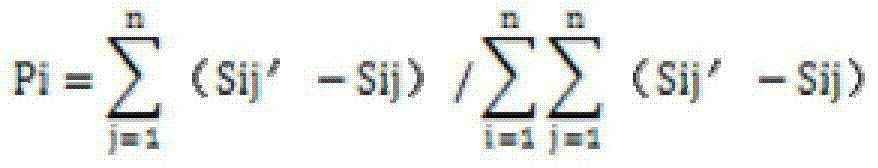Patents
Literature
163 results about "Predictor variable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Predictor Variable. A predictor variable is a variable used in regression to predict another variable. It is sometimes referred to as an independent variable if it is manipulated rather than just measured.
Method for predicting the therapeutic outcome of a treatment
InactiveUS6317731B1Improve accuracy and precisionHigh precisionBiological neural network modelsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionDiseaseNerve network
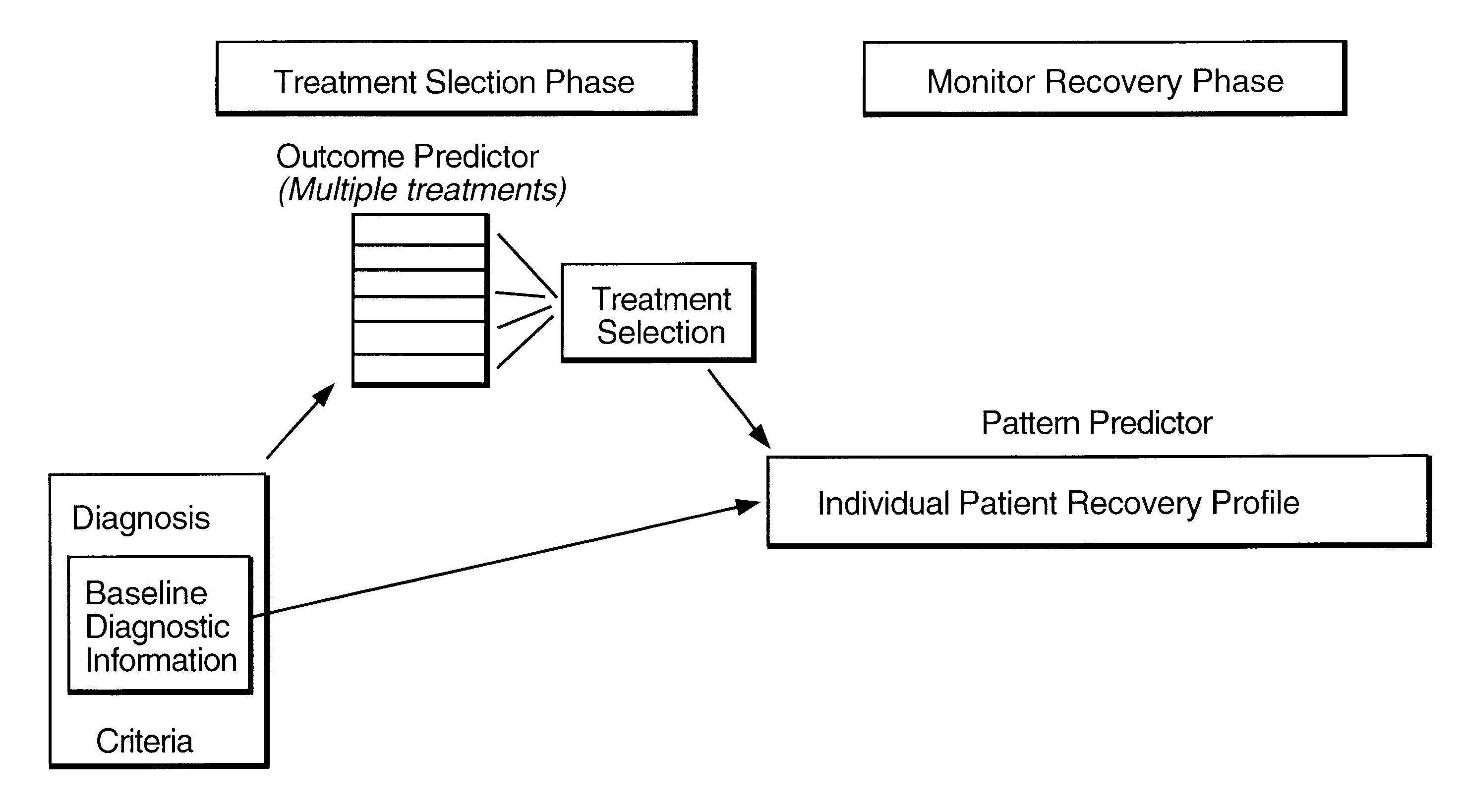
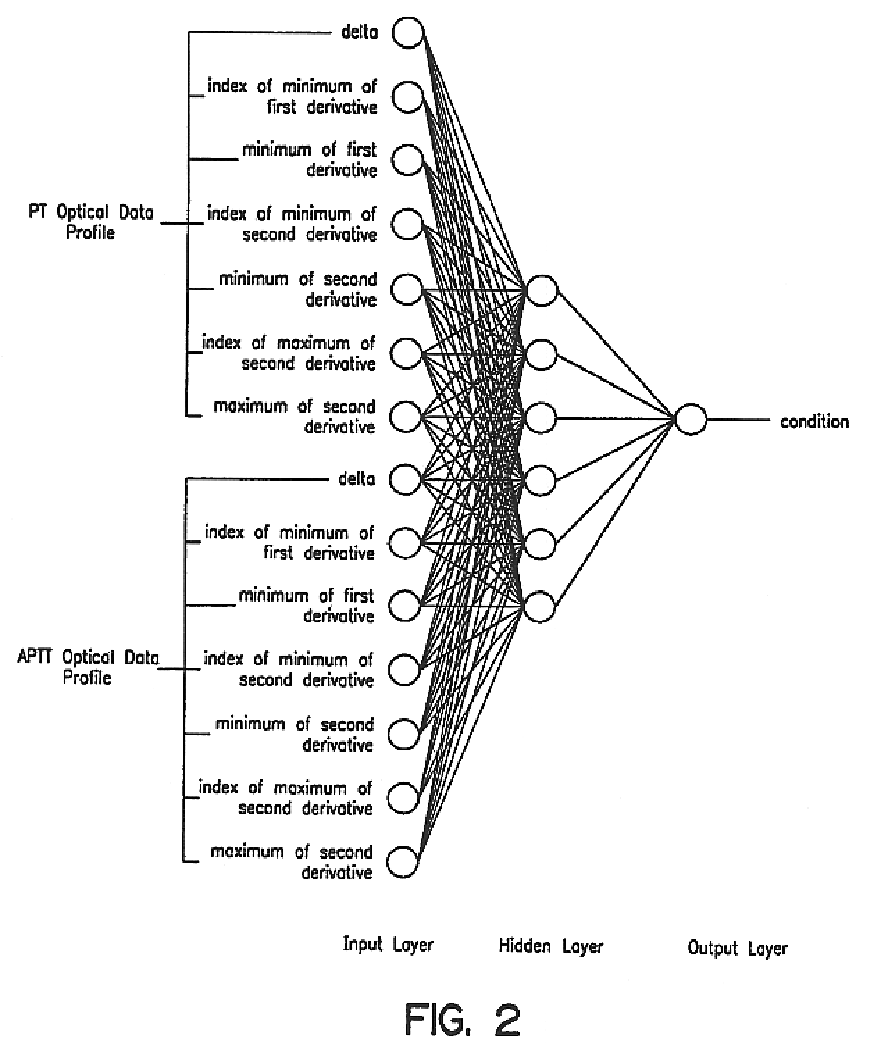
A method useful for facilitating choosing a treatment or treatment regime and for predicting the outcome of a treatment for a disorder which is diagnosed and monitored by a physician or other appropriately trained and licensed professional, such as for example, a psychologist, based upon the symptoms experienced by a patient. Unipolar depression is an example of such a disorder, however the model may find use with other disorders and conditions wherein the patient response to treatment is variable. In the preferred embodiment, the method for predicting patient response includes the steps of performing at least one measurement of a symptom on a patient and measuring that symptom so as to derive a baseline patient profile, such as for example, determining the symptom profile with time; defining a set of a plurality of predictor variables which define the data of the baseline patient profile, wherein the set of predictor variables includes predictive symptoms and a set of treatment options; deriving a model that represents the relationship between patient response and the set of predictor variables; and utilizing the model to predict the response of said patient to a treatment. A neural net architecture is utilized to define a non-linear, second order model which is utilized to analyze the patient data and generate the predictive database from entered patient data.
Owner:ADVANCED BIOLOGICAL LAB
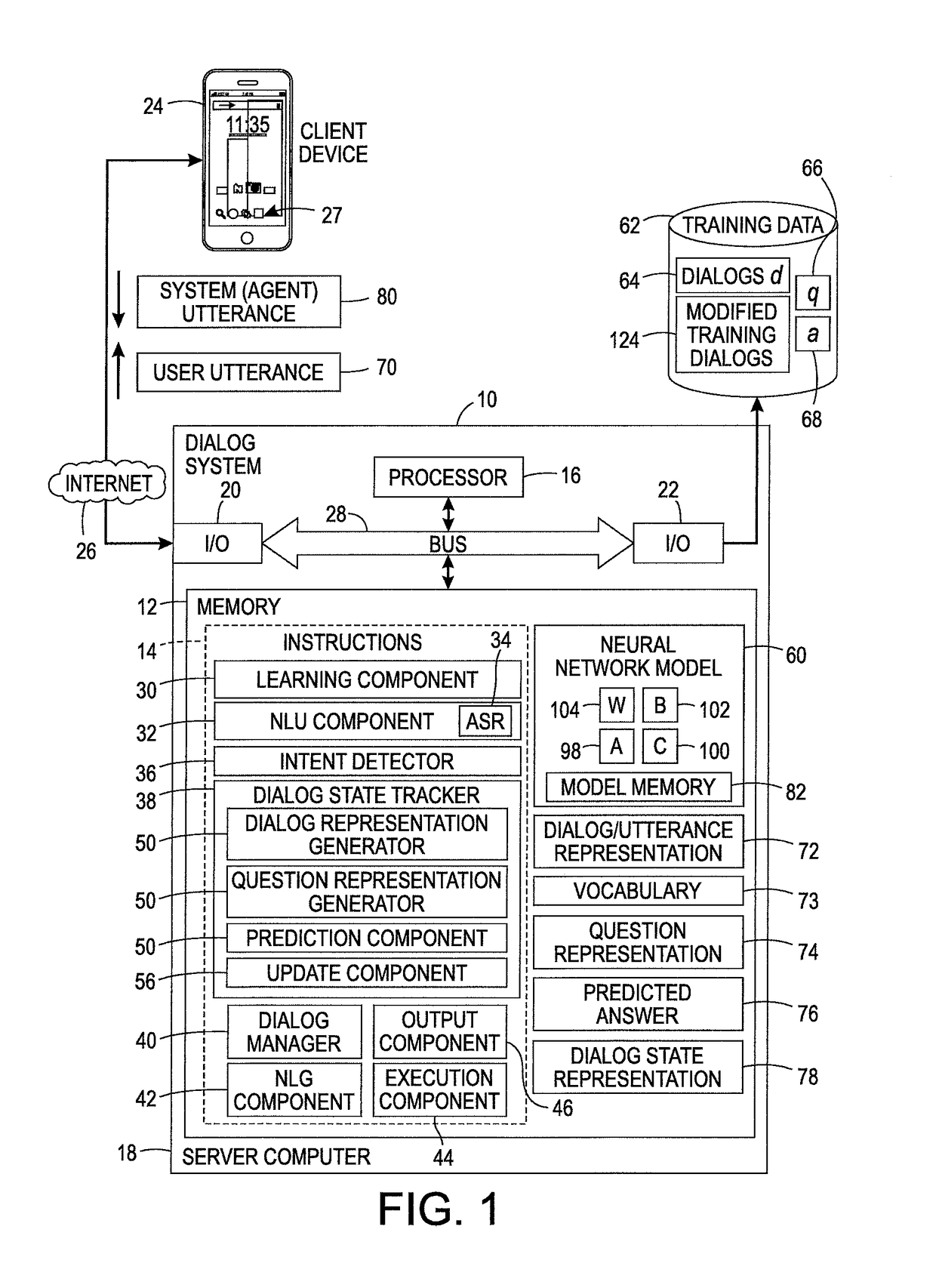
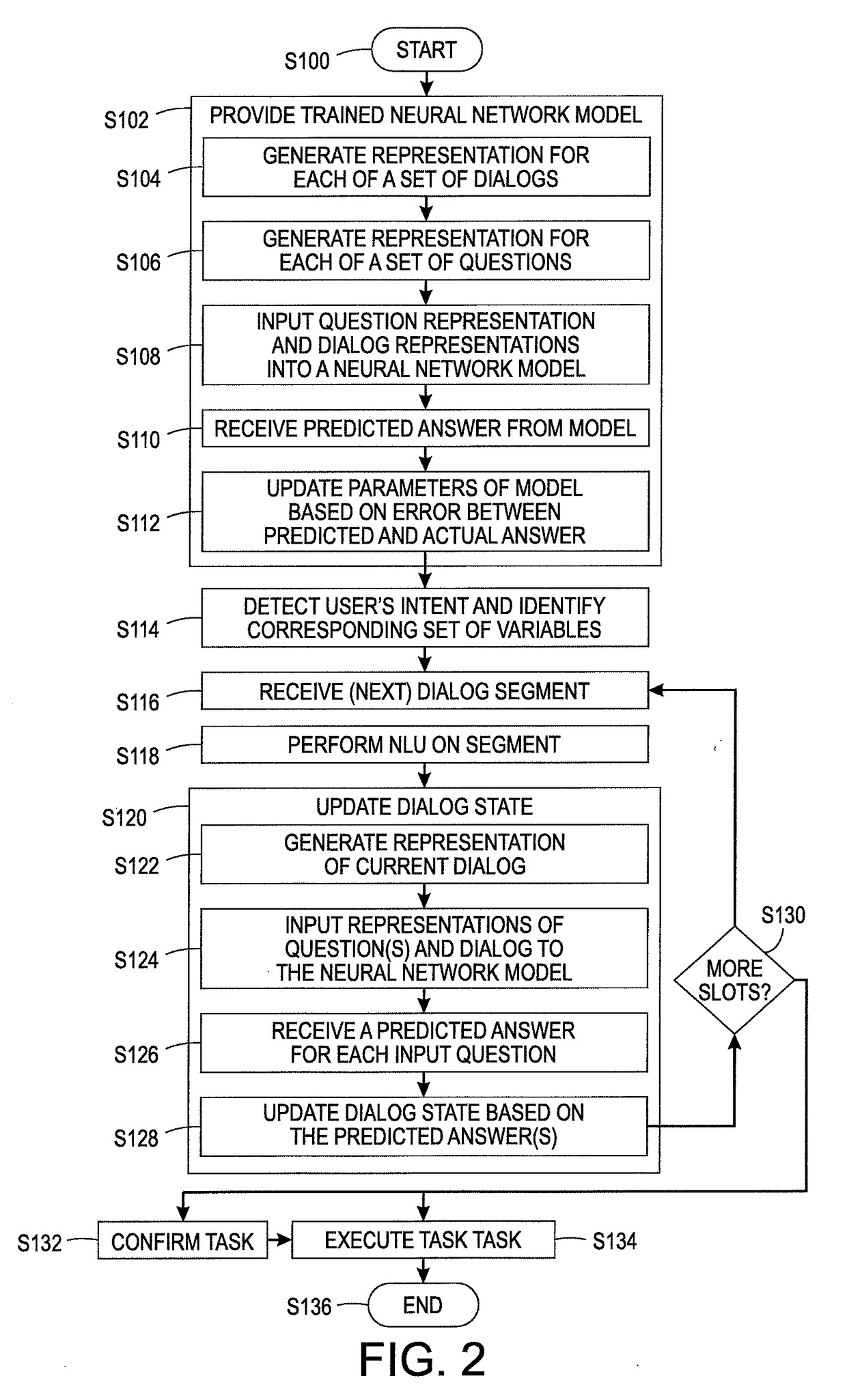
Machine reading method for dialog state tracking
ActiveUS20180137854A1Natural language data processingSpeech recognitionMachine learningNetwork model
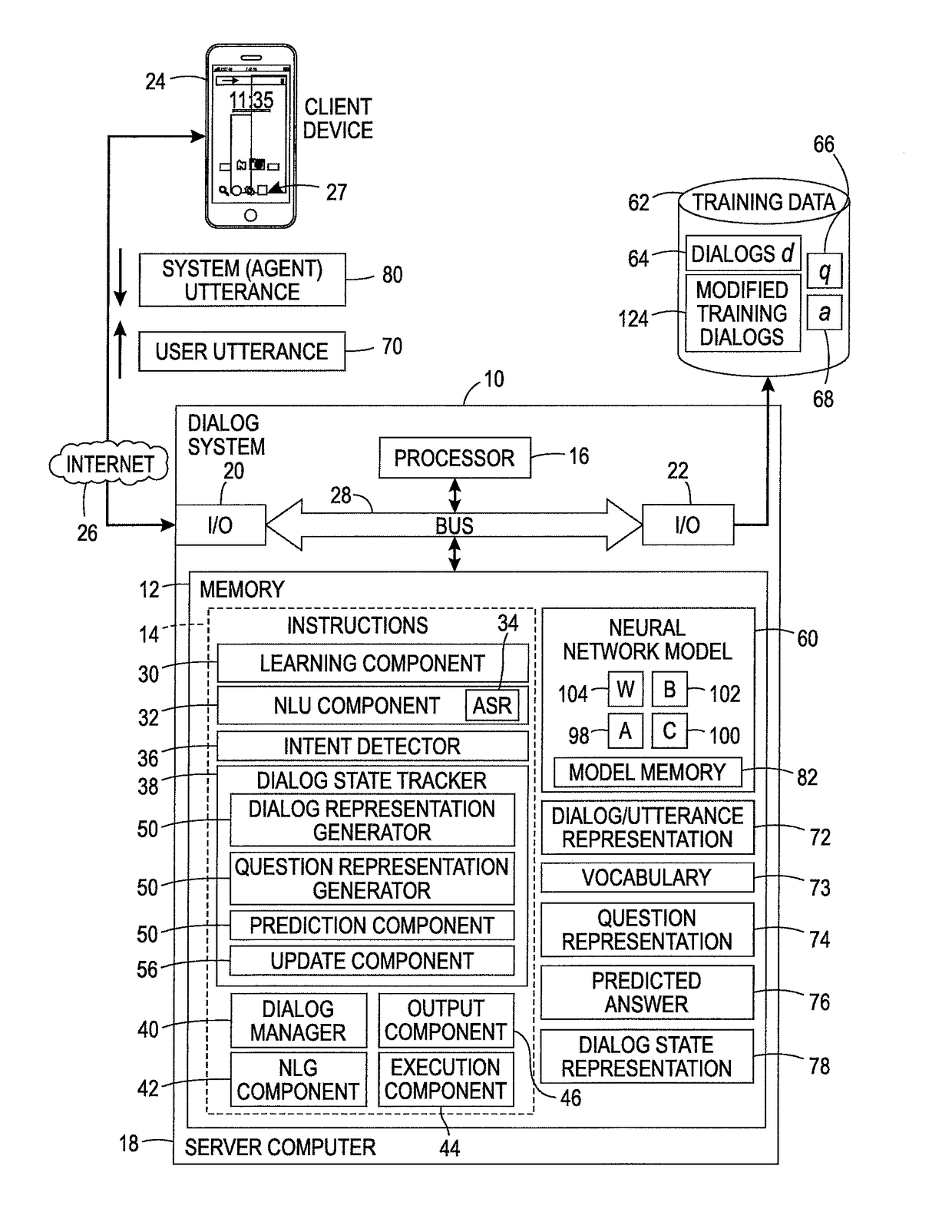
A method for dialog state tracking uses a neural network model, such as an MemN2N model, which has been trained to receive a representation of a question and a representation of a subpart of a dialog and to output an answer to the question. For at least one iteration, a subpart of a dialog is received. A representation of the subpart of the dialog is generated. The representation of the subpart of the input dialog and representation of a question are input to the trained neural network model. An answer is output by the neural network model, based on the representation of the question and the representation of the subpart of the input dialog. A dialog state for the dialog is updated, based on the answer to the question. The dialog state includes a set of variables. The updating includes predicting a value for at least one of the variables.
