Patents
Literature
1381 results about "Time division multiple access" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
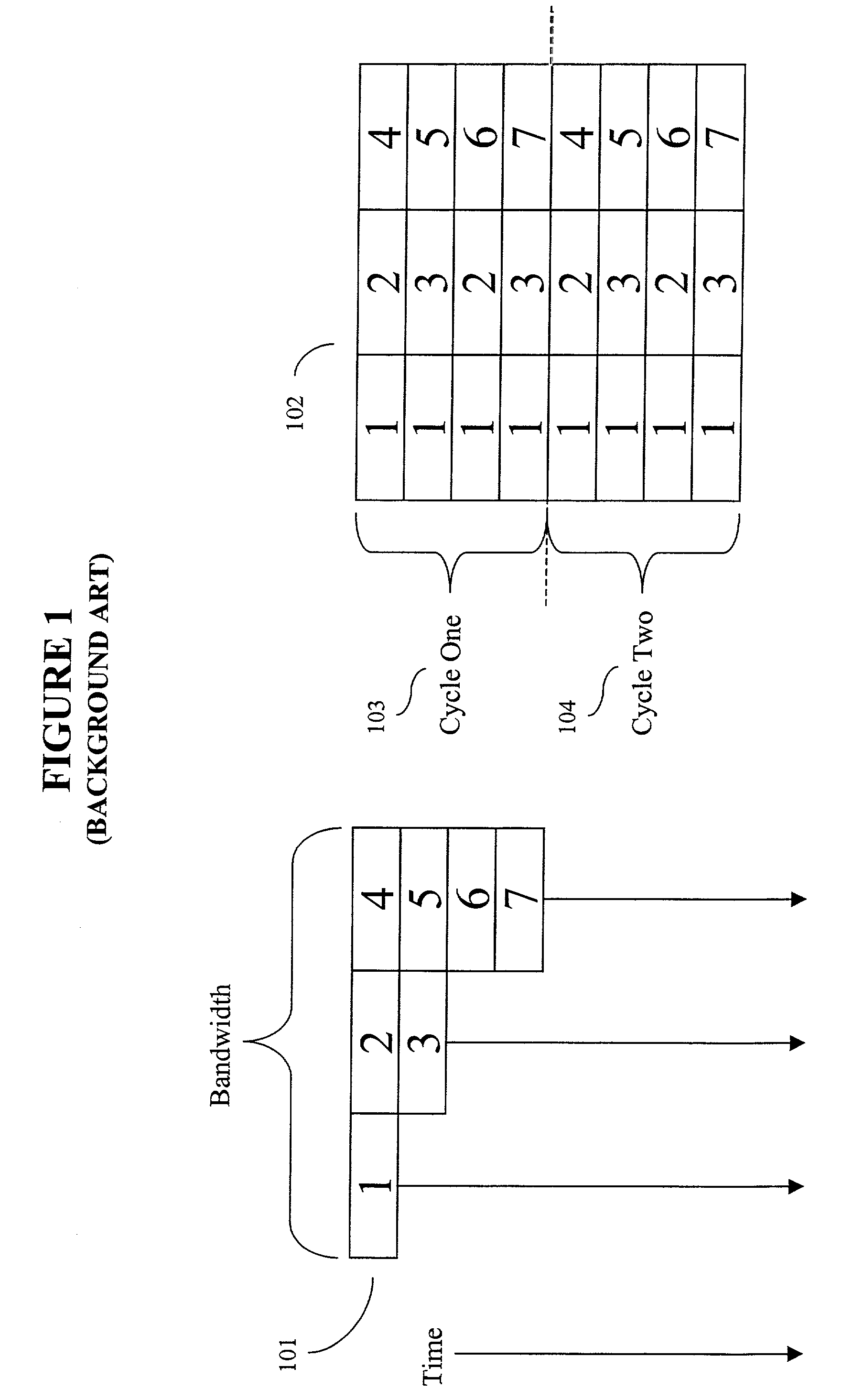
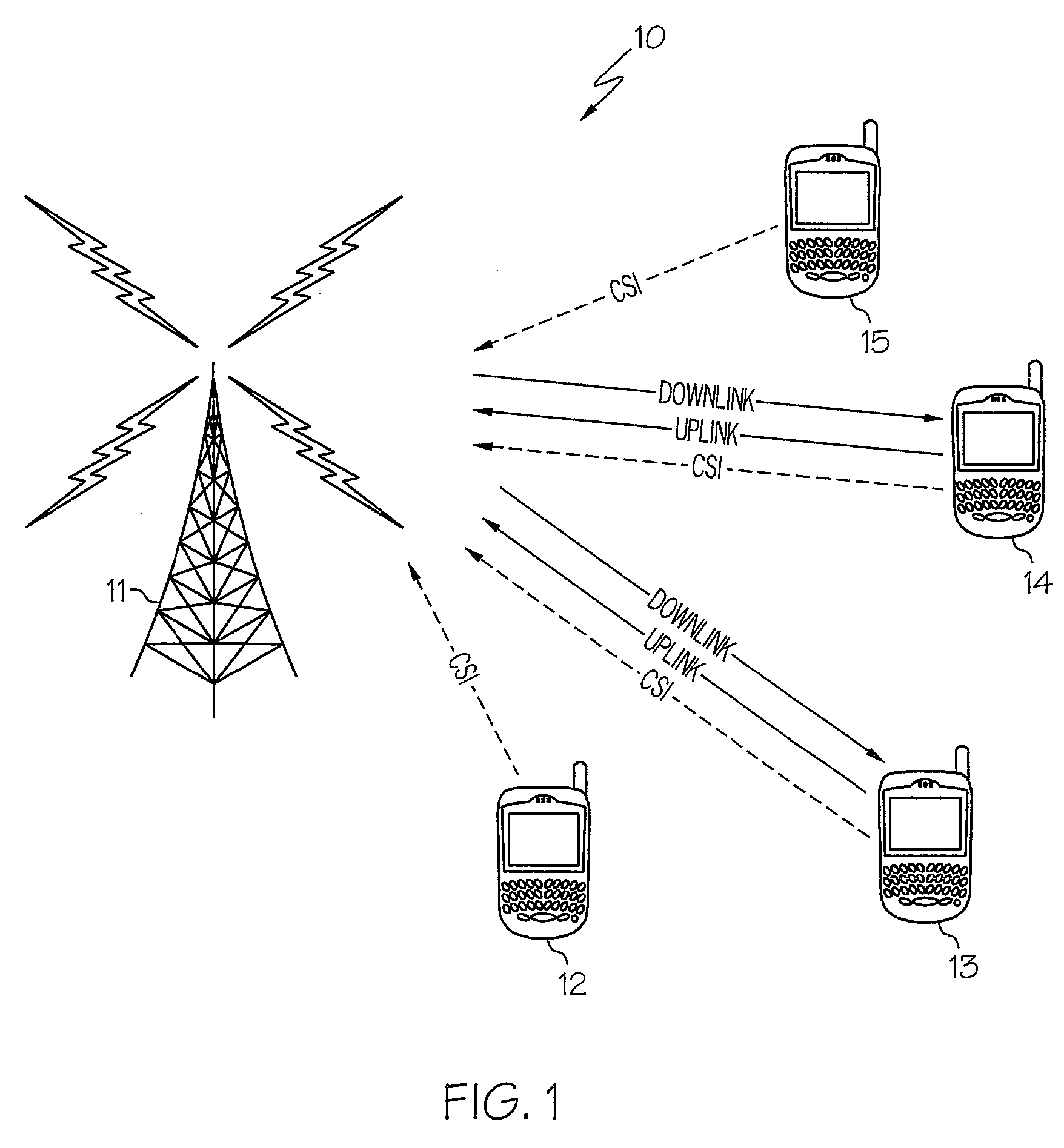
Time-division multiple access (TDMA) is a channel access method for shared-medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This allows multiple stations to share the same transmission medium (e.g. radio frequency channel) while using only a part of its channel capacity. TDMA is used in the digital 2G cellular systems such as Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), IS-136, Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) and iDEN, and in the Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) standard for portable phones. TDMA was first used in satellite communication systems by Western Union in its Westar 3 communications satellite in 1979. It is now used extensively in satellite communications, combat-net radio systems, and passive optical network (PON) networks for upstream traffic from premises to the operator. For usage of Dynamic TDMA packet mode communication, see below.
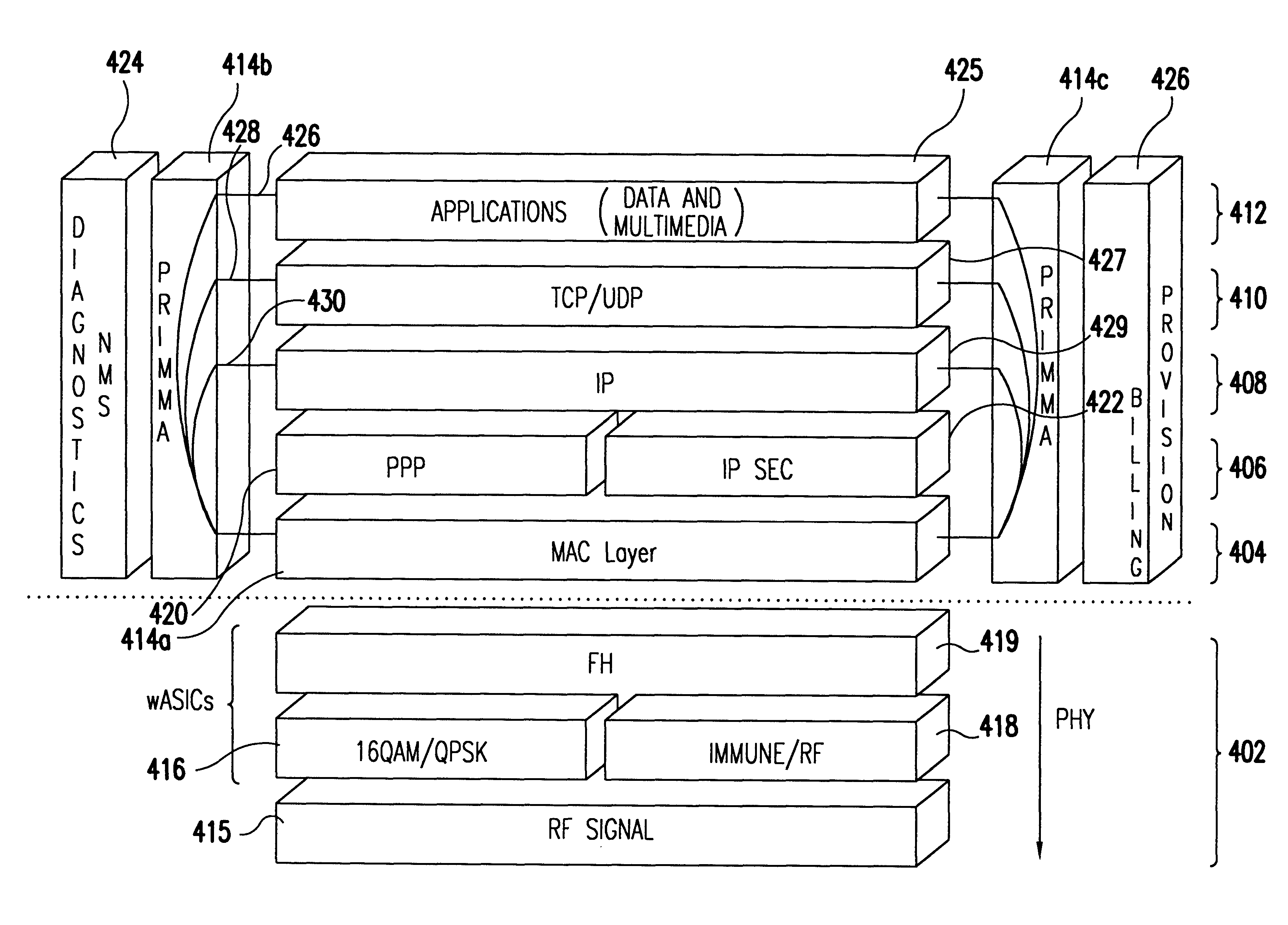
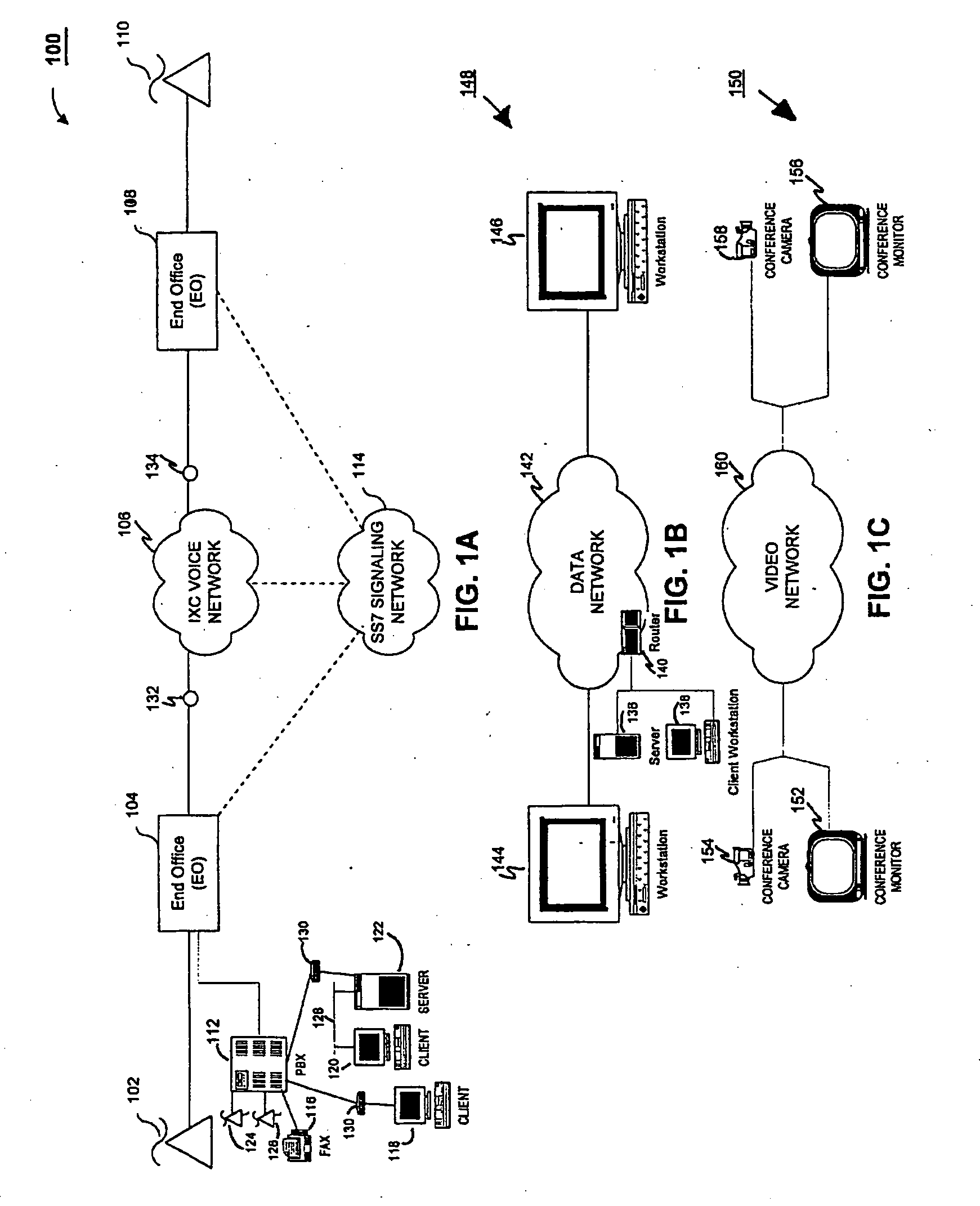
Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet-centric wireless point to multi-point (PTMP) transmission system architecture
InactiveUS6862622B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransport systemWorkstation
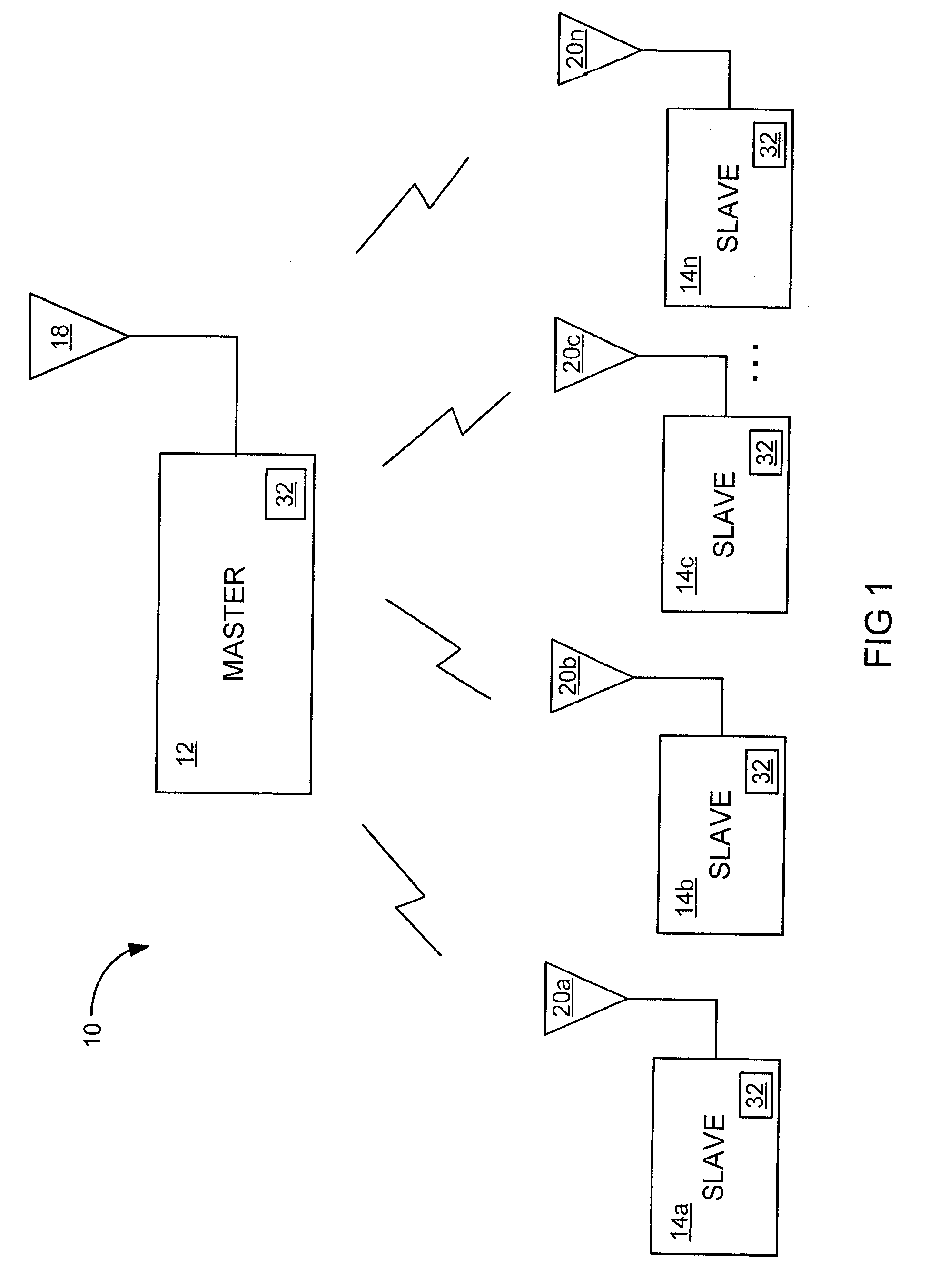
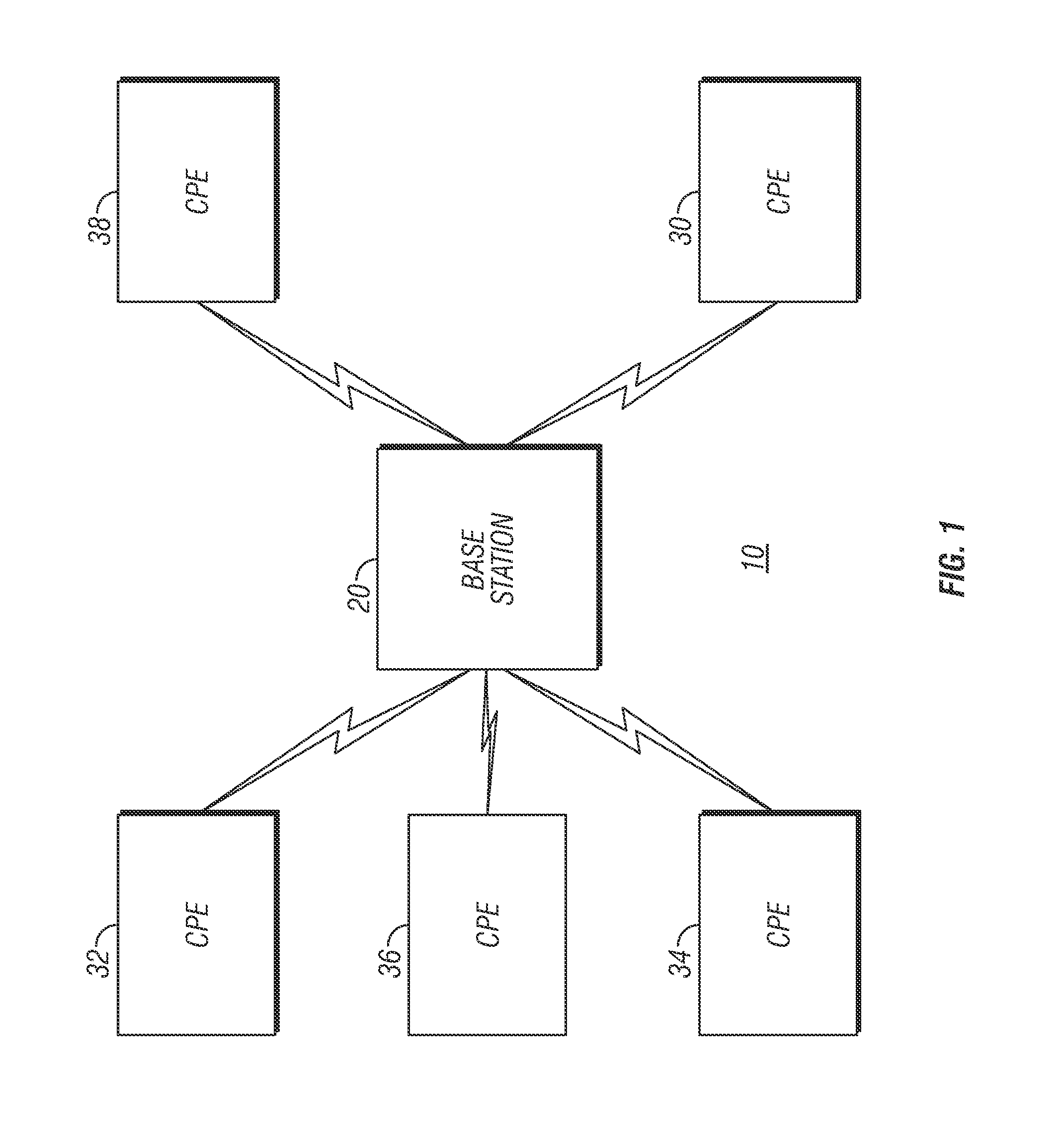
A packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system includes: a wireless base station communicating via a packet-centric protocol to a first data network; one or more host workstations communicating via the packet-centric protocol to the first data network; one or more subscriber customer premise equipment (CPE) stations coupled with the wireless base station over a shared bandwidth via the packet-centric protocol over a wireless medium; and one or more subscriber workstations coupled via the packet-centric protocol to each of the subscriber CPE stations over a second network. The packet-centric protocol can be transmission control protocol / internet protocol (TCP / IP). The packet-centric protocol can be a user datagram protocol / internet protocol (UDP / IP). The system can include a resource allocation means for allocating shared bandwidth among the subscriber CPE stations. The resource allocation is performed to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS). The wireless communication medium can include at least one of: a radio frequency (RF) communications medium; a cable communications medium; and a satellite communications medium. The wireless communication medium can further include a telecommunications access method including at least one of: a time division multiple access (TDMA) access method; a time division multiple access / time division duplex (TDMA / TDD) access method; a code division multiple access (CDMA) access method; and a frequency division multiple access (FDMA) access method.The first data network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN). The second network includes at least one of: a wireline network; a wireless network; a local area network (LAN); and a wide area network (WAN).
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
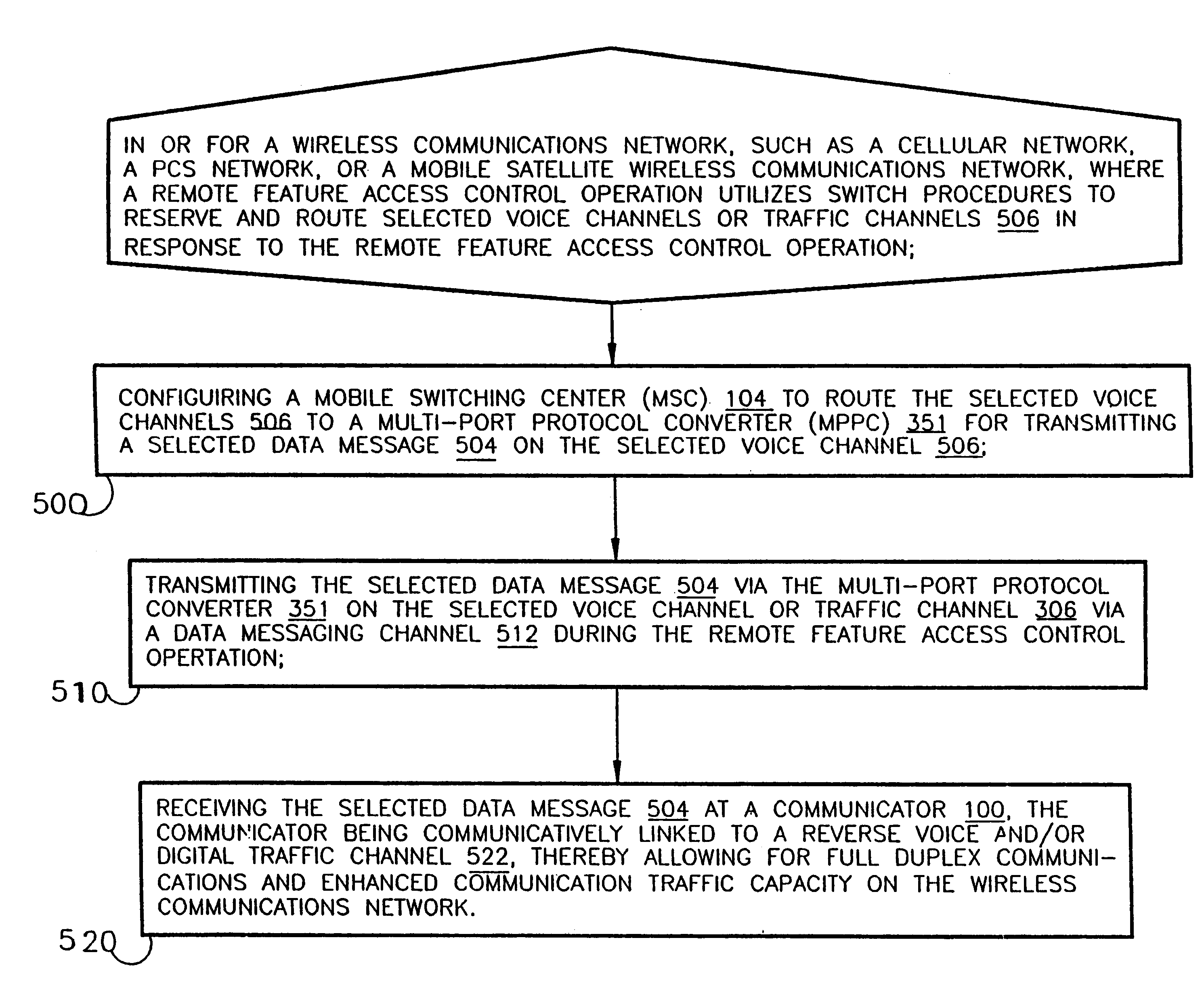
Time division multiple access downlink personal communications system voice and data debit billing method
InactiveUS6185198B1Increase capacityFunction increaseTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationCode division multiple accessControl channel
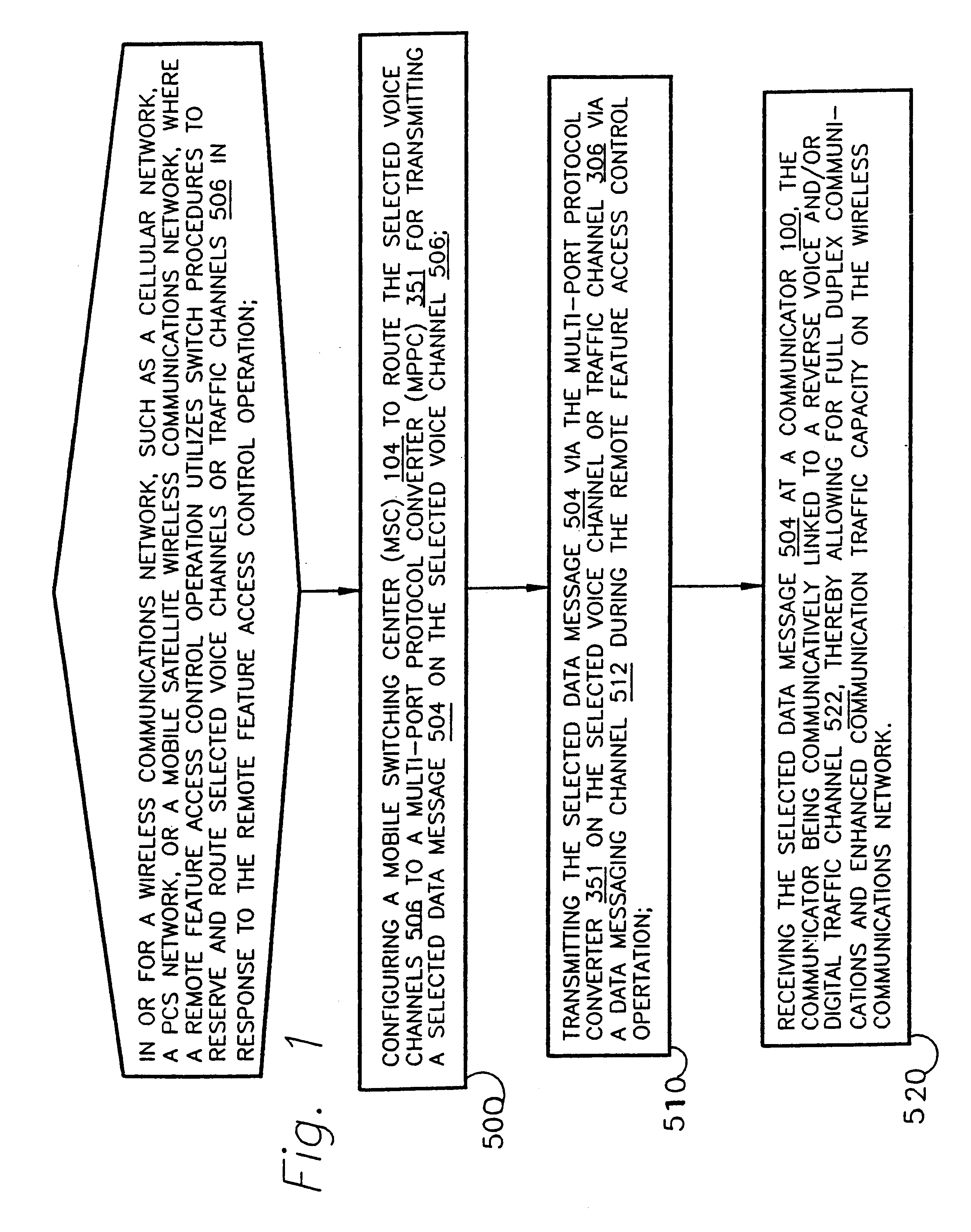
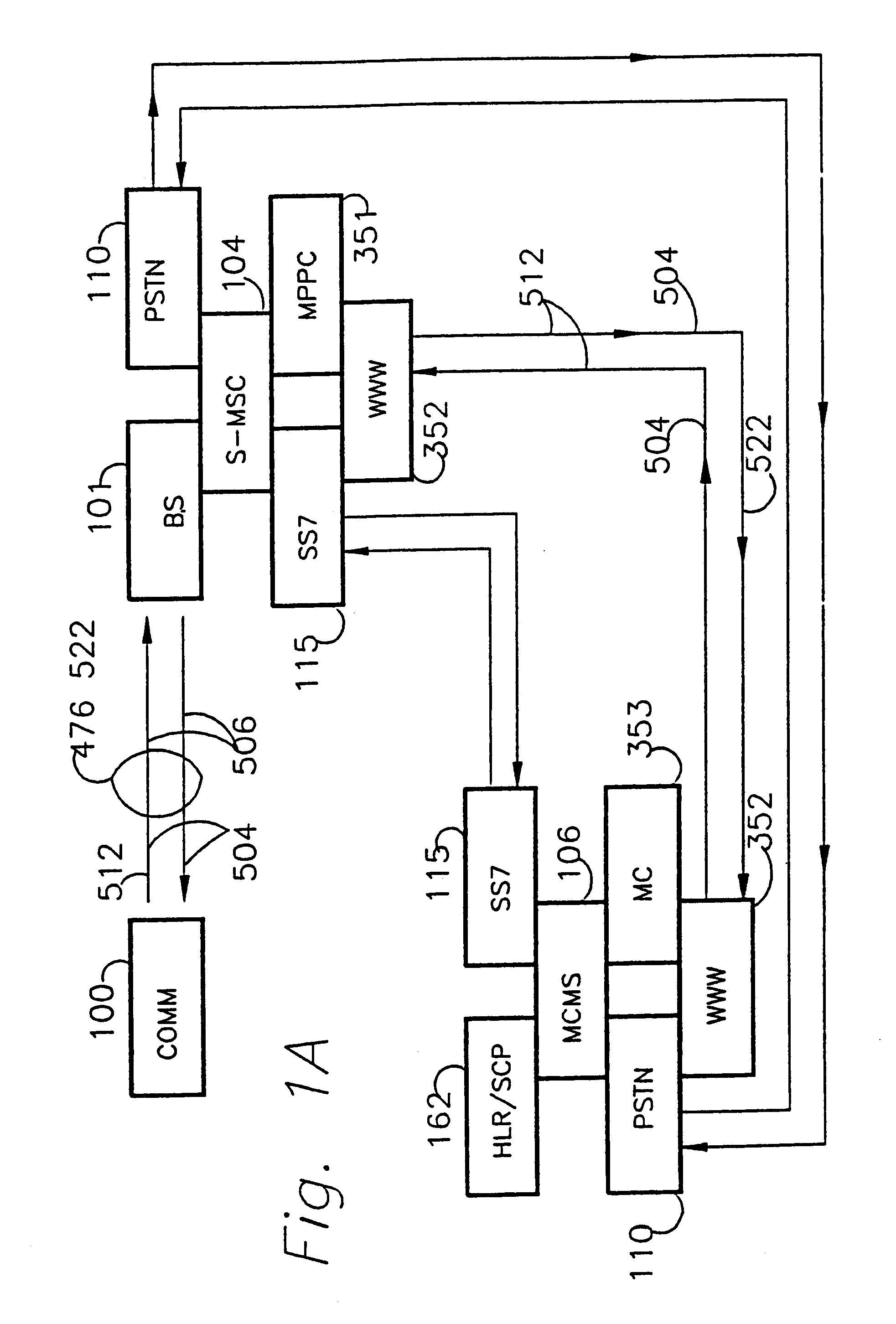
A method and apparatus for full-duplex data communication in or for a wireless communications network, such as a cellular network, PCS network, or mobile satellite network, where a remote feature access control operation utilizes a switch to reserve and route selected voice channels or traffic channels in response to the remote feature access control operation. The method comprising the steps of: configuring a mobile switching center (MSC) to route the selected voice channels to a multi-port protocol converter (MPPC) for transmitting a selected data message on the selected voice channel. Transmitting the selected data message via the multi-port protocol converter on the selected voice channel via a data messaging channel during the remote feature access control operation. Then the selected data message is received at a communicator, which is communicatively linked to a reverse voice and / or digital traffic channel of the wireless network, thereby providing for both forward and reverse messaging on the wireless communications network. An apparatus is disclosed for data communication in or for a wireless communications network for transmitting and receiving both forward and reverse voice, traffic, and control channel messages utilizing the disclosed methodology.
