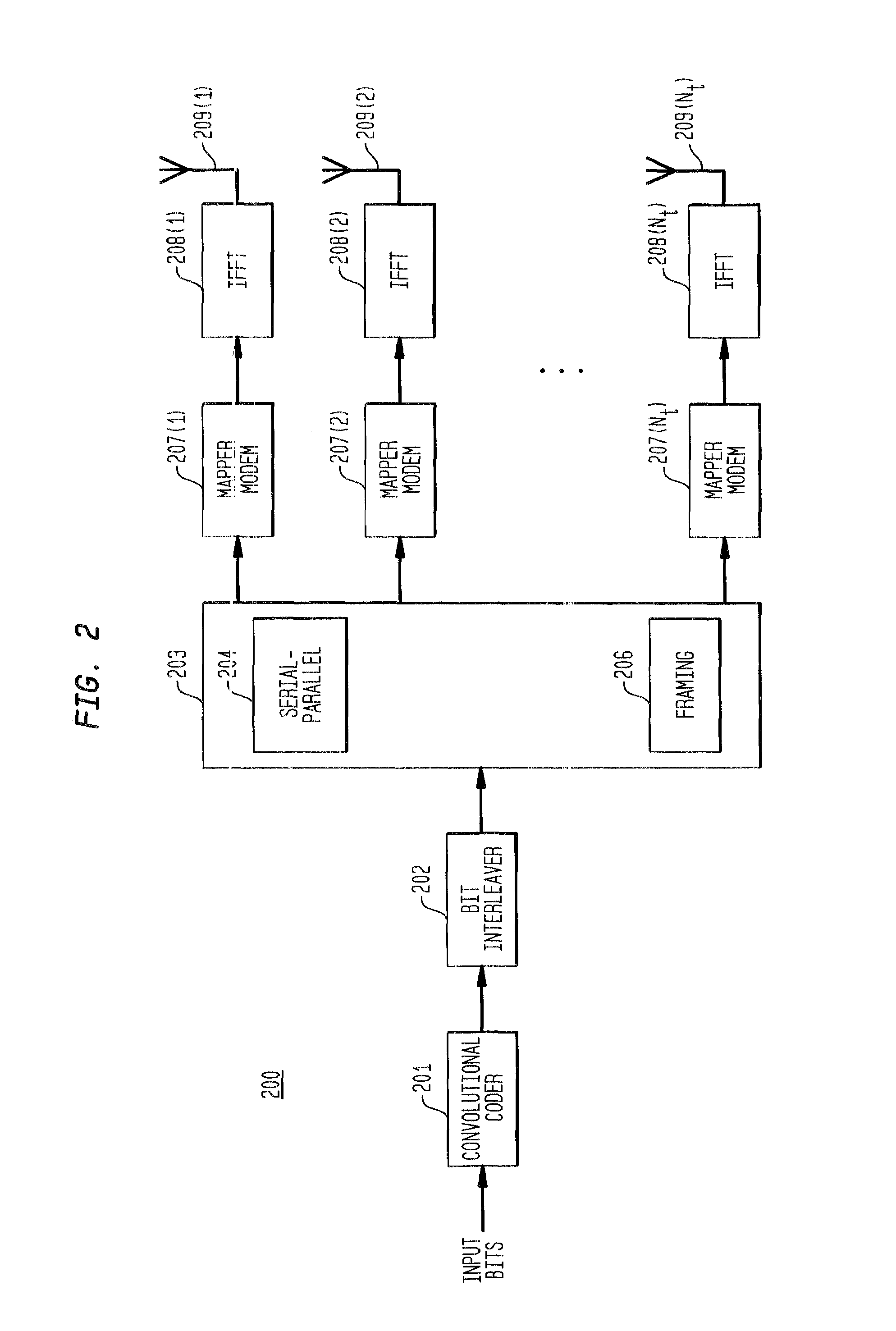
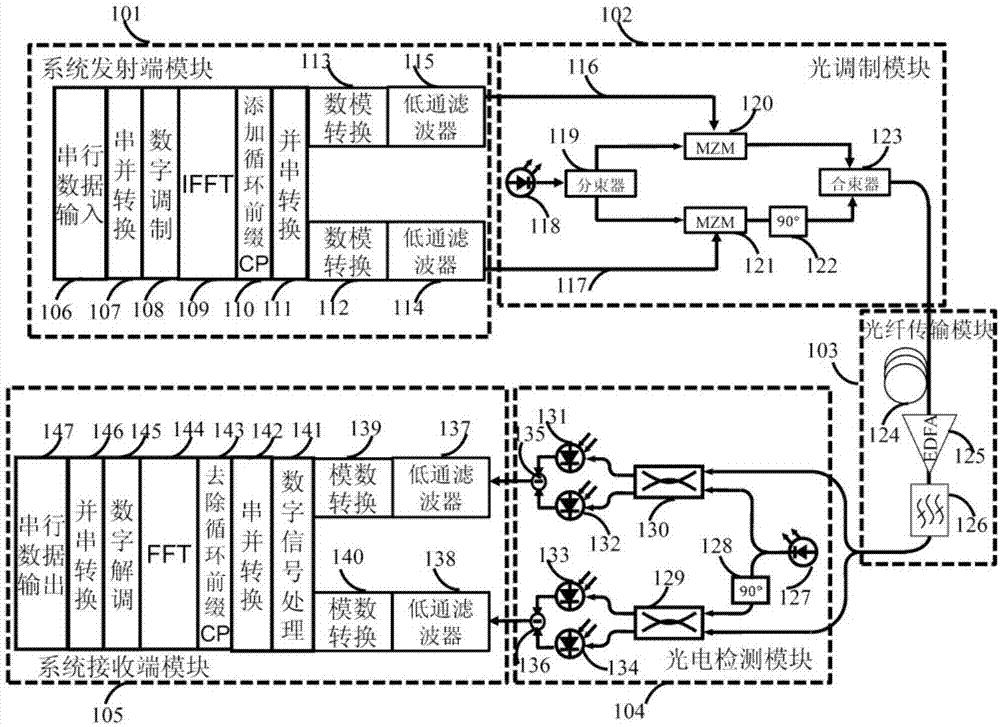
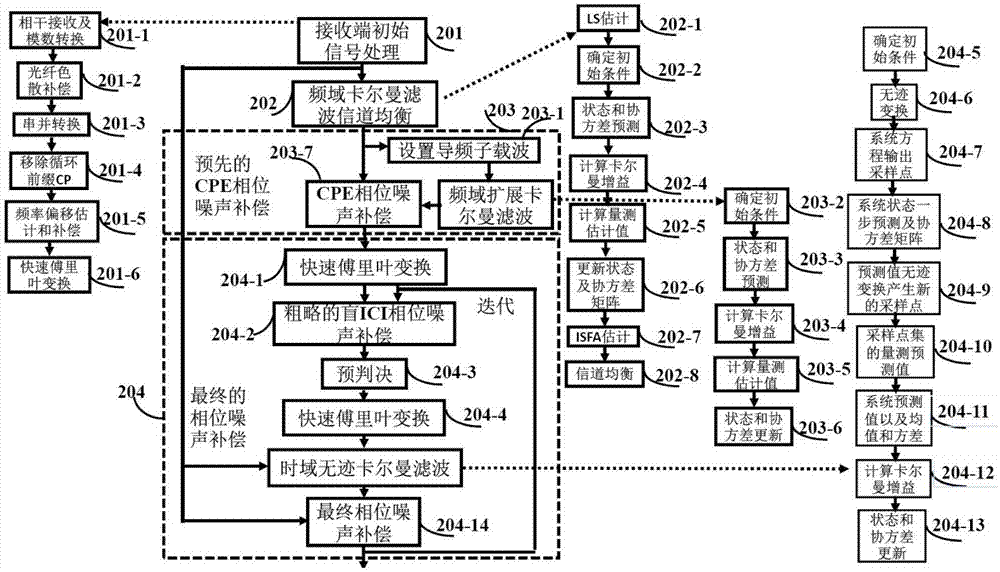
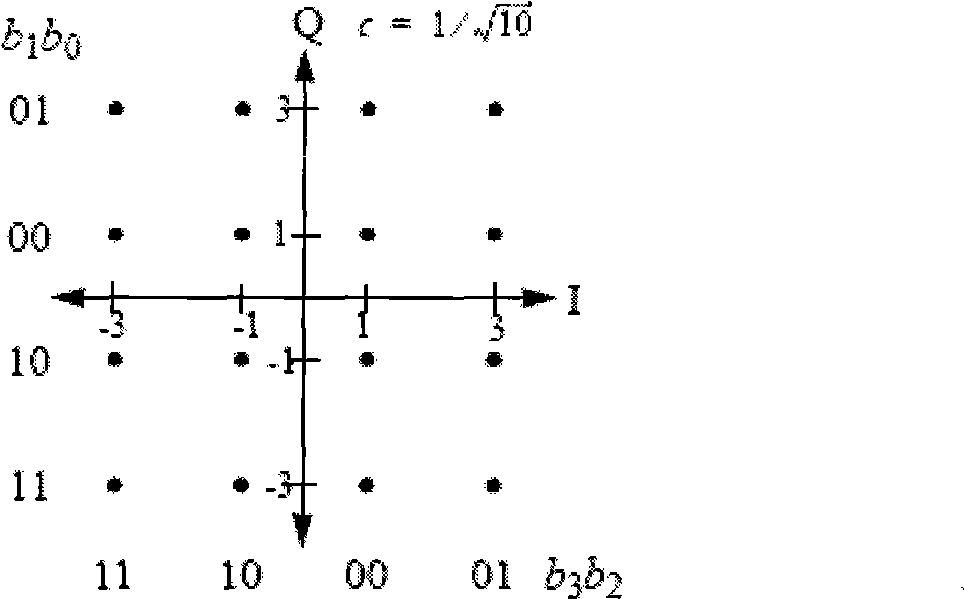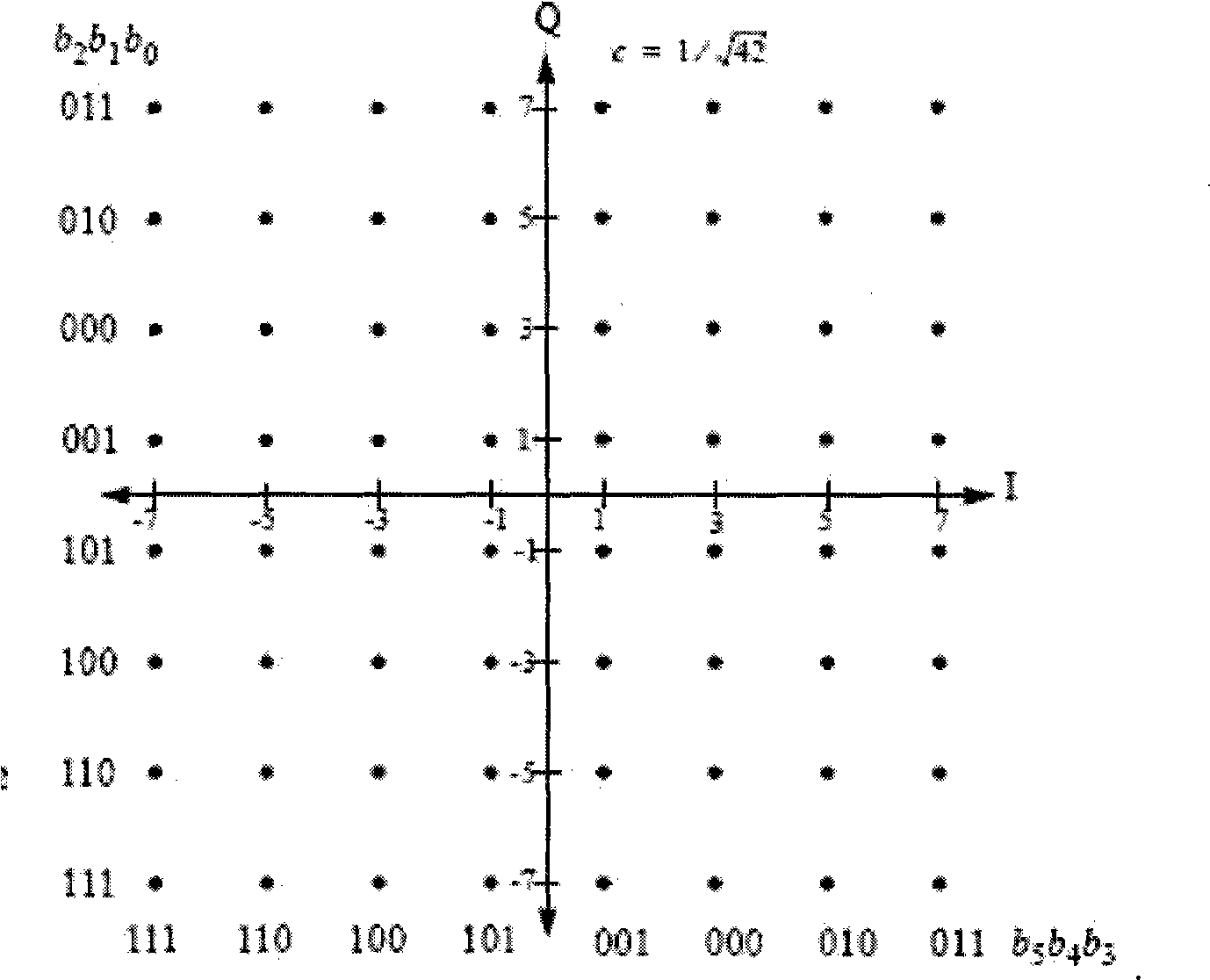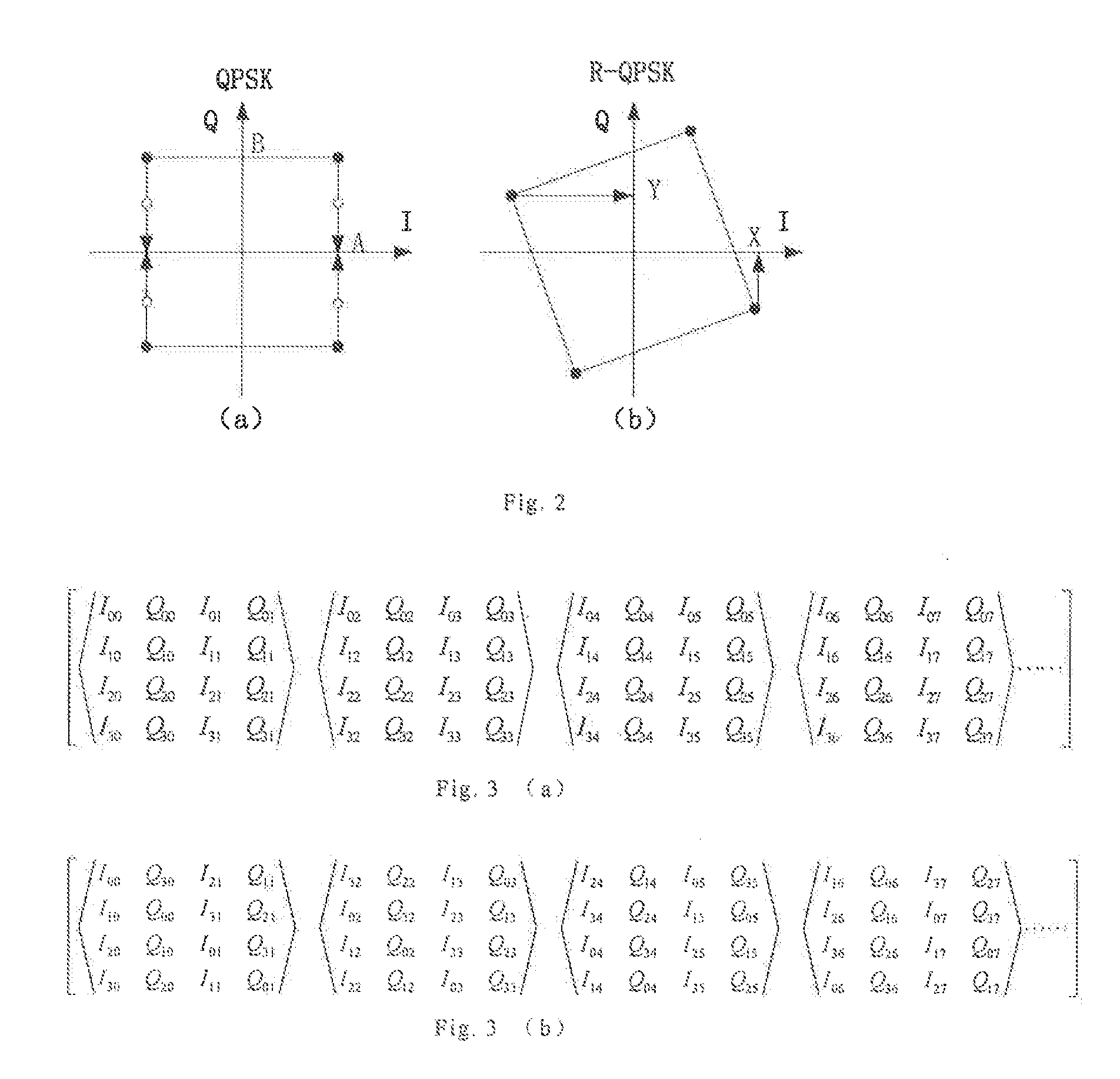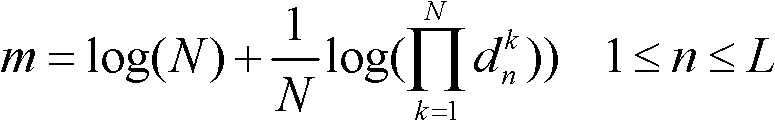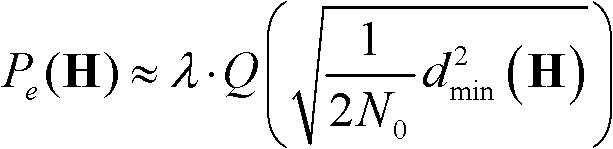Patents
Literature
483 results about "Higher-order modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
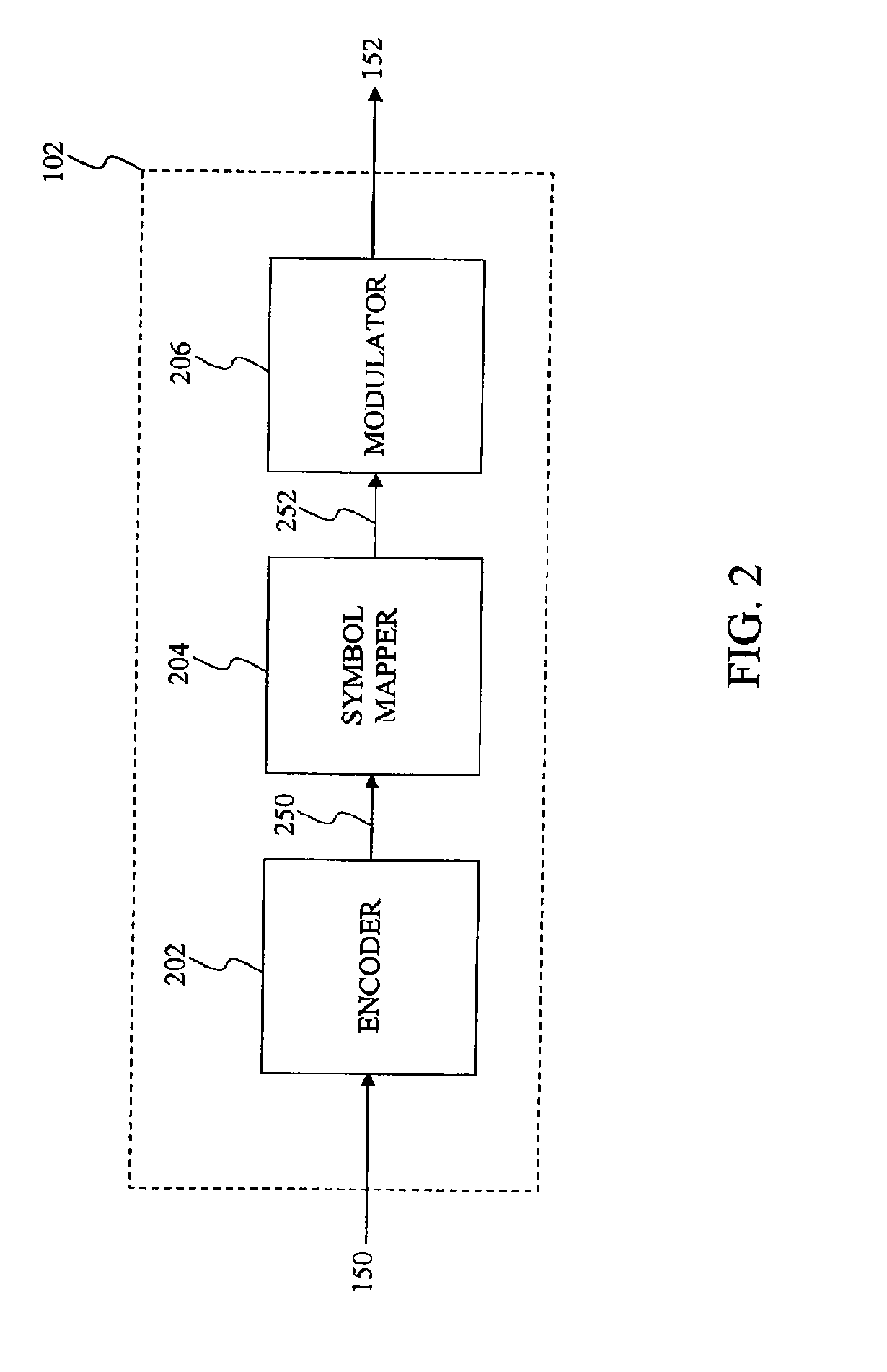
Higher-order modulation is a type of digital modulation usually with an order of 4 or higher. Examples: quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK), and m-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (m-QAM).
