Patents
Literature
4216results about How to "Improve overall utilization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
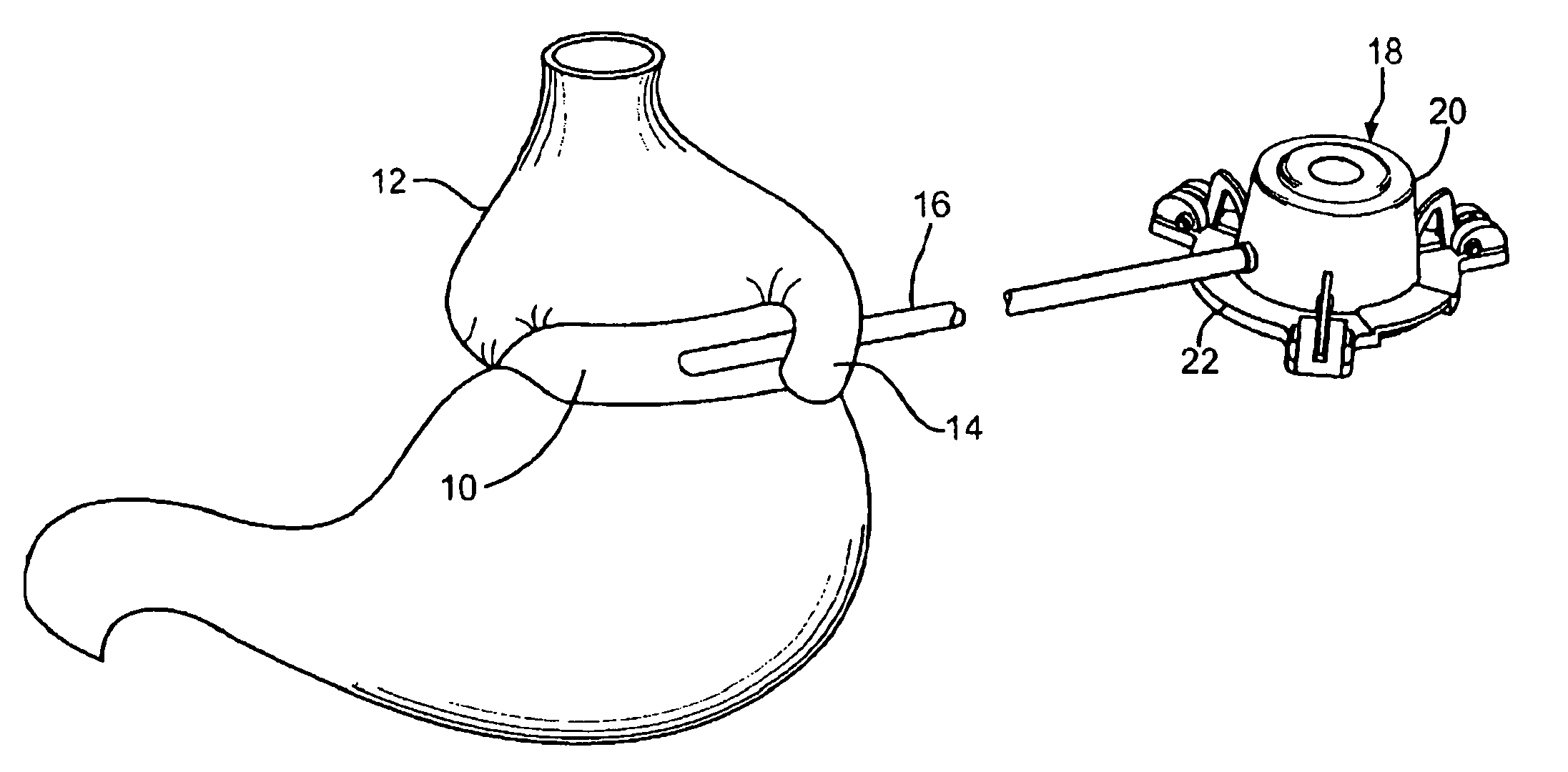
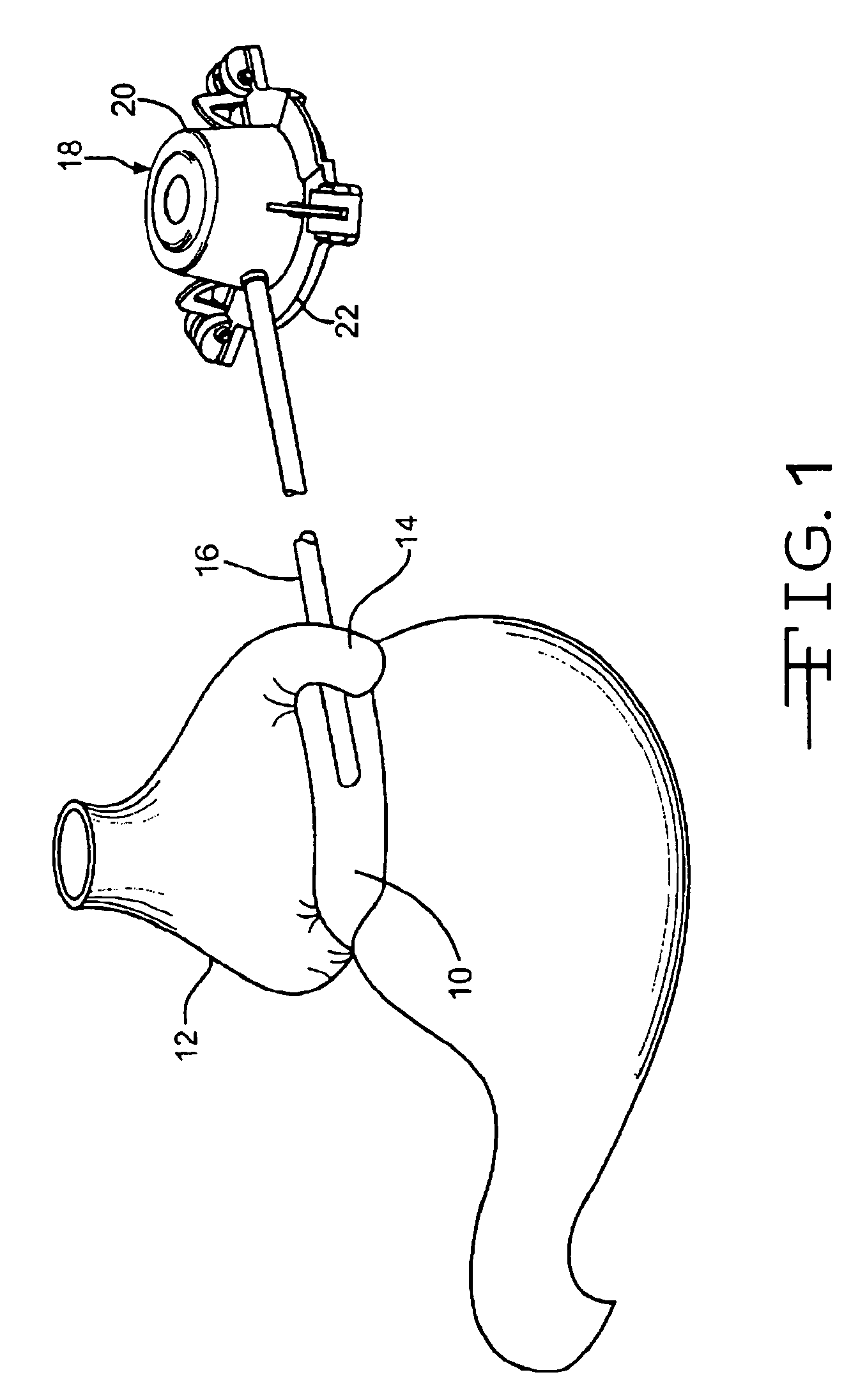
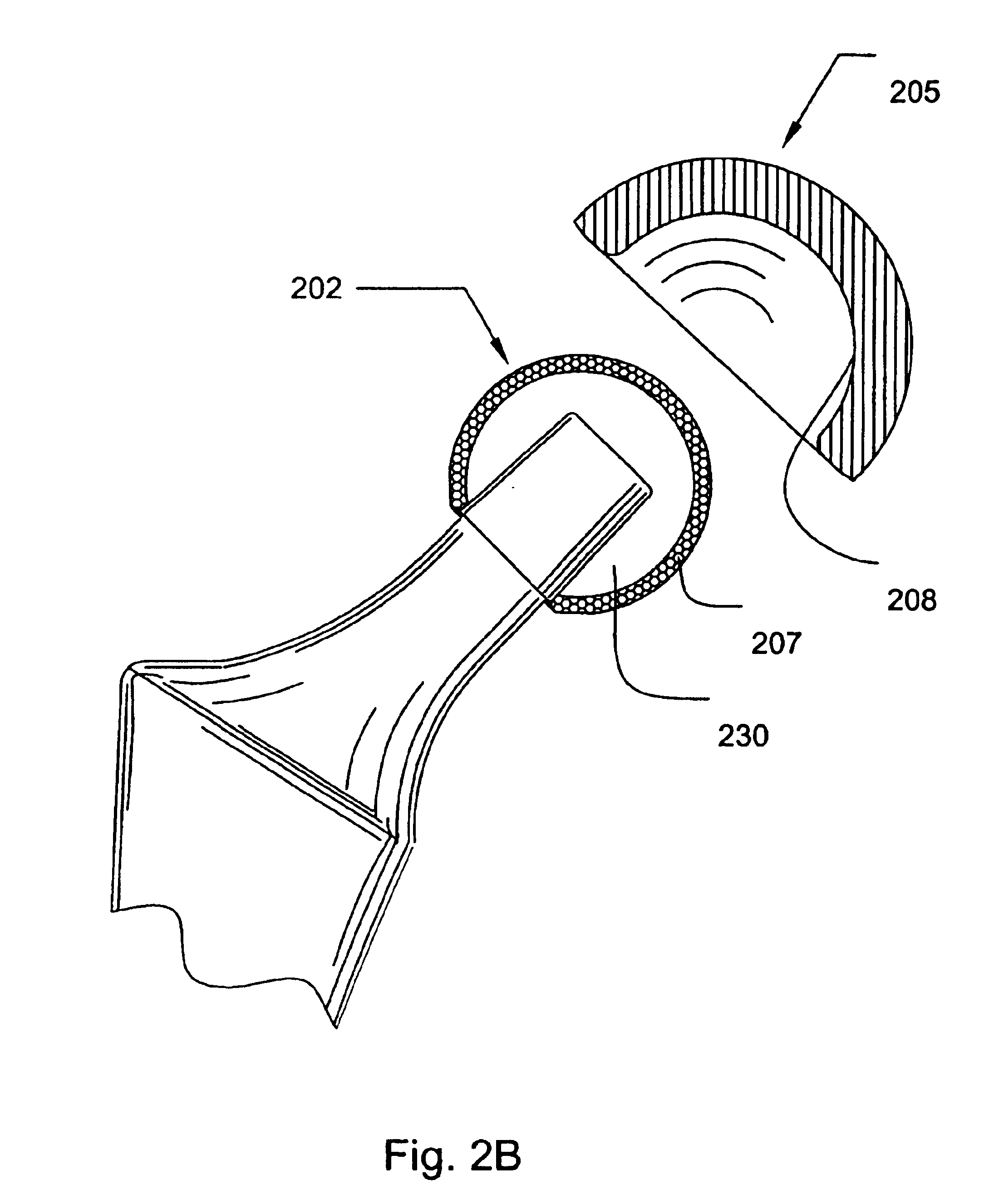
Subcutaneous self attaching injection port with integral moveable retention members
InactiveUS7862546B2Improve overall utilizationMedical devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesInjection portEngineering
A self attaching injection port has integral moveable fasteners which are moveable from a undeployed state to a deployed state engaging tissue. The fasteners may be disposed radially or tangentially, and rotated to pierce the fascia. The fasteners may be rigid or elastically deformable.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
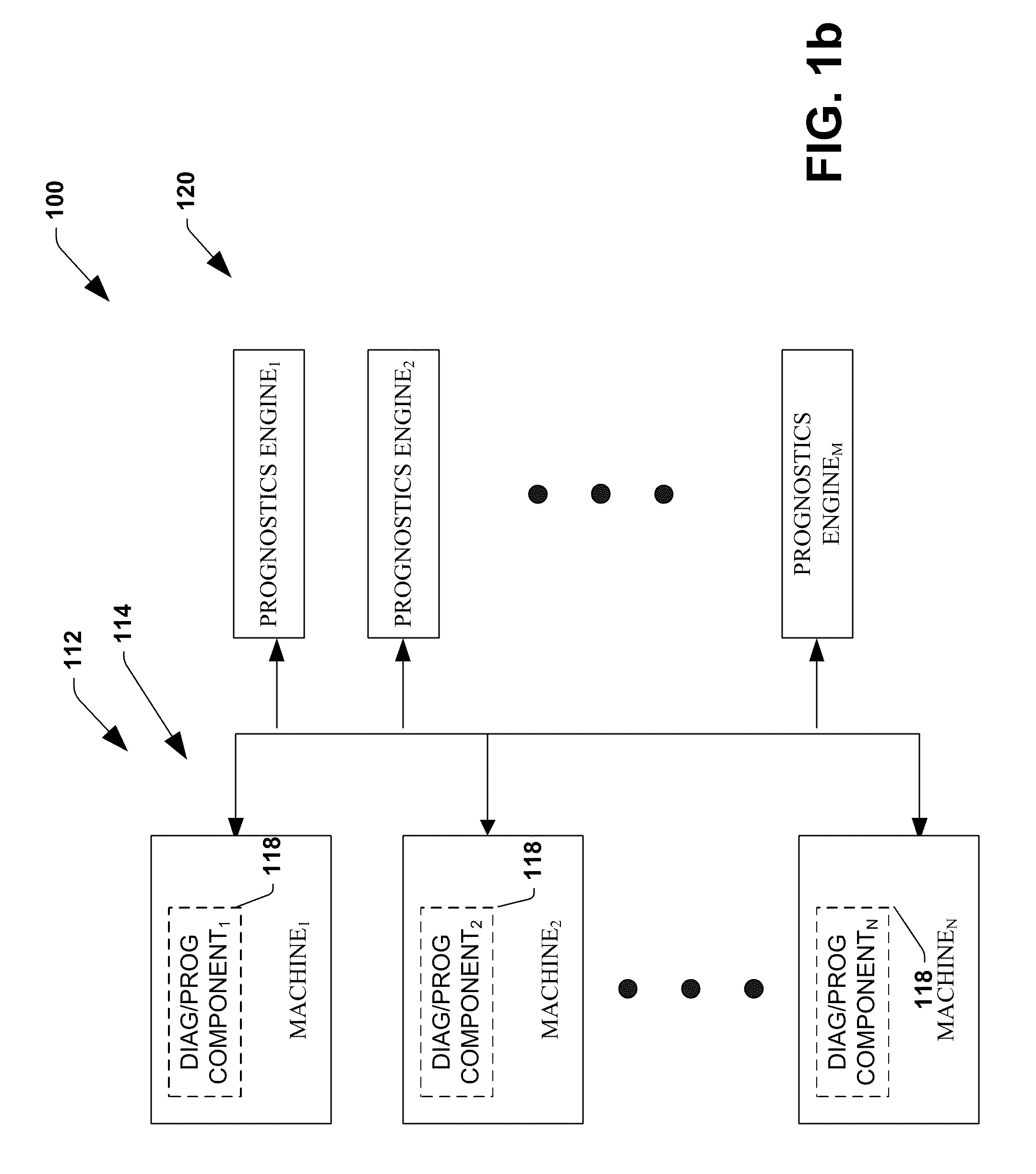
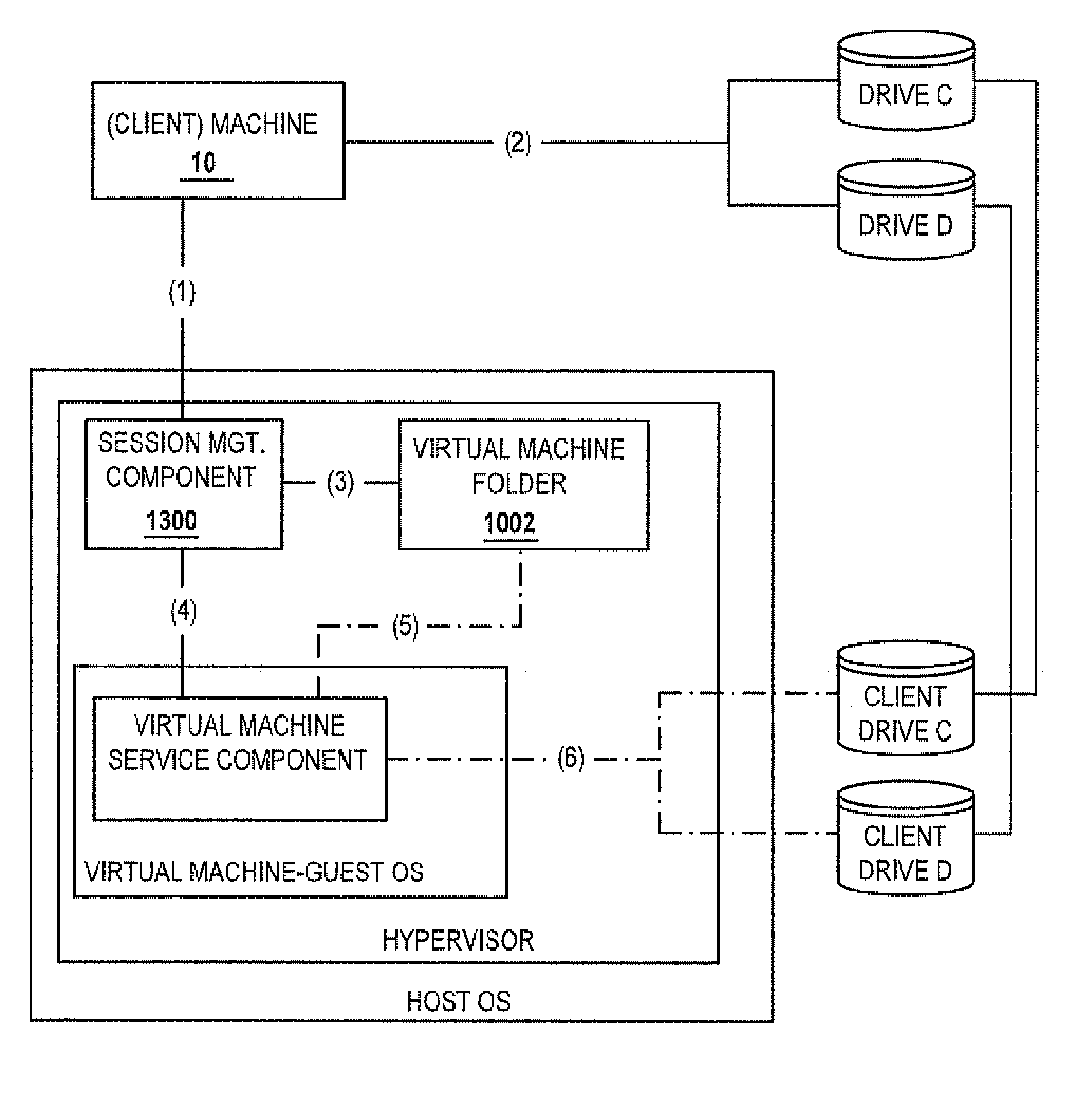
Methods and systems for interacting, via a hypermedium page, with a virtual machine executing in a terminal services session
ActiveUS20070171921A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationHyperlinkClient agent
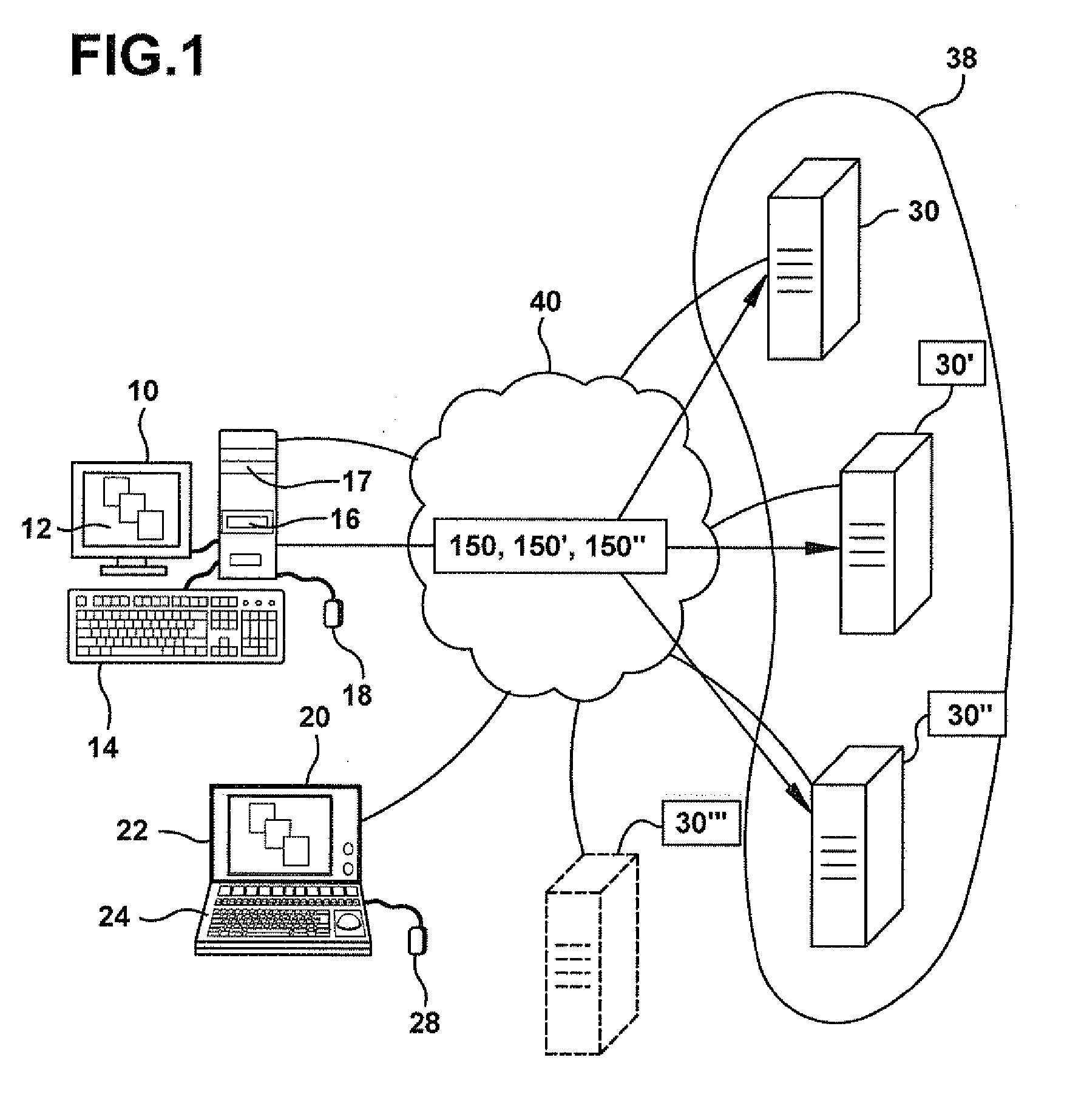
A method for making a hypermedium page interactive, the hypermedium page displayed by a network browser, includes the step of selecting a hyperlink on the hypermedium page displayed on a client machine, the hyperlink identifying a desired computing resource. A hyperlink configuration file is retrieved, the hyperlink configuration file corresponding to the hyperlink and identifying a server machine. A client agent is started on the client machine. The client agent creates, via a terminal services session, a communication link to a virtual machine executing on the server identified by the hyperlink configuration file, the virtual machine executed by a hypervisor executing in the terminal services session provided by an operating system executing on the server. The client agent receives data from the virtual machine and displays, on the client machine, the received data without intervention by the network browser.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Coating composition for multiple hydrophilic applications
InactiveUS20030203991A1Tough and durable and printable surfaceImprove wettabilityOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsColloidWear resistance
A coating composition is disclosed which comprises an aqueous polymeric matrix, a hydrophilic polymer, a colloidal metal oxide and a crosslinker. The coating composition when applied on medical devices is hydrophilic, shows improved lubricity, abrasion resistance and substrate adhesion on metallic or plastic substrates. The coating also shows improved water sheeting thus providing the coated substrates with anti-fog properties. The coating absorbs aqueous dye or stain solutions making the substrate suitable for printing.
