Patents
Literature
2836 results about "Time of flight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
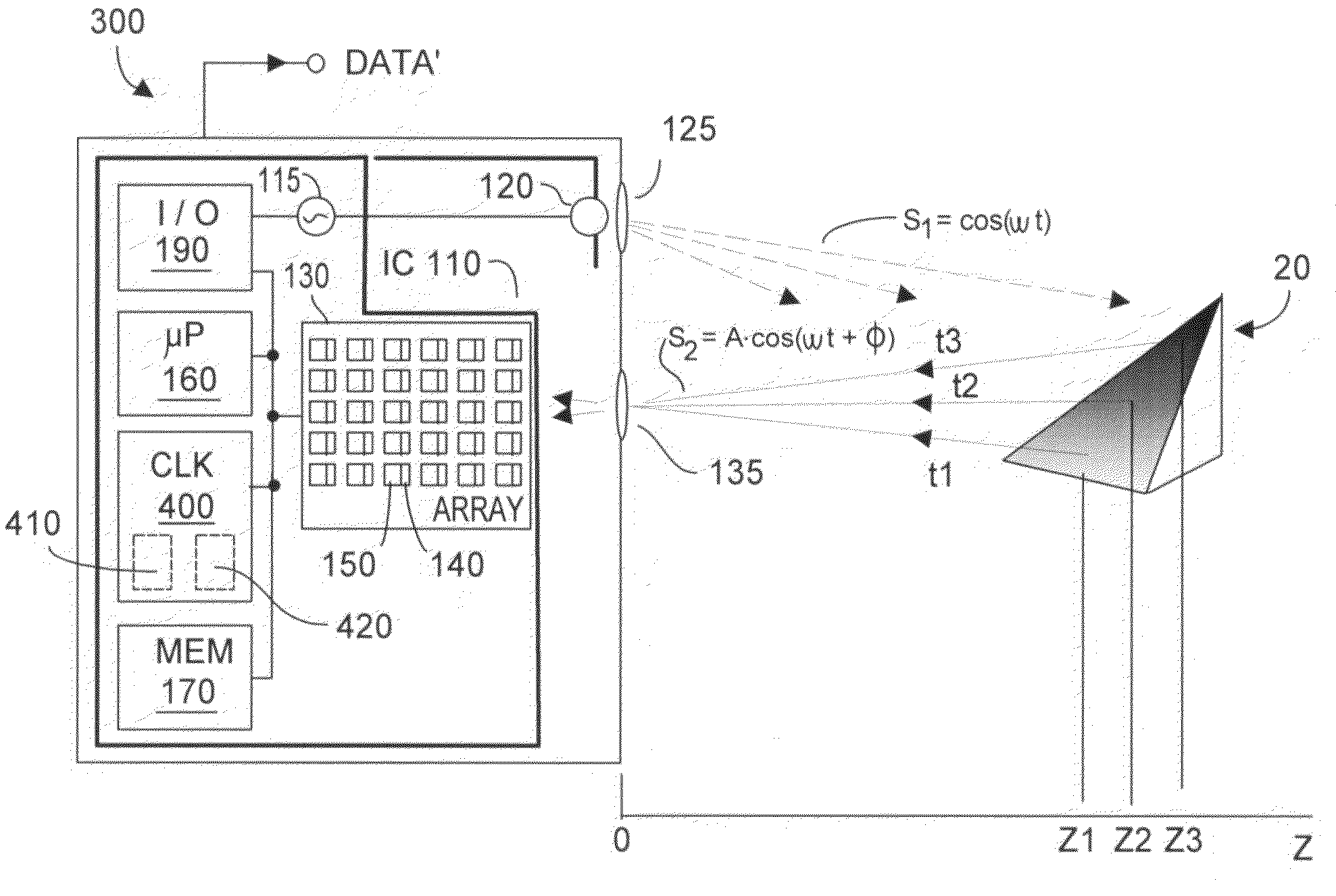
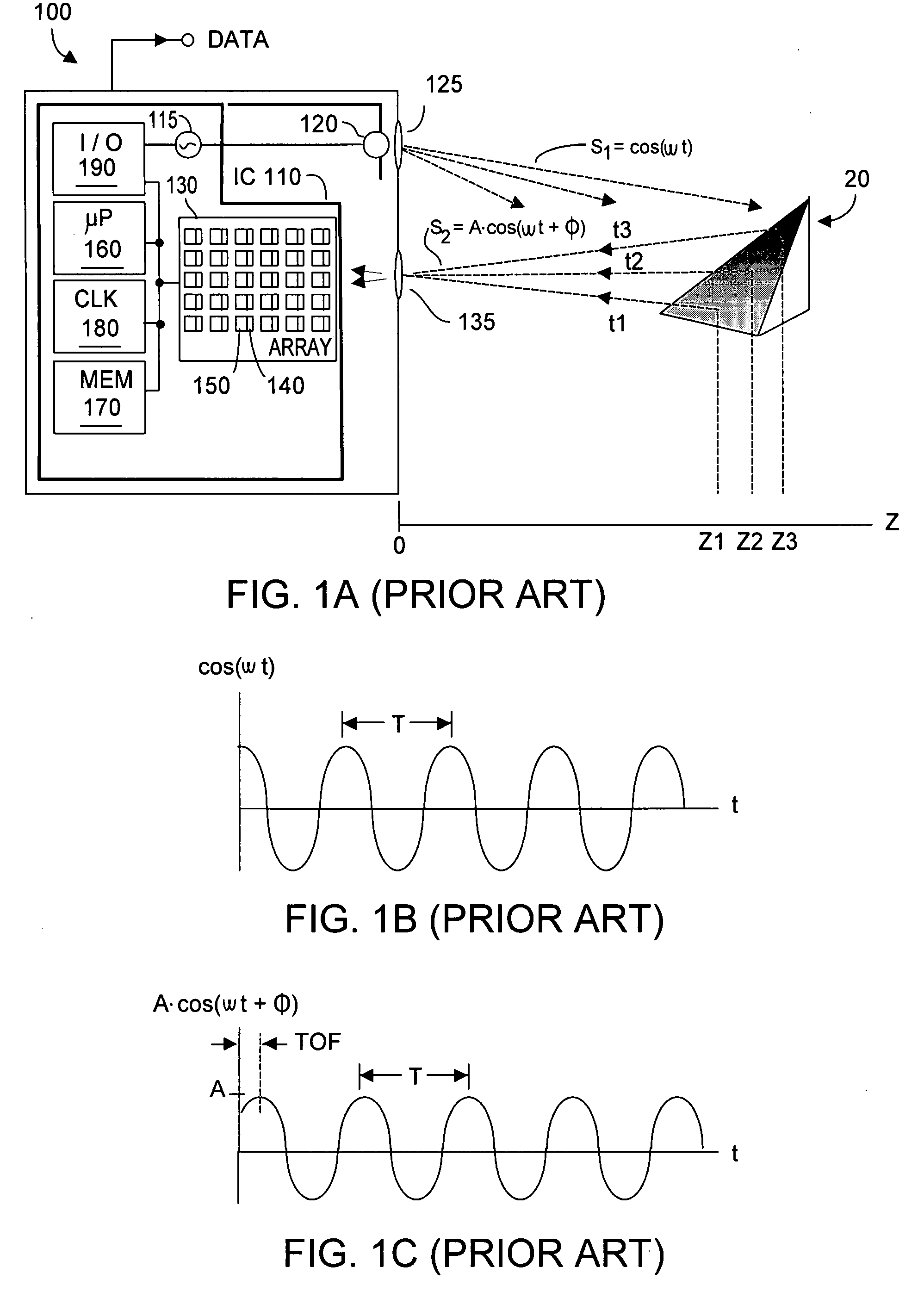
Time of flight (ToF) is the measurement of the time taken by an object, particle or wave (be it acoustic, electromagnetic, etc.) to travel a distance through a medium. This information can then be used to establish a time standard (such as an atomic fountain), as a way to measure velocity or path length, or as a way to learn about the particle or medium's properties (such as composition or flow rate). The traveling object may be detected directly (e.g., via an ion detector in mass spectrometry) or indirectly (e.g., by light scattered from an object in laser doppler velocimetry).
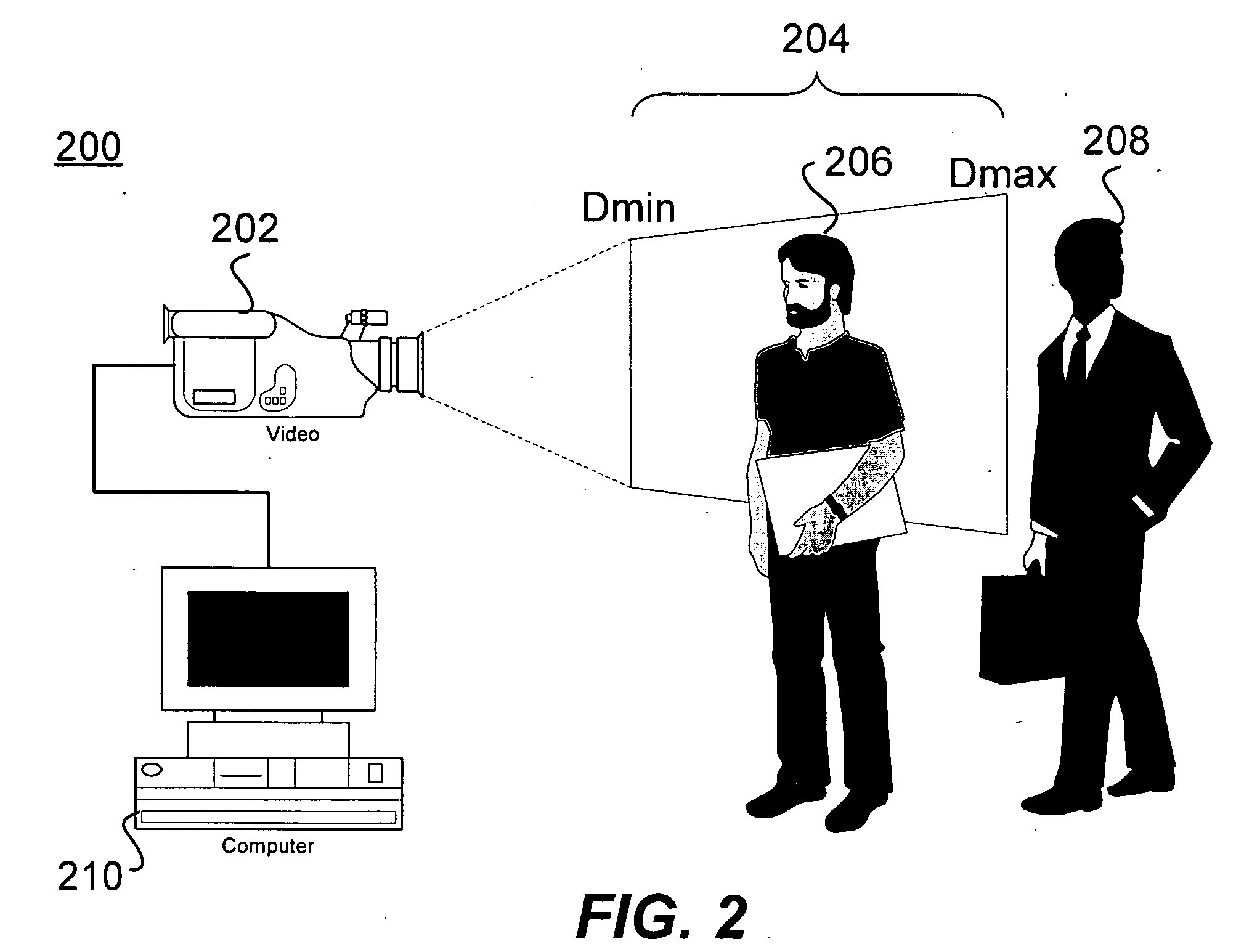
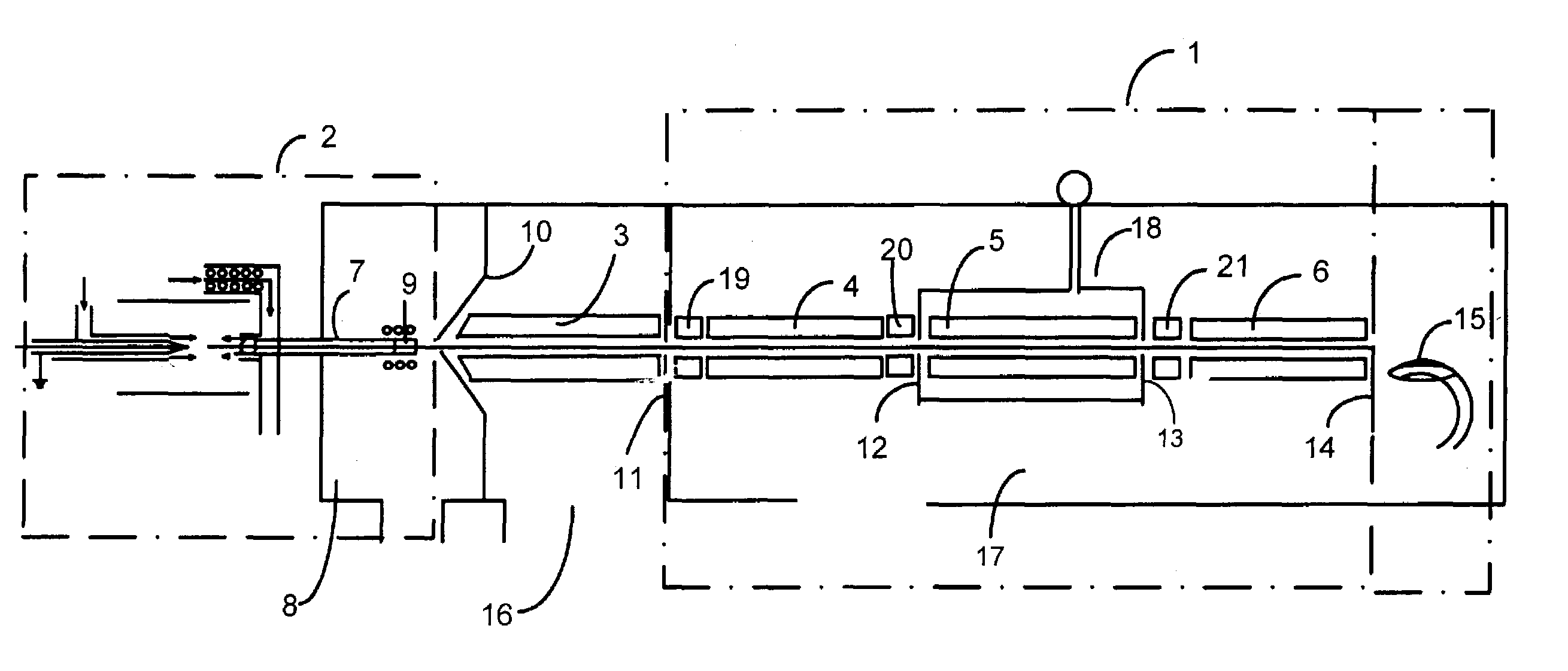
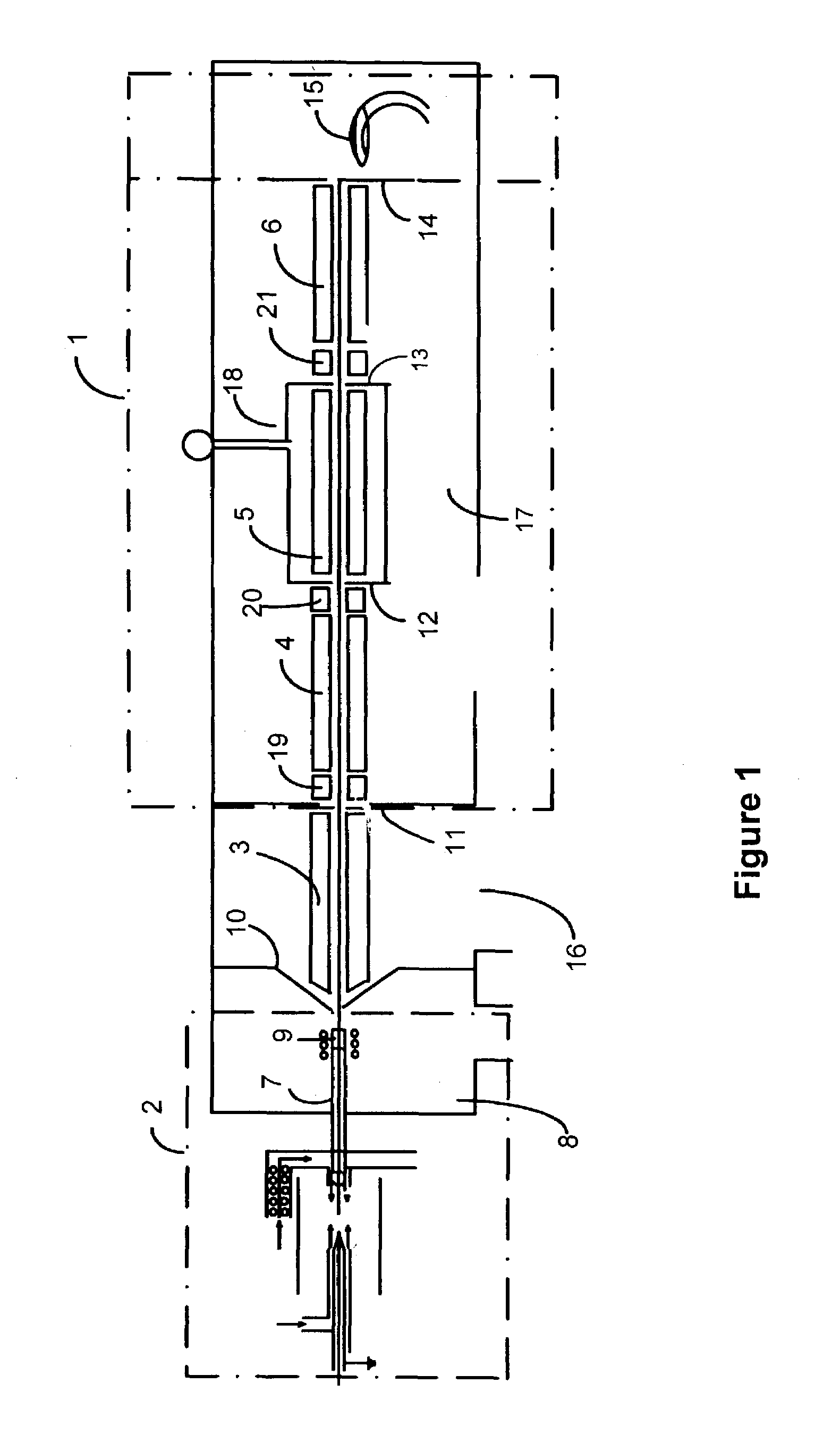
Dimensioning system with multipath interference mitigation
ActiveUS20160109224A1Reducing multipath distortionReduce distortionUsing optical meansMultipath interferenceLight beam
A system and method for measuring an item's dimensions using a time-of-flight dimensioning system is disclosed. The system and method mitigate multipath distortion and improve the accuracy of the measurements, especially in a mobile environment. To mitigate the multipath distortion, an imager captures an image of an item of interest. This image is processed to determine an illumination region corresponding item-of-interest's size, shape, and position. Using this information, an adjustable aperture's size, shape, and position are controlled so the light beam used in the time-of-flight analysis substantially illuminates the illumination region without first being reflected.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Ultra wideband precision geolocation system
InactiveUS6054950AEliminate needDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationUltra-widebandTransceiver
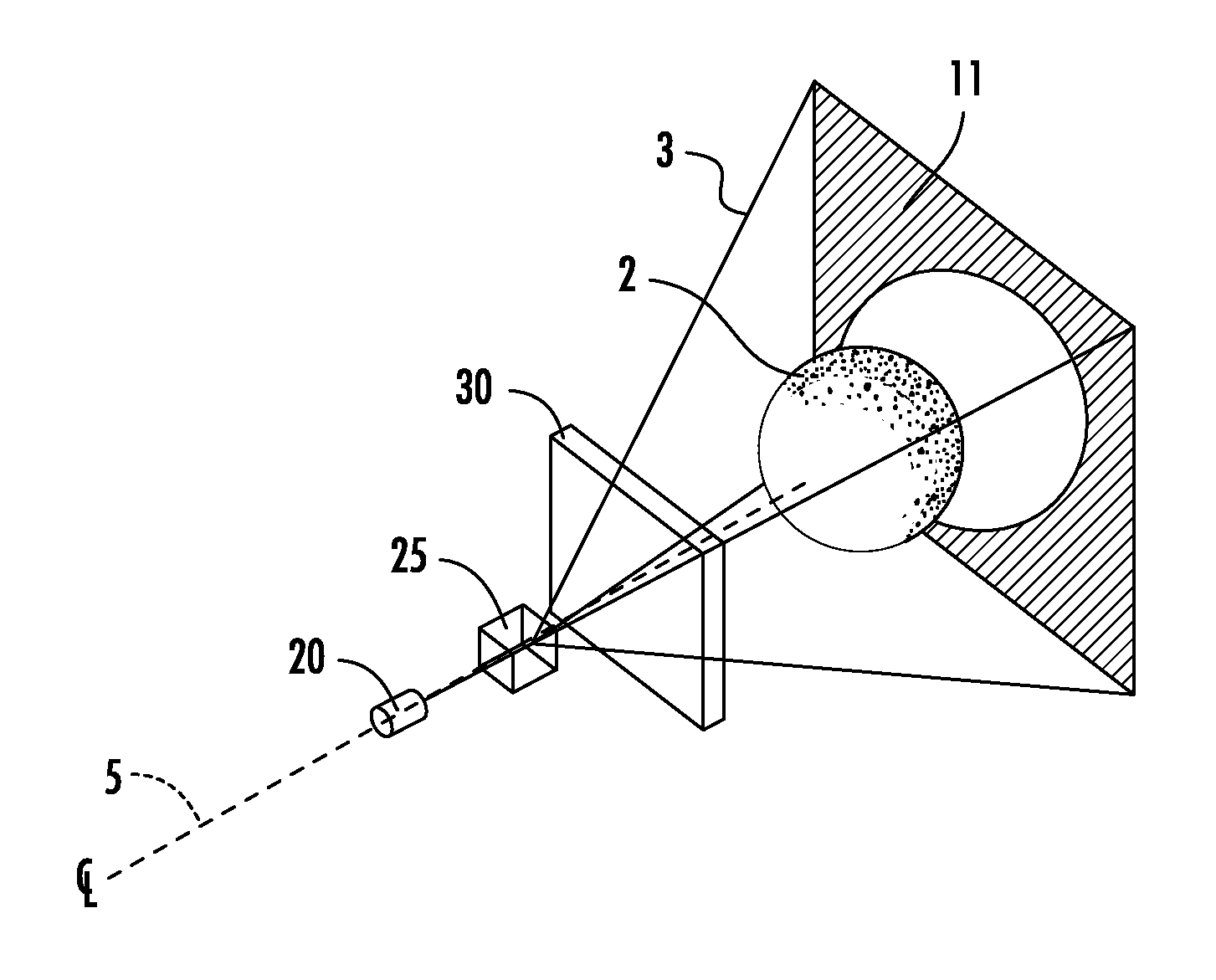
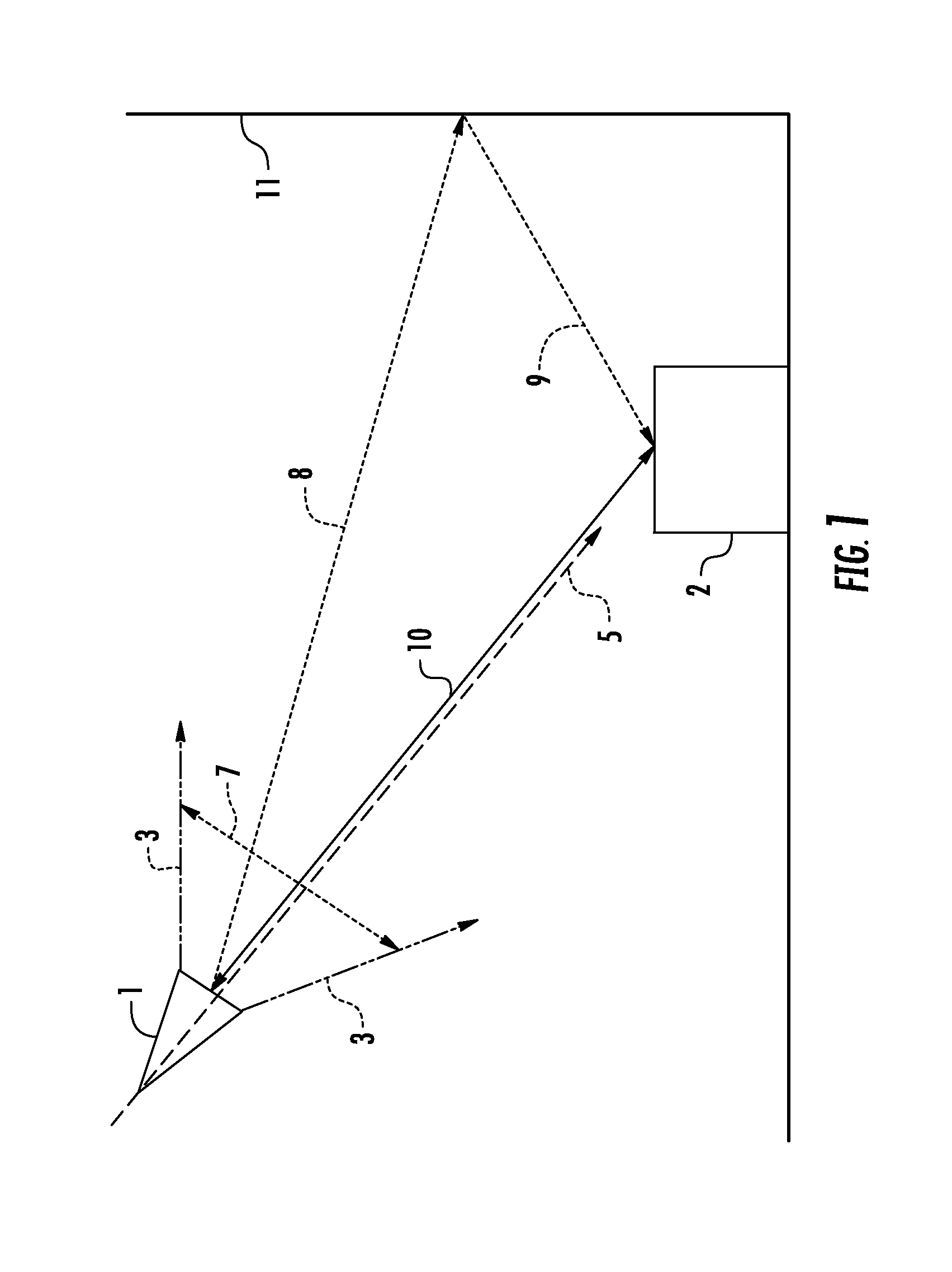
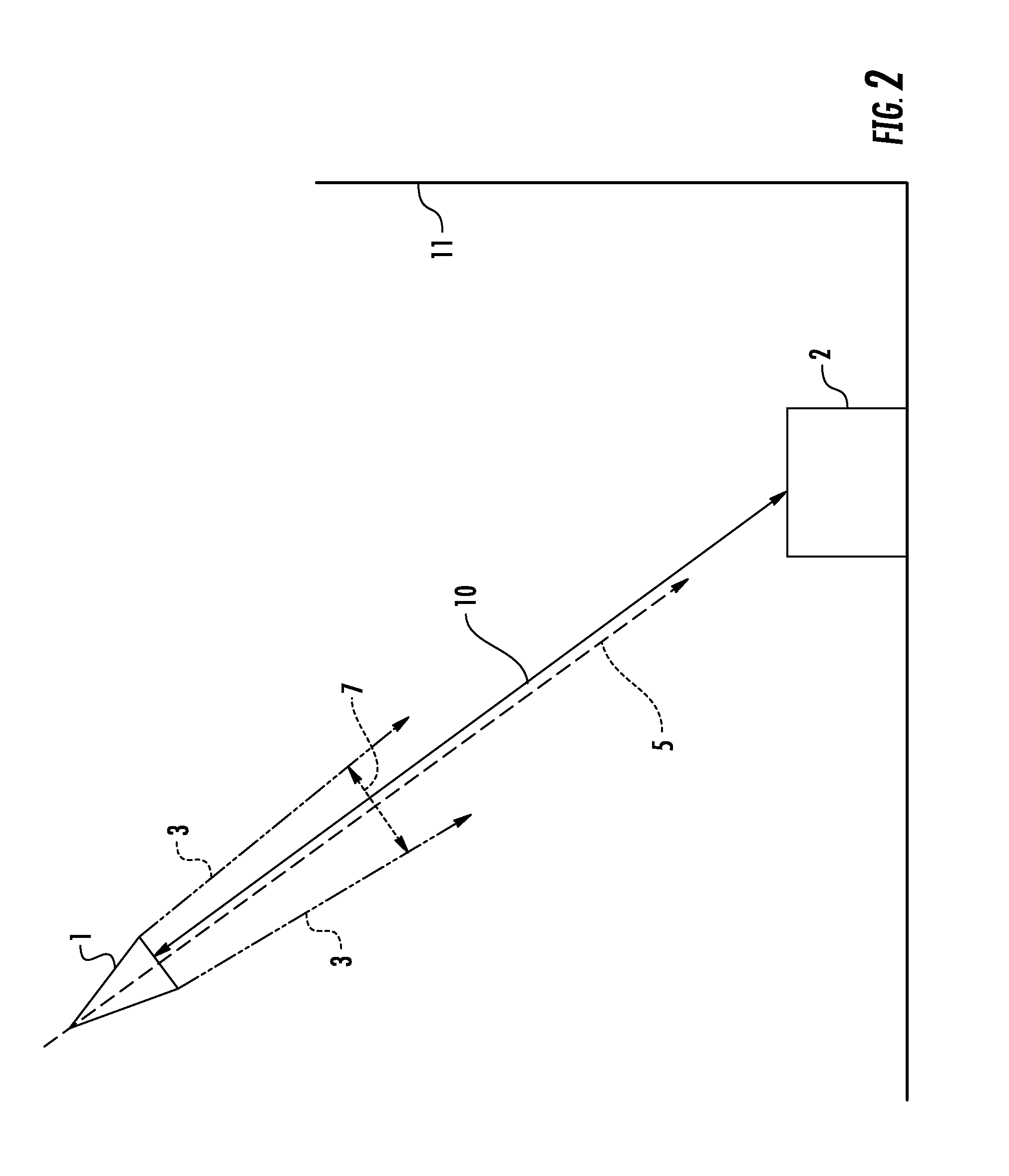
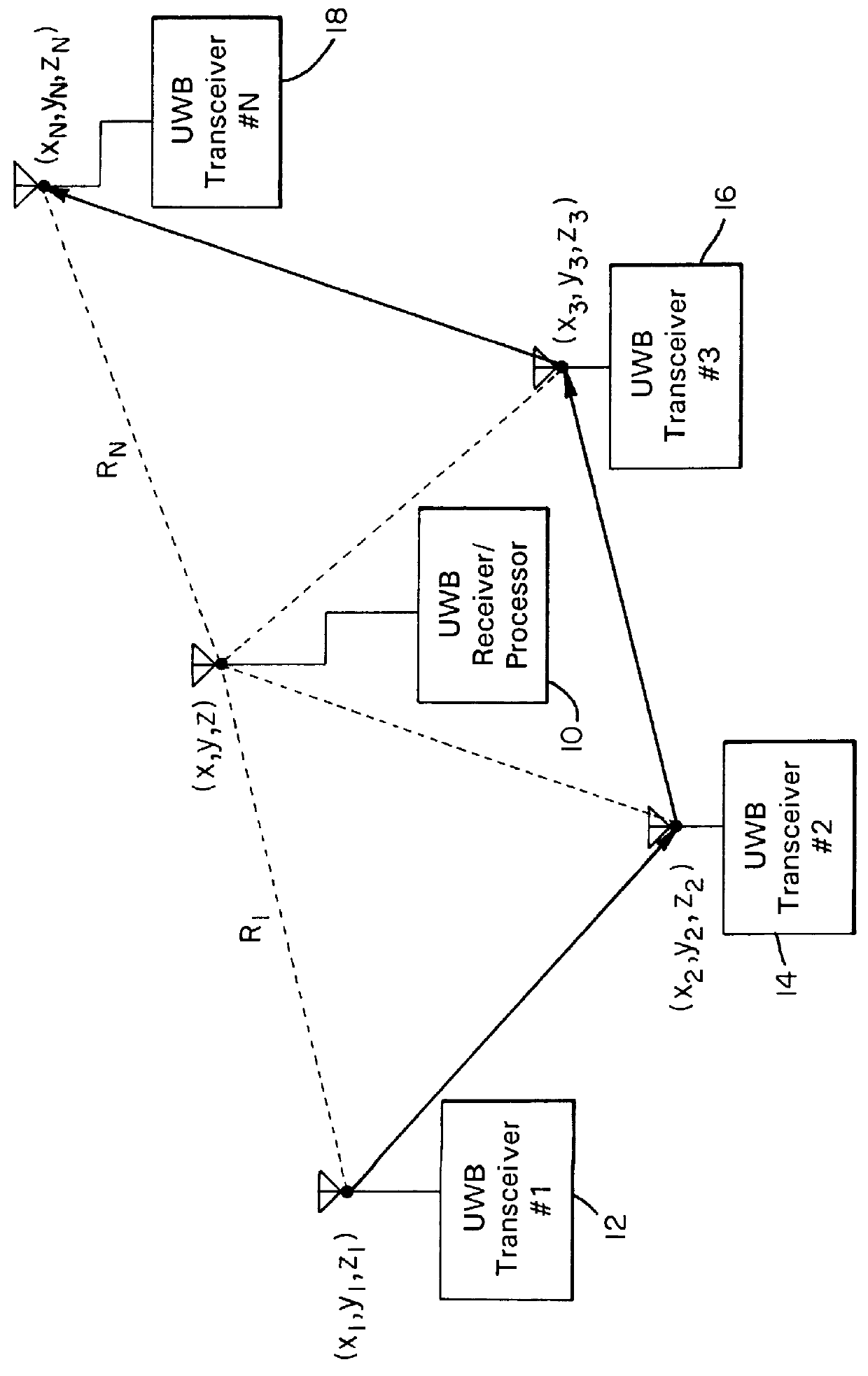
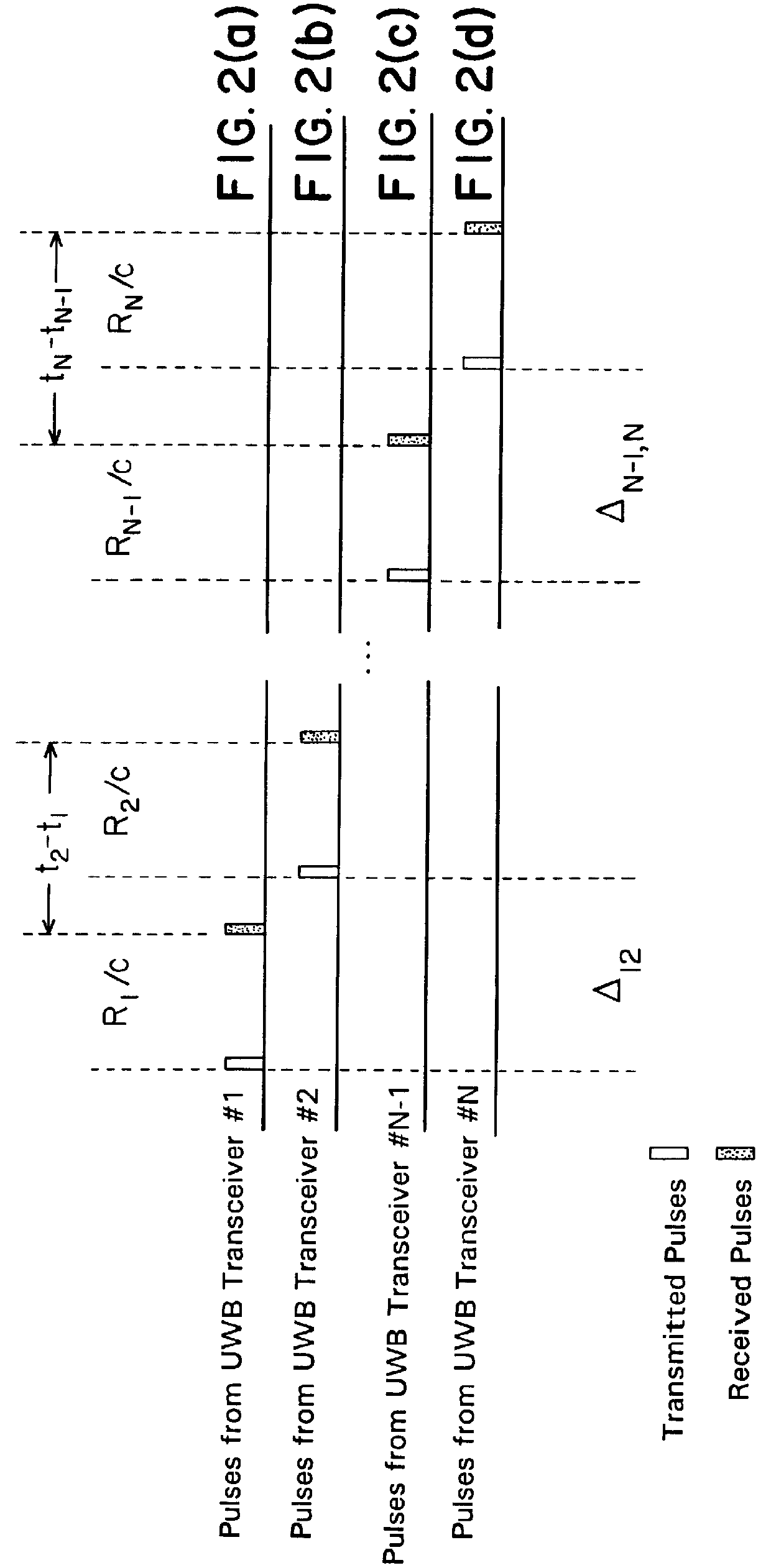
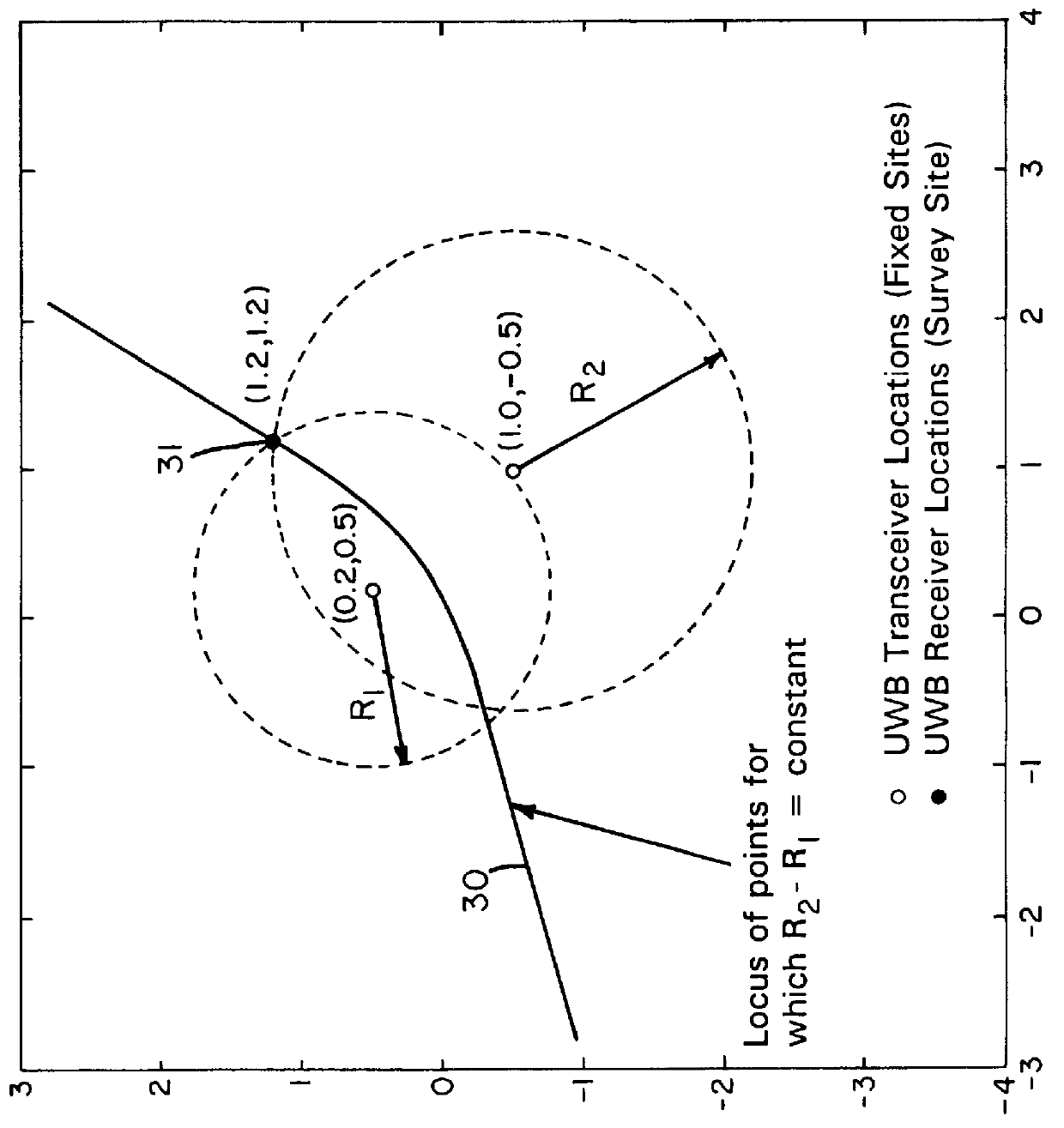
An ultra wideband (UWB) or short-pulse transmission system that enables precise tracking or geolocation of a target over distances of several kilometers. The system includes a set of N (where N>2) untethered UWB transceivers located at fixed positions, an untethered UWB receiver at the target, and a processor at the target for resolving time-of-flight measurement ambiguities of received pulses to determine precise geolocation by solving a set of equations according to time-of-flight measurements and surveyed positions of N-1 transceivers. To eliminate a clock distribution system, self-synchronizing of pulse timing is achieved by generating a start pulse at one of the untethered transceivers. Alternatively, a timing source may be provided by a GPS or other timing generator at the transceivers in order to synchronize emissions of their pulses.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Solid-state image sensor
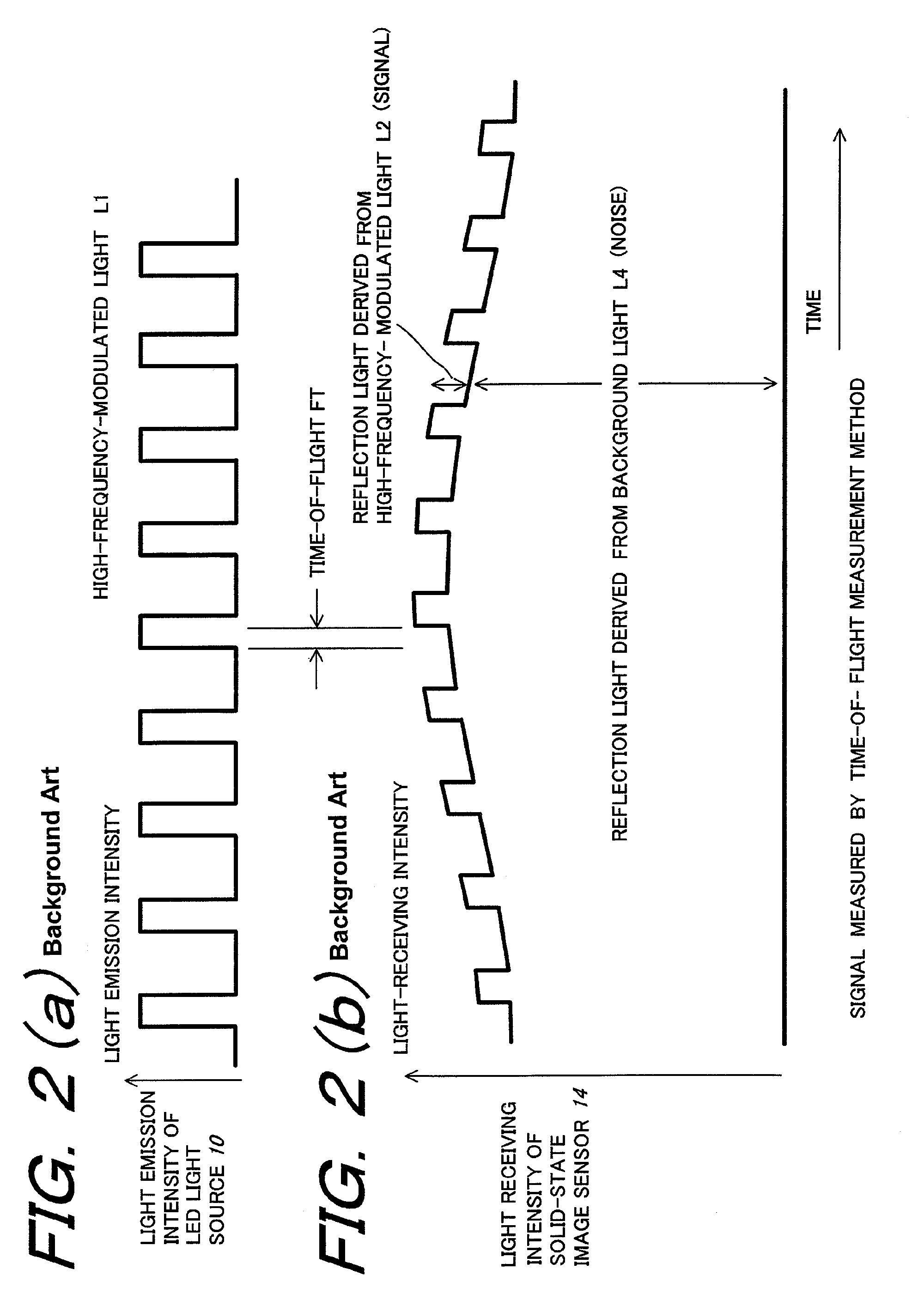
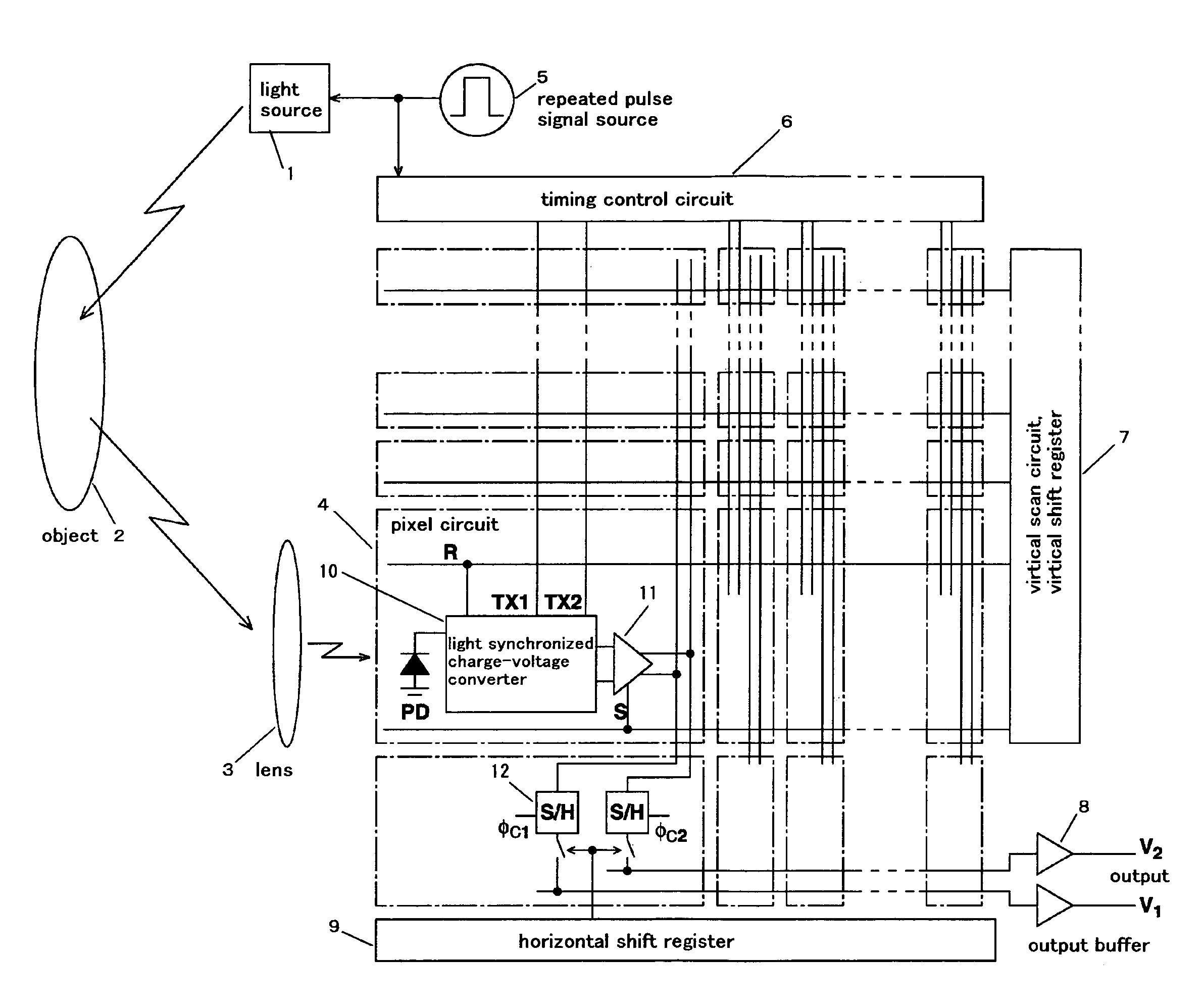
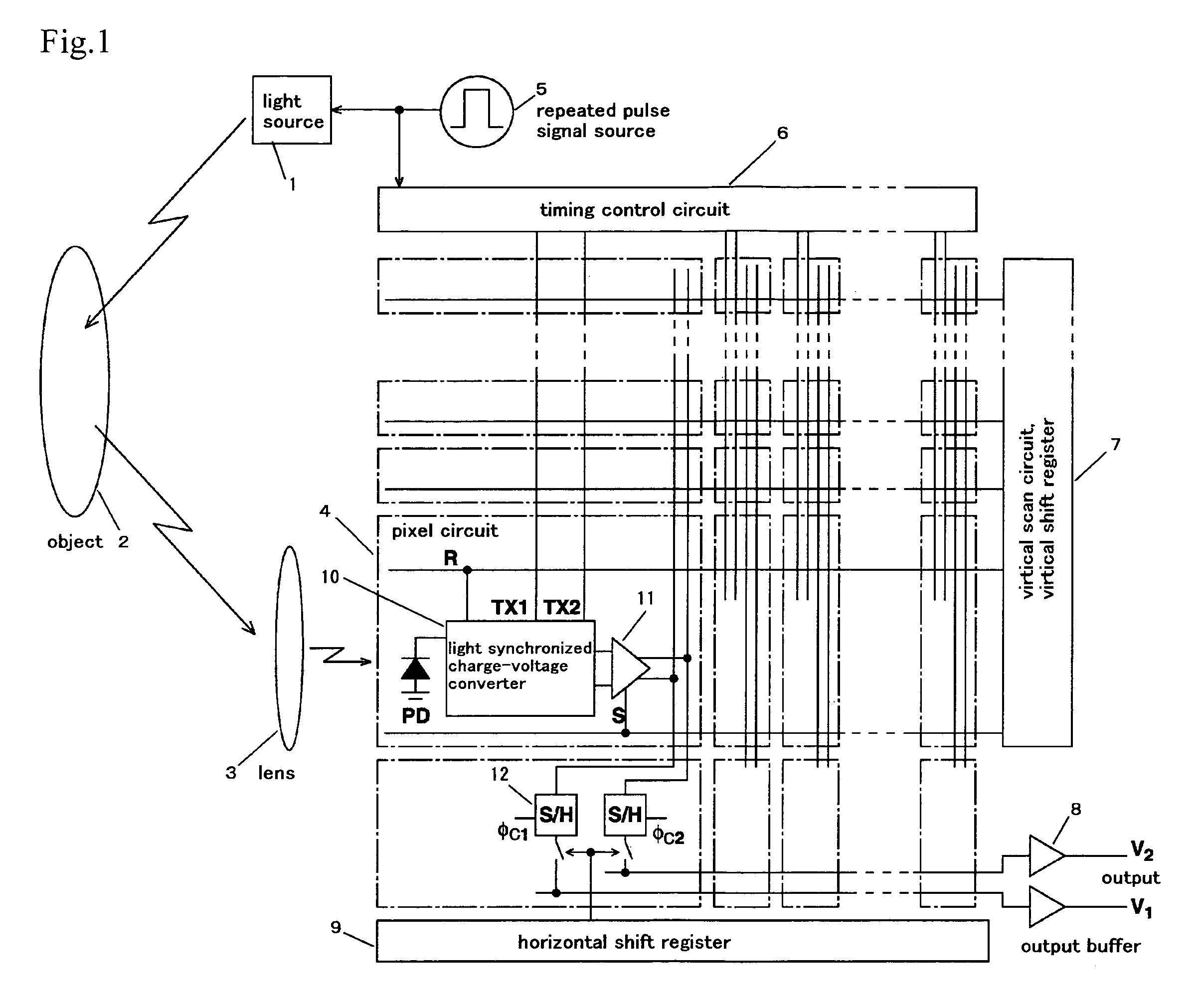
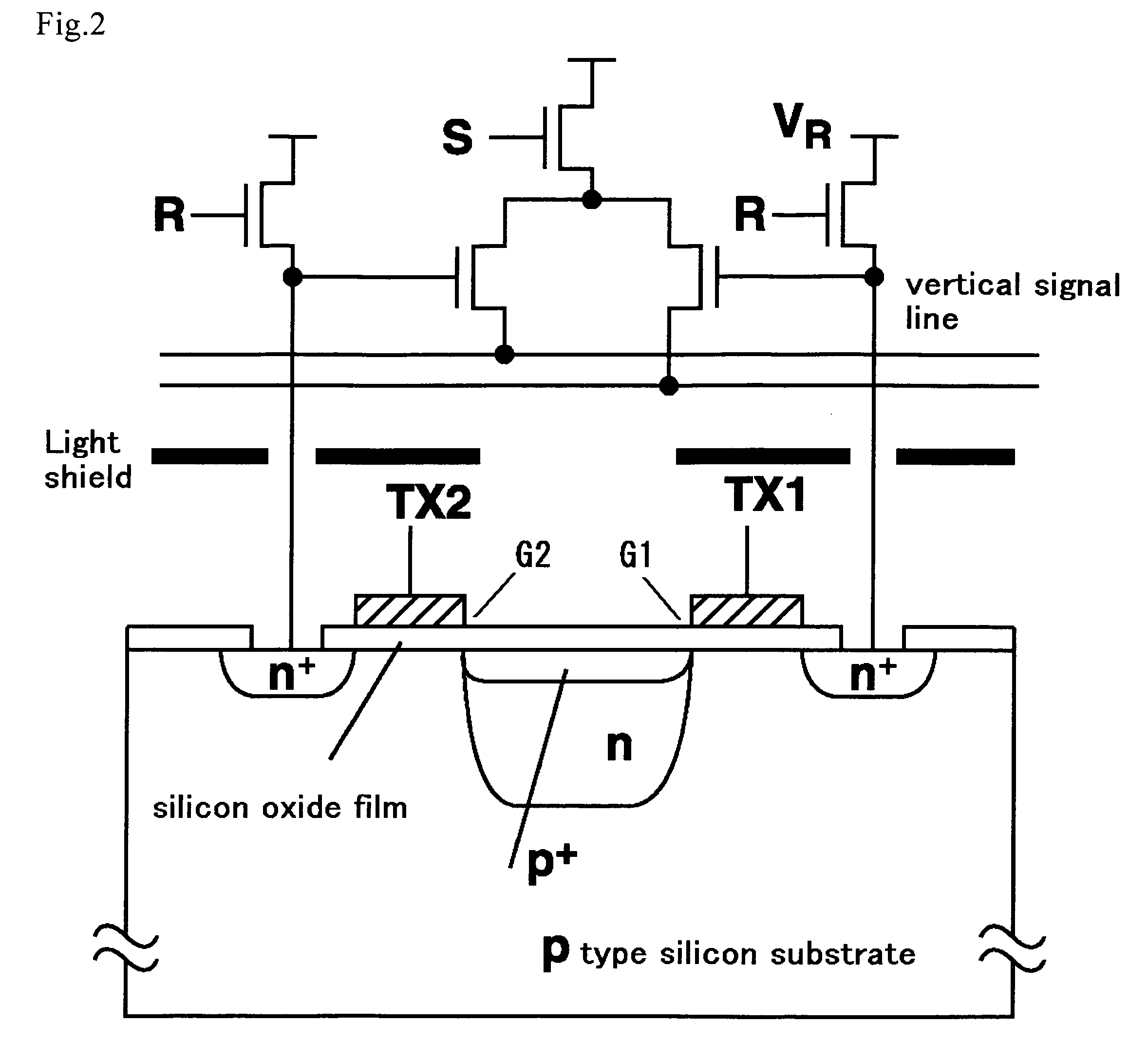
ActiveUS7683954B2Efficient extractionCancel noiseTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersLow noiseCapacitor
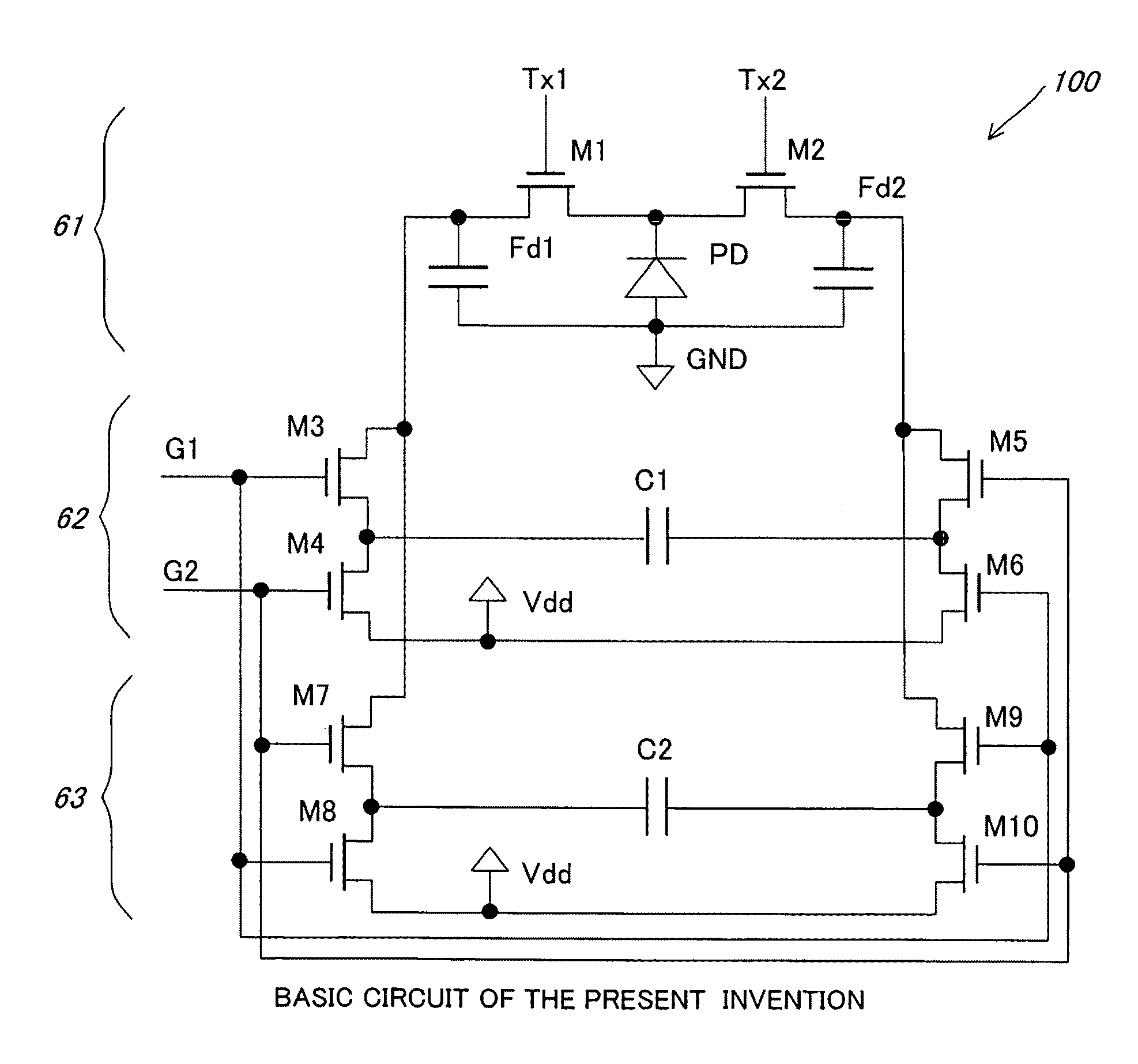
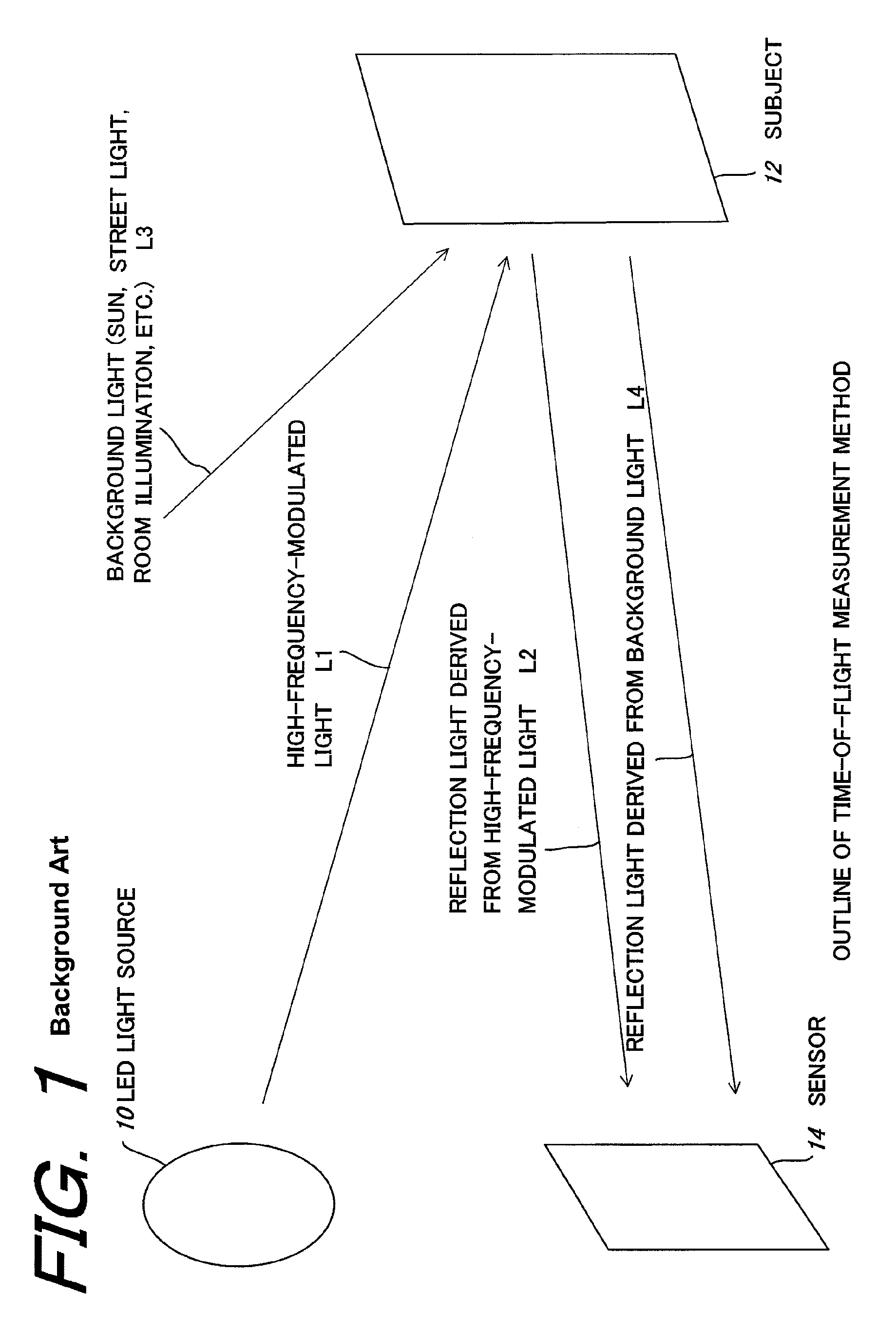
A solid-state image sensor of a charge sorting method used in a time-of-flight measurement method, in which noise derived from background light, which is caused by the reflection light from the subject derived from background light is eliminated, reflection light from the subject derived from a predetermined light source, which is previously set in the solid-state image sensor, is effectively extracted as a signal component to achieve high sensitivity and low noise, which is a solid-state image sensor that is equipped with a plurality of charge-storage sections, discriminates photoelectrons generated by incoming light on the incoming timing and sort to the above-described plurality of charge-storage sections, and measures the timing of the incoming light, in which the sensor has: a plurality of capacitors that capable of conducting to the plurality of charge-storage sections; and a control section that controls a conducted state between the above-described plurality of charge-storage sections and the above-described plurality of capacitors, in which by selectively conducting the above-described plurality of charge-storage sections and the above-described plurality of capacitors by the control of the above-described control section, the difference component of charge stored in the above-described plurality of charge-storage sections is extracted.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
