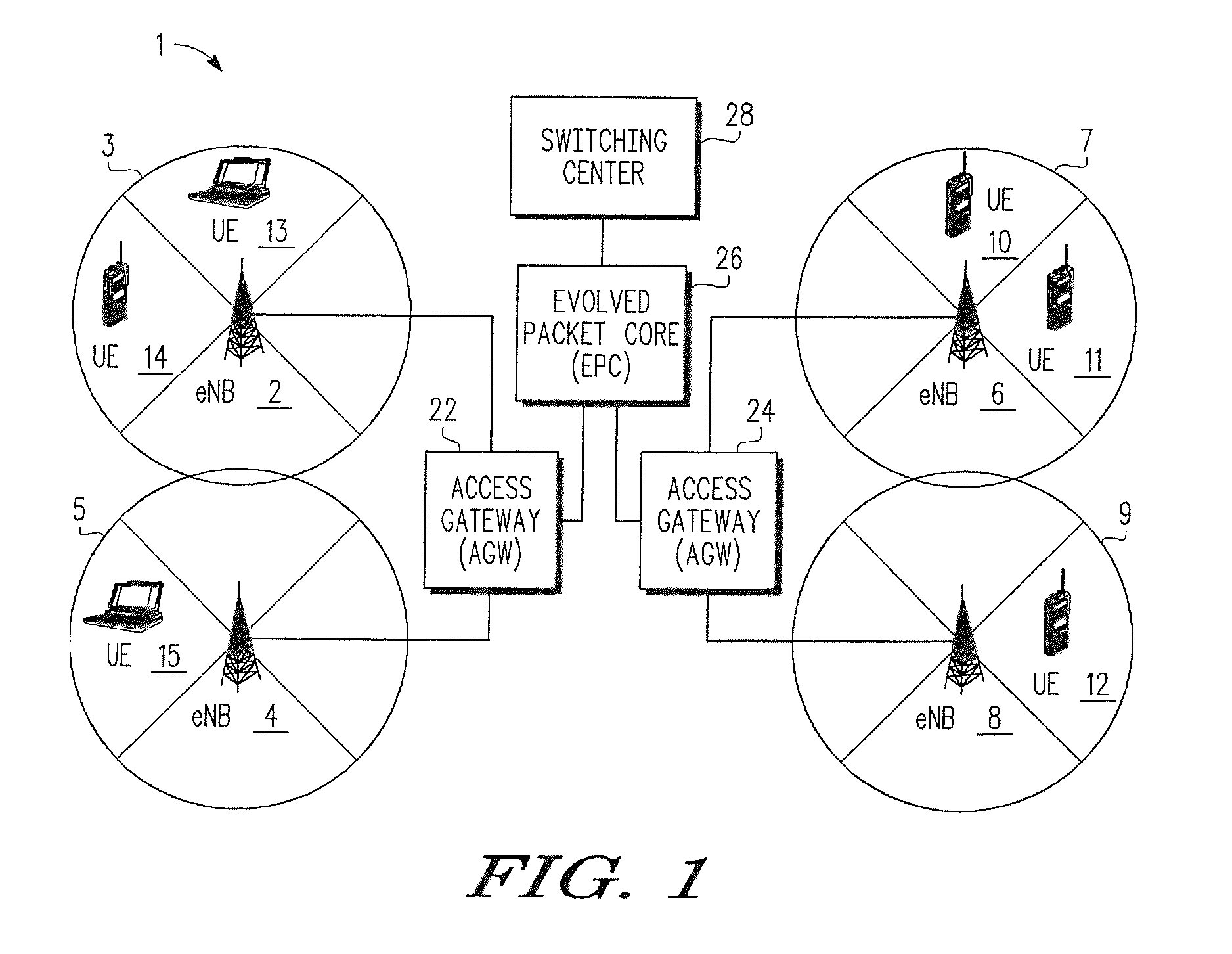
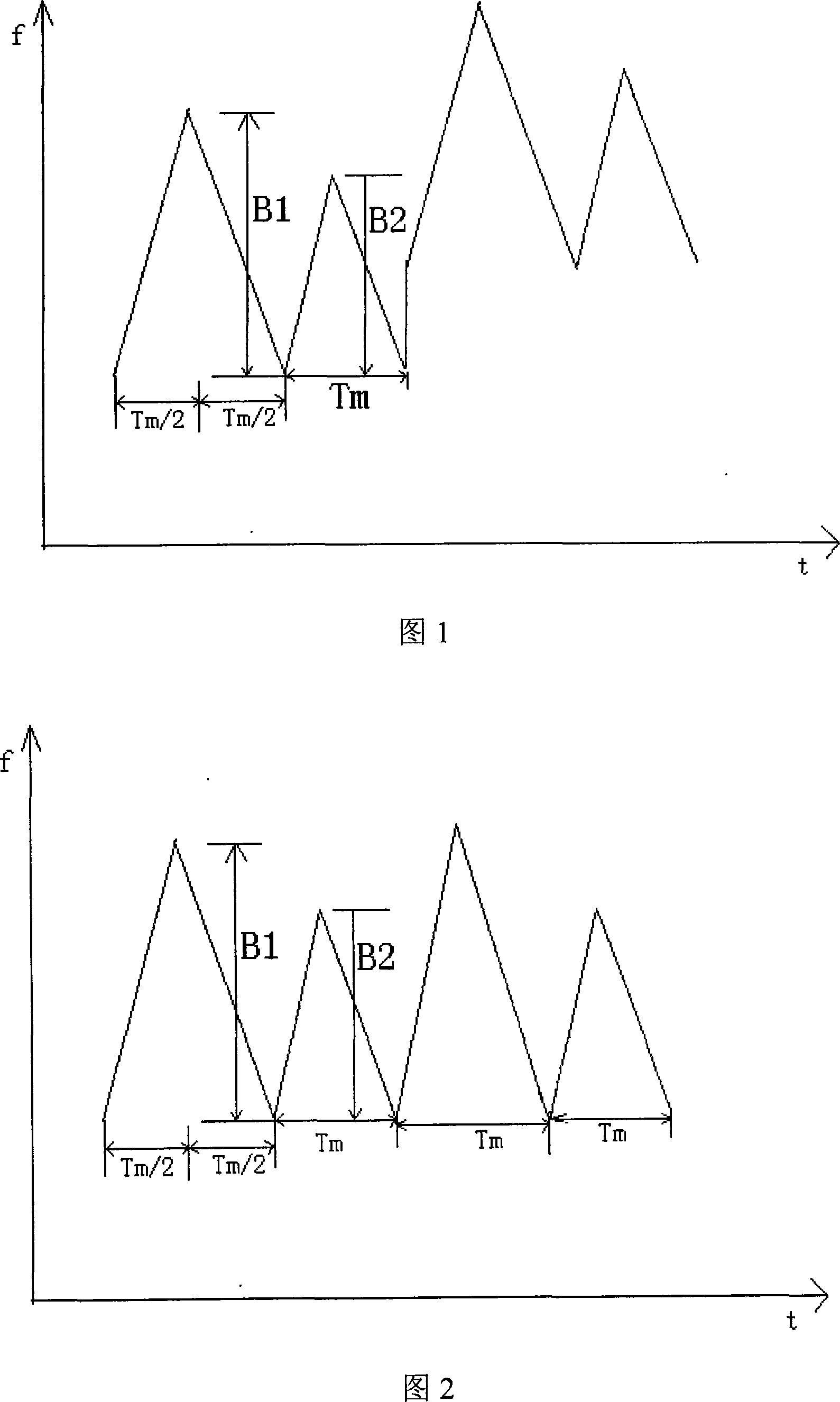Patents
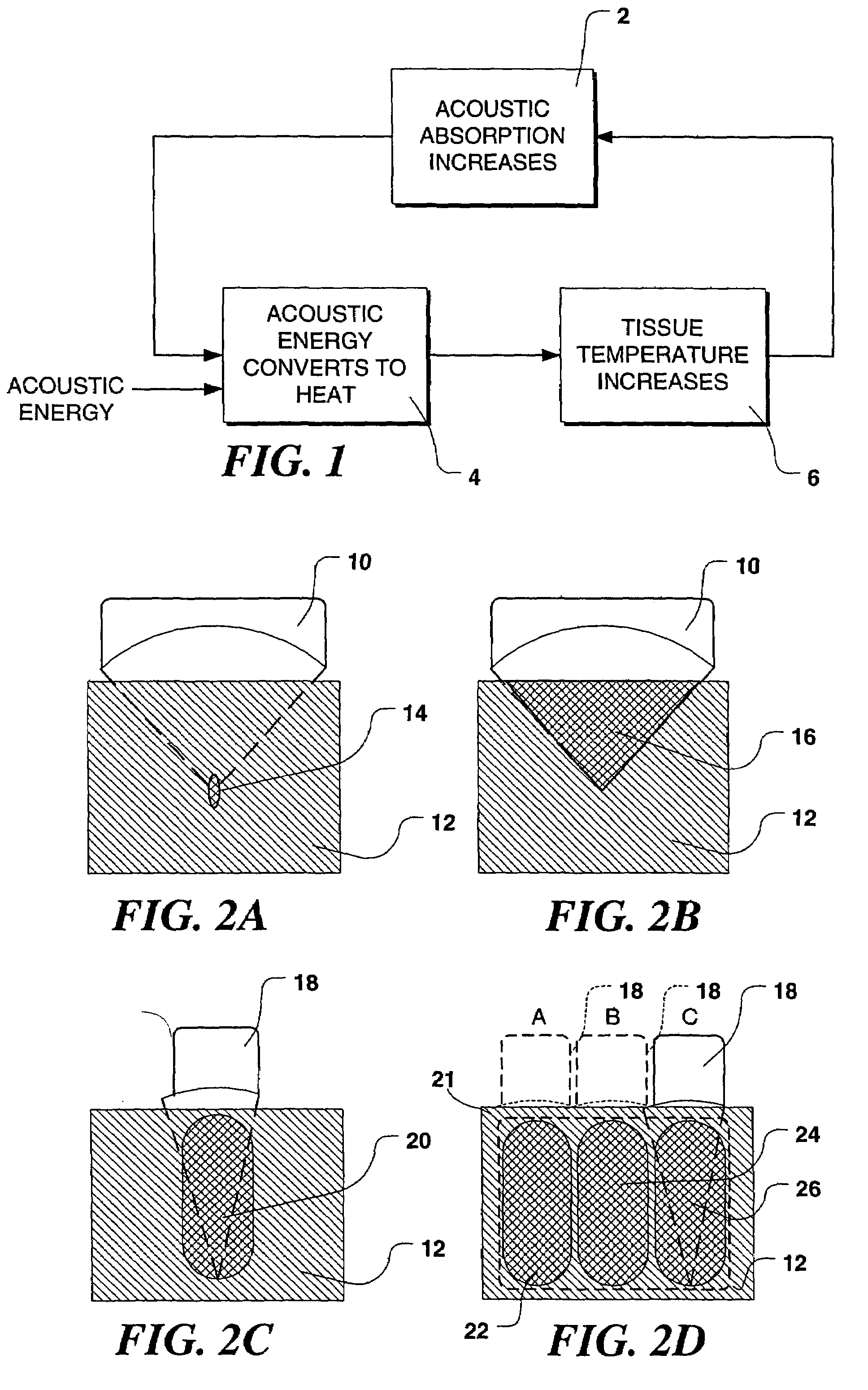
Literature
1972 results about "Continuous wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A continuous wave or continuous waveform (CW) is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency, typically a sine wave, that for mathematical analysis is considered to be of infinite duration. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a sinusoidal carrier wave is switched on and off. Information is carried in the varying duration of the on and off periods of the signal, for example by Morse code in early radio. In early wireless telegraphy radio transmission, CW waves were also known as "undamped waves", to distinguish this method from damped wave signals produced by earlier spark gap type transmitters.
Electrosurgical generator
ActiveUS7195627B2High peak power capabilityReduces delay and unwanted coagulation effectSurgical instruments for heatingPeak valueContinuous wave
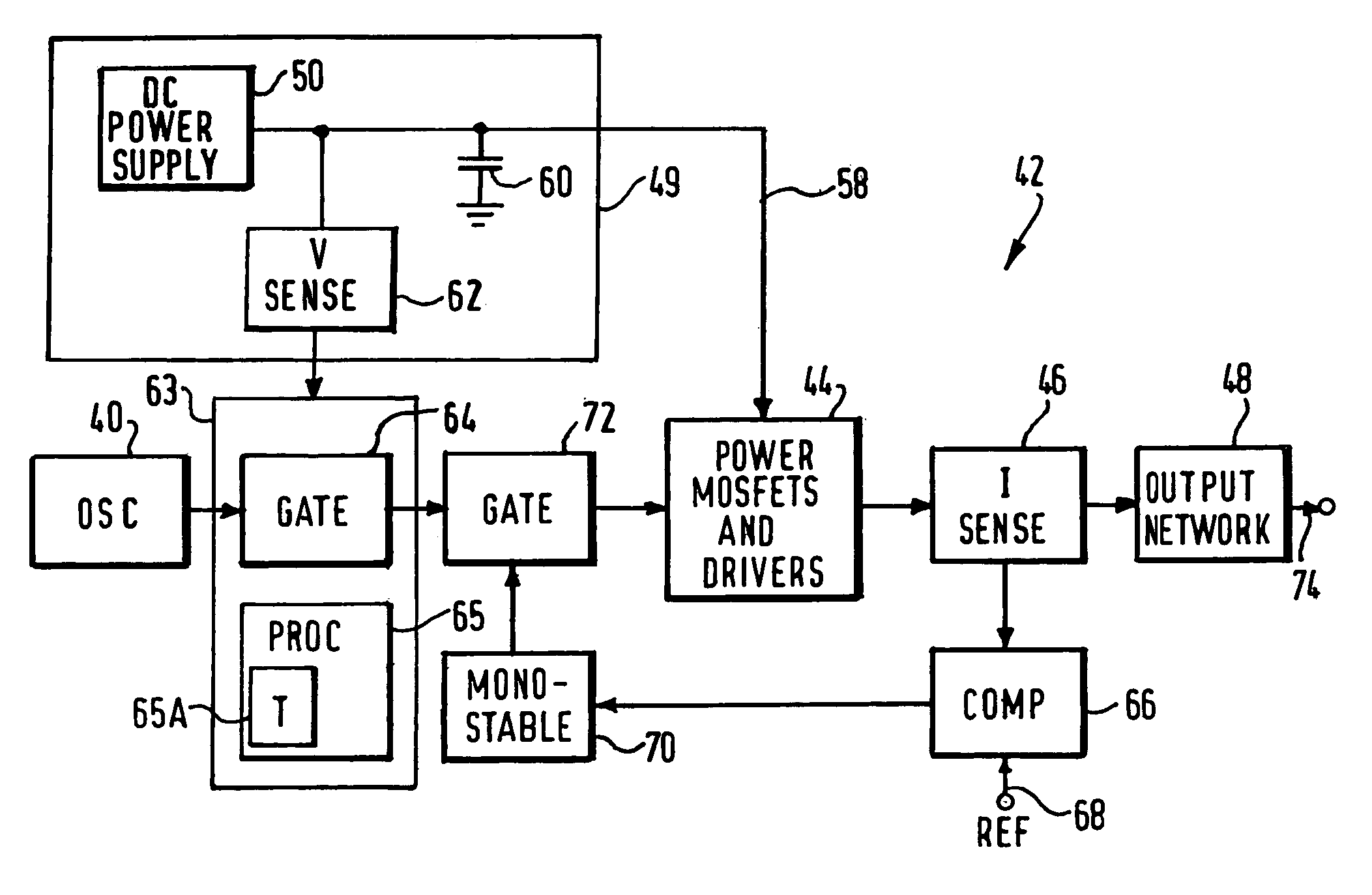
An electrosurgical generator for supplying RF power to an electrosurgical instrument for cutting or vaporising tissue has an RF output stage with RF output devices, a series-resonant output network and an RF output. The generator offers improved cutting and vaporising performance, especially in relation to the reliability with which an arc can be struck when presented with an initial load impedance load. This is achieved by virtue of the output stage being capable of maintaining output pulses of at least 1 kW peak by supplying the RF output devices from a large reservoir capacitor. An appropriate combination of cutting performance and haemostasis is provided by allowing for pulsed or continuous wave operation once an arc has been established, according to whether or not a surplus energy condition exists, as indicated by the voltage across the reservoir capacitor.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
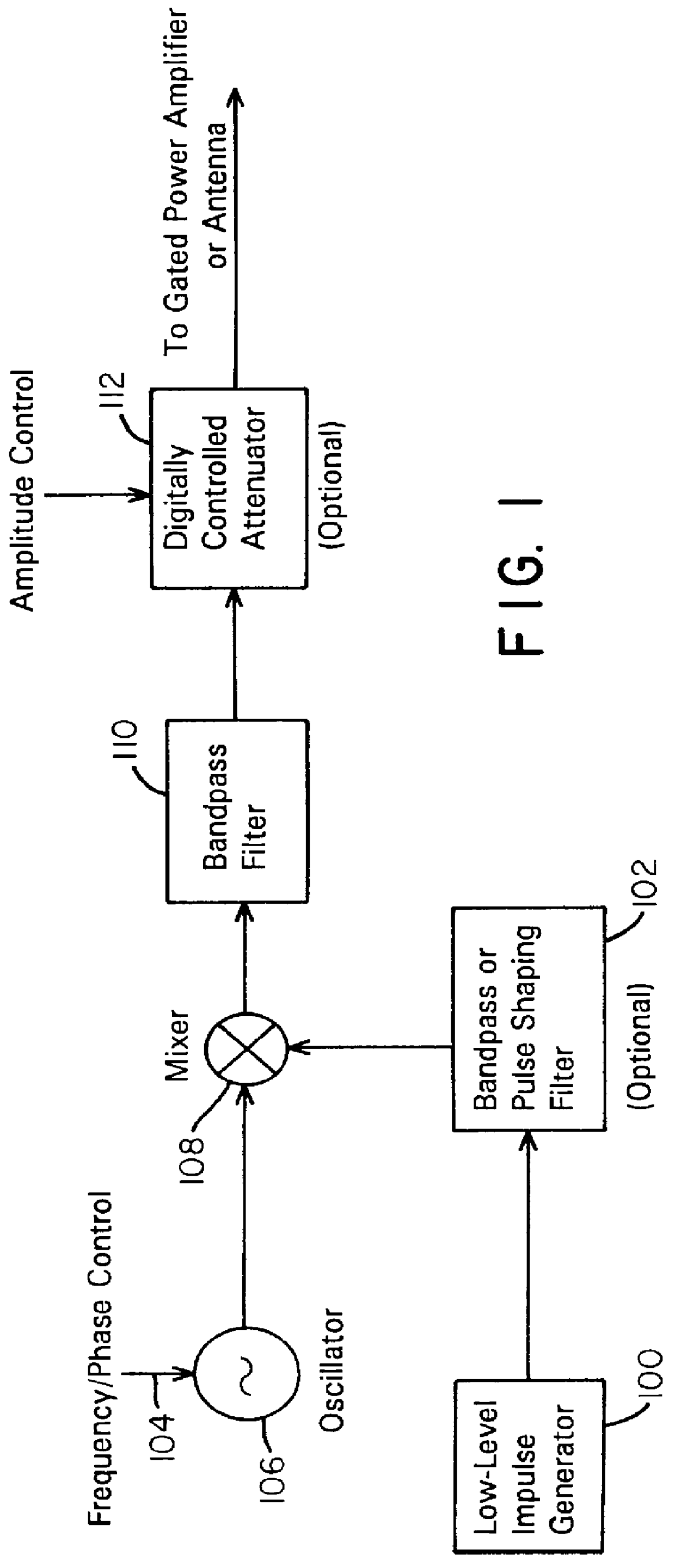
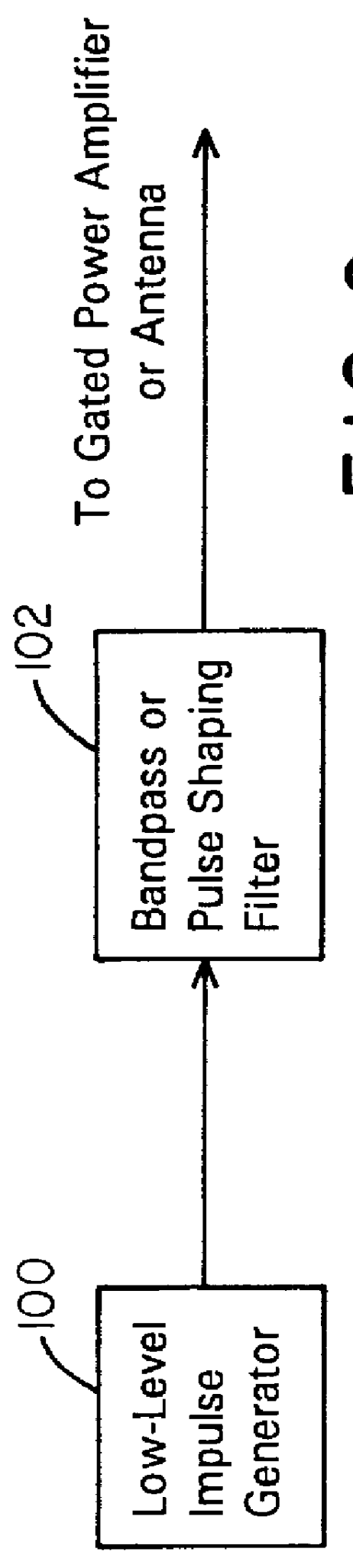
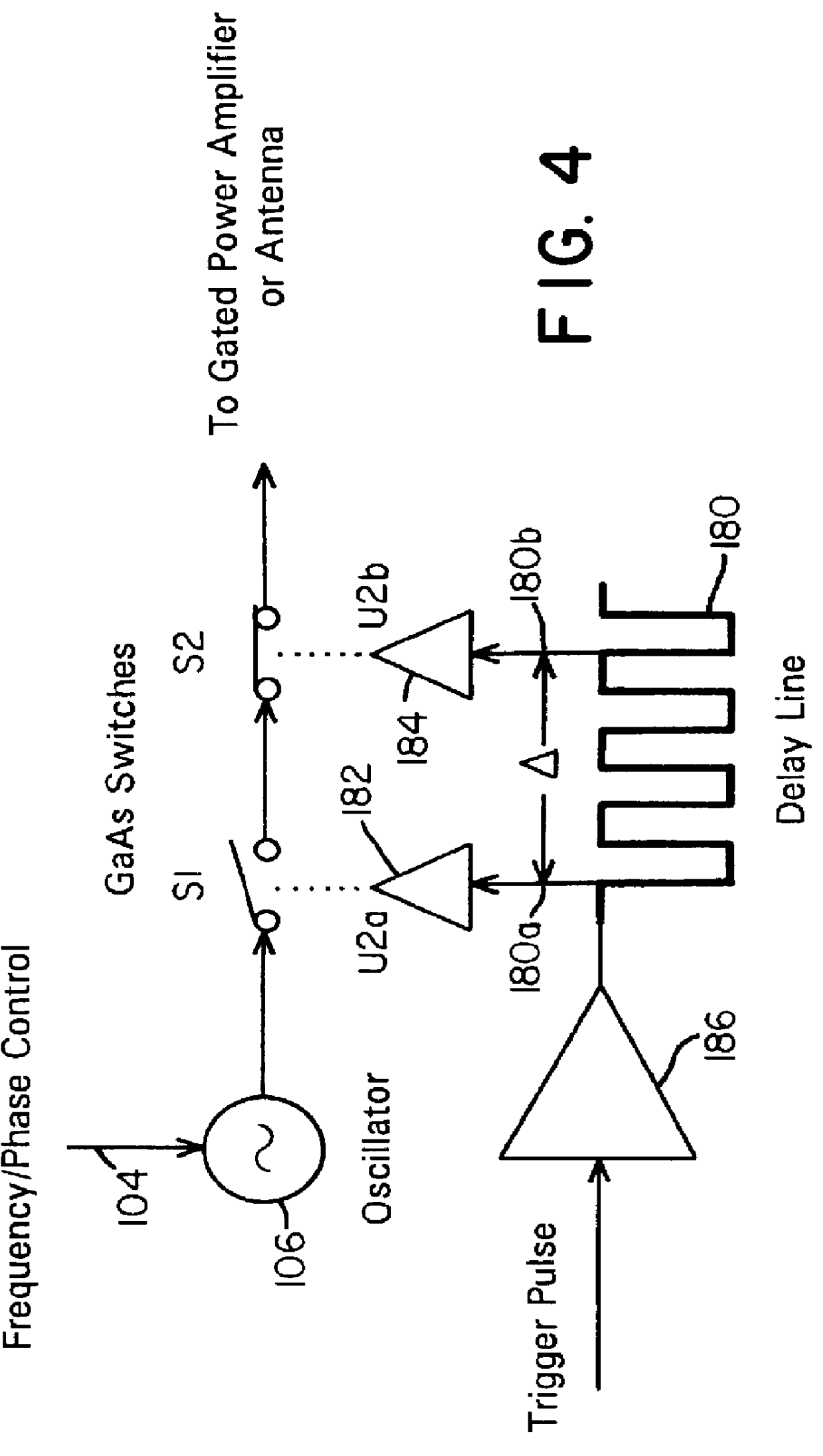
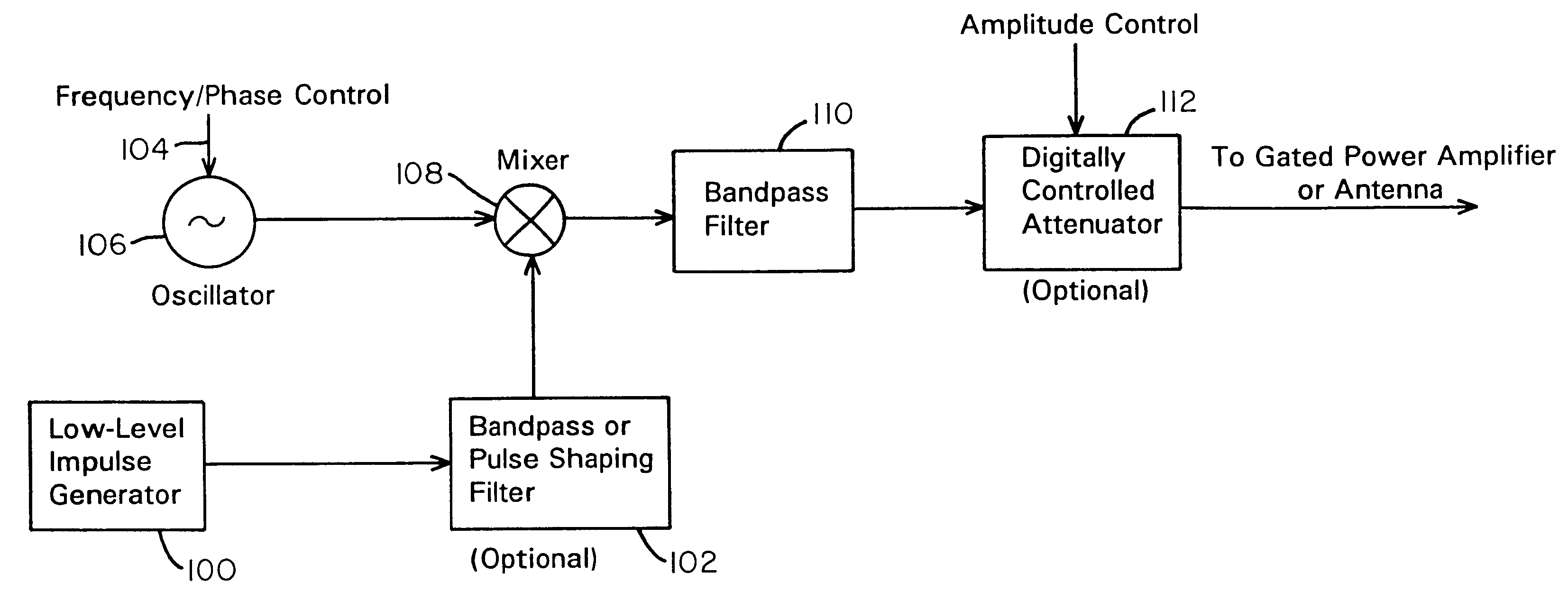
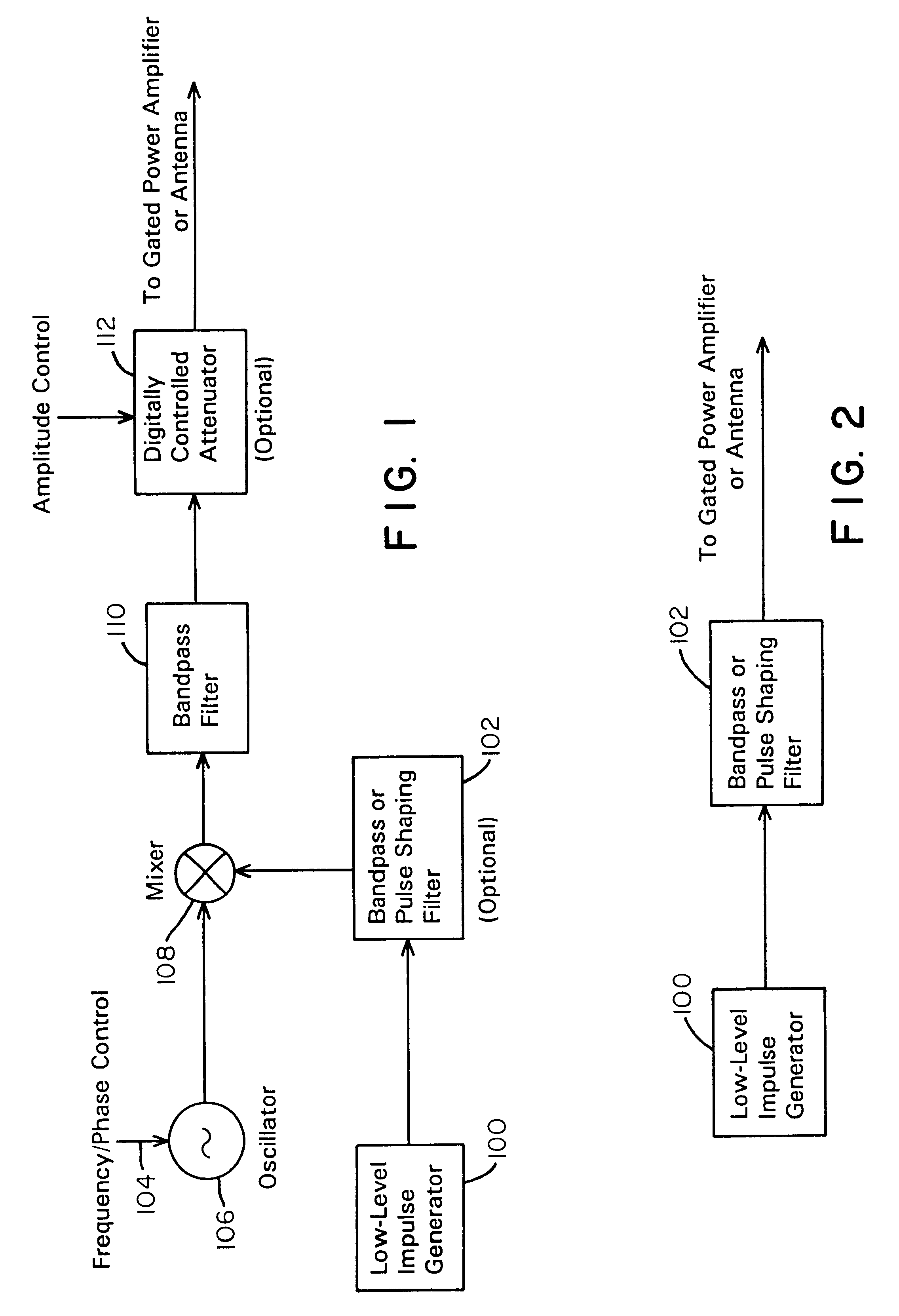
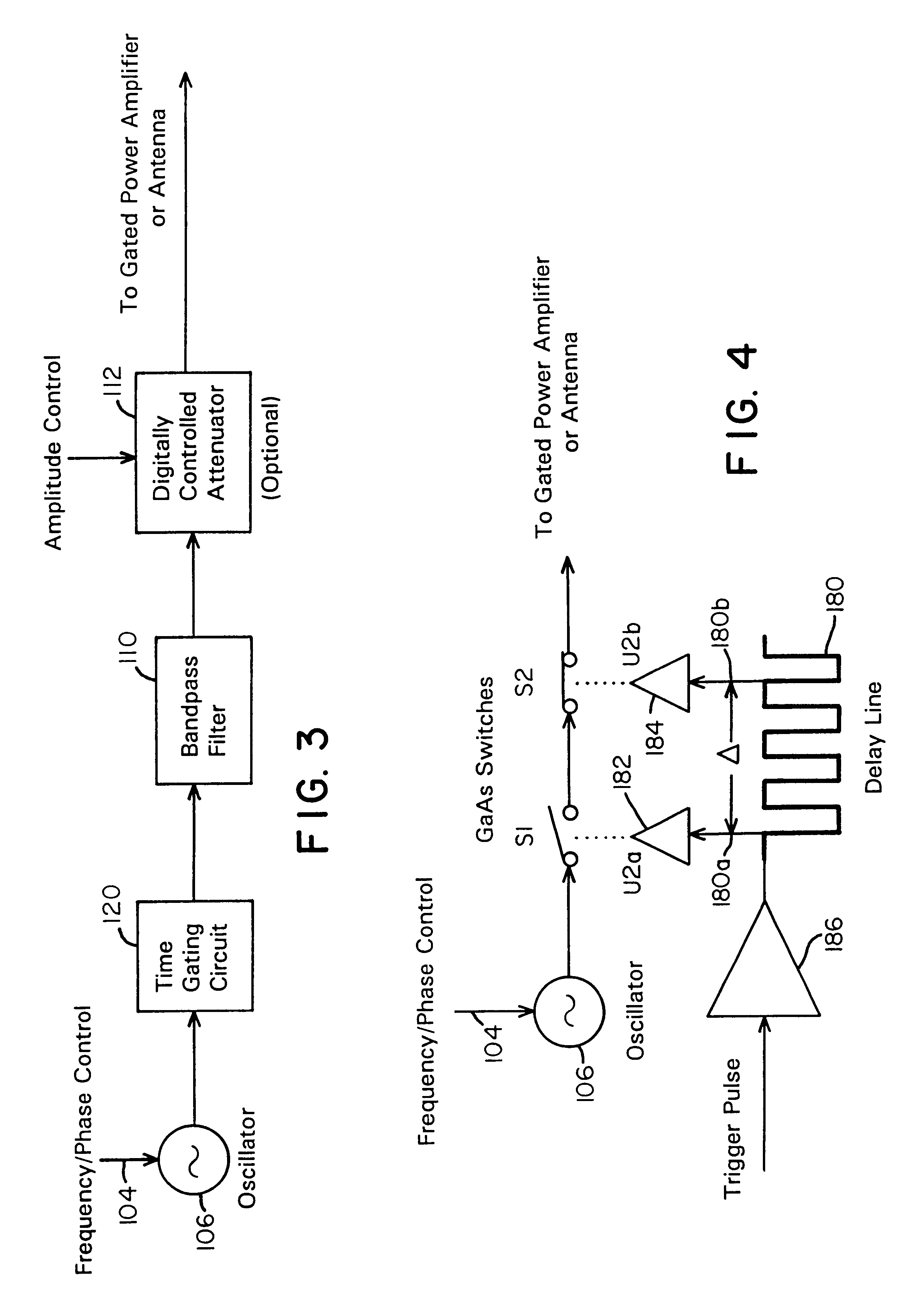
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
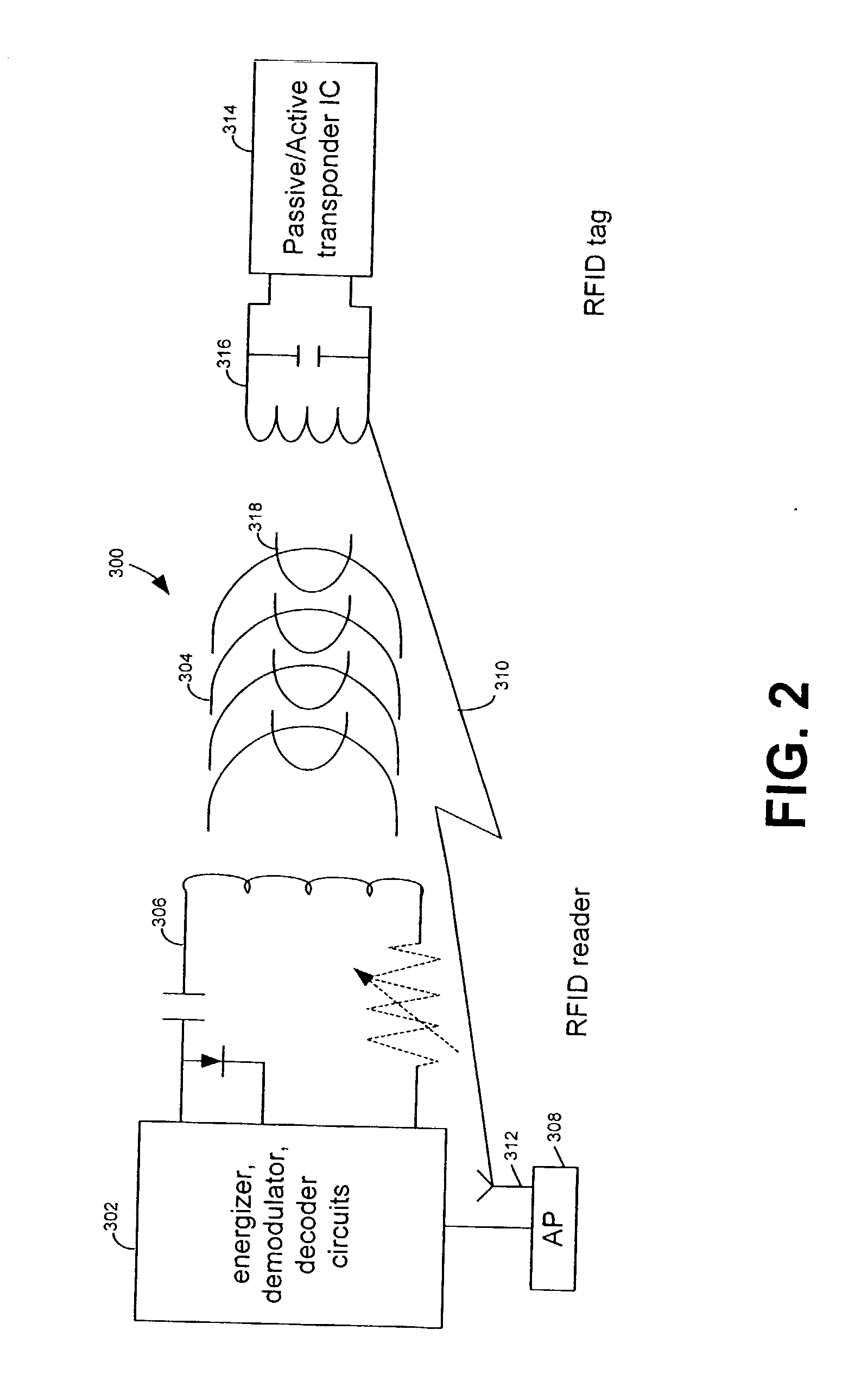
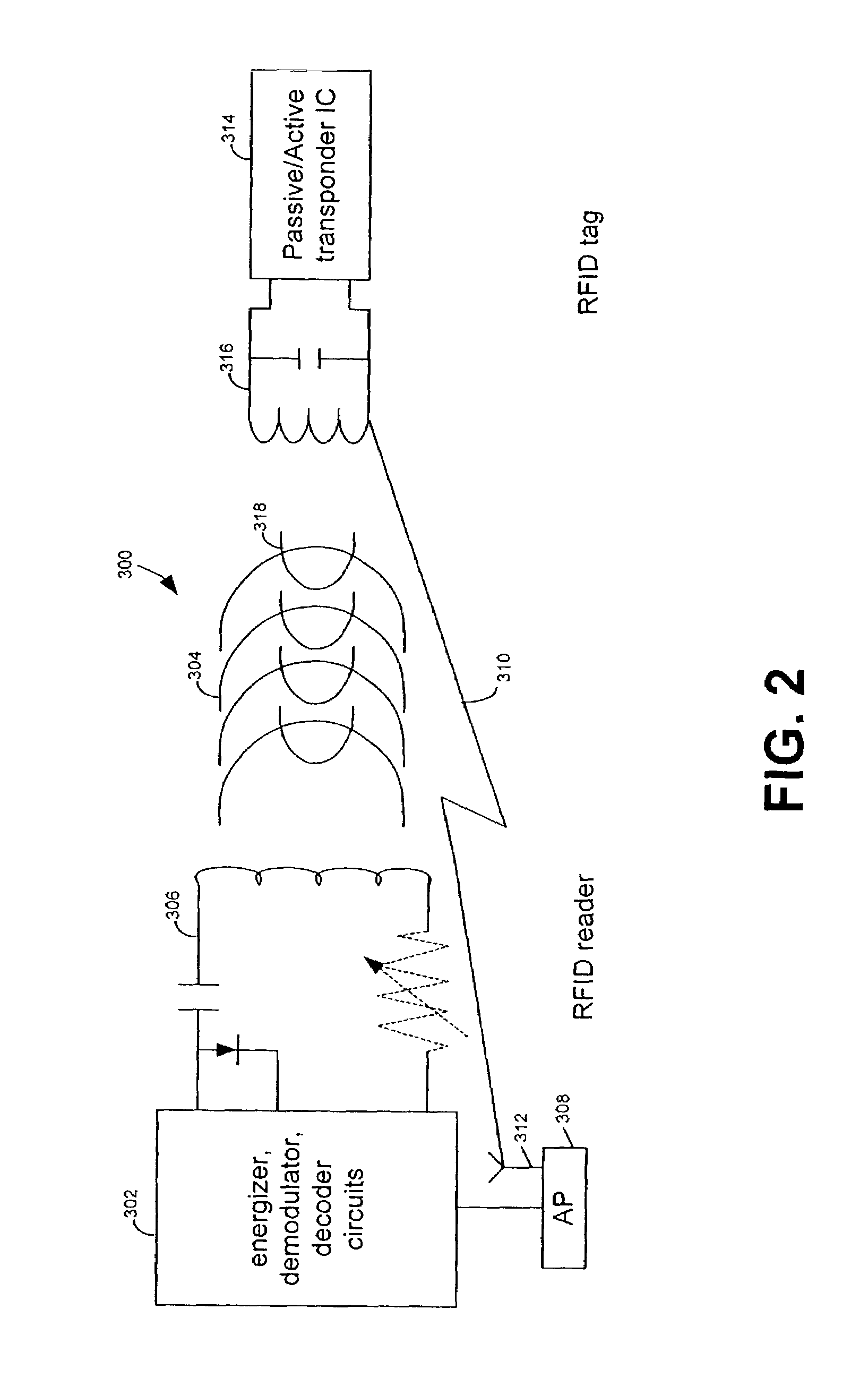
RFID device, system and method of operation including a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol compatible with RFID, bluetooth and/or IEEE 802.11x infrastructure
