Patents
Literature
1912 results about "Optical microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The optical microscope, often referred to as the light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast. Often used in the classroom and at home unlike the electron microscope which is used for closer viewing.
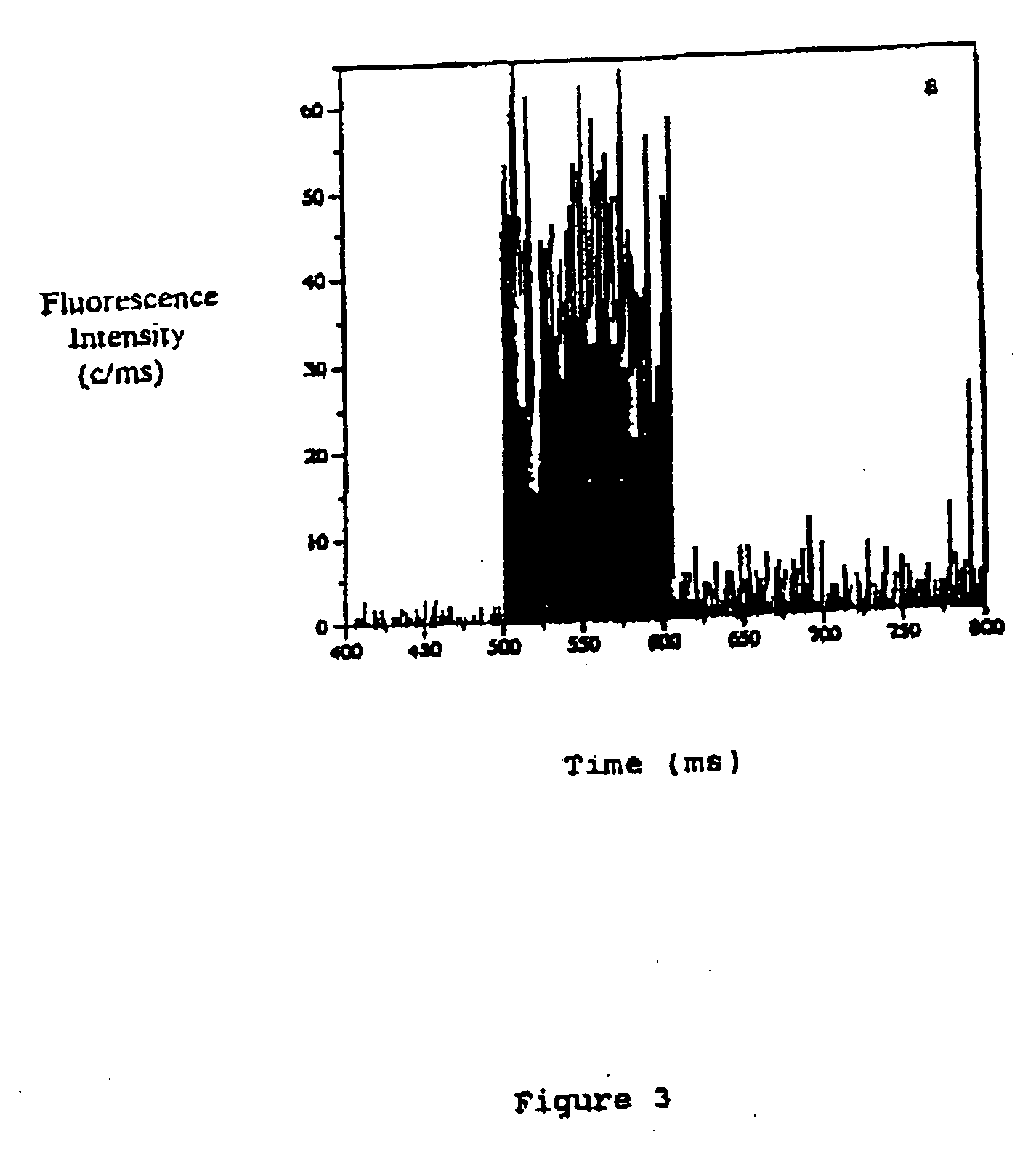
Spatial light interference microscopy and fourier transform light scattering for cell and tissue characterization
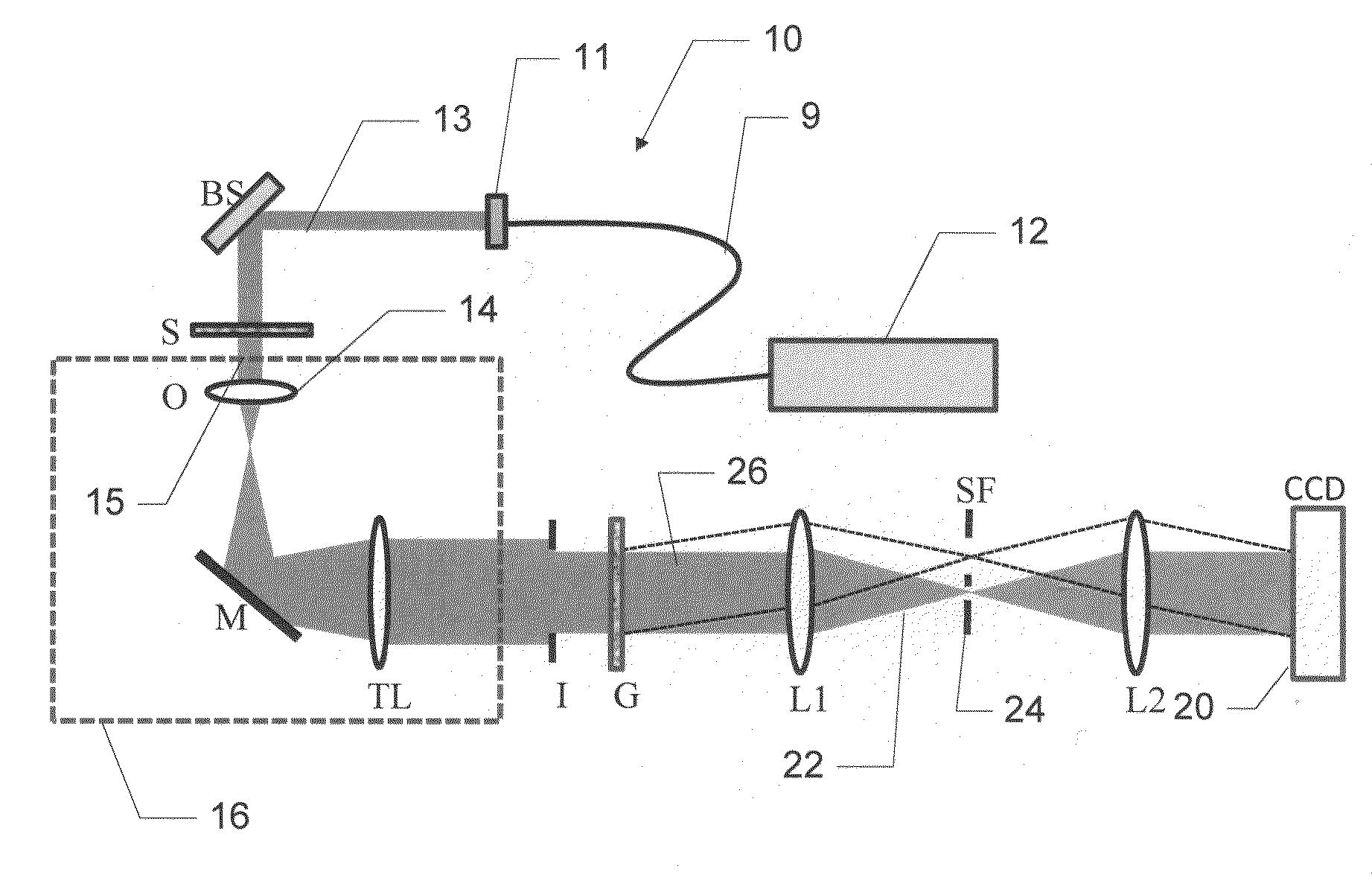
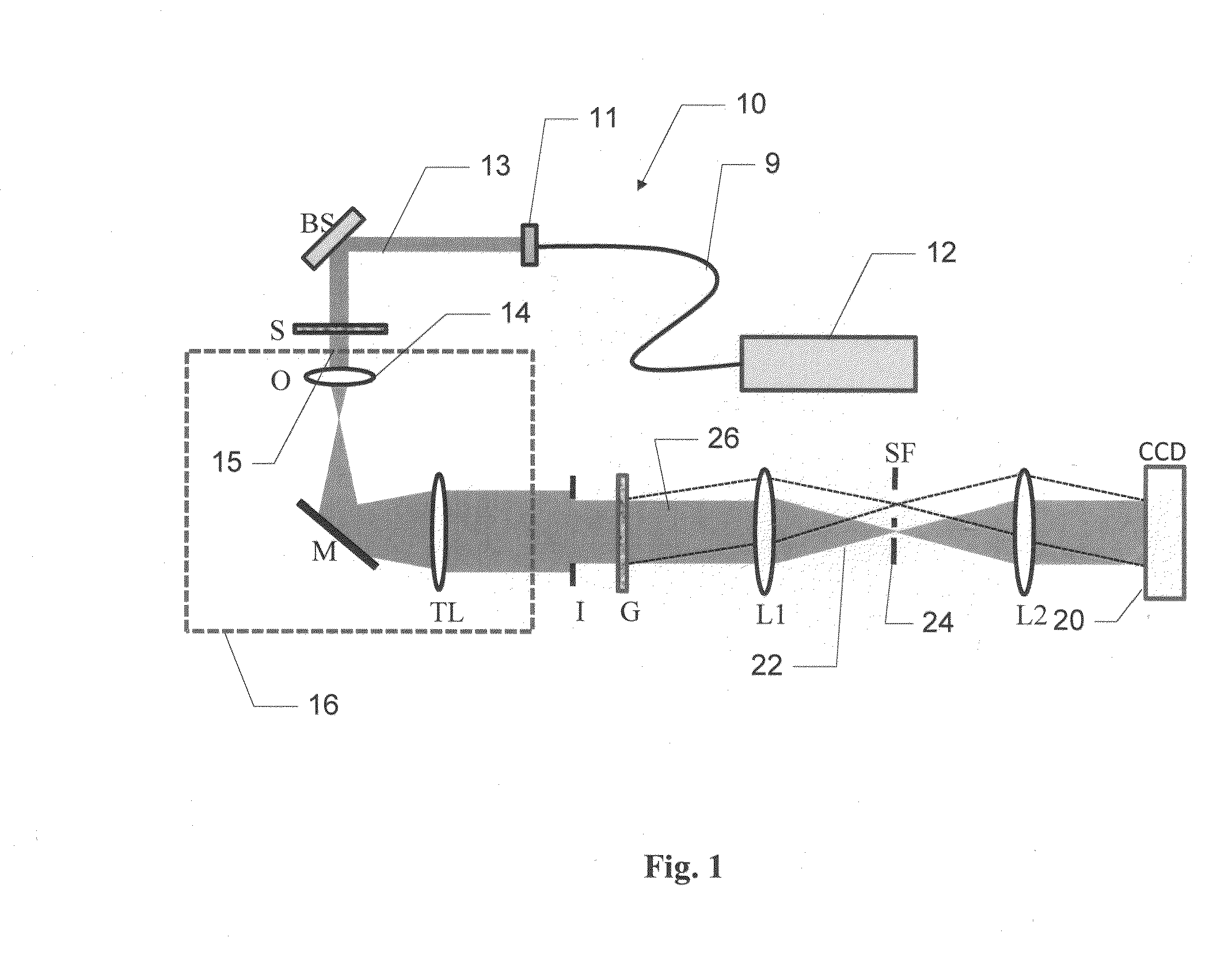
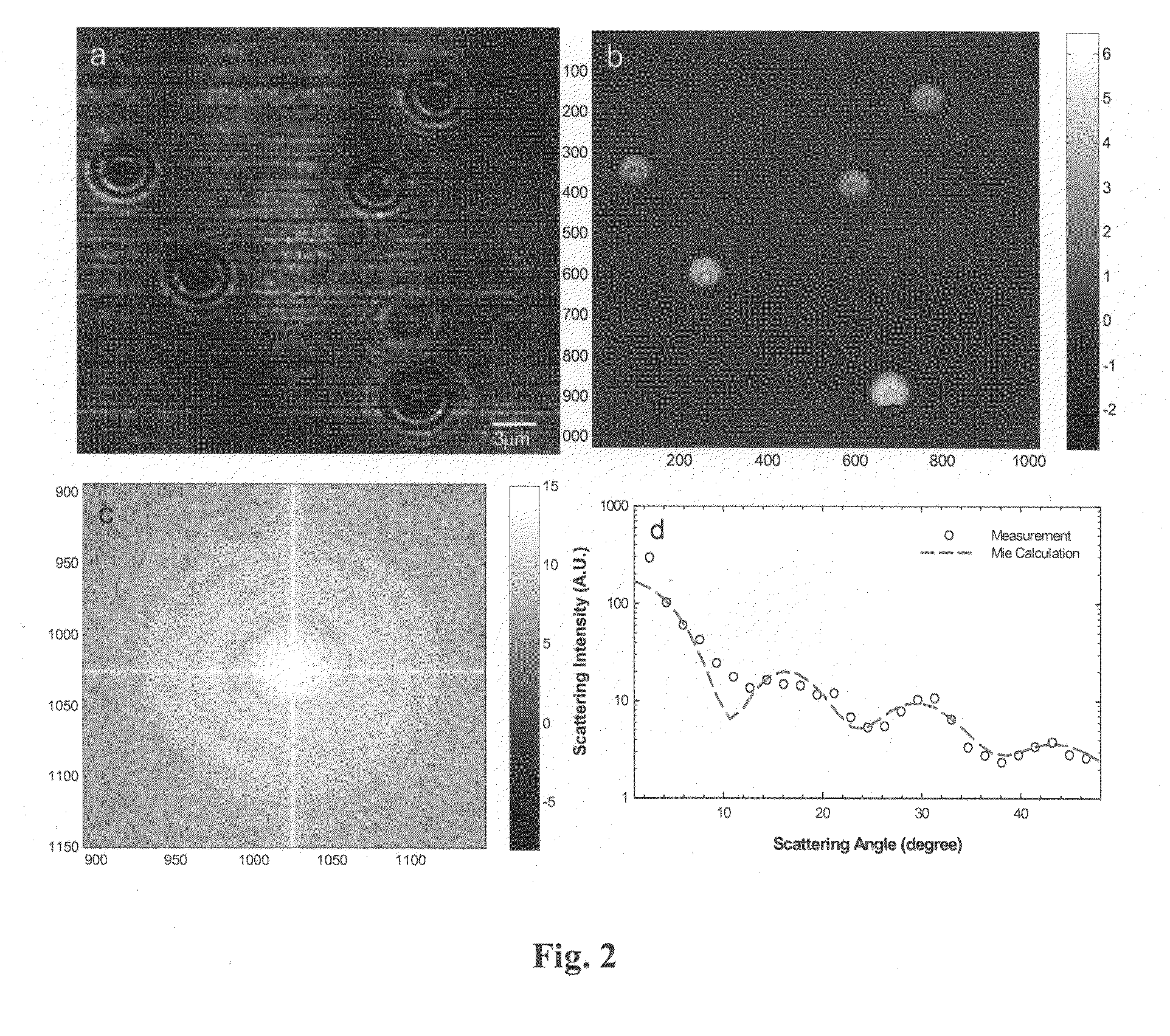
Methods and apparatus for rendering quantitative phase maps across and through transparent samples. A broadband source is employed in conjunction with an objective, Fourier optics, and a programmable two-dimensional phase modulator to obtain amplitude and phase information in an image plane. Methods, referred to as Fourier transform light scattering (FTLS), measure the angular scattering spectrum of the sample. FTLS combines optical microscopy and light scattering for studying inhomogeneous and dynamic media. FTLS relies on quantifying the optical phase and amplitude associated with a coherent image field and propagating it numerically to the scattering plane. Full angular information, limited only by the microscope objective, is obtained from extremely weak scatterers, such as a single micron-sized particle. A flow cytometer may employ FTLS sorting.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Optical probe for detecting or irradiating light and near-field optical microscope having such probe and manufacturing method of such probe
InactiveUS6215114B1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight irradiationNear field optical microscope
An optical prove for detecting or irradiating evanescent light is manufactured by forming a film having a regulated film thickness on a substrate, then forming a recess from the rear surface of the substrate, and forming a through hole in the film from the side of the recess by etching. The obtained optical probe has a micro-aperture at the tip of the through hole and usually, a plurality of optical probes each having a micro-aperture of uniform profile are formed on a single substrate. In the recess, light-receiving or light-irradiating means may be provided.
Owner:CANON KK
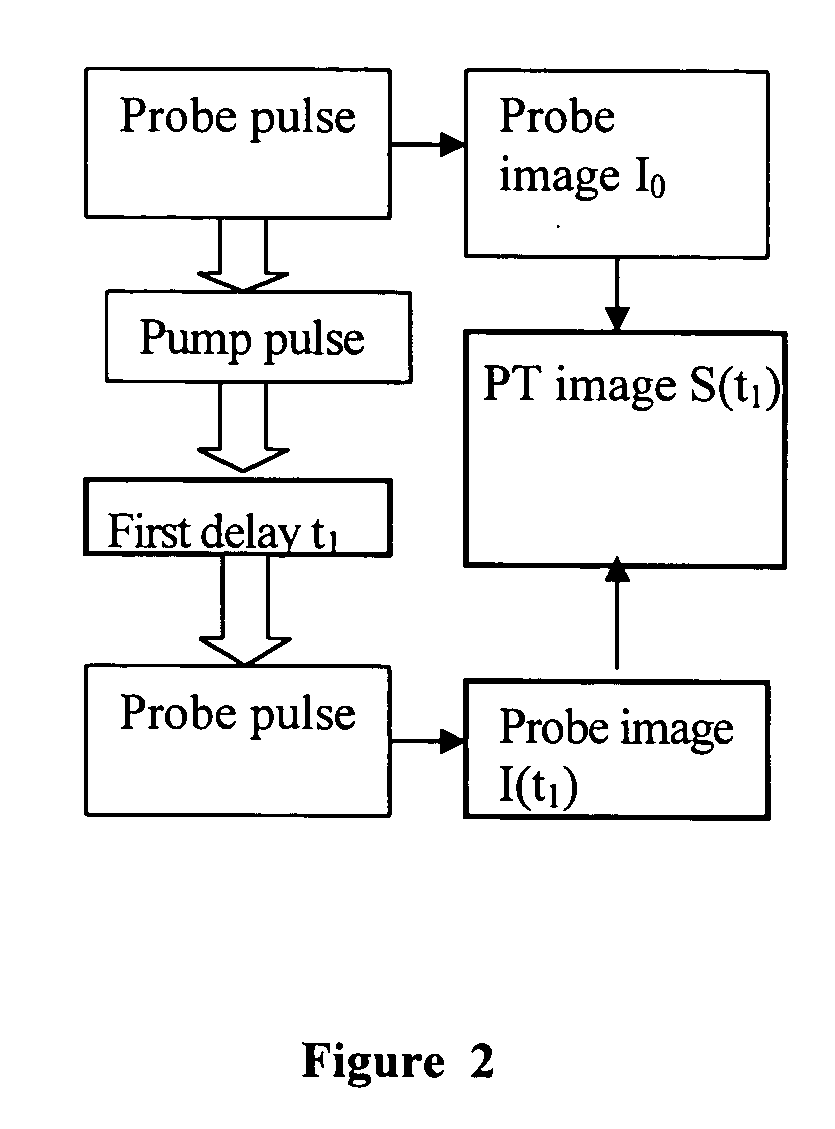
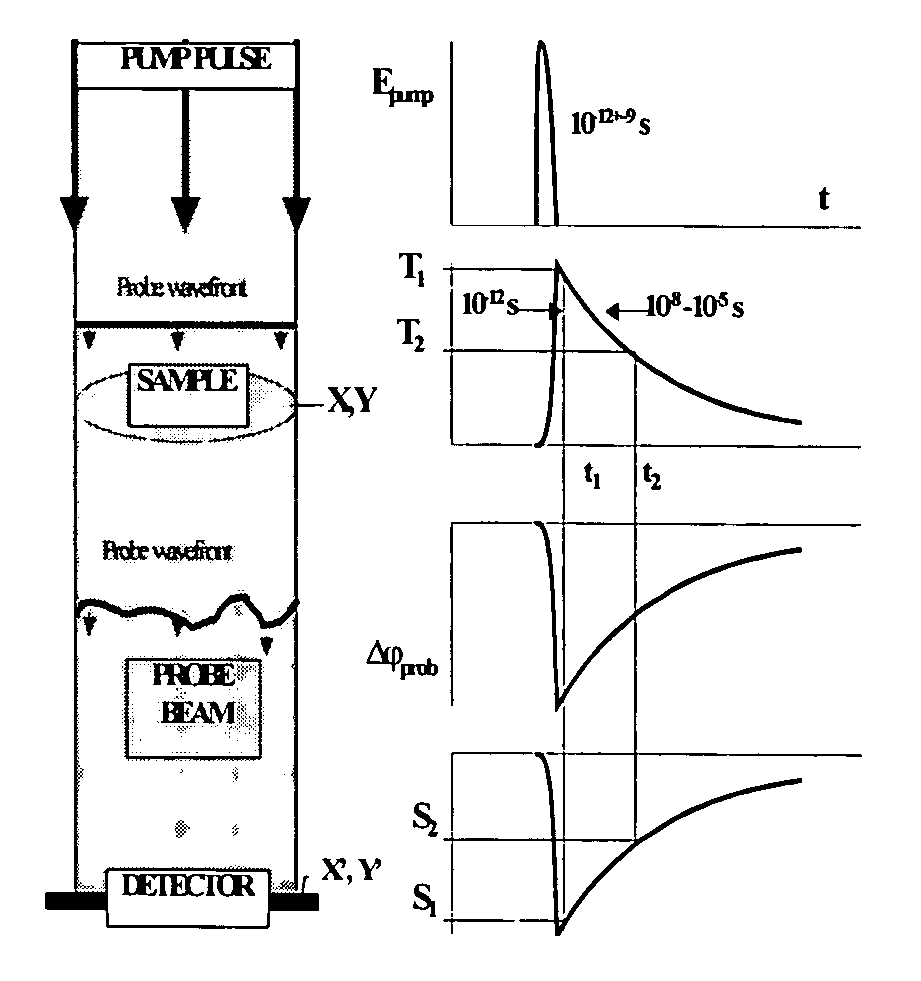
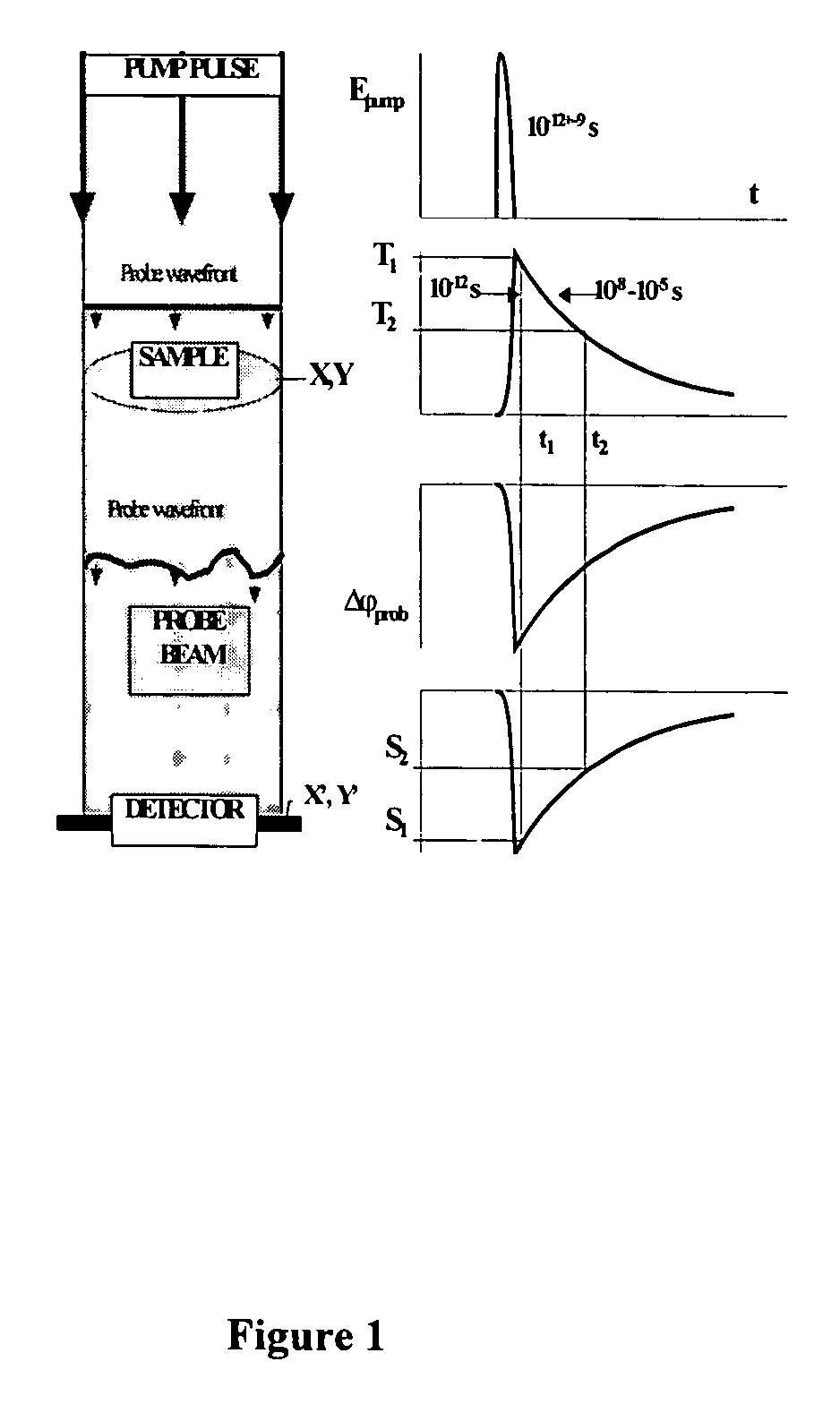
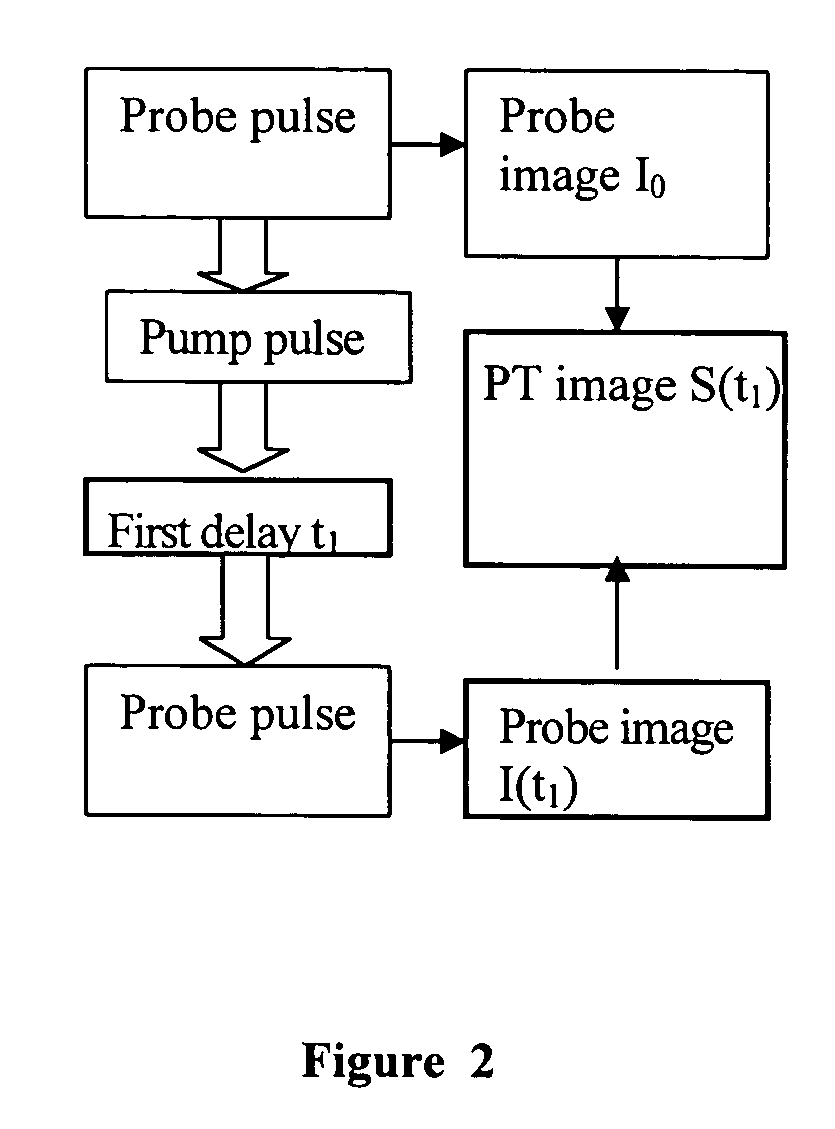
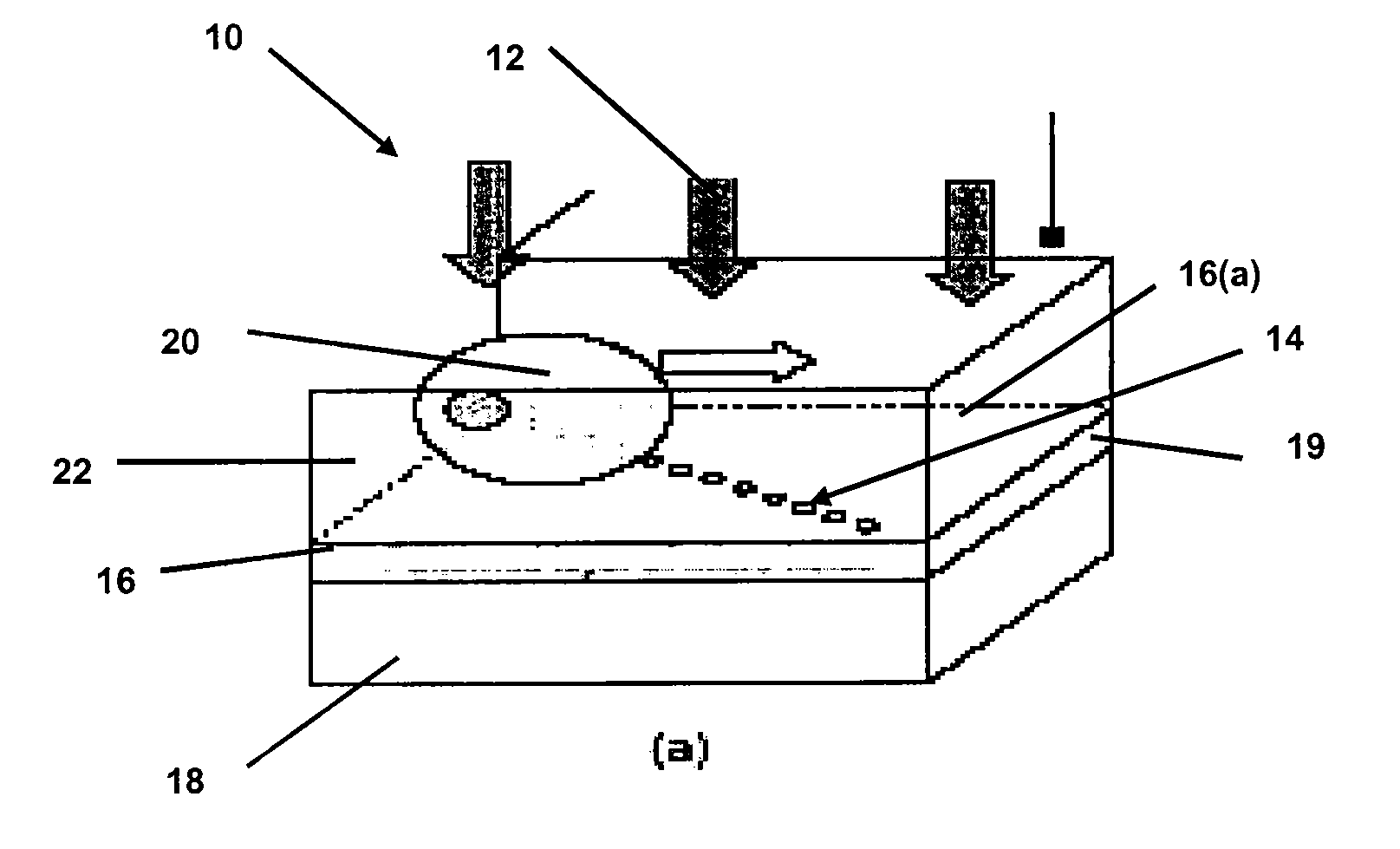
Method and device for photothermal examination of microinhomogeneities
InactiveUS20040085540A1Increase sensitivity and resolutionImprove resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsRefractive index
The invention relates to optical microscopy, in particular to methods for photothermal examination of absorbent microinhomogeneities using laser radiation sources and can be widely used in laser engineering, industry and biomedicine for examining relatively transparent objects containing submicron impurities, including the detection of local inclusions and defects in ultrapure optical and semiconductor materials and the non-destructive diagnosis of biological samples on a cellular and subcellular level. The aim of the invention is to increase the sensitivity, spatial resolution and informativity of examination of local absorbent microinhomogeinities in transparent objects and to measure said microinhomogeinities even when they are less than the used emission wavelength. The inventive method consists in radiating a sample with a pumping laser beam. The duration of the radiation is equal to or less than