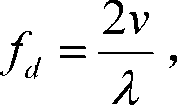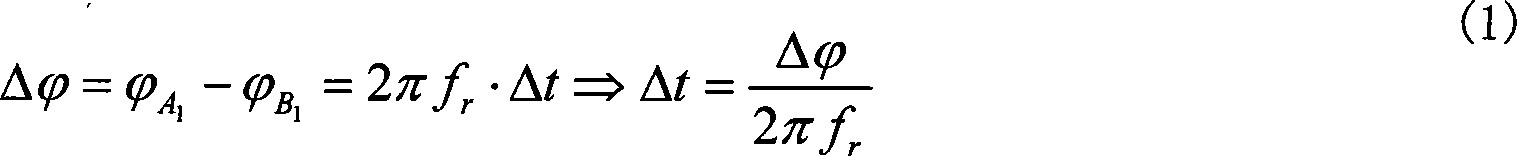Patents
Literature
2573 results about "Ranging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
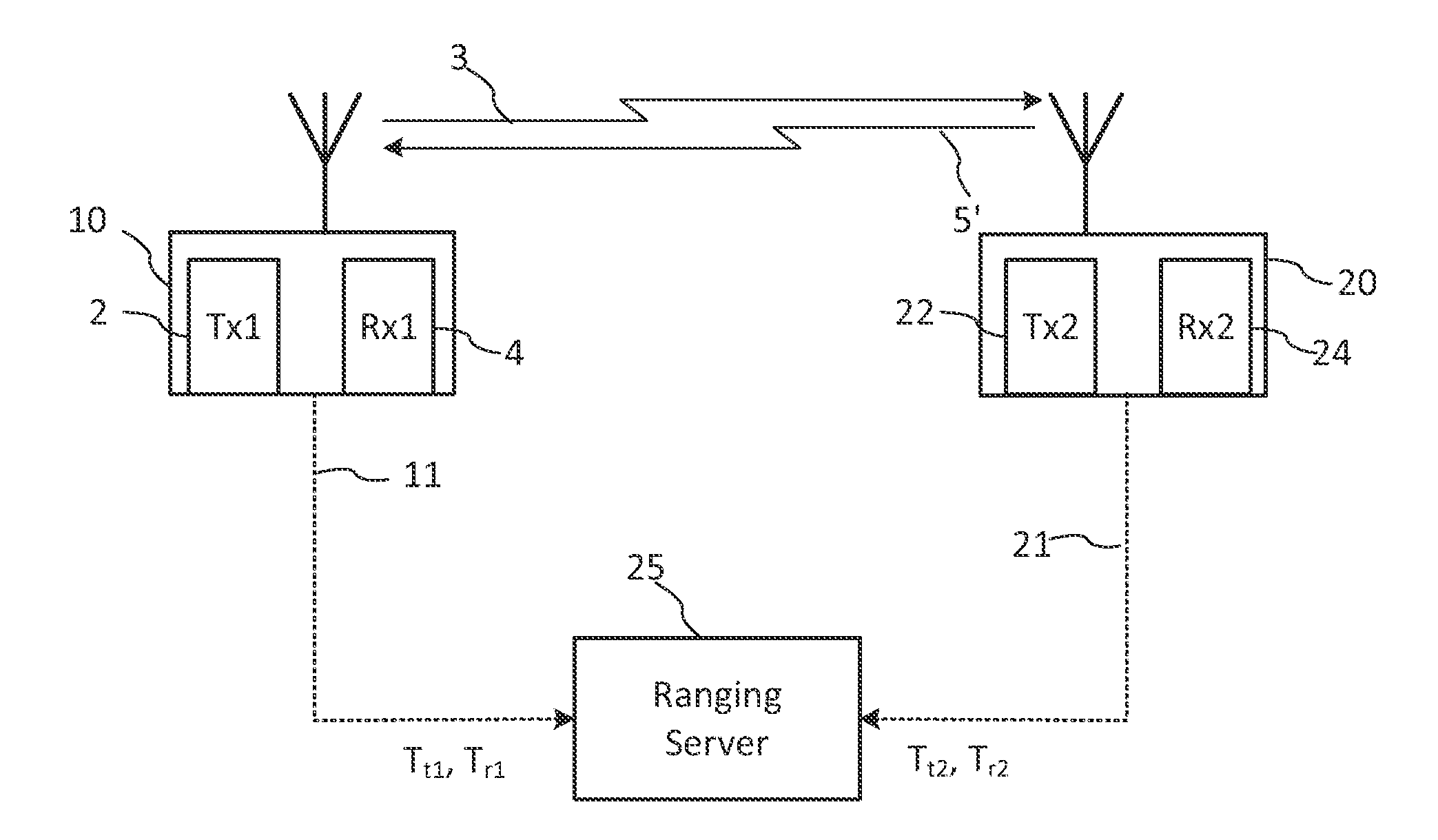
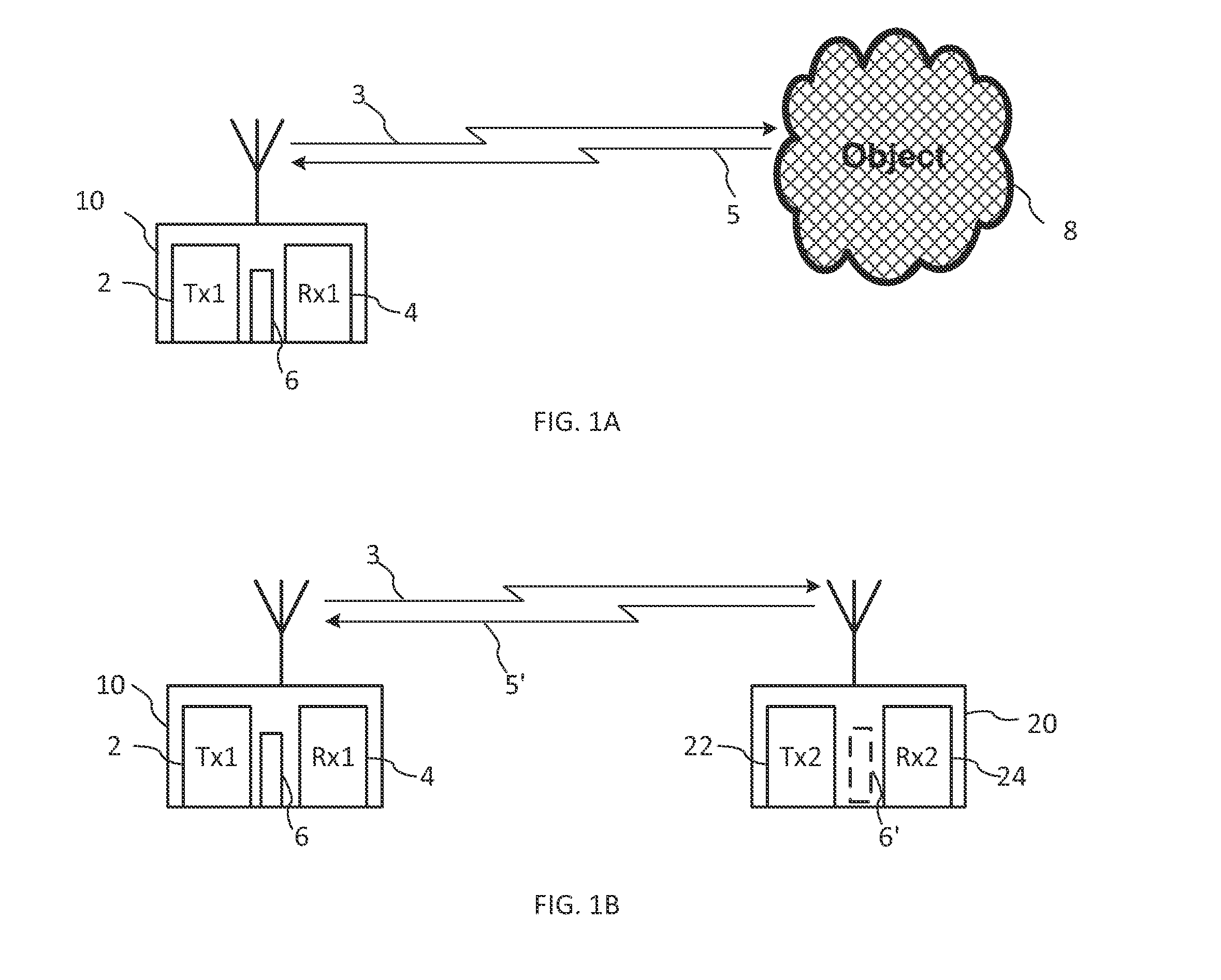
Ranging is a process or method to determine the distance from one location or position to another location or position. Another term for this method is lateration. Further development led to cooperative systems, where both locations are equipped with respective apparatus and thus provide bilateral measuring and to multilateral measurement between a larger set of locations, see multilateration. Members in the class of active ranging systems operate with unilateral transmission and passive reflections, as SONAR, RADAR and LIDAR. Special ranging makes use of actively synchronized transmission and travel time measurements, hence the time difference between several received signals is used to determine exact distances. This principle is used with SatNav, the Satellite Navigation class of systems. In conjunction with a standardized model of the Globe surface a certain location on the Globe may be determined with high accuracy. Ranging methods without accurate time synchronization of the receiver are called pseudorange, used e.g. in GPS positioning.
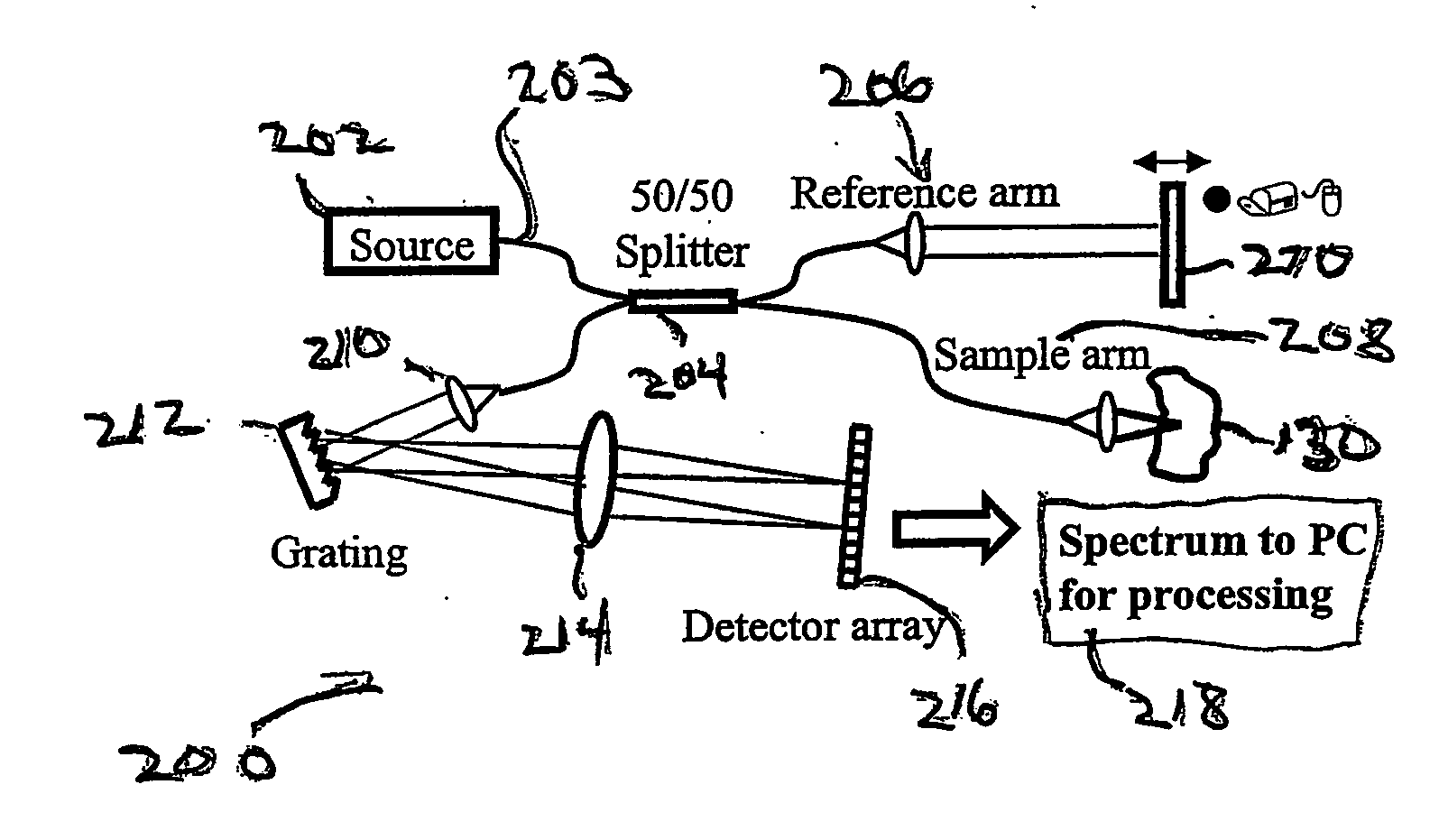
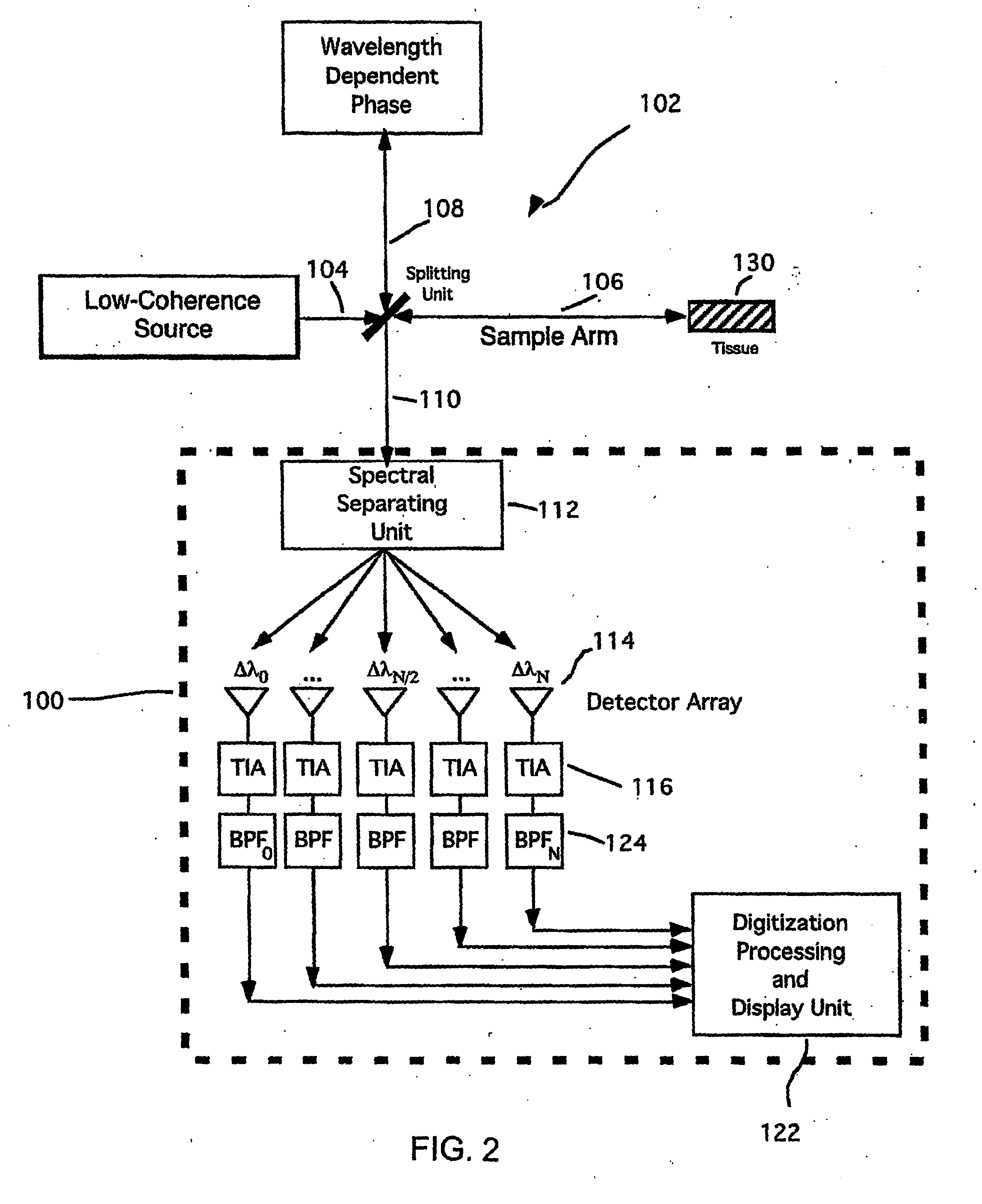
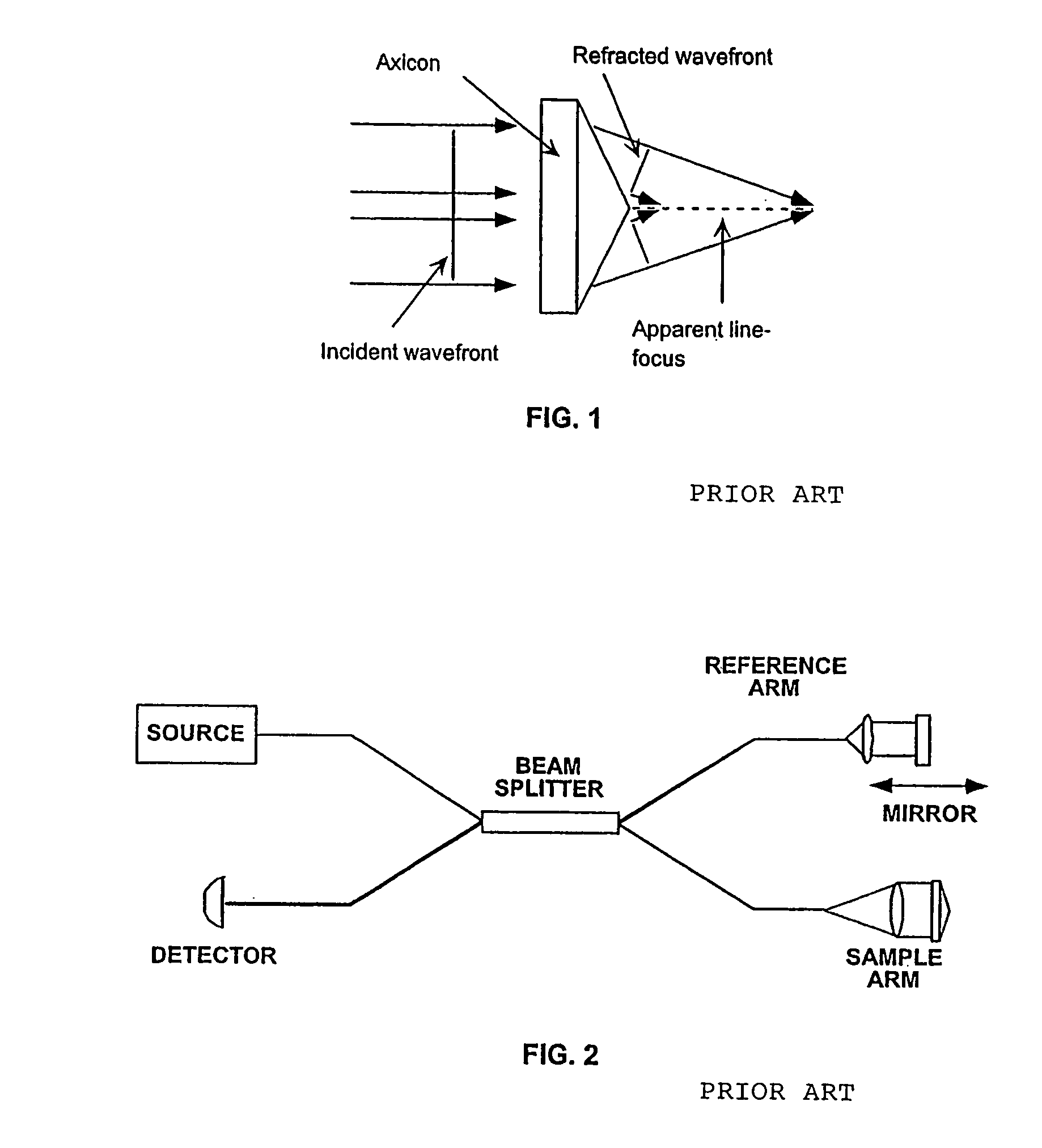
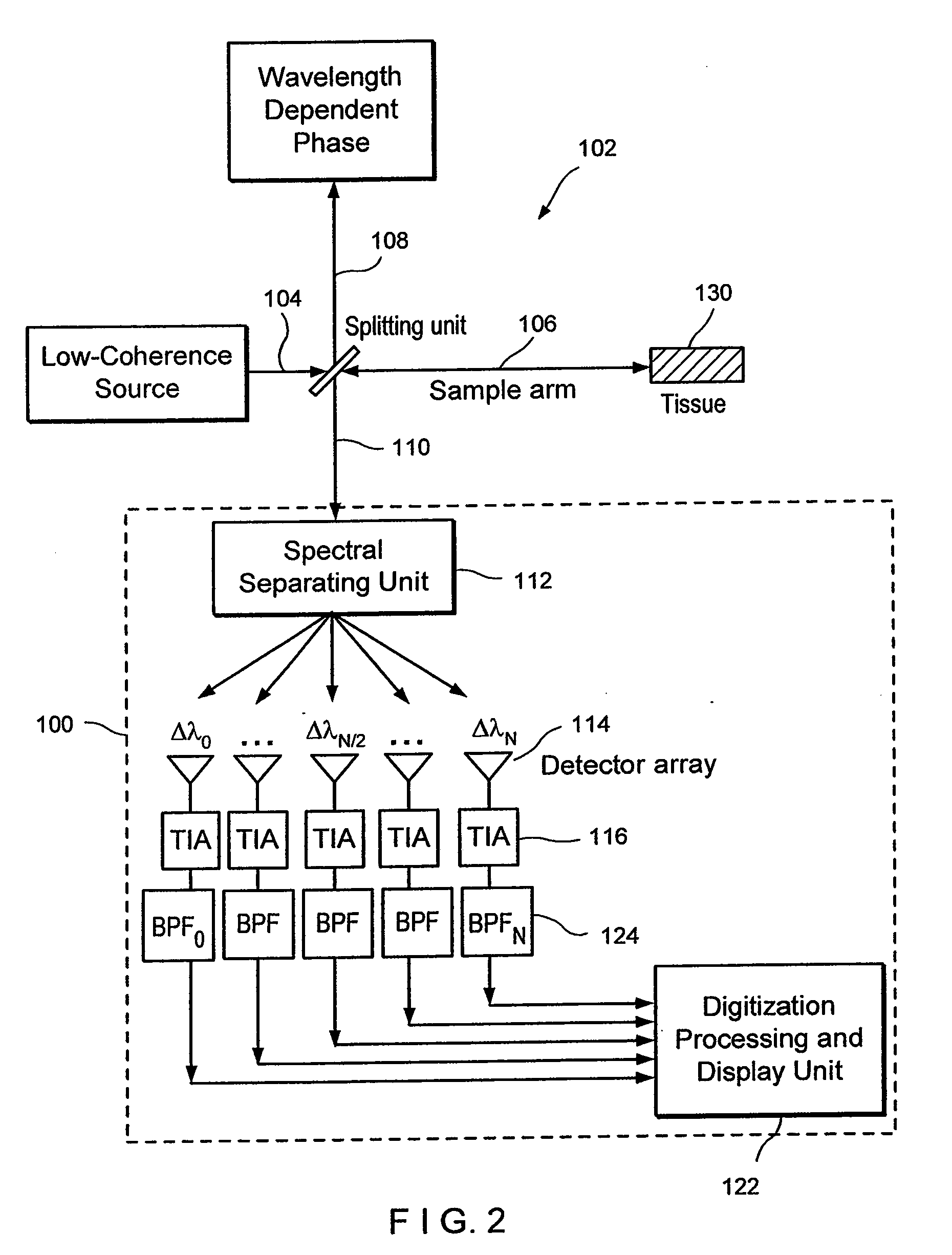
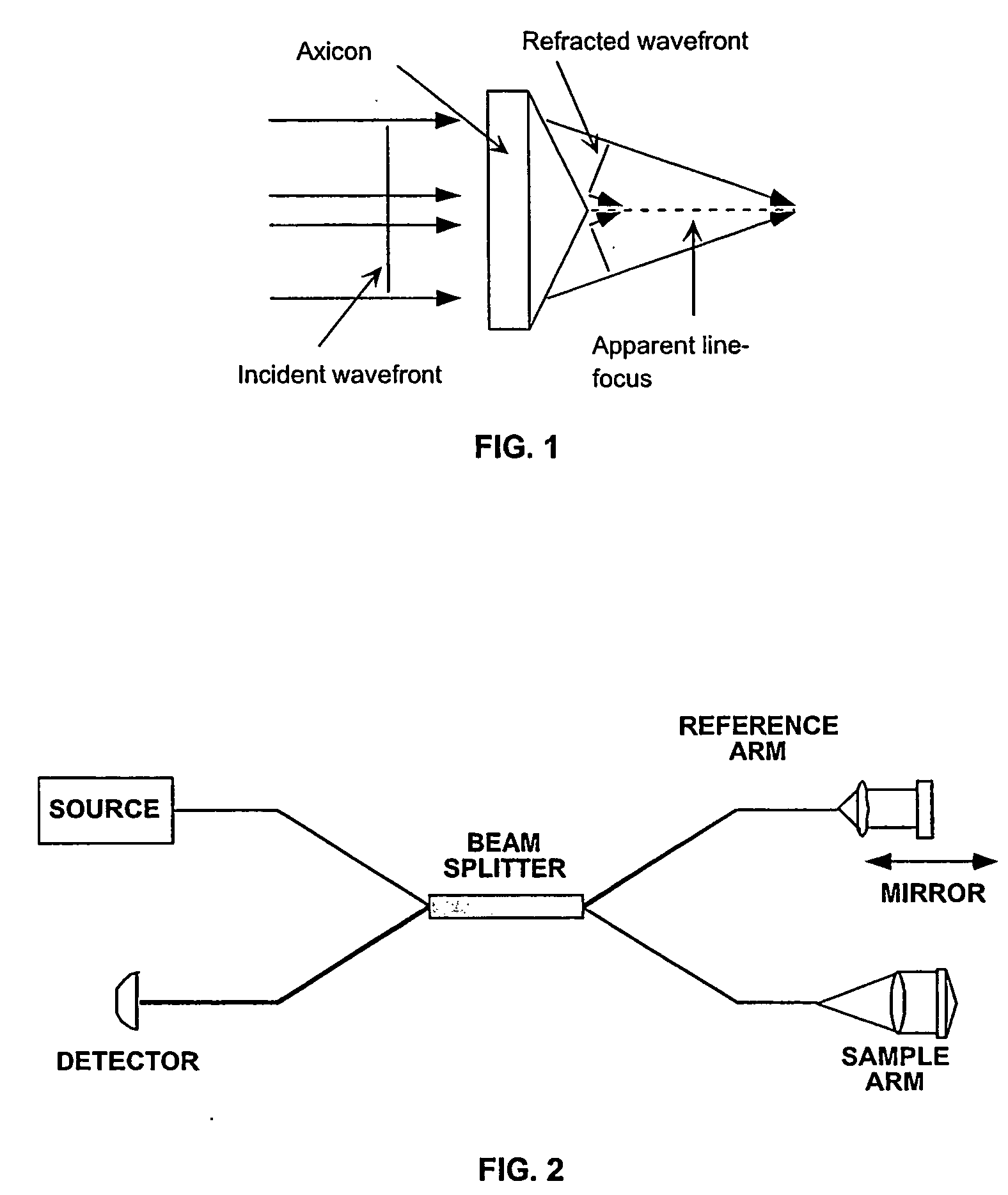
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20050018201A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
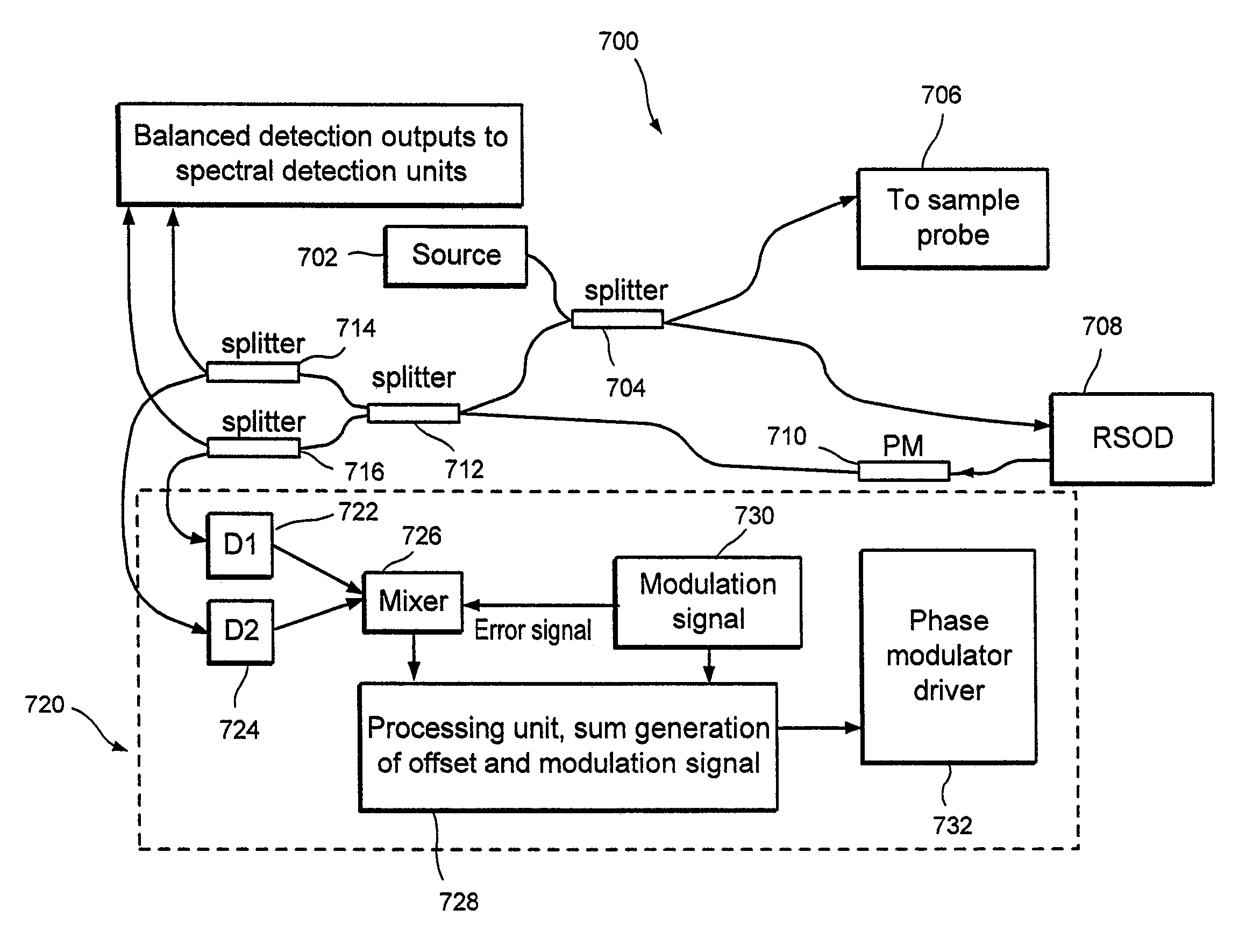
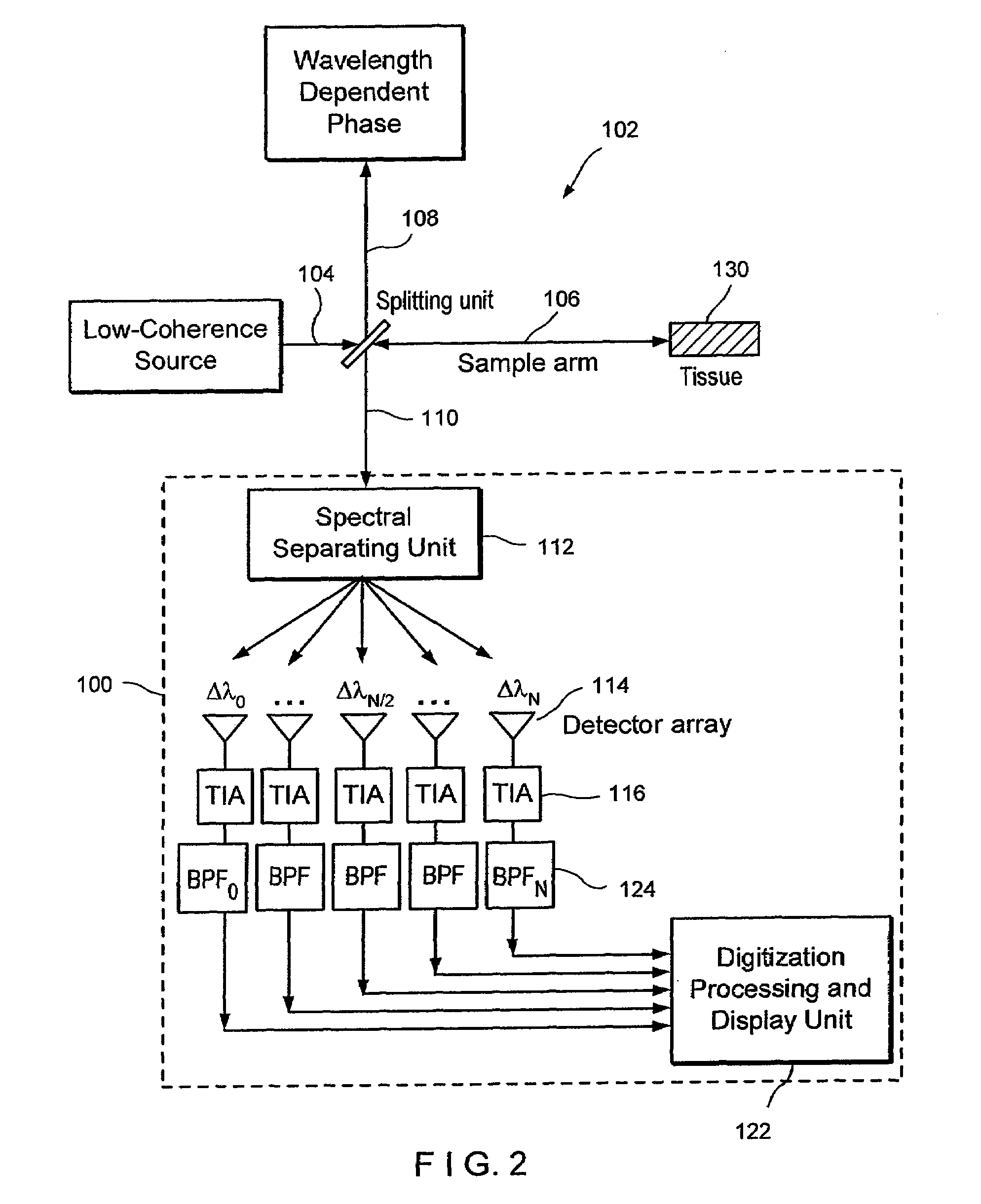
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
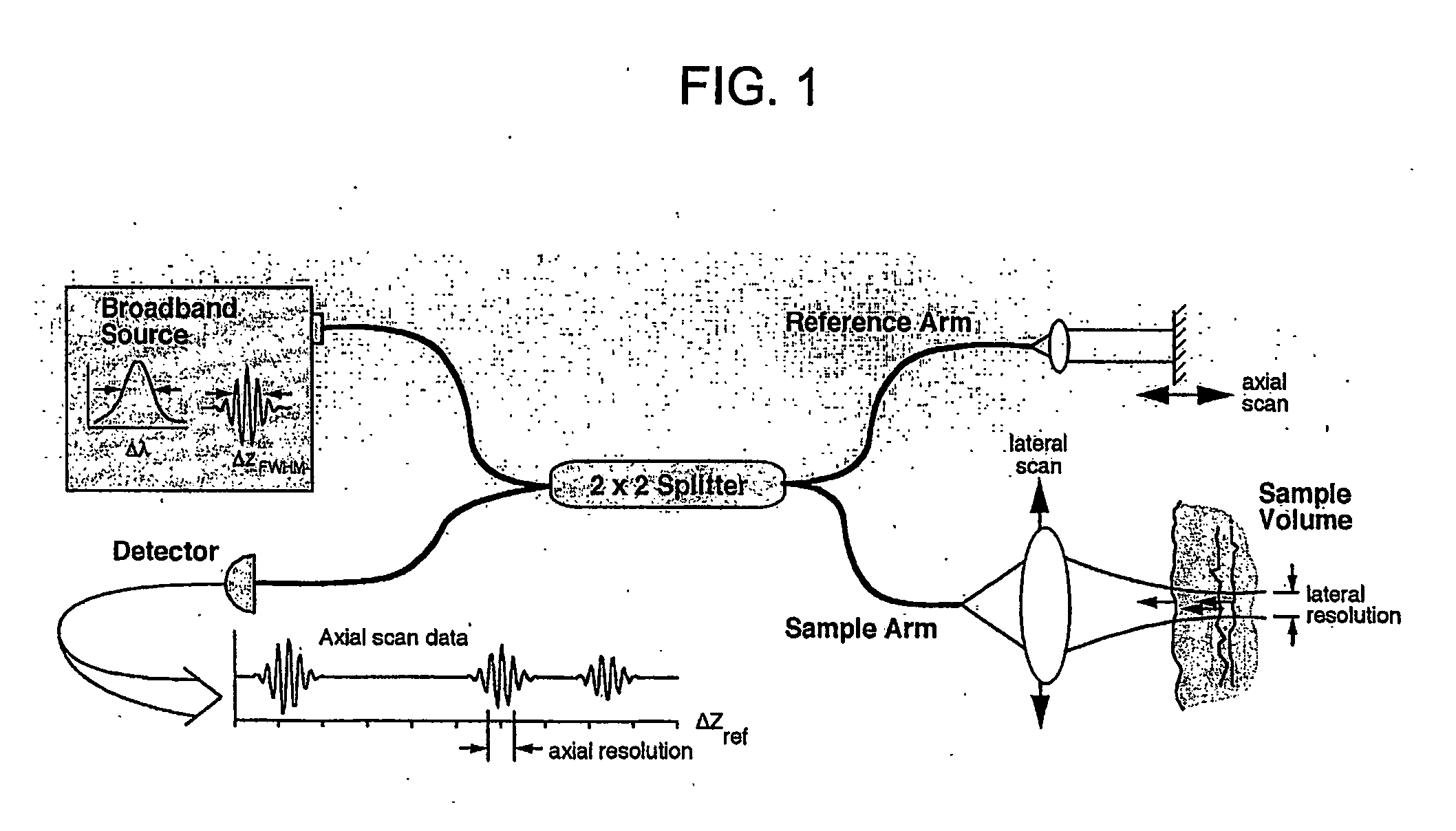
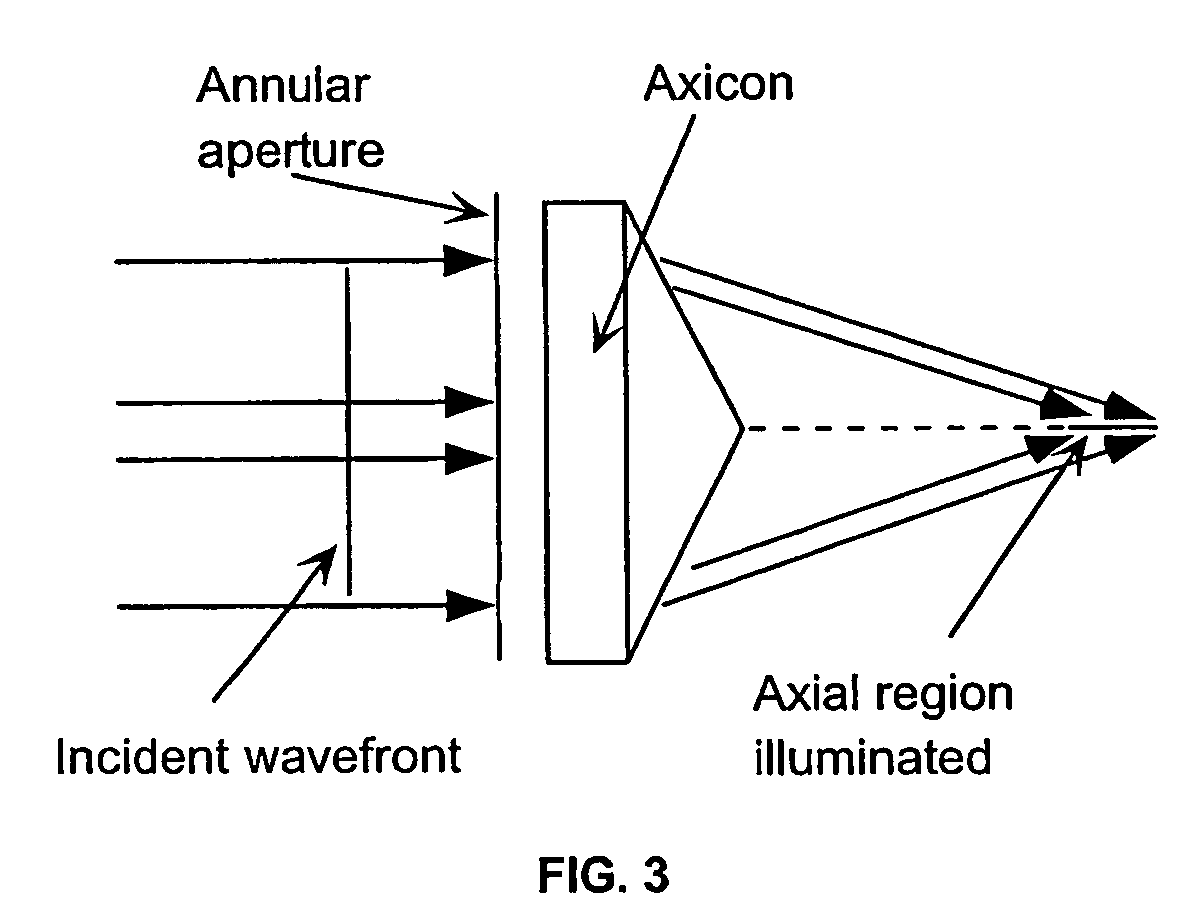
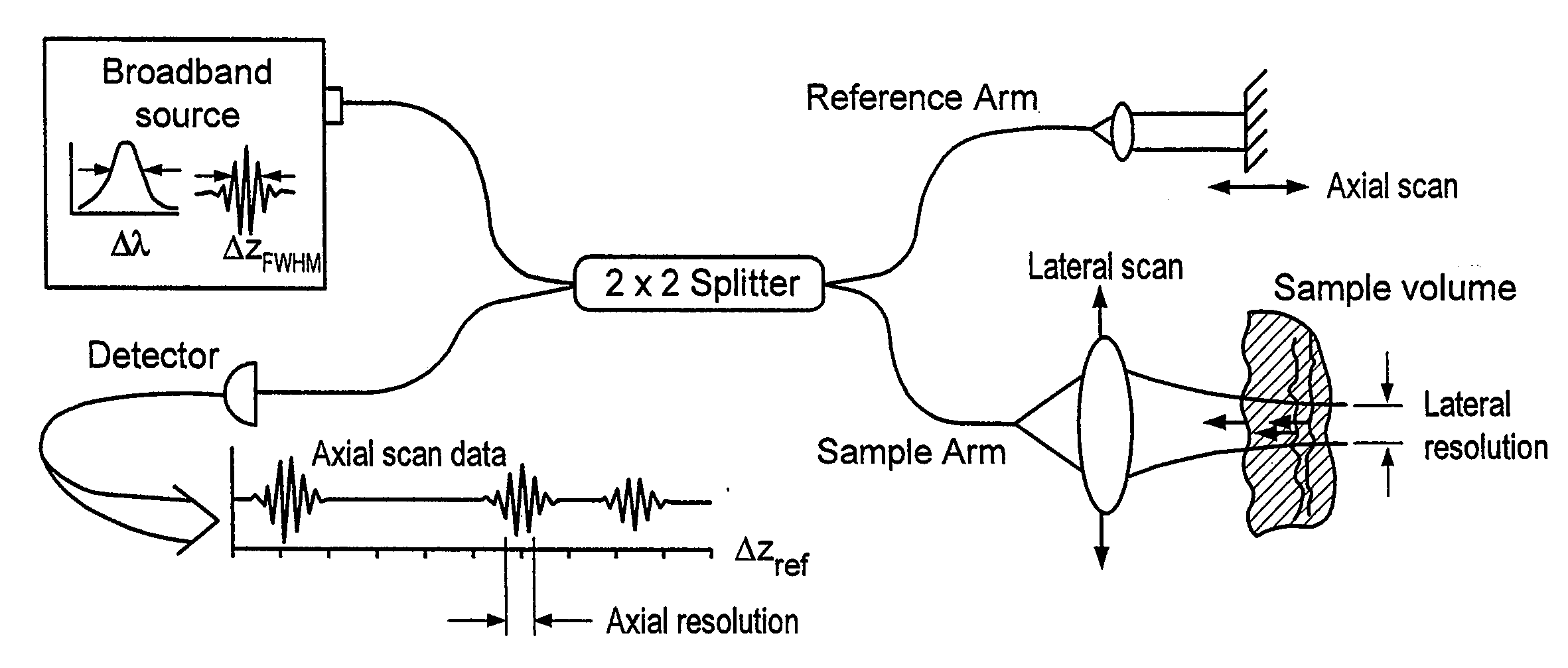
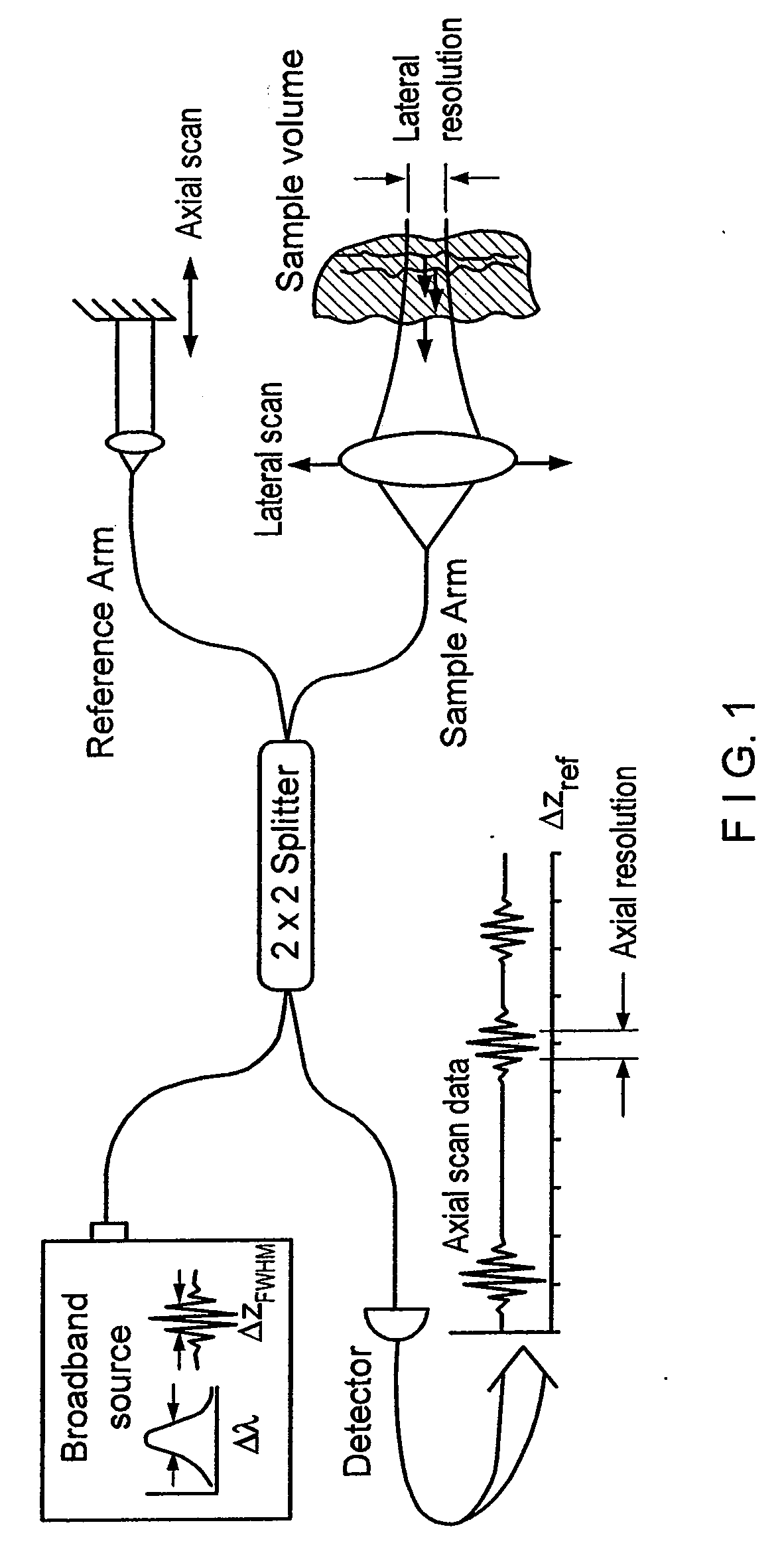
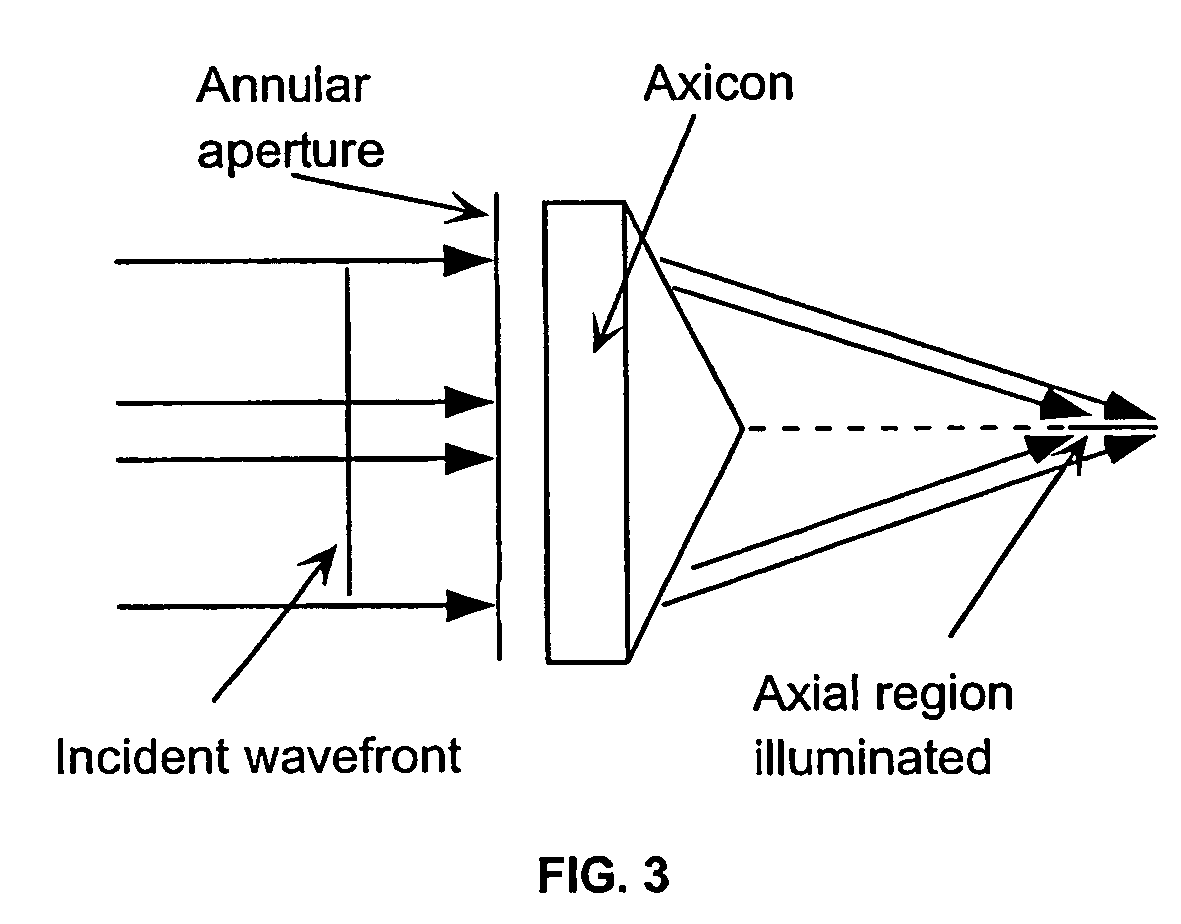
Apparatus and method for low coherence ranging