Owner:AERIS COMM
Method and a device for maintaining the performance quality of a code-division multiple access system in the presence of narrow band interference
InactiveUS6807405B1Reduce adverse effectsReducing and eliminating disruptionPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementContinuous scanningTime division multiple access
A method and device which dynamically detects, tracks and filters interfering signals with sufficient speed (i.e. within one IS-95 CDMA data frame period, or 20ms and fidelity to eliminate or greatly reduce the deleterious effects of narrow band interferor signals on a CDMA link. When inserted in an RF signal path an Adaptive Notch Filter (ANF) detects narrow band interferors above a threshold level within the CDMA signal. Detection is accomplished by continuous scanning of a preset excision band, e.g. a specified narrow band associated with an AMPS system. Detected interferors are then automatically acquired and suppressed. This is achieved by electronically placing a rejection notch at the frequency of the interferors. Multiple notch filters may be used to simultaneously suppress multiple interferors. In the absence of interferors a bypass mode is selected allowing the RF signal to bypass the notch. Upon detection of an interferor, a switch is made to a suppression mode where the interferor is steered through a first notch section and suppressed. Alternatively, an external control line may be used to select the bypass mode so that the signal is allowed to pass the notch section, regardless of interferer content.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPER CONDUCTOR CANADA CORP A CO INC UNDER THE LAWS OF CANADA +1
Low-power autonomous node for mesh communication network
ActiveUS20060029061A1Maximize power lifeEasy to usePower managementEnergy efficient ICTReal-time computingTime division multiple access
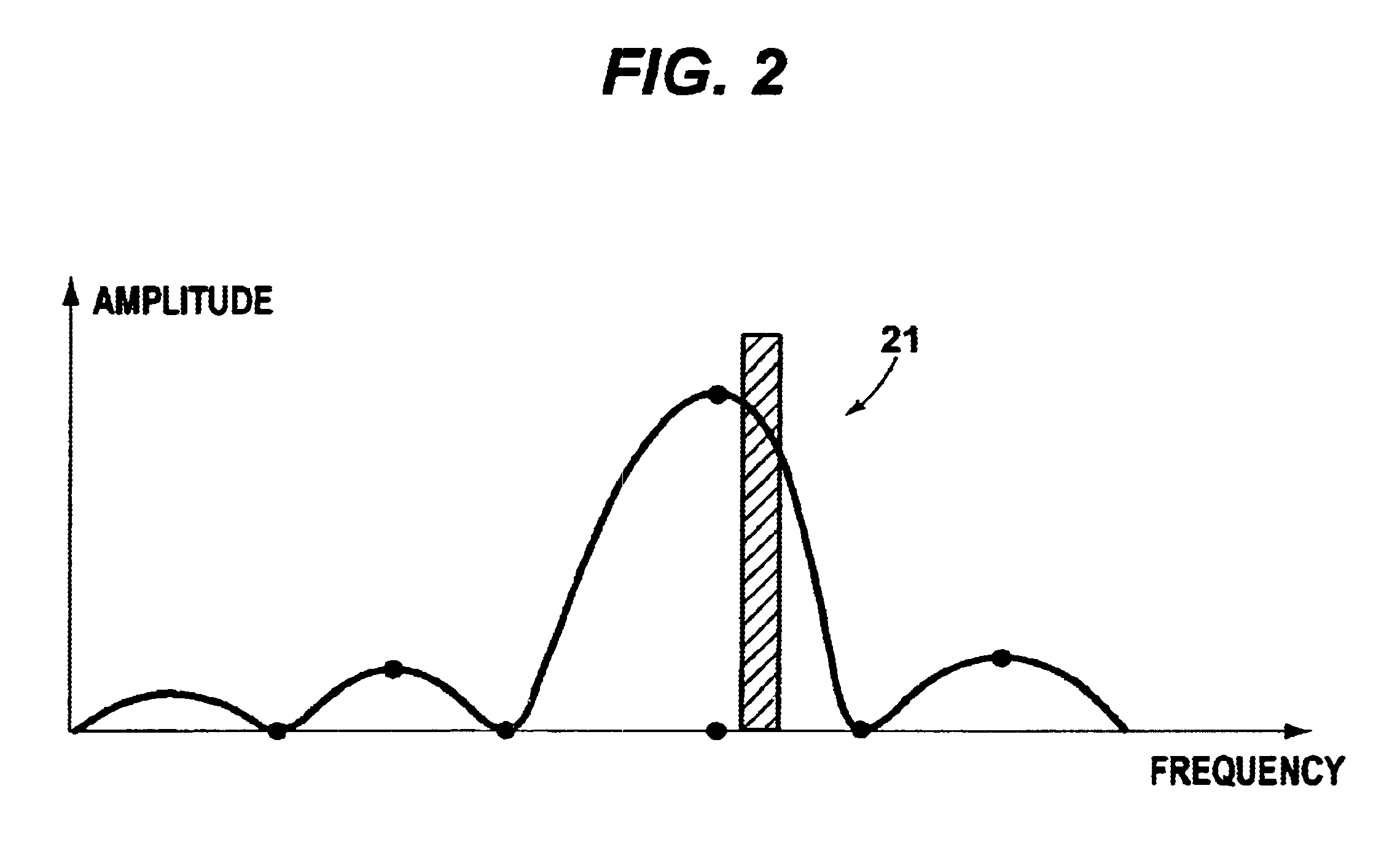
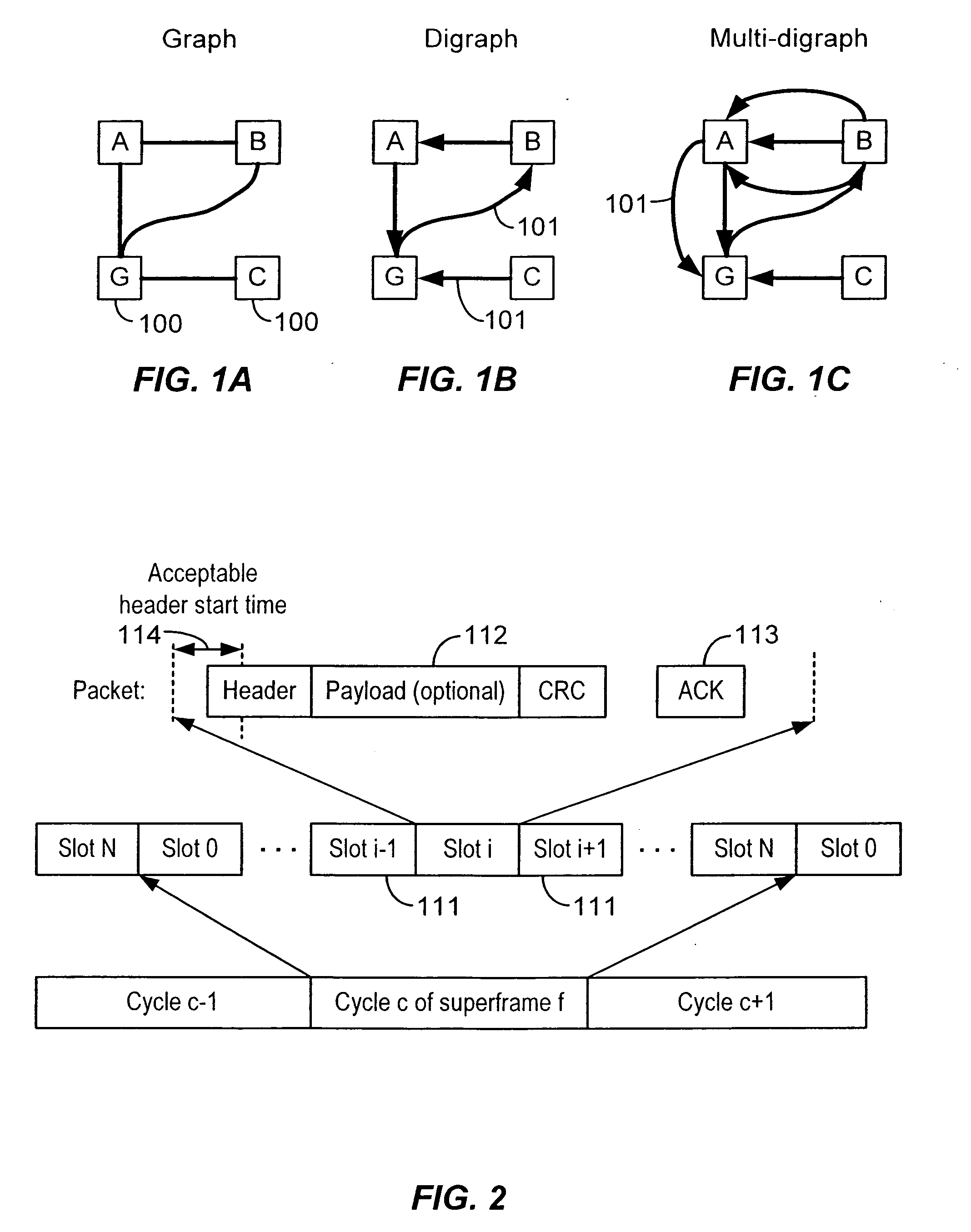
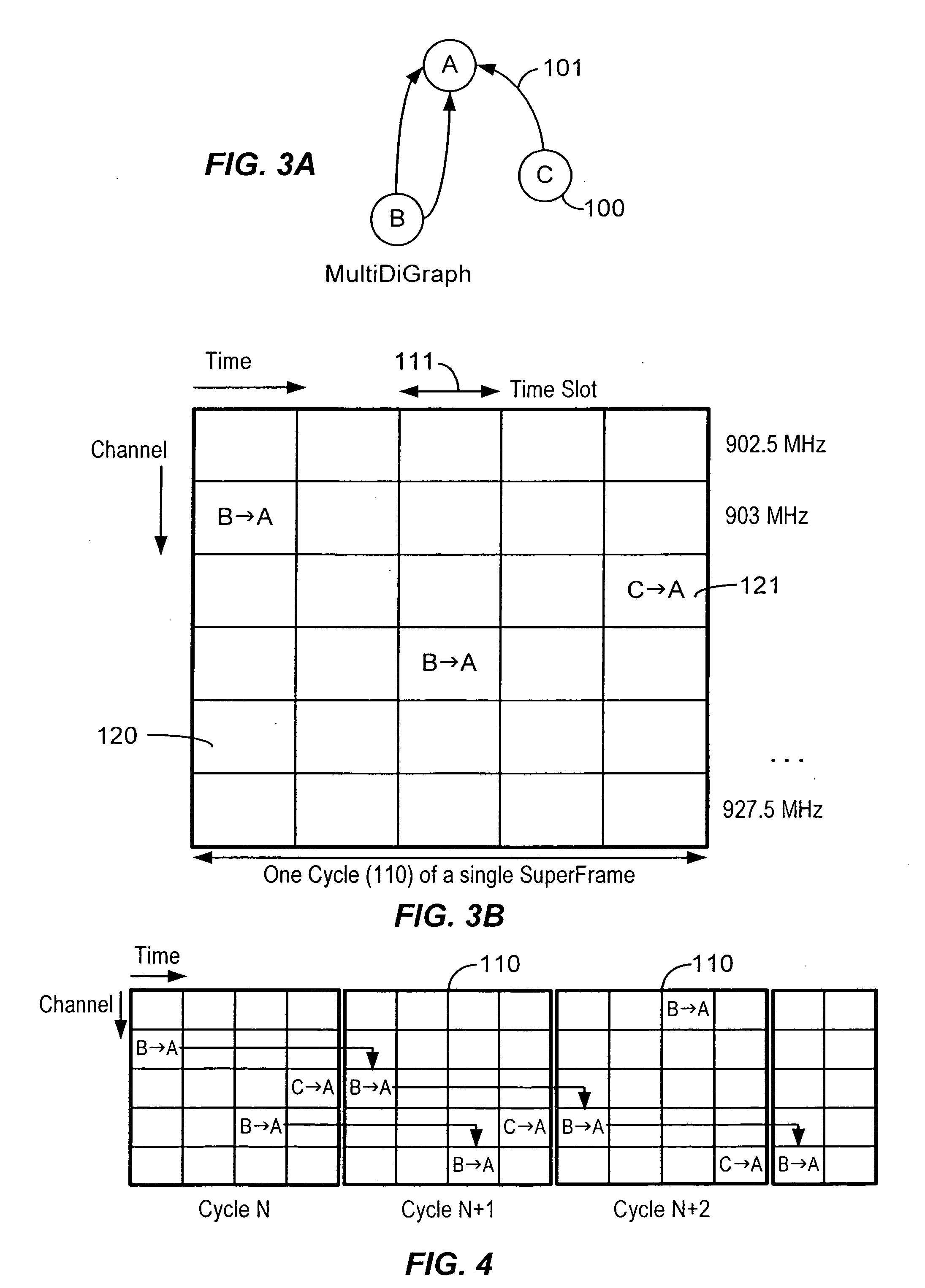
In a packet communication network, a method and apparatus for packet switched transport is provided among intelligent nodes wherein the duty cycling of the intelligent nodes is minimized in order to maximize power life using a synchronization algorithm that assures all nodes are able to propagate information through the network without undue use of transmission and reception power. Frequency hopping time-division multiple access supports packet communication between intelligent nodes via assigned directed links, each link being assigned to a time-channel offset (cell) in a superframe, so that a link carrying a packet string between any two intelligent nodes is active only during its assigned time slot. The result is efficient use of spectrum and minimal expenditure of power.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
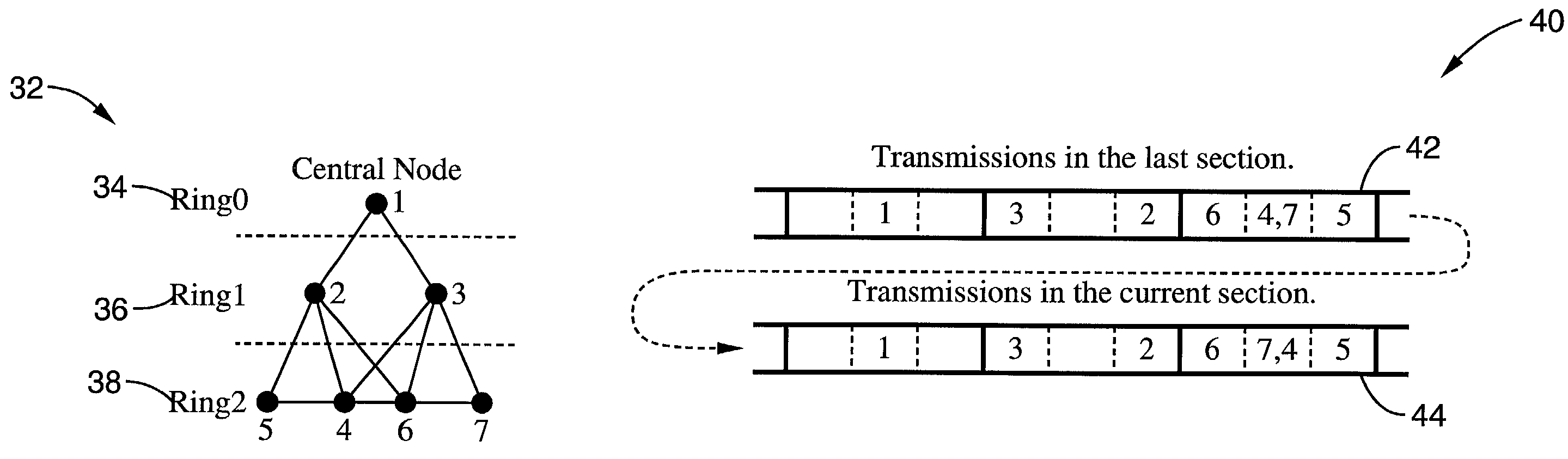
System and method for ad hoc network access employing the distributed election of a shared transmission schedule
InactiveUS20020067736A1Eliminate negotiationMore controlledNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessTransmission schedule
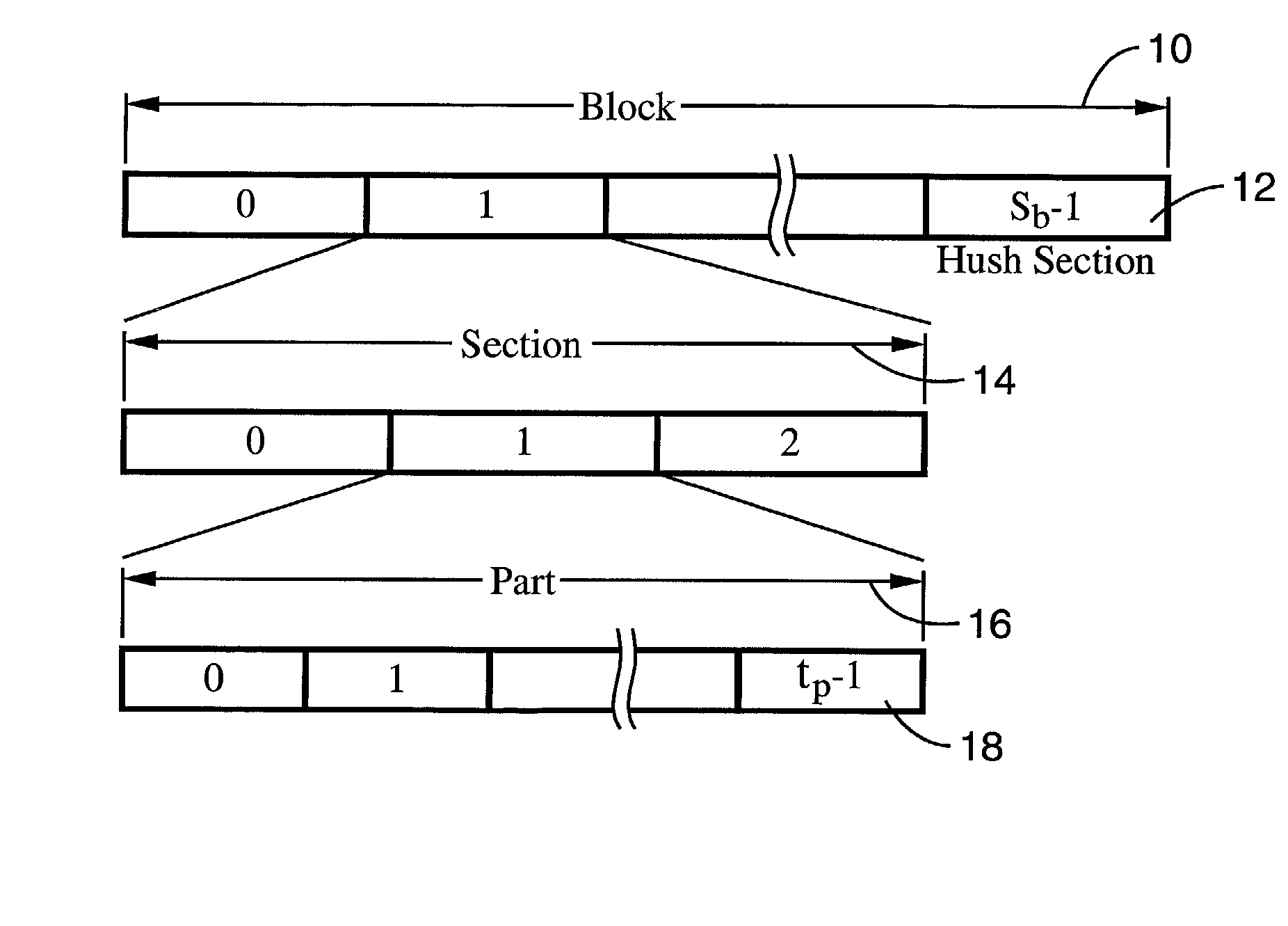
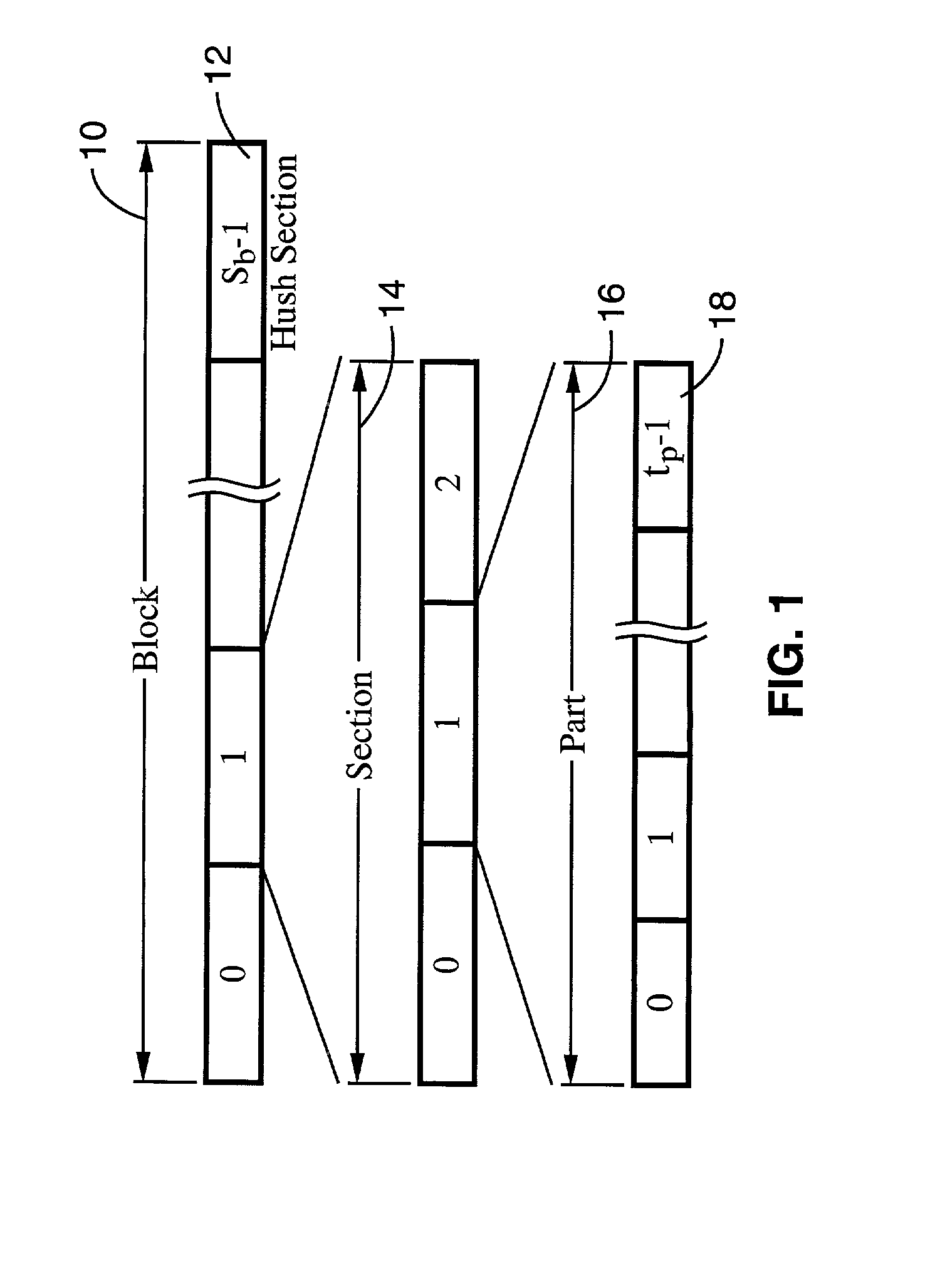
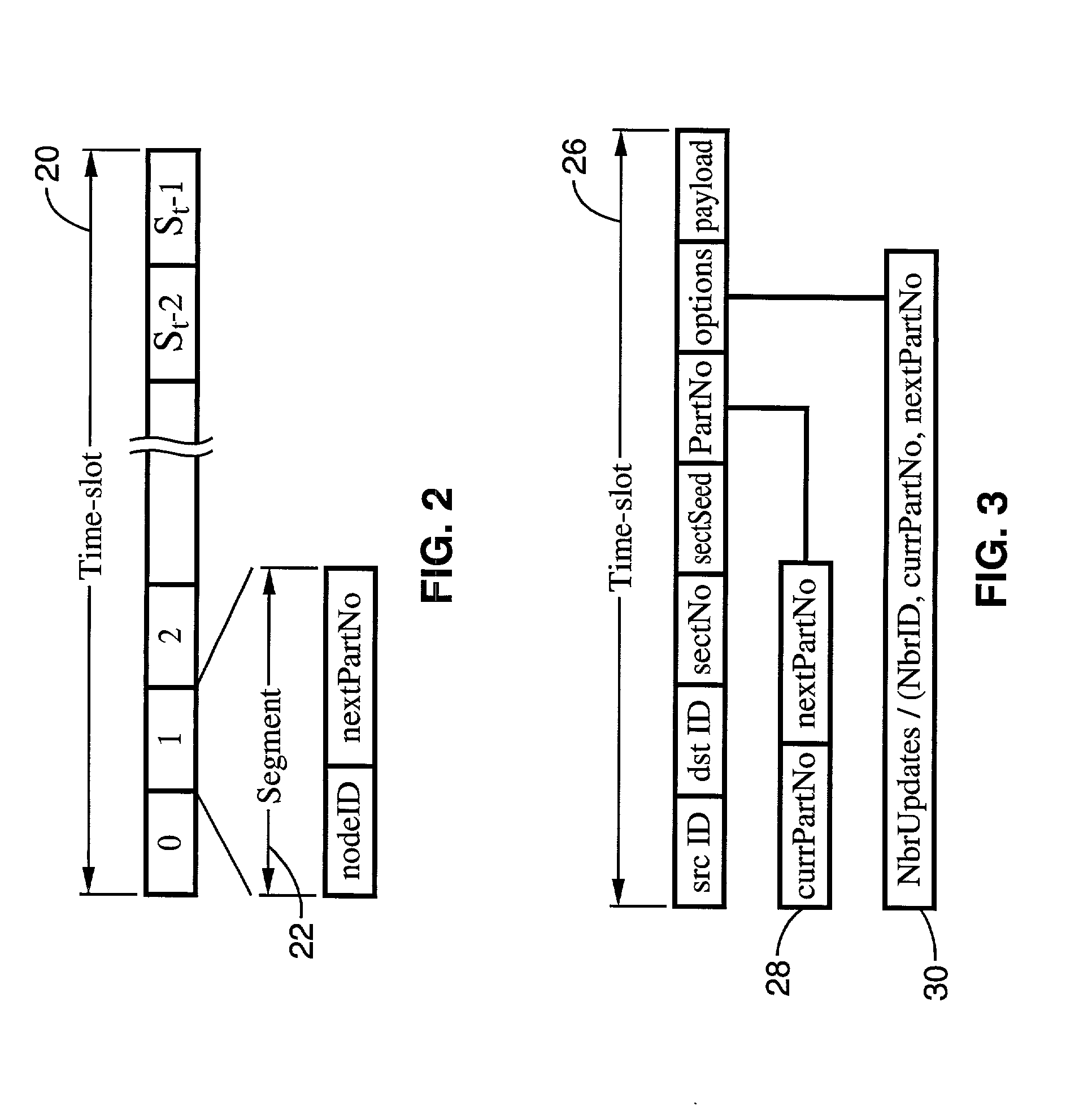
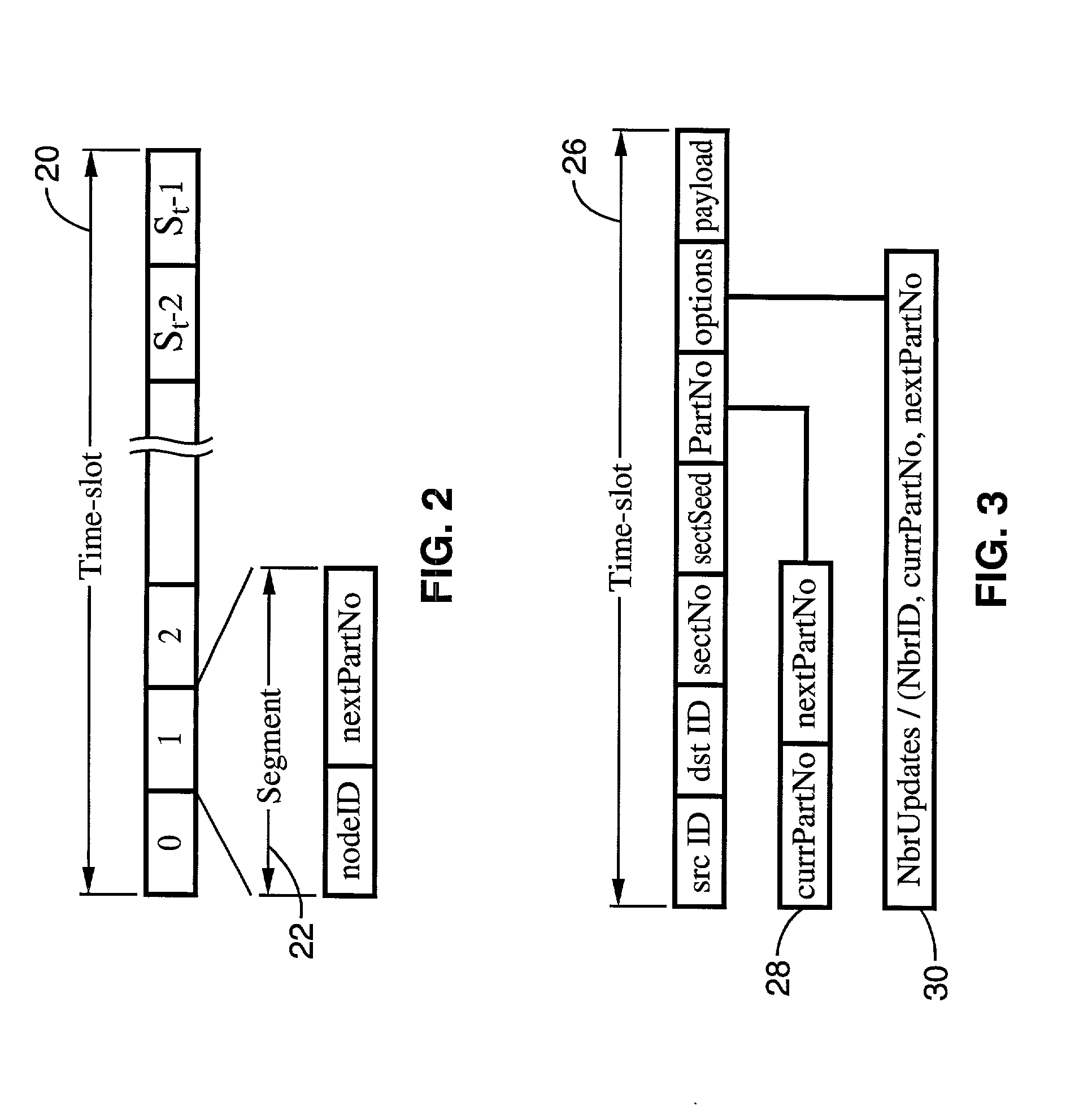
A system and method of providing distributed election of a shared transmission schedule within an ad hoc network. The invention includes a collision-free access protocol which resolves channel access contentions for time division multiple access (TDMA) of a single channel. Time-slots are organized into part numbers, which are included within sections, a sequence of which define a block. Each node is given a ring number according to its location within the network topology and maintains local neighbor information along with its own part number and message digest. Collision-free channel access is automatically scheduled and repetitious contention phases are resolved by a random permutation algorithm operating in message digests. An empty time-slot utilization method is also described and data packets may also be transmitted subject to a non-zero collision probability within a blind section of the block.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Power efficient wireless system for sensor network
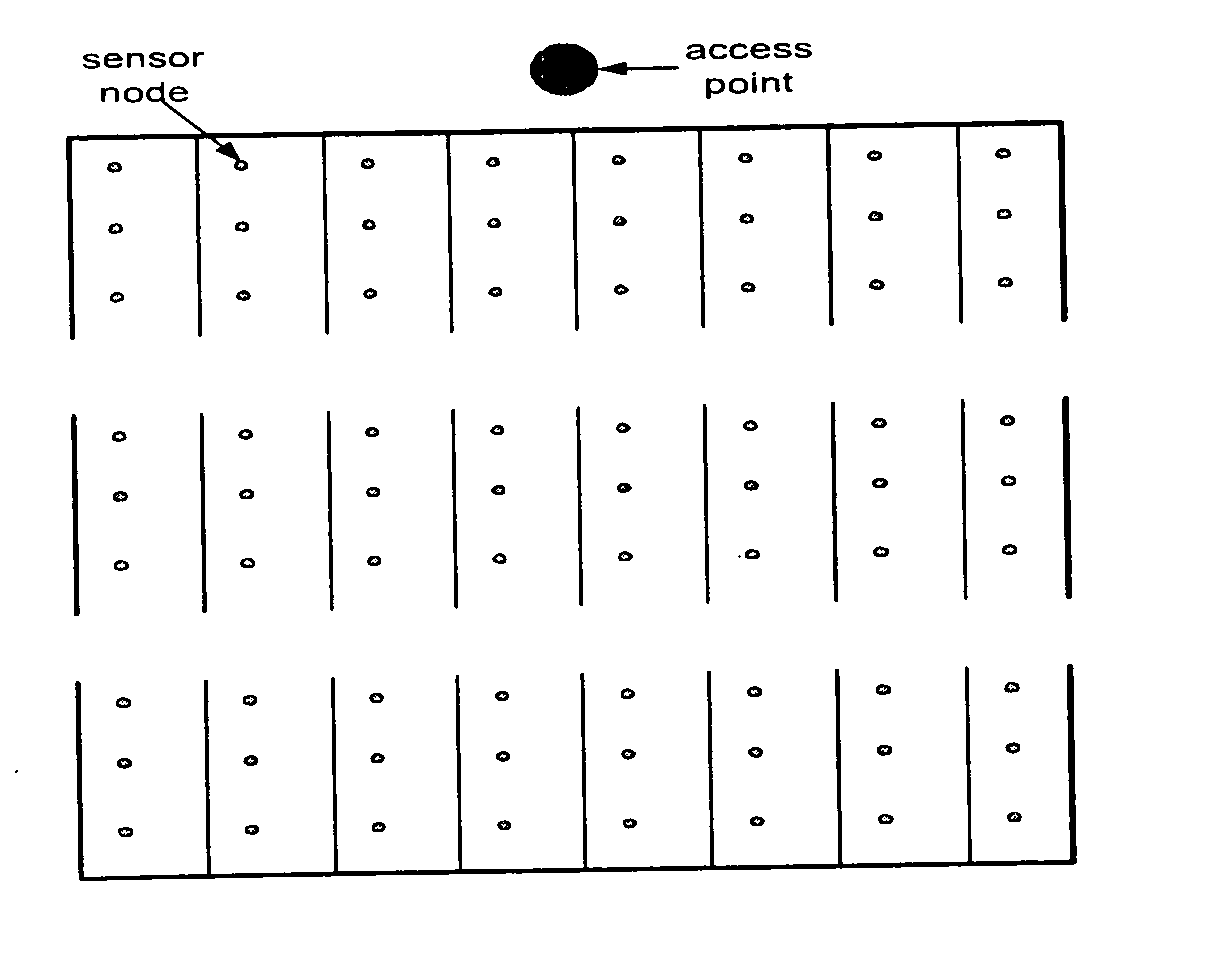
InactiveUS20050122231A1Reduce in quantityPower managementEnergy efficient ICTTime division multiple accessPower efficient