a representative time for cooling the examined microinhomogeinity. The relatively large surface of the sample is radiated, the shape thereof being greater than the wavelength of the used pumping laser. Thermal variations of the refractive index occurring in the sample as a result of absorption produced with the aid of the pumping beam are recorded by measuring parameters of a test laser beam. The diameter of the test beam is chosen in such a way that it is equal to or greater than the diameter of the pumping beam. A diffraction-limited phase distribution along the cross-section of the testing laser beam is transformed into an amplitude image, the microinhomogeinity properties being determined by measuring said amplitude image.
Owner:LAPOTKO TATIANA MS
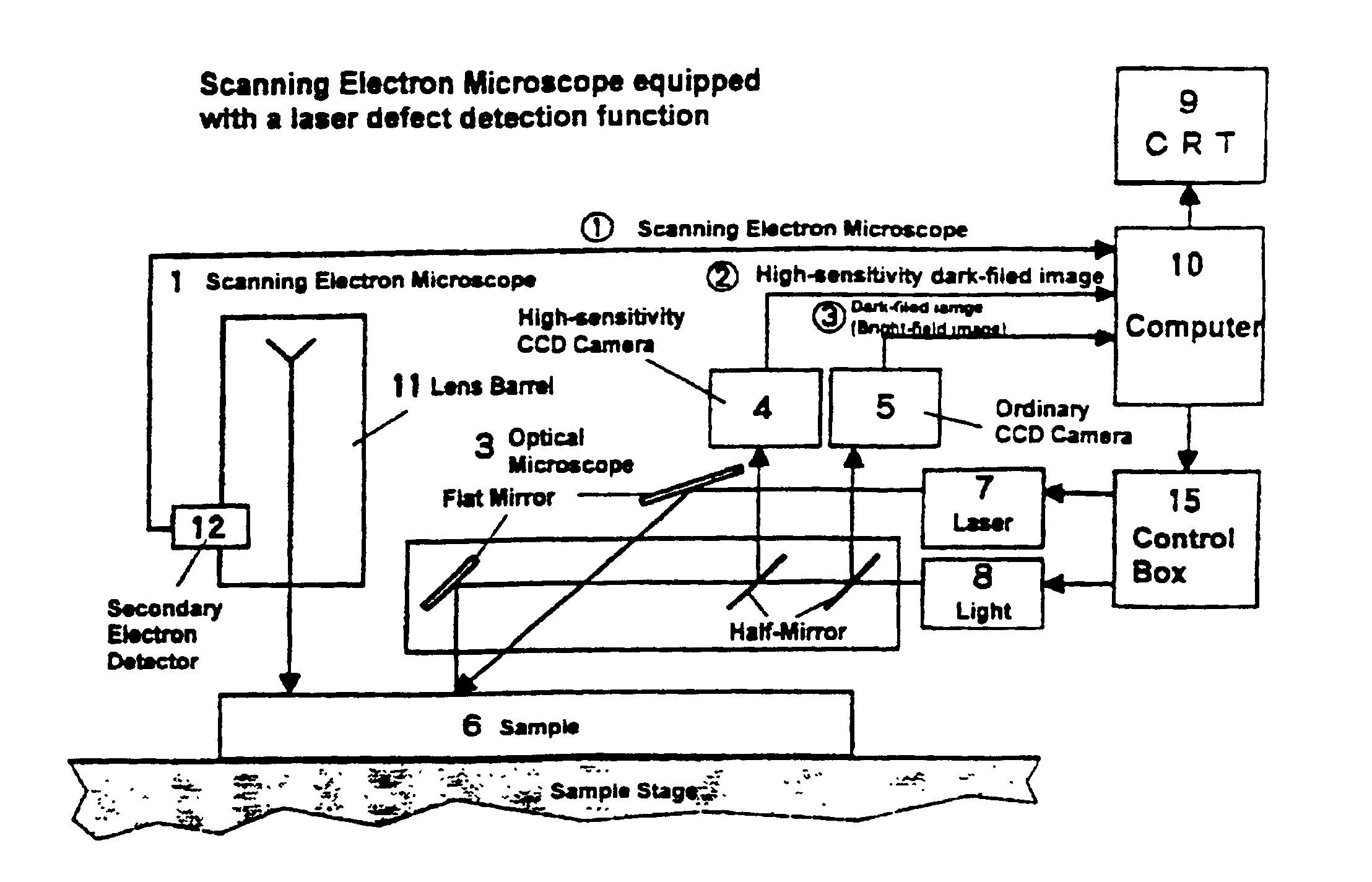
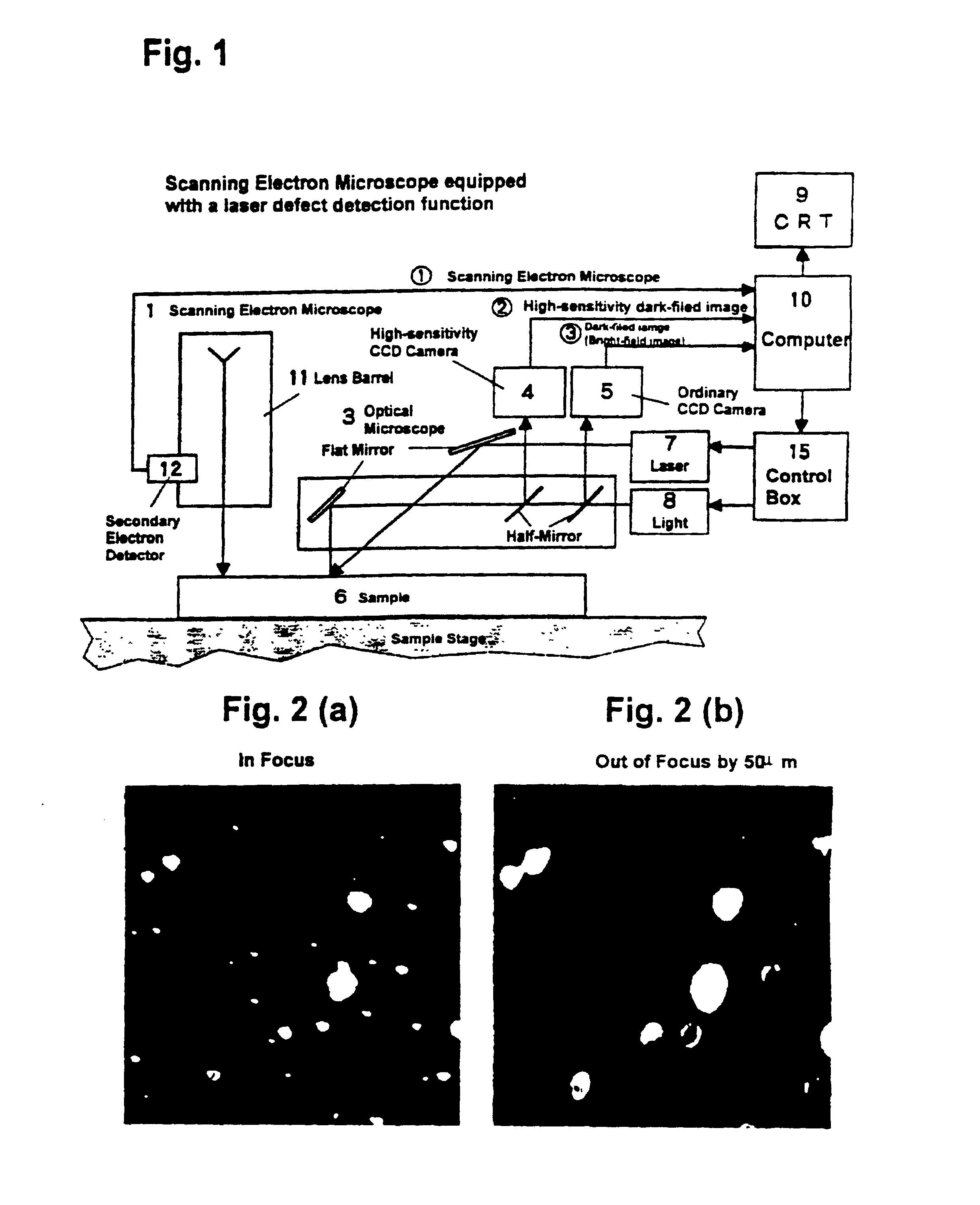
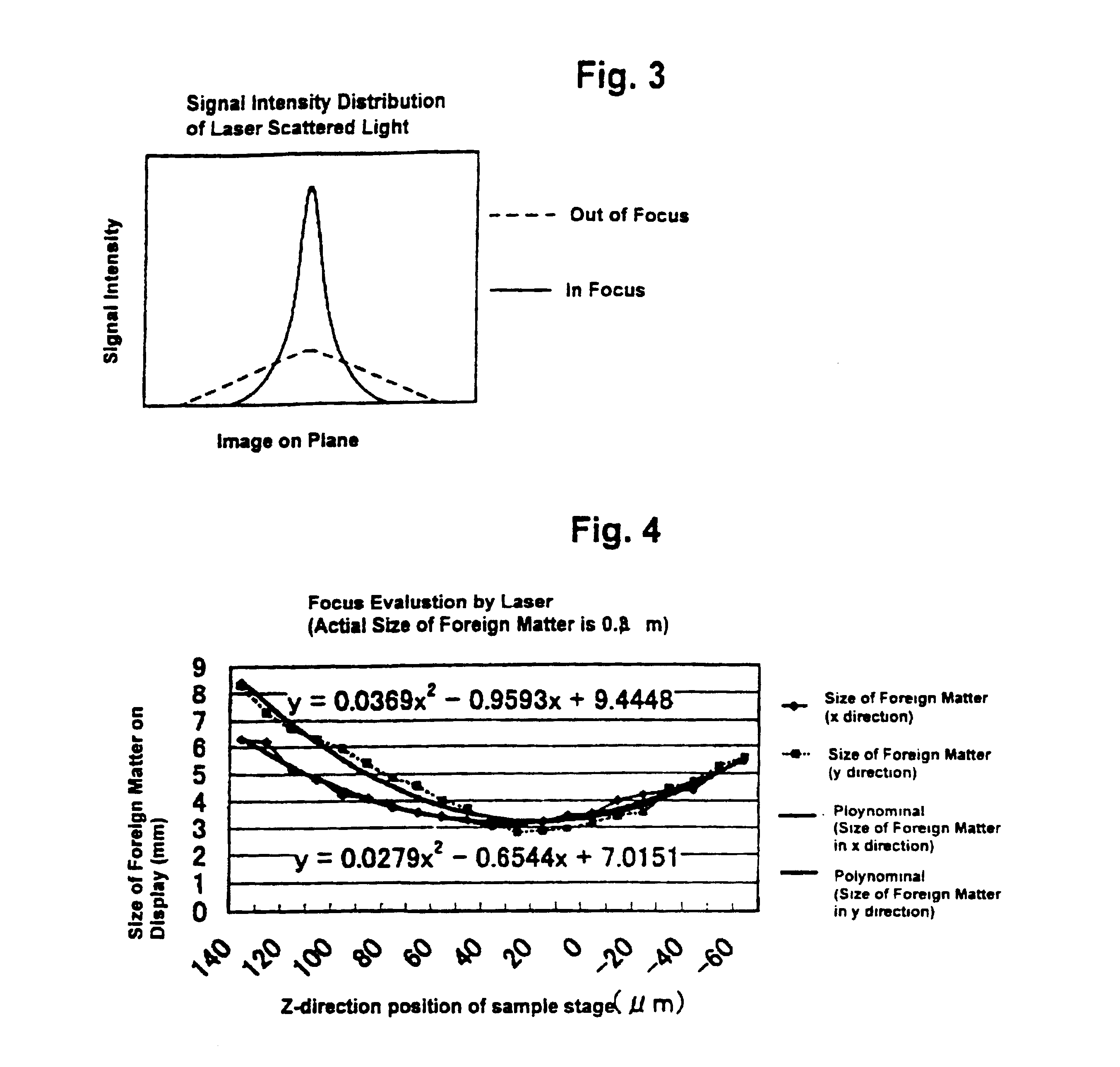
Automatic focusing system for scanning electron microscope equipped with laser defect detection function
InactiveUS6621082B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementImage detectionElectron microscope
A scanning electron microscope equipped with a laser defect detection function has an automatic focusing function that performs the steps of: obtaining a deviation (offset) amount between focal positions of an optical microscope and a scanning electron microscope; detecting a defect by a laser dark-field image of the optical microscope; analyzing the dark-field image to readjust a focus of the optical microscope to adjust a height of the optical microscope; and automatically adjusting a focus of the scanning electron microscope by adding a readjusted amount of the focus of the optical microscope to the offset amount before an observation is conducted by the scanning electron microscope.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
Method and device for photothermal examination of microinhomogeneities
InactiveUS7230708B2Improve resolutionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansRefractive indexLaser beams
The invention relates to optical microscopy, and more particularly to the methods for photothermal examination of absorbing microheterogeneities using laser radiation. The invention can be widely used in laser technique, industry, and biomedicine to examine transparent objects with absorbing submicron fragments, including detection of local impurities and defects in super-pure optical and semiconducting materials and non-destructive diagnostics of biological samples on cellular and subcellular levels.The object of the present invention is to increase sensitivity, spatial resolution and informative worth when examining local absorbing heterogeneities in transparent objects, as well as to detect the size of said heterogeneities even if said size is smaller than the radiation wavelength used.Said object is achieved by the pump beam irradiation of a sample, the duration of said irradiation not being longer than the characteristic time of cooling of the microheterogeneity observed. A relatively vast surface of the sample is irradiated at once, the size of said surface not being larger than the wavelength of the pump laser used. The refraction index thermal variations, induced by the pump beam in the sample and being the result of absorption, are registered by the parameter change of the probe laser beam. A chosen probe beam diameter should not be smaller than the pump beam diameter. The diffraction-limited phase distribution over the probe laser beam cross-section is transformed to an amplitude image using a phase contrast method. The properties of microheterogeneities are estimated by measuring said amplitude image.