Distance image sensor
ActiveUS7436496B2High sensitivityEnhanced charge transferTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersAudio power amplifierDelayed time
A distance image sensor for removing the background light and improving the charge transfer efficiency in a device for measuring the distance to an object by measuring the time-of-flight of the light.In a distance image sensor for determining the signals of two charge storage nodes which depend on the delay time of the modulated light, a signal by the background light is received from the third charge storage node or the two charge storage nodes in a period when the modulated light does not exist, and is subtracted from the signal which depends on the delay time of the two charge storage nodes, so as to remove the influence of the background. Also by using a buried diode as a photo-detector, and using an MOS gate as gate means, the charge transfer efficiency improves. The charge transfer efficiency is also improved by using a negative feedback amplifier where a capacitor is disposed between the input and output.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
Device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of modulated electromagnetic waves
InactiveUS7060957B2Low lighting powerExtend integration timePrismsSolid-state devicesPulse radiationData acquisition
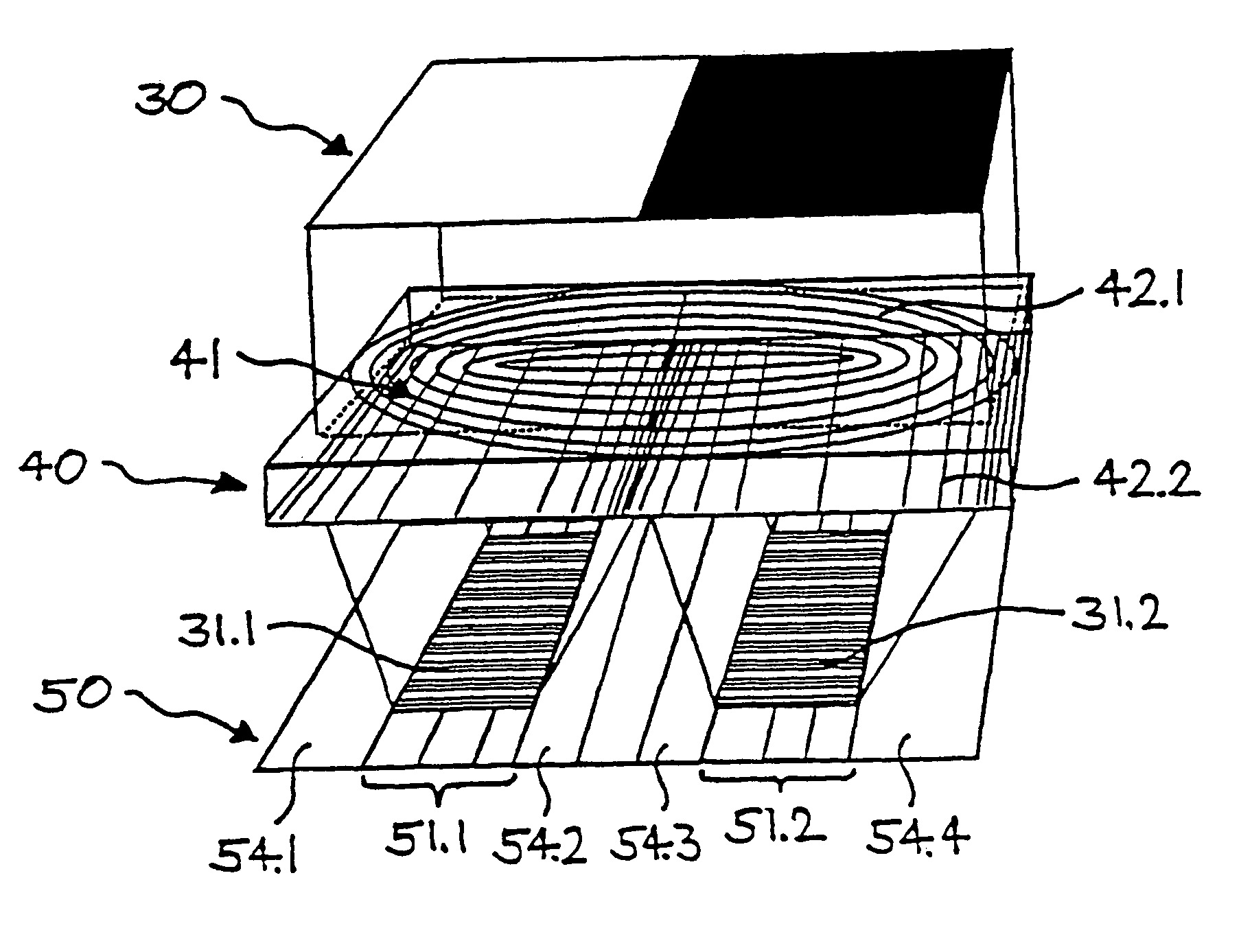
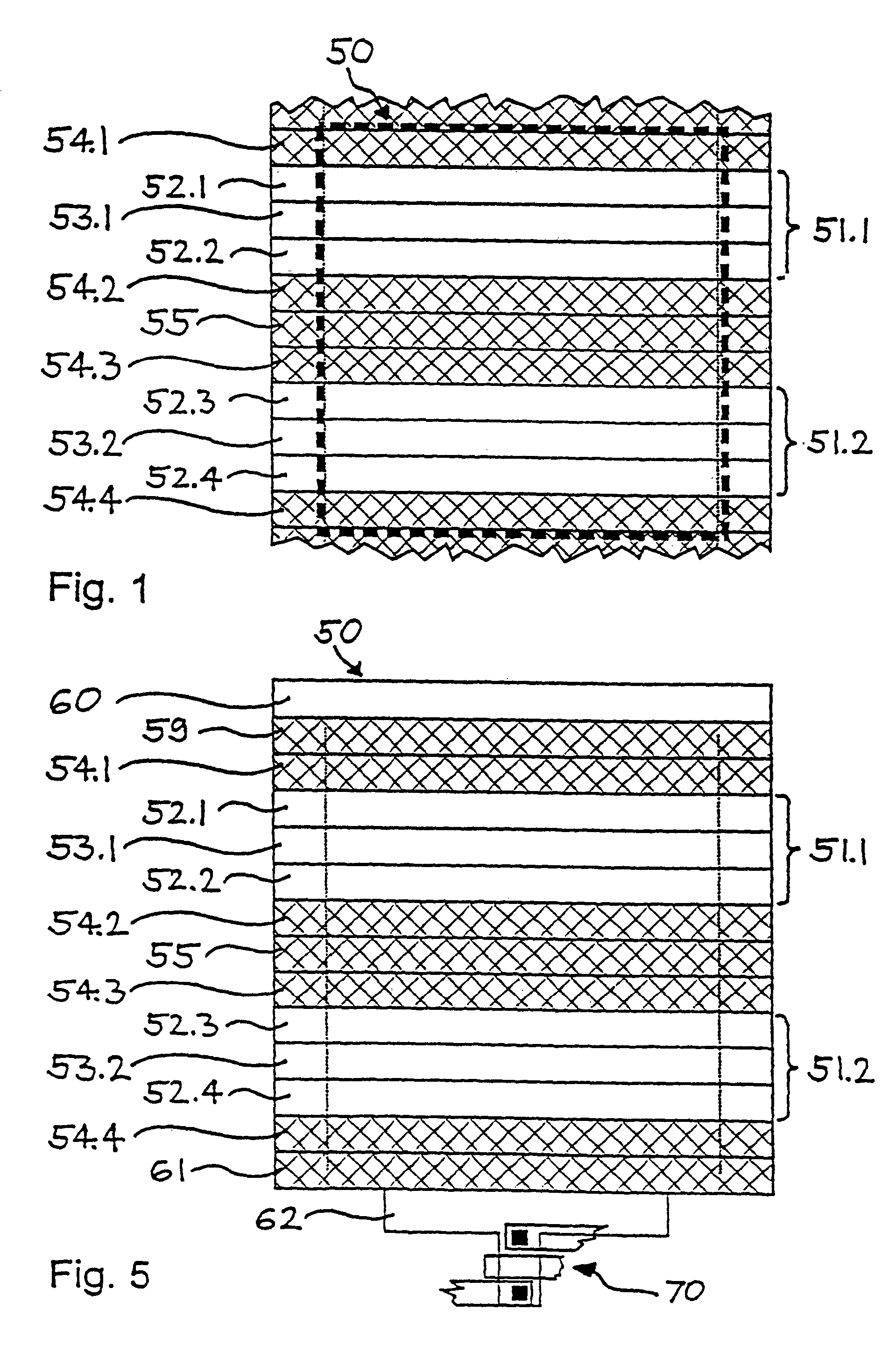
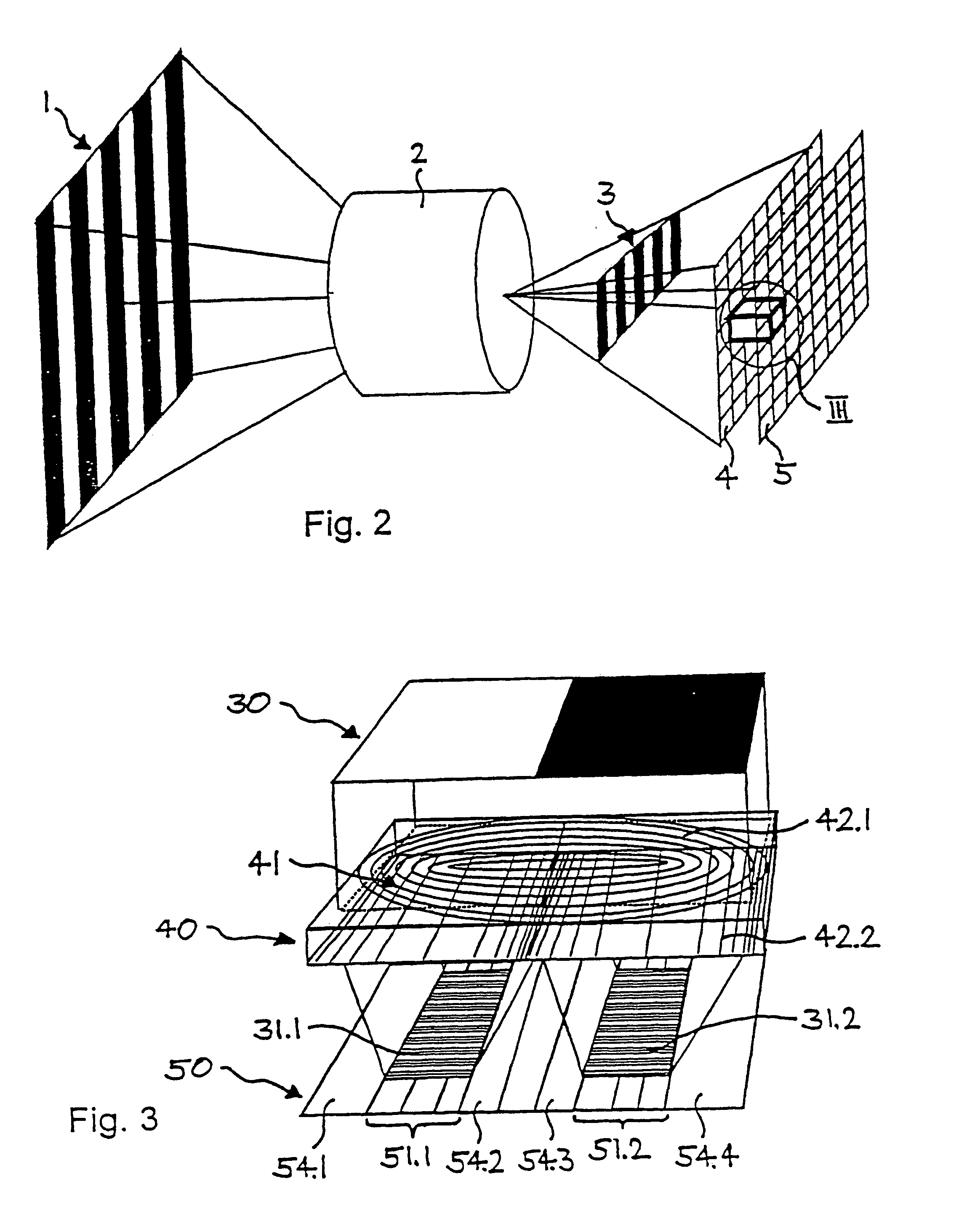
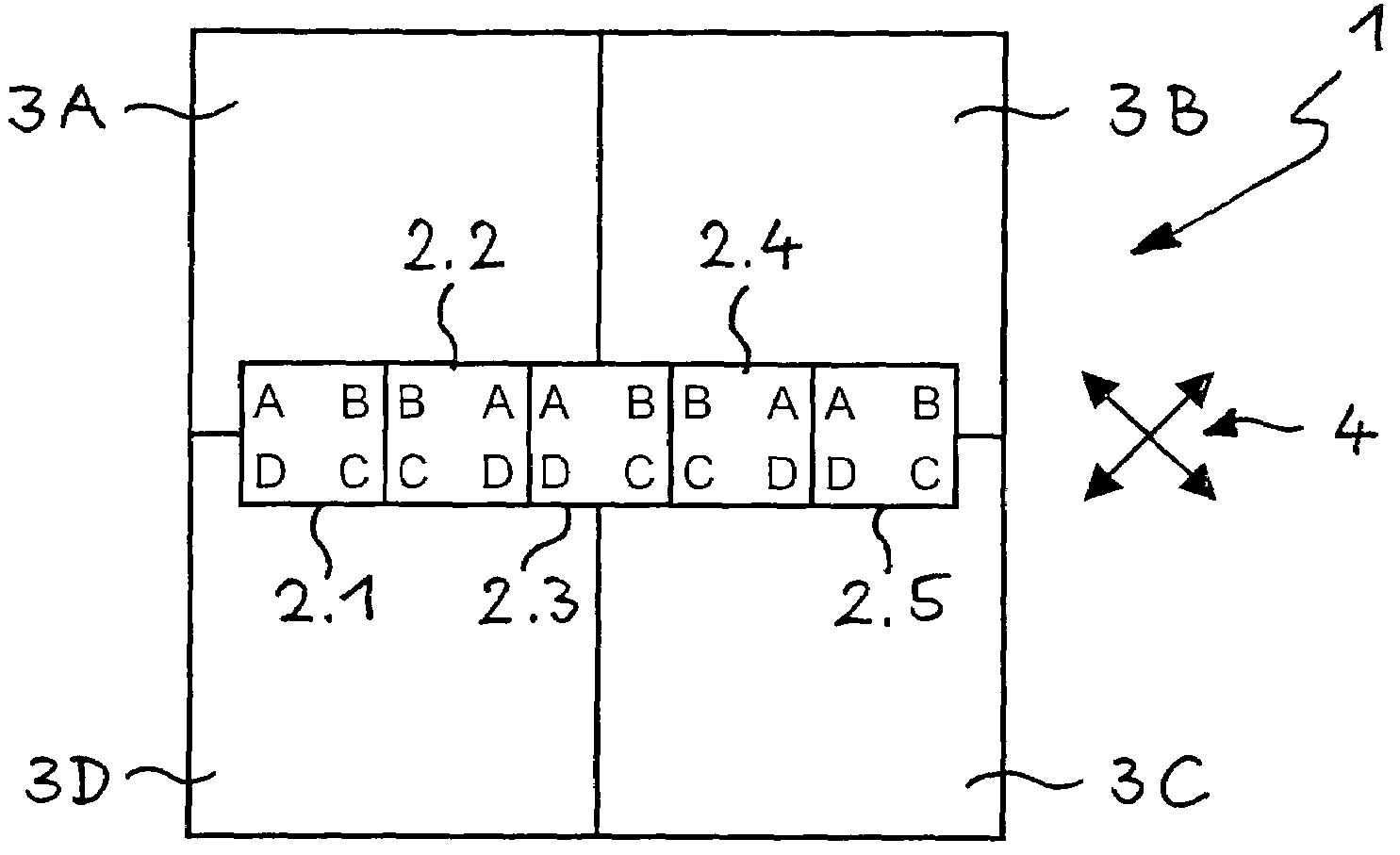
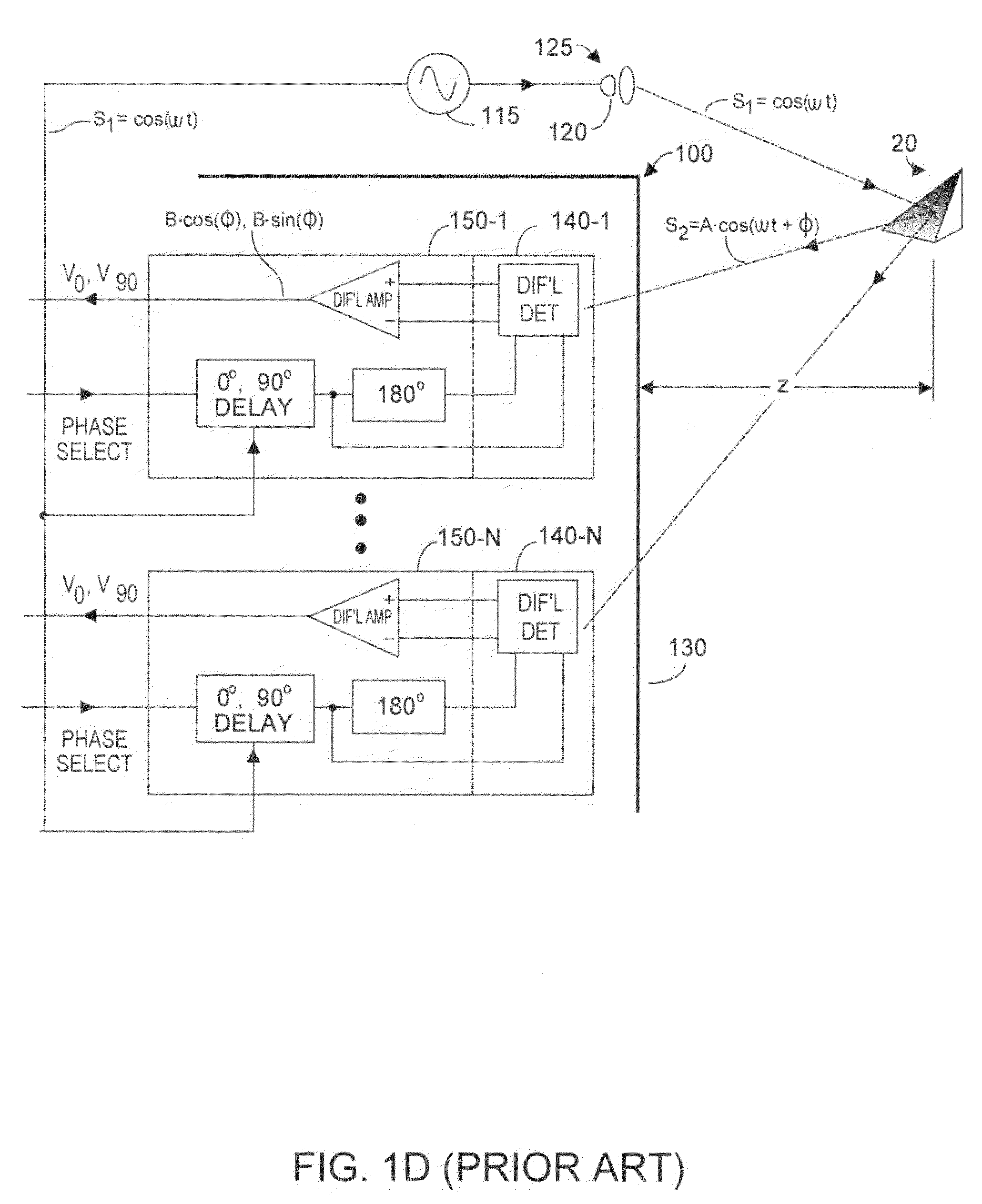
A device and method for spatially resolved photodetection and demodulation of temporally modulated electromagnetic waves makes it possible to measure phase, amplitude and offset of a temporally modulated, spatially coded radiation field. A micro-optical element (41) spatially averages a portion (30) of the scene and equally distributes the averaged intensity on two photo sites (51.1.51.2) close to each other. Adjacent to each of these photo sites (51.1) are two storage areas (54.1, 54.2) into which charge from the photo site can be moved quickly (with a speed of several MHz to several tens or even hundreds of MHz) and accumulated essentially free of noise. This is possible by employing the charge-coupled device (CCD) principle. The device combines a high optical fill factor, insensitivity to offset errors, high sensitivity even with little light, simultaneous data acquisition, small pixel size, and maximum efficiency in use of available signal photons for sinusoidal as well as pulsed radiation signals. The device and method may be used in a time-of-flight (TOF) range imaging system without moving parts, offering 2D or 3D range data.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Highly sensitive, fast pixel for use in an image sensor
ActiveUS7560701B2Overcomes speed limitationReasonable sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectric signalDemodulation
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
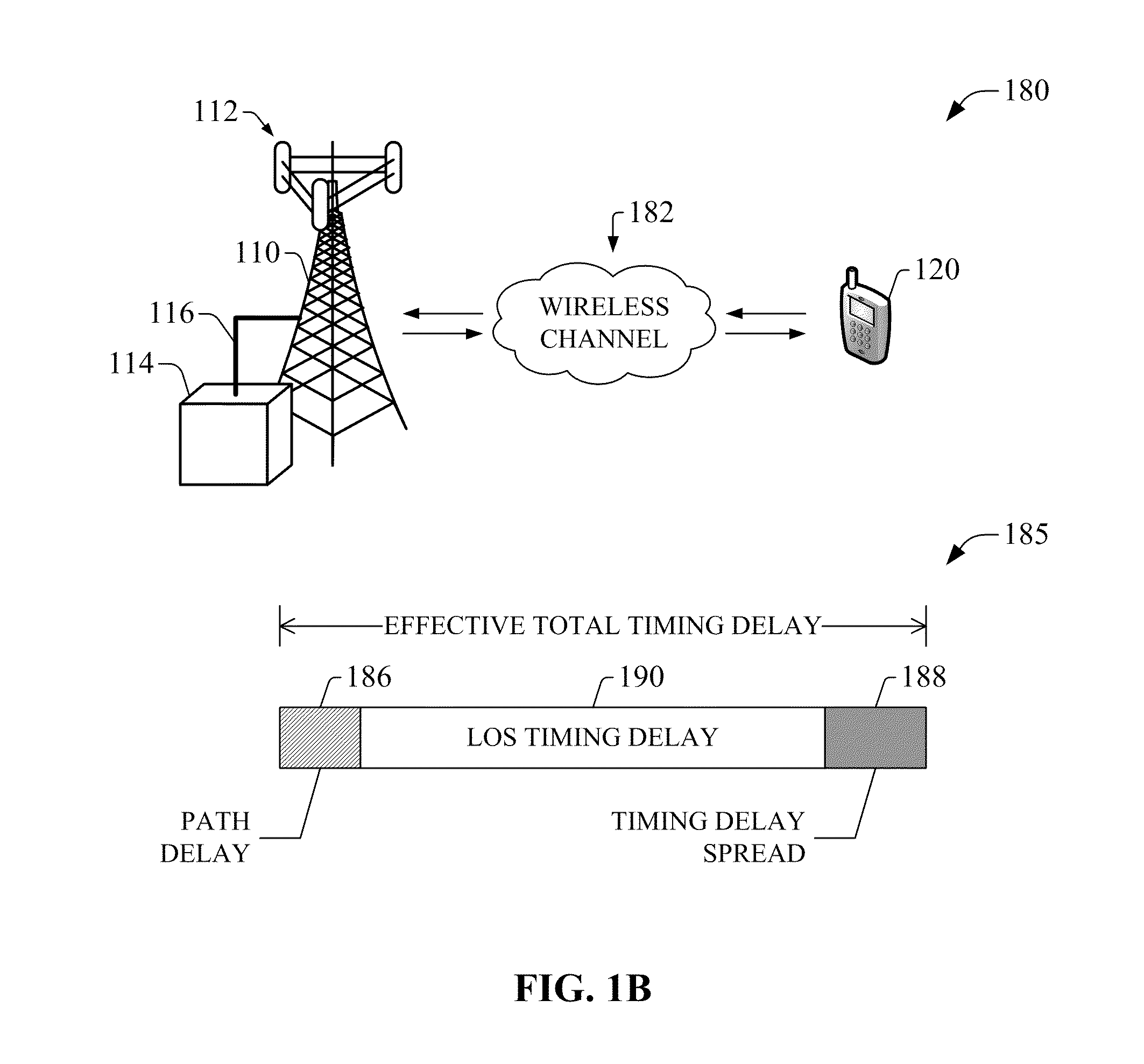
Compensation of propagation delays of wireless signals
ActiveUS20100190509A1Weakening rangeImprove accuracySynchronisation arrangementLocation information based servicePropagation delayRadio networks
System(s) and method(s) for compensation of propagation delay offsets of wireless signals. Compensation is accomplished through determination of an effective wireless signal propagation delay that accounts for signal path delay and propagation delay over the air. Such determination is based at least in part on statistical analysis of accurate location estimates of reference positions throughout a coverage sector or cell, and location estimates of the reference positions generated through time-of-flight (TOF) measurements of wireless signals. Determination of propagation or signal path delay offset also is attained iteratively based at least in part on reference location estimates and TOF location estimates. High-accuracy location estimates such as those obtained through global navigation satellite systems are employed as reference location estimates. Position of probes or wireless beacons, deployed throughout a sector or cell, also are employed as reference locations. Compensation of propagation delay offset improves accuracy of conventional TOF location estimates and radio network performance.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
System and method for position determination by impulse radio
InactiveUS6133876ADirection finders using radio wavesSatellite radio beaconingTransceiverDirectional antenna
