Patents
Literature
6413 results about "Ionization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ionization or ionisation, is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes.The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.
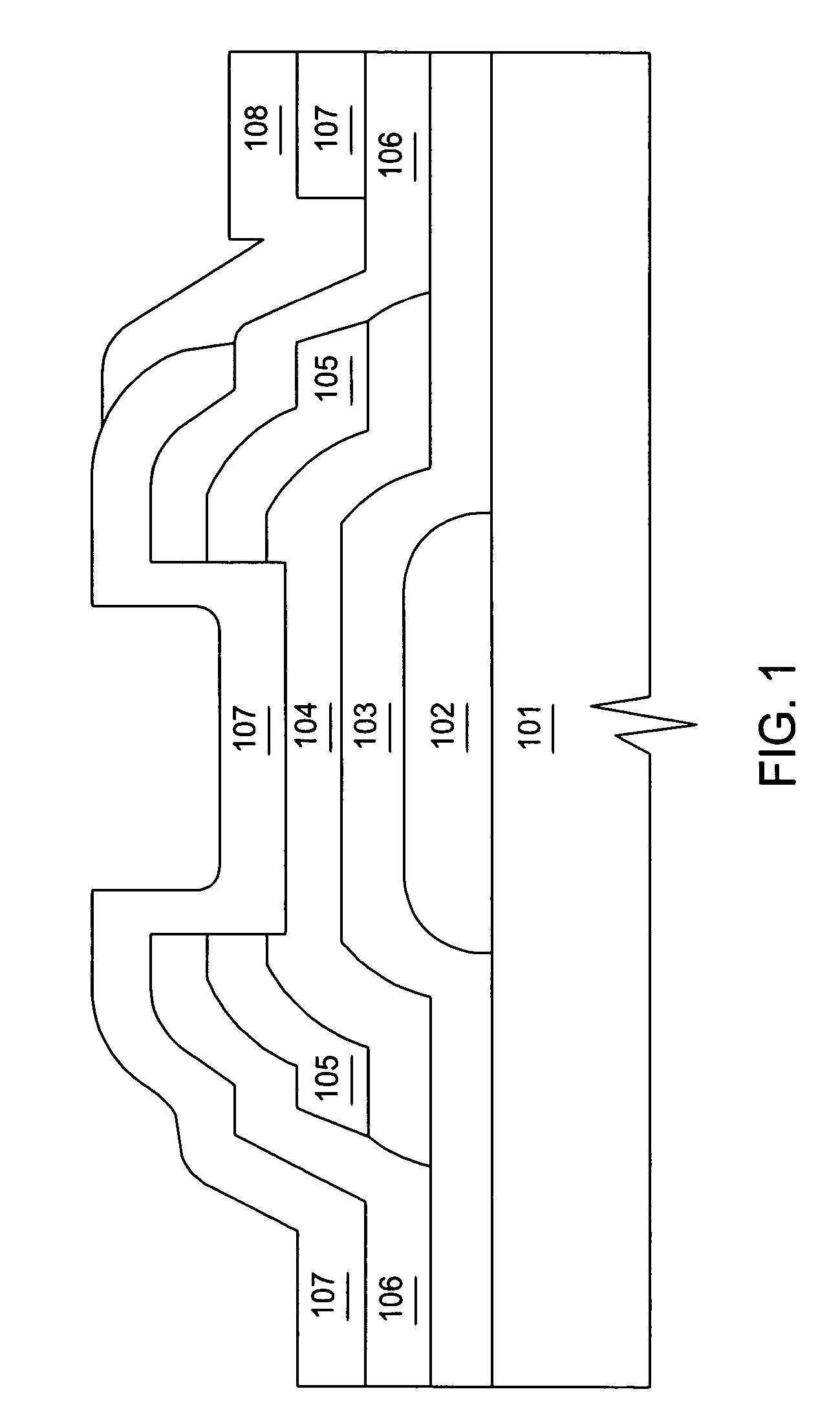
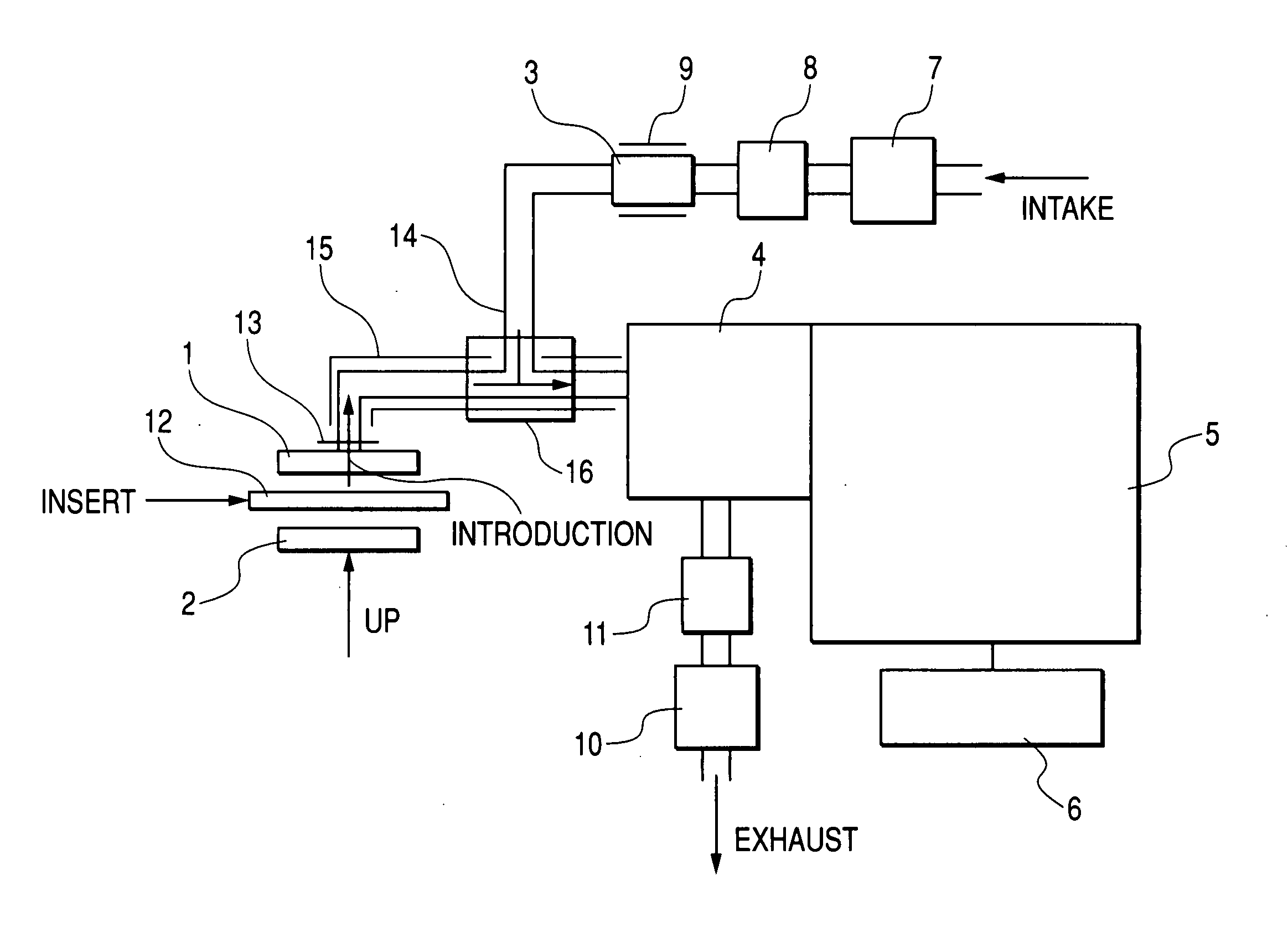
Method for sterilizing medical appliance
InactiveCN1634601AAvoid influenceImprove sterilization effectDiagnosticsSurgeryVacuum pressureMicrowave
A medical instrument sterilization method is disclosed, which characterizes in following process: pending medical instrument for sterilization treatment being placed in a closed container, then being vacuum pumped, the vacuum pressure of the container being controlled between 1 Pa to 1500 Pa, air and / or oxygen and / or inert gases are charged to closed container and the vacuum pressure being between 1 Pa to 1500 Pa, microwave is fed, the favorable power of which should make the gas charged into the container to generate ionization, the microwave be cut after the sterilization, then air being charged to release vacuum to finish the whole process.
Owner:吉林省中立实业有限公司
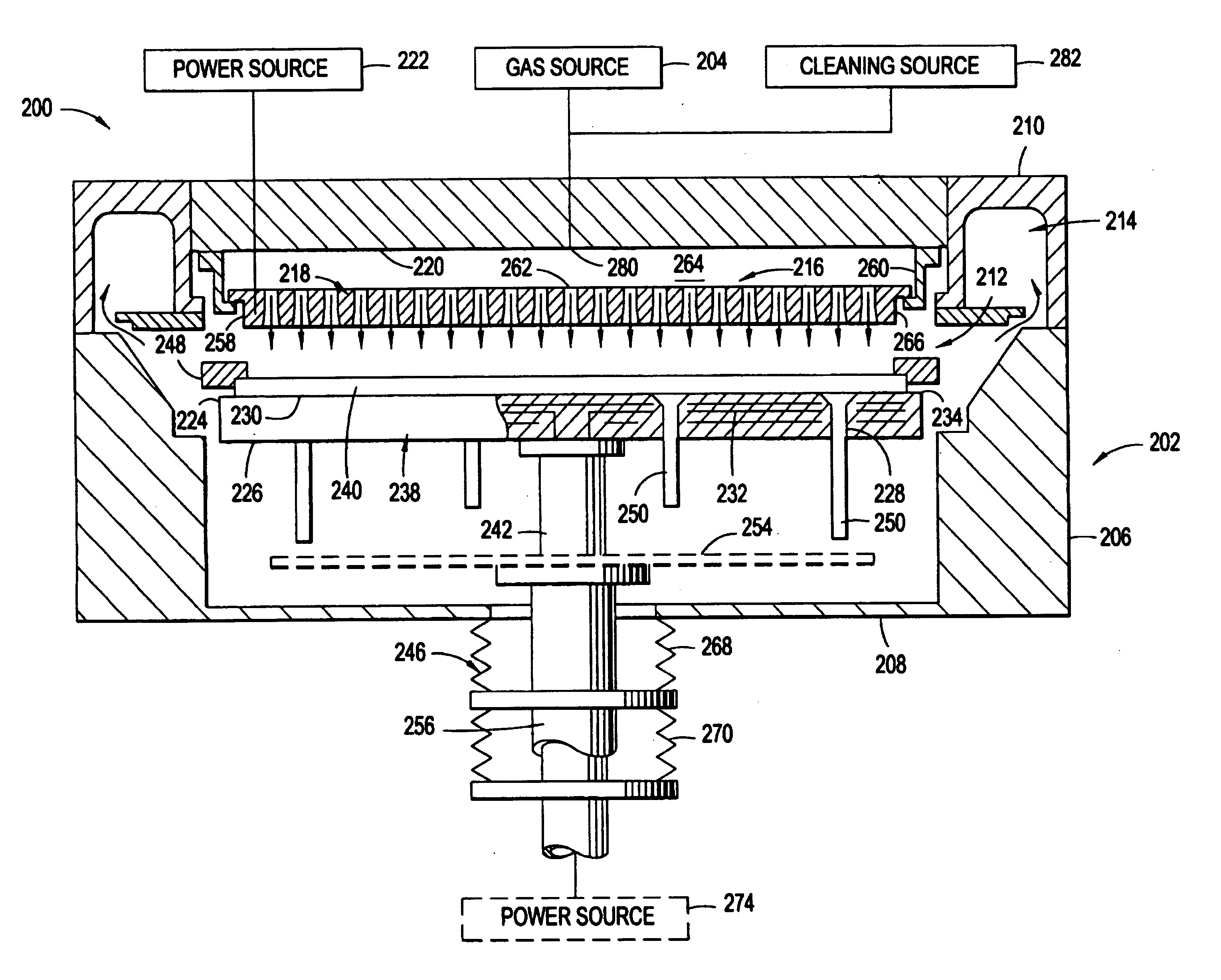
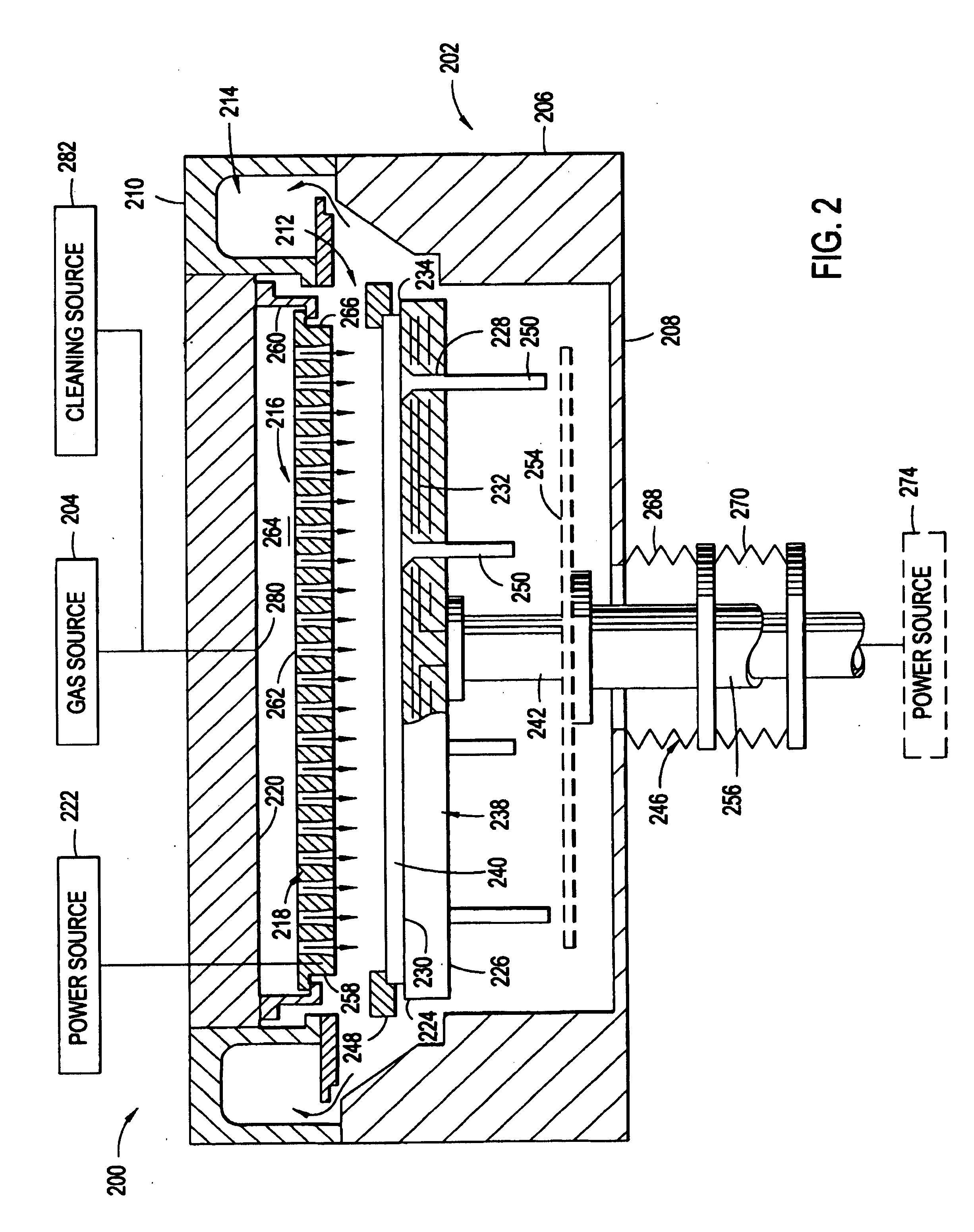
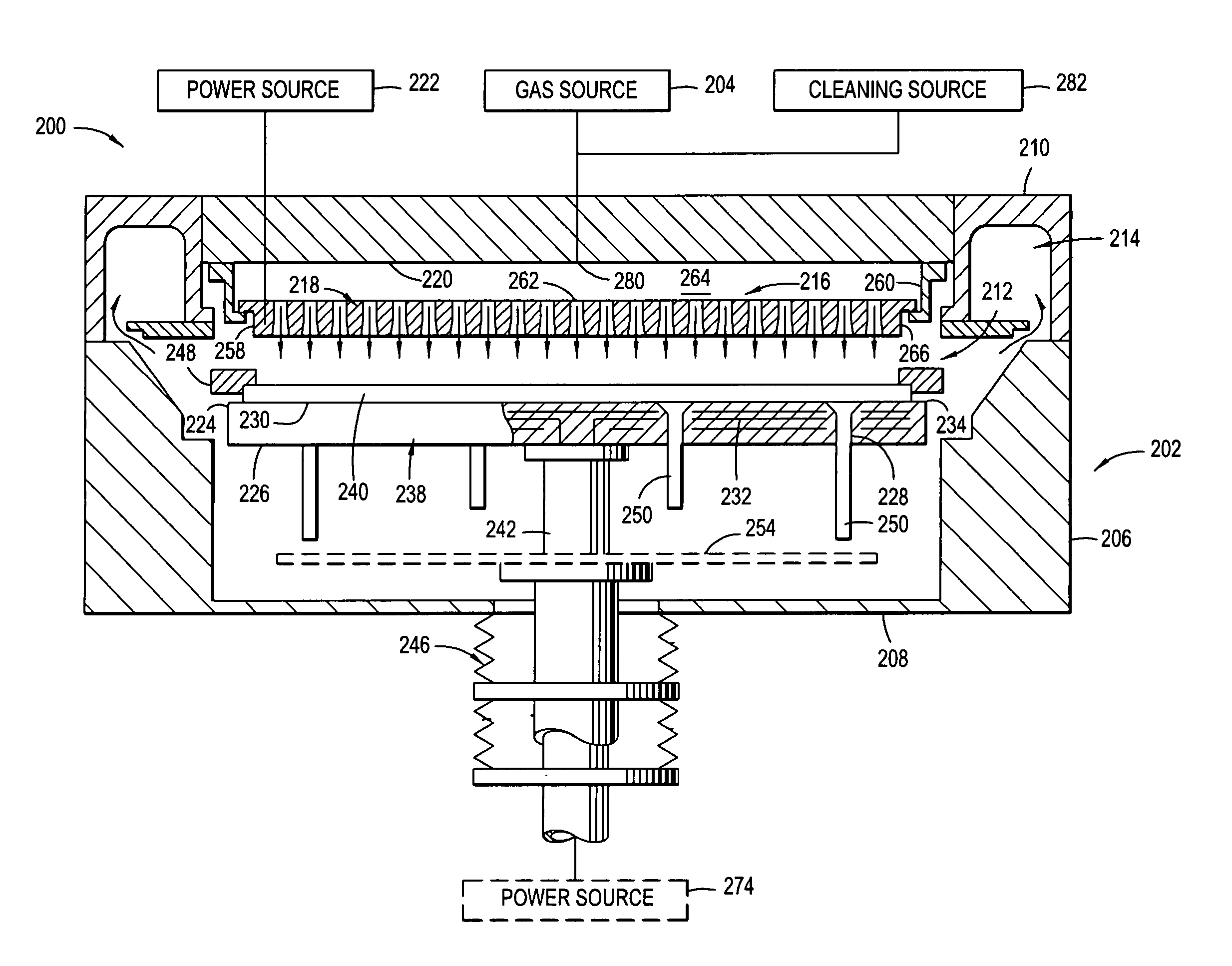
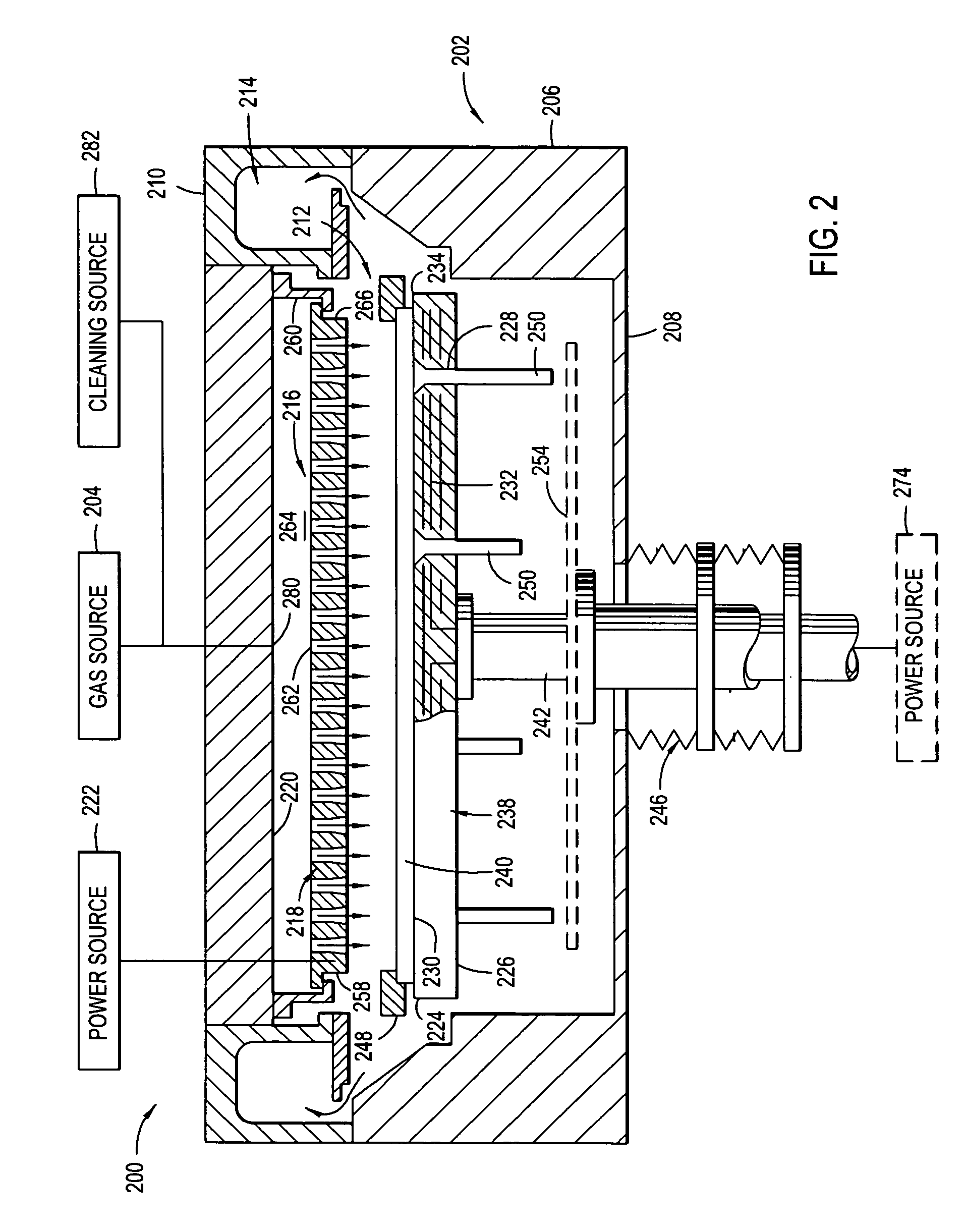
Plasma uniformity control by gas diffuser hole design
ActiveUS20050251990A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
Embodiments of a gas diffuser plate for distributing gas in a processing chamber are provided. The gas distribution plate includes a diffuser plate having an upstream side and a downstream side, and a plurality of gas passages passing between the upstream and downstream sides of the diffuser plate. The gas passages include hollow cathode cavities at the downstream side to enhance plasma ionization. The depths, the diameters, the surface area and density of hollow cathode cavities of the gas passages that extend to the downstream end can be gradually increased from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate to improve the film thickness and property uniformity across the substrate. The increasing diameters, depths and surface areas from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate can be created by bending the diffuser plate toward downstream side, followed by machining out the convex downstream side. Bending the diffuser plate can be accomplished by a thermal process or a vacuum process. The increasing diameters, depths and surface areas from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate can also be created computer numerically controlled machining. Diffuser plates with gradually increasing diameters, depths and surface areas of the hollow cathode cavities from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate have been shown to produce improved uniformities of film thickness and film properties.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plasma uniformity control by gas diffuser hole design
InactiveUS20060236934A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
Embodiments of a gas diffuser plate for distributing gas in a processing chamber are provided. The gas distribution plate includes a diffuser plate having an upstream side and a downstream side, and a plurality of gas passages passing between the upstream and downstream sides of the diffuser plate. The gas passages include hollow cathode cavities at the downstream side to enhance plasma ionization. The depths, the diameters, the surface area and density of hollow cathode cavities of the gas passages that extend to the downstream end can be gradually increased from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate to improve the film thickness and property uniformity across the substrate. The increasing diameters, depths and surface areas from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate can be created by bending the diffuser plate toward downstream side, followed by machining out the convex downstream side. Bending the diffuser plate can be accomplished by a thermal process or a vacuum process. The increasing diameters, depths and surface areas from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate can also be created computer numerically controlled machining. Diffuser plates with gradually increasing diameters, depths and surface areas of the hollow cathode cavities from the center to the edge of the diffuser plate have been shown to produce improved uniformities of film thickness and film properties.
