Patents
Literature
1871 results about "Reflective surfaces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reflective surfaces can deliver high solar reflectance (the ability to reflect the visible, infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths of the sun, reducing heat transfer to the surface) and high thermal emittance (the ability to radiate absorbed, or non-reflected, solar energy). Reflective surfaces are a form of geoengineering.
Optical communication device provided with a reflector and method for forming a reflector in an optical communication device
InactiveUS20070070490A1Small lossHigh bonding strengthMirrorsCoupling light guidesCompound (substance)Optical communication
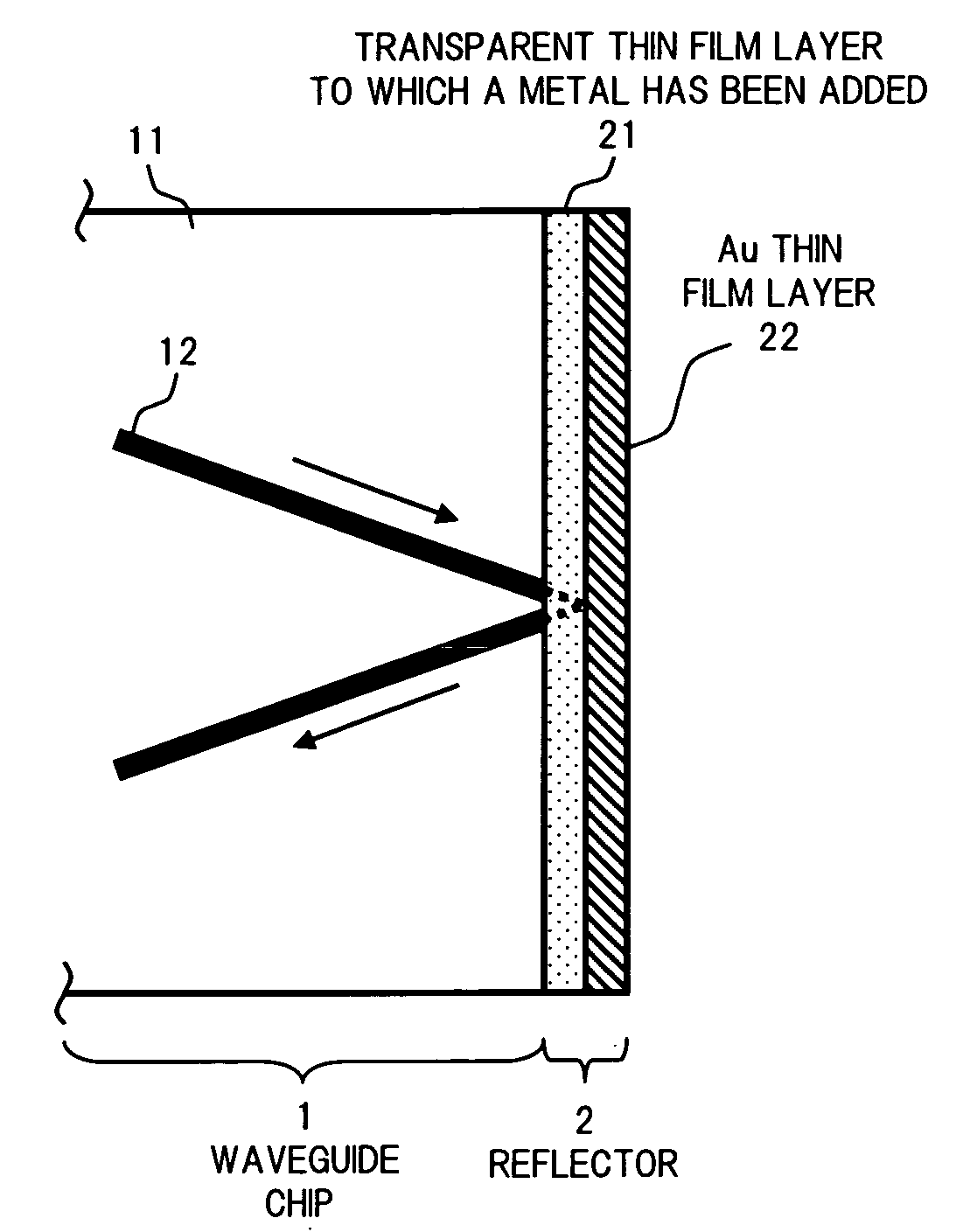
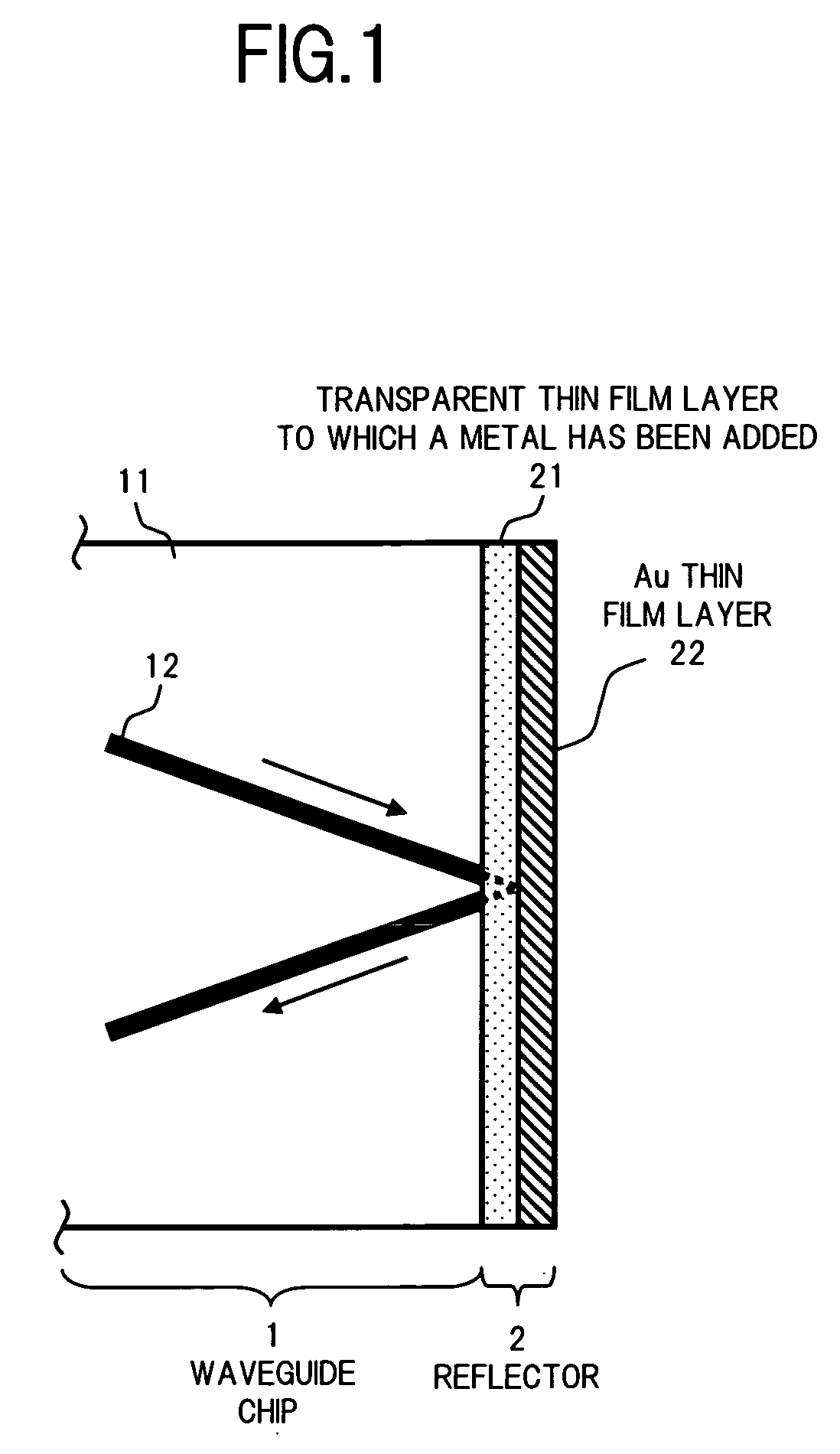
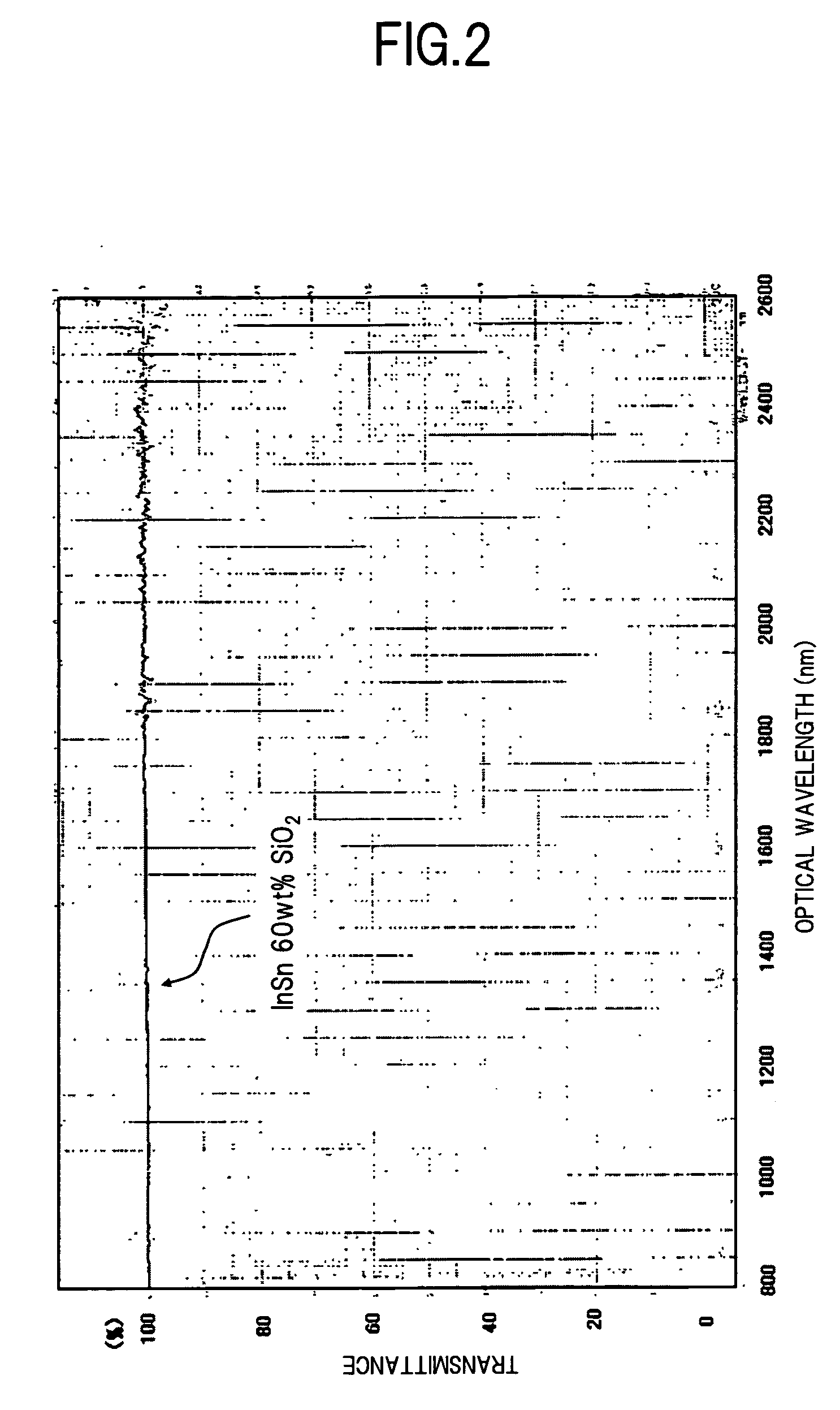
An optical communication device of the invention includes a reflector for reflecting the light that has reached one end surface of a waveguide chip to turn the optical path of the light. The reflector includes a transparent thin film layer formed on one end surface of the waveguide chip by using a material to which a metal that forms an intermetallic compound or the like with Au is added to a substance that is transparent to the light that propagates through the waveguide, as well as an Au thin film layer formed on the front surface of the transparent thin film layer. This allows formation of a reflector having an Au thin film layer as a reflecting surface in an optical medium with high adhesion strength. Thus, an optical communication device can be provided having a high reliability with little loss.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
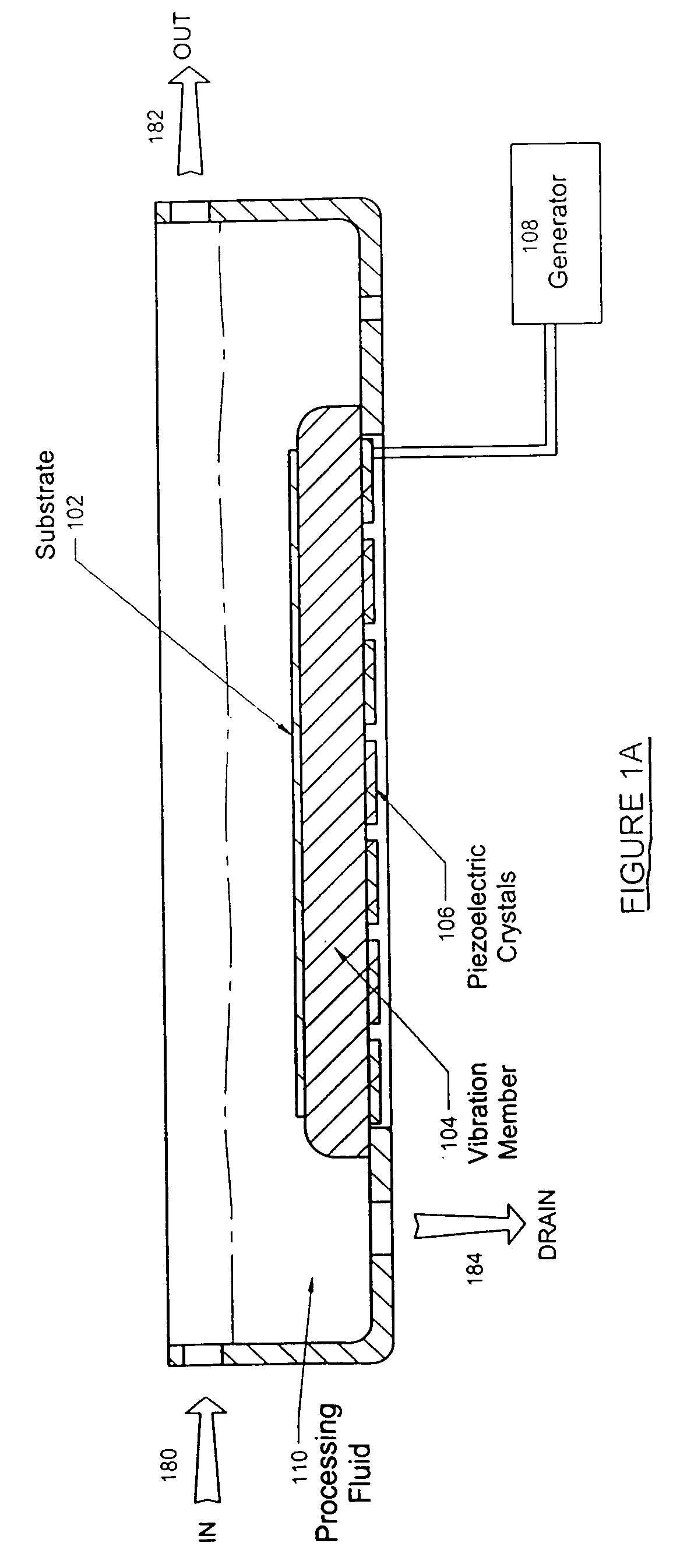
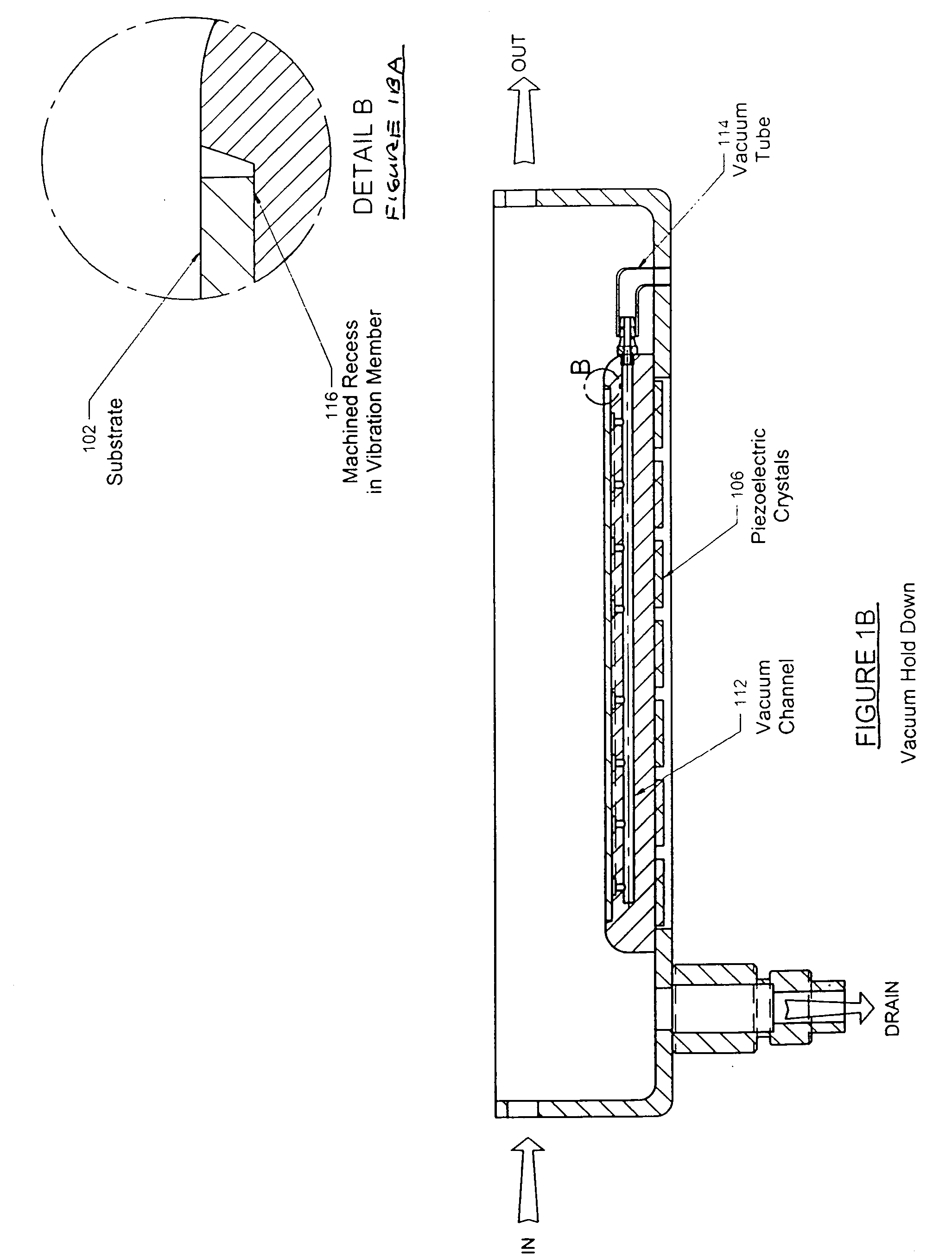
Method and apparatus to process substrates with megasonic energy
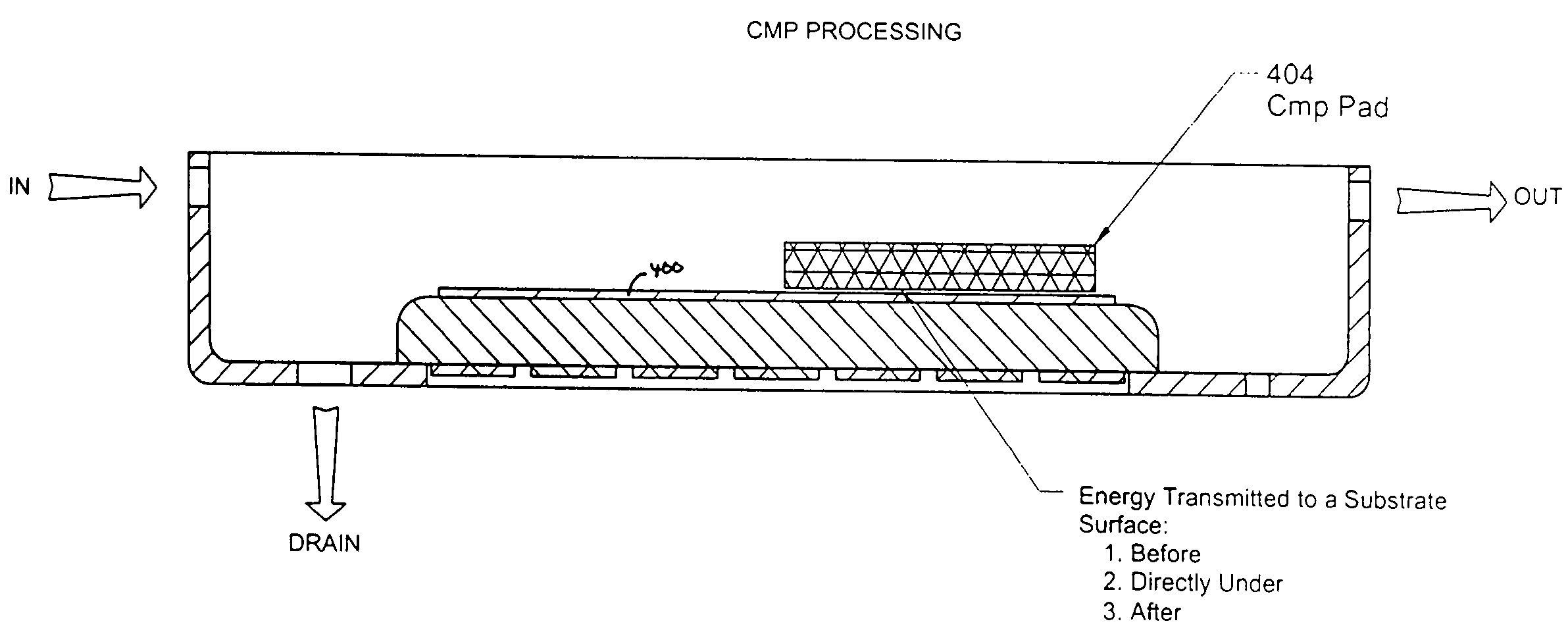
ActiveUS20050003737A1Uniform energyImprove uniformityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLiquid surface applicatorsEngineeringSubstrate surface
A variety of techniques may be employed, alone or in combination, to enhance contact between a processed substrate and applied megasonic energy. In accordance with one embodiment of the new invention, the vibration plate is brought into intimate contact with one surface of the substrate, while cleaning or processing fluid contacts the other. In accordance with an alternative embodiment of the present invention, a reflecting surface may be provided to cause emanated energy to be reflected back into the near field and make it more uniform. In accordance with another alternative embodiment of the present invention, energy may be transferred across a substrate bounded on both sides by liquid with incidence of megasonic energy that is either normal to the substrate surface or within a critical range of incident angles. In yet another embodiment, generated dilatational waves may be converted to surface waves prior to contacting the substrate.
Owner:P C T SYST
Methods and apparatus for spatial light modulation
ActiveUS20060187528A1Improve luminous efficiencyReduced Power RequirementsOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical cavityOptoelectronics
Improved apparatus and methods for spatial light modulation are disclosed which utilize optical cavities having both front and rear reflective surfaces. Light-transmissive regions are formed in the front reflective surface for spatially modulating light.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Trough reflectors for solar energy collectors
InactiveUS20080308094A1The process is simple and effectiveLow costSolar heating energyMirrorsEdge regionSolar thermal collector
A trough reflector for solar energy collection is constructed from transverse ribs which support a reflective surface. Side edge support rails mounted on ends of the ribs support linear edges of the reflective surface. The edge support rails have a channel-like construction with an inner flange member which is in contact with a top of the reflective surface, and a lip member extending from an outer flange member. The edge region of the reflective surface rests on the lip member with the edge of the reflective surface in contact with the outer flange member. A turning moment is applied to the edge regions of the reflective surface to ensure that the entire reflective surface is parabolic. An arcuate profile of ribs of the trough reflector is converted into a parabolic profile by the application of a force to the ends of the ribs.
Owner:MIRALITE
Nanocomposite microresonators
InactiveUS6876796B2High refractive indexGood optical performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicineIsolatorNanoparticle
A microresonator is provided that incorporates a composite material comprising a polymer matrix and nanoparticles dispersed therein. The microresonator includes the composite material having a shape that is bounded at least in part by a reflecting surface. The shape of the microresonator allows a discrete electromagnetic frequency to set up a standing wave mode. Advantageously, the polymer matrix comprises at least one halogenated polymer and the dispersed nanoparticles comprise an outer coating layer, which may also comprise a halogenated polymer. Methods for making composite materials and microresonators are also provided. Applications include, for example, active and passive switches, add / drop filters, modulators, isolators, and integrated optical switch array circuits.
Owner:PHOTON
OCT probe for eliminating ghost images
InactiveUS7805034B2Reduce the overall diameterIncrease the working distanceMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterPhoto irradiationMedicine
An OCT probe has a sheath to be inserted into a subject; and an optical system within the sheath, for changing the direction of light which propagates from a light source through an optical fiber to irradiate the light onto the subject through a transparent portion of the sheath, and for reflecting the light beam, which is reflected by the subject, to guide the light into the optical fiber. A light output surface, for causing the light to be output from the reflecting surface in a direction obliquely inclined with respect to the inner surface of the sheath, and a reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion, for preventing light reflected by the inner surface of the sheath from entering the optical fiber, are provided in the optical system. The reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion may be formed by providing a cut planar surface portion on the lens.
Owner:NAMIKI PRECISION JEWEL CO LTD