Owner:HYDROMER INC
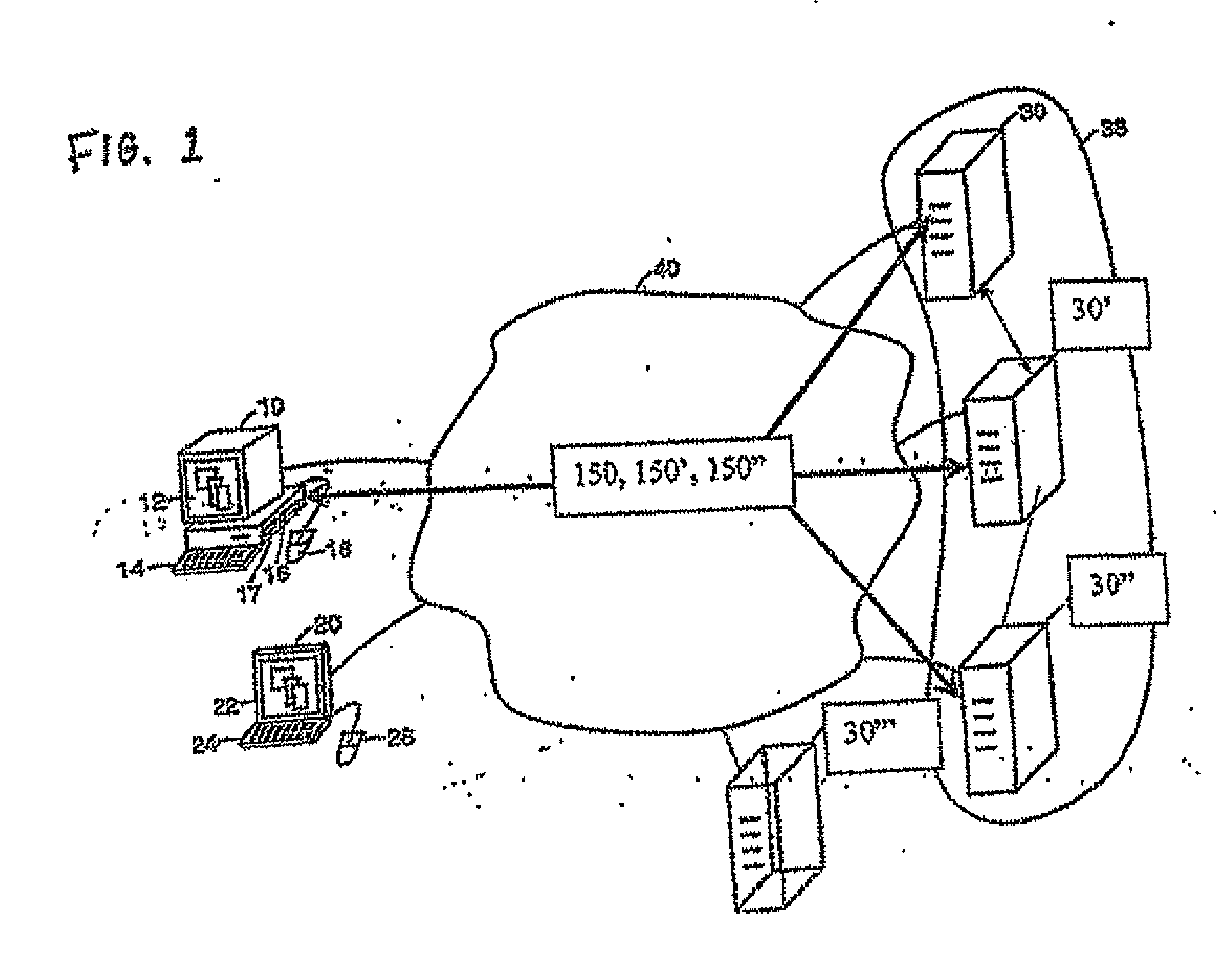
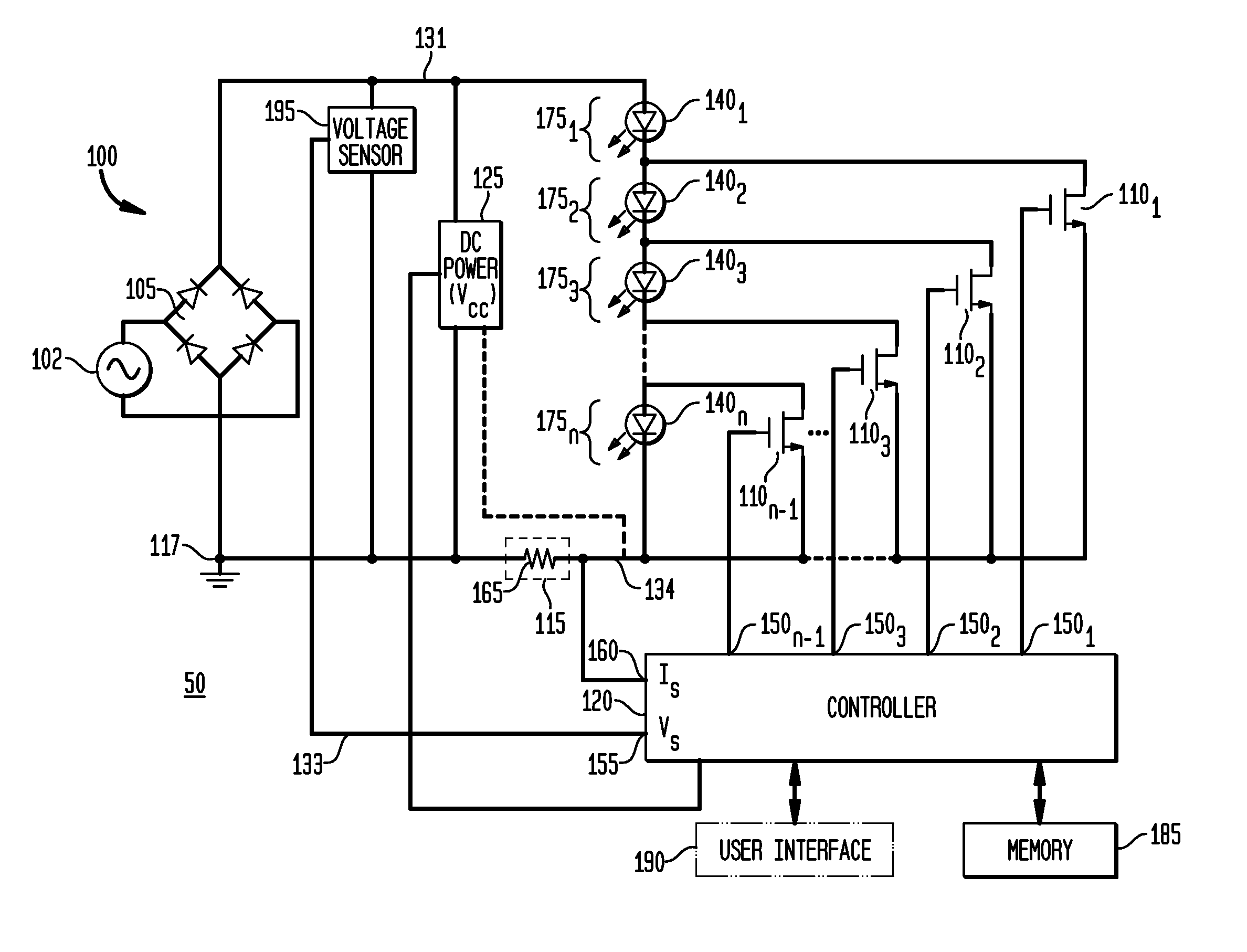
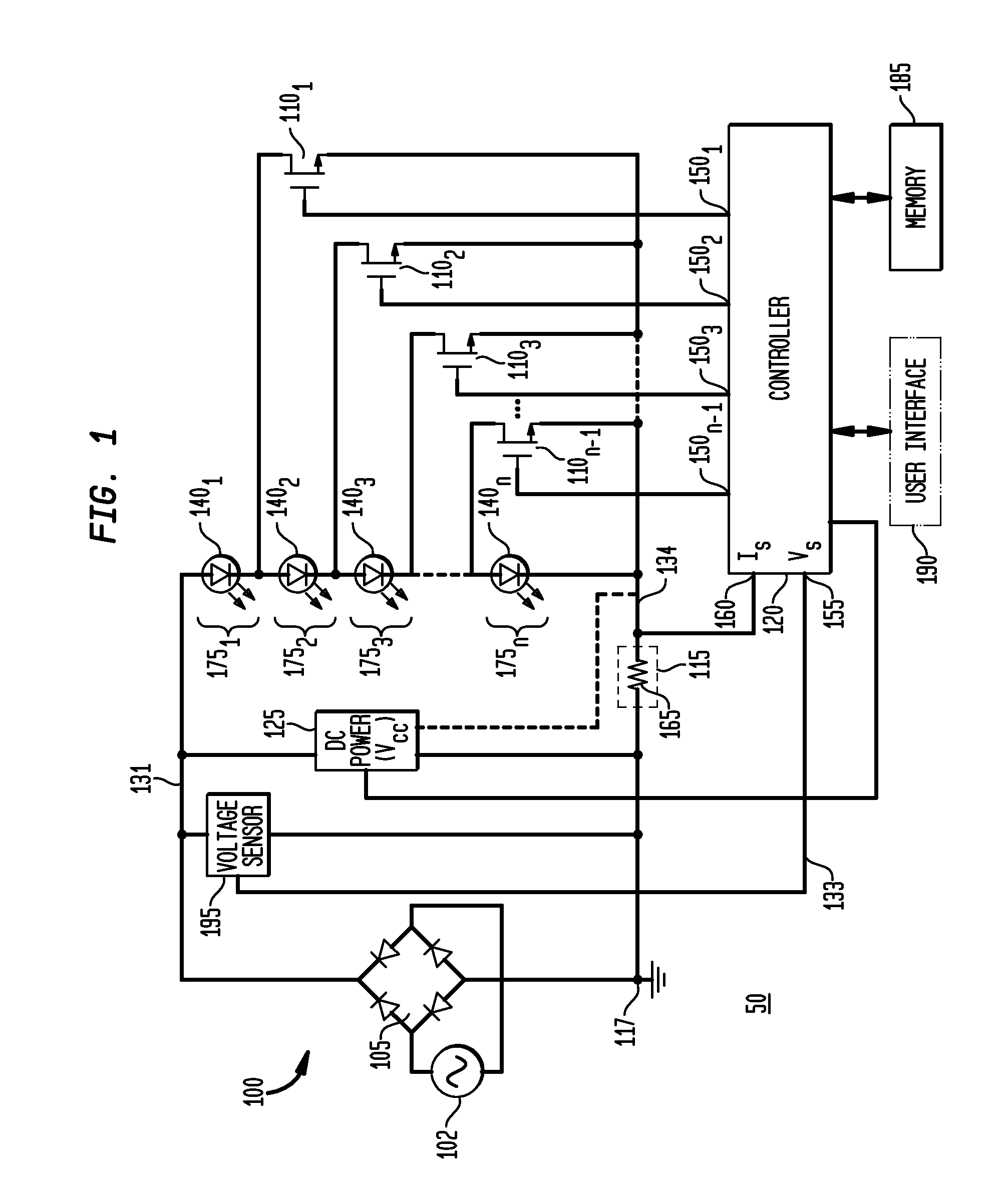
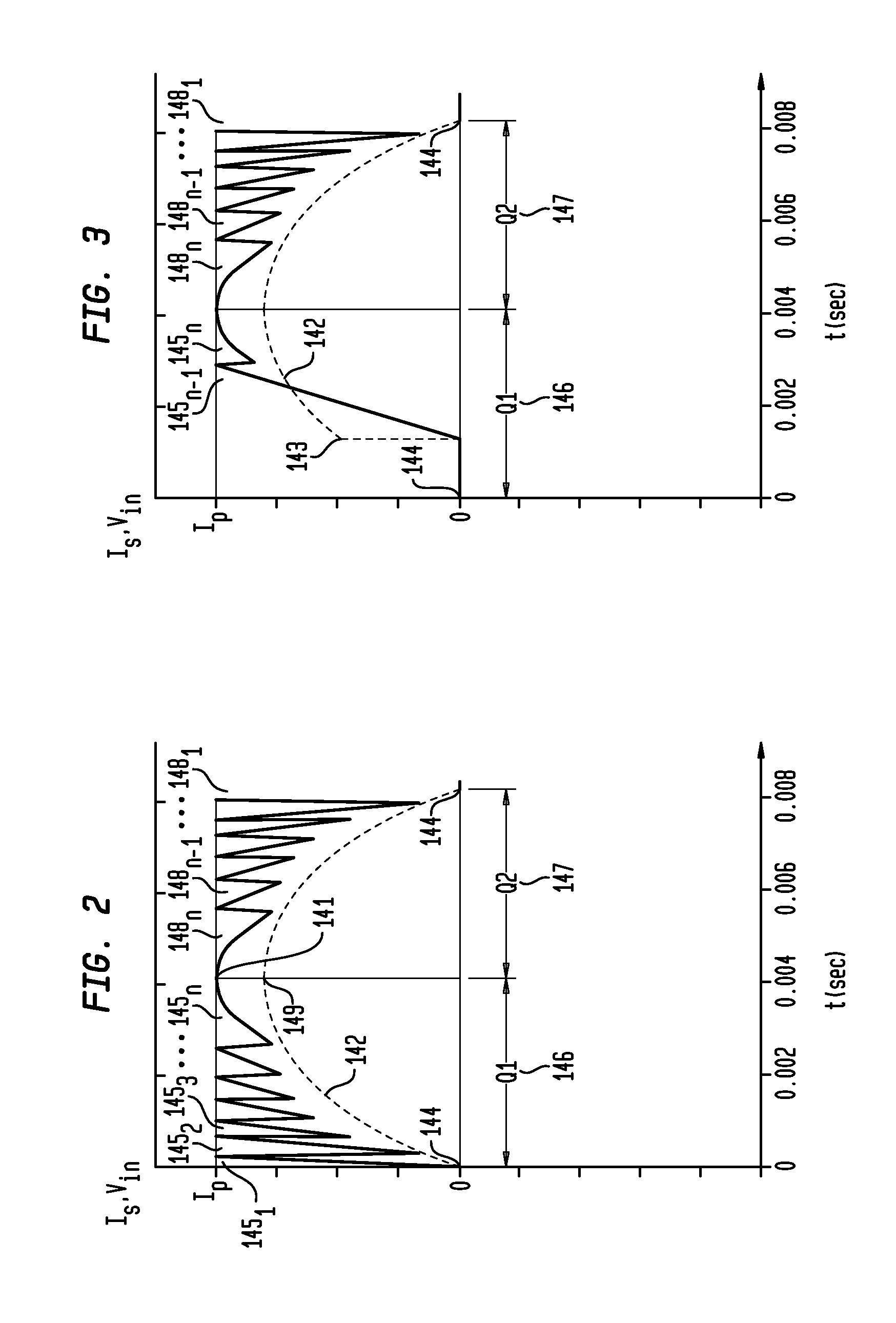
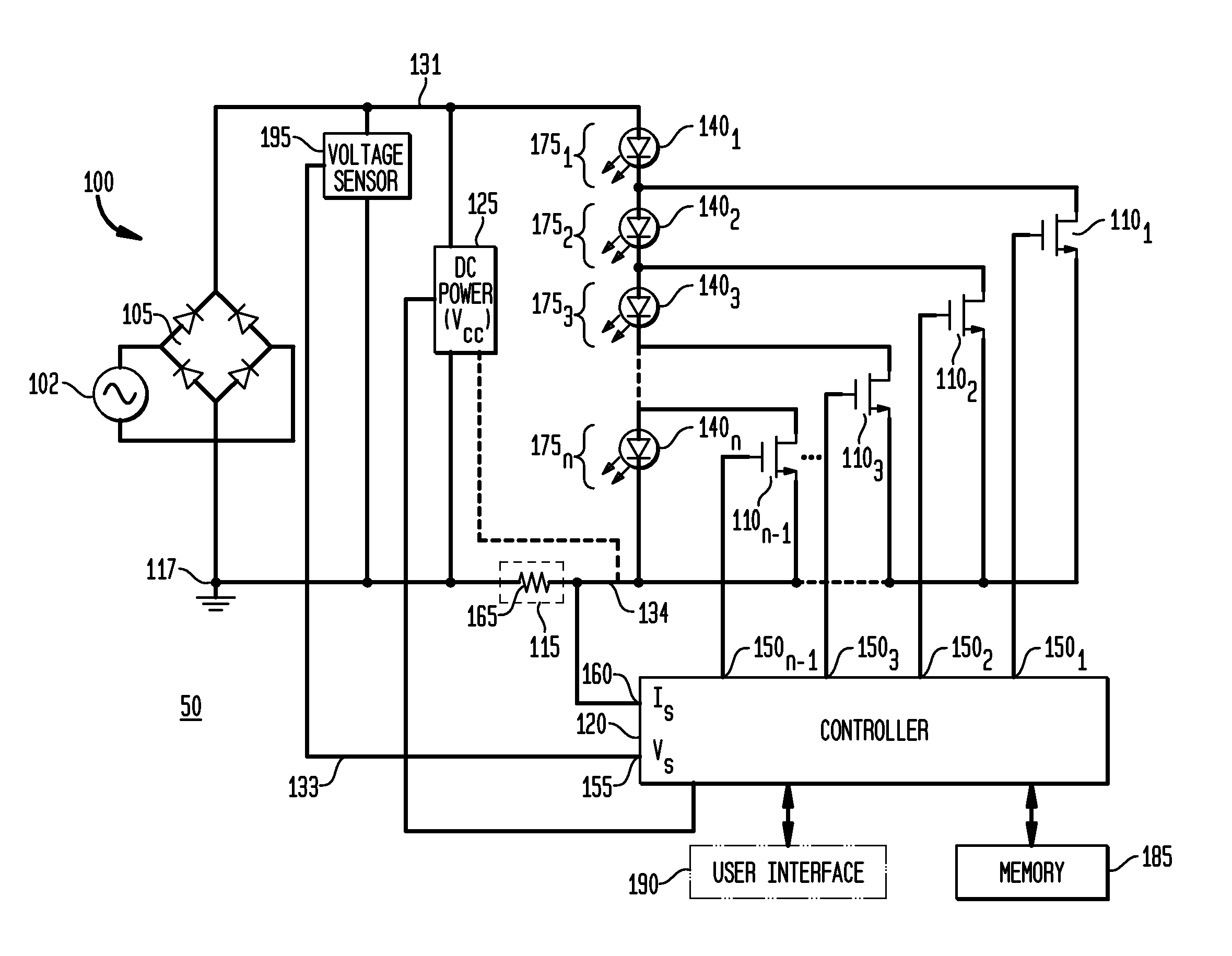
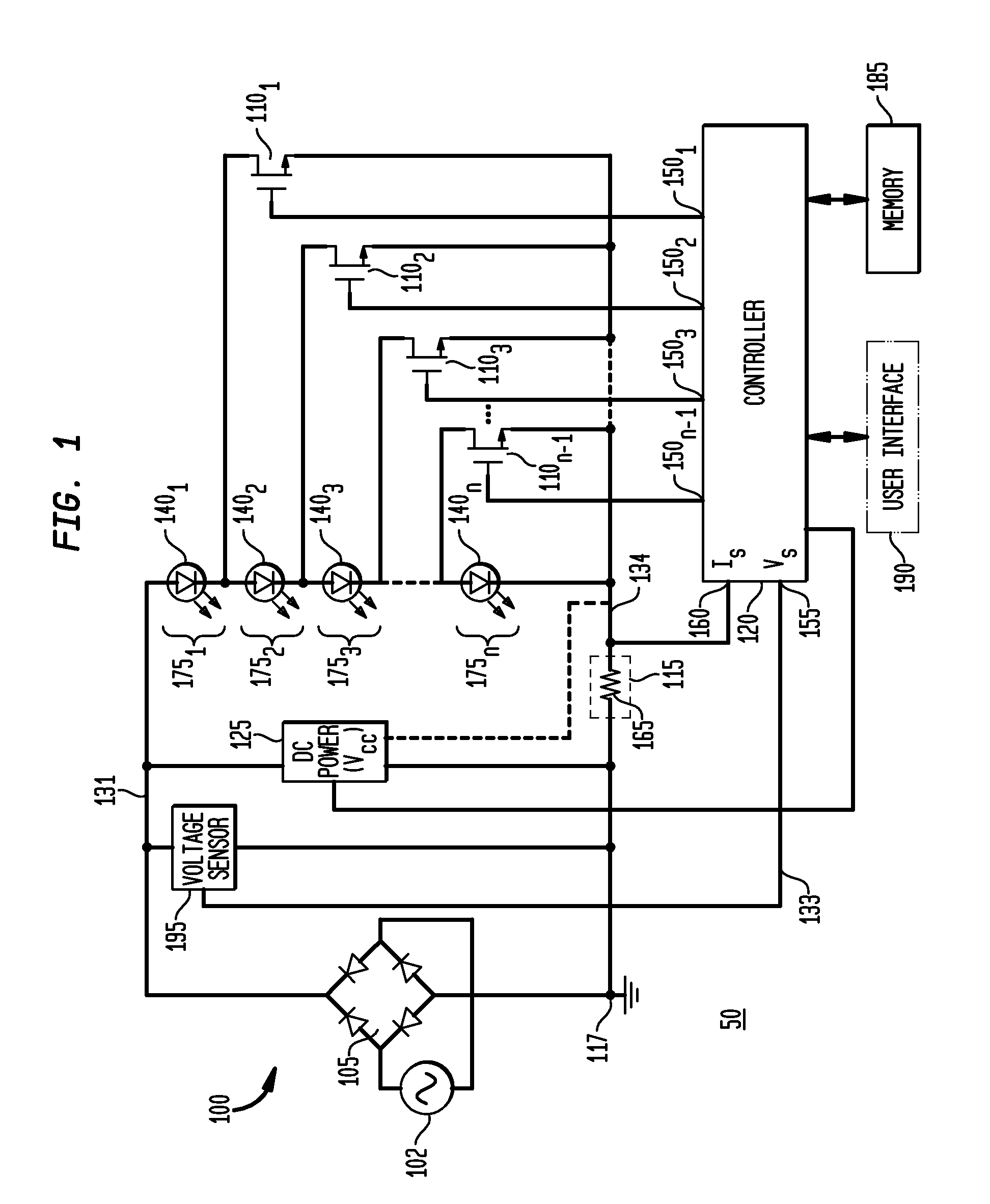
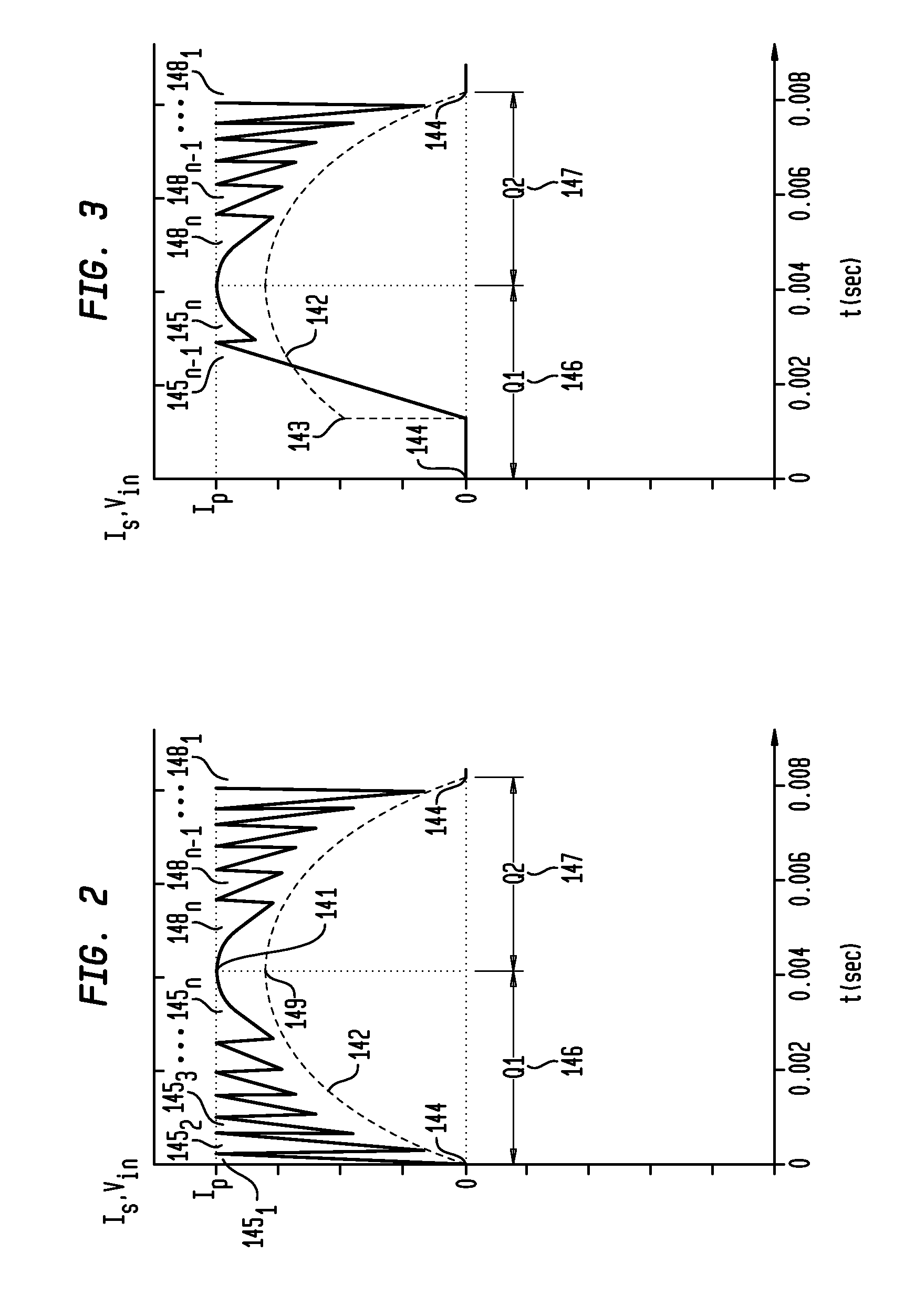
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20120081009A1Reduction in size and costImprove Utilization and EfficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentVoltage regulation
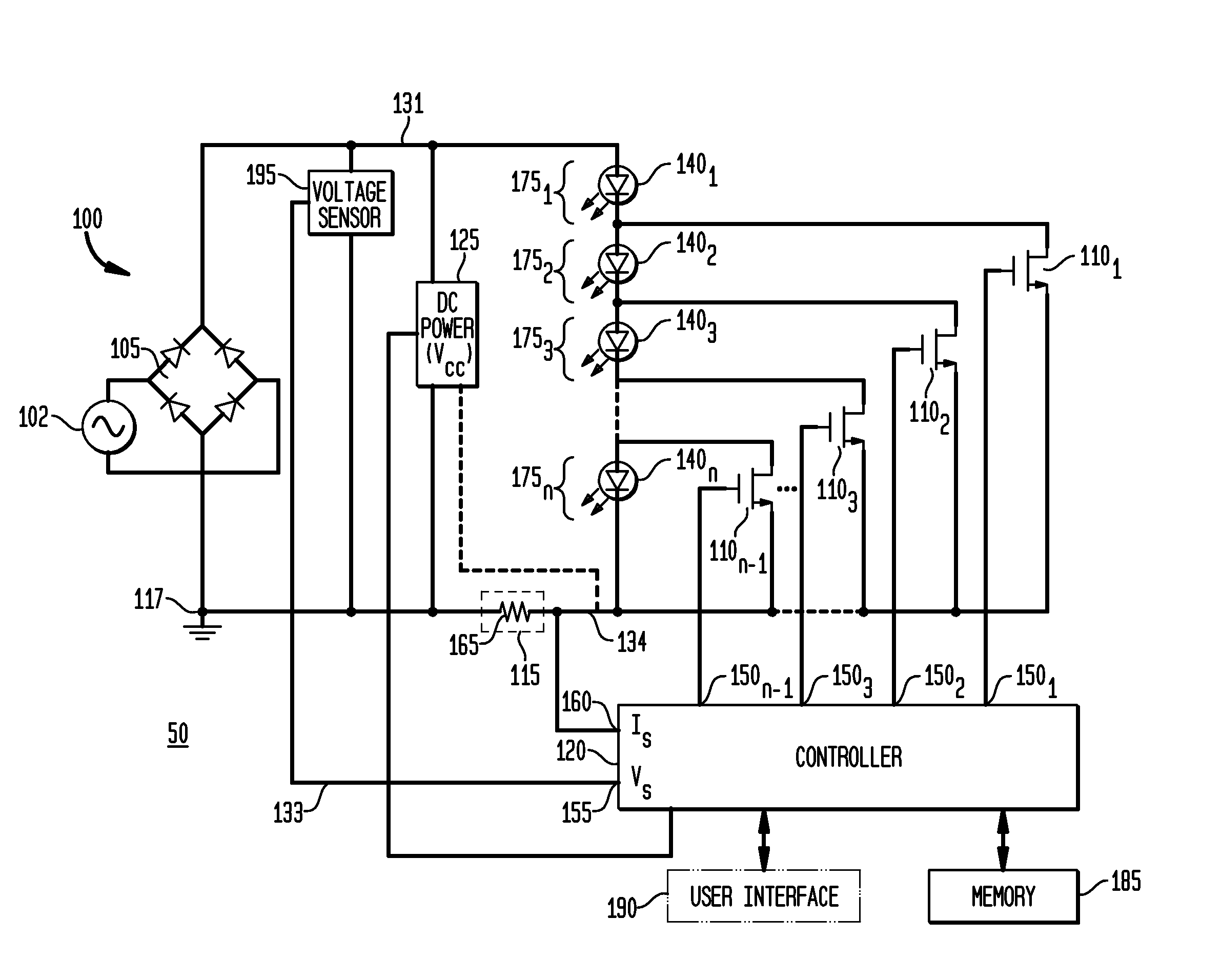
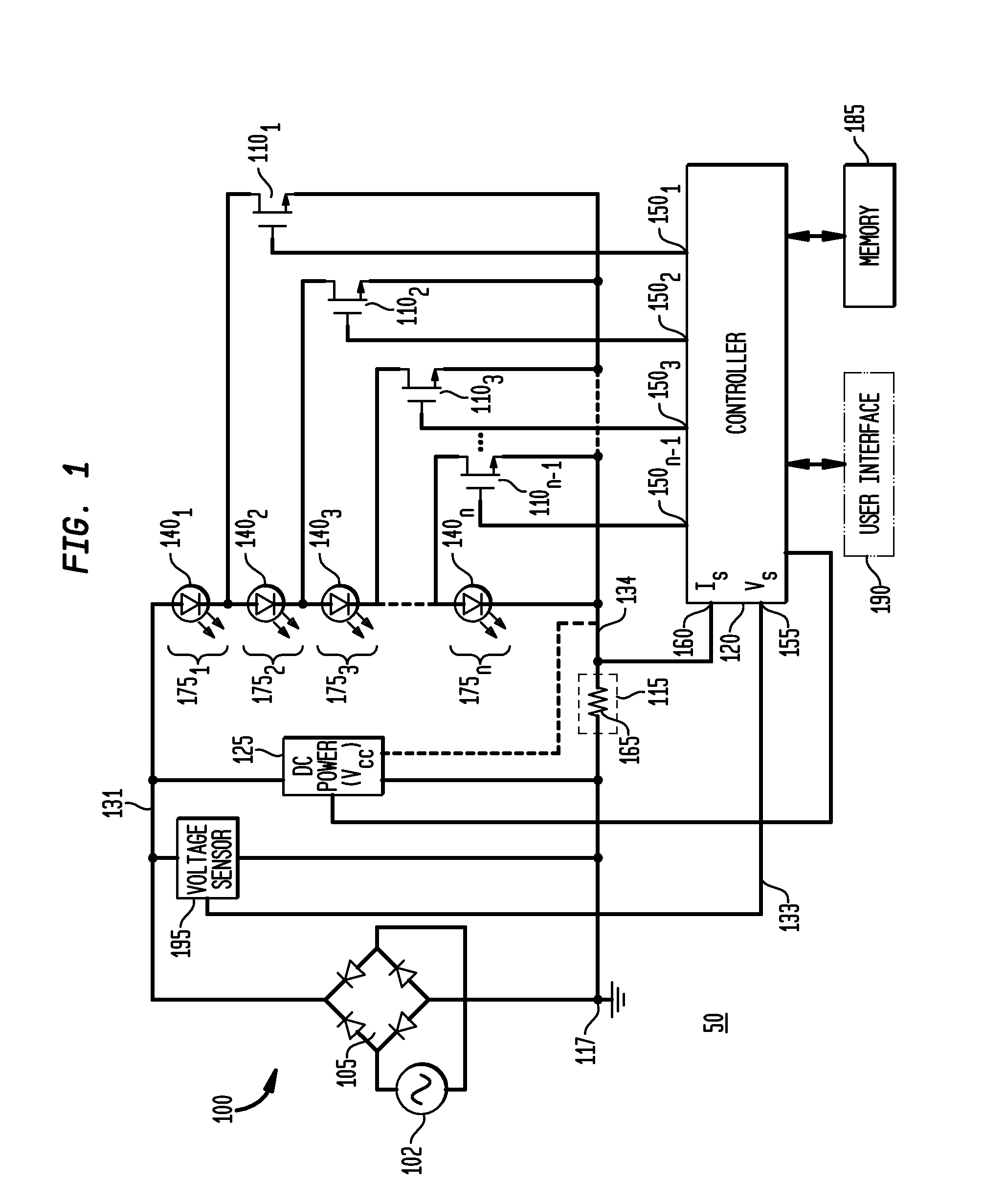
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a plurality of segments of LEDs; first and second current regulators; a current sensor; and a controller to monitor a current level through a series LED current path, and to provide for first or second segments of LEDs to be in or out of the series LED current path at different current levels. A voltage regulator is also utilized to provide a voltage during a zero-crossing interval of the AC voltage. In an exemplary embodiment, first and second segments of LEDs are both in the series LED current path regulated at a lower current level compared to when only the first segment of LEDs is in the series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20100308739A1Reduction in size and costImprove Utilization and EfficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentControl signal
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a first plurality of segments of LEDs; a plurality of switches coupled to the plurality of segments of LEDs to switch a selected segment into or out of a series LED current path in response to a control signal; a memory; and a controller which, in response to a first parameter and during a first part of an AC voltage interval, determines and stores in the memory a value of a second parameter and generates a first