A system and a method for position determination by impulse radio using a first transceiver having a first clock providing a first reference signal and a second transceiver placed spaced from the first transceiver. The system determines the position of the second transceiver. The second transceiver has a second clock that provides a second reference signal. A first sequence of pulses are transmitted from the first transceiver. The first sequence of pulses are then received at the second transceiver and the second transceiver is then synchronized with the first sequence of pulses. A second sequence of pulses are transmitted from the second transceiver. The first transceiver receives the second sequence of pulses and the first transceiver is synchronized with the second sequence of pulses. A delayed first reference signal is generated in response to the synchronization with the second sequence of pulses. A time difference between the delayed first reference signal and the first reference signal is then measured. The time difference indicates a total time of flight of the first and second sequence of pulses. The distance between the first and the second transceiver is determined from the time difference. The direction of the second transceiver from the first transceiver is determined using a directional antenna. Finally, the position of the second transceiver is determined using the distance and the direction.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
Visual tracking using depth data
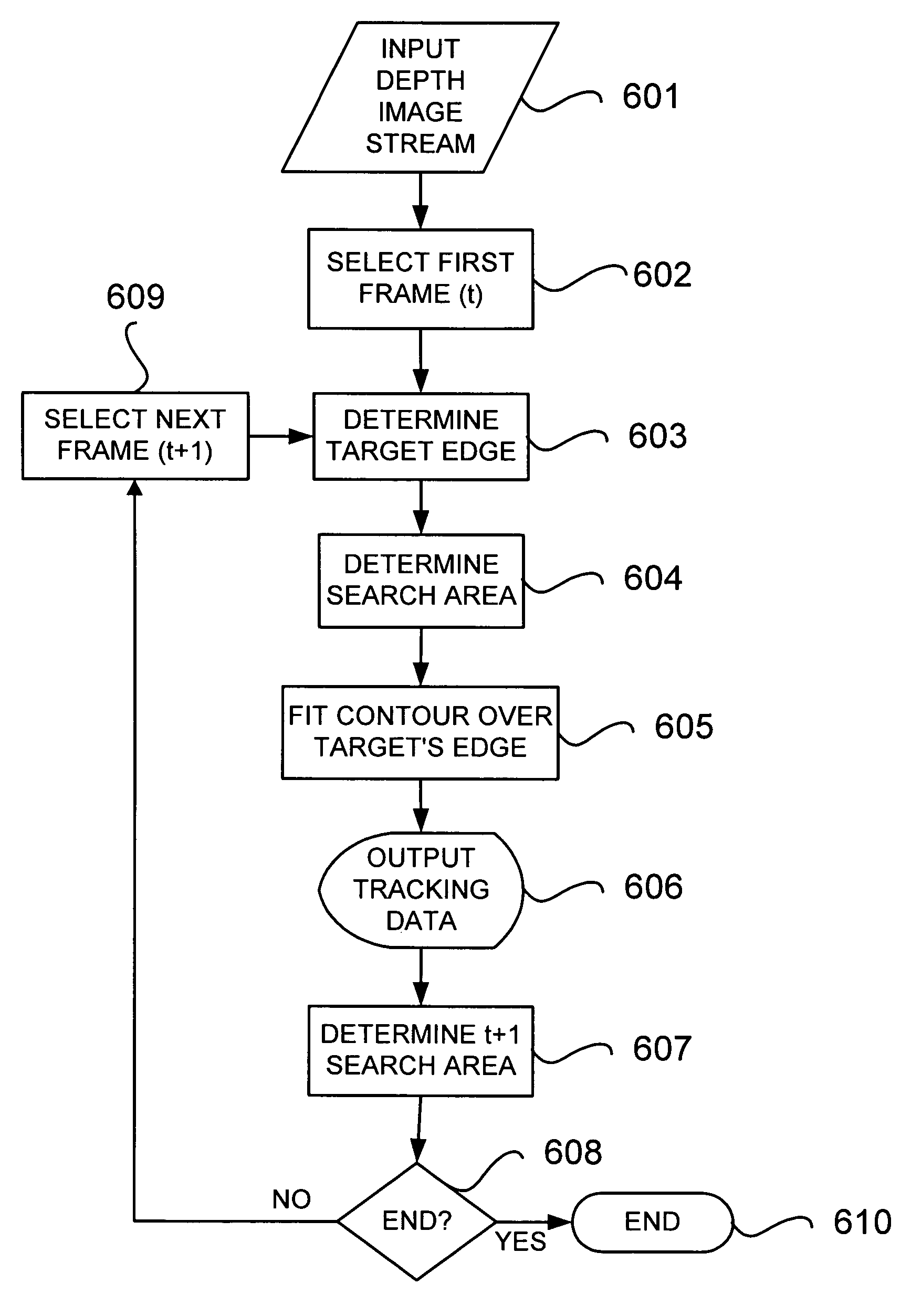
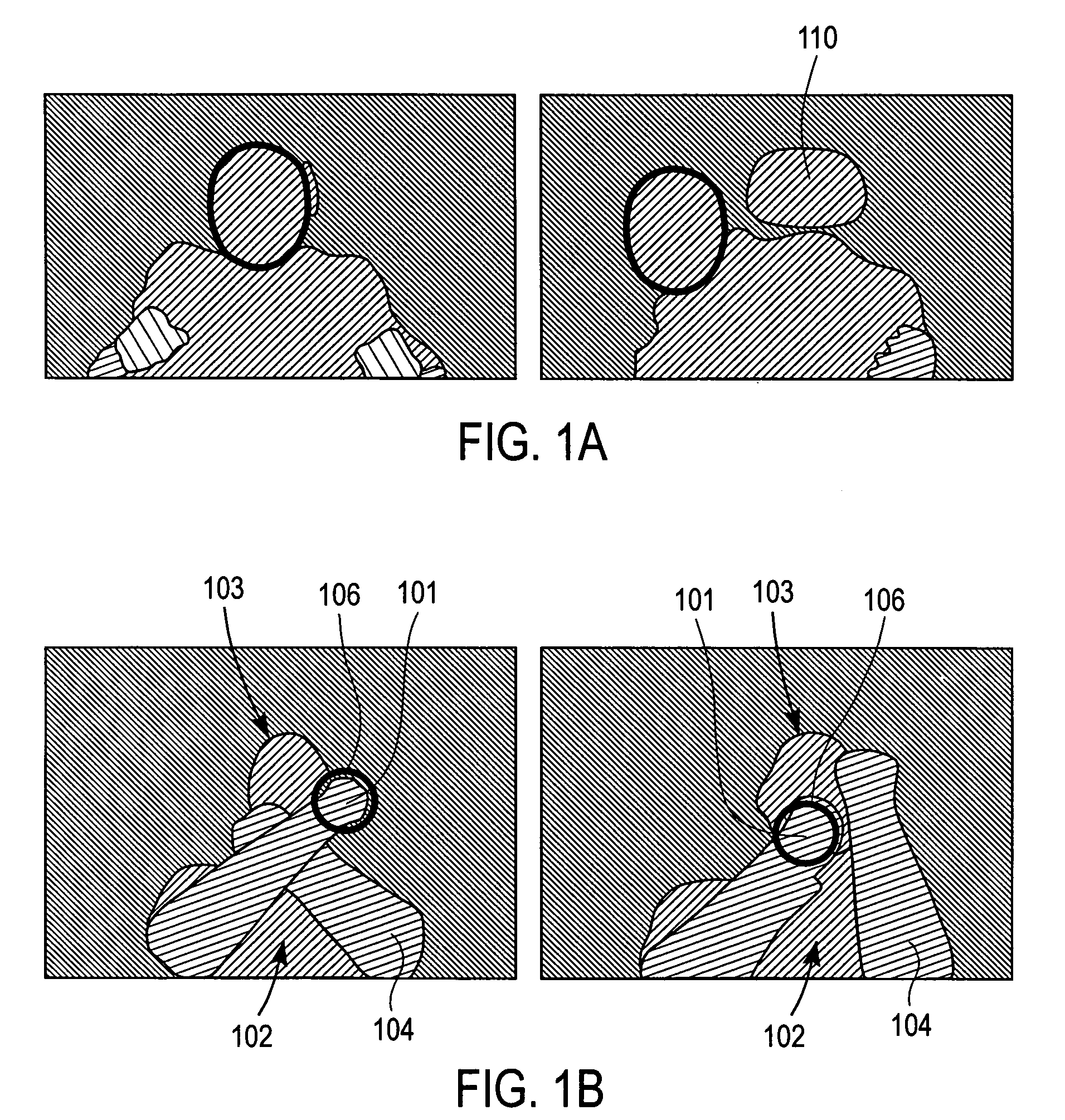
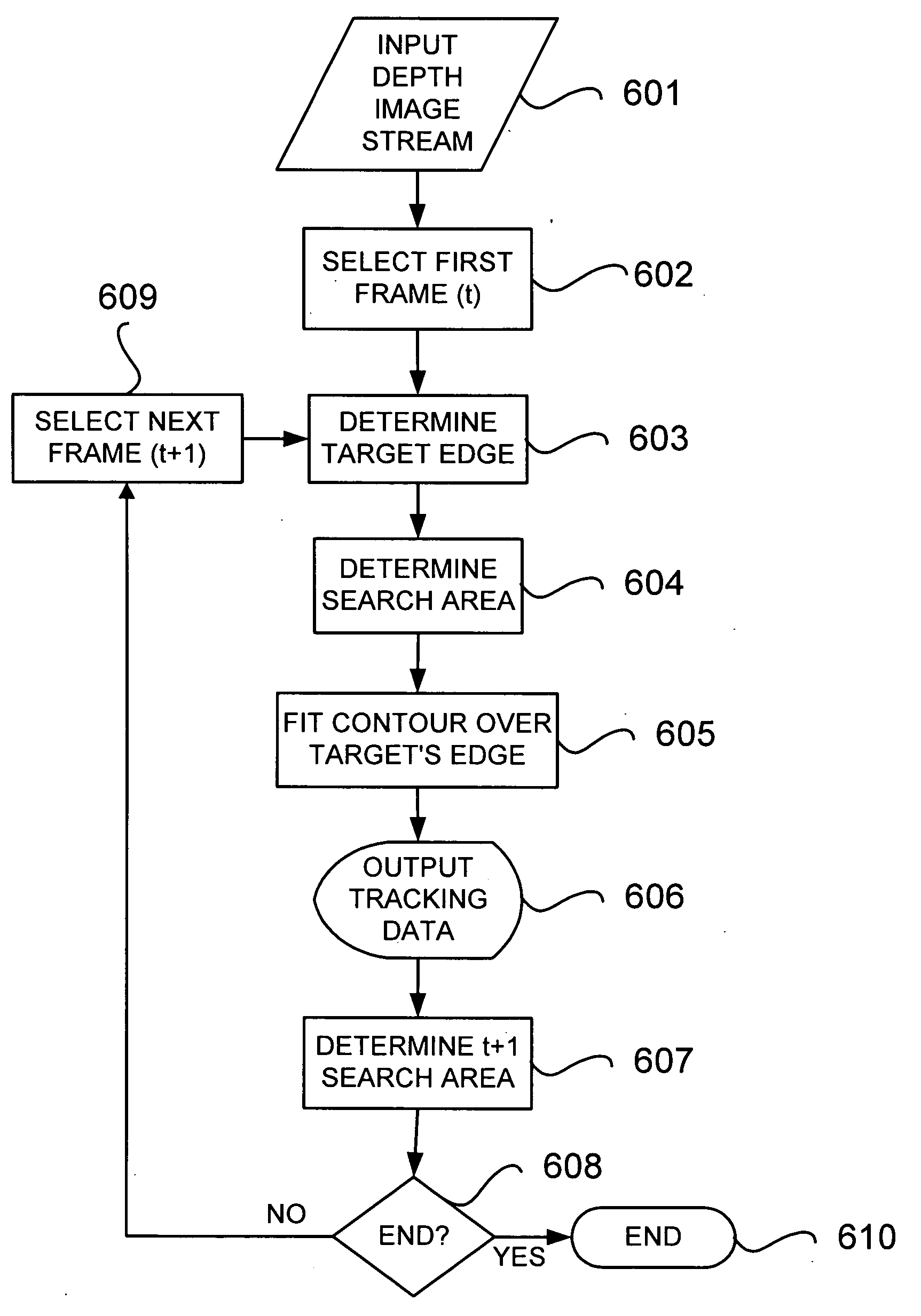
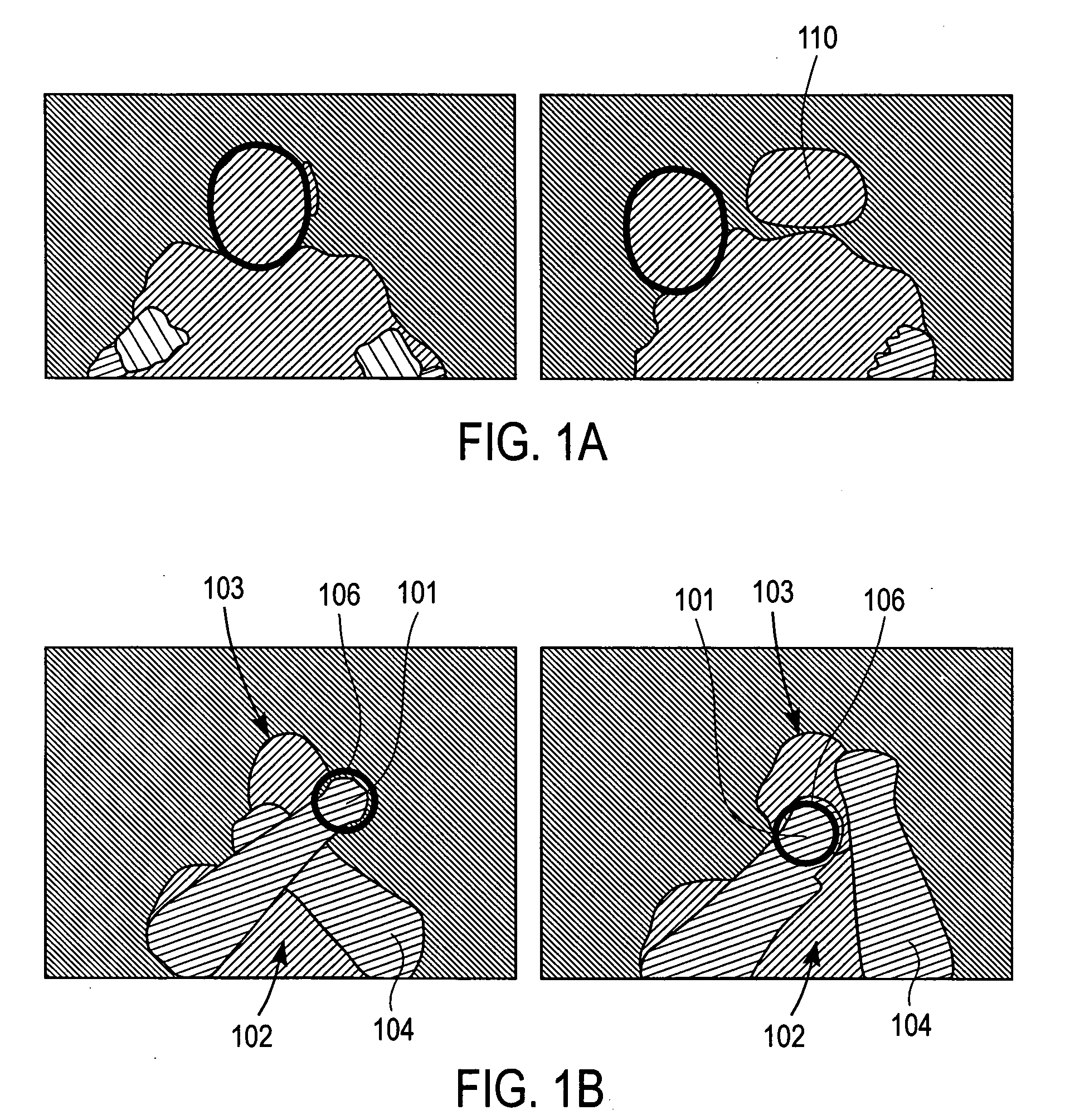
Real-time visual tracking using depth sensing camera technology, results in illumination-invariant tracking performance. Depth sensing (time-of-flight) cameras provide real-time depth and color images of the same scene. Depth windows regulate the tracked area by controlling shutter speed. A potential field is derived from the depth image data to provide edge information of the tracked target. A mathematically representable contour can model the tracked target. Based on the depth data, determining a best fit between the contour and the edge of the tracked target provides position information for tracking. Applications using depth sensor based visual tracking include head tracking, hand tracking, body-pose estimation, robotic command determination, and other human-computer interaction systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Visual tracking using depth data
Real-time visual tracking using depth sensing camera technology, results in illumination-invariant tracking performance. Depth sensing (time-of-flight) cameras provide real-time depth and color images of the same scene. Depth windows regulate the tracked area by controlling shutter speed. A potential field is derived from the depth image data to provide edge information of the tracked target. A mathematically representable contour can model the tracked target. Based on the depth data, determining a best fit between the contour and the edge of the tracked target provides position information for tracking. Applications using depth sensor based visual tracking include head tracking, hand tracking, body-pose estimation, robotic command determination, and other human-computer interaction systems.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Coupler with waveguide transition for an antenna in a radar-based level measurement system
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Cost-effective lidar sensor for multi-signal detection, weak signal detection and signal disambiguation and method of using same
InactiveUS20140211194A1Low costOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationSignal qualityEngineering
A lidar-based apparatus and method are used for multi-signal detection, weak signal detection and signal disambiguation through waveform approximation utilizing a multi-channel time-to-digital converter (TDC) electronic circuit, with each TDC having an individually adjustable voltage threshold. This advanced TDC-based pulse width time-of-flight (ToF) approach achieves the low cost associated with the TDC-based pulse width ToF approach while solving the signal quality issues associated with the standard single-threshold TDC-based approach.
Owner:QUANERGY SYST
Mass spectrometry with segmented RF multiple ion guides in various pressure regions