ActiveUS20030104848A1Near-field transmissionMemory record carrier reading problemsTransceiverAntenna impedance
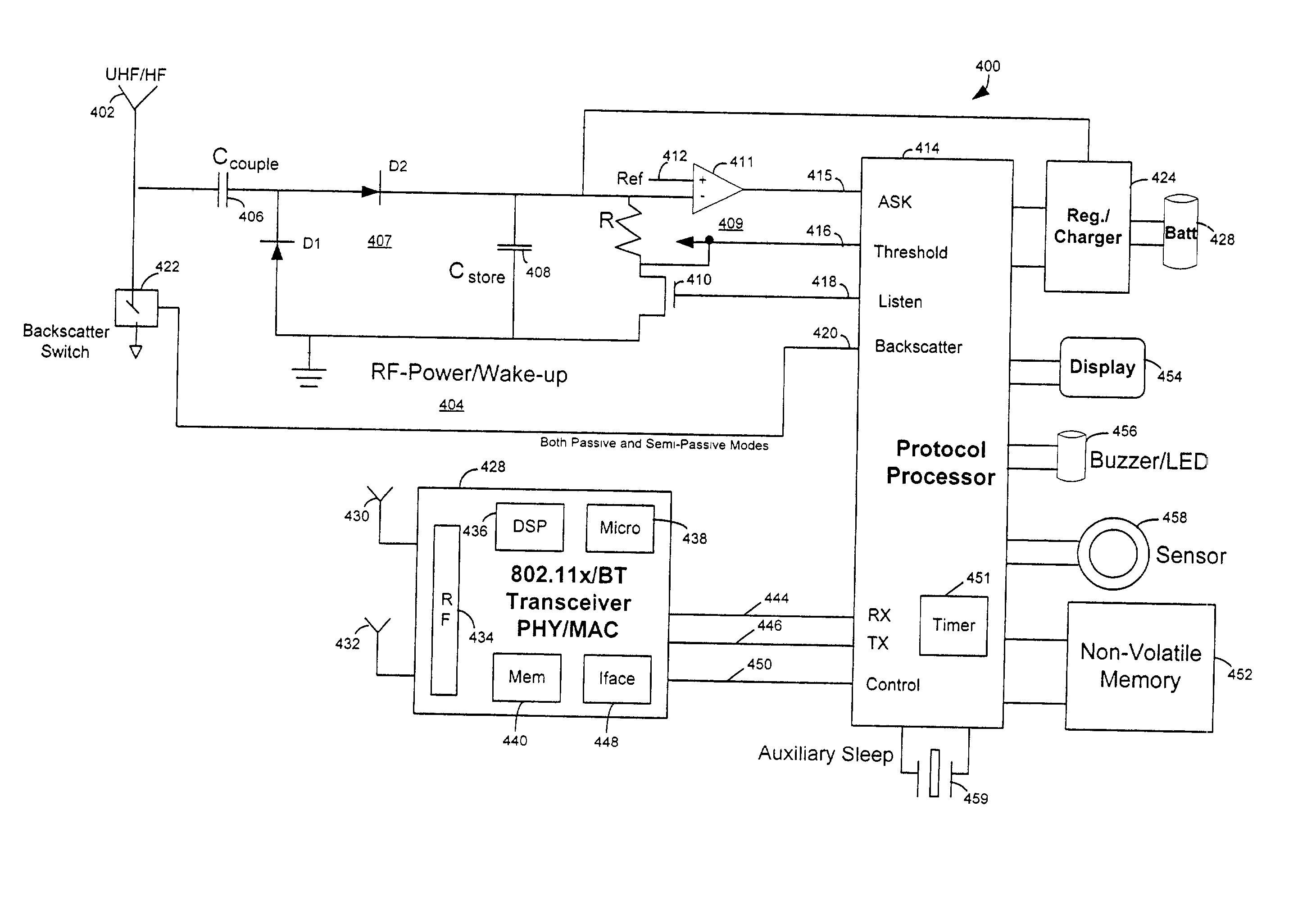
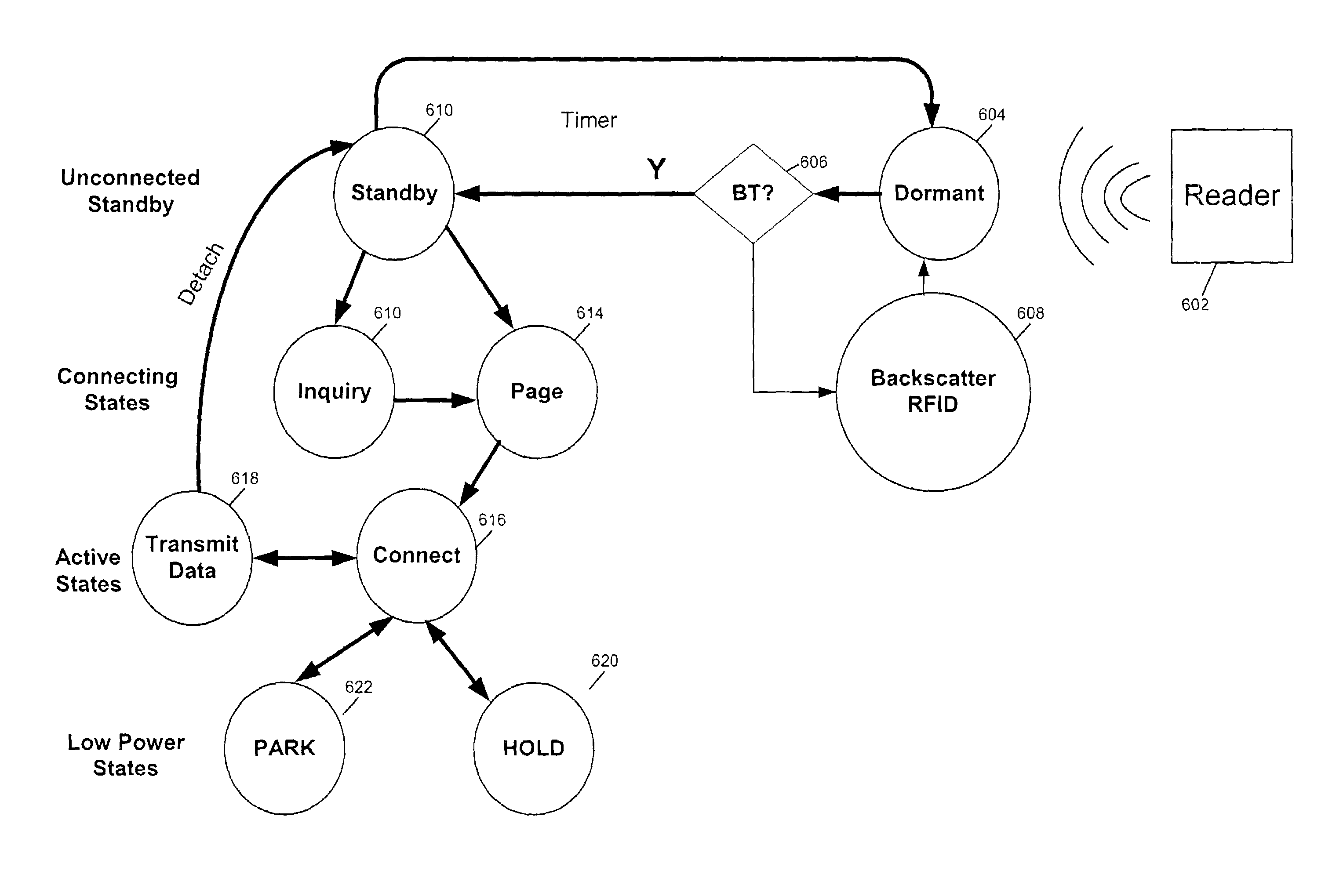
An RFID system includes a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol-compatible with existing 802.11x / Bluetooth Standards as well as RFID standards. The tag is linked to a multi-protocol Interrogator via a generated RF Continuous Wave (CW) field. The tag includes an antenna coupled to an RFID and a Bluetooth / 802.11x transceiver section. A Protocol Processor services RFID and transceiver sections and is coupled to the antenna via a backscatter switch. The Interrogator can switch the tag to an RFID backscatter radiation mode where the processor switches the antenna impedance to reflect the CW signal. For transceiver operation the processor switches antenna impedance in synchronization with a frame organized bit stream. For reception, the RFID section utilizes demodulation techniques, typically Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), and provides a wake up mode within a predetermined distance of the Interrogator. The transceiver may operate in a backscatter or regular mode as directed by an Access Point.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
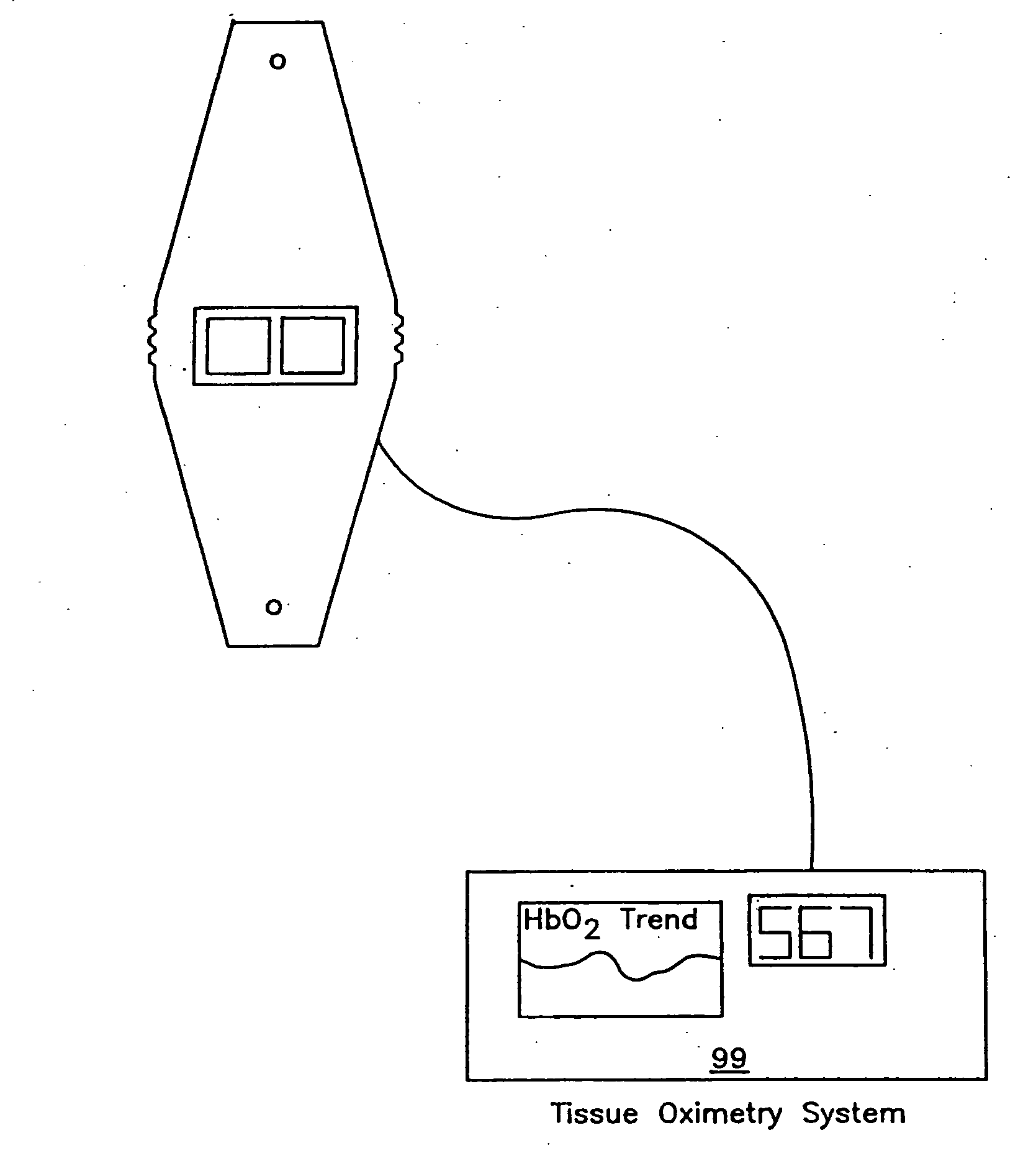
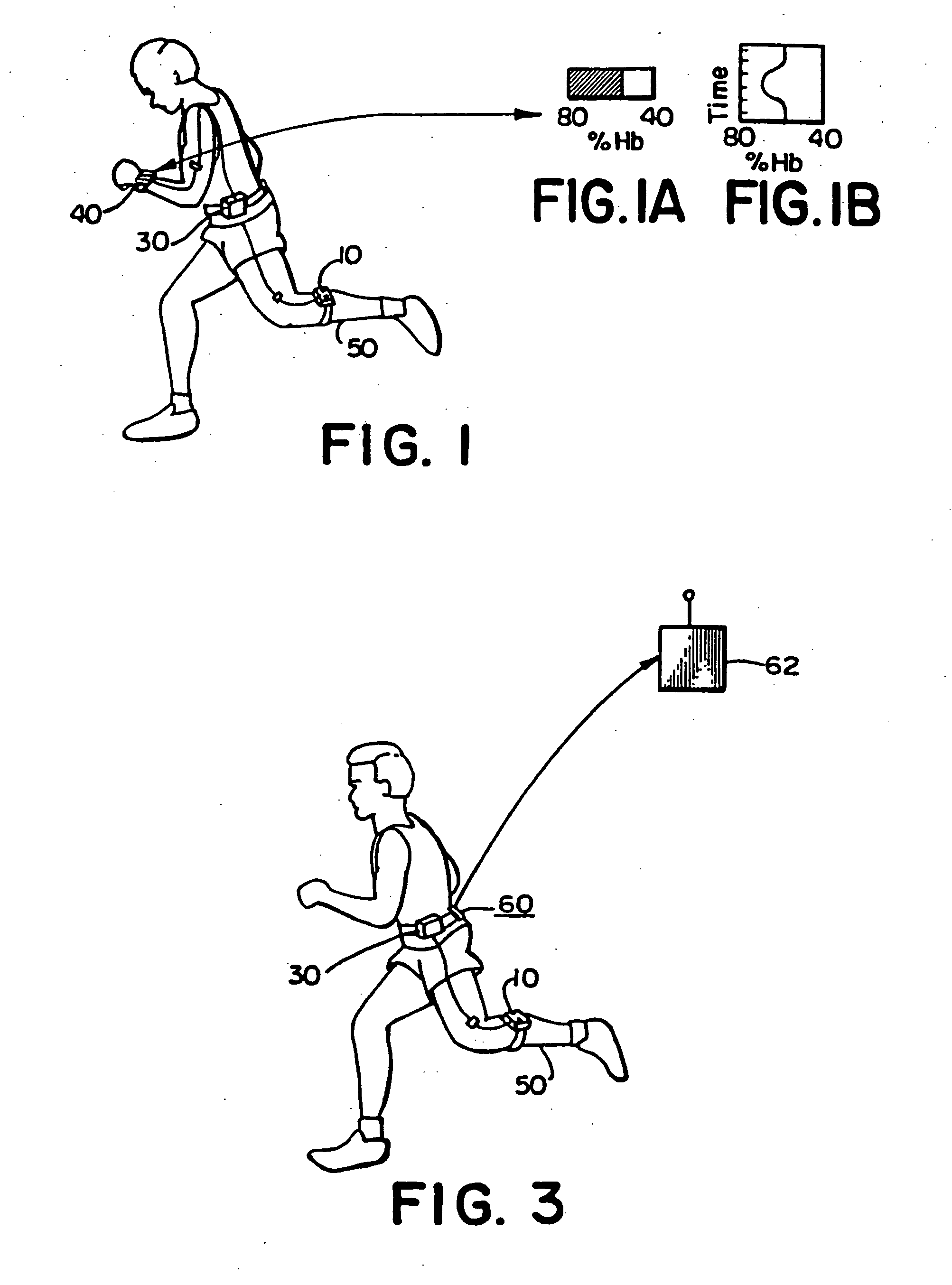
Hemoglobinometers and the like for measuring the metabolic condition of a subject
InactiveUS20050113656A1Performance of was minimizedEfficient couplingCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSkin surfaceContinuous wave
The present invention discloses a novel, user-wearable system for monitoring the oxygen concentration, or oxygenation trend, in the tissue of a subject undergoing aerobic stress. The system comprises a lightweight detector, worn against the skin surface of the subject, at the site being monitored. The system further includes wearable power pack and display means for displaying information indicative of the metabolic condition of the region being monitored. The detector preferably employs a continuous wave spectrophotometer having one or more sources of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between about 760 and 800 nanometers directed into the tissue of the subject. The detector utilizes photon migration to detect the portion of the transmitted radiation arriving at an adjacent skin region. The present invention also discloses methods for displaying the aerobic metabolic condition of a subject.