control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs into the series LED current path; and during a second part of the AC voltage interval, when a current value of the second parameter is substantially equal to the stored value, generates a second control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs out of the first series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Methods and systems for providing authorized remote access to a computing environment provided by a virtual machine
ActiveUS20070179955A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideProxy server
A method for providing authorized remote access to a computing environment provided by a virtual machine, includes the step of requesting, by a client machine, access to a resource. A collection agent gathers information about the client machine. A policy engine receives the gathered information. The policy engine makes an access control decision based on the received information. A computing environment already associated with the user is identified in response to the received information, the identified computing environment provided by a virtual machine. A broker server establishes, responsive to the access control decision, a connection between the client machine and the identified computing environment.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Methods and systems for assigning access control levels in providing access to resources via virtual machines
ActiveUS20070180493A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideProxy server
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Intergrated circuit and a method of cache remapping
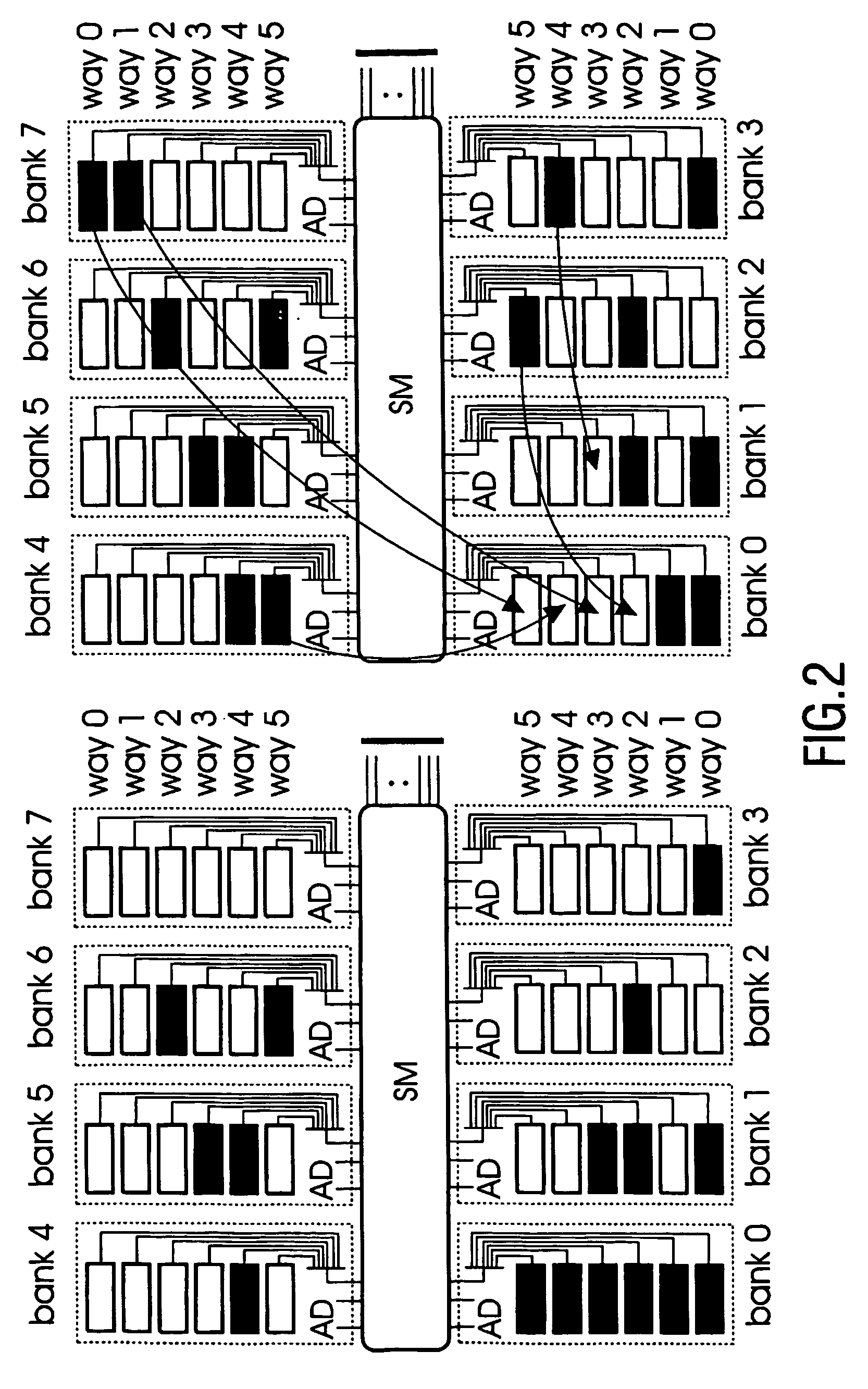