Owner:CHOI SOO YOUNG +9
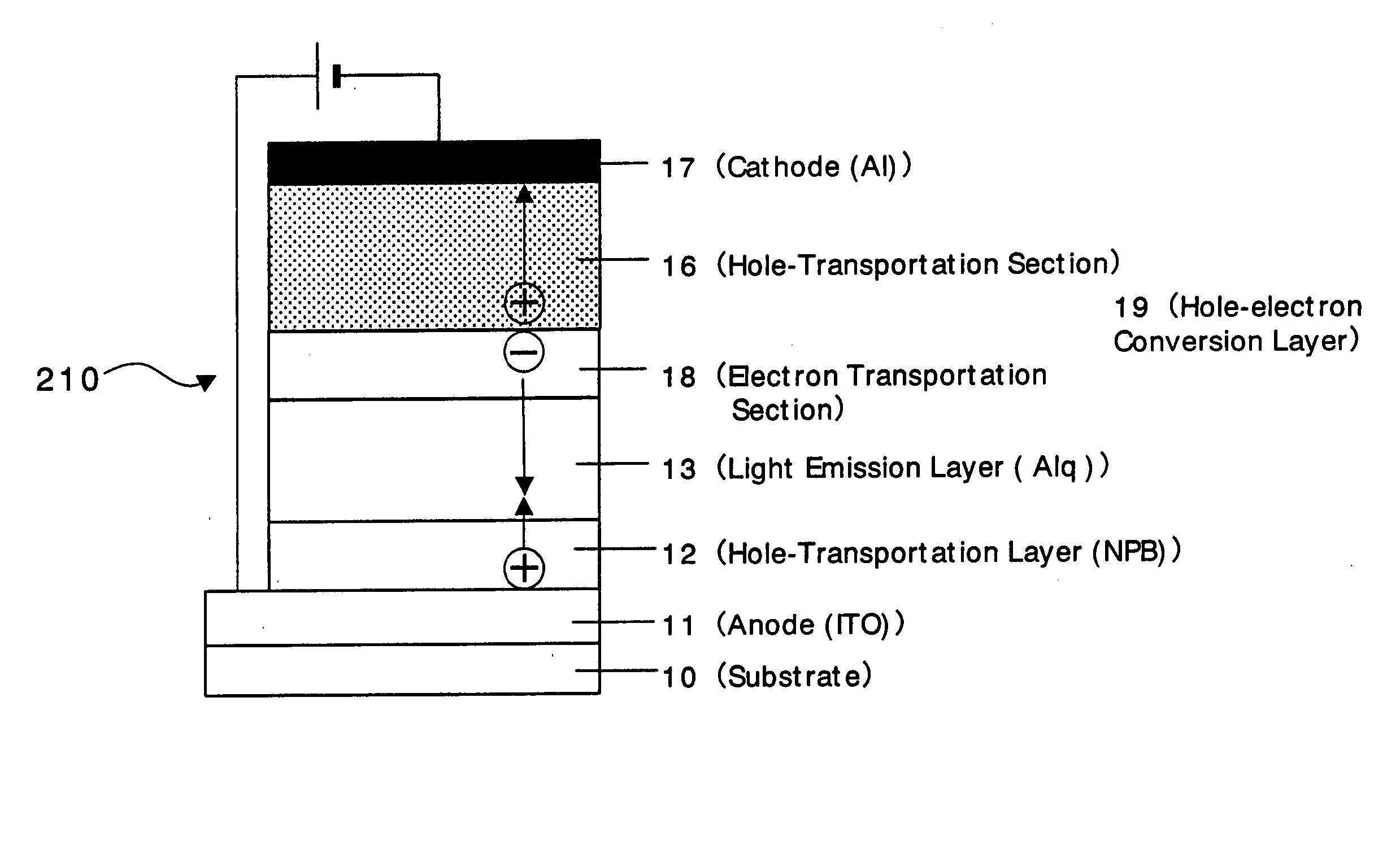
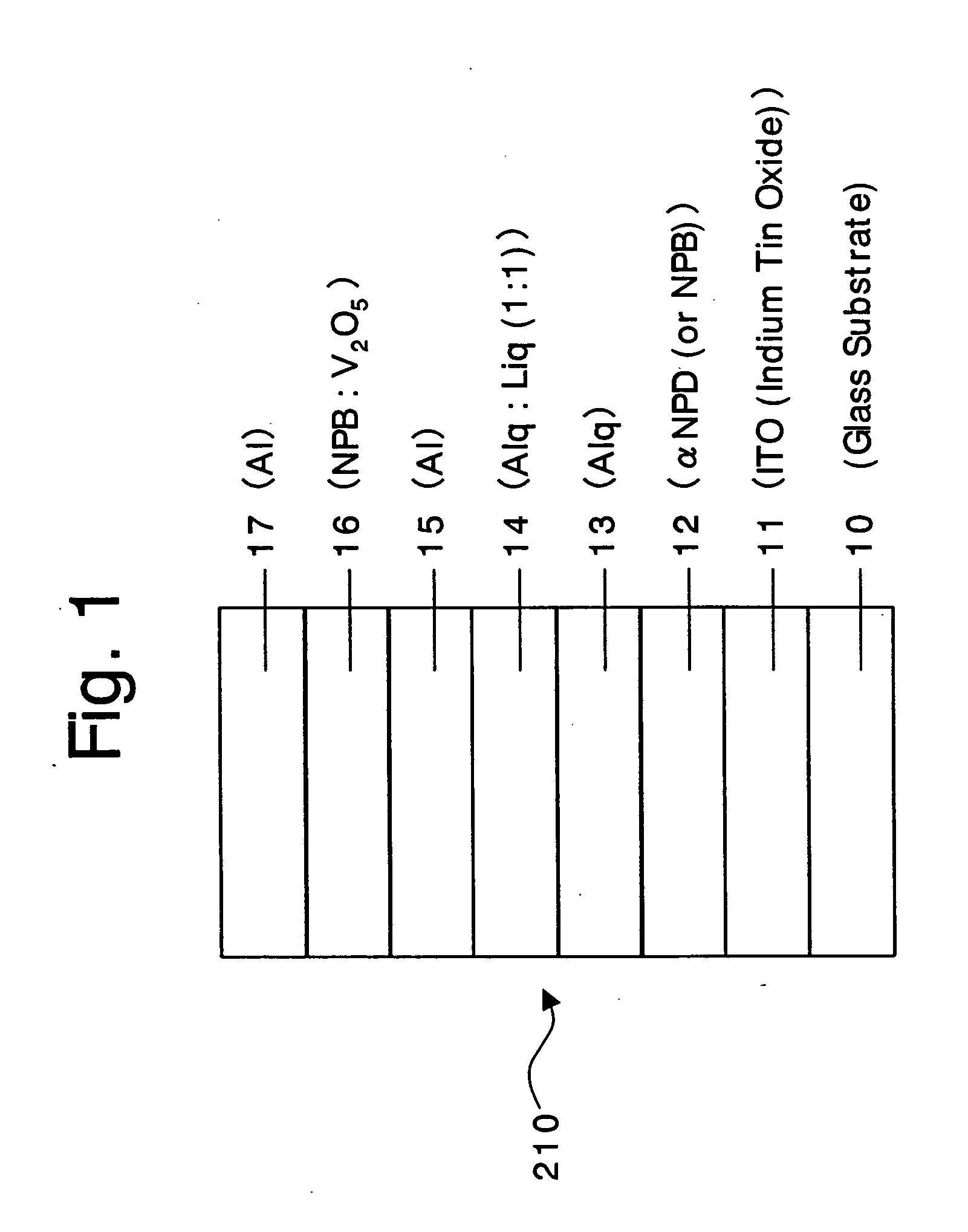
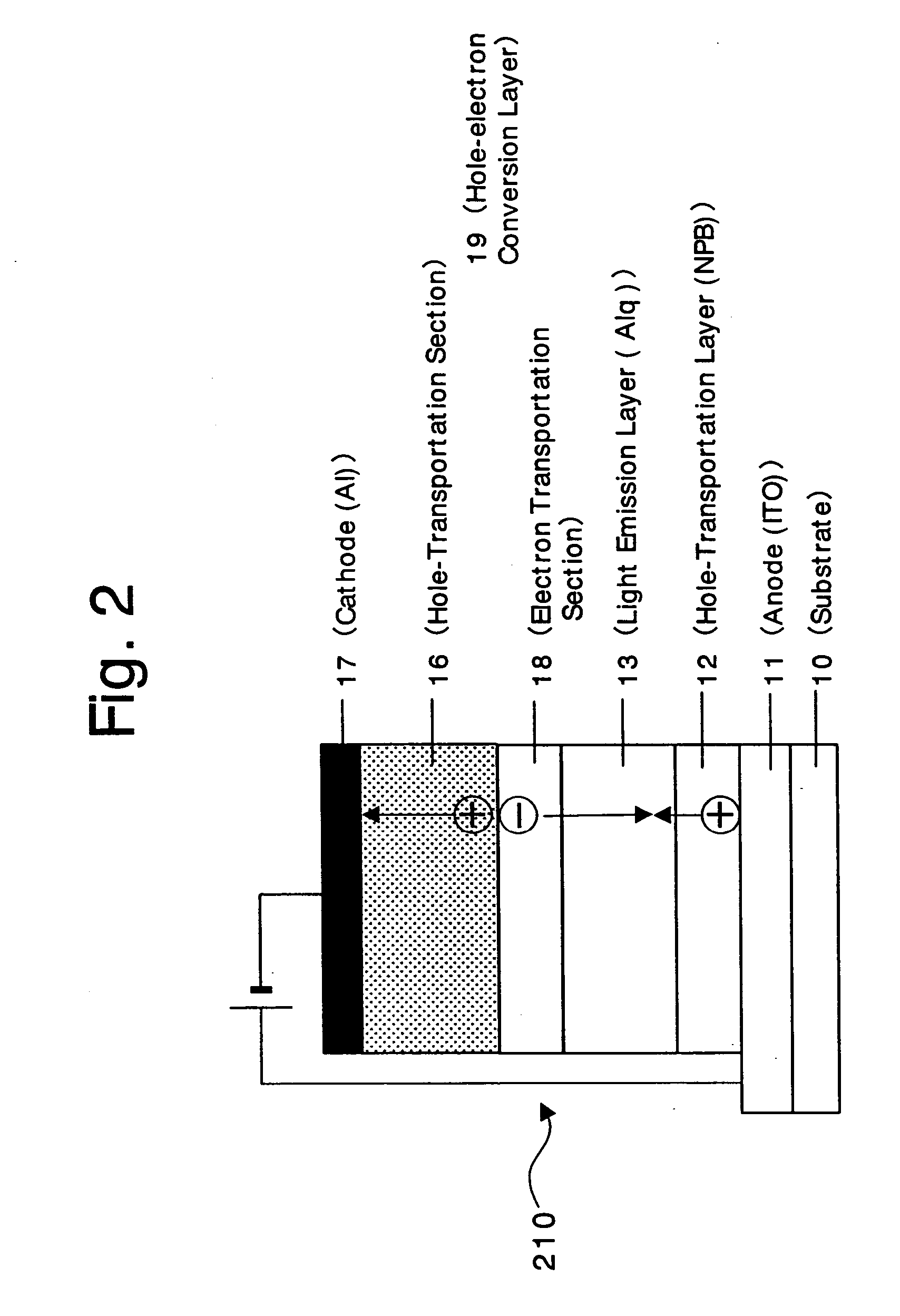
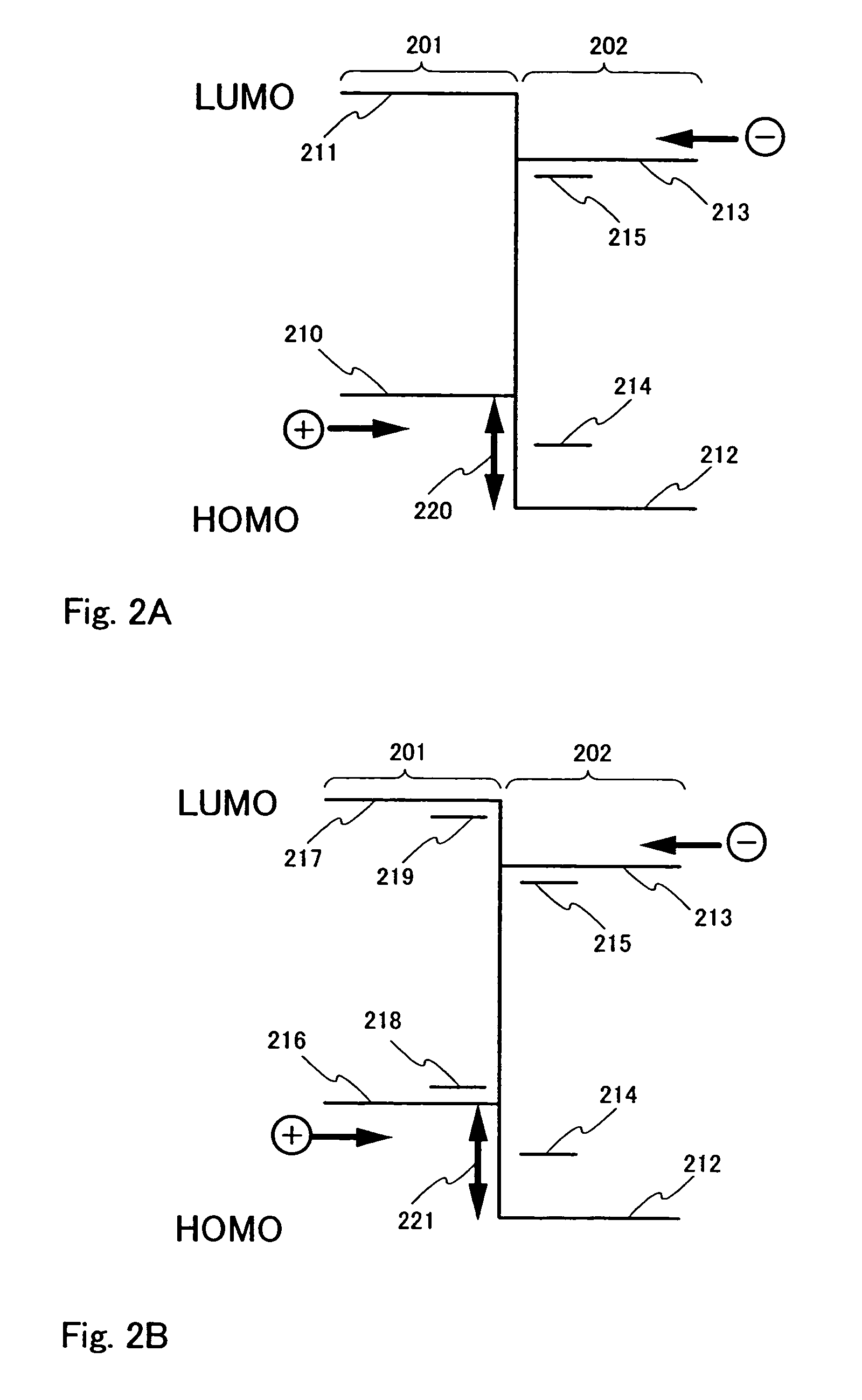
Organic devices, organic electroluminescent devices, organic solar cells, organic FET structures and production method of organic devices
ActiveUS20050098207A1TransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectronic transmissionOrganic solar cell
An organic device has a hole current-electron current conversion layer which comprises a laminate of an electron transportation section and a hole transportation section. The electron transportation section includes a charge transfer complex formed upon an oxidation-reduction reaction between a reduced low work function metal and an electron-accepting organic compound, the reduced metal being produced upon an in-situ thermal reduction reaction caused upon contact, through lamination or mixing by co-deposition, of an organic metal complex compound or an inorganic compound containing at least one metal ion selected from ions of low work function metals having a work function of not more than 4.0 eV, and a thermally reducible metal capable of reducing a metal ion contained in the organic metal complex compound or the inorganic compound in vacuum to the corresponding metal state, and the electron transportation section having the electron-accepting organic compound in the state of radical anions. The hole transportation section includes an organic compound having an ionization potential of less than 5.7 eV and an electron-donating property and an inorganic or organic substance capable of forming a charge transfer complex upon its oxidation-reduction reaction with the organic compound, the organic compound and the inorganic or organic substance being contacted through lamination or mixing, and the electron-donating organic compound is in the state of radical cations.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD +1
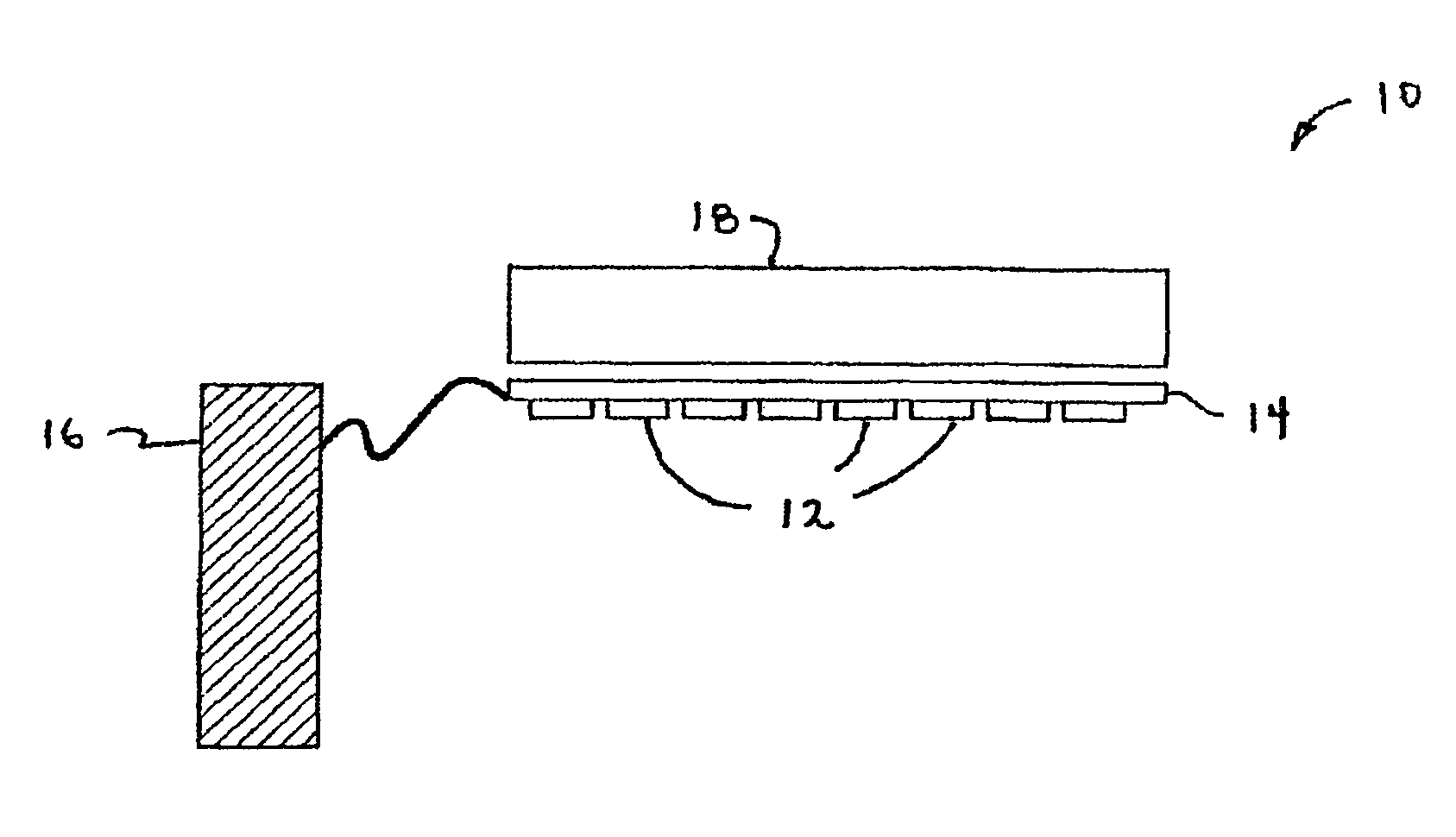
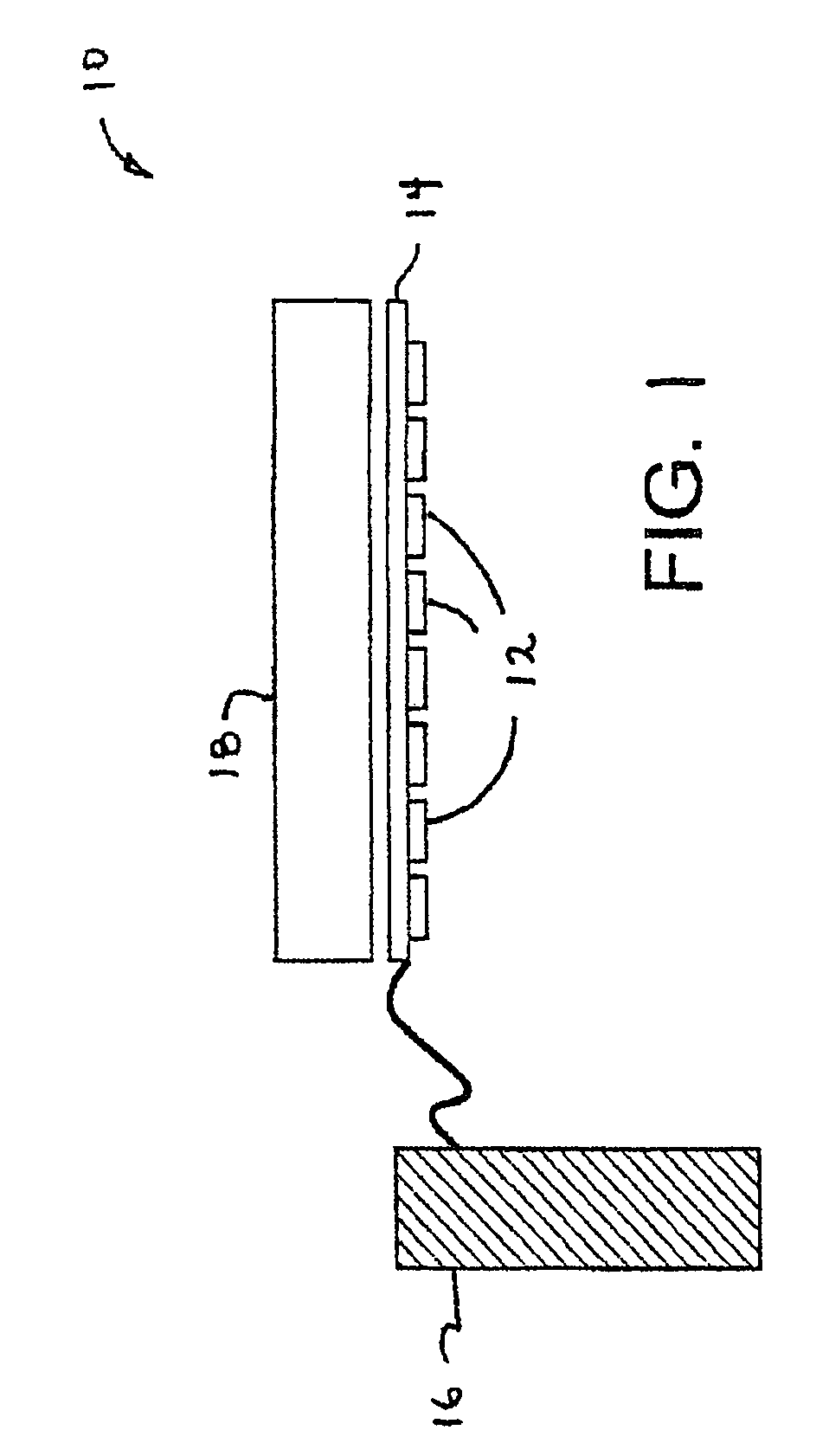
High efficiency solid-state light source and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS20050152146A1Eliminate needImprove light outputOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceDevice materialFluorescence
A high-intensity light source is formed by a micro array of a semiconductor light source such as a LEDs, laser diodes, or VCSEL placed densely on a liquid or gas cooled thermally conductive substrate. The semiconductor devices are typically attached by a joining process to electrically conductive patterns on the substrate, and driven by a microprocessor controlled power supply. An optic element is placed over the micro array to achieve improved directionality, intensity, and / or spectral purity of the output beam. The light module may be used for such processes as, for example, fluorescence, inspection and measurement, photopolymerzation, ionization, sterilization, debris removal, and other photochemical processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
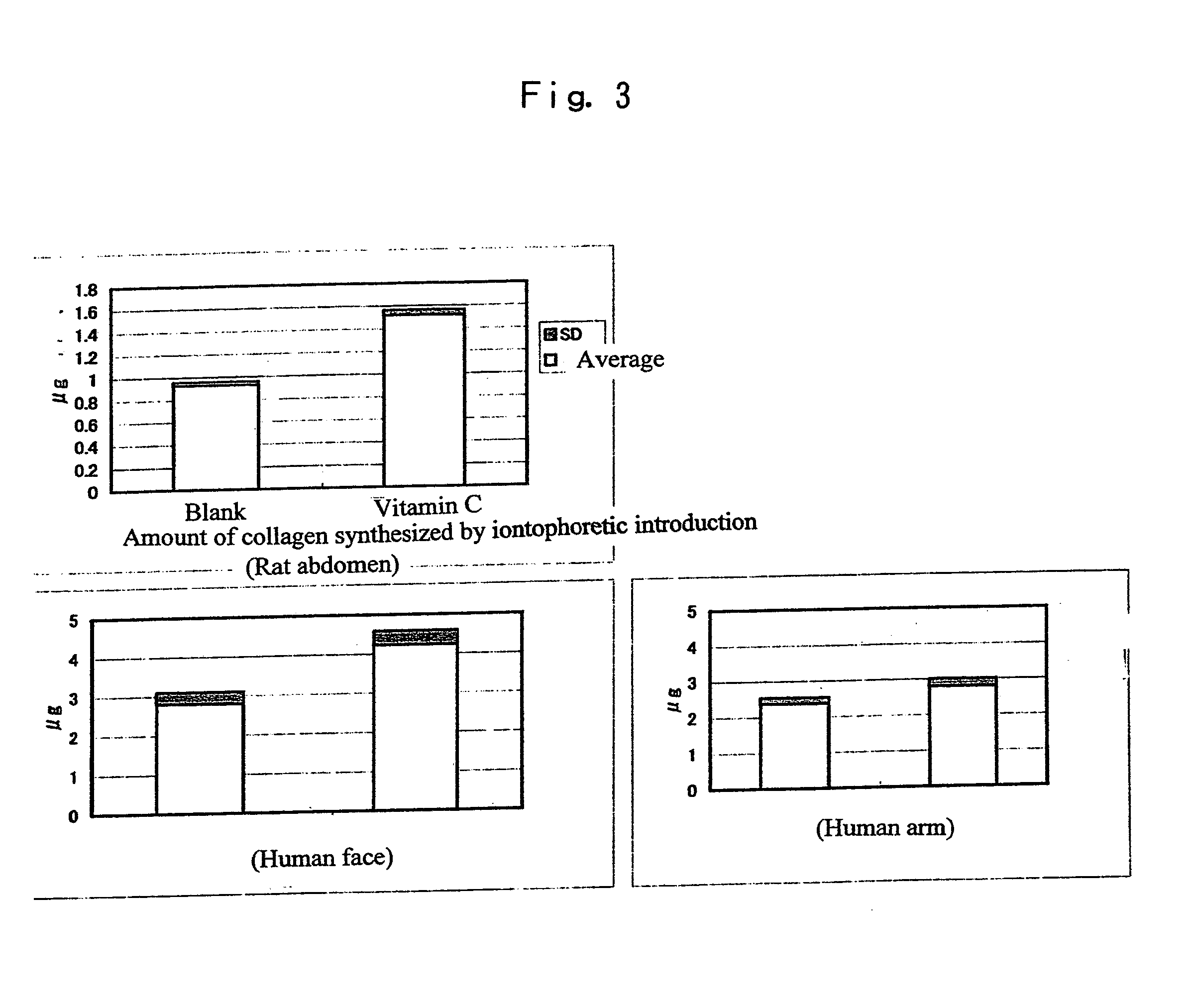
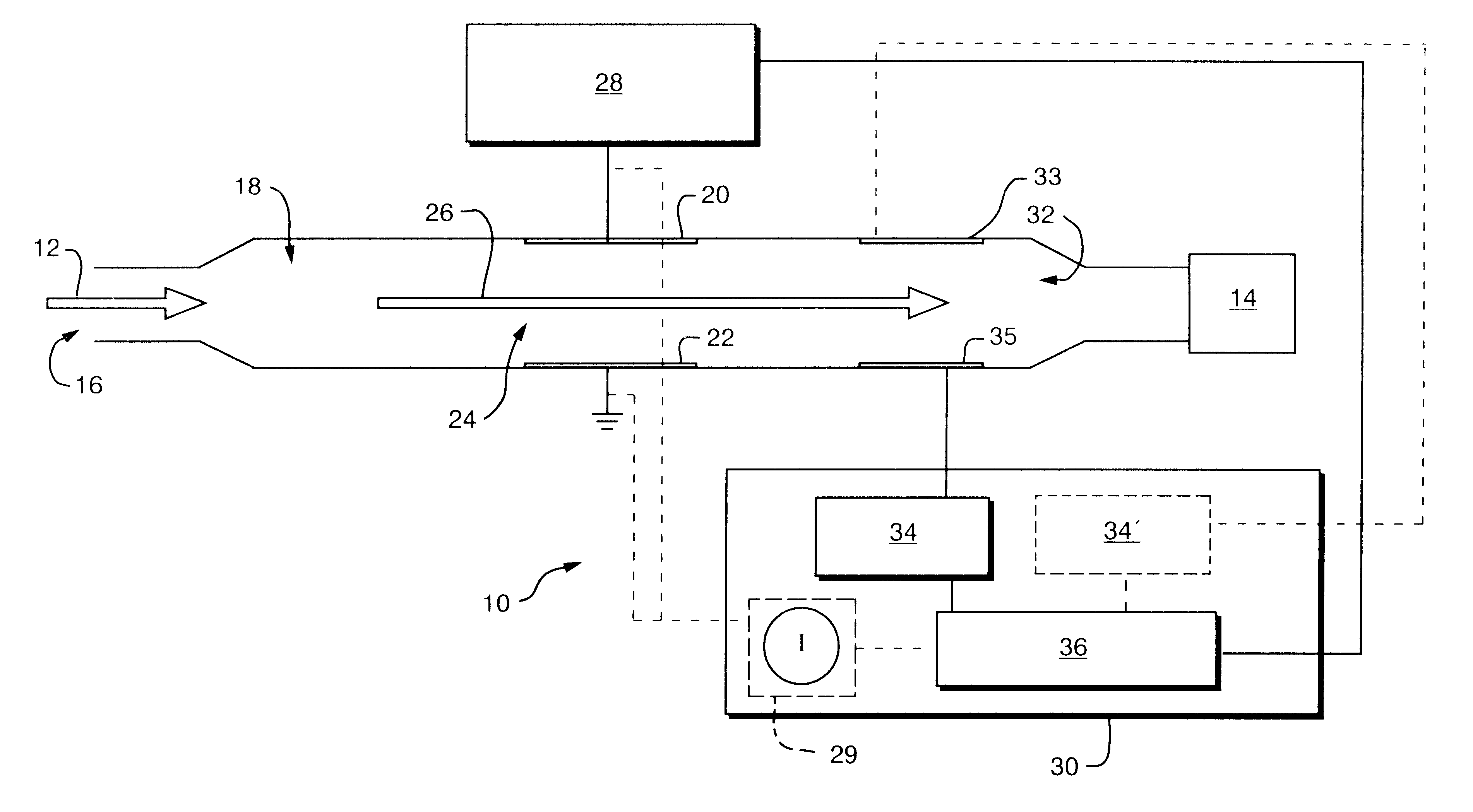
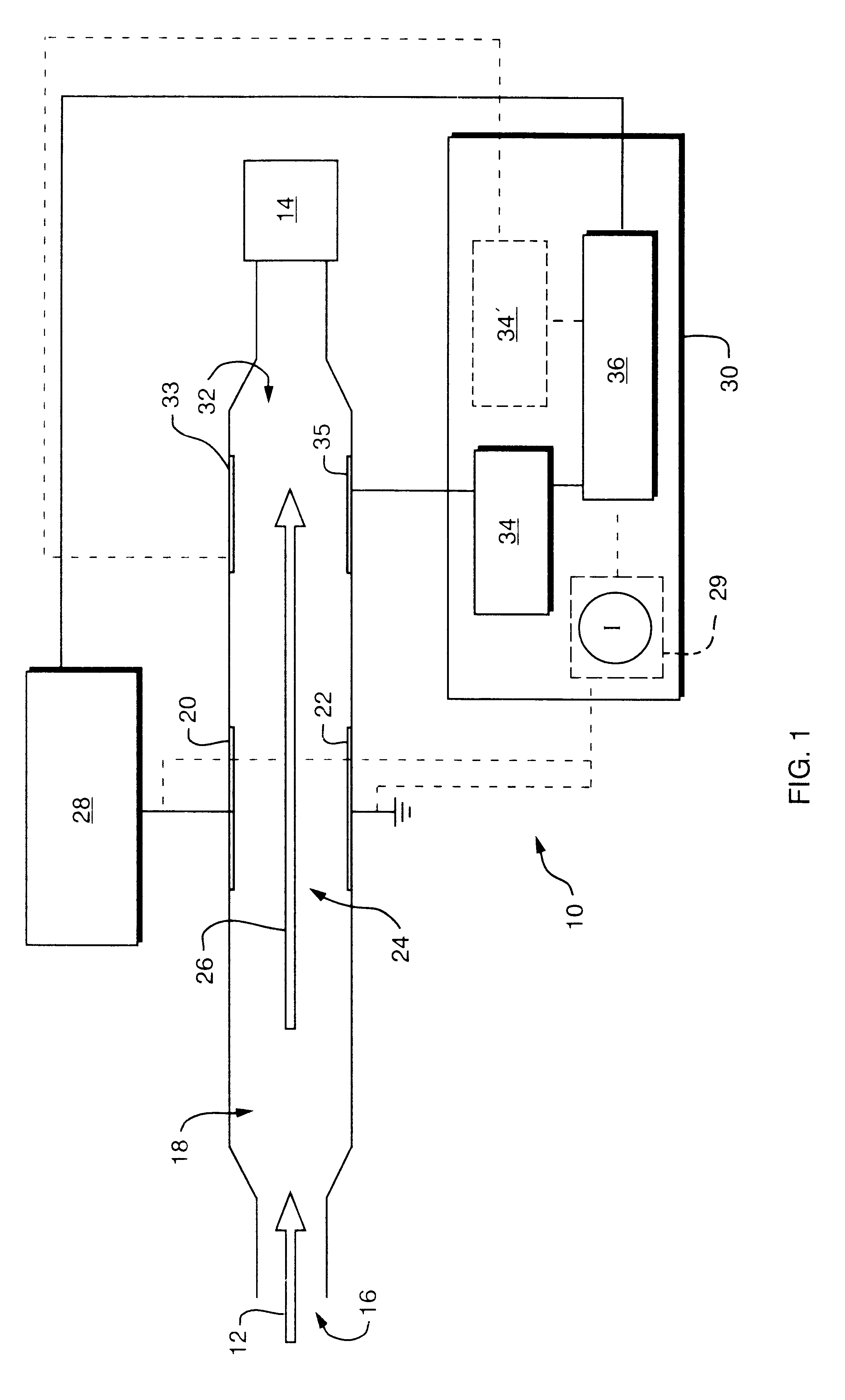
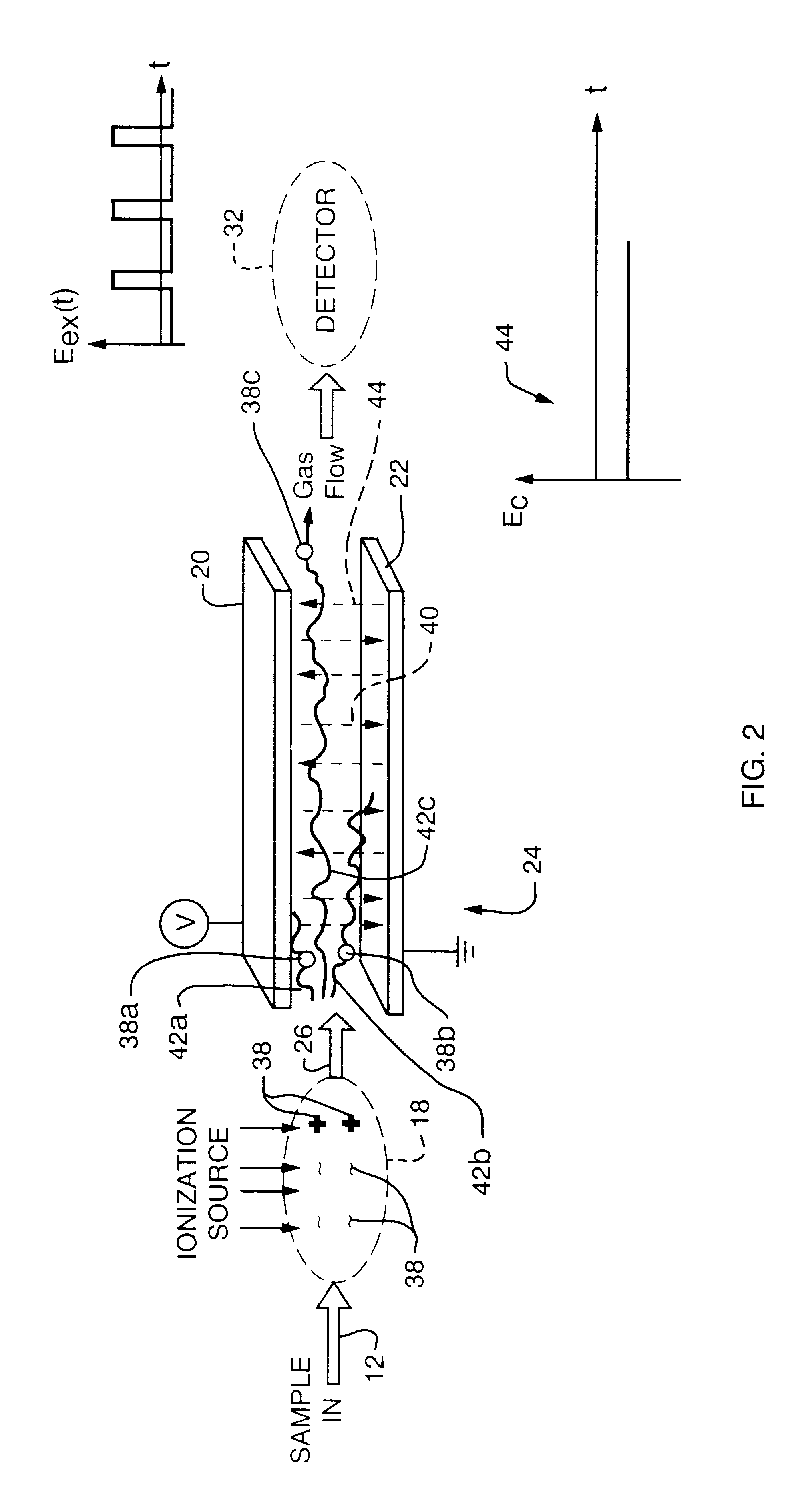
Method for the iontophoretic non-invasive determination of the in vivo concentration level of an inorganic or organic substance
The present invention relates to an vitro device for the removal of ionized substances from a membrane sample without mechanical penetration, which device comprises:(a) a positive electrode;(b) a negative electrode, and(c) electrical insulation between subpart (a) and (b), wherein the positive electrode, and the negative electrode, and electrical insulation are positioned on the same side of the membrane sample.The present invention also relates to a device for the removal of or delivery of ionized substances to a mammal through intact skin or mucosal membrane without mechanical penetration, which device comprises: (a) a positive electrode, (b) a negative electrode, and (c) an electrically insulating material between subpart (a) and (b), wherein the positive electrode, negative electrode and insulating material are physically positioned so that each present a common surface of the device for contact with the same surface of the skin or mucosal membrane of the mammal.The present invention also relates to the use of iontophoresis to determine the level of a charged molecule in a living mammal, and with the use of a feedback mechanism, administer appropriate levels of therapeutic substances.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus for detecting chemical substances and method therefor