Owner:XEROX CORP
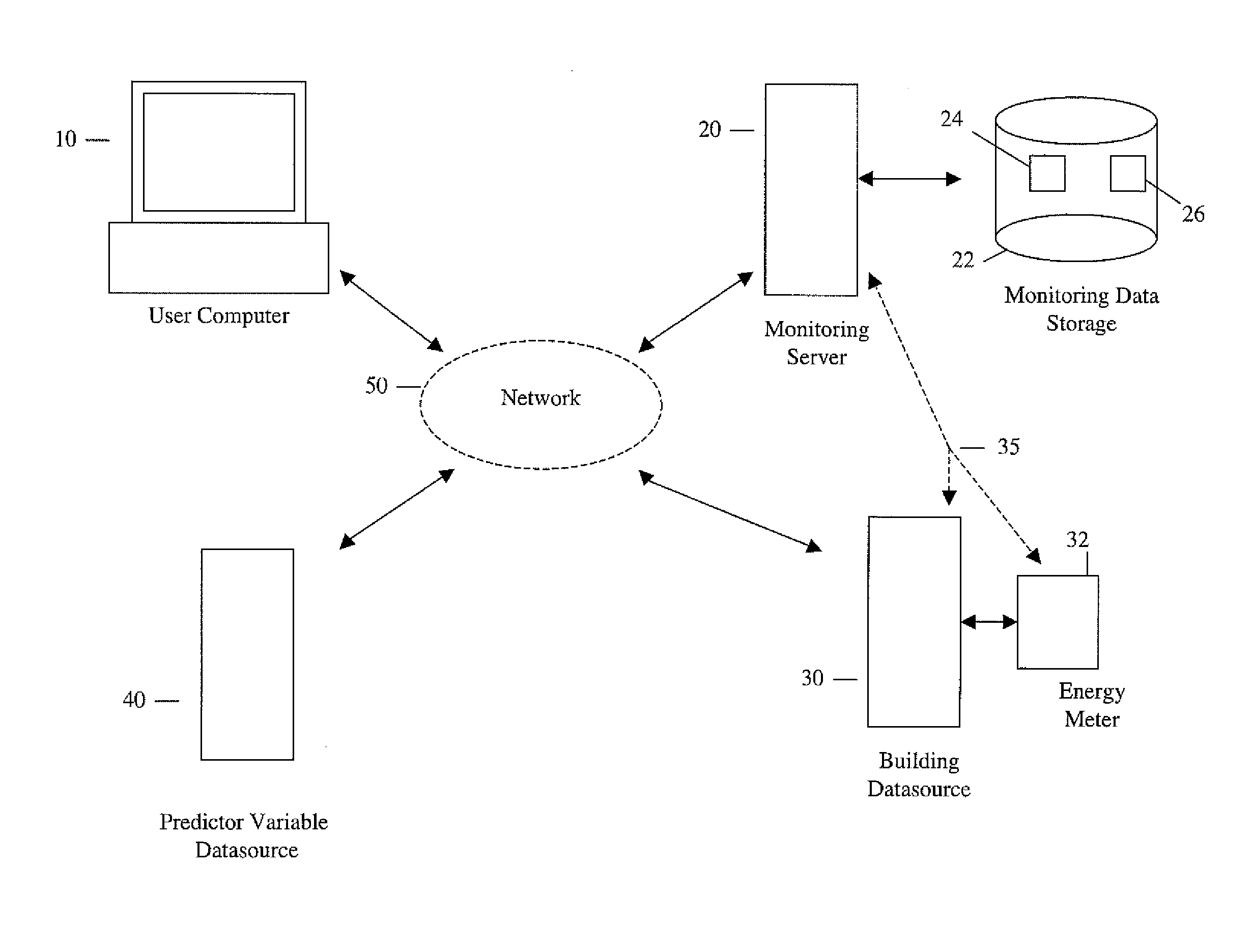
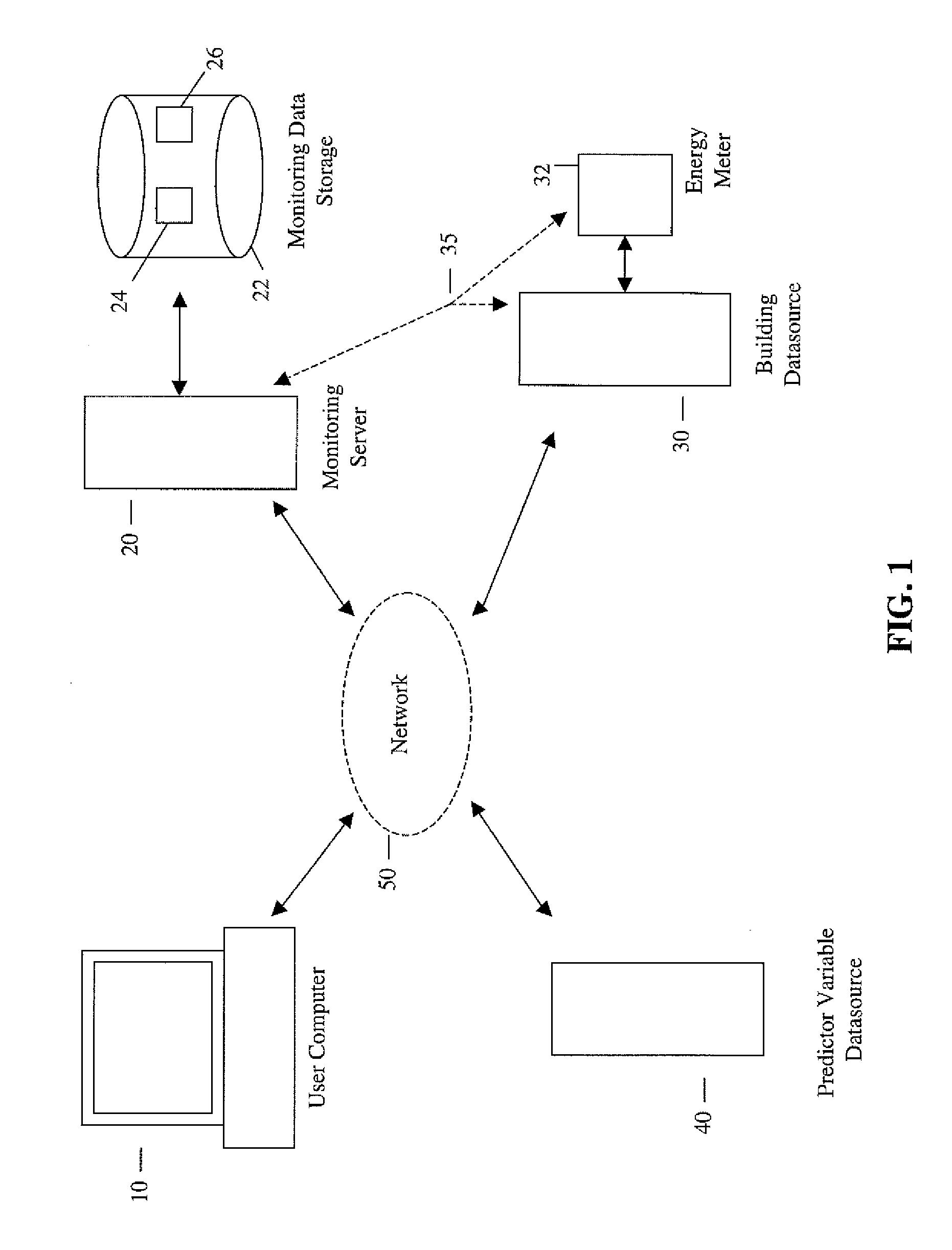
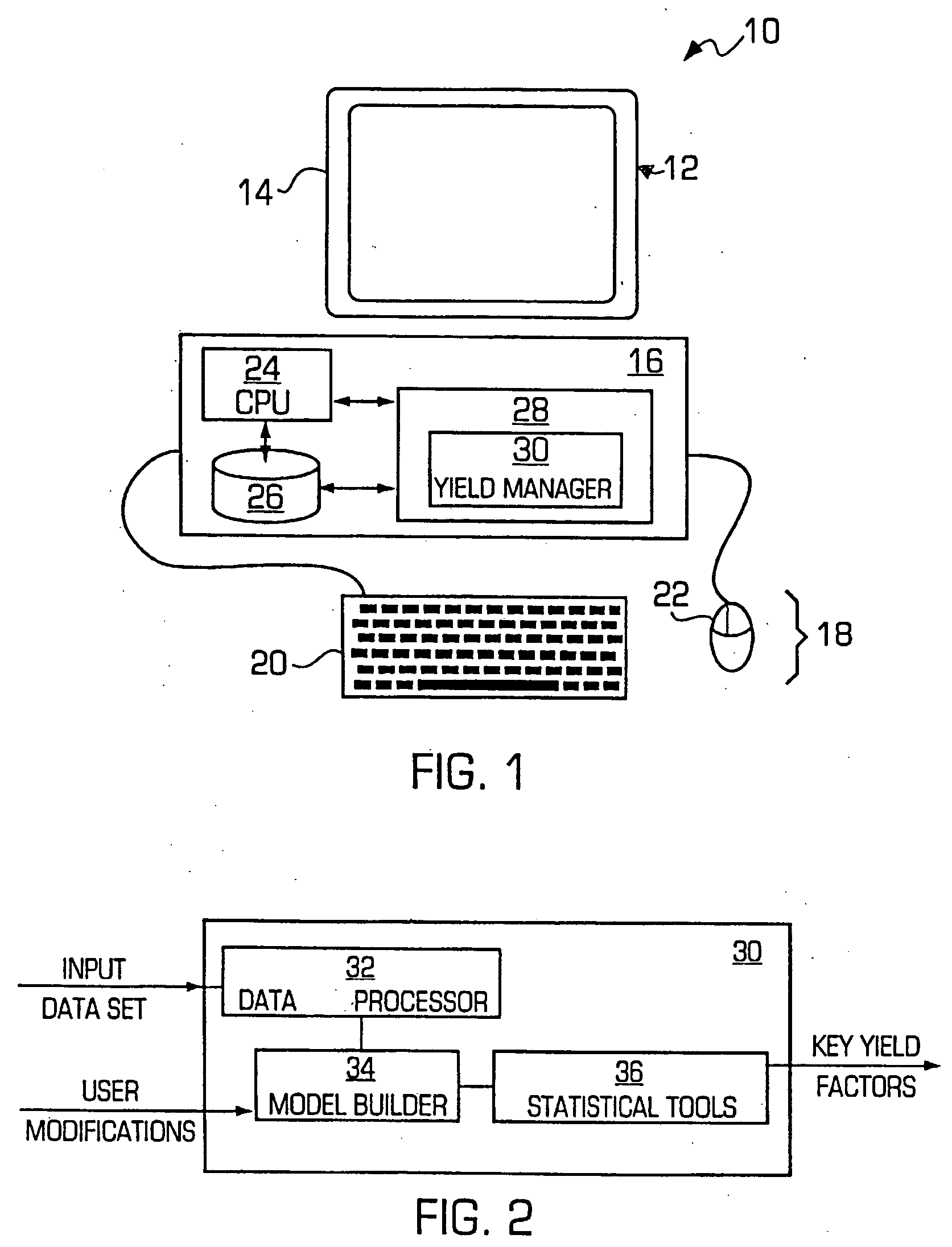
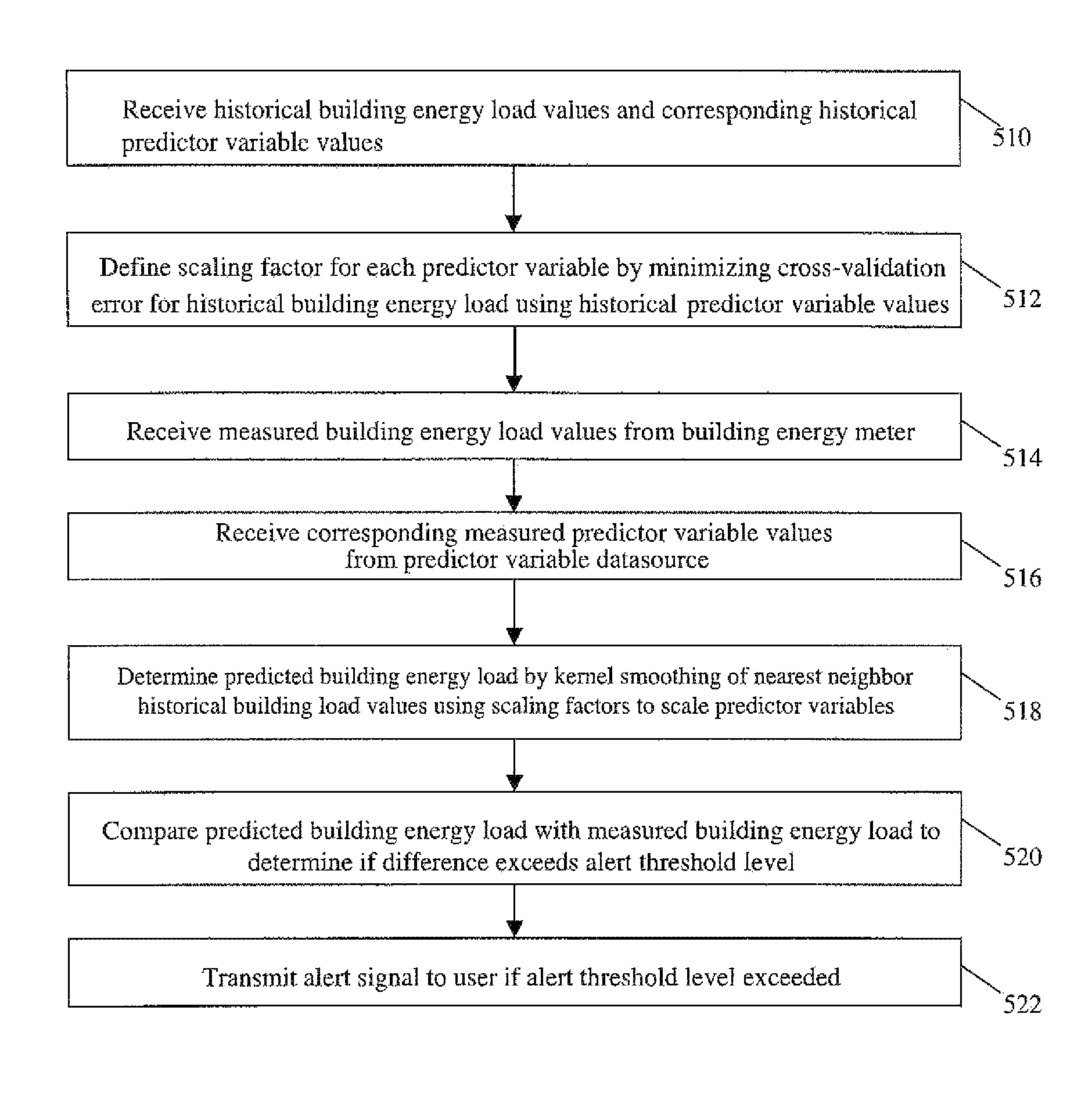
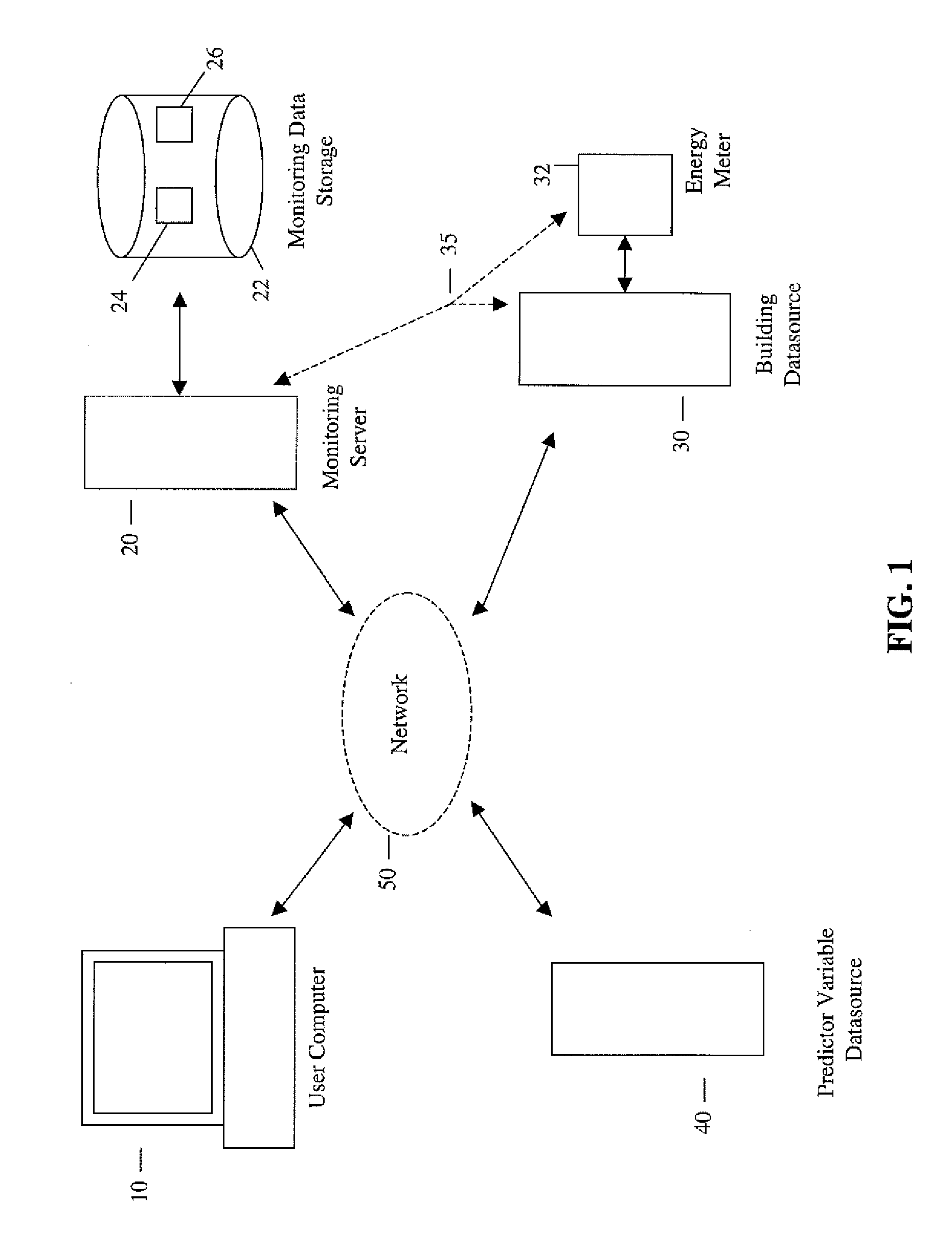
Systems and methods for predictive building energy monitoring
A system and method for predictive modeling of building energy consumption provides predicted building energy load values which are determined using kernel smoothing of historical building energy load values for a building using defined scaling factors for scaling predictor variables associated with building energy consumption. Predictor variables may include temperature, humidity, windspeed or direction, occupancy, time, day, date, and solar radiation. Scaling factor values may be defined by optimization training using historical building energy load values and measured predictor variable values for a building. Predicted and measured building energy load values are compared to determine if a preset difference threshold has been exceeded, in which case an alert signal or message is generated and transmitted to electronically and / or physically signal a user. The building energy monitoring system may be integrated with a building automation system, or may be operated as a separate system receiving building energy and predictor variable values.
Owner:YARDI SYST
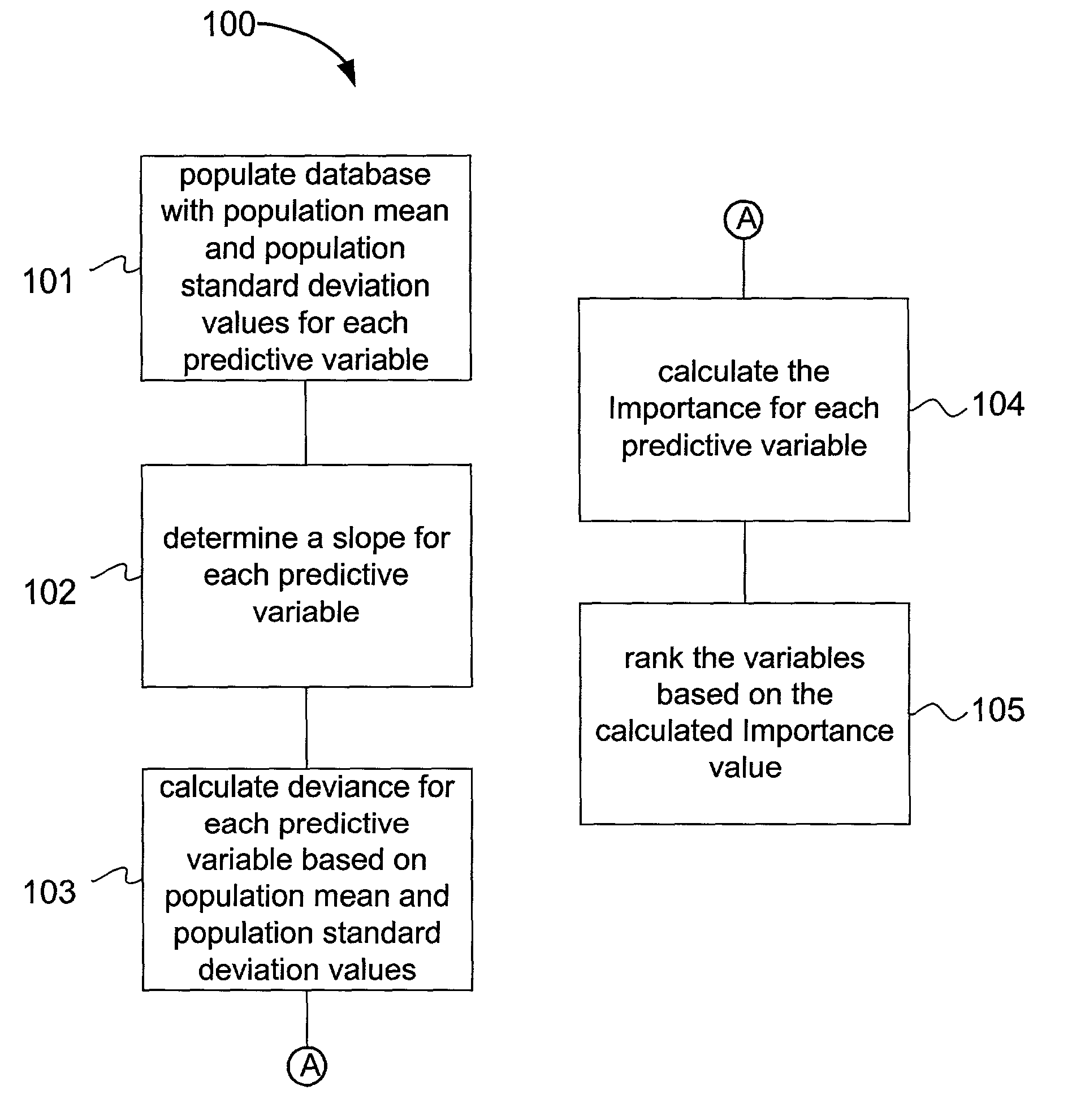
Methods and Systems for Determining the Importance of Individual Variables in Statistical Models
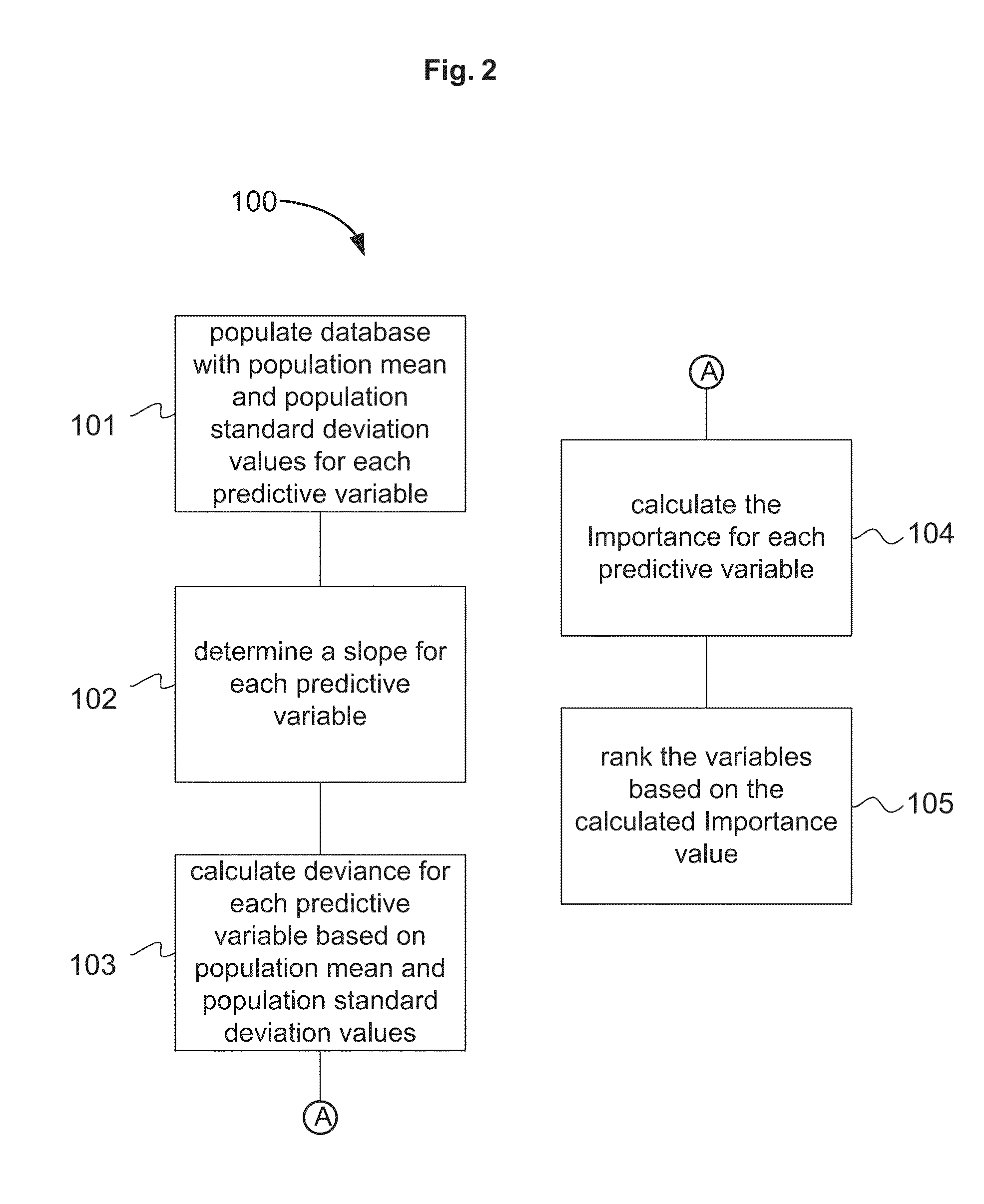
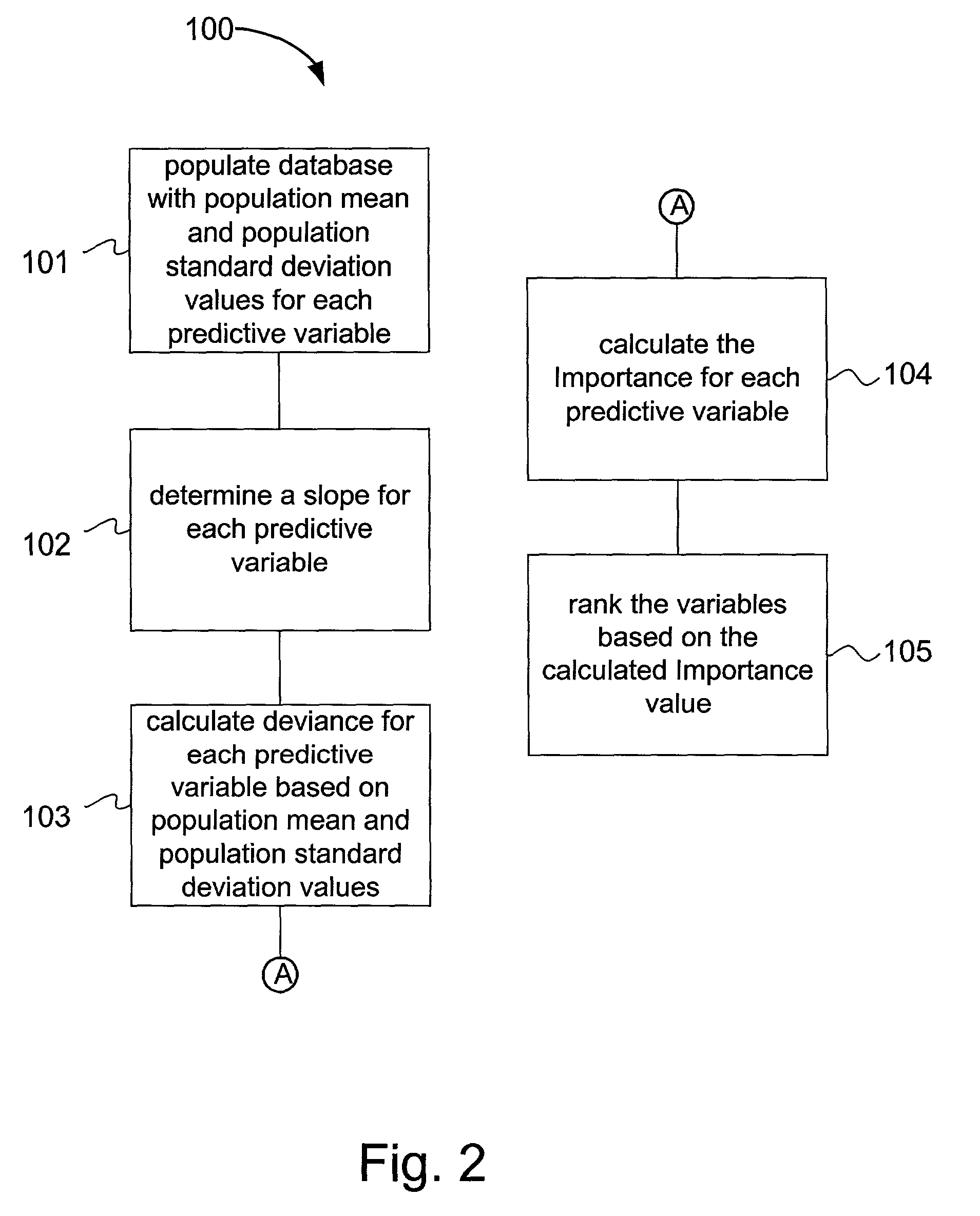
Methods and systems for determining the importance of each of the variables, or combinations of variables, that contribute to the overall score generated by a predictive statistical model are presented. In a specialized case, for each variable in the model, an importance is calculated based on the calculated slope and deviance of the predictive variable. In a more general case, for each variable in the model, an importance is calculated based on setting that variable to have the average value for the data set, and then calculating the change in score. The totality of variables (or combinations thereof) is then ranked by the Δscore, or a magnitude of it, such as |Δscore|.