InactiveUS7827372B2Improve overall utilizationRapid cachingError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit is provided with at least one processing unit (TM), a cache memory (L2 BANK) having a plurality of memory modules, and remapping means (RM) for performing an unrestricted remapping within said plurality of memory modules. Accordingly, faulty modules can be remapped without limitations in order to optimise the utilization of the memory modules by providing an even distribution of the faulty modules.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Method and apparatus for cleaning of a CVD reactor
InactiveUS20090269506A1Efficient and uniform remote plasma cleaningImprove efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingElectrostatic cleaningRemote plasmaOxygen
The present invention provides a process and an apparatus for remote plasma cleaning of a process chamber of a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) reactor. The reactive species are generated in a remote plasma unit and are introduced into the process chamber through a plurality of inlet holes. The reactive species are free radicals such as oxygen radicals, fluorine radicals, and the like. These reactive species react with the unwanted residues in the process chamber and generate volatile products. The invention also provides a method for controlling the flow rate of the reactive species.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
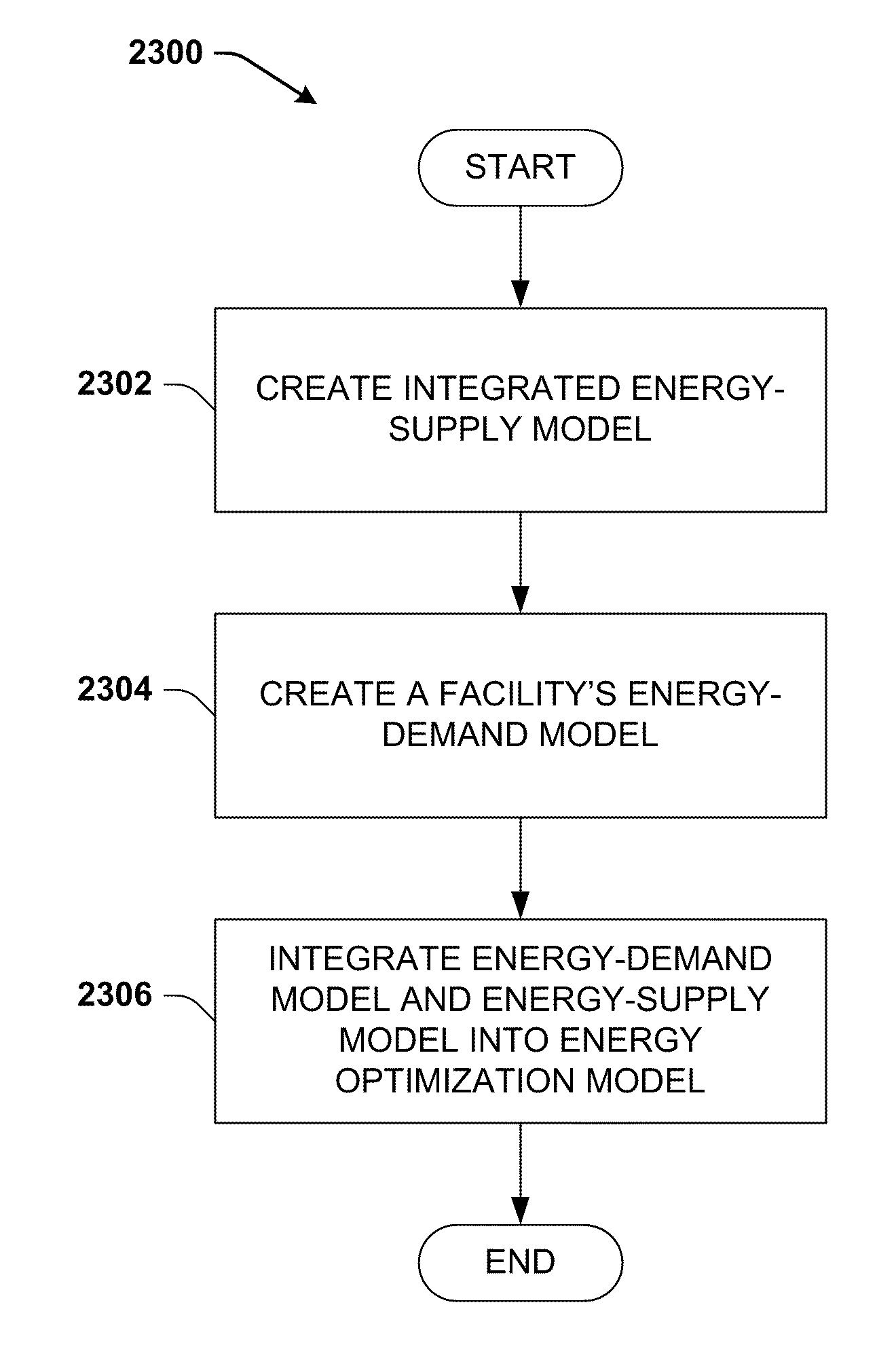
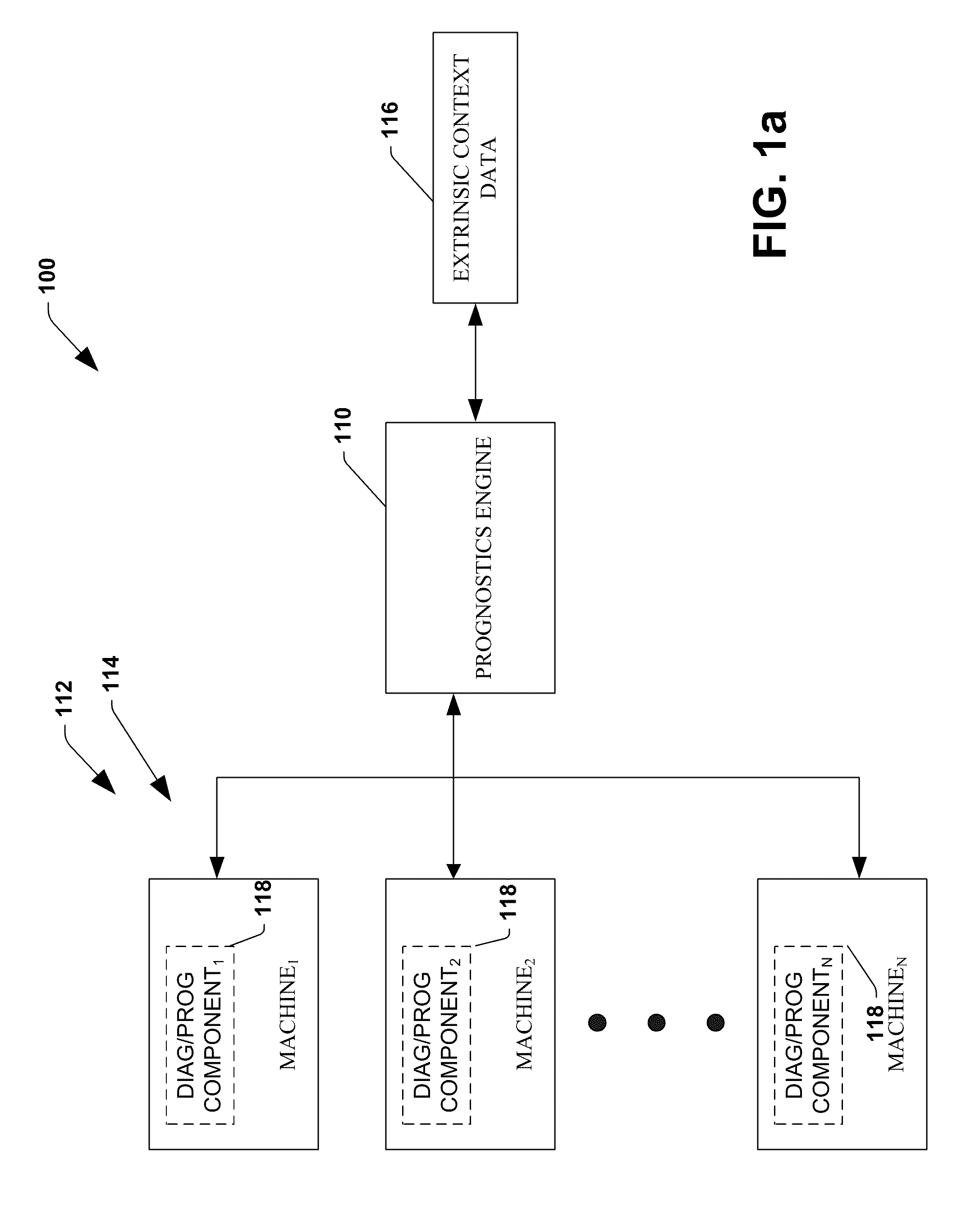
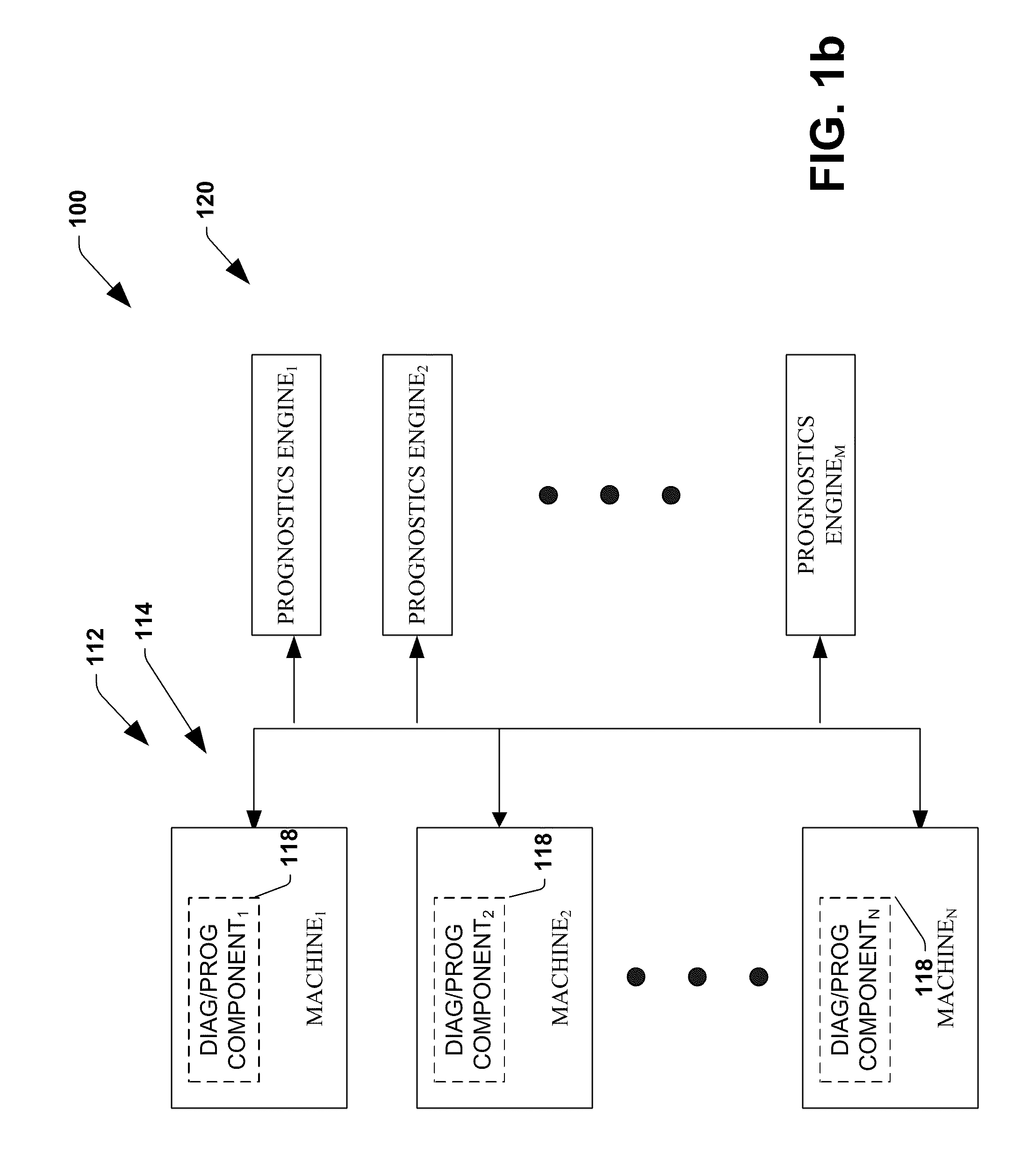
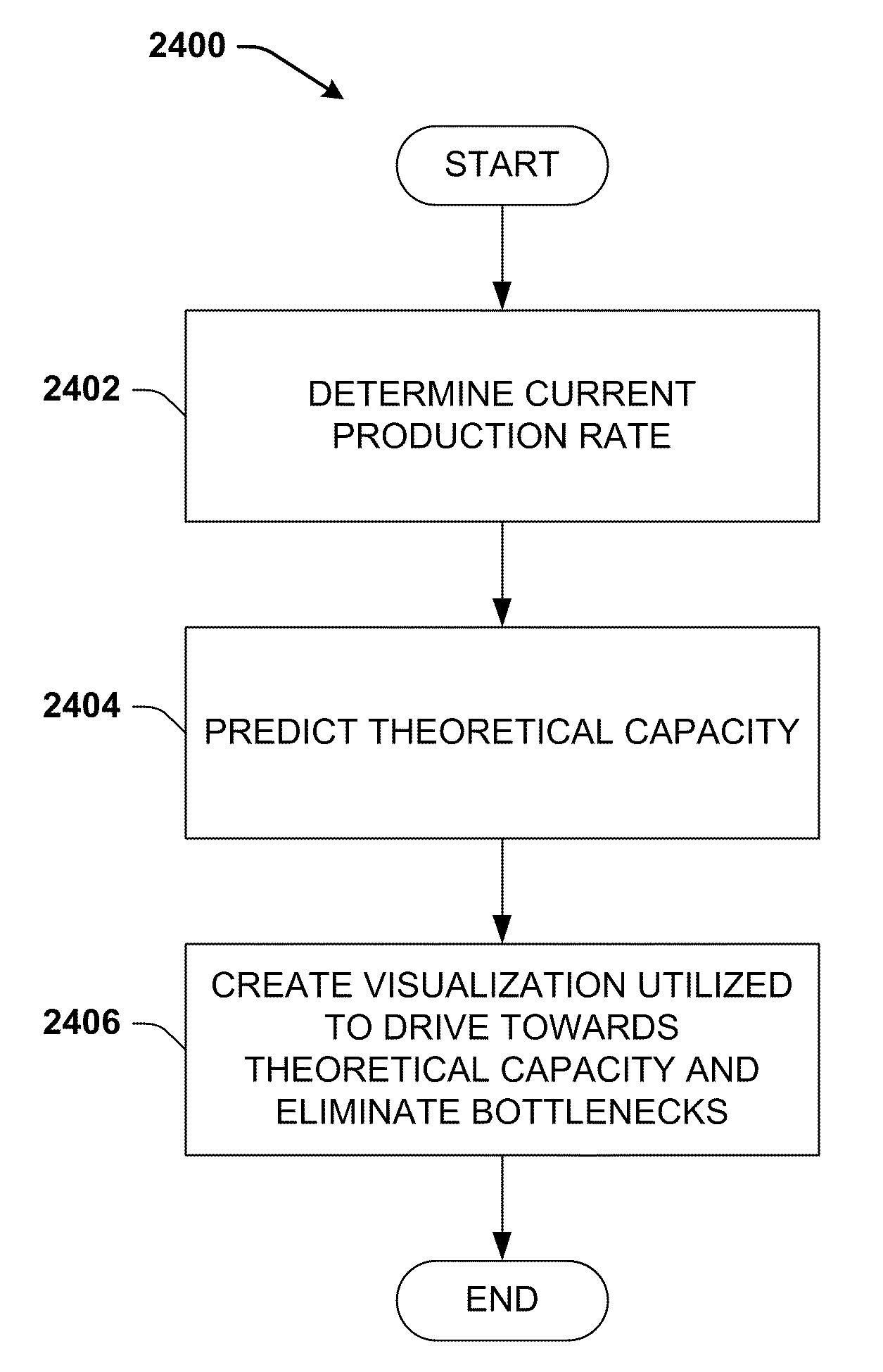
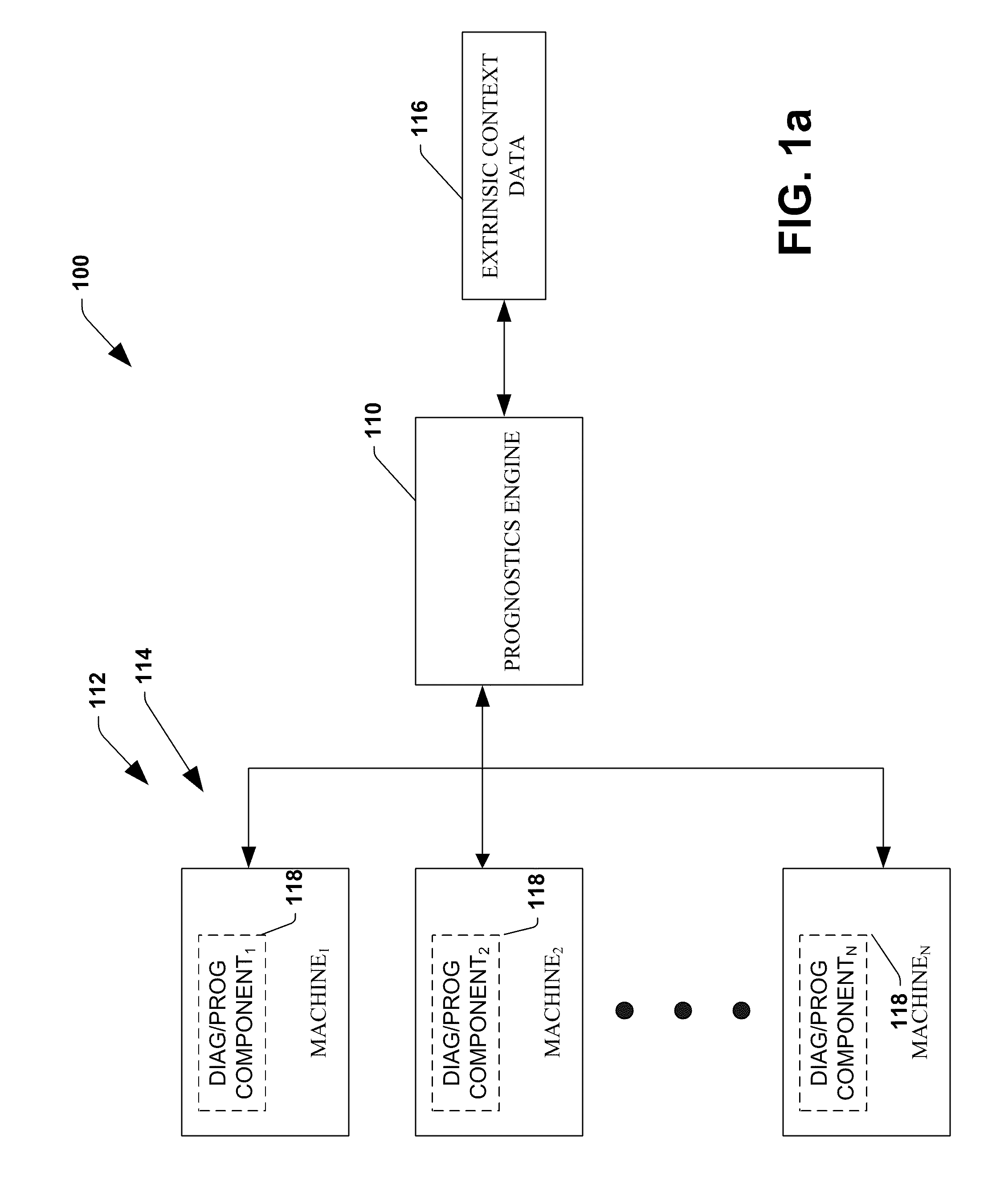
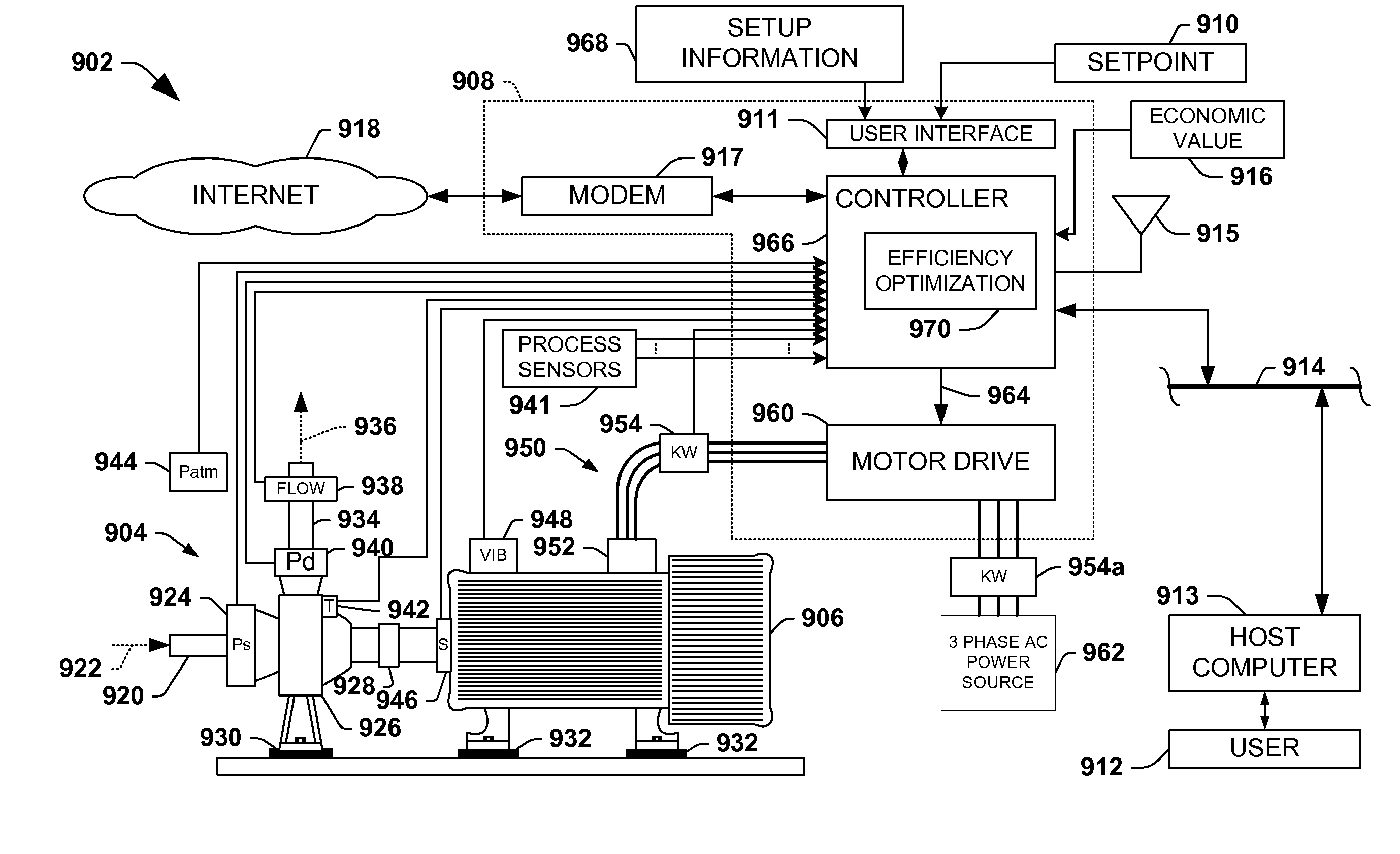
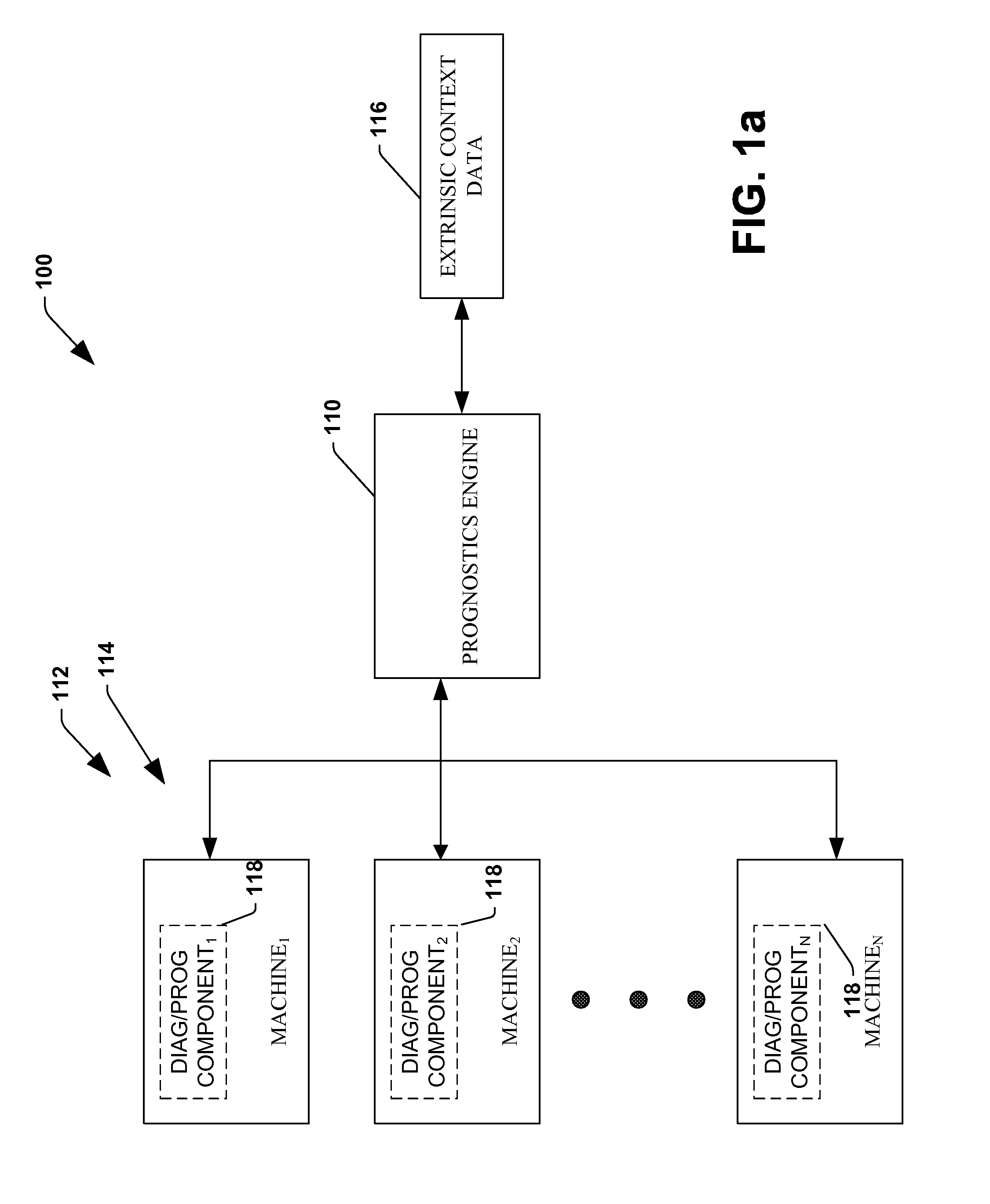
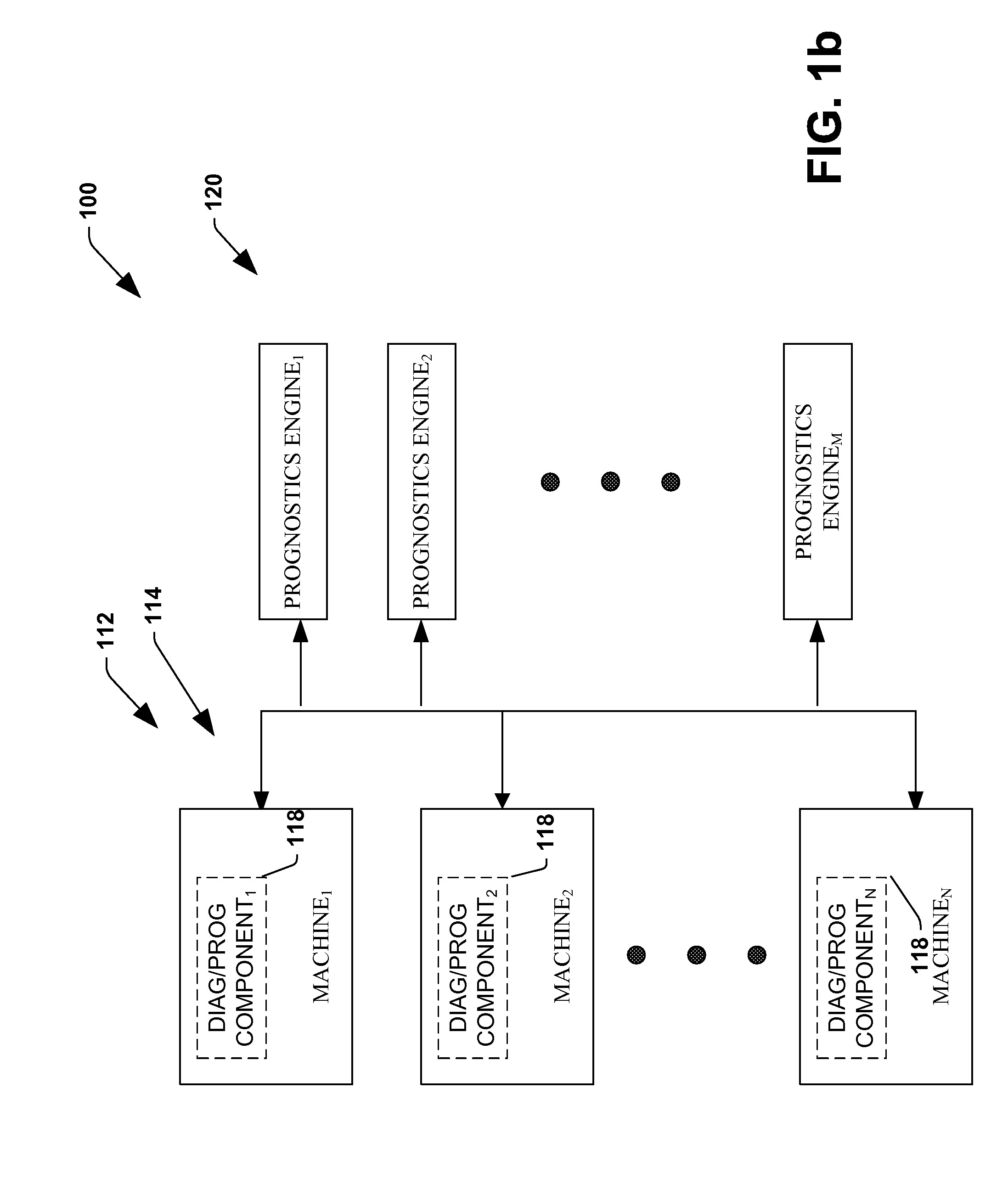
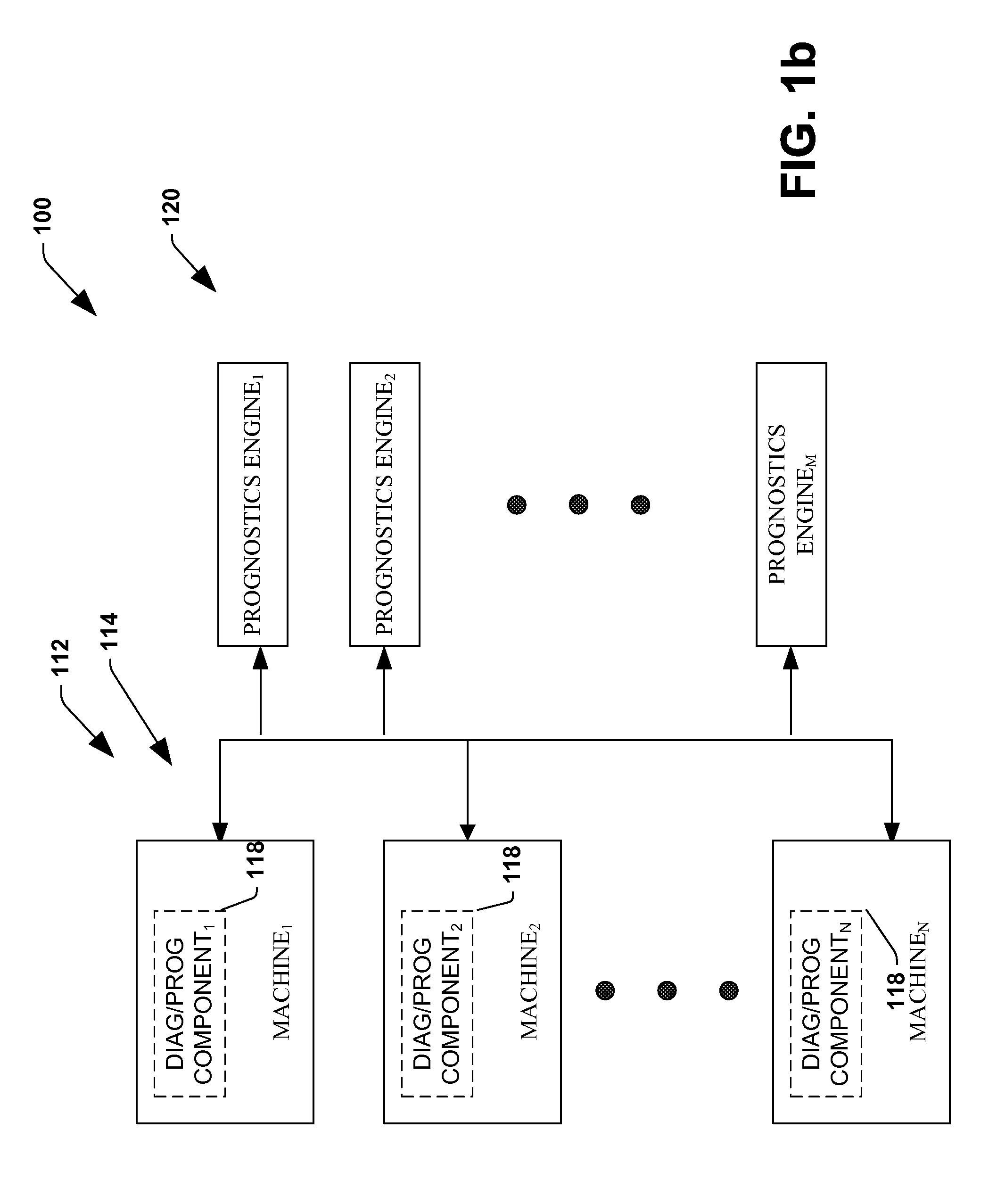
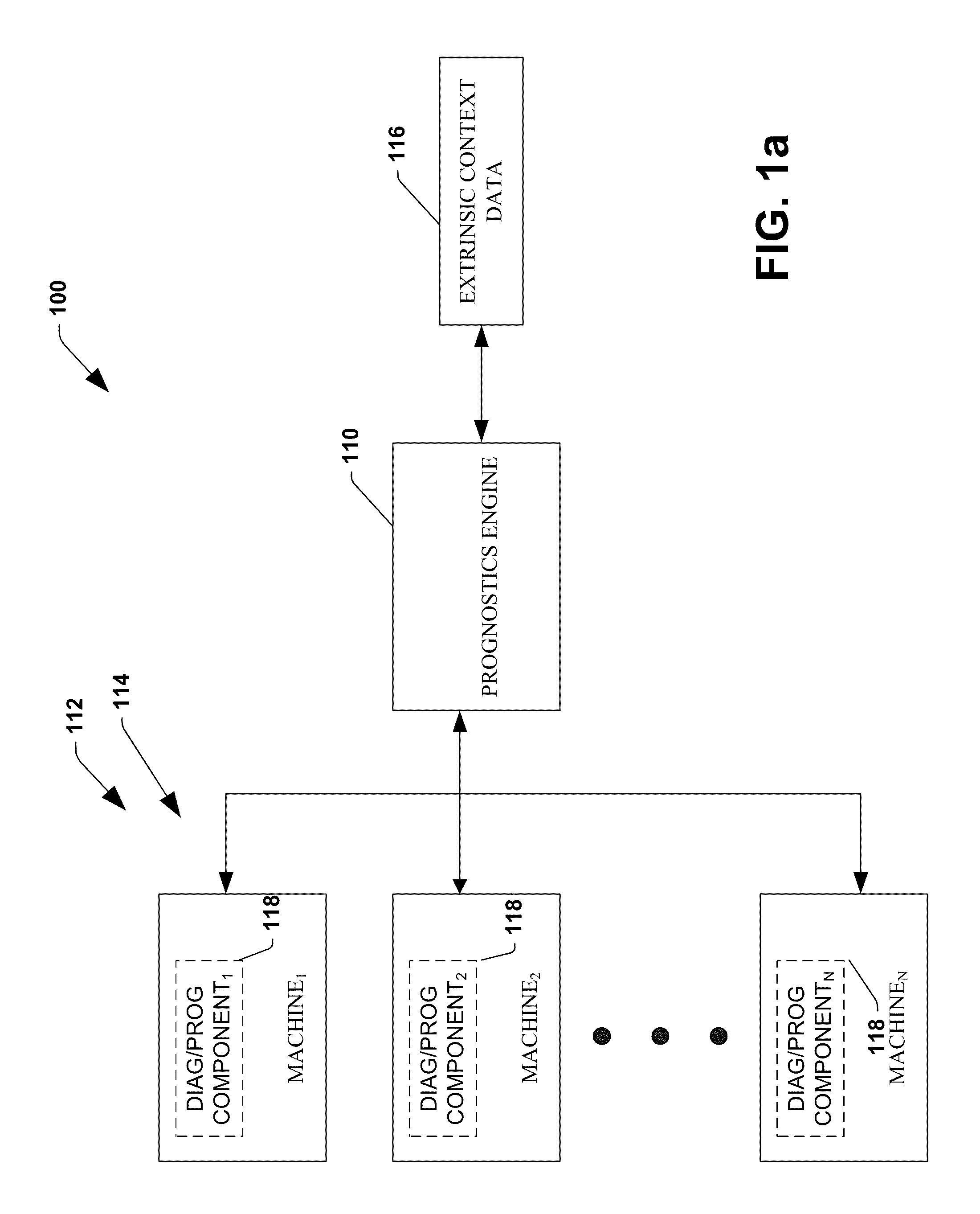
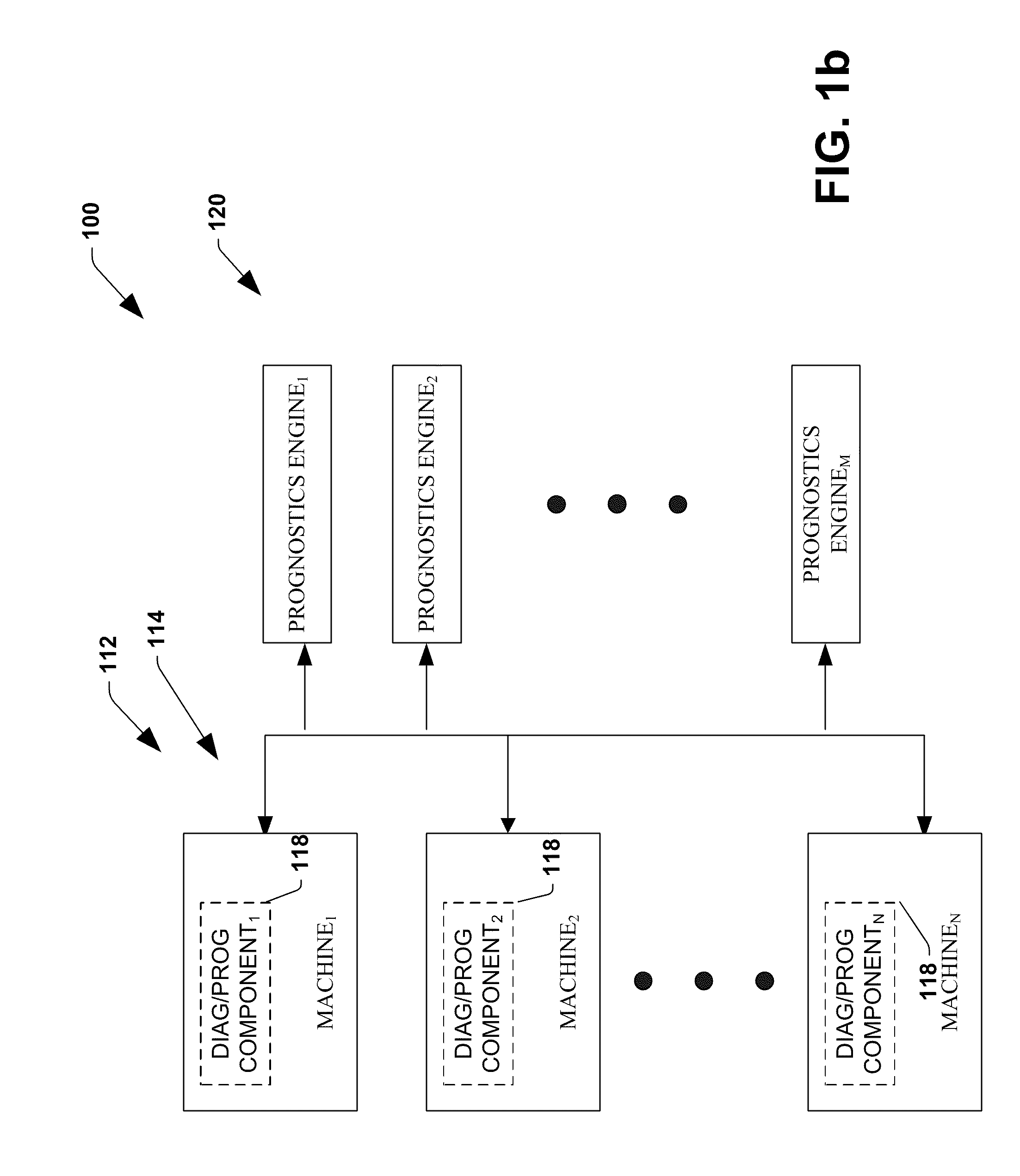
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
ActiveUS20090204267A1Minimizing power consumptionCost-optimizedMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlOperational costsMulti-objective optimization