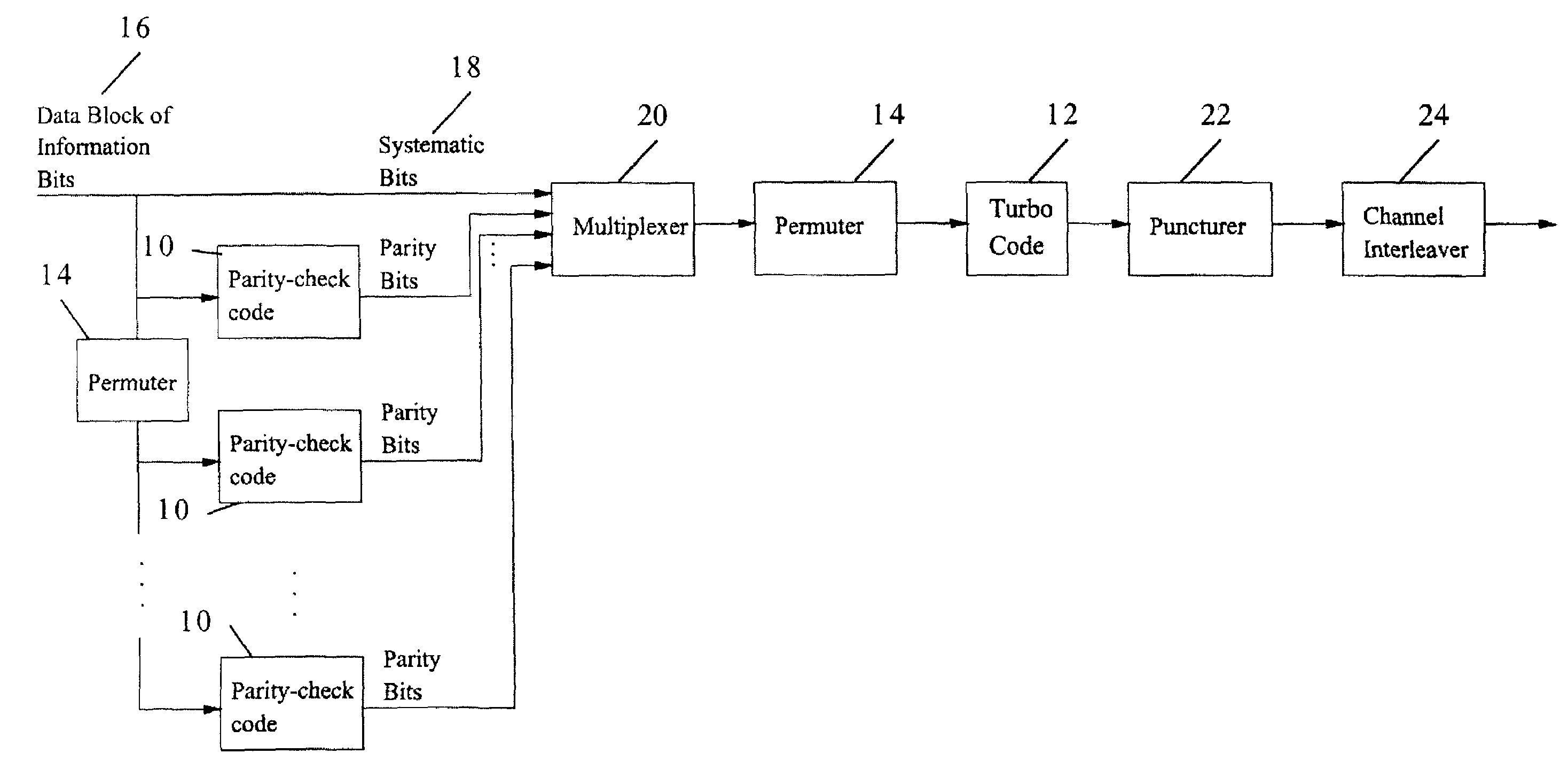
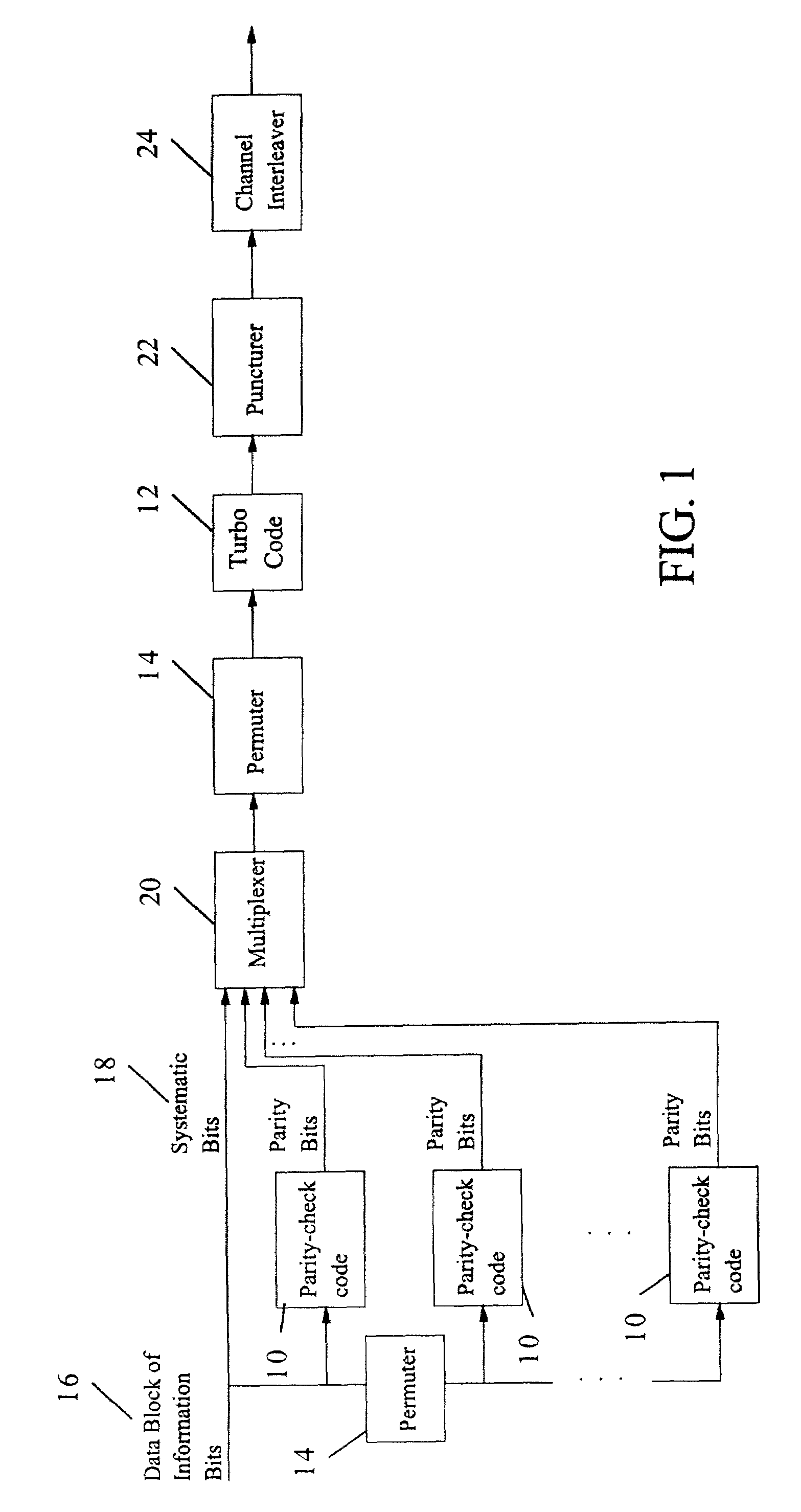
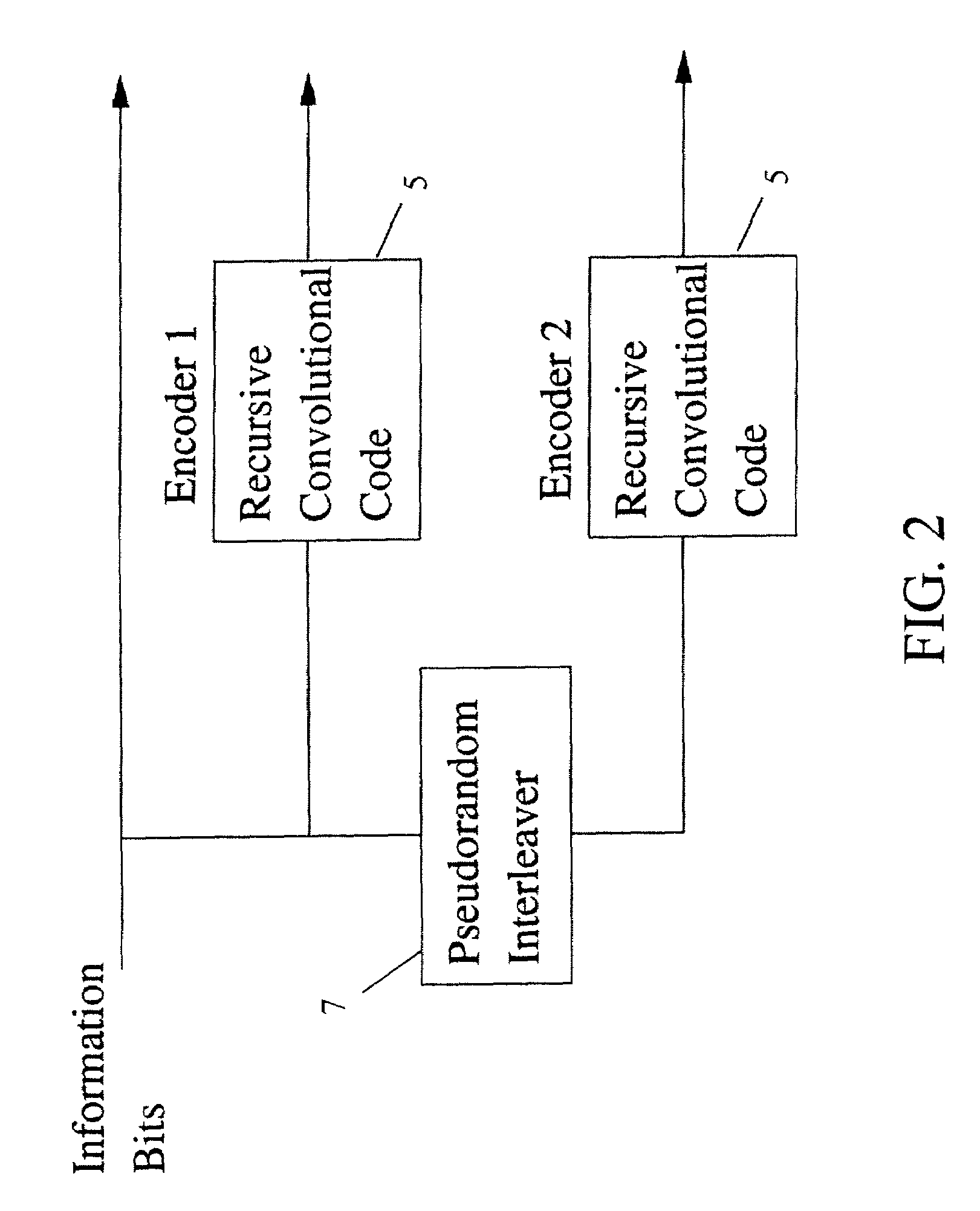
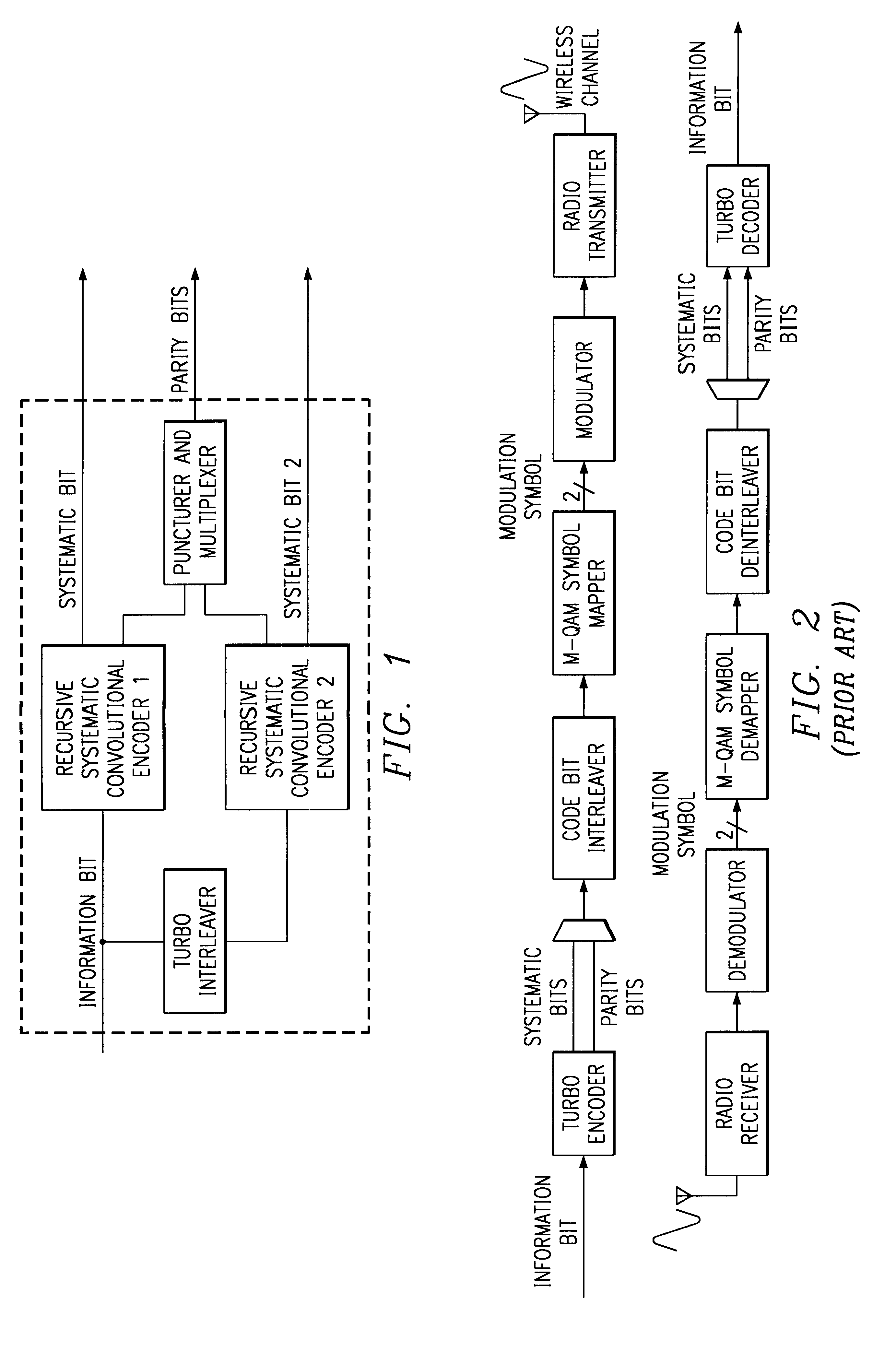
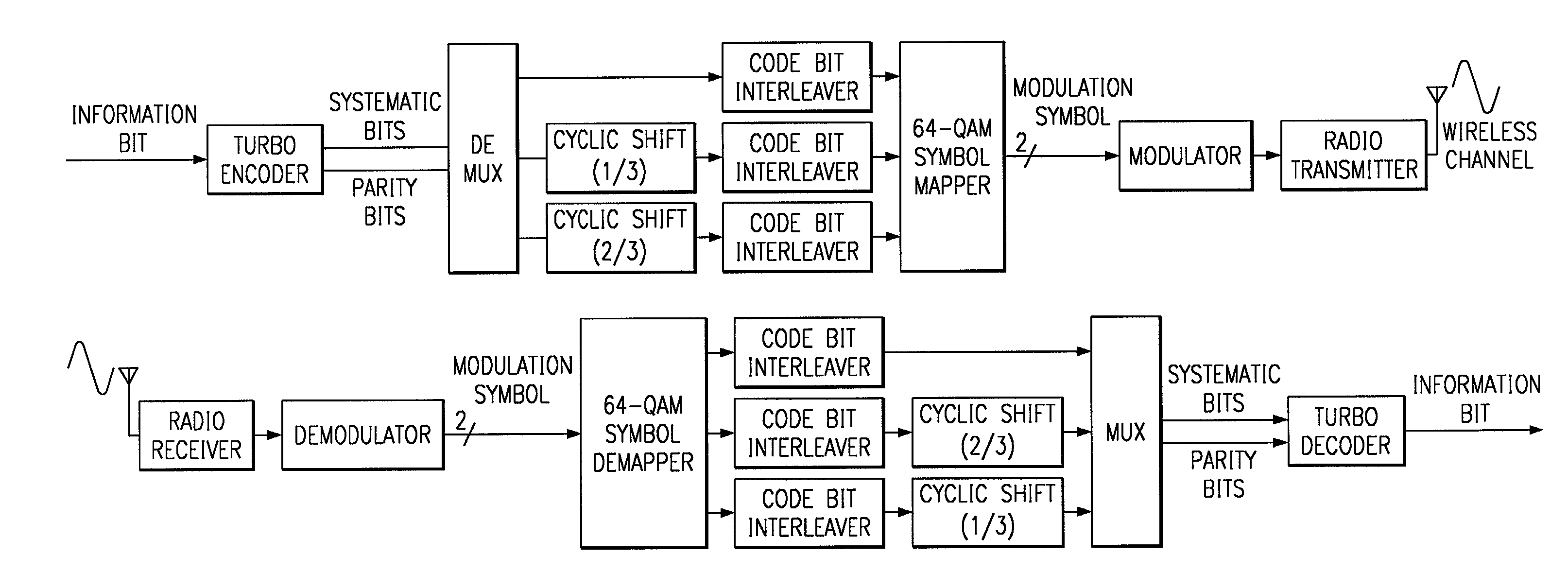
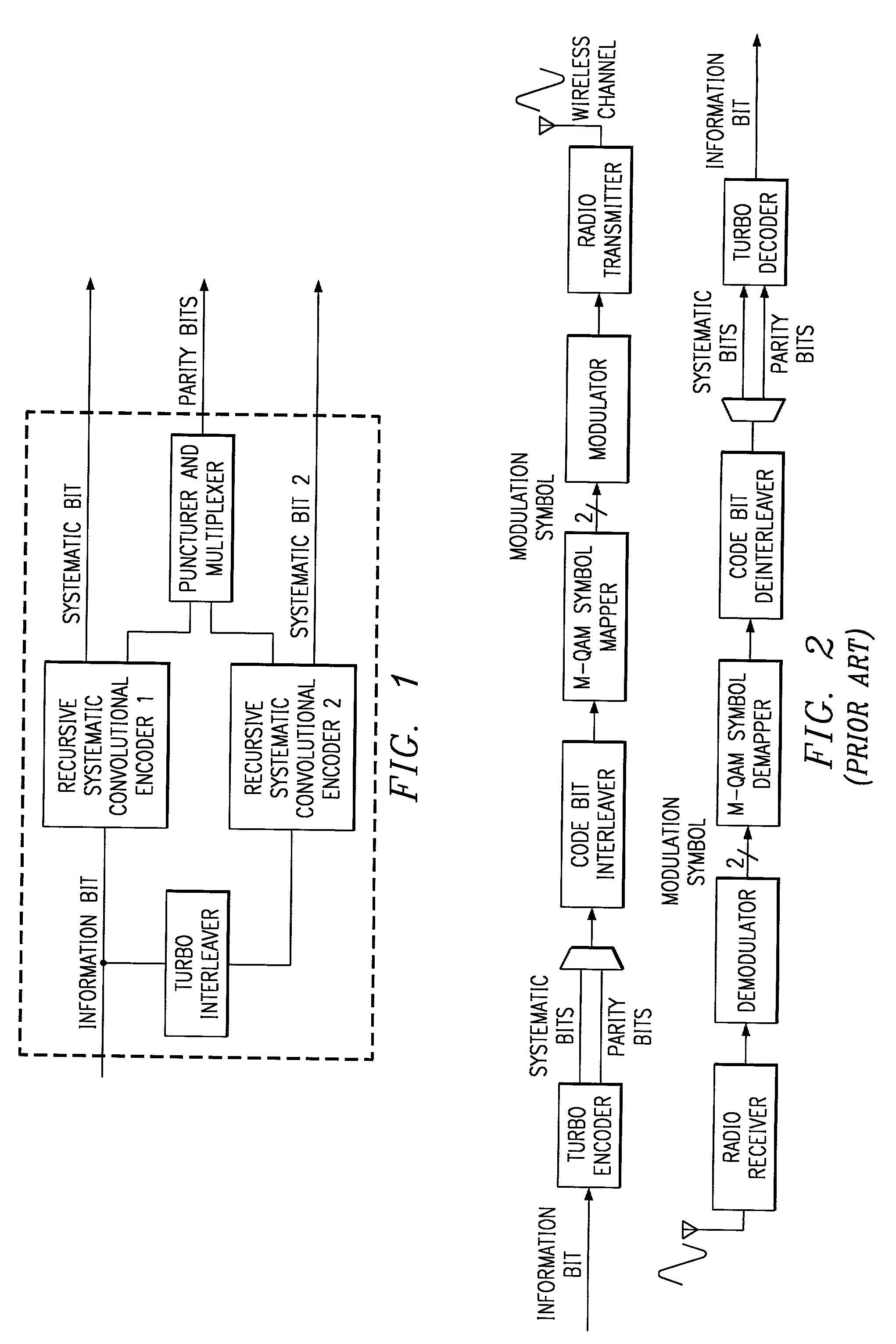
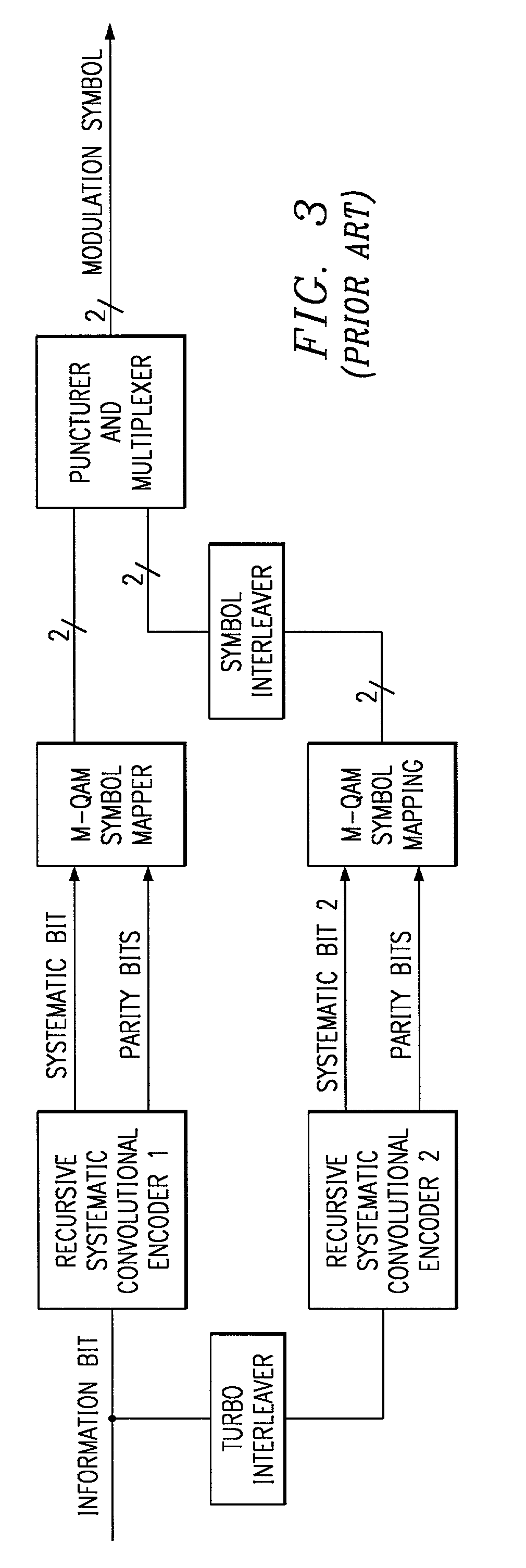
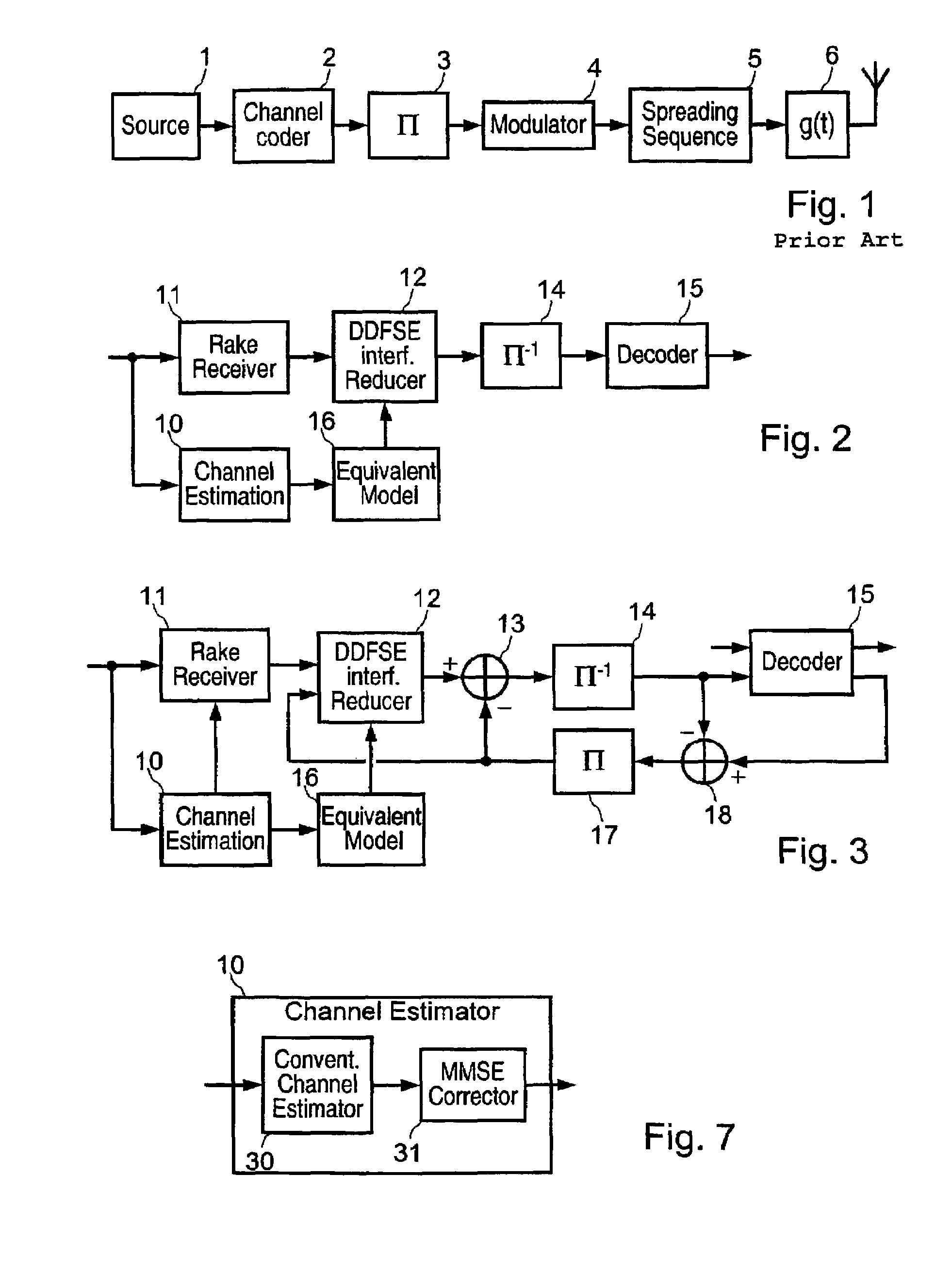
Method and coding means for error-correction utilizing concatenated parity and turbo codes
InactiveUS7093179B2Reduction in rateImprove overall utilizationError preventionError detection/correctionParallel computingTurbo coded
A method and apparatus for encoding and decoding data using an overall code comprising an outer parity-check and an inner parallel concatenated convolutional, or turbo code. The overall code provides error probabilities that are significantly lower than can be achieved by using turbo codes alone. The output of the inner code can be punctured to maintain the same turbo code rate as the turbo code encoding without the outer code. Multiple parity-check codes can be concatanated either serially or in parallel as outer codes. Decoding can be performed with iterative a posteriori probability (APP) decoders or with other decoders, depending on the requirements of the system. The parity-check code can be applied to a subset of the bits to achieve unequal error protection. Moreover, the techniques presented can be mapped to higher order modulation schemes to achieve improved power and bandwidth efficiency.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
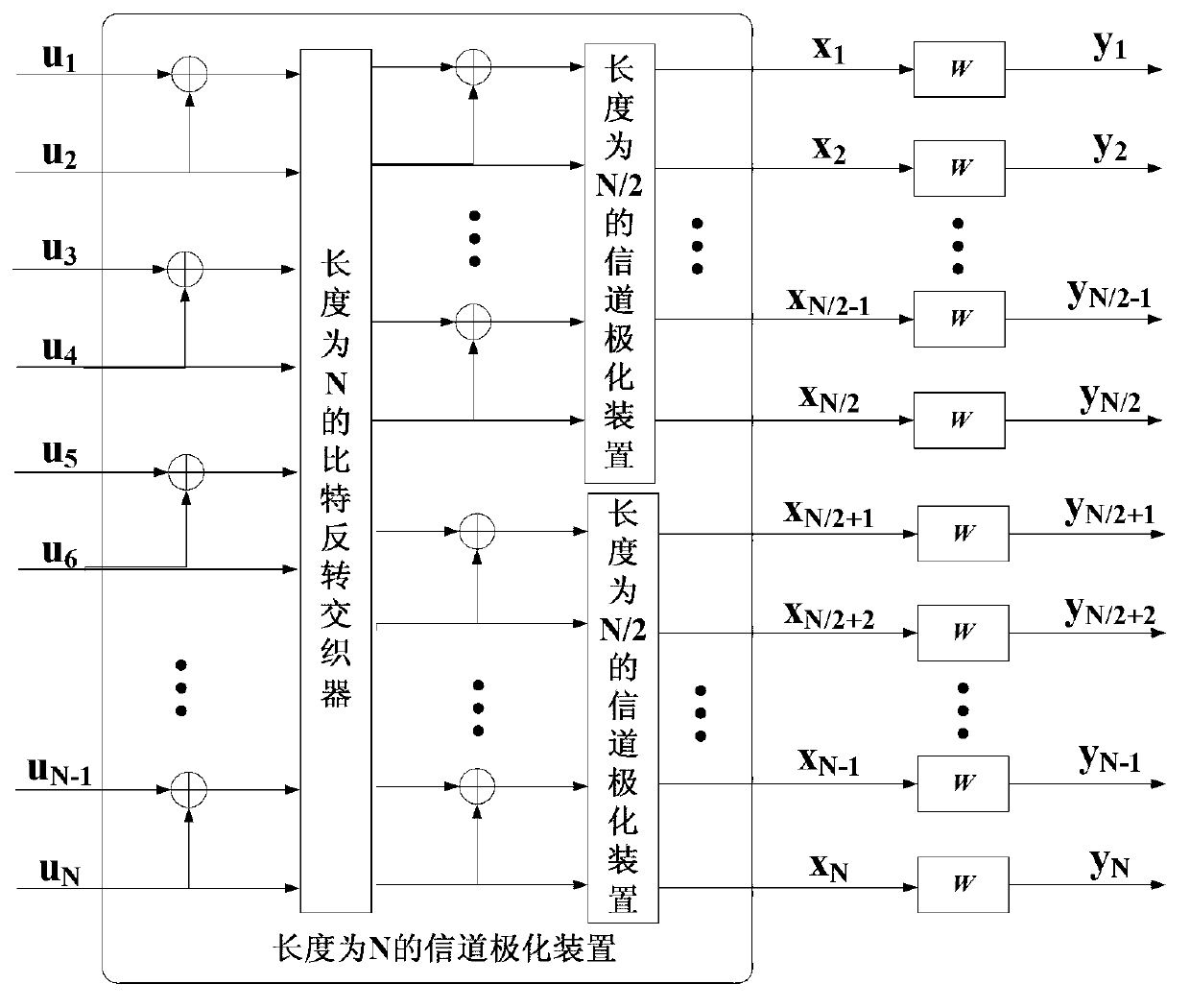
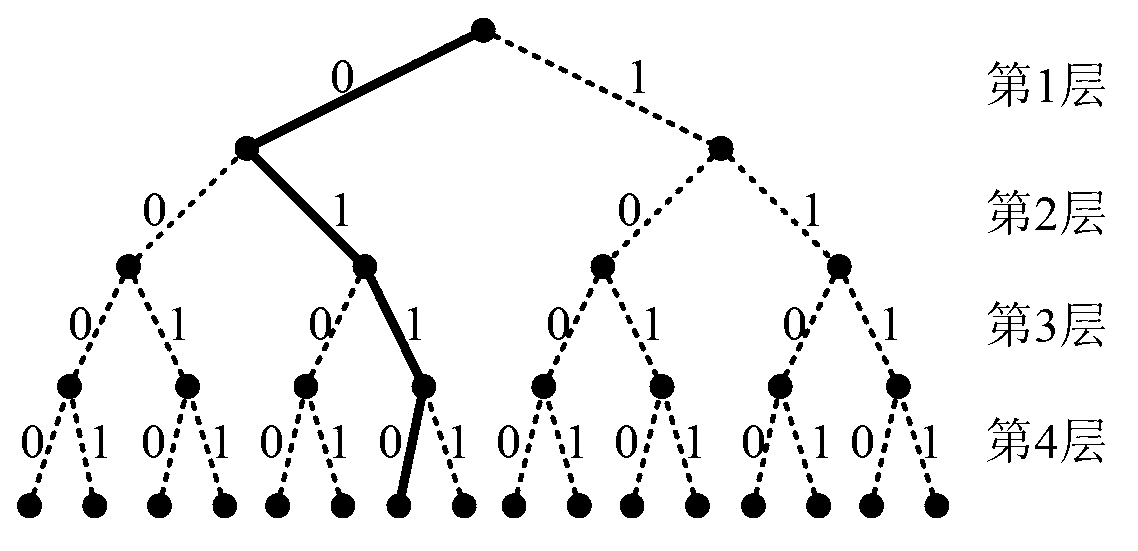
Random code length polar encoding method
InactiveCN103023618AImprove noise immunityError preventionCode conversionComputer hardwareCommunications system
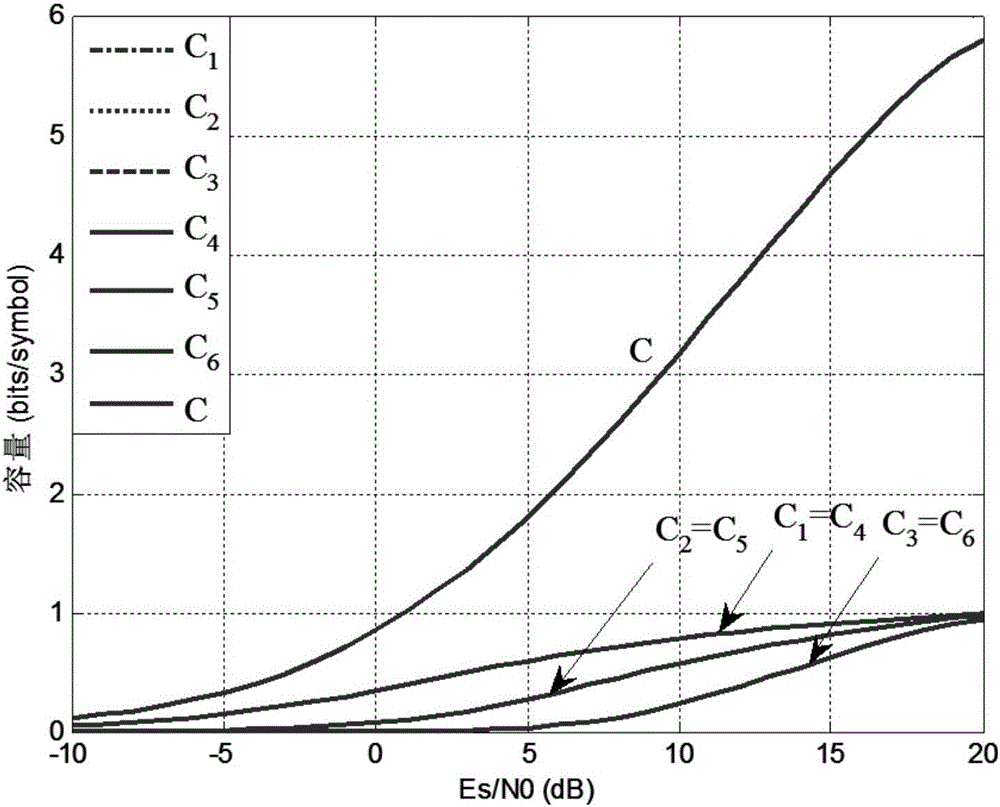
A random code length polar encoding method includes: during construction of a polar code, if the code length is not the power of 2, using a group of virtual channels with the capacity of zero for supplementing the channel number to be the power of 2; performing mixed mapping for each channel according to the capacity equalization principle; and performing polar conversion for the obtained channels, selecting the channels with higher capacity from converted channels according to the designed bitrate for transmitting information bit sequences, and using the rest channels for transmitting a known fixed bit sequence of a receiving end and a transmitting end. The method enables polar encoding to allow the code length to be an optional positive integer and is applicable to multi-carrier and high-order modulation systems, and the added perforating operation enables the encoding bit sequences outputted by an encoder to be optional in length; by means of channel mixed mapping, polar encoding can adapt to different component channels of parallel channels, so that anti-noise performance is good; and flexibility of using polar codes for a practical digital communication system is greatly improved, and accordingly the method has good application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
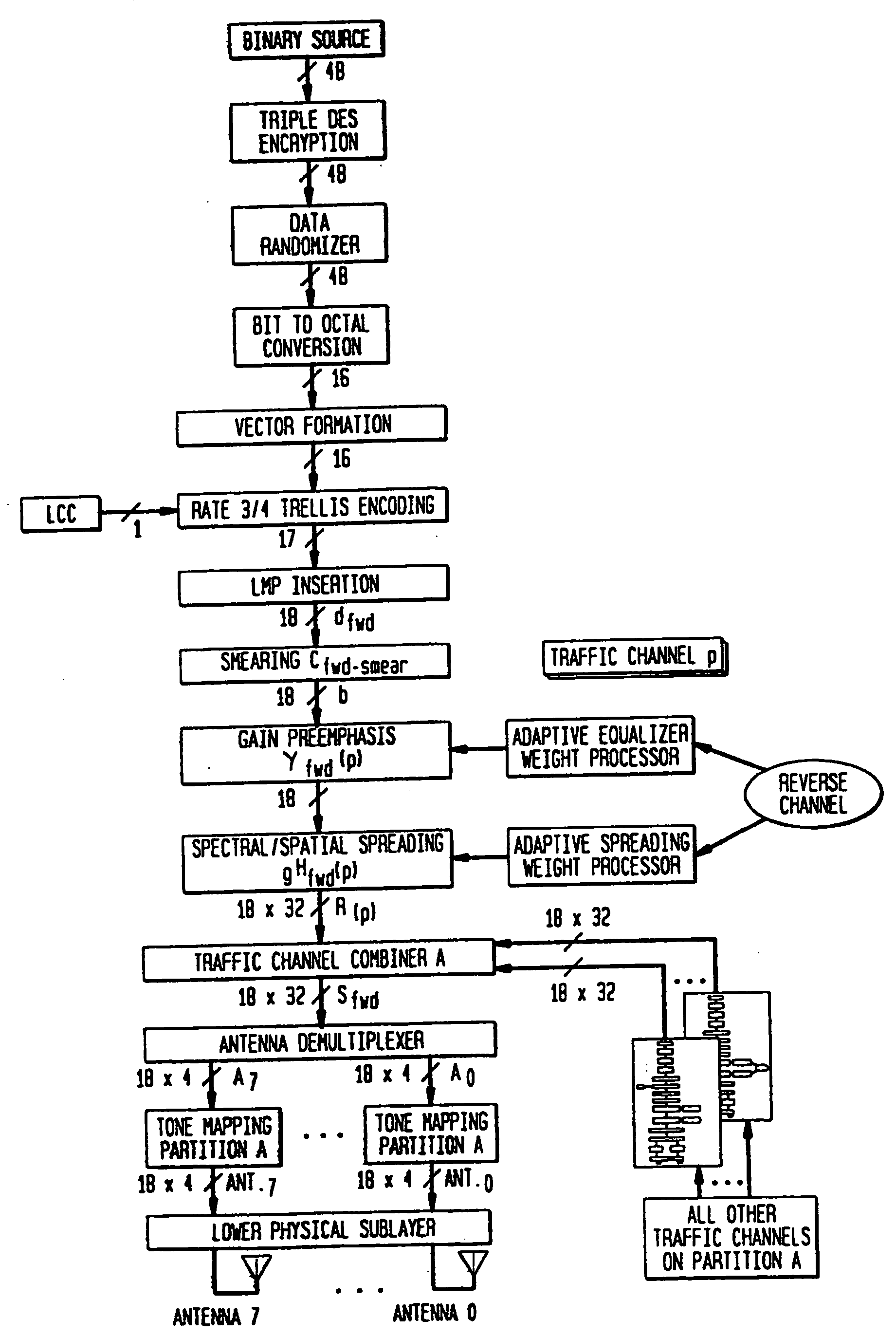
Highly bandwidth-efficient communications
InactiveUS20060193373A1Reduce distractionsSimple calculationSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
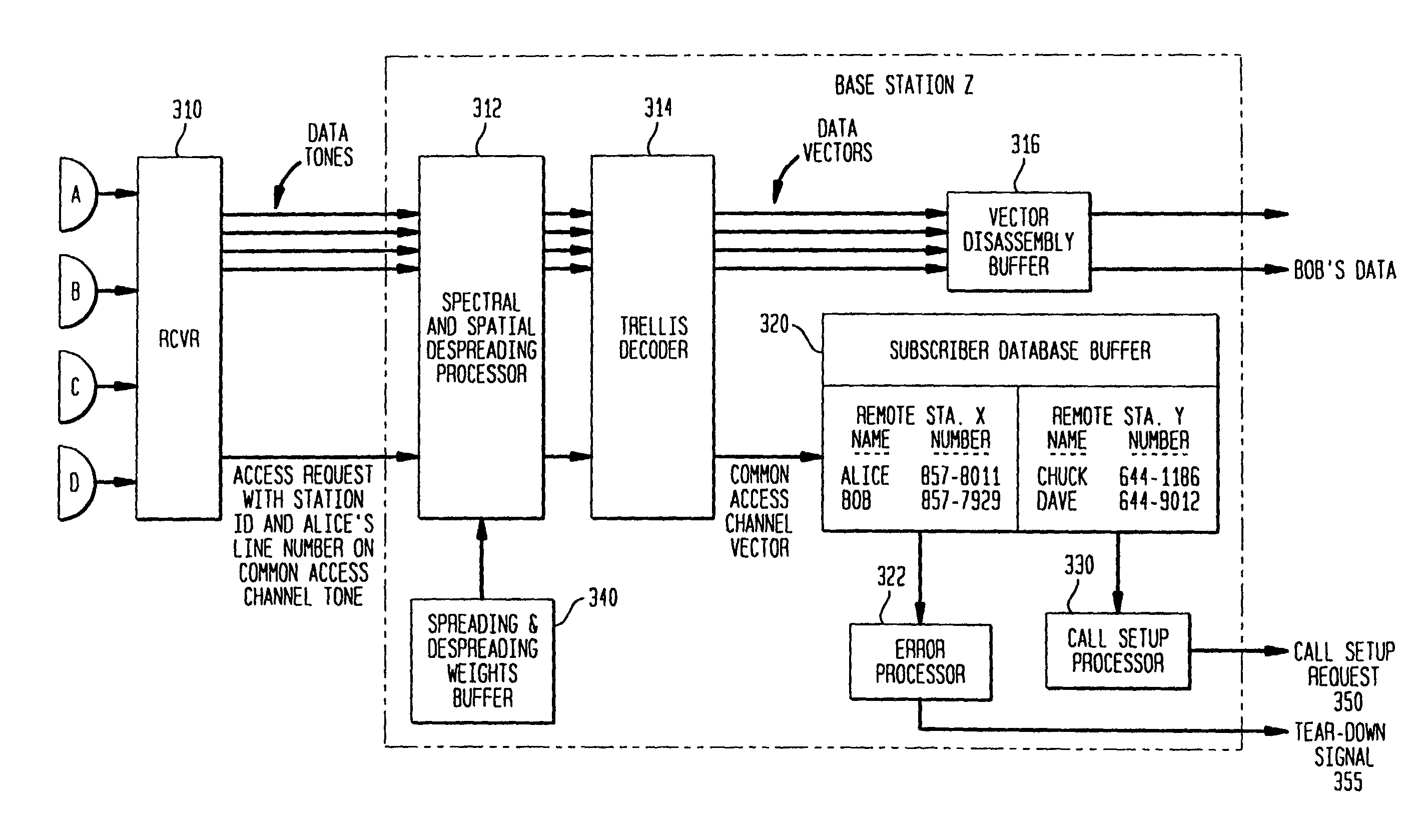
A discrete multitone stacked-carrier spread spectrum communication method is based on frequency domain spreading including multiplication of a baseband signal by a set of superimposed, or stacked, complex sinusoid carrier waves. In a preferred embodiment, the spreading involves energizing the bins of a large Fast Fourier transform (FFT). This provides a considerable savings in computational complexity for moderate output FFT sizes. Point-to-multipoint and multipoint-to-multipoint (nodeless) network topologies are possible. A code-nulling method is included for interference cancellation and enhanced signal separation by exploiting the spectral diversity of the various sources. The basic method may be extended to include multielement antenna array nulling methods for interference cancellation and enhanced signal separation using spatial separation. Such methods permit directive and retrodirective transmission systems that adapt or can be adapted to the radio environment. Such systems are compatible with bandwidth-on-demand and higher-order modulation formats and use advanced adaptation algorithms. In a specific embodiment the spectral and spatial components of the adaptive weights are calculated in a unified operation based on the mathematical analogy between the spectral and spatial descriptions of the airlink.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