ActiveUS20050061964A1High detection sensitivityPrevent false detectionStability-of-path spectrometersAnalysis using chemical indicatorsNon detectionData treatment
An apparatus for detecting chemical substances which is high in sensitivity and selectivity is provided. An organic acid or an organic acid salt is used to generate an organic acid gas from an organic acid gas generator 3 to be mixed with a sample gas for introduction into an ion source 4 for ionization, thereby obtaining a mass spectrum by a mass analysis region 5. A data processor 6 determines the detection or non-detection of a specific m / z of an organic acid adduct ion obtained by adding a molecule generated from the organic acid to a molecule with specific m / z generated from a target chemical substance to be detected based on the obtained mass spectrum. When there is an ion peak with the m / z of the organic acid adduct ion, the presence of the target chemical substance to be detected is determined, and an alarm is sounded. False detection can be prevented.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
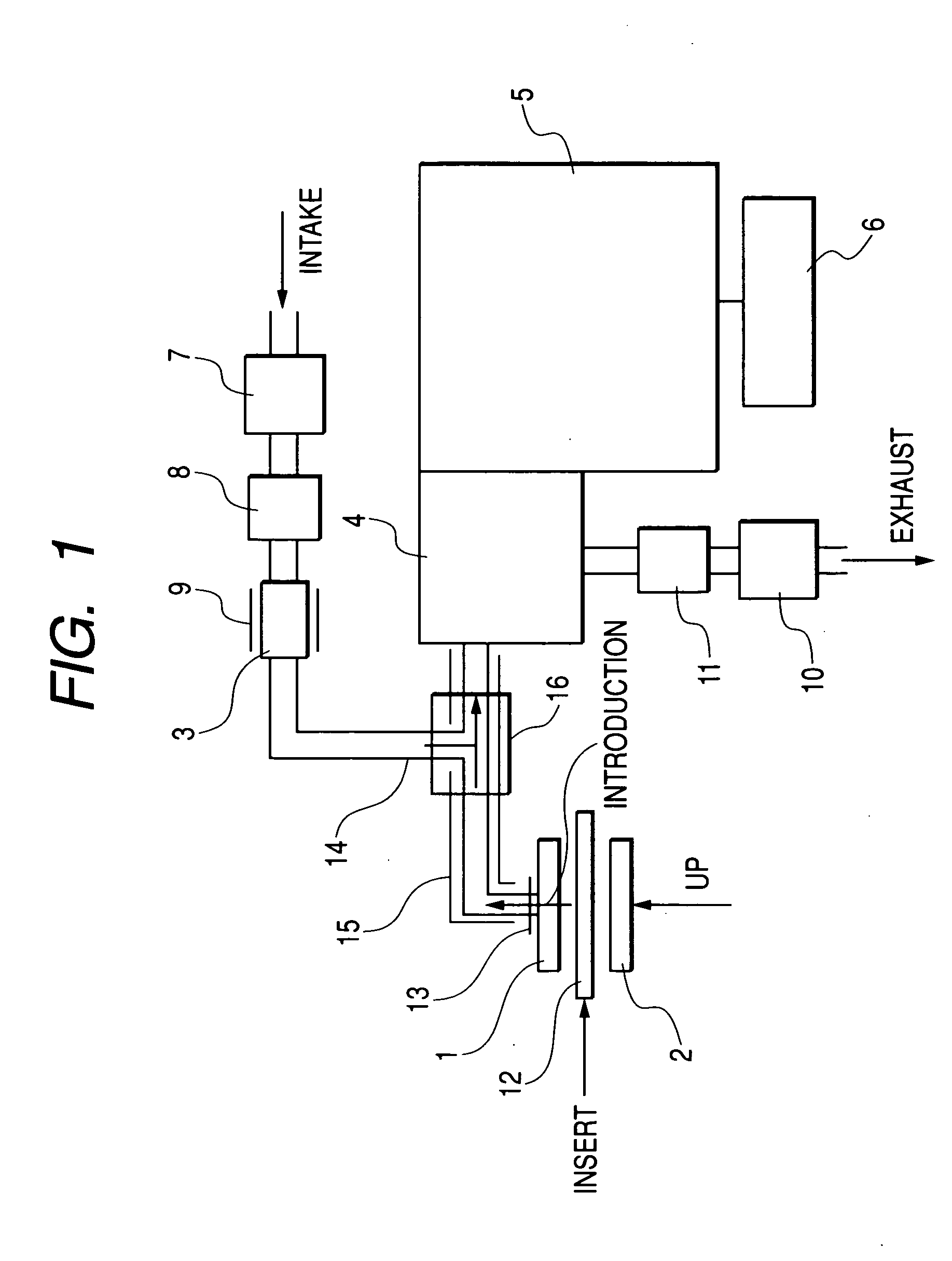
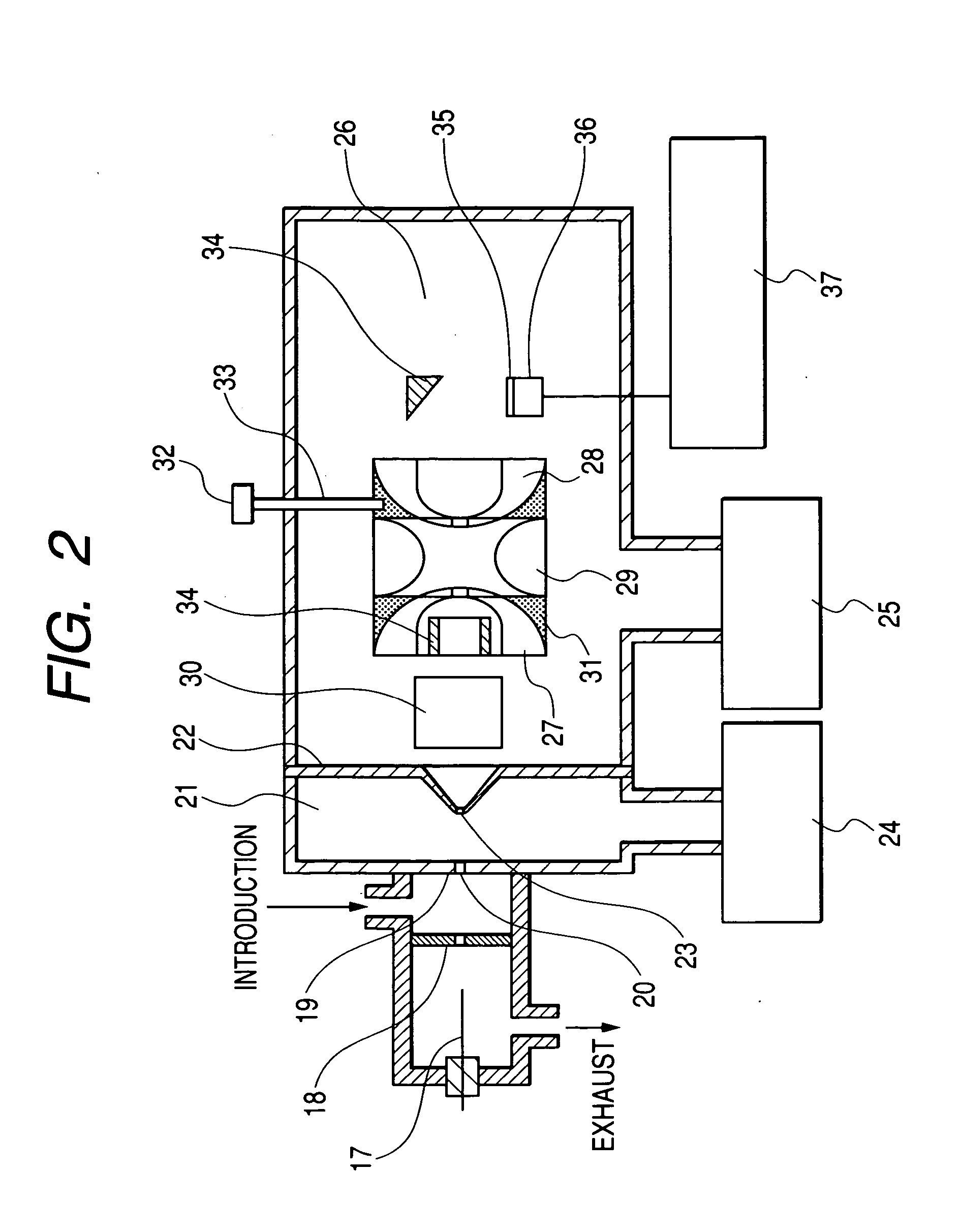
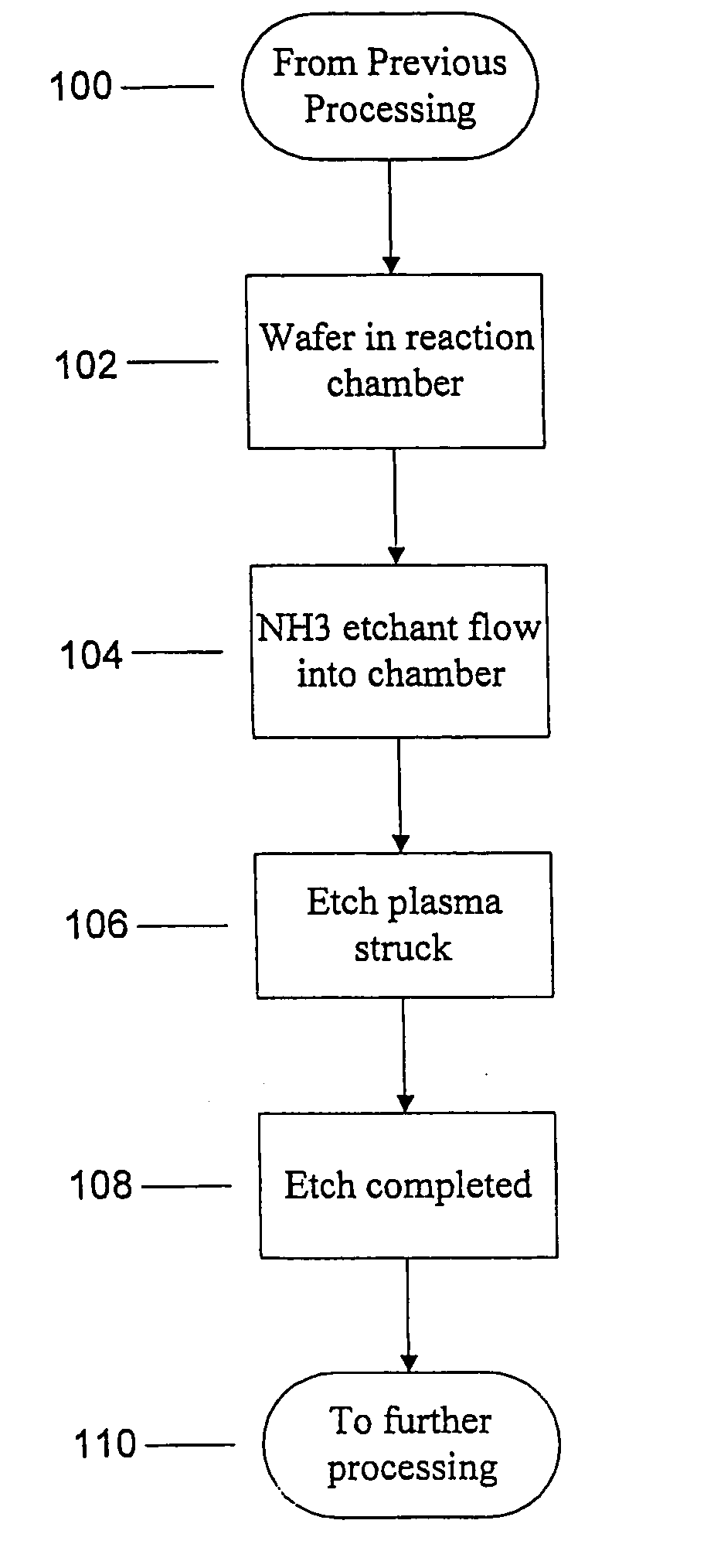
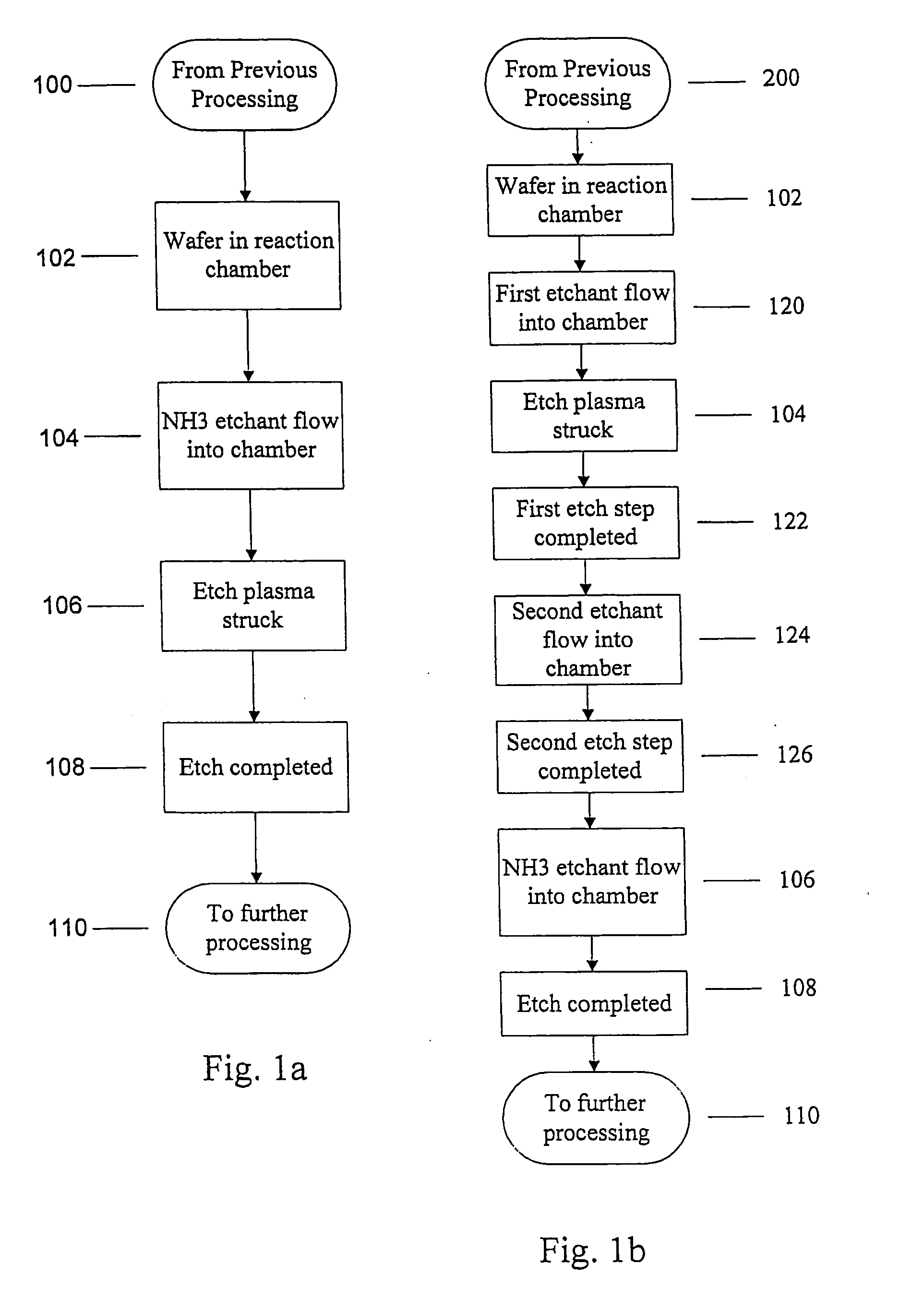
Use of ammonia for etching organic low-k dielectrics
InactiveUS20050003676A1Increase etch rateHigh selectivityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess chemistryElectricity
Method for etching organic low-k dielectric using ammonia, NH3, as an active etchant. Processes using ammonia results in at least double the etch rate of organic low-k dielectric materials than processes using N2 / H2 chemistries, at similar process conditions. The difference is due to the much lower ionization potential of NH3 versus N2 in the process chemistry, which results in significantly higher plasma densities and etchant concentrations at similar process conditions.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
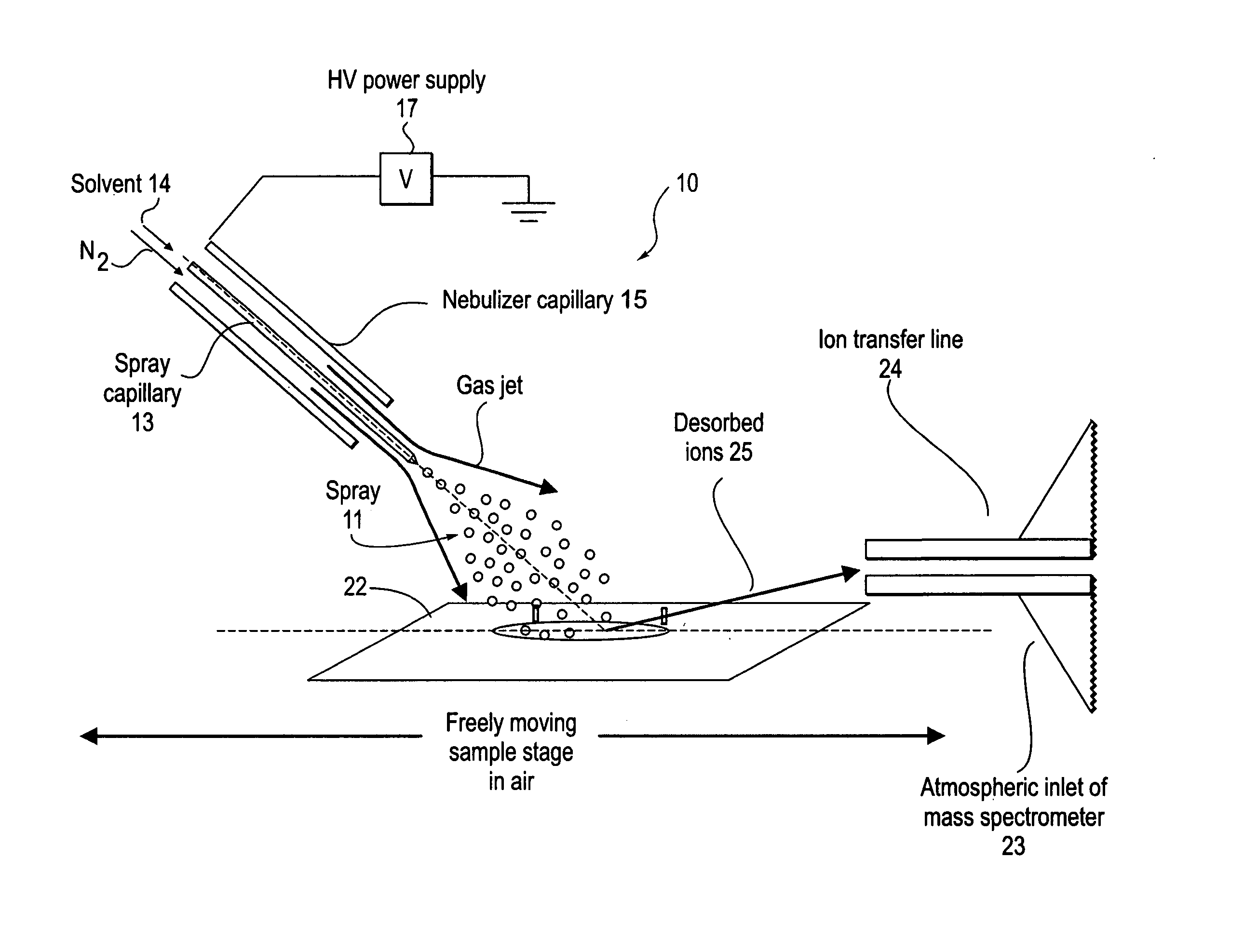
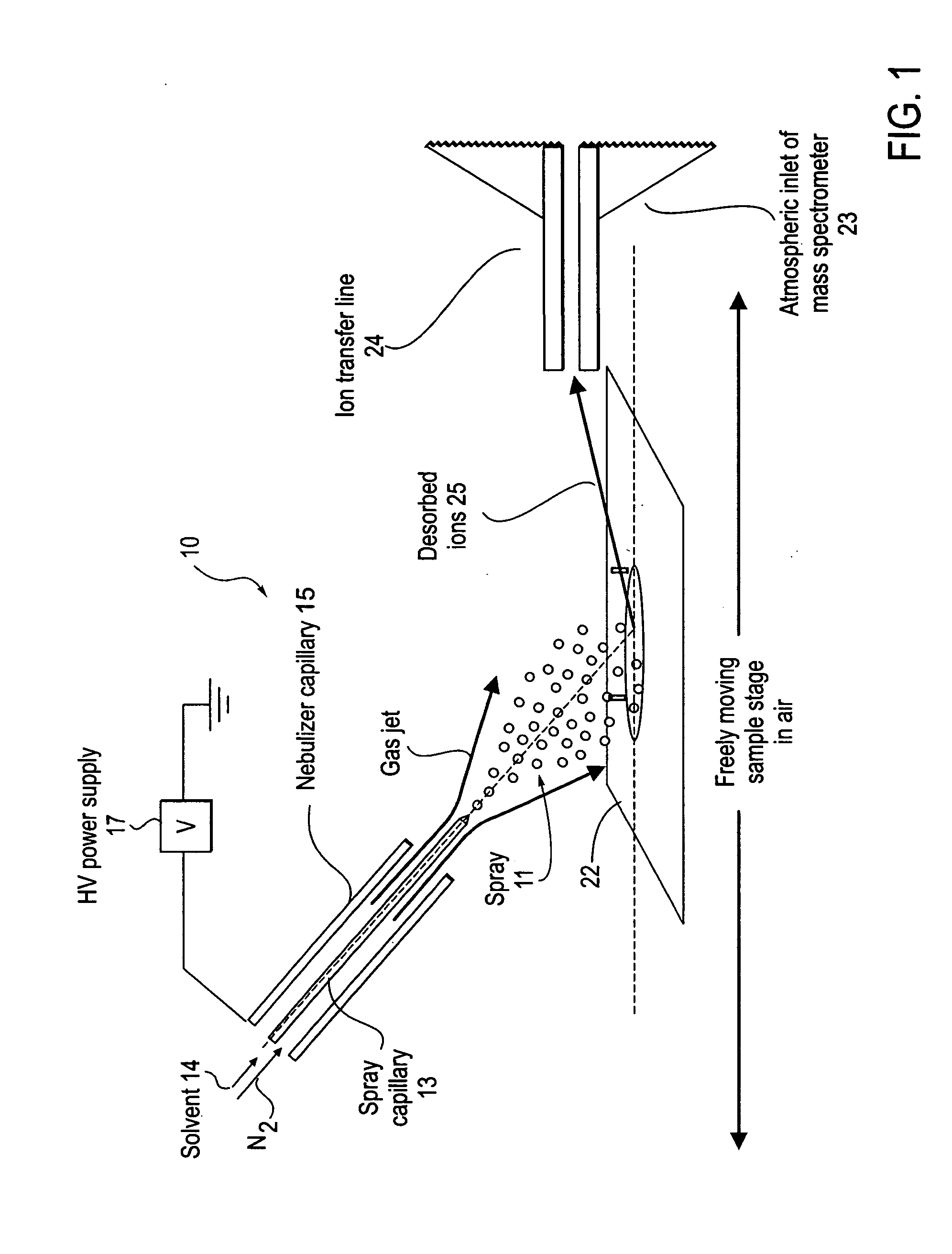
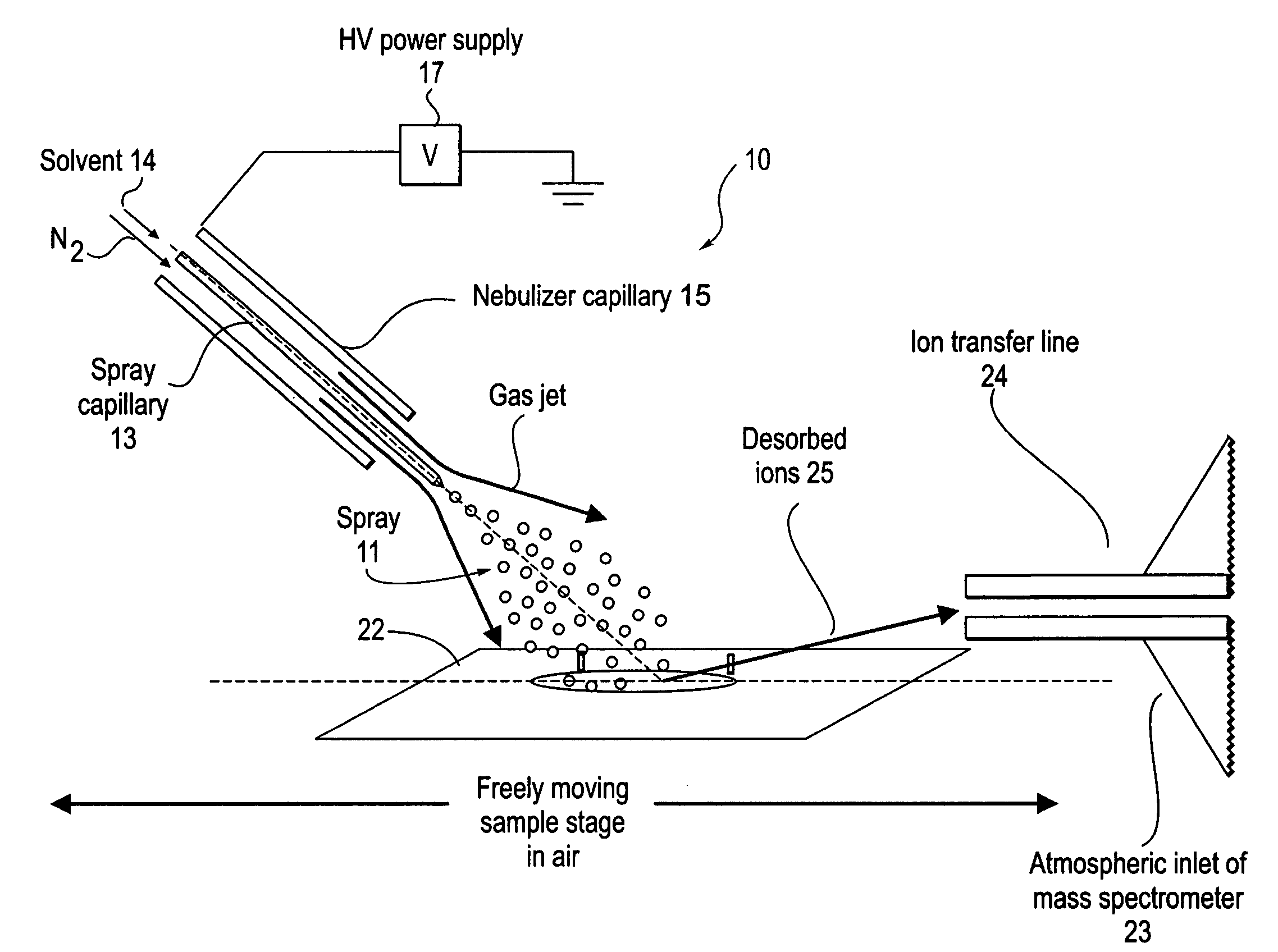
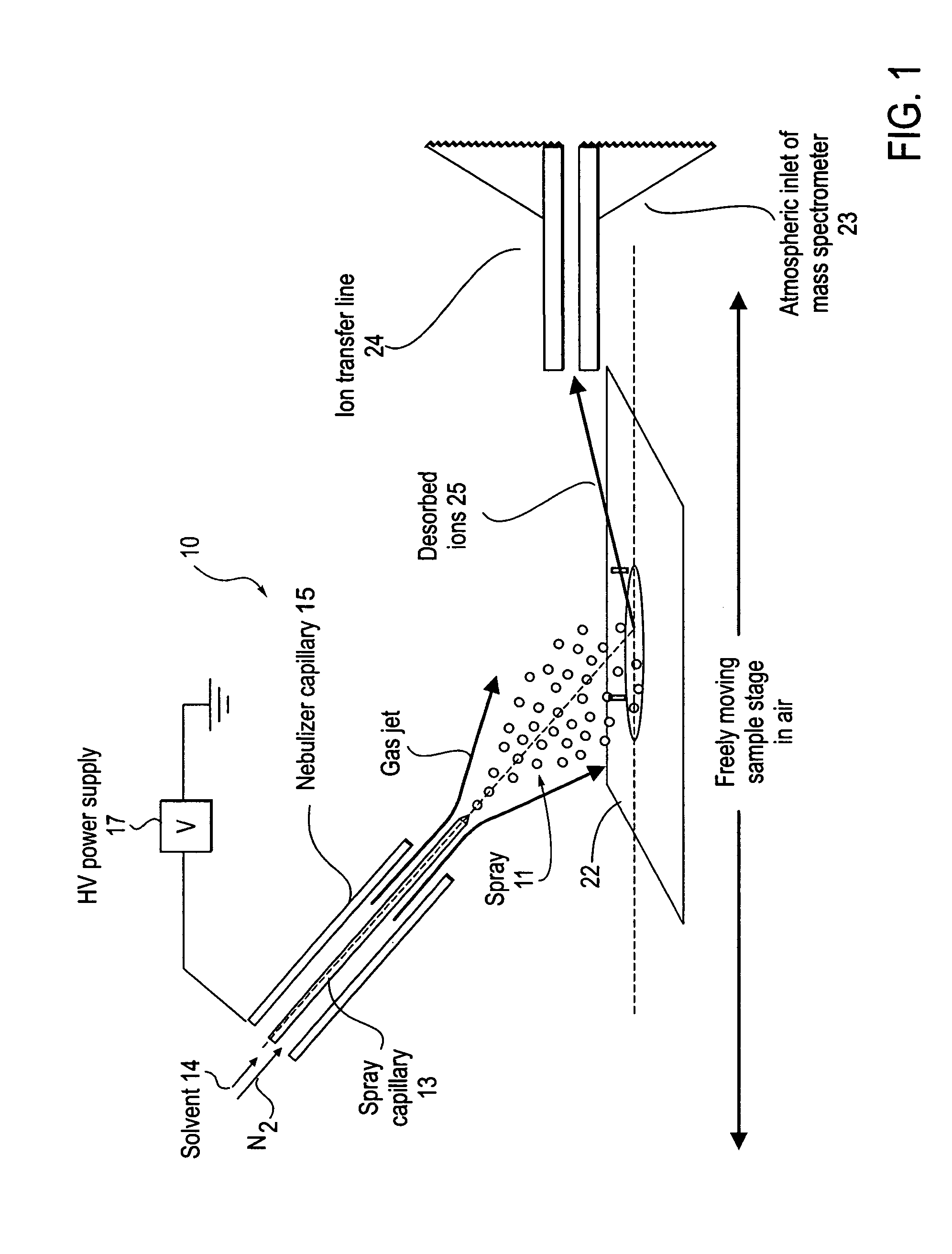
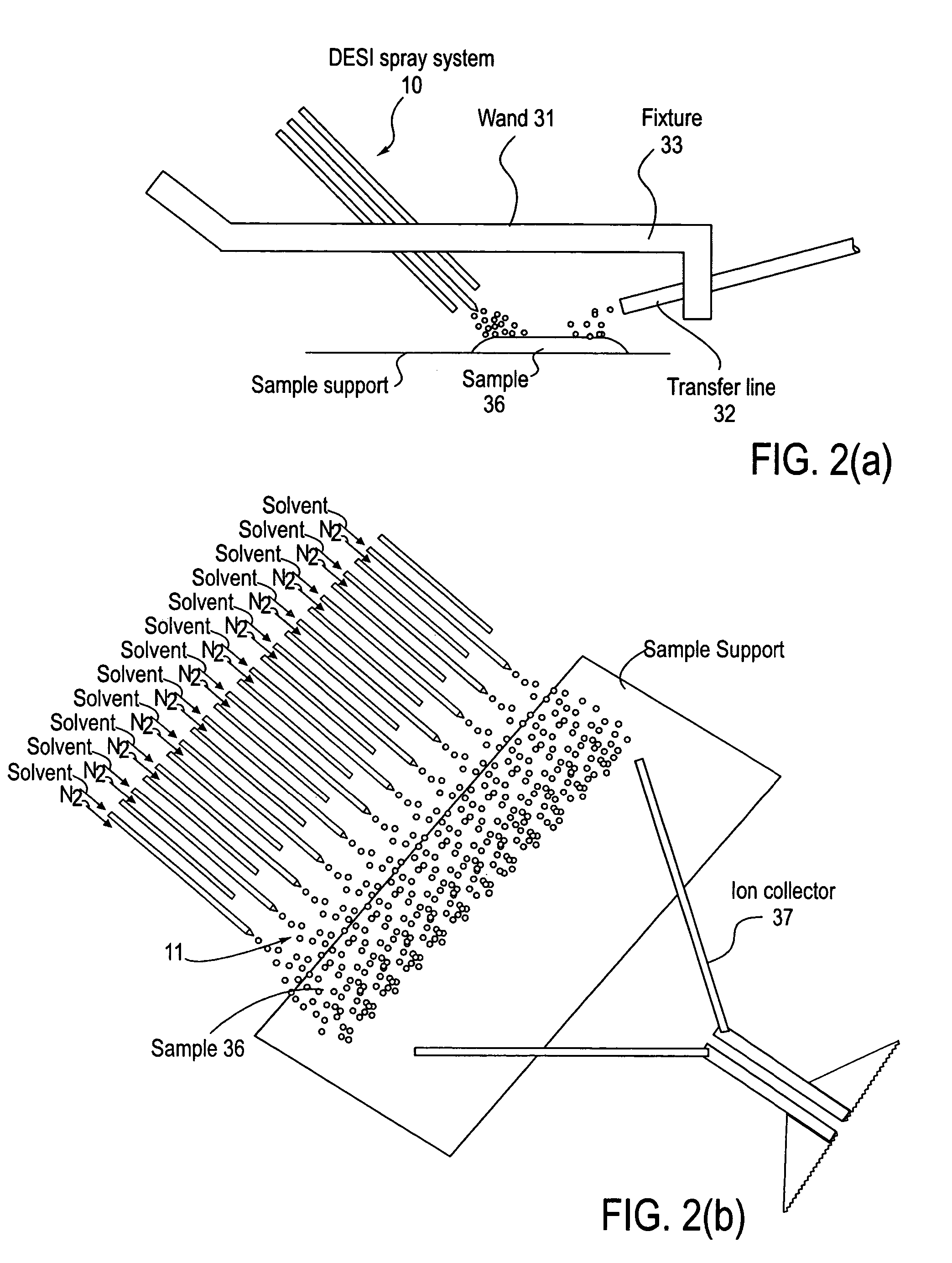
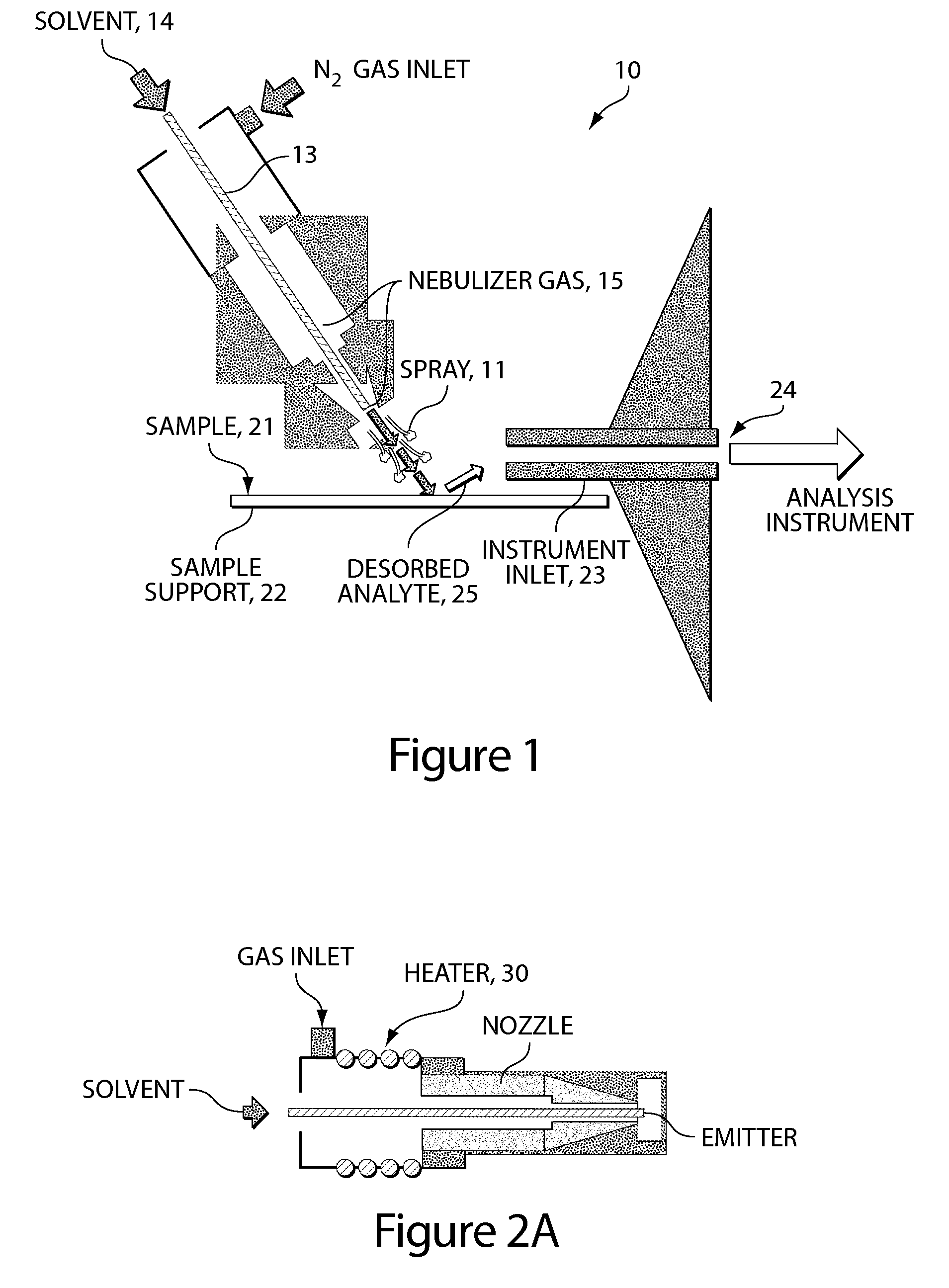
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
ActiveUS20050230635A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansIonizationDesorption electrospray ionization
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs, through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method and system for desorption electrospray ionization
ActiveUS7335897B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLycopeneElectrospray ionization
A new method and system for desorption ionization is described and applied to the ionization of various compounds, including peptides and proteins present on metal, polymer, and mineral surfaces. Desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) is carried out by directing charged droplets and / or ions of a liquid onto the surface to be analyzed. The impact of the charged particles on the surface produces gaseous ions of material originally present on the surface. The resulting mass spectra are similar to normal ESI mass spectra in that they show mainly singly or multiply charged molecular ions of the analytes. The DESI phenomenon was observed both in the case of conductive and insulator surfaces and for compounds ranging from nonpolar small molecules such as lycopene, the alkaloid coniceine, and small drugs, through polar compounds such as peptides and proteins. Changes in the solution that is sprayed can be used to selectively ionize particular compounds, including those in biological matrices. In vivo analysis is demonstrated.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Apparatus and Method for Plasma Ignition with a Self-Resonating Device
