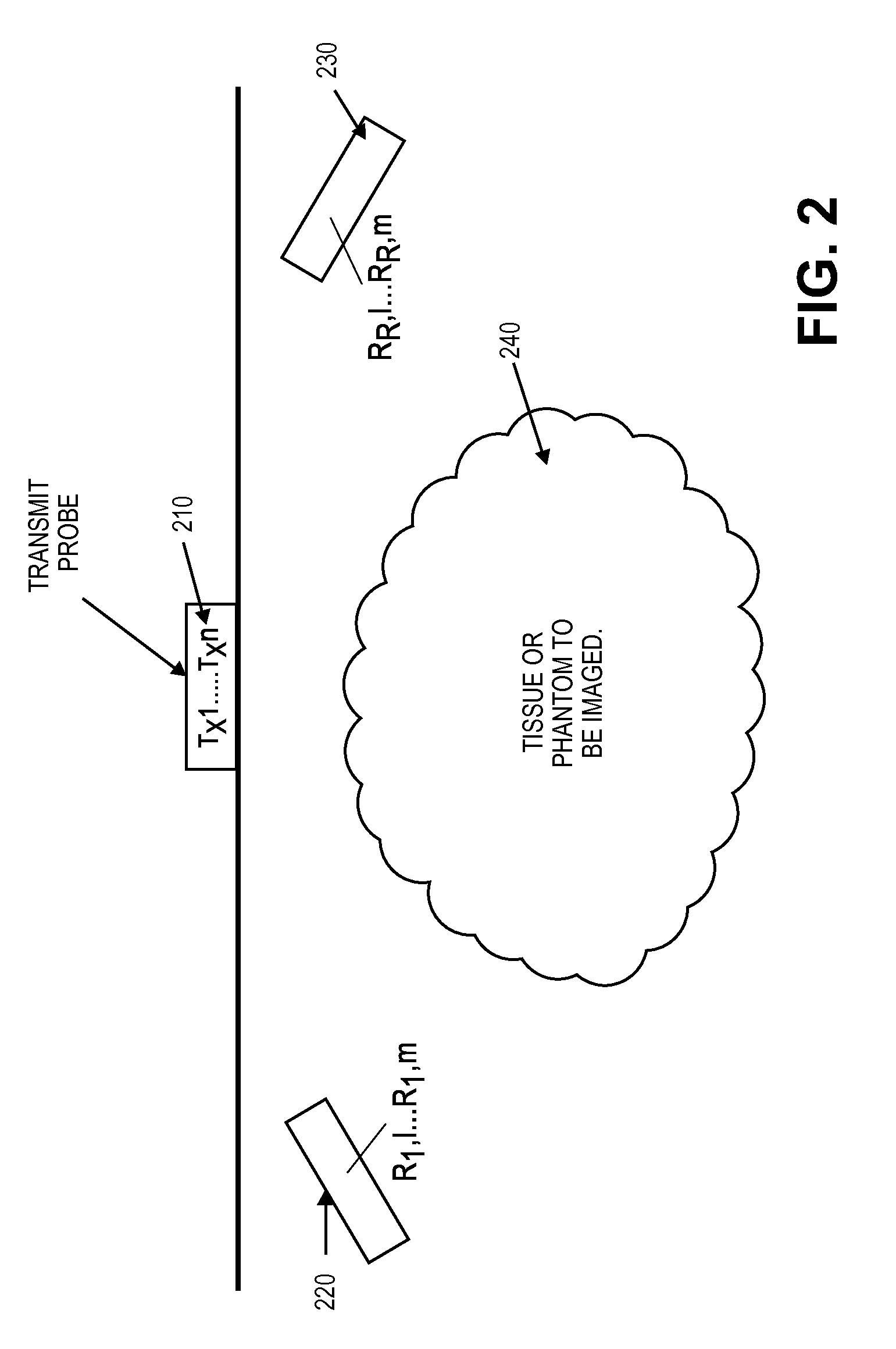
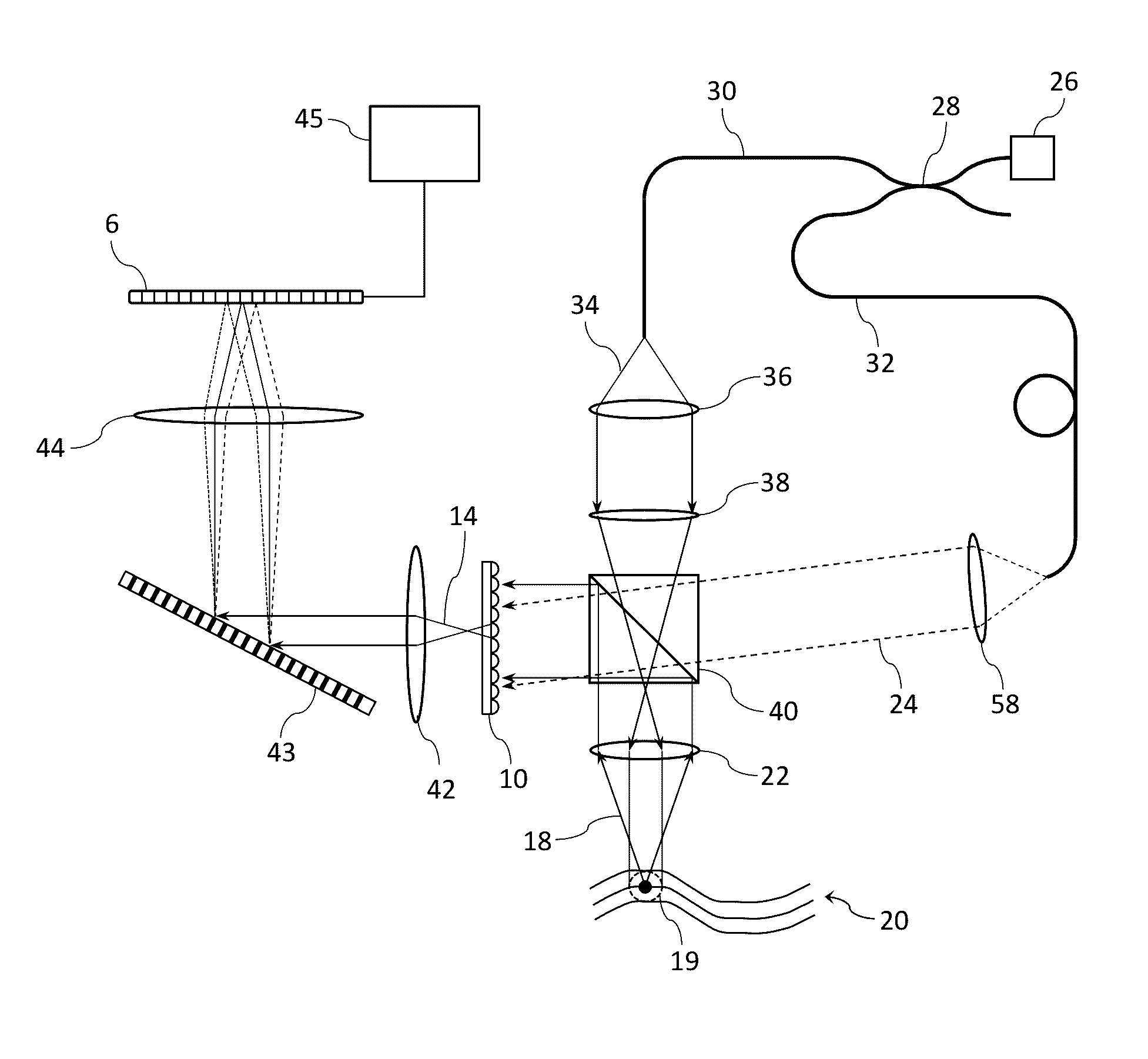
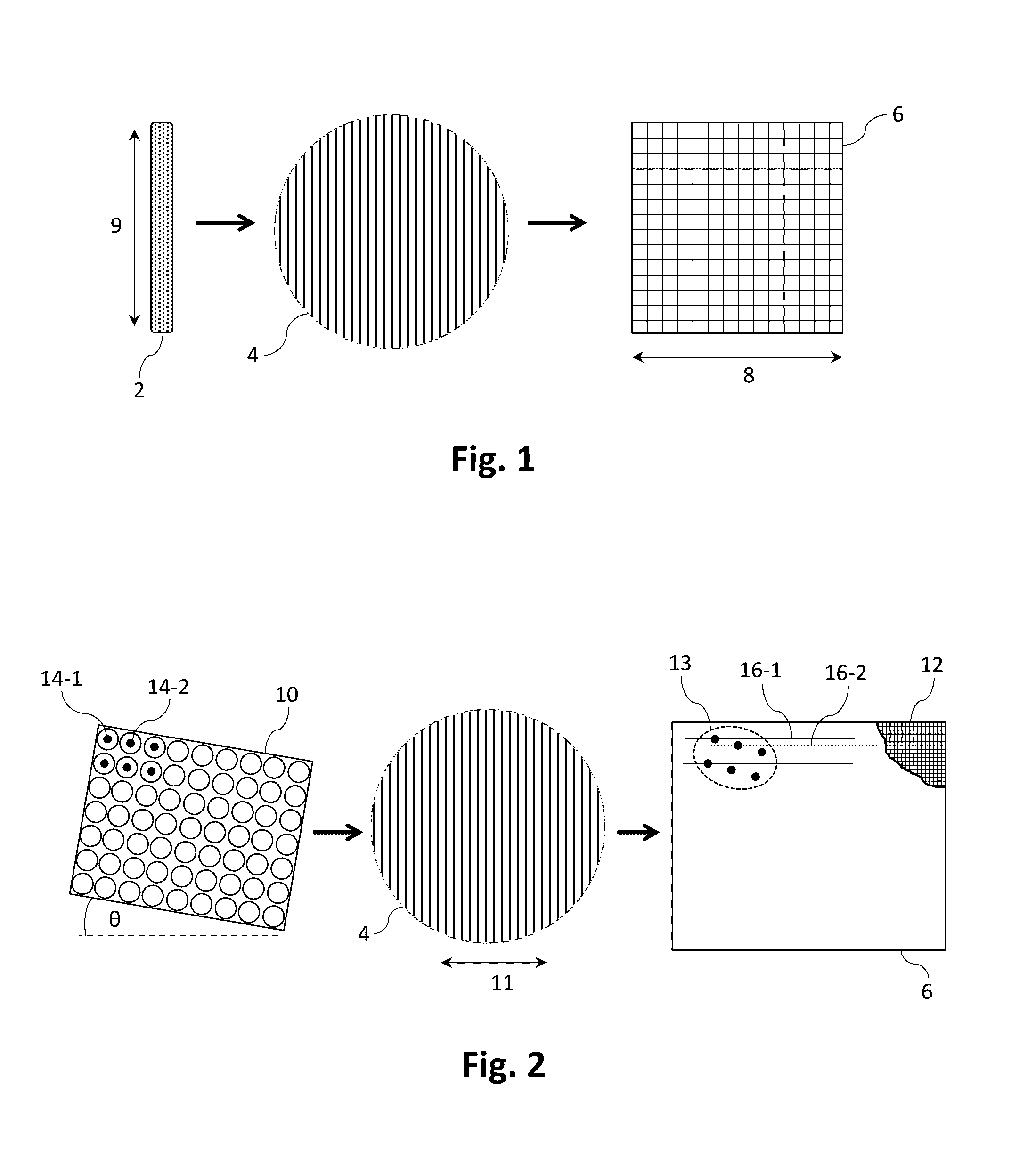
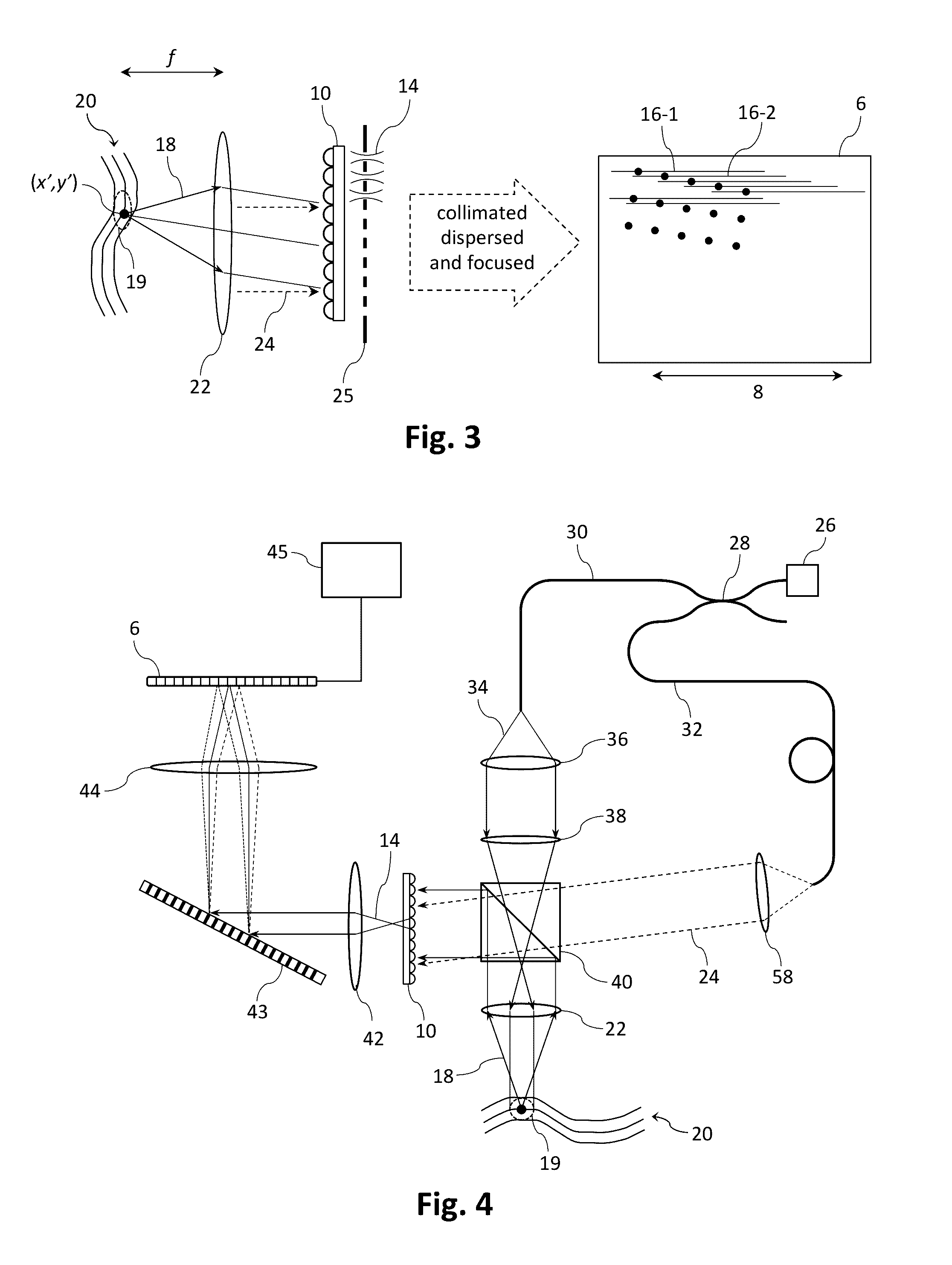
Patents
Literature
449 results about "Lateral resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Axial resolution, also known as longitudinal, depth or linear resolution resolution is resolution in the direction parallel to the ultrasound beam. The resolution at any point along the beam is the same; therefore axial resolution is not affected by depth of imaging.
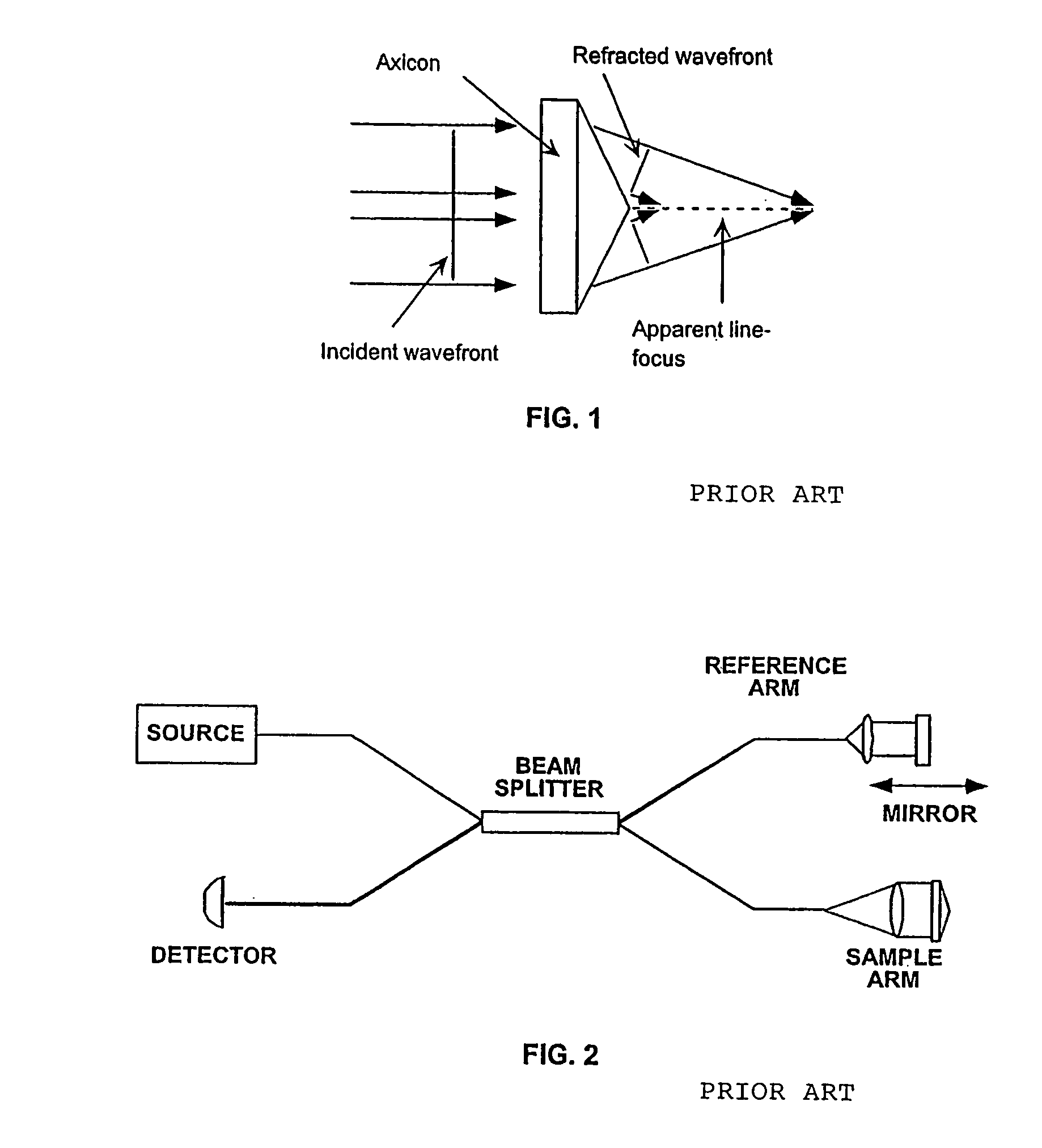
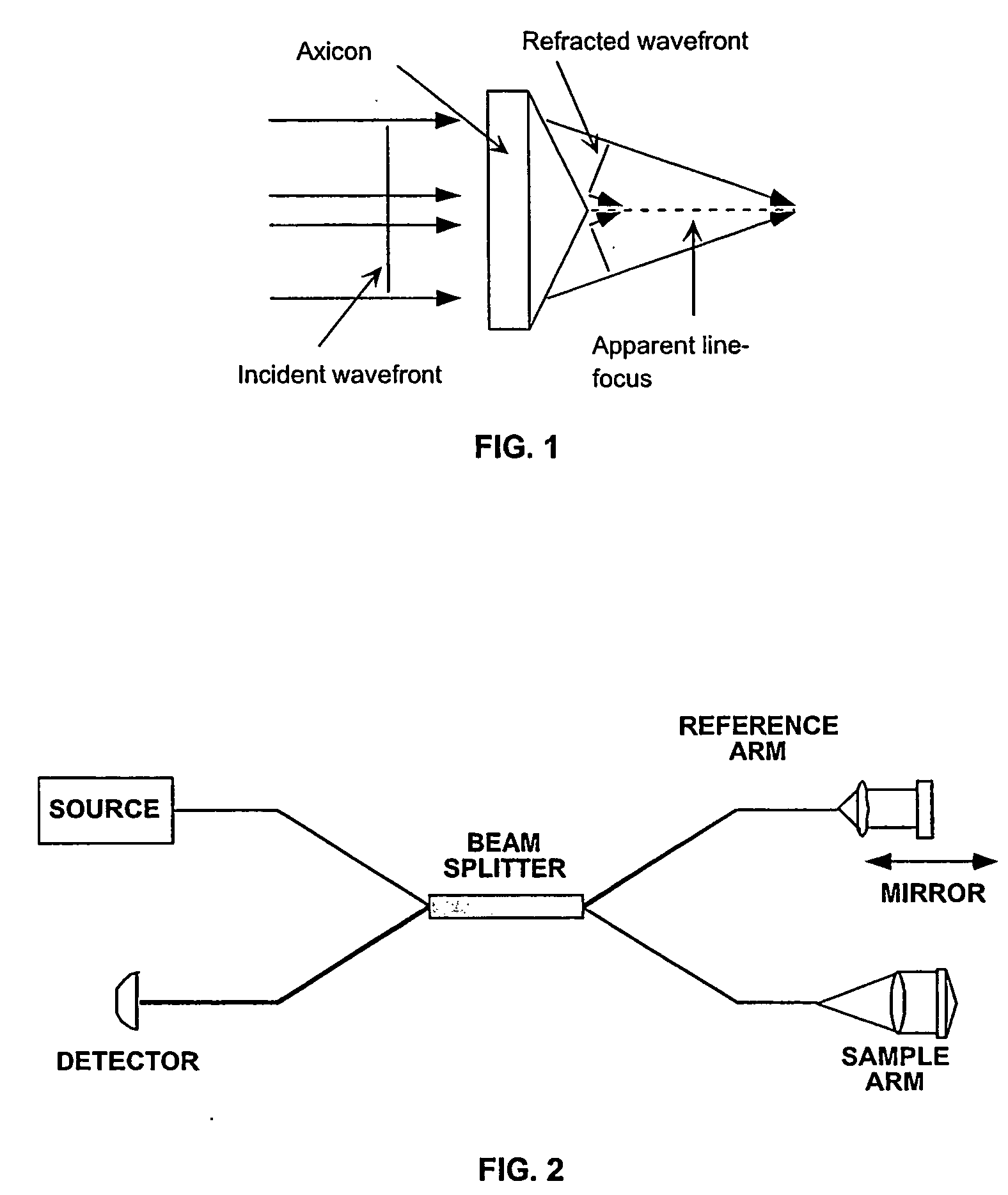
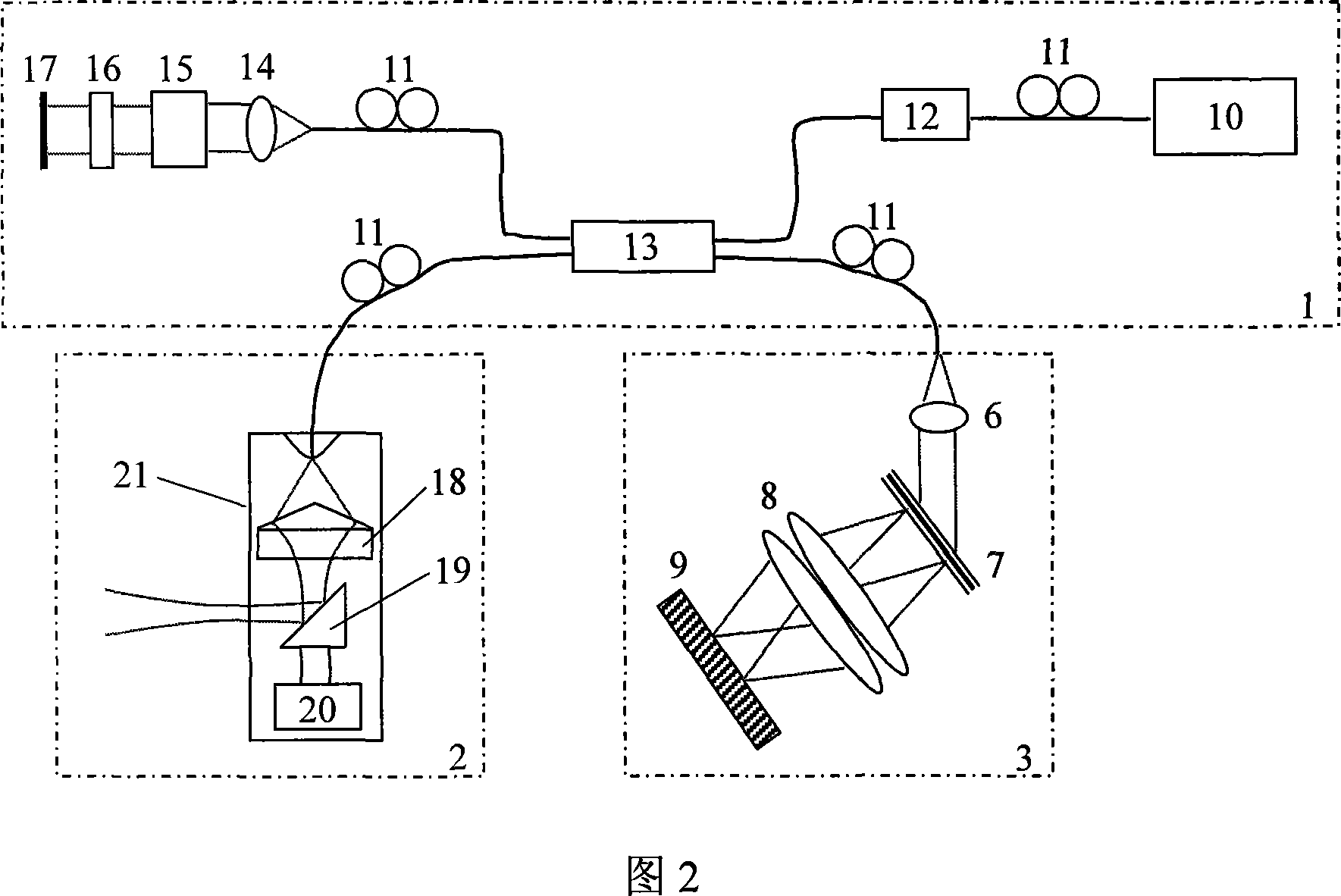
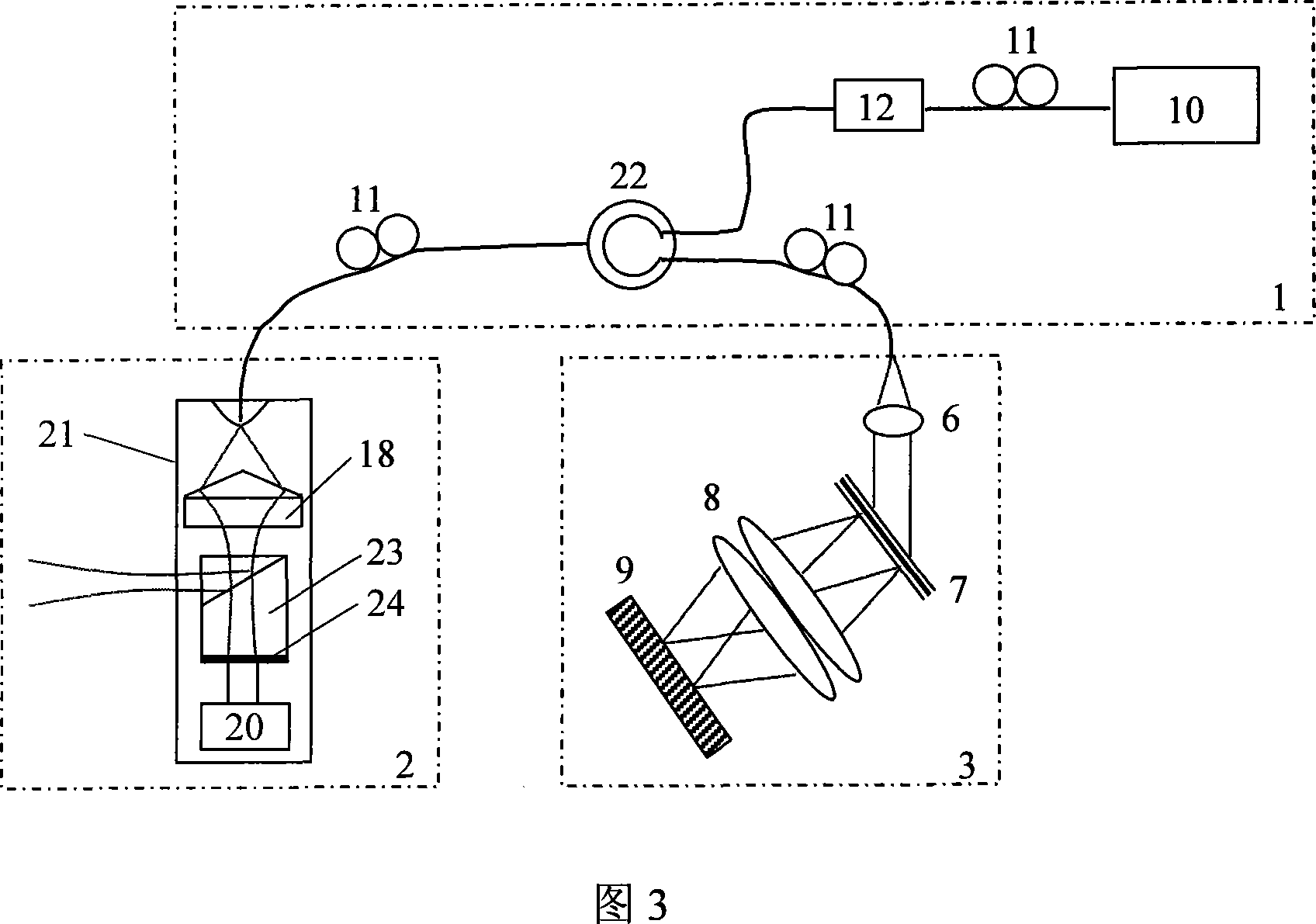
Apparatus and method for low coherence ranging
InactiveUS7310150B2Low costPotential compact sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansImage resolutionLateral resolution
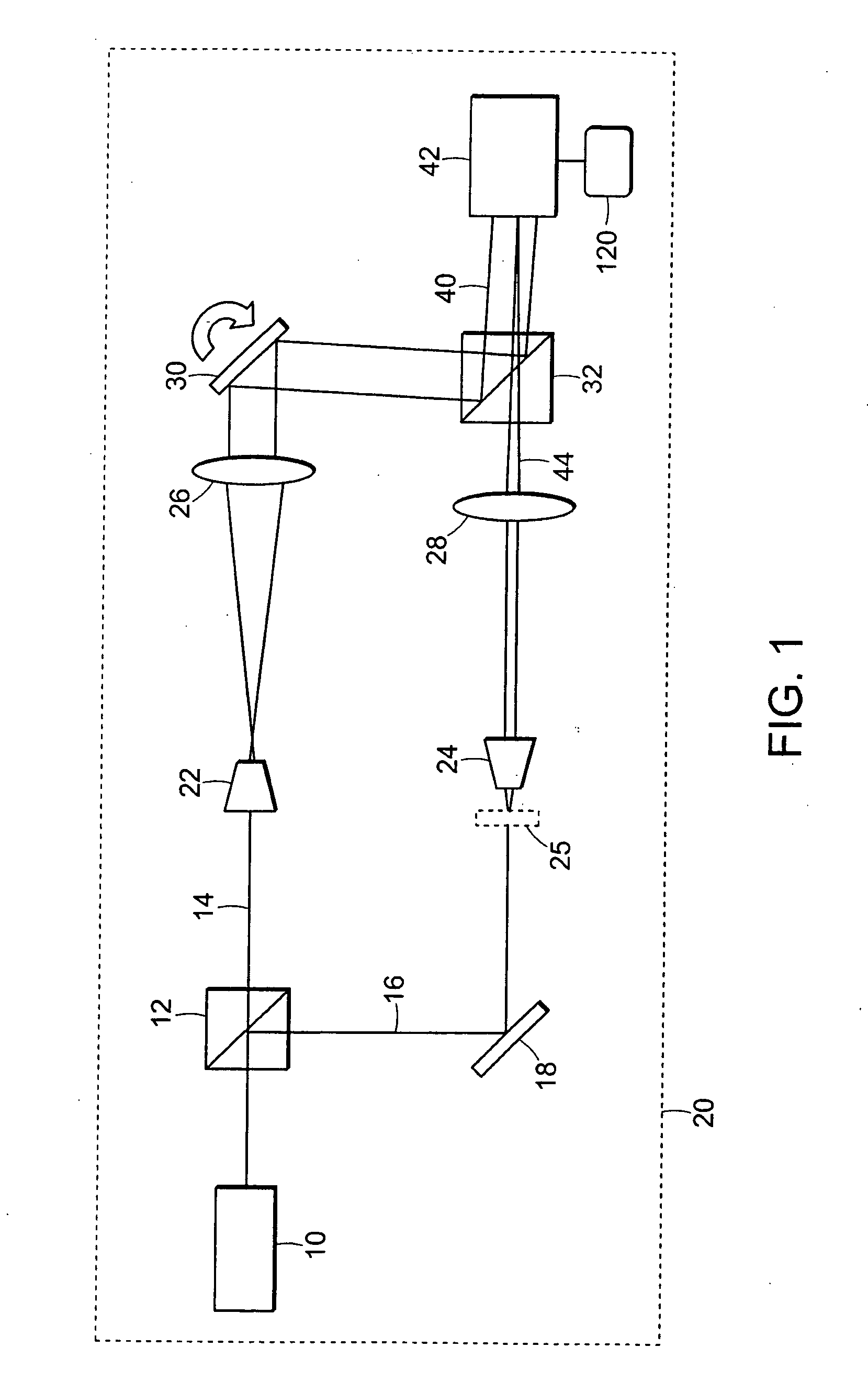
A system, apparatus and method for performing low coherence ranging of a sample with high transverse resolution and large depth of focus can be provided. For example, an optical ranging system including a light source can be used. Certain exemplary arrangement can be provided, e.g., a first arrangement for directing light from the light source to the sample, a second arrangement for directing reflected light from the sample to a detector, at least one detector, and a third arrangement for processing light data received by the detector and which generates an image can be utilized. Further, for example, an optical element can be provided which can have a transverse resolution defined as .Δris less than or equal to about μ5 m, and a depth of focus Δz of at least about 50 μm.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
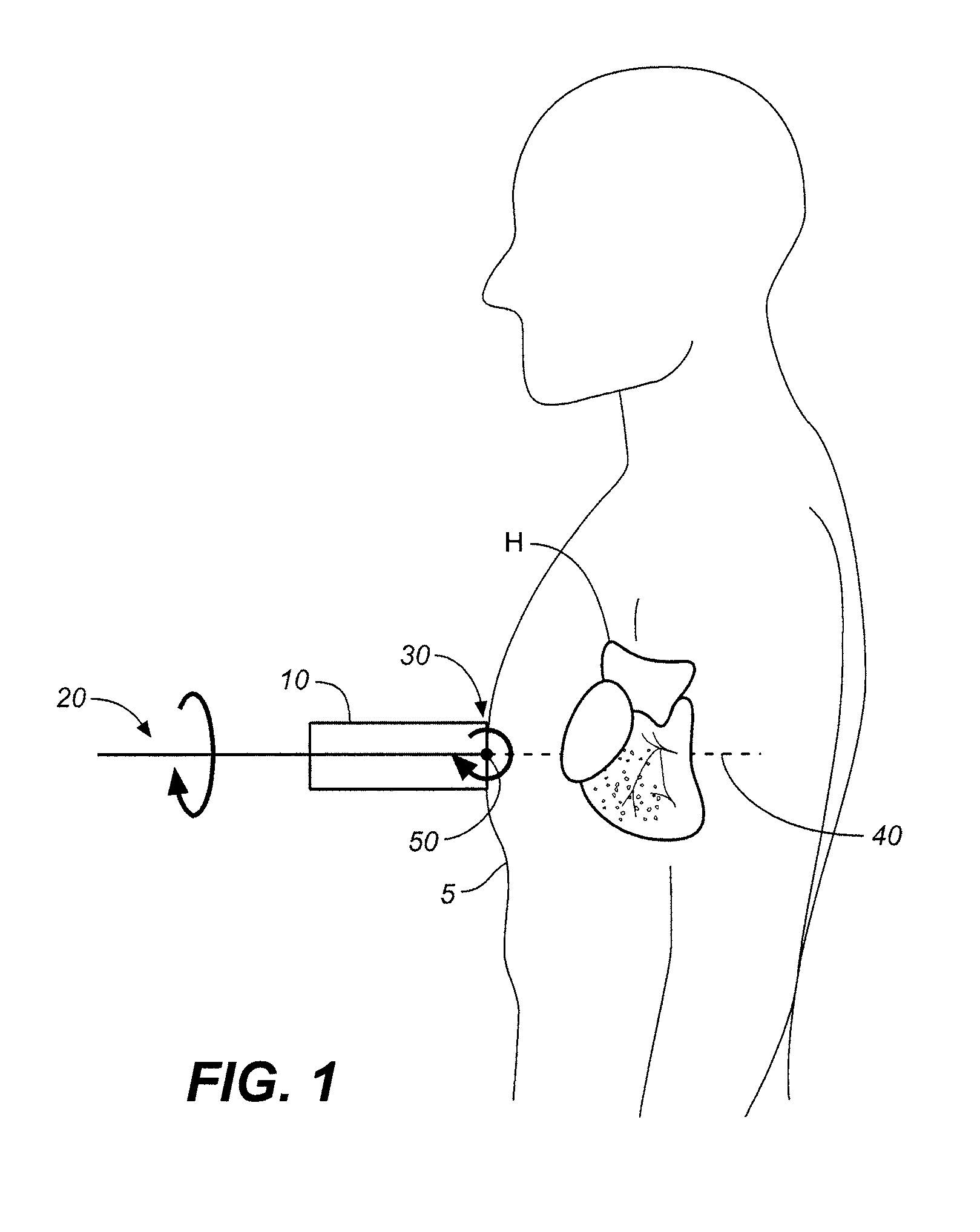
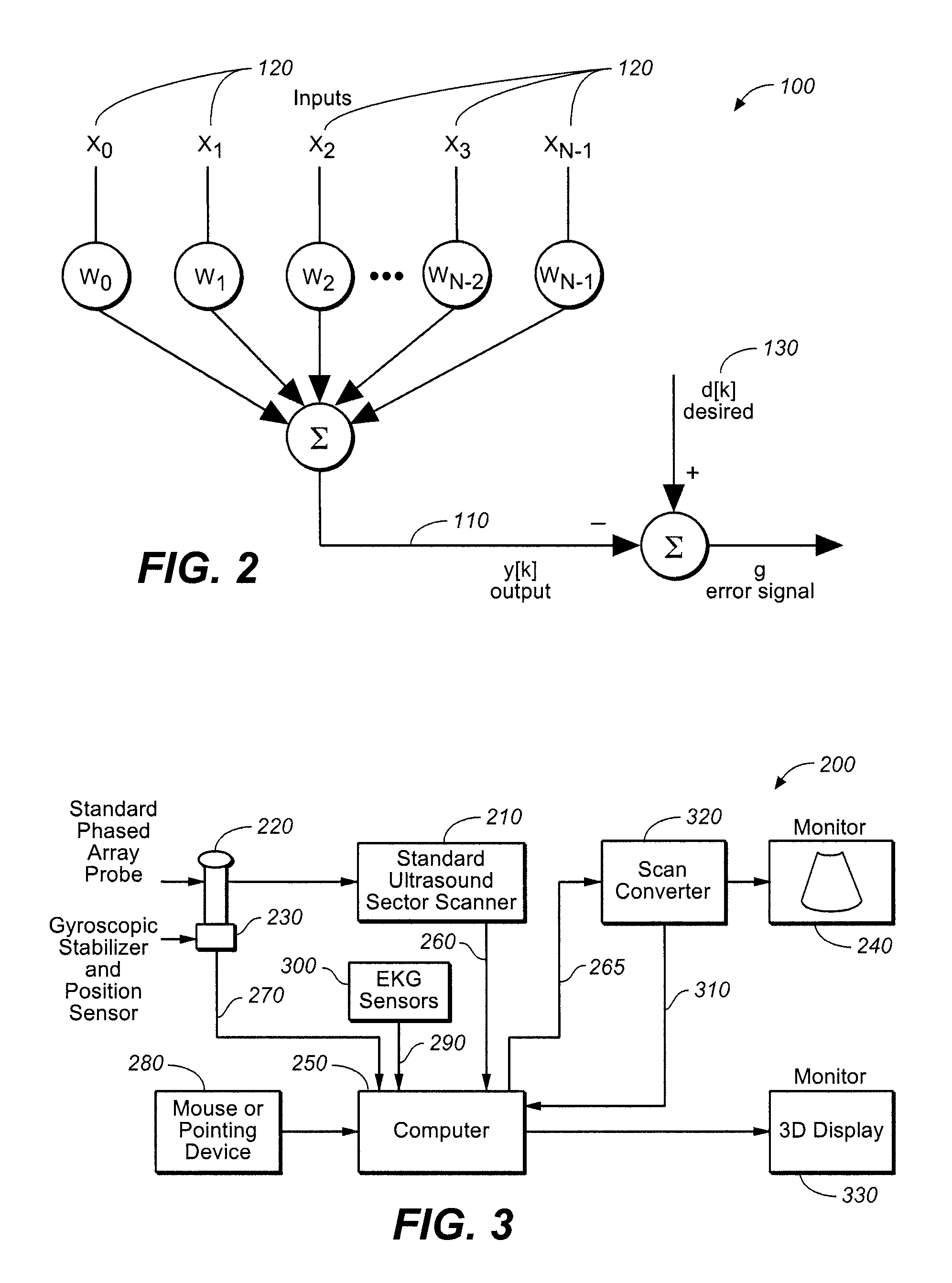
Method and apparatus to visualize the coronary arteries using ultrasound
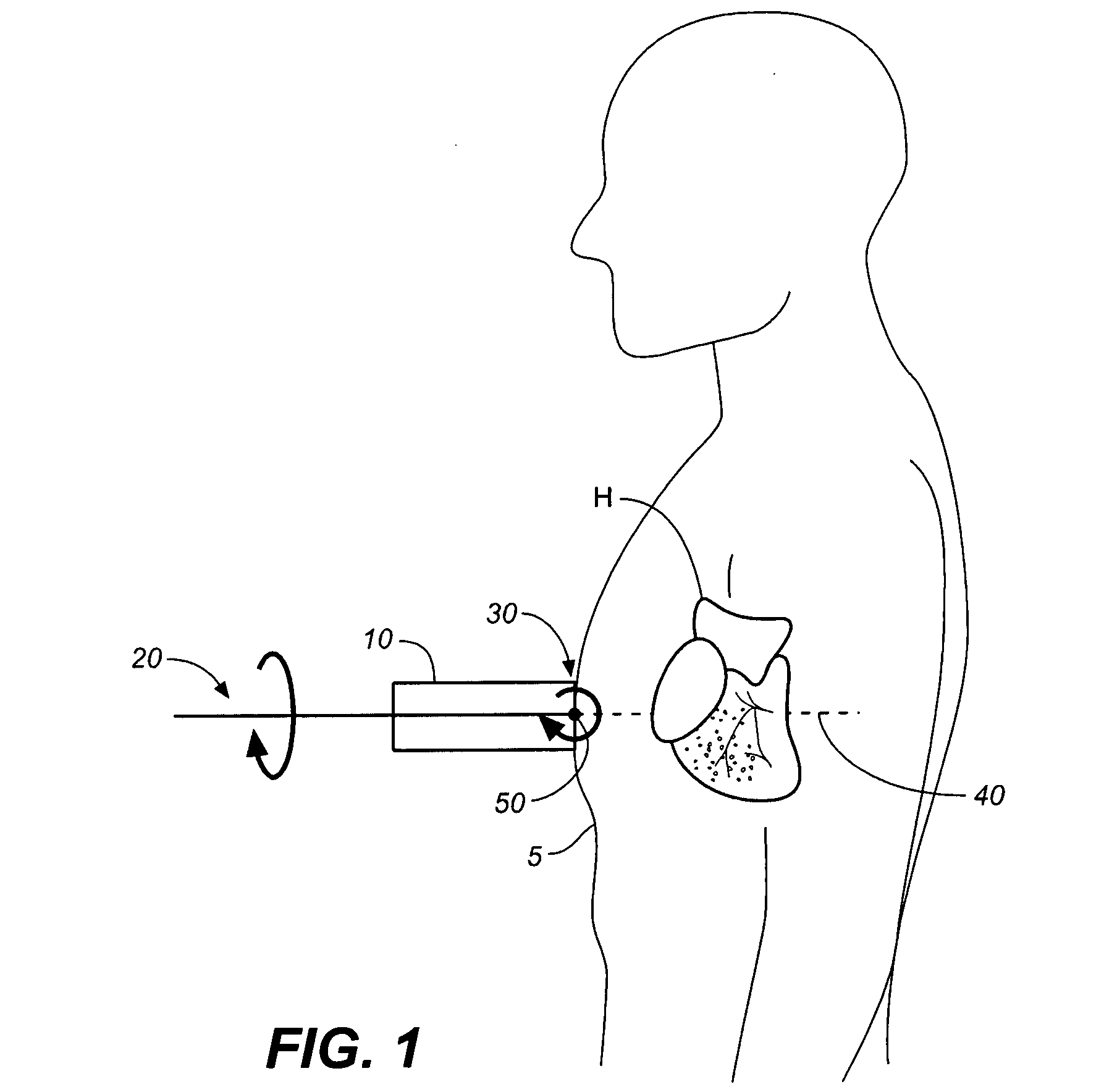
ActiveUS20070238999A1Improved three dimensional imageReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisBLOOD FILLEDScreening techniques
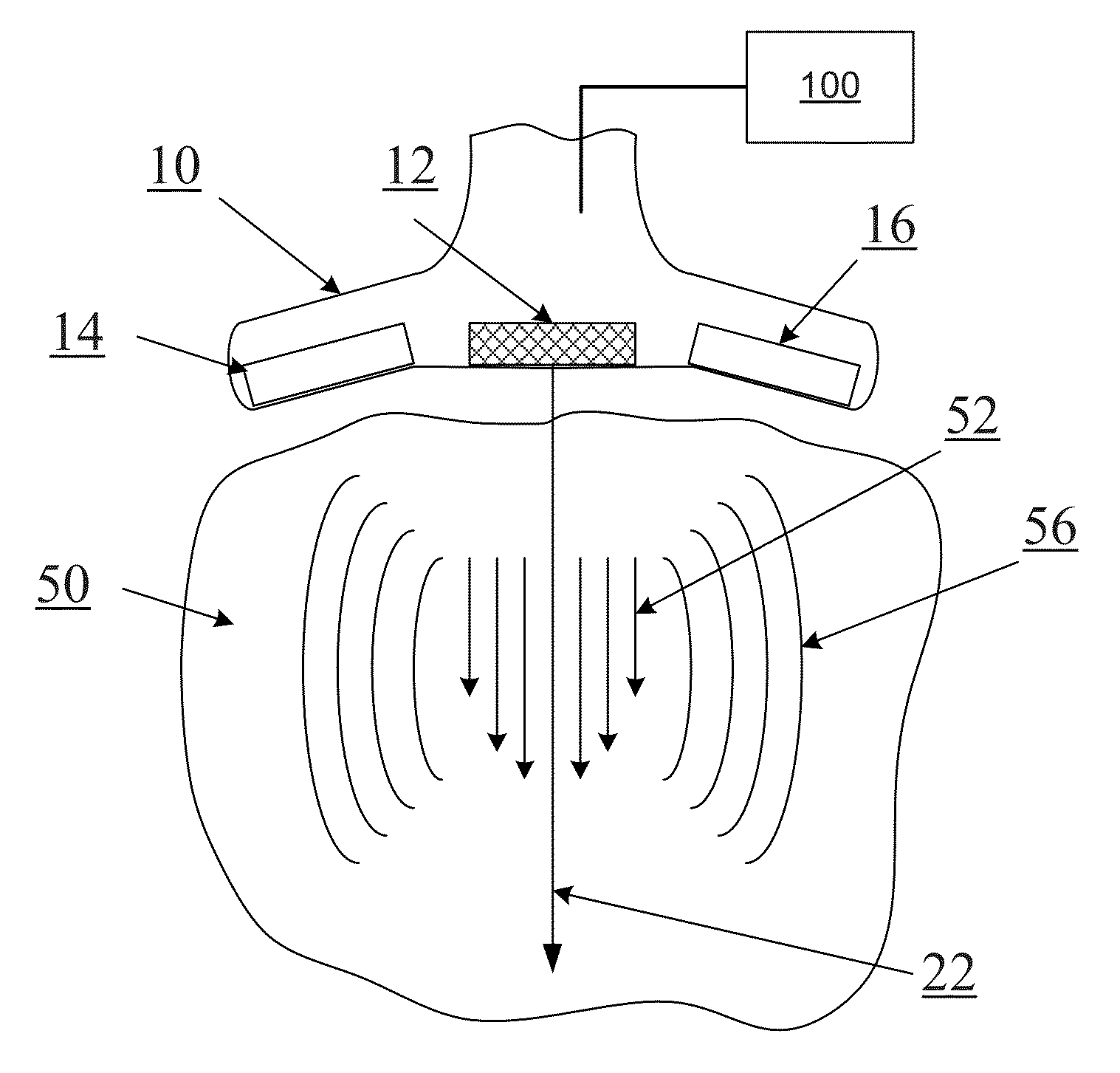
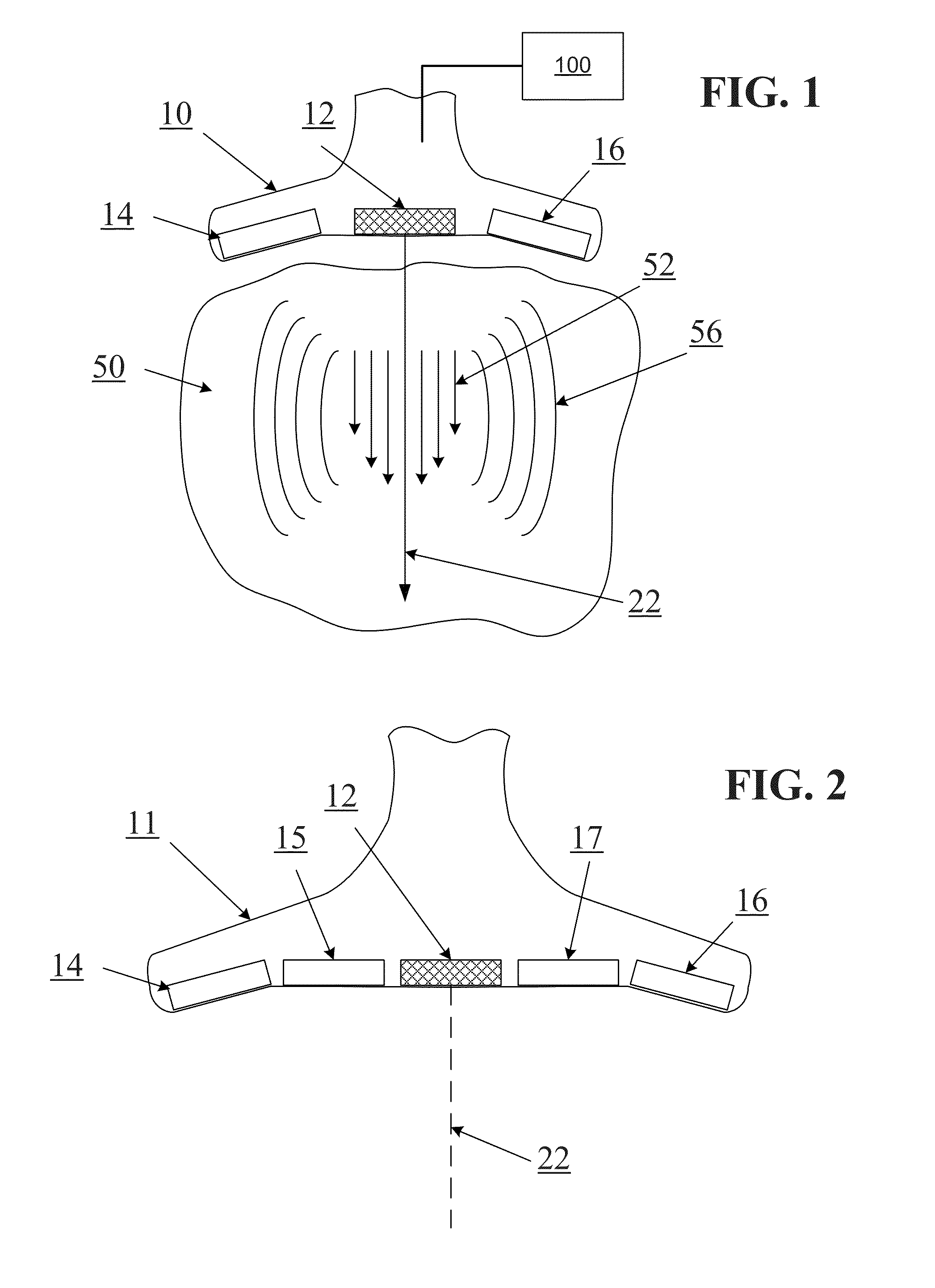
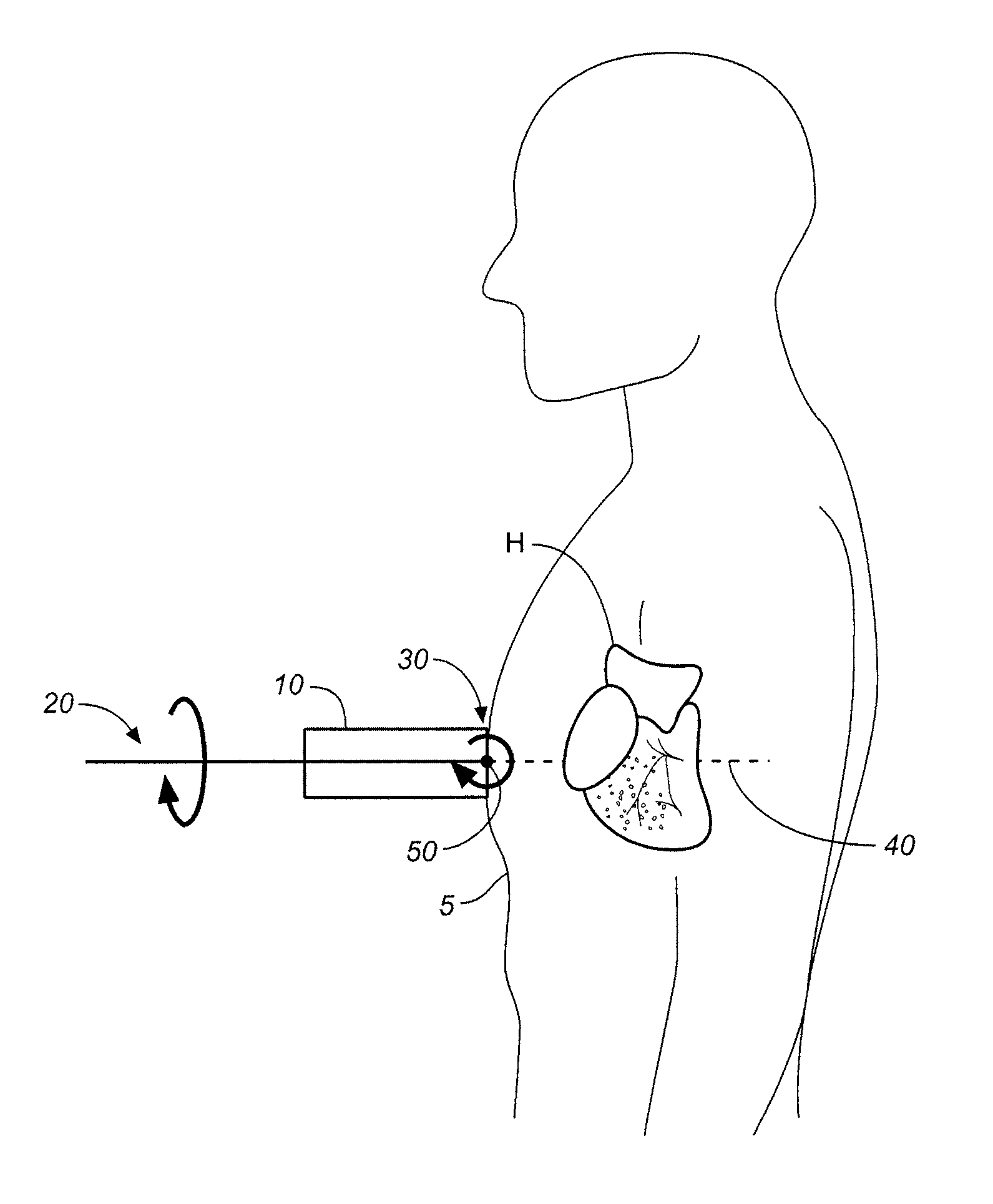
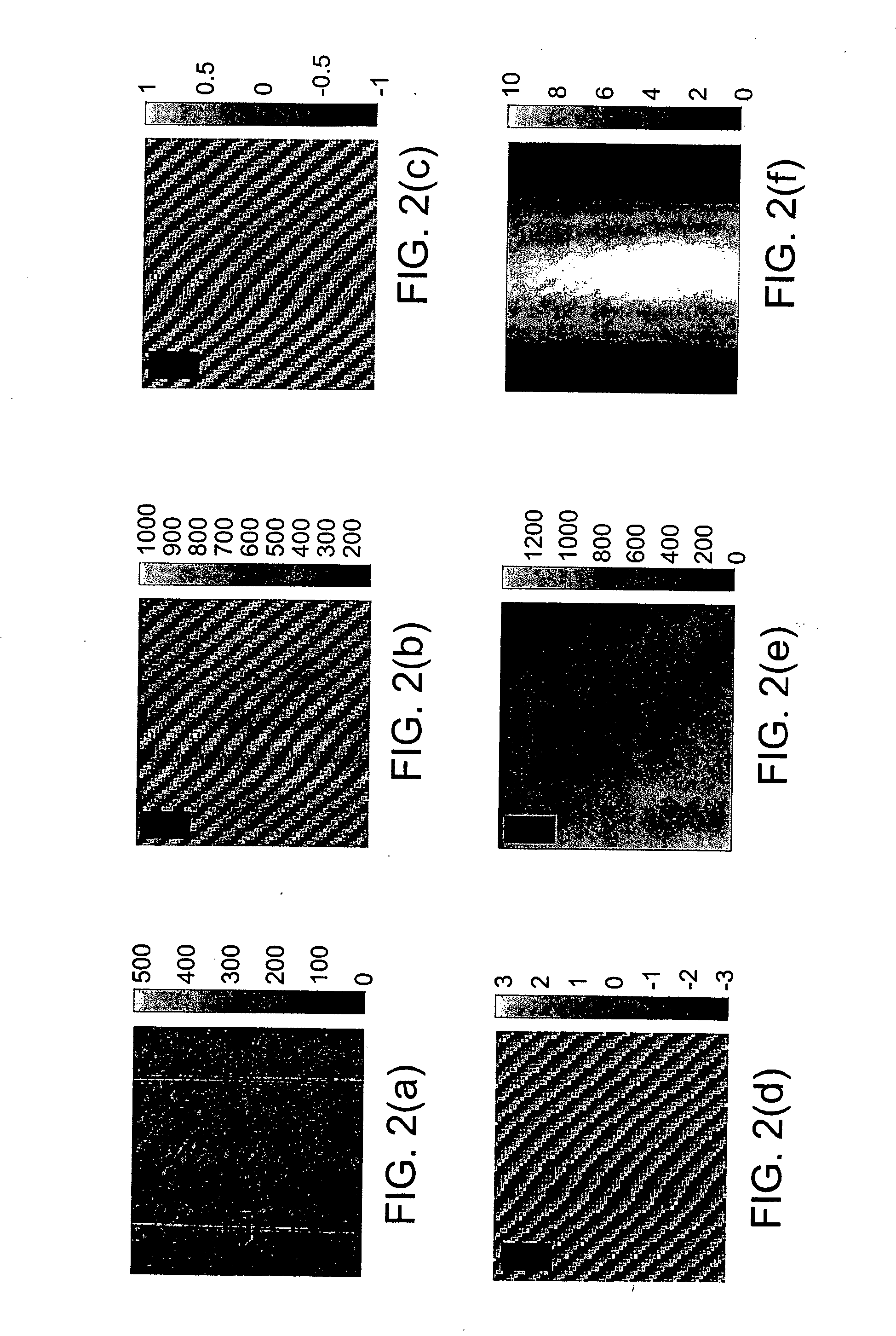
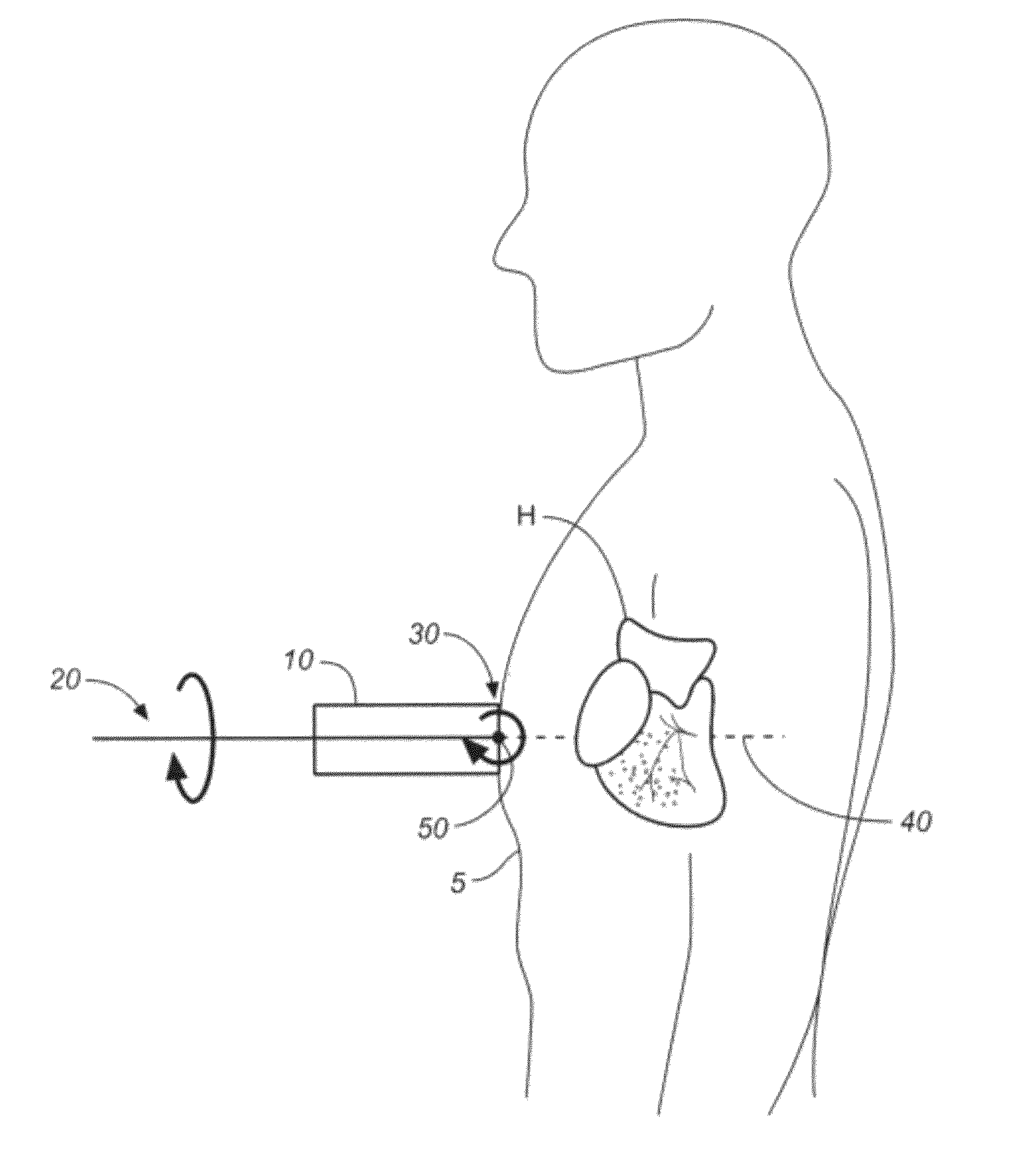
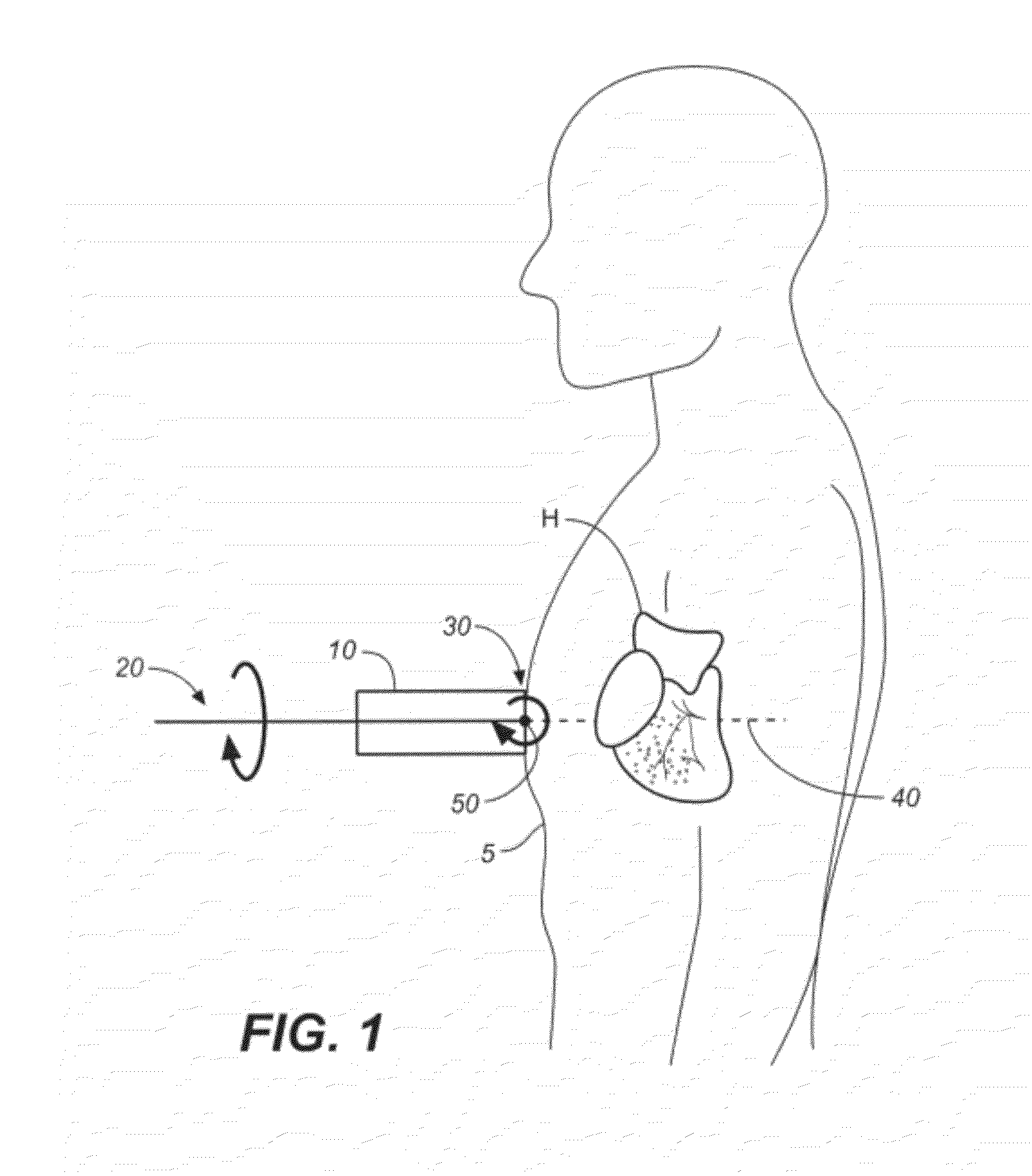
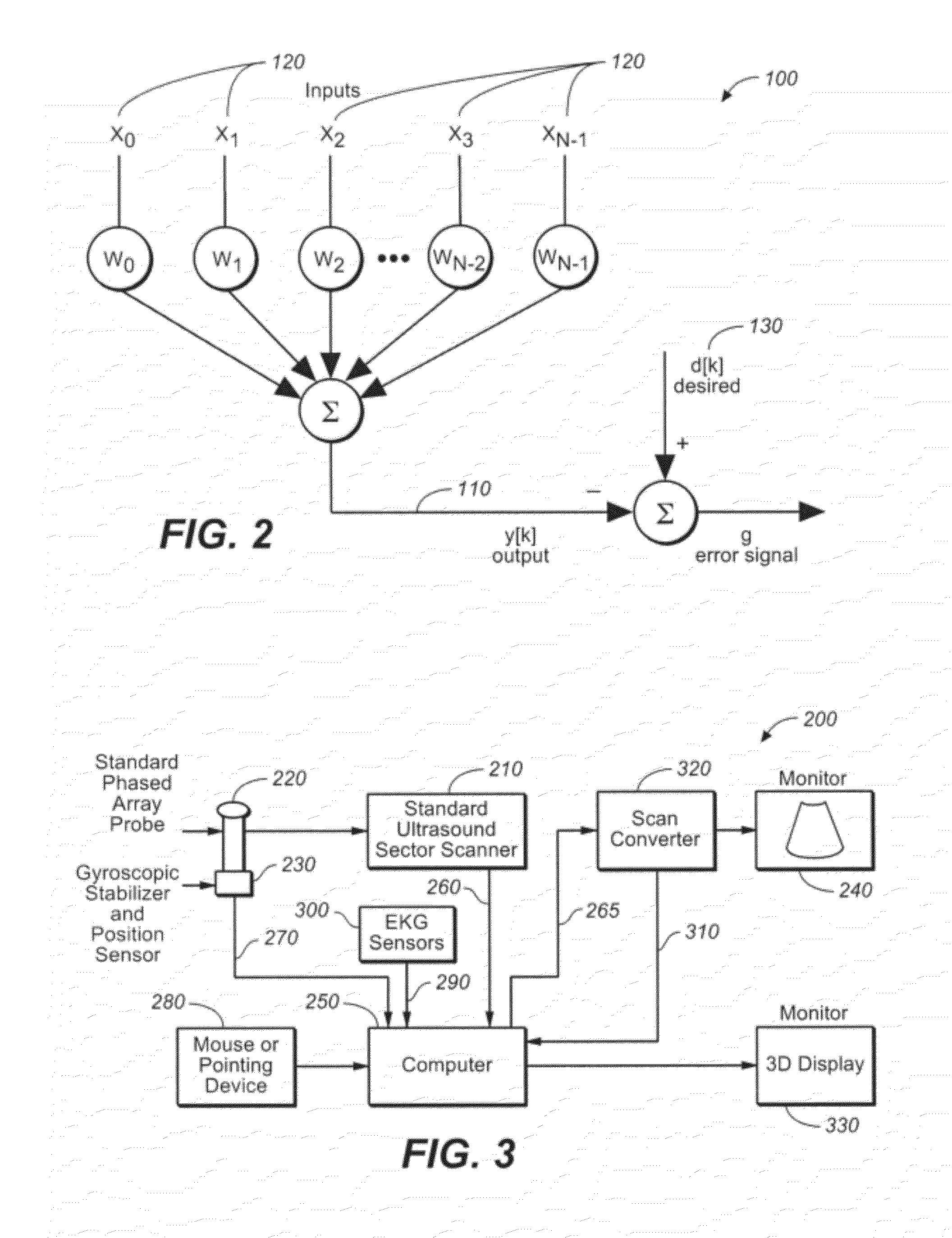
A non-invasive screening technique for visualizing coronary arteries which overcomes the problems of visualizing the curved arteries by projecting the three dimensional volume of the arteries onto a two dimensional screen. Blood filled areas, and in particular, the coronary arteries and veins, are highlighted to contrast them with other nearby tissues using non-linear classification and segmentation techniques. Data is gathered as a sequence of 2D slices stored as a 3D volume. Software is employed to interpolate voxels intermediate to the slices. Wiener filtering or LMS spatial filtering can be implemented on each 2D scan to improve lateral resolution and reduce noise prior to the use of the scan data with the classification and segmentation algorithms. A traditional handheld ultrasound probe is employed to enable the technician to locate the area of interest, but a gyroscopic stabilizer is added to minimize unwanted variation on two axes of rotation while scanning through angles on the third axis of rotation.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