Owner:CHANCE BRITTON
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
RFID device, system and method of operation including a hybrid backscatter-based RFID tag protocol compatible with RFID, bluetooth and/or IEEE 802.11x infrastructure
ActiveUS7215976B2Near-field transmissionMemory record carrier reading problemsTransceiverAntenna impedance
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
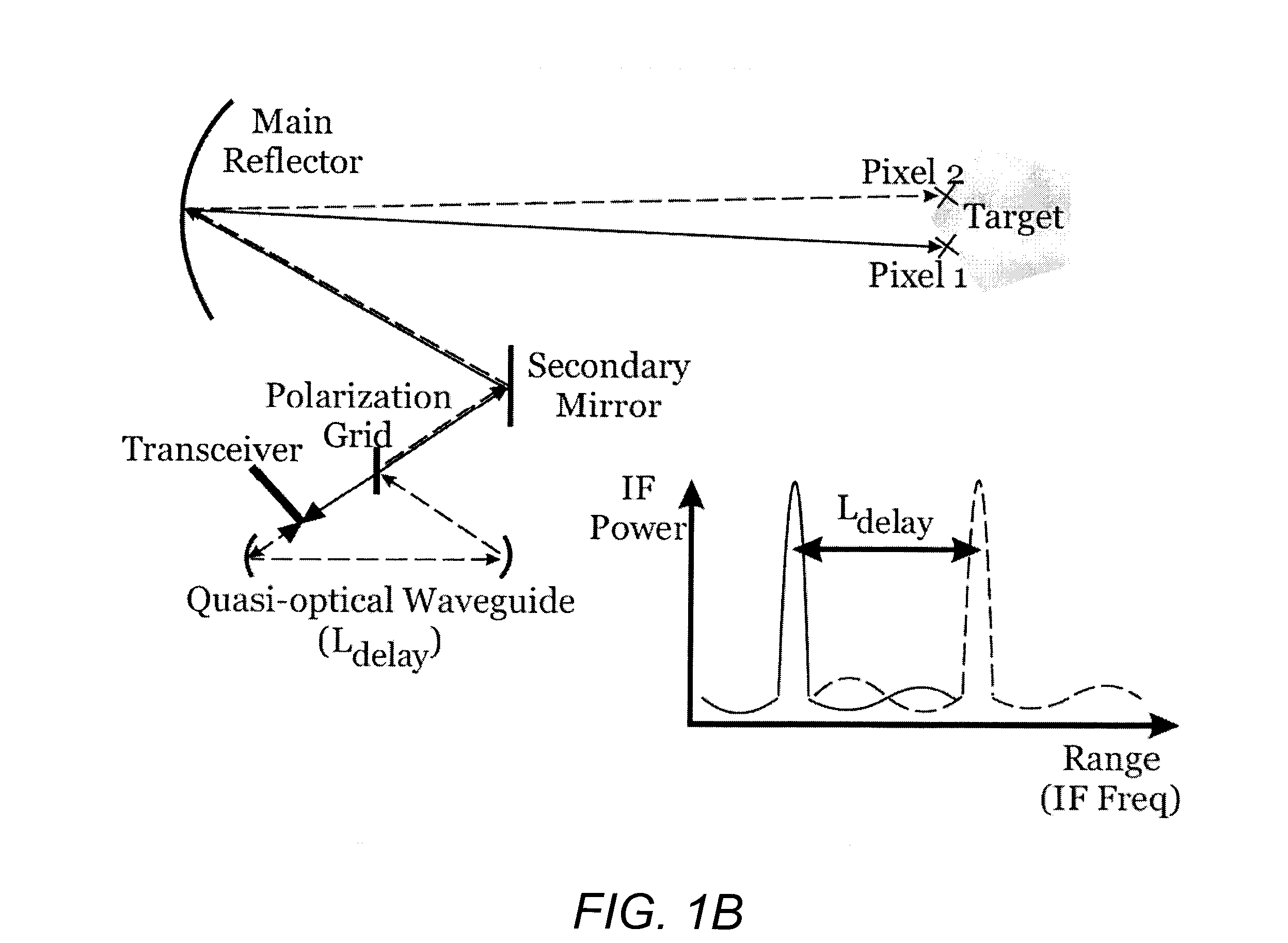
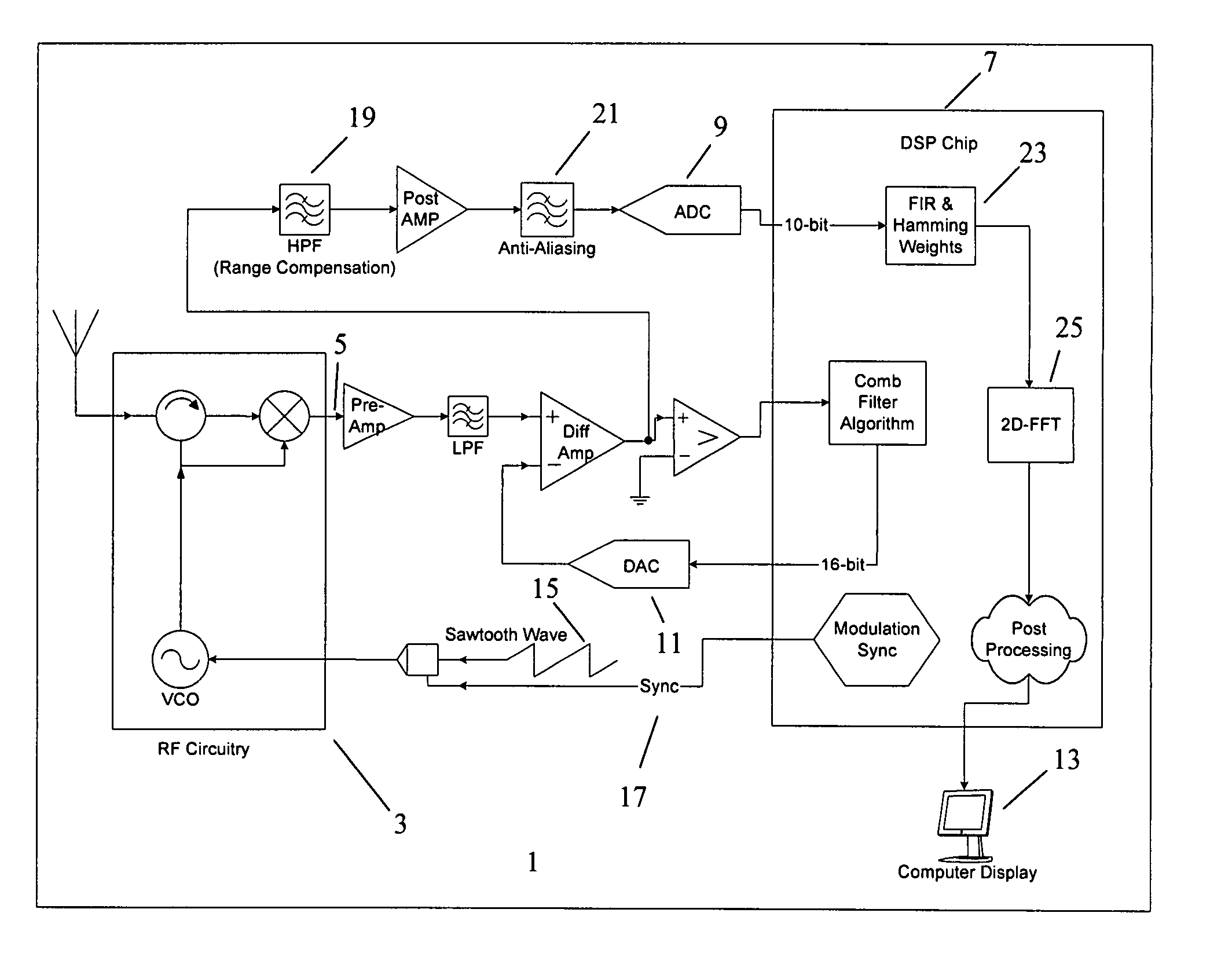
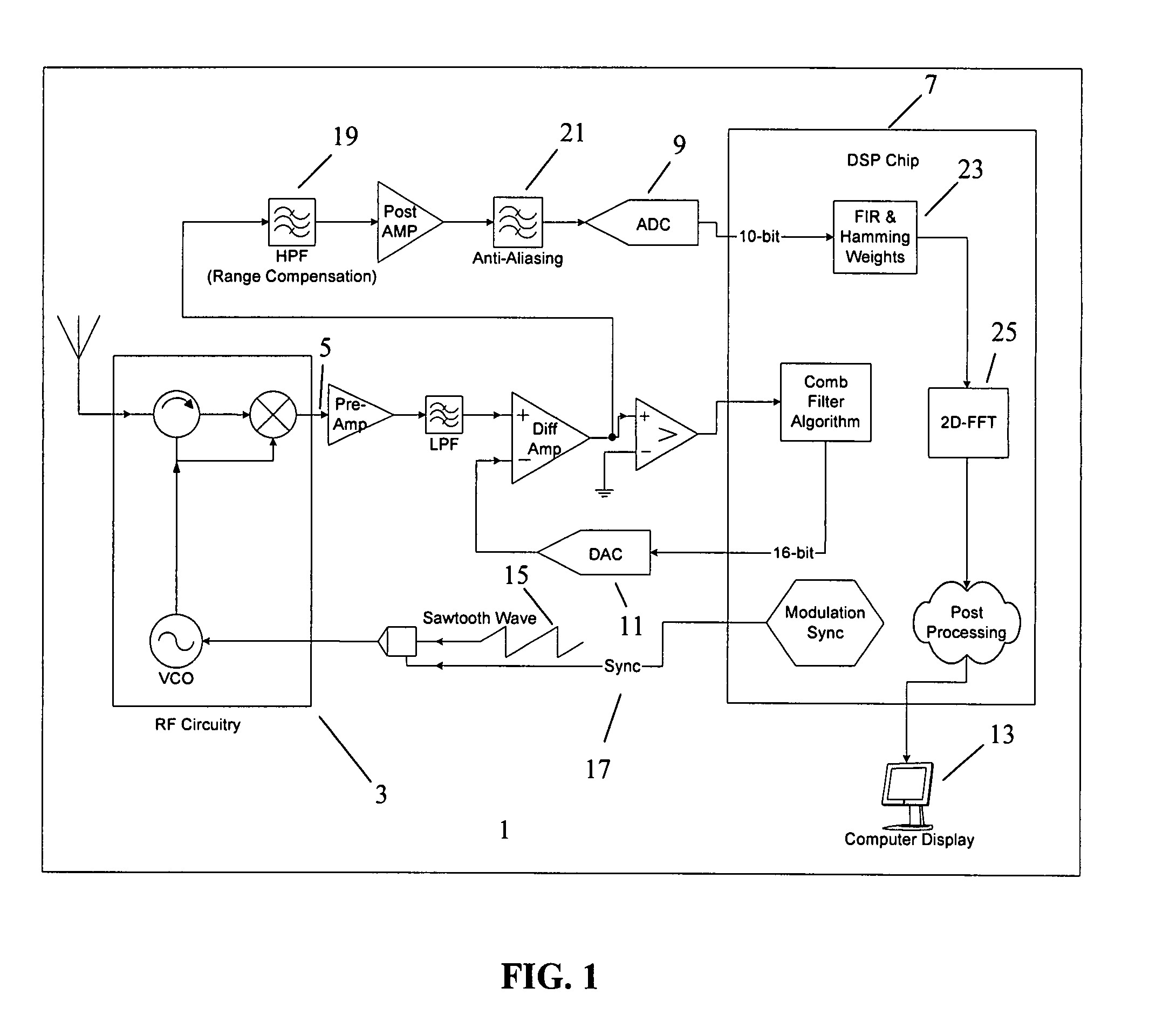
Multi-pixel high-resolution three-dimensional imaging radar
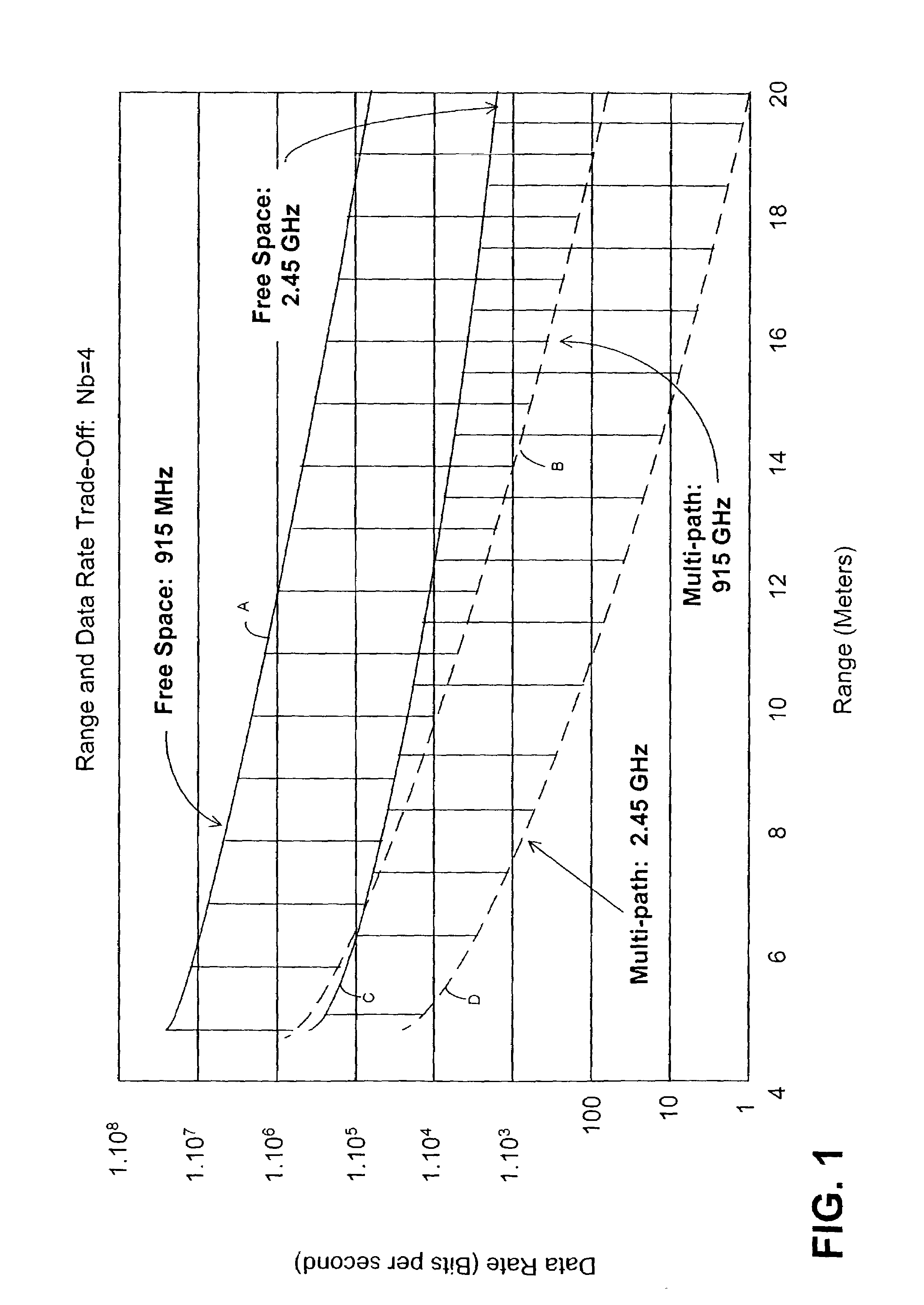
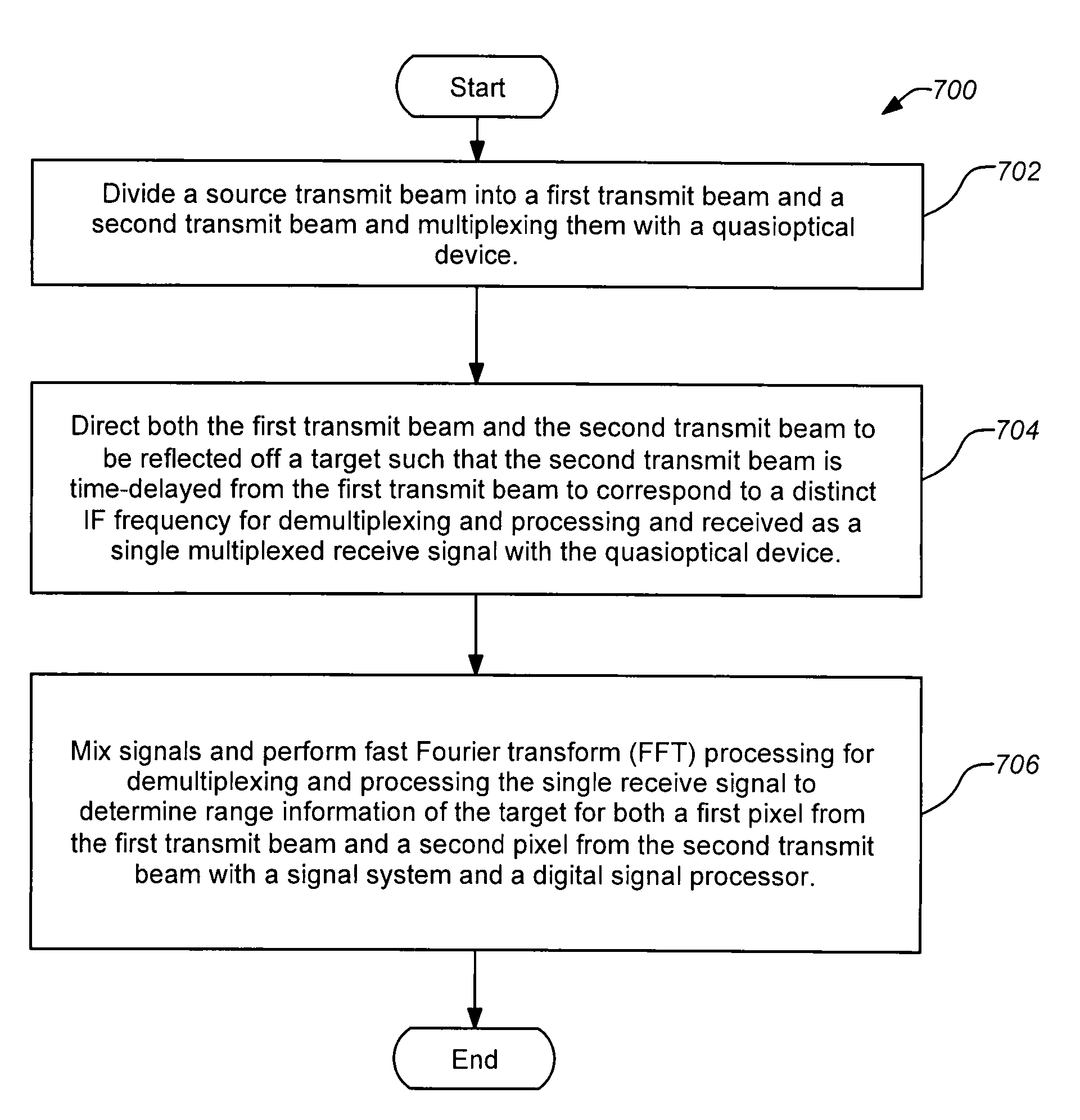
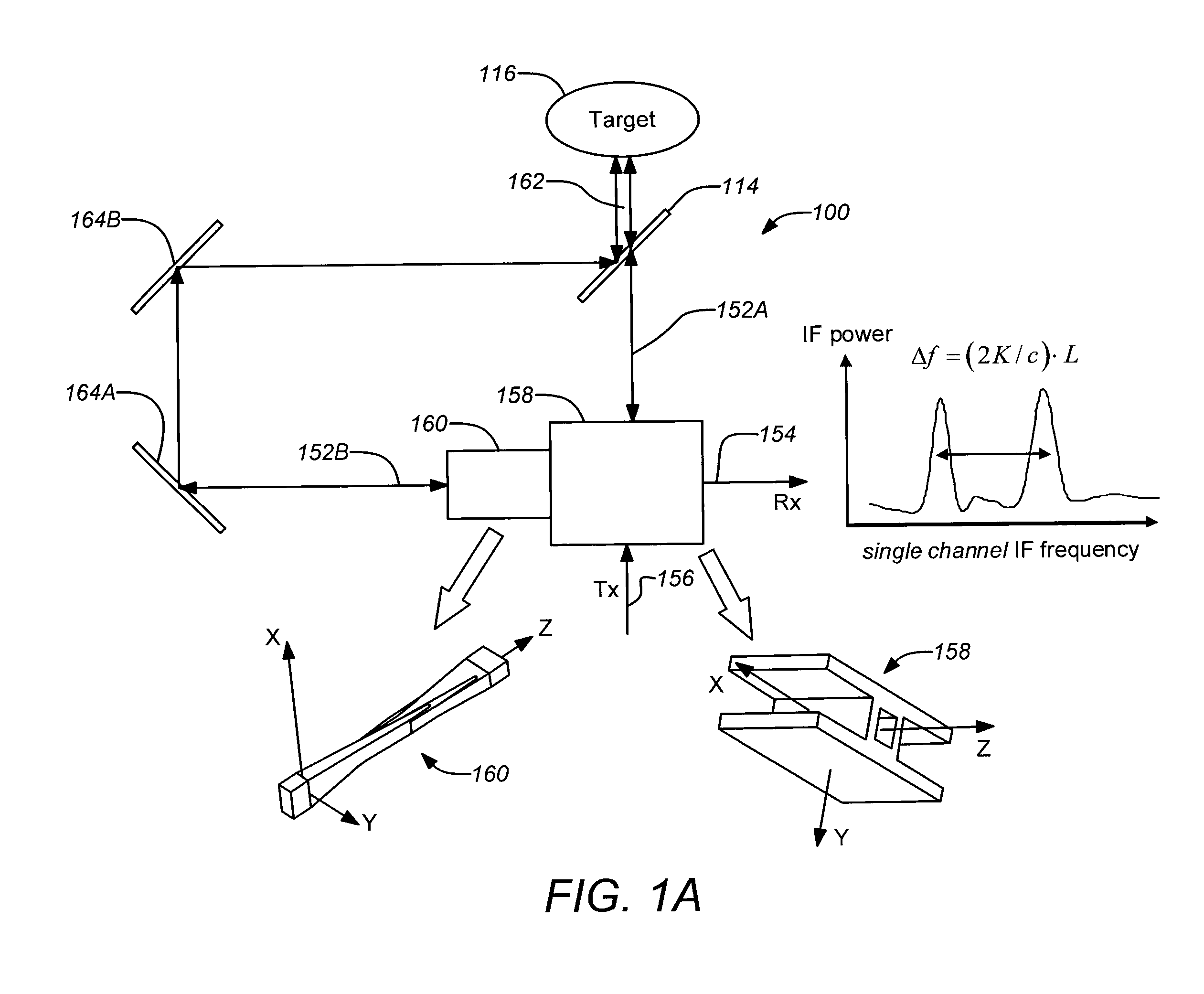
A three-dimensional imaging radar operating at high frequency e.g., 670 GHz radar using low phase-noise synthesizers and a fast chirper to generate a frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) waveform, is disclosed that operates with a multiplexed beam to obtain range information simultaneously on multiple pixels of a target. A source transmit beam may be divided by a hybrid coupler into multiple transmit beams multiplexed together and directed to be reflected off a target and return as a single receive beam which is demultiplexed and processed to reveal range information of separate pixels of the target associated with each transmit beam simultaneously. The multiple transmit beams may be developed with appropriate optics to be temporally and spatially differentiated before being directed to the target. Temporal differentiation corresponds to a different intermediate frequencies separating the range information of the multiple pixels. Collinear transmit beams having differentiated polarizations may also be implemented.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Copper barrier reflow process employing high speed optical annealing
InactiveUS20070032004A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
A method of forming a barrier layer for a thin film structure on a semiconductor substrate includes forming high aspect ratio openings in a base layer having vertical side walls, depositing a dielectric barrier layer comprising a dielectric compound of a barrier metal on the surfaces of the high aspect ratio openings including the vertical side walls and depositing a metal barrier layer comprising the barrier metal on the first barrier layer. The method further includes reflowing the metal barrier layer by (a) directing light from an array of continuous wave lasers into a line of light extending at least partially across the thin film structure, and (b) translating the line of light relative to the thin film structure in a direction transverse to the line of light.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
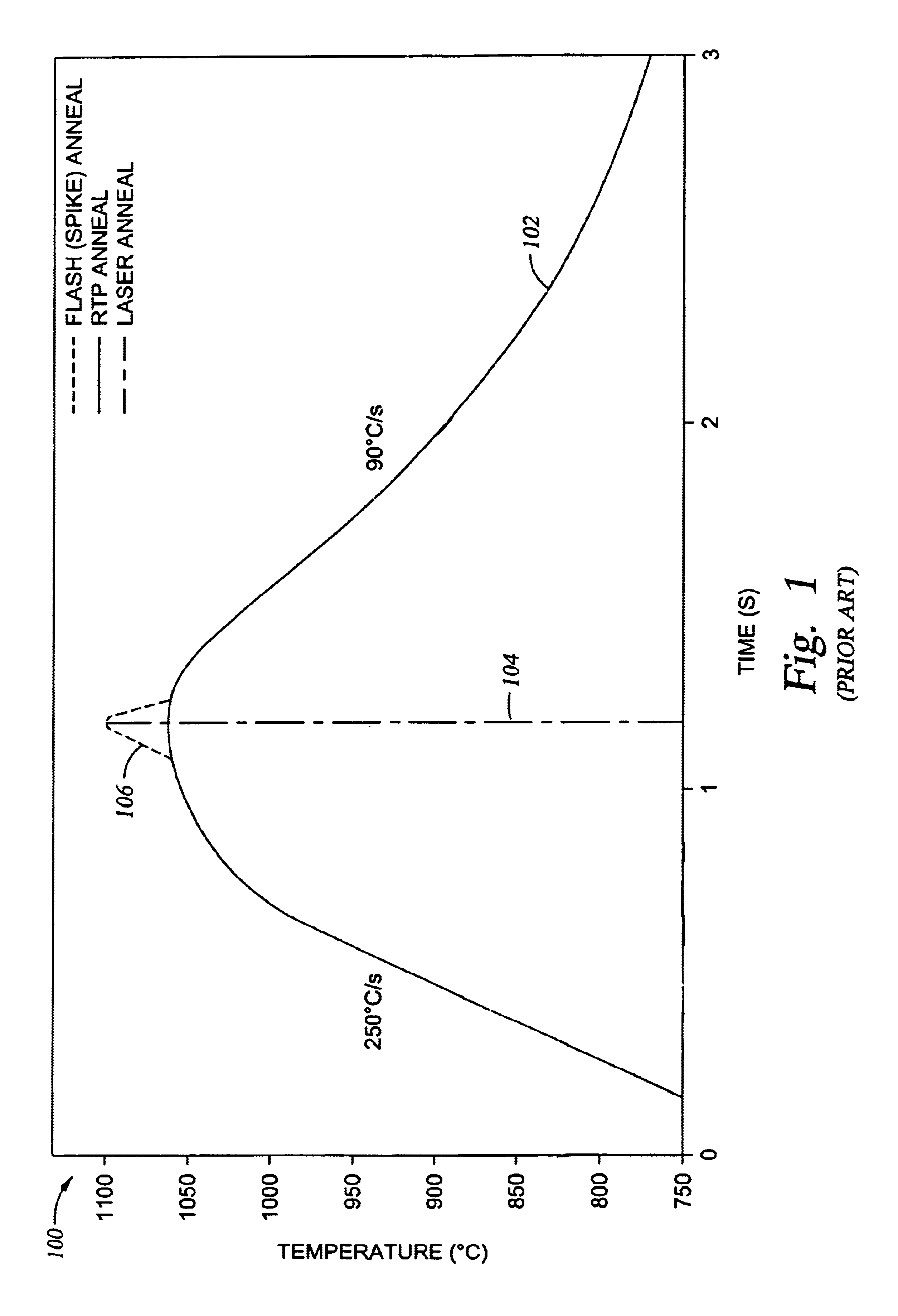
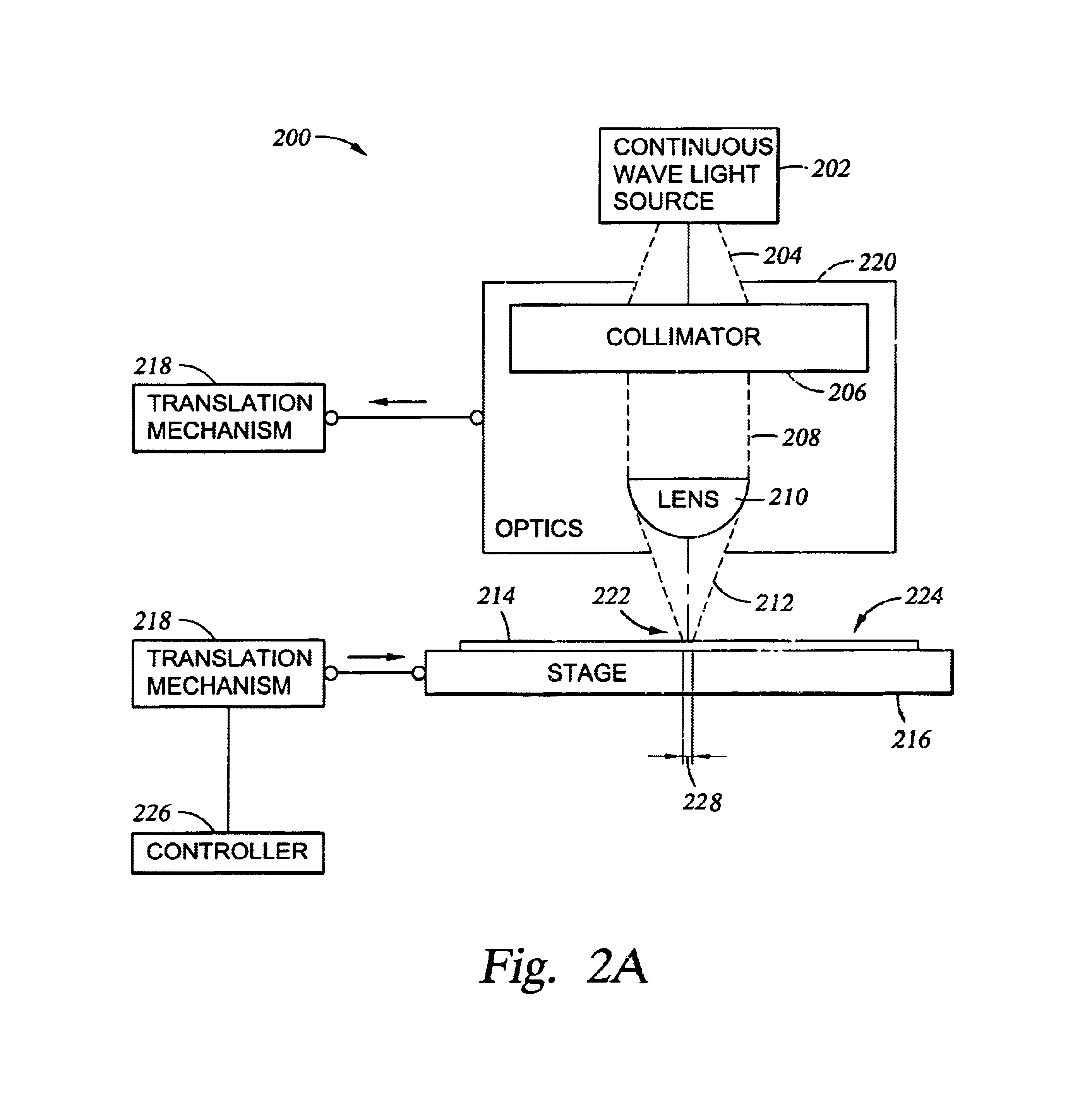
Thermal flux processing by scanning
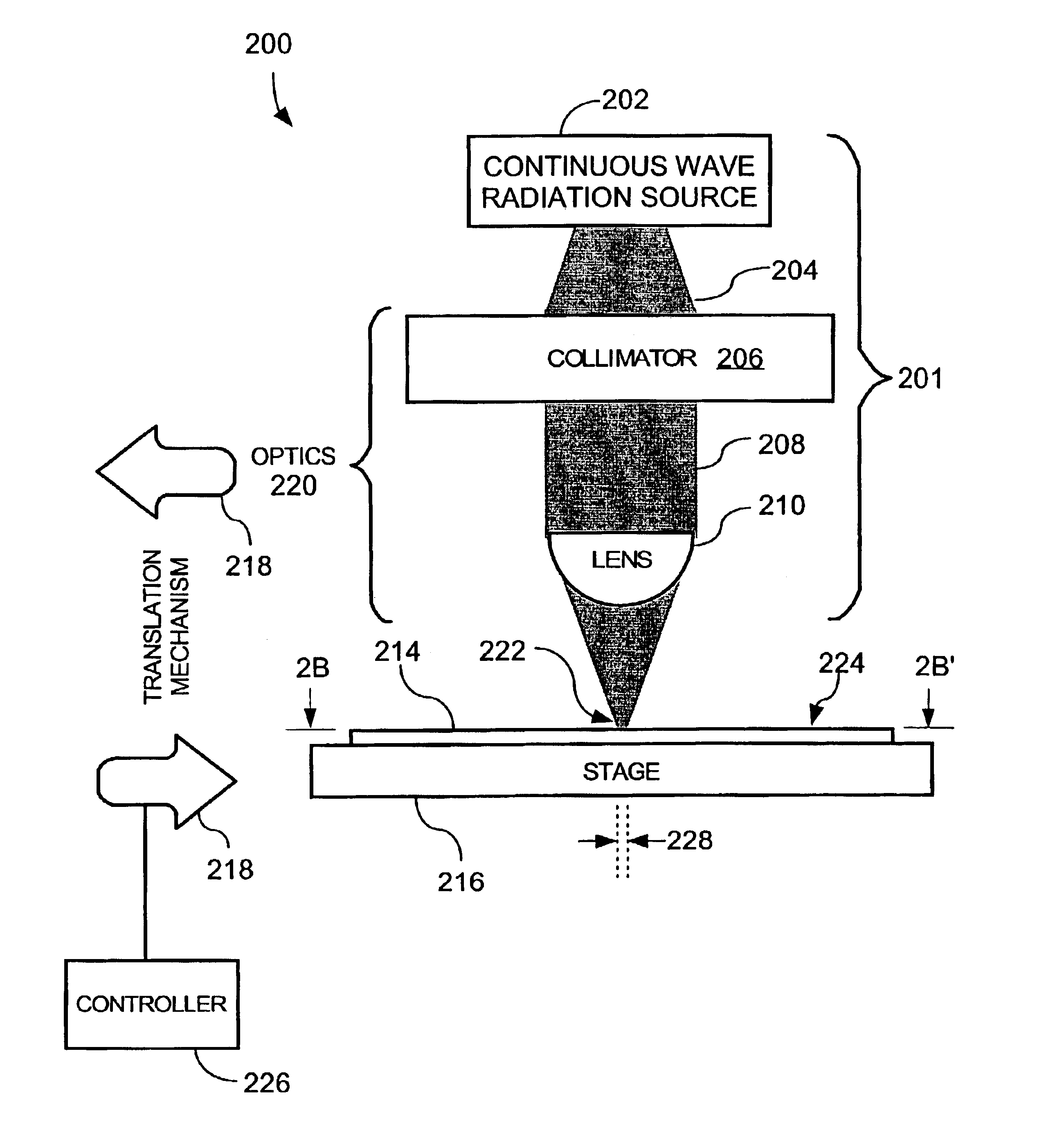
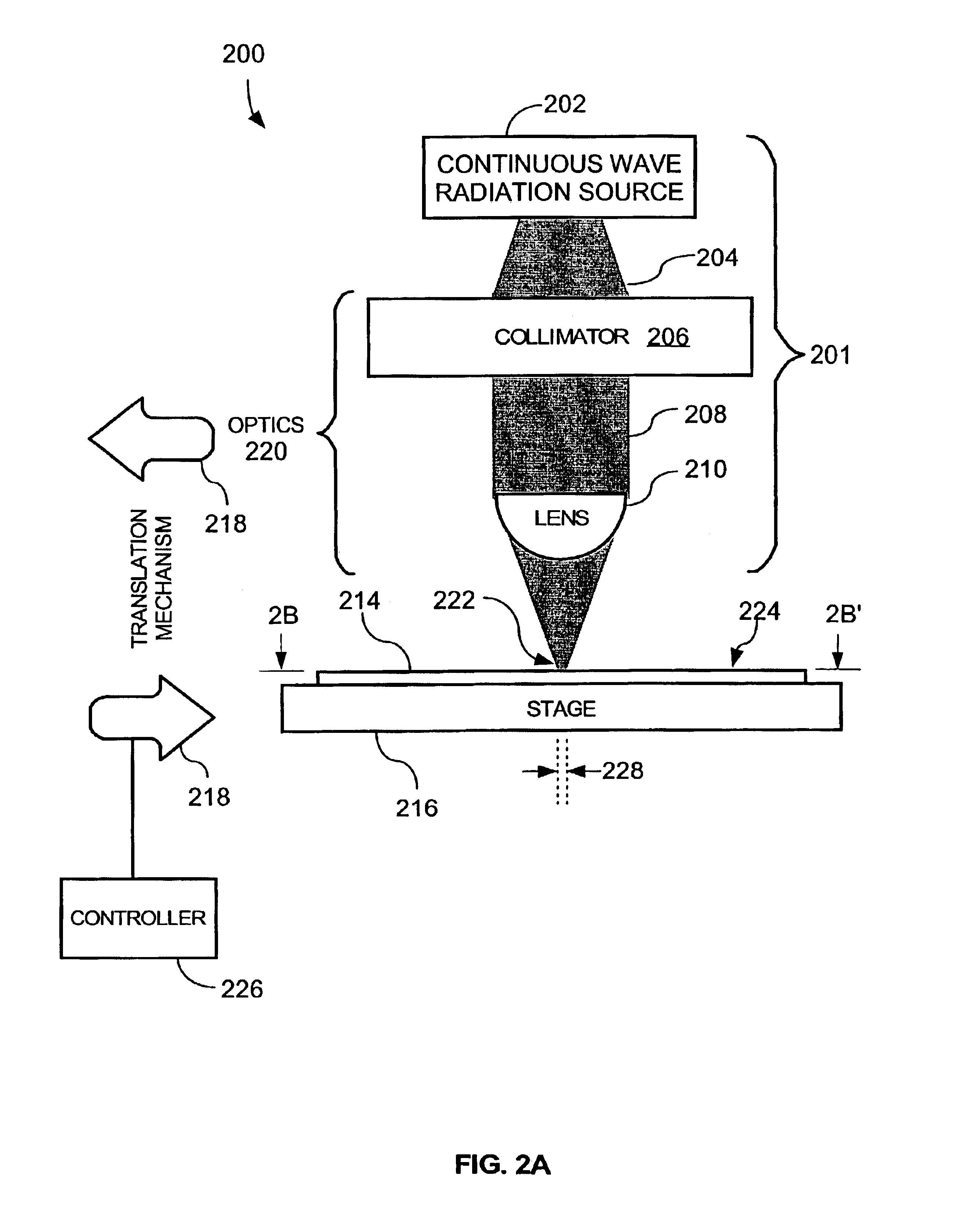
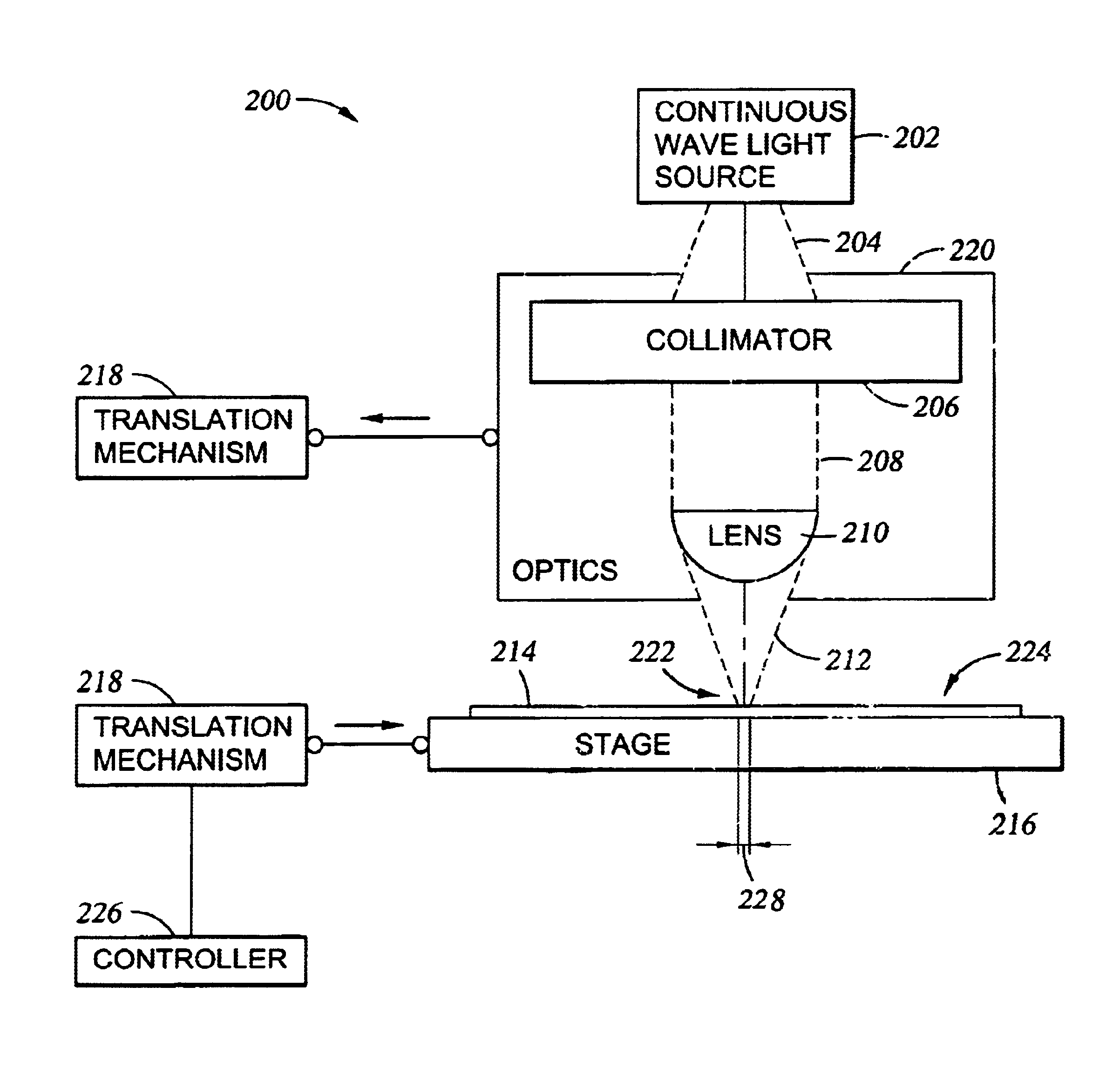
InactiveUS6987240B2Easy to controlReduced Power RequirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingHeat fluxComputerized system
The thermal processing device includes a stage, a continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source, a series of lenses, a translation mechanism, a detection module, and a computer system. The stage is configured to receive a substrate thereon. The continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source is disposed adjacent the stage, and is configured to emit continuous wave electromagnetic radiation along a path towards the substrate. The series of lenses is disposed between the continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source and the stage, and are configured to condense the continuous wave electromagnetic radiation into a line of continuous wave electromagnetic radiation on a surface of the substrate. The translation mechanism is configured to translate the stage and the line of continuous wave electromagnetic radiation relative to one another. The detection module is positioned within the path, and is configured to detect continuous wave electromagnetic radiation. The computer system is coupled to the detection module.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Laser Illuminator System