InactiveUS7310150B2Low costPotential compact sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansImage resolutionLateral resolution
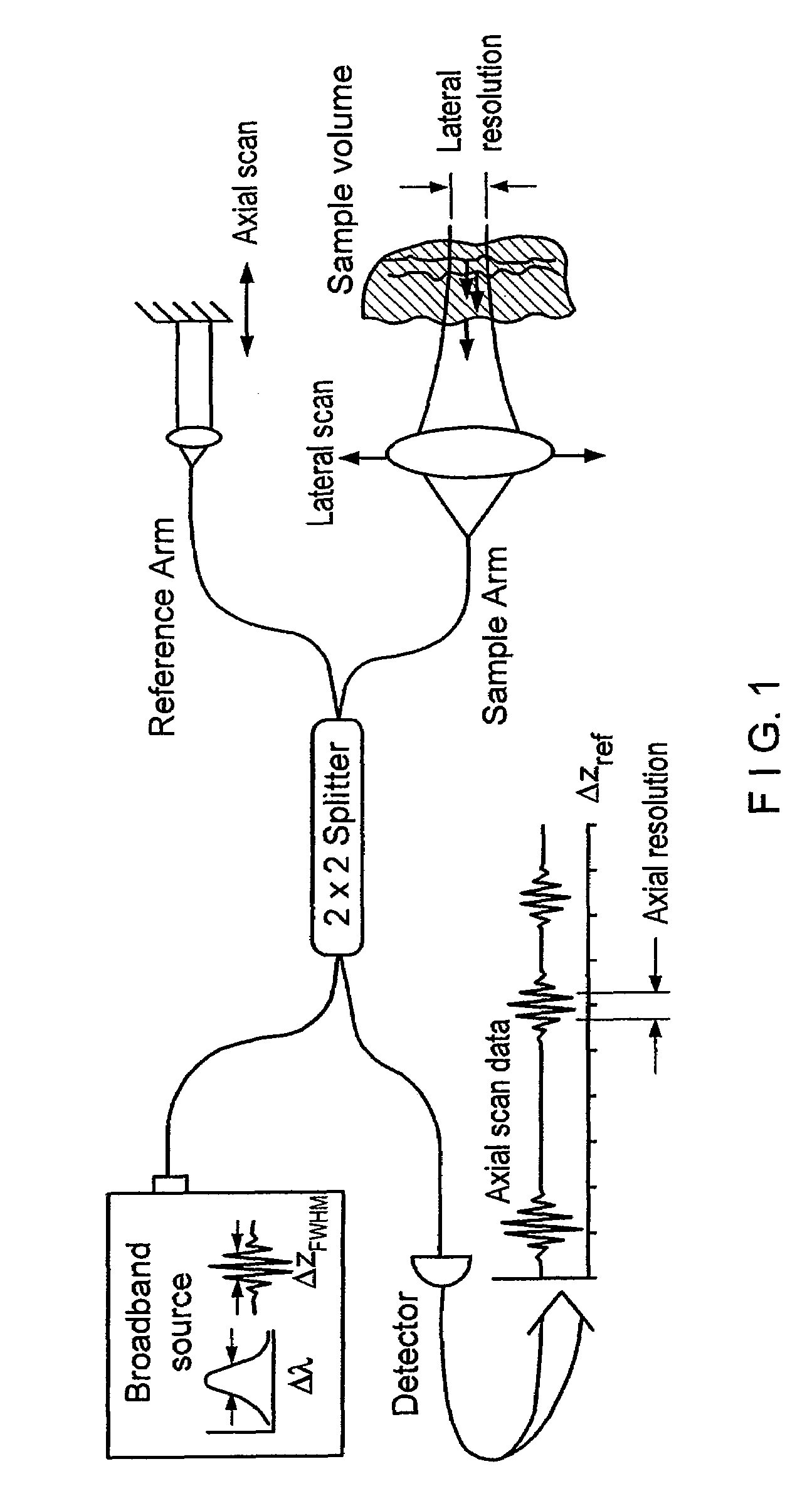
A system, apparatus and method for performing low coherence ranging of a sample with high transverse resolution and large depth of focus can be provided. For example, an optical ranging system including a light source can be used. Certain exemplary arrangement can be provided, e.g., a first arrangement for directing light from the light source to the sample, a second arrangement for directing reflected light from the sample to a detector, at least one detector, and a third arrangement for processing light data received by the detector and which generates an image can be utilized. Further, for example, an optical element can be provided which can have a transverse resolution defined as .Δris less than or equal to about μ5 m, and a depth of focus Δz of at least about 50 μm.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
High-resolution ranging and location finding using multicarrier signals
InactiveUS20120032855A1Direction finders using radio wavesError preventionModulation patternImage resolution
The invention relates to methods and systems for accurate ranging and geo-locationing using coherent multicarrier (CM) signals and based on a high-resolution estimation of a receiver timing offset in a signal receiver that receives ranging CM signals. A transmitter transmits a ranging CM signal having a known subcarrier modulation pattern. The receiver samples the ranging CM signal it receives reflected back from an object or from the remote transmitter, and processes the sampled signal that preserves relative subcarrier phases using a high-resolution model channel response function to determine the receiver timing offset with resolution much better than the receiver sampling period. The receiver timing offset is used to determine a flight time for the ranging CM signal with high accuracy.
