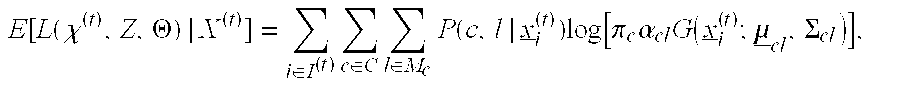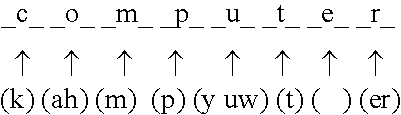Patents
Literature
143255 results about "Algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm (/ˈælɡərɪðəm/ ) is a sequence of instructions, typically to solve a class of problems or perform a computation. Algorithms are unambiguous specifications for performing calculation, data processing, automated reasoning, and other tasks.
Methods and apparatus for interpreting user selections in the context of a relation distributed as a set of orthogonalized sub-relations
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
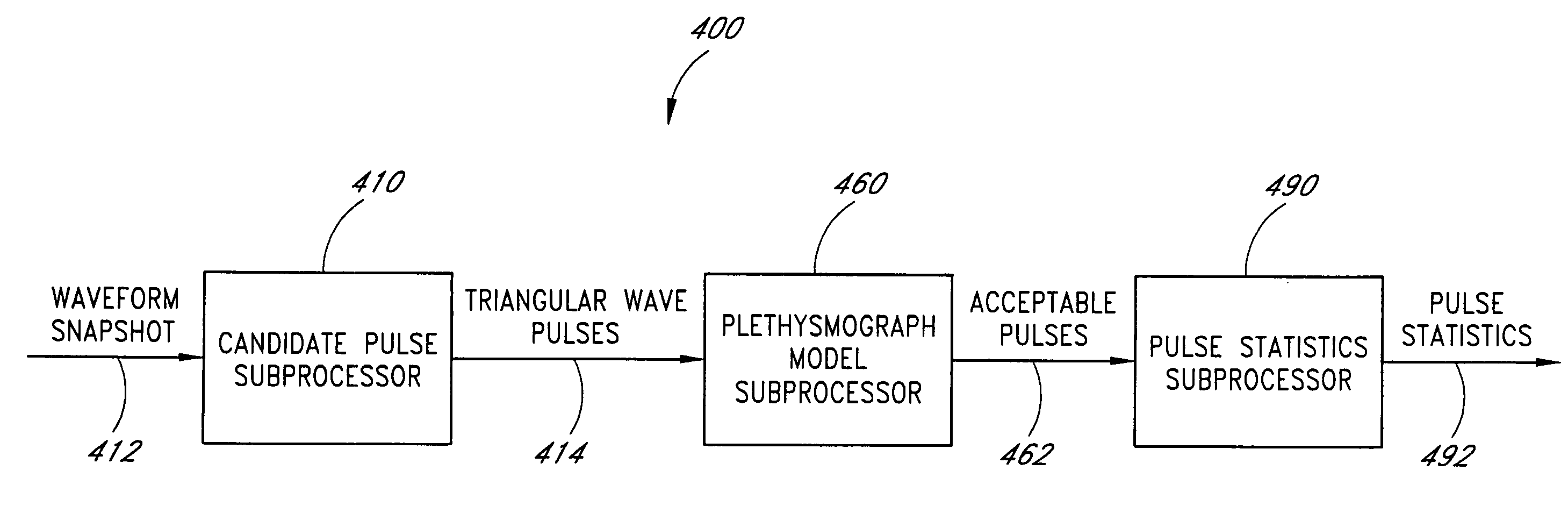
Plethysmograph pulse recognition processor
A time domain rule-based processor provides recognition of individual pulses in a pulse oximeter-derived photo-plethysmograph waveform.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method and system for determining an individual's state of attention
Owner:FICO MIRRORS SA
Predictive modeling of consumer financial behavior using supervised segmentation and nearest-neighbor matching
InactiveUS6839682B1Specific accurate targetingIncrease valueDiscounts/incentivesDigital computer detailsPredictive modellingAlgorithm
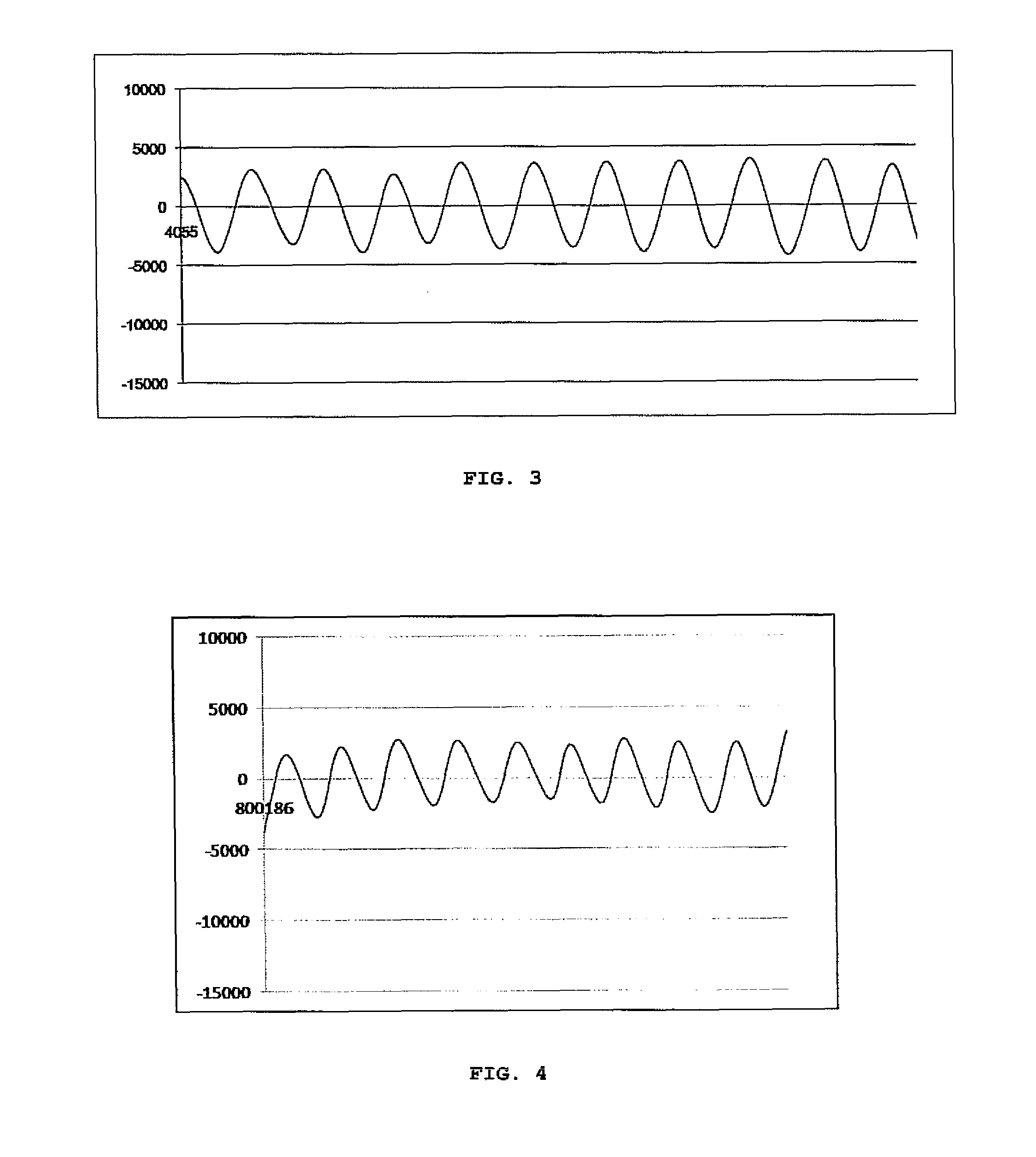
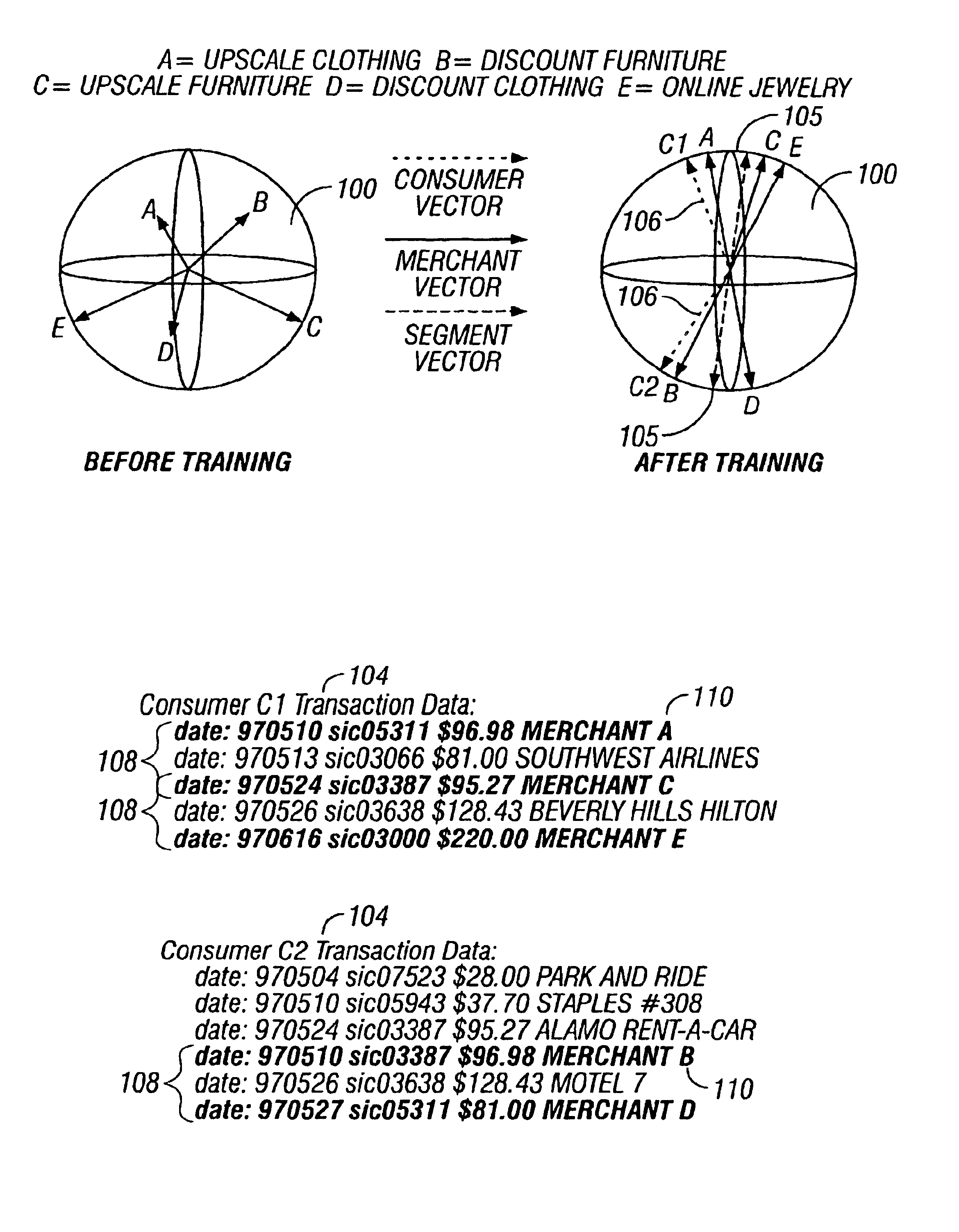
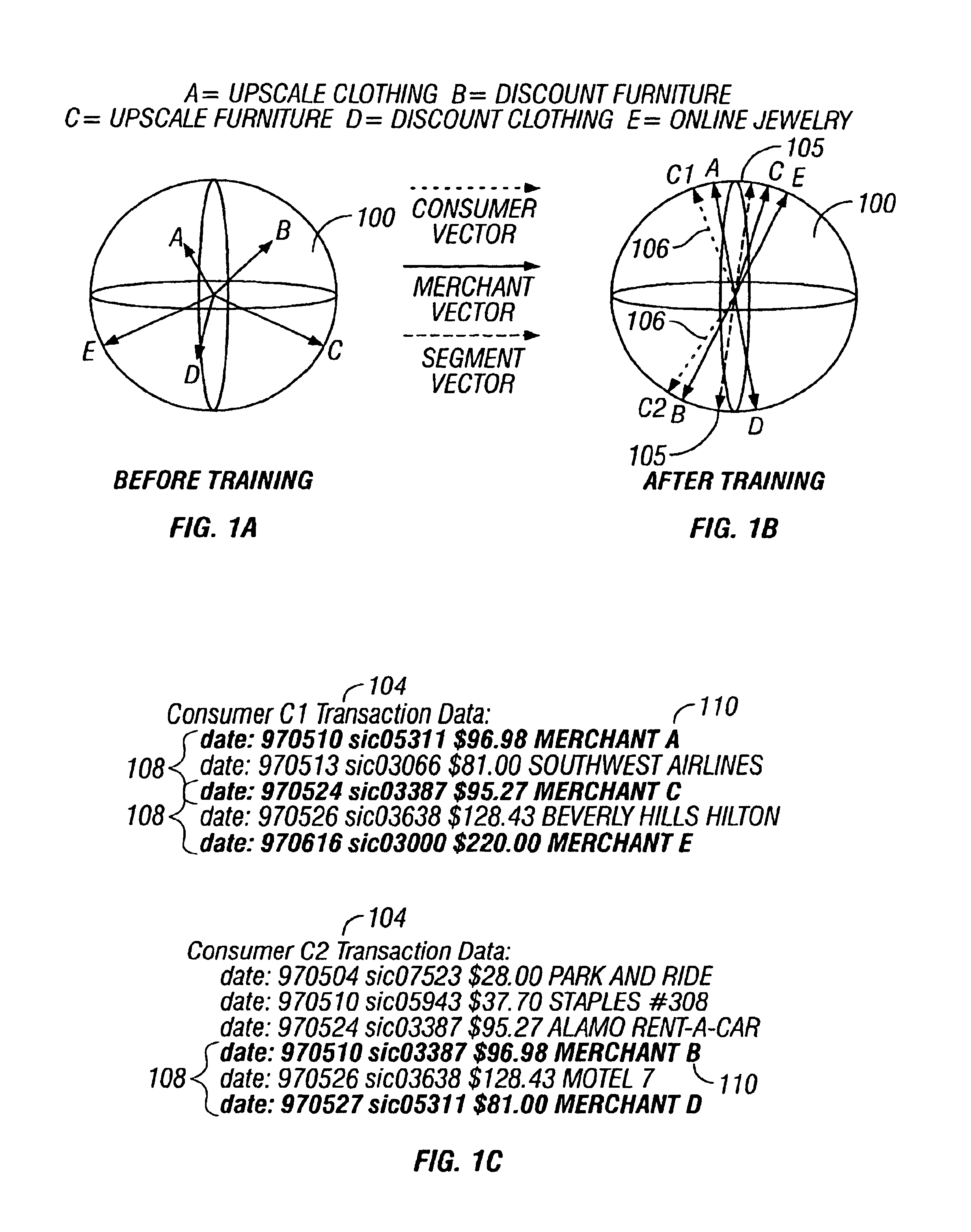
Predictive modeling of consumer financial behavior, including determination of likely responses to particular marketing efforts, is provided by application of consumer transaction data to predictive models associated with merchant segments. The merchant segments are derived from the consumer transaction data based on co-occurrences of merchants in sequences of transactions. Merchant vectors represent specific merchants, and are aligned in a vector space as a function of the degree to which the merchants co-occur more or less frequently than expected. Consumer vectors are developed within the vector space, to represent interests of particular consumers by virtue of relative vector positions of consumer and merchant vectors. Various techniques, including clustering, supervised segmentation, and nearest-neighbor analysis, are applied separately or in combination to generate improved predictions of consumer behavior.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Method and system for optimally searching a document database using a representative semantic space
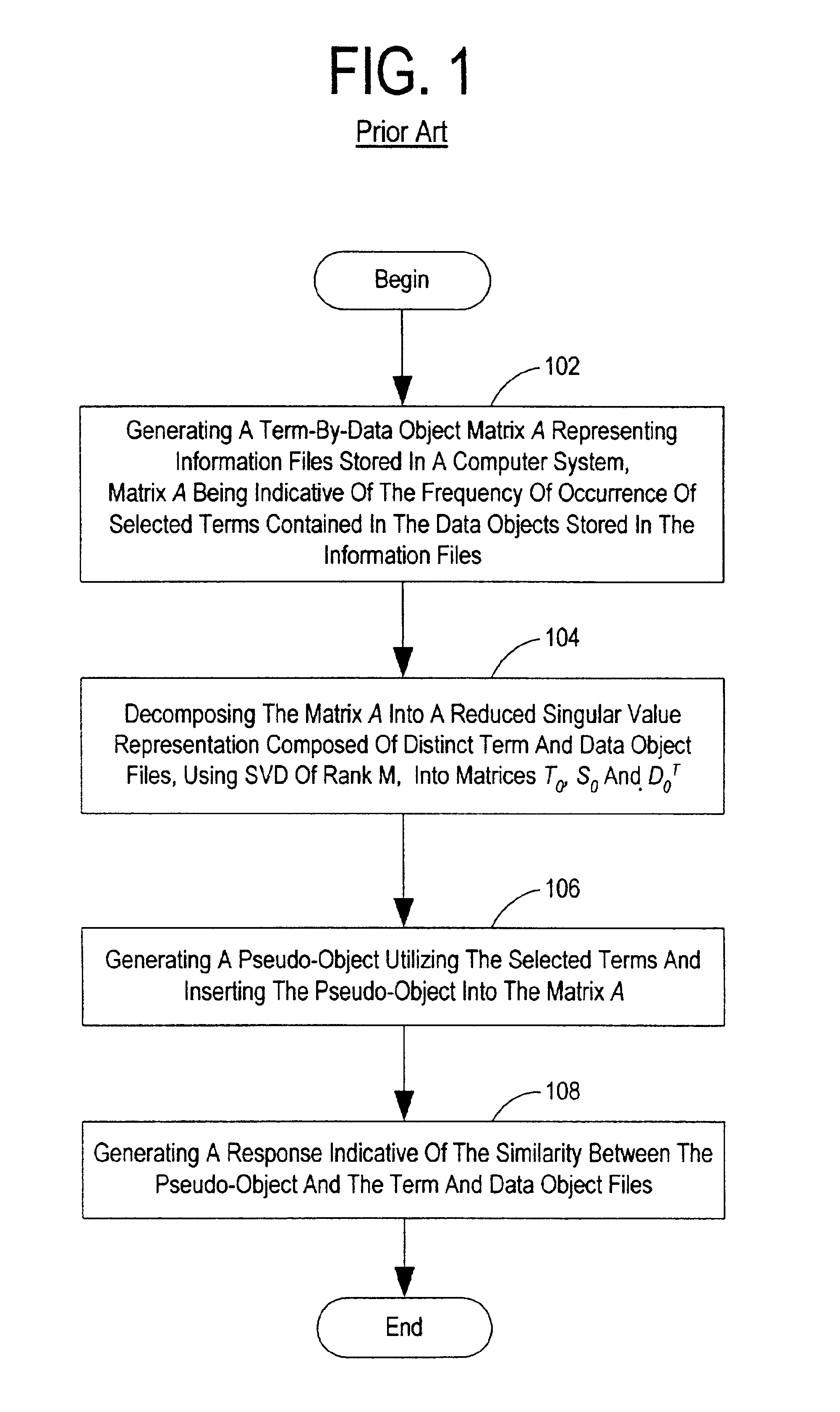
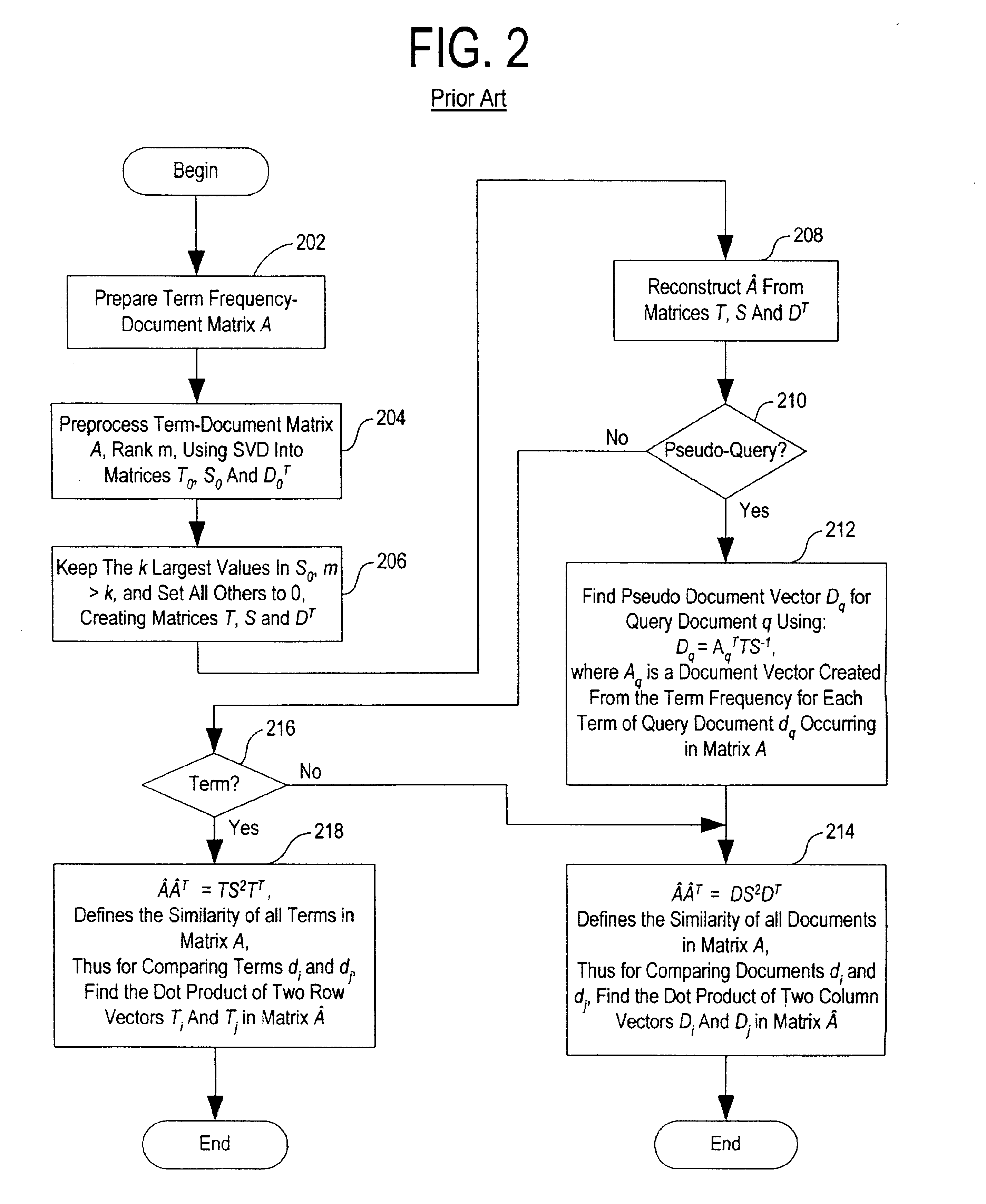
InactiveUS6847966B1Reduced dimensionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSingular value decompositionSubject matter
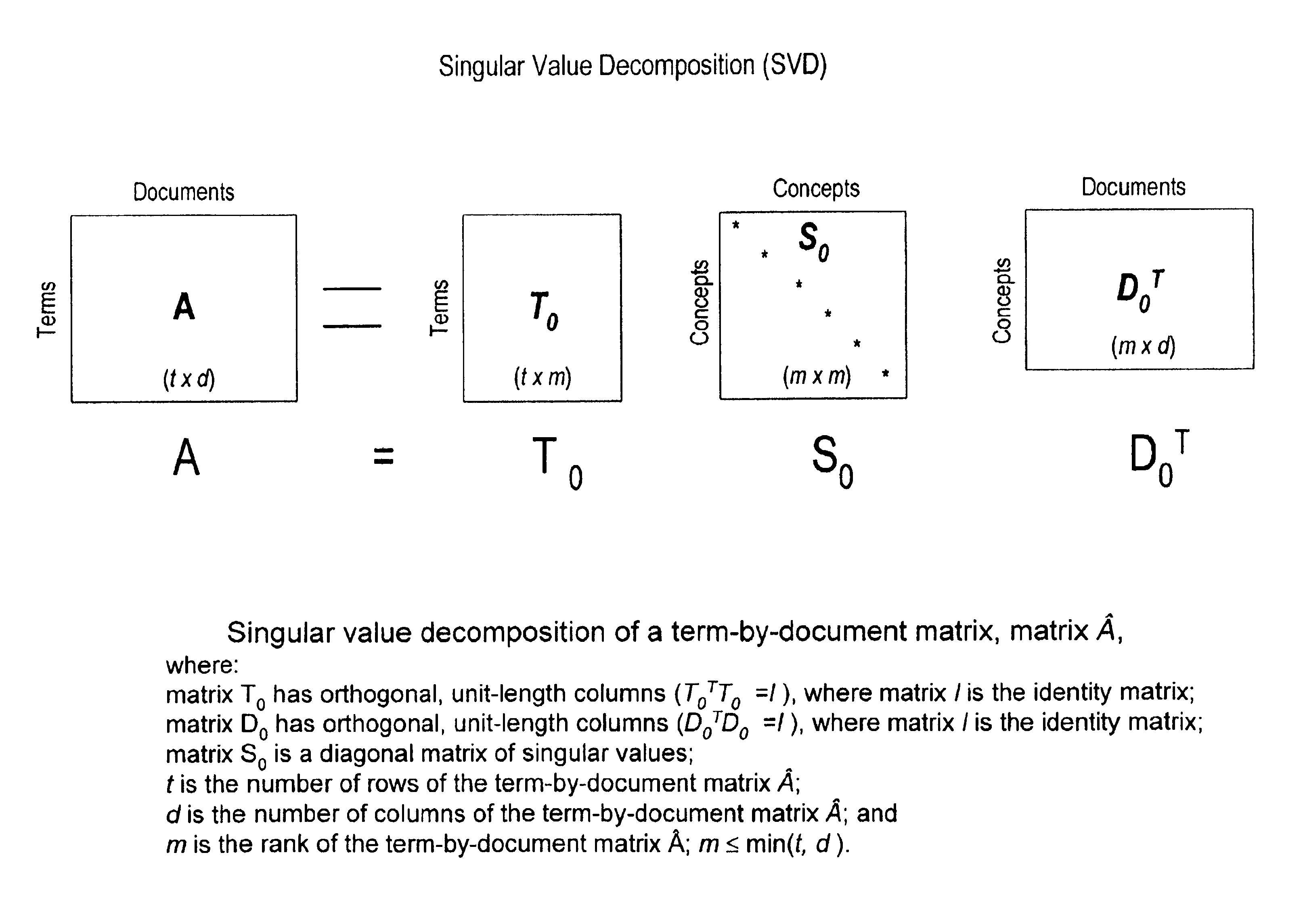
A term-by-document matrix is compiled from a corpus of documents representative of a particular subject matter that represents the frequency of occurrence of each term per document. A weighted term dictionary is created using a global weighting algorithm and then applied to the term-by-document matrix forming a weighted term-by-document matrix. A term vector matrix and a singular value concept matrix are computed by singular value decomposition of the weighted term-document index. The k largest singular concept values are kept and all others are set to zero thereby reducing to the concept dimensions in the term vector matrix and a singular value concept matrix. The reduced term vector matrix, reduced singular value concept matrix and weighted term-document dictionary can be used to project pseudo-document vectors representing documents not appearing in the original document corpus in a representative semantic space. The similarities of those documents can be ascertained from the position of their respective pseudo-document vectors in the representative semantic space.