InactiveUS7034292B1Reduce lossesEliminate and reduce numberIsotope separationSpectrometer combinationsFourier transform on finite groupsMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer is configured with individual multipole ion guides, configured in an assembly in alignment along a common centerline wherein at least a portion of at least one multipole ion guide mounted in the assembly resides in a vacuum region with higher background pressure, and the other portion resides in a vacuum region with lower background pressure. Said multipole ion guides are operated in mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation modes, in either a high or low pressure region, said region being selected according to the optimum pressure or pressure gradient for the function performed. The diameter, lengths and applied frequencies and phases on these contiguous ion guides may be the same or may differ. A variety of MS and MS / MSn analysis functions can be achieved using a series of contiguous multipole ion guides operating in either higher background vacuum pressures, or along pressure gradients in the region where the pressure drops from high to low pressure, or in low pressure regions. Individual sets of RF, + / −DC and resonant frequency waveform voltage supplies provide potentials to the rods of each multipole ion guide allowing the operation of ion transmission, ion trapping, mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation functions independently in each ion guide. The presence of background pressure maintained sufficiently high to cause ion to neutral gas collisions along a portion of each multiple ion guide linear assembly allows the conducting of Collisional Induced Dissociation (CID) fragmentation of ions by axially accelerating ions from one multipole ion guide into an adjacent ion guide. Alternatively ions can be fragmented in one or more multipole ion guides using resonant frequency excitation CID. A multiple multipole ion guide assembly can be configured as the primary mass analyzer in single or triple quadrupole mass analyzers with or without mass selective axial ejection. Alternatively, the multiple multipole ion guide linear assembly can be configured as part of a hybrid Time-Of-Flight, Magnetic Sector, Ion Trap or Fourier Transform mass analyzer.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
High-resolution ranging and location finding using multicarrier signals
InactiveUS20120032855A1Direction finders using radio wavesError preventionModulation patternImage resolution
The invention relates to methods and systems for accurate ranging and geo-locationing using coherent multicarrier (CM) signals and based on a high-resolution estimation of a receiver timing offset in a signal receiver that receives ranging CM signals. A transmitter transmits a ranging CM signal having a known subcarrier modulation pattern. The receiver samples the ranging CM signal it receives reflected back from an object or from the remote transmitter, and processes the sampled signal that preserves relative subcarrier phases using a high-resolution model channel response function to determine the receiver timing offset with resolution much better than the receiver sampling period. The receiver timing offset is used to determine a flight time for the ranging CM signal with high accuracy.
Owner:AMERISYS INC
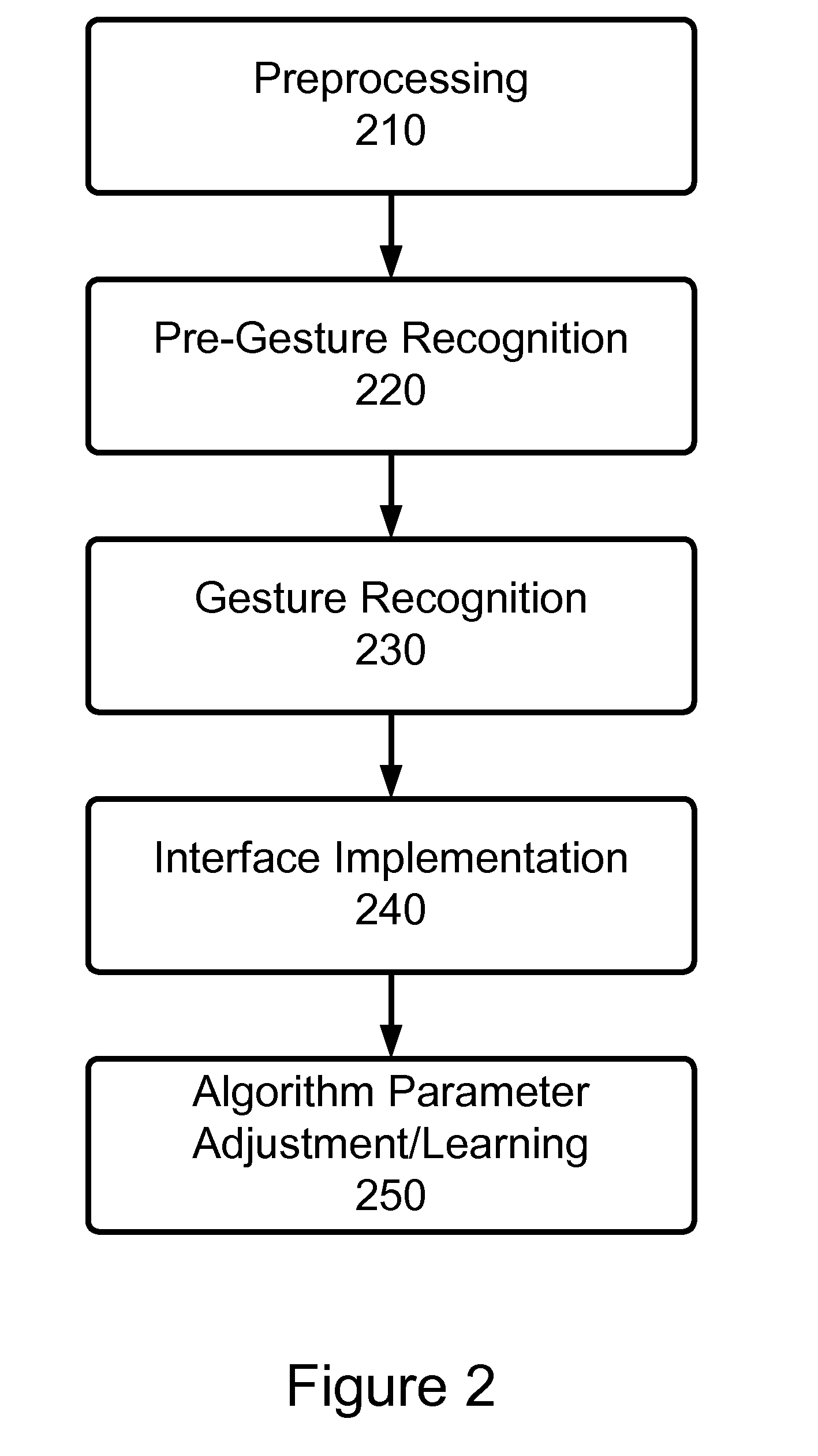
Systems and related methods for three dimensional gesture recognition in vehicles
ActiveUS20110286676A1Improve accuracyRobust implementationImage enhancementImage analysisIn vehicleComputer vision
A method and system for performing gesture recognition of a vehicle occupant employing a time of flight (TOF) sensor and a computing system in a vehicle. An embodiment of the method of the invention includes the steps of receiving one or more raw frames from the TOF sensor, performing clustering to locate one or more body part clusters of the vehicle occupant, locating the palm cluster of the vehicle occupant, calculating the location of the tip of the hand of the vehicle occupant, determining whether the hand has performed a dynamic or a static gesture, retrieving a command corresponding to one of the determined static or dynamic gestures, and executing the command.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Tilt-compensated laser rangefinder
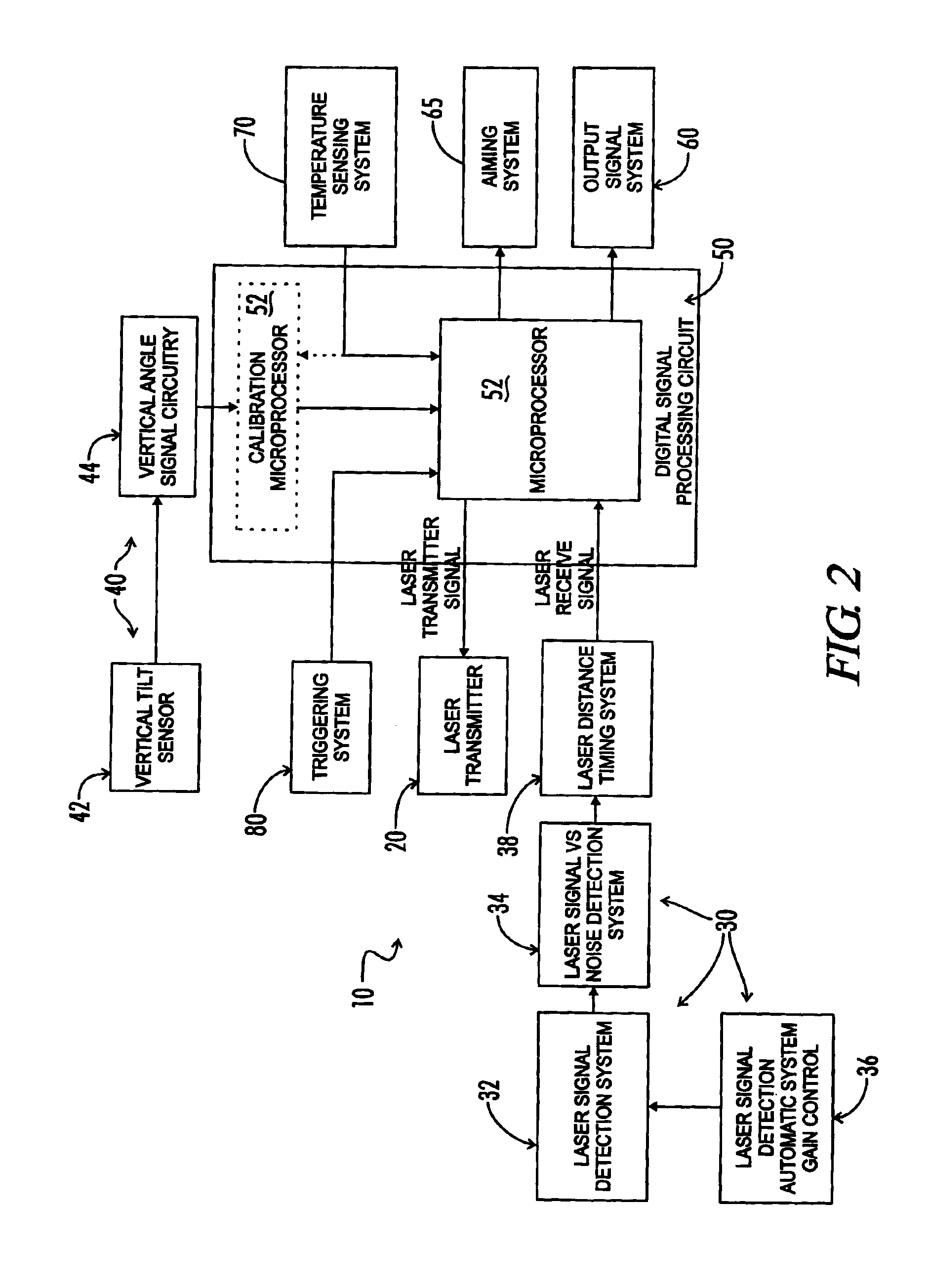
InactiveUS6873406B1Minimize impactError minimizationAngle measurementOptical rangefindersDigital signal processingInternal temperature
The present invention is a laser ranging device that incorporates an internal tilt sensor, an internal temperature sensor, and an internal pressure sensor. The tilt sensor is used to measure the target's vertical angle relative to the horizontal reference plane. Digital signal processing circuitry controls the firing of the laser pulse, calculation of time-of-flight range, measurement of the vertical angle of the tilt sensor, measurement of ambient temperature and storage of tilt sensor and temperature sensor calibration data. The digital signal processing circuitry then provides the user temperature corrected ballistic ranging information, including horizontal range. Additionally, an automatic gain control system minimizes the effects of target to target variance in reflectivity and its associated errors. It is also an object of this invention to electronically minimize errors in the measurement of a vertical angle caused by housing vibration and by temperature variance errors.