Owner:AMERISYS INC
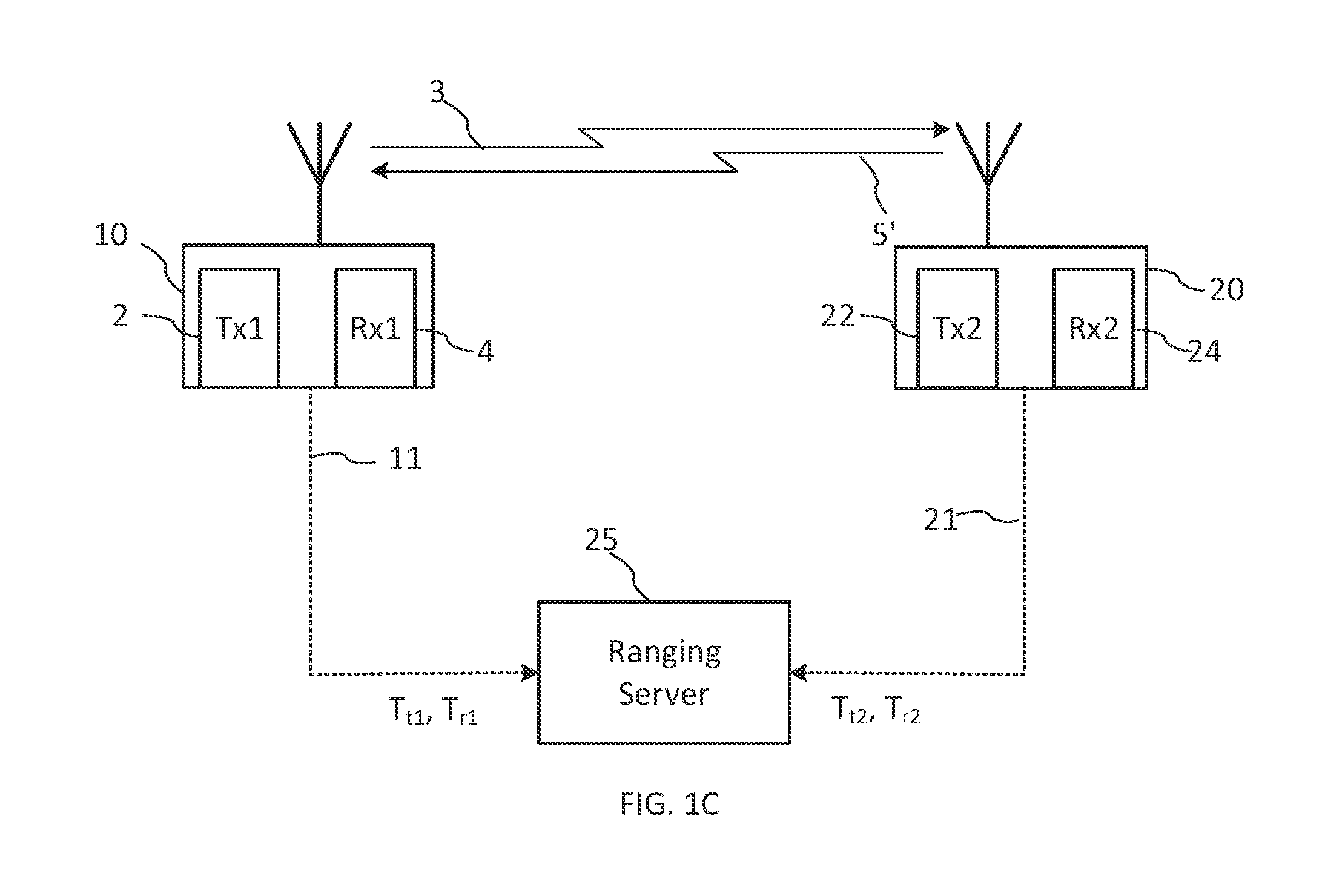
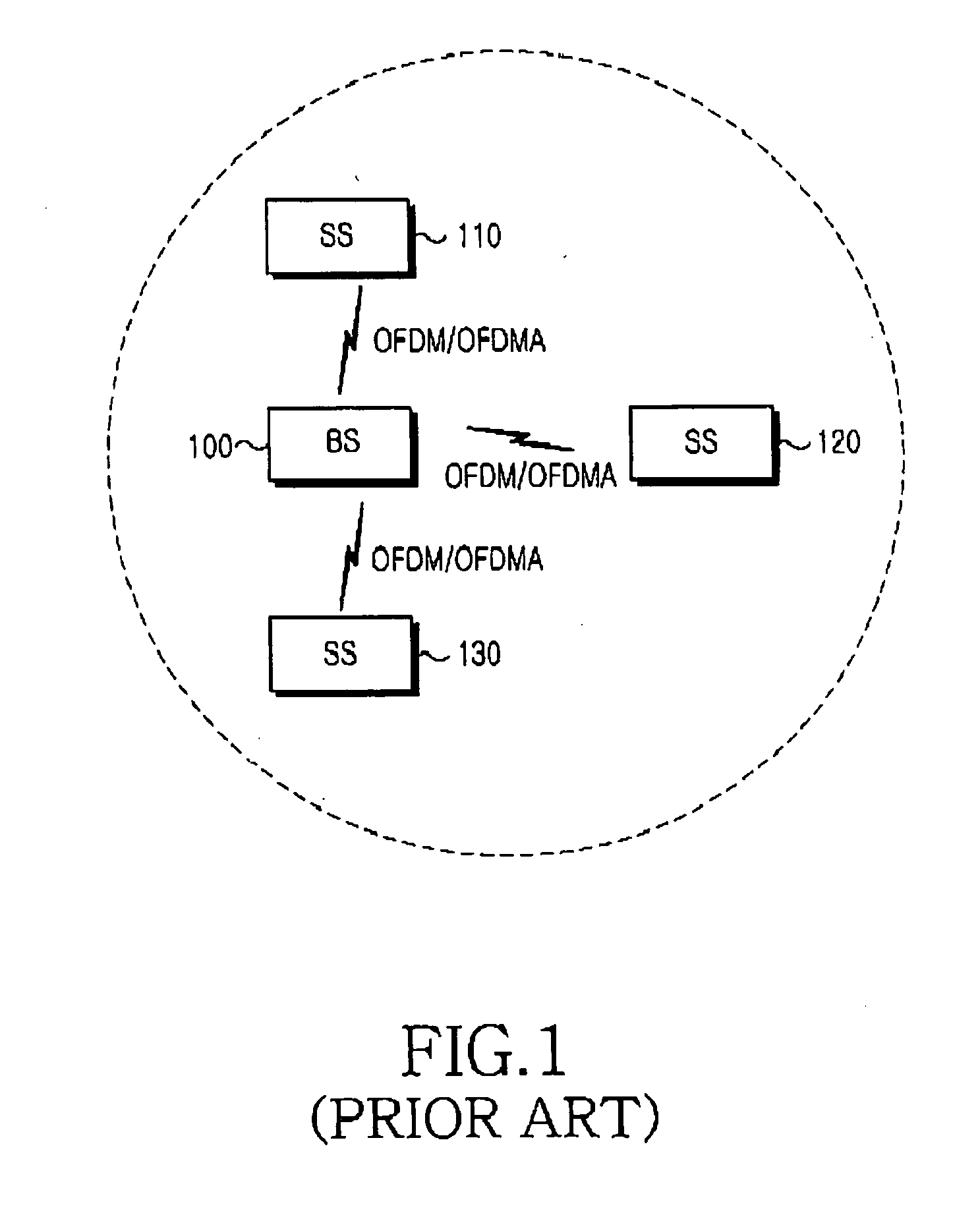
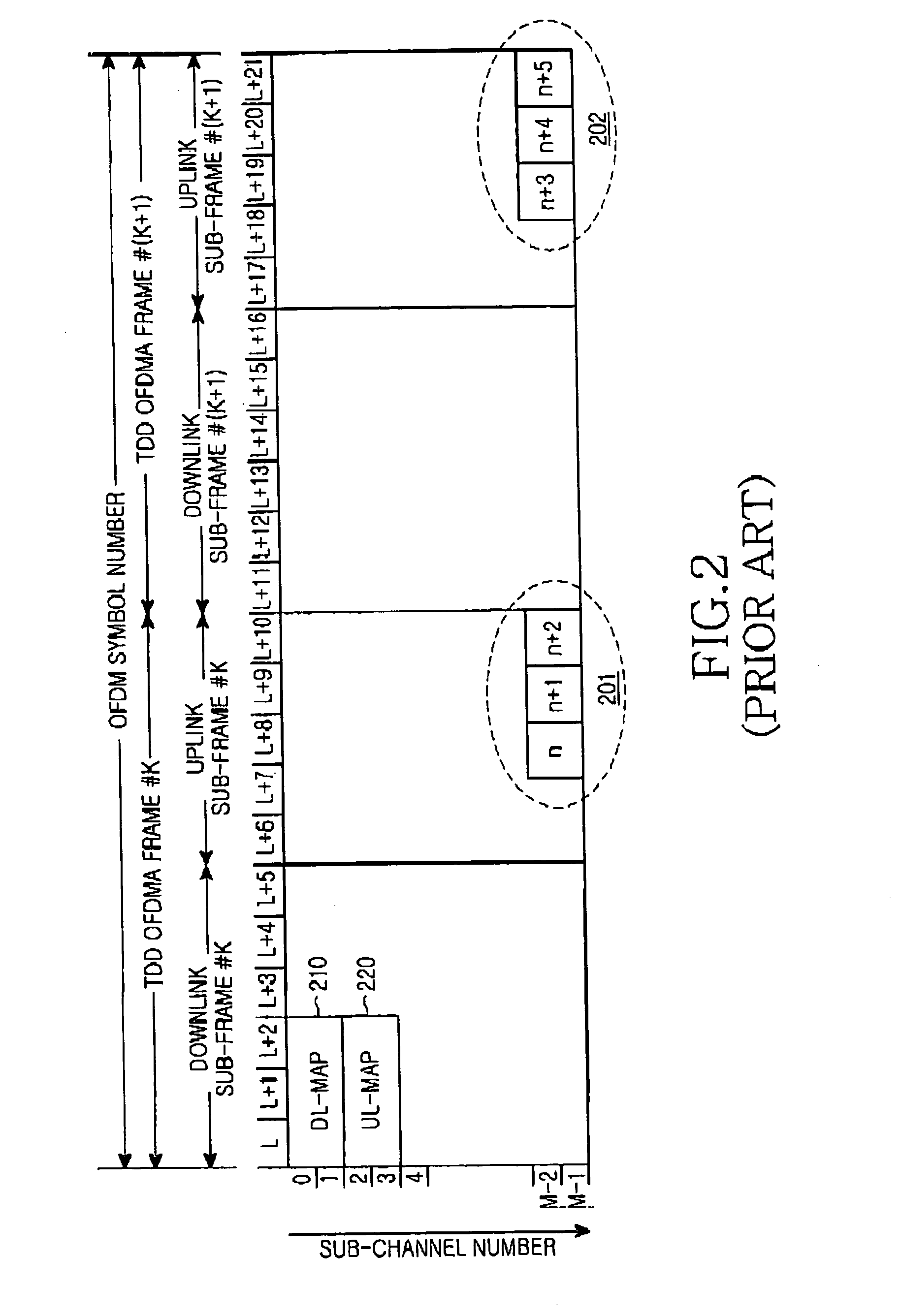
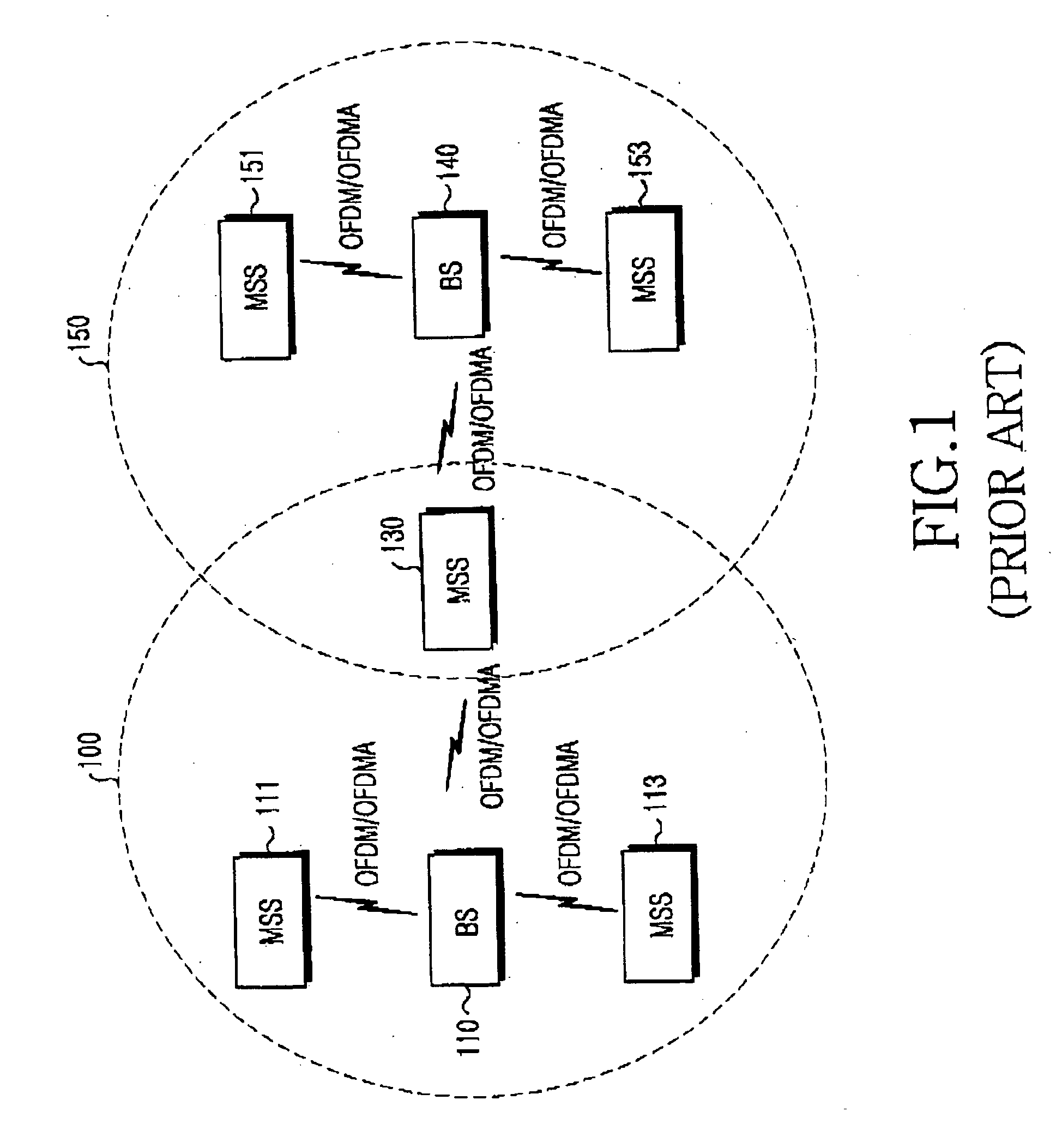
Ranging method in a mobile communication system using orthogonal frequency division multiple access
InactiveUS20050058058A1Minimizing access delayPreventing ranging code collisionData switching by path configurationOrthogonal multiplexControl communicationsNull state
Disclosed is a method for controlling an operational state of at least one subscriber stations in an OFDM / OFDMA communication system having ranging slots and ranging codes to be used for rangings. The subscriber station performing in a Null state, an initial ranging if an initial ranging request occurs, and transitioning from the Null state to an Idle state if the initial ranging is successful; transitioning to an Access state if a bandwidth request ranging request occurs in the Idle state, and performing in the Access state the bandwidth request ranging based on a random access technique; transitioning from the Access state to a Busy state if the random access-based bandwidth request ranging is successful, performing the bandwidth request ranging based on a scheduled access technique if the bandwidth request ranging request occurs in the Busy state, and transmitting data if the scheduled access-based bandwidth request ranging is successful; and transitioning to a Hold state if the data transmission is ended in the Busy state, and performing the scheduled access-based bandwidth request ranging if the bandwidth request ranging request occurs in the Hold state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7643153B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
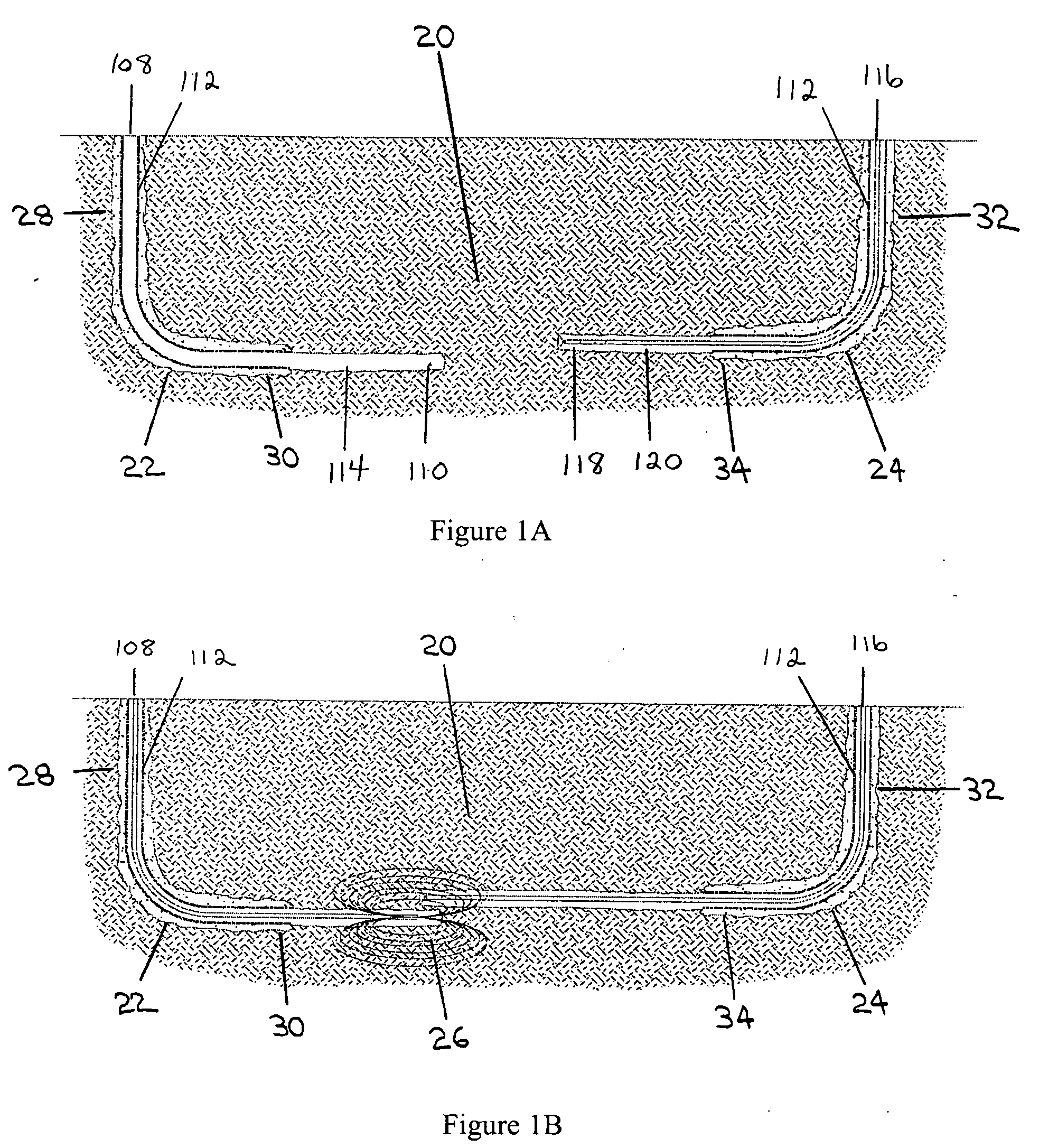
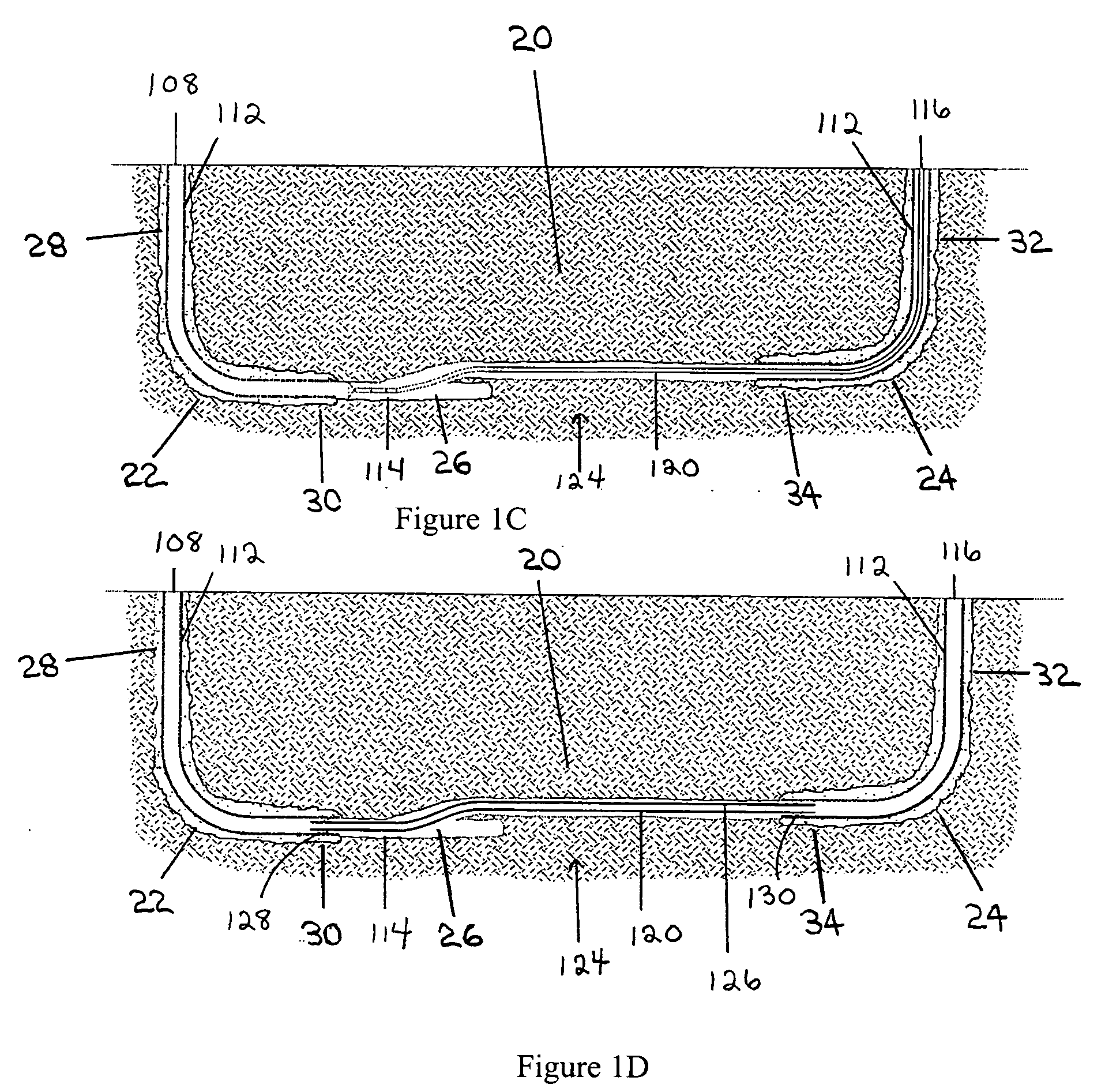
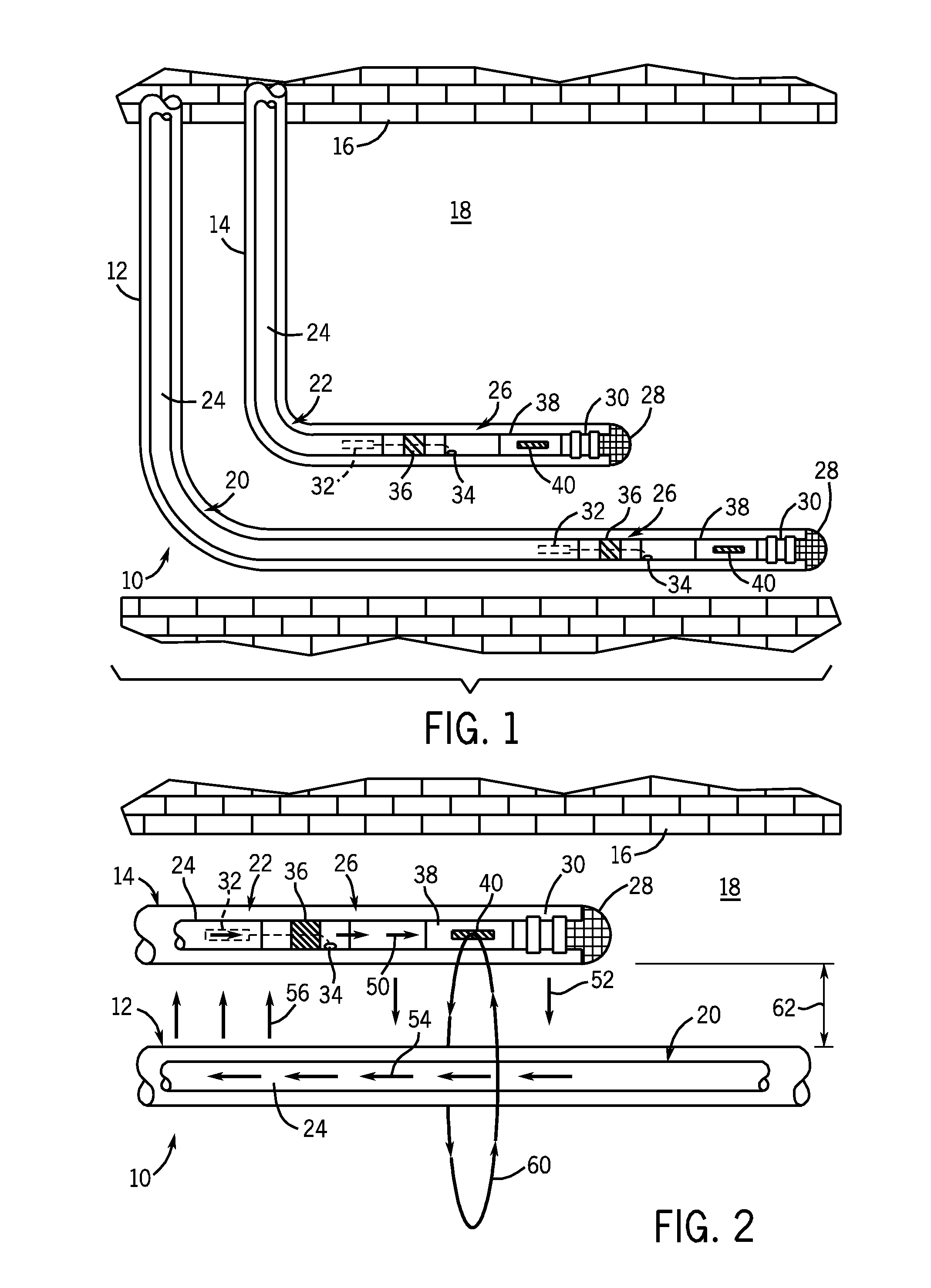
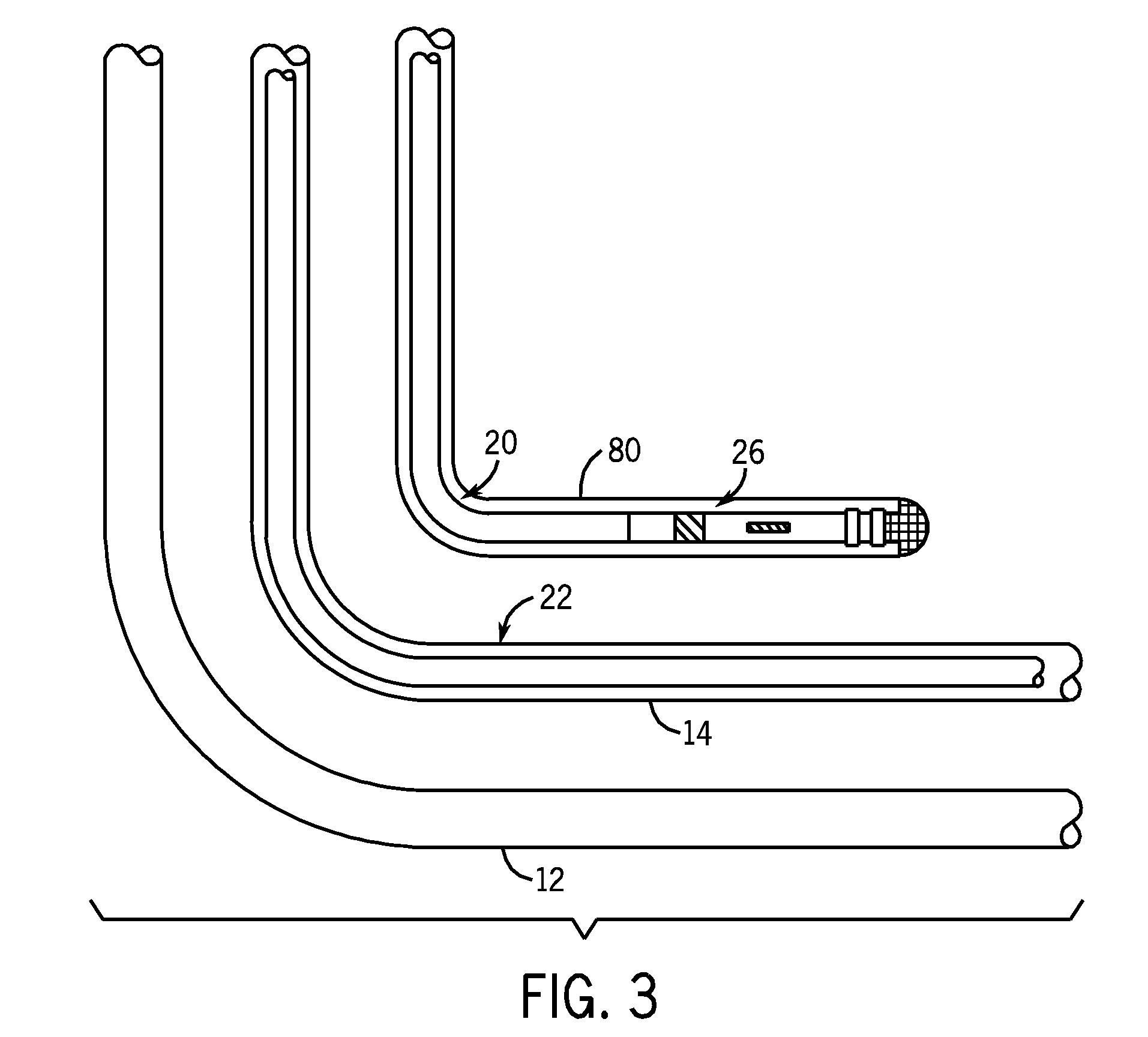
Methods and apparatus for drilling, completing and configuring U-tube boreholes
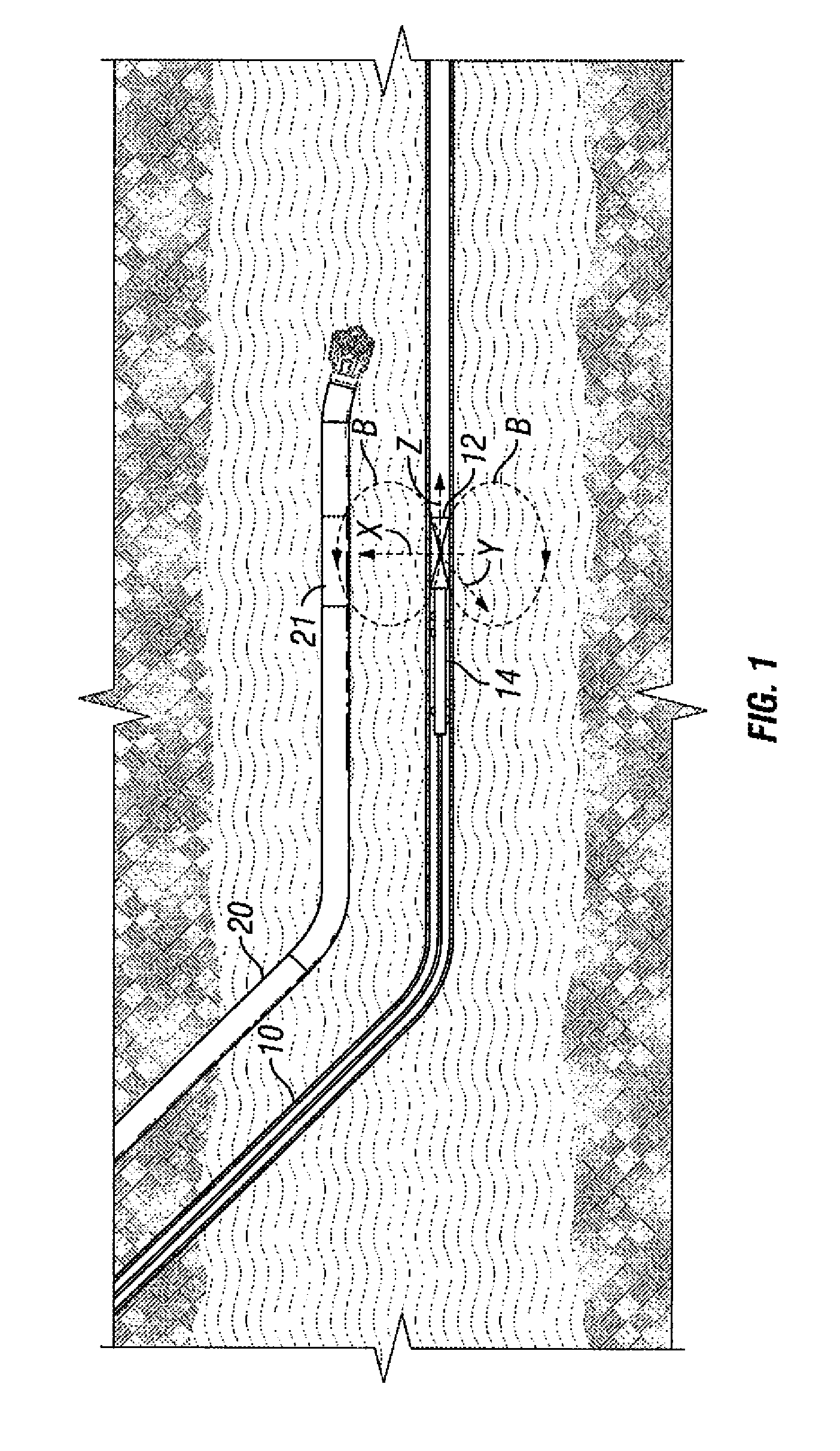
A borehole network including first and second end surface locations and at least one intermediate surface location interconnected by a subterranean path, and a method for connecting a subterranean path between a first borehole including a directional section and a second borehole including a directional section. A directional drilling component is drilled in at least one of the directional sections to obtain a required proximity between the first and second boreholes. An intersecting component is drilled, utilizing magnetic ranging techniques, from one directional section to provide a borehole intersection between the first and second boreholes, thereby connecting the subterranean path.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
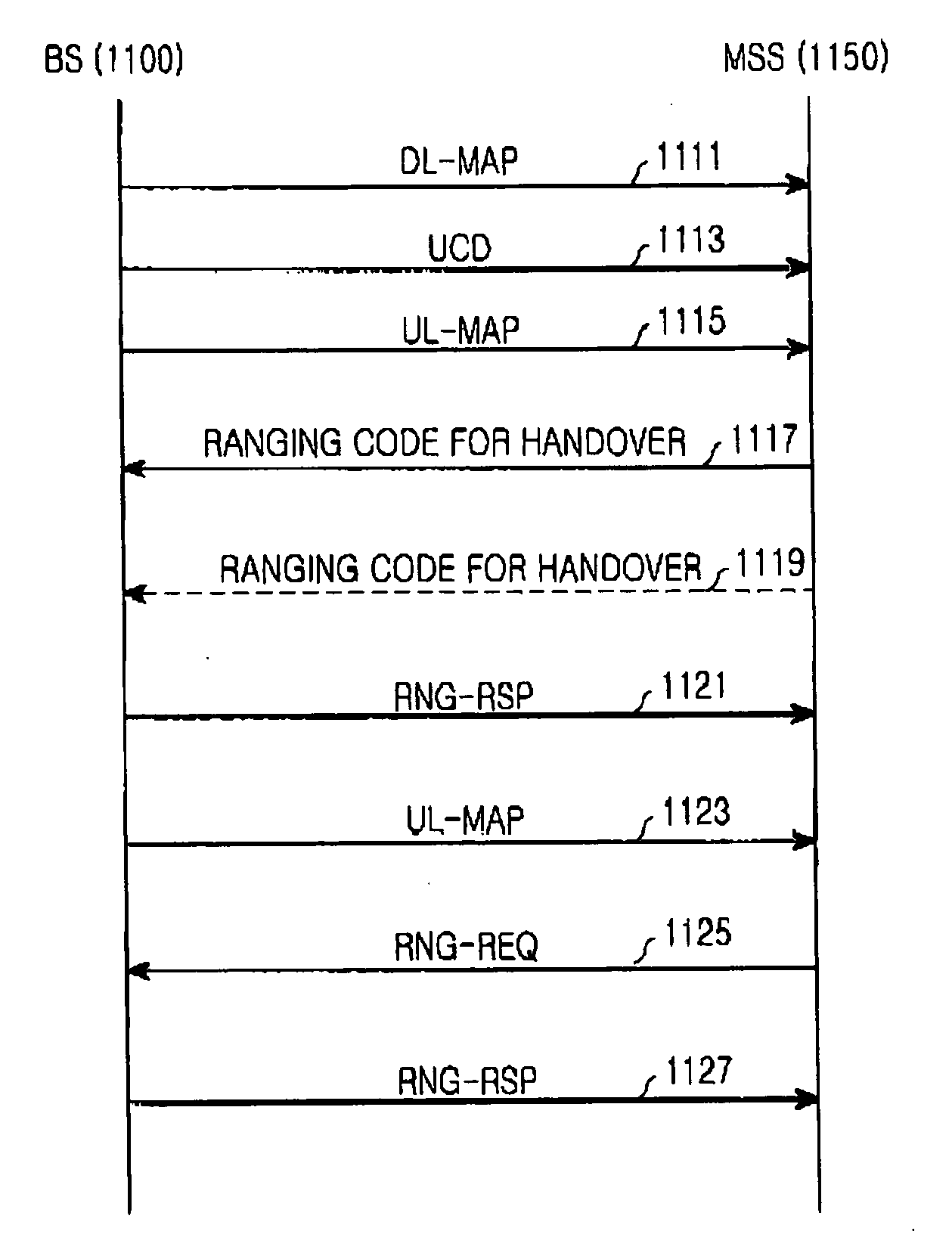
System and method for ranging for a fast handover in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050117539A1Reduce latencyData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemFrequency-division multiple access
A mobile communication system using an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) / orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) scheme. The method for assigning ranging codes in the OFDM / OFDMA communication system includes classifying rangings between a base station and a mobile subscriber station (MSS) of the OFDM / OFDMA communication system into an initial ranging, a periodic ranging, a bandwidth request ranging, and a handover ranging. A first number of ranging codes used for the rangings are created and a second number of ranging codes selected from the first number of ranging codes are assigned as handover ranging codes used for the handover ranging.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for rangings and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080097709A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
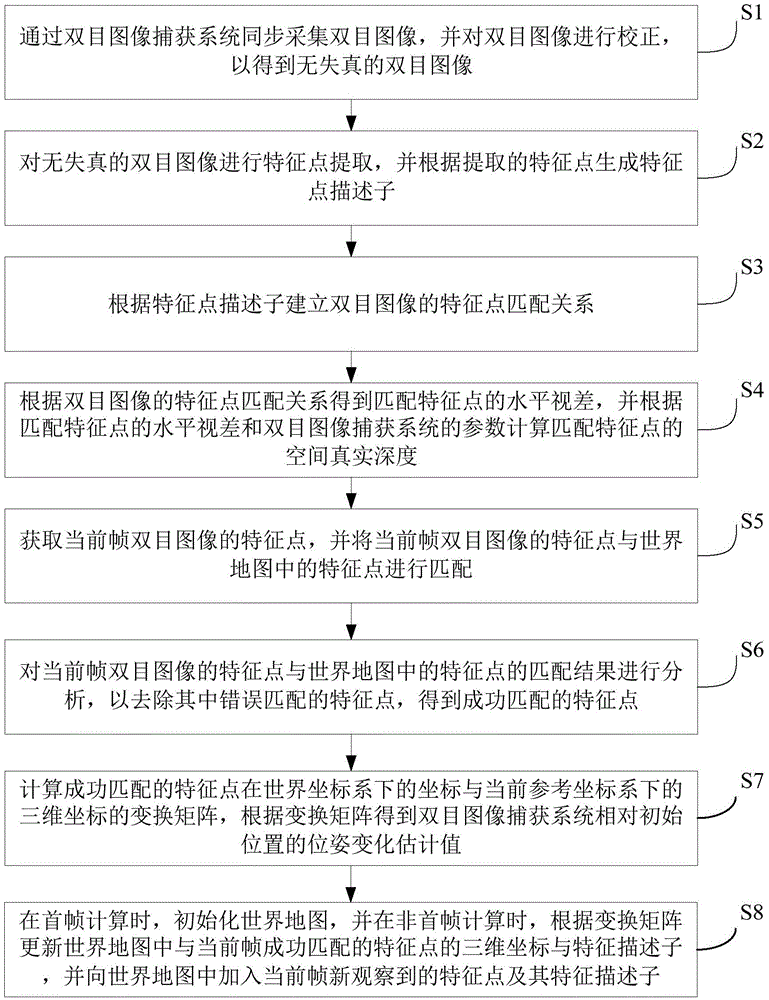
Apparatus for low coherence ranging
InactiveUS20050018200A1Low costPotential compact sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansImage resolutionLateral resolution
An apparatus for performing low coherence ranging of a sample with high transverse resolution and large depth of focus, comprising an optical ranging system comprising a light source, a means for directing light from the light source to the sample, a means for directing reflected light from the sample to a detector, at least one detector, a means for processing light data received by the detector and which generates an image; and an optical element having a transverse resolution defined as .Δris less than or equal to about 5 μm, and a depth of focus Δz of at least about 50 μm.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