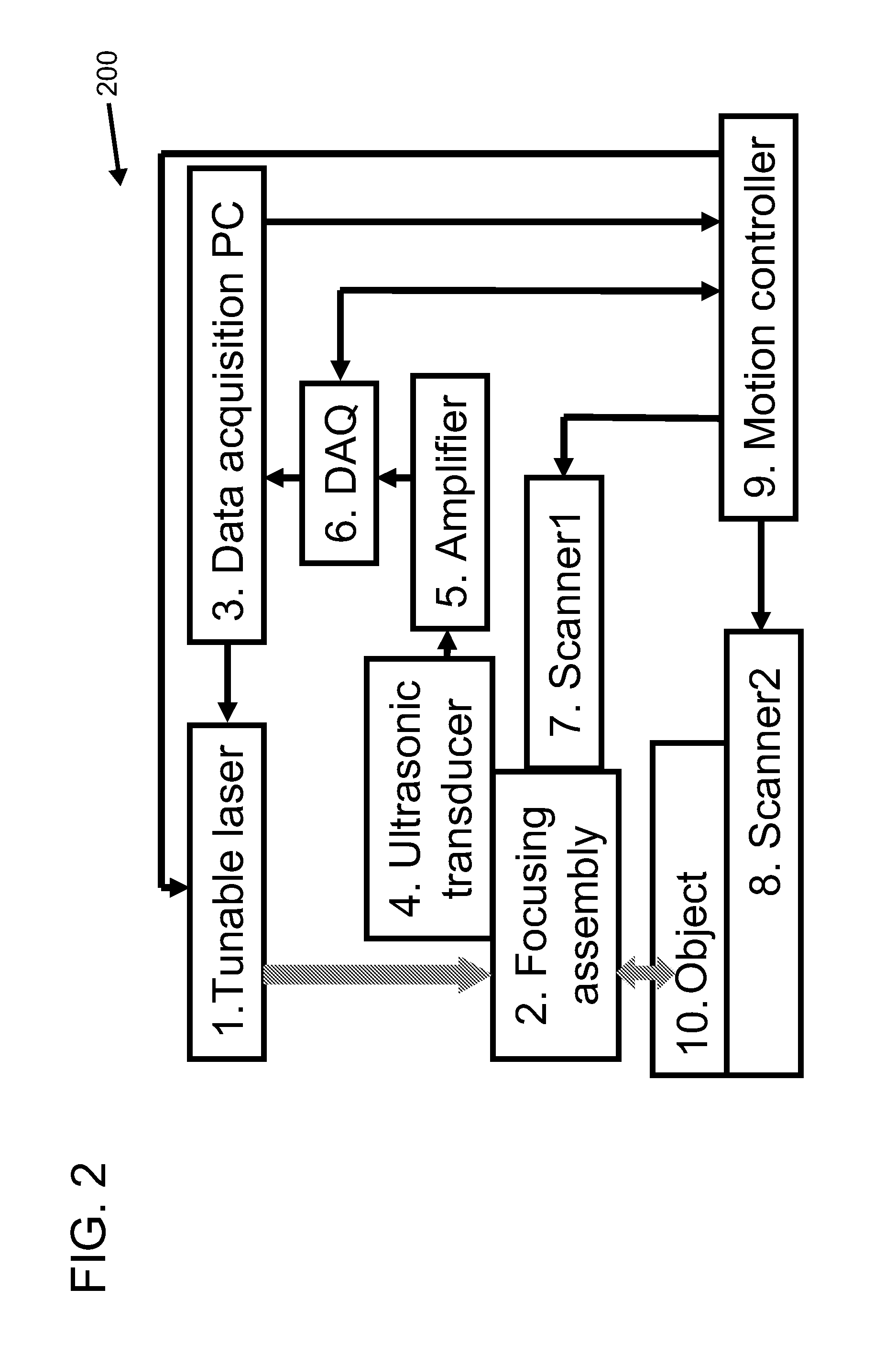
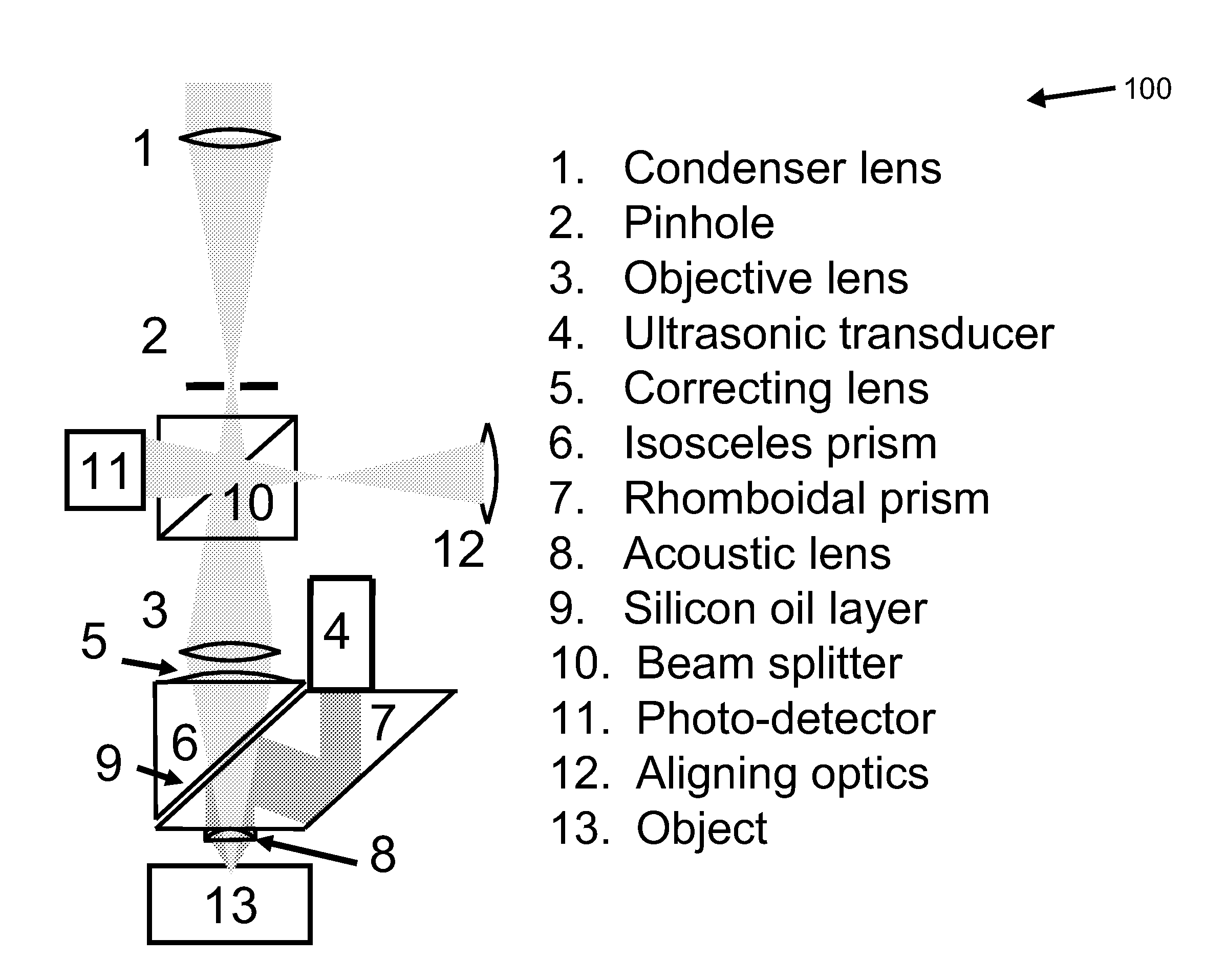
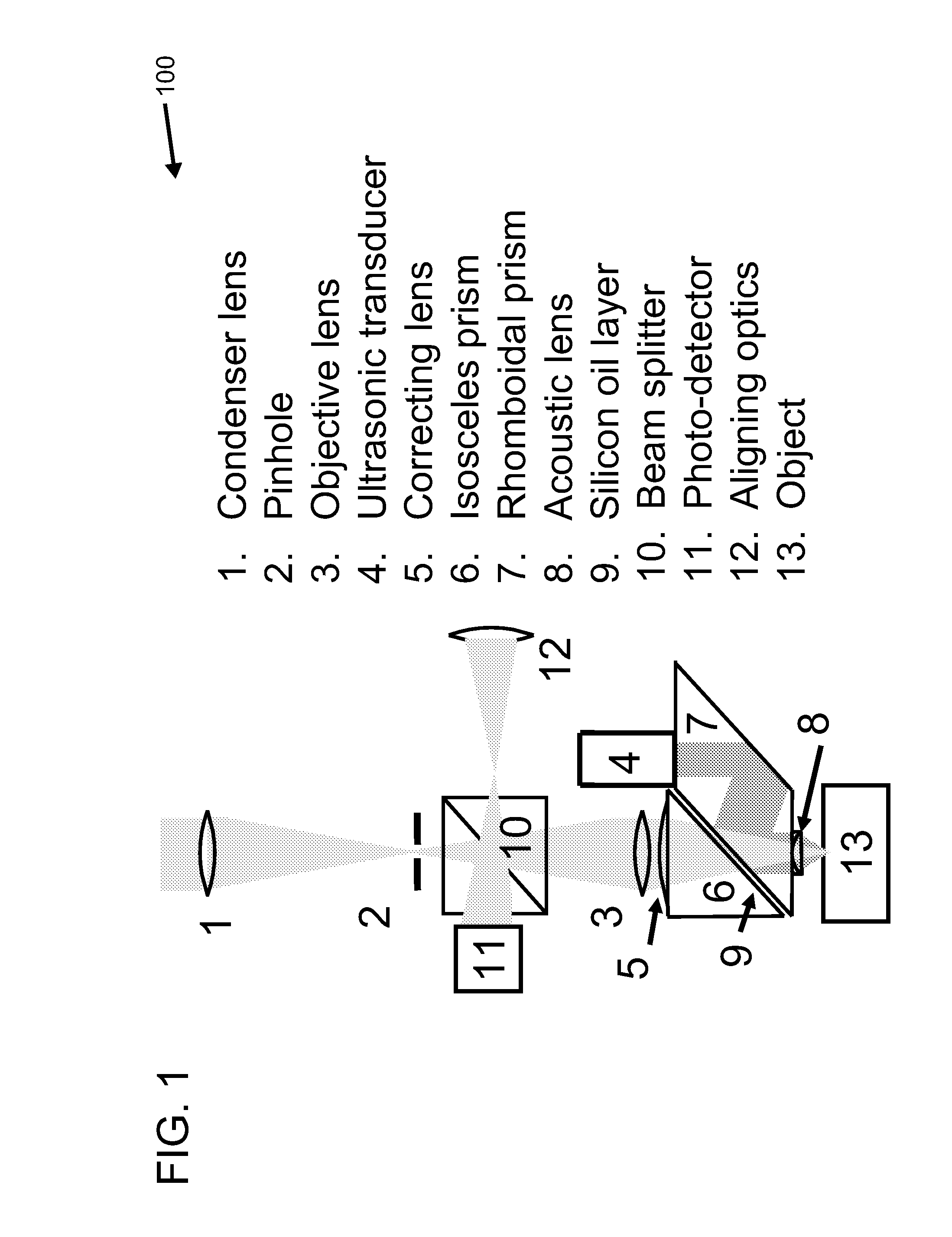
Confocal photoacoustic microscopy with optical lateral resolution
ActiveUS20100268042A1Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhotoacoustic microscopyUltrasonic sensor
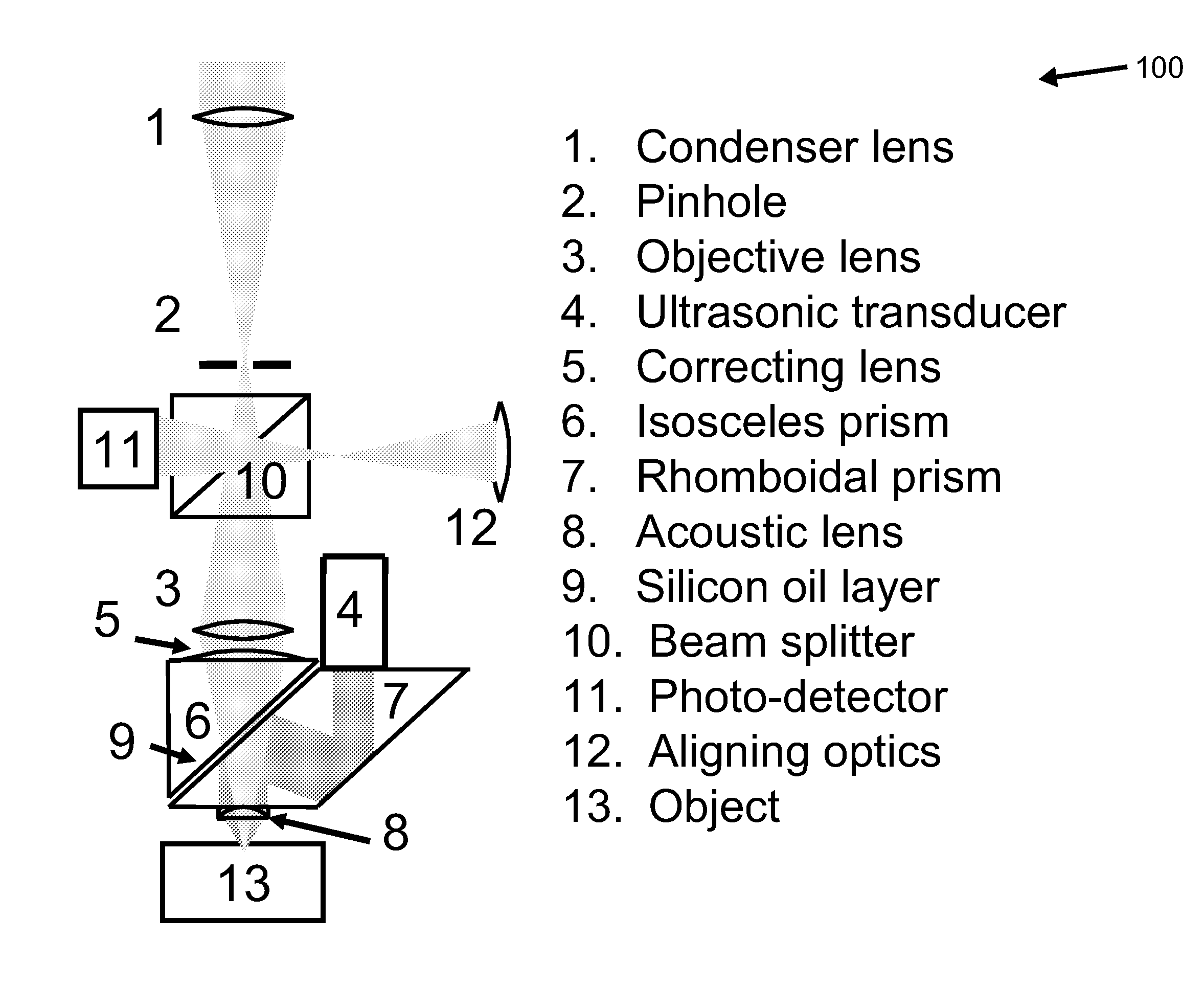
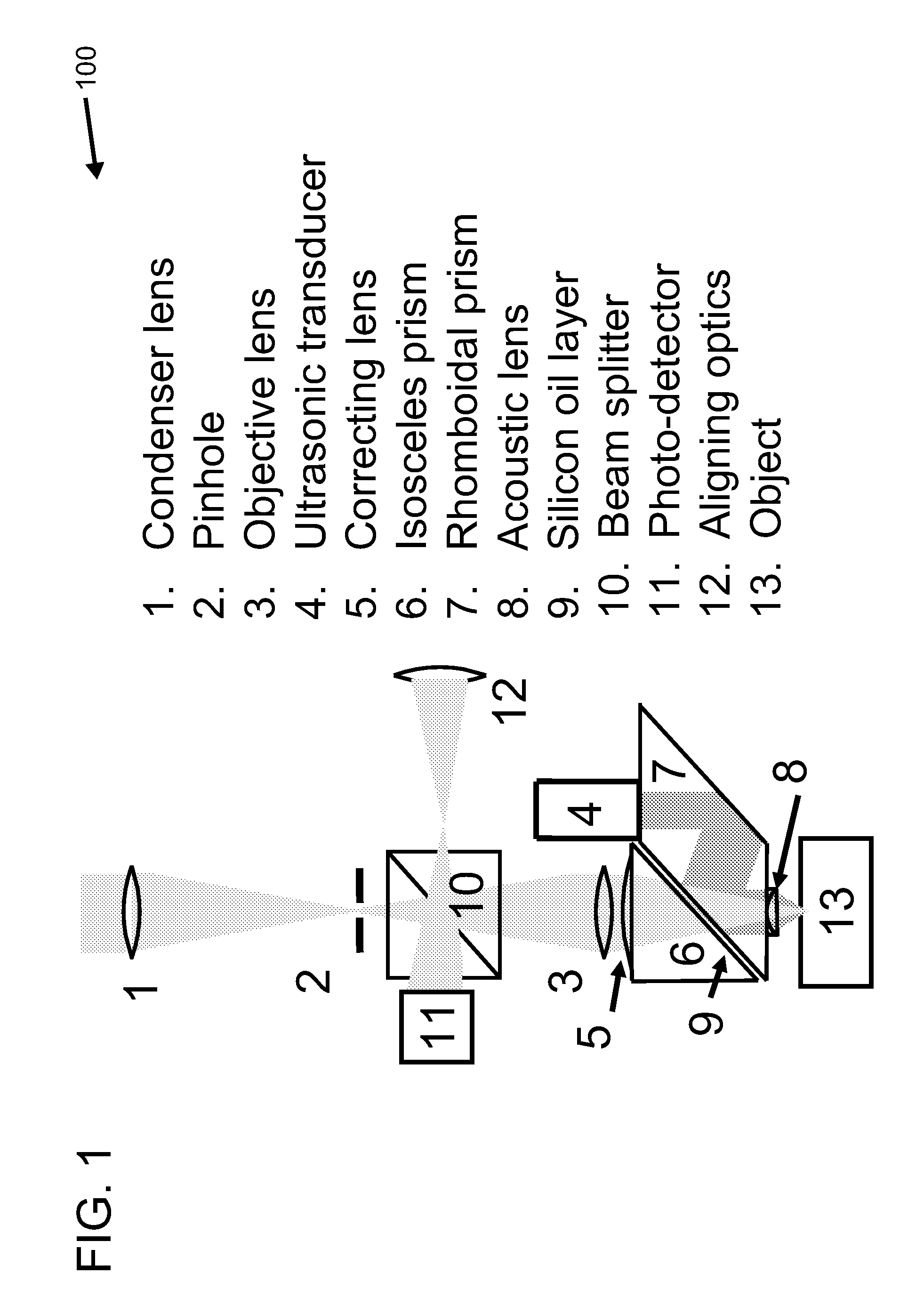
A confocal photoacoustic microscopy system includes a laser configured to emit a light pulse, a focusing assembly configured to receive the light pulse and to focus the light pulse into an area inside an object, an ultrasonic transducer configured to receive acoustic waves emitted by the object in response to the light pulse, and an electronic system configured to process the acoustic waves and to generate an image of the area inside the object. The focusing assembly is further configured to focus the light pulse on the object in such a way that a focal point of the focusing assembly coincides with a focal point of the at least one ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Apparatus for low coherence ranging
InactiveUS20050018200A1Low costPotential compact sizeScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansImage resolutionLateral resolution
An apparatus for performing low coherence ranging of a sample with high transverse resolution and large depth of focus, comprising an optical ranging system comprising a light source, a means for directing light from the light source to the sample, a means for directing reflected light from the sample to a detector, at least one detector, a means for processing light data received by the detector and which generates an image; and an optical element having a transverse resolution defined as .Δris less than or equal to about 5 μm, and a depth of focus Δz of at least about 50 μm.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
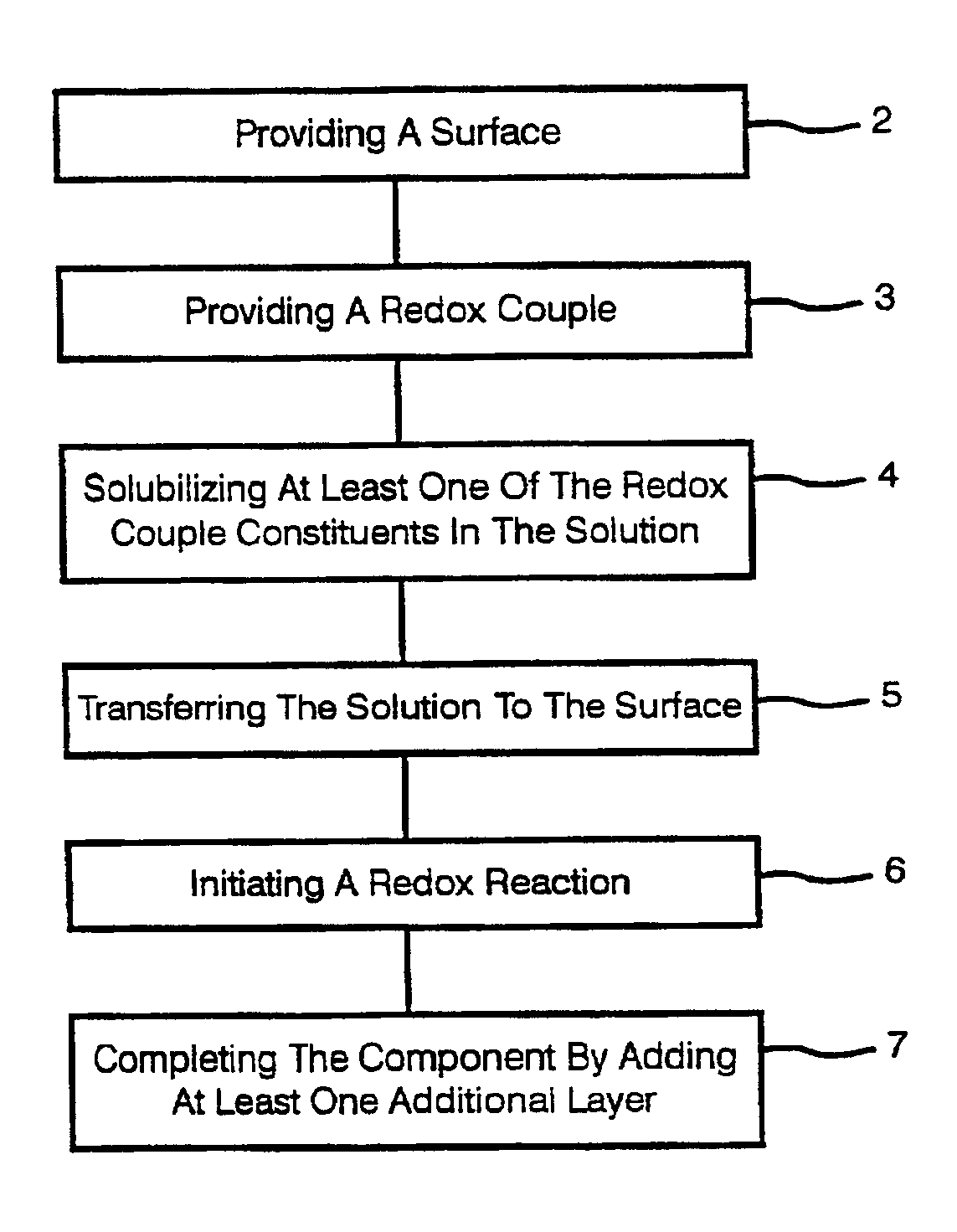
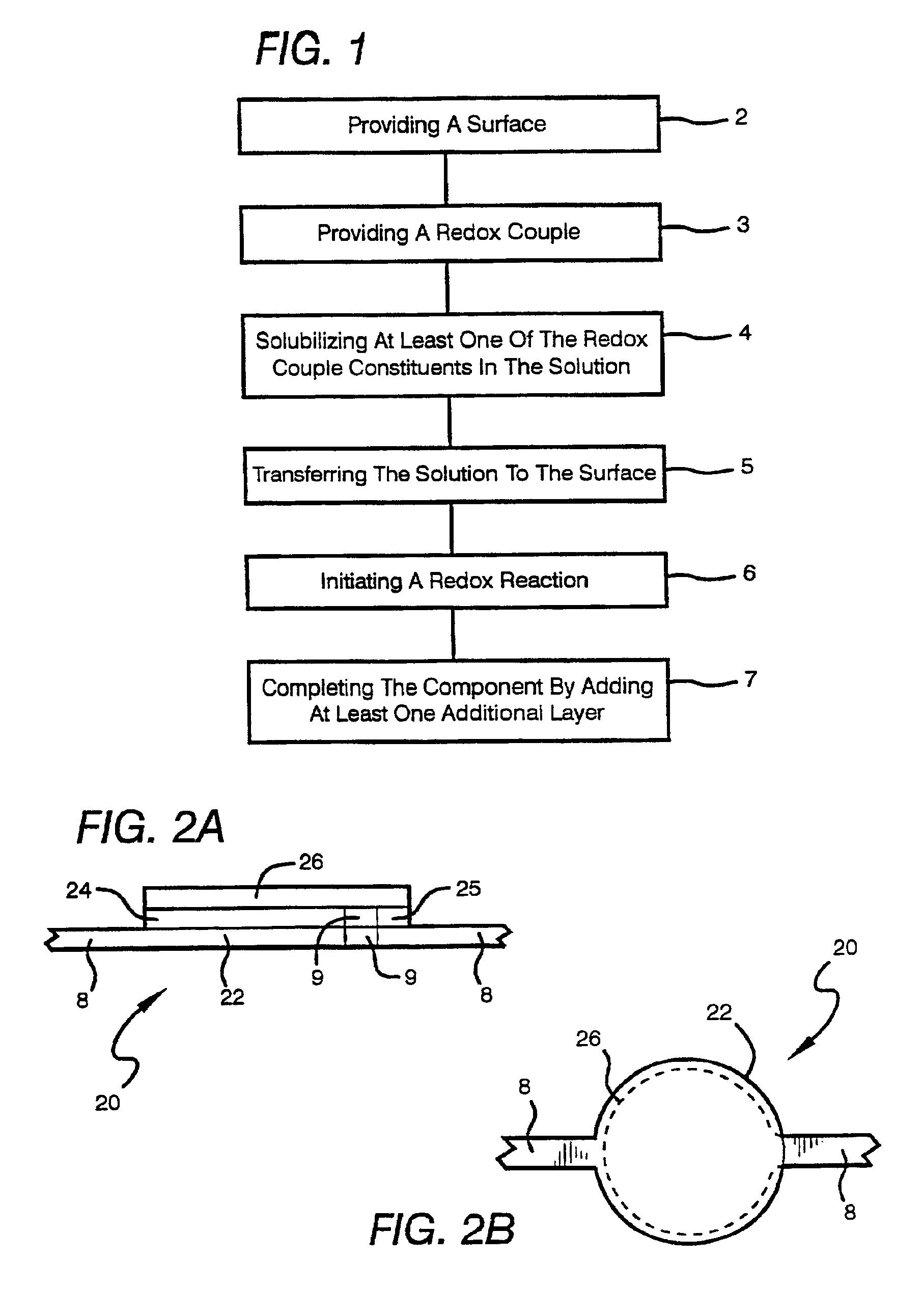
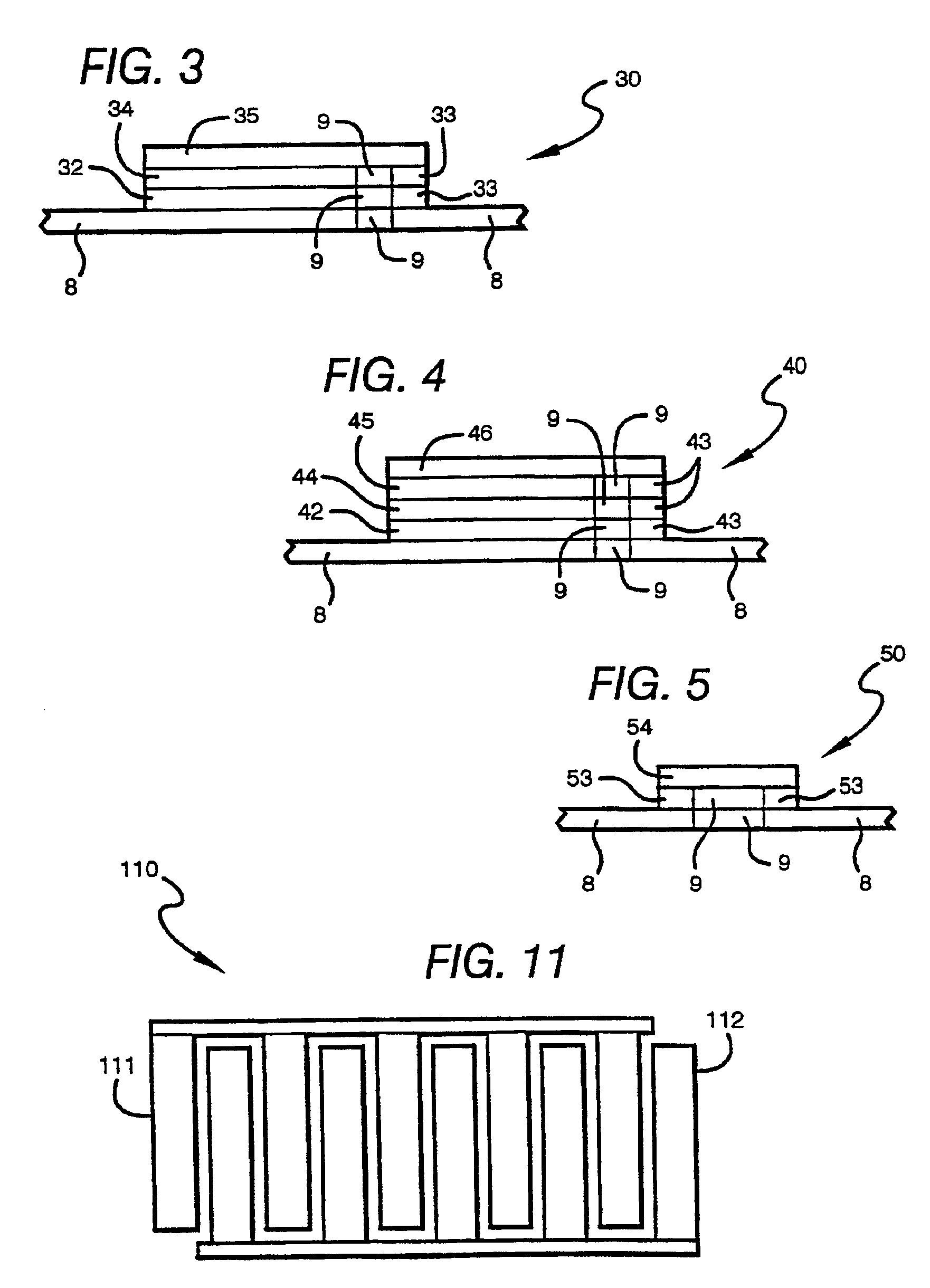
Printing of electronic circuits and components
InactiveUS6855378B1Reduce the content of particulate matterCell electrodesFinal product manufactureParticulatesHigh concentration
Methods are disclosed for printing (2-7) multilayer electronic components, and circuits on a surface (2), where at least one of the layers is formed by a redox reaction (6) occurring in a deposited solution (4, 5). Electronic components may comprise semiconductors such as in transistors or diode, or metal oxide or electrolyte such as in batteries or fuel cells, or are capacitors, inductors, and resistors. Preferably, the oxidizer of the redox reaction is a strong oxidizer, and the reducer is a strong reducer (3). Reactions are preferably sufficiently exothermic that they can be initiated (6), rather than driven to completion, by microwave or other suitable energy sources, and may yield substantially pure metal or metal oxide layers. The solution being deposited (5) may have either high concentrations of particulates, such as 60-80 wt. % of dry weight, or low concentrations of particulates, such as ≦5 wt. % or ≦2 wt. %. Low particulate content provides printing of structures having lateral resolution of ≦10 μm, ≦5 μm, or ≦1 μm.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