Owner:LAPOTKO TATIANA MS
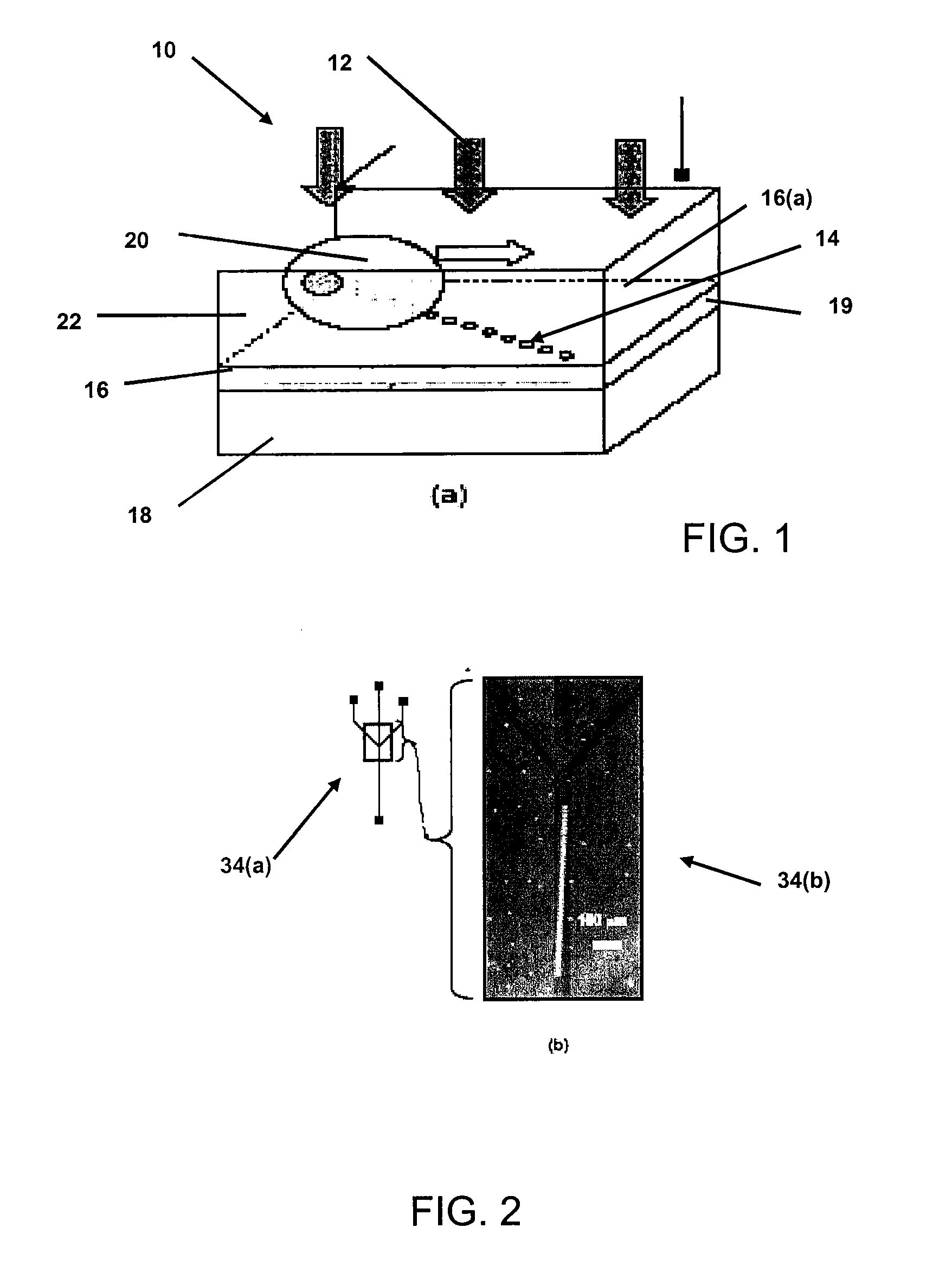
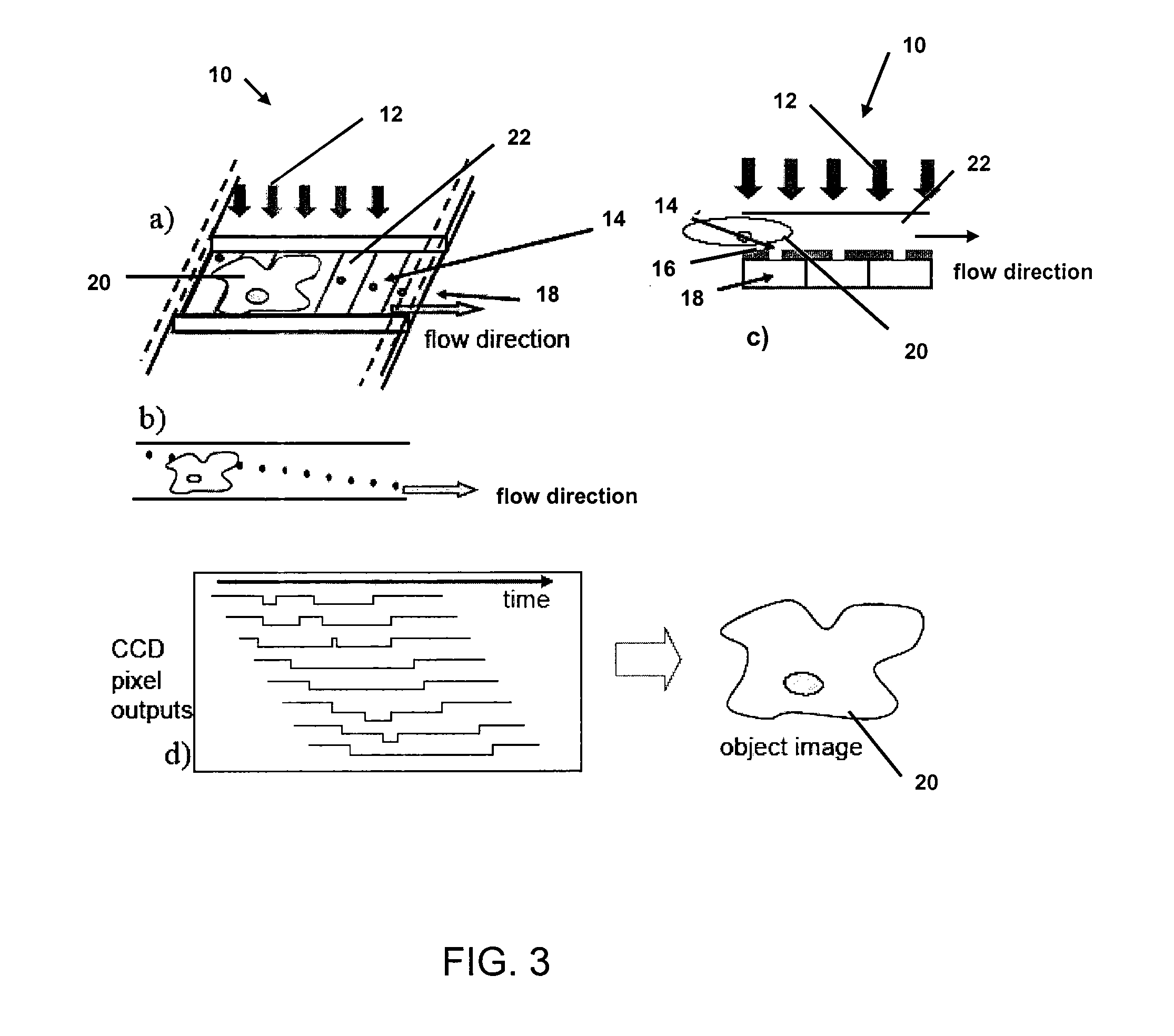
Optofluidic microscope device
InactiveUS20070207061A1High imaging throughput rateEasy to handleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyOptical flowMicroscope
An optofluidic microscope device is disclosed. The device includes a fluid channel having a surface and an object such as a bacterium or virus may flow through the fluid channel. Light transmissive regions of different sizes may be used to image the object.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Arrayed biomolecules and their use in sequencing
InactiveUS20050042649A1Reduce interferencePermit resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsVolumetric Mass DensityBiology
A device comprising an array of molecules immobilised on a solid surface is disclosed, wherein the array has a surface density which allows each molecule to be individually resolved, e.g. by optical microscopy. Therefore, the arrays of the present invention consist of single molecules that are more spatially distinct than the arrays of the prior art.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Confocal microscope
InactiveUS7339148B2Increase speedHigh image resolutionRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersCamera lensLight beam
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
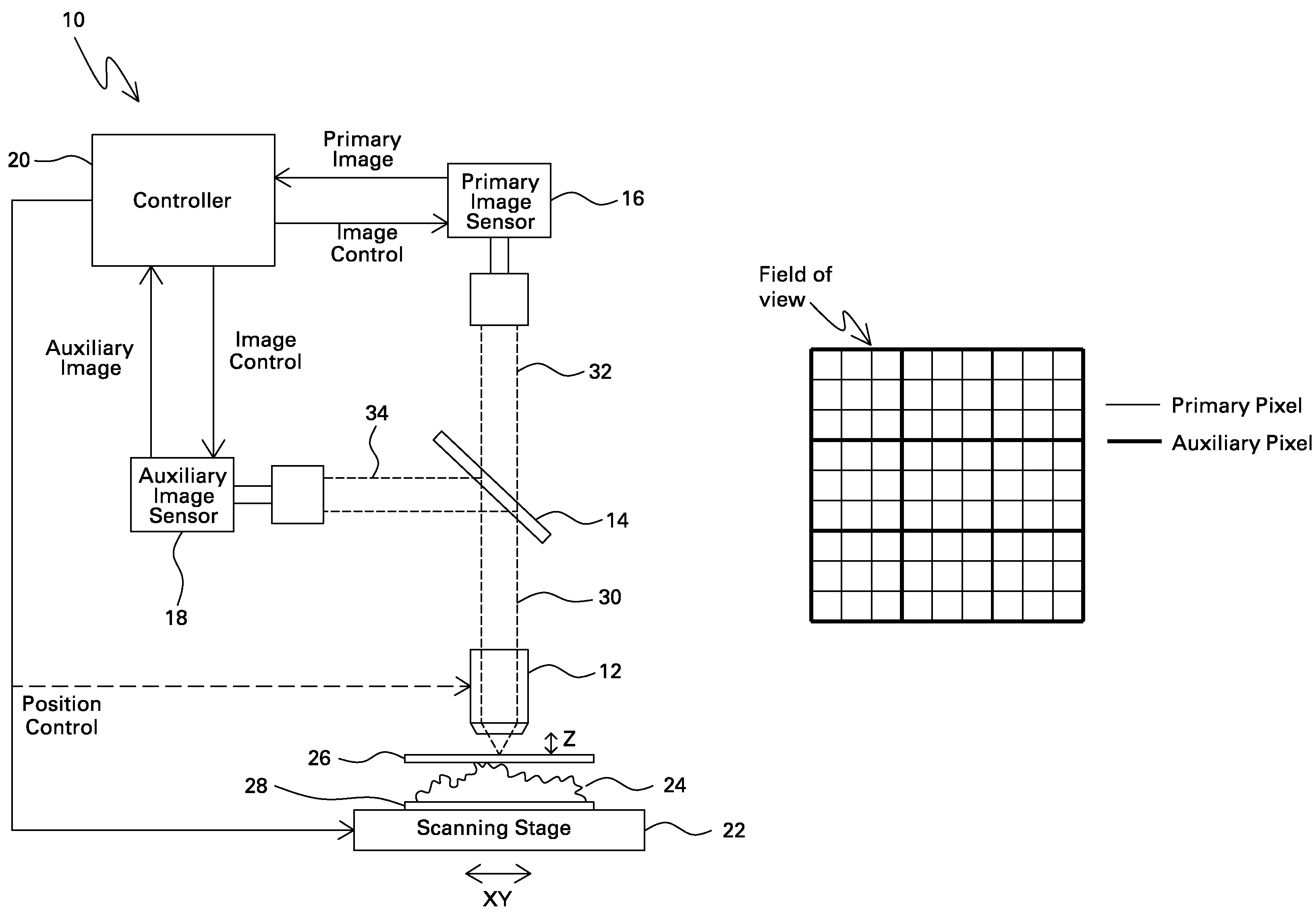
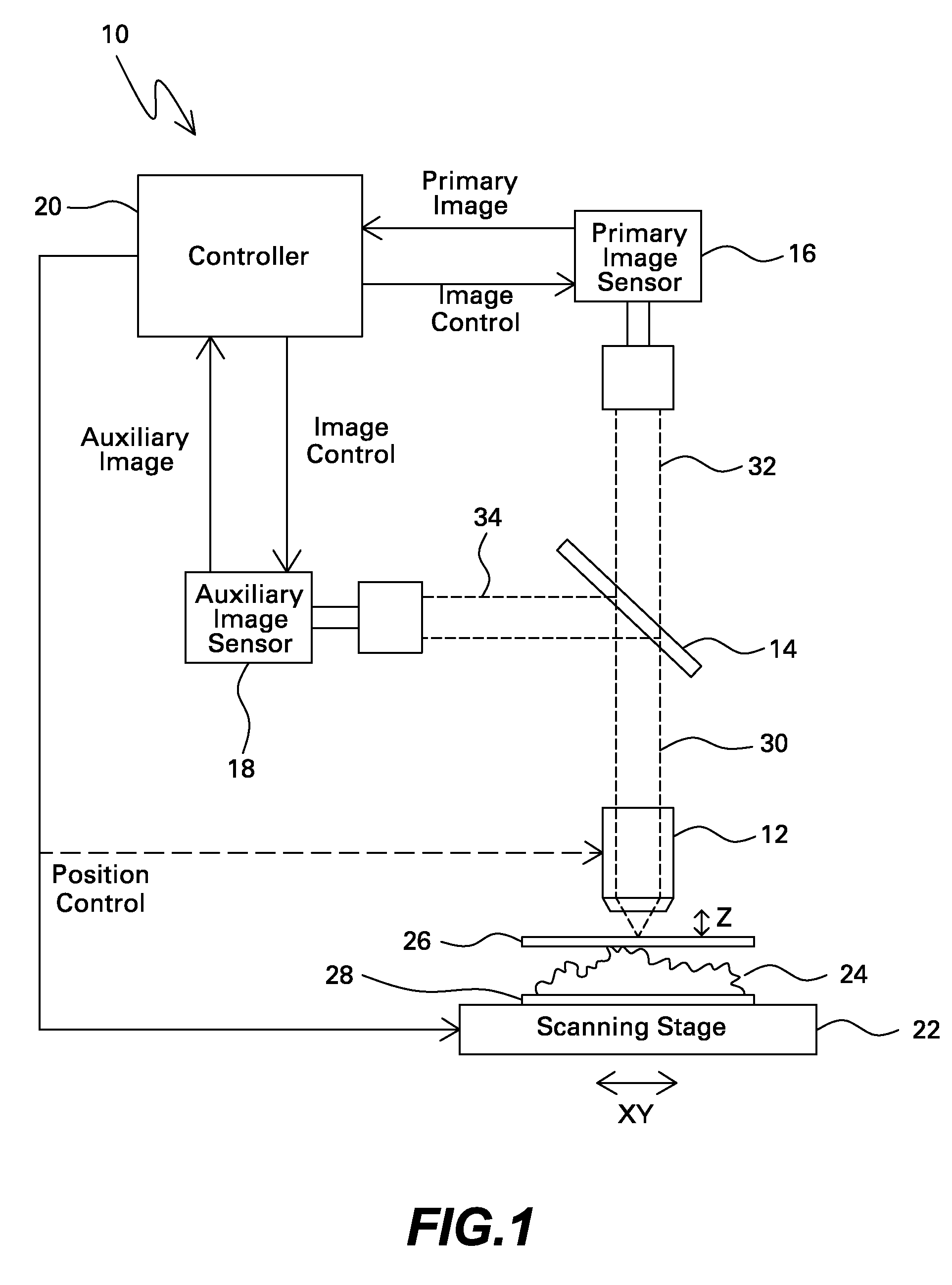
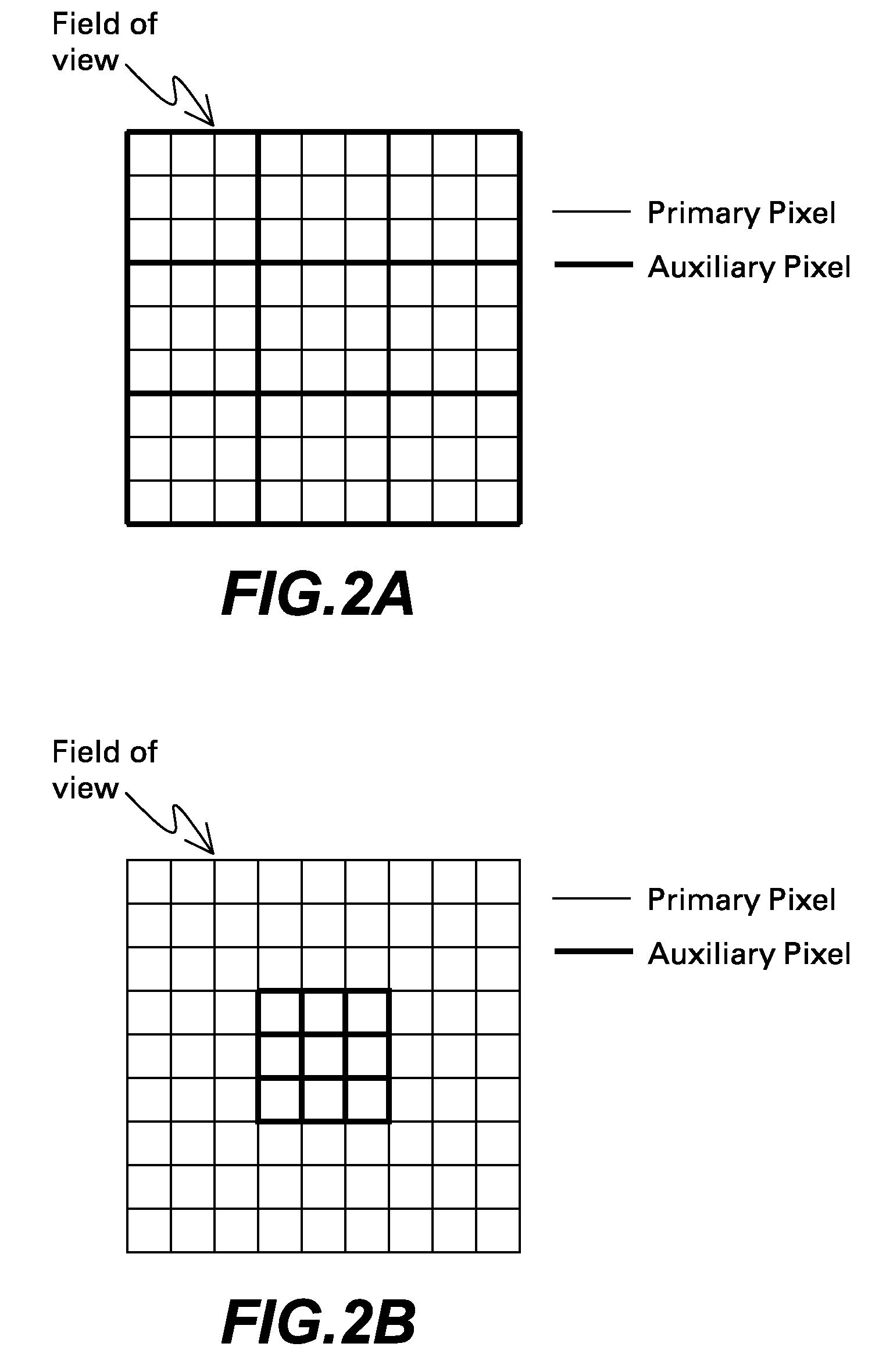
Microscope with dual image sensors for rapid autofocusing
A digital optical microscope includes a primary image sensor that generates a primary image of a sample at a primary frame rate, an auxiliary image sensor that generates an auxiliary image of the sample at an auxiliary frame rate that is faster than the primary frame rate, and a controller that adjusts a focal distance between an objective lens and the sample along an optical axis in response to the auxiliary image, thereby autofocusing the primary image on the sample. The primary image sensor generates the primary image in response to the autofocusing.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Carbon nanotube with a graphitic outer layer: process and application
InactiveUS6582673B1Increase profitLarge caliberMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentScanning probe microscopyNanometer size
A method for manufacturing carbon nanotubes with an integrally attached outer graphitic layer is disclosed. The graphitic layer improves the ability to handle and manipulate the nanometer size nanotube device in various applications, such as a probe tip in scanning probe microscopes and optical microscopes, or as an electron emitting device. A thermal chemical vapor deposition reactor is the preferred reaction vessel in which a transition metal catalyst with an inert gas, hydrogen gas and a carbon-containing gas mixture are heated at various temperatures in a range between 500° C. and 1000° C. with gases and temperatures being adjusted periodically during the reaction times required to grow the nanotube core and subsequently grow the desired outer graphitic layer.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
Transmission electron microscope sample preparation
InactiveUS6841788B1Easy to useProvide protectionElectric discharge tubesPreparing sample for investigationElectron microscopeThinning
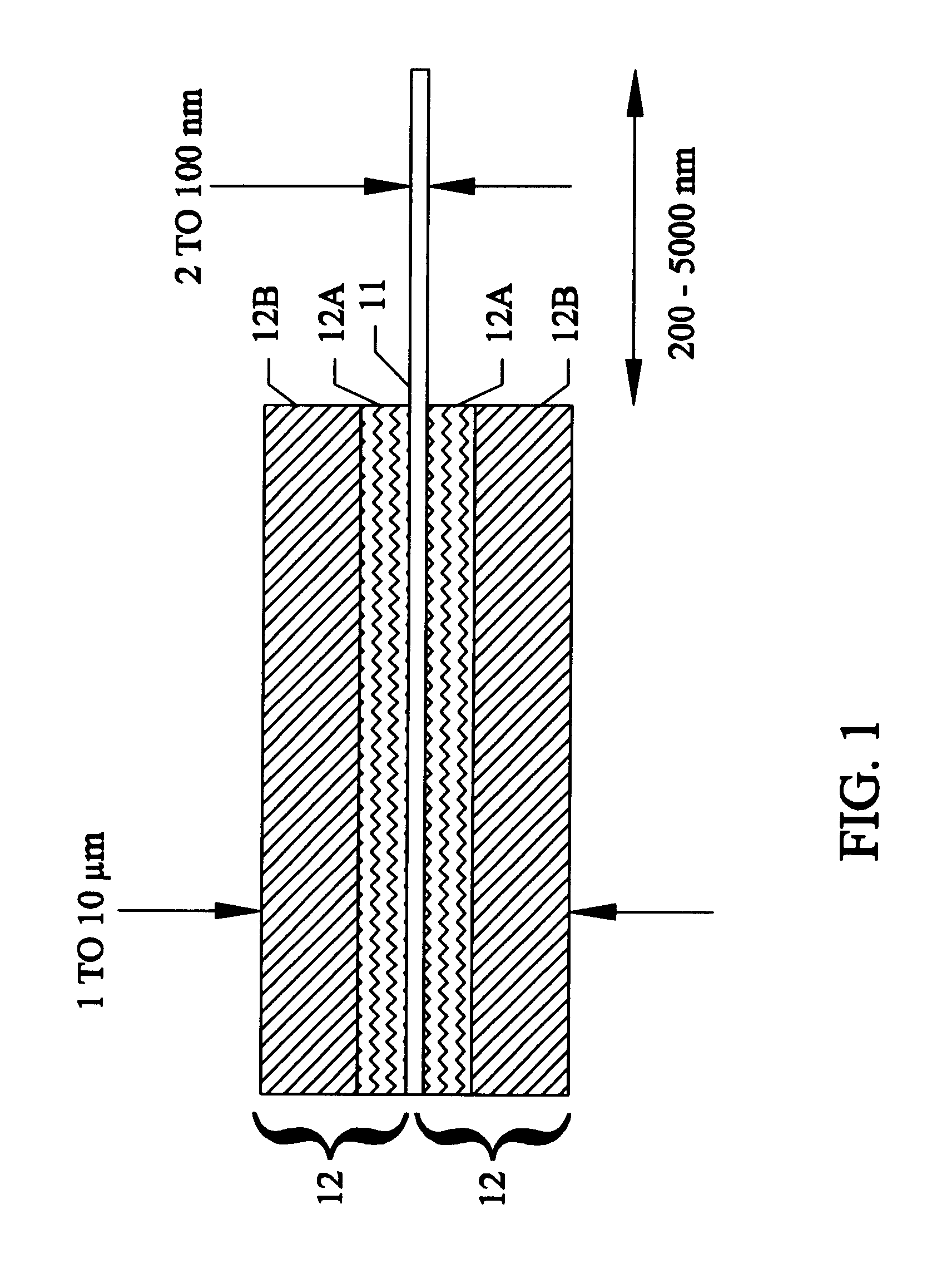
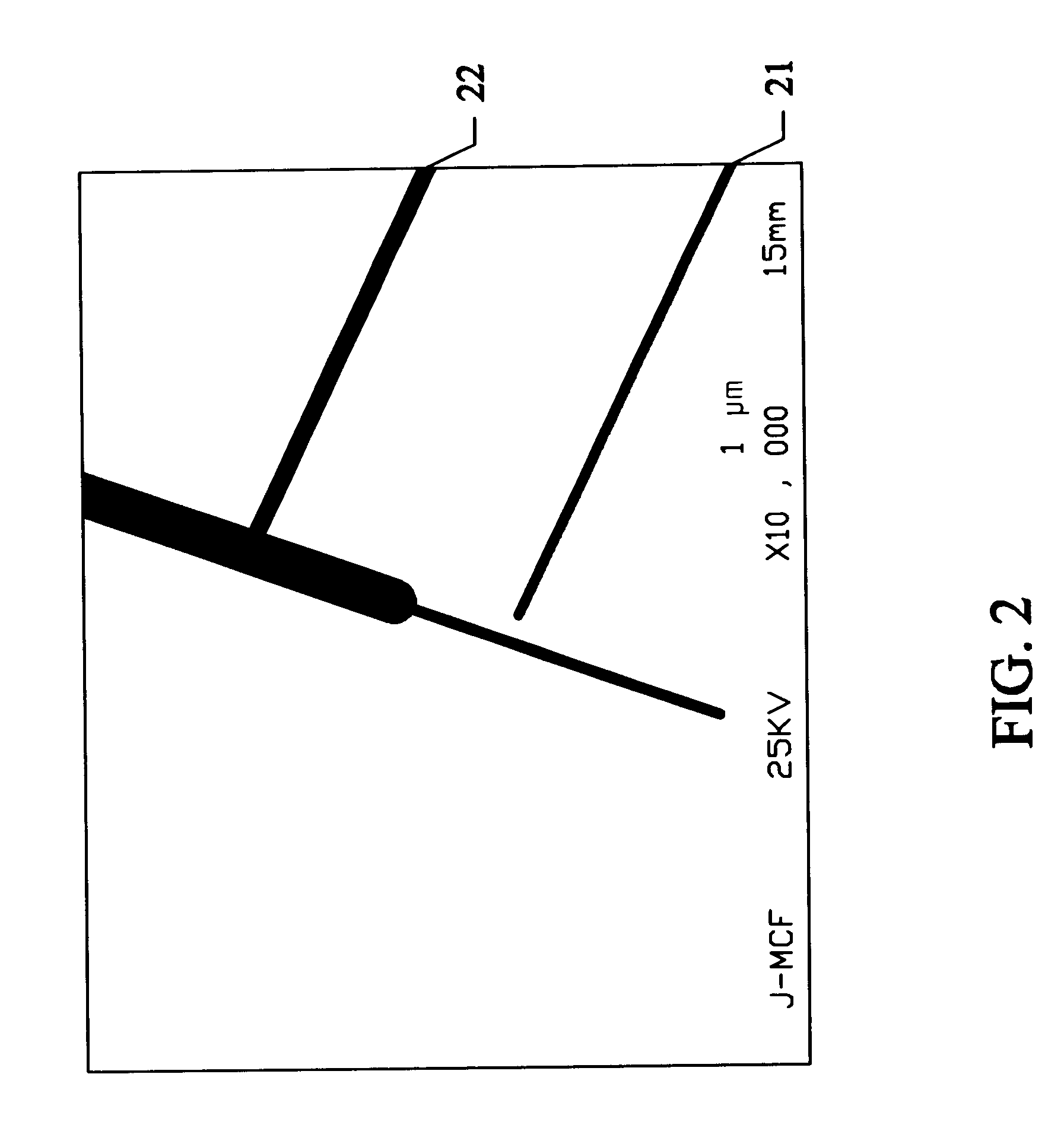
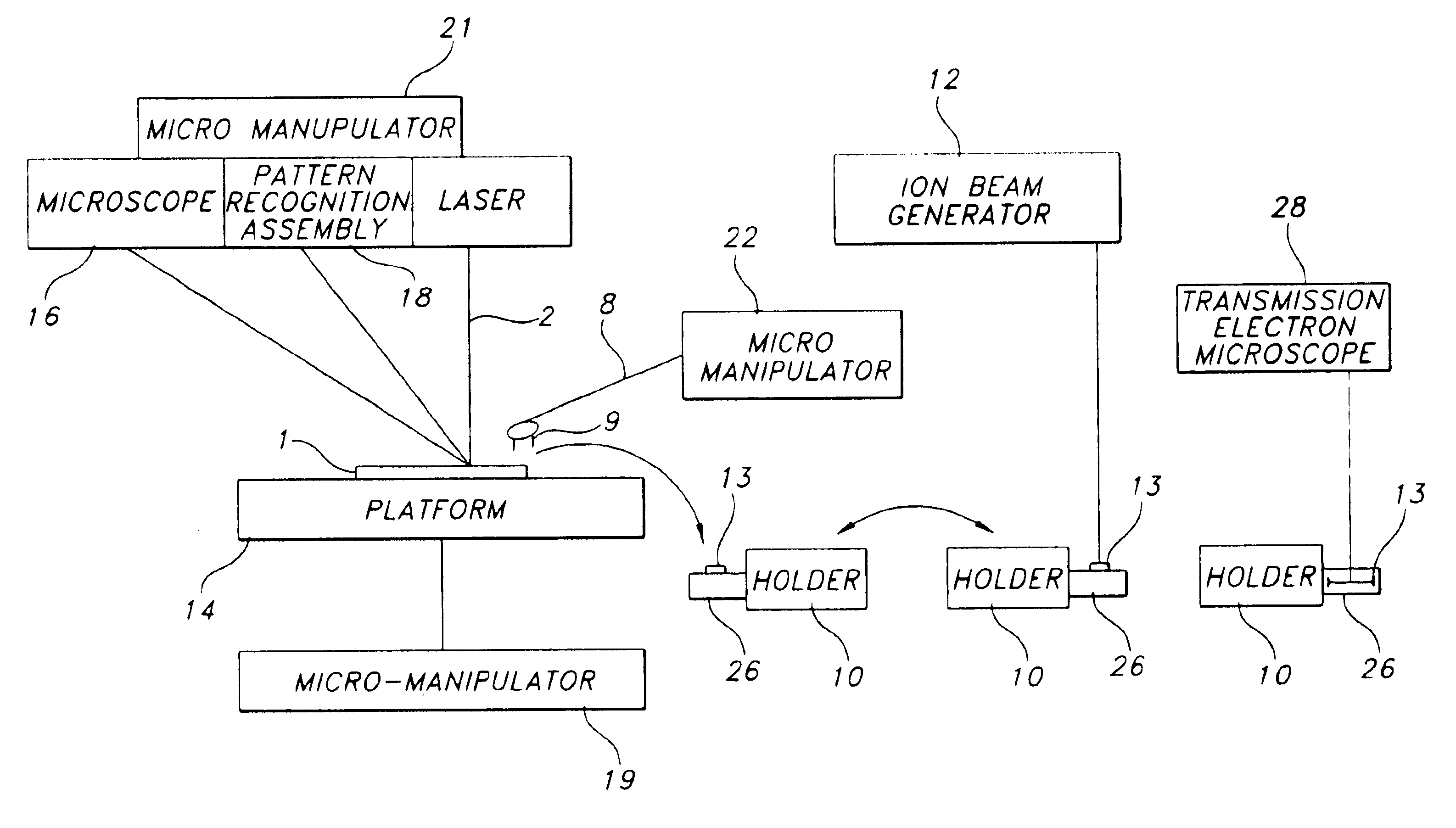
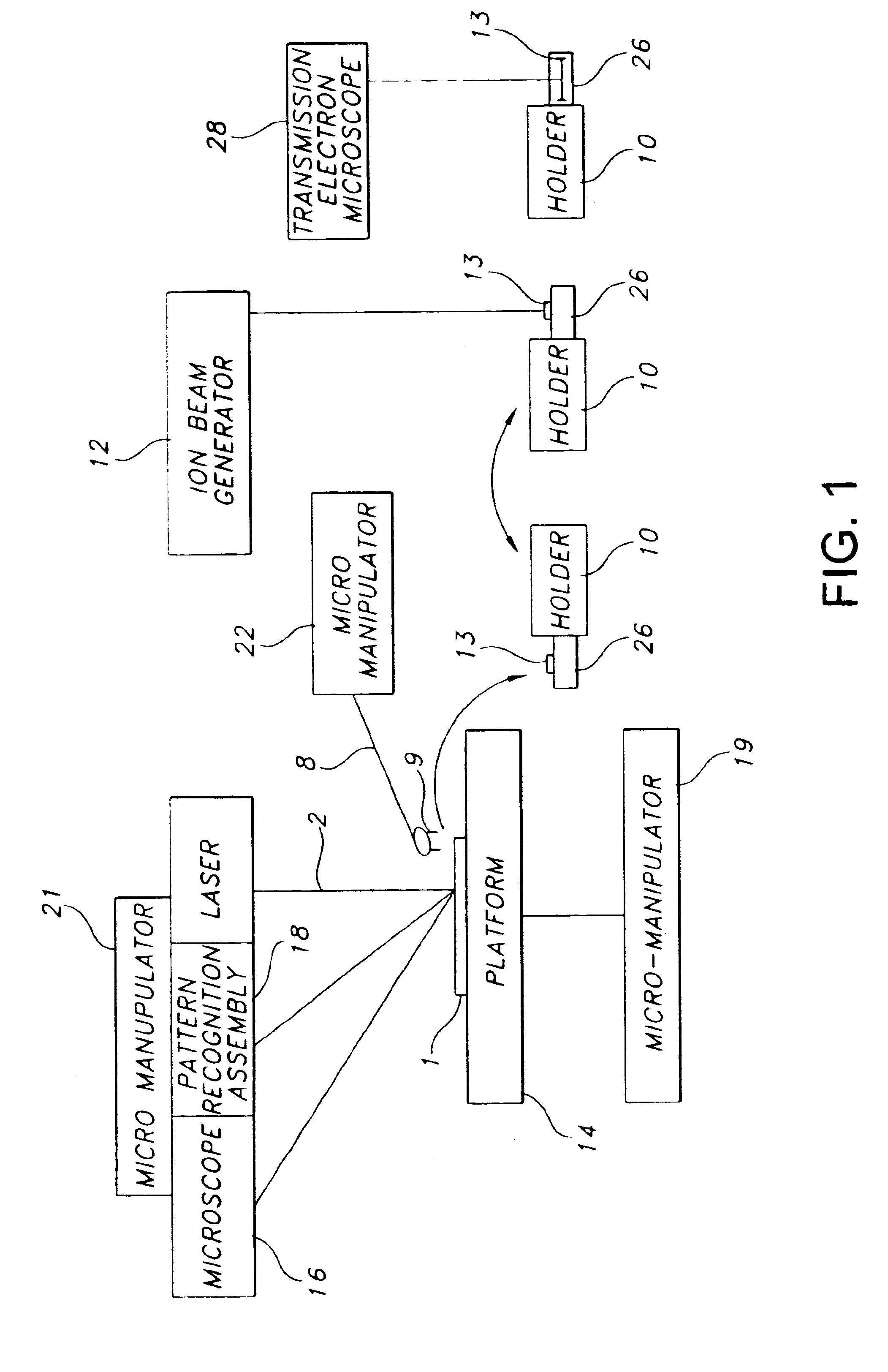
Sample preparation apparatus and method includes a wafer stage platform with an optical microscope and integrated pattern recognition to automatically address specific locations on the wafer sample of interest. A laser attaches to the optical microscope to mill a set pattern around the area of interest. A precision micro-manipulator engages the sample support structure, extracts the structure, and places the structure in a TEM holder or holder tip. The holder or holder tip can then be placed inside a FIB for final thinning, followed by direct transfer into the TEM.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR AMERICA
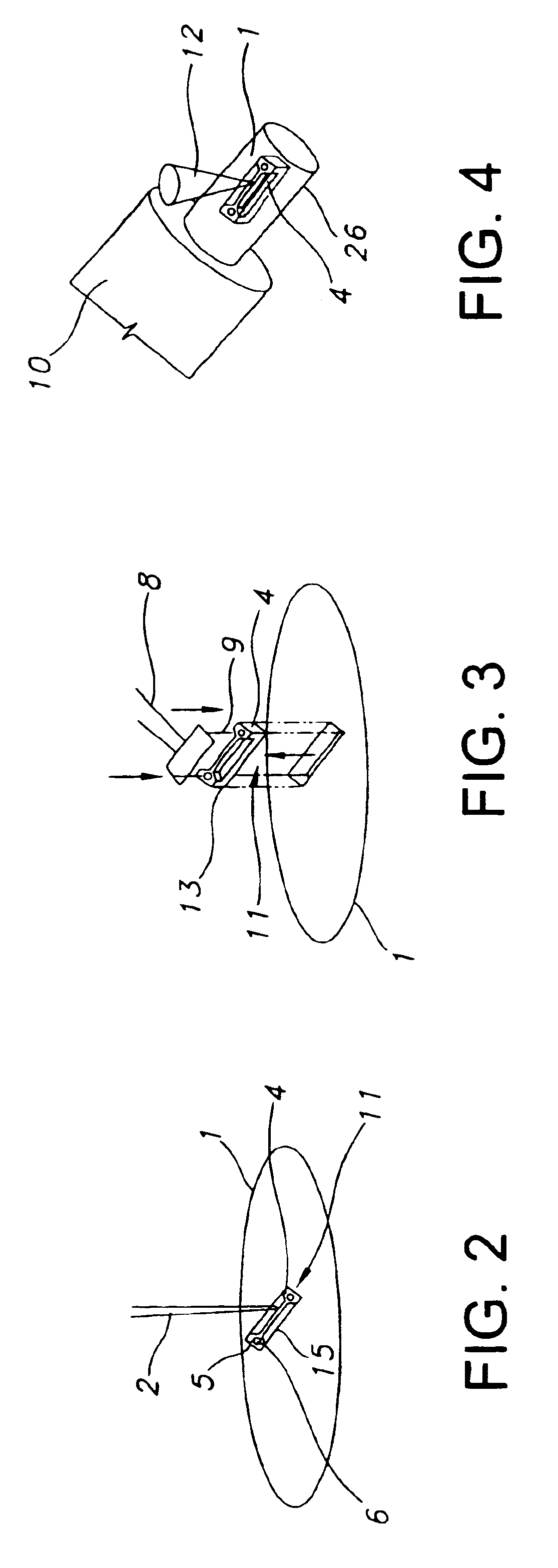
Fast-Scanning SPM Scanner and Method of Operating Same
ActiveUS20080223119A1Increased focus rangeImage data is accurateNanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsHigh bandwidthImage resolution
A high-bandwidth SPM tip scanner is provided that additionally includes an objective that is vertically movable within the scan head to increase the depth of focus for the sensing light beam. Movable optics also are preferably provided to permit targeting of the sensing light beam on the SPM's probe and to permit the sensing light beam to track the probe during scanning. The targeting and tracking permit the impingement of a small sensing light beam spot on the probe under direct visual inspection of focused illumination beam of an optical microscope integrated into the SPM and, as a result, permits the use of a relatively small cantilever with a commensurately small resonant frequency. A high-bandwidth tip scanner constructed in this fashion has a fundamental resonant frequency greater than greater than 500 Hz and a sensing light beam spot minor diameter of less than 10 μm. Images can be scanned on large samples having a largest dimension exceeding 7 mm with a resolution of less than 1 Angstrom and while scanning at rates exceeding 30 Hz.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Image processing and analysis of individual nucleic acid molecules
InactiveUS20030036067A1Improve throughputQuick buildBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideImaging processing
