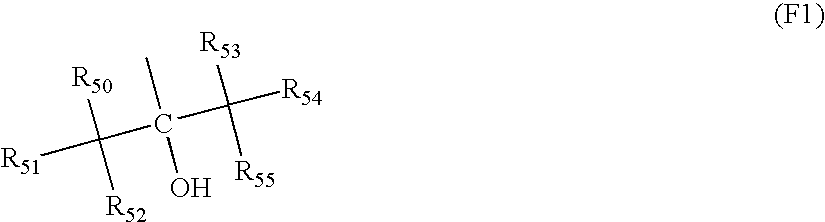Patents
Literature
688 results about "Fluence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In radiometry, radiant exposure or fluence is the radiant energy received by a surface per unit area, or equivalently the irradiance of a surface, integrated over time of irradiation, and spectral exposure or is the radiant exposure per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The SI unit of radiant exposure is the joule per square metre (J/m²), while that of spectral exposure in frequency is the joule per square metre per hertz (J⋅m⁻²⋅Hz⁻¹) and that of spectral exposure in wavelength is the joule per square metre per metre (J/m³)—commonly the joule per square metre per nanometre (J⋅m⁻²⋅nm⁻¹).
Marketplace illumination methods and apparatus
Methods and apparatus for providing illumination in a marketplace. In one example, radiation comprising variable color light is generated using a plurality of LEDs. One or more articles in the marketplace are illuminated with the generated radiation, and the spectral content of the generated radiation is controllably varied over a period of time so that a customer of the marketplace perceives a change in color and / or an illusion of motion associated with the article(s) due to a selective color interaction between the generated radiation and the article(s). Examples of marketplaces include, but are not limited to, consumer environments, work environments, sporting environments, entertainment environments, retail establishments, restaurants, museums, art galleries and the like.
Owner:PHILIPS LIGHTING NORTH AMERICA CORPORATION
Method of and apparatus in a filter tipping machine for manipulating a web
InactiveUS6229115B1More reliableLess expensiveCigarette manufactureLaser beam welding apparatusFiberAdhesive
A running web of tipping paper (one side of which is coated with a film of adhesive) in a filter cigarette making machine is subdivided into discrete uniting bands and / or is perforated by resorting to a single source or to two discrete sources of coherent radiation. Each source is associated with a control unit which initiates the emission of short-lasting flashes of coherent radiation. Such radiation is caused to impinge upon a diffractive focusing lens which focuses coherent radiation upon one or more masks having openings for coherent radiation which is to sever the web along transversely extending linear zones and / or to provide the web with desired arrays of perforations. The perforations permit atmospheric air to enter the column of tobacco smoke in a filter cigarette wherein the tobacco-containing portion and the filter mouthpiece are united by a perforated adhesive-coated uniting band.
Owner:HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG
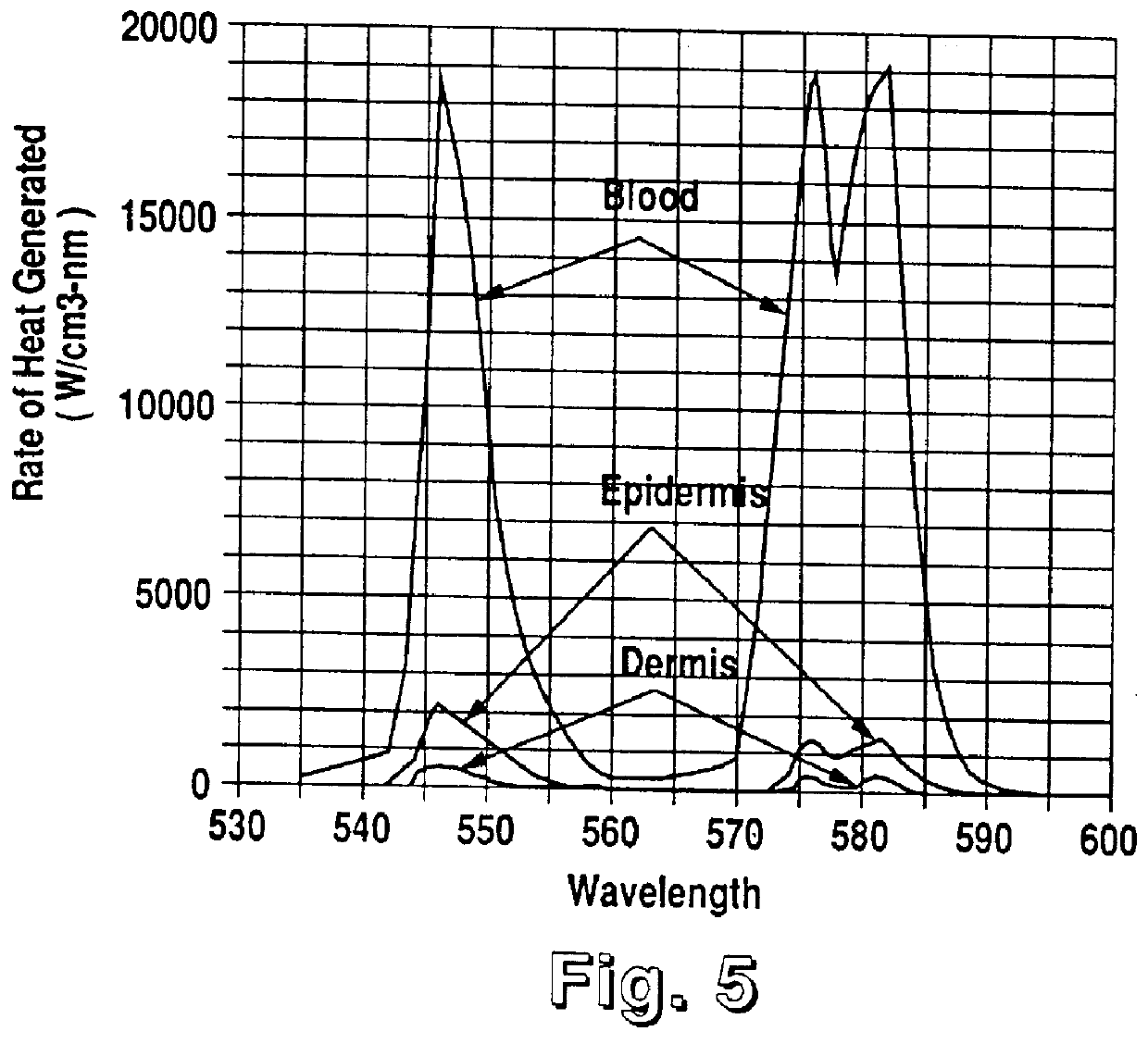
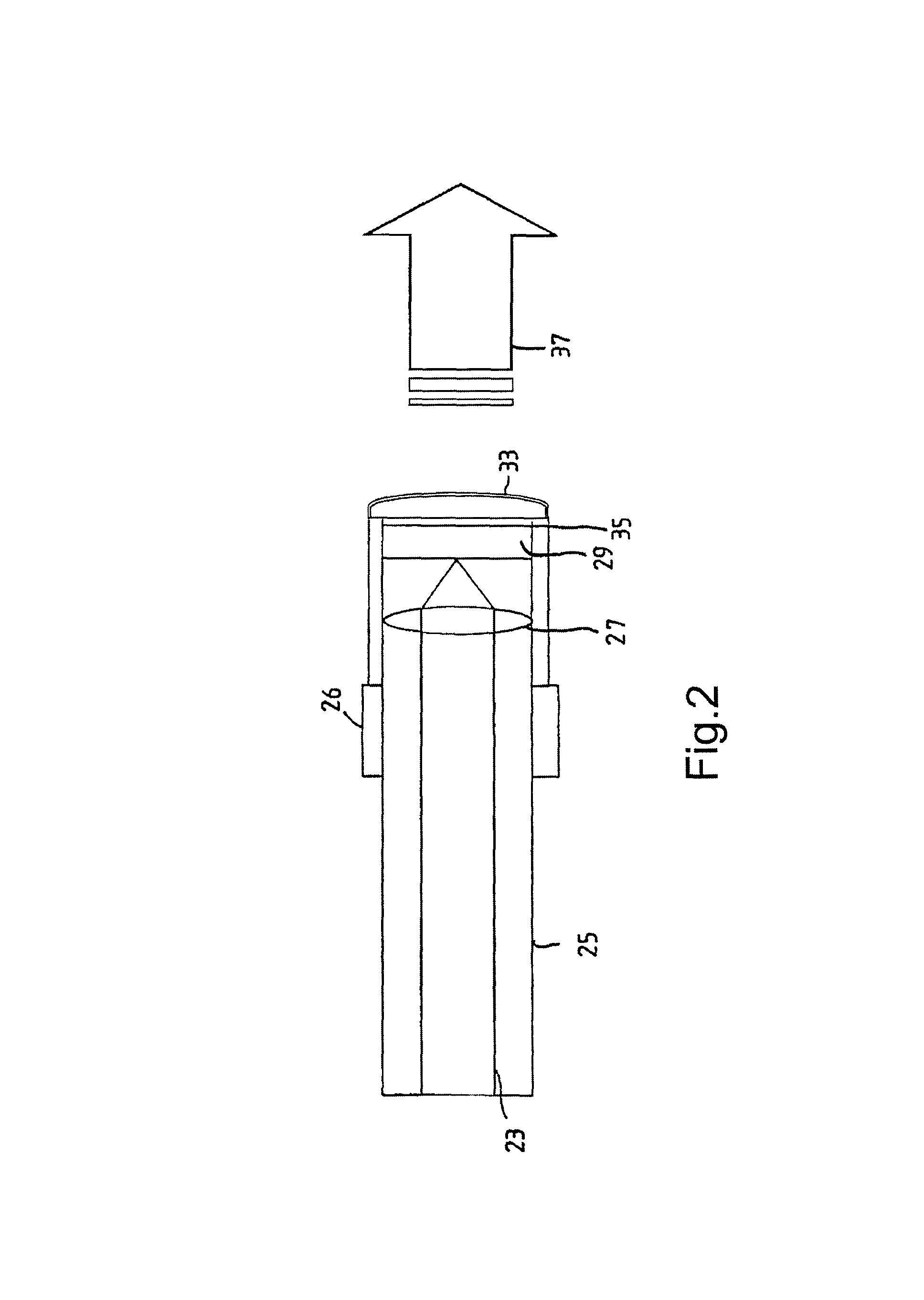
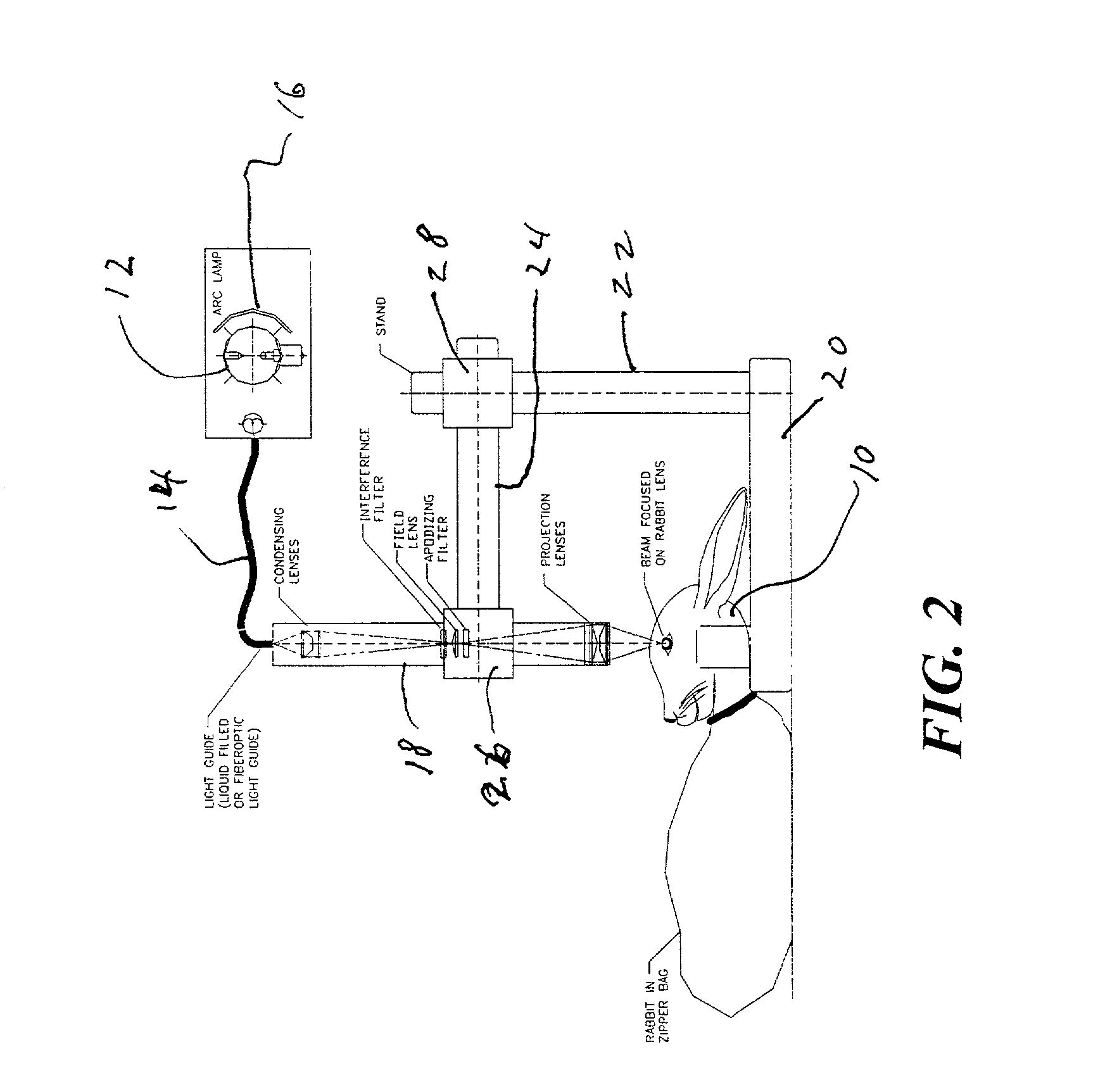
Optical system for treatment of vascular lesions
An improved optical system for treatment of disorders of the skin, especially vascular lesions, such as Port Wine Stains. The system irradiates the skin with radiation at a predetermined wavelength and cools the skin during a predetermined time interval in coordination with delivery of the radiation. The absorption of the radiation by the skin and the change in temperature of the skin is monitored by the system and the operation of the radiation delivery system is controlled to optimize treatment of the vascular lesion. The source of irradiation is an arc lamp and the cooling system delivers a cooling gas to a lens in contact with the skin. The cooling gas can be carbon dioxide, freon, or any other appropriate gas. The lens used has a high heat conductivity and may be formed of sapphire.
Owner:GHAFFARI SHAHRIAR
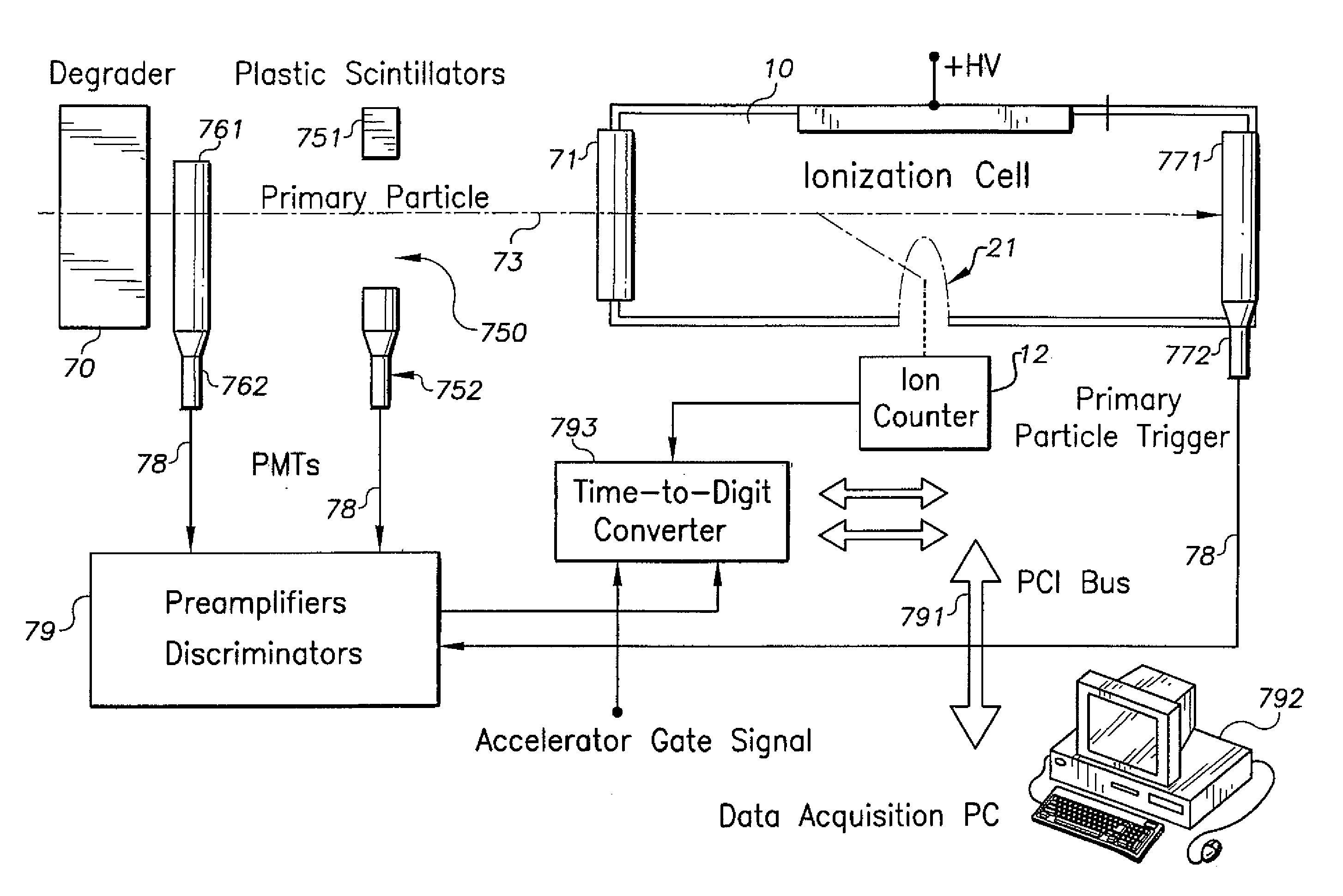
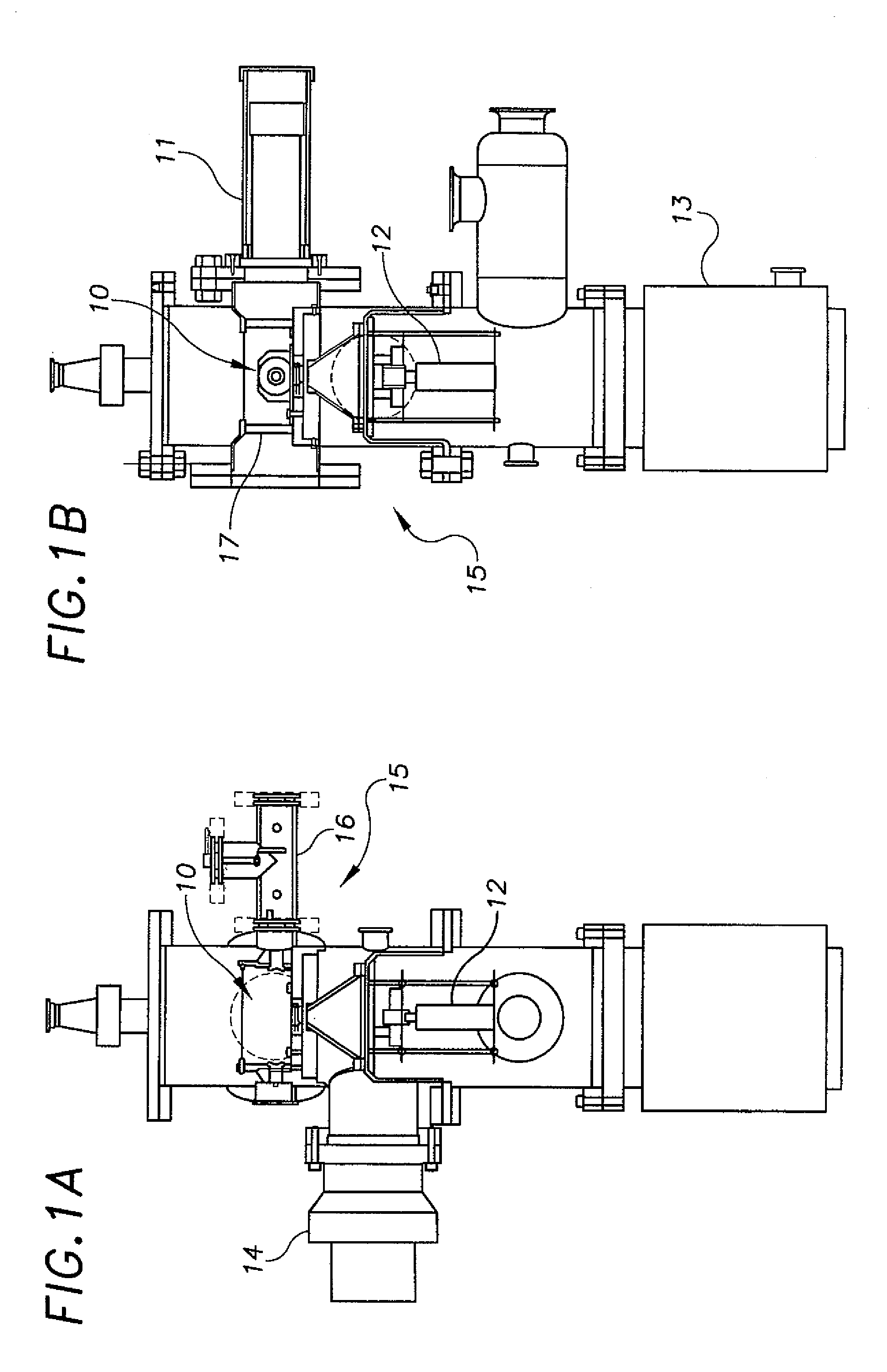
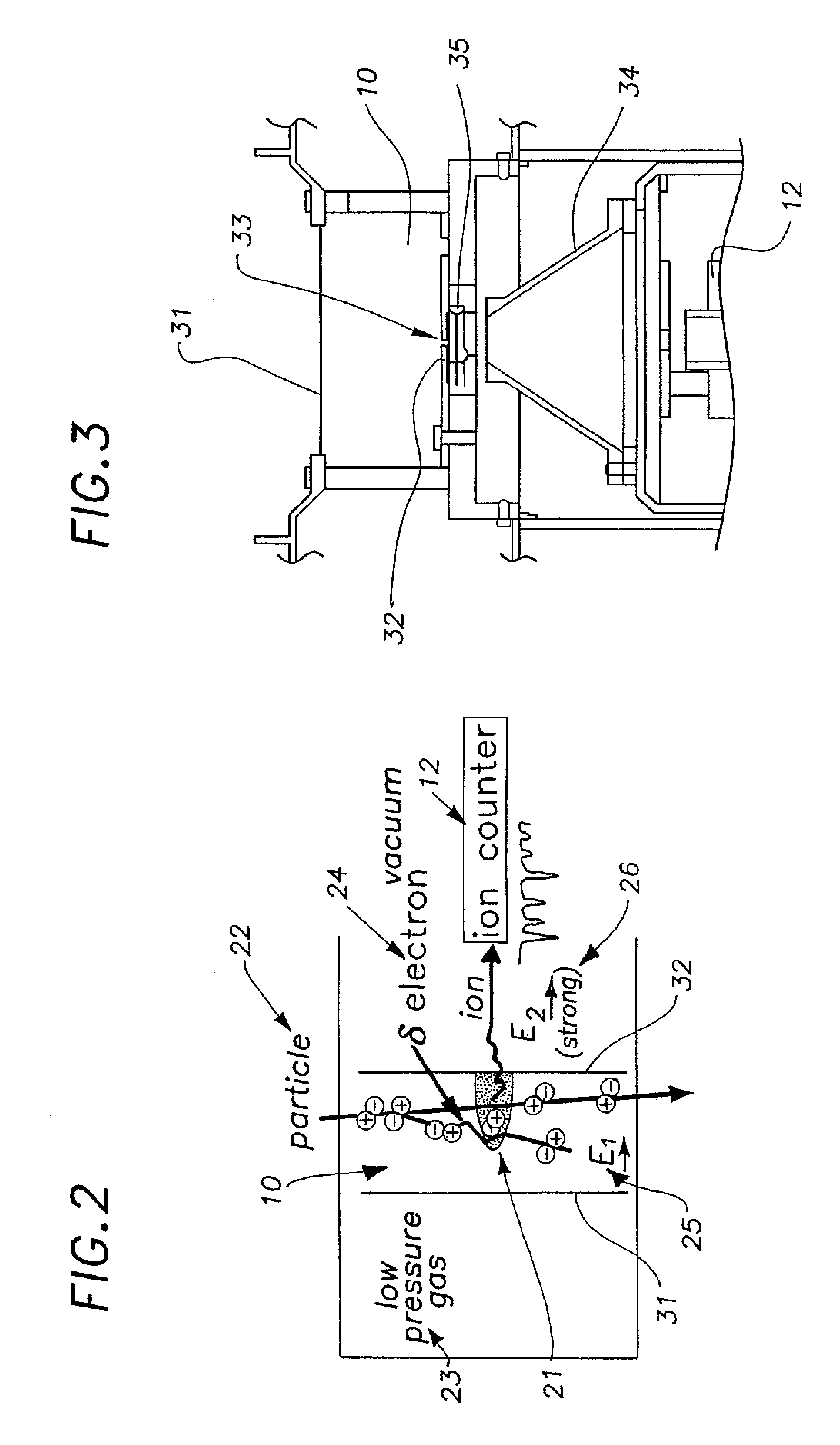
Nanodosimeter based on single ion detection
InactiveUS7081619B2Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFluenceDosimeter
A nanodosimeter device (15) for detecting positive ions induced in a sensitive gas volume by a radiation field of primary particle, comprising an ionization chamber (10) for holding the sensitive gas volume to be irradiated by the radiation field of primary particles; an ion counter system connected to the ionization chamber (10) for detecting the positive ions which pass through the aperture opening and arrive at the ion counter (12) at an arrival time; a particle tracking system for position-sensitive detection of the primary particles passing through the sensitive gas volume; and a data acquisition system capable of coordinating the readout of all data signals and of performing data analysis correlating the arrival time of the positive ions detected by the ion counter system relative to the position sensitive data of primary particles detected by the particle tracking system. The invention further includes the use of the nanodosimeter for method of calibrating radiation exposure with damage to a nucleic acid within a sample. A volume of tissue-equivalent gas is radiated with a radiation field to induce positive ions. The resulting positive ions are measured and compared with a determination of presence or extent of damage resulting from irradiating a nucleic acid sample with an equivalent dose of radiation.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIVERSITY +1
Adhesive bonding composition and method of use
A polymerizable composition includes at least one monomer, a photoinitiator capable of initiating polymerization of the monomer when exposed to light, and a phosphor capable of producing light when exposed to radiation (typically X-rays). The material is particularly suitable for bonding components at ambient temperature in situations where the bond joint is not accessible to an external light source. An associated method includes: placing a polymerizable adhesive composition, including a photoinitiator and energy converting material, such as a down-converting phosphor, in contact with at least two components to be bonded to form an assembly; and, irradiating the assembly with radiation at a first wavelength, capable of conversion (down-conversion by the phosphor) to a second wavelength capable of activating the photoinitiator, to prepare items such as inkjet cartridges, wafer-to-wafer assemblies, semiconductors, integrated circuits, and the like.