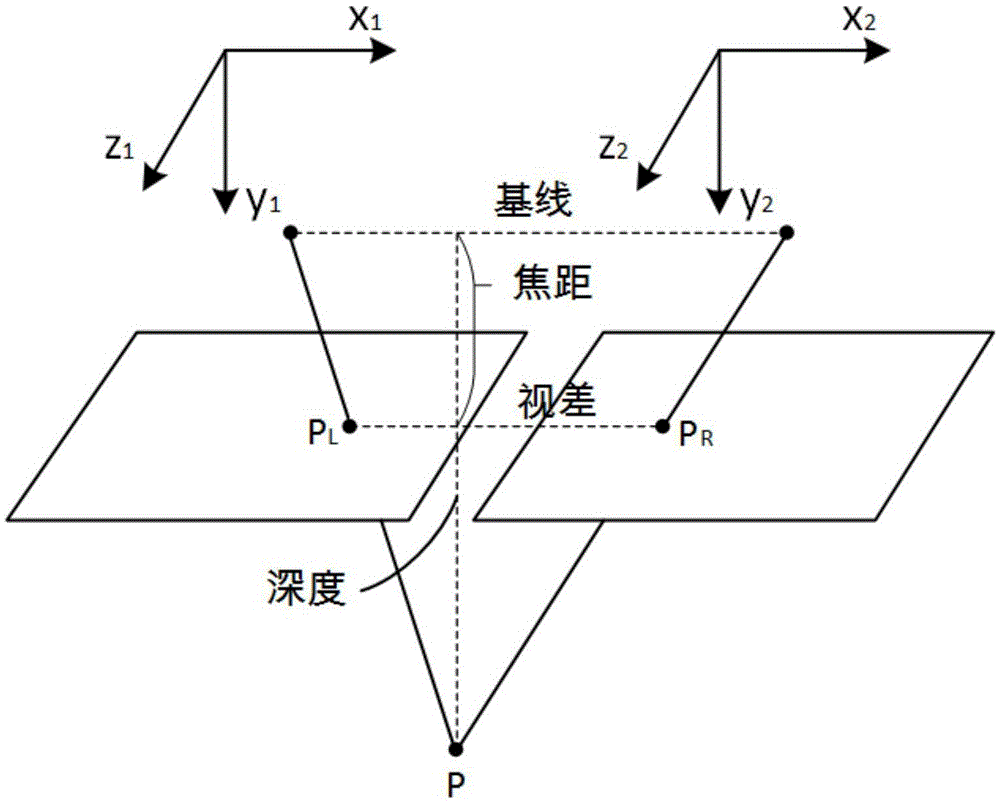
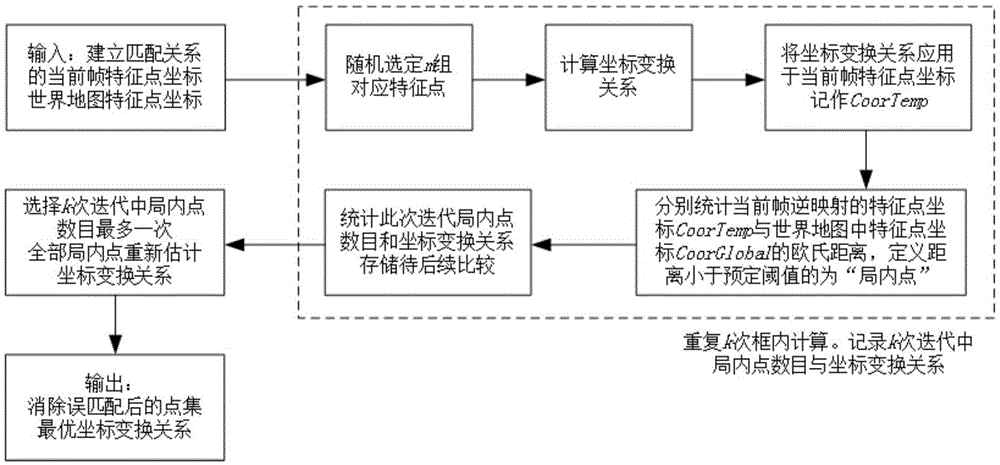
Visual ranging-based simultaneous localization and map construction method
ActiveCN105469405AReduce computational complexityEliminate accumulationImage enhancementImage analysisSimultaneous localization and mappingComputation complexity
The invention provides a visual ranging-based simultaneous localization and map construction method. The method includes the following steps that: a binocular image is acquired and corrected, so that a distortion-free binocular image can be obtained; feature extraction is performed on the distortion-free binocular image, so that feature point descriptors can be generated; feature point matching relations of the binocular image are established; the horizontal parallax of matching feature points is obtained according to the matching relations, and based on the parameters of a binocular image capture system, real space depth is calculated; the matching results of the feature points of a current frame and feature points in a world map are calculated; feature points which are wrongly matched with each other are removed, so that feature points which are successfully matched with each other can be obtained; a transform matrix of the coordinates of the feature points which are successfully matched with each other under a world coordinate system and the three-dimension coordinates of the feature points which are successfully matched with each other under a current reference coordinate system is calculated, and a pose change estimated value of the binocular image capture system relative to an initial position is obtained according to the transform matrix; and the world map is established and updated. The visual ranging-based simultaneous localization and map construction method of the invention has low computational complexity, centimeter-level positioning accuracy and unbiased characteristics of position estimation.
Owner:北京超星未来科技有限公司
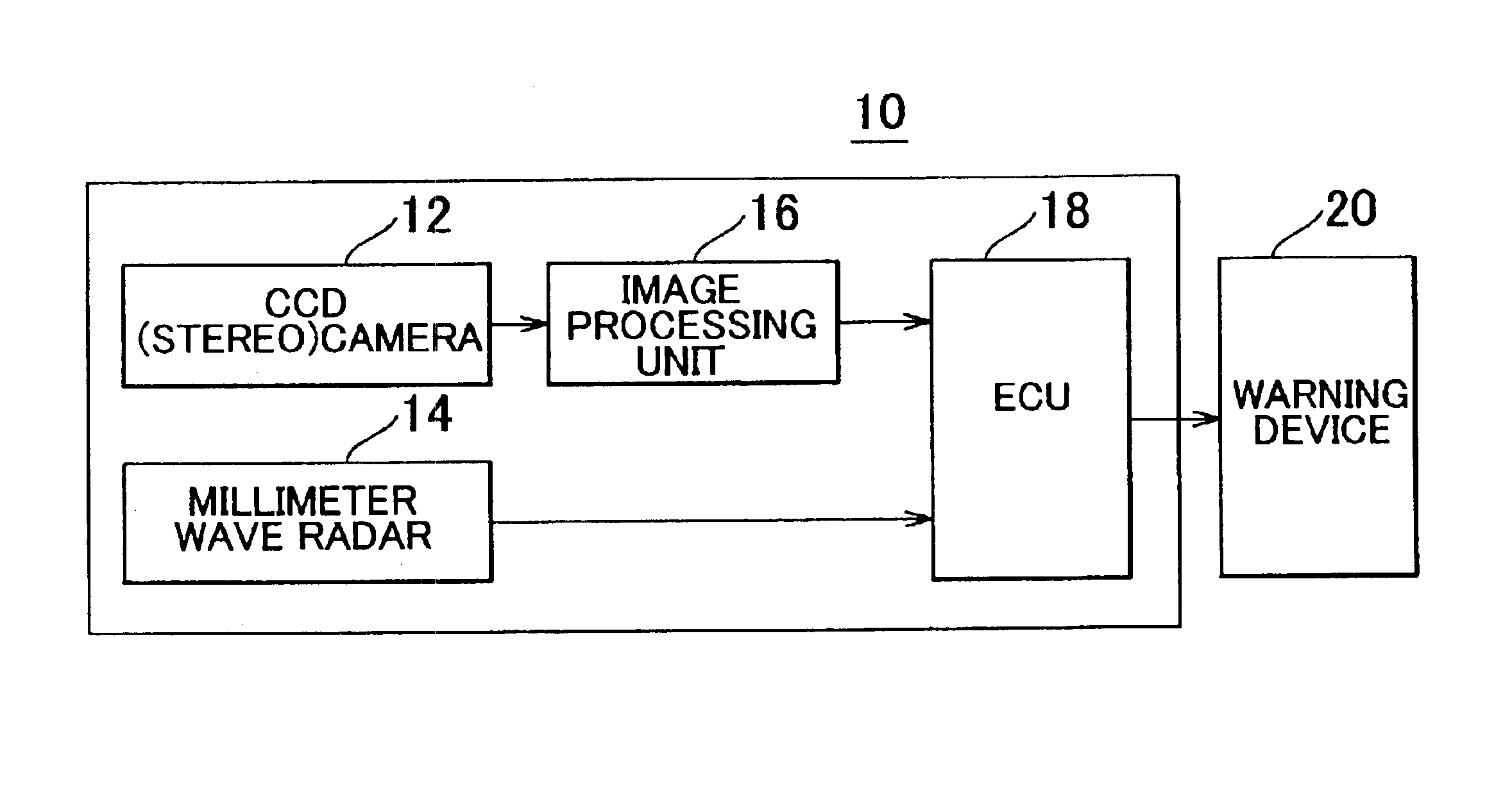
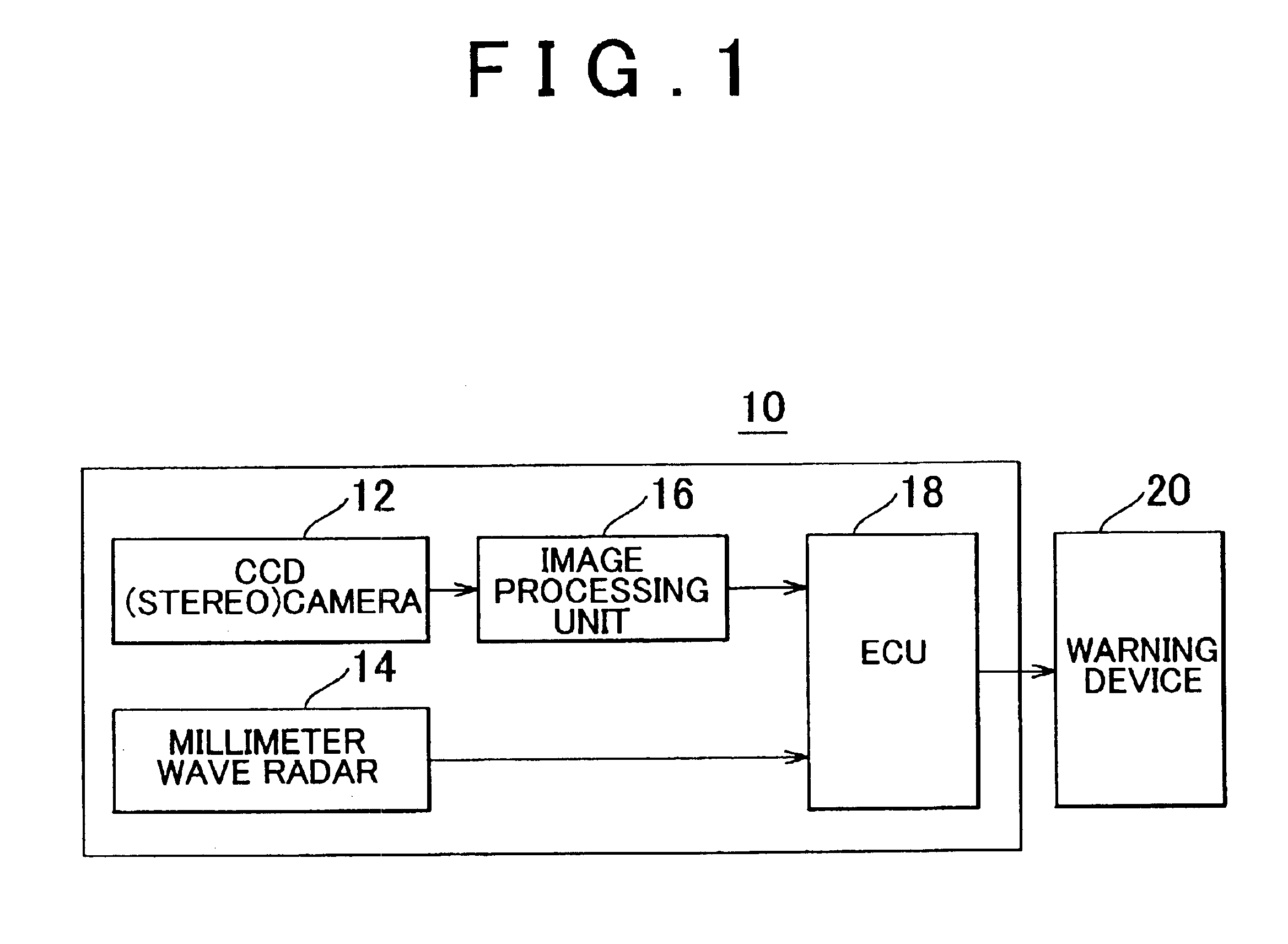
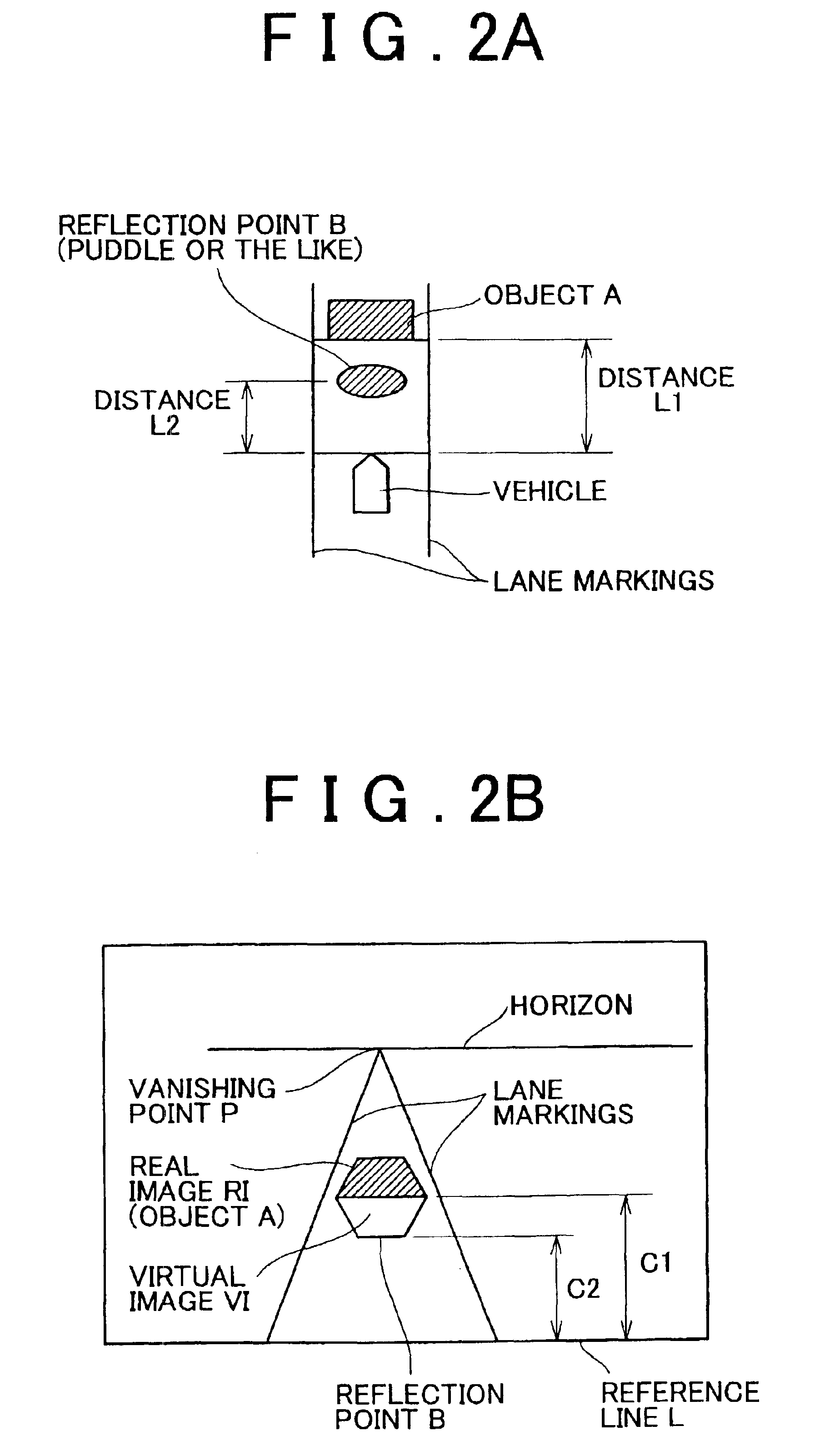
Obstacle detection device for vehicle and method thereof
InactiveUS6888447B2Minimize recognitionImprove accuracyOptical rangefindersPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementImaging processingRadar
An obstacle detection device for a vehicle that detects obstacles using a distance to an object calculated by image processing and a distance to the object calculated by radar ranging. This obstacle detection device includes a measuring portion that measures an amount of movement of the object at a predetermined interval of time by image processing and a measuring portion that measures an amount of movement of the object at a predetermined interval of time by radar ranging, and does not determine the object to be an obstacle when the two amounts of movement are not consistent.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
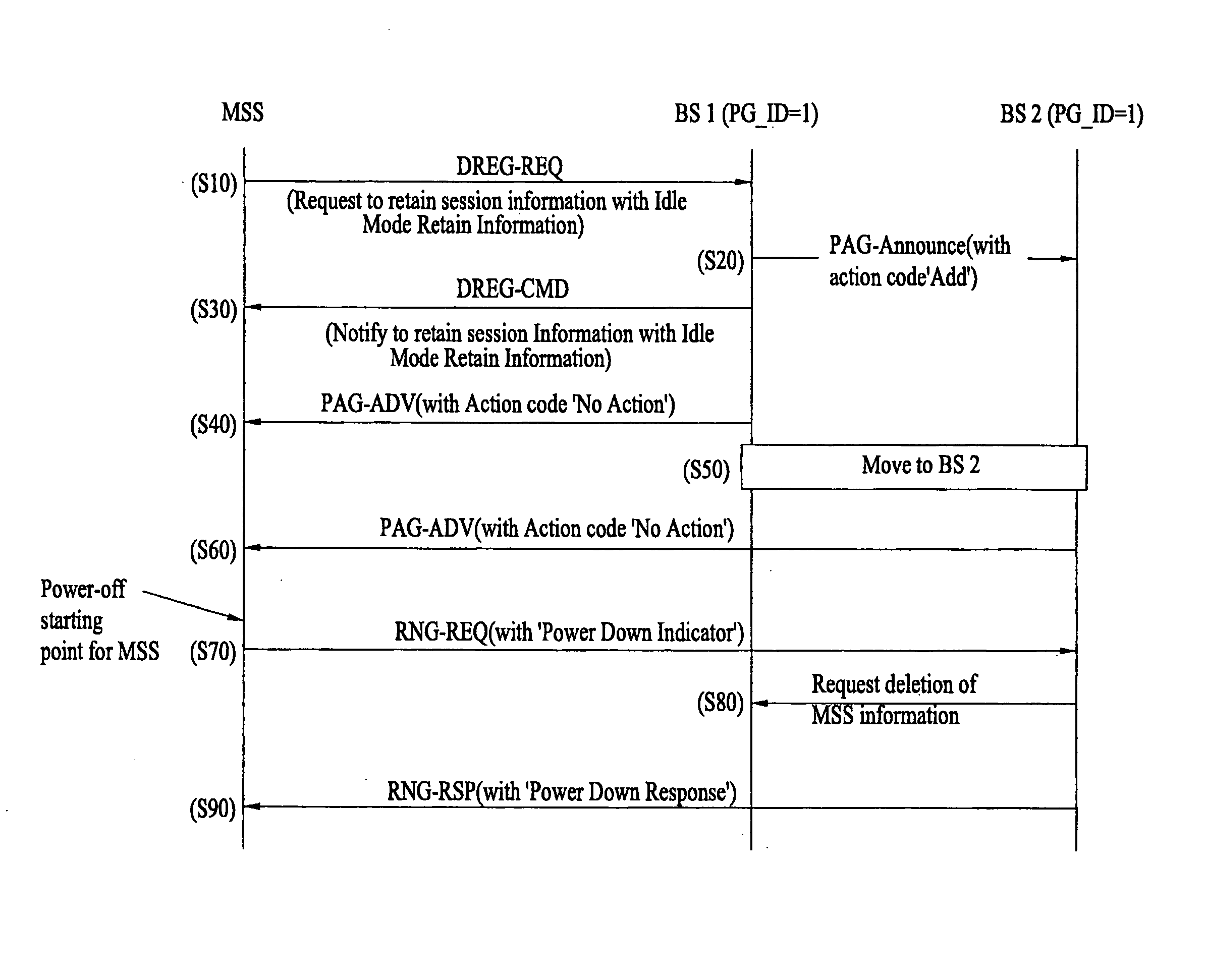
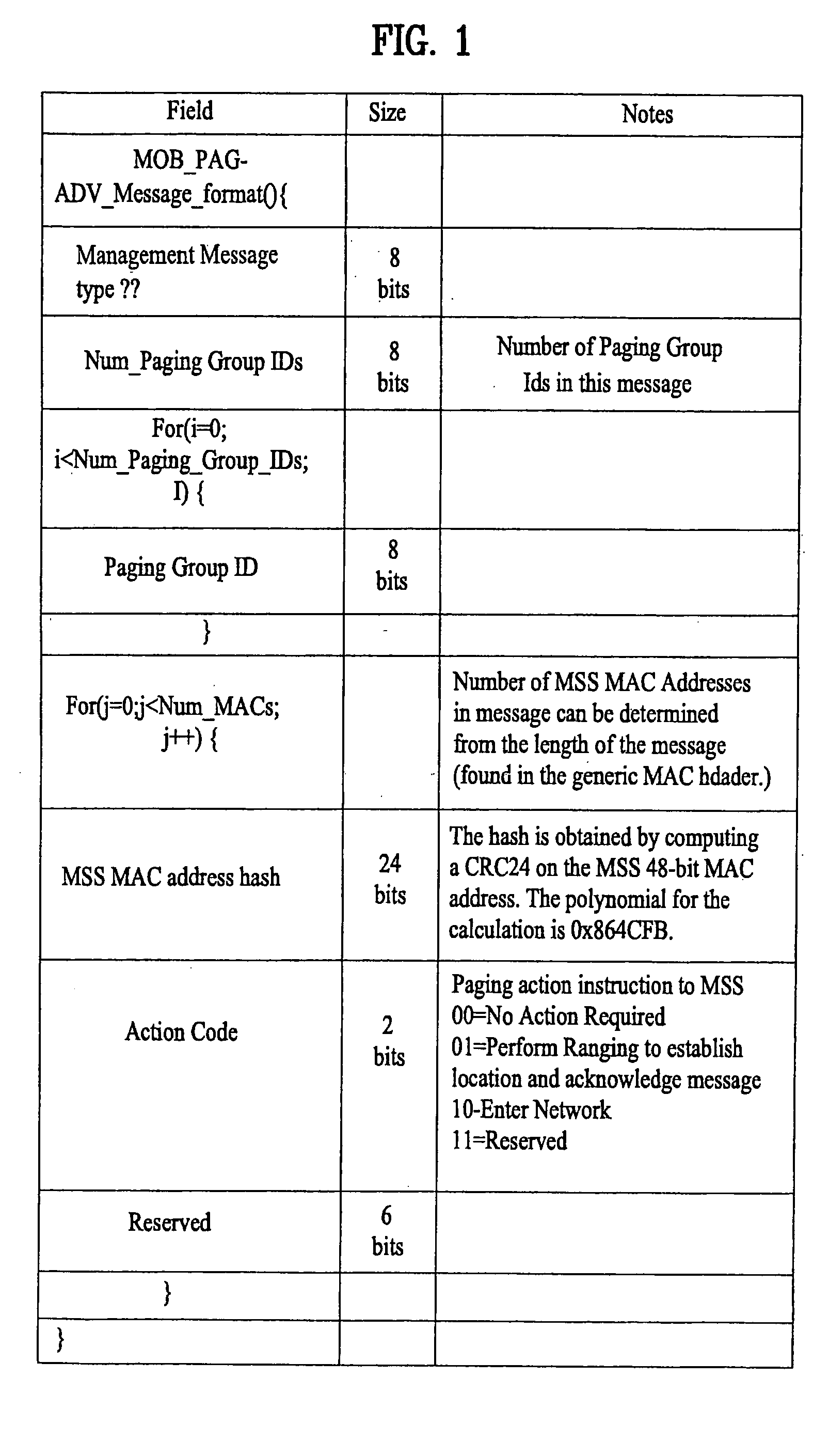
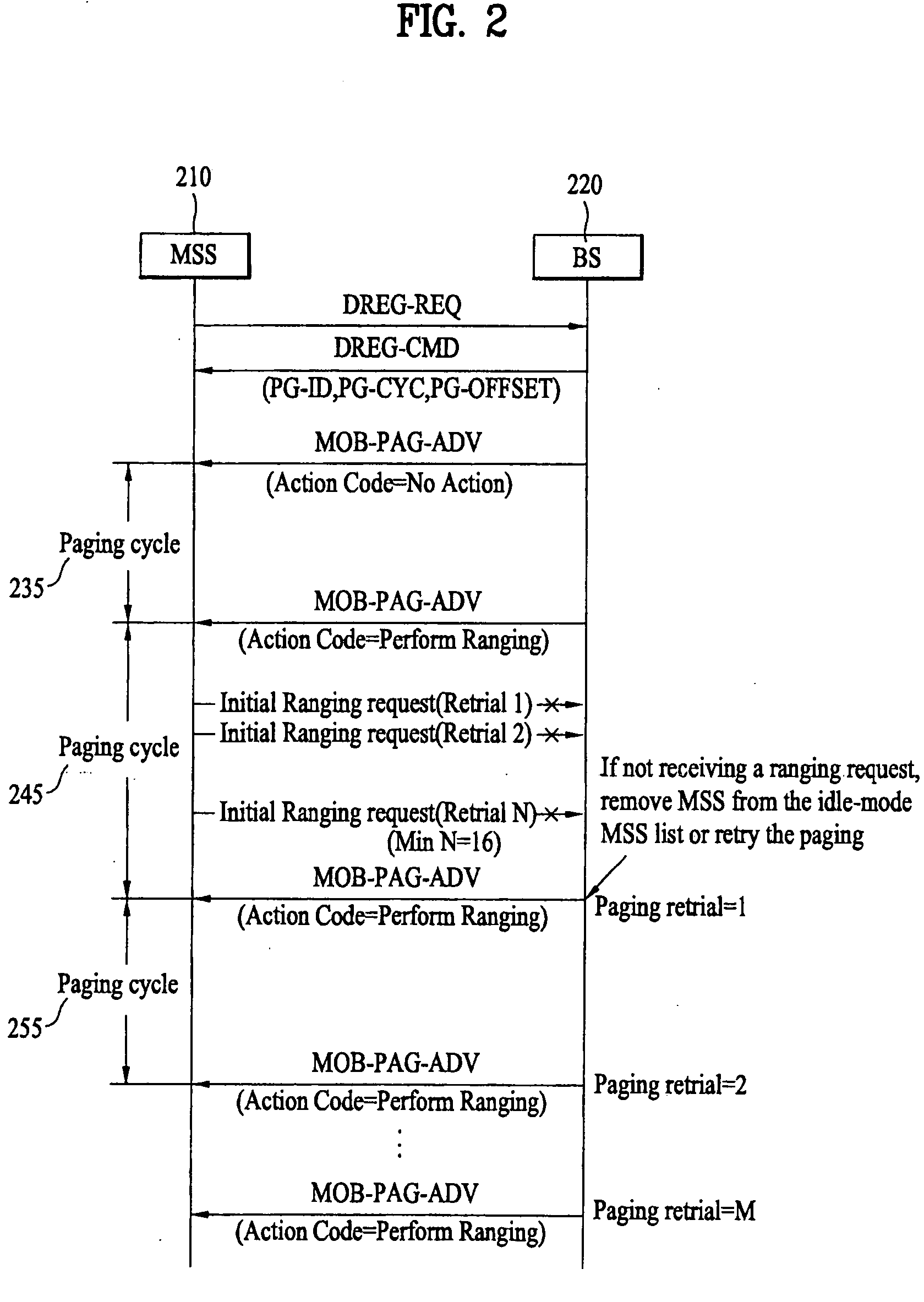
Verifying availability of idle-mode mobile subscriber station in wireless access system
ActiveUS20060009242A1Eliminate the problemPower managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAction CodeRanging
A method of verifying of a mobile subscriber station that is in an idle-mode includes requesting to a base station by the mobile subscriber station to enter an idle-mode, wherein the base station is associated with a paging group comprising a plurality of base stations, and receiving from the base station an idle-mode response command to enter the idle-mode. The method also includes receiving from the base station a paging command comprising an action code associated with performing ranging while the mobile subscriber station is in the idle-mode to verify availability of the mobile subscriber station with respect to the base station, wherein if the ranging is not successfully preformed with the base station during a predetermined period, the base station continues to transmit the paging command until a paging retrial count reaches a predetermined threshold.
