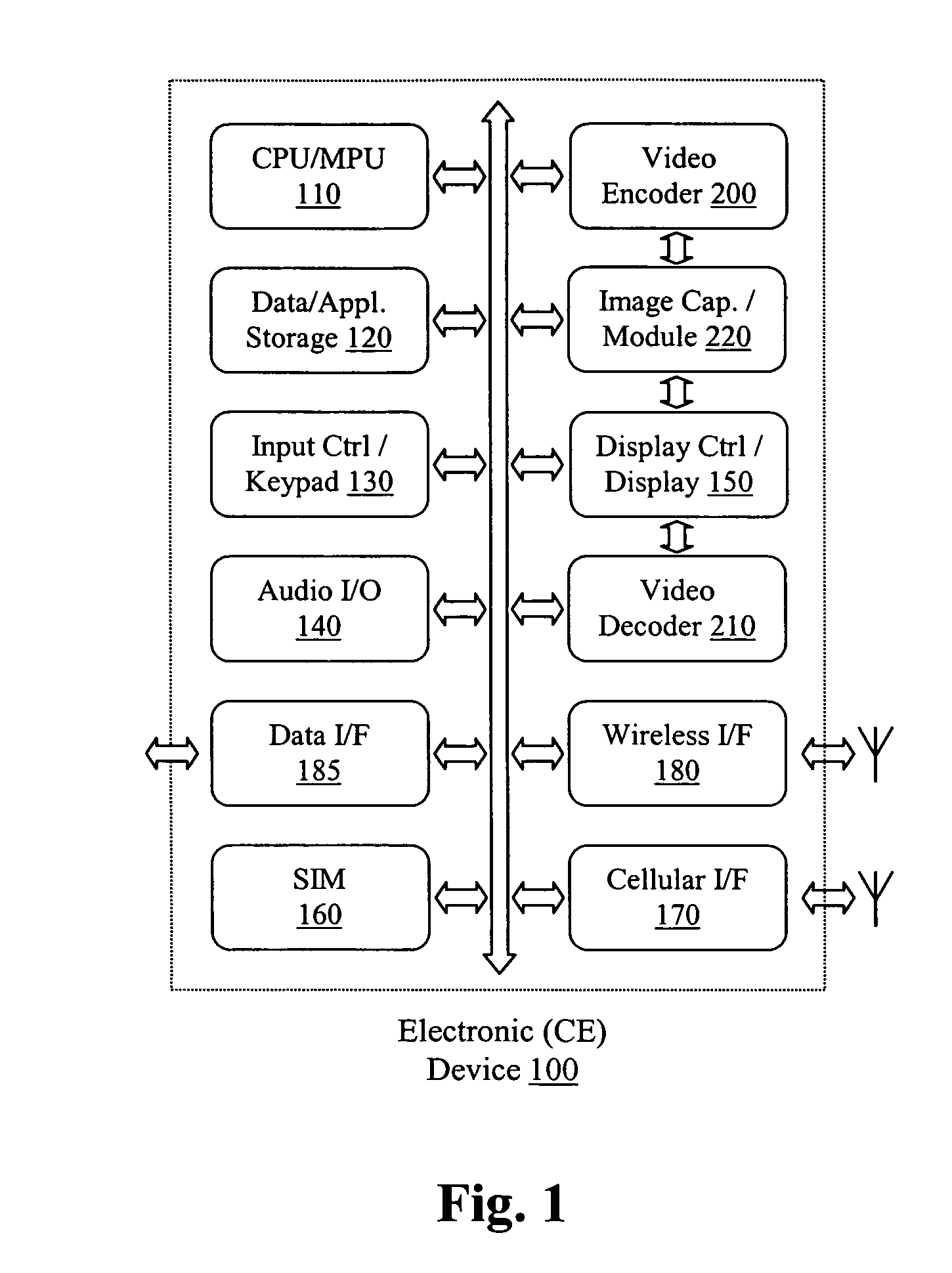
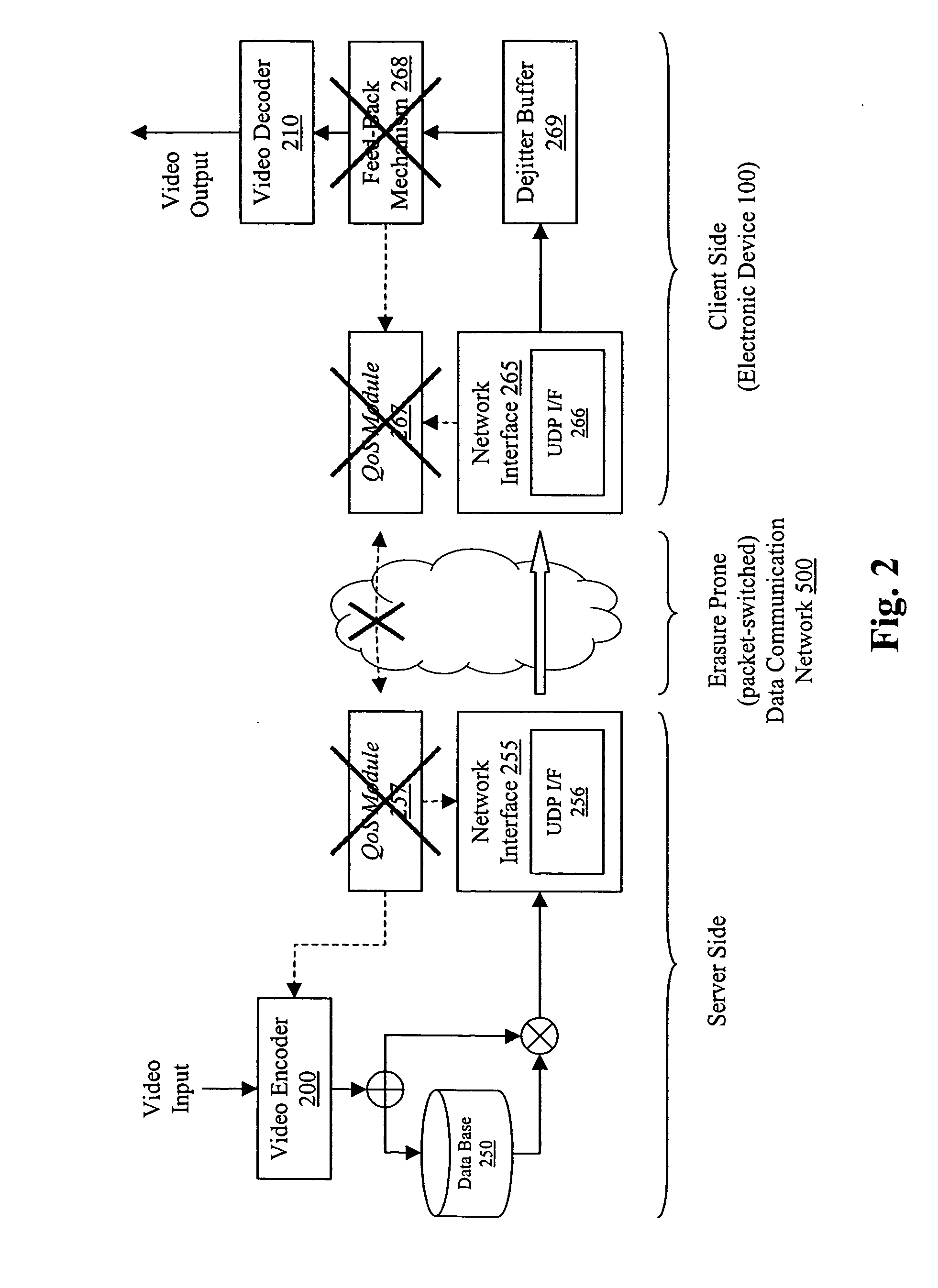
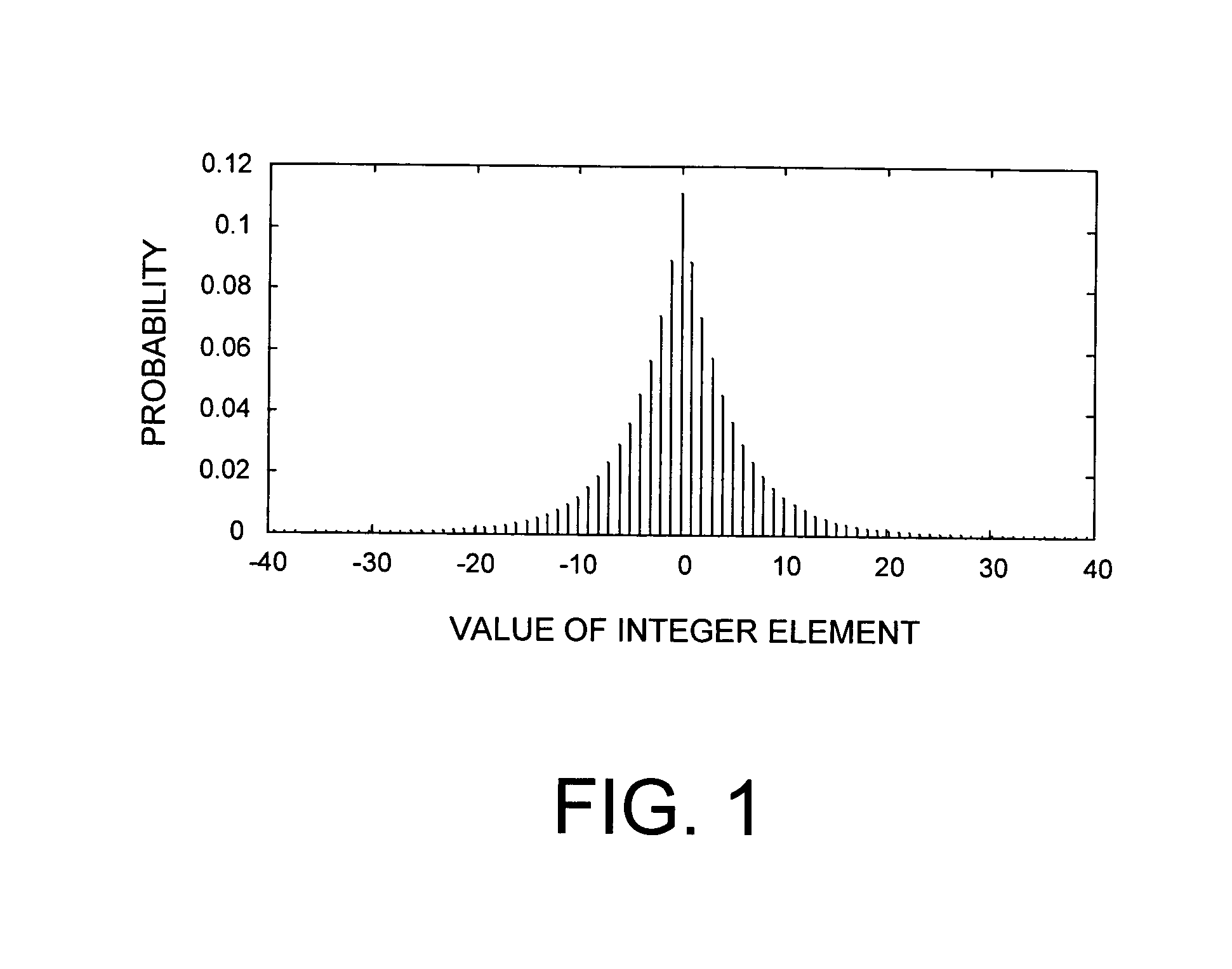
Patents
Literature
168 results about "Adaptive encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adaptive Huffman coding (also called Dynamic Huffman coding) is an adaptive coding technique based on Huffman coding. It permits building the code as the symbols are being transmitted, having no initial knowledge of source distribution, that allows one-pass encoding and adaptation to changing conditions in data.