A method for observing and determining the size of individual molecules and for determining the weight distribution of a sample containing molecules of varying size, which involves placing a deformable or nondeformable molecule in a medium, subjecting the molecule to an external force, thereby causing conformational and / or positional changes, and then measuring these changes. Preferred ways to measure conformational and positional changes include: (1) determining the rate at which a deformable molecule returns to a relaxed state after termination of the external force, (2) determining the rate at which a molecule becomes oriented in a new direction when the direction of the perturbing force is changed, (3) determining the rate at which a molecule rotates, (4) measuring the length of a molecule, particularly when it is at least partially stretched, or (5) measuring at least one diameter of a spherical or ellipsoidal molecule. Measurements of relaxation, reorientation, and rotation rates, as well as length and diameter can be made using a light microscope connected to an image processor. Molecule relaxation, reorientation and rotation also can be determined using a microscope combined with a spectroscopic device. The invention is particularly useful for measuring polymer molecules, such as nucleic acids, and can be used to determine the size and map location of restriction digests. Breakage of large polymer molecules mounted on a microscope slide is prevented by condensing the molecules before mounting and unfolding the molecules after they have been placed in a matrix.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
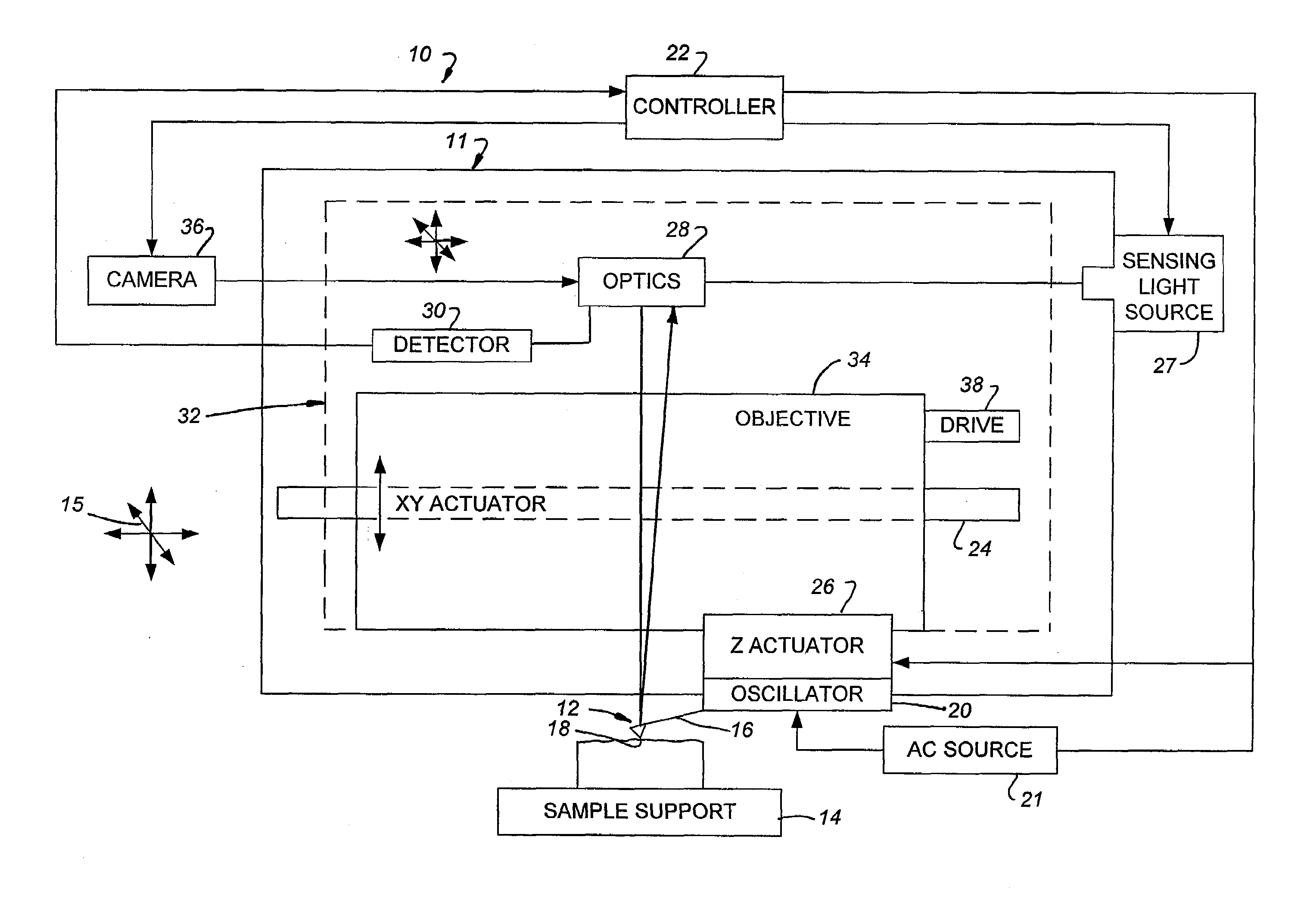
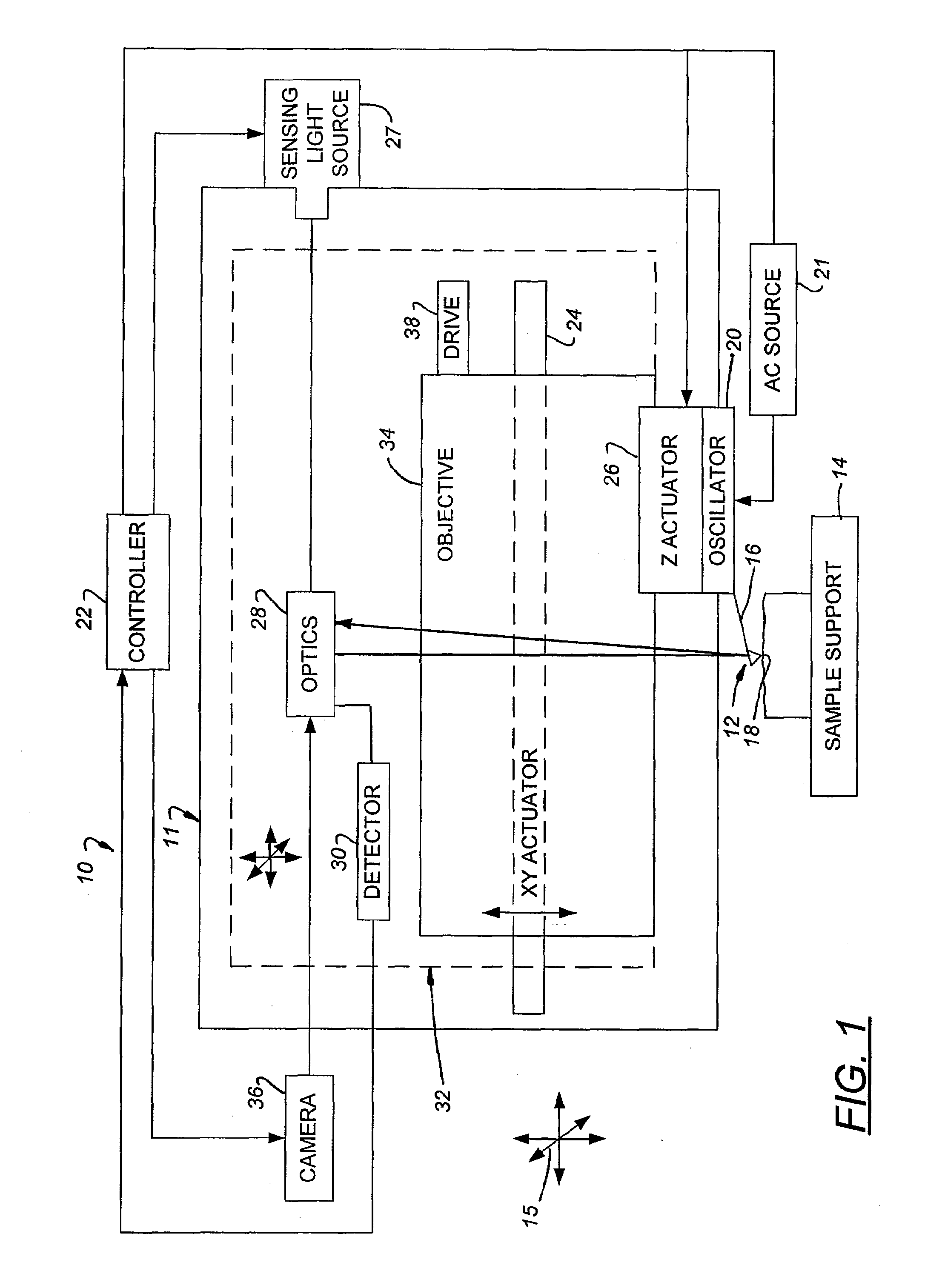
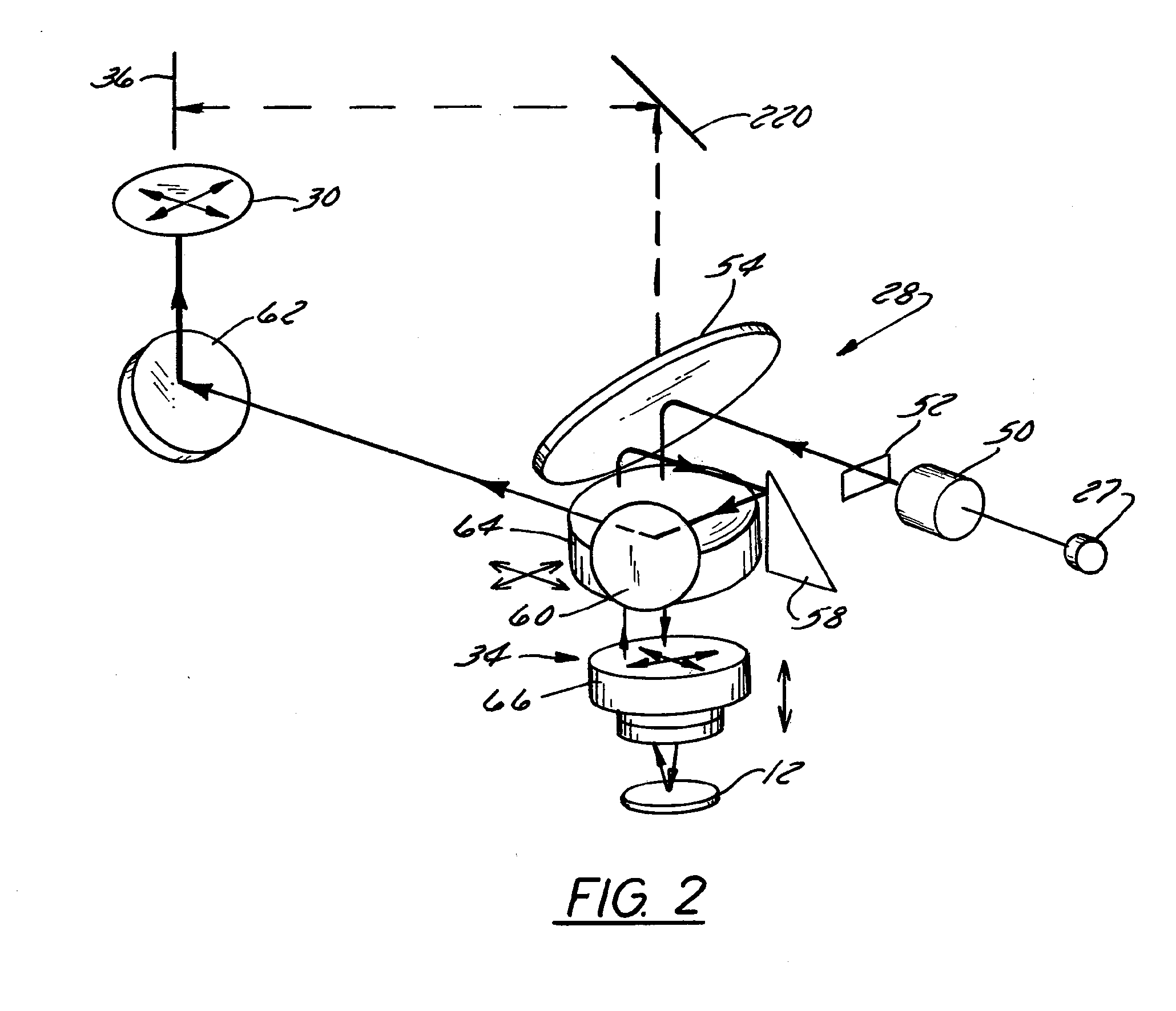
Auto-focusing method and device for use with optical microscopy
InactiveUS7109459B2Rapid positioningAvoid the needElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesOptical axisElectromagnetic radiation
An auto-focusing method and device are presented for determining an in-focus position of a sample supported on a substrate plate made of a material transparent with respect to incident electromagnetic radiation. The method utilizes an optical system capable of directing incident electromagnetic radiation towards the sample and collecting reflections of the incident electromagnetic radiation that are to be detected. A focal plane of an objective lens arrangement is located at a predetermined distance from a surface of the substrate, which is opposite to the sample-supporting surface of the substrate. A continuous displacement of the focal plane relative to the substrate along the optical axis of the objective lens arrangement is provided, while concurrently directing the incident radiation towards the sample through the objective lens arrangement to thereby focus the incident radiation to a location at the focal plane of the objective lens arrangement. Reflected components of the electromagnetic radiation to a location objective lens arrangement are continuously detected. The detected reflected components are characterized by a first intensity peak corresponding to an in-focus position of said opposite surface of the substrate, and a second intensity peak spaced in time from the first intensity peak and corresponding to an in-focus position of said sample-supporting surface of the substrate. This technique enables imaging of the sample when in the in-focus position of the sample-supporting surface of the substrate.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Integrated method for enriching and detecting rare cell in biological fluid sample
ActiveCN101587043APromote universal applicationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationRed blood cellFluorescence
Owner:CYTTEL BIOSCI BEIJING
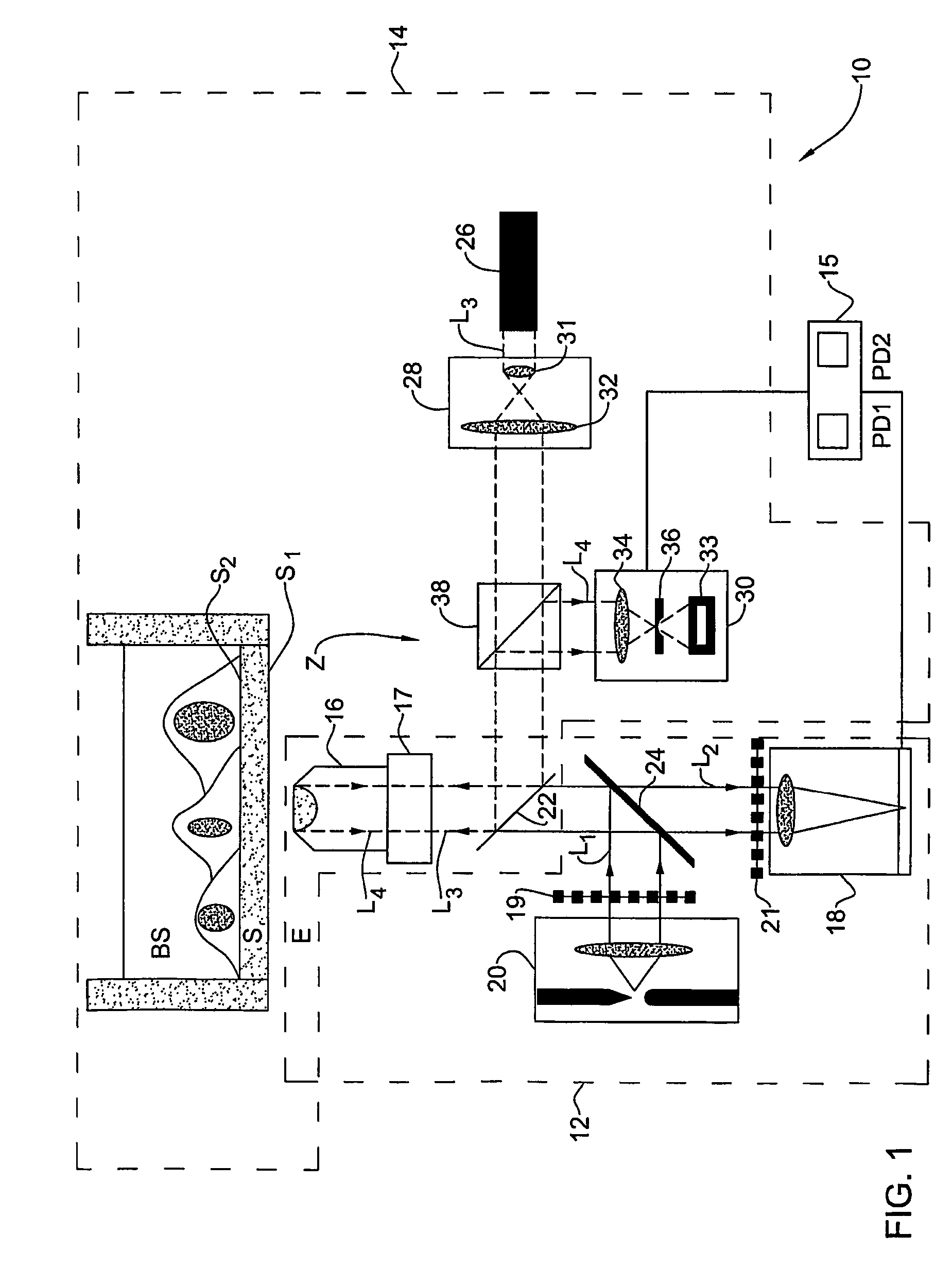
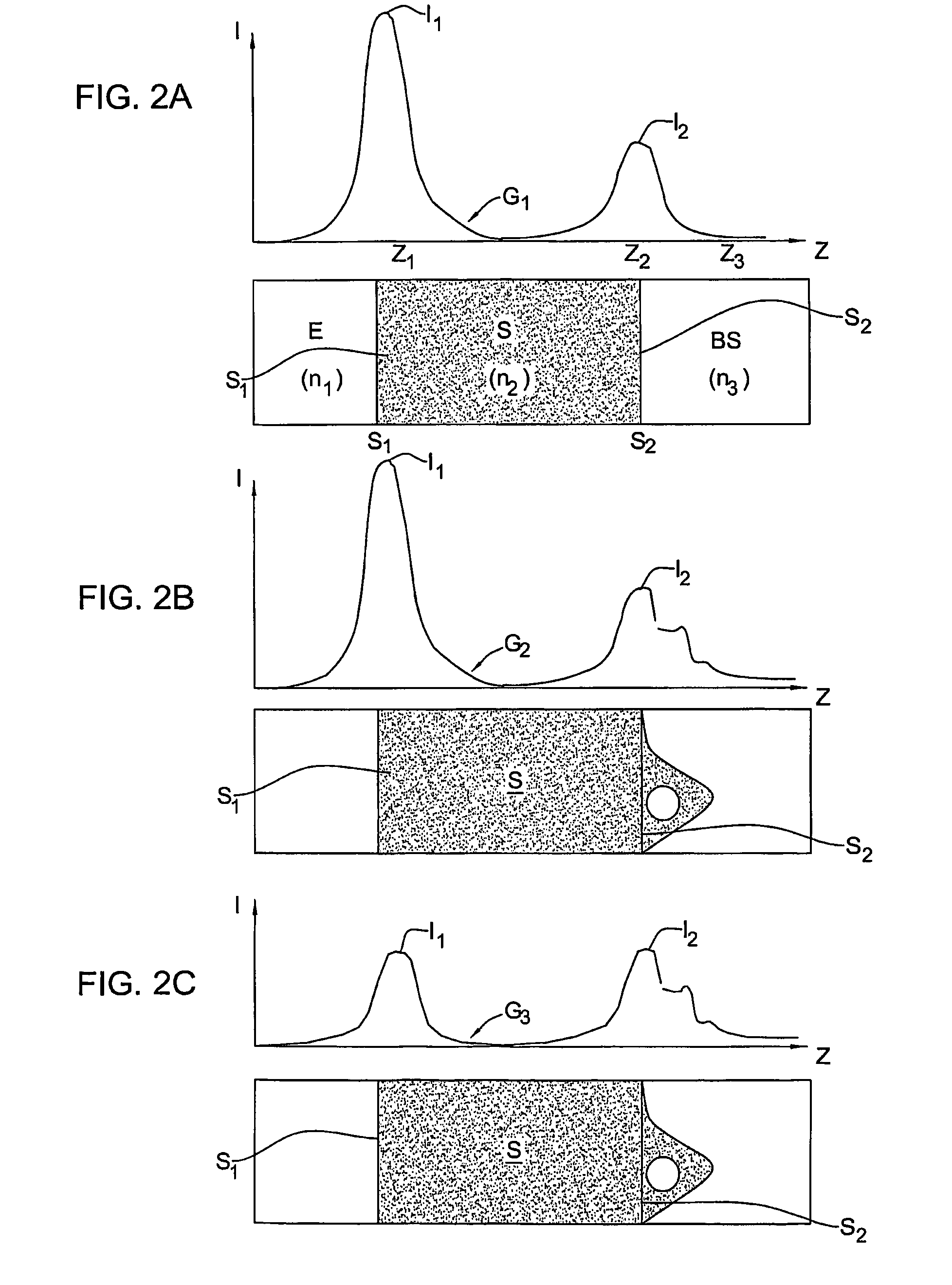
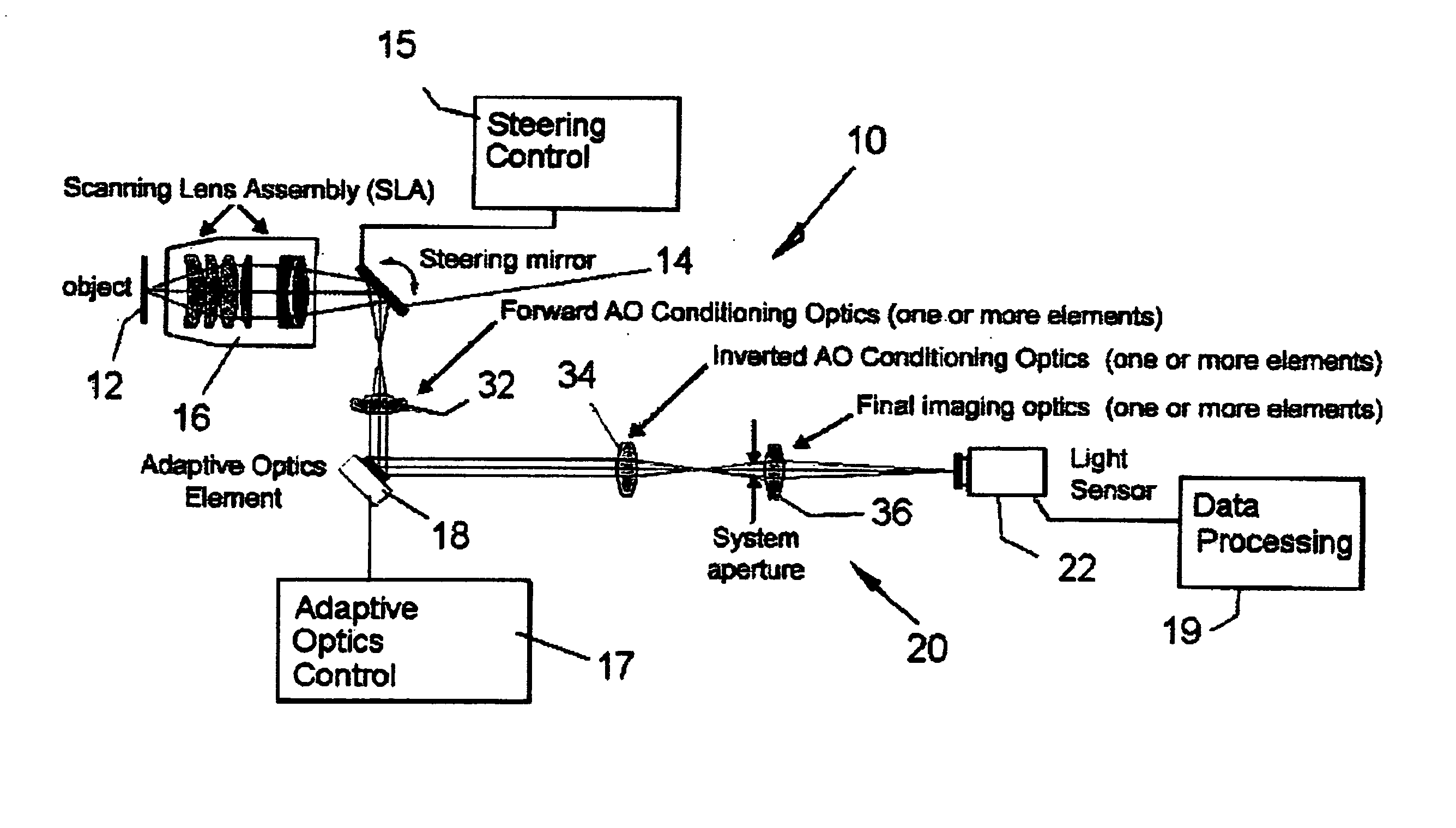
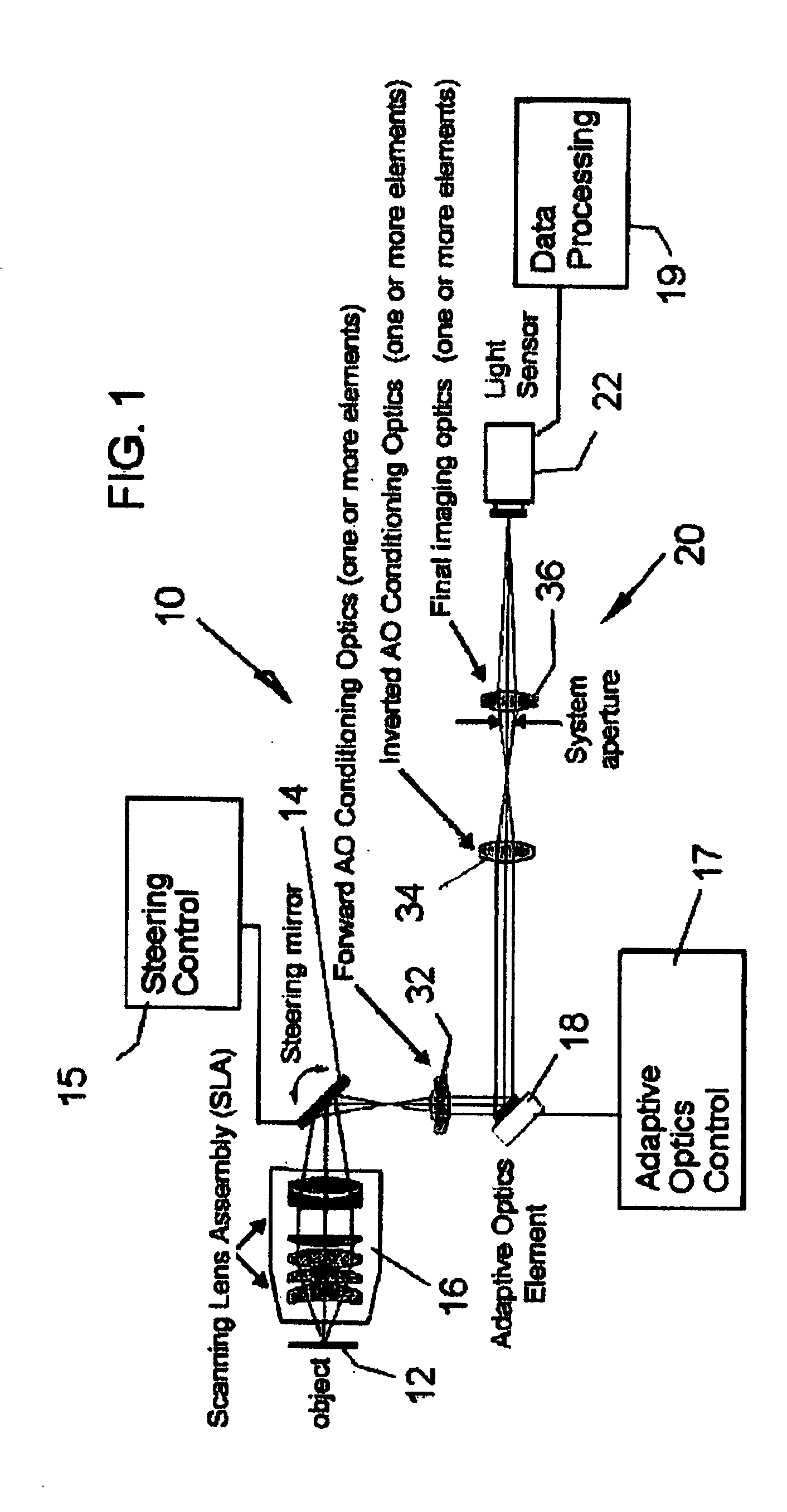
Adaptive-scanning optical microscope
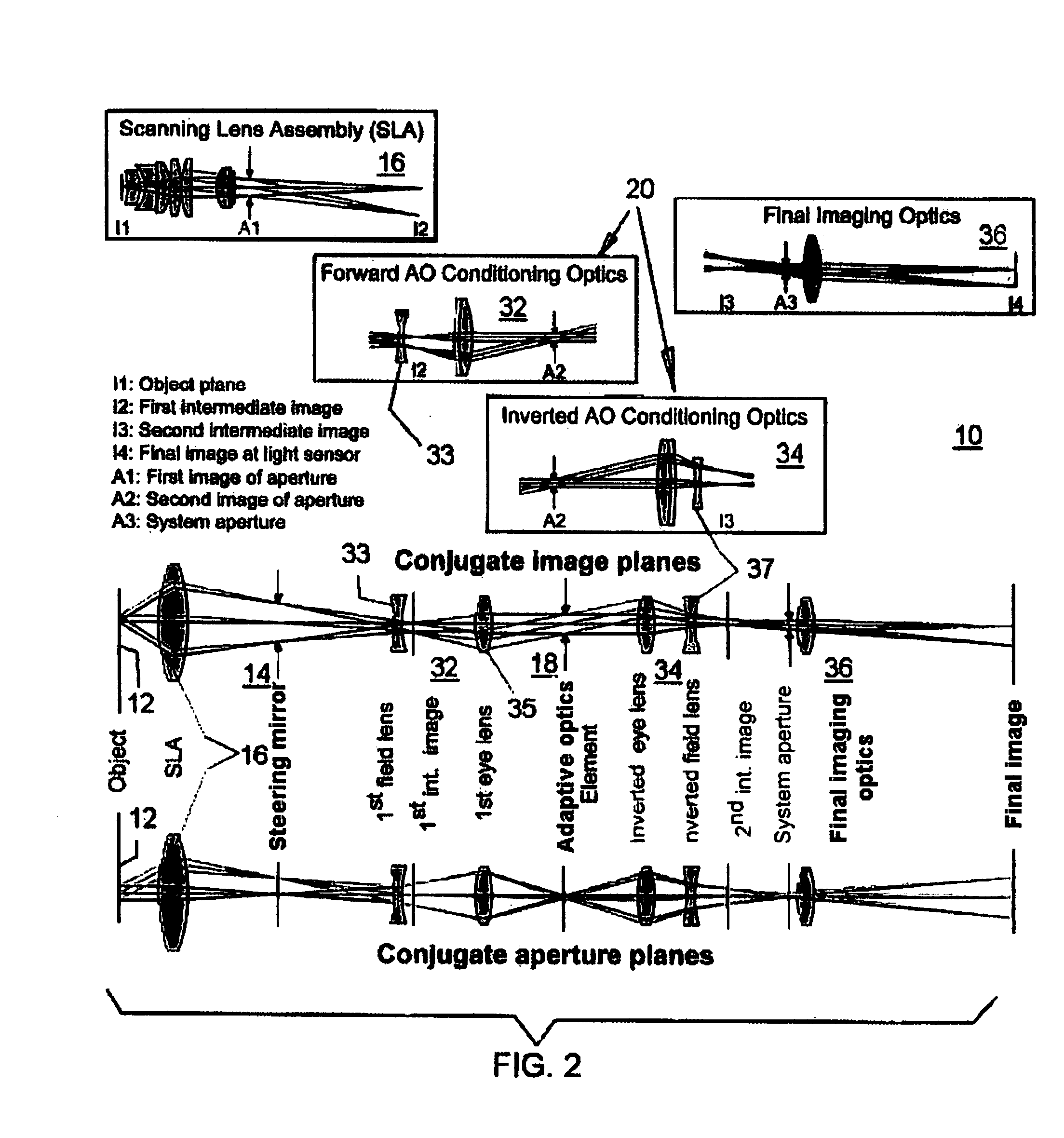
ActiveUS20070253057A1Improve performanceScanner lens is simplifiedMicroscopesPosition dependentOptical aberration
An adaptive scanning optical microscope has a scanner lens assembly for acquiring images from different parts of an object plane and for forming a preferably curved image field having at least some aberration which varies as a function of the part of the object plane from which the image is acquired. A steering mirror selects the field of view and steers light from the object and along a light path from the object plane to a final image plane. An adaptive optics element receives the steered light from the object and compensates for the field position dependent optical aberrations and additional optics are along at least part of the light path for conditioning and focusing the light as it moves from the steering mirror, past the adaptive optics element and to the final image plane.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
3-d optical microscope
ActiveUS20080291532A1Low costReliable and accurate imagingMicroscopesSteroscopic systemsImage contrastFocal position
A 3-D optical microscope, a method of turning a conventional optical microscope into a 3-D optical microscope, and a method of creating a 3-D image on an optical microscope are described. The 3-D optical microscope includes a processor, at least one objective lens, an optical sensor capable of acquiring an image of a sample, a mechanism for adjusting focus position of the sample relative to the objective lens, and a mechanism for illuminating the sample and for projecting a pattern onto and removing the pattern from the focal plane of the objective lens. The 3-D image creation method includes taking two sets of images, one with and another without the presence of the projected pattern, and using a software algorithm to analyze the two image sets to generating a 3-D image of the sample. The 3-D image creation method enables reliable and accurate 3-D imaging on almost any sample regardless of its image contrast.