Owner:PANTECH CORP
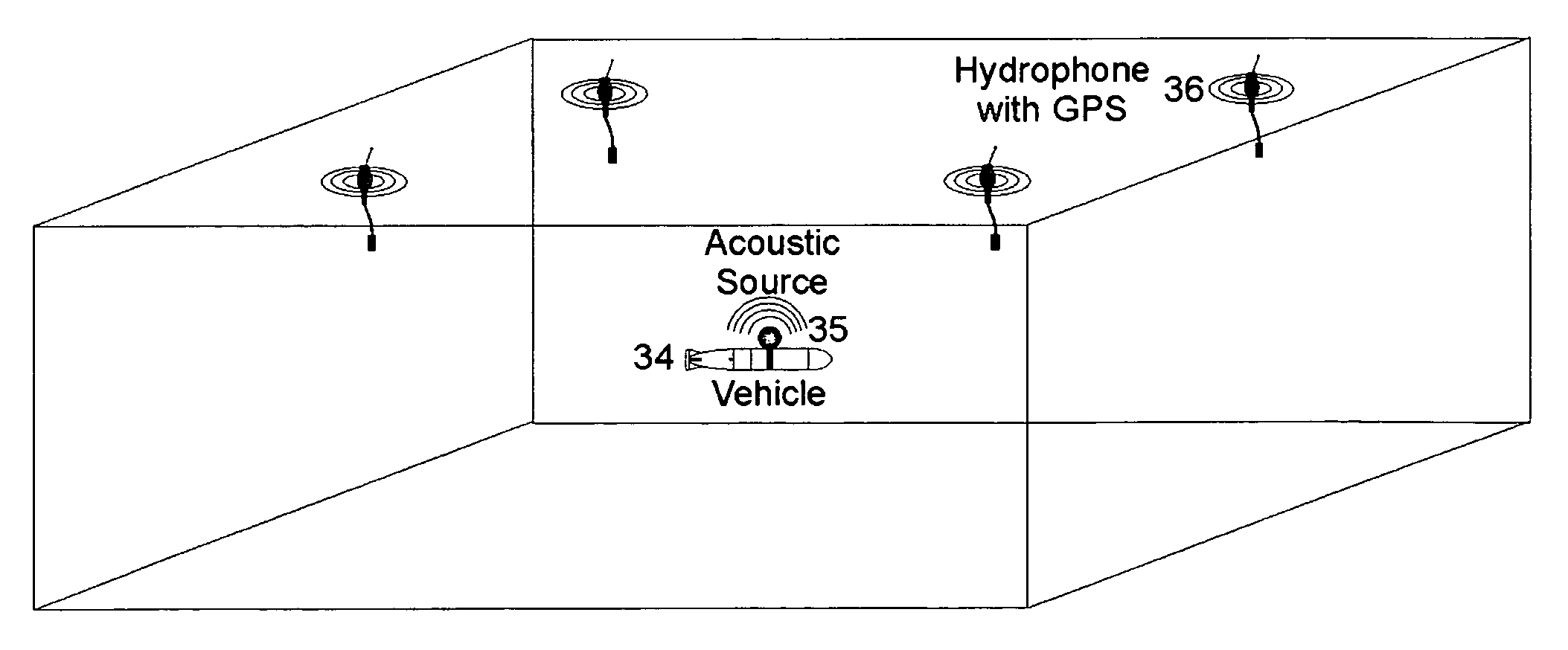
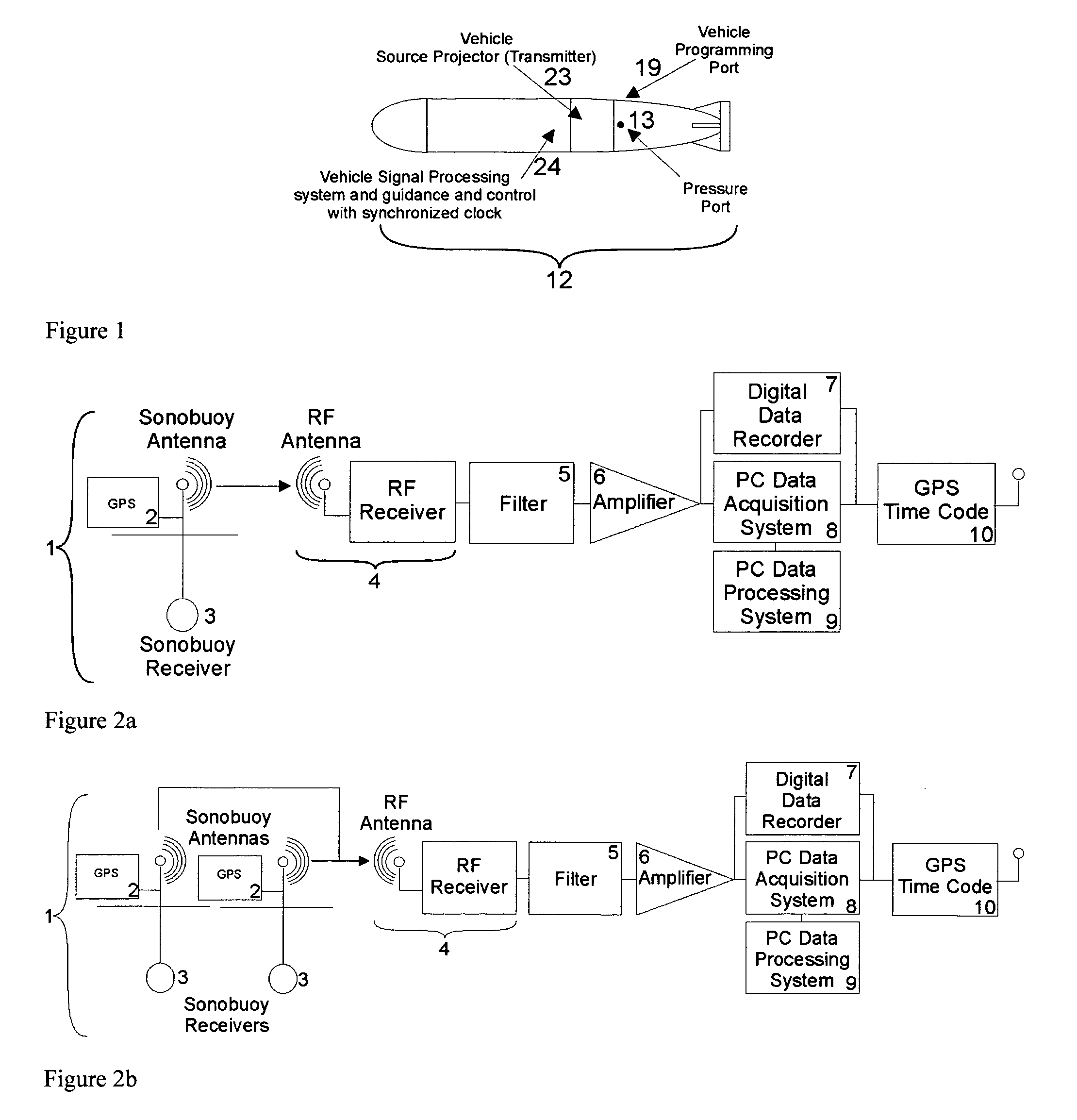
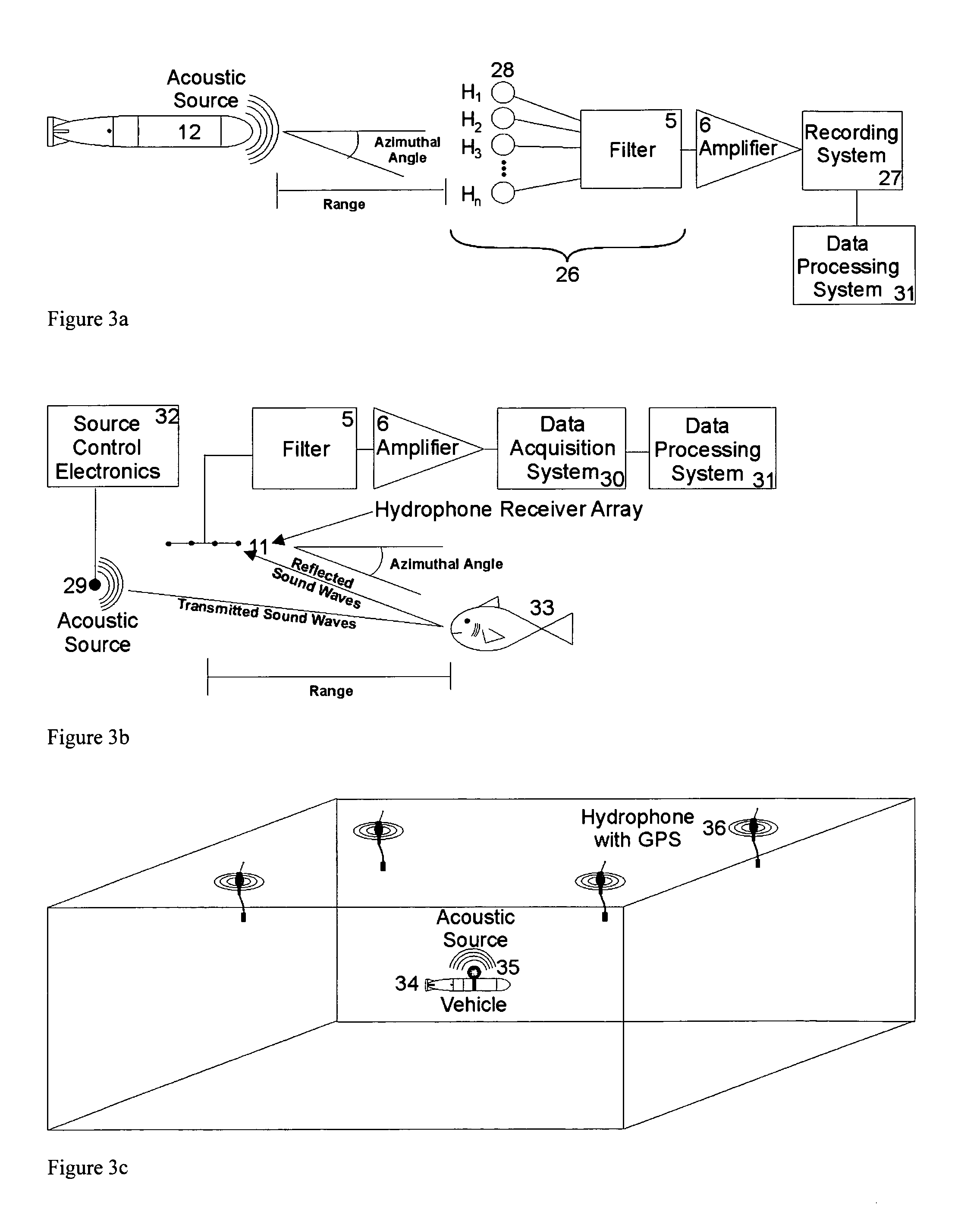
Methods of and systems for continually measuring the range between mobile underwater vehicles carrying acoustical signal transmitters and remotely deployed synchronized underwater acoustical receivers provided with signal processing for continually determining such range during the underwater moving of the vehicle, and for measuring acoustic underwater transmission loss, geoacoustical properties and for other purposes
ActiveUS20080165617A1Improve practicalitySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionAcoustic wave reradiationOcean bottomContinuous measurement
Invention relates to a novel method of and system for ranging between an acoustic source carried on an unmanned or autonomous undersea mobile vehicle (UUV or AUV) and preferably a plurality of hydrophone receivers remotely deployed from the vehicle in predetermined patterns, generally suspended from sonobuoys equipped with above-the-sea relay radio transmitting antennas, and with time synchronization provided amongst the source and the receivers, wherein the time delay from the transmissions of the source is measured by utilizing special signal processing, enabling range to be measured in close to real time by determining the product of the sound velocity and the measured time delay, and with the process continually and periodically being repeated throughout the duration of the vehicle run. Given the range, the system may then be used to measure the acoustical properties of and / or receiver system performance in the sea or other water body, such as transmission or propagation loss TL, channel impulse response, bottom geoacoustic properties, source level, receiver sensitivity calibration, sonar operator readiness and sonar receiver performance and the like. Further, in situ measured data can be assimilated with models to enable more accurate prediction of the ocean environment than could be obtained from either individually.
Owner:OCEAN ACOUSTICAL SERVICES ADN INSTR SYST OASIS INC
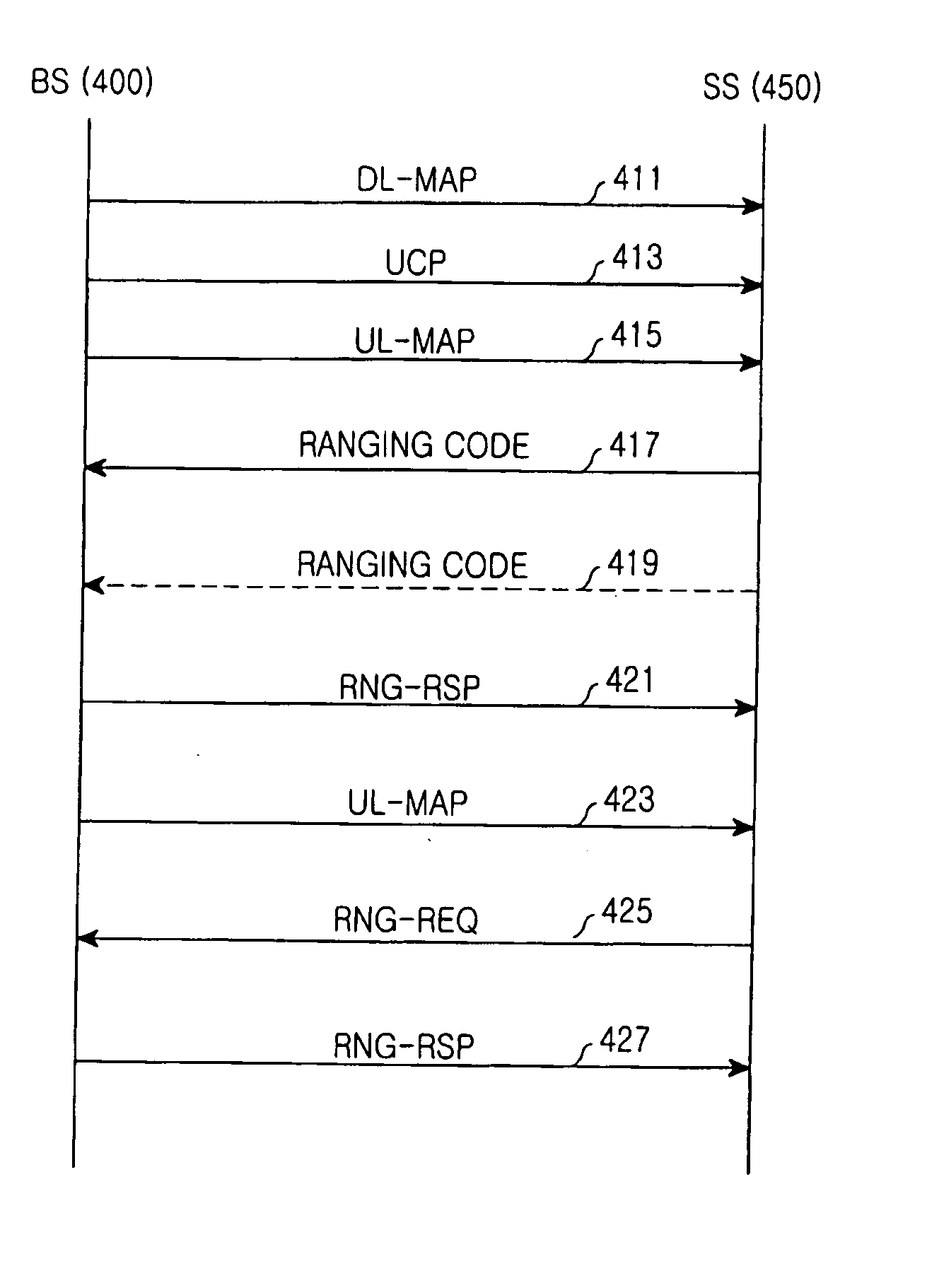
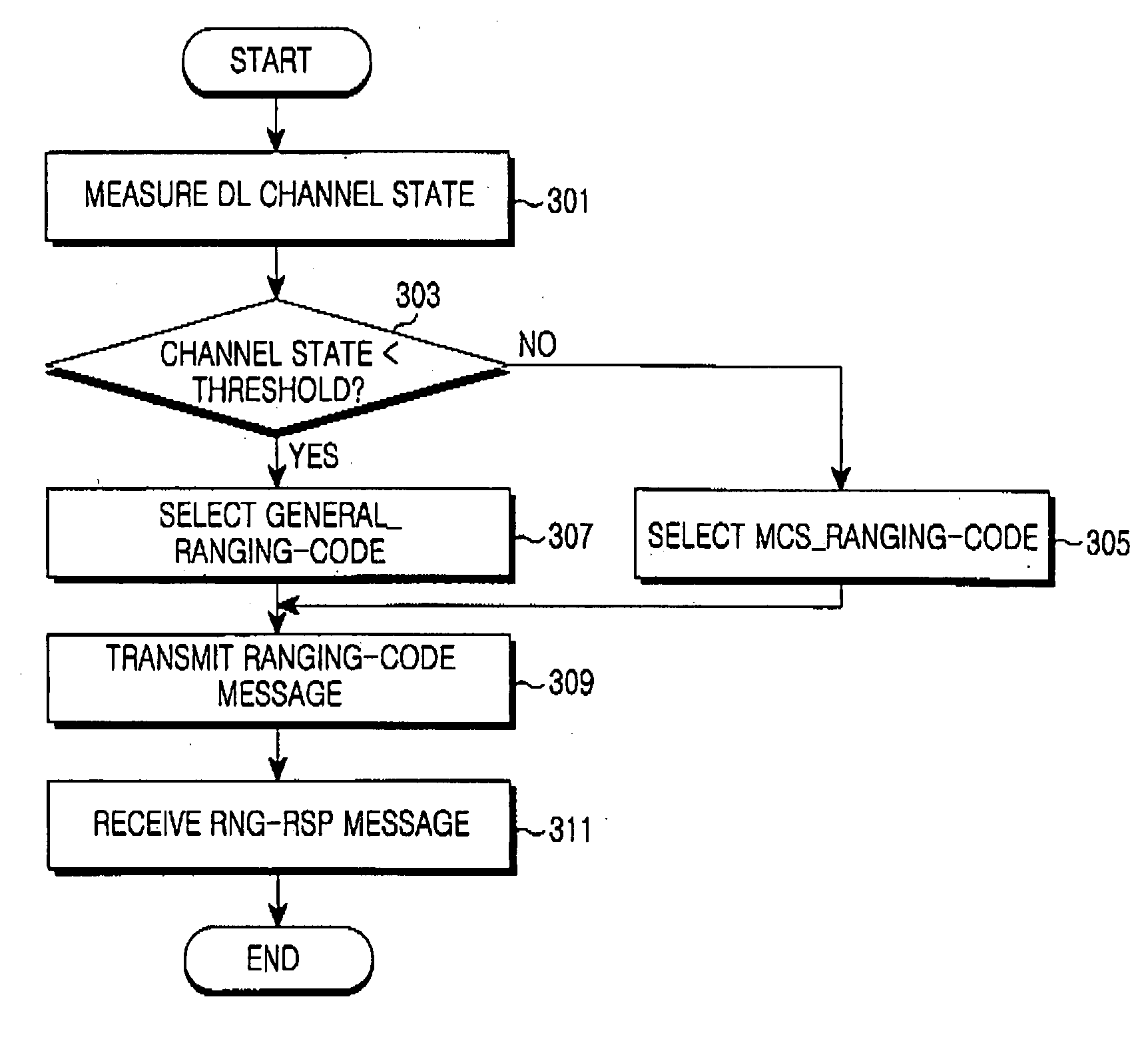
Method and system for ranging in communication system
InactiveUS20070202882A1Synchronisation arrangementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsChannel state informationCommunications system
A method is provided a ranging method in a communication system. The method includes measuring the state of a channel between an Mobile Station (MS) and a Base Station (BS) when recognizing a need for ranging with the BS after acquiring synchronization with the BS; setting a channel state information code corresponding to the measured channel state; and transmitting a ranging code message including the set channel state information code to the BS to perform the ranging.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
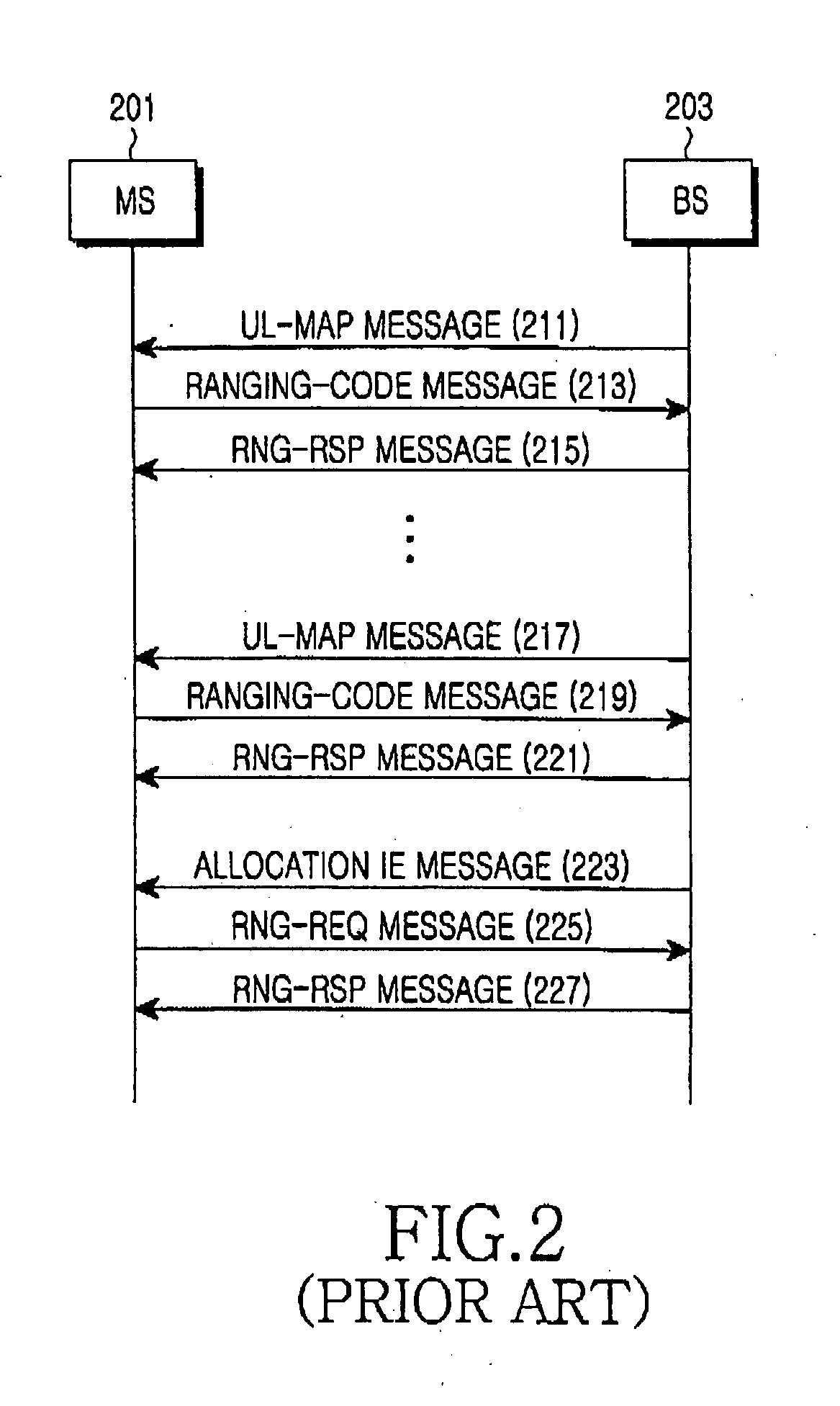
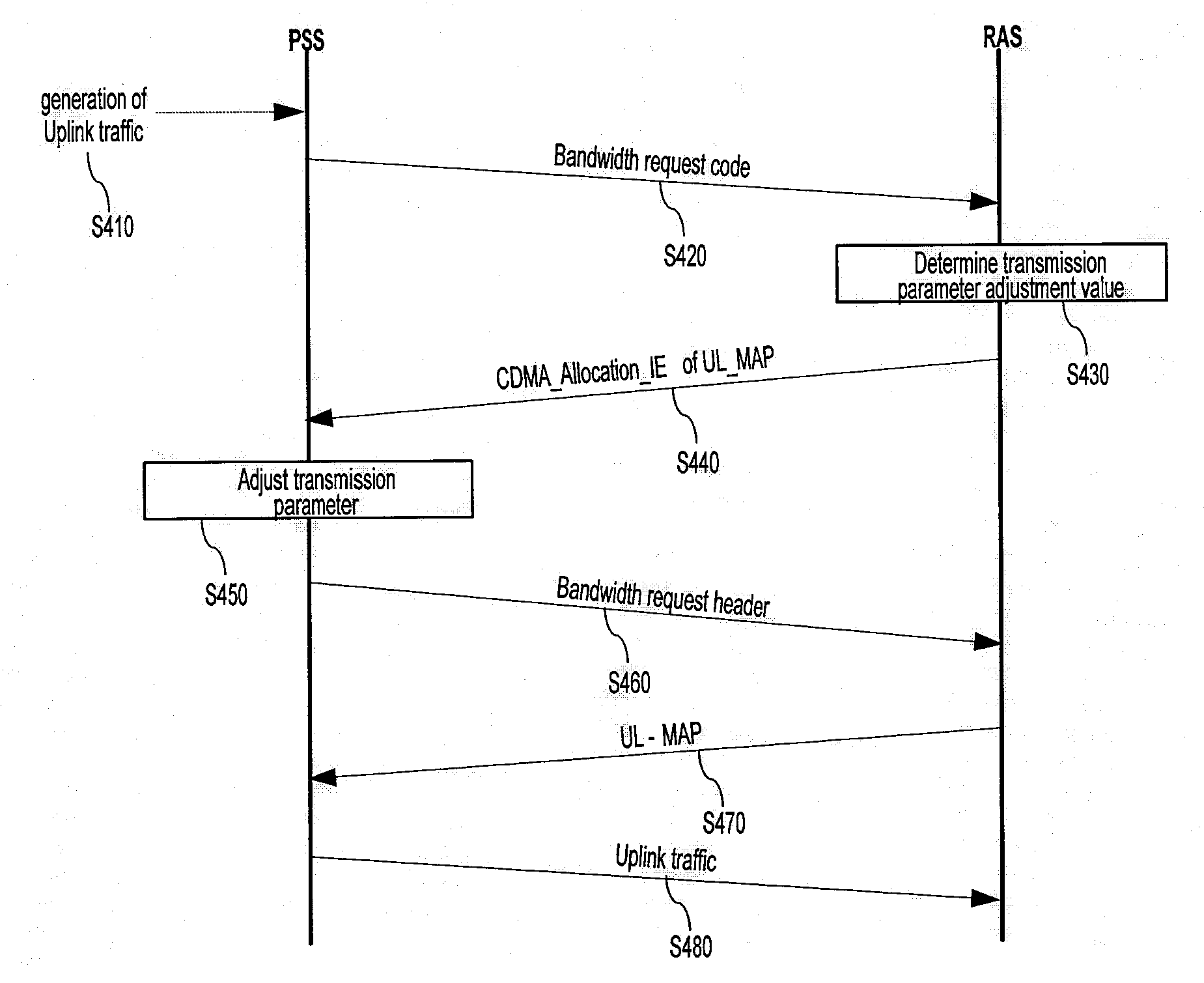
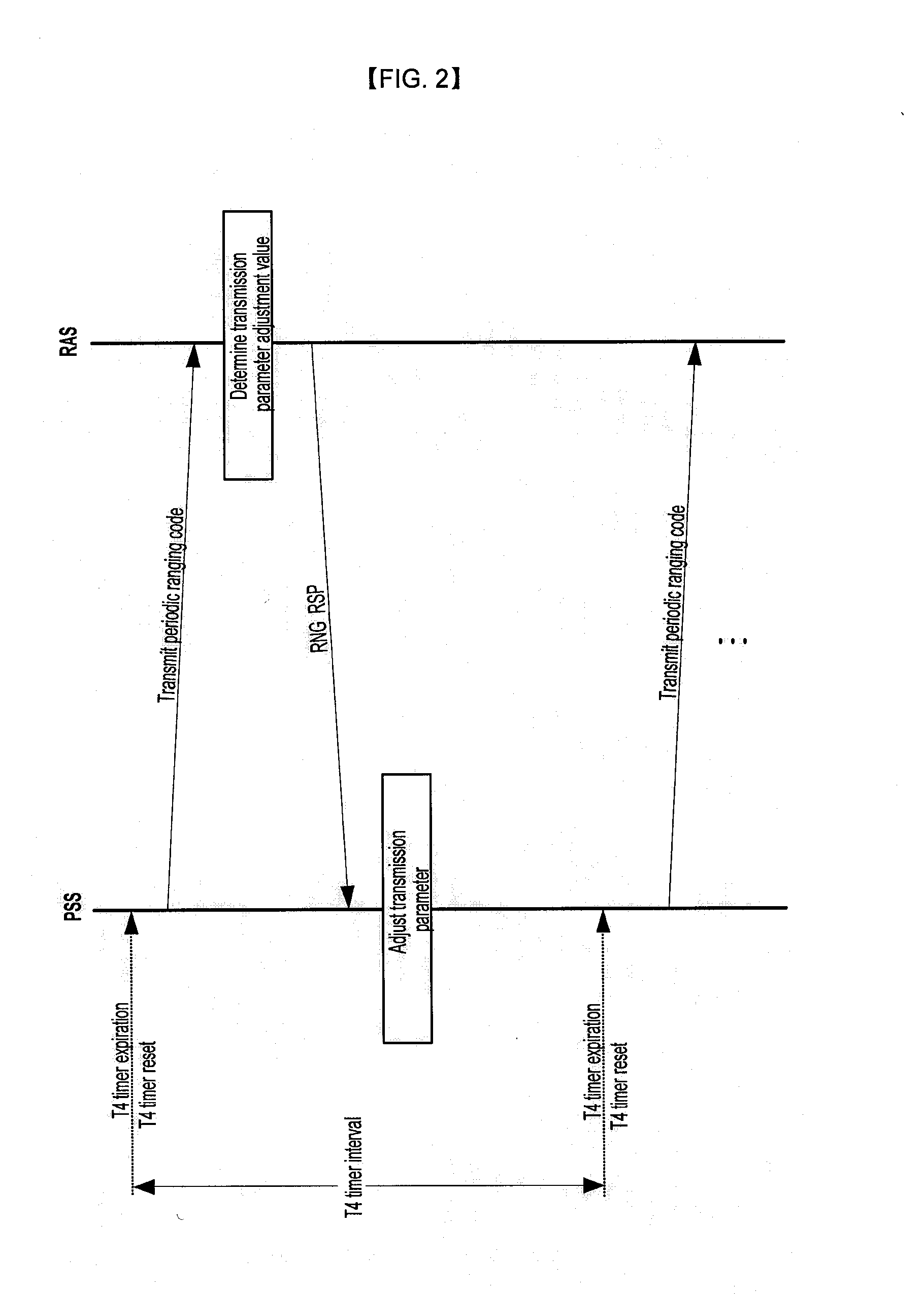
Method for Ranging with Bandwidth Request Code
InactiveUS20080232330A1Network traffic/resource managementCode division multiplexData transmissionTimer
The present invention relates to a ranging method using a bandwidth request code. For this purpose, the present invention provides a ranging method that includes transmitting a bandwidth request code for requesting a bandwidth for uplink traffic transmission from a radio access station, receiving a CDMA_Allocation_IE of a UL_MAP that includes uplink radio resource information from the radio access station, adjusting a transmission parameter according to an adjustment value included in the CDMA_Allocation_IE when periodic ranging performance is checked through the CDMA_Allocation_IE, checking whether the adjusted transmission parameter has an optimum value, and resetting a timer for periodic ranging, and a CDMA_Allocation_IE structure of a UL_MAP for the same. According to the present invention, delay in uplink data transmission of a portable subscriber station can be reduced by including a ranging parameter for a bandwidth request code in a UL_MAP, and a downlink bandwidth can be efficiently used by a radio access station by eliminating a process of RNG_RSP transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +4
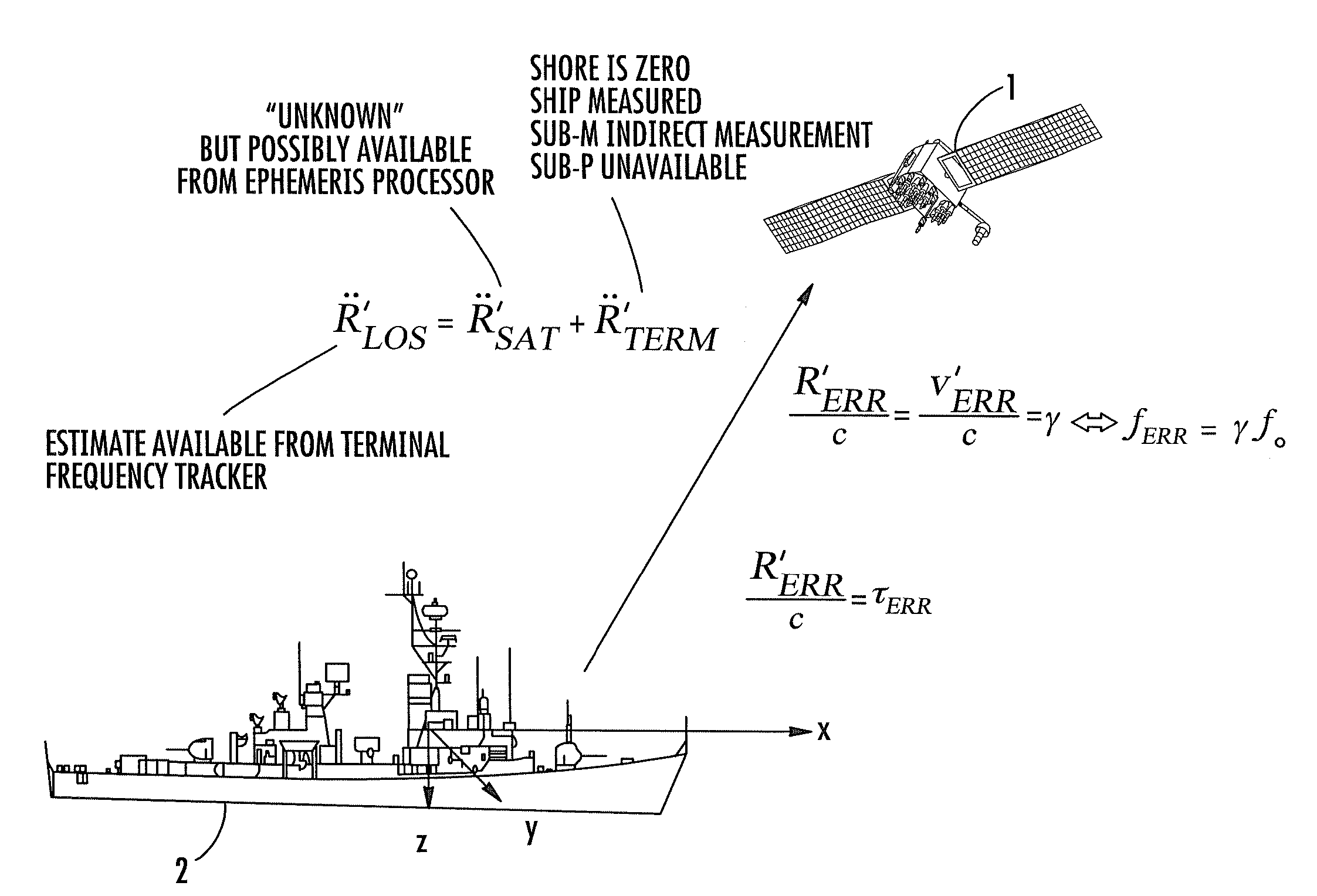
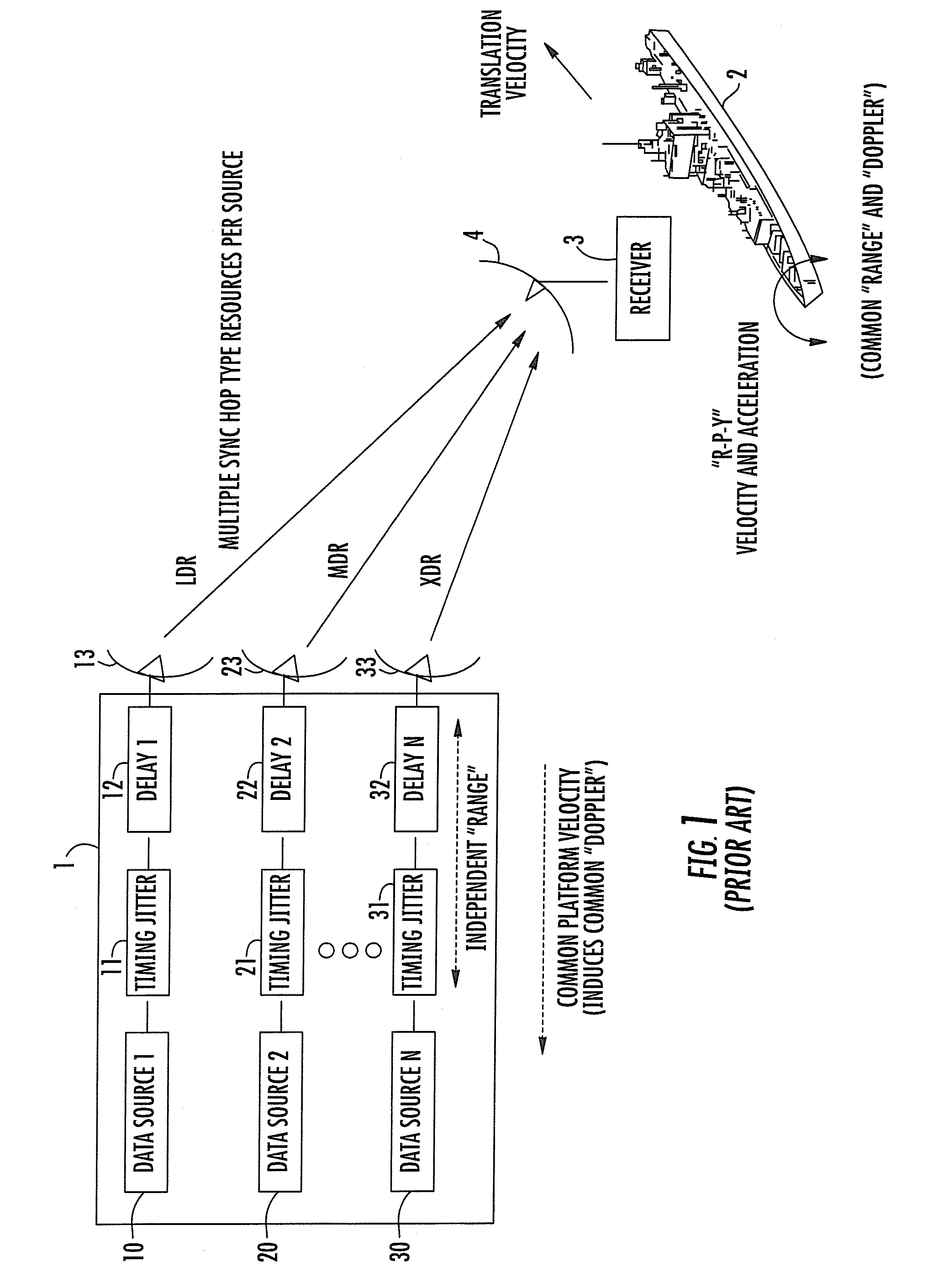
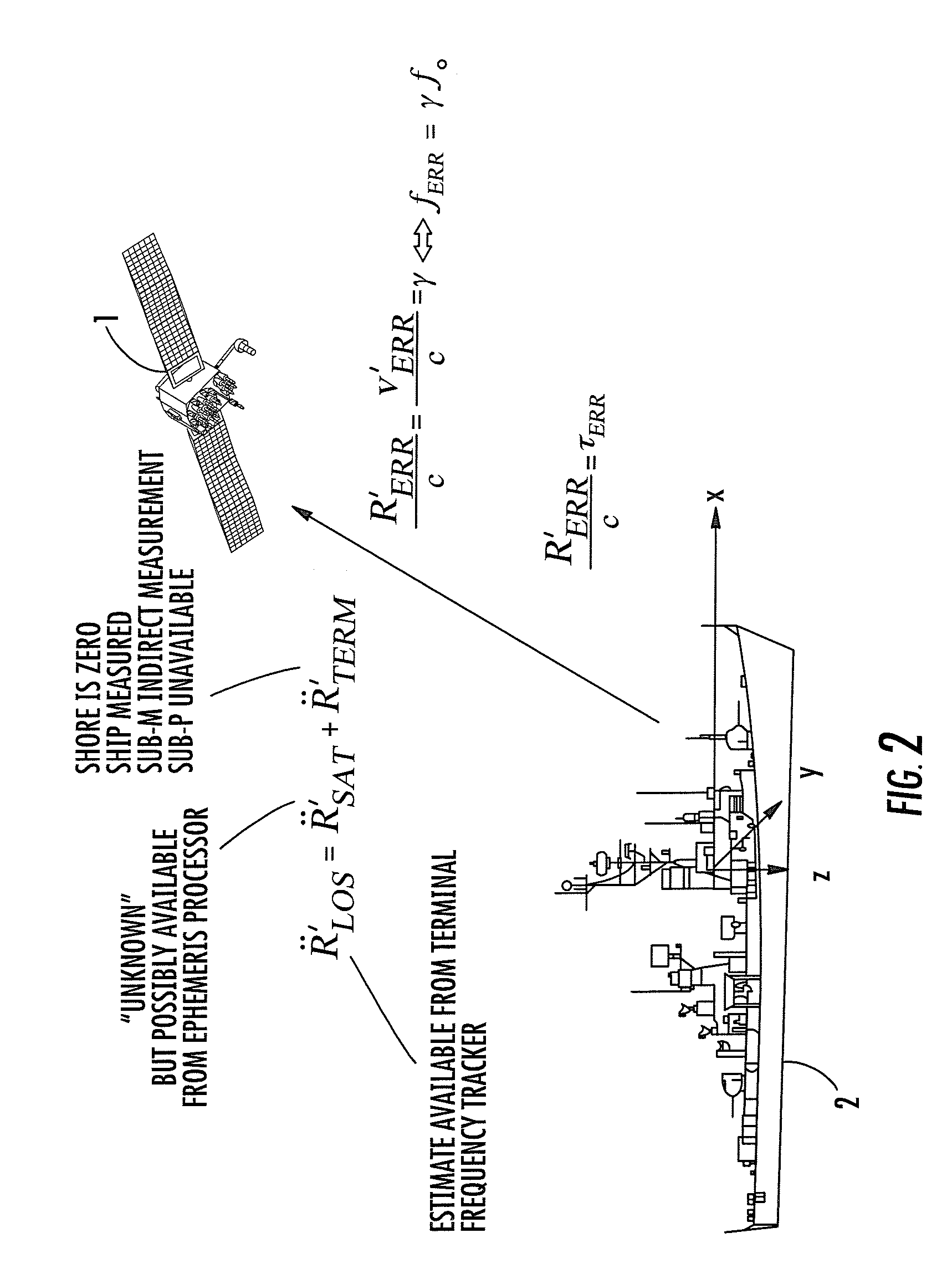
Time/frequency recovery of a communication signal in a multi-beam configuration using a kinematic-based kalman filter and providing a pseudo-ranging feature
InactiveUS20070218931A1Inability to efficientlyEffectively obviatedSynchronisation arrangementRadio transmissionErrors measurementKalman filter