Owner:KLDISCOVERY ONTRACK LLC
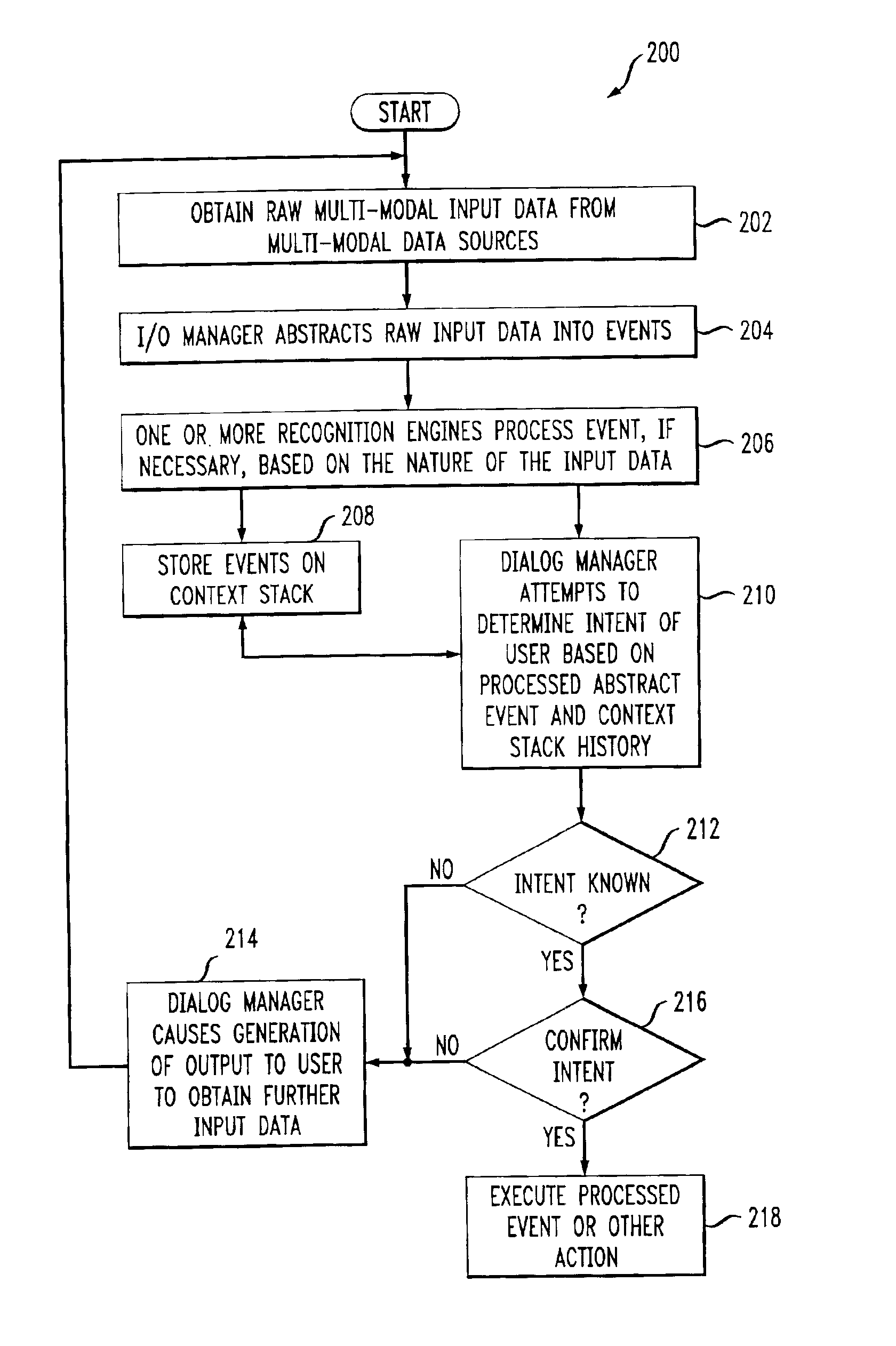
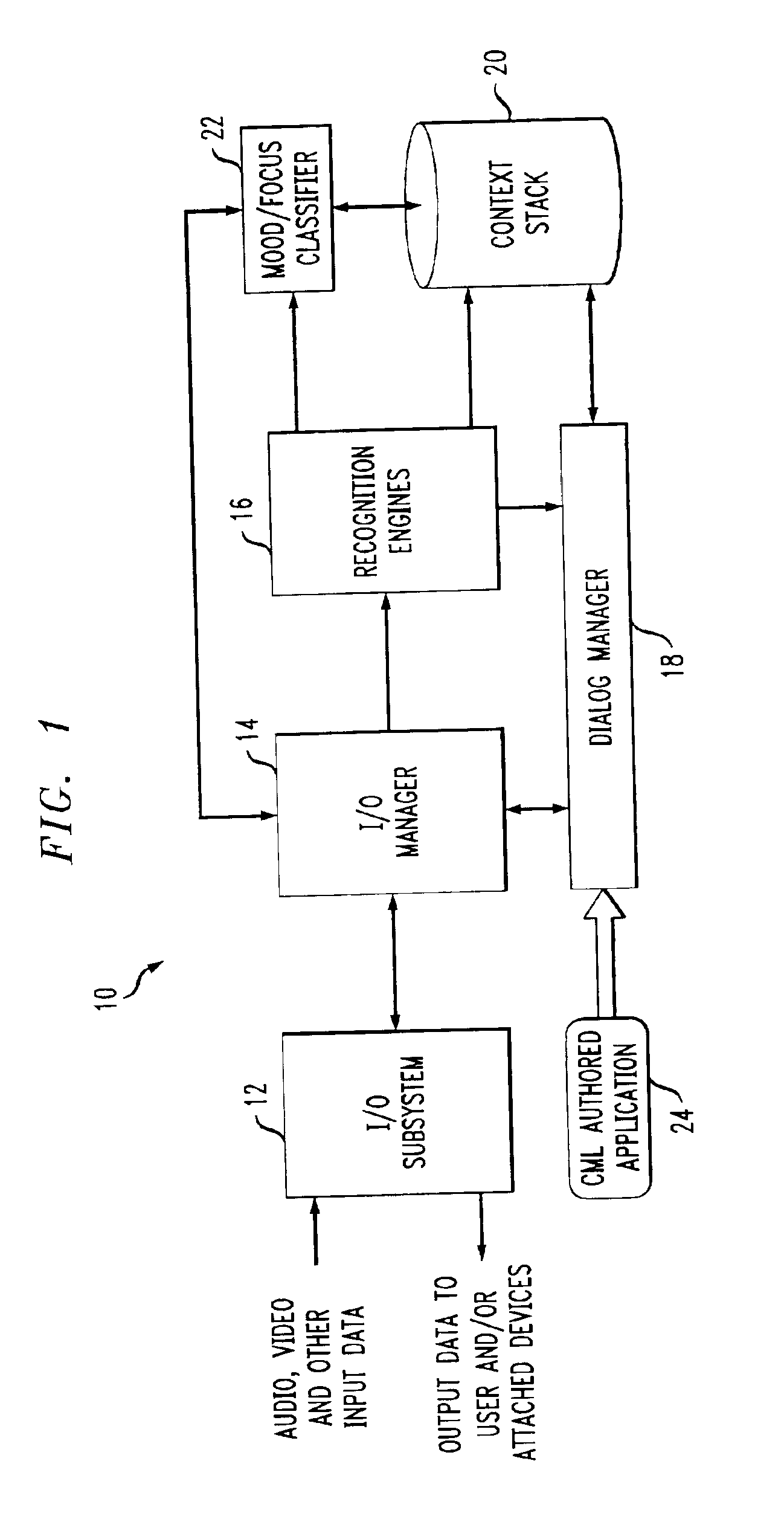
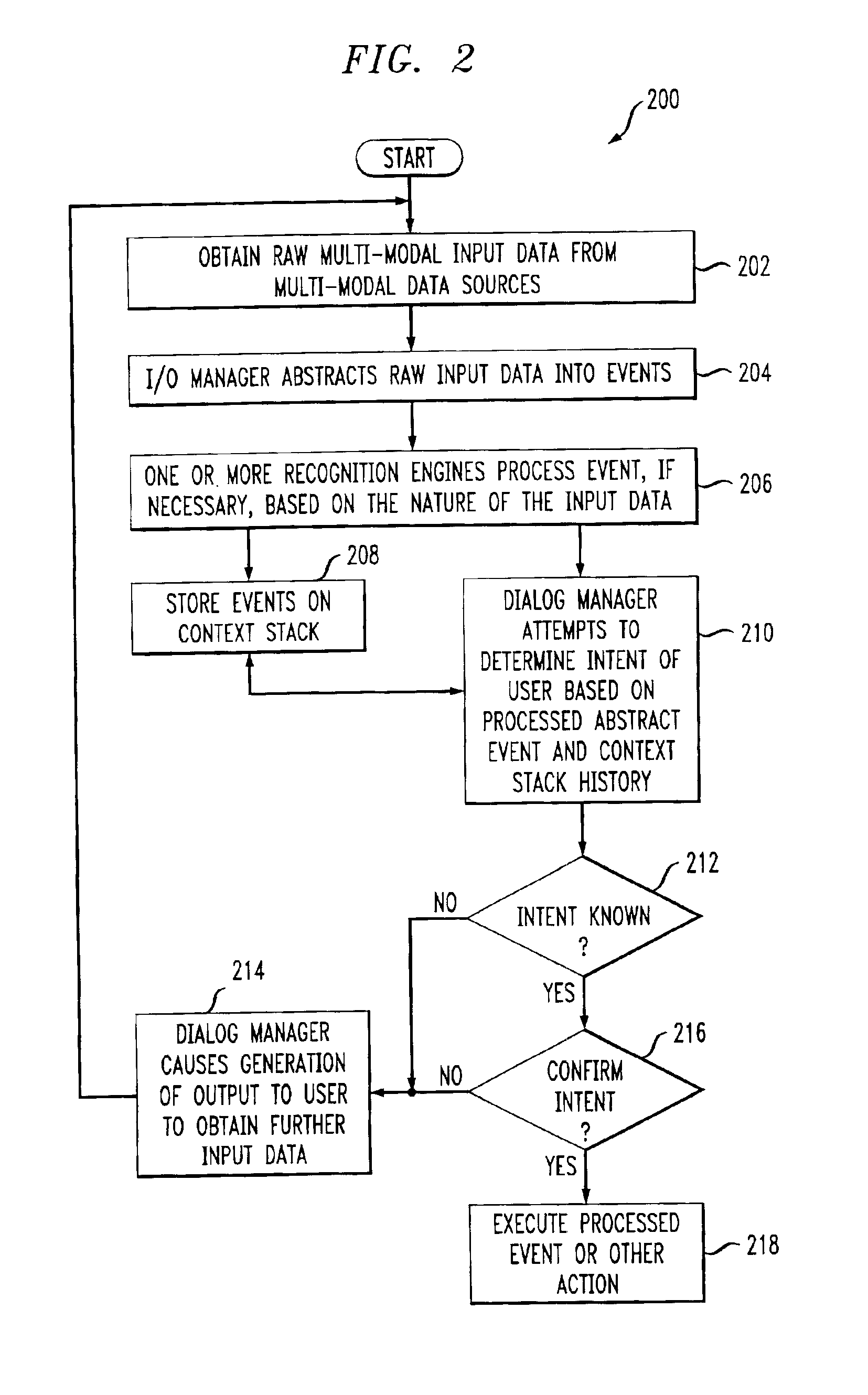
System and method for multi-modal focus detection, referential ambiguity resolution and mood classification using multi-modal input
InactiveUS6964023B2Effective conversational computing environmentInput/output for user-computer interactionData processing applicationsOperant conditioningComputer science
Owner:IBM CORP
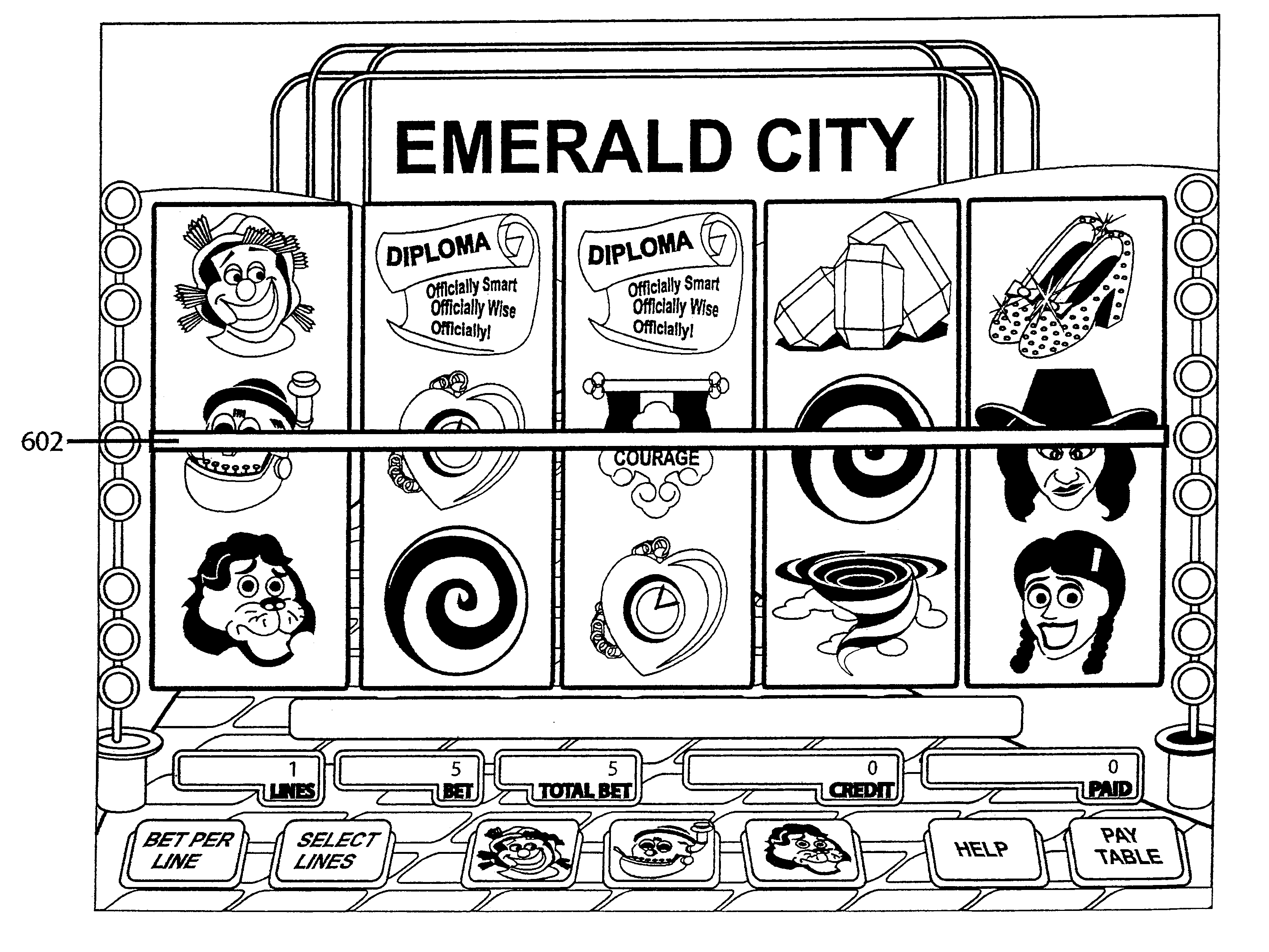
Slot machine game having a plurality of ways to designate one or more wild symbols (select-a-wild)
InactiveUS6604740B1Card gamesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingAlgorithmComputer graphics (images)
A slot machine enables a player to select one or more symbols as wild symbols ("Select-A-Wild"). In one embodiment, the game displays three spin buttons. Each spin button is permanently associated with a symbol. All of the associated symbols have matching symbols on the reel strips. Each of the associated symbols have the same probability of appearing on the reel strips. The player selects a wild symbol by pressing a spin button. The symbol associated with the pressed spin button acts as a wild symbol for that spin. After each spin, the player receives awards for all winning combinations.