Owner:DELOITTE DEV
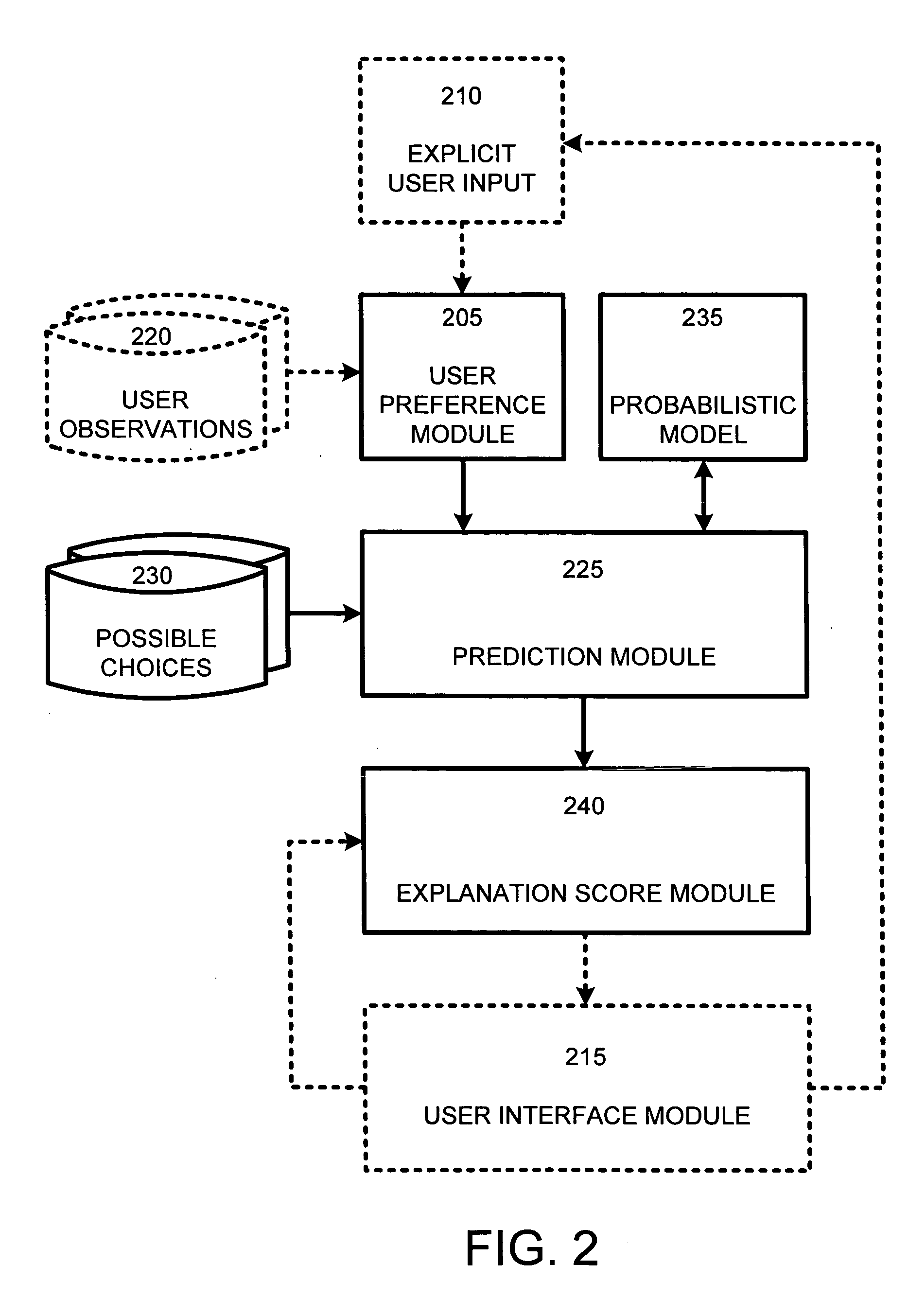
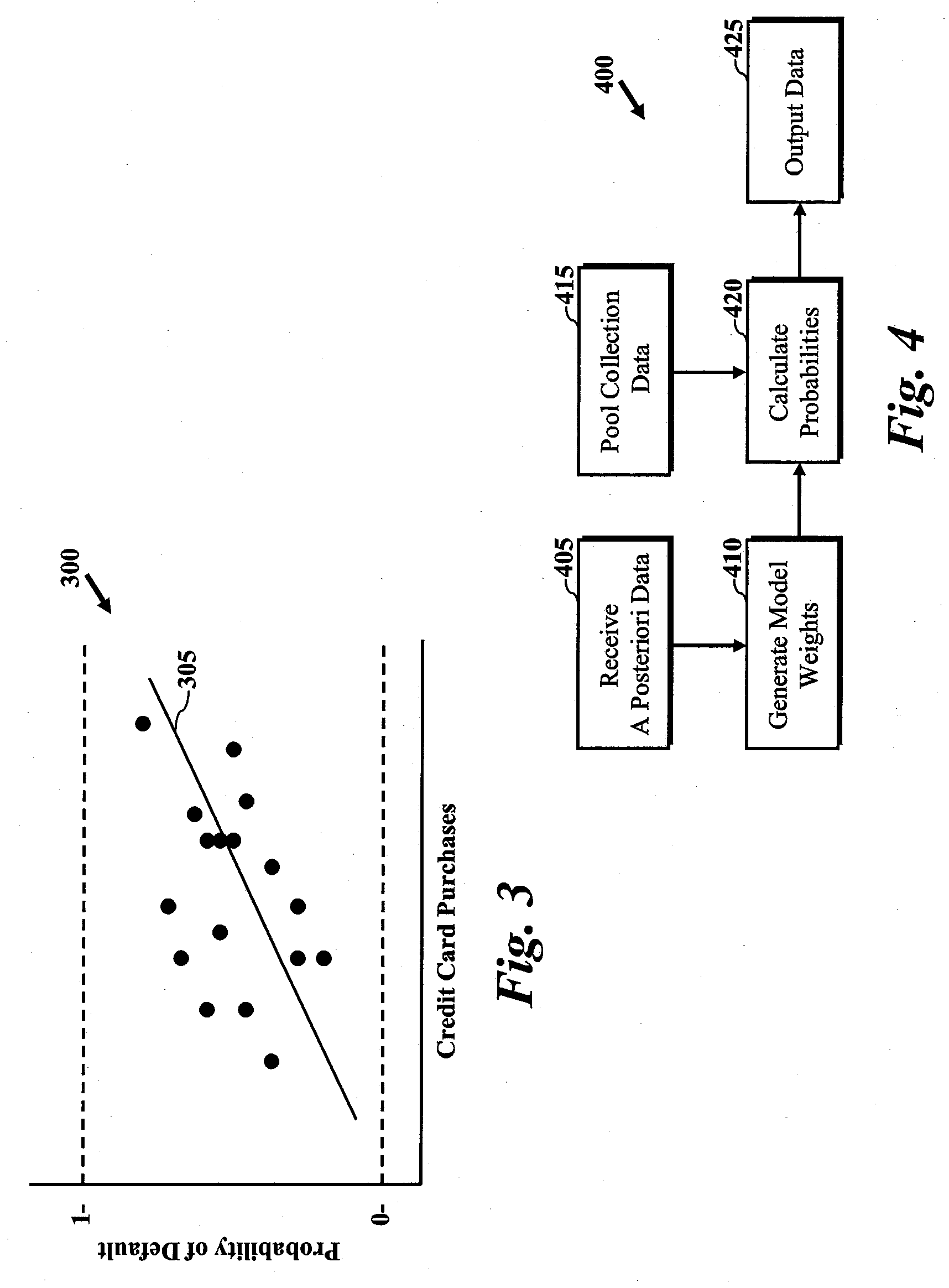
System and process for automatically explaining probabilistic predictions
The system and method of the present invention automatically assigns “scores” to the predictor / variable value pairs of a conventional probabilistic model to measure the relative impact or influence of particular elements of a set of topics, items, products, etc. in making specific predictions using the probabilistic model. In particular, these scores measure the relative impact, either positive or negative, that the value of each individual predictor variable has on the posterior distribution of the target topic, item, product, etc., for which a probability is being determined. These scores are useful for understanding why each prediction is made, and how much impact each predictor has on the prediction. Consequently, such scores are useful for explaining why a particular prediction or recommendation was made.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for dynamic determination of disease prognosis
InactiveUS20060289020A1Predictive powerImprove predictive performanceSurgeryMedical automated diagnosisPredictor variablePatient data
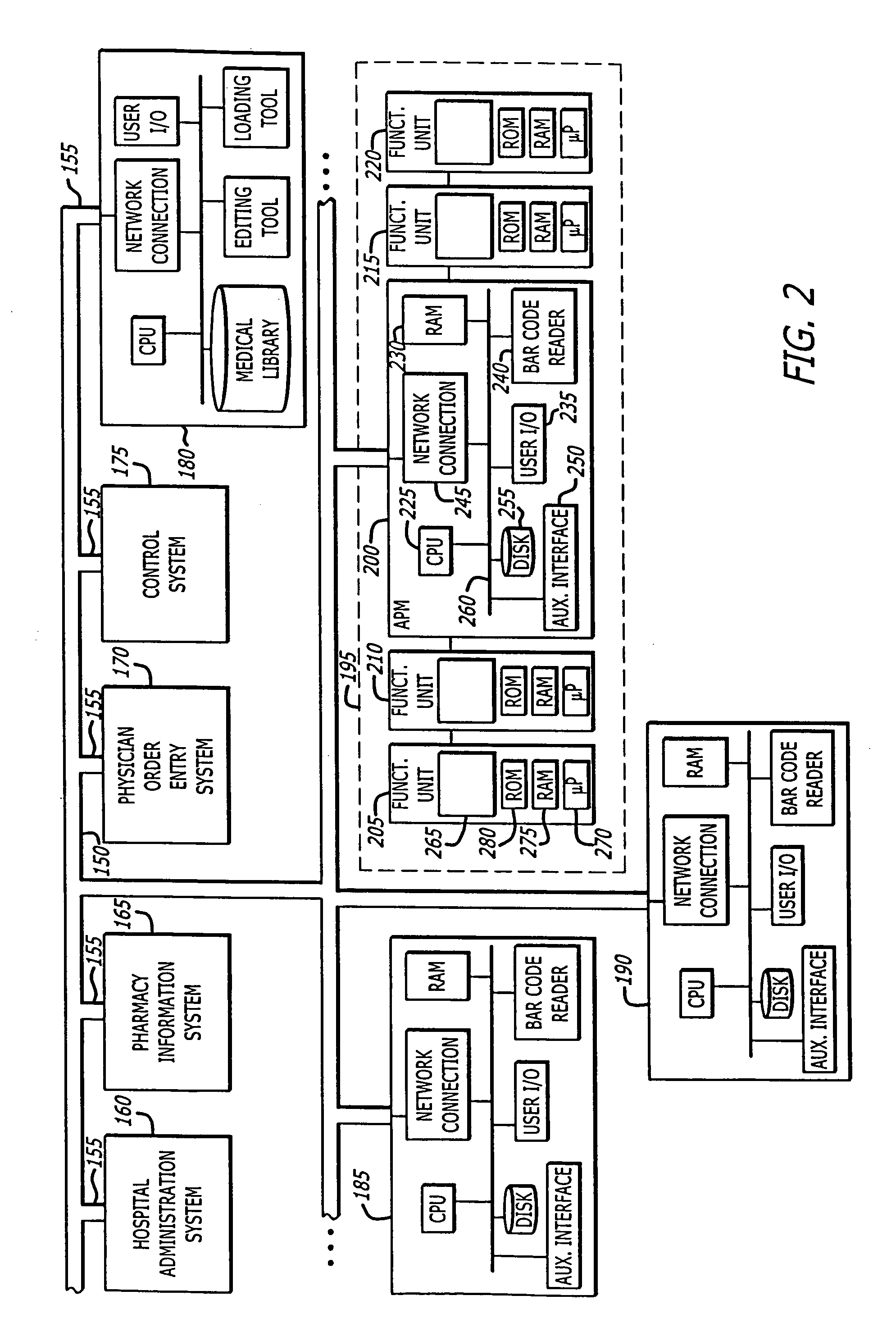
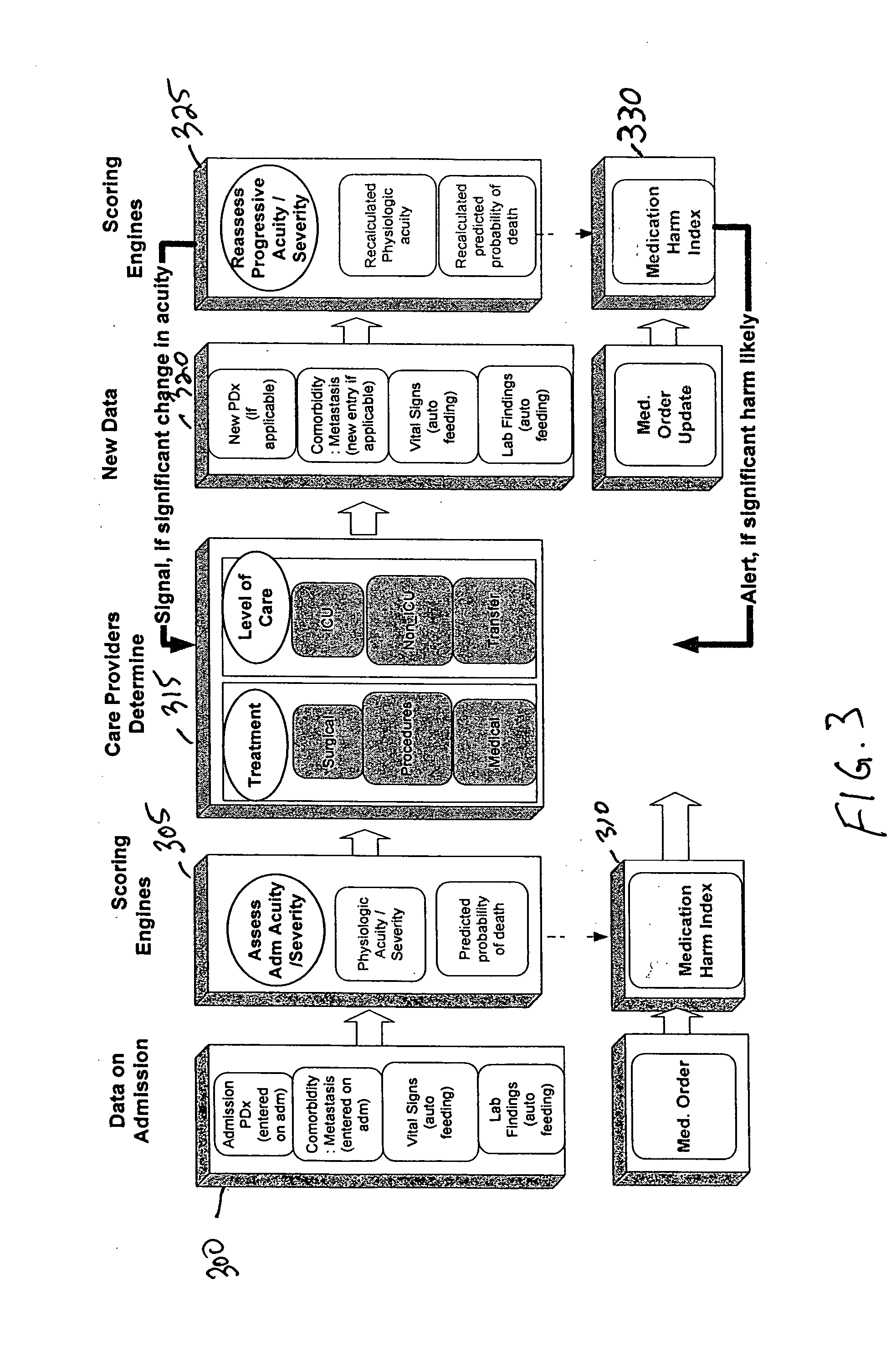
A method of obtaining and processing patient data and patient treatment data to provide a prognosis parameter related to a patient's disease state is provided. The method identifies and calculates coefficients related to appropriate predictor variables which are then used by the prediction model to calculate the prognosis parameter. The prediction model may be a logistic regression model. The method may also be used to assess the level of care being provided to patients, as well as providing a way of assessing the outcome of the patient's condition as a function of treatment. A method of calculating a harm index reflective of the risk of treatment is also provided.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
Prediction processing system and method of use and method of doing business
InactiveUS20130254146A1Improve accuracyIncrease impactMathematical modelsForecastingData miningEvent based
A prediction processing system, method, and method for doing business is disclosed. The prediction processing system can collect, process and publish event-outcome information. The prediction processing system can dynamically filter participants into groupings and iteratively optimize odds calculations over time. A proposal framework consisting of a various abstract proposal types can model and settle propositions. Game propositions can be automatically generated based on event categorization relationships. The prediction processing system can provide game players or others with access to collective intelligence, including prediction information and information derived from prediction information. The prediction processing system can create groupings of better-performing predictors and provide them with additional information not generally available. Better-performing predictors can be provided with additional stakes to increase the weight of their predictions in odds calculations. The prediction processing system can provide access to event-outcome information on a for-fee subscription basis.
Owner:KOODBEE
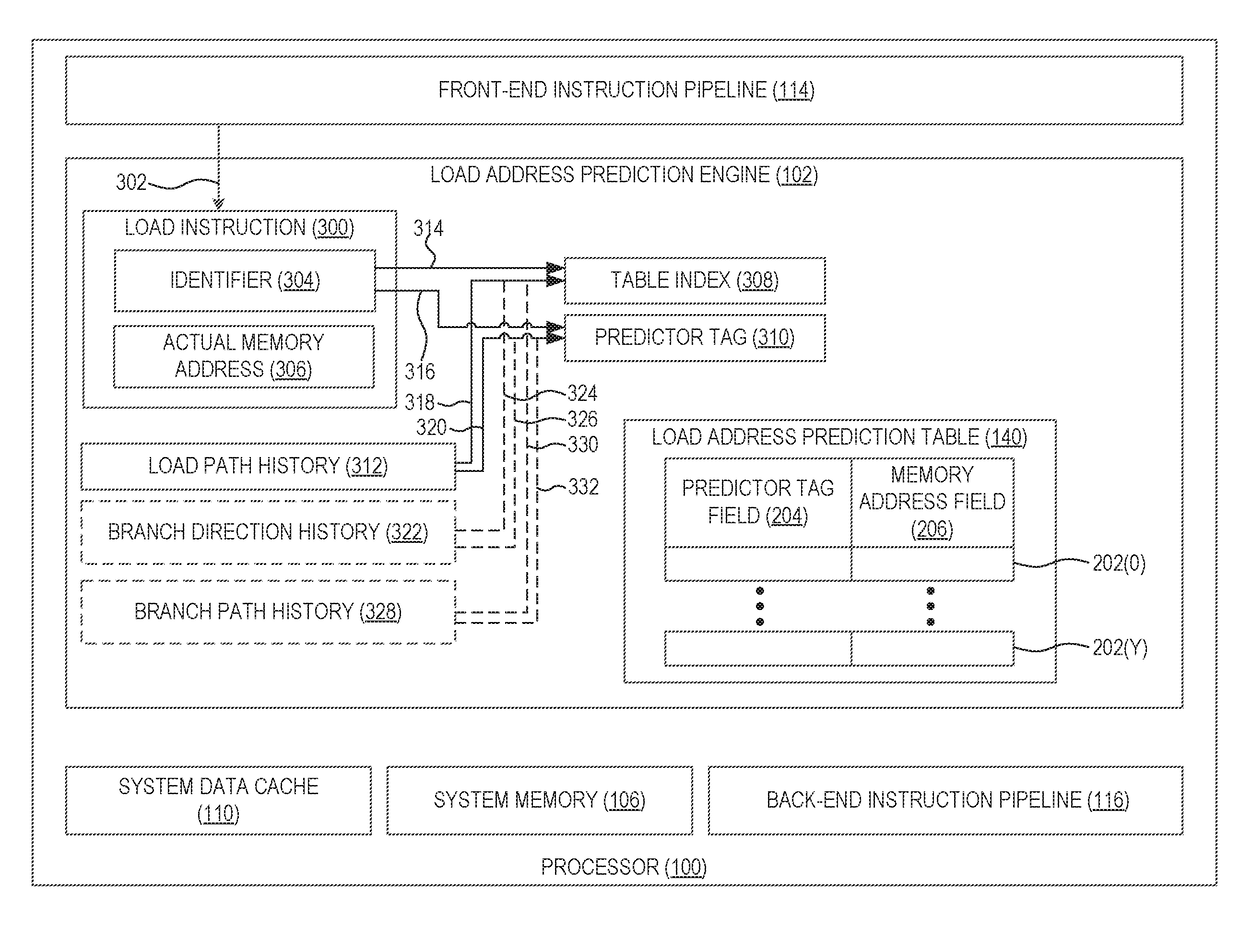
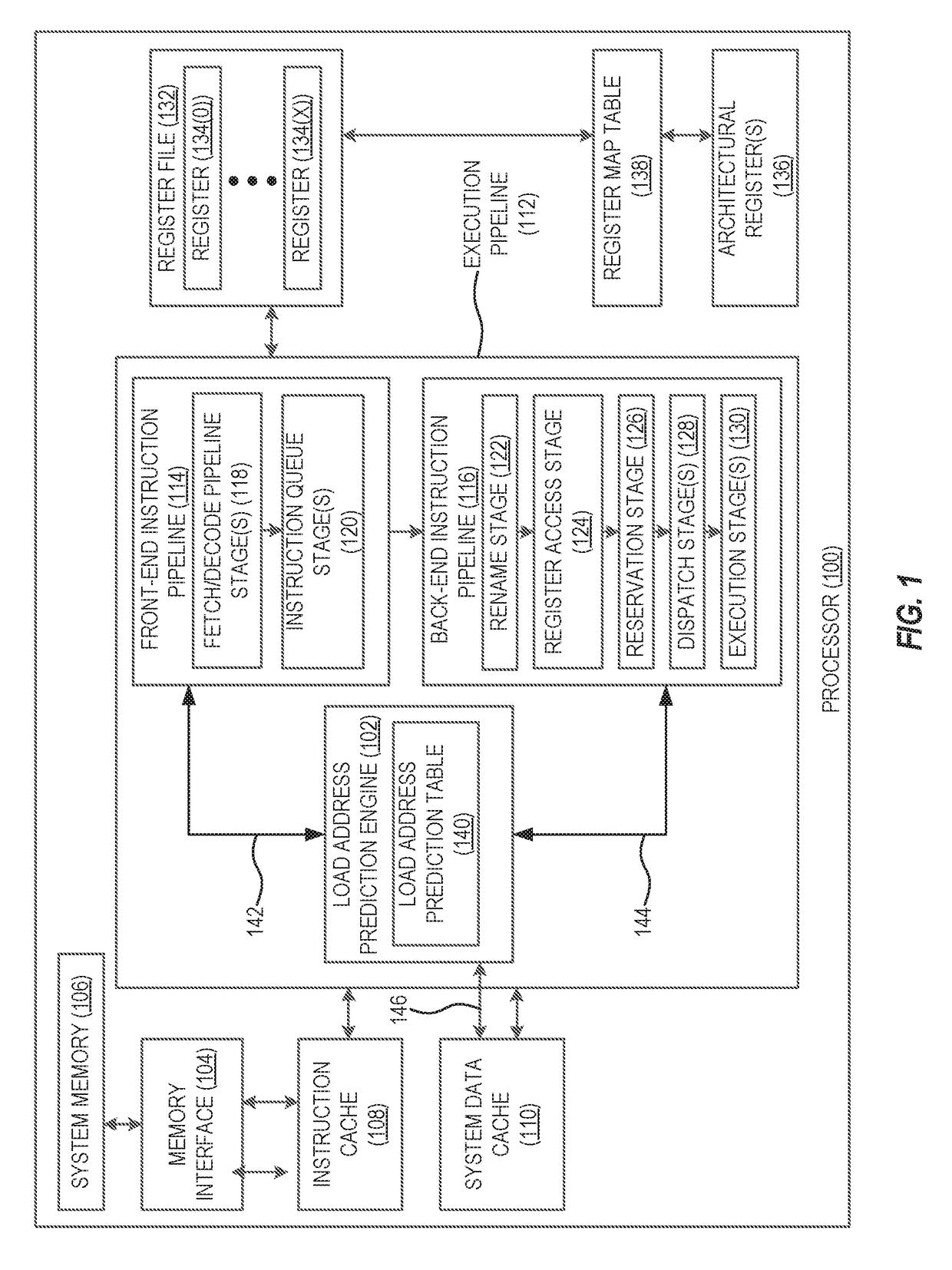
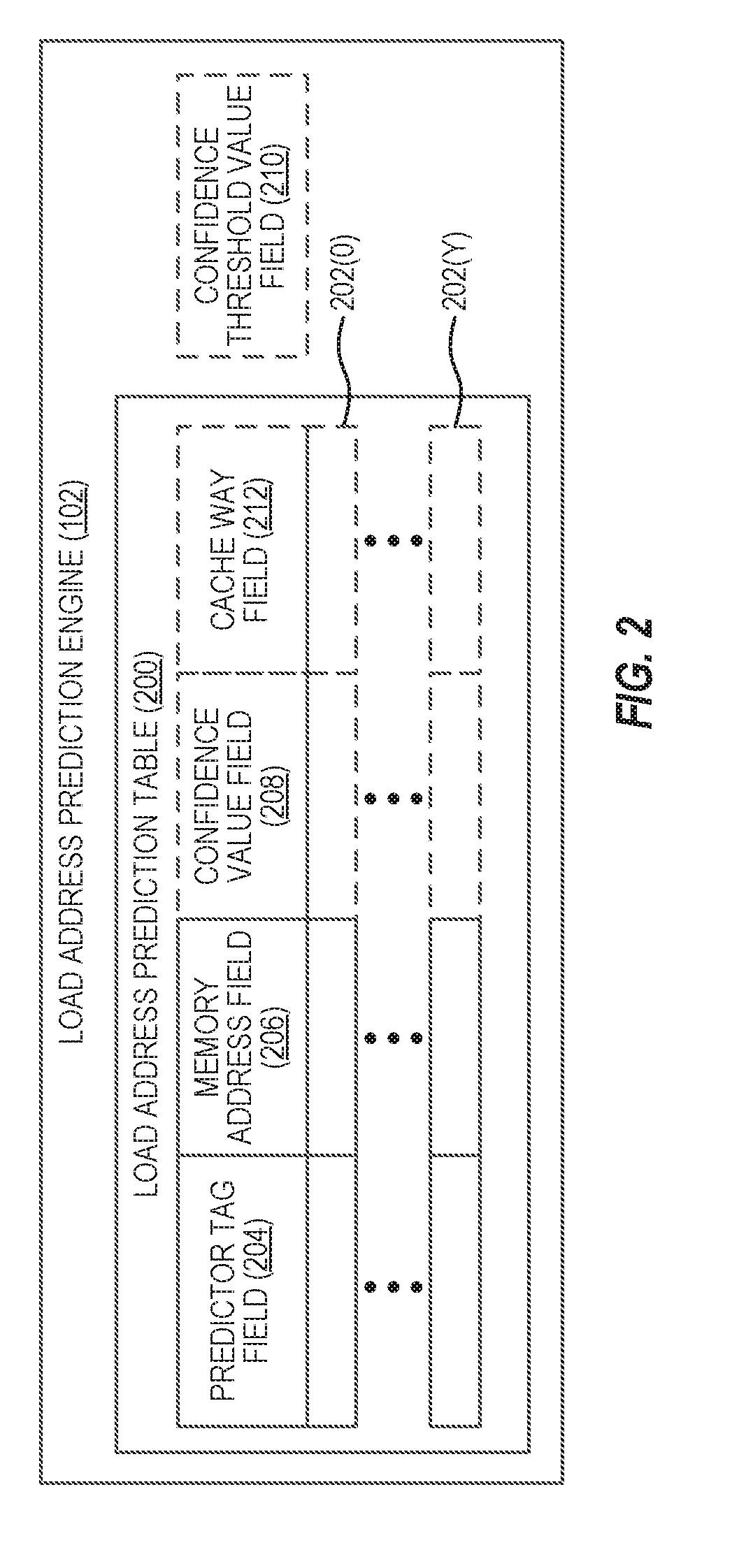
Providing load address predictions using address prediction tables based on load path history in processor-based systems
ActiveUS20170286119A1Improve efficiencyImprove processor performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressPredictor variable
Aspects disclosed in the detailed description include providing load address predictions using address prediction tables based on load path history in processor-based systems. In one aspect, a load address prediction engine provides a load address prediction table containing multiple load address prediction table entries. Each load address prediction table entry includes a predictor tag field and a memory address field for a load instruction. The load address prediction engine generates a table index and a predictor tag based on an identifier and a load path history for a detected load instruction. The table index is used to look up a corresponding load address prediction table entry. If the predictor tag matches the predictor tag field of the load address prediction table entry corresponding to the table index, the memory address field of the load address prediction table entry is provided as a predicted memory address for the load instruction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