Substrate-guided relays for use with scanned beam light sources
Substrate-guided relays that employ light guiding substrates to relay images from sources to viewers in optical display systems. The substrate-guided relays are comprised of an input coupler, an intermediate substrate, and an output coupler. In some embodiments, the output coupler is formed in a separate substrate that is coupled to the intermediate substrate. The output coupler may be placed in front of or behind the intermediate substrate, and may employ two or more partially reflective surfaces to couple light from the coupler. In some embodiments, the input coupler is coupled to the intermediate substrate in a manner that the optical axis of the input coupler intersects the optical axis of the intermediate substrate at a non-perpendicular angle.
Owner:MICROVISION
Vehicular lamp
InactiveUS20080013333A1Reduce in quantityLowering of cost and size and power consumptionMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideOptical axis
A vehicular lamp including an LED(s), a reflector having a reflective surface that reflects light from the LED(s) in the forward direction of the lamp, and a flat (plate-like) light guide(s) to which the light from the LED(s) is incident from one side of the light guide(s) and which radiates the light in the forward direction from another side. Light in the vicinity of the optical axis of the LED(s) is incident to the light guide(s), and other light is reflected by the reflective surface of the reflector, so that a part of light of the LED(s) is irradiated by the light guide(s), and other light is reflected and irradiated by the reflector, thus reducing the number of LEDs used and the size and power consumption of the lamp.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
System and method for gas analysis using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy
ActiveUS20060123884A1Increase productionReduce equipment downtimeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis using microwave meansGas analysisGas detector
A method for analyzing gas concentration using doubly resonant photoacoustic spectroscopy, and a doubly resonant photaoacoustic gas detector comprising: i) a continuous wave light beam whose wavelength coincides with an absorption wavelength of a gaseous analyte; ii) a closed path optical cavity having at least two reflective surfaces; iii) an acoustic resonator chamber contained within said optical cavity, and comprising an acoustic sensor for detecting sound waves generated by a gaseous analyte present within said chamber, the light beam passing sequentially into, through and out of said chamber, and being repeatedly reflected back and forth through said chamber, and being modulated at a frequency which is equal to or equal to one-half of an acoustic resonance frequency of said acoustic resonator chamber.
Owner:LI COR
Lateral laser fiber for high average power and peak pulse energy
ActiveUS7909817B2Minimize reflectionAvoid seizuresSurgical instrument detailsFree rotationRefractive index
An improved optical fiber comprising a waveguide with an input for coupling focused laser energy into the waveguide and communicating electromagnetic radiation in a propagation direction to an internally reflective tip of the waveguide, a tissue contacting surface wherein the light path from the reflecting surface to the transmitting surface in substantially homogenous in refractive index and cooled by fluid flow. In minimizing the variations in refractive index within the lateral light path, while providing active cooling directly below the tissue contact surface, the invention prevents internal reflections and beam distortion and greatly improves the efficiency and durability of the laterally directing probe. Free rotation of the tissue contact surface, about the lateral tip, may be provided and tissue vaporization efficiency may be improved by providing a morcellating tool on the tissue contact surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Smoke detector and method of detecting smoke
ActiveUS20060261967A1Small sizeReduce complexityMaterial analysis by optical meansFire alarm smoke/gas actuationSmoke detectorsEngineering
A smoke detector that includes at least one image-forming reflective surface, at least one light source and at least one light sensor. In operation, at least one light source emits light from a first area thereon and the reflective surface focuses the light onto a second area that includes at least one light sensor, wherein the first area is smaller than the second area.
Owner:GE SECURITY INC
Imaging Light Guide With Reflective Turning Array
ActiveUS20170075119A1Increase brightnessImprove optical efficiencyMirrorsPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideDiffraction optics
An imaging light guide has a waveguide and an in-coupling diffractive optic formed on the waveguide and disposed to direct image-bearing light beams into the waveguide. An array of two or more at least partially reflective surfaces are oriented in parallel and disposed to expand the image-bearing light beams from the in-coupling diffractive optic in a first dimension and to direct the expanded image-bearing light beams toward an out-coupling diffractive optic. The out-coupling diffractive optic is formed on the waveguide and disposed to expand the image-bearing light beams in a second dimension orthogonal to the first dimension and to direct the image-bearing light beams toward a viewer eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
Inflatable heliostatic solar power collector
ActiveUS20100229850A1Low costImprove conversion efficiencyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyHydrocotyle bowlesioidesCollector device
Increased utilization of solar power is highly desirable as solar power is a readily available renewable resource with power potential far exceeding total global needs; and as solar power does not contribute to pollutants associated with fossil fuel power, such as unburned hydrocarbons, NOx and carbon dioxide. The present invention provides low-cost inflatable heliostatic solar power collectors, which can be stand-alone units suitable for flexible utilization in small, medium, or utility scale applications. The inflatable heliostatic power collectors use a reflective surface or membrane “sandwiched” between two inflated chambers, and attached solar power receivers which may be of photovoltaic and / or solar thermal types. Modest concentration ratios enable benefits in both reduced cost and increased conversion efficiency, relative to simple prior-art flat plate solar collectors.
