Patents
Literature
52977results about "Digital video signal modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
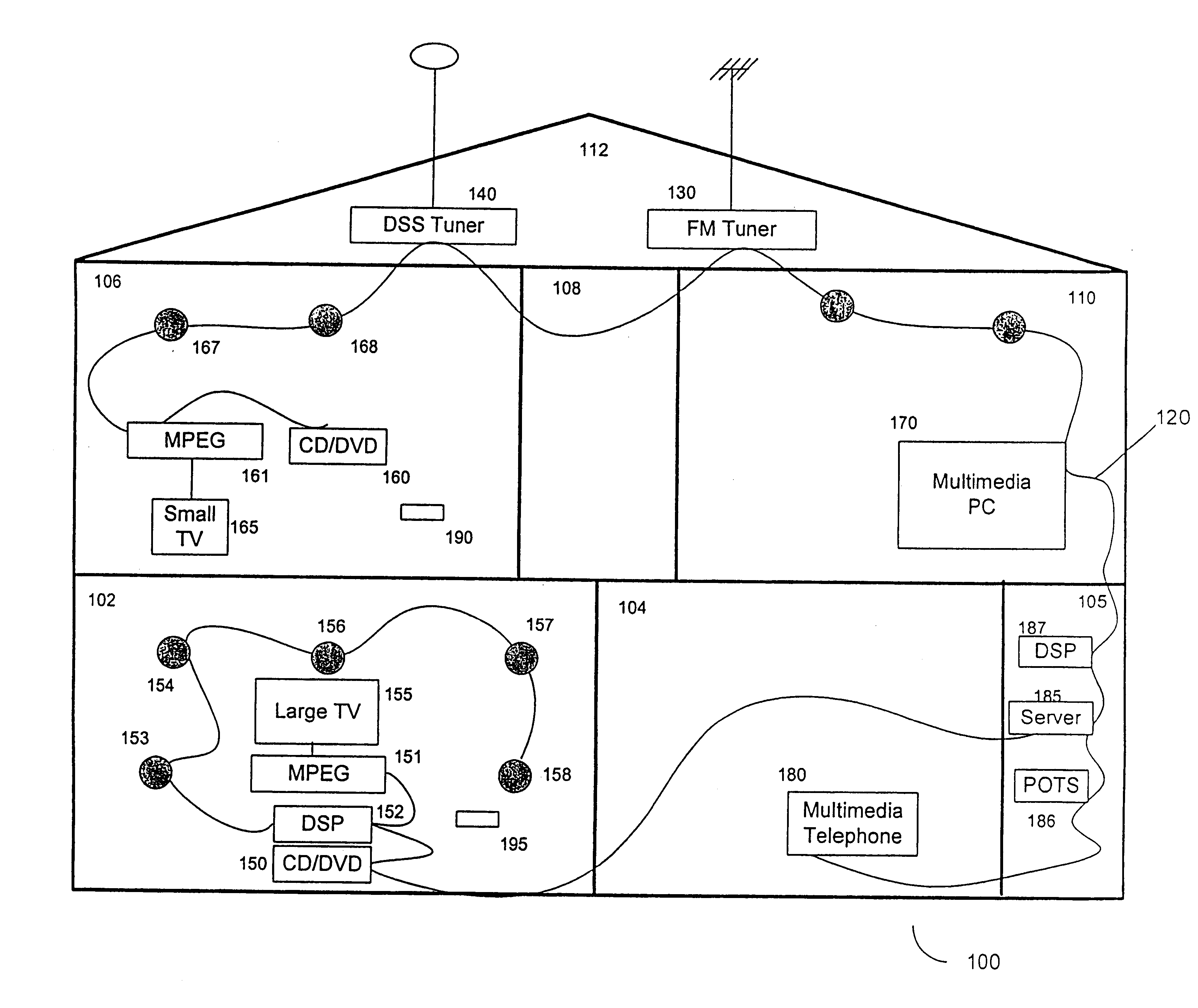
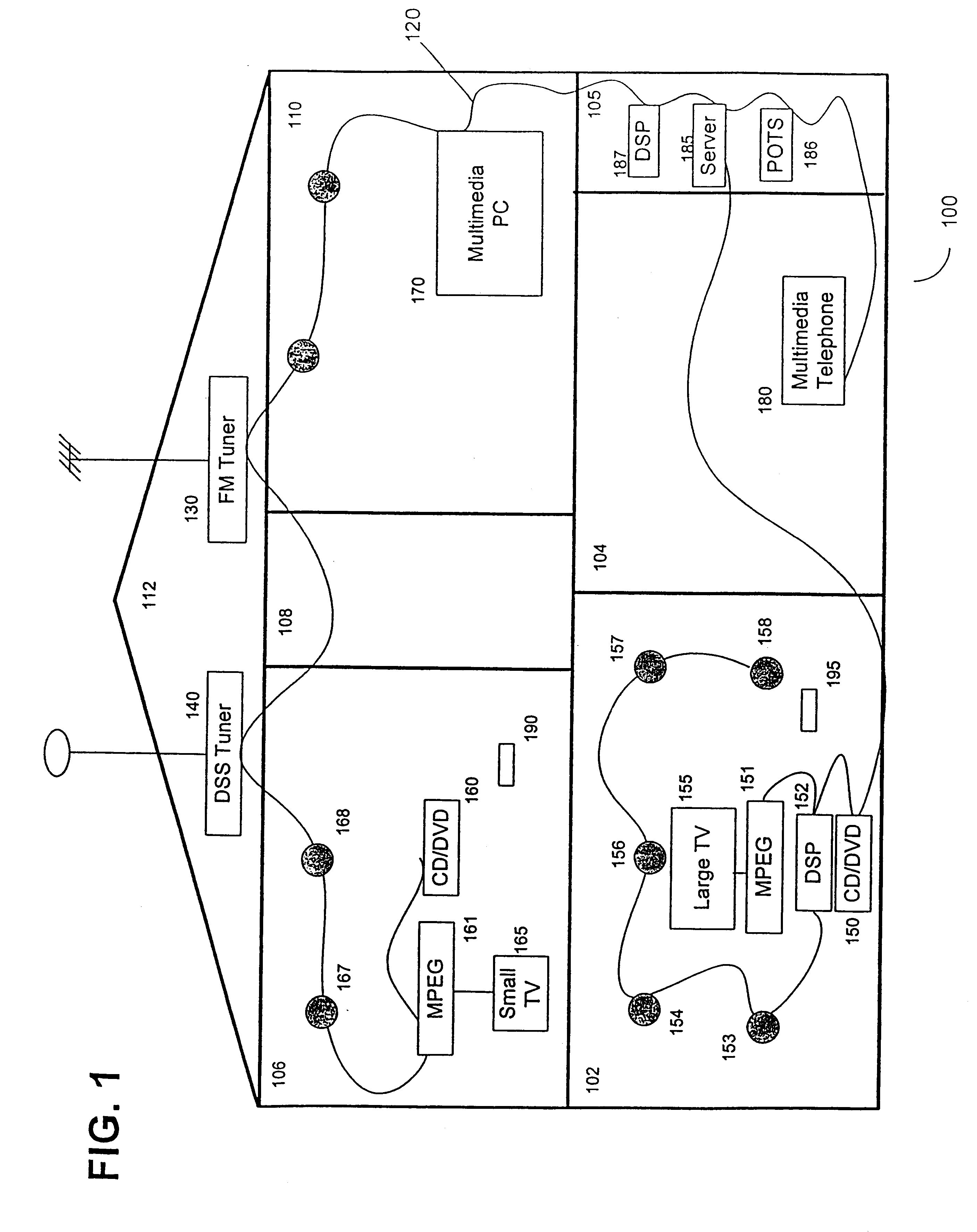
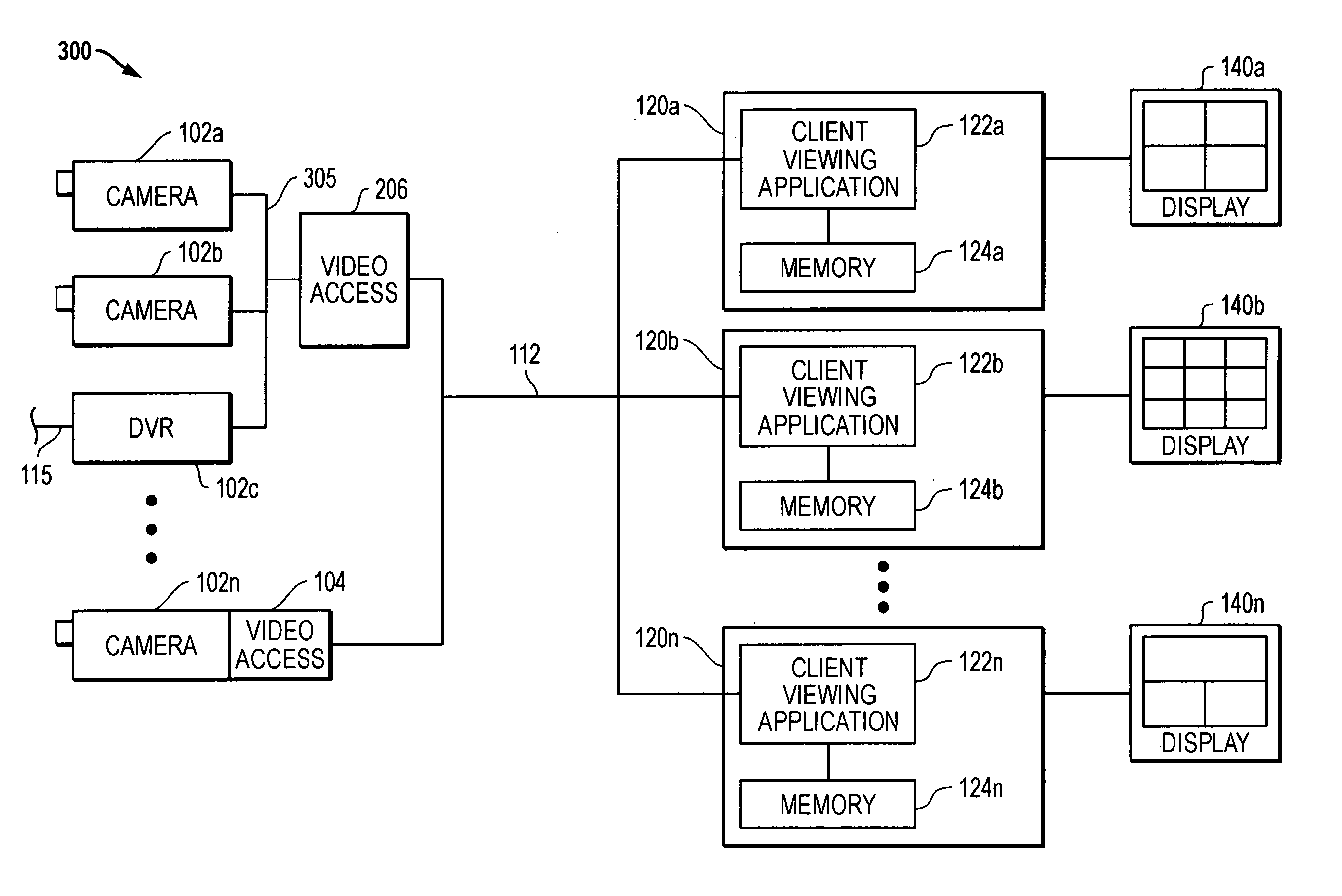
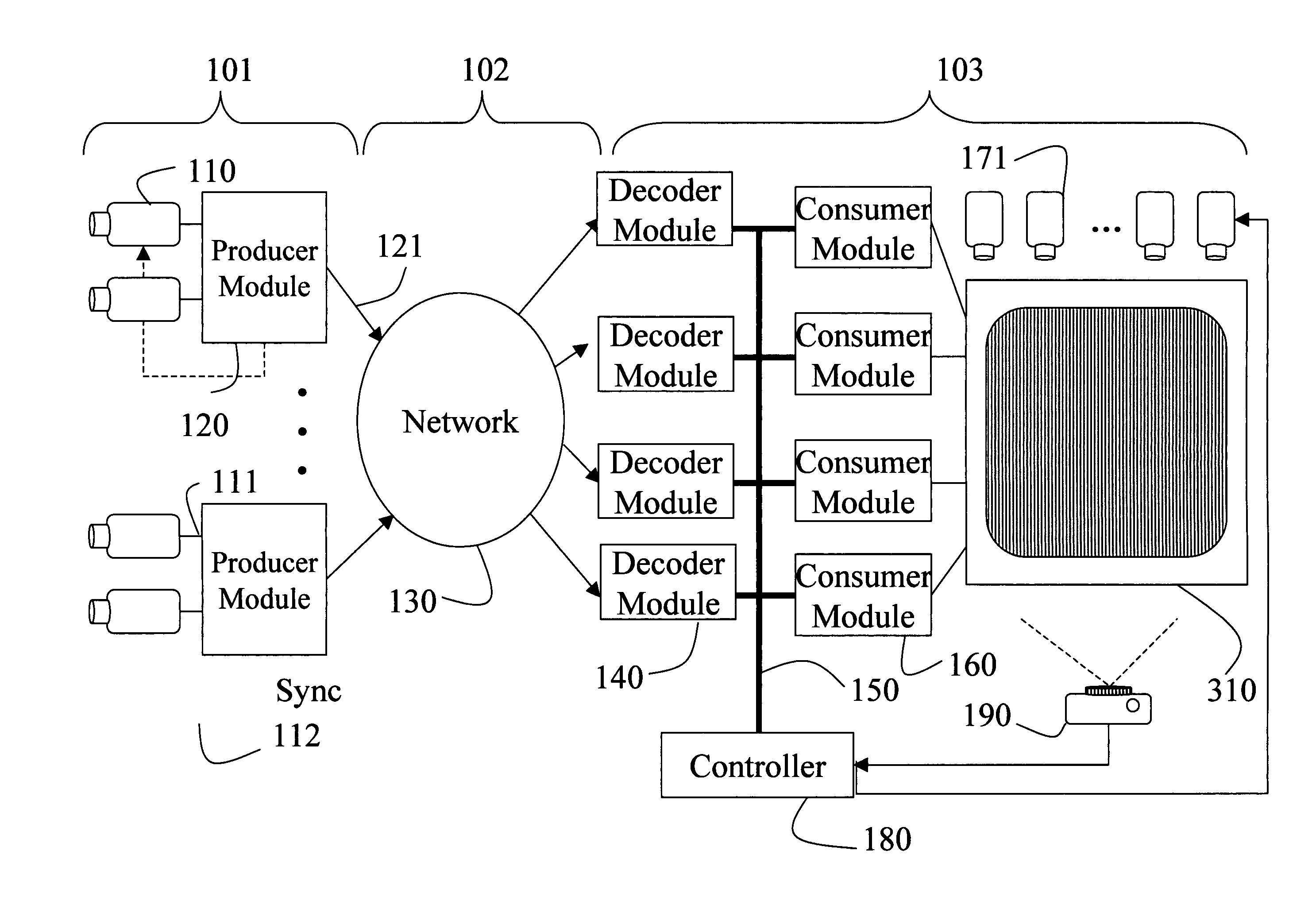
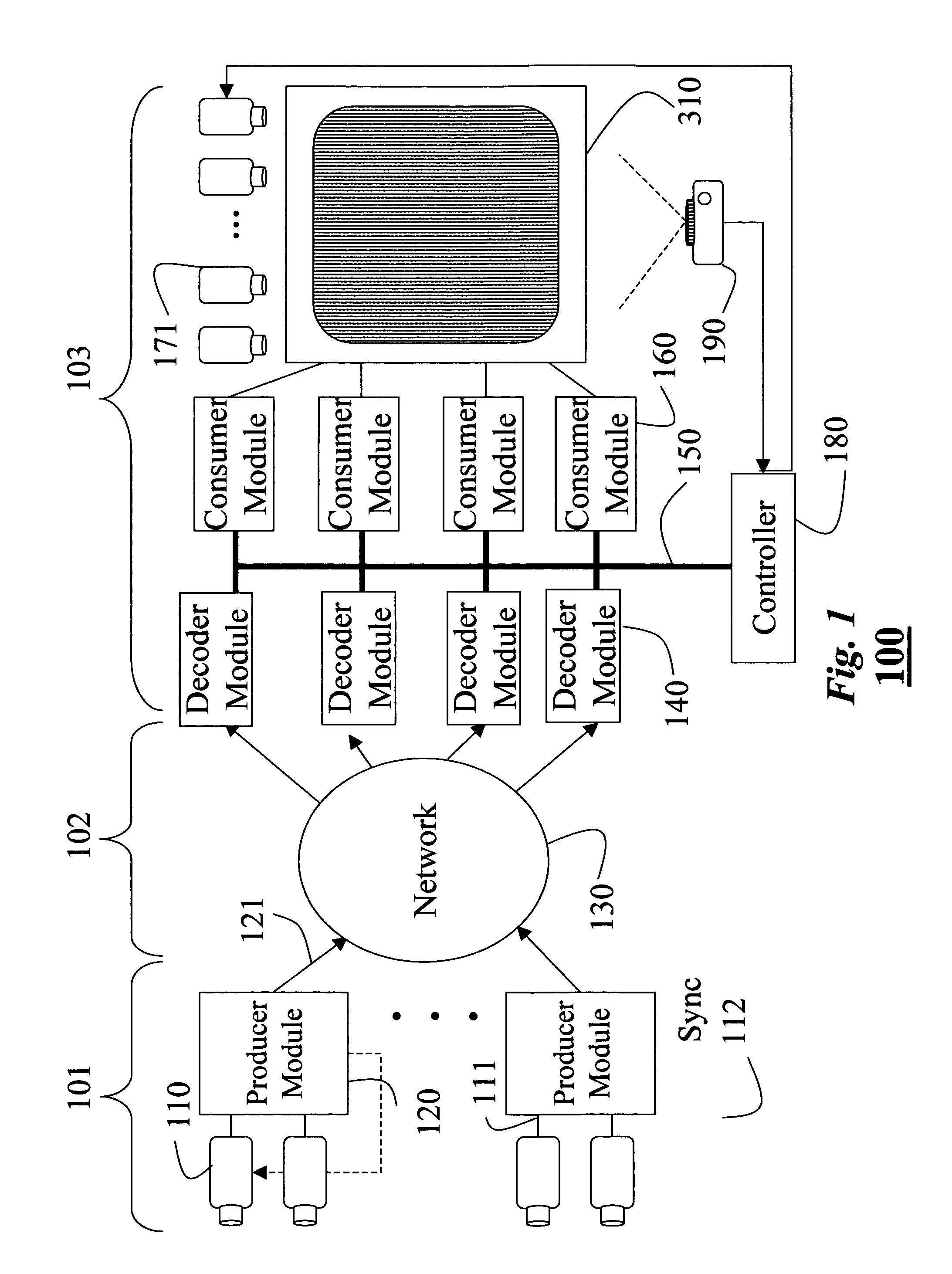
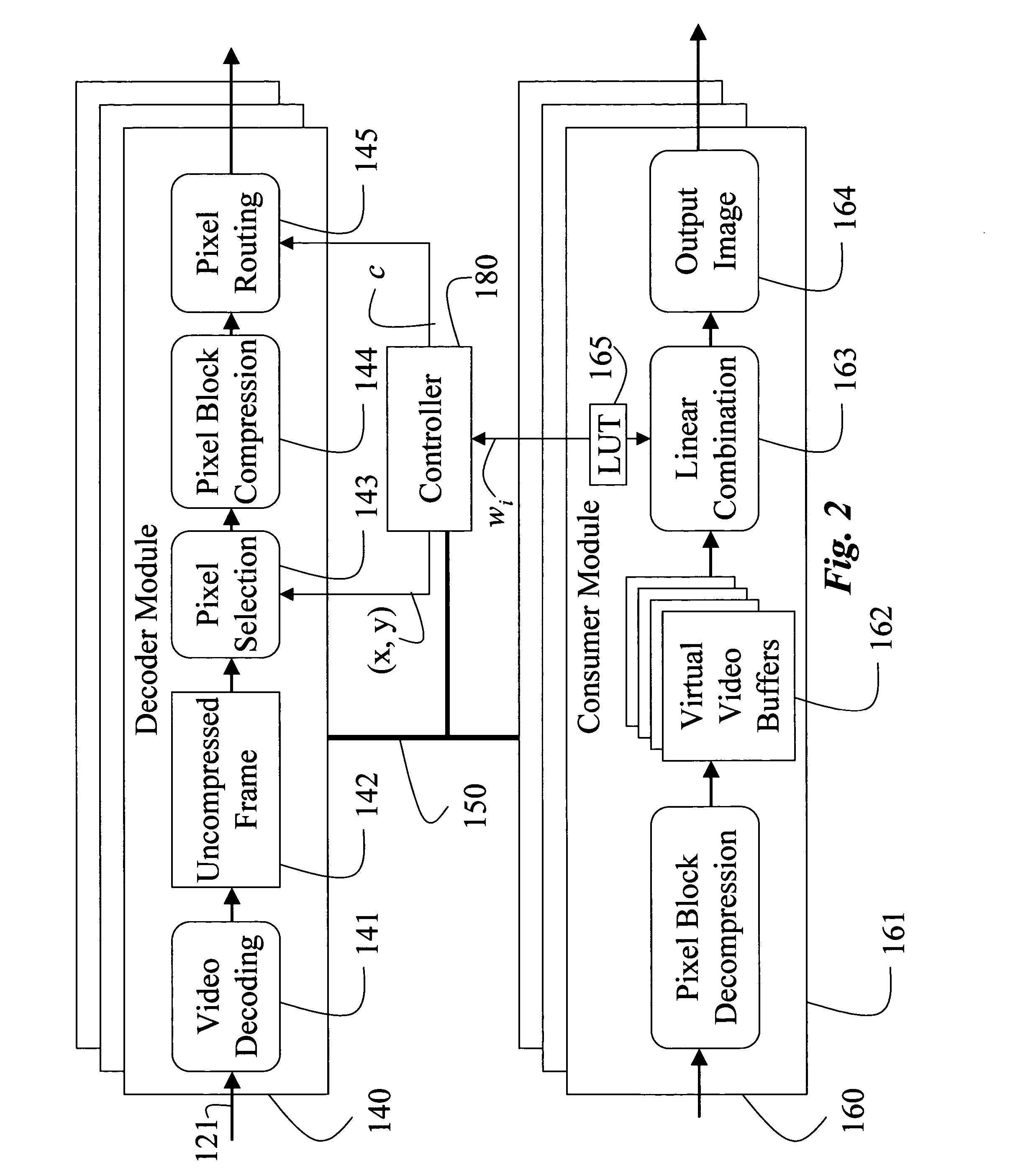
Synchronous network for digital media streams
InactiveUS6611537B1Avoid collisionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexData streamNetwork clock
A network adapter for a synchronous logical ring network operates on existing physical twisted-pair telephone topologies. Information propagates around the logical ring, reaching every device on each revolution around the network. Network devices are full-duplex, transmitting and receiving information on every clock cycle. Network devices arbitrate to be elected the network clock device. By synchronizing all network devices to a single reference clock, and providing fixed frames of information propagating around the network at consistent time intervals, the logical ring network ensures that information propagates from one device to another at consistent time intervals. The fixed-length frames are divided into two independent streams: a data stream for the distribution of real-time continuous digital media streams; and a system command stream for the distribution of system commands.
Owner:CENTILLIUM COMM
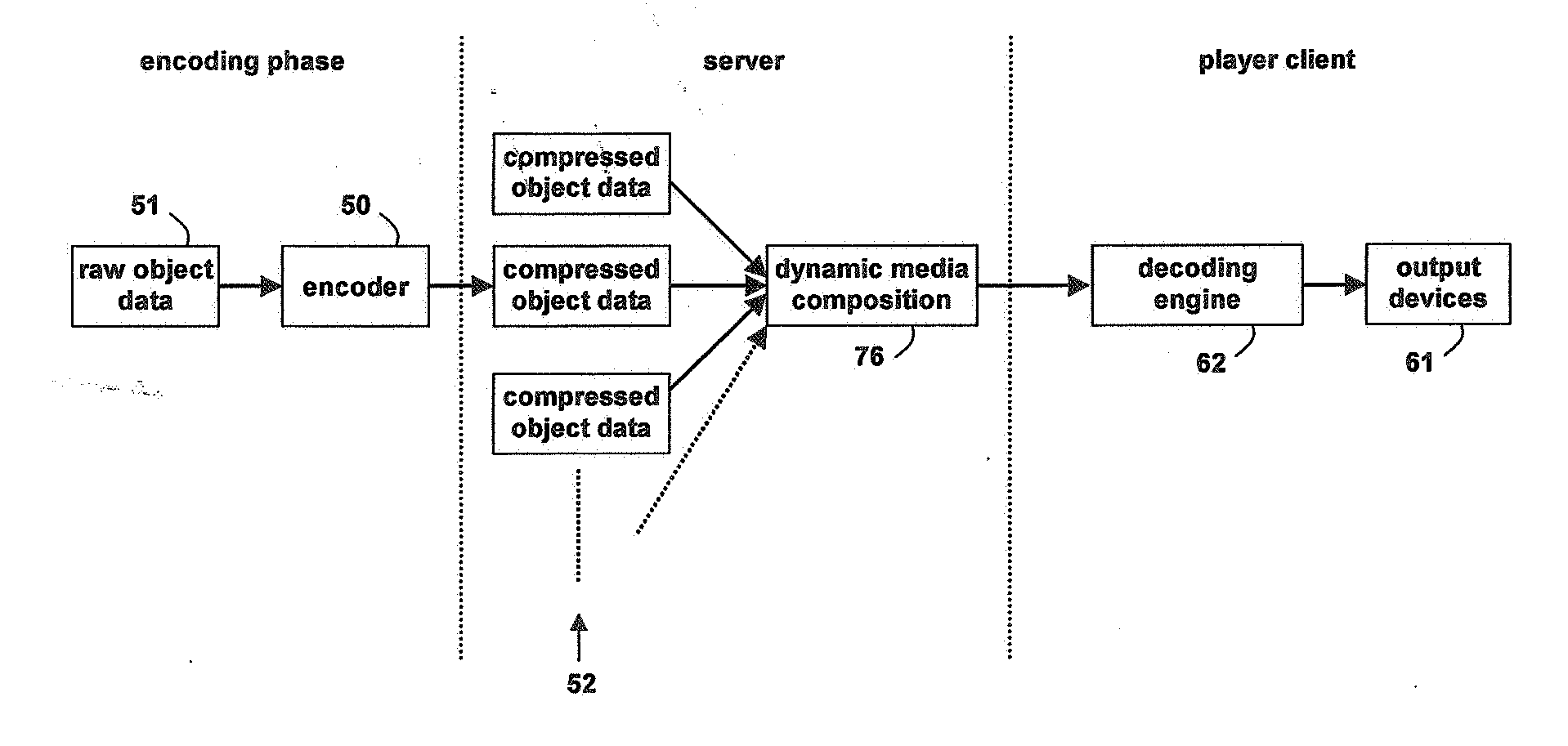
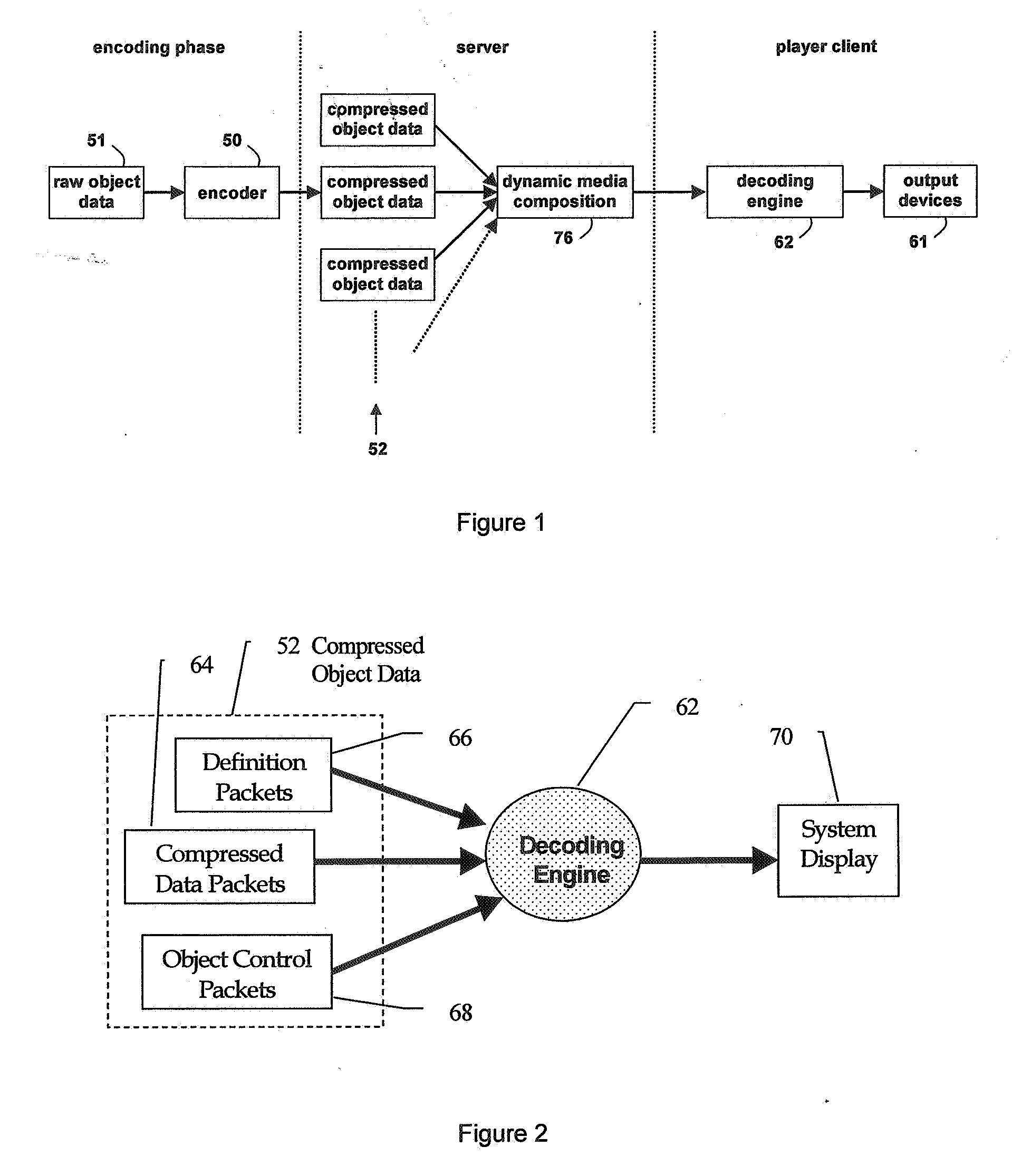
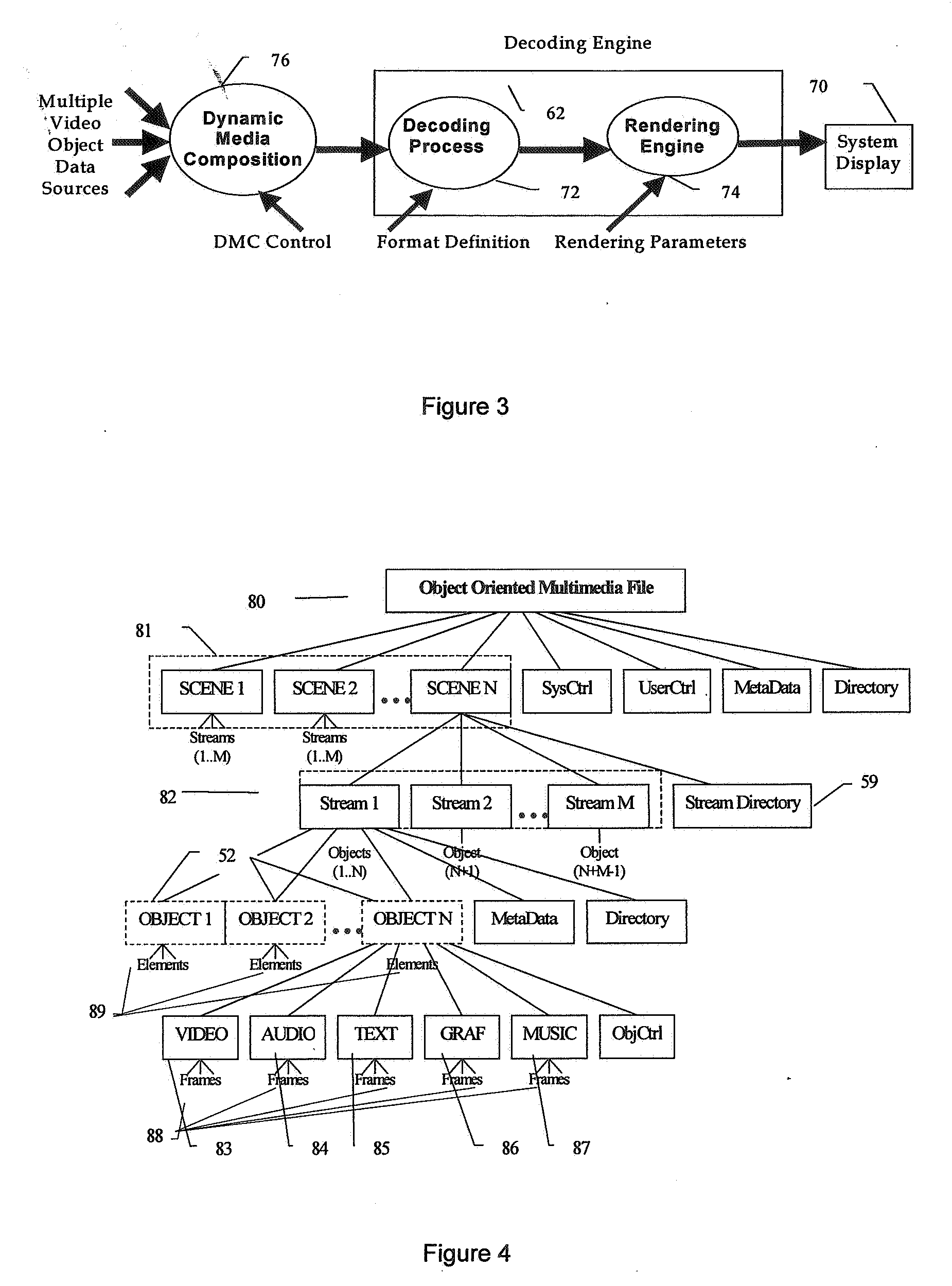
Object oriented video system
InactiveUS20070005795A1Reduce colorNo extra data overhead and processing overheadTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionGraphicsData stream
A method of generating an object oriented interactive multimedia file, including encoding data comprising at least one of video, text, audio, music and / or graphics elements as a video packet stream, text packet stream, audio packet stream, music packet stream and / or graphics packet stream respectively, combining the packet streams into a single self-contained object, said object containing its own control information, placing a plurality of the objects in a data stream, and grouping one or more of the data streams in a single contiguous self-contained scene, the scene including format definition as the initial packet in a sequence of packets. An encoder for executing the method is provided together with a player or decoder for parsing and decoding the file, which can be wirelessly streamed to a portable computer device, such as a mobile phone or a PDA. The object controls provide rendering and interactive controls for objects allowing users to control dynamic media composition, such as dictating the shape and content of interleaved video objects, and control the objects received.