Owner:IGT
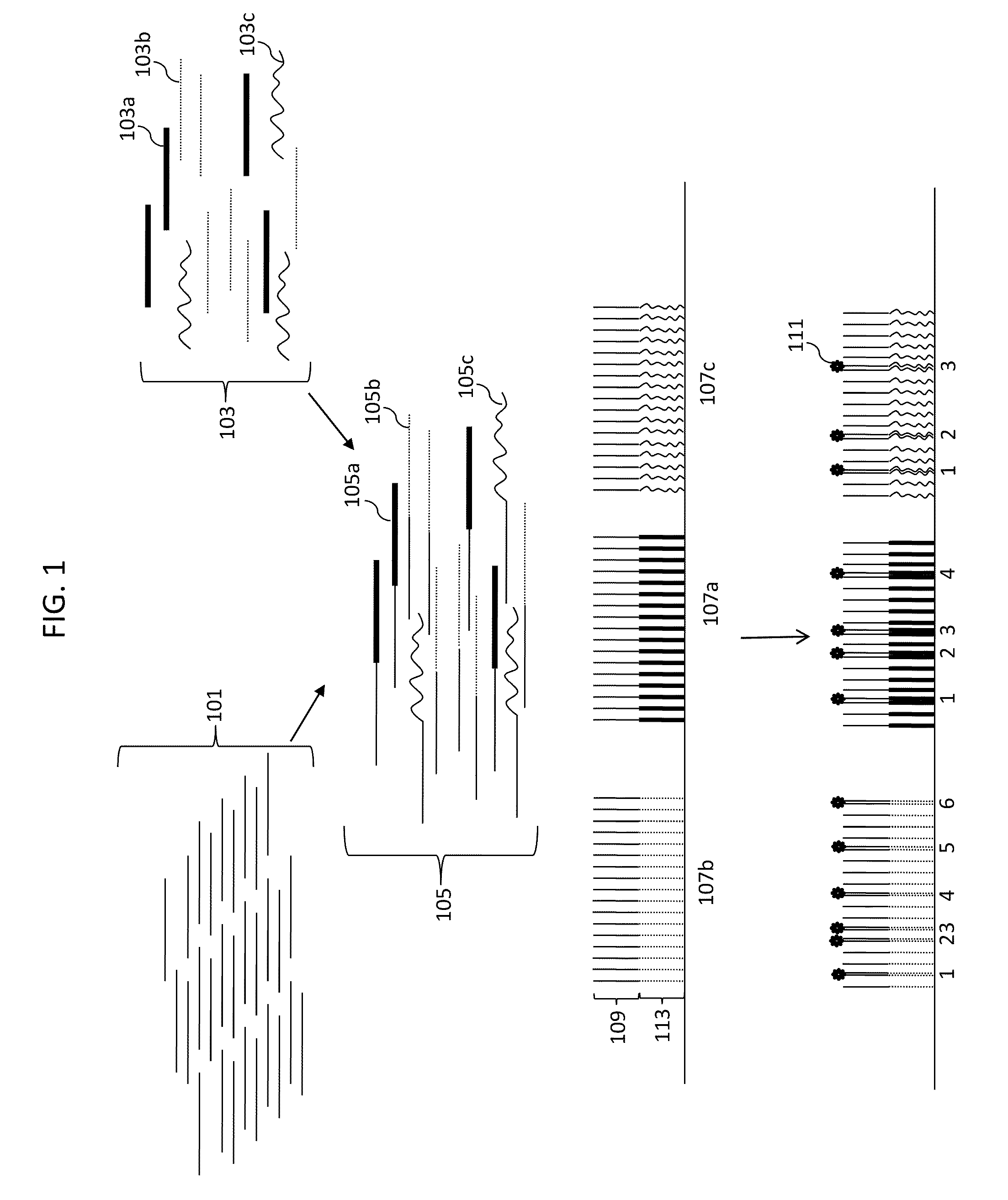
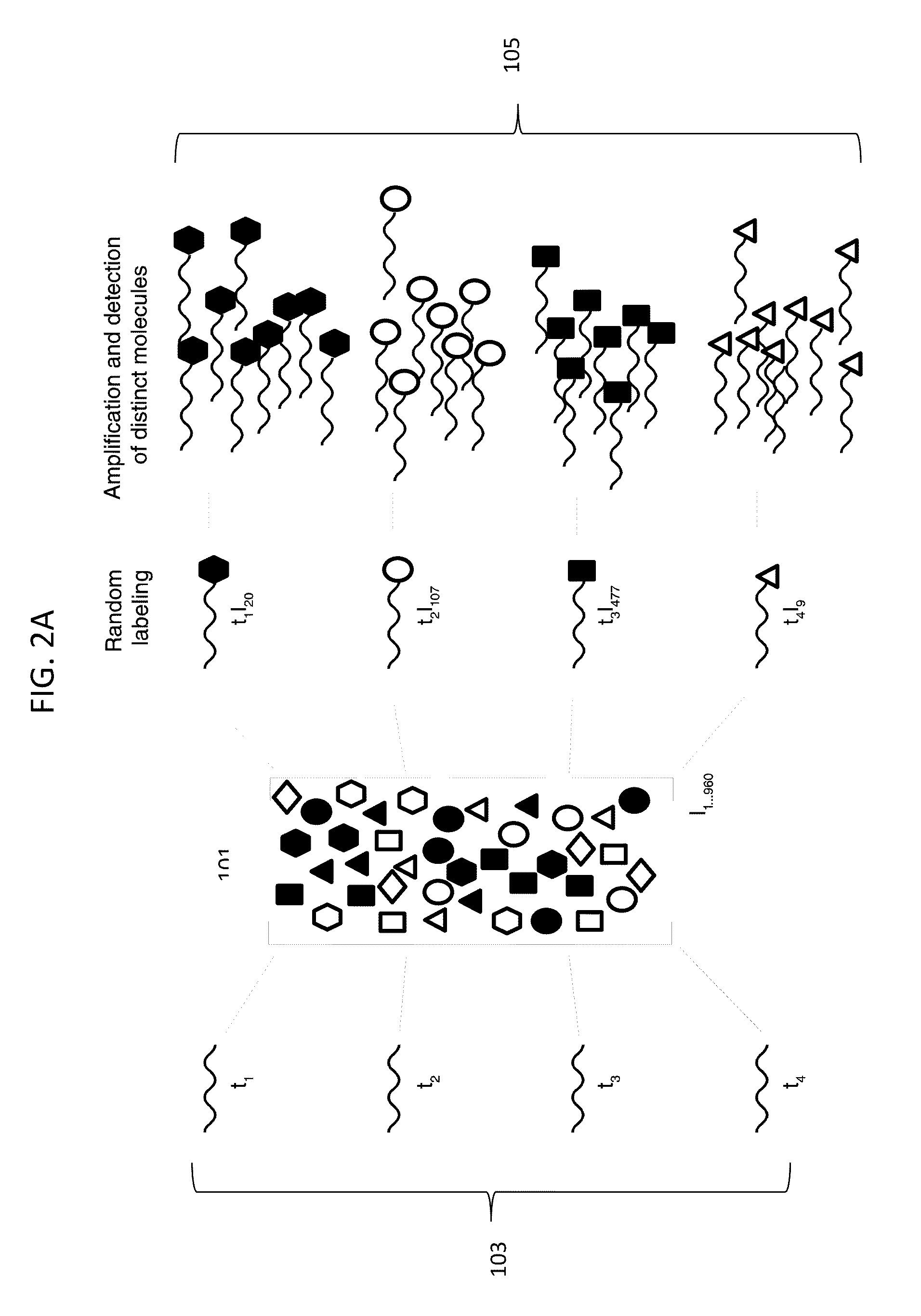
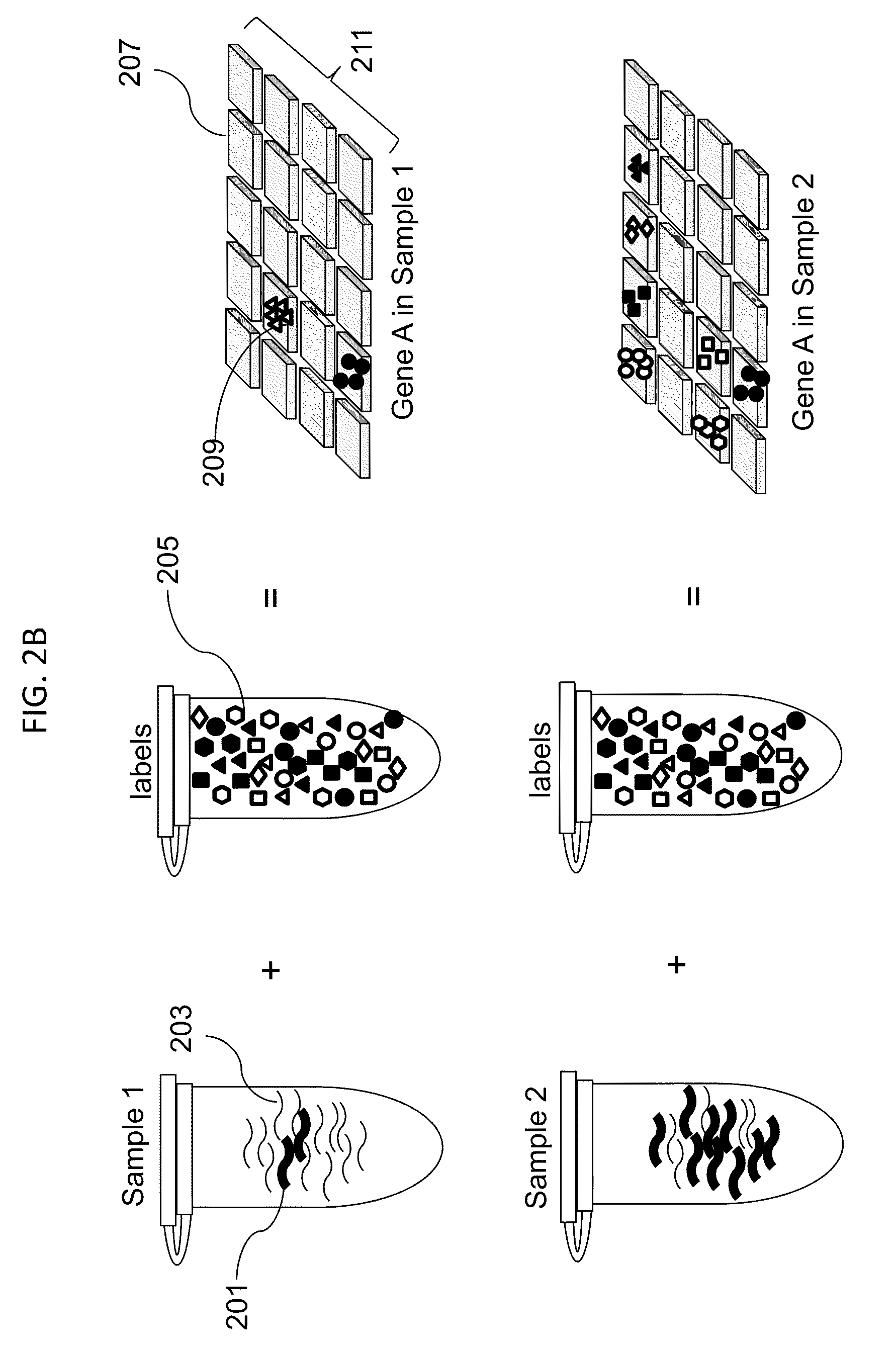
Digital counting of individual molecules by stochastic attachment of diverse labels
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Methods and systems for annotating biomolecular sequences
A method of annotating biomolecular sequences. The method comprises (a) computationally clustering the biomolecular sequences according to a progressive homology range, to thereby generate a plurality of clusters each being of a predetermined homology of the homology range; and (b) assigning at least one ontology to each cluster of the plurality of clusters, the at least one ontology being: (i) derived from an annotation preassociated with at least one biomolecular sequence of each cluster; and / or (ii) generated from analysis of the at least one biomolecular sequence of each cluster thereby annotating biomolecular sequences.
Owner:COMPUGEN
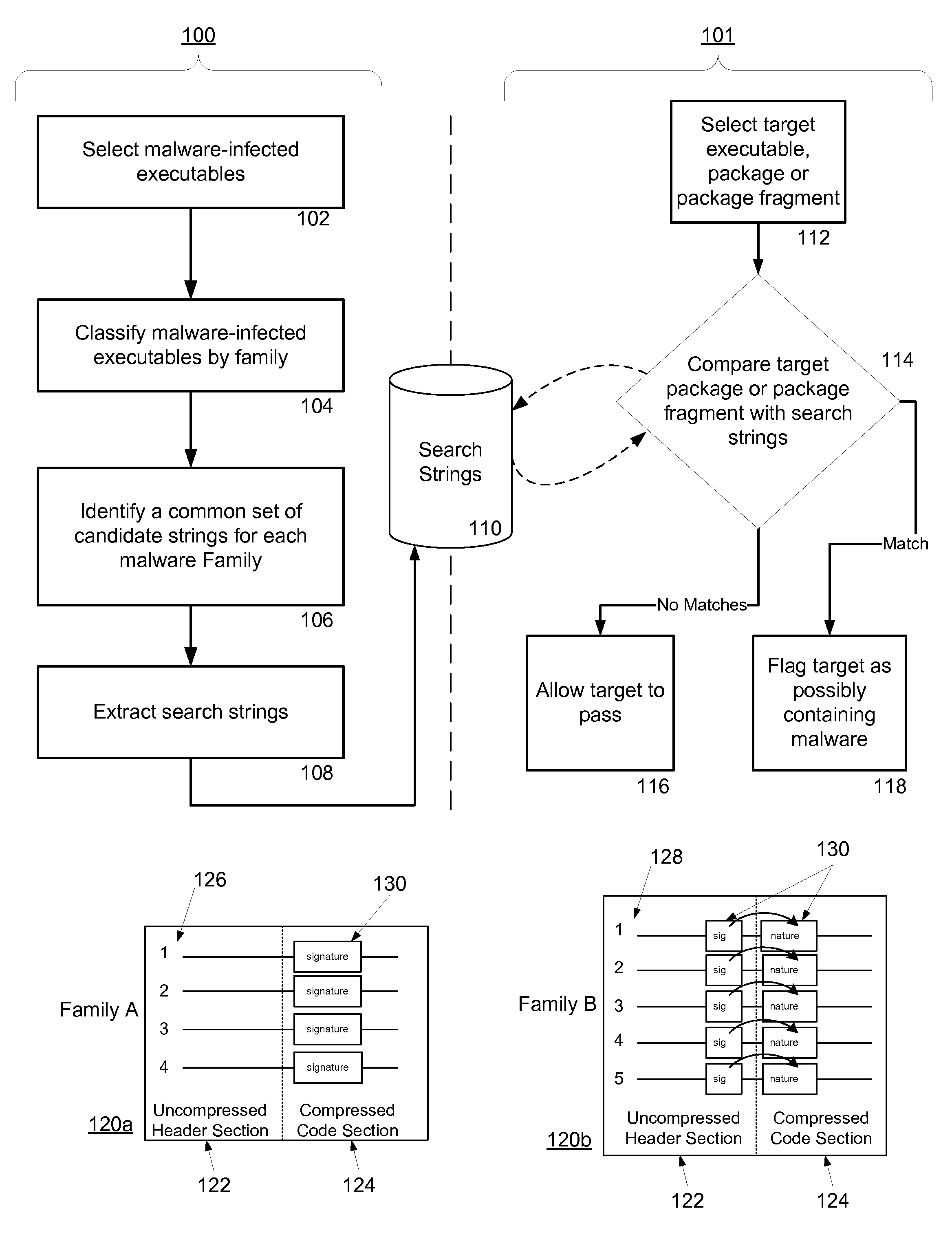
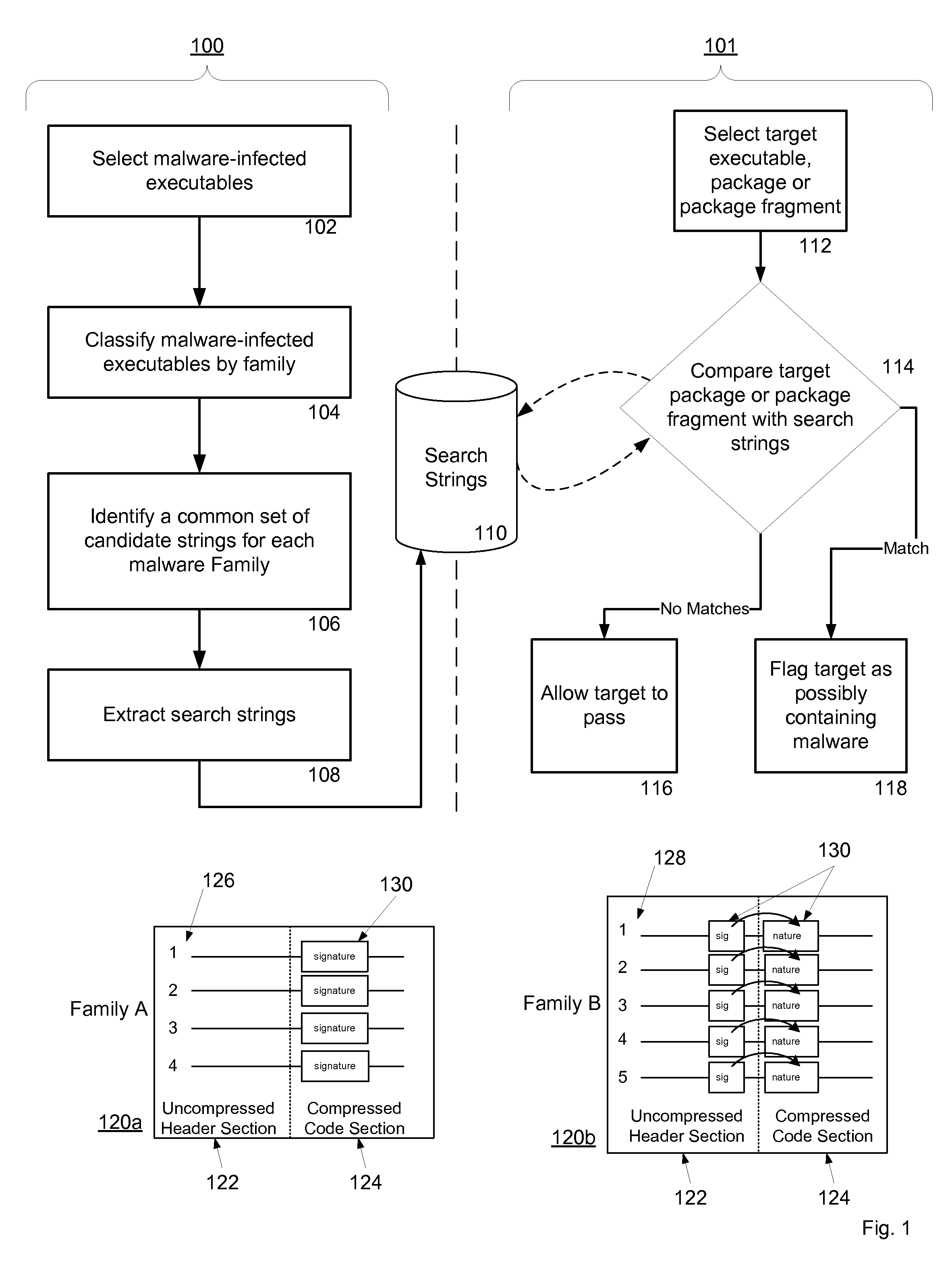
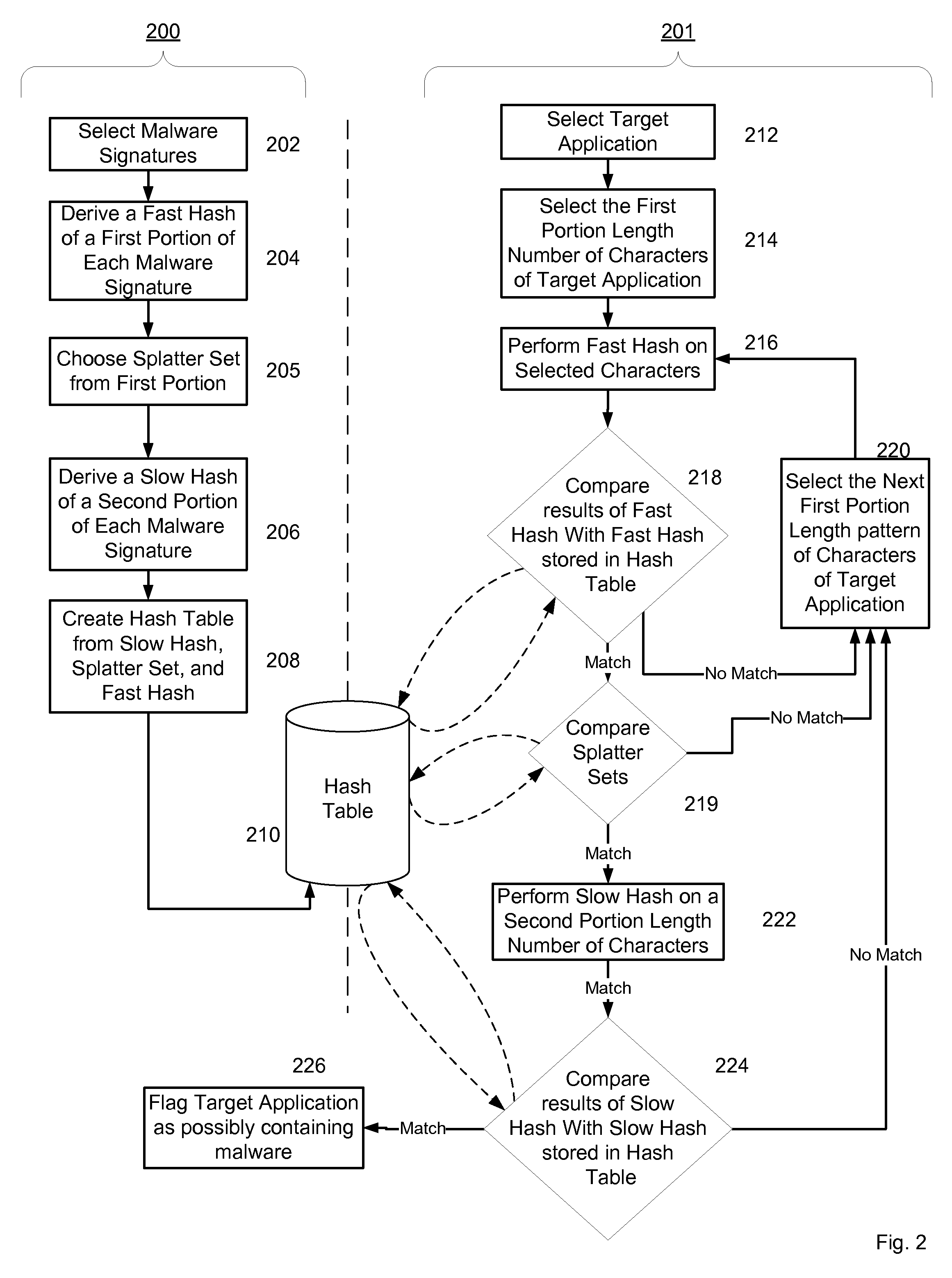
Malware Modeling Detection System And Method for Mobile Platforms
ActiveUS20070240217A1Suitable for useReliable detectionMemory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationFeature setAlgorithm
A system and method for detecting malware by modeling the behavior of malware and comparing a suspect executable with the model. The system and method extracts feature elements from malware-infected applications, groups the feature elements into feature sets, and develops rules describing a malicious probability relationship between the feature elements. Using malware-free and malware-infected applications as training data, the system and method heuristically trains the rules and creates a probability model for identifying malware. To detect malware, the system and method scans the suspect executable for feature sets and applies the results to the probability model to determine the probability that the suspect executable is malware-infected.
Owner:PULSE SECURE
System and method for improving the accuracy of audio searching
ActiveUS7725318B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAlgorithmSearch terms
A system and method for improving the accuracy of audio searching using multiple models to process an audio file or stream to obtain search tracks. The search tracks are processed to locate at least one search term and generate multiple search results. The number of search results is equivalent to the number of models used to process the audio stream. The search results are combined to generate a unified search result. The multiple models may represent different languages, dialects and accents.