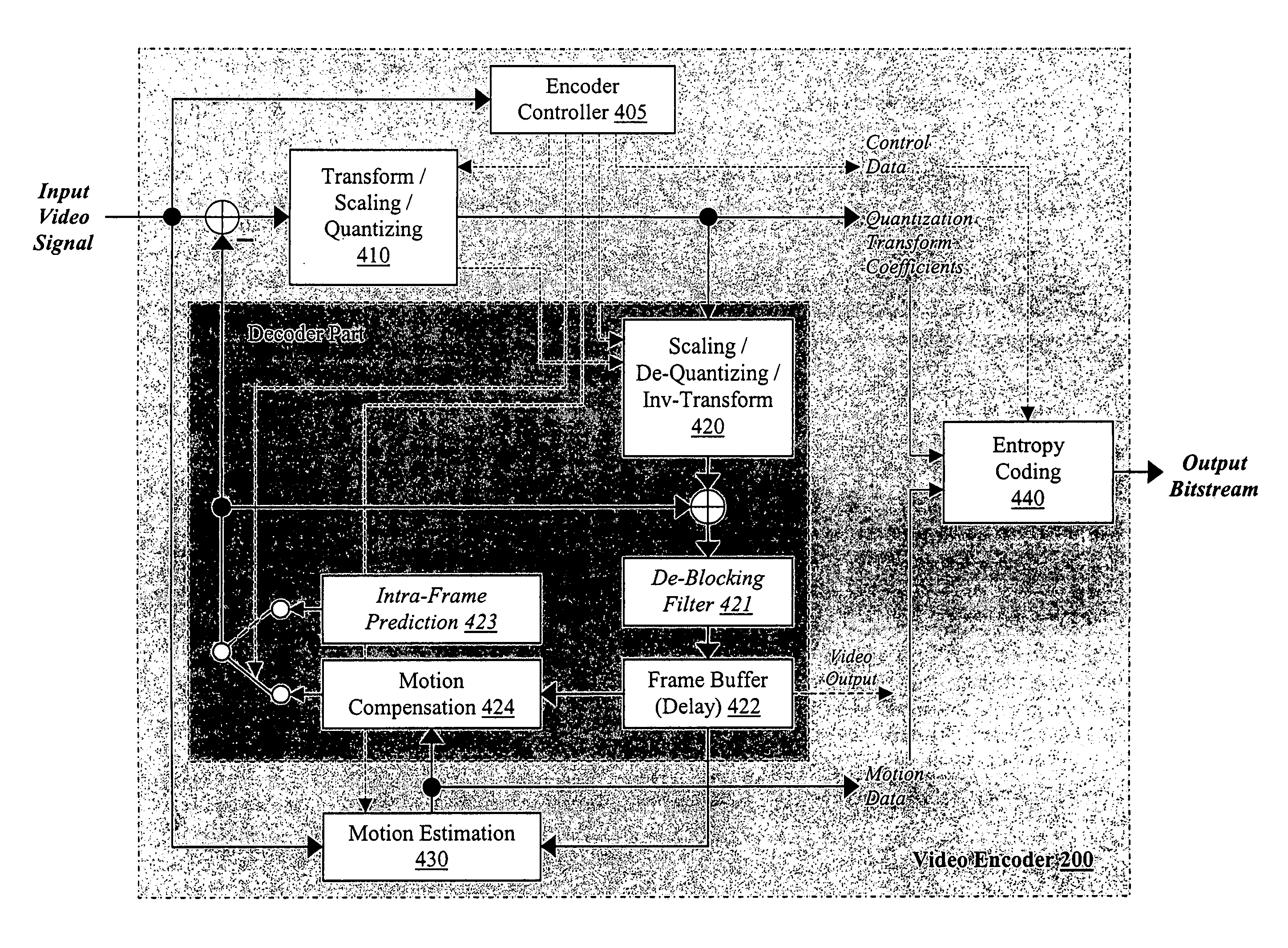
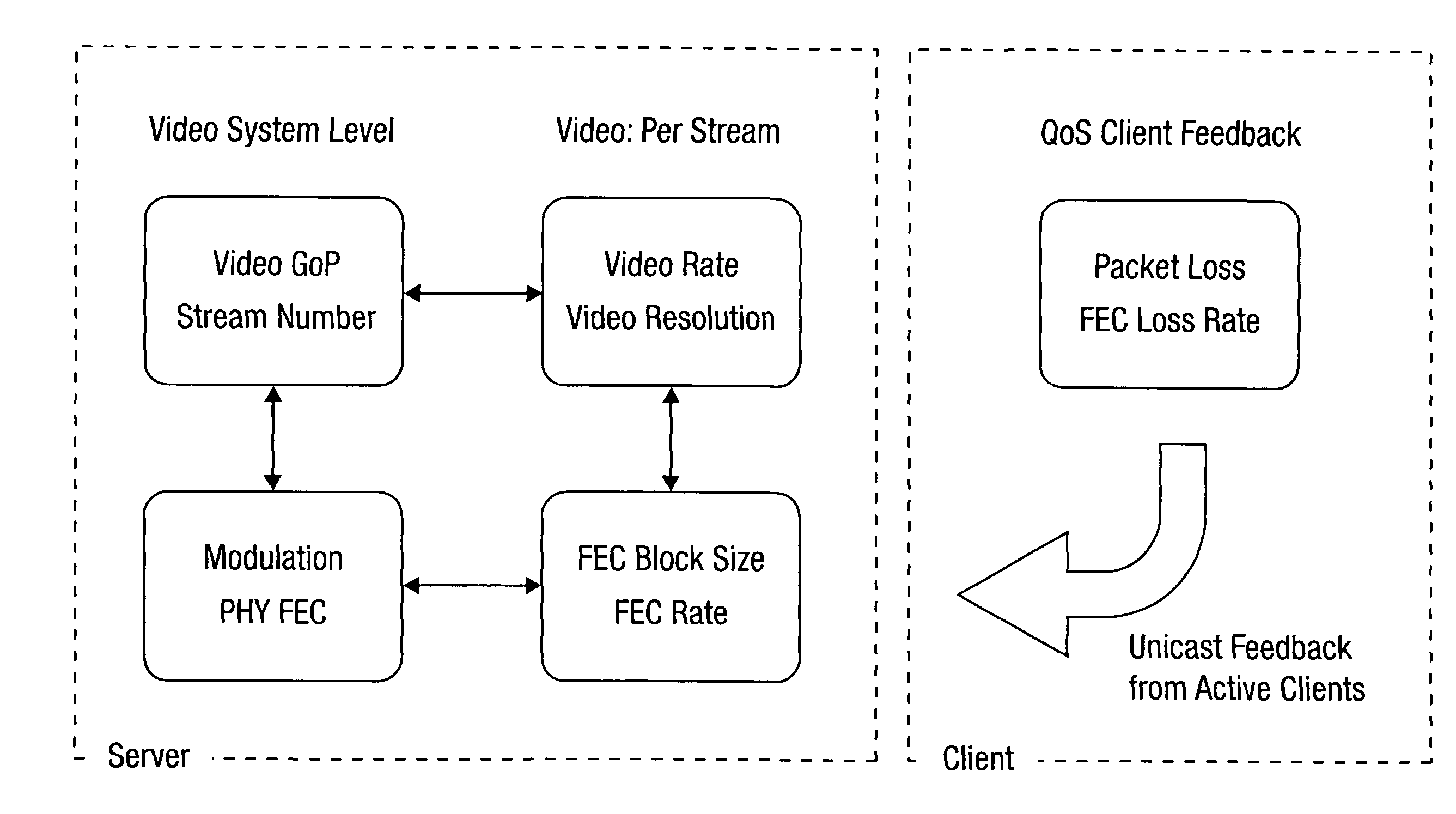
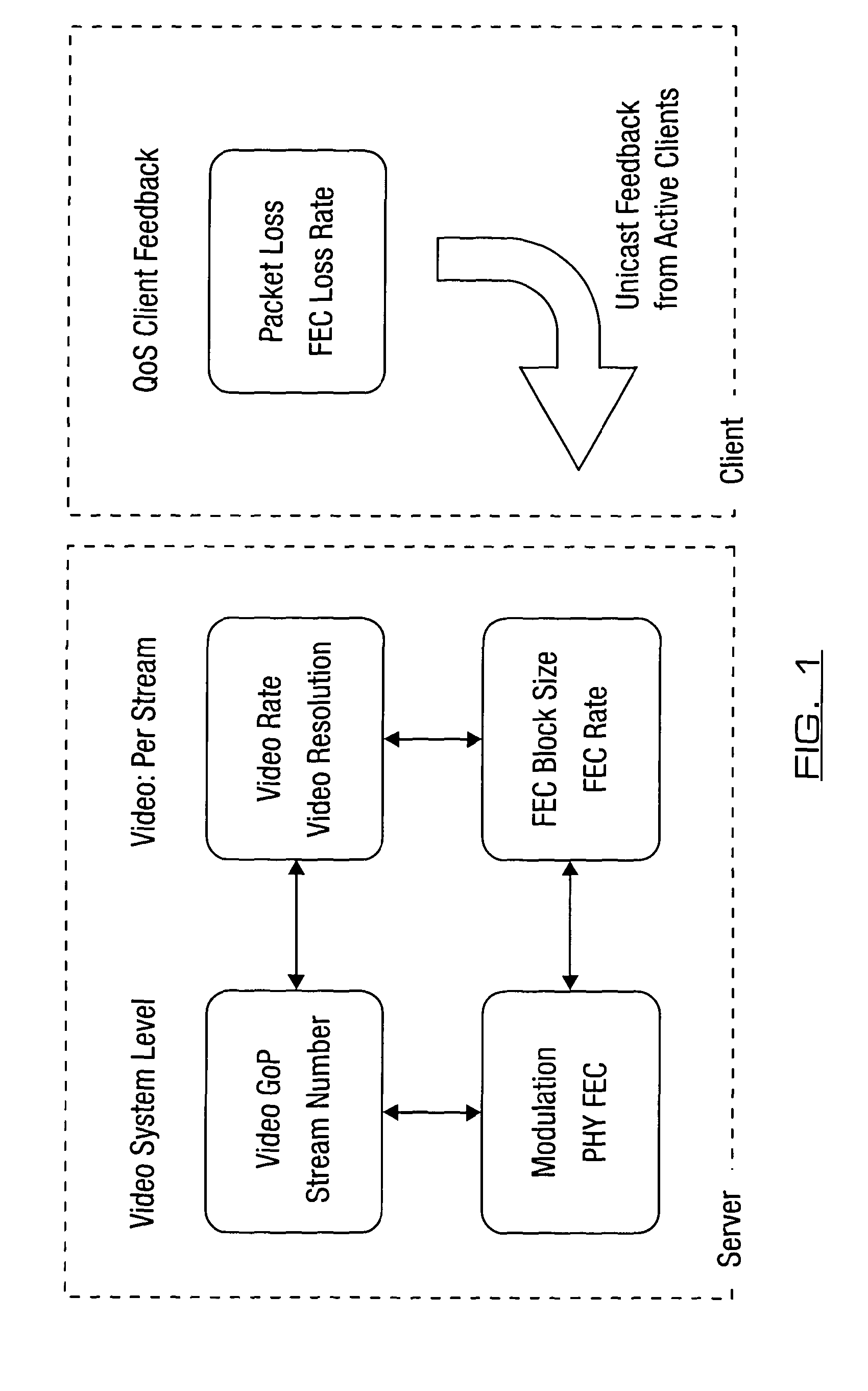