Owner:ACTIVESKY
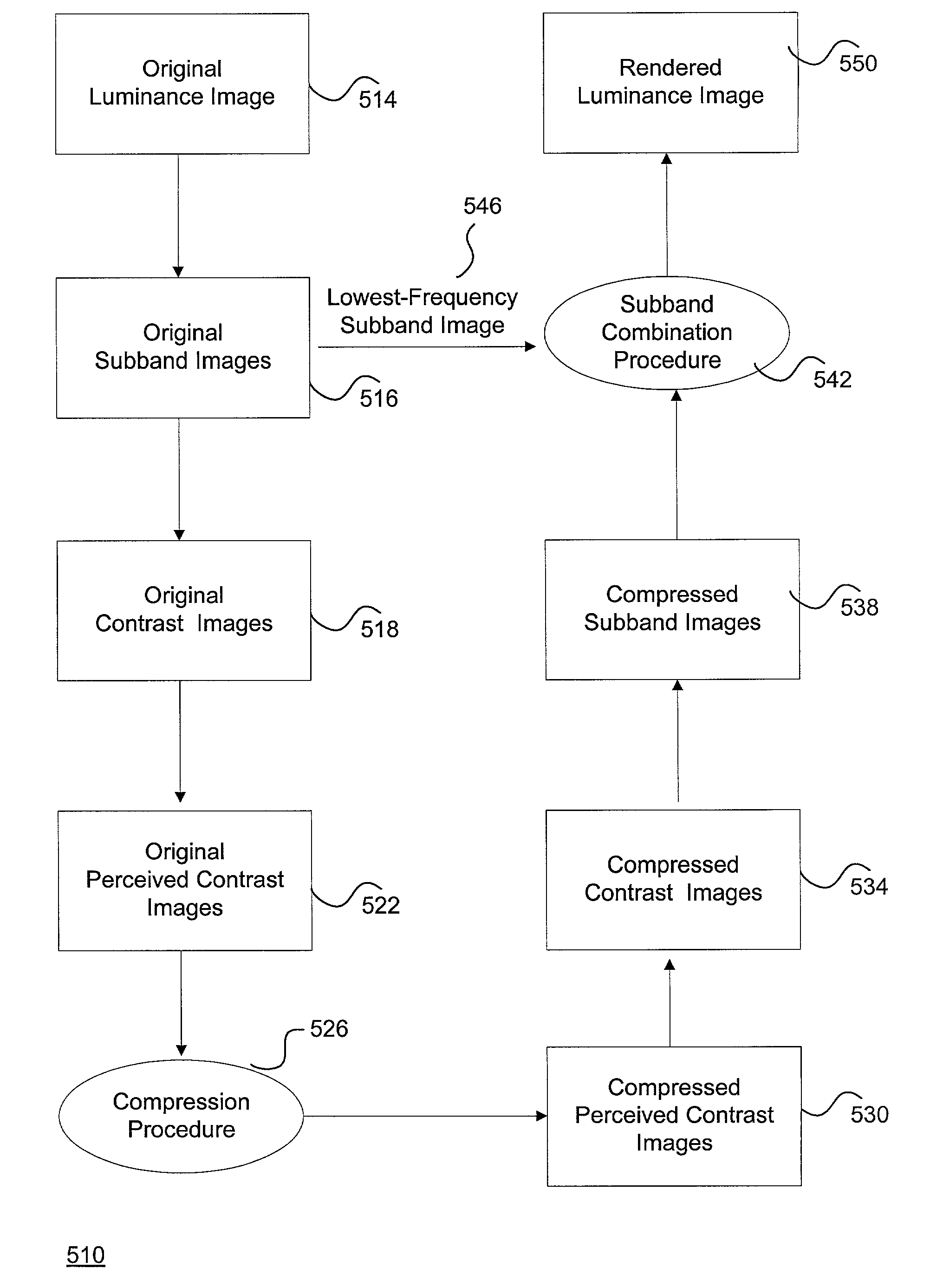
System and method for effectively rendering high dynamic range images
InactiveUS6993200B2High imagingEffectively renderingImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Image conversion
A system and method for rendering high dynamic range images includes a rendering manager that divides an original luminance image into a plurality of original subband images. The rendering manager converts the original subband images into original contrast images which are converted into original perceived contrast images. The rendering manager performs a compression procedure upon the original perceived contrast images to produce compressed perceived contrast images. The rendering manager converts the compressed perceived contrast images into compressed contrast images which are converted into compressed subband images. The rendering manager performs a subband combination procedure for combining the compressed subband images together with a lowest-frequency subband image to generate a rendered luminance image. The rendering manager may combines the rendered luminance image with corresponding chrominance information to generate a rendered composite image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Image processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS6496598B1Improve the three-dimensional effectImproving stereoscopic image pairImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage transfer
An image conversion system for converting monoscopic images for viewing in three dimensions including: an input means adapted to receive the monoscopic images; a preliminary analysis means to determine if there is any continuity between a first image and a second image of the monoscopic image sequence; a secondary analysis means for receiving monoscopic images which have a continuity, and analyzing the images to determine the speed and direction of motion, and the depth, size and position of objects; a first processing means for processing the monoscopic images based on data received from the preliminary analysis means or the secondary analysis means; a second processing means capable of further processing images received from the first processing means; a transmission means capable of transferring the processed images to a stereoscopic display system.
Owner:DYNAMIC DIGITAL DEPTH RES
Color adaptive watermarking
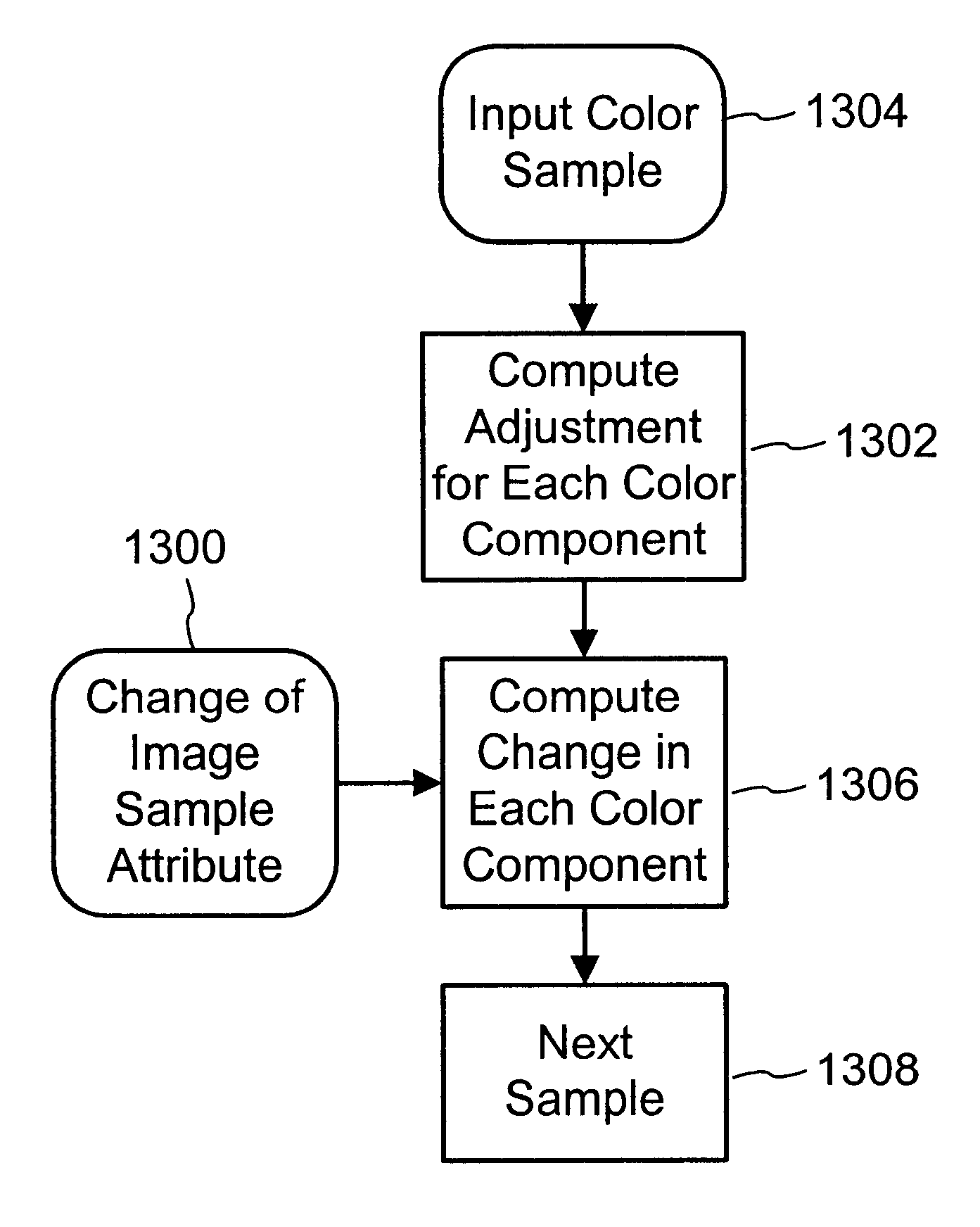
InactiveUS6590996B1Effectively create and manipulateReduce the amount requiredPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningColor mappingComputer graphics (images)
A color mapping process enhances a watermark by computing a change in colors that is less visible for a given watermark strength. The mapping process provides smooth transitions from one color region to another, and may be implemented efficiently with a 3D look up table. A user interface scheme enables the user to control encoding of the watermark in desired color regions.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
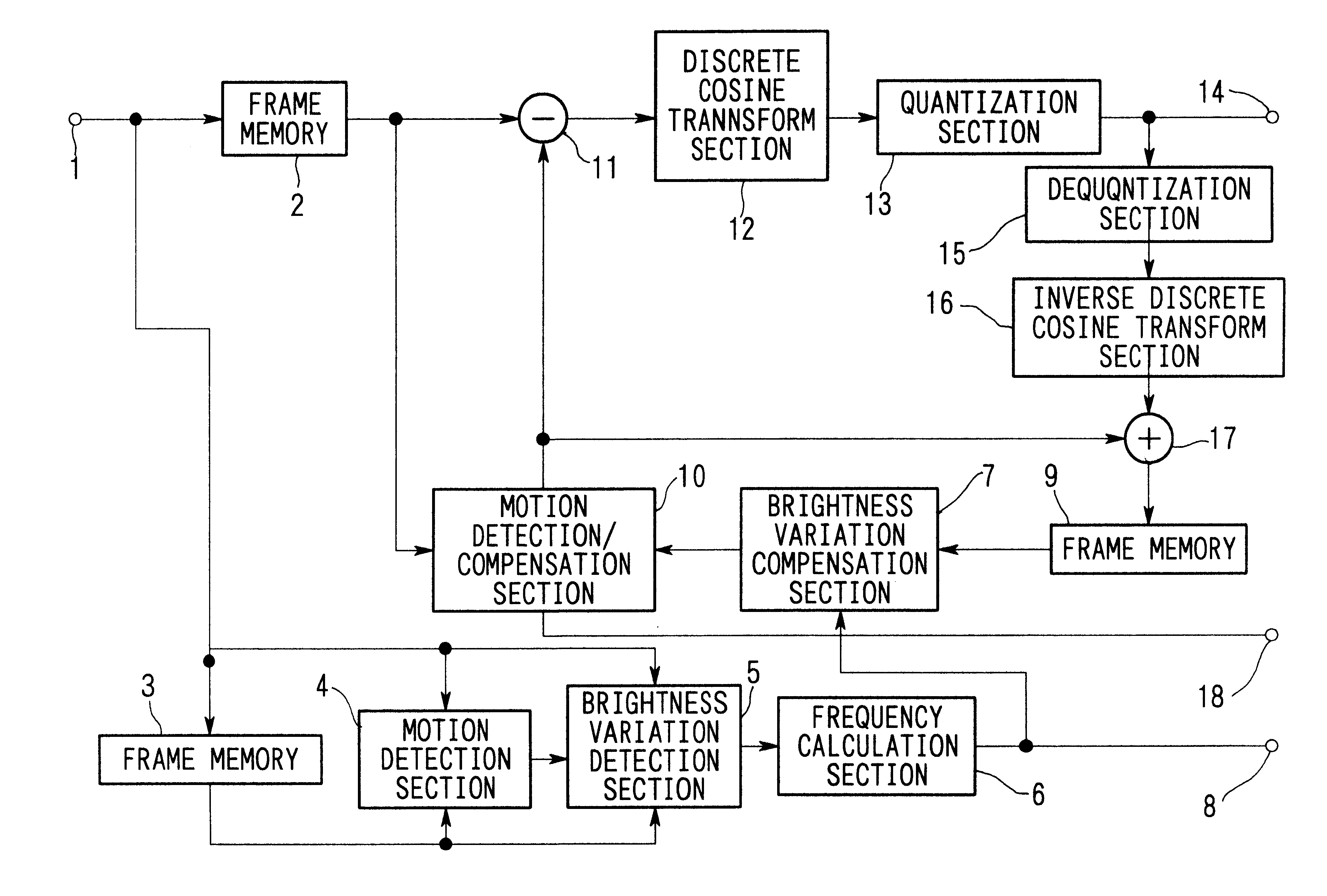
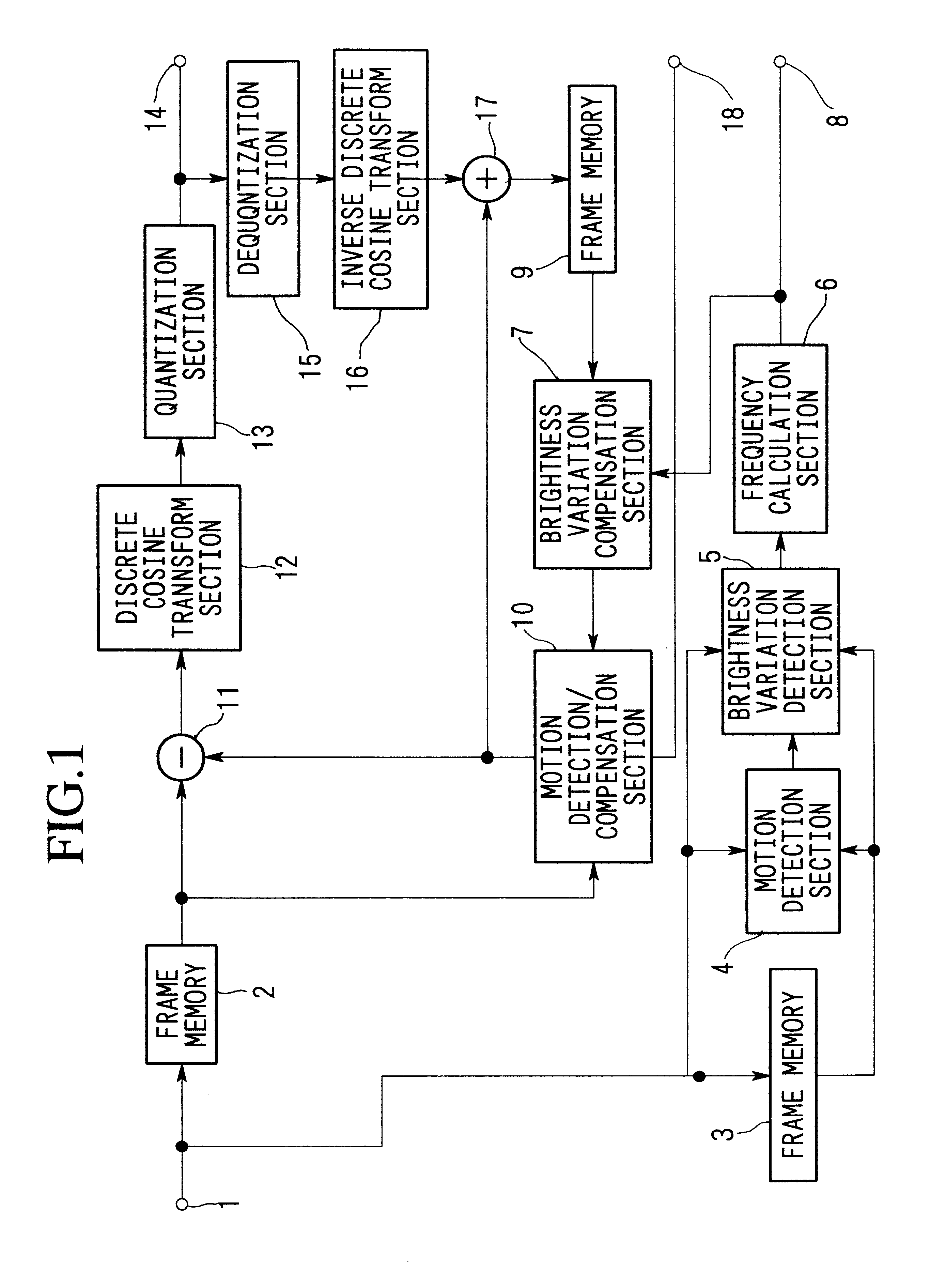
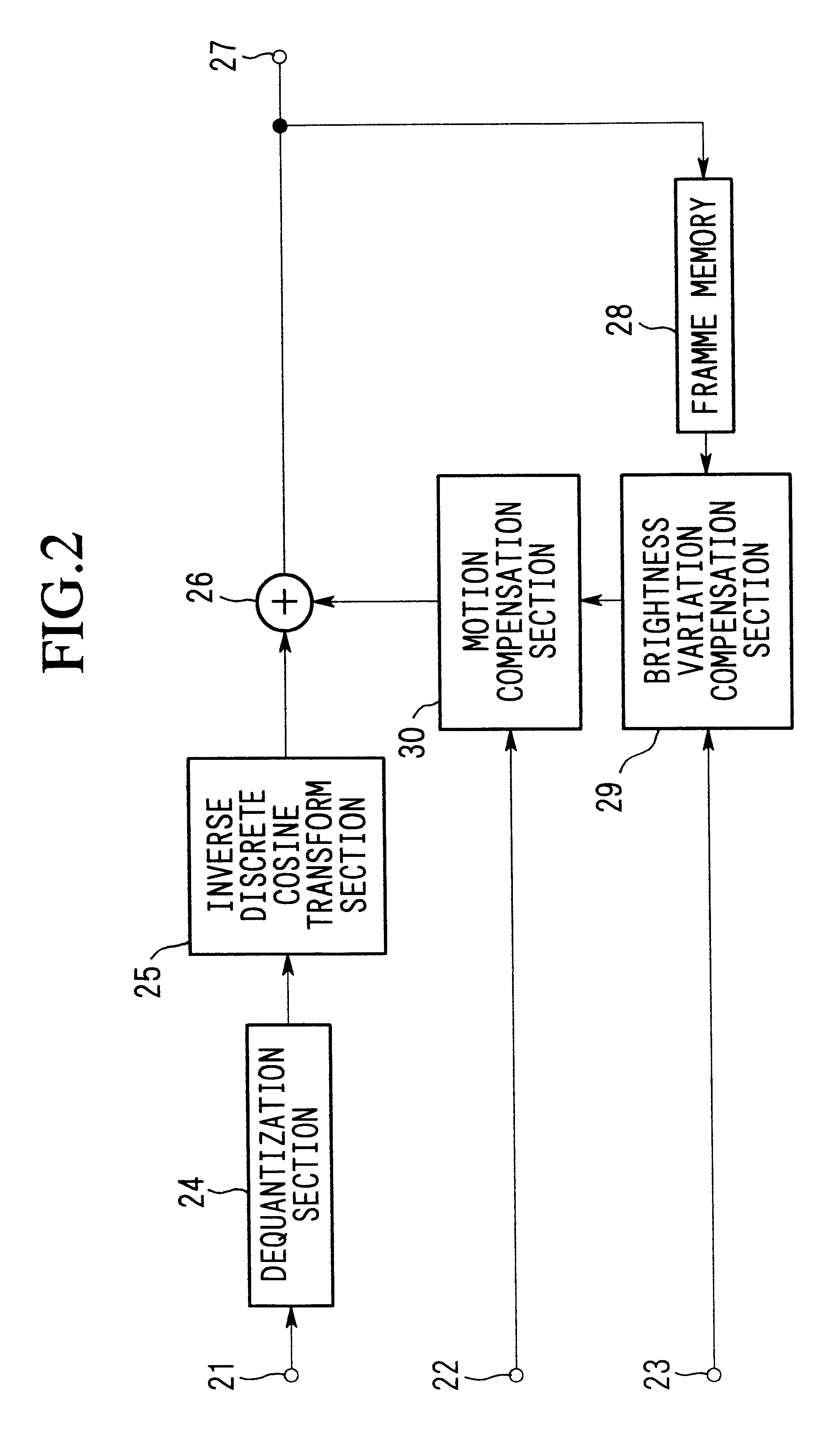
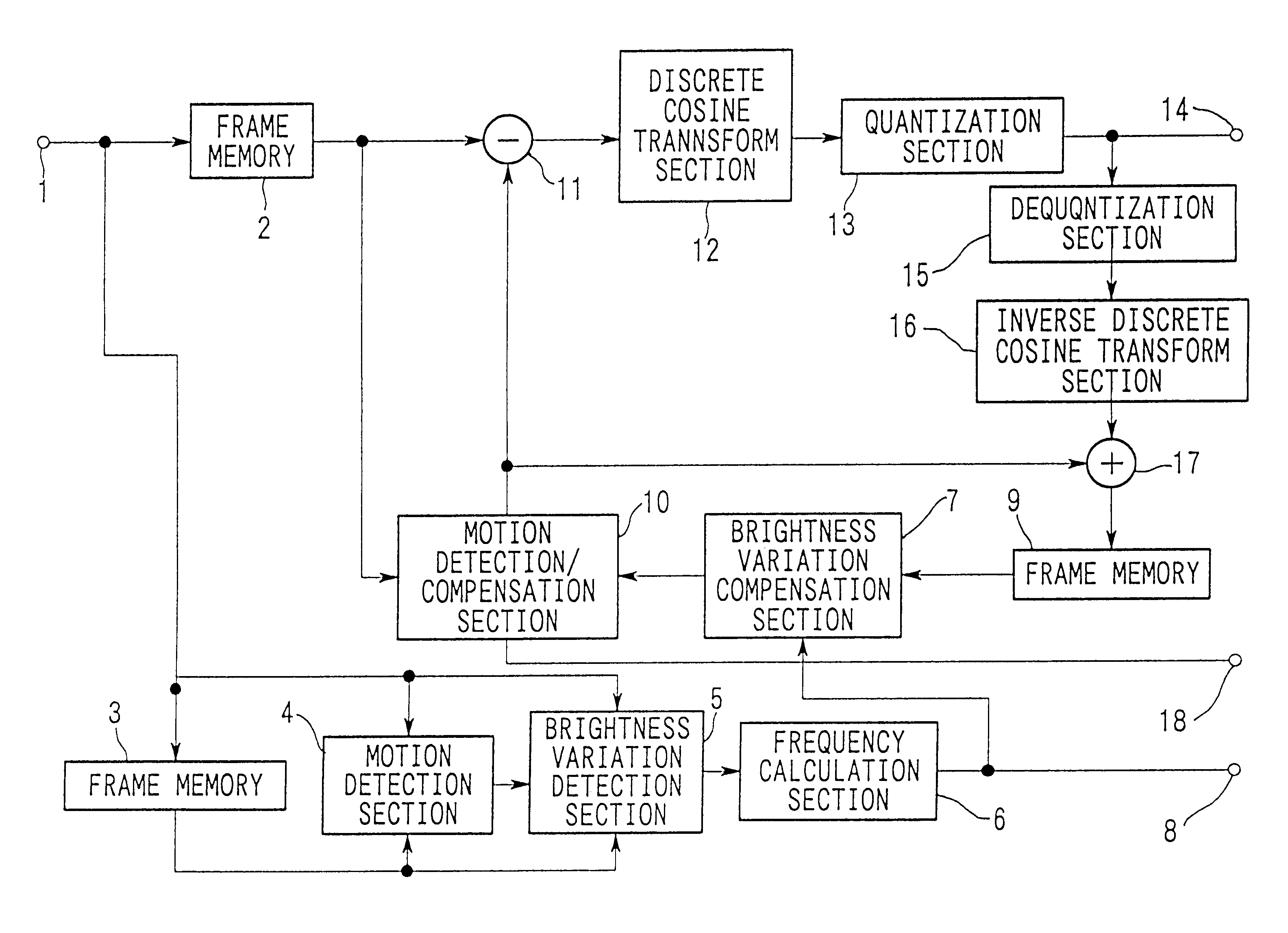
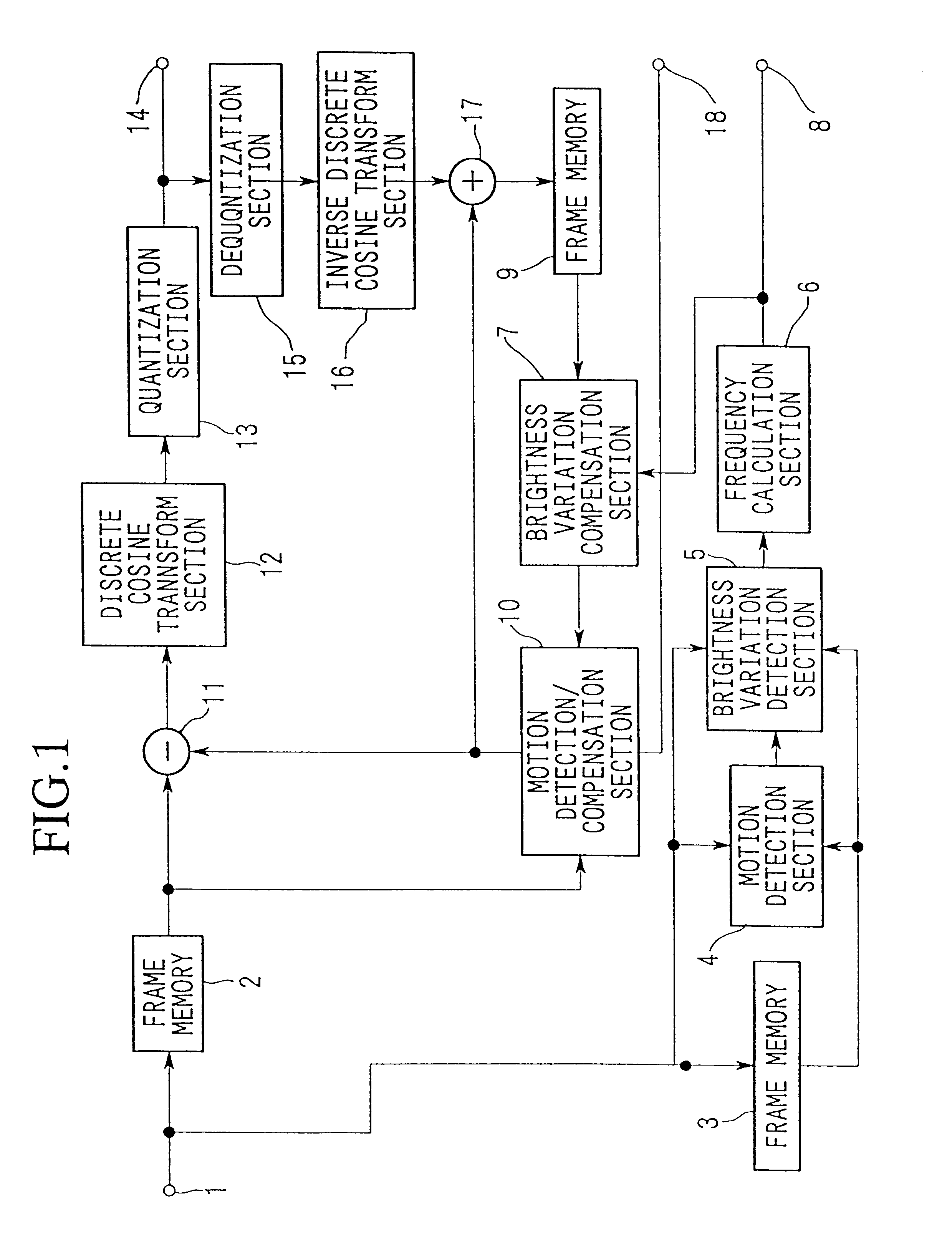
Brightness-variation compensation method and coding/decoding apparatus for moving pictures
InactiveUS6266370B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingReference image
A moving image brightness variation compensation method for encoding digital moving images for transmission and storage, and for image processing when editing moving images, the moving image brightness variation compensation method comprising a step of compensating for overall brightness variations by correcting a luminance value x of each pixel according to the formula DC.x+DB, wherein DB is a parameter indicating a gain change and DC is a parameter indicating a contrast change, the parameters representing overall luminance changes between a reference image plane and an image plane being processed.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
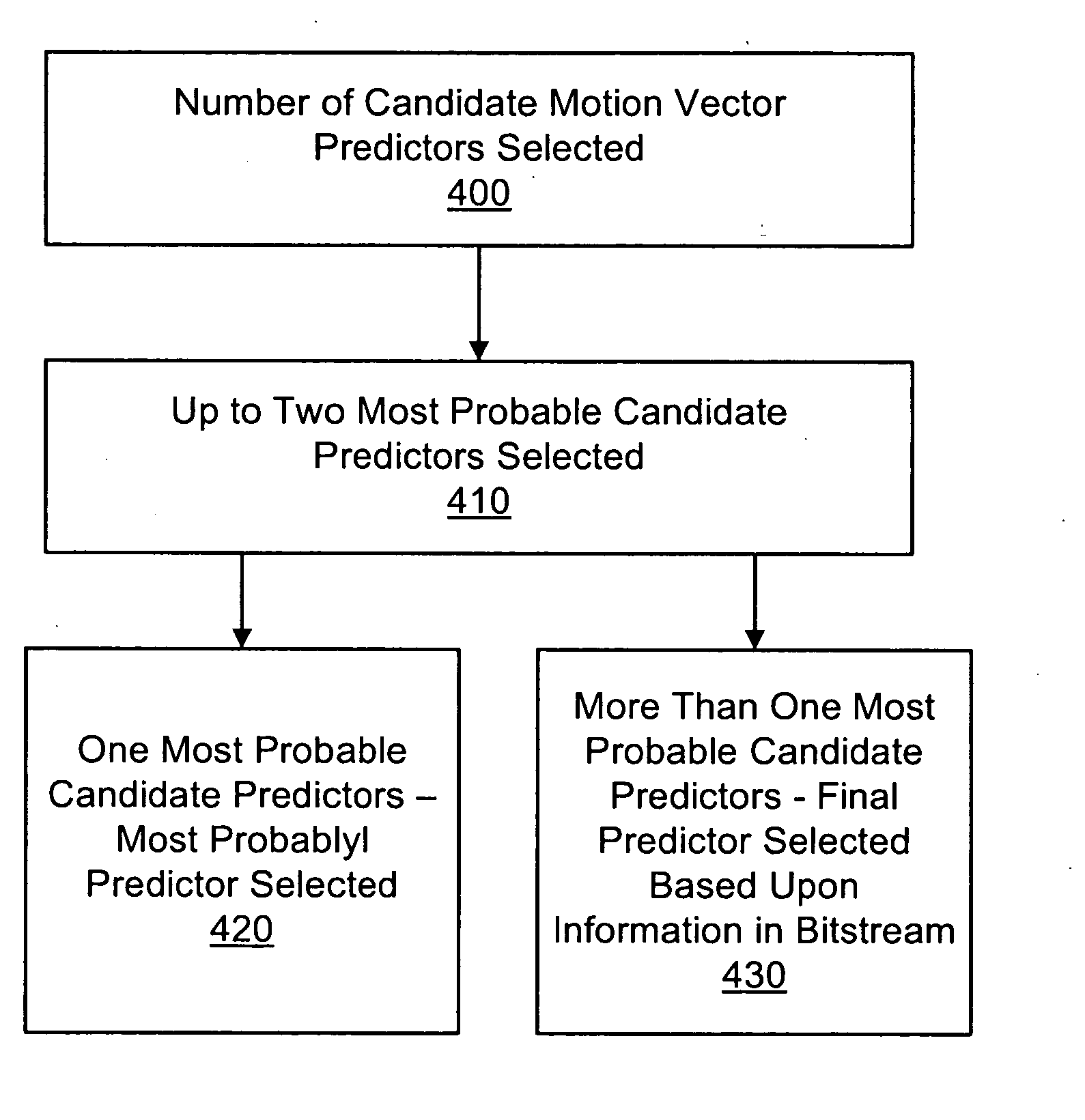