ActiveUS20170303382A1Reduce frequencyMinimizationElectric discharge tubesPlasma techniqueEngineeringIonization
Methods and apparatus for igniting a process plasma within a plasma chamber are provided. One or more self-resonating devices are positioned within a plasma chamber relative to a plasma generation volume within the plasma chamber. The plasma generation volume is defined by the plasma chamber. Each of the self-resonating devices generates an ignition plasma. The ignition plasmas cause a partial ionization of an ignition gas. The partially ionized ignition gas allows for ignition of a process plasma by applying an electric field to the plasma generation volume.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Skin beautification cosmetic system using iontophoresis device, ultrasonic facial stimulator, and cosmetic additive
InactiveUS20050191252A1Skin safeImprove responseCosmetic preparationsElectrotherapyAging skinsCosmetic component
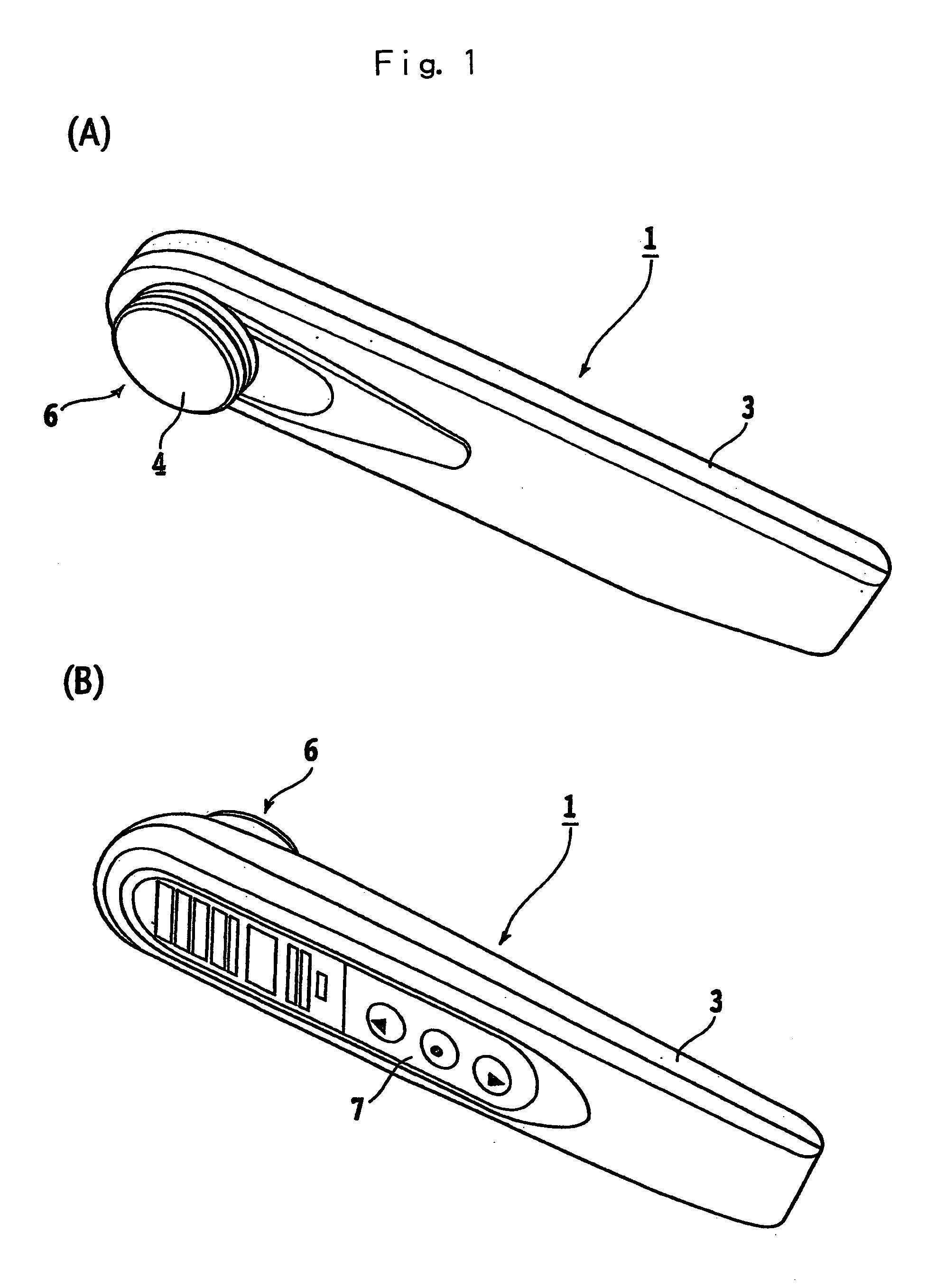
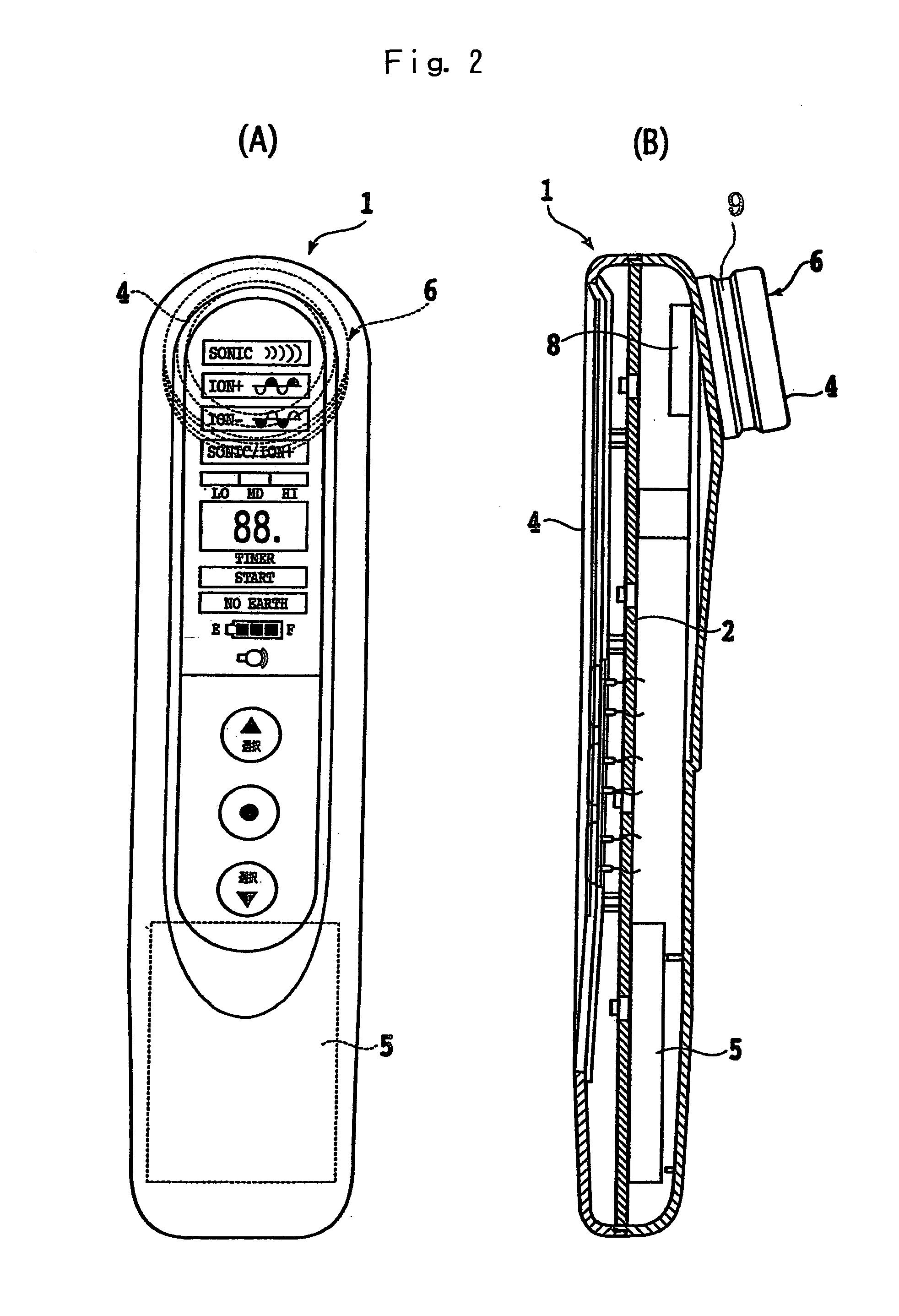
A skin beautification cosmetic system comprising an iontophoresis device, an infrared (including far infrared) generator, an ultrasonic vibrator, and a cosmetic composition is disclosed. The system ensures effective action of moisturizing and whitening cosmetics without causing any problem in the skin. By specifying the type of cosmetic to be used, the system can ensure a more effective beautification action, can improve dry skin and aging skin which adversely affect the female skin, and can decompose and remove melanin. Moisturizing and / or whitening cosmetic components such as hydrophilic gel and ultrafine gel are applied to the face or skin or impregnated in a skin contact member section, following which iontophoresis high frequency vibration is applied to the face or skin for a prescribed period of time using an ultrasonic vibrator 3 with built-in high ionization iontophoresis device 2 and infrared generator 9.
Owner:JAPAN NATURAL LAB
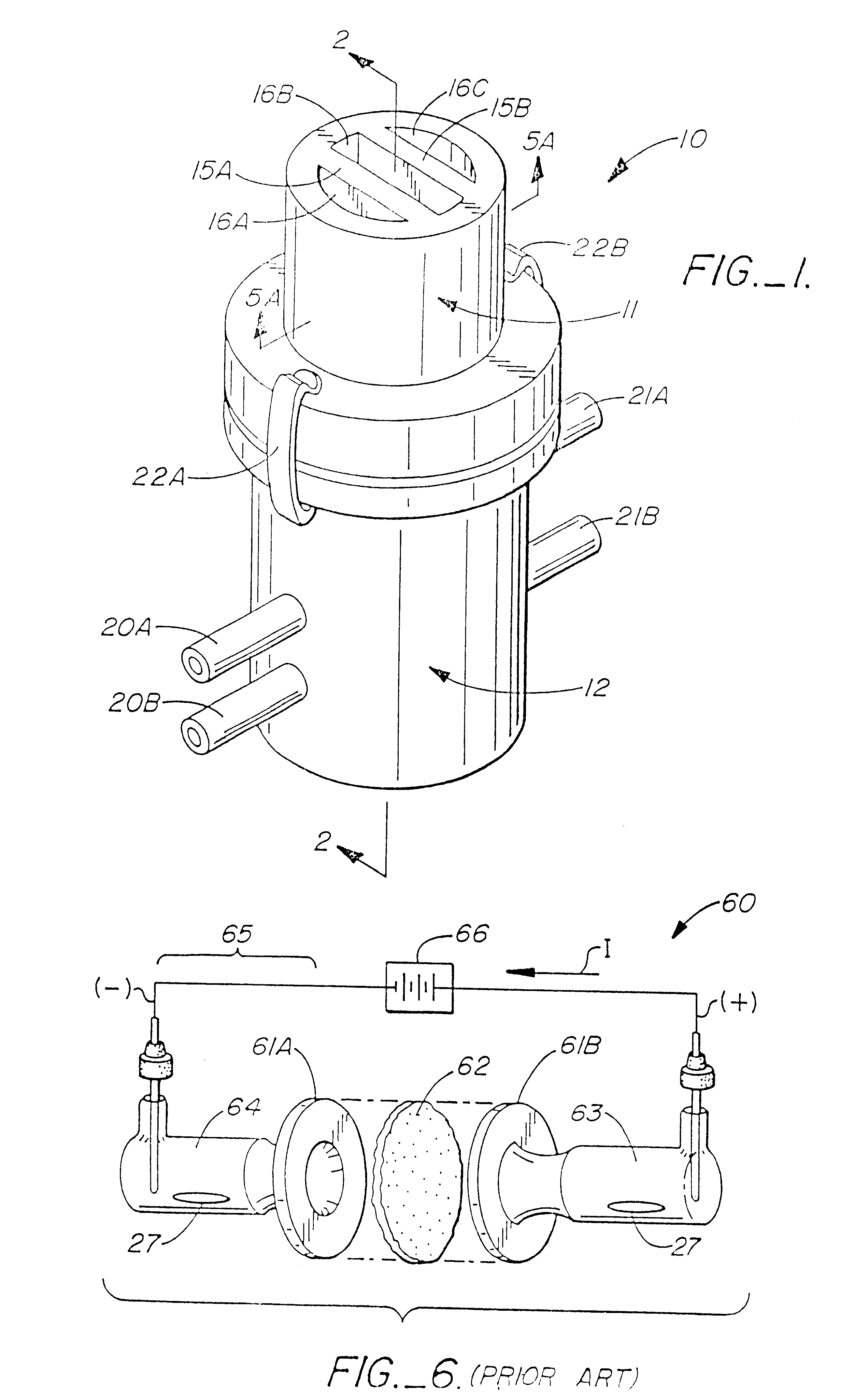
Longitudinal field driven field asymmetric ion mobility filter and detection system
InactiveUS6512224B1Improve accuracyHigh resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersNon symmetricIon-mobility spectrometry
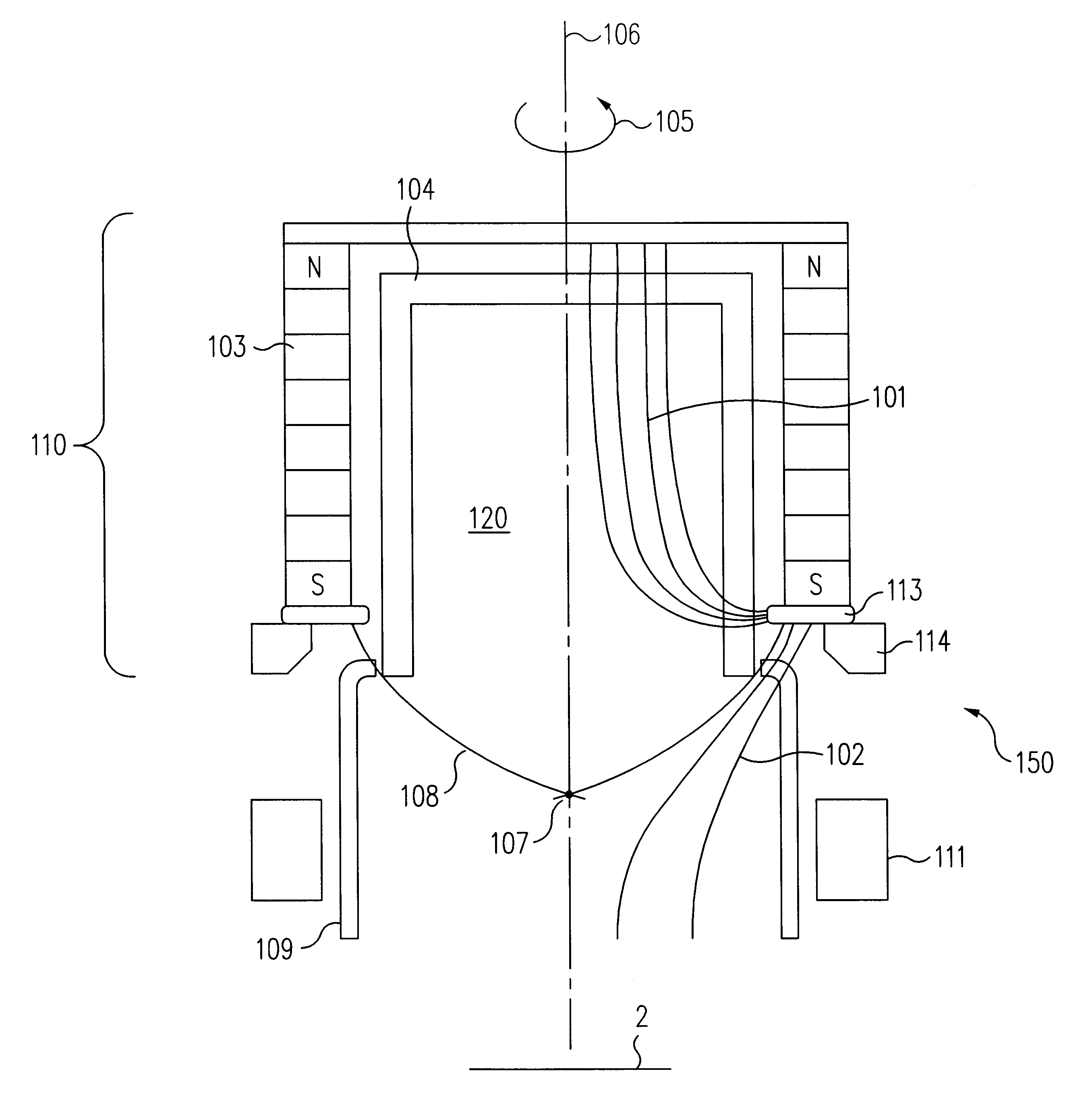
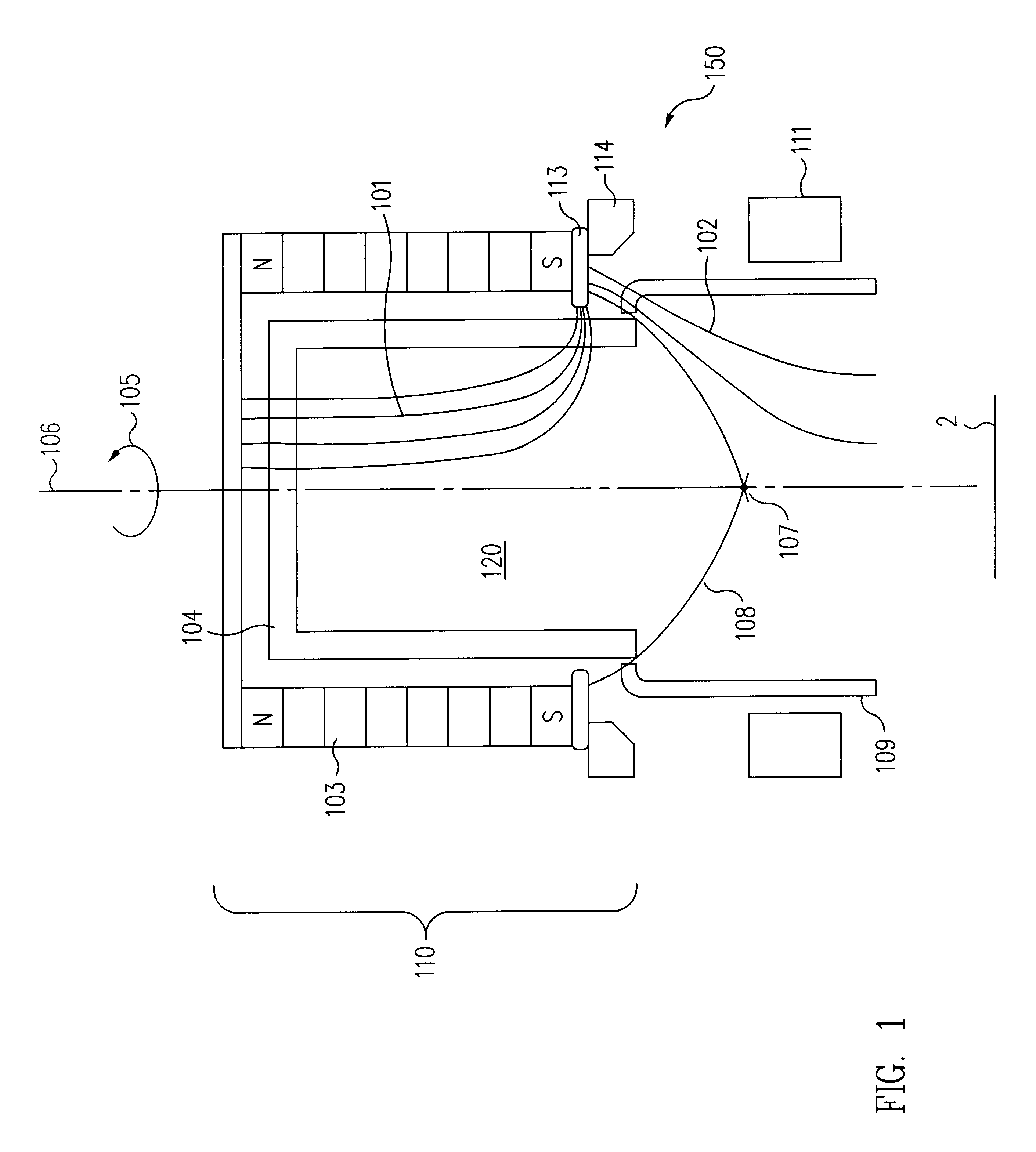
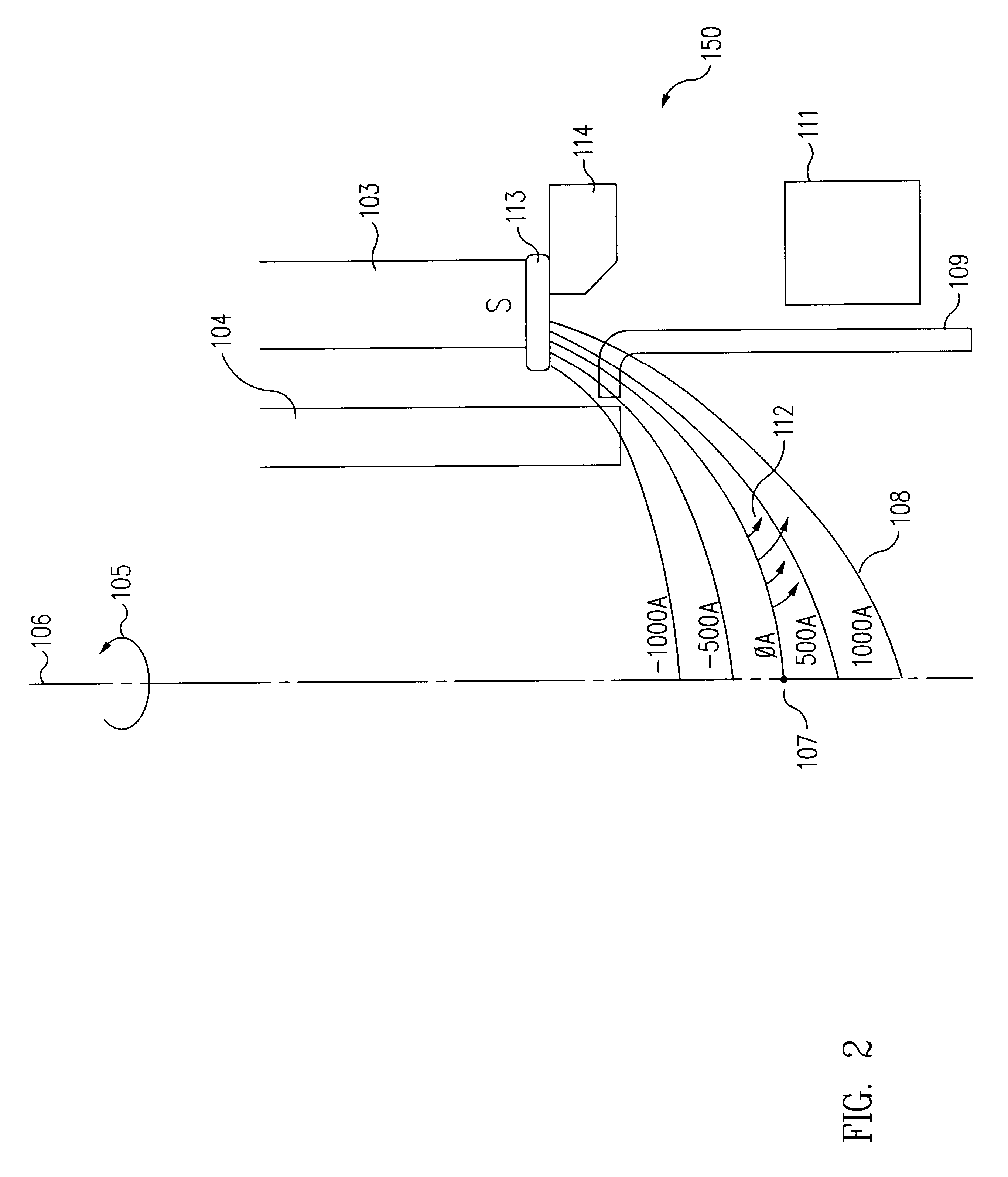
An asymmetric field ion mobility spectrometer with an ionization source for ionizing a sample media and creating ions. An ion filter is disposed in the analytical gap downstream from the ionization source for creating an asymmetric electric field to filter the ions. An ion flow generator for creating an electric field in a direction transverse to the asymmetric electric field and which propels the ions through the asymmetric electric field towards a detector.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Ion source
InactiveUS6849854B2Electric arc lampsMaterial analysis by optical meansElectron flowTitanium nitride
An ion source 10 for producing a beam of ions from a plasma is disclosed. A plasma is created at the center of an anode 12 by collisions between energetic electrons and molecules of an ionizable gas. The electrons are sourced from a cathode filament 11 and are accelerated to the anode 12 by an applied electric potential. A projection of the anode and a magnetic field having an axis aligned with the axis of the anode act together to concentrate the flow of electrons to the center of the anode 12. The ionizable gas is introduced into an ionization region 13 of the ion source 10 at the point of concentrated electron flow. Ions created in the ionization region are expelled from the ion source as an ion beam centred on the axis of the magnetic field. The surfaces of the anode are coated with an electrically conductive non-oxidising layer of Titanium Nitride to prevent a build up of an insulating layer on the anode.