Owner:NICE SYSTEMS
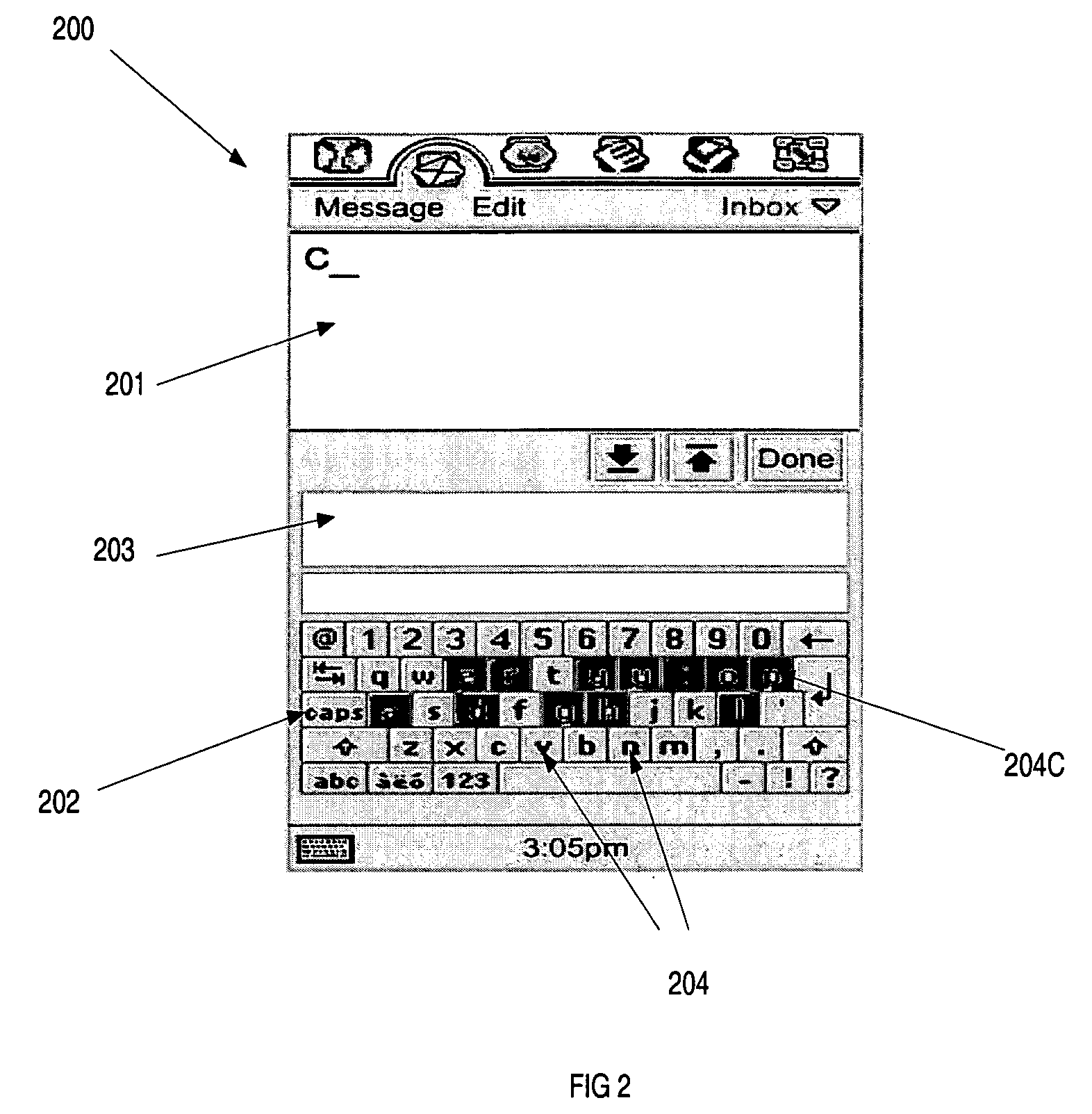
Entering a character into an electronic device
ActiveUS7443316B2Easy for to identify wantedEasy for to see and also to selectInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmEngineering
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
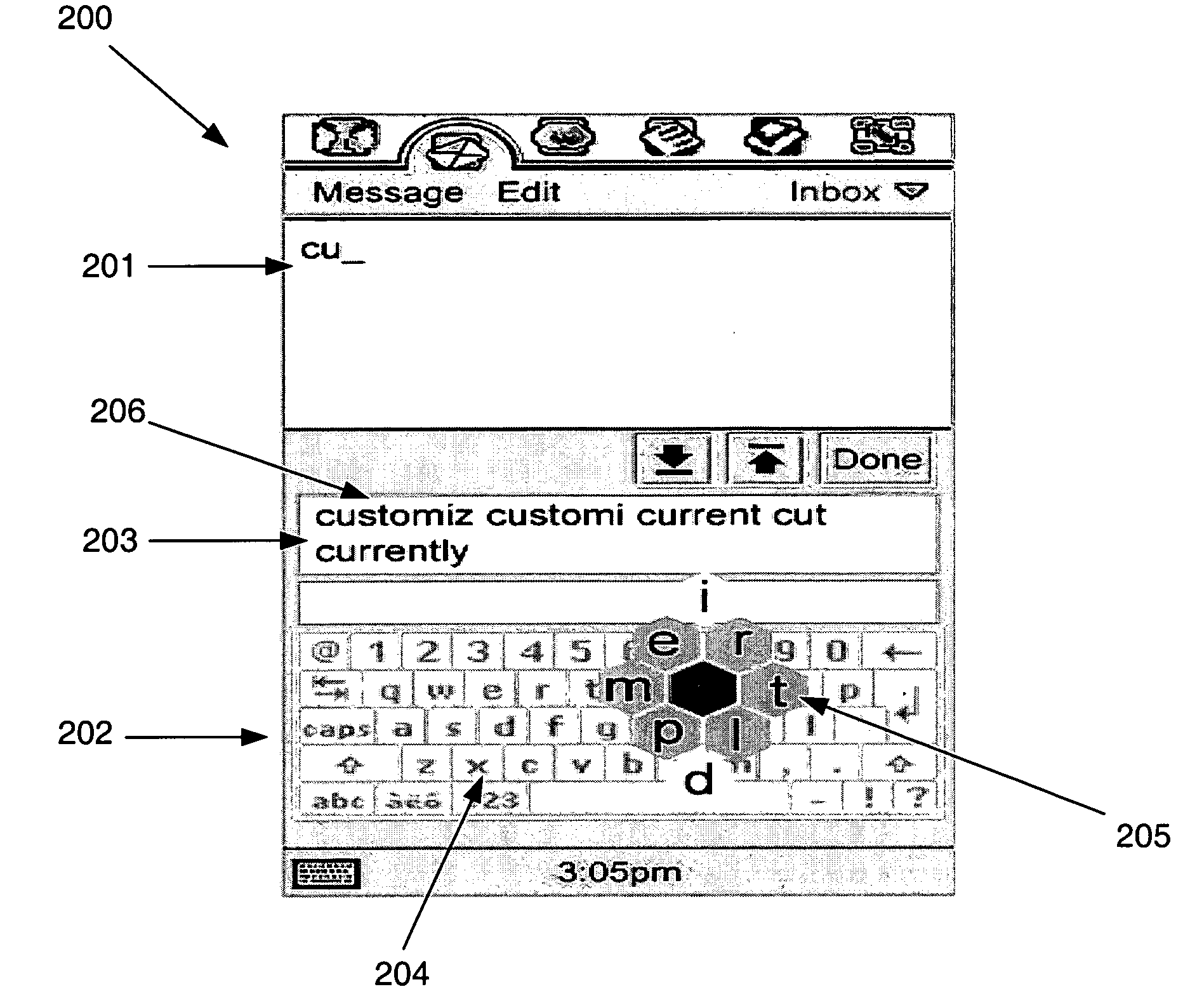
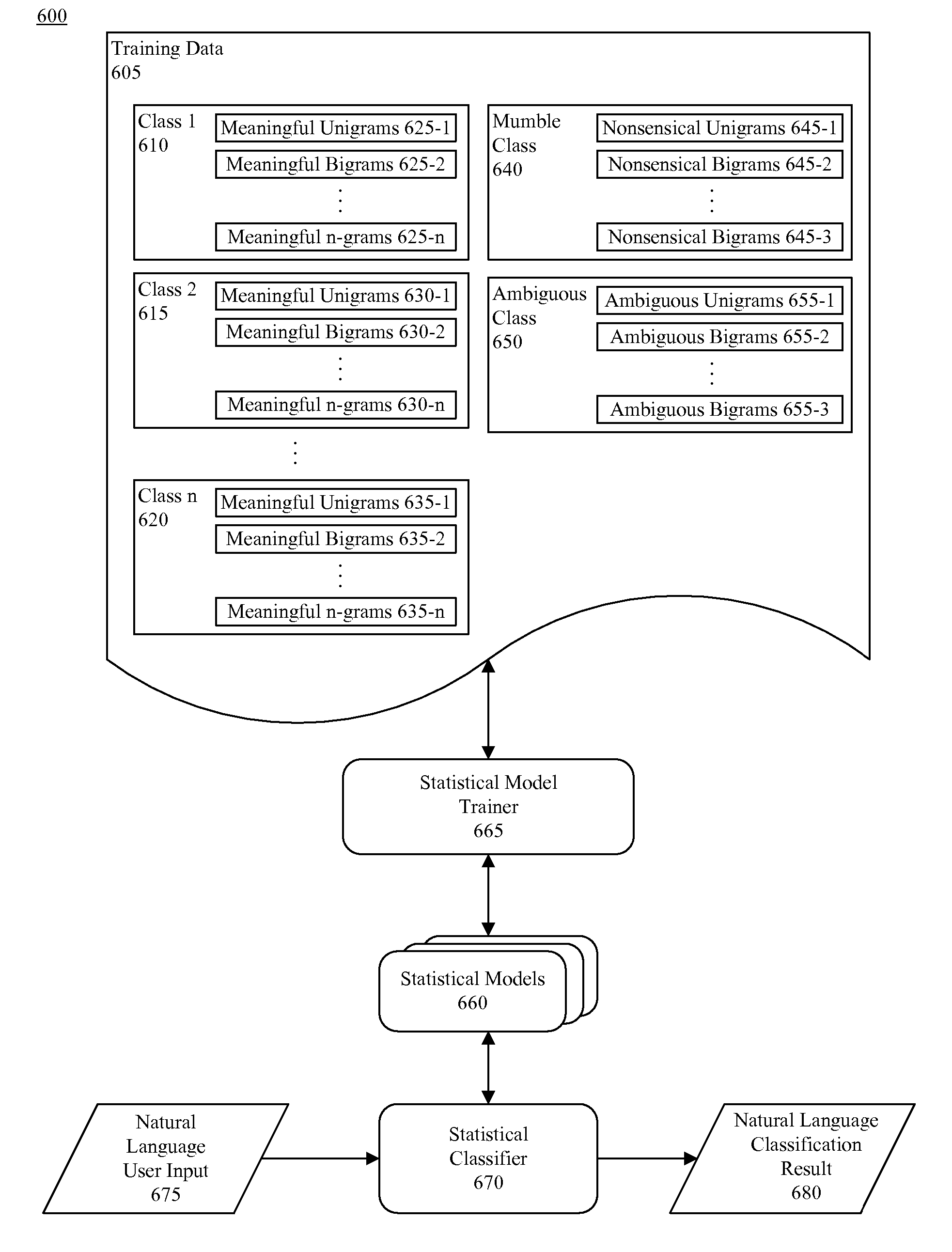
Identification and rejection of meaningless input during natural language classification
ActiveUS7707027B2Digital data information retrievalNatural language data processingAlgorithmComputer science
A method for identifying data that is meaningless and generating a natural language statistical model which can reject meaningless input. The method can include identifying unigrams that are individually meaningless from a set of training data. At least a portion of the unigrams identified as being meaningless can be assigned to a first n-gram class. The method also can include identifying bigrams that are entirely composed of meaningless unigrams and determining whether the identified bigrams are individually meaningless. At least a portion of the bigrams identified as being individually meaningless can be assigned to the first n-gram class.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
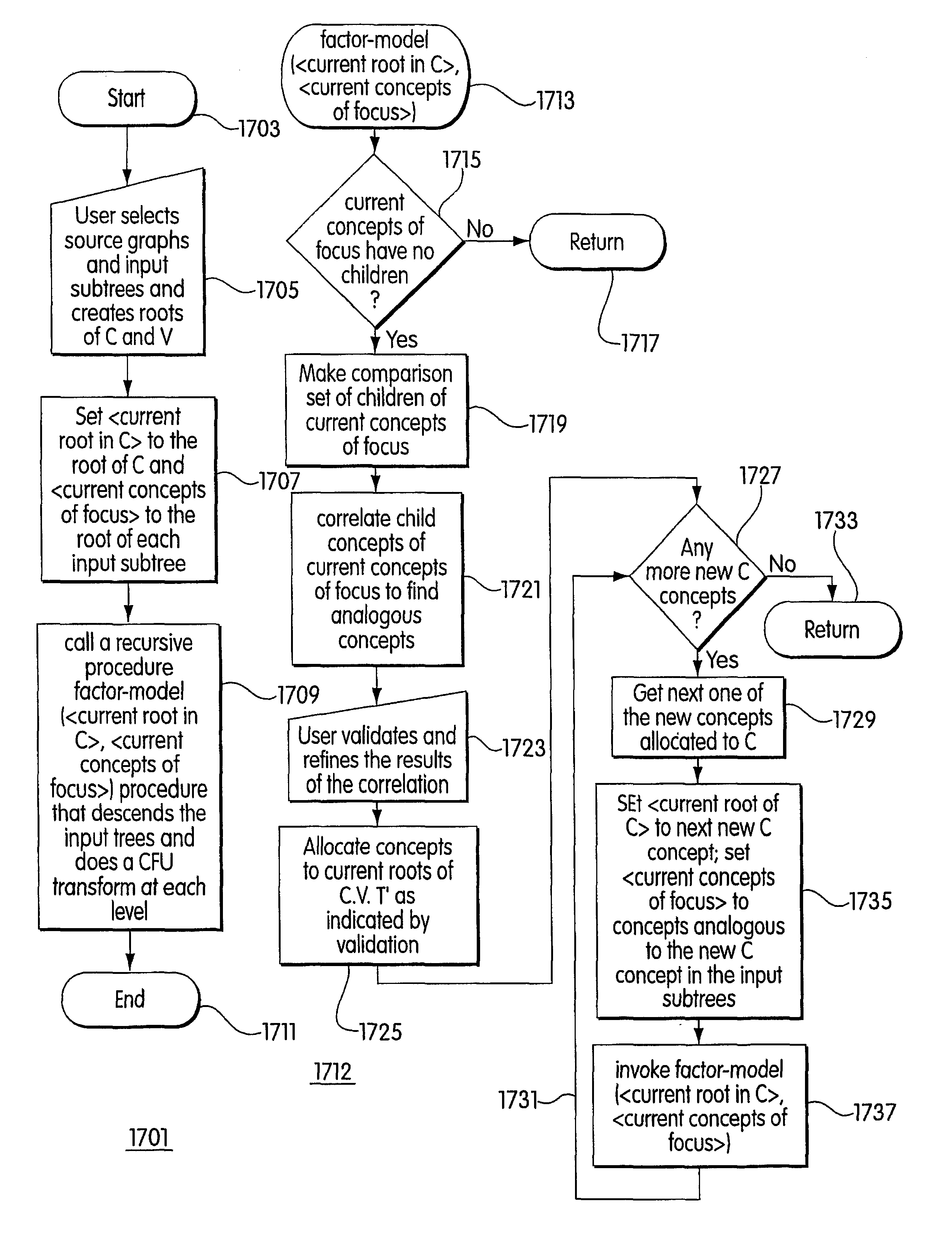
Conceptual factoring and unification of graphs representing semantic models
InactiveUS6847979B2Easily and efficiently producedData processing applicationsDrawing from basic elementsAlgorithmPresentation semantics
Techniques for factoring one or more source graphs into a composite graph containing nodes representing analogous elements of the source graphs and a variability graph containing nodes representing differences in the source graphs. The composite graph is made by taking analogous input trees from the source graphs and traversing the trees from top to bottom looking for nodes in each tree at each level that are analogous to the nodes at that level in the other input trees. The sets of analogous nodes are found by first automatically correlating the nodes in the level currently being examined. Correlation may, for example, be based on similar values of a property of the nodes being correlated. Representations of the sets of correlated nodes are then displayed to a user, who indicates which sets of correlated nodes are in fact analogous. The user may also indicate that the nodes in a set of correlated nodes are not analogous or that nodes that were found by the automatic correlation not to be autonomous are in fact. The analogous nodes are allocated to a corresponding node at a corresponding level in the composite graph; the other nodes are allocated to a set of anomalous nodes. One application for the techniques is managing graphs which are models of catalogs of items.
Owner:POPPET INT
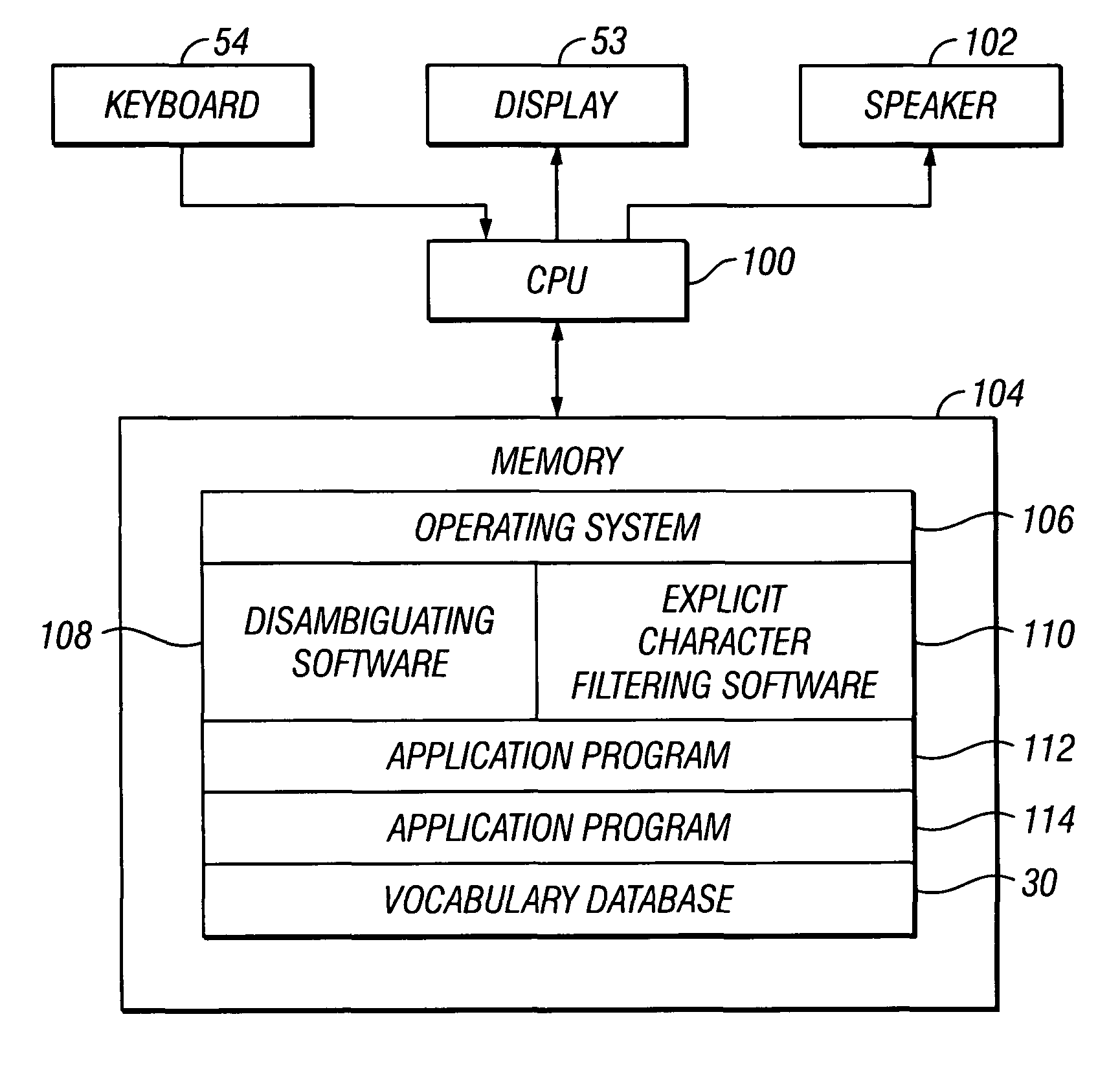
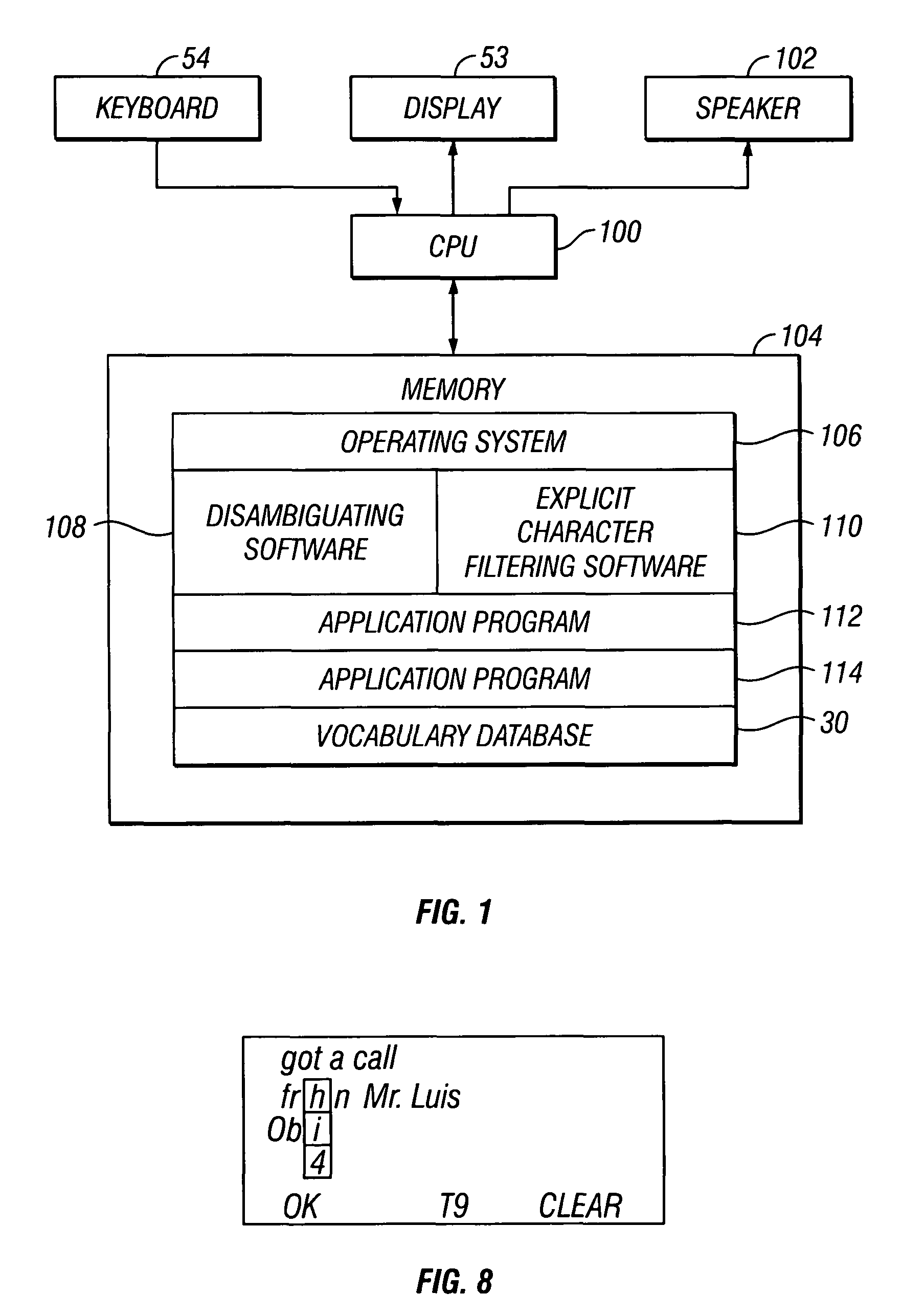
Explicit character filtering of ambiguous text entry
InactiveUS7712053B2Input/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingProgramming languageAlgorithm
Owner:TEGIC COMM
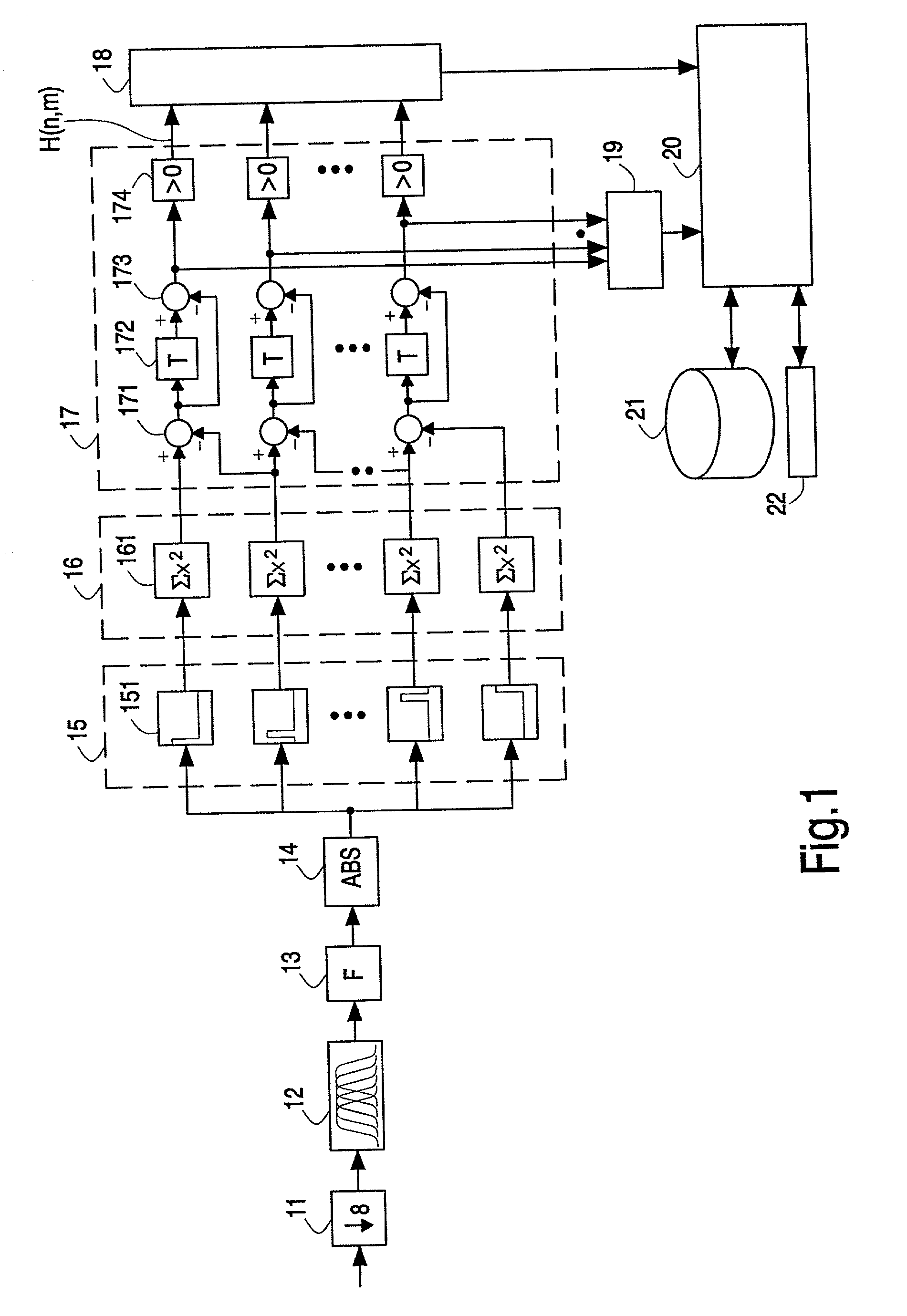
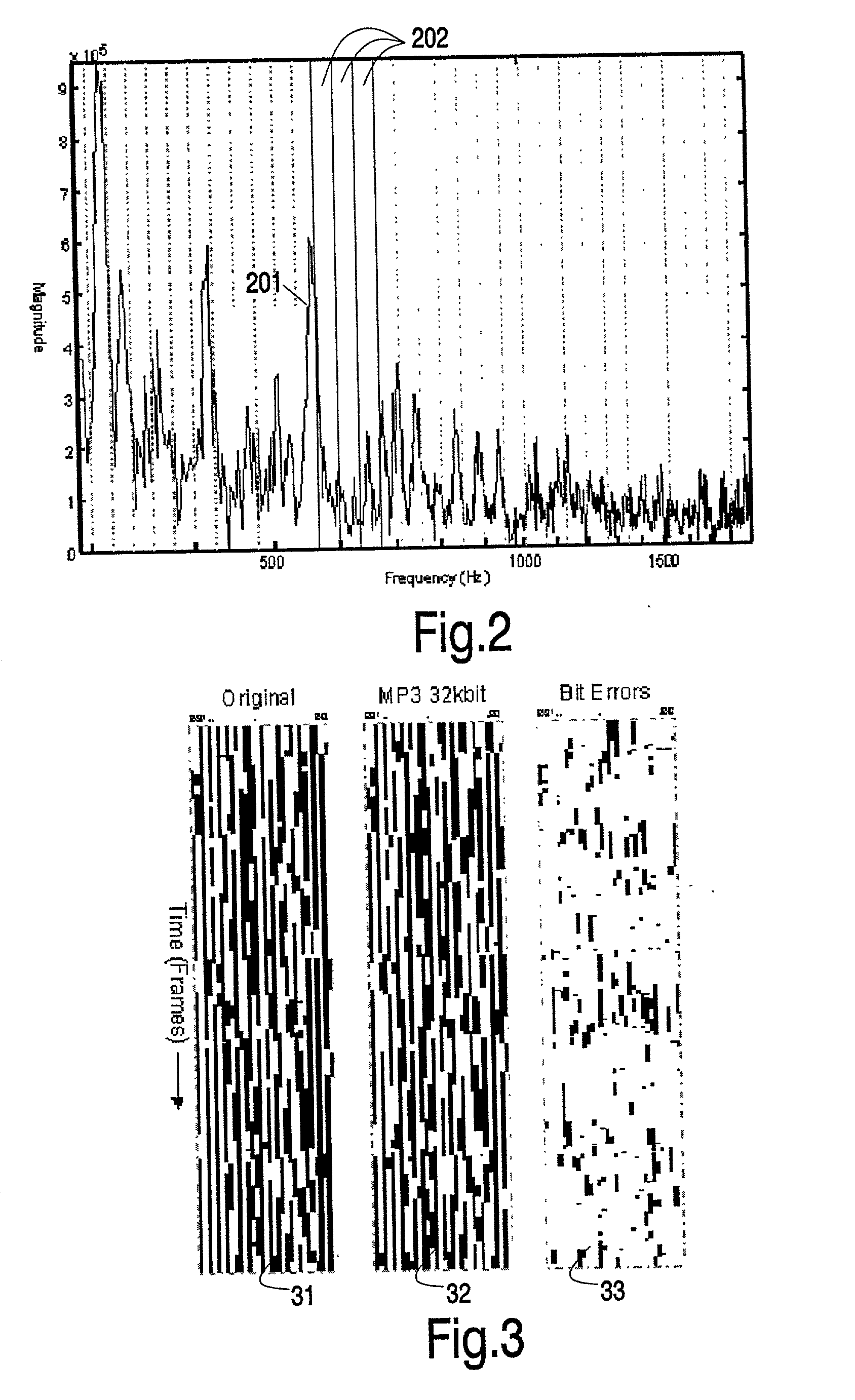
Generating and matching hashes of multimedia content
ActiveUS20020178410A1RobustRobust hashingElectrophonic musical instrumentsCode conversionFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