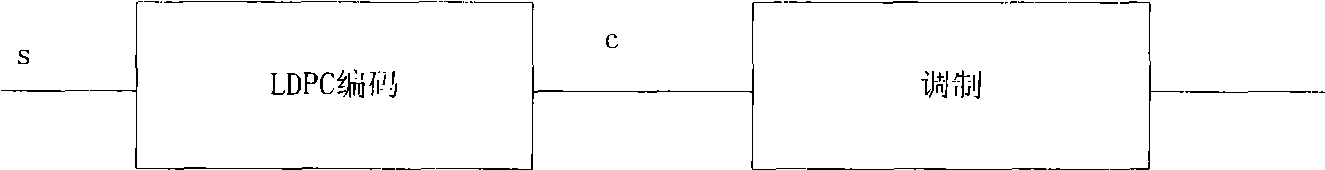
LDPC code encoding modulation method and apparatus
ActiveCN101488819APremium Coded Modulation GainError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeTheoretical computer science
The invention embodiment provides a coded modulation method for low density parity check code, a low density parity check code coded processing can be performed for an information sequence to obtain a code word, and the interweave processing can be performed for the code word, then the modulated processing can be performed for the code word by interweave processing; meanwhile, the invention embodiment also provides a coded modulation apparatus for the low density parity check code. The technical scheme disclosed by the invention embodiment is based on the importance of low density parity check code degree distribution, and the different bits on a star map in high order modulation have different reliabilities, and the excellent coded modulation gain can be obtained.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Highly bandwidth-efficient communications
InactiveUS7106781B2Efficient processingEnhance signal to noise and interference ratio of signalSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
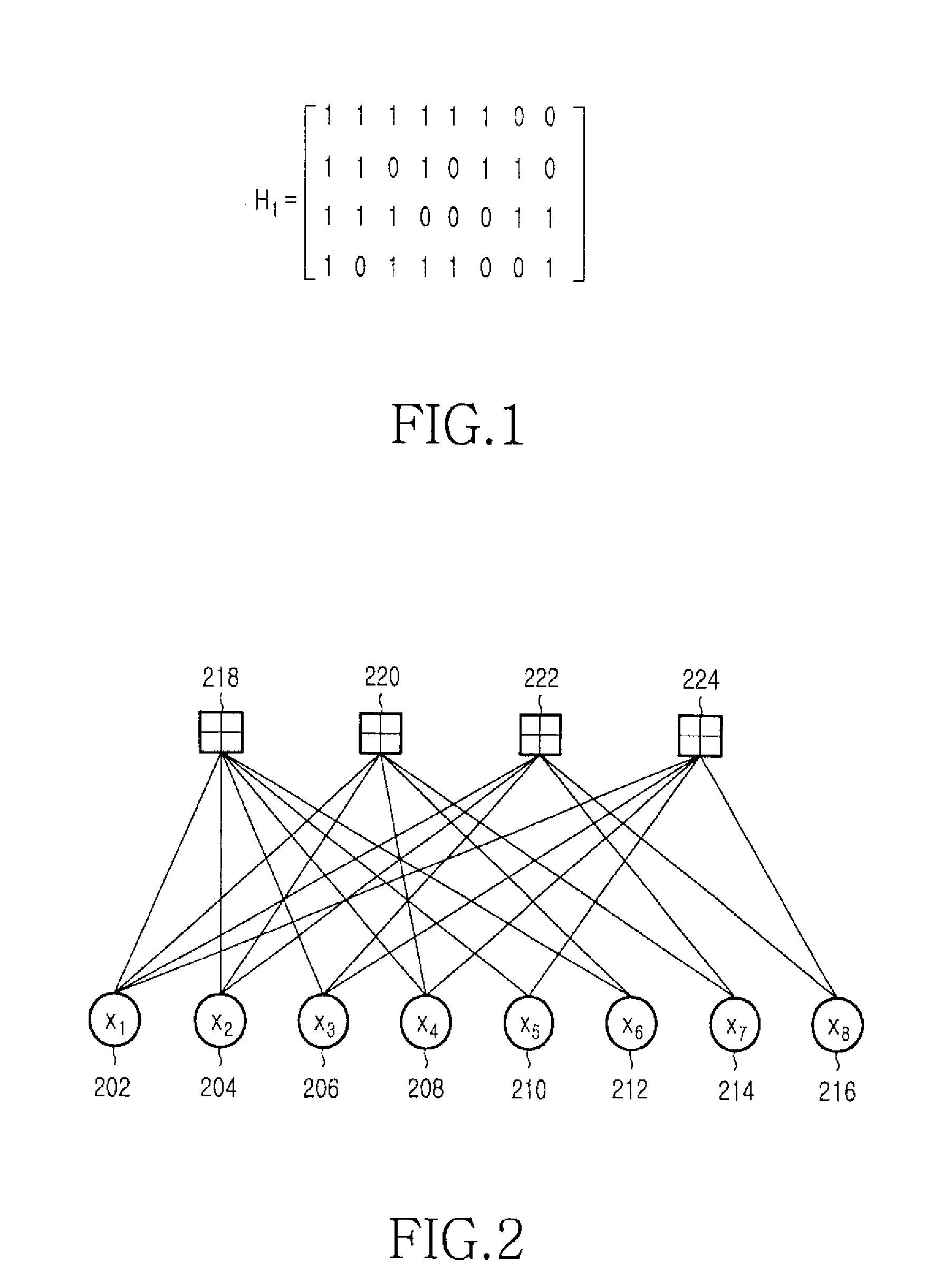
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in a communication system using low density parity check code
ActiveUS20090125781A1Reduce signal distortionImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsError correction/detection using LDPC codesCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
A method for transmitting data in a communication system using a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) matrix includes generating an LDPC codeword by encoding information data bits, interleaving the LDPC codeword, mapping the interleaved LDPC codeword to a modulation signal, and generating a mapped signal by mapping the LDPC codeword bits separately to a bit corresponding to a real part and a bit corresponding to an imaginary part of said modulation signal, among bits constituting the modulation signal, generating a modulation signal by high-order-modulating the mapped signal and Radio Frequency (RF)-processing the modulation signal, and transmitting the RF-processed signal via a transmission antenna.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
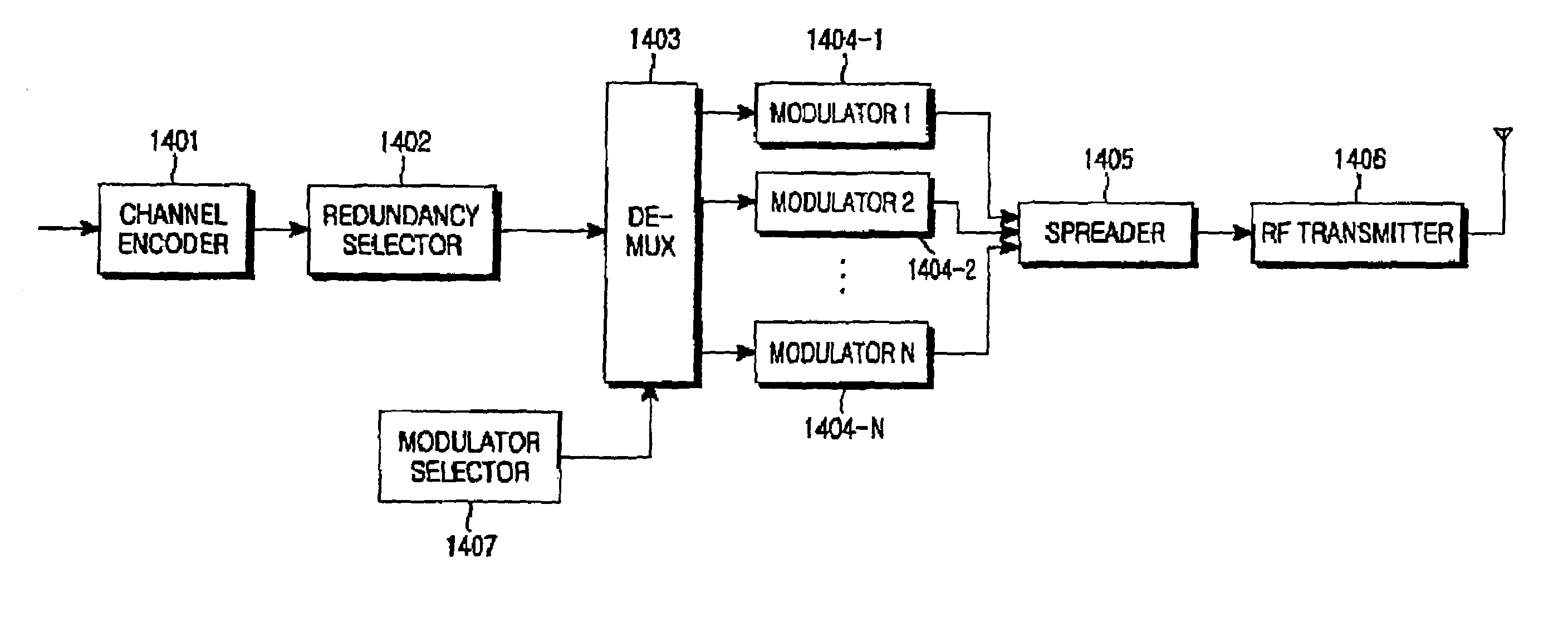
Preamble with modified signal field (SIG) for use in wireless communications
A wireless communication device (‘device’) is configured to generate an OFDM / A packet that includes at least one OFDM / A symbol that includes at least one SIG having SIG information modulated on only even (or odd) sub-carriers and does not include any information modulated on odd (or even) sub-carriers of a set of OFDM / A sub-carriers. The set of OFDM / A sub-carriers may be all or less than all of available sub-carriers. The device may generate the packet to include a preamble and a payload such that the payload, which may be composed of at least one additional OFDM / A symbol, includes data modulated on some or all of the sub-carriers of the set of OFDM / A sub-carriers. The device can modulate and transmit SIG information and data differently within the preamble and the payload (e.g., with higher ordered modulation or MCS for the data and less power per sub-carrier than for the preamble).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for transmitting MCS instructing information
InactiveCN103580788AImprove throughputImprove spectral efficiencyModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter specific arrangementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Frequency spectrum
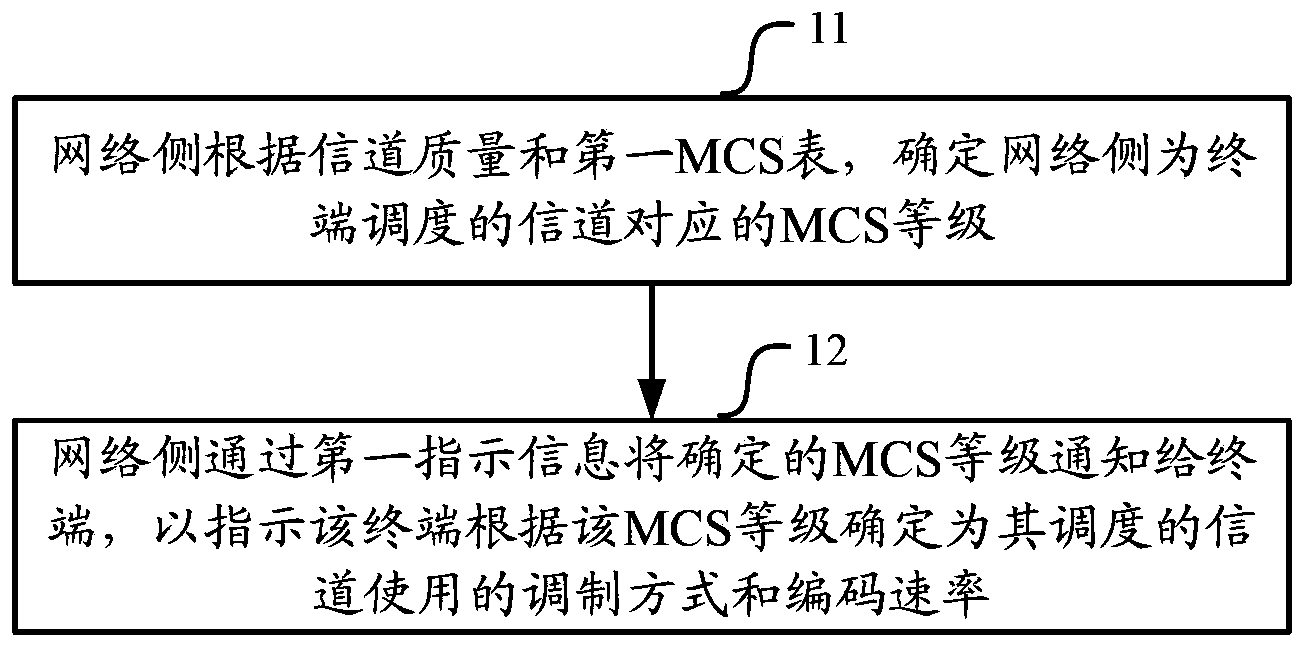
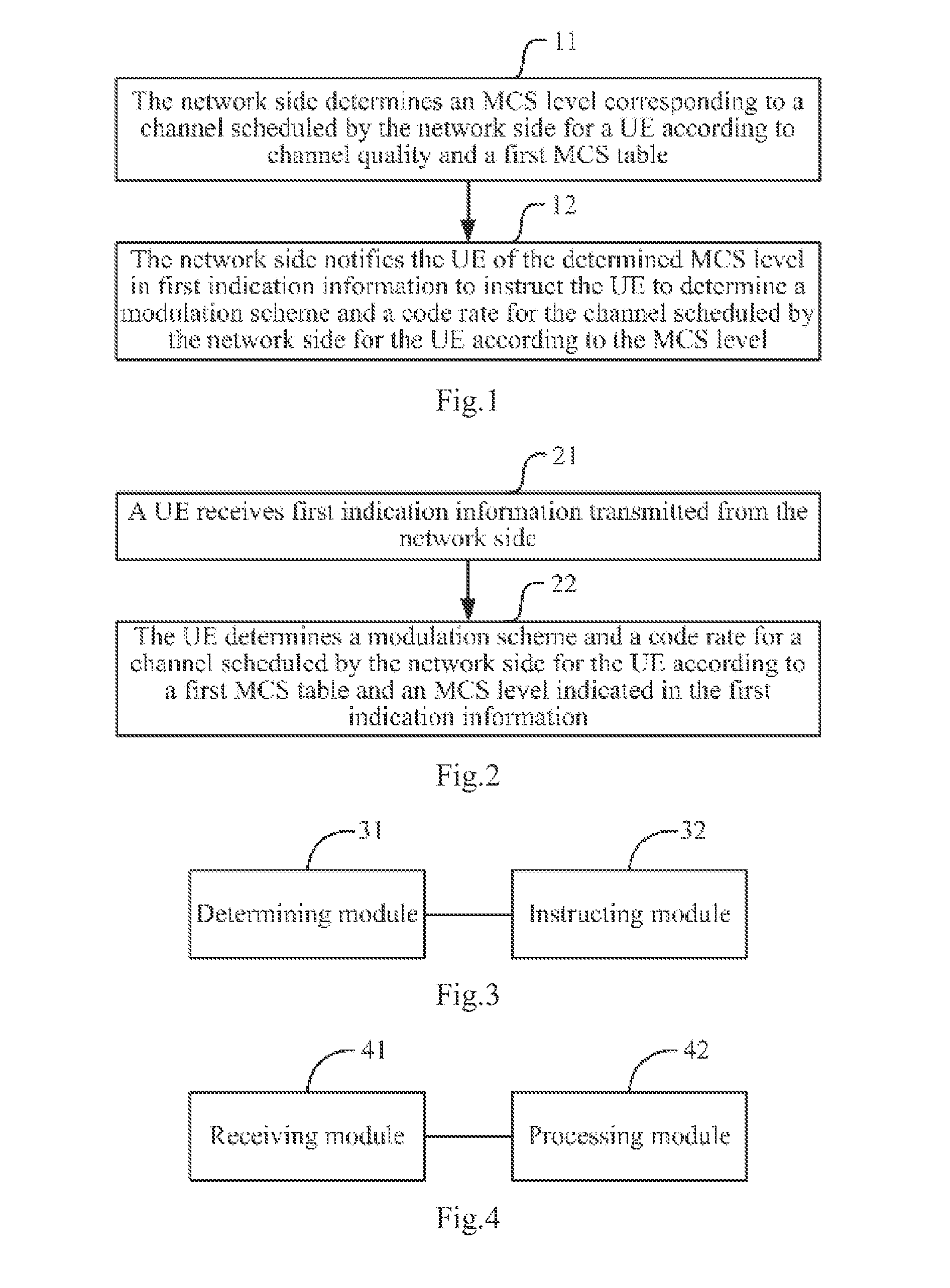
The present application relates to the field of wireless communications, and in particular, to an indication method and device for a modulation coding scheme. It is used for solving the problem that in an existing LTE / LTE-A system, a higher-order modulation scheme cannot be supported, thereby limiting the further improvement of throughput in an application scenario of a high signal-to-noise ratio. The method of the embodiments of the present application includes: according to the channel quality and a first MCS table, a network side determining an MCS grade corresponding to a channel assigned to a terminal; and by means of first indication information, notifying the terminal of the determined MCS grade, so as to indicate to the terminal to determine a modulation scheme and coding rate used by the channel assigned thereto according to the MCS grade, wherein the first MCS table at least contains corresponding records of an MCS index and a TBS index corresponding to a modulation scheme with a modulation order greater than 6. The embodiments of the present application introduce a higher-order modulation scheme into an existing LTE / LTE-A system, improving the spectrum efficiency.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