Owner:SAINTECH
Boron ionization for aluminum oxide etch enhancement
Embodiments described herein generally provide a method for performing a semiconductor precleaning process. More specifically, embodiments provided herein relate to boron ionization for aluminum oxide etch enhancement. A process for removing native oxide from aluminum may utilize ionized boron alone or in combination with a halogen plasma. The ionized boron may provide improved aluminum oxide etching properties while being highly selective for native oxides more generally.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Organic electroluminescence element and an exposure unit and image-forming apparatus both using the element
ActiveUS20050248267A1Large quantity of lightOrganic electroluminescence element can be enhancedDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectron injectionWork function
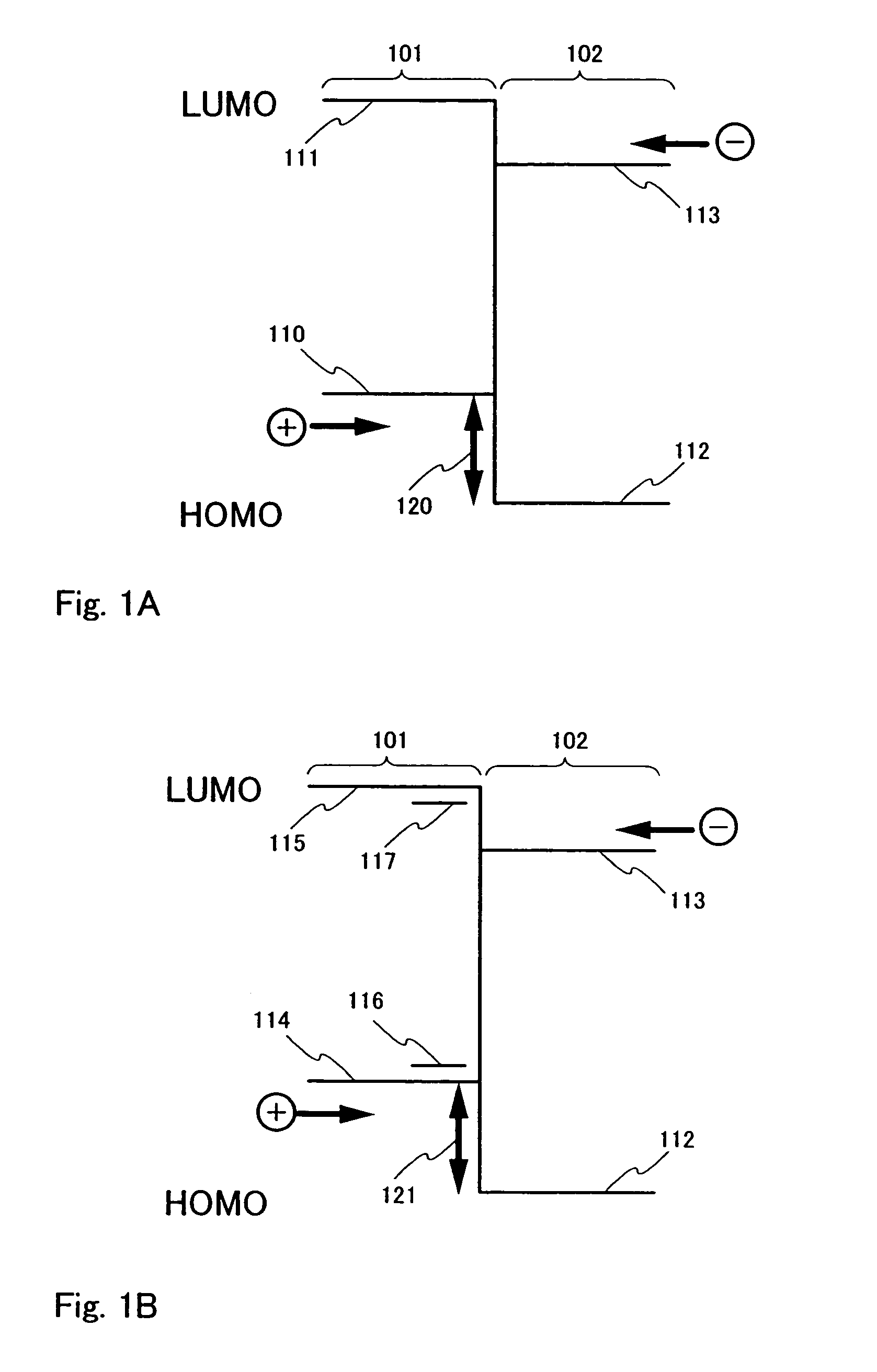
The invention has an object of providing an organic electroluminescence element with a large emitted light quantity, an exposure unit and an image-forming apparatus both using the element. The organic electroluminescence element in accordance with the invention has, on a substrate, an anode acting as a hole injection electrode, a cathode acting as an electron injection electrode, a plurality of light emission layers each having a light emission region and a charge generation layer injecting electrons into the light emission layer lying close to the anode and injecting holes into the light emission layer lying close to the cathode, these layers being arranged between the anode and the cathode, and is configured so that the work function of the charge generation layer is set higher than the ionization potential of the light emission layer lying close to the anode.
Owner:JOLED INC
Organic electroluminescence device and phenylenediamine derivative
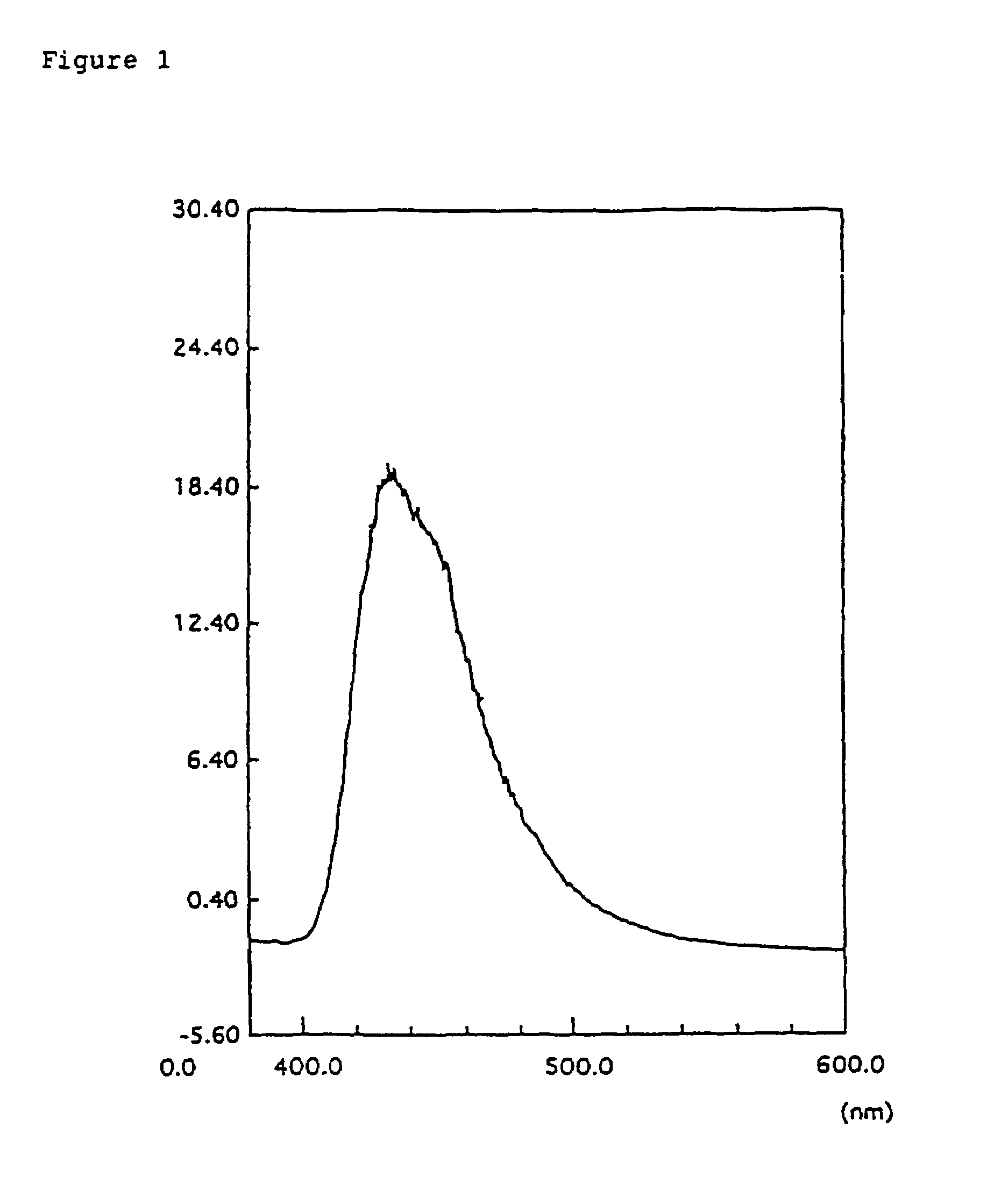
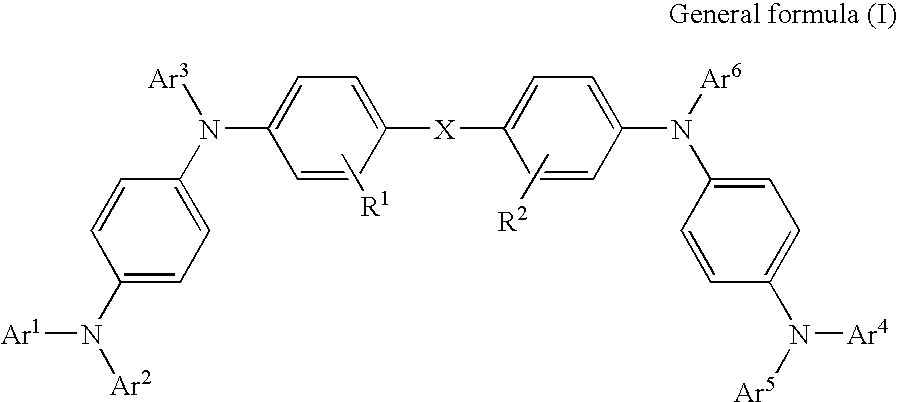
InactiveUS7399537B2Reduce the driving voltageSmall ionization potentialOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectron holeCharge injection
The invention is to provide an organic EL device having a long life time that can reduce the driving voltage of the organic EL device, and to provide a material having a small ionization potential and exhibiting a large hole mobility by using as a layer or a zone. The organic electroluminescence device comprises a pair of electrodes and an organic light emitting layer sandwiched in the electrodes, characterized in that a hole transporting zone provided between the electrodes comprises the phenylenediamine derivative represented by the specific structural formulae, and the phenylenediamine derivative has a hole mobility of 10−4 cm2 / V·s or more upon using as a layer or a zone, with the organic light emitting layer containing a charge injection auxiliary.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
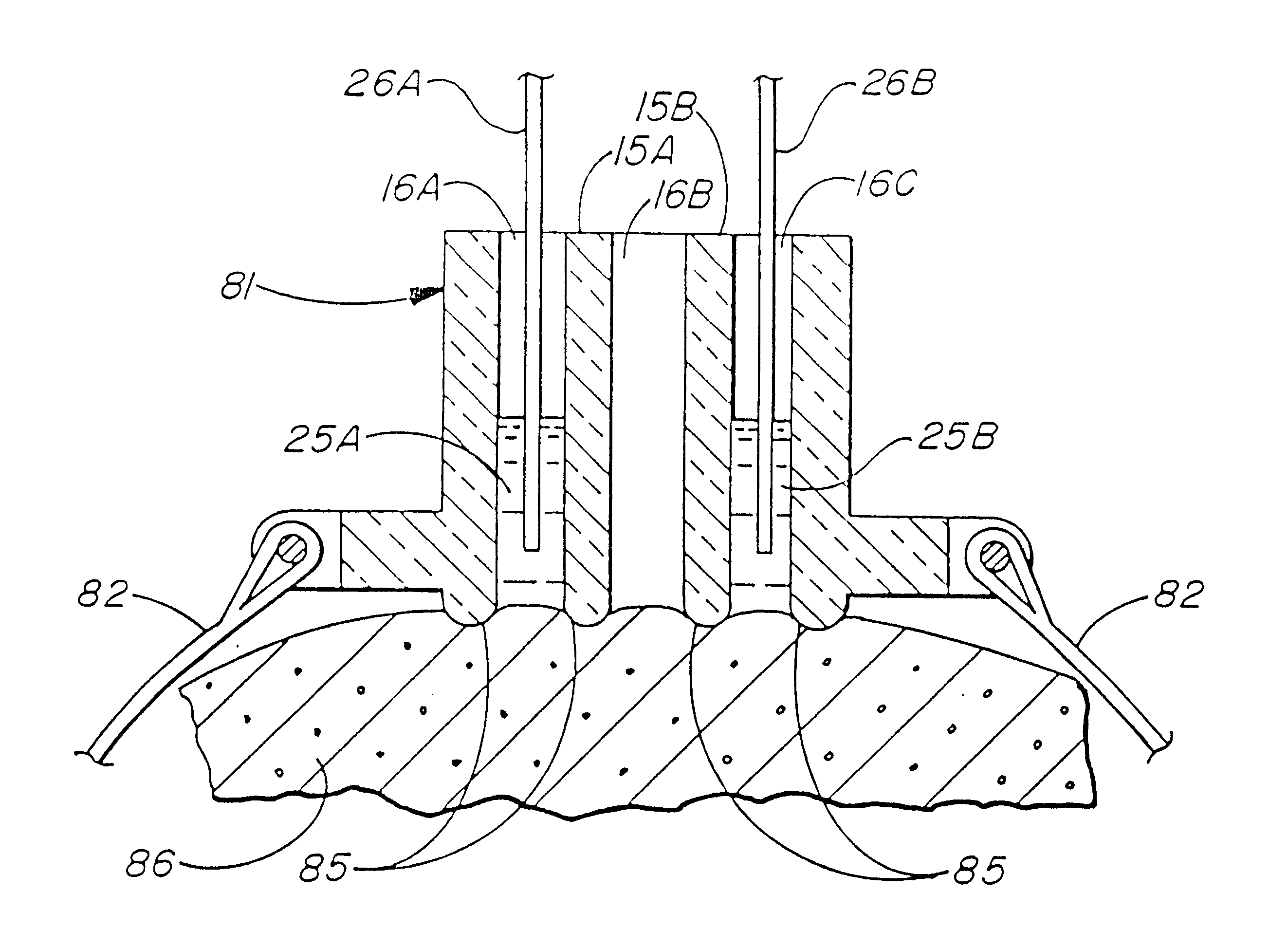
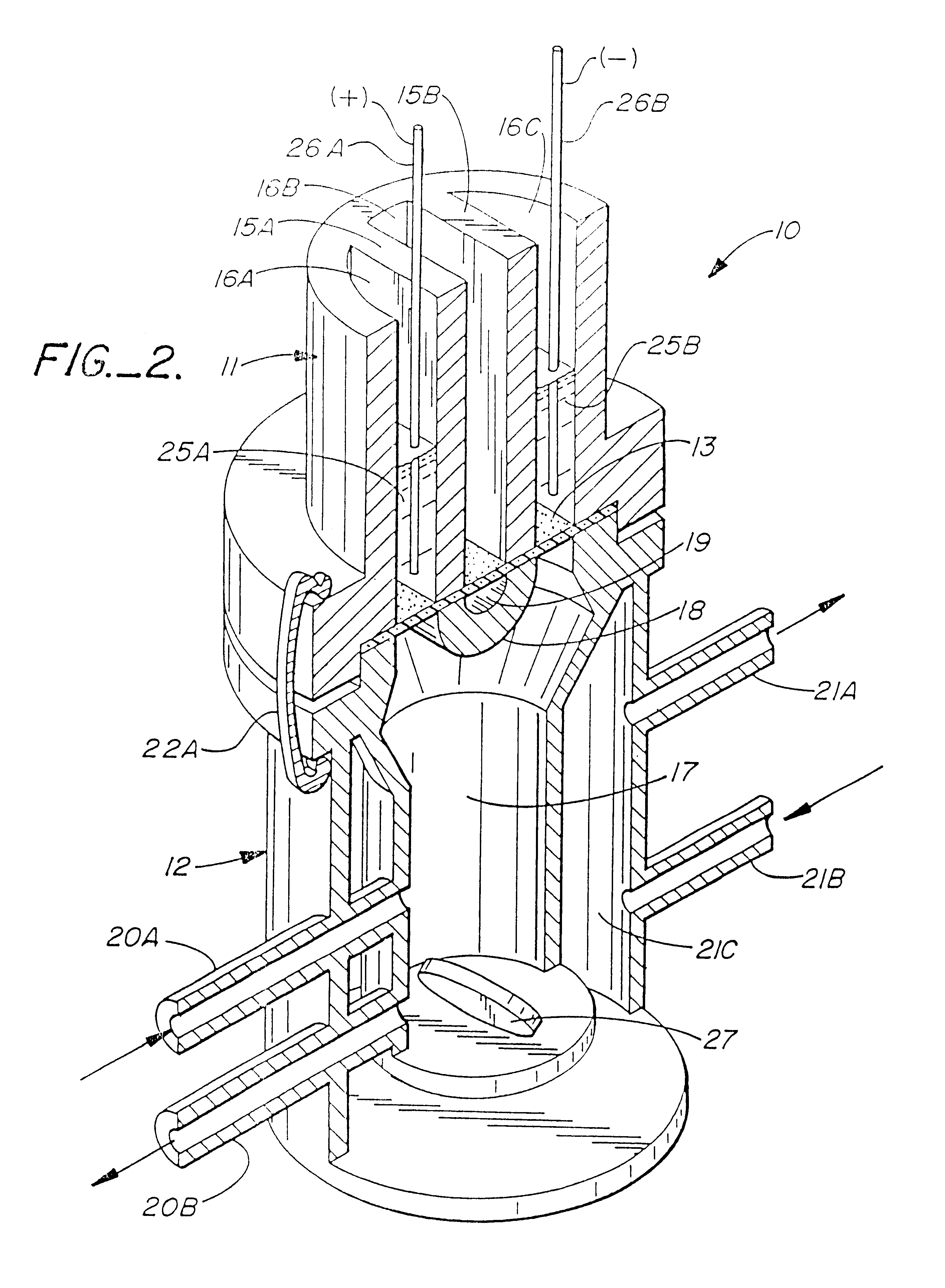
Laminated tube for the transport of charged particles contained in a gaseous medium
InactiveUS6943347B1Reduce gas loadControl flowElectron/ion optical arrangementsIsotope separationGas phaseMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
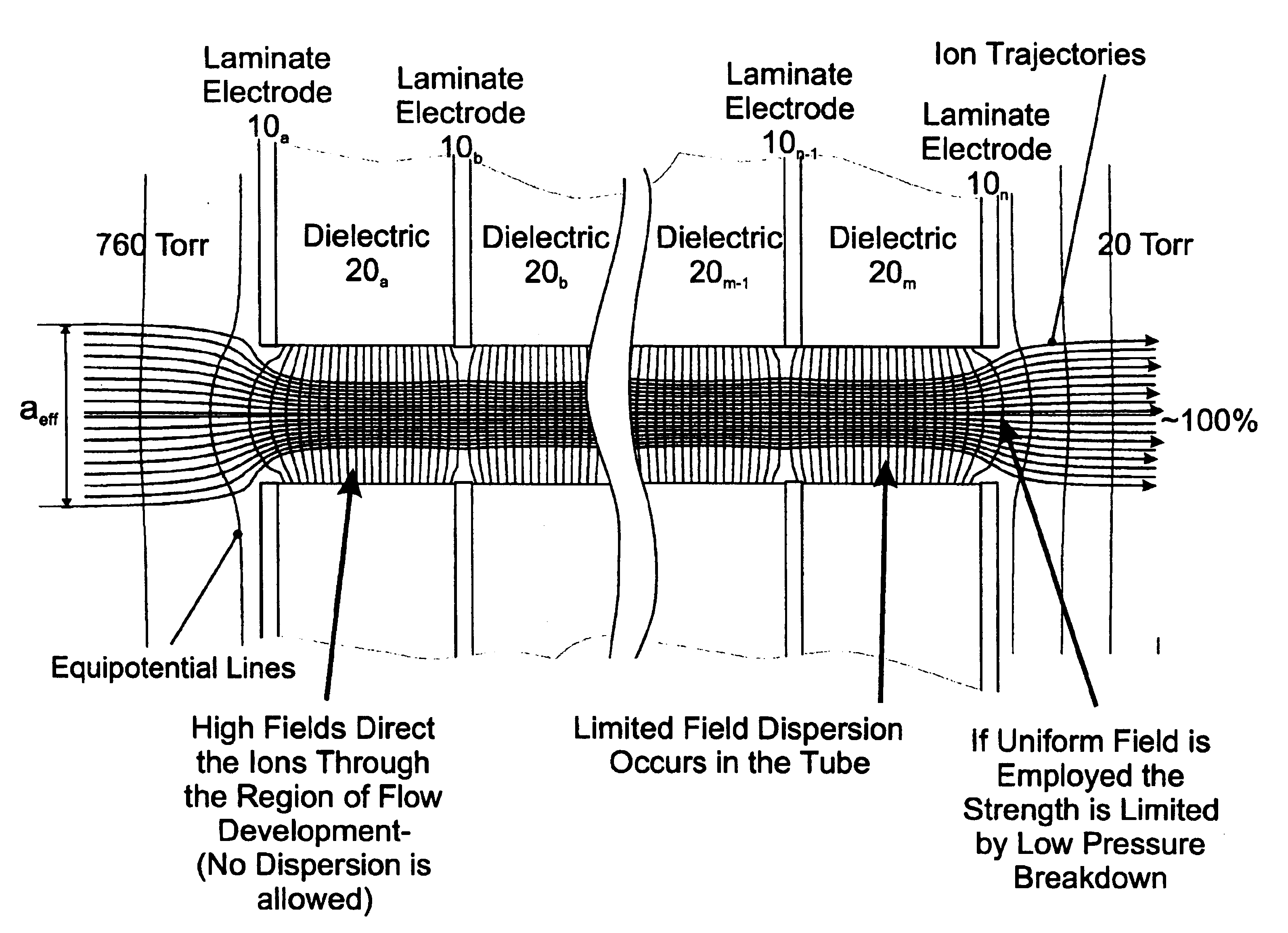
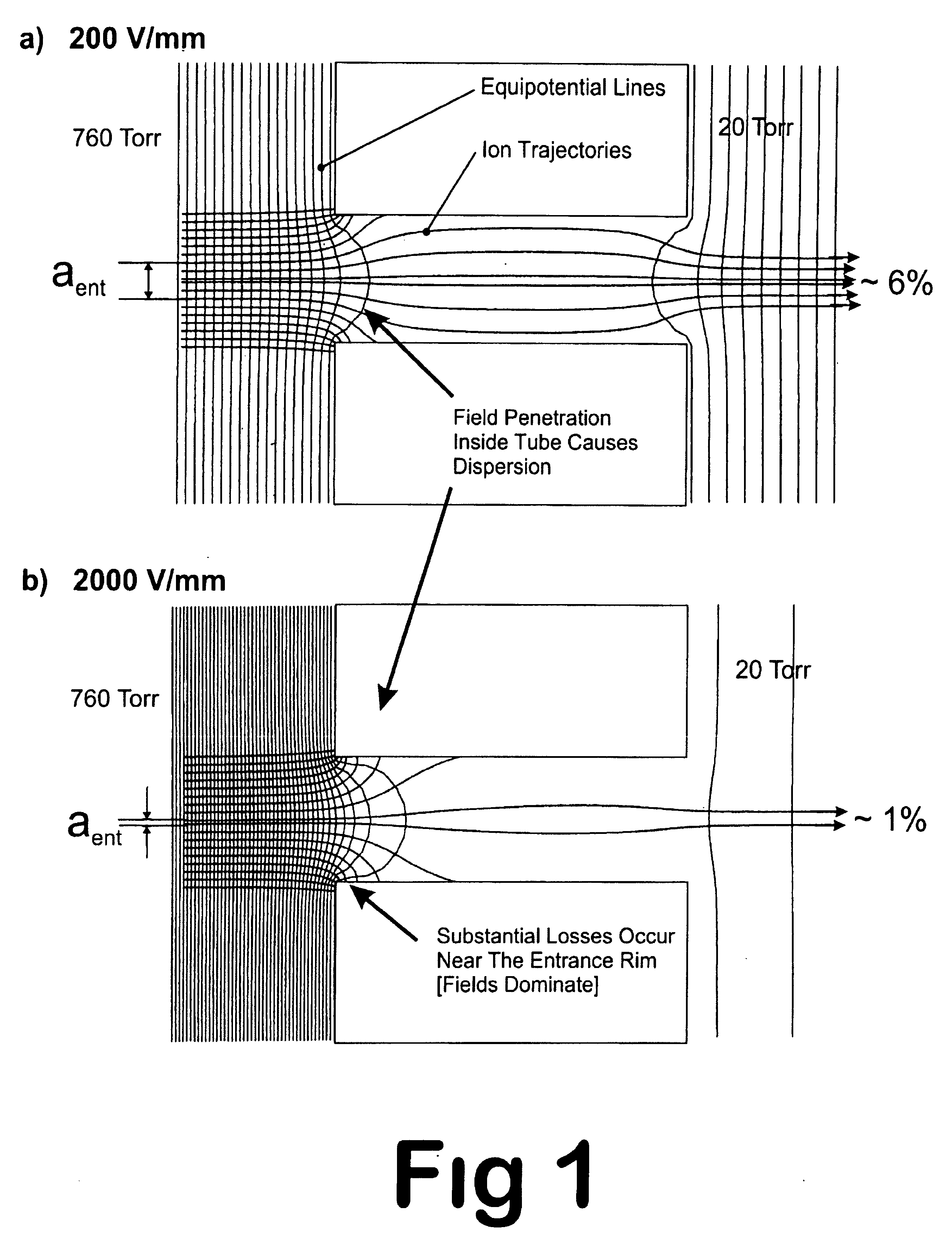
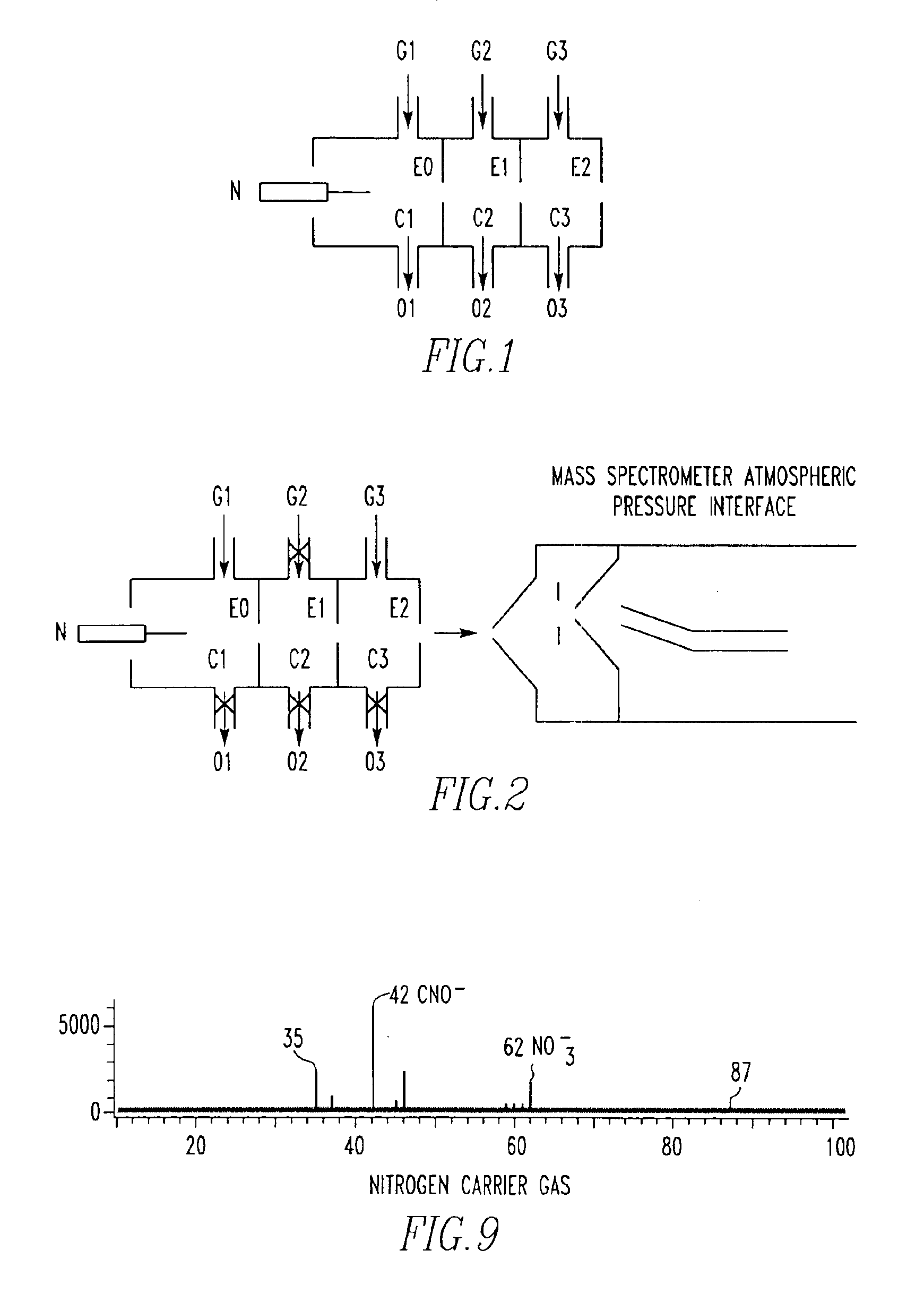
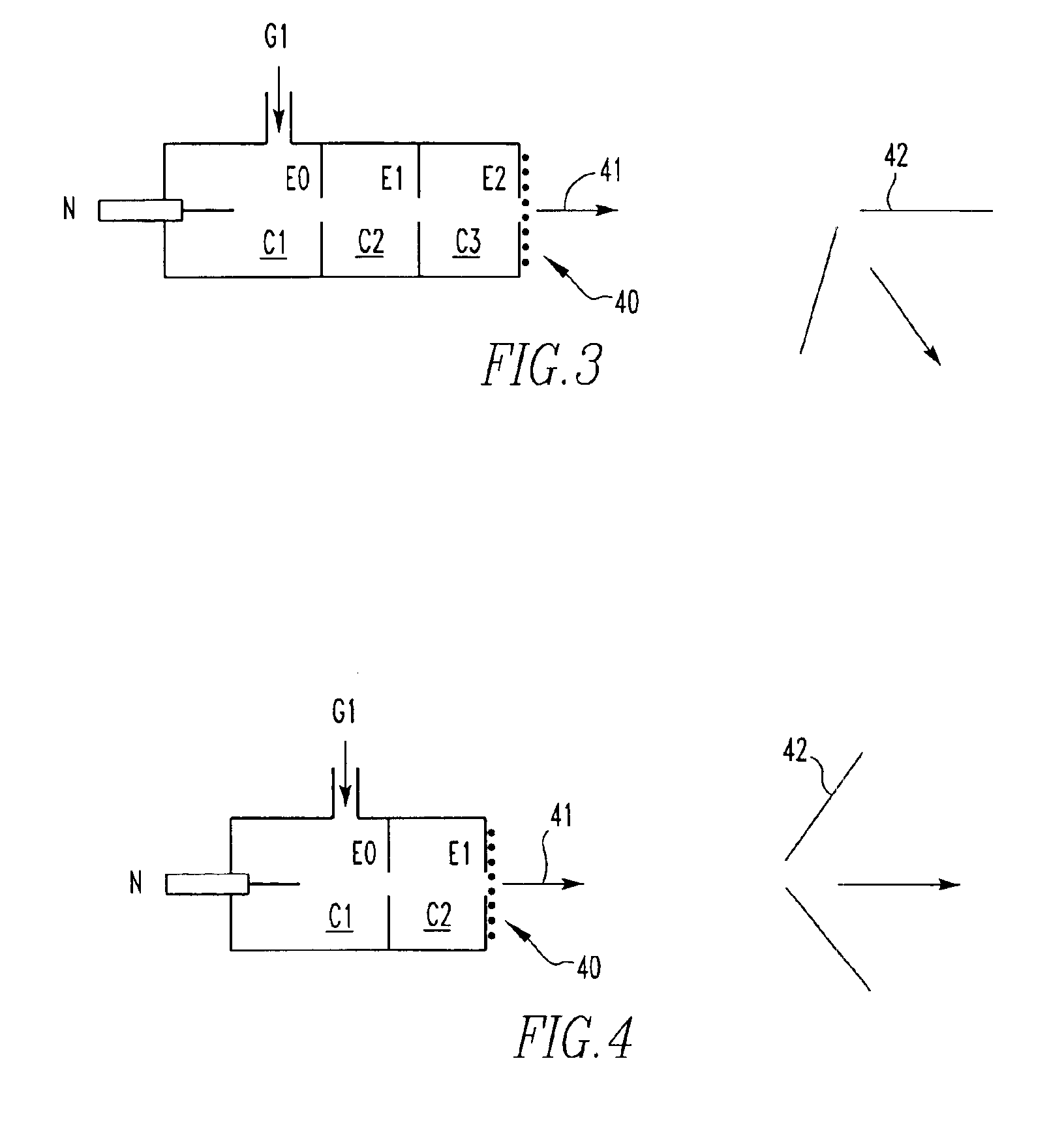
