Patents
Literature
12929 results about "Resource allocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In economics, resource allocation is the assignment of available resources to various uses. In the context of an entire economy, resources can be allocated by various means, such as markets or planning.
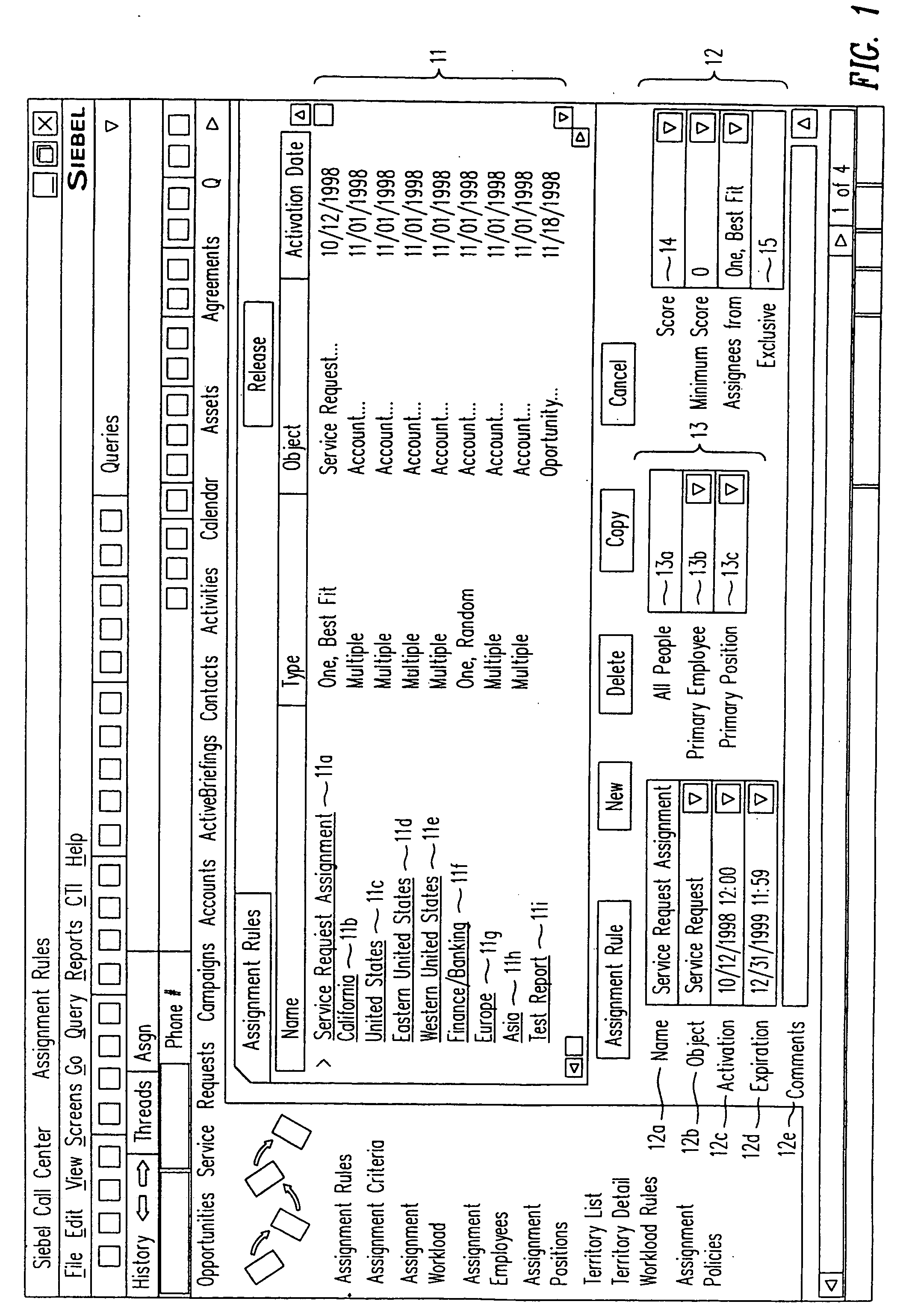
Assignment manager
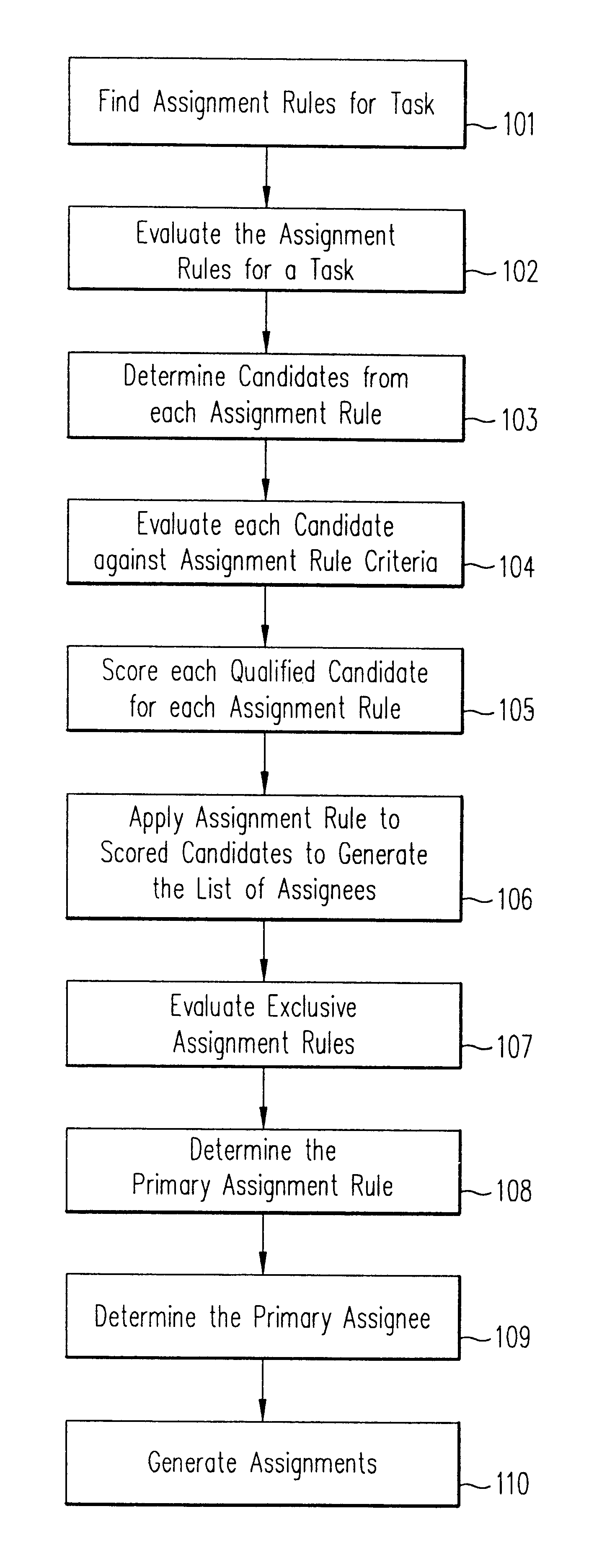
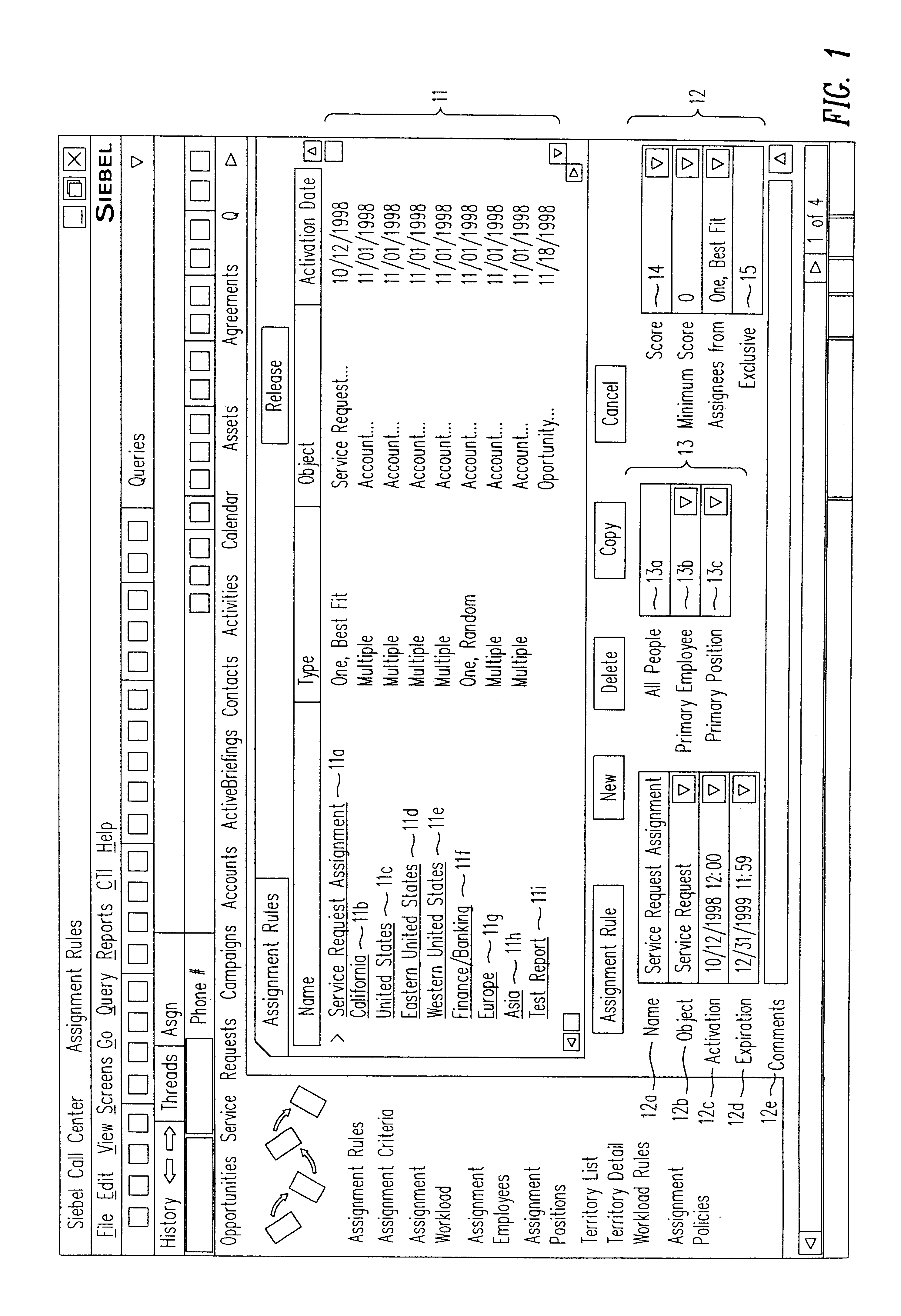
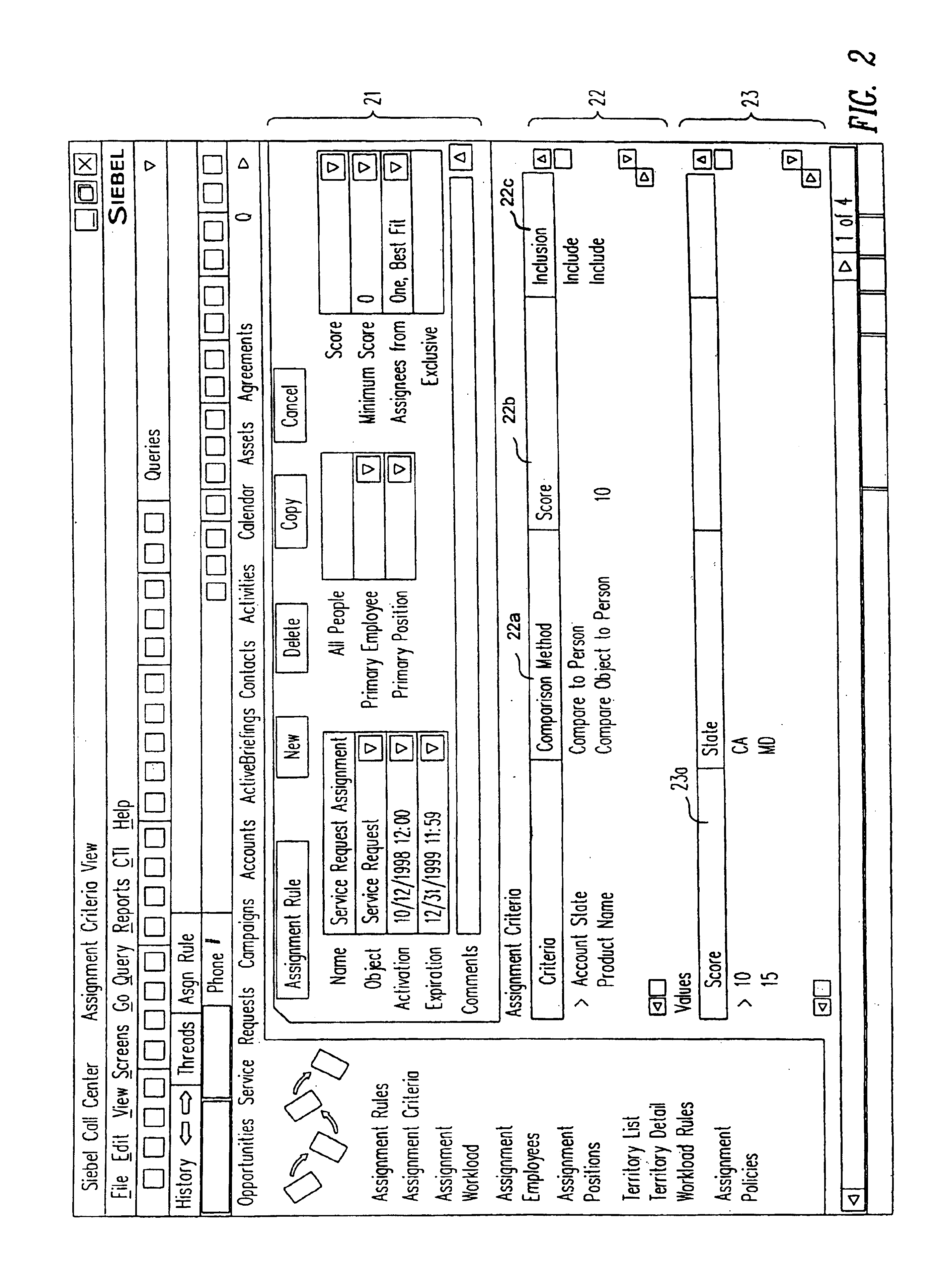
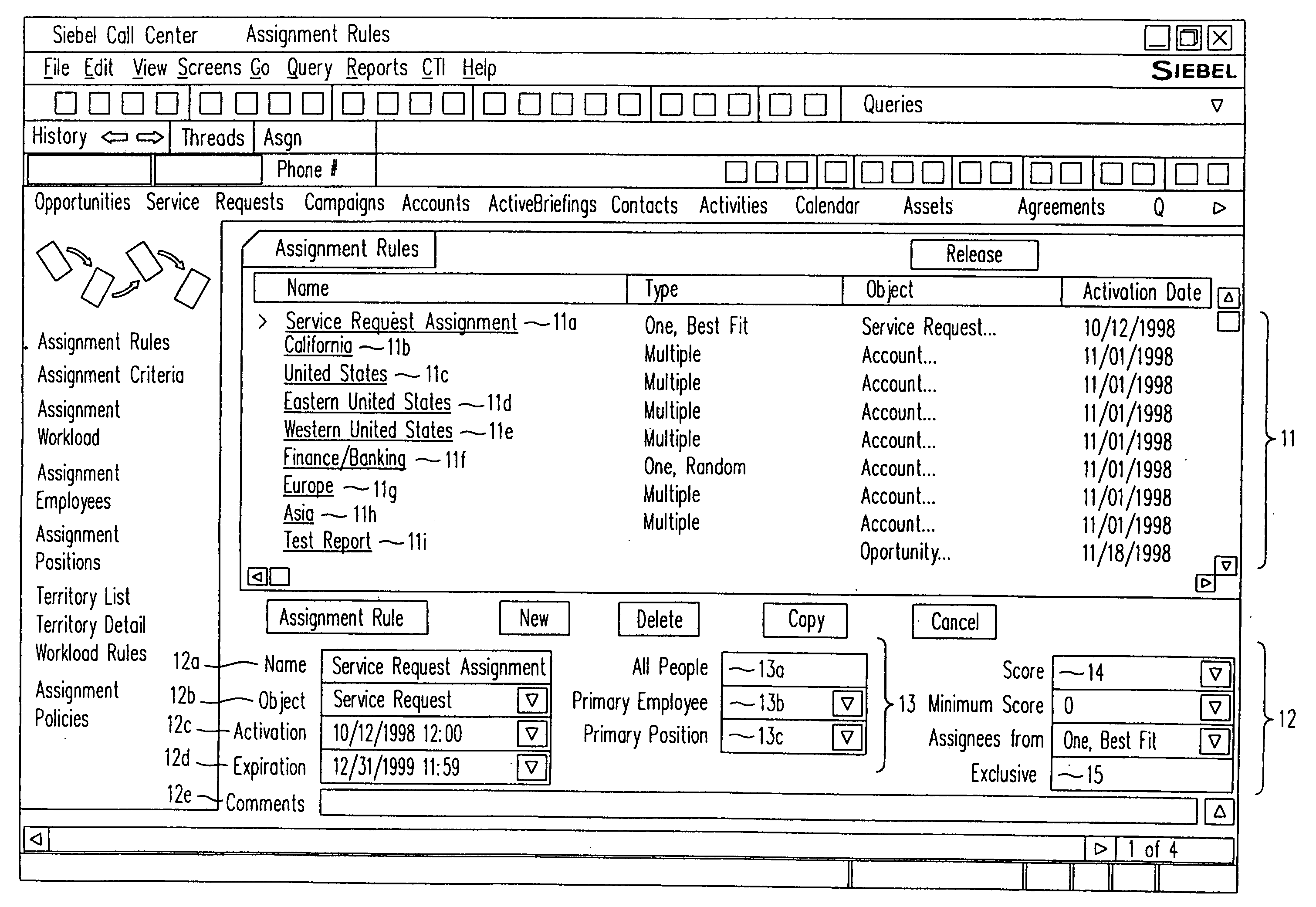
A method, a program product, and a system for assigning resources to tasks in a rule based, resource constrained system. This is done by receiving as inputs tasks and task attributes; resources and resource attributes; and assignment rules. These inputs are used to searching a database of tasks, task attributes, and assignment rules thereof, to search a database of resources including resource attributes thereof, and to retrieve resources based upon the resource attributes. Resources are assigned to tasks based upon matches and scores of the resource attributes, the task attributes, and the assignment rules.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
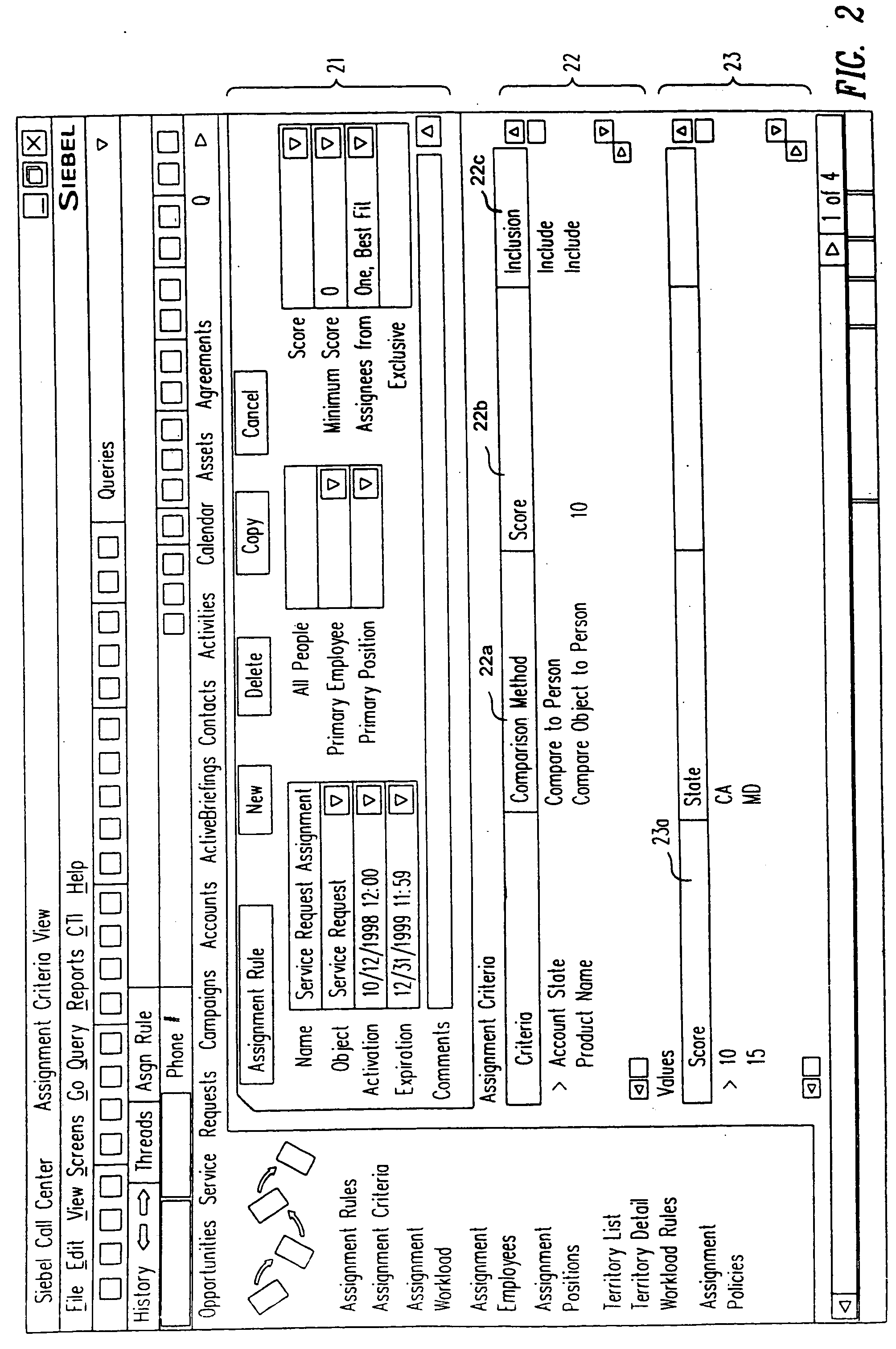
Assignment manager
InactiveUS20050091098A1ResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsResource basedResource allocation
A method, a program product, and a system for assigning resources to tasks in a rule based, resource constrained system. This is done by receiving as inputs tasks and task attributes; resources and resource attributes; and assignment rules. These inputs are used to searching a database of tasks, task attributes, and assignment rules thereof, to search a database of resources including resource attributes thereof, and to retrieve resources based upon the resource attributes. Resources are assigned to tasks based upon matches and scores of the resource attributes, the task attributes, and the assignment rules.
Owner:SIEBEL SYST INC
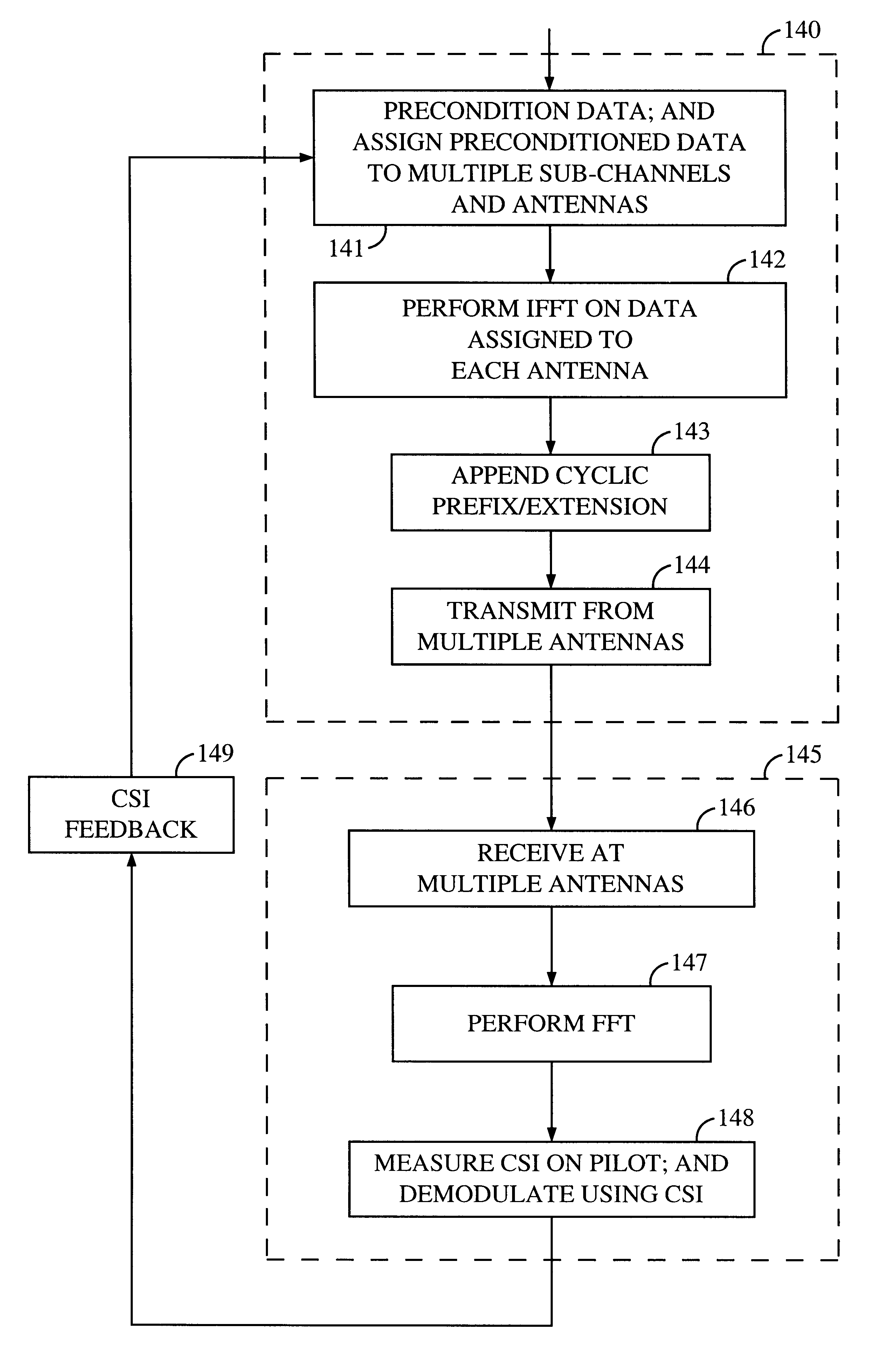
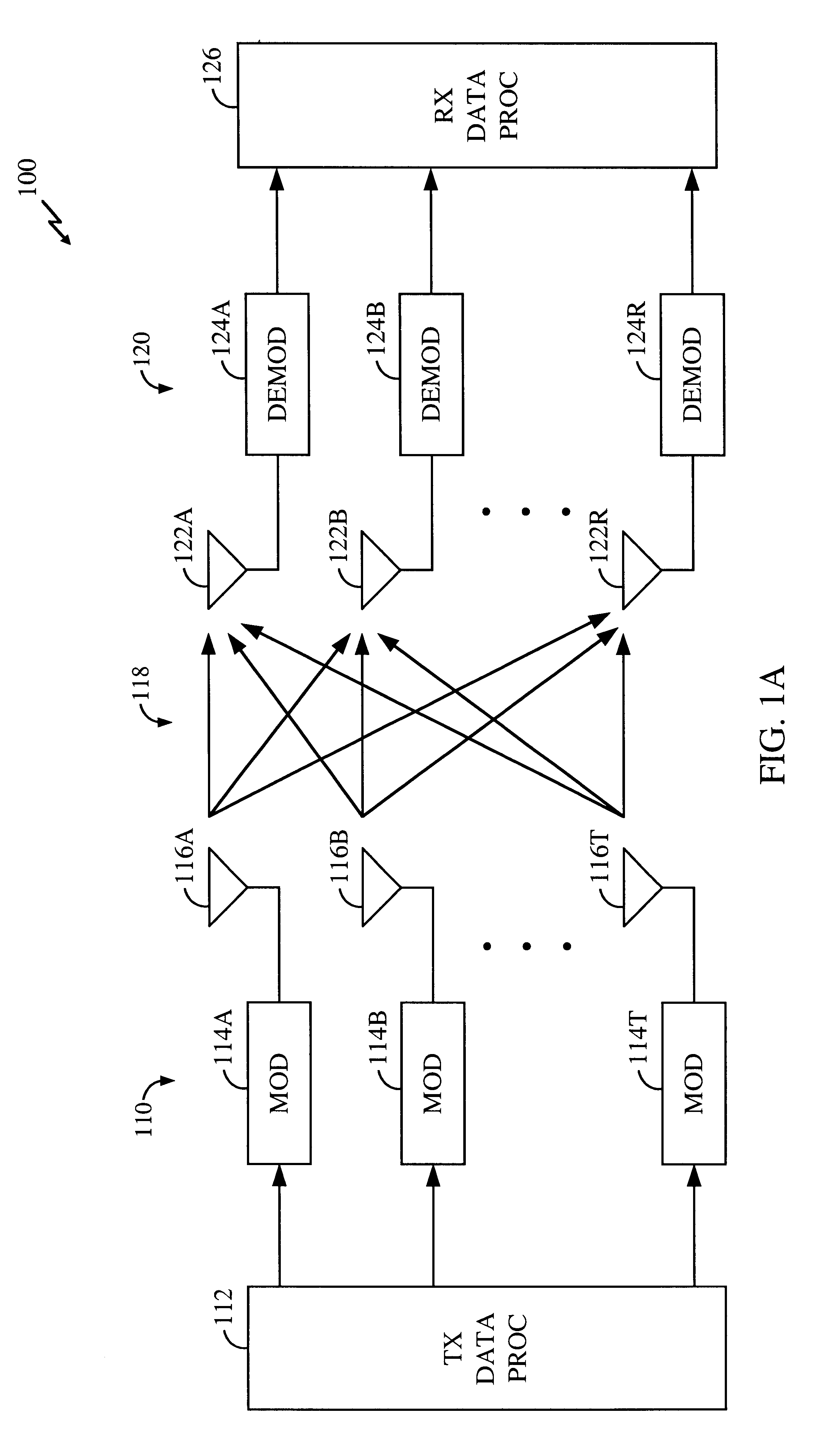
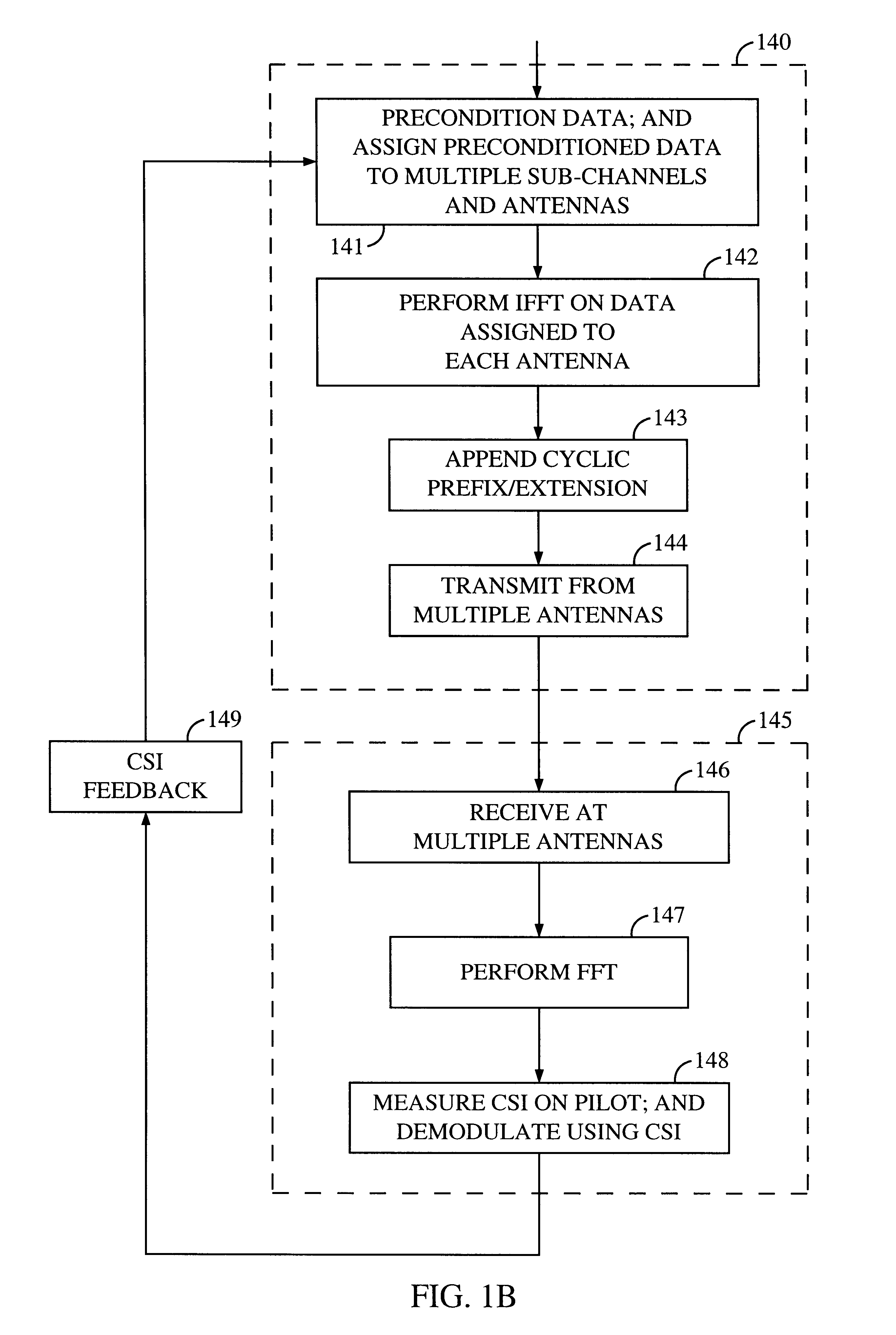
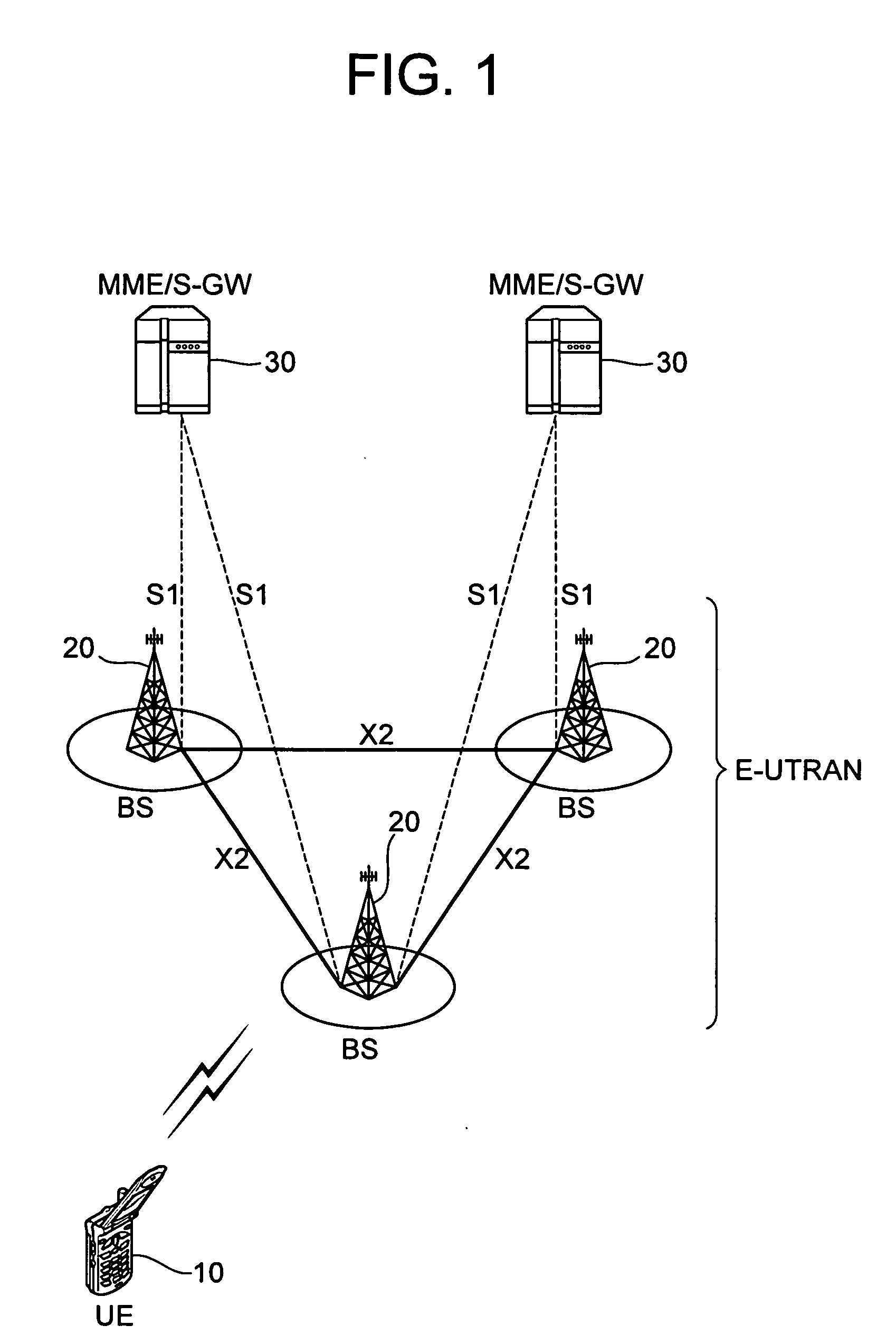
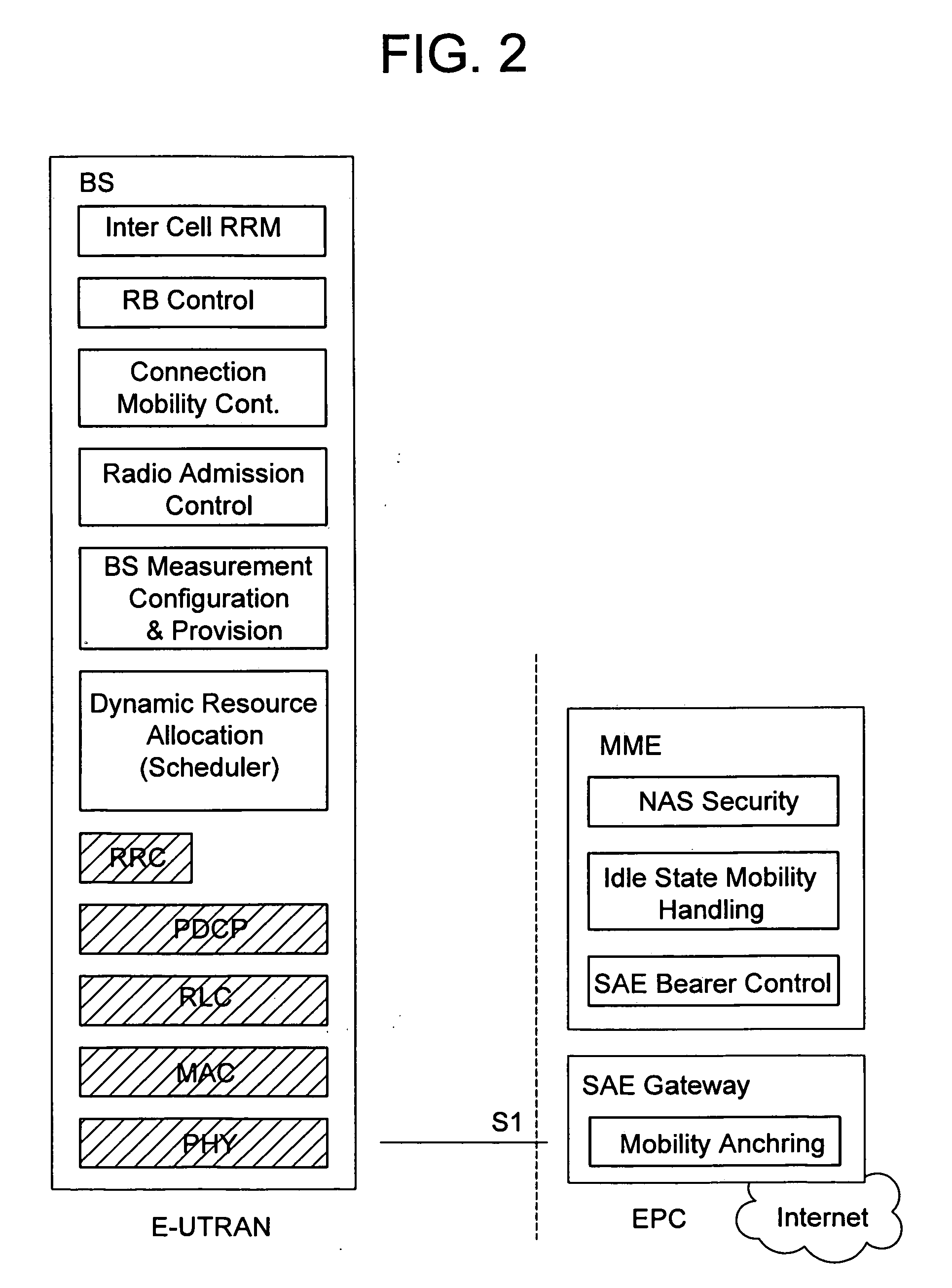
Method and apparatus for measuring reporting channel state information in a high efficiency, high performance communications system
InactiveUS6473467B1Efficient sharingInterference minimizationSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityChannel state informationCommunications system
Channel state information (CSI) can be used by a communications system to precondition transmissions between transmitter units and receiver units. In one aspect of the invention, disjoint sub-channel sets are assigned to transmit antennas located at a transmitter unit. Pilot symbols are generated and transmitted on a subset of the disjoint sub-channels. Upon receipt of the transmitted pilot symbols, the receiver units determine the CSI for the disjoint sub-channels that carried pilot symbols. These CSI values are reported to the transmitter unit, which will use these CSI values to generate CSI estimates for the disjoint sub-channels that did not carry pilot symbols. The amount of information necessary to report CSI on the reverse link can be further minimized through compression techniques and resource allocation techniques.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
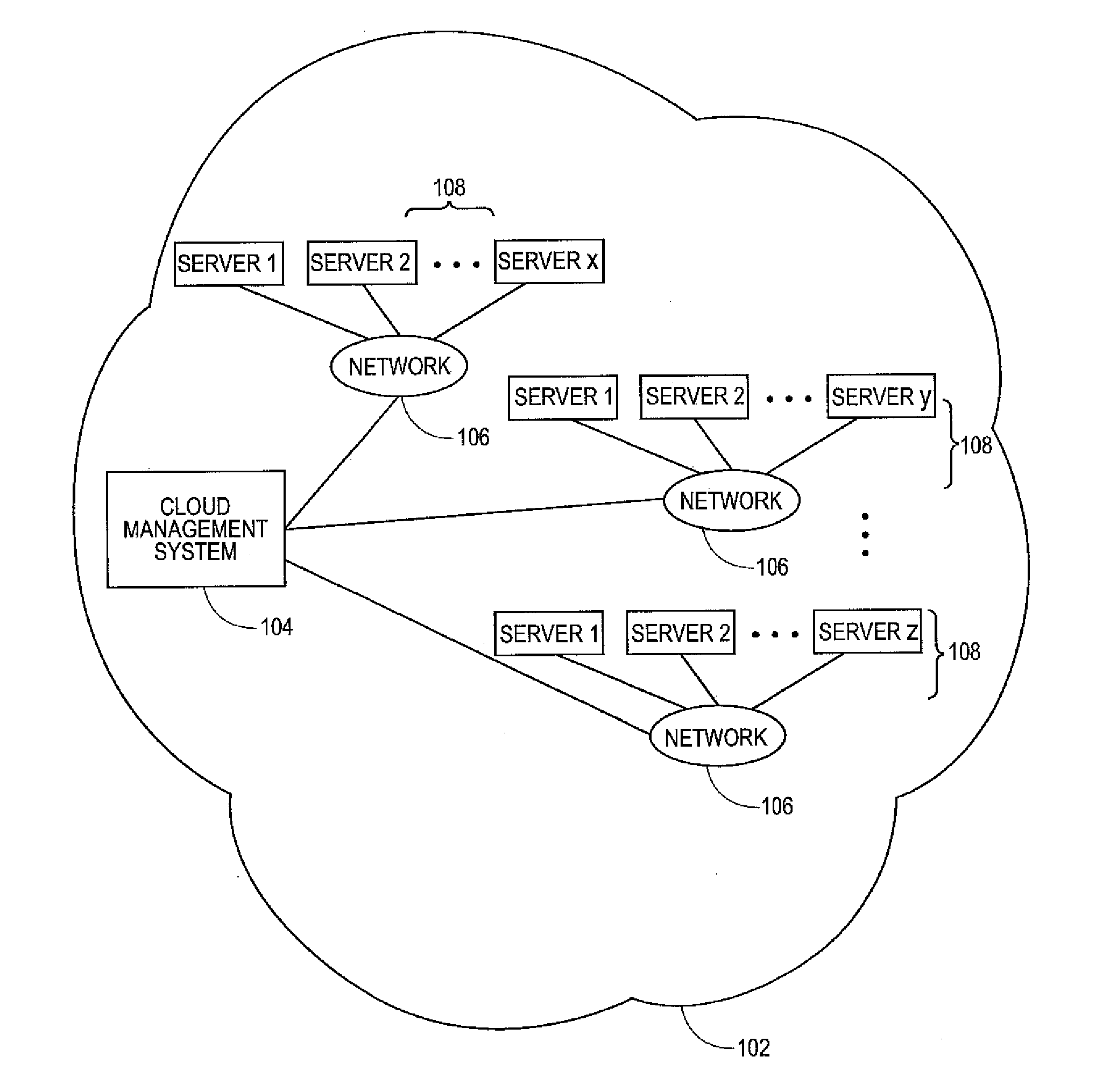
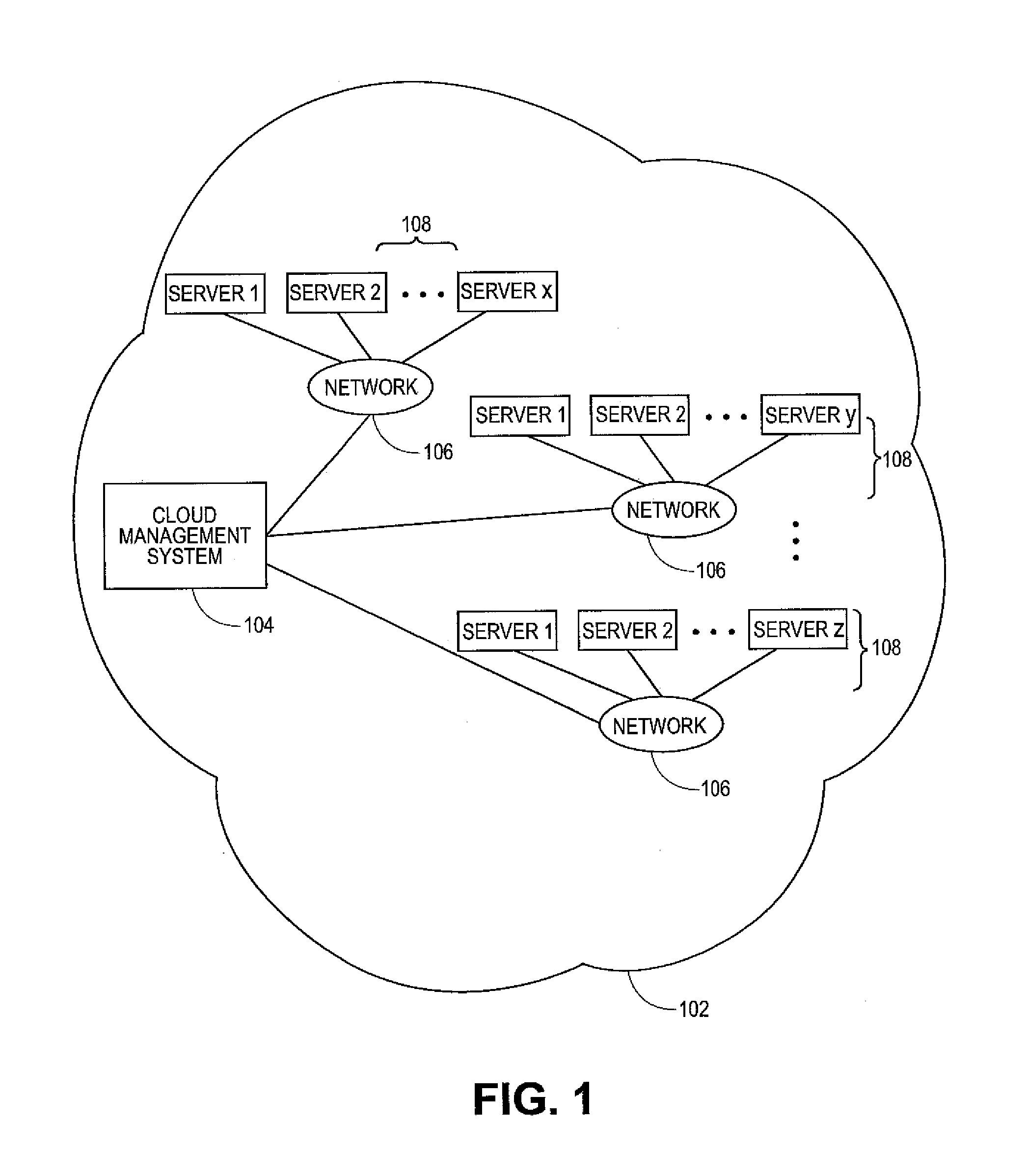
Methods and systems for load balancing in cloud-based networks
ActiveUS20090300210A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlCloud baseResource allocation
Owner:RED HAT
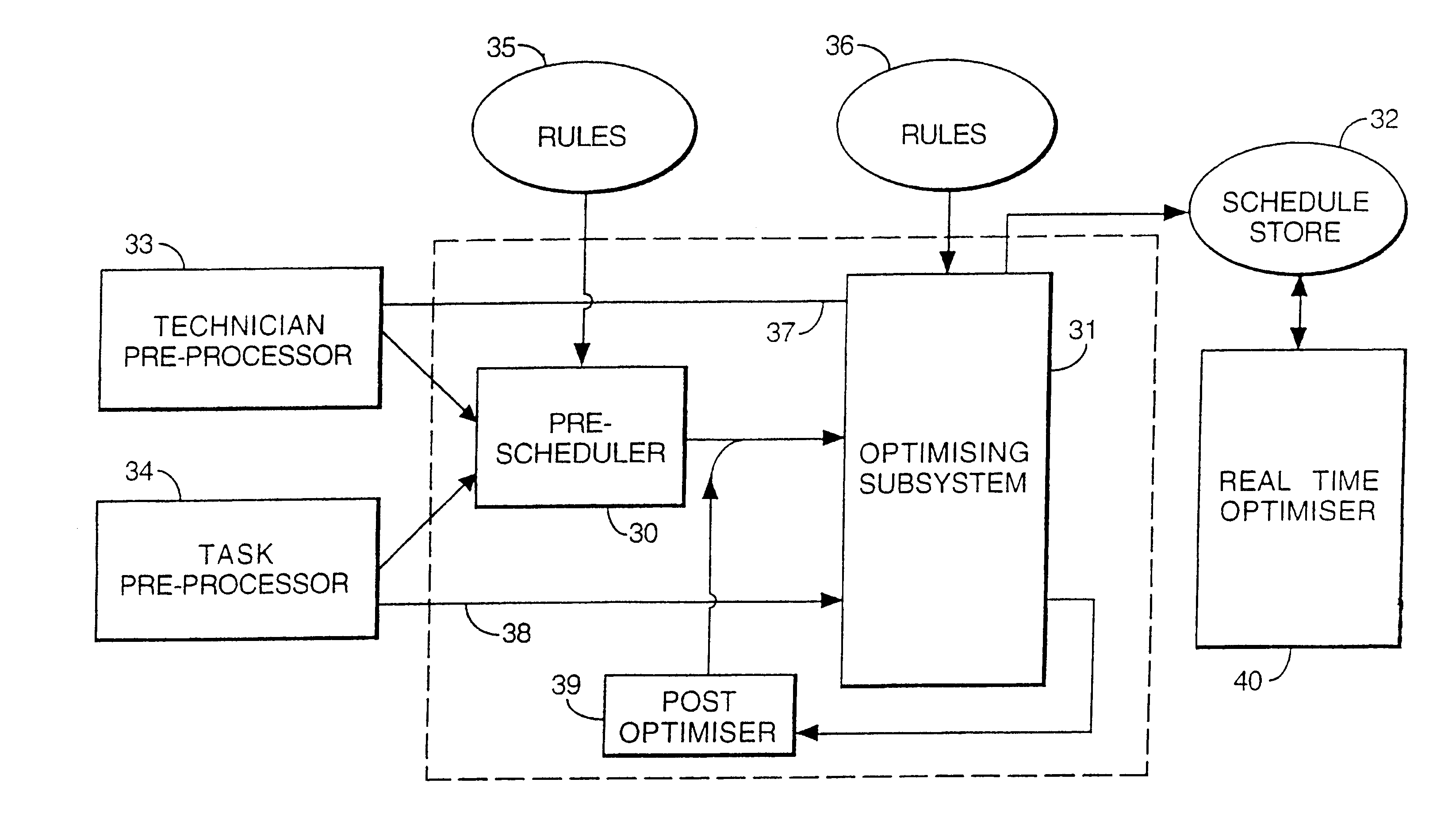
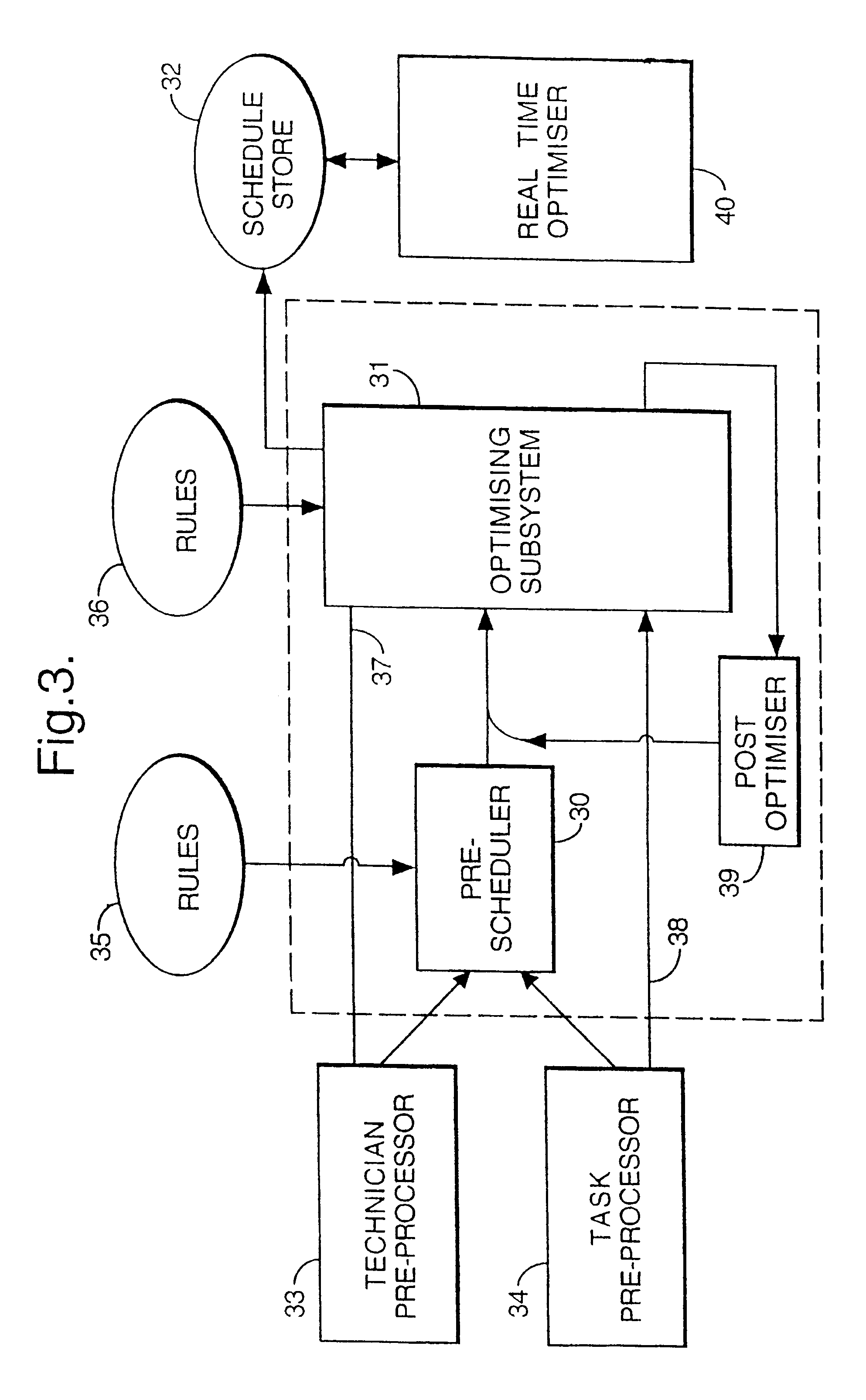
Method and apparatus for resource allocation when schedule changes are incorporated in real time
InactiveUS6578005B1Improve distributionEasy to solveResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsTime scheduleRule-based system