Combined motion vector and reference index prediction for video coding
ActiveUS20090304084A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove compression efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo encoding
A system and method for improving the coding efficiency of motion vector information in video coding. According to various embodiments, a list of motion vector predictor candidates is arranged according to predefined rules. Each motion vector also has a reference index associated with it. One of the motion vector candidates is then selected as a predictor based on predefined rules, or the selection is explicitly signaled in the bitstream. The reference index associated with the selected motion vector is used as a reference index for the current block. The reference index is predicted along with the motion vector. Such embodiments can improve the compression efficiency of modern video codecs.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
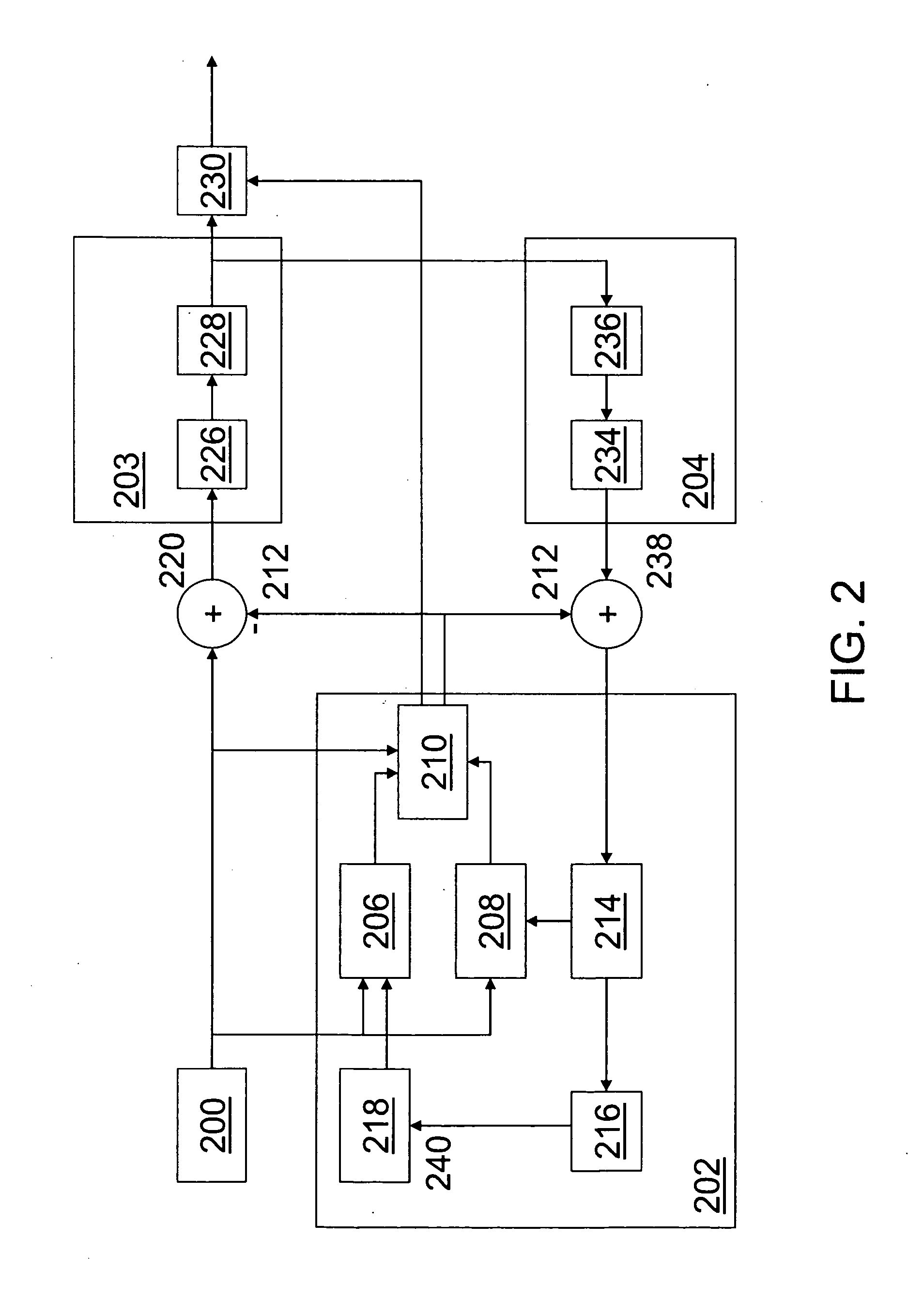
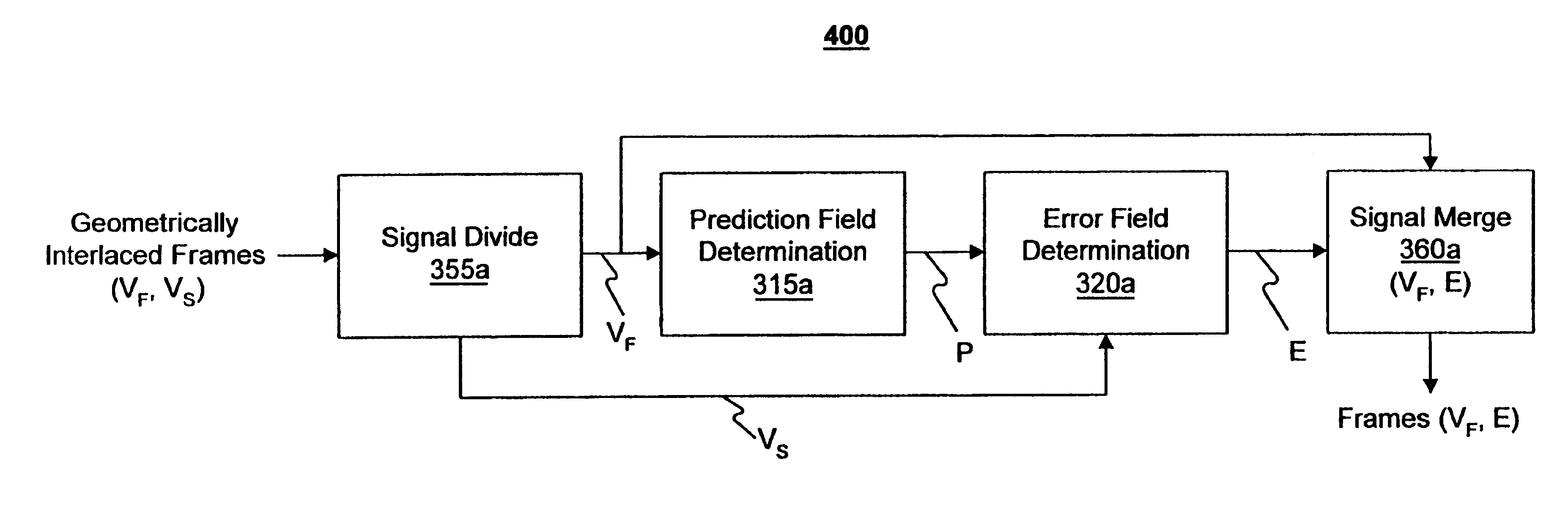
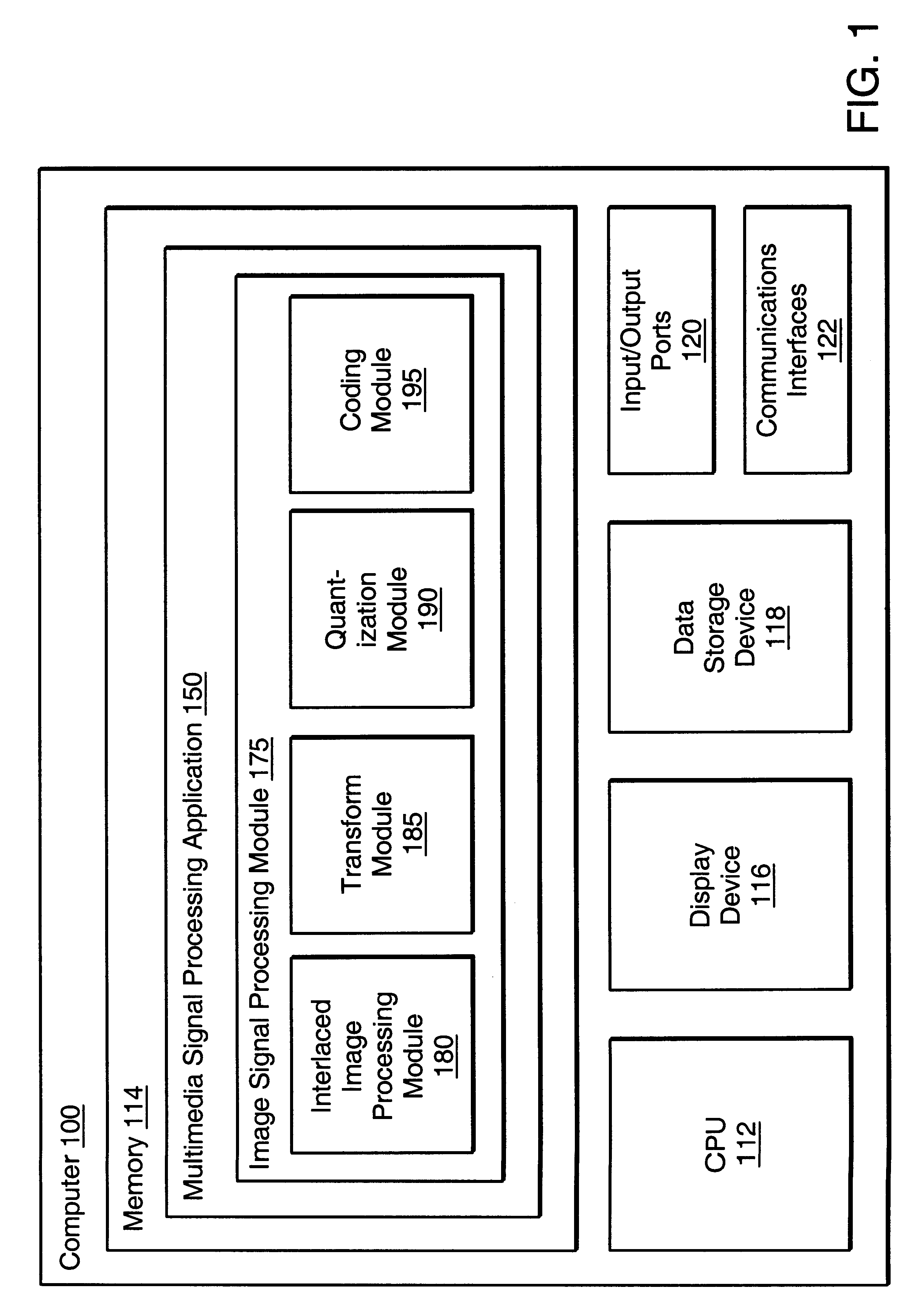
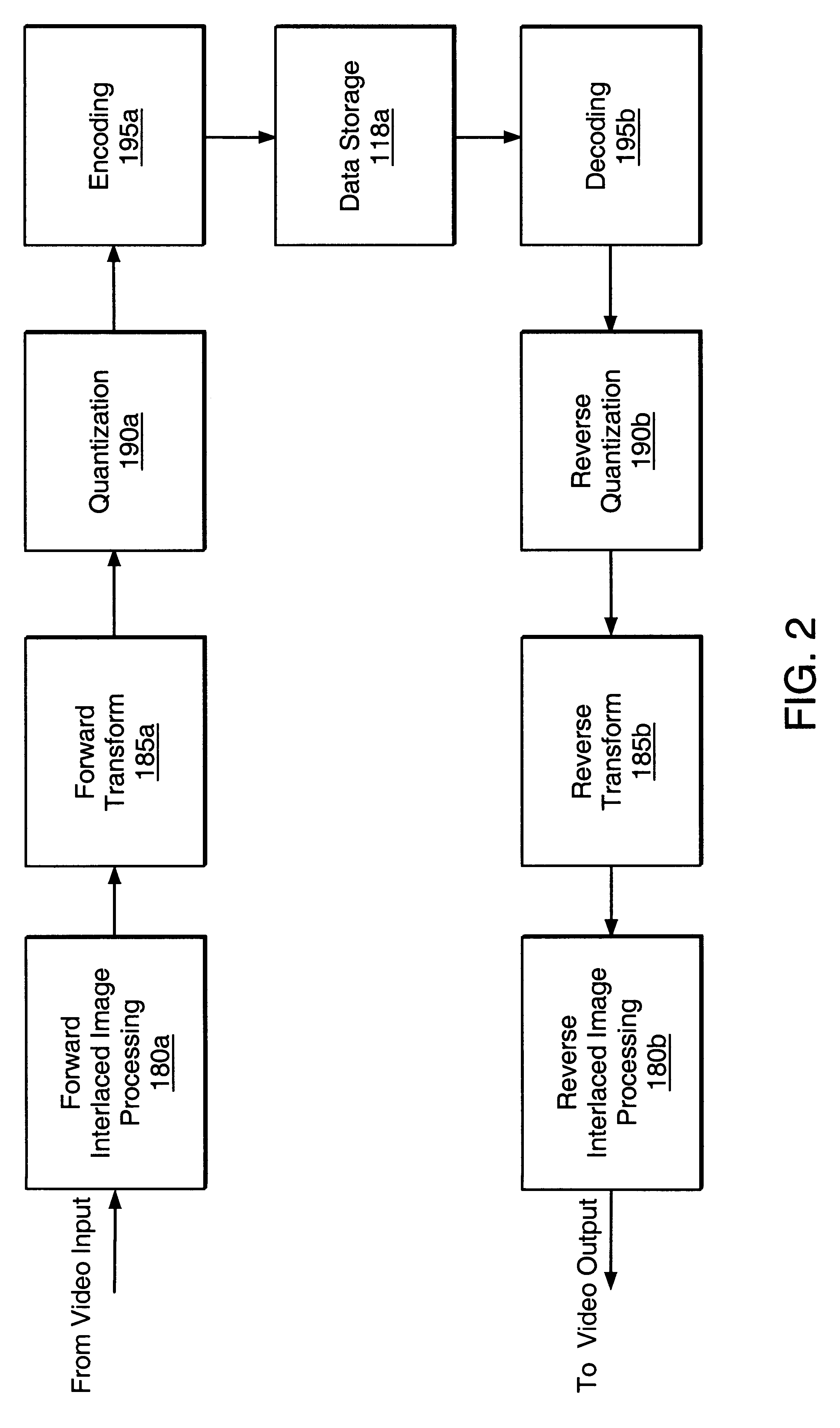
Apparatus and method for optimized compression of interlaced motion images
InactiveUS6289132B1Easy to compressAvoid inefficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImaging processingInterlaced video
Owner:QUVIS +1
Brightness-variation compensation method and coding/decoding apparatus for moving pictures
InactiveUS6456658B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImaging processingReference image
A moving image brightness variation compensation method for encoding digital moving images for transmission and storage, and for image processing when editing moving images, the moving image brightness variation compensation method comprising a step of compensating for overall brightness variations by correcting a luminance value x of each pixel according to the formula DC.x+DB, wherein DB is a parameter indicating a gain change and DC is a parameter indicating a contrast change, the parameters representing overall luminance changes between a reference image plane and an image plane being processed.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
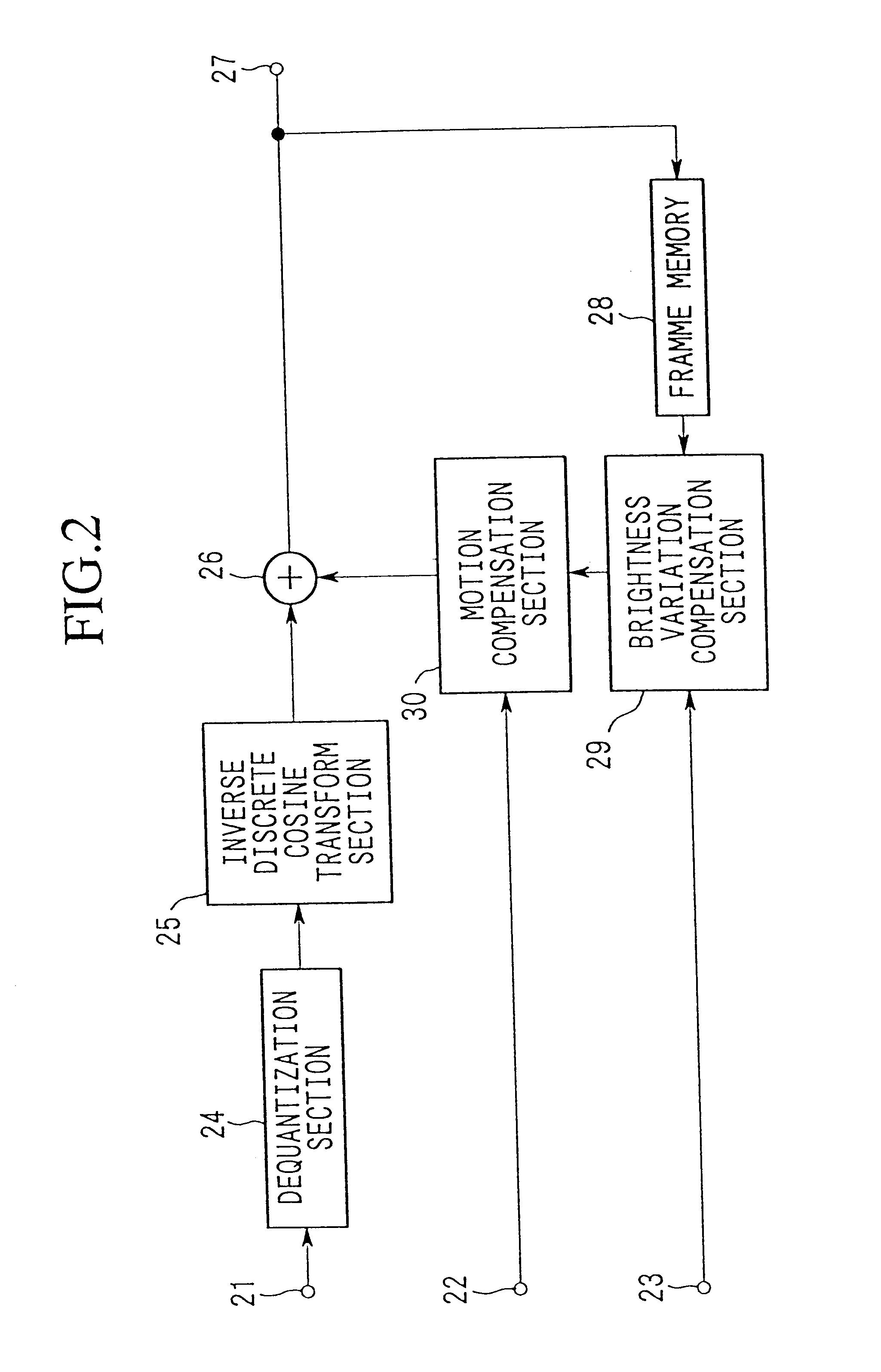
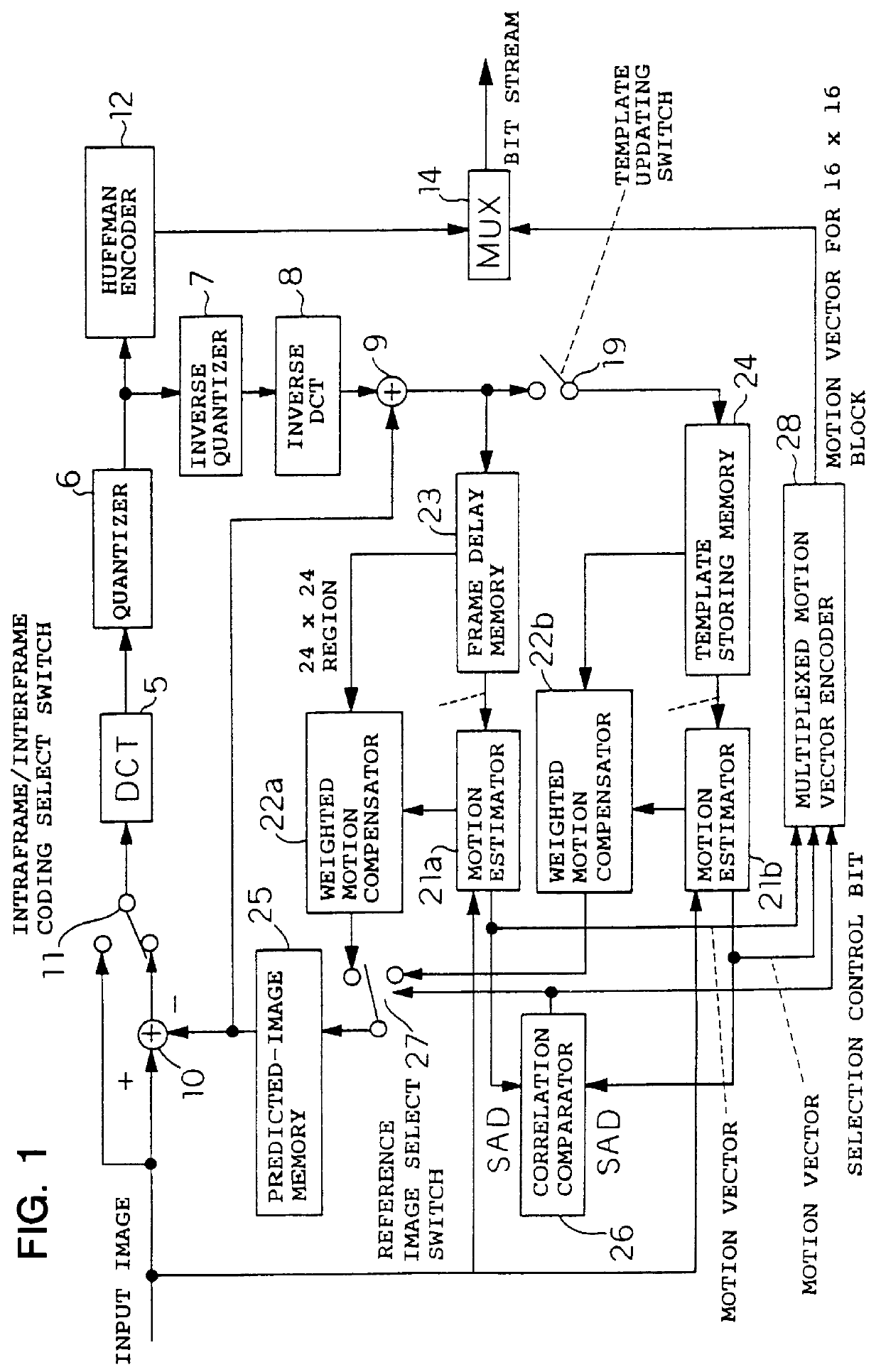
Image coding and decoding apparatus and methods thereof
InactiveUS6081551APicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionExtensibilityMotion vector
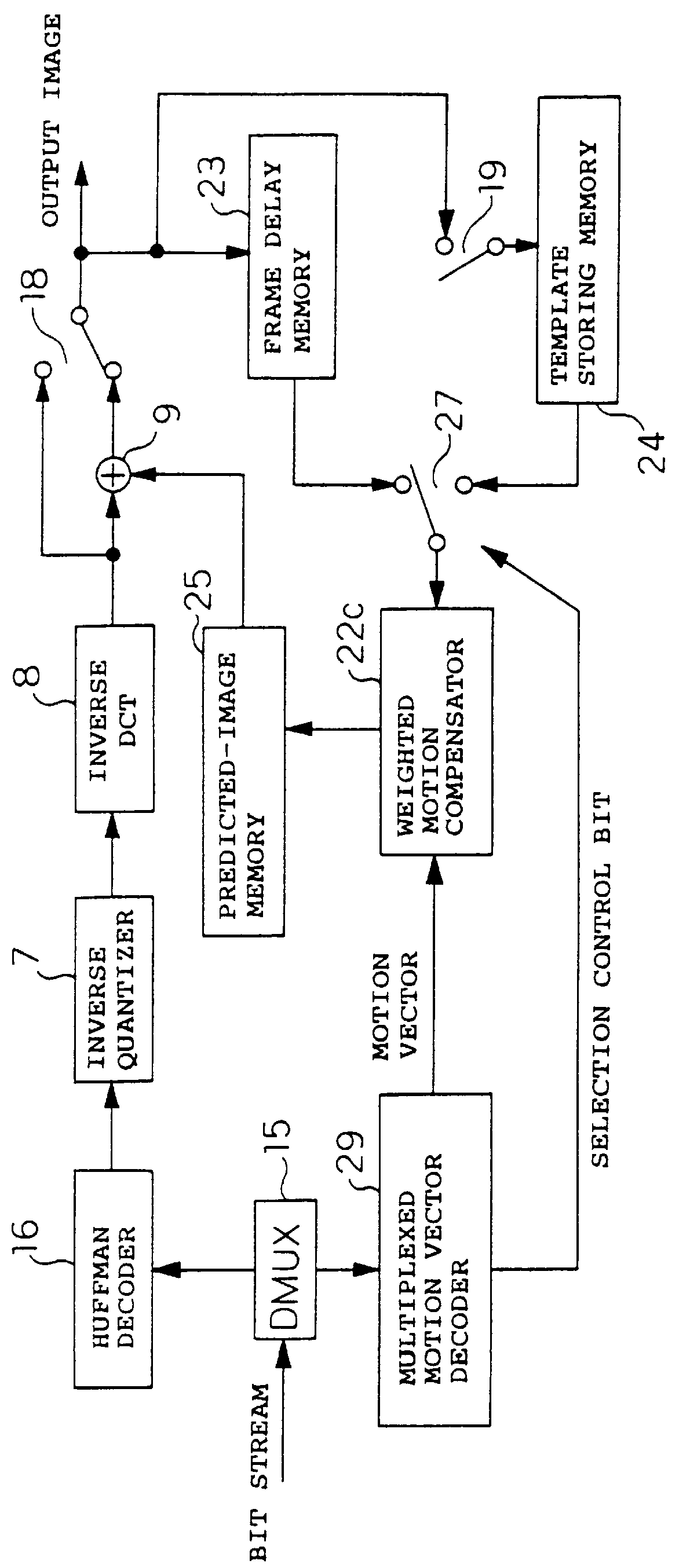
To achieve an image encoding apparatus that has extensibility by not limiting an image to be referenced, and that can reduce processing time satisfactorily if the processing of an ordinary frame is skipped, the apparatus of the present invention comprises: motion detecting means for detecting a motion vector for each block of a prescribed size from a reference image and an input image; weighted motion-compensation means for, based on the detected motion vector, extracting from the reference image an area of a prescribed size which is wider than the prescribed block size and which contains an area corresponding to each block of the input image, and for creating a predicted image for the input image by applying a predetermined weight to each of pixels in the wider area and by using the weighted pixels of the wider area; a predicted-image memory for storing the predicted image; encoding means for taking a residual between the stored predicted image and the input image, and for encoding the residual; and decoding means for decoding the encoded image data and thereby obtaining a reference image.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
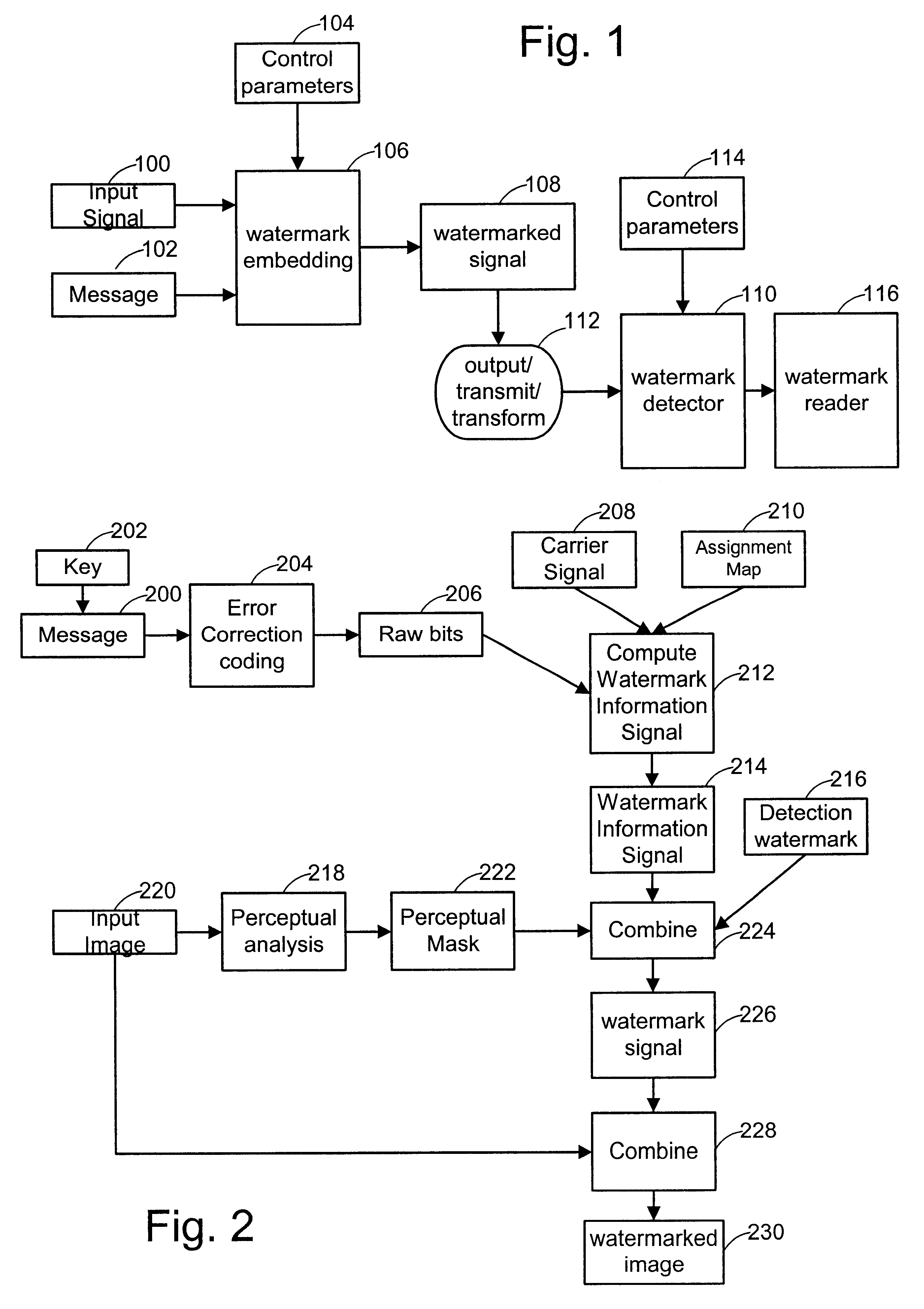
Method and apparatus for embedding data, including watermarks, in human perceptible images
InactiveUS6031914AGood autocorrelationPromote generationElectric signal transmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
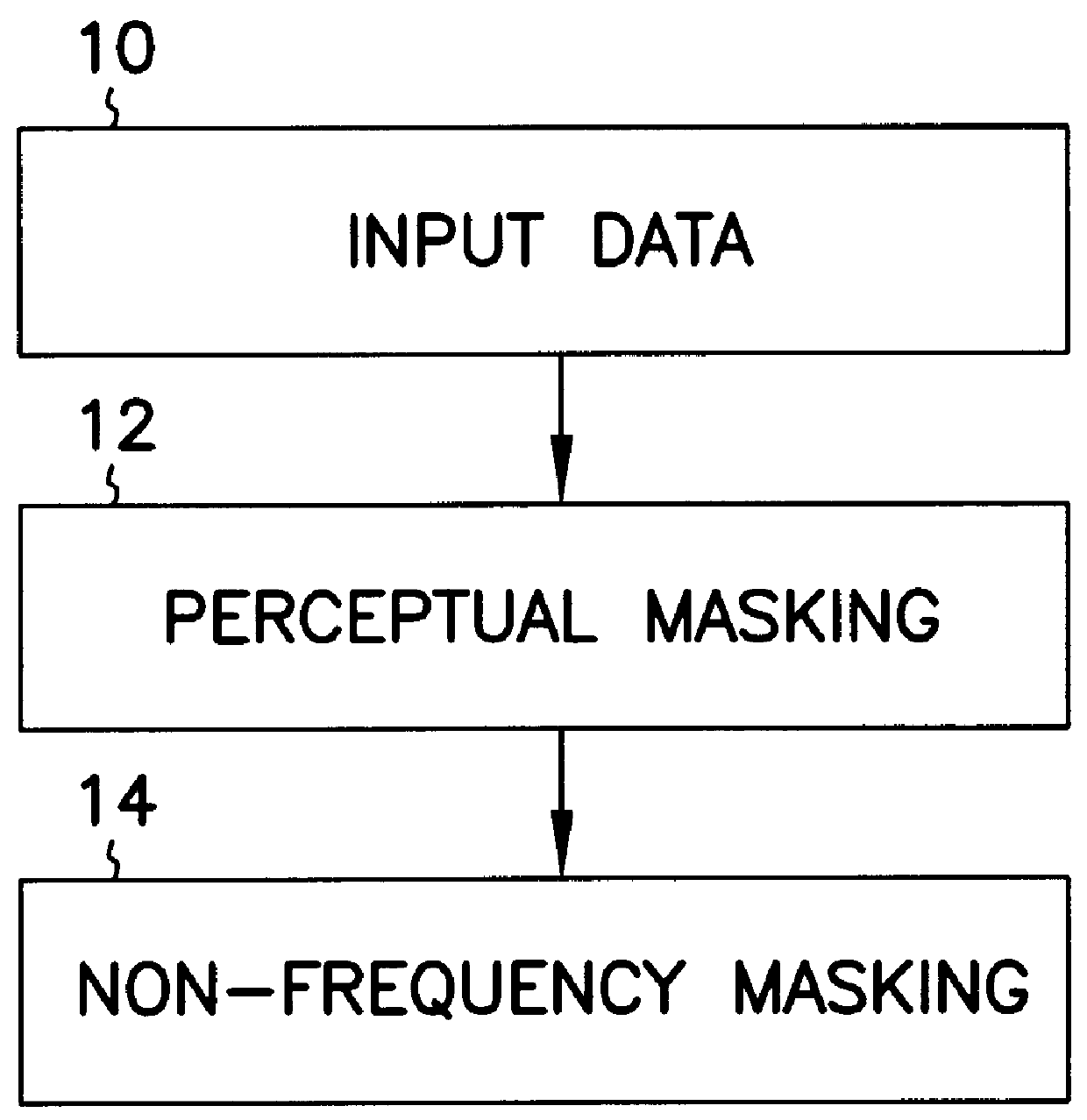
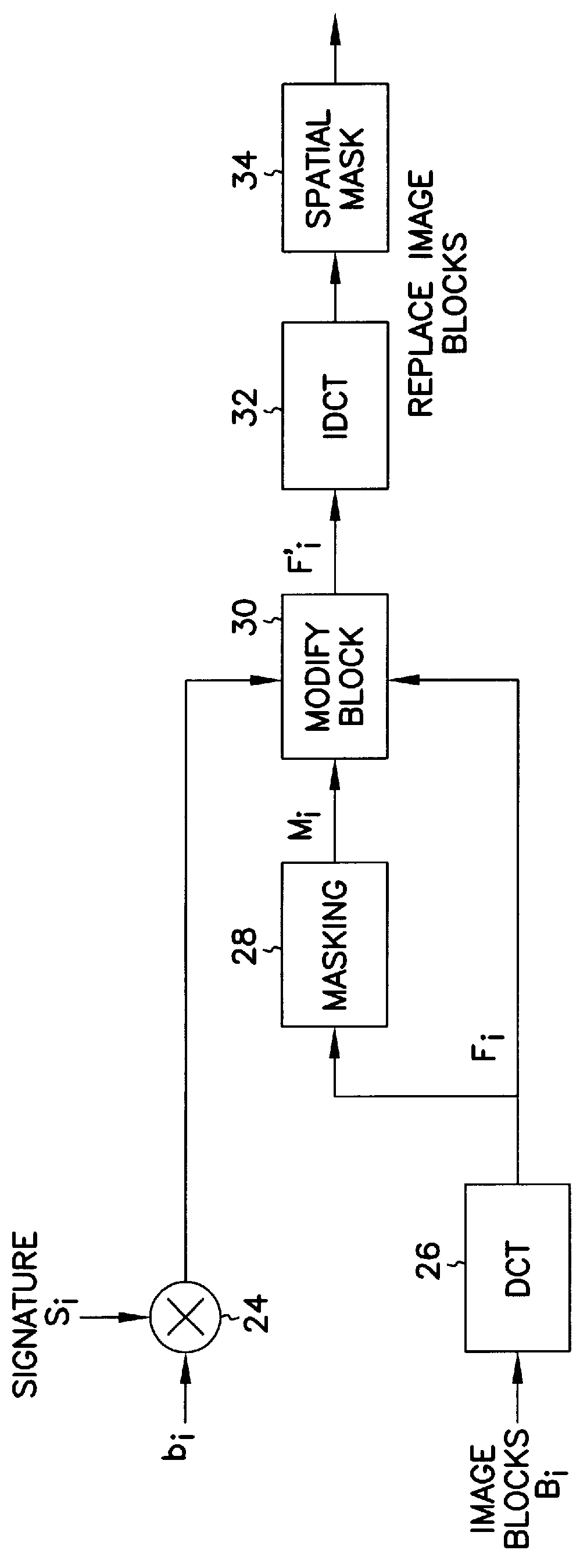