A power efficient system architecture that exploits the characteristics of sensor networks in order to decrease the power consumption in the network. The primary characteristic of sensor networks is that the destination of all the data packets in the network is a central data collector and this central data collector, which is usually denoted as access point (AP), has unlimited transmission power and energy whereas the sensor nodes have limited battery energy and transmission power. The system uses the AP to directly synchronize and explicitly schedule the nodes' transmissions over Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) time slots.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for dynamic neighbor discovery within wireless networks using time division multiple access (TDMA)
InactiveUS20060198346A1Improve reliabilityAvoid collisionSpatial transmit diversityTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessComputer science
An Ad-Hoc wireless network according to the present invention employs a TDMA based neighbor discovery protocol, where each network node is assigned a unique time slot to broadcast neighbor discovery packets or messages. A primary controller node is dynamically designated to perform the time slot assignments. A dynamic selection of a secondary or backup controller node is further provided in case of failure of the primary controller node. The present invention further includes flooding techniques based upon TDMA. A TDMA HELLO flood is used to distribute a small number of common parameters to network nodes by placing or piggybacking the information within the neighbor discovery messages. A CNR flood is based on the principles of a RAKE type receiver and used to distribute time slot assignments to the entire network.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Spatial division multiple access for wireless networks
ActiveUS7352718B1Doubling and of network throughputIncrease system capacityPower managementPolarisation/directional diversityWireless mesh networkSystem capacity
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology in conjunction with the IEEE 802.11 standard enables simultaneous communication of data packets to or from multiple users in the same frequency. Spatial divisional multiple access (SDMA) is thus provided. In this way, system capacity can be increased to an extent that depends on available antenna resources and the multipath characteristics of the communication channel. Doubling or quadrupling of network throughput can be achieved.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Providing space division multiple access in a wireless network
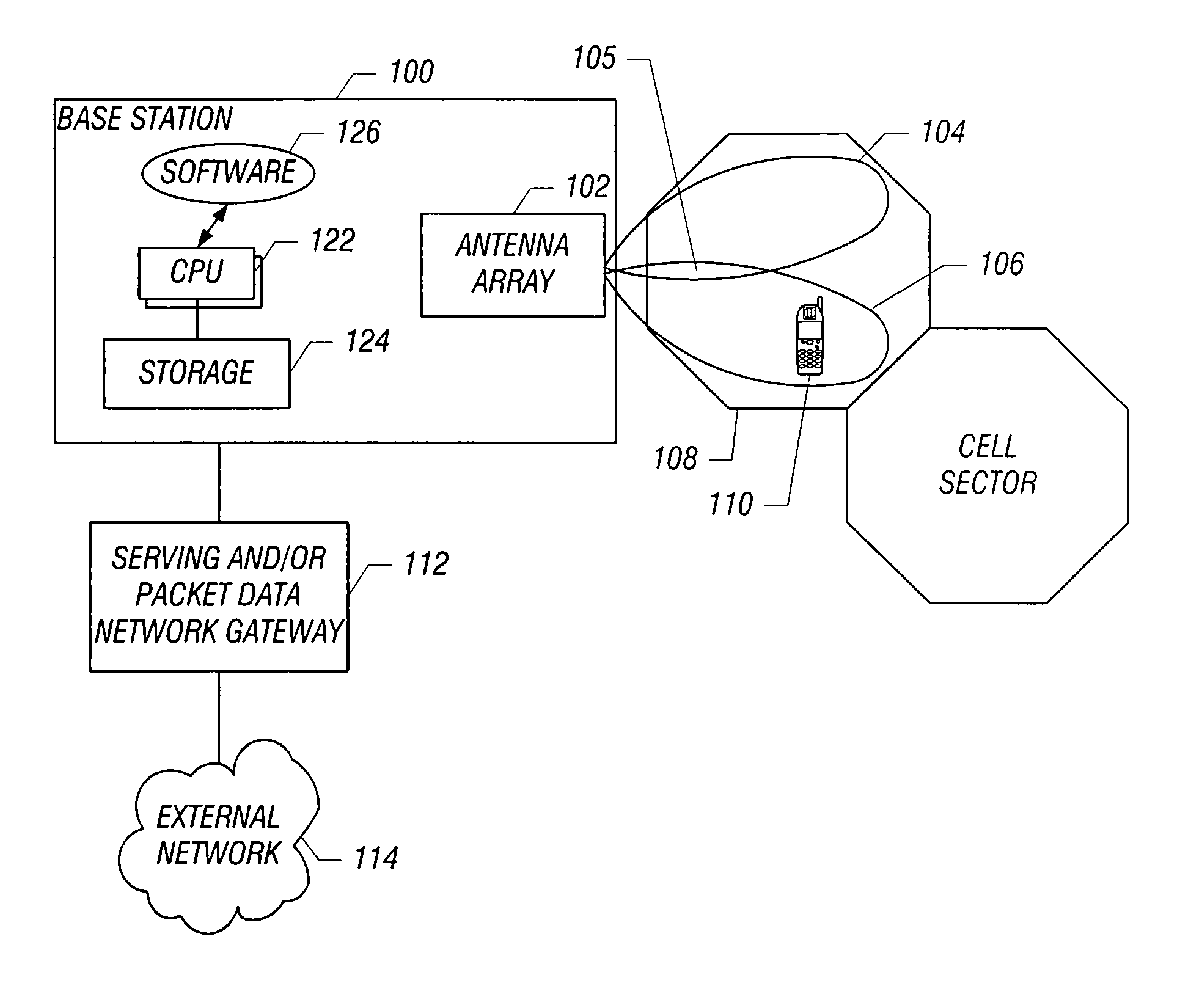
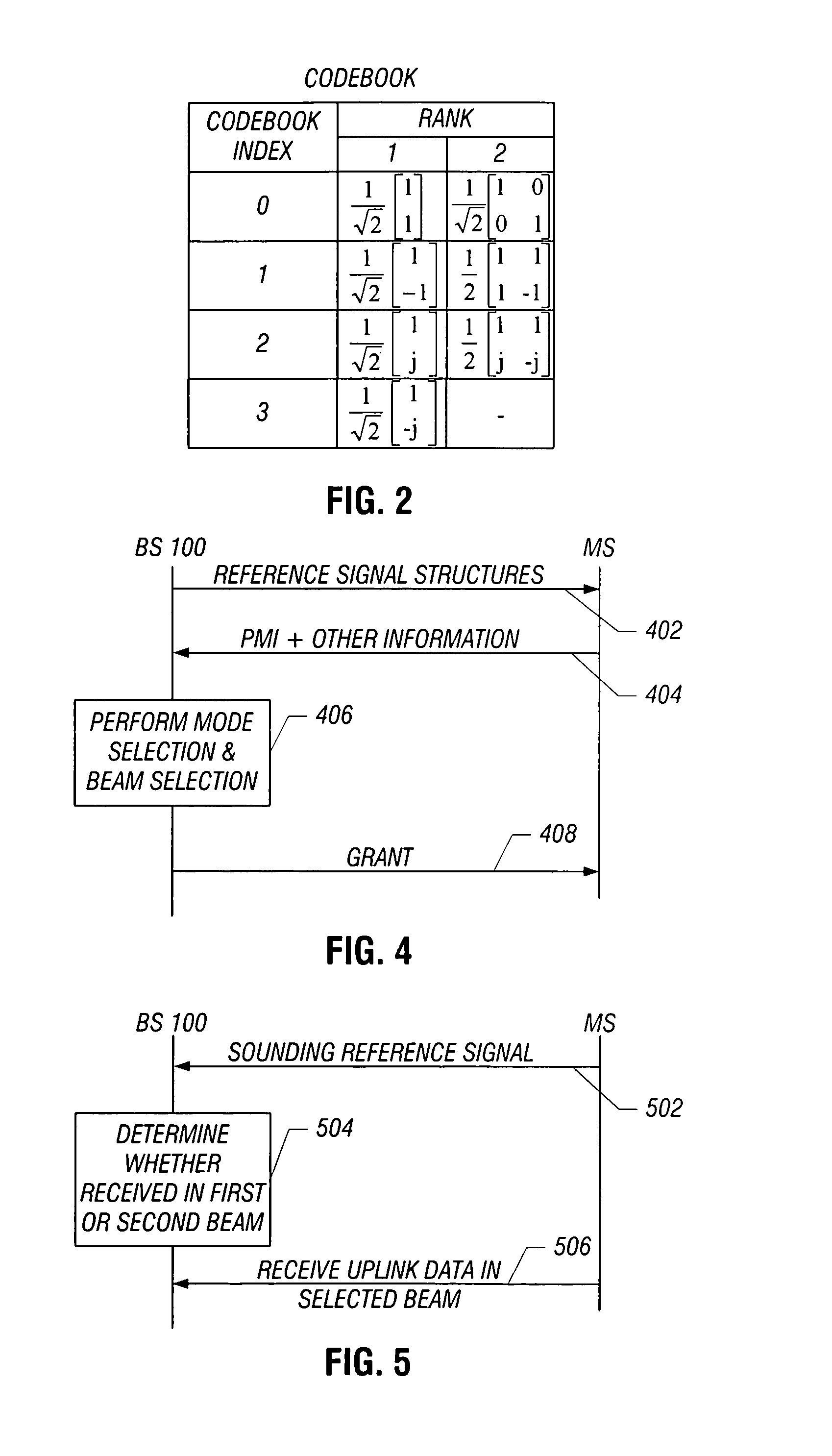
To provide space division multiple access in a wireless network, plural beams are transmitted within a cell segment. Different information sets are sent in the corresponding plural beams, where one or more of the information sets are detectable by a mobile station depending upon a location of the mobile station in the cell segment. An indication responsive to which of the different information sets is detected by the mobile station is received, and beam selection from among the plural beams is performed according to the received indication.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
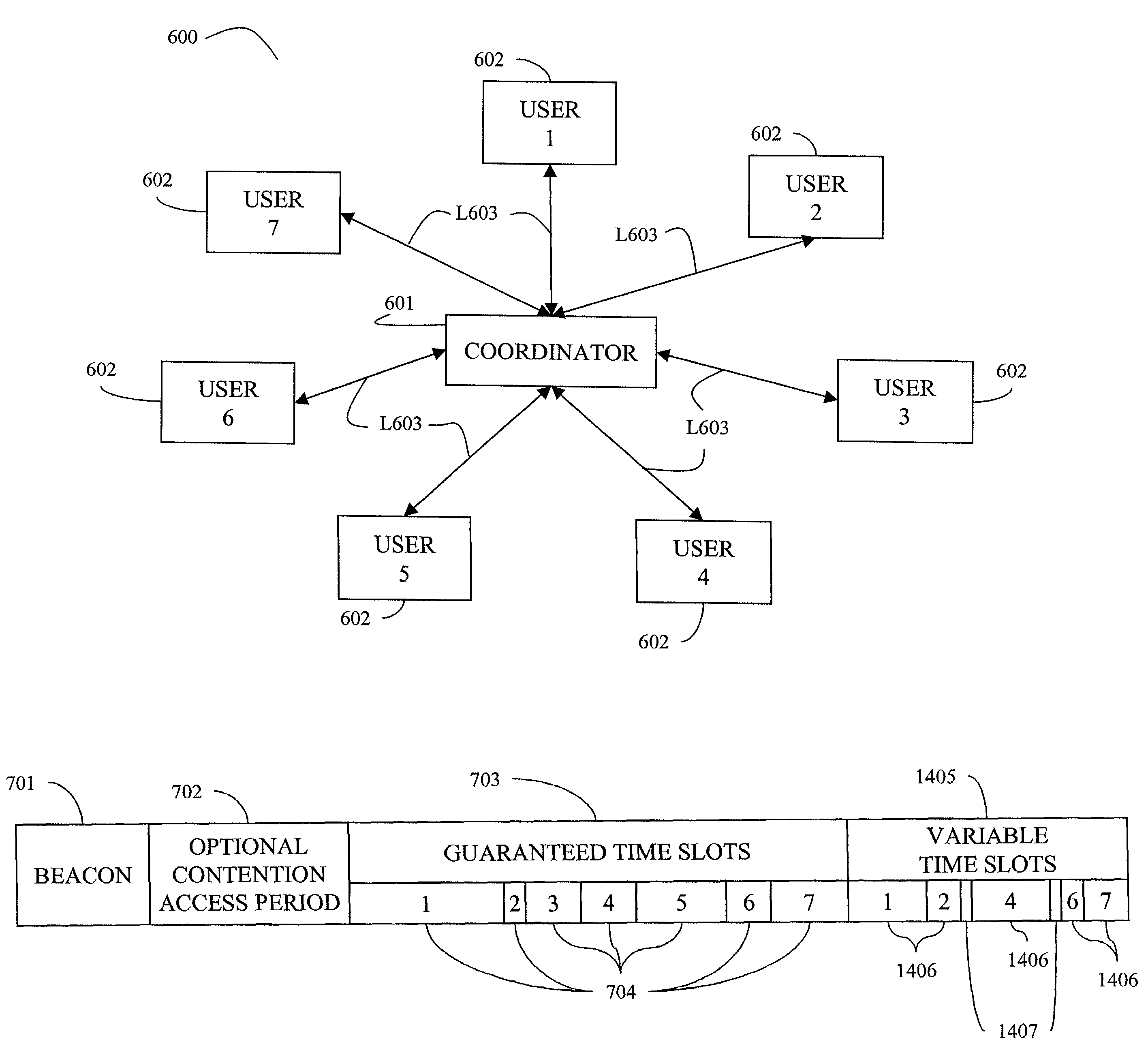
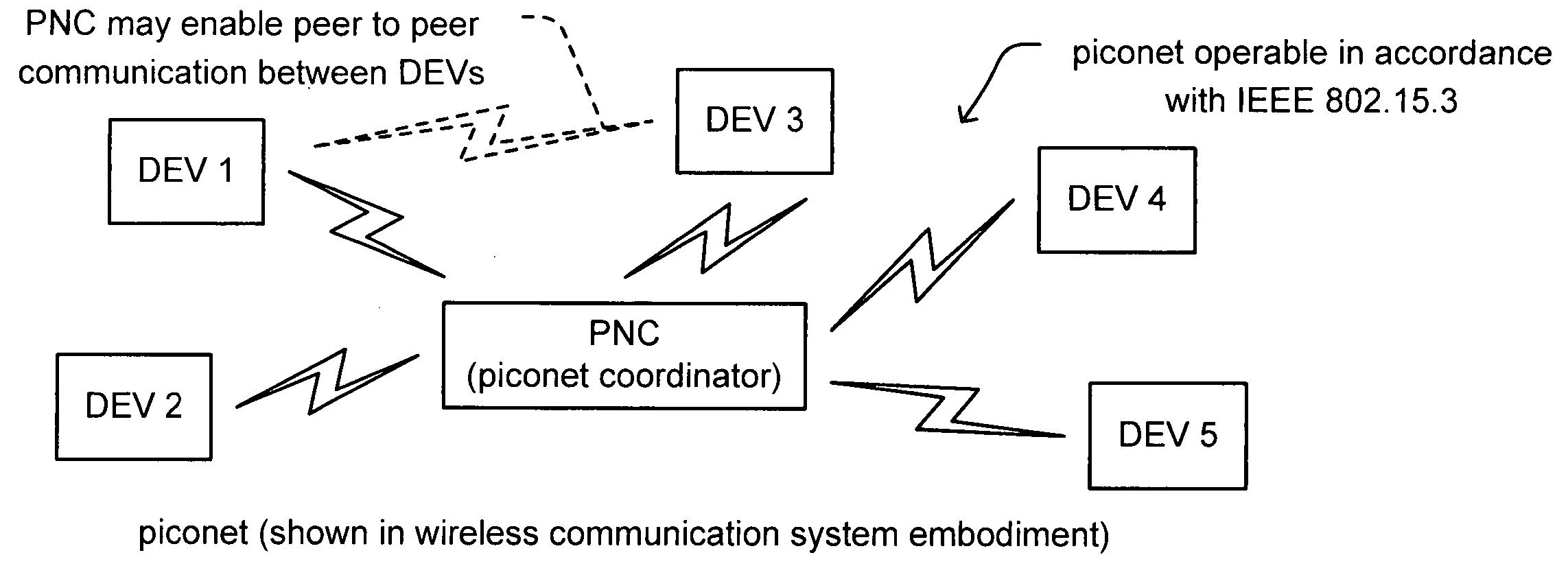
System, method, and computer program product for sharing bandwidth in a wireless personal area network or a wireless local area network
InactiveUS7110380B2Maximize battery lifeFair and power-efficientPower managementEnergy efficient ICTTime division multiple accessStart time
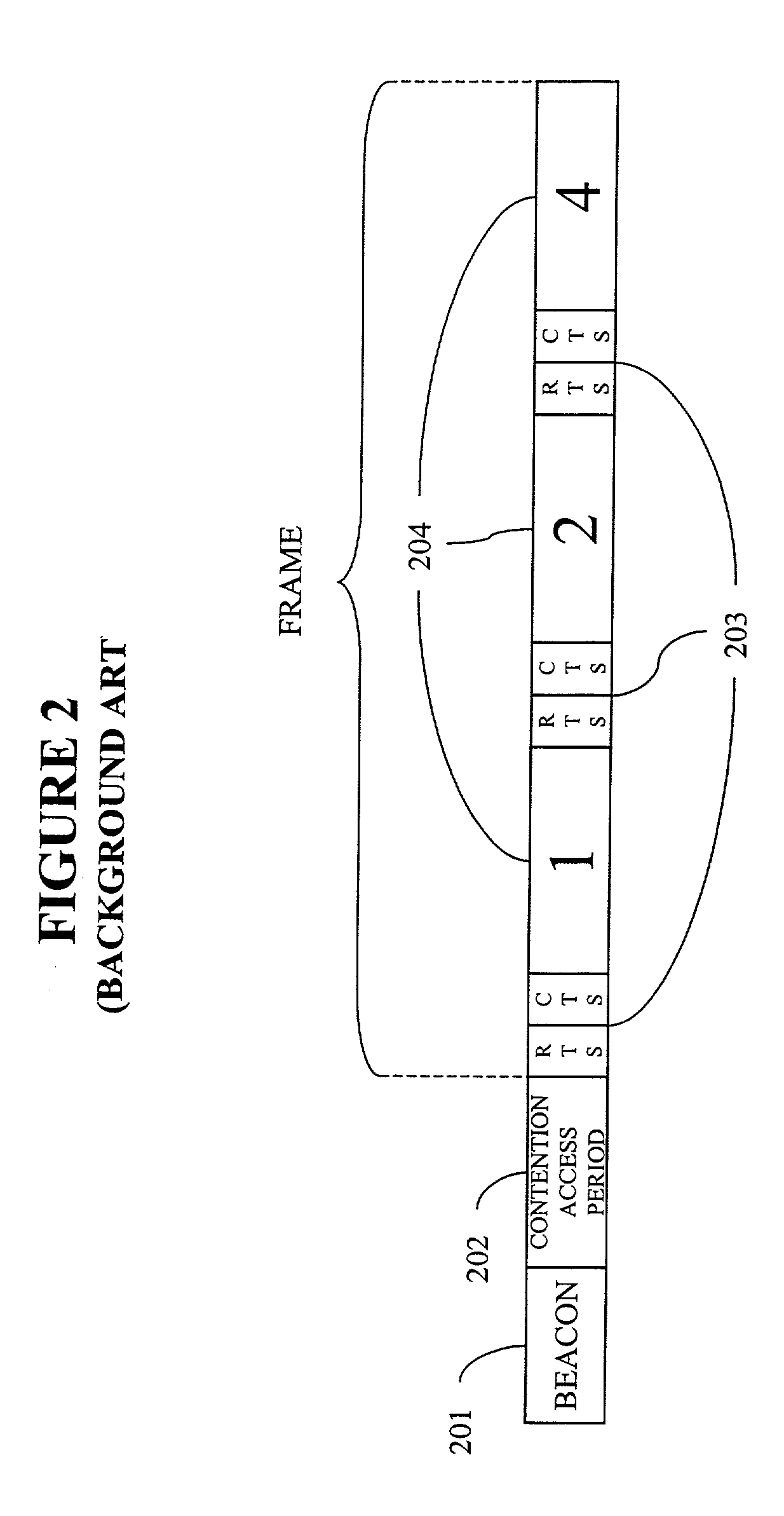
A system, method, and computer program product for sharing bandwidth by a plurality of devices in a wireless personal area network or a wireless local area network. A media access control protocol frame includes a beacon signal sent from a coordinator including coordination information to each of the devices of the WPAN, an optional contention access period, and a contention free period that includes an additional shared period that is managed as a slot cycle time division multiple access period, a polling period, or as management period. The coordination information includes a device-unique start time indicator and a transmission duration defining a guaranteed time slot within the contention free period of the frame for each of the networked devices. Each of the network devices sleeps while not receiving the beacon and not transmitting data during their guaranteed time slot, thereby reducing power consumption as compared to slot cycle time division multiple access or polling schemes which require listening by all devices during the contention free period.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Information processing system and information processing apparatus