Hashes are short summaries or signatures of data files which can be used to identify the file. Hashing multimedia content (audio, video, images) is difficult because the hash of original content and processed (e.g. compressed) content may differ significantly. The disclosed method generates robust hashes for multimedia content, for example, audio clips. The audio clip is divided (12) into successive (preferably overlapping) frames. For each frame, the frequency spectrum is divided (15) into bands. A robust property of each band (e.g. energy) is computed (16) and represented (17) by a respective hash bit. An audio clip is thus represented by a concatenation of binary hash words, one for each frame. To identify a possibly compressed audio signal, a block of hash words derived therefrom is matched by a computer (20) with a large database (21). Such matching strategies are also disclosed. In an advantageous embodiment, the extraction process also provides information (19) as to which of the hash bits are the least reliable. Flipping these bits considerably improves the speed and performance of the matching process.
Owner:GRACENOTE
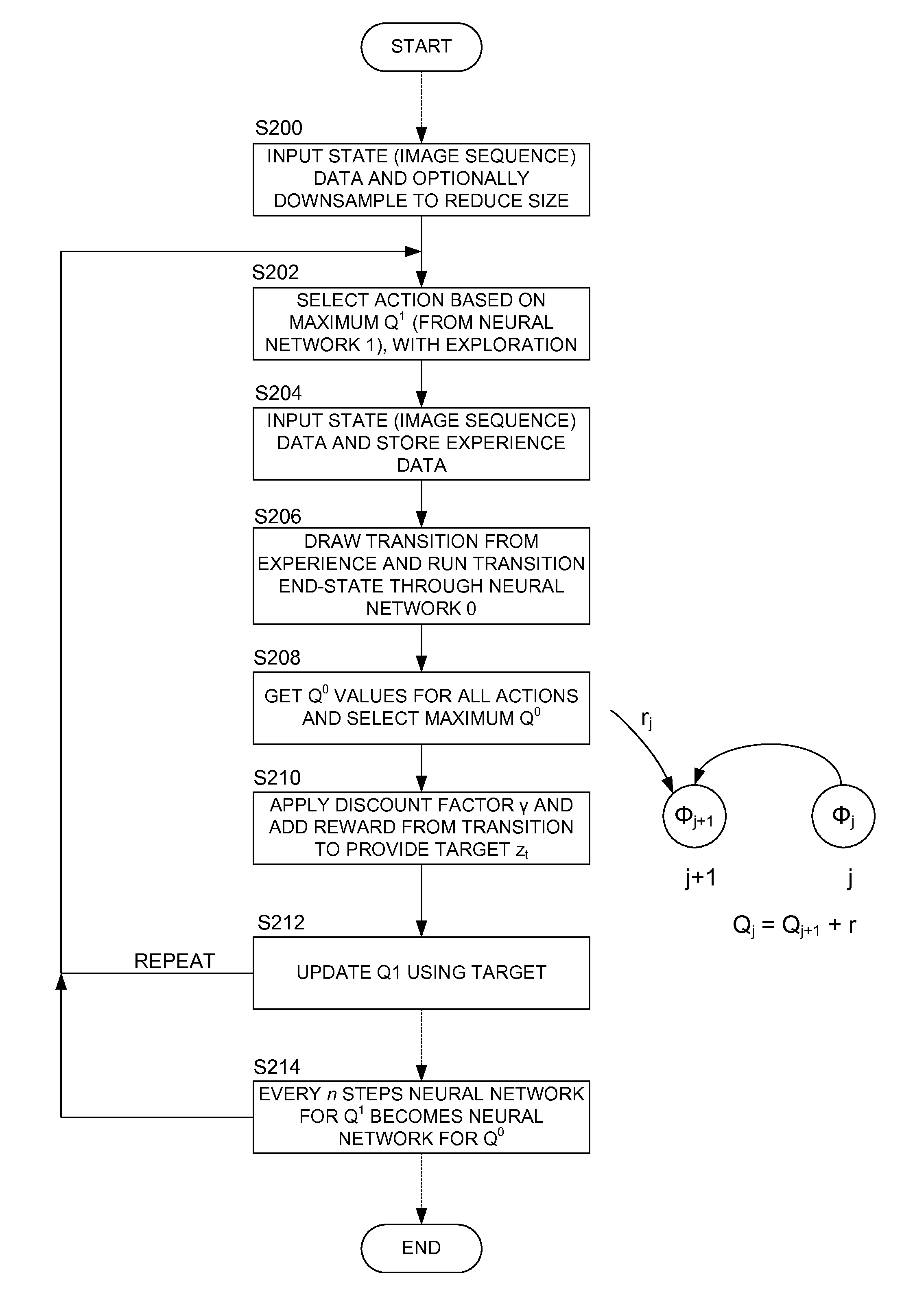
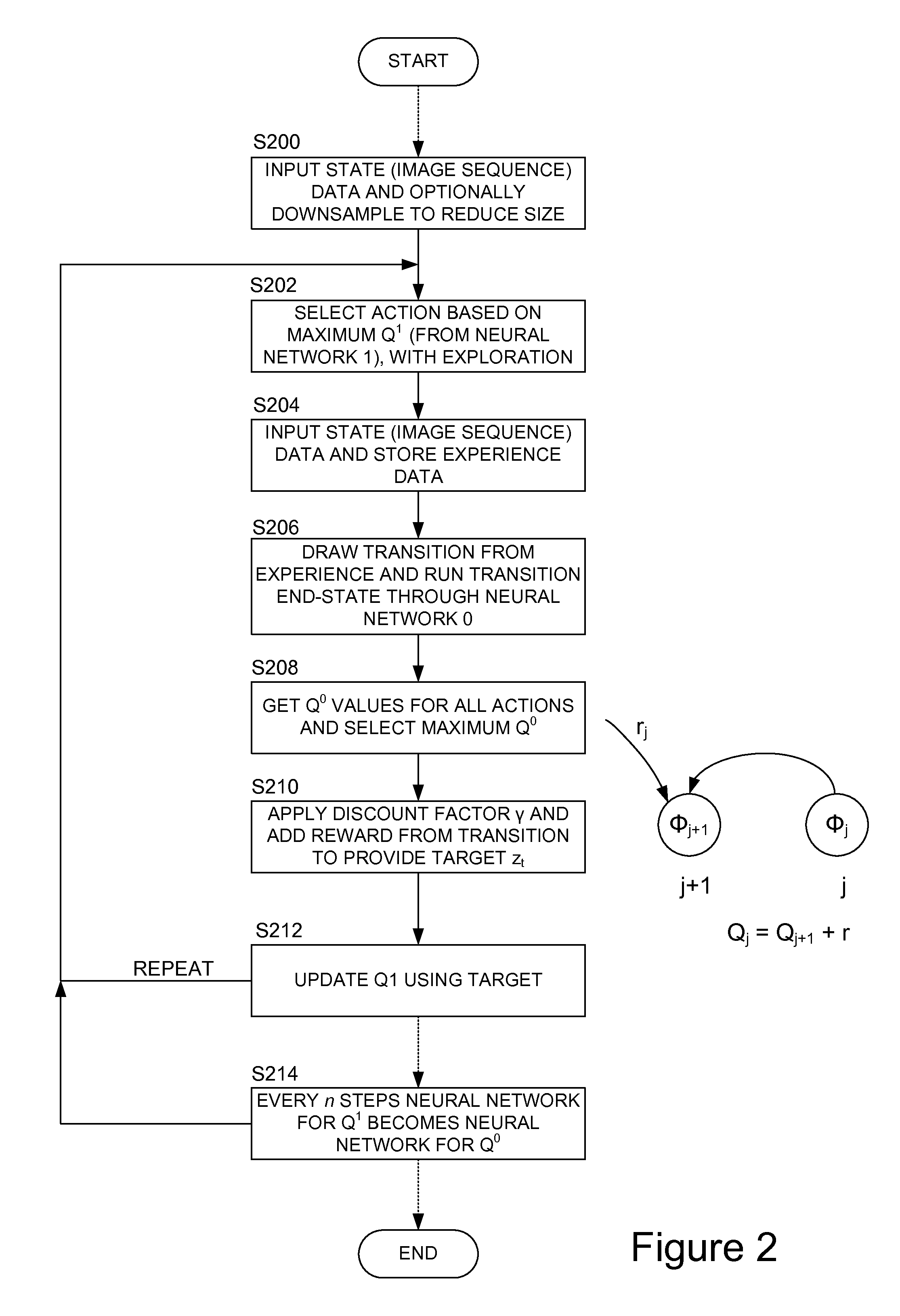
Methods and apparatus for reinforcement learning
ActiveUS20150100530A1Reduce computing costLarge data setDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeAlgorithmReinforcement learning
Owner:DEEPMIND TECH LTD
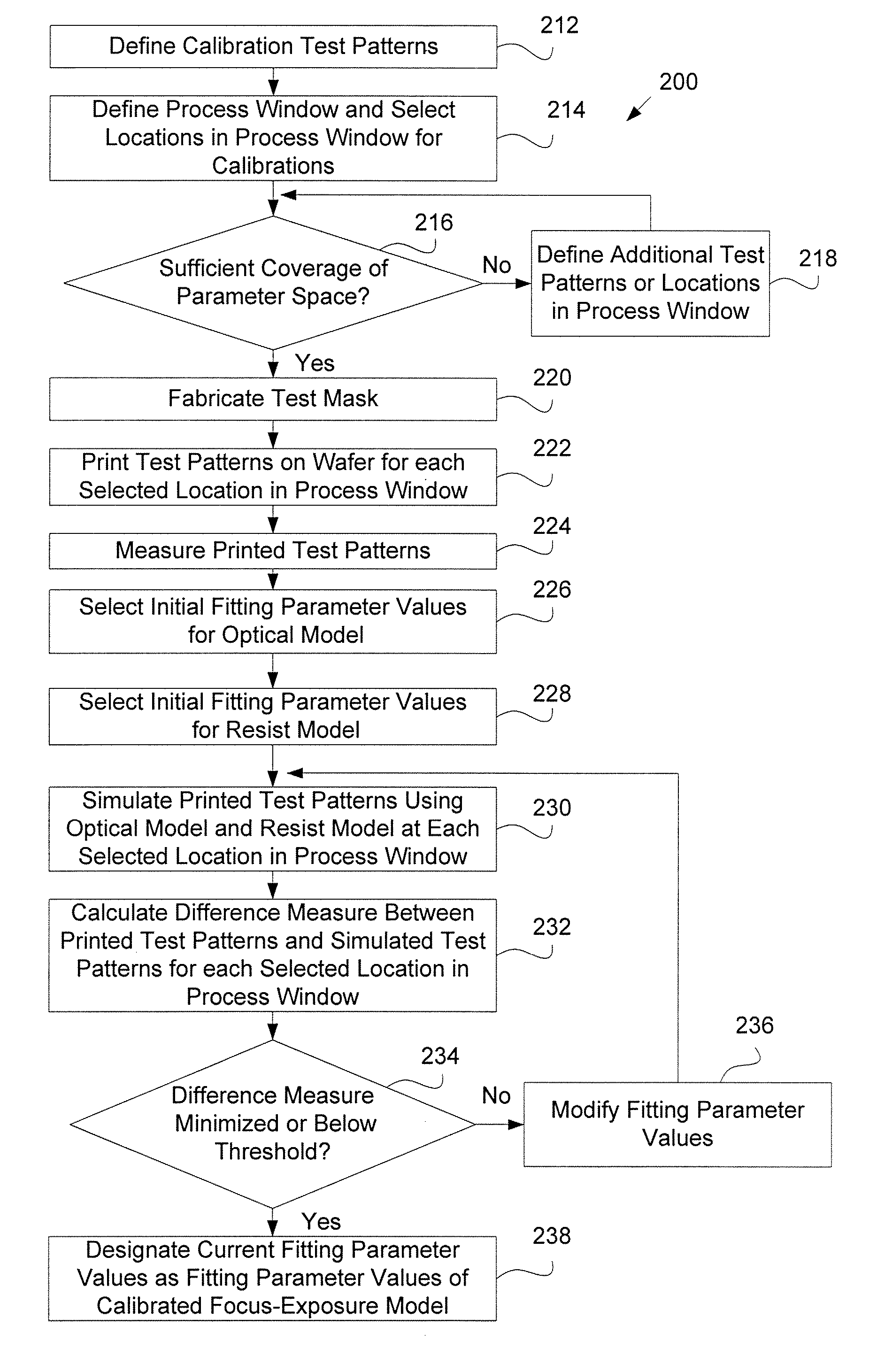
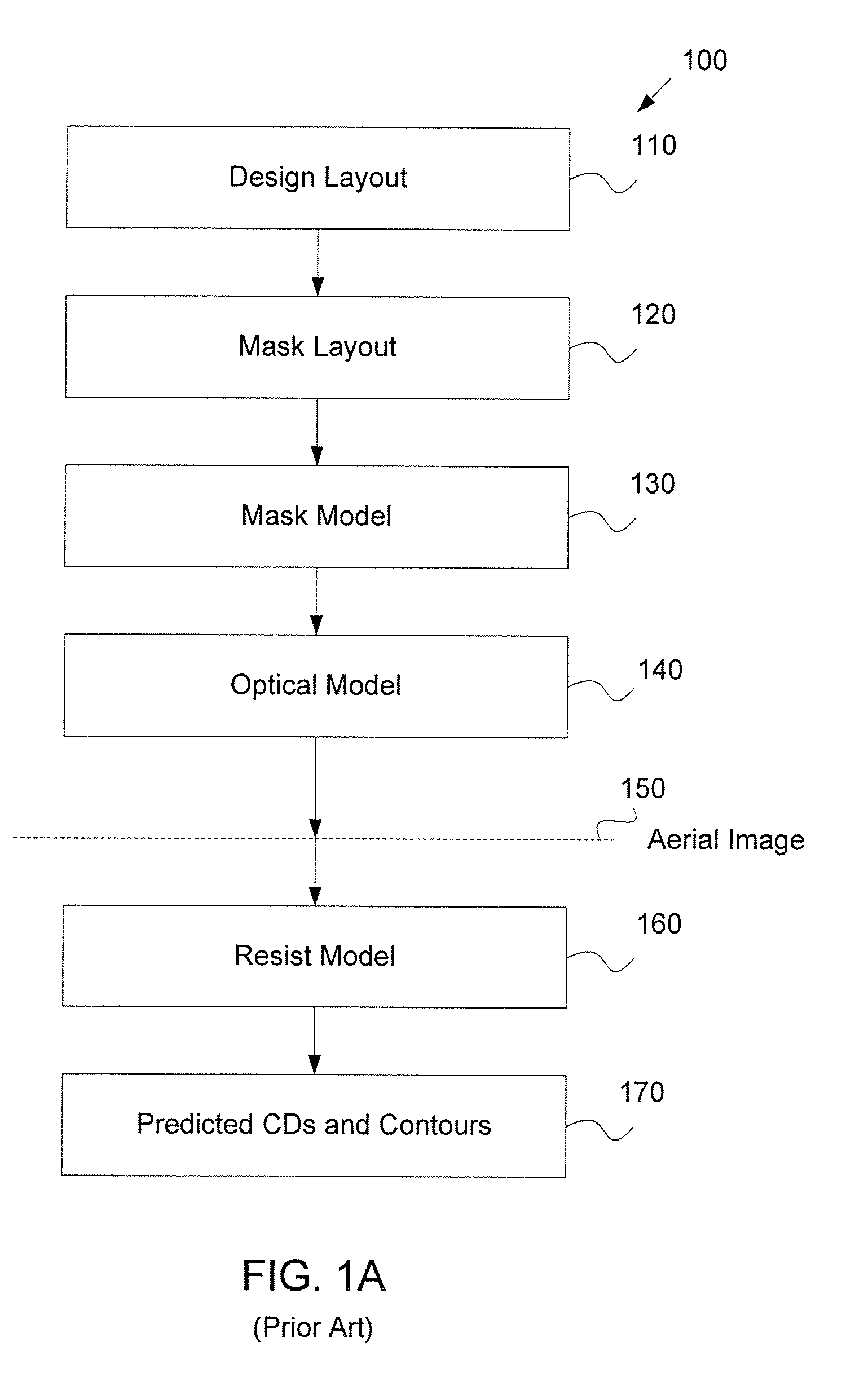
System and method for creating a focus-exposure model of a lithography process
ActiveUS20070031745A1Good accuracy and robustnessPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithography processAlgorithm
A system and a method for creating a focus-exposure model of a lithography process are disclosed. The system and the method utilize calibration data along multiple dimensions of parameter variations, in particular within an exposure-defocus process window space. The system and the method provide a unified set of model parameter values that result in better accuracy and robustness of simulations at nominal process conditions, as well as the ability to predict lithographic performance at any point continuously throughout a complete process window area without a need for recalibration at different settings. With a smaller number of measurements required than the prior-art multiple-model calibration, the focus-exposure model provides more predictive and more robust model parameter values that can be used at any location in the process window.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
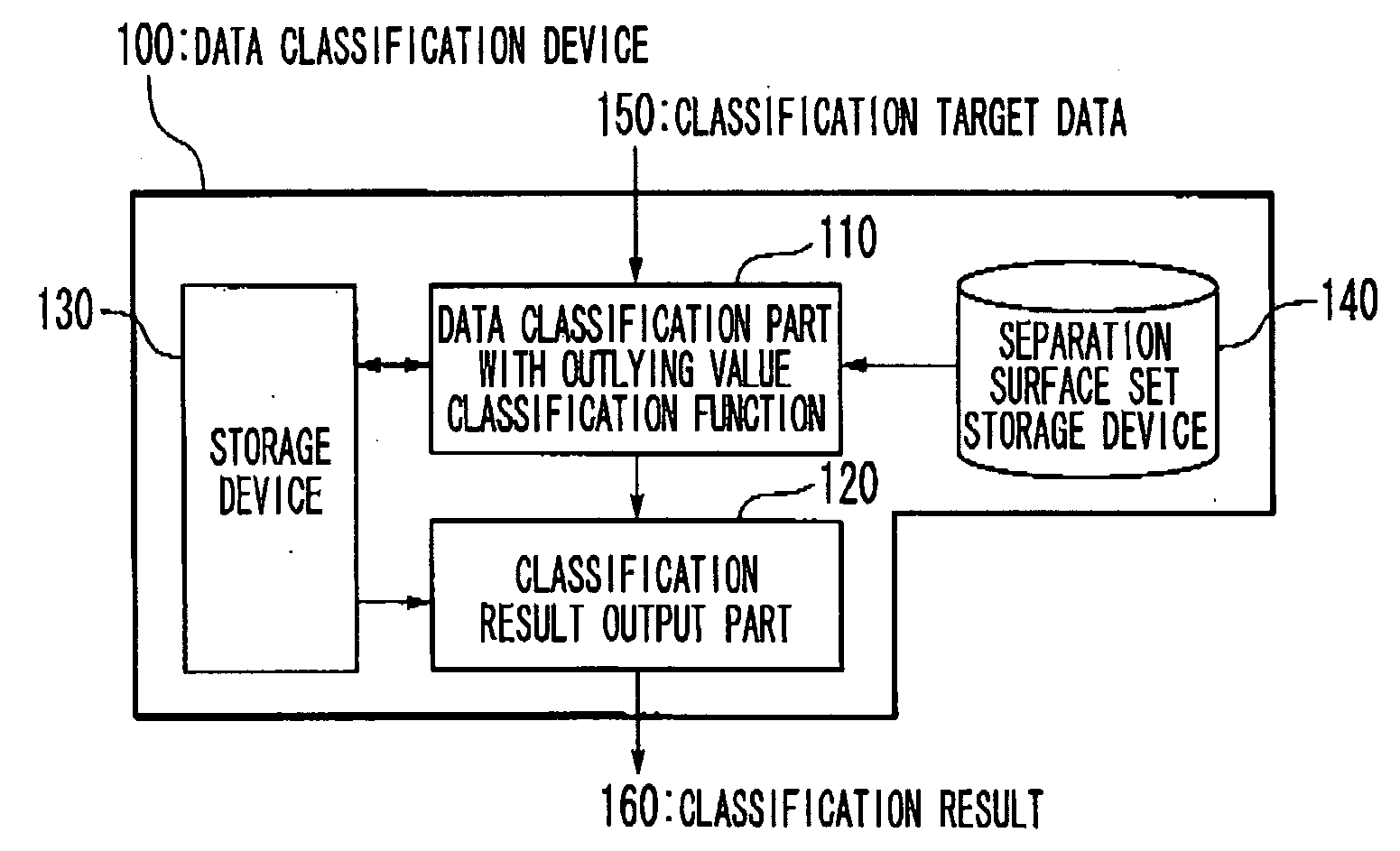
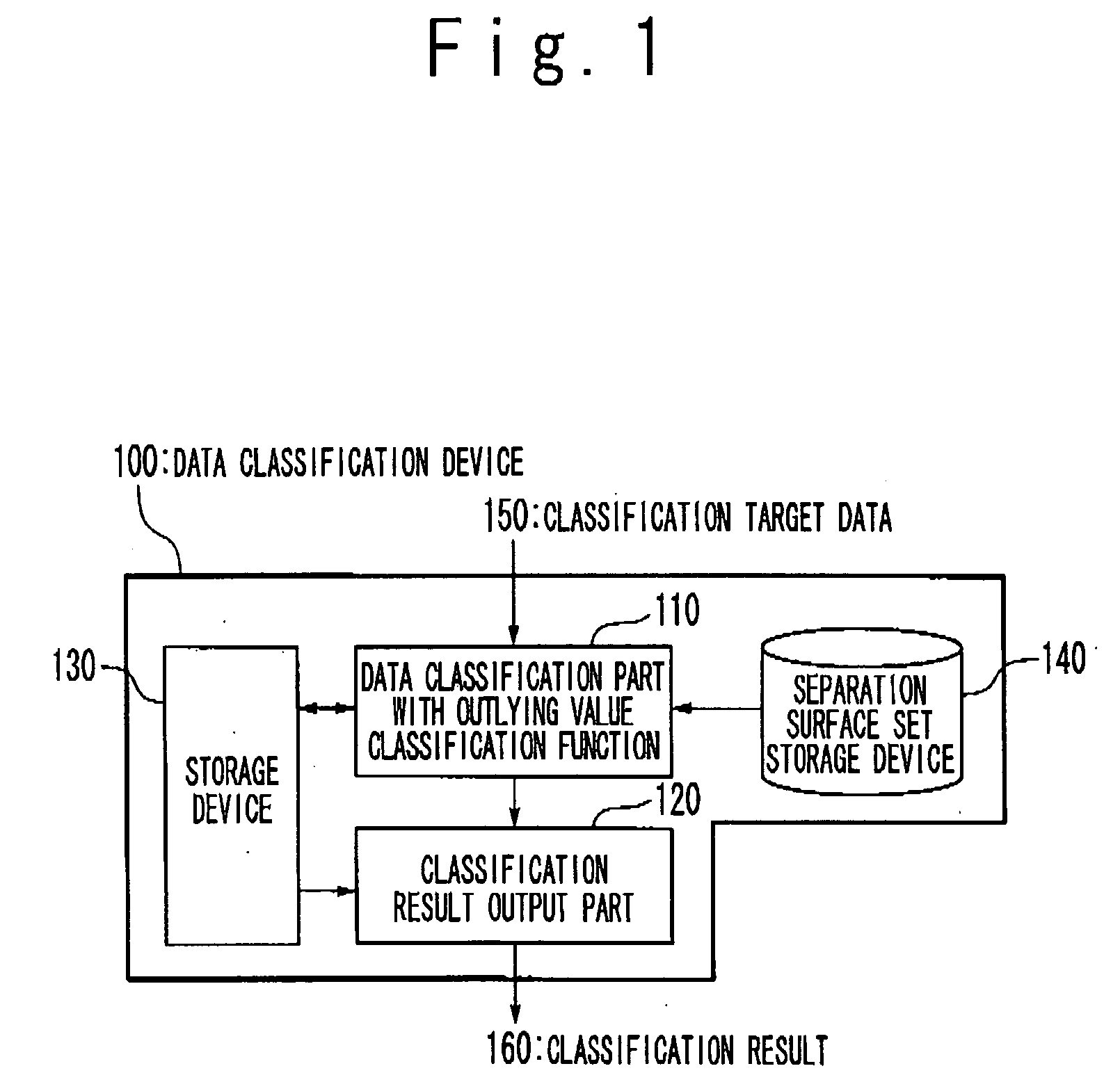
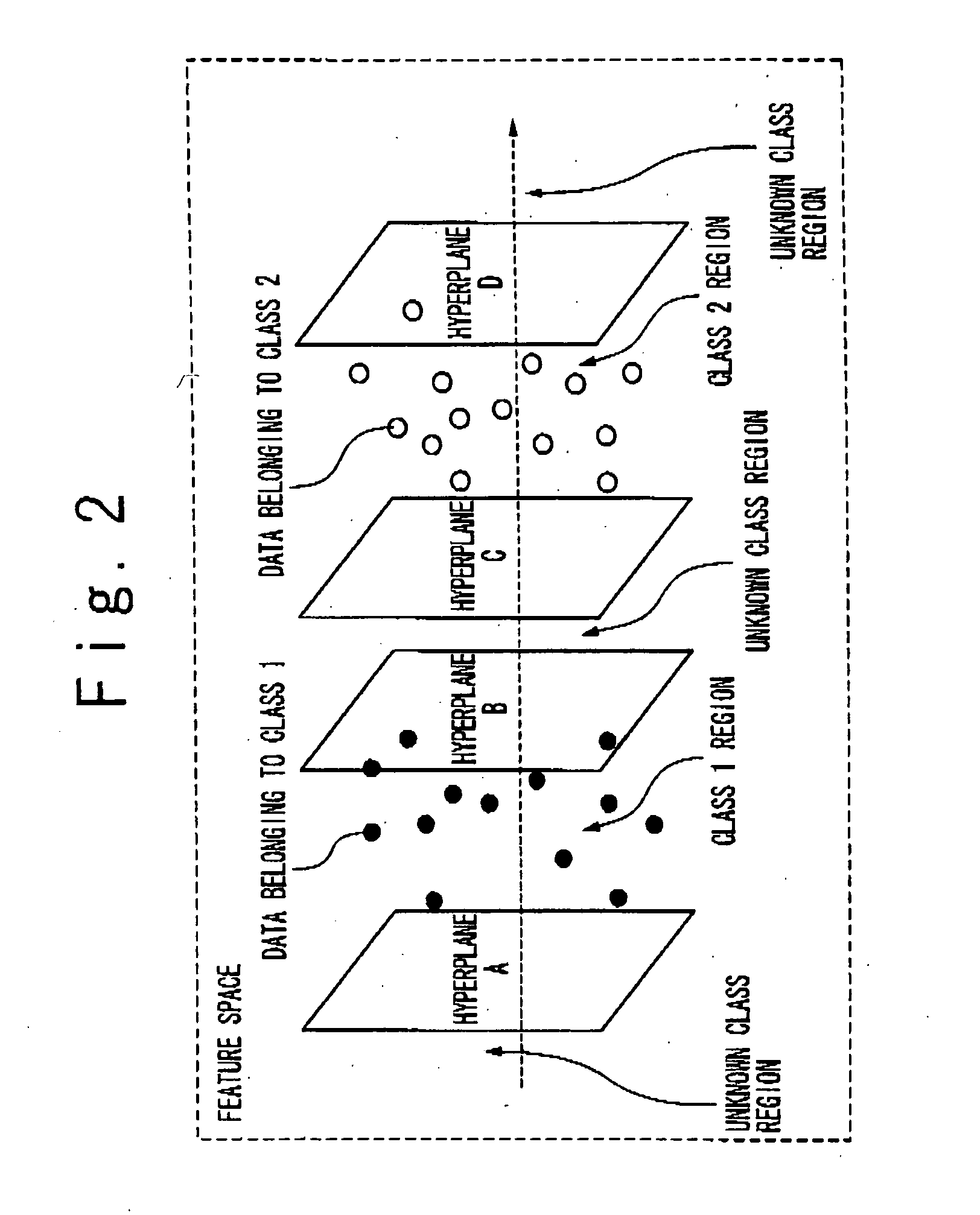
Data classification method and data classification device
ActiveUS20100250542A1Improve reliabilityHigh data reliabilityDigital data processing detailsKernel methodsAlgorithmCharacteristic space