A technique for hiding of data, including watermarks, in human-perceptible images, that is, image host data, is disclosed. In one embodiment a method comprises three steps. In the first step, data to be embedded is inputted. In the case of a watermark, this data is a unique signature, and may be a pseudo-noise (PN) code. In the case of hidden data to be embedded in the host data, this data is the hidden data itself, or the hidden data as spread against the frequency spectrum by a pseudo-noise (PN) code. In the second step, the inputted data is embedded within the host data, in accordance with a perceptual mask of the host data. The perceptual mask determines the optimal locations within the host data to insert the inputted data. In the case of images, these optimal locations are determined by reference to the human visual system. In the third step, the host data, with the embedded data, is further masked by a non-frequency mask. In the case of image data, the non-frequency mask is a spatial mask.
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
Foveated image coding system and method for image bandwidth reduction
InactiveUS6252989B1Increase in sizeQuick implementationDigitally marking record carriersPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData compressionImaging quality
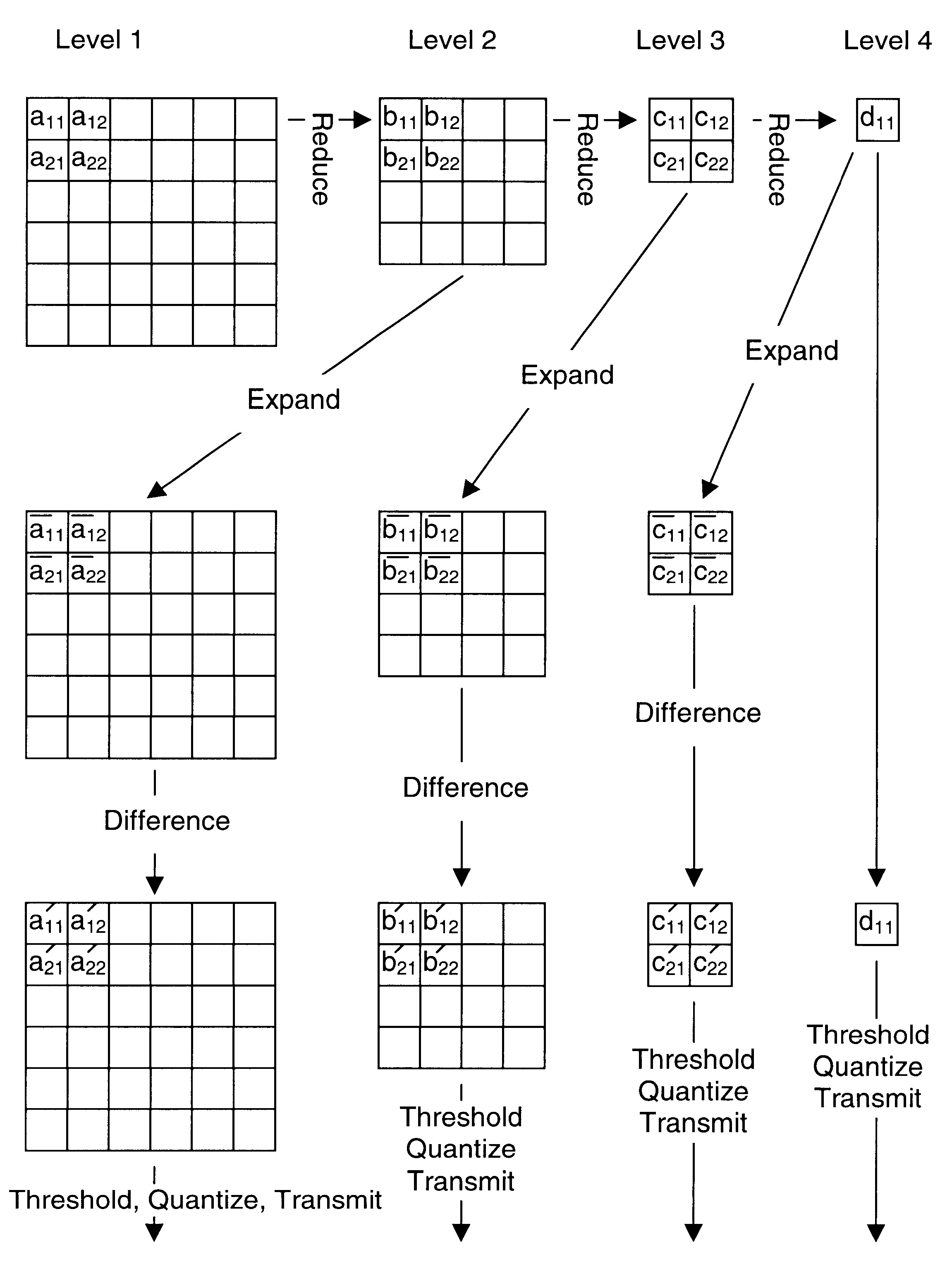
A foveated imaging system, which can be implemented on a general purpose computer and greatly reduces the transmission bandwidth of images has been developed. This system has demonstrated that significant reductions in bandwidth can be achieved while still maintaining access to high detail at any point in an image. The system is implemented with conventional computer, display, and camera hardware. It utilizes novel algorithms for image coding and decoding that are superior both in degree of compression and in perceived image quality and is more flexible and adaptable to different bandwidth requirements and communications applications than previous systems. The system utilizes novel methods of incorporating human perceptual properties into the coding the decoding algorithms providing superior foveation. One version of the system includes a simple, inexpensive, parallel pipeline architecture, which enhances the capability for conventional and foveated data compression. Included are novel applications of foveated imaging in the transmission of pre-recorded video (without eye tracking), and in the use of alternate pointing devices for foveation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
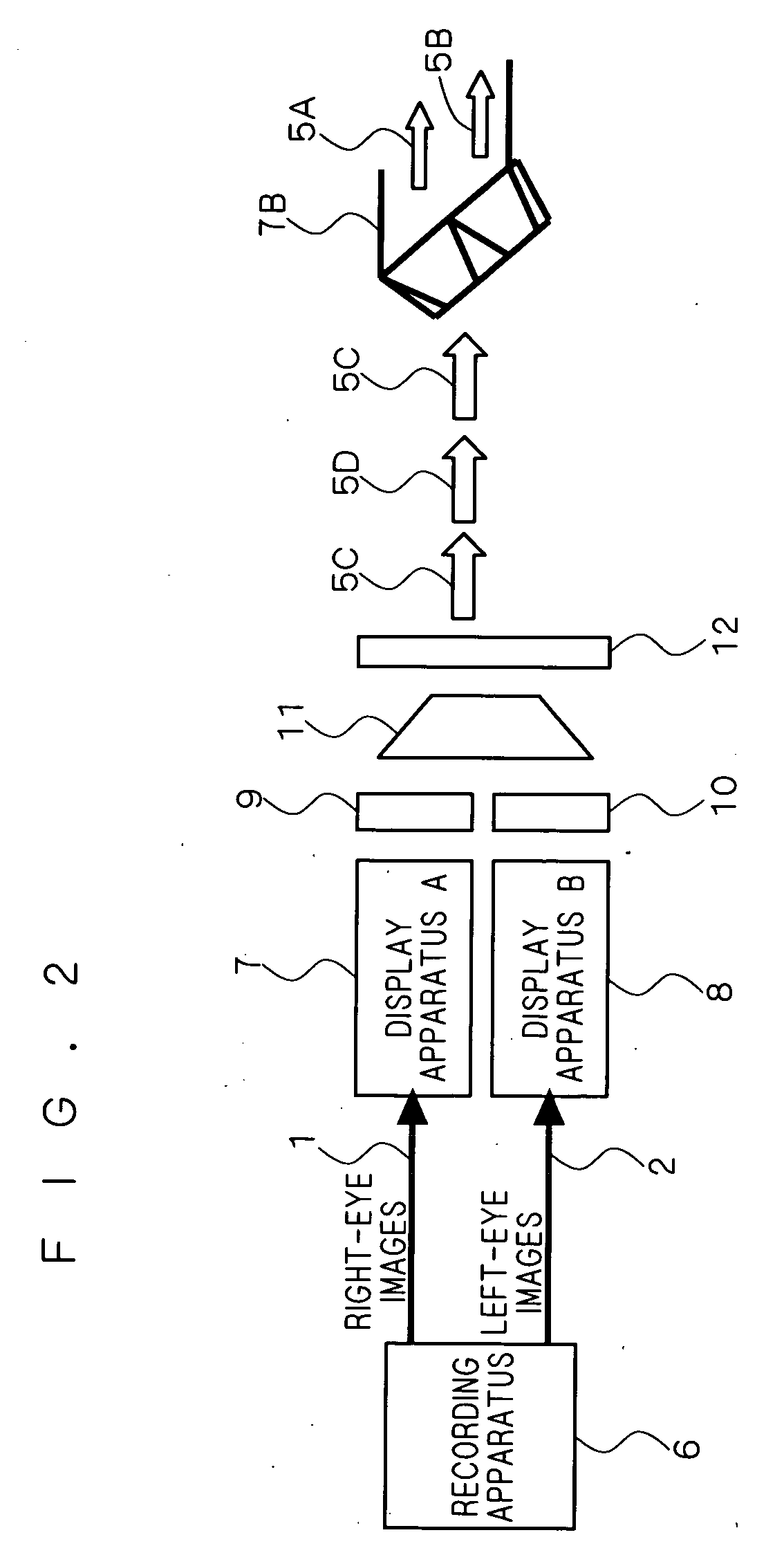
Stereoscopic video recording method, stereoscopic video recording medium, stereoscopic video reproducing method, stereoscopic video recording apparatus, and stereoscopic video reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20090142041A1Easy to recordPromote reproductionTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsParallaxStereoscopic video
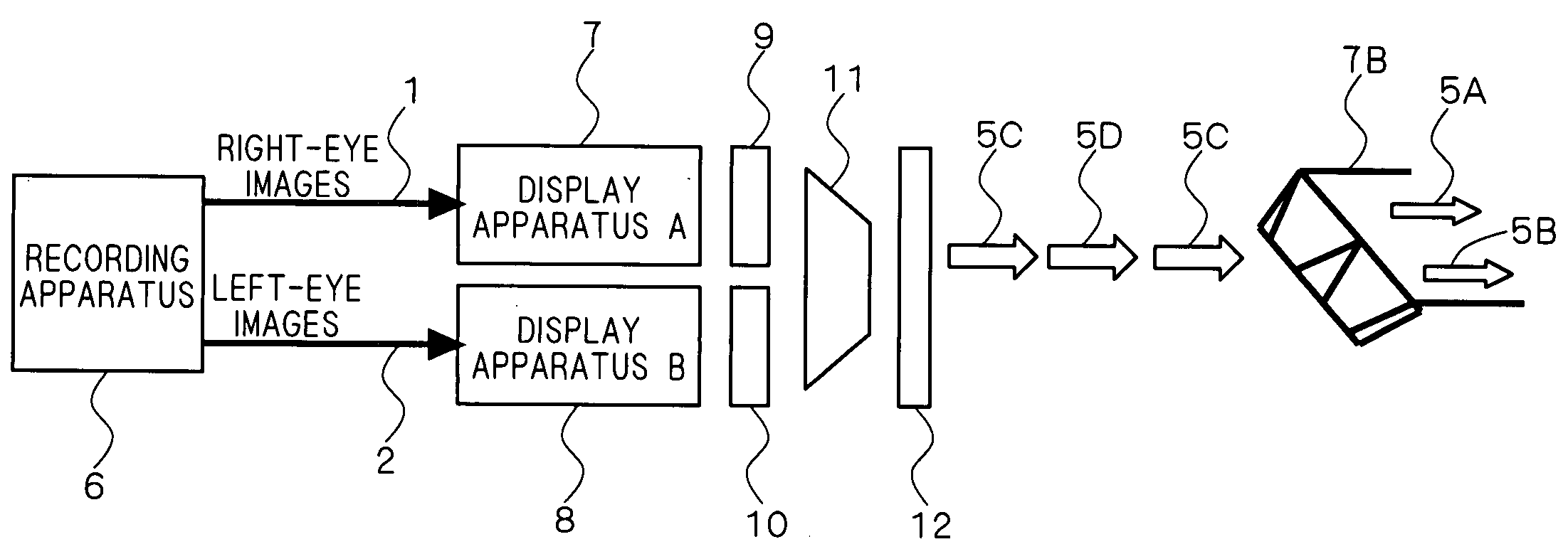
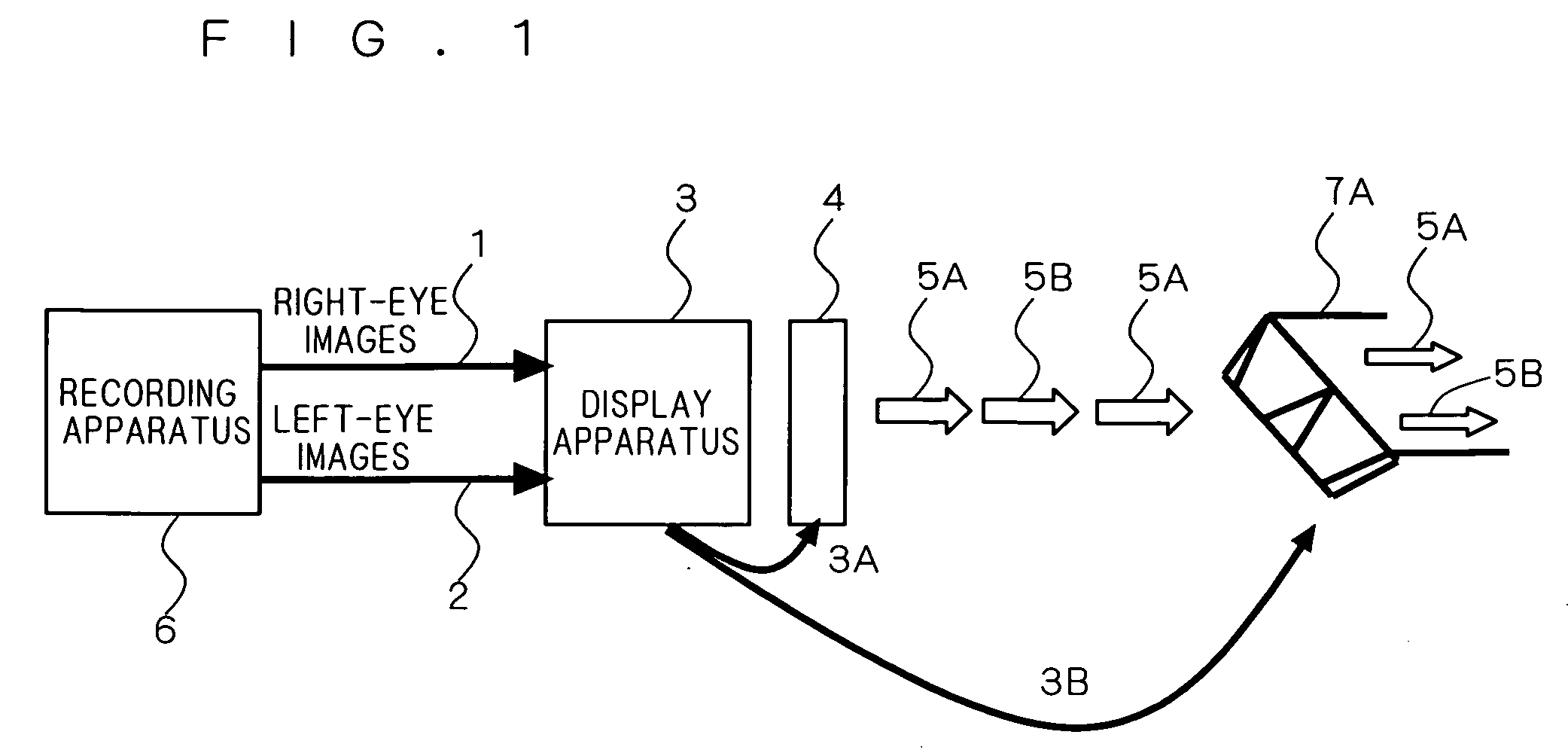
An object of the present invention is to provide a stereoscopic video recording method, a stereoscopic video recording medium, a stereoscopic video reproducing method, a stereoscopic video recording apparatus, and a stereoscopic video reproducing apparatus that are capable of more optimally performing recording and reproduction of stereoscopic video. According to one solving means of the present invention, a stereoscopic video recording method records, in a recording medium, stereoscopic video including left-eye images (2) and right-eye images (1) utilizing parallax information, by using a stereoscopic video recording apparatus (6). From video content that contains stereoscopic images, the method grasps the amount of variation in parallactic angle having a given or larger value, a variation time that the variation in parallactic angle takes, and the number of times that the variation in parallactic angle occurs. The method then calculates an evaluation value that corresponds to the degree of eye fatigue on the basis of the amount of variation, the variation time, and the number of times of the variation, encodes the video content in such a manner that the evaluation value is within a given range, and records the encoded video content in the recording medium.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