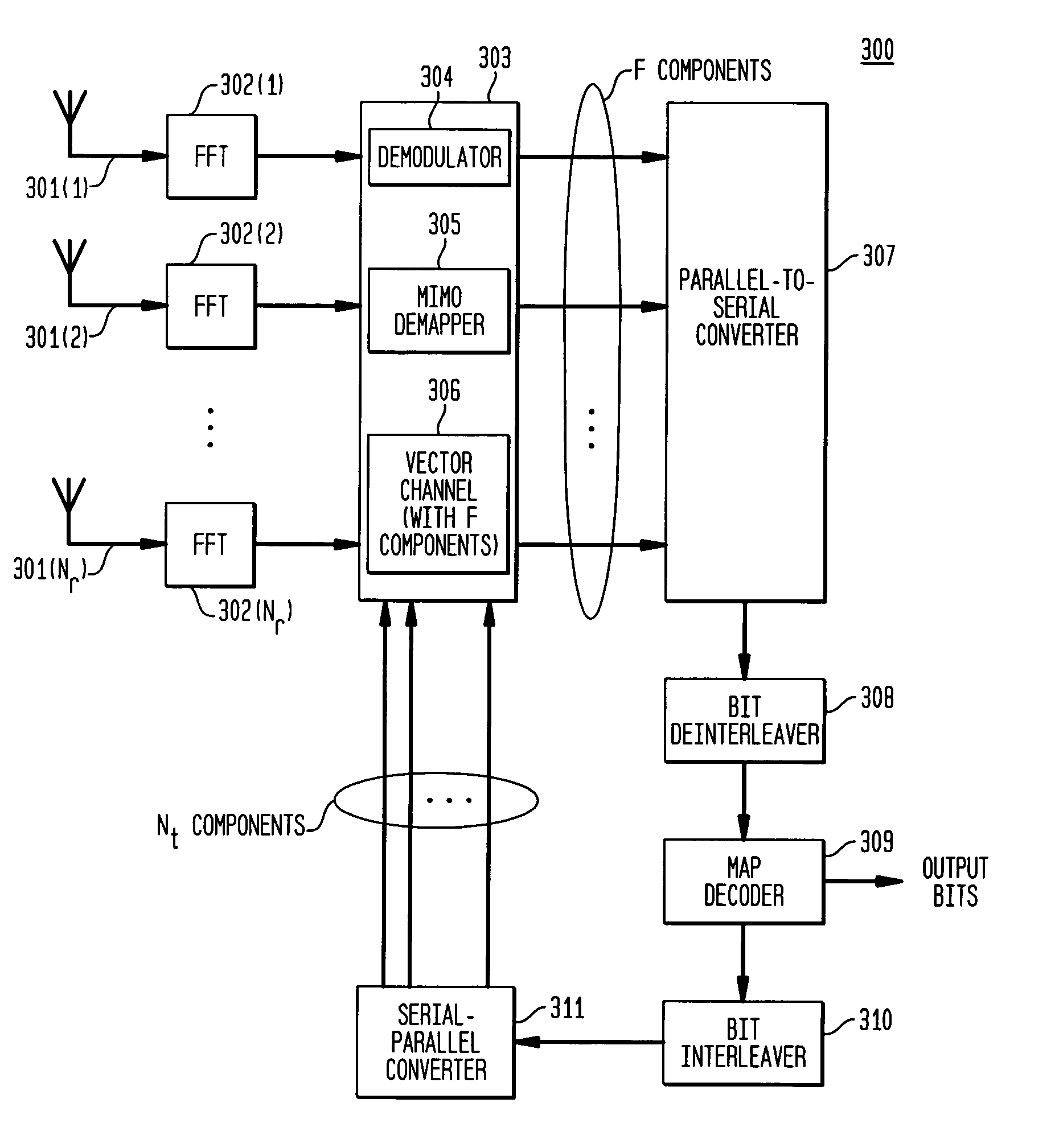
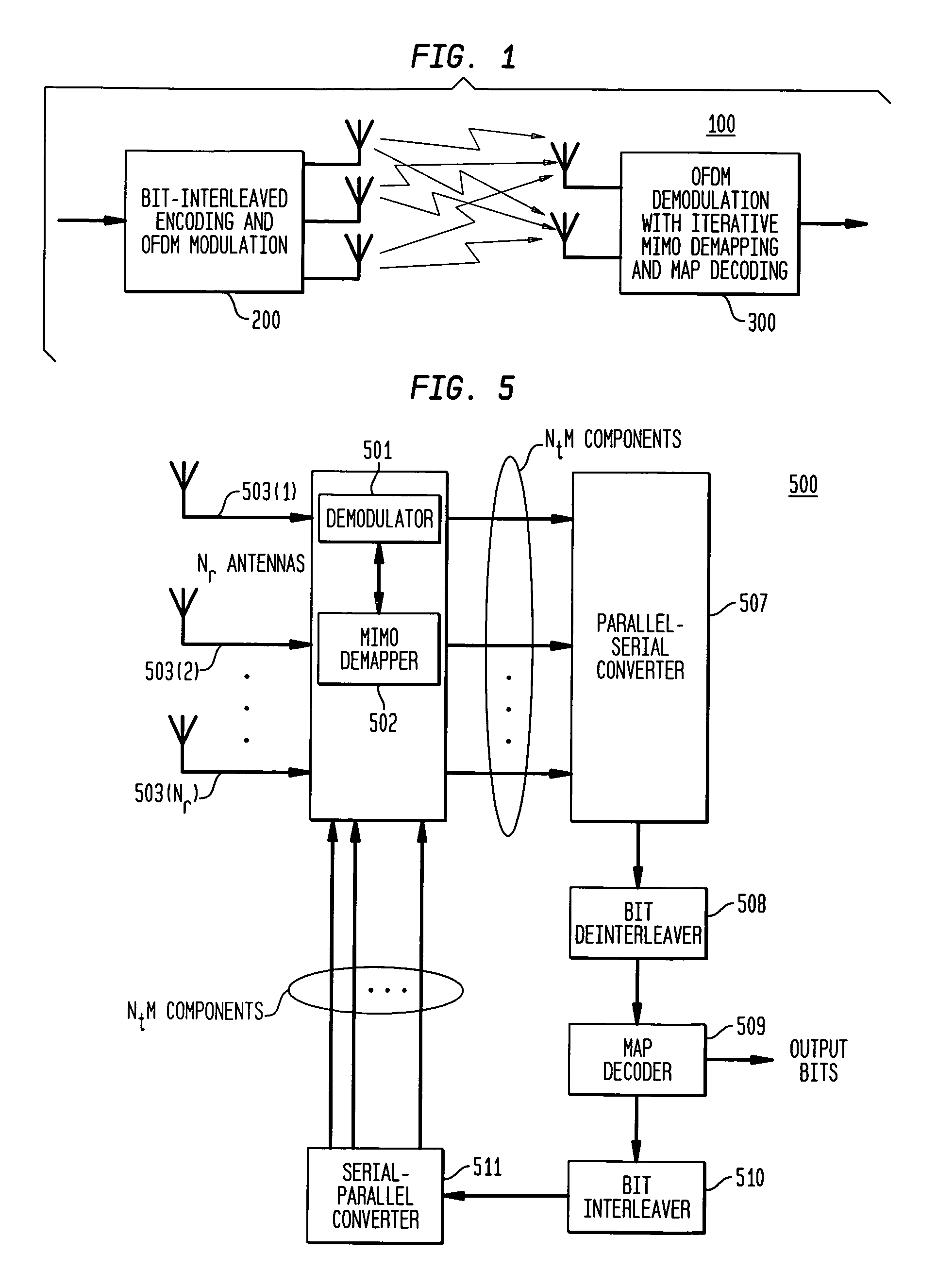
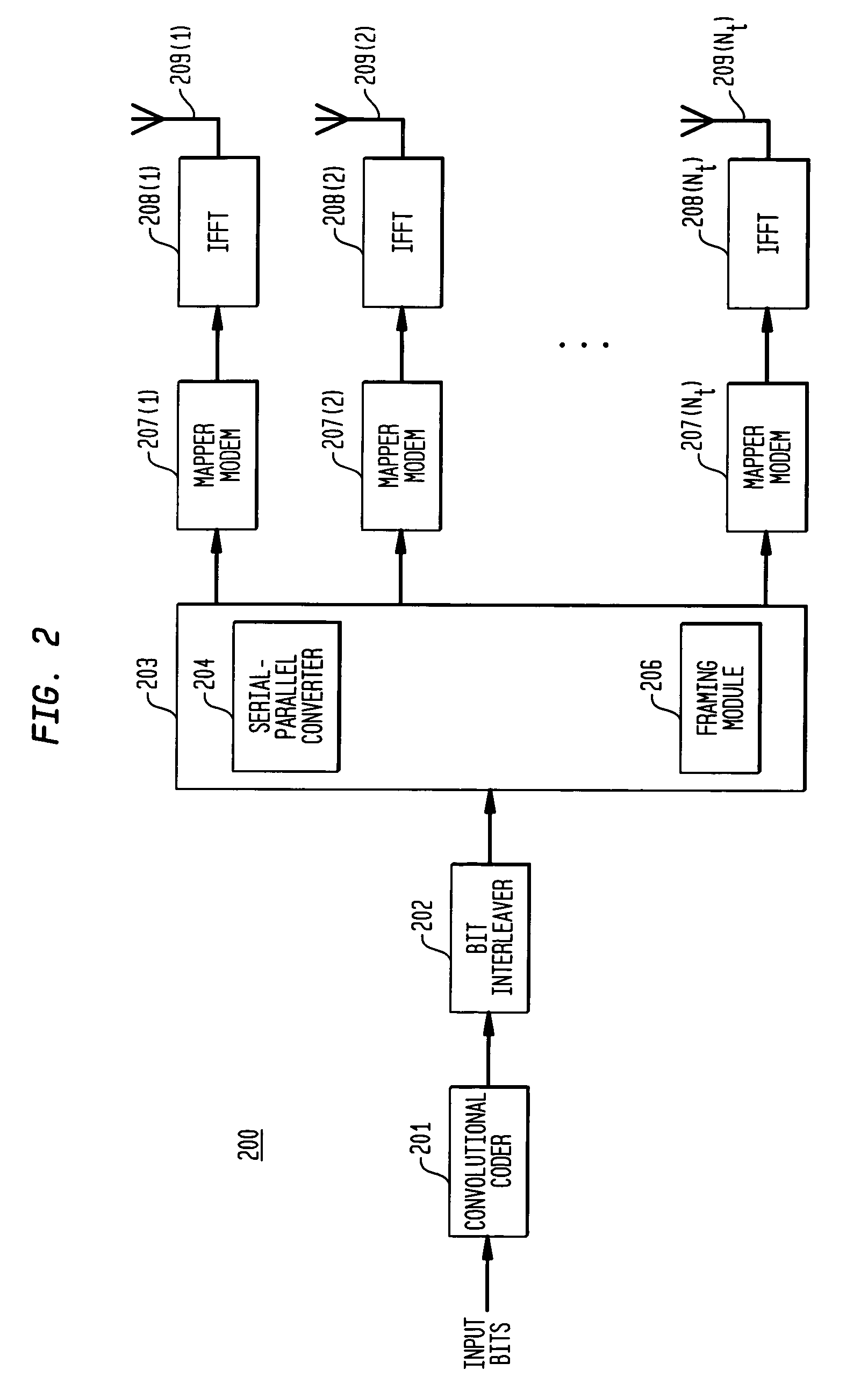
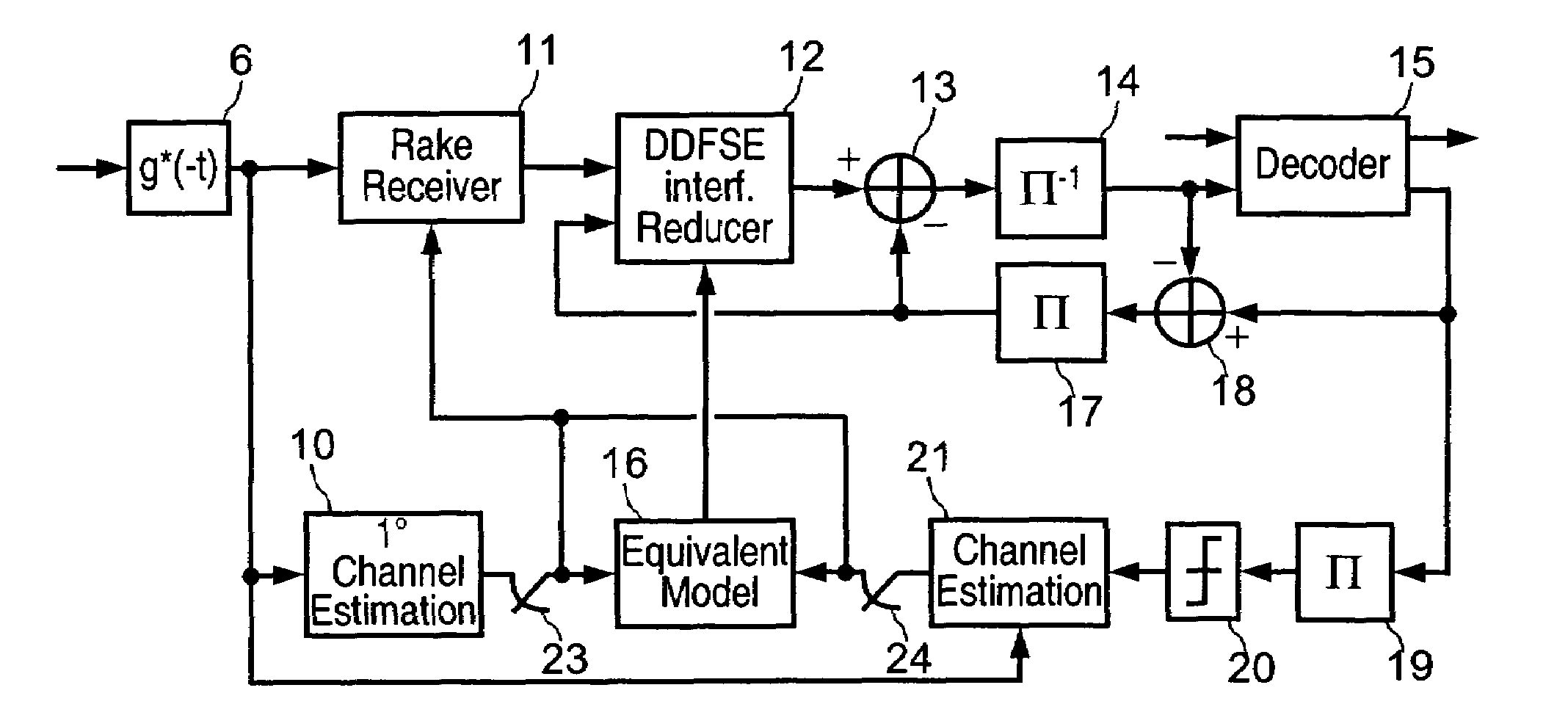
Reduced complexity receiver for space-time- bit-interleaved coded modulation
InactiveUS7095812B2Improve bit error rate performanceReduce in quantityData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionMulti inputRadio channel
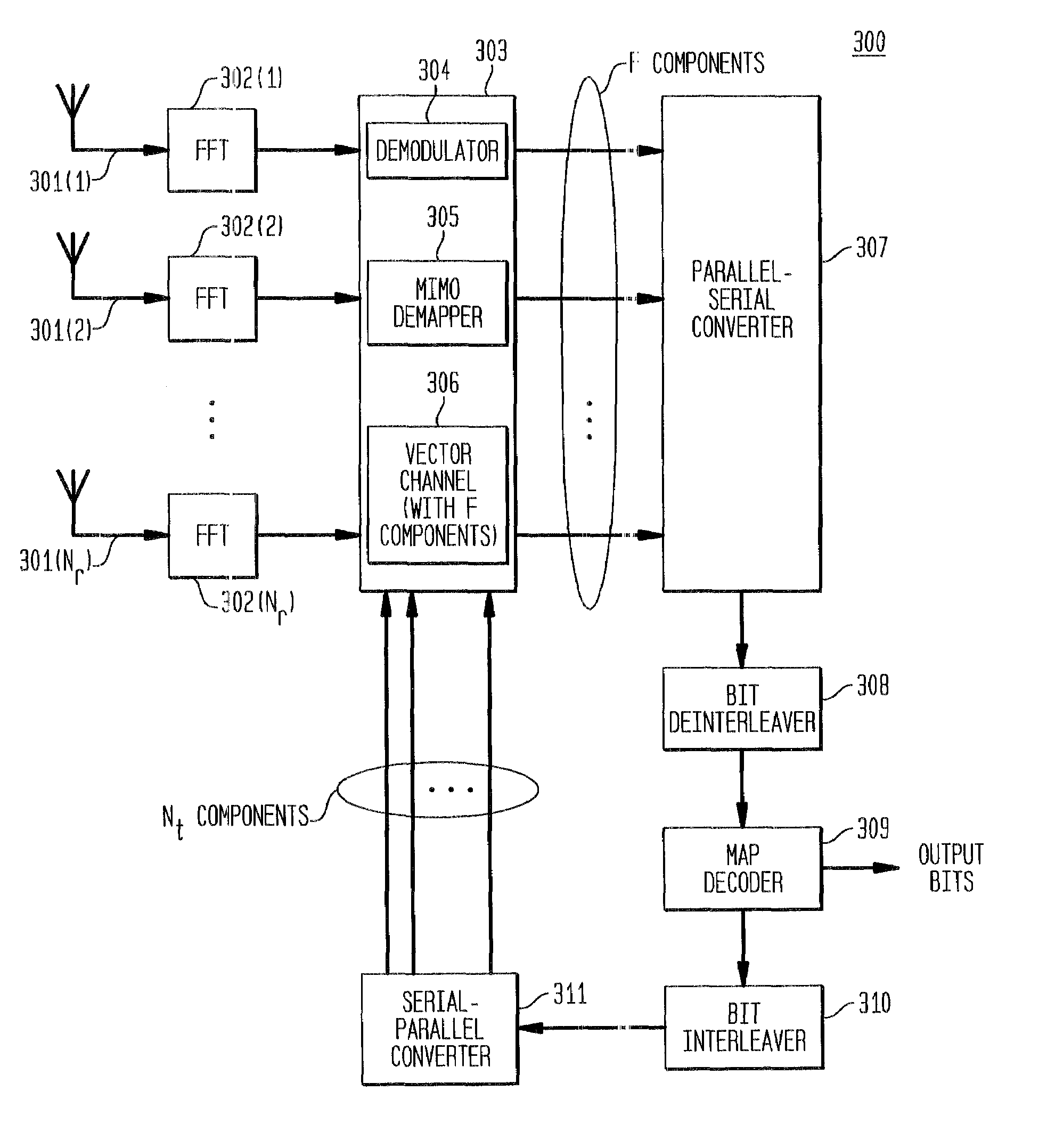
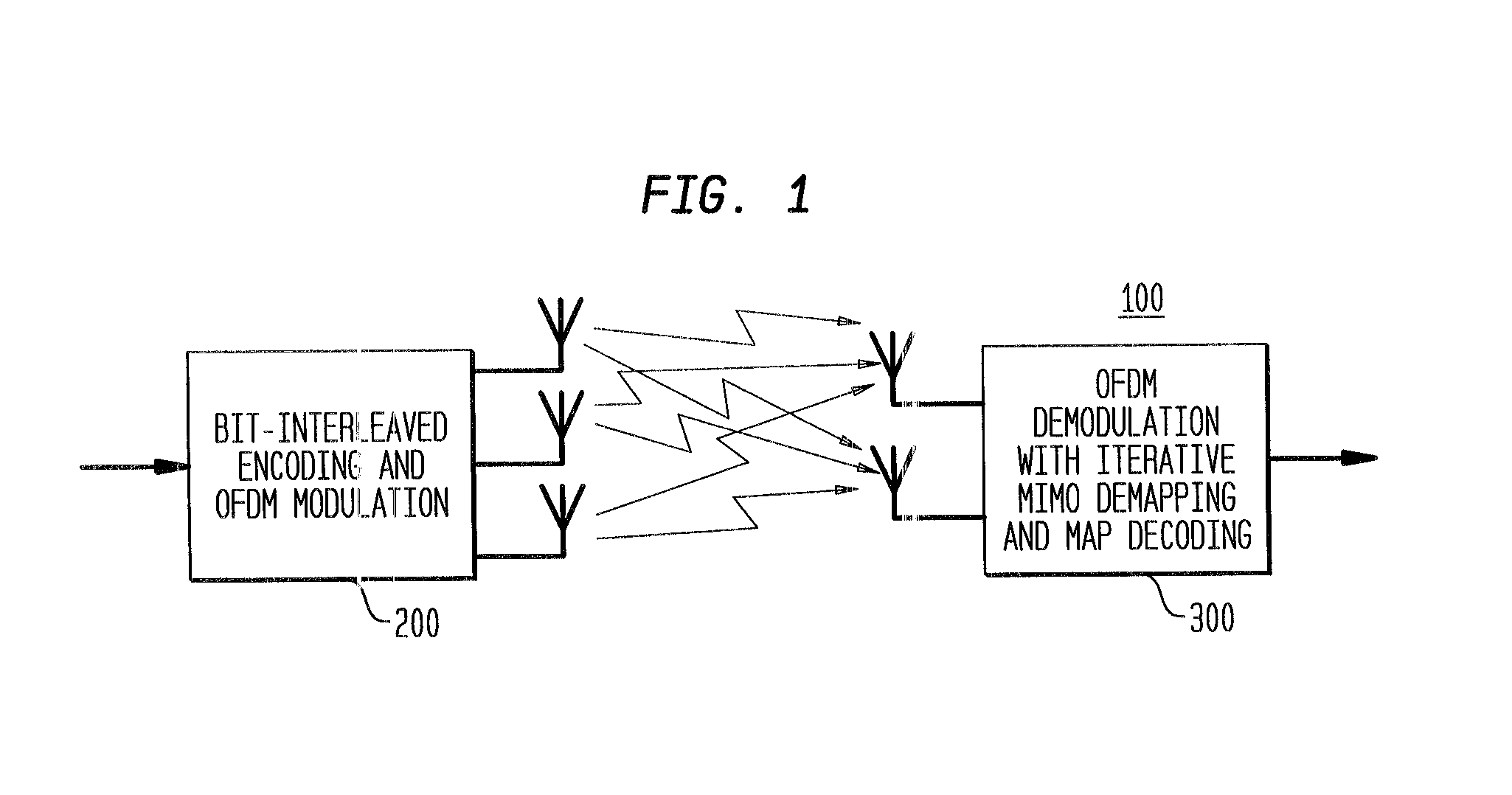
A system employs space-time coding characterized at the transmitter by bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) combined with modulating several streams of the BICM encoded data for transmission over two or more antennas. Space-time coding techniques improve transmission efficiency in radio channels by using multiple transmit and / or receive antennas and coordination of the signaling over these antennas. Bit-interleaved coded modulation provides good diversity gain with higher-order modulation schemes that employ binary convolutional codes. A receiver demodulates the received signals and applies multi-input, multi-output (MIMO) demapping to estimate the BICM encoded bitstream. After deinterleaving of the BICM encoded bitstream, maximum a posteriori (MAP) decoding is applied to the resulting bit stream to generate soft output values. By applying well-known turbo-decoding principles to iteratively demap and decode, the overall receiver performance is significantly improved. The MIMO demapping and MAP decoding processes exchange likelihood information to improve the bit error rate performance over several iterations of demapping / decoding. By generating tentative decisions for transmitted bits, the overall number of evaluations used for demapping may be reduced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
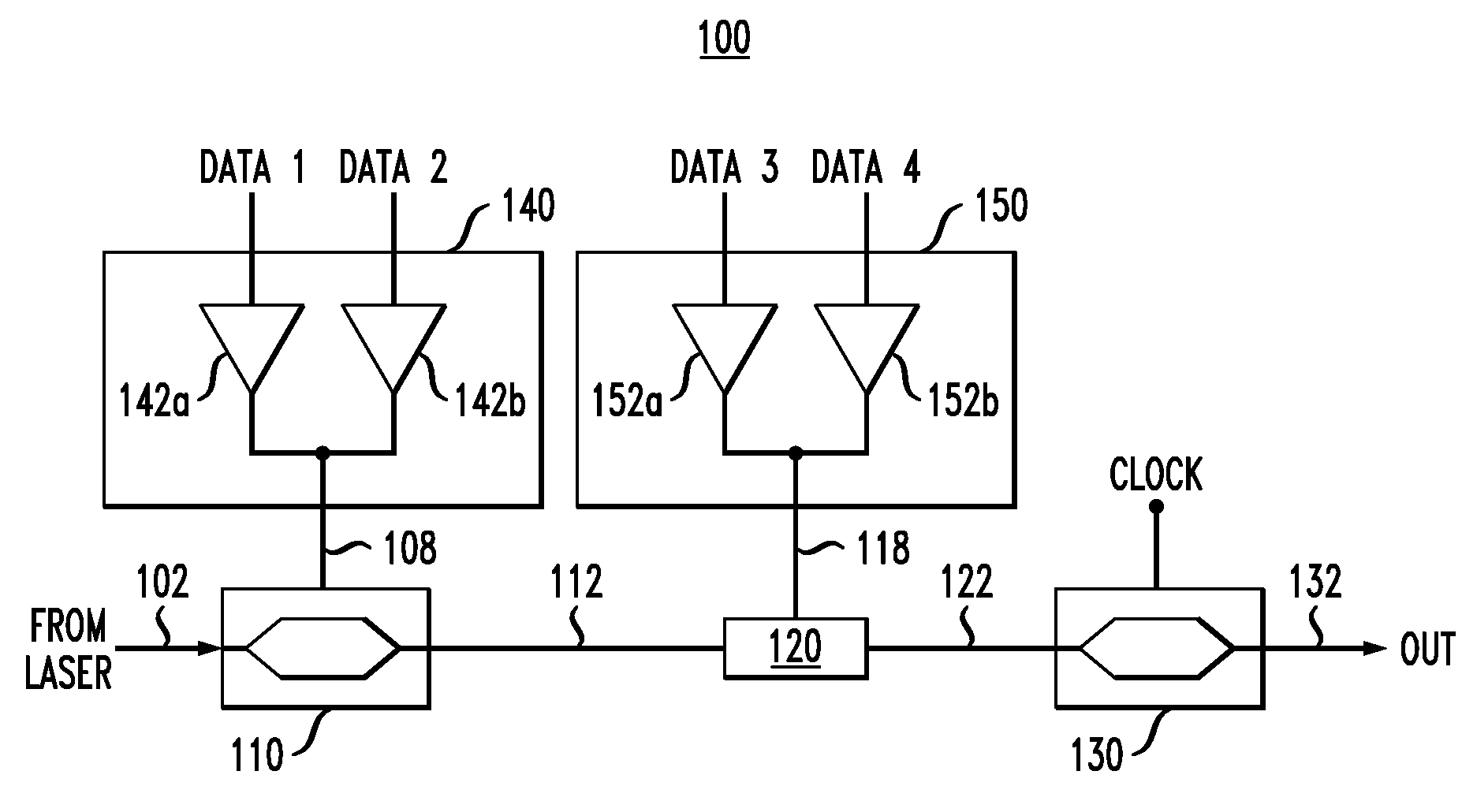
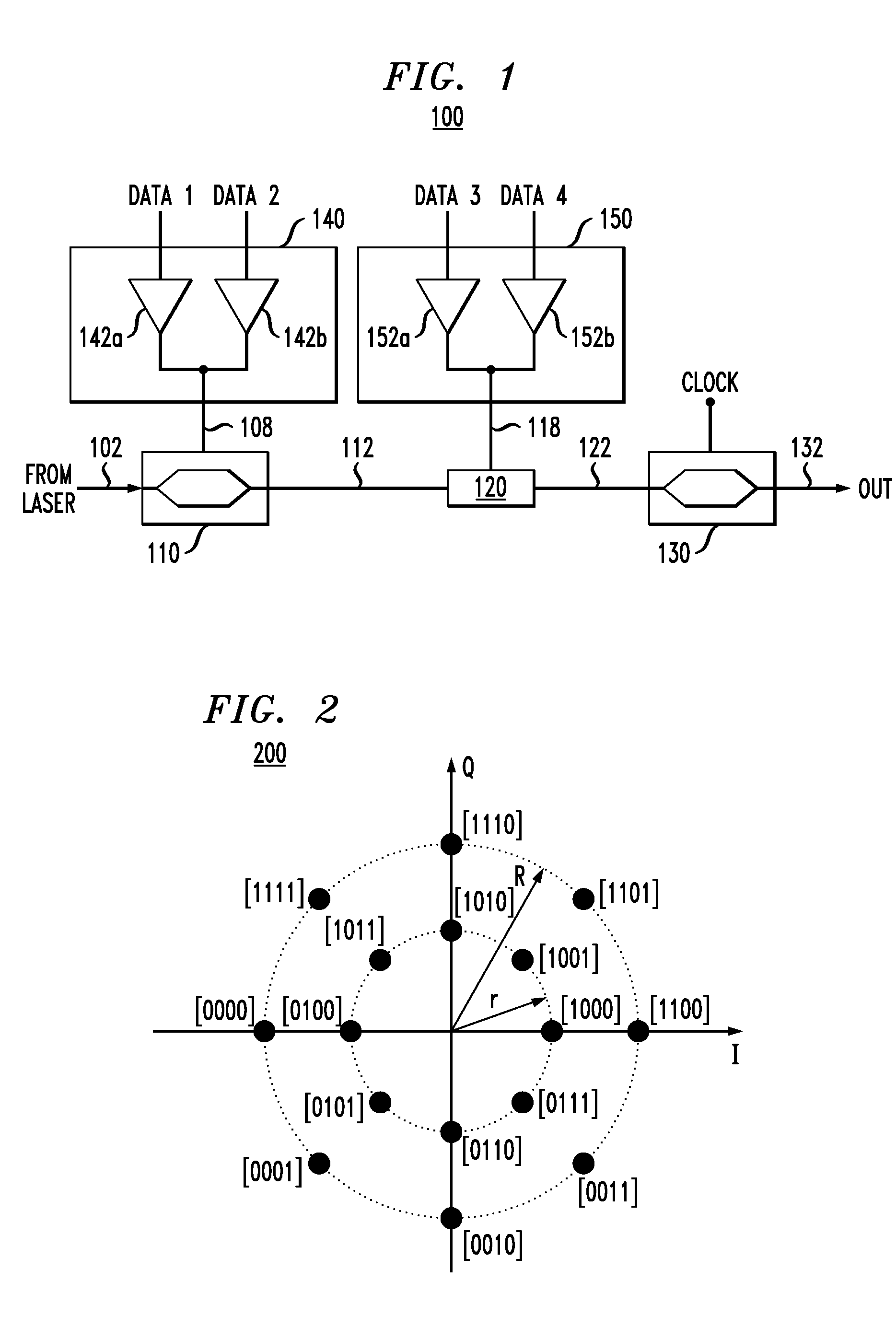
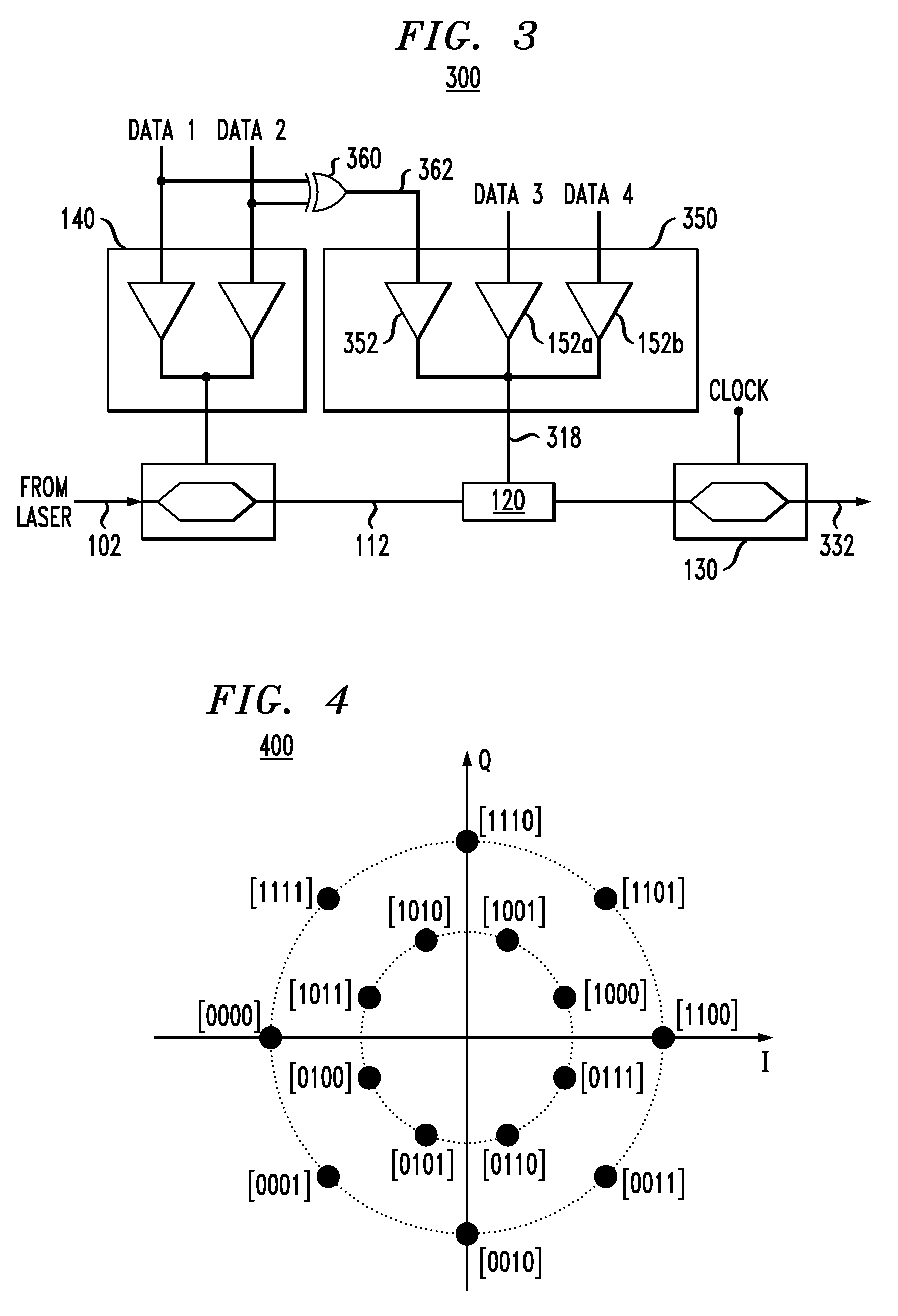
Method and apparatus for prioritizing information protection in high order modulation symbol mapping
InactiveUS6476734B2Increase chanceImprove performanceCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareHigher-order modulation
Owner:APPLE INC
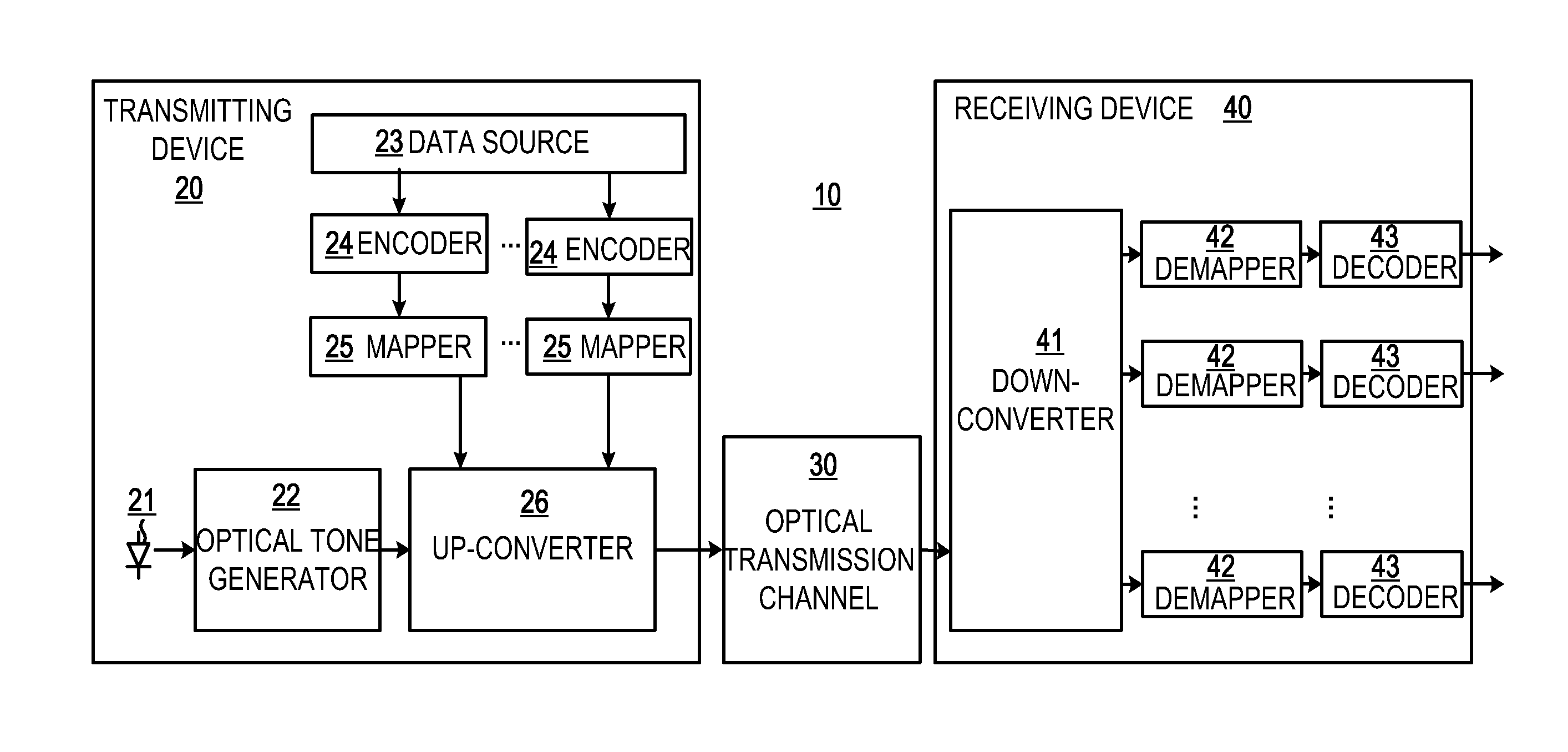
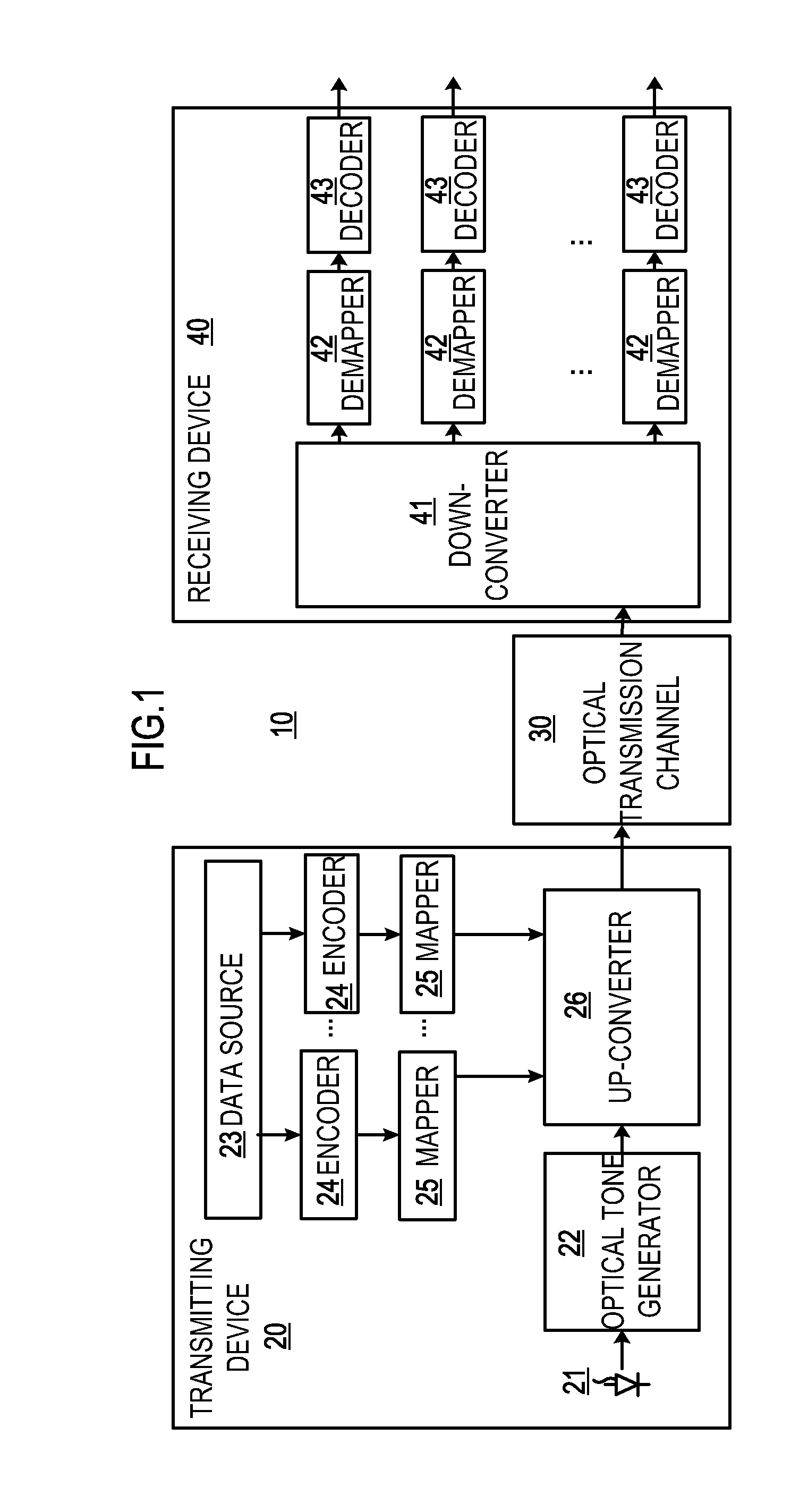
Optical Communication System, Device and Method Employing Advanced Coding and High Modulation Order
ActiveUS20120141135A1Improve system sensitivityIncrease speedError preventionPolarisation multiplex systemsFrequency changerCommunications system
A transmitting device, a receiving device, an optical communication system, and associated methods are provided. The transmitting device transmits an optical signal containing data, and comprises: an optical tone generator for generating at least one optical tone; at least one encoder for performing advanced coding on at least one data signal respectively, each of the at least one data signal carrying a part of the data; at least one mapper for performing high order modulation on the at least one coded data signal; and an up-converter for up-converting the at least one high-order-modulated data signal into the optical signal to be outputted through the at least optical tone. Thereby, high speed (e.g., over 1-Tb / s) transmission per single channel over a long-haul distance (e.g. over 1000-km) with error-free recovery may be achieved.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
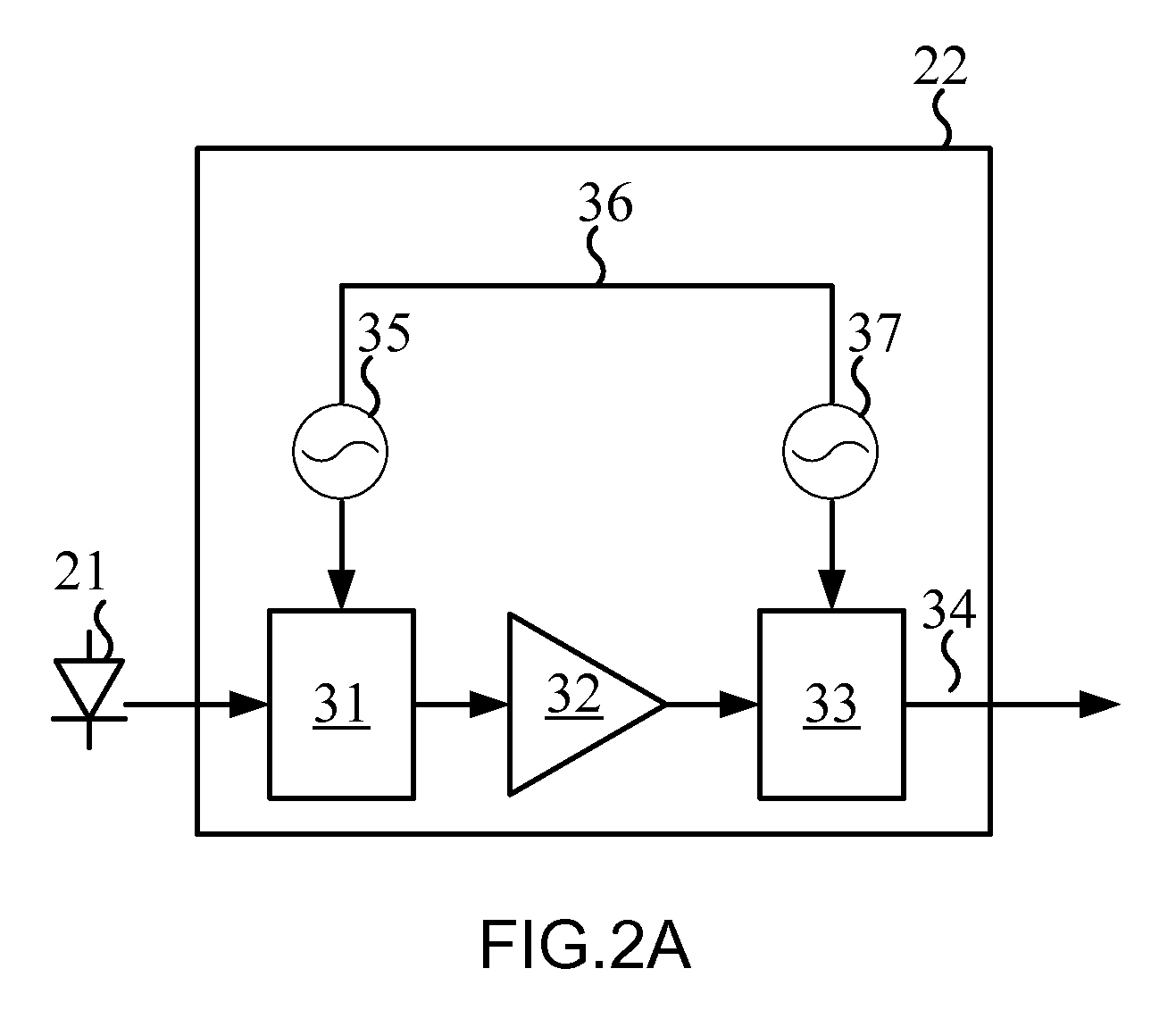
Optical modulator for higher-order modulation
According to one embodiment of the invention, a 16-QAM optical modulator has a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) coupled to a drive circuit that drives the MZM based on two electrical binary signals. The output of the MZM corresponds to an intermediary constellation consisting of four constellation points arranged on a straight line in the corresponding in-phase / quadrature-phase (I-Q) plane. Two of these constellation points correspond to a zero phase, and the remaining two constellation points correspond to a phase of π radian. The 16-QAM optical modulator further has a phase shifter that modulates the output of the MZM based on two additional electrical binary signals. The resulting optical output signal corresponds to a star 16-QAM constellation, which is produced by incremental rotation of the intermediary constellation.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method and apparatus for prioritizing information protection in high order modulation symbol mapping