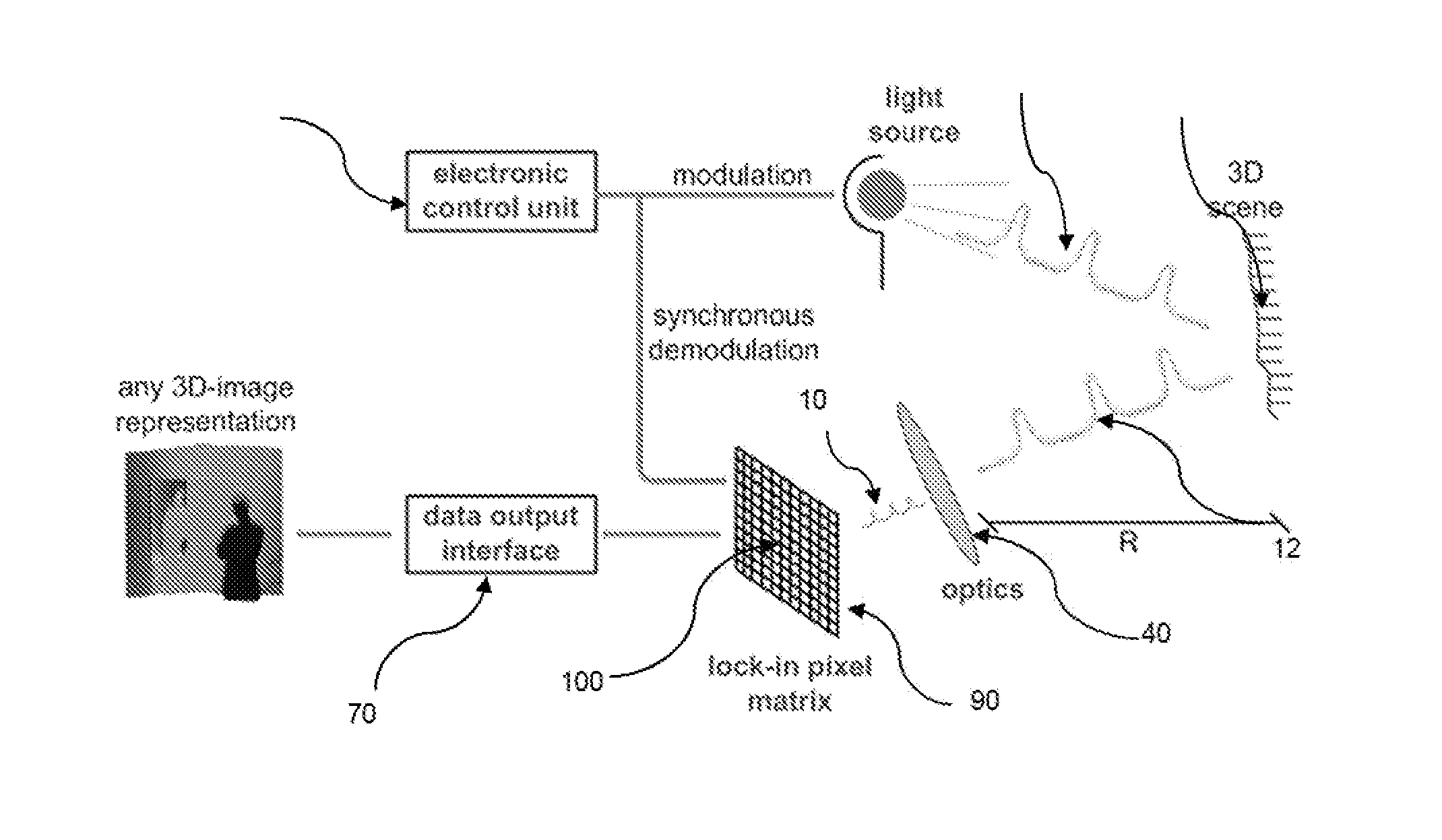
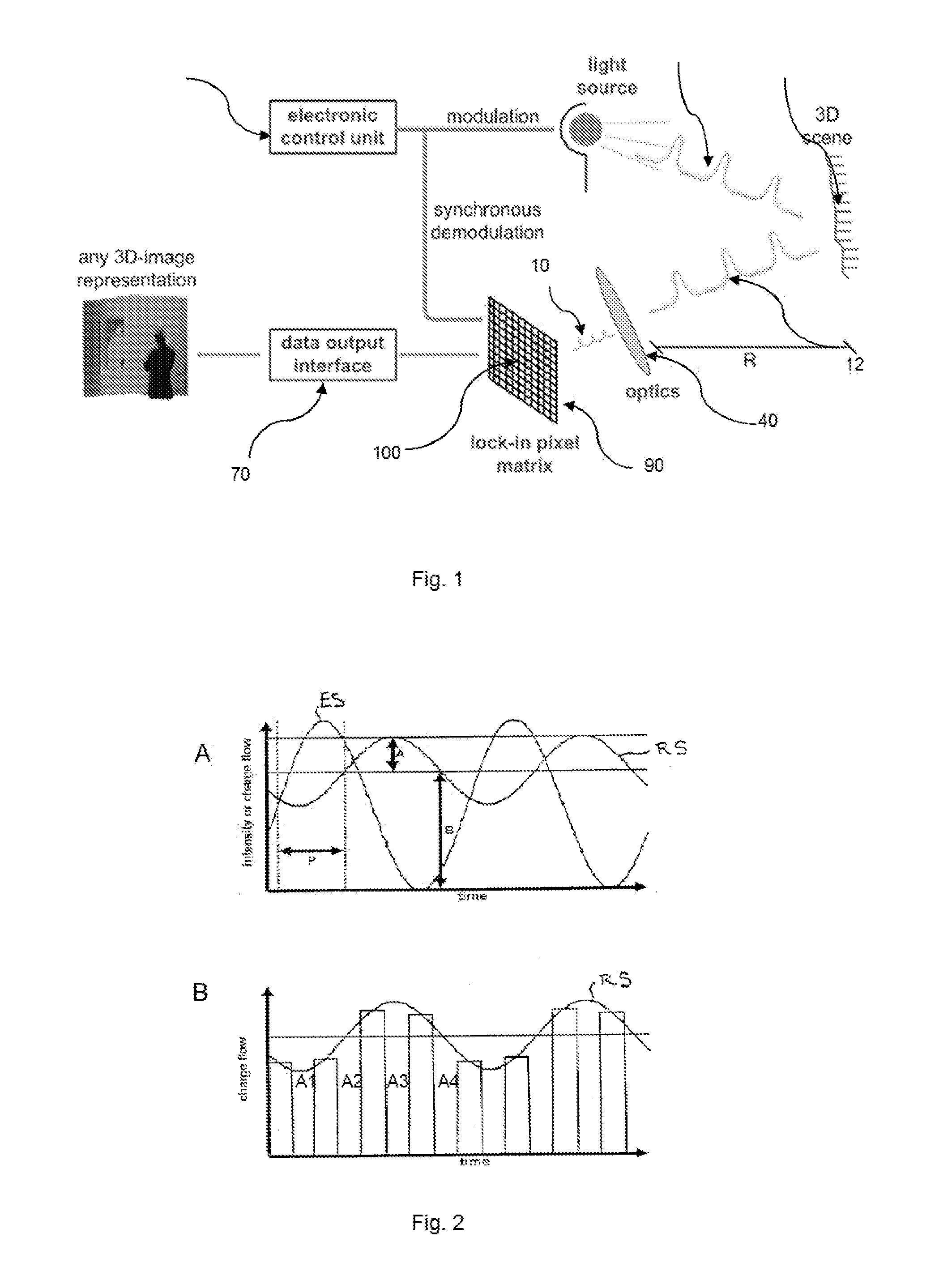
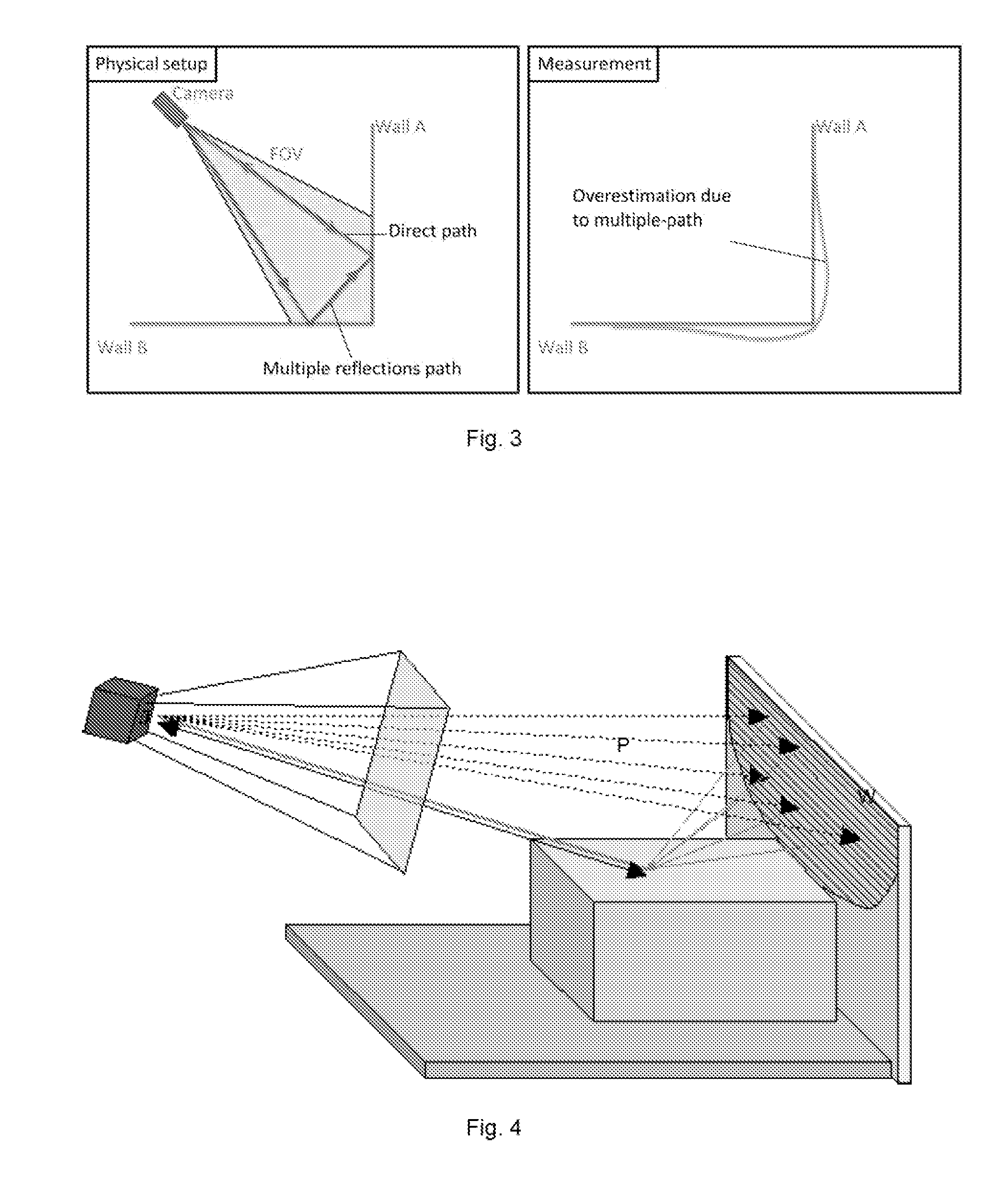
Method to Compensate for Errors in Time-of-Flight Range Cameras Caused by Multiple Reflections
ActiveUS20130148102A1Increase horizontal resolutionLowering lateral resolutionOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationImage resolutionMulti path
Due to their parallel illumination and acquisition for all the pixels, today's state-of-the-art time-of-flight (TOF) range cameras suffer from erroneous measurements caused by multiple reflections in the scene. The invention proposes to compensate for the multi-path fusing the results obtained by applying two spatially different illumination schemes, typically one to achieve highest possible lateral resolution and for the second one structuring the emitted light and by doing so lowering the lateral resolution but limiting the impact of multiple reflections.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Method and system for high resolution ultrasonic imaging of small defects or anomalies.
InactiveUS6128092ARadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySonificationSynthetic aperture focusing
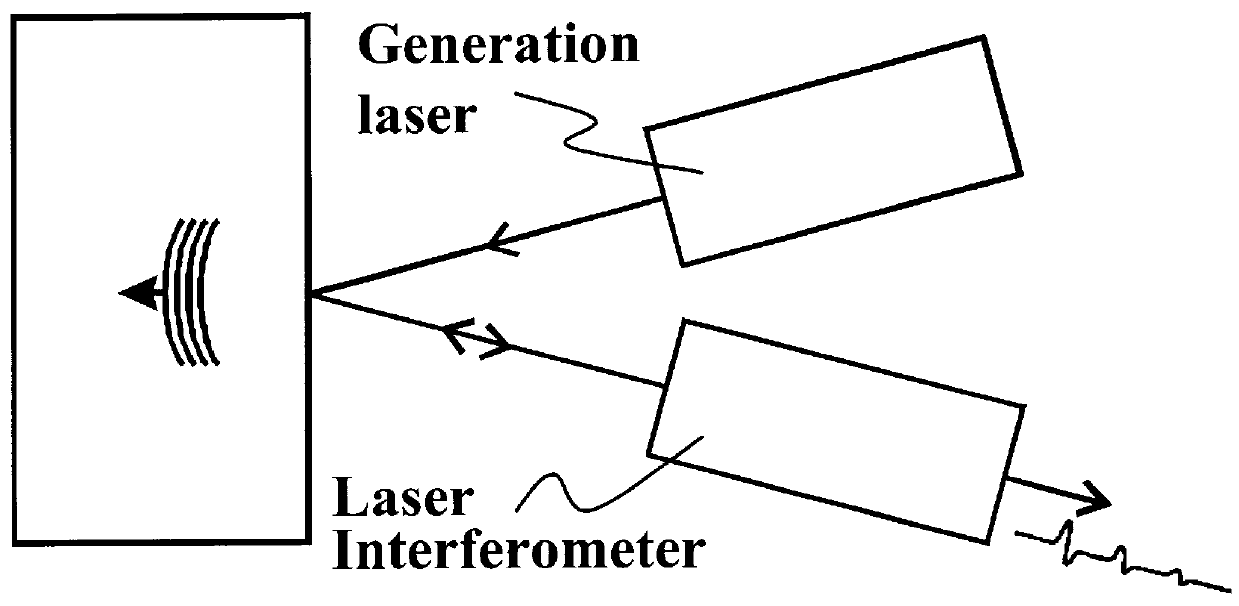
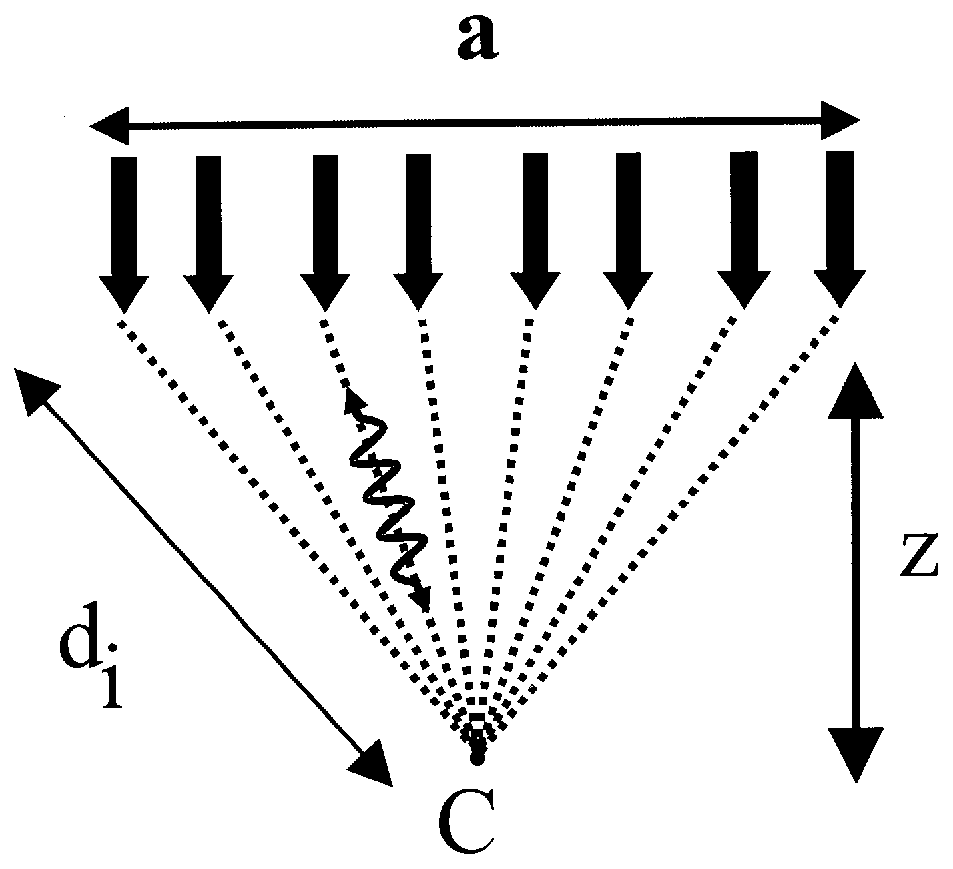
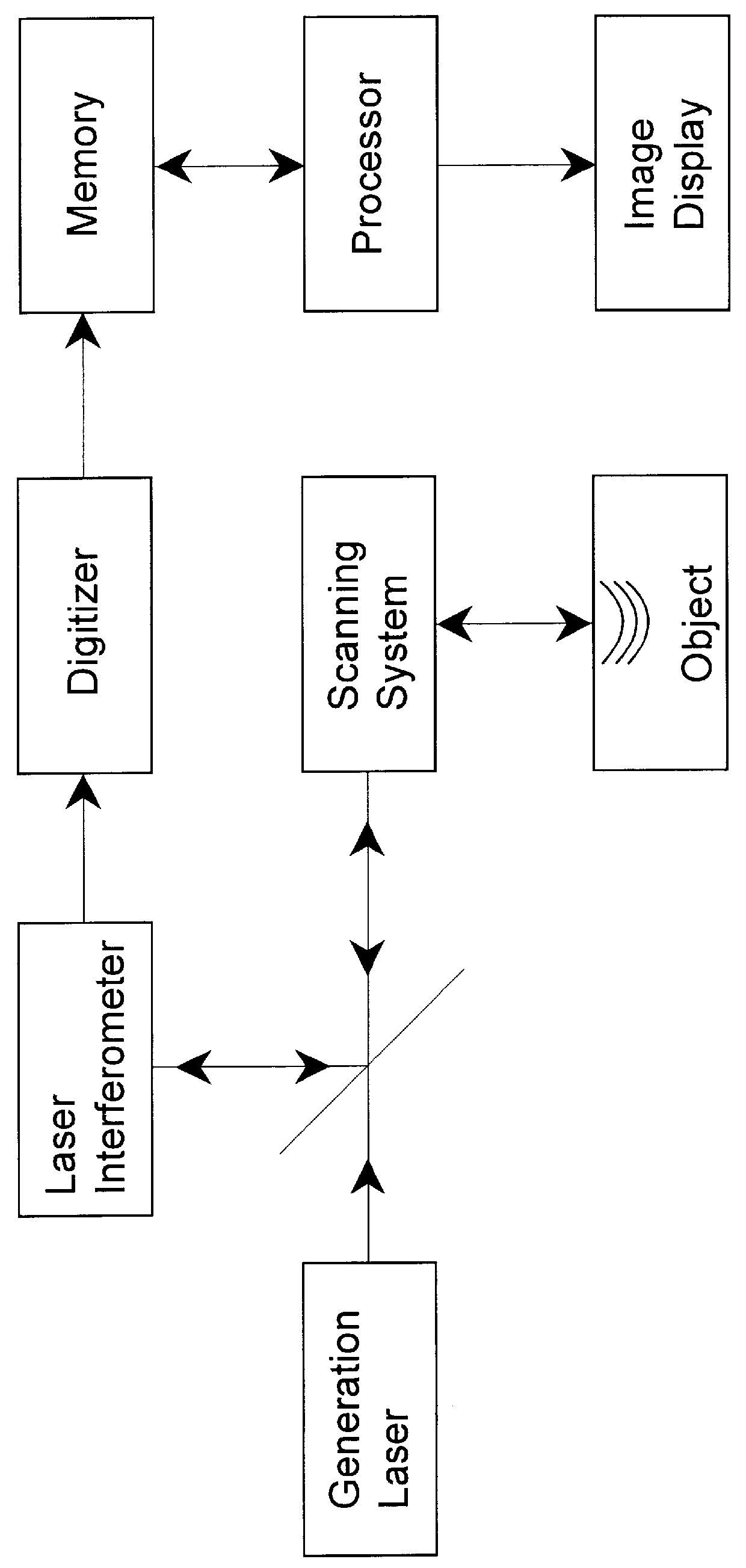
A method and system is provided for enhanced ultrasonic detection and imaging of small defects inside or at the surface of an object. The Synthetic Aperture Focusing Technique (SAFT) has been used to improve the detectability and to enhance images in conventional ultrasonics and this method has recently been adapted to laser-ultrasonics. In the present invention, an improved version of the frequency-domain SAFT (F-SAFT) based on the angular spectrum approach is described. The method proposed includes temporal deconvolution of the waveform data to enhance both axial and lateral resolutions, control of the aperture and of the frequency bandwidth to improve signal-to-noise ratio, as well as spatial interpolation of the subsurface images. All the above operations are well adapted to the frequency domain calculations and embedded in the F-SAFT data processing. The aperture control and the spatial interpolation allow also a reduction of sampling requirements to further decrease both inspection and processing times. This method is of particular interest when ultrasound is generated by a laser and detected by either a contact ultrasonic transducer or a laser interferometer.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
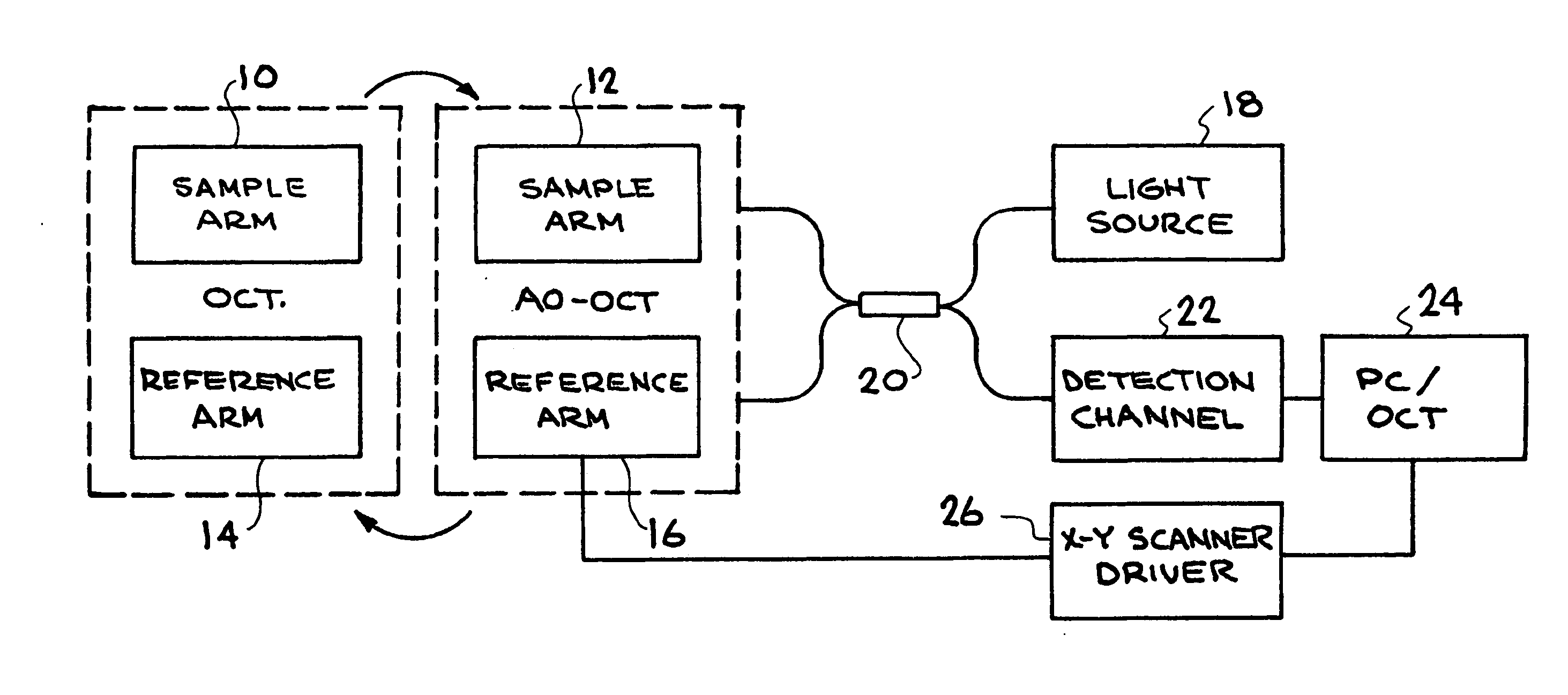
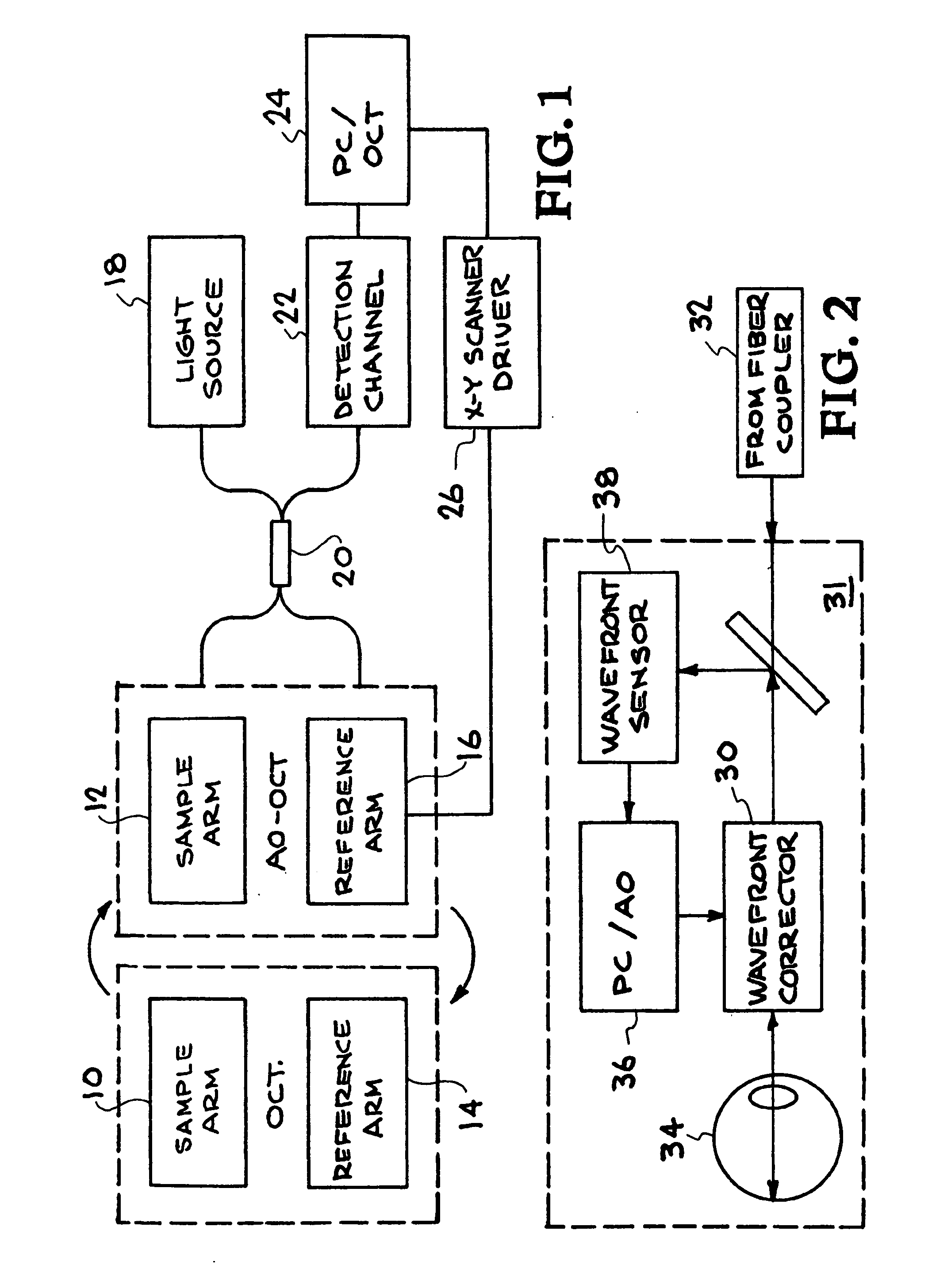
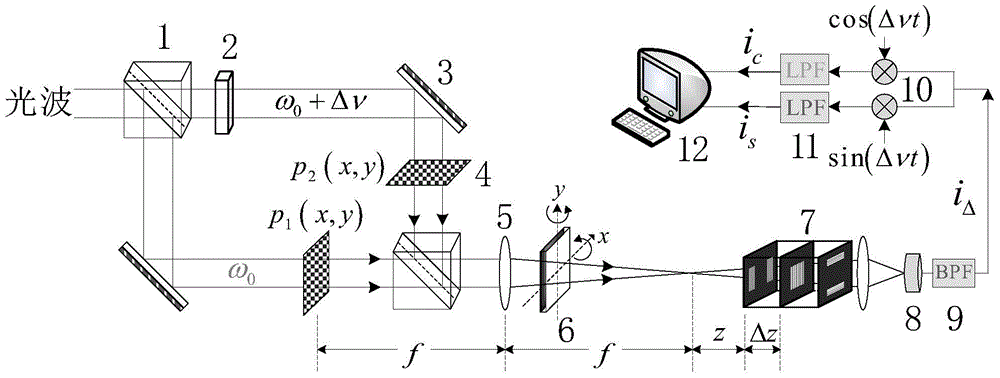
High-resolution retinal imaging using adaptive optics and fourier-domain optical coherence tomography
ActiveUS20070258095A1Precise positioningMinimize eye motionUsing optical meansOthalmoscopesMicroscopic blood vesselHuman eye