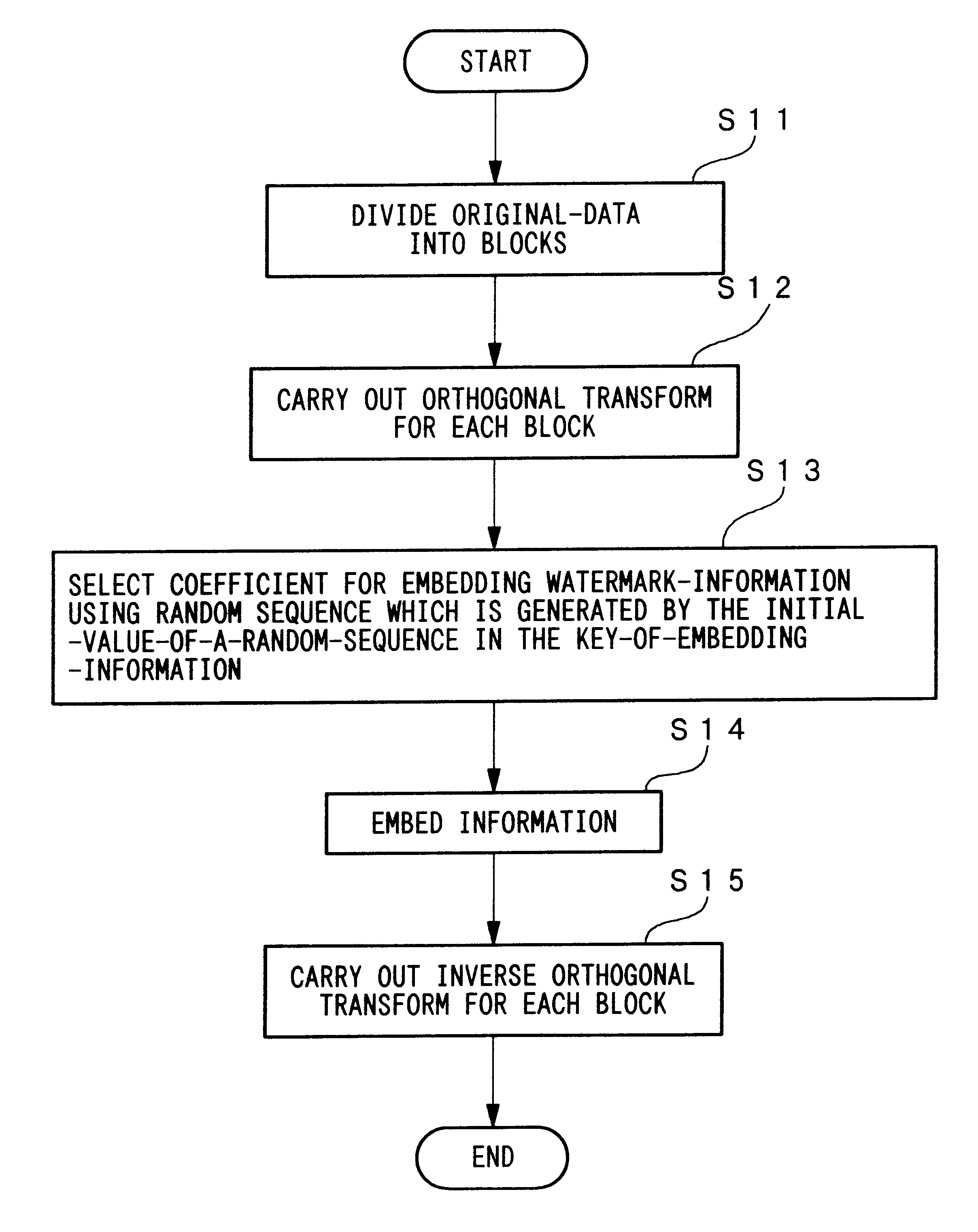
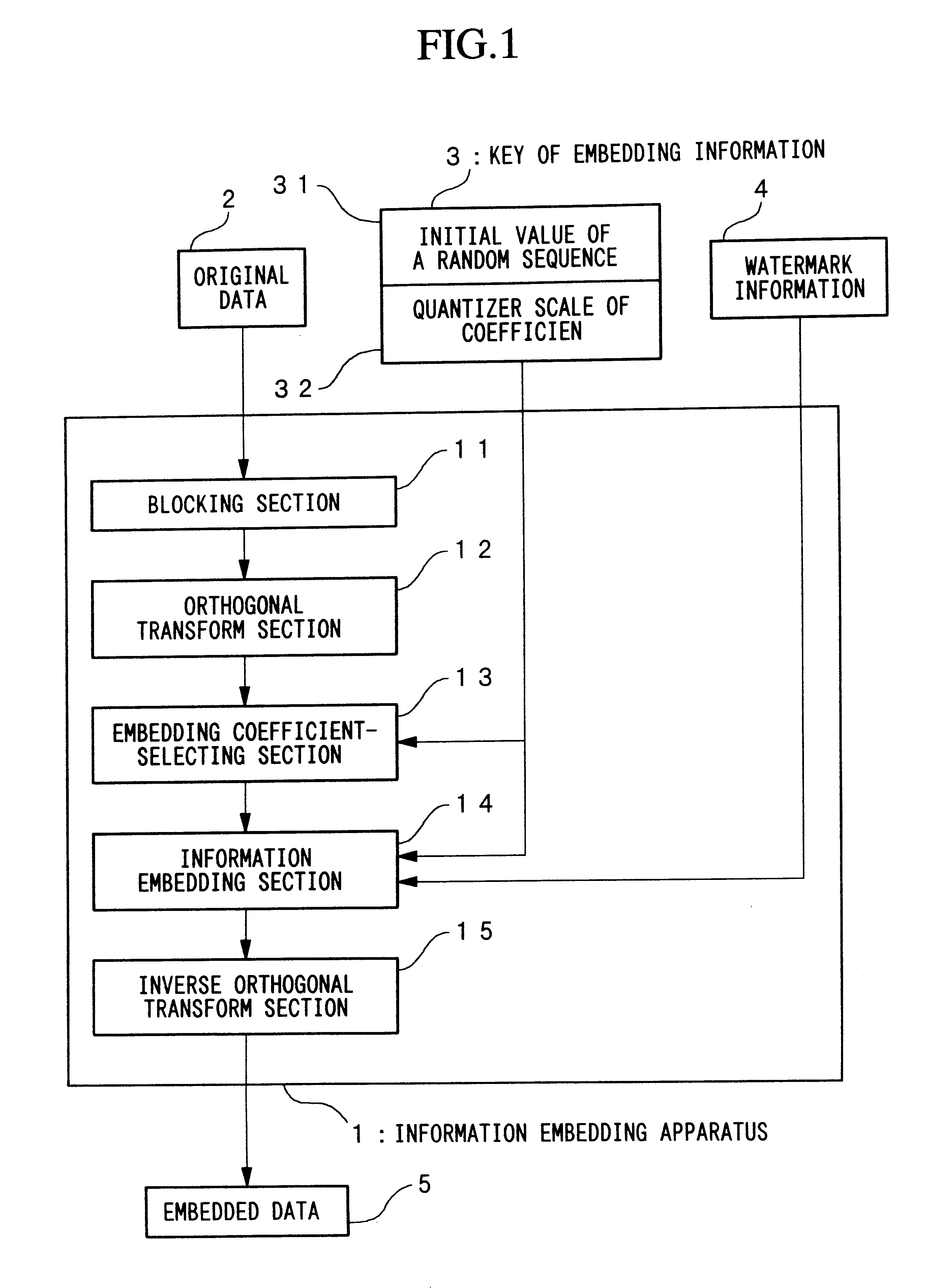
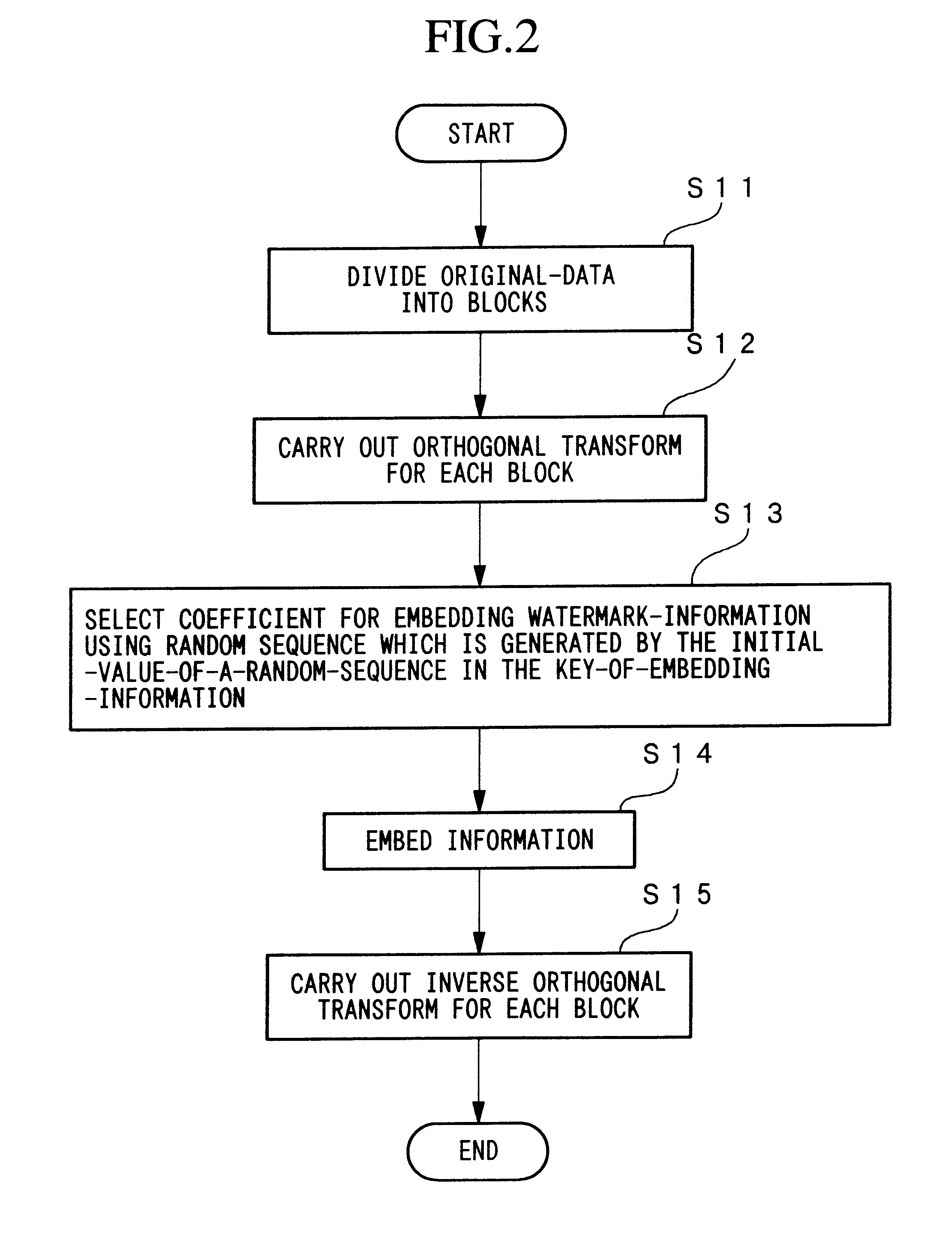
Method for embedding and reading watermark-information in digital form, and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS6185312B1Information can be droppedOther printing matterCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation embeddingOrthogonal transformation
An apparatus for embedding information comprises: a blocking step for dividing data to be processed into blocks; an orthogonal transform step for obtaining coefficients by carrying out orthogonal transformation for each block; an embedding coefficient selecting step for determining coefficients in which the watermark-information will be embedded by using a random sequence which is generated by initial value; an information embedding step for sequentially embedding the watermark-information, which has arbitrary length of bits, by quantizing value of said coefficients using a predetermined value for quantization; and an inverse orthogonal transform step for carrying out inverse orthogonal transformation for modified coefficients to form block in which the watermark-information is embedded, as well as combining the divided blocks and reconstructing the original form.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Fast-start streaming and buffering of streaming content for personal media player
ActiveUS20060095472A1Improve experienceReduce bitratePulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast-related systemsClient-sideDigitization
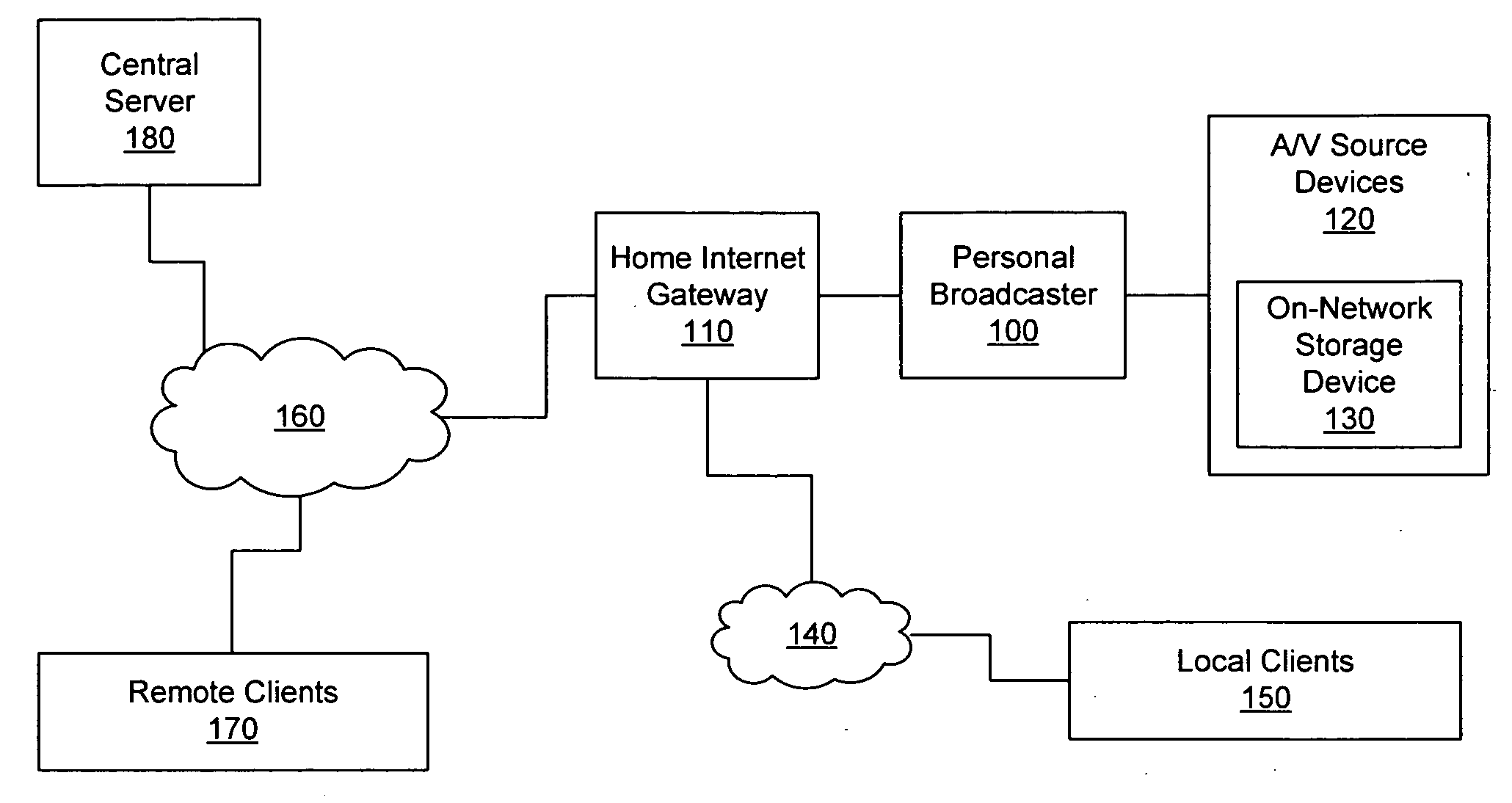
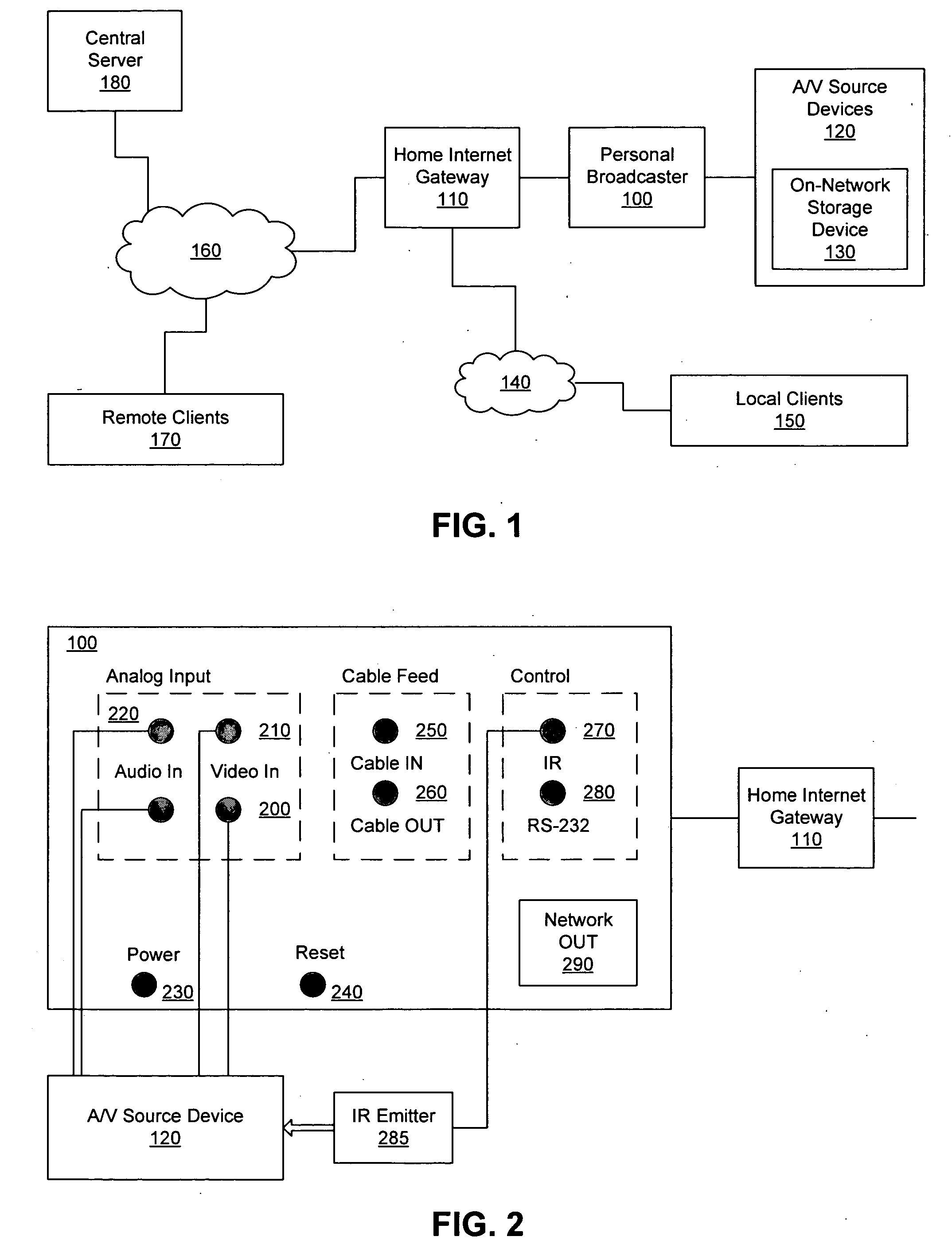
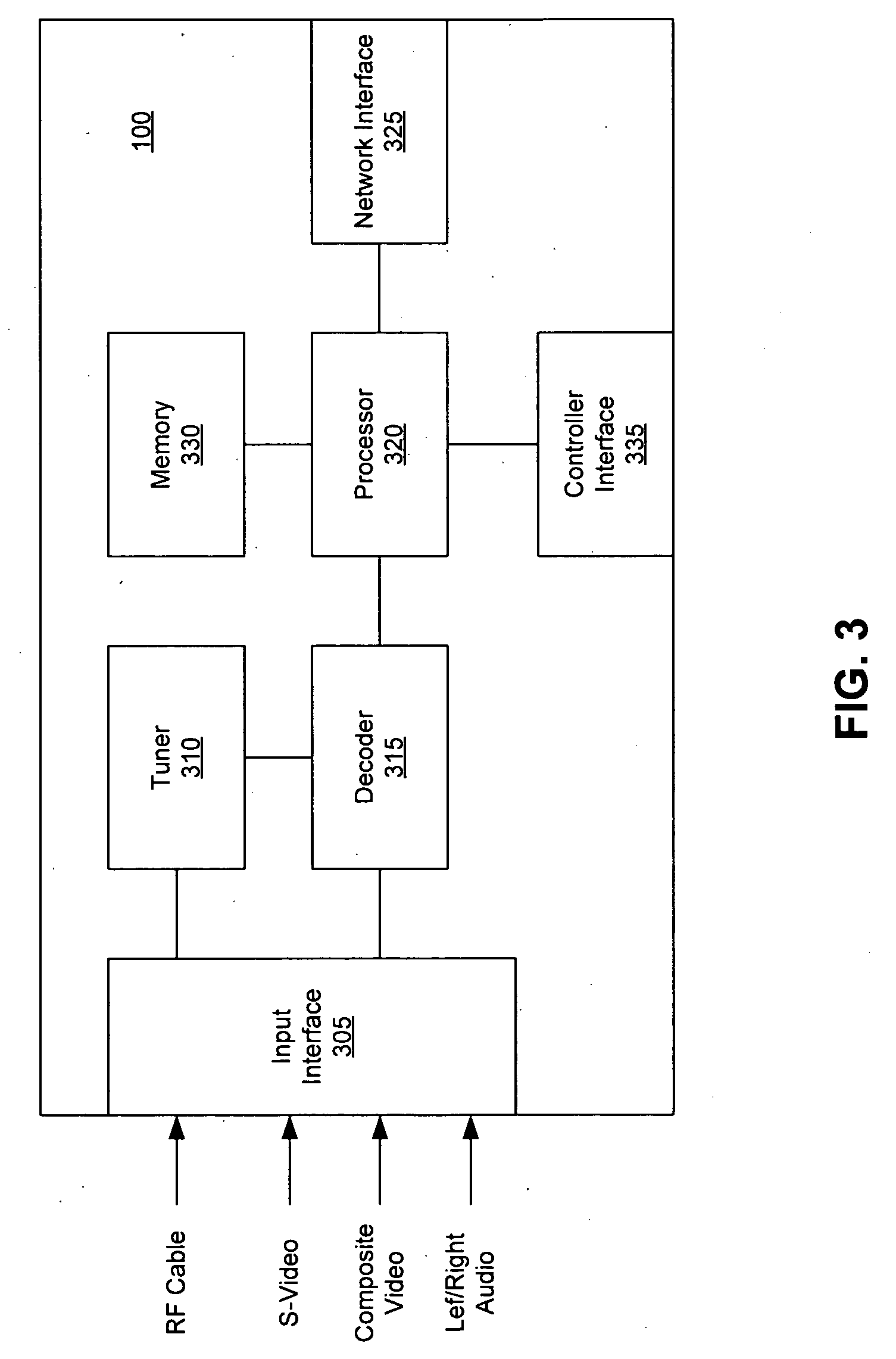
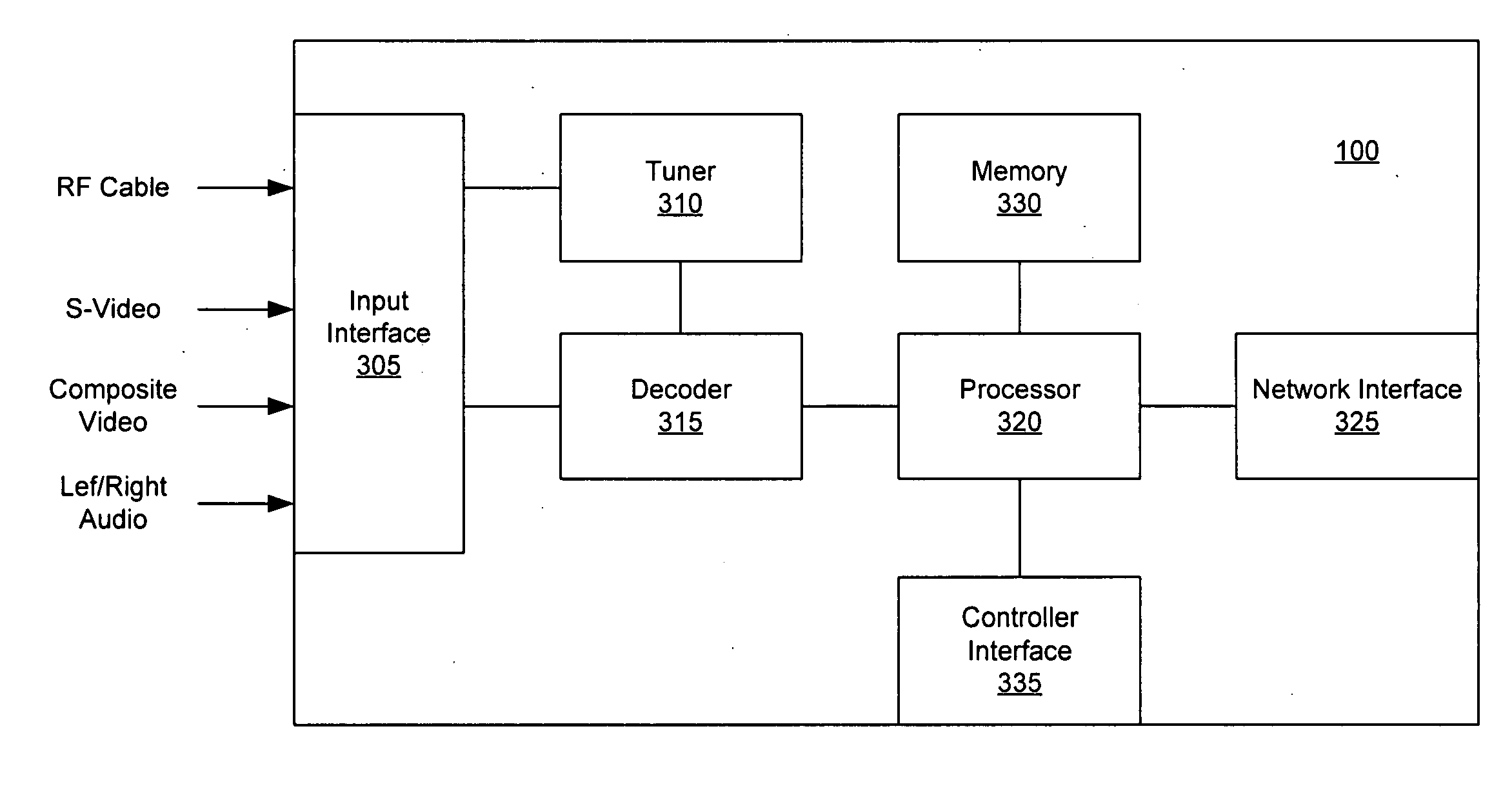
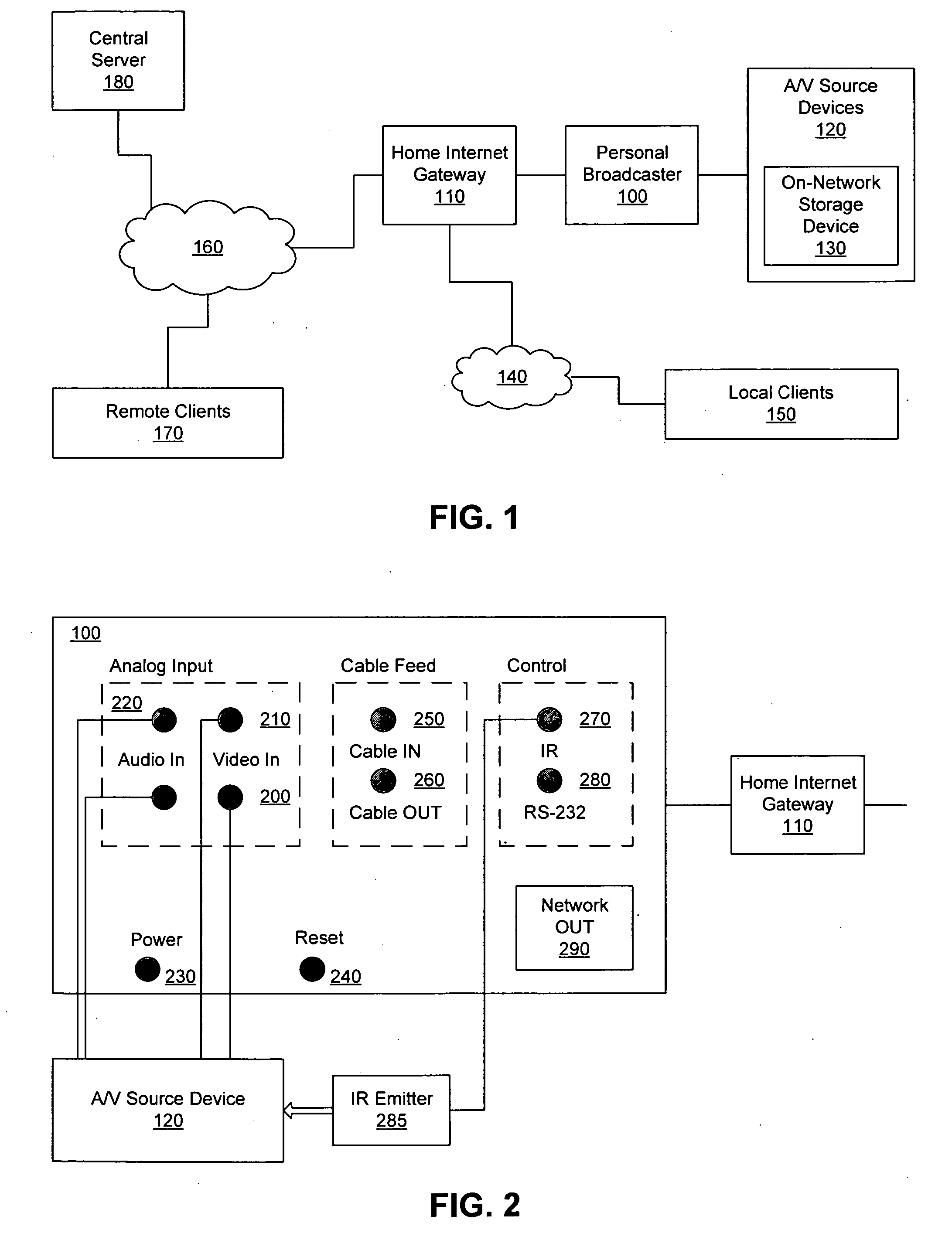
A personal media broadcasting system enables video distribution over a computer network and allows a user to view and control media sources over a computer network from a remote location. A personal broadcaster receives an input from one or more types of media sources, digitizes and compresses the content, and streams the compressed media over a computer network to a media player running on any of a wide range of client devices for viewing the media. The system may allow the user to issue control commands (e.g., “channel up”) from the media player to the broadcaster, causing the source device to execute the commands. The broadcaster and the media player may employ several techniques for buffering, transmitting, and viewing the content to improve the user's experience.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
Personal media broadcasting system with output buffer
ActiveUS20060095401A1Improve experienceReduce bitratePulse modulation television signal transmissionBroadcast-related systemsClient-sideDigitization
A personal media broadcasting system enables video distribution over a computer network and allows a user to view and control media sources over a computer network from a remote location. A personal broadcaster receives an input from one or more types of media sources, digitizes and compresses the content, and streams the compressed media over a computer network to a media player running on any of a wide range of client devices for viewing the media. The system may allow the user to issue control commands (e.g., “channel up”) from the media player to the broadcaster, causing the source device to execute the commands. The broadcaster and the media player may employ several techniques for buffering, transmitting, and viewing the content to improve the user's experience.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
Generating and matching hashes of multimedia content
ActiveUS20020178410A1RobustRobust hashingElectrophonic musical instrumentsCode conversionFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
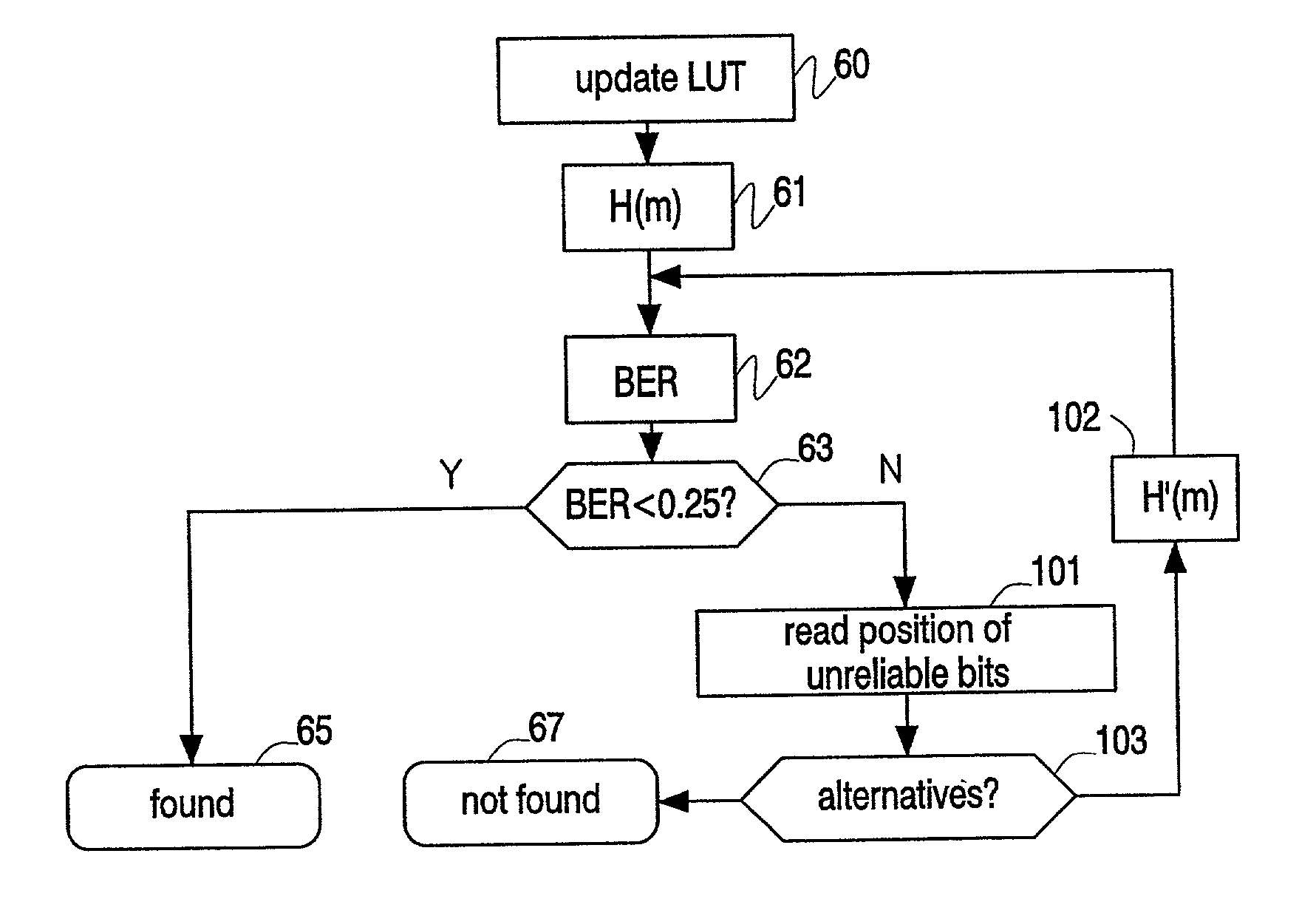
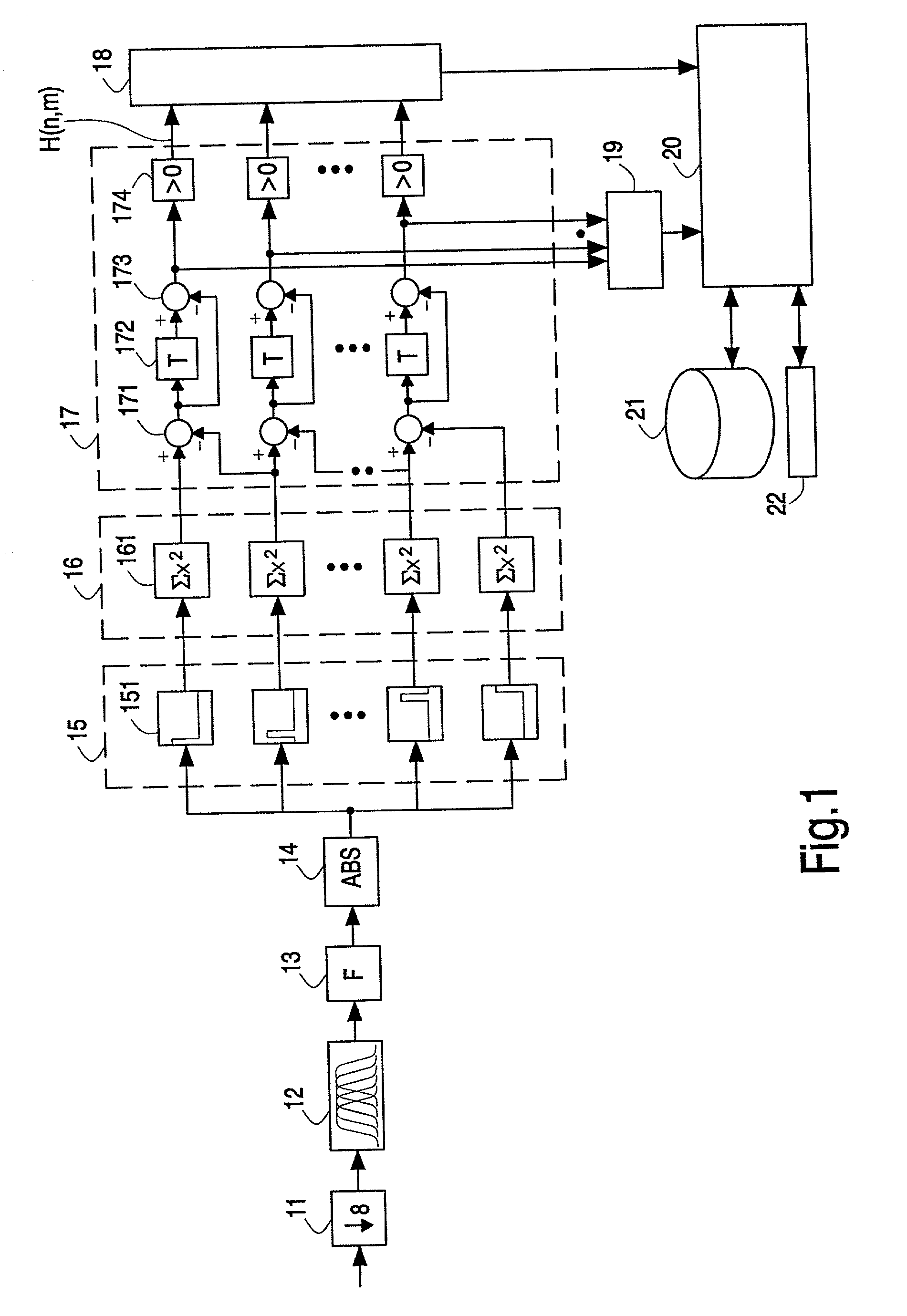