InactiveUS20020126763A1Increase chanceImproved decoder performanceCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareHigher-order modulation
Owner:APPLE INC
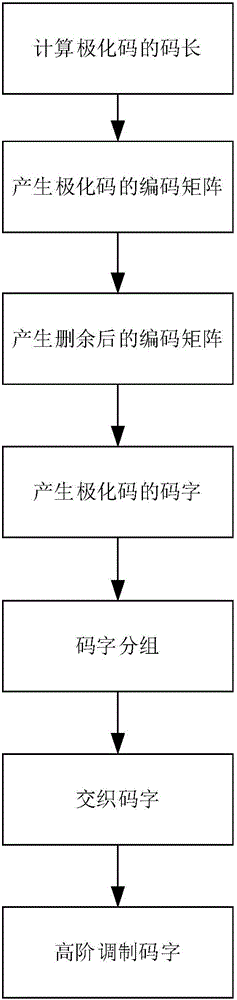
Polar code encoding modulation method applicable to any high-order modulation
ActiveCN106230489AImprove performanceOvercoming the lack of high complexitySpatial transmit diversityError correction/detection using block single space codingChannel capacityComputer science
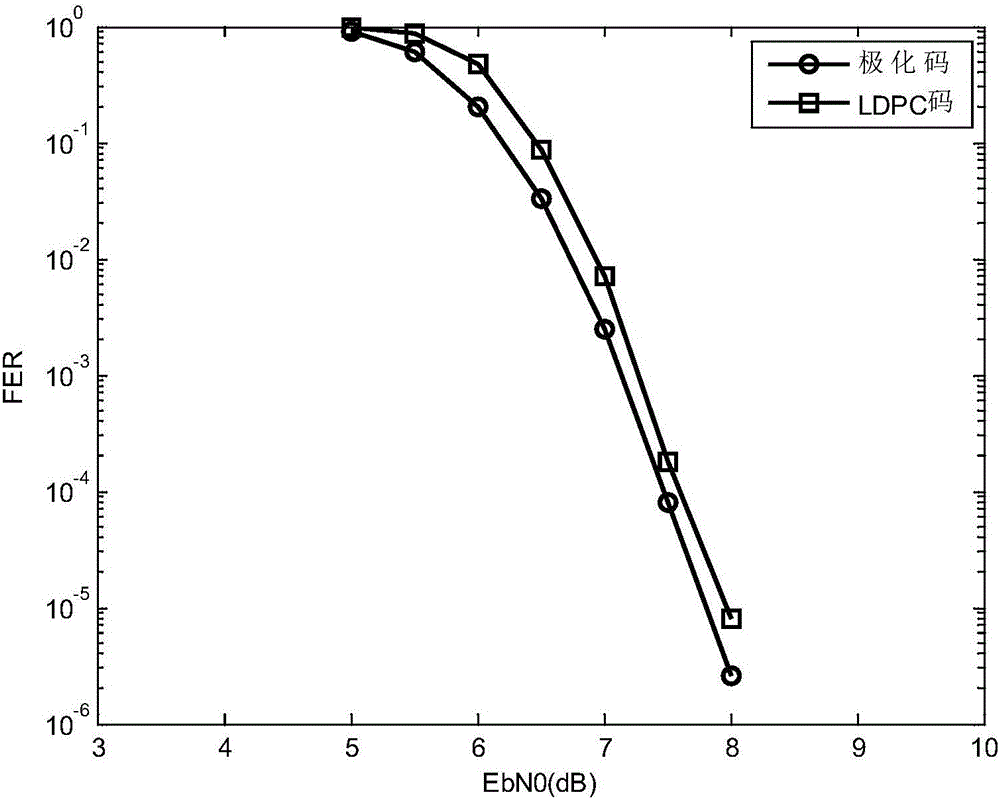
The invention discloses a polar code encoding modulation method applicable to any high-order modulation. The method comprises the concrete steps of (1), calculating the code length of a polar code; (2), generating an encoding matrix of the polar code; (3), generating the encoding matrix after puncturing; (4), generating code words of the polar code; (6) interleaving the code words; and (7), carrying out high-order modulation. According to the method, the code words are interleaved by employing a grouping interleaving technology, the polar effect of a channel is intensified with the combination of the polar characteristic of the polar code itself and the capacity differences of high-order modulation sub-channels, and the performance of the polar code is improved. According to the method, the encoding matrix is punctured according to a column weight, the decoding delay is reduced, and the programming realization complexity of a decoding algorithm in a programmable device is reduced. The flexibility of the polar code in the high-order modulation is improved, and the polar code has good performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Space-time bit-interleaved coded modulation for wideband transmission
ActiveUS7359313B2Improve bit error rate performancePhase-modulated carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexMulti inputBroadband transmission
A system employs space-time coding characterized at the transmitter by bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) combined with multi-carrier Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) modulation. Space-Time coding techniques improve transmission efficiency in radio channels by using multiple transmit and / or receive antennas and coordination of the signaling over these antennas. Bit-interleaved coded modulation provides good diversity gain with higher-order modulation schemes that employ binary convolutional codes. OFDM modulation allows for wideband transmission over frequency selective radio channels. A receiver demodulates the OFDM signal and applies multi-input, multi-output (MIMO) demapping to estimate the BICM encoded bitstream. After deinterleaving of the BICM encoded bitstream, maximum a posteriori (MAP) decoding is applied to the resulting bit stream to generate soft output values. The MIMO demapping and MAP decoding processes exchange likelihood information to improve the bit error rate performance over several iterations of demapping / decoding. By applying well-known turbo-decoding principles to iteratively demap and decode, the overall receiver performance is significantly improved.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
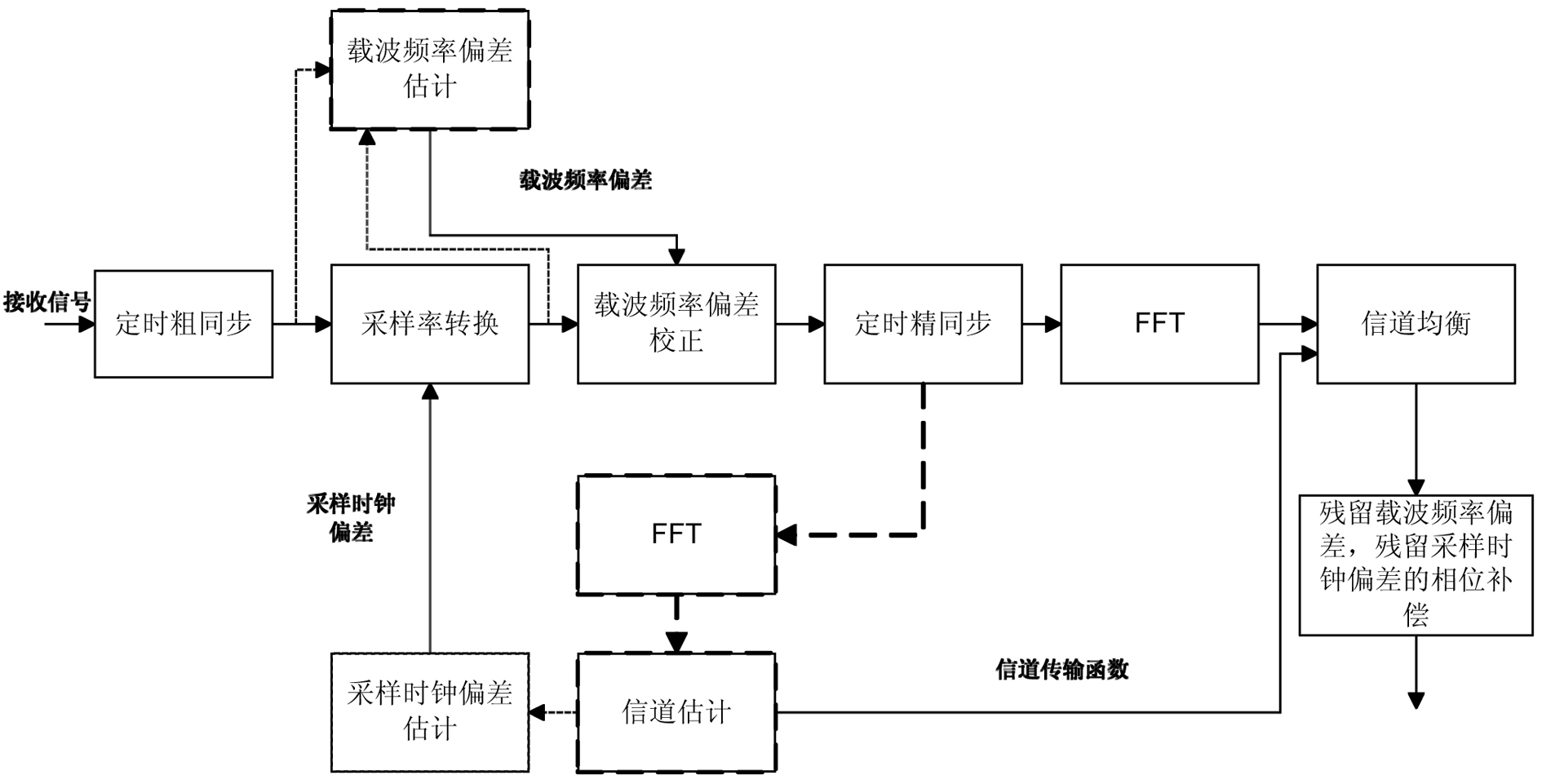
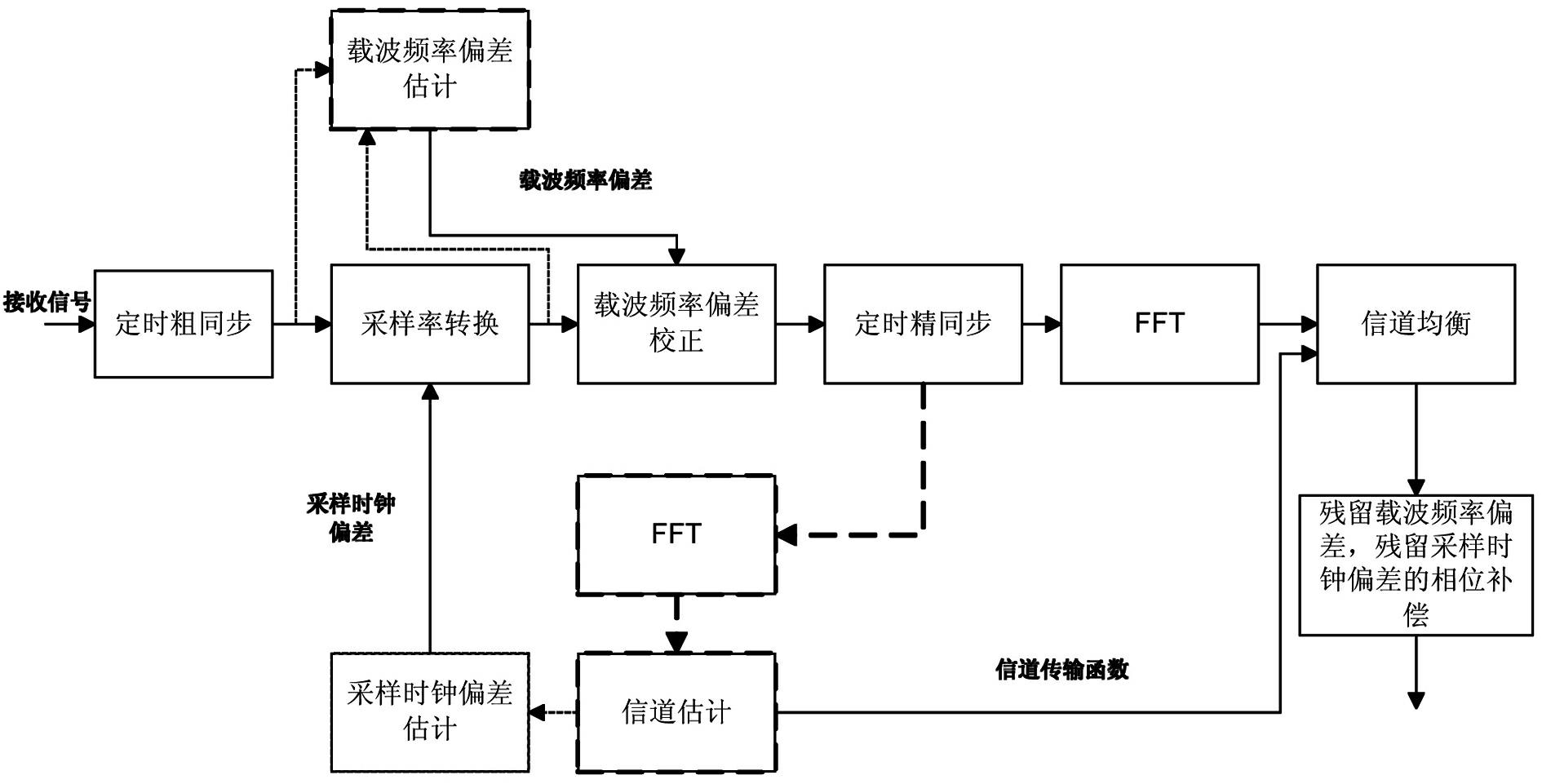
Synchronized method of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system
InactiveCN102075486AAvoid the impact of timing fine synchronizationMeet needsMulti-frequency code systemsCarrier frequency offsetCarrier signal
The invention provides a synchronized method of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system. The invention discloses an associated synchronized method of frame synchronization, carrier frequency synchronization and sampling clock synchronization. Carrier frequency offset estimation, channel estimation and fine estimation of symbol timing offset are performed again after sampling clock offset correction is finished, thereby avoiding influences of sampling clock offset on the carrier frequency offset estimation, the channel estimation and the fine estimation of the symbol timing offset, compensating phase deflection caused by the residual carrier frequency offset and the sampling clock offset simultaneously, greatly improving the synchronized performance, and meeting the demands of a high-order modulated system. In addition, due to aiming at a low time-varying channel, the channel estimation is required to be performed once only, thereby reliving the complexity of the system.