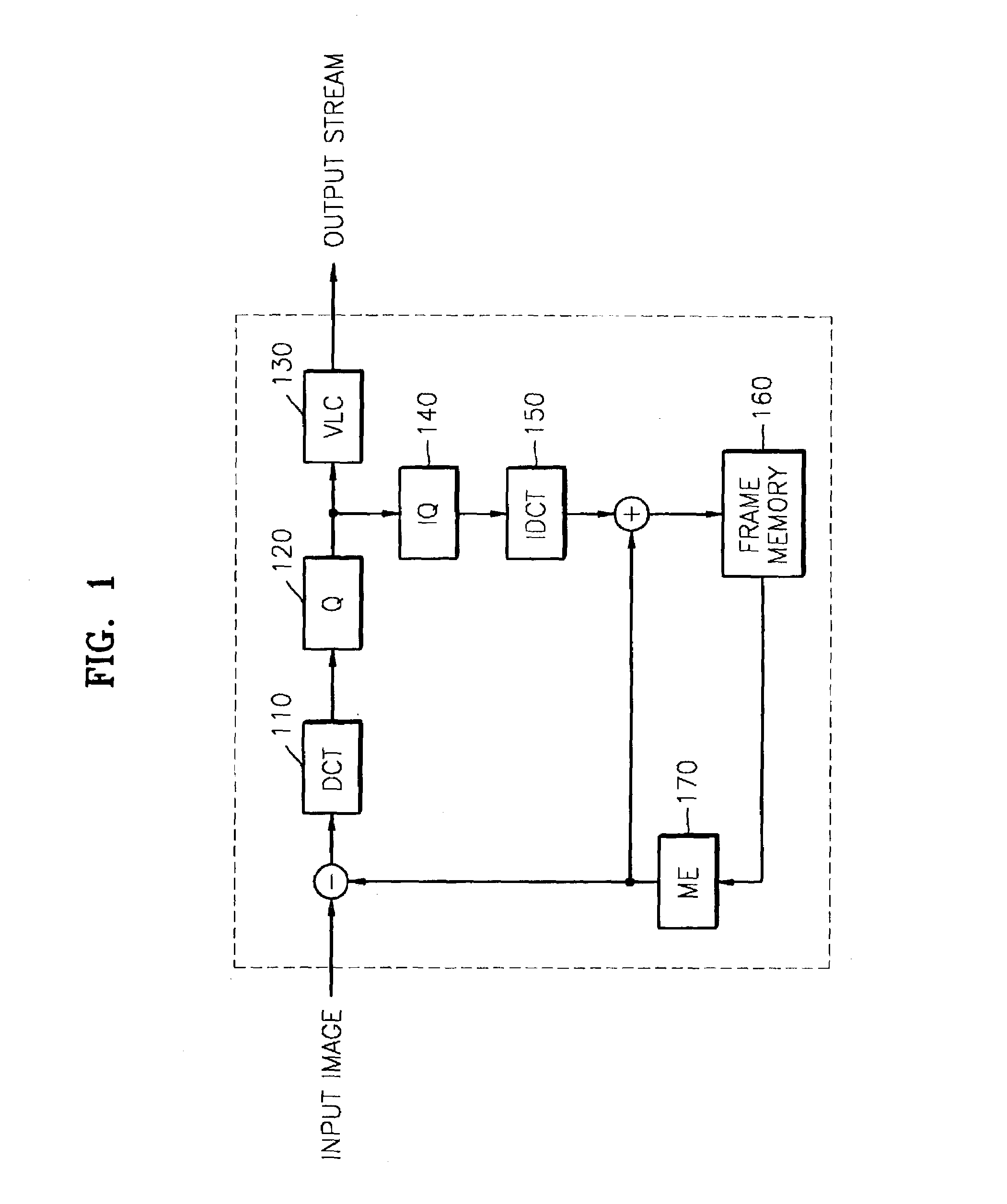
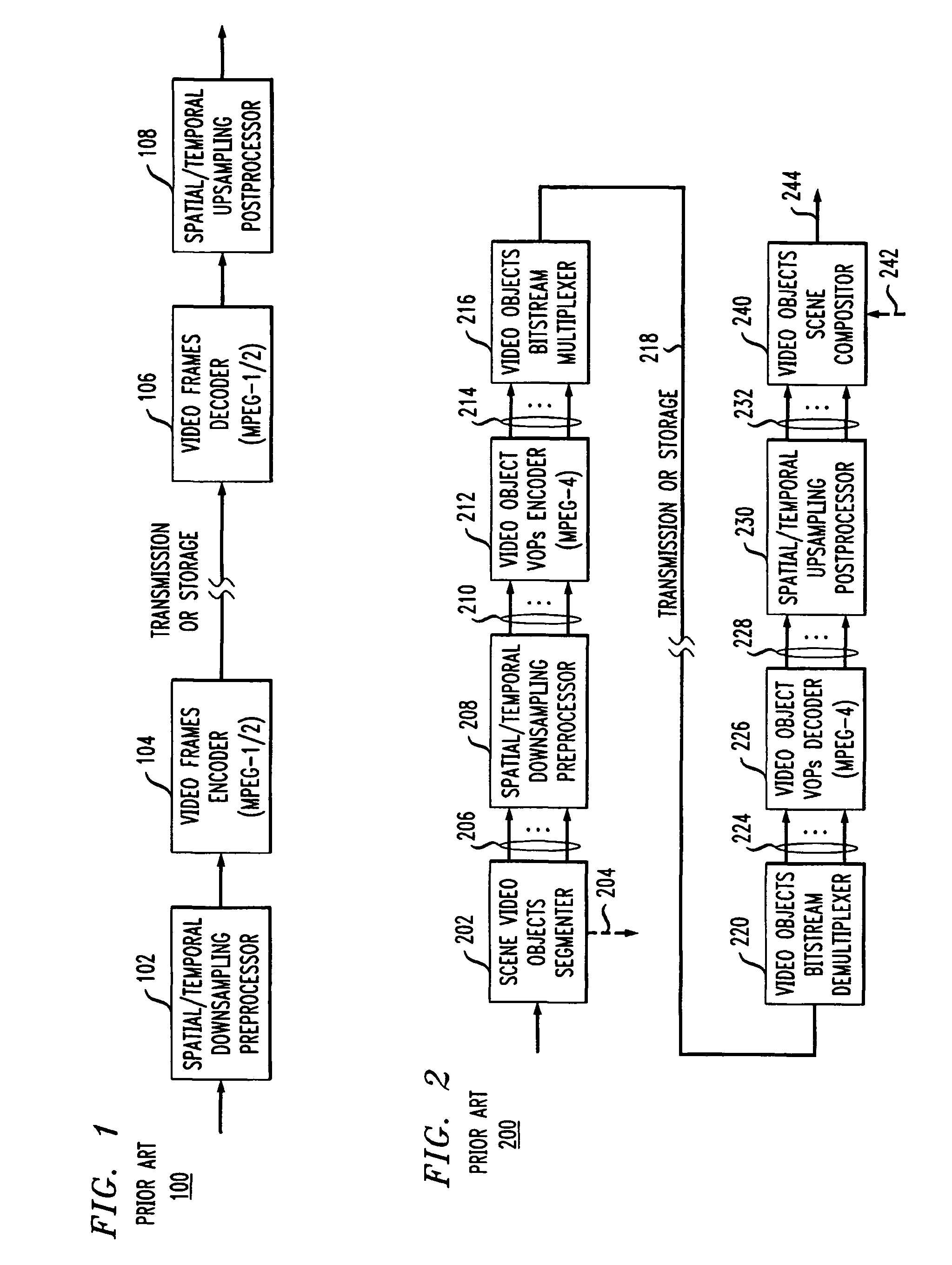
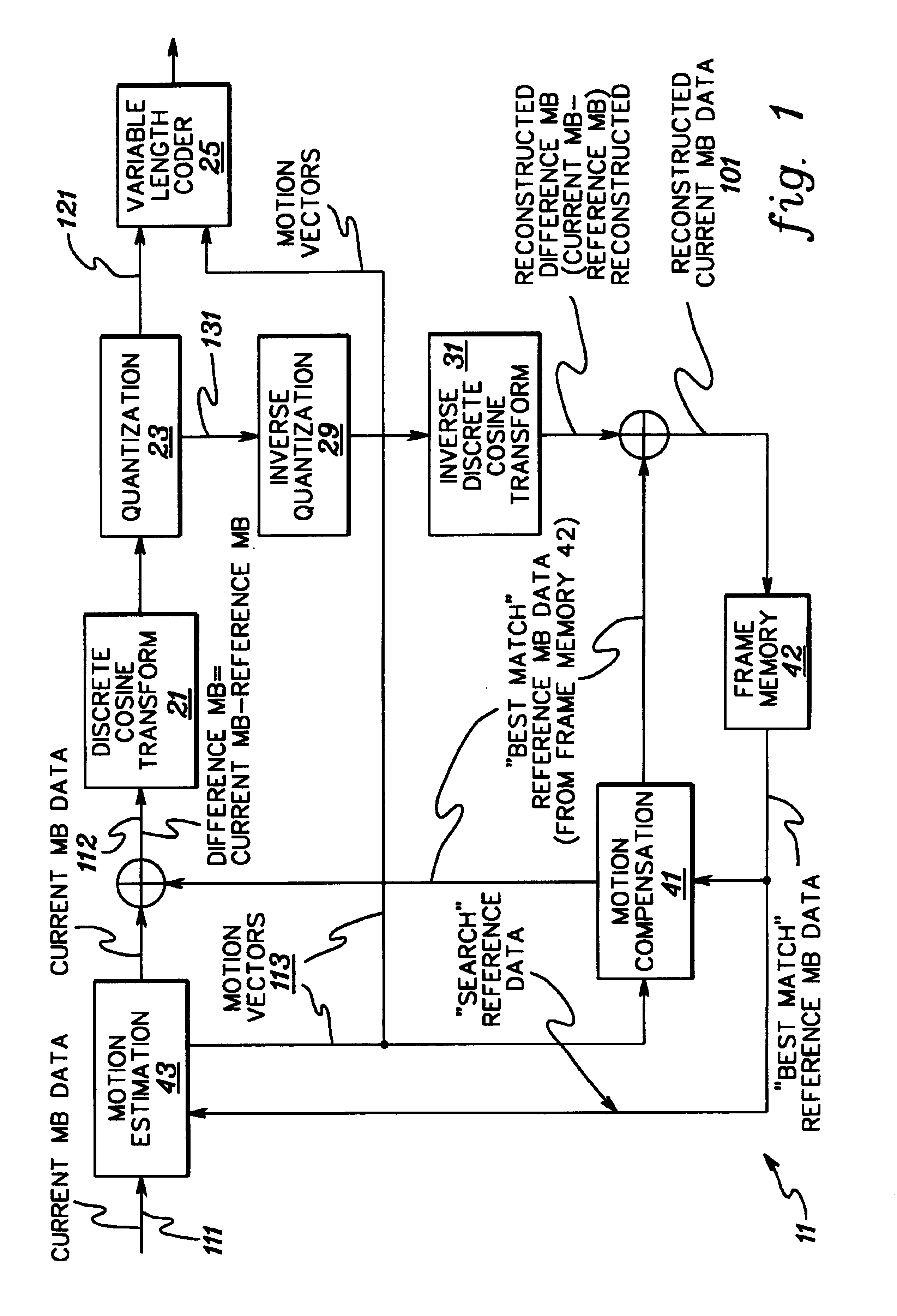