Owner:KLA CORP
Scanning tunnel microscope
PCT No. PCT / JP88 / 00804 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 5, 1990 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 5, 1990 PCT Filed Aug. 12, 1988 PCT Pub. No. WO89 / 01603 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 23, 1989A scanning tunnel microscope is arranged by a combination of an optical microscope and a tunnel scanning unit. The scanning tunnel unit includes a probe held to be spaced apart from a sample placed on a sample table by a predetermined interval in an axial direction, and an actuator for axially moving the sample table and the probe to a tunnel region and relatively and three-dimensionally driving the sample table and the probe. An objective lens and the probe are arranged such that the axis of the probe of the scanning tunnel unit is aligned with an optical axis of the objective lens of the optical microscope. The sample and the probe are axially moved and brought into the tunnel region, and the sample is scanned in its surface direction while the sample and the probe are finely moved in the axial direction and a tunnel current is kept constant, thereby performing an STM observation of an observation surface of the sample. The objective lens of the optical microscope is axially moved to obtain an in-focus state, and the field of the STM observation surface is observed as an optical microscopic image through an eyepiece lens.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Charged particle beam apparatus
InactiveUS20130284924A1Improve throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesMolecular physicsMicroscope
There is provided an apparatus which can accurately carry out focusing of an optical microscope mounted on a charged particle beam apparatus while restraining an increase in an apparatus cost and a reduction in a throughput. An approximate polynomial is formed based on a focus map of the optical microscope which is previously measured, and a control amount which adds a difference between a piece of wafer height information at that occasion and a piece of wafer height information in actual observation to the approximate polynomial is inputted as a focus control value of the optical microscope.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Defect detection method and defect detection device and defect observation device provided with same
ActiveUS20120274931A1Improve throughputLow costPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsPupilElectron microscope
The disclosed device, which, using an electron microscope or the like, minutely observes defects detected by an optical appearance-inspecting device or an optical defect-inspecting device, can reliably insert a defect to be observed into the field of an electron microscope or the like, and can be a device of a smaller scale. The electron microscope (5), which observes defects detected by an optical appearance-inspecting device or by an optical defect-inspecting device, has a configuration wherein an optimal microscope (14) that re-detects defects is incorporated, and a spatial filter and a distribution polarization element are inserted at the pupil plane when making dark-field observations using this optical microscope (14). The electron microscope (5), which observes defects detected by an optical appearance-inspecting device or an optical defect-inspecting device, has a configuration wherein an optimal microscope (14) that re-detects defects is incorporated, and a distribution filter is inserted at the pupil plane when making dark-field observations using this optical microscope (14).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Adaptive phase contrast microscope
InactiveUS20120257040A1Region can be greatEnhance the imageColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMicro platePhase image
An optical microscope is provided with an adjustable optical phase ring. The adjustable ring provides a way to compensate for distortion in the visible phase ring before the light reaches the sample. In an inverted microscope, when observing transparent cells under a liquid, the visible light phase ring is distorted. By the use of a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) in place of a fixed ring, the projected ring is adjusted to realign the light and produce phase. In a typical micro plate, the meniscus formed produces a lens effect that is realigned by providing changes in the position and pattern, to allow phase imaging over a wider portion of the well. The realignment of the ring can be manual or automated and can be dynamically adjusted based upon an observed image of the sample.
Owner:KAIROS INSTR
3-d optical microscope
ActiveUS7729049B2Low costReliable and accurate imagingMicroscopesSteroscopic systemsImage contrastFocal position
A 3-D optical microscope, a method of turning a conventional optical microscope into a 3-D optical microscope, and a method of creating a 3-D image on an optical microscope are described. The 3-D optical microscope includes a processor, at least one objective lens, an optical sensor capable of acquiring an image of a sample, a mechanism for adjusting focus position of the sample relative to the objective lens, and a mechanism for illuminating the sample and for projecting a pattern onto and removing the pattern from the focal plane of the objective lens. The 3-D image creation method includes taking two sets of images, one with and another without the presence of the projected pattern, and using a software algorithm to analyze the two image sets to generating a 3-D image of the sample. The 3-D image creation method enables reliable and accurate 3-D imaging on almost any sample regardless of its image contrast.