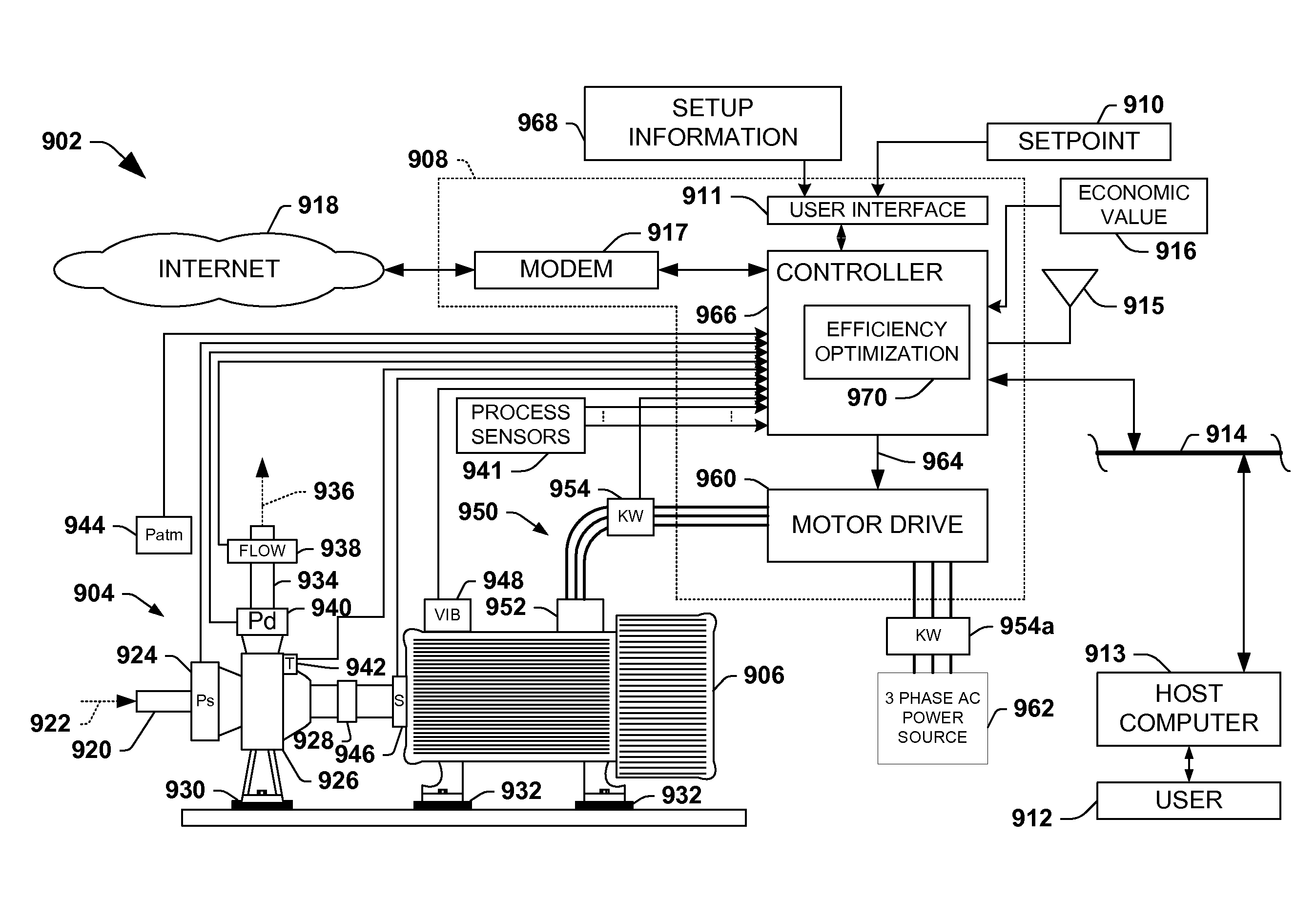
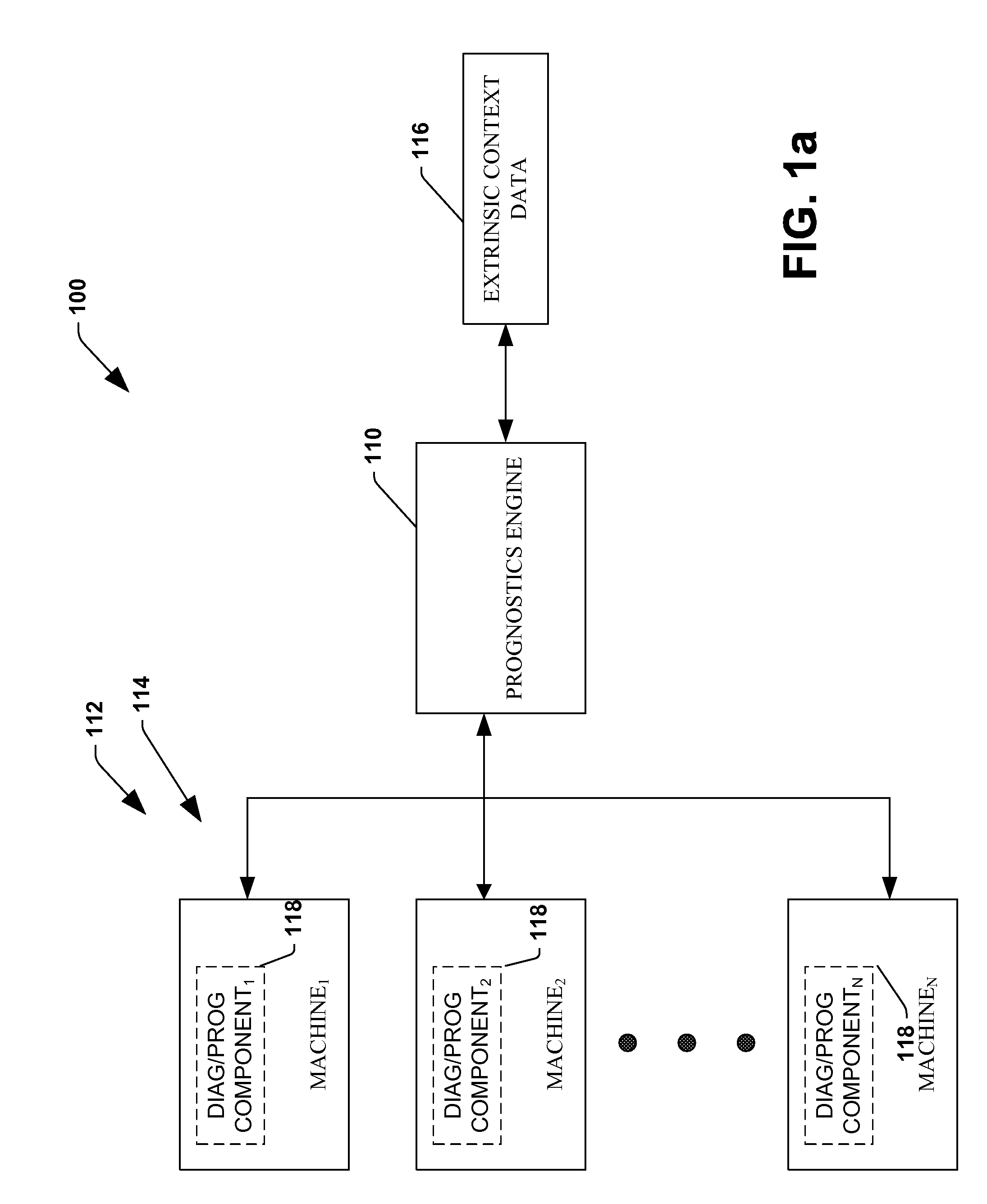
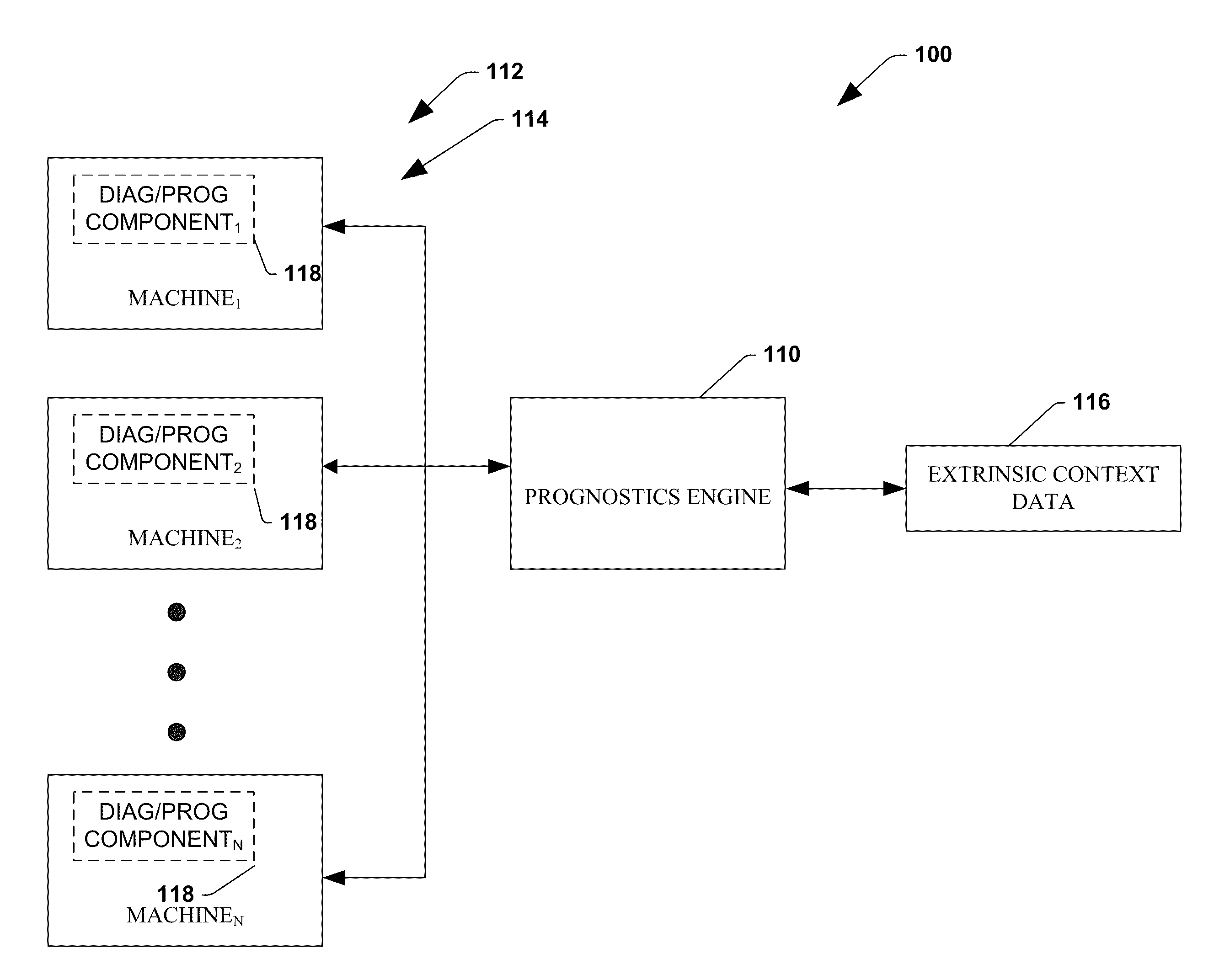
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Methods and systems for selecting a method for execution, by a virtual machine, of an application program
ActiveUS20070180450A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideClient machine
A method for selecting a method of execution for an application includes the step of receiving credentials. A plurality of applications available to a client machine is enumerated responsive to the received credentials. A request to execute an enumerated application is received. One of a predetermined number of methods for executing the requested application is selected responsive to a policy, the predetermined number of methods including a method for executing the requested application in a computing environment provided by a virtual machine.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
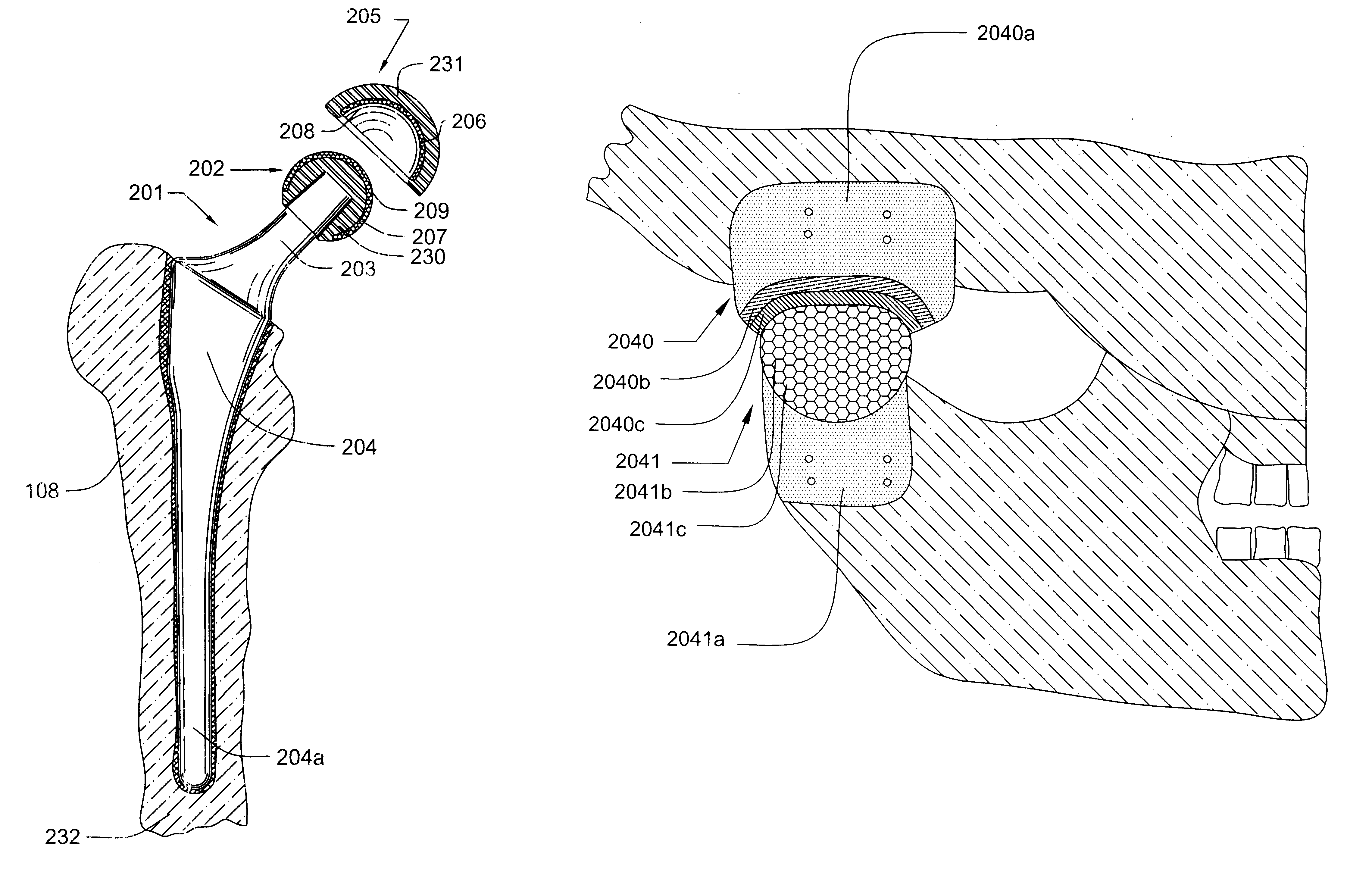
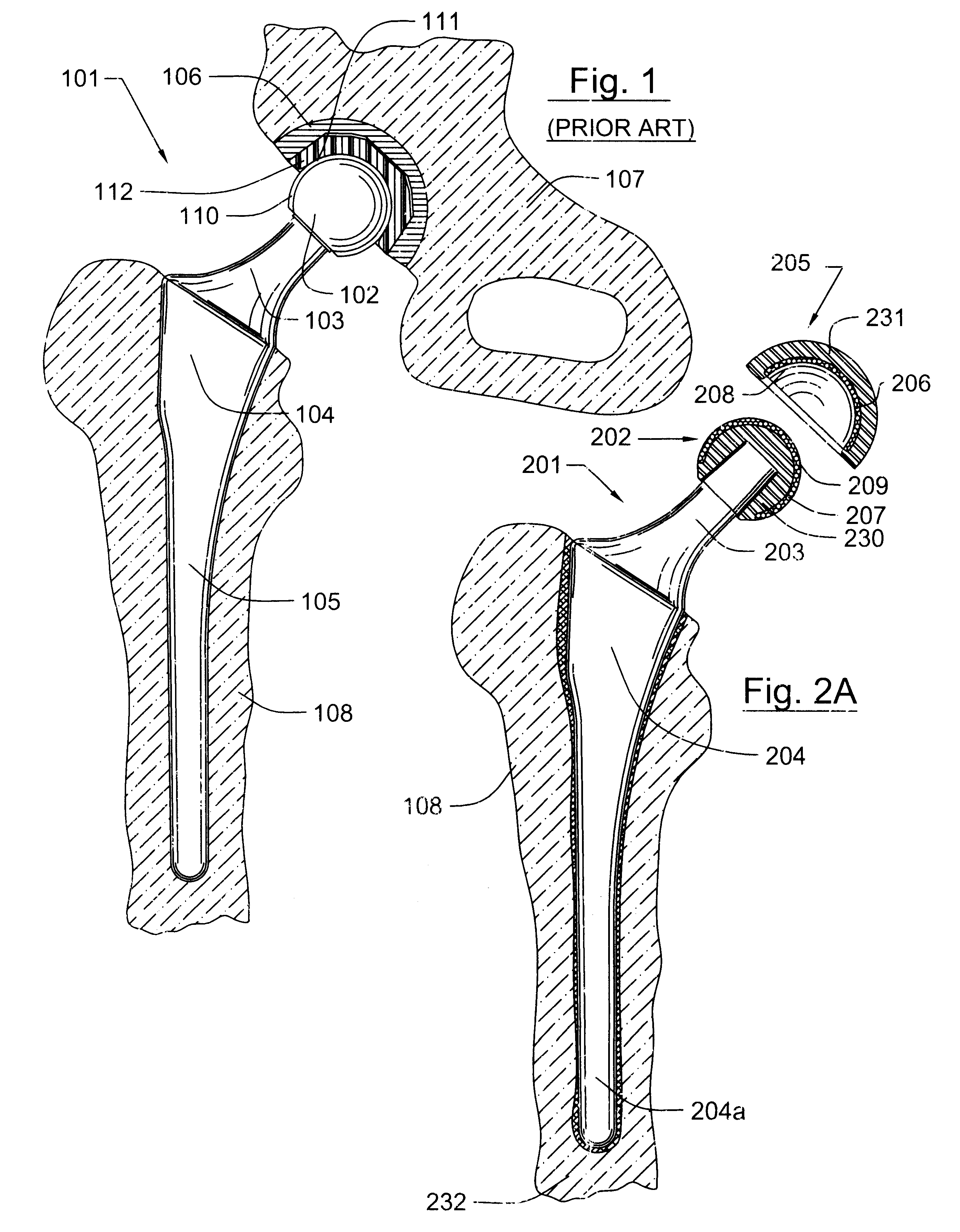
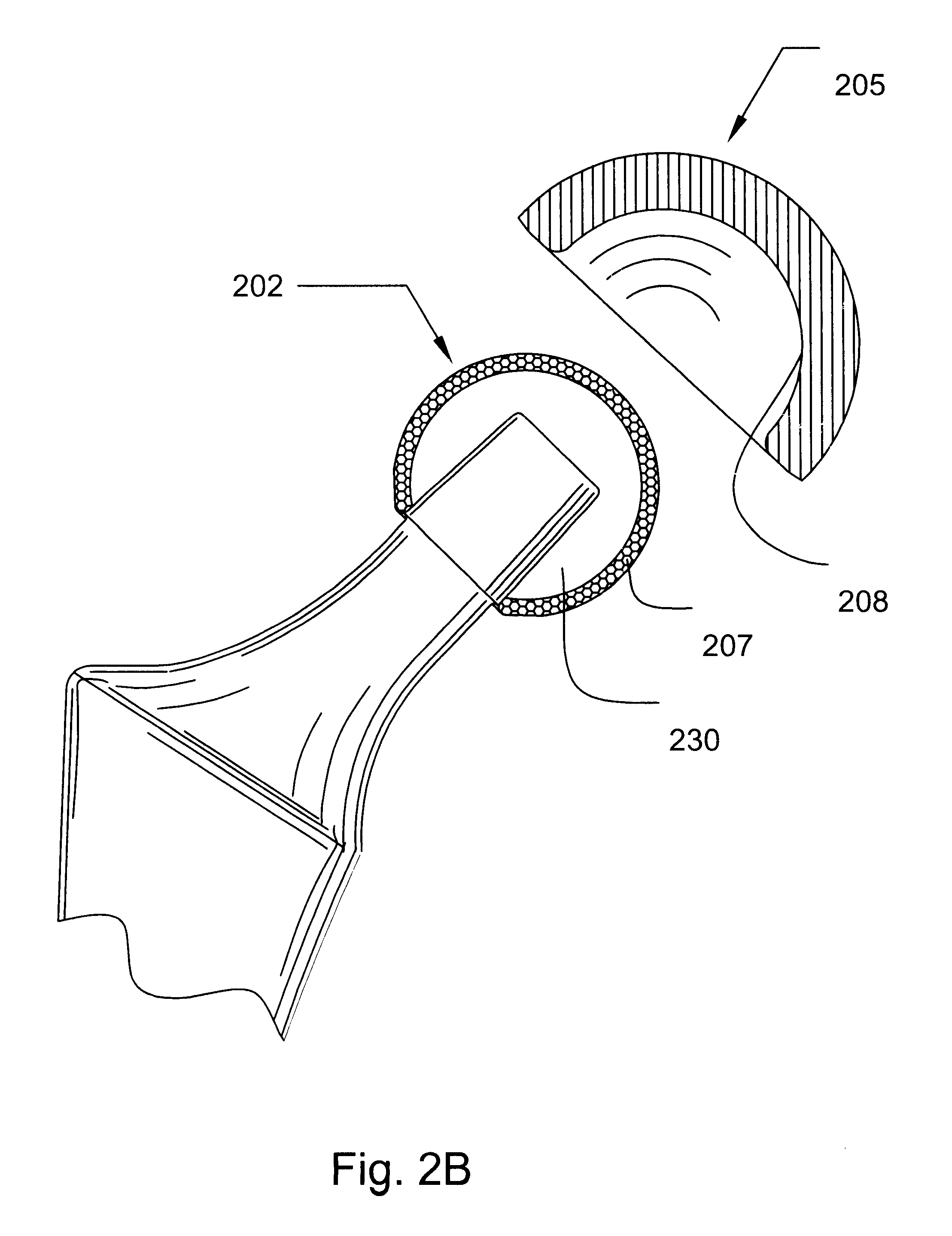
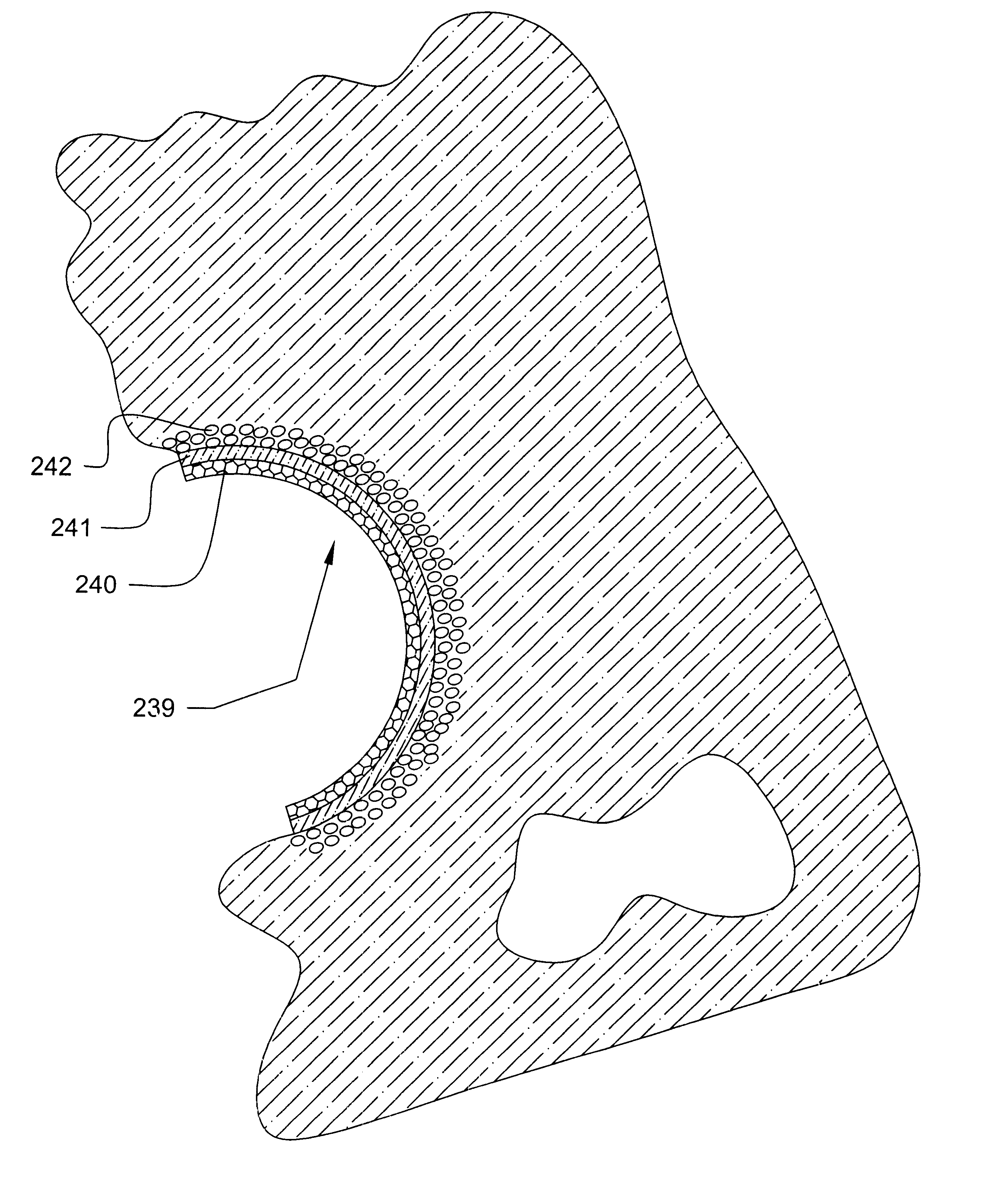
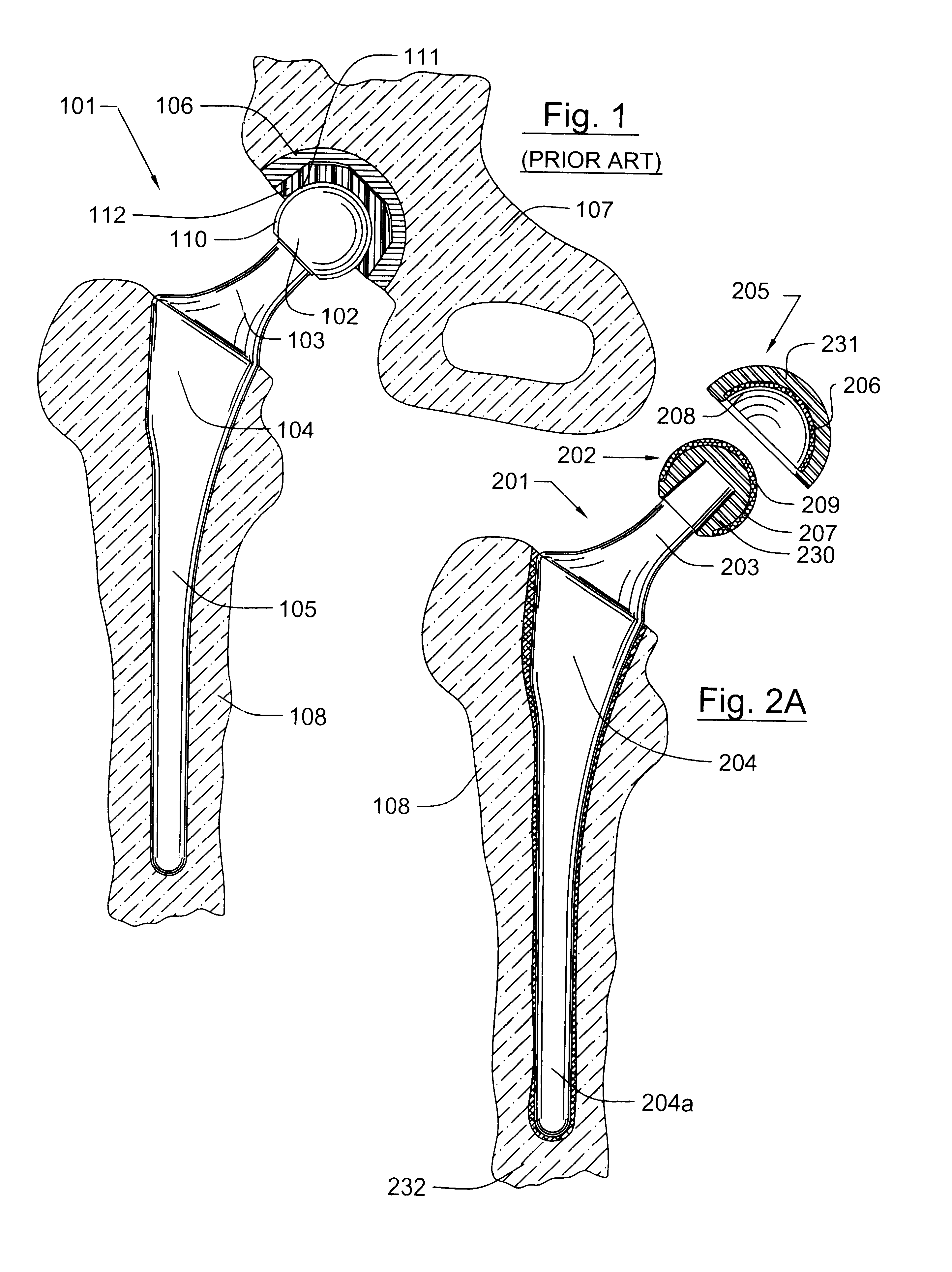
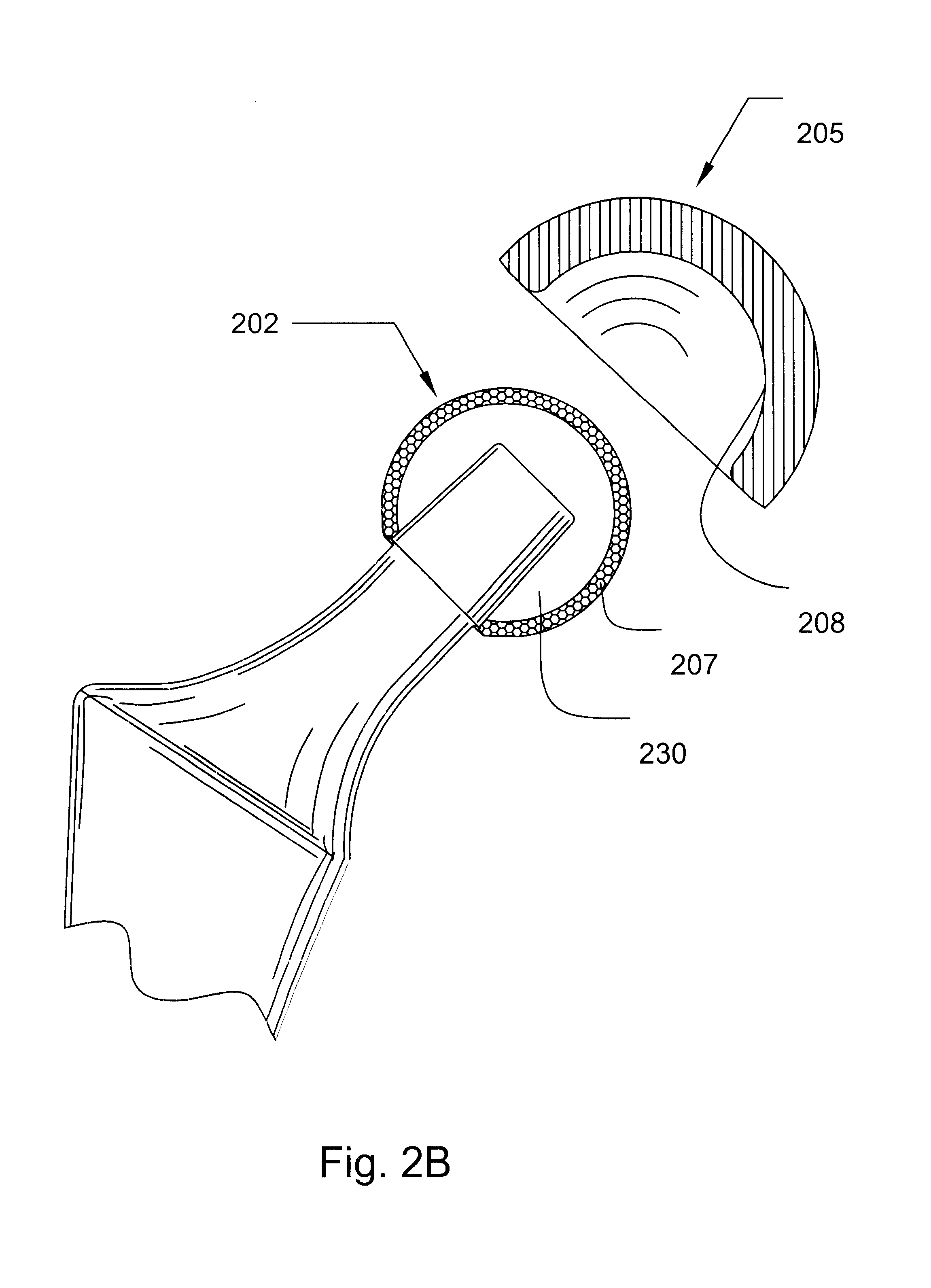
Prosthetic hip joint having a polycrystalline diamond articulation surface and a plurality of substrate layers
InactiveUS6793681B1Less disruptiveLimit stressJoint implantsFemoral headsPolycrystalline diamondProsthesis
Prosthetic joints, components for prosthetic joints, superhard bearing and articulation surfaces, diamond bearing and articulation surfaces, substrate surface topographical features, materials for making joints, bearing and articulation surfaces, and methods for manufacturing and finishing the same, and related information are disclosed, including a prosthetic hip joint having a polycrystalline diamond articulation surface and a plurality of substrate layers.