Hashes are short summaries or signatures of data files which can be used to identify the file. Hashing multimedia content (audio, video, images) is difficult because the hash of original content and processed (e.g. compressed) content may differ significantly. The disclosed method generates robust hashes for multimedia content, for example, audio clips. The audio clip is divided (12) into successive (preferably overlapping) frames. For each frame, the frequency spectrum is divided (15) into bands. A robust property of each band (e.g. energy) is computed (16) and represented (17) by a respective hash bit. An audio clip is thus represented by a concatenation of binary hash words, one for each frame. To identify a possibly compressed audio signal, a block of hash words derived therefrom is matched by a computer (20) with a large database (21). Such matching strategies are also disclosed. In an advantageous embodiment, the extraction process also provides information (19) as to which of the hash bits are the least reliable. Flipping these bits considerably improves the speed and performance of the matching process.
Owner:GRACENOTE
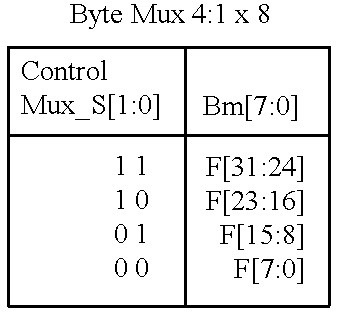
Memory module including scalable embedded parallel data compression and decompression engines
InactiveUS6879266B1Low costSmall data storage requirementMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTParallel compressionParallel computing
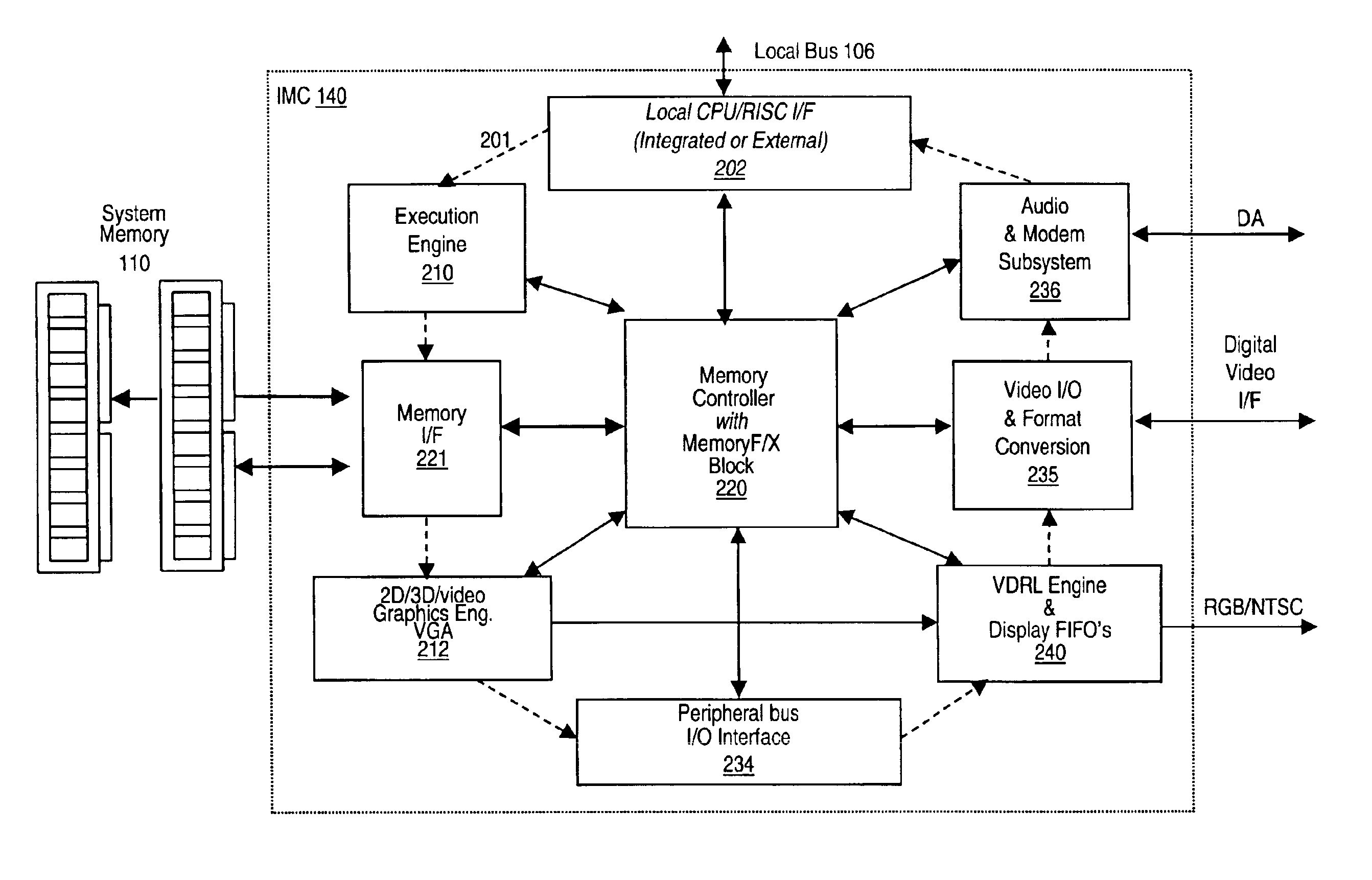
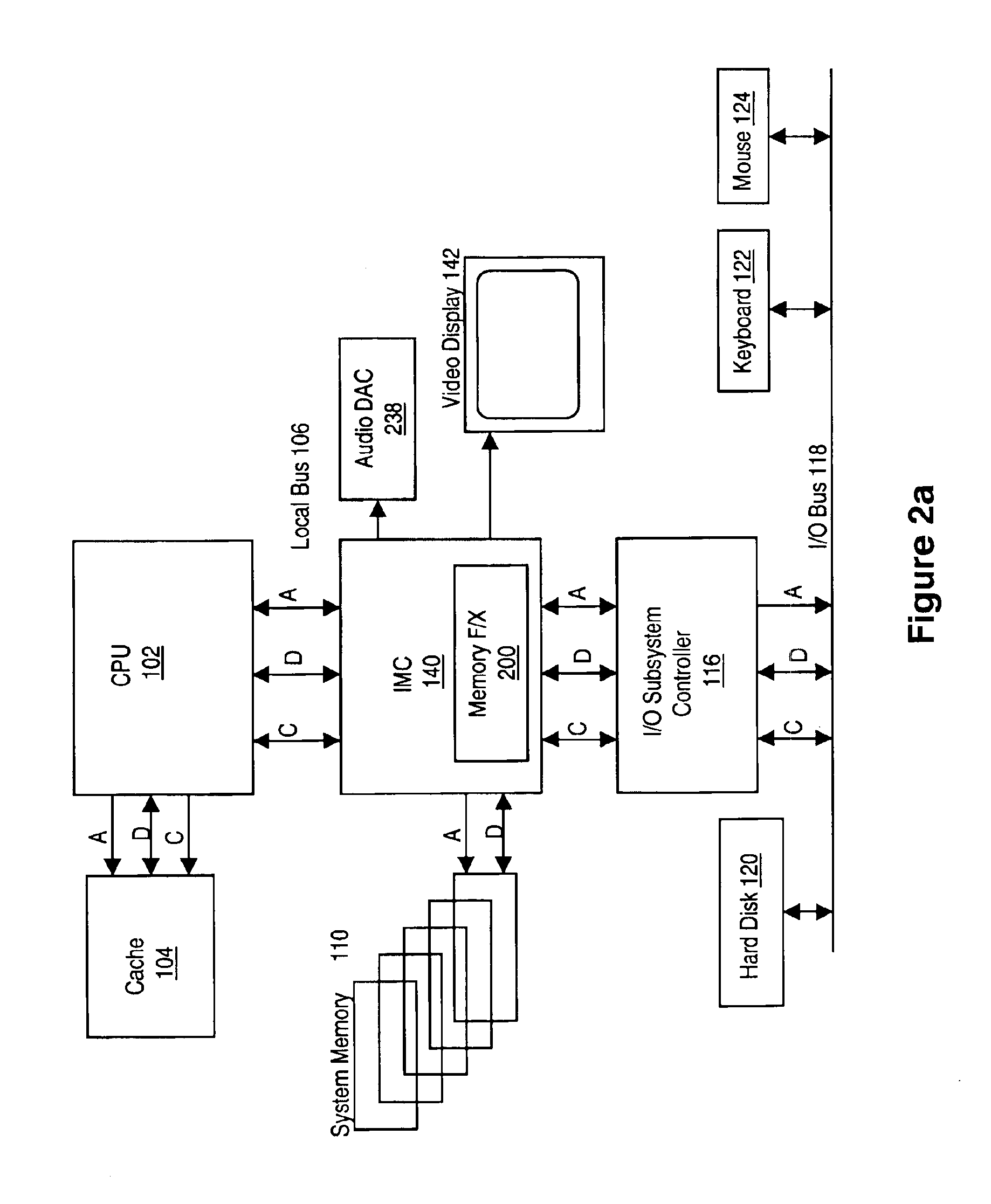
An memory module including parallel data compression and decompression engines for improved performance. The memory module includes MemoryF / X Technology. To improve latency and reduce performance degradations normally associated with compression and decompression techniques, the MemoryF / X Technology encompasses multiple novel techniques such as: 1) parallel lossless compression / decompression; 2) selectable compression modes such as lossless, lossy or no compression; 3) priority compression mode; 4) data cache techniques; 5) variable compression block sizes; 6) compression reordering; and 7) unique address translation, attribute, and address caches. The parallel compression and decompression algorithm allows high-speed parallel compression and high-speed parallel decompression operation. The memory module-integrated data compression and decompression capabilities remove system bottlenecks and increase performance. This allows lower cost systems due to smaller data storage, reduced bandwidth requirements, reduced power and noise.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Systems and methods for providing high-resolution regions-of-interest
InactiveUS20070024706A1Less video compressionEnhanced color formatColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsRegion of interestHigh resolution
Systems and methods for providing high-quality region of interest (HQ-ROI) viewing within an overall scene by enabling one or more HQ-ROIs to be viewed in a controllable fashion, as higher quality ‘windows-within-a-window’ of regions (spatial subsets) of a scene.
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
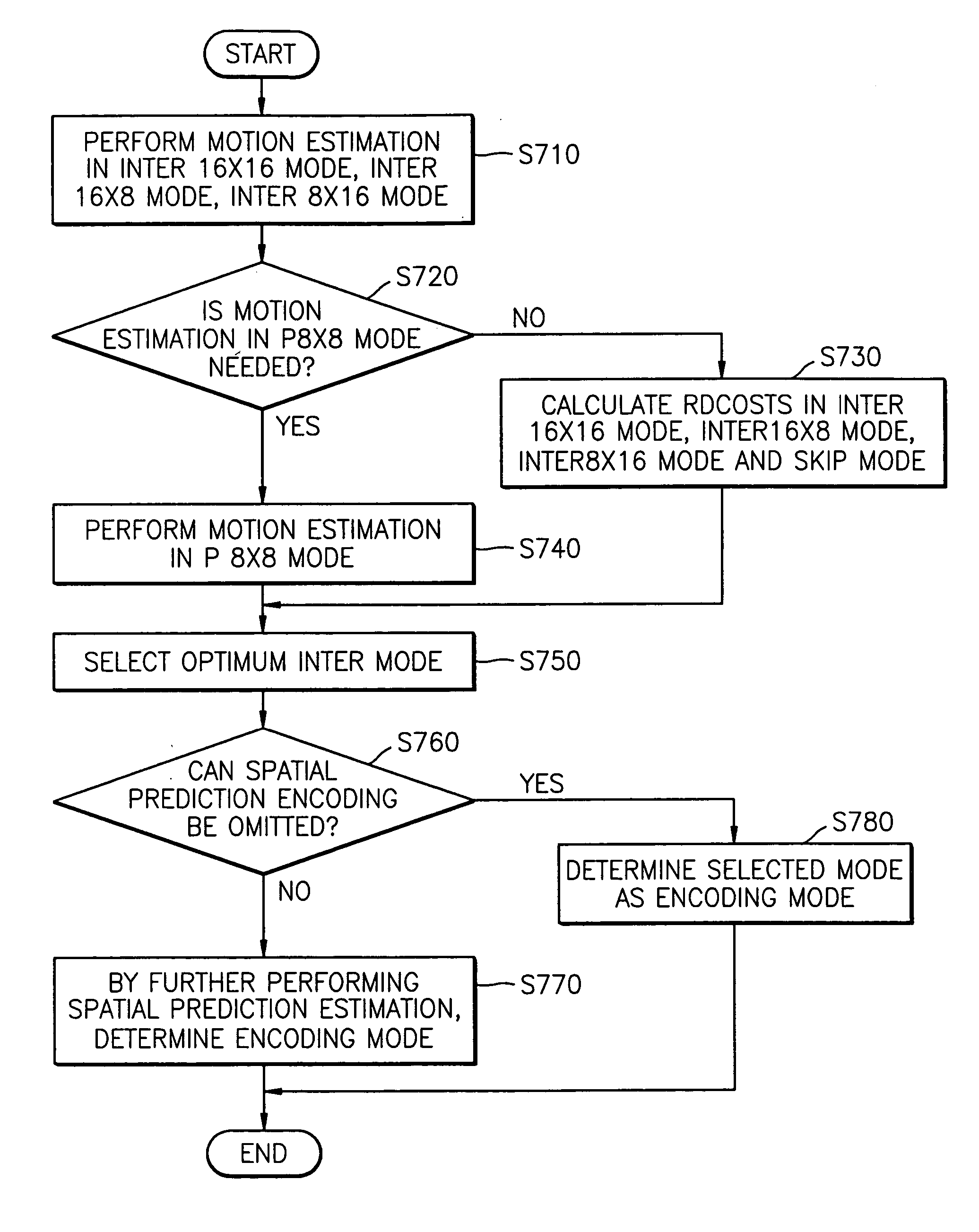
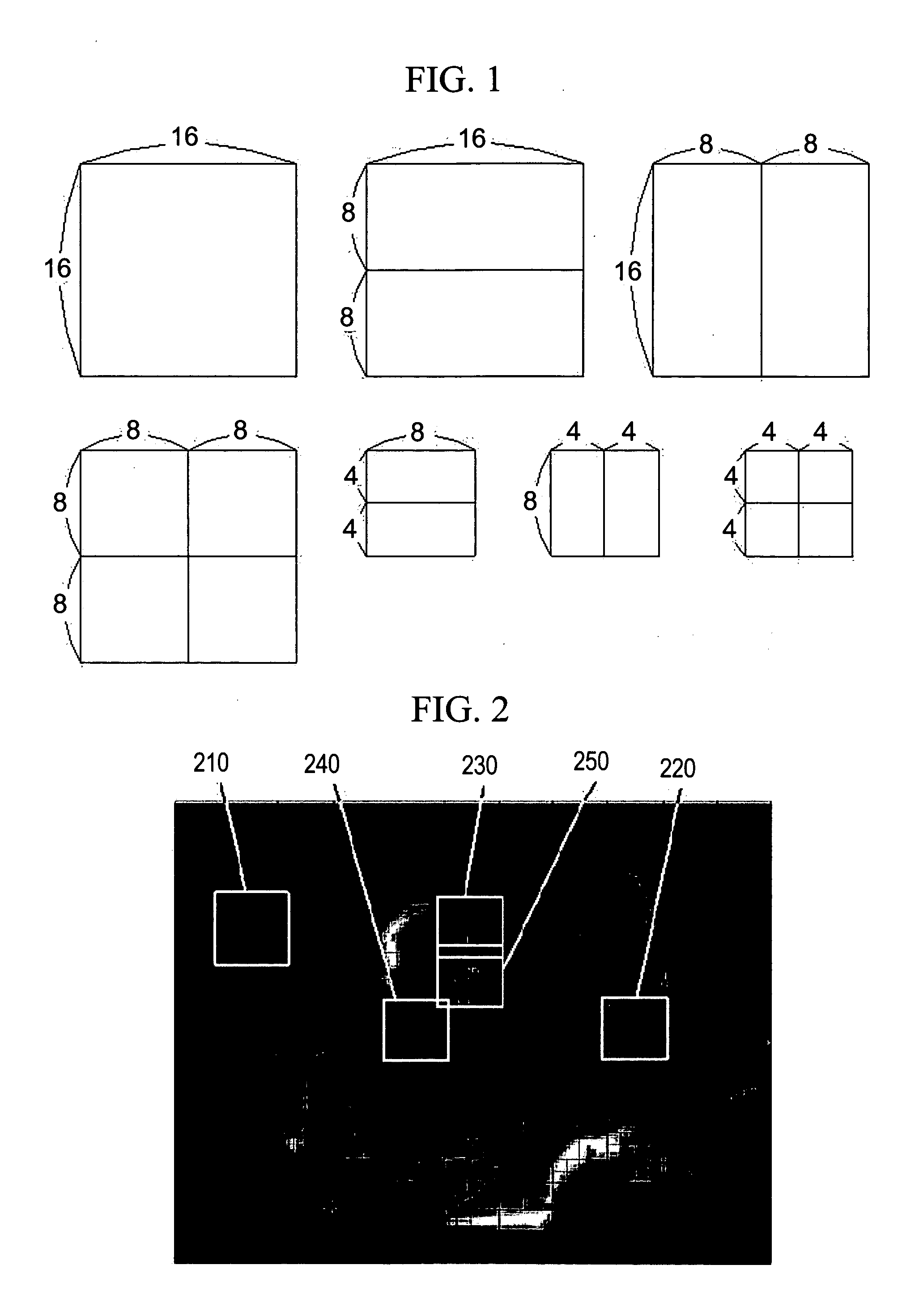
Method of encoding mode determination, method of motion estimation and encoding apparatus
InactiveUS20050135484A1Efficiently omittedQuick fixTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpatial predictionRate distortion
Motion estimation of a macro block in inter16×16, inter16×8, and inter8×16 modes is performed and a determination of whether to further perform motion estimation in a P8×8 mode is made. Motion estimation in P8×8 mode is either omitted or performed and one mode is determined according to a rate distortion cost of the respective modes. Spatial prediction encoding may then be performed or omitted based on comparing the rate distortion cost of the one mode with a predetermined value. Accordingly, by selectively omitting variable block motion estimation and spatial prediction encoding which are the most complicated operations in an H.264 encoder, determining an encoding mode is rapidly performed such that encoding speed increases.