An improved tube for accepting gas-phase ions and particles contained in a gas by allowing substantially all the gas-phase ions and gas from an ion source at or greater than atmospheric pressure to flow into the tube and be transferred to a lower pressure region. Transport and motion of the ions through the tube is determined by a combination of viscous forces exerted on the ions by the flowing gas molecules and electrostatic forces causing the motion of the ions through the tube and away from the walls of the tube. More specifically, the tube is made up of stratified elements, wherein DC potentials are applied to the elements so that the DC voltage on any element determines the electric potential experience by the ions as they pass through the tube. A precise electrical gradient is maintained along the length of the stratified tube to insure the transport of the ions. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving the sensitivity of mass spectrometry or ion mobility spectrometers when coupled to atmospheric and above atmospheric pressure ionization sources. An alternate embodiment of this invention applies an AC voltage to one or more of the conducting elements in the laminate.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
Extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus
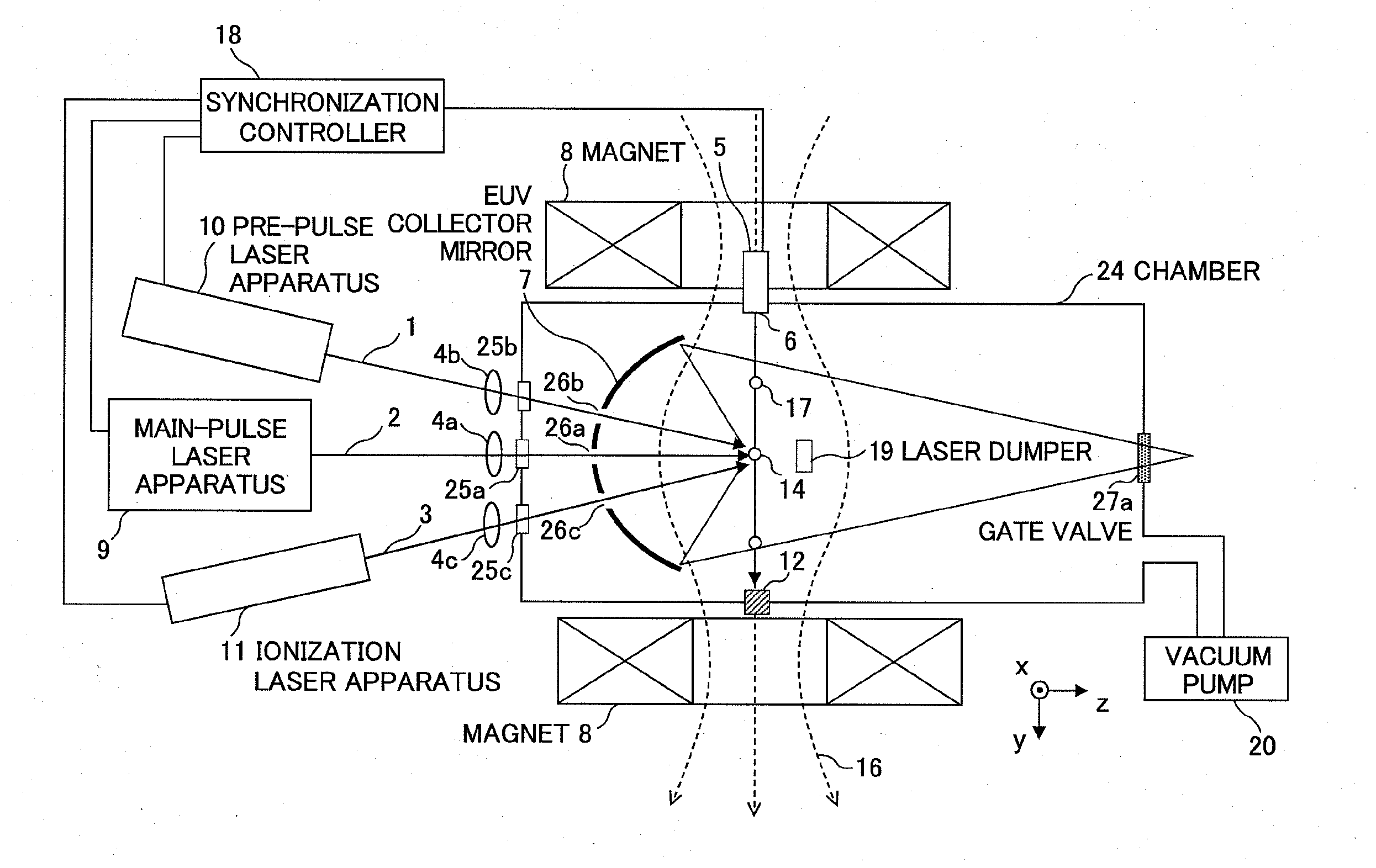
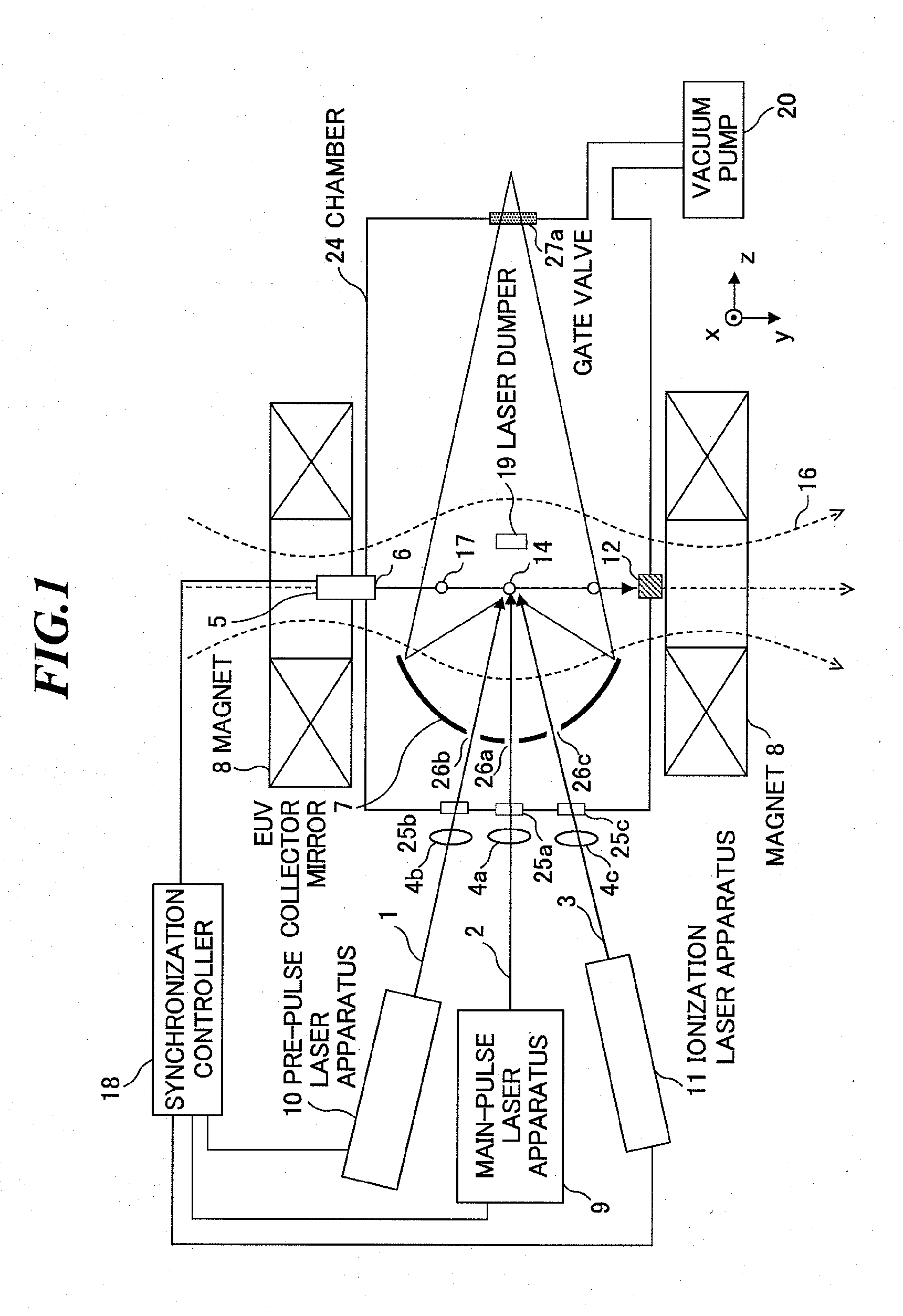
ActiveUS20100181503A1Improve efficiencyDamage to coatingRadiation pyrometryPhotomechanical apparatusExtreme ultravioletIonization
In an EUV light source apparatus, a collector mirror is protected from debris damaging a mirror coating. The EUV light source apparatus includes: a chamber in which extreme ultraviolet light is generated; a target supply unit for supplying a target material into the chamber; a plasma generation laser unit for irradiating the target material within the chamber with a plasma generation laser beam to generate plasma; an ionization laser unit for irradiating neutral particles produced at plasma generation with an ionization laser beam to convert the neutral particles into ions; a collector mirror for collecting the extreme ultraviolet light radiated from the plasma; and a magnetic field or electric field forming unit for forming a magnetic field or an electric field within the chamber so as to trap the ions.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
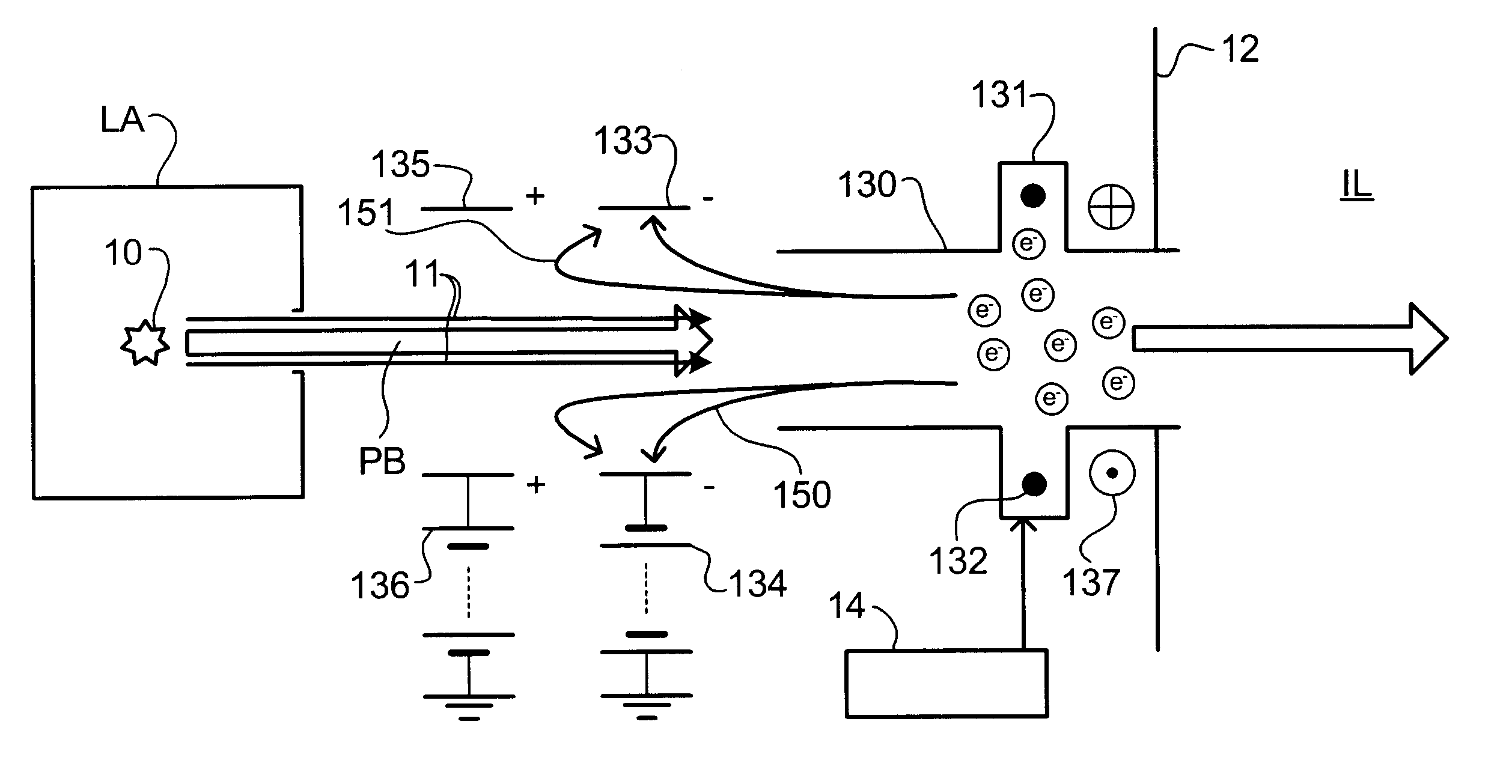
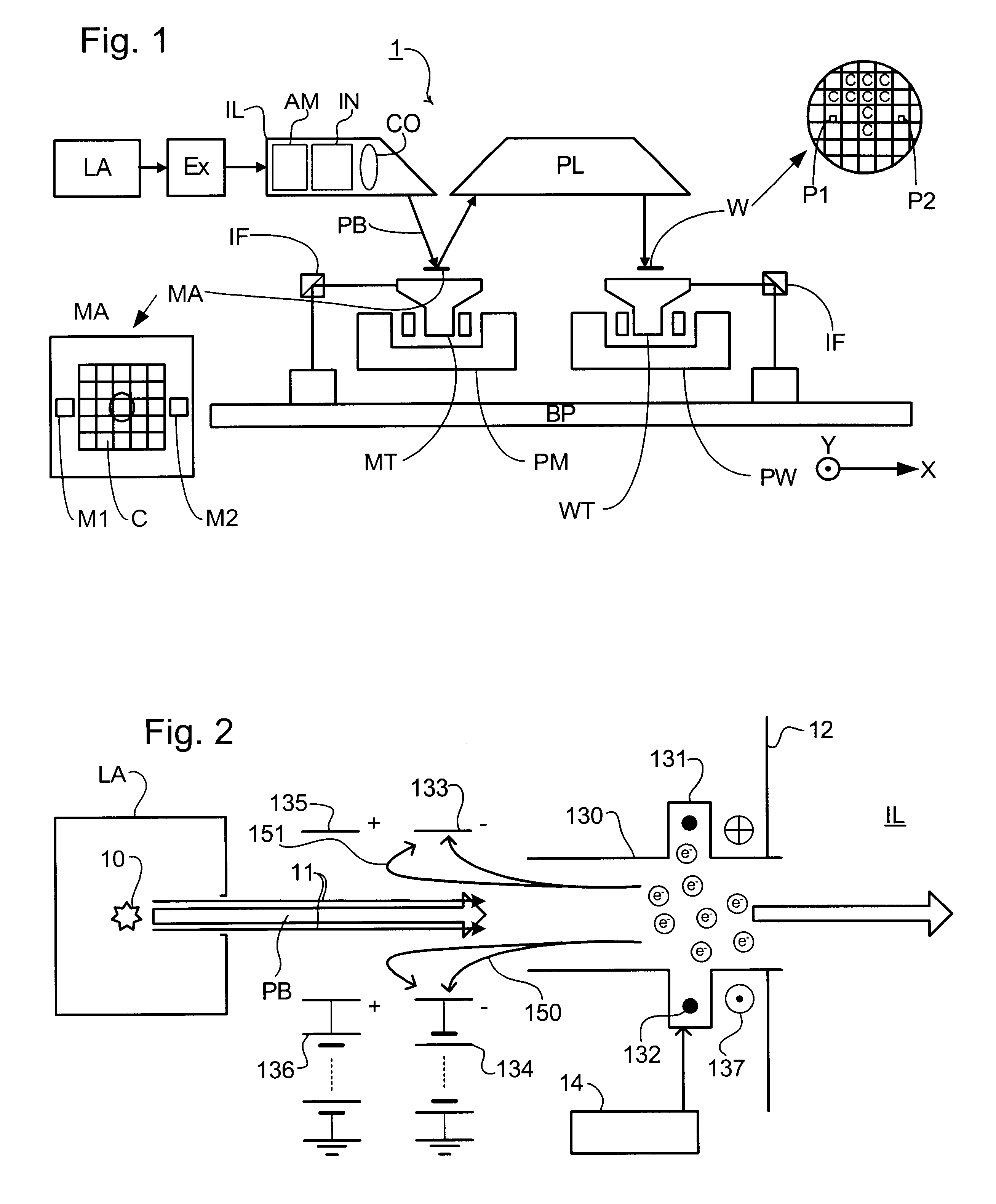
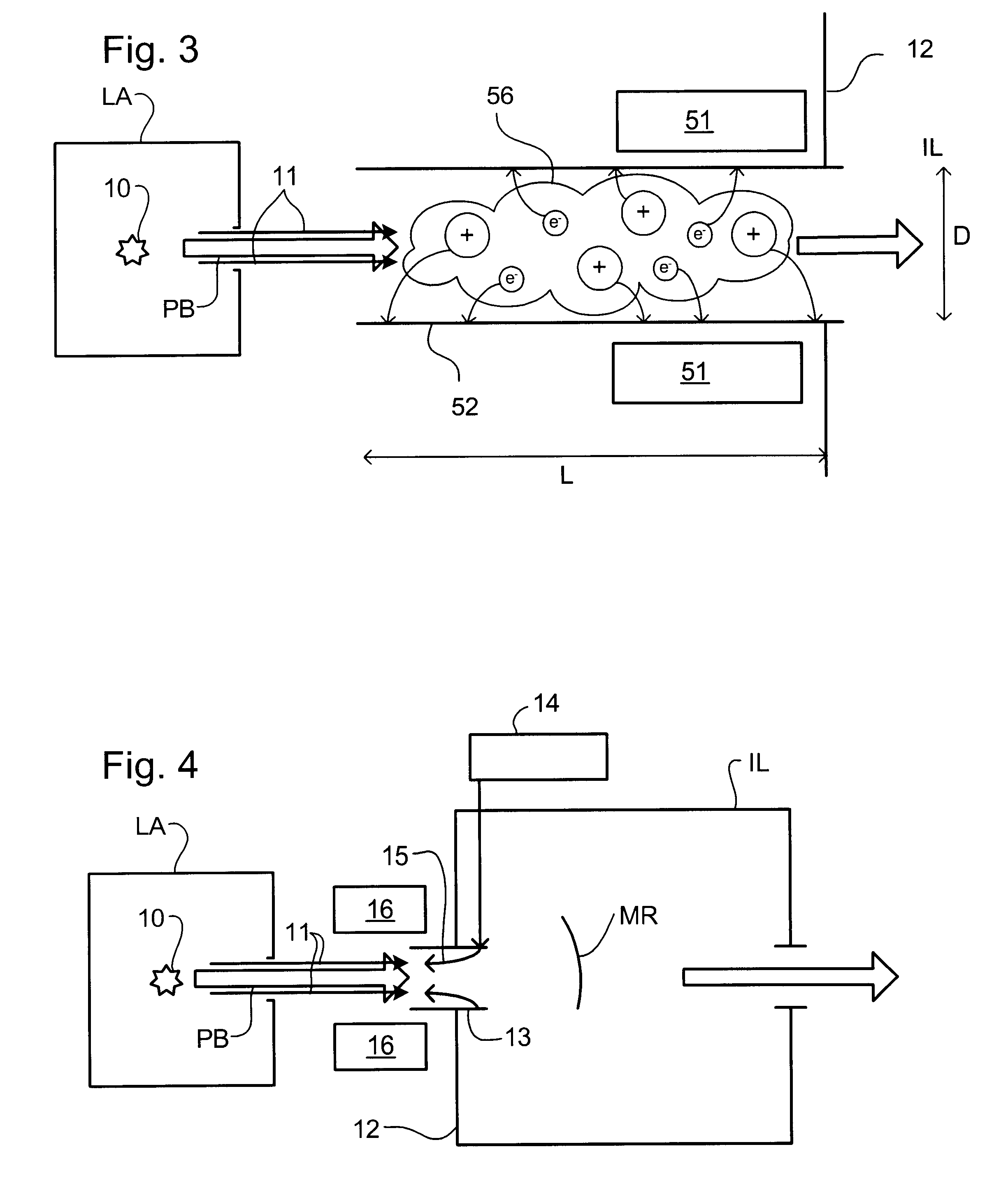
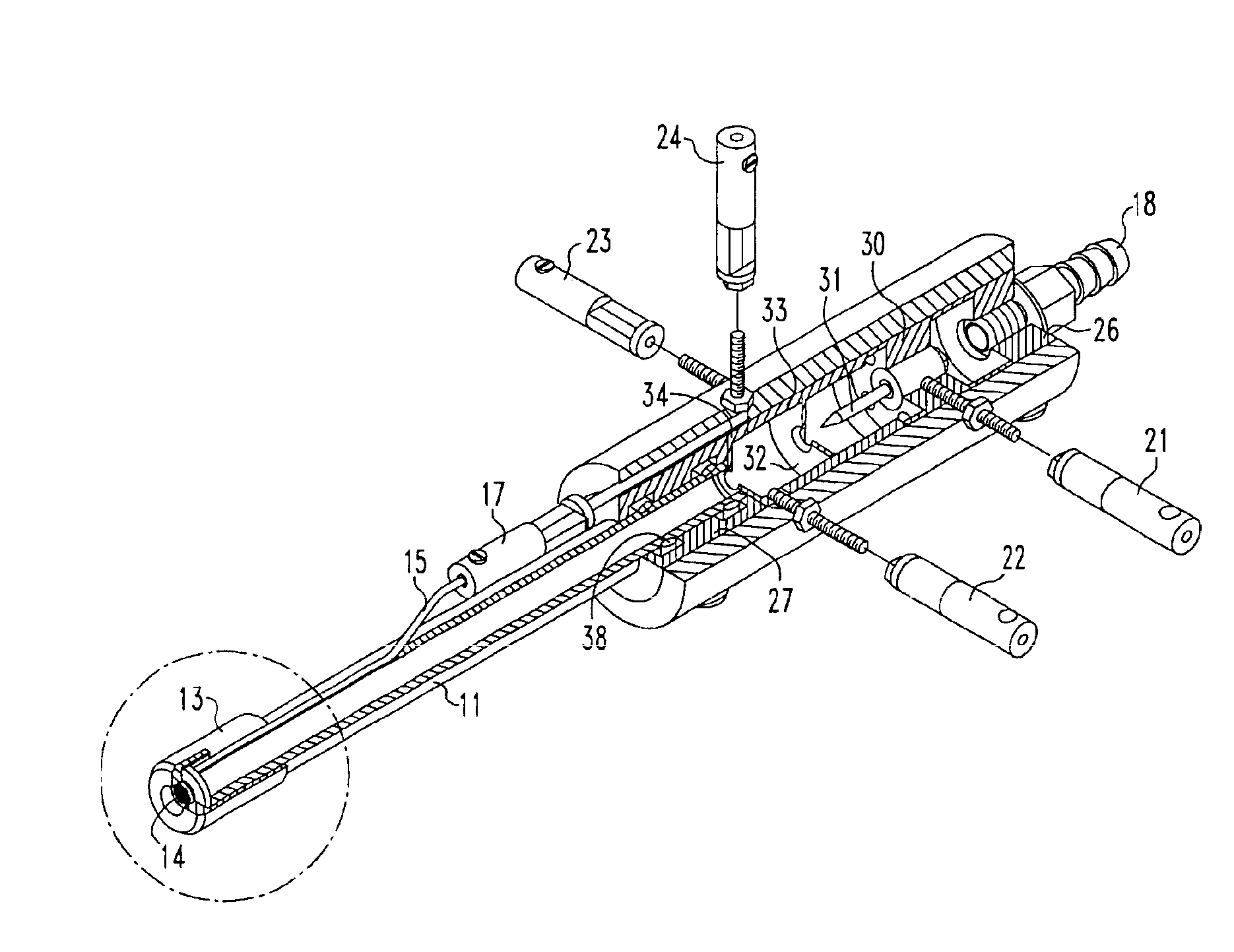
Lithographic projection apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS6614505B2Good removal effectImprove the ionization effectInvestigating moving sheetsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIonizationGas supply
Contaminant particles travelling with a projection beam in a lithographic projection apparatus are ionized. A purge gas may be attracted towards getter plates provided upstream of the purge gas supply. A magnetic field traps electrons generated by the ionizer to improve the ionization of the purge gas. The contaminant particles can be ionized by generating a plasma in a tube having a greater length than width.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Atmospheric pressure ion source
A non-radioactive atmospheric pressure device for ionization of analytes comprises an atmospheric pressure chamber having an inlet for carrier gas, a first electrode at one end, and a counter-electrode at the other end of the chamber for creating an electrical discharge in the carrier gas thus creating metastable neutral excited-state species. Optionally, a grid is provided to generate electrons or ions by contact with the excited-state species. The carrier gas containing the excited-state species or the electrons generated therefrom is directed at an analyte at atmospheric pressure near ground potential to form analyte ions.