Owner:DIAMICRON
Methods and systems for providing access to a computing environment
ActiveUS20070186212A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationClient-sideClient machine
A method for providing access to a computing environment includes the step of receiving, by a broker machine, a request from a client machine for access to a computing environment, the request including an identification of a user of the client machine. One of a plurality of virtual machines is identified, the identified virtual machine providing the requested computing environment. One of a plurality of execution machines is identified, the identified execution machine executing a hypervisor providing access to hardware resources required by the identified virtual machine. A connection is established between the client machine and the identified virtual machine.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Prosthetic hip joint having sintered polycrystalline diamond compact articulation surfaces
InactiveUS6290726B1Improve wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesProsthesis
Prosthetic joints, components for prosthetic joints, superhard bearing and articulation surfaces, diamond bearing and articulation surfaces, substrate surface topographical features, materials for making joints, bearing and articulation surfaces, and methods for manufacturing and finishing the same, and related information are disclosed, including a prosthetic hip joint having sintered polycrystalline diamond articulation.
Owner:DIAMICRON
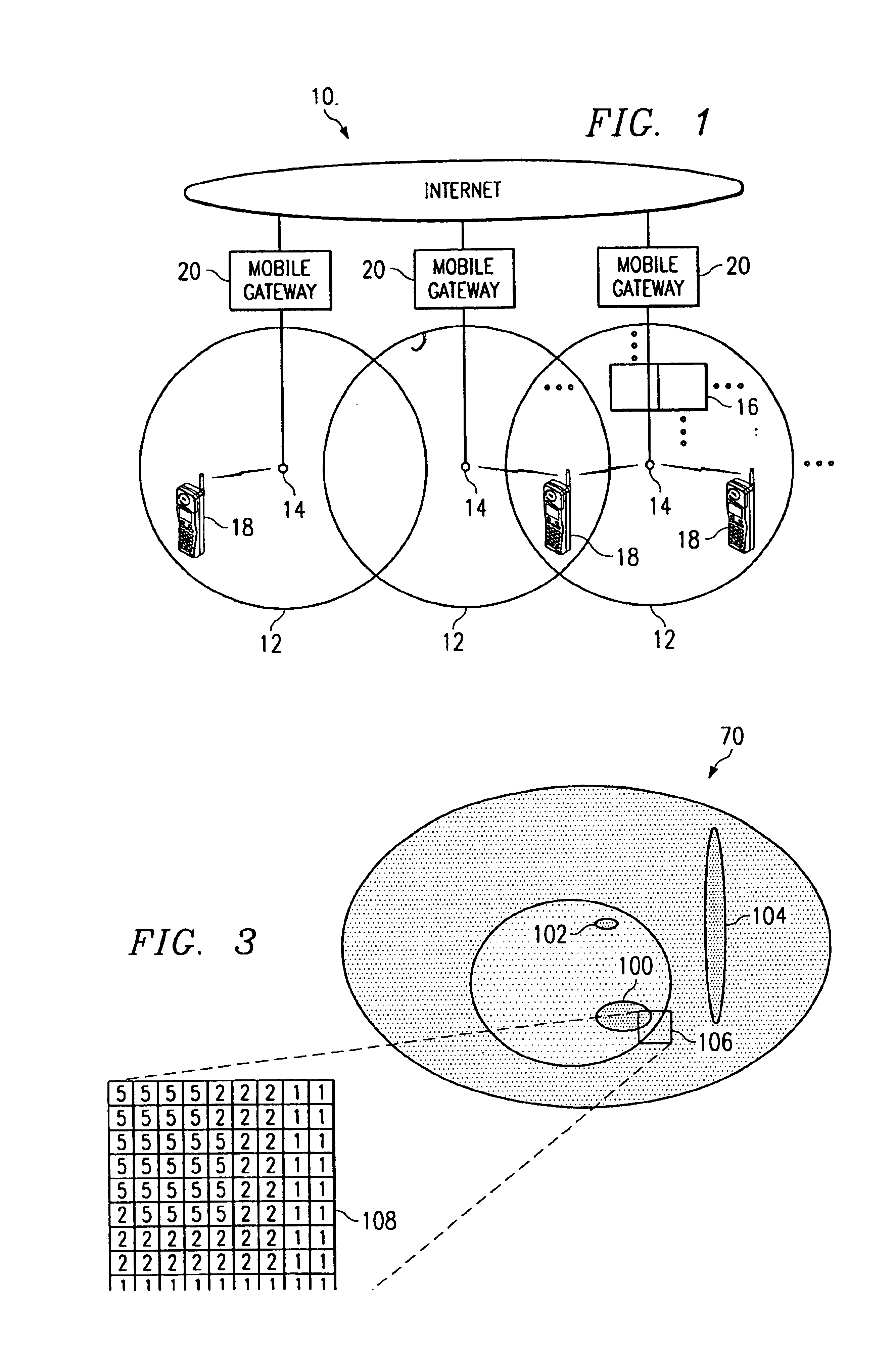
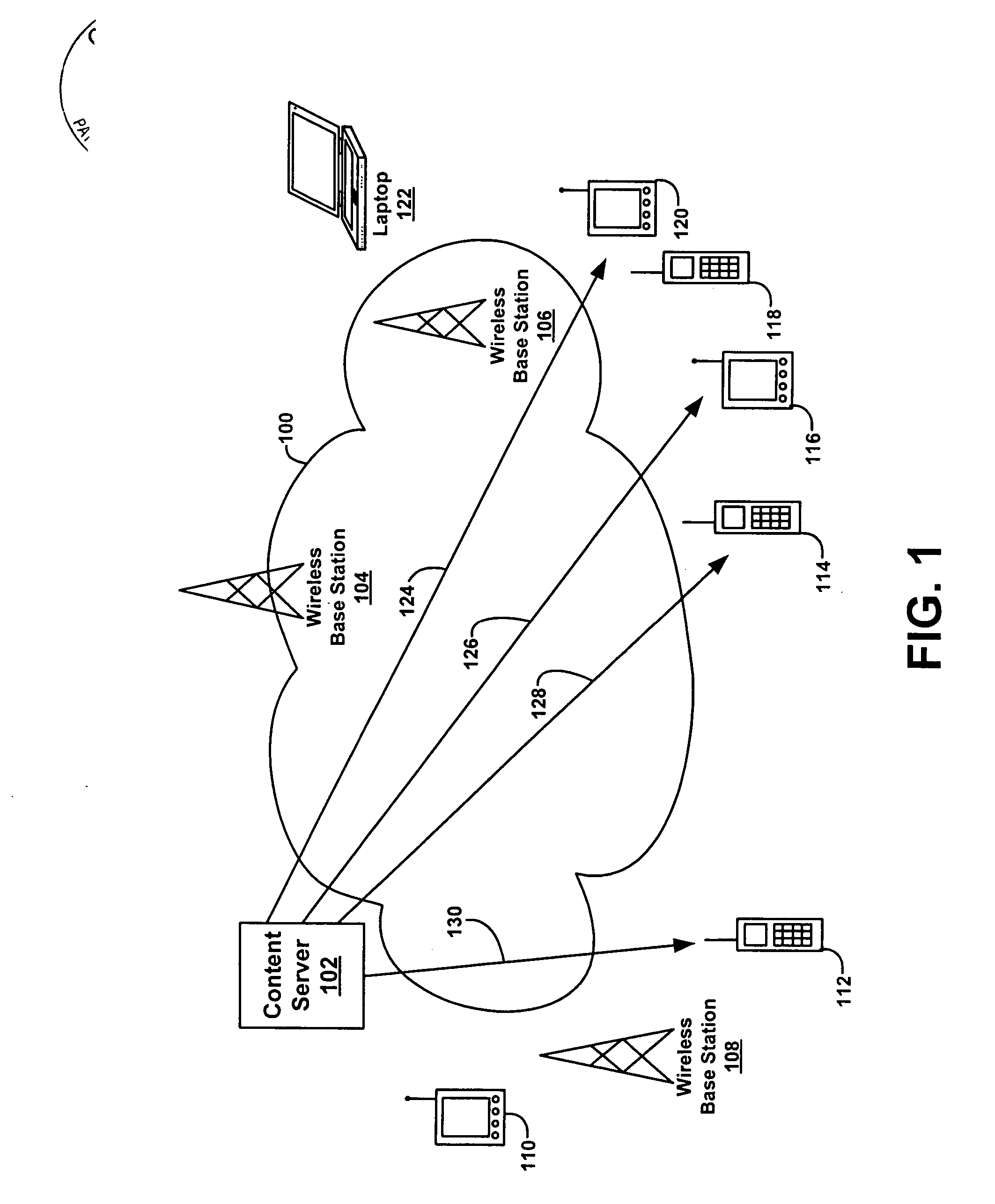
Method and system for allocating bandwidth in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS6850764B1Accurately estimateAccurately determineAccounting/billing servicesNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunicationsGeolocation
A method and system for allocating bandwidth in a wireless communications network includes a geo-location tool and an allocation engine. The geo-location tool is operable to receive data for a wireless communications network that includes a plurality of geo-location areas and to estimate bandwidth parameters for a geo-location based on the data. The allocation engine is operable to allocate bandwidth in the geo-location area based on its bandwidth parameters.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Solution-based fabrication of photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20050183767A1Improve overall utilizationLow costMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleSolar cell
An ink for forming CIGS photovoltaic cell active layers is disclosed along with methods for making the ink, methods for making the active layers and a solar cell made with the active layer. The ink contains a mixture of nanoparticles of elements of groups IB, IIIA and (optionally) VIA. The particles are in a desired particle size range of between about 1 nm and about 500 nm in diameter, where a majority of the mass of the particles comprises particles ranging in size from no more than about 40% above or below an average particle size or, if the average particle size is less than about 5 nanometers, from no more than about 2 nanometers above or below the average particle size. The use of such ink avoids the need to expose the material to an H2Se gas during the construction of a photovoltaic cell and allows more uniform melting during film annealing, more uniform intermixing of nanoparticles, and allows higher quality absorber films to be formed.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS20090210081A1Improve overall utilizationImprove efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionForecastingMachine selectionOperational costs
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
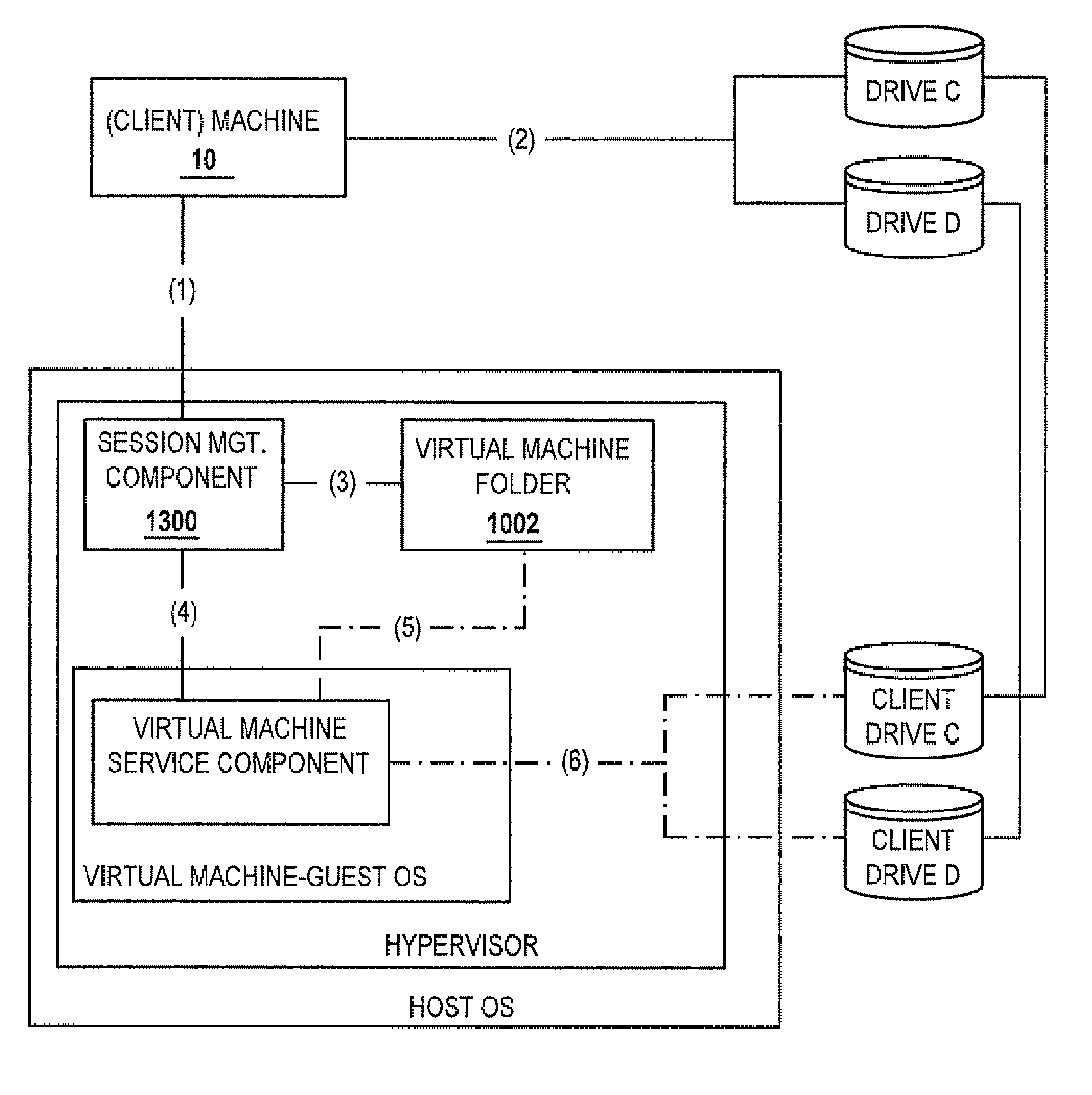
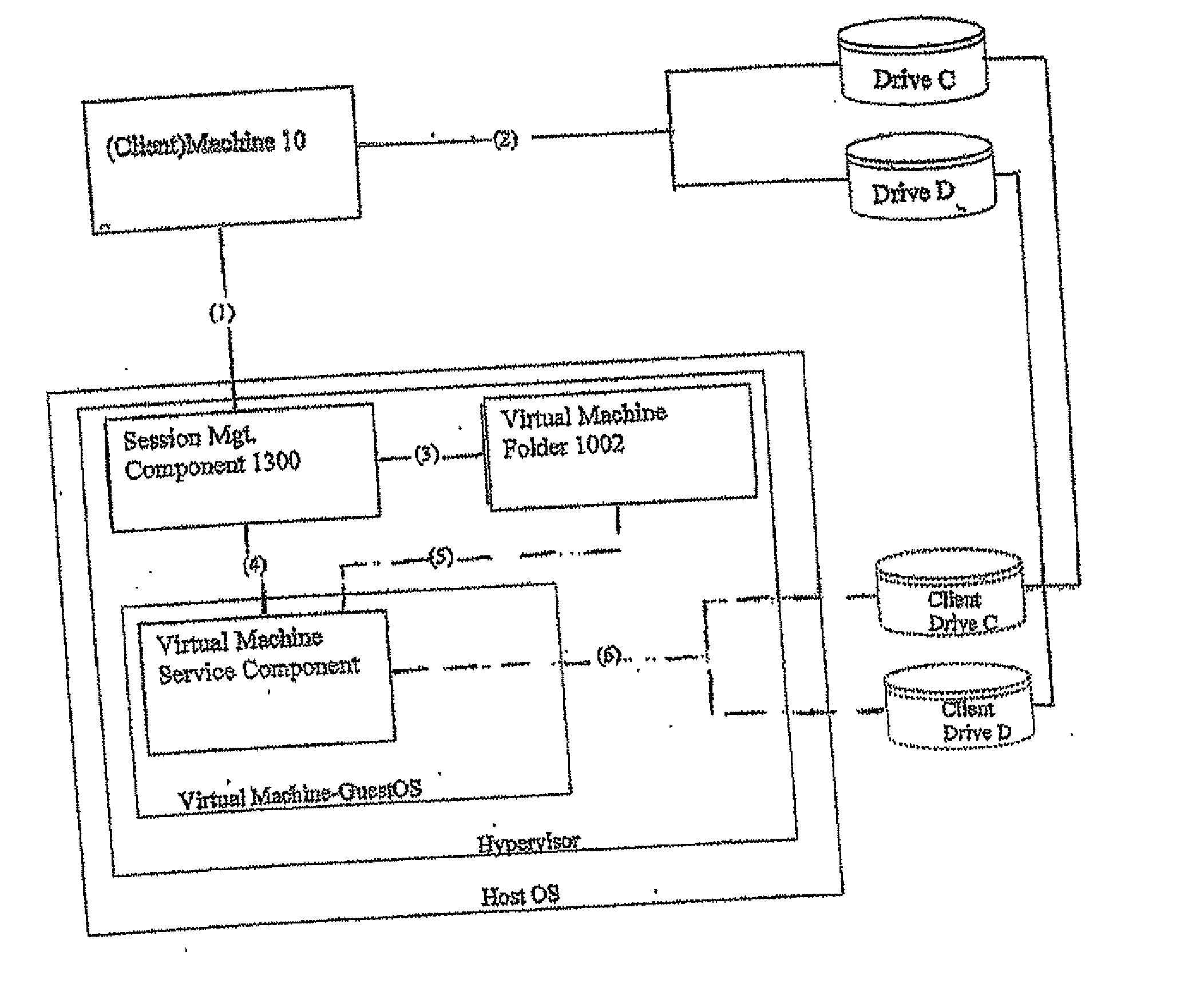
Methods and systems for providing access to a computing environment provided by a virtual machine executing in a hypervisor executing in a terminal services session
ActiveUS20070180448A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationSession managementClient-side
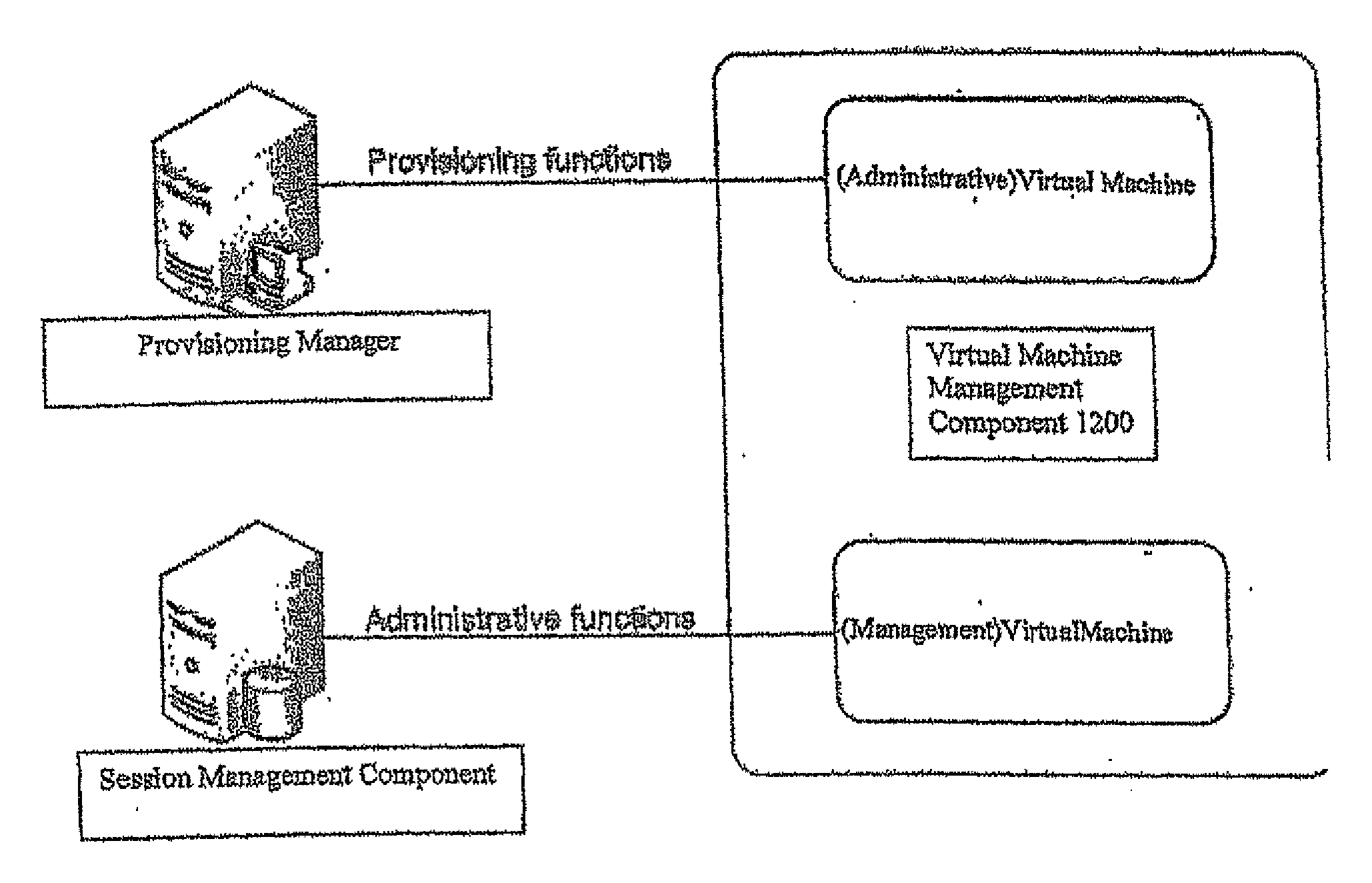
A method for providing access to a computing environment includes the step of receiving, by a broker machine, a request from a client machine for access to a computing environment, the request including an identification of a user of the client machine. One of a plurality of virtual machines is identified by a session management component, the identified virtual machine providing the requested computing environment. One of a plurality of execution machines is identified, the identified execution machine providing a terminal services session in which a hypervisor executes to provide access to hardware resources required by the identified virtual machine. The hypervisor launches the identified virtual machine. A connection is established between the client machine and the identified virtual machine, via the terminal services session.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20100308738A1Small sizeLow costElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentControl signal
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a first plurality of segments of LEDs; a plurality of switches coupled to the plurality of segments of LEDs to switch a selected segment into or out of a series LED current path in response to a control signal; a current sensor; and a controller which, in response to a first parameter and during a first part of an AC voltage interval, generates a first control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs into the series LED current path; and during a second part of the AC voltage interval, generates a second control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs out of the first series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
ActiveUS20090204234A1Minimize power consumptionLow costSimulator controlForecastingMachine selectionOperational costs
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Methods and systems for providing remote access to a computing environment provided by a virtual machine
ActiveUS20070180449A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationVirtualizationOperational system
A method for providing remote access to a computer environment provided by a virtual machine includes the step of receiving authentication information associated with a user of a client machine. Based on the received authentication information, a computer environment provided by a virtualized operating system and already associated with the user is identified. A connection is established between the client machine and the identified computing environment
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Diamond-surfaced cup for use in a prosthetic joint
InactiveUS6488715B1Improve wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionFinger jointsWrist jointsArticular surfacesSacroiliac joint
Prosthetic joints, components for prosthetic joints, superhard bearing and articulation surfaces, diamond bearing and articulation surfaces, substrate surface topographical features, materials for making joints, bearing and articulation surfaces, and methods for manufacturing and finishing the same, and related information are disclosed, including a diamond-surfaced cup for use in a prosthetic joint.