A plurality of resources, typically service operatives, are allocated to a plurality of tasks by a method in which initial information relating to the tasks to be allocated and the resources available to perform the tasks is provided. An initial series of schedules is first generated allocating resources to the tasks, and then modifying the individual schedule of at least one resource in response to updated information. Changes to individual schedules may be made in response to such updated information independently of the schedule generation. The initial, series of schedules may be generated in a two-stage process in which a rule-based system allocates tasks selected as being difficult to allocate (e.g., because they are linked to other tasks). then a stochastic (non-systematic) search system compiles the rest of the schedule. Periodically, the stochastic system may be interrupted to allow a further rule-based system to analyze the schedules created thus far, and fix the best ones in the schedule, so that the stochastic system can then concentrate on improving the remaining schedules. In order to allow the system to handle rapid changes in the requirements for tasks and the resources, on a scale faster than the time required to generate the schedules, a schedule modification system is arranged to make changes in the short term in between schedule updates delivered by the schedule generation system.
Owner:TRIMBLE MRM
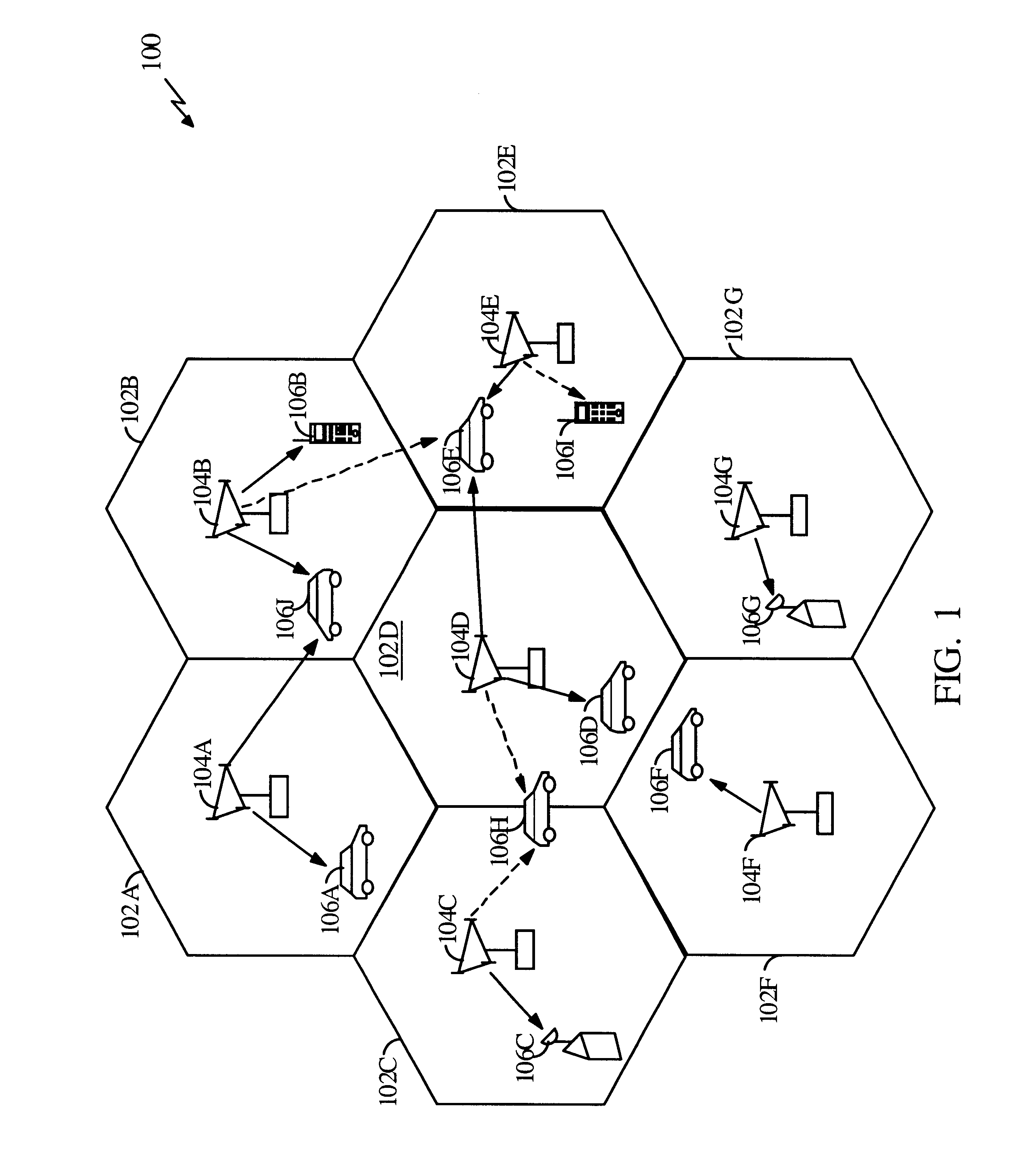
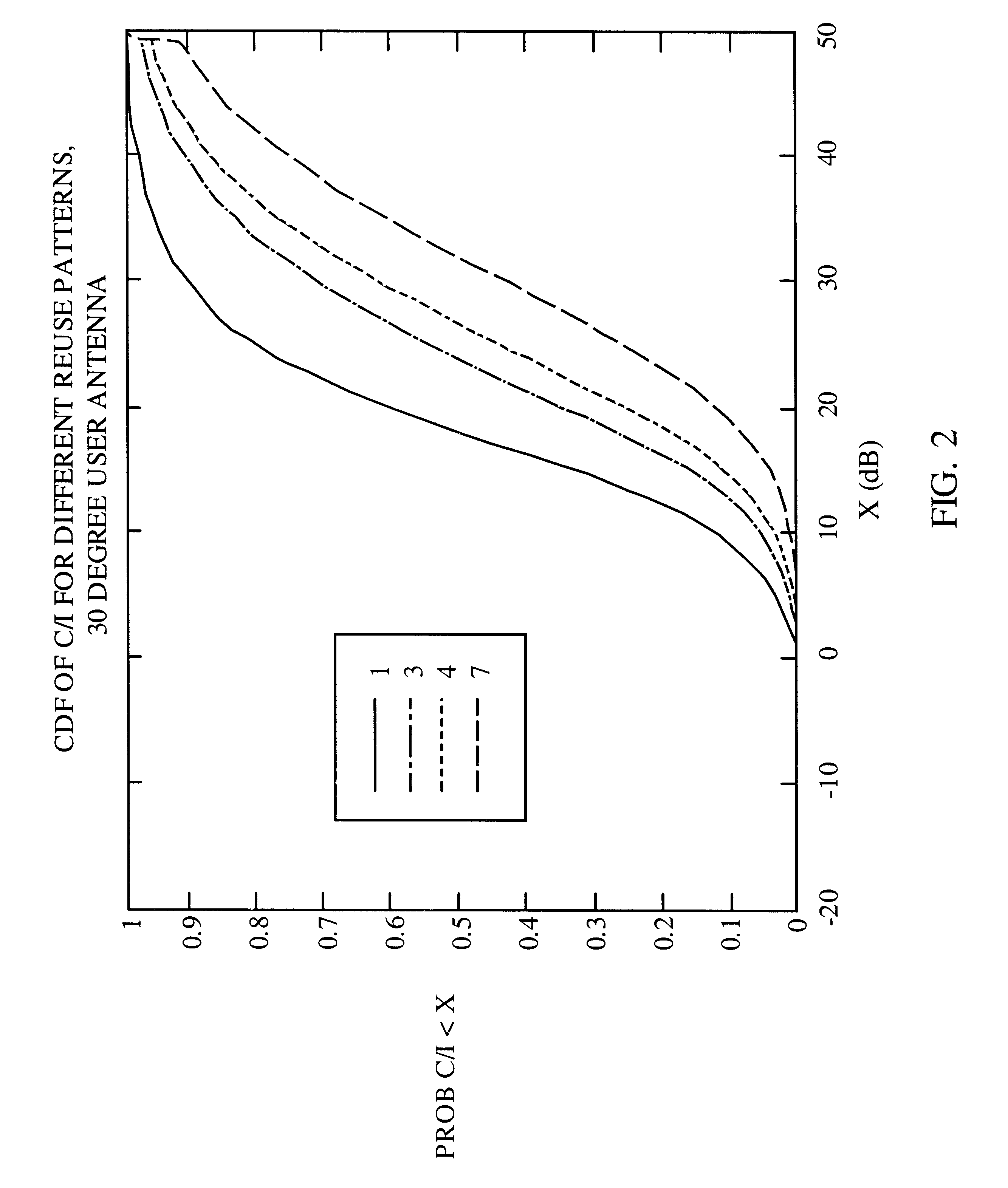
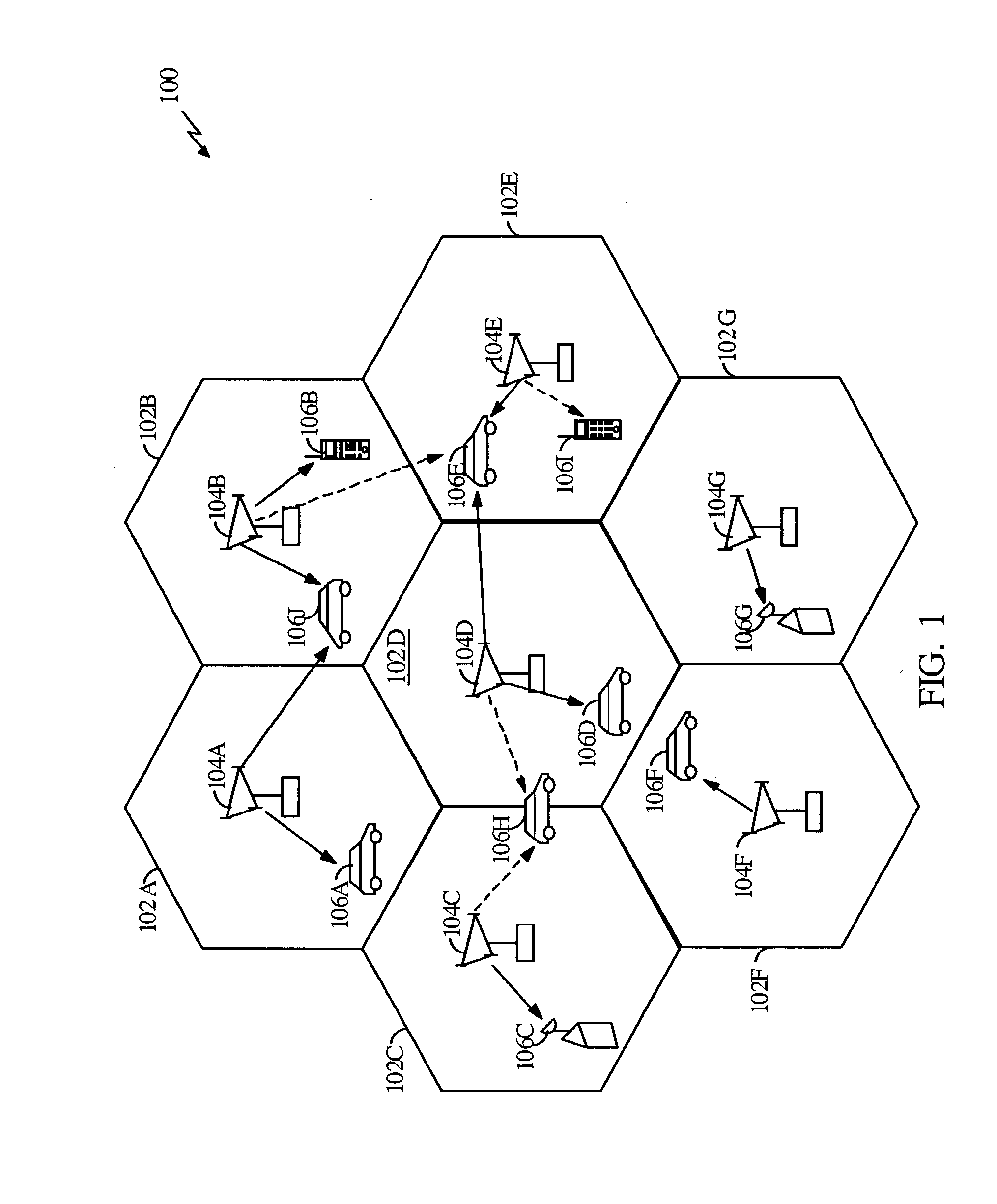
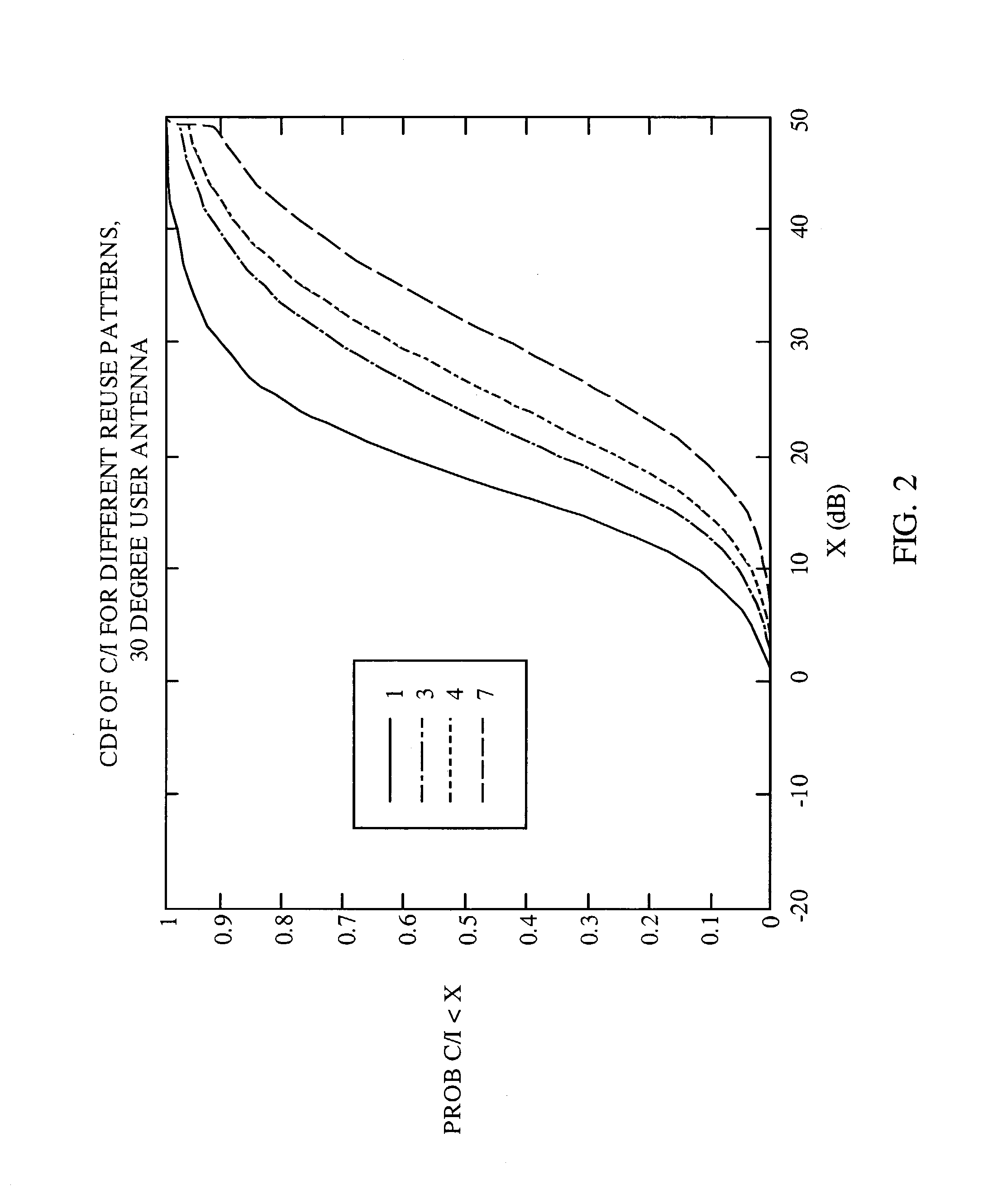
Method and apparatus for controlling transmissions of a communications systems
InactiveUS6493331B1Reduce the amount of noiseLower Level RequirementsEnergy efficient ICTPower managementControl communicationsSystem requirements
In some aspects, each cell in the communications system can be designed to operate in accordance with a set of back-off factors that identify the reductions in peak transmit power levels for the channels associated with the back-off factors. The back-off factors are defined to provide the required power to a large percentage of the users while reducing the amount of interference. In some other aspects, the cells operate using an adaptive reuse scheme that allows the cells to efficiently allocate and reallocate the system resources to reflect changes in the system. A reuse scheme is initially defined and resources are allocated to the cells. During operation, changes in the operating conditions of the system are detected and the reuse scheme is redefined as necessary based on the detected changes. For example, the loading conditions of the cells can be detected, and the resources can be reallocated and / or the reuse scheme can be redefined. In yet other aspects, techniques are provided to efficiency schedule data transmissions and to assign channels to users. Data transmissions can be scheduled based on user priorities, some fairness criteria, system requirements, and other factors. Users are assigned to available channels based on a number of channel assignment schemes. Channel metrics are also provided, which can be used to prioritize users and for channel assignments.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
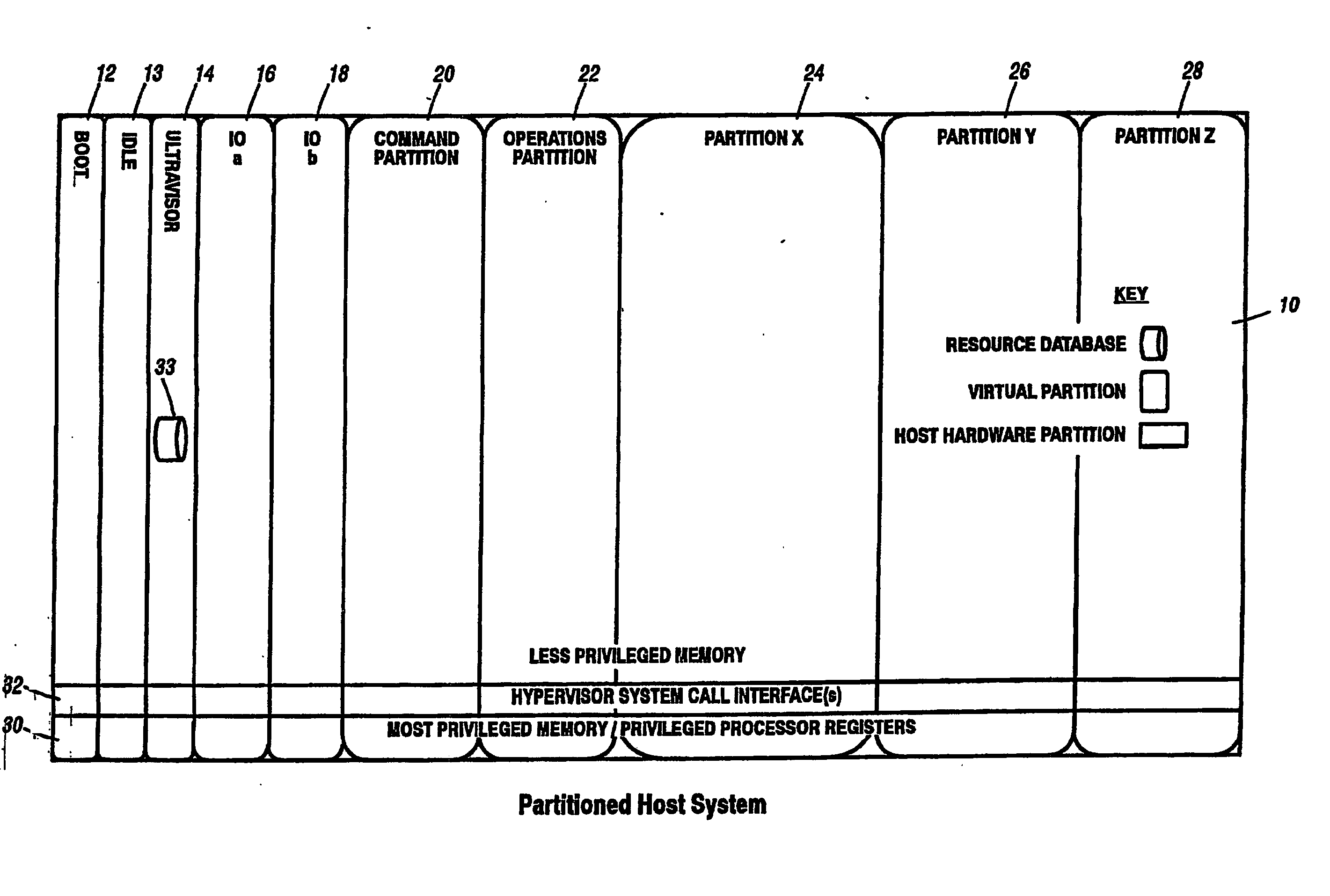
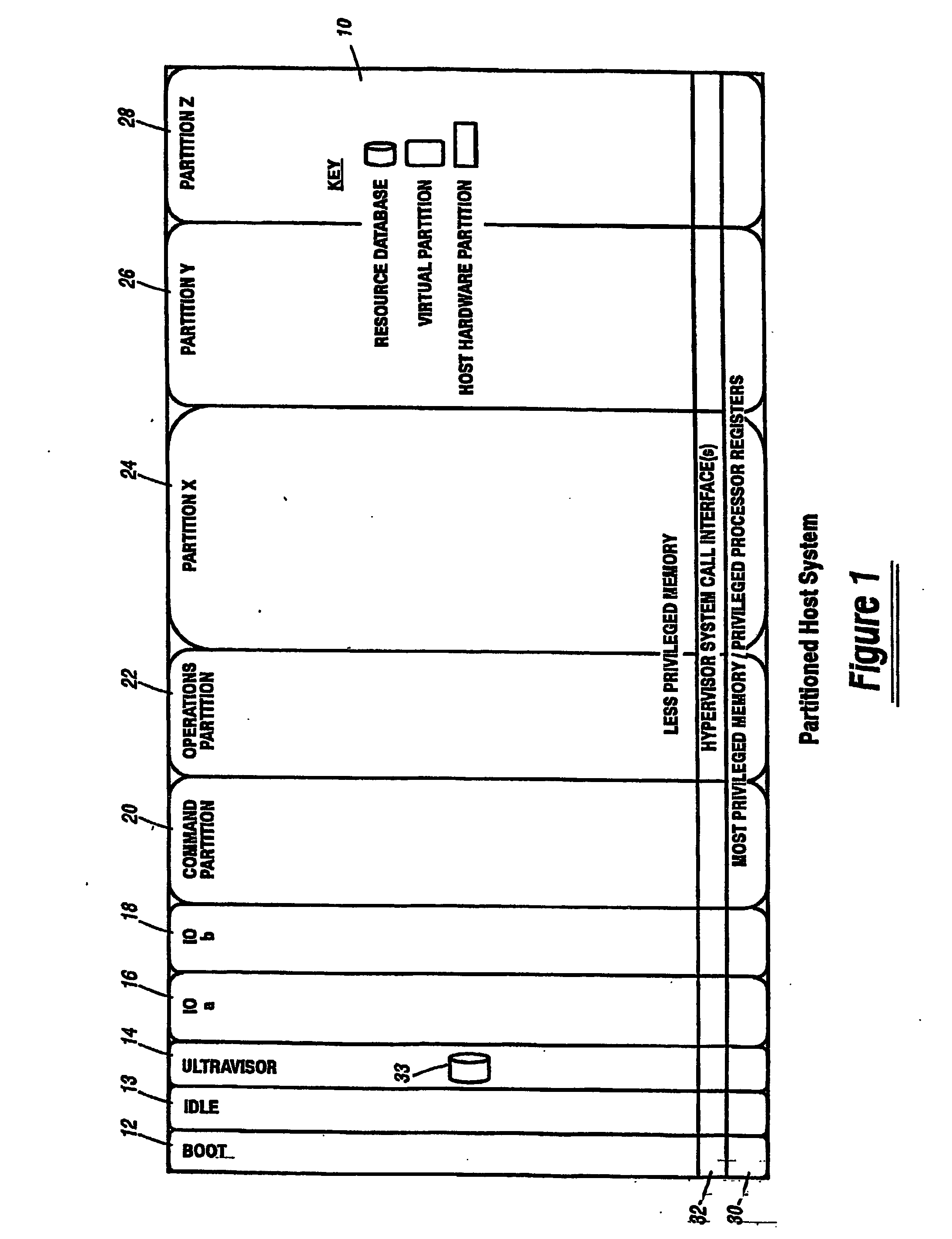
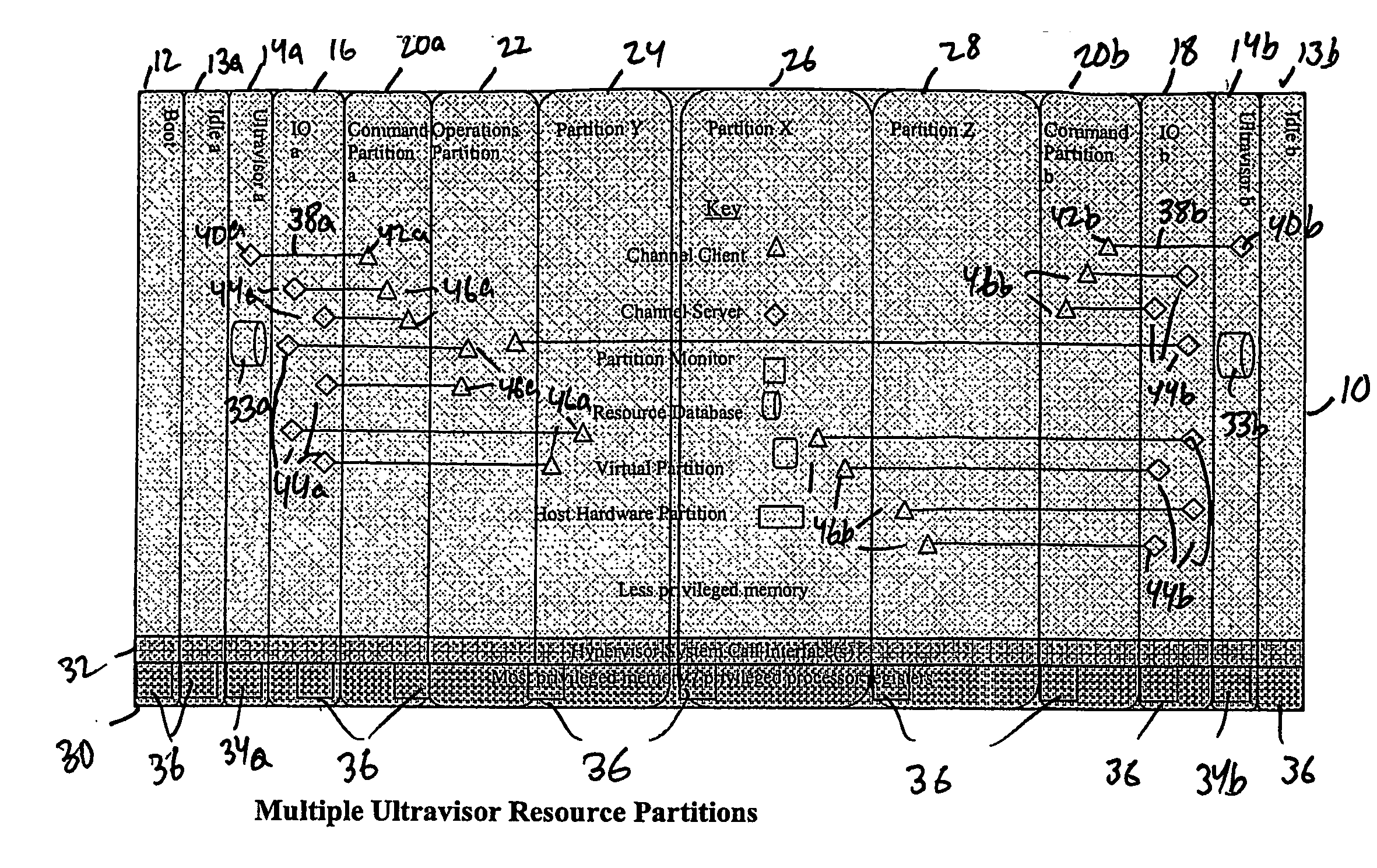
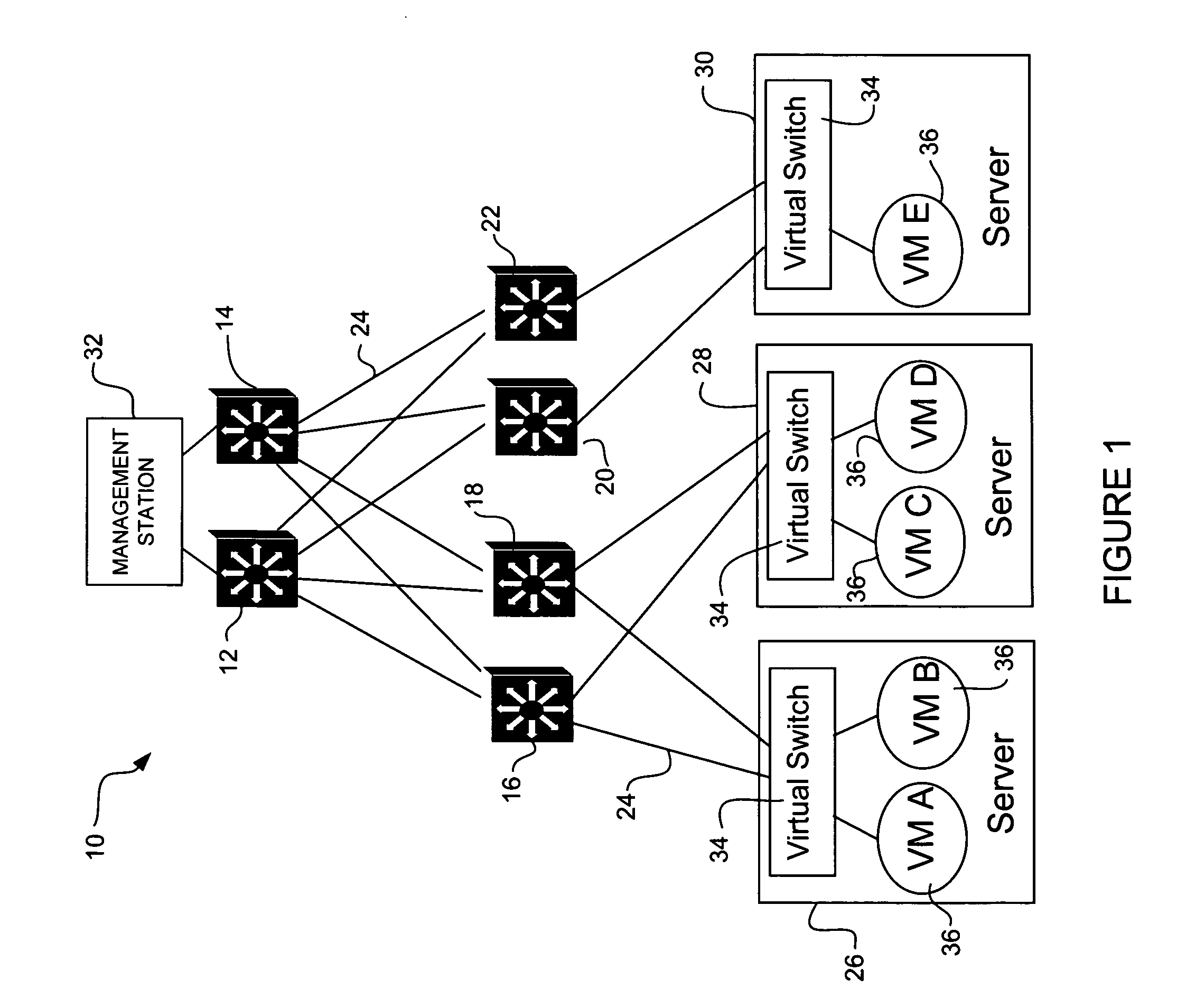
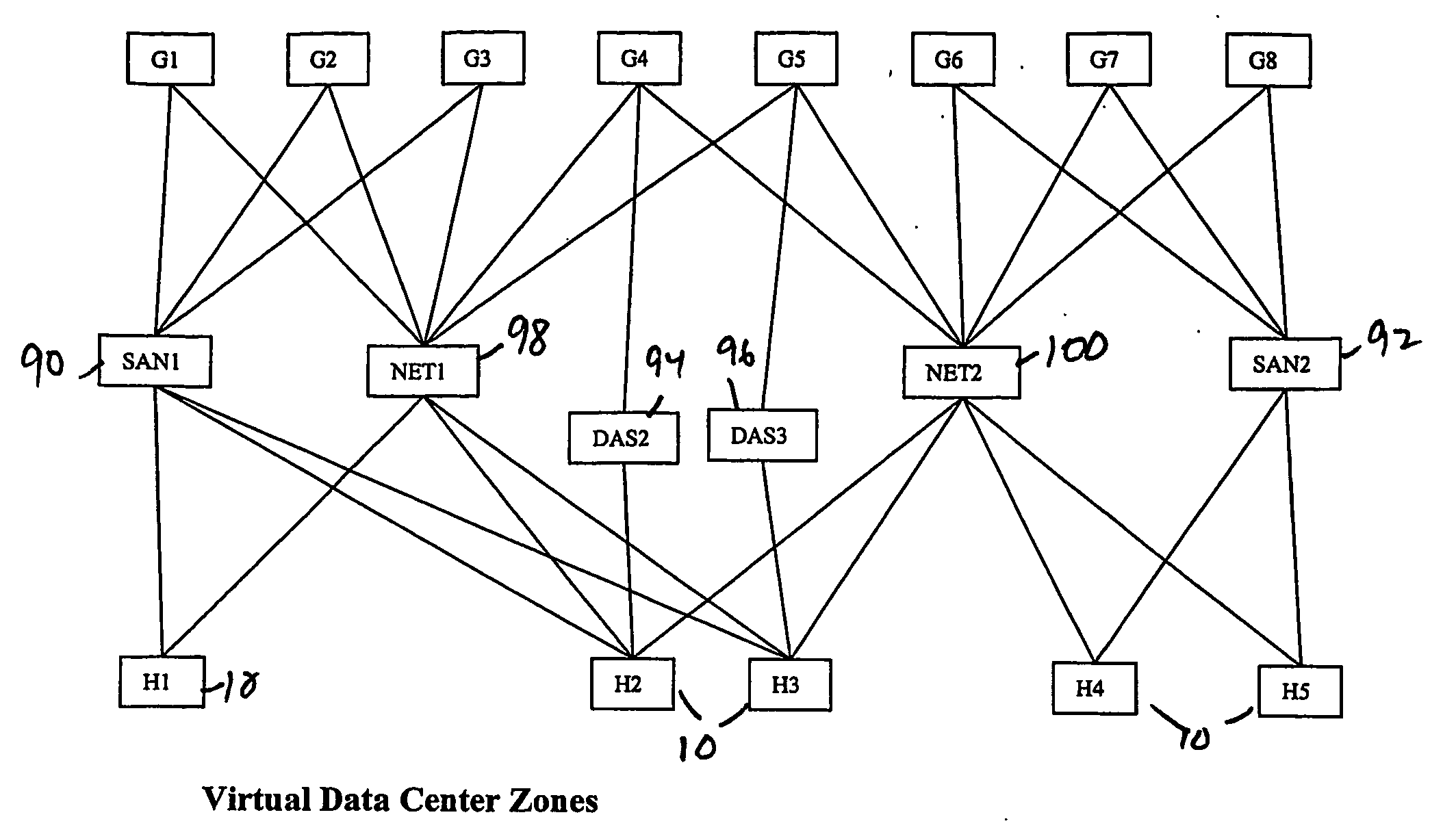
Virtual data center that allocates and manages system resources across multiple nodes
ActiveUS20070067435A1Improve securityExcessive removalError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemData center
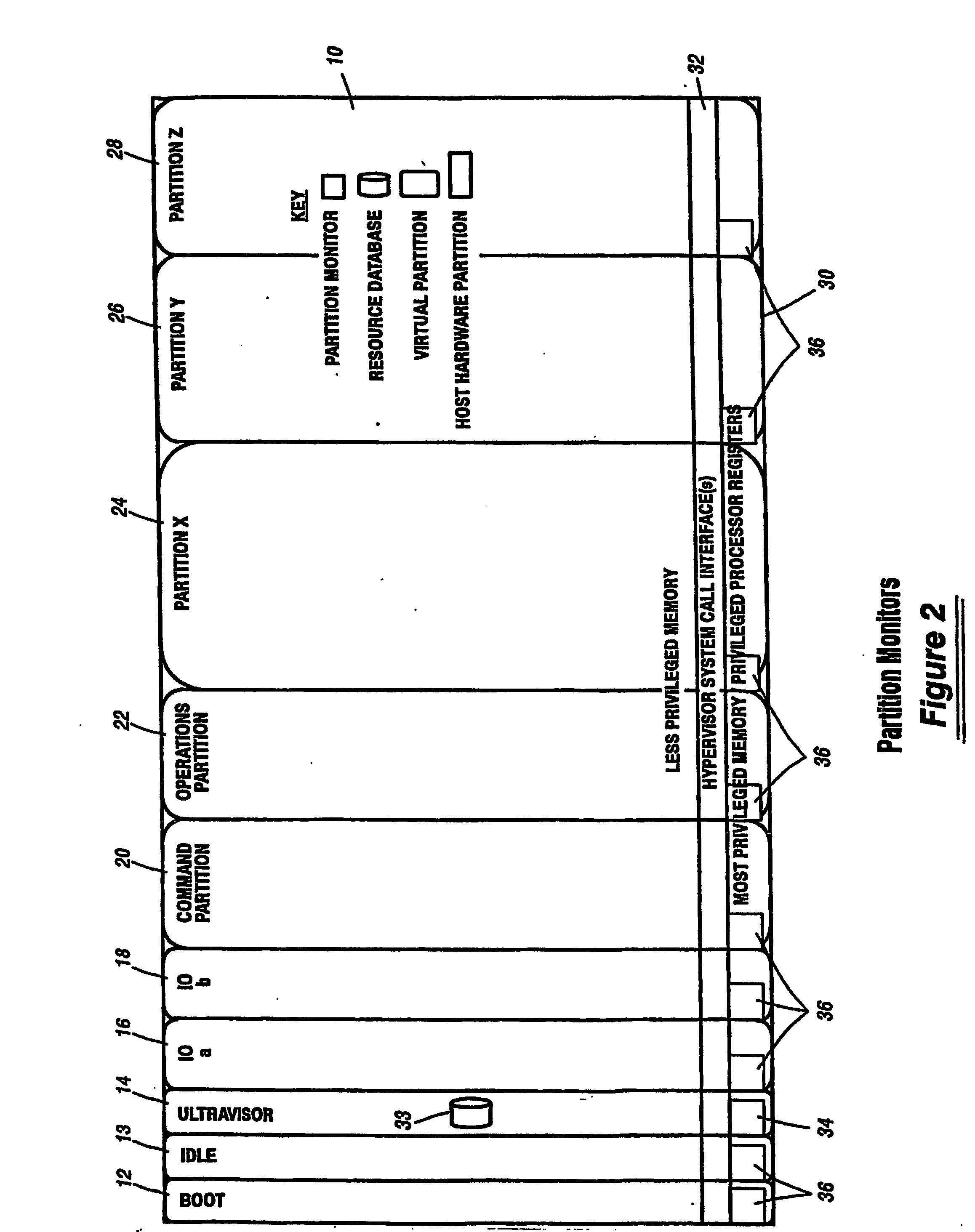
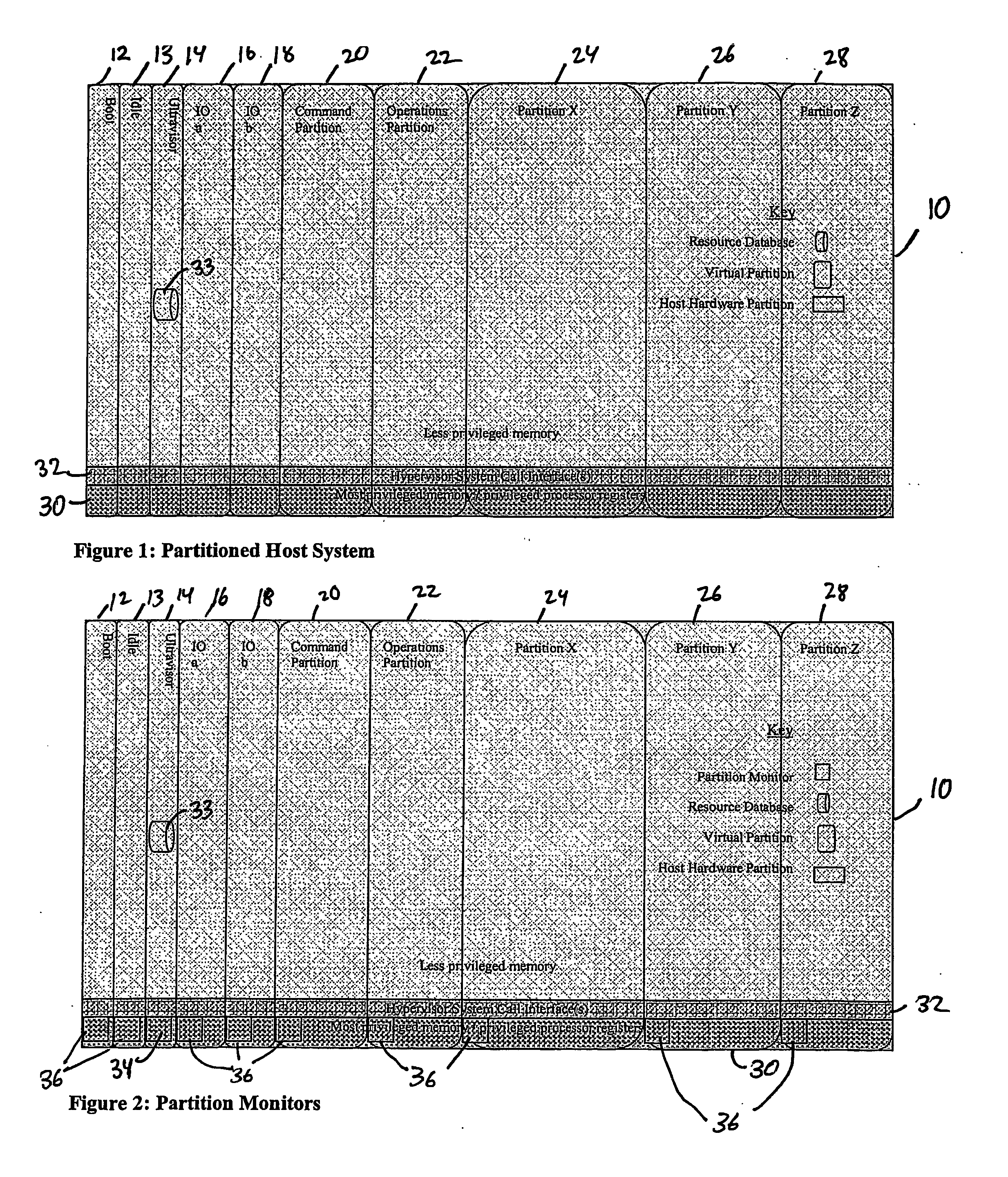
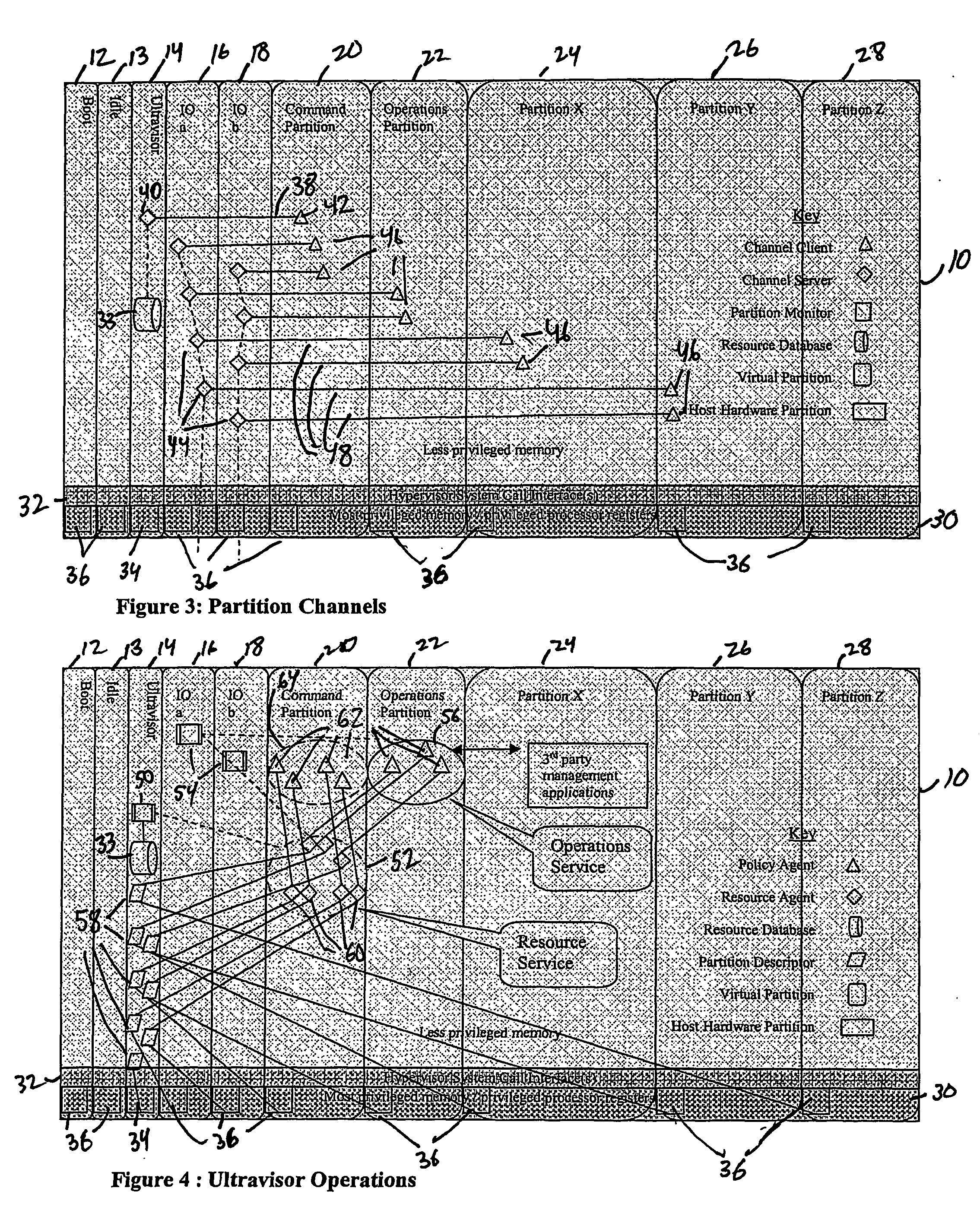
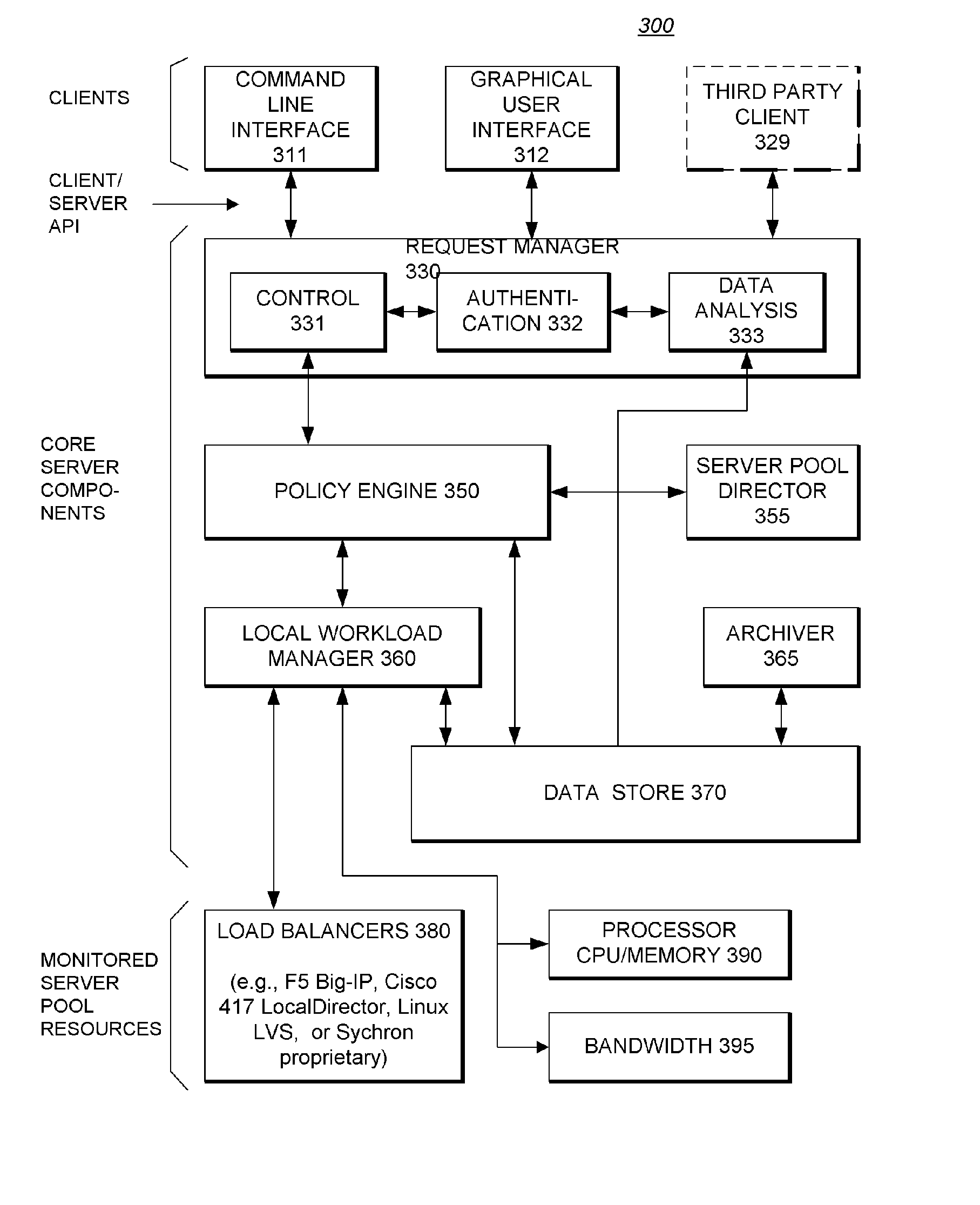
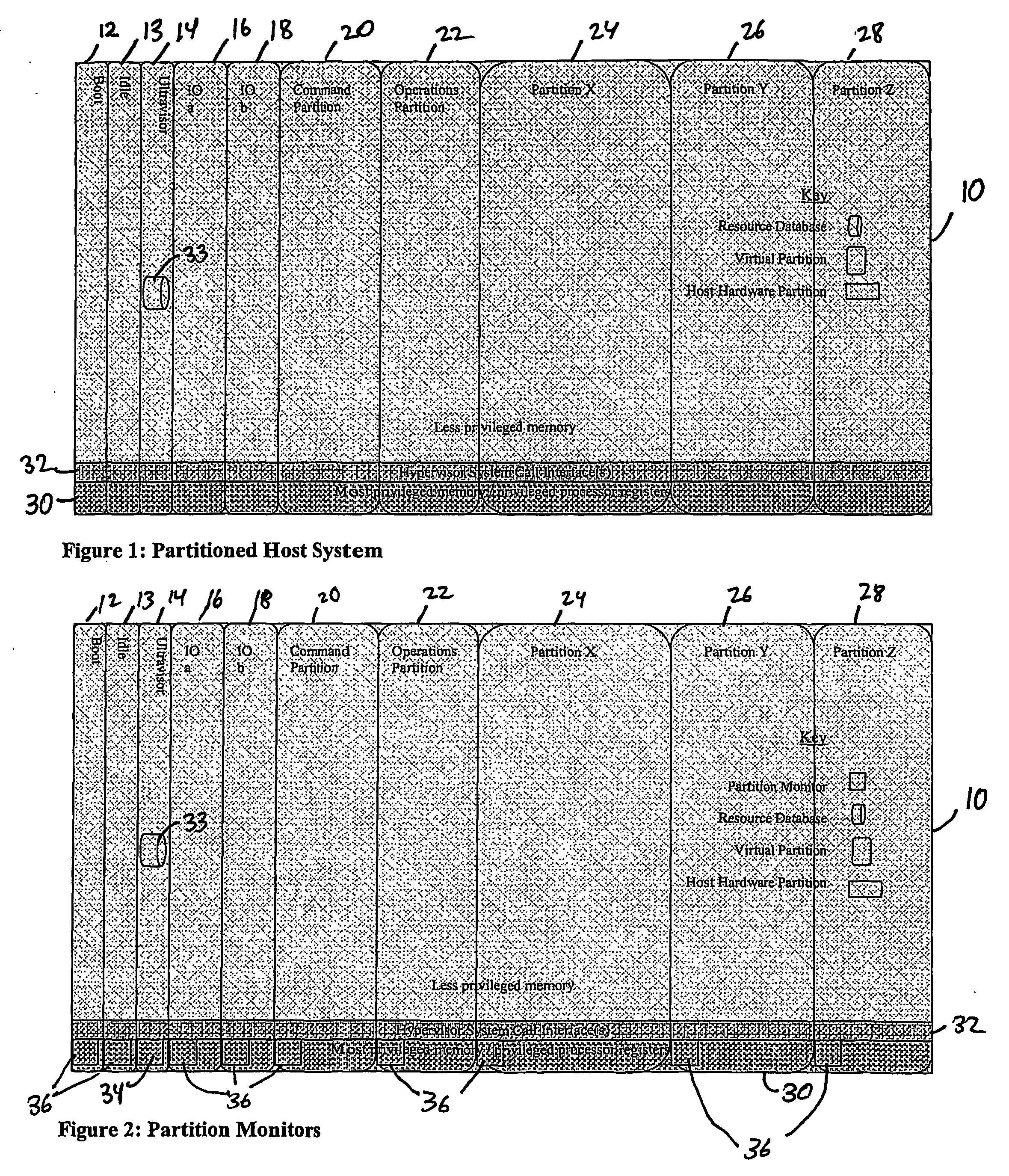
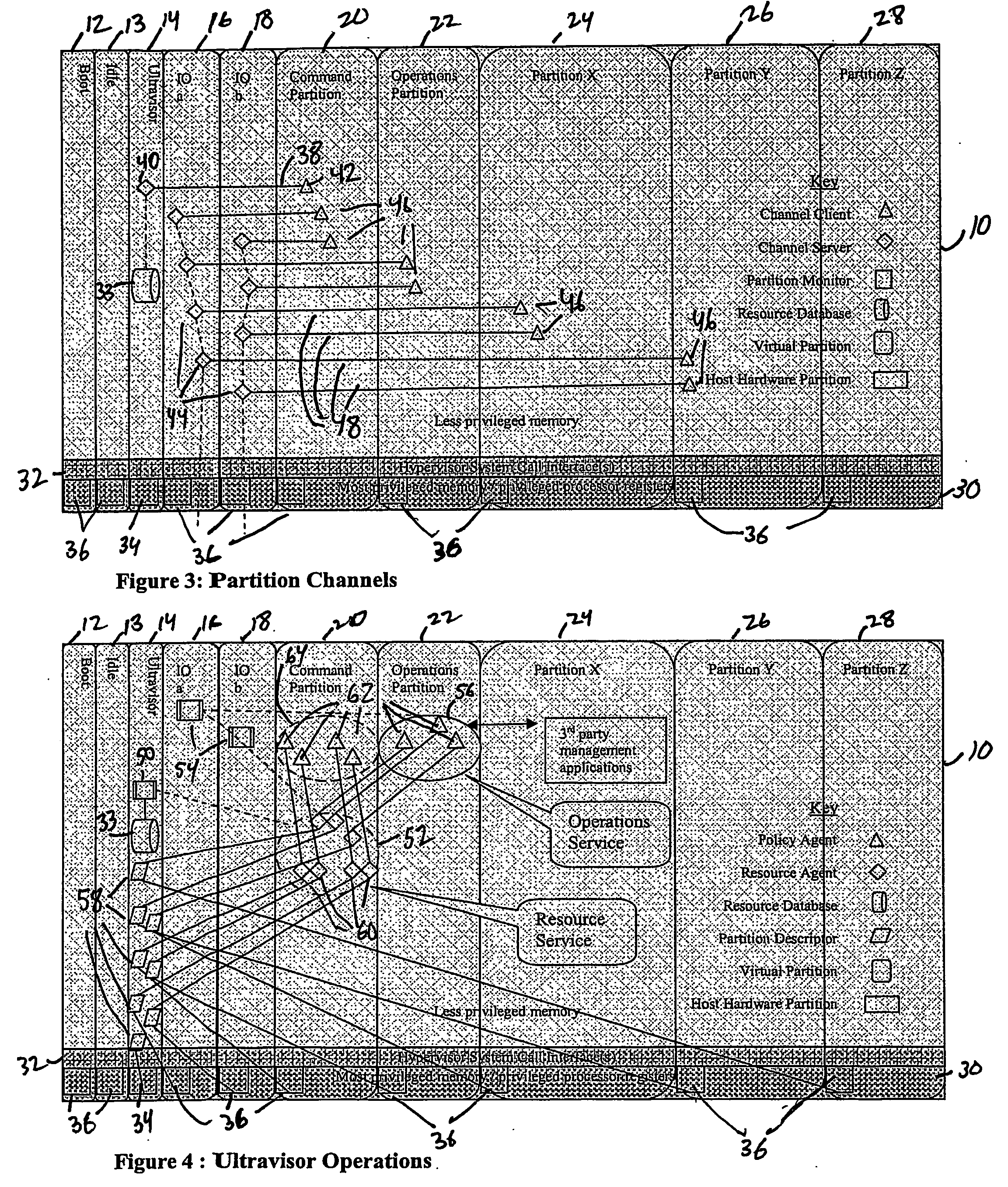