Owner:IMMUNOLIGTHT LLC +1
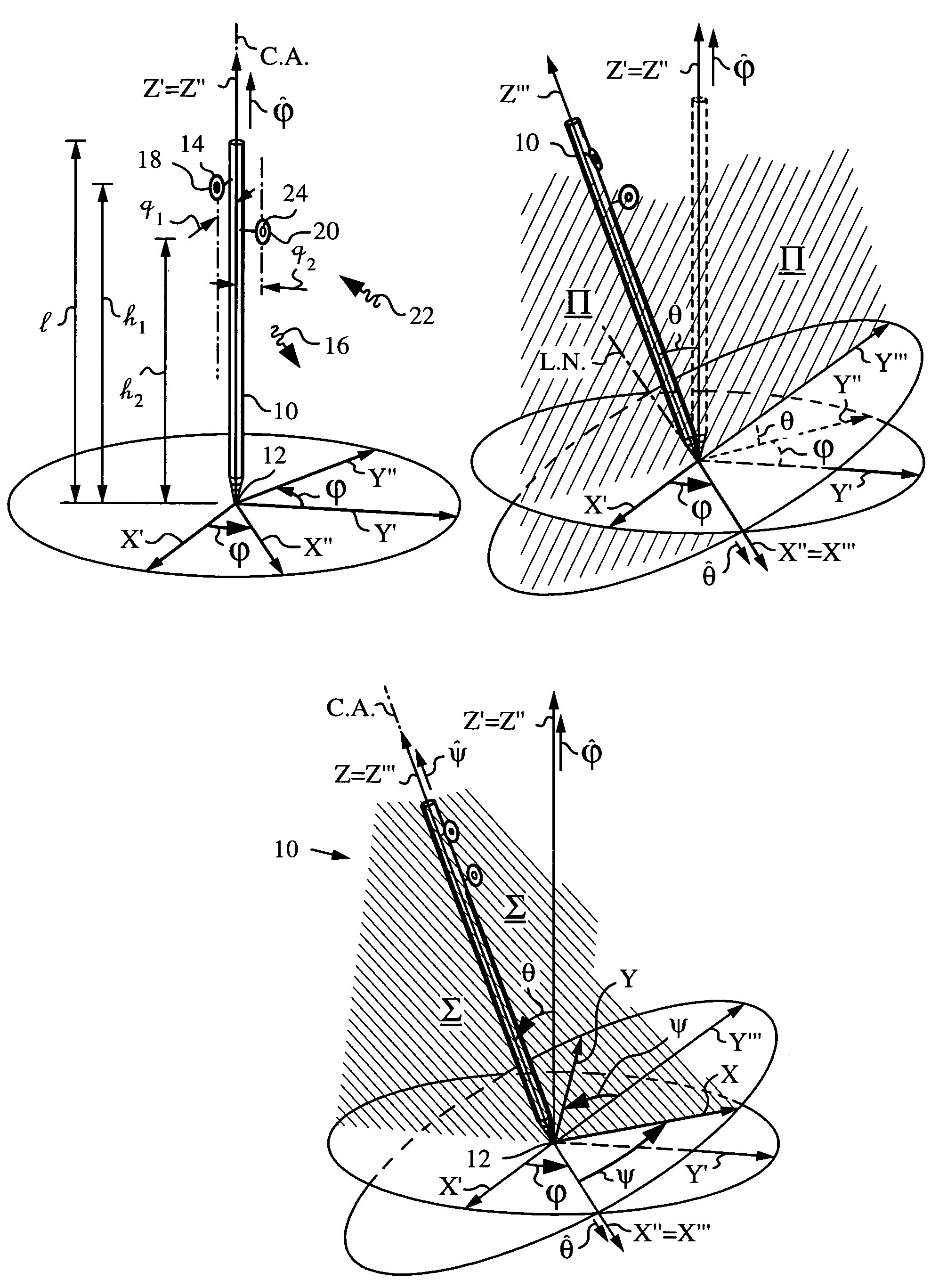
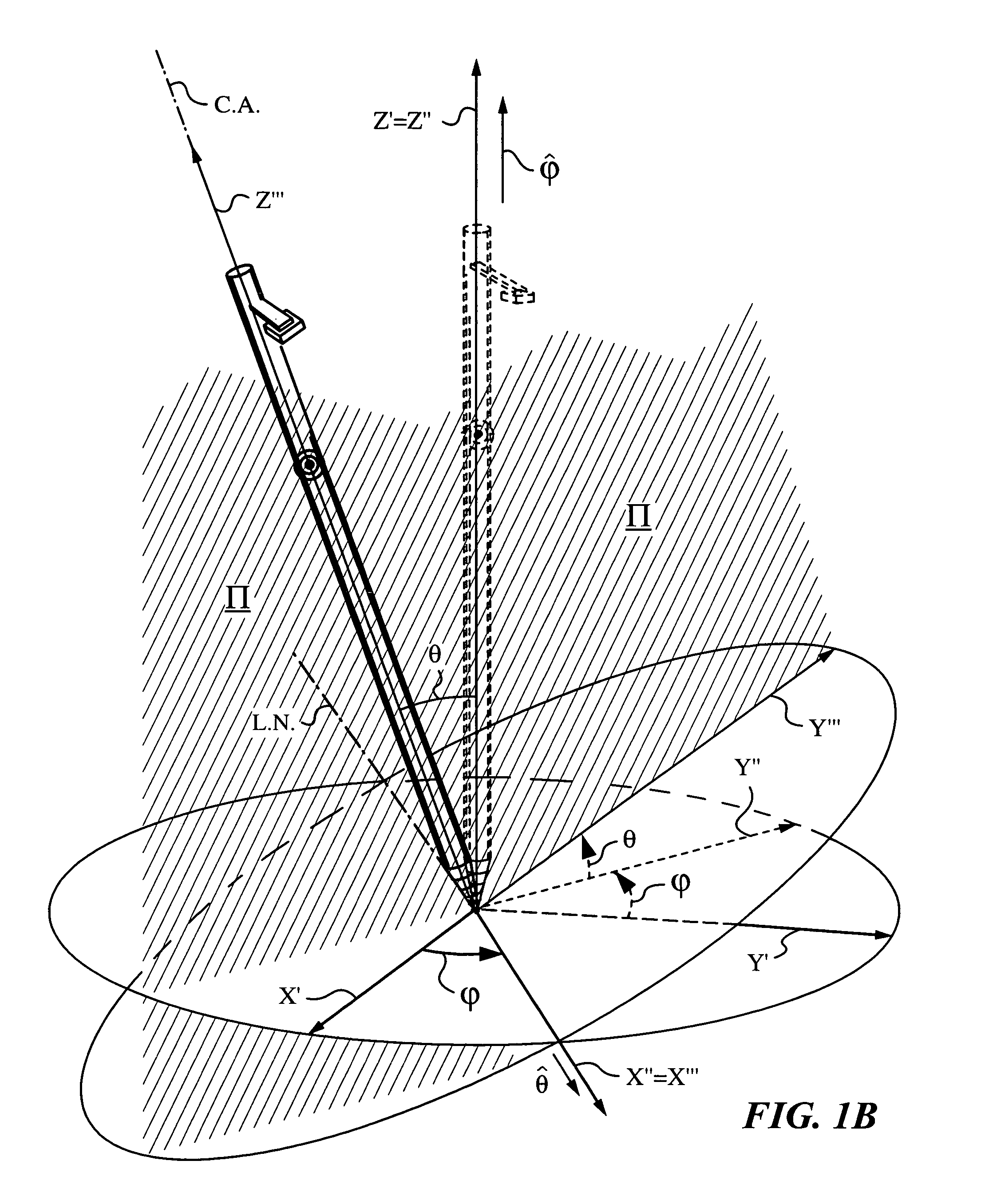
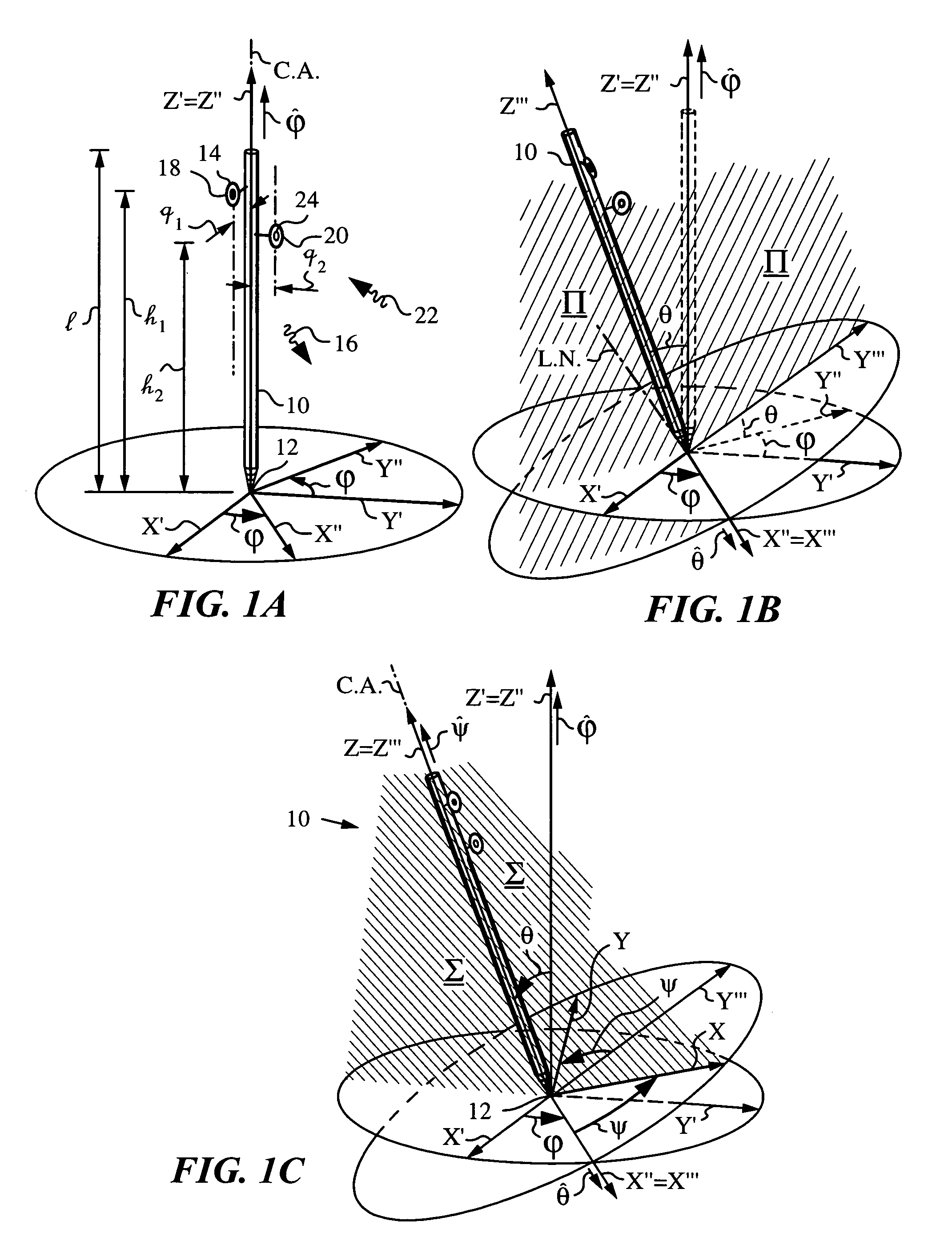
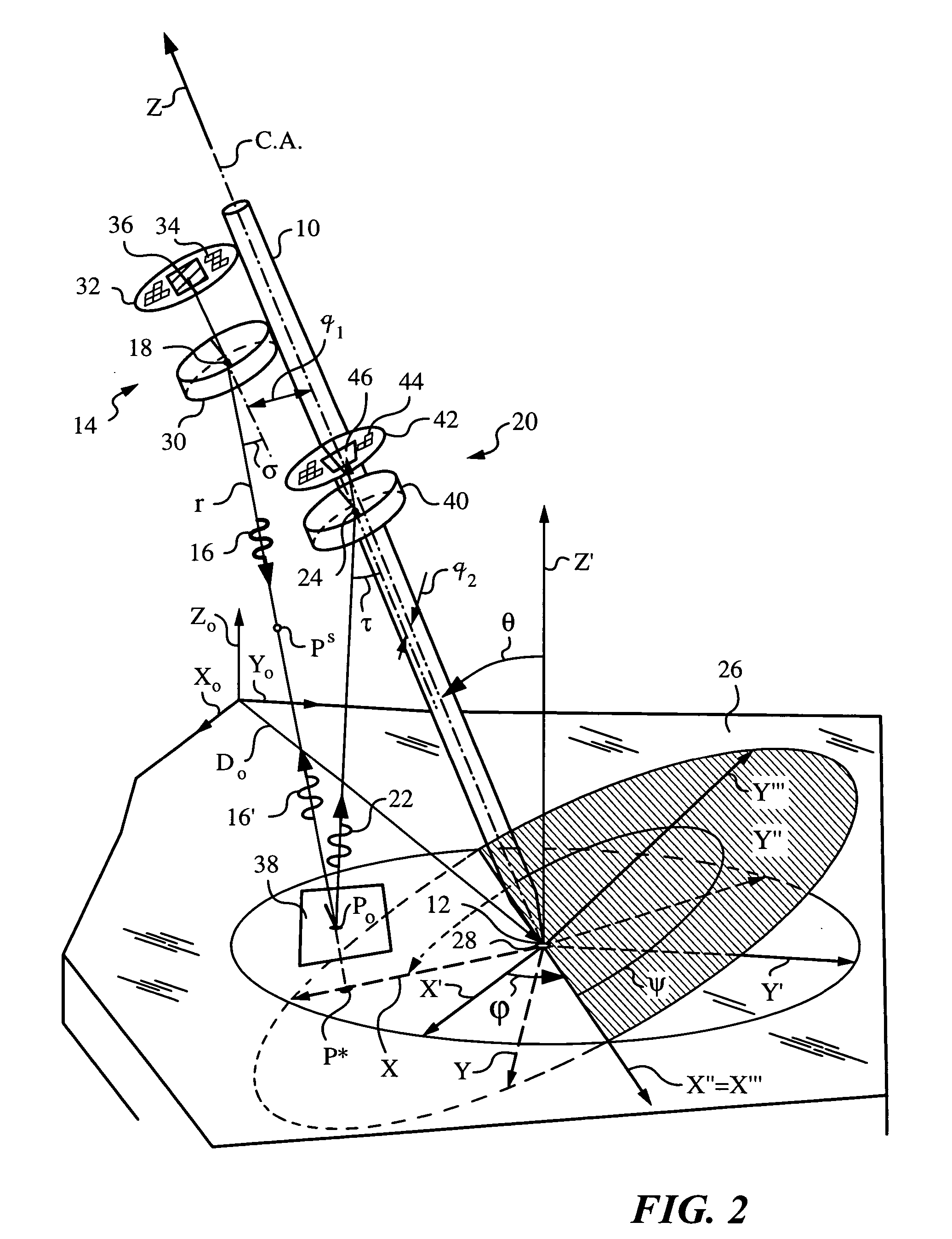
Apparatus and method for determining orientation parameters of an elongate object
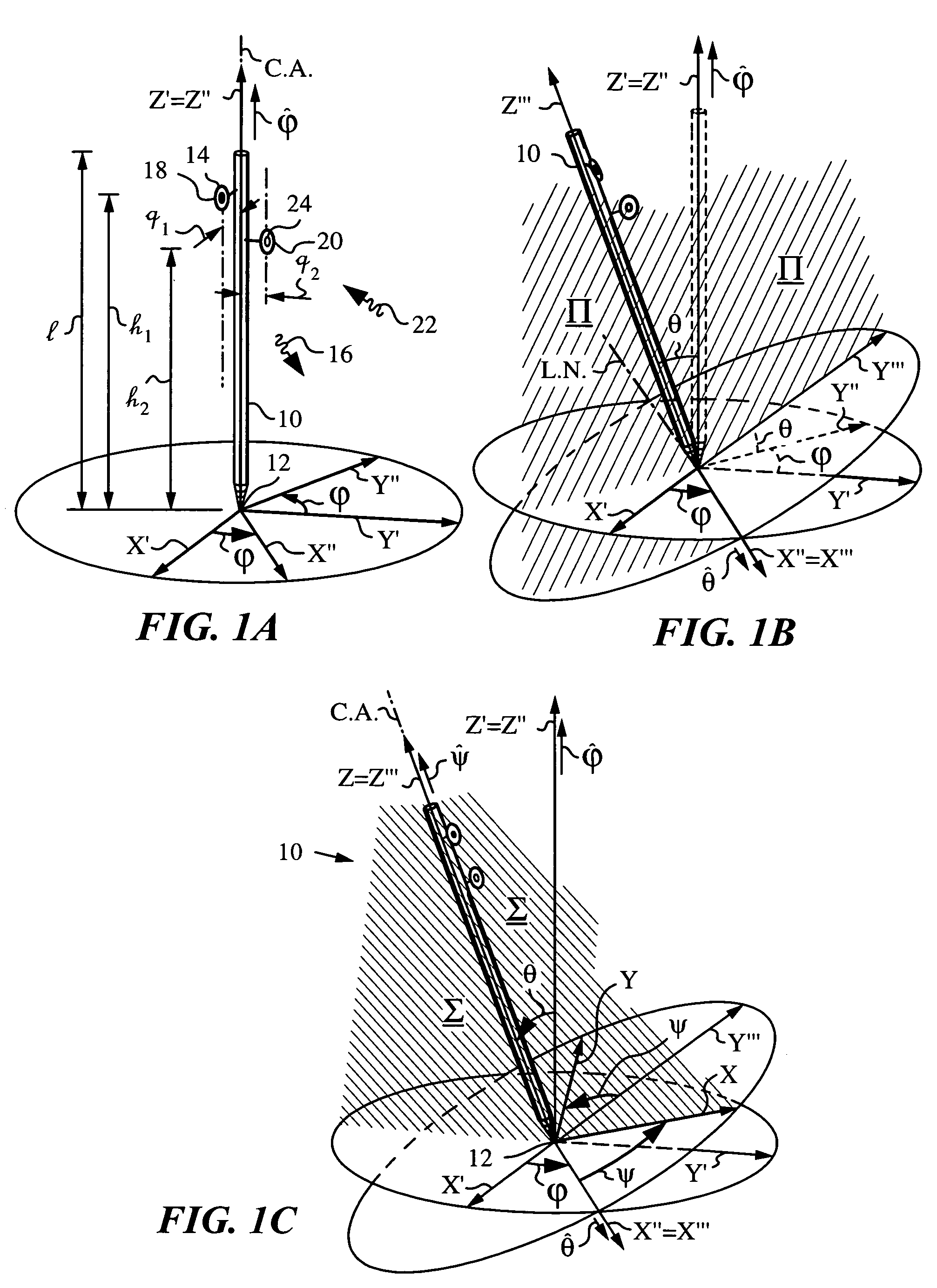
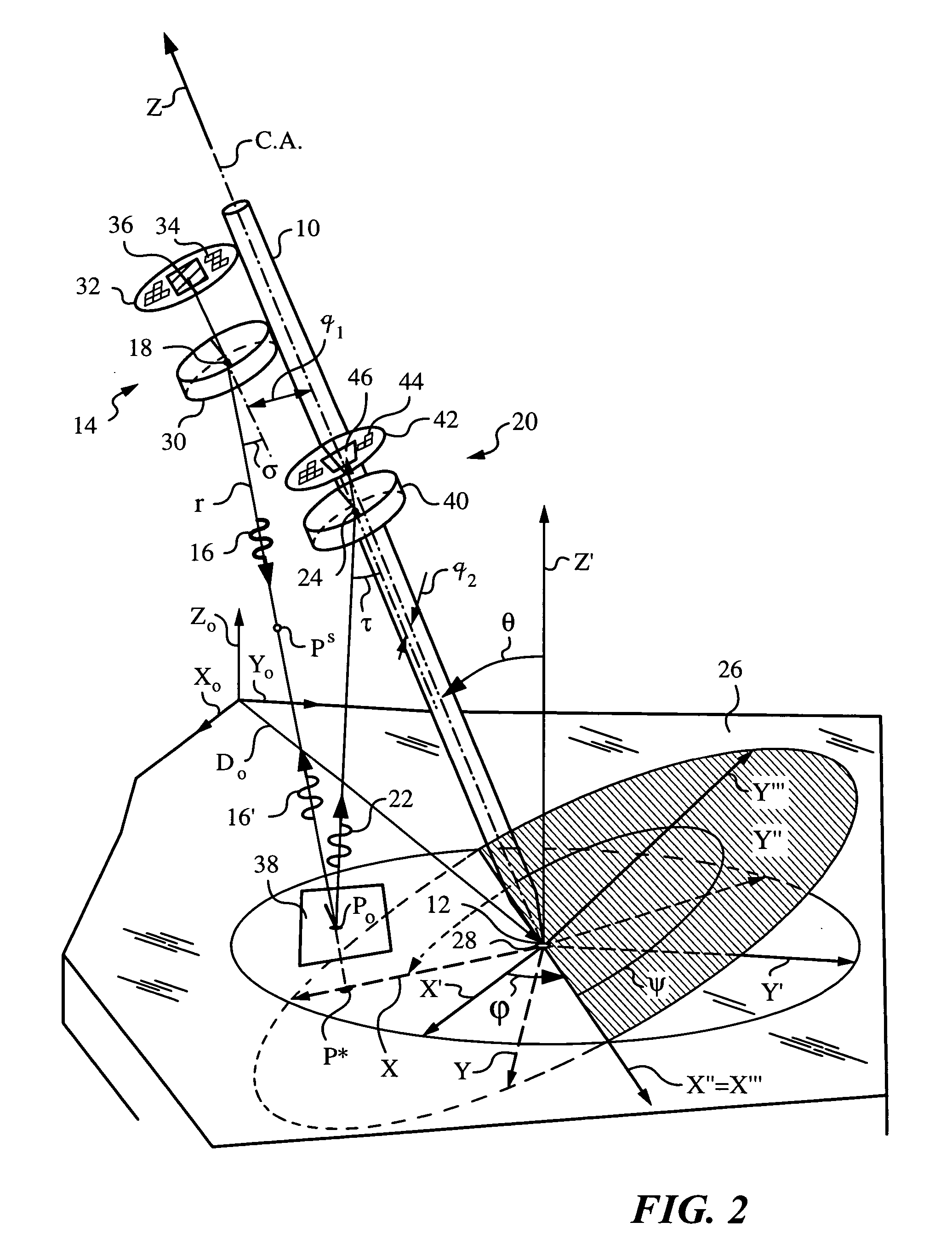
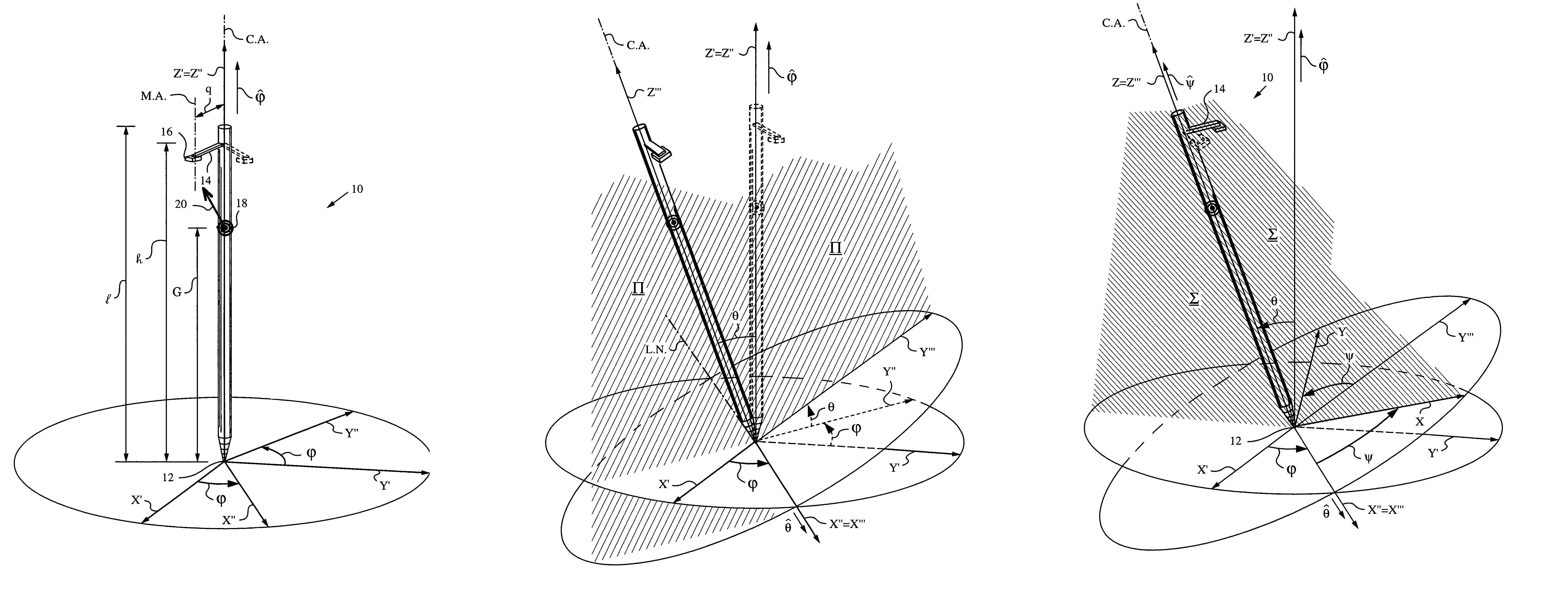
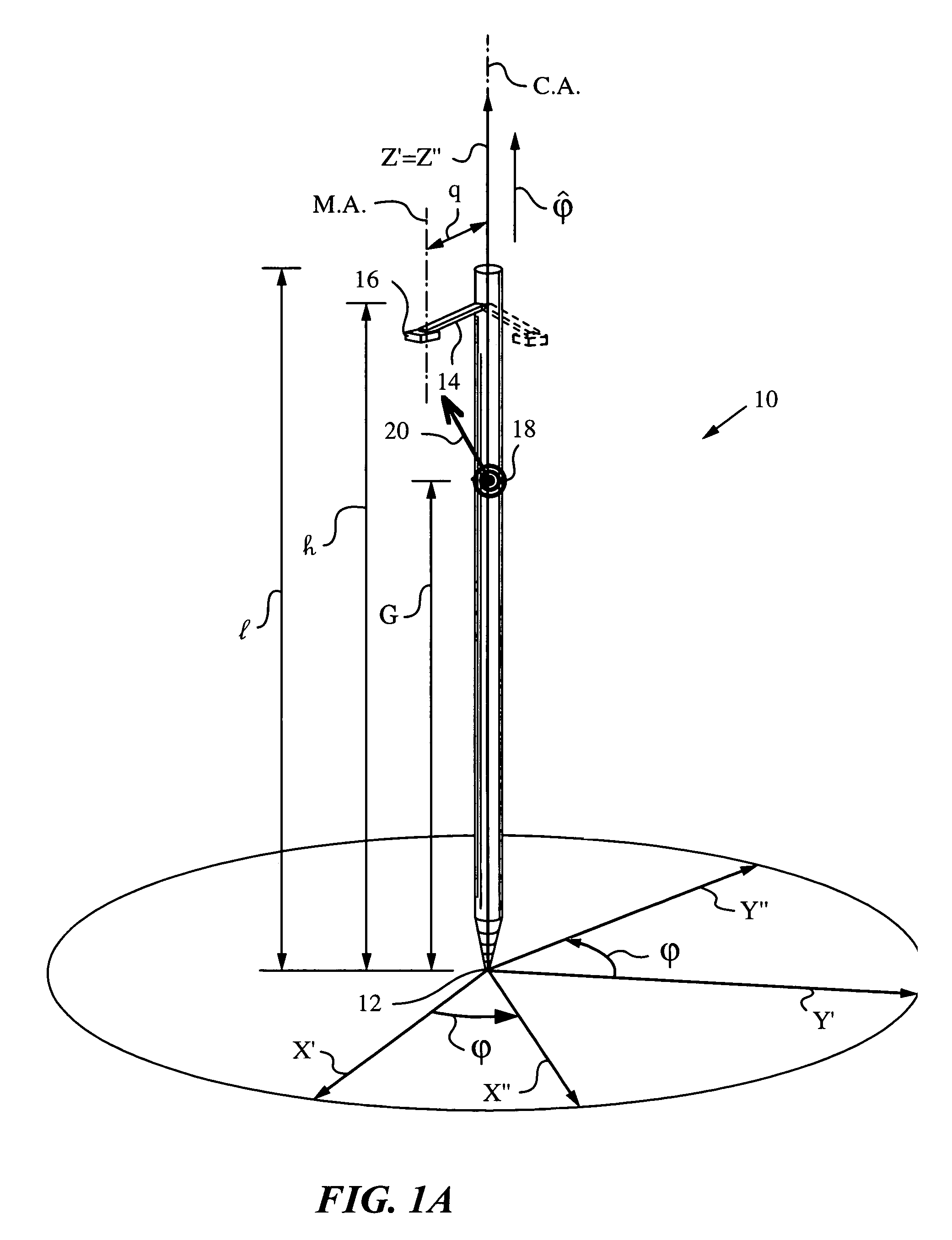
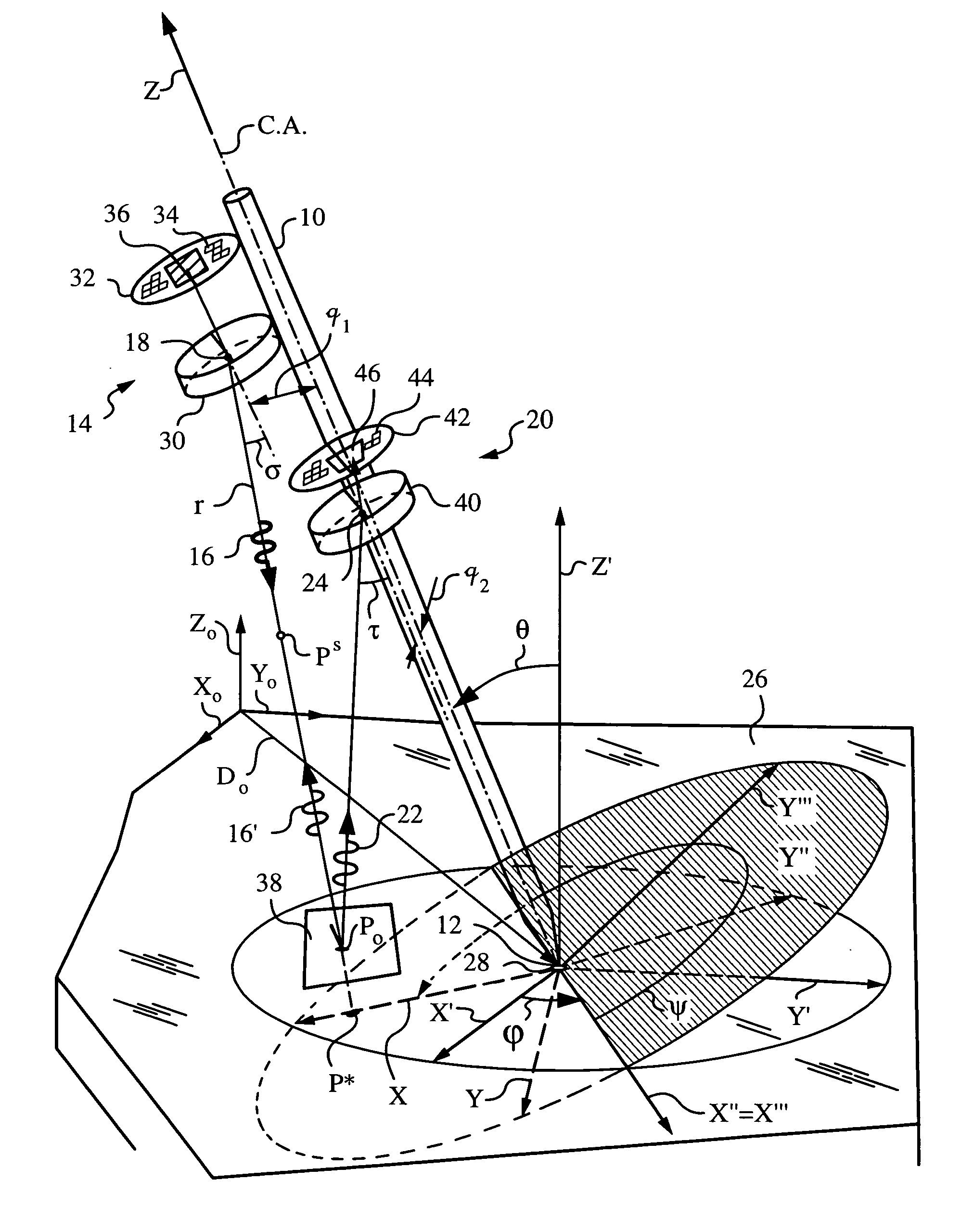
An apparatus and method employing principles of stereo vision for determining one or more orientation parameters and especially the second and third Euler angles θ, ψ of an elongate object whose tip is contacting a surface at a contact point. The apparatus has a projector mounted on the elongate object for illuminating the surface with a probe radiation in a known pattern from a first point of view and a detector mounted on the elongate object for detecting a scattered portion of the probe radiation returning from the surface to the elongate object from a second point of view. The orientation parameters are determined from a difference between the projected and detected probe radiation such as the difference between the shape of the feature produced by the projected probe radiation and the shape of the feature detected by the detector. The pattern of probe radiation is chosen to provide information for determination of the one or more orientation parameters and can include asymmetric patterns such as lines, ellipses, rectangles, polygons or the symmetric cases including circles, squares and regular polygons. To produce the patterns the projector can use a scanning arrangement or a structured light optic such as a holographic, diffractive, refractive or reflective element and any combinations thereof. The apparatus is suitable for determining the orientation of a jotting implement such as a pen, pencil or stylus.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Apparatus and method for determining an inclination of an elongate object contacting a plane surface
An apparatus and method for determining an inclination angle θ between an axis of an elongate object such as a cane, a pointer or a jotting implement such as a pen, pencil, stylus or the like and a normal to a plane surface at times when a tip of the elongate object is contacting that plane surface. The apparatus has an emitter mounted on the object for illuminating the plane surface with a probe radiation at an angle σ with respect to the axis of the object. The apparatus also has a detector mounted on the elongate object for detecting a radiation characteristic of a scattered portion of the probe radiation returning