InactiveUS7106382B2Television system detailsSpatial transmit diversityInformation processingTime division multiple access
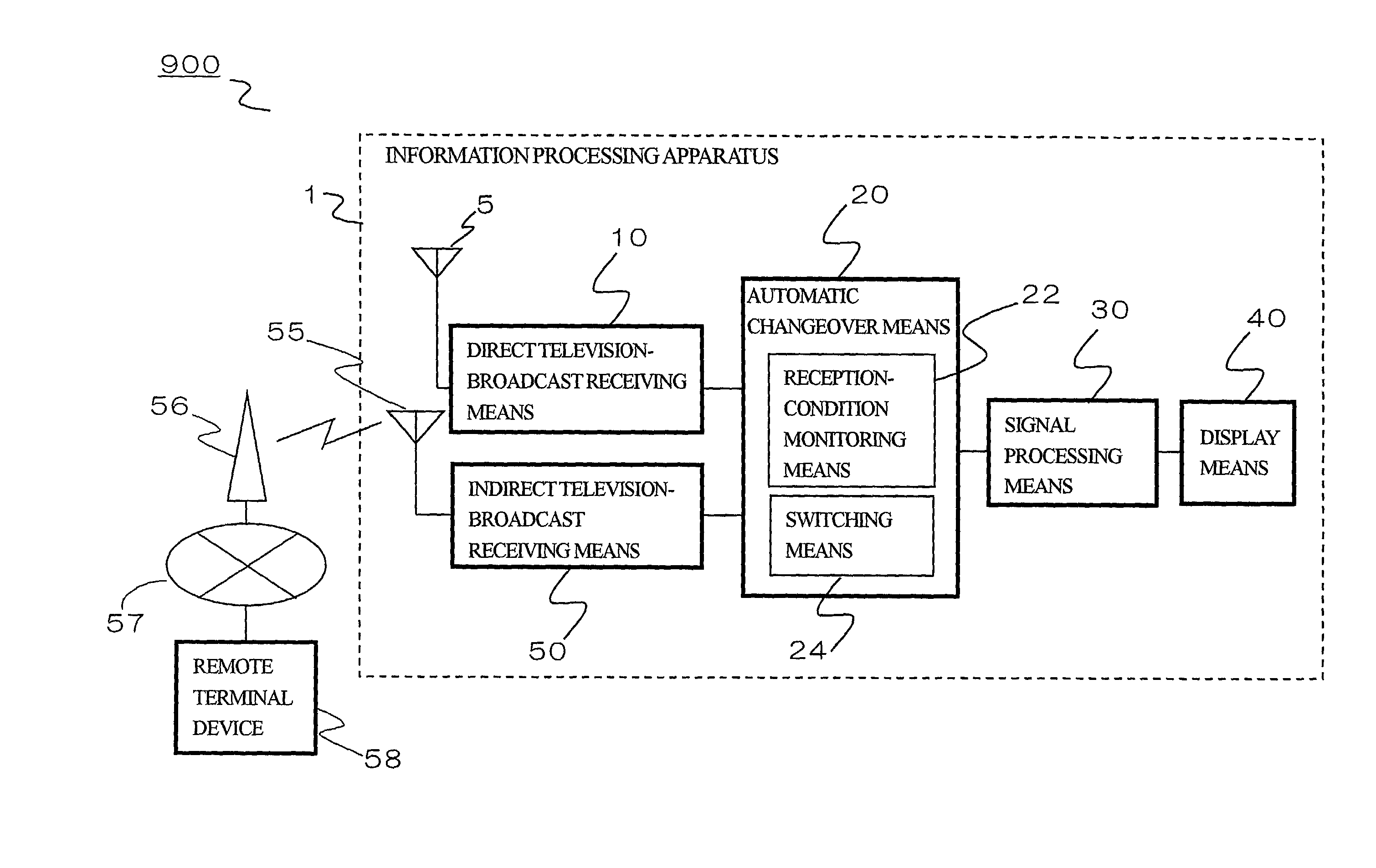
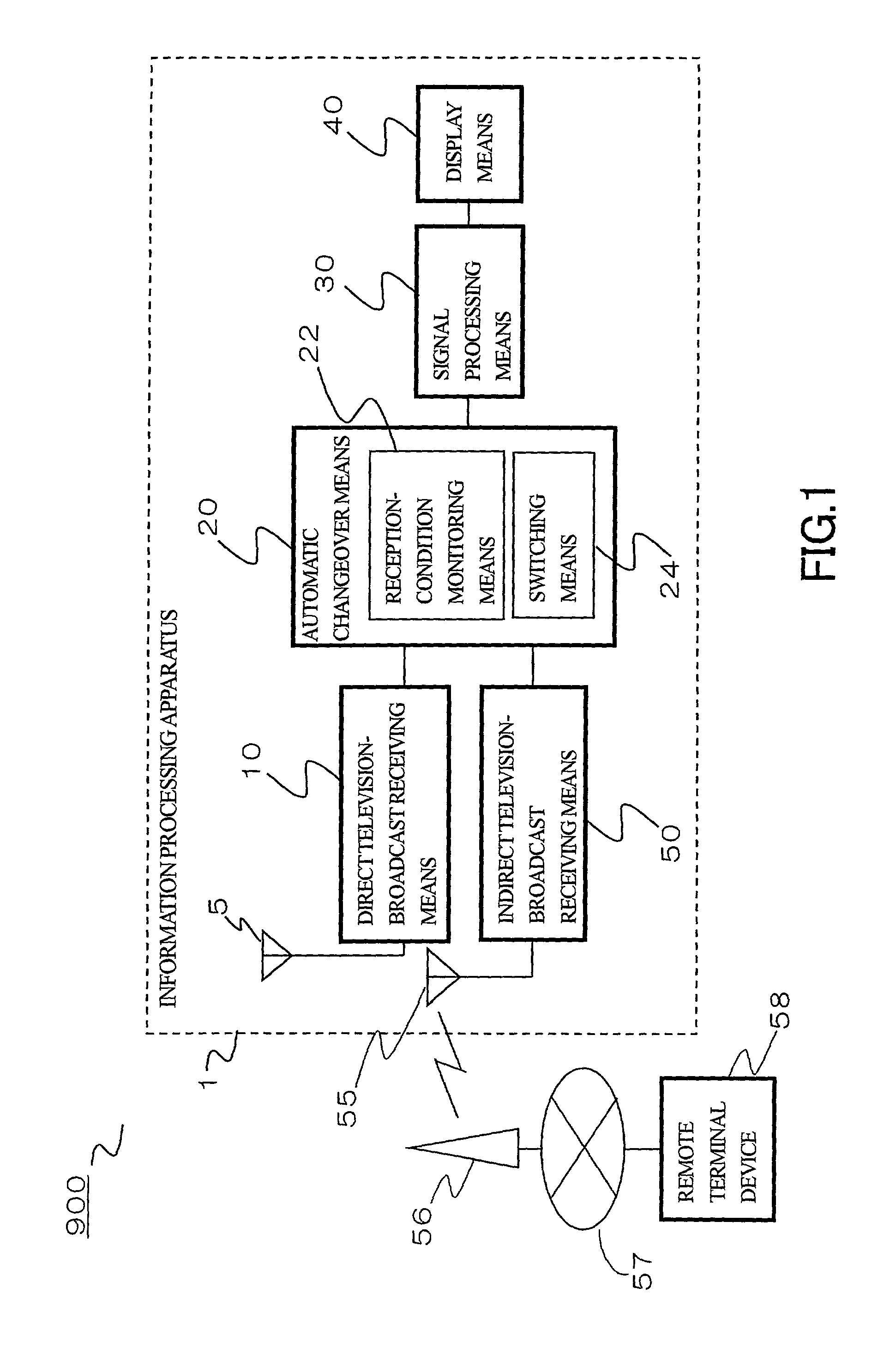
An information processing system and apparatus receiving a television broadcast includes: a direct receiving unit directly receiving television broadcast waves; an indirect receiving unit indirectly receiving the television broadcast waves; and a switching unit determining whether the television broadcast waves are to be received by the direct receiving unit or the indirect receiving unit by switching between the direct receiving unit and the indirect receiving unit based on their reception conditions. With this configuration, it is possible to obtain television-broadcast video signals from the selected receiving unit. The indirect receiving unit is preferably formed of a communication device provided with a wireless cellular telephone function using a wideband code division multiple access (W-CDMA) system in which signals having a large transmission capacity can be transmitted and received, or a communication device provided with a wireless LAN communication function.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Time division multiple access over broadband modulation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6891841B2Accurate resolutionBroadband local area networksTime-division optical multiplex systemsTime division multiple accessBurst transmission
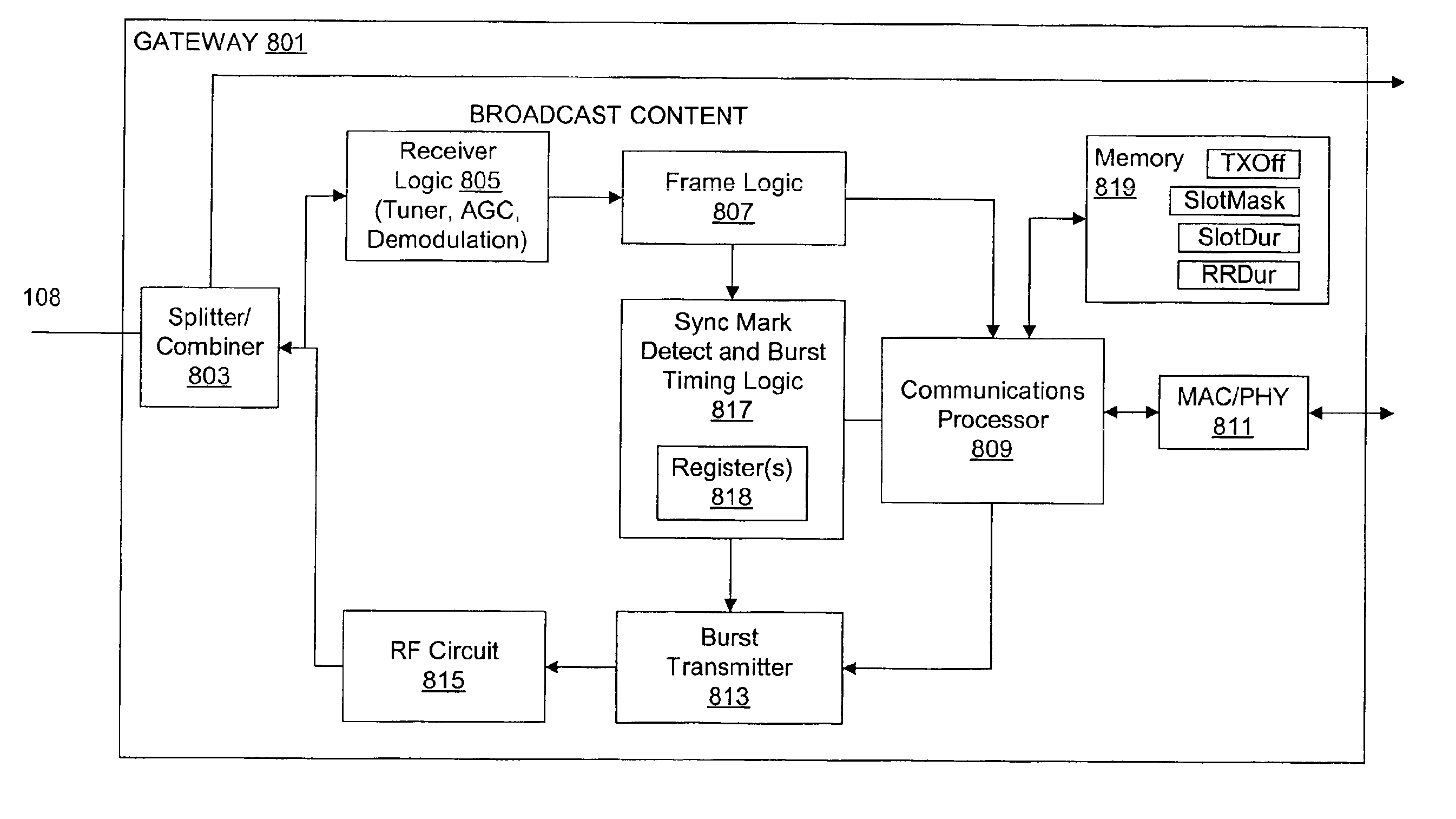
A communication system is disclosed for providing dedicated bandwidth to at least one subscriber location for transmitting to a common point of distribution via an HFC network. In an embodiment of the invention, the communication system includes a channel interface module and at least one gateway coupled across the HFC network. The channel interface module is located at the point of distribution and includes a transmitter that transmits a windowing signal via the HFC network. The gateway is located at a subscriber location and includes a processor that encapsulates subscriber data into data cells suitable for burst transmission, receive logic that receives the windowing signal, timing logic that indicates burst transmission times only at programmed time slots within each of repeating transmission windows based on the windowing signal and a predetermined transmission timing offset, and a burst transmitter that burst transmits subscriber data cells in a predetermined upstream frequency channel when indicated by the timing logic.
Owner:INCEPTIA +1
Communication method and wireless communication system for realizing multi-user dispatching
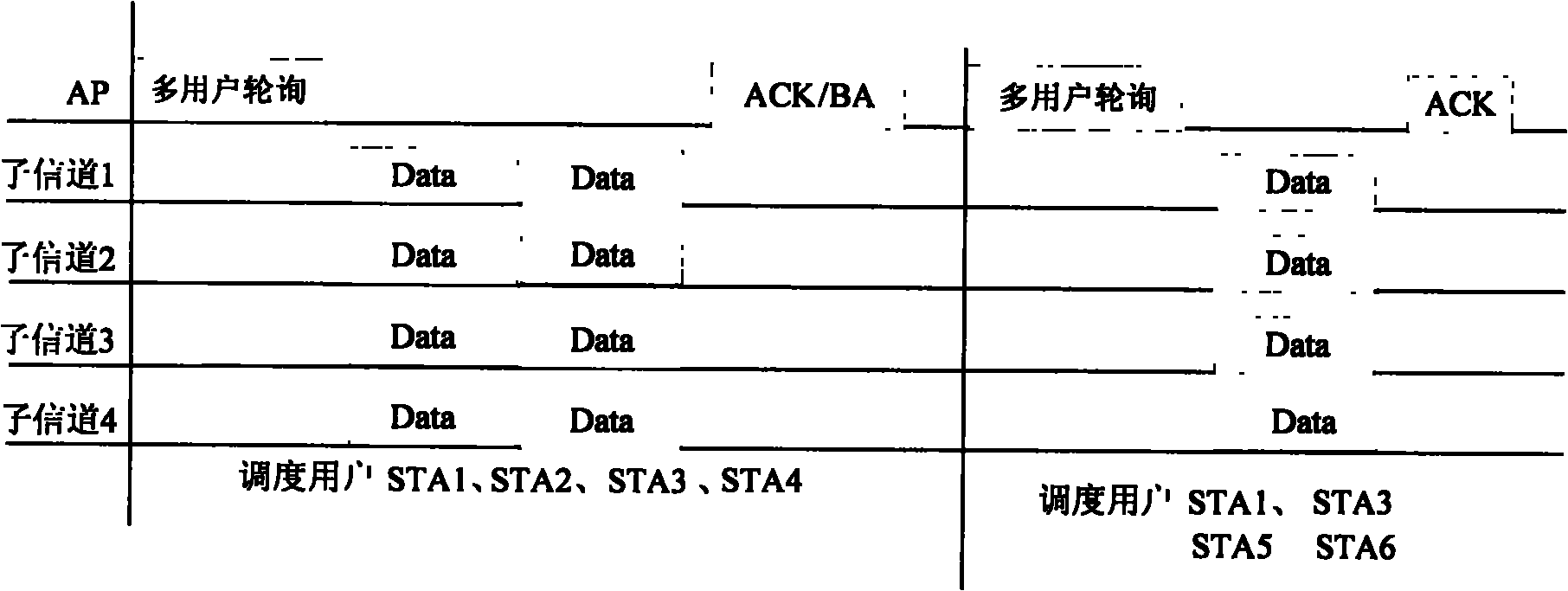
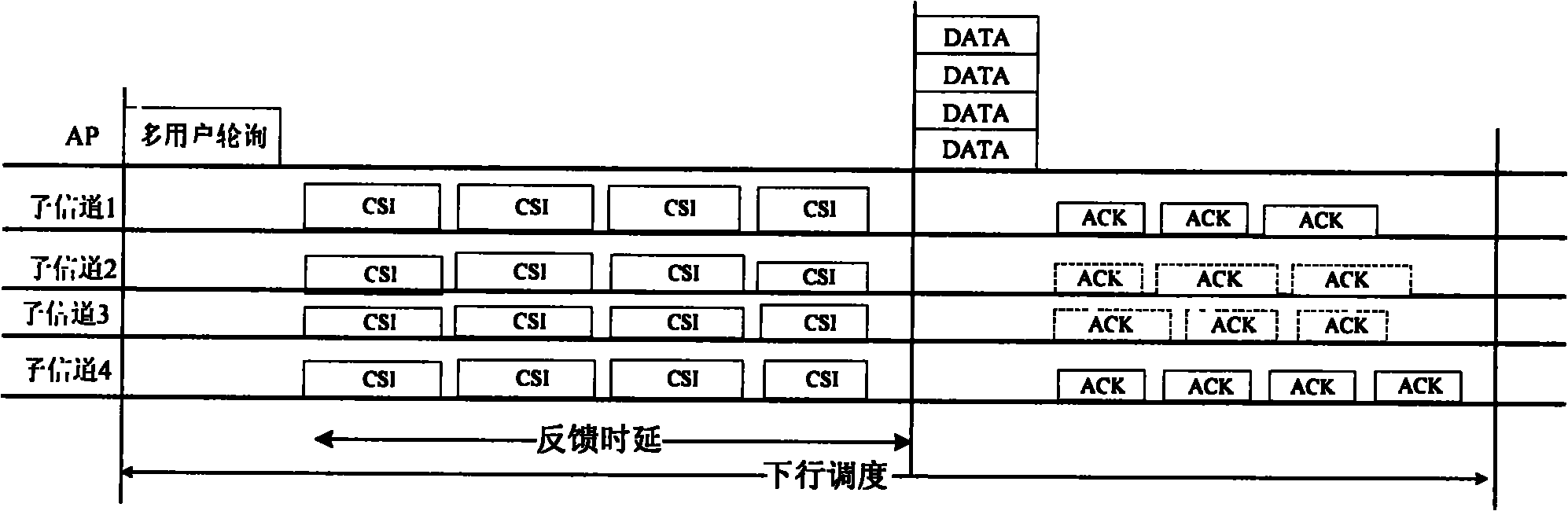
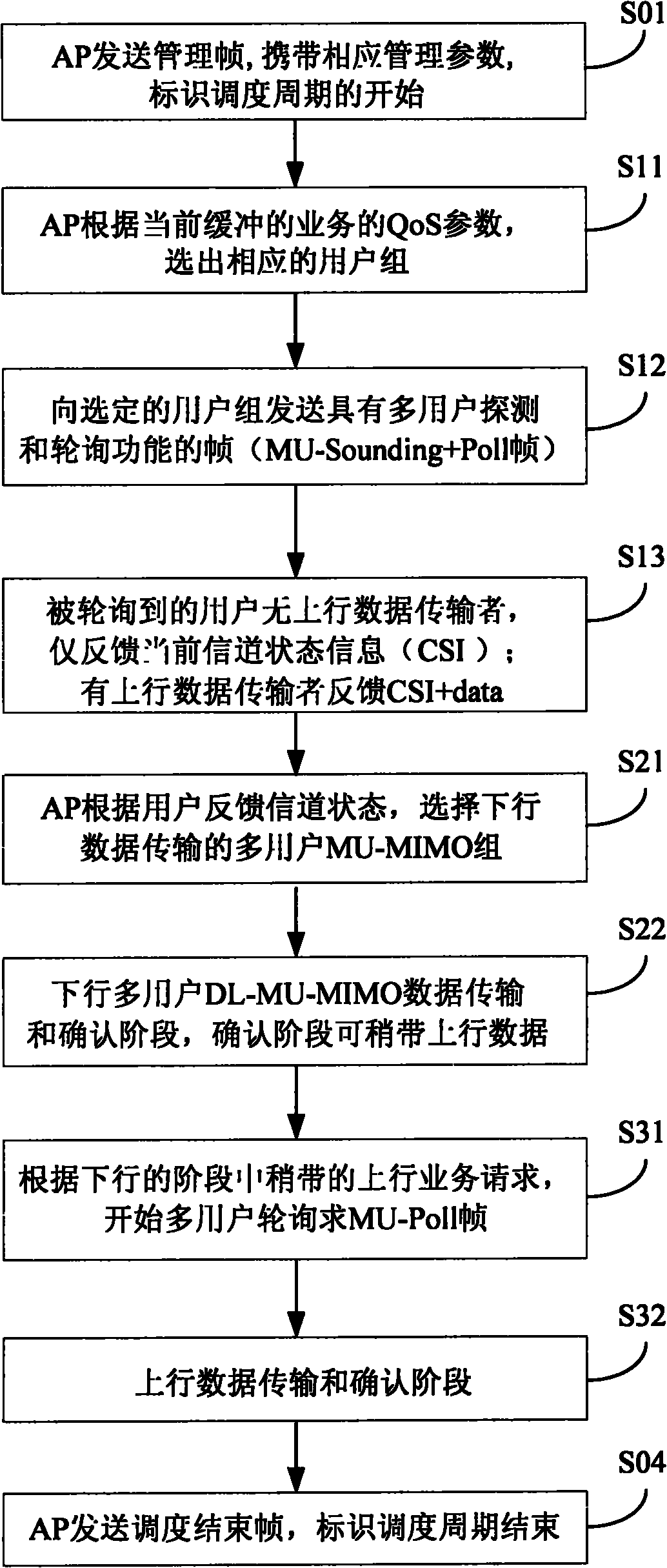
ActiveCN102013959AGood for Uplink SchedulingAccess to meetMulti-frequency code systemsWireless communicationUplink transmissionMultiple input
The invention discloses a communication method and wireless communication system for realizing multi-user dispatching. The method comprises the following steps: refining and multiplexing are carried out on physical resources in the wireless communication system so that multiple users can simultaneously access the physical resources in parallel; downlink transmission is carried out based on orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) and multi-user-multiple-input and multiple-output (MU-MIMO) mechanism, and uplink transmission is carried out based on OFDMA or OFDMA+time division multiple access (OFMA+TDMA); an access point sends a multi-user polling frame or channel detection frame which carries an uplink transmission resource indication; a user station transmits data and feeds back channel status information according to the resource indication; and the system selects a user group for downlink data transmission and sends data to the users in the user group. According to the invention, a media access control (MAC) layer dispatching mechanism allowing multiple users to access simultaneously is achieved, and uplink and downlink services are comprehensively considered to realize two-way communication in the wireless communication system, thus the access delay can be obviously reduced, the system throughput can be obviously improved, and the requirement of accessing more multi-media services can be met.