Owner:OPTI LOGIC CORP
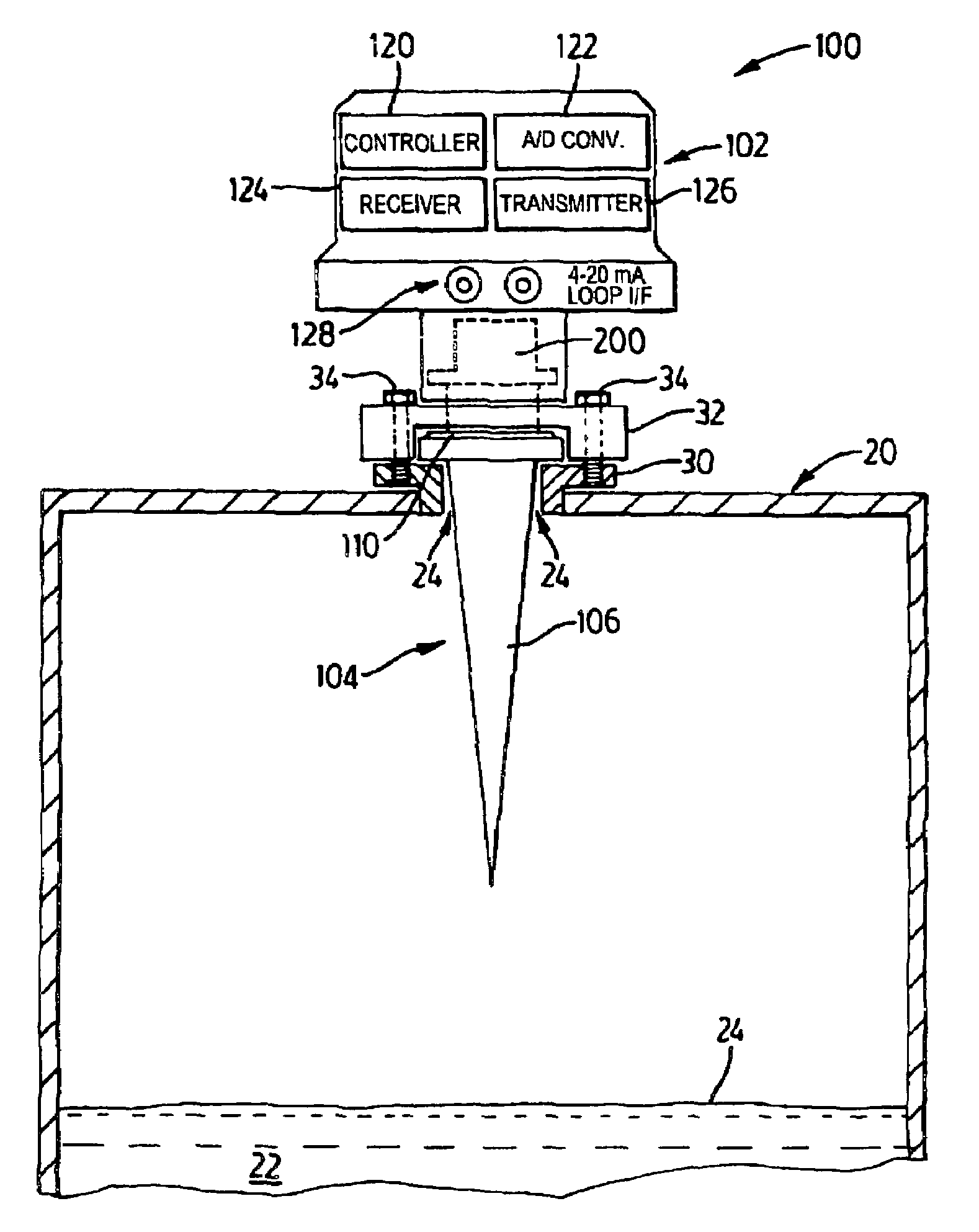
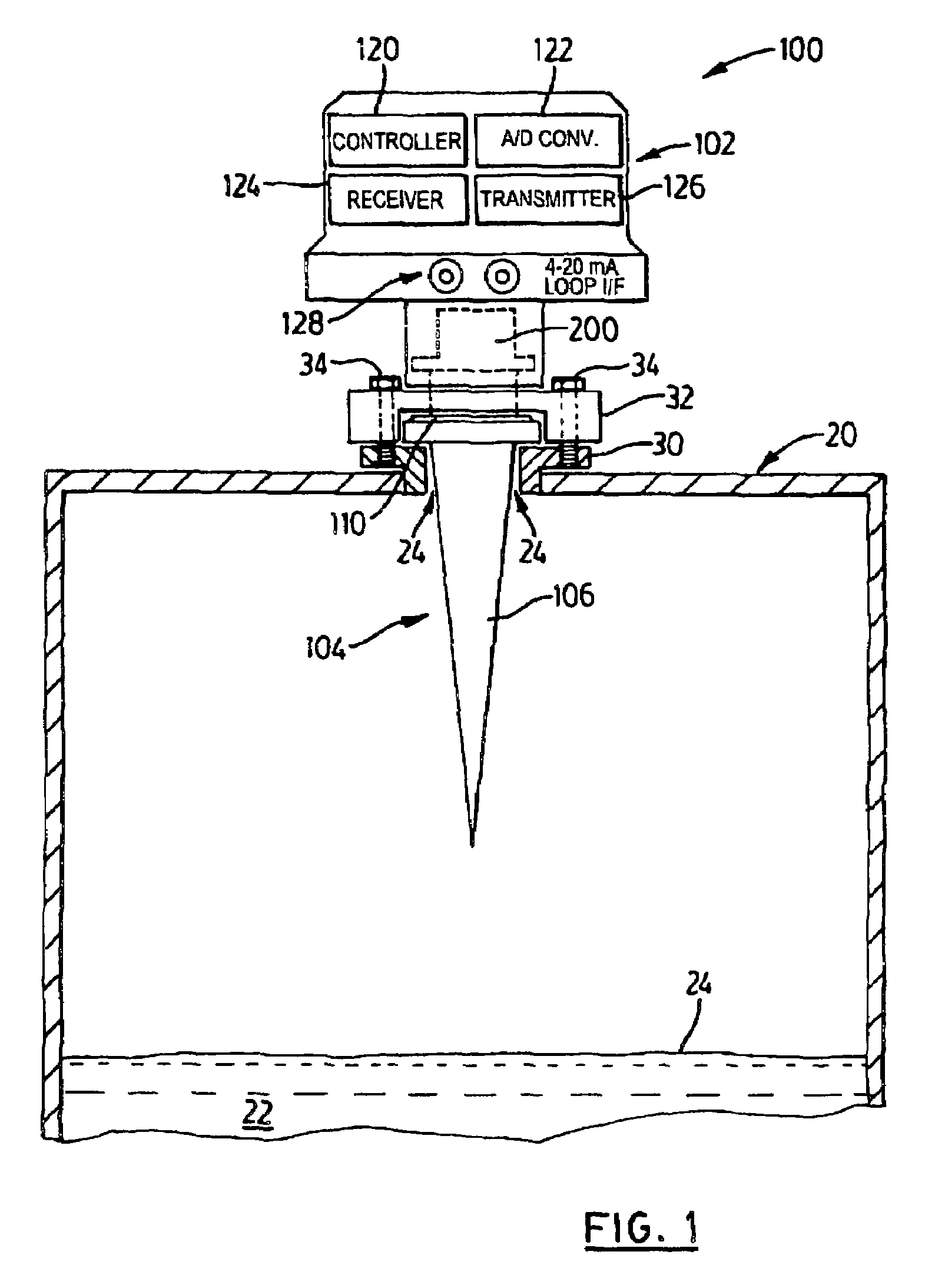
Vehicle classification and axle counting sensor system and method
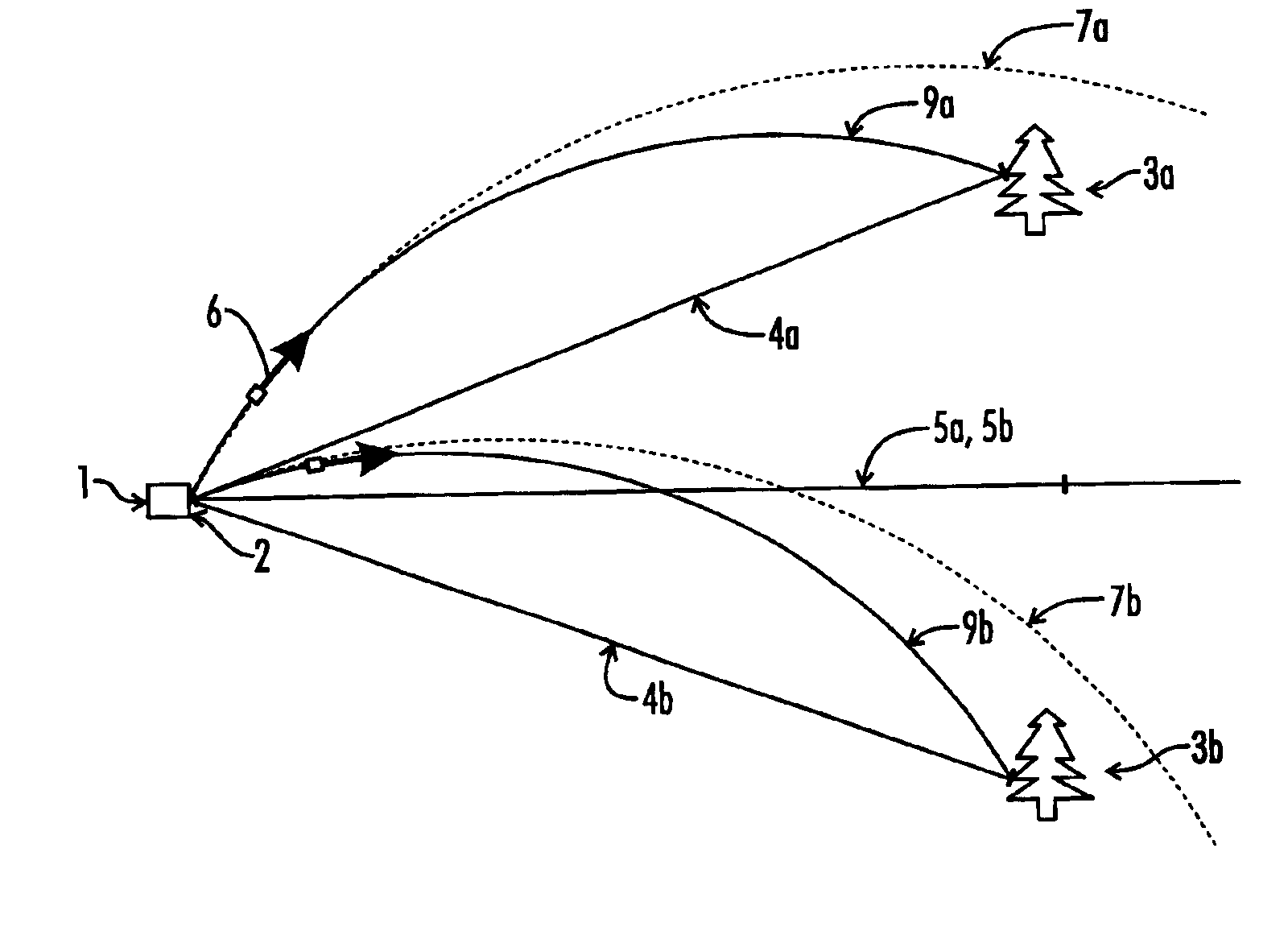
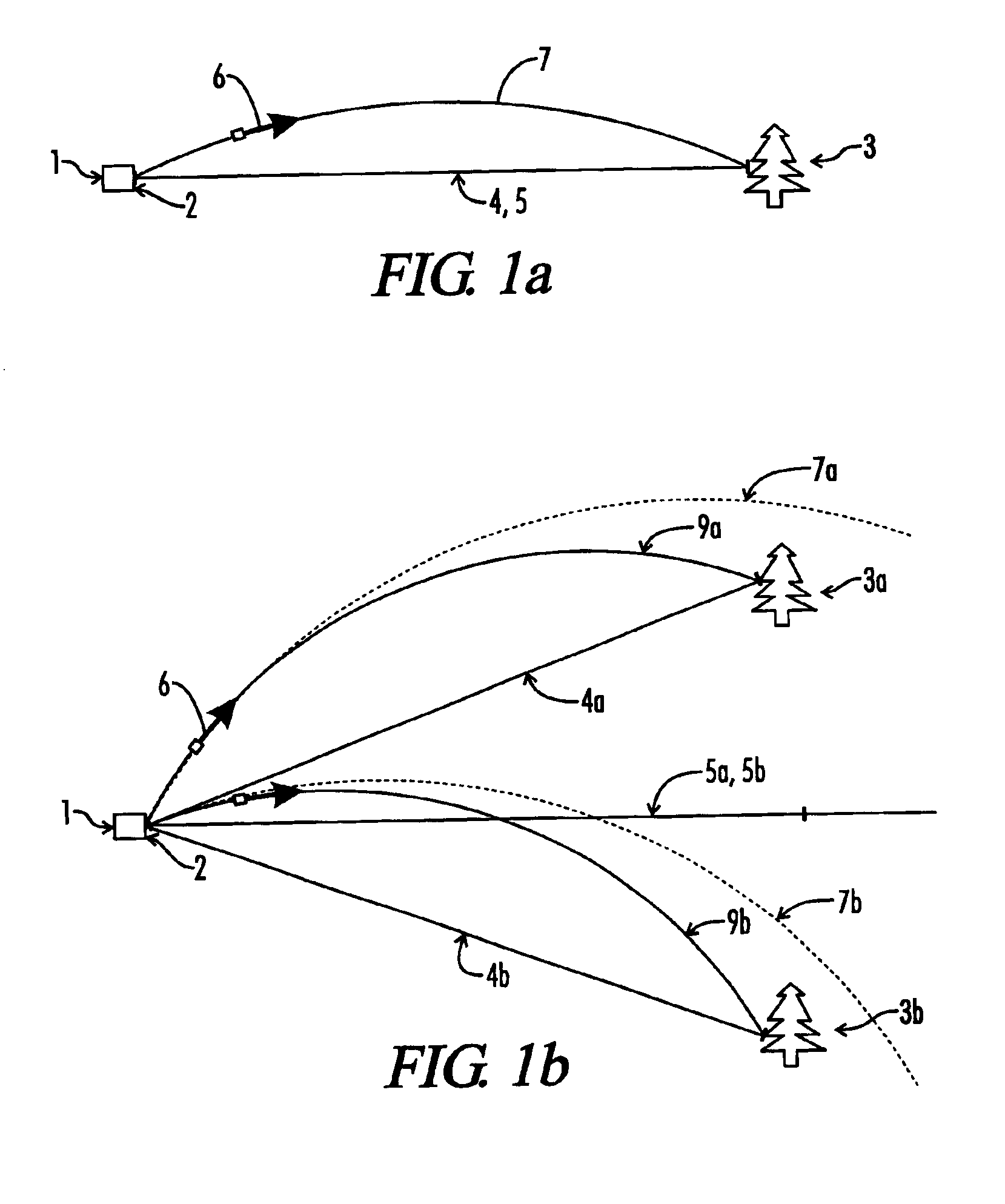
InactiveUS20020140924A1Accurately determinedAccurate detectionOptical rangefindersDetection of traffic movementRoad surfaceVehicle detection
A vehicle detection and classification sensor provides accurate 3D profiling and classification of highway vehicles for speeds up to 100 mph. A scanning time-of-flight laser rangefinder is used to measure the distance to the highway from a fixed point above the road surface and then measure the distance to the surfaces of any vehicle that is viewed by the sensor. The beam is pulsed at a high repetition rate for determining vehicle speeds with a high accuracy and uses the calculated speed and consecutive range measurements as the vehicle moves past the sensor to develop a three-dimensional profile of the vehicle. An algorithm is applied to the three-dimensional profile for providing a vehicle-classification. A laser is also used to count the number of axles associated with the vehicle.
Owner:WANGLER RICHARD J +3
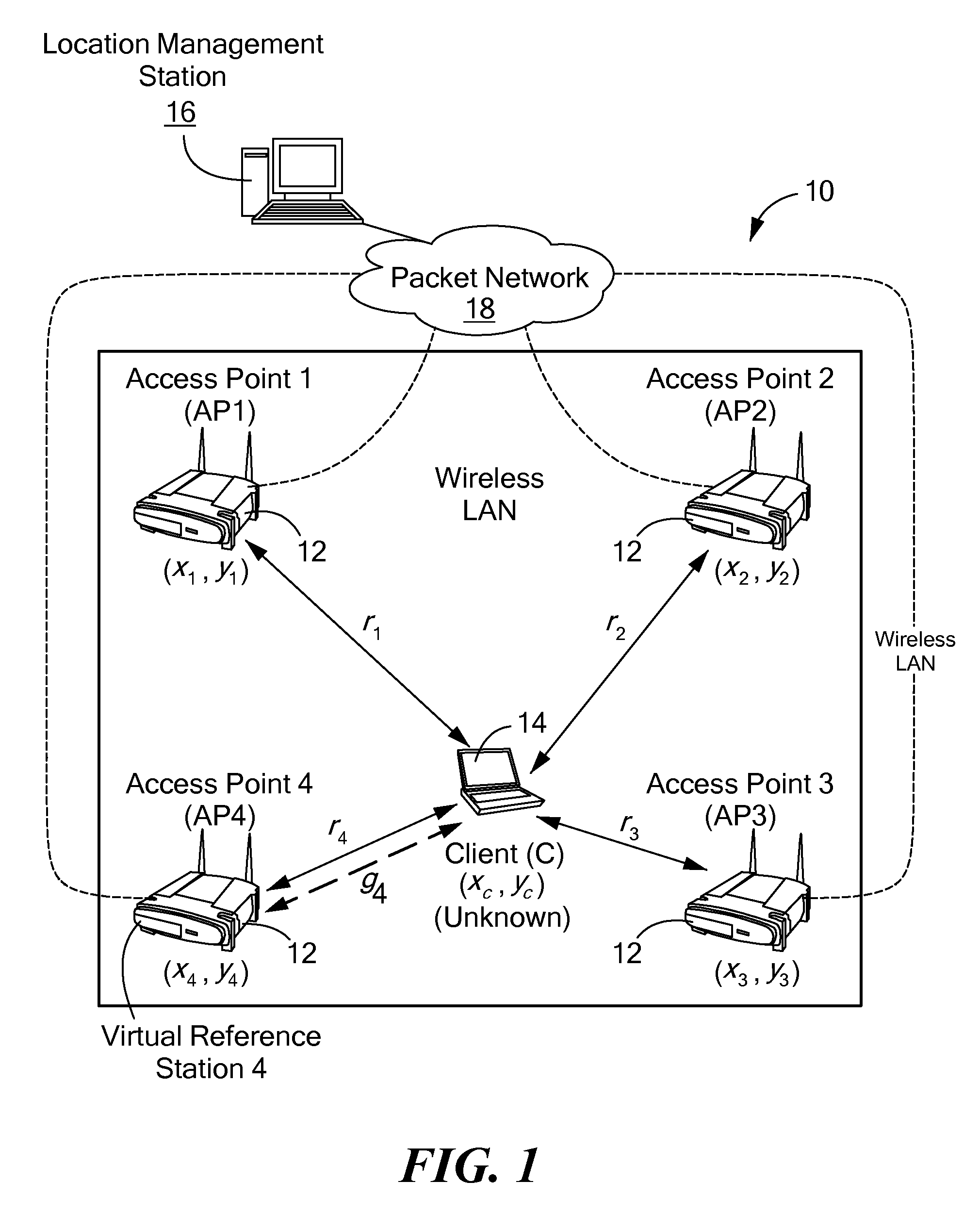
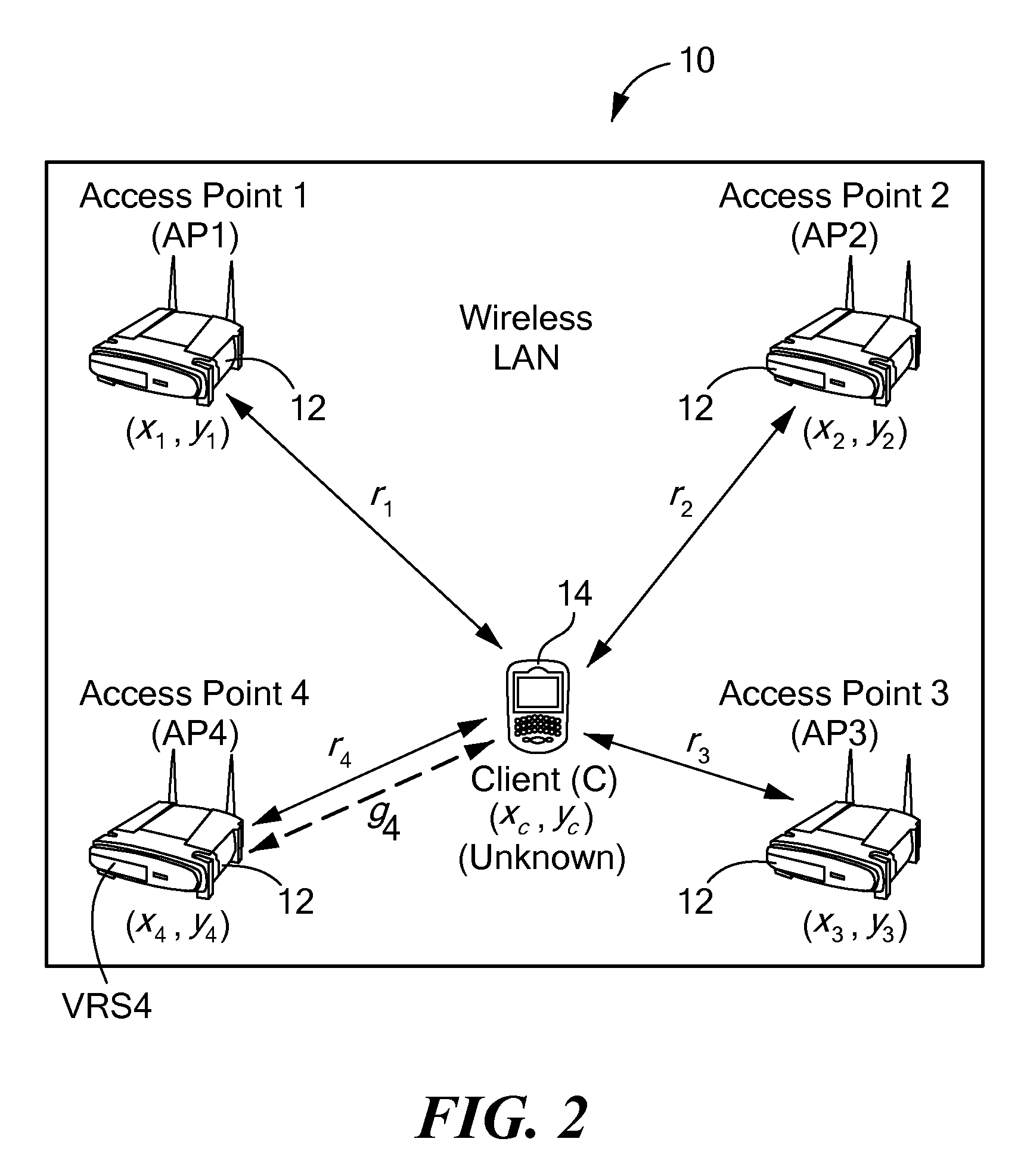
Method and system for wireless lan-based indoor position location
A method and system for position location of clients in wireless local area networks. (WLANs). The position location technique utilizes time-of-flight (TOF) measurements of signals transmitted from a client to a number of wireless access points (APs) or vice versa to determine distances. Round-trip time (RTT) measurement protocols are used to estimate TOF and distances between the client at an unknown position and the WLAN APs. The method and system improves positioning accuracy by identifying and mitigating non-line-of sight (NLOS) errors such as multipaths. Trilateration algorithms are utilized in combination with median filtering of measurements to accurately estimate the position of the client.
