wireless gateway. The invention includes a processing unit running on a wireless device controlled by an affiliated address control program. The processing unit includes a processing unit with a subject processor, a program store for holding an apparatus control program, a network address sub-processor, an address array referrer, an input mechanism, a display device for selecting retrieved affiliated addresses, and a high speed memory for holding site address selectors and associated content buffer. The wireless device communicates with a network via conventional wireless communication means which provides a path for updating the content buffer and array referrer, as well as transference of other types of sensory data. Means for predicting search failures is also integrated into the apparatus control program of the processing unit. Data received from the wireless gateway is statistically preprocessed then supplied to a processor called a network address sub-processor. The system then incorporates sorted affiliated addresses into the system on the wireless device to make possible a real-time detector system for a wireless device accessing content through a wireless gateway. The system may be offered as a service benefit for wireless device subscription or as a per occurrence chargeable item for a wireless subscriber. The system relieves the standard “hit-or-miss” method for affiliated address selection and site address storage and retrieval.
Owner:MOBULAR TECH
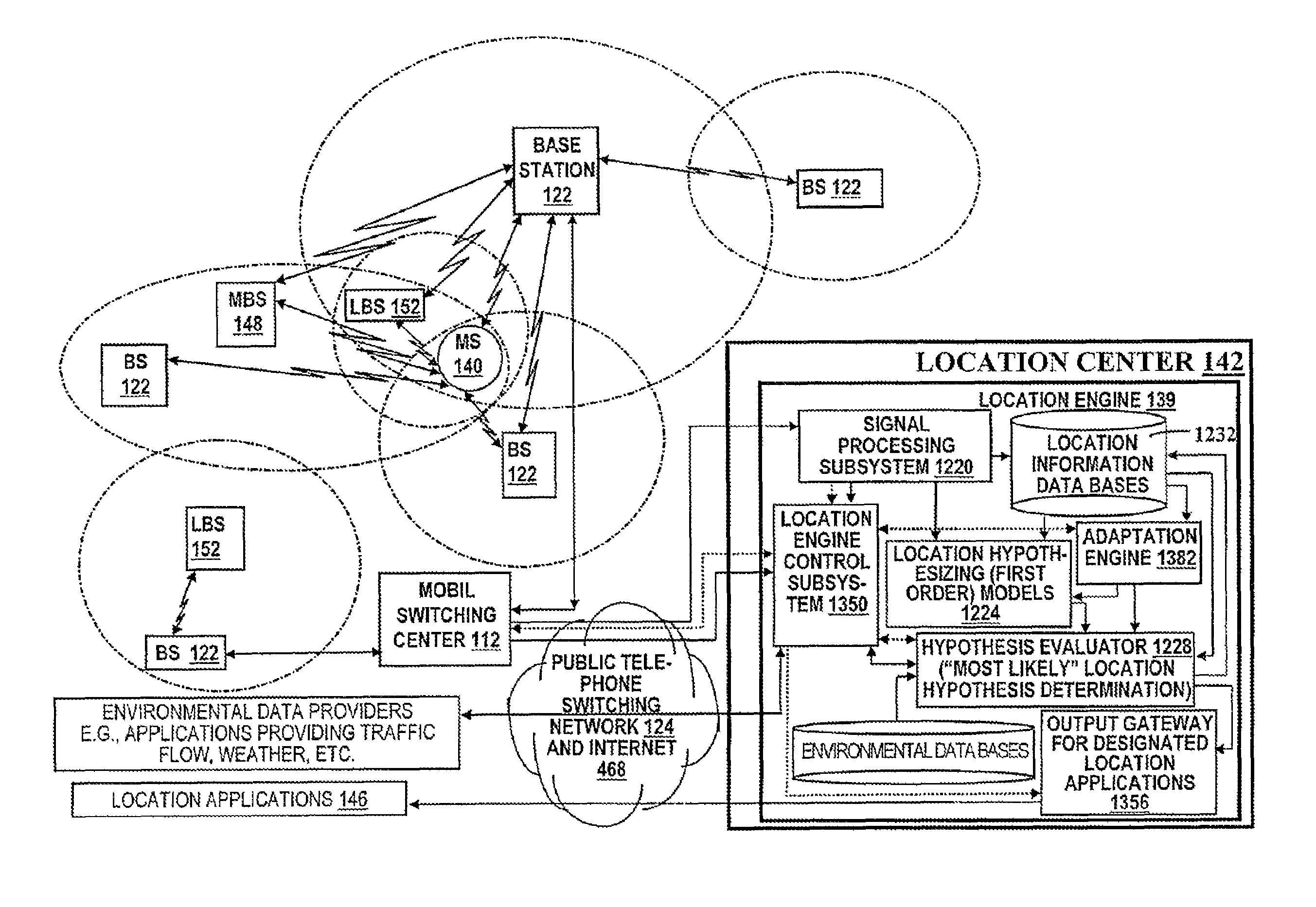
Wireless location routing applications and architecture therefor
InactiveUS7903029B2Accurate locationInstruments for road network navigationDirection finders using radio wavesInternet communicationModularity
A system for wirelessly locating mobile station / units (MS) and using resulting location determinations for providing a product or service is disclosed. The system is useful for routing an MS user to a plurality of desired locations, alerting an MS user to a nearby desired product or service based on satisfaction of user criteria, and providing enhanced security and 911 response. In one embodiment, the system responds to MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location processing sites. A plurality of locating technologies including those based on: (1) TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) timing advance; (5) GPS and network assisted GPS, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from low cost base stations