A virtualization infrastructure that allows multiple guest partitions to run within a host hardware partition. The host system is divided into distinct logical or virtual partitions and special infrastructure partitions are implemented to control resource management and to control physical I / O device drivers that are, in turn, used by operating systems in other distinct logical or virtual guest partitions. Host hardware resource management runs as a tracking application in a resource management “ultravisor” partition, while host resource management decisions are performed in a higher level command partition based on policies maintained in a separate operations partition. The conventional hypervisor is reduced to a context switching and containment element (monitor) for the respective partitions, while the system resource management functionality is implemented in the ultravisor partition. The ultravisor partition maintains the master in-memory database of the hardware resource allocations and serves a command channel to accept transactional requests for assignment of resources to partitions. It also provides individual read-only views of individual partitions to the associated partition monitors. Host hardware I / O management is implemented in special redundant I / O partitions. Operating systems in other logical or virtual partitions communicate with the I / O partitions via memory channels established by the ultravisor partition. The guest operating systems in the respective logical or virtual partitions are modified to access monitors that implement a system call interface through which the ultravisor, I / O, and any other special infrastructure partitions may initiate communications with each other and with the respective guest partitions. The guest operating systems are modified so that they do not attempt to use the “broken” instructions in the x86 system that complete virtualization systems must resolve by inserting traps. System resources are separated into zones that are managed by a separate partition containing resource management policies that may be implemented across nodes to implement a virtual data center.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Method and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information for carrier aggregated spectrums
InactiveUS20100271970A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
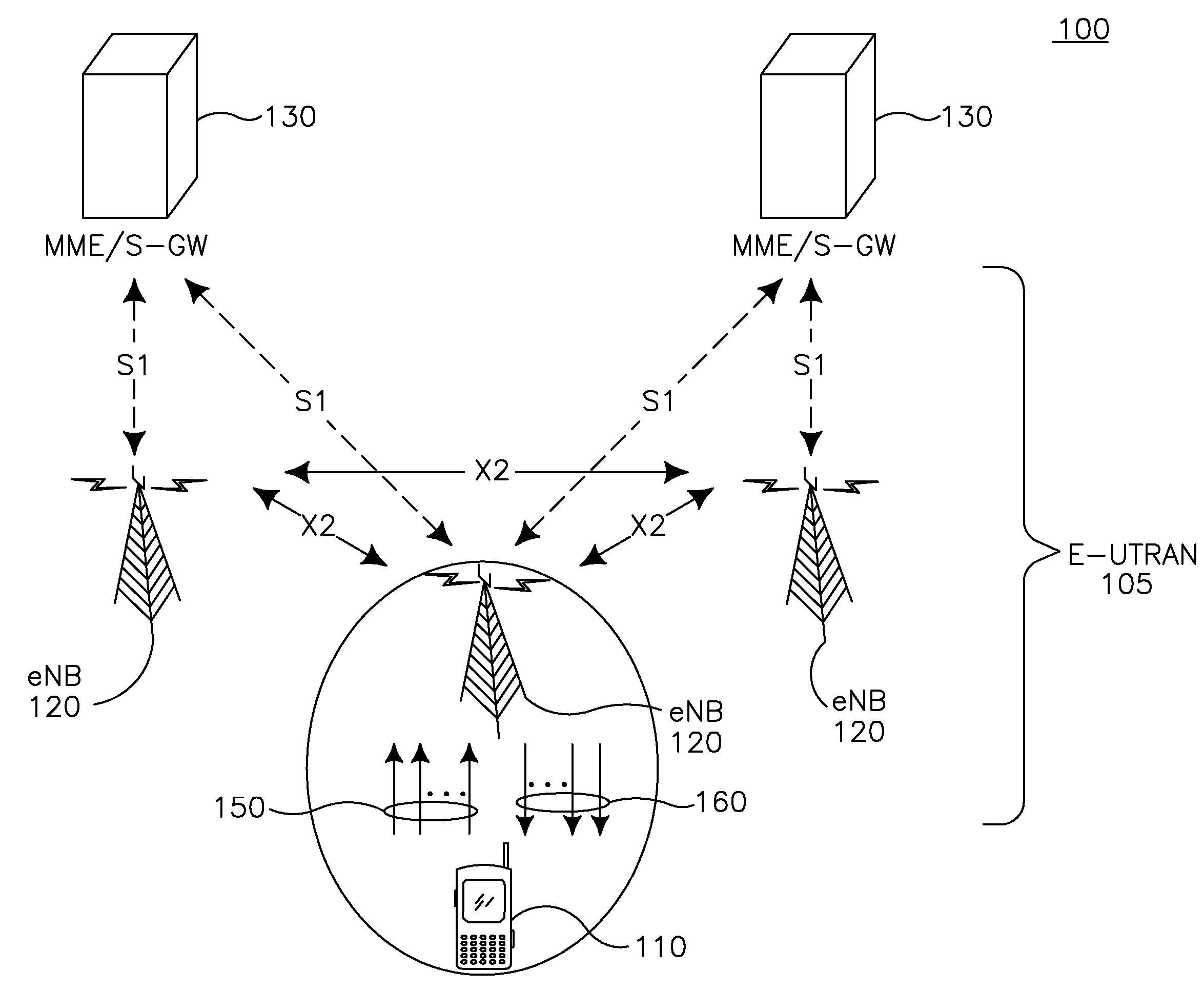
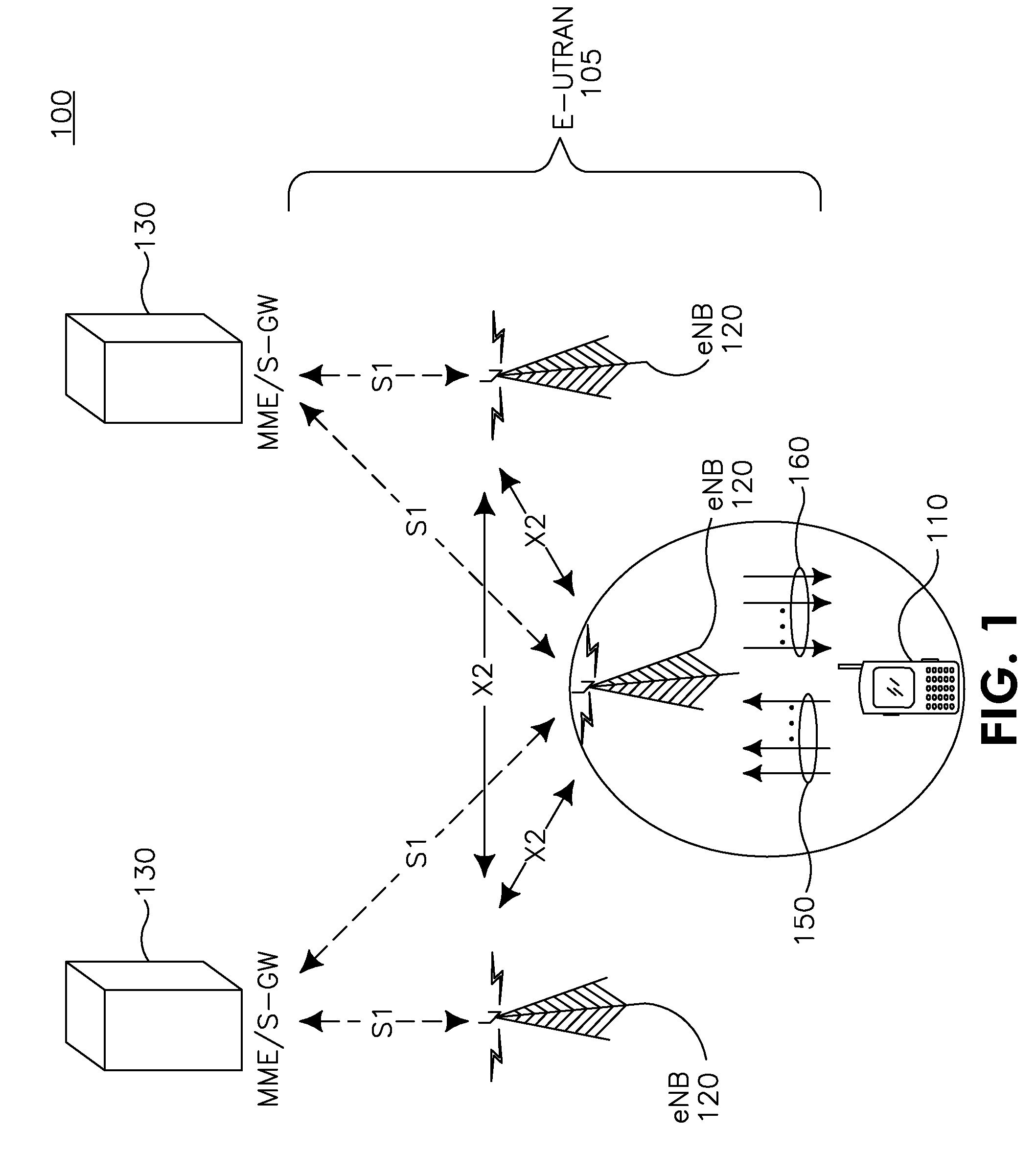
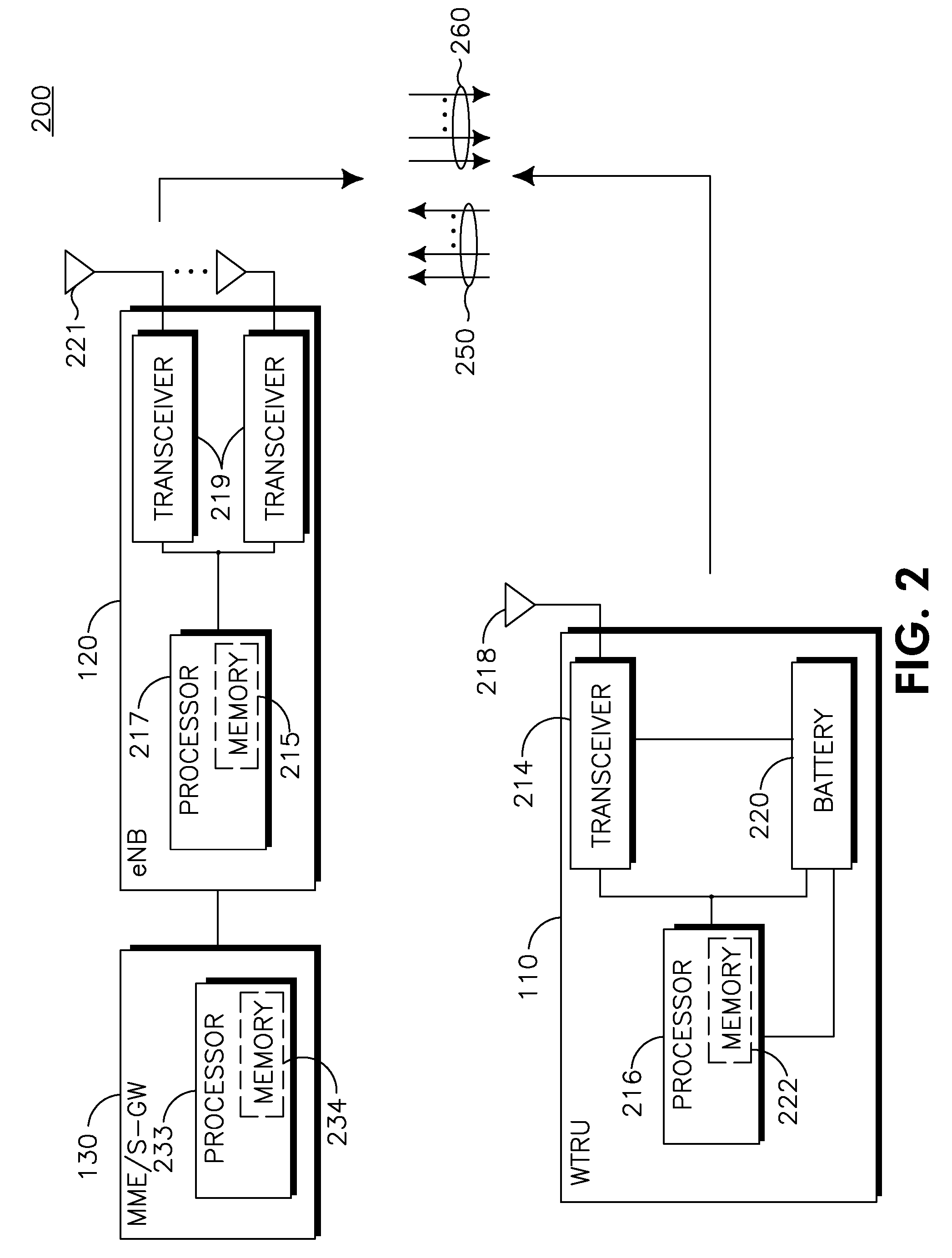
Methods and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information (UCI) in carrier aggregated spectrums are disclosed. UCI may include, but is not limited to, Precoding Matrix Indicator (PMI), Rank Indication (RI), Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), Acknowledge / Not Acknowledge (ACK / NACK) and Scheduling Request (SR). For symmetric carrier aggregation, uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) component carriers may be paired and use physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) in each UL component carrier to send UCI for the corresponding DL component carrier. For asymmetric carrier aggregation, methods are provided for UCI transmission and resource allocation depending on component carrier configuration or assignment. Methods are provided for multiple and single component carrier configurations that may further provide backward compatibility.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
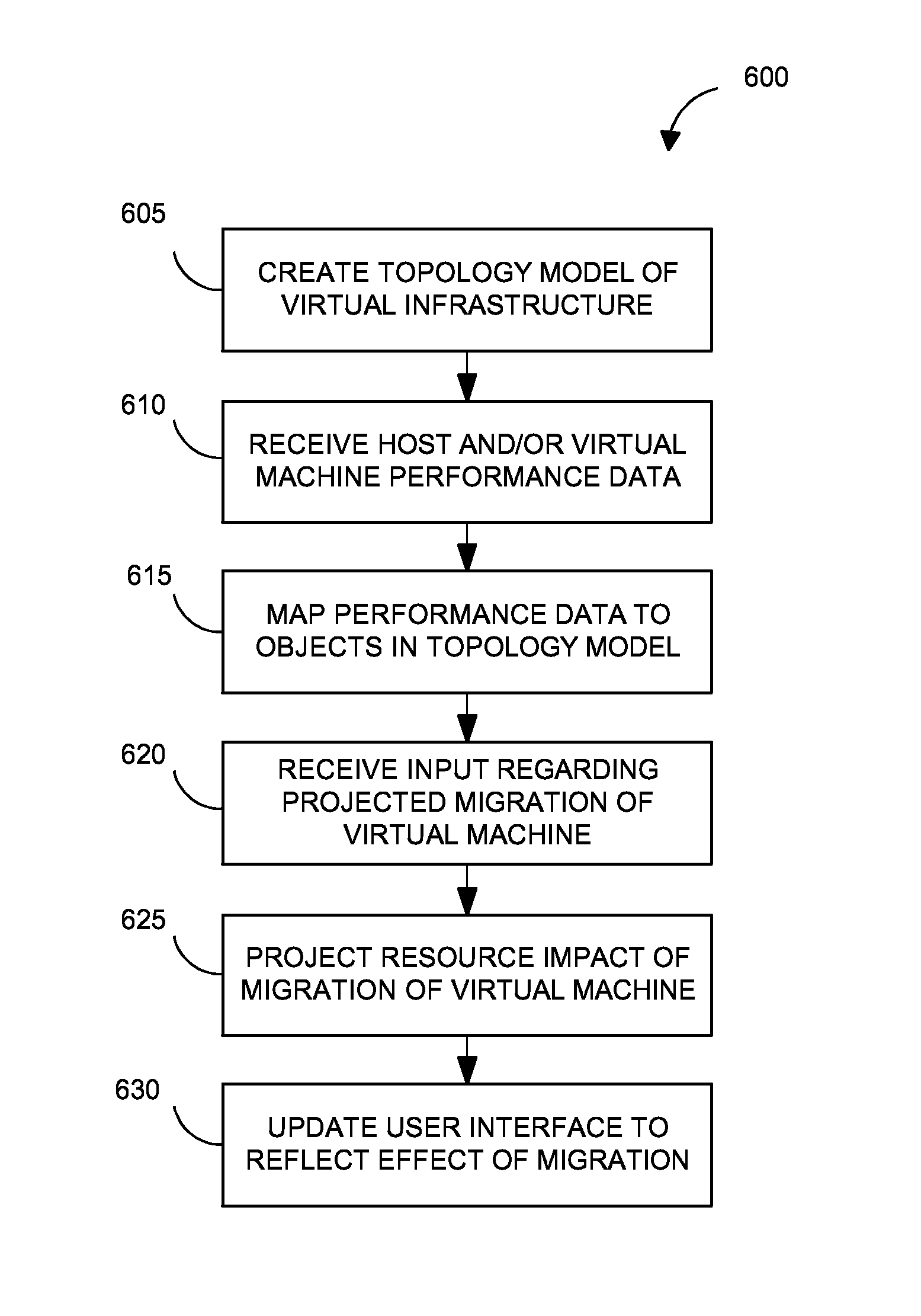
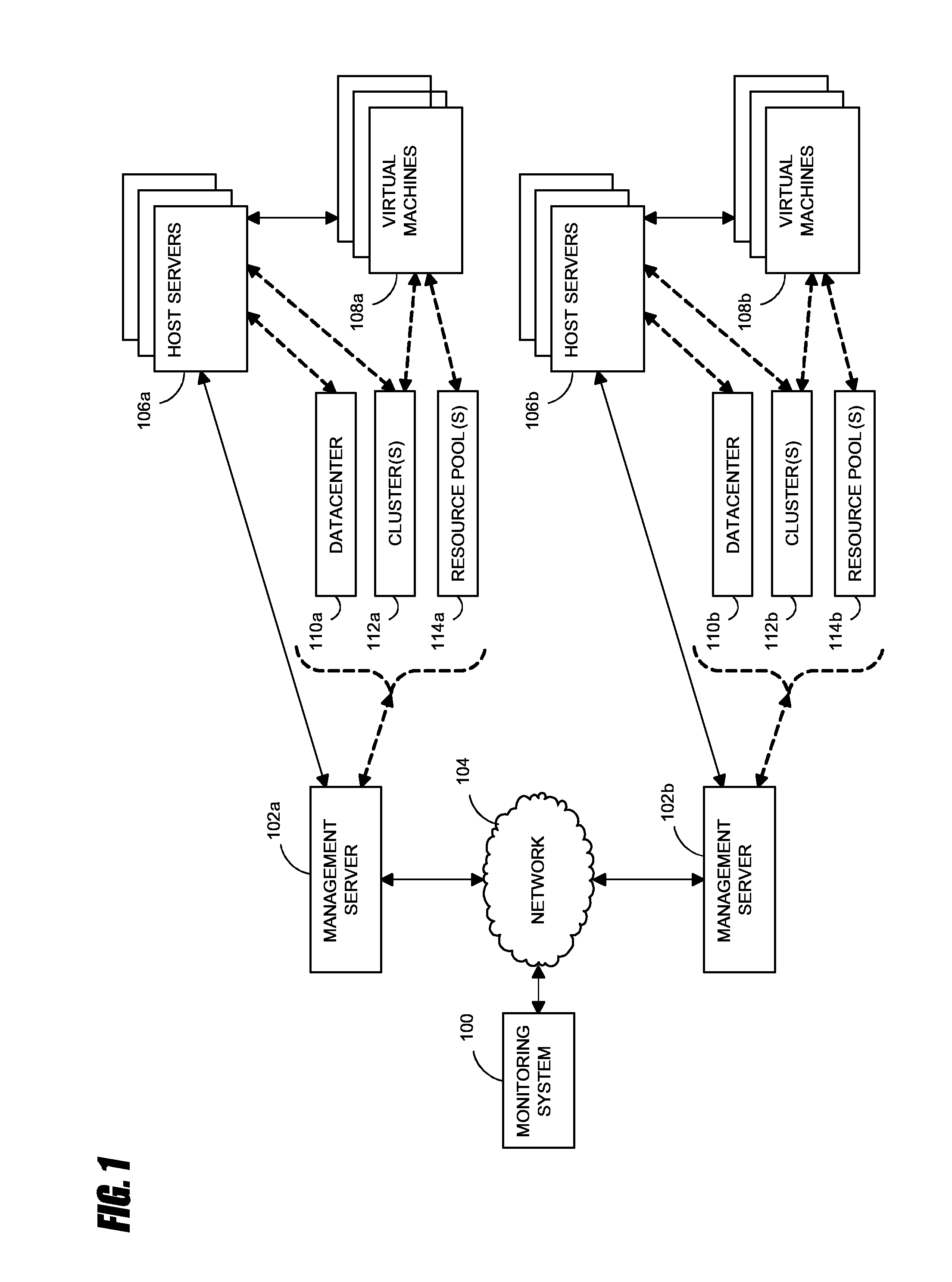
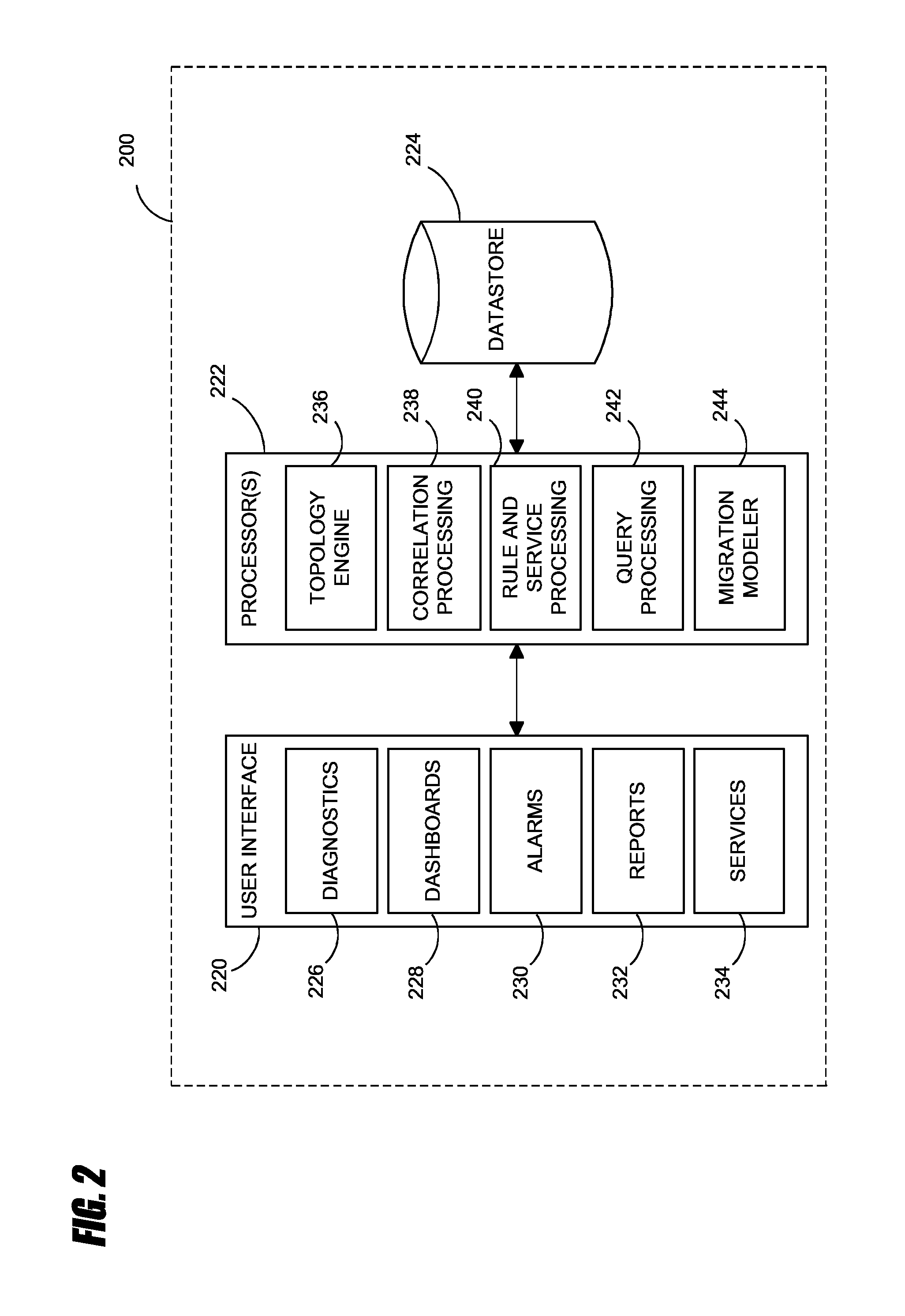
Systems and methods for analyzing performance of virtual environments
InactiveUS8175863B1Effective and efficient diagnosisResource allocationError detection/correctionMonitoring systemSmart surveillance