InactiveUS20130163627A1Improve thermal conductivityHeat dissipation fastSolid-state devicesSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLow inductance
An optical illuminator using Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) is disclosed. Optical modules configured using single VCSEL and VCSEL arrays bonded to a thermal submount to conduct heat away from the VCSEL array, are suited for high power and high speed operation. High speed optical modules are configured using single VCSEL or VCSEL arrays connected to a high speed electronic module on a common thermal submount or on a common Printed Circuit Board (PCB) platform including transmission lines. The electronic module provides low inductance current drive and control functions to operate the VCSEL and VCSEL array. VCSEL apertures are designed for a desired beam shape. Additional beam shaping elements are provided for VCSELs or VCSEL arrays, for desired output beam shapes and / or emission patterns. VCSEL arrays may be operated in continuous wave (CW) or pulse operation modes in a programmable fashion using a built-in or an external controller.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Method and apparatus for automotive radar sensor
InactiveUS20050225481A1Low costAdditional imaging capabilityAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSolid-state devicesEngineeringWaveguide
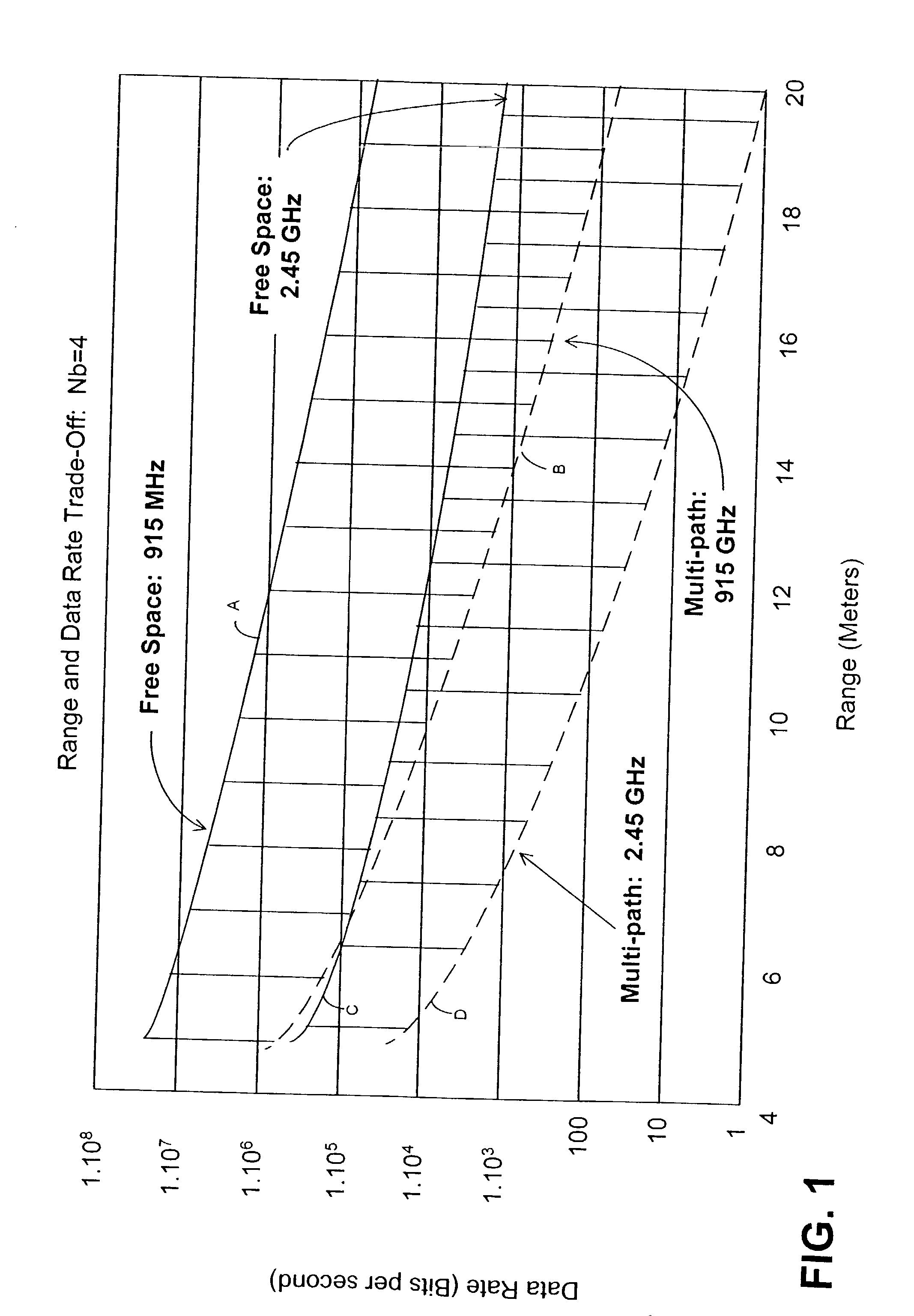
Methods and apparatus are presented which reduce the overall cost and increase the imaging capability for medium and long range automotive radar sensing applications through the combination of a high signal-to-noise ratio and wide dynamic range radar waveform and architecture, antenna arrangement, and a low cost packaging and interconnection method. In accordance with aspects of the present invention, one way a high signal-to-noise ratio and wide dynamic range imaging radar with reduced cost can be achieved is through the combination of a pulsed stepped-frequency-continuous-wave waveform and electrically beam-switched radar architecture, utilizing a planar package containing high-frequency integrated circuits as well as integrated high-frequency waveguide coupling ports, coupled to a multi-beam waveguide-fed twist-reflector narrow beam-width antenna. Other methods and apparatus are presented.
Owner:GHZ TR CORP
Optical fiber switch
Optical fiber switches operated by electrical activation of at least one laser light modulator through which laser light is directed into at least one polarizer are used for the sequential transport of laser light from a single laser into a plurality of optical fibers. In one embodiment of the invention, laser light from a single excitation laser is sequentially transported to a plurality of optical fibers which in turn transport the laser light to separate individual remotely located laser fuel ignitors.The invention can be operated electro-optically with no need for any mechanical or moving parts, or, alternatively, can be operated electro-mechanically. The invention can be used to switch either pulsed or continuous wave laser light.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
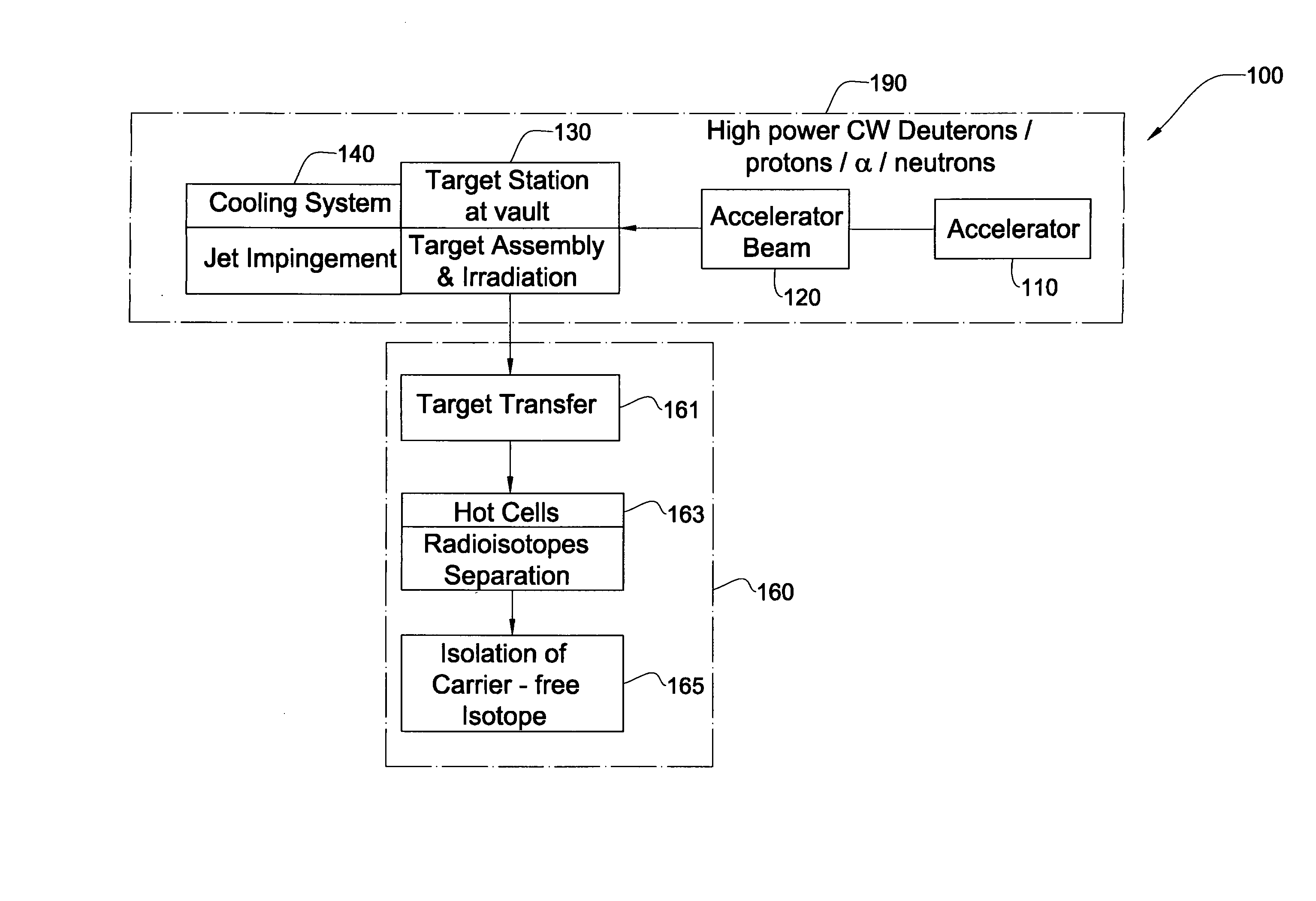
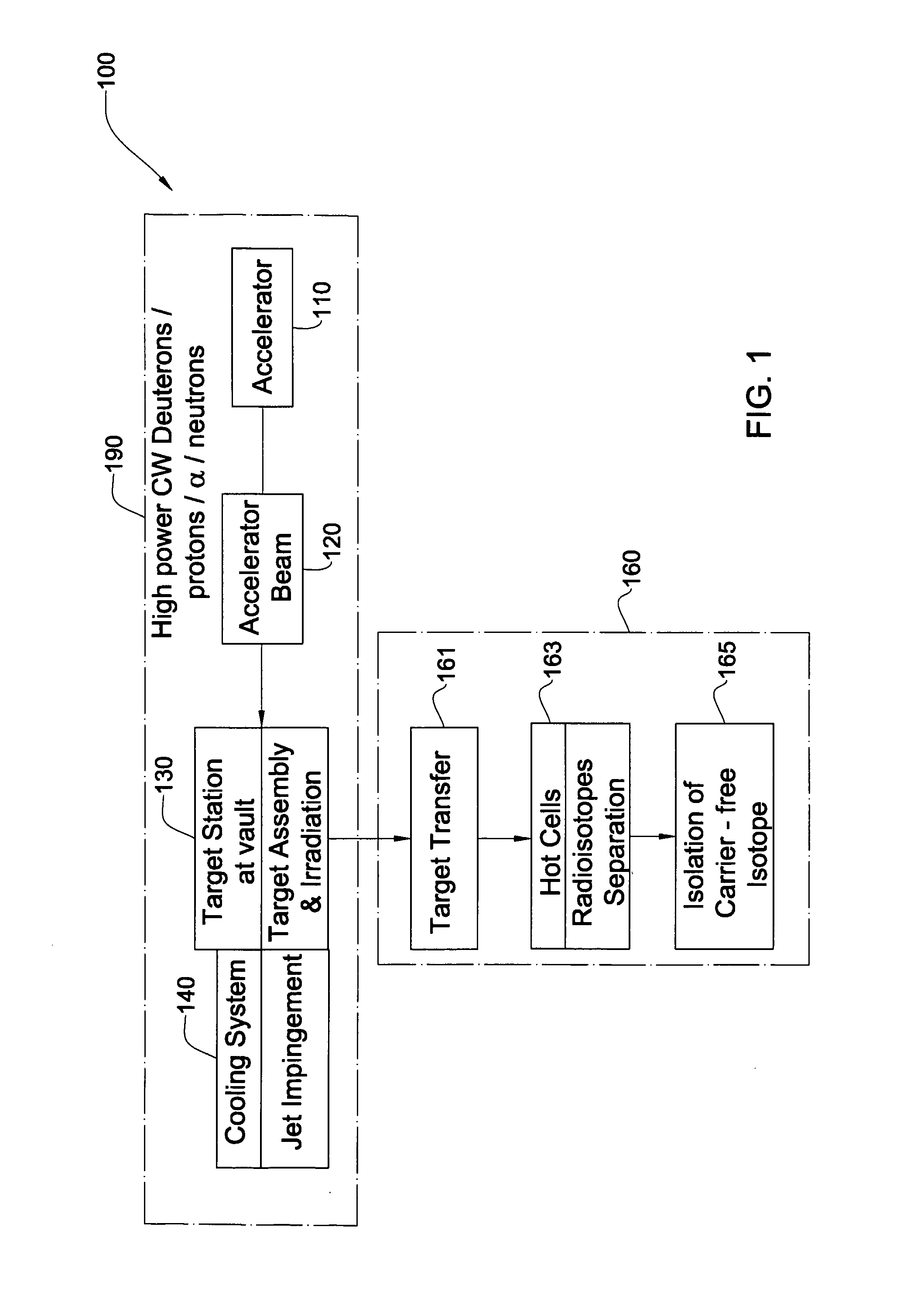
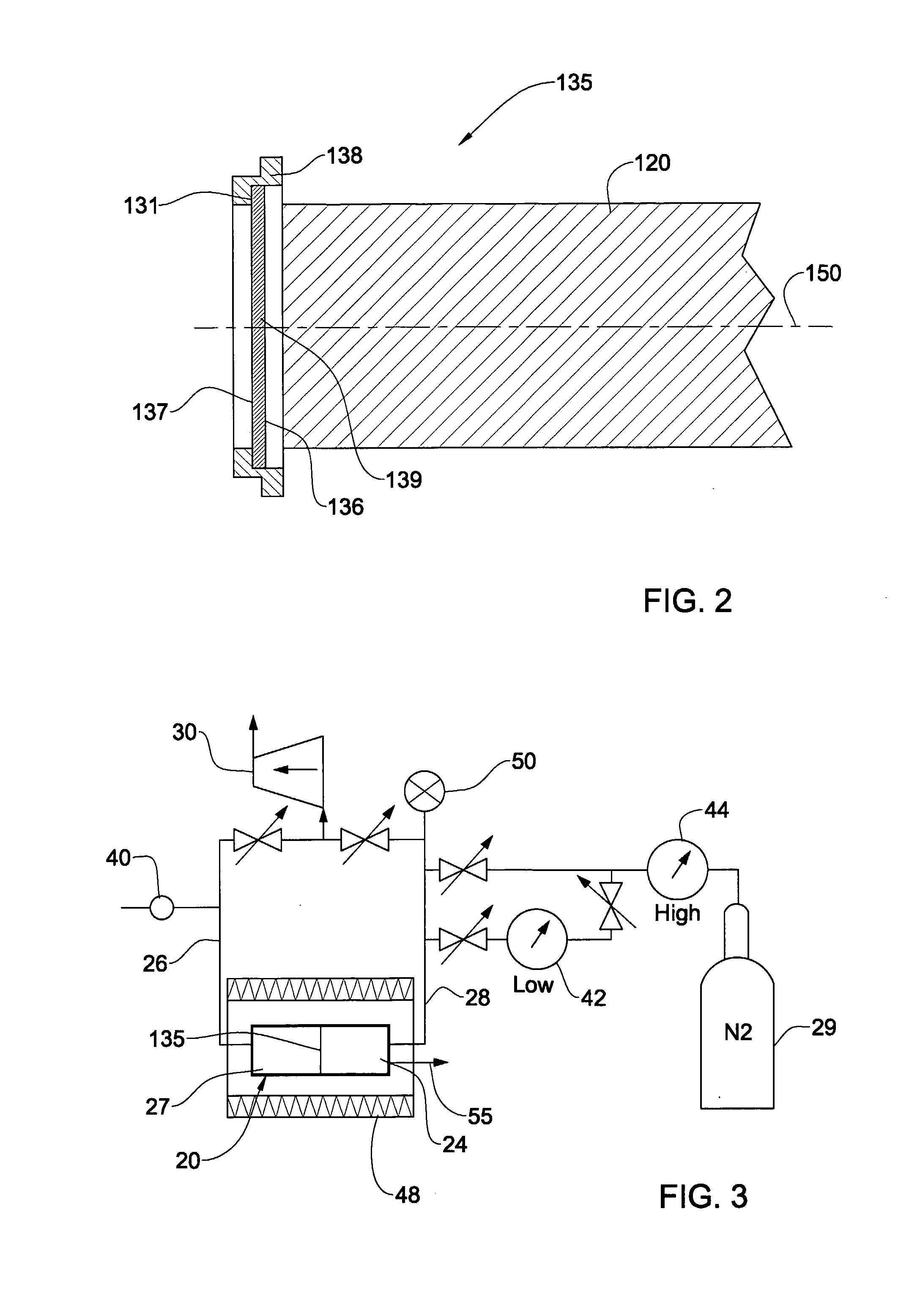
Method And System For Production Of Radioisotopes, And Radioisotopes Produced Thereby
InactiveUS20070297554A1Avoid communicationAvoid contaminationConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear targetsHeat fluxParticle beam
A system and method for the production of radioisotopes by the transmutation of target isotopic material bombarded by a continuous wave particle beam. An ion source generates a continuous wave ion beam, irradiating an isotope target, which is cooled by transferring heat away from the target at heat fluxes of at least about 1 kW / cm2.