Owner:RIC ENTERPRISES
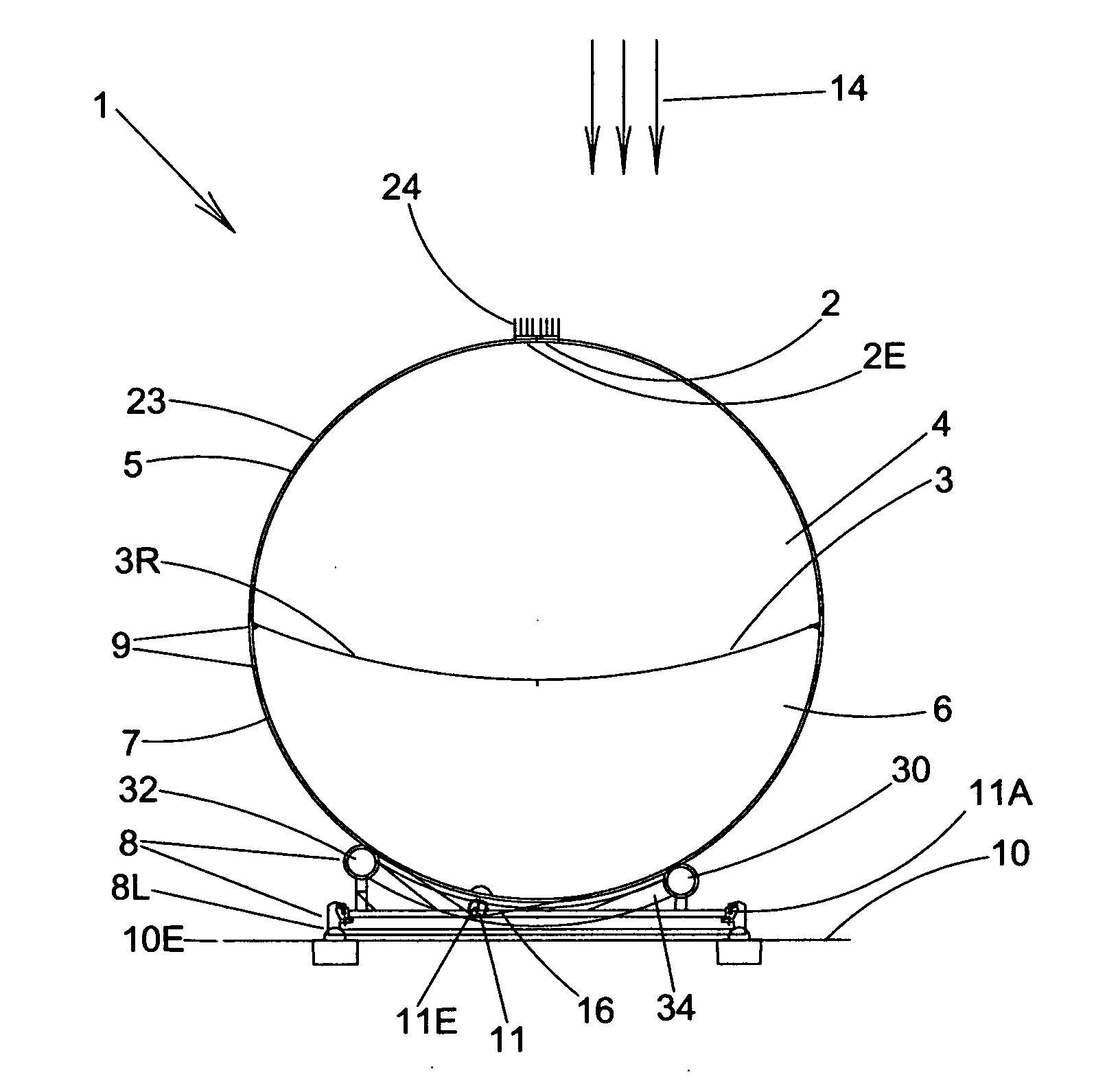
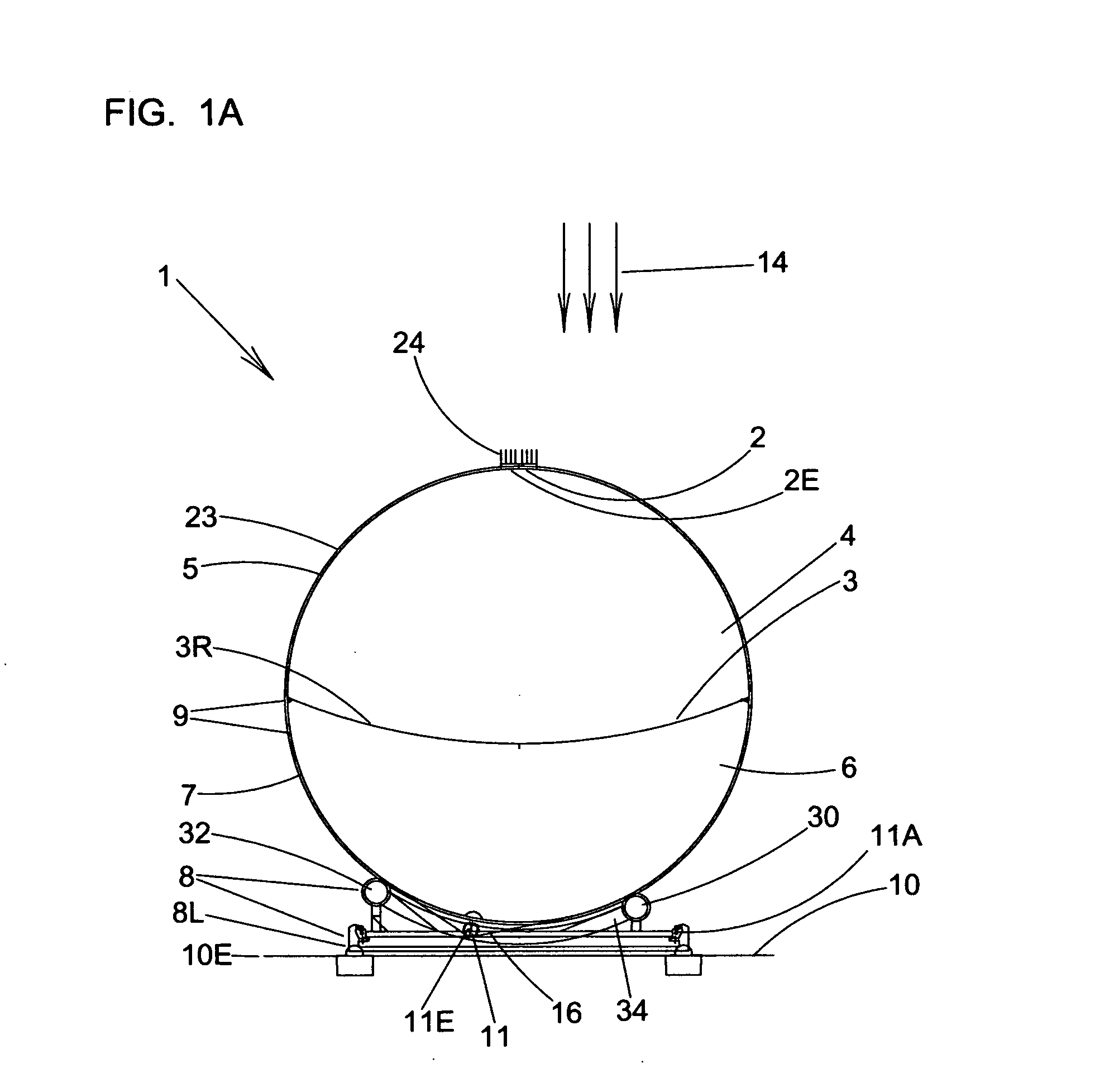
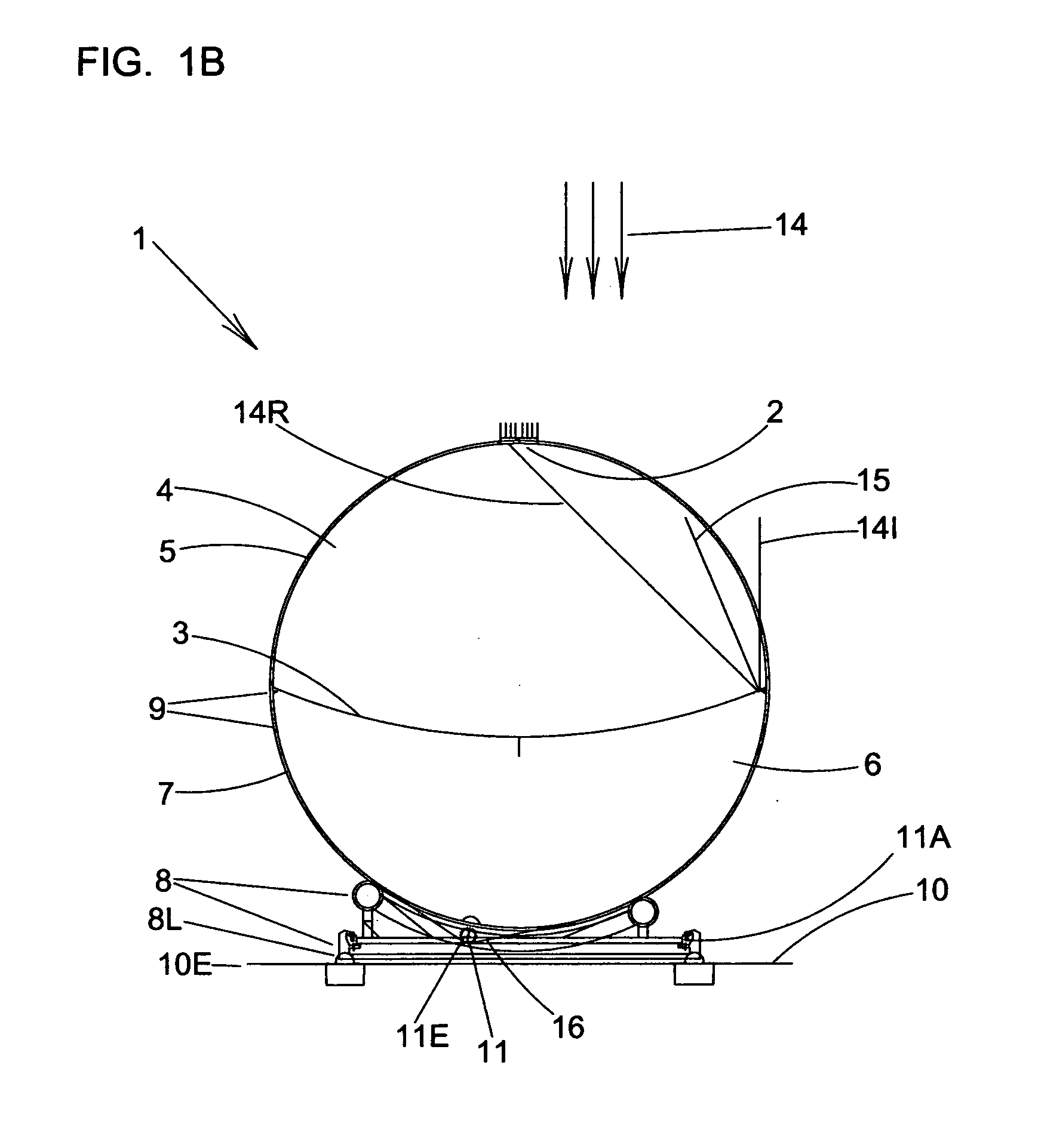
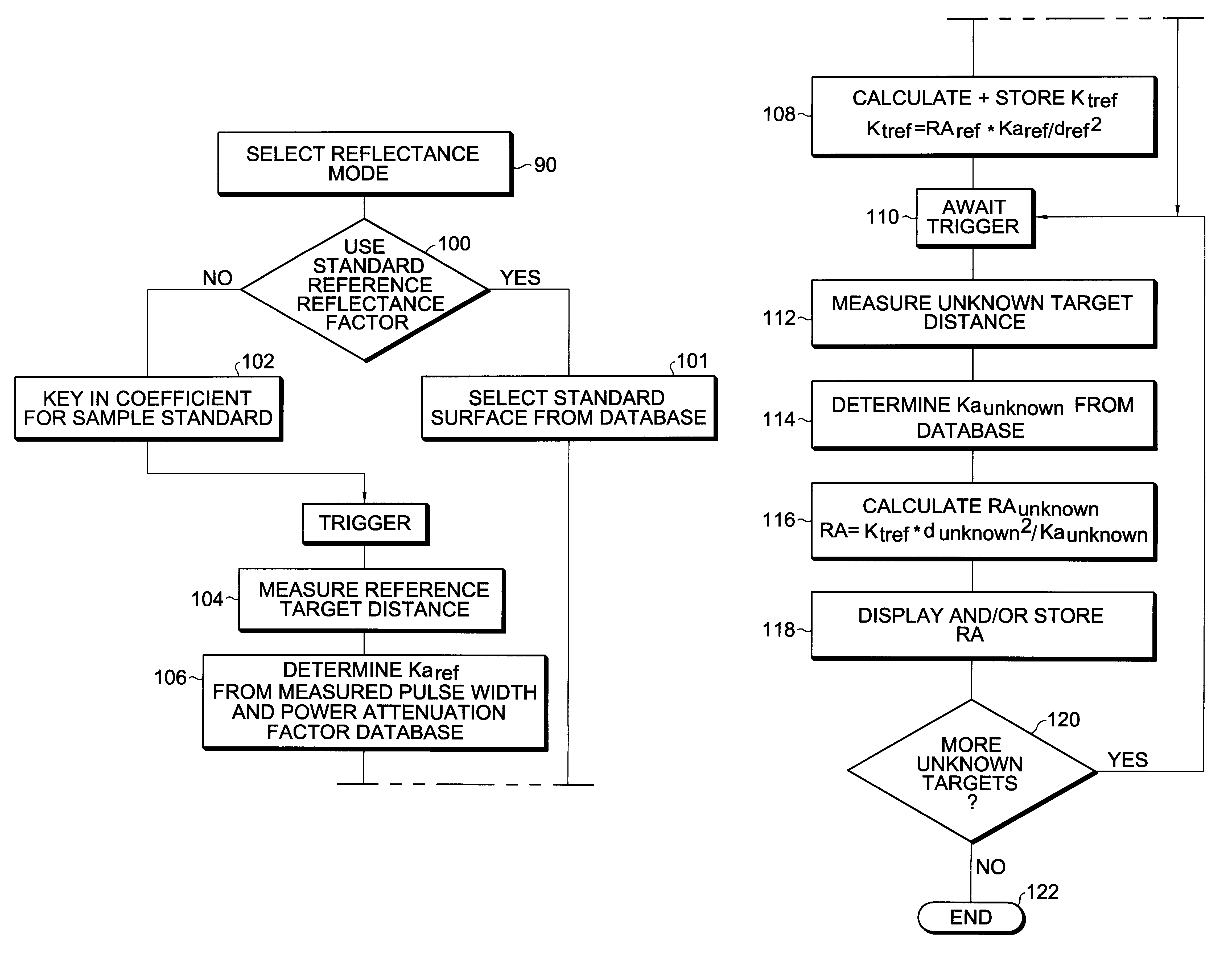
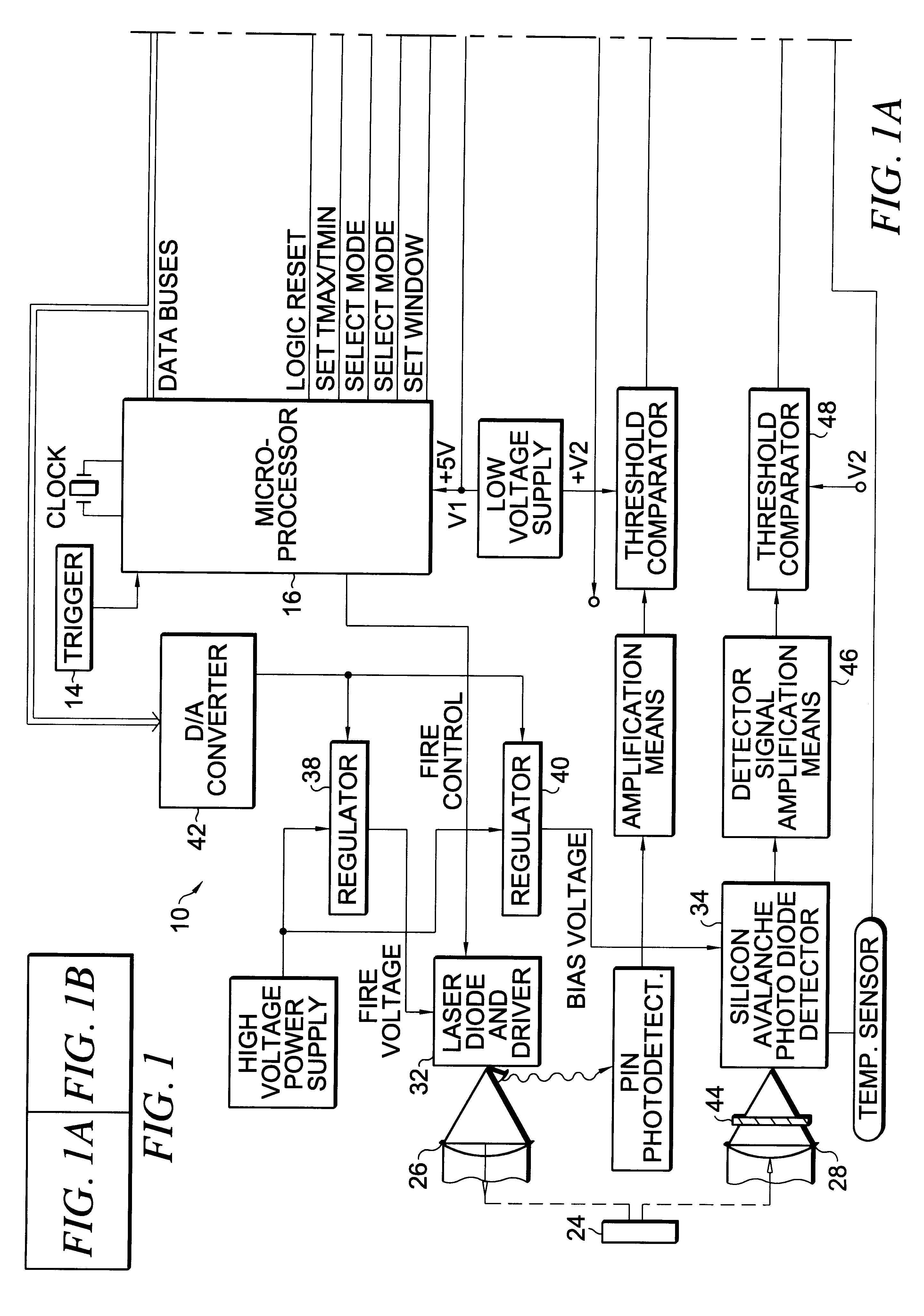
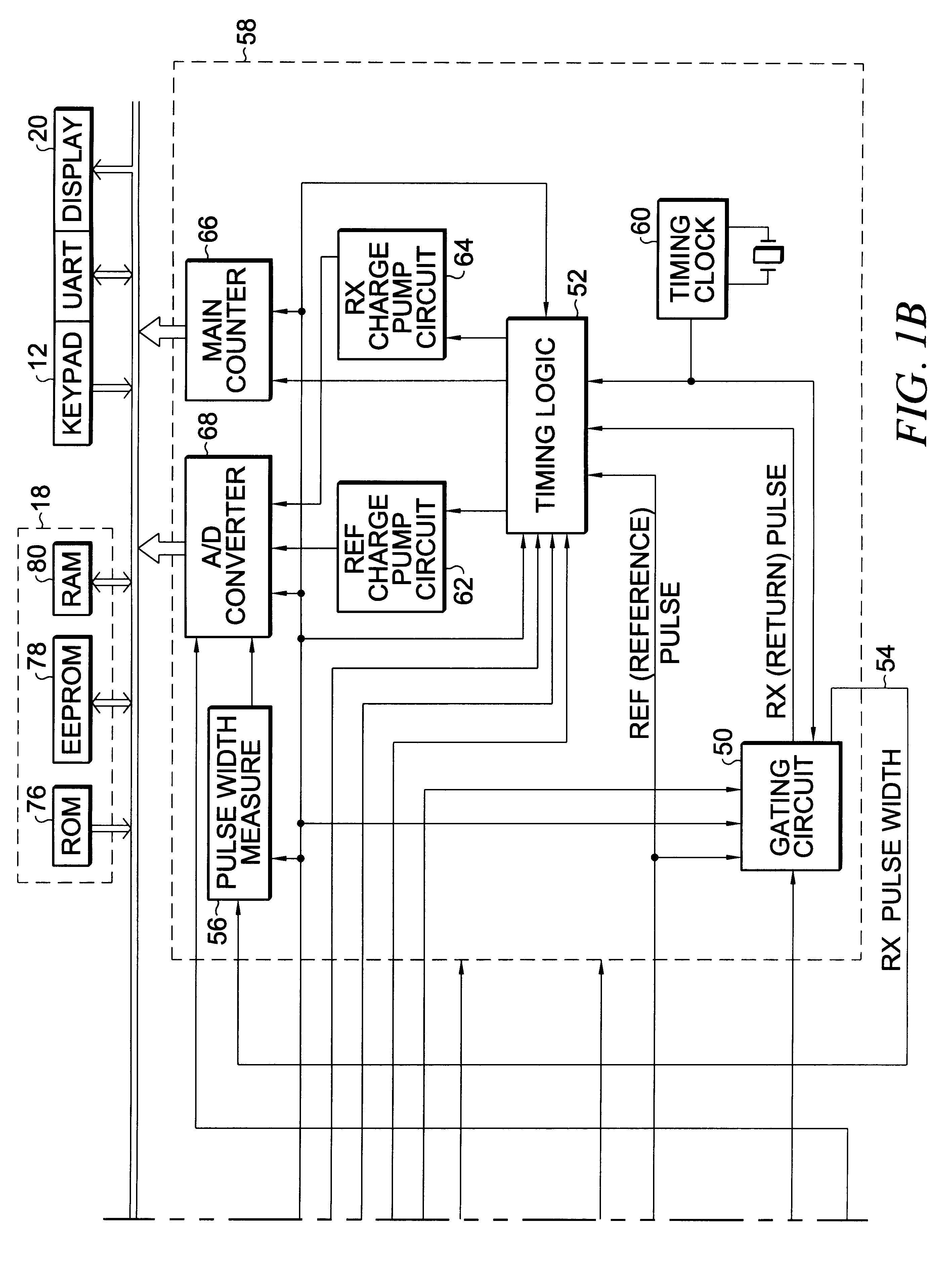
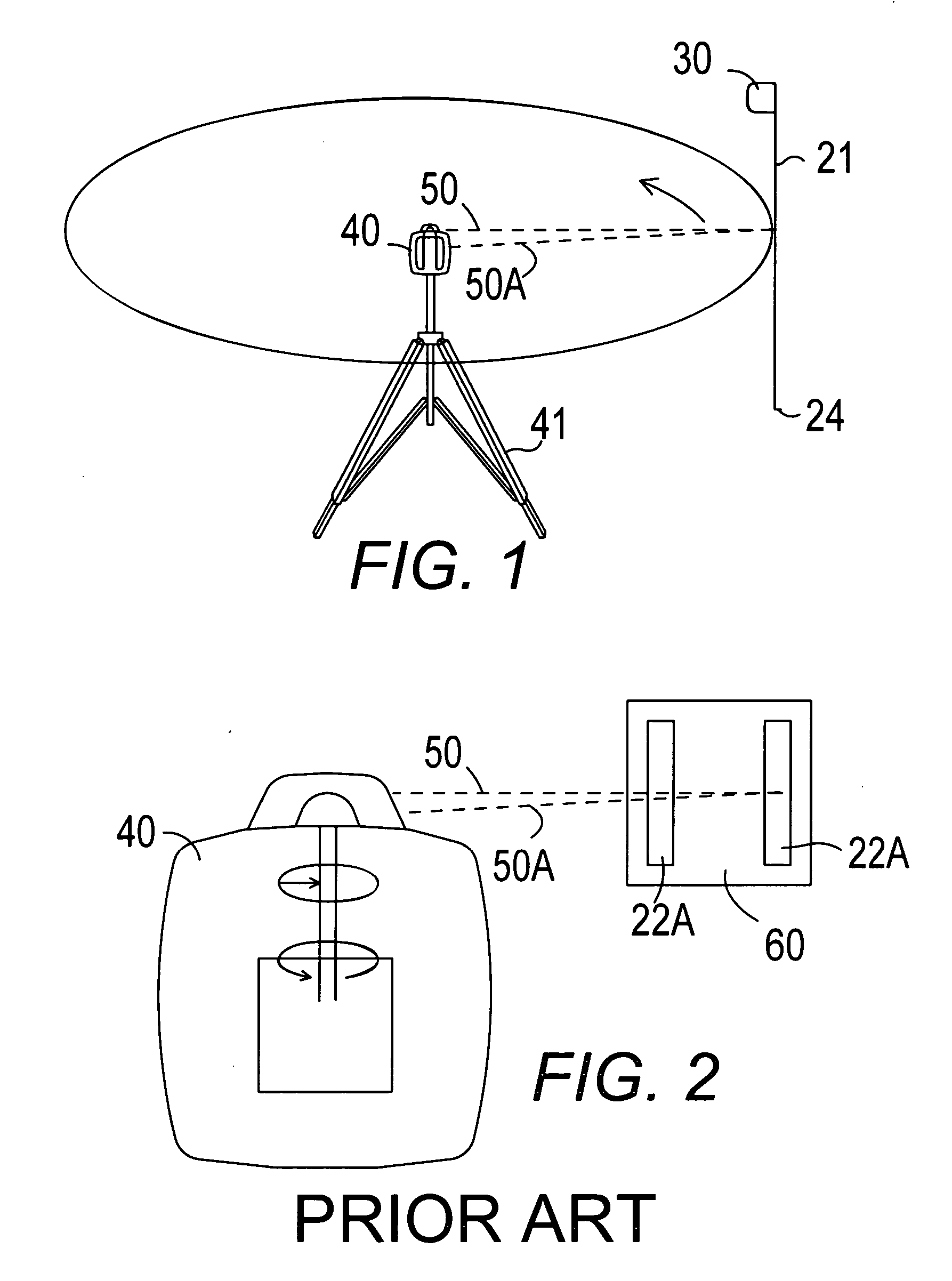
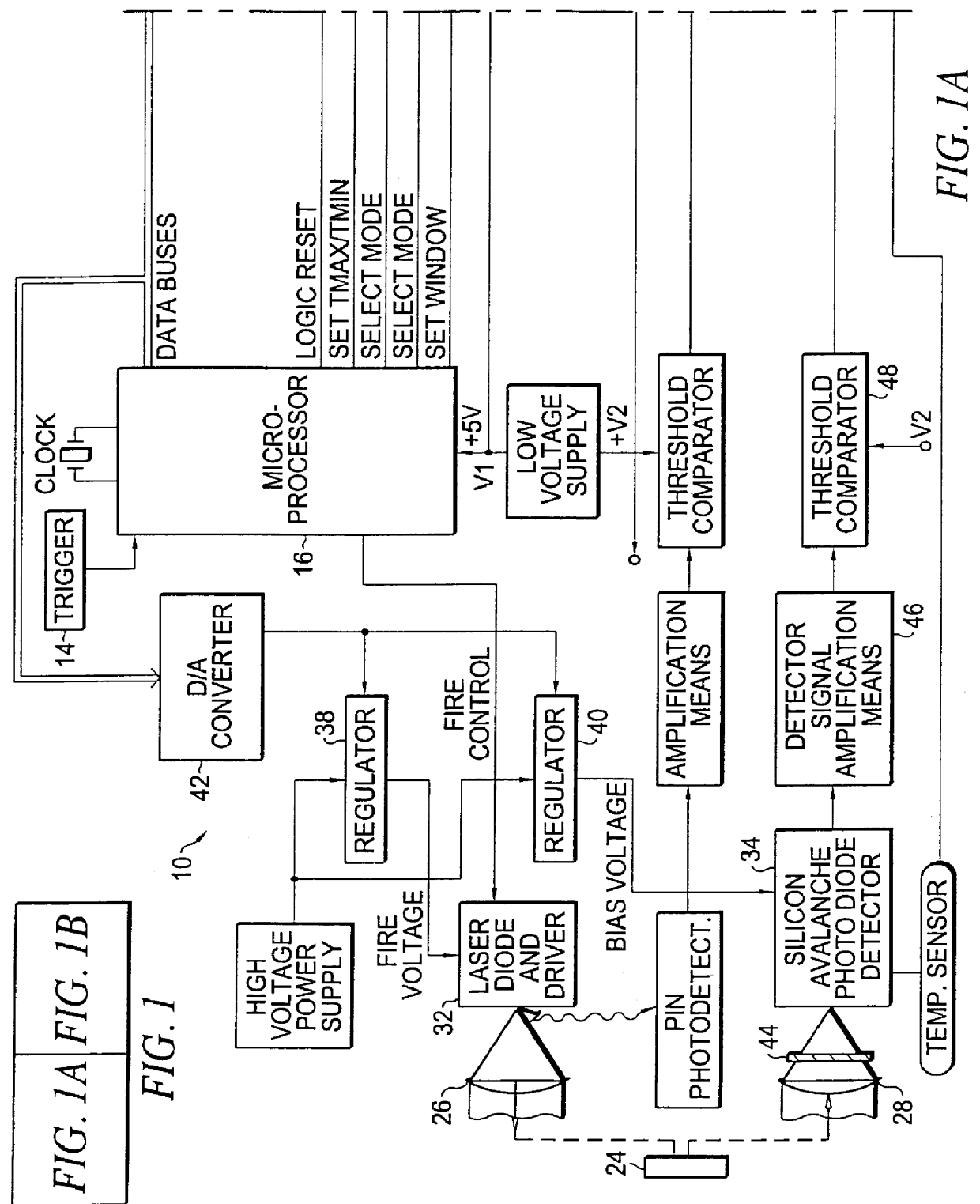
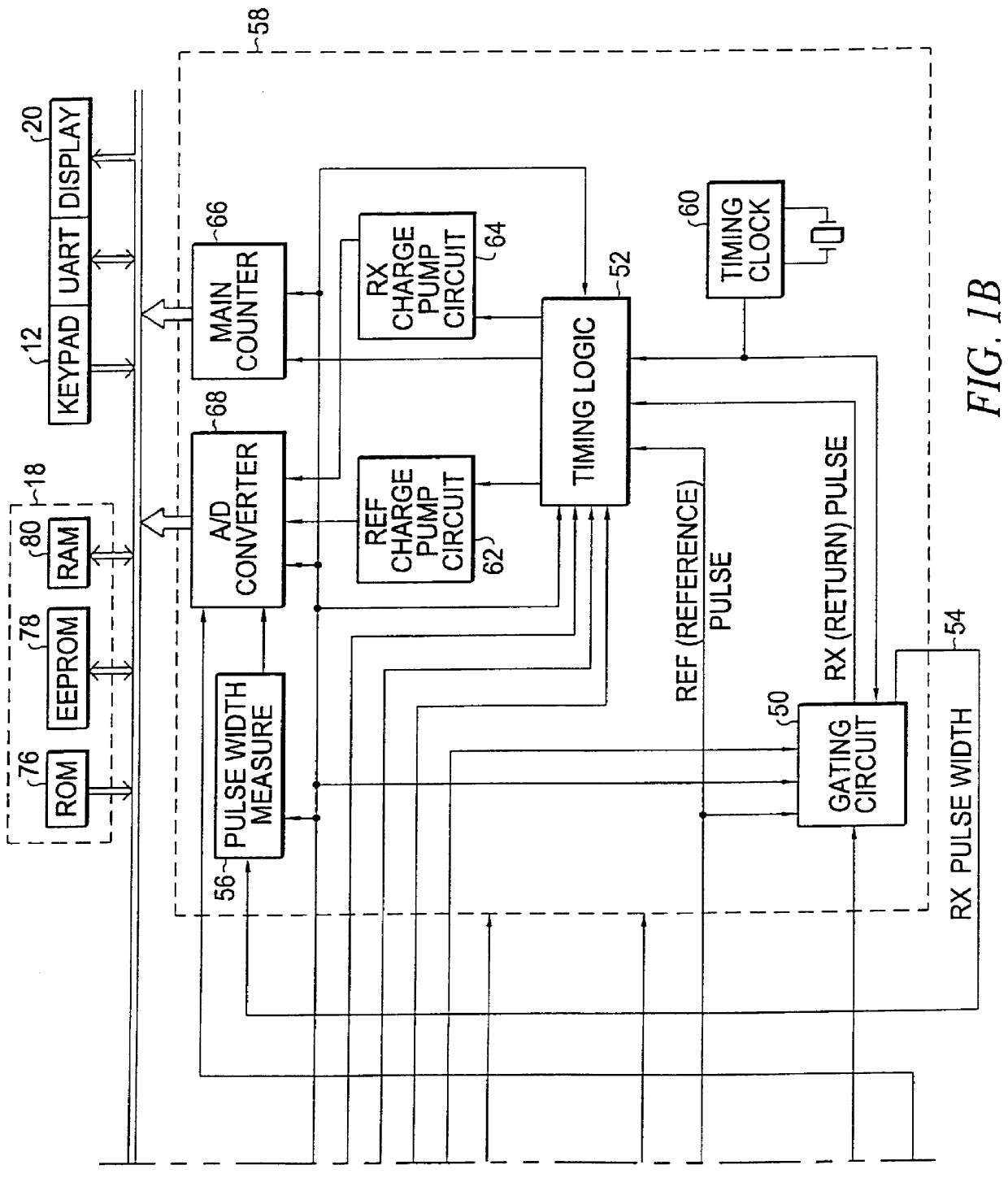
Apparatus and method for determining precision reflectivity of highway signs and other reflective objects utilizing an optical range finder instrument
An apparatus and method for measuring coefficients of retroreflectance of retroreflective surfaces such as road signs involves use of a modified light based range finder. The apparatus includes a power attenuation factor data base which relates pulse width of received pulses to power attenuation of the transmitted pulses. The range finder calculates target range based on time of flight of light pulses. The apparatus automatically calculates the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance for an unknown reflective surface being measured by comparison of the measurement to a reading with the same instrument of a known reflectance standard. The method involves either recalling a stored standard reference reflectance factor or determining a reflectance factor via the range finder for a sample of retroreflective material with a predetermined coefficient of retroreflectance, and then measuring the distance to an unknown target, determining a power attenuation factor from the received pulse width from the unknown target and then calculating the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance based upon these determined values of power attenuation factor, distance and the reference reflectance factor.