Owner:DAEYANG FOUND SEJONG UNIV +1
Audio and video decoder circuit and system
InactiveUS6369855B1Accelerates memory block moveAvoid confictTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionCoprocessorNetwork packet
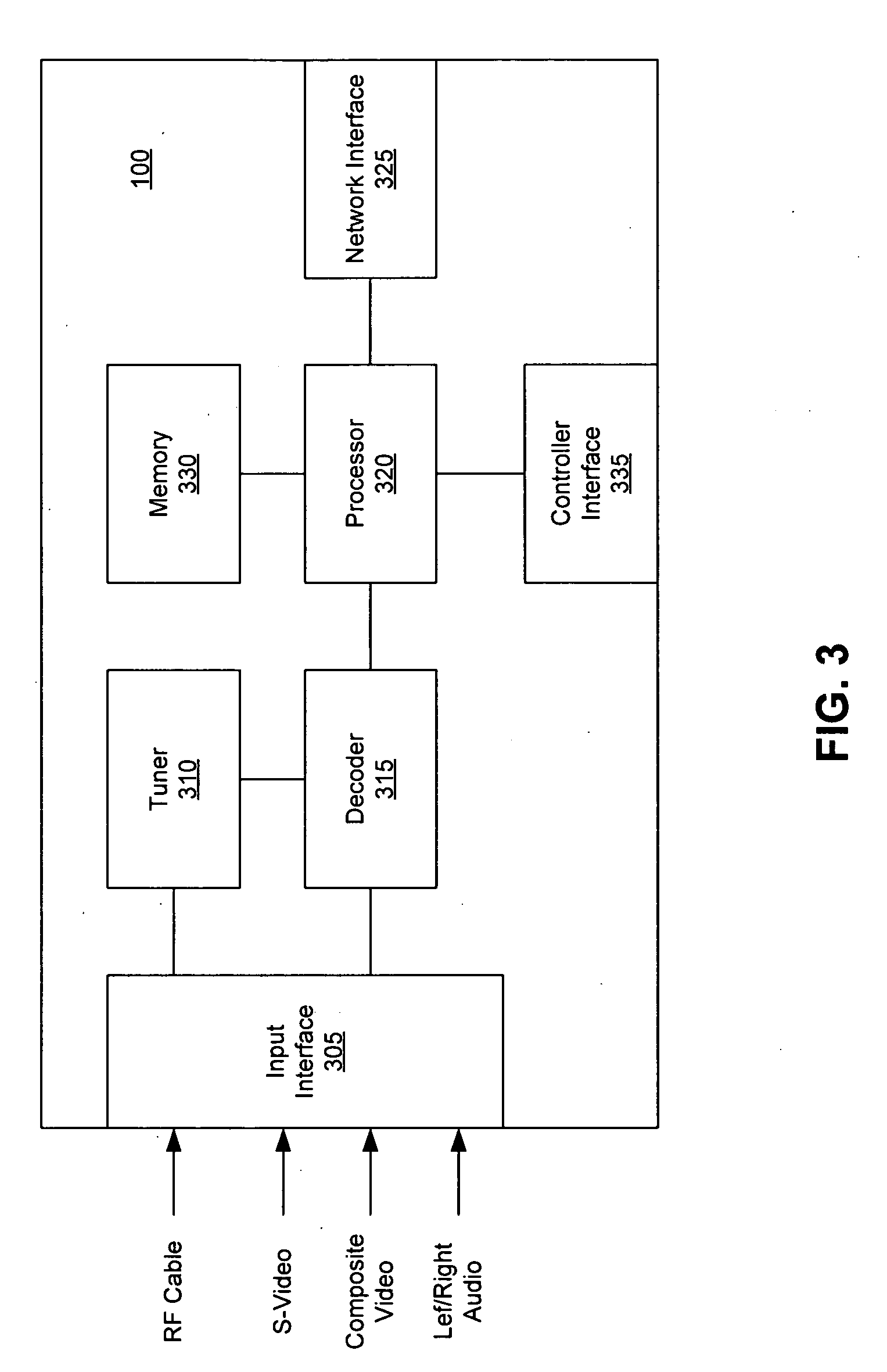
An improved audio-visual circuit is provided that includes a transport packet parsing circuit for receiving a transport data packet stream, a CPU circuit for initializing said integrated circuit and for processing portions of said data packet stream, a ROM circuit for storing data, a RAM circuit for storing data, an audio decoder circuit for decoding audio portions of said data packet stream, a video decoder circuit for decoding video portions of said data packet stream, an NTSC / PAL encoding circuit for encoding video portions of said data packet stream, an OSD coprocessor circuit for processing OSD portions of said data packets, a traffic controller circuit moving portions of said data packet stream between portions of said integrated circuit, an extension bus interface circuit, a P1394 interface circuit, a communication coprocessors circuit, an address bus connected to said circuits, and a data bus connected to said circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for use in camera and systems employing same
ActiveUS20070002159A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesControl signalImage resolution
There are many inventions described herein. Some aspects are directed to methods and / or apparatus to provide relative movement between optics, or portion(s) thereof, and sensors, or portion(s) thereof, in a digital camera. The relative movement may be in any of various directions. In some aspects, relative movement between an optics portion, or portion(s) thereof, and a sensor portion, or portion(s) thereof, are used in providing any of various features and / or in the various applications disclosed herein, including, for example, but not limited to, increasing resolution, optical and electronic zoom, image stabilization, channel alignment, channel-channel alignment, image alignment, lens alignment, masking, image discrimination, range finding, 3D imaging, auto focus, mechanical shutter, mechanical iris, multi and hyperspectral imaging, and / or combinations thereof. In some aspects, movement is provided by actuators, for example, but not limited to MEMS actuators, and by applying appropriate control signal thereto.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
3D television system and method
InactiveUS20050185711A1Increase flexibilityHigh resolutionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTelevision systemTransmission network
A three-dimensional television system includes an acquisition stage, a display stage and a transmission network. The acquisition stage includes multiple video cameras configured to acquire input videos of a dynamically changing scene in real-time. The display stage includes a three-dimensional display unit configured to concurrently display output videos generated from the input videos. The transmission network connects the acquisition stage to the display stage.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
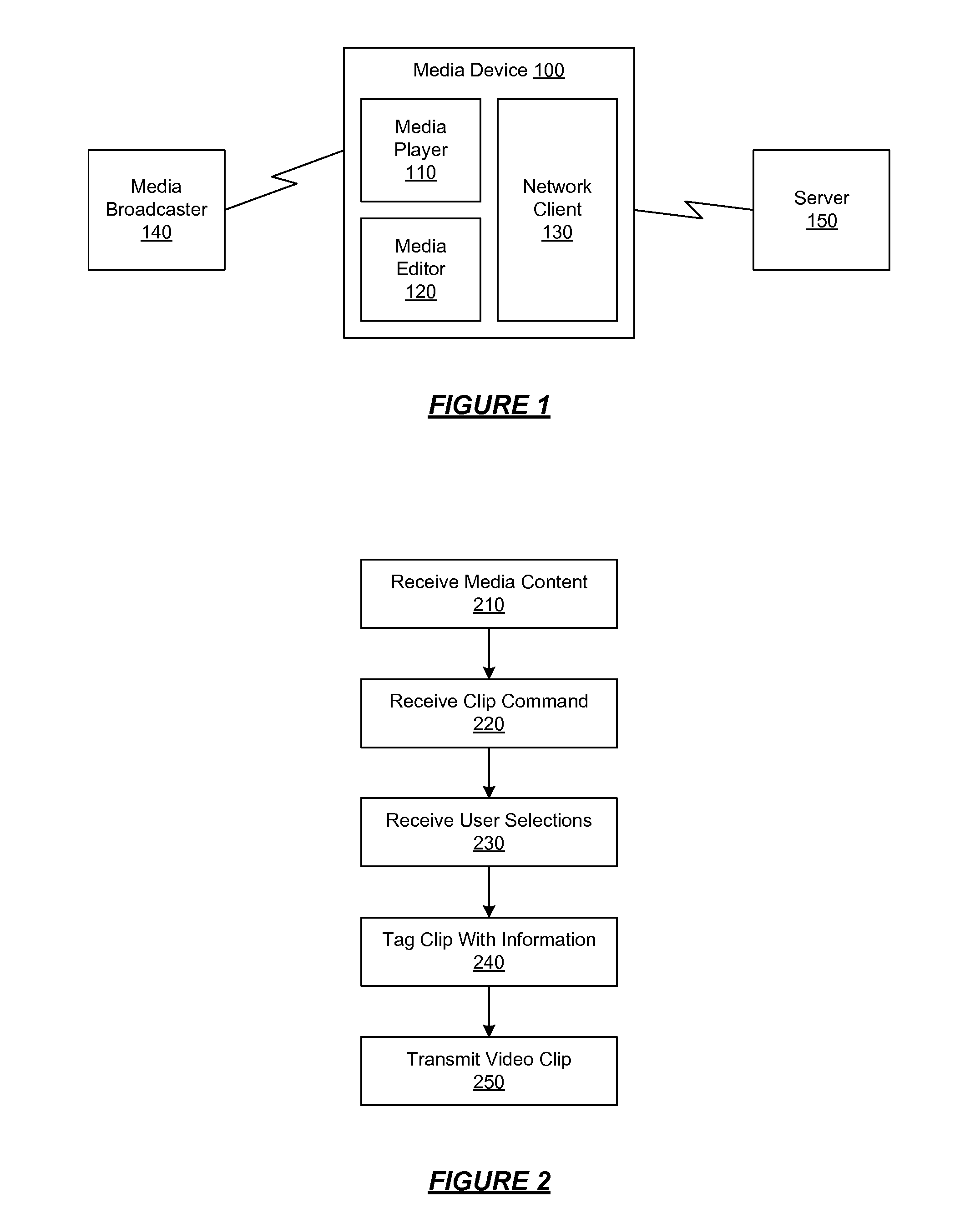
Management of Shared Media Content
ActiveUS20070198532A1GenerateGenerate advertising revenueFinanceAdvertisementsShared mediumMedia content
A media device allows users to watch and capture portions from a media broadcast. Users may then share the captured media content items with other users, for example, by uploading the items to a community website. Before providing requested media content items to other users, the website may combine advertisements with the media content items. The website may receive advertising revenue from advertisers and may share the advertising revenue with owners of the media content items in exchange for their permission to provide the media content items. The advertisers may provide restrictions on how the advertisements are combined with the media content items, and the content owners may provide restrictions on how the media content items are provided to the users.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
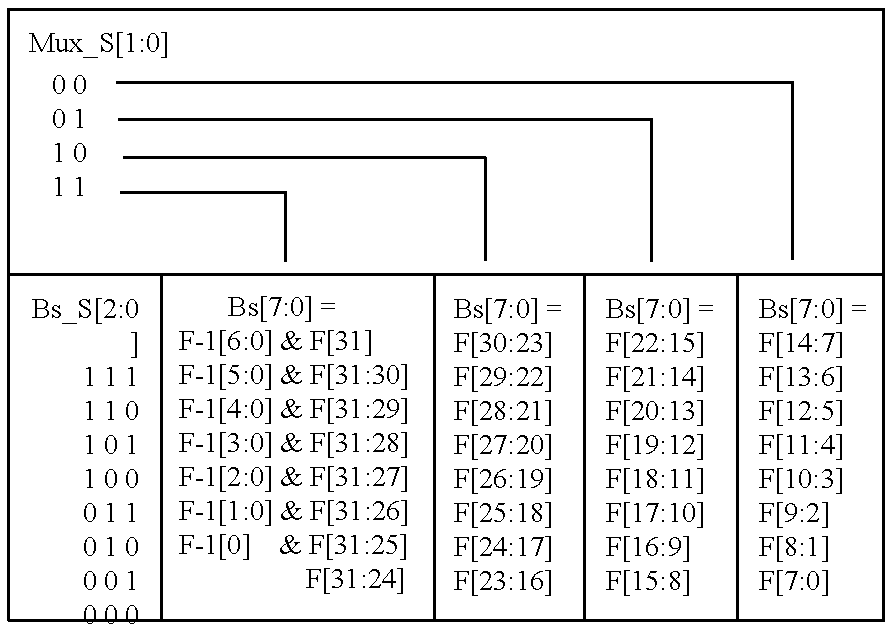
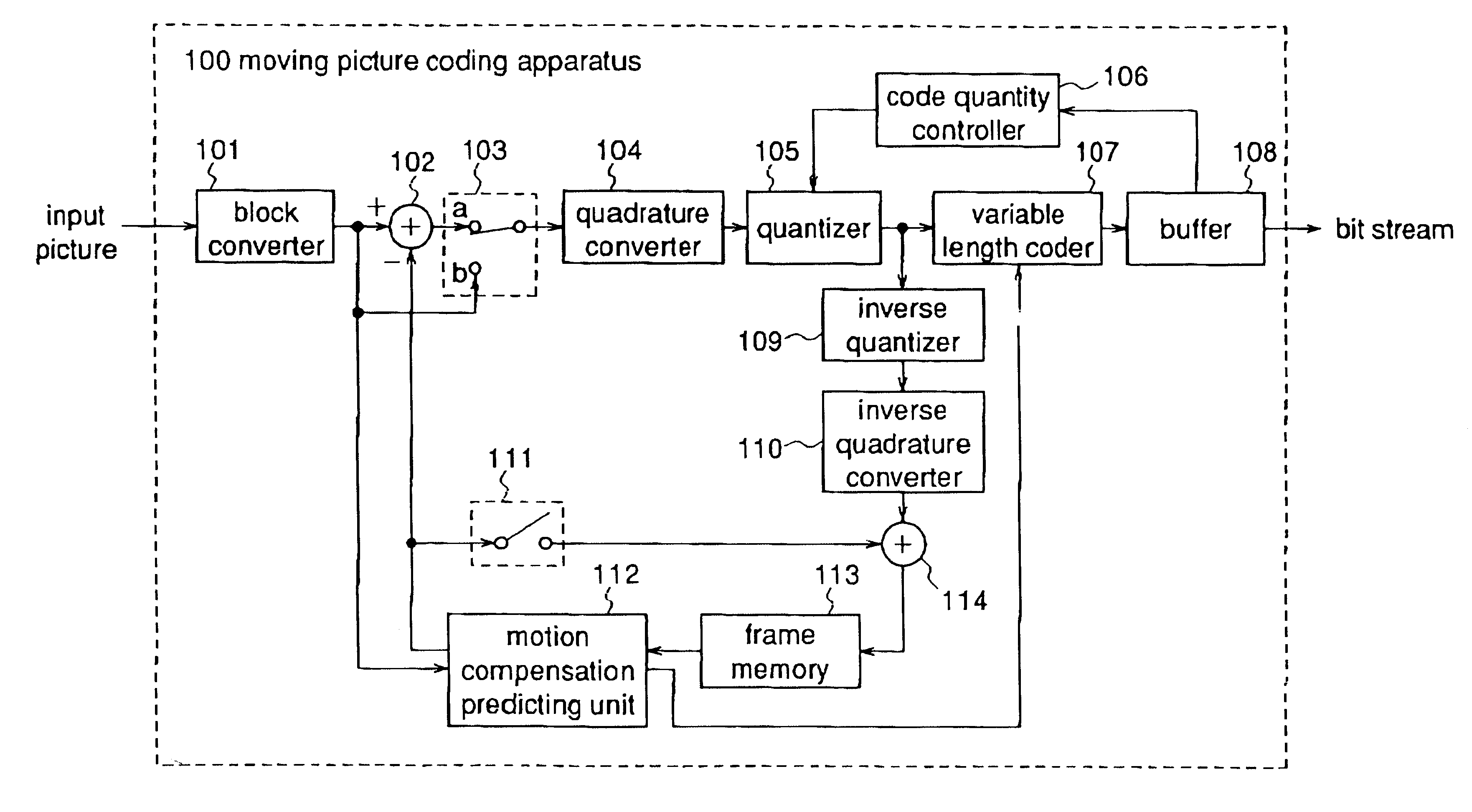
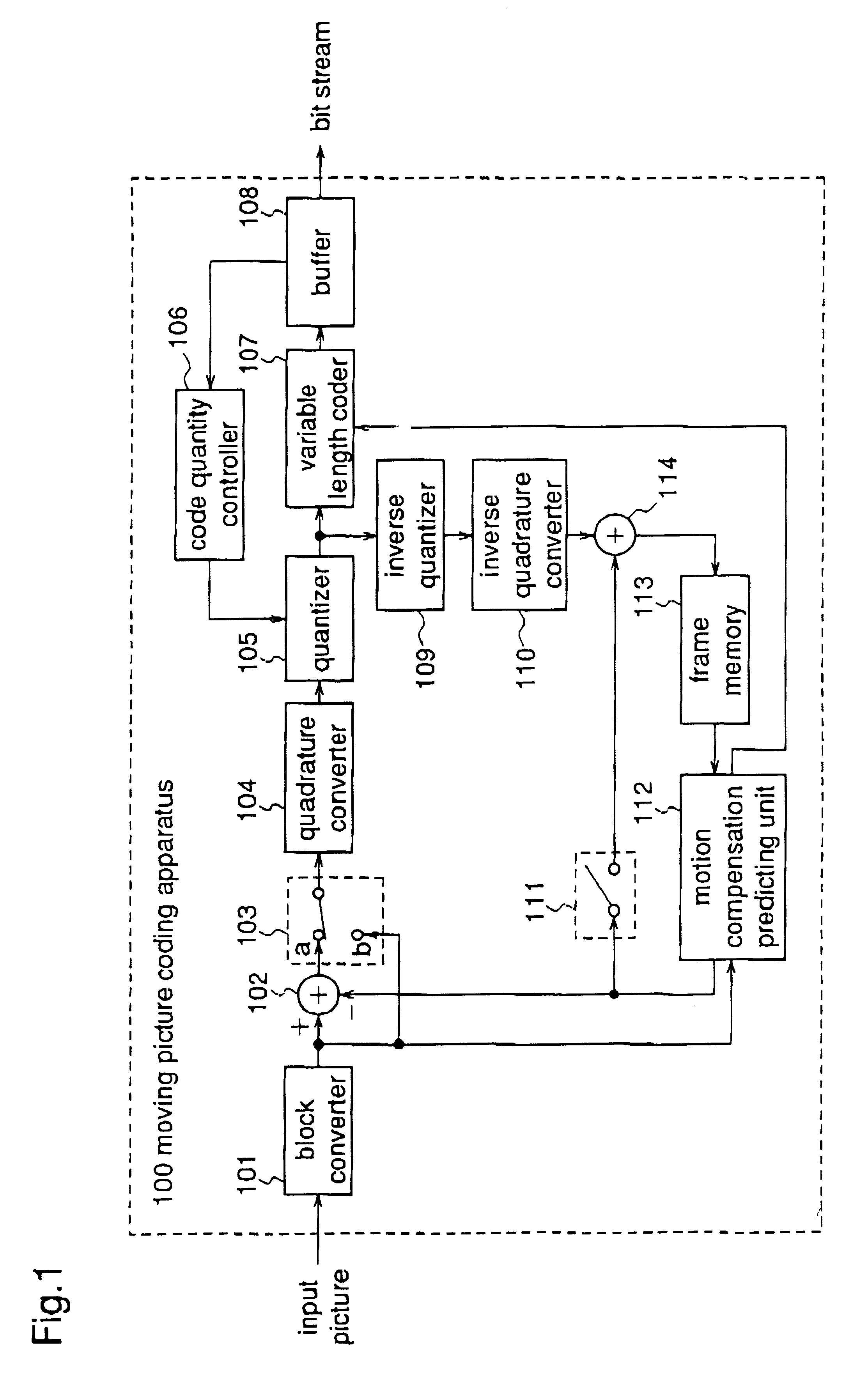
Moving picture variable bit rate coding apparatus, moving picture variable bit rate coding method, and recording medium for moving picture variable bit rate coding program
InactiveUS6259739B1Improved coding resultIncrease the compression ratioTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesComputer scienceTime processing
A moving picture variable bit rate coding apparatus receives digitized moving pictures and subjects them to coding according to a variable bit rate method using real time processing in response to the input of the pictures. The apparatus performs variable bit rate coding in real time by sequentially performing blocking, conversion processing, quantization processing, and generation of bit streams in response to the input of digitized moving picture data, and setting a quantization scale used for quantization corresponding to a quantity of generated bit streams to perform coding processing and control of quantization in parallel.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
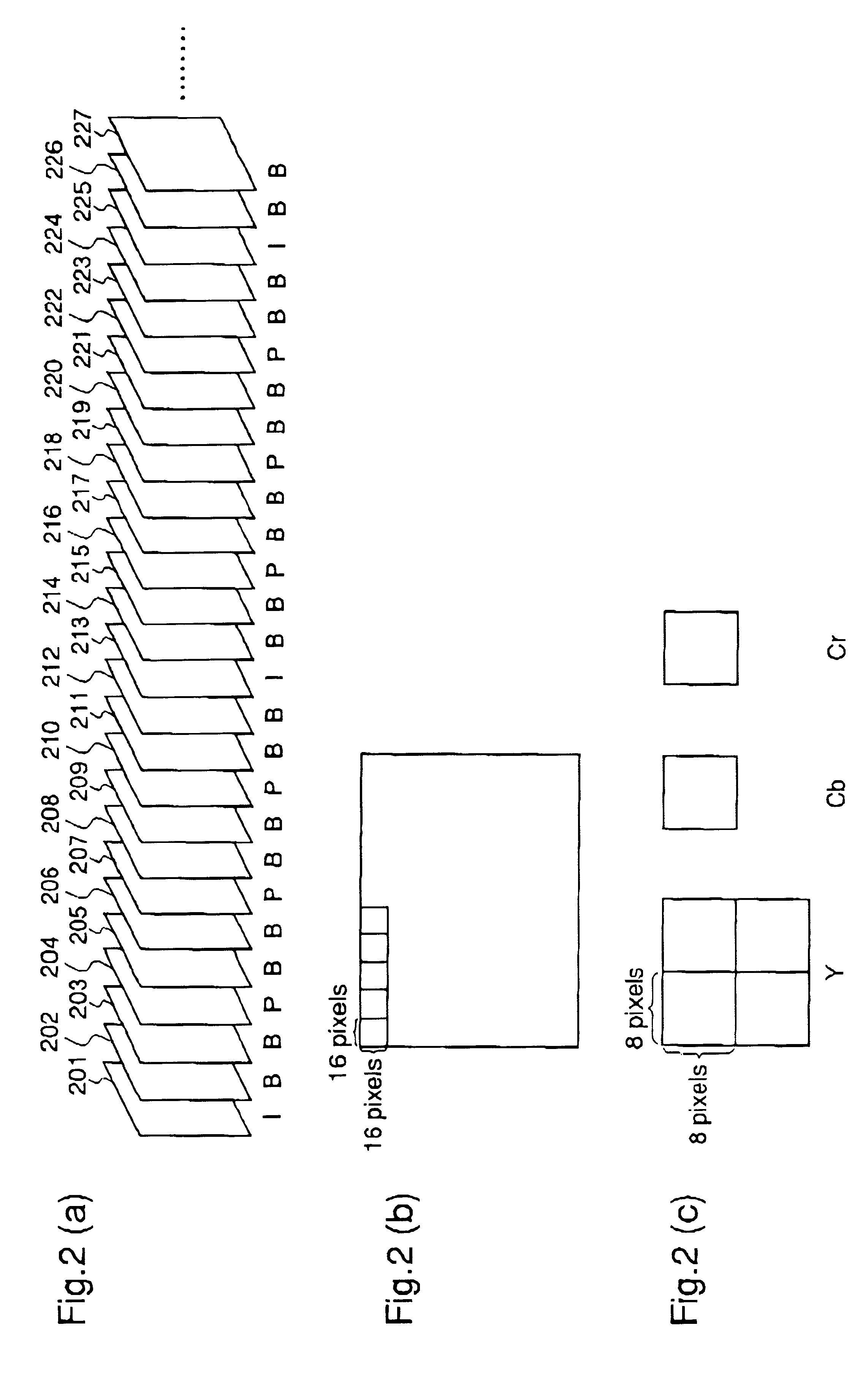
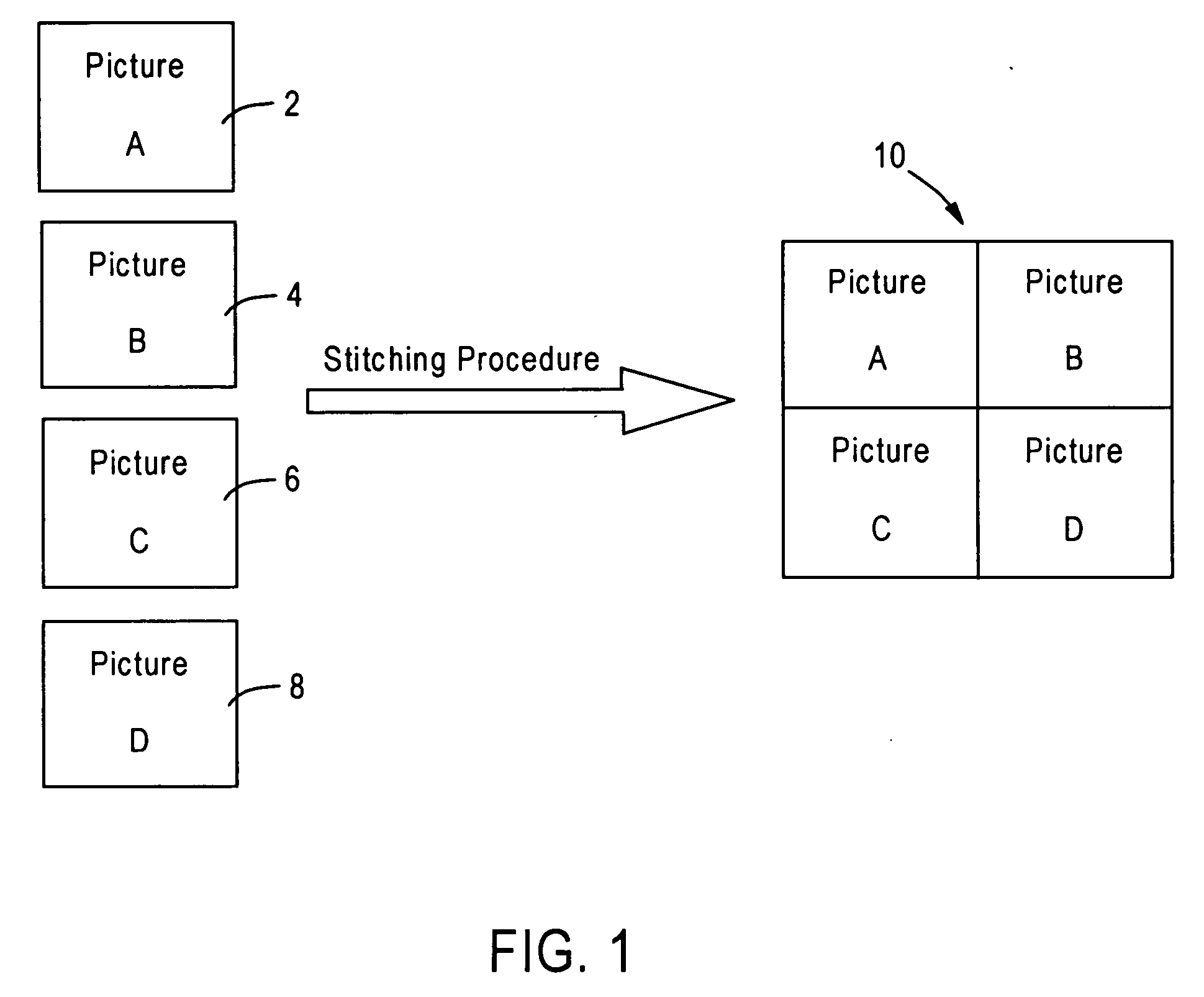
Stitching of video for continuous presence multipoint video conferencing
InactiveUS20050008240A1Avoid mistakesTelevision system detailsTelevision conference systemsVideo bitstreamVideo sequence
A drift-free hybrid method of performing video stitching is provided. The method includes decoding a plurality of video bitstreams and storing prediction information. The decoded bitstreams form video images, spatially composed into a combined image. The image comprises frames of ideal stitched video sequence. The method uses prediction information in conjunction with previously generated frames to predict pixel blocks in the next frame. A stitched predicted block in the next frame is subtracted from a corresponding block in a corresponding frame to create a stitched raw residual block. The raw residual block is forward transformed, quantized, entropy encoded and added to the stitched video bitstream along with the prediction information. Also, the stitched raw residual block is inverse transformed and dequantized to create a stitched decoded residual block. The residual block is added to the predicted block to generate the stitched reconstructed block in the next frame of the sequence.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Method and device for monitoring and analyzing signals
A method and system for monitoring and analyzing at least one signal are disclosed. An abstract of at least one reference signal is generated and stored in a reference database. An abstract of a query signal to be analyzed is then generated so that the abstract of the query signal can be compared to the abstracts stored in the reference database for a match. The method and system may optionally be used to record information about the query signals, the number of matches recorded, and other useful information about the query signals. Moreover, the method by which abstracts are generated can be programmable based upon selectable criteria. The system can also be programmed with error control software so as to avoid the re-occurrence of a query signal that matches more than one signal stored in the reference database.