Owner:SOREQ NUCLEAR RES CENT ISRAEL ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION
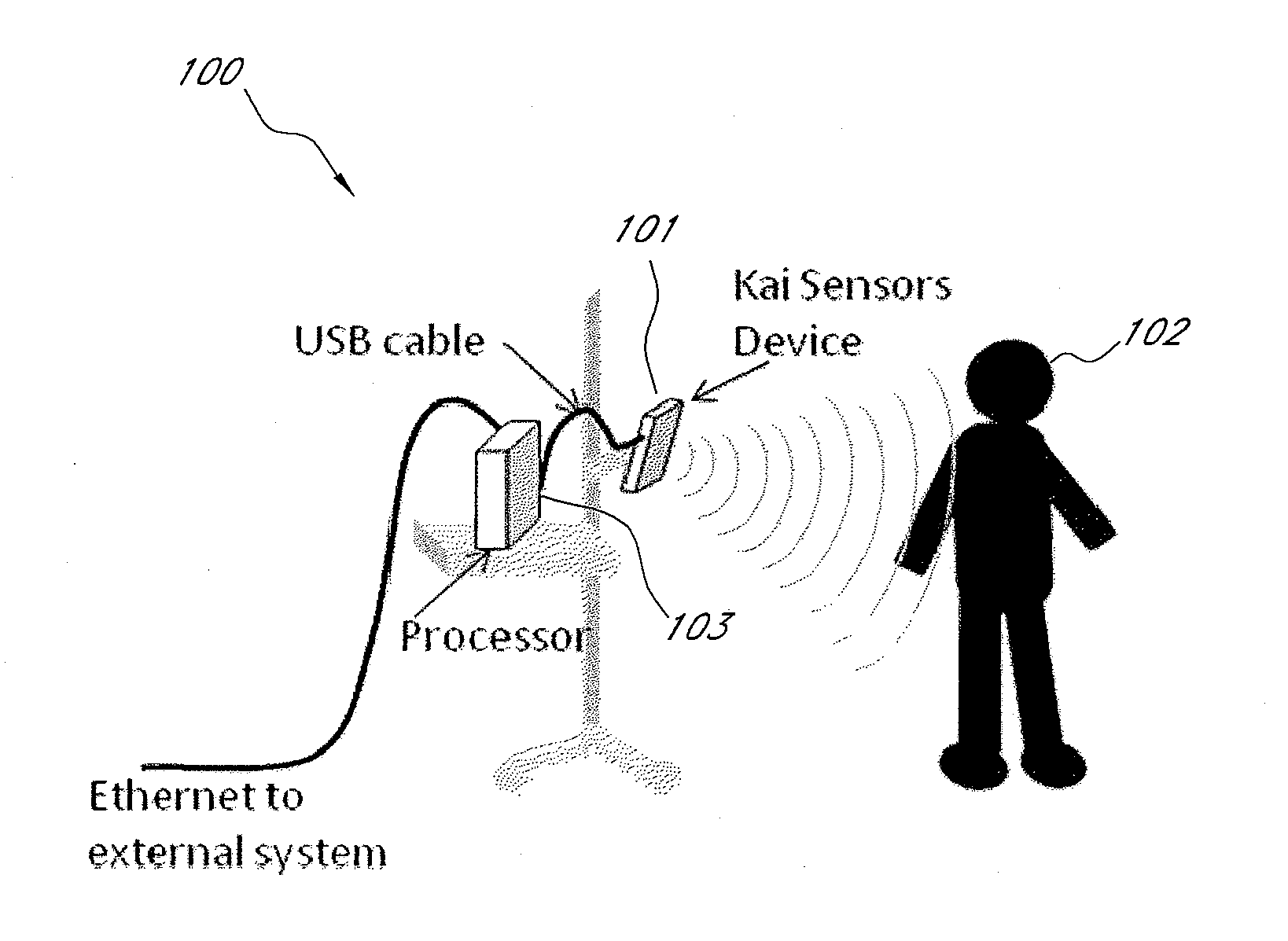
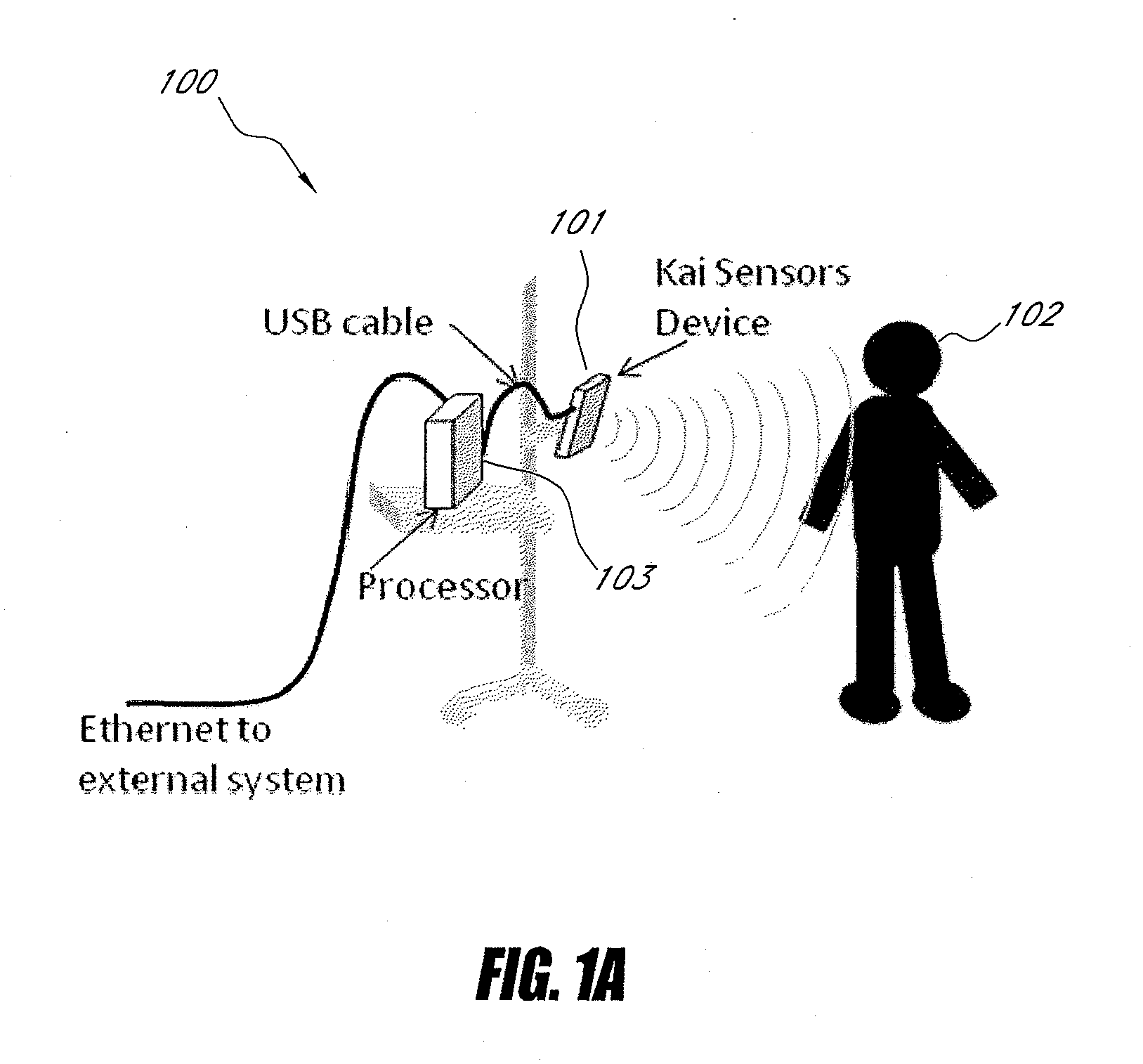
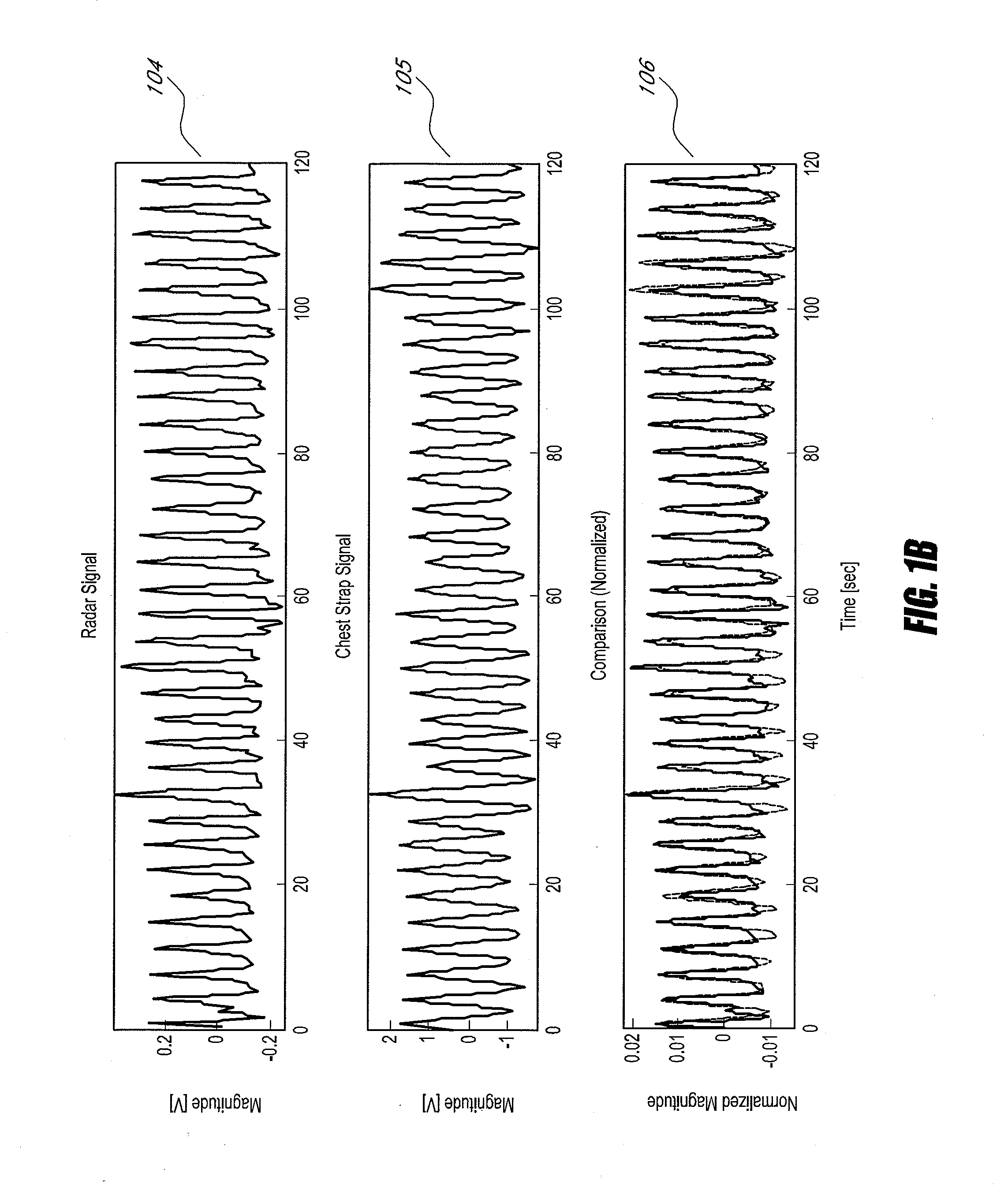
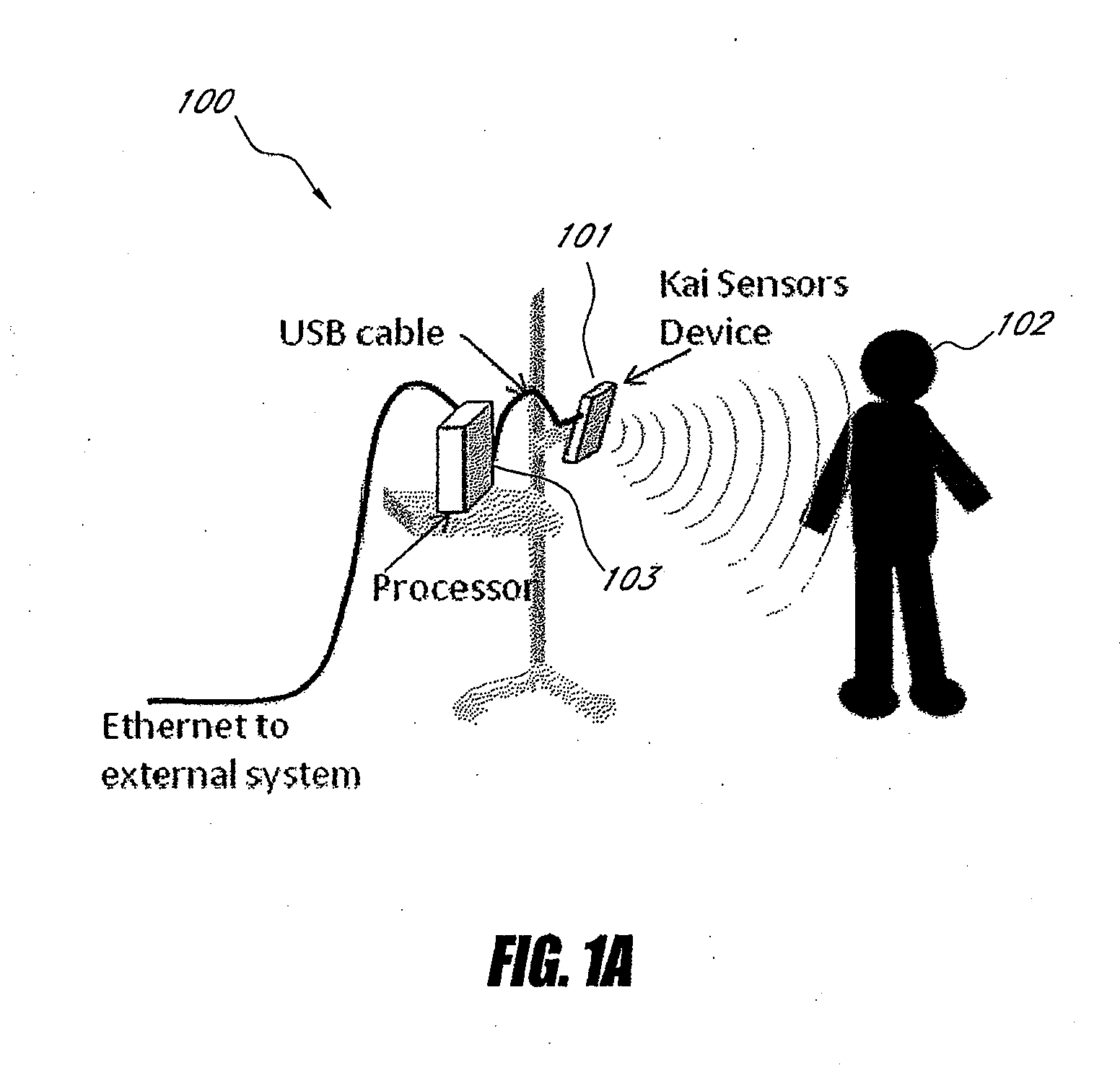
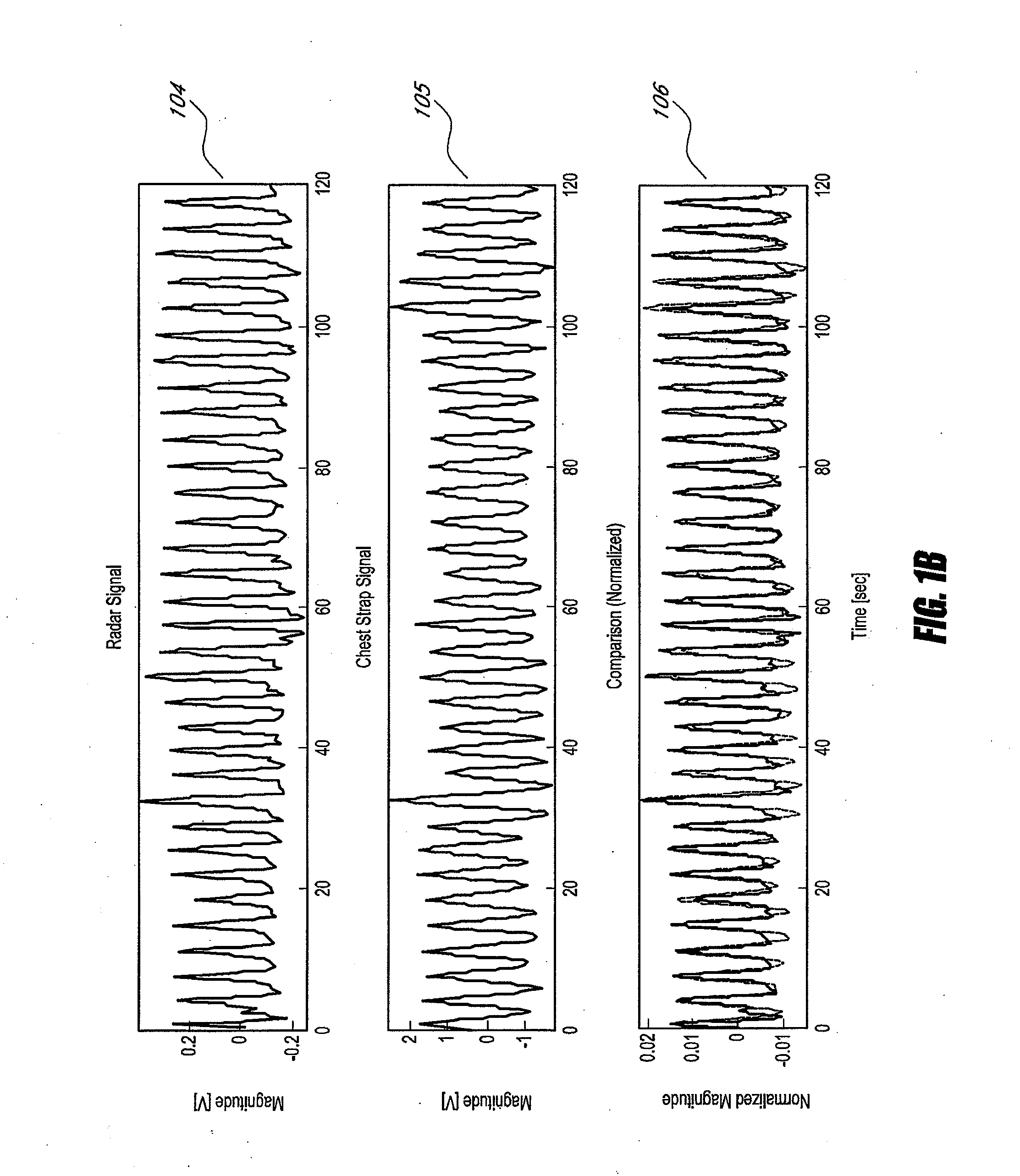
Systems and methods for non-contact multiparameter vital signs monitoring, apnea therapy, sway cancellation, patient identification, and subject monitoring sensors
InactiveUS20120022348A1Minimize signal powerElectrotherapyCatheterElectromagnetic radiationDigitization
Aspects of the of the disclosure relate to a non-contact physiological motion sensor and a monitor device that can incorporate use of the Doppler effect. A continuous wave of electromagnetic radiation can be transmitted toward one or more subjects and the Doppler-shifted received signals can be digitized and / or processed subsequently to extract information related to the cardiopulmonary motion in the one or more subjects. The extracted information can be used, for example, to determine apneic events and / or to provide apnea therapy to subjects when used in conjunction with an apnea therapy device. In addition, methods of use are disclosed for sway cancellation, realization of cessation of breath, integration with multi-parameter patient monitoring systems, providing positive providing patient identification, or any combination thereof.
Owner:KAI MEDICAL
Selective Deposition Modeling Using CW UV LED Curing
ActiveUS20090267269A1Auxillary shaping apparatus3D object support structuresUltravioletContinuous wave
A continuous-wave (CW) ultraviolet (UV) curing system for solid freeform fabrication (SFF) is provided, wherein the curing system is configured to provide an exposure of UV radiation for one or more layers of UV-curable material. One or more UV exposures may initiate curing of a curable material in the layer dispensed by a solid freeform fabrication apparatus. One approach to provide the single or multiple UV exposures is the use of one or more UV LEDs, which generate UV radiation without generating any substantial amounts of infrared (IR) radiation at the same time. This allows for the curing process to be energy efficient and also allows for the SFF system to be far less complex.
Owner:3D SYST INC
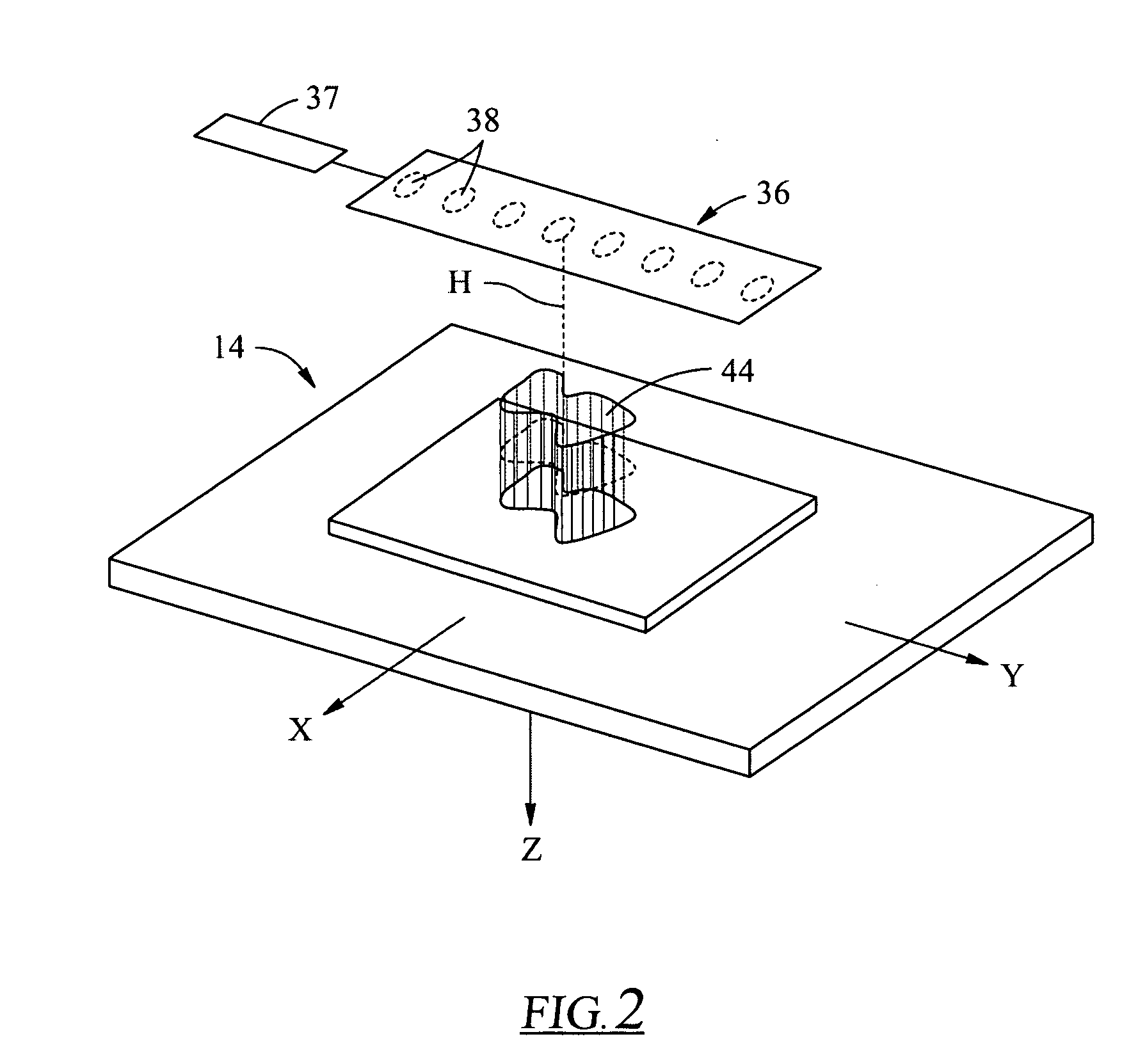
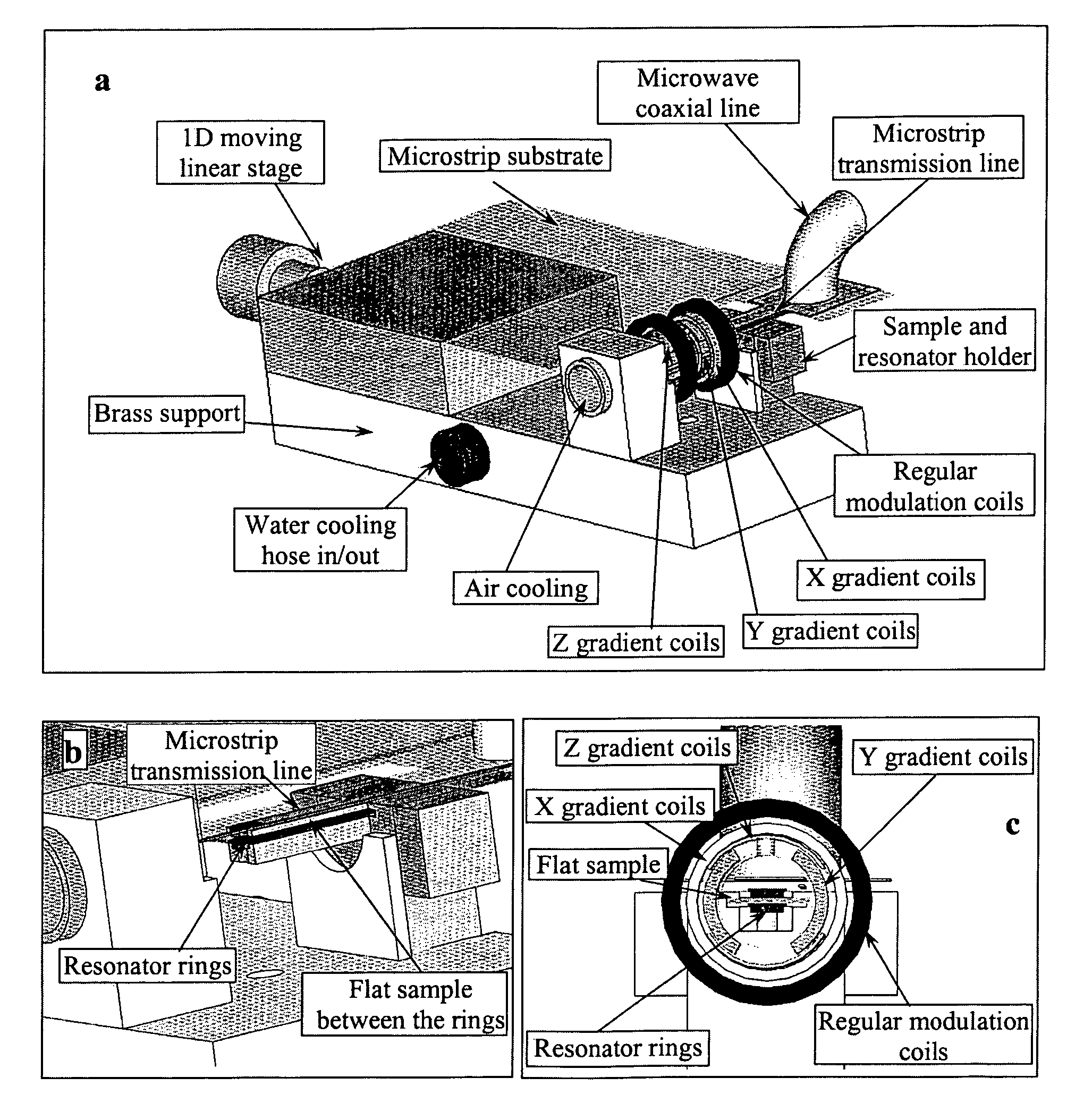
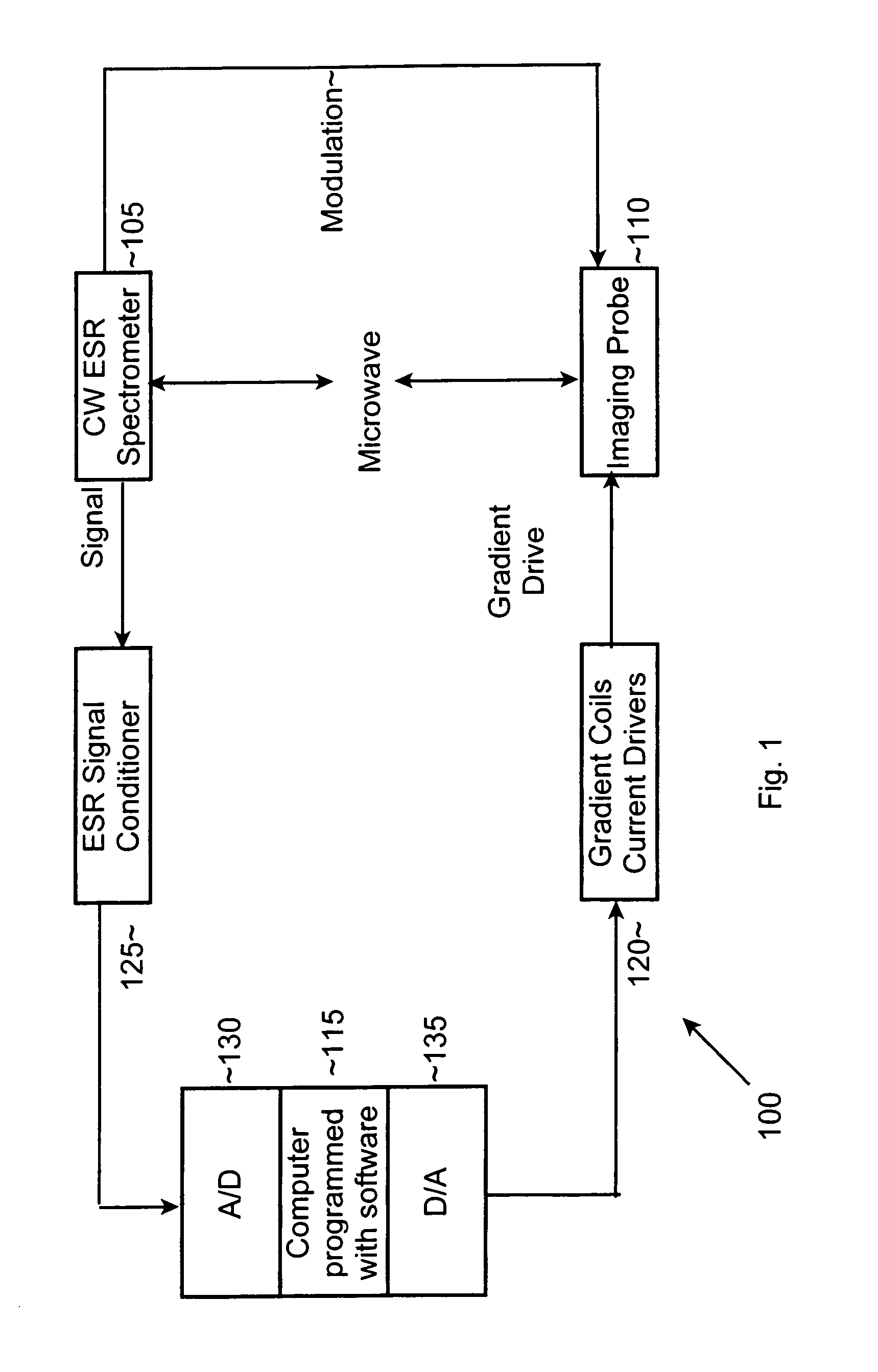
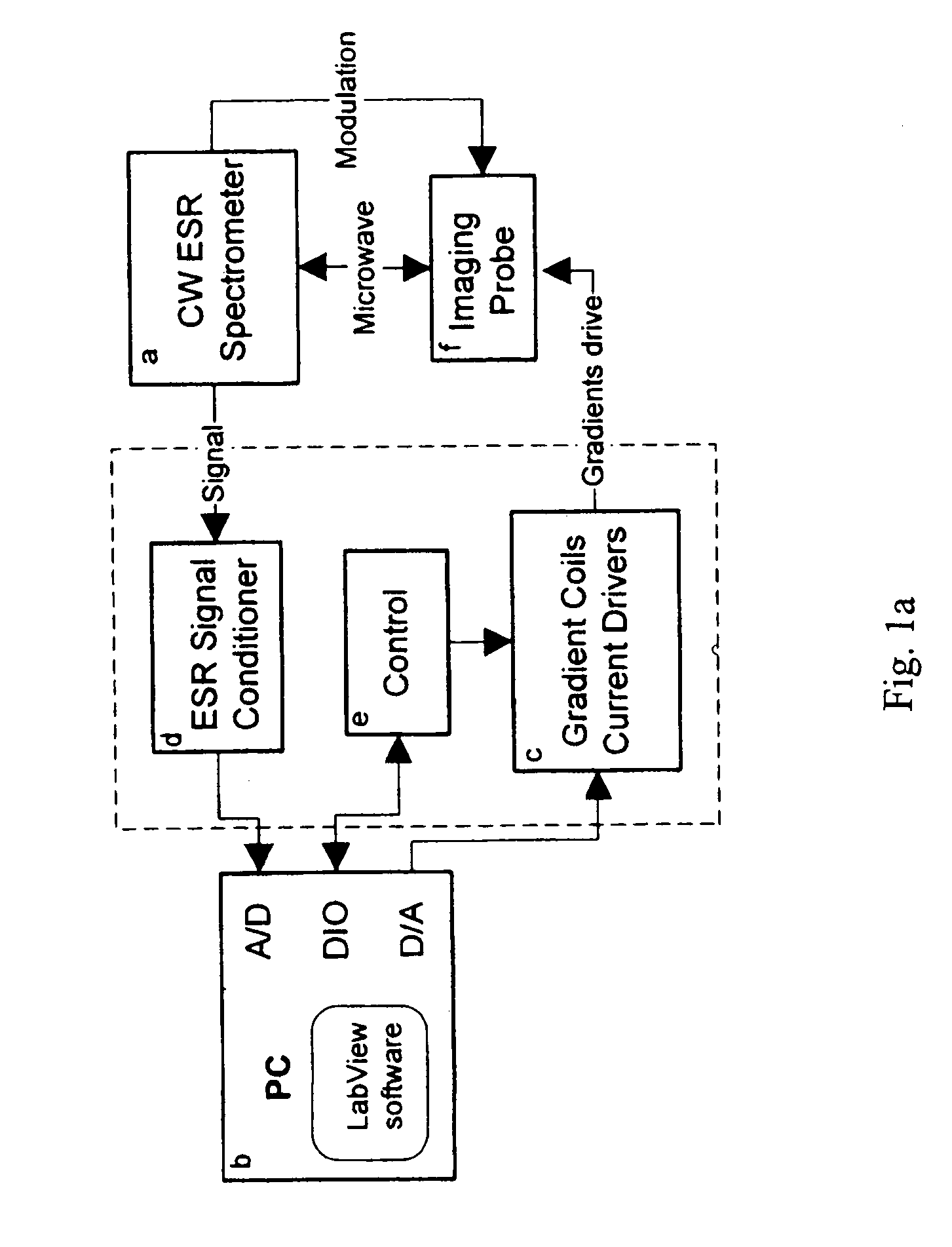
Electron spin resonance microscope for imaging with micron resolution
InactiveUS7403008B2Increase concentrationSmall effective volumeMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionPermittivityElectron
ESR microscope systems and methods for examining specimens using both continuous wave and pulsed modes in the 9 to 60 GHz range. The ESR microscope uses an image probe comprising gradient coils in addition to conventional modulation coils (in continuous wave mode) or magnetic field bias coils (in pulse mode), and a resonator constructed from high permittivity material. The systems and methods also involves the use of sample containers that permit the precise placement of samples in relation to the image probe. The microscope uses a microstrip or thin coaxial or dielectric antenna to obtain a high coupling coefficient to the specimen being imaged. The microscope systems provide resolution at the single micron level, and permit the observation of images comprising tens to hundreds of pixels for each of two or three dimensions in a few minutes. Novel stable radicals used as the imaging media are also described.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
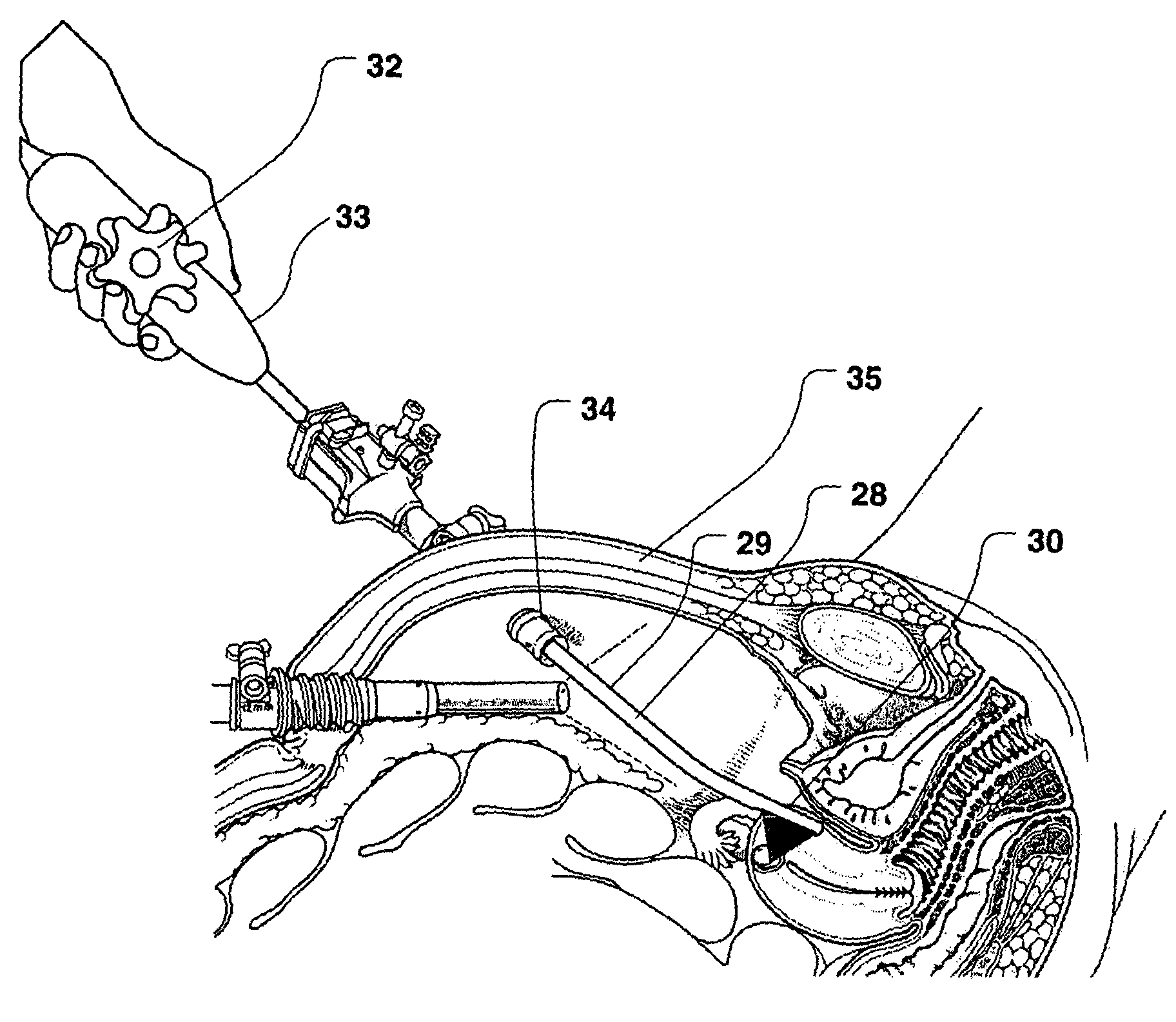
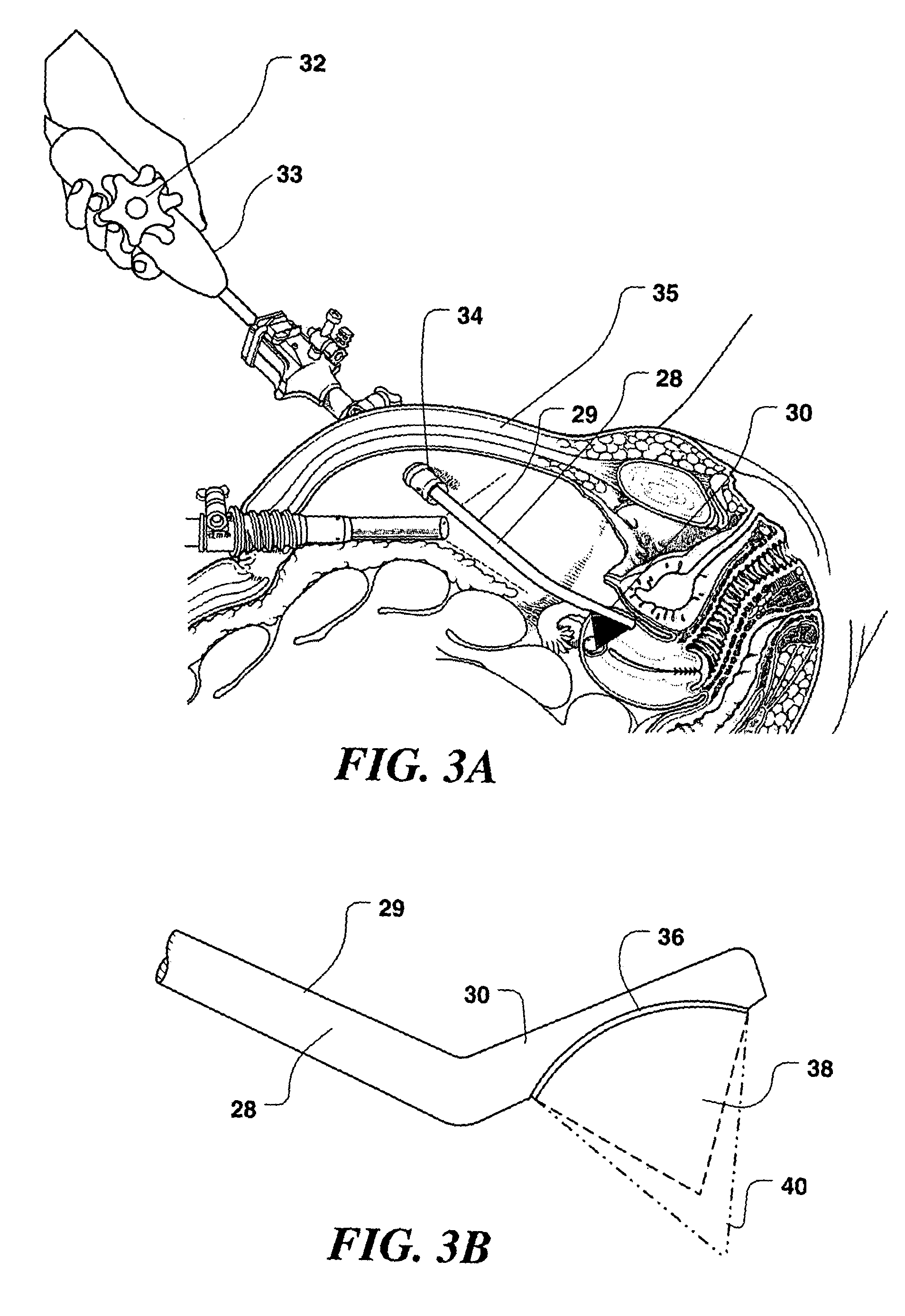
Method and device for sub-dermal tissue treatment
InactiveUS20050055018A1Avoid heat damageAvoid tissue damageUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingCavitationHand held