Owner:AVAYA INC +1
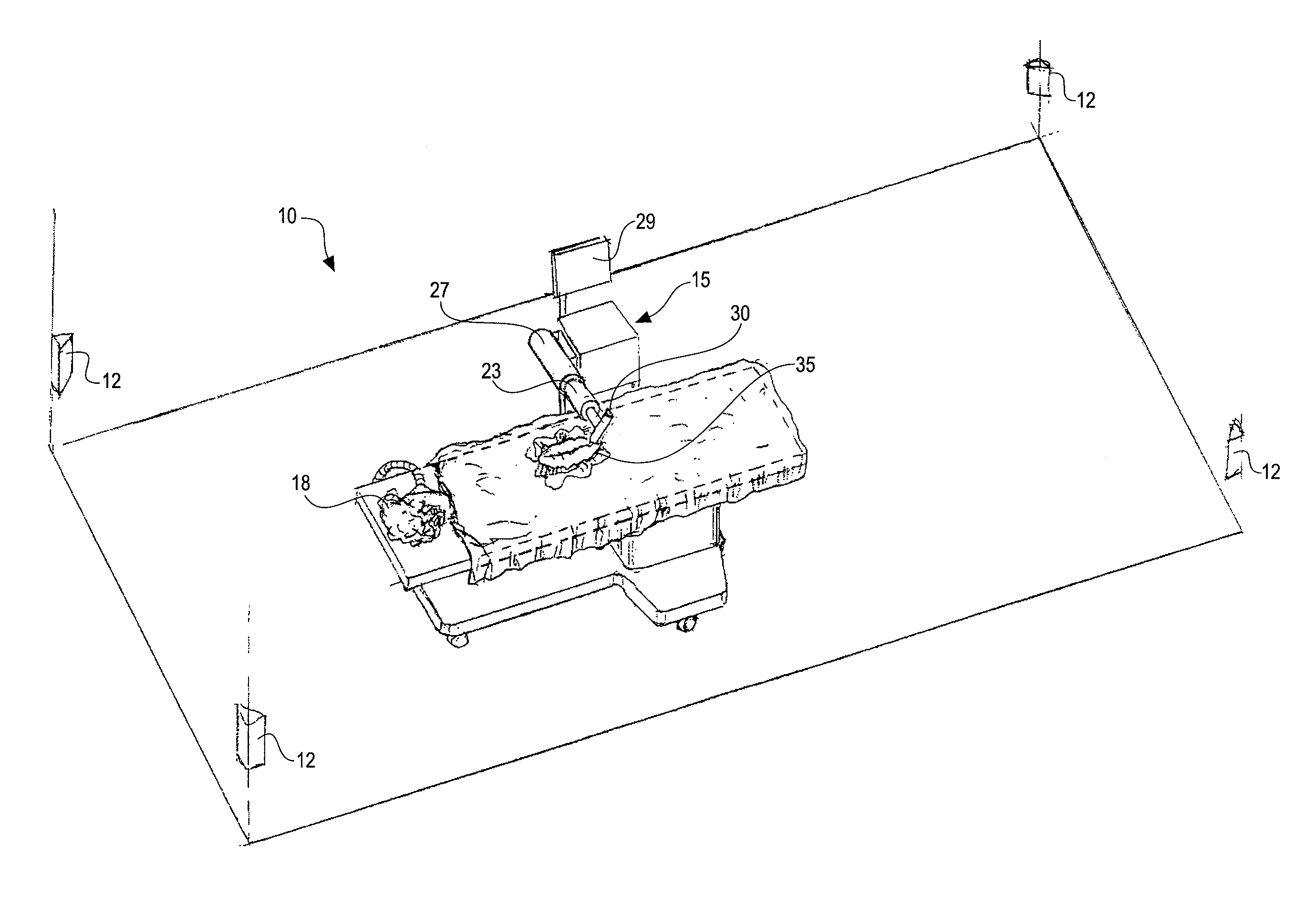
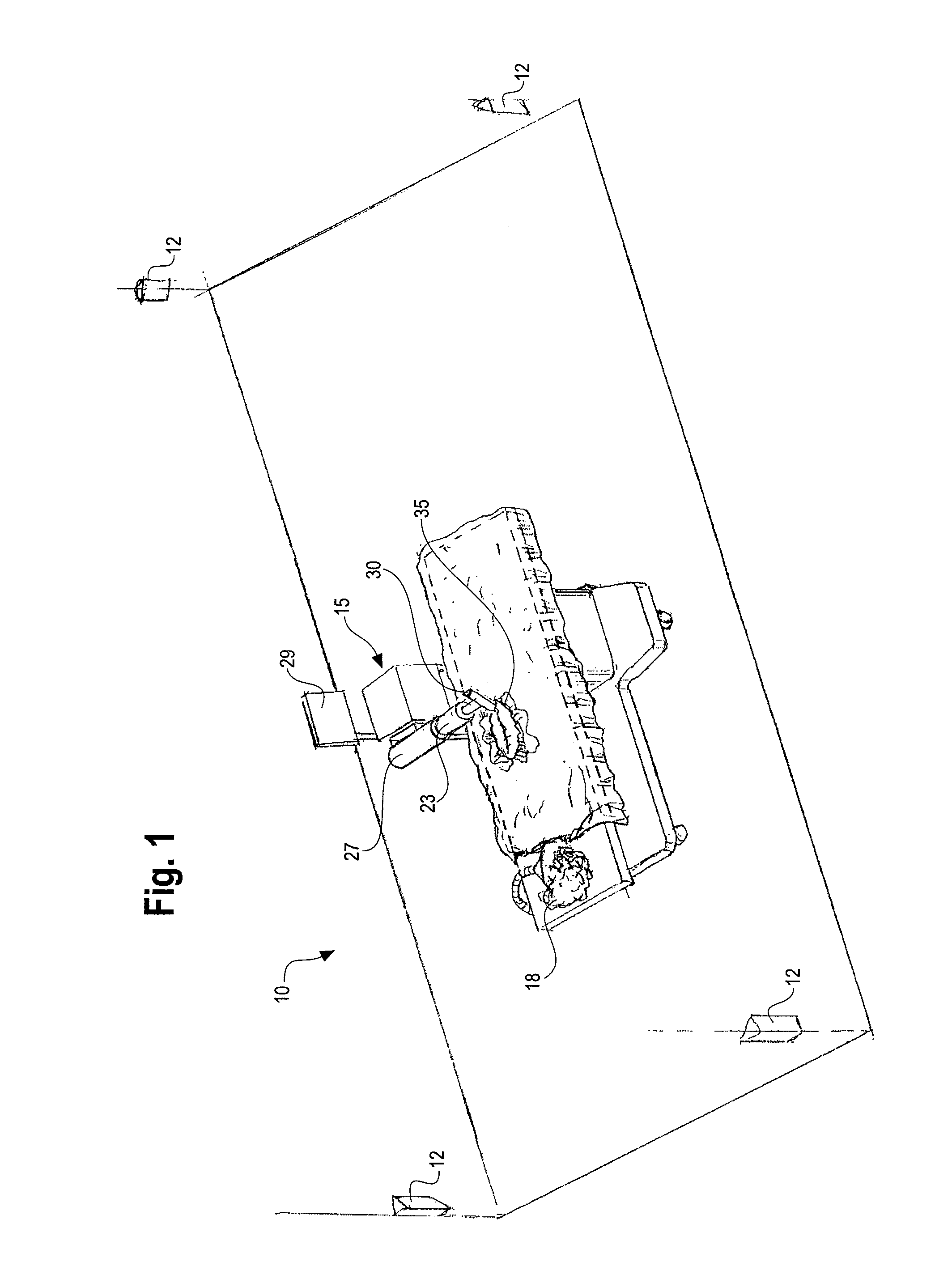
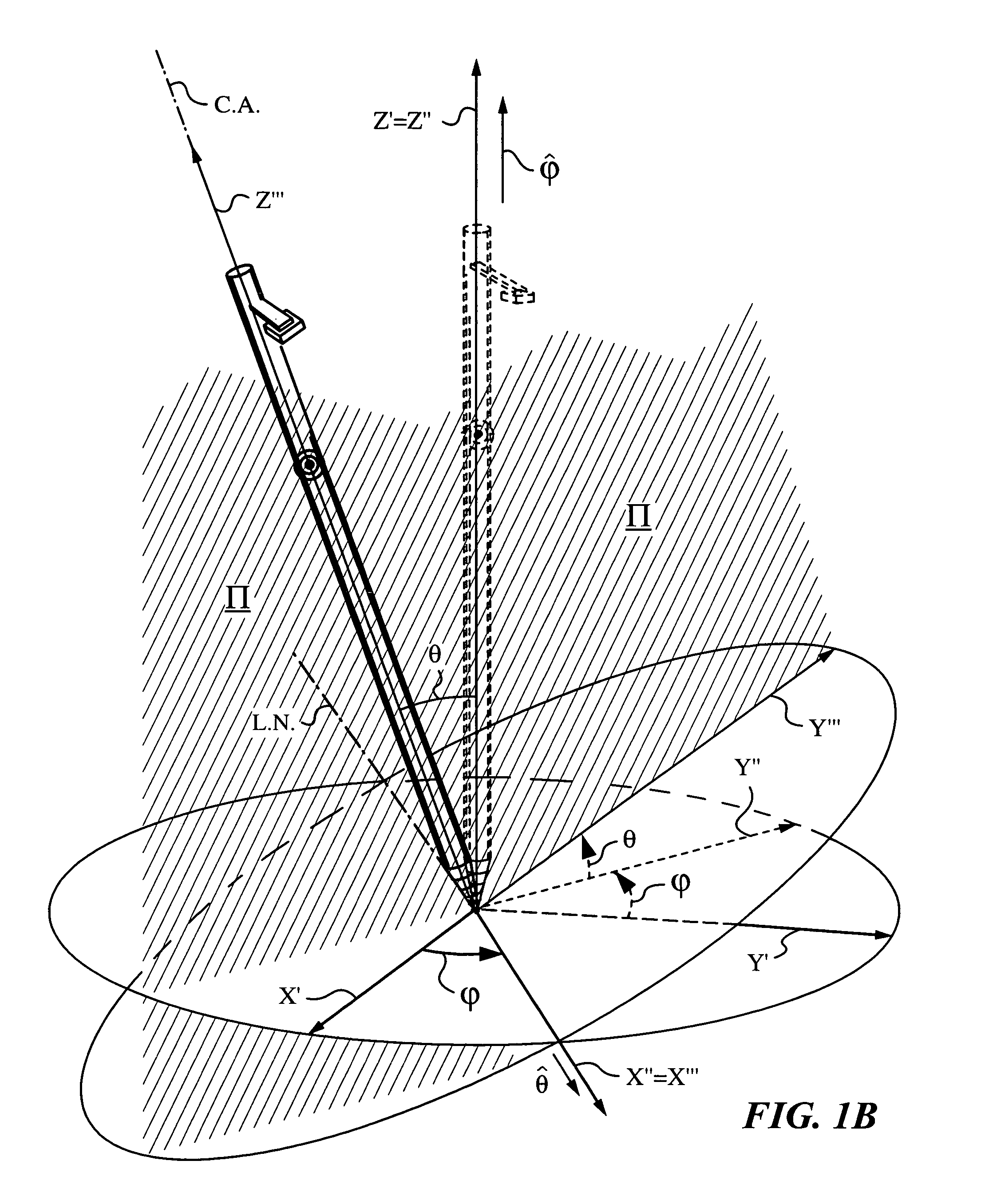
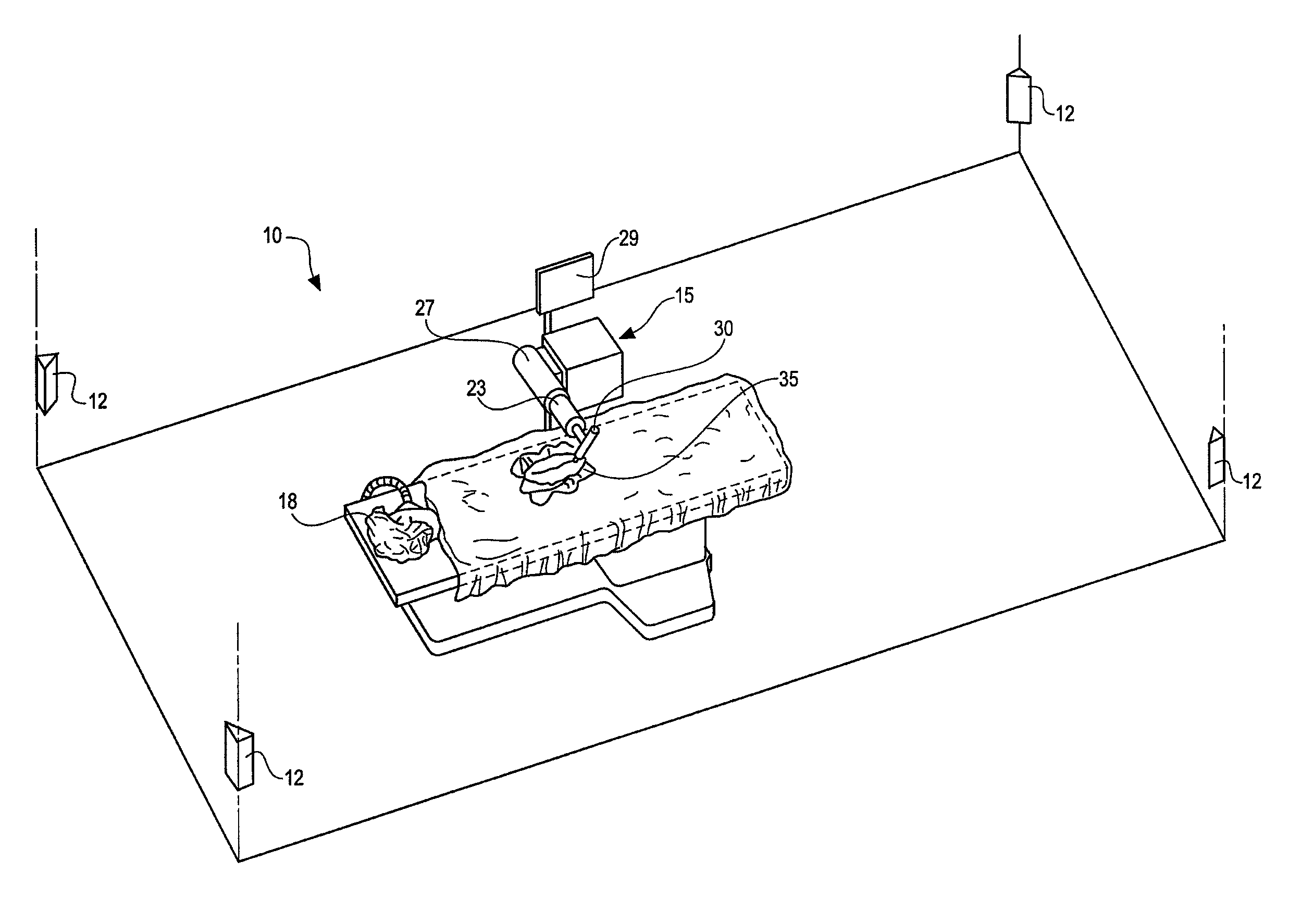
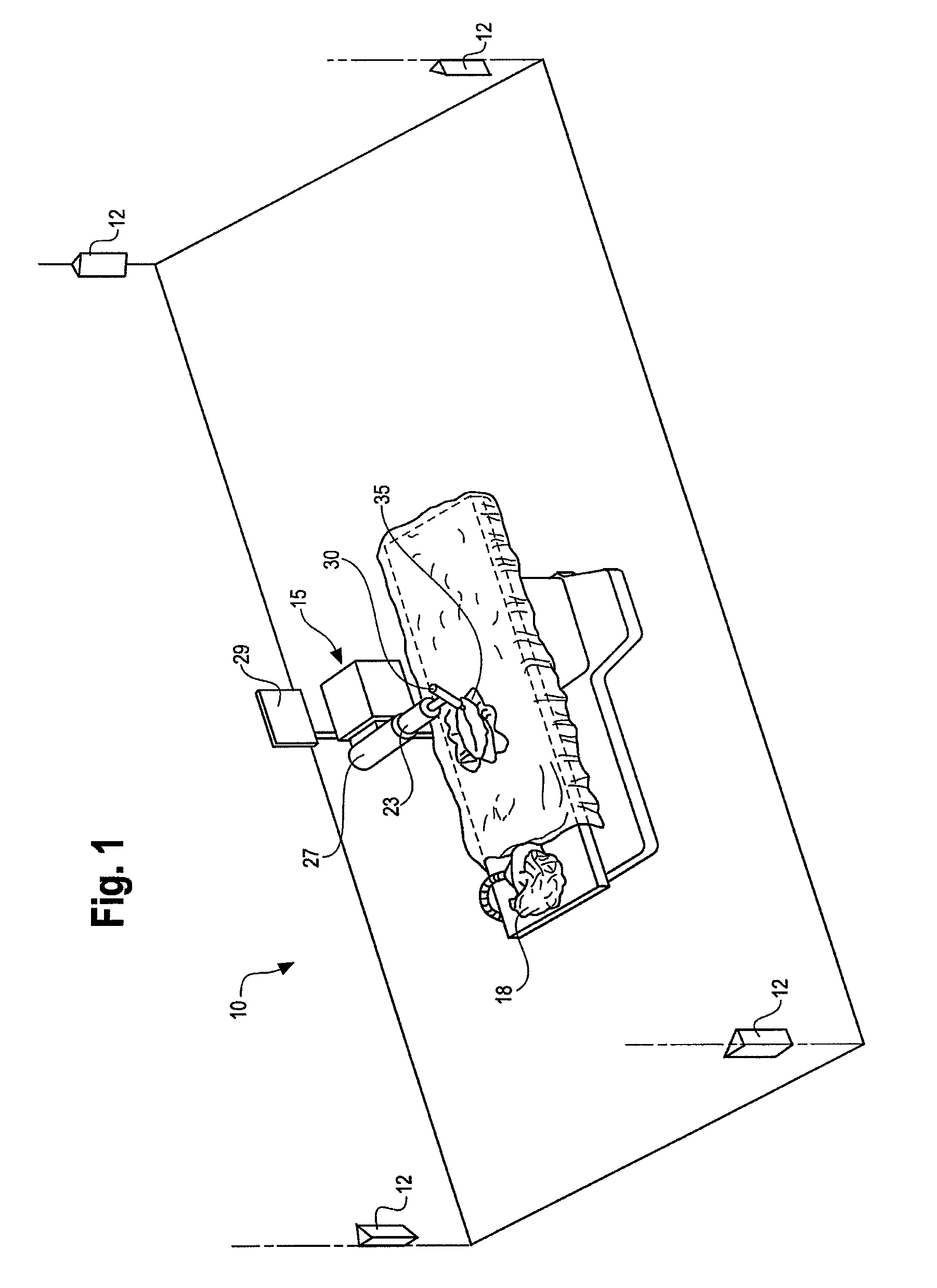
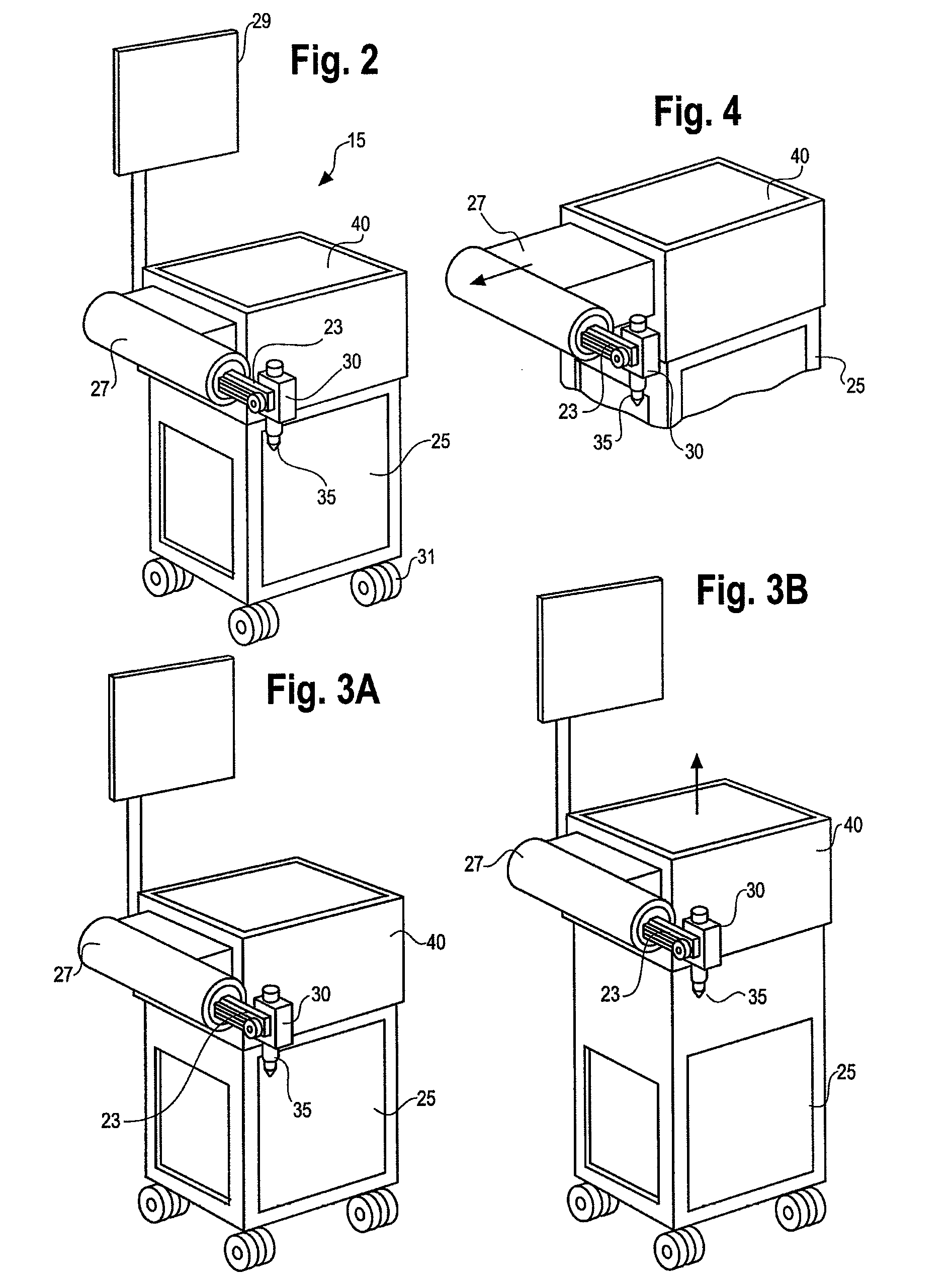
Method and system for performing invasive medical procedures using a surgical robot
ActiveUS8219178B2Degree of precisionInternal osteosythesisSurgical needlesGuidance systemSurgical robot
A method and system for performing invasive procedures includes a surgical robot which is controlled by a guidance system that uses time of flight calculations from RF transmitters embedded in the robot, surgical instrument, and patient anatomy. Sensors around the room detect RF transmissions emitted by the RF transmitters and drive the robot according to a preprogrammed trajectory entered into the guidance system.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL +1
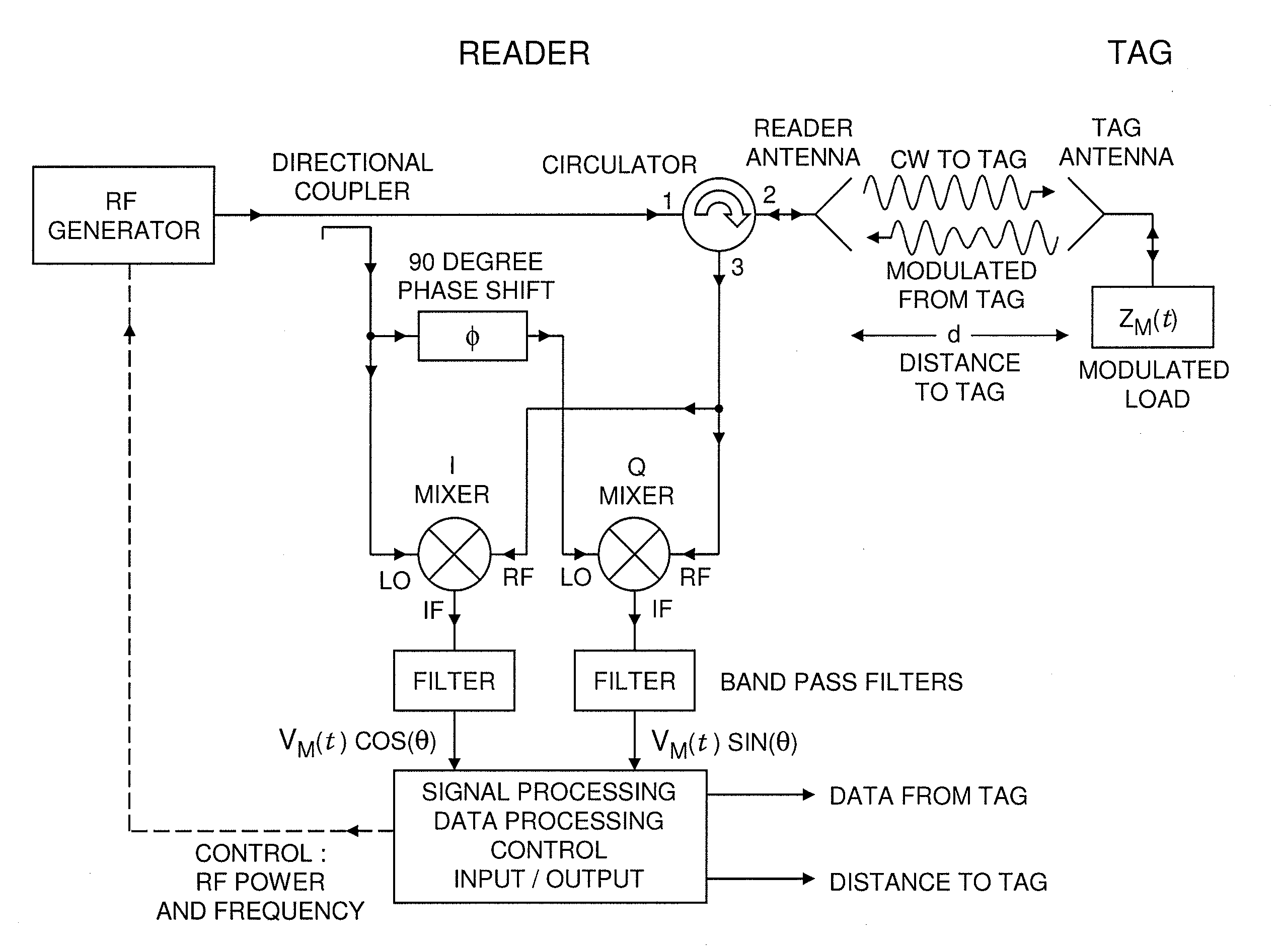
System and method for measurement of distance to a tag by a modulated backscatter RFID reader
ActiveUS20110187600A1Easy to controlDirection finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAudio power amplifierEngineering
Distance to a modulated backscatter tag is measured with a RFID reader that measures changes in phase with frequency of modulated backscattered RF signals. Measured distances are linked to a specific tag. The effects of other sources of reflected and interfering signals are mitigated. The techniques eliminate the need for high RF bandwidth used in time-of-flight methods, and may be used with linear, limiting or other types of amplifiers in the reader receiver. Unambiguous distance to a tag may be found using the derivative of phase with RF frequency of the modulated signal backscattered by a tag. The distance to a tag can be measured with an accuracy on the order of a centimeter. The techniques utilize the characteristics of cooperative backscatter tags (transponders, labels, etc.). New readers implement the techniques which may use unmodified tags.
Owner:AMTECH SYST
Method and system to avoid inter-system interference for phase-based time-of-flight systems
ActiveUS7405812B1Likelihood of interferenceReduce distractionsOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationClock rateOptical energy
Inter-system interference cross-produce P12 is reduced in a phase-based TOF system by randomizing instantaneous phase and / or frequency within a capture interval (or detection integration period). In one aspect, the TOF clock system frequency preserves long-term clock frequency stability but intentionally includes random or pseudo-random clock noise. The noise ensures the generated clock signals are temporally imperfect and lack substantial perfect periodicity. A second aspect causes the TOF clock system to hop frequency, preferably pseudo-randomly. TOF system homodyning favors detection of optical energy whose frequency correlates to the time-varying frequency of the emitted optical energy. Thus, the varying spectral spacing of the emitted optical energy reduces likelihood that an adjacent TOF system at any given time will emit optical energy of an interfering frequency. At least one aspect is employed, both aspects being mutually complementary to reduce the cross-correlation product P12 without substantially affecting TOF system performance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Robust lidar sensor for broad weather, shock and vibration conditions
InactiveUS20160047901A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser transmitterVibration control
An apparatus and method are used for real-time wide-field-of-view ranging with a time-of-flight lidar sensor having one or a plurality of laser emitters and one or a plurality of photodetectors. When a plurarity of laser emitters are used, they are preferably copackaged or are in the form of an integrated multi-emitter chip or emitting multi-chip module in a single package, and when a plurarity of photoreceivers are used, they are preferably copackaged or are in the form of an integrated multi-photoreceiver chip or photoreceiving multi-chip module in a single package. Furthermore, the apparatus comprises any combination of (a) no moving external parts in contact with the environment, (b) wireless energy and data transfer between the static and the moving parts of the lidar, and (c) protective body, sealant and / or damage-resistant tamper-resistant theft-resistant cage.