Owner:KAMA TECH CORP +1
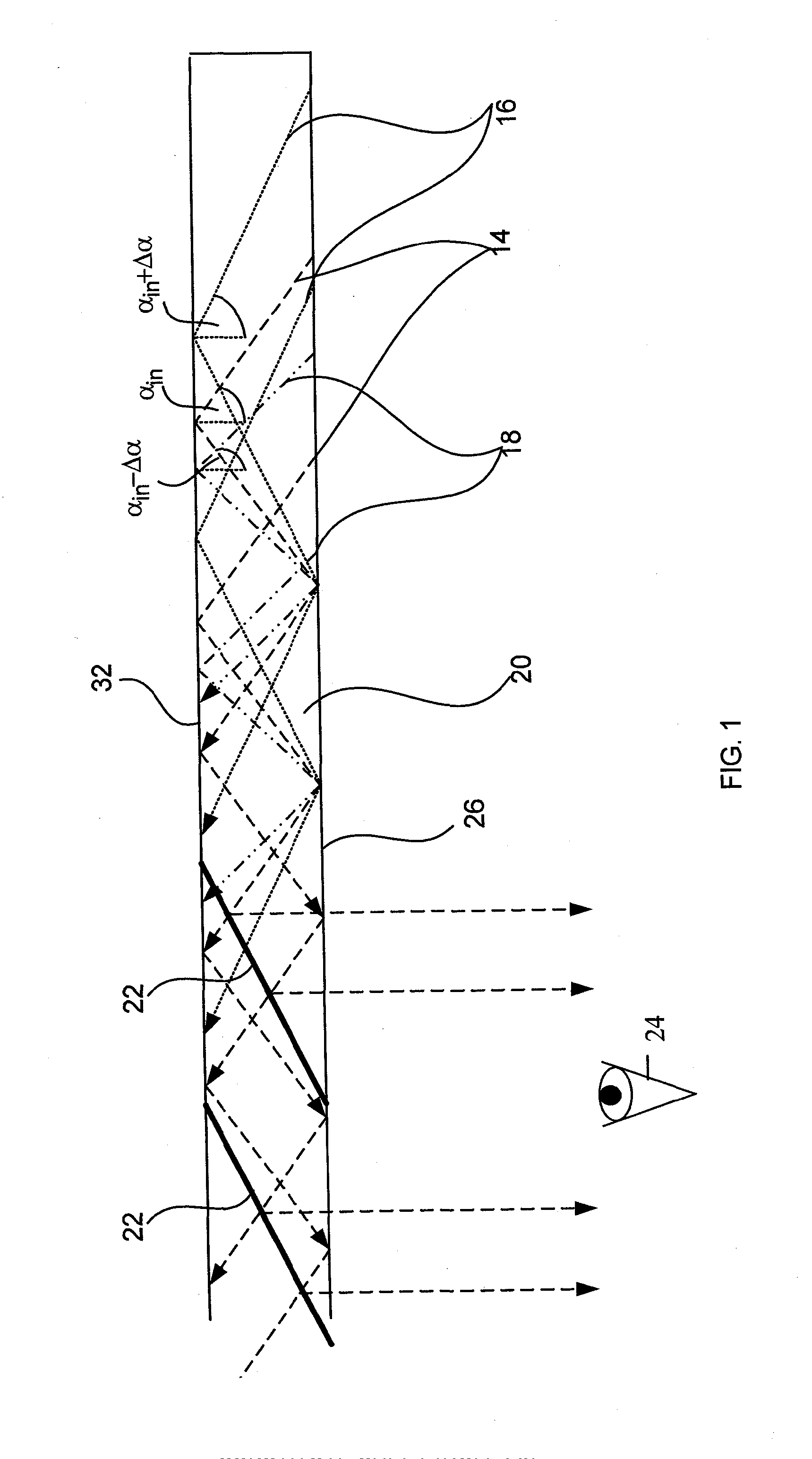
Compact head-mounted display system
ActiveUS20170045744A1Facilitates exploitationLarge EMB valuePrismsPolarising elementsTotal internal reflectionEngineering
There is provided an optical system, including a light-transmitting substrate (20) having at least two major surfaces (26) and edges, an optical prism (54) having at least a first (58), a second (56) and a third (60) surface, for coupling light waves having a given field-of-view into the substrate by total internal reflection, at least one partially reflecting surface located in the substrate, the partially reflecting surface being orientated non-parallelly with respect to the major surfaces of the substrate, for coupling light waves out of the substrate, at least one of the edges (50) of the substrate is slanted at an oblique angle with respect to the major surfaces, the second surface of the prism is located adjacent to the slanted edge of the substrate, and a part of the substrate located next to the slanted edge is substantially transparent, wherein the light waves enter the prism through the first surface of the prism, traverse the prism without any reflection and enter the substrate through the slanted edge.
Owner:LUMUS LTD
Laser cladding of tubes
InactiveUS20090291197A1Reducing dust and back spatterLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge heatingEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to an apparatus for laser cladding of a curved surface comprising: (a) an elongated arm having first and second ends and defining a chamber through the arm from the first end to the second end; (b) a laser delivery source connected to a focusing lens mounted in a housing within an opening on the first end of the arm for delivering a laser beam through the chamber; (c) a delivery head mounted on the second end of the arm comprised of (i) an enclosure having an inlet for receiving the laser and an outlet for delivering the laser to the curved surface, (ii) a powder nozzle for delivering a cladding powder to an inner surface of the curved surface, and (iii) a reflective surface for reflecting the laser to exit through the outlet; (d) mounting means for rotating the curved surface for the cladding of the curved surface; and (e) indexing means for moving the arm substantially parallel to a longitudinal axis of the curved surface so as to clad the curved surface during the rotation of the curved surface. Typically, the curved surface is part of the inner surface of a tube used in industrial applications.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
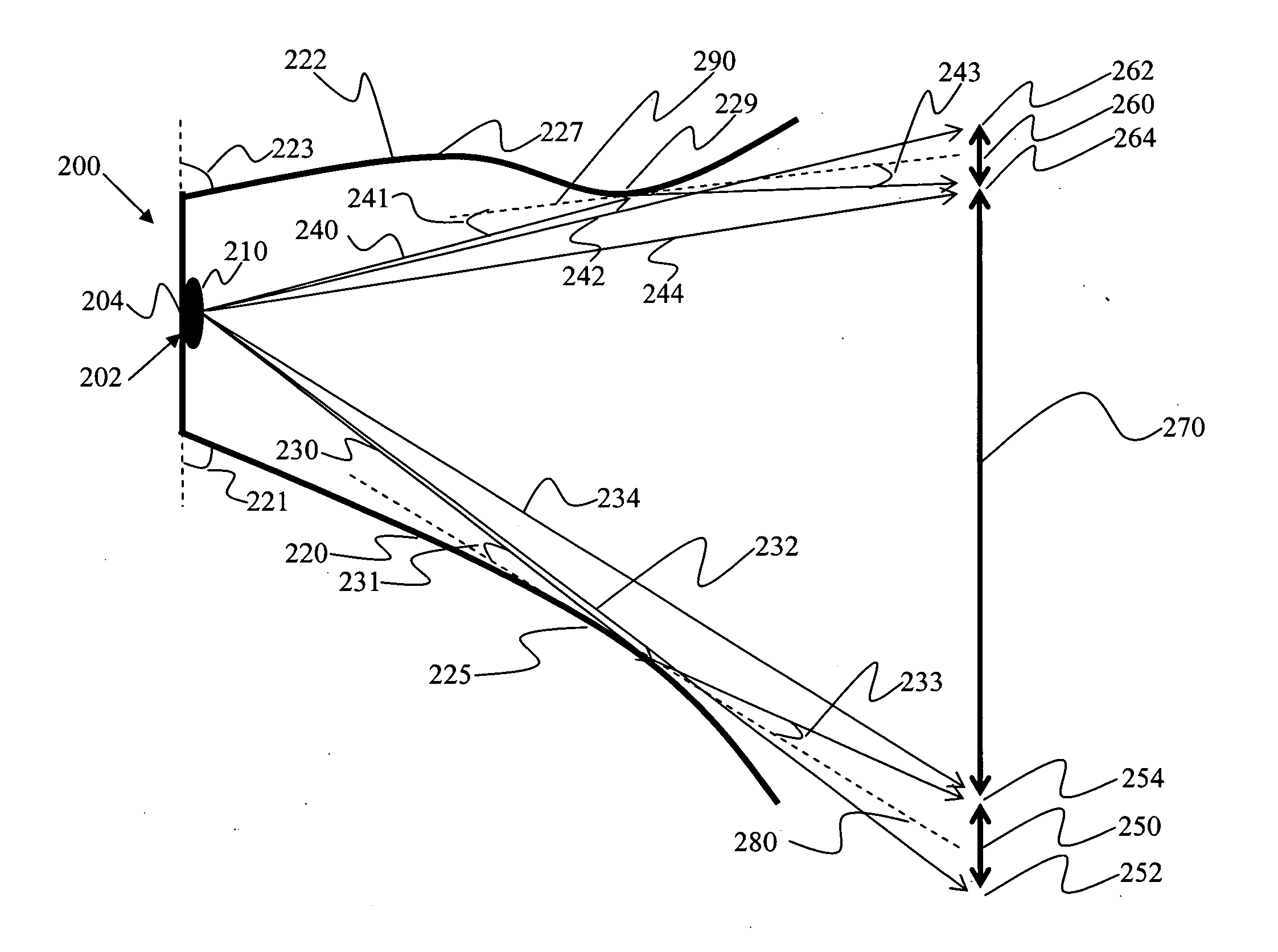
Scanning interferometer for aspheric surfaces and wavefronts
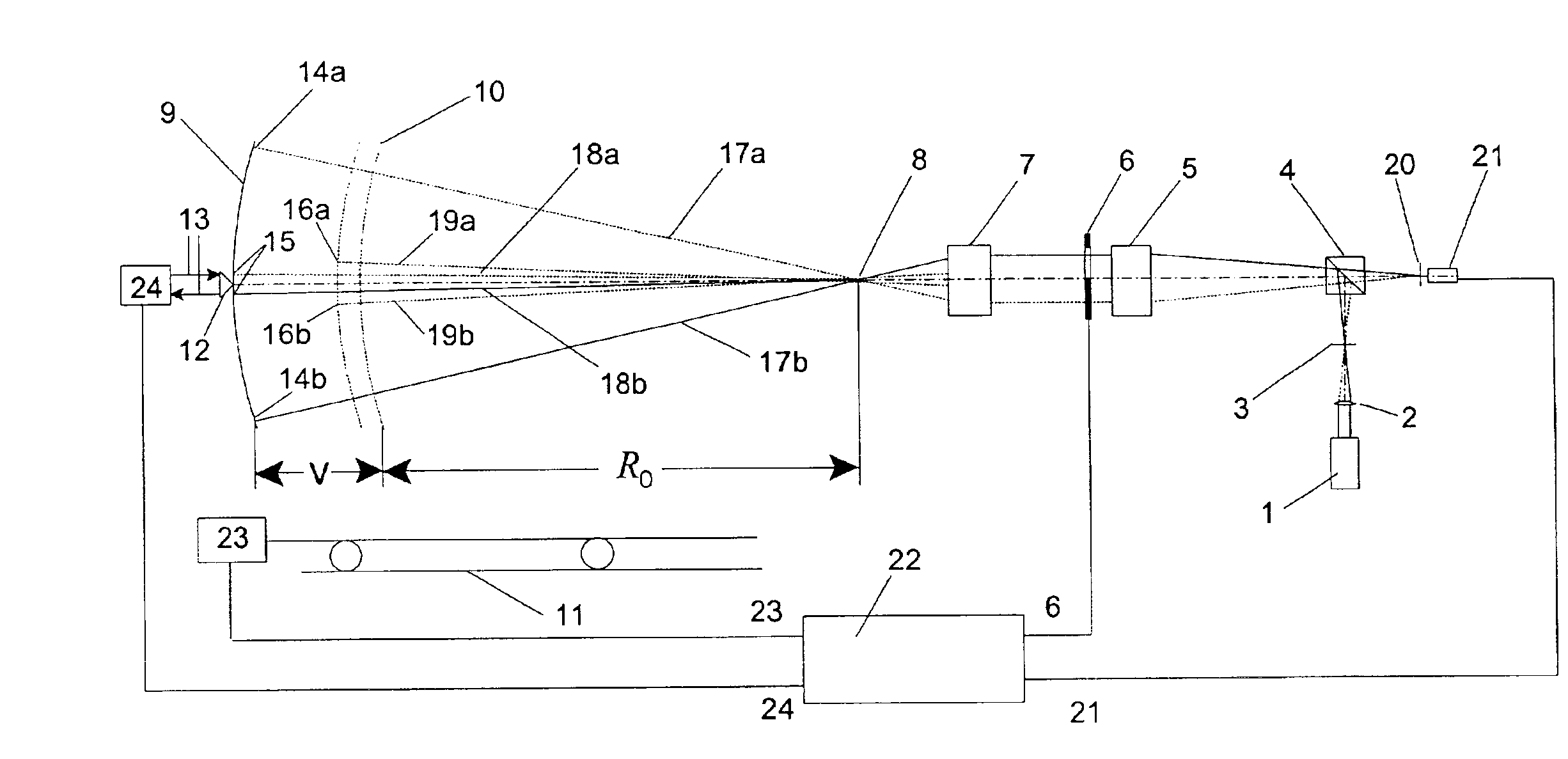
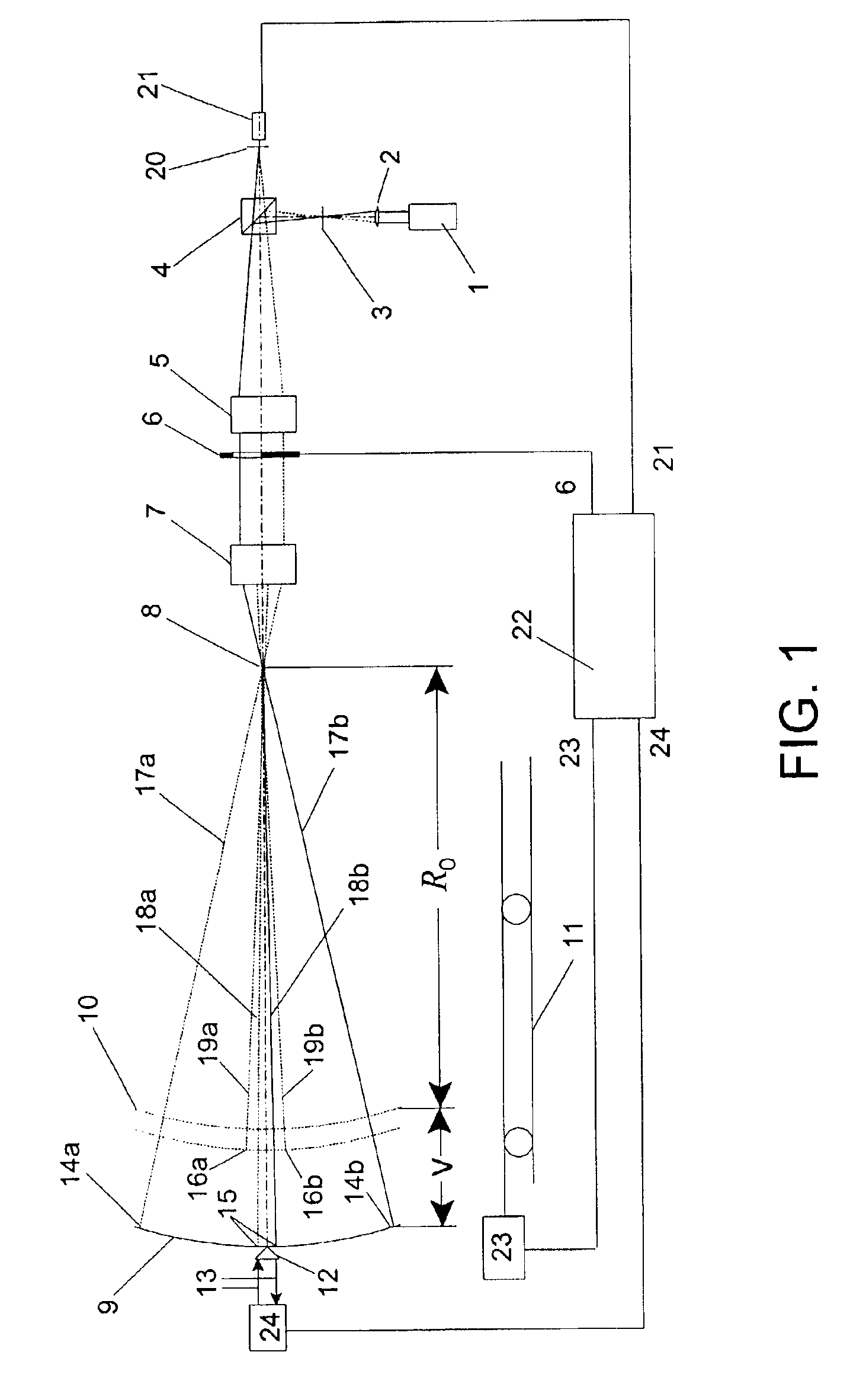
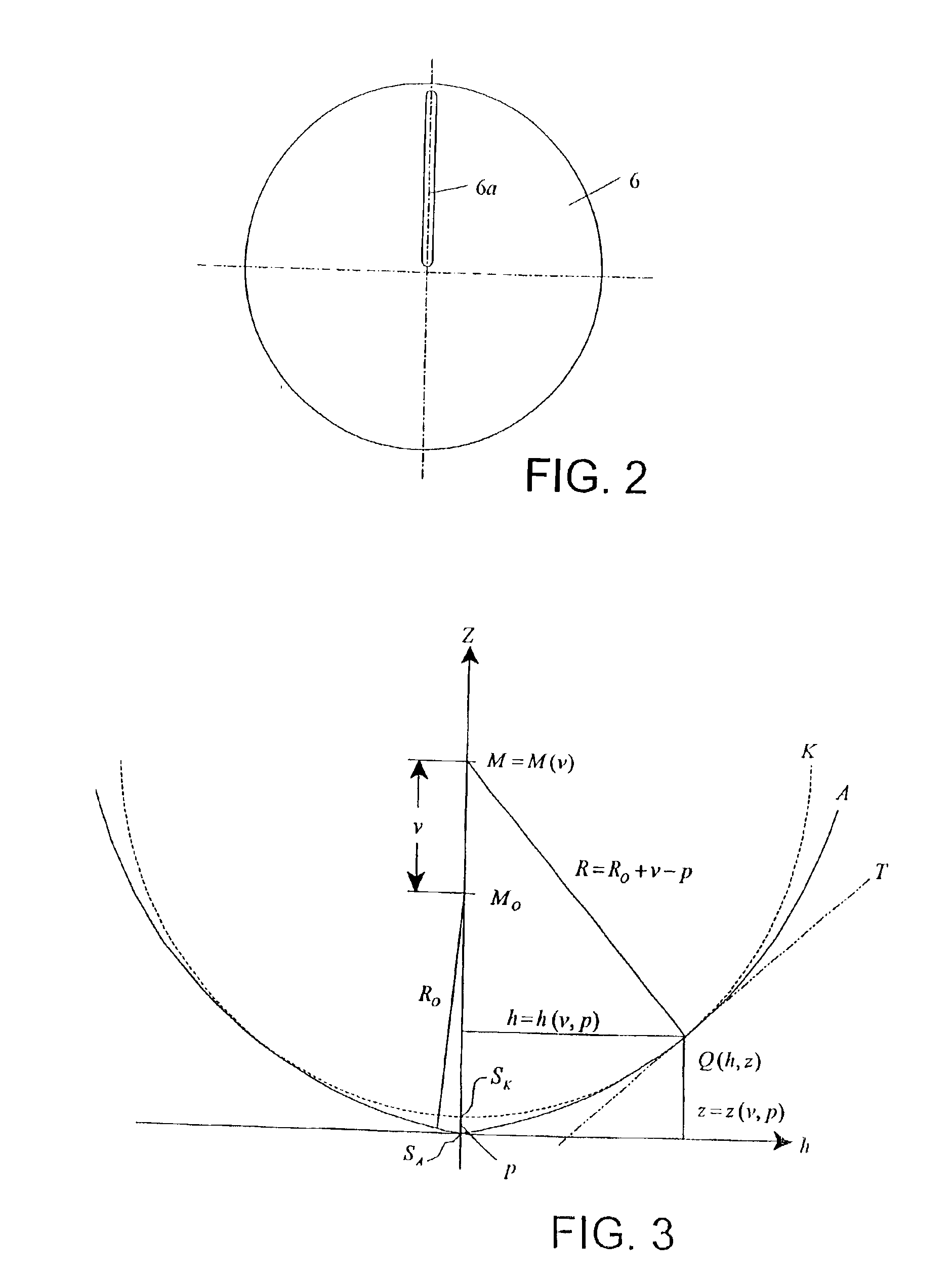
Interferometric scanning method(s) and apparatus for measuring rotationally and non-rotationally symmetric test optics either having aspherical surfaces or that produce aspherical wavefronts. A spherical or partial spherical wavefront is generated from a known origin along an optical axis. The test optic is aligned with respect the optical axis and selectively moved along it relative to the known origin so that the spherical wavefront intersects the test optic at the apex of the aspherical surface and at radial positions where the spherical wavefront and the aspheric surface intersect at points of common tangency. An axial distance, ν, and optical path length, p, are interferometrically measured as the test optic is axially scanned by the spherical wavefront where ν is the distance by which the test optic is moved with respect to the origin and p is the optical path length difference between the apex of an aspherical surface associated with the test optic and the apex of the circles of curvature that intersect the aspherical surface at the common