Owner:DIAMICRON
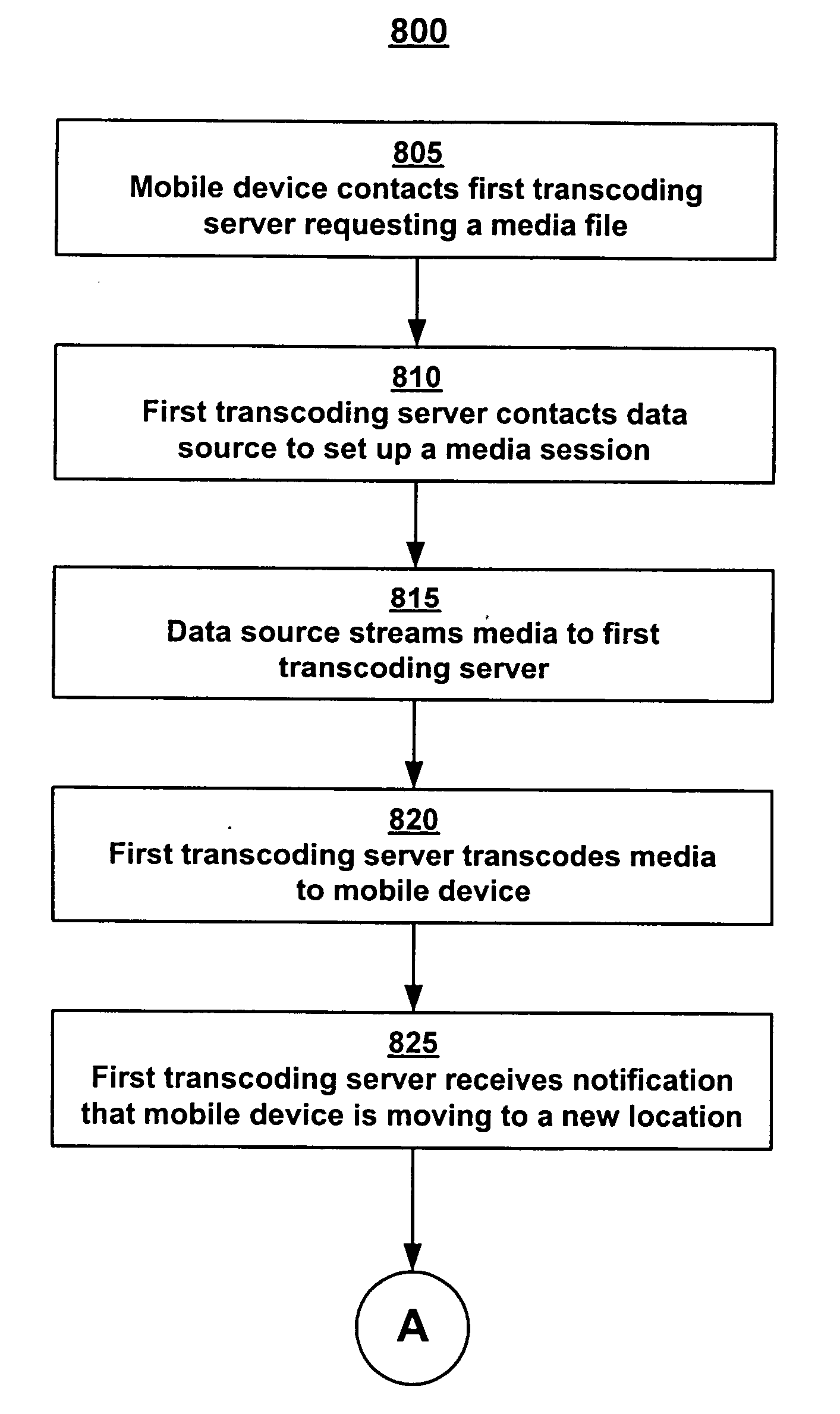
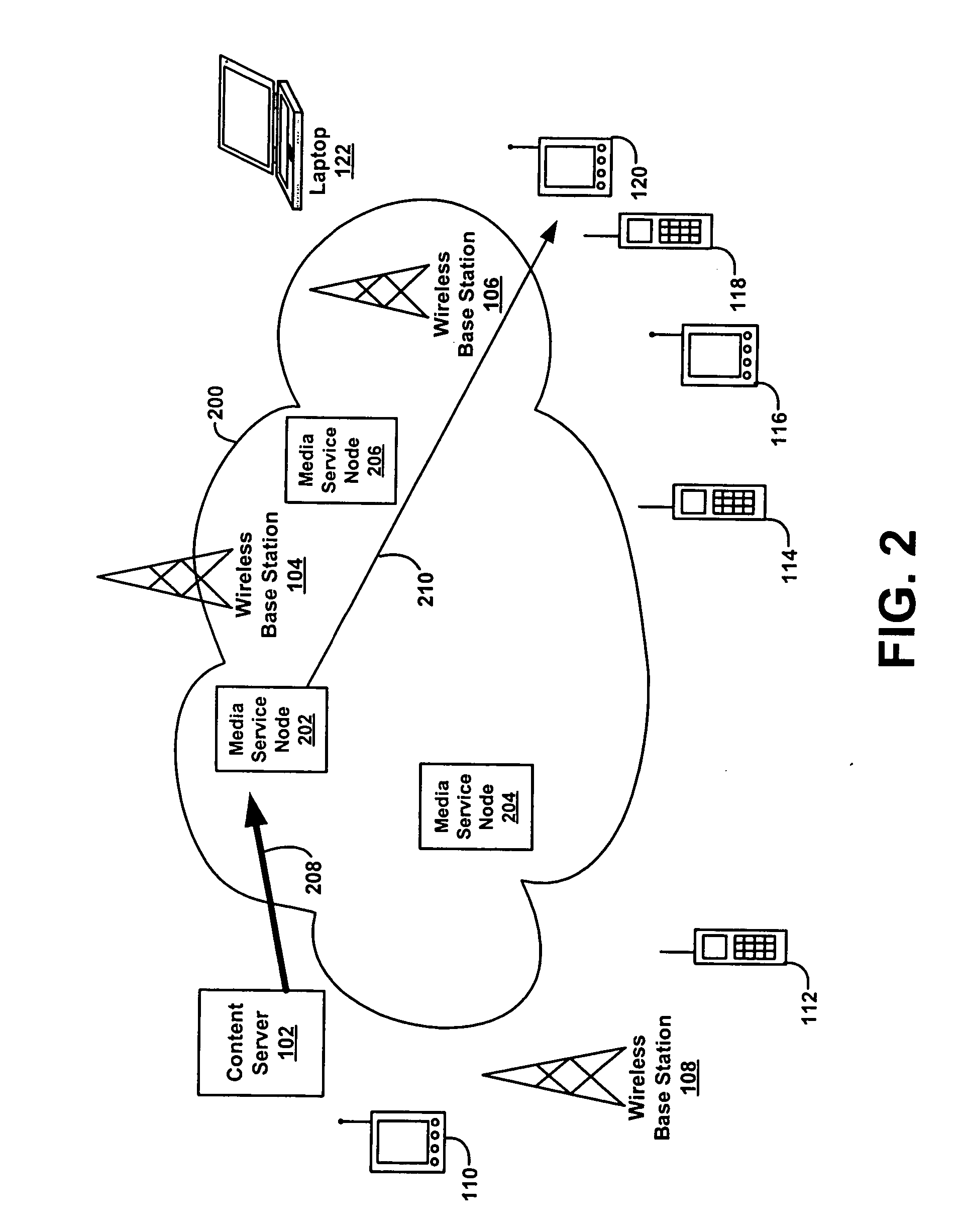
Method for managing a streaming media service
InactiveUS20050005025A1Improve overall utilizationDigital computer detailsWireless commuication servicesClient-sideService component
One embodiment of the invention includes a method for managing a streaming media service. The method includes receiving a request for a streaming media service from a client. The streaming media service includes a plurality of media services components. Additionally, the method includes determining which media service component of the plurality of media services components to assign to a service node of a plurality of service nodes of a network. The method also includes informing each service node assigned to perform a media service component of the plurality of media services components enabling the streaming media service to be performed on a streaming media.
Owner:HARVILLE MICHAEL +5
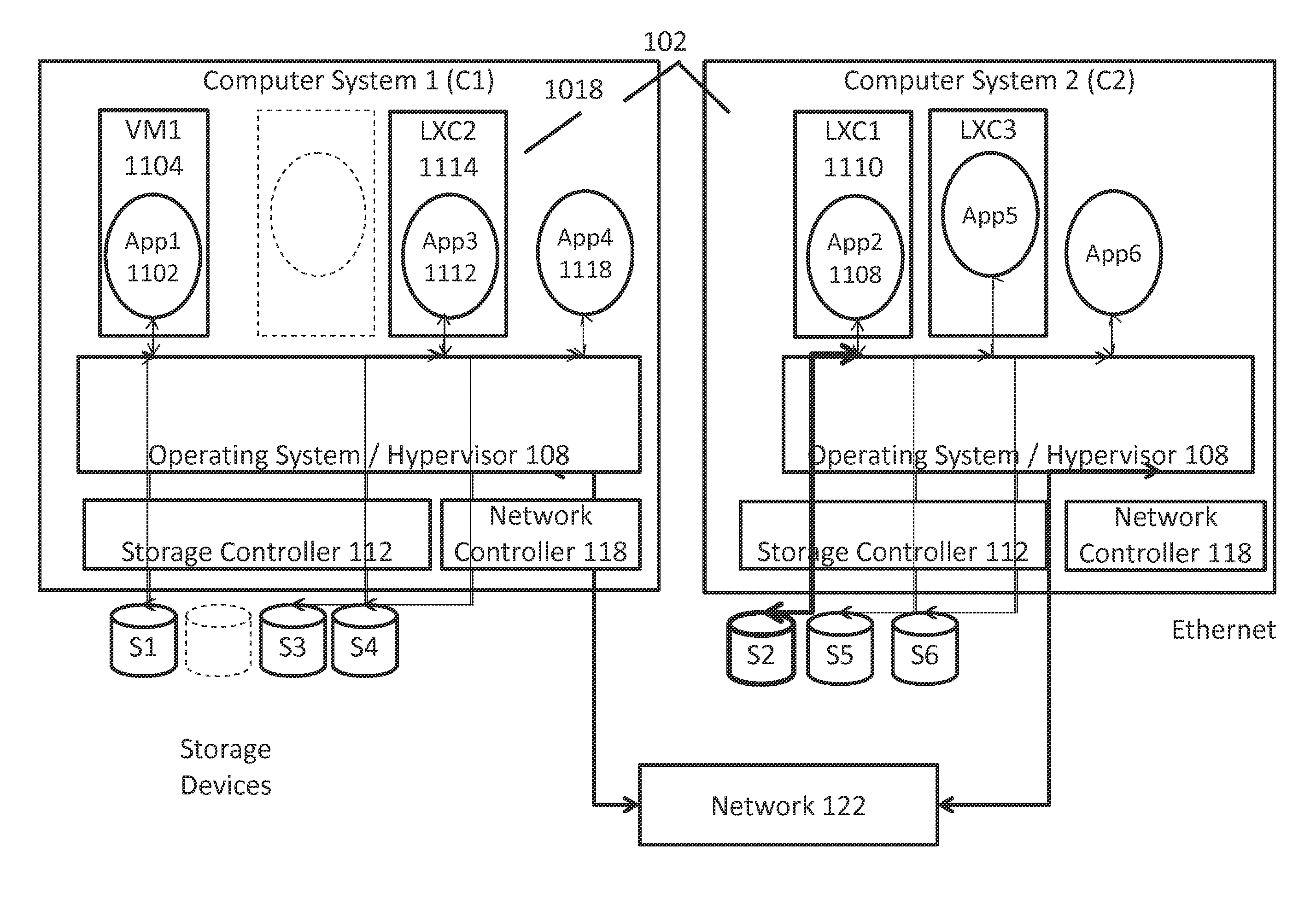
Methods and systems for converged networking and storage
InactiveUS20150254088A1Easy programmingImprove performanceResource allocationDigital computer detailsTraffic capacityNetwork interface controller
A device includes a converged input / output controller that includes a physical target storage media controller, a physical network interface controller and a gateway between the storage media controller and the network interface controller, wherein gateway provides a direct connection for storage traffic and network traffic between the storage media controller and the network interface controller.
Owner:DIAMANTI INC
Method and coding means for error-correction utilizing concatenated parity and turbo codes
InactiveUS7093179B2Reduction in rateImprove overall utilizationError preventionError detection/correctionParallel computingTurbo coded
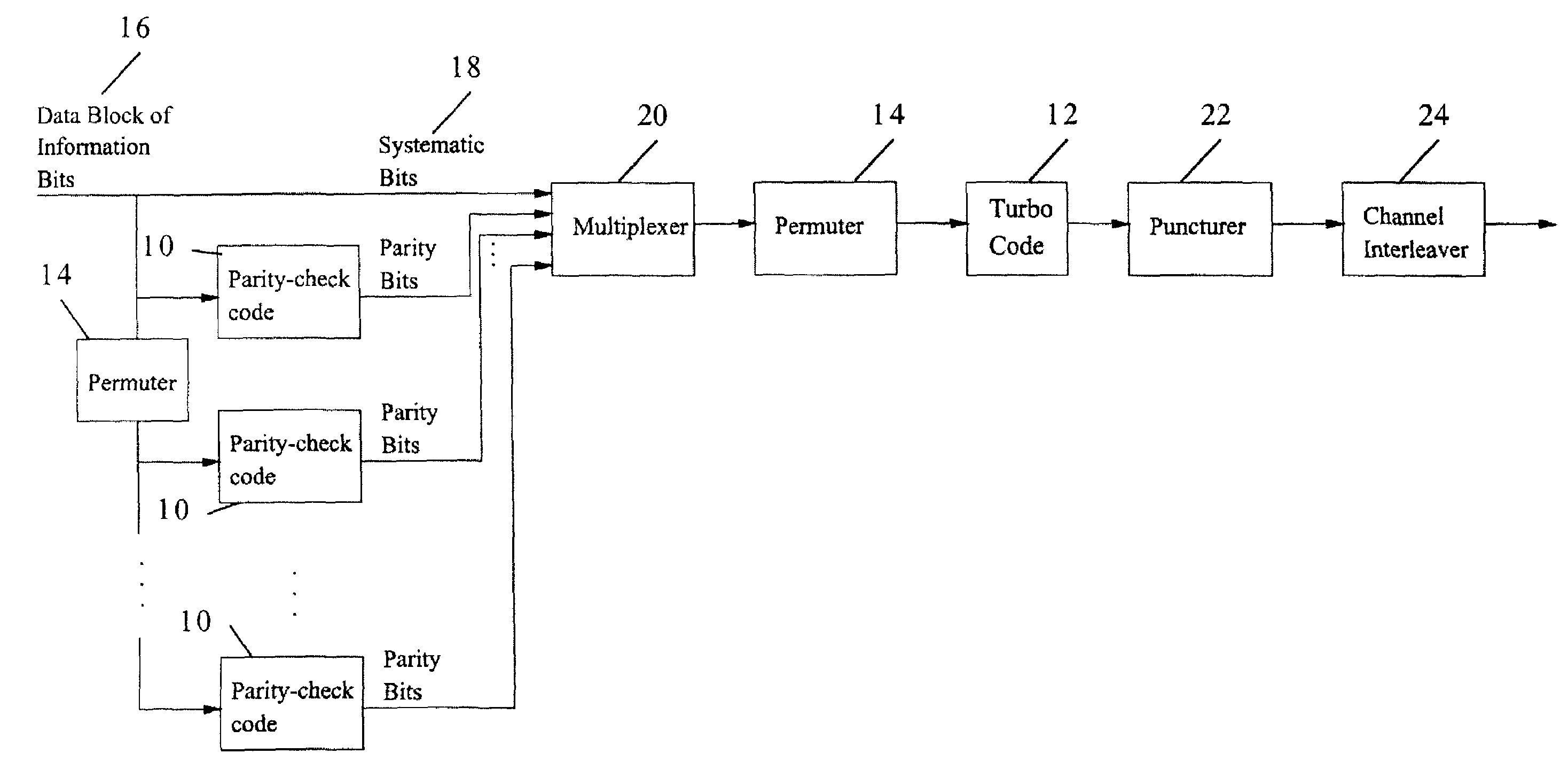
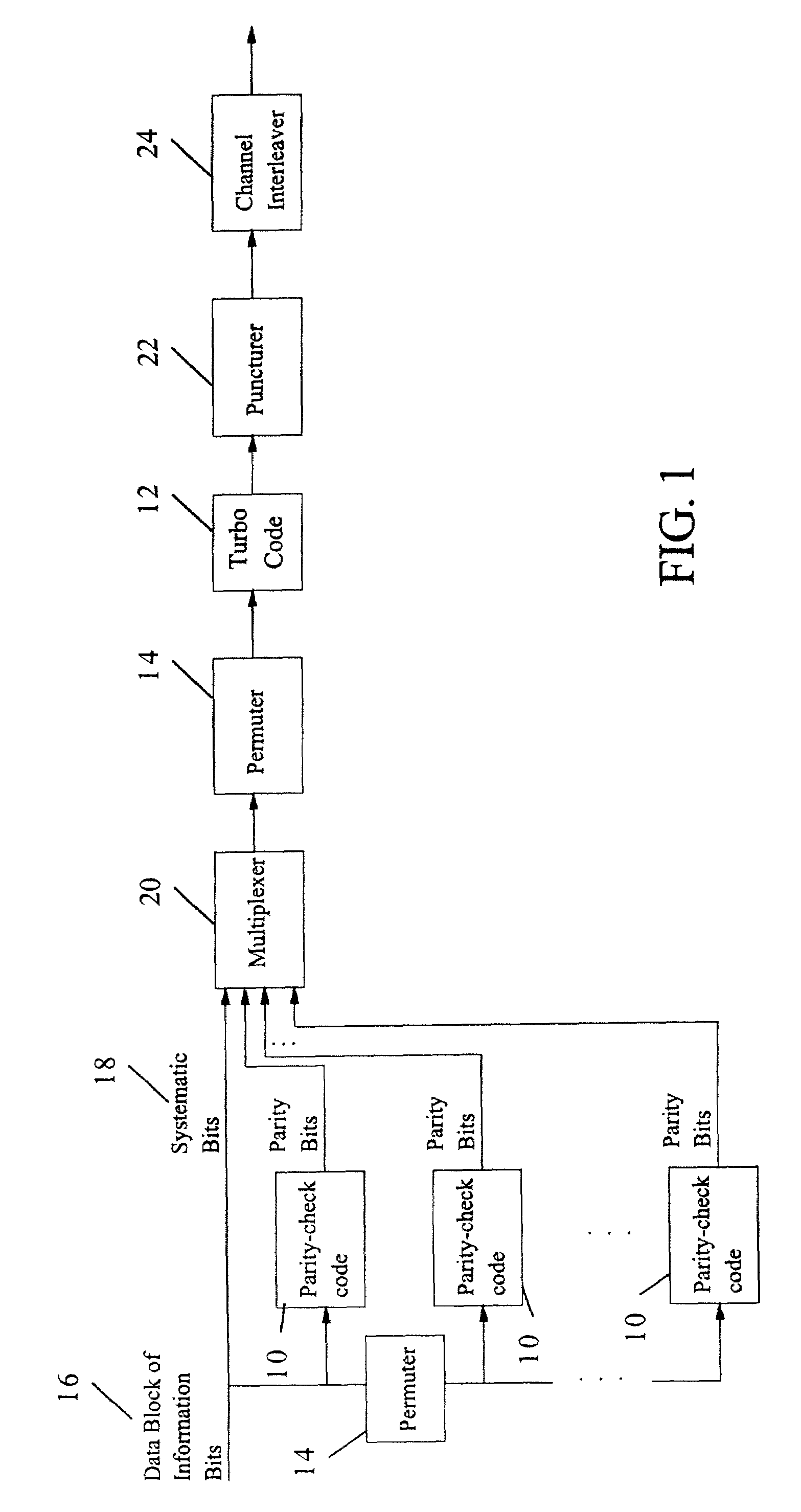
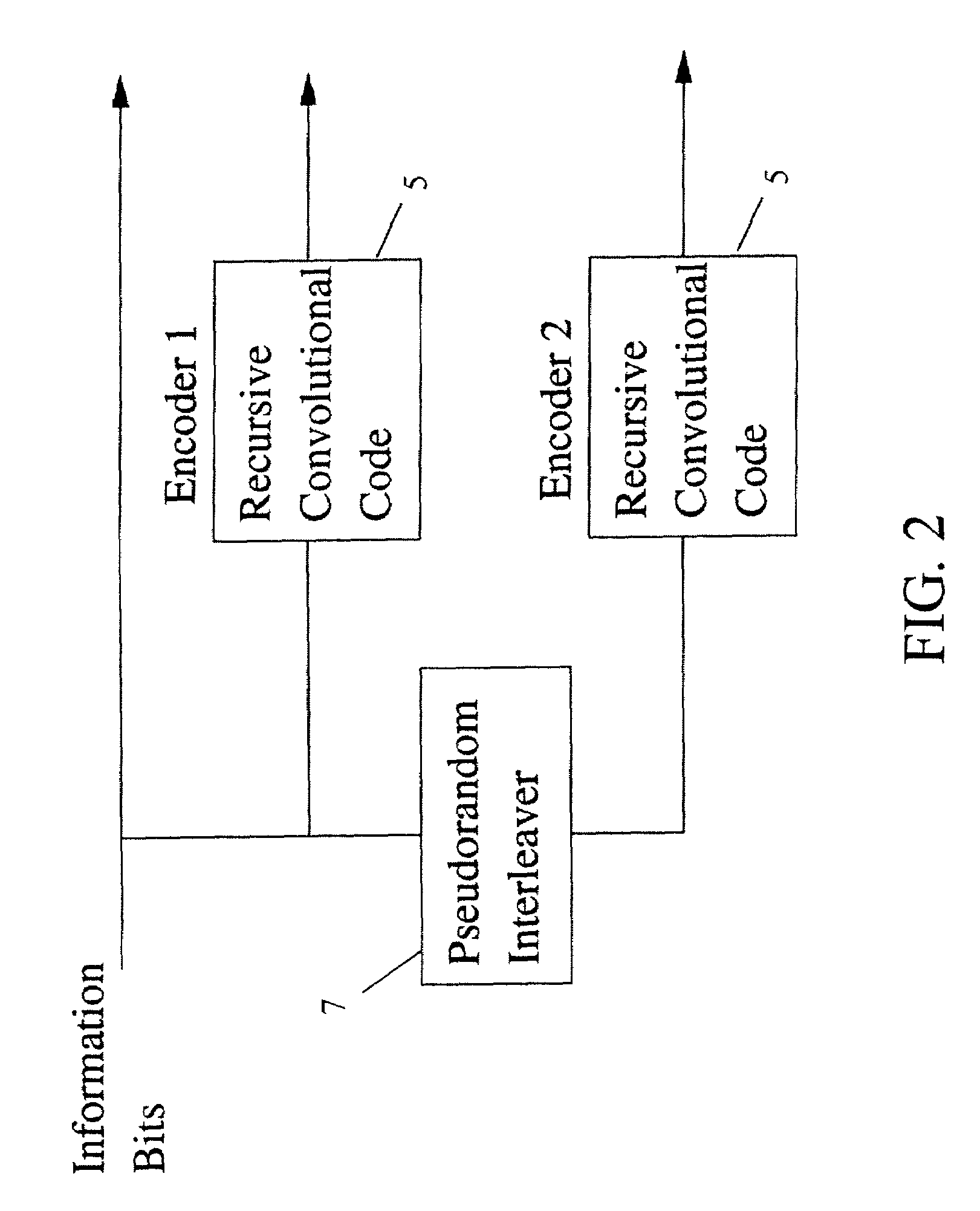
A method and apparatus for encoding and decoding data using an overall code comprising an outer parity-check and an inner parallel concatenated convolutional, or turbo code. The overall code provides error probabilities that are significantly lower than can be achieved by using turbo codes alone. The output of the inner code can be punctured to maintain the same turbo code rate as the turbo code encoding without the outer code. Multiple parity-check codes can be concatanated either serially or in parallel as outer codes. Decoding can be performed with iterative a posteriori probability (APP) decoders or with other decoders, depending on the requirements of the system. The parity-check code can be applied to a subset of the bits to achieve unequal error protection. Moreover, the techniques presented can be mapped to higher order modulation schemes to achieve improved power and bandwidth efficiency.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
Catalytic hydrogenation process utilizing multi-stage ebullated bed reactors
InactiveUS6270654B1Easy to processAvoid poor resultsCatalytic naphtha reformingHydrocarbon oil crackingChemistryBoiling point
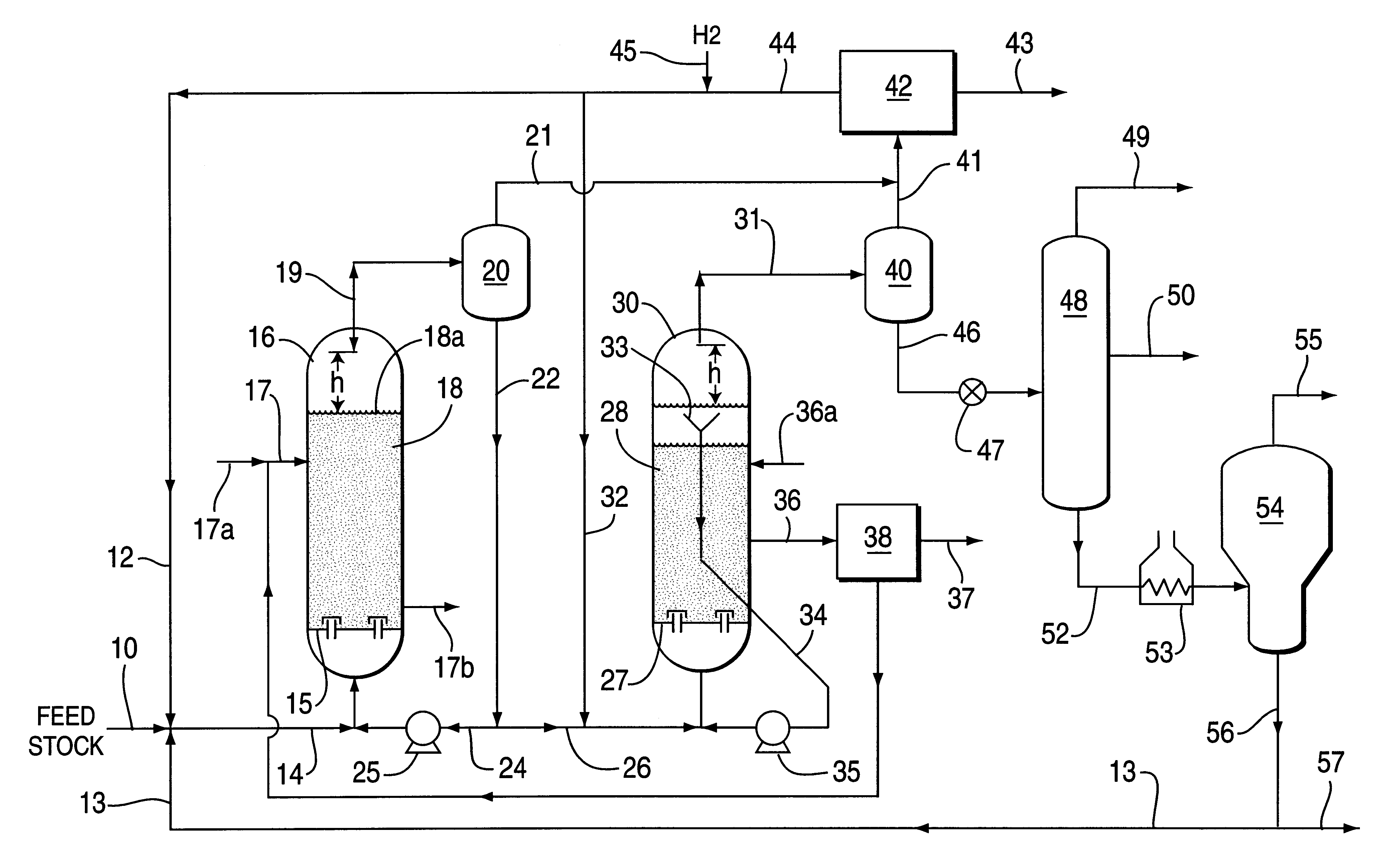
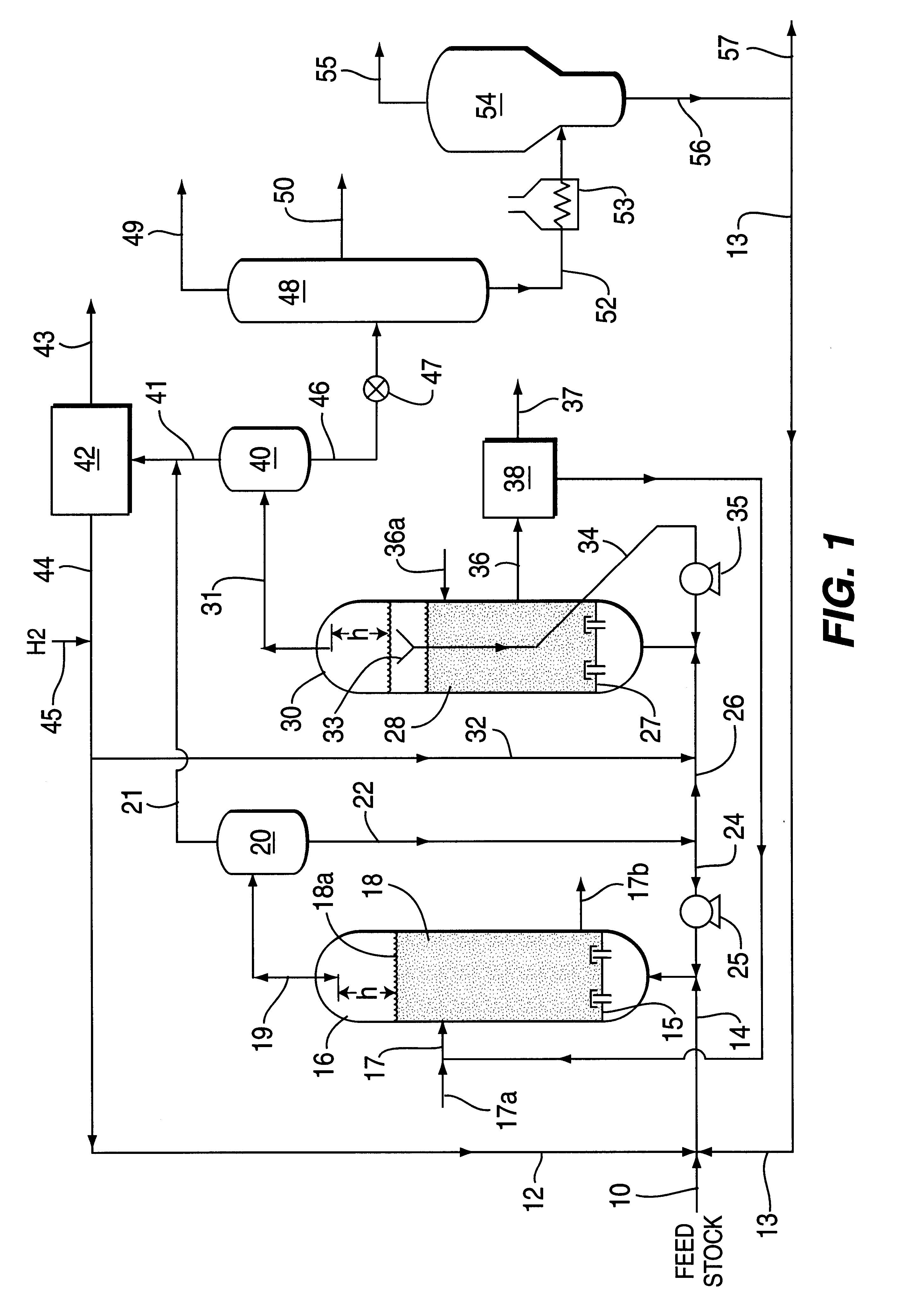
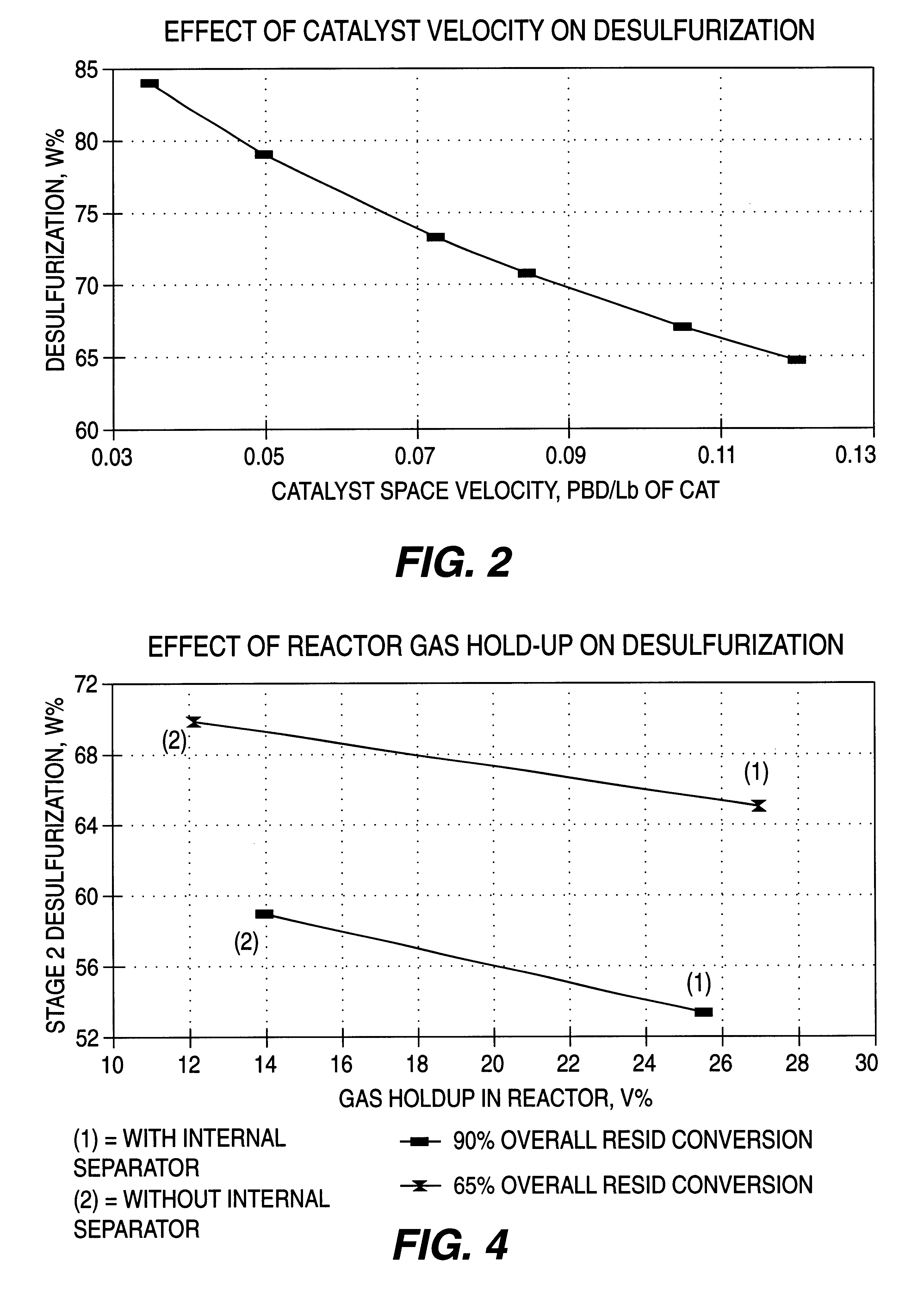
A process for catalytic multi-stage hydrogenation of heavy carbonaceous feedstocks using catalytic ebullated bed reactors is operated at selected flow and operating conditions so as to provide improved reactor operations and produce increased yield of lower boiling hydrocarbon liquid and gas products. The disclosed process advantageously takes advantage of an external gas / liquid separation unit associated with the first stage reactor to allow for a more efficient and effective catalytic hydrocracking process. The more efficient process is primarily a result of the increased catalyst loading and lower gas hold-up in the ebullated reactors.