A separation surface set storage part stores information defining a plurality of separation surfaces which separate a feature space into at least one known class region respectively corresponding to at least one known class and an unknown class region. Each of the at least one known class region is separated from outside region by more than one of the plurality of separation surfaces which do not intersect to each other. A data classification apparatus determine a classification of a classification target data whose inner product in the feature space is calculable by calculating to which region of the at least one known class region and the unknown class region determined by the information stored in the separation surface set storage part the classification target data belongs. A method and apparatus for data classification which can simultaneously perform identification and outlying value classification with high reliability in a same procedure are provided.
Owner:NEC CORP
Robust anomaly detection and regularized domain adaptation of classifiers with application to internet packet-flows
InactiveUS20120284791A1Maximize aggregate statistical significanceMaximizesMathematical modelsMemory loss protectionCredit cardAlgorithm
Sound, robust methods identify the most suitable, parsimonious set of tests to use with respect to prioritized, sequential anomaly detection in a collected batch of sample data. While the focus is on detecting anomalies in network traffic flows and classifying network traffic flows into application types, the methods are also applicable to other anomaly detection and classification application settings, including detecting email spam, (e.g. credit card) fraud detection, detecting imposters, unusual event detection (for example, in images and video), host-based computer intrusion detection, detection of equipment or complex system failures, as well as of anomalous measurements in scientific experiments.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Action Detection and Activity Classification
ActiveUS20130190903A1Physical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesActivity classificationAlgorithm
Activities, actions and events during user performance of physical activity may be detected using various algorithms and templates. Templates may include an arrangement of one or more states that may identify particular event types and timing between events. Templates may be specific to a particular type of activity (e.g., types of sports, drills, events, etc.), user, terrain, time of day and the like.
Owner:NIKE INC
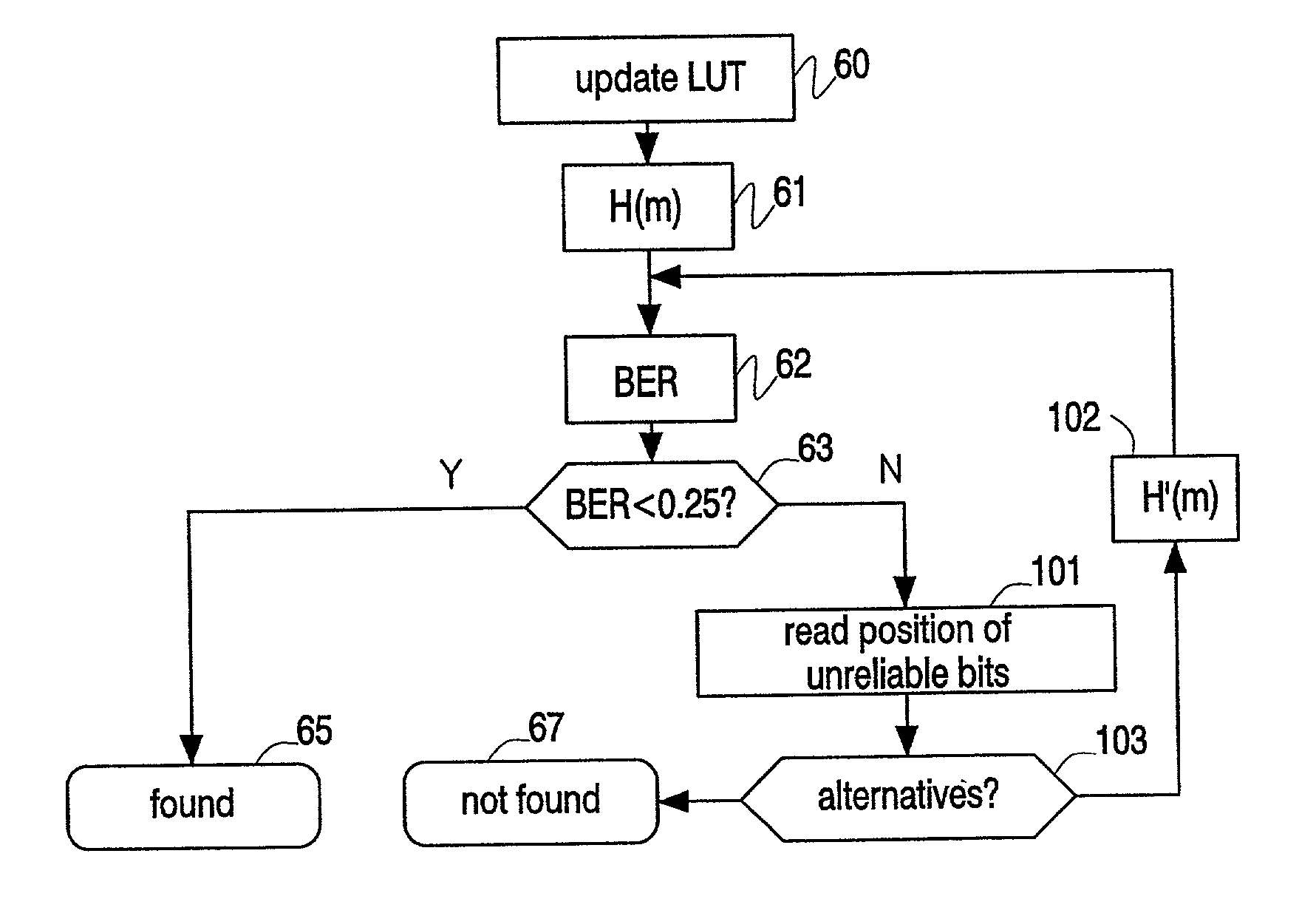
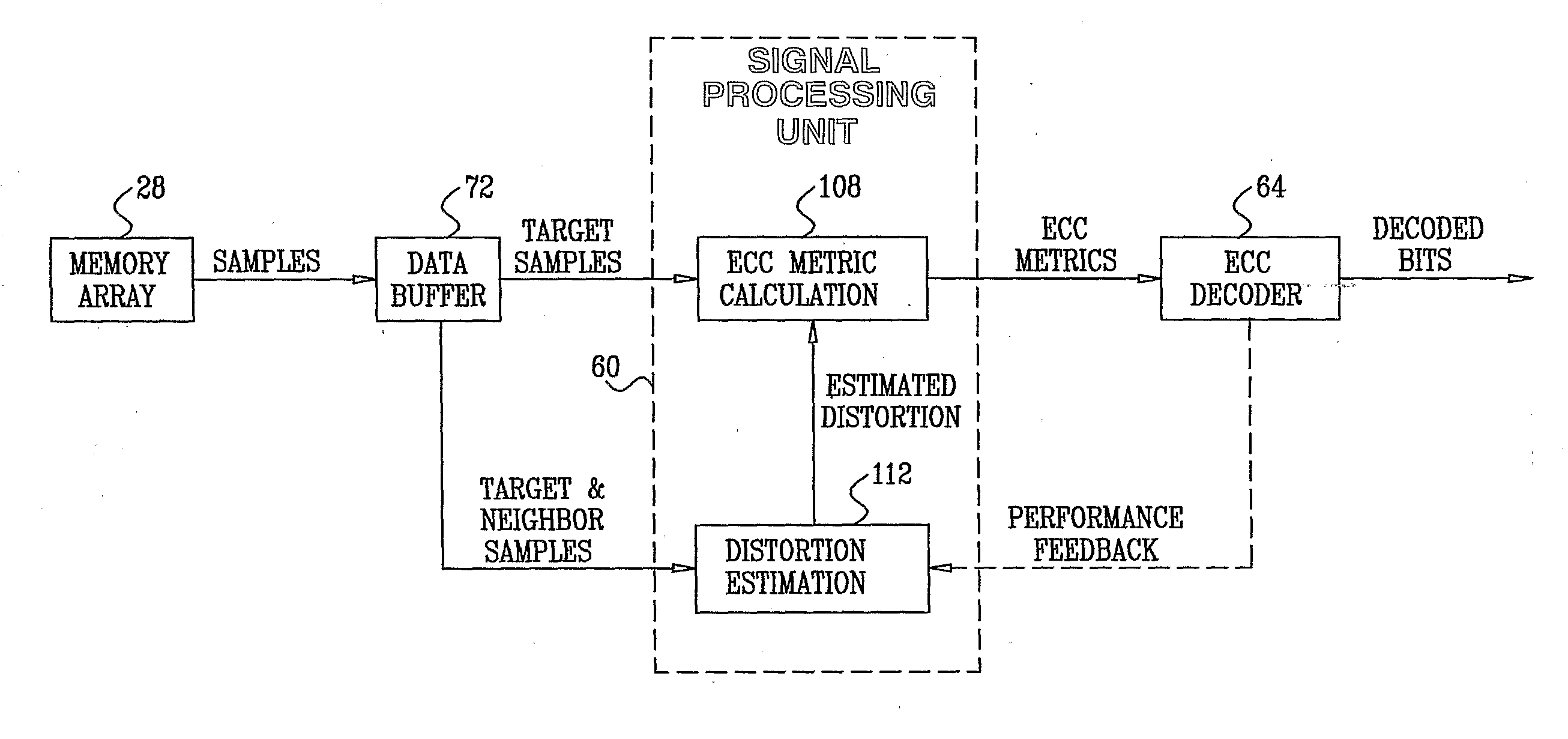
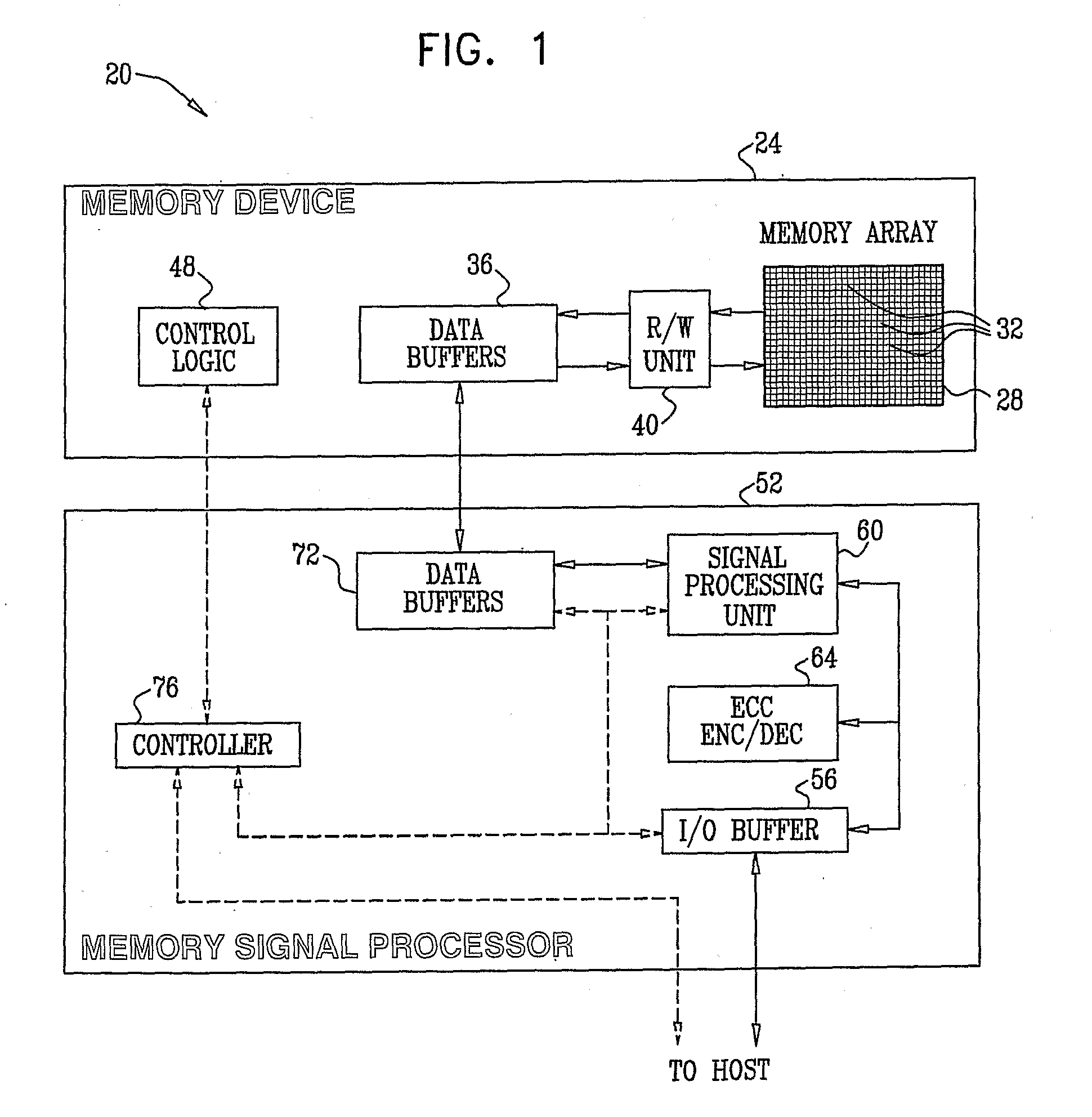
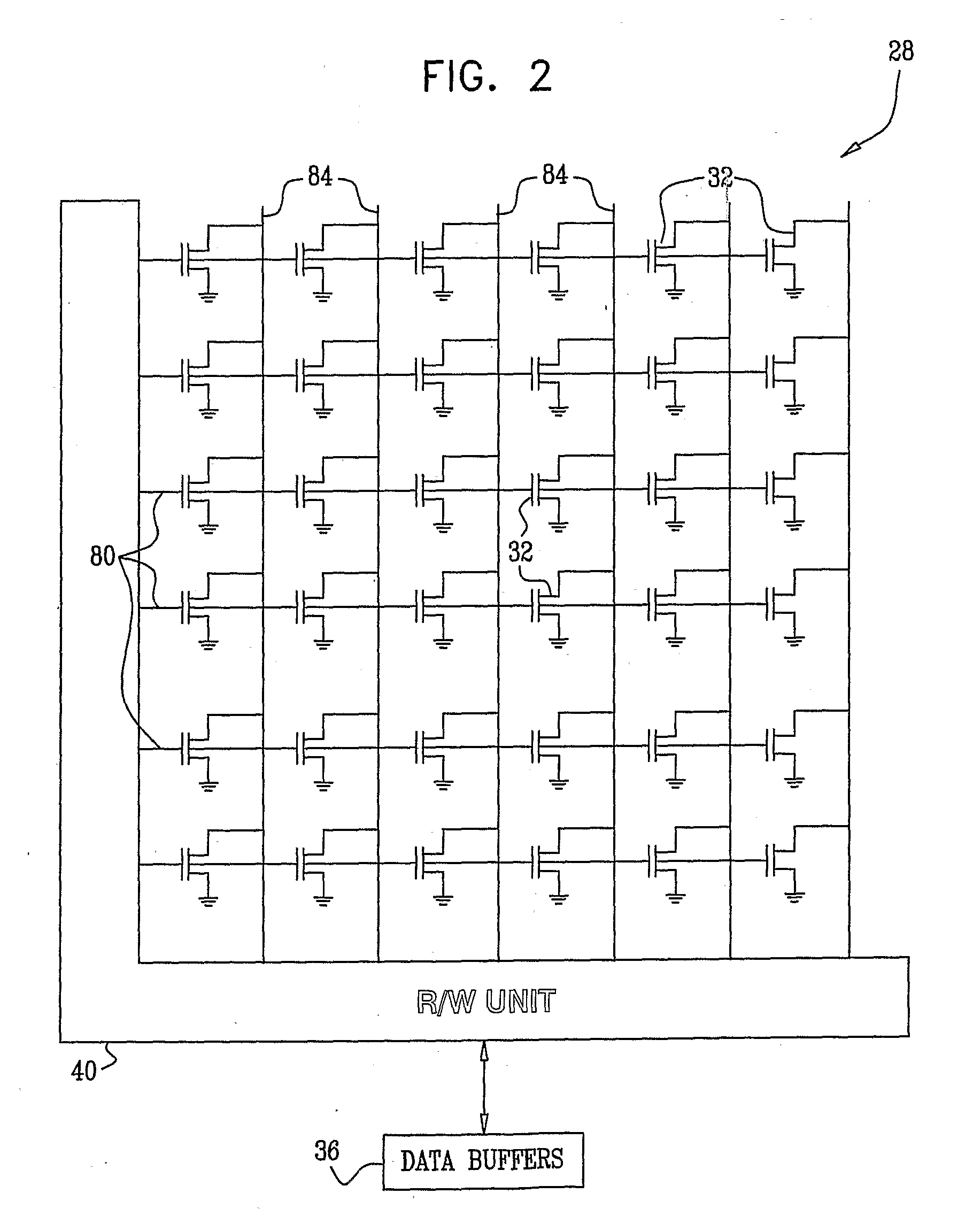
Combined distortion estimation and error correction coding for memory devices
ActiveUS20090024905A1Improve performanceData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionCalculation errorDistortion
A method for operating a memory device (24) includes encoding data using an Error Correction Code (ECC) and storing the encoded data as first analog values in respective analog memory cells (32) of the memory device. After storing the encoded data, second analog values are read from the respective memory cells of the memory device in which the encoded data were stored. At least some of the second analog values differ from the respective first analog values. A distortion that is present in the second analog values is estimated. Error correction metrics are computed with respect to the second analog values responsively to the estimated distortion. The second analog values are processed using the error correction metrics in an ECC decoding process, so as to reconstruct the data.