from the plane surface and a computing unit for deriving the inclination angle θ from the radiation characteristic. A scanning arrangement, such as a uniaxial or biaxial scanner, or a light guiding optic can be used for varying angle σ, and the probe radiation can be emitted in the form of a scan beam. Preferably, the emitter and detector of the scattered portion of the probe radiation are integrated and the scattered portion of the probe radiation whose characteristic is being measured is the back-scattered portion. The radiation characteristic detected by the detector can be the intensity, polarization, time-of-flight or any combination thereof.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
Defective pixel compensation method
InactiveUS6618185B2Microbiological testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpatial light modulatorFluence
The present invention relates to a method for compensating the impact of at least one defective pixel with a known position in a spatial light modulator (SLM) when creating a pattern of the SLM on a work piece covered with a layer sensitive to electromagnetic radiation. A source for emitting electromagnetic radiation is provided. Said radiation is illuminating said SLM having a plurality of modulating elements (pixels). In a writing pass an image of said modulator is projected on said work piece. A compensation for defective pixels in at least one other writing pass is performed. The invention also relates to an apparatus for performing said method.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
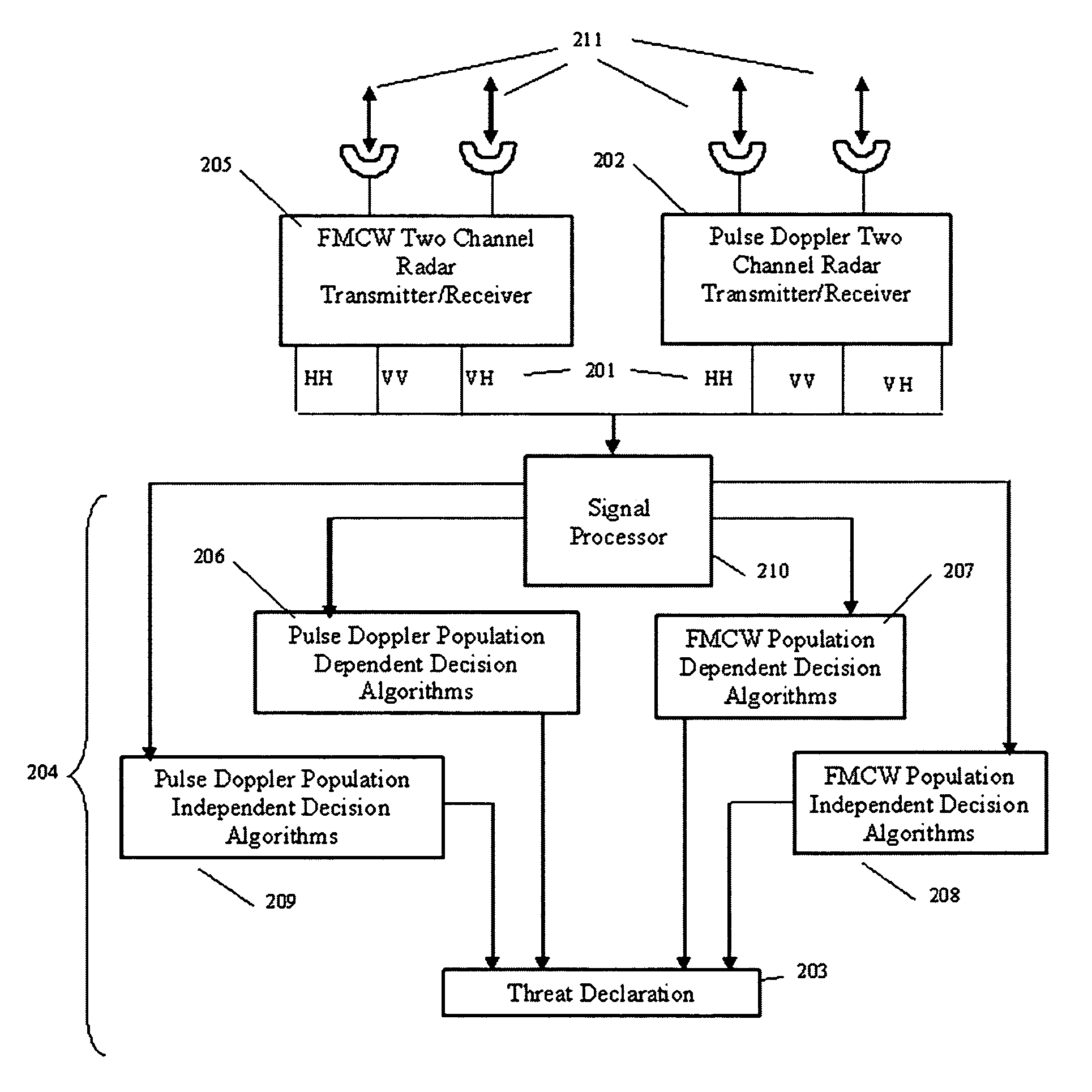
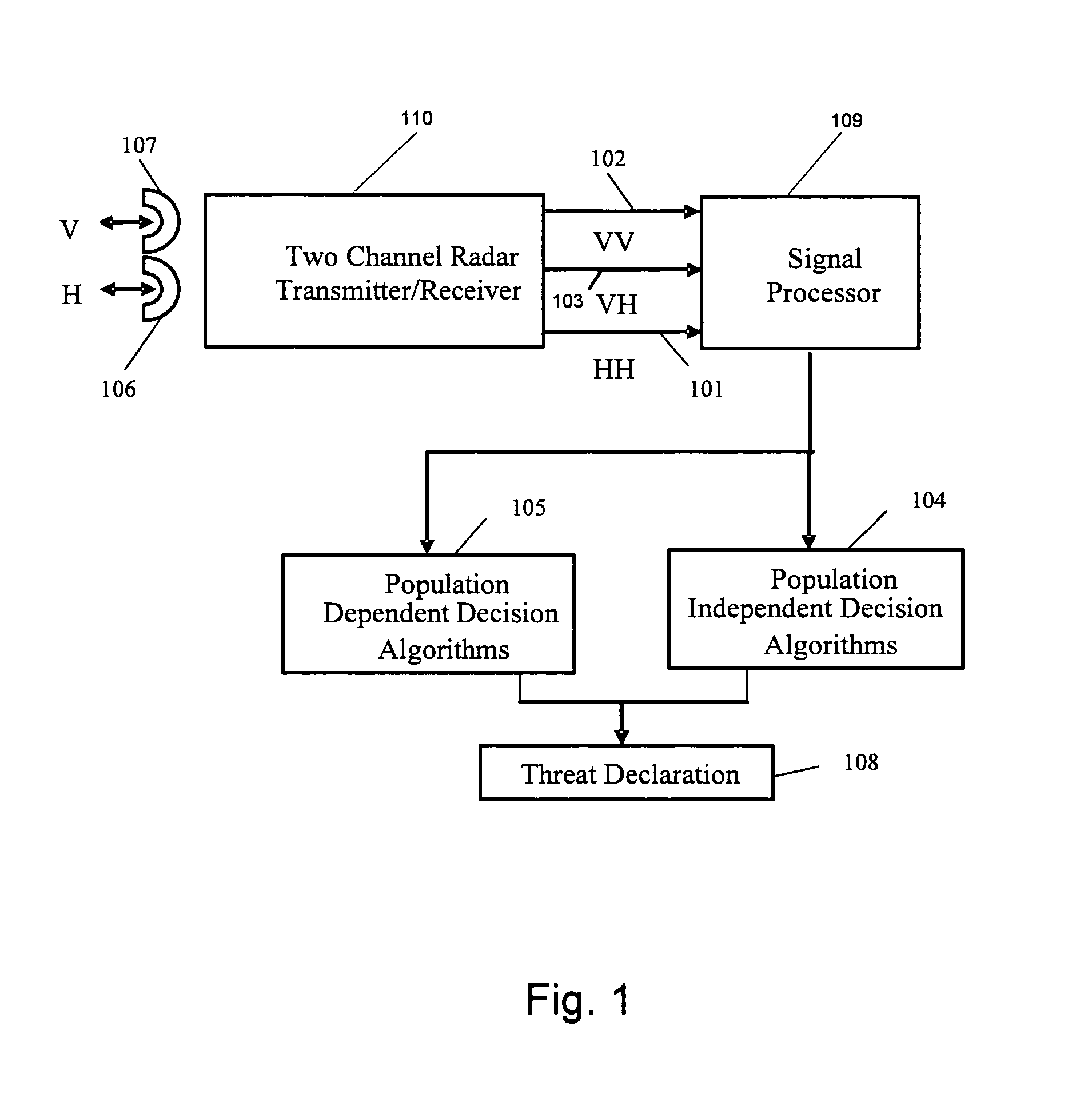
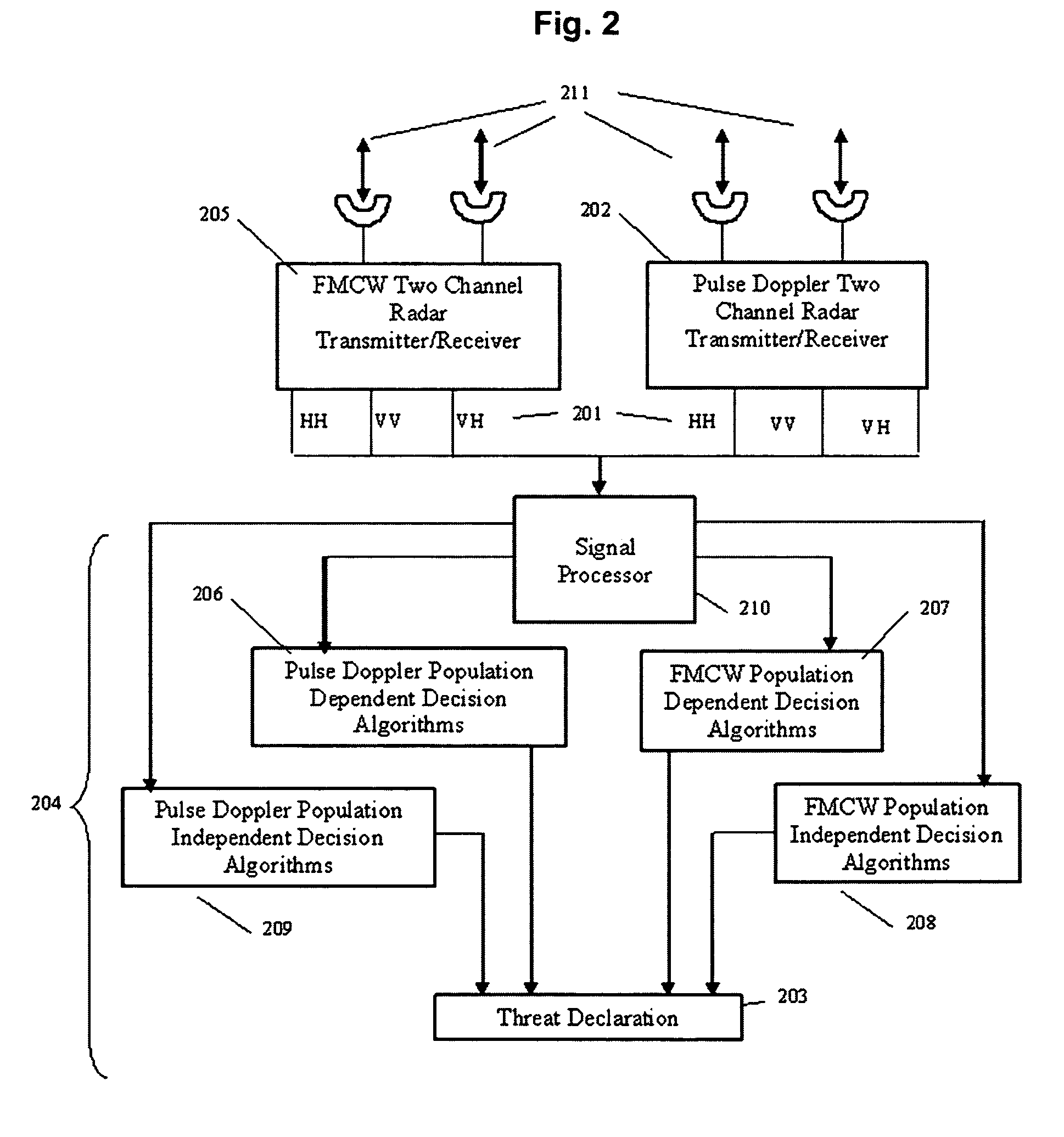
Methods and apparatus for detecting threats using radar
Methods and apparatus for early detection and identification of a threat such as individuals carrying hidden explosive materials, land mines on roads, etc. are disclosed. One method comprises illuminating a target with radiation at a first polarization, collecting first radiation reflected from the target which has the same polarization as the first polarization, illuminating a target with radiation at a second polarization, and collecting second radiation reflected from the target which has the same polarization as the second polarization. A threat determination is then made based on the difference between the energy values of the first and second collected radiations. In other embodiments, the difference between energy values is used in conjunction with an evaluation of the returned energy in comparison with returned energy from other targets in order to additionally assess whether the primary target is a threat.