Owner:KLA CORP
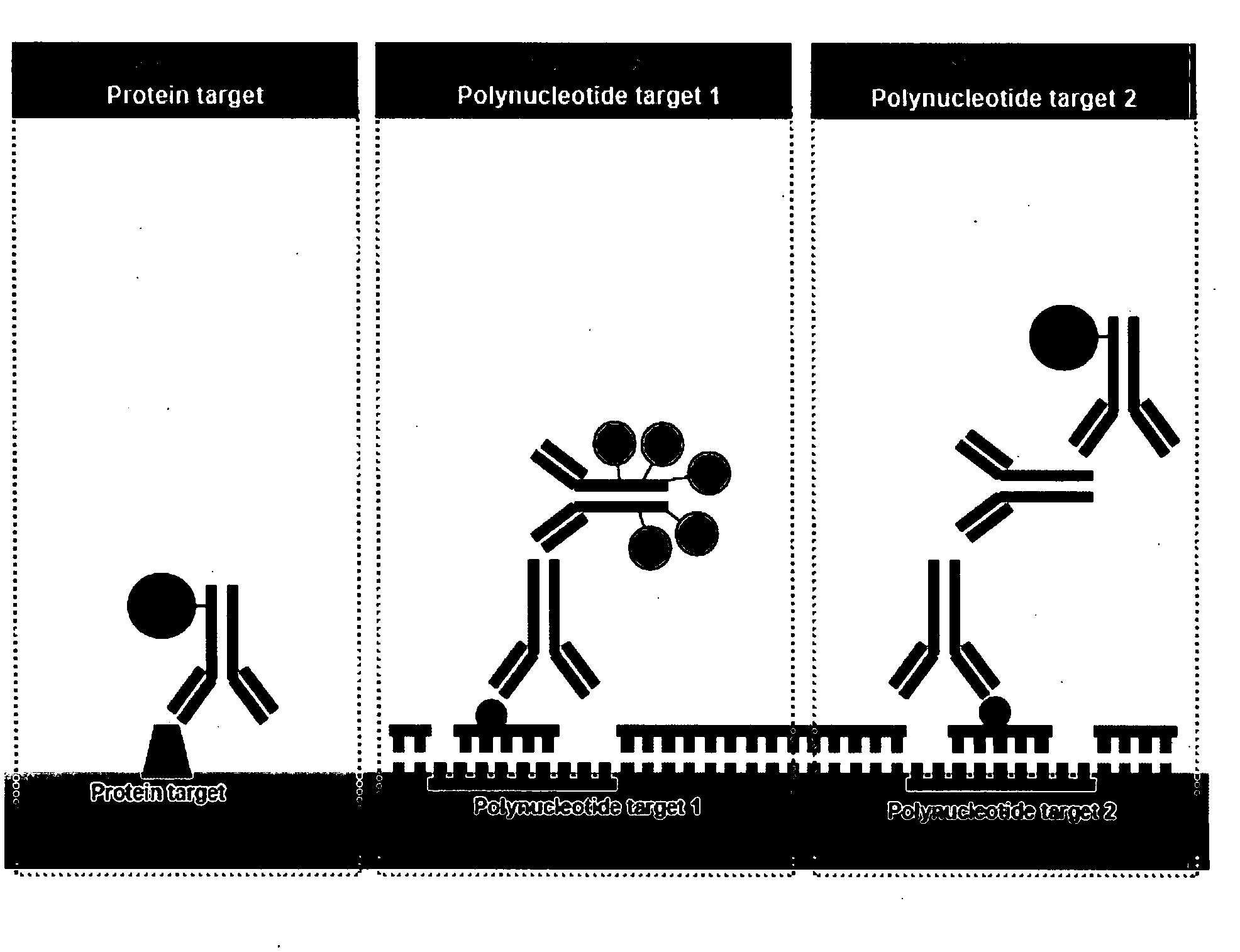
Multicolor chromogenic detection of biomarkers
InactiveUS20080299555A1Facilitates chromogenic detection of signalThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHistocytochemistryChemiluminescence
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assembles of articles and methodology for detecting multiple target molecules in a sample, such as in a tissue sample. In particular, site-specific deposition of elemental metal is used in conjunction with other means of detection, such as other chromogenic, radioactive, chemiluminescent and fluorescent labeling, to simultaneously detect multiple targets, such a gene, a protein, and a chromosome, in a biological sample. More particularly the multiple targets may be labeled with the specifically deposited metal and other chromogenic labels to allow chromogenic immunohistochemical (IHC) detection in situ by using bright field light microscope.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Optical detection and analysis of particles
InactiveUS7399600B2Simple to useEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationParticle methodPhotodetection
Method and apparatus for the single particle detection of submicron structures such as biological molecules and viruses utilises an optical element (100) comprising an optically transparent substrate (1) partially coated with a thin film of metal (2) illuminated with an optical beam (4) incident on a non-metal coated region (3) of the surface of the optical element at a point adjacent or close to the metal coated region of the optical element such that the beam propagates above but close and substantially parallel to the metal surface defining a measurement zone from within which submicron particles (7) contained in a sample (6) placed in contact with the optical element scatter or emit light which can be detected in the far field by conventional photodetection systems. The apparatus can be configured in a flow cell or optical microscope configuration.
Owner:MALVERN INSTRUMENTS
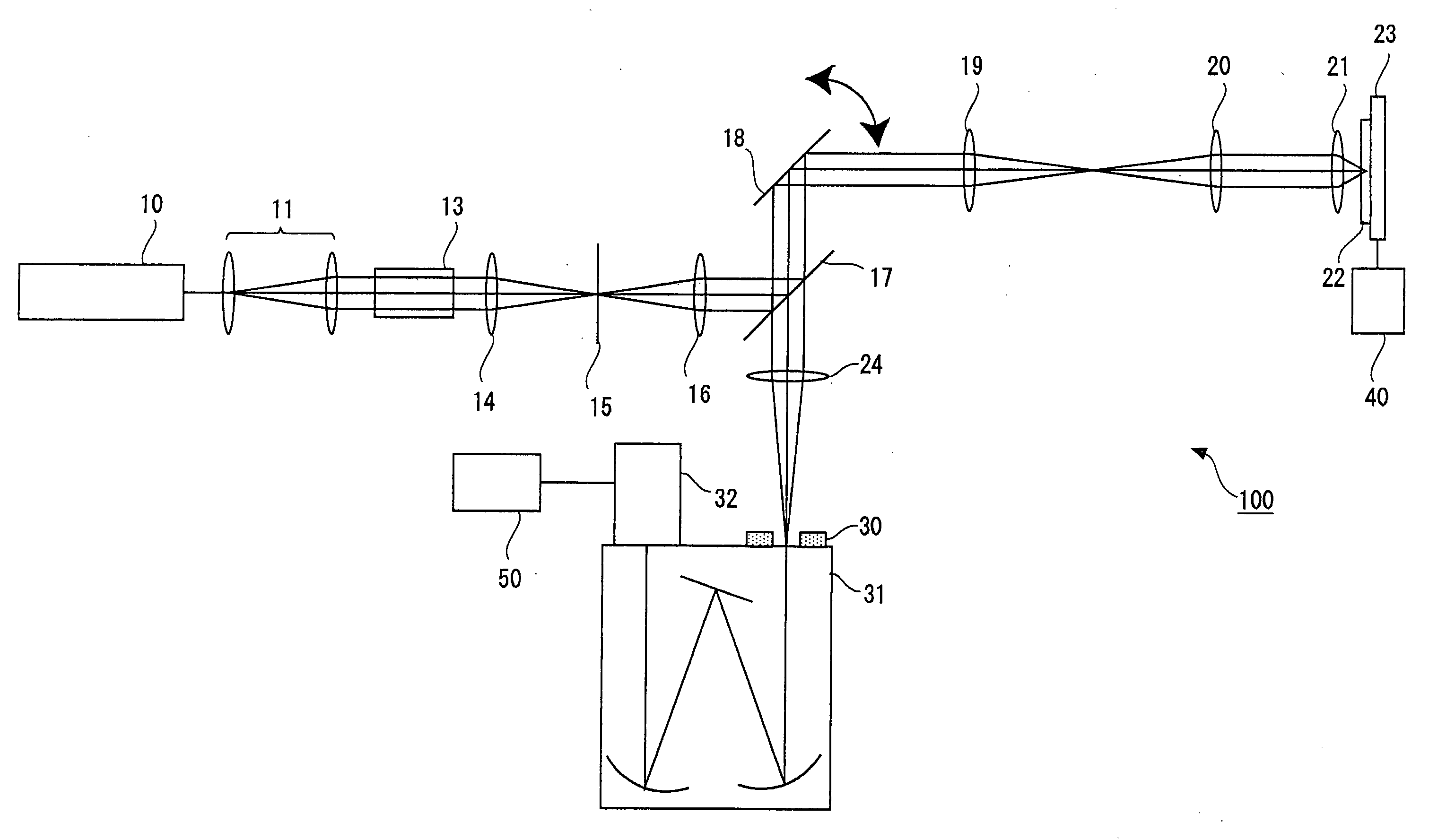
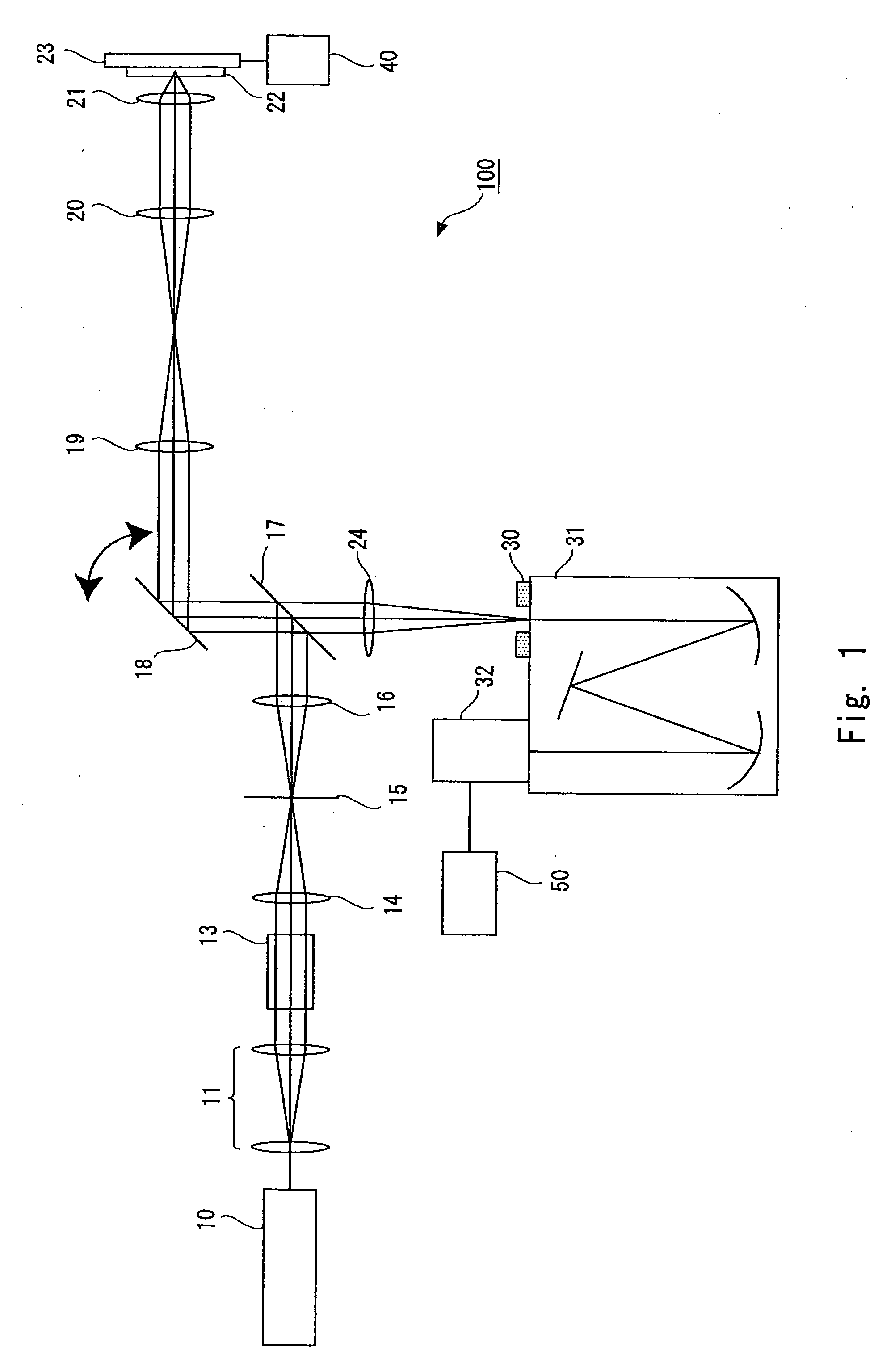
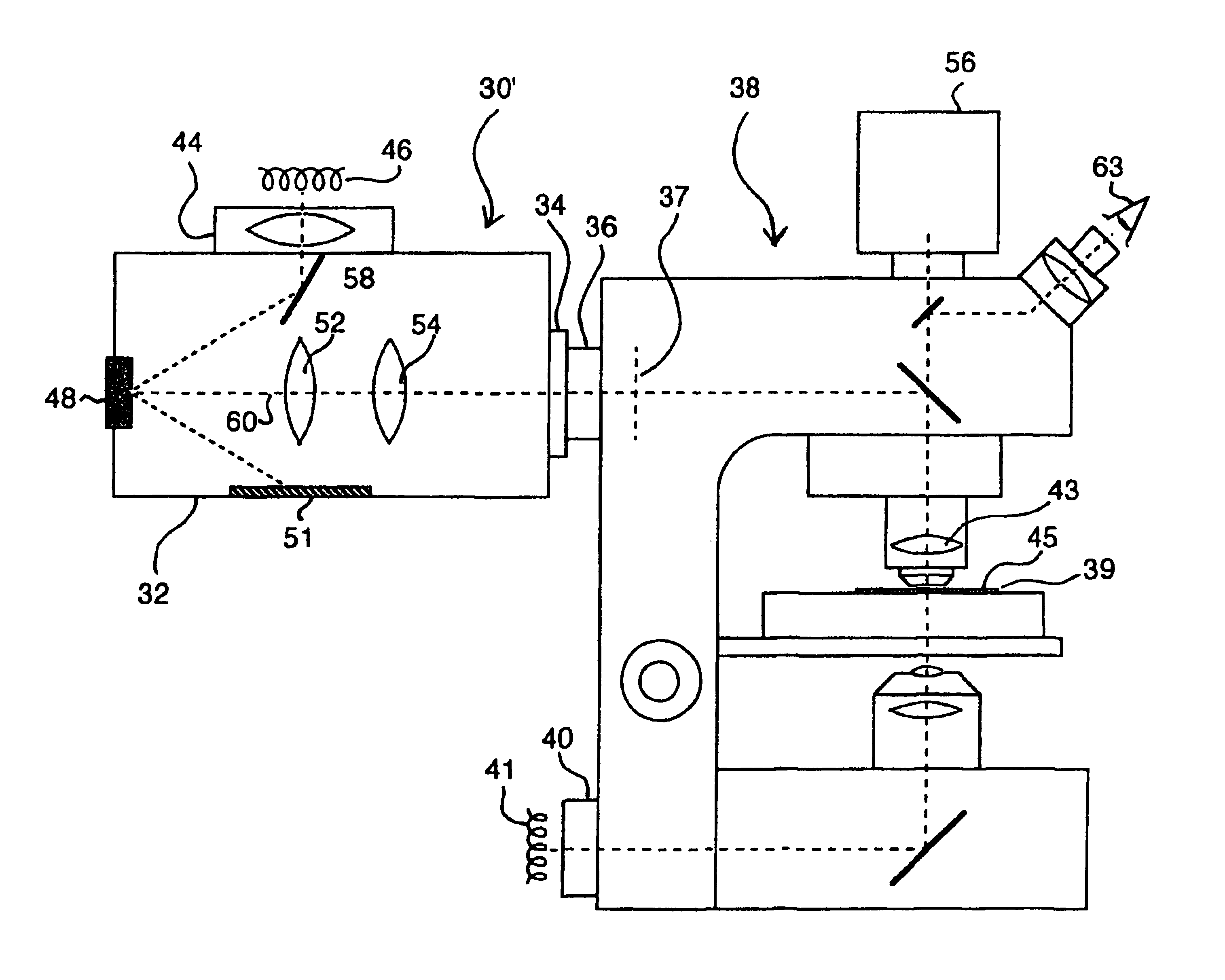
Optical microscope and spectrum measuring method
ActiveUS20070132994A1High precision measurementUniform scanning speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splitterLight beam
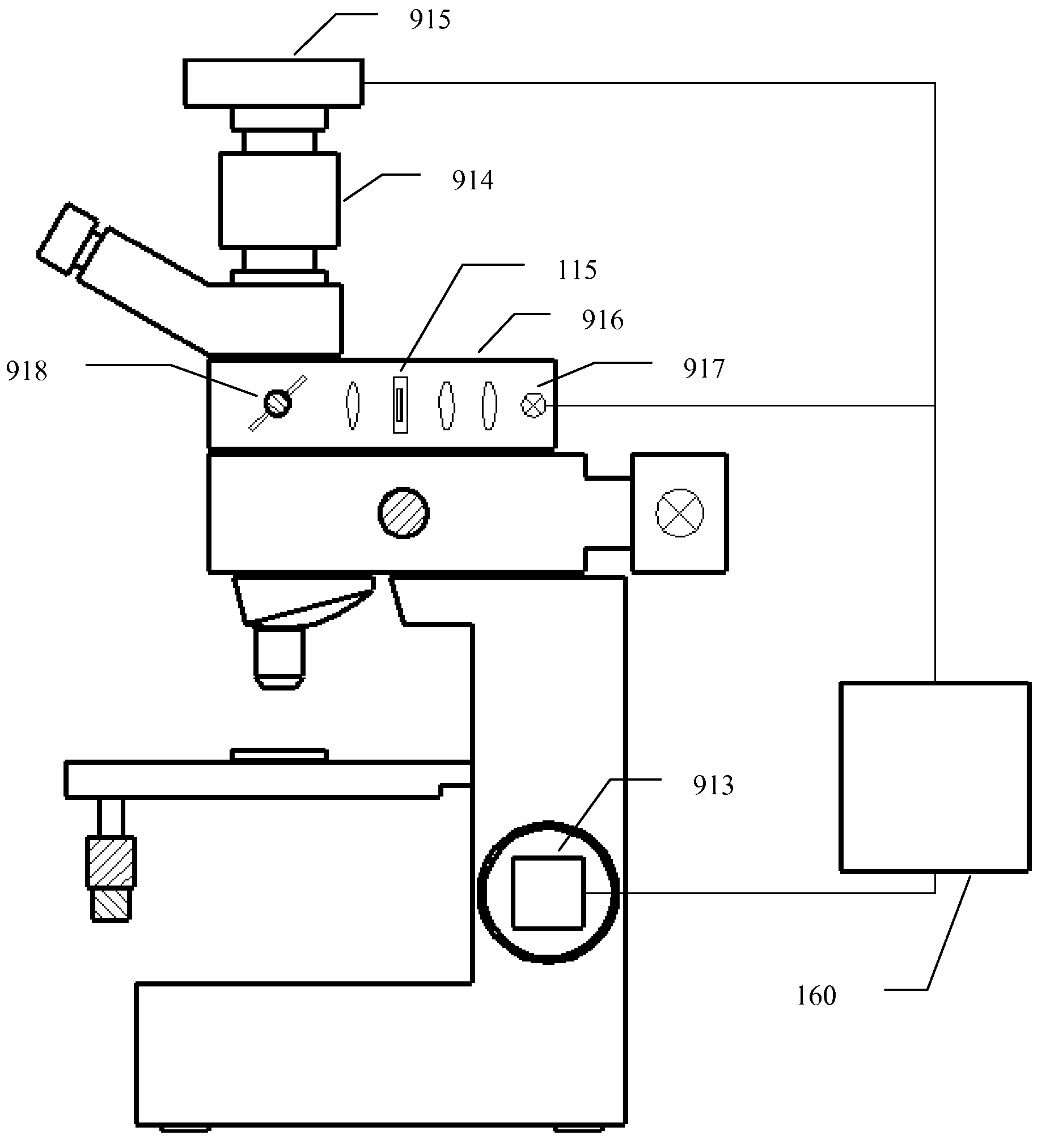
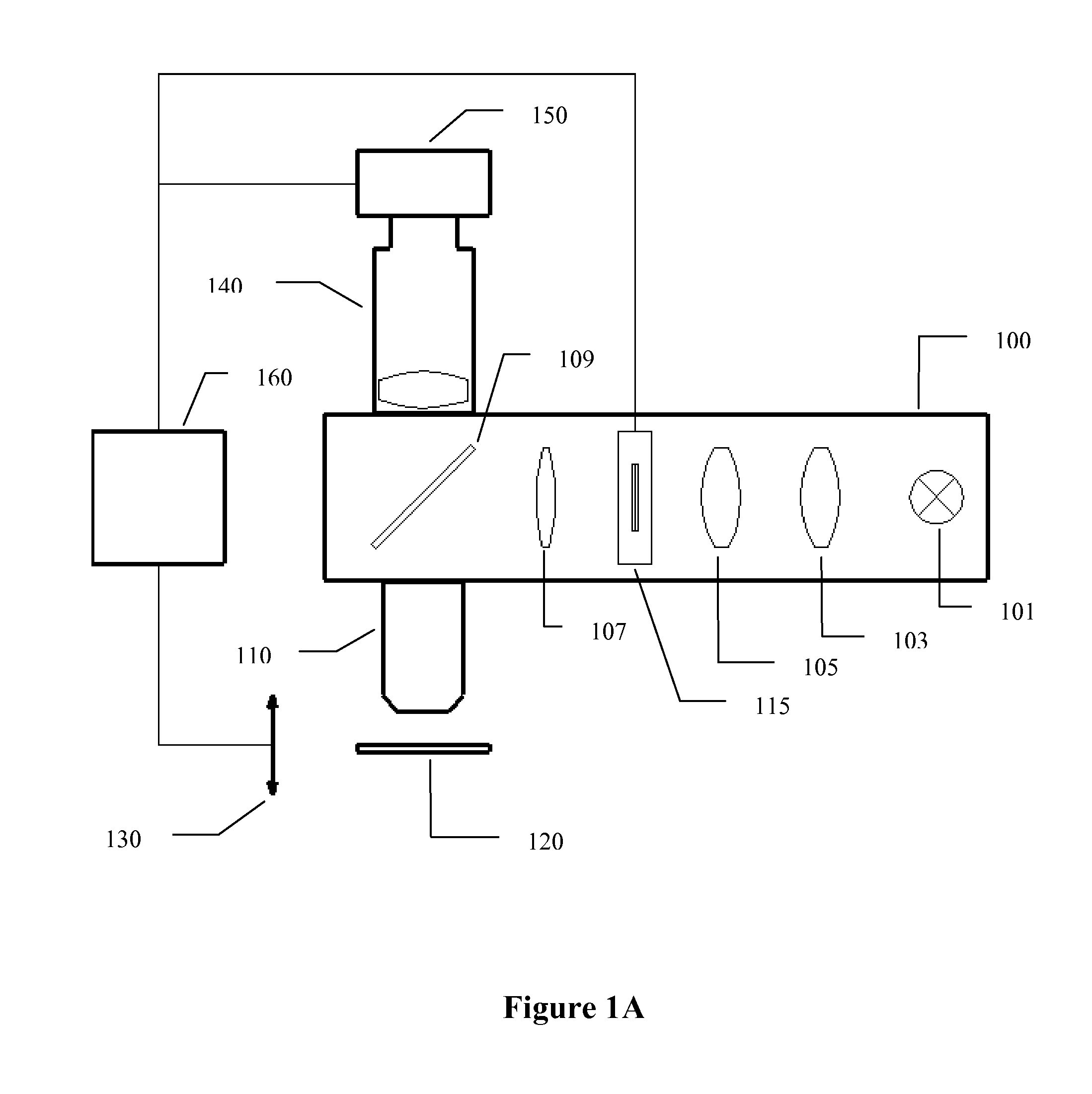
An optical microscope according to a first embodiment of the present invention includes: a laser light source; a Y-directional scanning unit moving the light beam in a Y direction; an objective lens; a X-directional scanning unit moving the light beam in a X direction; a beam splitter provided in an optical path from the Y-directional scanning unit to the sample, and separating outgoing light out of the light beam incident on the sample, which exits from the sample toward the objective lens from the light beam incident on the sample from the laser light source; a spectroscope having an entrance slit extending along the Y direction and spatially dispersing the outgoing light passed through the entrance slit in accordance with a wavelength of the light; and a detector detecting the outgoing light dispersed by the spectroscope.