Owner:APPLE INC
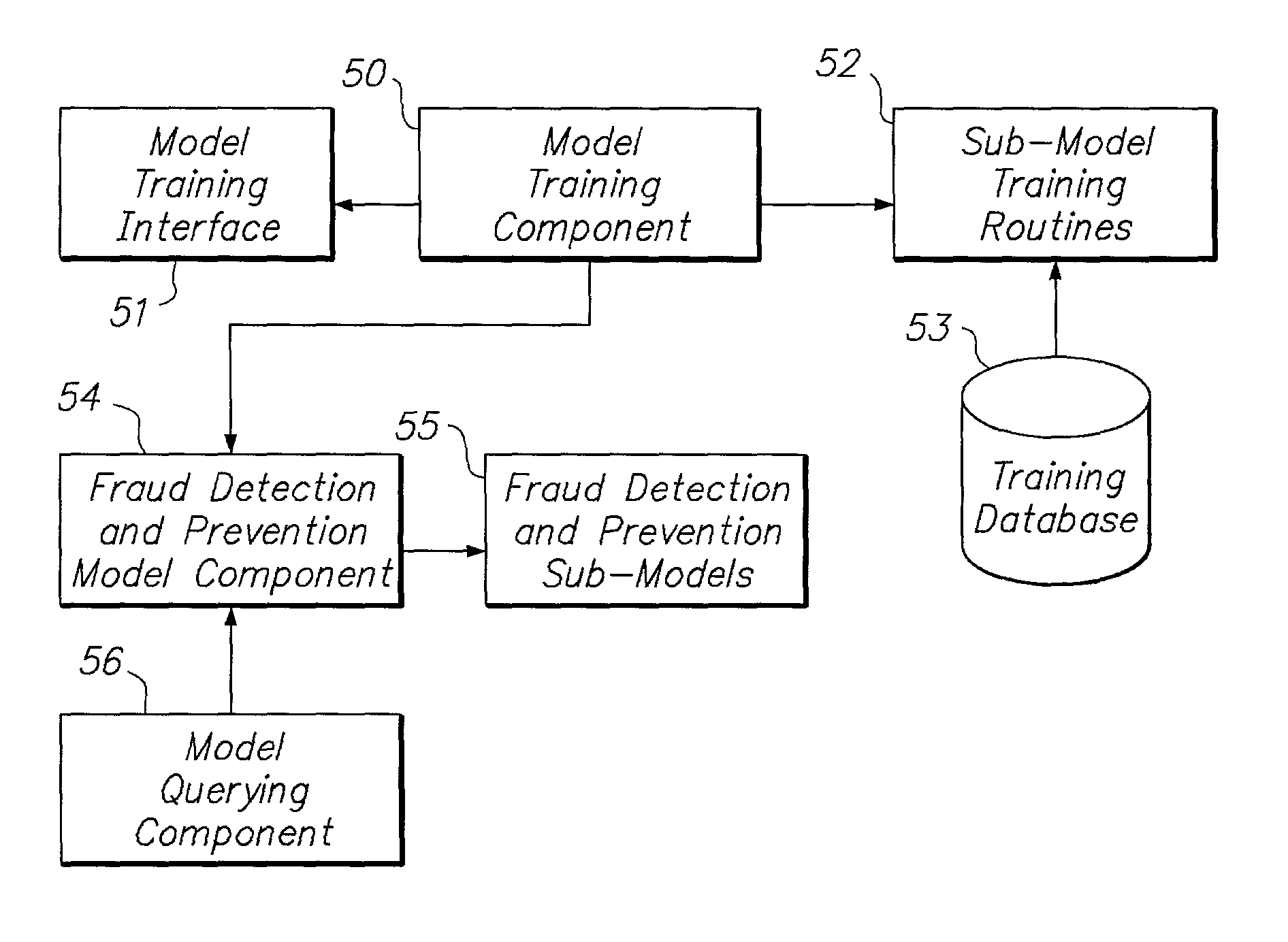
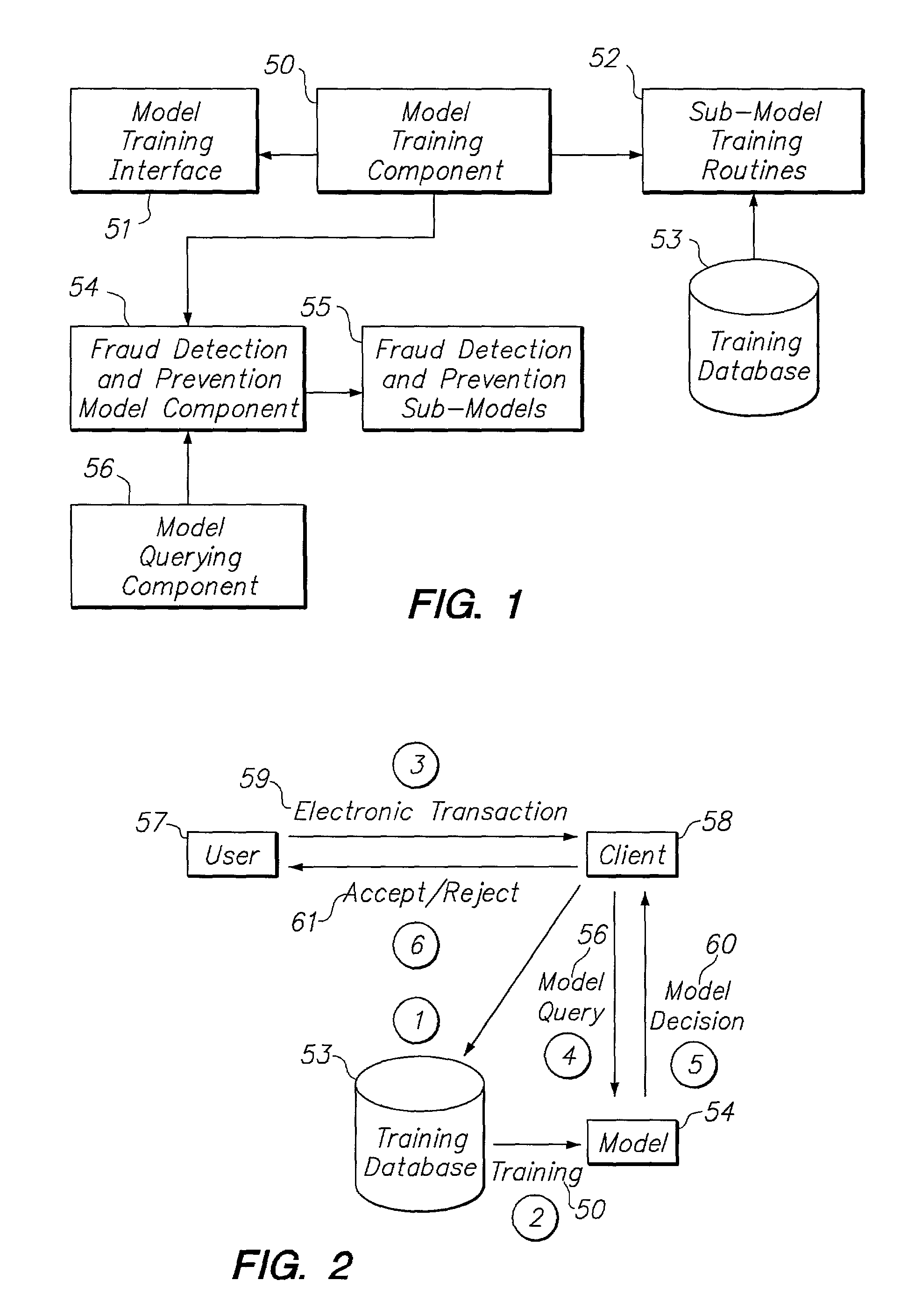
Systems and methods for dynamic detection and prevention of electronic fraud
The present invention provides systems and methods for dynamic detection and prevention of electronic fraud and network intrusion using an integrated set of intelligent technologies. The intelligent technologies include neural networks, multi-agents, data mining, case-based reasoning, rule-based reasoning, fuzzy logic, constraint programming, and genetic algorithms. The systems and methods of the present invention involve a fraud detection and prevention model that successfully detects and prevents electronic fraud and network intrusion in real-time. The model is not sensitive to known or unknown different types of fraud or network intrusion attacks, and can be used to detect and prevent fraud and network intrusion across multiple networks and industries.
Owner:BRIGHTERION
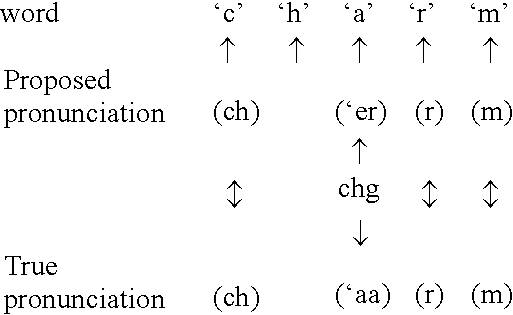
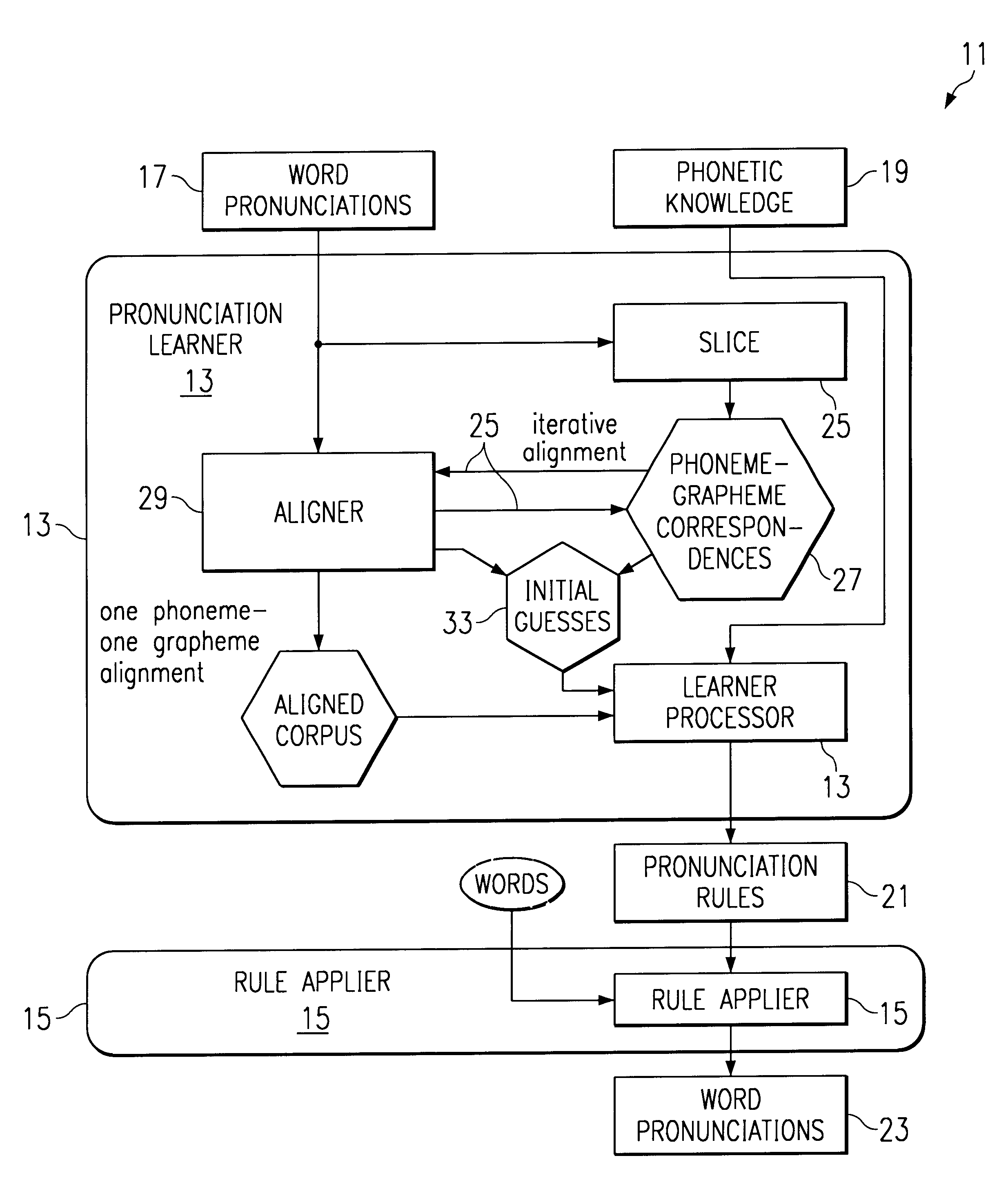
Rule-based learning of word pronunciations from training corpora
A text-to-pronunciation system (11) includes a large training set of word pronunciations (19) and an extractor for extracting language specific information from the training set to produce pronunciations for words not in its training set. A learner (13) forms pronunciation guesses for words in the training set and for finding a transformation rule that improves the guesses. A rule applier (15) applies the transformation rule found to guesses. The learner (13) repeats the finding of another rule and the rule applier (15) applies the new rule to find the rules that improves the guesses the most.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Quasi-monte carlo light transport simulation by efficient ray tracing
InactiveUS20090167763A1Efficient and accurateSuitable for implementation3D-image rendering3D modellingGraphicsGraphic system
Methods, systems, devices and computer program code (software) products operable within a computer graphics system or other computer system enable quasi-Monte Carlo (QMC) light transport simulation by efficient ray tracing.
Owner:MENTAL IMAGES
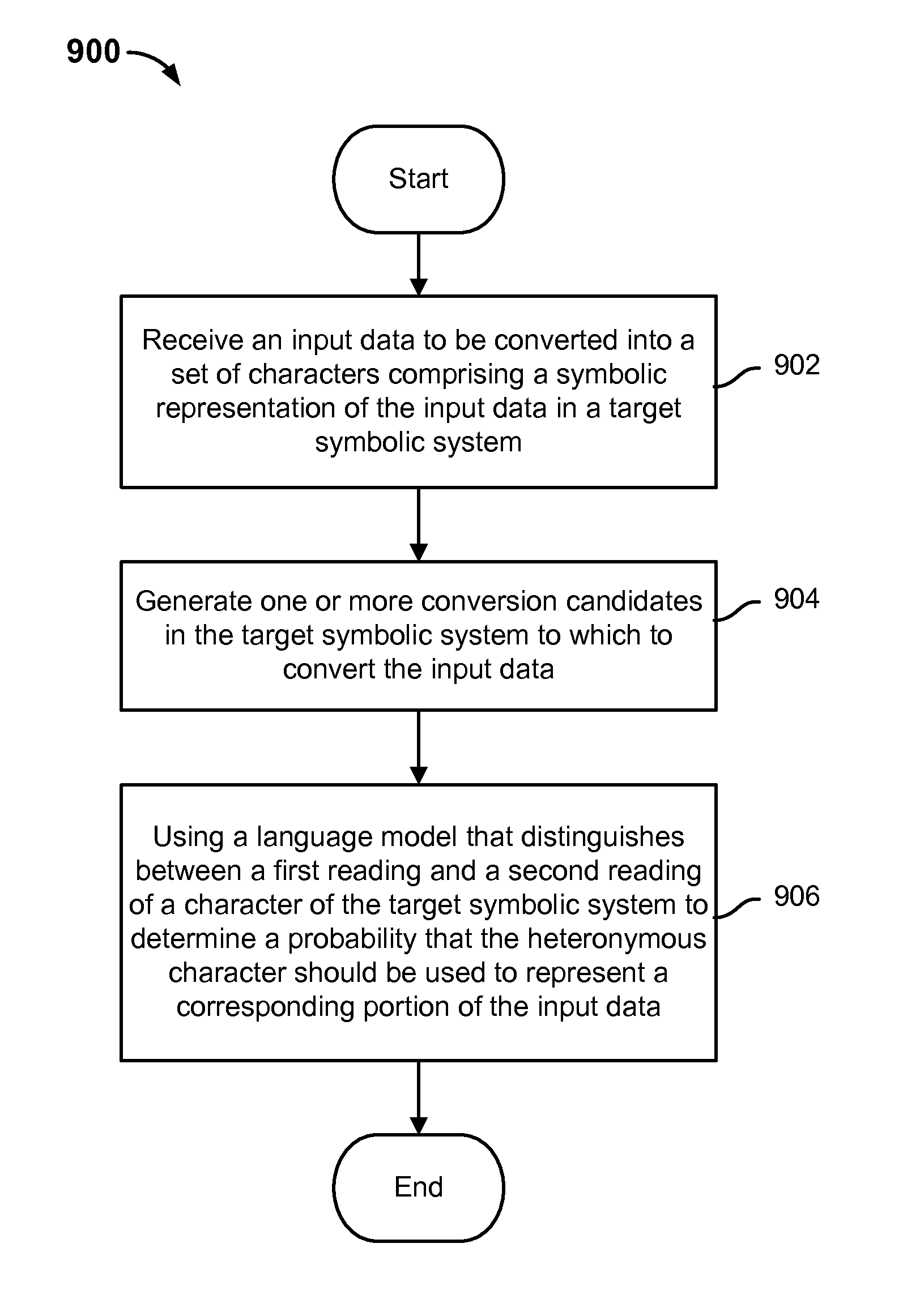
Method for disambiguating multiple readings in language conversion
Disambiguating multiple readings in language conversion is disclosed, including: receiving an input data to be converted into a set of characters comprising a symbolic representation of the input data in a target symbolic system; and using a language model that distinguishes between a first reading and a second reading of a character of the target symbolic system to determine a probability that the heteronymous character should be used to represent a corresponding portion of the input data.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of generating attribute cardinality maps
InactiveUS6865567B1The result is accurateSmall sizeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalResource consumptionAlgorithm
This invention provides a novel means for creating a histogram for use in minimizing response time and resource consumption when optimizing a query in a database, and other like structures, the histogram being created by placing ordered elements into specific range until the next element to be considered for inclusion in the range is a predetermined distance from the (generalized) mean value associated with the elements within the range, whereupon that next element is placed in the following range. Similarly, the following ranges are closed when the next element to be considered for inclusion in the range is greater than a predetermined distance from the (generalized) mean value associated with the elements in that range, whereupon that next element is placed in the following range. For each range, the location and size of the range is recorded with, for example, the mean value, the slope or other attribute characterizing one or more elements in the range. The invention has also applications in pattern recognition, message routing, and in actuarial sciences.