Owner:WISTARIA TRADING INC
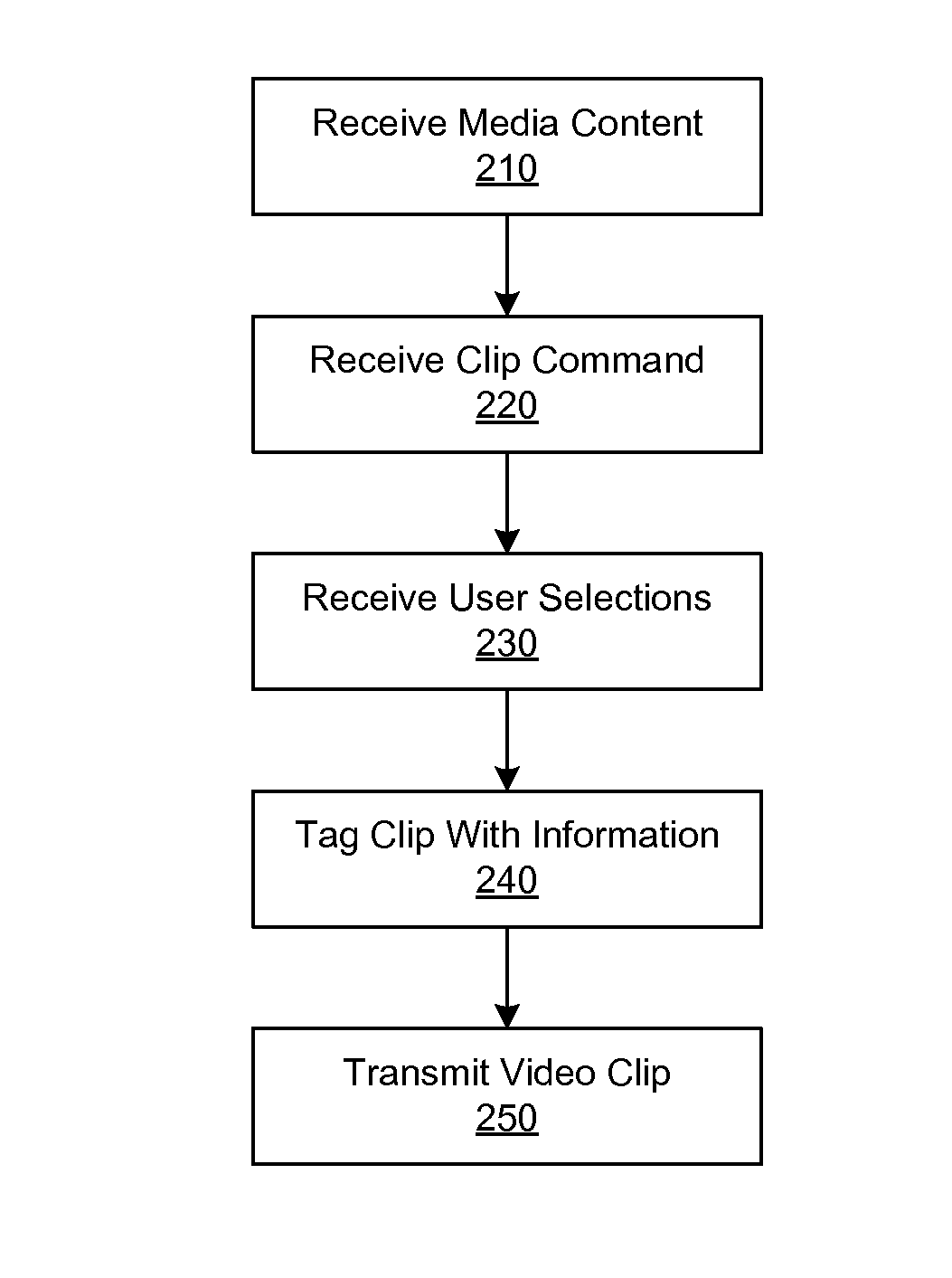
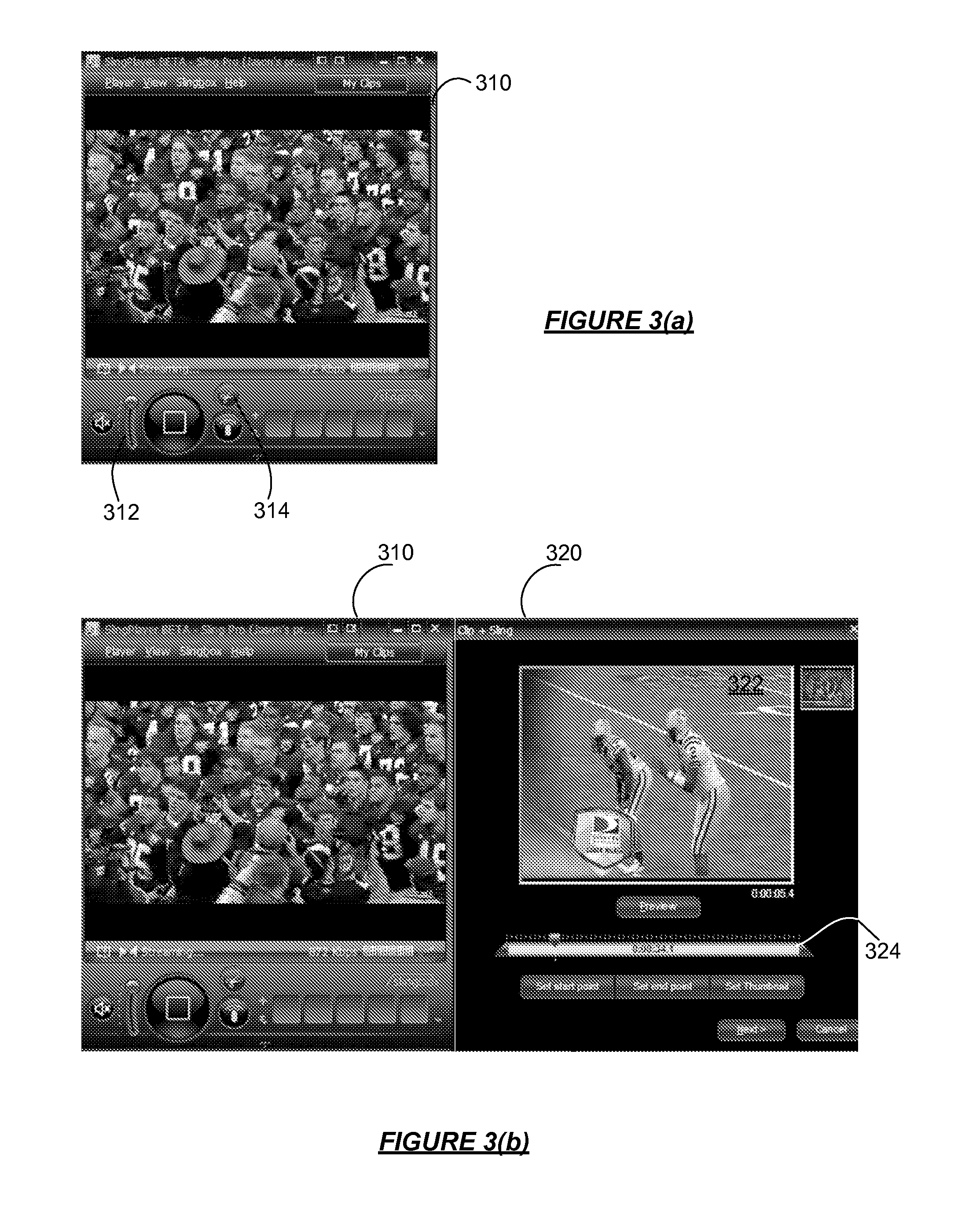
Capturing and Sharing Media Content
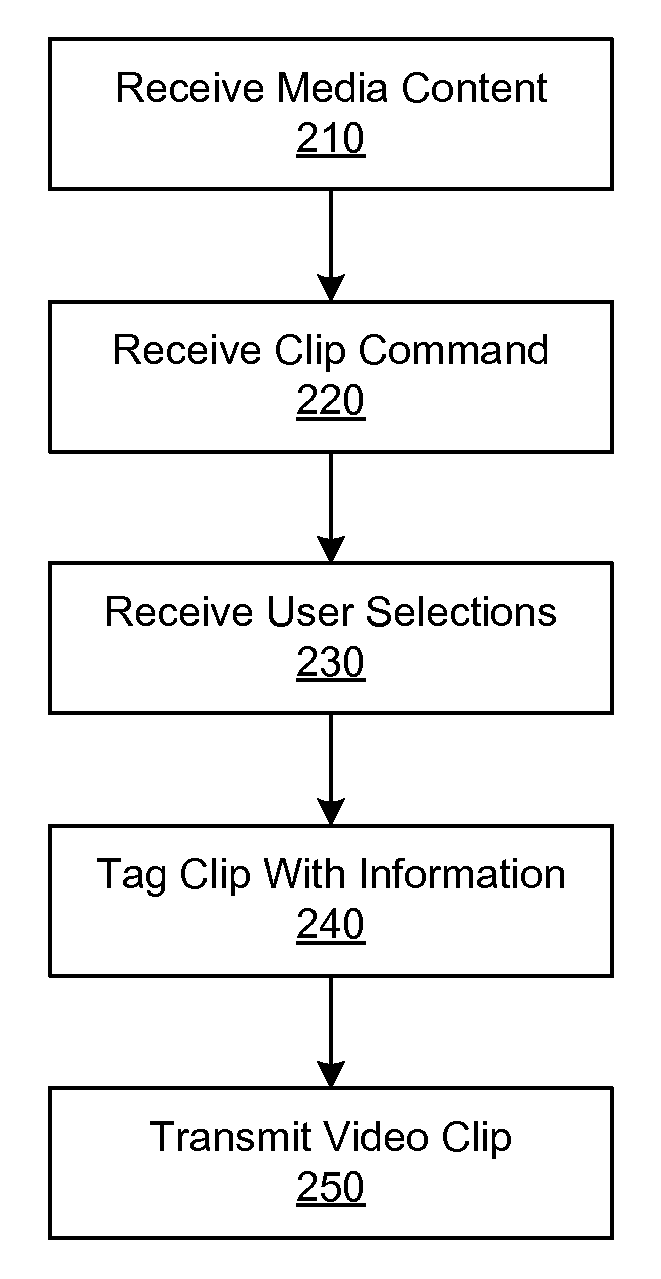
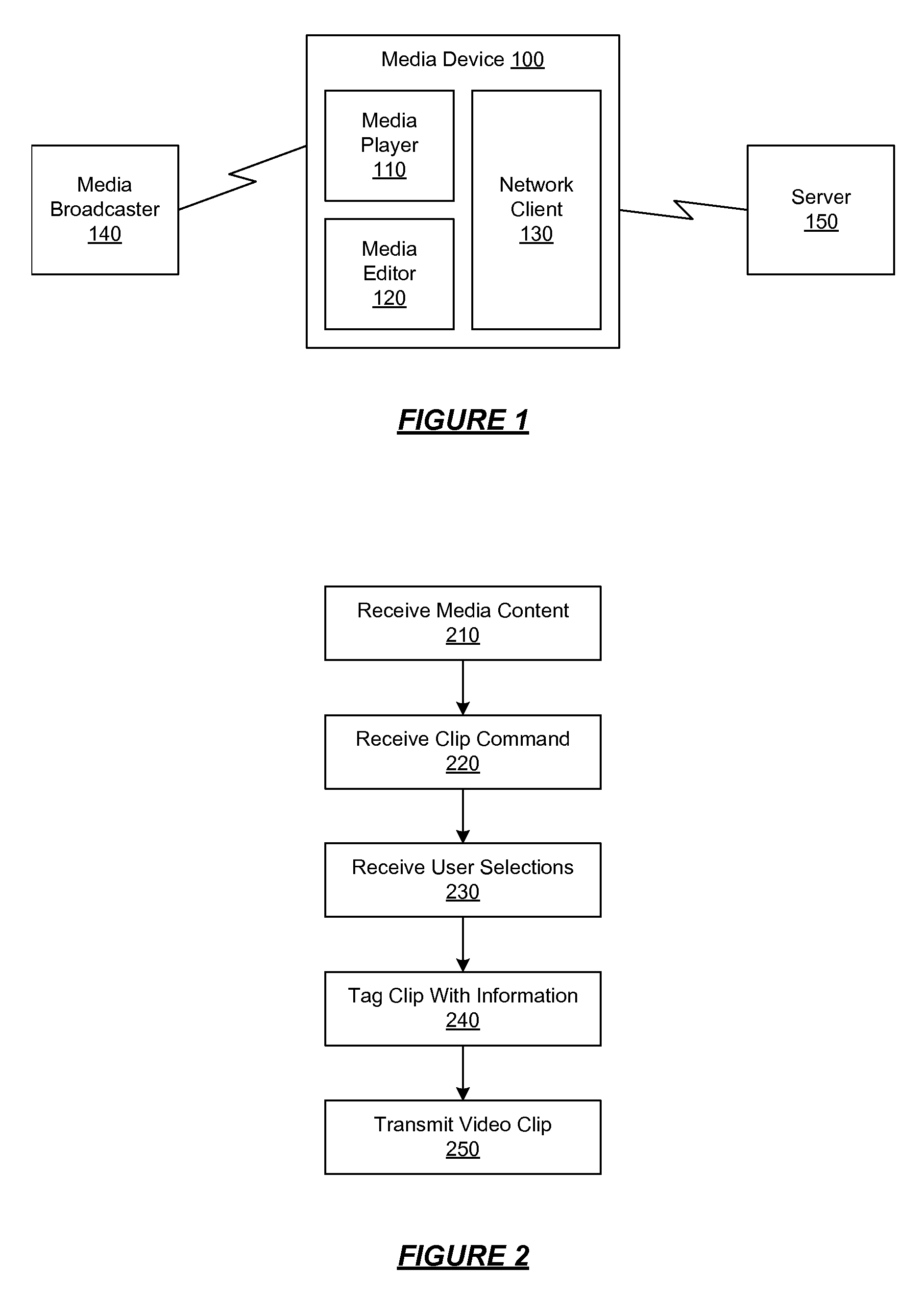
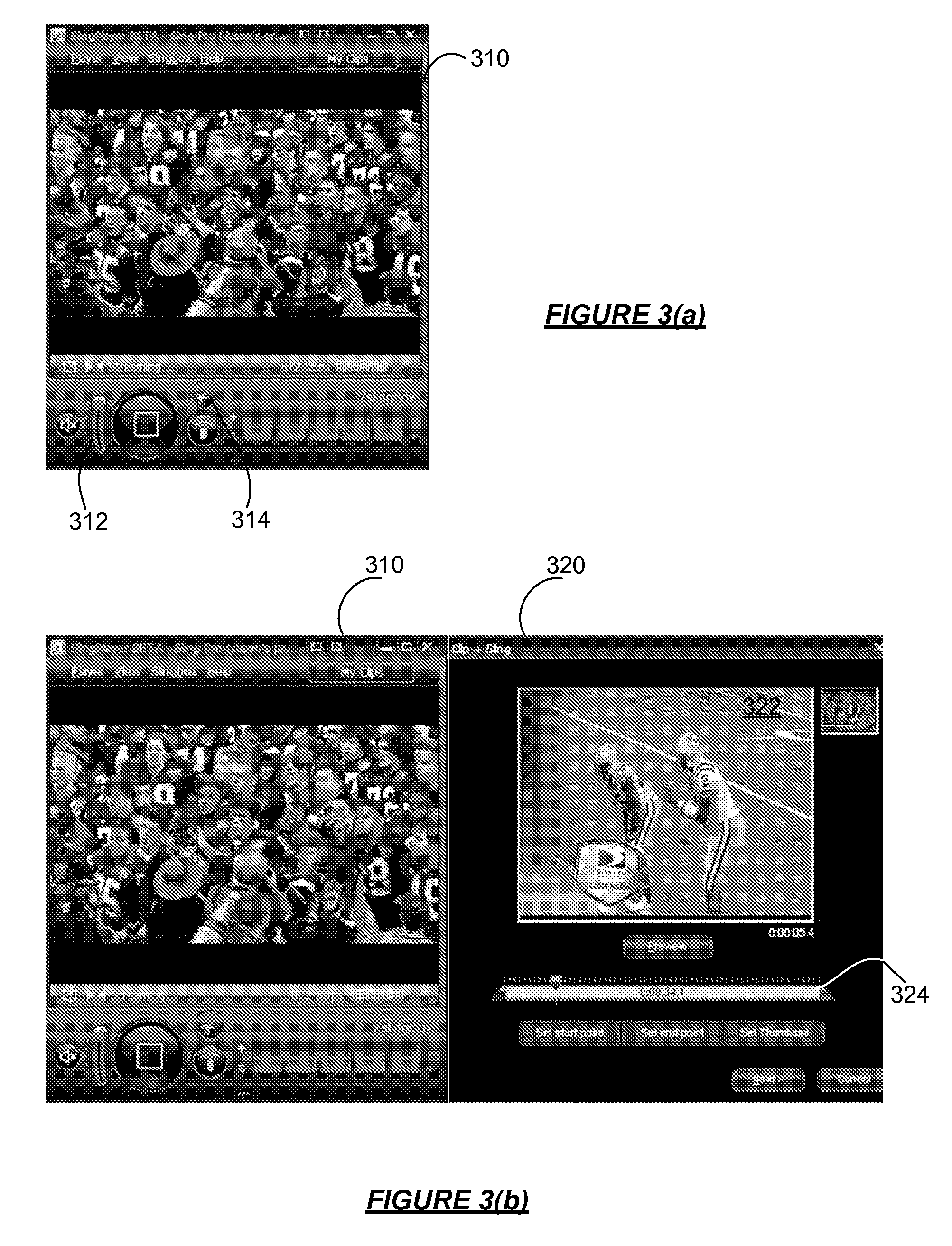
ActiveUS20070168543A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsBroadcast-related systemsWeb siteShared medium
A media device allows users to watch and capture portions from a media stream. Users may then share the captured media content with other users. In one embodiment, the media device receives a media stream, plays the media stream, and caches a portion of the media stream as it is being played. A user can define a media clip by selecting its boundaries in the cached portion of the media stream. The media device creates the media clip based on the user's input and enables the user to transmit the media clip to another system, such as a community website for sharing it with other users.
Owner:SLING MEDIA LLC
Video frame encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20050169374A1Improve effectivenessDecrease in code efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAdaptive encodingContext model
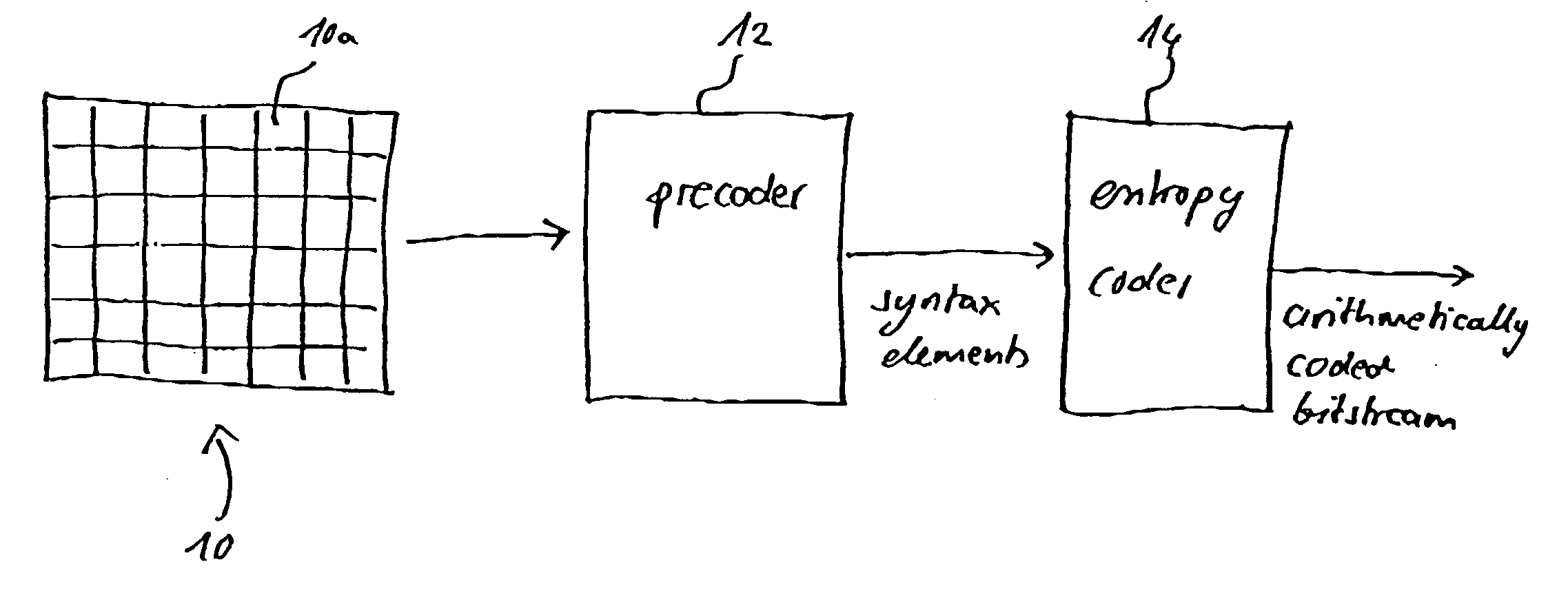
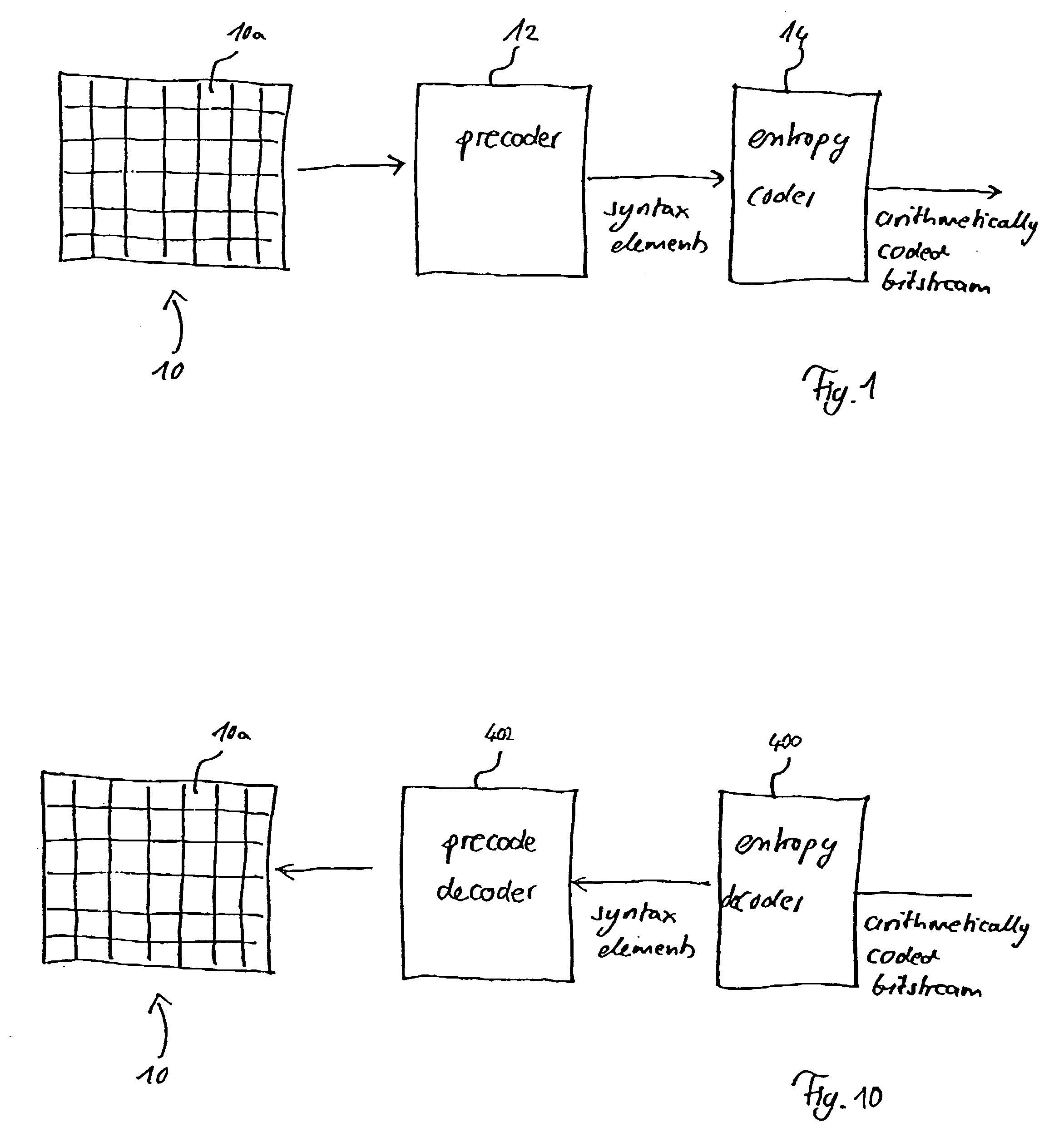
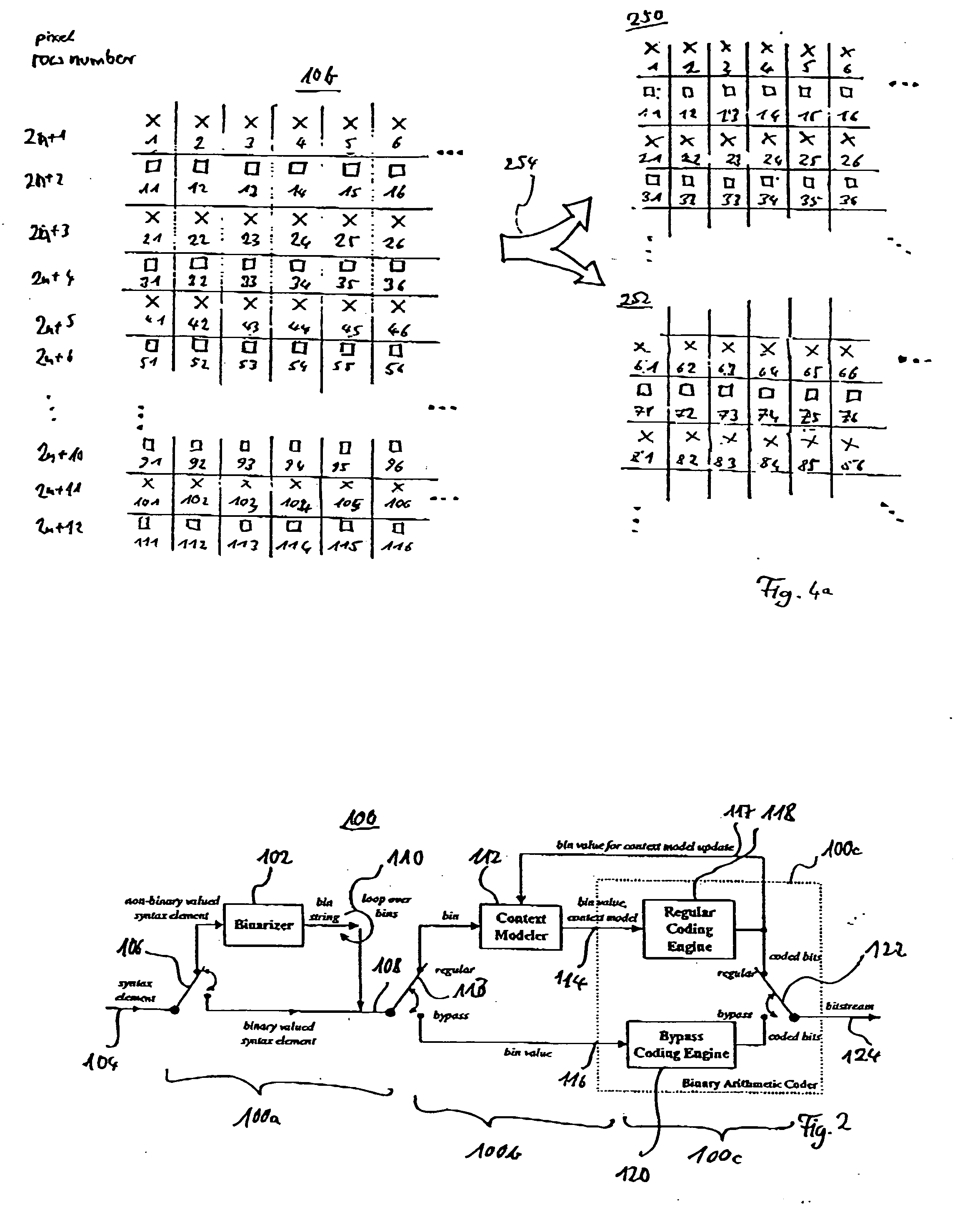
A video frame arithmetical context adaptive encoding and decoding scheme is presented which is based on the finding, that, for sake of a better definition of neighborhood between blocks of picture samples, i.e. the neighboring block which the syntax element to be coded or decoded relates to and the current block based on the attribute of which the assignment of a context model is conducted, and when the neighboring block lies beyond the borders or circumference of the current macroblock containing the current block, it is important to make the determination of the macroblock containing the neighboring block dependent upon as to whether the current macroblock pair region containing the current block is of a first or a second distribution type, i.e., frame or field coded.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Apparatus and method for processing video data
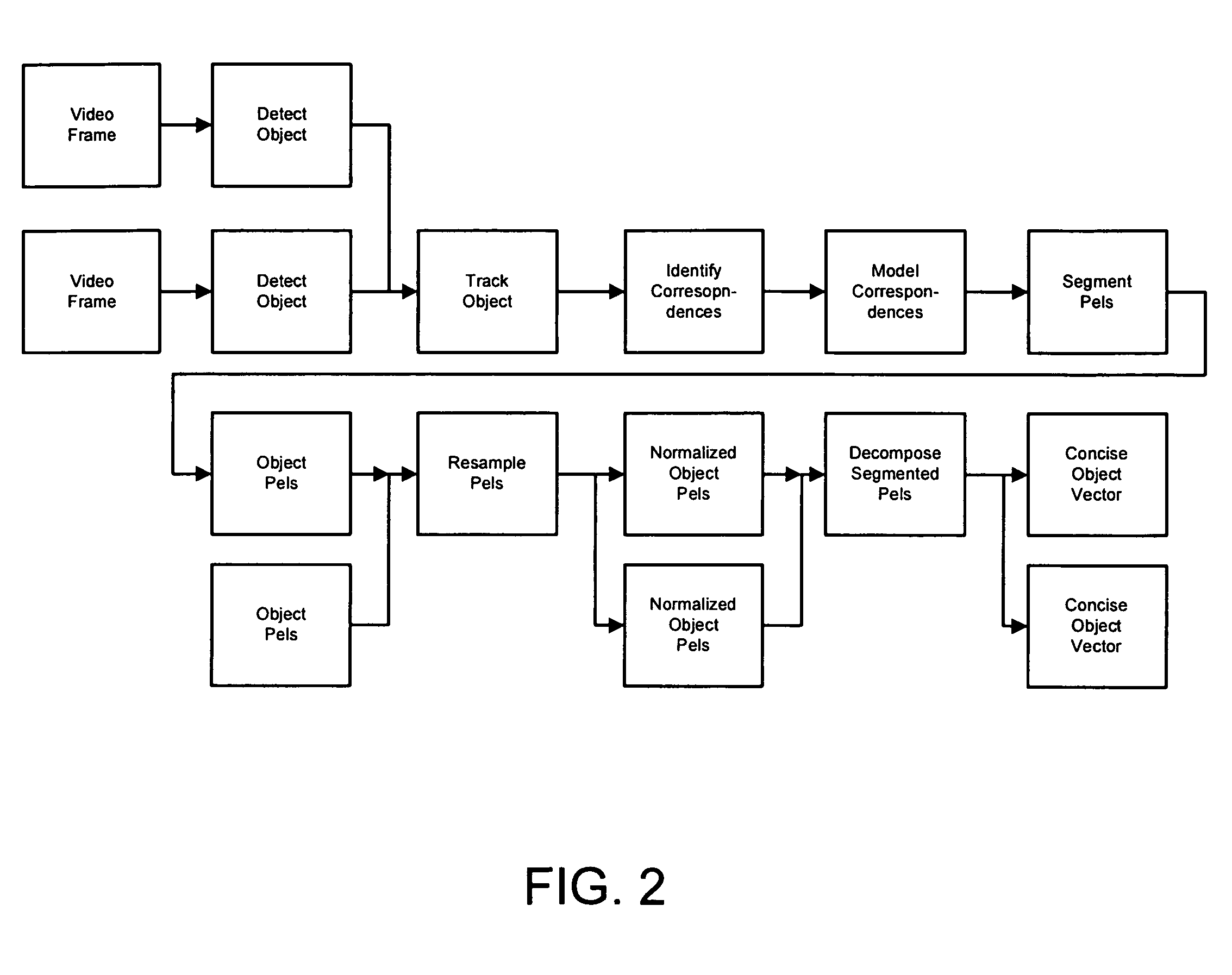
ActiveUS7158680B2Increases robustness and applicabilityReduce non-linearityImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionComputer graphics (images)
An apparatus and methods for processing video data are described. The invention provides a representation of video data that can be used to assess agreement between the data and a fitting model for a particular parameterization of the data. This allows the comparison of different parameterization techniques and the selection of the optimum one for continued video processing of the particular data. The representation can be utilized in intermediate form as part of a larger process or as a feedback mechanism for processing video data. When utilized in its intermediate form, the invention can be used in processes for storage, enhancement, refinement, feature extraction, compression, coding, and transmission of video data. The invention serves to extract salient information in a robust and efficient manner while addressing the problems typically associated with video data sources
Owner:EUCLID DISCOVERIES LLC
Popular searches
Image coding Digital video signal modification Selective content distribution Home automation networks Synchronous/start-stop systems Data switching by path configuration Multiple digital computer combinations Simultaneous/sequential multiple television signal transmission Special data processing applications Multimedia data retrieval
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com