Owner:深圳市阿派斯实业有限公司
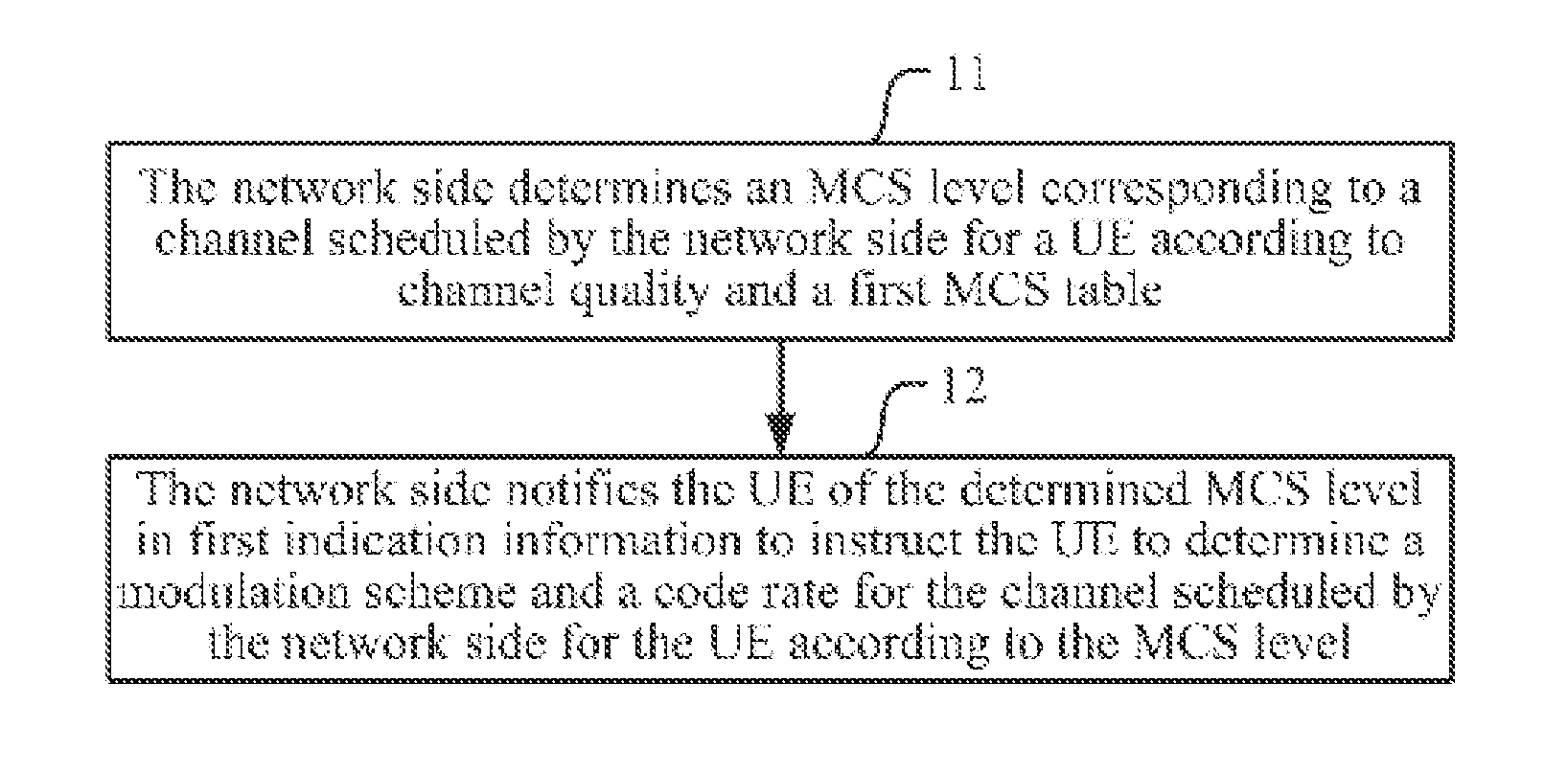
Method and device for transmitting mcs indication information
ActiveUS20150200746A1Improve throughputImprove signal-to-noise ratioModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter specific arrangementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Frequency spectrum
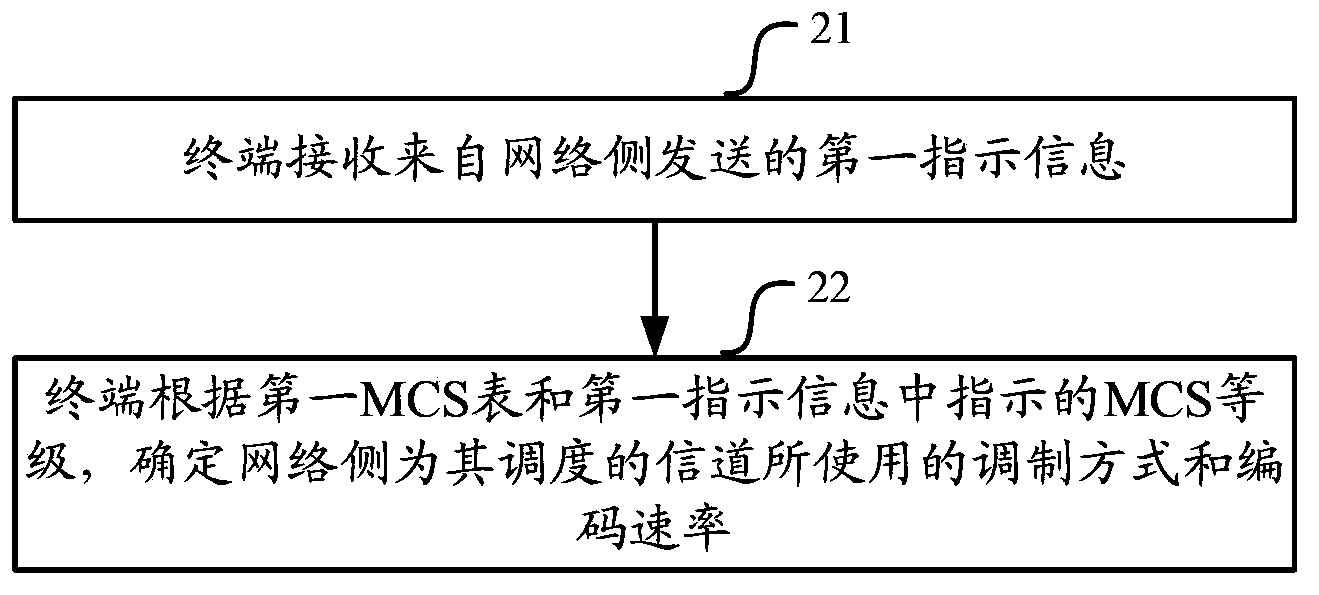
The present application relates to the field of wireless communications, and in particular, to an indication method and device for a modulation coding scheme. It is for solving the problem that in an existing LTE / LTE-A system, a higher-order modulation scheme cannot be supported, thereby limiting the further improvement of throughput in an application scenario of a high signal-to-noise ratio. The method of the embodiments of the present application includes: according to the channel quality and a first MCS table, a network side determining an MCS level corresponding to a channel scheduled for a UE; and by means of first indication information, notifying the UE of the determined MCS level, so as to indicate to the UE to determine a modulation scheme and code rate for the channel scheduled therefor according to the MCS grade, wherein there are at least corresponding entries of MCS indexes and TBS indexes corresponding to modulation schemes at higher modulation orders than 6 in the first MCS table. The embodiments of the present application introduce a higher-order modulation scheme into an existing LTE / LTE-A system, improving the spectrum efficiency.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
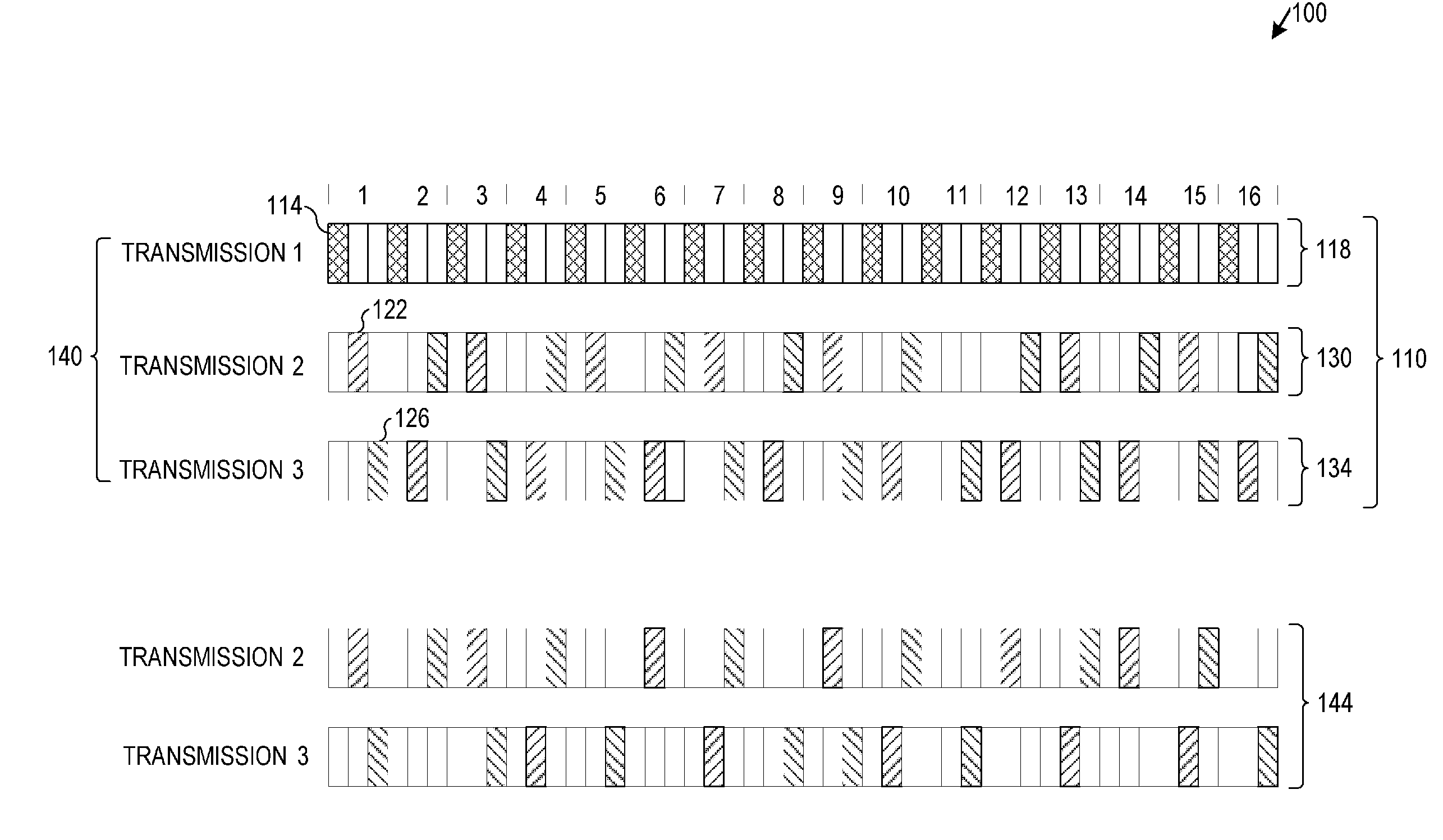
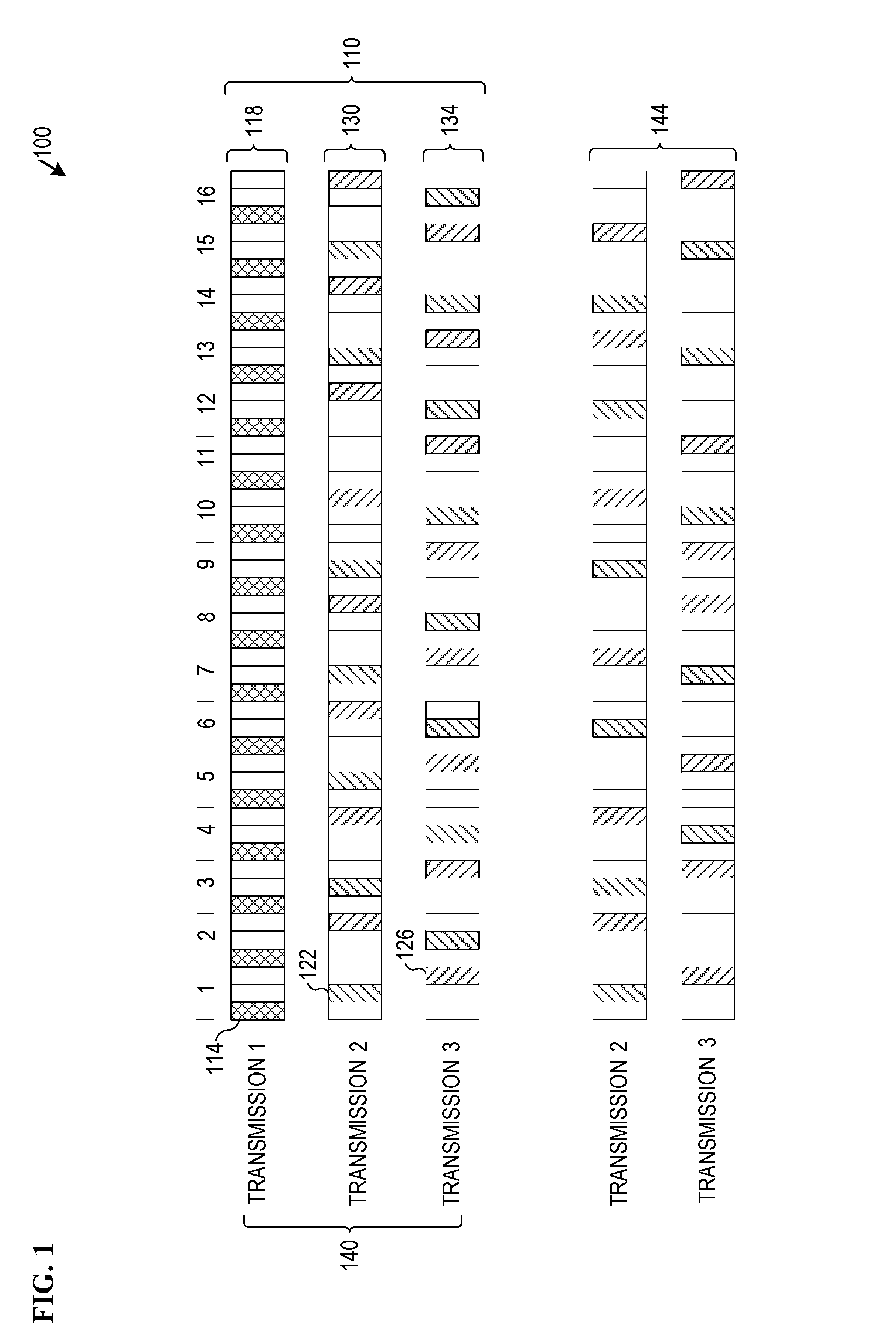
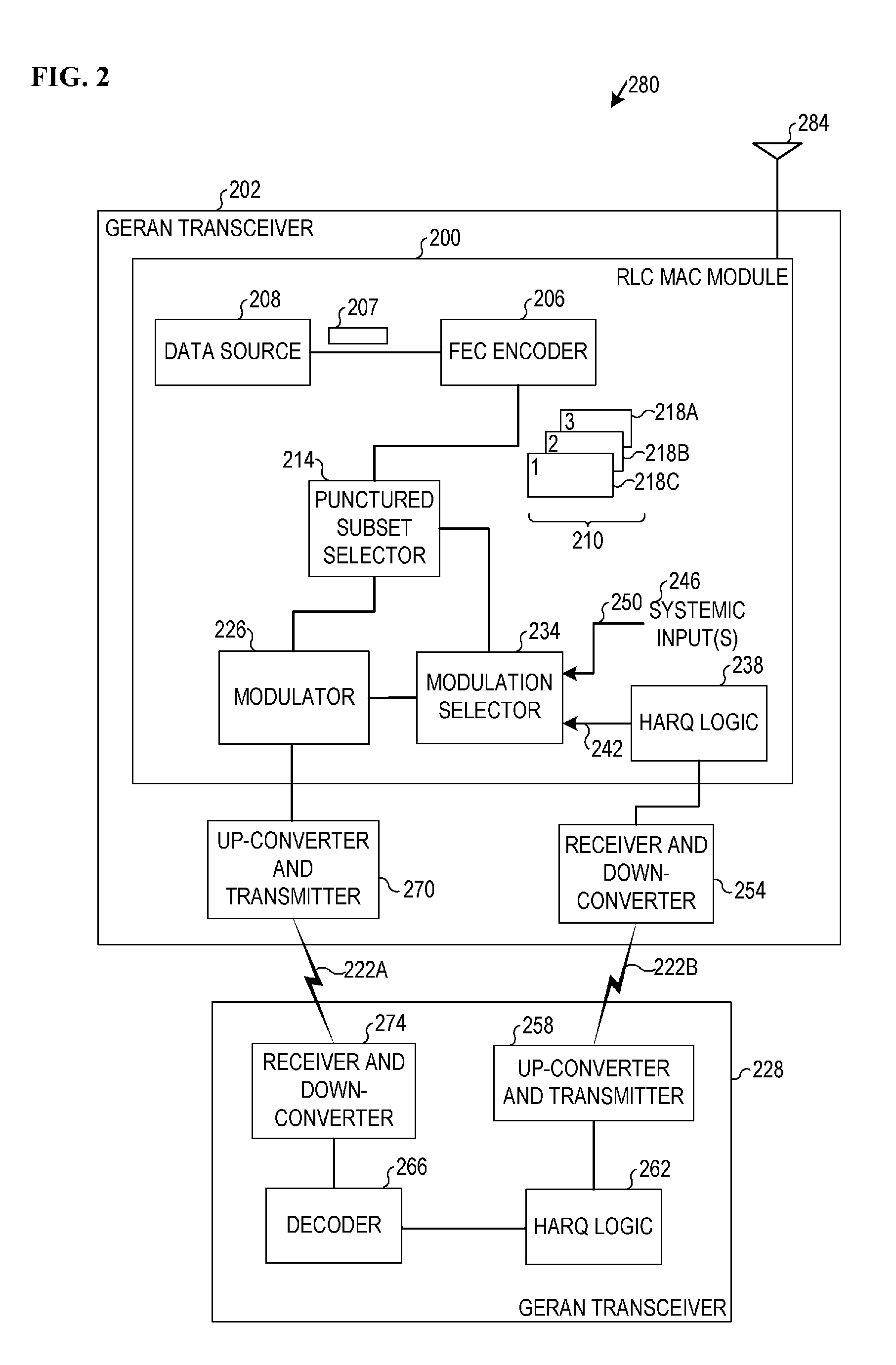
Incremental redundancy using high-order modulation and coding schemes
ActiveUS20080002565A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionRadio Link ControlMedia access control
Embodiments of a radio link control media access control module and associated methods may be described herein. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
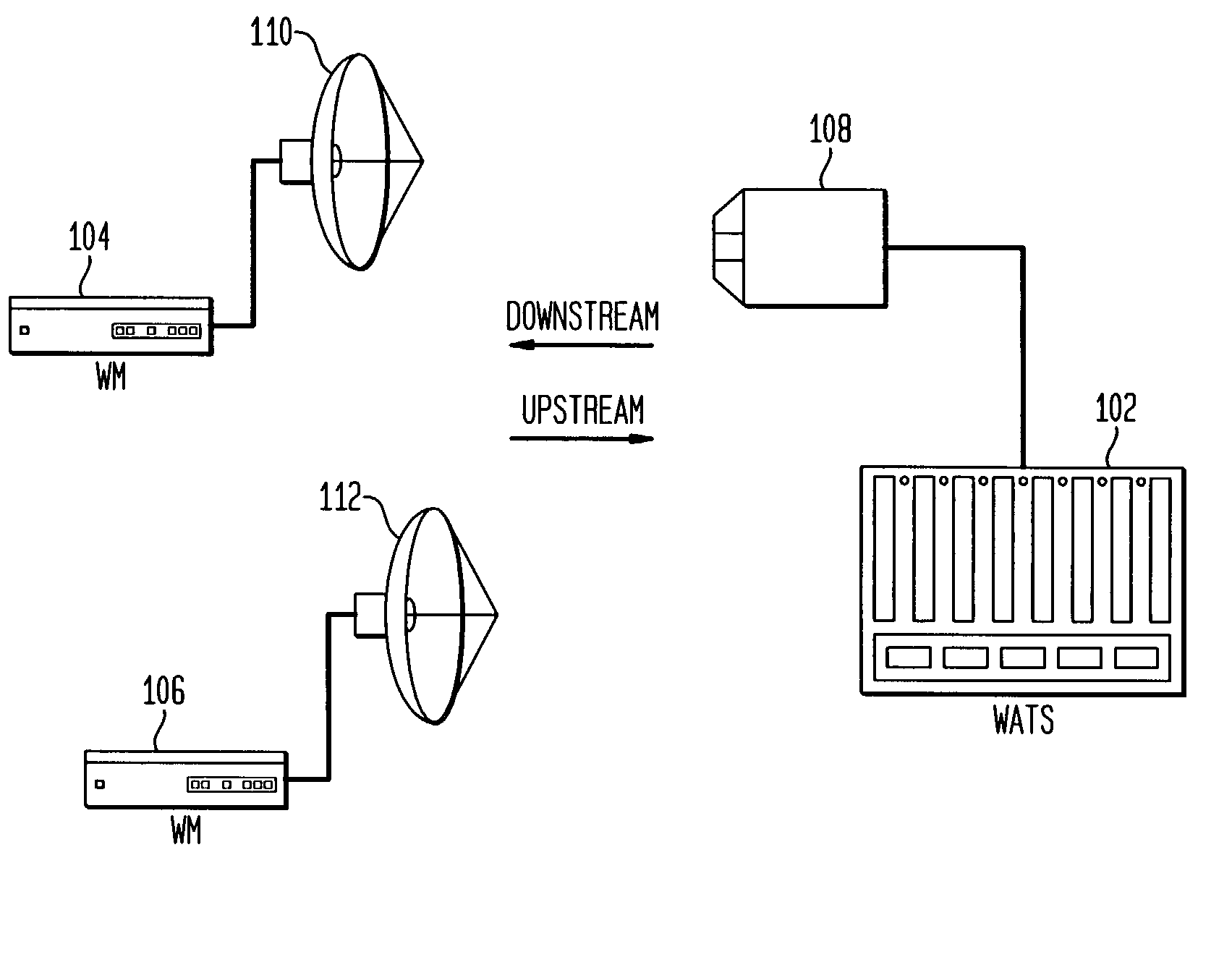
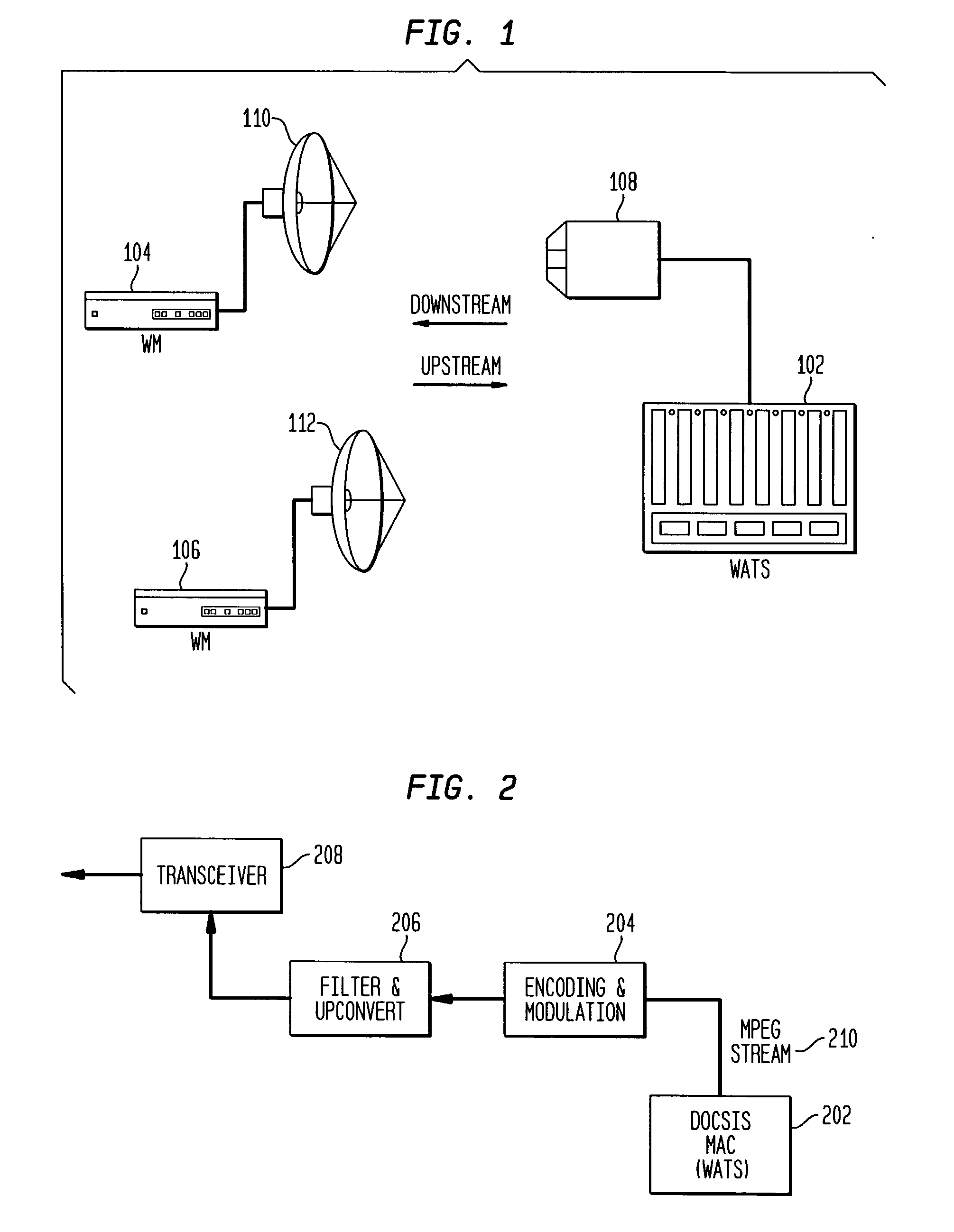
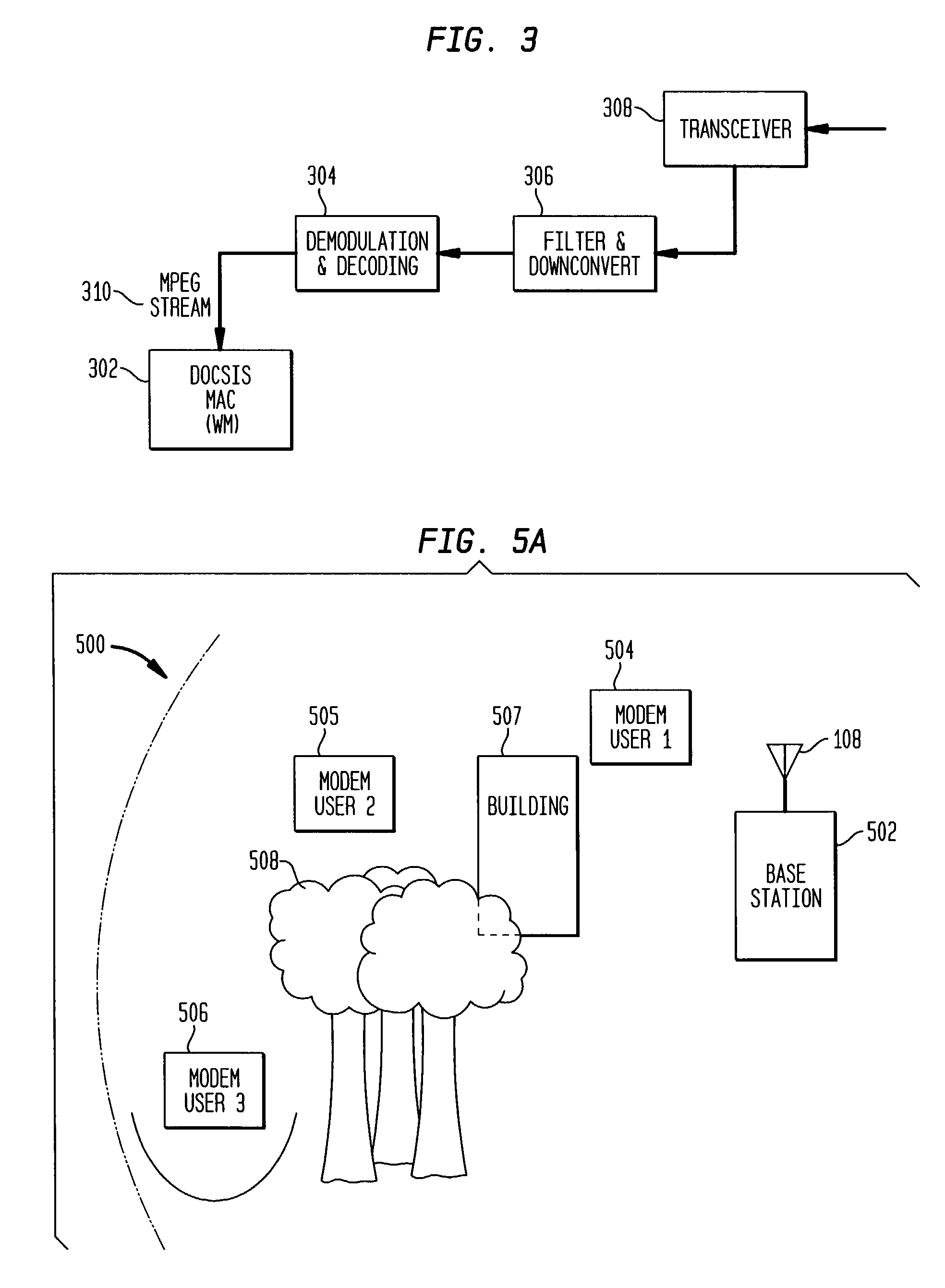
Downstream adaptive modulation in DOCSIS based communications systems
InactiveUS20030176161A1Signal strengthCompensation changesBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityModem device
A downstream adaptive modulation system and method. The downstream adaptive modulation system comprises a wireless access termination system and one or more wireless modems. The wireless access termination system includes a plurality of queues and a parser. The parser parses data traffic onto the plurality of queues. Each queue is associated with a different coding and modulation scheme. Each of the one or more wireless modems receives data traffic from the plurality of queues based on the wireless modem's ability to demodulate and decode the signal from each of the plurality of queues. When a wireless modem experiences a change in signal strength, the present invention enables the wireless modem to adapt to data from other queues to compensate for the change in signal strength. Thus, if the signal strength improves over a period of time, the wireless modem may receive data at a higher order modulation and FEC code rate. If the signal strength weakens over a period of time, the wireless modem may receive data at a lower order modulation and FEC code rate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multi-antenna codebook selection modulation method for solving weak scattering
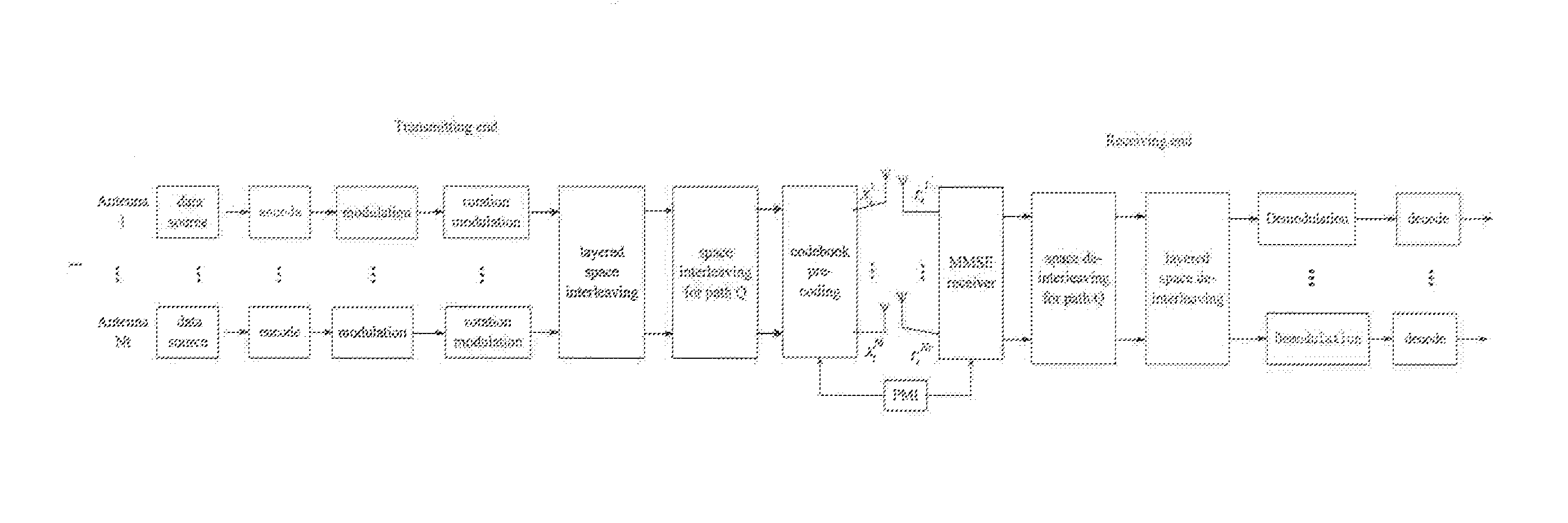
InactiveUS20130251058A1Increase diversityReduce error rateSpatial transmit diversityChannel estimationDiversity schemeHigher-order modulation
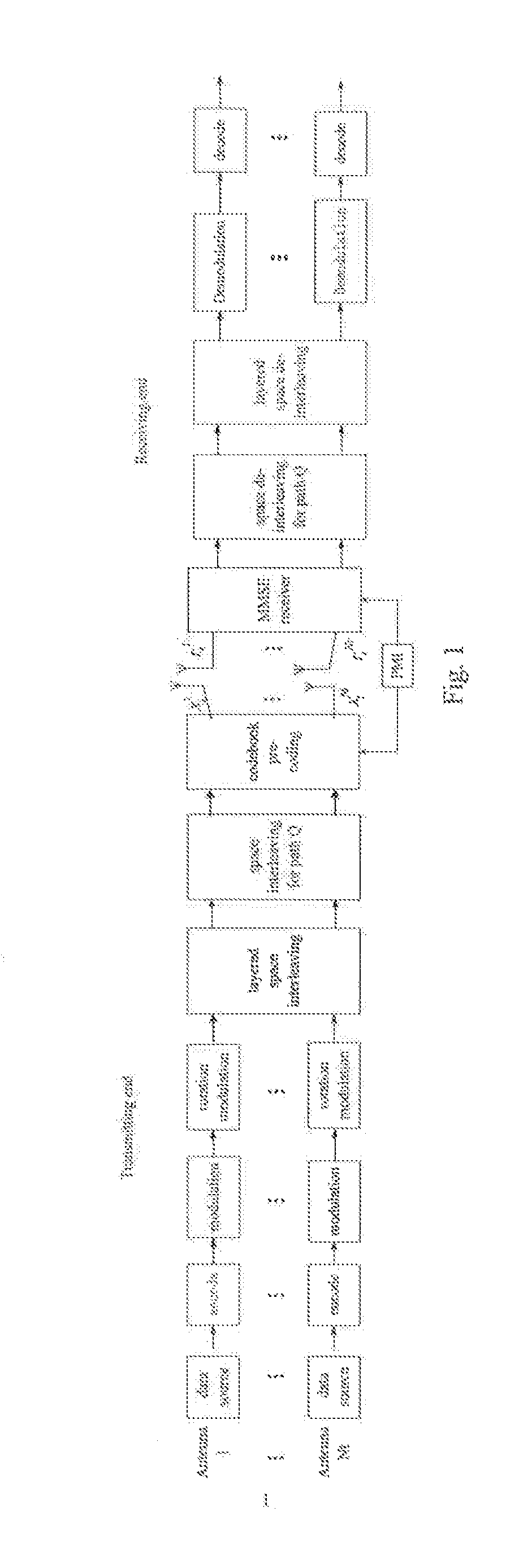
A multi-antenna codebook selection modulation method for solving weak scattering is provided by the present invention. The method obtains higher diversity gain from a combination of multi-antenna codebook pre-coding and a rotation modulation solution by designing a new codebook selection rule. The present invention employs a design solution of designing a higher-order modulation diversity and space interleaver to obtain the higher diversity gain. In addition, the number of transmission antennas and the number of rotation modulation dimension can be set arbitrarily. However, the present invention takes the number Nt of transmission antennas to be equal to the number D of rotation modulation dimension in order to obtain higher diversity gain. In this way, the method evenly disperses signals of each dimension after D-dimensional rotation to each antenna through space interleaving technique, so that the signals of each dimension suffer different fading, thus enabling space diversity gain. With the present invention, the data of a transmitting end are pre-coded by using a channel value estimated for an ideal channel.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sub-optimal iterative receiver method and system for a high-bit-rate CDMA transmission system
ActiveUS7298778B2Close to optimum performanceHigh order modulationError preventionOther decoding techniquesSpread factorSpreading factor
A reception method and receiver structure that are relatively simple, that have close to optimum performance, and that use high order modulation combined with a low spreading factor are disclosed. The method receives a signal transmittal in the form of sequences of coded binary symbols comprising both predefined pilot symbols and date symbols multiplied by a spreading sequence. The method also includes a step of determining a channel estimate using received predefined pilot symbols. A system for receiving a signal transmitted on a multipath transmission channel using a spread spectrum technique and low spreading factor is also disclosed.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving data in a communication system using low density parity check code