Intelligent monitoring systems and methods for virtual environments are disclosed that understand various components of a virtual infrastructure and how the components interact to provide improved performance analysis to users. In certain examples, a monitoring system assesses the performance of virtual machine(s) in the context of the overall performance of the physical server(s) and the environment in which the virtual machine(s) are running. For instance, the monitoring system can track performance metrics over a determined period of time to view changes to the allocation of resources to virtual machines and their location(s) on physical platforms. Moreover, monitoring systems can utilize past performance information from separate virtual environments to project a performance impact resulting from the migration of a virtual machine from one physical platform to another.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Computer system para-virtualization using a hypervisor that is implemented in a partition of the host system
ActiveUS20070028244A1Improve securityExcessive removalError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemSystem call
A virtualization infrastructure that allows multiple guest partitions to run within a host hardware partition. The host system is divided into distinct logical or virtual partitions and special infrastructure partitions are implemented to control resource management and to control physical I / O device drivers that are, in turn, used by operating systems in other distinct logical or virtual guest partitions. Host hardware resource management runs as a tracking application in a resource management “ultravisor” partition, while host resource management decisions are performed in a higher level command partition based on policies maintained in a separate operations partition. The conventional hypervisor is reduced to a context switching and containment element (monitor) for the respective partitions, while the system resource management functionality is implemented in the ultravisor partition. The ultravisor partition maintains the master in-memory database of the hardware resource allocations and serves a command channel to accept transactional requests for assignment of resources to partitions. It also provides individual read-only views of individual partitions to the associated partition monitors. Host hardware I / O management is implemented in special redundant I / O partitions. Operating systems in other logical or virtual partitions communicate with the I / O partitions via memory channels established by the ultravisor partition. The guest operating systems in the respective logical or virtual partitions are modified to access monitors that implement a system call interface through which the ultravisor, I / O, and any other special infrastructure partitions may initiate communications with each other and with the respective guest partitions. The guest operating systems are modified so that they do not attempt to use the “broken” instructions in the x86 system that complete virtualization systems must resolve by inserting traps.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
System Providing Methodology for Policy-Based Resource Allocation
A system providing methodology for policy-based resource allocation is described. In one embodiment, for example, a system for allocating computer resources amongst a plurality of applications based on a policy is described that comprises: a plurality of computers connected to one another through a network; a policy engine for specifying a policy for allocation of resources of the plurality of computers amongst a plurality of applications having access to the resources; a monitoring module at each computer for detecting demands for the resources and exchanging information regarding demands for the resources at the plurality of computers; and an enforcement module at each computer for allocating the resources amongst the plurality of applications based on the policy and information regarding demands for the resources.