can be activated, in various combinations, by system embodiments. MS location difficulties resulting from poor location accuracy / reliability and / or poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:MOBILE MAVEN
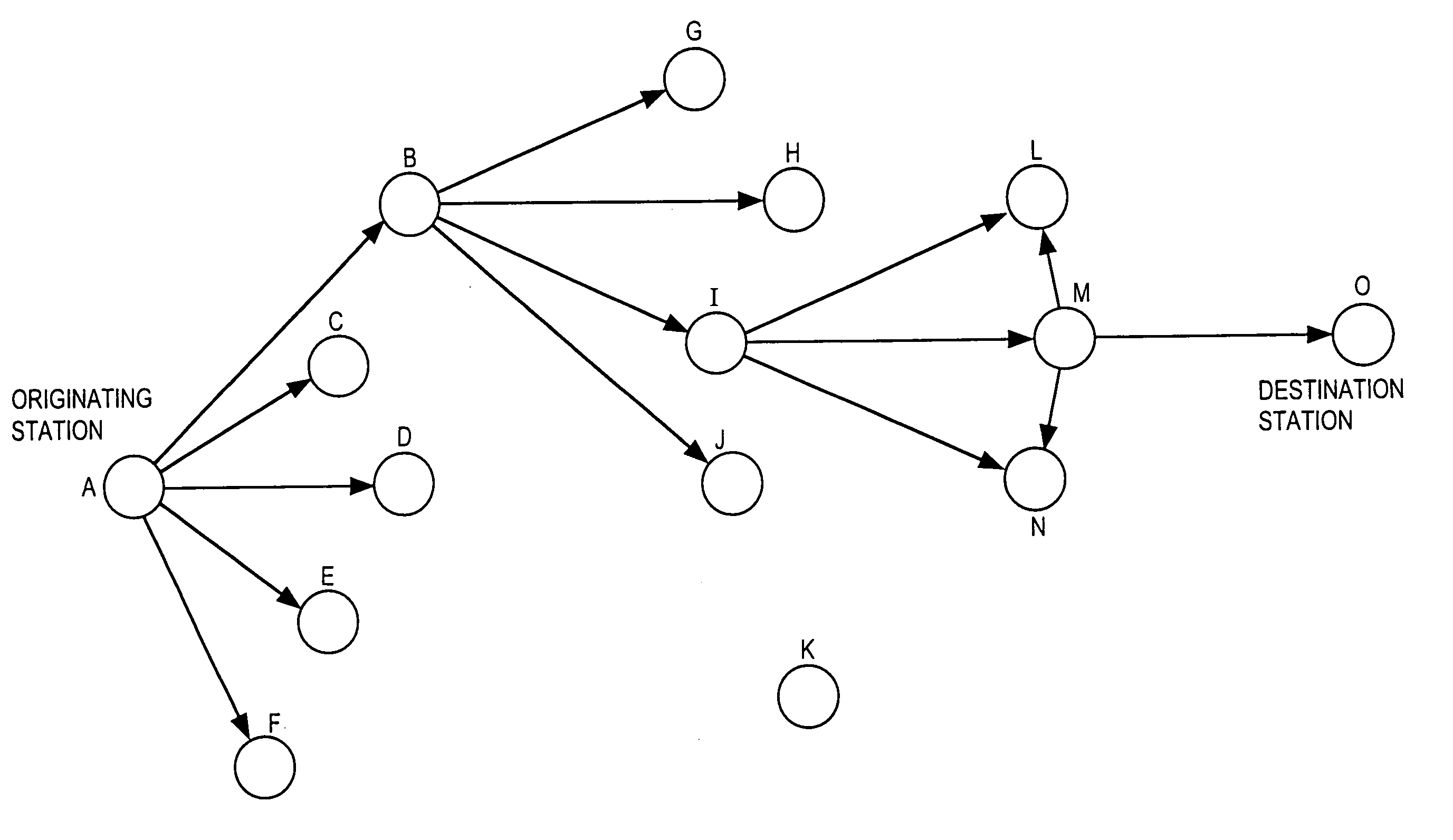
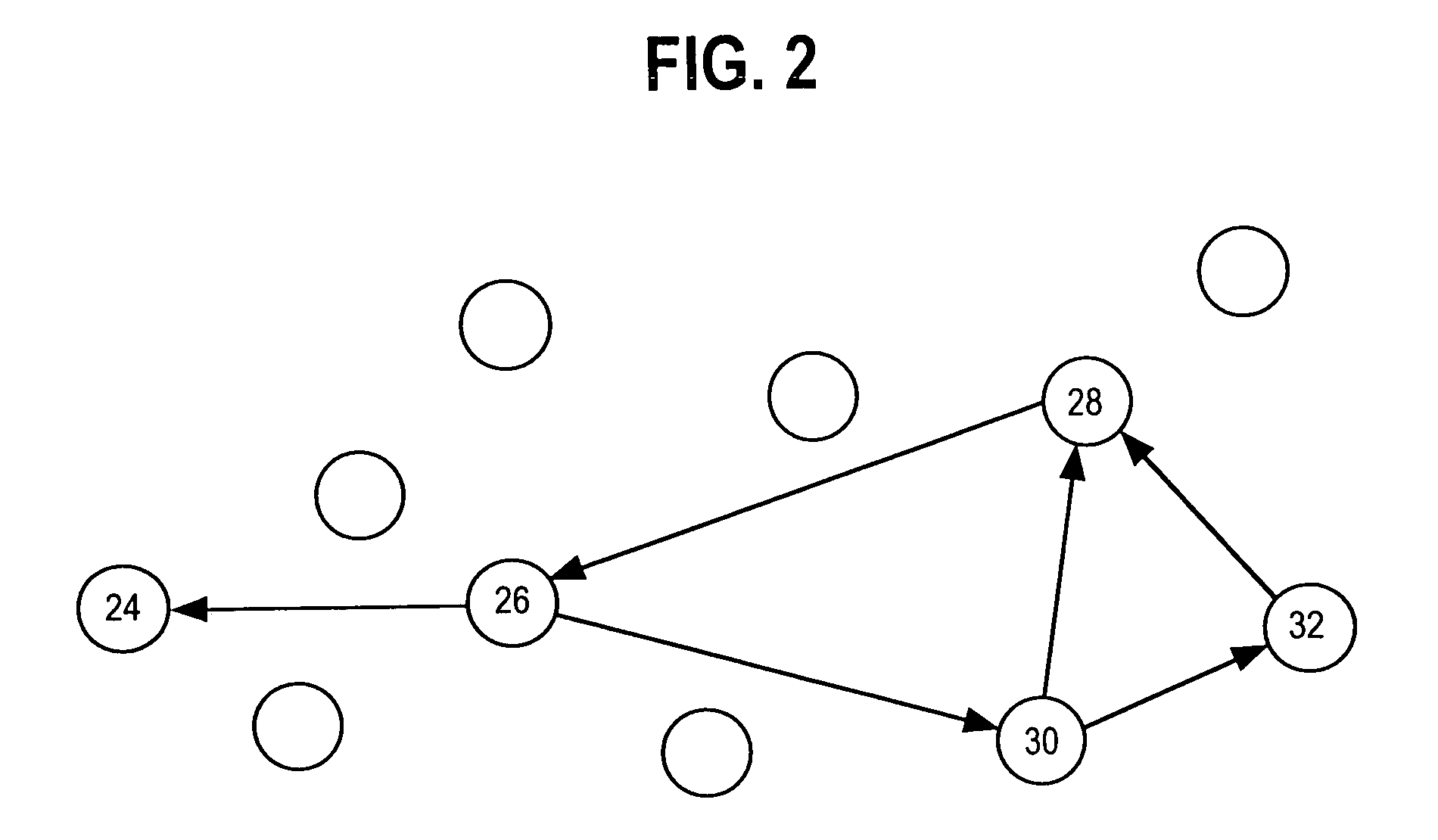
Multi-hop packet radio networks
InactiveUS6965568B1Control rateIncrease probabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer networkTransceiver
An adaptive communication system utilises opportunistic peak-mode transmissions to transmit data between originating and destination stations, via one or more intermediate stations. Each station monitors the activity of other stations in the network, storing connectivity information for use in subsequent transmissions. Each station also sends out probe signals from time to time, to establish which other stations are in range. Messages are then sent across the network from station to station, with confirmation data being transmitted back to the originating station, until the destination station is reached. Old messages, which would otherwise clog the network, are timed out and deleted. A communication network and transceiver apparatus for use in the network are also disclosed.