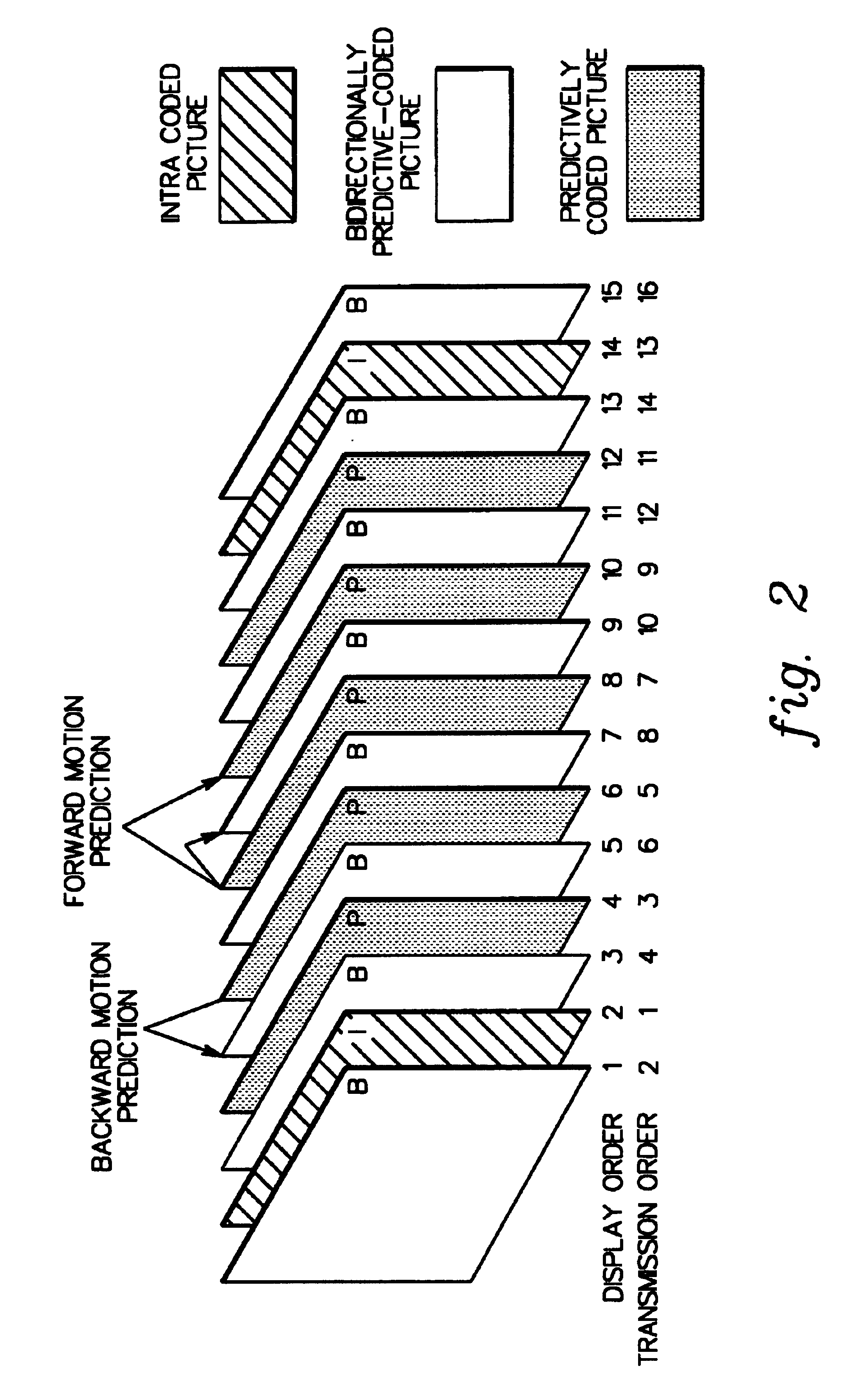
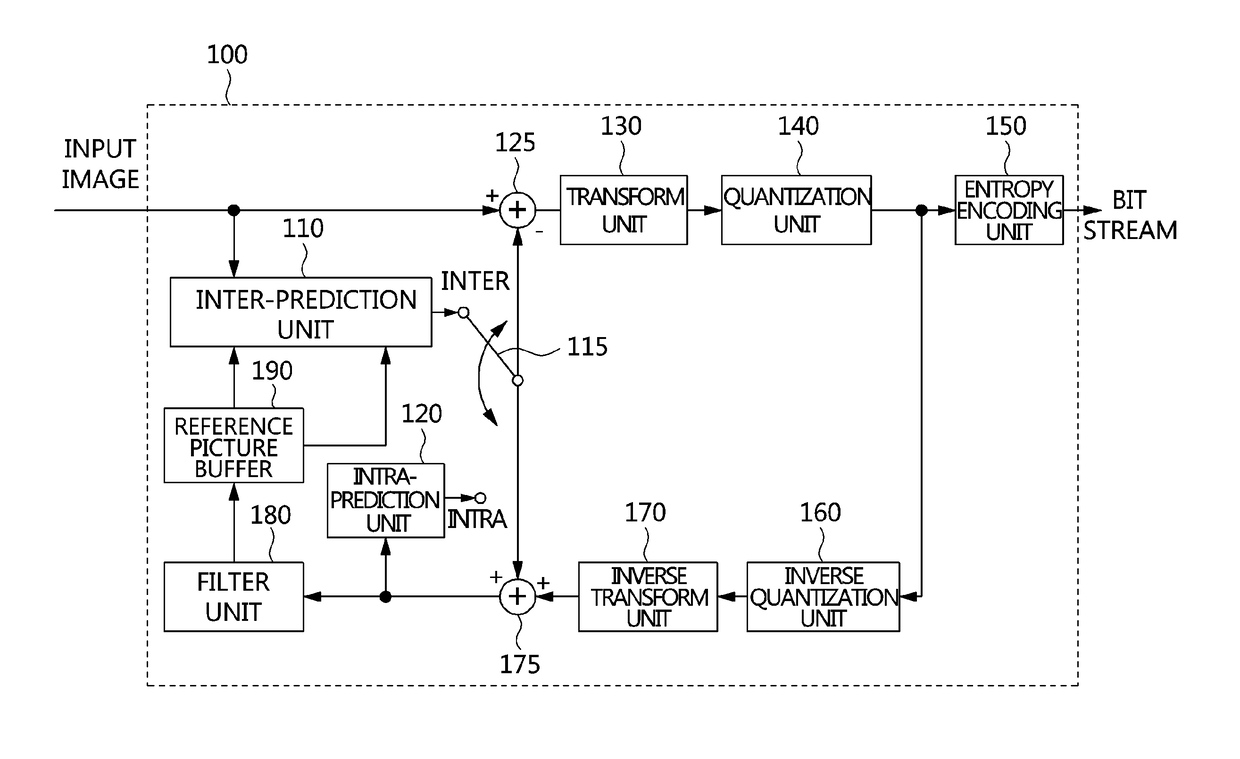
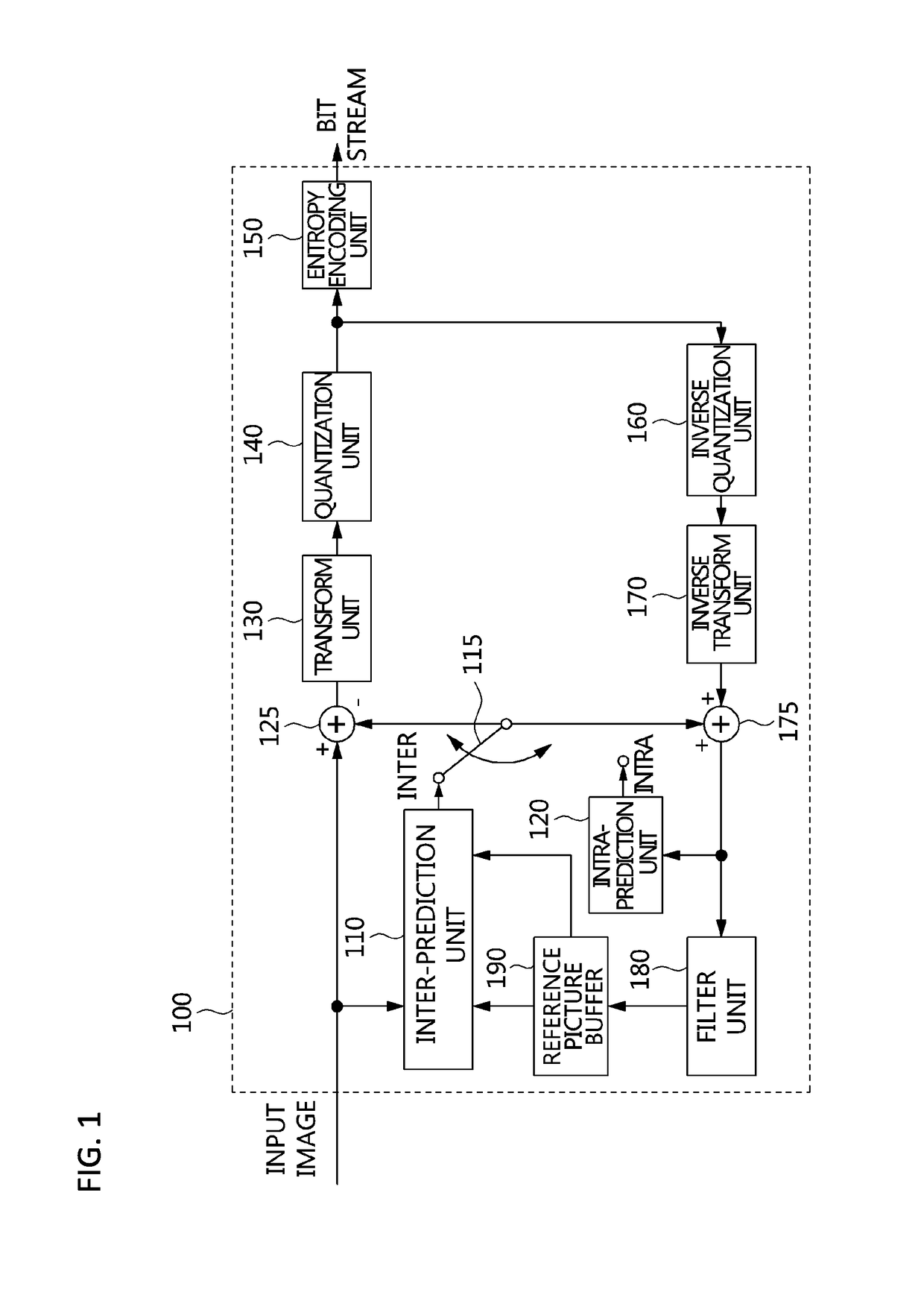