Owner:CAVALIER NEWCO +1
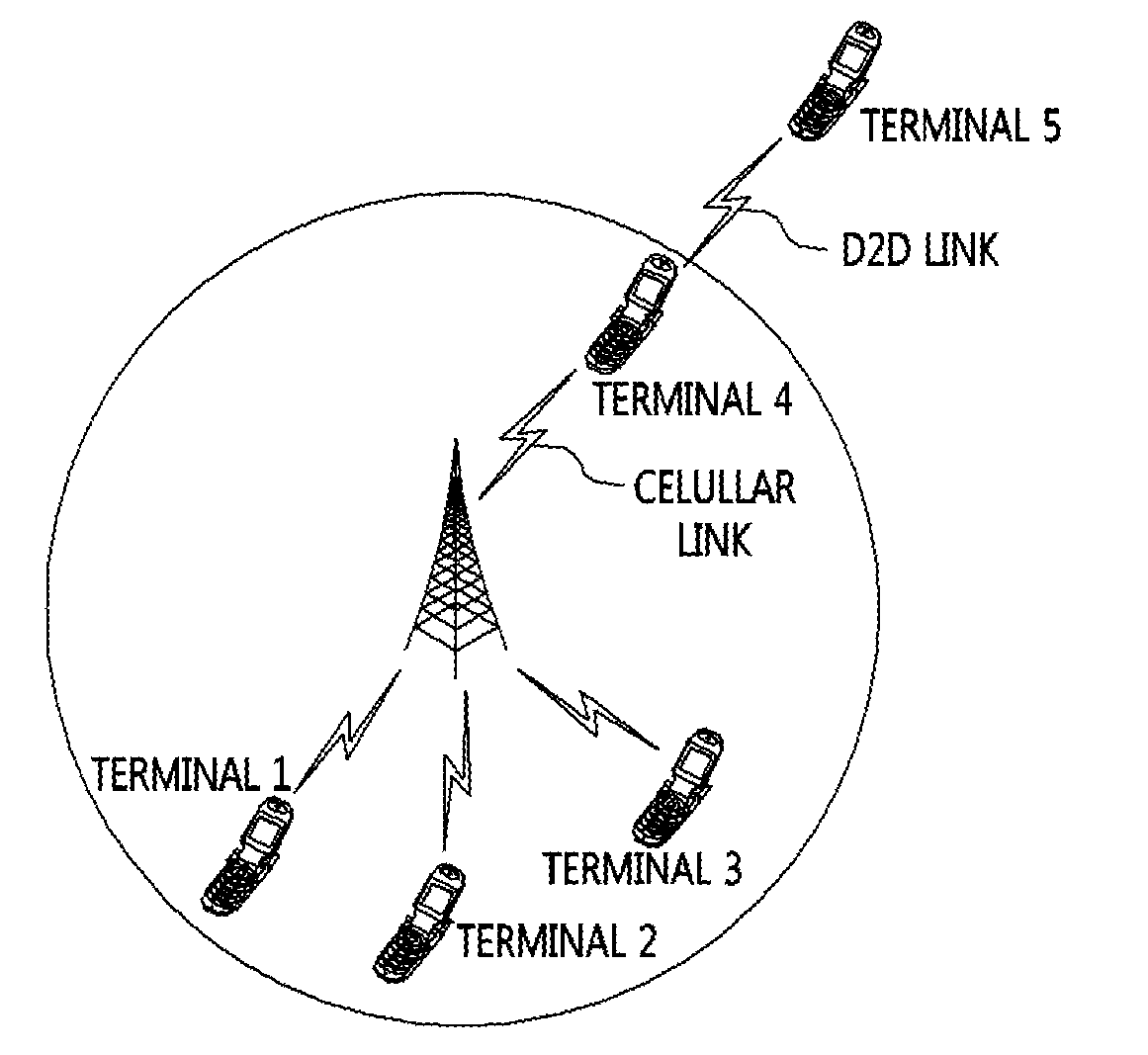
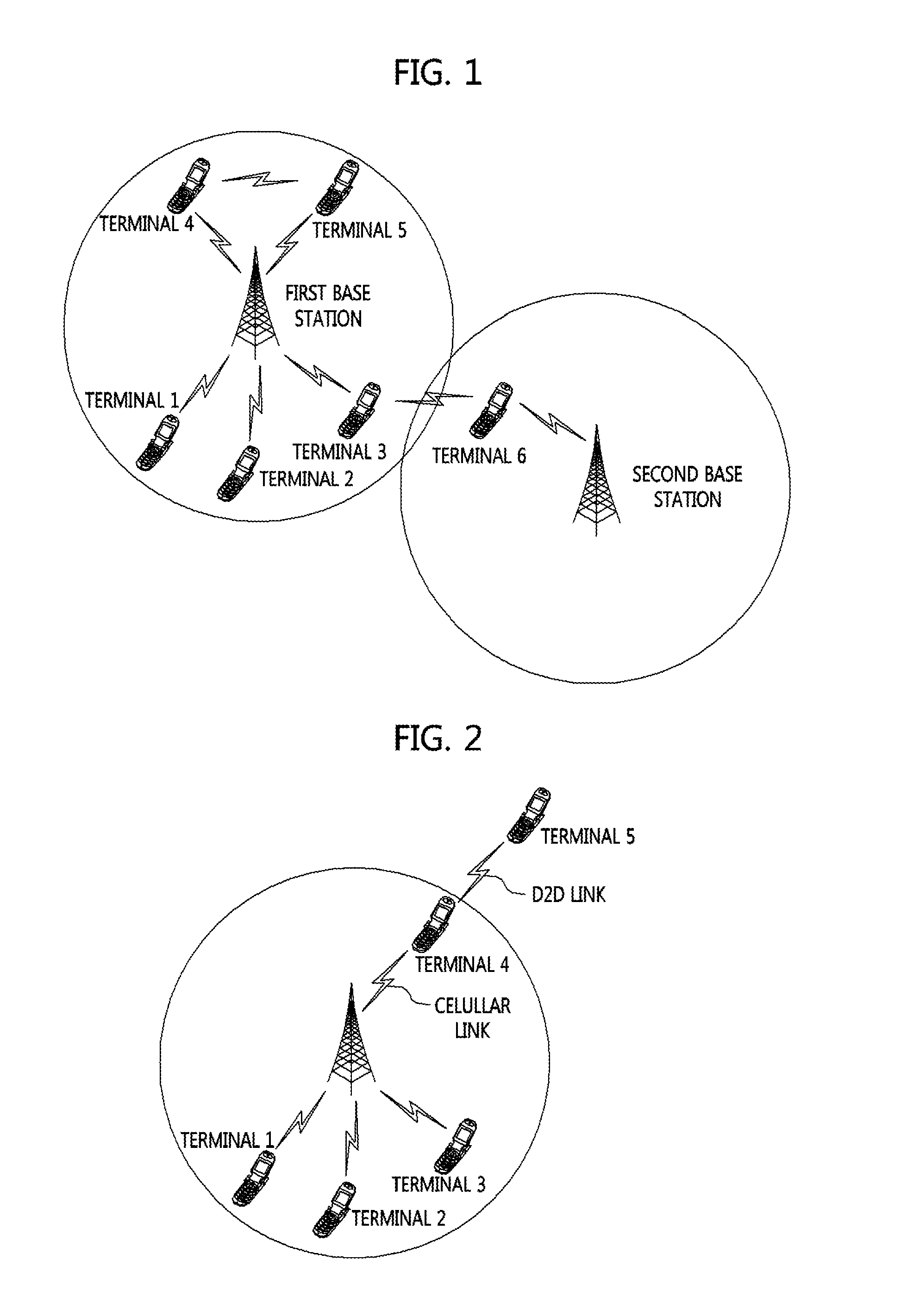
Apparatus and method for dynamic communication resource allocation for device-to-device communications in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20120093098A1Facilitate communicationPower managementSynchronisation arrangementCommunications systemDirect device
An apparatus, system and method to dynamically manage an allocation of communication resources for direct device-to-device communications between a plurality of wireless communication devices in a wireless communication system. In one embodiment, the apparatus (410) includes a communication resource allocator (420) configured to: (1) select a master communication device of a plurality of wireless communication devices that form a device-to-device group, (2) provide an allocation of communication resources for device-to-device group that facilitate direct device-to-device communications therebetween. The apparatus (410) also includes a message generator (430) configured to assemble messages that include the allocation of the communication resources.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet-centric wireless point to multi-point (PTMP) transmission system architecture
InactiveUS6862622B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransport systemWorkstation
A packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system includes: a wireless base station communicating via a packet-centric protocol to a first data network; one or more host workstations communicating via the packet-centric protocol to the first data network; one or more subscriber customer premise equipment (CPE) stations coupled with the wireless base station over a shared bandwidth via the packet-centric protocol over a wireless medium; and one or more subscriber workstations coupled via the packet-centric protocol to each of the subscriber CPE stations over a second network. The packet-centric protocol can be transmission control protocol / internet protocol (TCP / IP). The packet-centric protocol can be a user datagram protocol / internet protocol (UDP / IP). The system can include a resource allocation means for allocating shared bandwidth among the subscriber CPE stations. The resource allocation is performed to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS). The wireless communication medium can include at least one of: a radio frequency (RF) communications medium; a cable communications medium; and a satellite communications medium. The wireless communication medium can further include a telecommunications access method including at least one of: a time division multiple access (TDMA) access method; a time division multiple access / time division duplex (TDMA / TDD) access method; a code division multiple access (CDMA) access method; and a frequency division multiple access (FDMA) access method.The first data network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN). The second network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN).
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
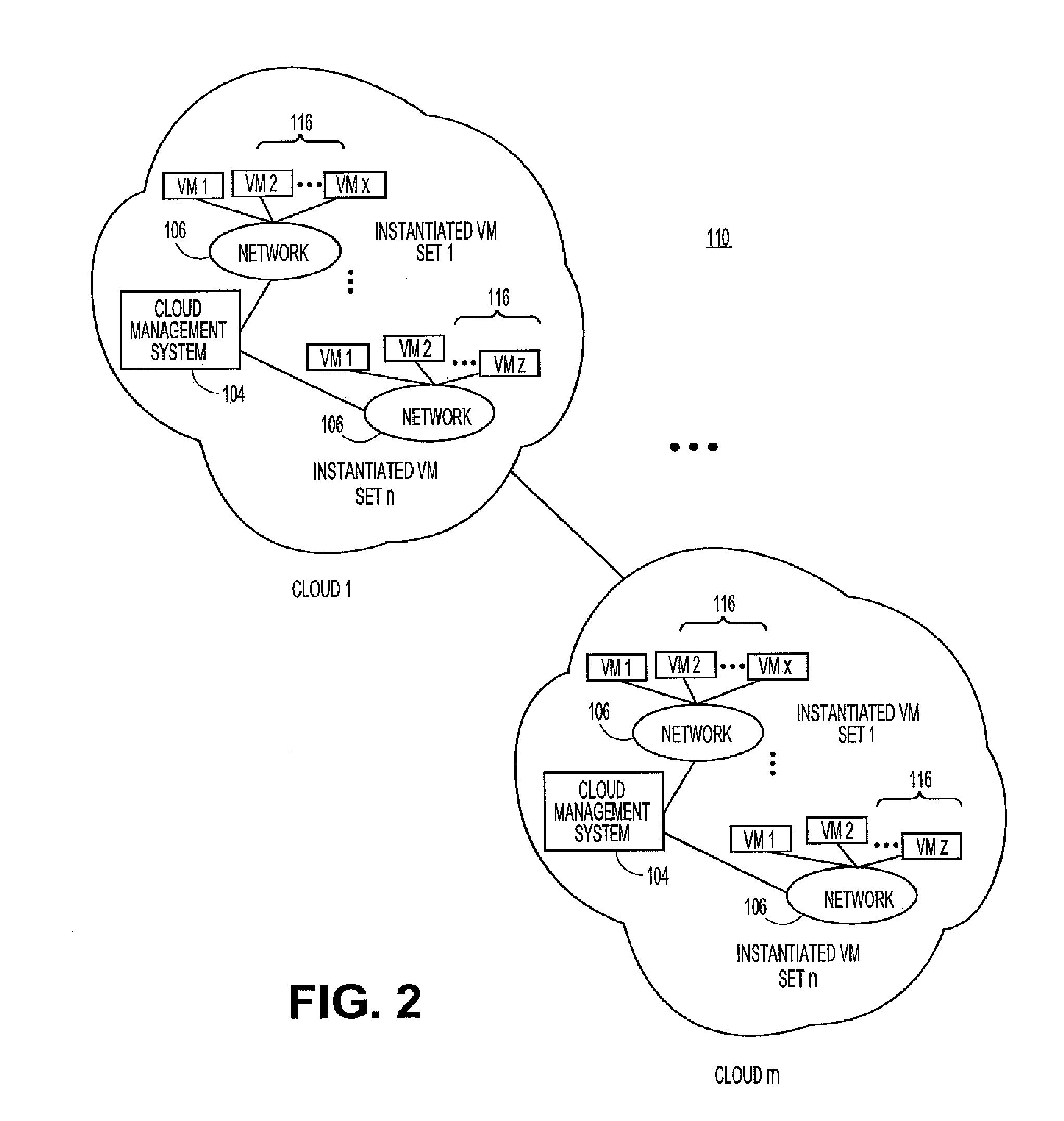
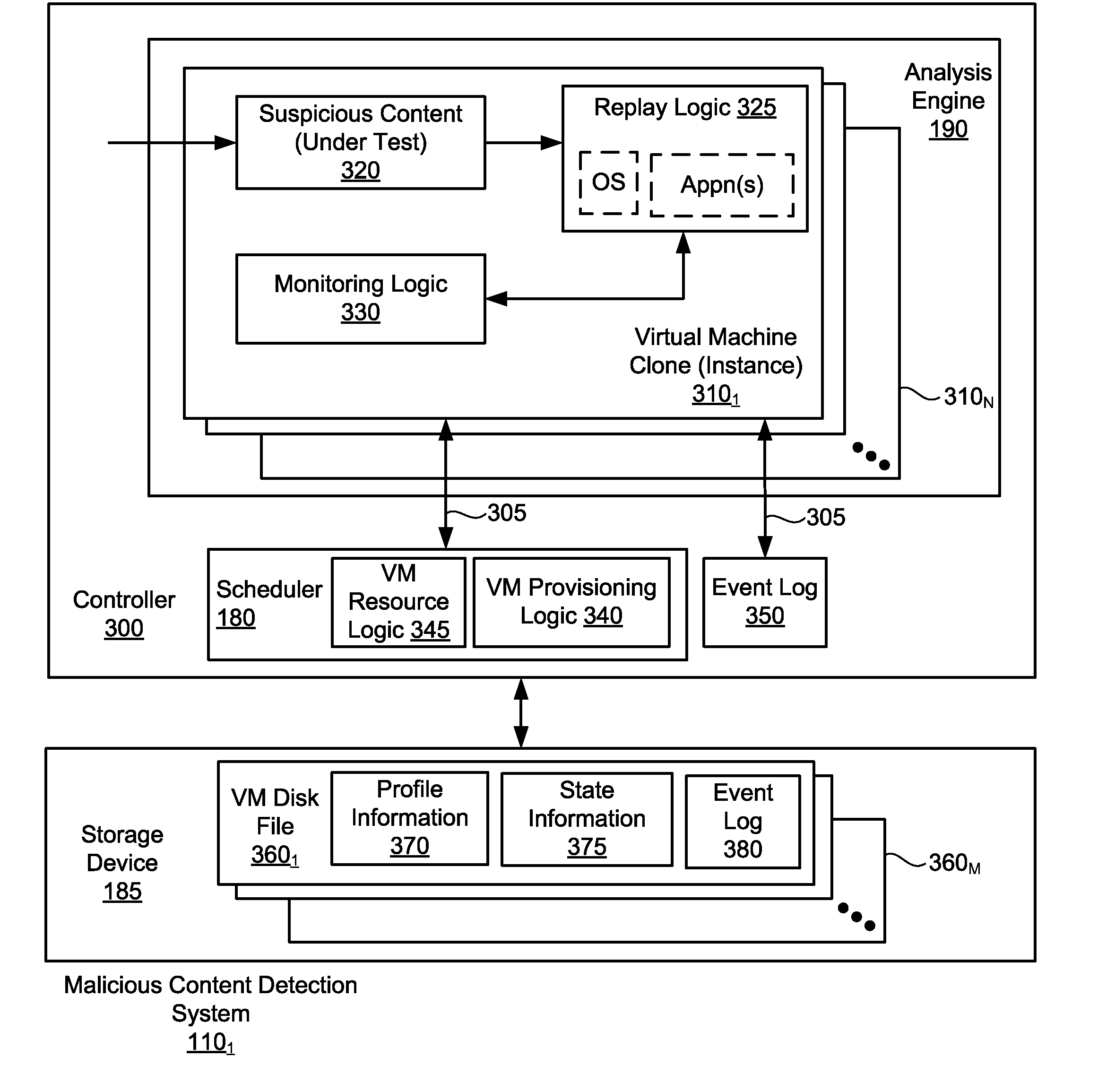
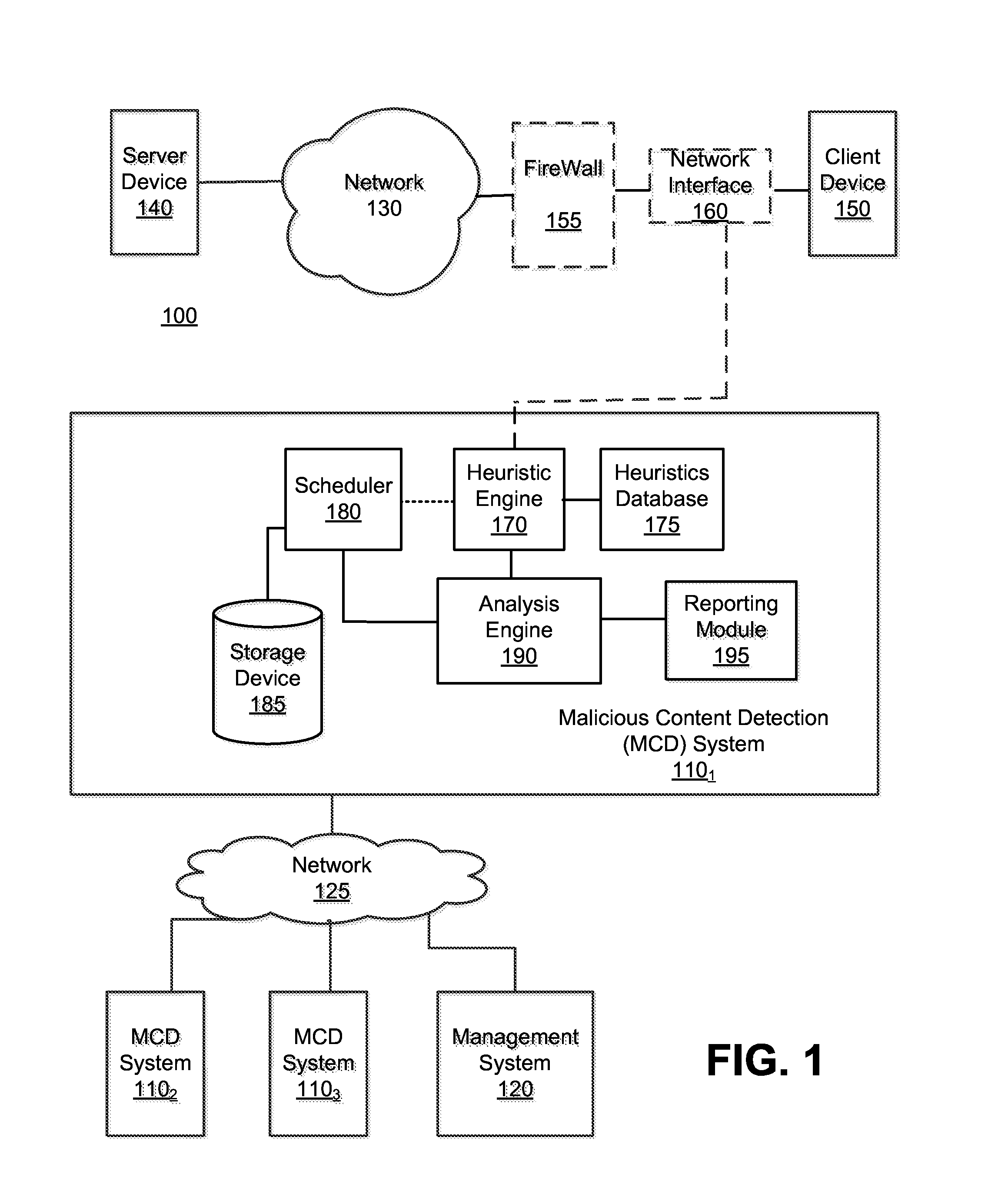
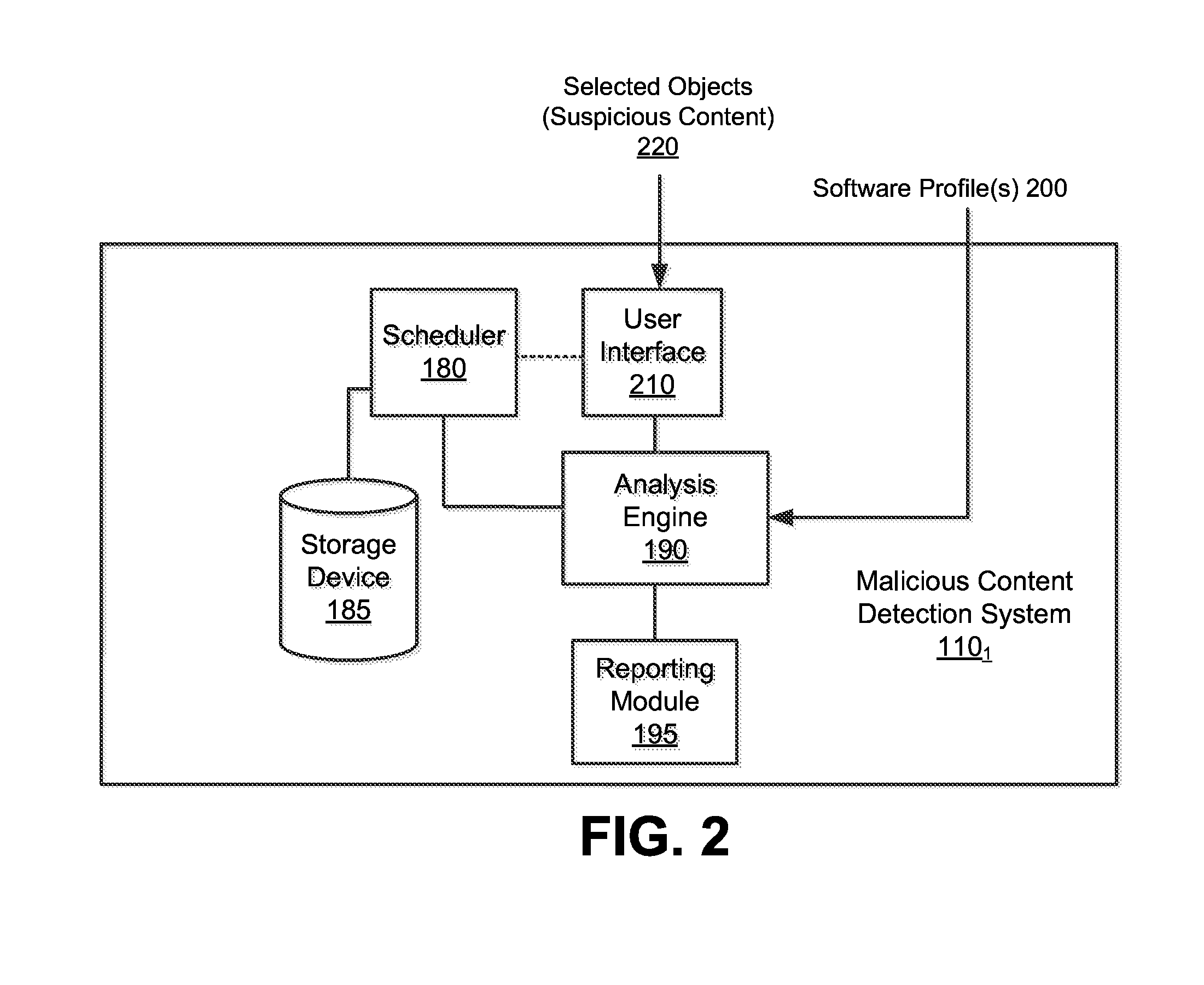
Optimized resource allocation for virtual machines within a malware content detection system
According to one embodiment, a computerized method comprises operations of instantiating a first virtual machine instance and a second virtual machine instance to run concurrently with the first virtual machine instance. The first virtual machine instance provides a first virtual operating environment while the second virtual machine instance is adapted to share the resources allocated to the first virtual machine instance. The second virtual machine instance is further adapted to allocate additional resources upon conducting a Copy-On Write operation.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
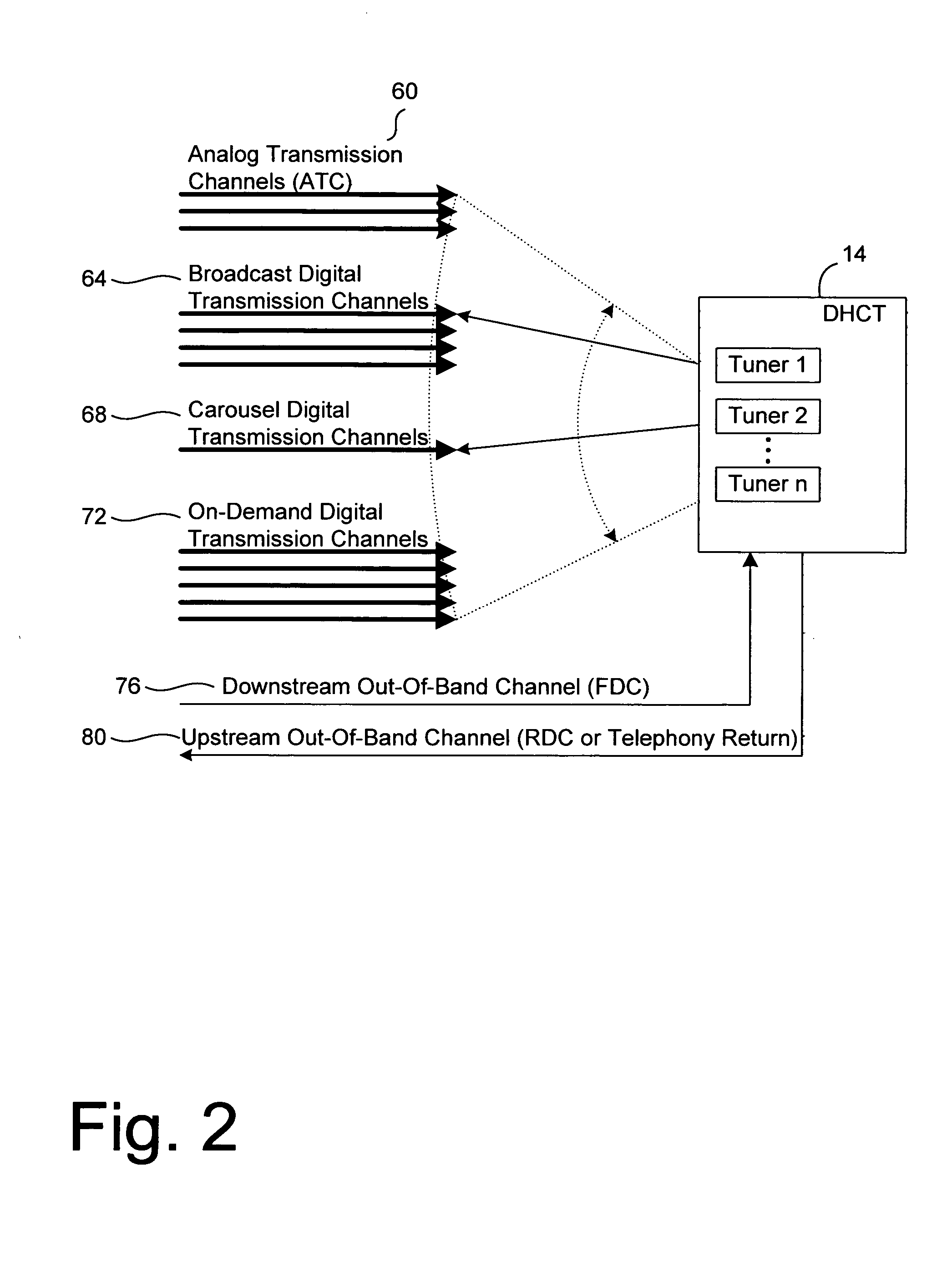
Systems and method for adaptive scheduling and dynamic bandwidth resource allocation management in a digital broadband delivery system
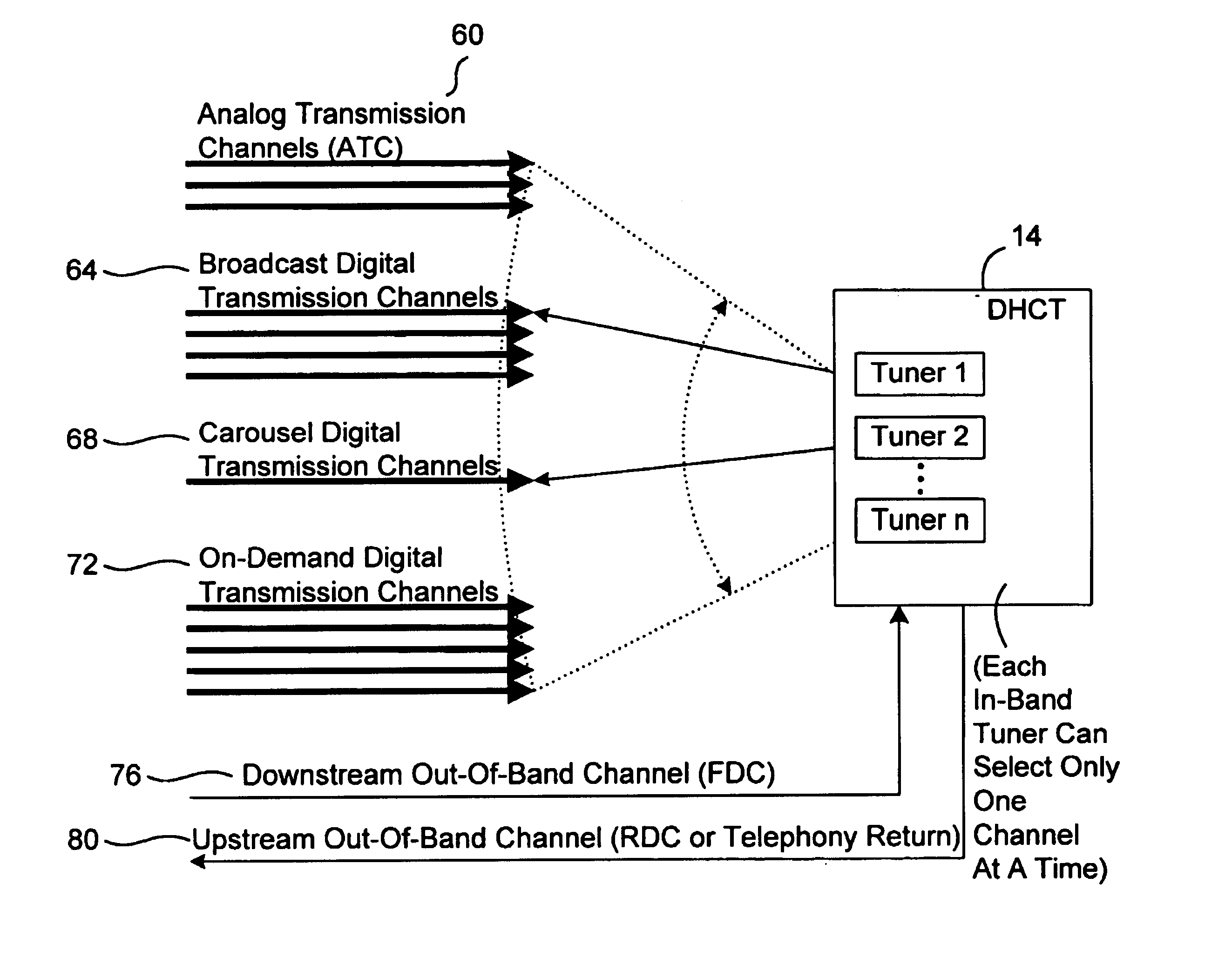
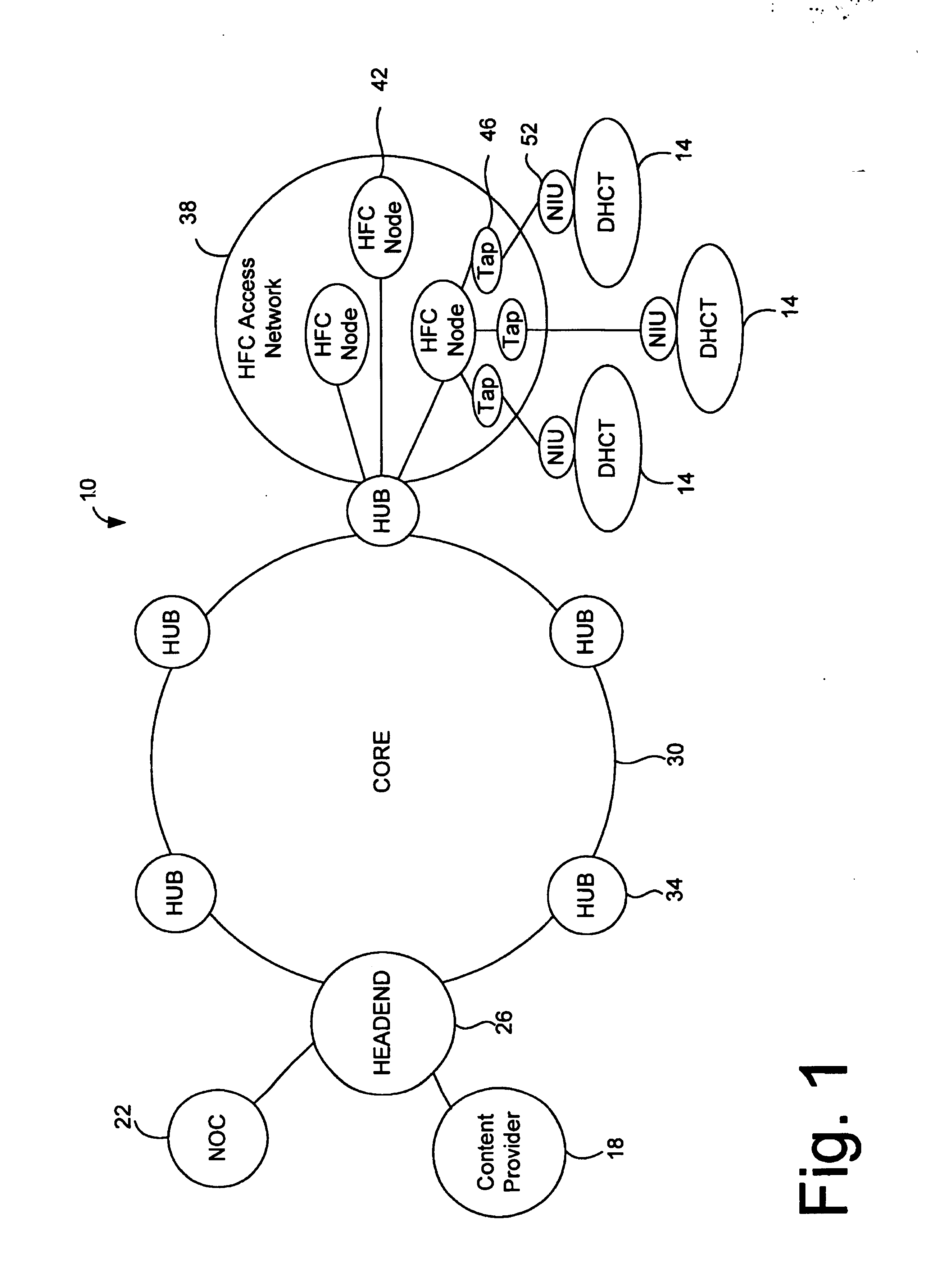
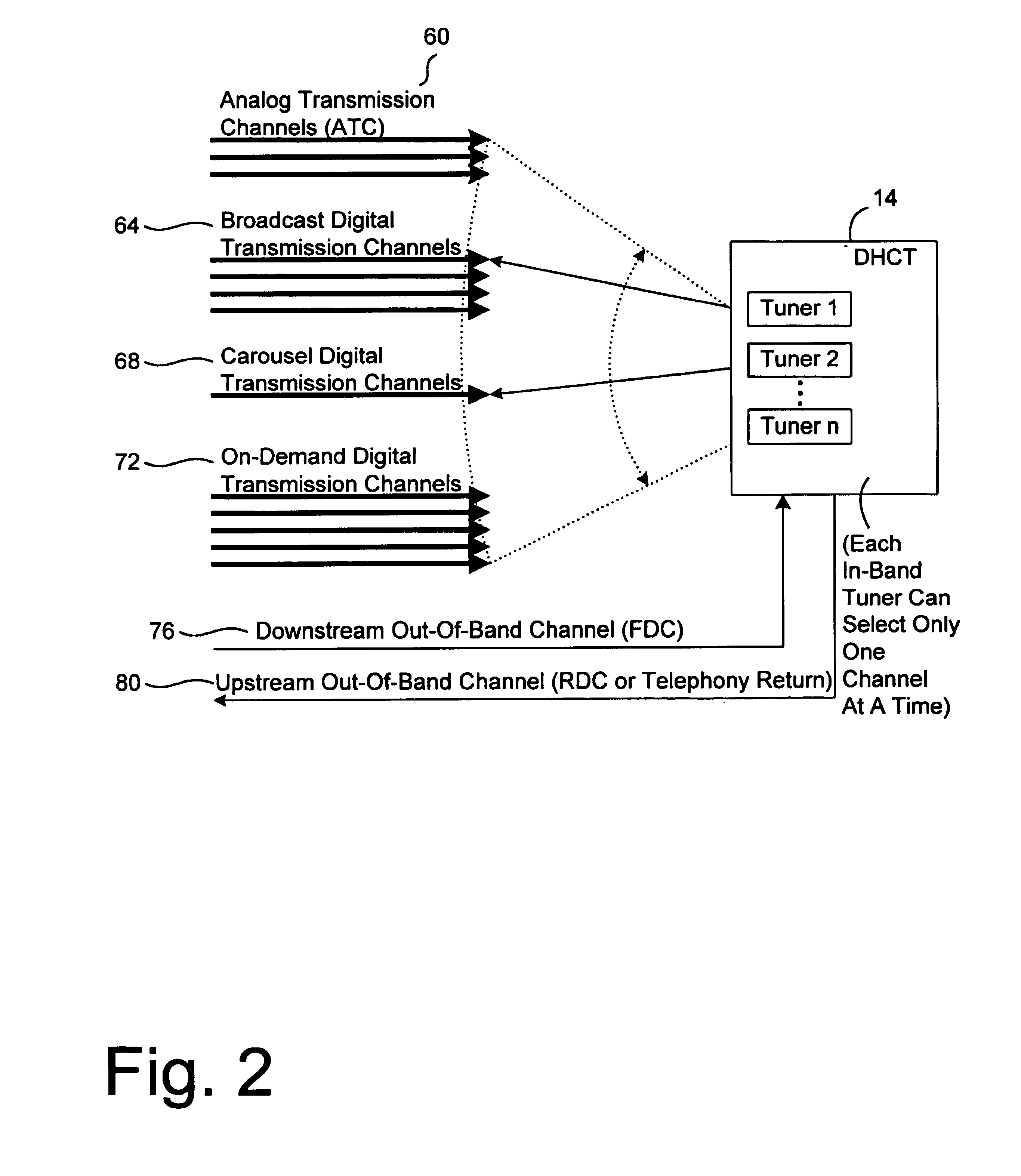
InactiveUS20050071882A1Bandwidth to be flexibly and efficiently-allocatedTelevision system detailsResource management arrangementsTransmission channelBroadband
A technique for allocating bandwidth in a digital broadband delivery system (DBDS) using a bandwidth allocation manager to dynamically assign a content delivery mode to a plurality of digital transmission channels based on an allocation criteria received from a subscriber is disclosed herein. The bandwidth allocation manager determines a bandwidth allocation schedule for a predetermined bandwidth based on allocation criteria comprising a criteria received from a subscriber. The allocation criteria received from the subscriber may comprise a subscriber reservation request which is processed by the bandwidth allocation manager to determine the bandwidth allocation schedule.