Owner:BEIJING NUFRONT MOBILE MULTIMEDIA TECH
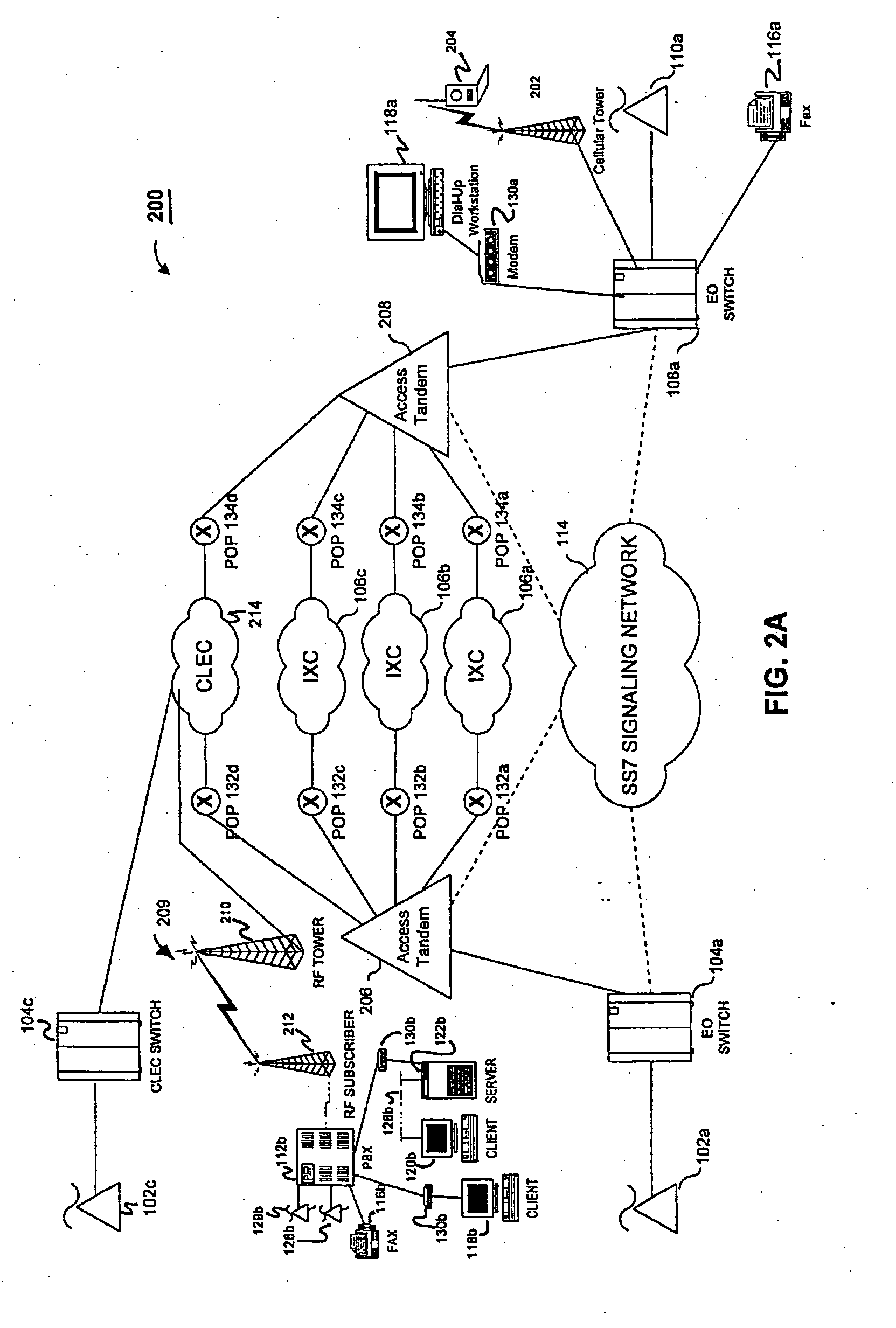
Transmission control protocol/internet protocol (TCP/IP) packet-centric wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system architecture
InactiveUS20050232193A1Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceCode division multiple access
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Dual mode satellite/cellular terminal
InactiveUS6084865APower managementTransmission control/equalisingTime division multiple accessDual mode
A method and apparatus of communicating information using Time Division Multiple Access and adaptive transmission and reception are disclosed. Signal bursts are transmitted from TDMA transmitters to a TDMA receiver wherein the transmitter codes the information and transmits coded information to the receiver using at least one of two timeslots of a plurality of timeslots in a repetitive TDMA frame period. Both of the two timeslots are received whether or not the transmitter has transmitted using one or two timeslots and the received signals are classified as intended and non-intended. Successively received signals classified as intended are then assembled into a block for decoding to reproduce the information.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
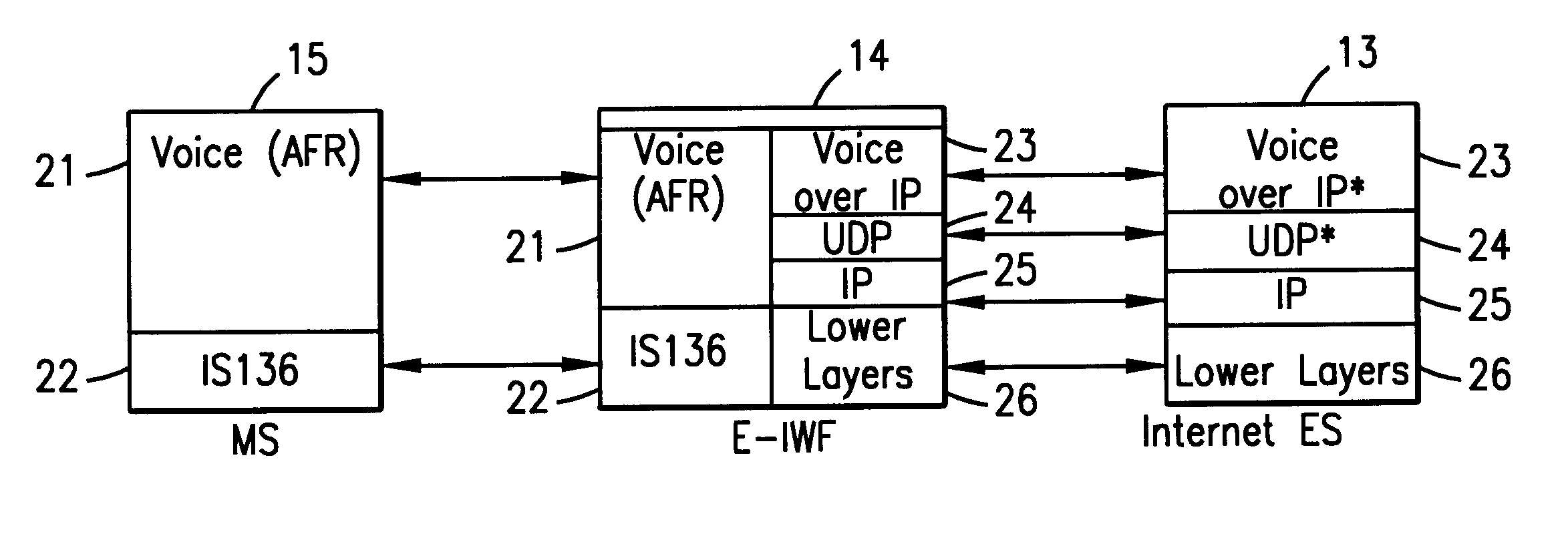
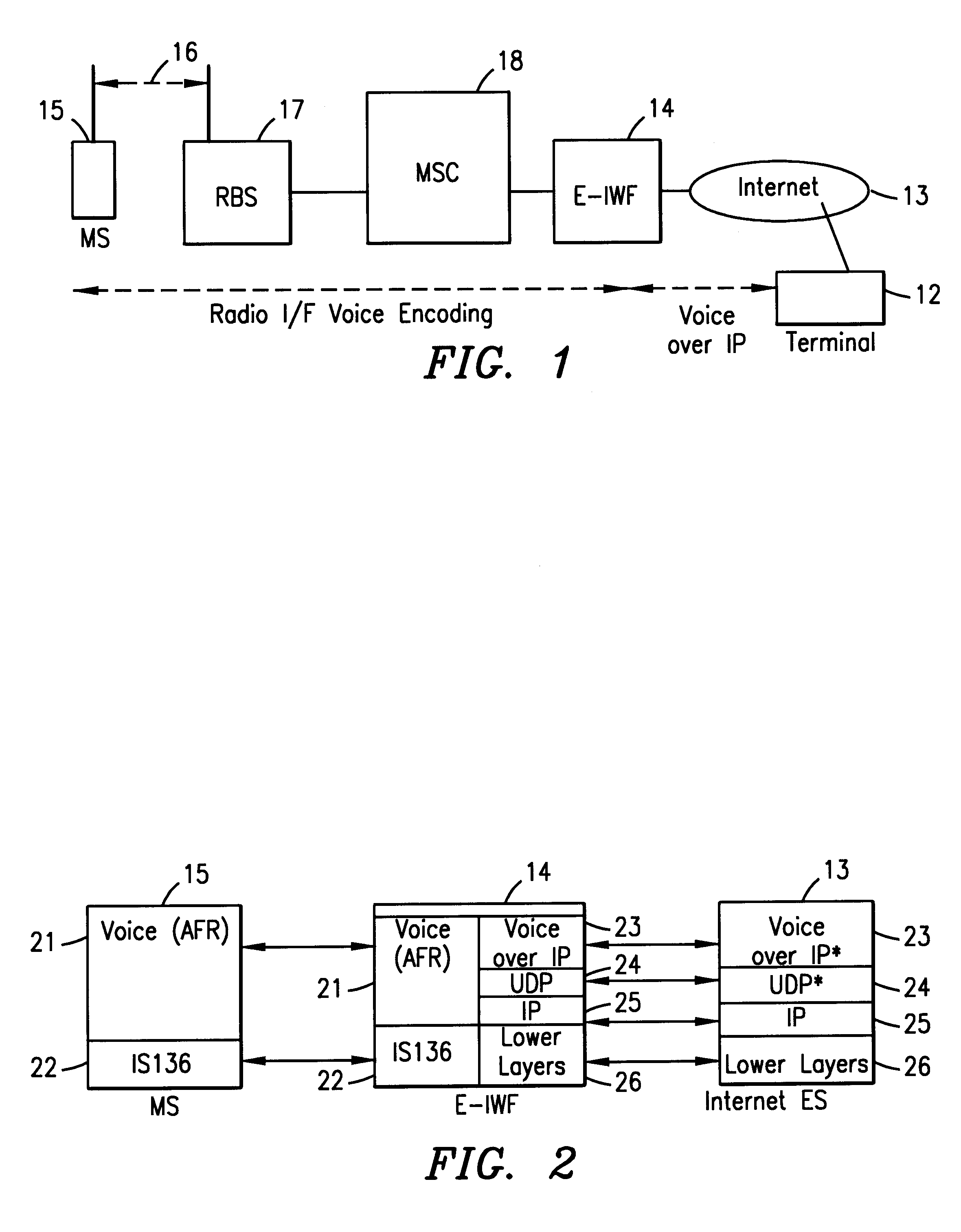
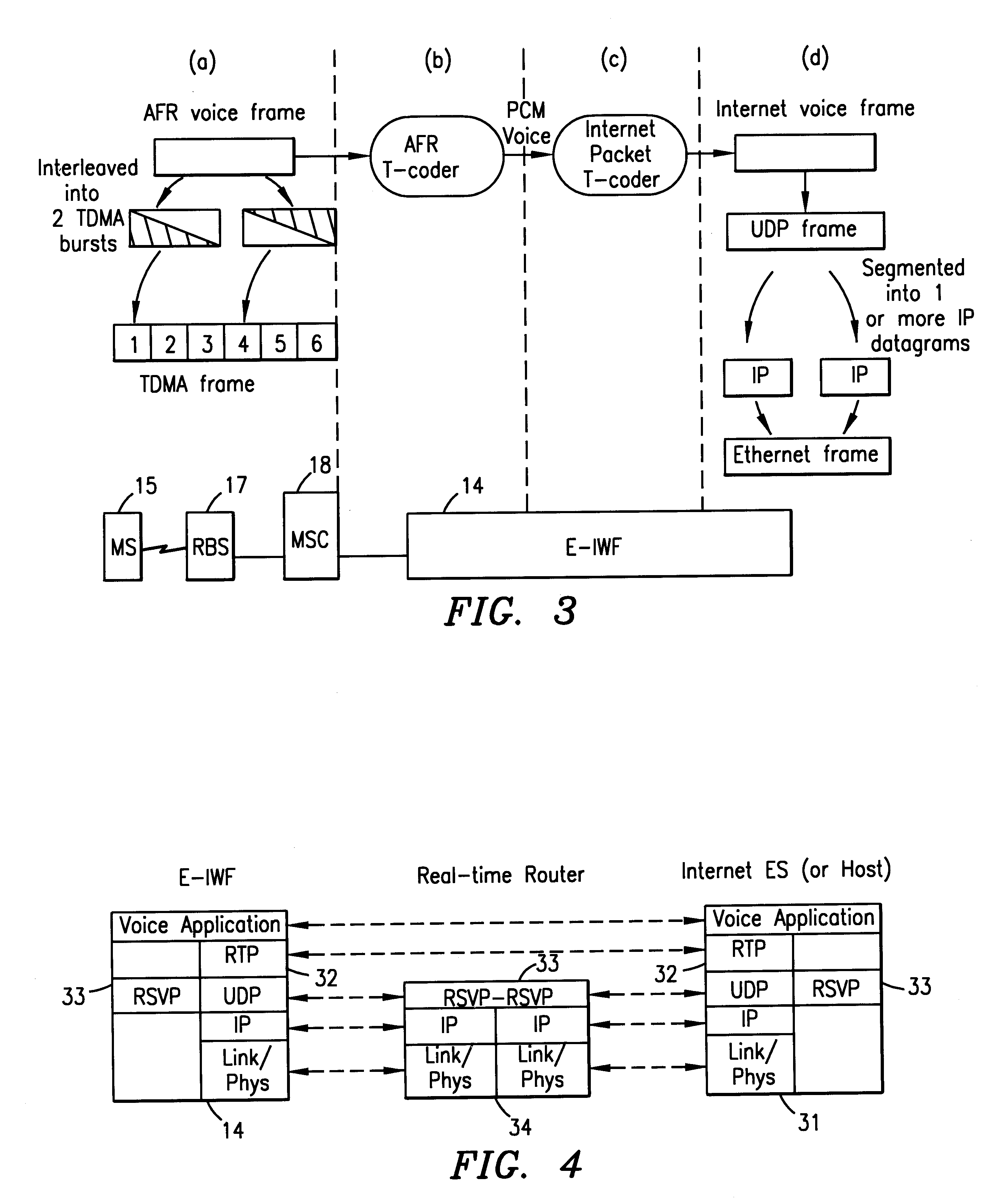
Enhanced interworking function for interfacing digital cellular voice and fax protocols and internet protocols
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
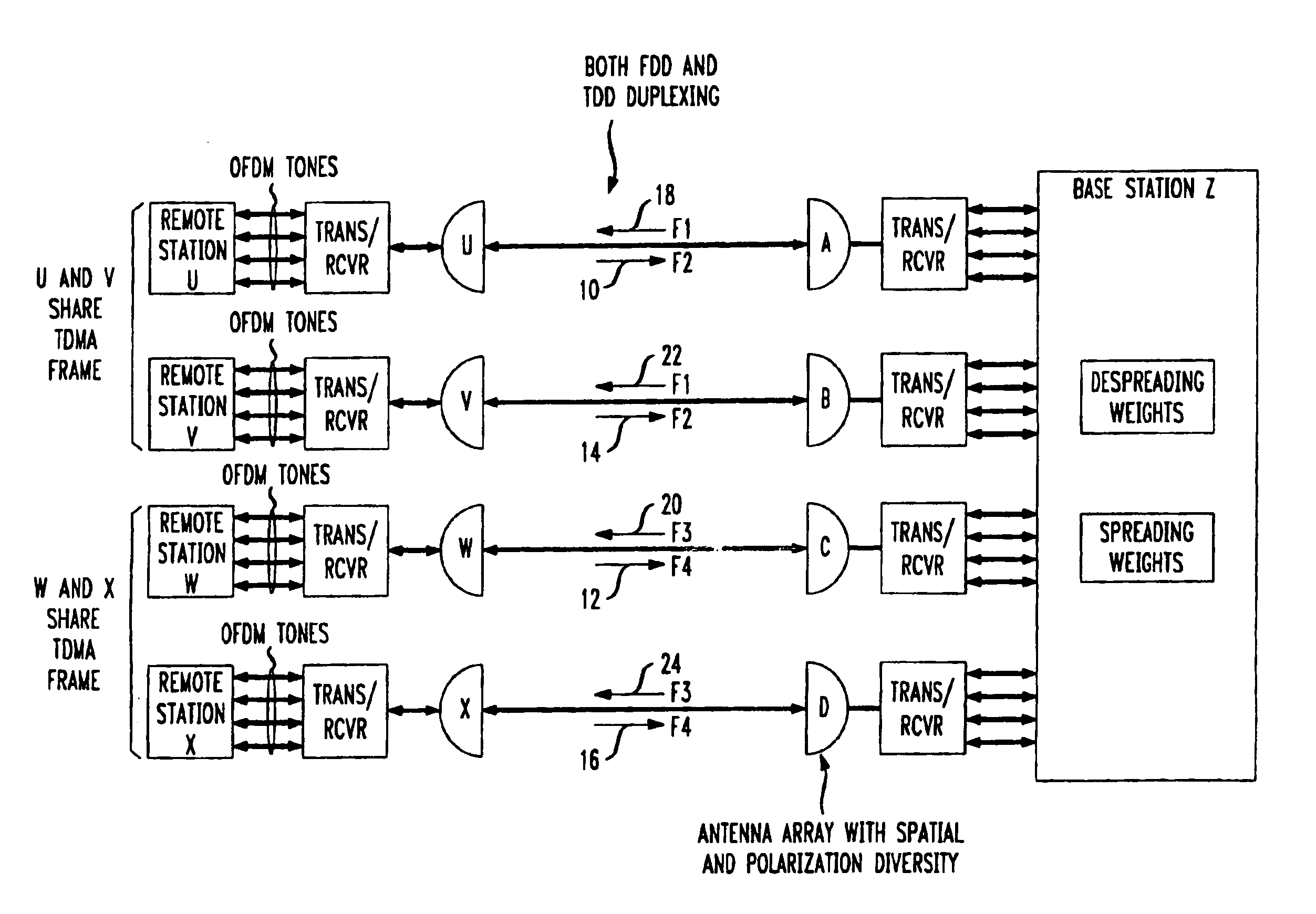
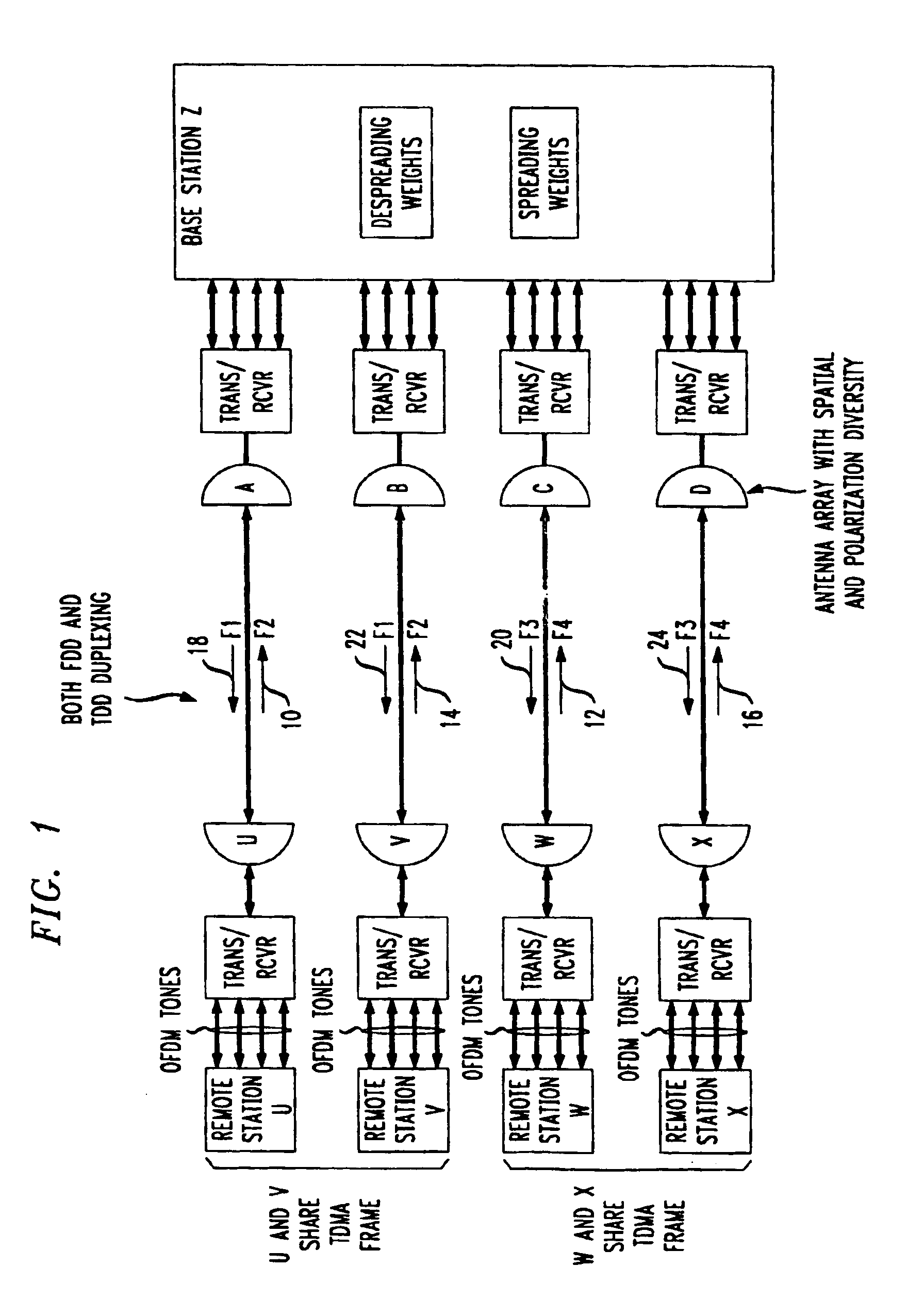
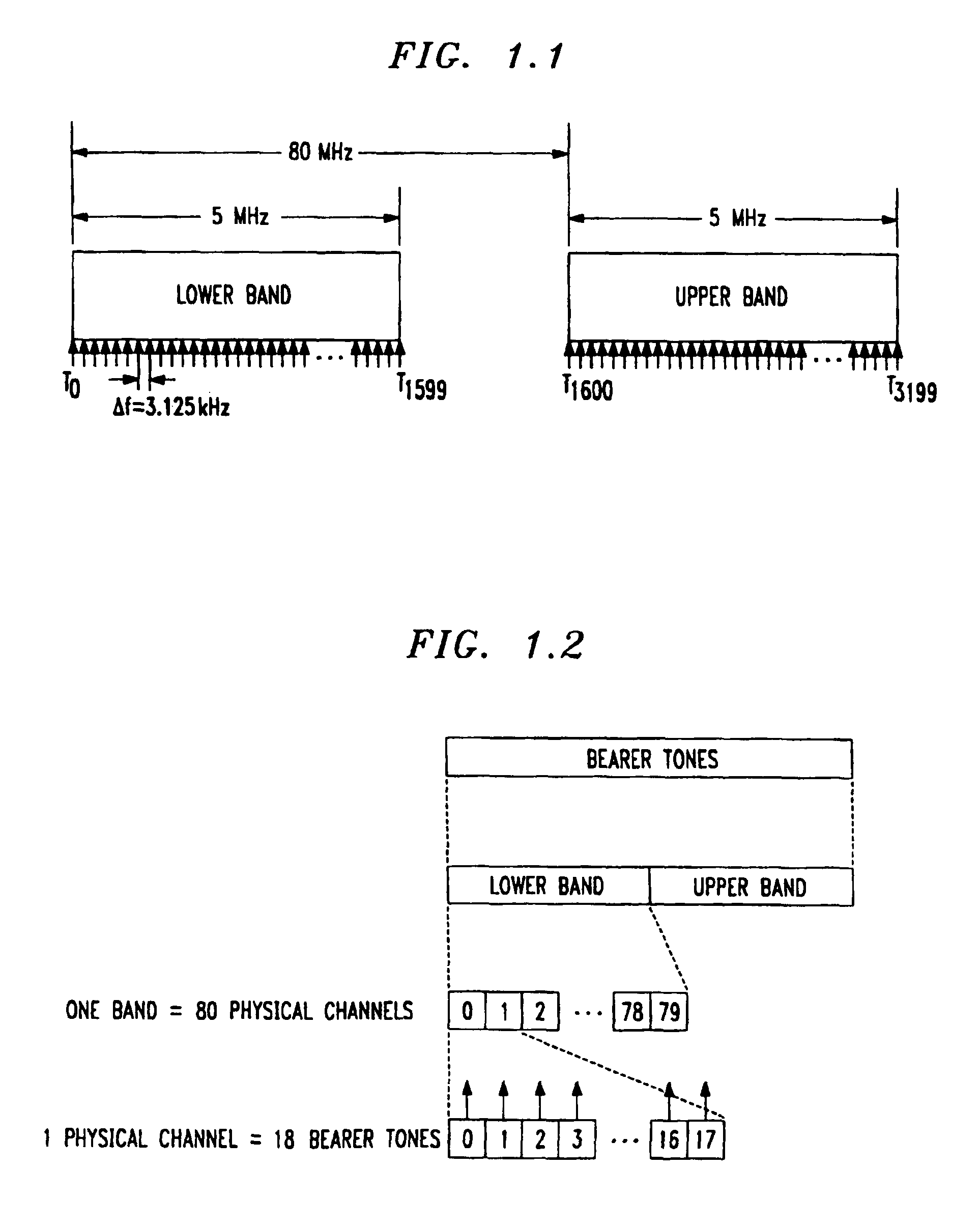
Method for frequency division duplex communications
InactiveUS6853629B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyQuality improvementSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsPolarization diversity
The high quality PCS communications are enabled in environments where adjacent PCS service bands operate with out-of-band harmonics that would otherwise interfere with the system's operation. The highly bandwidth-efficient communications method combines a form of time division duplex (TDD), frequency division duplex (FDD), time division multiple access (TDMA), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), spatial diversity, and polarization diversity in various unique combinations. The method provides excellent fade resistance. The method enables changing a user's available bandwidth on demand by assigning additional TDMA slots during the user's session.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Method and apparatus for multicasting real time traffic in wireless ad-hoc networks
InactiveUS6721290B1Speed up decision making processSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of servicePacket loss
A real-time multicast scheduler method and apparatus is presented, to facilitate multicasting of real-time constant bit rate data in wireless ad-hoc networks. Constant bit rate traffic cannot tolerate delay jitter. However, a small amount of packet losses may be tolerable. In order to ensure the provisioning of a desired level of quality of service, bandwidth is reserved on the multicast structure. A goal of the real-time multicast scheduler is to avoid packet collisions and to facilitate color re-use, where "color" is defined as a channel selected as a combination of time-division multiple access, frequency-division multiple access, and code-division multiple access schemes. The real-time multicast scheduler provides a self-healing network which corrects for disconnections caused by node movement and nodes moving out of range of each other, while accounting for colors already assigned for data transmission in order to prevent packet collisions.
Owner:HRL LAB
Synchronized UWB piconets for SOP (Simultaneously Operating Piconet) performance
ActiveUS20050090200A1Improve overall utilizationImprove trustSynchronisation arrangementSynchronisation information channelsTime division multiple accessEngineering
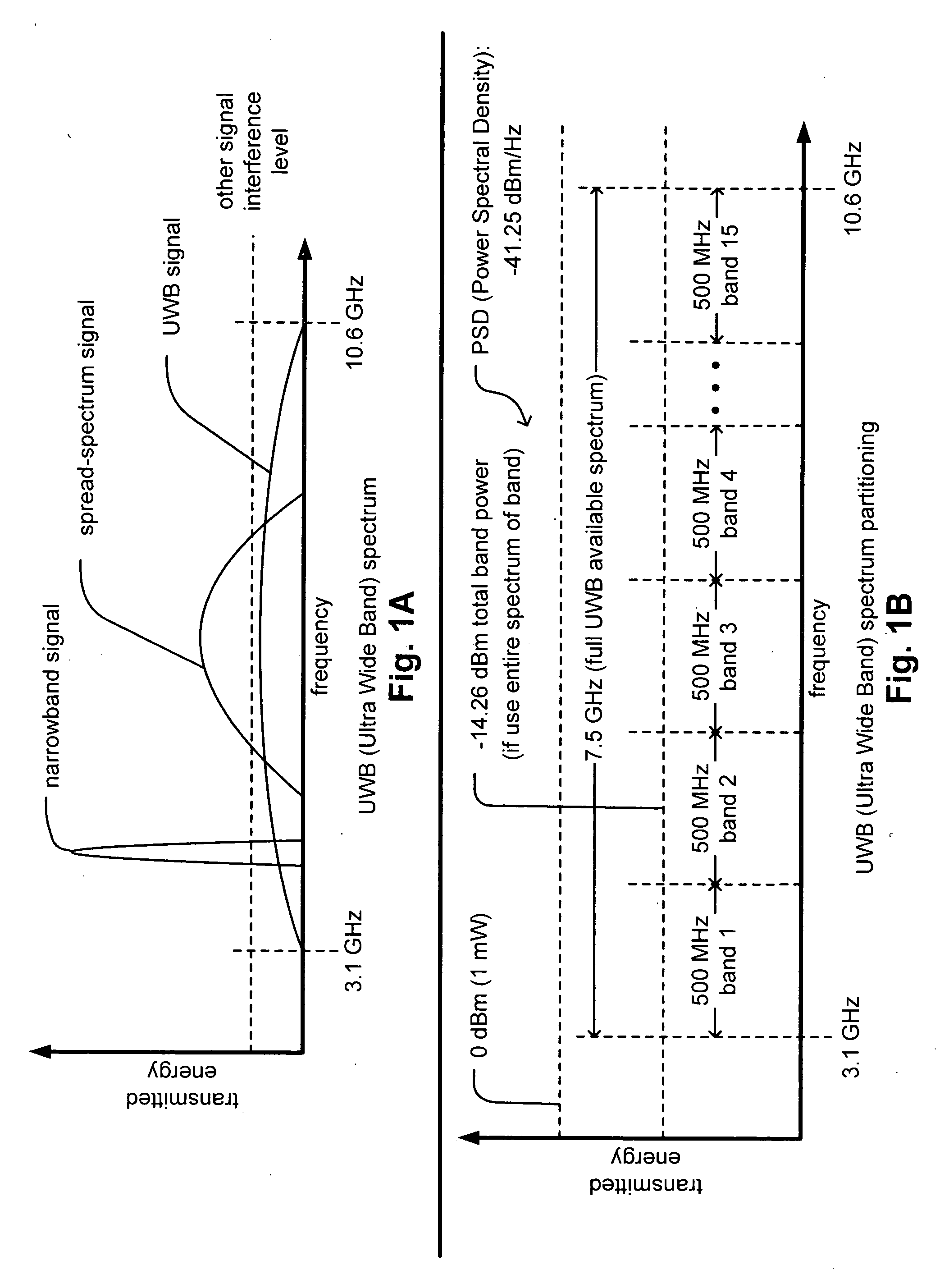
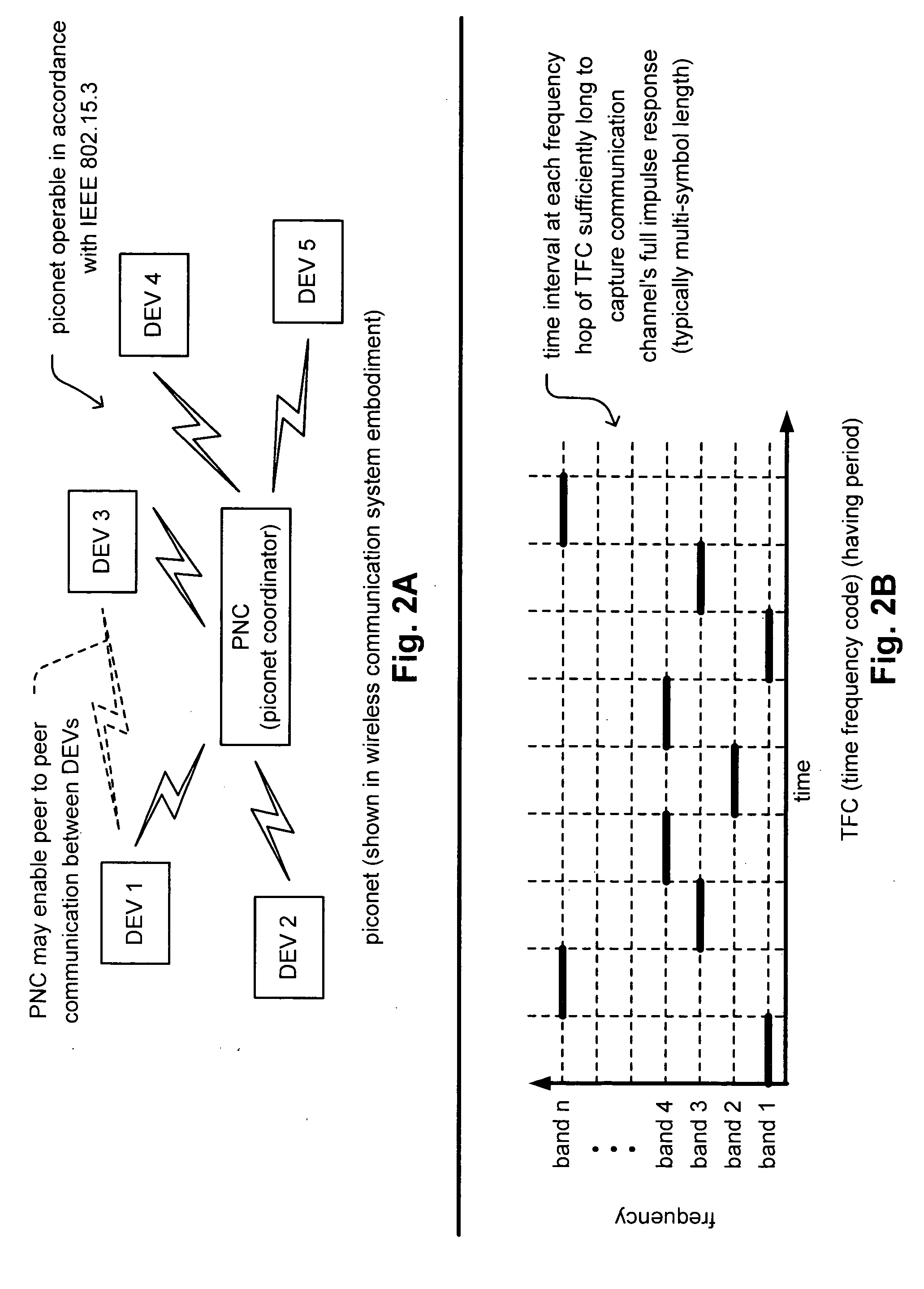