points of tangency. Coordinates of the aspherical surface are calculated wherever the circles of curvature have intersected the aspherical surface and in correspondence with the interferometrically measured distances, ν and p. Afterwards, the shape of the aspheric surface is calculated. Where the test optic comprises a refracting optic a known spherical reflecting surface is provided upstream of the refracting optic for movement along the optical axis and a known wavefront is made to transit the refracting optic, reflects from the known spherical surface, again transits the refracting optic traveling towards the known origin after which the interferogram is formed. In another aspect of the invention, a spherical reference surface is provided to form a Fizeau that is used to generate phase information for measuring spheres, mild aspheres, and multiple mild aspheres.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Polarizing turning film using total internal reflection
A light redirecting article redirects light toward a target angle. The light redirecting article has an input surface for accepting incident illumination over a range of incident angles and an output surface with a plurality of light redirecting structures, each light redirecting structure having an internal reflection surface oriented at a first angle with respect to the plane of the input surface and an exit surface for emitting an output light at an emitted light angle, wherein the exit surface is oriented at a second angle relative the plane of the input surface. For incident illumination at a principal angle greater than 60 degrees from normal, light is reflected from the internal reflection surface and emitted from the exit surface at an emitted light angle that is within 5 degrees of the target angle.
Owner:SK MICROWORKS SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Optical unit, vehicle monitor, and obstruction detector
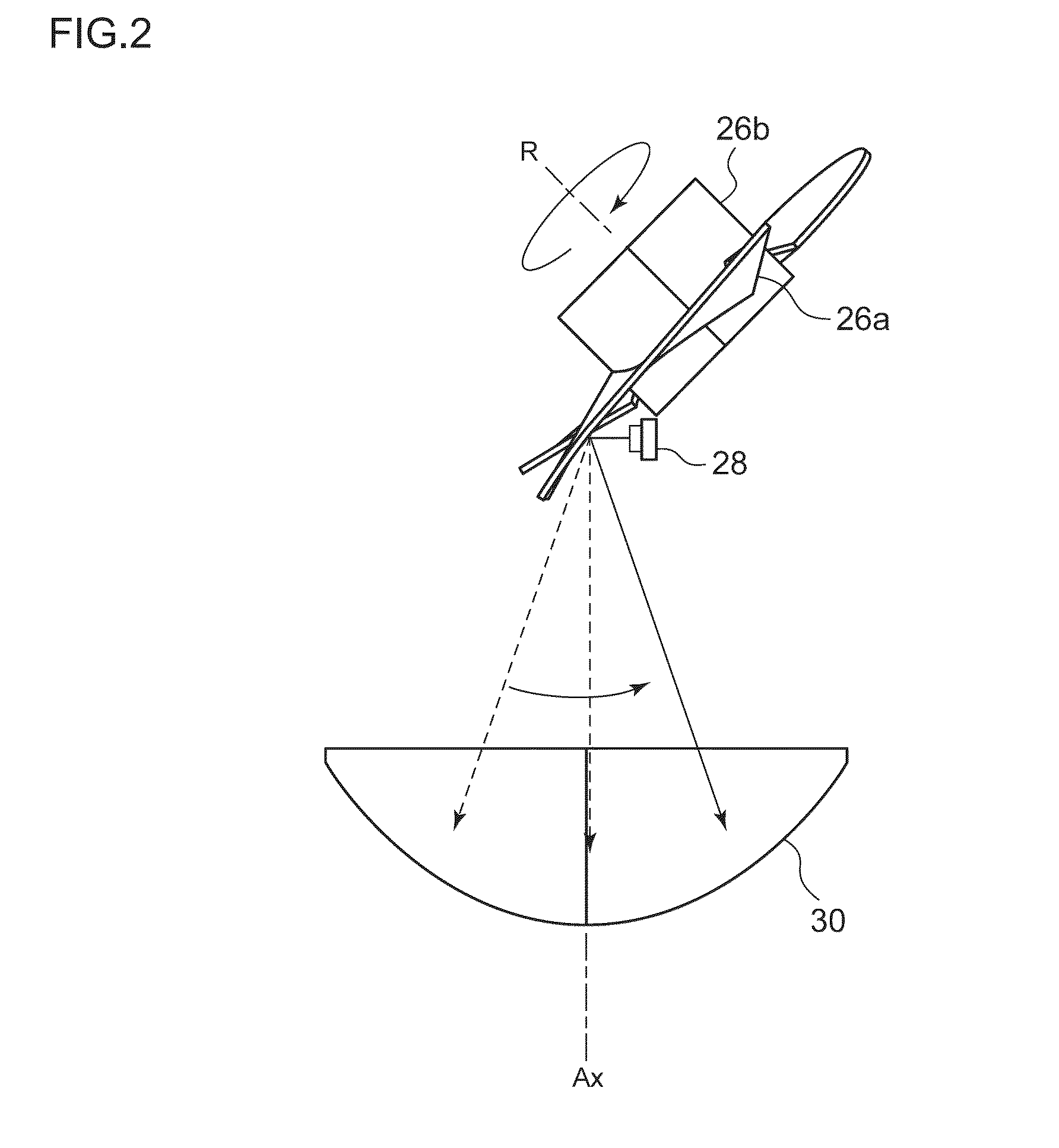
ActiveUS20130038736A1Easy to useAccurately and easily detects a vehicle travelingPoint-like light sourcePortable electric lightingOptical axisMechanical engineering
Disclosed is an optical unit wherein a rotating reflector rotates about a rotation axis in one direction, while reflecting light emitted from a light source. The rotating reflector is provided with a reflecting surface such that the light reflected by the rotating reflector, while rotating, forms a desired light distribution pattern, said light having been emitted from the light source. The light source is composed of light emitting elements. The rotation axis is provided within a plane that includes an optical axis and the light source. The rotating reflector is provided with, on the periphery of the rotation axis, a blade that functions as the reflecting surface.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Optical interferometric pressure sensor
InactiveUS20070089524A1Raise the gradeFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsFluid pressure measurement by optical meansOptical reflectionEngineering
A capacitive vacuum measuring cell has a first housing body and a membrane, both of Al2O3 ceramic or sapphire. The membrane is planar with a peripheral edge joined by a first seal to the first housing body to form a reference vacuum chamber. A second housing body of Al2O3 ceramic or sapphire opposite the membrane, is joined to the peripheral edge of the membrane by a second seal to form a measurement vacuum chamber. A port connects the vacuum measuring cell to a medium to be measured. At least in the central area of the first housing body, an optical transparent window is formed and at least the central region of the membrane has an optically reflective surface. Outside the reference vacuum chamber, in opposition to and at a distance from the window, an optical fibre is arranged for feeding in and out light onto the surface of the membrane.