This invention permits retinal images to be acquired at high speed and with unprecedented resolution in three dimensions (4×4×6 μm). The instrument achieves high lateral resolution by using adaptive optics to correct optical aberrations of the human eye in real time. High axial resolution and high speed are made possible by the use of Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography. Using this system, we have demonstrated the ability to image microscopic blood vessels and the cone photoreceptor mosaic.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
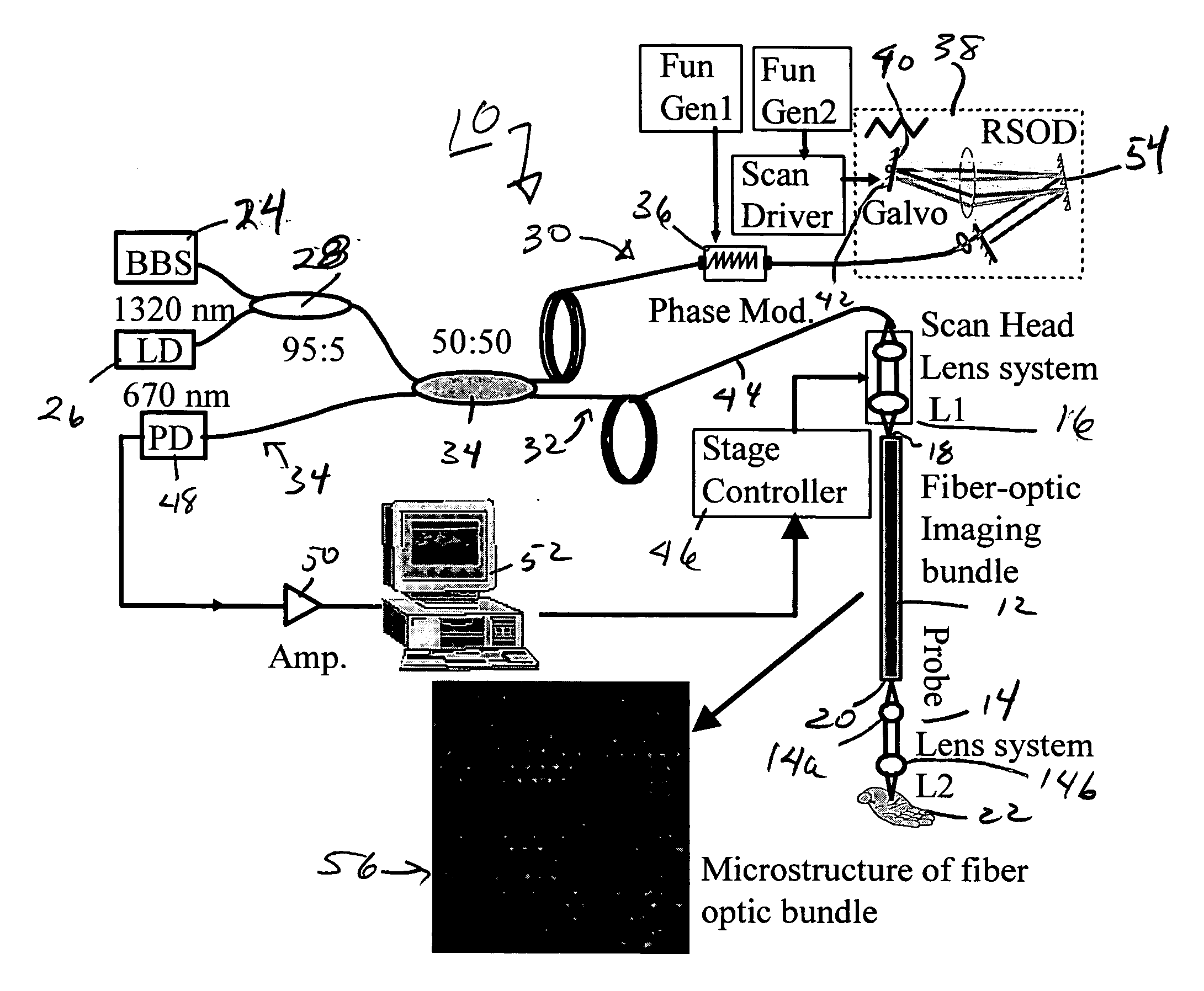
Optical coherent tomographic (OCT) imaging apparatus and method using a fiber bundle
InactiveUS20070038119A1Reduce back reflectionHigh resolution imageDiagnostics using tomographyUsing optical meansEngineeringLight-emitting diode
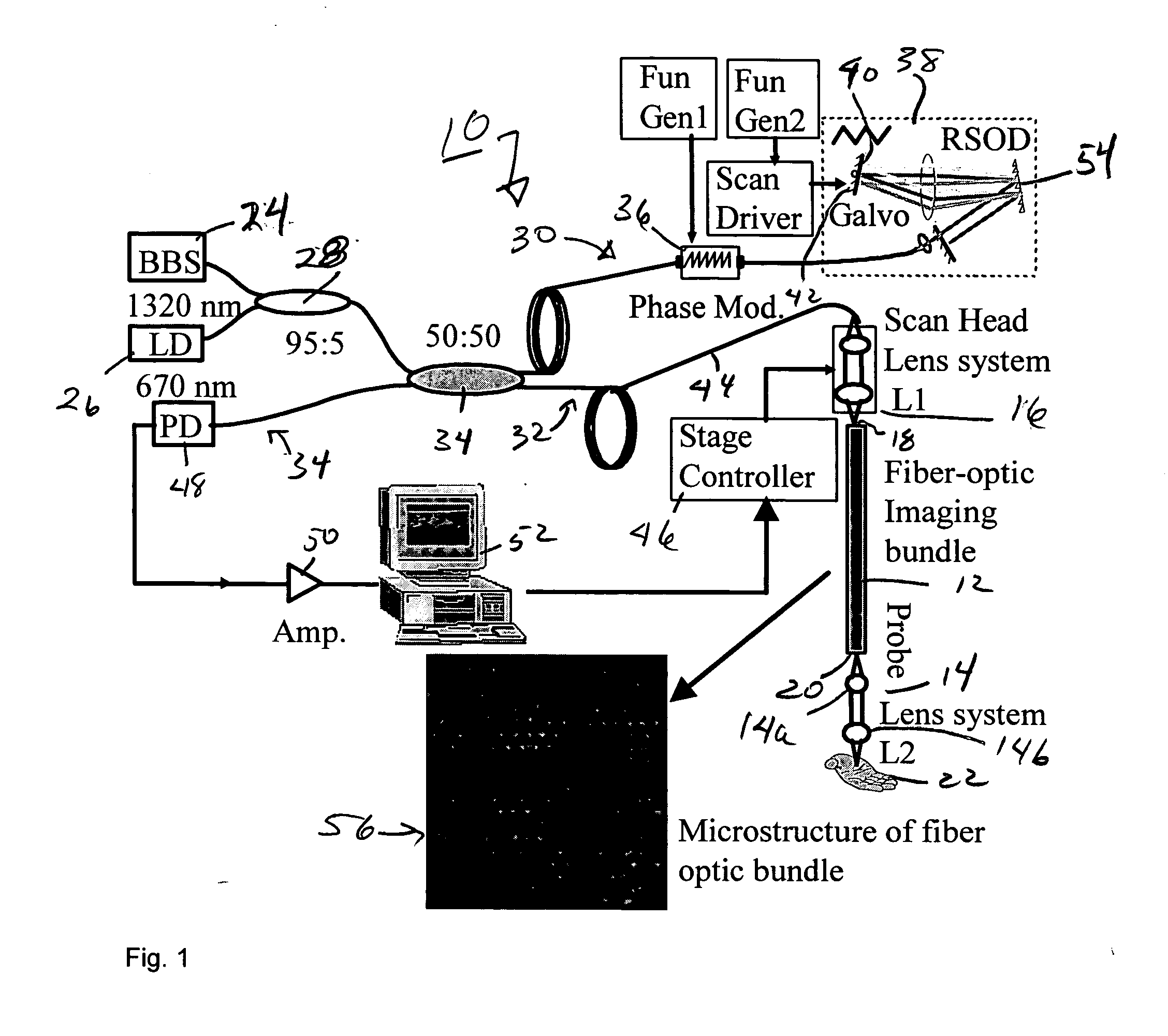
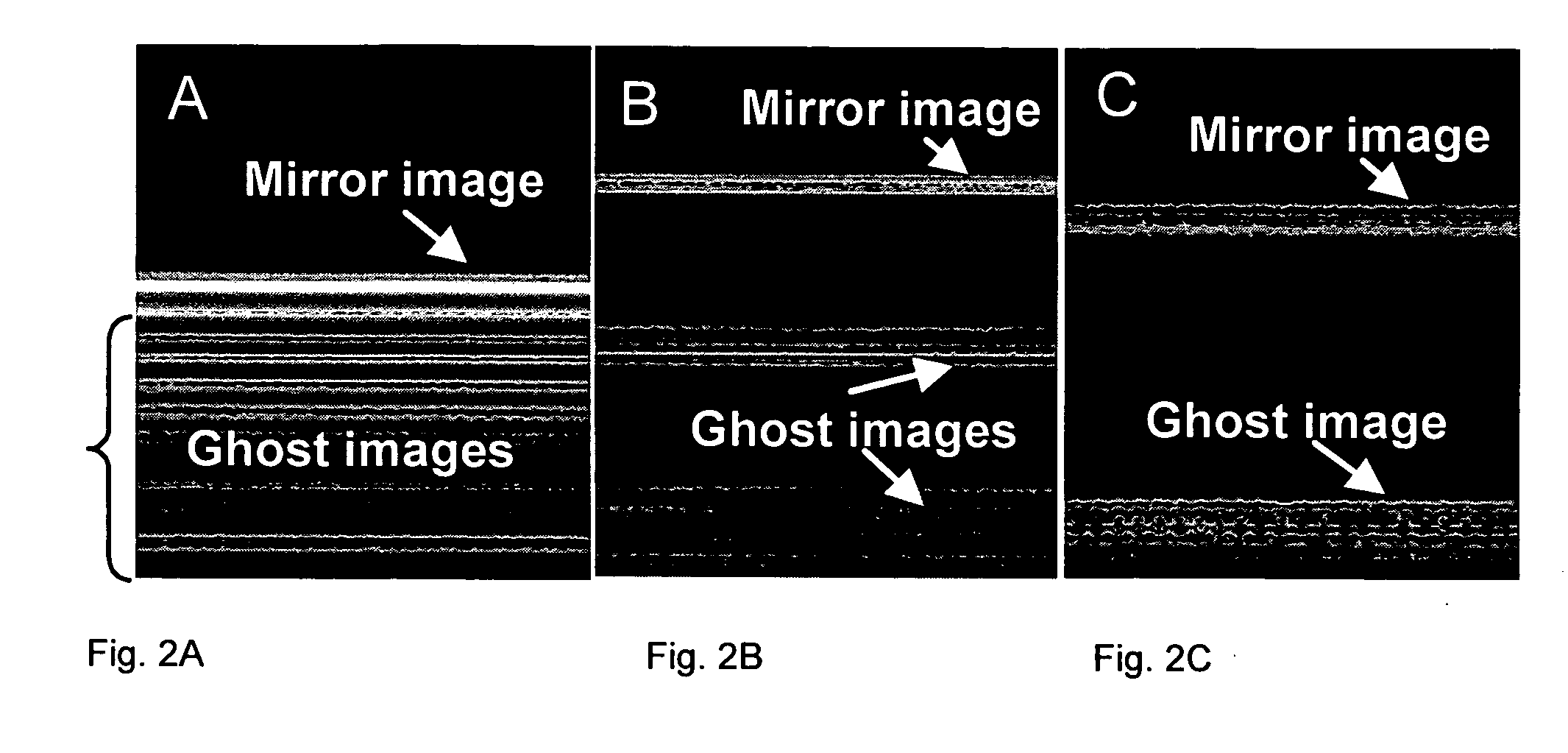
A fiber-optic bundle based optical coherence tomography (OCT) probe method is demonstrated in a multimode optical fiber bundle based OCT system. The system can achieve a lateral resolution of 12 μm and an axial resolution of 10 μm using a super-luminescent diode source. This imaging approach eliminates any moving parts in the probe and has a primary advantage for use in extremely compact and safe OCT endoscopes to image internal organs and great potential to be combined with confocal endoscopic microscopy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for optical imaging via spectral encoding
ActiveUS20070081236A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMethod using image detector and image signal processingAnatomical structuresImage resolution
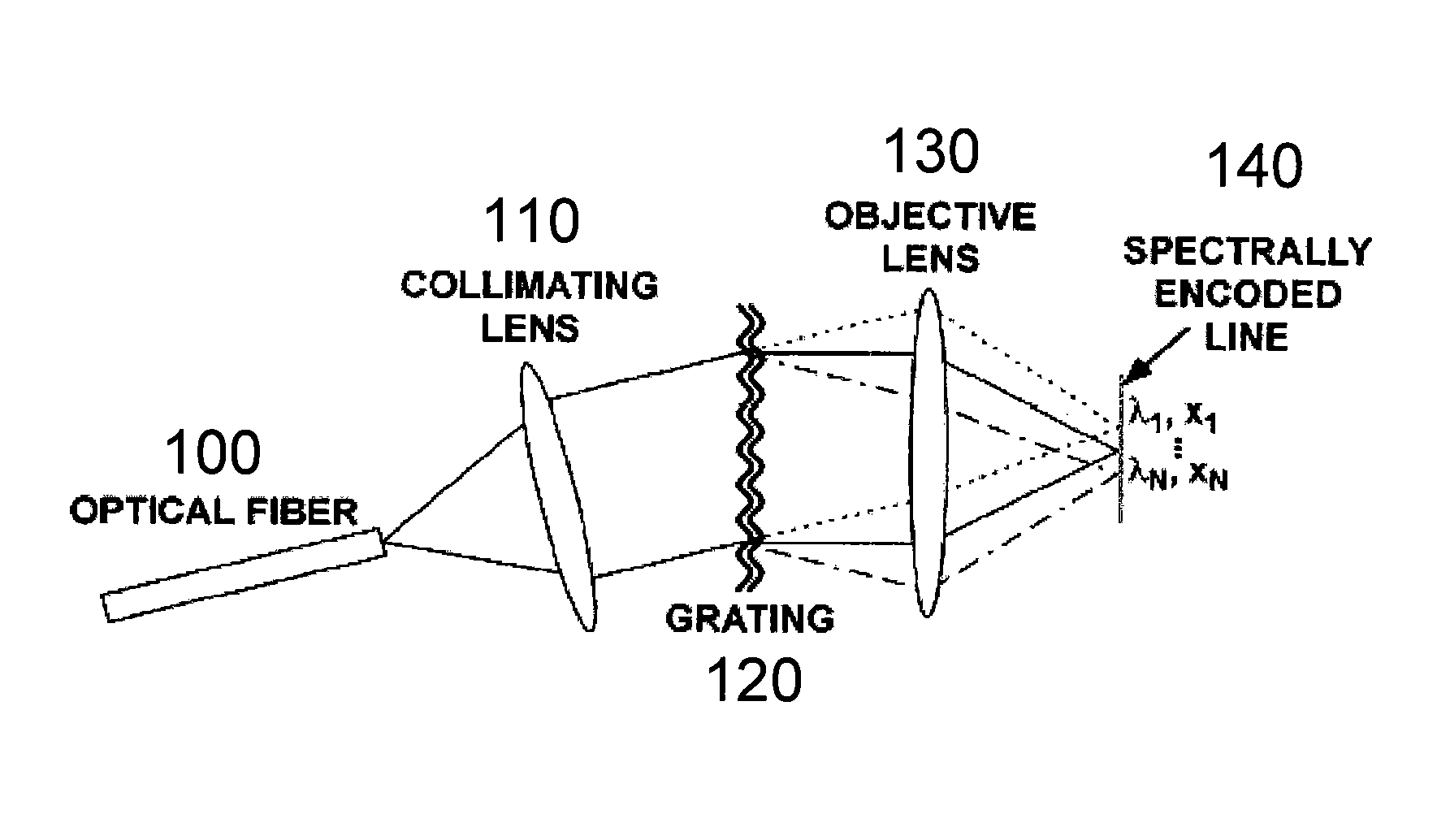
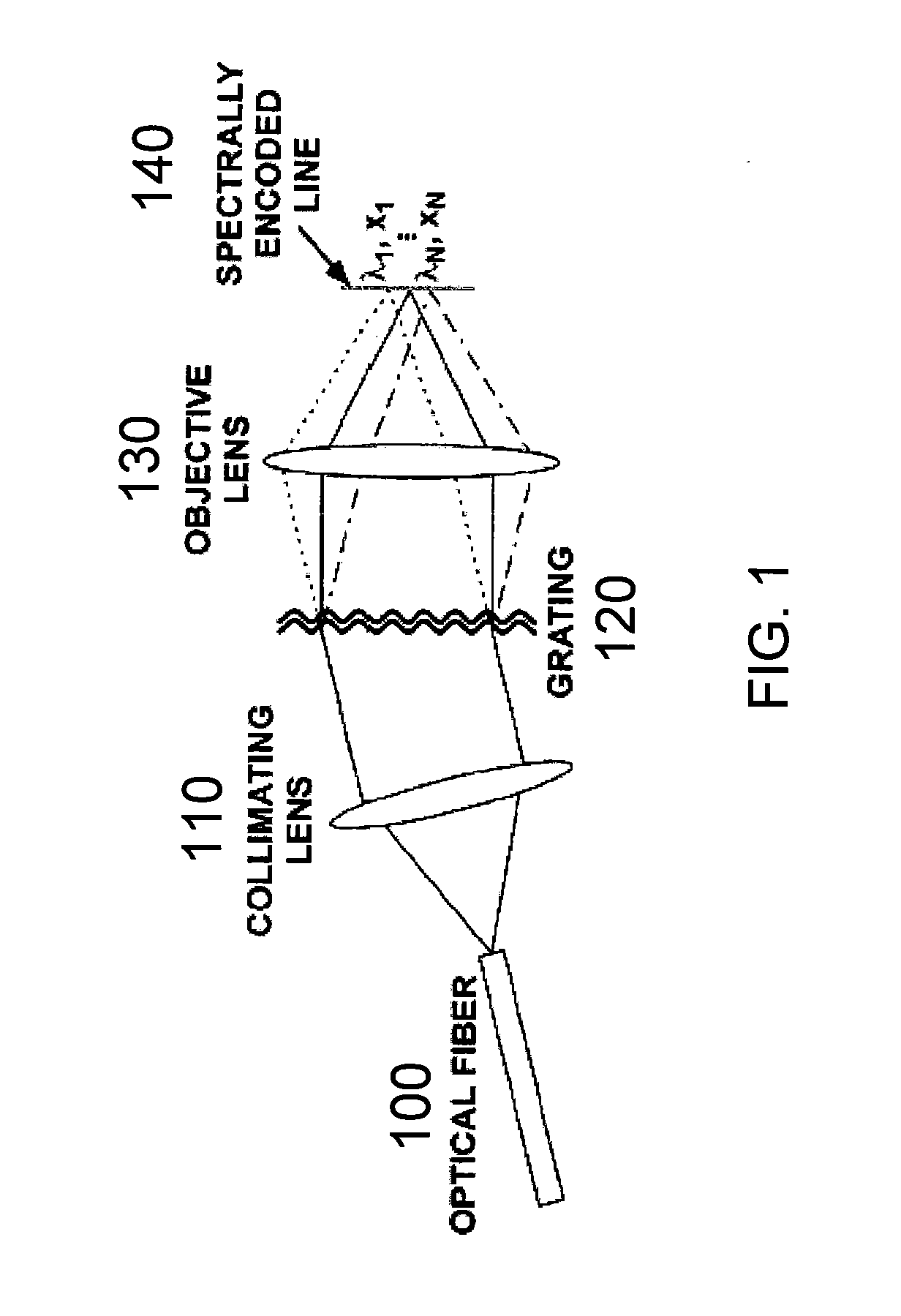
Method, apparatus and arrangement according an exemplary embodiment of the present invention can be provided for generating an image of at least one portion of an anatomical structure. For example, the portion can have an area greater than about 1 mm2, and the image can have a resolution a transverse resolution that is below about 10 μm. For example, light can be scanned over such portion so as to generate first information which is related to the portion, where the light may be provided through a diffraction arrangement to generate a spectrally dispersed line. Method, apparatus and arrangement according to a further exemplary embodiment of the present invention can be provided for positioning a radiation or optical beam within an anatomical structure based on signals generated by scanning a portion of the structure using the same or a different beam.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Determining Material Stiffness Using Multiple Aperture Ultrasound
ActiveUS20130218012A1High resolutionHigh imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSonification
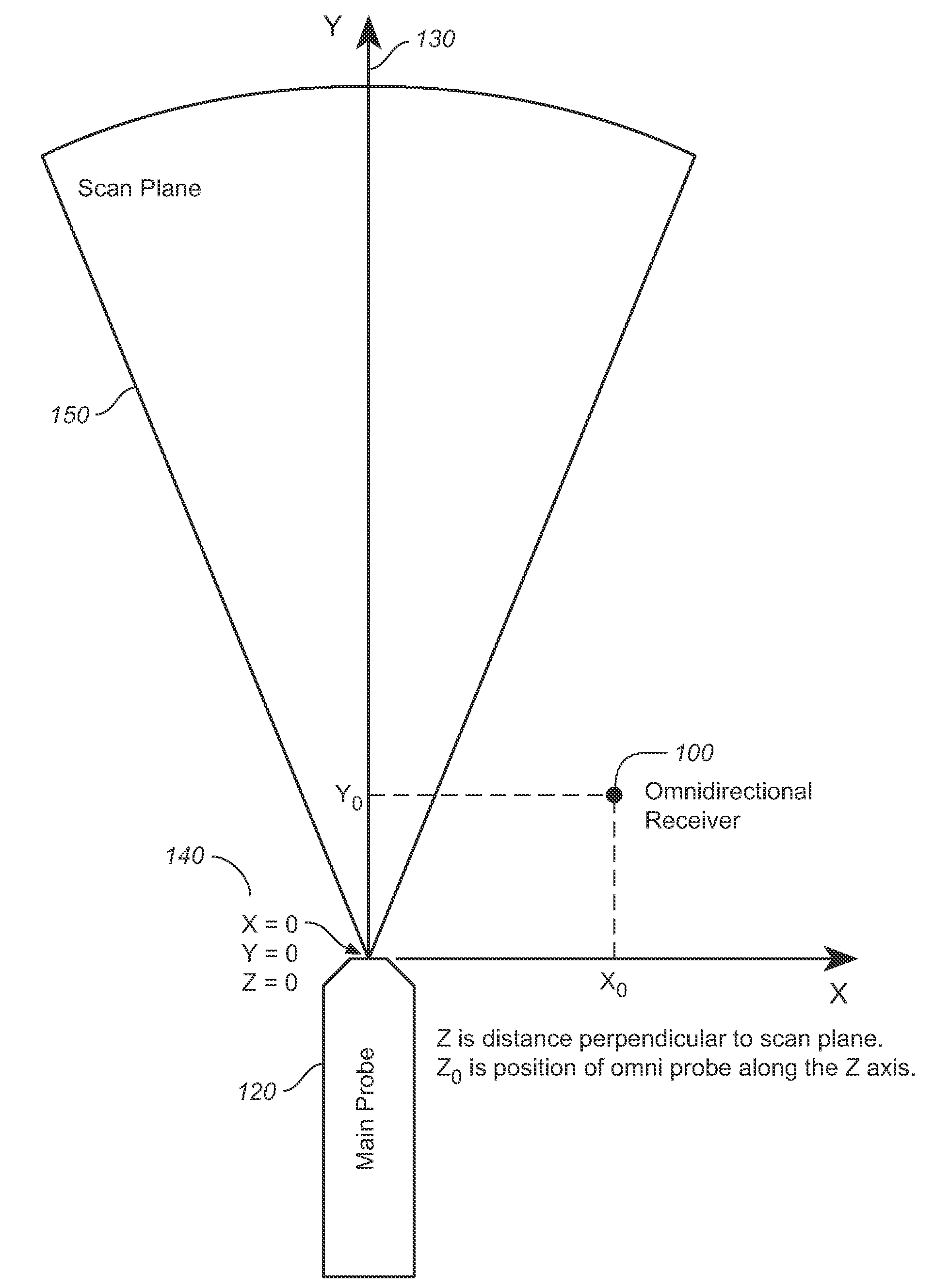
Changes in tissue stiffness have long been associated with disease. Systems and methods for determining the stiffness of tissues using ultrasonography may include a device for inducing a propagating shear wave in tissue and tracking the speed of propagation, which is directly related to tissue stiffness and density. The speed of a propagating shear wave may be detected by imaging a tissue at a high frame rate and detecting the propagating wave as a perturbance in successive image frames relative to a baseline image of the tissue in an undisturbed state. In some embodiments, sufficiently high frame rates may be achieved by using a ping-based ultrasound imaging technique in which unfocused omni-directional pings are transmitted (in an imaging plane or in a hemisphere) into a region of interest. Receiving echoes of the omnidirectional pings with multiple receive apertures allows for substantially improved lateral resolution.