A downlink time / frequency tracker for a receiver terminal, which may be mounted to a static platform on the earth, or to a dynamic platform, such as a ship. The tracker is operative to acquire and track time and frequency variations in time- and frequency-hopped synchronization signals from different data rate sources in a dynamic platform, such as a satellite. Characteristics of the Kalman filter are updated in accordance with data representative of timing error and frequency error measurements carried out on the synchronization signals, as well as data representative of local kinematic domain measurements carried out with respect to the receiver terminal. The Kalman filter outputs minimum mean square error estimates of timing and frequency errors in the receiver terminal's demodulator clock. These error estimates are used to synchronize the demodulator's clock with the clock embedded in the downlink signal, so as to enable demodulation and recovery of data.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
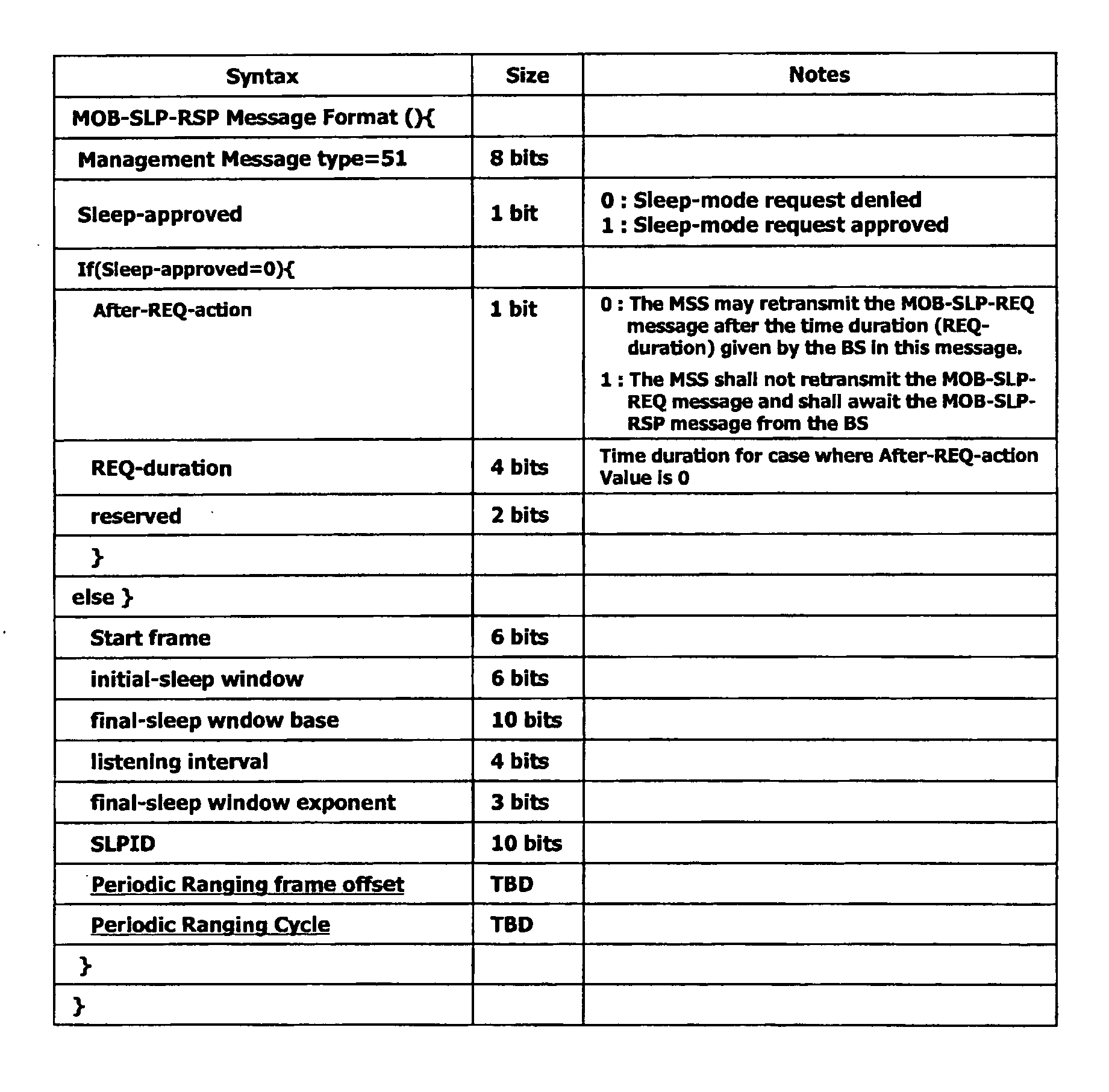
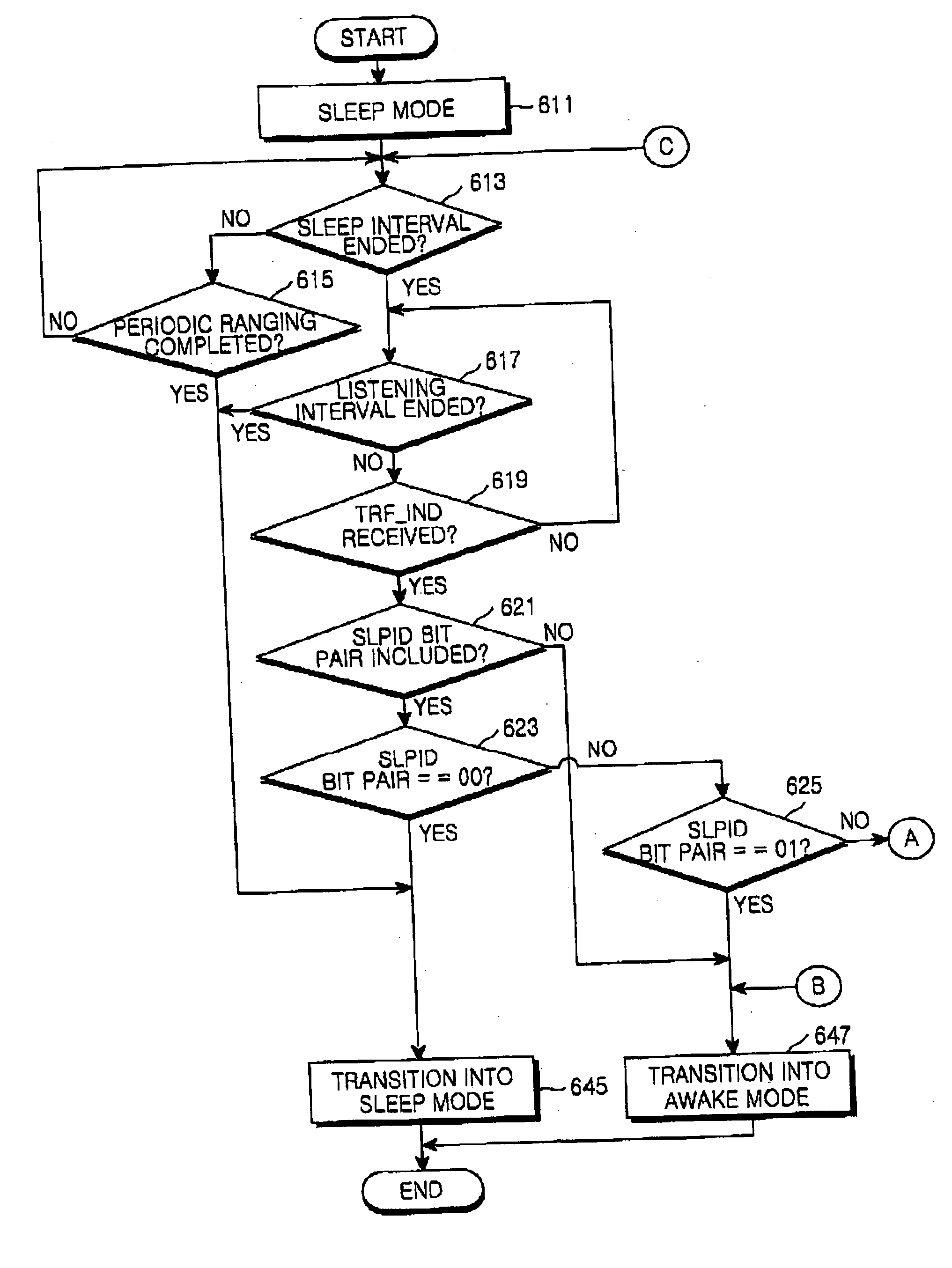
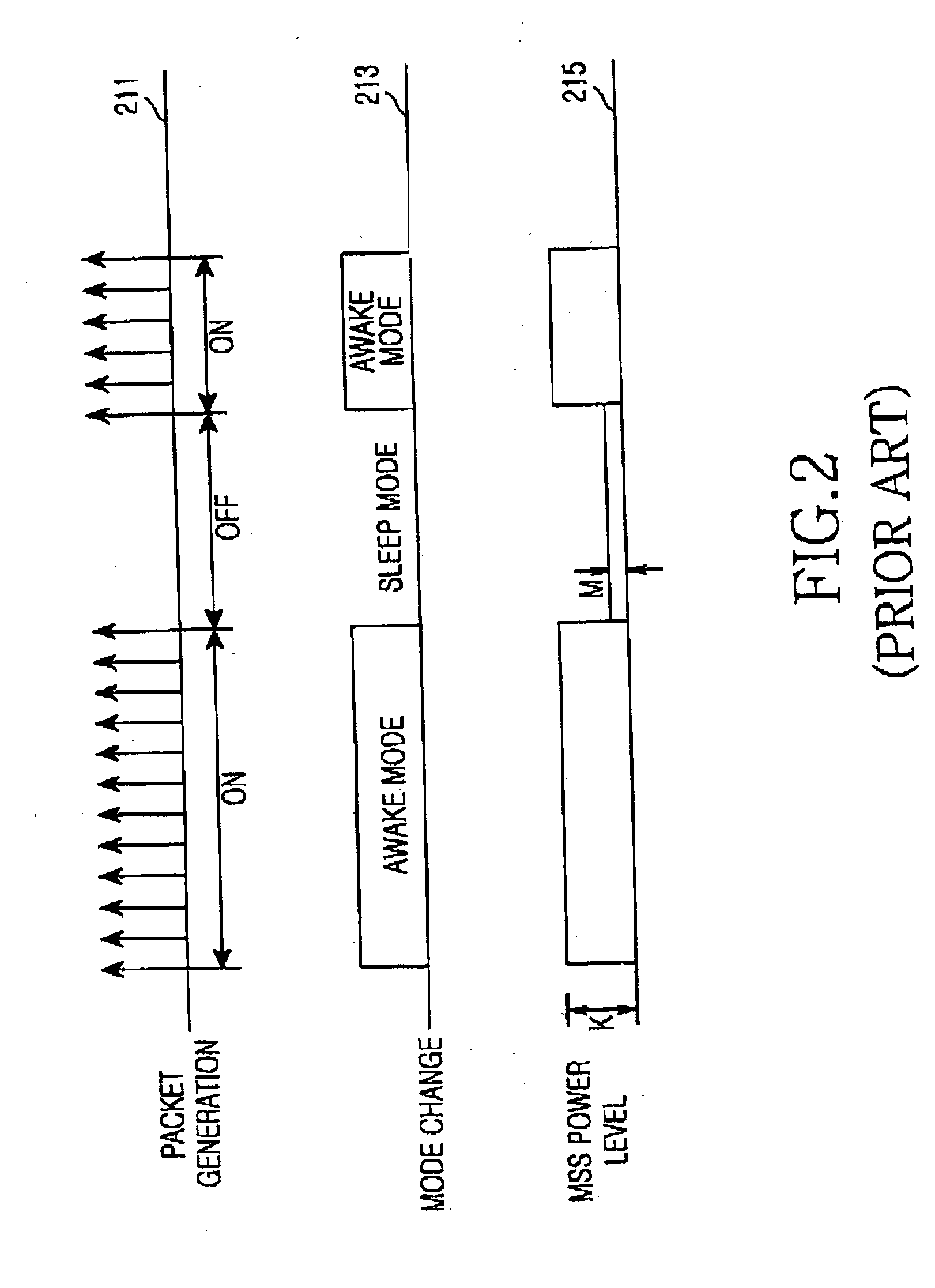
Periodic ranging in a wireless access system for mobile station in sleep mode
InactiveUS20060030305A1Eliminate the problemPower managementSubstation equipmentSleep timeMobile station
A method of performing a ranging process between a base station and a mobile station in sleep mode in a wireless access system, wherein the base station provides the mobile station with an initial notification of a periodic ranging time that occurs during a sleep time interval and during which the mobile station is to perform the ranging process, the initial notification included in a first message indicating whether the mobile station should terminate sleep mode to receive downlink data, and wherein the base station provides the mobile station with subsequent notifications of periodic ranging times that occur during the sleep time interval, the subsequent notifications indicated in a second message, the second message transmitted to the mobile station as part of the ranging process such that the mobile station performs a plurality of ranging processes within the sleep time interval.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Magnetization of target well casing strings tubulars for enhanced passive ranging
InactiveUS20060131013A1Small diameterCost effectiveElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveySection planeMagnetic poles
A method for magnetizing a wellbore tubular is disclosed. The method includes magnetizing a wellbore tubular at three or more discrete locations on the tubular. In exemplary embodiments the magnetized wellbore tubular includes at least one pair of opposing magnetic poles located between longitudinally opposed ends of the tubular. Wellbore tubulars magnetized in accordance with this invention may be coupled to one another to provide a magnetic profile about a section of a casing string. Passive ranging measurements of the magnetic field about the casing string may be utilized to survey and guide drilling of a twin well. Such an approach advantageously obviates the need for simultaneous access to both wells.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for rejecting rain clutter in a radar system
InactiveUS6127965ADue to rain clutter are dramatically reducedReduces false alarmsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPatch arrayRadar systems
A method and apparatus for detecting the presence of objects in a vehicle operator's blind spots. The apparatus comprises a side-facing Doppler radar system using continuous wave (CW) transmission with frequency modulation (FM) operation from a frequency modulation switching technique. The radar system determines the presence, range and closing rate of detected targets. The radar system detects targets even when operated in adverse weather conditions and will not generate false warnings due to rain clutter caused by wet roads and other wet surroundings. The radar system uses ranging techniques to reject false targets that are detected outside of a predetermined target detection zone. In accordance with the present invention, the radar system indicates that a target is detected if and only if any part of the target is within the detection zone and it: (1) remains in front of the antenna for at least TH1 seconds; (2) is at a range between Rangemin and Rangemax; and (3) is moving faster than Closing-Speedmin relative to the antenna. By rejecting targets that are closer than Rangemin feet to the antenna, false alarms due to rain clutter are dramatically reduced. Also, by rejecting targets that are further than Rangemax feet from the antenna, the radar system reduces false alarms caused by wet foliage and other wet "non-road" surroundings. In one embodiment, the radar system uses a patch array antenna oriented into a diamond-shape configuration to effectively create a natural linear amplitude taper that aids in rejecting clutter caused by wet road surfaces.