Owner:INFICON GMBH
Reduced angular emission cone illumination leds
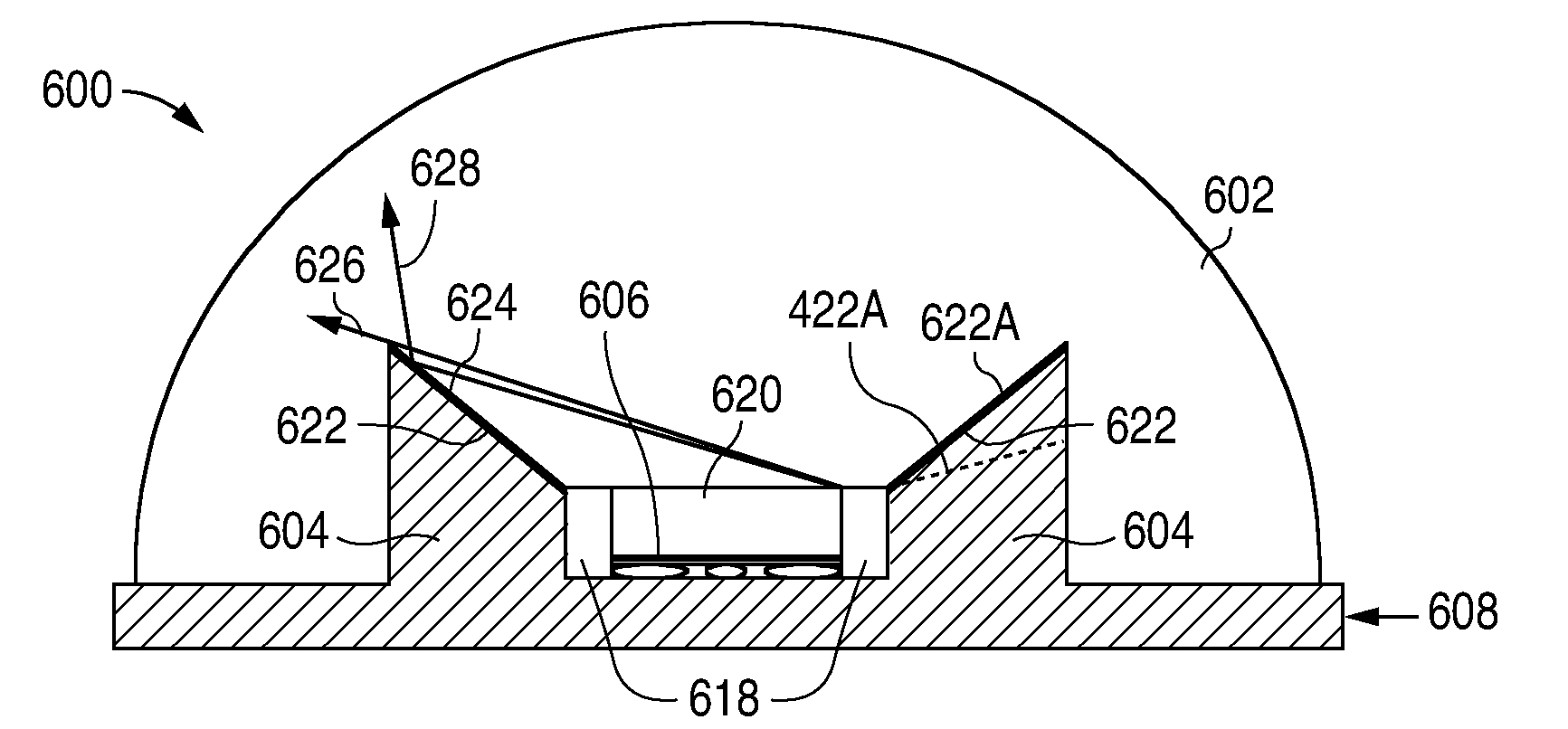
InactiveUS20110062470A1Reduces light emission angleSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emissionLight-emitting diode
A light emitting diode (LED) package includes a support, an LED die mounted on the support, a reflector around the LED die, and a lens over the LED die. The reflector has an angled reflective surface that limits the light emission angle from the LED package. The reflector is a part of the lens or the support.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
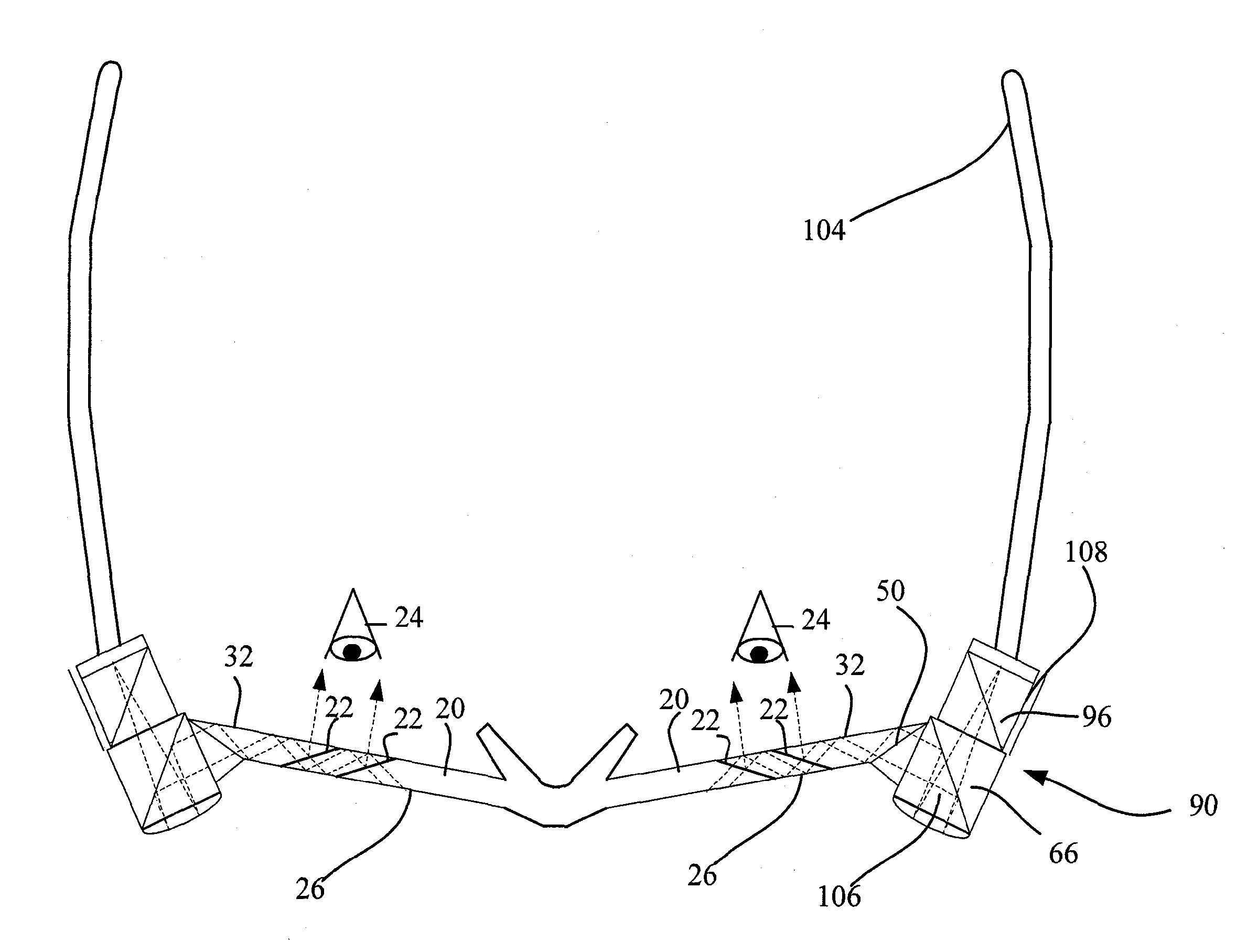
Augmented reality eyewear
Eyewear for displaying a virtual image comprising first and second lenses, a light source in optical communication with at least one of the lenses, and a reflective surface situated within at least one of the lenses and configured to direct light projected into the lens from the light source toward a corresponding eye of the wearer for display as a virtual image. Another eyewear comprising a lens(es) configured to display a virtual image, a frame for supporting the lens(es) within a field of vision of the wearer, and electronics for operating the eyewear, the electronics being integrally embedded within one or more components of the frame.
Owner:LAFORGE OPTICAL INC
Vehicle headlamp
ActiveUS20100194276A1Dispersion errorReliably achieveVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourcePower savingHeadlamp
A vehicle headlamp is provided with: a fixed reflector having reflecting surfaces made of parabola-based free curved faces; movable reflectors having reflecting surfaces made of parabola-based free curved faces; and semiconductor-type light sources having light emitting chips shaped like a planar rectangle. When the movable reflectors are positioned in a first location, a light distribution pattern for low beam is obtained. When the movable reflectors are positioned in a second location, light distribution patterns for high beams are obtained. When the movable reflectors are positioned in a third location, light distribution patterns for daytime running light are obtained. As a result, the vehicle headlamp can achieve downsizing, weight reduction, power saving, and cost reduction.
Owner:ICHIKOH IND LTD
Lighting unit reflector
InactiveUS20070247856A1Reduce dark band areaWide areaMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceDark bandLight source
A lighting unit that includes a light source and a reflector assembly upon which the light source is mounted. The reflector assembly includes a first reflector having a first curved reflective surface extending away from the light source, and a second reflector having a second curved reflective surface extending away from the light source. The first curved reflective surface faces and opposes the second curved reflective surface. The first curved reflective surface has a curvature that is different from that of the second curved reflective surface. The first and second curved reflective surfaces both preferably terminate in convexities that reduce the size of dark band areas of illumination.
Owner:LEOTEK ELECTRONICS
Retroreflective article
A retroreflective article that exhibits suitable retroreflective luminance under dry and dynamic wet conditions. The article includes an enclosed-lens retroreflective sheeting that, under dry conditions, exhibits a coefficient of retroreflective luminance of about 40 (millicandela / m2) / lux as measured by ASTM D 4061-94 and, under dynamic wet conditions the sheeting increases in coefficient of retroreflective luminance. The article further includes a plurality of retroreflective elements partially embedded in a light transmissible bonding layer on the front, reflective surface of the retroreflective sheeting.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Catadioptric projection objective with an in-line, single-axis configuration
InactiveUS20060082905A1Prevent fallingPhotomechanical apparatusOptical elementsOptoelectronicsProjection system
A catadioptric objective for a microlithography projection system has an in-line single-axis arrangement of lenses and reflectors. The catadioptric portion of the objective includes a catadioptric lens element with at least one reflective surface or surface portion reflecting light back into the lens, so that the catadioptric lens element interacts with light rays through reflection as well as refraction.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Optical system for a fundus camera