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Method and apparatus to visualize the coronary arteries using ultrasound
ActiveUS8105239B2Improved three dimensional imageReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisBLOOD FILLEDScreening techniques
A non-invasive screening technique for visualizing coronary arteries which overcomes the problems of visualizing the curved arteries by projecting the three dimensional volume of the arteries onto a two dimensional screen. Blood filled areas such as the coronary arteries and veins, are highlighted to contrast with other nearby tissues using non-linear classification and segmentation techniques. Data is gathered as a sequence of 2D slices stored as a 3D volume. Software interpolates voxels intermediate to the slices. Wiener filtering or LMS spatial filtering can be implemented on each 2D scan to improve lateral resolution and reduce noise prior to the use of the scan data with the classification and segmentation algorithms. A traditional handheld ultrasound probe is employed to enable the technician to locate the area of interest, but a gyroscopic stabilizer is added to minimize unwanted variation on two axes of rotation.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
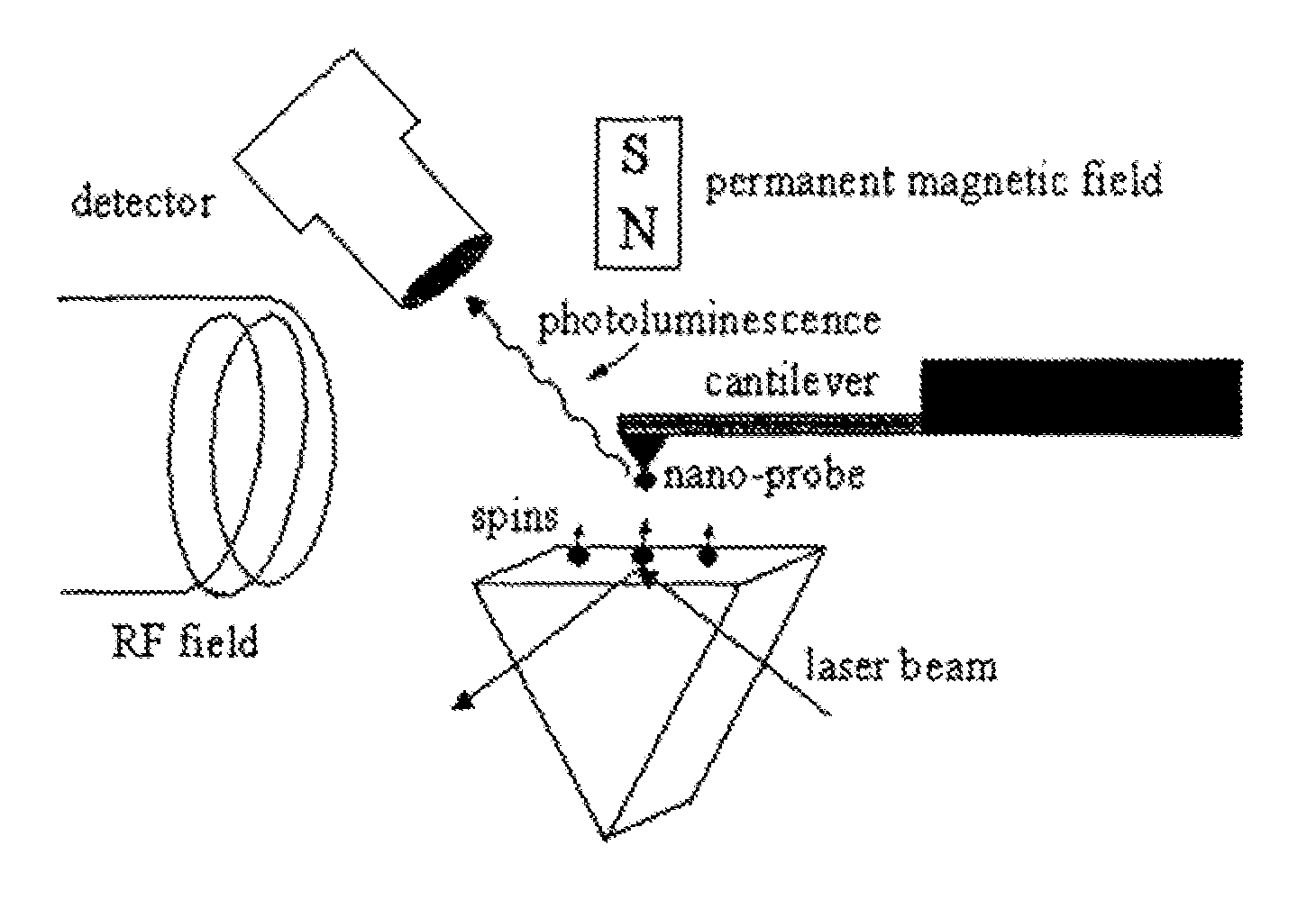
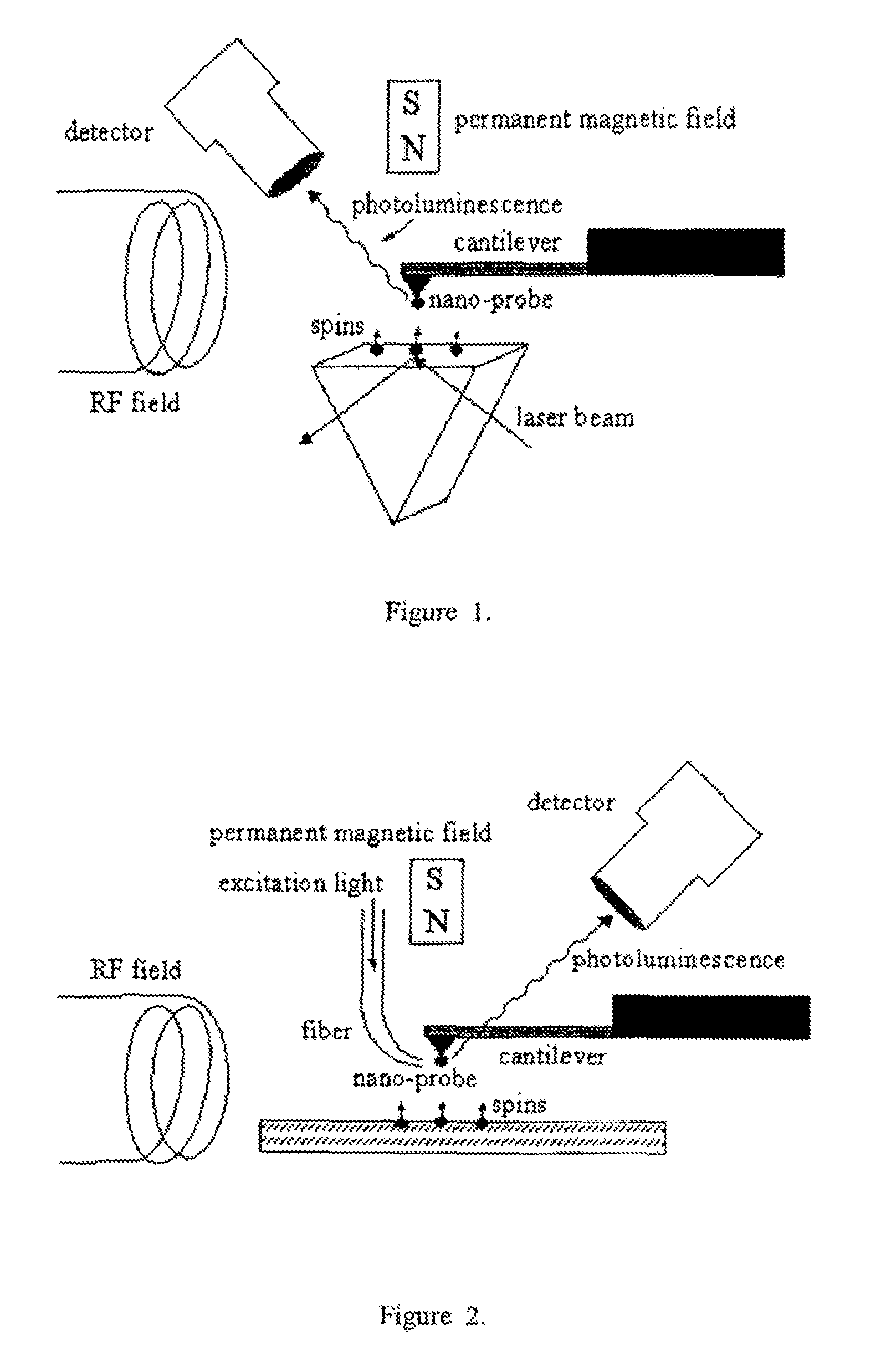
Spin microscope based on optically detected magnetic resonance
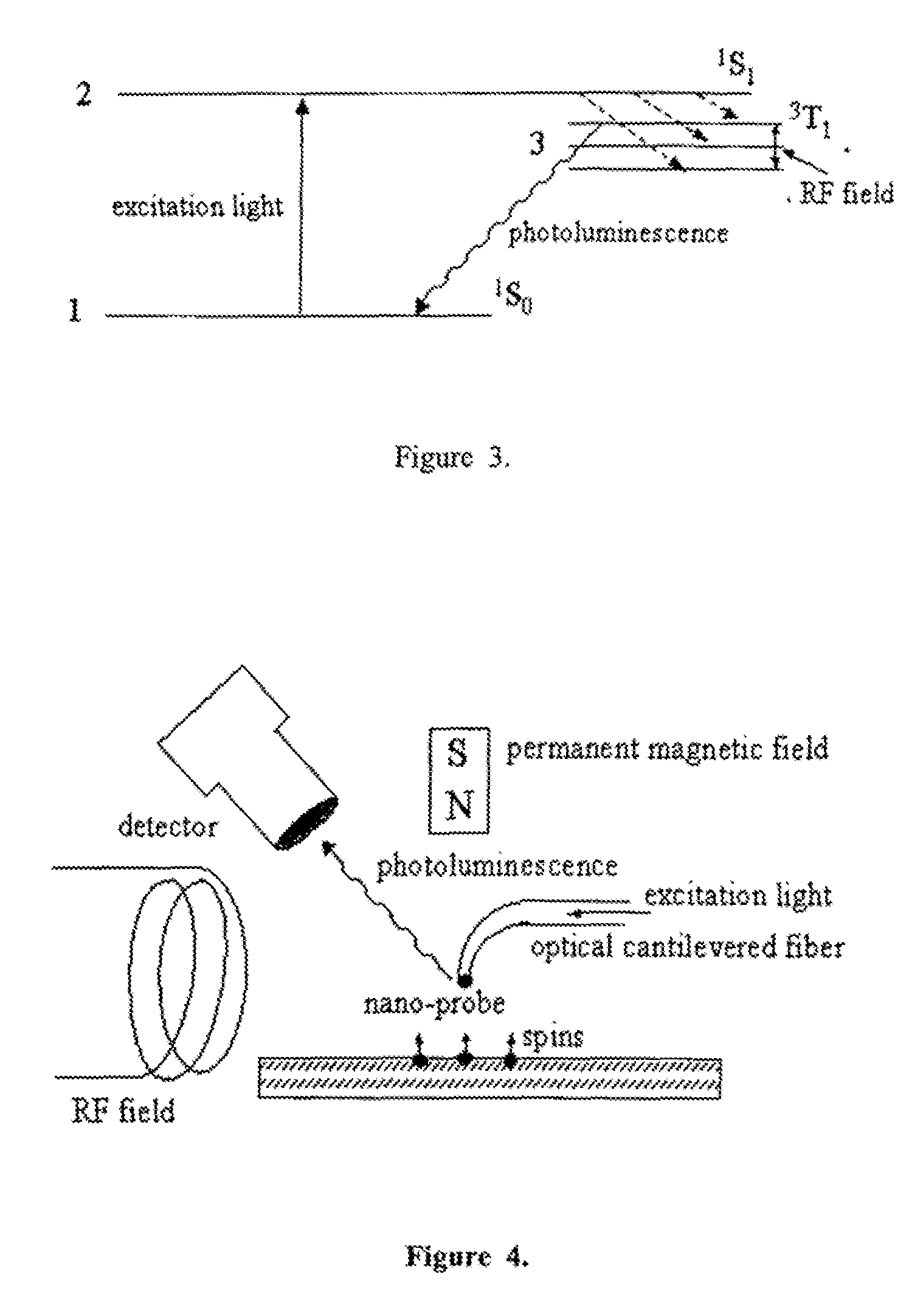
InactiveUS7608820B1NanomagnetismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic force microscopePhotoluminescence
The invention relates to scanning magnetic microscope which has a photoluminescent nanoprobe implanted in the tip apex of an atomic force microscope (AFM), a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) or a near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) and exhibits optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) in the vicinity of unpaired electron spins or nuclear magnetic moments in the sample material. The described spin microscope has demonstrated nanoscale lateral resolution and single spin sensitivity for the AFM and STM embodiments.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
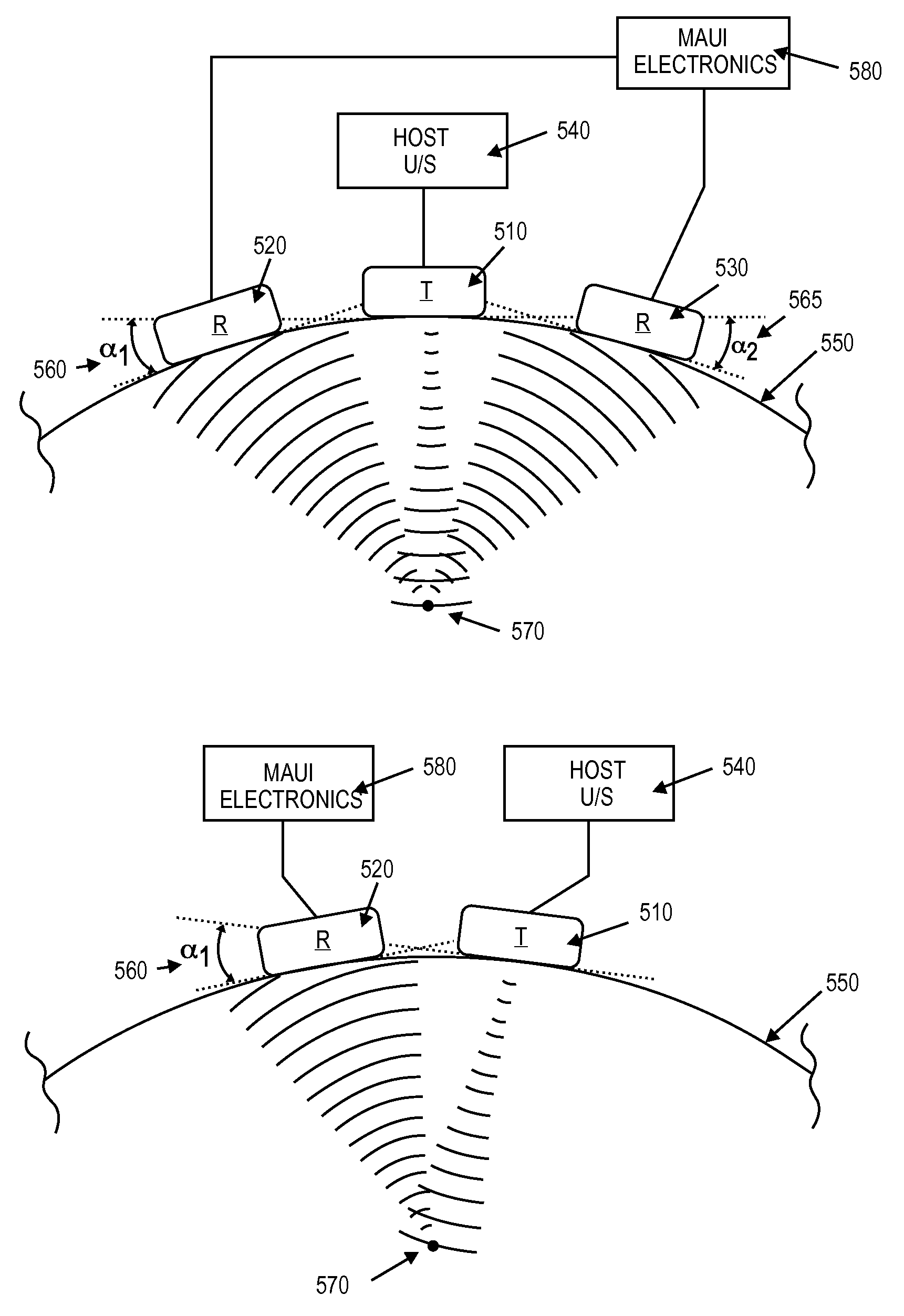
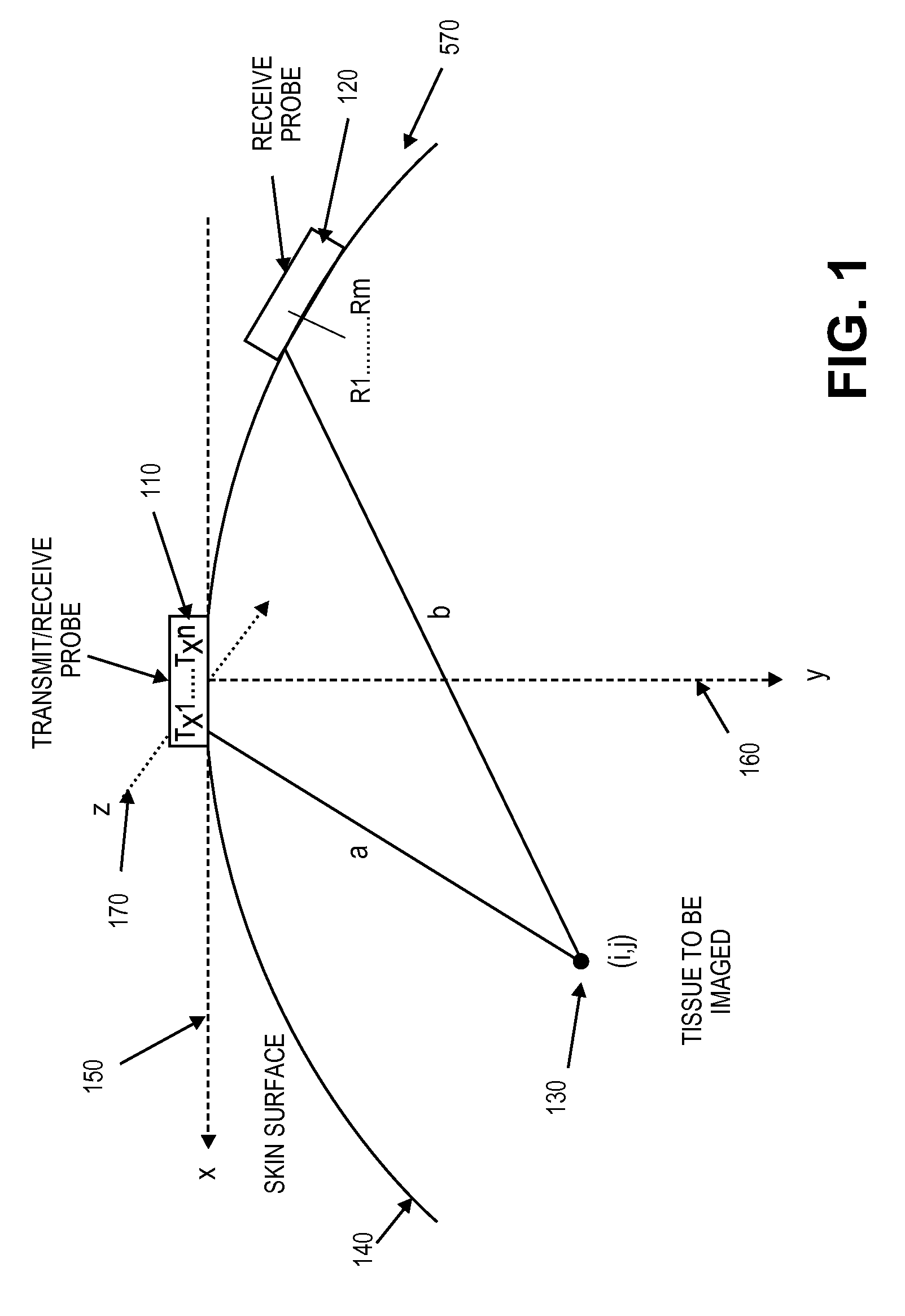
Method and apparatus to produce ultrasonic images using multiple apertures
ActiveUS8007439B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioNarrow thicknessDiagnostic probe attachmentOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationSignal-to-noise ratio
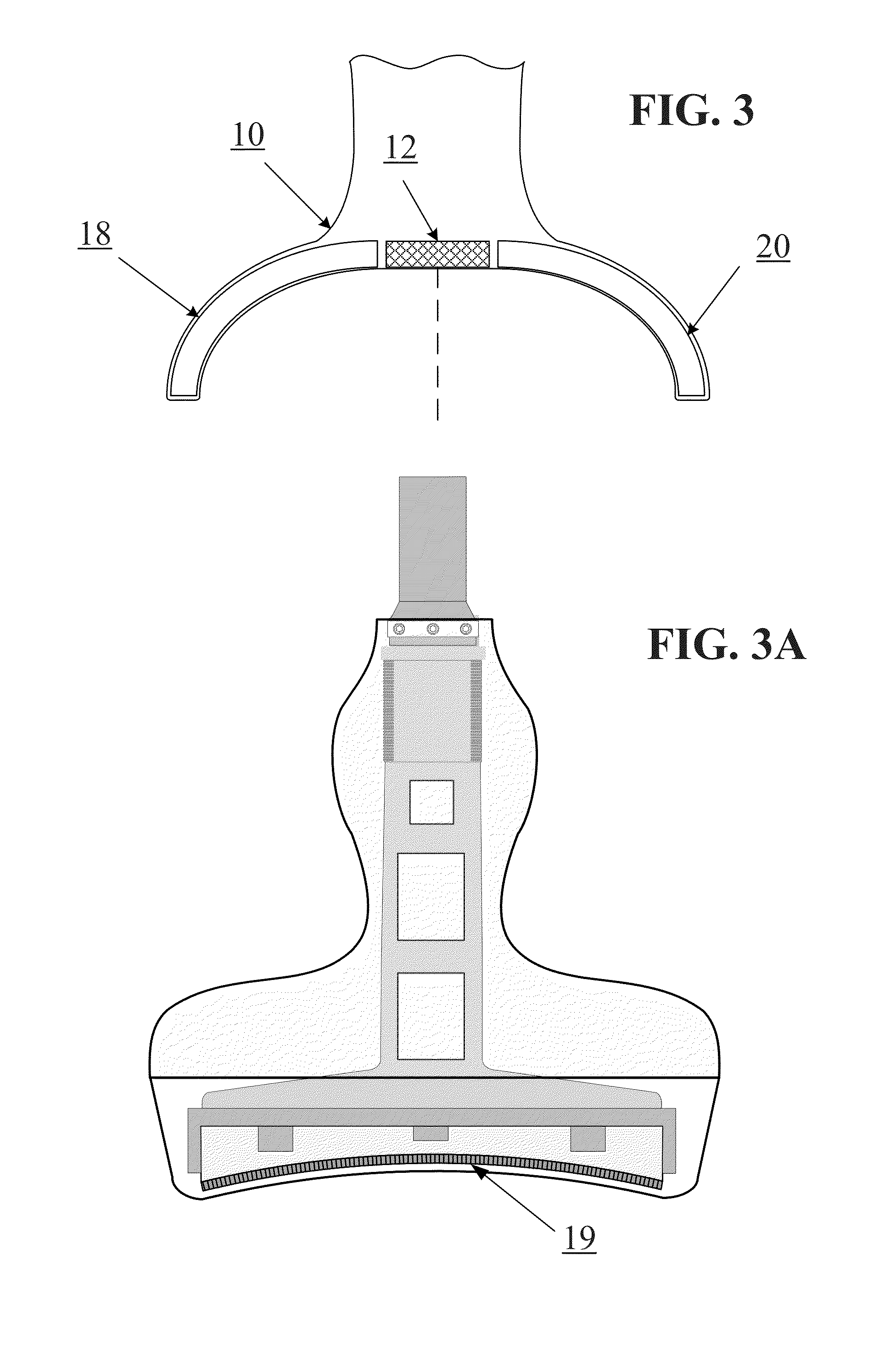
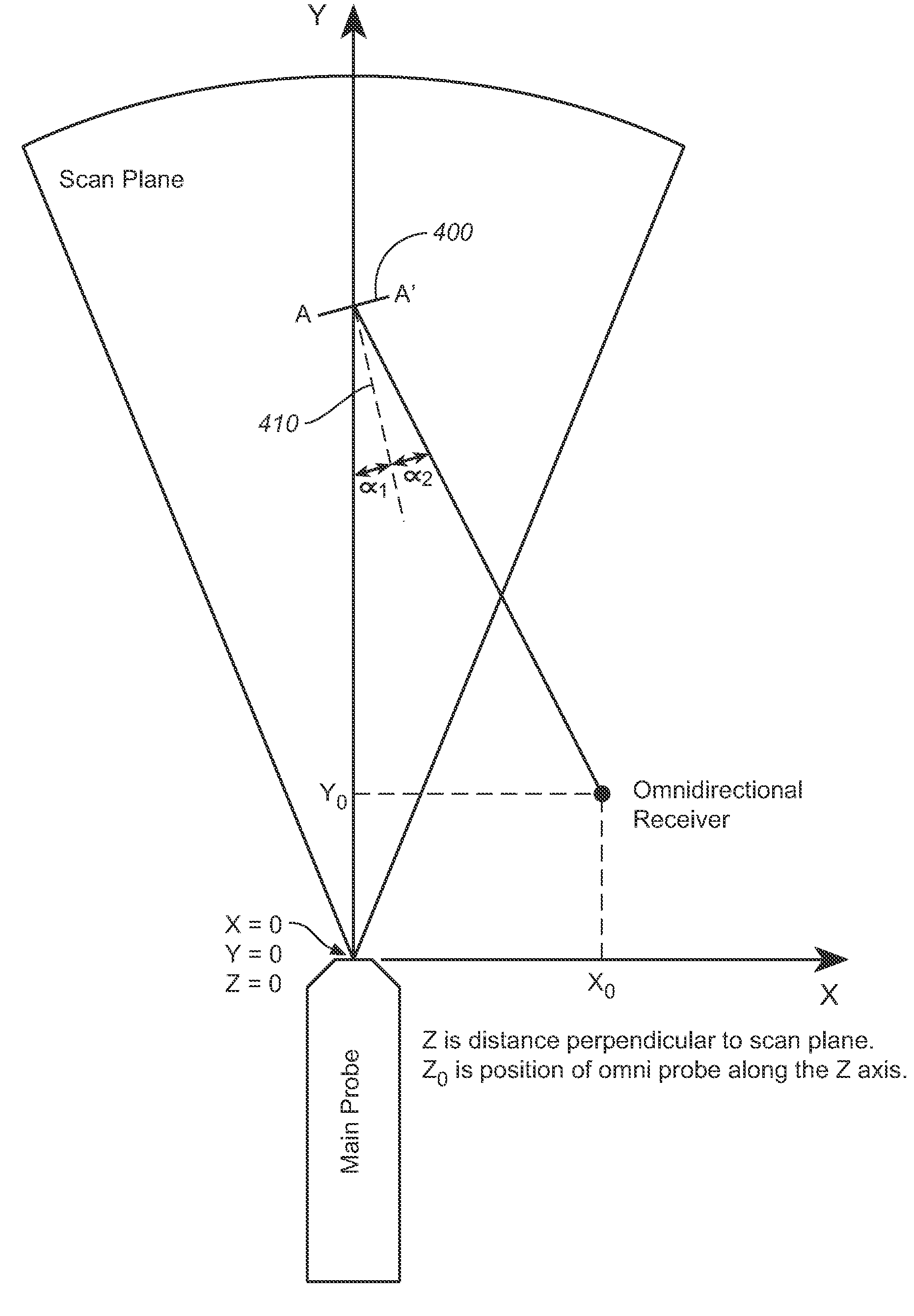
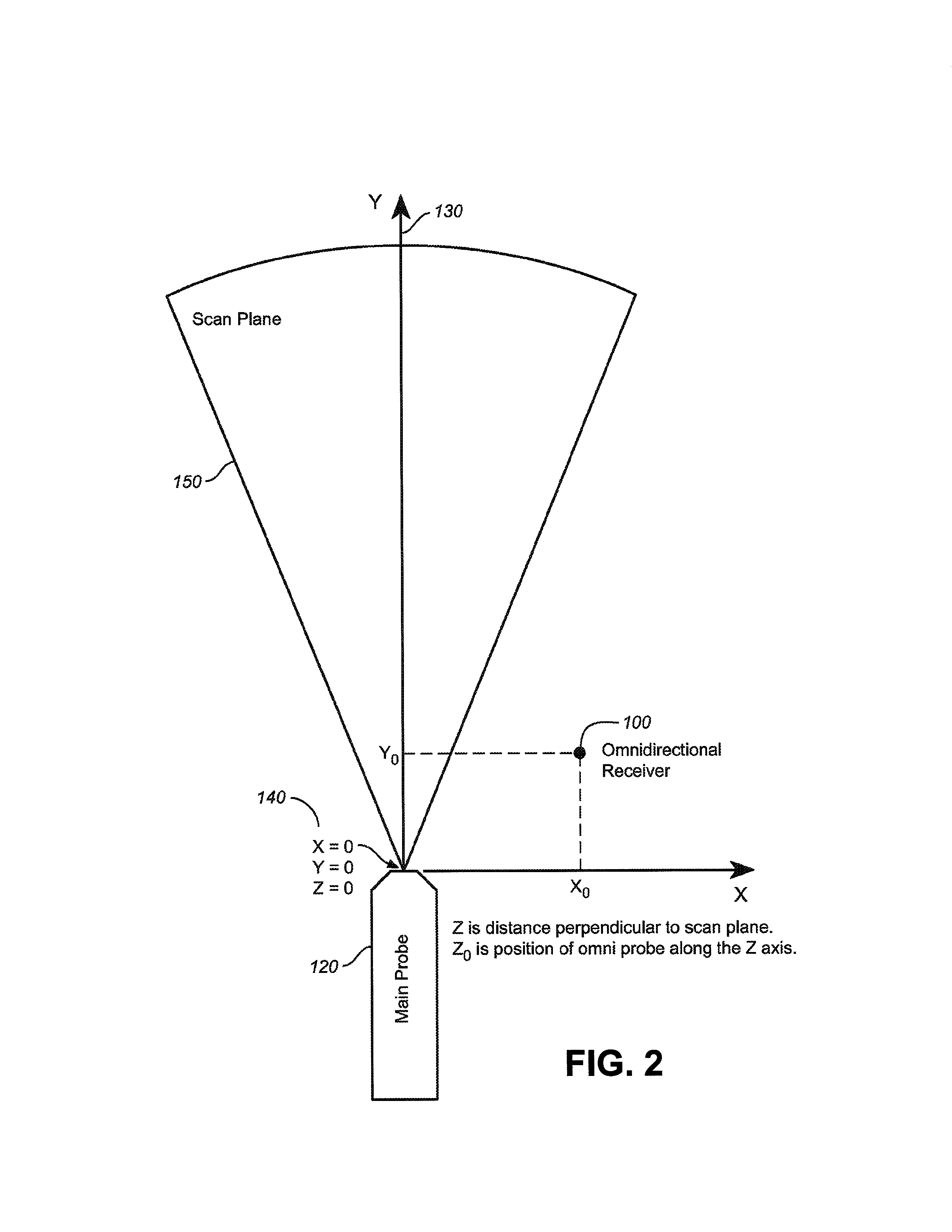
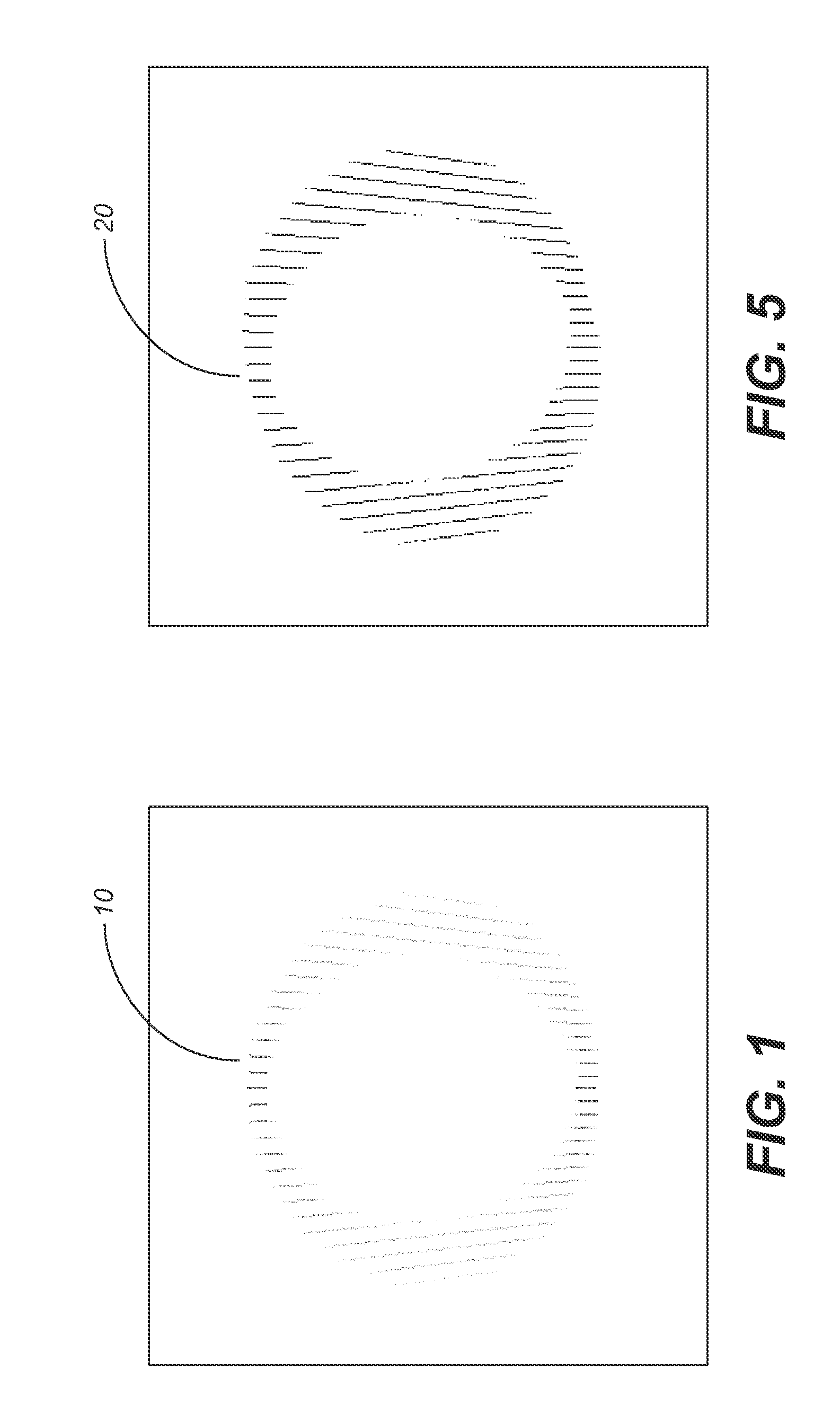