Owner:BENDIX COMML VEHICLE SYST LLC
Method for drilling wells in close relationship using magnetic ranging while drilling
Methods for drilling wells using magnetic ranging while drilling to position the wells with respect to one another are provided. In accordance with one embodiment, a method of drilling a well includes leaving a drill string in position within a primary well, and drilling a secondary well using the drill string as a target for magnetic ranging while drilling such that the secondary well is positioned with a specified orientation relative to the drill string.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
High precision speed-measuring distance-measuring radar system and method
ActiveCN101236253AImprove electro-optic efficiencyReduce power consumptionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsLocal oscillator
The invention relates to a high precision speed and distance measuring laser radar system and a speed and distance measuring method. The basic principle of the invention is as follows: linear chirp modulation and pseudo-random code modulation of lasers are performed; most lasers after modulation are taken as outgoing lasers and transmitted by a telescope; a small part of the lasers is taken as local oscillator beams and used for coherent detection; laser echo signals are divided into two parts; distance information is obtained after related operation of one part of the laser echo signals and original pseudo-random codes; the frequency difference of the local oscillator beams and echo signal beams is obtained after coherent detection of the other part of the laser echo signals and the local oscillator beams and pulse compression, and simultaneously comprises the distance information and Doppler shift; the Doppler shift is obtained through mathematical manipulation, thereby speed information is obtained. The high precision speed and distance measuring laser radar system and a speed and distance measuring method of the invention is characterized in that the speed information and the distance information of a target can be obtained with high precision.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHONGKE TIANWEI TECH
System and method for periodic ranging in sleep mode in broadband wireless access communication system
A method and a system for periodic ranging in a sleep mode of a broadband wireless access communication system having an awake mode in which data to be transmitted between a mobile subscriber station (MSS) and a base station (BS) exists and the sleep mode in which data to be transmitted between the MS and the BS does not exist, the sleep mode having a sleep interval and a listening interval, the MSS being capable and incapable of receiving data in the listening interval and in the sleep interval, respectively. The BS reports to the MSS in a listening interval before the sleep interval that the MSS must perform the periodic ranging in the sleep interval when the BS detects that it is necessary for the MSS in the sleep mode to perform the periodic ranging at a particular time point in the sleep interval.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
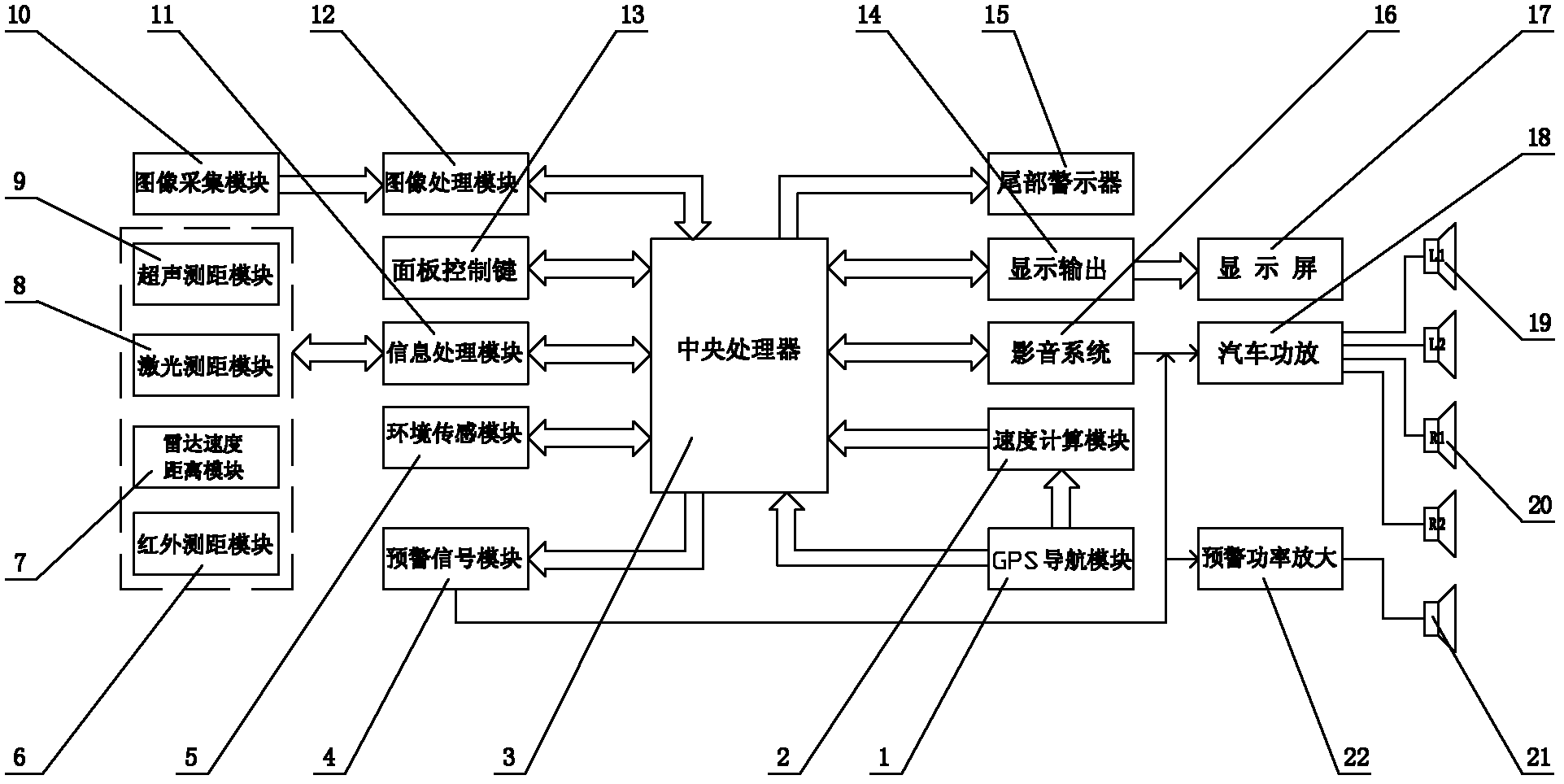
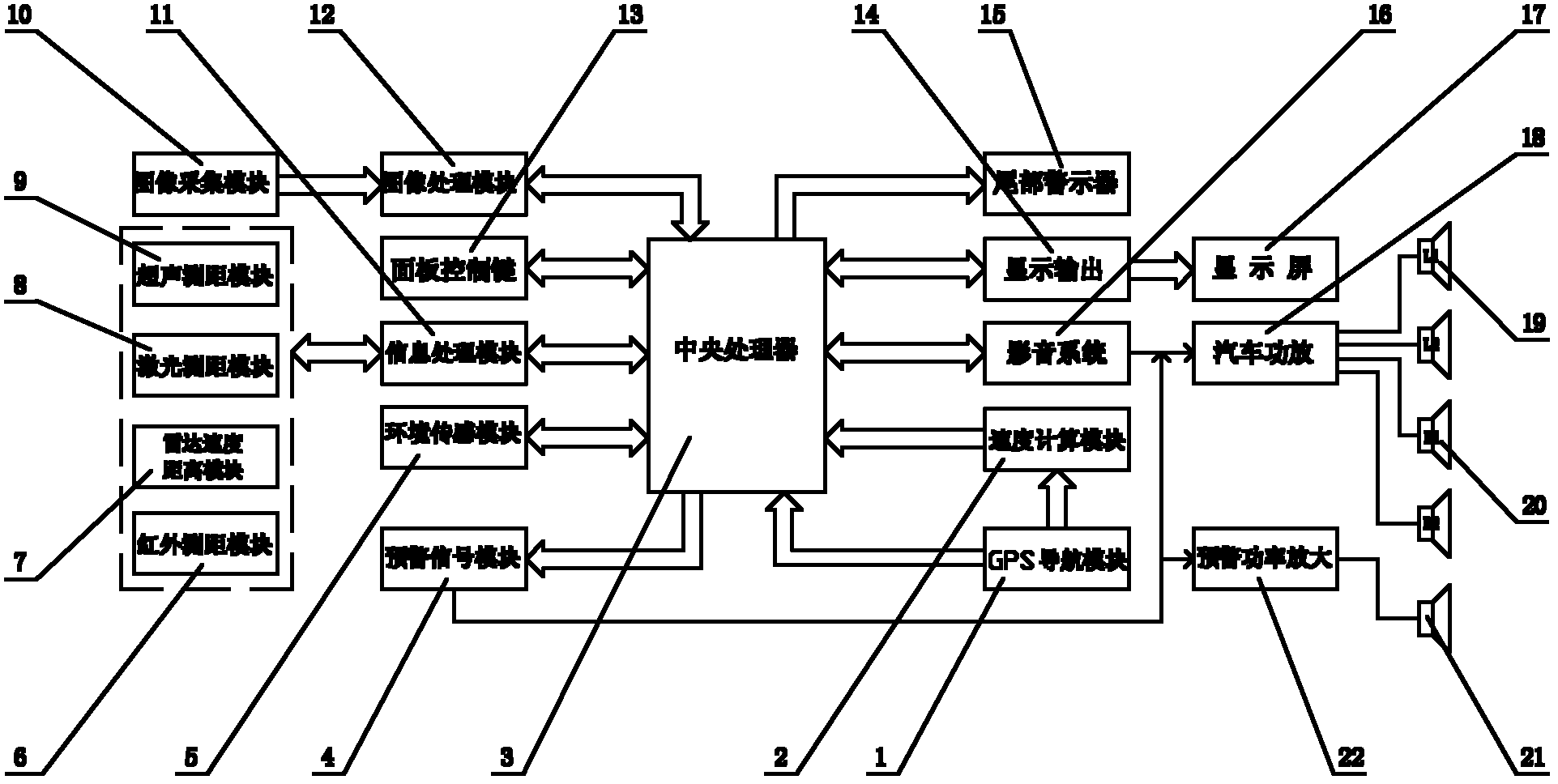
Intelligent vehicle-mounted GPS (global positioning system) navigation anti-collision warning system
The invention discloses an intelligent vehicle-mounted GPS (global positioning system) navigation anti-collision warning system which consists of a GPS navigation module, a speed computation module, a central processing unit, an early warning signal module, an environment sensing module, an infrared distance measuring module, a radar speed distance module, a laser distance measuring module, an ultrasound distance measuring module, an image collecting module, an information processing module, an image processing module, a tail warning device, an audio video system, a display screen and an early warning power amplifier, wherein the speed is detected by the GPS, and the distance is detected by the distance measuring module, dangers which can cause tailgating at the front and at the back of a vehicle can be founded in time, so that a driver can be warned to travel normally and drive safely, functions of GPS navigation and audio video are realized, and no part of a vehicle control system needs to be changed.
Owner:朱庆平
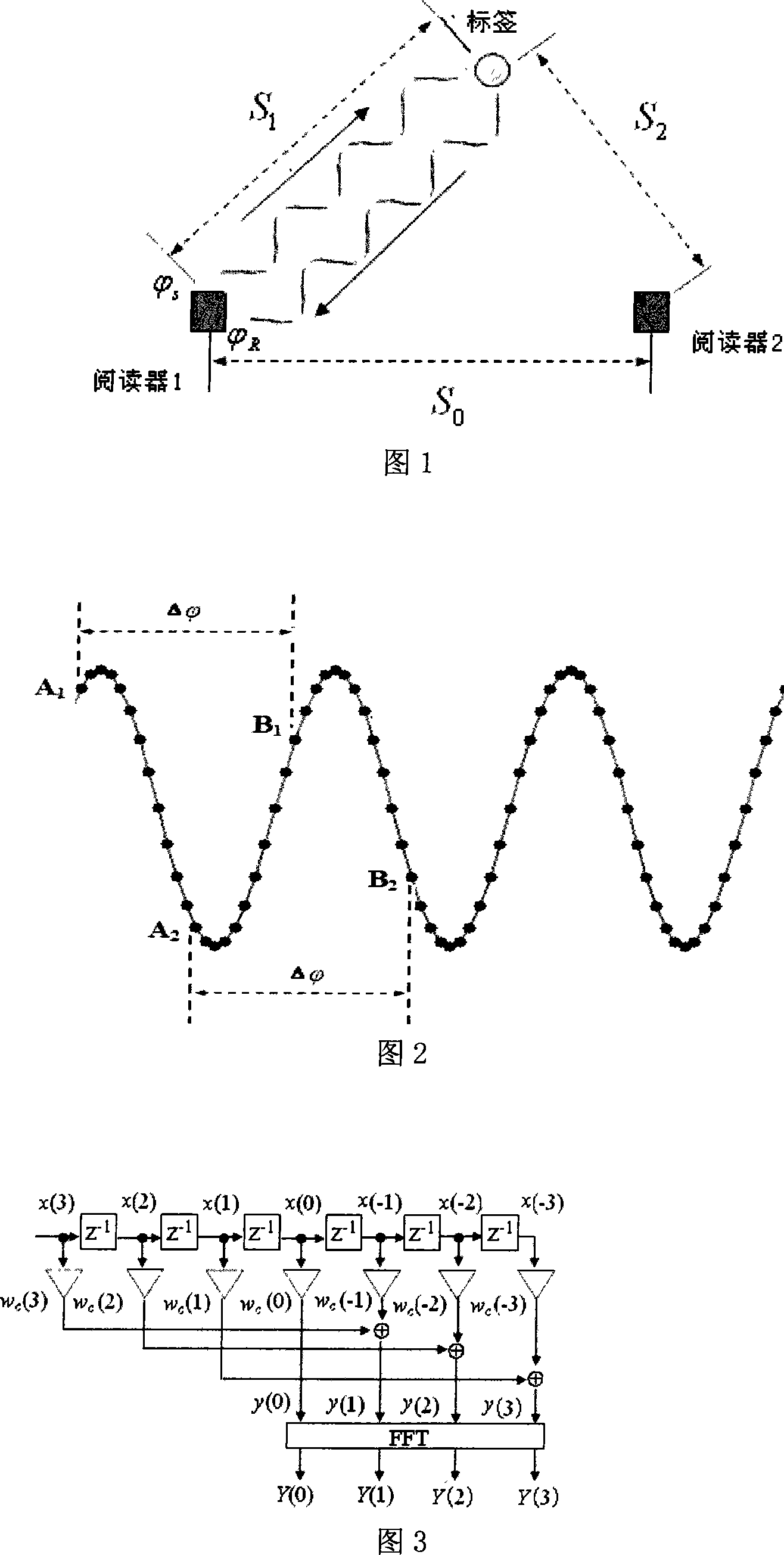
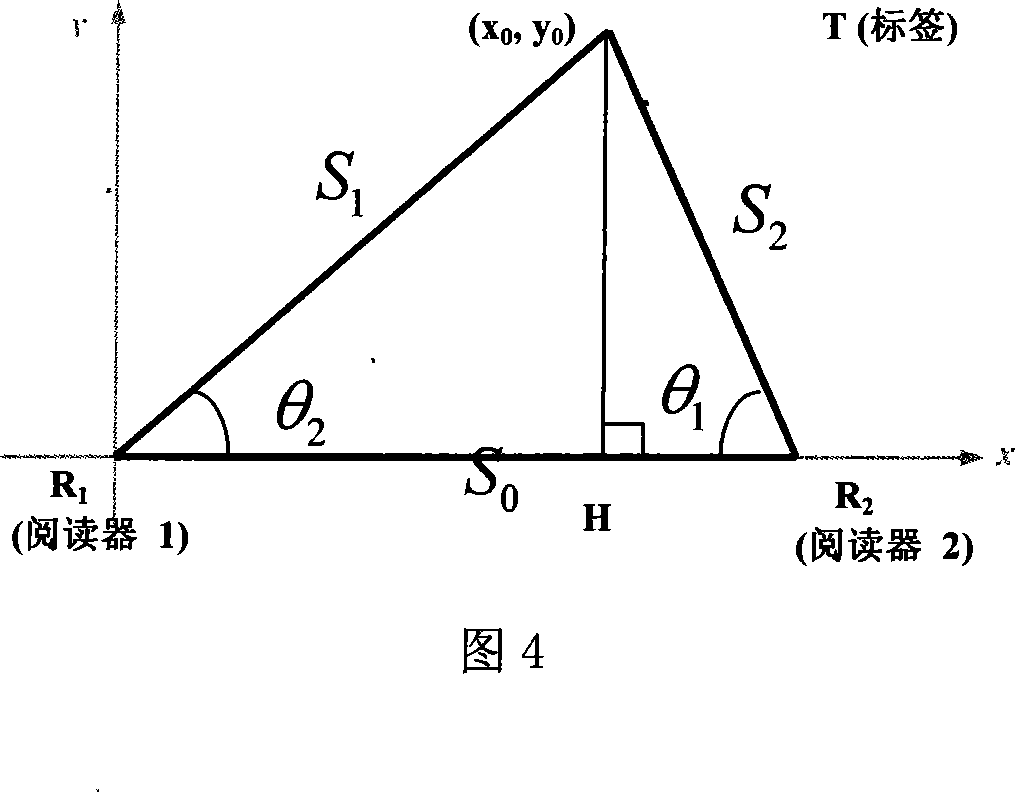
RFID radio positioning method based on phase difference ranging
A RFID radio positioning method by utilizing phase-difference to measure out distance includes binding radio frequency countermark on object to be measured, setting at least two readers on positions within 1-10 meter surrounding said object, knowing position of each reader and distance between the two, emitting and receiving electromagnetic wave by each reader through its own antenna, measuring phase-difference of emission phase and reception phase to confirm distance between radio frequency countermark to each reader and calculating out position of said countermark according to geometric relation of said countermark to readers.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
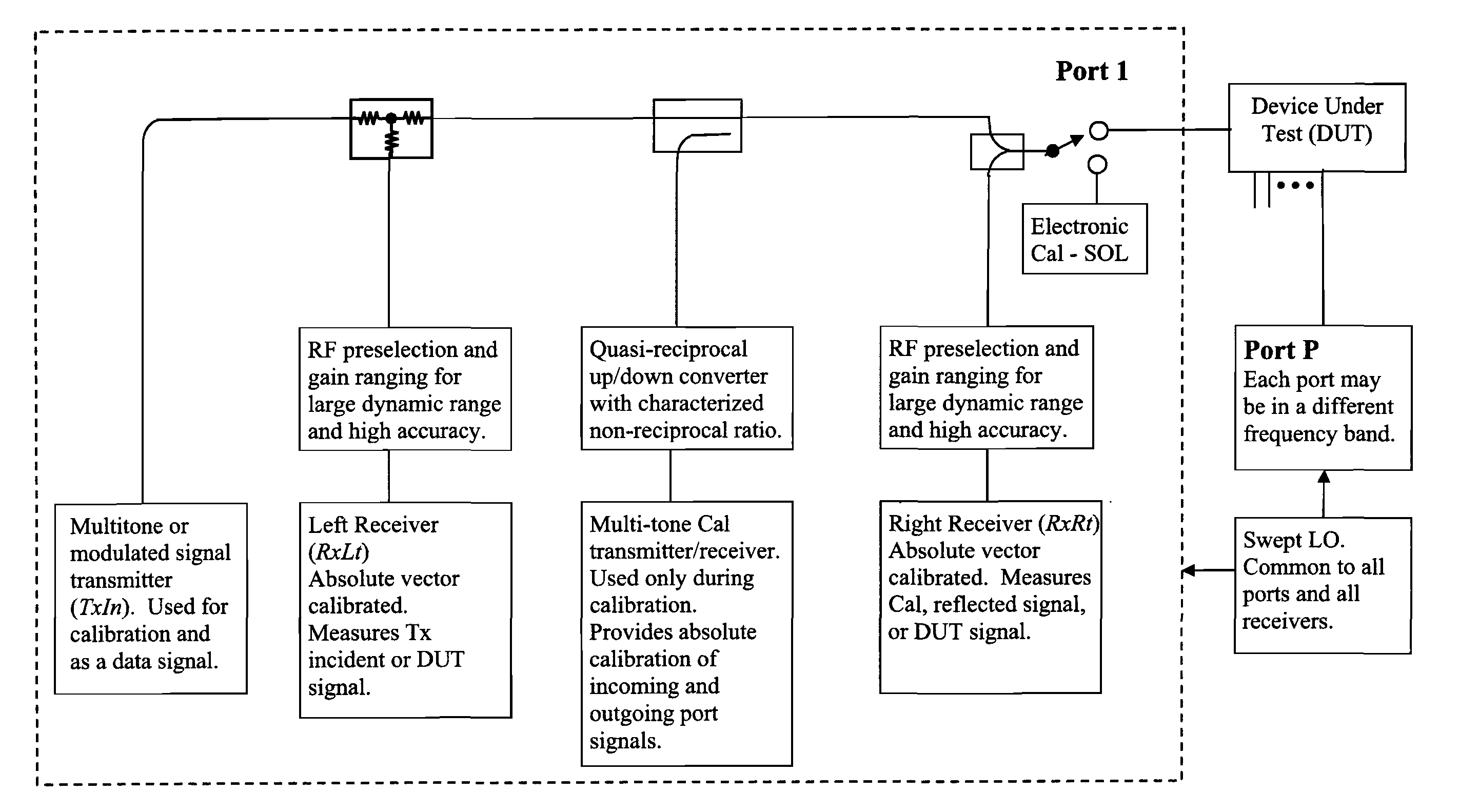
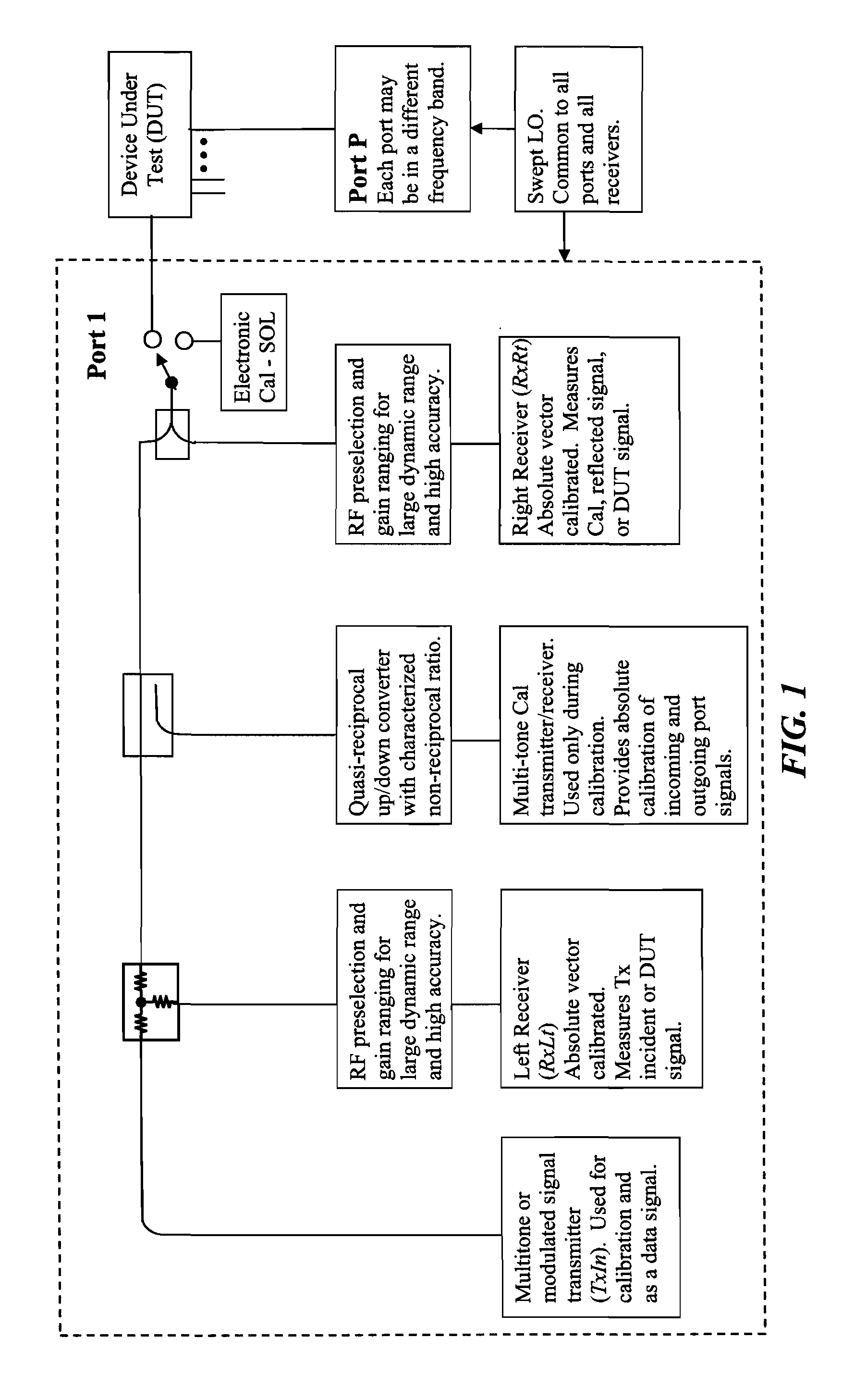
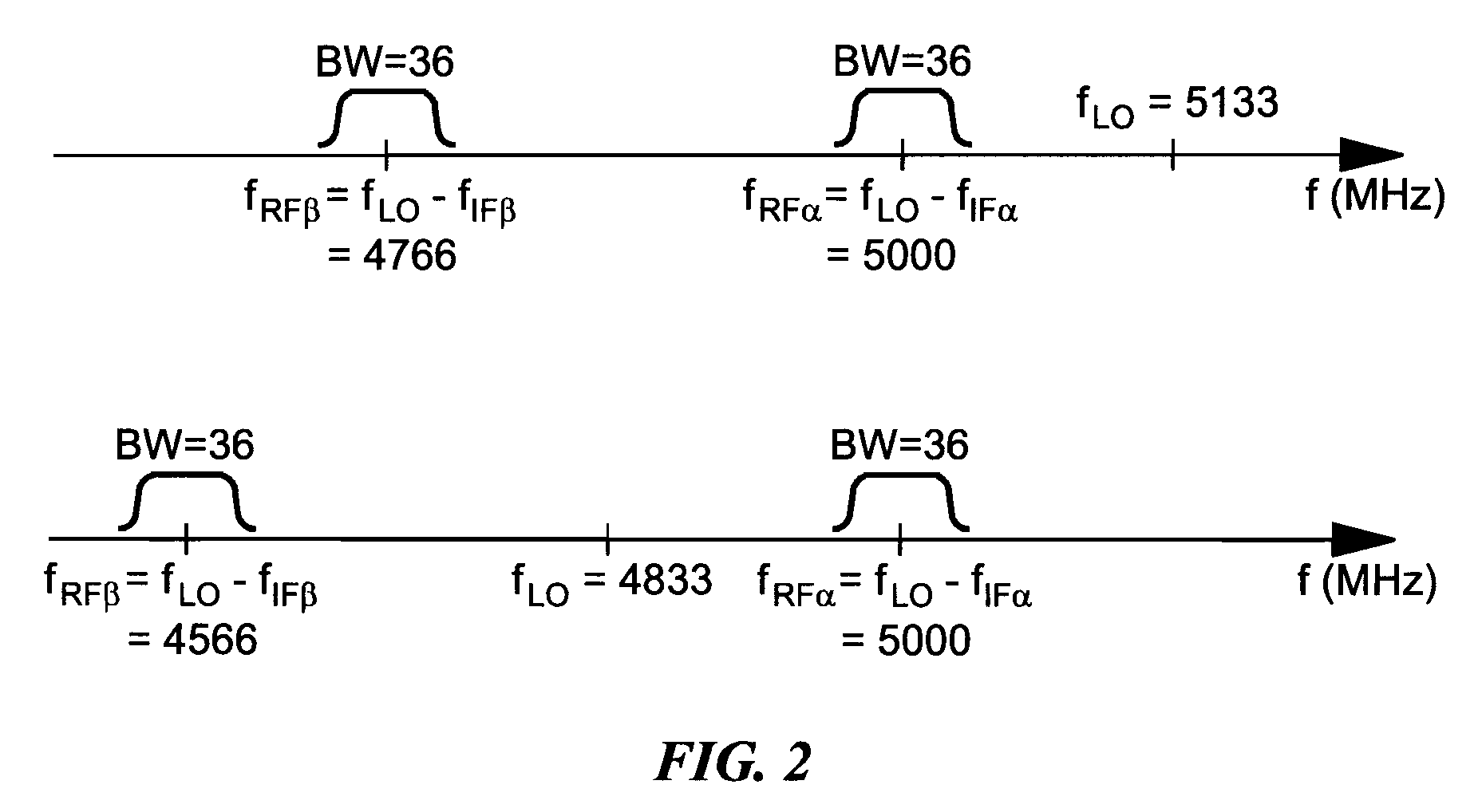
Vector signal measuring system, featuring wide bandwidth, large dynamic range, and high accuracy
A new measurement system, with two receiver channels per measurement port, has been developed that provides absolute magnitude and absolute phase relationship measurements over wide bandwidths. Gain ranging is used at RF to provide optimum noise performance and a swept YIG preselector filter is used to avoid spurious signals. A new absolute vector error correction method is used to calibrate the measurement system in order to allow for absolute vector measurements, and it also removes the time-varying responses caused by the swept YIG preselector filters. A quasi-reciprocal mixer with a characterized non-reciprocal ratio is used to provide the absolute calibration standard. The two receiver channels can be adapted to a wide variety of applications, including wide bandwidth vector signal analyzer measurements, mixer measurements, and harmonic measurements. The two-channels can also be used as an absolute calibrated transmitter / reflectometer.