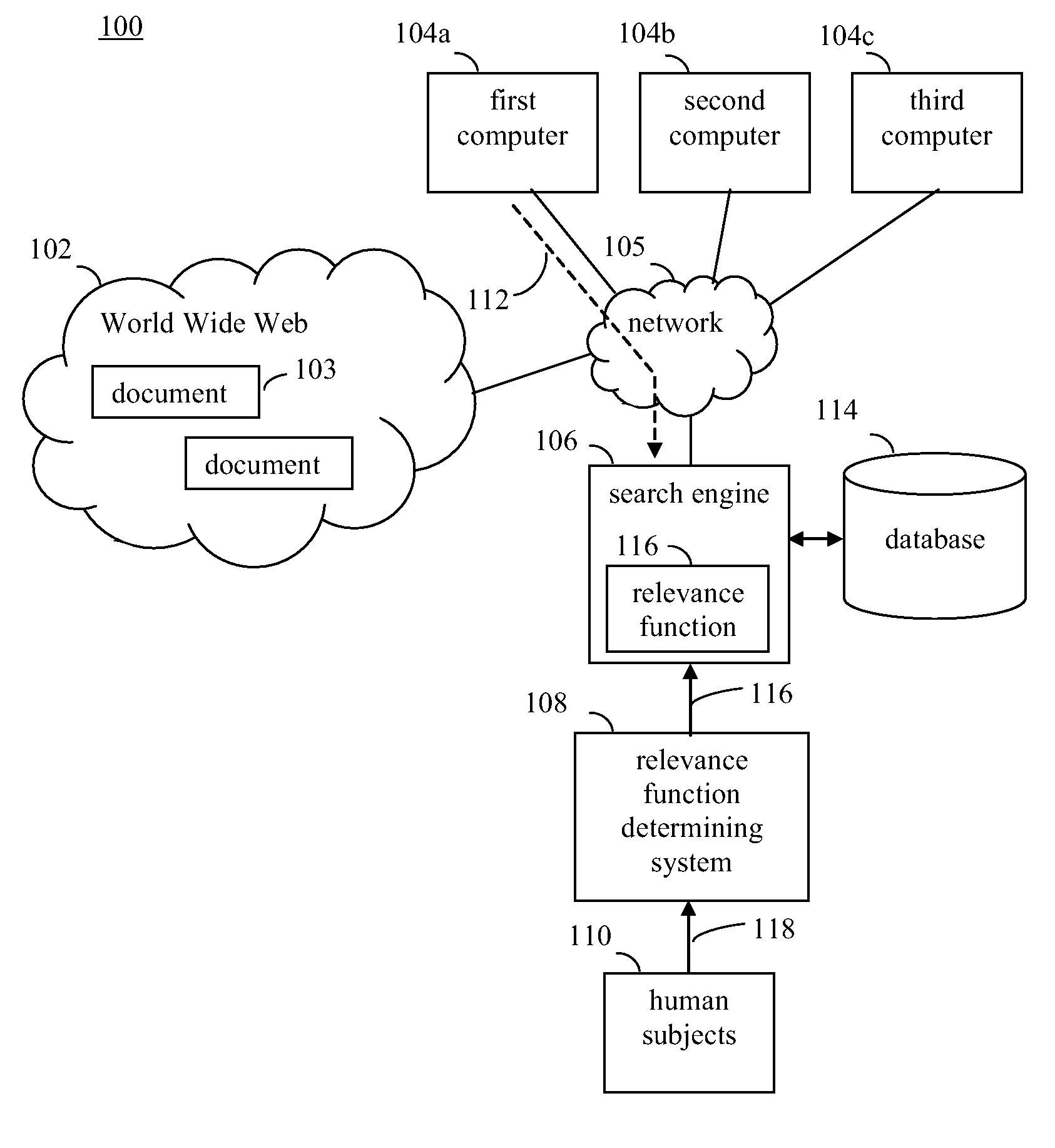
Determining a relevance function based on a query error derived using a structured output learning technique
InactiveUS8005774B2Improve efficiencyMinimize sumDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPredictor variableAlgorithm
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for generating relevance functions for ranking documents obtained in searches are provided. One or more features to be used as predictor variables in the construction of a relevance function are determined. The relevance function is parameterized by one or more coefficients. An ideal query error is defined that measures, for a given query, a difference between a ranking generated by the relevance function and a ranking based on a training set. According to a structured output learning framework, values for the coefficients of the relevance function are determined to substantially minimize an objective function that depends on a continuous upper bound of the defined ideal query error. The query error is determined using a structured output learning technique. The query error is defined as a maximum over a set of permutations.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
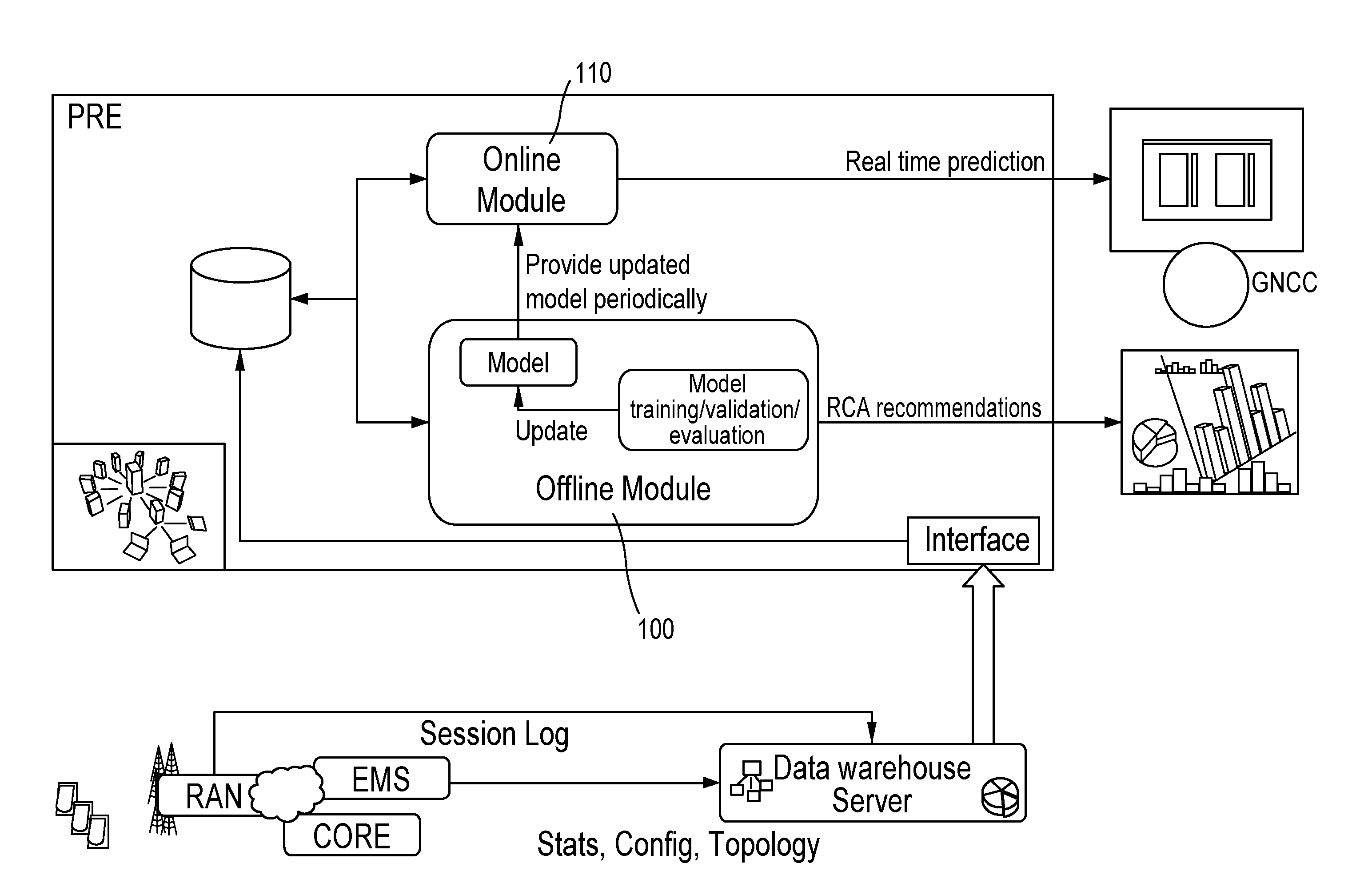
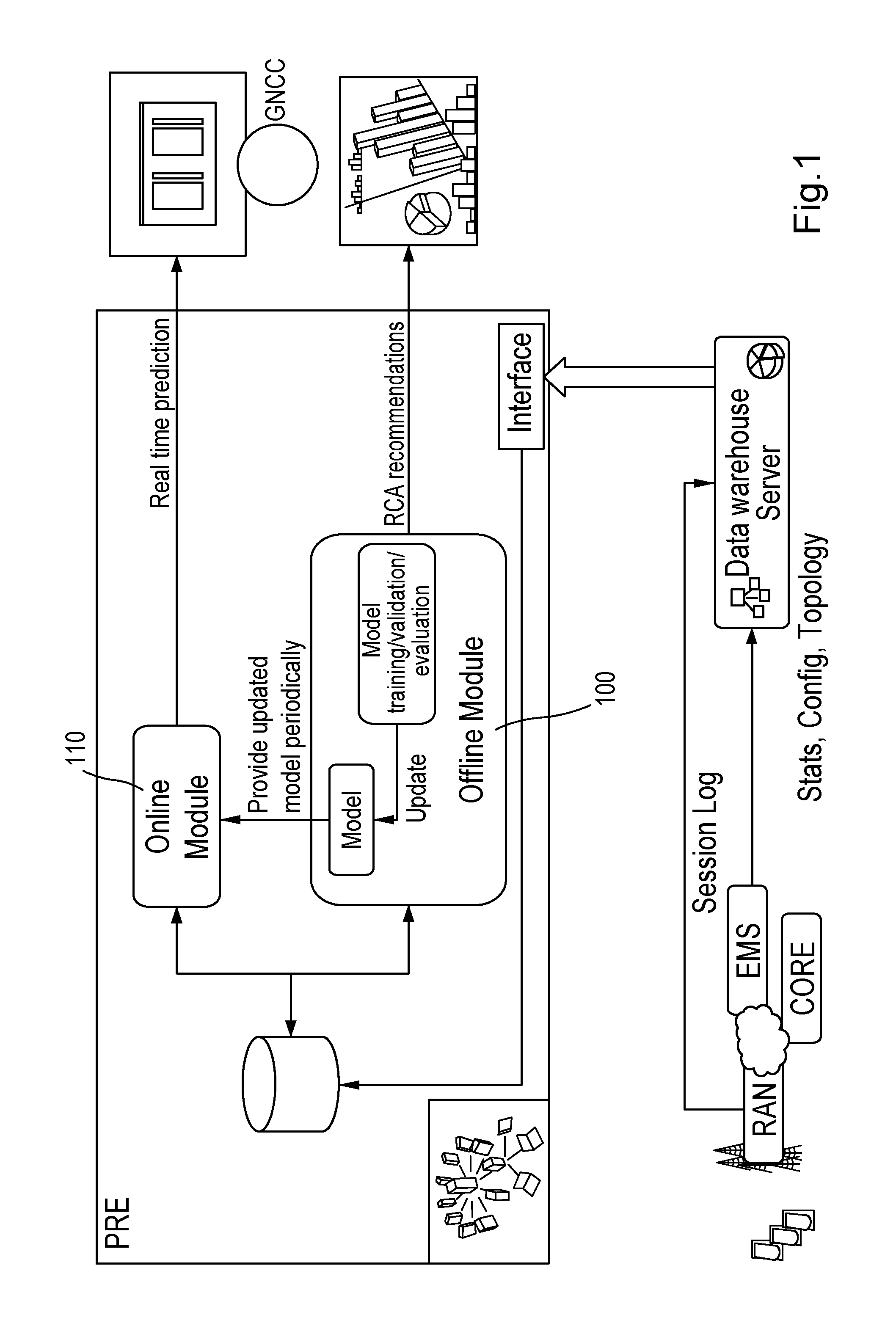
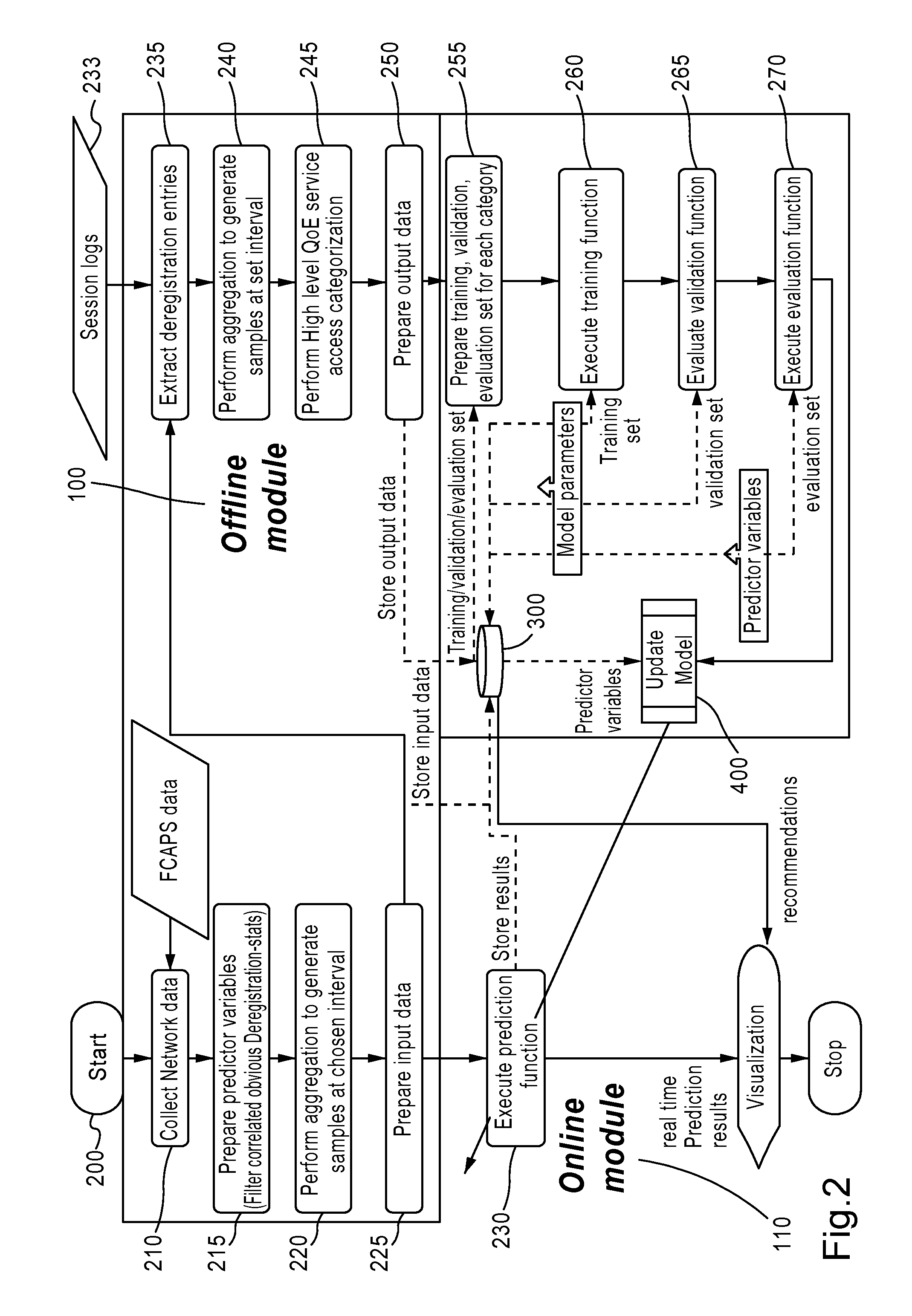
Method and system for prediction and root cause recommendations of service access quality of experience issues in communication networks
ActiveUS20130238534A1Digital computer detailsMachine learningPredictor variablePredictive regression
Embodiments of the invention utilize advanced statistical data analytics to predict and provide recommendations for root-cause analysis for service access QoE issues in networks, such as 3G / 4G networks. Using FCAPS data as predictor variables, embodiments are configured to set up the problem as a predictive regression or classification problem to estimate service access QoE related indicators. Some embodiments perform training and tuning of various non-linear statistical modelling algorithms, based for example on tree and ensemble methods, using network deregistration information from RAN logs.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
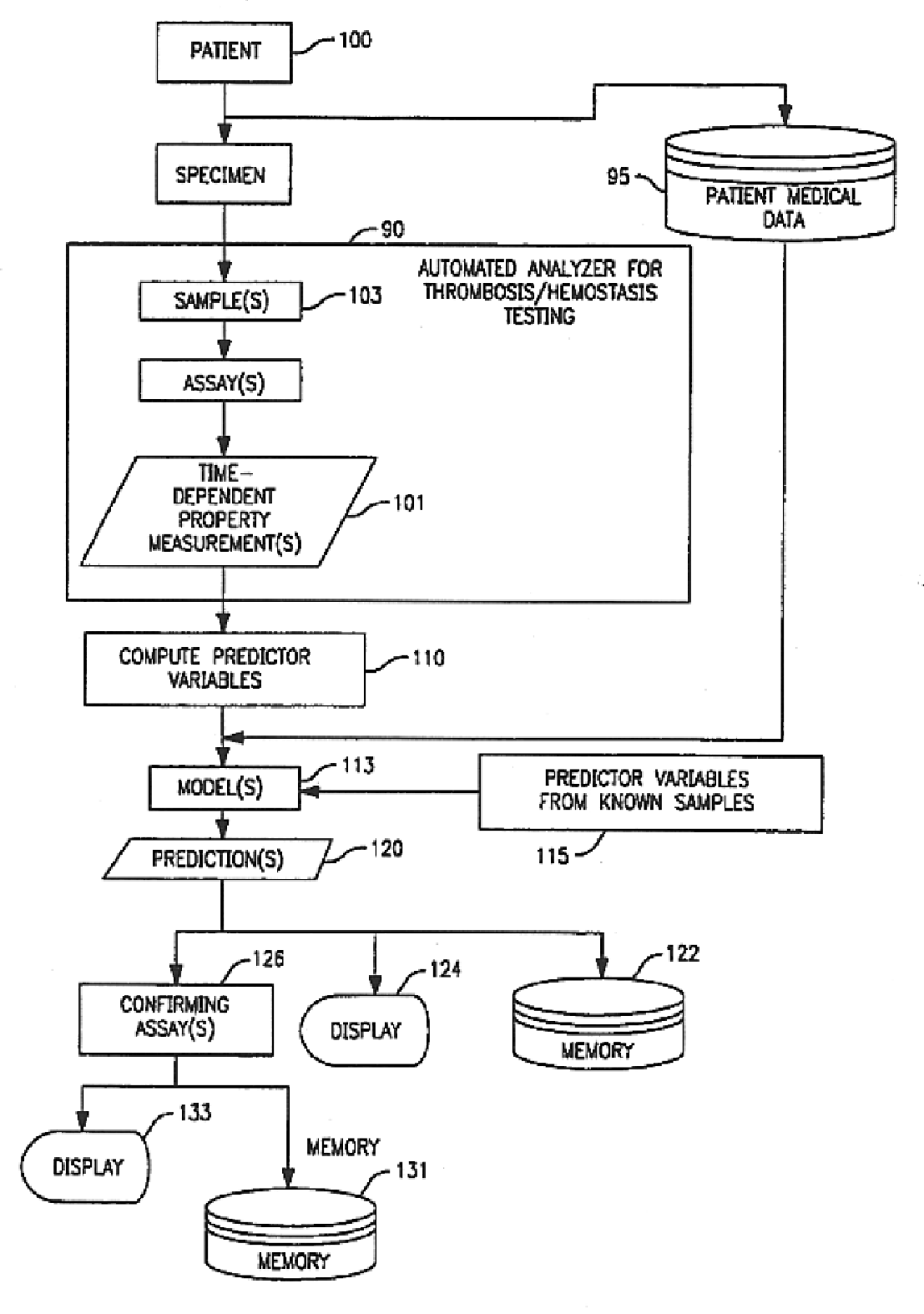
Method and apparatus for predicting the presence of haemostatic dysfunction in a patient sample
InactiveUS6898532B1Predict dysfunctionMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesFunctional disturbancePredictor variable
A method is disclosed for predicting the presence of haemostatic dysfunction. At least one time-dependent measurement on an unknown sample is performed and a respective property of the sample is measured over time so as to derive a time-dependent measurement profile. One or more predictor variables, including initial slope, are defined which sufficiently define the data of the time-dependent measurement profile. A model is then derived that represents the relationship between the abnormality and the set of predictor variables. Subsequently, the model is utilized to predict haemostatic dysfunction, such as septicemia or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC
Automated predictive modeling of business future events based on historical data
InactiveUS7720782B2Accurate representationFinanceDigital computer detailsPredictive modellingCluster based
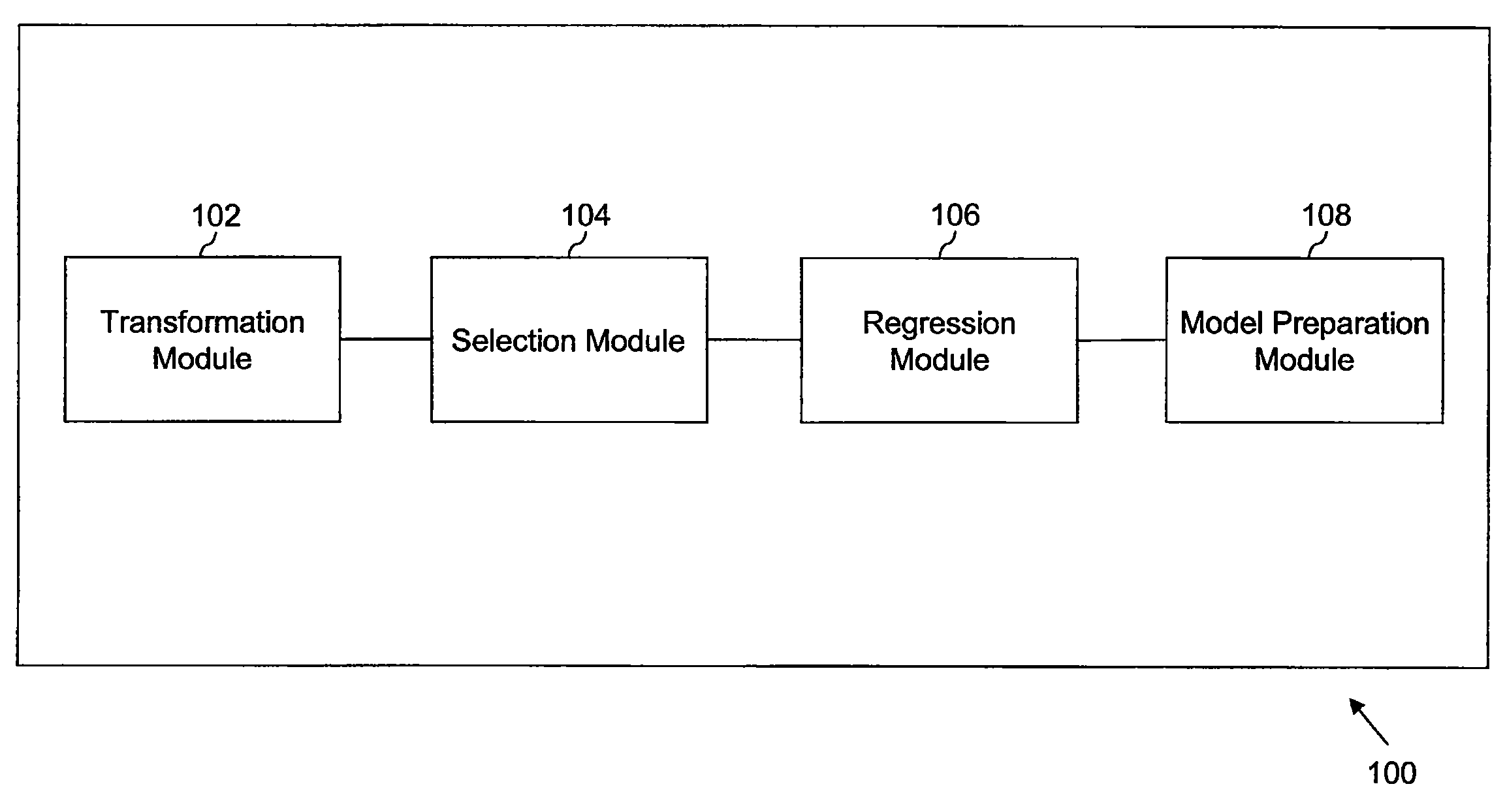
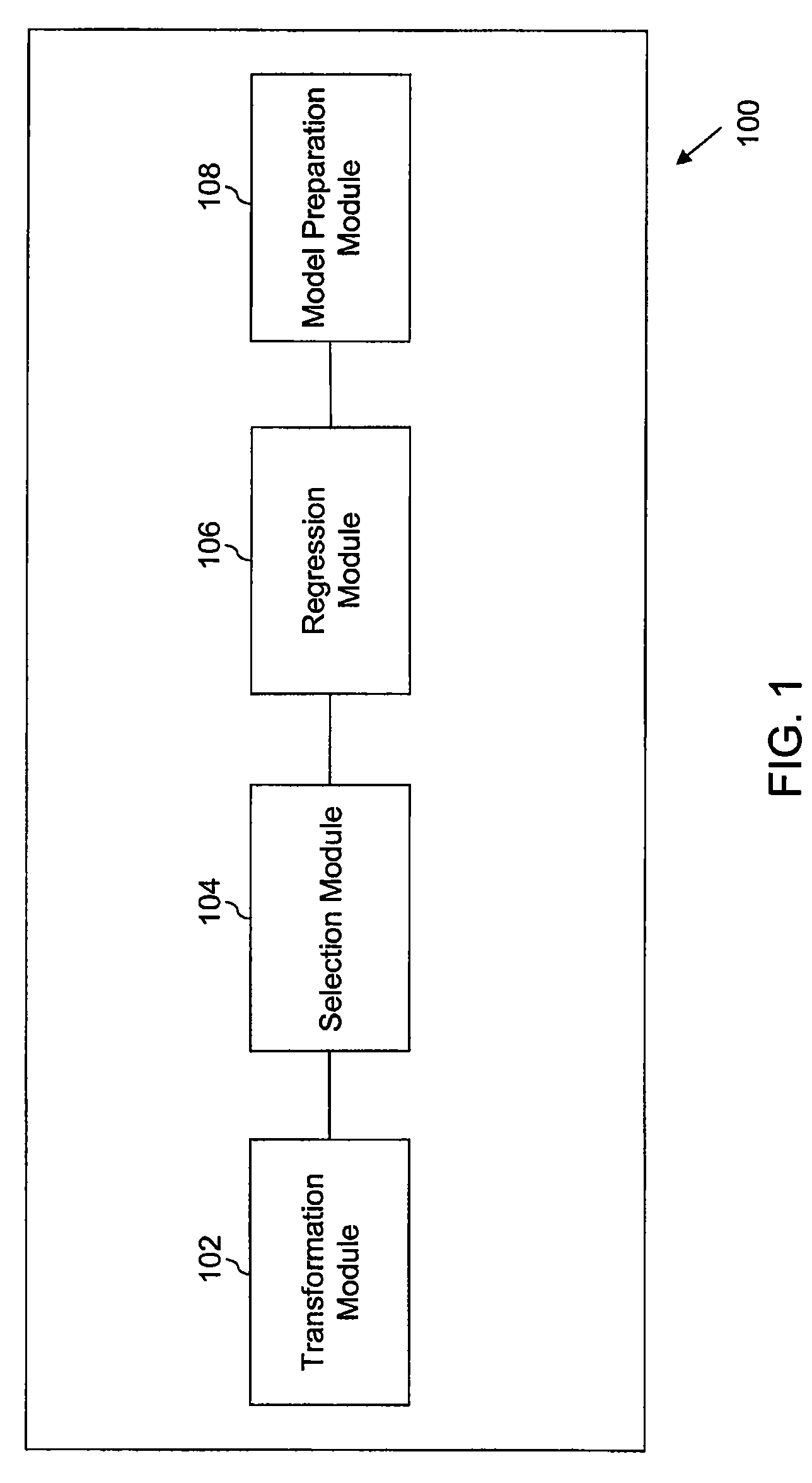
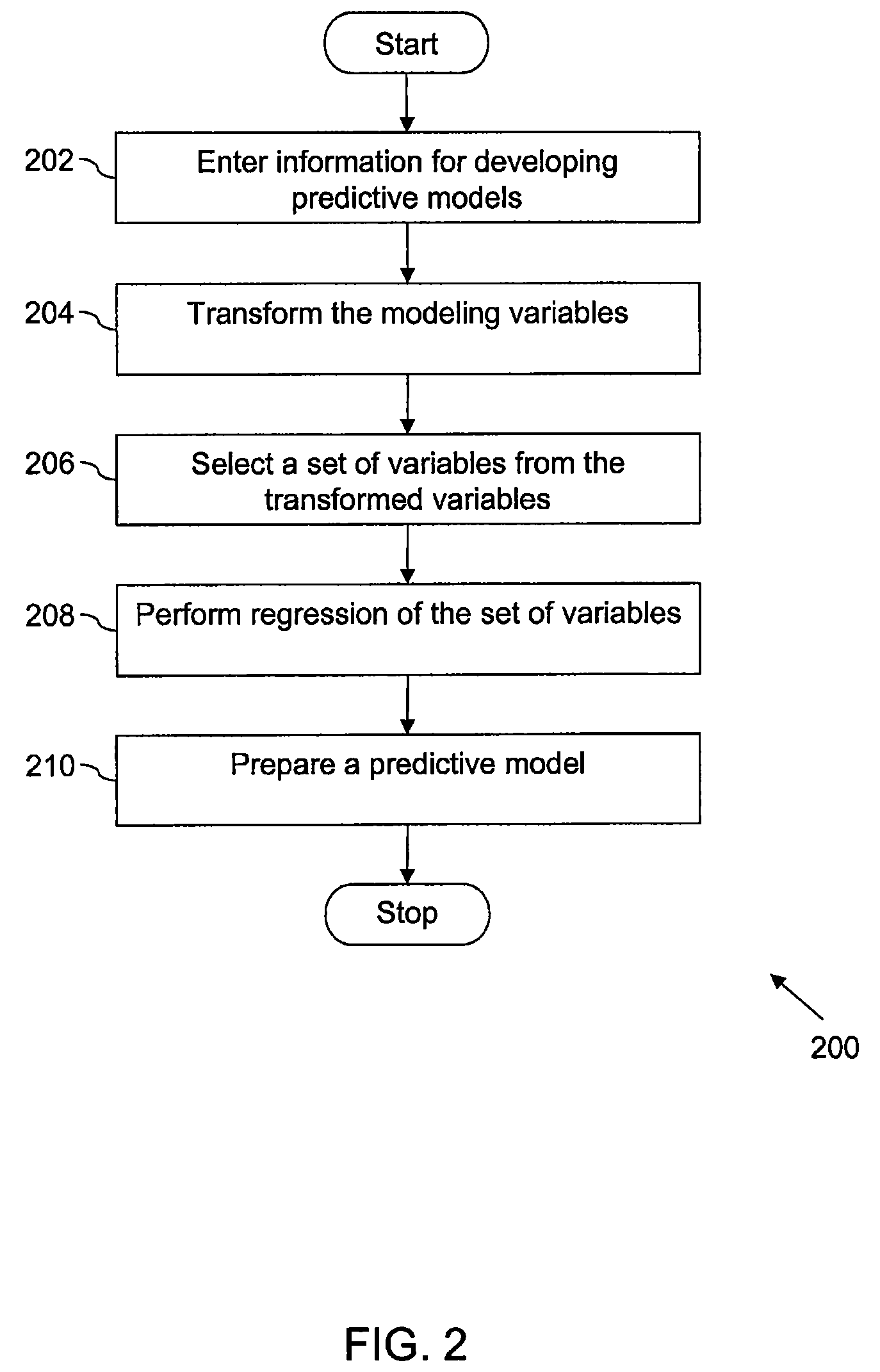