ActiveUS8230295B2Reduce signal distortionImprove performanceModulated-carrier systemsError correction/detection using LDPC codesCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
A method for transmitting data in a communication system using a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) matrix includes generating an LDPC codeword by encoding information data bits, interleaving the LDPC codeword, mapping the interleaved LDPC codeword to a modulation signal, and generating a mapped signal by mapping the LDPC codeword bits separately to a bit corresponding to a real part and a bit corresponding to an imaginary part of said modulation signal, among bits constituting the modulation signal, generating a modulation signal by high-order-modulating the mapped signal and Radio Frequency (RF)-processing the modulation signal, and transmitting the RF-processed signal via a transmission antenna.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
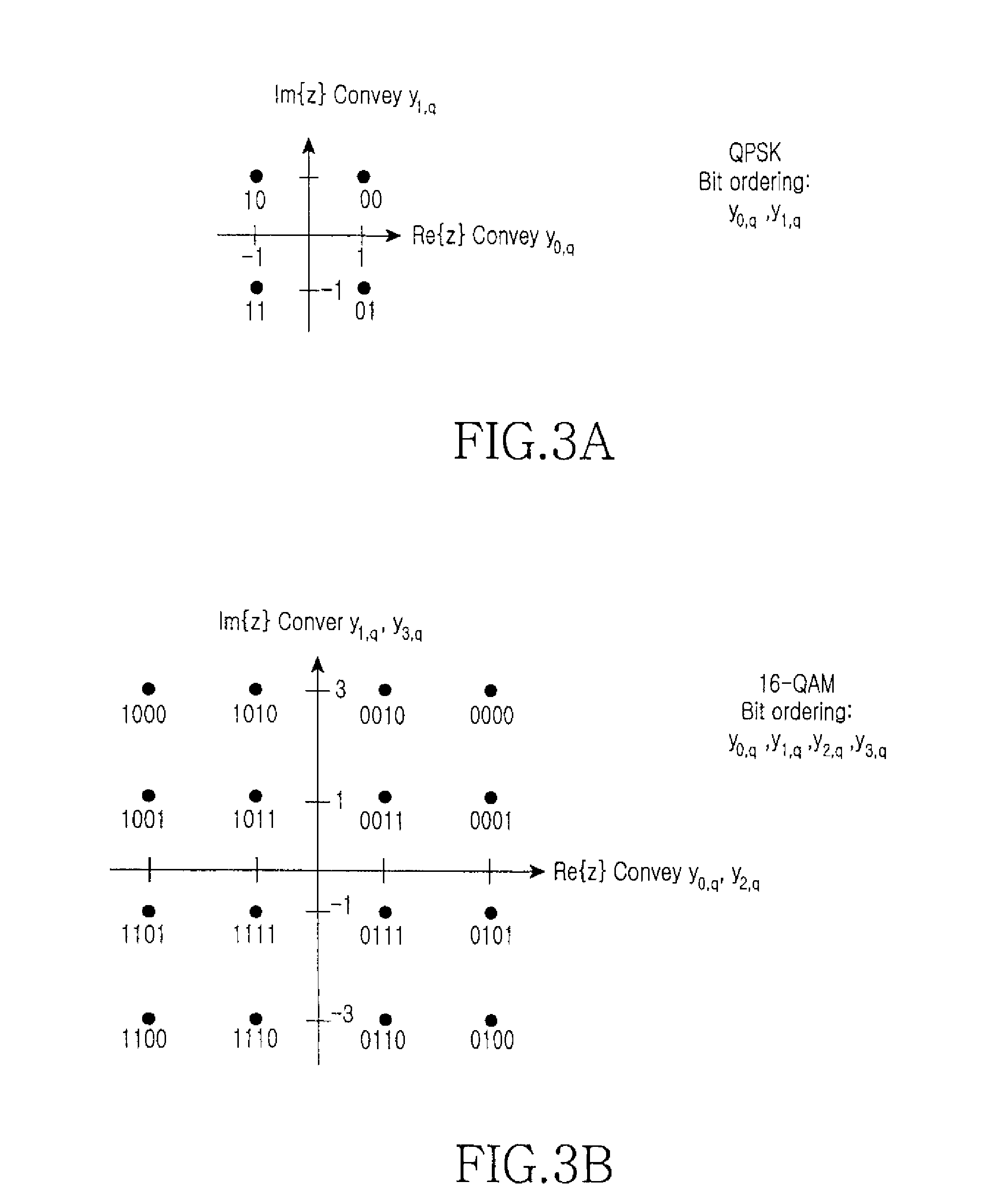
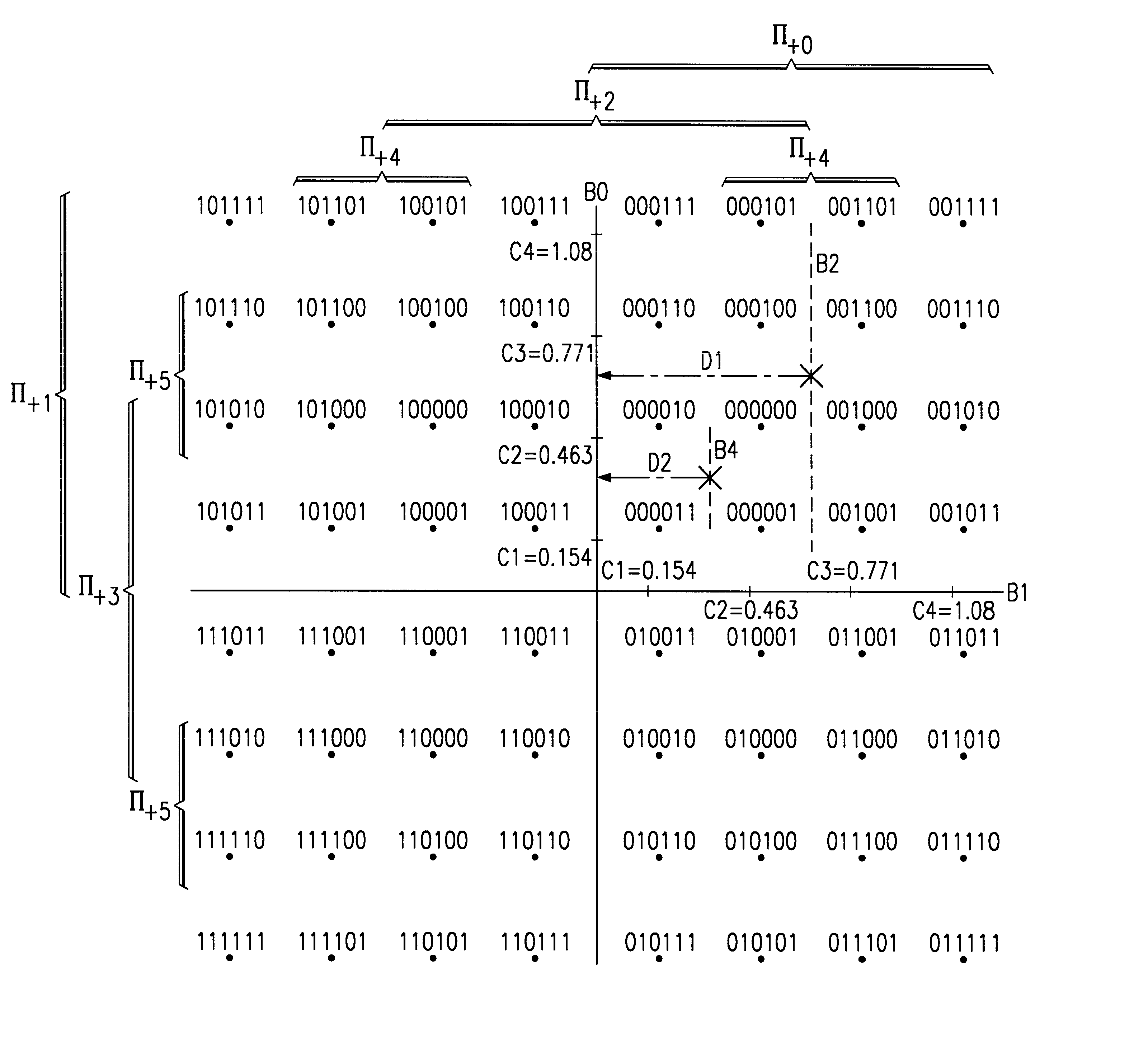
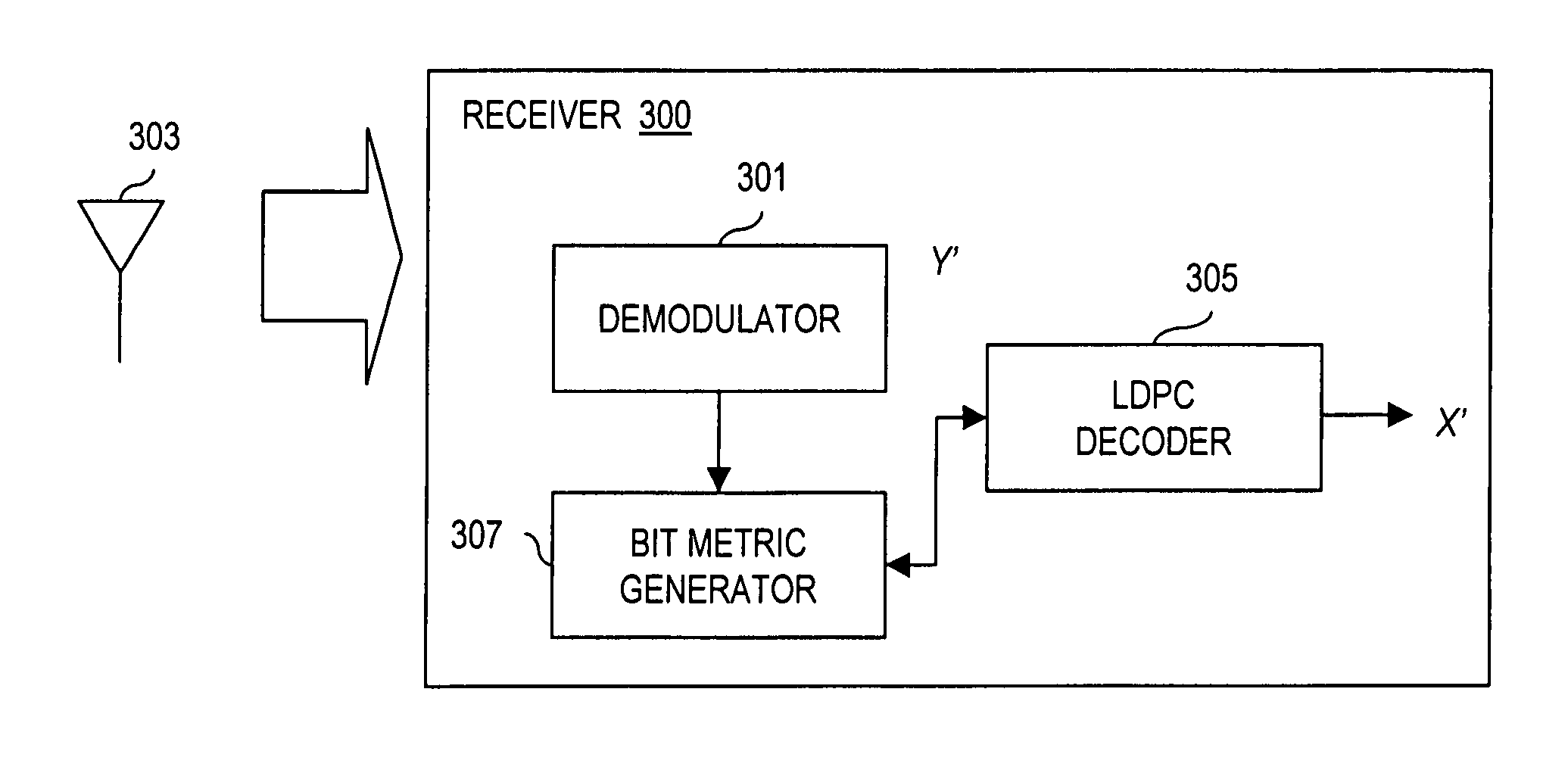
Soft-decision metric generation for higher order modulation
InactiveUS7076000B2Data representation error detection/correctionDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionTheoretical computer scienceSymbol of a differential operator
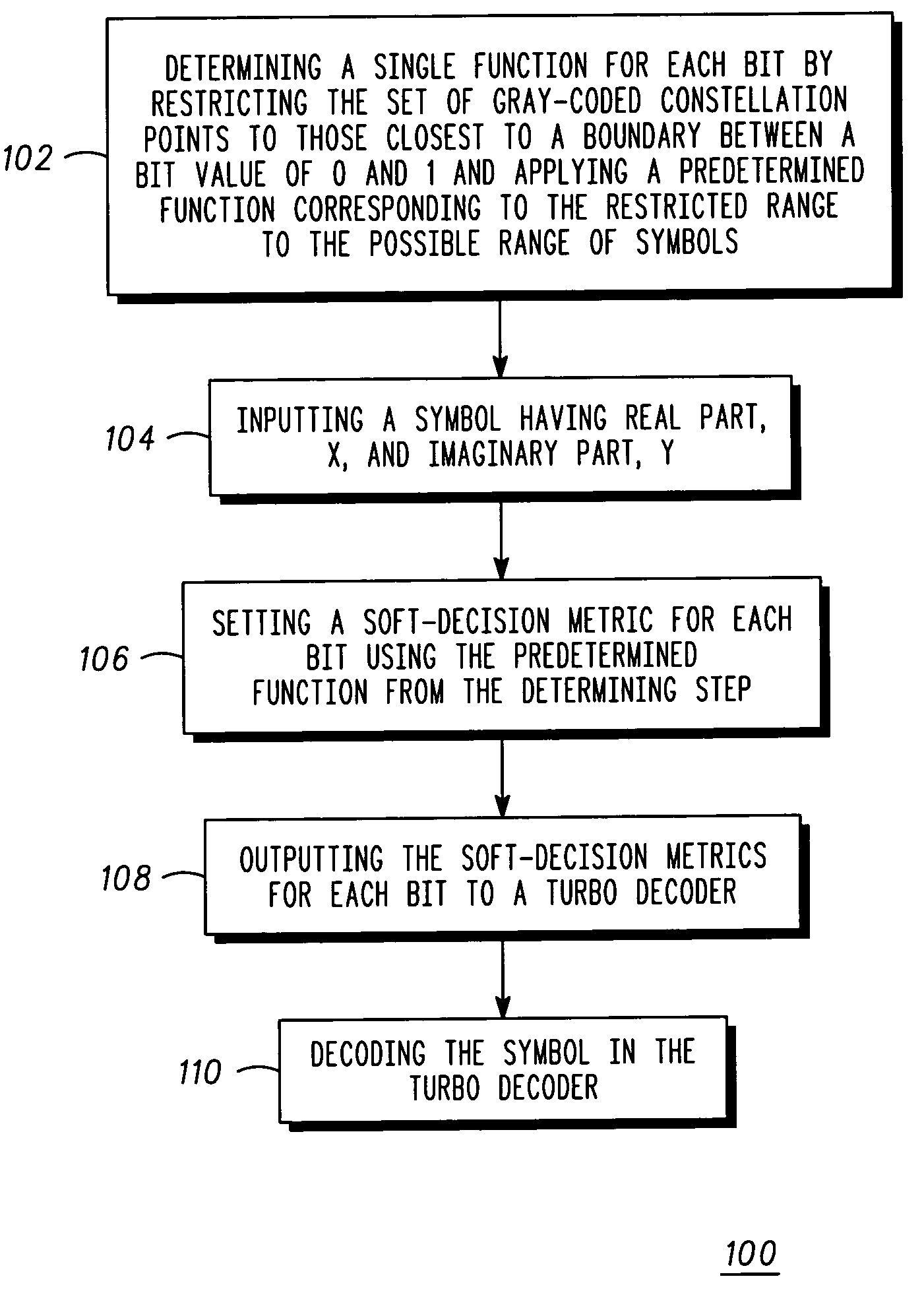
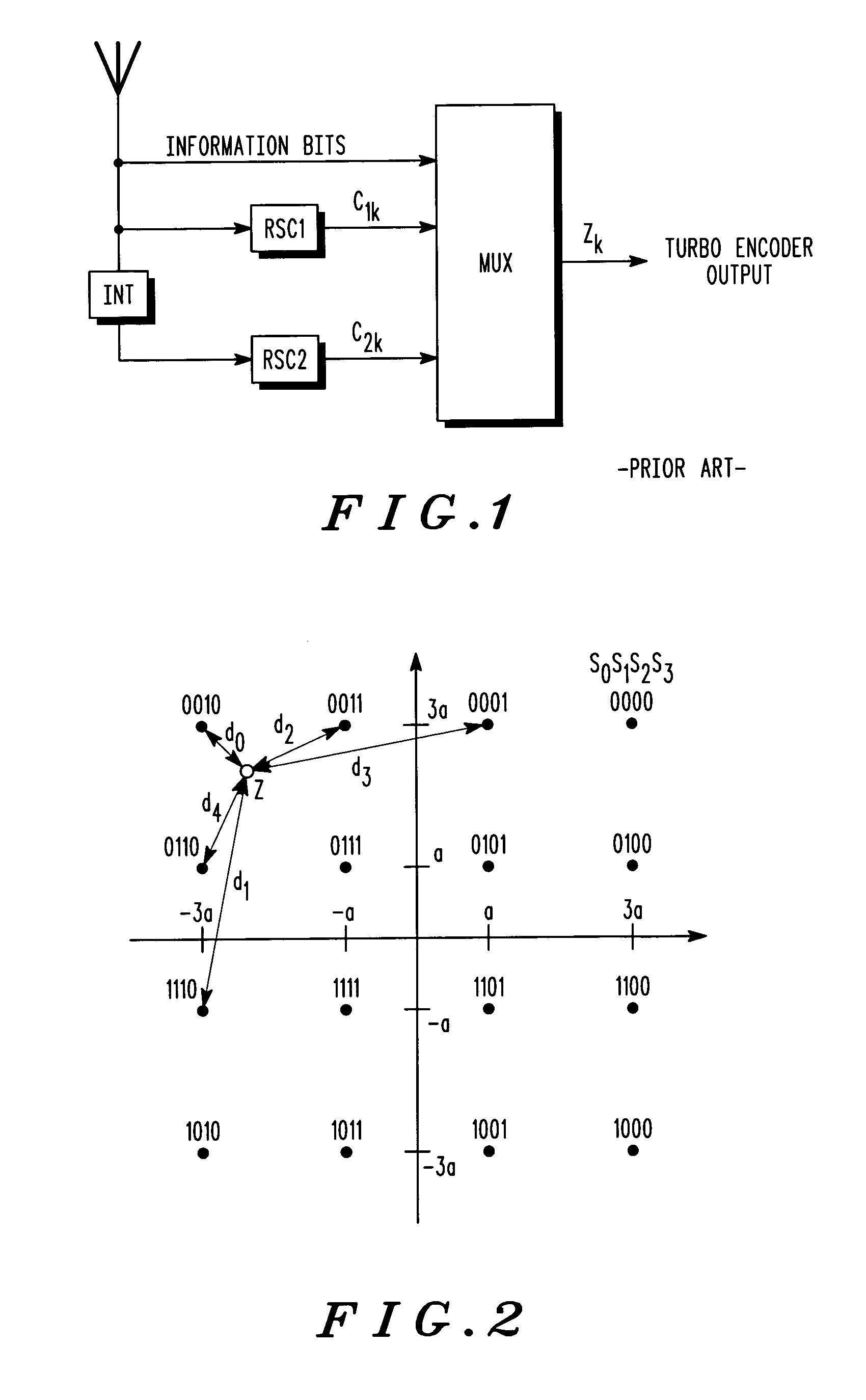
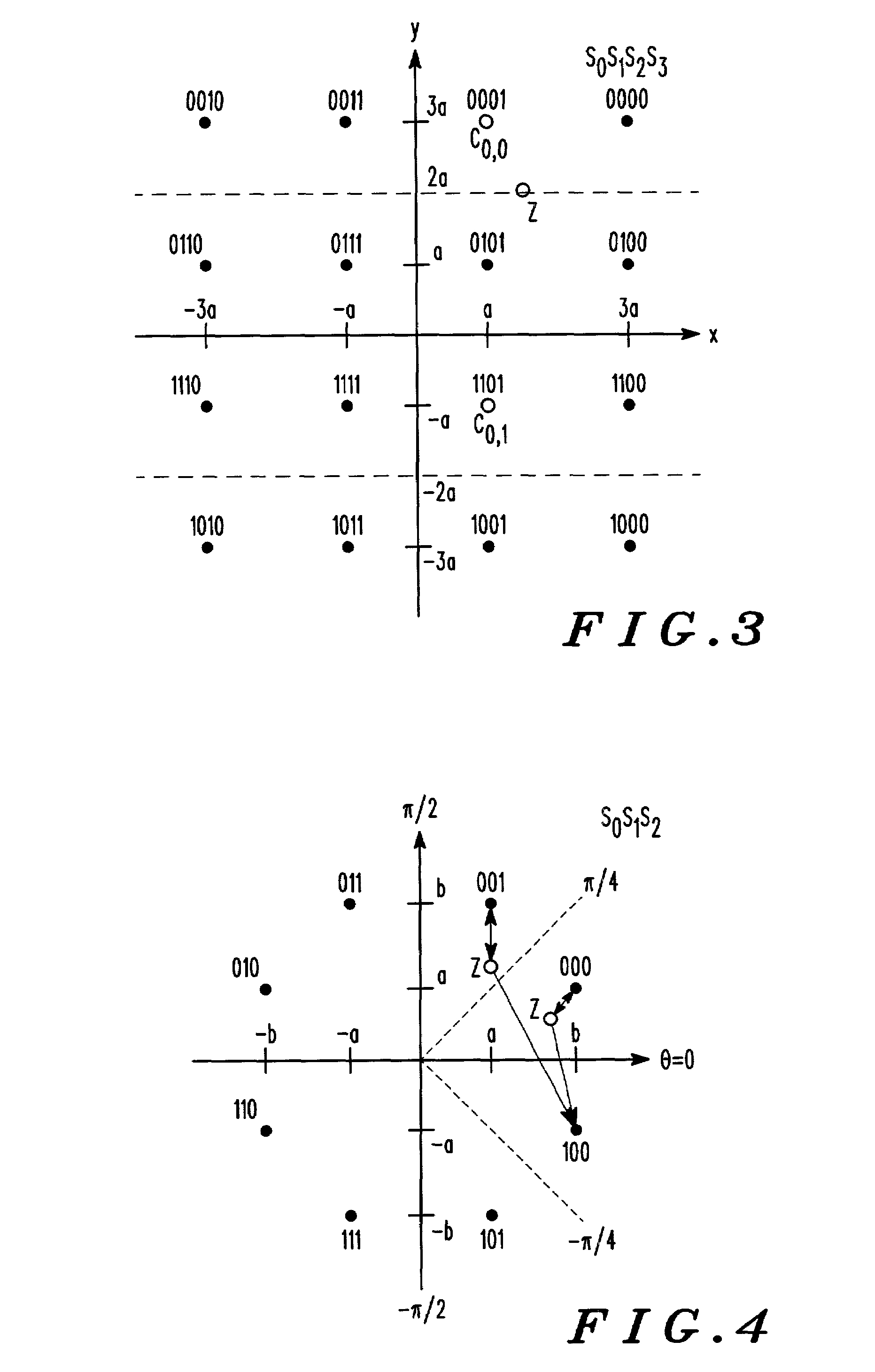
A method (100) for simplifying soft-decision metric decisions in a M-ary modulation system includes determining (102) a single function for a soft-decision metric for each bit in a symbol by restricting the set of all possible Gray-coded constellation points to those closest to a boundary between a bit value of 0 and 1 for each bit in the input symbol and applying a predetermined function corresponding to the range of restricted constellation points to the entire possible range of symbols. A next step includes inputting (104) a symbol having real part, x, and an imaginary part, y. A next step includes (106) setting a soft-decision metric for each bit in the symbol using the predetermined function from the determining step (102).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Satellite communincation system utilizing low density parity check codes
ActiveUS20050063484A1High bandwidthImprove efficiencyError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionCommunications systemAs Directed
An approach for reliably communicating over a satellite in support of a communication service including, for example, as direct broadcast satellite and data service, is disclosed. An input message is encoded, yielding a structured Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) coded message. The coded message is modulated according to a high order modulation scheme that has a signal constellation representing more than two symbols per signaling point—e.g., 8-PSK (Phase Shift Keying) and 16-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation). The system includes a transmitter configured to propagate the modulated signal over the satellite. The above approach is particularly applicable to bandwidth constrained communication systems requiring high data rates.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
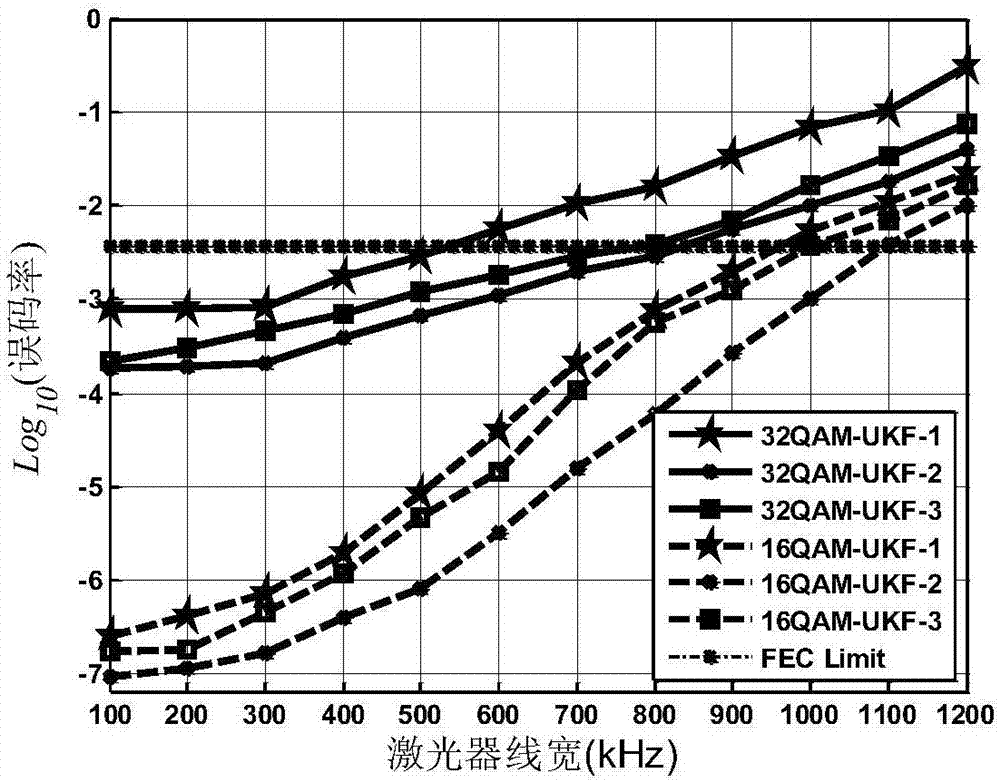
Large line width CO-OFDM system phase noise compensation method of time domain unscented Kalman filter
ActiveCN107395282ALess carrierGood phase noise equalizationDistortion/dispersion eliminationMulti-frequency code systemsPhase noiseFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a phase noise compensation method suitable for large line width and high order modulation CO-OFDM system. The method comprises the following steps: performing channel equalization on training symbol data of a receiving terminal after performing Kalman filter on the same in the frequency domain; setting pilot frequency subcarrier data with certain intervals for each OFDM symbol on a transmitting terminal, and performing preset CPE phase noise estimation and compensation at pilot frequency subcarriers in the frequency domain based on extended Kalman filter (EKF); and finally, converting frequency domain data subjected to CPE phase noise compensation into the time domain, and realizing blind ICI phase noise compensation by using the Avg-BL method, then performing pre- judgment, converting the frequency domain data subjected to the judgment into the time domain, applying time domain data and original time domain data of the receiving terminal to time domain unscented Kalman filter, calculating a final phase noise compensation value, and performing compensation. By adoption of the phase noise compensation method, a better phase noise equalization effect is obtained, and the spectrum utilization rate of the system is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for determining modulation scheme for retransmission in a communication system
ActiveUS7133462B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemComputer science
A method and apparatus for determining an optimum modulation scheme for a retransmission in a communication system supporting HARQ. When two modulation schemes are available, at an initial transmission, information is modulated in the lower-order modulation scheme if a first MPR is less than a first threshold, and in the higher-order modulation scheme if the first MPR is greater than or equal to the first threshold. Here, an MPR is determined by an EP size, the number of available Walsh codes, and the number of slots per sub-packet that are used for a transmission. To select one of the modulation schemes for a retransmission, a second MPR is calculated using an EP size, the number of available Walsh codes, and the number of slots per sub-packet that are used for the retransmission. If the first MPR is equal to or less than a second threshold greater than the first threshold, the lower-order modulation scheme is selected. If the second MPR is greater than the second threshold, the higher-order modulation scheme is selected.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