Owner:IFP NORTH AMERICA
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
ActiveUS20090204245A1Minimize power consumptionLow costForecastingTechnology managementOperational costsMachine selection
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
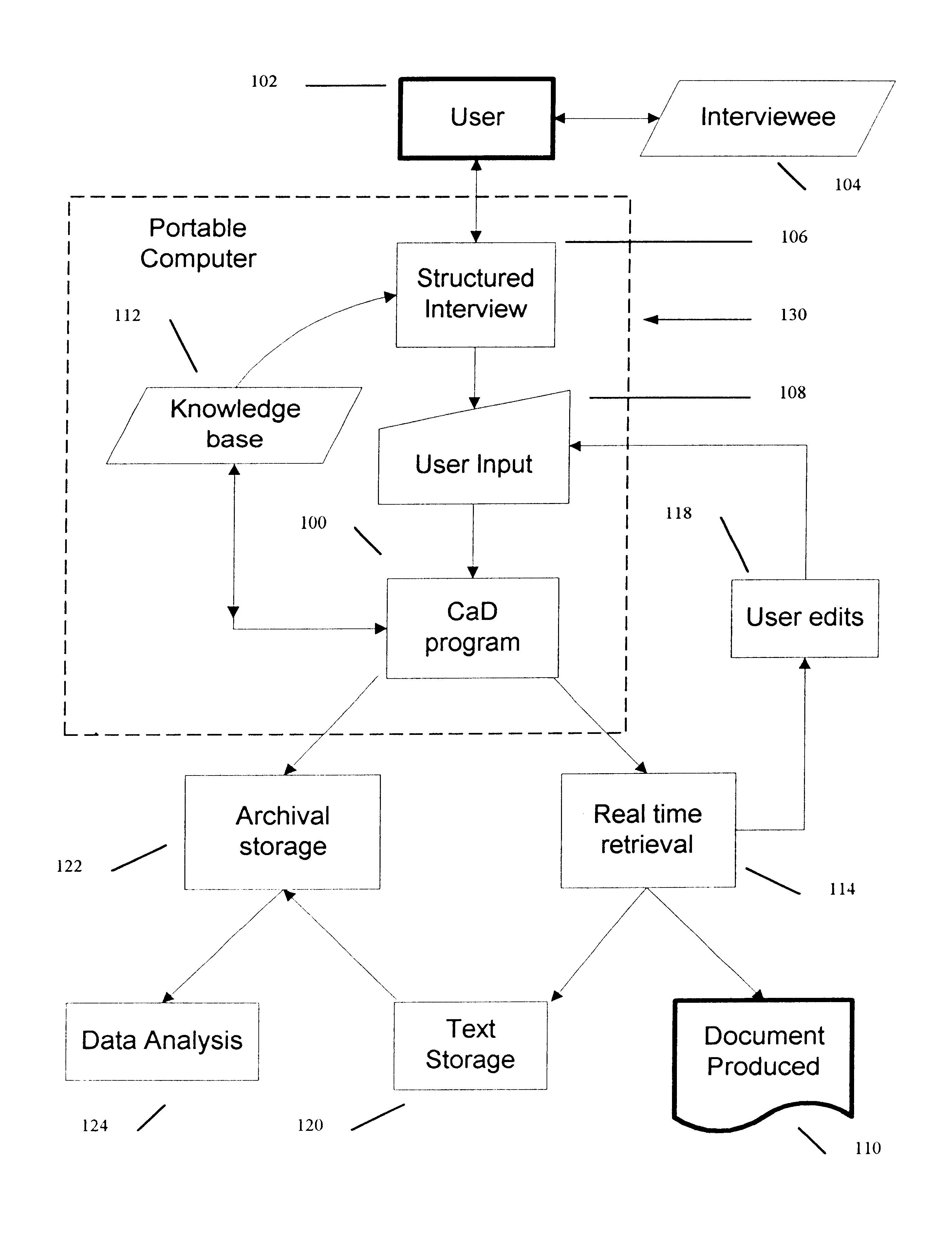
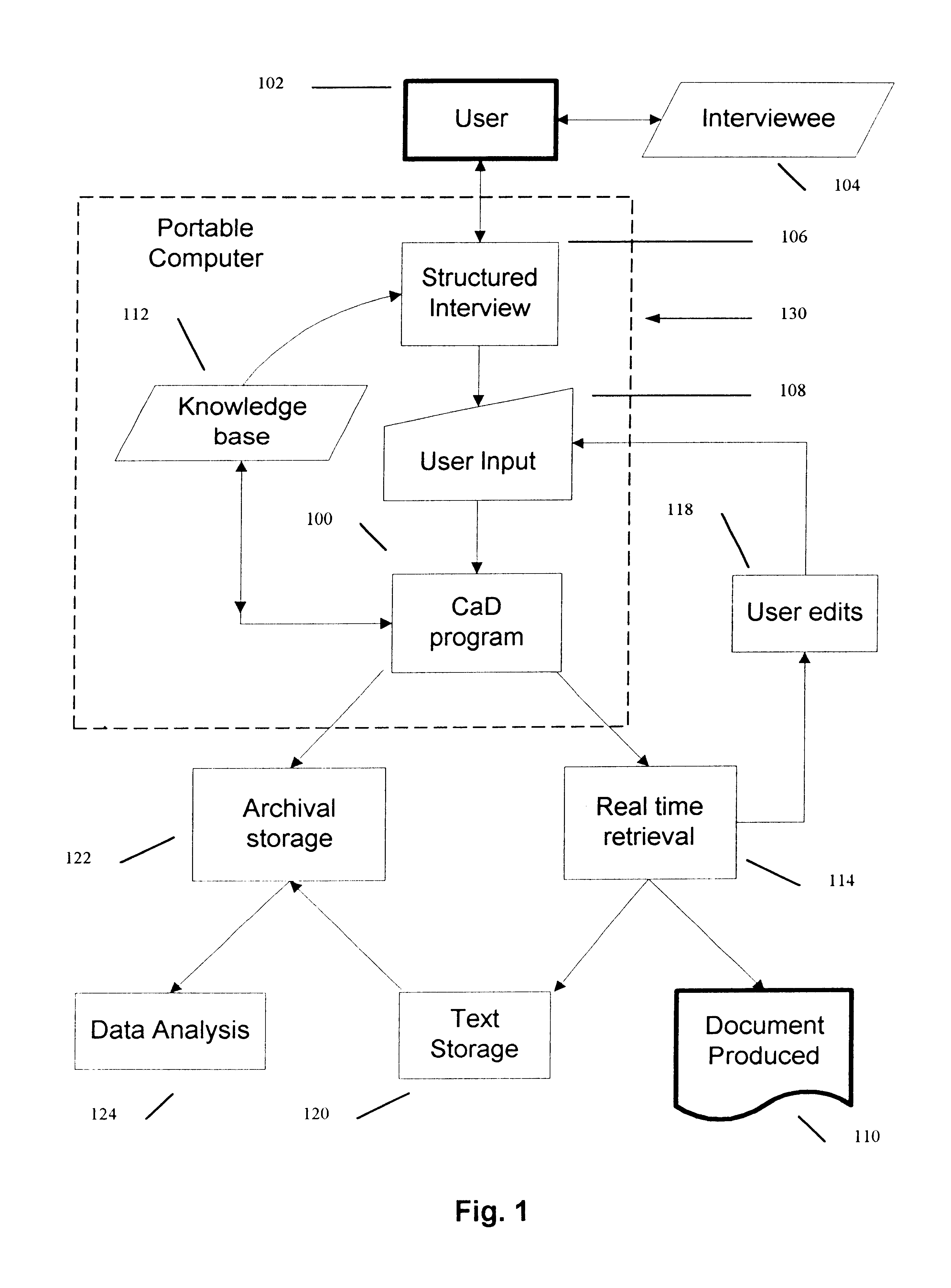
Method for production of medical records and other technical documents
InactiveUS6684188B1Improve overall utilizationEffective use timeData processing applicationsSurgeryMedical recordDocument preparation
A computer implemented system for the production of medical records, legal documents and other frequently produced semi-technical documents. This is accomplished by generating an intelligent computer-guided interview and the use of serialized scriptable objects. Major program elements include a knowledge base text file, a parse engine, and an execution module. The knowledge base uses a unique rule syntax. The parse engine converts the textual knowledge base file to a compiled binary representation which can then be interpreted by the execution module. The execution module leads the user through the interview by generating a series of questions and presents possible answers in the form of pick lists. The data is recorded with a computer pen and collated into a document file. This file is coded in binary format and can be written to and recalled from disk. If the file is recalled from disk the user can continue to answer questions or change answers previously given. The result is a mobile computing system whereby data is input in a structured format. When the program is executed the user is prompted for answers to questions and, based upon the user's response, the final document can change considerably. Depending upon each answer, the program may change the subsequent questions being asked, change the list associated with a question, change the text being generated, or change the entire structure of the document. The data collected may be also be stored in a database for analysis at a later date. Finally, the data collected is output in a narrative text format which can be tailored according to the traditions and expectations of the user's profession. The program will output the text via a printer or it can be transmitted via electronic means.
Owner:MITCHELL GEOFFREY C +1
Methods and systems for interacting, via a hypermedium page, with a virtual machine
InactiveUS20070180447A1Low costReduce difficultyDigital data information retrievalInterprogram communicationClient agentHyperlink
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
System and method for dynamic multi-objective optimization of machine selection, integration and utilization
InactiveUS20090204237A1Minimize power consumptionLow costForecastingTechnology managementOperational costsMachine selection
The invention provides control systems and methodologies for controlling a process having computer-controlled equipment, which provide for optimized process performance according to one or more performance criteria, such as efficiency, component life expectancy, safety, emissions, noise, vibration, operational cost, or the like. More particularly, the subject invention provides for employing machine diagnostic and / or prognostic information in connection with optimizing an overall business operation over a time horizon.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
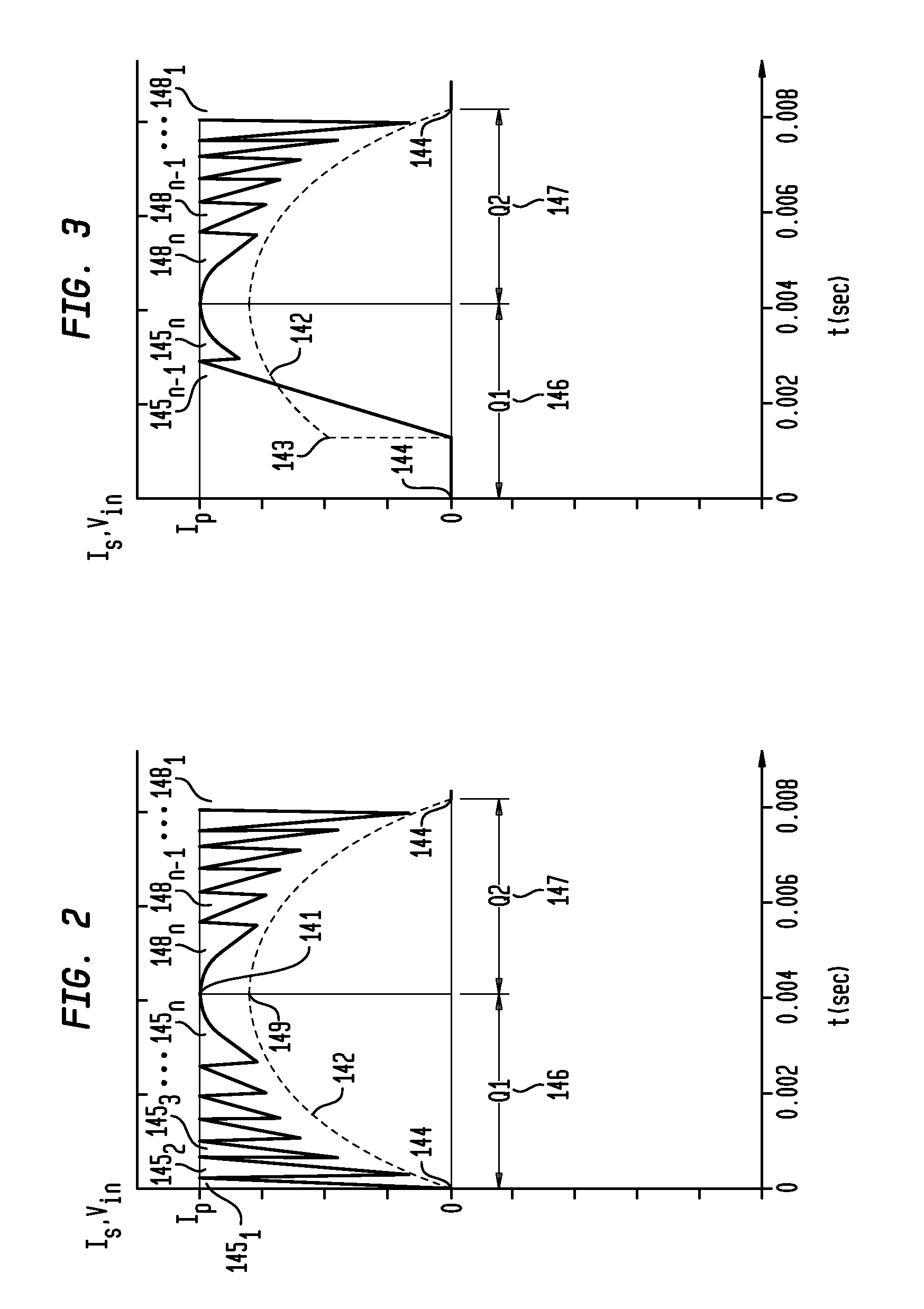
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com