Owner:KOSOWSKY LESTER
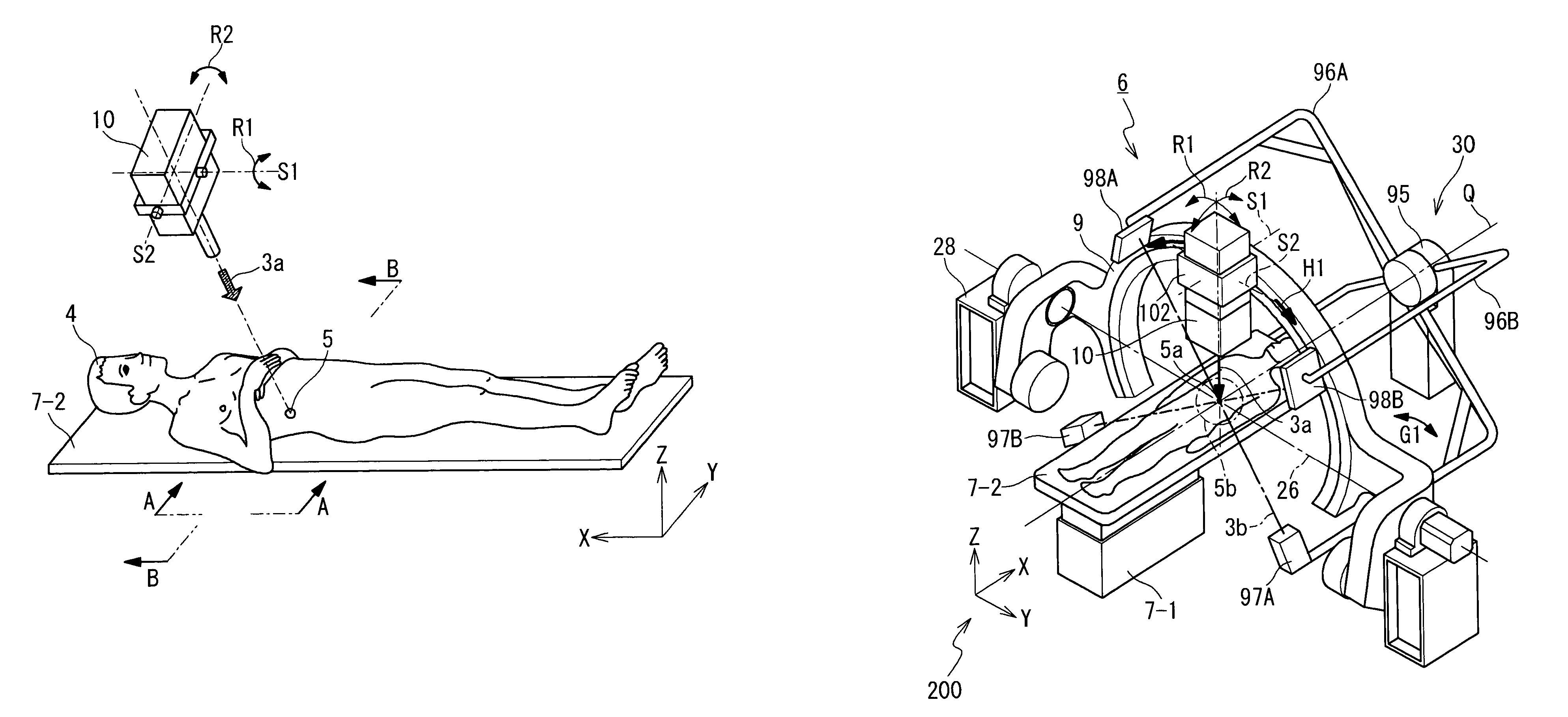
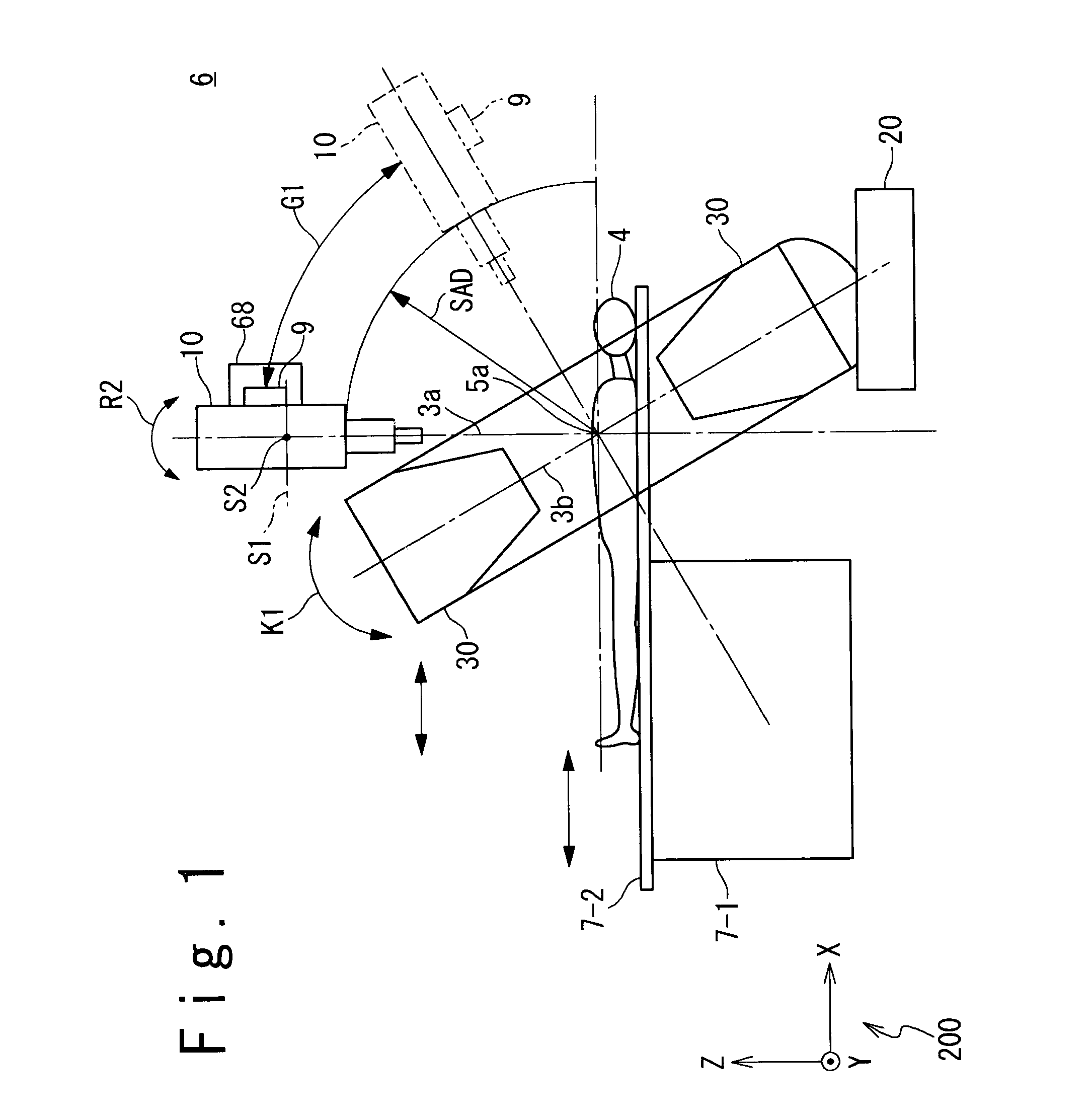
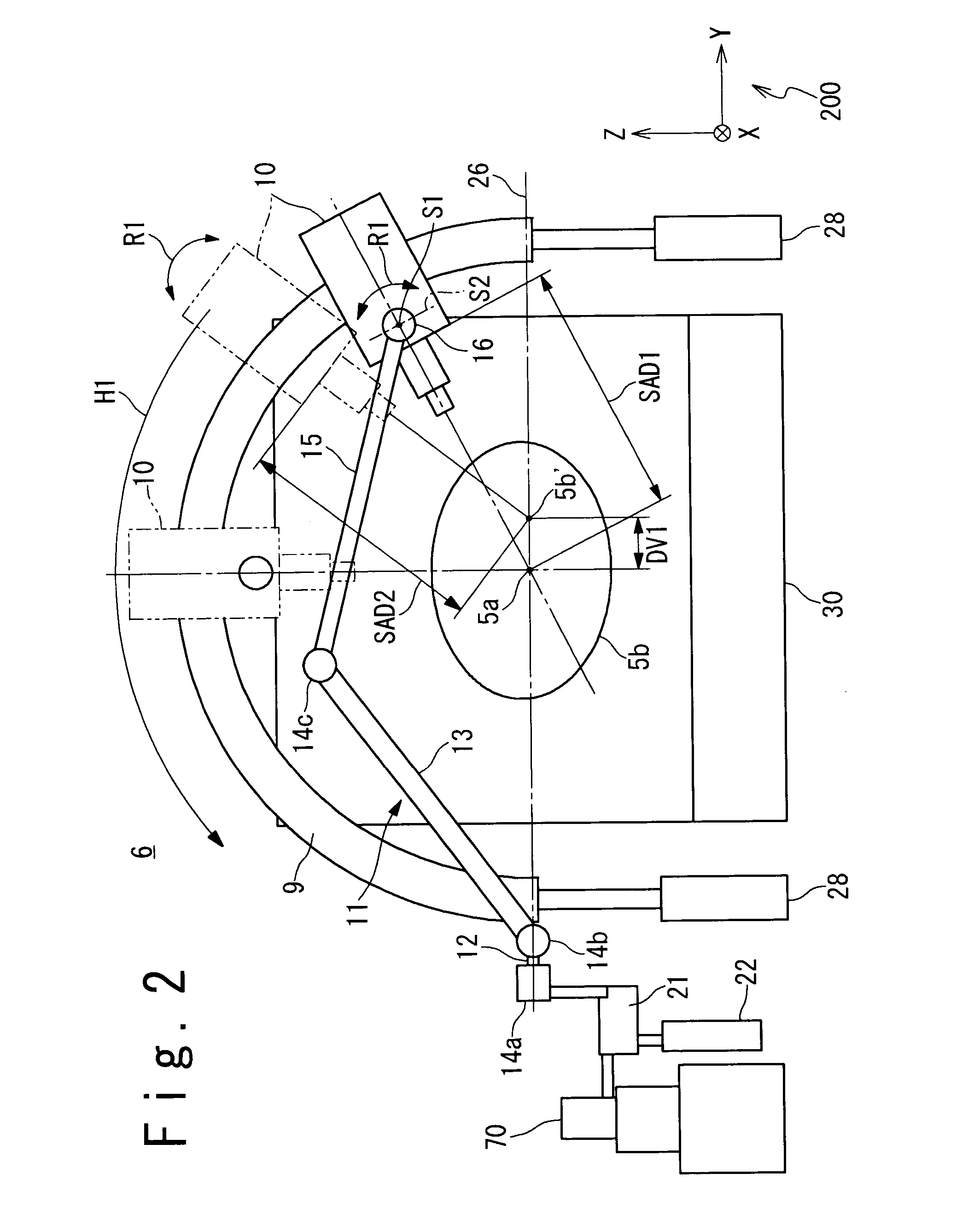
Radiotherapy device
InactiveUS7085347B2Reduced drive mechanismReduce the burden onDiagnosticsSurgeryFluenceTreatment field
The radiotherapy apparatus in the present invention includes a bed, a radiation irradiating head, head swing mechanisms, a precise inspection unit and a control unit. The bed carries a subject. The radiation irradiating head irradiates a treatment radiation to a treatment field of the subject. The head swing mechanisms, which are coupled to the radiation irradiating head, swings the head of the radiation irradiating head so that the treatment radiation emitted from the radiation irradiating head pursues the motion of the treatment field. The precise inspection unit obtains a diagnosis image containing the treatment field. The control unit controls the positions of the head swing mechanisms so that an irradiation field of the radiation irradiating head pursues the treatment field, based on the diagnosis image, the position of the radiation irradiating head and the state of the swung head. Then, the control unit controls the radiation irradiating head so that the treatment radiation is irradiated from the radiation irradiating head, after the positional control of the head swing mechanisms.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Delivery system for post-operative power adjustment of adjustable lens
InactiveUS6905641B2Easy to useLess potential riskSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryFluencePost operative
A method and instrument to irradiate a light adjustable lens, for example, inside a human eye, with an appropriate amount of radiation in an appropriate intensity pattern by first measuring aberrations in the optical system containing the lens; aligning a source of the modifying radiation so as to impinge the radiation onto the lens in a pattern that will null the aberrations. The quantity of the impinging radiation is controlled by controlling the intensity and duration of the irradiation. The pattern is controlled and monitored while the lens is irradiated.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
Positive photosensitive composition
InactiveUS20030077540A1High sensitivityBroad defocus latitudePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsActinic RaysFluence
A positive photosensitive composition comprising (A) a specific acid generator that generates an acid upon irradiation of an actinic ray or radiation, and (B) a resin that has a monocyclic or polycyclic alicyclic hydrocarbon structure and is decomposed by the action of an acid to increase solubility in an alkali developing solution.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
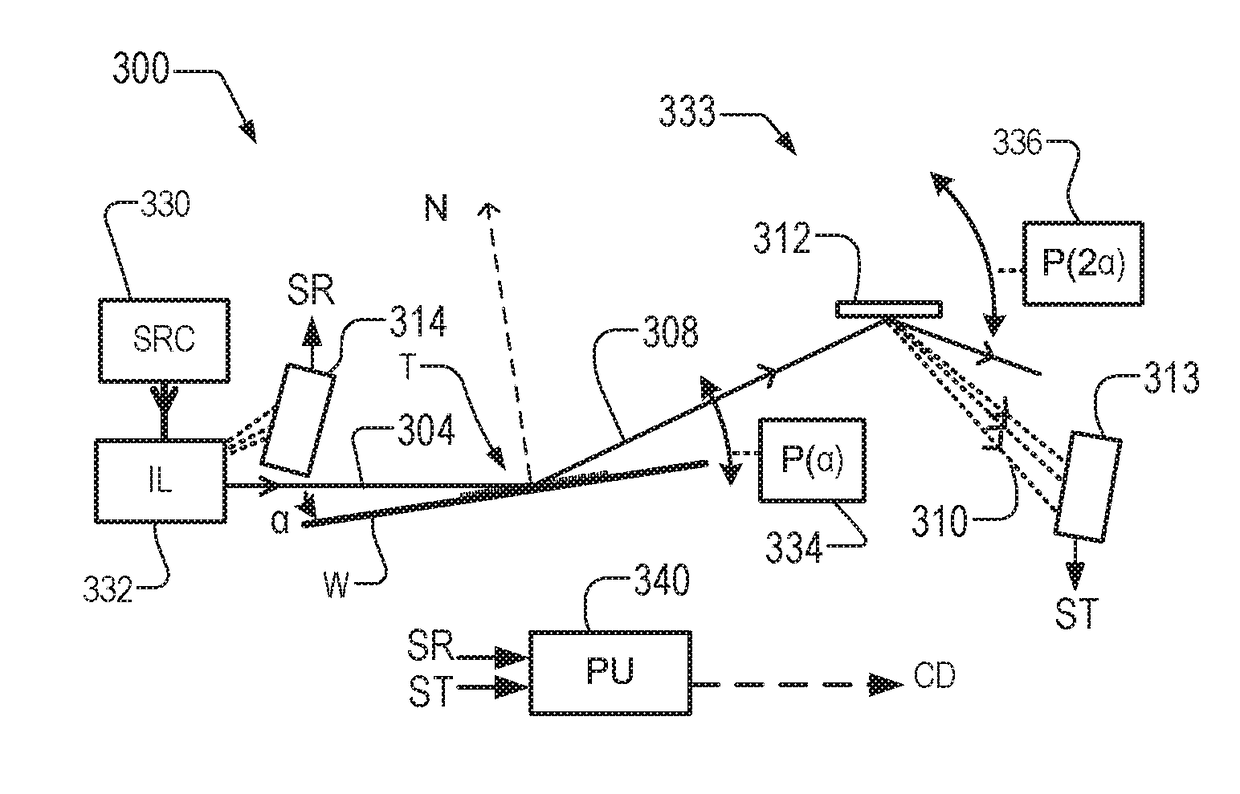
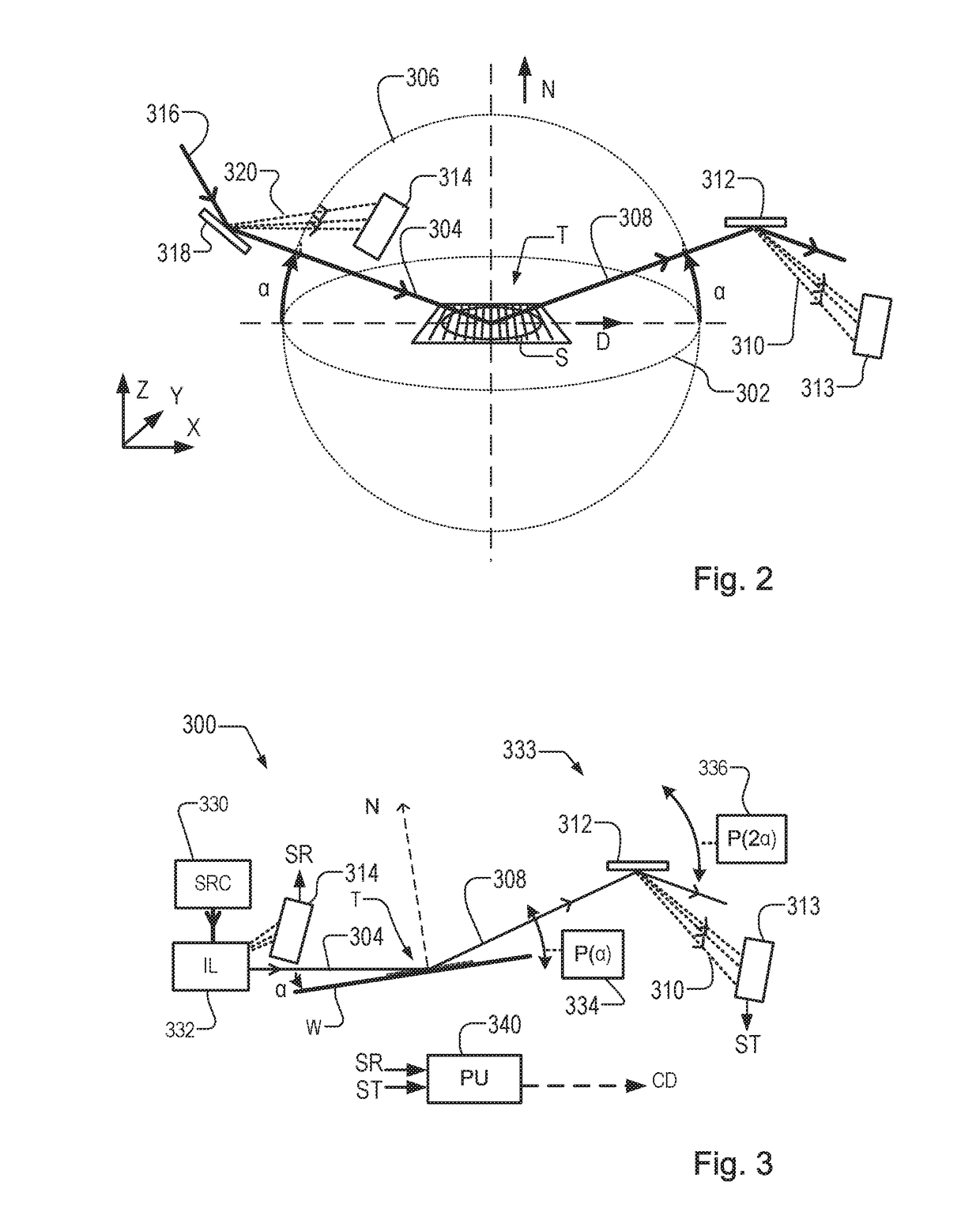
Metrology Methods, Metrology Apparatus and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20170184981A1Precise structureIncrease the angle of incidenceOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAction spectrumMetrology
Hybrid metrology apparatus (1000, 1100, 1200, 1300, 1400) measures a structure (T) manufactured by lithography. An EUV metrology apparatus (244, IL1 / DET1) irradiates the structure with EUV radiation and detects a first spectrum from the structure. Another metrology apparatus (240, IL2 / DET2) irradiates the structure with second radiation comprising EUV radiation or longer-wavelength radiation and detects a second spectrum. Using the detected first spectrum and the detected second spectrum together, a processor (MPU) determines a property (CD / OV) of the structure. The spectra can be combined in various ways. For example, the first detected spectrum can be used to control one or more parameters of illumination and / or detection used to capture the second spectrum, or vice versa. The first spectrum can be used to distinguish properties of different layers (T1, T2) in the structure. First and second radiation sources (SRC1, SRC2) may share a common drive laser (LAS).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
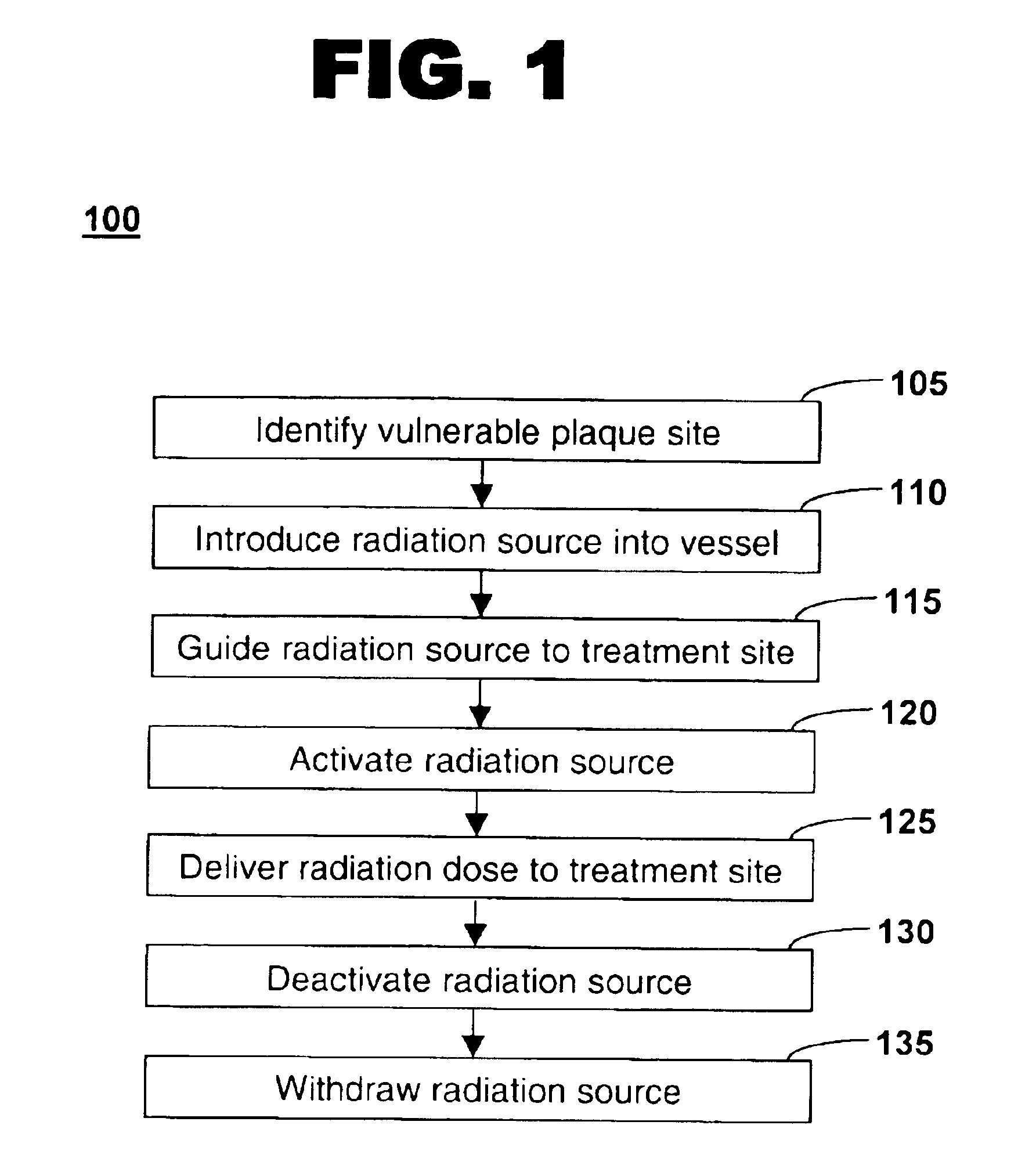
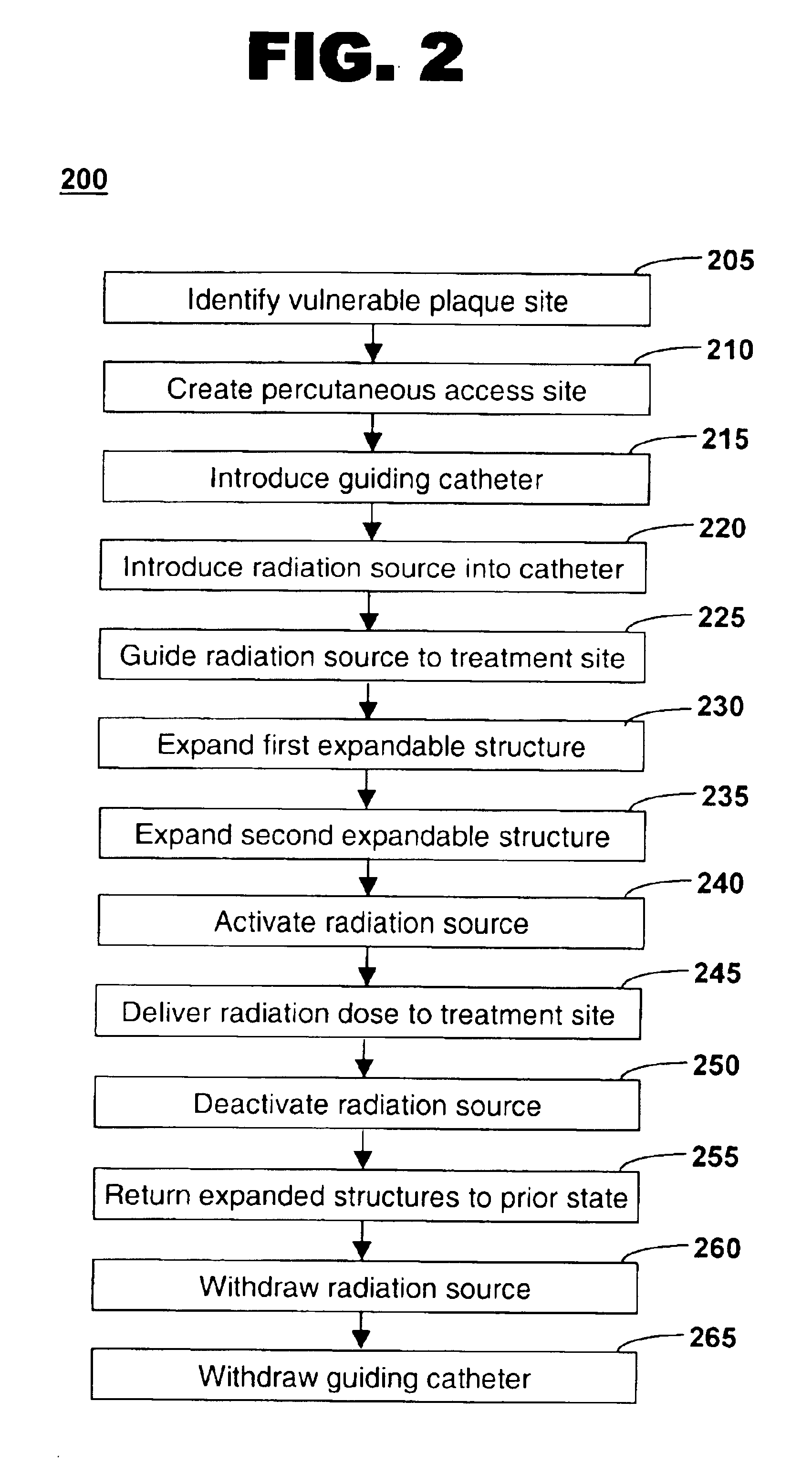
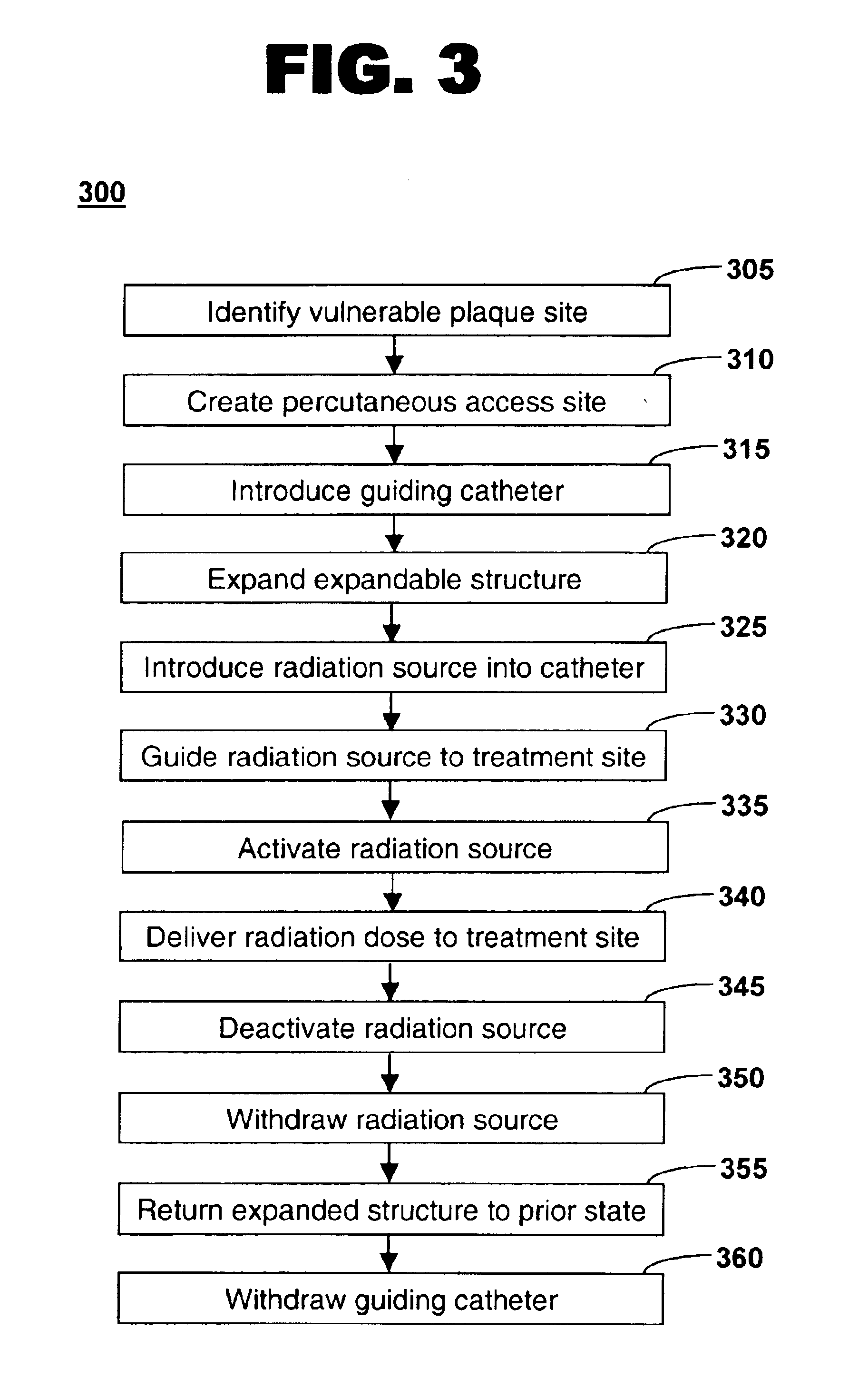
Method of treating vulnerable plaque using a catheter-based radiation system
The invention provides a method of treating vulnerable plaque at a site in a vessel. A vulnerable plaque site is identified for treatment. A radiation source is introduced into a vessel containing a vulnerable plaque site identified for treatment. The radiation source is guided to a position adjacent to the treatment site. A therapeutically effective dose of radiation is delivered to the vulnerable plaque site. As the radiation impinges upon the wall of the lumen, it promotes cell growth. Such growth can serve to strengthen the thin fibrous cap found atop a vulnerable plaque lesion. With the lesion thus stabilized, time is provided for the use of statin drugs or other agents to shrink or remove the lipid pool beneath the cap.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Radiation probe and detecting tooth decay
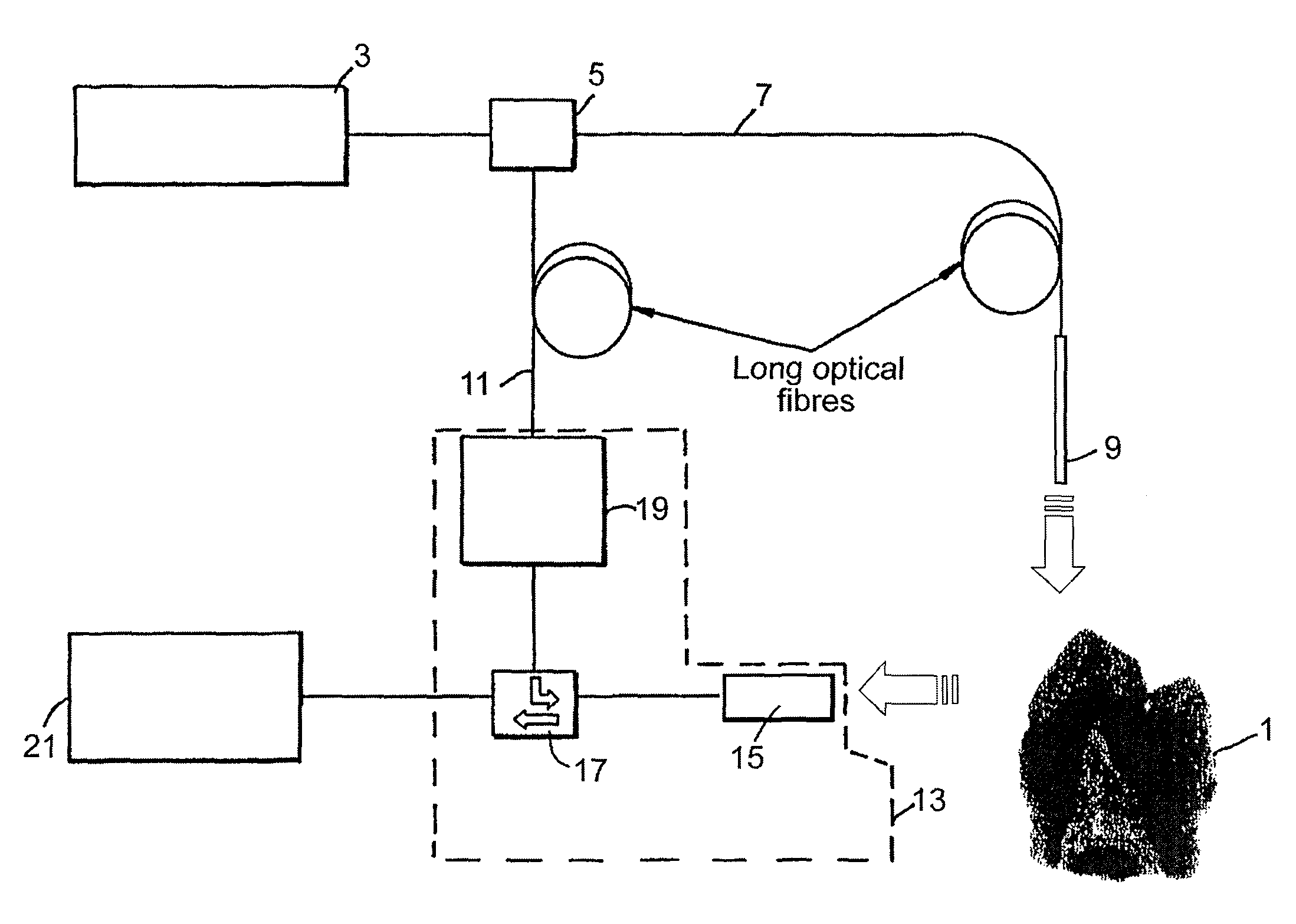
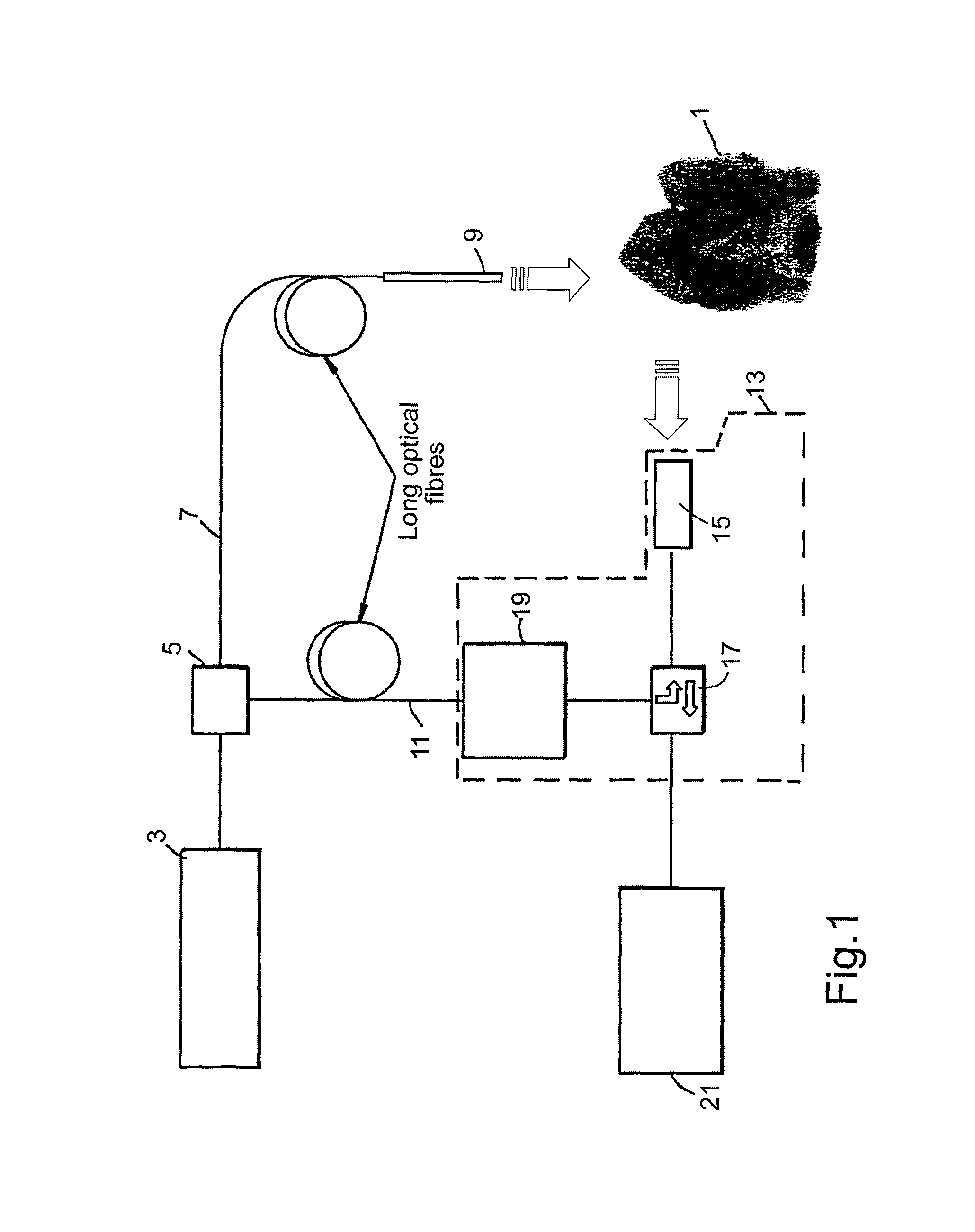
ActiveUS8027709B2Maximize contrastHigh porosityTeeth fillingSurgeryCementum cariesFrequency conversion
A probe assembly for examining a sample, the assembly including a probe, a fiber optic cable for communicating signals to and / or from the probe, an emitter for emitting radiation to irradiate the sample and an electro-magnetic radiation detector for detecting radiation which is transmitted or reflected from the sample. The emitter includes a frequency conversion member which emits radiation in response to being irradiated with input radiation which has a different frequency to that of the emitted radiation. At least one of the emitter or detector is located in the probe. The probe is particularly for use as an endoscope or for imaging teeth. The invention also extends to a method of imaging teeth, and apparatus for imaging diseased teeth, for example, teeth with caries or suffering from periodontal disease.