Owner:DVORAK STEVEN L +1
Method and System for Ultrasonic Signaling, Ranging and Location Tracking
ActiveUS20140192622A1Minimize audible artifactUser privacy is enhancedBeacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMultilaterationFrequency modulation
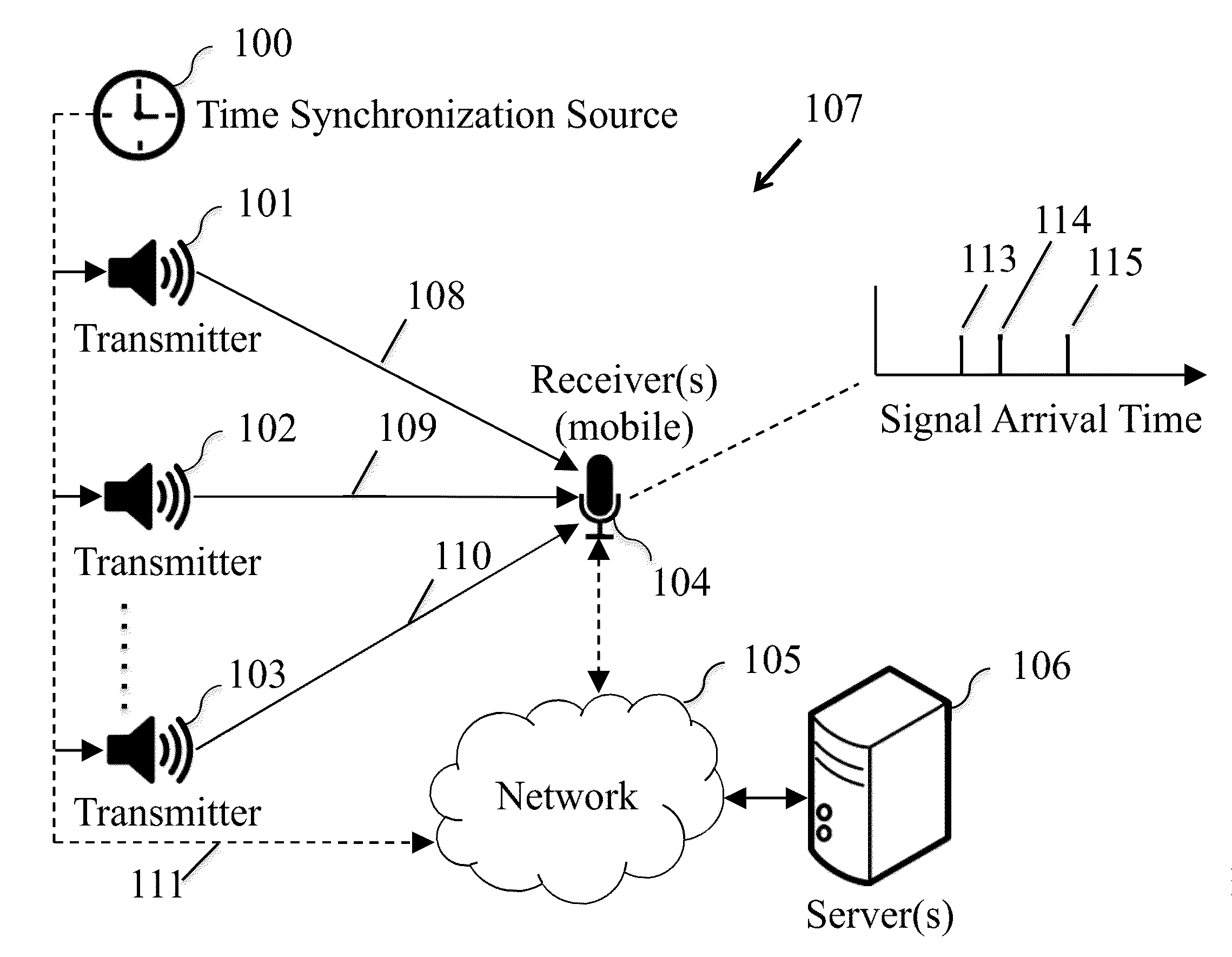
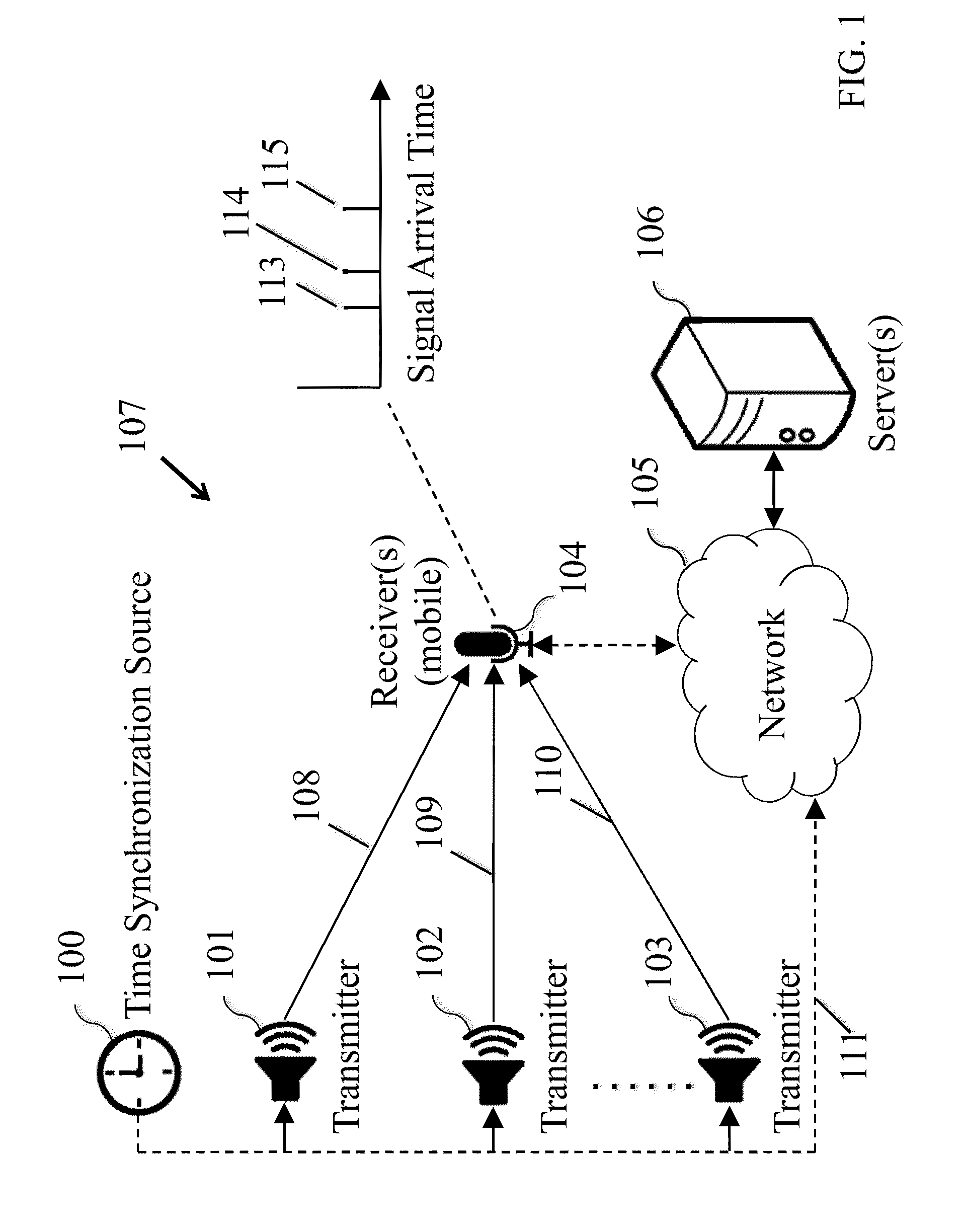
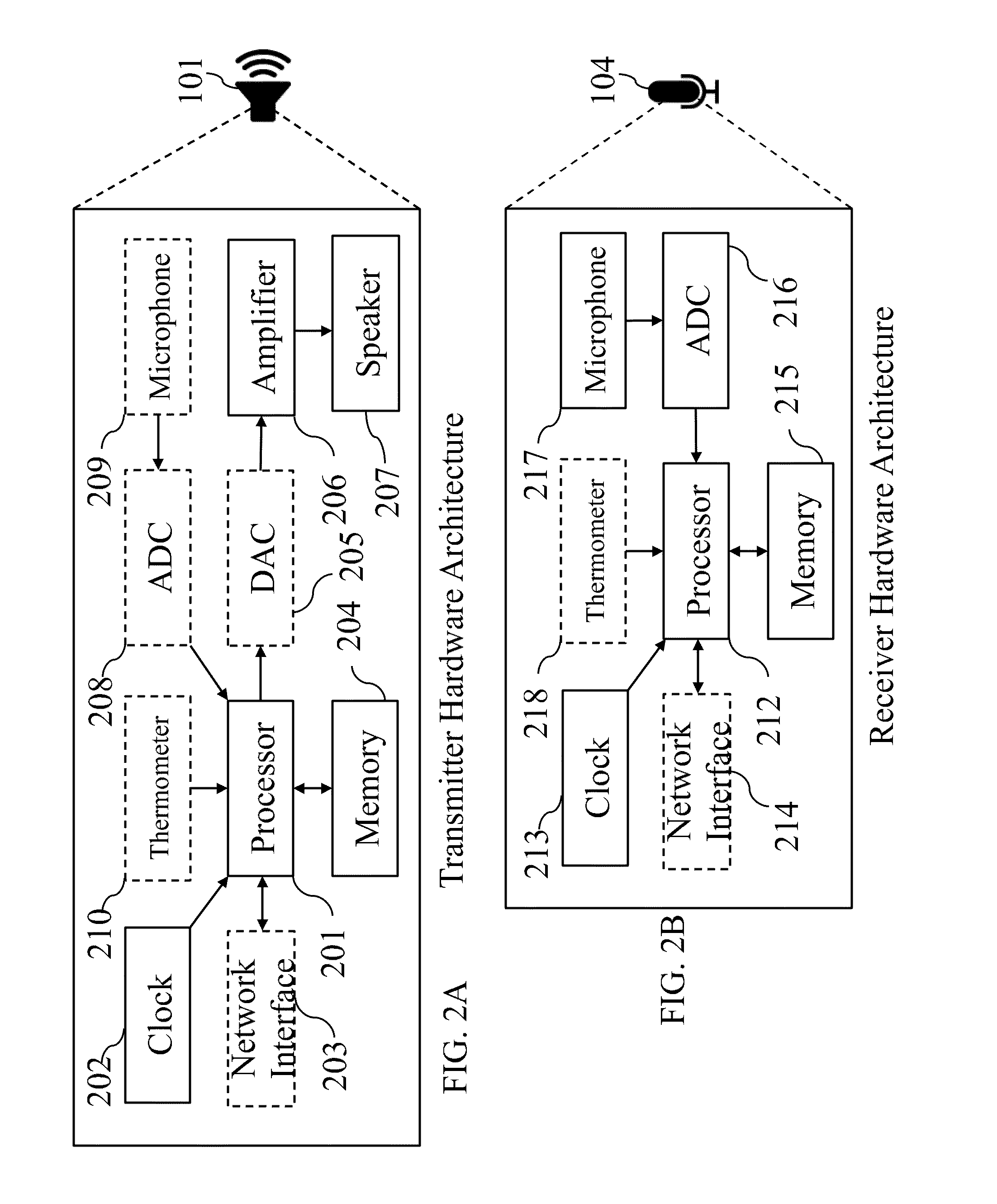
An indoor ultrasonic location tracking system that can utilize standard audio speakers to provide indoor ranging information to modern mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. The method uses a communication scheme based on linearly increasing frequency modulated chirps in the audio bandwidth just above the human hearing frequency range where mobile devices are still sensitive. The method uses gradual frequency and amplitude changes that minimize human perceivable (psychoacoustic) artifacts derived from the non-ideal impulse response of audio speakers. Chirps also benefit from Pulse Compression, which improves ranging resolution and resilience to both Doppler shifts and multi-path propagation that plague indoor environments. The method supports the decoding of multiple unique identifier packets simultaneously. A Time-Difference-of-Arrival pseudo-ranging technique allows for localization without explicit synchronization with the broadcasting infrastructure. An alternate received signal strength indicator based localization technique allows less accurate localization at the benefit of sparser transmission infrastructure.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
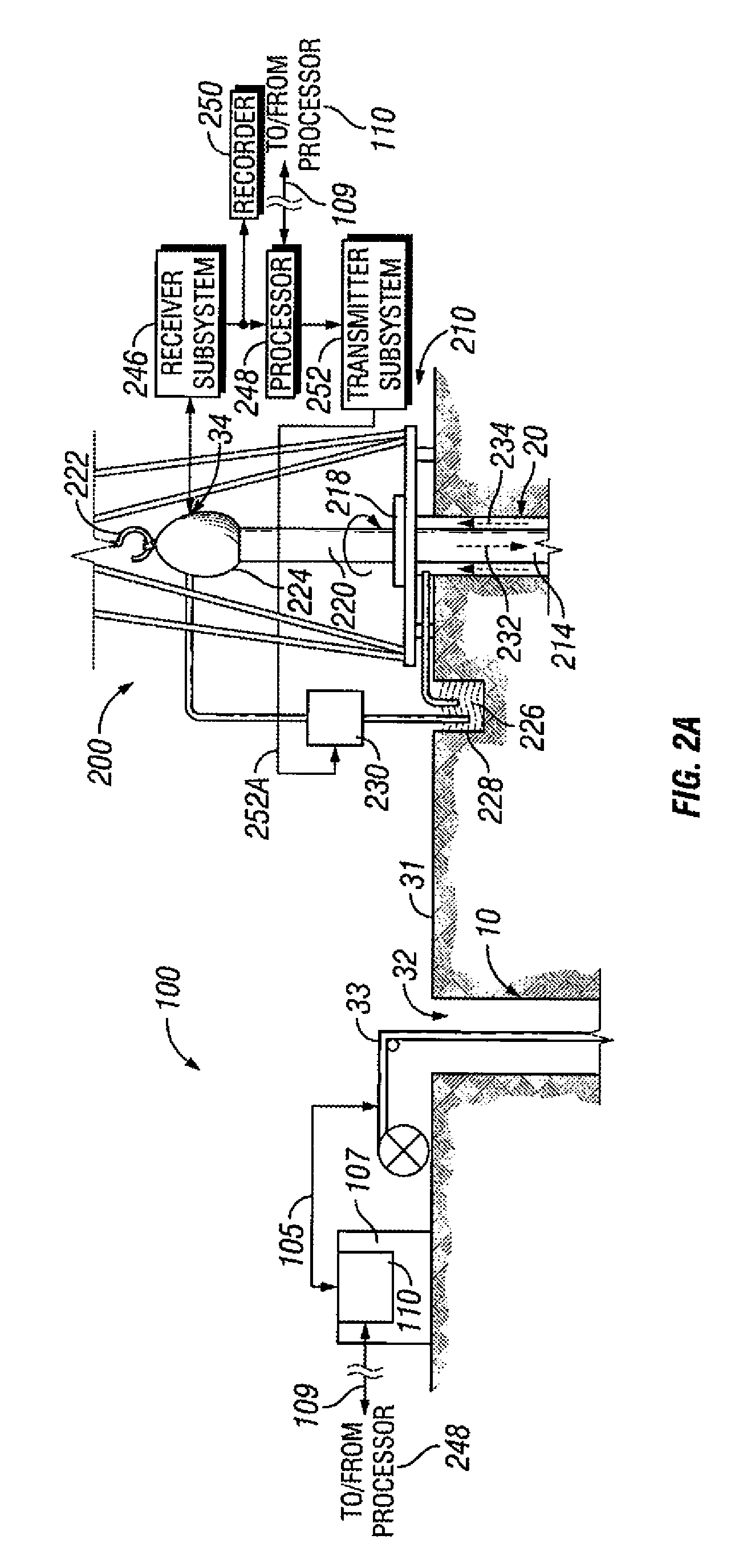
Magnetic ranging and controlled earth borehole drilling
InactiveUS20090308657A1High and variable magnetic permeabilityReduce magnetic field strengthSurveyConstructionsAtomic physicsRanging
A method for determining the distance and / or direction of a second earth borehole with respect to a first earth borehole, includes the following steps: providing, in the first borehole, first and second spaced apart magnetic field sources; providing, in the second borehole, a magnetic field sensor subsystem for sensing directional magnetic field components; activating the first and second magnetic field sources, and producing respective first and second outputs of the magnetic field sensor subsystem, the first output being responsive to the magnetic field produced by the first magnetic field source, and the second output being responsive to the magnetic field produced by the second magnetic field source; and determining distance and / or direction of the second earth borehole with respect to the first earth borehole as a function of the first output and the second output.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
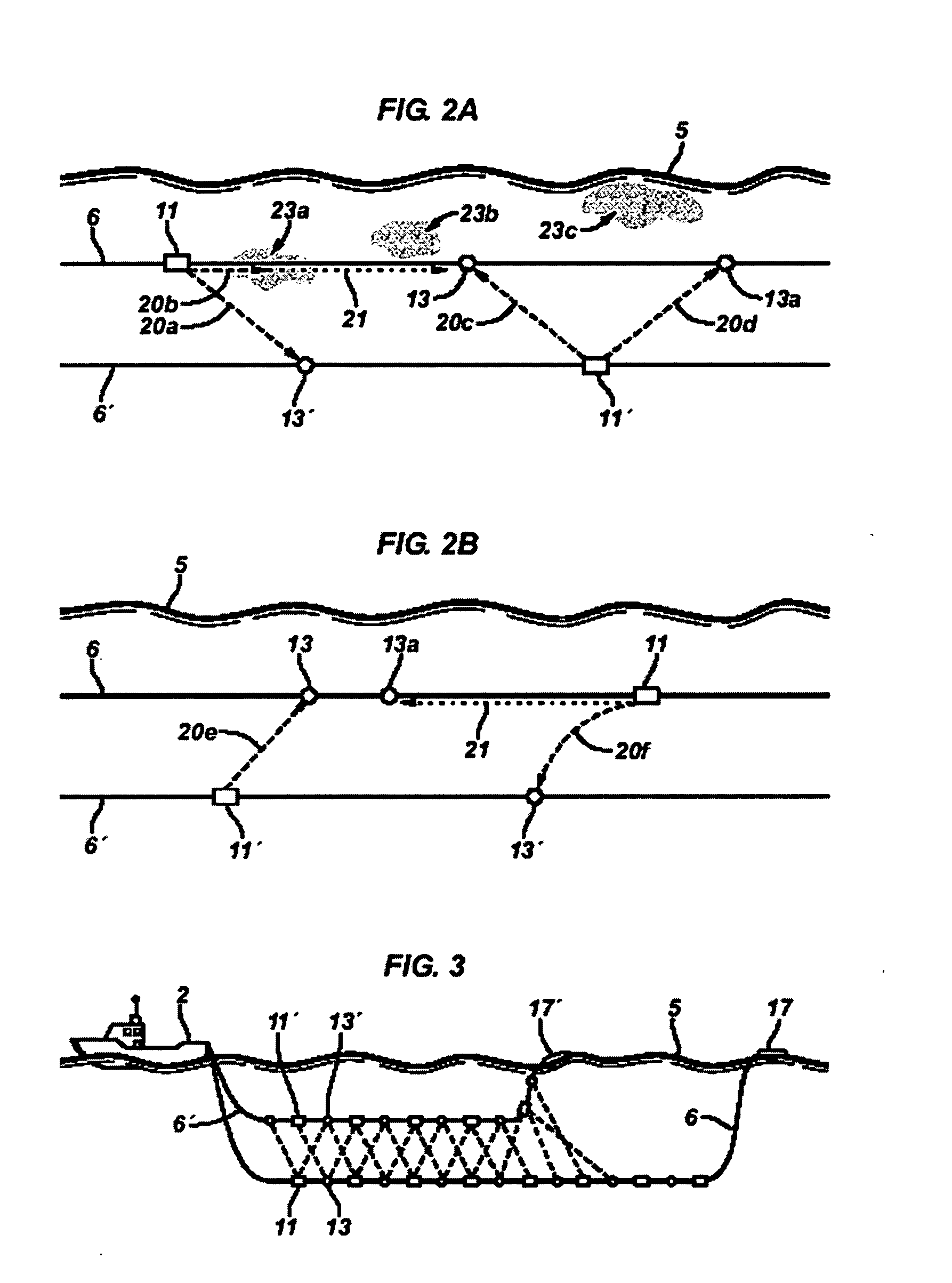
Systems and methods for seismic streamer positioning
InactiveUS20060215489A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationSubject matterPositioning system
Systems and methods for determining position of one or more seismic streamers are disclosed. One system embodiment includes a seismic streamer towed by a towing vessel at a first depth; at least one positioning streamer towed by the towing vessel at a second depth different than the first depth; and an acoustic ranging system between the seismic and positioning streamers It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
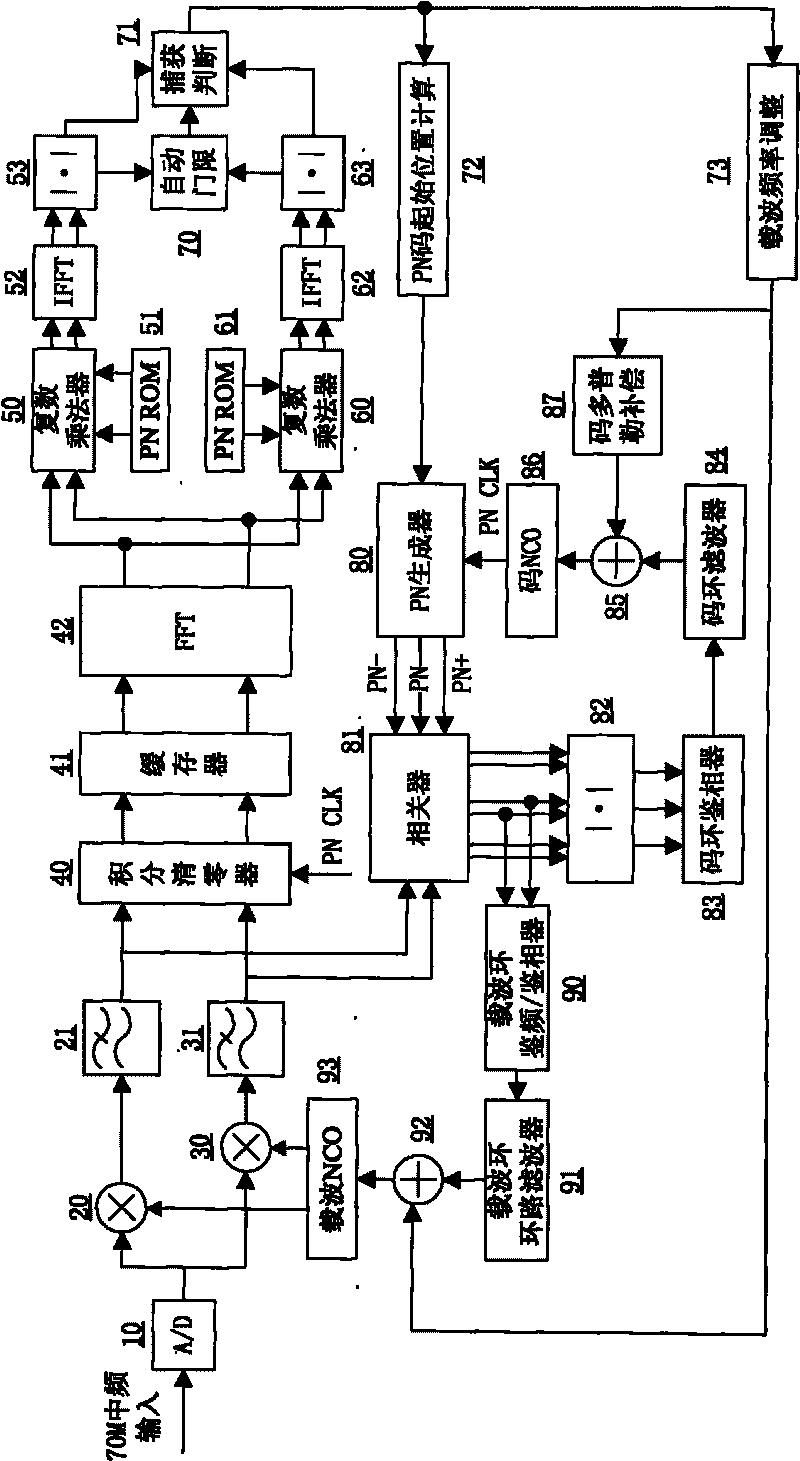
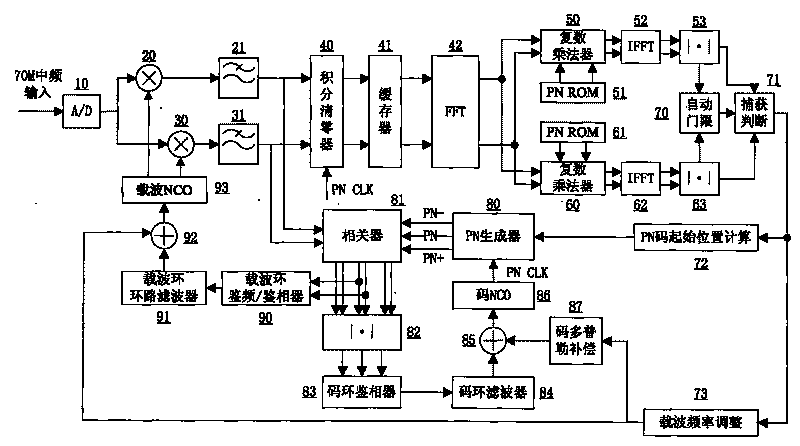
Intermediate frequency direct sequence spread spectrum receiver for satellite ranging
InactiveCN101726746AReduce resource consumptionFast captureSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorLow-pass filter
The invention relates to an intermediate frequency direct sequence spread spectrum receiver for satellite ranging, which consists of 37 parts of a front-end A / D, an FFT module, a local PN code generator, a correlator, an automatic threshold calculation module and the like. The connection relationship is as follows: the output of the front-end A / D and the output of a carrier tracking loop NCO are respectively connected to an in-phase branch multiplier and an orthogonal branch multiplier, the input of the front-end A / D and the input of the carrier tracking loop NCO enter into an in-phase branch FIR low-pass filter and an orthogonal branch FIR low-pass filter, consequently, on the one hand, the output is sent to an integral zero clearing device, then the output which is sent to the FFT module, a branch 1 local PN code memory ROM and a branch 2 local PN code memory ROM enters into a branch 1 complex multiplier and a branch 2 complex multiplier, the output is sent to a branch 1 root mean square module and a branch 2 root mean square module, the output is sent to the threshold calculation module and a capturing and judging module for carrying out code catching; and on the other hand, the output is sent to the correlator and the local PN code generator for carrying out code tracking. The output of the correlator is simultaneously sent into a frequency discriminator / phase discriminator of the carrier tracking loop and then enters into a loop filter of the carrier tracking loop, and the output of the loop filter of the carrier tracking loop enters into the carrier tracking loop NCO for carrying out carrier tracking.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Hybrid RF network with high precision ranging
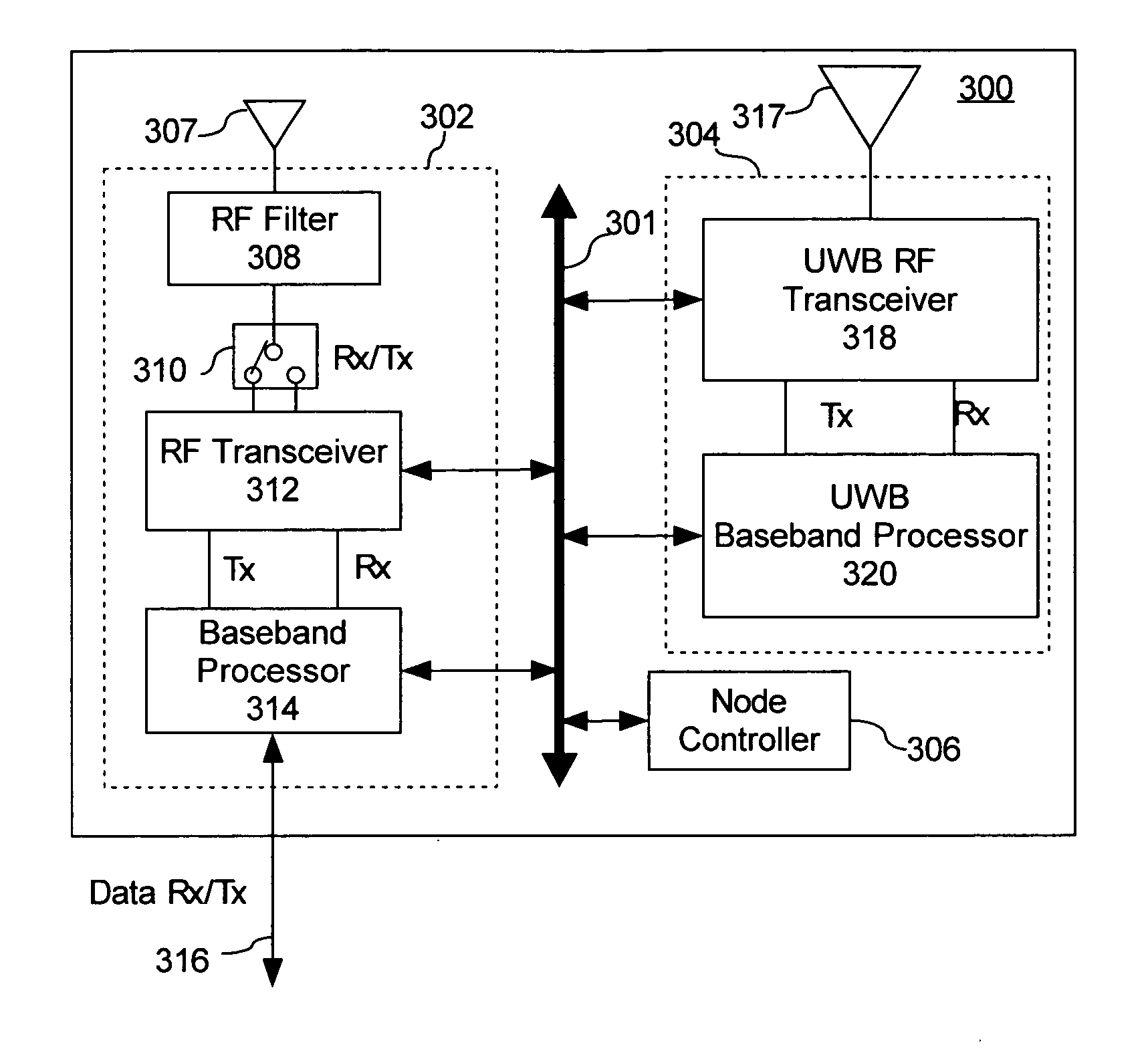
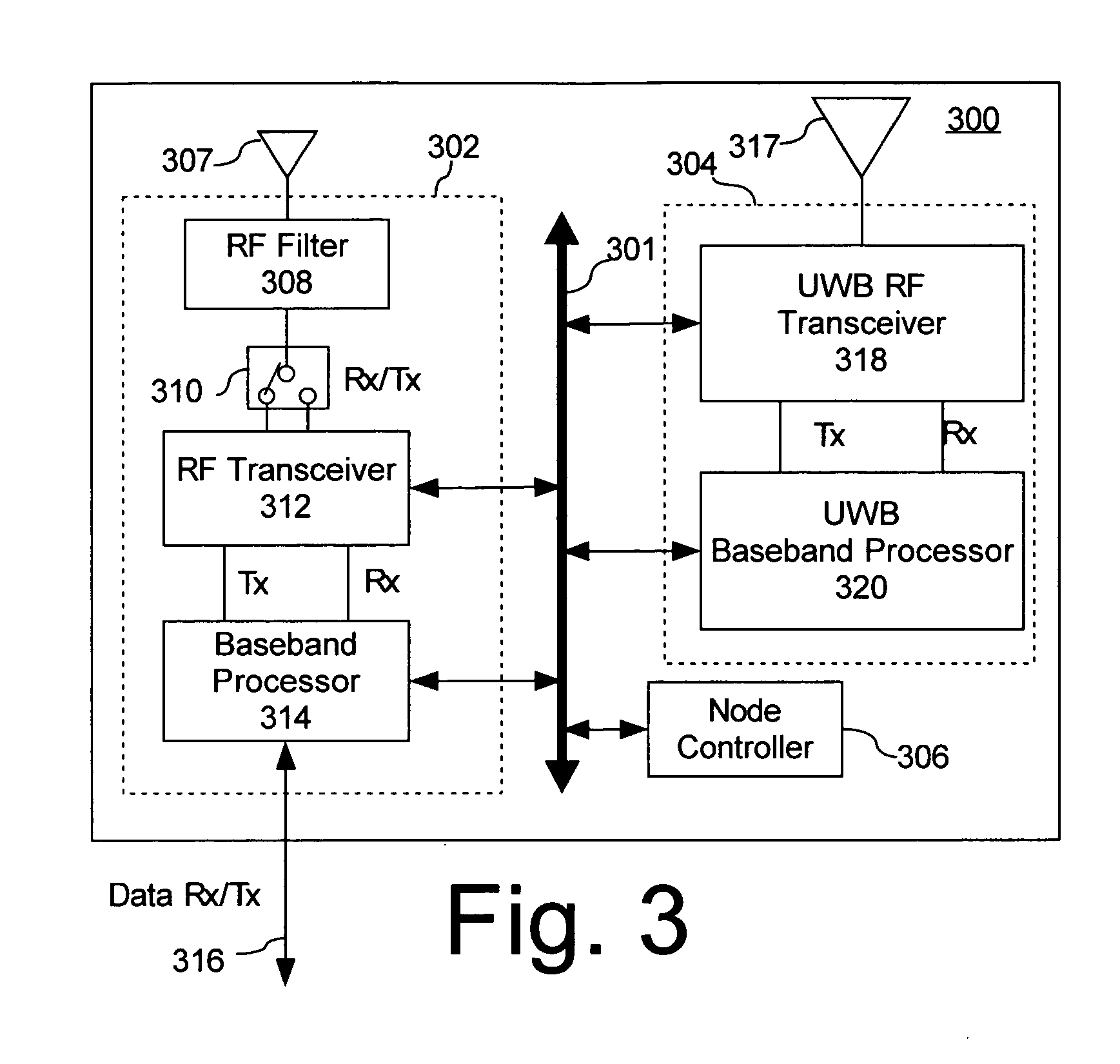
InactiveUS20070081505A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesUltra-widebandTransceiver
A wireless network can include two or more nodes (300), each having an ultra wideband (UWB) transceiver (304) configured for determining a range between the nodes using UWB ranging techniques. In addition, each node (300) has a narrow-band transceiver (302) for communicating data between each of the nodes (300) using a narrow-band radio protocol.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com