Owner:TRITON US VP ACQUISITION CO
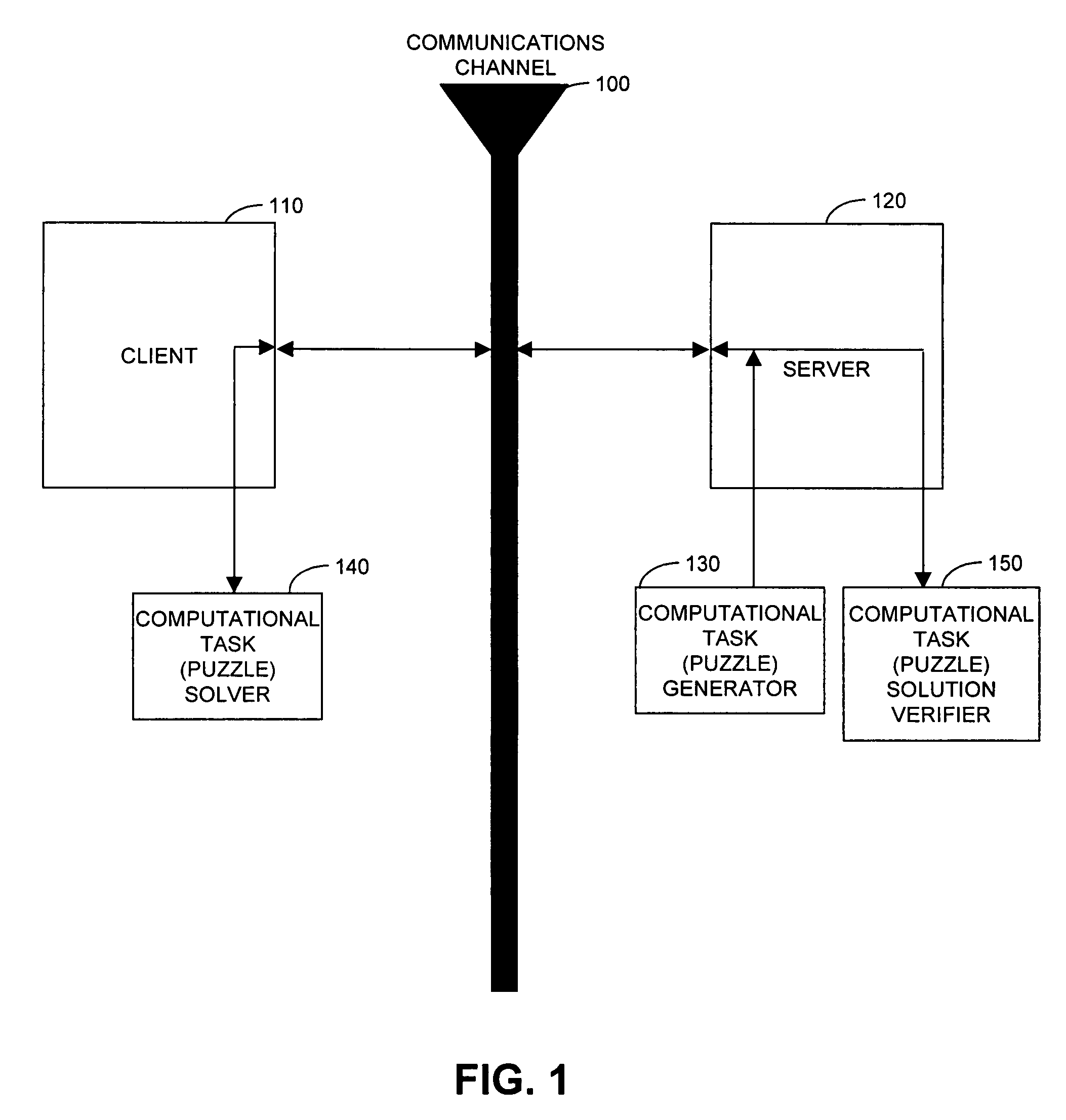
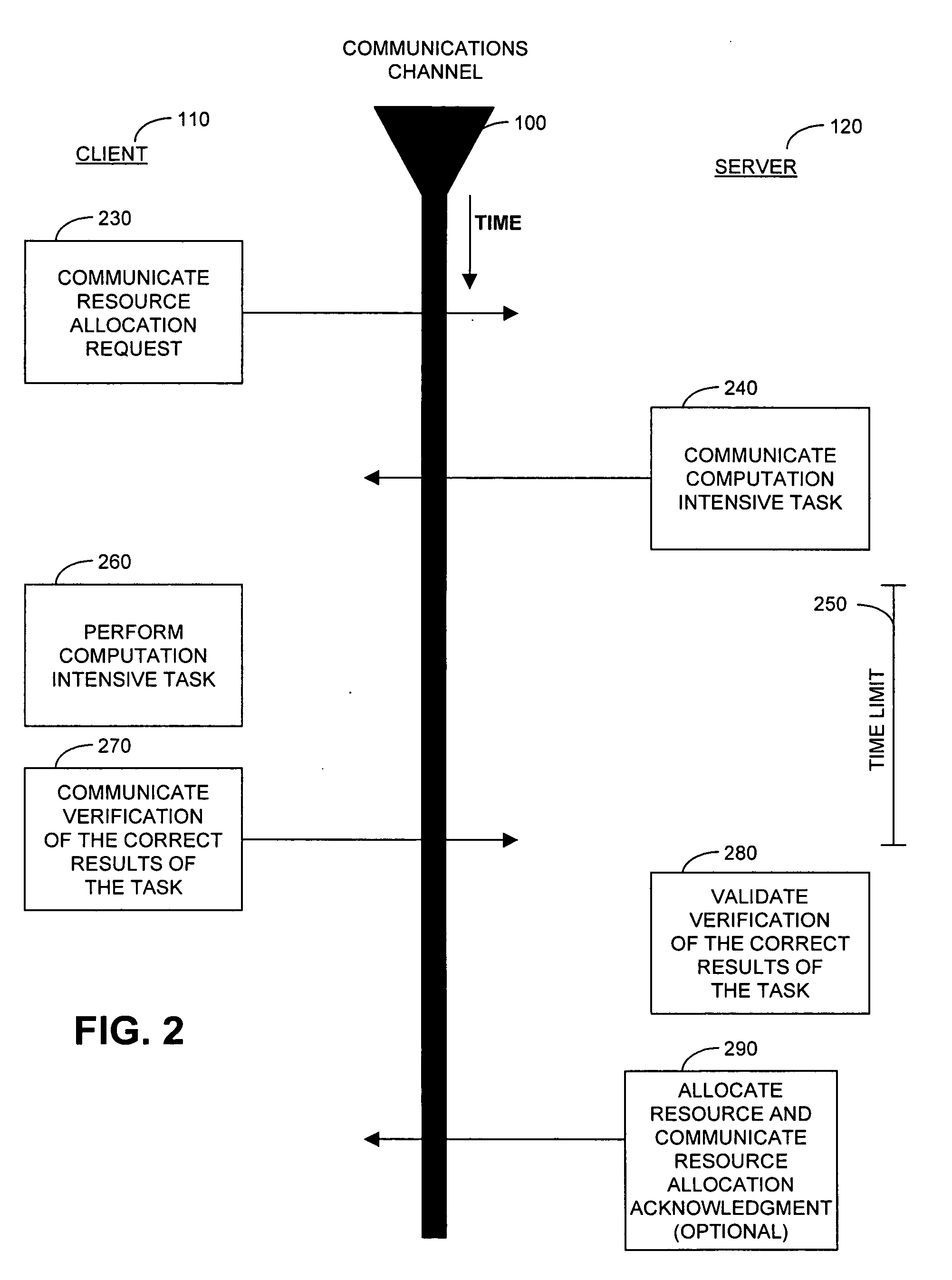
Cryptographic countermeasures against connection depletion attacks
InactiveUS7197639B1Ensure correct executionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCountermeasureTime limit
This invention relates to cryptographic communications methods and systems that protect a server from a connection depletion attack. Specifically, the invention presents a method for allocating a resource comprising the steps of receiving a resource allocation request from a client, imposing a computational task and a time limit for correct completion of the task upon the client, verifying that the task was performed correctly within the time limit, and allocating the resource if the task was correctly performed within the time limit.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
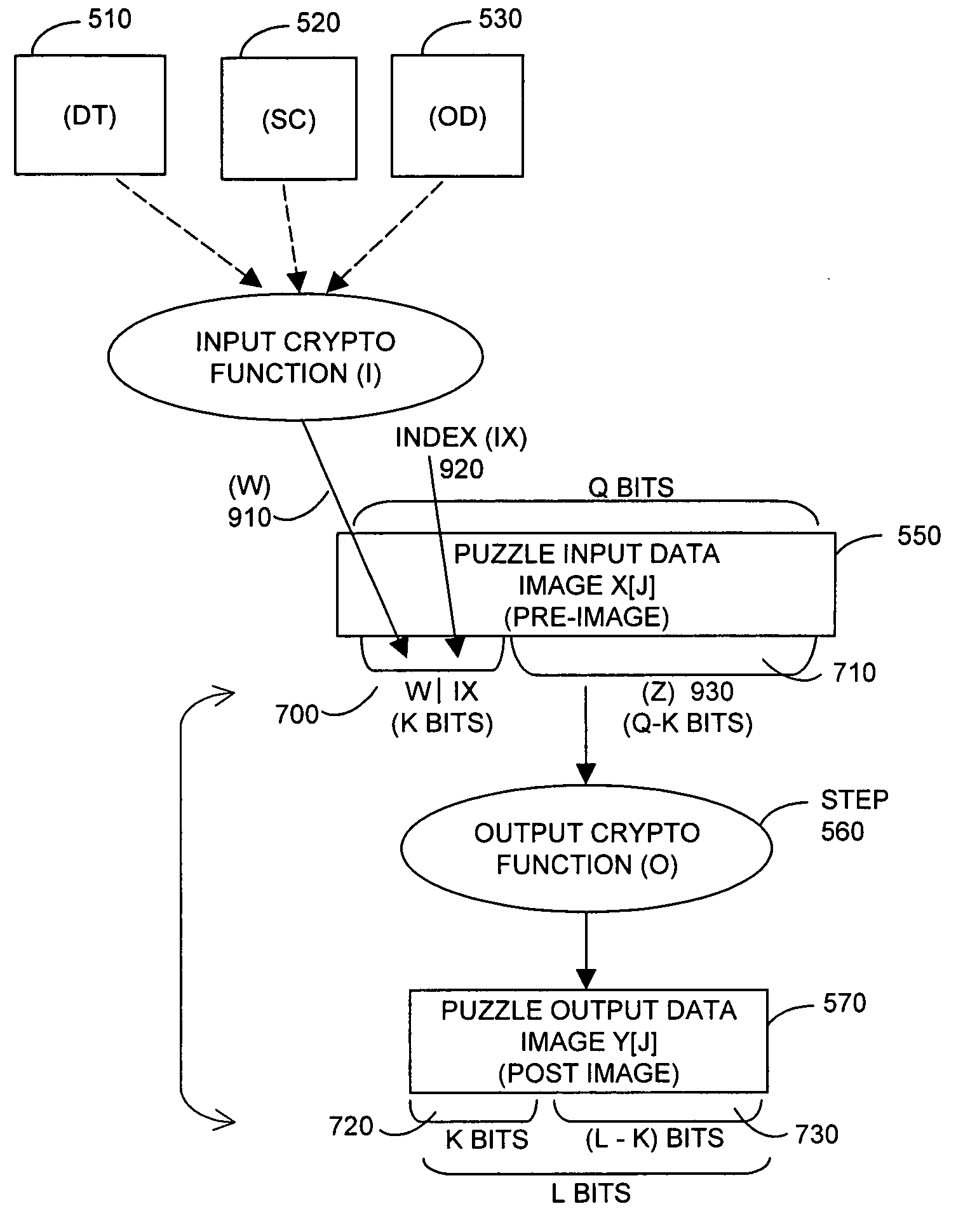
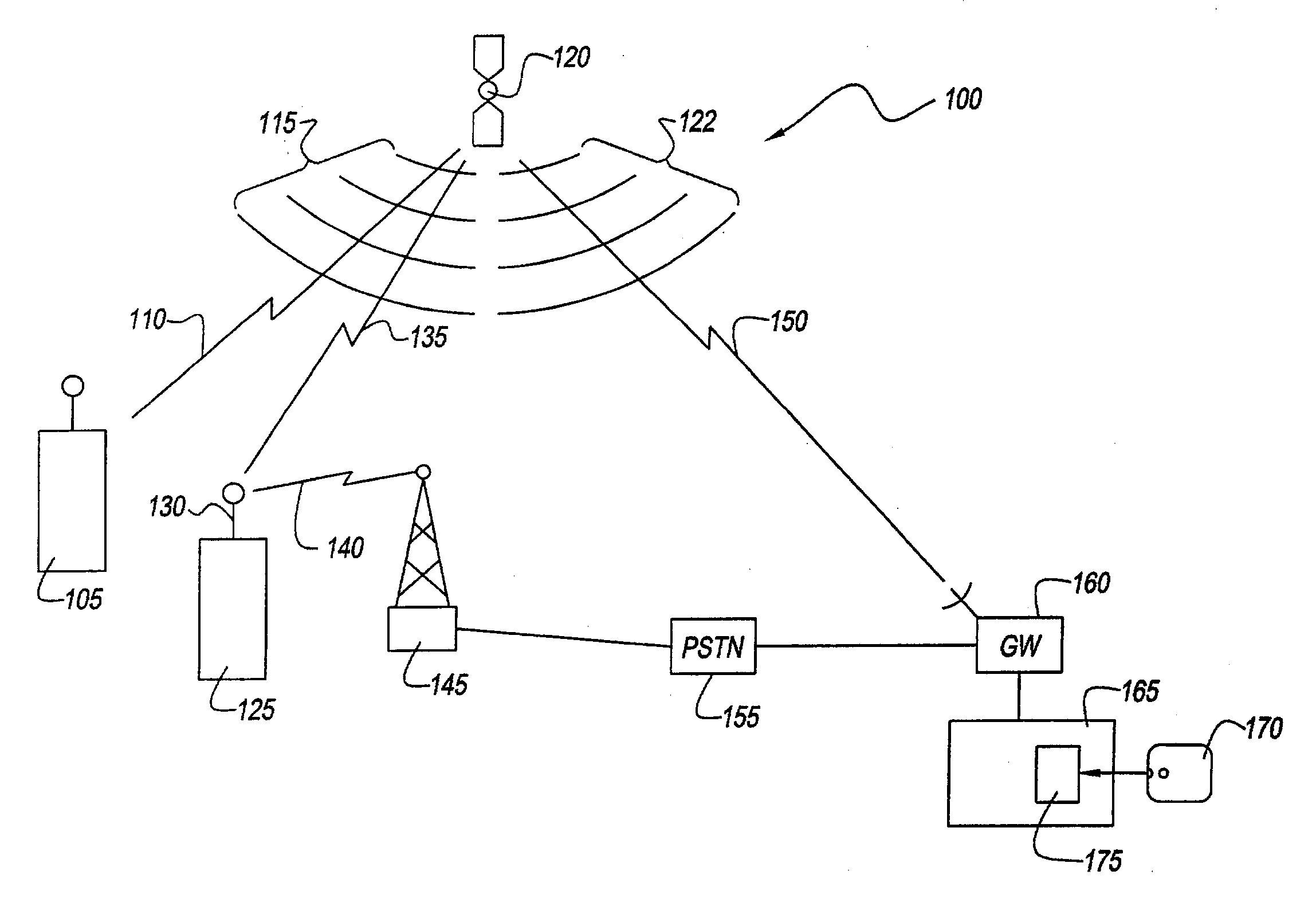
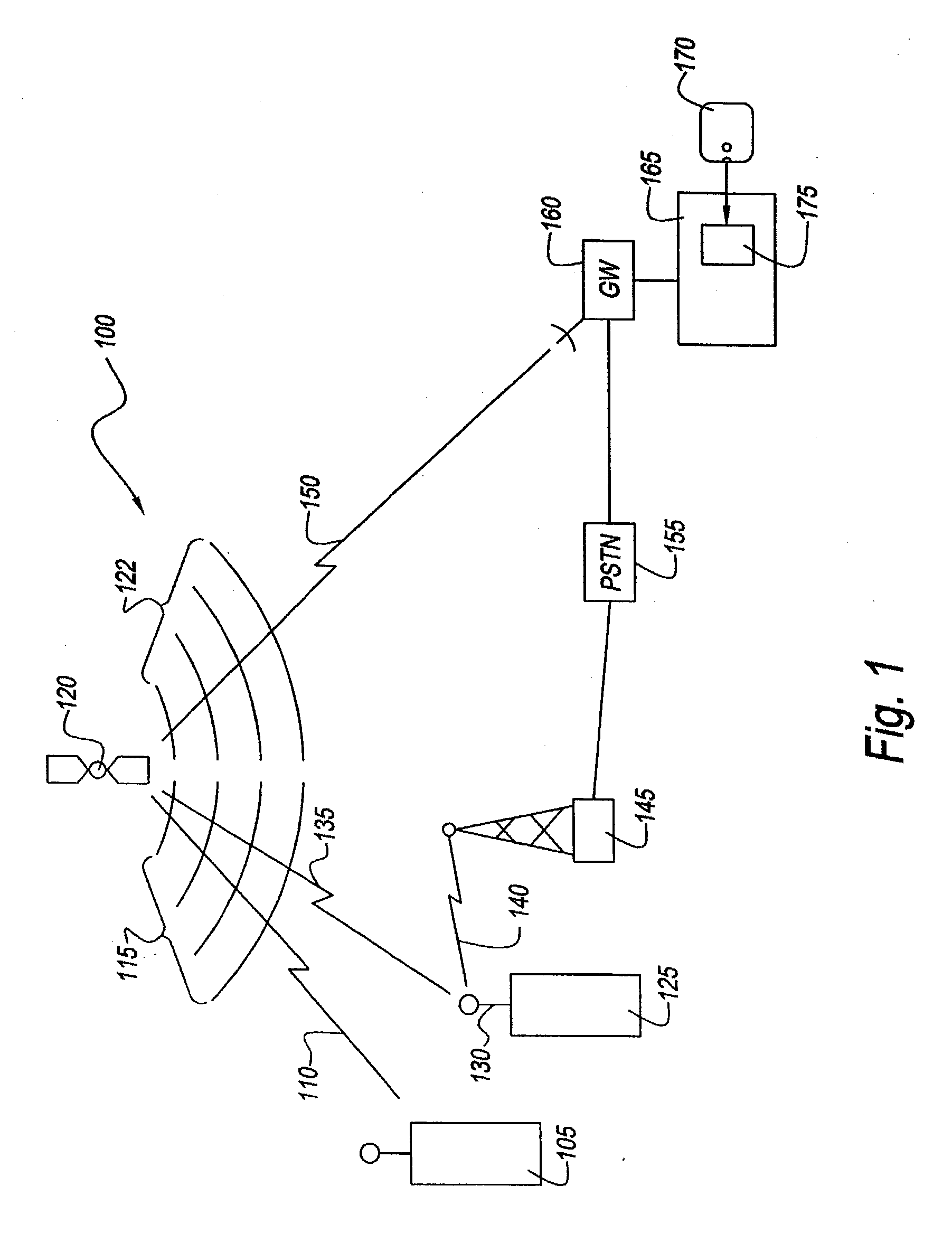
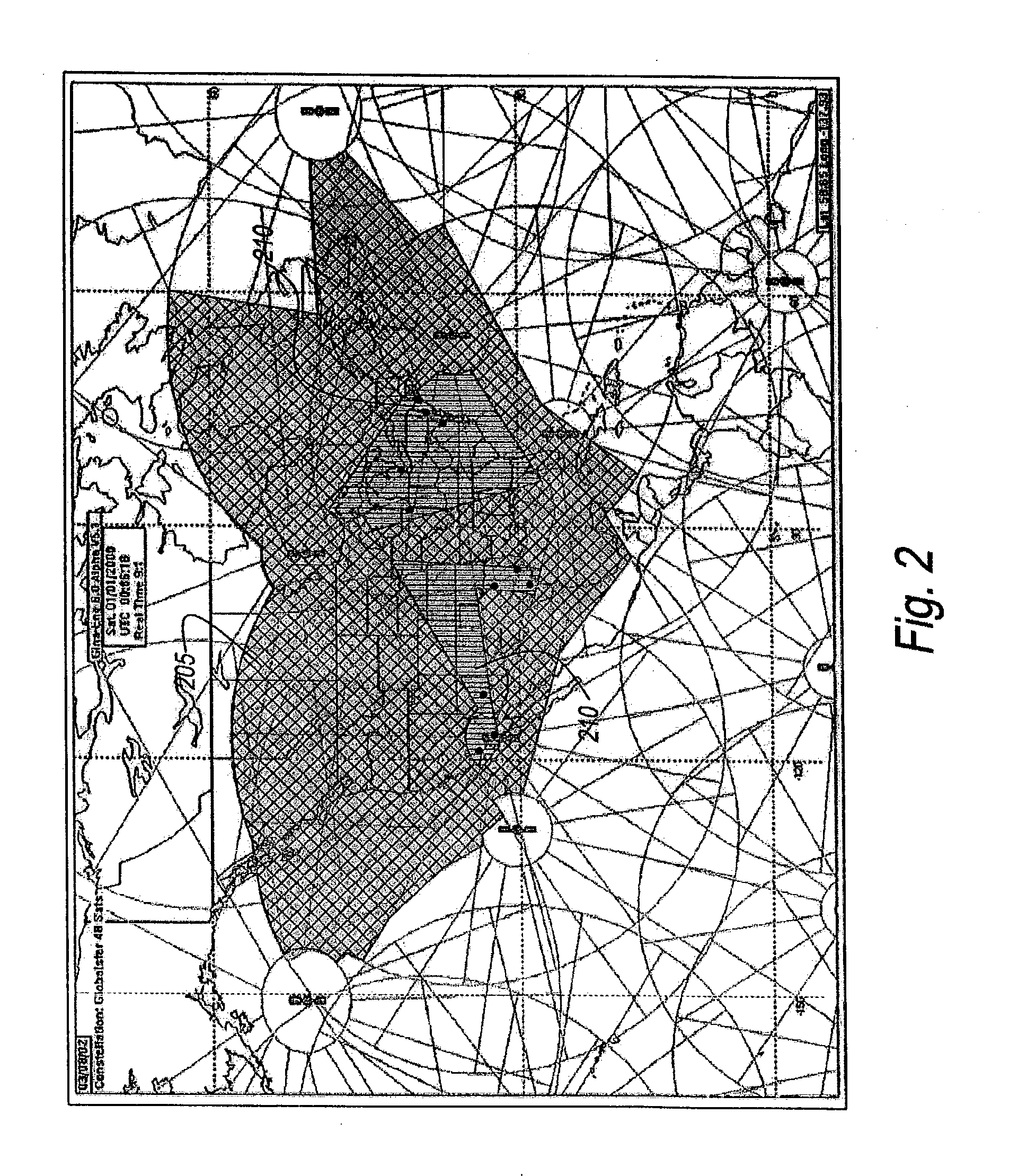
Resource allocation to terrestrial and satellite services
ActiveUS20040072539A1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission control/equalisingGround systemResource allocation
There is provided a method for improving an allocation of resources, i.e., frequency and power, to terrestrial services and satellite services that use a same frequency band. The method includes determining a demand (DS) for a resource by users of a satellite system, determining a demand (DT) for the resource by users of a terrestrial system, and allocating the resource between the satellite system and the terrestrial system based on a ratio of DS to DT.