A combination of an ultrasonic scanner and an omnidirectional receive transducer for producing a two-dimensional image from the echoes received by the single omnidirectional transducer is described. Two-dimensional images with different noise components can be constructed from the echoes received by additional transducers. These can be combined to produce images with better signal to noise ratios and lateral resolution. Also disclosed is a method based on information content to compensate for the different delays for different paths through intervening tissue is described. Specular reflections are attenuated by using even a single omnidirectional receiver displaced from the insonifying probe. The disclosed techniques have broad application in medical imaging but are ideally suited to multi-aperture cardiac imaging using two or more intercostal spaces. Since lateral resolution is determined primarily by the aperture defined by the end elements, it is not necessary to fill the entire aperture with equally spaced elements. In fact, gaps can be left to accommodate spanning a patient's ribs, or simply to reduce the cost of the large aperture array. Multiple slices using these methods can be combined to form three-dimensional images.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Confocal photoacoustic microscopy with optical lateral resolution
ActiveUS8454512B2Vibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhotoacoustic microscopyElectronic systems
A confocal photoacoustic microscopy system includes a laser configured to emit a light pulse, a focusing assembly configured to receive the light pulse and to focus the light pulse into an area inside an object, an ultrasonic transducer configured to receive acoustic waves emitted by the object in response to the light pulse, and an electronic system configured to process the acoustic waves and to generate an image of the area inside the object. The focusing assembly is further configured to focus the light pulse on the object in such a way that a focal point of the focusing assembly coincides with a focal point of the at least one ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method and apparatus to produce ultrasonic images using multiple apertures
ActiveUS20080103393A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioNarrow thicknessDiagnostic probe attachmentOrgan movement/changes detectionImaging ProceduresIntercostal space
A combination of an ultrasonic scanner and an omnidirectional receive transducer for producing a two-dimensional image from the echoes received by the single omnidirectional transducer is described. Two-dimensional images with different noise components can be constructed from the echoes received by additional transducers. These can be combined to produce images with better signal to noise ratios and lateral resolution. Also disclosed is a method based on information content to compensate for the different delays for different paths through intervening tissue is described. Specular reflections are attenuated by using even a single omnidirectional receiver displaced from the insonifying probe. The disclosed techniques have broad application in medical imaging but are ideally suited to multi-aperture cardiac imaging using two or more intercostal spaces. Since lateral resolution is determined primarily by the aperture defined by the end elements, it is not necessary to fill the entire aperture with equally spaced elements. In fact, gaps can be left to accommodate spanning a patient's ribs, or simply to reduce the cost of the large aperture array. Multiple slices using these methods can be combined to form three-dimensional images.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