Owner:TERAVIEW
Delivery system for post-operative power adjustment of adjustable lens
InactiveUS20020100990A1Less potential riskMore versatile in generating different irradiation intensity patternsSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryFluencePost operative
A method and instrument to irradiate a light adjustable lens, for example, inside a human eye, with an appropriate amount of radiation in an appropriate intensity pattern by first measuring aberrations in the optical system containing the lens; aligning a source of the modifying radiation so as to impinge the radiation onto the lens in a pattern that will null the aberrations. The quantity of the impinging radiation is controlled by controlling the intensity and duration of the irradiation. The pattern is controlled and monitored while the lens is irradiated.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
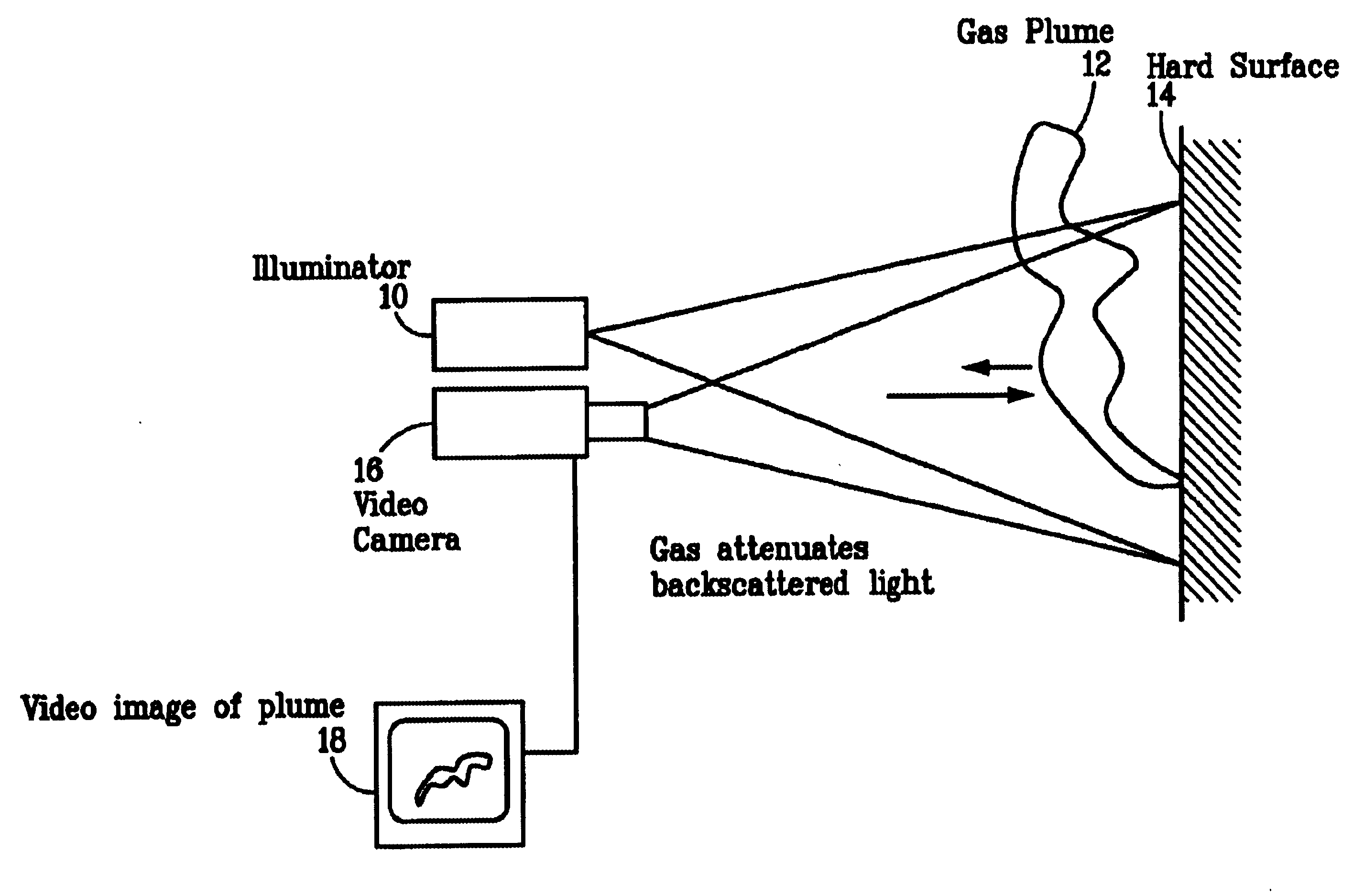
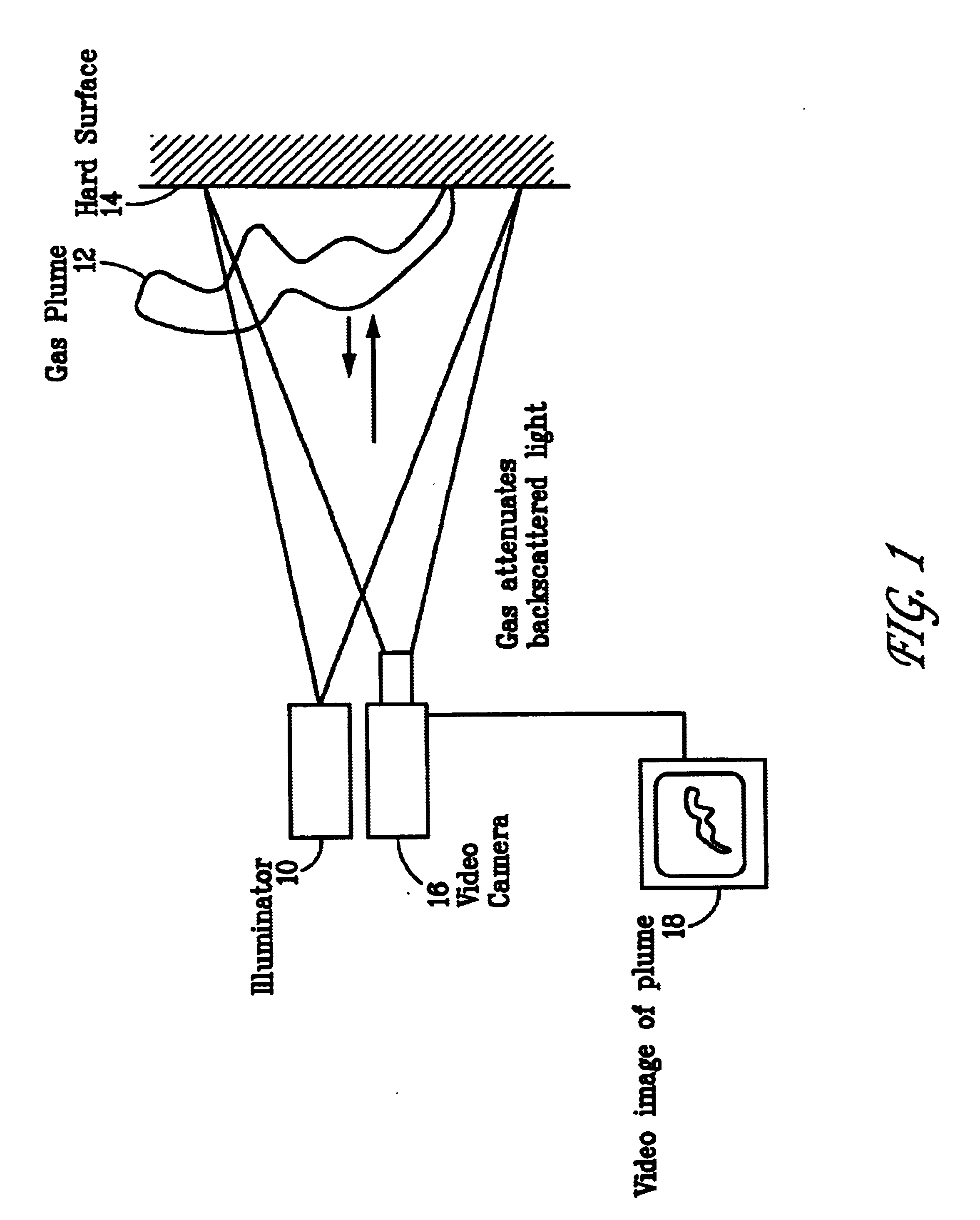
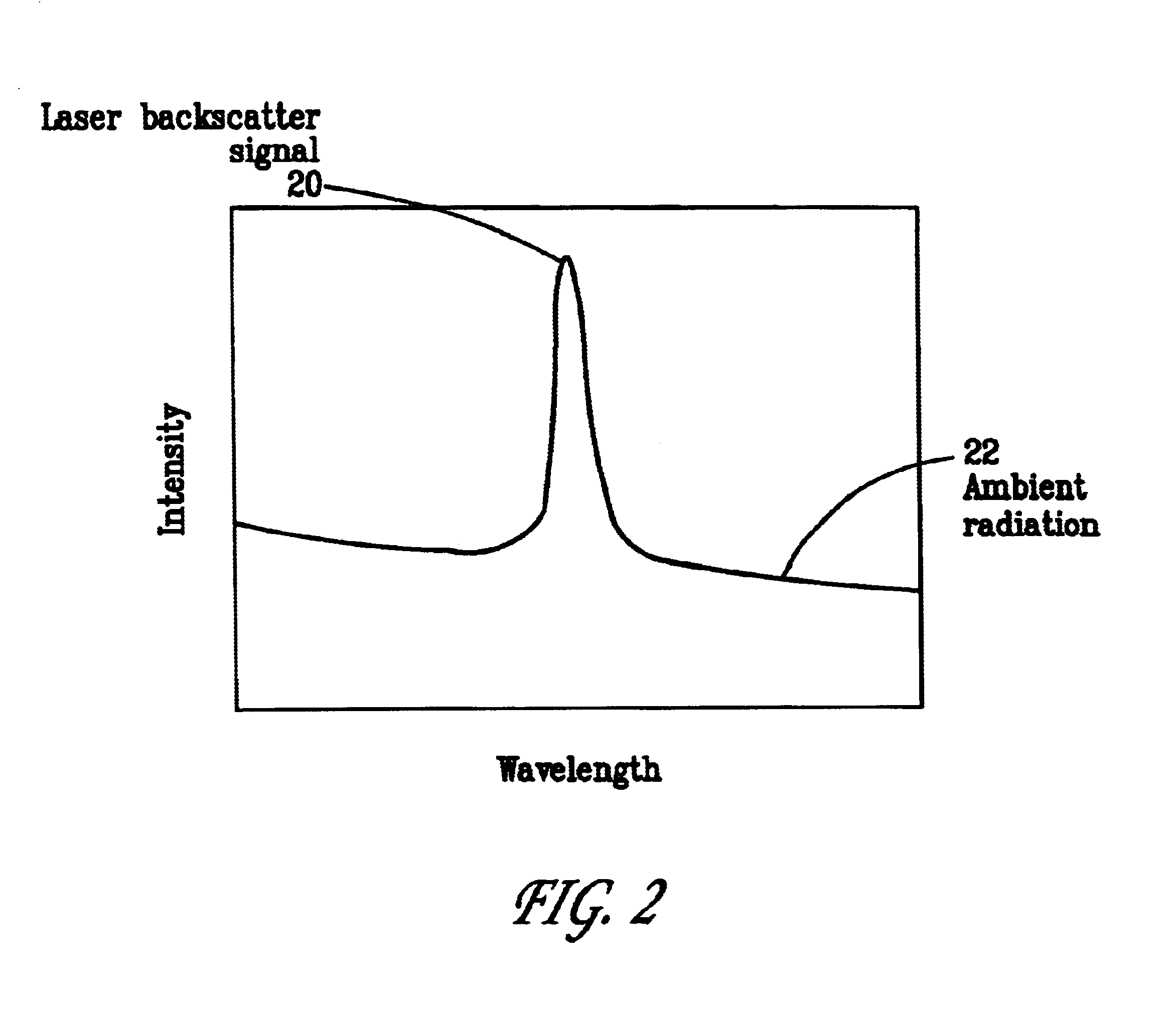
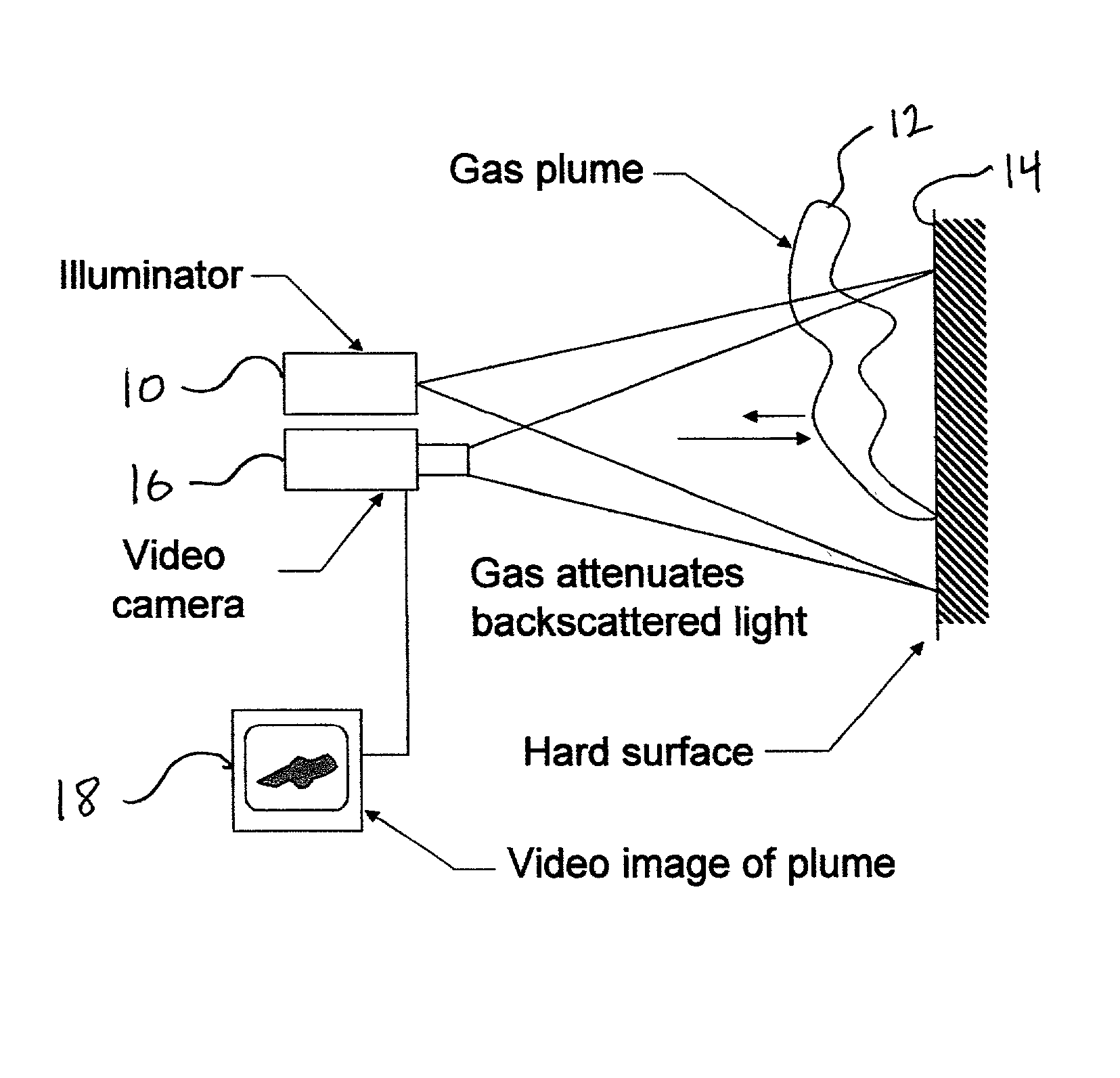
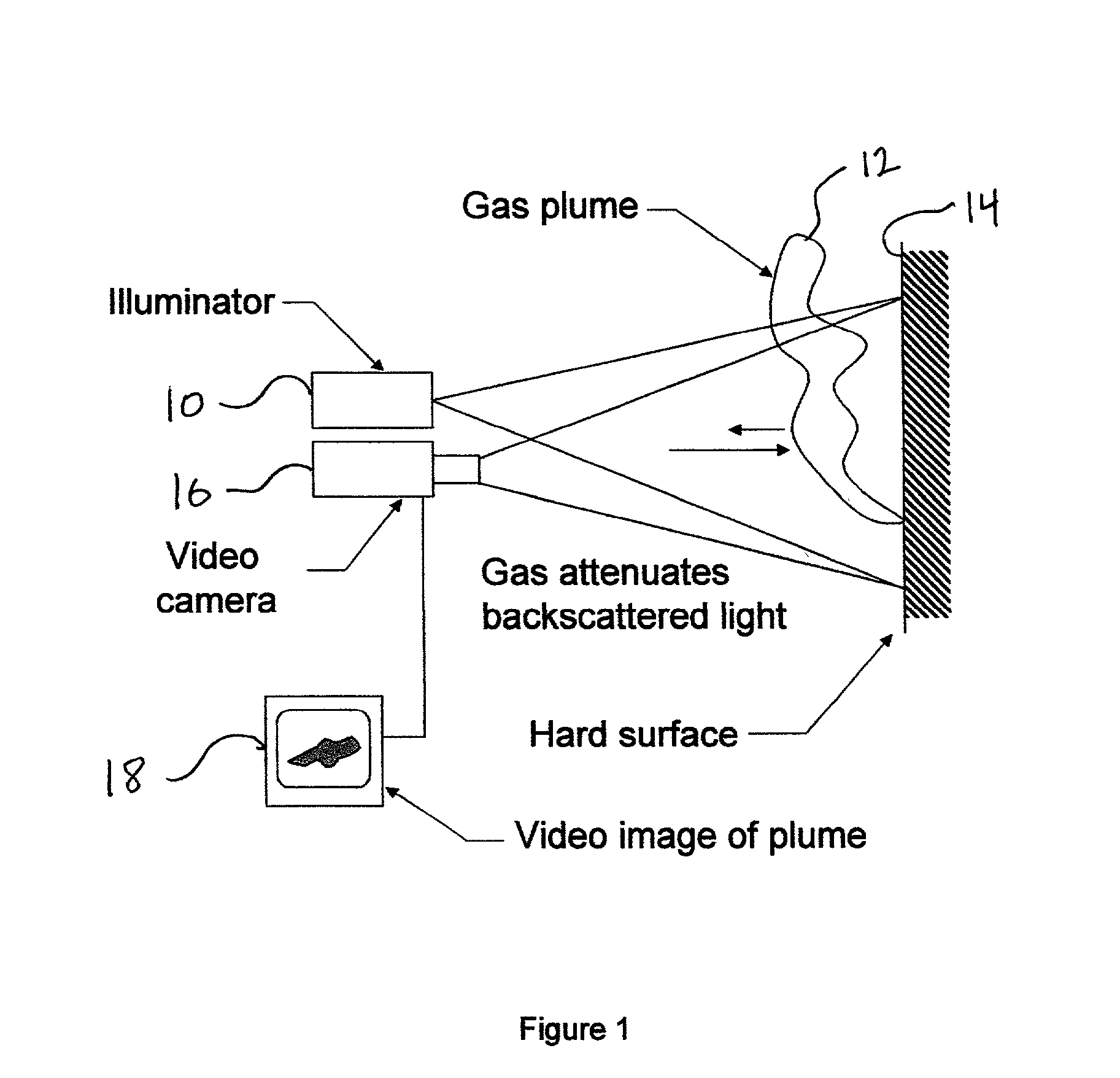
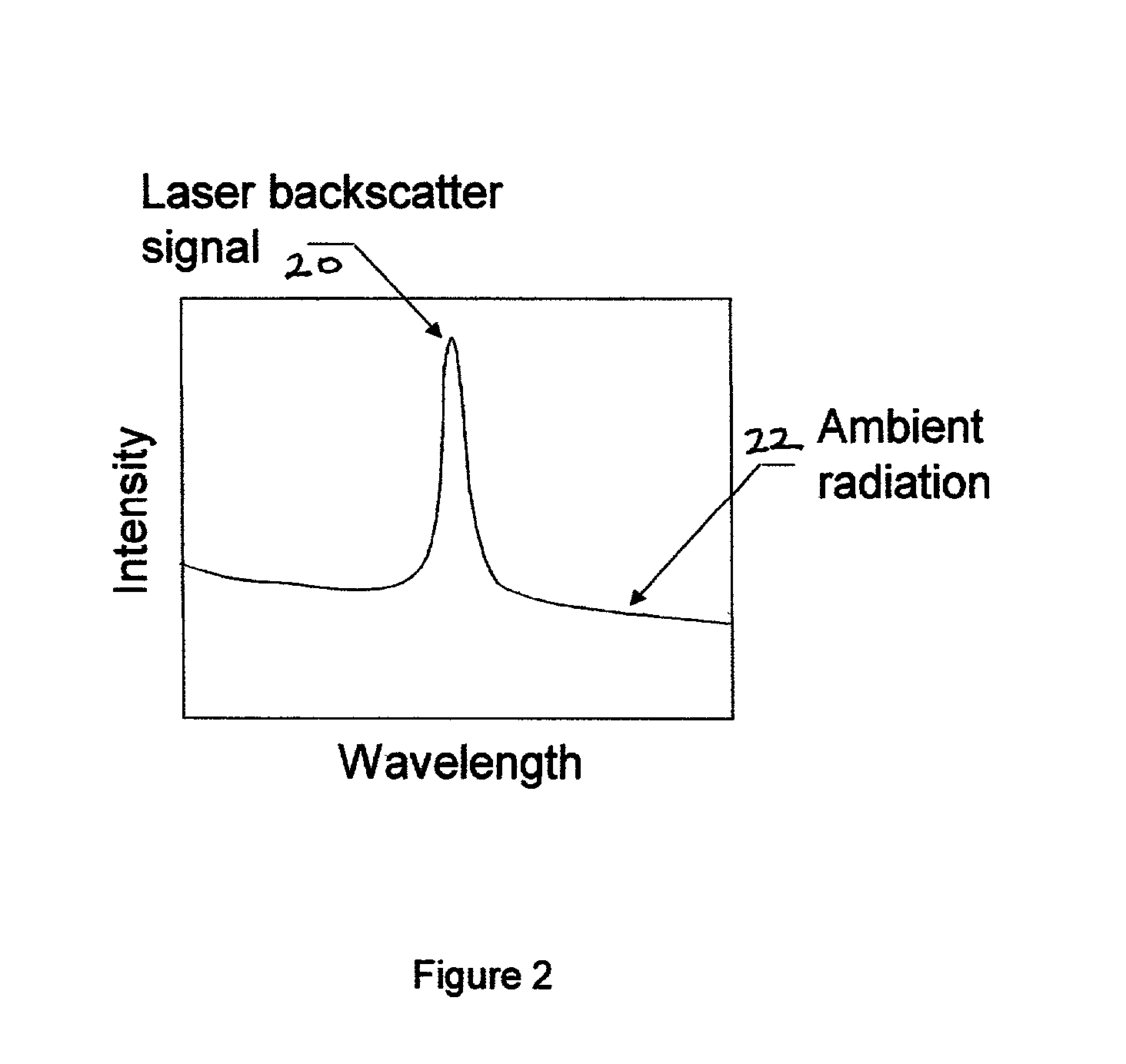
Pulsed laser linescanner for a backscatter absorption gas imaging system
InactiveUS6690472B2Enhanced signalMaximize attenuationScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsMobile vehicleFluence
An active (laser-illuminated) imaging system is described that is suitable for use in backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI). A BAGI imager operates by imaging a scene as it is illuminated with radiation that is absorbed by the gas to be detected. Gases become "visible" in the image when they attenuate the illumination creating a shadow in the image. This disclosure describes a BAGI imager that operates in a linescanned manner using a high repetition rate pulsed laser as its illumination source. The format of this system allows differential imaging, in which the scene is illuminated with light at least 2 wavelengths-one or more absorbed by the gas and one or more not absorbed. The system is designed to accomplish imaging in a manner that is insensitive to motion of the camera, so that it can be held in the hand of an operator or operated from a moving vehicle.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
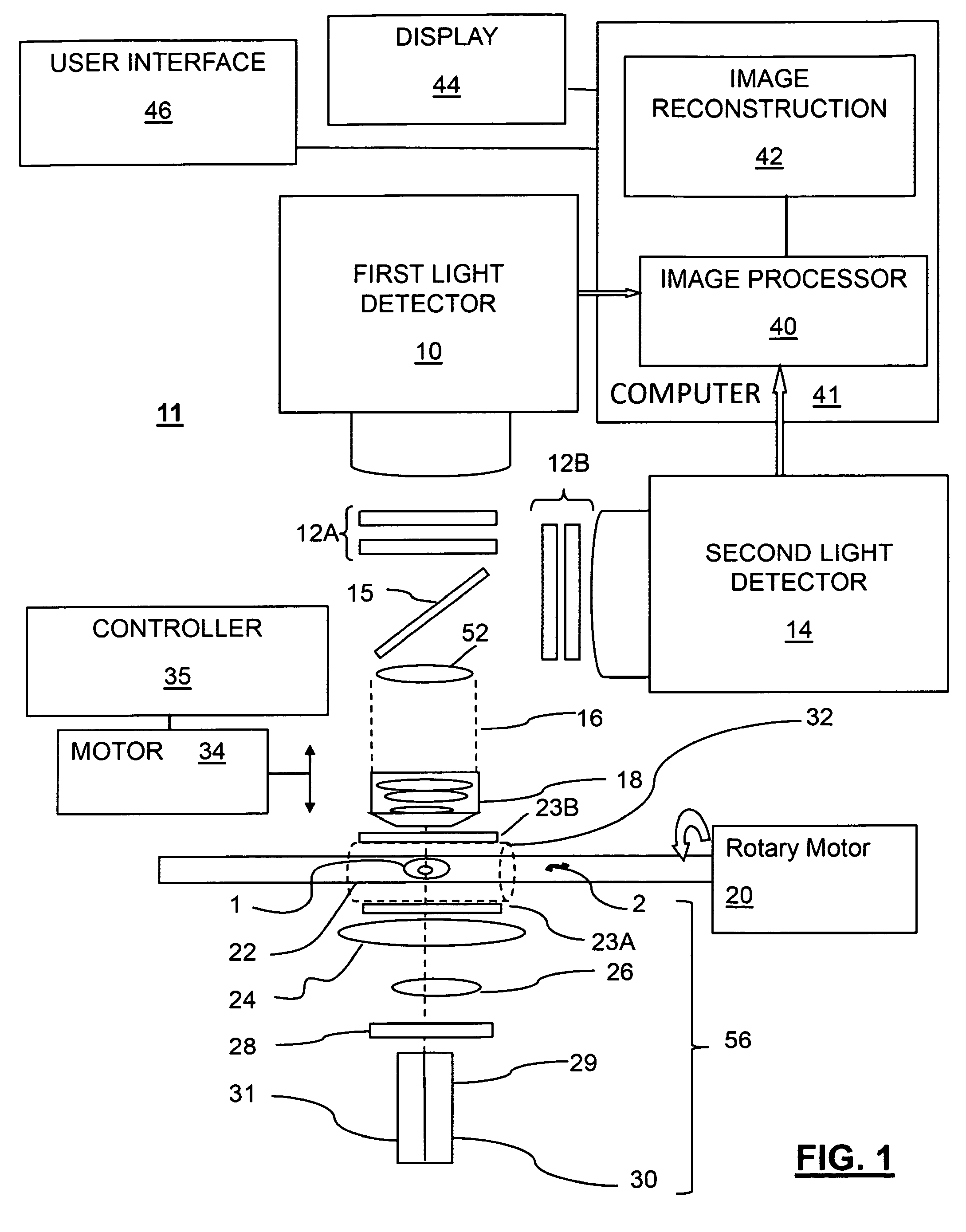
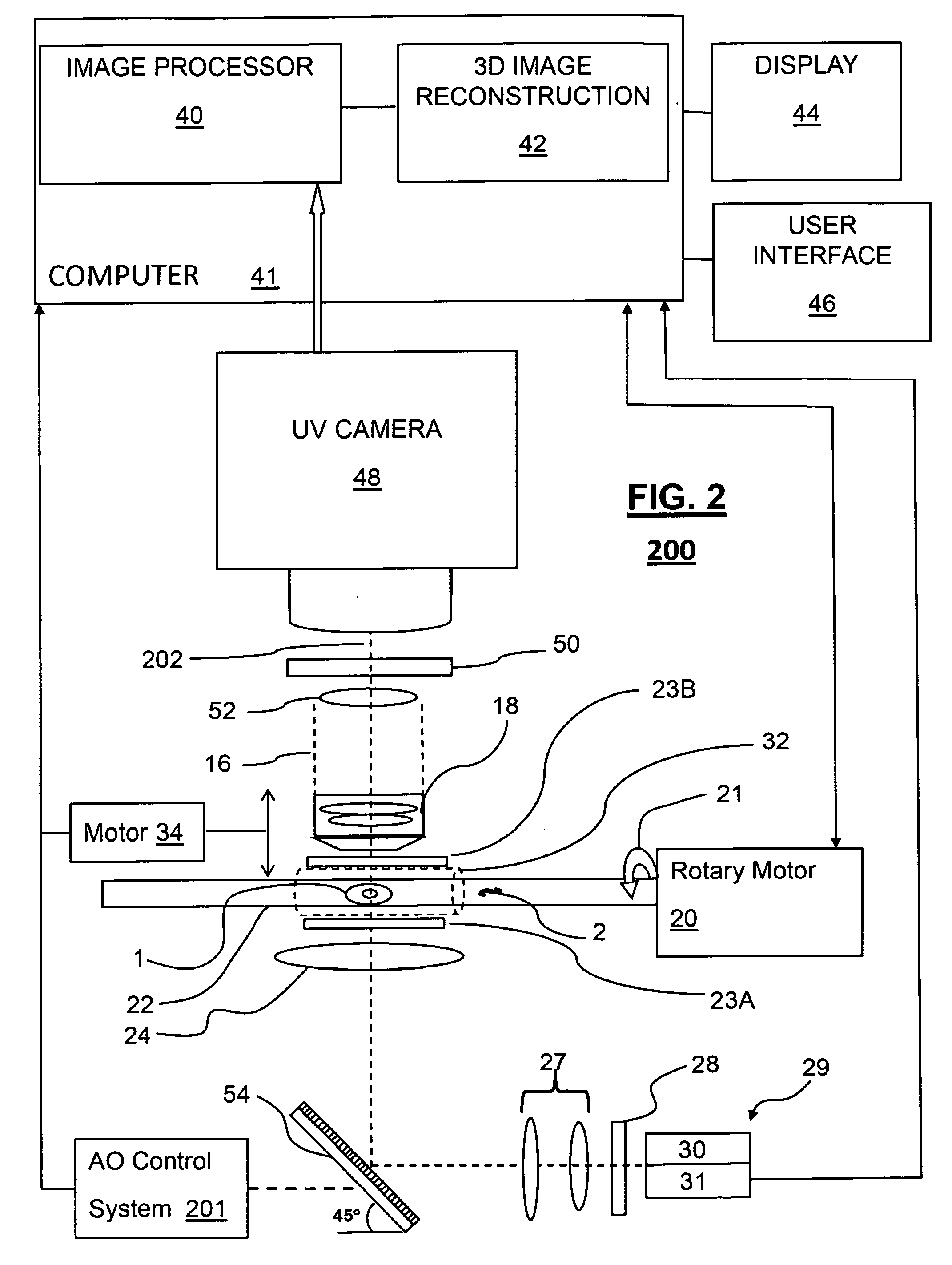
3D imaging of live cells with ultraviolet radiation
InactiveUS20090208072A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical tomographyFluence
A method for 3D imaging of cells in an optical tomography system includes moving a biological object relatively to a microscope objective to present varying angles of view. The biological object is illuminated with radiation having a spectral bandwidth limited to wavelengths between 150 nm and 390 nm. Radiation transmitted through the biological object and the microscope objective is sensed with a camera from a plurality of differing view angles. A plurality of pseudoprojections of the biological object from the sensed radiation is formed and the plurality of pseudoprojections is reconstructed to form a 3D image of the cell.
Owner:VISIONGATE
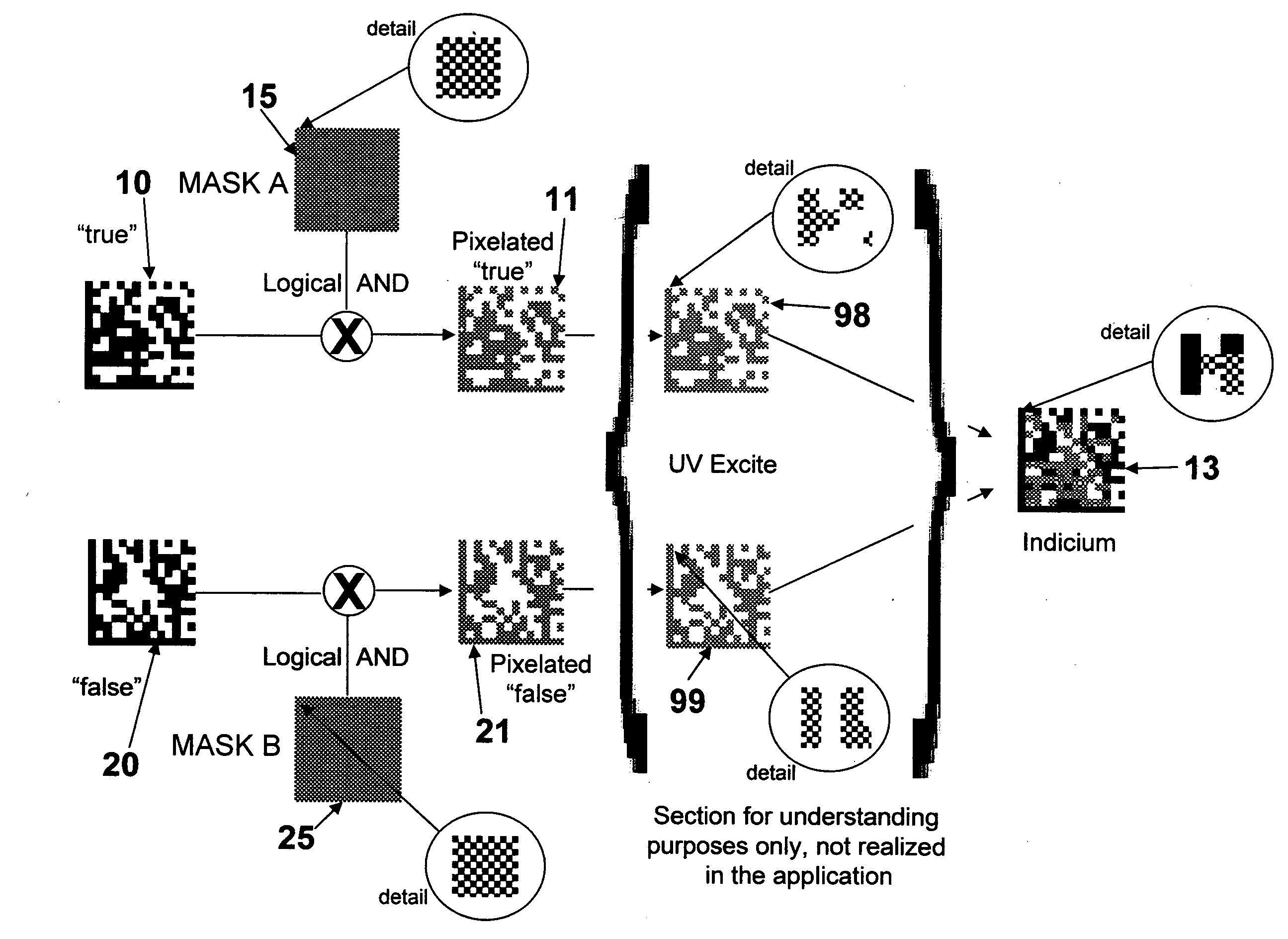
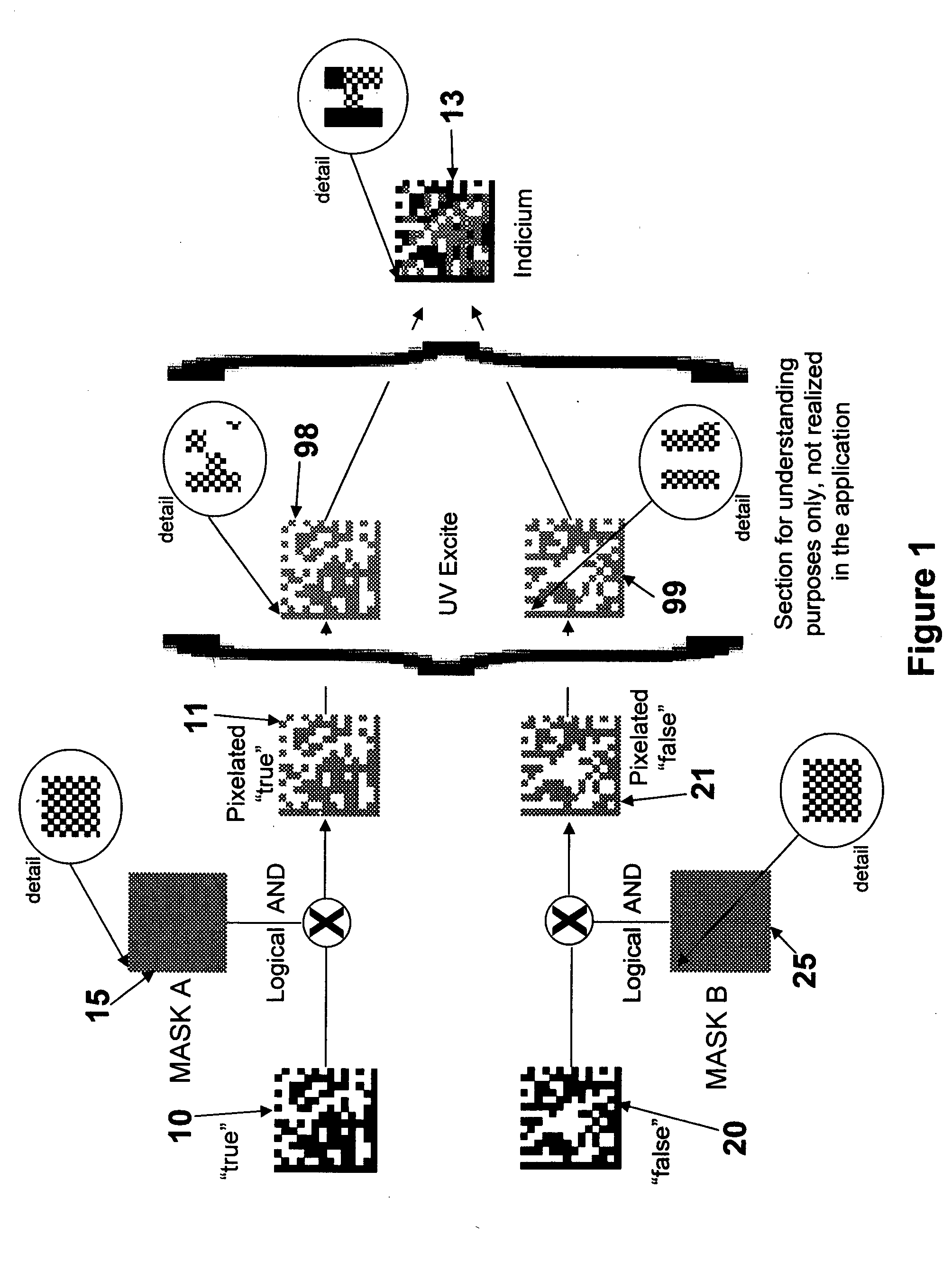
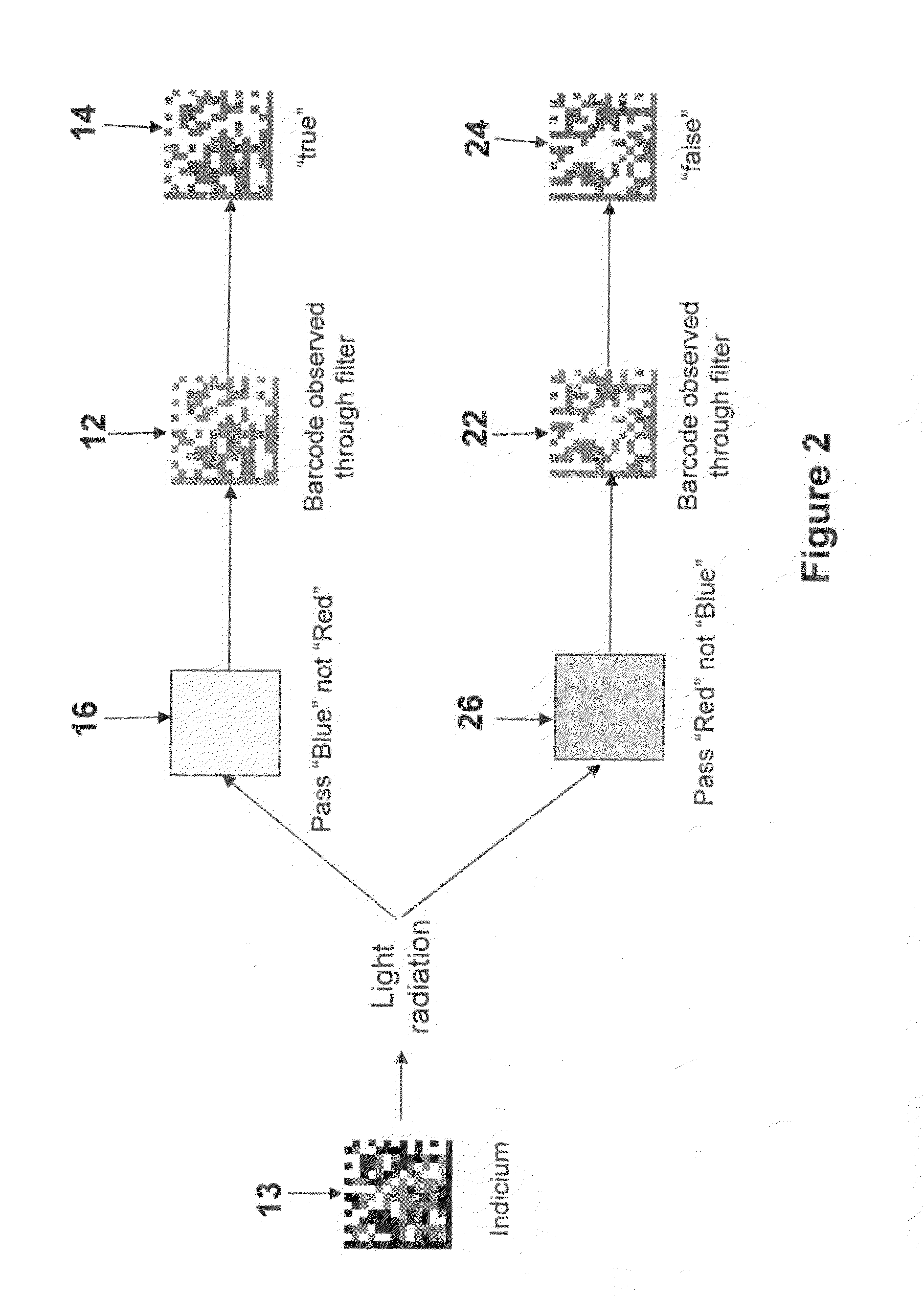
Method and system for creating and reading multi-color co-planar emissive indicia using printable dyes and pigments
ActiveUS20080252066A1Minimize area of overprintingEasy to useOther printing matterDuplicating/marking methodsFluenceSpectral filtering
A method and system for identifying, tracking, and / or authenticating objects that is simple to apply and to use by an intended user, but is extremely difficult to counterfeit or compromise by an unintended user. Also disclosed is a multi-color, co-planar indicium made of a combination of printed patterns of multiple inks. The printed patterns may be modified by software-generated masks to ensure that the patterns are co-planar. The indicium is undecipherable unless irradiated with specified wavelengths of light radiation, filtered through specified spectral filters, and read and decoded by an electronic image reader. The indicium may be visible or covert. The indicium encodes unique true information about the object and may encode nonsensical or intentionally incorrect information as a further deterrent to unauthorized use. The method permits the indicia to be applied to objects at high processing speeds possible with inkjet printing.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Pulsed laser linescanner for a backscatter absorption gas imaging system