InactiveUS20100014052A1Suppression of blurDimension of can be minimizeEye diagnosticsOptical elementsCatoptricsDioptre
The invention is directed to an optical system for a fundus camera for reflection-free opthalmoscopy having a beam path with refractive and reflective optical elements which are used substantially in common for illumination and observation or recording. An imaging mirror system substantially comprising a plurality of reflecting optical elements in the form of mirrors and is provided for illuminating and imaging the fundus. At least one optical element, for example, mirror, is formed as a freeform mirror with an imaging, reflecting freeform surface. The optical elements are arranged in a housing in a precisely defined position and attitude relative to one another in such a way that an imaging of the reflecting surfaces of the optical elements on the image of the imaged retina is prevented within a wide diopter range of the patient's eye to be examined.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Flashlight with lens for transmitting central and off-axis light sources
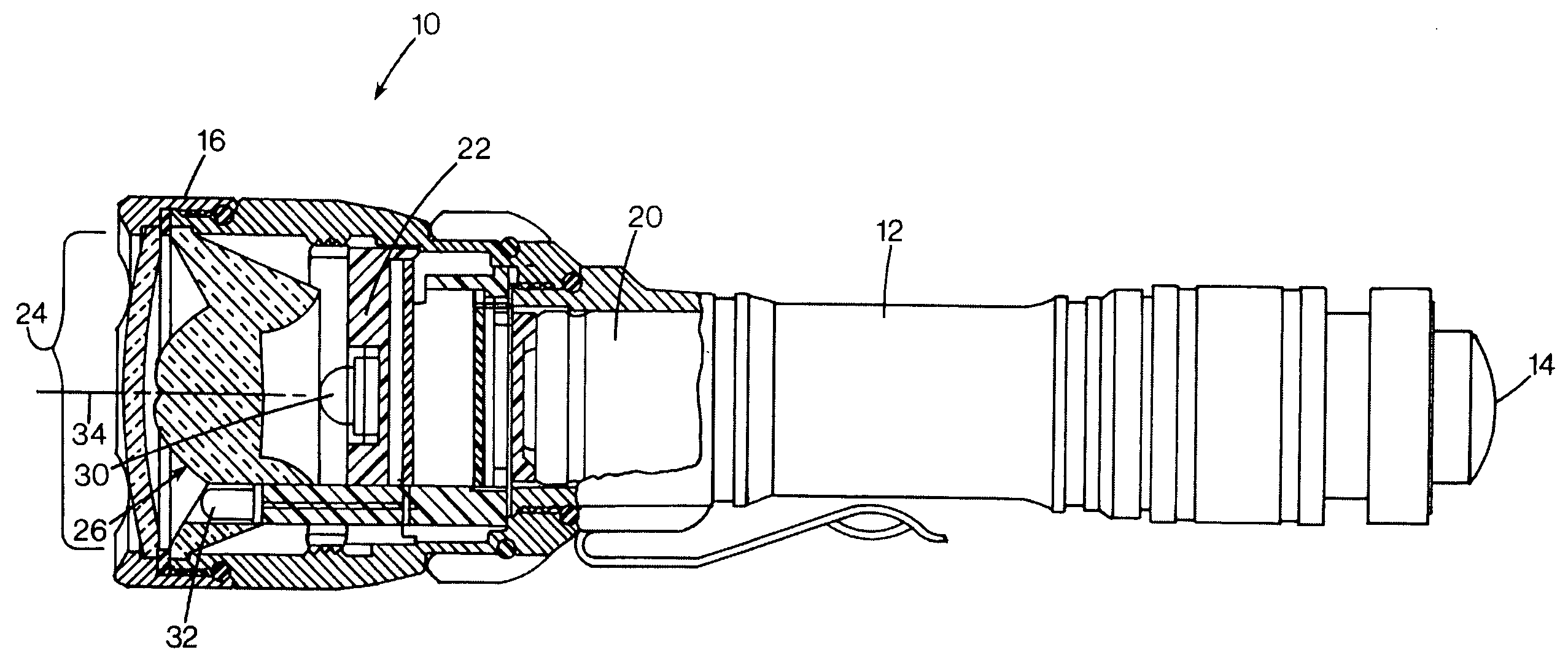
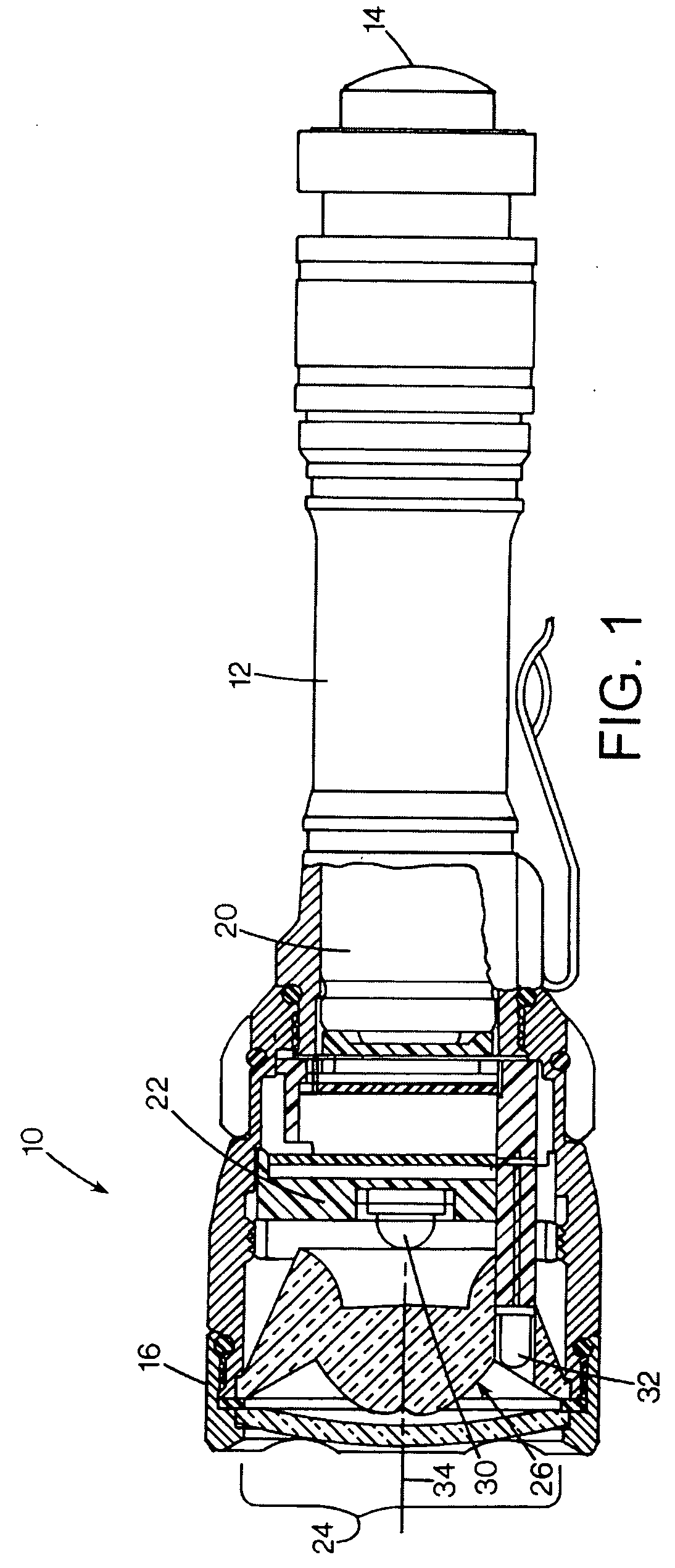
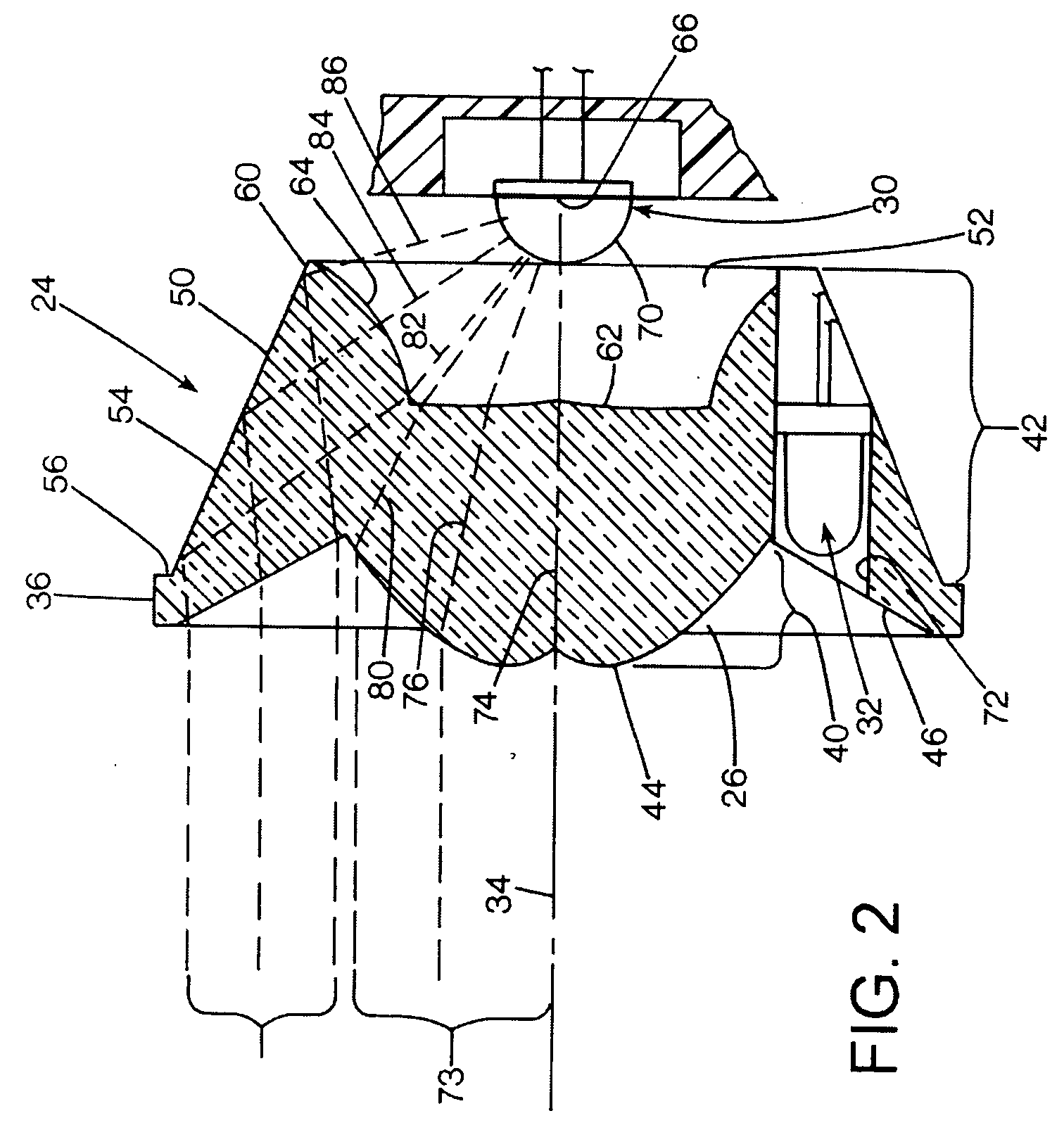
ActiveUS20050122711A1Overcome limitationsLight source combinationsPoint-like light sourceOptical axisFirst light
A flashlight has a lens having an optical axis, with a first light source positioned on the optical axis. A second light source is spaced apart from the first light source away from the optical axis, and the lens has an aperture registered with the second light source. The lens may have a central portion configured to transmit axially-emitted light from the first light source, and the lens having a peripheral portion having an internally reflective surface configured to reflect laterally-emitted light from the light source in a direction more closely aligned with the optical axis. The first light source may be positioned within a recess in the lens, and the aperture may be formed in the peripheral portion of the lens. The light sources may be LEDs, and may be of different colors.
Owner:SUREFIRE LLC
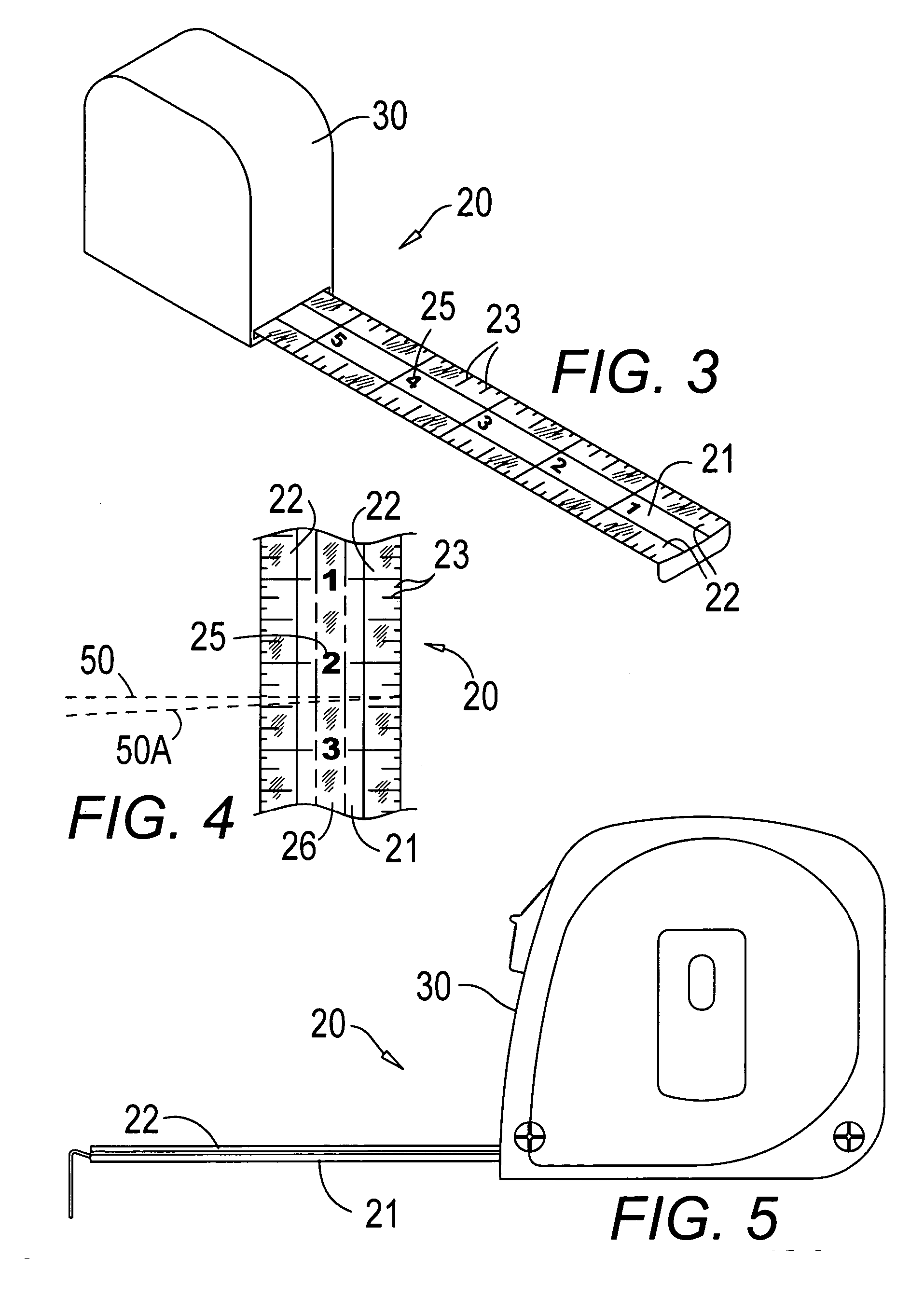
Light reflective and light enhancing tape measure
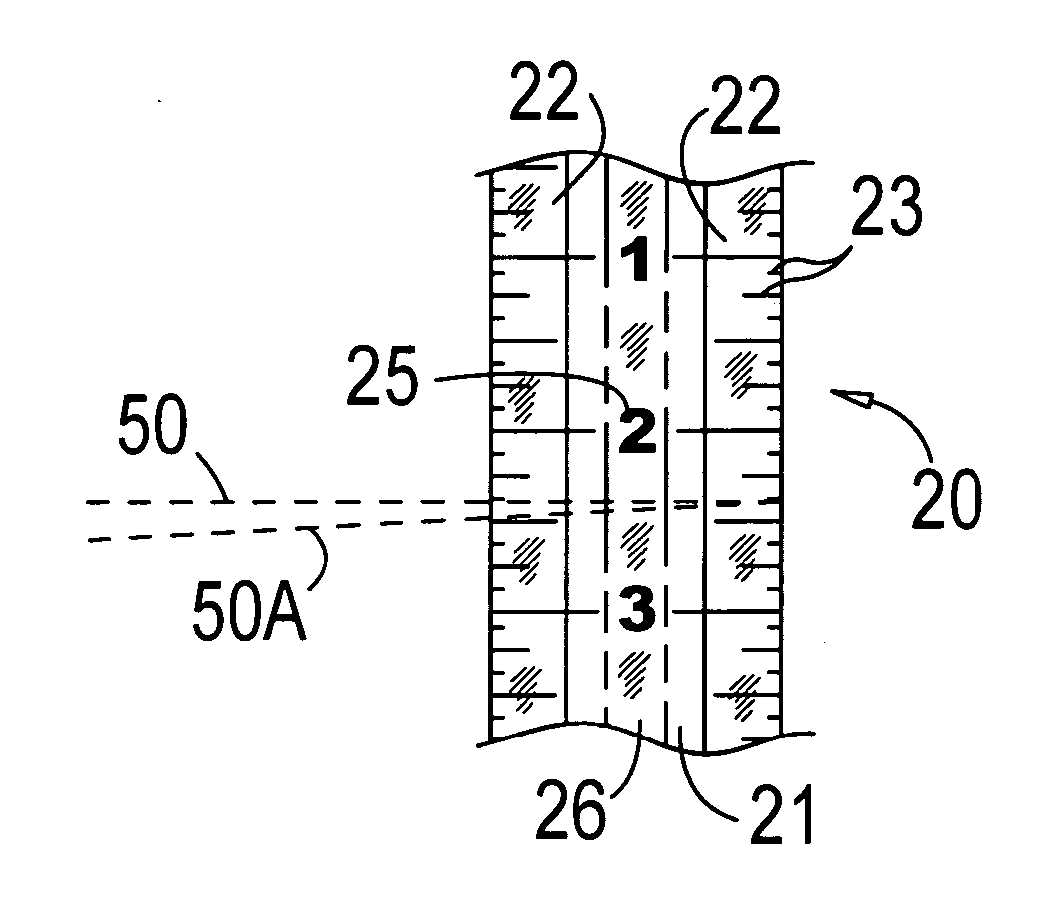
InactiveUS20070017111A1Easy to readReduce usageSurveyor's staffsMovable markersLight reflexOptoelectronics
A tape measure or other measuring surface has an attached pair of light enhancing reflective surfaces in conjunction with the numbers and measurement lines for use with rotating laser light instruments and light enhancement for readability. Reflective and glow in the dark surfaces may also be applied.
Owner:HOBACK JOHN F +1
Apparatus and method for determining precision reflectivity of highway signs and other reflective objects utilizing an optical range finder instrument
An apparatus and method for measuring coefficients of retroreflectance of retroreflective surfaces such as road signs involves use of a modified light based range finder. The apparatus includes a power attenuation factor data base which relates pulse width of received pulses to power attenuation of the transmitted pulses. The range finder calculates target range based on time of flight of light pulses. The apparatus automatically calculates the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance for an unknown reflective surface being measured by comparison of the measurement to a reading with the same instrument of a known reflectance standard. The method involves either recalling a stored standard reference reflectance factor or determining a reflectance factor via the range finder for a sample of retroreflective material with a predetermined coefficient of retroreflectance, and then measuring the distance to an unknown target, determining a power attenuation factor from the received pulse width from the unknown target and then calculating the absolute coefficient of retroreflectance based upon these determined values of power attenuation factor, distance and the reference reflectance factor.
Owner:KAMA TECH (HK) LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com