Owner:GLOBALSTAR INC
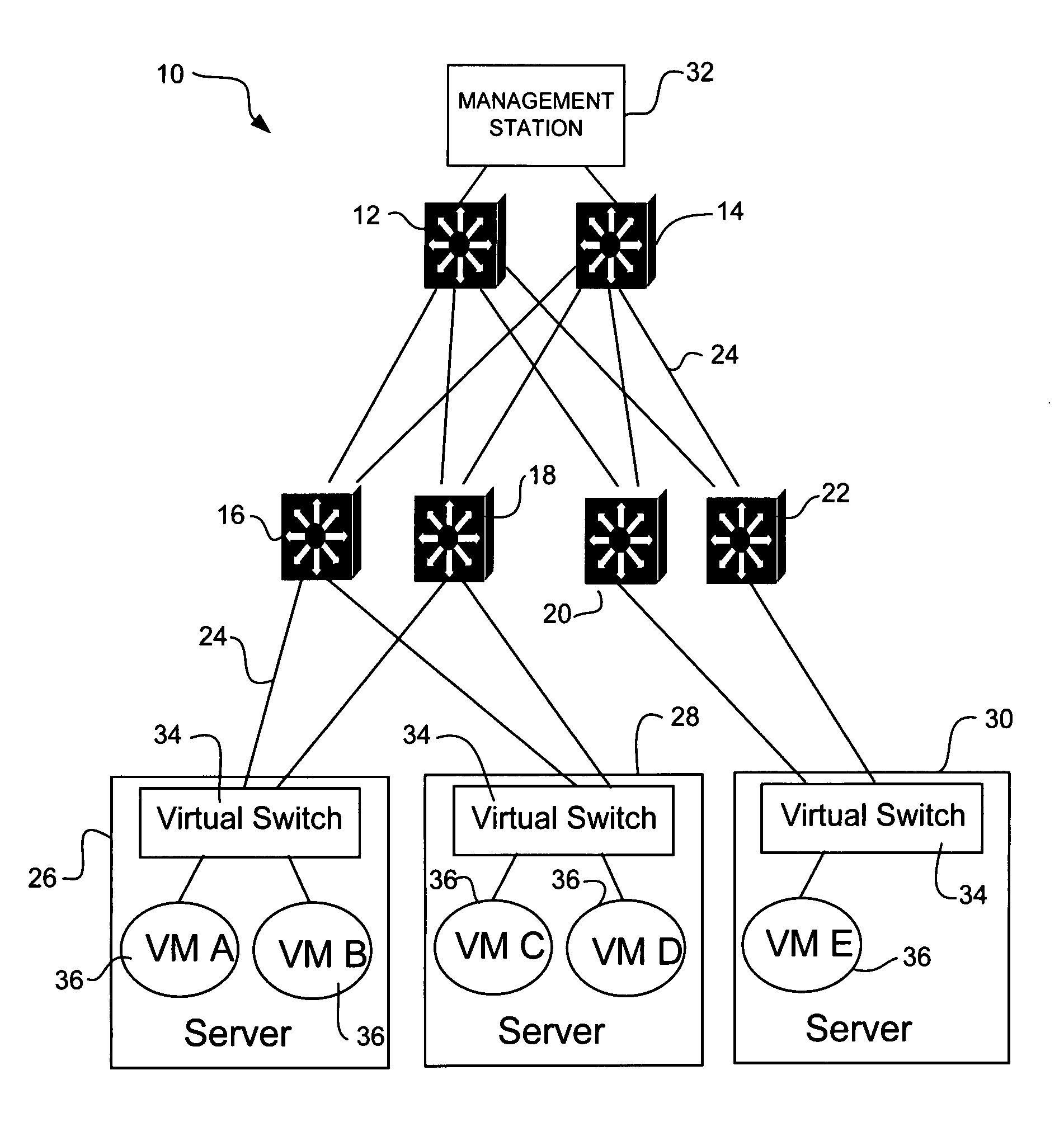
Dynamic distribution of virtual machines in a communication network
In one embodiment, a method generally includes monitoring network traffic associated with a first network device comprising at least one of a plurality of virtual machines and determining if a parameter exceeds a predefined threshold at the first network device. If the parameter exceeds the predefined threshold, one of the virtual machines is selected to move to a second network device, the second network device selected based on network information, and the virtual machine is moved. An apparatus for resource allocation is also disclosed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for establishing a device-to-device link connection and scheduling for device-to-device communication and terminal relaying
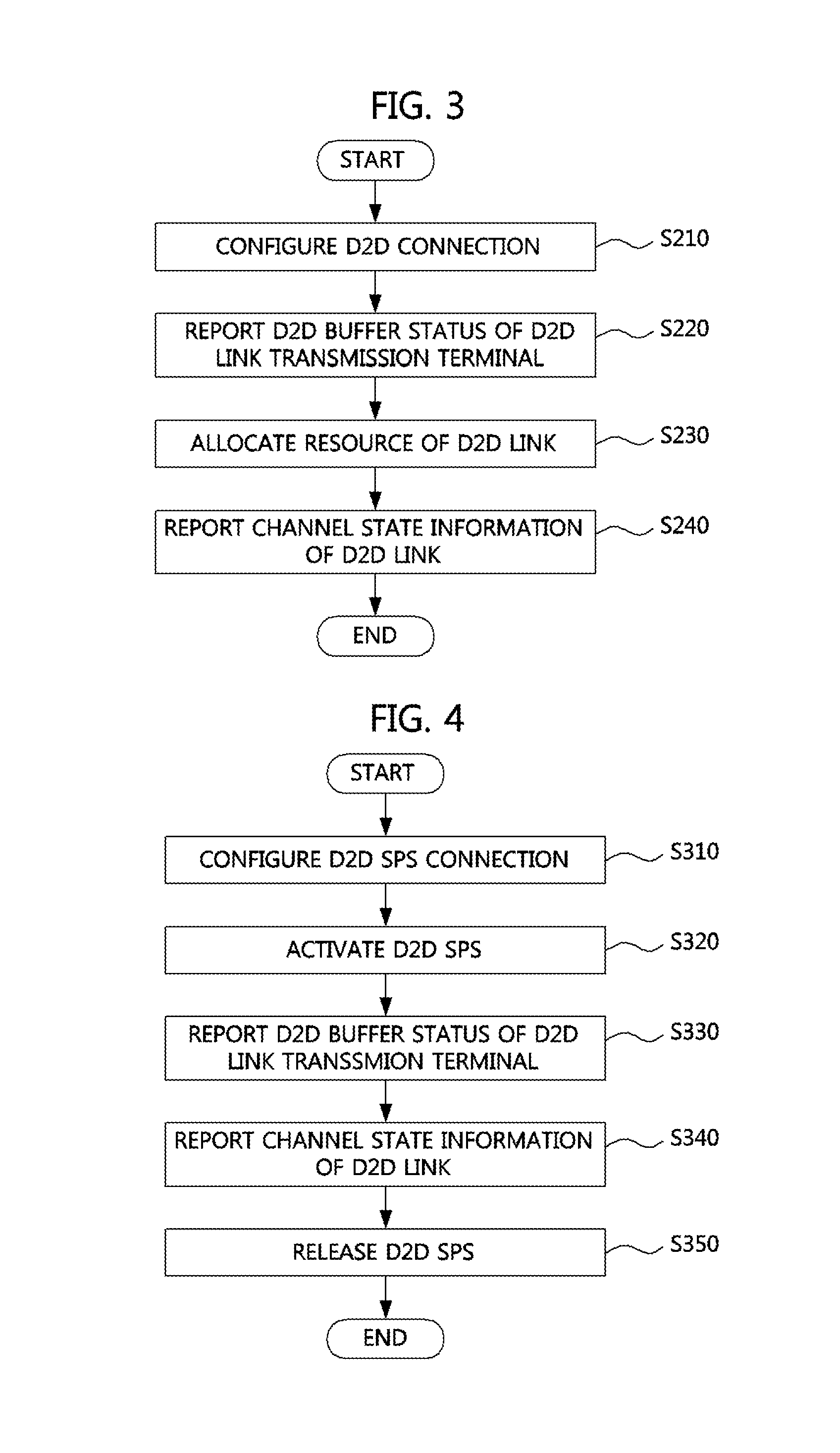
Disclosed is a method for establishing a device-to-device link connection and scheduling for device-to-device communication and terminal relaying. The method for operating a terminal according to the present invention comprises the following steps: receiving information on the establishment of a D2D link; reporting a state of a D2D buffer of the D2D link to a base station; and receiving information on the D2D link resource allocation based on the report on the D2D buffer state. The scheduling method for D2D communication according to the present invention enables dynamic scheduling to be performed on a subframe unit basis, and enables semi-continuous scheduling for continuous data transmission for a D2D communication link.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Systems and methods for adaptive scheduling and dynamic bandwidth resource allocation management in a digital broadband delivery system
InactiveUS6986156B1Flexibly efficiently allocatedTelevision system detailsResource management arrangementsTransmission channelBroadband
Owner:TRITON US VP ACQUISITION CO
Para-virtualized computer system with I/0 server partitions that map physical host hardware for access by guest partitions
InactiveUS20070061441A1Improve efficiencyImprove securityError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsOperational systemSystem call
A virtualization infrastructure that allows multiple guest partitions to run within a host hardware partition. The host system is divided into distinct logical or virtual partitions and special infrastructure partitions are implemented to control resource management and to control physical I / O device drivers that are, in turn, used by operating systems in other distinct logical or virtual guest partitions. Host hardware resource management runs as a tracking application in a resource management “ultravisor” partition, while host resource management decisions are performed in a higher level command partition based on policies maintained in a separate operations partition. The conventional hypervisor is reduced to a context switching and containment element (monitor) for the respective partitions, while the system resource management functionality is implemented in the ultravisor partition. The ultravisor partition maintains the master in-memory database of the hardware resource allocations and serves a command channel to accept transactional requests for assignment of resources to partitions. It also provides individual read-only views of individual partitions to the associated partition monitors. Host hardware I / O management is implemented in special redundant I / O partitions. Operating systems in other logical or virtual partitions communicate with the I / O partitions via memory channels established by the ultravisor partition. The guest operating systems in the respective logical or virtual partitions are modified to access monitors that implement a system call interface through which the ultravisor, I / O, and any other special infrastructure partitions may initiate communications with each other and with the respective guest partitions. The guest operating systems are modified so that they do not attempt to use the “broken” instructions in the x86 system that complete virtualization systems must resolve by inserting traps.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
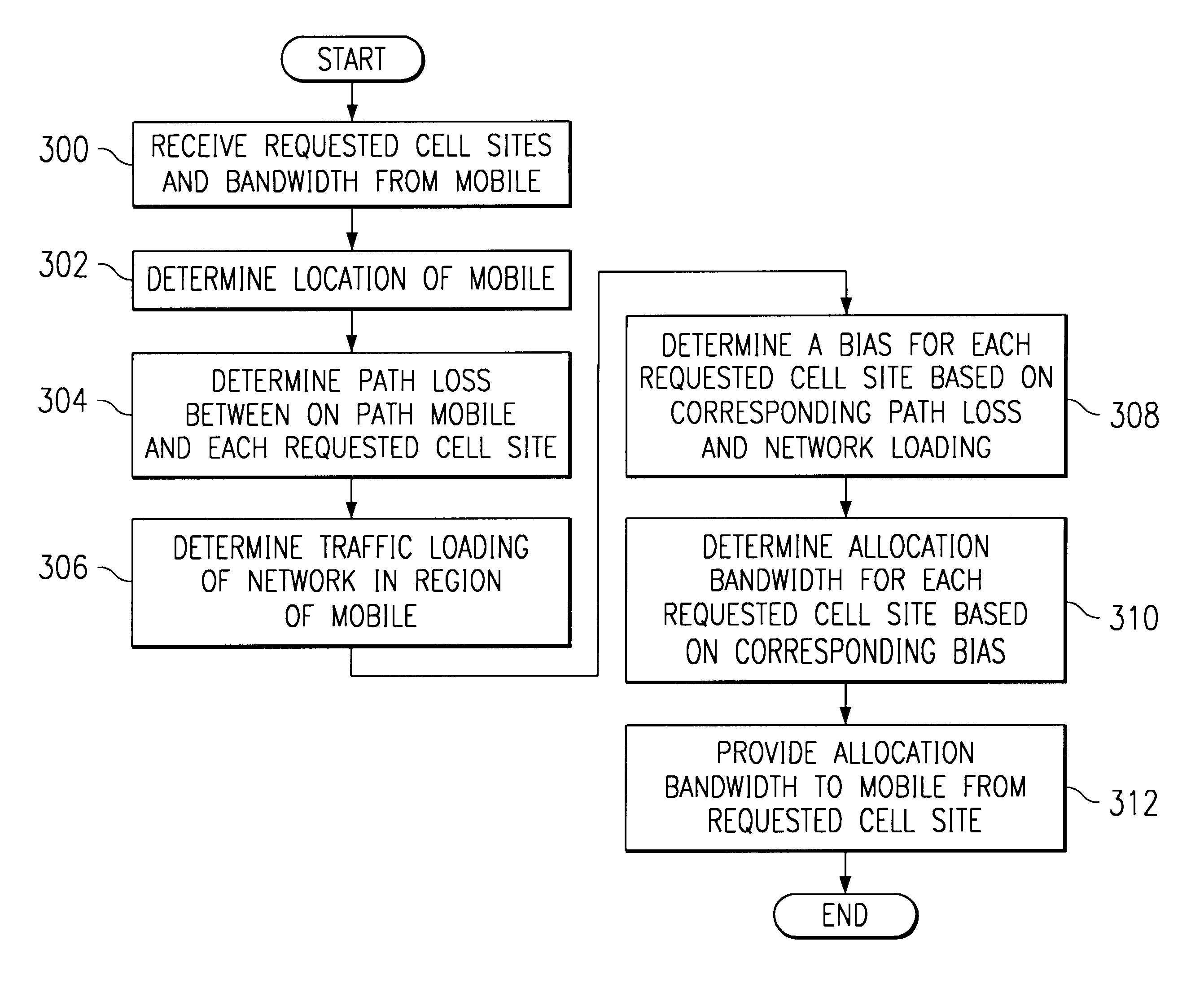
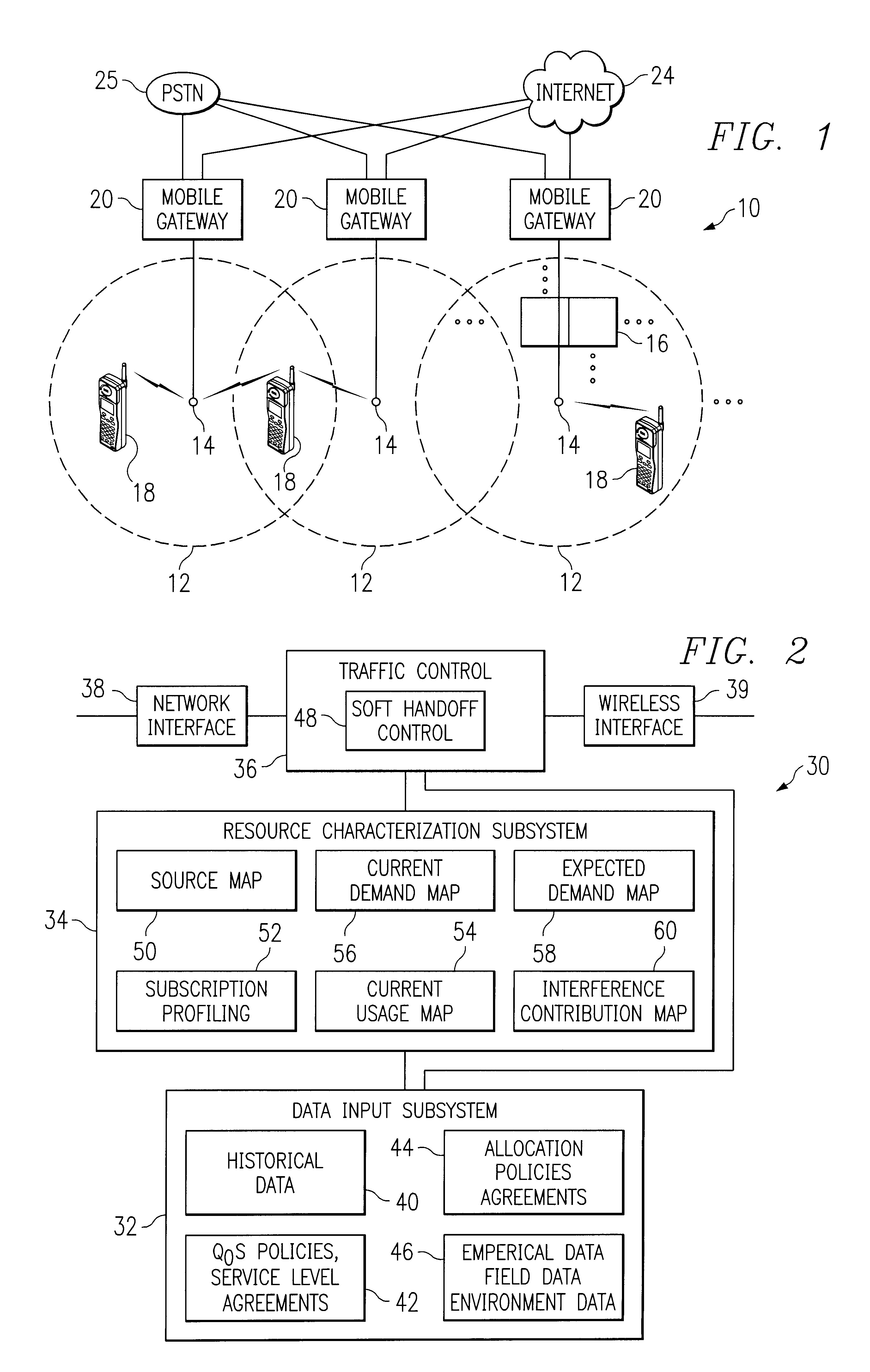
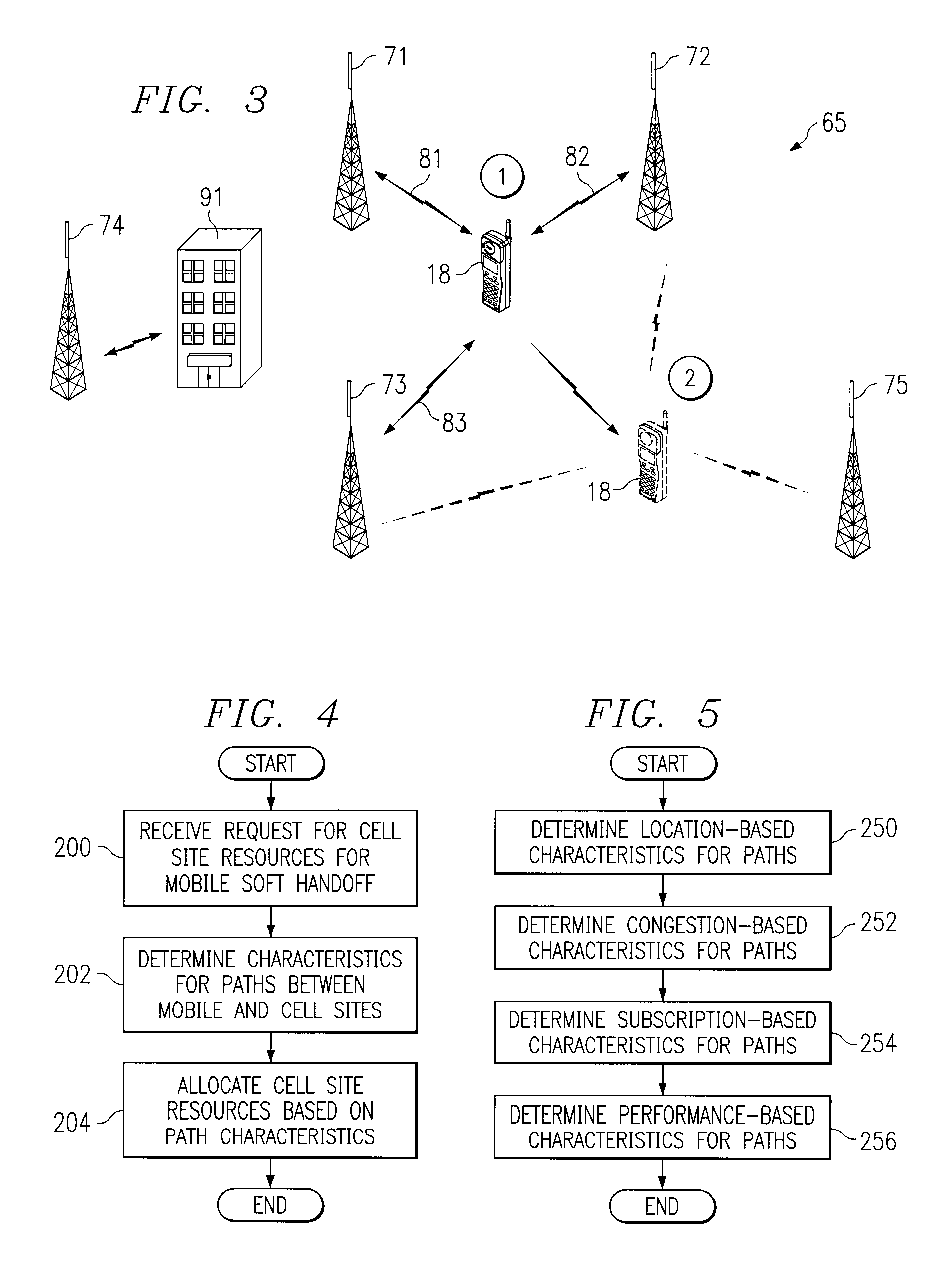
Method and system for dynamic soft handoff resource allocation in a wireless network
InactiveUS6907243B1Resource allocatedMinimize air-link congestionPower managementAccounting/billing servicesTelecommunicationsMobile device
A method and system for dynamic soft handoff resource allocation in a wireless communications network includes determining a wireless path characteristic individually for each path of a macro diversity connection between a mobile device and a plurality of wireless sites. Wireless resources are allocated for the macro diversity connection between the mobile device and the wireless sites based on the wireless path characteristic. The wireless path characteristic includes a location-based characteristic, a congestion-based characteristic, a subscriber-based characteristic and / or a performance-based characteristic.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
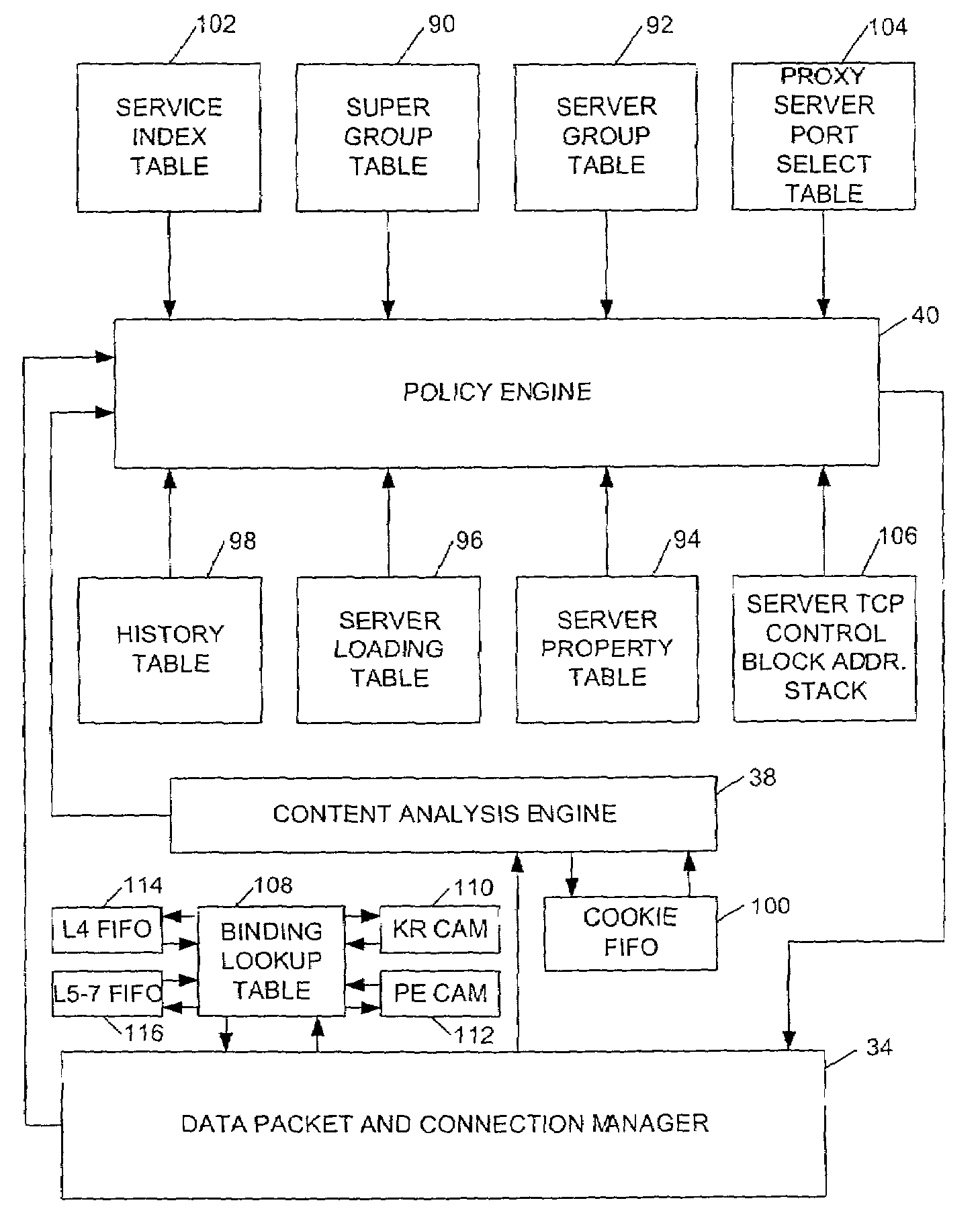
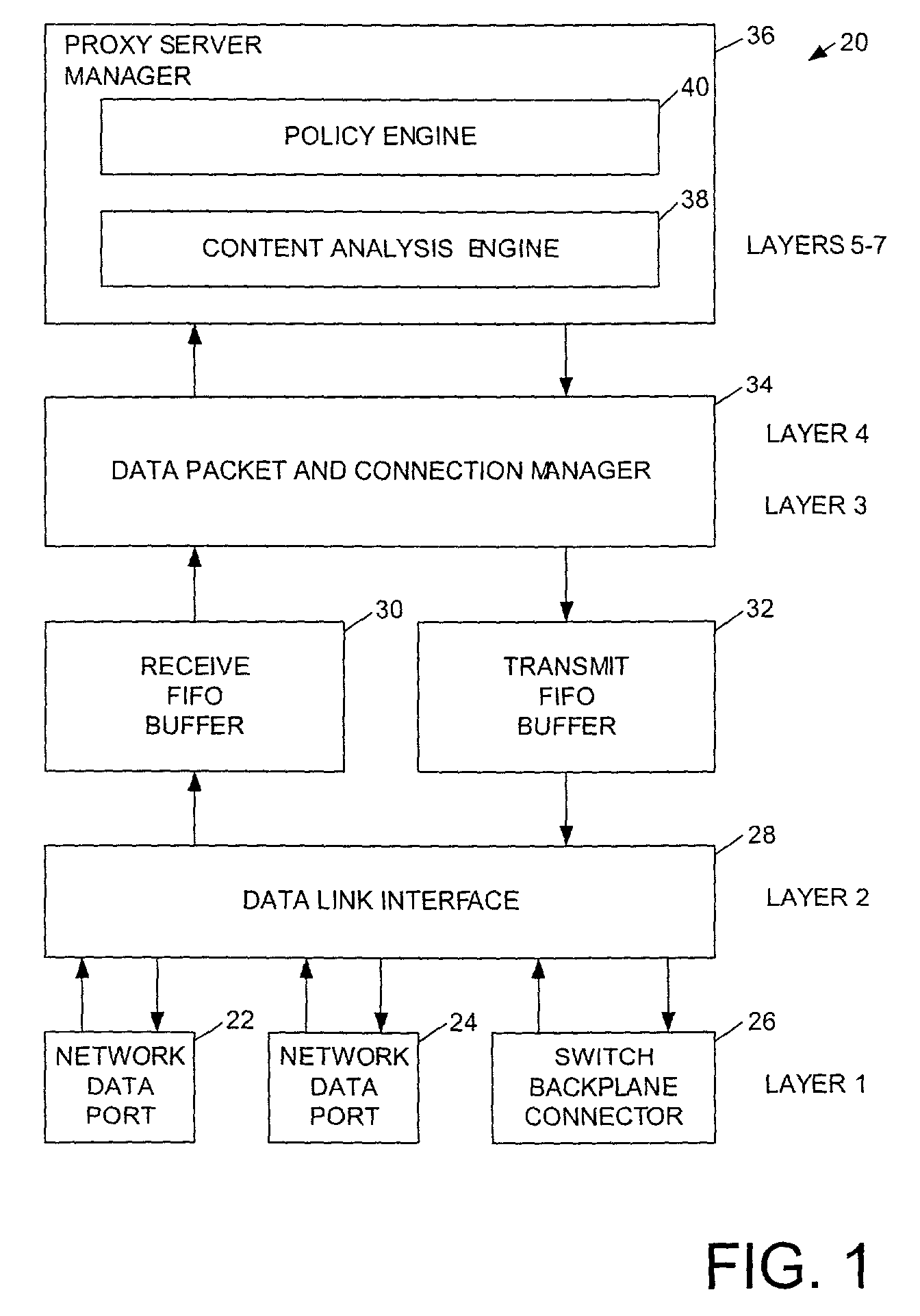
Method of and system for allocating resources to resource requests
ActiveUS7321926B1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsResource allocationBalance strategy
A system and method of allocating a resource to a service request. Servers are virtually assigned through a hierarchy including groups of servers and super groups of the groups of servers. Each service request type is associated with a service index that determines both a super group and a load balancing policy for that service request type. A load balancing policy may be applied to select a group of servers among several server groups associated with the super group. Another load balancing policy is applied to the selected group of servers to select a server to handle the service request. The hierarchical data structure allows servers to be configured into overlappable, arbitrary subsets that can address service requests matching configured content rules. Load balancing policies can be selected by service request type.