Owner:NANOPHOTON
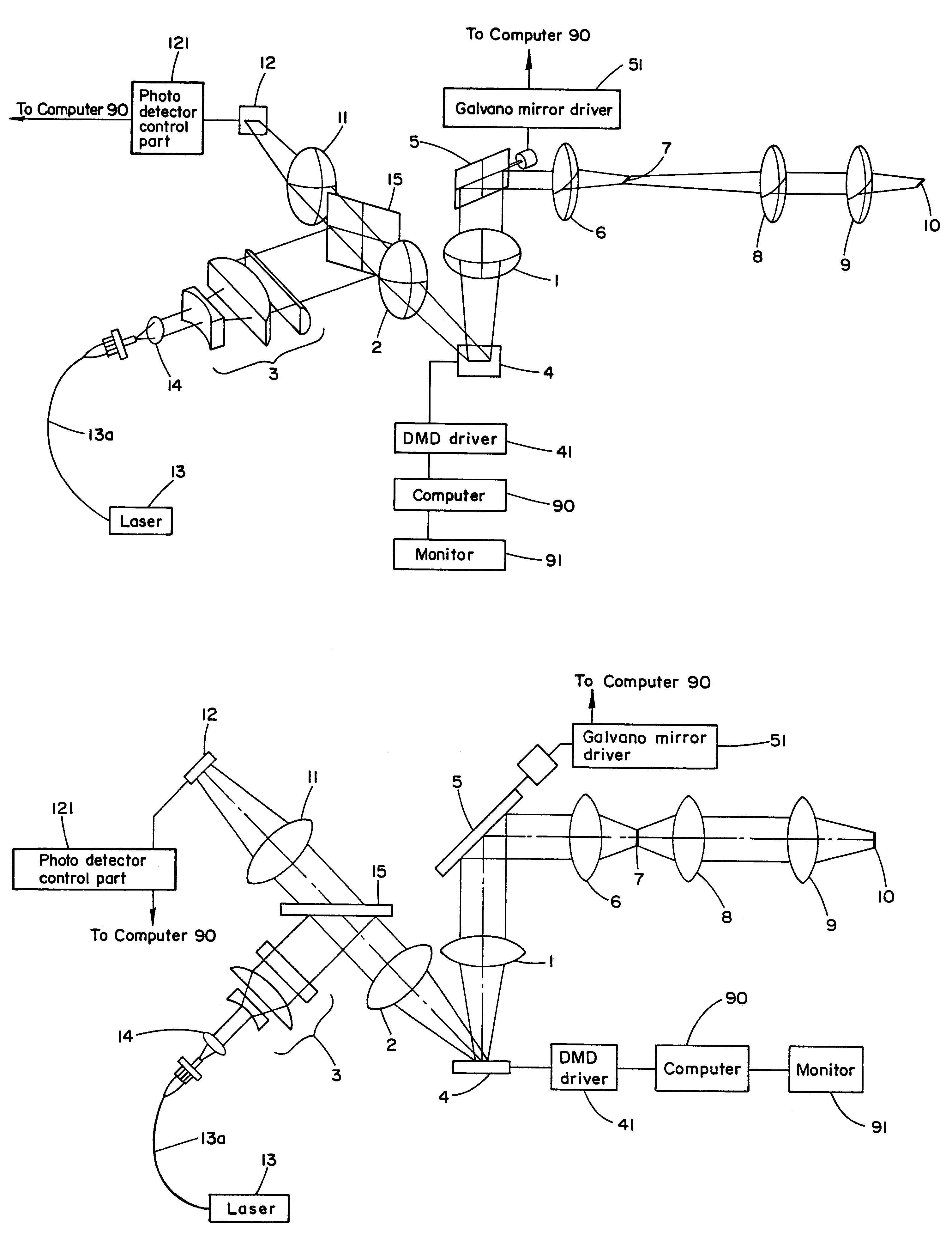
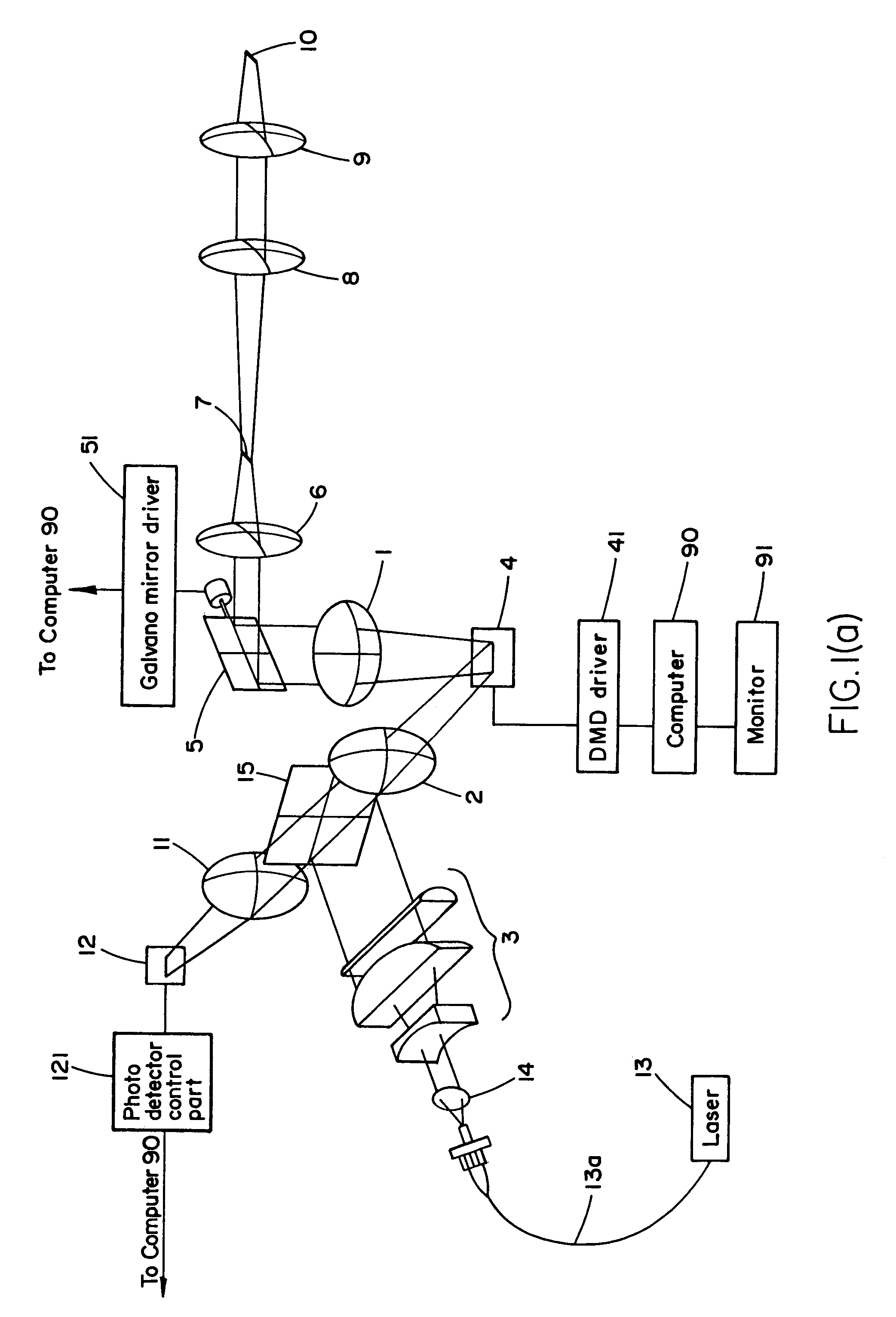
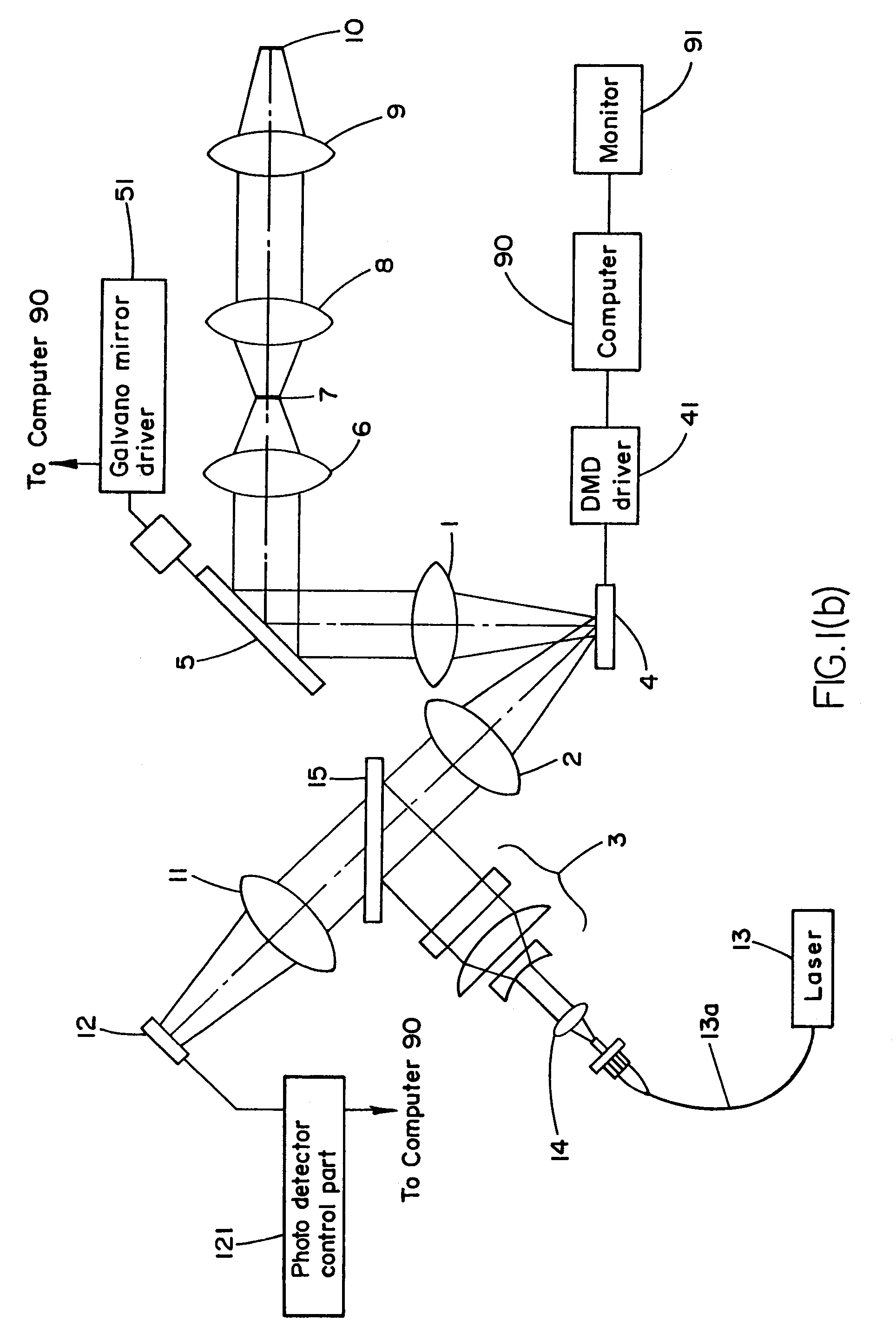
Spatial light modulator apparatus
InactiveUS6885492B2Low costPerforms betterStatic indicating devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatial light modulatorDigital interface
A spatial light modulator apparatus for an optical microscope system including an optical head with a mounting flange for mounting the optical head to a port of the microscope, a DMD for generating a pattern image of light, a light source mount for receiving a source of illumination, and one or more optical elements for directing light from the source of illumination to the DMD and to direct the pattern image generated by the DMD to the microscope. A DMD controller has a digital input and is connected to the DMD for driving the individual micromirrors of the DMD to generate the pattern image. A pattern generation subsystem is configured to output pattern image data and a digital interface is connected between the digital input of the DMD controller and the pattern generation subsystem, the digital interface configured to provide a digital drive signal to the DMD controller corresponding to the pattern image data.
Owner:ANDOR TECH PLC
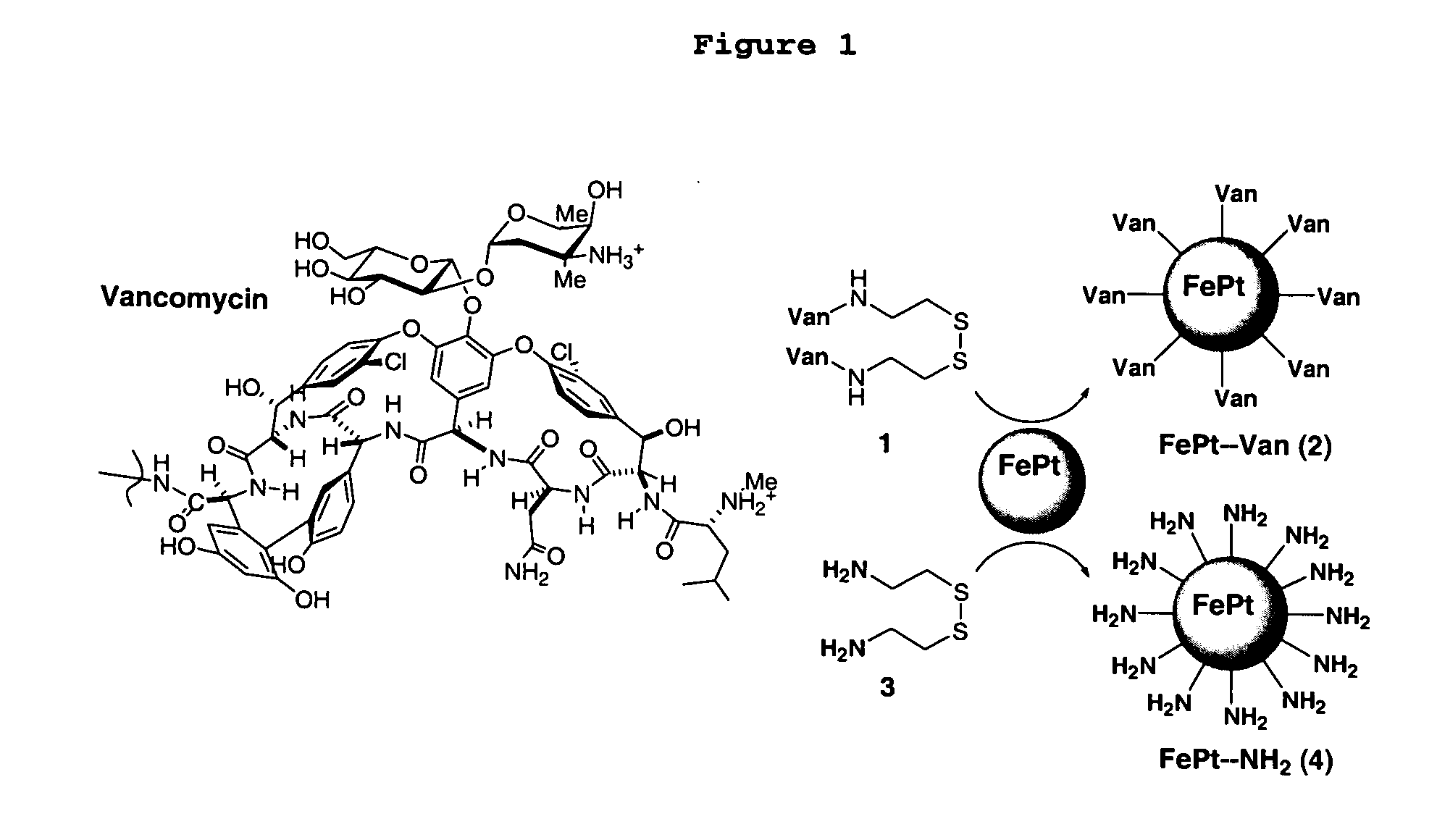
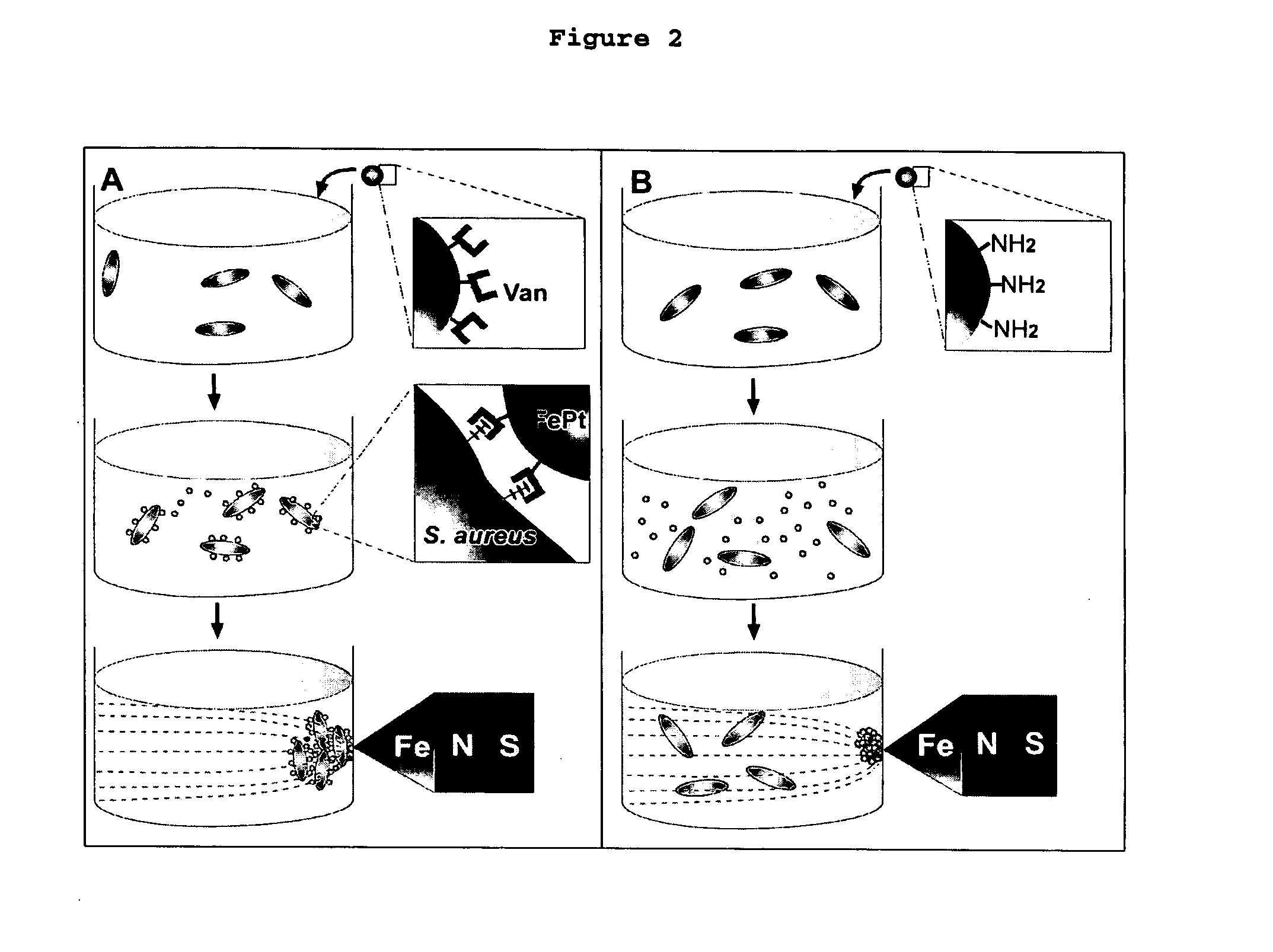
Biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for pathogen detection
InactiveUS20060292555A1High sensitivityEasy to reportNanotechMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetite NanoparticlesBiology
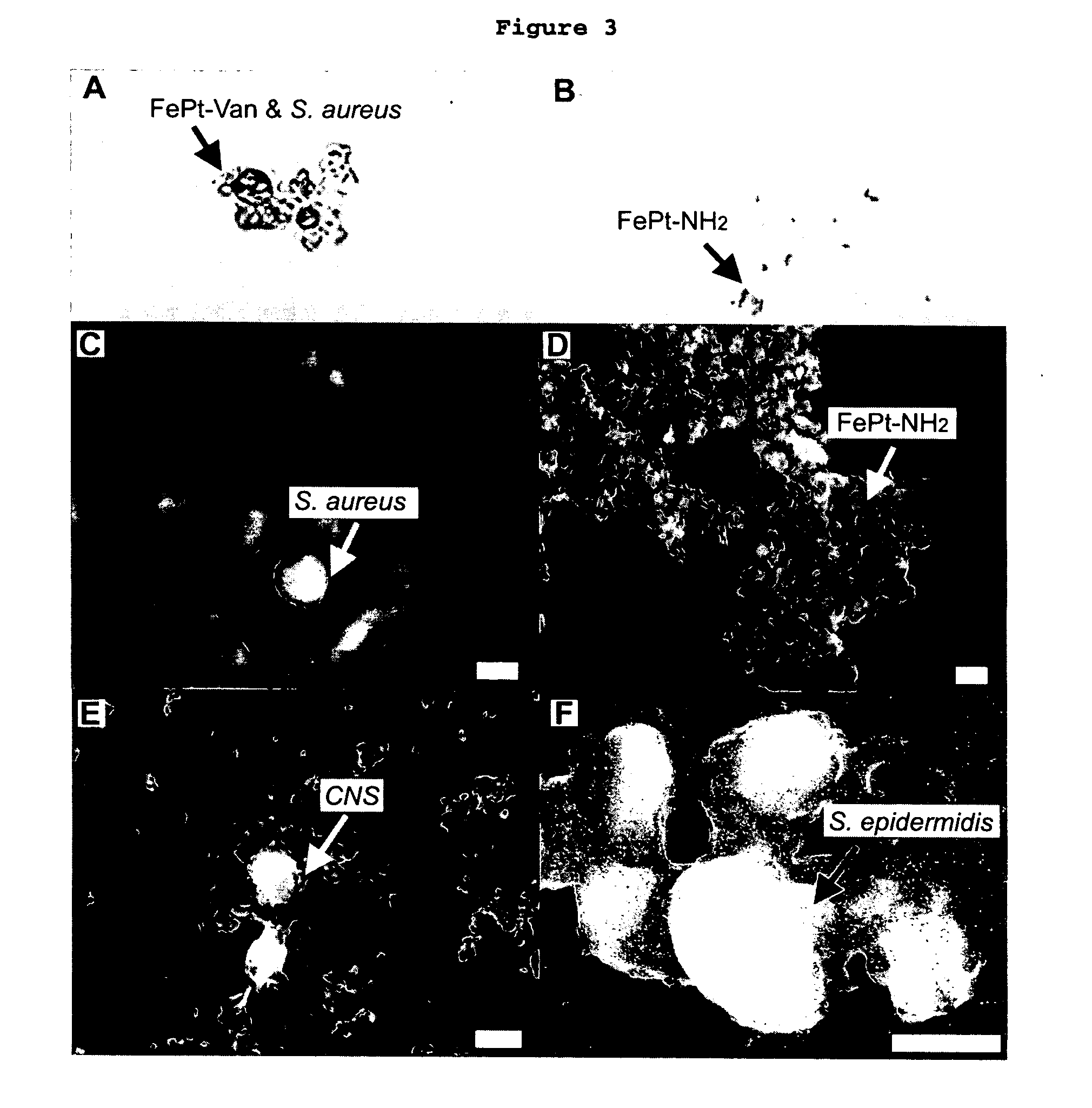
This invention provides a method of detecting pathogens comprising the steps of: (a) contacting a sufficient amount of biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles with an appropriate sample for an appropriate period of time to permit the formation of complexes between the pathogens in the sample and the nanoparticles; (b) using a magnetic field to aggregate said complexes; and (c) detecting said complexes. The method may further comprise the additional step of removing said complexes. The biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles are preferably a conjugate of vancomycin and FePt. The pathogens may be bacteria or viruses, and the sample may be a solid, liquid, or gas. Detection may involve conventional fluorescence assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), optical microscope, electron microscope, or a combination thereof. The sensitivity of detection for the method is at least as low as 10 colony forming units (cfu) of the pathogens in one milliliter of solution within one hour.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
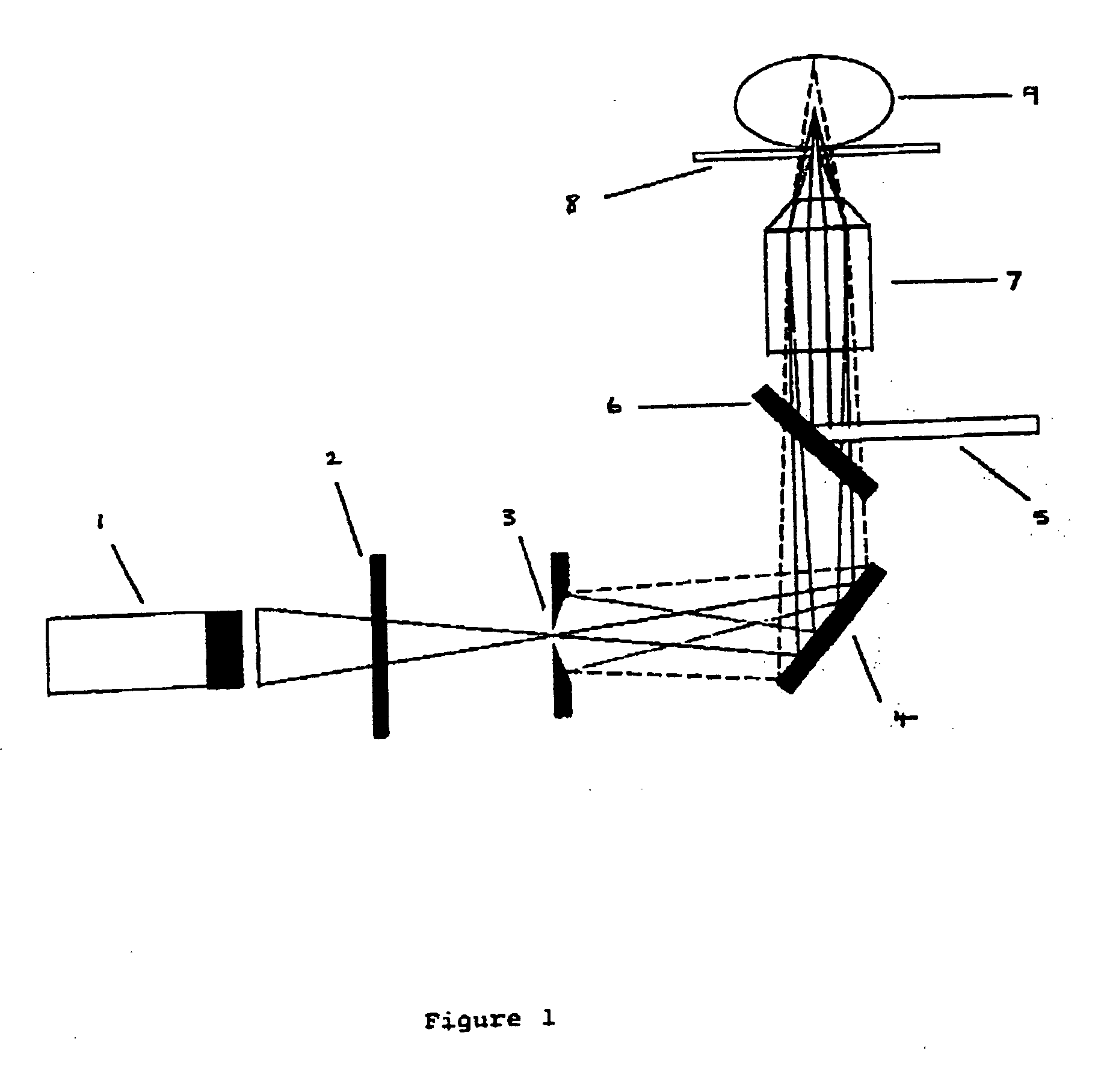
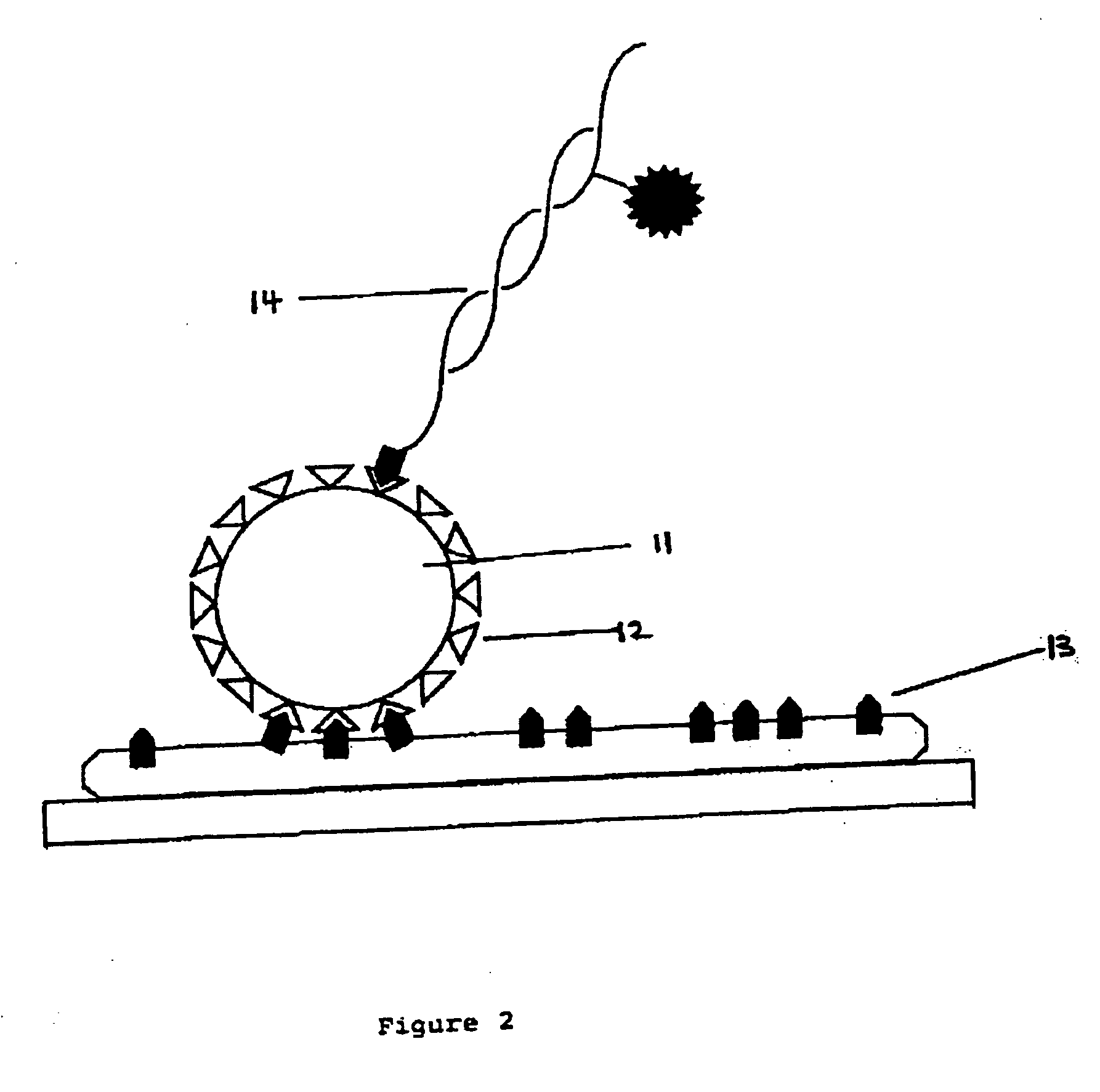
Contact-field optical microscope
InactiveUS7006741B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBundled fibre light guidePhotocathodeOpto electronic
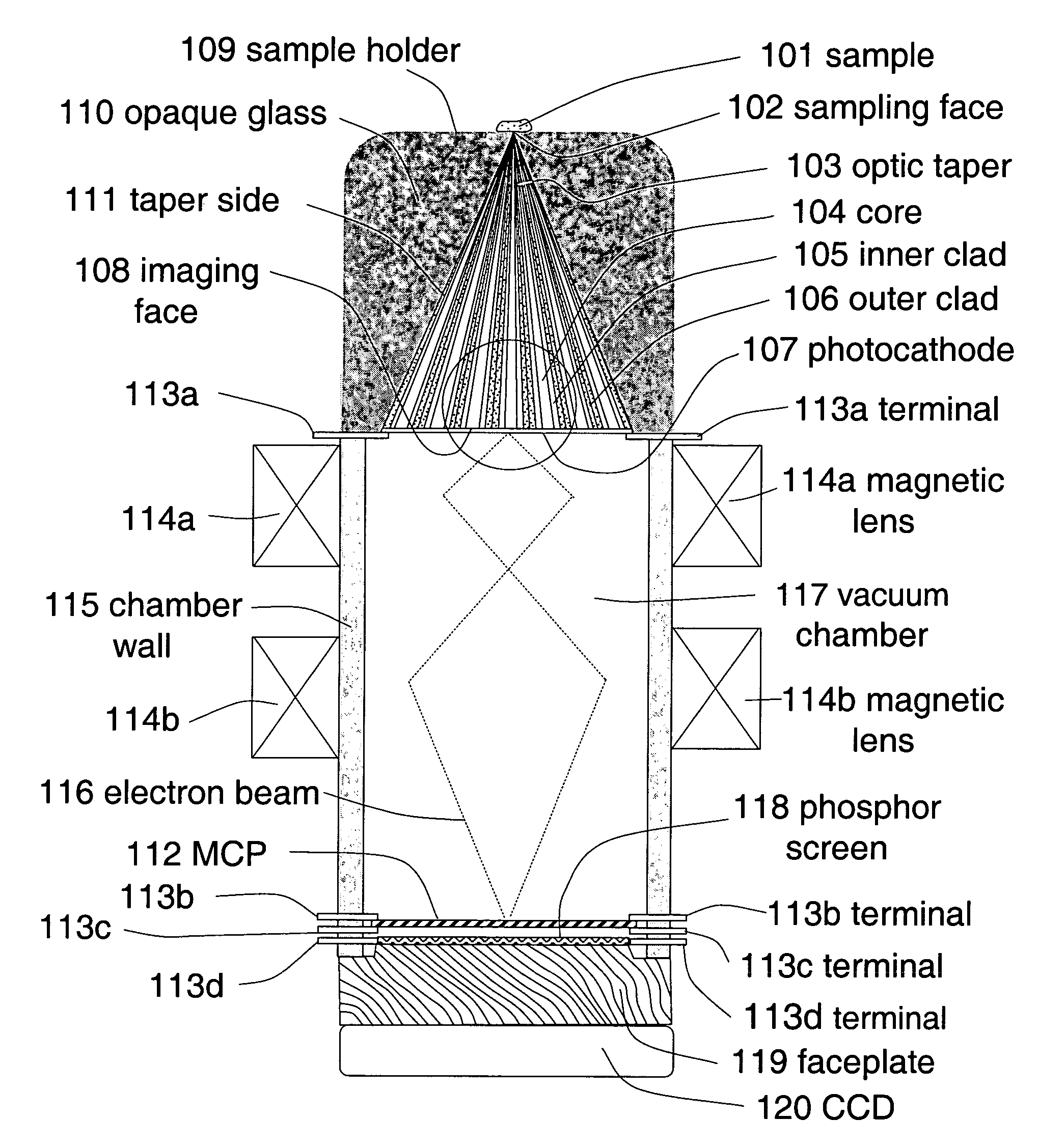
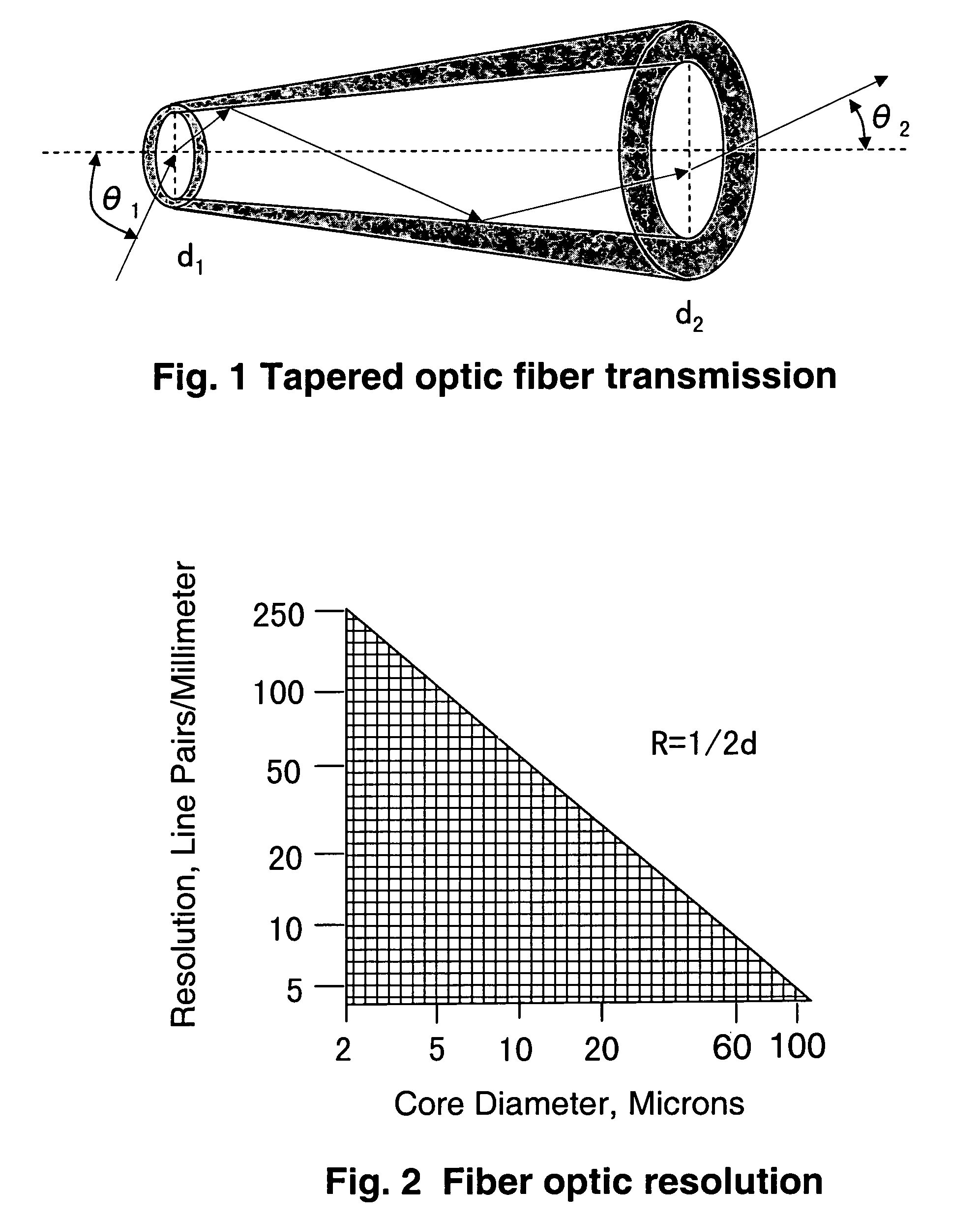