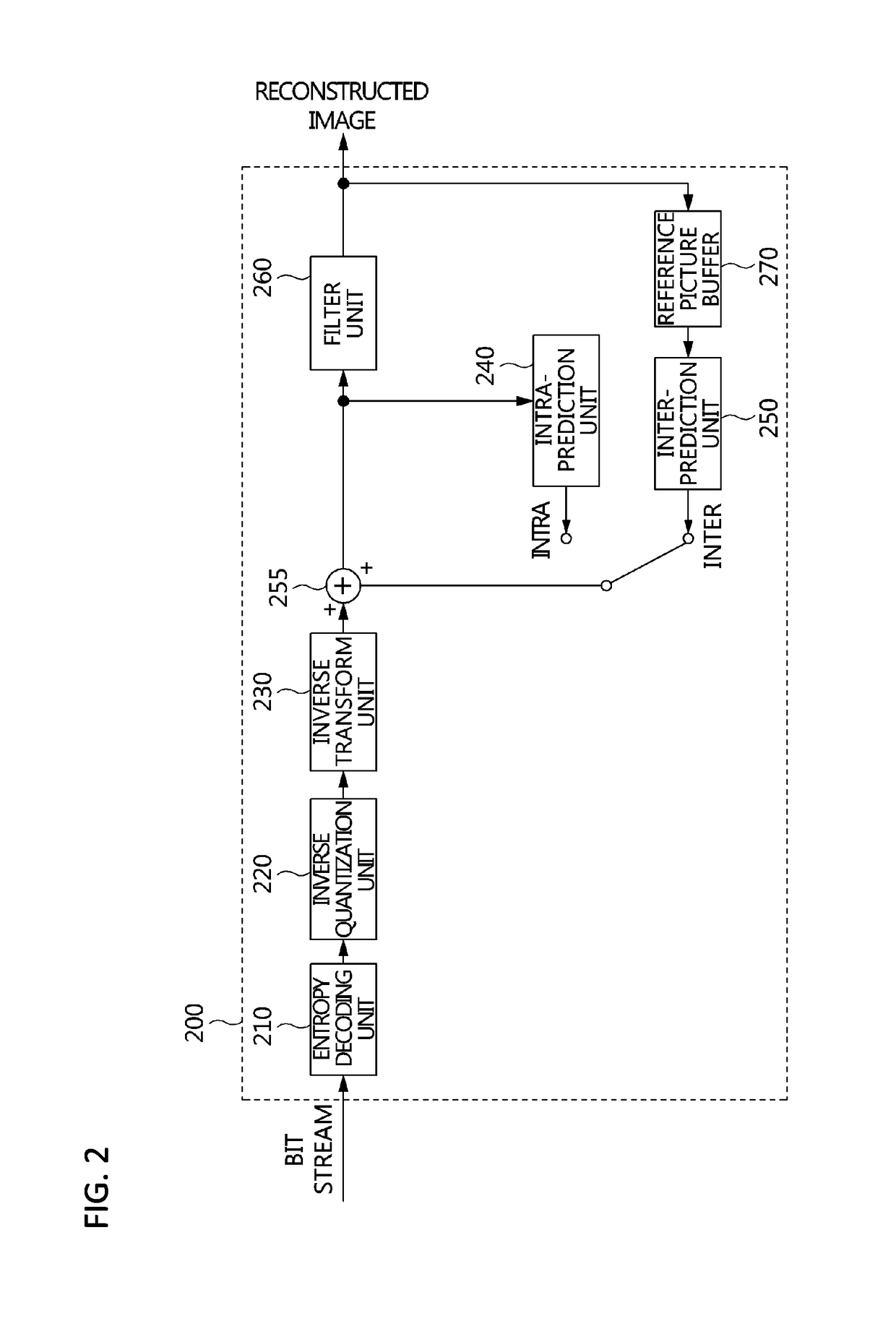
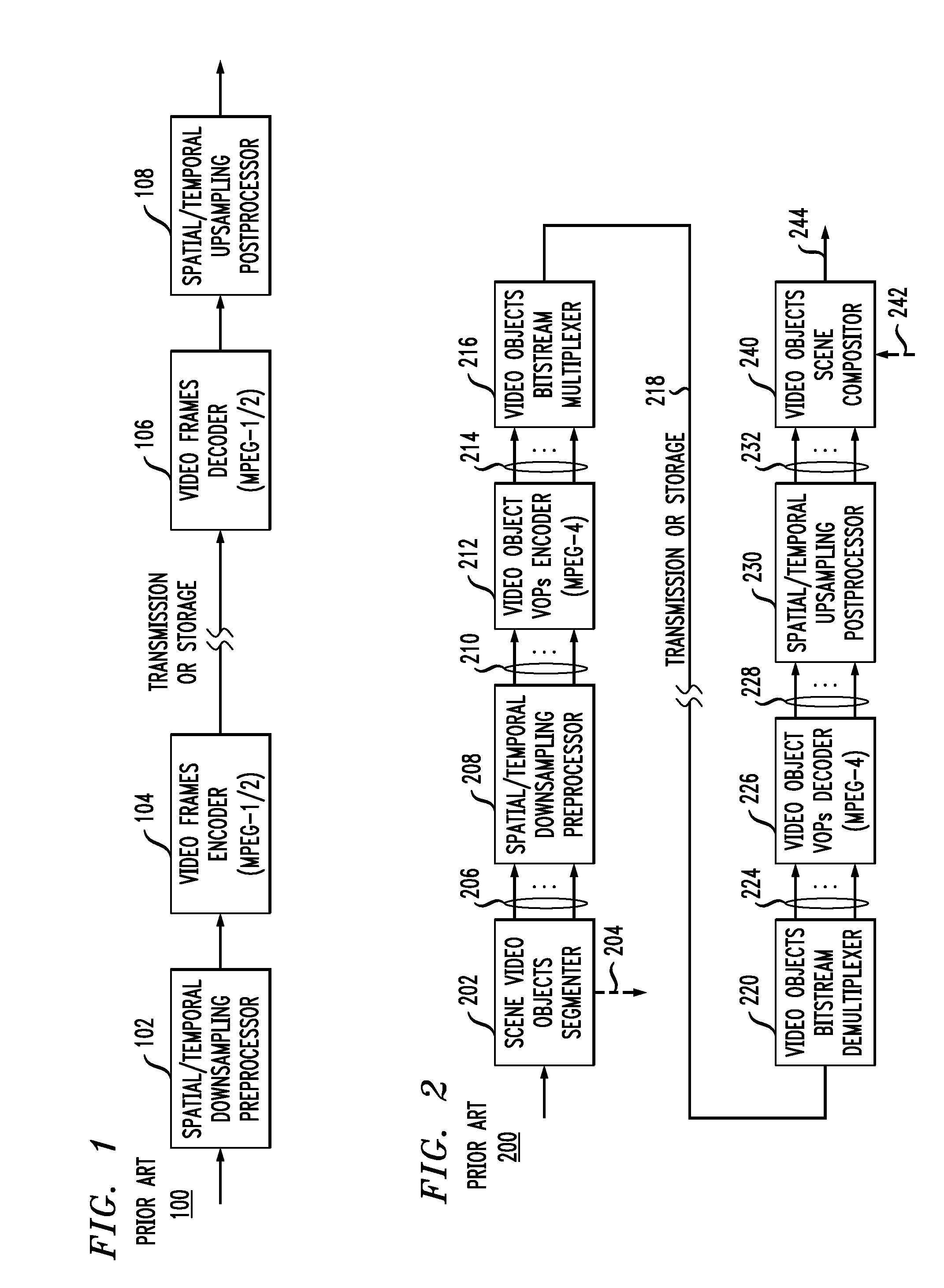
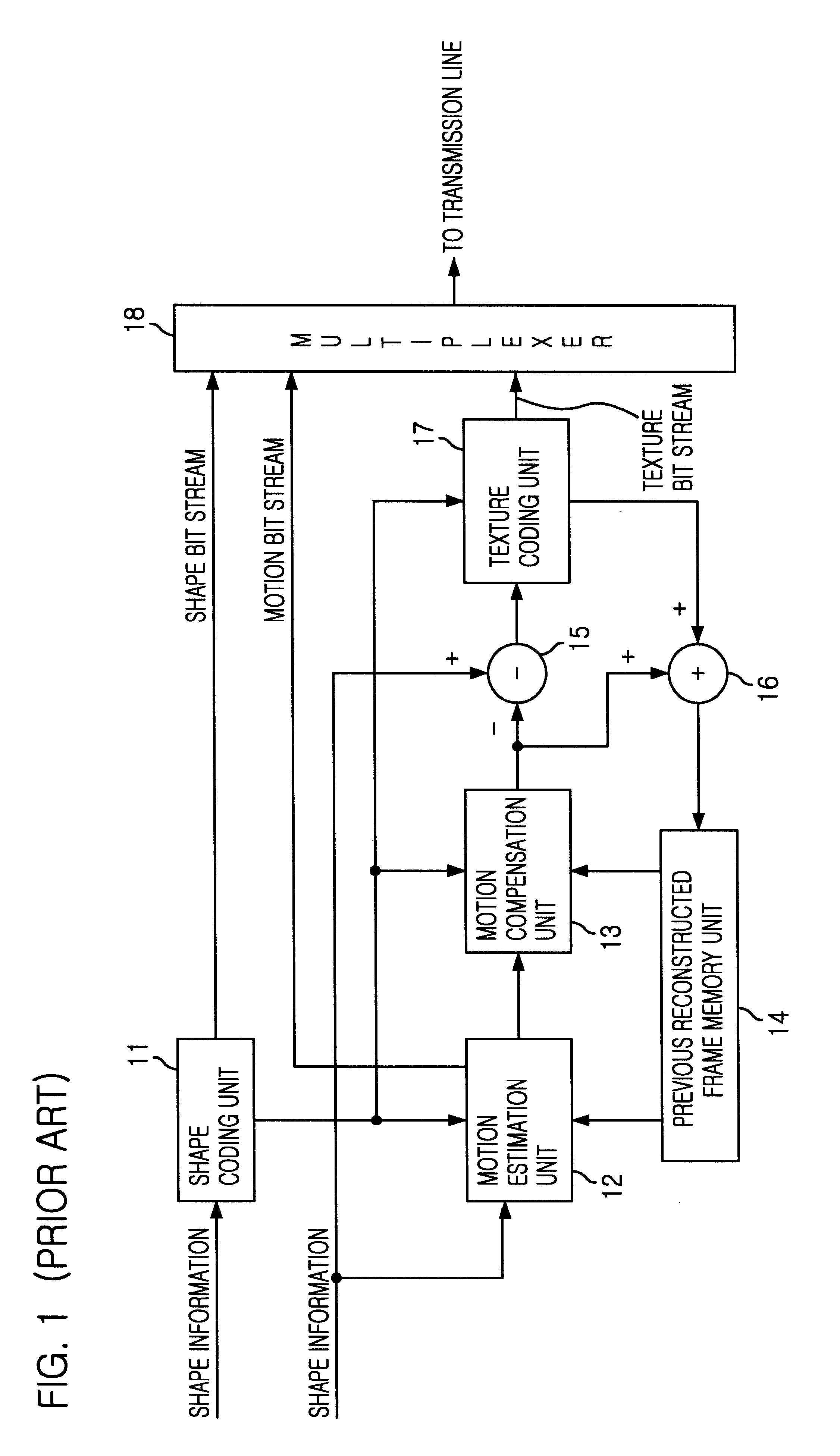
Video frame encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20050169374A1Improve effectivenessDecrease in code efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAdaptive encodingContext model
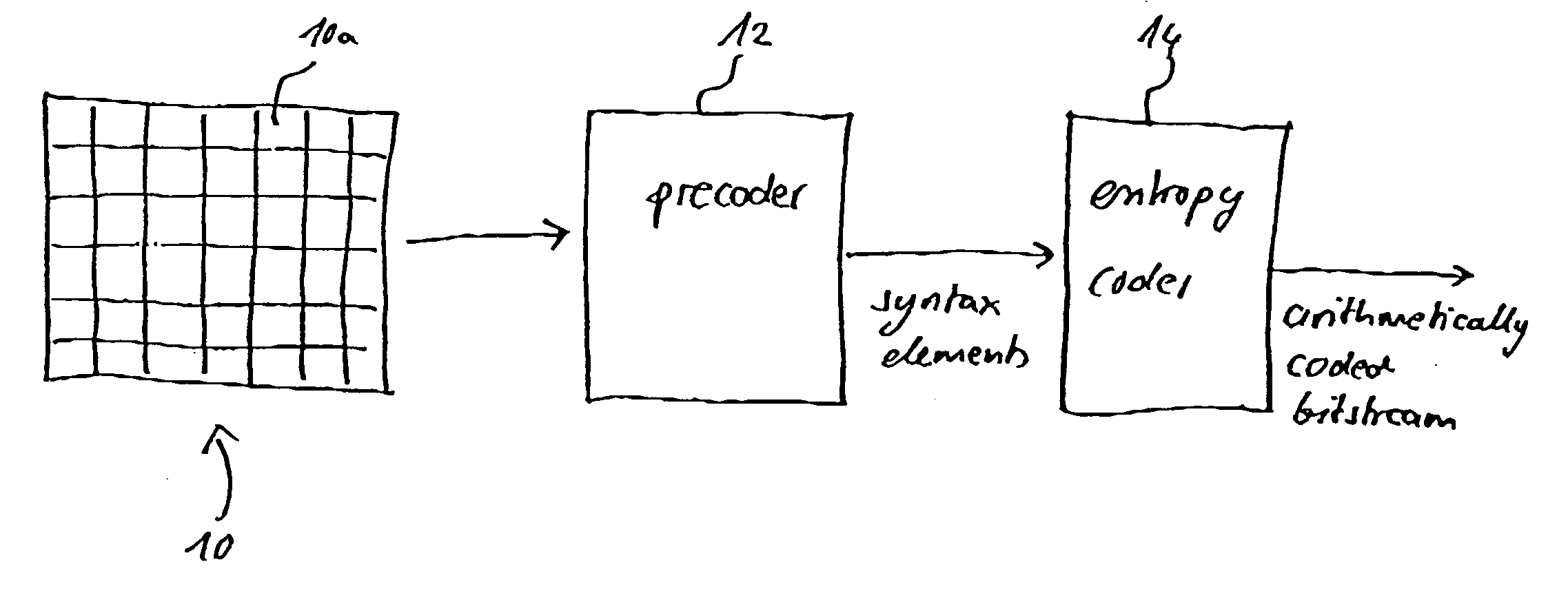
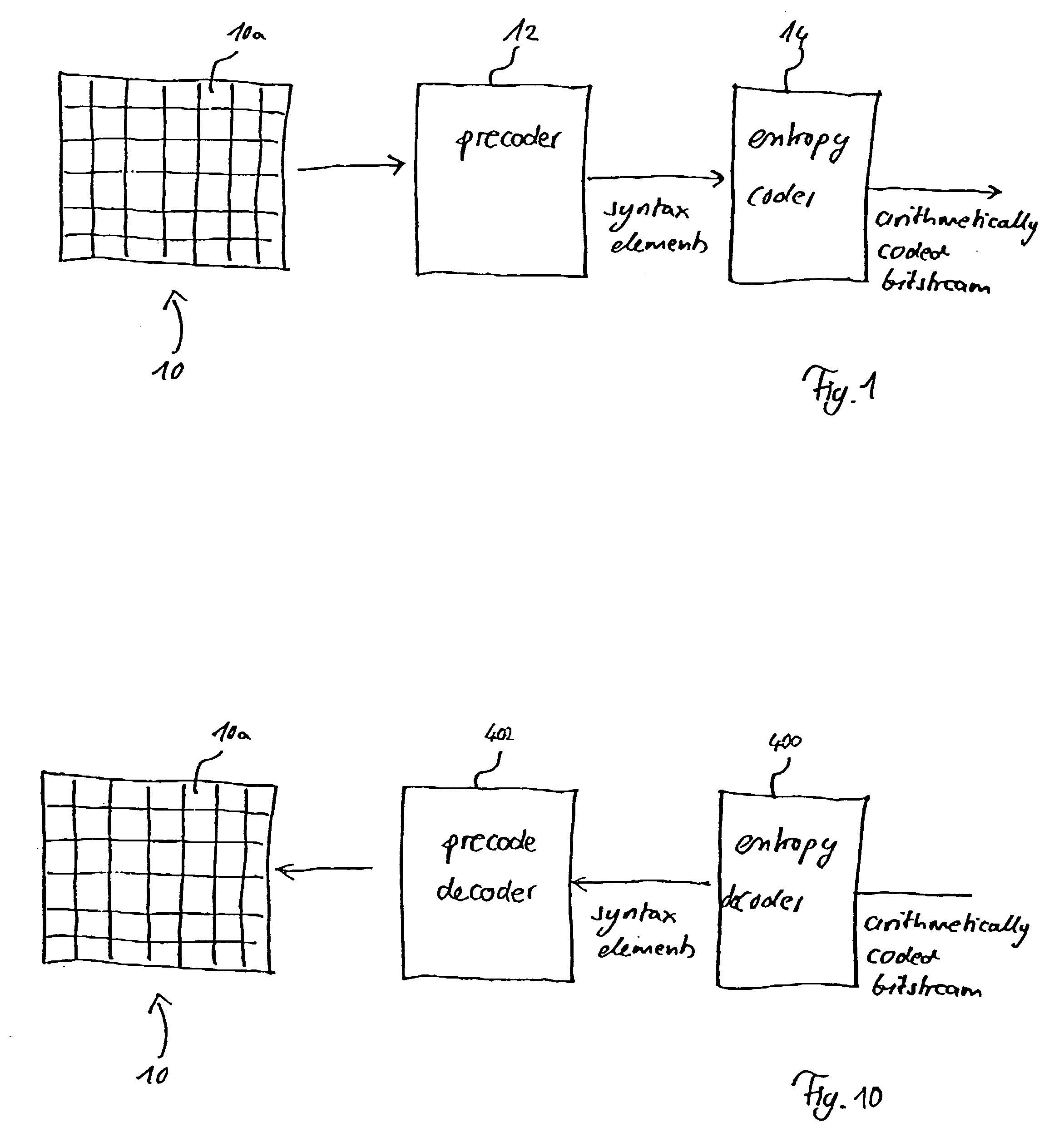