Predictive models are developed automatically for a plurality of modeling variables. The plurality of modeling variables is transformed, based on a transformation rule. A clustering of the transformed modeling variables is performed to create variable clusters. A set of variables is selected from the variable clusters based on a selection rule. A regression of the set of variables is performed to determine prediction variables. The prediction variables are utilized in developing a predictive model. The development of the predictive model may include modification of the predictive model, review of the plurality of transformations, and validation of the predictive model.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
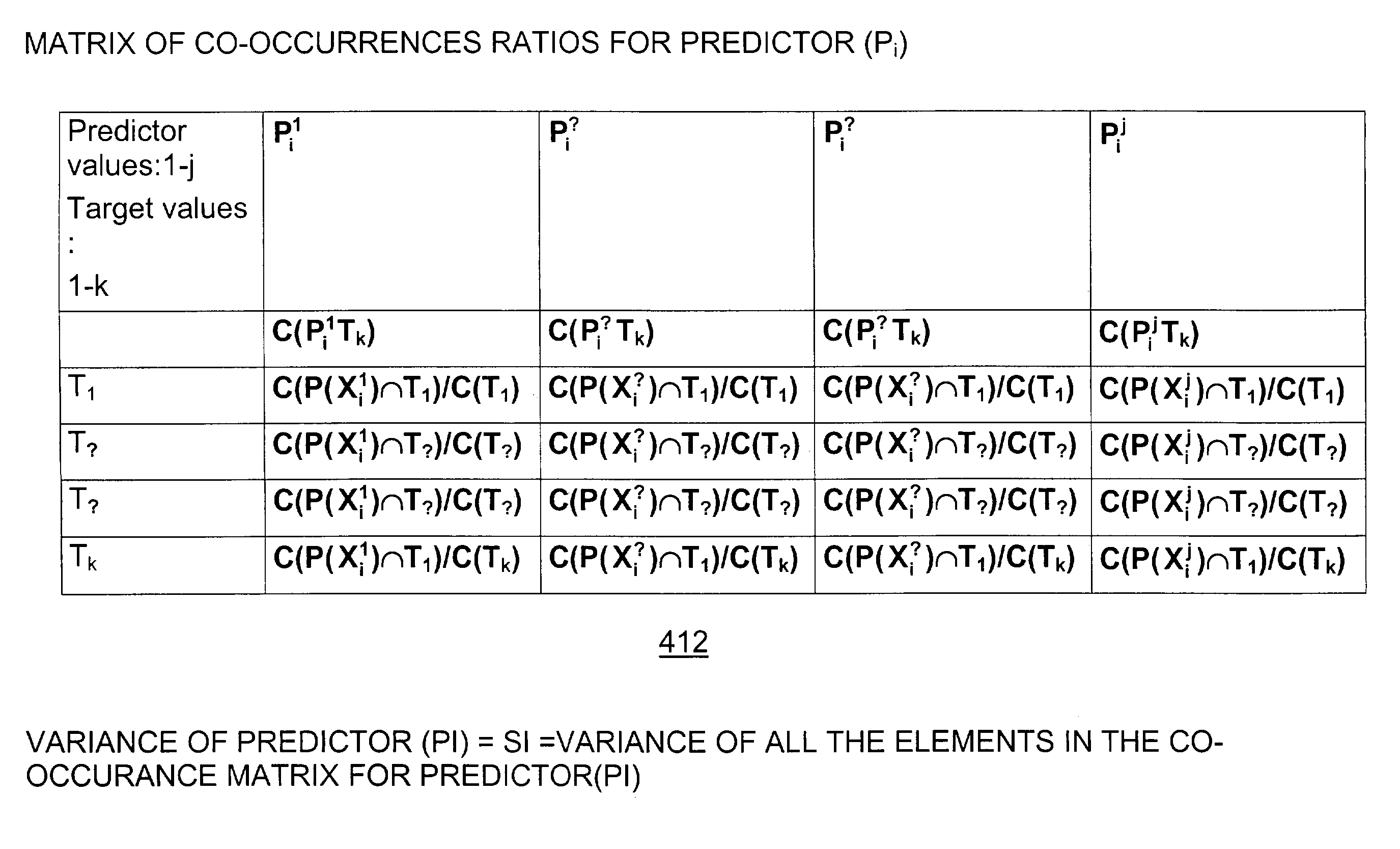
Data mining model building using attribute importance
ActiveUS7219099B2Reducing resourceShorten the timeMathematical modelsData processing applicationsData dredgingData set
A system, method, and computer program product that uses attribute importance (AI) to reduce the time and computation resources required to build data mining models, and which provides a corresponding reduction in the cost of data mining. Attribute importance (AI) involves a process of choosing a subset of the original predictive attributes by eliminating redundant, irrelevant or uninformative ones and identifying those predictor attributes that may be most helpful in making predictions. A new algorithm Predictor Variance is proposed and a method of selecting predictive attributes for a data mining model comprises the steps of receiving a dataset having a plurality of predictor attributes, for each predictor attribute, determining a predictive quality of the predictor attribute, selecting at least one predictor attribute based on the determined predictive quality of the predictor attribute, and building a data mining model including only the selected at least one predictor attribute.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
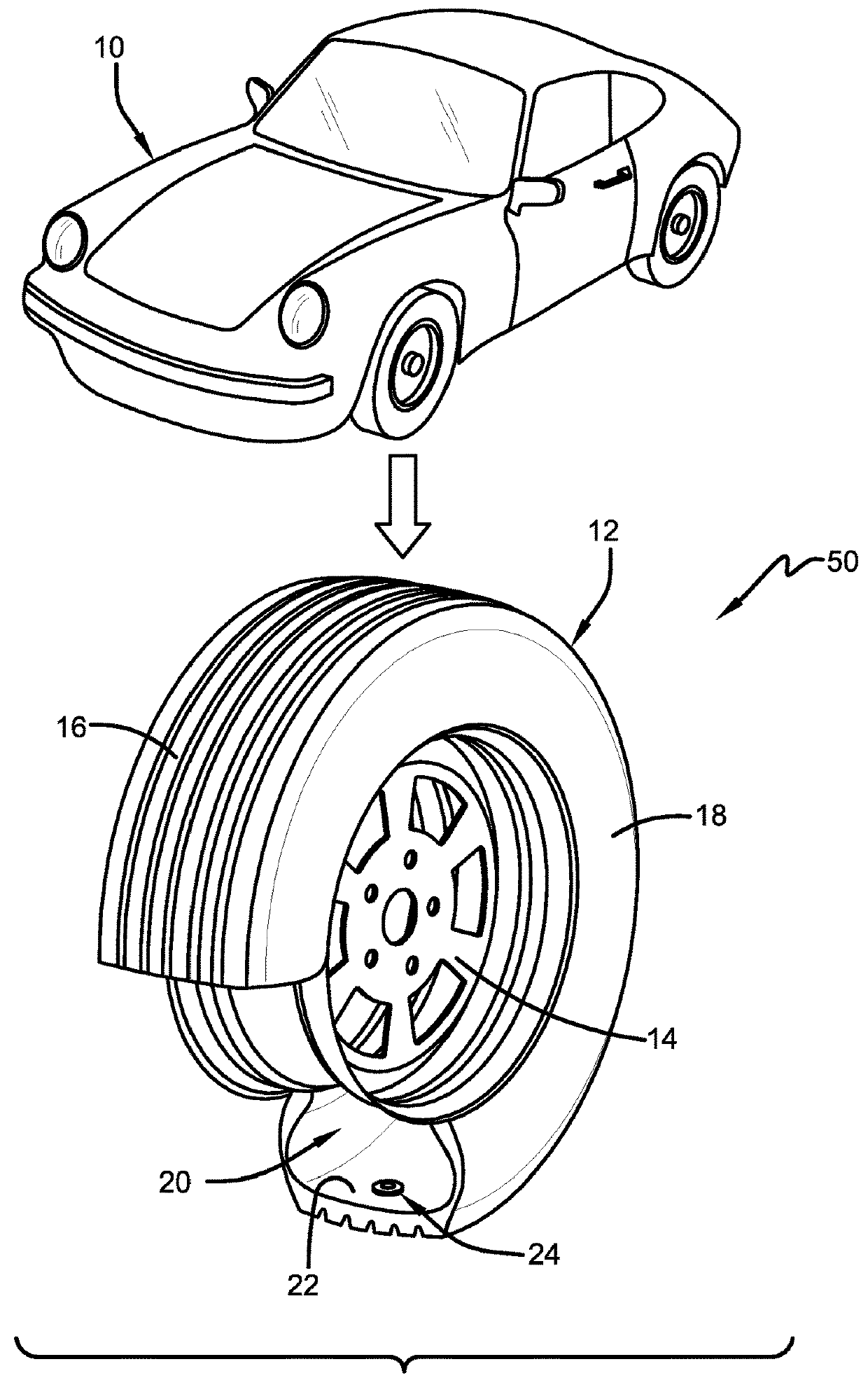
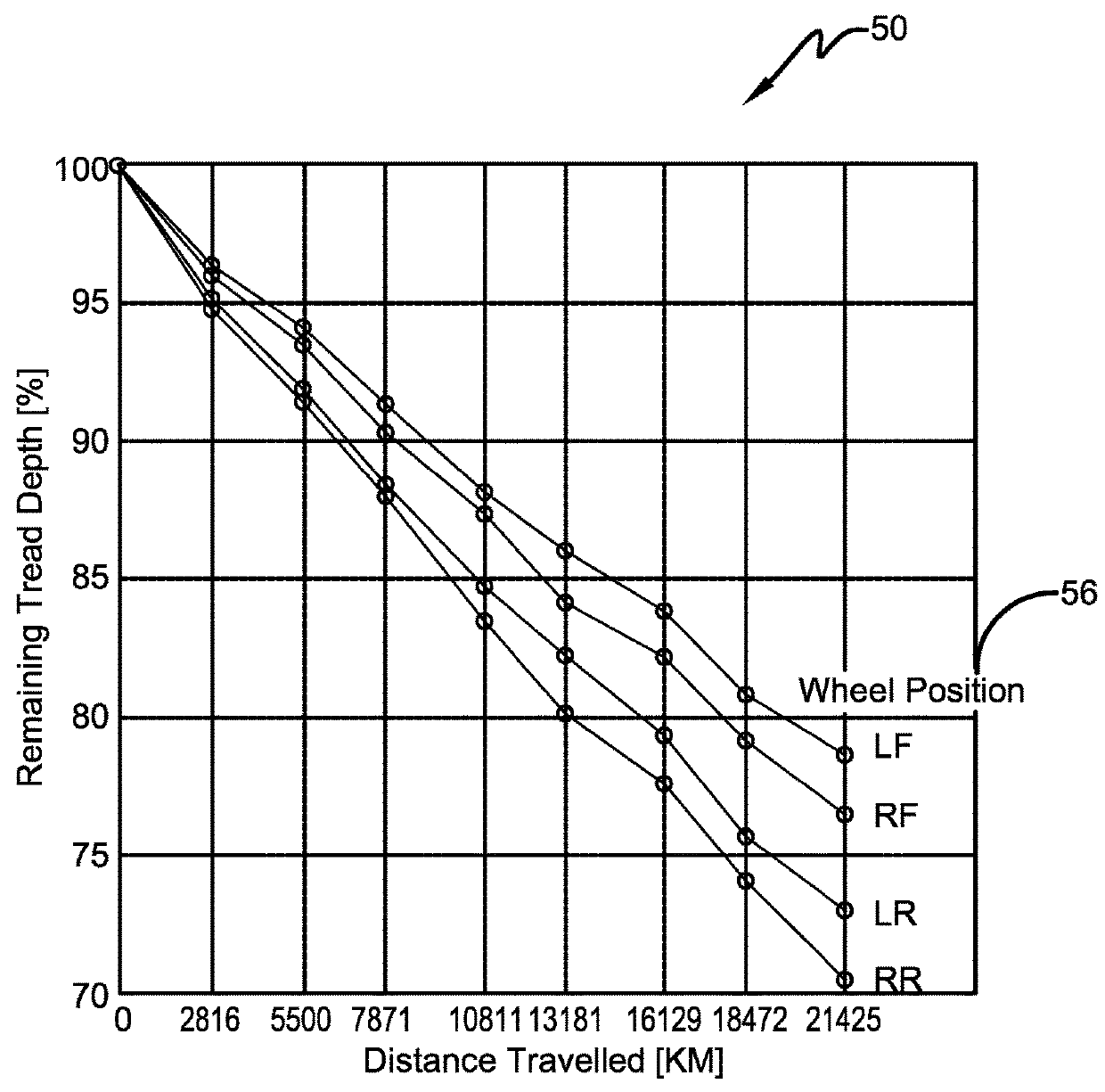
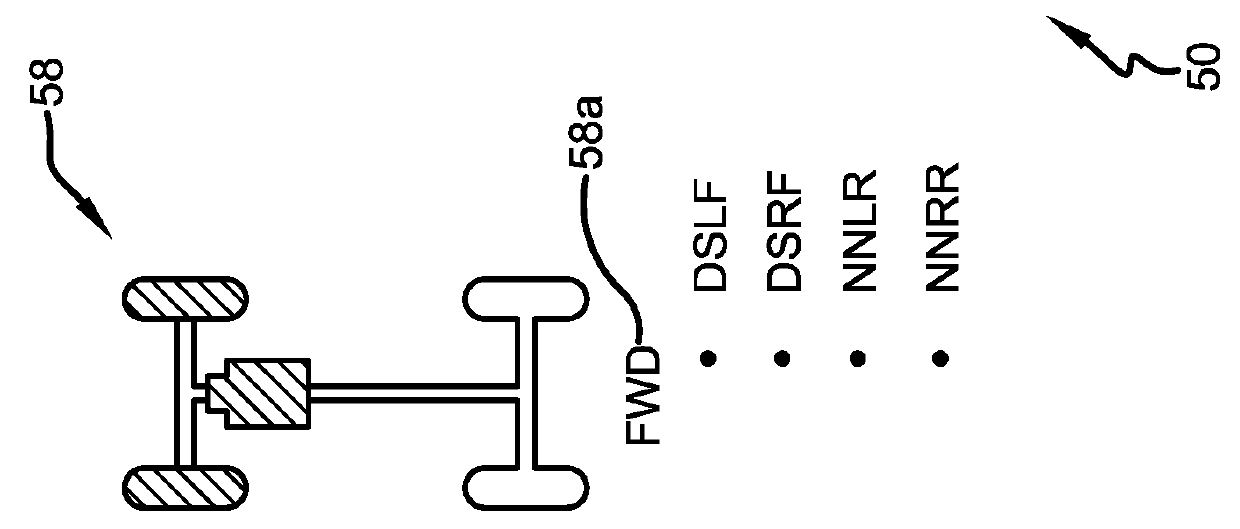
Model based tire wear estimation system and method
A tire wear estimation system is provided. The system includes at least one tire that supports a vehicle. At least one sensor is affixed to the tire to generate a first predictor. A lookup table or a database stores data for a second predictor. One of the predictors includes at least one vehicle effect. A model receives the predictors and generates an estimated wear rate for the at least one tire.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Method and system for determining the importance of individual variables in a statistical model
A method and system for determining the importance of each of the variables that contribute to the overall score of a model for predicting the profitability of an insurance policy. For each variable in the model, an importance is calculated based on the calculated slope and deviance of the predictive variable. Since the score is developed using complex mathematical calculations combining large numbers of parameters with predictive variables, it is often difficult to interpret from the mathematical formula for example, why some policyholders receive low scores while other receive high scores. Such clear communication and interpretation of insurance profitability scores is critical if they are used by the various interested insurance parties including policyholders, agents, underwriters, and regulators.
Owner:DELOITTE DEV
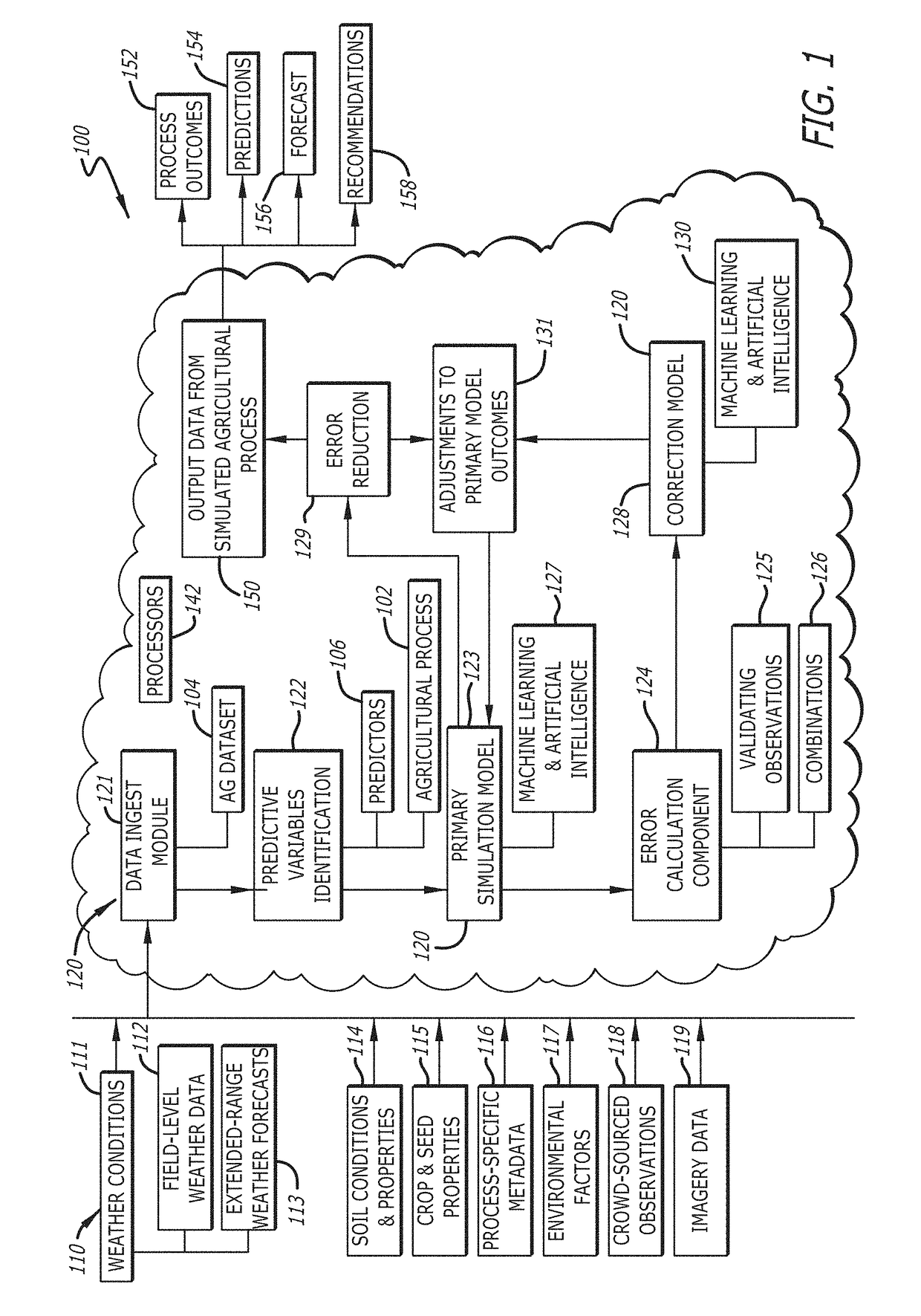
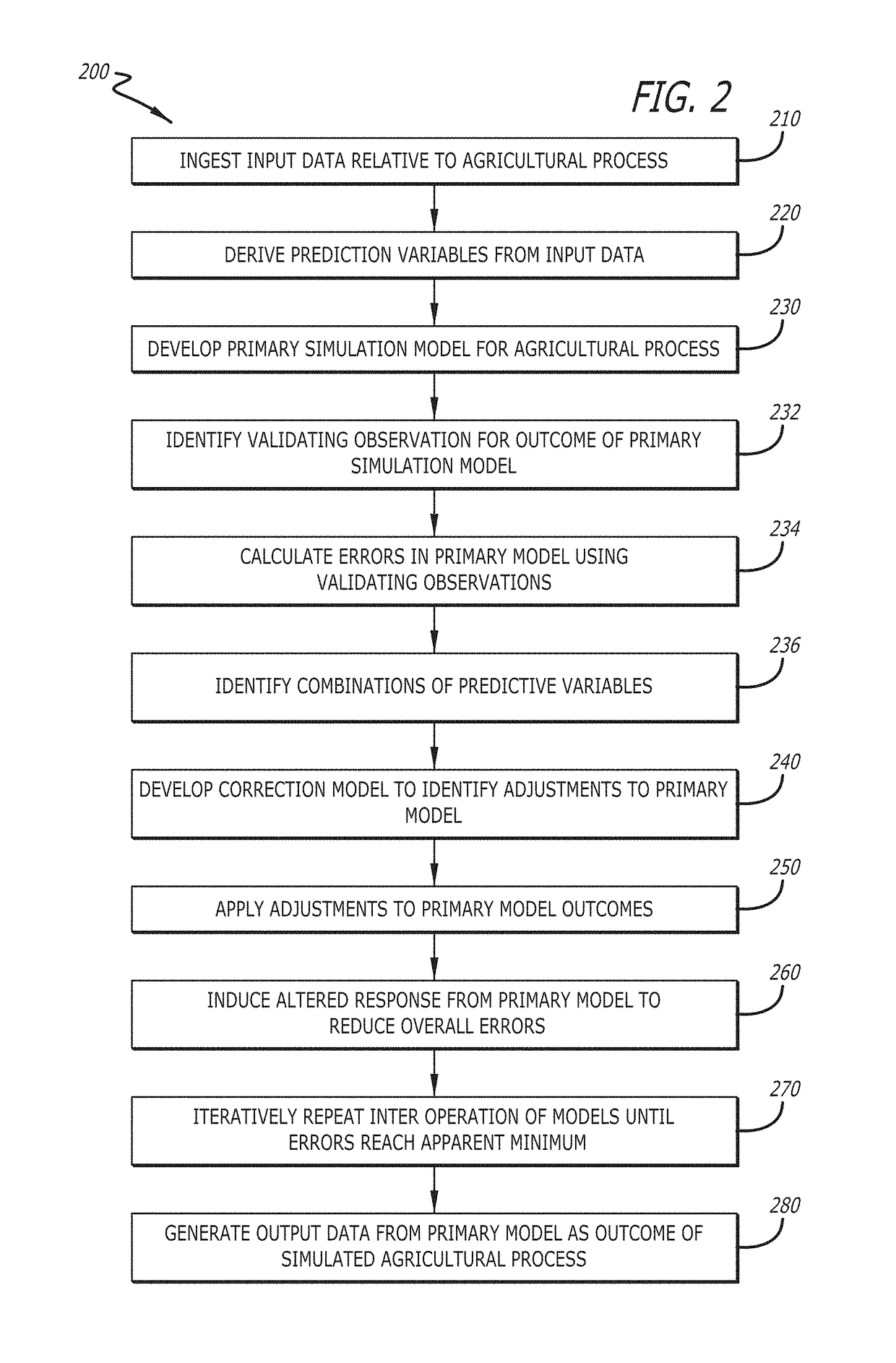
Development of complex agricultural simulation models from limited datasets
PendingUS20190050510A1Reduce model errorData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationData setPredictor variable
A multi-step iterative process for simulating complex agricultural situations where limited sets of data are available for such problems first predicts an outcome for each situation in a particular dataset, using initial assumptions of an applied primary model. The process then uses the errors across these situations to identify where opportunities exist among relevant predictive variables for the model to make changes to a response to such predictor variables to reduce the errors when averaged across all situations. The process then develops a correction model to identify adjustments based on combinations of the predictive variables, and applies the adjustments to the primary model to induce an altered outcome.