Owner:QUANERGY SYST
Multiple Pulse, LIDAR Based 3-D Imaging
ActiveUS20170219695A1Minimize impactOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight beamPulse sequence
Methods and systems for performing multiple pulse LIDAR measurements are presented herein. In one aspect, each LIDAR measurement beam illuminates a location in a three dimensional environment with a sequence of multiple pulses of illumination light. Light reflected from the location is detected by a photosensitive detector of the LIDAR system during a measurement window having a duration that is greater than or equal to the time of flight of light from the LIDAR system out to the programmed range of the LIDAR system, and back. The pulses in a measurement pulse sequence can vary in magnitude and duration. Furthermore, the delay between pulses and the number of pulses in each measurement pulse sequence can also be varied. In some embodiments, the multi-pulse illumination beam is encoded and the return measurement pulse sequence is decoded to distinguish the measurement pulse sequence from exogenous signals.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Noninvasive glucose sensing methods and systems
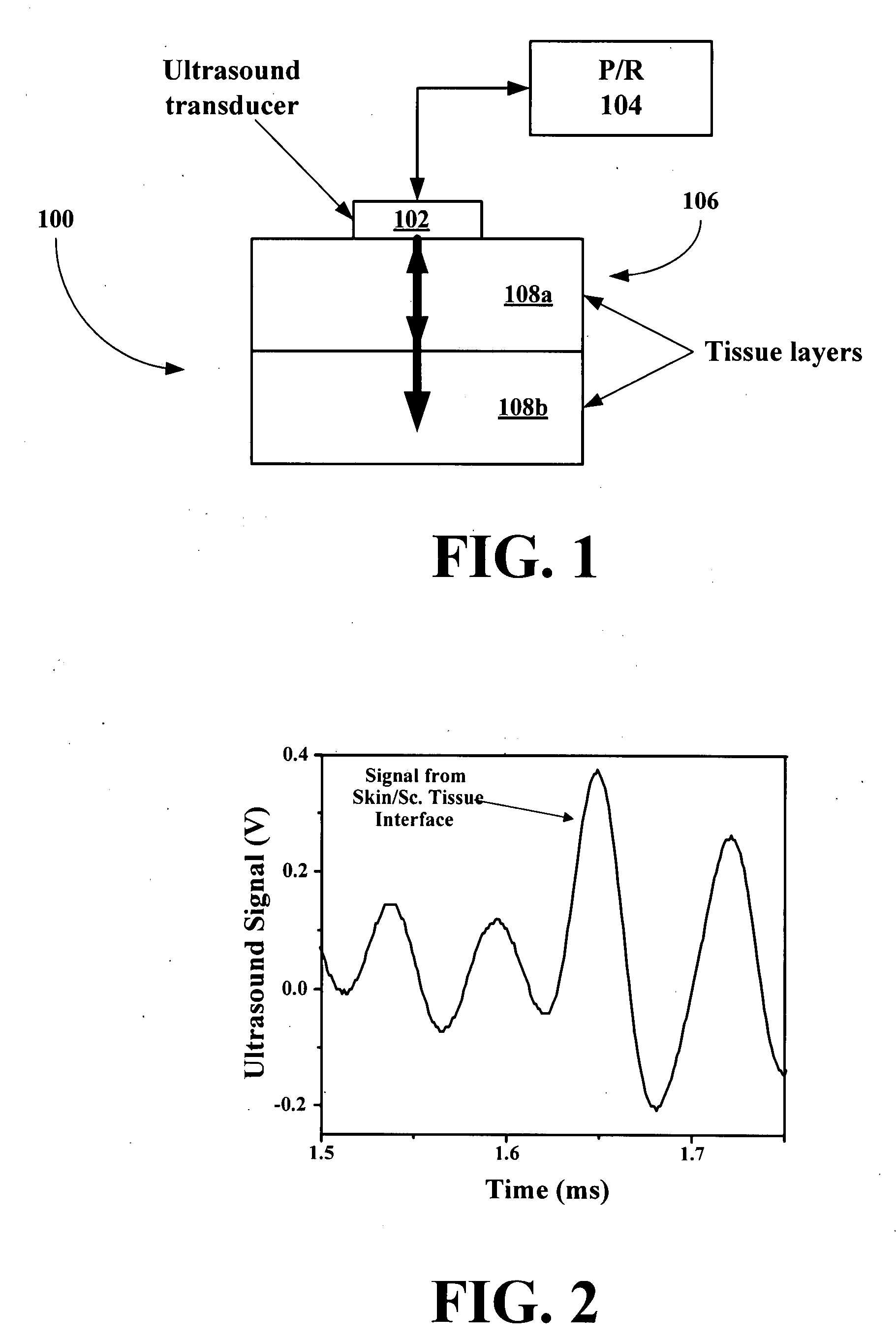
ActiveUS20070255141A1Reduce complicationsReduce mortalityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsMedicineD-Glucose
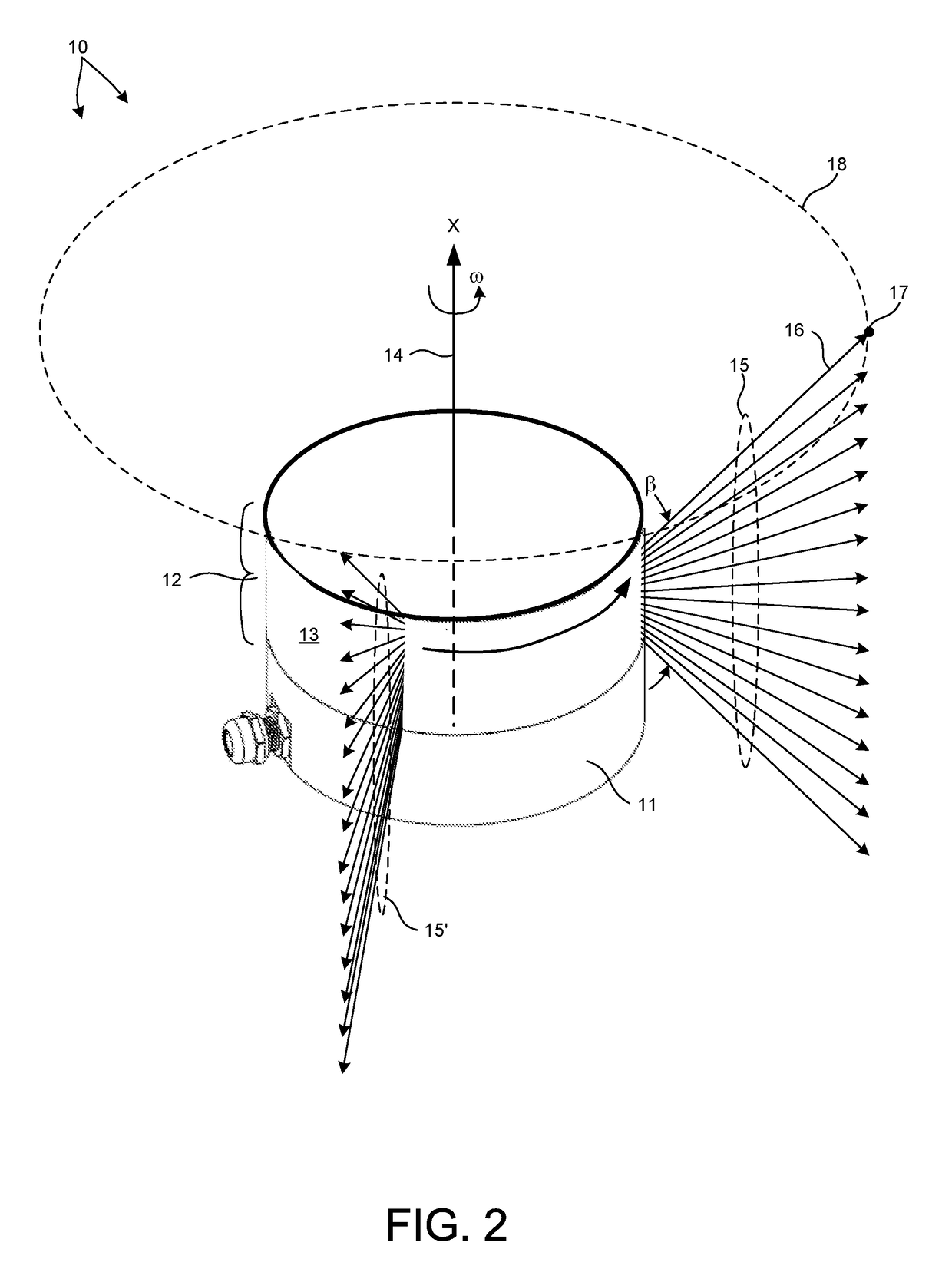
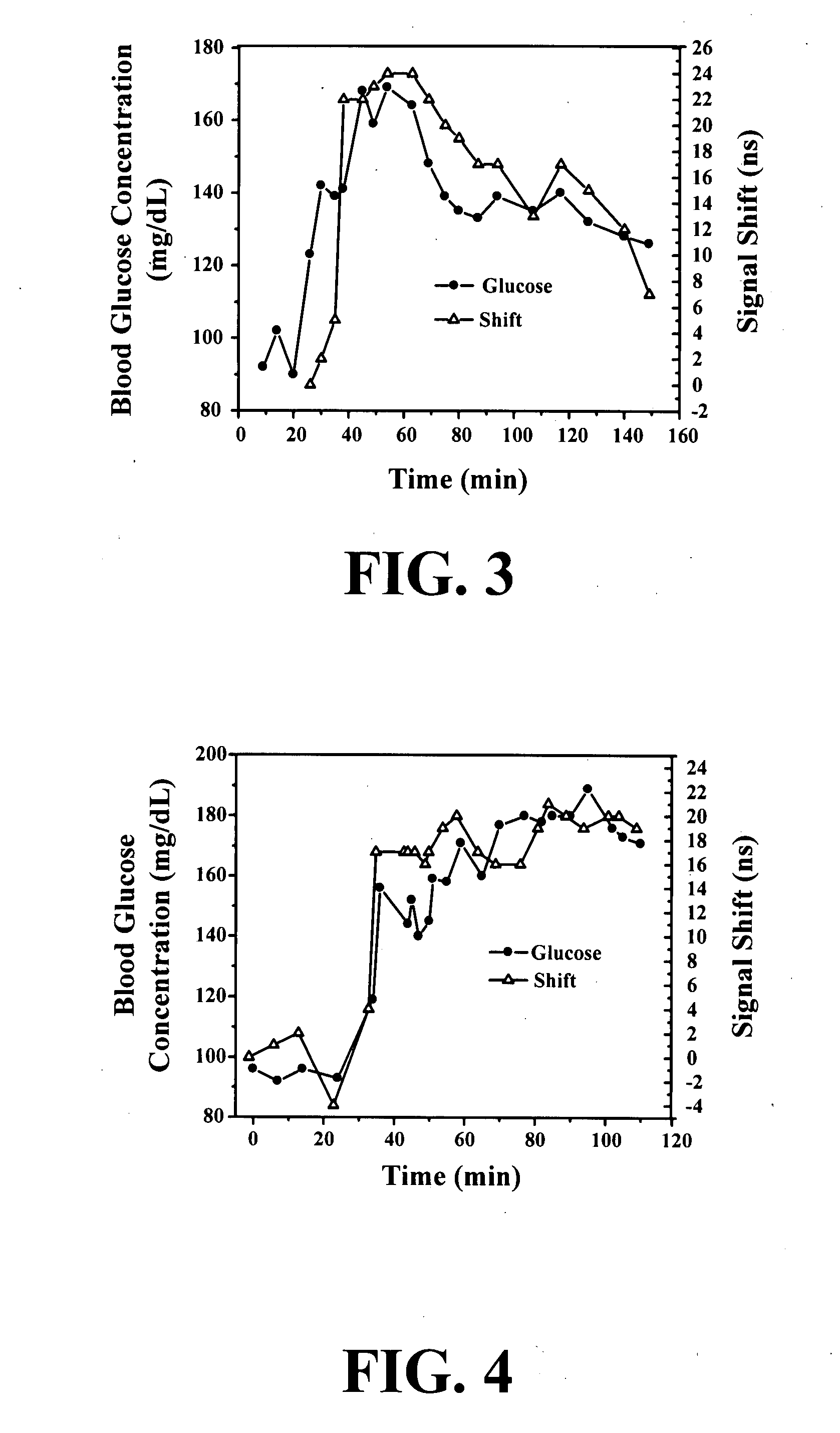
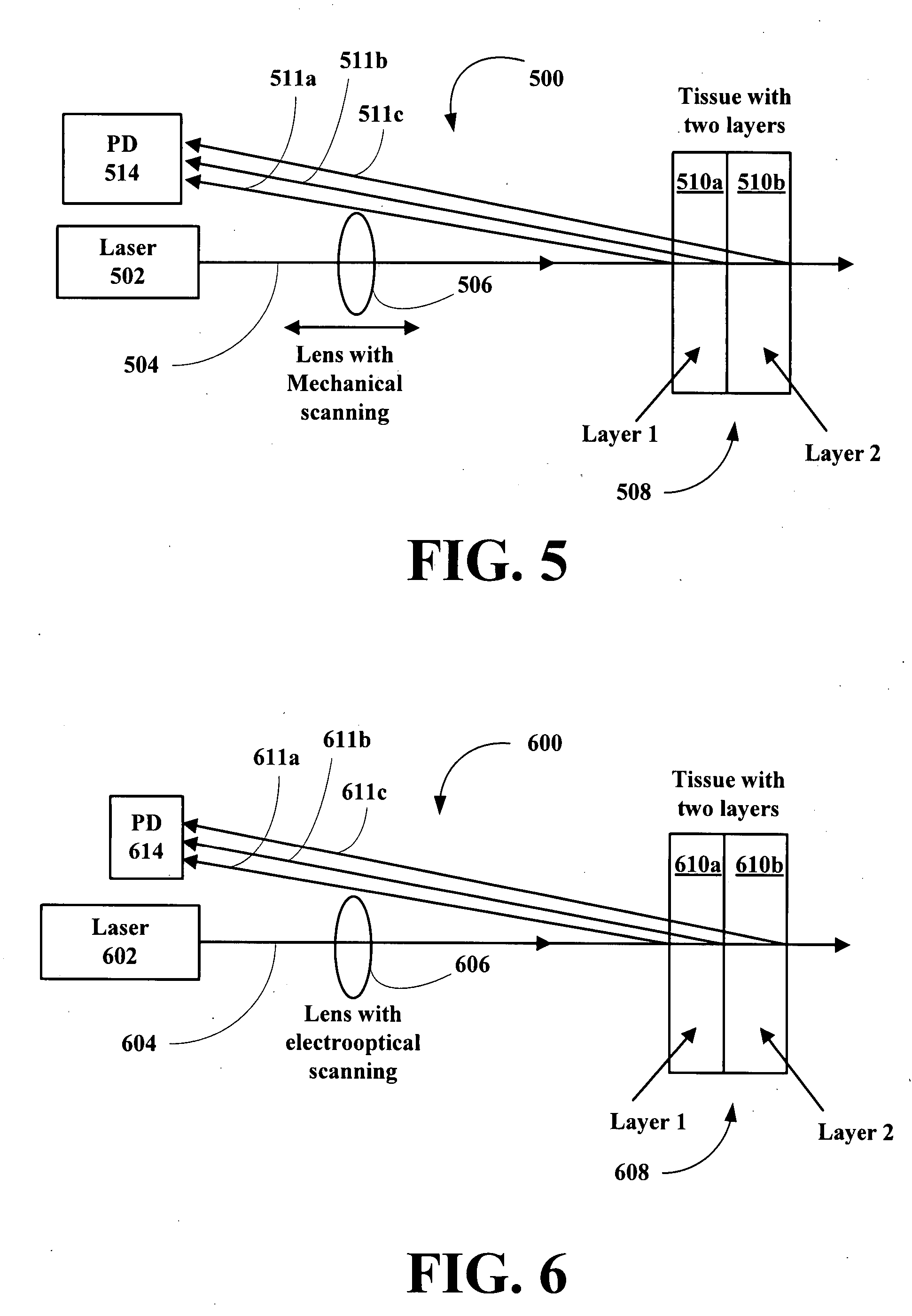
New methods and systems for noninvasive glucose monitoring and sensing with electromagnetic waves or ultrasound are disclosed. The methods are based on absolute or relative measurement of tissue dimensions (or changes in the dimensions) including, but not limited to: thickness, length, width, diameter, curvature, roughness as well as time of flight of ultrasound and optical pulses and optical thickness, which change with changing blood glucose concentrations. By measuring noninvasively absolute or relative changes in at least one dimension of at least one tissue or tissue layer or absolute or relative changes in time of flight of ultrasound or optical pulses, one can monitor blood glucose concentration noninvasively.
Owner:ESENALIEV RINAT O +1
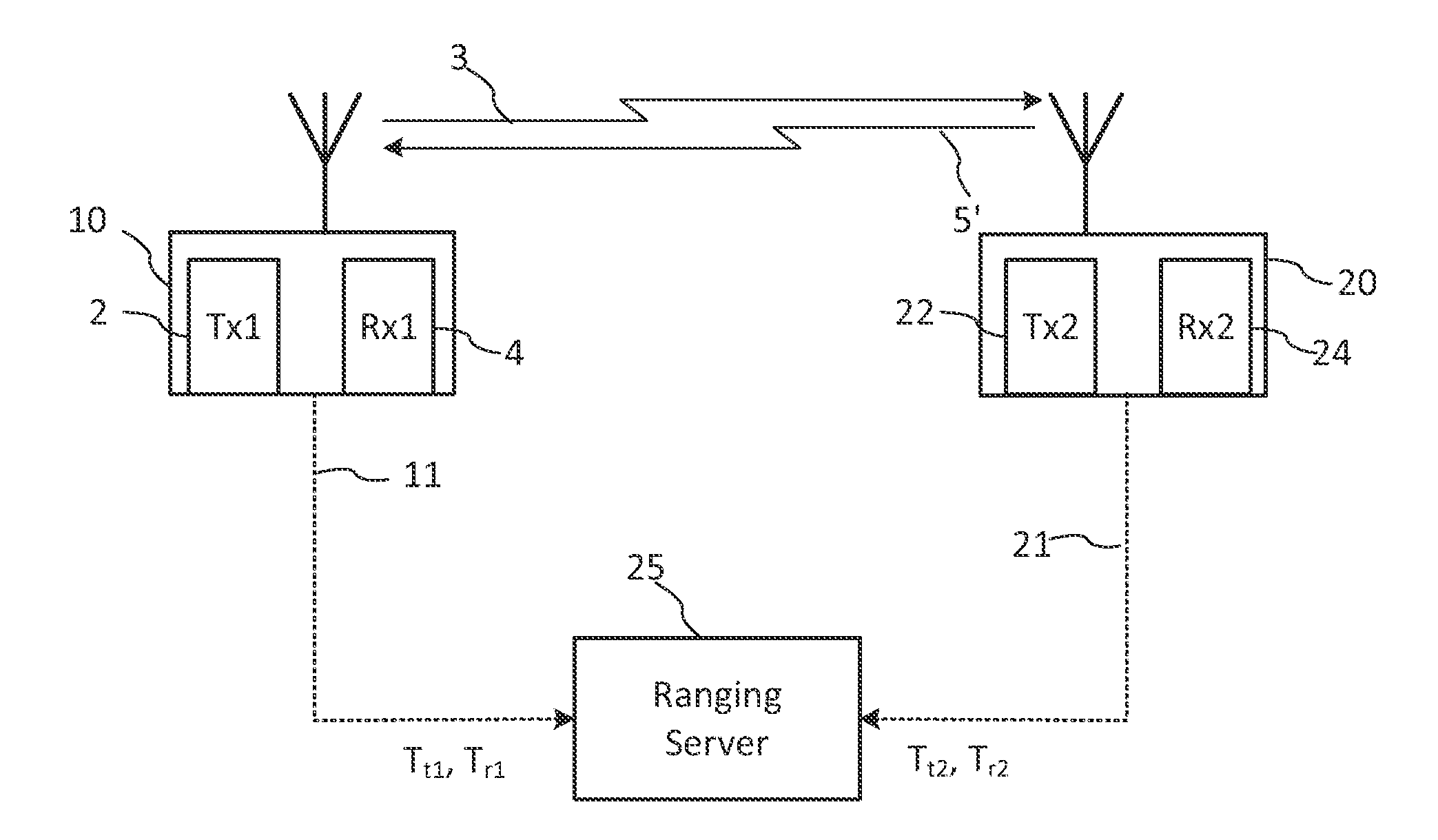
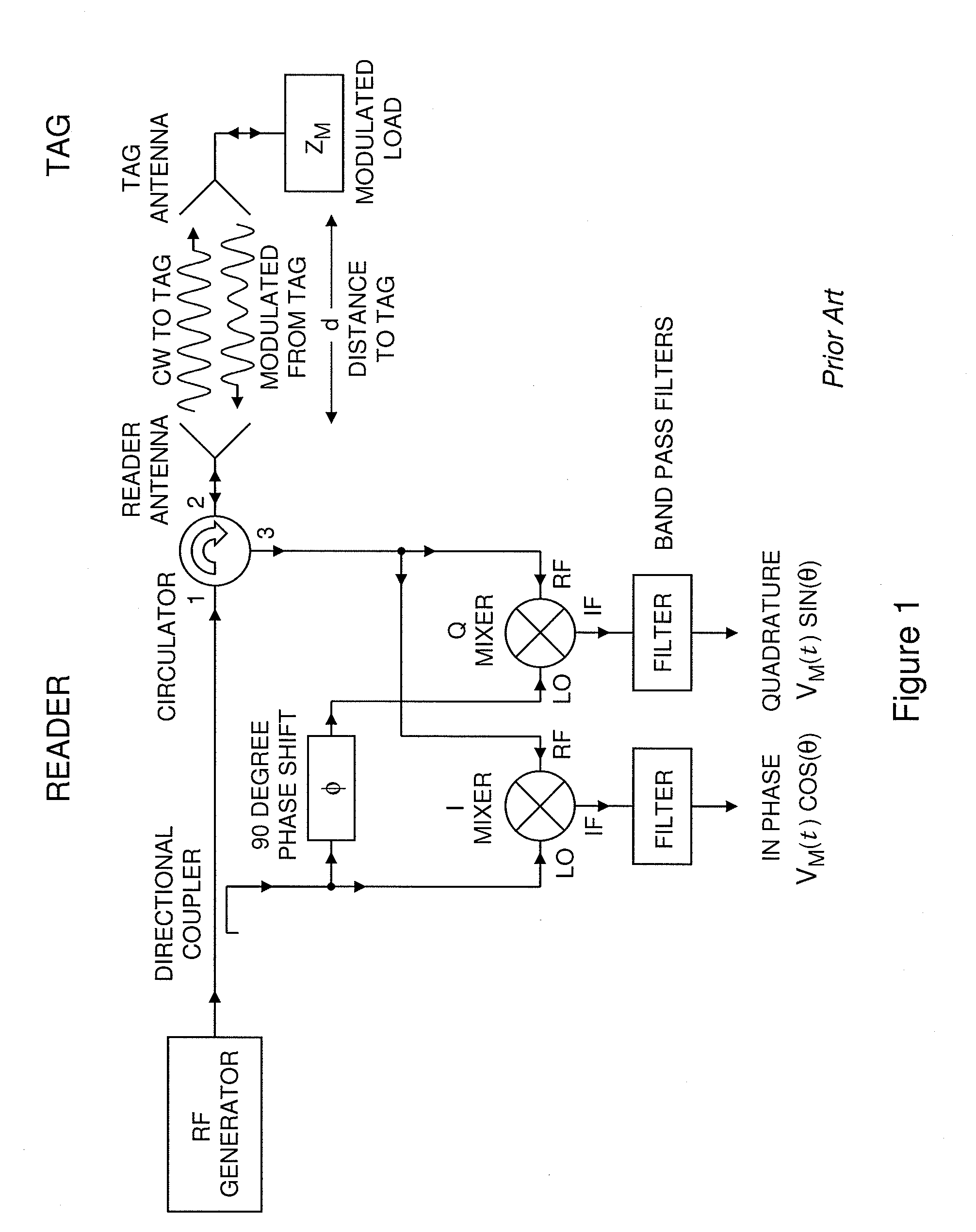
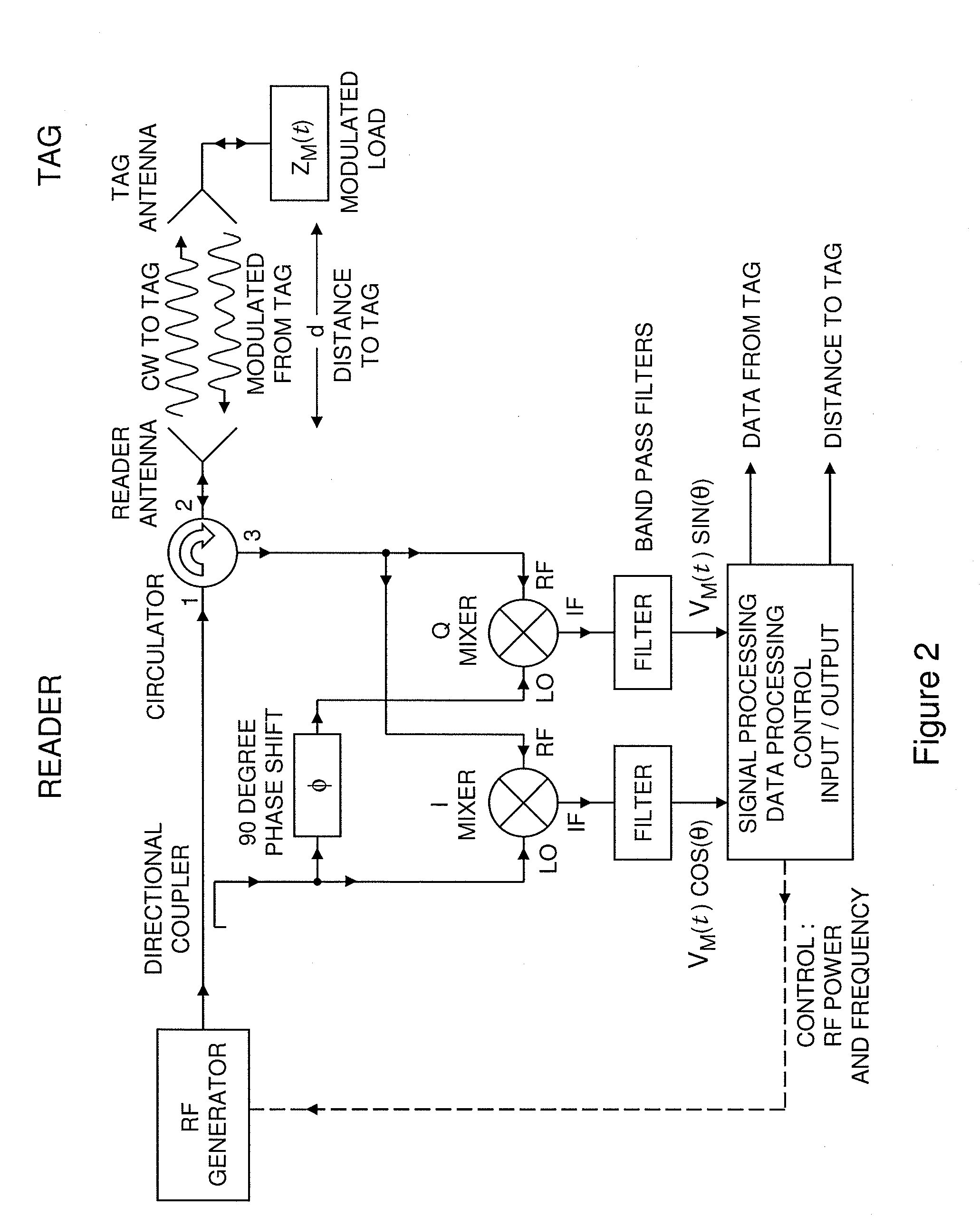
System and method for distance measurement by inphase and quadrature signals in a radio system
InactiveUS6295019B1Direction finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverTime delays
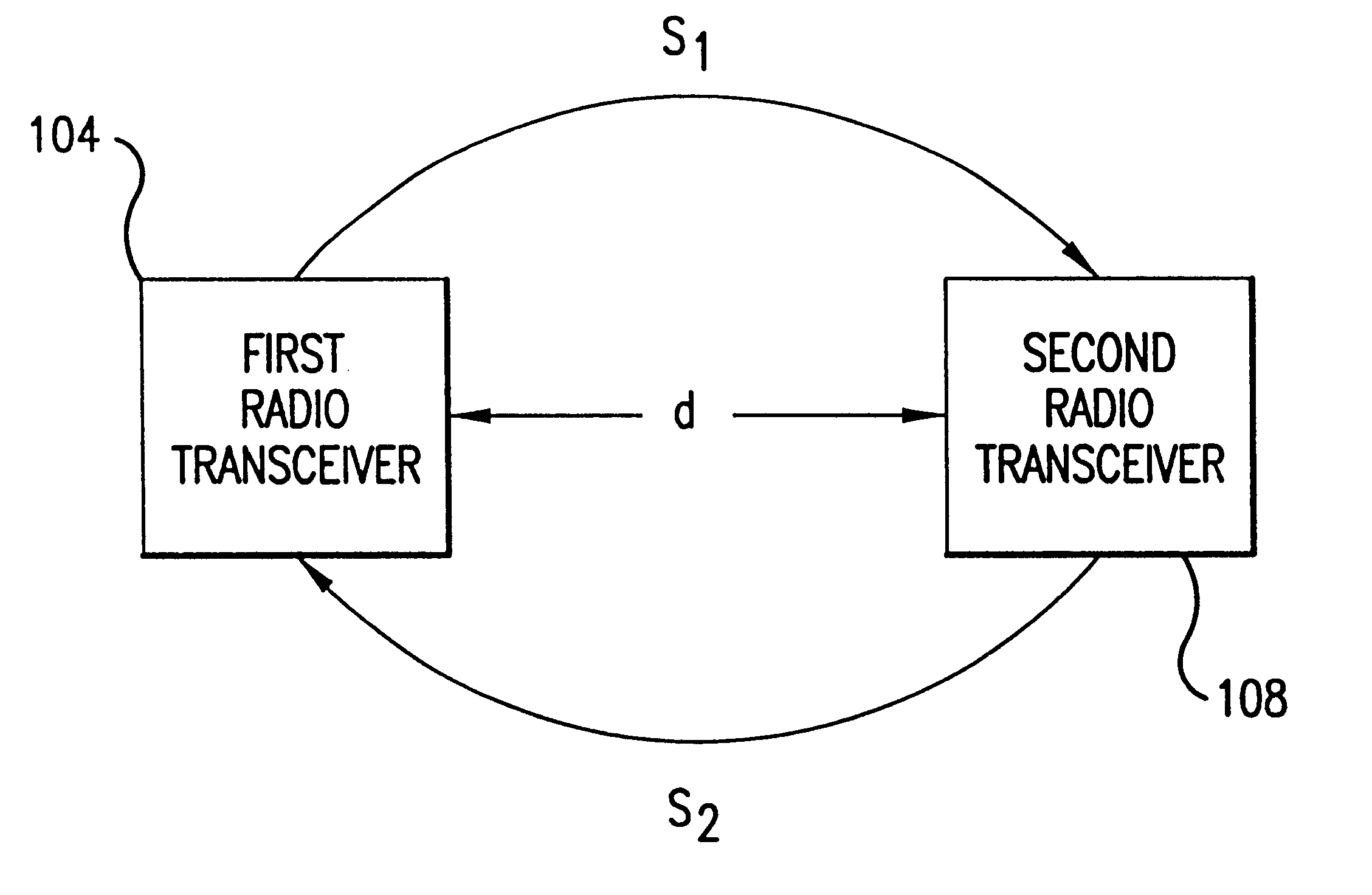
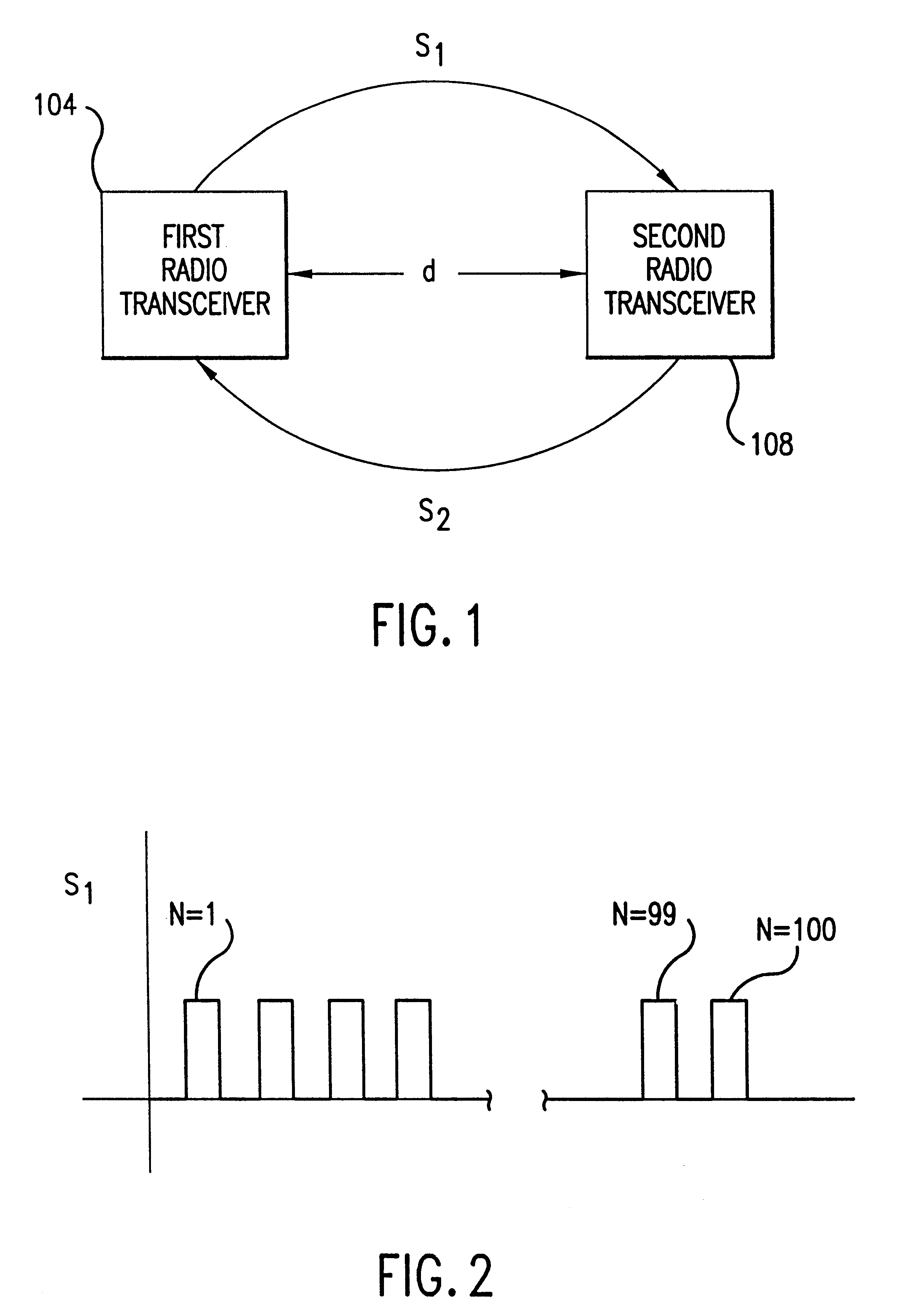
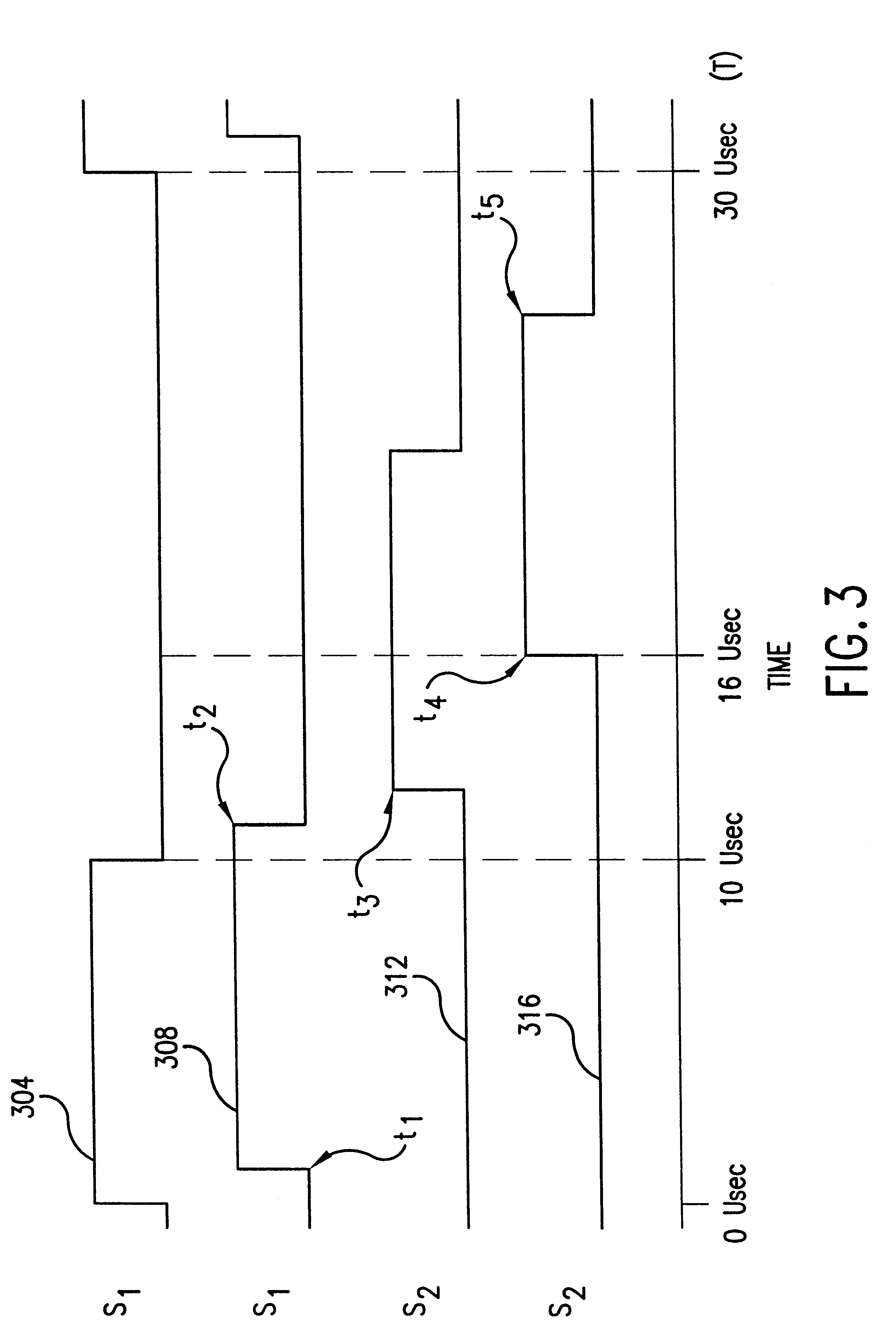
A system and a method for distance measurement utilizes a radio system. The distance is measured by determining the time it takes a pulse train to travel from a first radio transceiver to a second radio transceiver and then from the second radio transceiver back to the first radio transceiver. The actual measurement is a two step process. In the first step, the distance is measured in coarse resolution, and in the second step, the distance is measured in fine resolution. A first pulse train is transmitted using a transmit time base from the first radio transceiver. The first pulse train is received at a second radio transceiver. The second radio transceiver synchronizes its time base with the first pulse train before transmitting a second pulse train back to the first radio transceiver, which then synchronizes a receive time base with the second pulse train. The time delay between the transmit time base and the receive time base can then be determined. The time delay indicates the total time of flight of the first and second pulse trains. The time delay comprises coarse and fine distance attributes. The coarse distance between the first and second radio transceivers is determined. The coarse distance represents the distance between the first and second radio transceivers in coarse resolution. An in phase (I) signal and a quadrature (Q) signal are produced from the time delay to determine the fine distance attribute. The fine distance indicates the distance between the first and second transceivers in fine resolution. The distance between the first and second radio transceivers is then determined from the coarse distance and the fine distance attributes.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
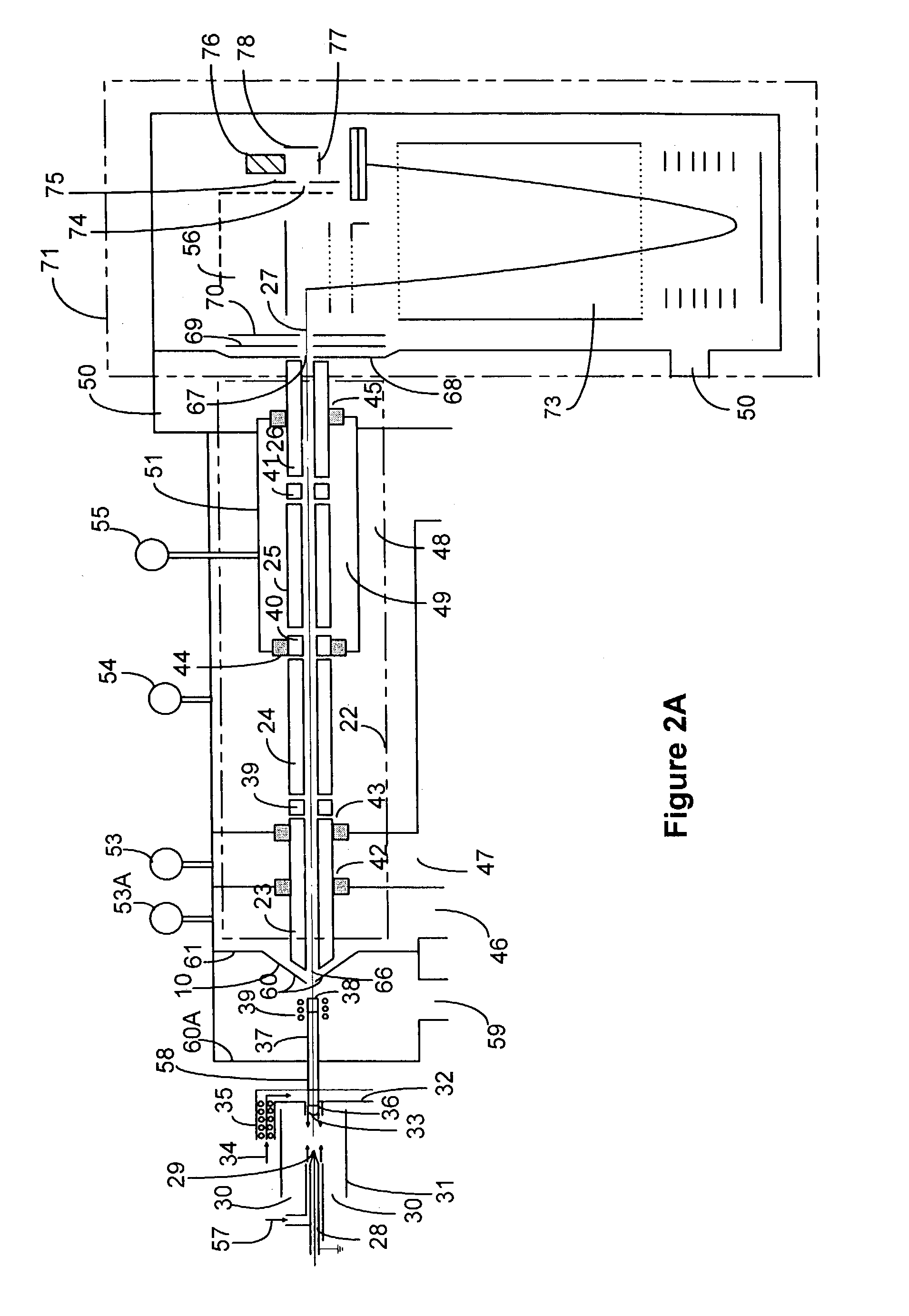
Dimensioning system
ActiveUS20100208039A1Enhanced third dimension accuracyMechanically simpleUsing optical meansRobotQuality controlLaser pulse shaping
The present invention determines the dimensions and volume of an object by using a novel 3-D camera that measures the distance to every reflective point in its field of view with a single pulse of light. The distance is computed by the time of flight of the pulse to each camera pixel. The accuracy of the measurement is augmented by capture of the laser pulse shape in each camera pixel. The camera can be used on an assembly line to develop quality control data for manufactured objects or on a moving or stationary system that weighs as well as dimensions the objects. The device can also ascertain the minimum size of a box required to enclose an object.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