System and method for non-invasive lysis of sub-dermal tissue by means of focused ultrasonic energy, the system comprising: a source of ultrasonic energy adapted to operate in continuous wave mode and to focus ultrasonic energy in a focal zone within the sub-dermal tissue, the ultrasonic energy being adapted to induce tissue cavitation in the focal zone; means for continuous displacement of the source over the skin surface; and means for determining a safe speed for the displacement, the safe speed allowing to avoid thermal tissue damage. The source of ultrasonic energy is accommodated in a hand-held applicator including a wheeled traction system powered by an electric drive.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Systems and methods for non-contact multiparameter vital signs monitoring, apnea therapy, apnea diagnosis, and snore therapy
InactiveUS20130030257A1Minimize signal powerRestore muscle toneElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesMonitoring systemContinuous wave
Aspects of the of the disclosure relate to a non-contact physiological motion sensor and a monitor device that can incorporate use of the Doppler effect. A continuous wave of electromagnetic radiation can be transmitted toward one or more subjects and the Doppler-shifted received signals can be digitized and / or processed subsequently to extract information related to the cardiopulmonary motion in the one or more subjects. The extracted information can be used, for example, to determine apneic events and / or snoring events and / or to provide apnea or snoring therapy to subjects when used in conjunction with an apnea or snoring therapy device. In addition, methods of use are disclosed for sway cancellation, realization of cessation of breath, integration with multi-parameter patient monitoring systems, providing positive providing patient identification, or any combination thereof.
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
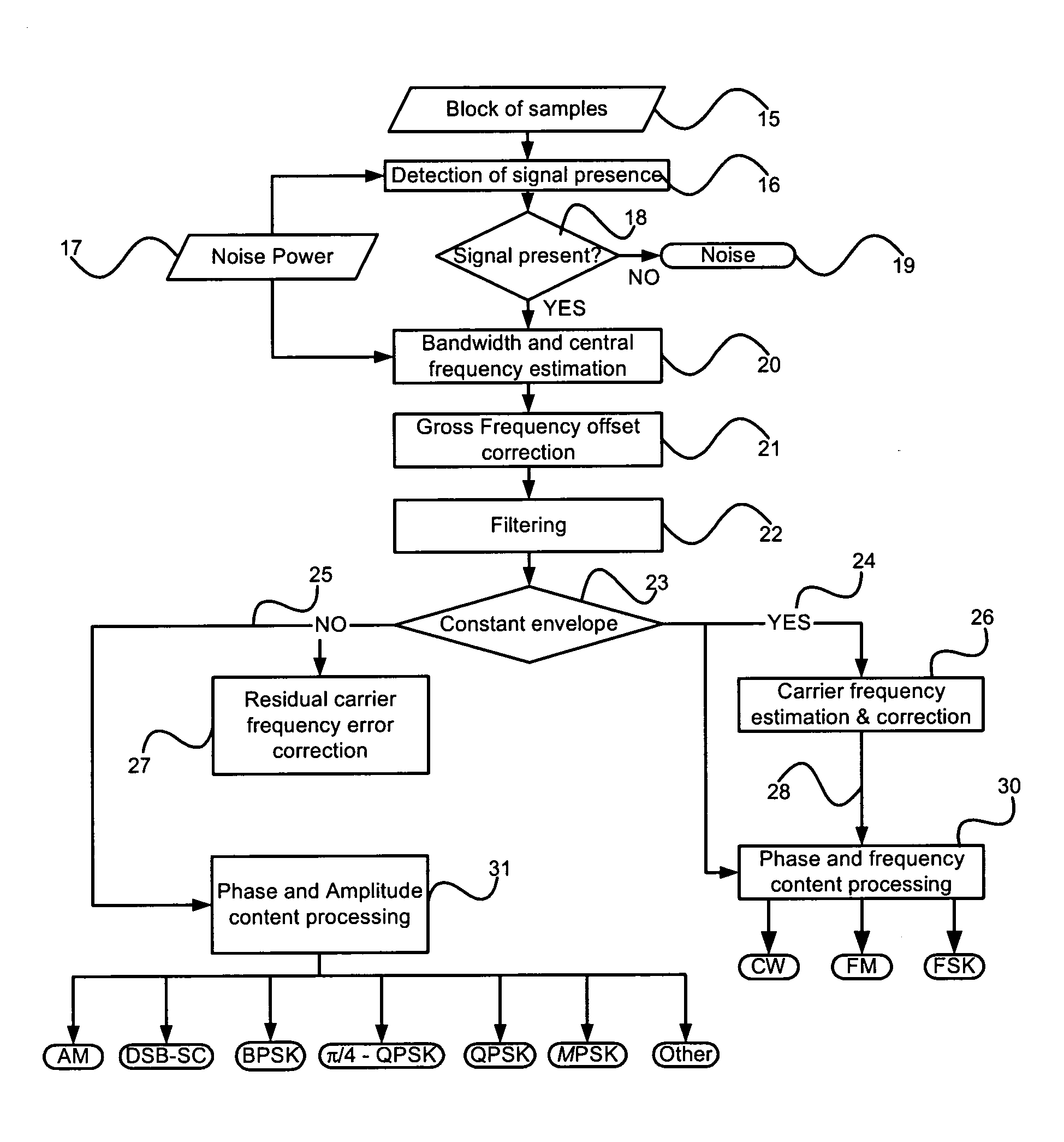
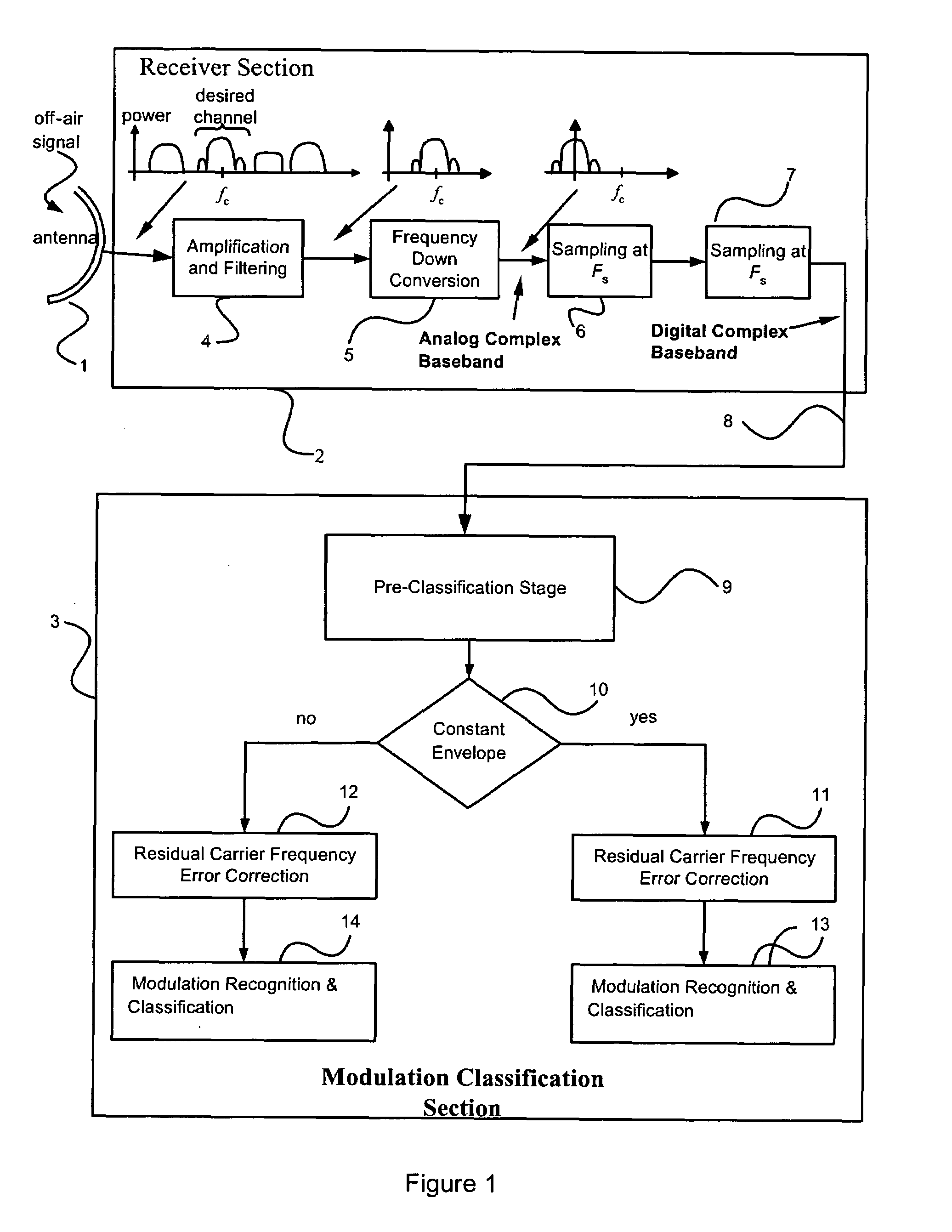
Method and system for detecting and classifying the modulation of unknown analog and digital telecommunications signals
InactiveUS7428270B1Accurate classificationHigh precisionModulation type identificationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal classificationCarrier signal
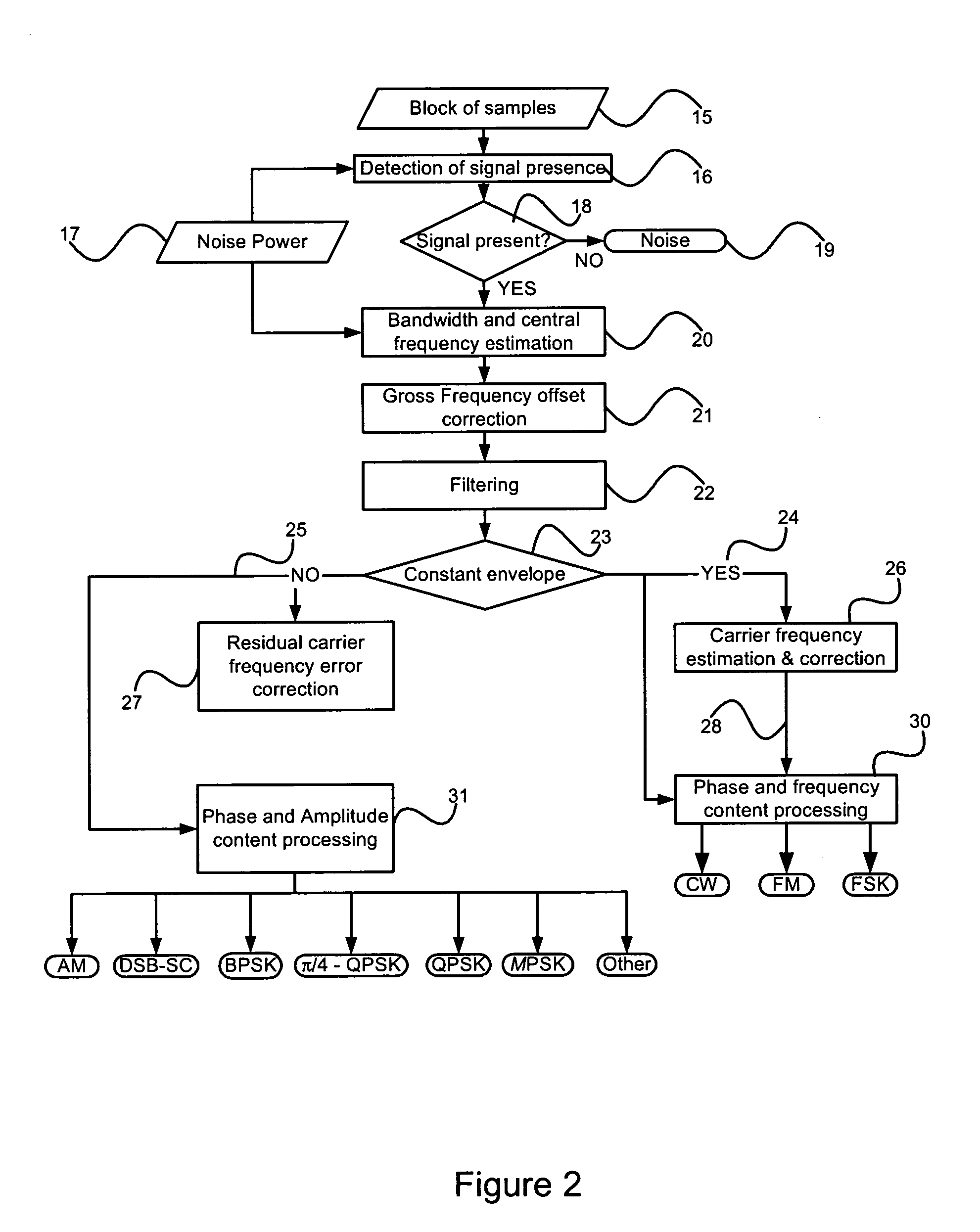
Disclosed is a unique system and method for recognizing the type of modulation embedded in an unknown complex baseband signal, comprising a receiver section for extracting the complex baseband signal from a modulated signal having a carrier frequency, and comprising an orderly series of signal processing functions for (a) estimating the bandwidth of the unknown signal, (b) removing the out-of-band noise and correcting gross carrier frequency errors, (c) discriminating between constant envelope and irregular envelope signals, (d) estimating and correcting residual carrier frequency errors, (e) classifying a constant envelope signal into one of the following modulation formats: {Continuous Wave (CW), Frequency Modulation (FM), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)}, and (f) classifying an irregular envelope signal into one of the following modulation formats: {Amplitude Modulation (AM), Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC), Binary Shift Keying (BPSK), Quaternary Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), π / 4-shifted QPSK, M-ary PSK (MPSK), and OTHER classes}.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Short-range frequency-modulation continuous wave FMCW radar anti-interference method
ActiveCN101089653AWork reliablyEasy to implementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionContinuous waveFrequency modulation
An anti-interfering method of short-range FMCW radar includes designing a set of pseudo-random code according to occasion of radar, distributing different pseudo-random code to different radar operated at different area, applying different pseudo-random code to modulate frequency start-point of FM emission signal for the same radar on each cycle, making frequency-mixture on received echo signal by utilizing emission signal, using filter to filter off interference signal and applying FM signal processing means to treat reserved usable signal for obtaining object distance and speed information in high resolution.