Owner:DTN LLC
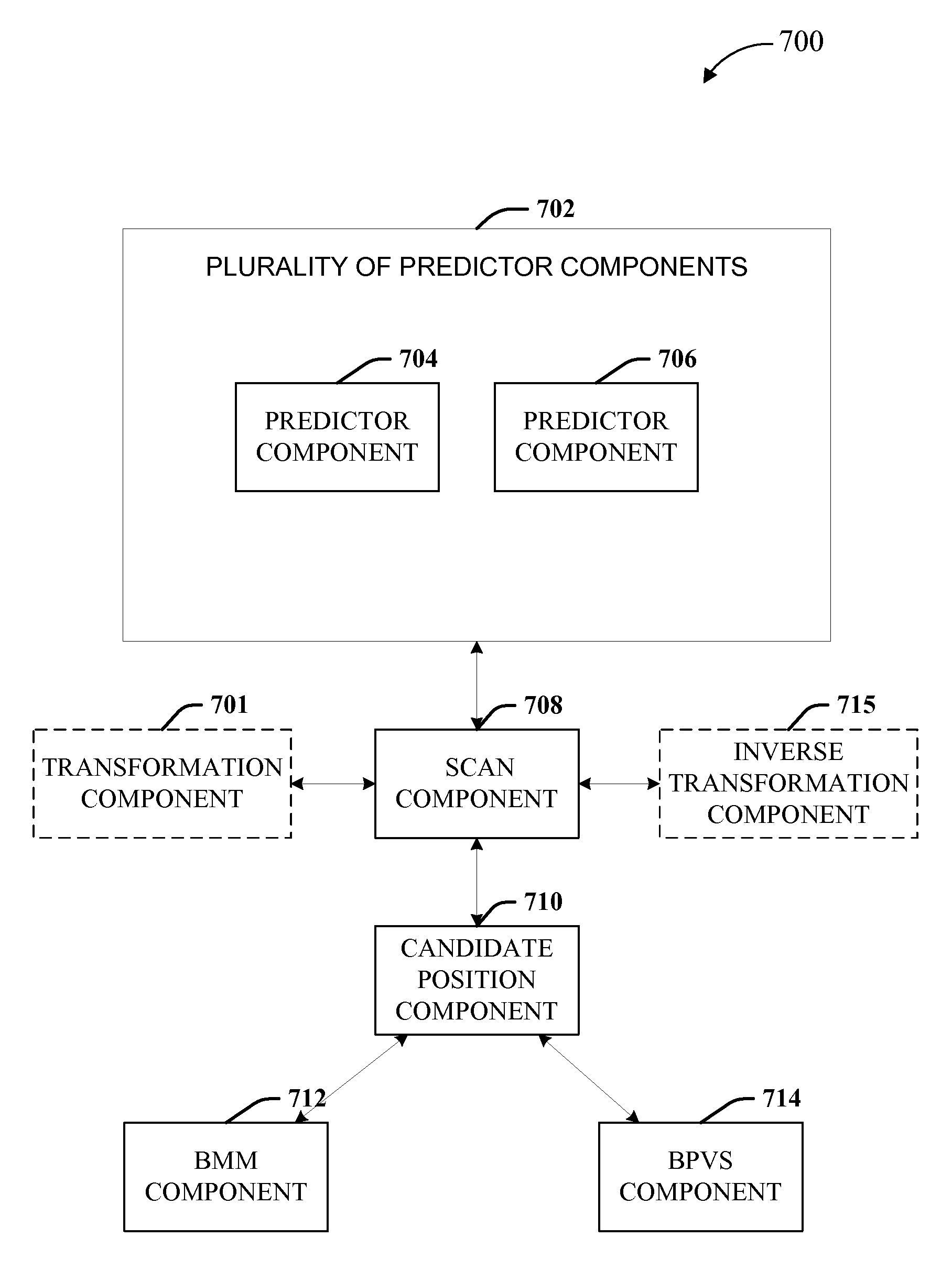
Methods and Apparatuses of Video Processing with Overlapped Block Motion Compensation in Video Coding Systems
InactiveUS20190387251A1Reduce in quantityDigital video signal modificationReference samplePredictor variable
Exemplary video processing methods and apparatuses for coding a current block determine a number of OBMC blending lines for a boundary between a current block and a neighboring block according to motion information, a location of the current block, or a coding mode of the current block. OBMC is applied to the current block by blending an original predictor of the current block with an OBMC predictor for the number of OBMC blending lines. Some other exemplary video processing methods and apparatuses for coding a current block extend reference samples fetched from a buffer by a padding method to generate padded sample, and OBMC is applied to the current block or a neighboring block by blending an original predictor with an OBMC predictor generated from the extended reference samples.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Decision support systems and methods
ActiveUS7562063B1Character and pattern recognitionKnowledge representationPredictor variableCombined use
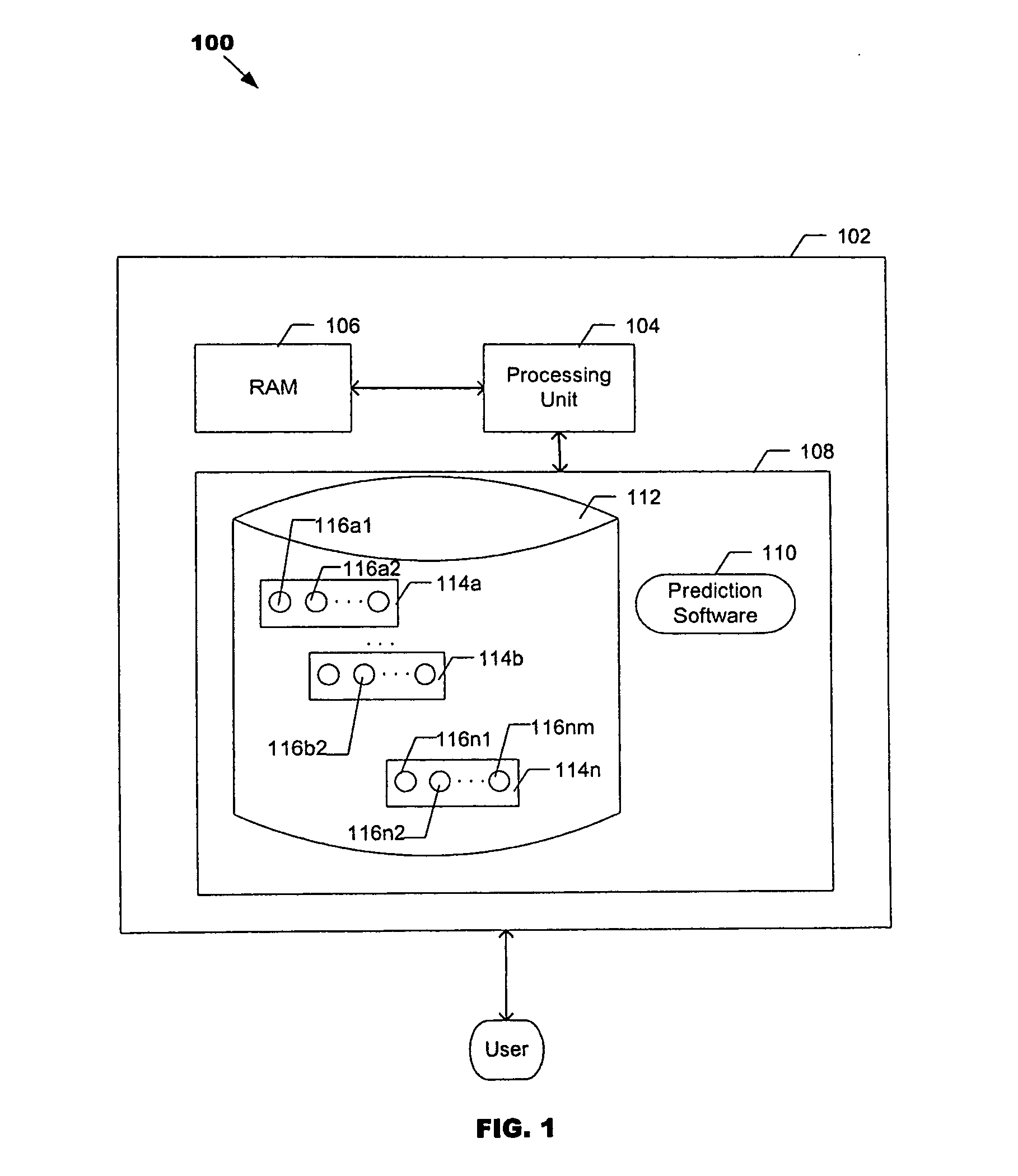
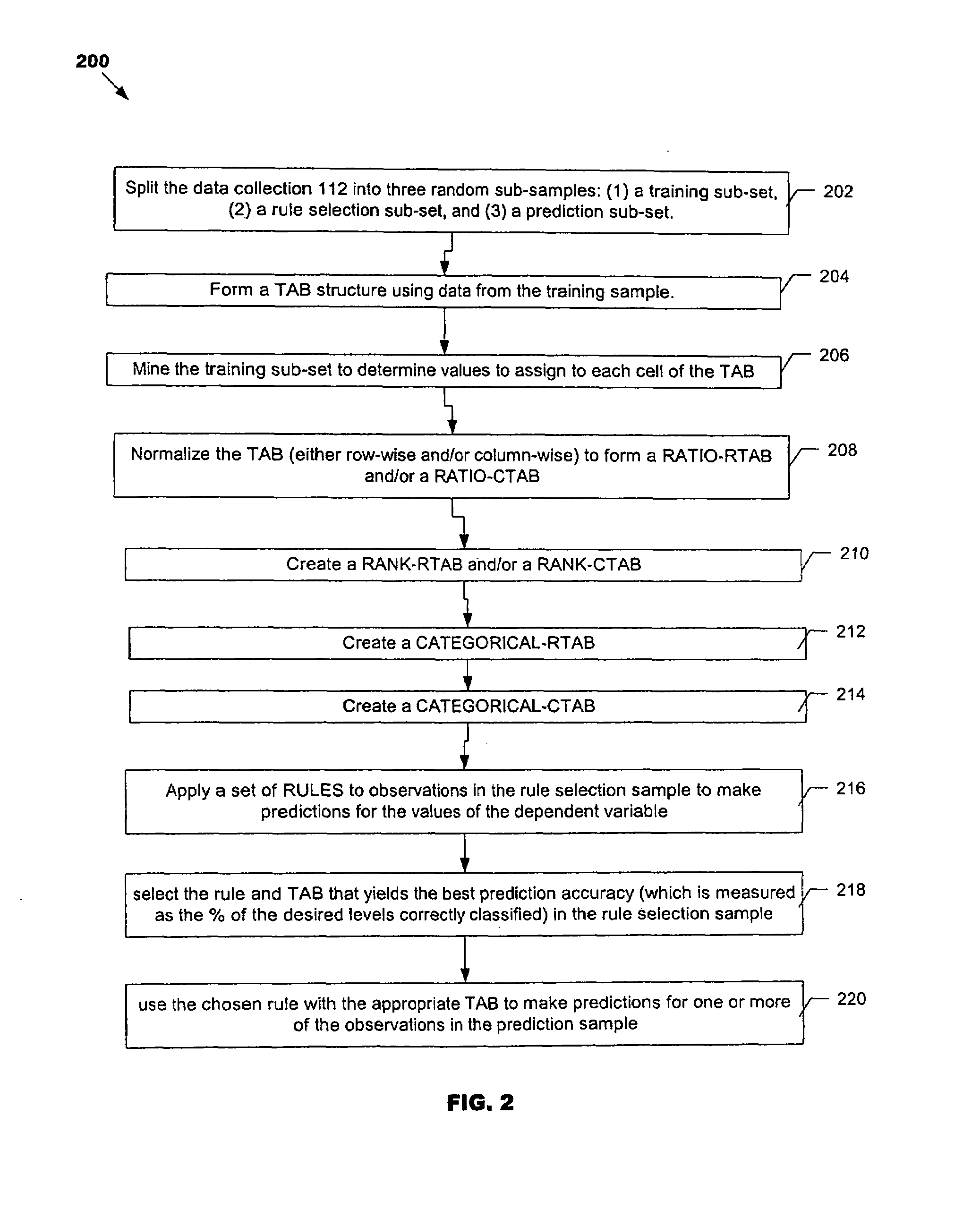
In one aspect, the invention is based on a process that combines information present in a joint distribution of the predictor variables and the variable (or variables) to be predicted. This information may be captured in the form of a table or other like data structure that includes a set of vectors (referred to as a “TAB”). The process uses the information in the TAB in conjunction with one or more rules. In one embodiment, a set of different rules are applied to the TAB to determine which rule in the set produces the most accurate predictions. The RULE that produces the most accurate predictions is then used in conjunction with observed information to make predictions.
Owner:CHATURVEDI ANIL
Automated model development process
ActiveUS20180075175A1High strengthReduce in quantityFinanceDesign optimisation/simulationSoftware development processData set
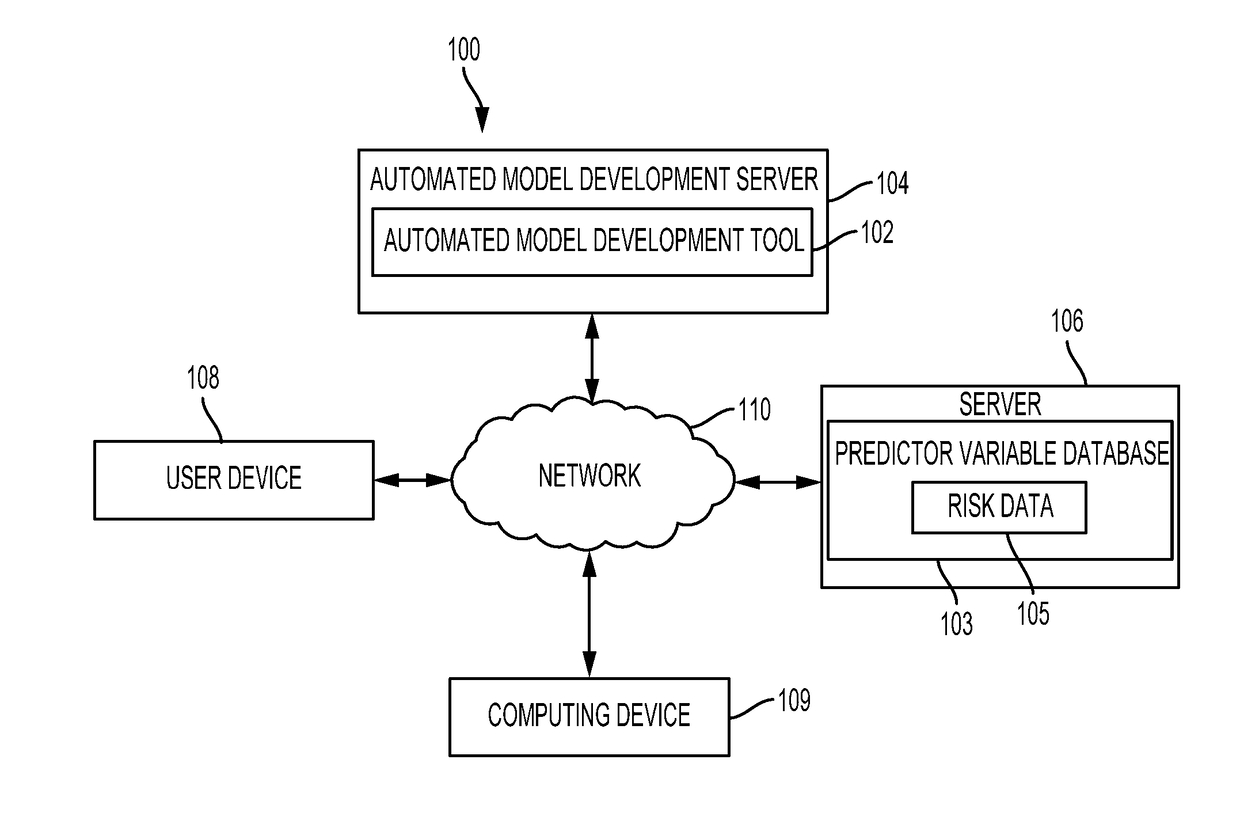
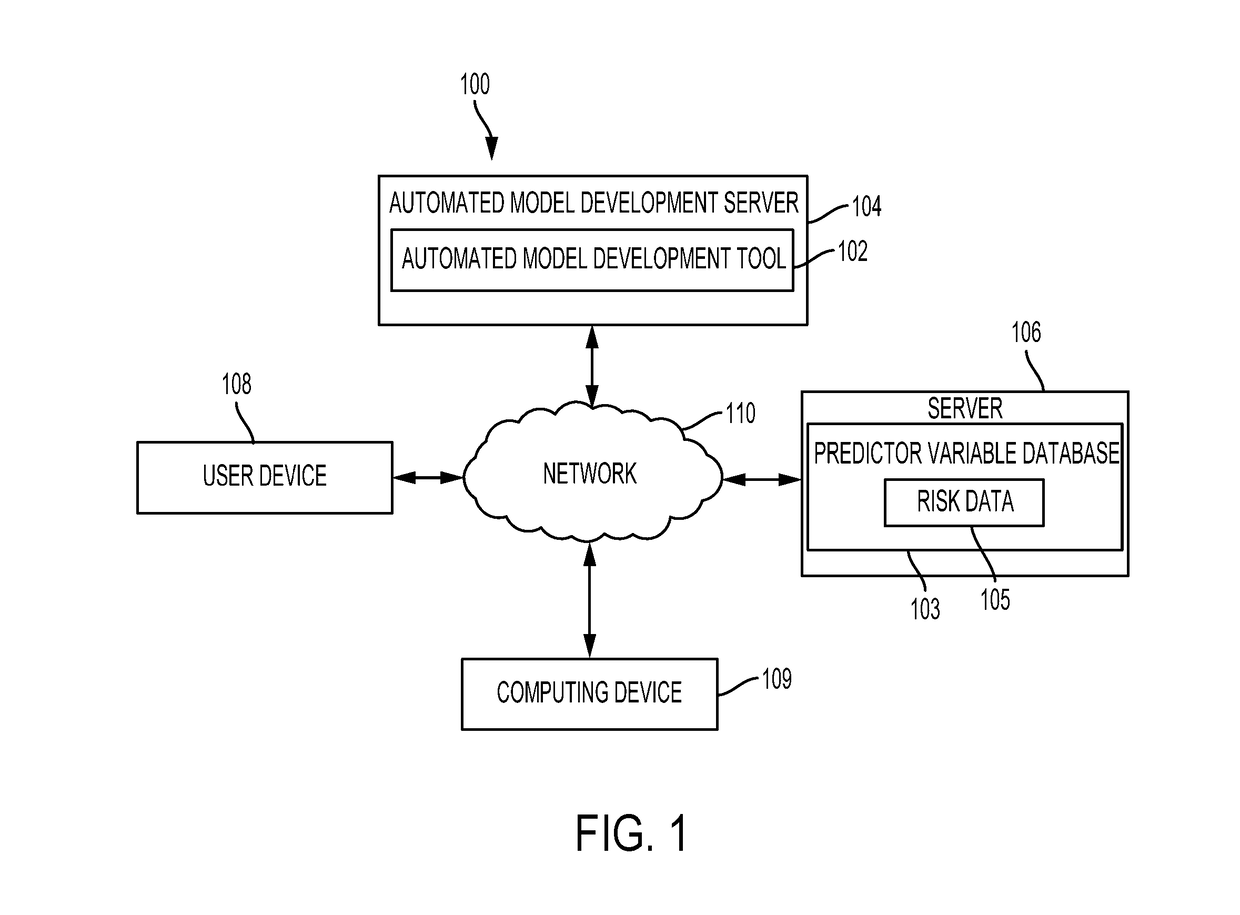
An automated model development tool can be used for automatically developing a model (e.g., an analytical model). The automated model development tool can perform various automated operations for automatically developing the model including, for example, performing automated operations on variables in a data set that can be used to develop the model. The automated operations can include automatically analyzing the predictor variables. The automated operations can also include automatically binning (e.g., combining) data associated with the predictor variables to provide monotonicity between the predictor variables and one or more output variables. The automated operations can further include automatically reducing the number of predictor variables in the data set and using the reduced number of predictor variables to develop the analytical model. The model developed using the automated model development tool can be used to identify relationships between predictor variables and one or more output variables in various machine learning applications.