Apparatus and method for determining an inclination of an elongate object contacting a plane surface
An apparatus and method for determining an inclination angle θ between an axis of an elongate object such as a cane, a pointer or a jotting implement such as a pen, pencil, stylus or the like and a normal to a plane surface at times when a tip of the elongate object is contacting that plane surface. The apparatus has an emitter mounted on the object for illuminating the plane surface with a probe radiation at an angle σ with respect to the axis of the object. The apparatus also has a detector mounted on the elongate object for detecting a radiation characteristic of a scattered portion of the probe radiation returning from the plane surface and a computing unit for deriving the inclination angle θ from the radiation characteristic. A scanning arrangement, such as a uniaxial or biaxial scanner, or a light guiding optic can be used for varying angle σ, and the probe radiation can be emitted in the form of a scan beam. Preferably, the emitter and detector of the scattered portion of the probe radiation are integrated and the scattered portion of the probe radiation whose characteristic is being measured is the back-scattered portion. The radiation characteristic detected by the detector can be the intensity, polarization, time-of-flight or any combination thereof.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Method and system for performing invasive medical procedures using a surgical robot
ActiveUS8219177B2Degree of precisionSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsGuidance systemSurgical robot
A method and system for performing invasive procedures includes a surgical robot which is controlled by a guidance system that uses time of flight calculations from RF transmitters embedded in the robot, surgical instrument, and patient anatomy. Sensors around the room detect RF transmissions emitted by the RF transmitters and drive the robot according to a preprogrammed trajectory entered into the guidance system.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL +1
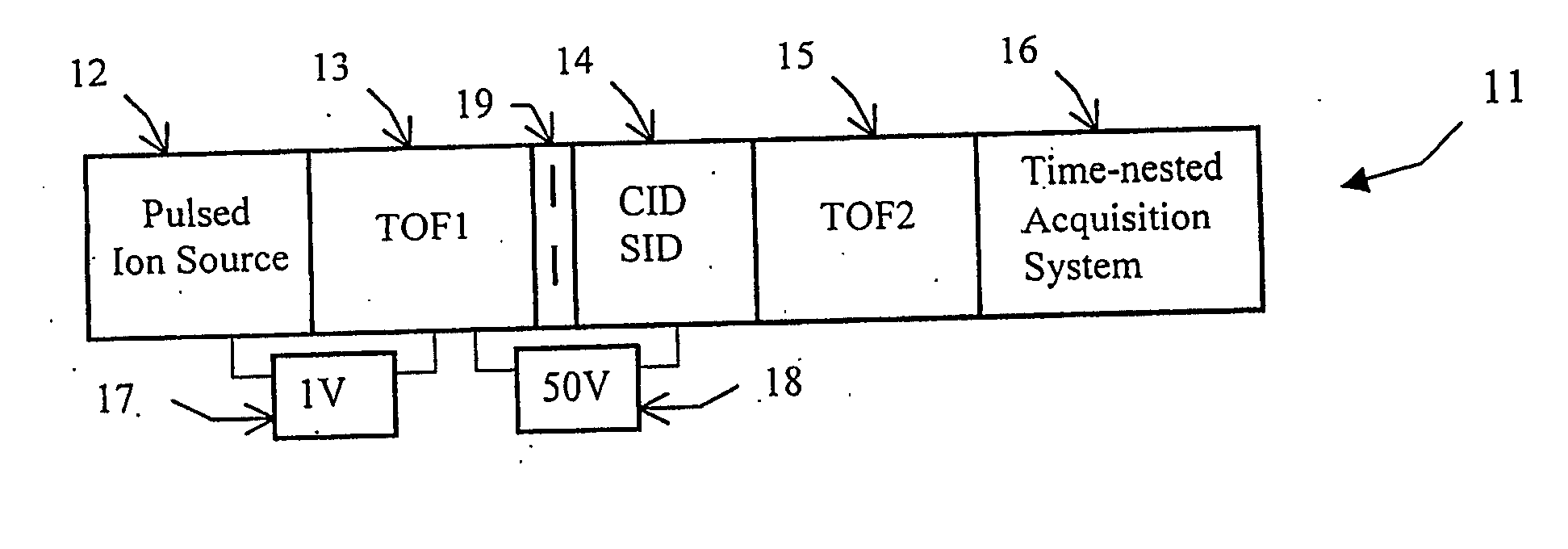
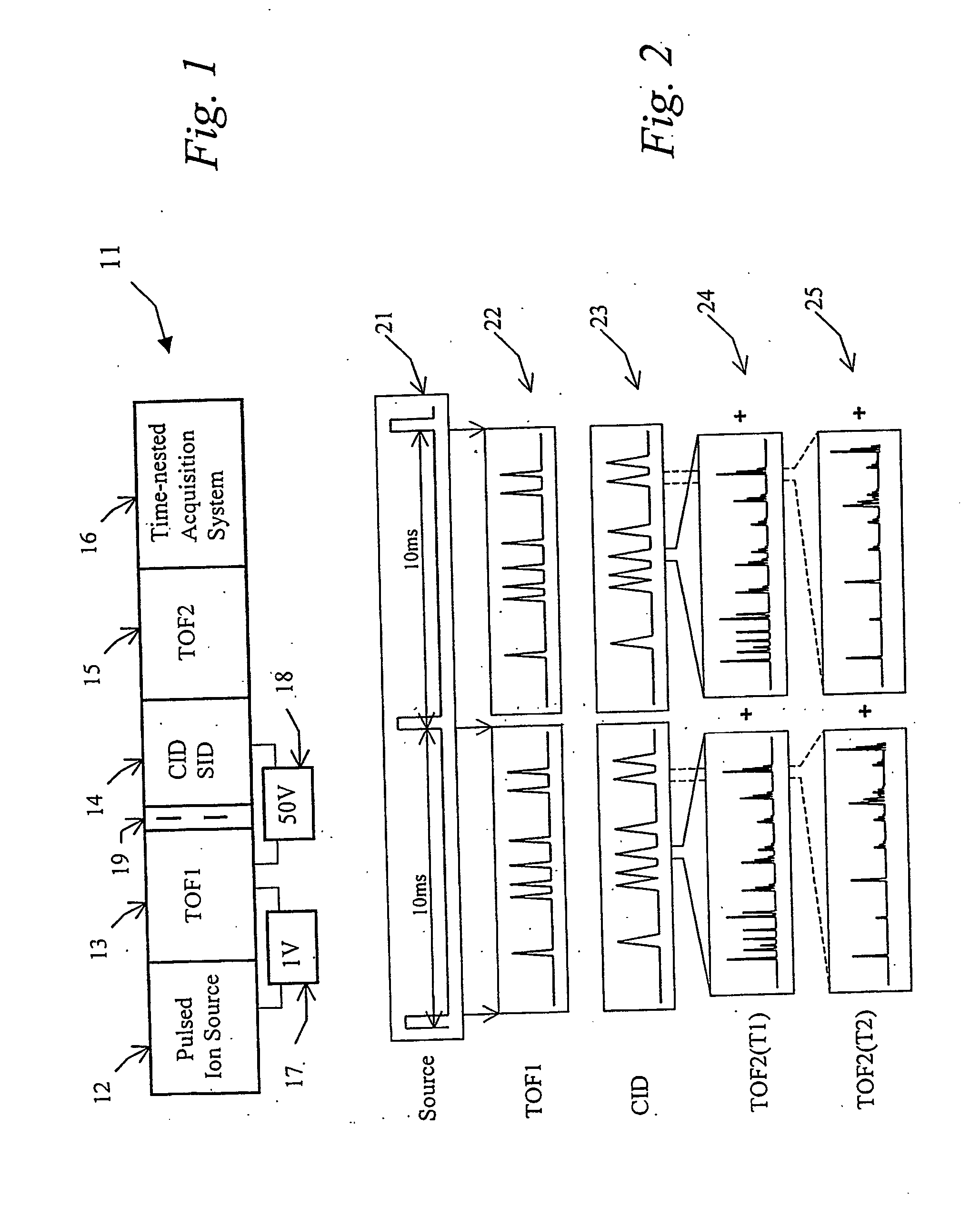
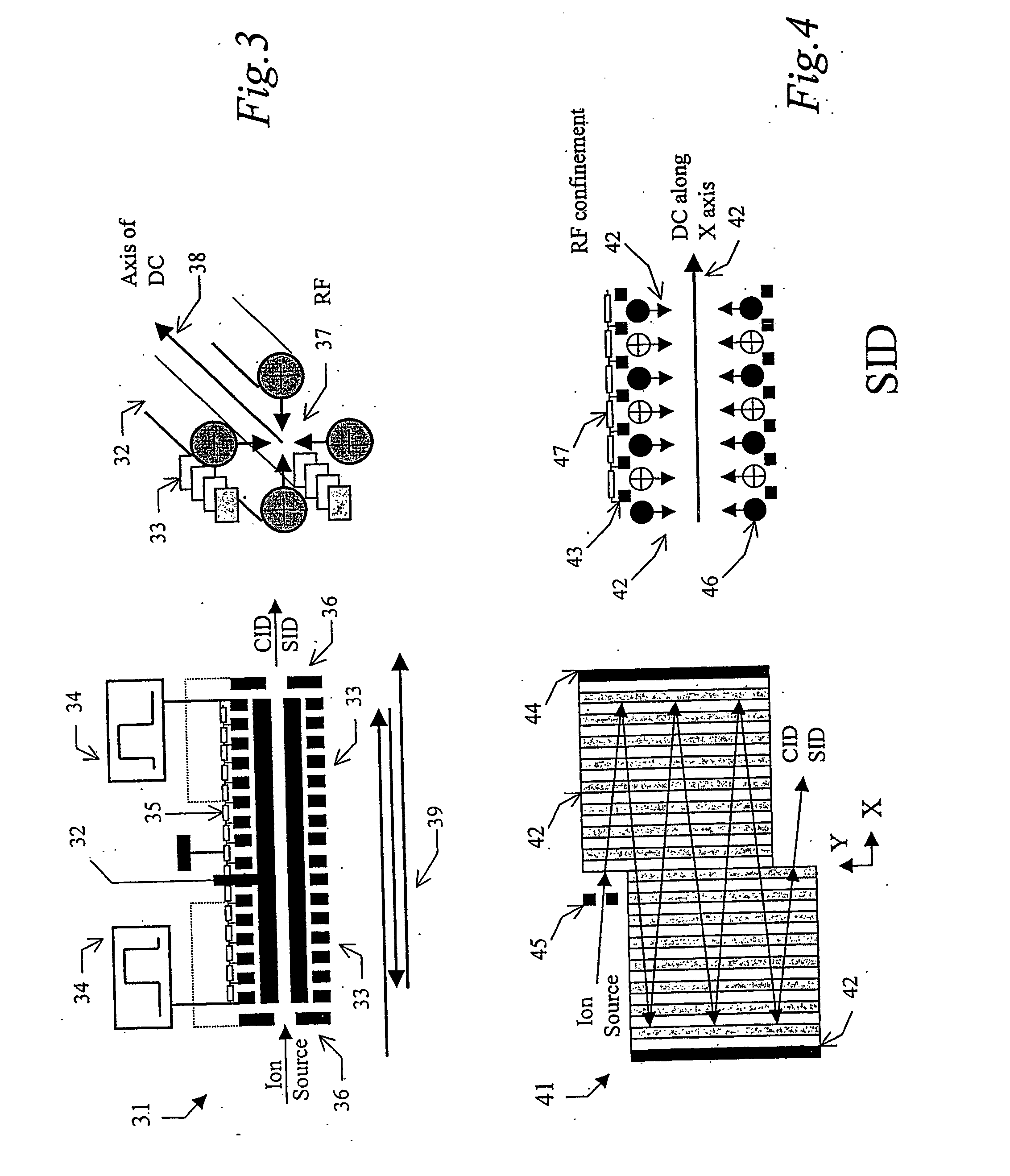
Tandem time of flight mass spectrometer and method of use
InactiveUS20050242279A1Rapid MS-MS analysisEasy to separateTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationRelative energyMass analyzer
To provide comprehensive (i.e. rapid and sensitive) MS-MS analysis, the inventor employs a time-nested separation, using two time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometers. Parent ions are separated in a slow and long TOF1, operating at low ion energy (1 to 100 eV), and fragment ions are mass analyzed in a fast and short TOF2, operating at much higher keV energy. Low energy fragmentation cell between TOF1 and TOF2 is tailored to accelerate fragmentation and dampening steps, mostly by shortening the cell and employing higher gas pressure. Since separation in TOF1 takes milliseconds and mass analysis in TOF2—microseconds, the invention provides comprehensive MS-MS analysis of multiple precursor ions per single ion pulse. Slow separation in TOF1 becomes possible with an introduction of novel TOF1 analyzers. The TOF-TOF could be implemented using a static TOF1, here described on the examples of spiratron, planar and cylindrical multi-pass separators with griddles spatial focusing ion mirrors. Higher performance is expected with the use of novel hybrid TOF1 analyzers, combining radio frequency (RF) and quadratic DC fields. RF field retains low-energy ions within TOF1 analyzer, while quadratic DC field improves resolution by compensate for large relative energy spread.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Personnel location and monitoring system and method for enclosed facilities
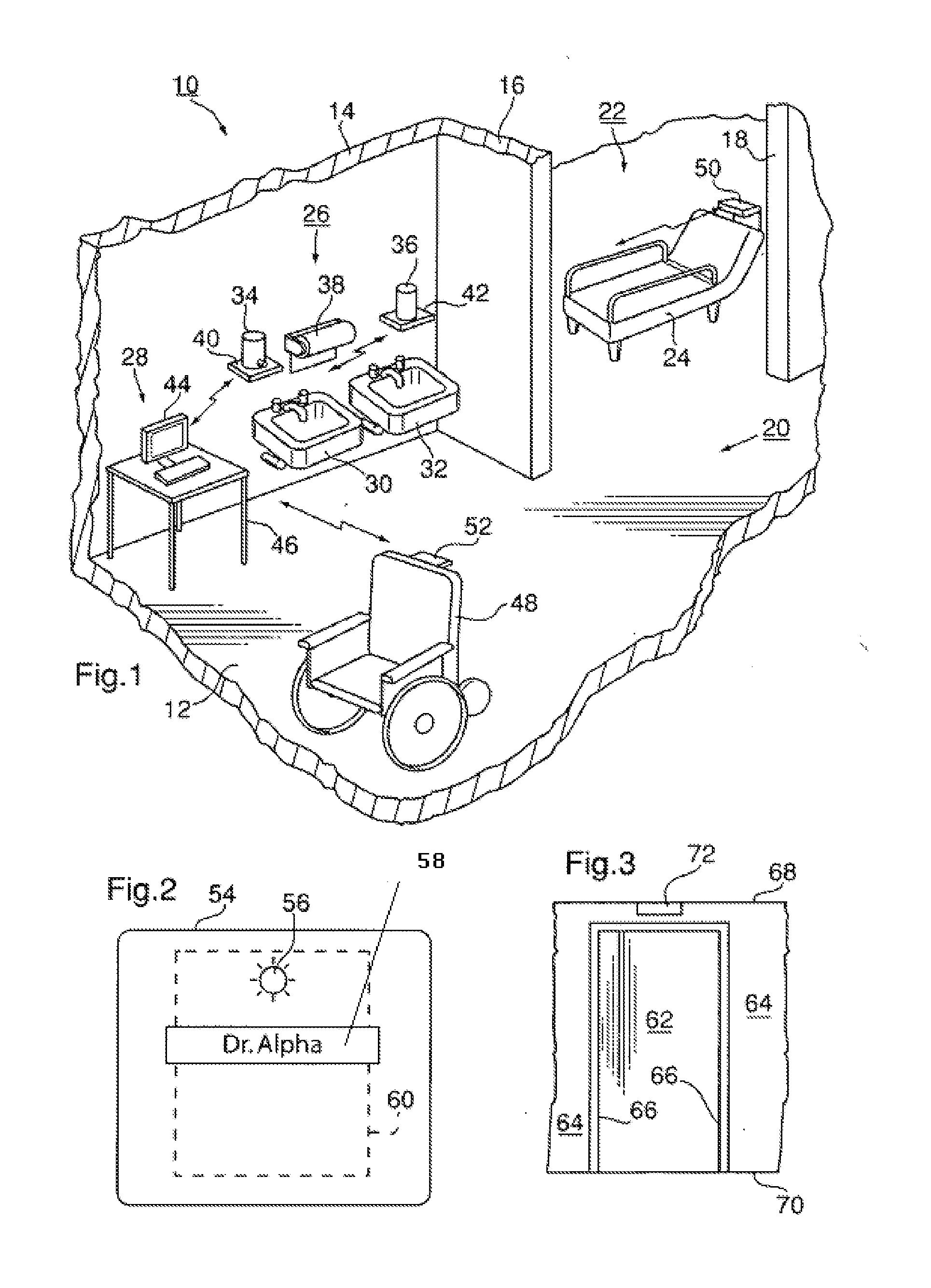
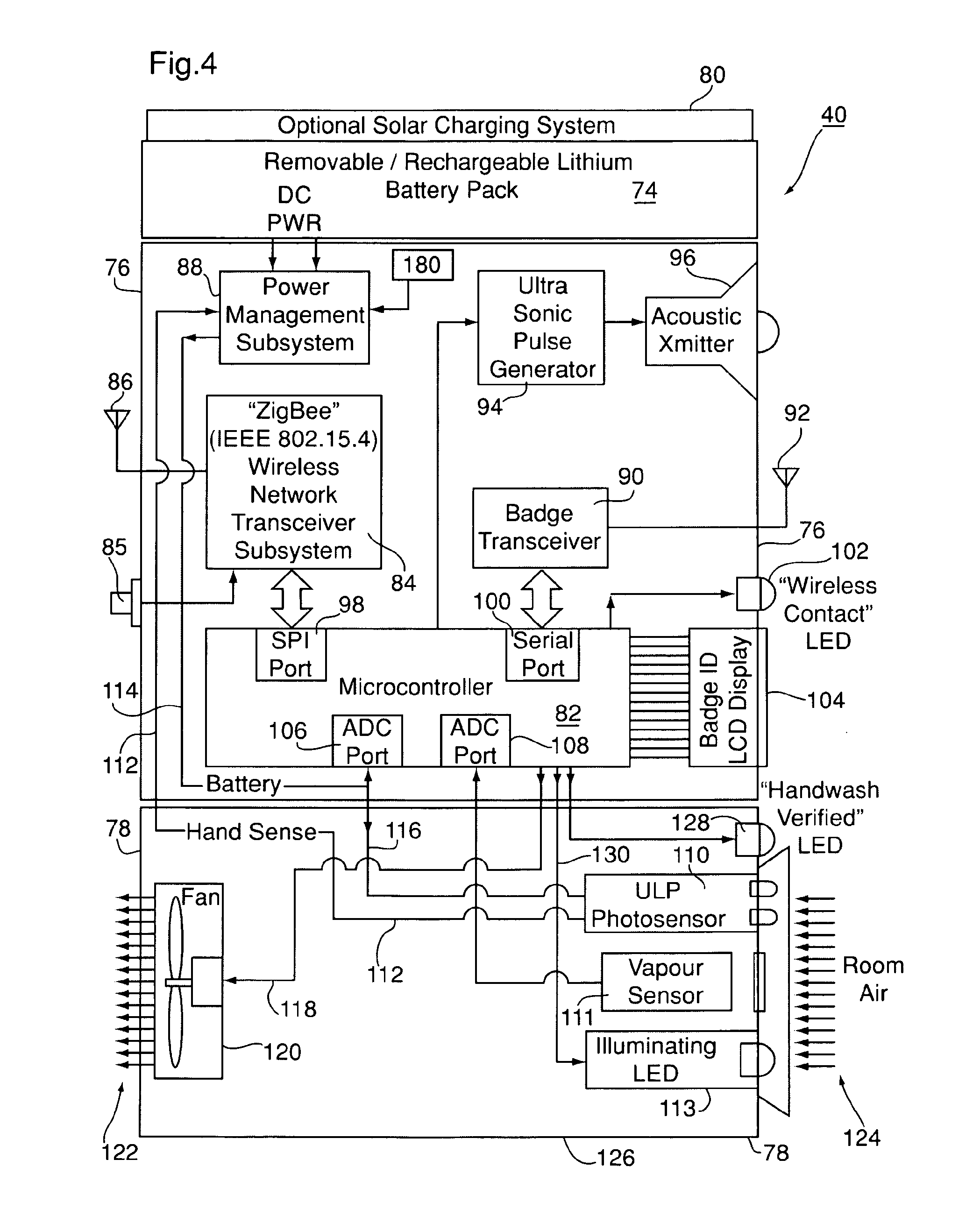
InactiveUS20110227740A1Limit power usageMeet growth requirementsRegistering/indicating time of eventsPosition fixationMotion detectorMonitoring system
A wireless time-of-flight distance measurement device a motion detector is used at each of a plurality of stations in a wireless network in an enclosed facility to accurately locate a badge-wearing person near the station. The location, badge number and time of detection are transmitted through the network and stored in a computer memory. In a healthcare facility, hand washing detectors are located at some of the stations and caused to energize a hand wash status indicator light on the badge when the wearer has washed his or her hands. The light remains “on” for only a certain length of time, but will be extinguished sooner by a monitor device near each patient when the healthcare worker leaves the vicinity of the patient. These events also are transmitted and stored so that a timed record of each worker's hand washing and visits to patients is created.
Owner:XHALE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com