InactiveUS20020071122A1Enhanced signalMaximize attenuationScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsFluenceRadiation
An active (laser-illuminated) imaging system is described that is suitable for use in backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI). A BAGI imager operates by imaging a scene as it is illuminated with radiation that is absorbed by the gas to be detected. Gases become "visible" in the image when they attenuate the illumination creating a shadow in the image. This disclosure describes a BAGI imager that operates in a linescanned manner using a high repetition rate pulsed laser as its illumination source. The format of this system allows differential imaging, in which the scene is illuminated with light at least 2 wavelengths-one or more absorbed by the gas and one or more not absorbed. The system is designed to accomplish imaging in a manner that is insensitive to motion of the camera, so that it can be held in the hand of an operator or operated from a moving vehicle.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
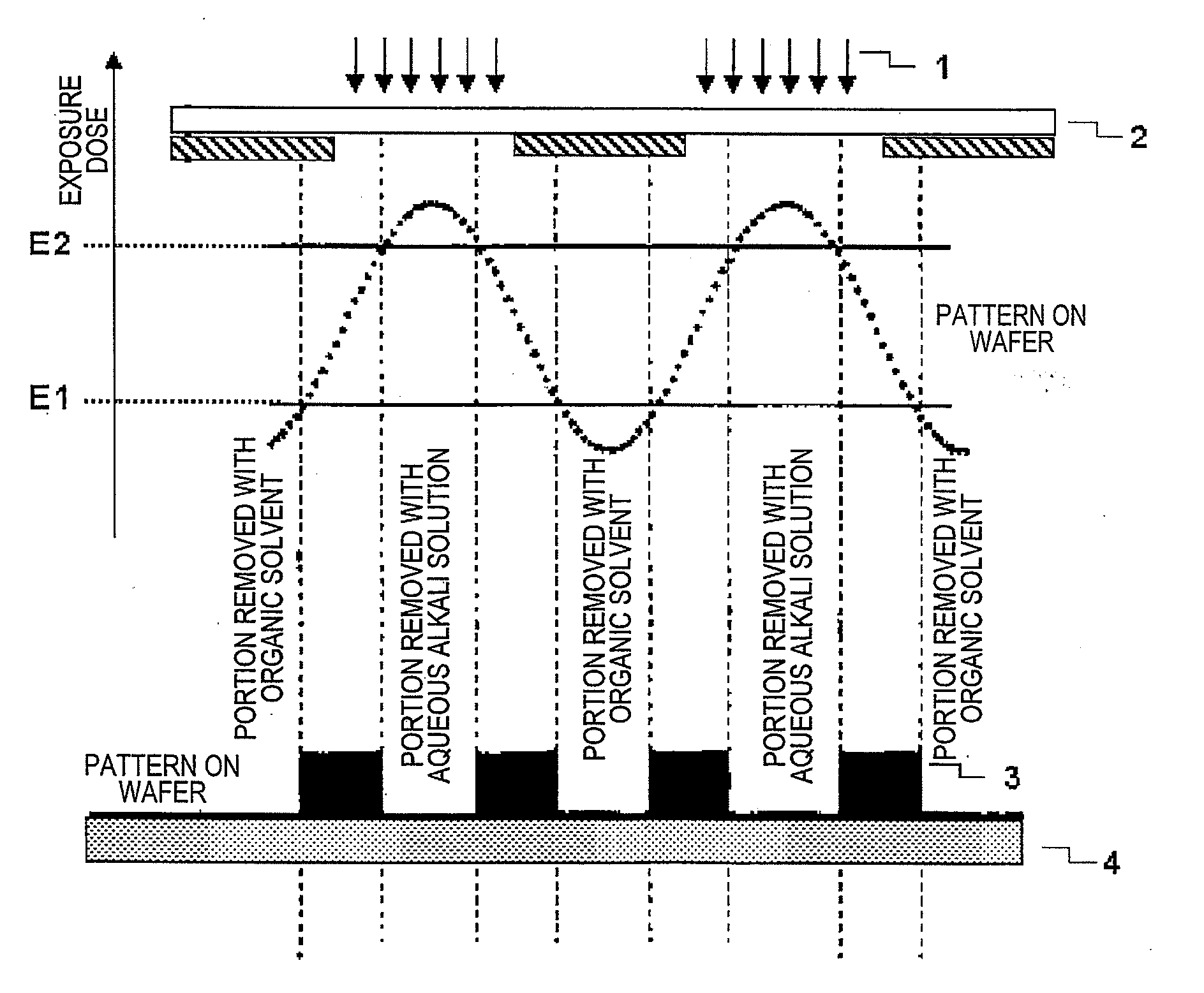
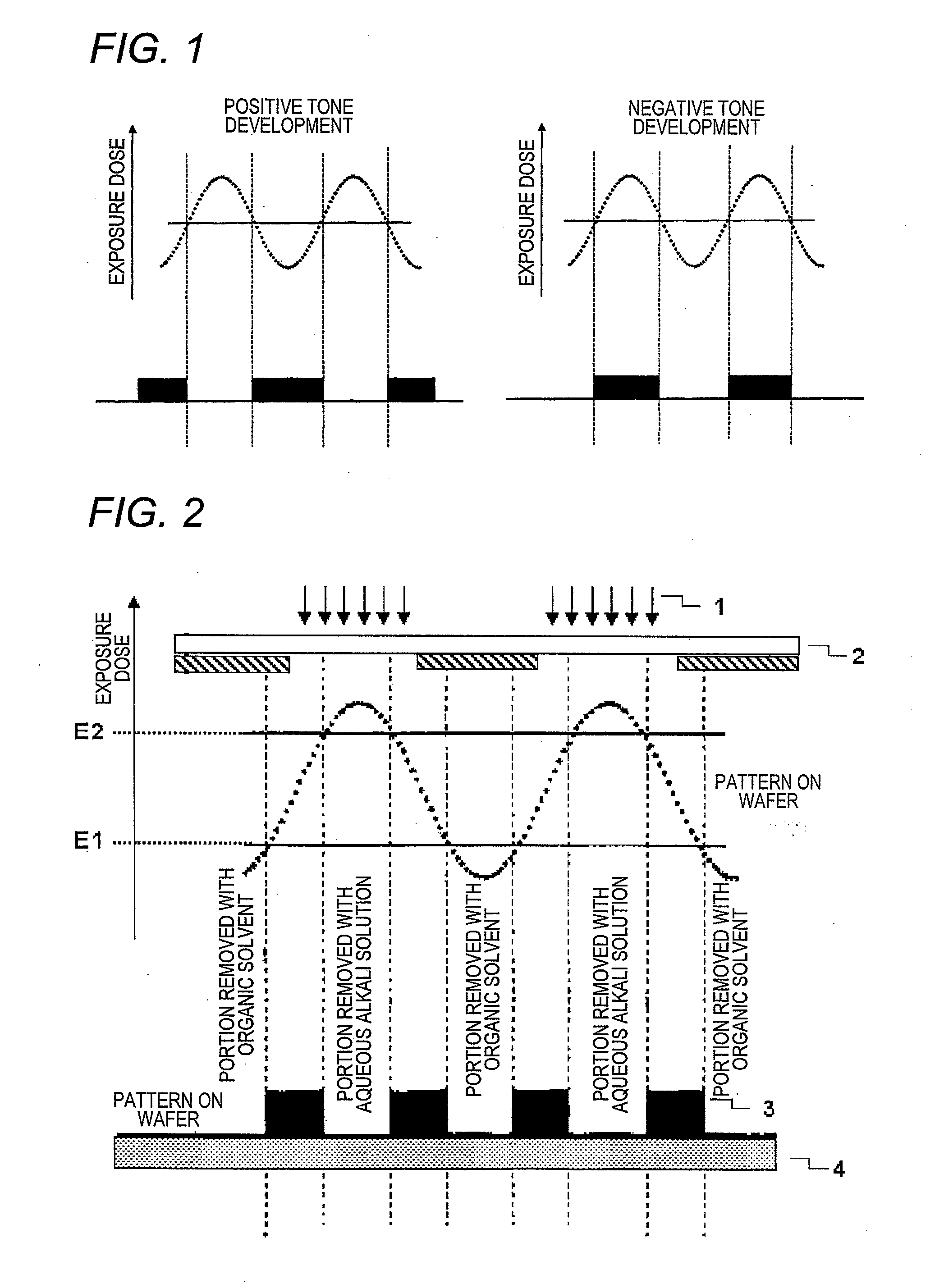
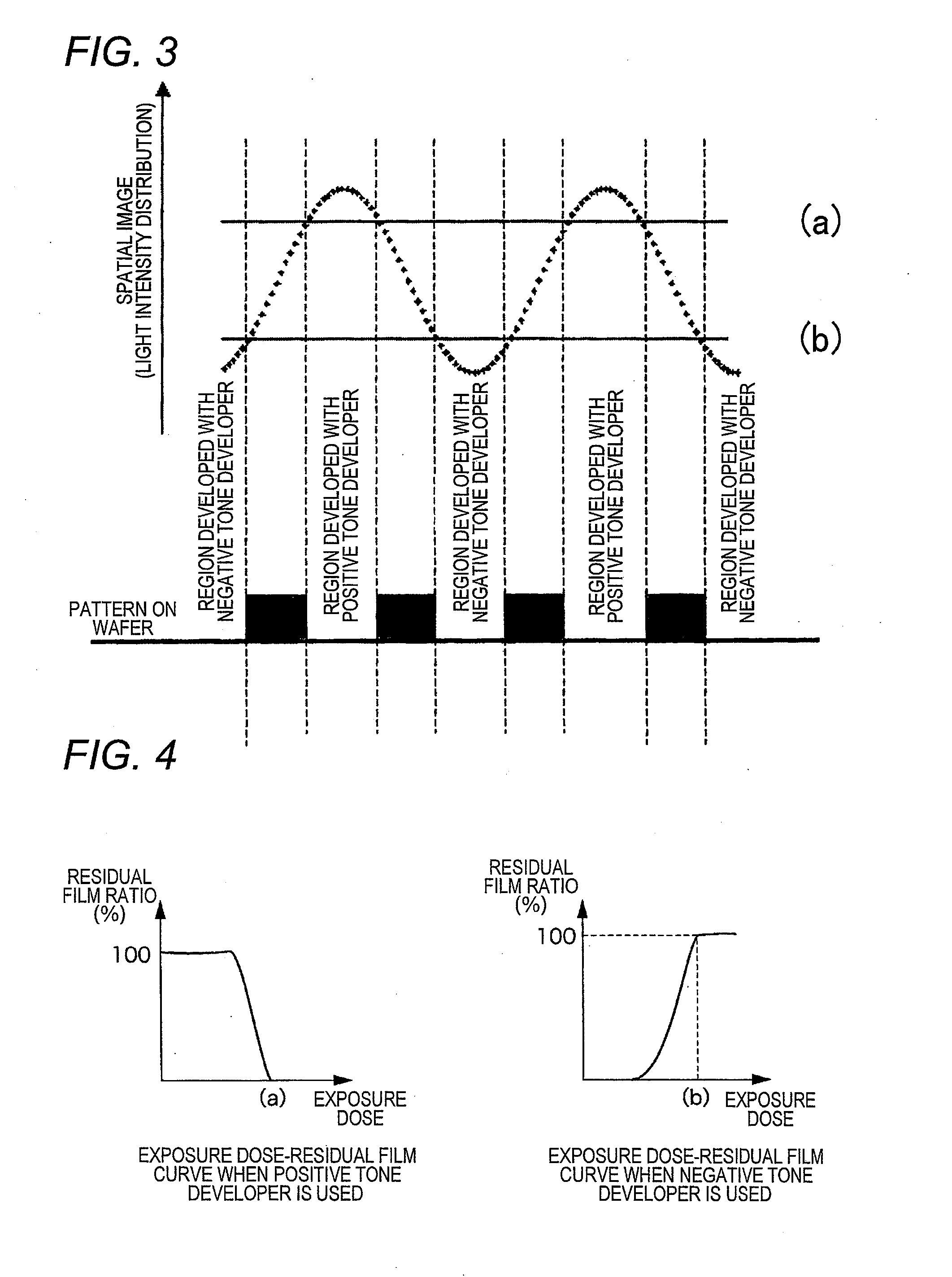
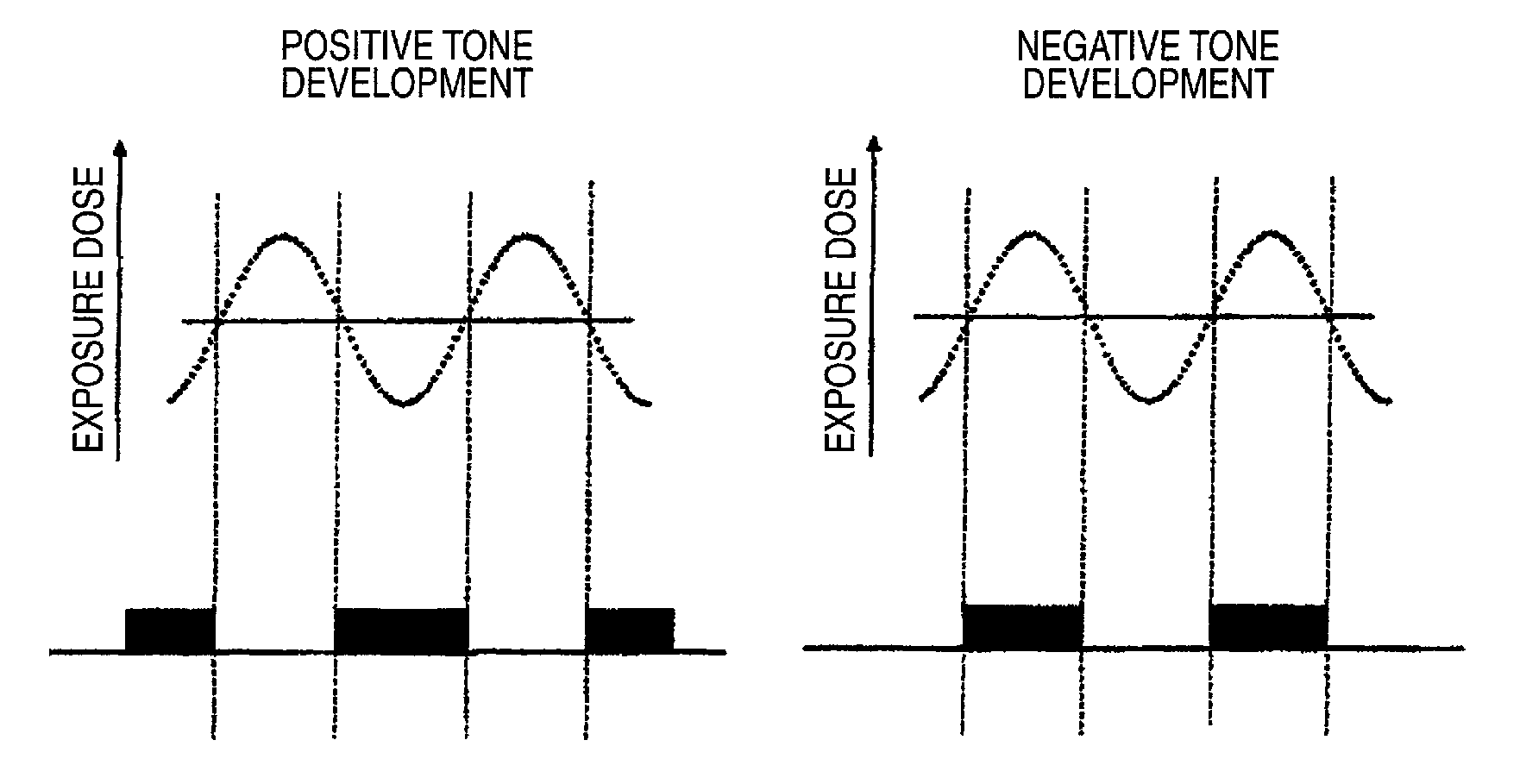
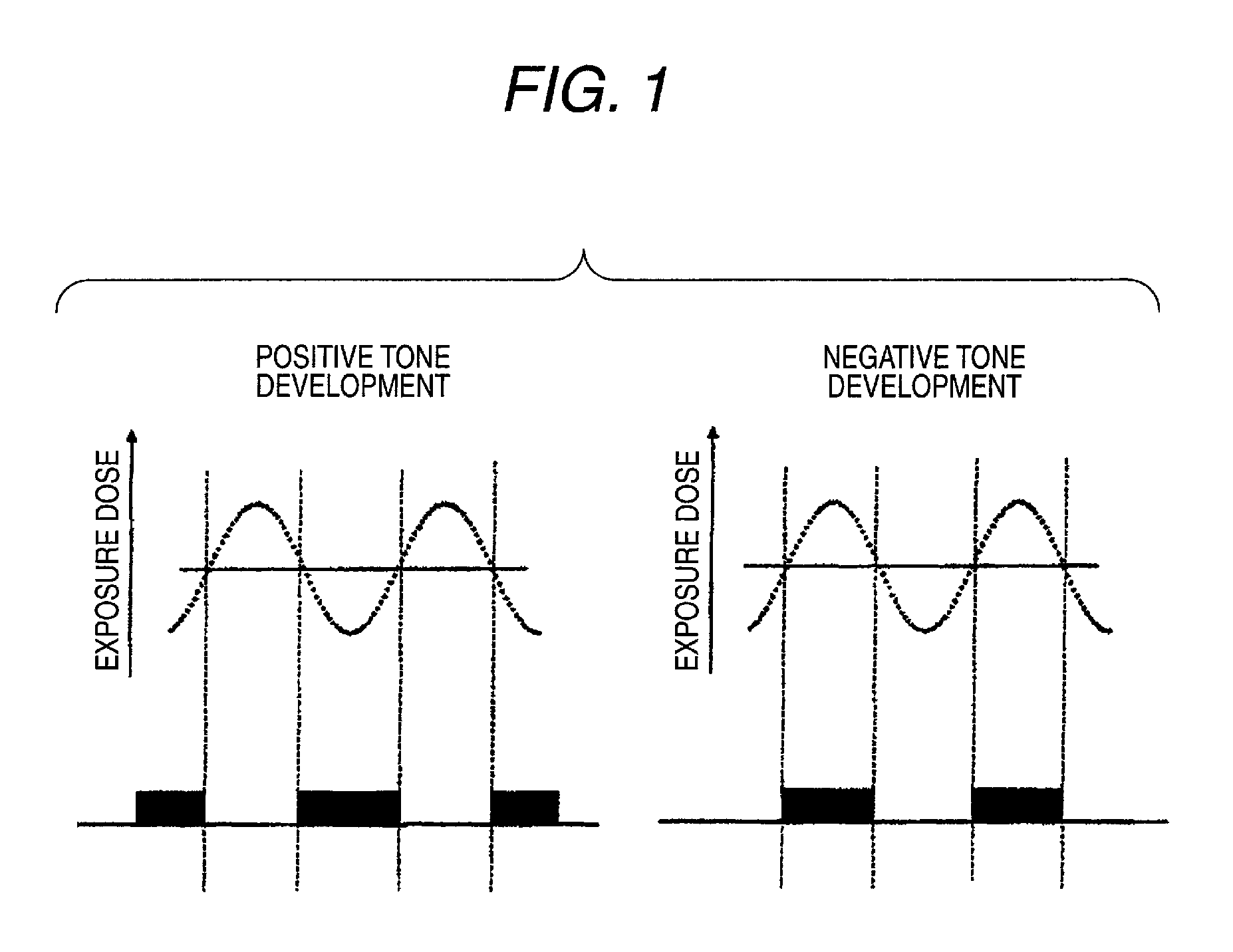
Pattern forming method, and resist composition, developer and rinsing solution used in the pattern forming method
InactiveUS20100040971A1Reduced line edge roughnessGood size uniformityPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusDispersityActinic Rays
A pattern forming method comprising a step of applying a resist composition whose solubility in a negative tone developer decreases upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation and which contains a resin having an alicyclic hydrocarbon structure and a dispersity of 1.7 or less and being capable of increasing the polarity by the action of an acid, an exposure step, and a development step using a negative tone developer; a resist composition for use in the method; and a developer and a rinsing solution for use in the method, are provided, whereby a pattern with reduced line edge roughness and high dimensional uniformity can be formed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Apparatus and method for determining orientation parameters of an elongate object
ActiveUS20050195387A1Apparent advantageInput/output for user-computer interactionAngle measurementSymmetric caseFluence
An apparatus and method employing principles of stereo vision for determining one or more orientation parameters and especially the second and third Euler angles θ, ψ of an elongate object whose tip is contacting a surface at a contact point. The apparatus has a projector mounted on the elongate object for illuminating the surface with a probe radiation in a known pattern from a first point of view and a detector mounted on the elongate object for detecting a scattered portion of the probe radiation returning from the surface to the elongate object from a second point of view. The orientation parameters are determined from a difference between the projected and detected probe radiation such as the difference between the shape of the feature produced by the projected probe radiation and the shape of the feature detected by the detector. The pattern of probe radiation is chosen to provide information for determination of the one or more orientation parameters and can include asymmetric patterns such as lines, ellipses, rectangles, polygons or the symmetric cases including circles, squares and regular polygons. To produce the patterns the projector can use a scanning arrangement or a structured light optic such as a holographic, diffractive, refractive or reflective element and any combinations thereof. The apparatus is suitable for determining the orientation of a jotting implement such as a pen, pencil or stylus.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
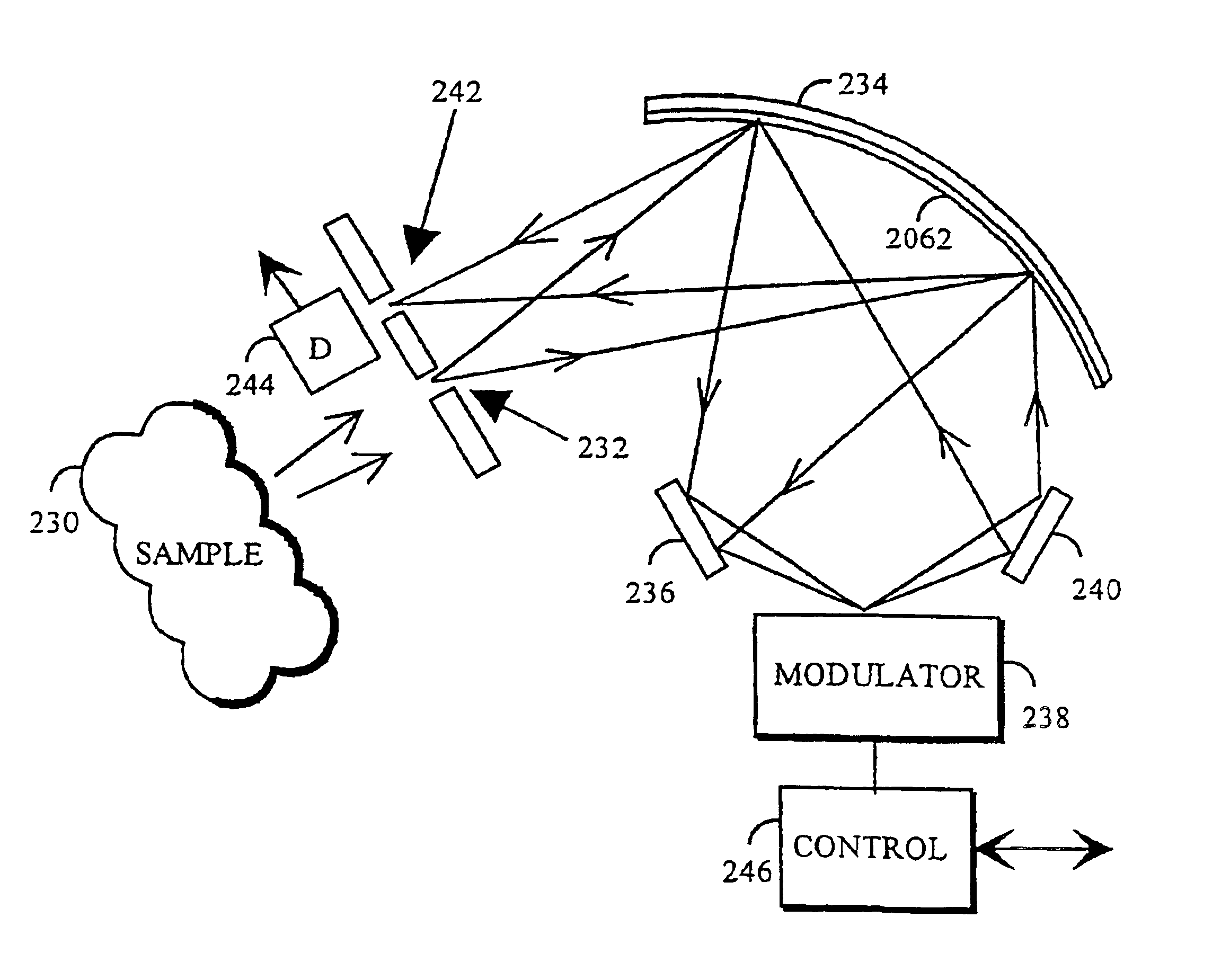
Spectrometer and method for measuring optical spectrum