Synchronized UWB piconets for SOP (Simultaneously Operating Piconet) performance. A common backbone (either wired or wireless) is employed that provides a common CLK (clock signal) to all of the various PNCs (piconet coordinators) of various piconets that may operate within a sufficiently close region such that interference could undesirably occur. By providing a very reliable CLK signal from a common backbone to all of the PNCs of the various piconets operating within a substantially close proximity to one another, very precise synchronization may be ensured for all of the communications performed therein. The various piconets may then even operate using TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access)—whose performance would be substantially compromised without effective synchronization. In addition, combined TFC (time frequency code) and TDMA may also be employed to support the communications therein thereby providing even another degree of orthogonality that provided by TDMA alone.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and Apparatus for Using Multicarrier Interferometry to Enhance optical Fiber Communications
InactiveUS20070025421A1Energy efficient ICTWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime domainTime division multiple access
Owner:LOT 41 ACQUISITION FOUND +1
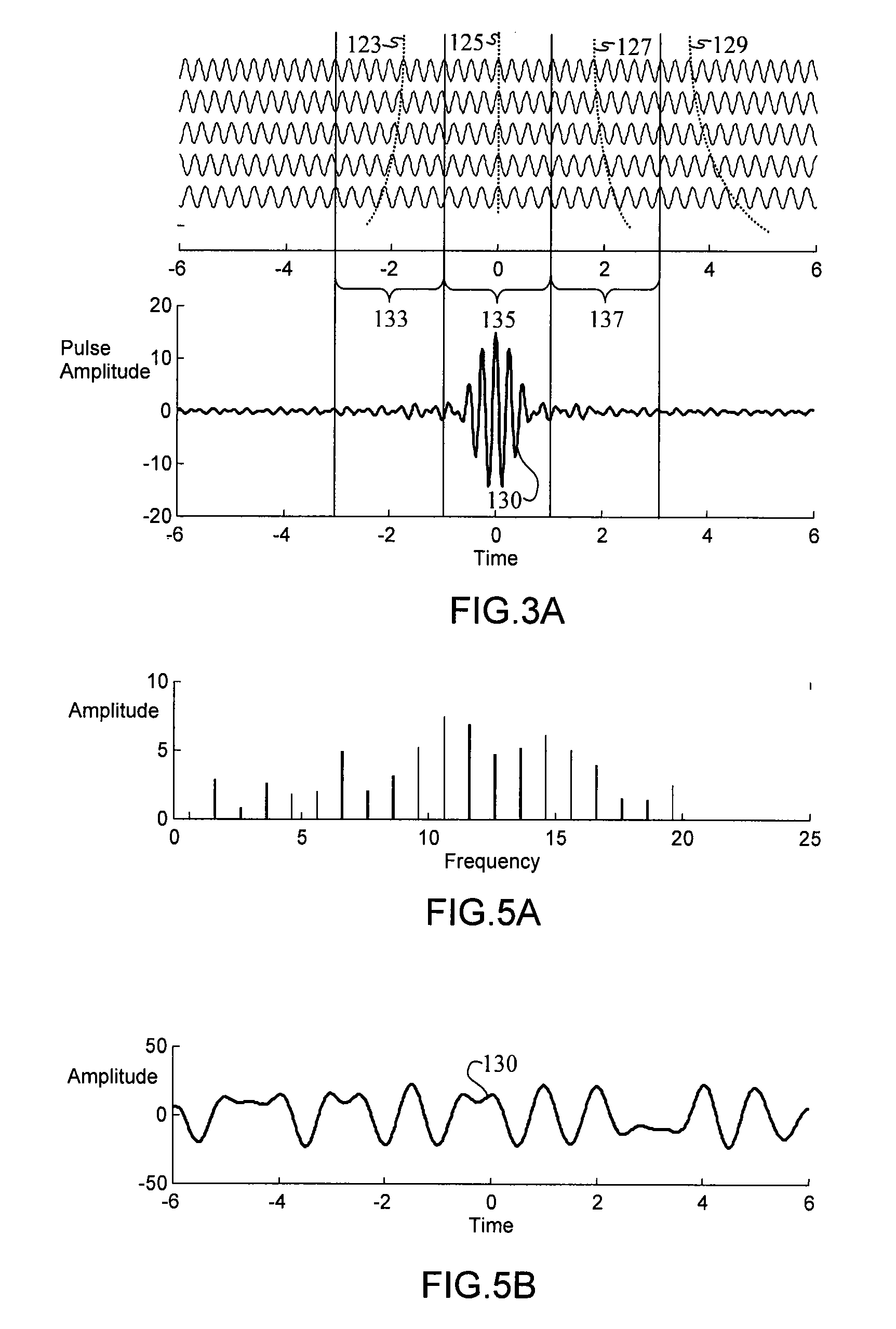
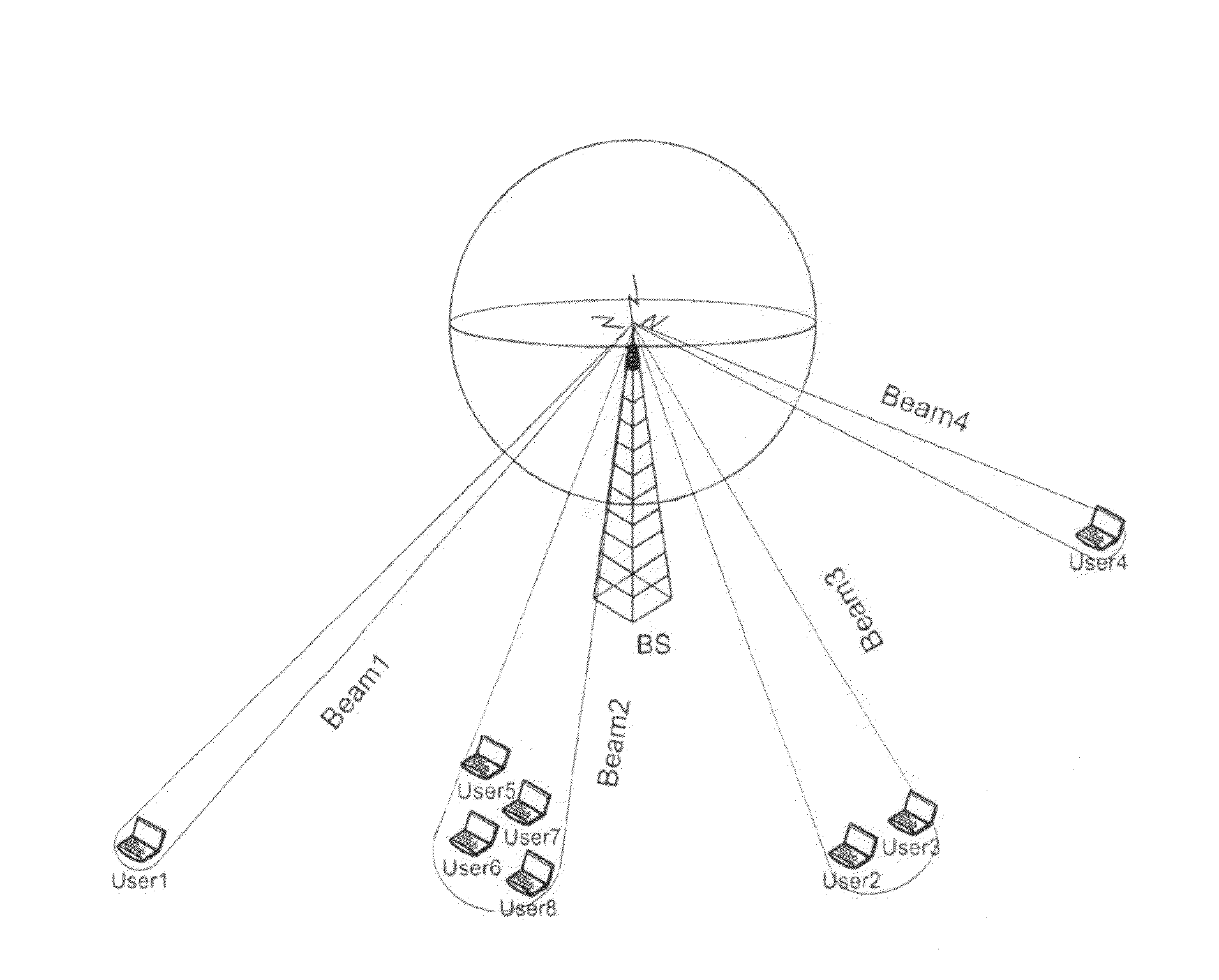
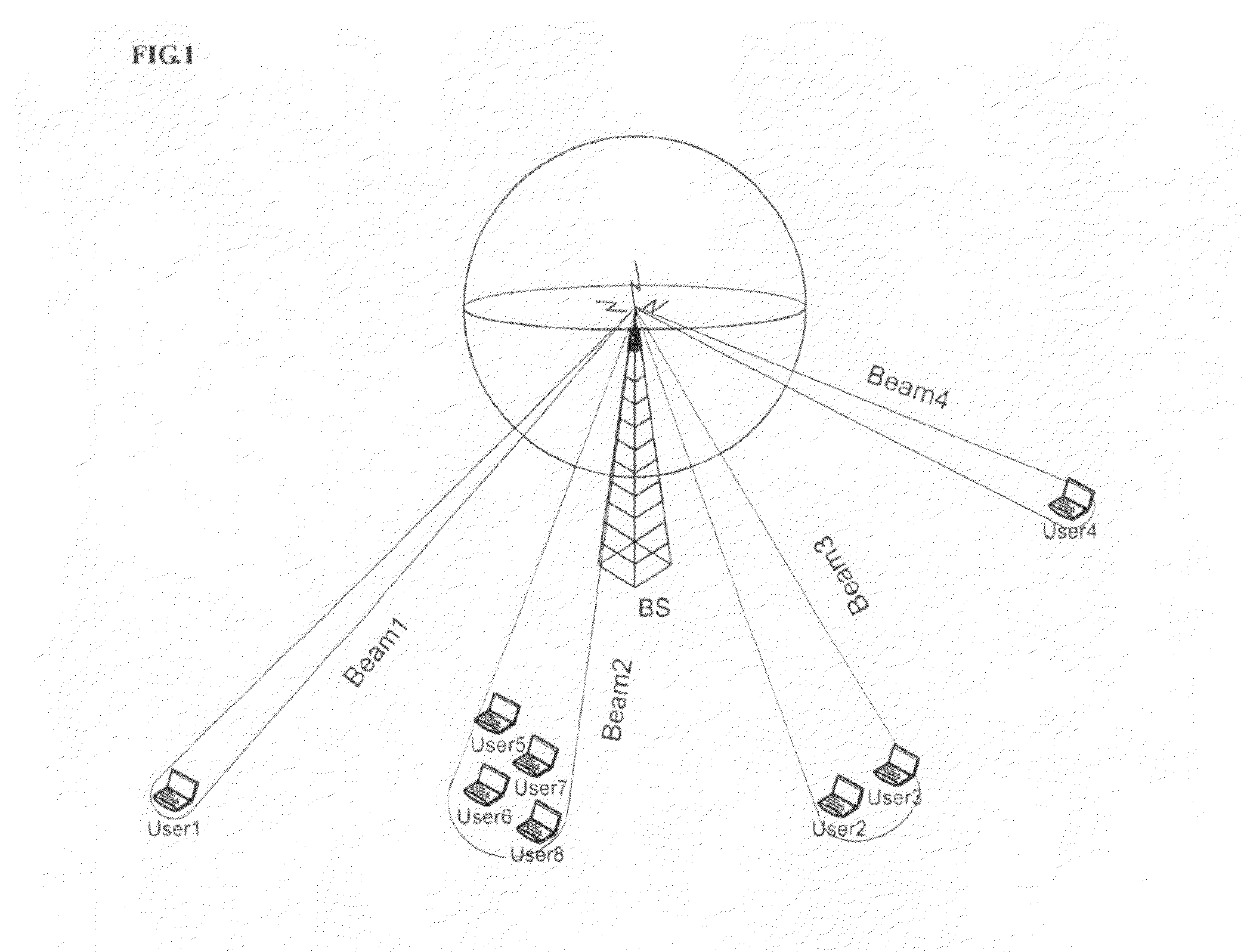
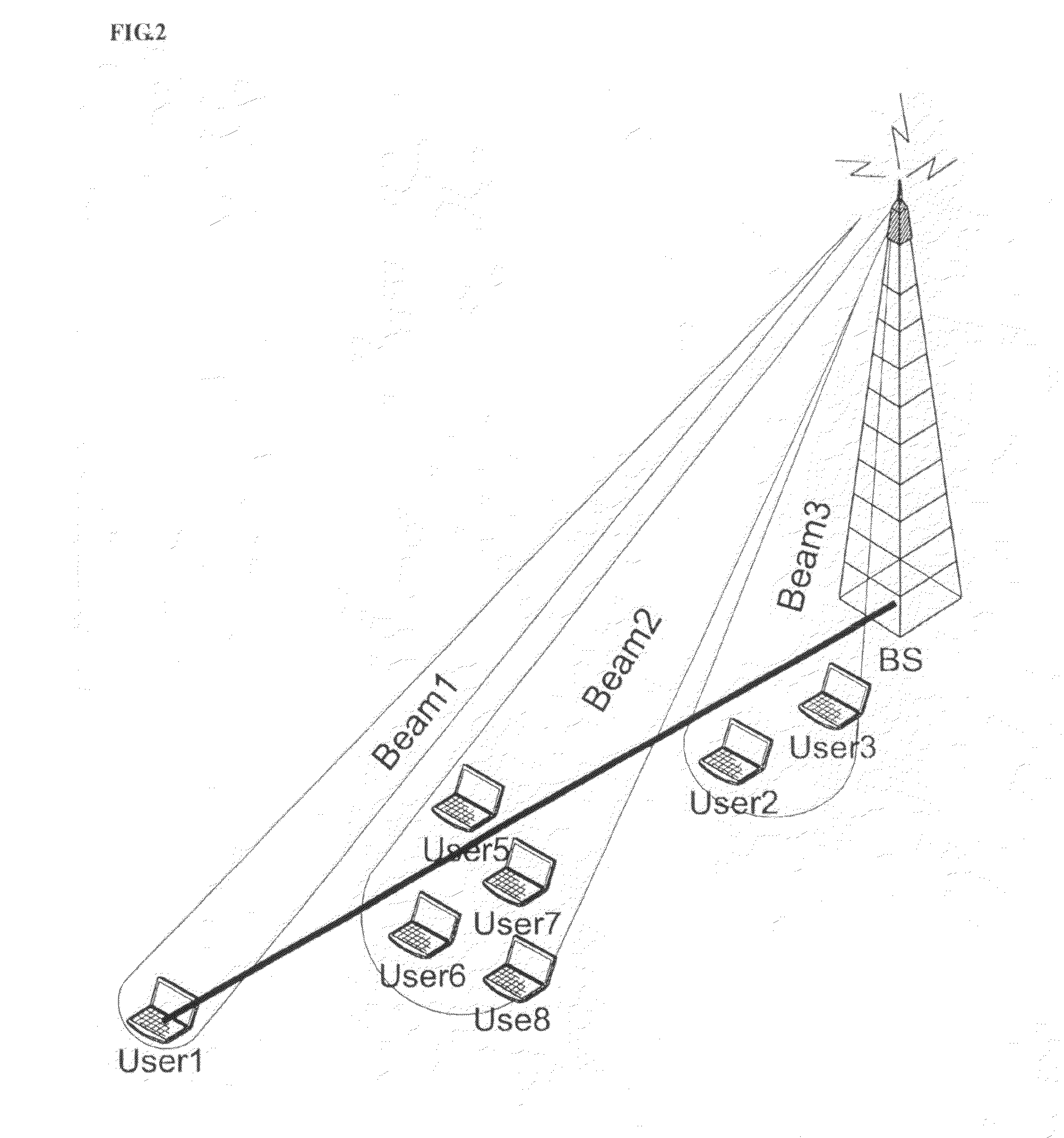
Beam division multiple access system and method for mobile communication system
InactiveUS20100165914A1Maximize the use of spaceEfficiently space resourceRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesTime division multiple accessCode division multiple access
The present invention is related to a beam division multiple access system and a method thereof. The base station according to the present invention comprises a initial mobile station information receiver for receiving initial mobile station information that a mobile station omnidirectionally transmits in an initial communication step, a mobile station location and speed detector for detecting a location and a moving speed of the mobile station from the initial mobile station information, a downlink beam generator for generating a downlink beam based on the location and the moving speed of the mobile station transferred from the mobile station location and speed detector, and adjusting at least one of a width and a direction of each the downlink beam, and a downlink beam transmitter for transmitting the downlink beam generated by the downlink beam generator to the mobile station through a phase array antenna.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
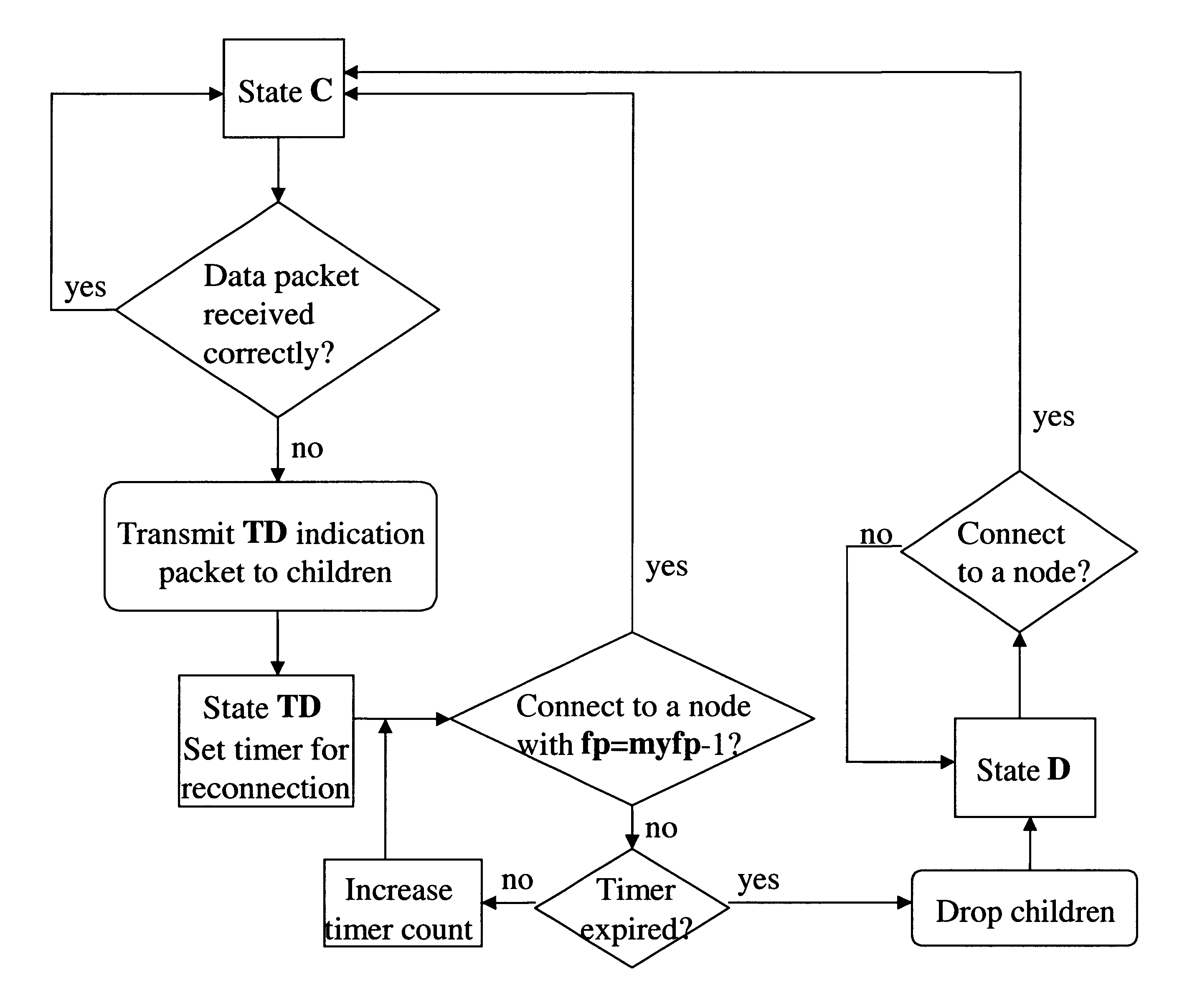
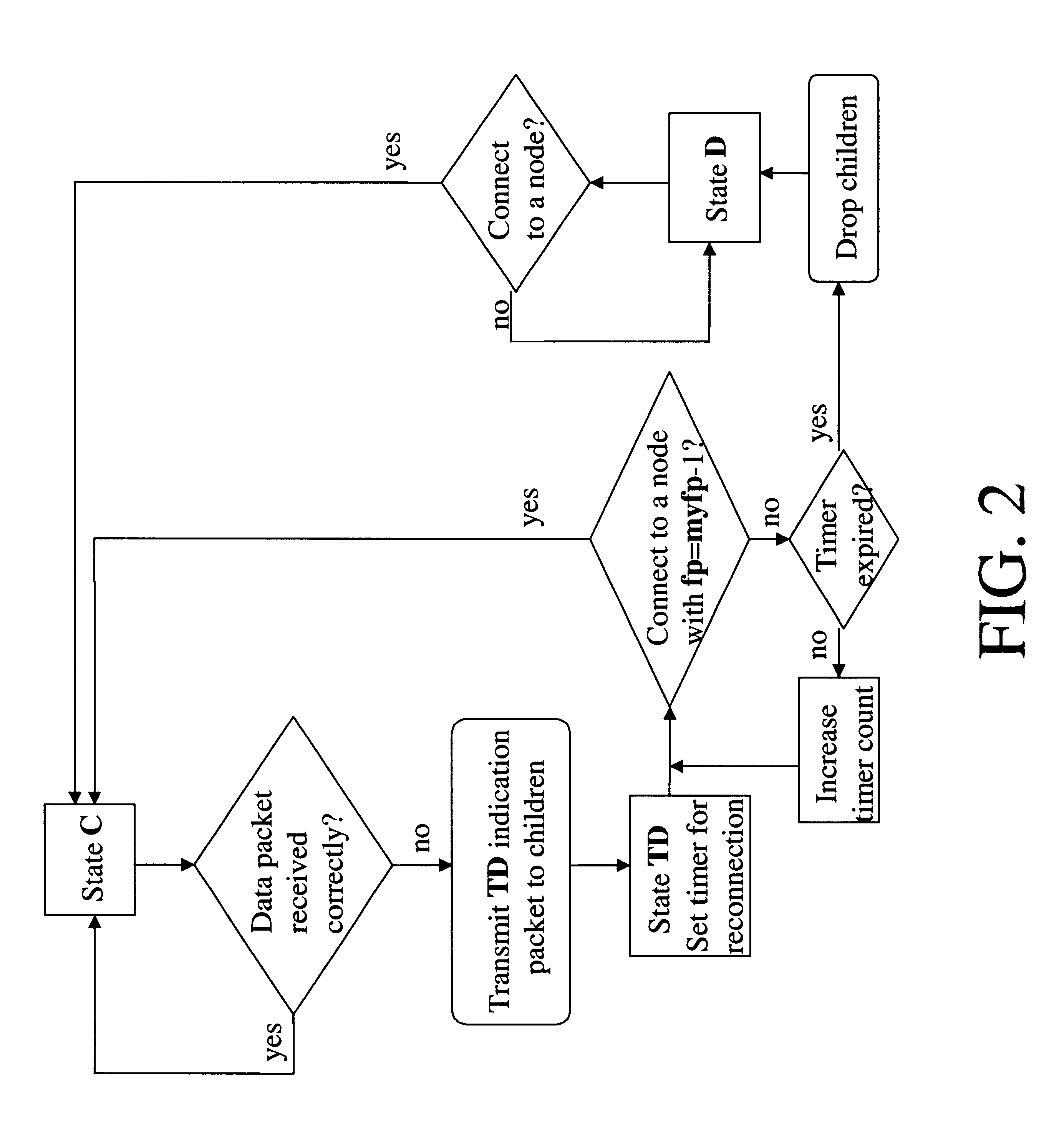
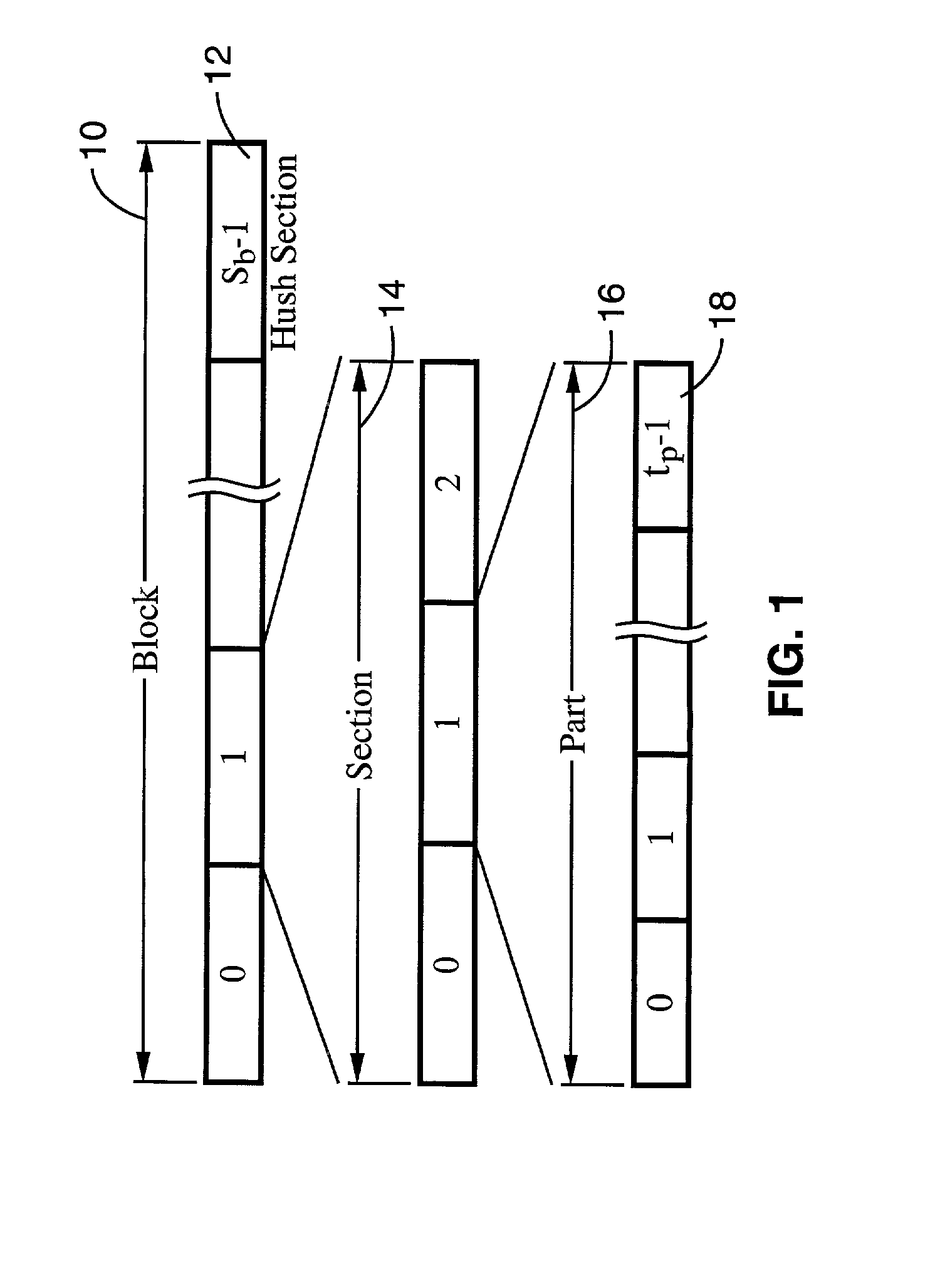
Apparatus and method for managing variable-sized data slots within a time division multiple access frame
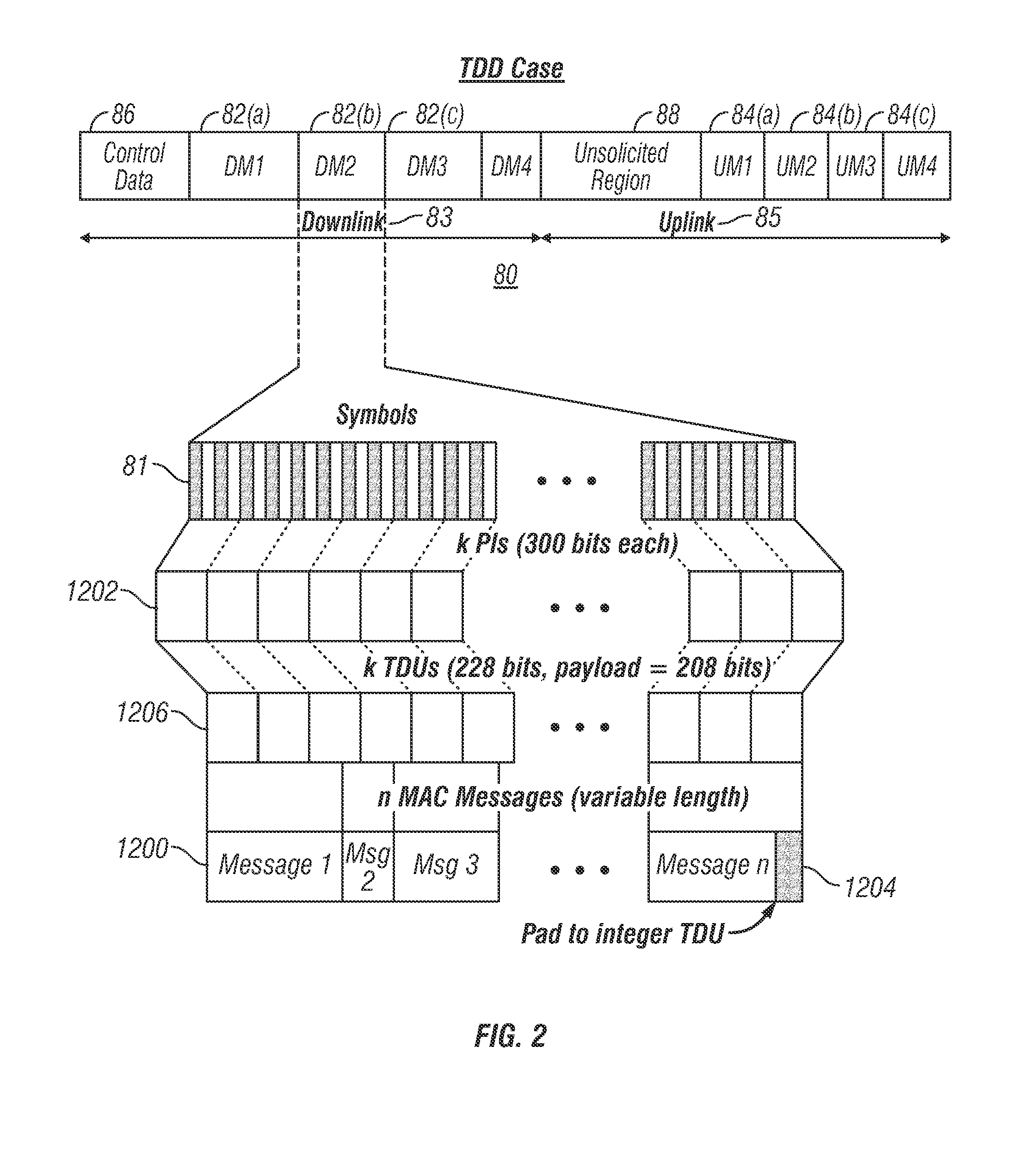
InactiveUS6944148B1Easy to useWider transferTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationReference modelQuality of service
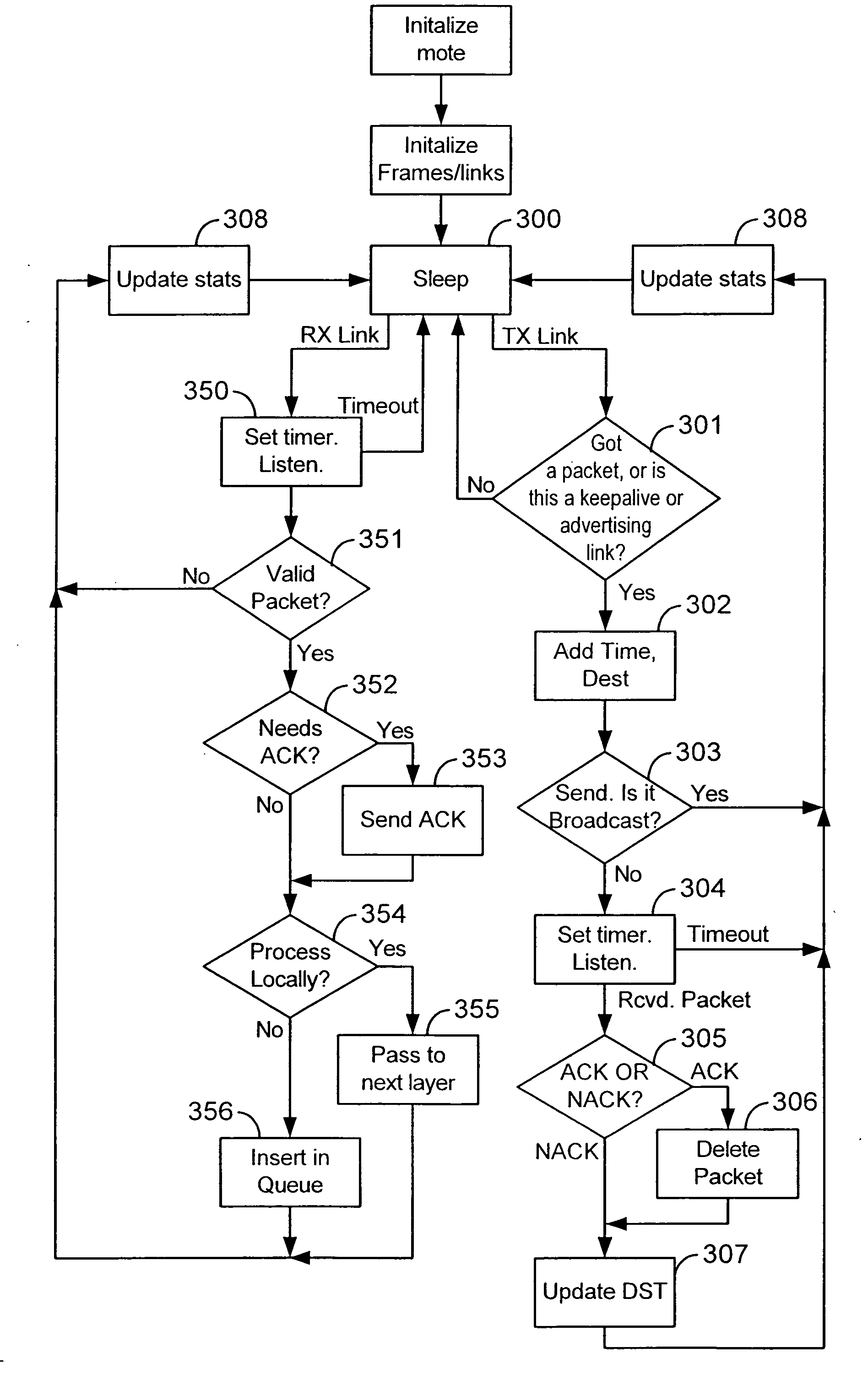
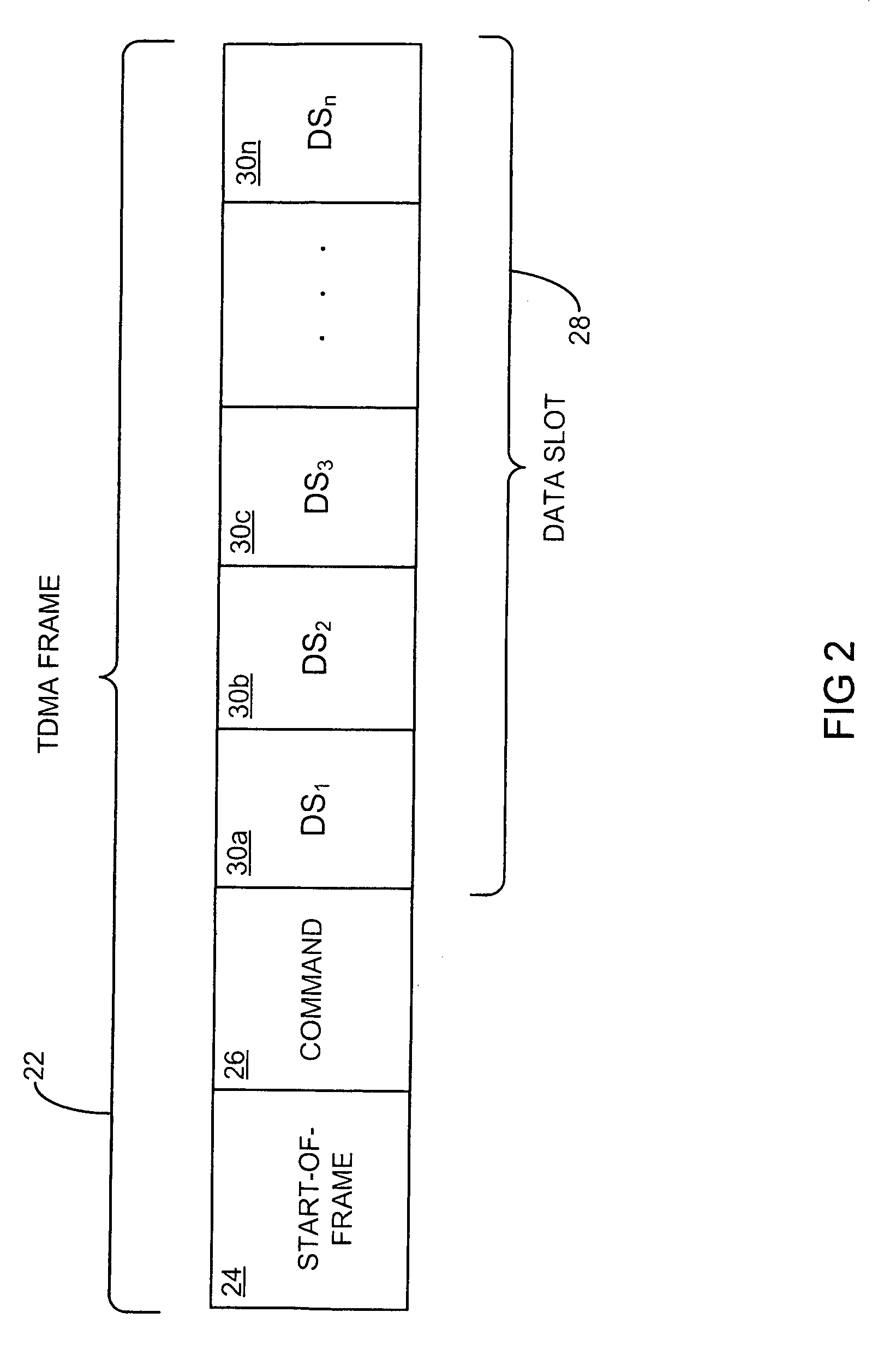
A reliable Medium Access Control layer protocol and method employing centralized management of communication in a Time Division Multiple Access network architecture. The Medium Access Control layer protocol implements Quality of Service guaranties to the layers of the Open Systems Interconnection reference model above the Medium Access Control layer by providing guaranteed bandwidth links within the bandwidth range specified by those layers. The Medium Access Control layer protocol further provides variable data slot requisition, variable data slot allocation, dynamic data slot reallocation, and data slot deallocation.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
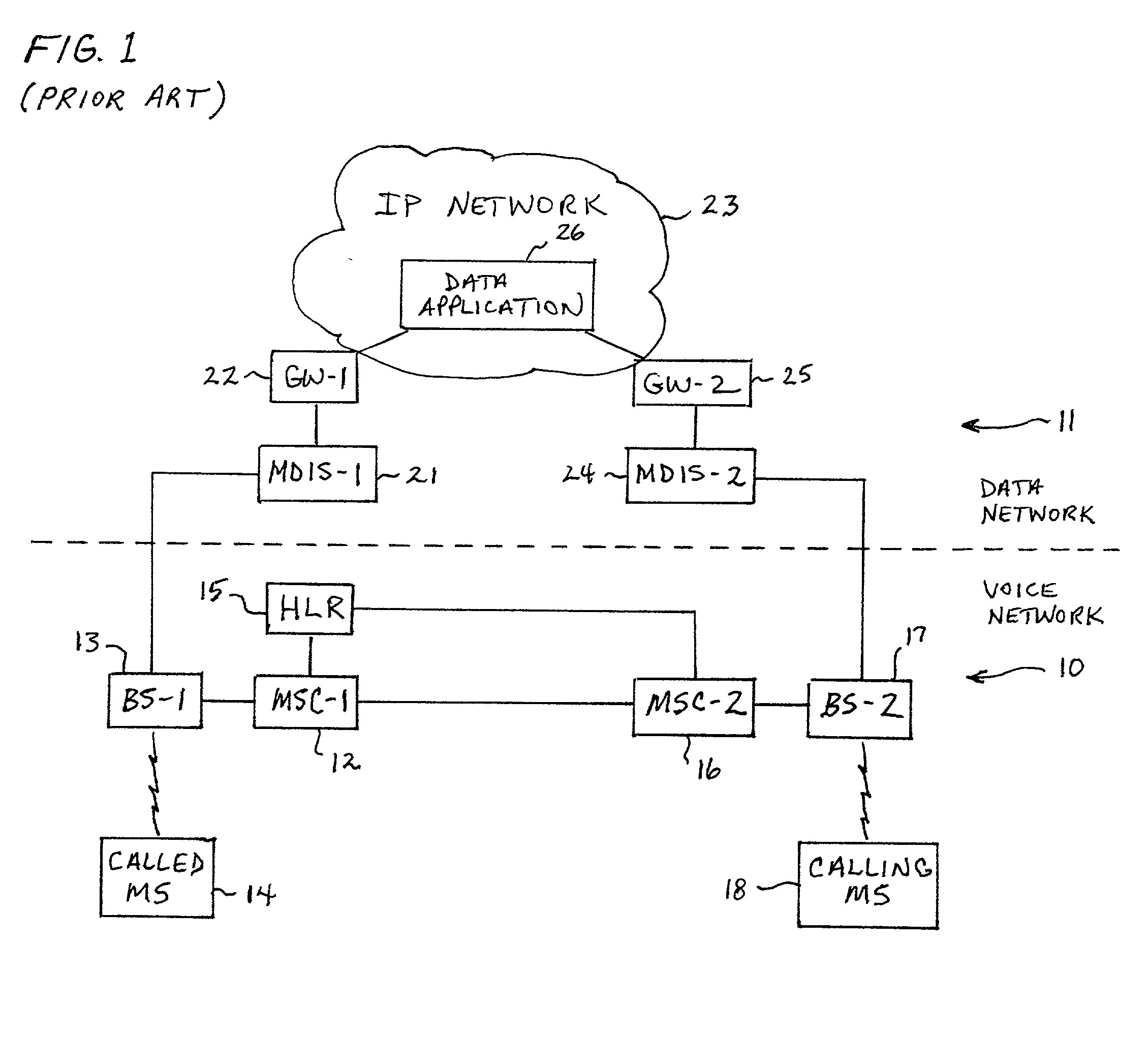
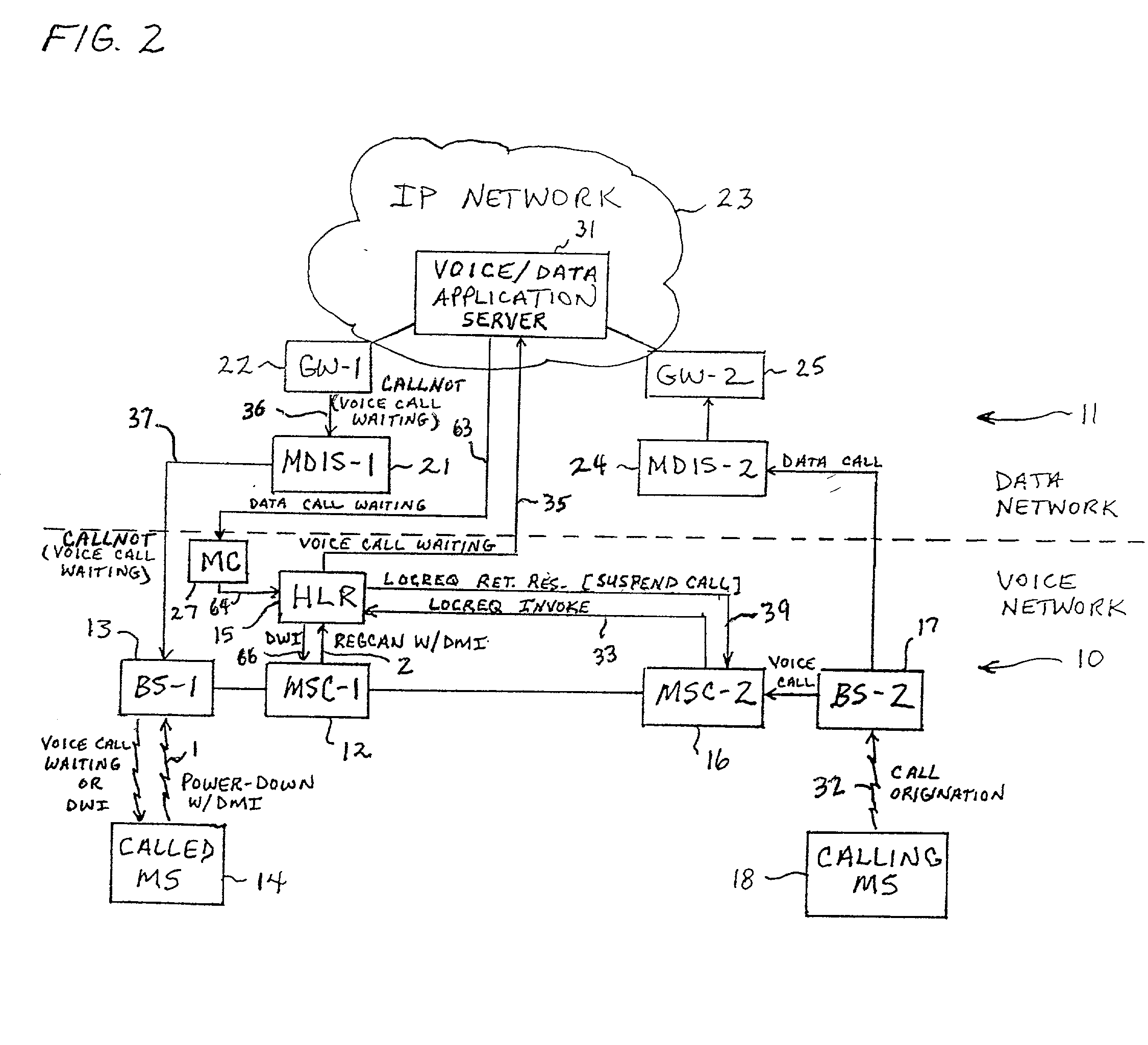
System and method of providing voice and data features in a time division multiple access (TDMA) network
InactiveUS20020111167A1Avoid expirationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesTime division multiple accessShort Message Service
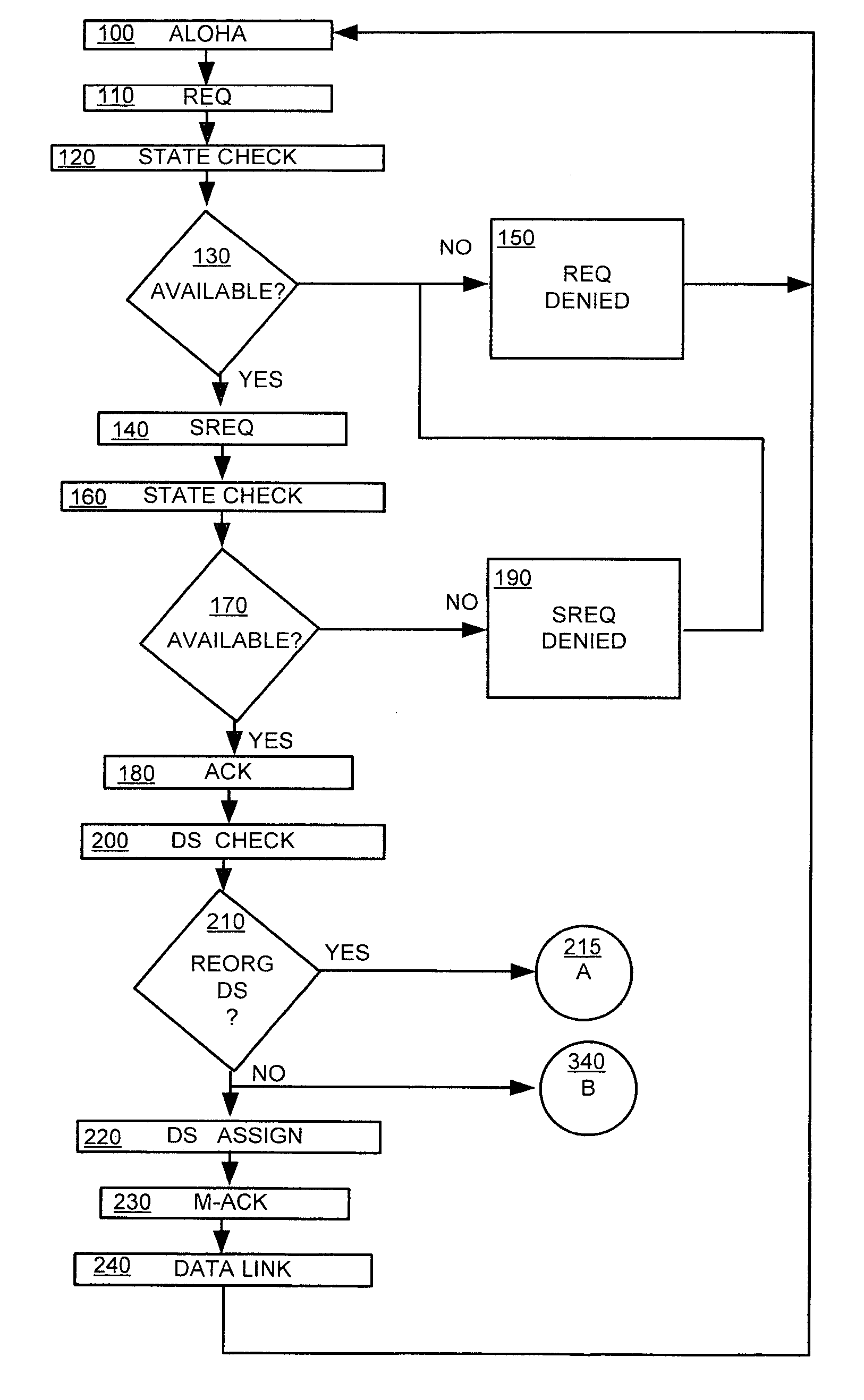
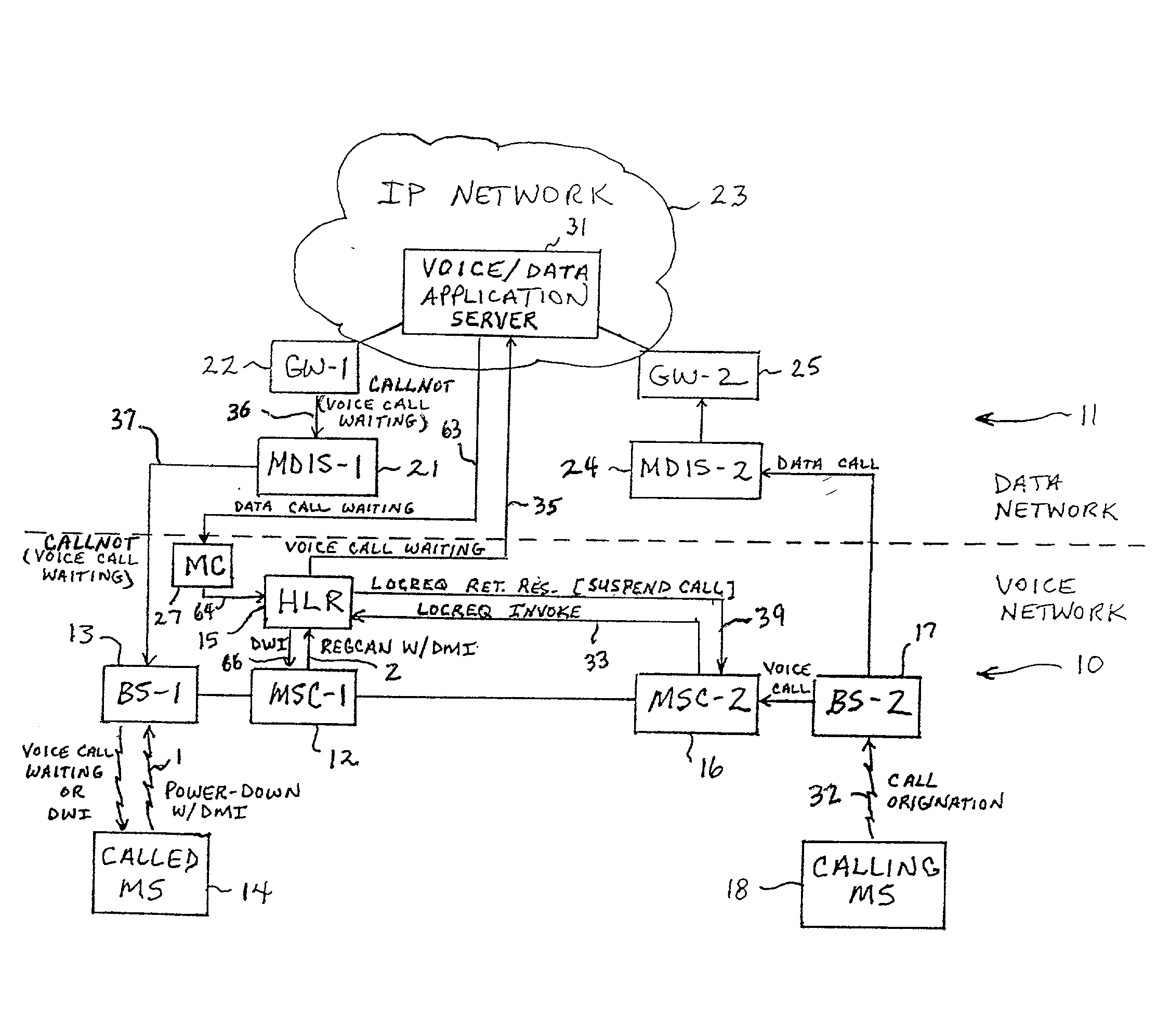