Owner:IWICS INC
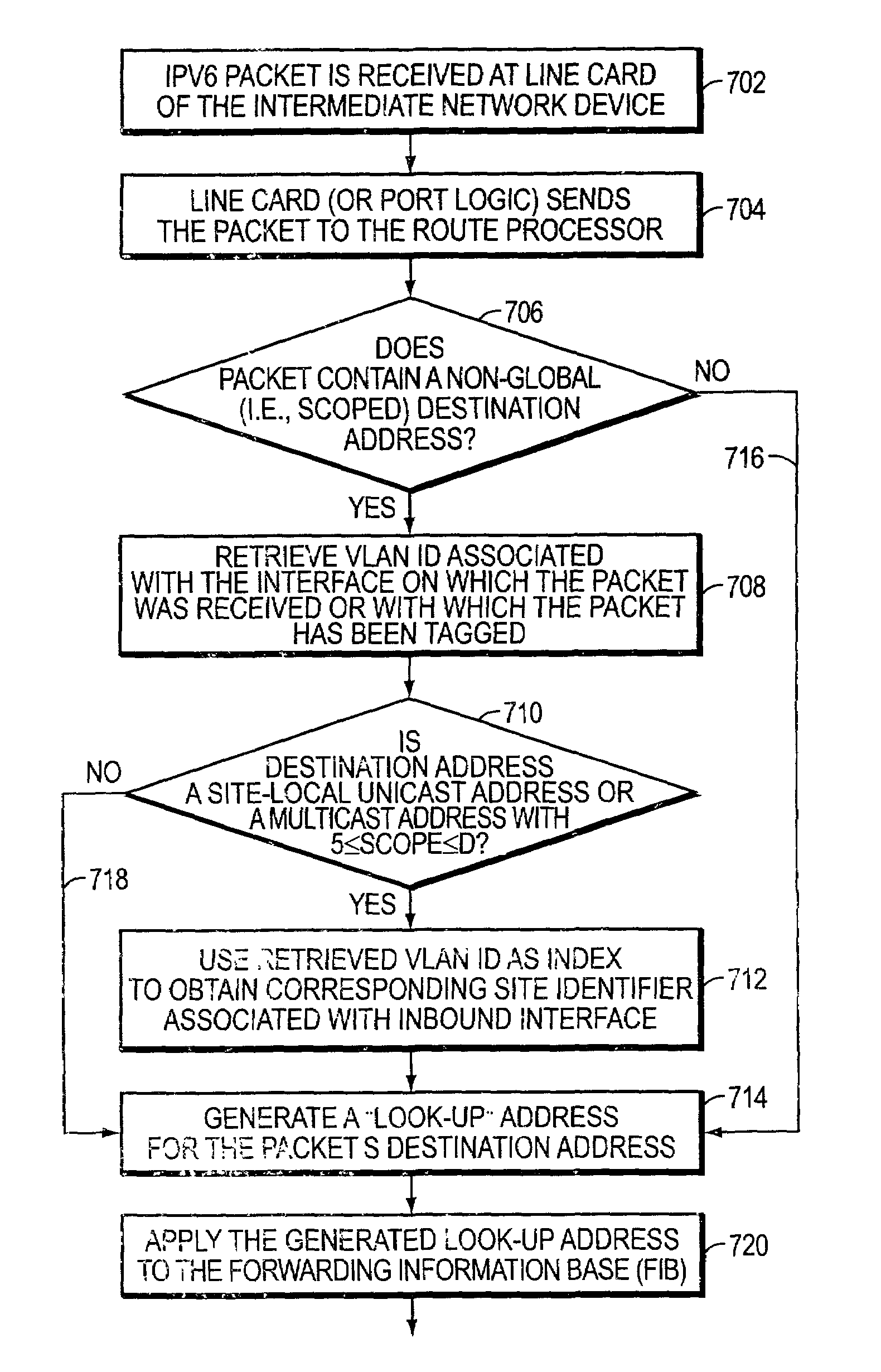
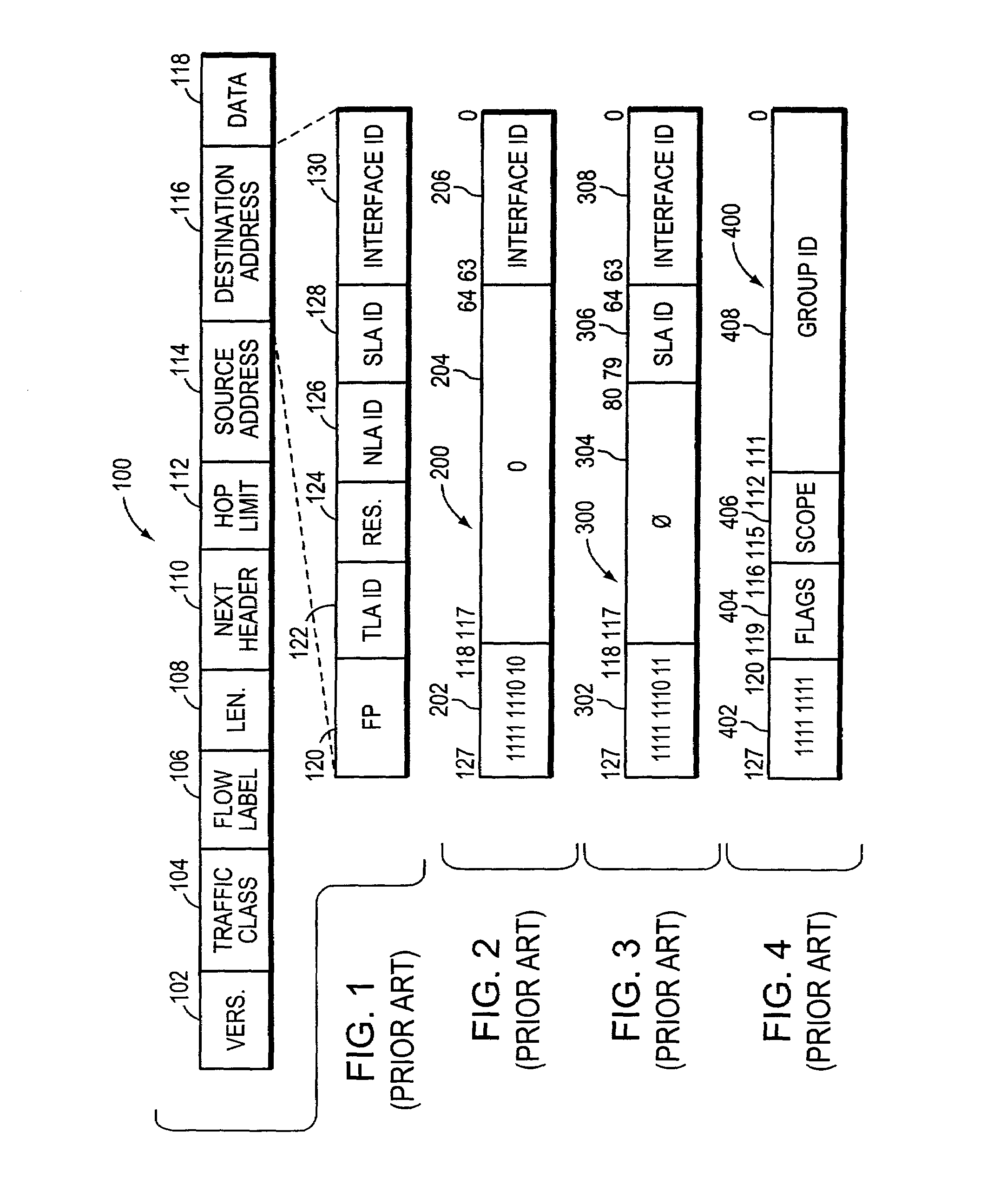
System and method for deriving IPv6 scope identifiers and for mapping the identifiers into IPv6 addresses
InactiveUS7095738B1Efficient and high-speedSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsInformation repositoryVirtual LAN
A system and method for use at an intermediate network device employs Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) designations as Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) link identifiers, and maps VLAN designations to IPv6 site identifiers (IDs). The system also generates a compacted look-up address based on the destination address specified within a received network message, such as an IPv6 packet. For a network message having a link-local unicast destination address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a site-local unicast address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a multicast destination address, if the address's scope value is between hexadecimal “2” and “4” inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. If the scope value is between hexadecimal “5” and “D”, inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. The look-up addresses are applied to a forwarding information base (FIB) to derive the outbound interface(s) from which the message is to be forwarded.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com