Owner:JEOL USA
Light emitting element and light emitting device
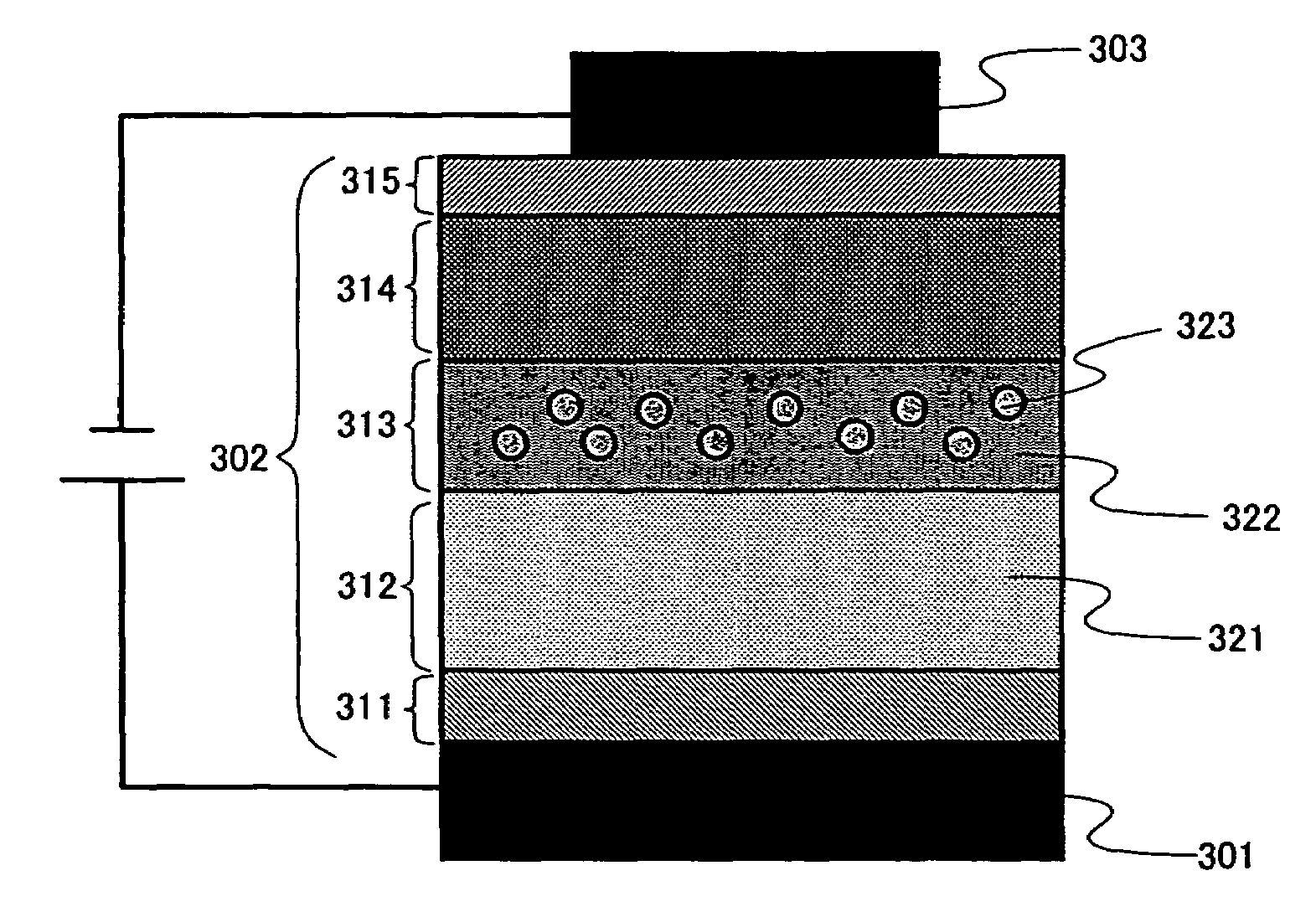
InactiveUS7943925B2Improve light emission efficiencyImprove efficiencyLamination ancillary operationsDischarge tube luminescnet screensHigh concentrationPeak value
A high efficient white emission light emitting element having peak intensity in each wavelength region of red, green, and blue is provided. Specifically, a white emission light emitting element having an emission spectrum that is independent of current density is provided. A first light emitting layer 312 exhibiting blue emission and a second light emitting layer 313 containing a phosphorescent material that generates simultaneously phosphorescent emission and excimer emission are combined. In order to derive excimer emission from the phosphorescent material, it is effective to disperse a phosphorescent material 323 having a high planarity structure such as platinum complex at a high concentration of at least 10 wt % to a host material 322. Further, the first light emitting layer 312 is provided to be in contact with the second light emitting layer 313 at the side of an anode. Ionization potential of the second light emitting layer 313 is preferably larger by 0.4 eV than that of the first light emitting layer 312.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
High efficiency solid-state light source and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS8192053B2Improve efficiencyIncrease powerOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceHigh intensity light
A high-intensity light source is formed by a micro array of a semiconductor light source such as a LEDs, laser diodes, or VCSEL placed densely on a liquid or gas cooled thermally conductive substrate. The semiconductor devices are typically attached by a joining process to electrically conductive patterns on the substrate, and driven by a microprocessor controlled power supply. An optic element is placed over the micro array to achieve improved directionality, intensity, and / or spectral purity of the output beam. The light module may be used for such processes as, for example, fluorescence, inspection and measurement, photopolymerzation, ionization, sterilization, debris removal, and other photochemical processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Solvent system of hardly soluble drug with improved dissolution rate
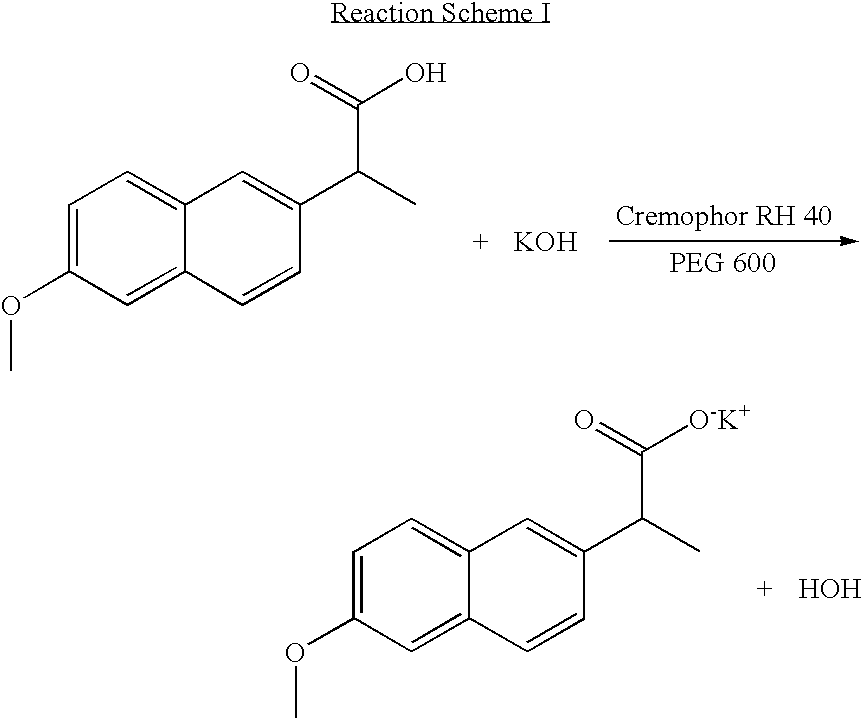
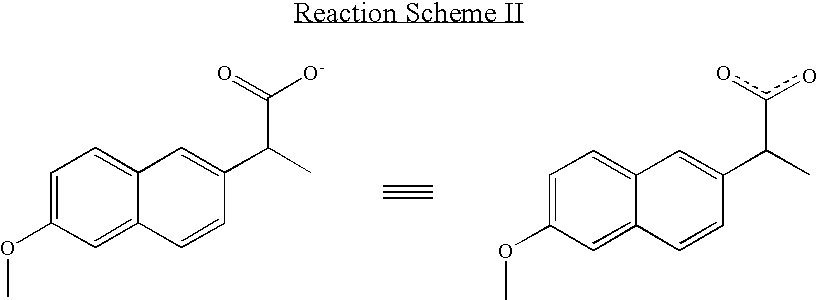
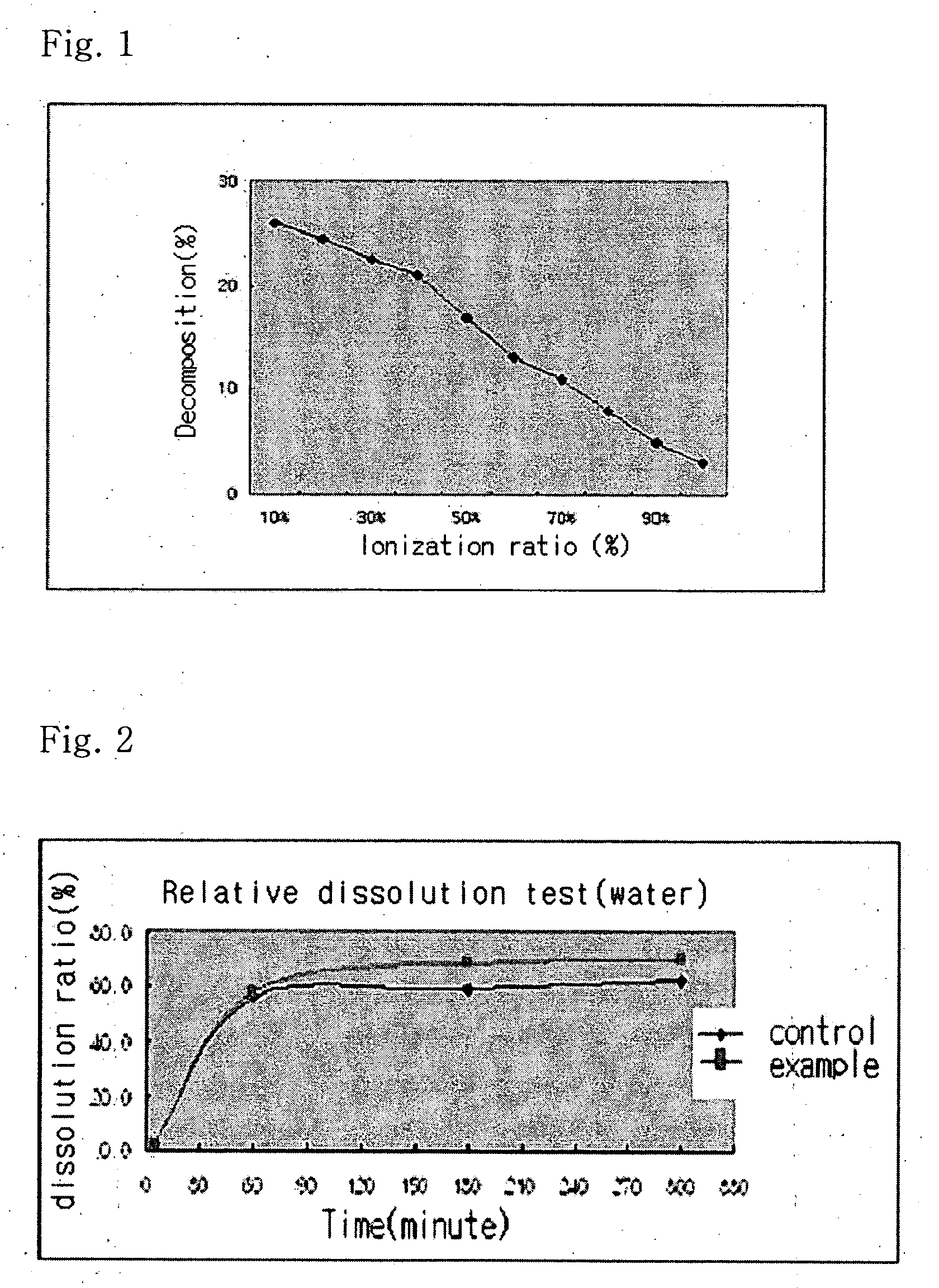
InactiveUS20040157928A1Good disintegrationPromote dissolutionBiocideAntipyreticDissolutionIonization
The present invention relates to a solvent system with improved disintegration degree and dissolution ratio of a hardly soluble drug by highly concentrating the drug through partial ionization, and by establishing optimal conditions for enhancing bioavailability of the drug, such as the co-relation between the acid drug and the accompanied components, ionization degree of a solvent system, use of an appropriate cation acceptance, water content, selection of optimal mixing ratio of the respective components and use of specific surfactants, and to a pharmaceutical preparation comprising the same. The solvent system of the invention has advantages in that it can enhance bioavailability by improving the disintegration degree and dissolution ratio of a hardly soluble drug and also provide a capsule with a sufficiently small volume to permit easy swallowing.
Owner:R & P KOREA
Electrostatic filter cartridge for a tower air cleaner
InactiveUS20080314250A1Improve removal efficiencyImprove drainage capacityHuman health protectionMagnetic separationParticulatesTower
The disclosed electrostatic precipitator cartridge for a tower air cleaner in accord with the present invention is low-cost, because constructed of injected molded plastics material and stamped and extruded metal components. It is easy to clean, not only because it's constitutive metal parts and plastic components are machine washable but also because the cartridge as a whole is machine washable, the pieces and components are designed and arranged to prevent intracartridge fluid buildup or retention after washing, thereby eliminating any electrical shorting or arcing or other undesirable phenomena resulting therefrom that could interfere with the operation of the electrostatic filter cartridge. It is mechanically stable and has high particulate collection efficiency because it's ionizer bars have a predetermined preferably air foil shape that provides improved ionization efficiency and that imparts improved torsion stability rendering it possible to provide taller electrostatic filter cartridges and / or greater cleaning power.
Owner:LASKO OPERATION HLDG LLC
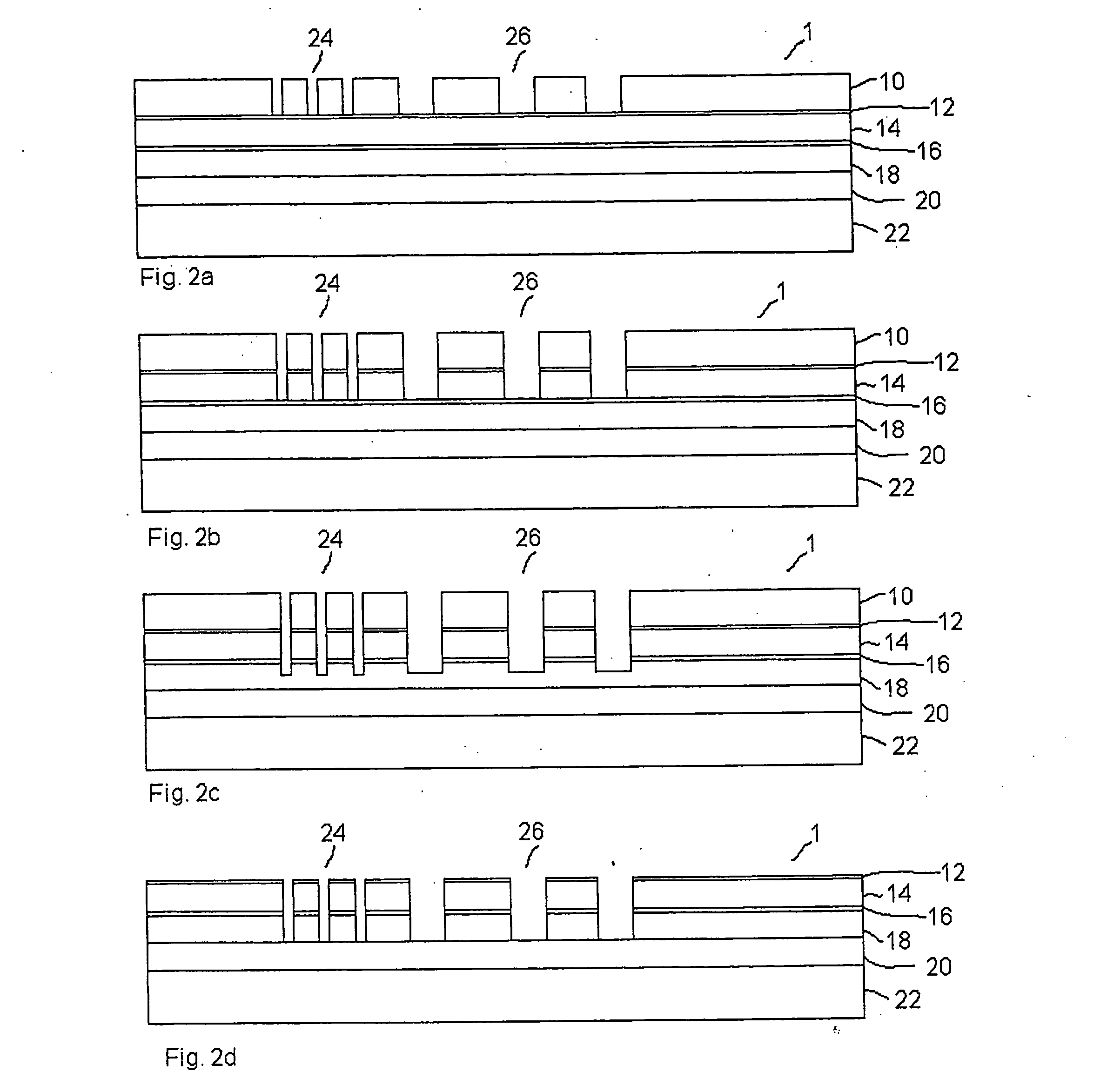
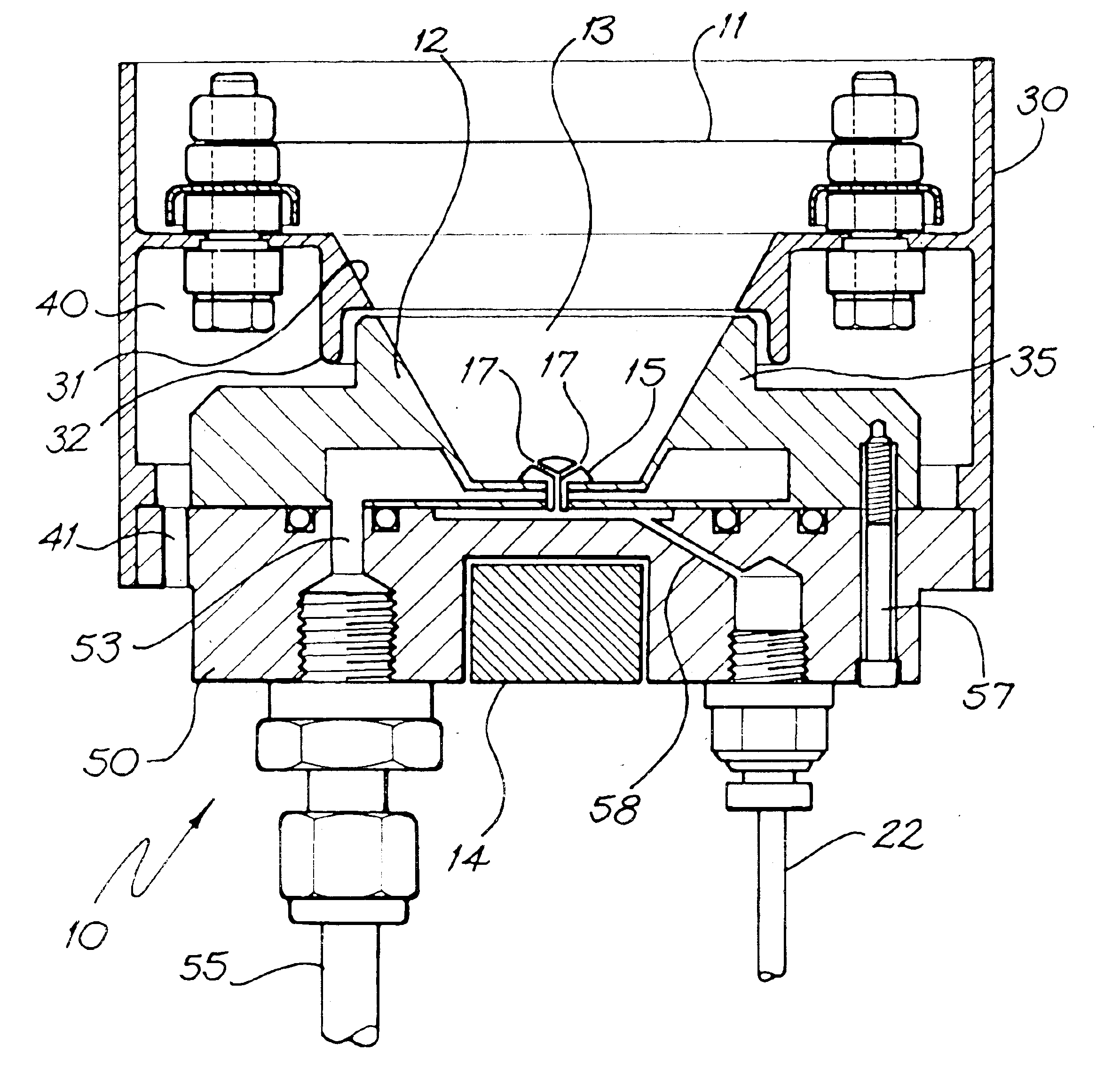
Surface-enhanced affinity capture for desorption and detection of analytes
InactiveUS6027942AFacilitate desorption/ionizationAccurately determineTime-of-flight spectrometersComponent separationAnalyteDesorption
This invention relates generally to a mass spectrometer probe and a method of using said probe for desorption and ionization of analytes. The sample probe comprises an affinity reagent on the probe surface, wherein the affinity reagent is capable of selectively binding an analyte. An analyte bound to the affinity reagent can be desorbed by a high energy source and detected in the mass spectrometer. The probe and methods are useful in detection and analysis of macromolecules such as proteins or other biomolecules.