Owner:EQUIFAX INC
Standardized Modeling Suite
ActiveUS20120239375A1Easy accessPromote generationResourcesSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPredictor variableGoal variable
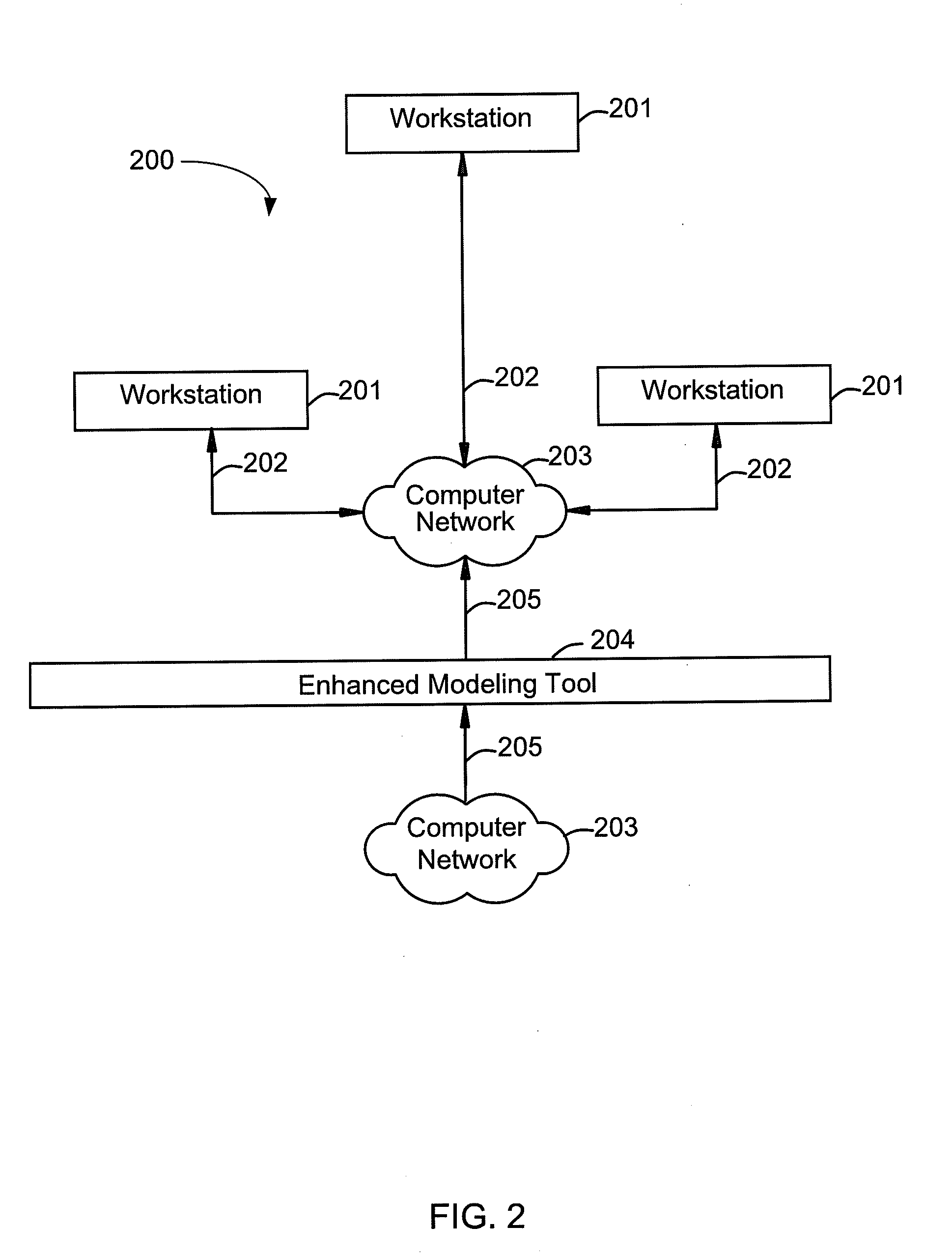
An enhanced modeling tool associated with an entity may facilitate end-to-end modeling of problems in any application space. The enhanced modeling tool may collect modeling data from a variety of sources, check the collected data, find the best predictor variables for a given target variable, estimate the model, implement the model, and validate the model. The output of each of these steps may be in a standardized format to allow other steps to directly incorporate the output. An additional feature of the system may include a reporting capability that generates supporting documents related to model governance and risk compliance.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
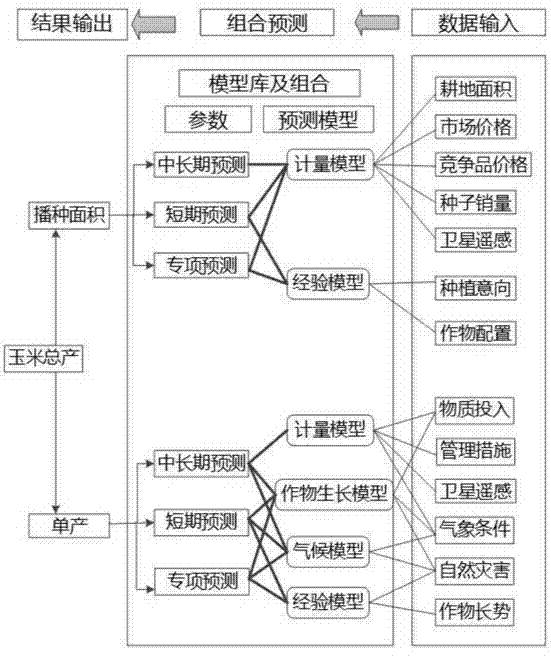
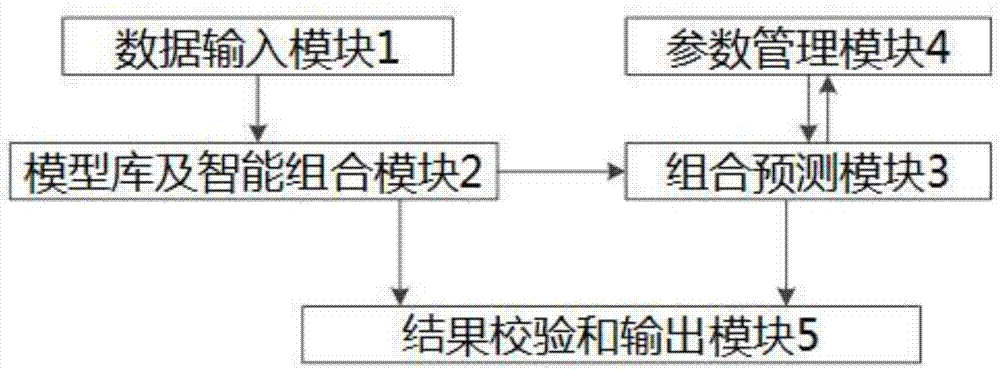
Maize yield combined prediction system and method
InactiveCN104732299AHigh precisionAchieve short termForecastingPredictor variableApplicability domain
The invention discloses a maize yield combined prediction system and method. The prediction system comprises a data input module, a model base and intelligent combined module, a combined prediction module, a parameter management module and a result check and output module. The prediction method includes the steps that yield prediction is divided into sown area prediction and per-unit-yield prediction, models are selected to be combined according to predicted targets, the weights of sub-models of the combined model are determined according to the basic data change amplitude, the combined prediction result is acquired according to weight distribution of the combined model and checked, and finally the combined prediction result is output through diagrams and characters. Different prediction models are correspondingly combined according to different prediction durations, prediction variable factors and prediction basic data, maize yield prediction is pertinently conducted, the prediction result is higher in accuracy, the application range is wider, short-period and medium-and-long-term dynamic prediction can be achieved at the same time, and agricultural research requirements are met.
Owner:AGRI INFORMATION INST OF CAS
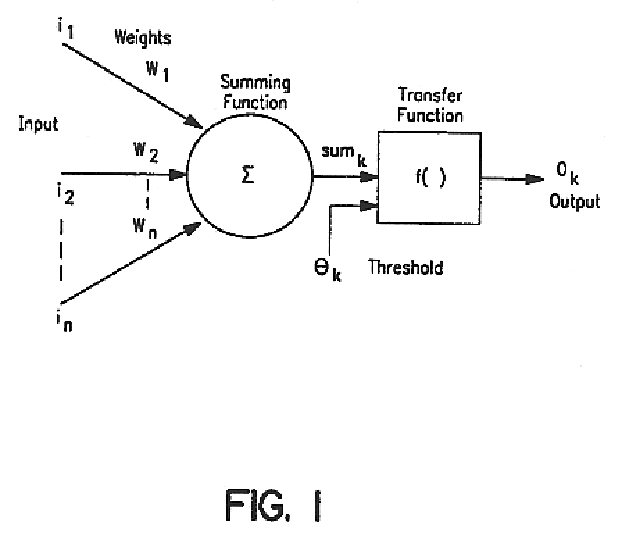
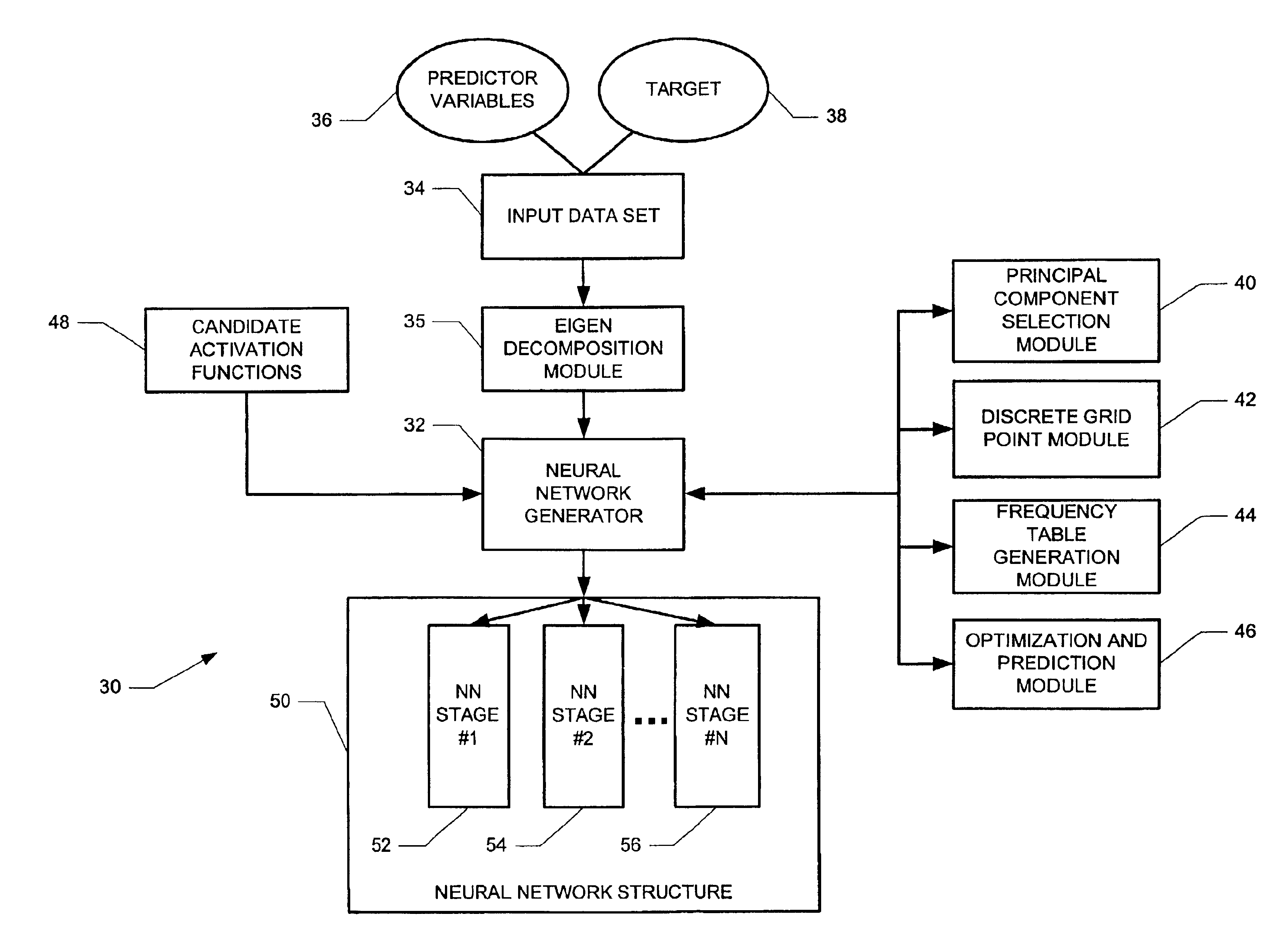
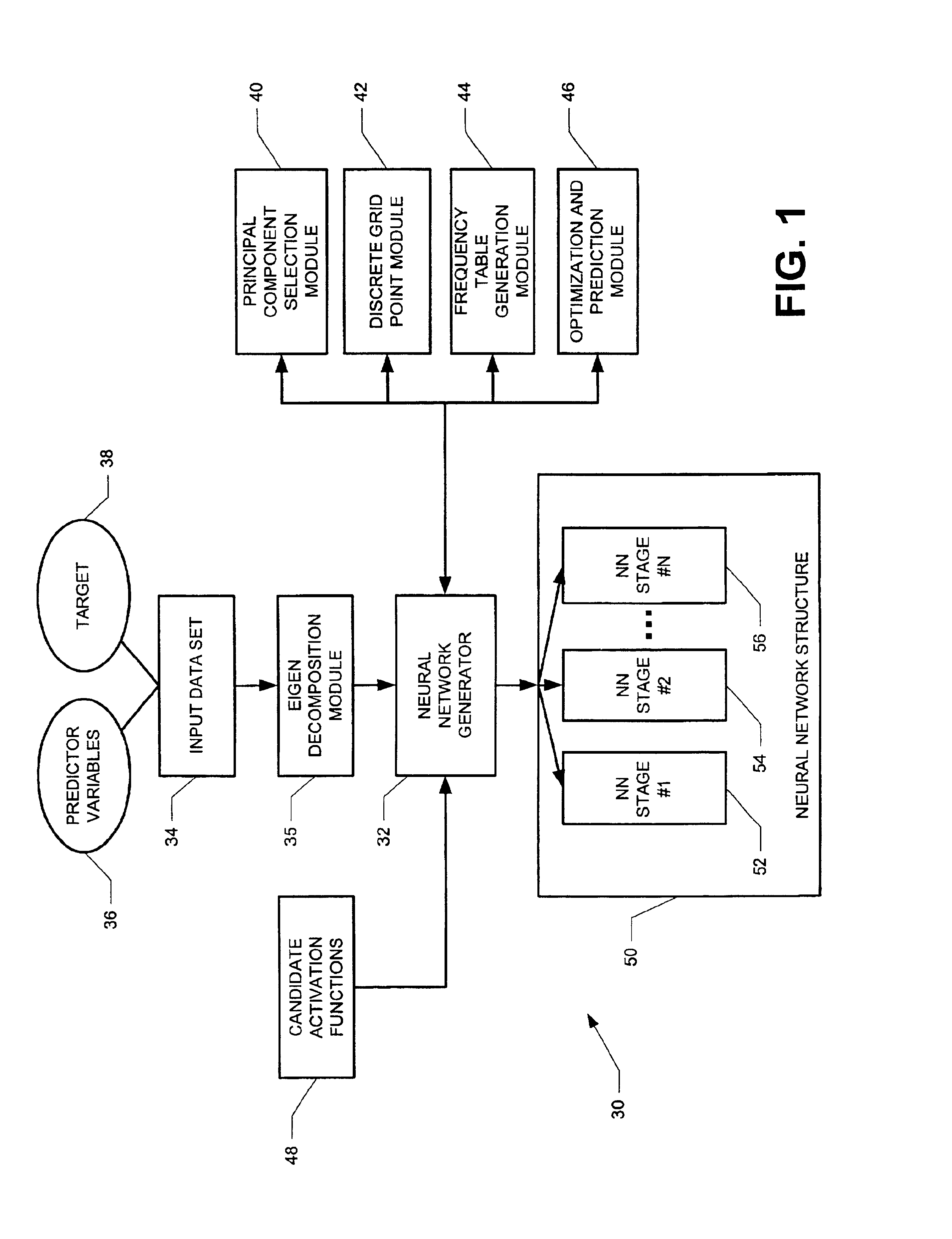
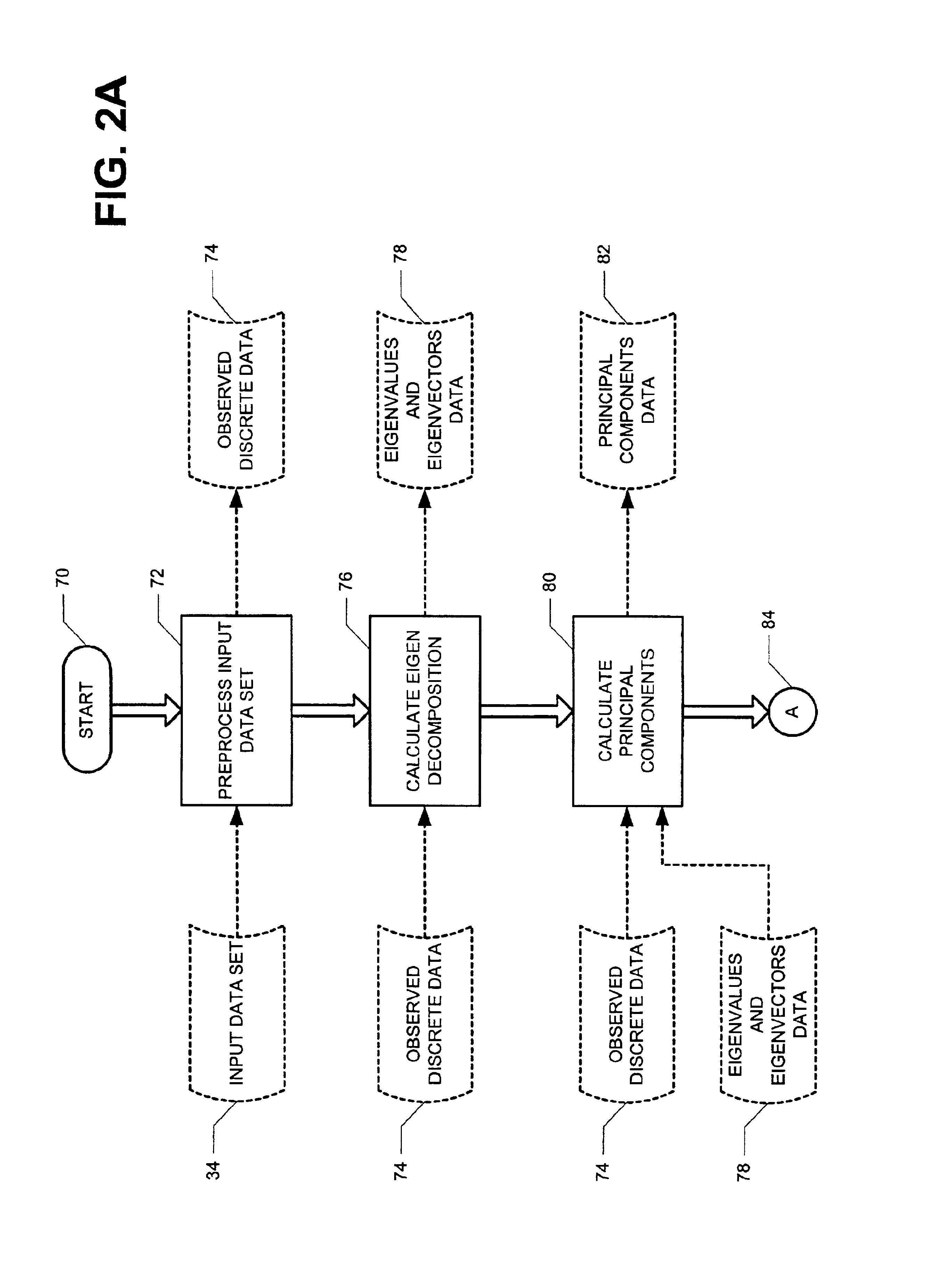
Hybrid neural network generation system and method
ActiveUS6941289B2Overcome disadvantagesDigital computer detailsDigital dataData setPredictor variable
A computer-implemented method and system for building a neural network is disclosed. The neural network predicts at least one target based upon predictor variables defined in a state space. First, an input data set is retrieved that includes the predictor variables and at least one target associated with the predictor variables for each observation. In the state space, a number of points is inserted in the state space based upon the values of the predictor variables. The number of points is less than the number of observations. A statistical measure is determined that describes a relationship between the observations and the inserted points. Weights and activation functions of the neural network are determined using the statistical measure.
Owner:SAS INSTITUTE
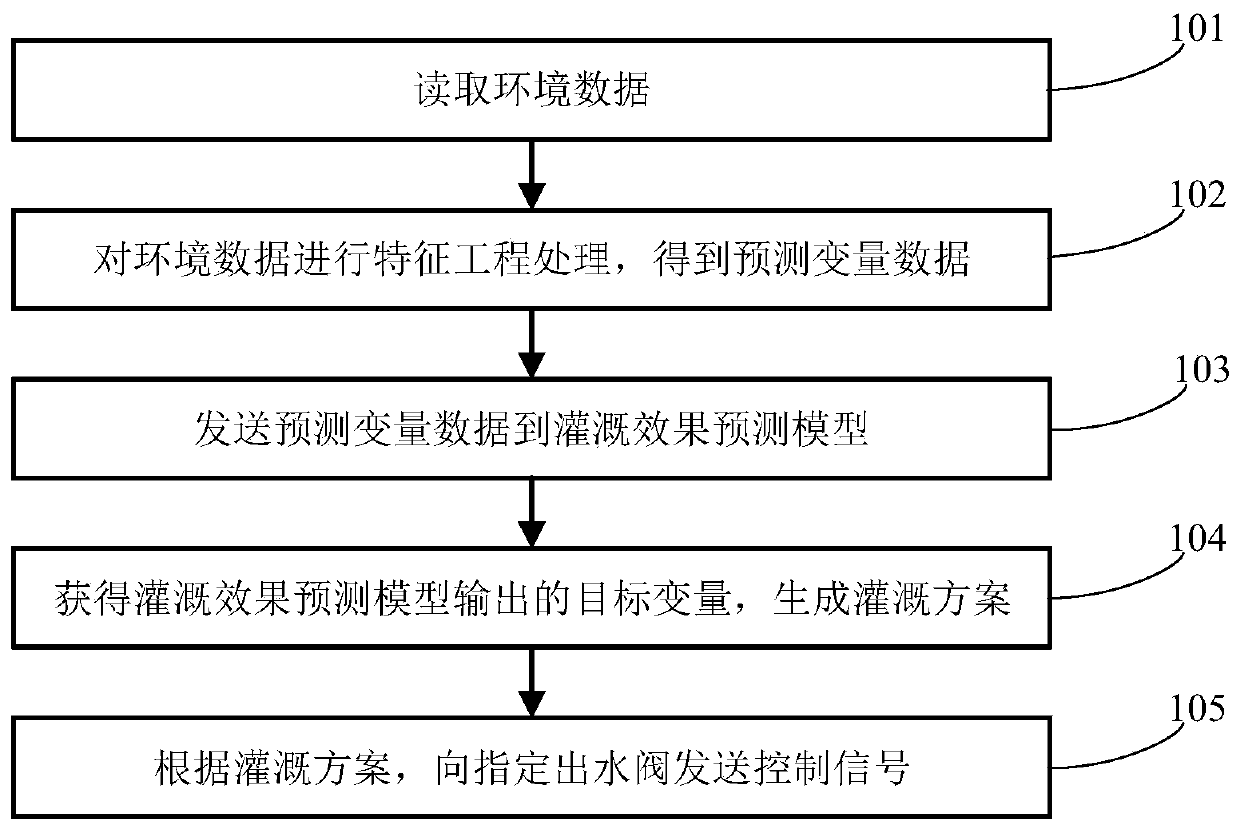
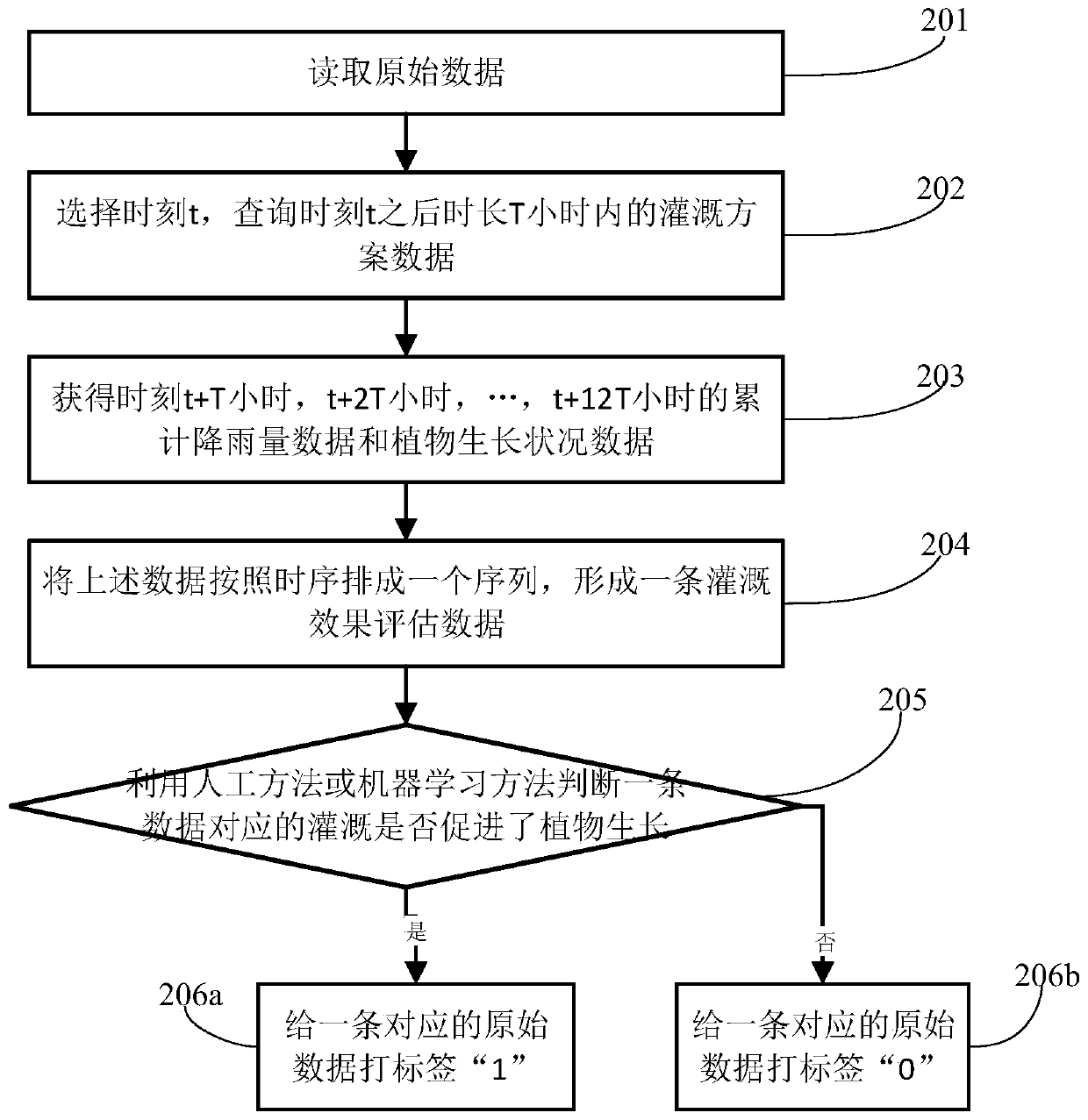
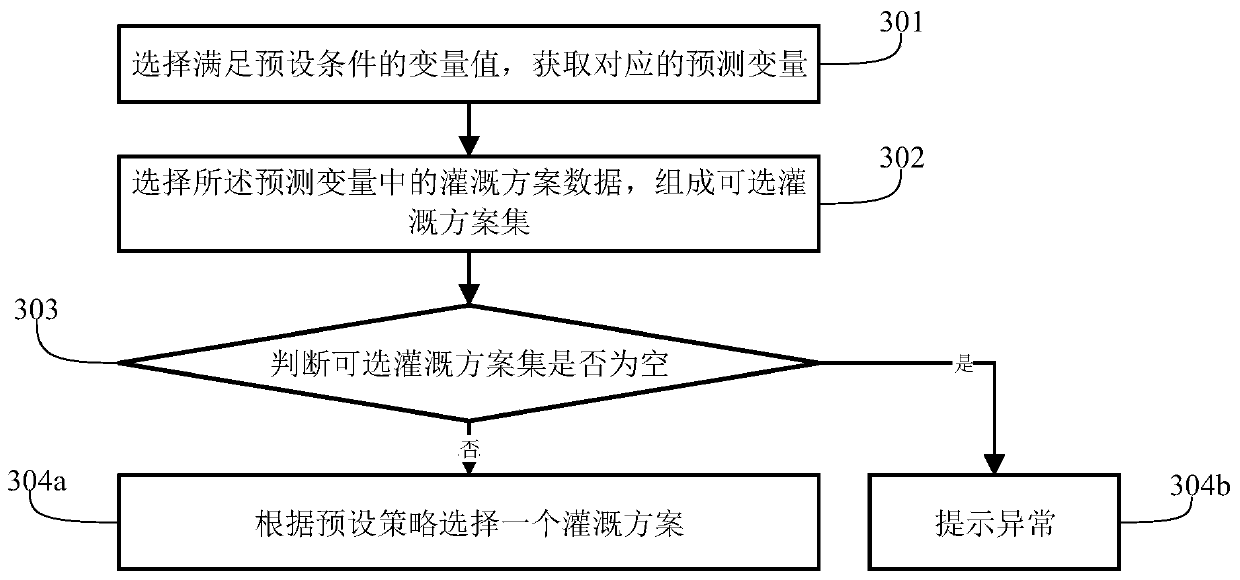
Irrigation method and device based on machine learning
ActiveCN111369093AReduce harmEnsure production increaseClimate change adaptationWatering devicesEnvironmental resource managementControl signal
The invention relates to the technical field of intelligent irrigation, and provides an irrigation method and device based on machine learning, and the method comprises the steps: reading environmentdata which comprises weather, soil humidity and plant growth condition data; performing feature engineering processing on the environment data to obtain prediction variable data; sending the prediction variable data to an irrigation effect prediction model, the irrigation effect prediction model being obtained based on labeled historical data training, the label being generated by using a manual method or a machine learning method; obtaining a target variable value output by the irrigation effect prediction model, and generating an irrigation scheme by utilizing the target variable value; andsending a control signal to the water outlet valve with the specified number according to the irrigation scheme. The irrigation opportunity is modeled and controlled based on plant growth conditions and environmental factors, the problem that irrigation cannot be carried out at the optimal opportunity through manual decision making or decision making based on a single environmental factor can be solved, the crop yield can be ensured, and labor and water resources are saved.