A broad-spectrum, high spatial and time resolution contact-field optical microscope comprises a fiber optical taper, a vacuum chamber, a photocathode, a magnetic lens photoelectron image enlarger, a micro-channel plate image intensifier, a phosphor screen and a CCD. Sample is placed directly in contact with a smaller sampling face of the optical taper. Light which is emitted, reflected or transmitted by the sample is launched into each of the fiber core ends on the sampling face and conveyed by the optical fibers to a larger imaging face of the optical taper, thereby presenting an enlarged image at the imaging face. The image is converted into a photoelectron image by photocathode which is deposited on the surface of the imaging face. The photoelectron image is further enlarged by magnetic lenses and intensified by micro-channel plate. The enlarged and enhanced electron image is displayed on phosphor screen and coupled through faceplate to CCD.
Owner:YU BI
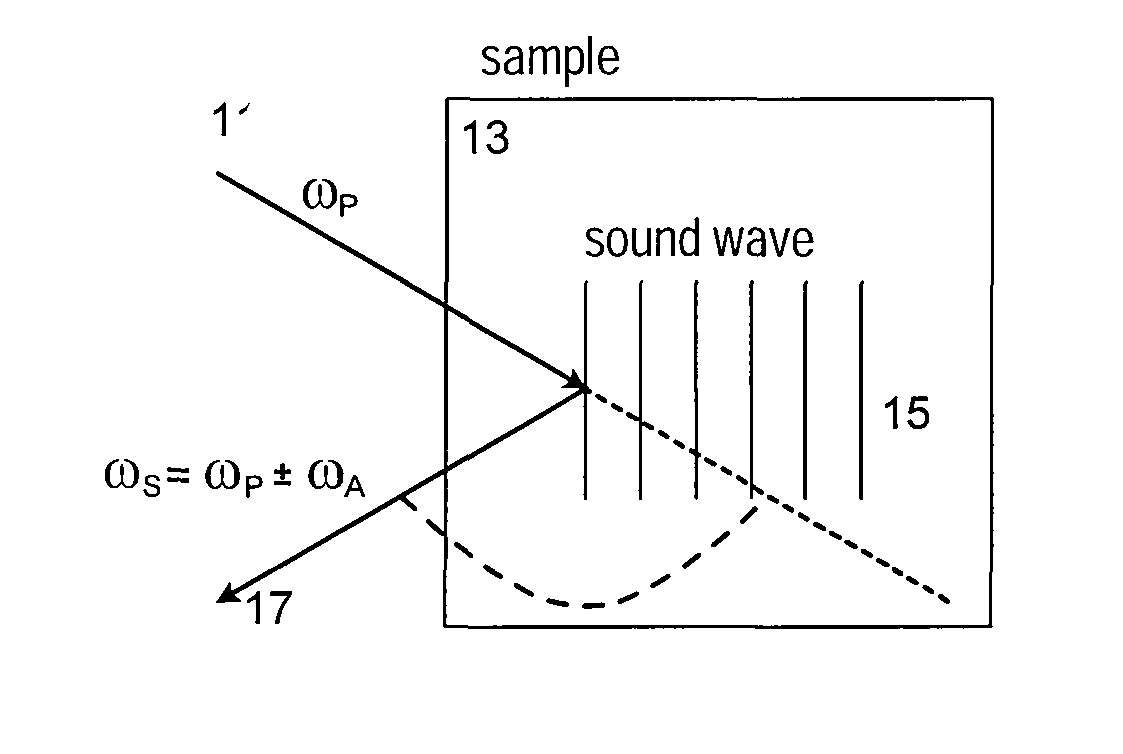
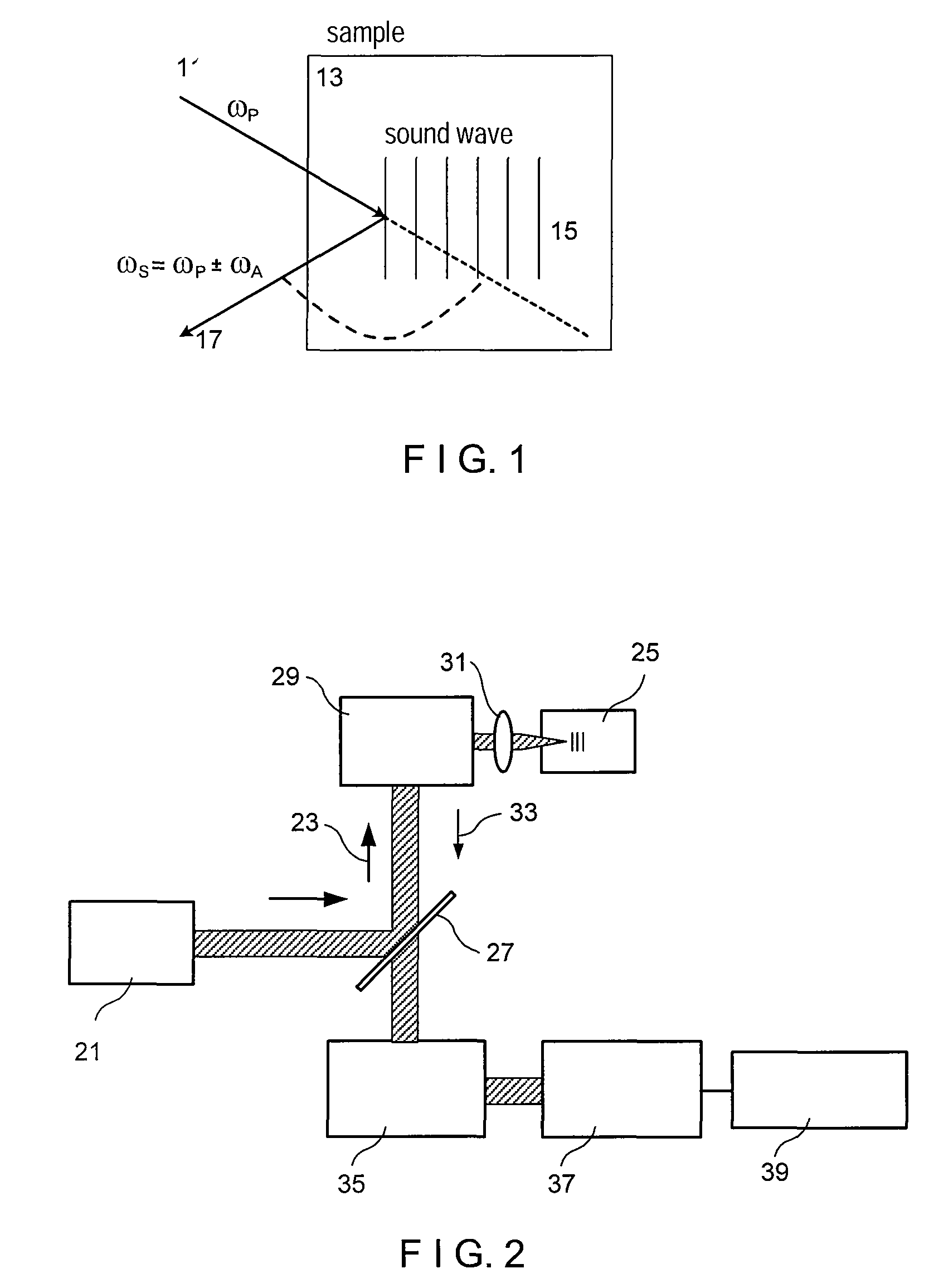
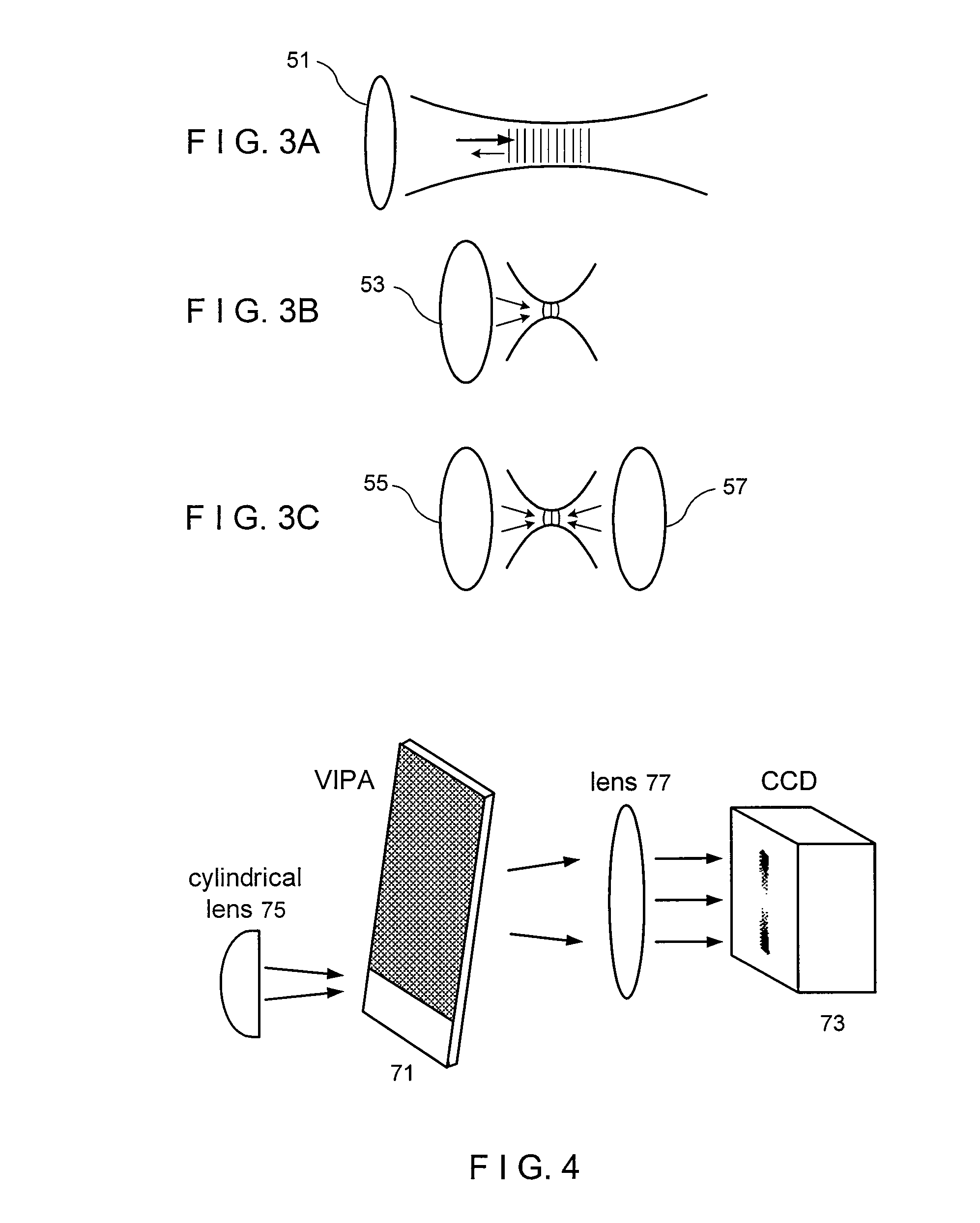
Methods, arrangements and systems for obtaining information associated with a sample using optical microscopy
ActiveUS8115919B2Radiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyAcoustic waveElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Online material biaxial static-dynamic performance test platform under service temperature
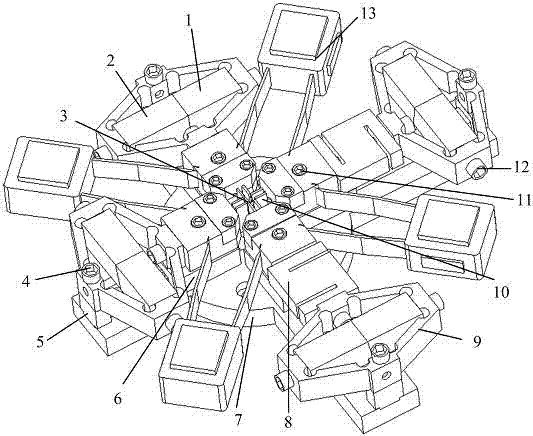
ActiveCN104502202AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesAlloyEngineering
The invention relates to an online material biaxial static-dynamic performance test platform under service temperature, belonging to the field of precision drive. The large-stroke biaxial synchronous identical-speed or synchronous different-speed displacement output is realized by virtue of four groups of piezoelectric actuators which are orthogonally distributed, and the biaxial static tensile test or dynamic fatigue test for a block-shaped material or a film material with a characteristic size being in a millimeter scale can be carried out under a high / low temperature service condition by combining with an embedded high temperature electrothermal alloy sheet / parr patch. The online material biaxial static-dynamic performance test platform is likely to use in conjunction with a scanning electron microscope with a relatively-large vacuum cavity or other microimaging device with an open-type carrier space, such as an optical microscope, an atomic power microscope and a high speed camera, so that the multimode biaxial static tensile test or the large-frequency-range biaxial dynamic fatigue test can be carried out, and the research for the microstructure evolution behavior and fatigue failure mechanism of various structural materials or functional materials under a complicated service condition such as a high / low temperature condition and a static-dynamic plane stress condition can be facilitated.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com