Owner:南京精益安防系统科技有限公司
Radar microsensor for detection, tracking, and classification
InactiveUS20080106460A1Noise minimizationRemove unwanted amplitude modulationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsImage resolution
The subject invention pertains to a frequency modulation continuous wave (FMCW) radar system. Embodiments relate to methods of improving the performance of such a FMCW system and improving the value of the information provided by such a FMCW system. In an embodiment of the subject invention, the IF level can be monitored while sweeping the frequency of the system through at least a portion of the frequency range of the system. In a specific embodiment, the system is then set to the frequency that produces the minimum IF level, which is the frequency that produces the minimum AM signal level. Embodiments of the invention pertain to techniques for expediting the adaptation of the comb filter to the signal when the system is turned on. In an embodiment, in order to reduce the number of detection calculations a processor performs every frame, a method of quickly determining the largest peaks in the RDM is implemented. Embodiments of the subject invention relate to a method for processing a radar signal that classifies two or more targets. A specific embodiment of a method for processing the radar signal classifies a human target or other target(s) using amplitude values in time-consecutive range-Doppler maps. Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method for processing a radar signal for improving the performance of FMCW detection, tracking, and classification algorithms. Embodiments improve such performance by increasing the SNR and velocity measurement resolution of slow moving targets while minimizing DSP computational and memory requirements in two-dimensional FFT range-velocity processing.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Thermal flux processing by scanning
InactiveUS7005601B2Easy to controlShort annealing timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingHeat fluxContinuous wave
The thermal flux processing device includes a continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source, a stage, optics, and a translation mechanism. The continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source is preferably a diode / s. The stage is configured to receive a semiconductor substrate thereon. The optics are preferably disposed between the continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source and the stage. Also, the optics are configured to focus continuous wave electromagnetic radiation from the continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source into a line of continuous wave electromagnetic radiation on an upper surface of the semiconductor substrate. A length of the line of continuous wave electromagnetic radiation extends across an entire width of the semiconductor substrate. The translation mechanism is configured to translate the stage and the line of continuous wave electromagnetic radiation relative to one another, and preferably includes a chuck for securely grasping the substrate. A method for thermally processing a semiconductor substrate is also provided.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
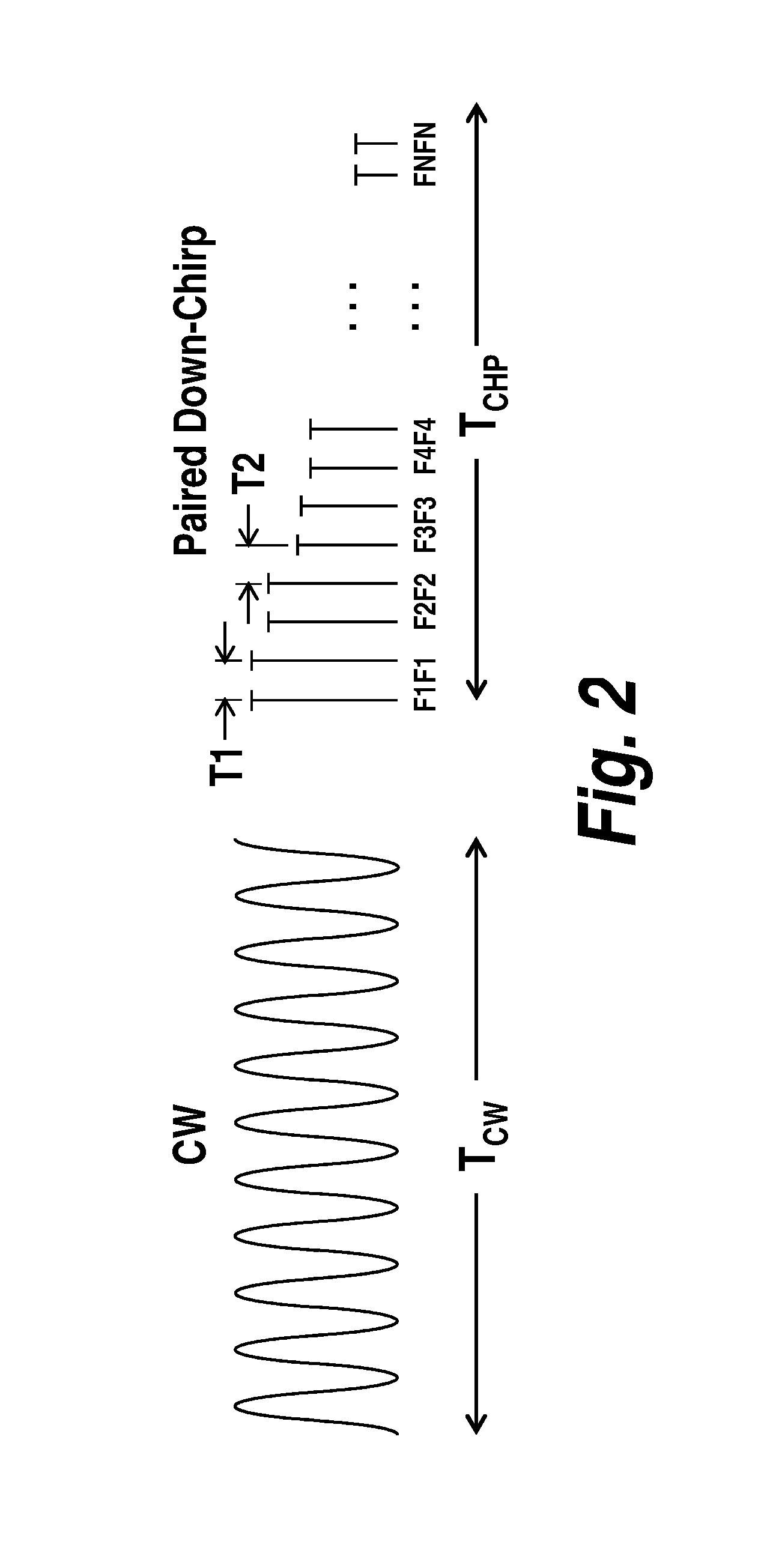
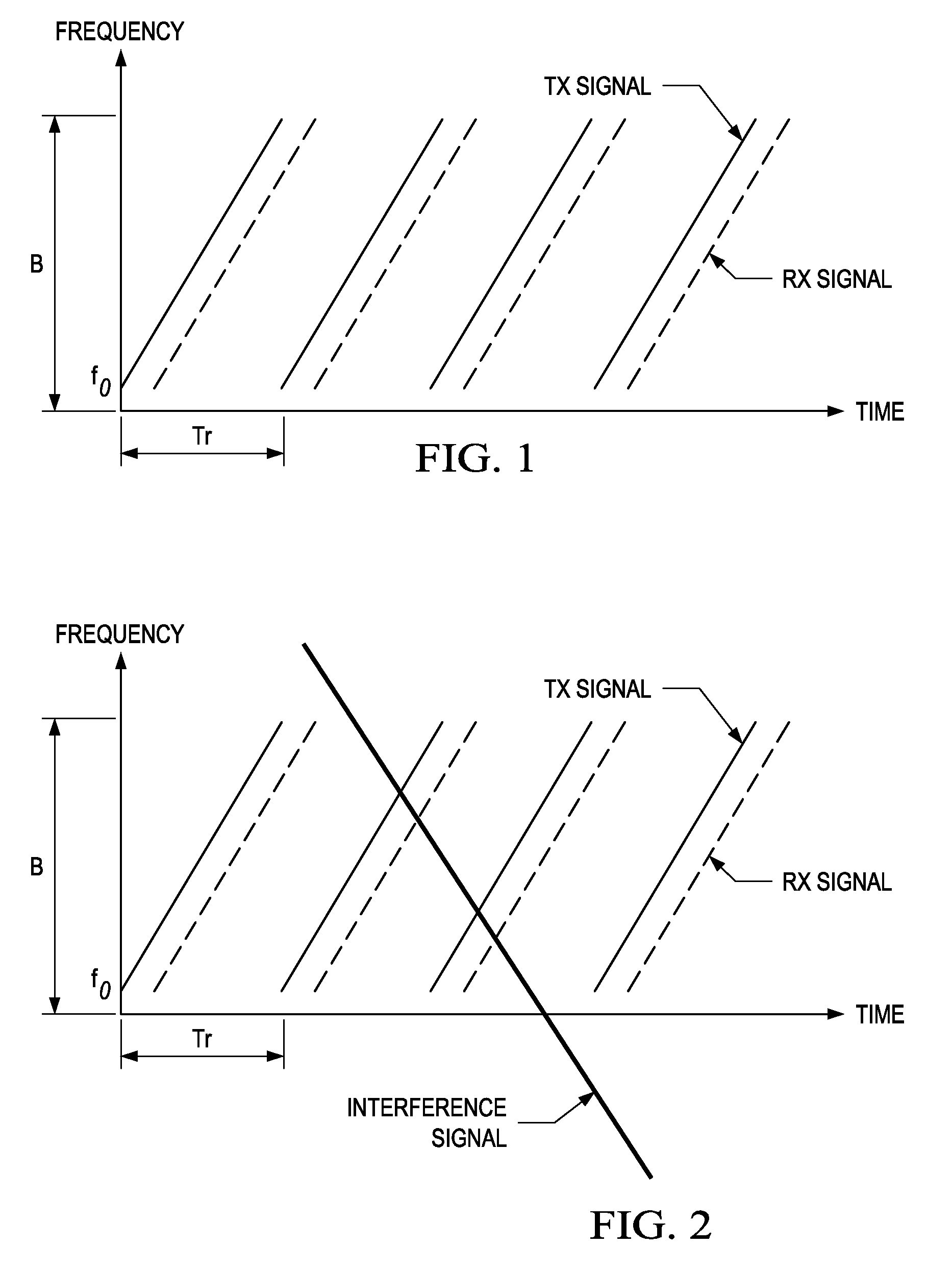
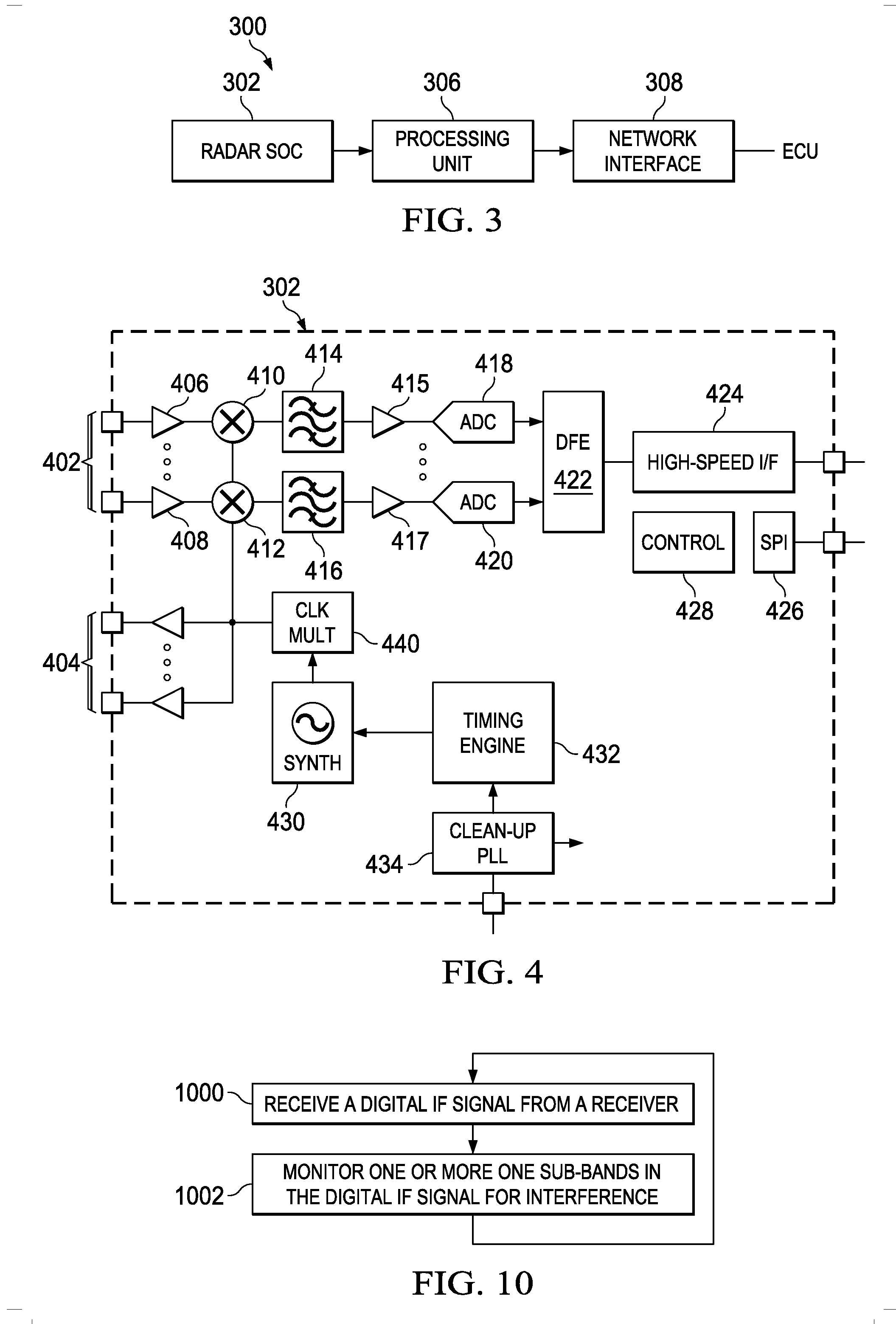
Radar system and method for determining range, relative velocity and bearing of an object using continuous-wave and chirp signals
Determining distance and relative speed includes a transmitter transmitting electromagnetic signals defined by a plurality of sections, a first section comprising a continuous-wave (CW) signal, a second section comprising a chirp electromagnetic signal, the chirp electromagnetic signal comprising a plurality of subsections. A detector detects reflected signals being the transmitted electromagnetic signals reflected from an object, and comprising a reflected CW signal and a reflected chirp signal. The detector detects the reflected signals by: (i) generating a plurality of samples of the reflected CW signal, and (ii) generating a plurality of samples of the reflected chirp signal. A processor determines a first set of phase differences among the plurality of samples of the reflected CW signal and a second set of phase differences among the plurality of samples of the reflected chirp signal, and processes the first and second sets of phase differences to determine the distance, relative speed and bearing.
Owner:ARRIVER SOFTWARE LLC (N D GES D STAATES DELAWARE)
Controlled high efficiency lesion formation using high intensity ultrasound
InactiveUS7470241B2Effective treatmentHigh strengthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound deviceTransducer
An ultrasound system used for both imaging and delivery high intensity ultrasound energy therapy to treatment sites and a method for treating tumors and other undesired tissue within a patient's body with an ultrasound device. The ultrasound device has an ultrasound transducer array disposed on a distal end of an elongate, relatively thin shaft. In one form of the invention, the transducer array is disposed within a liquid-filled elastomeric material that more effectively couples ultrasound energy into the tumor, that is directly contacted with the device. Using the device in a continuous wave mode, a necrotic zone of tissue having a desired size and shape (e.g., a necrotic volume selected to interrupt a blood supply to a tumor) can be created by controlling at least one of the f-number, duration, intensity, and direction of the ultrasound energy administered. This method speeds the therapy and avoids continuously pausing to enable intervening normal tissue to cool.
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
System and method for gas analysis using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS20060123884A1Increase productionReduce equipment downtimeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis using microwave meansGas analysisGas detector
A method for analyzing gas concentration using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy, and a doubly resonant photaoacoustic gas detector comprising: i) a continuous wave light beam whose wavelength coincides with an absorption wavelength of a gaseous analyte; ii) a closed path optical cavity having at least two reflective surfaces; iii) an acoustic resonator chamber contained within said optical cavity, and comprising an acoustic sensor for detecting sound waves generated by a gaseous analyte present within said chamber, the light beam passing sequentially into, through and out of said chamber, and being repeatedly reflected back and forth through said chamber, and being modulated at a frequency which is equal to or equal to one-half of an acoustic resonance frequency of said acoustic resonator chamber.
Owner:LI COR
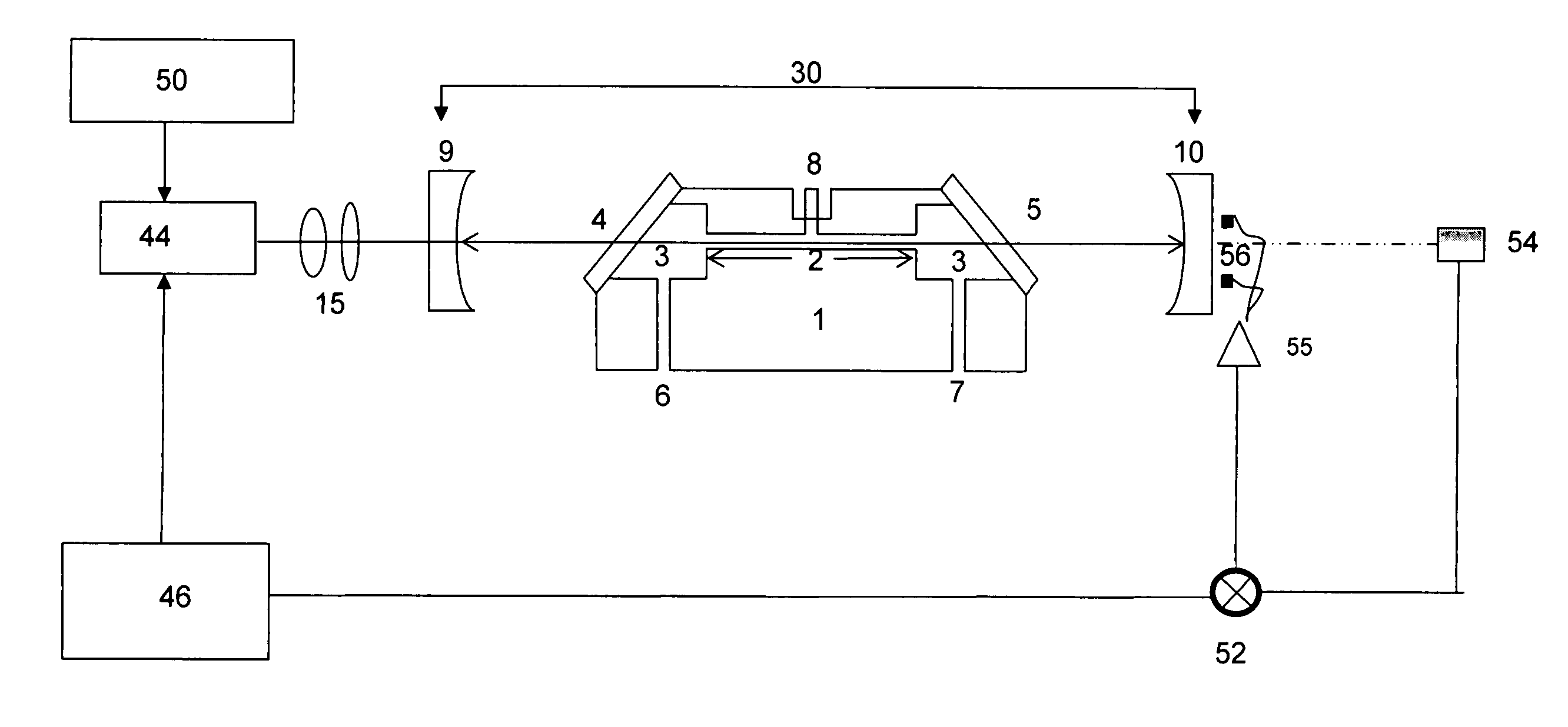
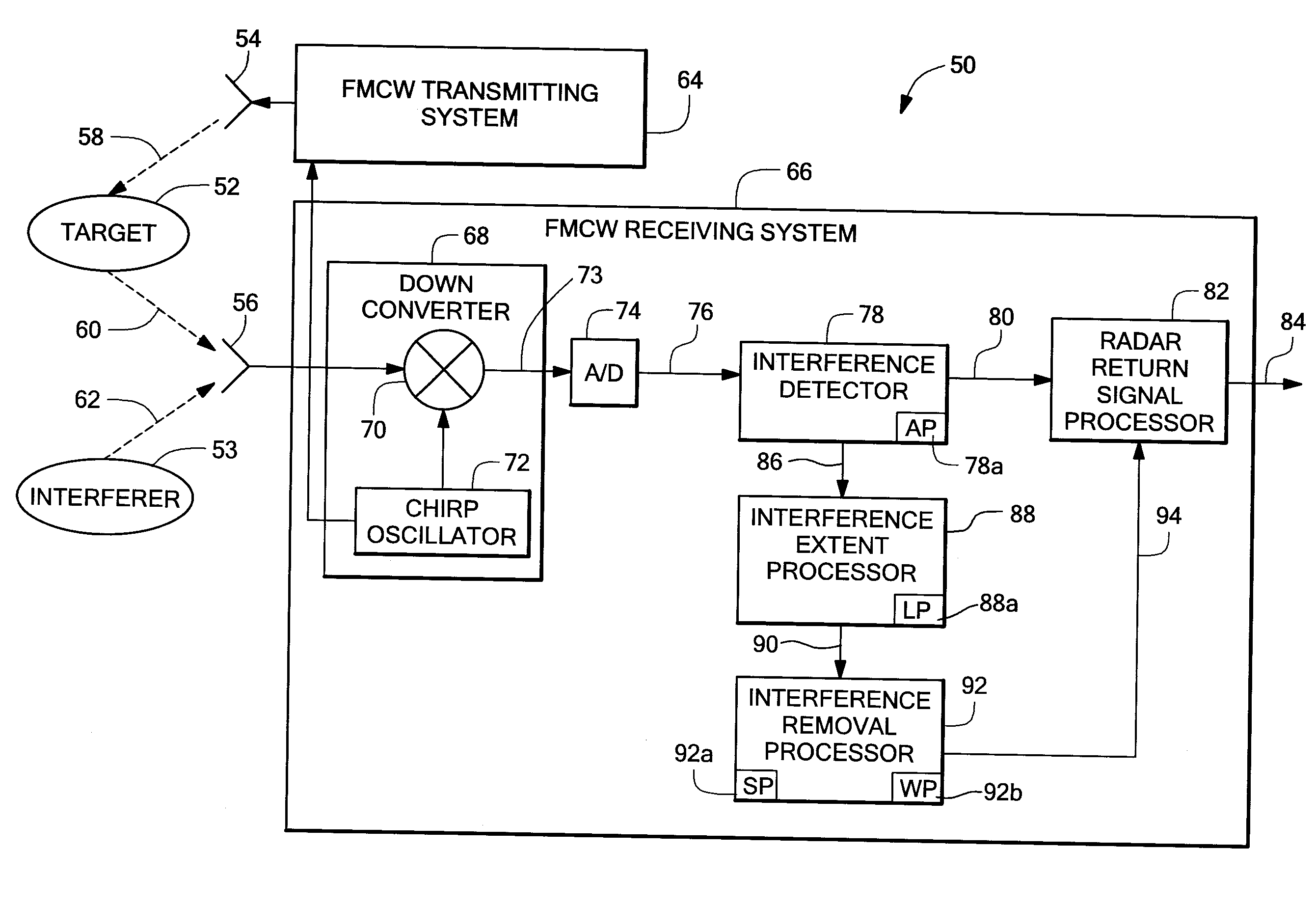
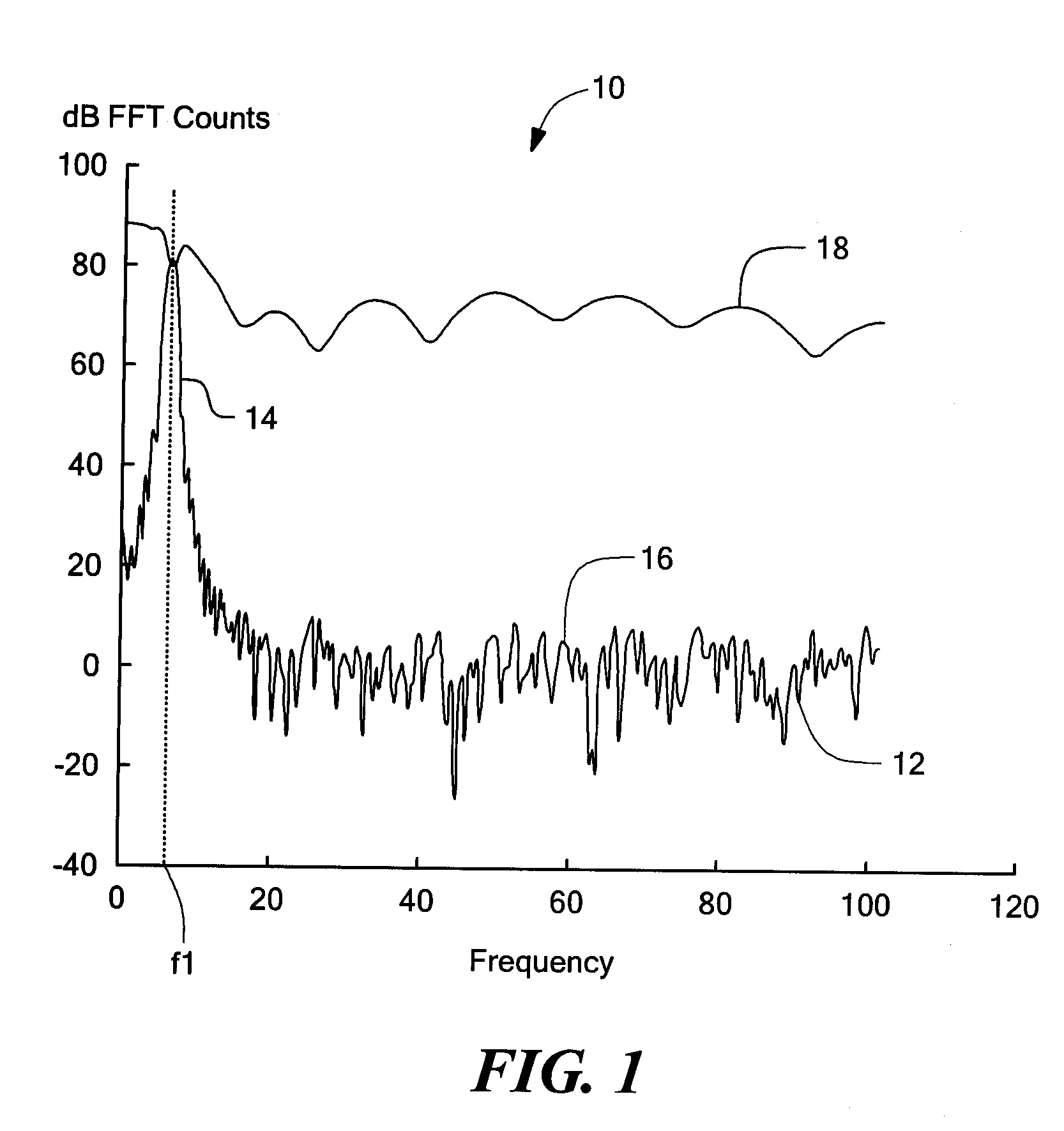
System and method for reducing the effect of a radar interference signal
ActiveUS20070120731A1Avoid interfering signalsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumTransmitted power
A system and method are provided to reduce the effect of an interfering signal in a radar return signal for a frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar. Once the interfering signal is detected, an extent of the interfering signal is determined and the data that was corrupted by the interfering signal is not included in the processing of the radar return signal. This allows the radar to detect a target in the presence of the interfering signal. The system and method can benefit any FMCW radar that is within the range of an interfering radar source (e.g. another FMCW radar, a police radar gun, a pulse radar, etc.) operating in the same frequency band as the FMCW radar. An alternative arrangement provides a system and method for determining the frequency of the interfering signal and then avoiding transmitting power in that portion of the frequency spectrum where the interfering signal is present.