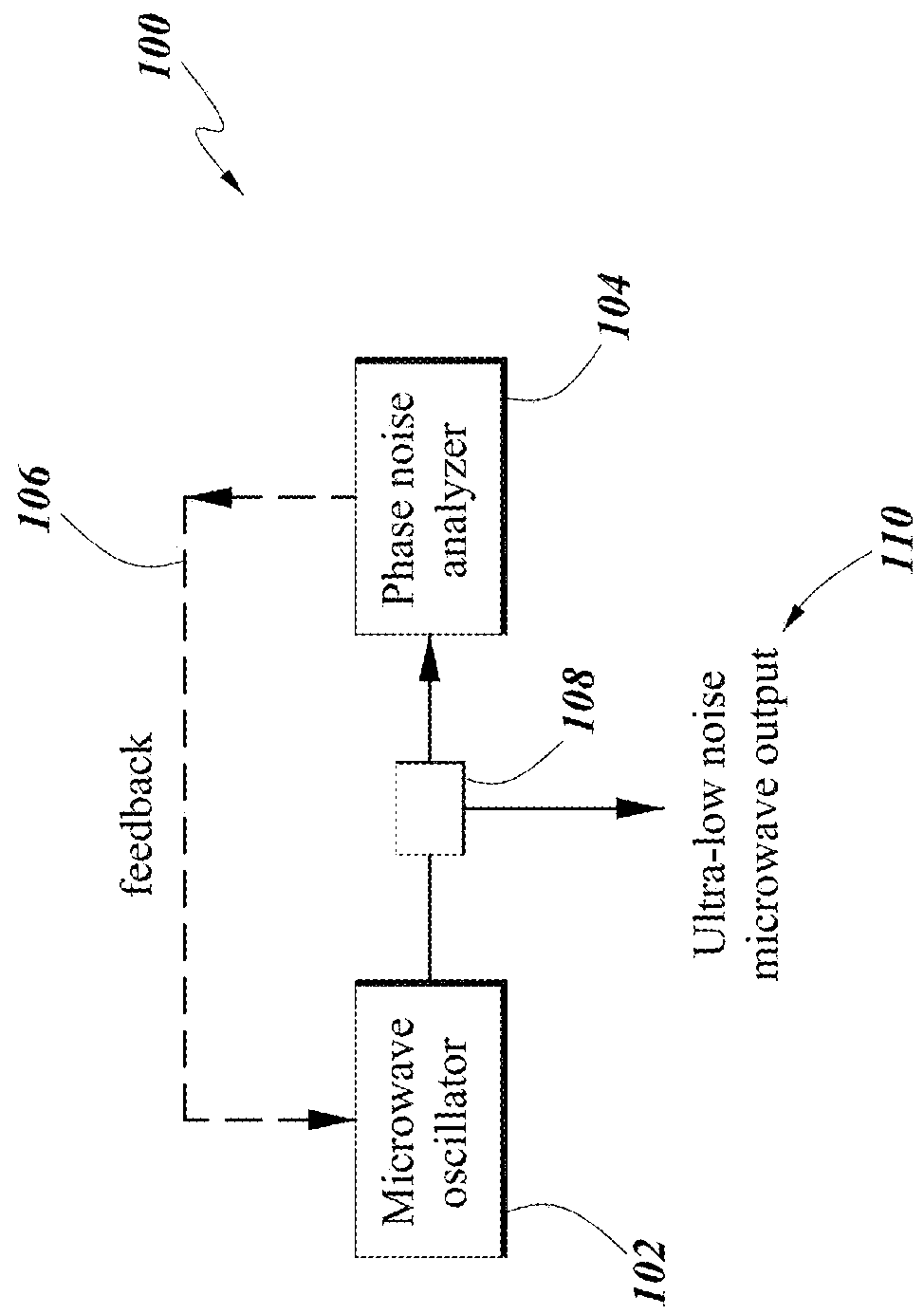
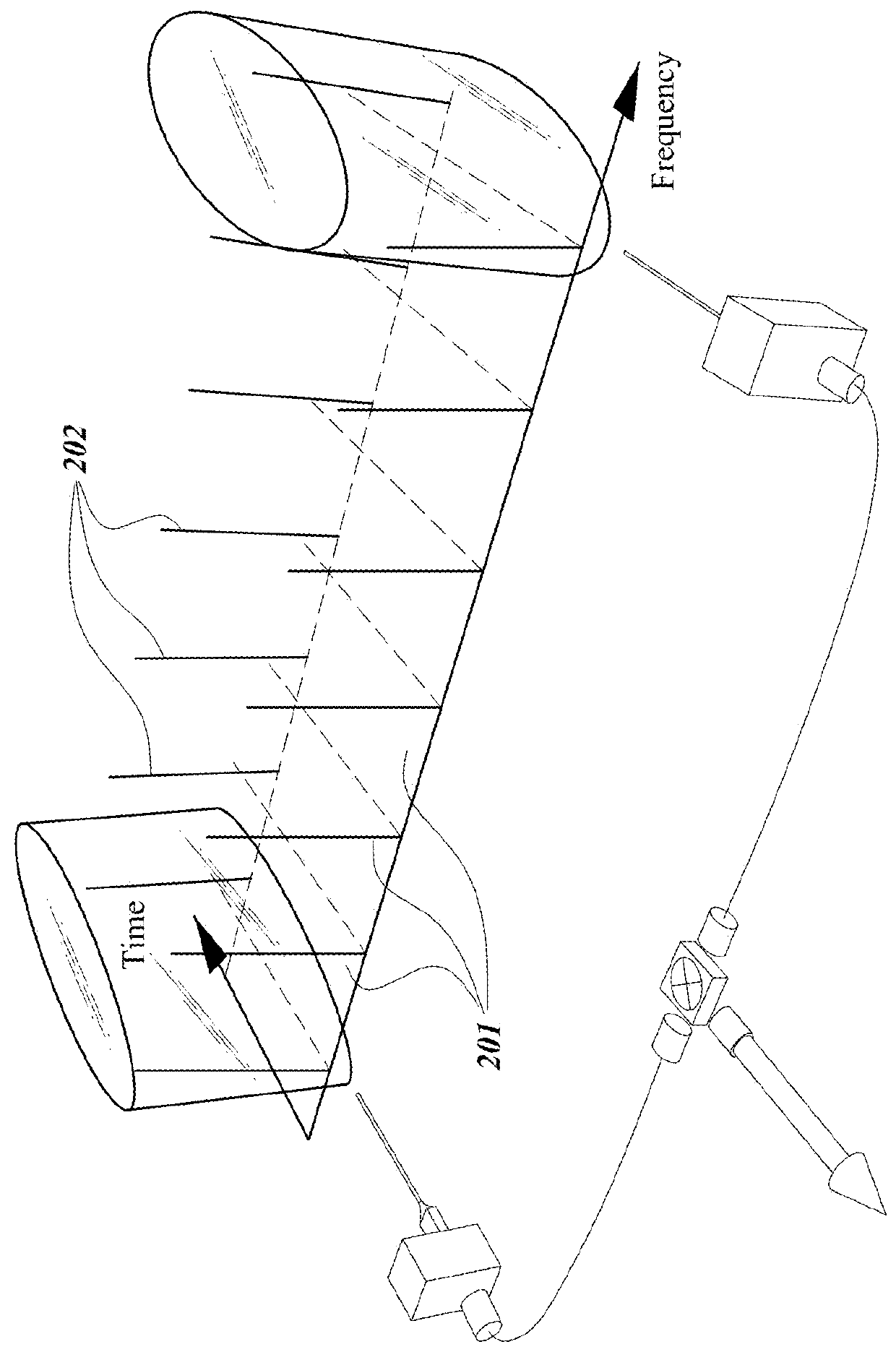
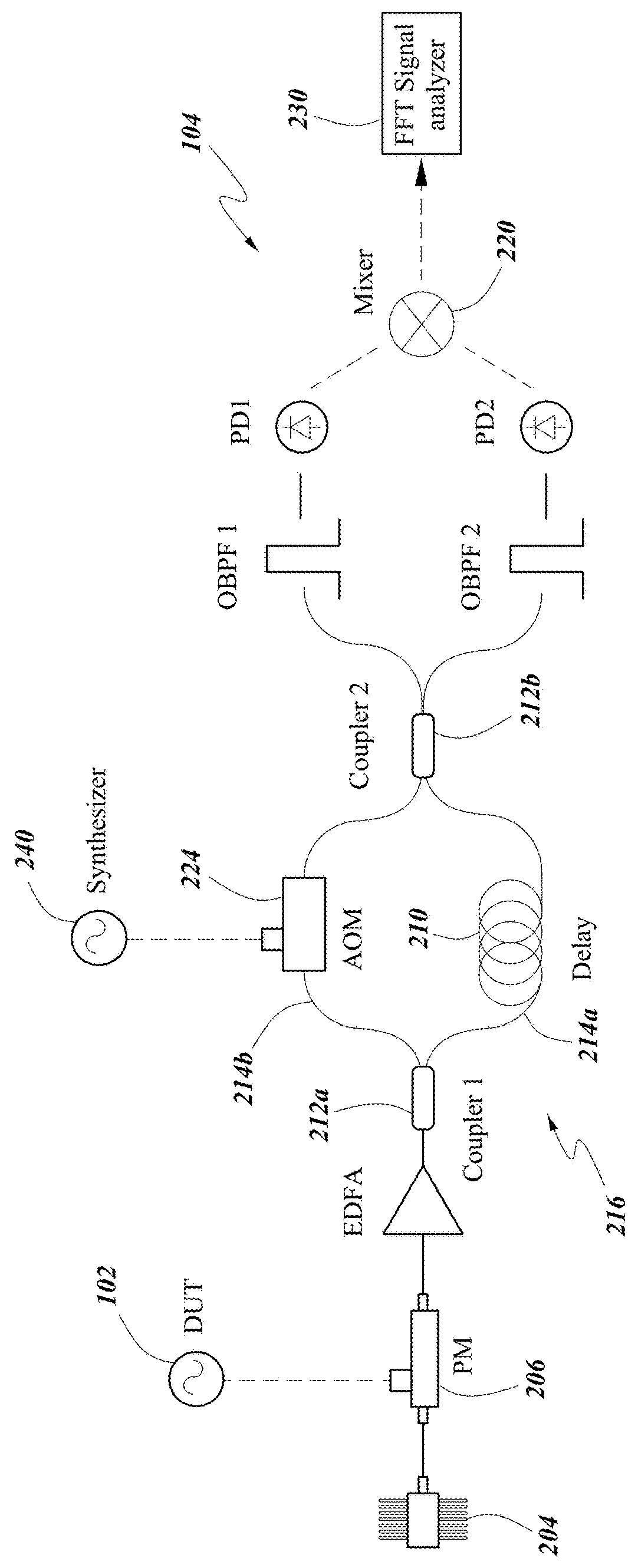
Ultra-low noise photonic phase noise measurement system for microwave signals
InactiveUS20180180655A1Reduce the noise floorHigh sensitivitySpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementLow noisePhase noise
Systems and methods for precision phase noise measurements of radio frequency (RF) oscillators are provided. An RF signal under test can be modulated on a continuous wave (cw) laser carrier frequency via generation of modulation sidebands using an appropriate modulator. A photonic delay line can be implemented as a self-heterodyne detection system for the phase noise, allowing for photonic down-conversion of the phase noise measurement to direct current (DC). The self-heterodyne detection system allows detection outside of any 1 / f noise issues. Ultra-low phase noise detection for RF frequencies in a range from below 1 GHz to beyond 100 GHz is enabled with a low noise floor in the whole frequency range. Higher-order modulation sidebands can further reduce the noise floor of the system. Ultra-low noise RF (microwave) output can be generated. The RF signal under test can be generated by a dielectric resonance oscillator or opto-electronic oscillator.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
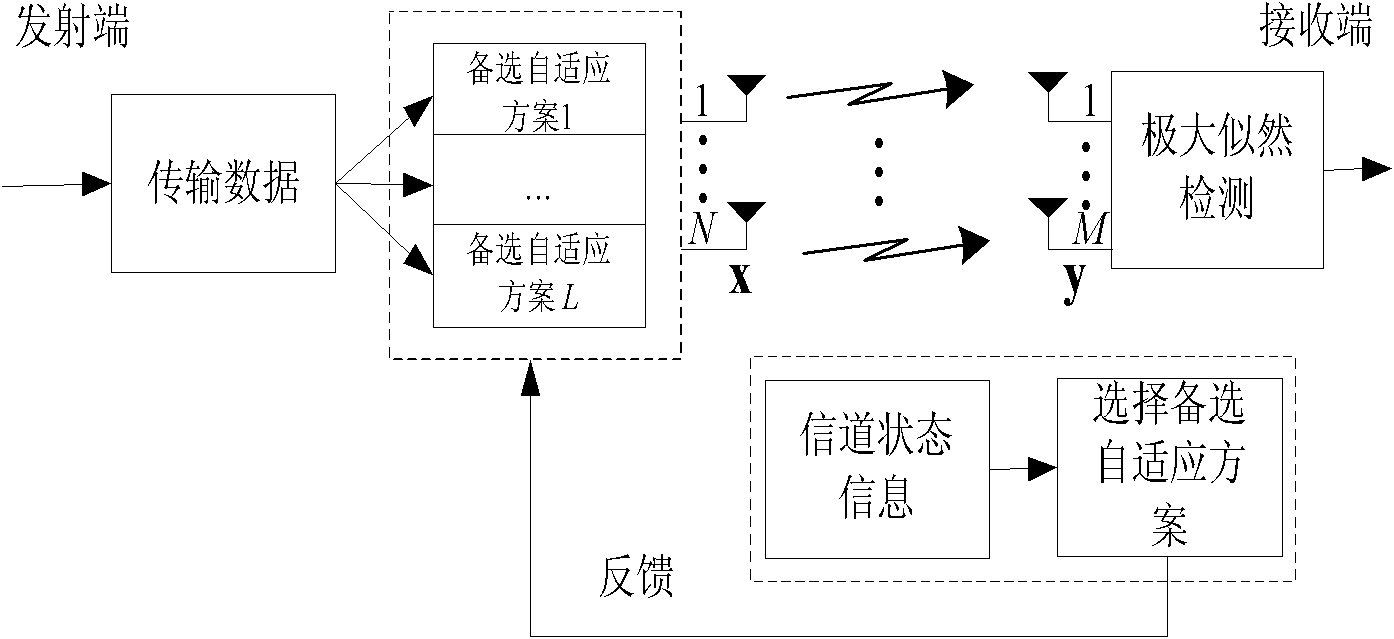
Adaptive spatial modulation method
InactiveCN102130755AFighting the effects of declineReduce bit error rateError prevention/detection by diversity receptionCurrent channelData transmission
The invention discloses an adaptive spatial modulation method. For the problem of weaker anti-interference capacity of the conventional multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system based on spatial modulation, the method comprises the following steps of: taking differences among channels corresponding to each transmitting antenna into full consideration, adjusting a mapping mode of transmitting data according to the state of the channels, namely selecting an optimized adaptive transmission scheme which adapts to the current channel, wherein each MIMO transmitting antenna adopts different modulation modes, namely properly selecting orders of modulation according to the state of the current channel; adopting a high-order modulation scheme when the channel of the transmitting antenna is better; and adopting a low-order modulation scheme when the channel of the transmitting antenna is worse. By adoption of the modulation method provided by the invention, influence on fading of transmitting-receiving channels can be prevented effectively, and the error rate of data transmission is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) Encoded Higher Order Modulation
InactiveUS20090129484A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionTheoretical computer scienceLow density
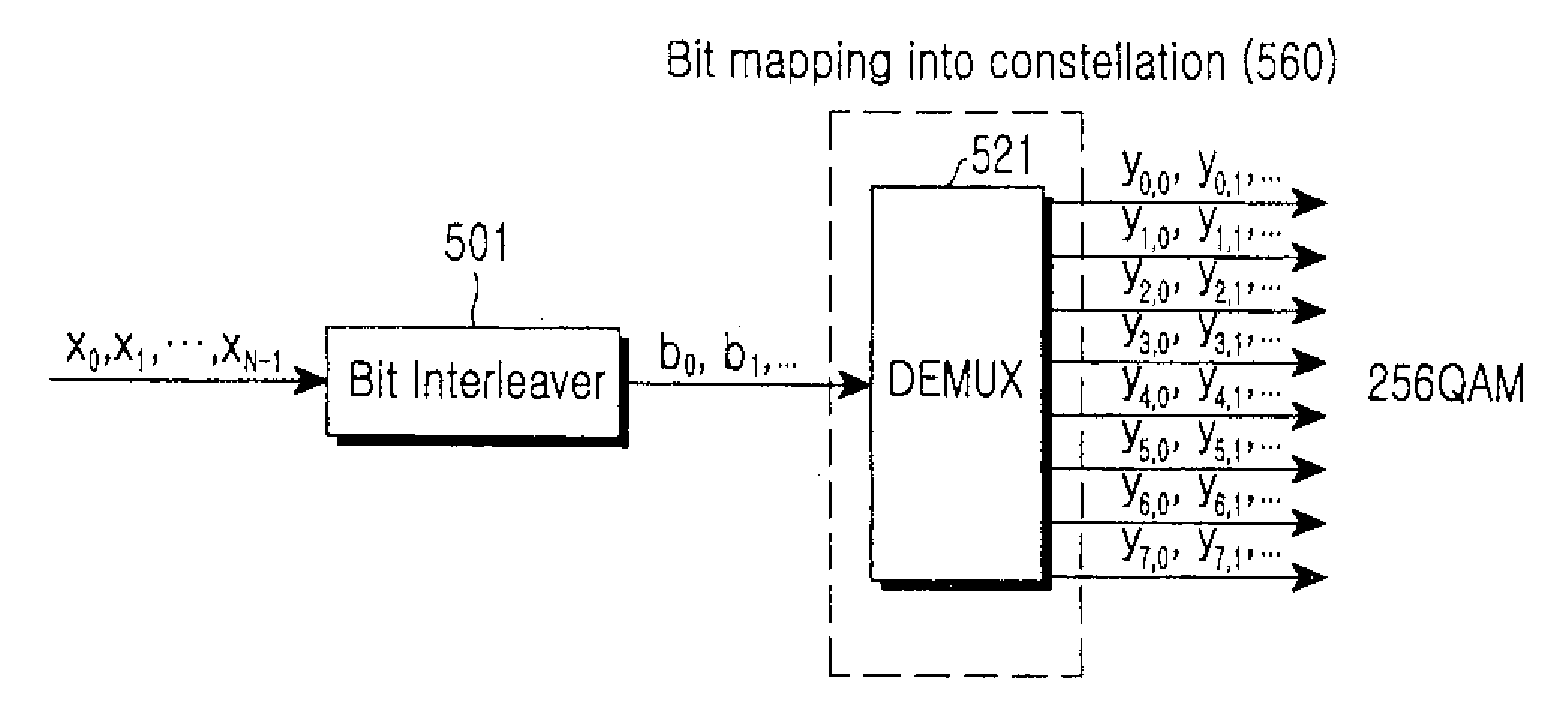
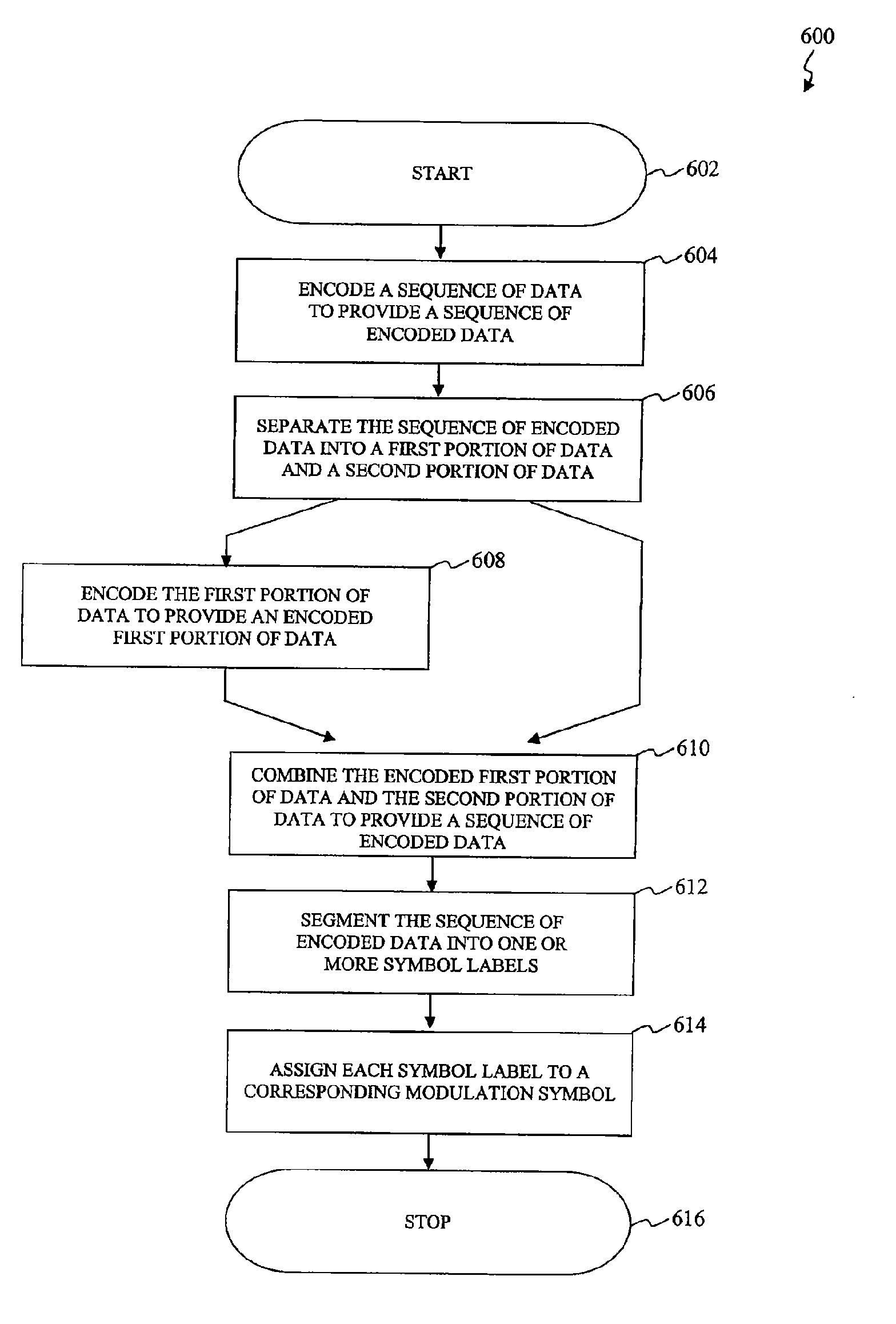
A method and apparatus is disclosed to map a sequence of data to Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) constellation symbols. The method and apparatus encodes only a portion of the sequence of data and leaves a remaining portion of the sequence of data unencoded. The encoded portion of the sequence of data and the remaining unencoded portion of the sequence of data are then mapped into modulation symbols of the QAM constellation. The encoded portion of the sequence of data selects subsets of the QAM constellation, and the remaining unencoded portion of the sequence of data determines a specific modulation symbol within each subset of the QAM constellation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
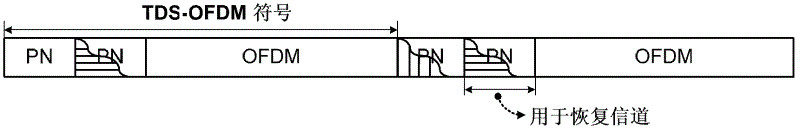
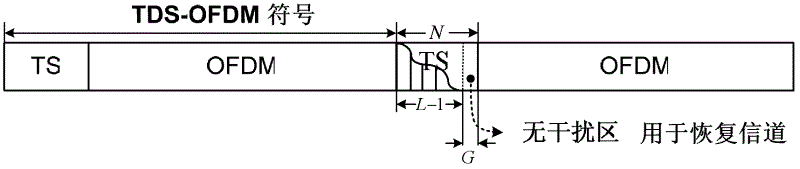
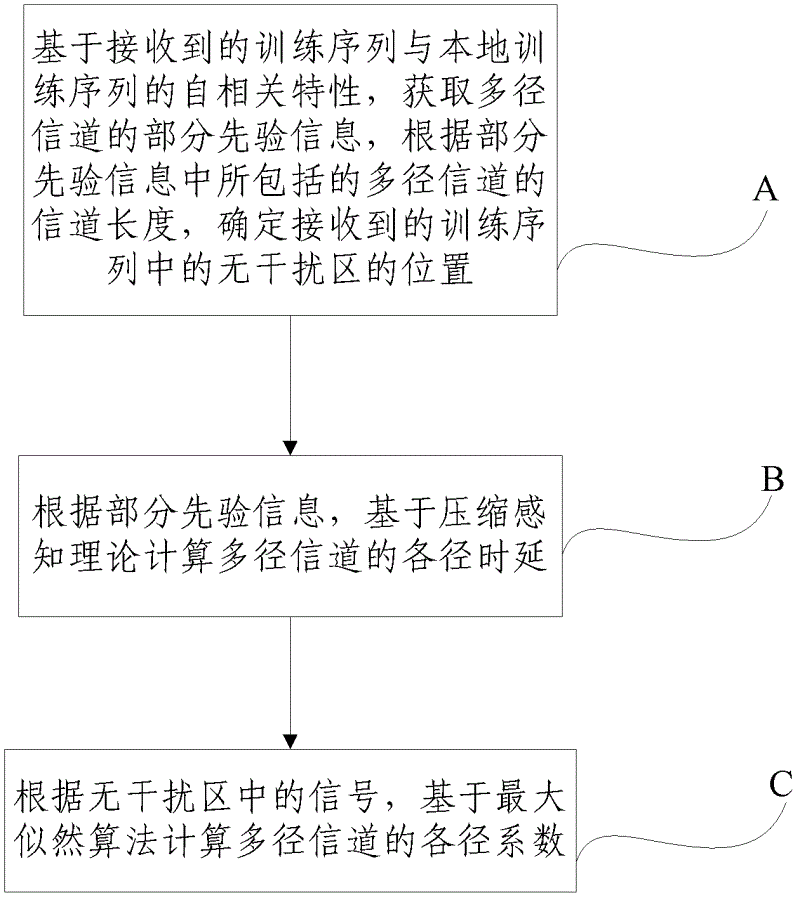
Transmission method of time domain synchronous-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (TDS-OFDM) based on theory of compressive sensing
InactiveCN102624658ABaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumDynamic channel
The invention discloses a transmission method of time domain synchronous-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (TDS-OFDM) based on a theory of compressive sensing and relates to the field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of self-correlation properties of a received training sequence and a local training sequence, obtaining parts of prior information of multi-path channels, and confirming a position of a non-interference area in the received training sequence according to the channel length of the multi-path channels included in parts of the prior information; according to parts of the prior information and on the basis of the theory of compressive sensing, calculating time delay of each path of the multi-path channels; and according to signals in the non-interference area and on the basis of a maximum likelihood algorithm, calculating coefficient of each path of the multi-path channels. According to the transmission method of the TDS-OFDM based on the theory of the compressive sensing, two technical problems that the TDS-OFDM is difficult to support high order modulation of 256 quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) and the performance deterioration in dynamic channels is obvious are solved, and a strong theoretical and technical support is provided so that digital terrestrial multimedia broadcasting (DTMB) can catch up with and surpass the advanced international levels in key performance indicators of spectral efficiency, high-speed motion and receiving and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com