Owner:OOMMEN BASANTKUMAR JOHN +1
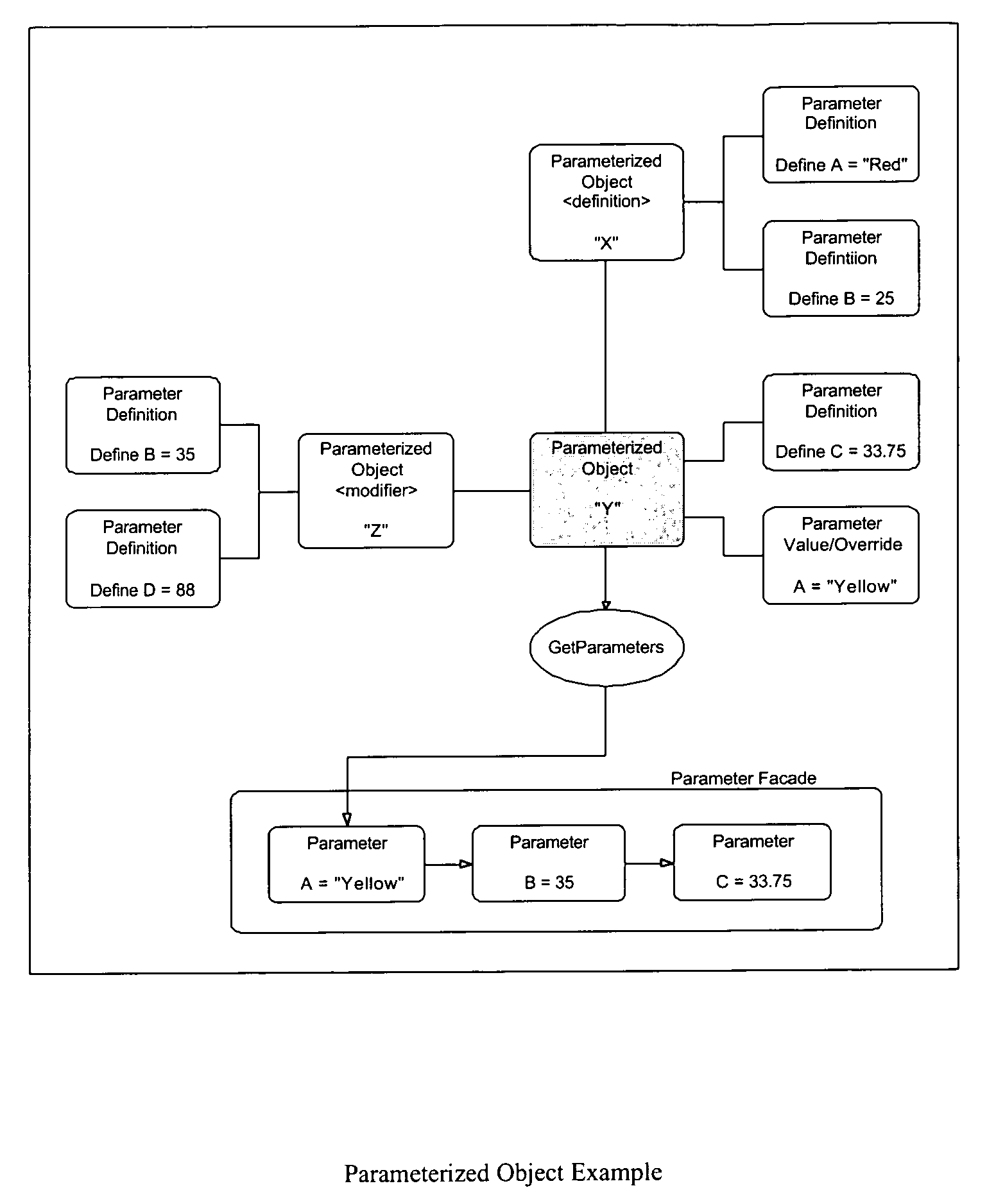
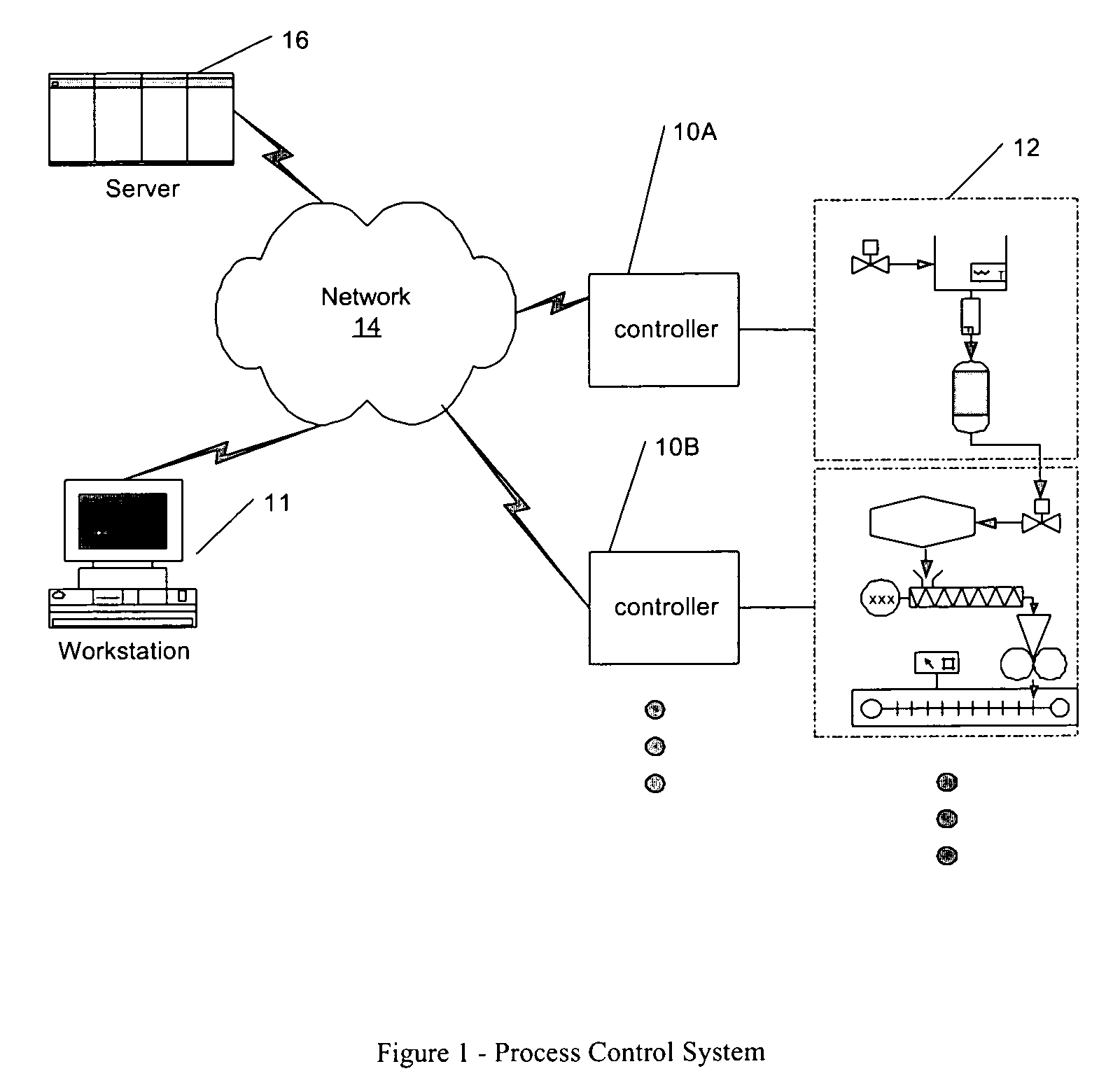
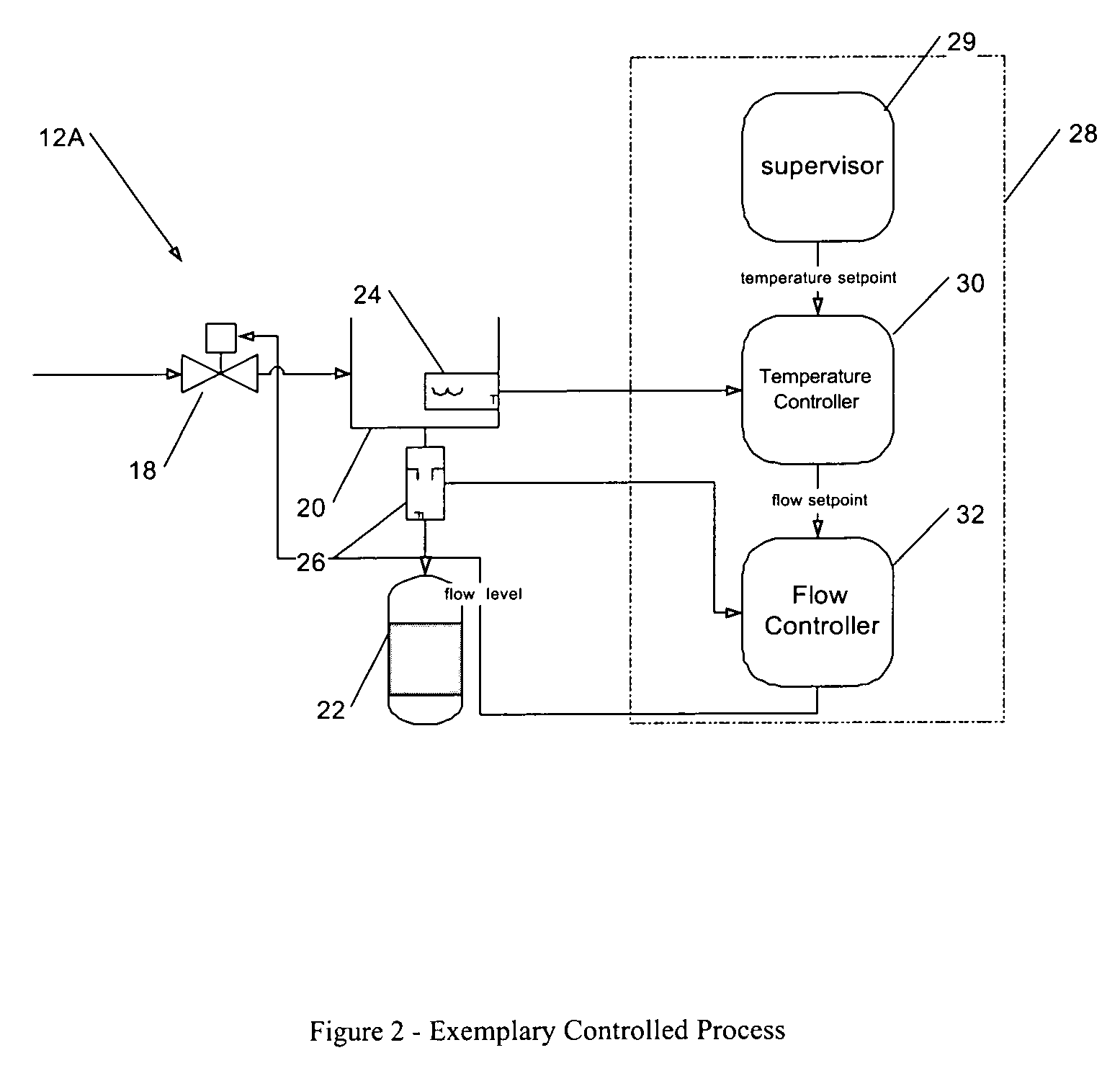
Process control configuration system with parameterized objects
InactiveUS7096465B1OptimizationConfiguration of process controlProgramme controlProgram loading/initiatingControl systemModel system
A process control system is configured via manipulation of objects that model system components, e.g., sensors, blocks, control processors, historians, workstations, etc. Individual objects include parameters that characterize the underlying components and / or the behavior of the objects themselves. These parameters are derived from the “parents,” from which the objects are created. Derived characteristics need not be defined explicitly but, rather, are defined implicitly or by reference. These derived characteristics may be overridden for an individual object and, thereby, its progeny. Although objects have class-like characteristics (i.e., insofar as they are definitional in nature), they can be created at configuration time, without the need for recompilation.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
Forecasting using interpolation modeling
InactiveUS7072863B1FinanceComputation using non-denominational number representationGoal variablePredictor variable
Owner:C4CAST COM
Method and apparatus for enhanced estimation of an analyte property through multiple region transformation
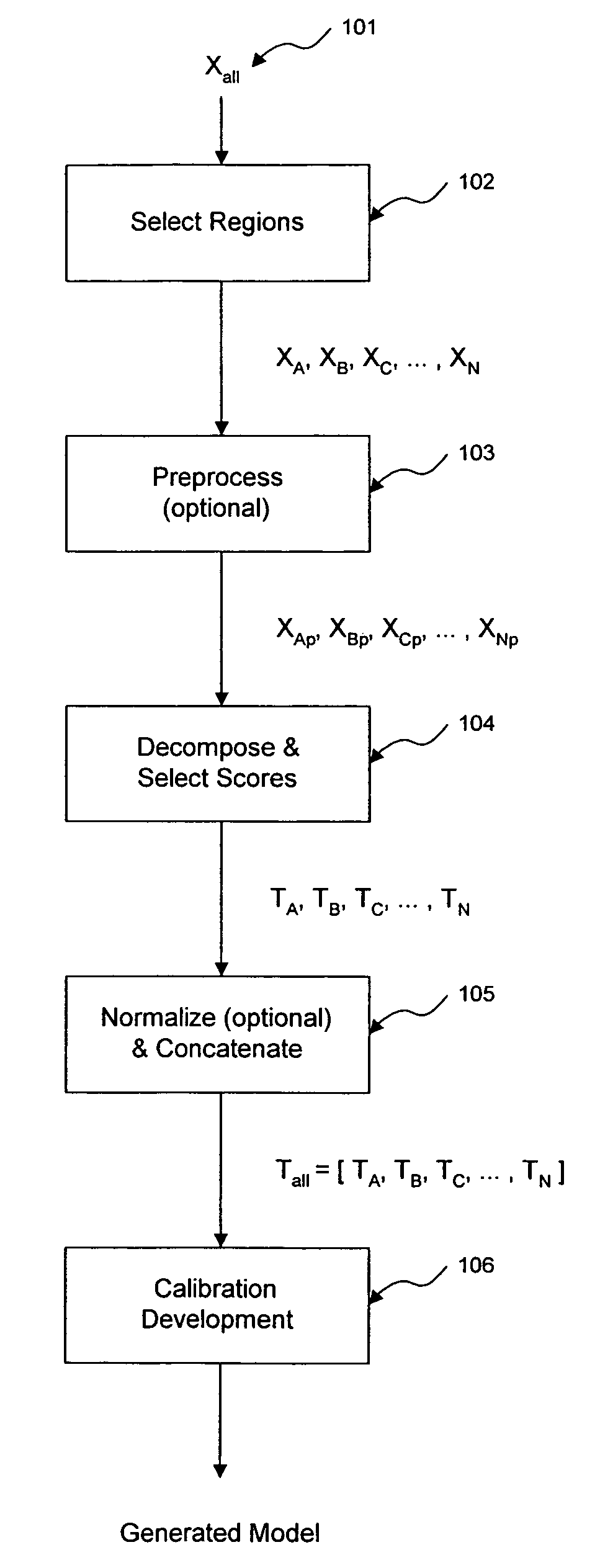
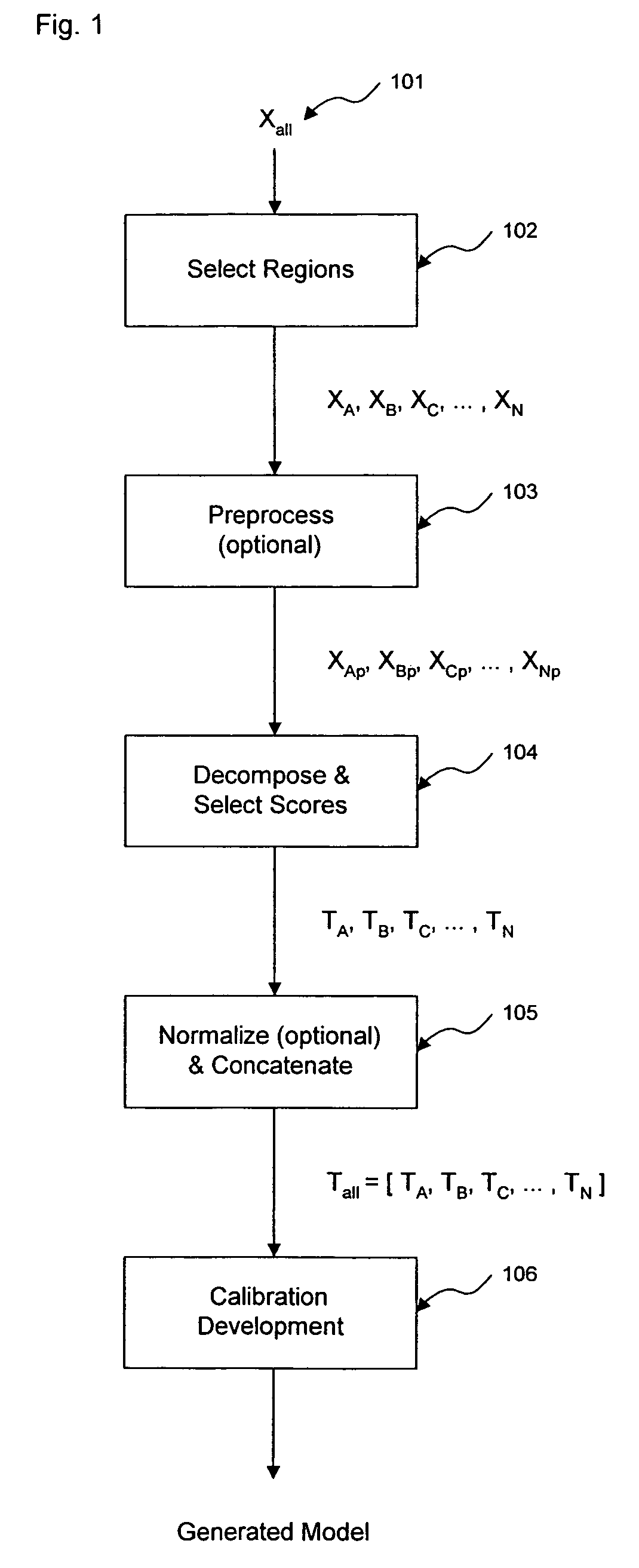
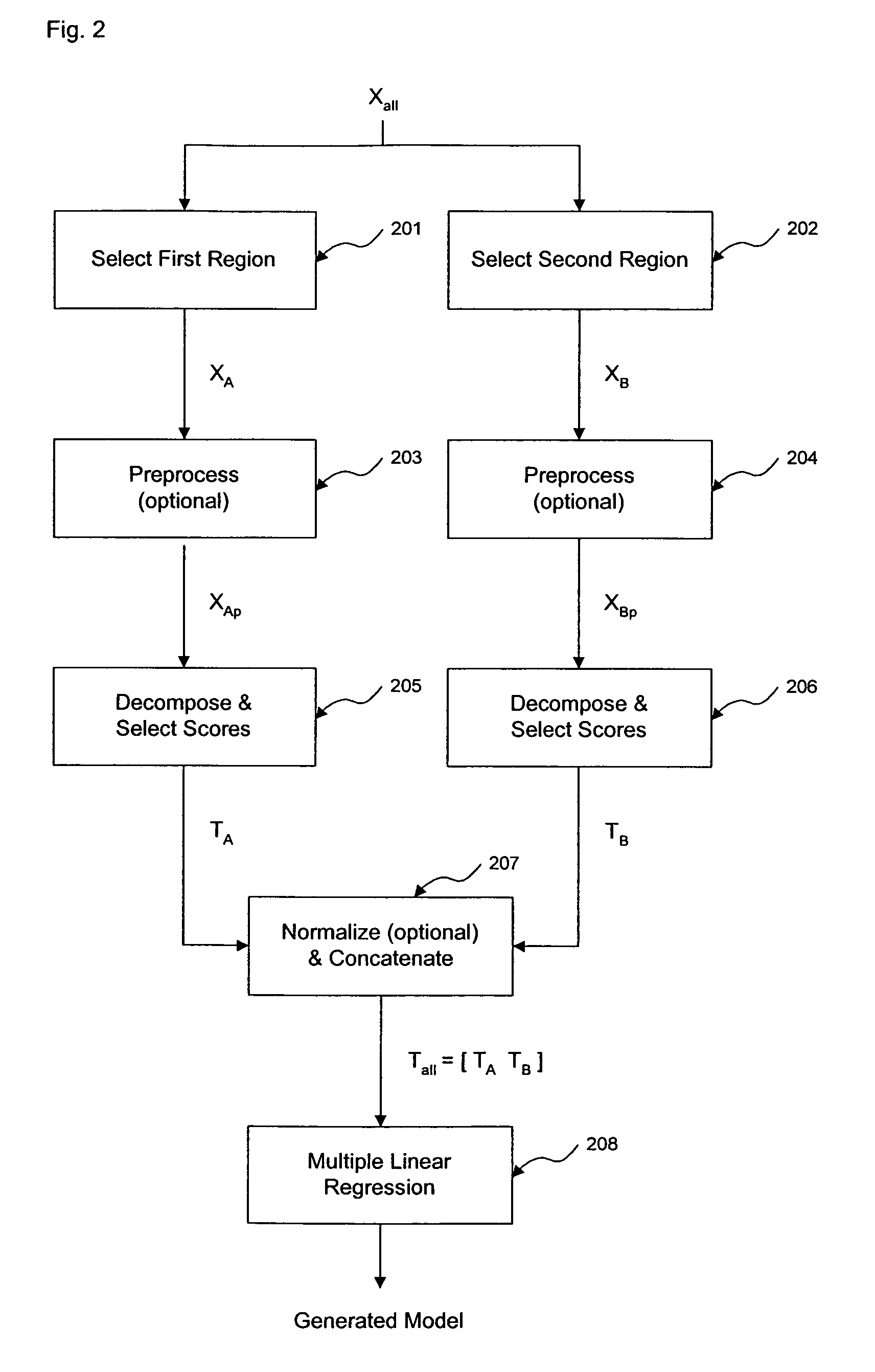
ActiveUS7620674B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteDecomposition
The invention comprises transformation of a section of a data block independently of the transformation of separate or overlapping data blocks to determine a property related to the original matrix, where each of the separate or overlapping data blocks are derived from an original data matrix. The transformation enhances parameters of a first data block over a given region of an axis of the data matrix, such as signal-to-noise, without affecting analysis of a second data block derived from the data matrix. This allows for enhancement of analysis of an analyte property, such as concentration, represented within the original data matrix. A separate decomposition and factor selection for each selected data matrix is performed with subsequent score matrix concatenization. The combined score matrix is used to generate a model that is subsequently used to estimate a property, such as concentration represented in the original data matrix.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com