A system and method of providing voice and data feature interaction in a Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) radio telecommunication network having a data network overlay. An incoming voice call is established with a called mobile station (MS) when the called MS is operating in a data mode. An indicator is set in the called MS's user profile indicating that the called MS is operating in the data mode. The called MS is notified through the data network overlay that the incoming voice call is waiting. If the call is accepted, it is delivered to the called MS. The system may also establish an incoming data call with the called MS when the called MS is operating in a voice mode. A Short Message Service message center notifies the called MS that a data call is waiting. If the call is accepted, it is delivered to the called MS.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for ad hoc network access employing the distributed election of a shared transmission schedule
InactiveUS7046639B2Eliminate CollisionsControl moreNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessTransmission schedule
A system and method of providing distributed election of a shared transmission schedule within an ad hoc network. The invention includes a collision-free access protocol which resolves channel access contentions for time division multiple access (TDMA) of a single channel. Time-slots are organized into part numbers, which are included within sections, a sequence of which define a block. Each node is given a ring number according to its location within the network topology and maintains local neighbor information along with its own part number and message digest. Collision-free channel access is automatically scheduled and repetitious contention phases are resolved by a random permutation algorithm operating in message digests. An empty time-slot utilization method is also described and data packets may also be transmitted subject to a non-zero collision probability within a blind section of the block.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Transmitter directed code division multiple access system using path diversity to equitably maximize throughput
InactiveUS6449490B1Power managementTransmission control/equalisingTime division multiple accessCommunications system
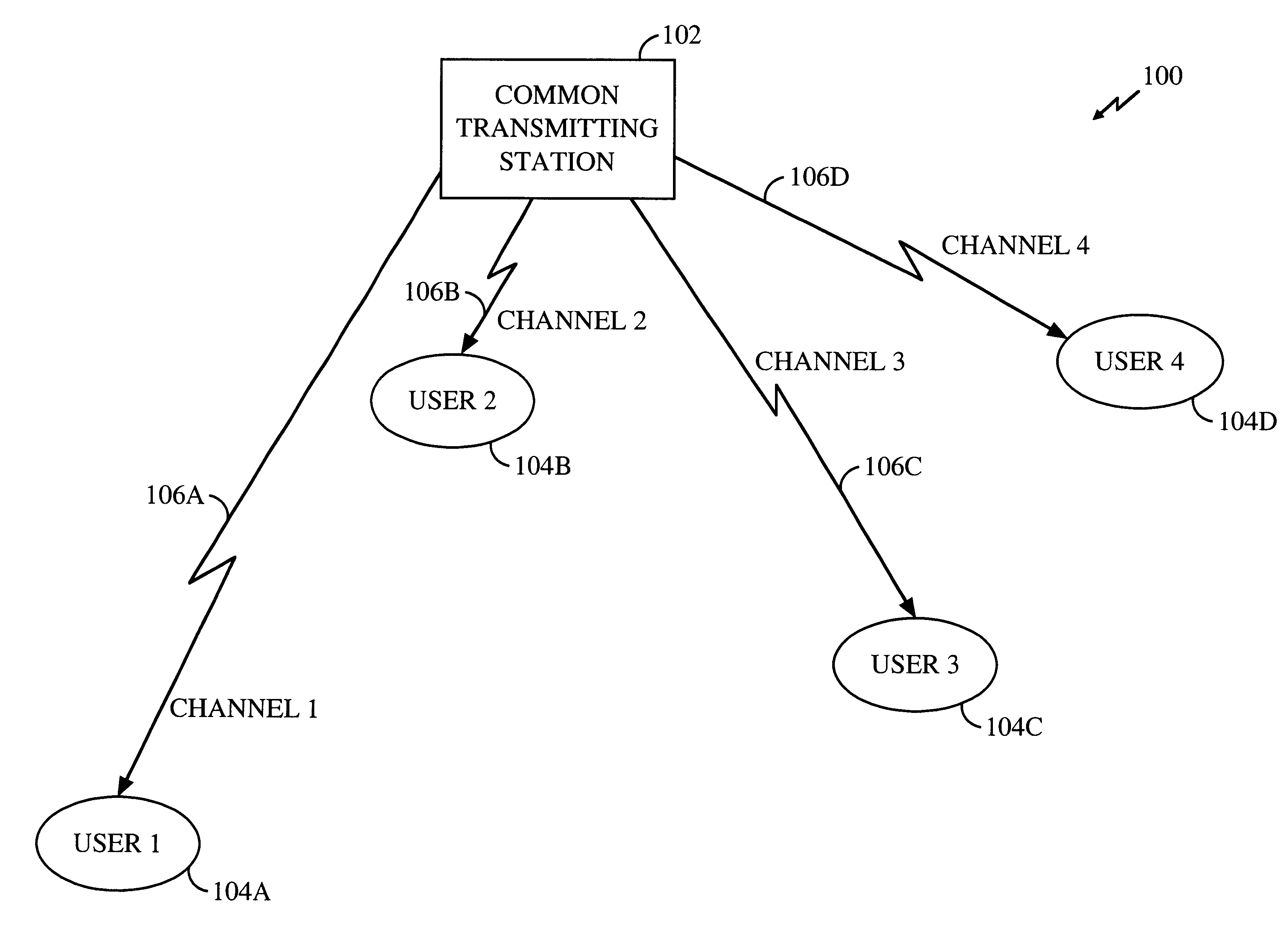
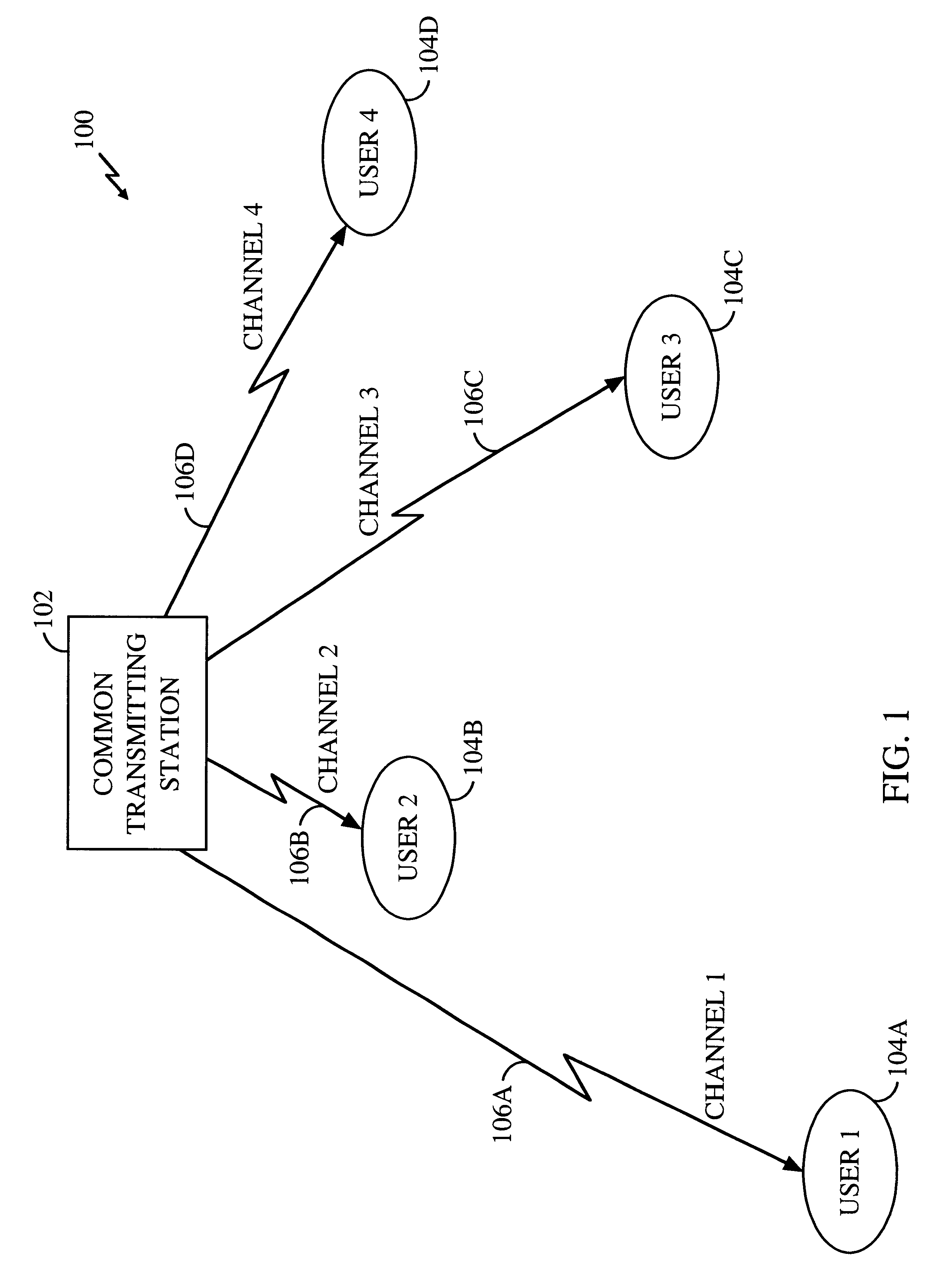
A transmitter directed, distributed receiver using path diversity provided by the distribution of the receiver. Advantage is taken of the uncorrelated variations over time in the condition of channels between a common transmitter and several users. The greater the variation in the channel condition of a particular channel over time, the greater the increase in total system throughput provided. An access metric represents the instantaneous channel condition of the communication system between each user and the transmitter with respect to the average channel condition of each channel. Alternatively, the access metric represent the instantaneous channel condition with respect to the average data throughput over that channel. The common transmitting station uses the access metric to directly compare the desirability of granting each channel access with the desirability of granting each other channel access. The user that has the greatest access metric is provided access to the channel.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Framing for an adaptive modulation communication system
ActiveUS7197022B2Synchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessCommunications system
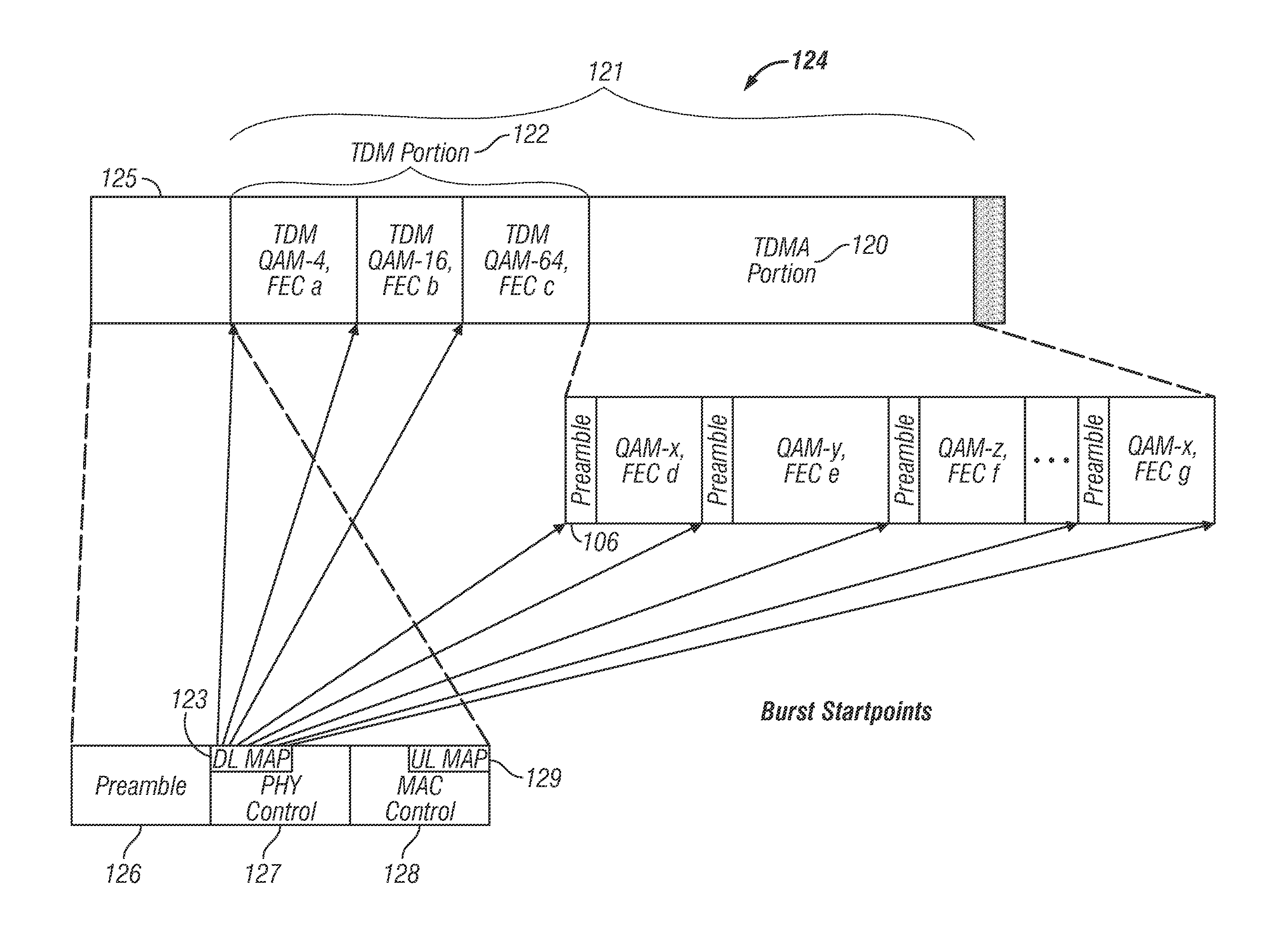
A system and method for mapping a combined frequency division duplexing (FDD) Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) / Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) downlink subframe for use with half-duplex and full-duplex terminals in a communication system. Embodiments of the downlink subframe vary Forward Error Correction (FEC) types for a given modulation scheme as well as support the implementation of a smart antennae at a base station in the communication system. Embodiments of the system are also used in a TDD communication system to support the implementation of smart antennae. A scheduling algorithm allows TDM and TDMA portions of a downlink to efficiently co-exist in the same downlink subframe and simultaneously support full and half-duplex terminals. The algorithm further allows the TDM of multiple terminals in a TDMA burst to minimize the number of map entries in a downlink map. The algorithm limits the number of downlink map entries to not exceed 2n+1, where n is the number of DL PHY modes (modulation / FEC combinations) employed by the communication system.