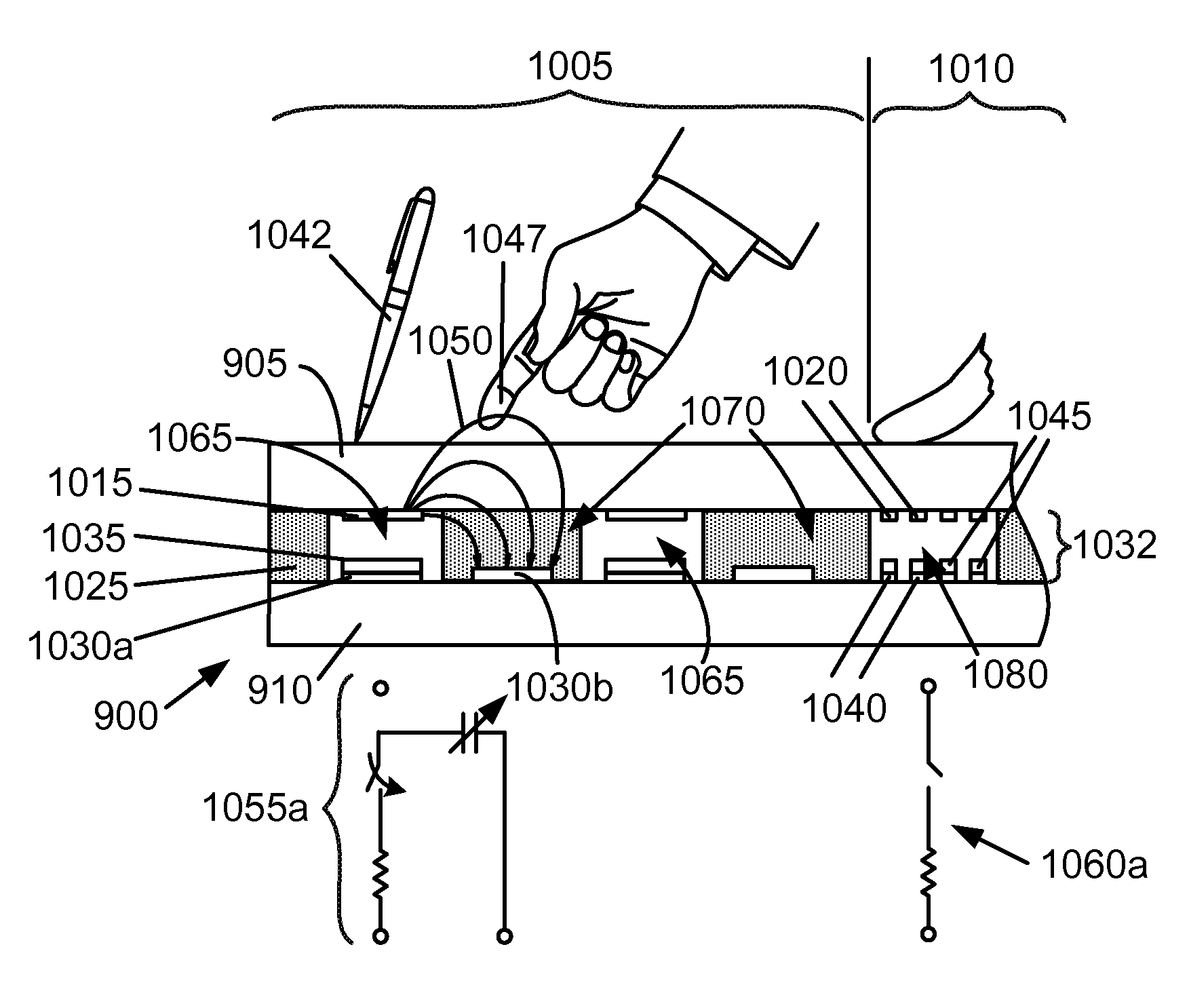
Touch, handwriting and fingerprint sensor with elastomeric spacer layer
Use of a compliant, elastomeric layer between upper and lower substrates of the combination sensor can increase the sensitivity to applied pressure or force from a stylus, while increasing the lateral resolution for a given sensel pitch. The elastomeric material may have an index of refraction that is substantially similar to that of the upper and lower substrates. The elastomeric material may include open regions for the inclusion of force-sensitive resistors. With careful selection of the elastomeric and FSR materials, the loss of transmissivity that can accompany air gaps can be minimized.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
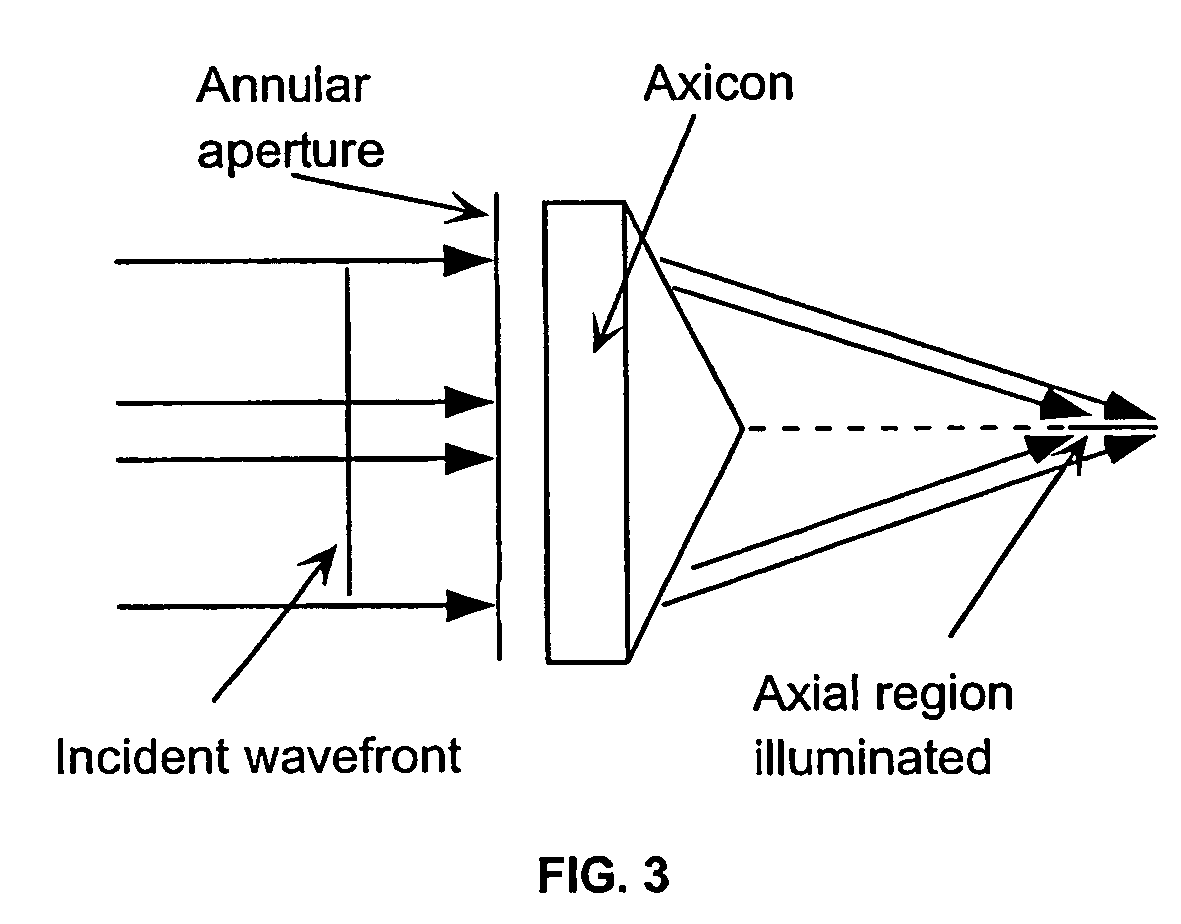
Method and system for obtaining an extended-depth-of-field volumetric image using laser scanning imaging
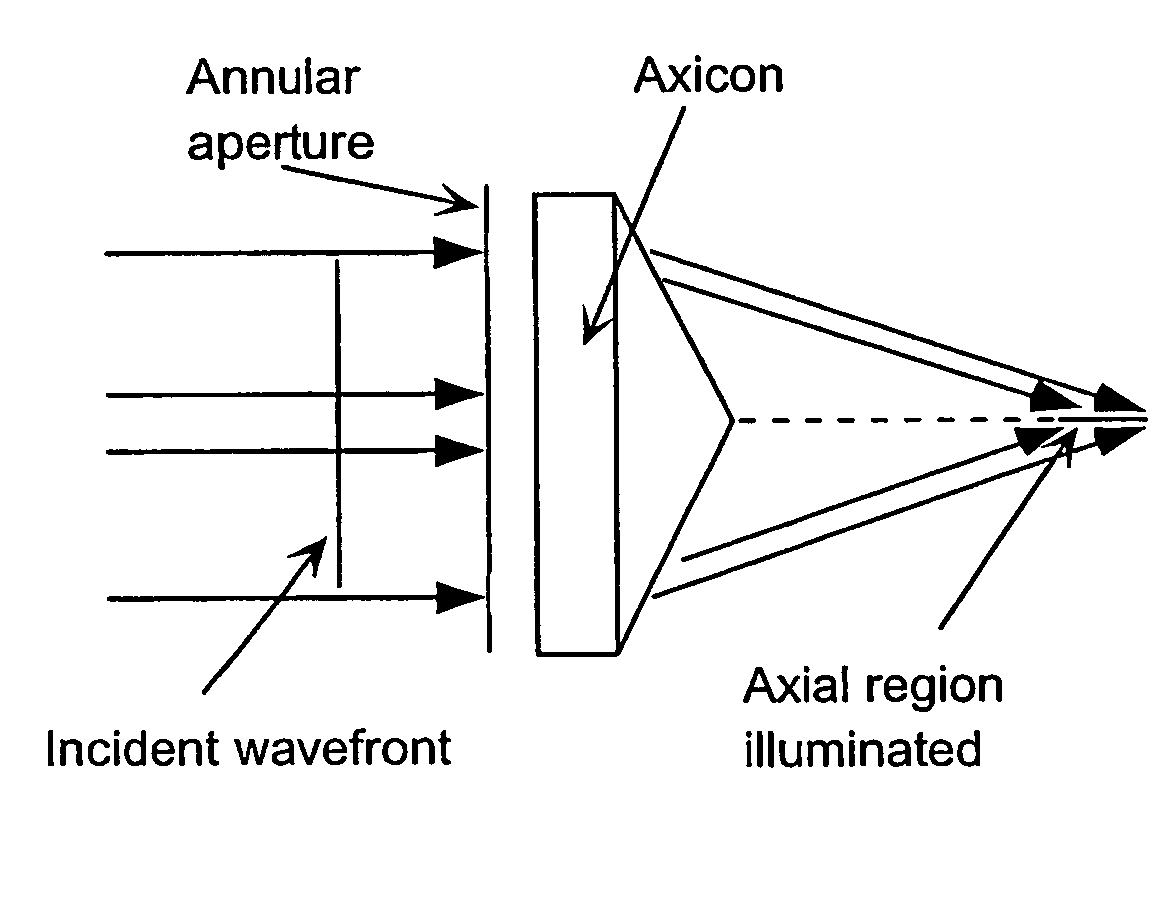
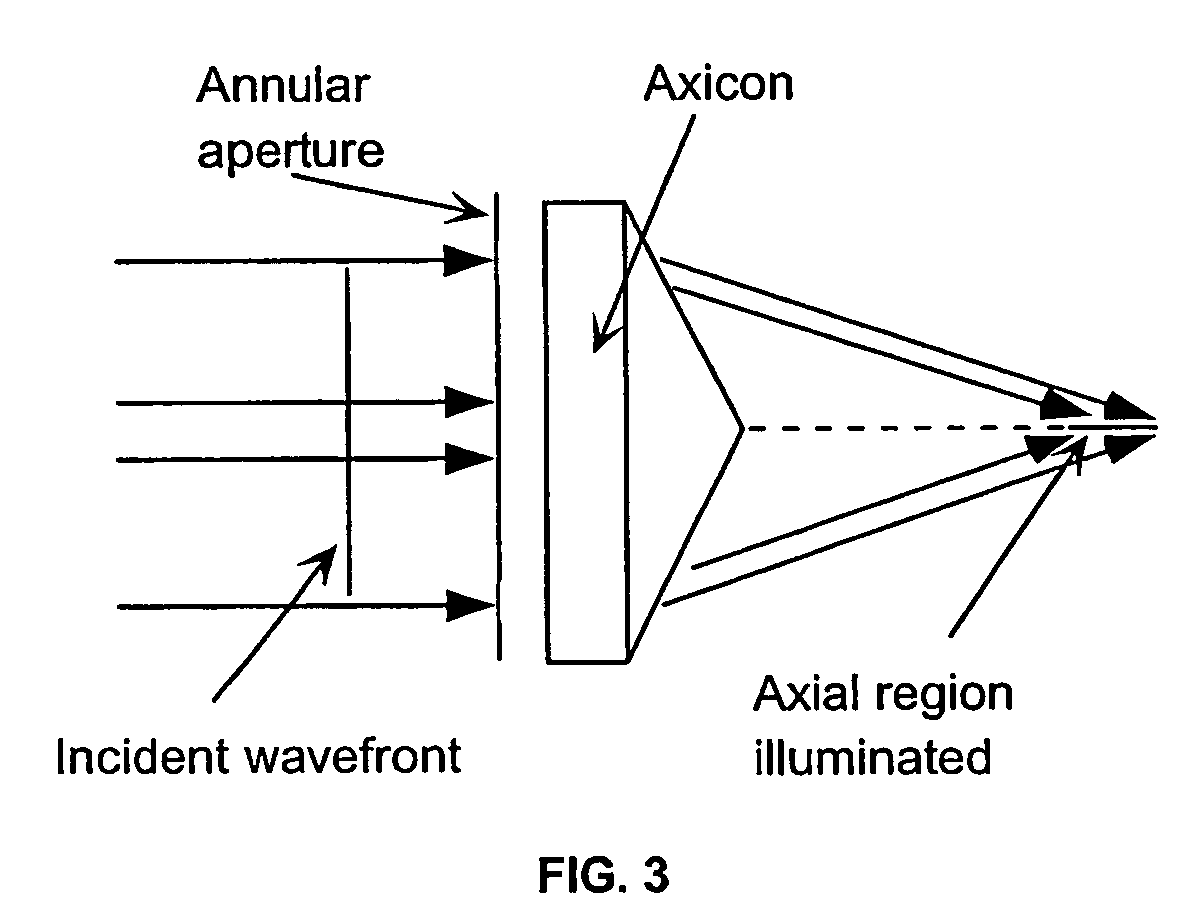
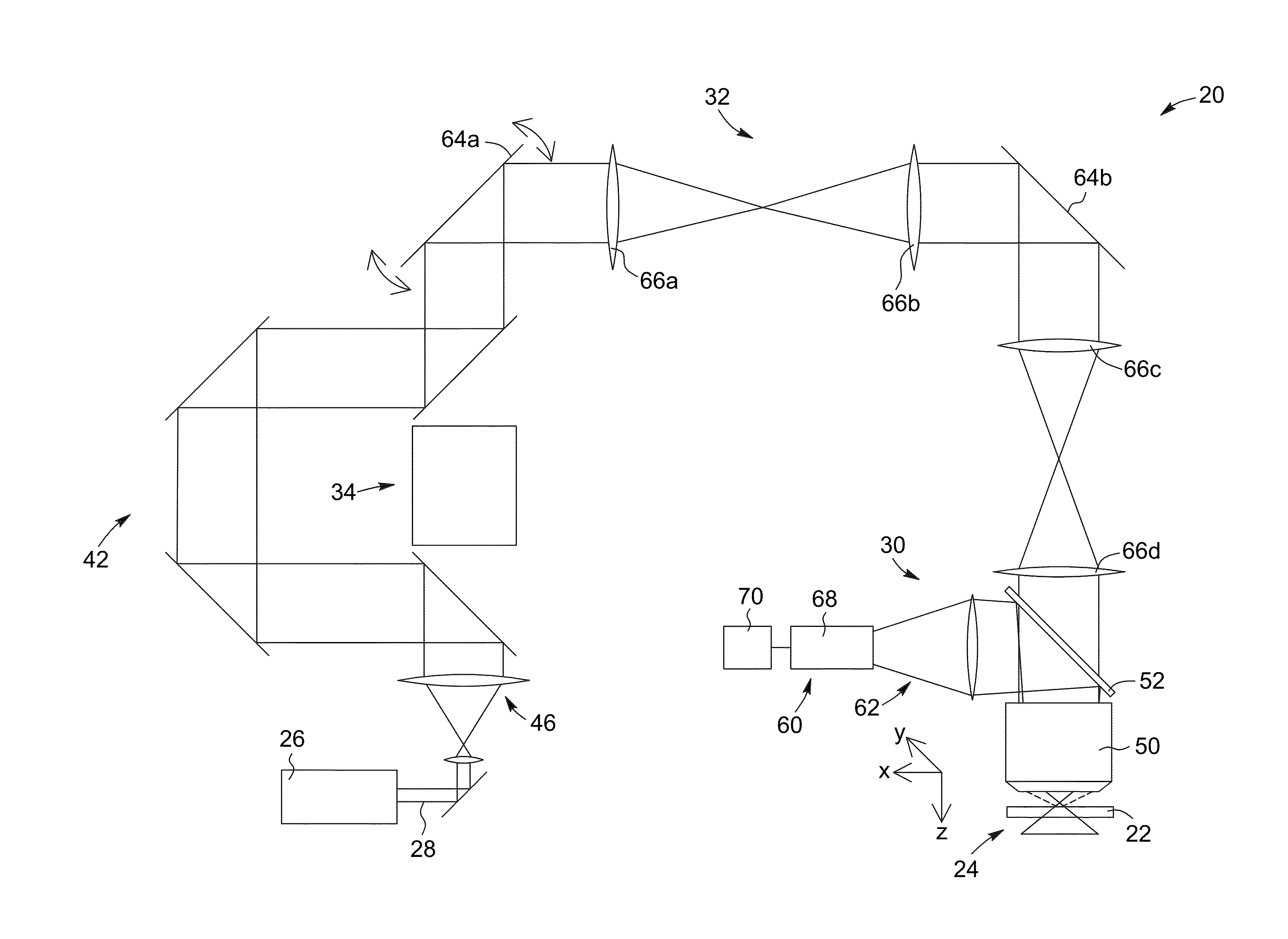
A laser scanning imaging system and method for obtaining an extended-depth-of-field image of a volume of a sample are provided. The system includes a laser module generating an input laser beam, a beam shaping module including an axicon and a Fourier-transform lens, and an imaging module including an objective lens and a detecting assembly. The axicon, Fourier-transform lens and objective lens are formed and disposed to successively convert the input laser beam into an intermediate non-diffracting beam, an intermediate annular beam, and an excitation non-diffracting beam. The excitation beam is projected onto the sample and has a depth of field and transverse resolution together defining a three-dimensional excitation region. The detecting assembly collects electromagnetic radiation from the excitation region to obtain one pixel of the extended-depth-of-field image. The system further includes a two-dimensional scanning module for scanning the excitation beam over the sample and build, pixel-by-pixel, the extended-depth-of-field image.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
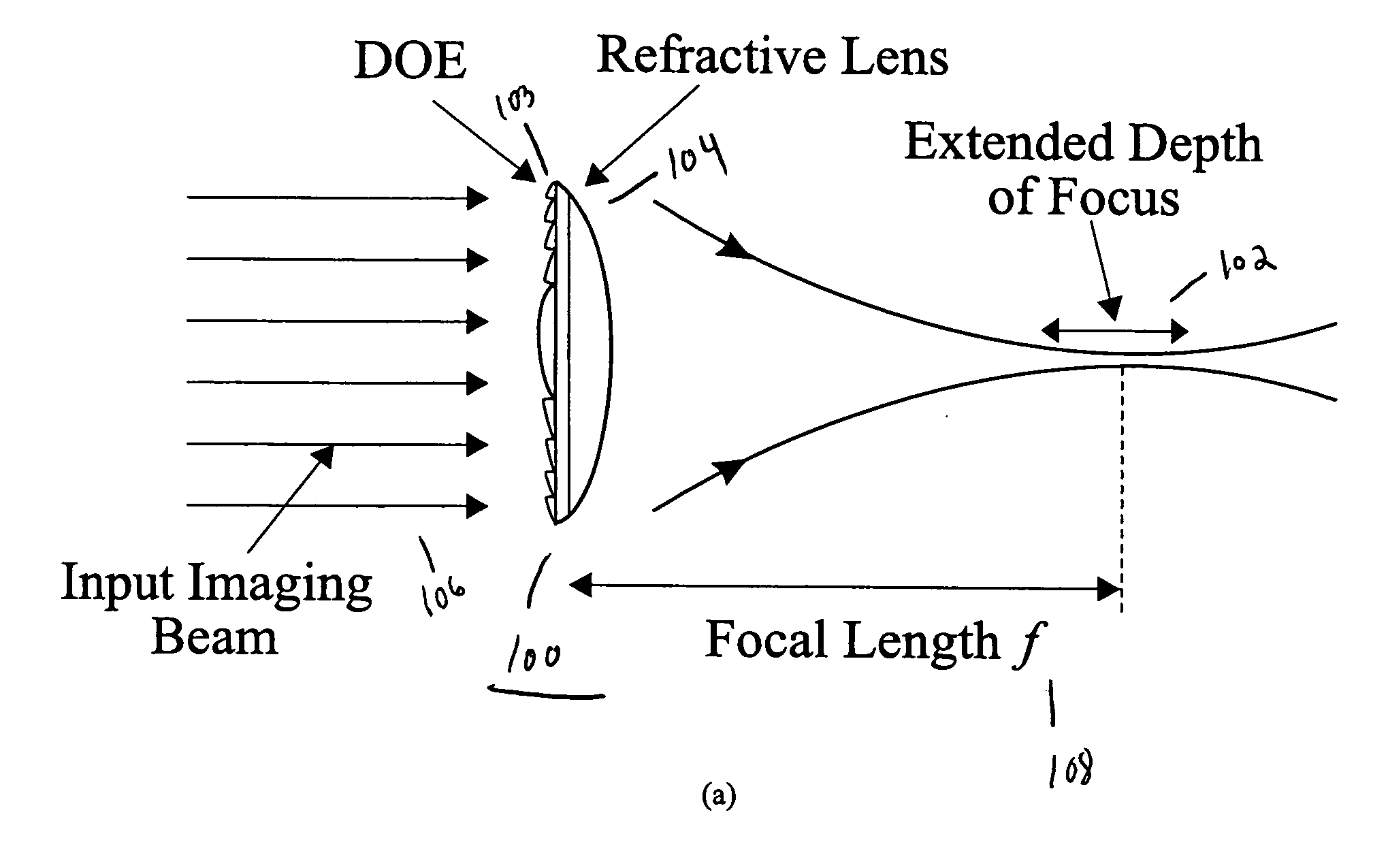
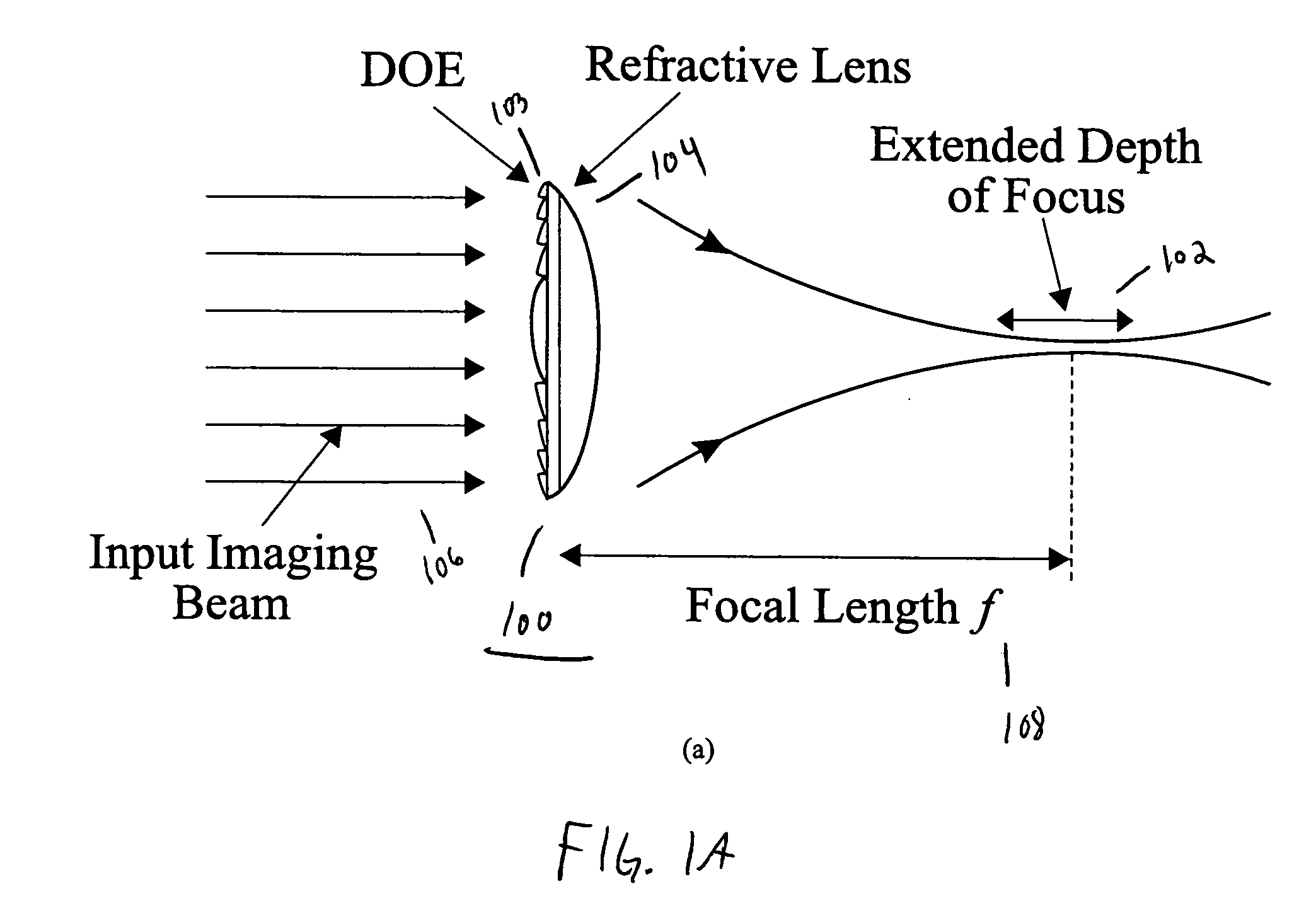
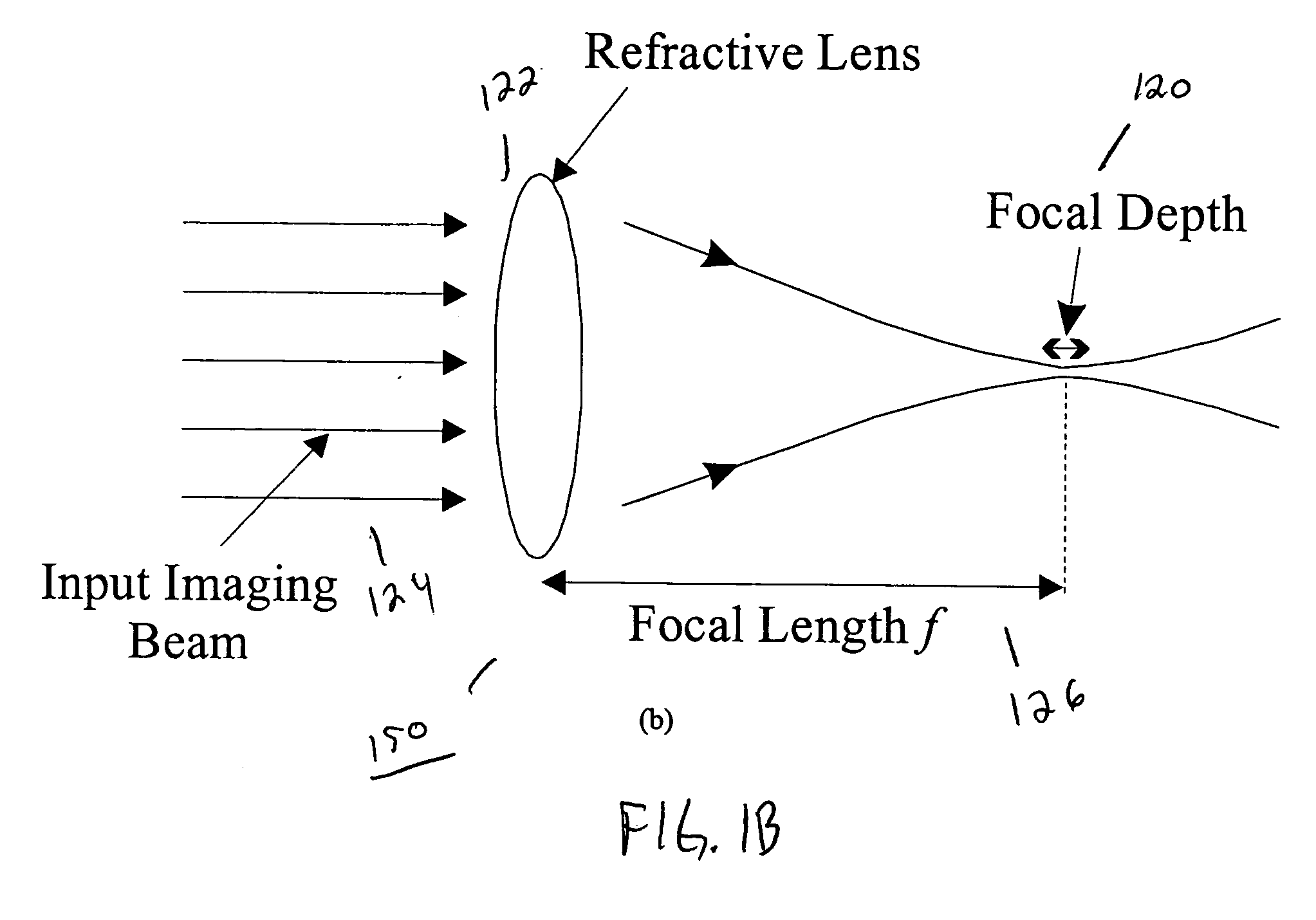
Achromatic imaging lens with extended depth of focus
InactiveUS20060082882A1Reduce overall chromatic aberrationIncrease depth of focusDiffraction gratingsMountingsImage resolutionOptoelectronics
A lens includes a diffractive surface having an etched structure and a refractive surface having a curved structure. The lens reduces chromatic aberration of incident light and extends depth of focus. In one alternative, the etched structure is a calculated phase pattern or a pattern that is embossed or diamond tuned. In another alternative, the curved structure is convex shaped or concave shaped. In yet another alternative, the lens is an imaging lens wherein high lateral resolution of incident light is preserved.