InactiveUS6870619B1Reduce impactSmall surface areaRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical radiationFluence
An entrance slit of the spectrometer is illuminated with optical radiation. An optical component images the entrance slit to an optical modulator by the optical radiation and disperses the optical radiation into a spectrum. The spectrum is modulated by the optical modulator The optical component composes spectral non-dispersive measurement radiation of the spectrum and images the entrance slit included in the measurement radiation to an exit slit which may be the same one as the exit slit or a different one. Measurement radiation is detected from the entrance slit with a detector, which converts the measurement radiation into an electrical measurement signal.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Pattern forming method
ActiveUS7985534B2Increase exposureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusActinic RaysFluence
A pattern forming method, includes: (i) a step of applying a resist composition whose solubility in a positive tone developer increases and solubility in a negative tone developer decreases upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation, the resist composition containing a resin capable of increasing a polarity by the action of an acid; (ii) an exposure step; (iii) a step of performing development by using a negative tone developer to form a resist pattern; and (iv) a step of causing a crosslinked layer-forming material to act on the resist pattern to crosslink the resin constituting the resist pattern and the crosslinked layer-forming material, thereby forming a crosslinked layer. According to the present invention, a method for forming a pattern having an effectively micro-dimensioned trench or hole pattern without generation of a scum is provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiation sources and radiation scanning systems with improved uniformity of radiation intensity
InactiveUS6954515B2Uniform radiation intensityImproved intensity distributionRadiation/particle handlingCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingFluenceX-ray
A radiation source is disclosed comprising a source of charged particles that travel along a path. Target material lies along the path to generate radiation upon impact by the beam. A magnet is provided to deflect the beam prior to impacting the target. The magnet may generate a time-varying magnetic field or a constant magnetic field. A constant magnetic field may be varied spatially across the beam. The magnet may be an electromagnet or a permanent magnet. In one example, deflection of the beam results in impact of the beam on the target along a plurality of axes. In another example, portions of the beam are differentially deflected. The source may thereby irradiate an object to be scanned with more uniform radiation. The charged particles may be electrons or protons and the radiation may be X-ray or gamma ray radiation, or neutrons. Scanning systems incorporating such sources, methods of generating radiation and methods of examining objects are disclosed, as well.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Automated plant analysis method, apparatus, and system using imaging technologies
ActiveUS20030142852A1Promotes good identificationPromotes discriminationRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesPlant rootsCyst
The present invention relates to an apparatus, method, software algorithm and system for evaluating plants for conditions or characteristics. In one aspect, the method can include imaging at least a portion of the plant and evaluating the image for discriminating condition(s) or characteristic(s) of interest. In one example, soybean roots are imaged and the image is evaluated to discriminate between soybean cyst nematode (SCN) cysts and the plant roots to count the number of SCN cysts for the plant. In another embodiment, a plant is illuminated by a ultra-violet radiation selected to cause photo-induced fluorescence of a target, e.g. SCN cysts. The fluorescence emitted is collected and analyzed to discriminate between the target and the remainder of the plant.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
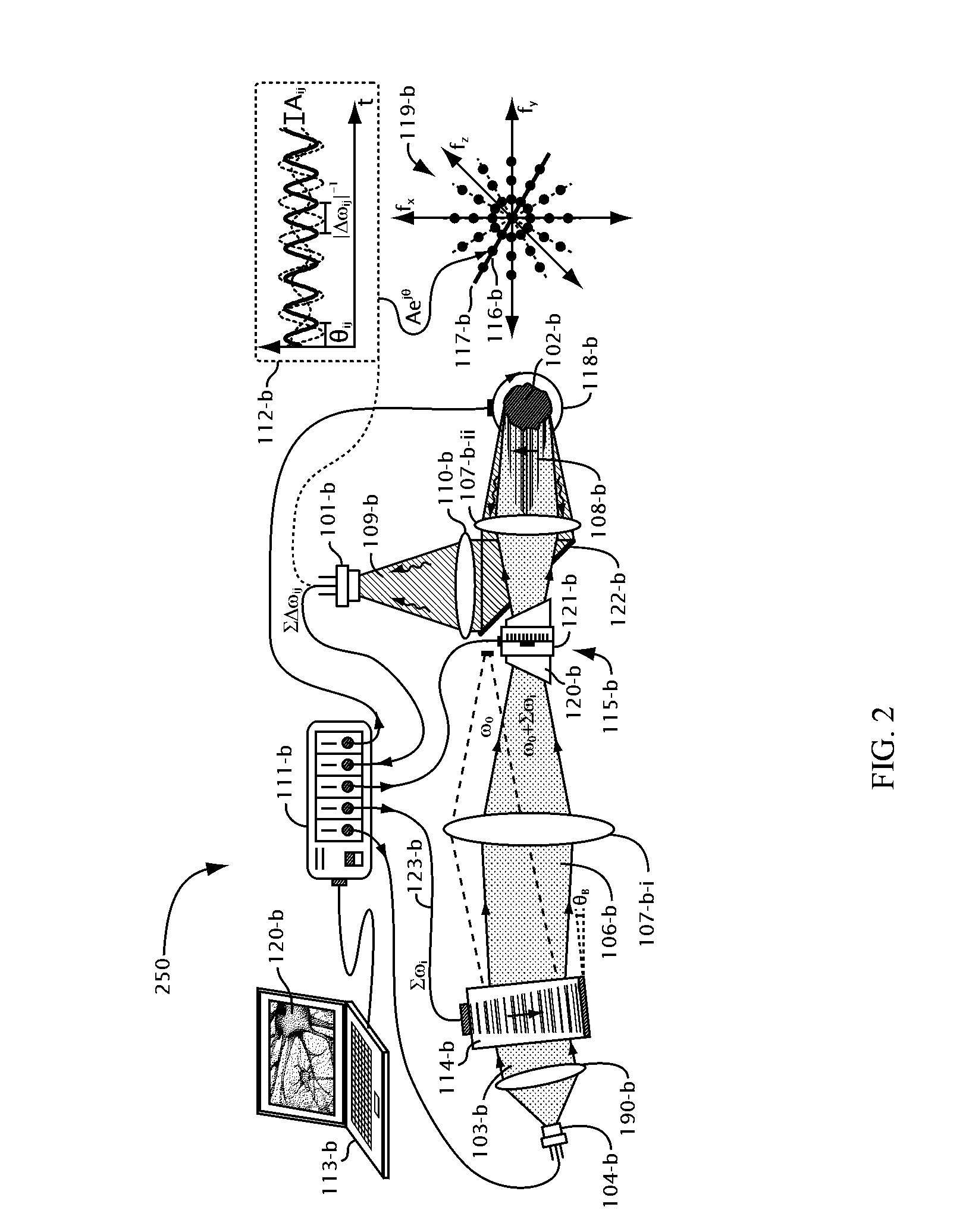
Fourier domain sensing