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
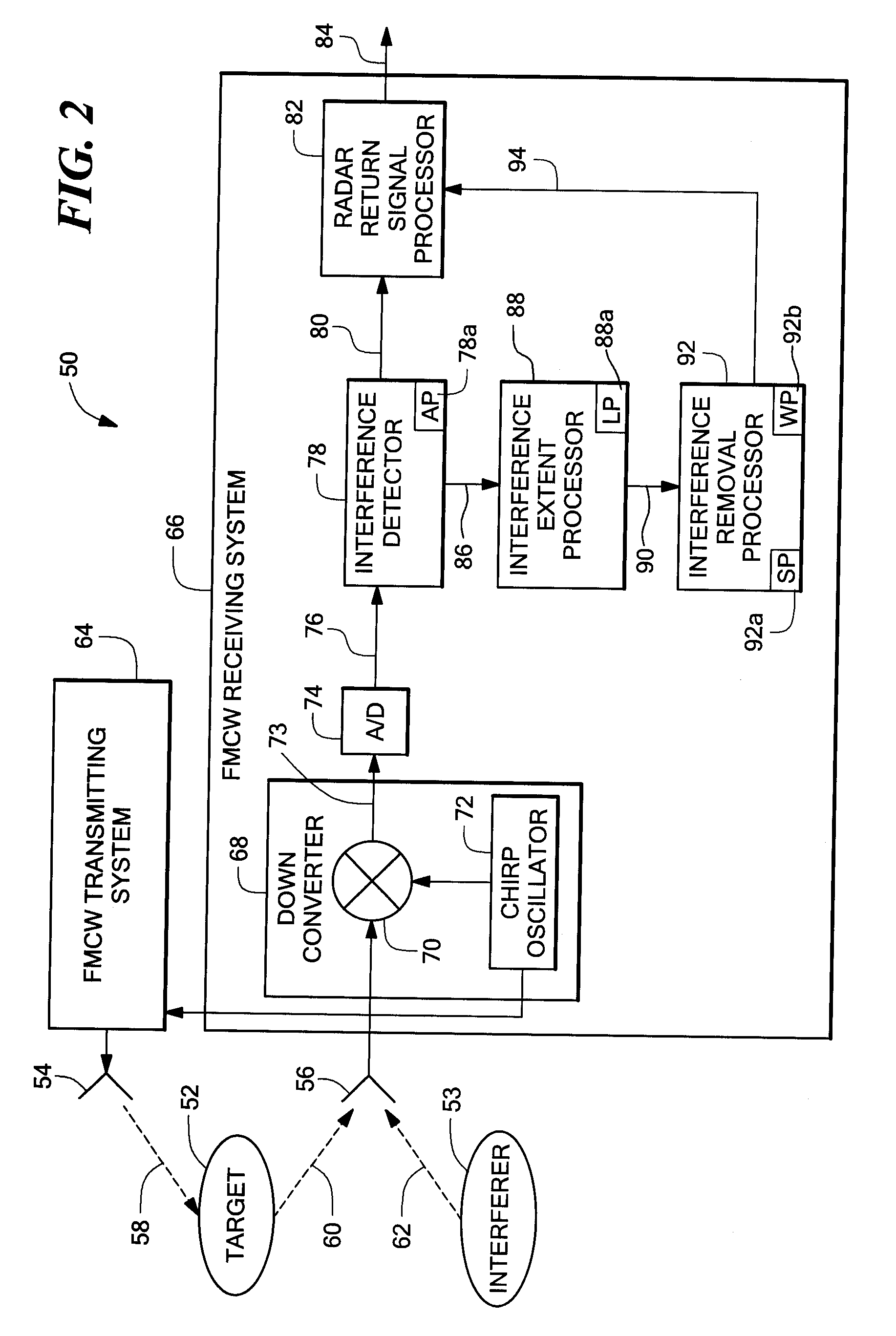
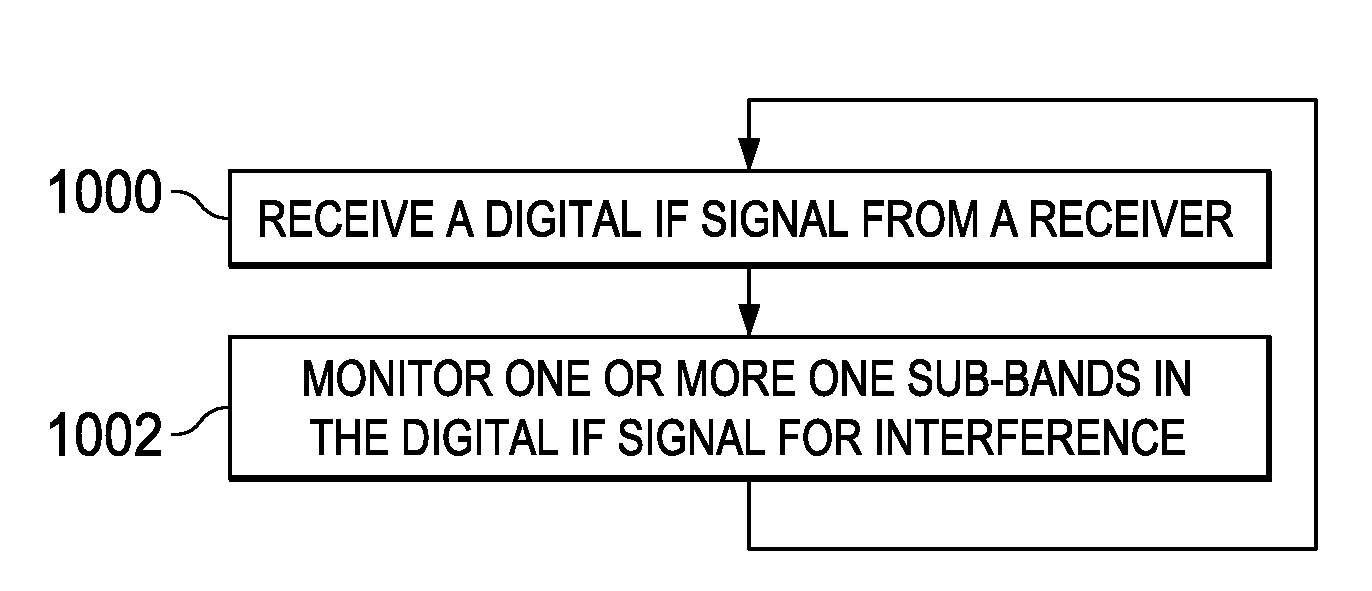
Interference Detection in a Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) Radar System
A frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar system is provided that includes a receiver configured to generate a digital intermediate frequency (IF) signal, and an interference monitoring component coupled to the receiver to receive the digital IF signal, in which the interference monitoring component is configured to monitor at least one sub-band in the digital IF signal for interference, in which the at least one sub-band does not include a radar signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
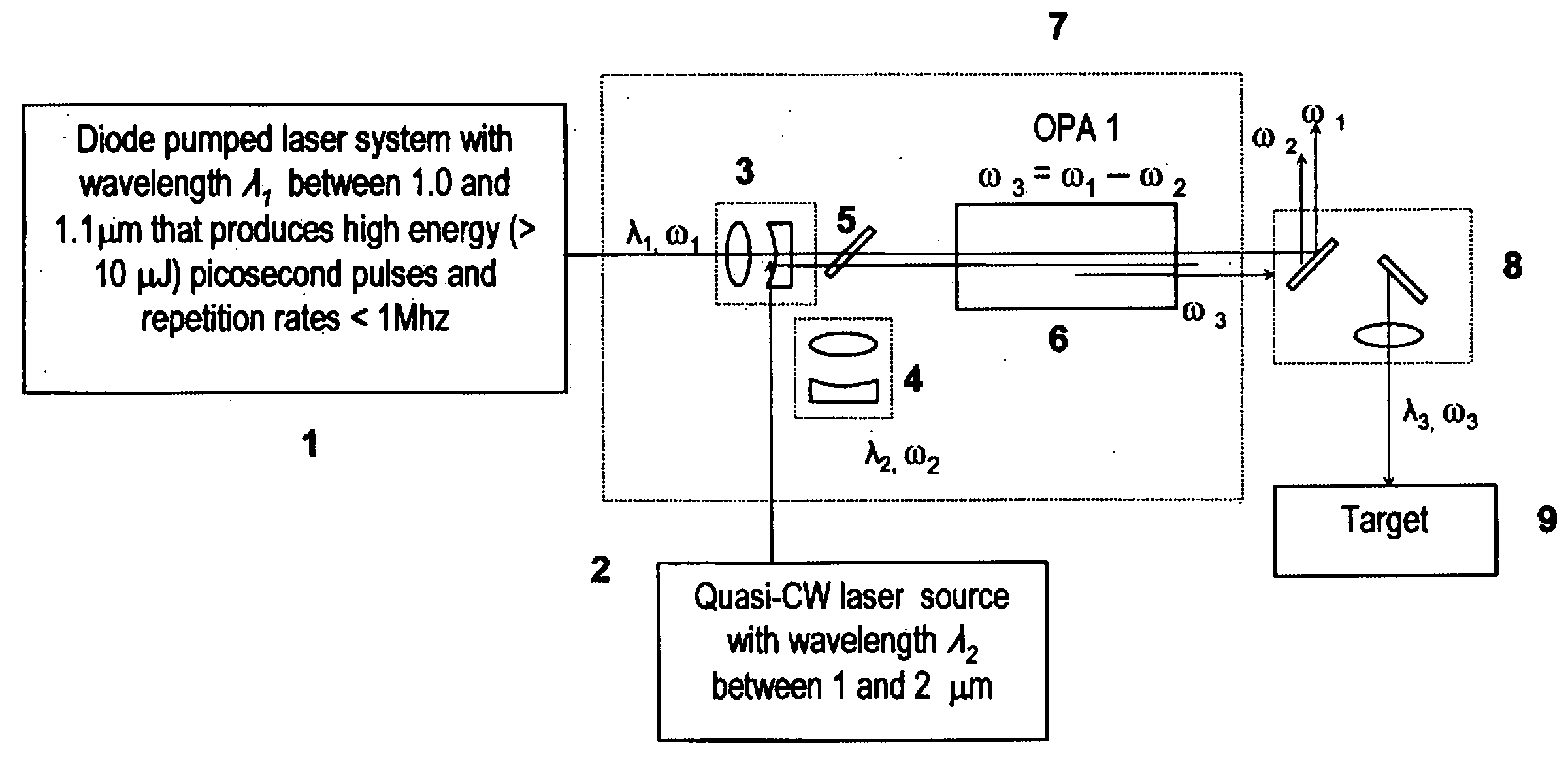
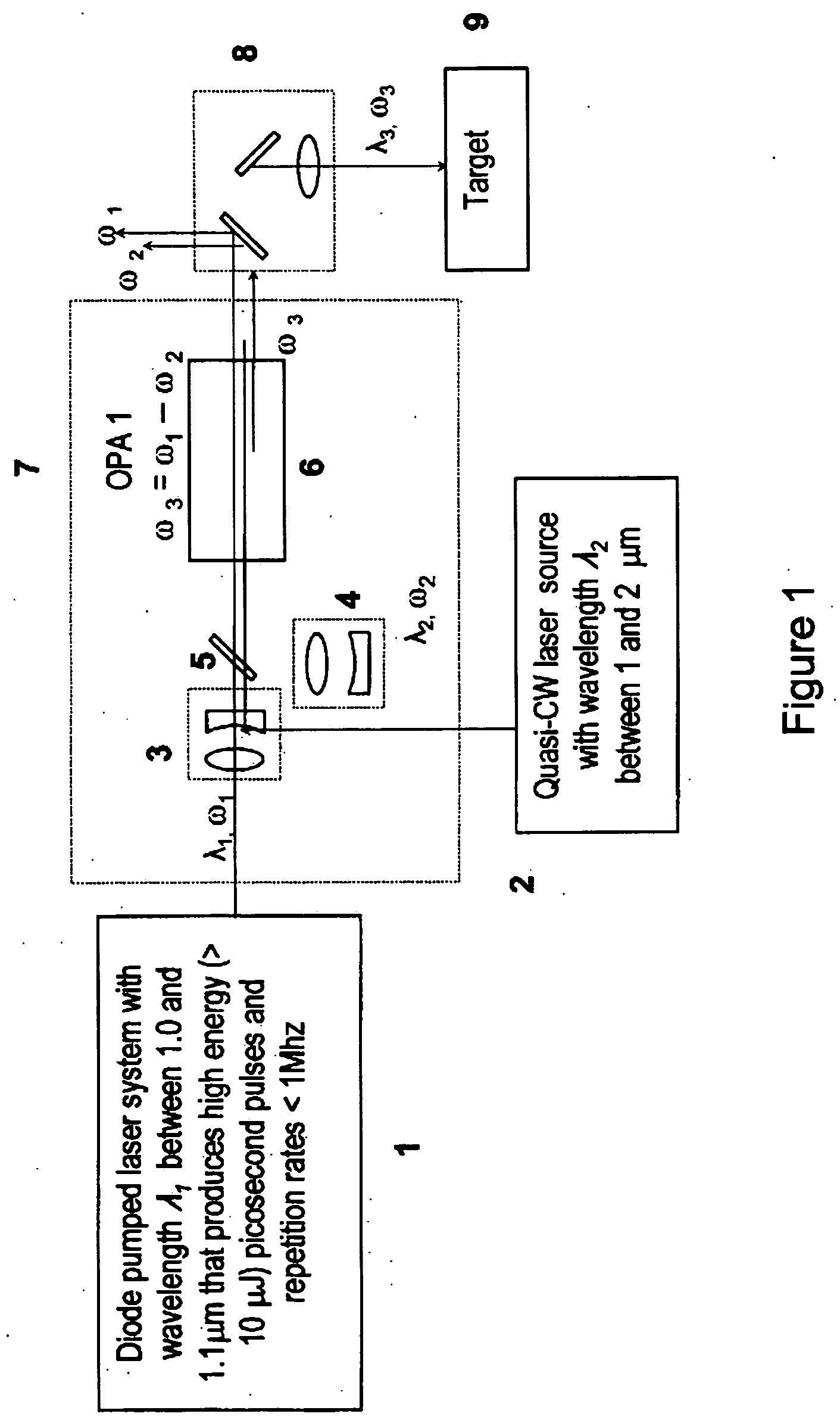
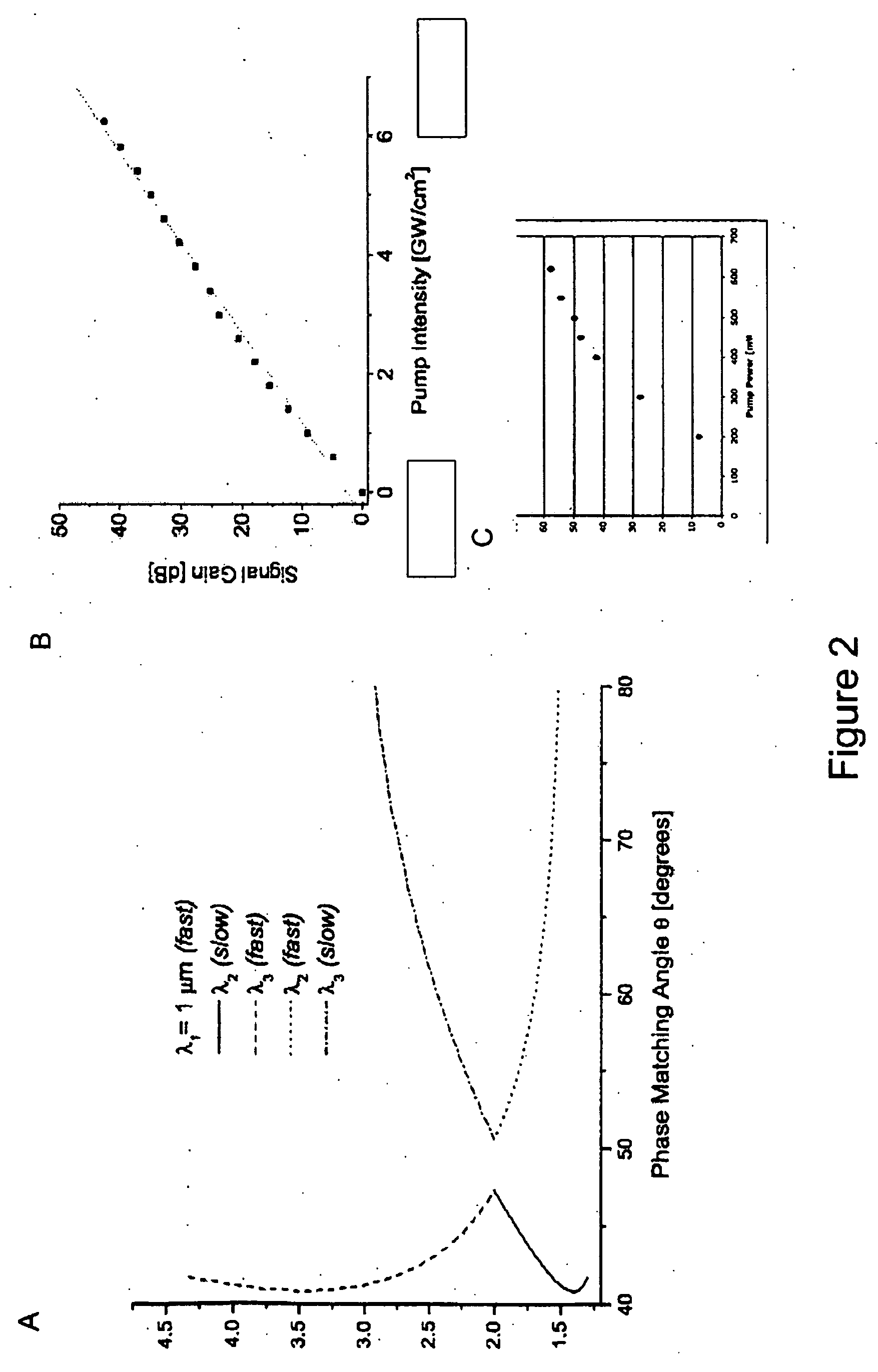
Laser system for generation of high-power sub-nanosecond pulses with controlable wavelengths in 2-15 mum region
ActiveUS20060153254A1Big spaceSubstantial temporal overlapLaser using scattering effectsSurgical instrument detailsSystems designHigh energy
A laser system capable of efficient production of high energy sub-nanosecond pulses in the 2-15 μm spectral region is disclosed. Diode pumped solid state lasers are used as pump sources. The system design is simple, reliable and compact allowing for easy integration. The laser system includes a combination of compact solid-state ˜1 micron laser sources, producing high power picosecond pulses, with optical parametric amplification and a quasi-continuous wave laser for seeding the amplification process that enables the efficient conversion of the high power ˜1 micron laser radiation to tuneable mid-infrared sub-ns pulses. New parametric processes are presented for achieving high gains in bulk nonlinear crystals. Furthermore, a method of exceeding the fundamental conversion efficiency limit of direct three wave mixing is presented. The compact and robust nature of this novel laser system opens up the use of high power and high peak power mid-infrared laser pulses to a wide variety of important medical and dental applications.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION
Radio frequency tag and reader with asymmetric communication bandwidth
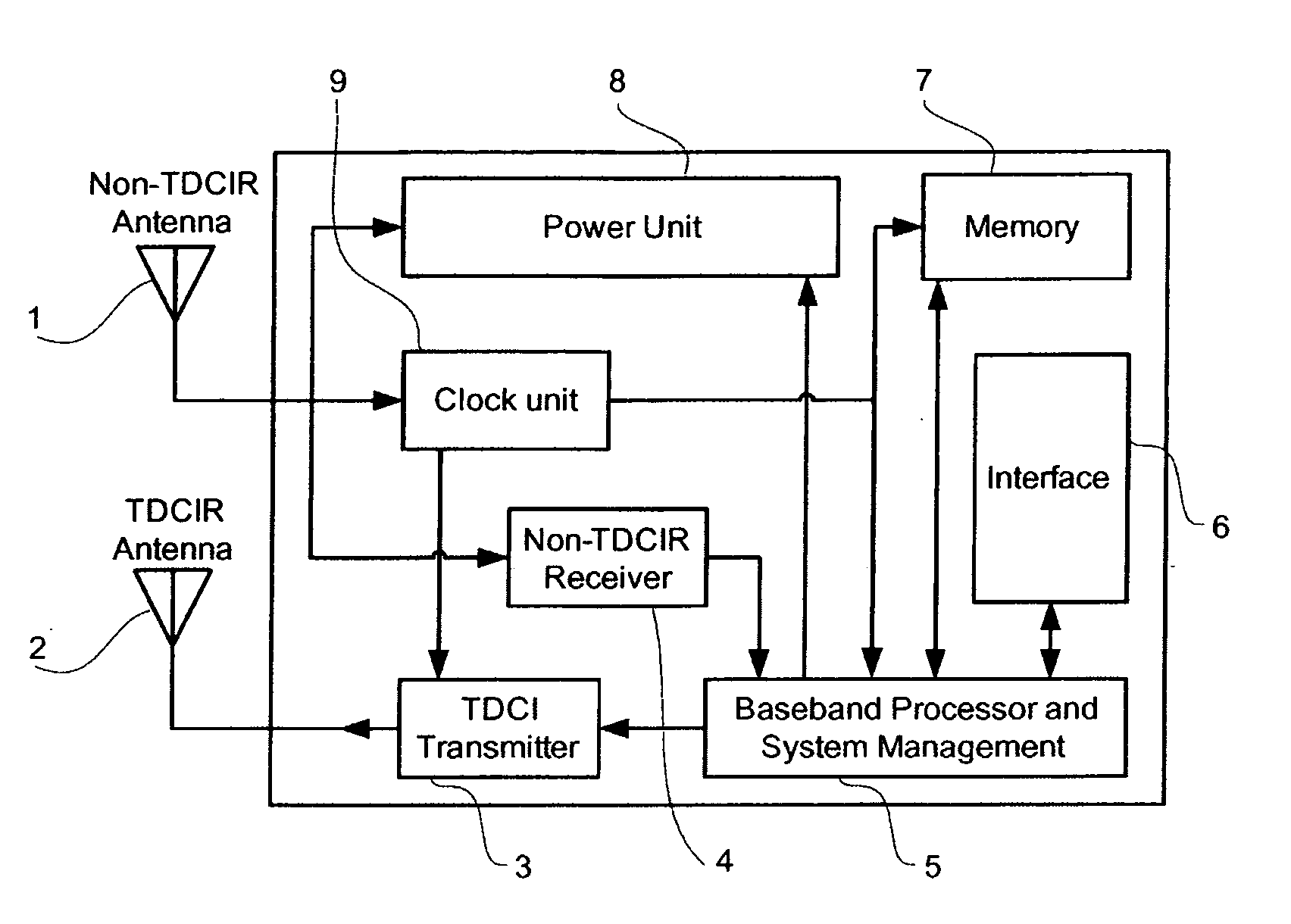
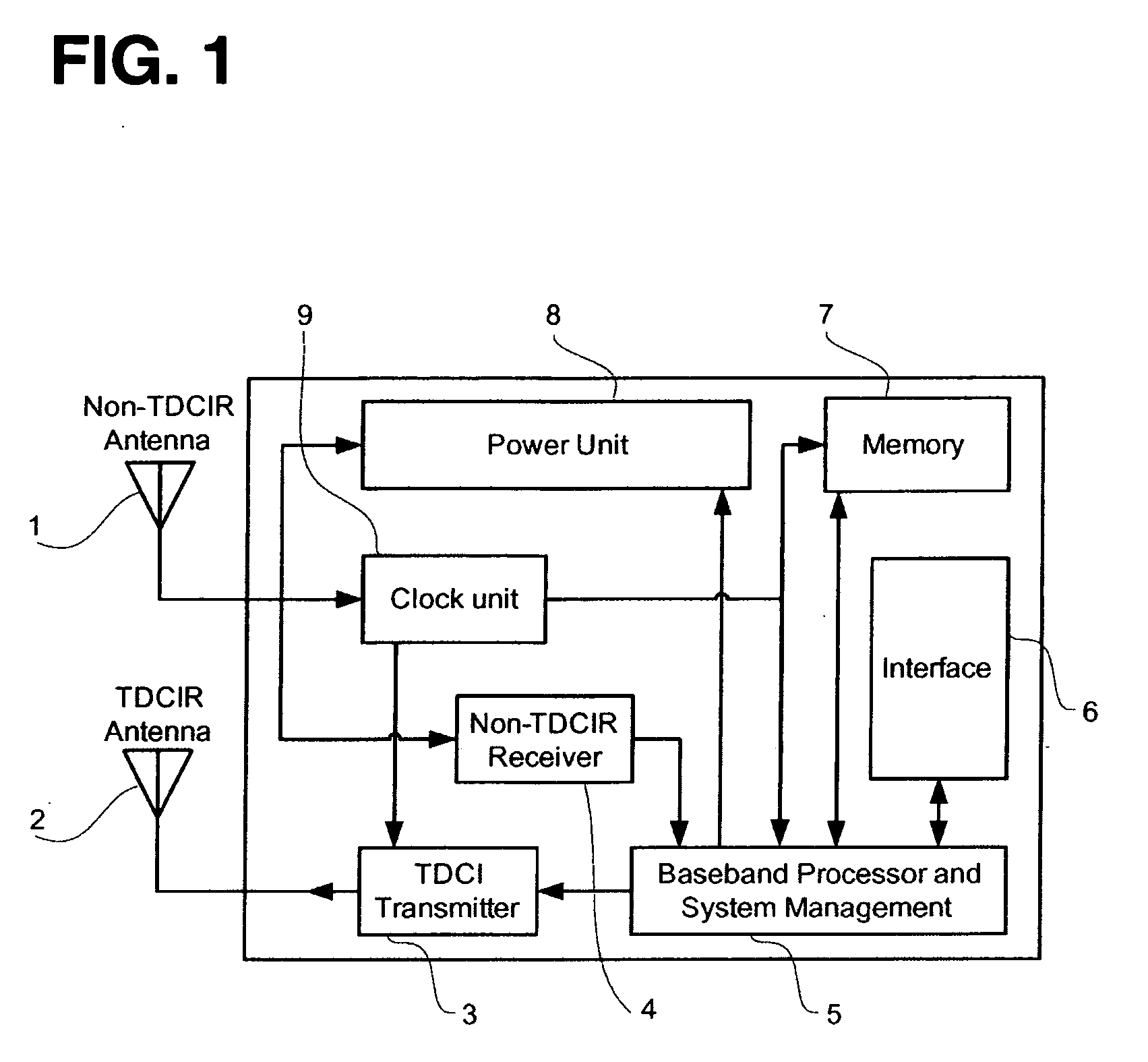
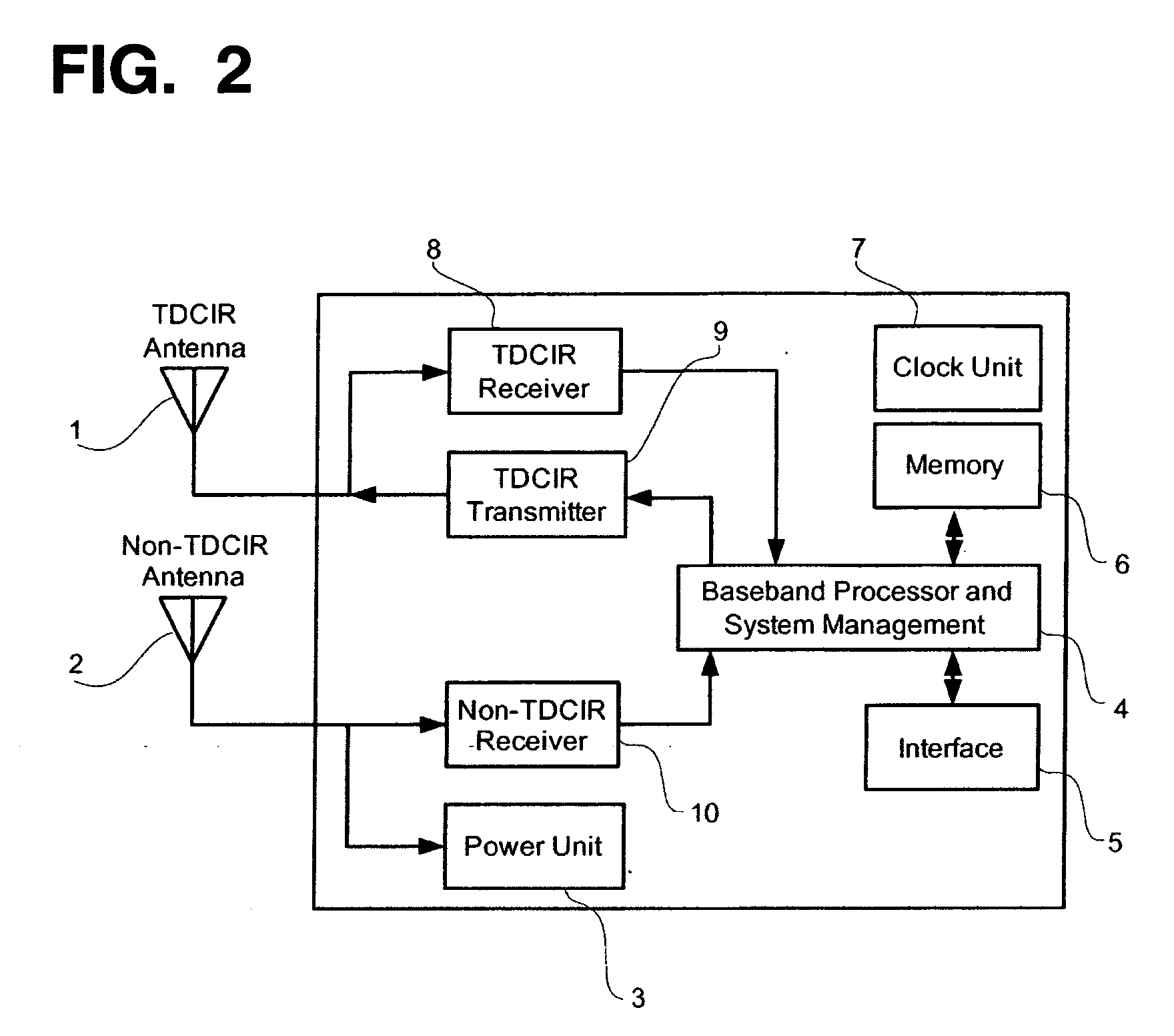
InactiveUS20060103535A1Increase speedIncrease data rateMemory record carrier reading problemsTransmissionCarrier signalElectromagnetic pulse
An asymmetric bandwidth communication system enables wireless communication between interrogators / readers and transponders / tags. A transponder transmits TDCIR (Time Domain Carrierless Impulse Radio) signals in the uplink direction and receives non-TDCIR signals, such as electromagnetic continuous waves, in the downlink direction. The transponder may receive partial or whole power from non-TDCIR signals. The TDCIR utilizes electromagnetic impulses with short duration and ultra wide bandwidth. It offers high data rate reliable communication at low power and design complexity. It also demonstrates resilience against path fading, selective absorption and reflection by physical matters and excellent location determination capabilities.
Owner:TAGARRAY
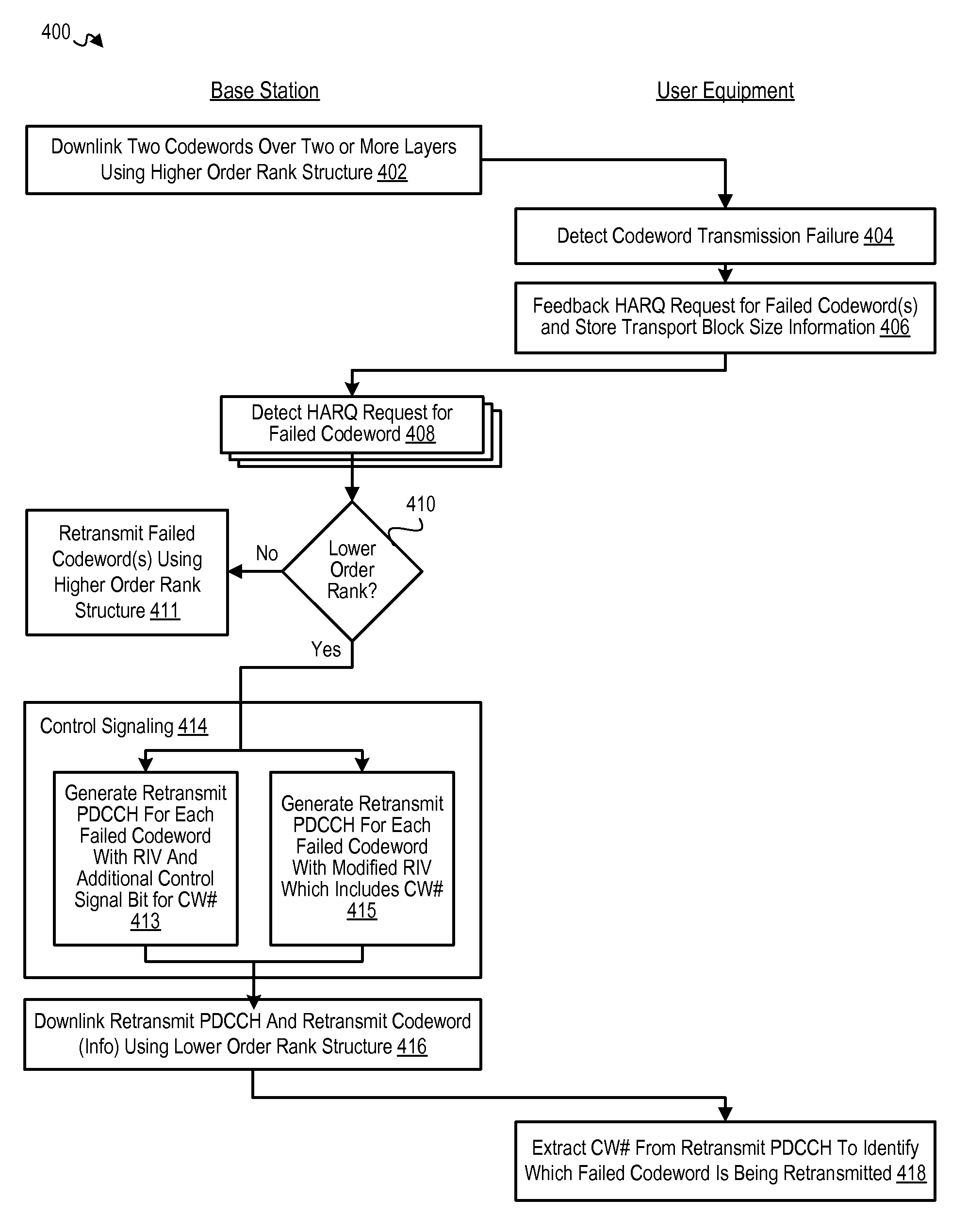
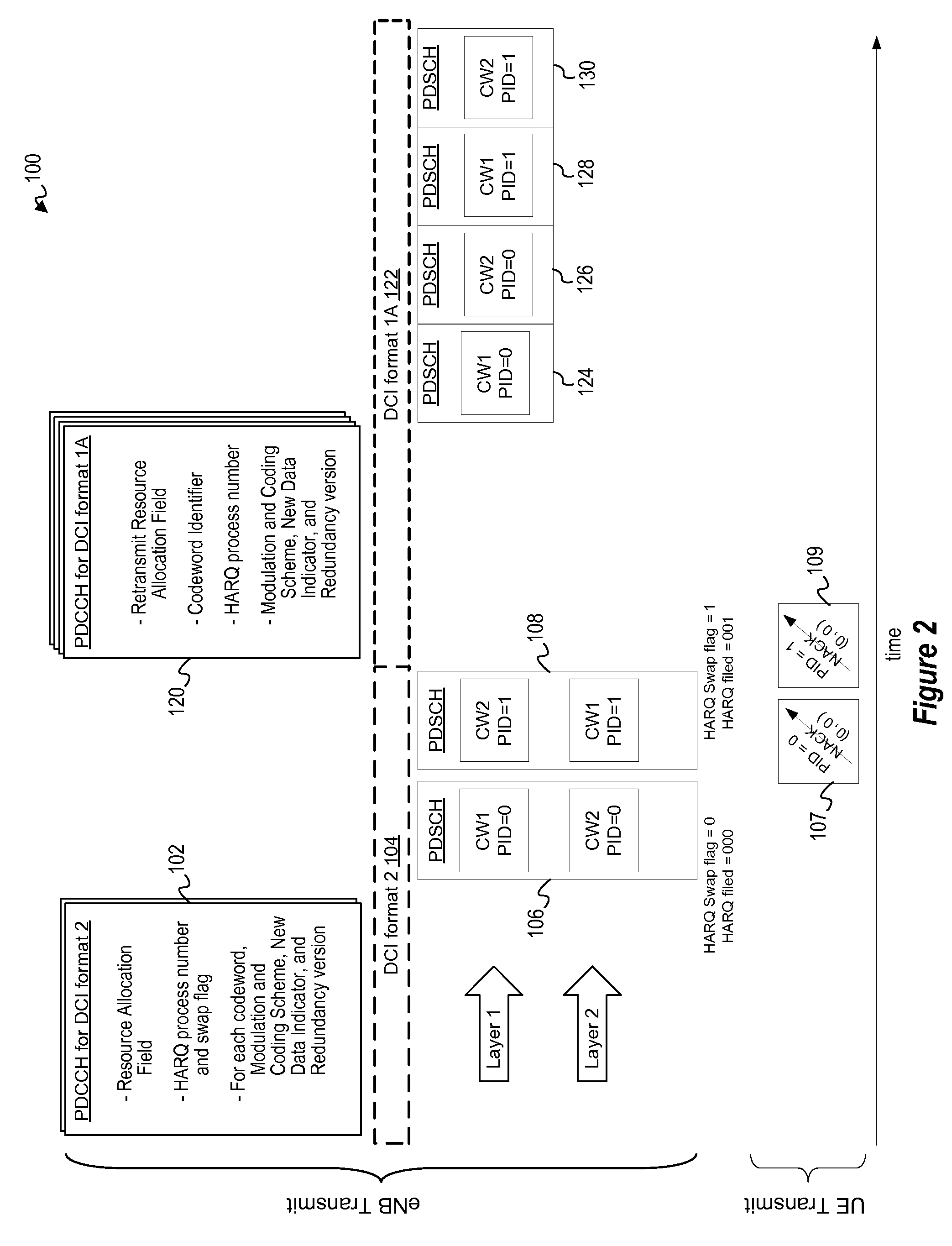
Method for efficient control signaling of two codeword to one codeword transmission
ActiveUS8245092B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemStation
In a wireless communication system (200), a compact control signaling scheme is provided for signaling the selected retransmission mode and codeword identifier for a codeword retransmission when one of a plurality of codewords (CW1, CW2) being transmitted over two codeword pipes to a receiver (201.i) fails the transmission and when the base station / transmitter (210) switches from a higher order channel rank (231) to a lower order channel rank (241), either by including one or more additional signaling bits in the control signal (240) to identify the retransmitted codeword, or by re-using existing control signal information in a way that can be recognized by the subscriber station / receiver to identify the retransmitted codeword. With the compact control signal, the receiver (201.i) is able to determine which codeword is being retransmitted and to determine the corresponding time-frequency resource allocation for the retransmitted codeword.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com