Owner:NEW SPAN OPTO TECH
Endoscopic imaging system in bulk optics biopsy spectral coverage OCT
InactiveCN101032390ASolve the problem that dynamic focus cannot be used to ensure lateral resolutionQuality of reliefEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringBeam splitterPrism
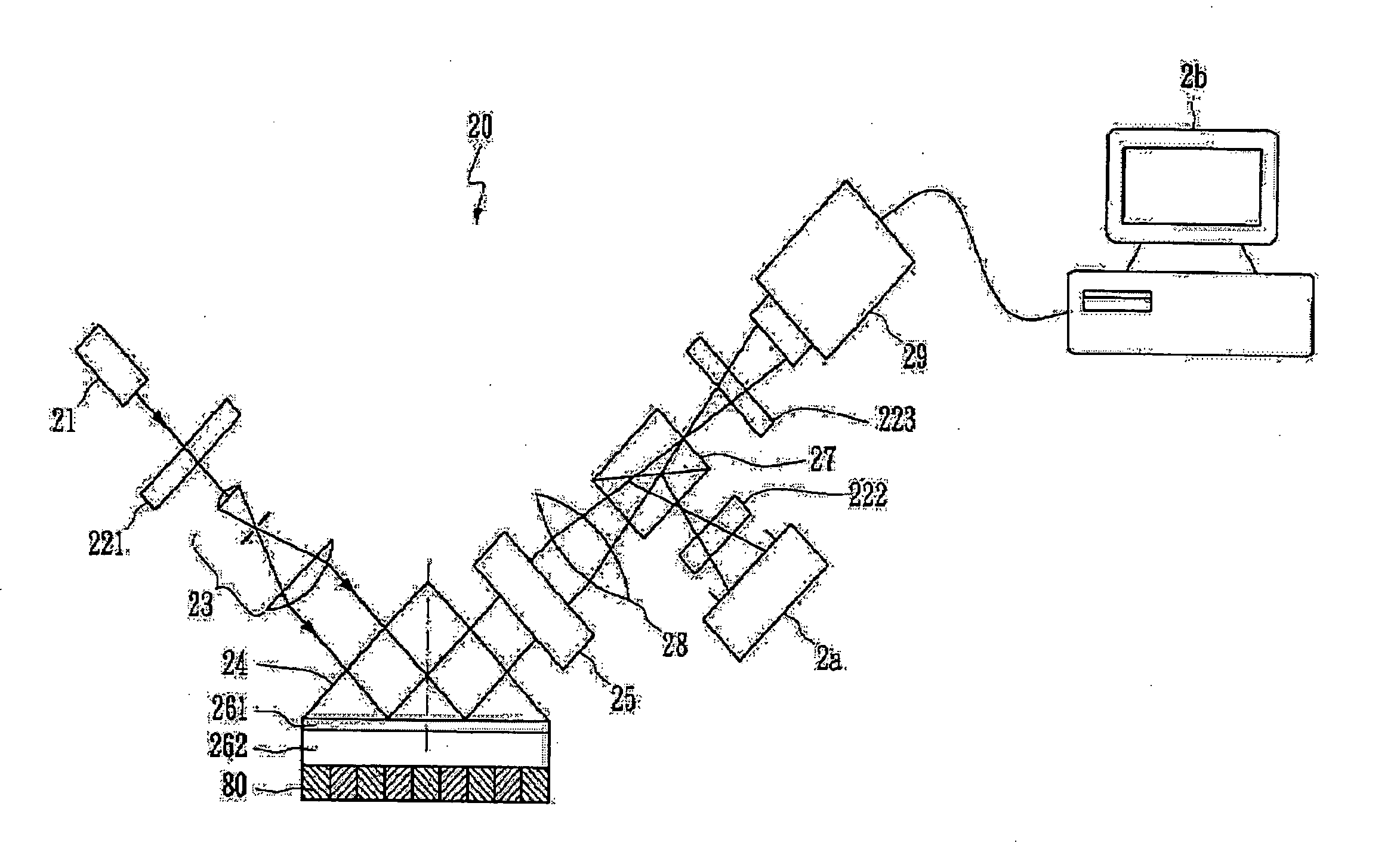
The present invention discloses one kind of spectral-domain optical coherent tomography endoscopic image system for in vivo optical biopsy, and the system includes one fiber optical interferometer, one imaging probe, one detection unit, one image acquiring card and one computer. The detection unit has grating spectrograph for high imaging speed, and the imaging probe has axial axicon lens and inside rotating right angle prism or circularly symmetric beam splitter combined to ensure high transverse resolution in the whole depth range, so as to realize circularly scanning endoscopic imaging. The present invention proposes two embodiments of circularly scanning probe and their corresponding system structures. The present invention may be applied in the optical endoscopic biopsy and analytic study of oral cavity, respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multiple Aperture Ultrasound Array Alignment Fixture
ActiveUS20100268503A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration apparatusUltrasound imagingUltrasonic sensor
Increasing the effective aperture of an ultrasound imaging probe by including more than one probe head and using the elements of all of the probes to render an image can greatly improve the lateral resolution of the generated image. In order to render an image, the relative positions of all of the elements must be known precisely. A calibration fixture is described in which the probe assembly to be calibrated is placed above a test block and transmits ultrasonic pulses through the test block to an ultrasonic sensor. As the ultrasonic pulses are transmitted though some or all of the elements in the probe to be tested, the differential transit times of arrival of the waveform are measured precisely. From these measurements the relative positions of the probe elements can be computed and the probe can be aligned.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
High resolution 3-d spectral domain optical imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160345820A1Improved high resolution optical imageProvide usageReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayDepth of field
Methods and apparatus are presented for obtaining high-resolution 3-D images of a sample over a range of wavelengths, optionally with polarisation-sensitive detection. In preferred embodiments a spectral domain OCT apparatus is used to sample the complex field of light reflected or scattered from a sample, providing full range imaging. In certain embodiments structured illumination is utilised to provide enhanced lateral resolution. In certain embodiments the resolution or depth of field of images is enhanced by digital refocusing or digital correction of aberrations in the sample. Individual sample volumes are imaged using single shot techniques, and larger volumes can be imaged by stitching together images of adjacent volumes. In preferred embodiments a 2-D lenslet array is used to sample the reflected or scattered light in the Fourier plane or the image plane, with the lenslet array suitably angled with respect to the dispersive axis of a wavelength dispersive element such that the resulting beamlets are dispersed onto unique sets of pixels of a 2-D sensor array.
Owner:CYLITE
Multiple aperture ultrasound array alignment fixture
ActiveUS8473239B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting/calibration apparatusUltrasound imagingSonification
Increasing the effective aperture of an ultrasound imaging probe by including more than one probe head and using the elements of all of the probes to render an image can greatly improve the lateral resolution of the generated image. In order to render an image, the relative positions of all of the elements must be known precisely. A calibration fixture is described in which the probe assembly to be calibrated is placed above a test block and transmits ultrasonic pulses through the test block to an ultrasonic sensor. As the ultrasonic pulses are transmitted though some or all of the elements in the probe to be tested, the differential transit times of arrival of the waveform are measured precisely. From these measurements the relative positions of the probe elements can be computed and the probe can be aligned.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
System and method for Hilbert phase imaging
ActiveUS20060291712A1Enable quantificationSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological cellImage resolution
Hilbert phase microscopy (HPM) as an optical technique for measuring high transverse resolution quantitative phase images associated with optically transparent objects. Due to its single-shot nature, HPM is suitable for investigating rapid phenomena that take place in transparent structures such as biological cells. A preferred embodiment is used for measuring biological systems including measurements on red blood cells, while its ability to quantify dynamic processes on the millisecond scale, for example, can be illustrated with measurements on evaporating micron-size water droplets.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Surface plasmon resonance microscope using common-path phase-shift interferometry
InactiveUS20060119859A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsRefractive indexPhase shift interferometry
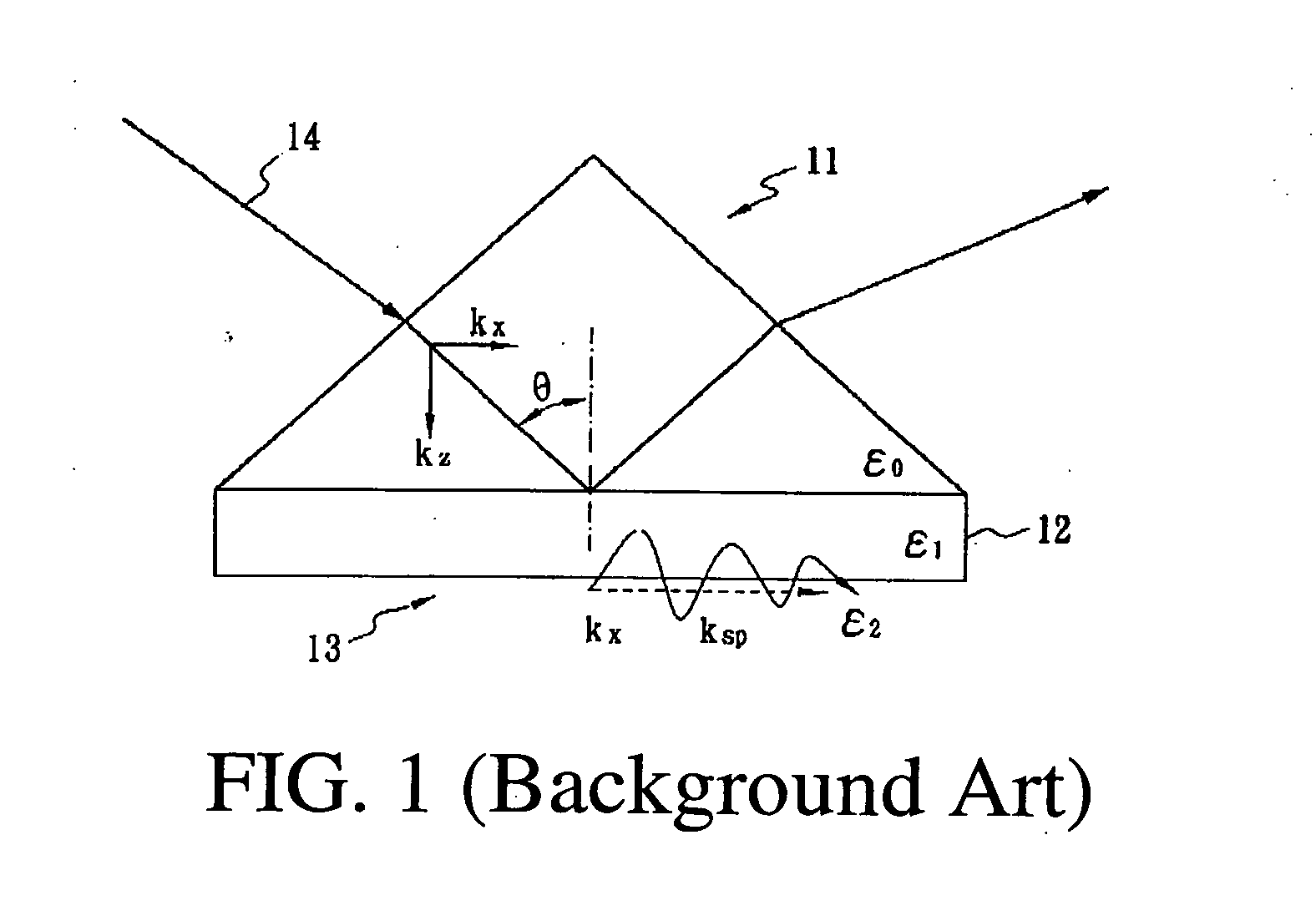
The present invention integrates the surface plasmon resonance and common-path phase-shift interferometry techniques to develop a microscope for measuring the two-dimensional spatial phase variation caused by biomolecular interactions on a sensing chip without the need for additional labeling. The common-path phase-shift interferometry technique has the advantage of long-term stability, even when subjected to external disturbances. Hence, the developed microscope meets the requirements of the real-time kinetic studies involved in biomolecular interaction analysis. The surface plasmon resonance microscope of the present invention using common-path phase-shift interferometry demonstrates a detection limit of 2×10−7 refractive index change, a long-term phase stability of 2.5×10−4π rms over four hours, and a spatial phase resolution of 10−3 π with a lateral resolution of 100 μm.
Owner:PHALANX BIOTECH GROUP
Method and apparatus for x-ray microscopy
ActiveUS20170261442A1Large pixel sizeImprove detection efficiencyImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-rayNanoscopic scale
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray microscopy using an array of micro-beams having a micro- or nano-scale beam intensity profile to provide selective illumination of micro- or nano-scale regions of an object. An array detector is positioned such that each pixel of the detector only detects x-rays corresponding to a single micro- or nano-beam. This allows the signal arising from each x-ray detector pixel to be identified with the specific, limited micro- or nano-scale region illuminated, allowing sampled transmission image of the object at a micro- or nano-scale to be generated while using a detector with pixels having a larger size and scale. Detectors with higher quantum efficiency may therefore be used, since the lateral resolution is provided solely by the dimensions of the micro- or nano-beams. The micro- or nano-scale beams may be generated using an arrayed x-ray source or a set of Talbot interference fringes.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Method and device for observing photoacoustic imaging in single-array element and multi-angle mode based on compressive sensing
ActiveCN102068277ALow costReduce acquisition timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringArray elementField-programmable gate array
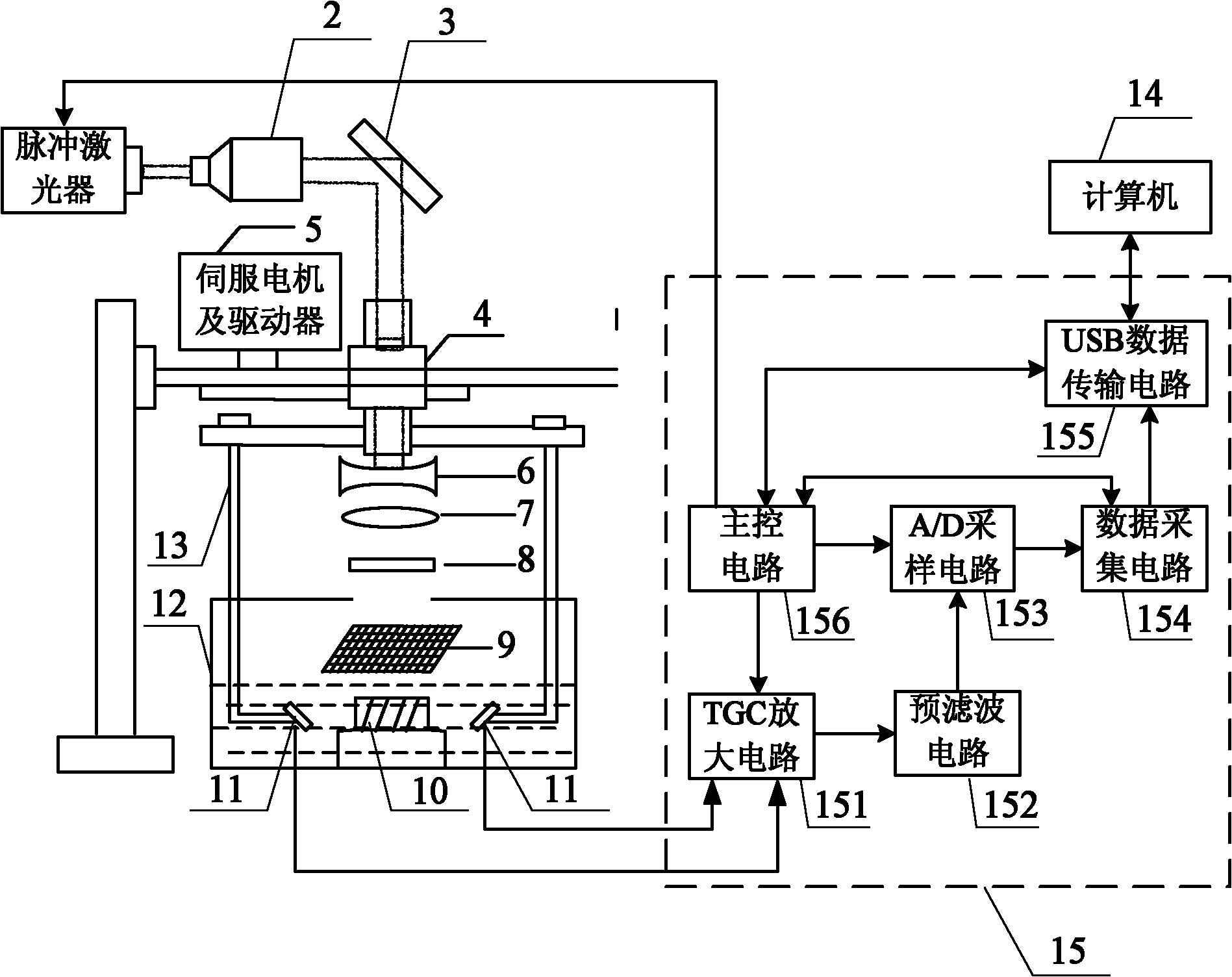
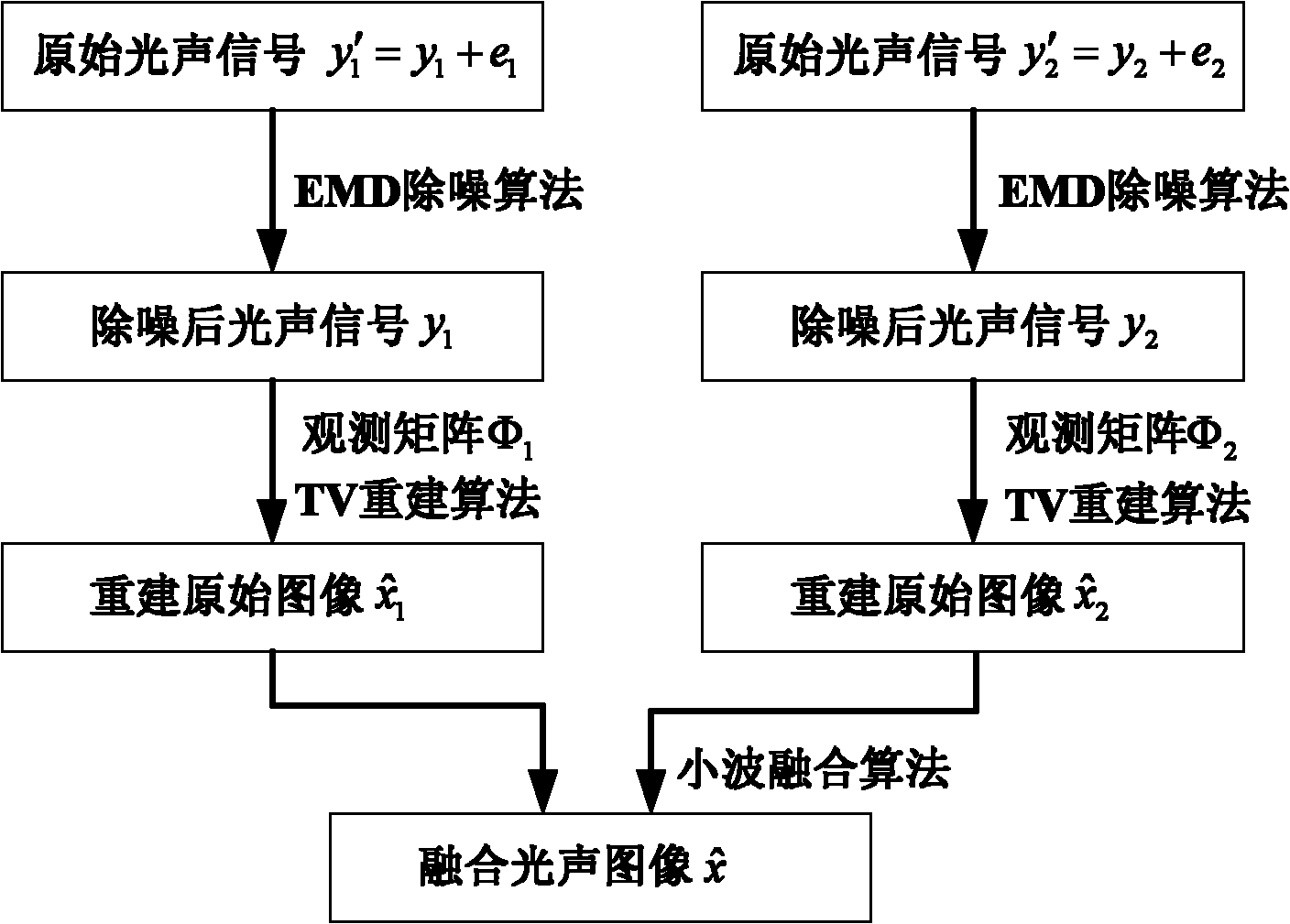
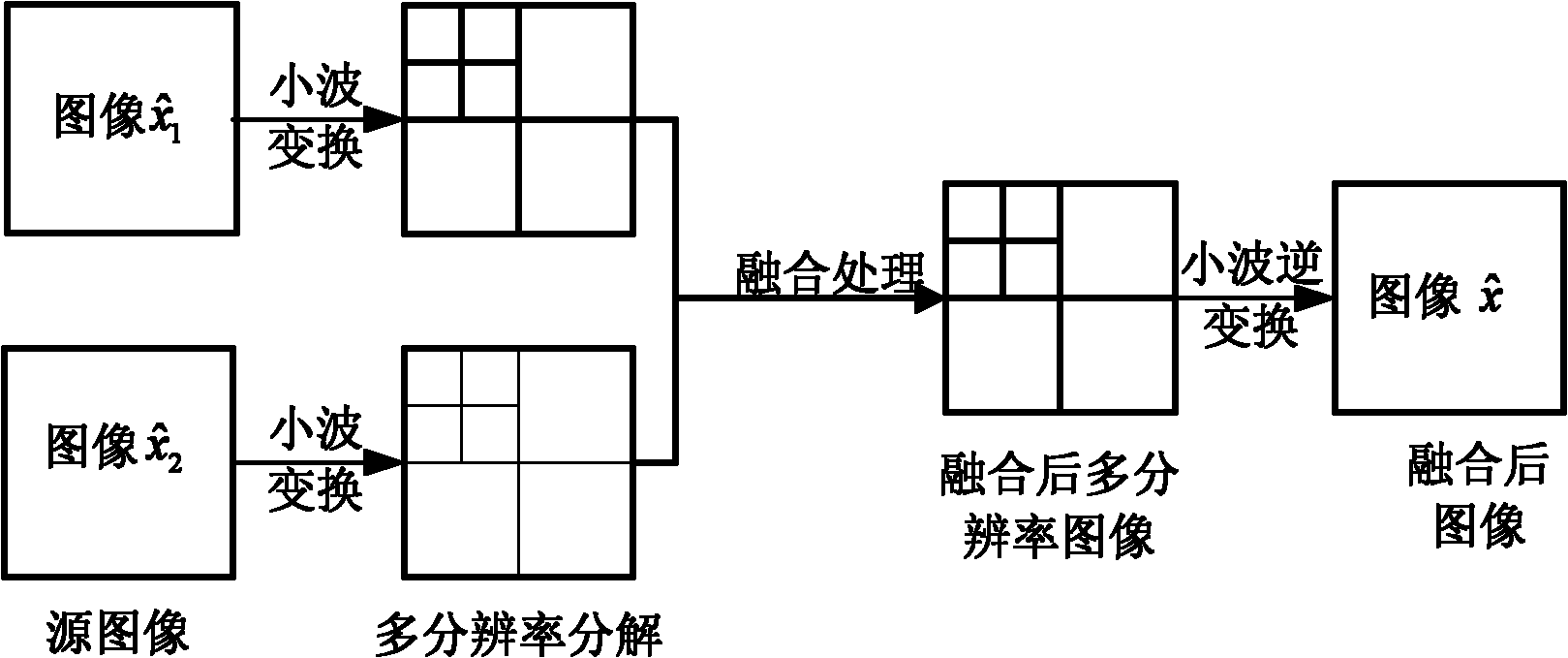
The invention relates to a method and device for observing photoacoustic imaging in a single-array element and multi-angle mode based on compressive sensing, belonging to the technical field of photoacoustic imaging and aiming at solving the problems of serious artefact, deformed images, high hardware cost and poor lateral resolution of images in the existing photoacoustic technology for imaging biological tissues. The method comprises the following steps: leading a pulsed laser to emit pulsed laser beams, irradiating the pulsed laser beams upon the biological tissues by using an optical maskto generate photoacoustic signals, observing and acquiring the photoacoustic signals synchronously by using two angled single array element ultrasonic probes, amplifying the photoacoustic signals, sending the photoacoustic signals to an A / D (analog to digital) converter, sampling uniformly, inputting acquired photoacoustic image data into a computer by using an FPGA (field programmable gate array), and reconstructing and fusing photoacoustic images by using the computer. Due to the adoption of a hardware platform and a processing mechanism which is rapidly constructed based on the compressivesensing algorithm by using the single array element ultrasonic probes to acquire the photoacoustic signals in parallel, the high resolution of the images are ensured on the premise that the sampled data are reduced and the acquiring time is shortened. The device for imaging is easy to operate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for improving optical scanning holographic tomography effect
InactiveCN104159094ASmall viewing impactEvenly distributed noiseImage enhancementSteroscopic systemsOptical scanning holographyOptical tomography
The invention discloses a method for improving an optical scanning holographic tomography effect, and belongs to the field of optical tomography. The method can solve the defect in the conventional optical scanning technology that restored section images have louder out-of-focus noise, in real time. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing a random phase in the optics encryption technique, changing a certain pupil function in a conventional optical scanning holographic system into a stochastic phase pupil function, and equaling restore of out-of-focus layer images into decryption under the condition of mistakenly decrypting a secret key, thereby enabling the out-of-focus layer images overlaid on the restored section images to be gaussian white noise with statistical independence and greatly reducing the influence of the out-of-focus noise on the focus layer images. Meanwhile the out-of-focus noise can also be filtered through design of a gaussian filter, so that the longitudinal resolution of the system can be improved; besides, through the adoption of the method, the bandwidth of the optical transfer function is wider, and the transverse resolution of the restored section images can be higher.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
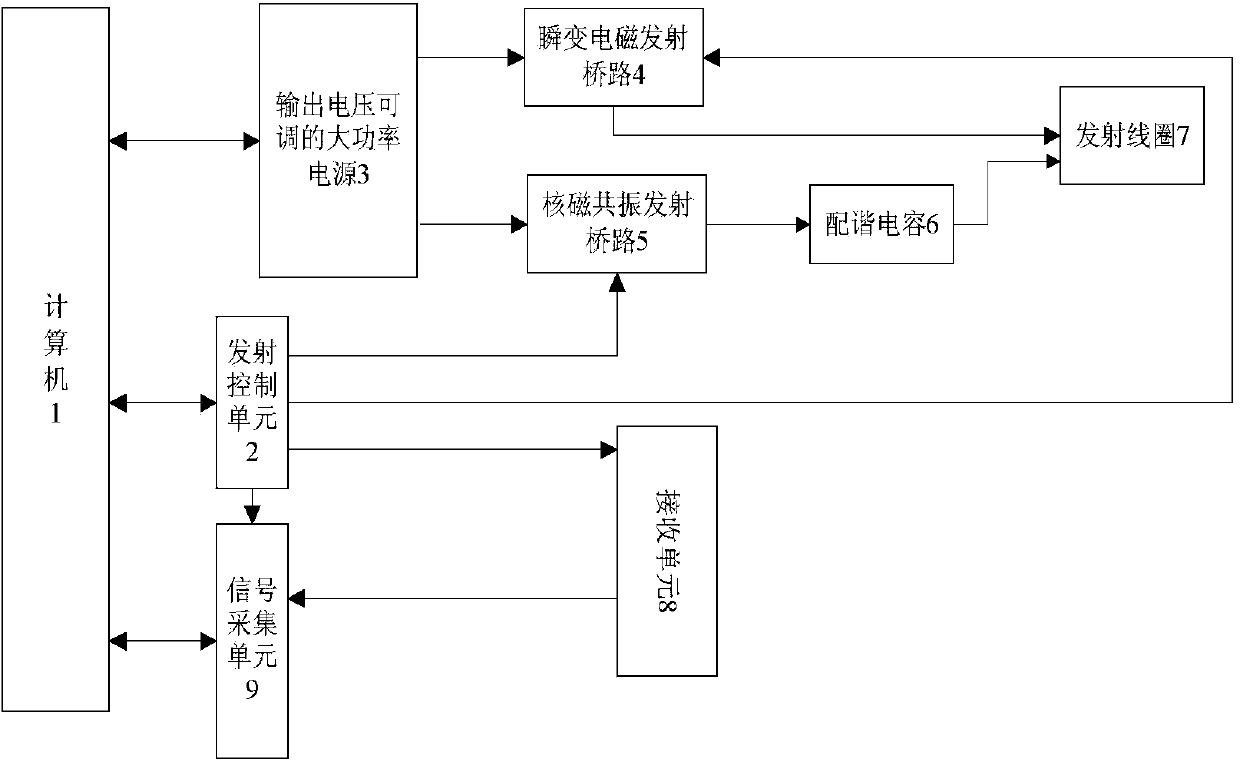
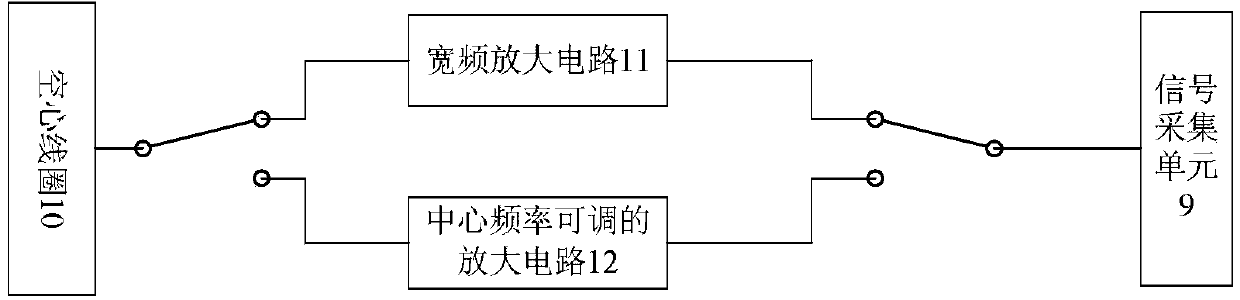
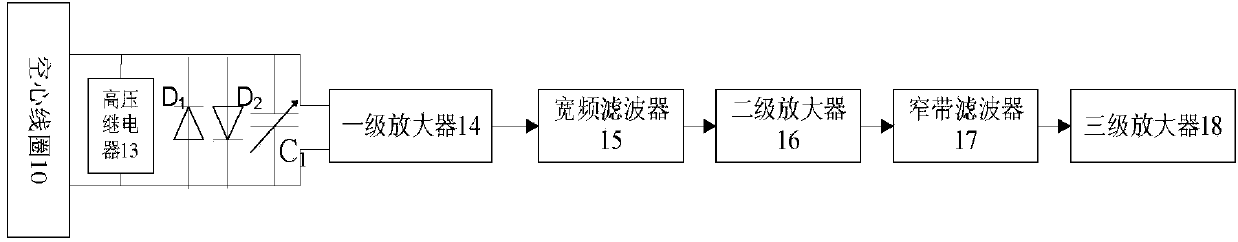
Underground water detection device and detection method based on combination of nuclear magnetic resonance and transient electromagnetic method
InactiveCN103809206AImprove adaptabilityIncrease horizontal resolutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceCapacitanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to underground water detection device and detection method based on the combination of nuclear magnetic resonance and transient electromagnetic method. The underground water detection device is formed by connecting a computer with a transient electromagnetic emission bridge circuit and a nuclear magnetic resonance emission bridge circuit through a high-power power supply with an adjustable output voltage, connecting the nuclear magnetic resonance emission bridge circuit with an emission coil through a harmonic capacitor, connecting the computer with the nuclear magnetic resonance emission bridge circuit and the transient electromagnetic emission bridge circuit through an emission control unit respectively, and connecting the emission control unit with the nuclear magnetic resonance emission bridge circuit and the transient electromagnetic emission bridge circuit respectively. The underground water detection device has the prominent advantages that the limit of a test site is avoided by using a hollow coil, thus increasing the transverse resolution of nuclear magnetic resonance detection. The underground water detection device can be much conveniently applied in underground engineering for narrow spaces such as tunnels and mine excavation roadways, the dimensions of a reception device are greatly reduced, and the spatial constraint is lower, thus the underground water detection device can be used for much accurately detecting a water-containing body; the problems of time consumption, cost consumption and labour consumption during pavement for a large coil are solved, the working efficiency is increased, and the working cost is reduced.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method and Apparatus to Visualize the Coronary Arteries Using Ultrasound
ActiveUS20120116226A1Improved three dimensional imageReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisBLOOD FILLEDScreening techniques
A non-invasive screening technique for visualizing coronary arteries which overcomes the problems of visualizing the curved arteries by projecting the three dimensional volume of the arteries onto a two dimensional screen. Blood-filled areas such as the coronary arteries and veins, are highlighted to contrast with other nearby tissues using non-linear classification and segmentation techniques. Data is gathered as a sequence of 2D slices stored as a 3D volume. Software interpolates voxels intermediate to the slices. Wiener filtering or LMS spatial filtering can be implemented on each 2D scan to improve lateral resolution and reduce noise prior to the use of the scan data with the classification and segmentation algorithms. A traditional handheld ultrasound probe is employed to enable the technician to locate the area of interest, but a gyroscopic stabilizer is added to minimize unwanted variation on two axes of rotation.
Owner:MAUI IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com