Owner:WI LAN INC +1
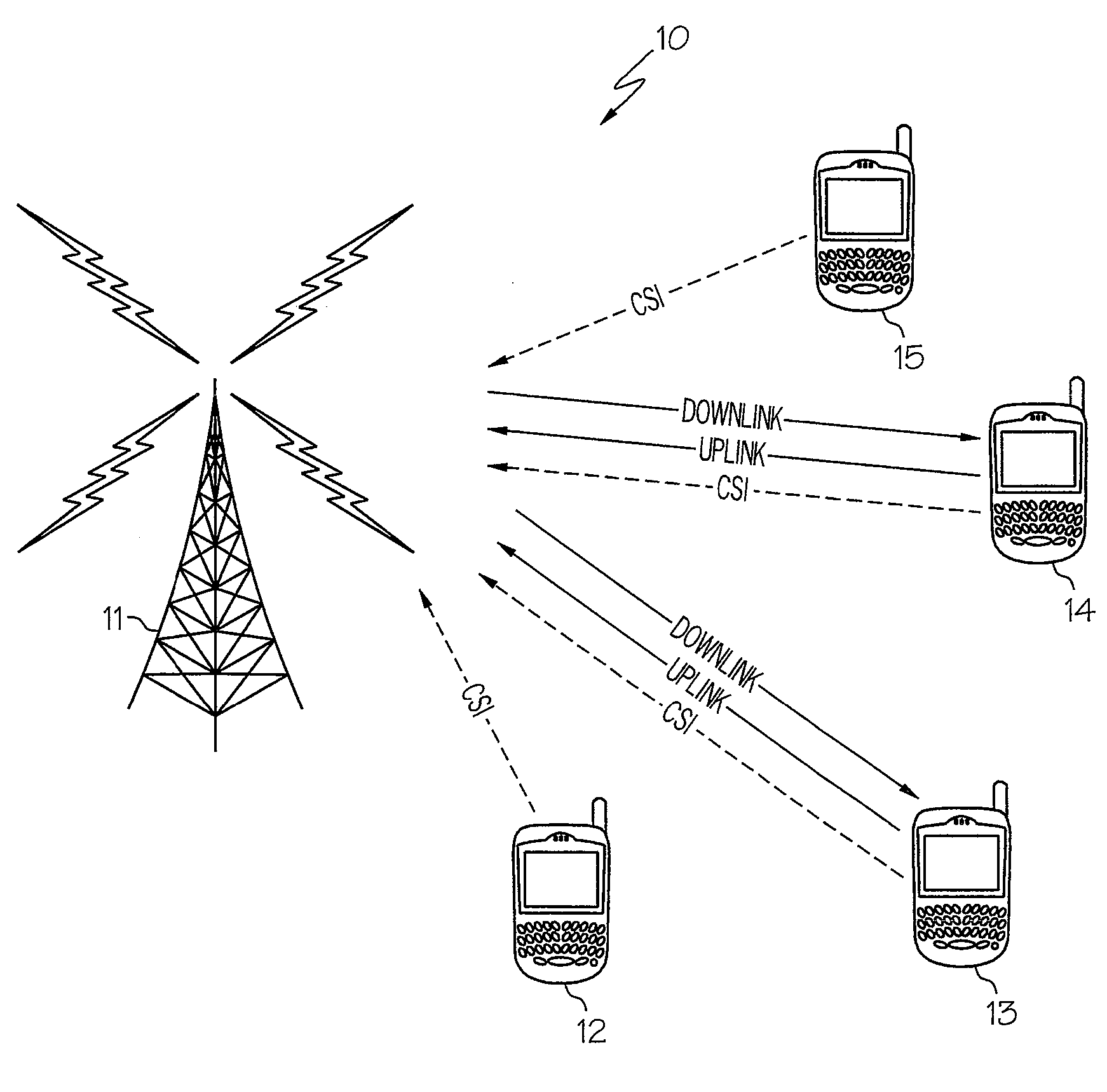
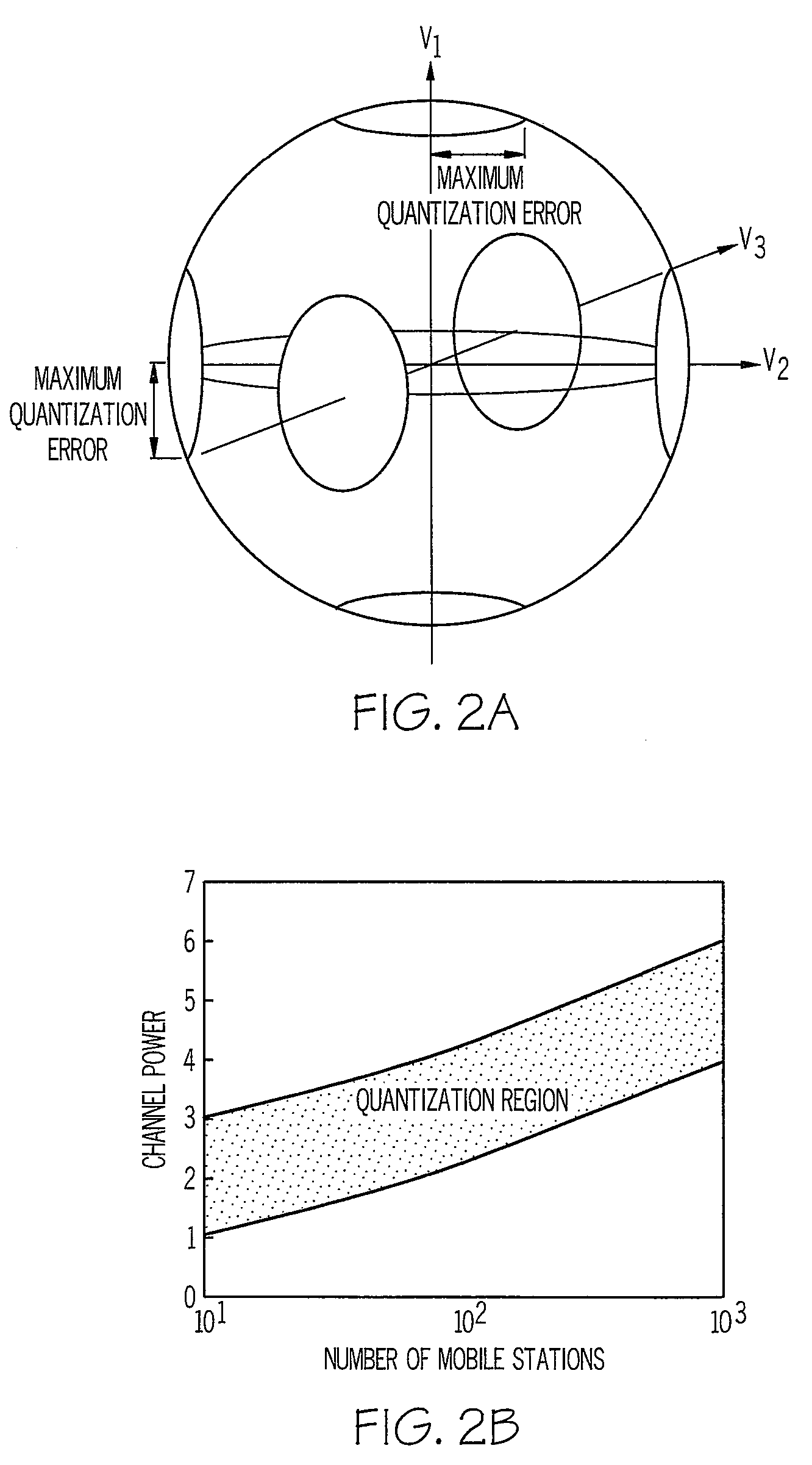
Method and apparatus for performing space division multiple access in a wireless communication network
A method and apparatus for performing space division multiple access in wireless communications are disclosed. After the receipt of a set of training data from a base station, an estimated channel state information (CSI) is then generated by a mobile station. The CSI is subsequently quantized. The mobile station then determines whether or not the quantized CSI falls within a set of thresholds. If the quantized CSI falls within the set of thresholds, the mobile then sends feedback information to the base station to allow the base station to consider the mobile station as one of the mobile station candidates available for data communications. Otherwise, if the quantized CSI falls outside the set of thresholds, the mobile station then discards the quantized CSI.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
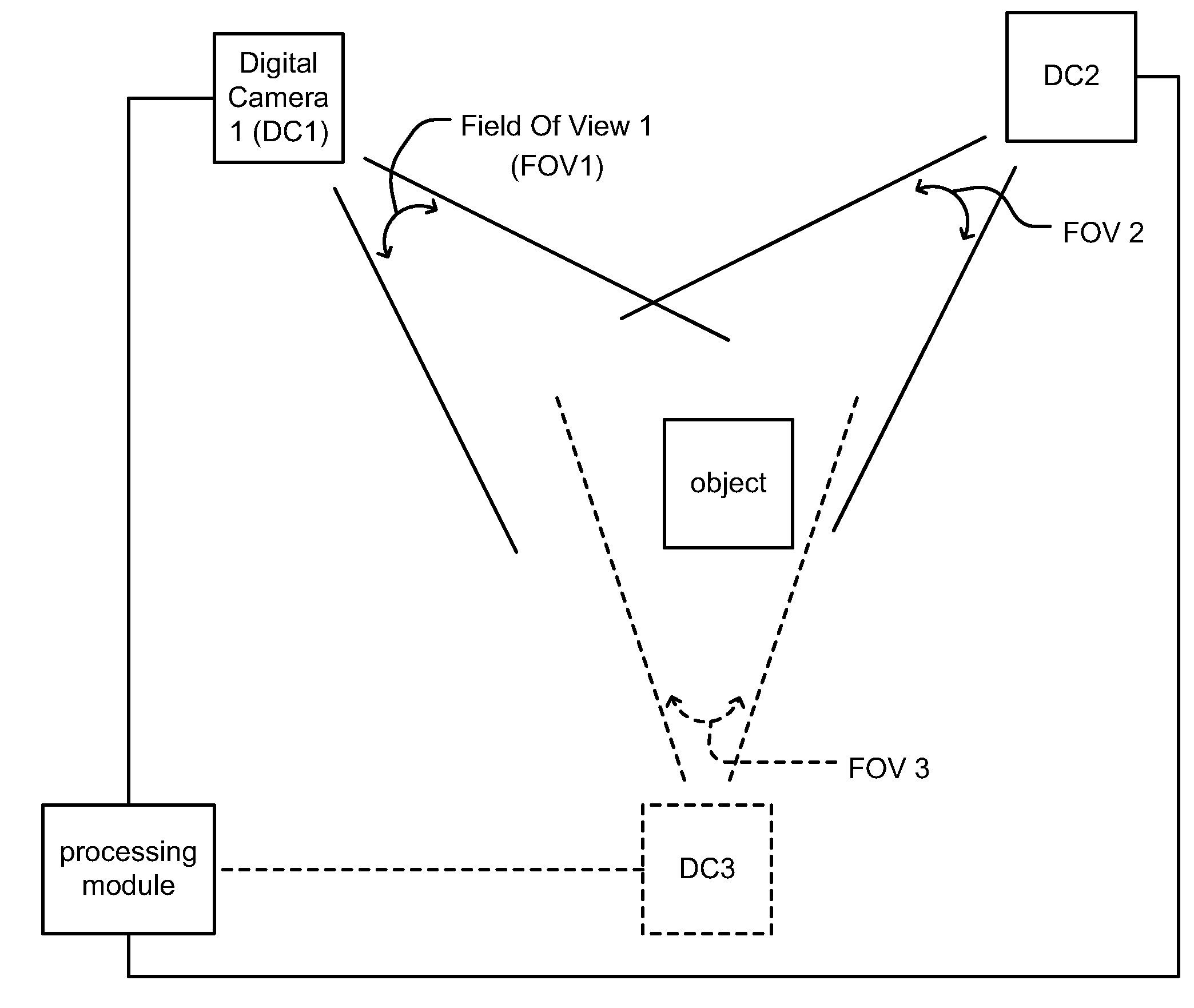
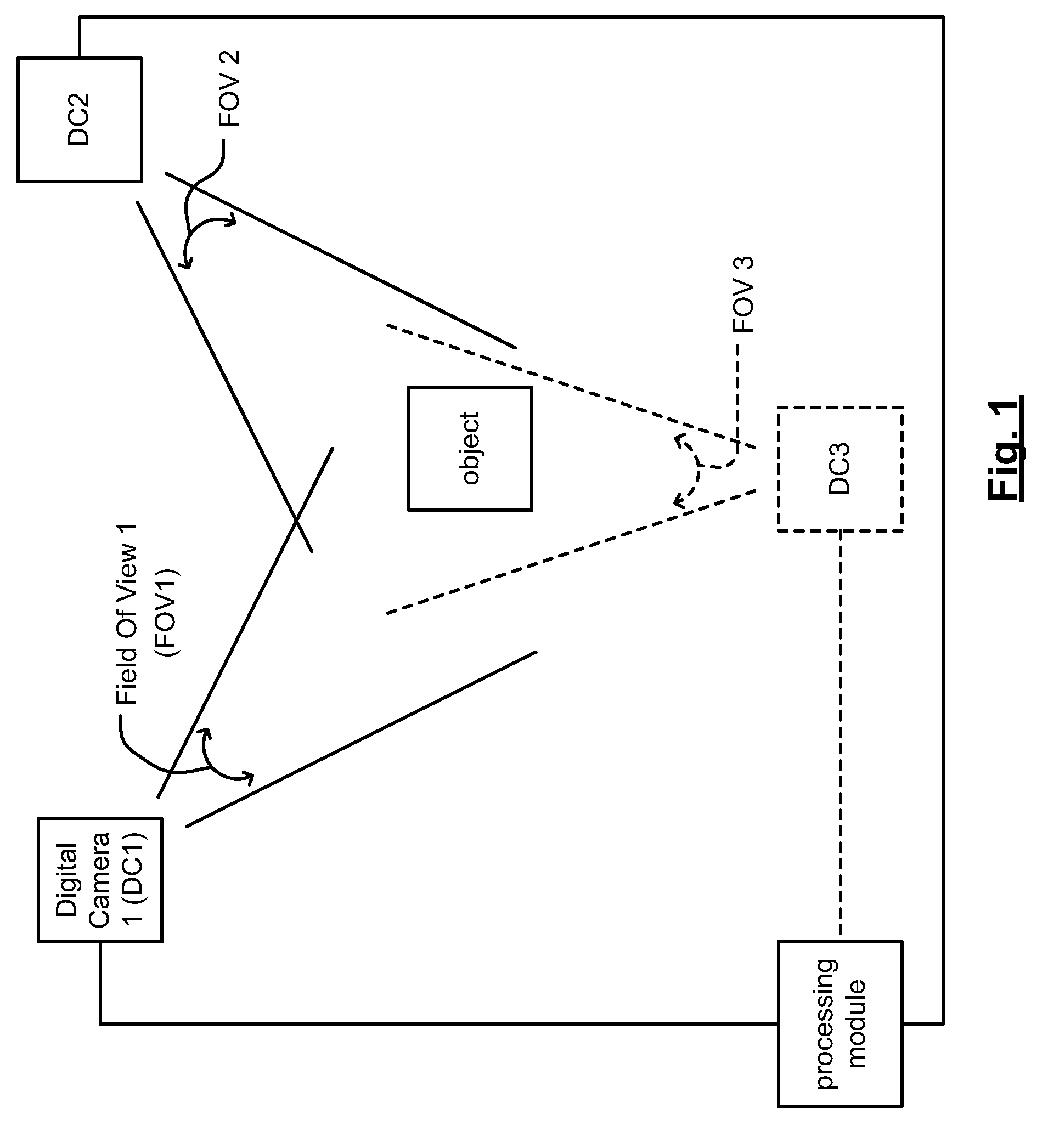
Position detection and/or movement tracking via image capture and processing
InactiveUS20080316324A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionCode division multiple accessPerformed Imaging
Position detection and / or movement tracking via image capture and processing. Digital cameras perform image capture of one or more objects within a particular region (e.g., a physical gaming environment). A game module or processing module processes the images captured by the digital cameras to identify a position of and / or track movement of objects (e.g., a player, a gaming object, a game controller, etc.). Various digital image processing techniques may be employed including pattern recognition of objects, color recognition / distinction, intensity recognition / distinction, relative size comparison, etc. to identify objects and / or track their movement. The coupling between the digital cameras and the game module or processing module may be wired, wireless, or a combination thereof. If wireless, any number of different signaling means may be employed including Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) signaling, Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) signaling, or Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) signaling.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method for frequency division duplex communications
InactiveUS20030156570A1Efficient communicationEasy to separateSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsTime division multiple access
The high quality PCS communications are enabled in environments where adjacent PCS service bands operate with out-of-band harmonics that would otherwise interfere with the system's operation. The highly bandwidth-efficient communications method combines a form of time division duplex (TDD), frequency division duplex (FDD), time division multiple access (TDMA), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), spatial diversity, and polarization diversity in various unique combinations. The method provides excellent fade resistance. The method enables changing a user's available bandwidth on demand by assigning additional TDMA slots during the user's session.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Hybrid DSMA/CDMA (digital sense multiple access/code division multiple access) method with collision resolution for packet communications
InactiveUS7075971B2Avoid collisionEffective distributionPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelPacket communicationTime division multiple access
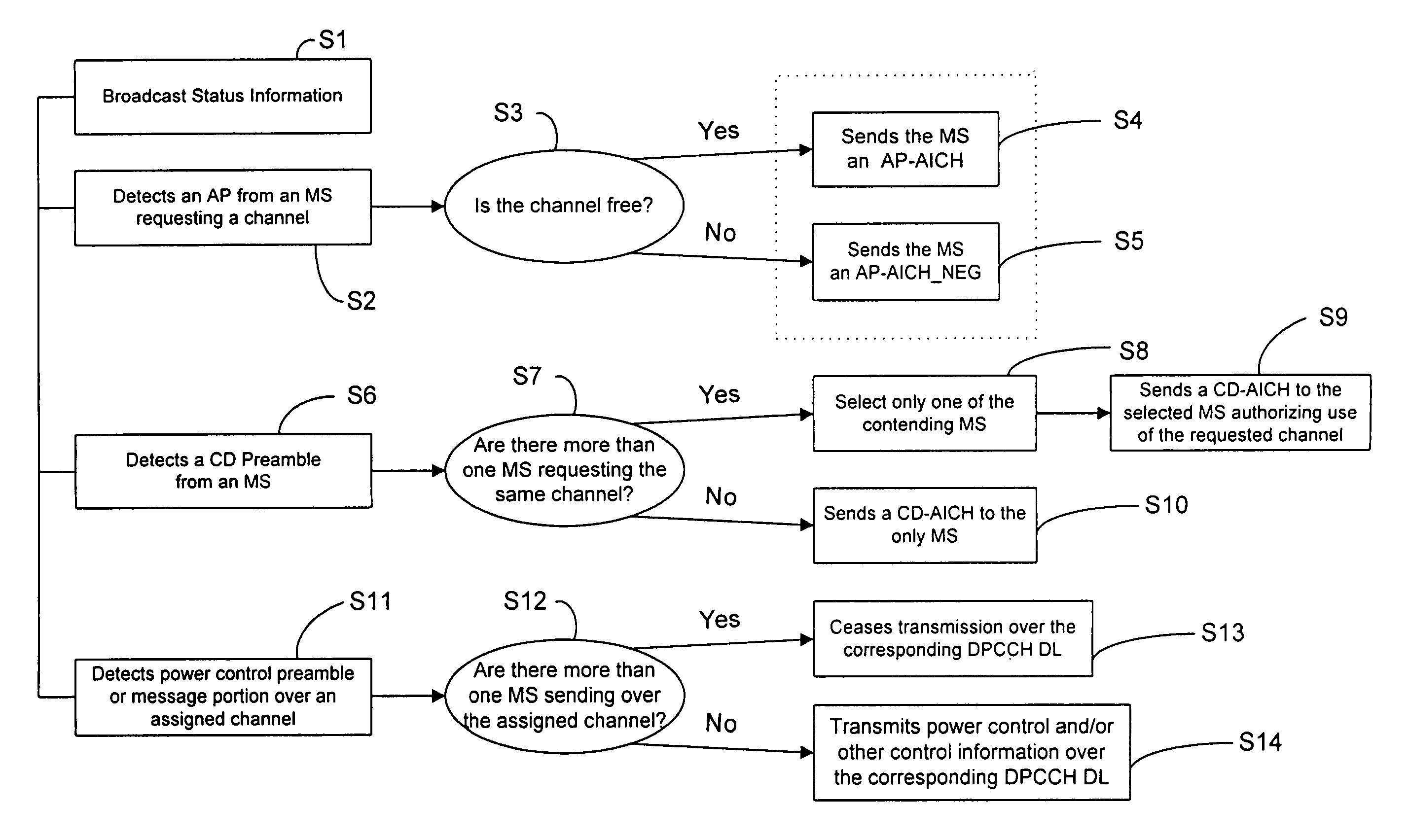
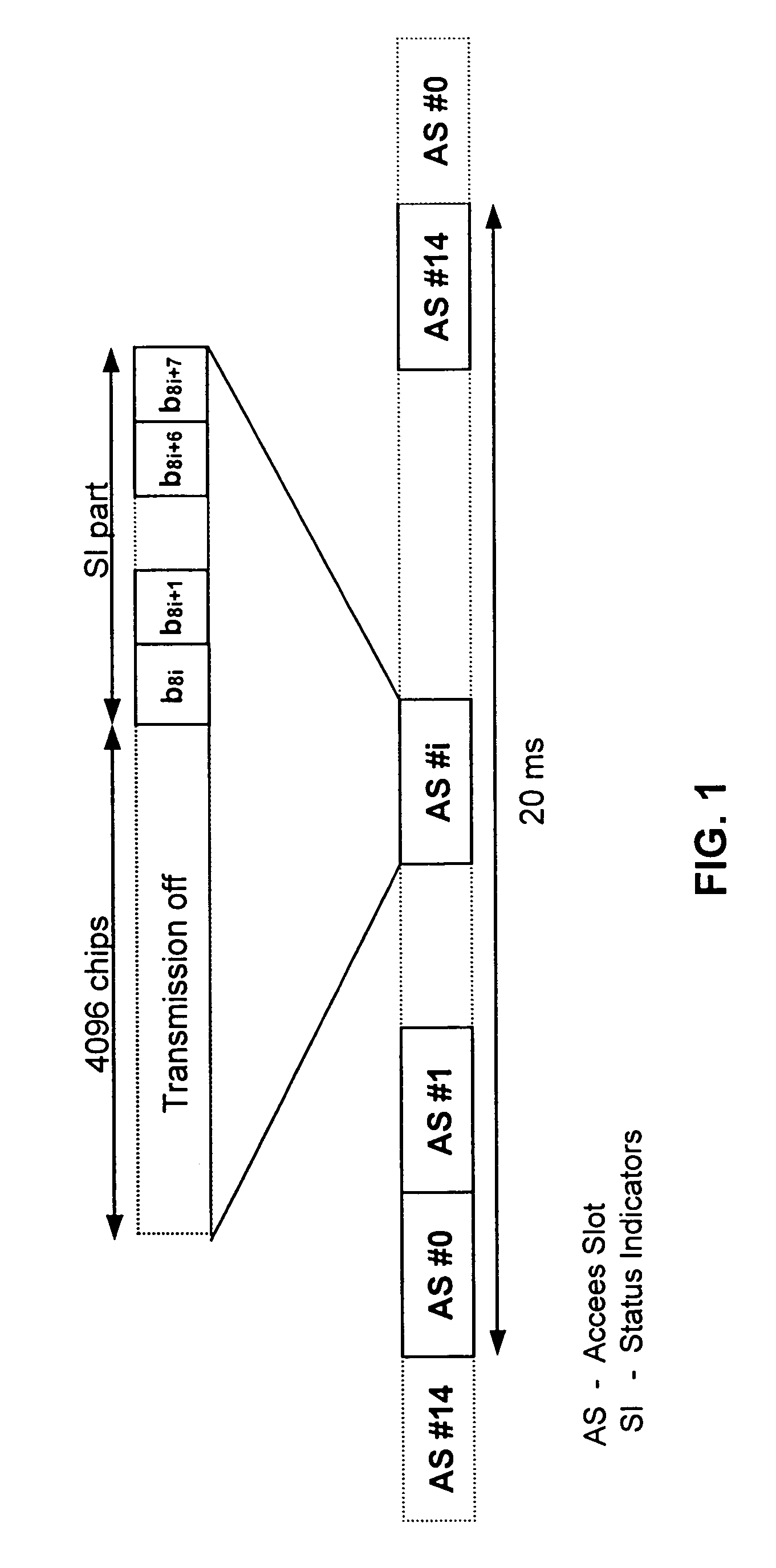
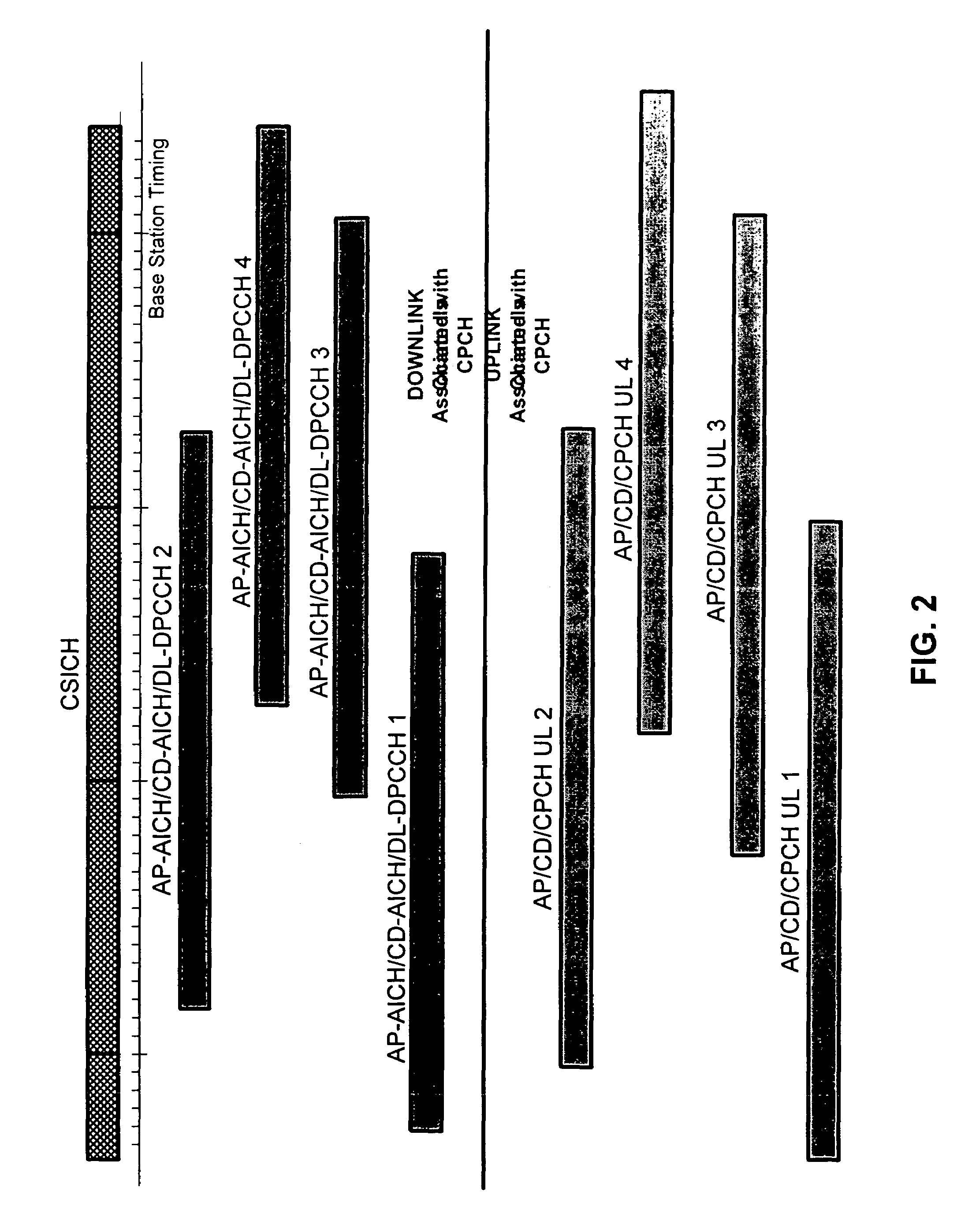
A hybrid DSMA-CR / CDMA methodology provides efficient access to one of a group of packet channels in a spread spectrum wireless communication network. The base station broadcasts status information as to the availability and / or available data rates for each packet channel or group of channels. Each mobile station uses the status information to select an available channel and / or a channel with sufficient data rate. The mobile station then starts transmission of a series of access preambles, each of which contains a signature corresponding to the selected channel. The mobile station transmits the preambles at increasing power levels. When the base station detects a preamble transmission, the base station responds with a corresponding acknowledgement essentially permitting the mobile station to send its packet data along with any closed-loop power control information over the selected channel.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com