Owner:HUTCHENS T WILLIAM
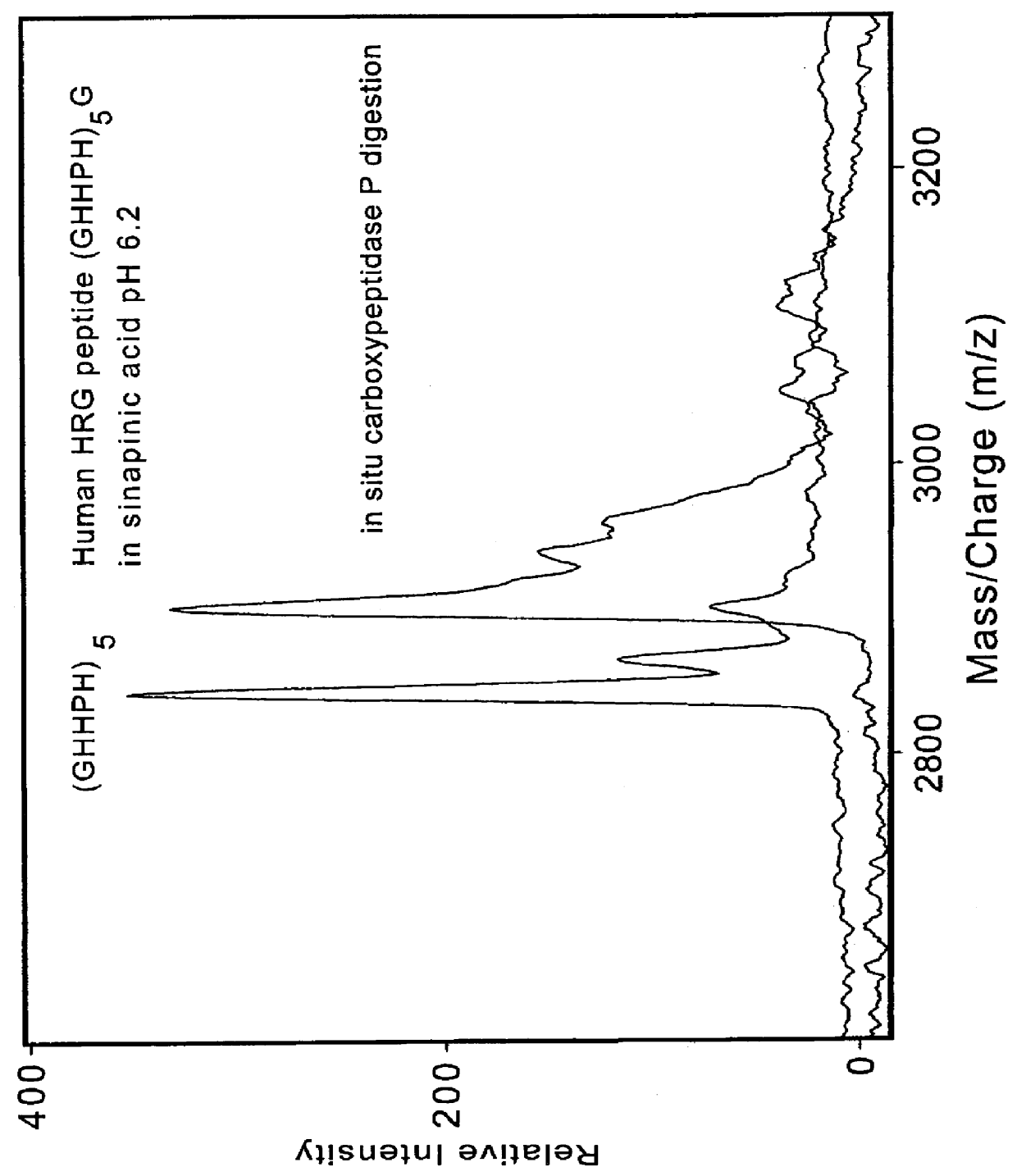
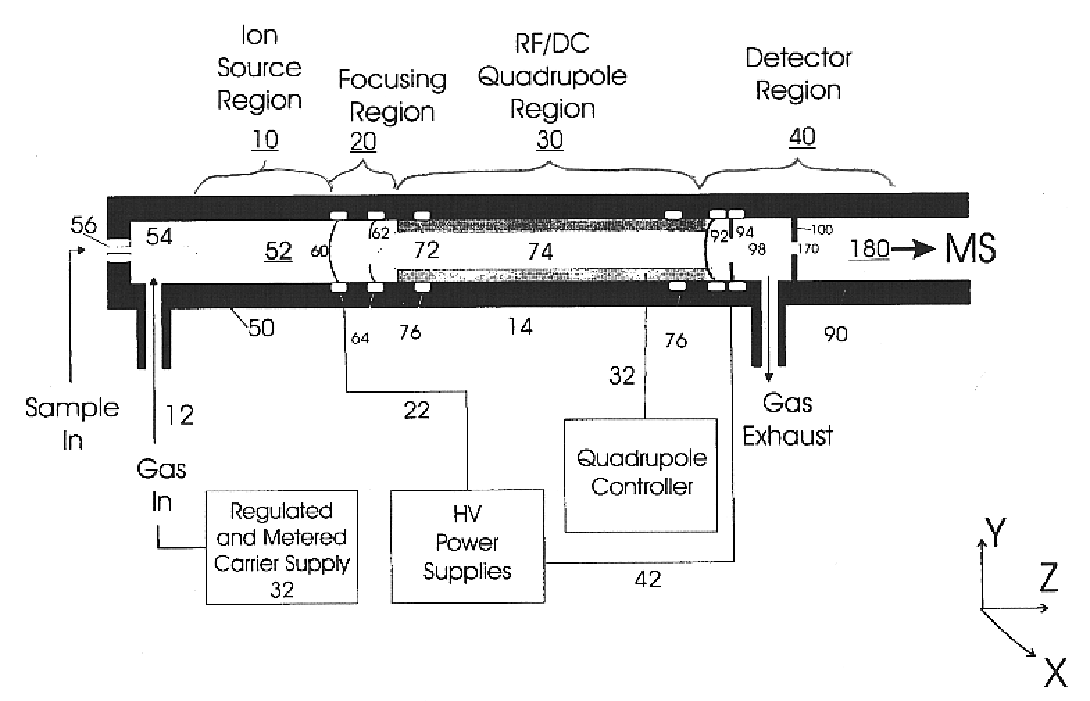
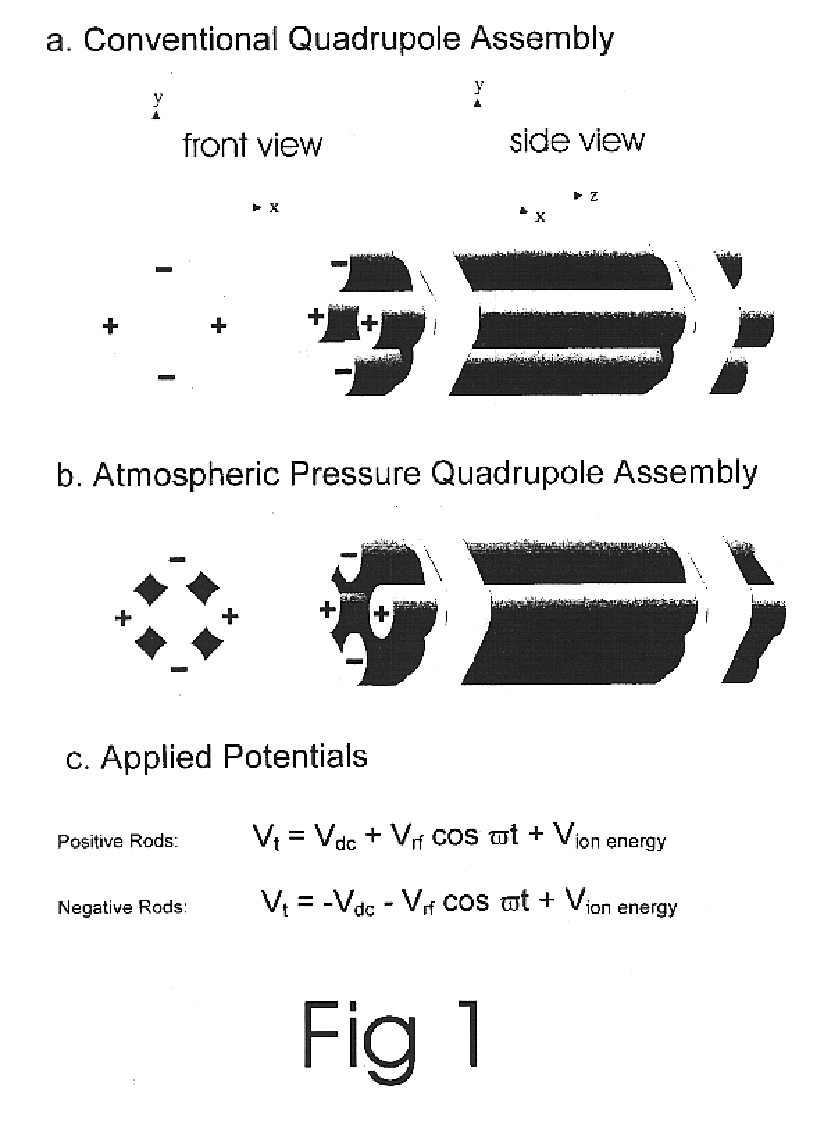
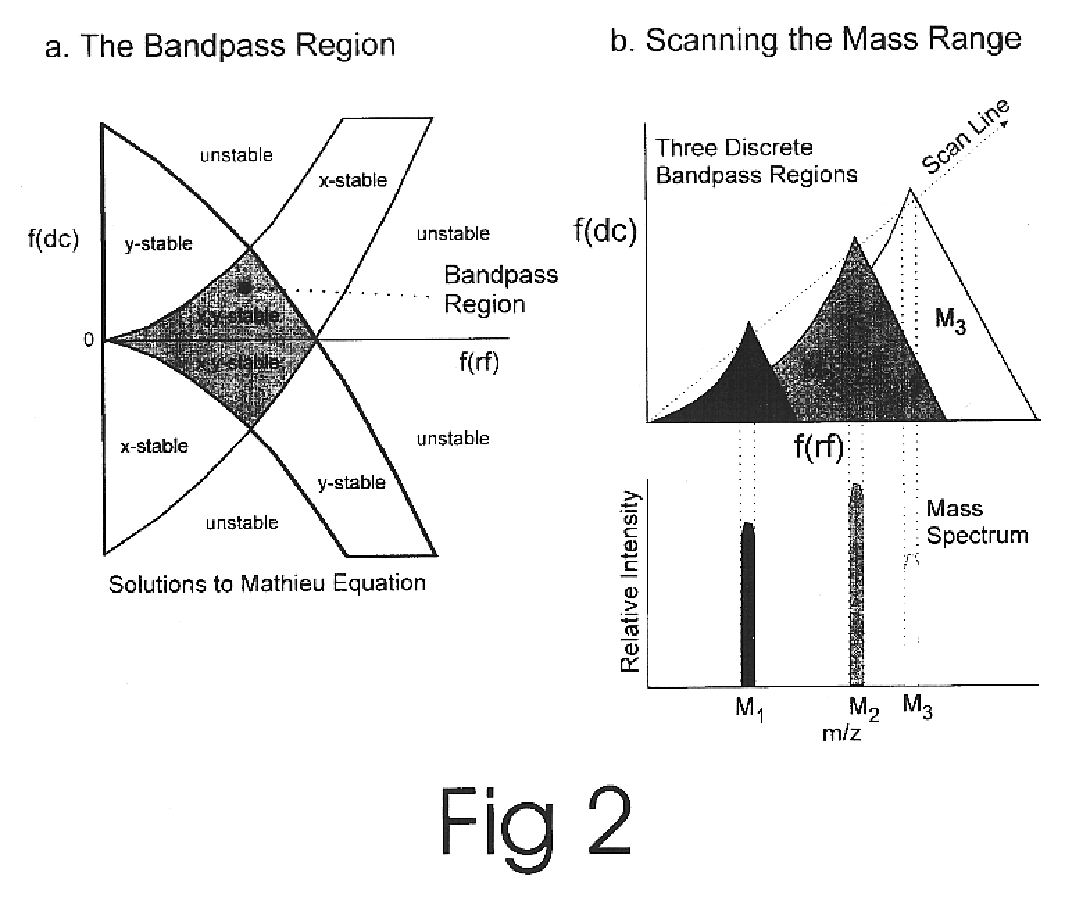
Apparatus and method for focusing and selecting ions and charged particles at or near atmospheric pressure
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for focusing, separating, and detecting gas-phase ions using the principles of quadrupole fields, substantially at or near atmospheric pressure. Ions are entrained in a concentric flow of gas and travel through a high-transmission element into a RF / DC quadrupole, through a second high-transmission element, and then impact on an ion detector, such as a faraday plate; or through an aperture with subsequent identification by a mass spectrometer. Ions with stable trajectories pass through the RF / DC quadrupole while ions with unstable trajectories drift off-axis collide with the rods and are lost. Embodiments of this invention are devices and methods for focusing, separating and detecting gas-phase ions without the need for a vacuum chamber when coupled to atmospheric ionization sources.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
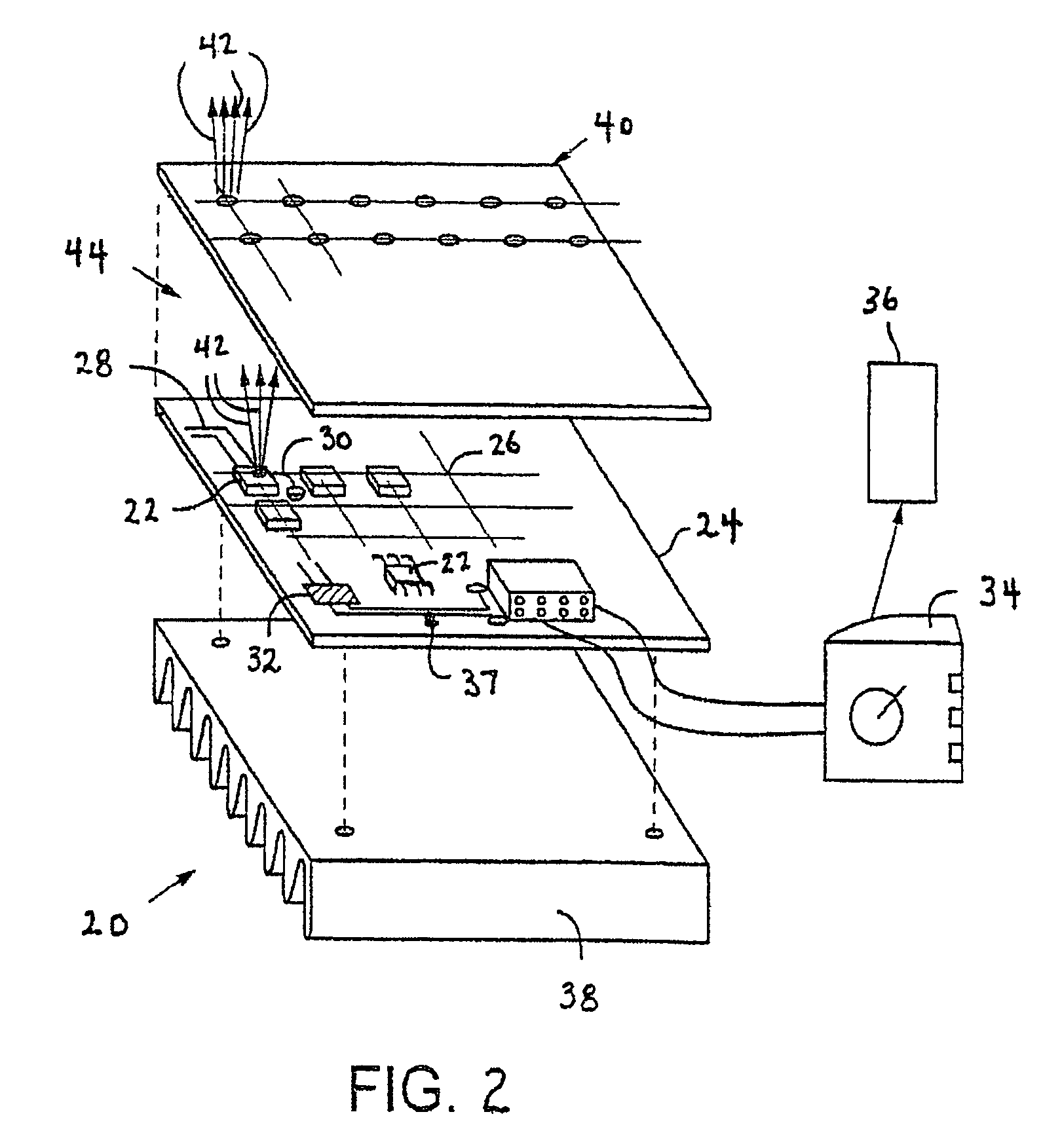
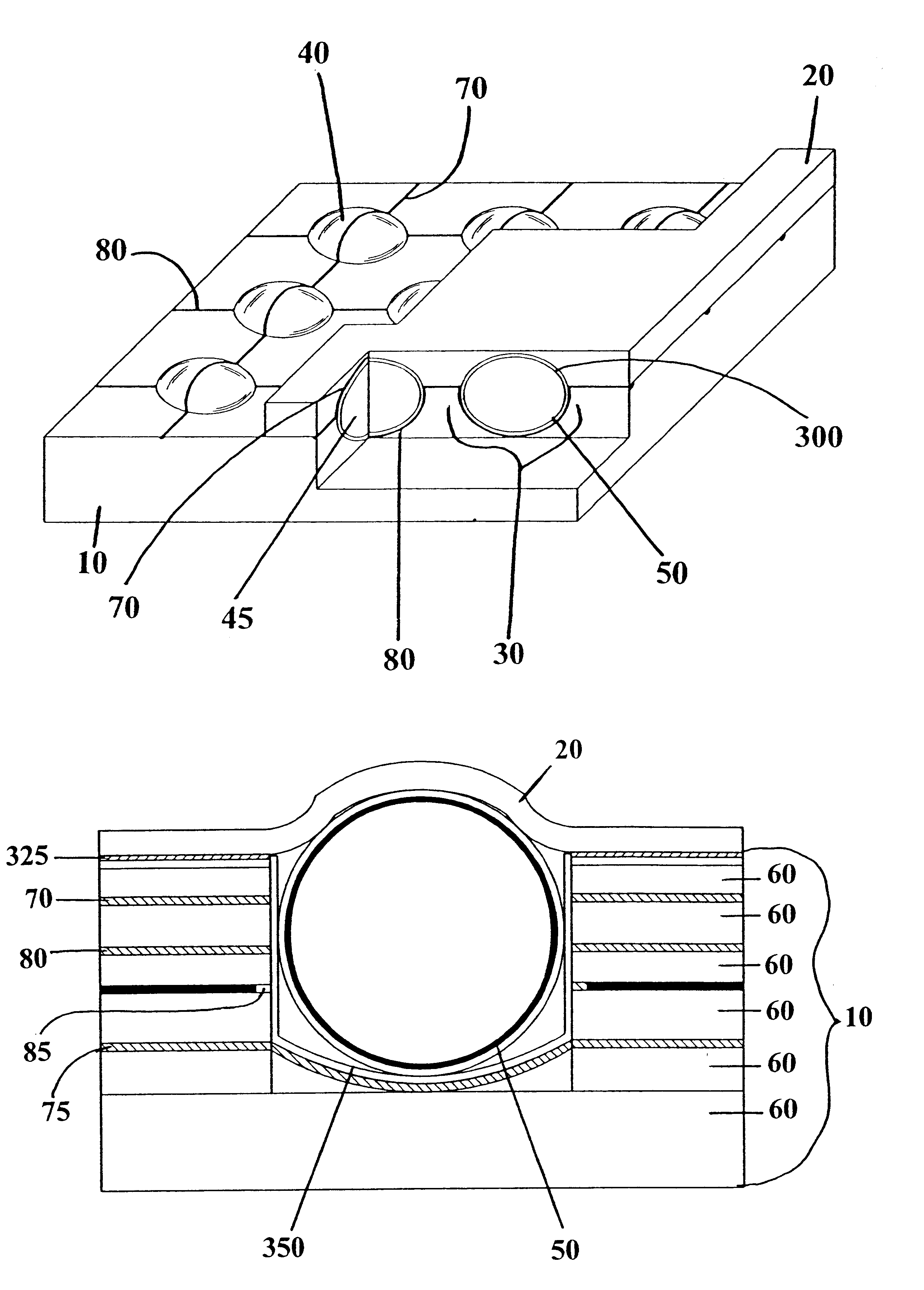
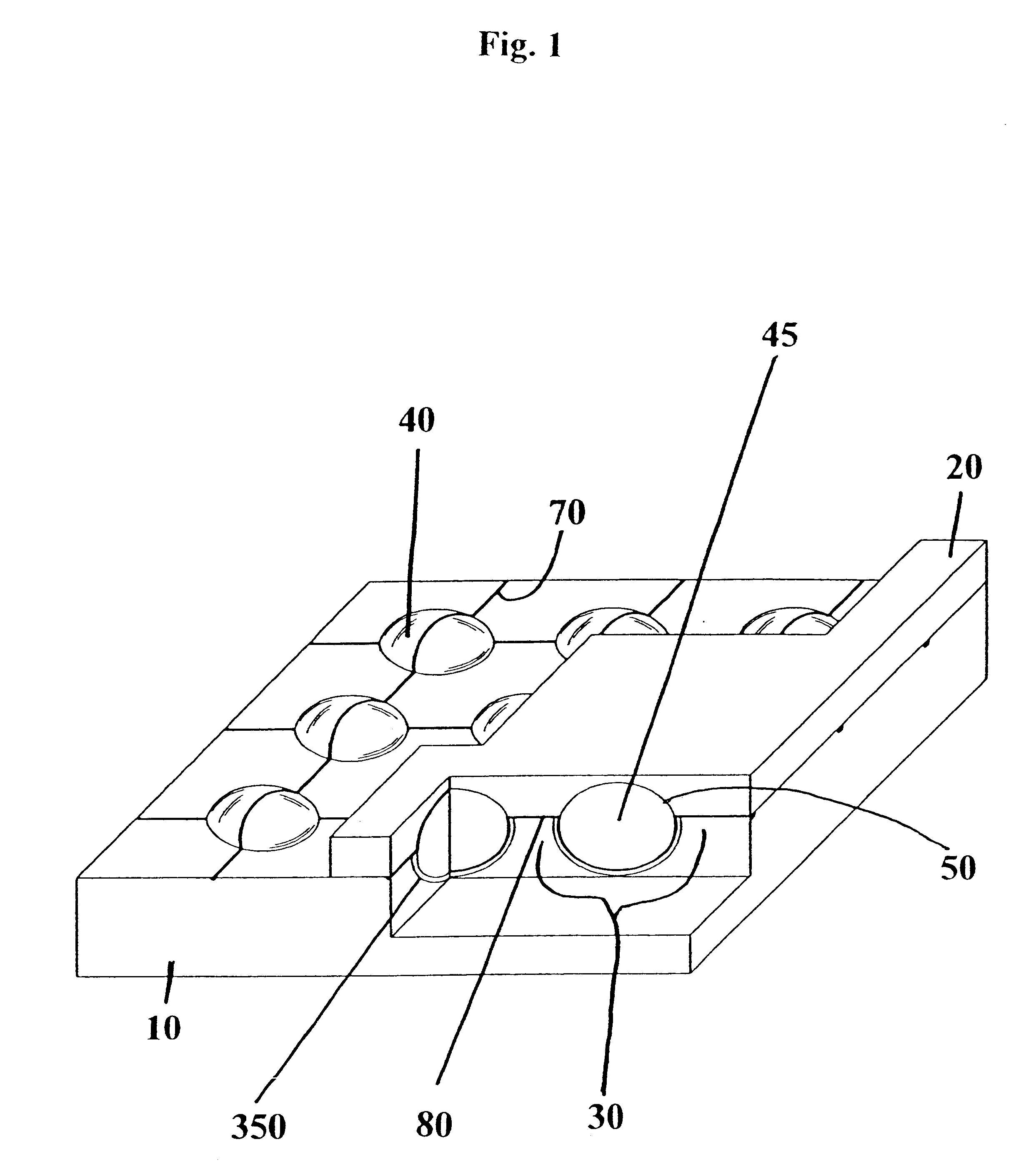
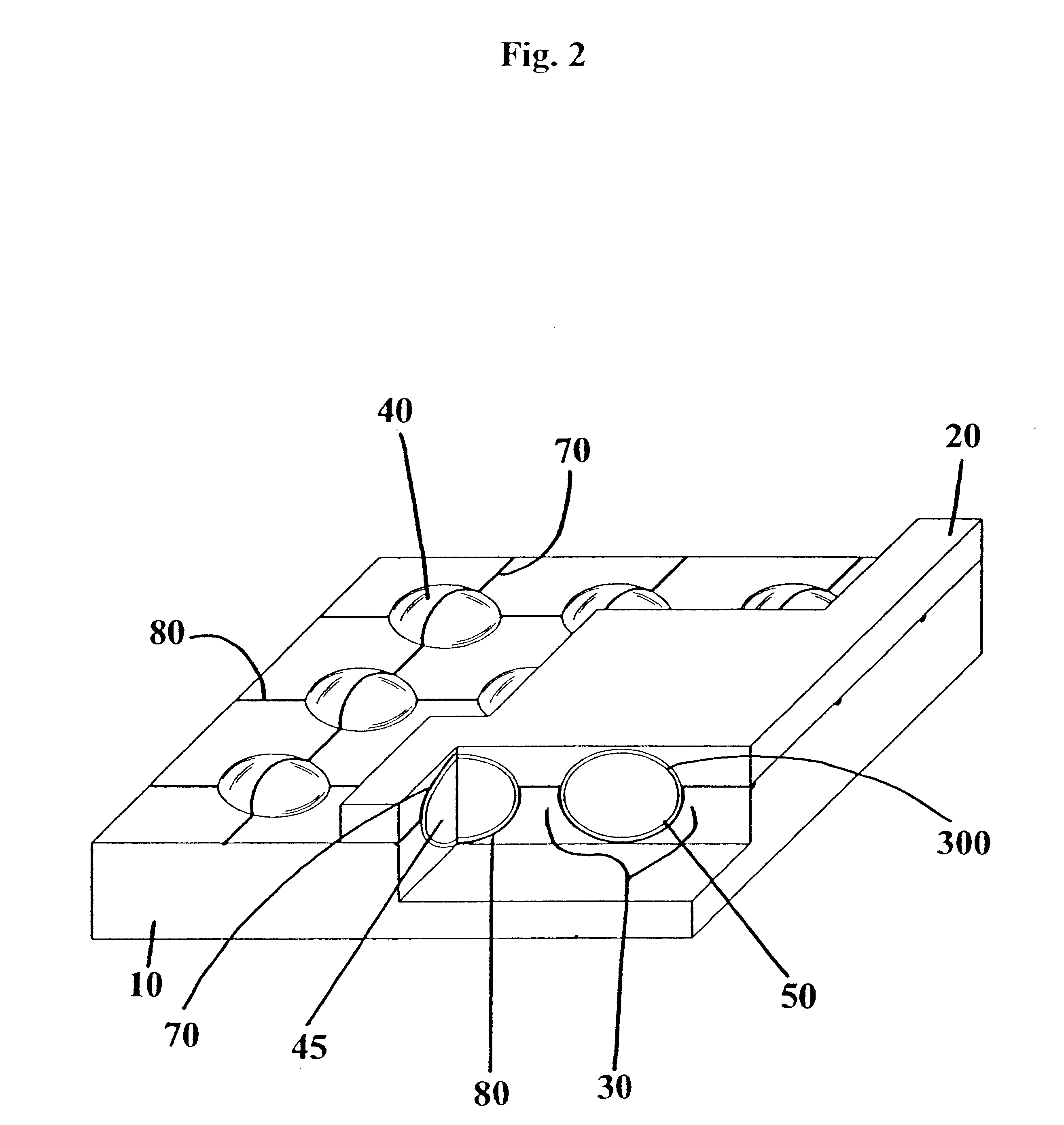
Socket for use with a micro-component in a light-emitting panel
InactiveUS6545422B1Sufficient resolutionManufactured very thinEmission spectroscopyStatic indicating devicesIonizationVoltage
An improved light-emitting panel having a plurality of micro-components at least partially disposed in a socket and sandwiched between two substrates is disclosed. Each micro-component contains a gas or gas-mixture capable of ionization when a sufficiently large voltage is supplied across the micro-component via at least two electrodes.
Owner:LEIDOS
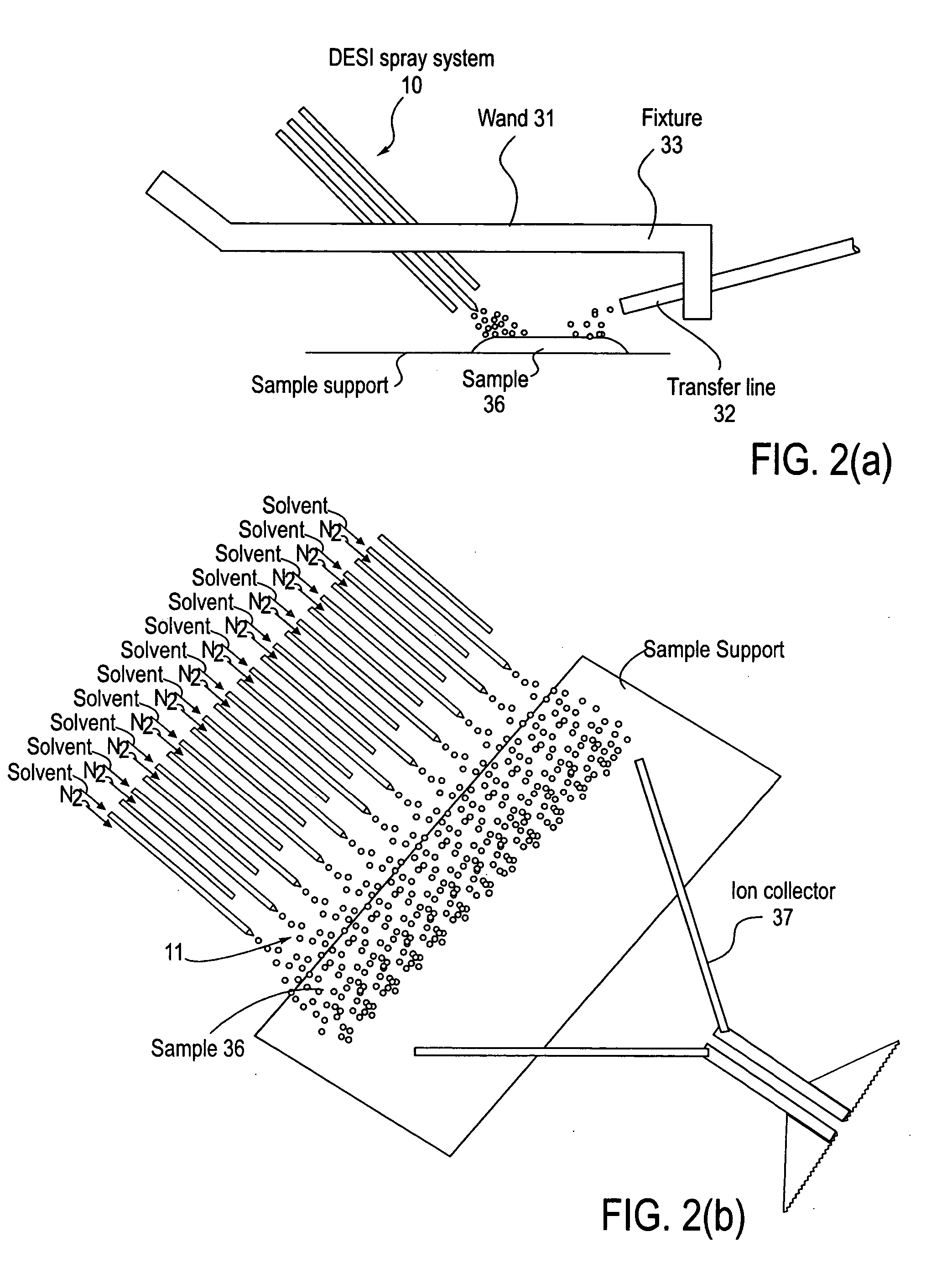
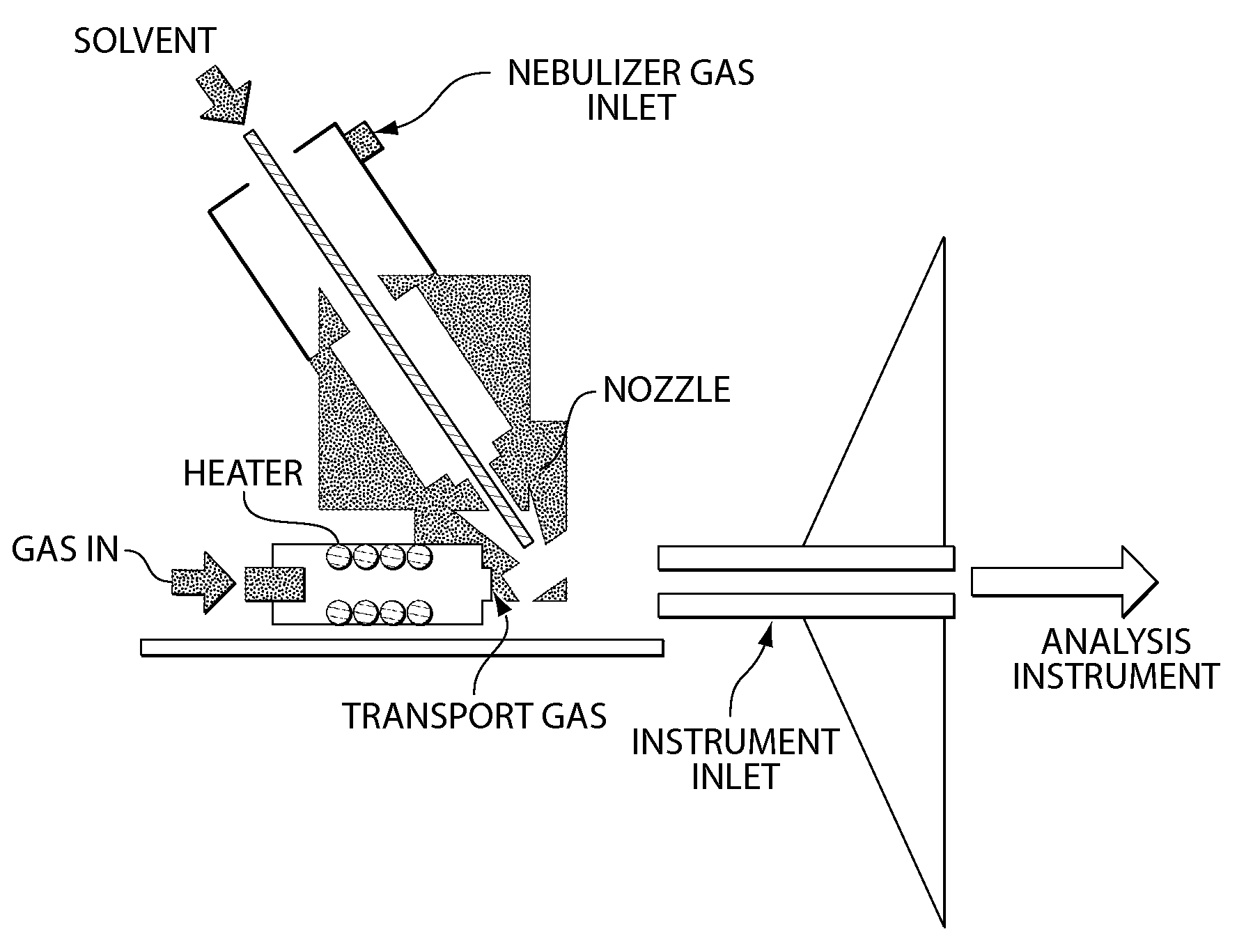
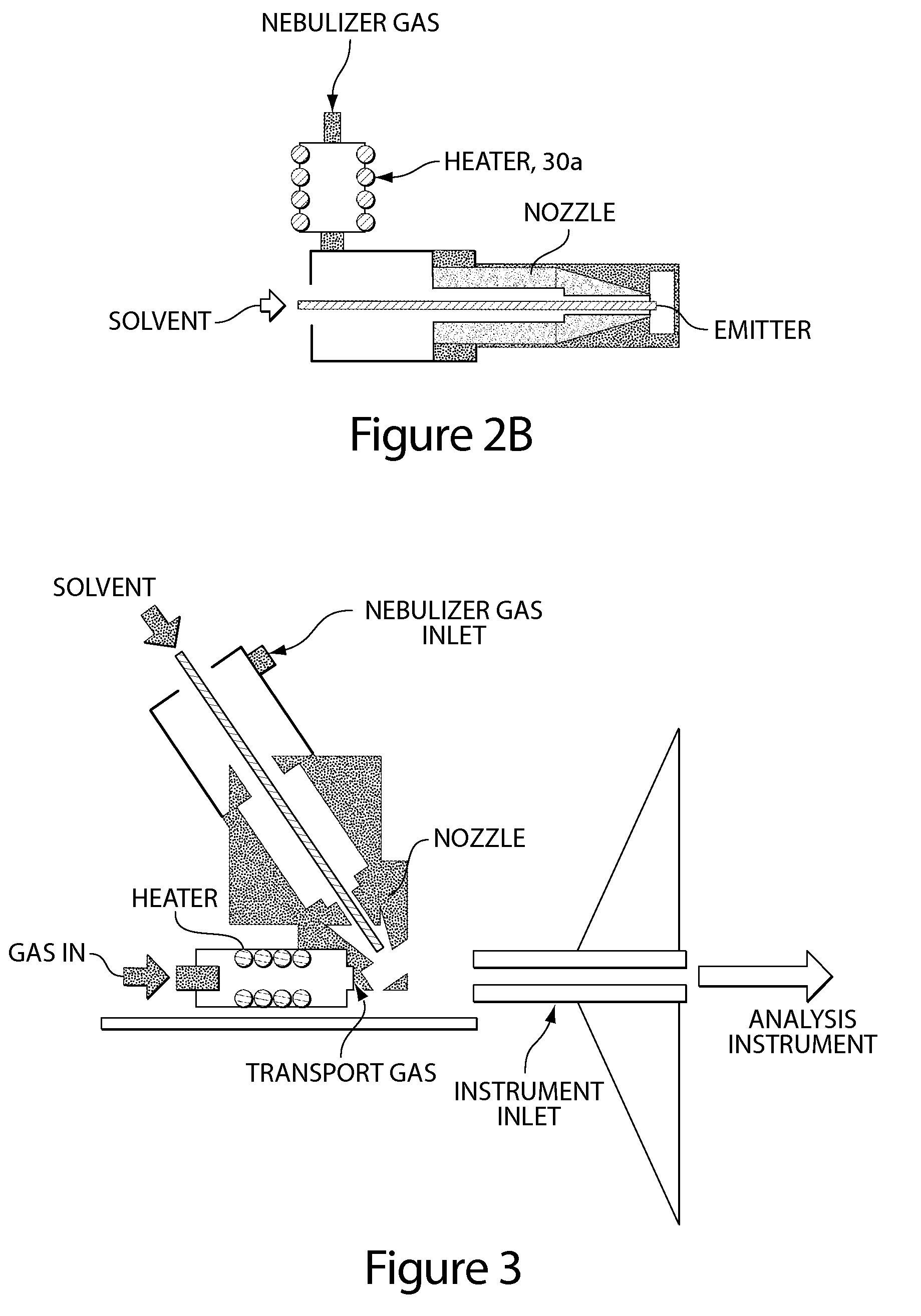
Method and apparatus for embedded heater for desorption and ionization of analytes
ActiveUS20100078550A1Enhance spot resolutionSmall sizeTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionDesolvationInstrumentation
A heated DESI spray device provides improved resolution or control of analyte desorption at a target locus on a sample. Heating controls spot size and enhances resolution in an imaging mode without impairing signal level. Additionally or alternatively the heated DESI spray may control desorption kinetics of a target analyte or otherwise control analyte discrimination in detection mode. One embodiment of the DESI spray is heated by heating nebulizing gas that accompanies the electrosprayed solvent. Another embodiment heats a separate gas stream that transports or directs desorbed material to the ion aperture of an analysis instrument. Heating may reduce size of primary droplets, alter the impact dynamics or the energy delivered by the spray to the surface, reduce size of secondary droplets and / or assure desolvation, improve species selectivity or otherwise affect sampling and enhance the ion signal level.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com