Owner:RPX CORP
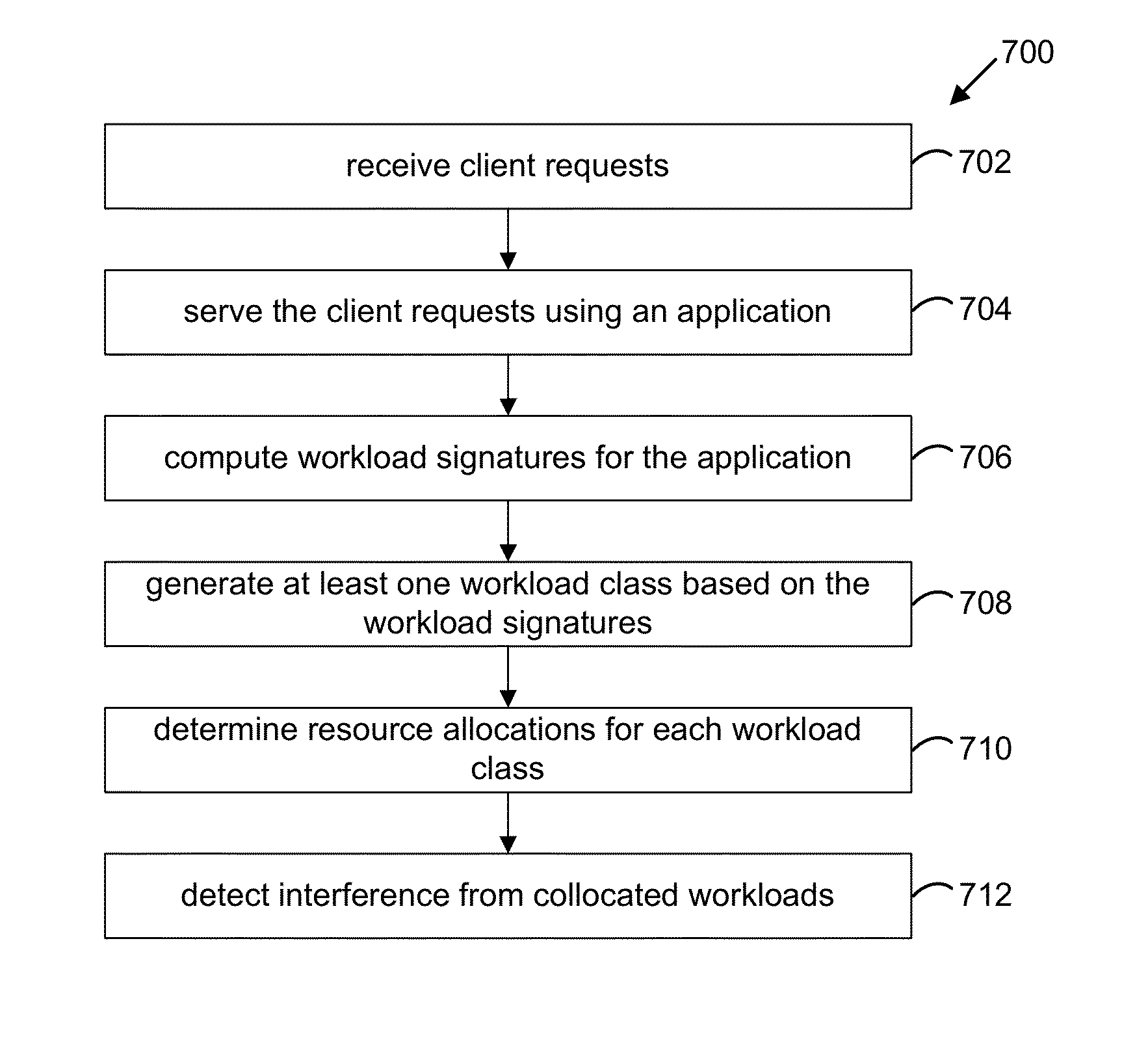
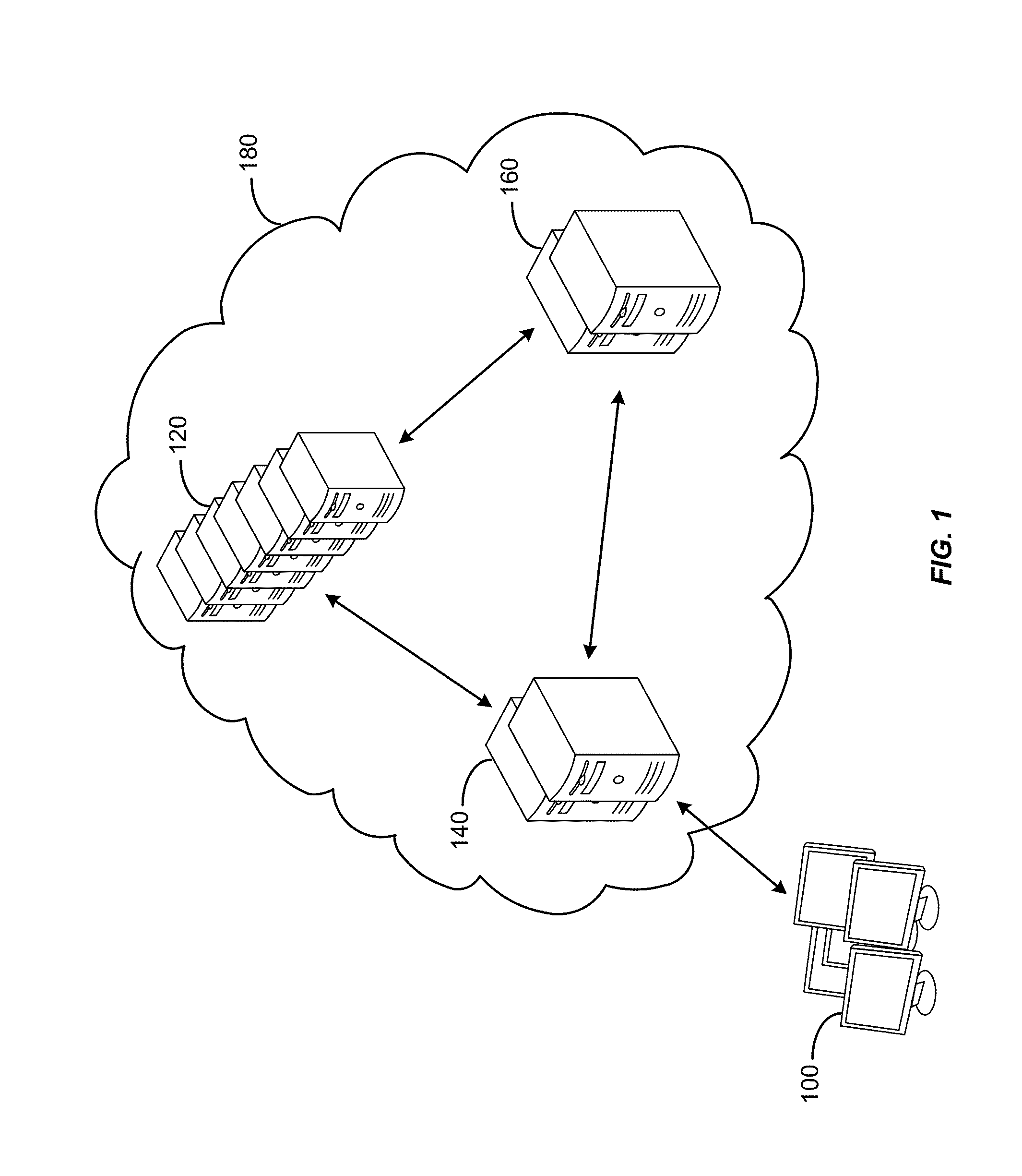
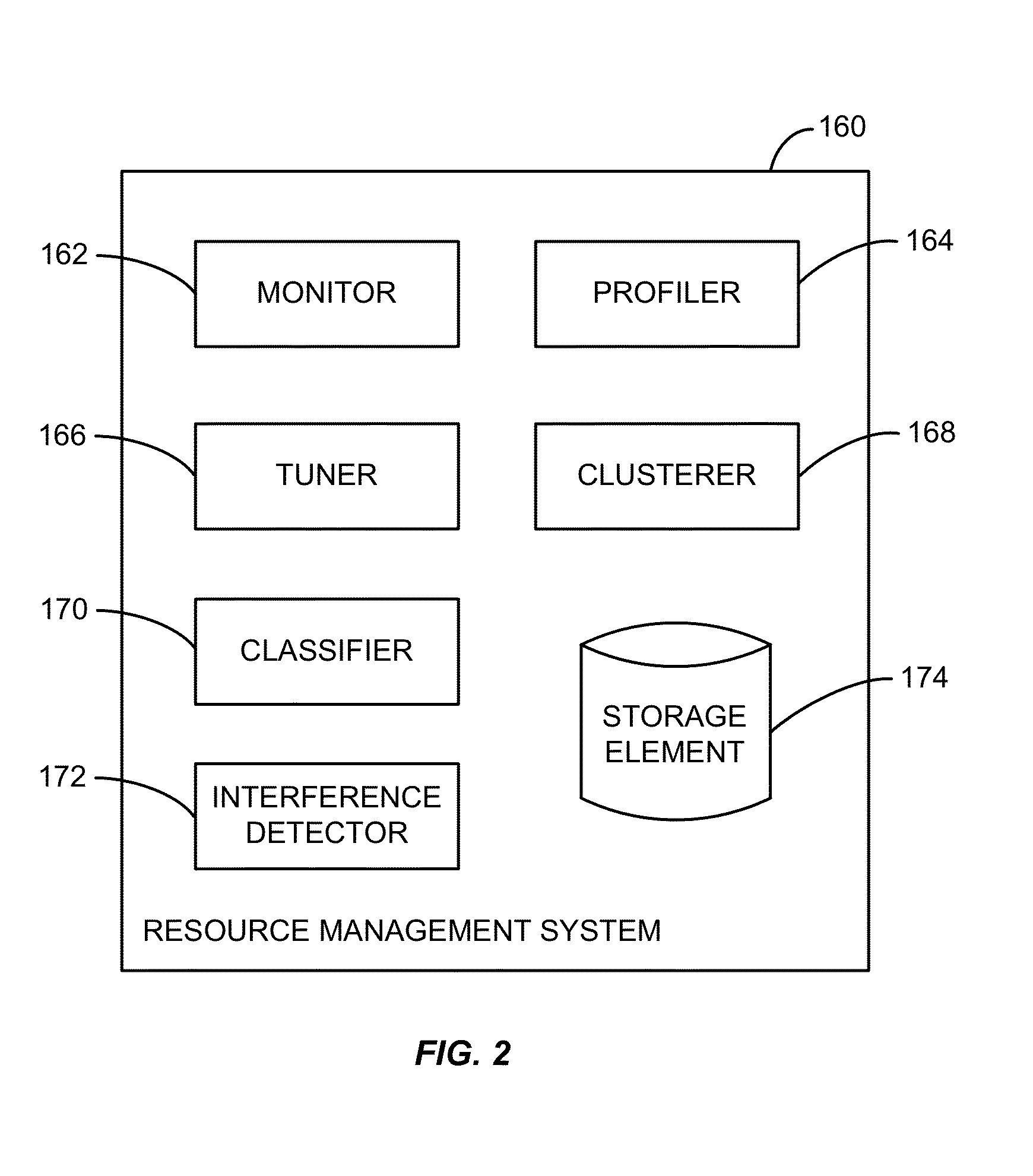
Accelerating resource allocation in virtualized environments using workload classes and/or workload signatures
Systems, methods, and apparatus for managing resources assigned to an application or service. A resource manager maintains a set of workload classes and classifies workloads using workload signatures. In specific embodiments, the resource manager minimizes or reduces resource management costs by identifying a relatively small set of workload classes during a learning phase, determining preferred resource allocations for each workload class, and then during a monitoring phase, classifying workloads and allocating resources based on the preferred resource allocation for the classified workload. In some embodiments, interference is accounted for by estimating and using an “interference index”.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL) +1
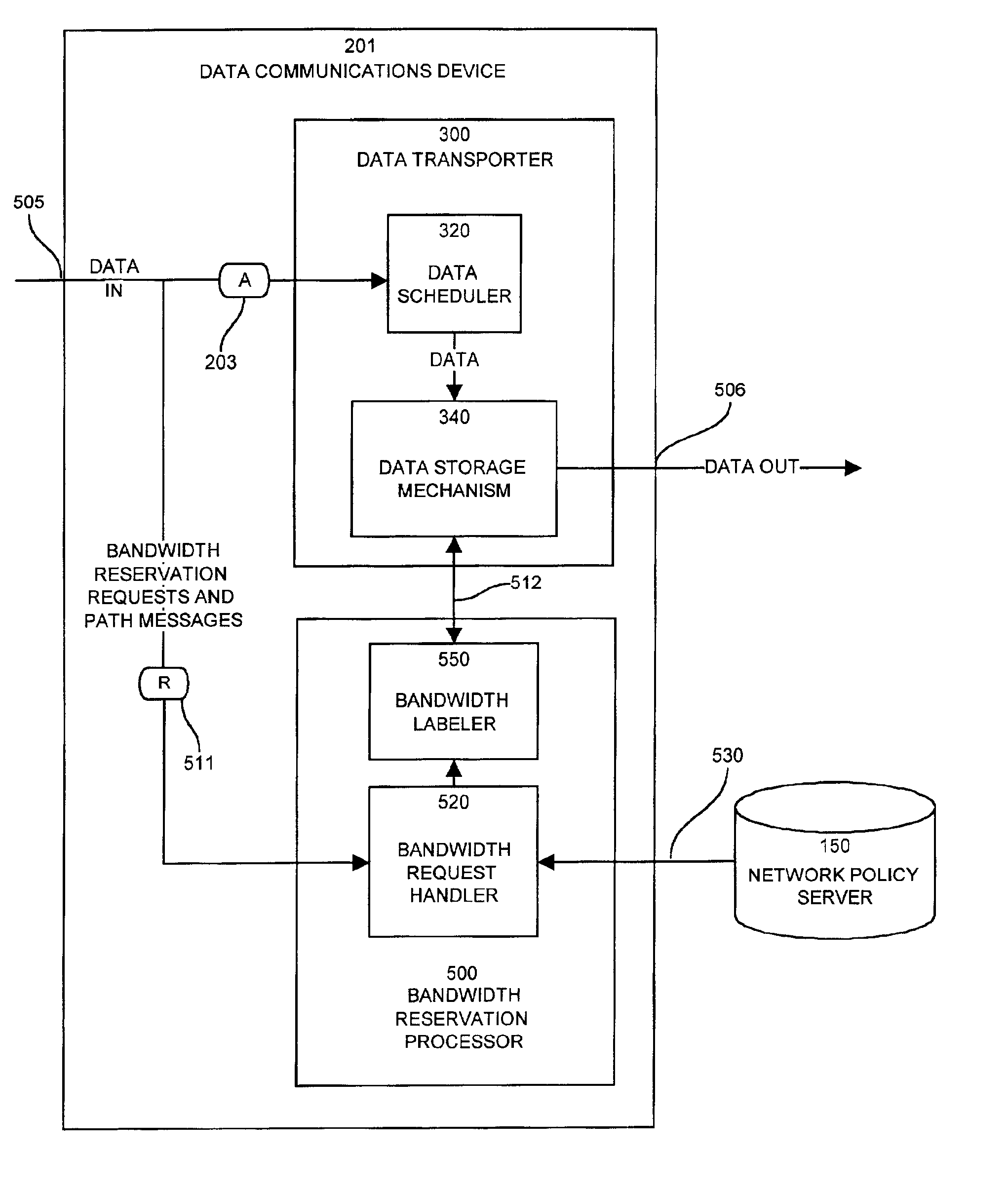
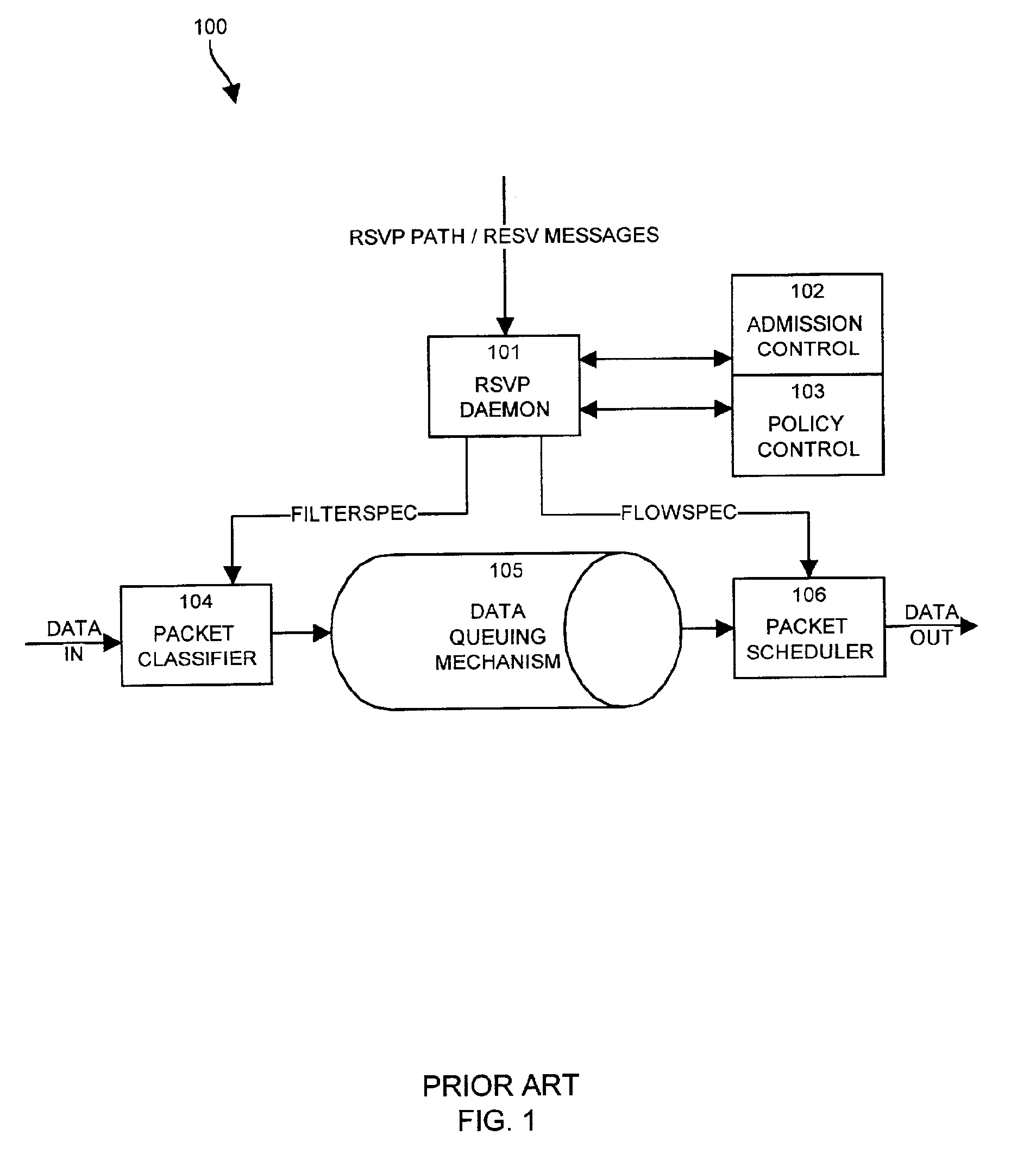
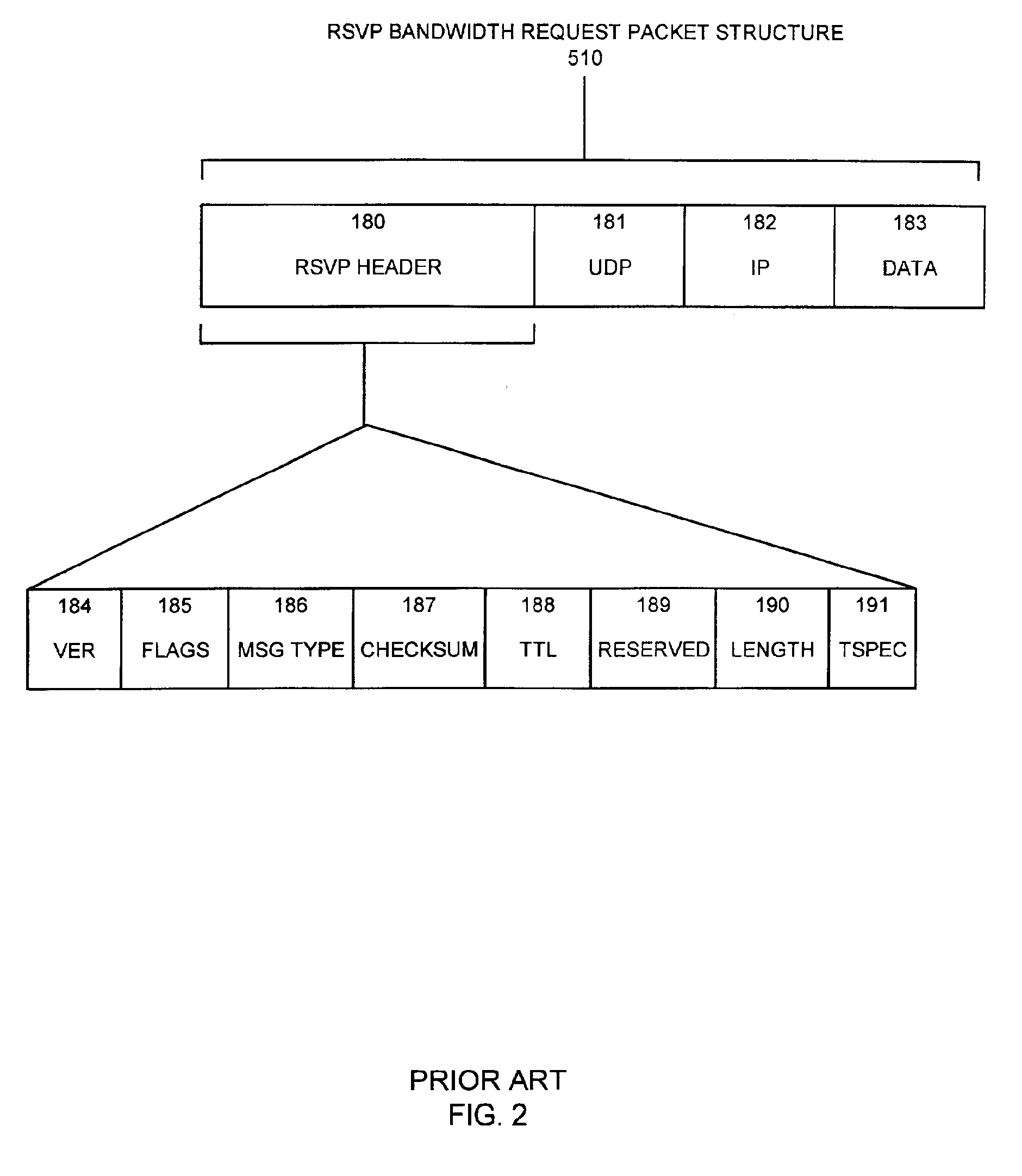
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
A system capable of dynamically reserving bandwidth and adjusting bandwidth reservations for active sessions of data communication in a data communications device is provided. The system generally separates the operation of bandwidth allocation and adjustment from the operation of data transport through the device, thereby allowing bandwidth reservations and adjustments to be made without disturbing sessions of data communication that are actively being transported through the device. The system can accept requests to allocate or reserve bandwidth in a data communications device using bandwidth reservation protocols such as RSVP. The reservation requests create sender state data that can be used to compute resource allocation data. The resource allocation data can be used to label data storage locations in a data storage mechanism according to the required bandwidth reservations. A data scheduling apparatus, which is ignorant of particular sessions and specific amounts of reserved bandwidth, examines data and deposits data into data storage locations having a label corresponding to a session identification specified in the data, if any. If an unknown or no session identification is specified in the data, the data scheduler deposits data into a data storage location that is unlabeled or that has an unreserved label. Thus session bandwidth is determined by the percentage of labeled data storage locations for the session. Changes in bandwidth reservations are reflected in the separate operation of alterations made in the data storage labeling scheme, and do not affect the data scheduler, or data dequeuing mechanisms, thus allowing data sessions to continue without interruption during bandwidth adjustments.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for controlling transmissions of a communications system
InactiveUS20030123425A1Reduce the amount of noiseLower Level RequirementsPower managementEnergy efficient ICTAdaptive reuseTransmitted power
In some aspects, each cell in the communications system can be designed to operate in accordance with a set of back-off factors that identify the reductions in peak transmit power levels for the channels associated with the back-off factors. The back-off factors are defined to provide the required power to a large percentage of the users while reducing the amount of interference. In some other aspects, the cells operate using an adaptive reuse scheme that allows the cells to efficiently allocate and reallocate the system resources to reflect changes in the system. A reuse scheme is initially defined and resources are allocated to the cells. During operation, changes in the operating conditions of the system are detected and the reuse scheme is redefined as necessary based on the detected changes. In yet other aspects, techniques are provided to efficiency schedule data transmissions and to assign channels to users.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
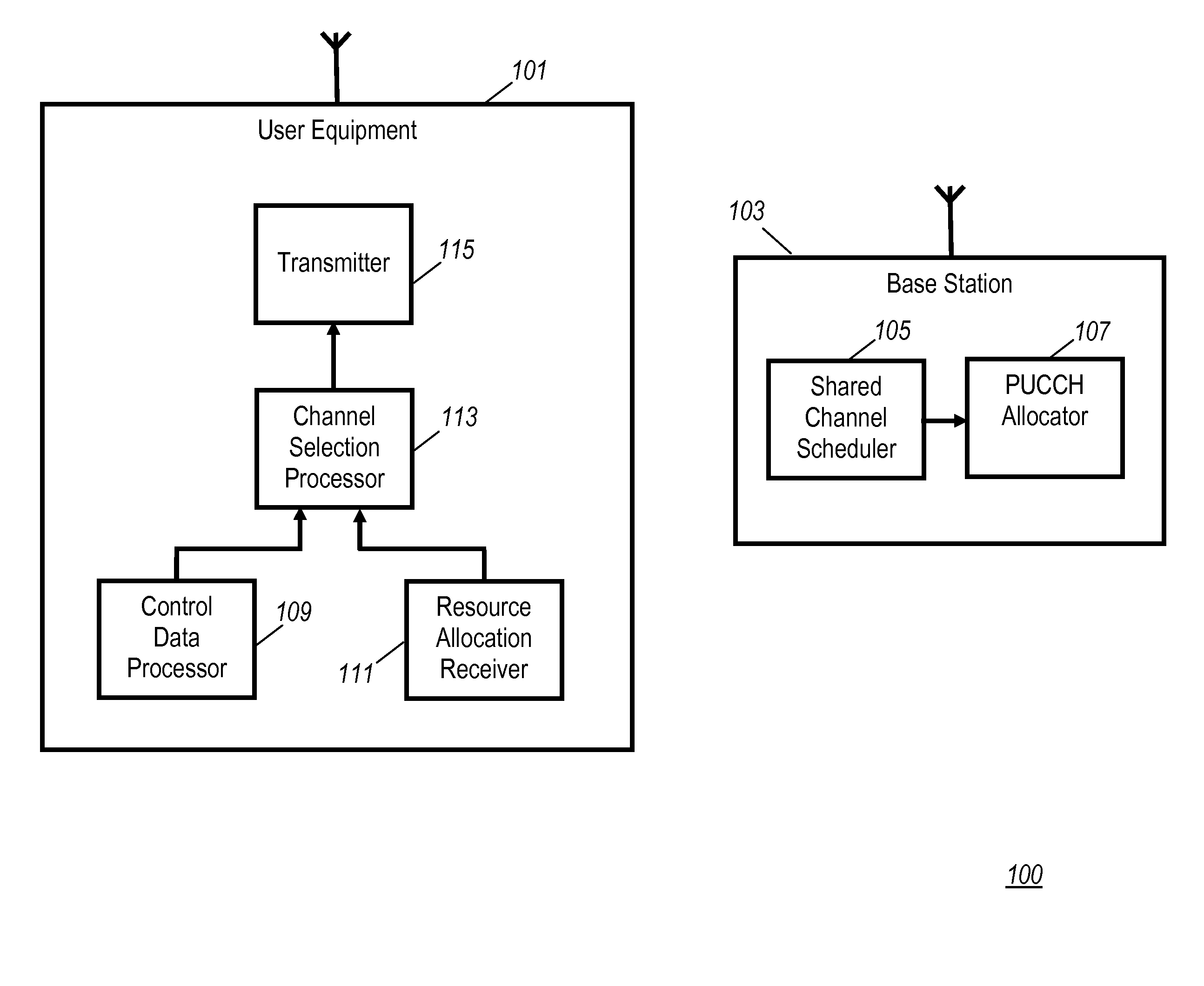
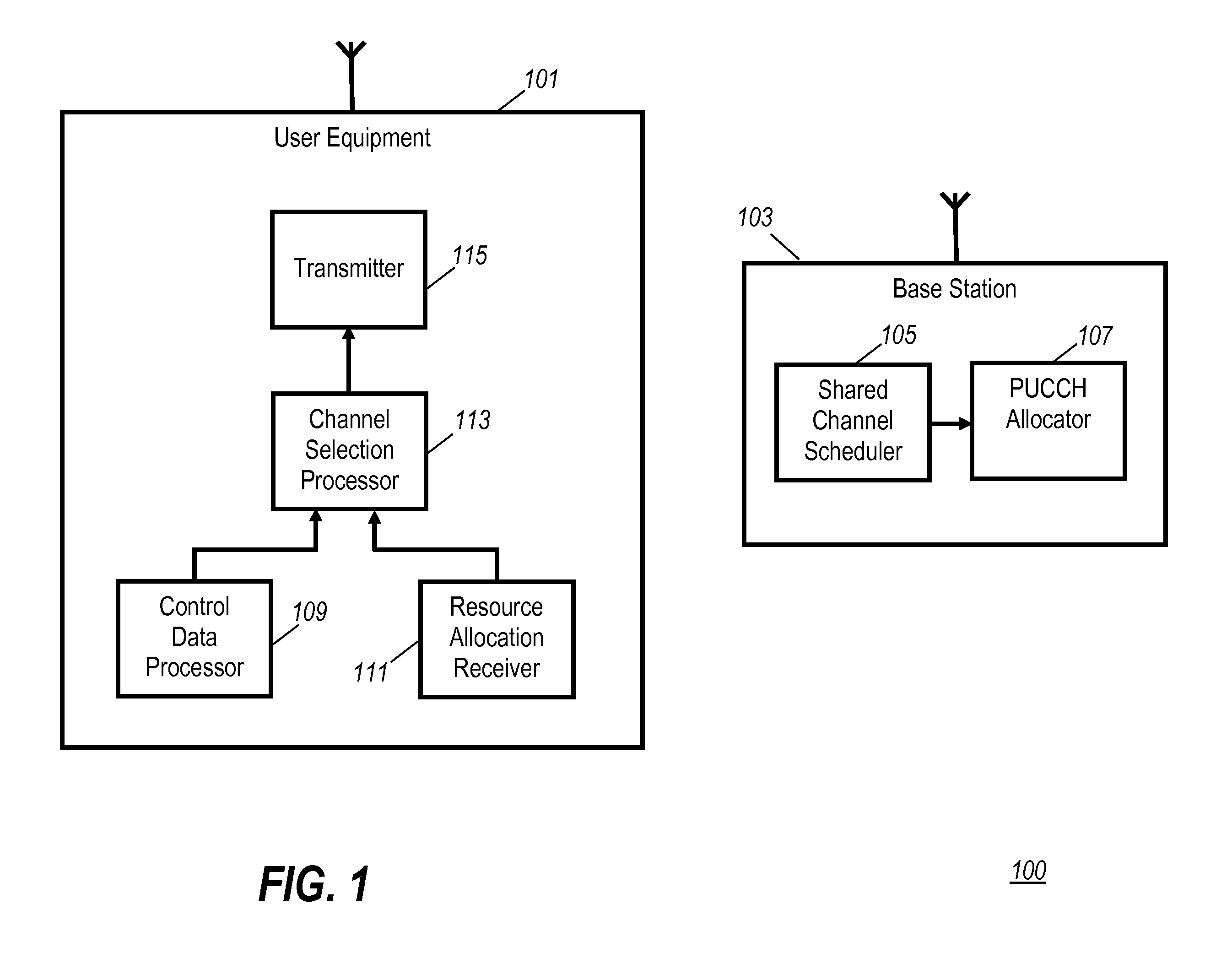
Use of the physical uplink control channel in a 3rd generation partnership project communication system
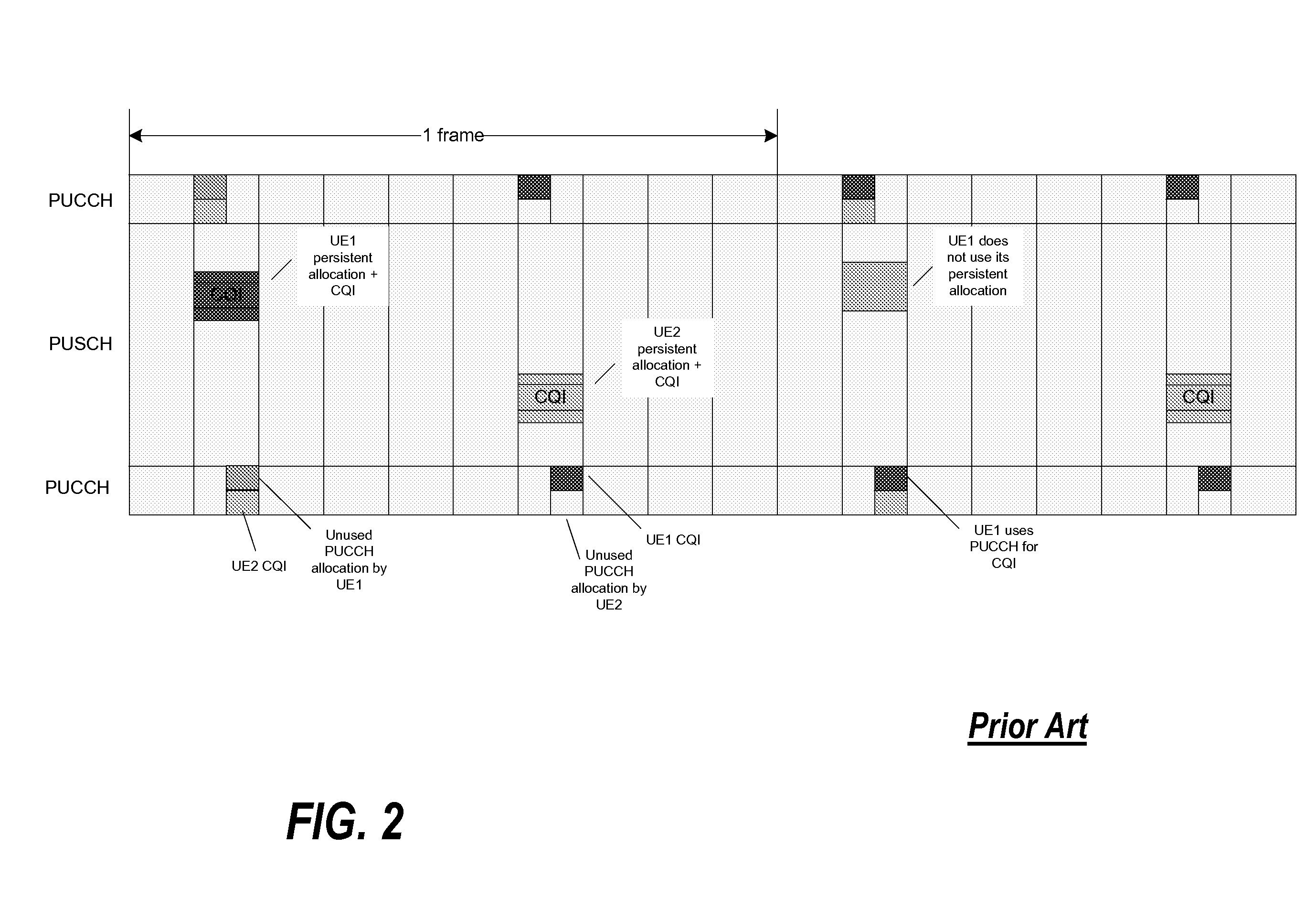
ActiveUS20080311919A1Easy to optimizeEfficient use of resourcesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignalling characterisationCommunications systemControl channel
In a 3rd Generation Partnership Project, 3GPP, communication system a base station comprises a scheduler allocating communication resource of at least one of a Physical Uplink Shared CHannel, PUSCH, and a Physical Downlink Shared CHannel, PDSCH to a User Equipment (UE). The scheduling may either be a dynamic scheduling wherein a resource allocation for a single frame is provided to the UE or a persistent scheduling wherein a resource allocation for a plurality of frames is provided to the UE. A resource allocator assigns resource of a Physical Uplink Control CHannel, PUCCH, to the UE dependent on whether dynamic scheduling or persistent scheduling is performed by the scheduler for the UE. The UE transmits uplink control data on a physical uplink channel which is selected as the PUCCH or the PUSCH in response to whether persistent scheduling is used for the UE. The invention allows e.g. reduced PUCCH loading.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Uplink resource allocation in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20090116434A1Transmission path divisionInter user/terminal allocationTelecommunicationsUplink transmission
The present invention relates to a method and mobile terminal for requesting resources for transmitting data on uplink within a mobile communication system. Further the invention relates to a network entity for allocating uplink resources to mobile terminal. To provide a flexible scheduling scheme for uplink transmission, the invention proposes different scheduling procedures based on a request grant scheme. The resource request of the mobile terminal is provided via a contention-based channel, while all further communication uses scheduled resources. Consequently subsequent transmissions of user data and / or scheduling information utilize scheduled resources.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
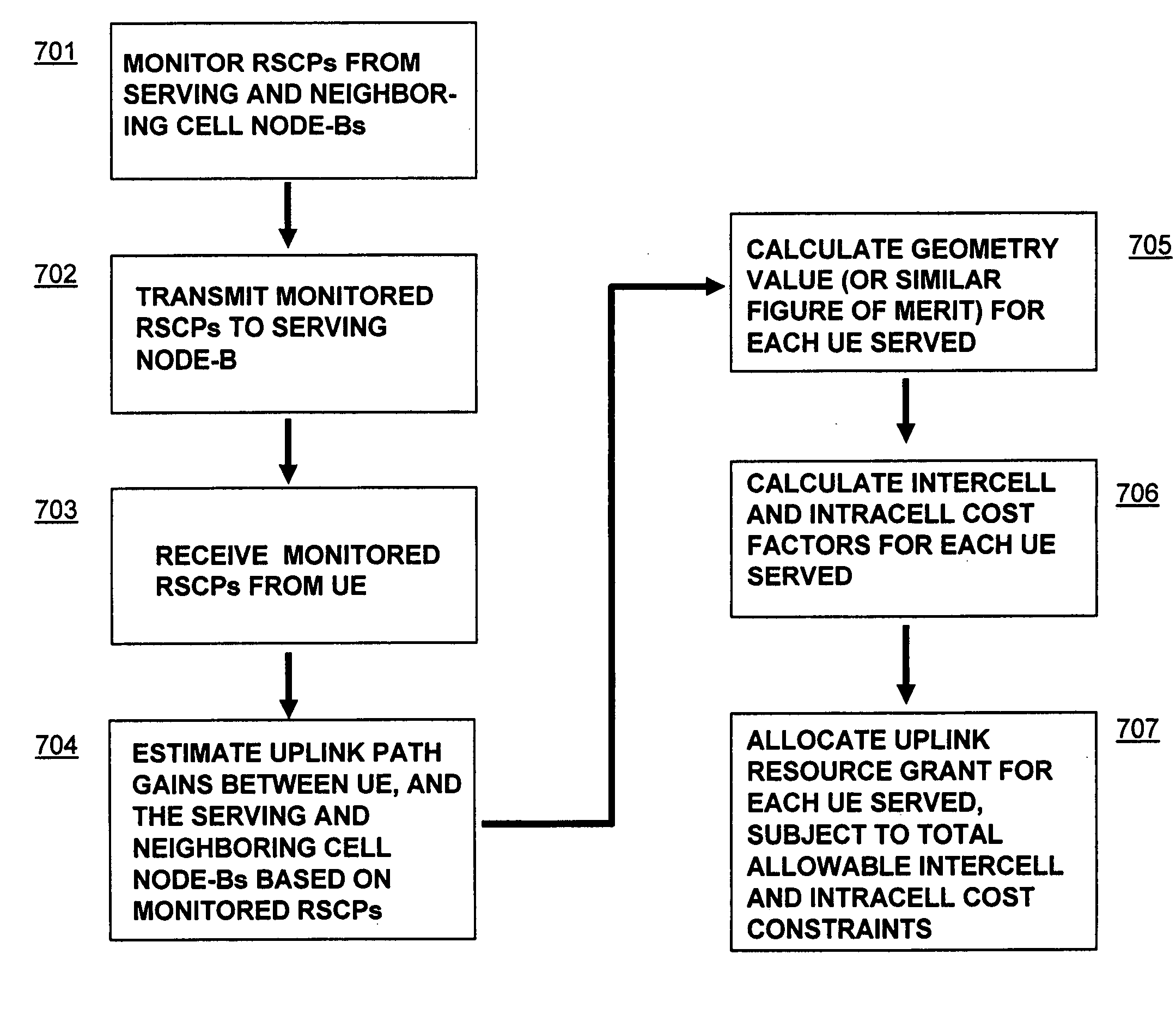
Uplink resource allocation to control intercell interference in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070042784A1Avoid elevationSuitable characteristicPower managementReceivers monitoringCommunications systemUplink transmission
Embodiments of the present invention exploit the reciprocity of radio channels in TDD, and longer-term correlation between average uplink and downlink path losses in FDD wireless communication systems to enable distributed schedulers in an enhanced uplink system to allocate uplink transmission resources while preemptively managing intercell interference levels. Each cell's base station transmits a downlink reference signal at a known transmission power level. A mobile station monitors the received signal strength of the downlink reference signals from multiple base stations. The transmitted and received signal strength levels can be used by the mobile station to estimate the amount of intercell interference that the mobile station's uplink transmissions cause, and the mobile station's uplink transmission parameters are adjusted accordingly. In further embodiments, the received reference signal power levels, or values derived therefrom, are transmitted by the mobile station to its serving base station, where a scheduling algorithm uses the information to adjust one or more transmission parameters relating to a grant of uplink transmission resources to the UE, thereby controlling the intercell interference generated by the mobile station's uplink transmissions.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method of performing random access procedure in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090186613A1Reliable data transmissionSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource allocation
A method includes transmitting a random access preamble, receiving a random access response as a response of the random access preamble, wherein the random access response comprises an uplink resource assignment and a request for transmission of a Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), and transmitting the CQI in the uplink resource assignment.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com