Owner:TIANYUN RONGCHUANG DATA TECH BEIJING CO LTD
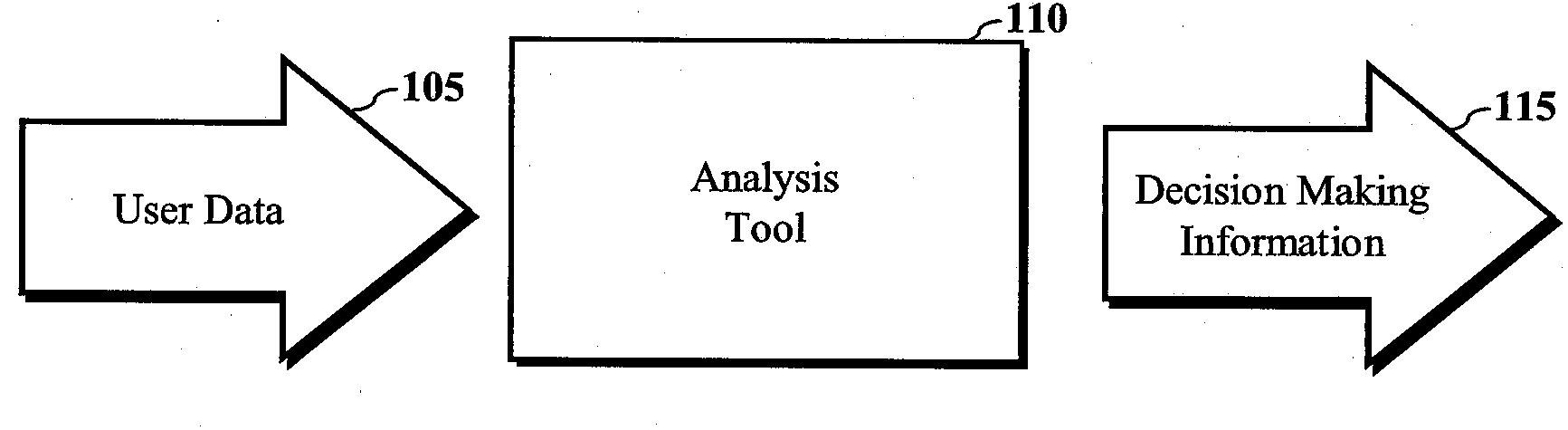
Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Data to Provide Decision Making Information
InactiveUS20090177612A1Fuzzy logic based systemsSpecific program execution arrangementsPredictor variableAnalysis data
Method and apparatus for analyzing data to provide decision making information. In one embodiment, a method includes receiving data corresponding to an agent for one or more predictor variables of a model, and calculating coefficients of the model based, at least in part, on a logistic regression analysis for a response variable to determine probability densities of the response variable, wherein the response variable is associated with the one or more predictor variables. The method may further include performing a computational analysis of the response variable based on the probability densities of the response variable to determine variation in the probability densities of the response variable, and generating a decision matrix, reflecting probabilities of one or more response variables and analysis values.
Owner:VALUE CREATION INST
Generalized lossless data hiding using multiple predictors
InactiveUS20080285790A1Character and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsGratingPredictor variable
A system and methodology for encoding or decoding hidden data, such as a digital watermark, in visual raster media is provided. The lossless data hiding methodology uses multiple predictors to choose an embedding location to be either a low variance region or a high variance region. Bijective mirror mapping is used to encode hidden data at an embedding location and bijective pixel value shifting is performed to ensure reversibility back to the original image without additional information. The system and methodology can be used either in the spatial domain or the wavelet domain. The Peak Signal to Noise Ratio and the payload capacity are relatively high with the methodology.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP +1
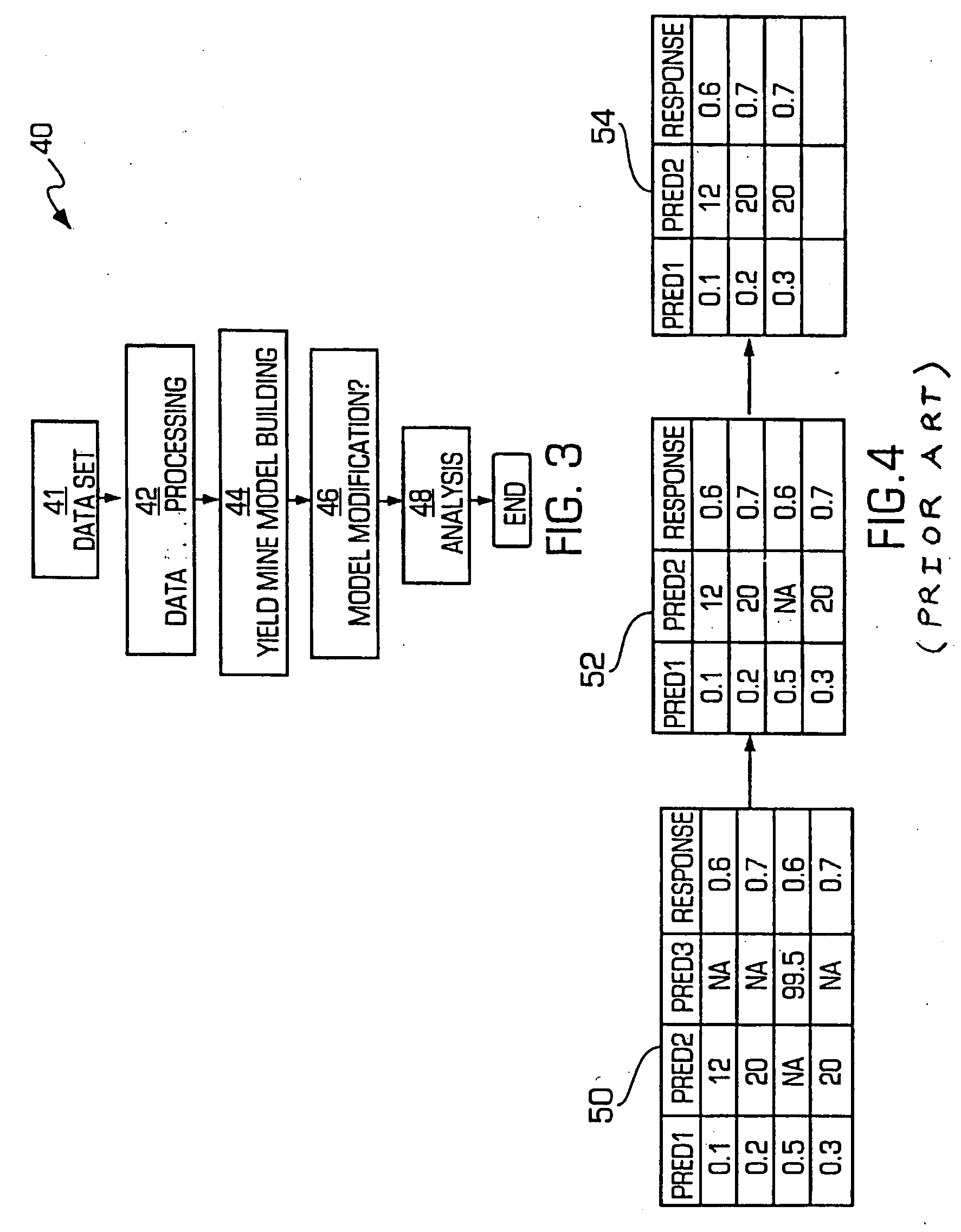
Semiconductor yield management system and method
InactiveUS20060095237A1Easy to useEasy to interpretSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementComputation using non-denominational number representationData setAnalysis data
A system and method for yield management are disclosed wherein a data set containing one or more prediction variable values and one or more response variable values is input into the system. The system can process the input data set to remove prediction variables with missing values and data sets with missing values based on a tiered splitting method to maximize usage of all valid data points. The processed data can then be used to generate a model that may be a decision tree. The system can accept user input to modify the generated model. Once the model is complete, one or more statistical analysis tools can be used to analyze the data and generate a list of the key yield factors for the particular data set.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Systems and methods for predictive building energy monitoring
A system and method for predictive modeling of building energy consumption provides predicted building energy load values which are determined using kernel smoothing of historical building energy load values for a building using defined scaling factors for scaling predictor variables associated with building energy consumption. Predictor variables may include temperature, humidity, windspeed or direction, occupancy, time, day, date, and solar radiation. Scaling factor values may be defined by optimization training using historical building energy load values and measured predictor variable values for a building. Predicted and measured building energy load values are compared to determine if a preset difference threshold has been exceeded, in which case an alert signal or message is generated and transmitted to electronically and / or physically signal a user. The building energy monitoring system may be integrated with a building automation system, or may be operated as a separate system receiving building energy and predictor variable values.
Owner:YARDI SYST
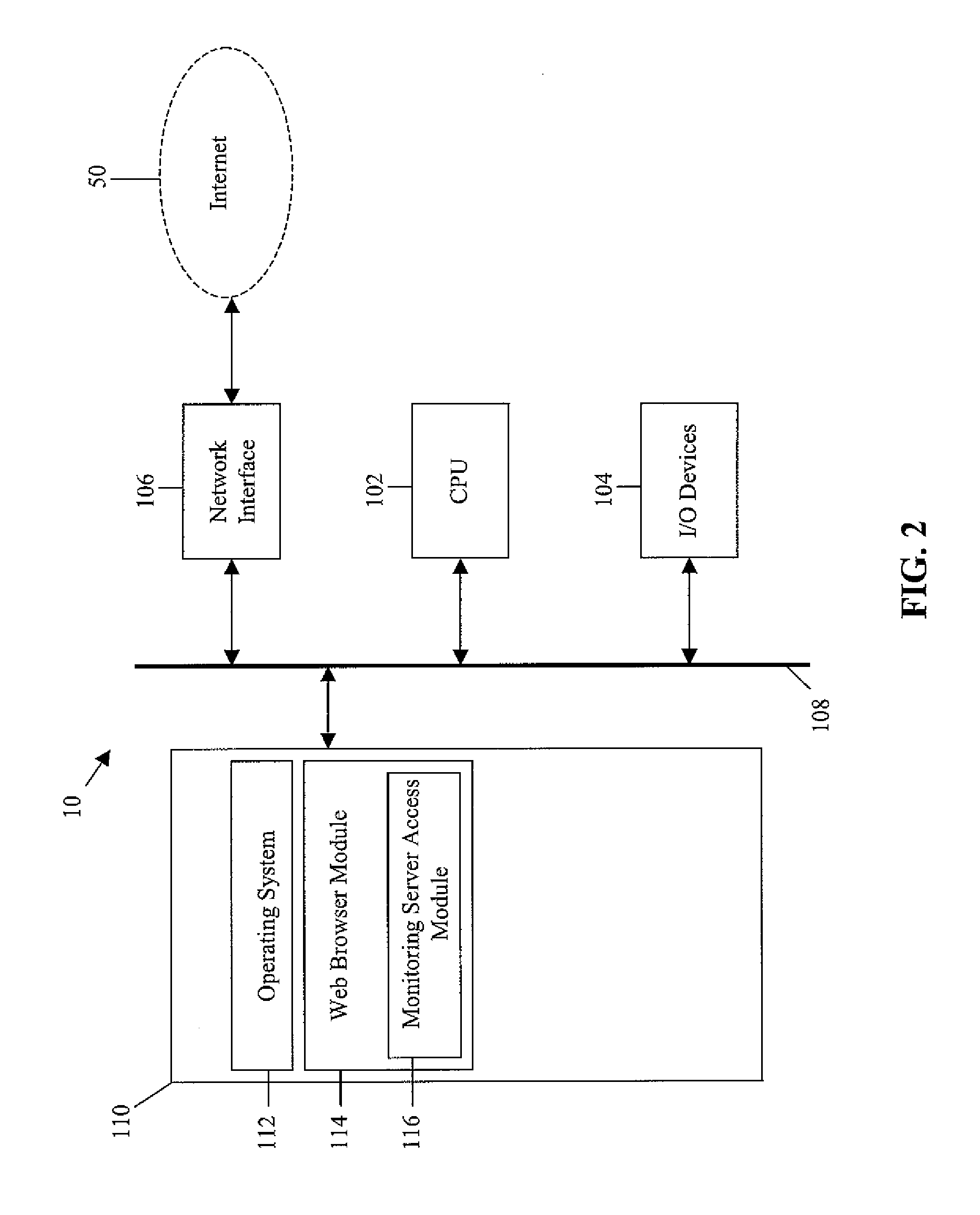
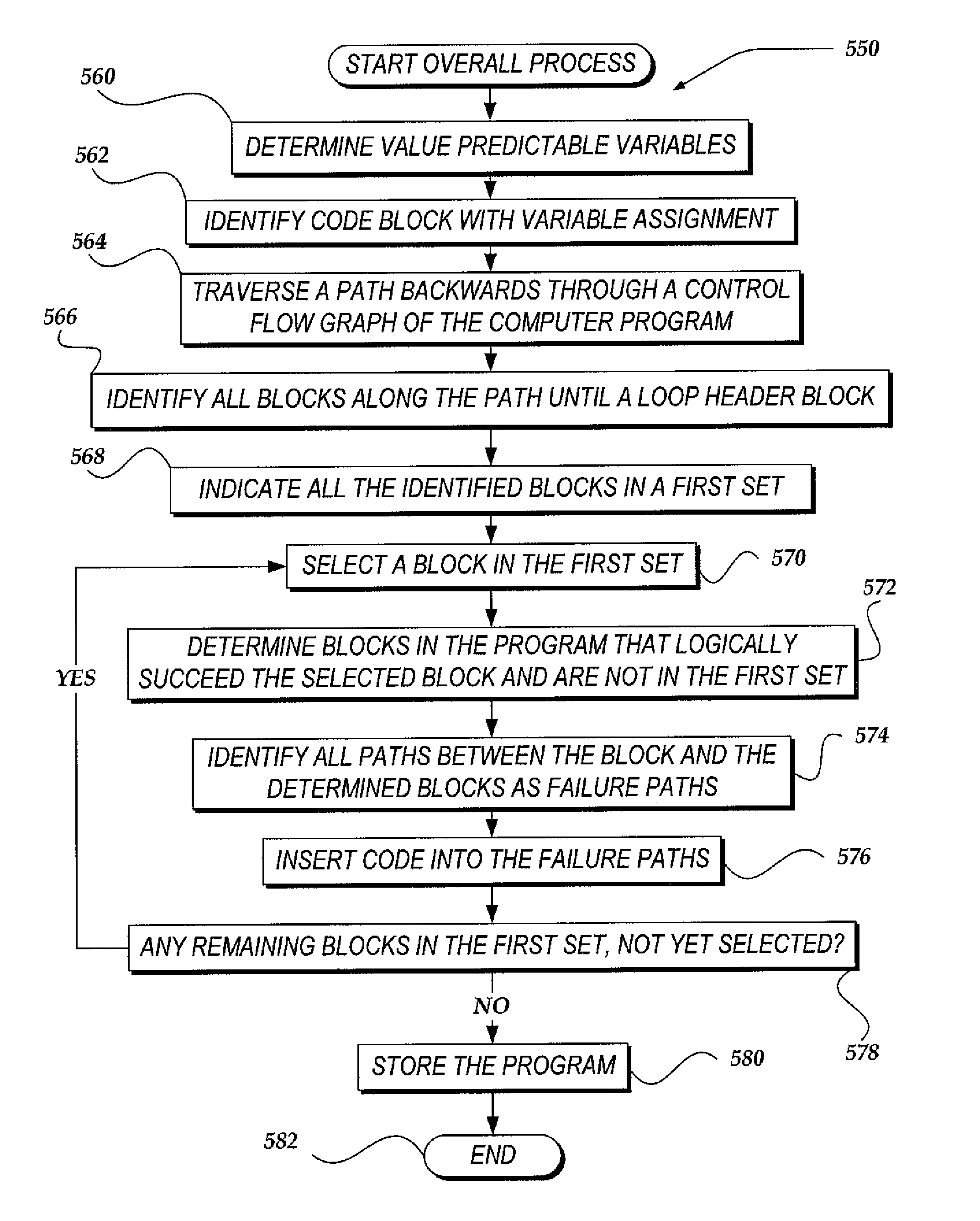
Value predictable variable scoping for speculative automatic parallelization with transactional memory
ActiveUS8239843B2Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsCoding blockPredictor variable
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Optimization of ranking measures as a structured output problem
InactiveUS20090138463A1Improve efficiencyMinimize sumDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPredictor variableRanking
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for generating relevance functions for ranking documents obtained in searches are provided. One or more features to be used as predictor variables in the construction of a relevance function are determined. The relevance function is parameterized by one or more coefficients. An ideal query error is defined that measures, for a given query, a difference between a ranking generated by the relevance function and a ranking based on a training set. According to a structured output learning framework, values for the coefficients of the relevance function are determined to substantially minimize an objective function that depends on a continuous upper bound of the defined ideal query error.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Resource Allocation Based on Available Predictions
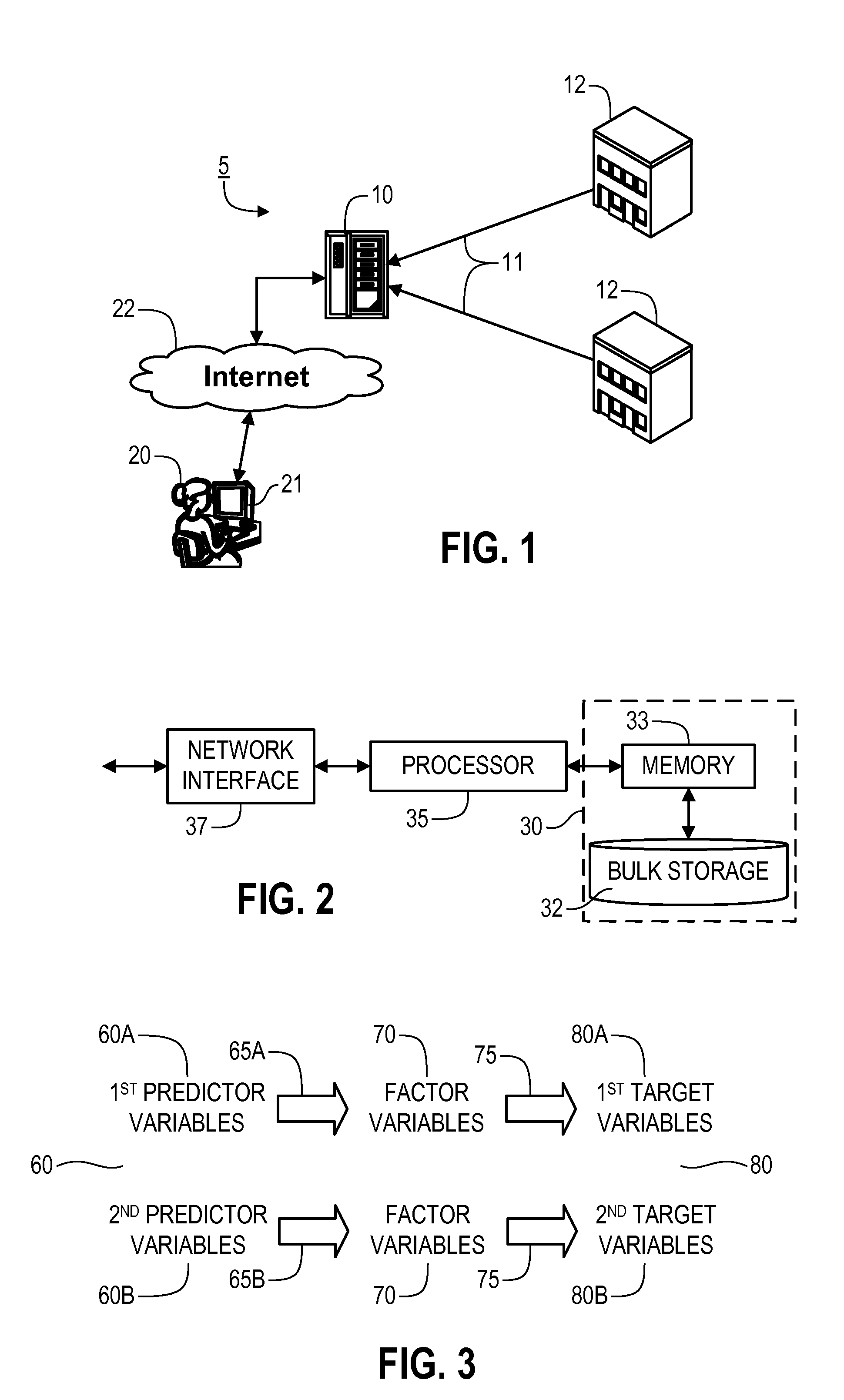
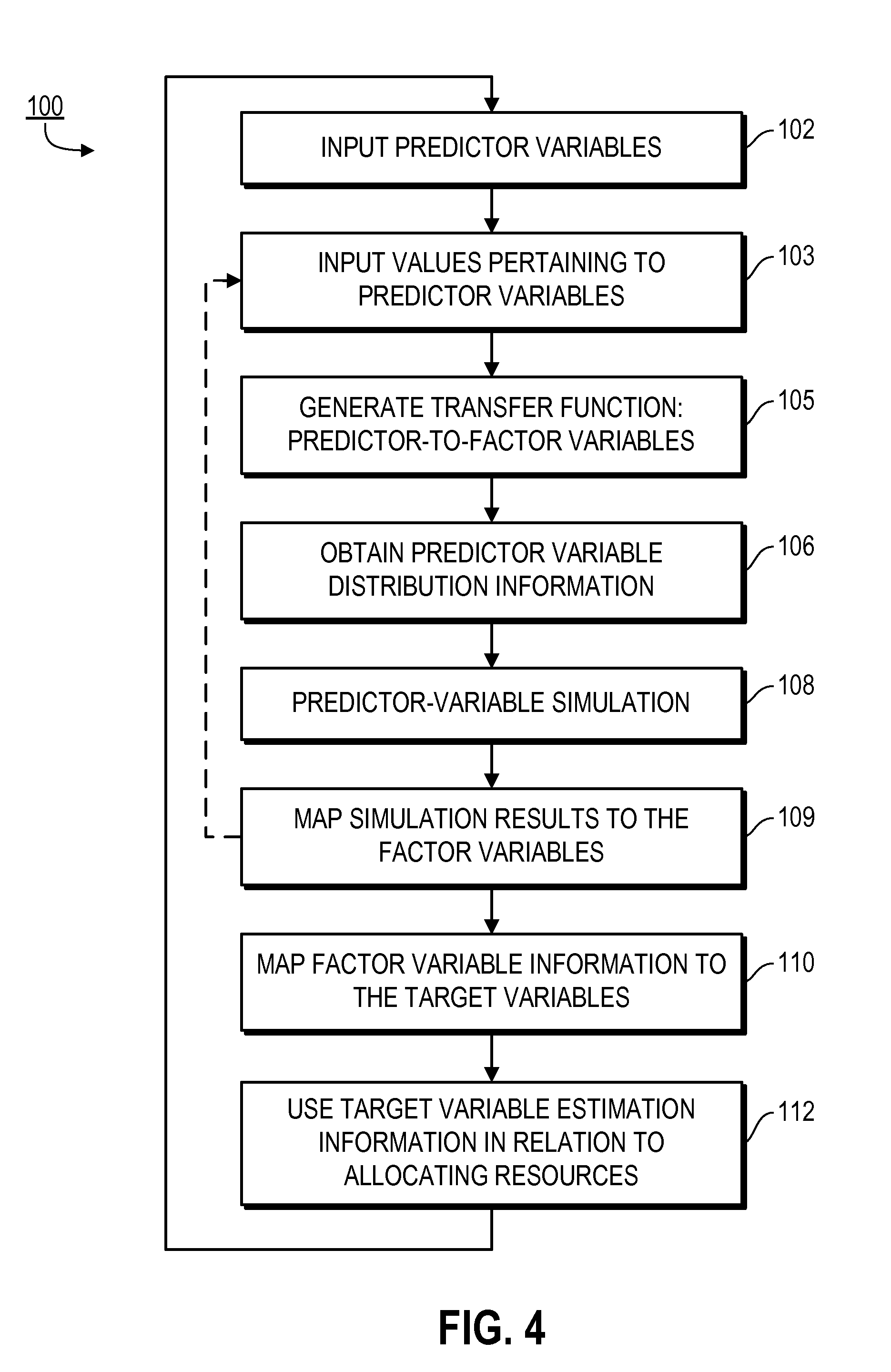
Provided are systems, methods and techniques for facilitating allocation of resources based on available data estimates, using steps to: input a set of predictor variables and data values pertaining to them; generate a first transfer function that maps values for the predictor variables to values for a predefined set of factor variables; generate distribution information for the predictor variables based on the input data values; conduct a simulation using the distribution information for the predictor variables; map the simulated values for the predictor variables to information regarding the factor variables, using the first transfer function; map such information to estimation information for a set of target variables using a second transfer function; and display the estimation information, use the estimation information to recommend a purchase or sale of an asset, and / or directly purchase and / or sell an asset based on the estimation information.
Owner:C4CAST COM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com