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are provided for measuring one or more sinusoidal Fourier components of an object. A structured second radiation is generated by spatially modulating a first radiation. The structured second radiation illuminates the object, The structured second radiation is scaled and oriented relative to the object. The object produces a third radiation in response to the illuminating. A single-element detector detects a portion of the third radiation from multiple locations on the object substantially simultaneously for each spatial modulation of the first radiation and for each orientation of the second radiation. A time-varying signal is produced based on said detected portion of the third radiations. One or more characteristics of the one or more sinusoidal Fourier components of the object are estimated based on the time-varying signal.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Ink composition, inkjet recording method, printed material, and process for producing lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS20070211111A1Improve curing effectImprove adhesionDuplicating/marking methodsInksFluencePlanographic printing
An ink composition is provided that includes (A) an N-vinyllactam, (B) a radically polymerizable compound, and (C) a polymerization initiator, the content of the N-vinyllactam (A) being at least 10 wt % of the ink total weight, and the content ratio by weight of (A):(B) being 1:8.5 to 1:1. There is also provided an inkjet recording method that includes (a1) a step of discharging the ink composition onto a recording medium and (b1) a step of curing the ink composition by irradiating the discharged ink composition with actinic radiation. A printed material recorded by the inkjet recording method is also provided. Furthermore, a process for producing a lithographic printing plate is provided that includes (a2) a step of discharging the ink composition onto a hydrophilic support and (b2) a step of curing the ink composition by irradiating the discharged ink composition with actinic radiation so as to form a hydrophobic image on the hydrophilic support by curing the ink composition.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
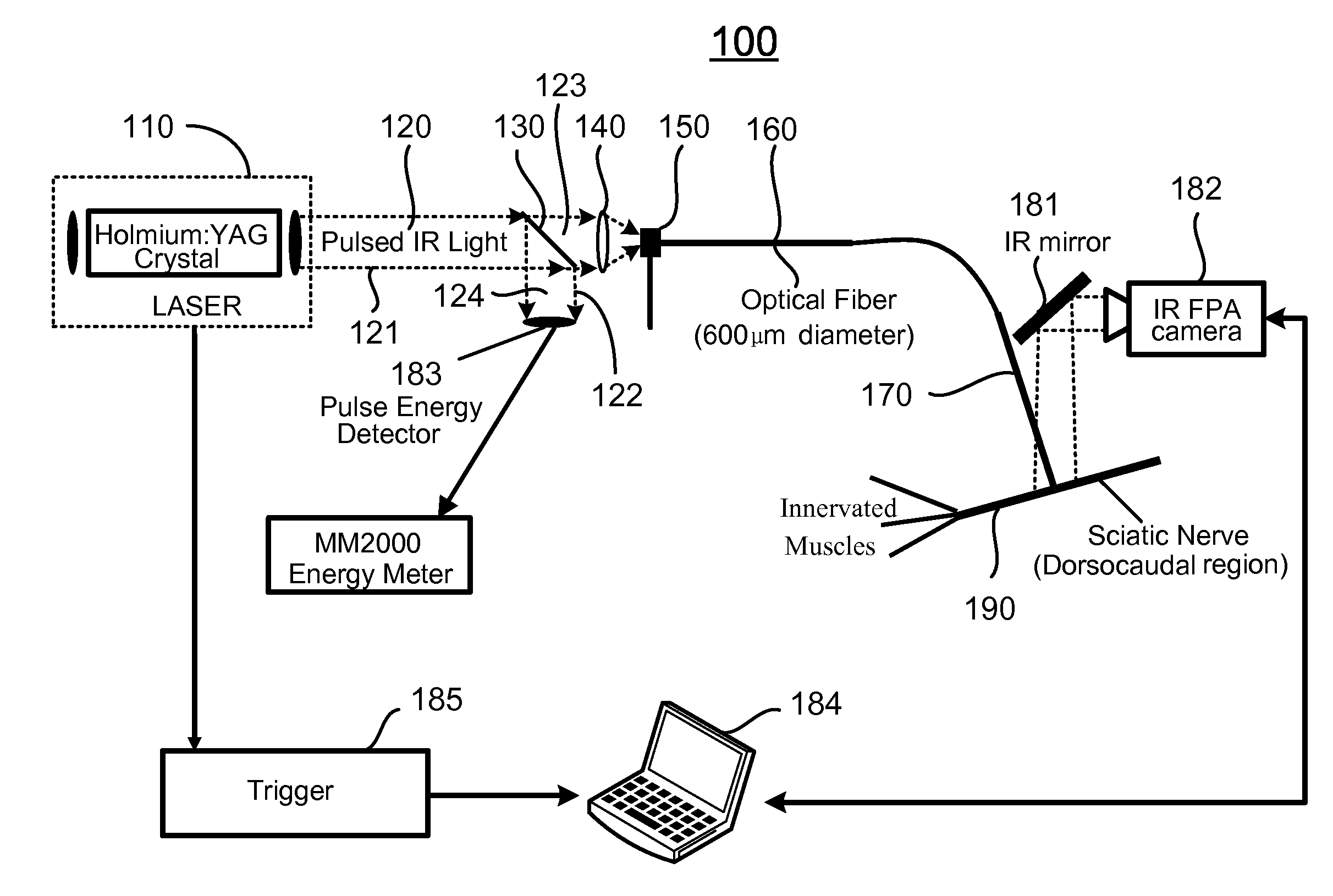
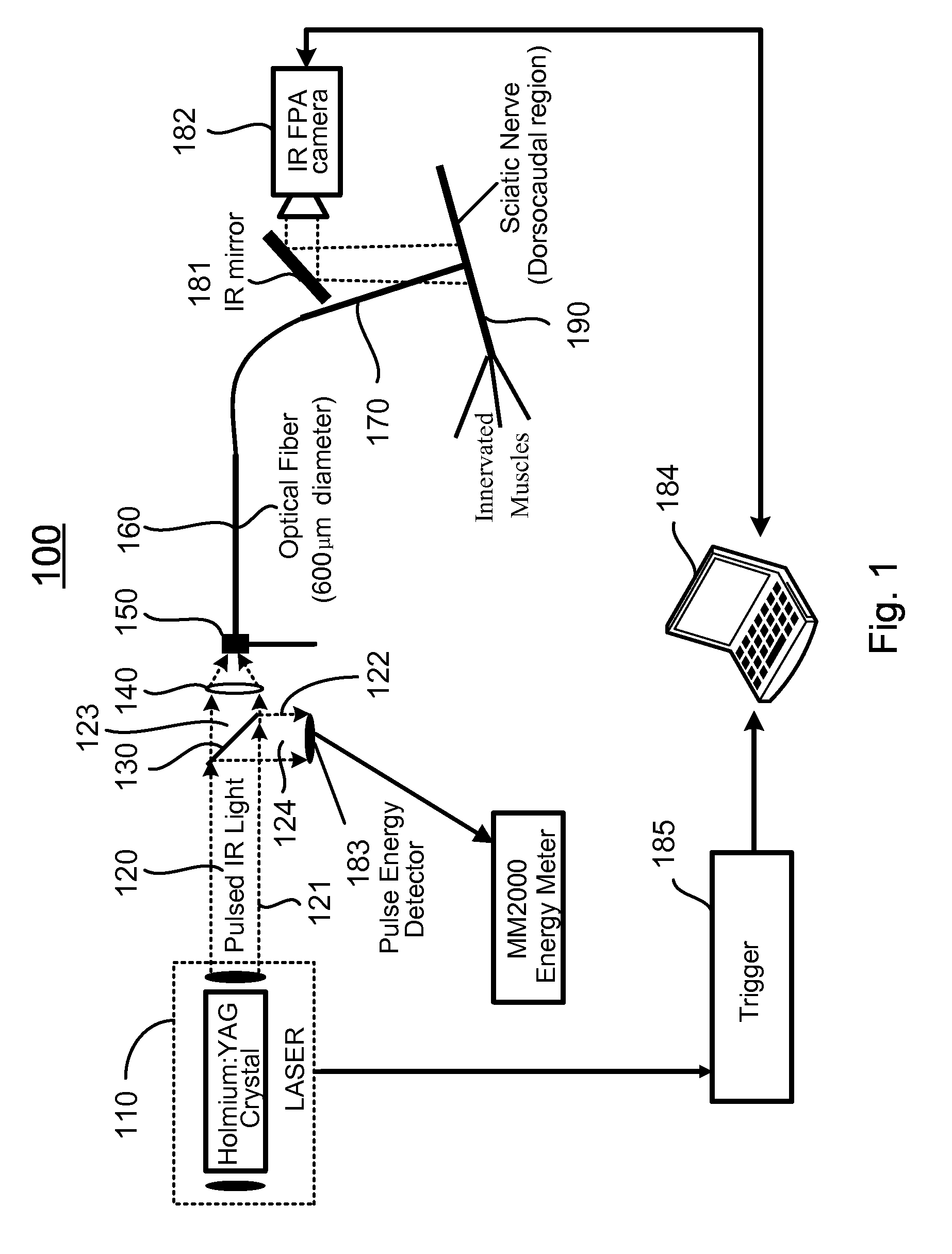
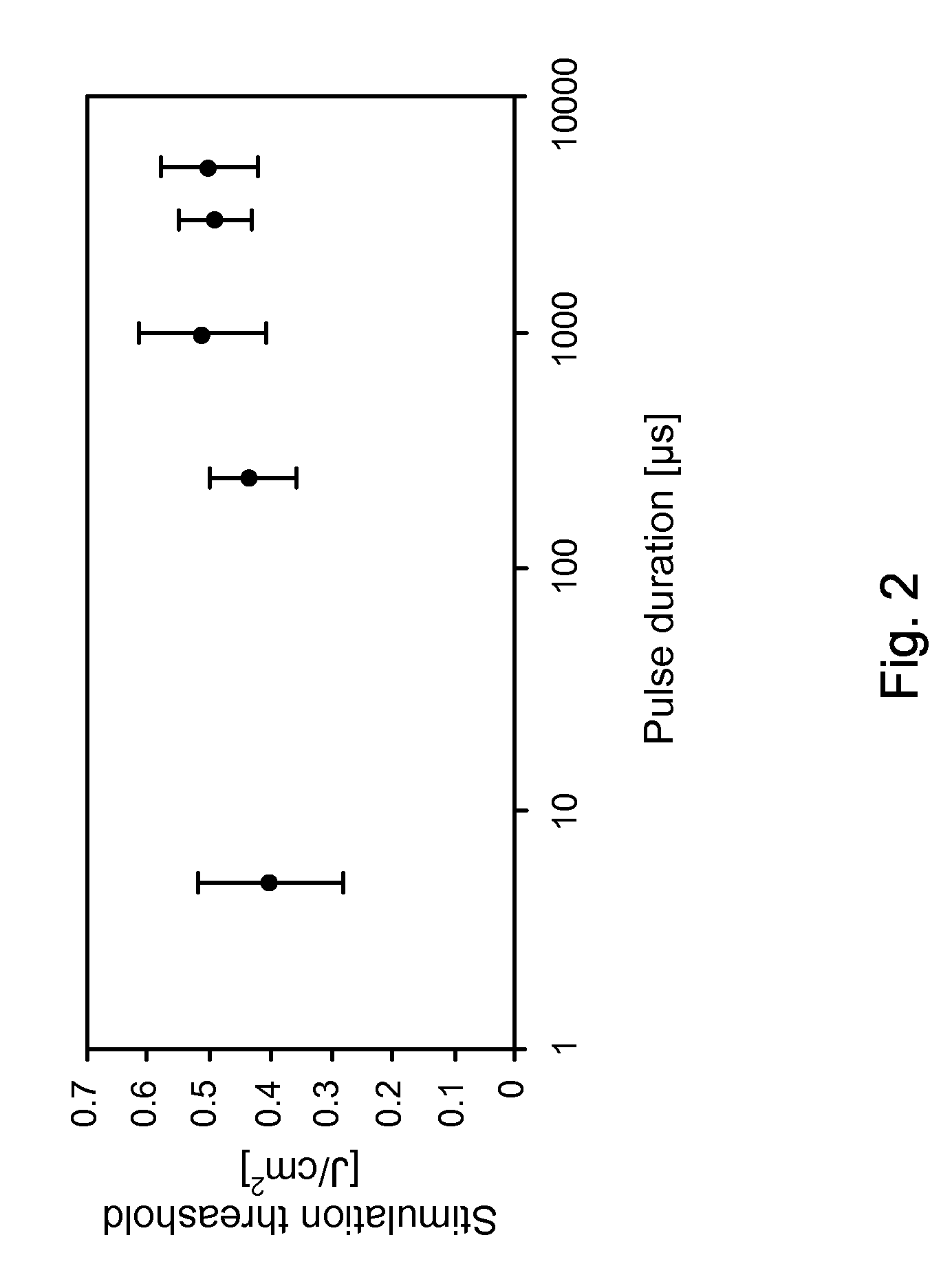
Apparatus and methods for optical stimulation of neural tissues
InactiveUS20090069871A1Minimal tissue damageSubstantial temperature increaseDiagnosticsSurgeryFluenceOptical stimulation
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a method for stimulating neural tissue of a living subject. In one embodiment, the method has the steps of generating at least one beam of radiation; introducing at least one of one or more chromophores and one or more optical agents to a target neural tissue; and delivering the at least one beam of radiation to the target neural tissue, wherein the at least one beam of radiation is delivered with a radiant exposure that causes a thermal gradient in the target neural tissue, thereby stimulating the target neural tissue.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
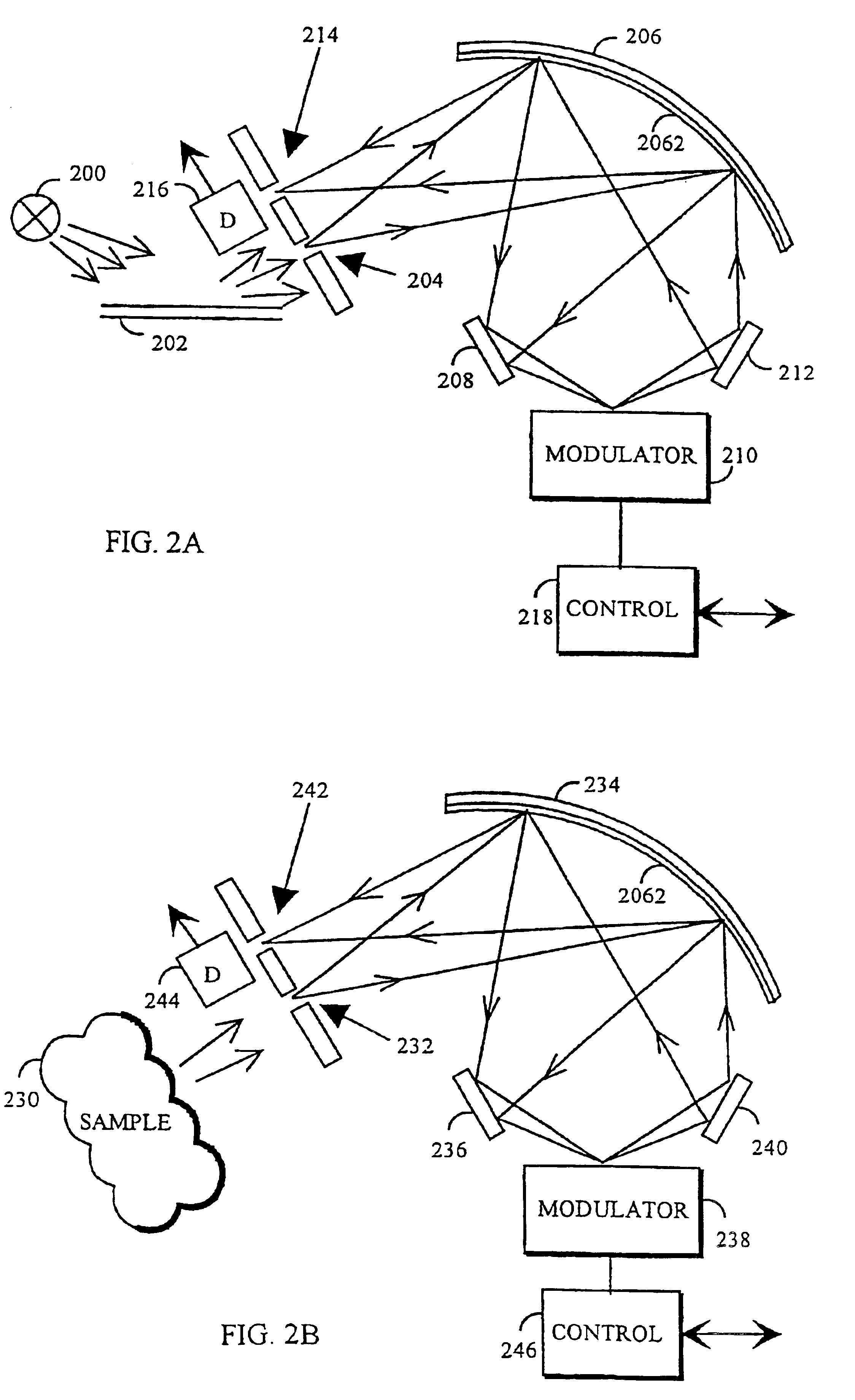
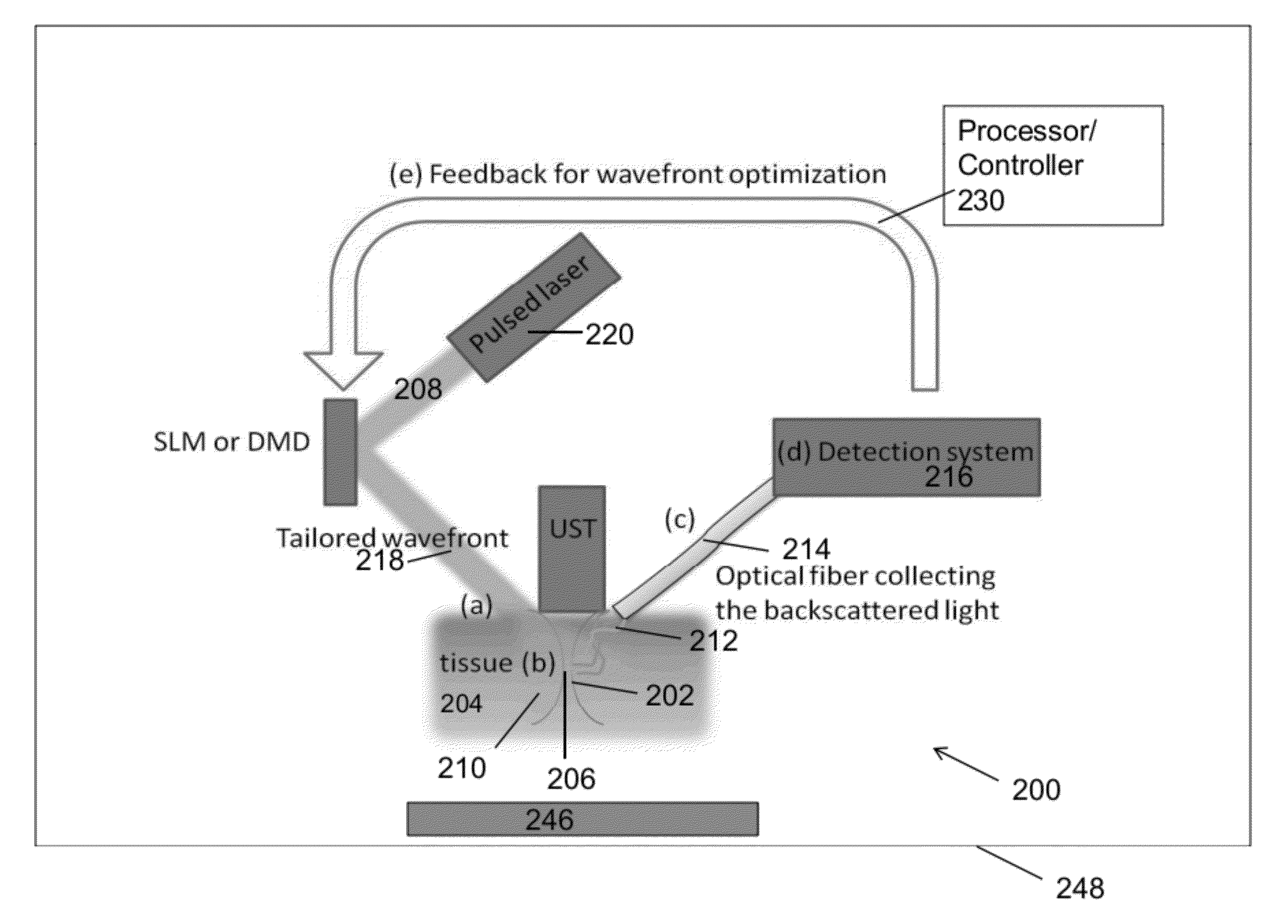
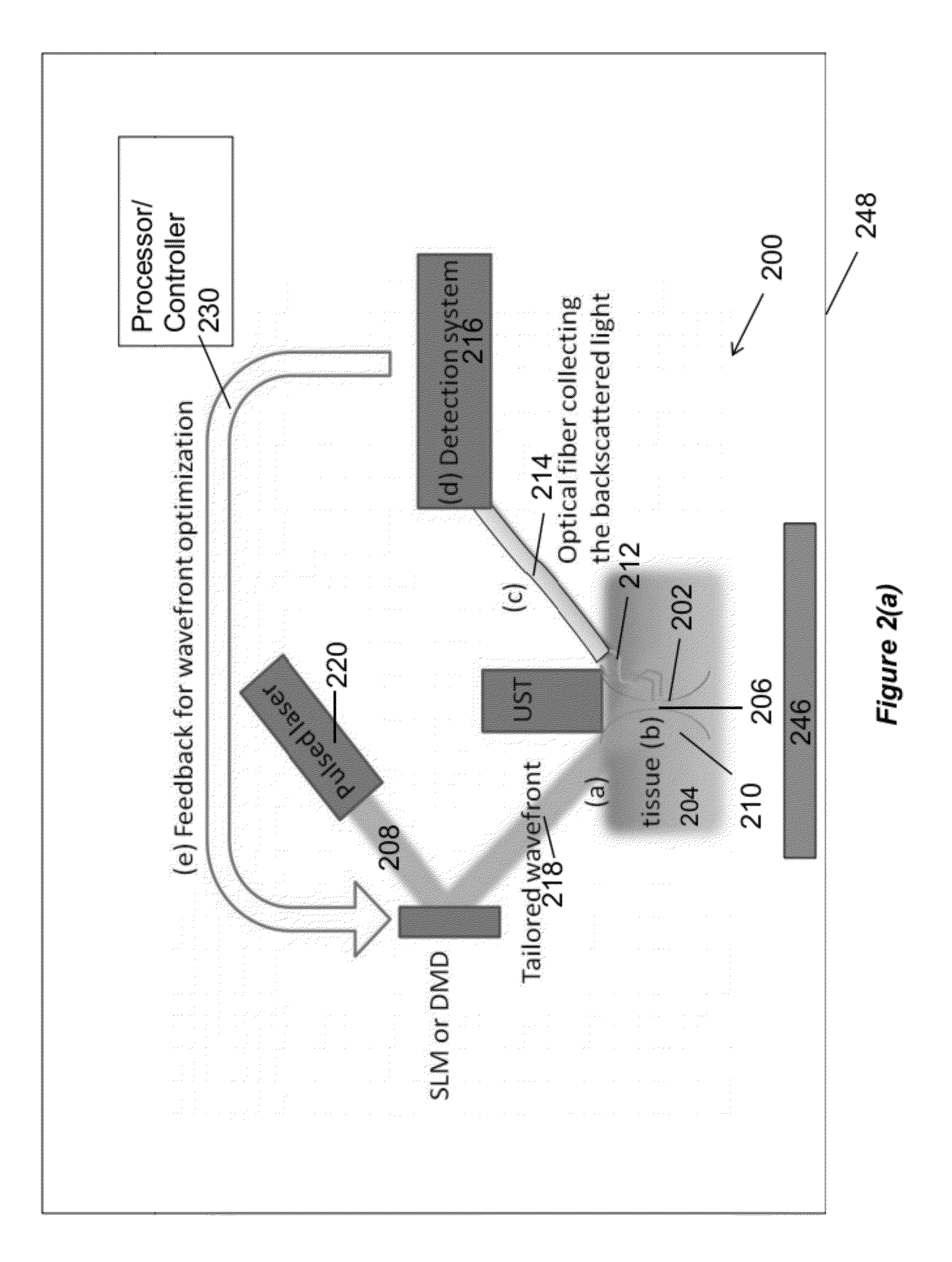
Acoustic-assisted iterative wave form optimization for deep tissue focusing
ActiveUS20120070817A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWavefrontFluence
A method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for irradiating one or more targets within a sample with electromagnetic (EM) radiation. One or more targets within the sample are controllably defined with an acoustic field. The sample is irradiated with input EM radiation having an input wavefront. An amount of frequency shifted EM radiation is detected, wherein at least some of the input EM radiation that passes through the acoustic field at the targets is shifted in frequency to form the frequency shifted EM radiation. The input wavefront is modified, using feedback comprising the amount of the frequency shifted EM radiation that is detected, into a modified wavefront. The sample is irradiated using the input EM radiation comprising the modified wavefront, and the process is repeated as desired.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com