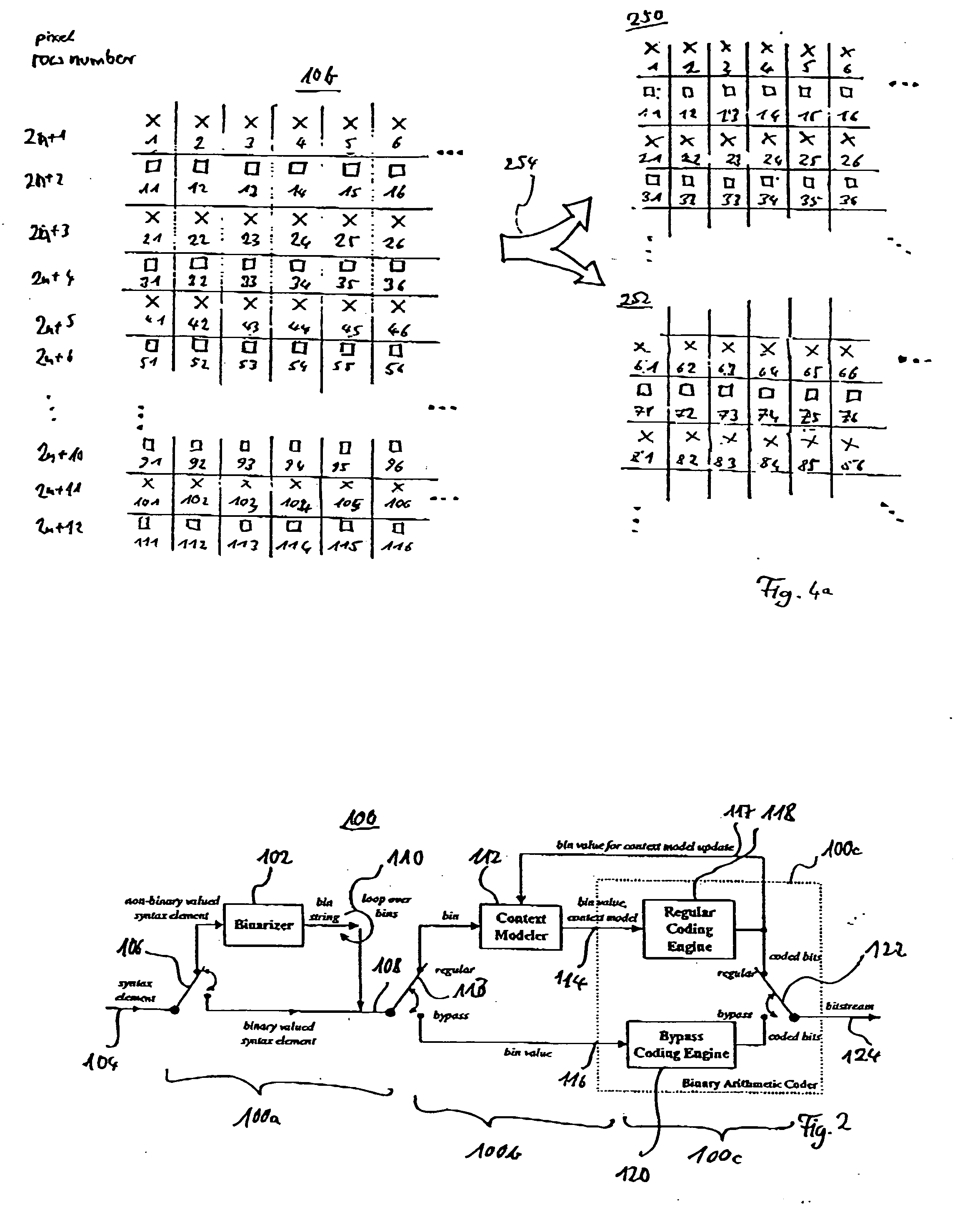
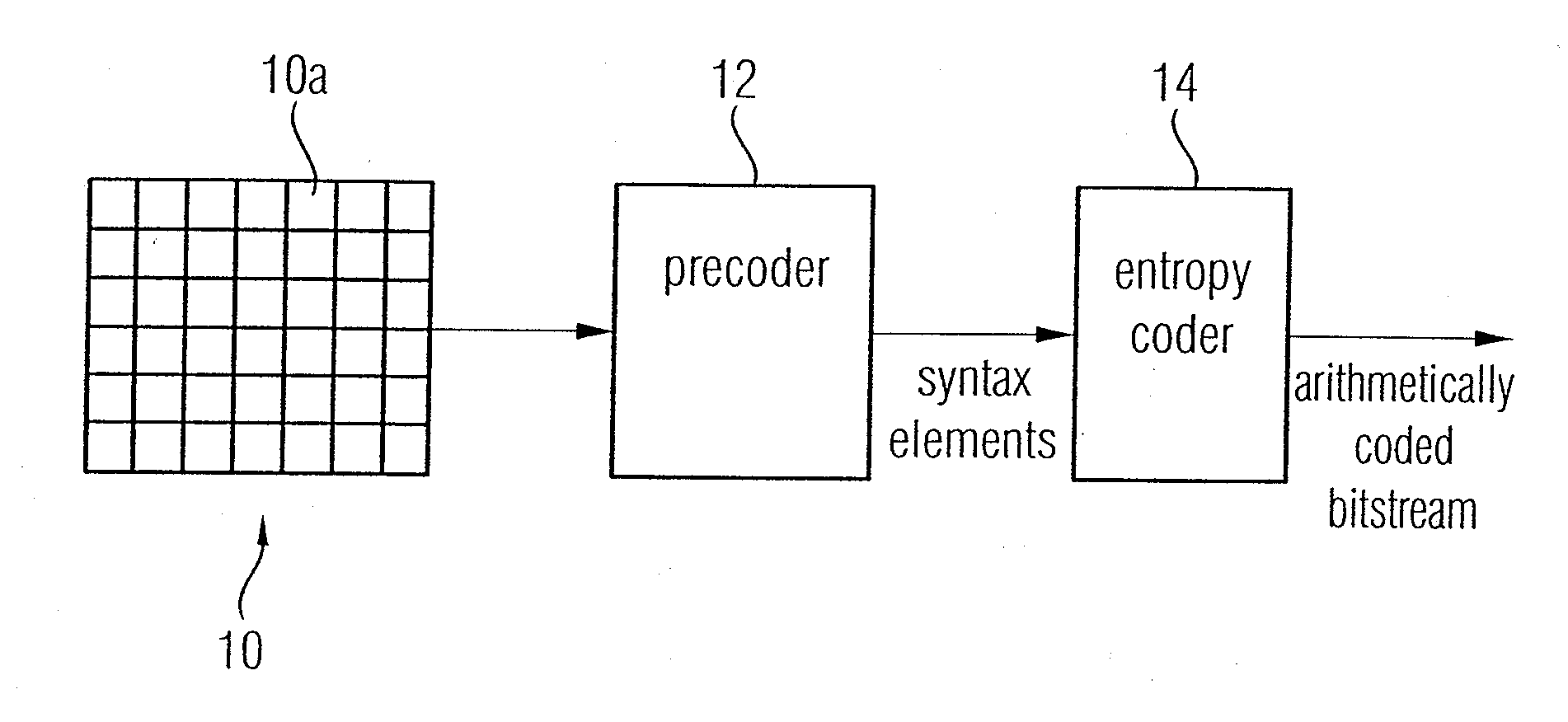
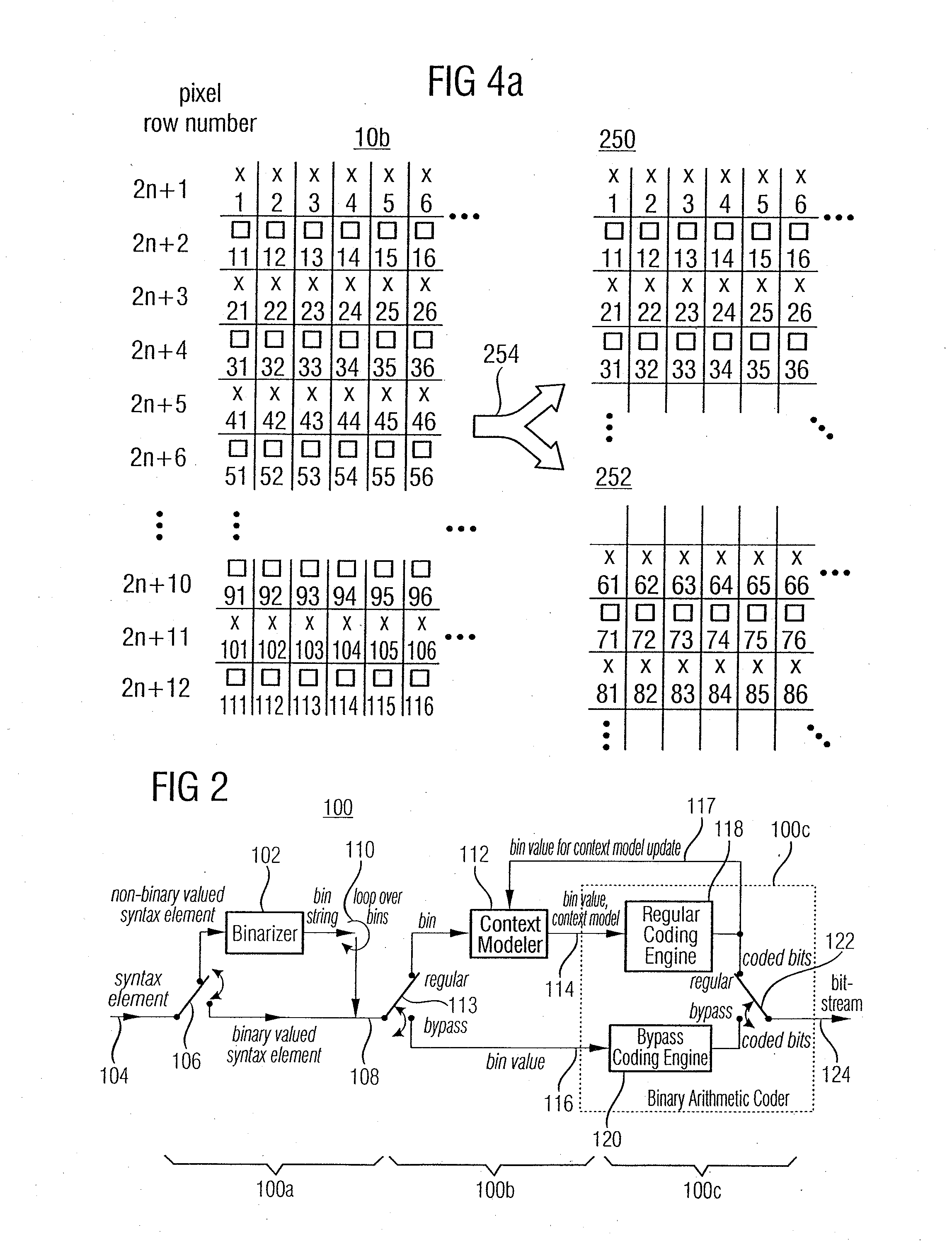
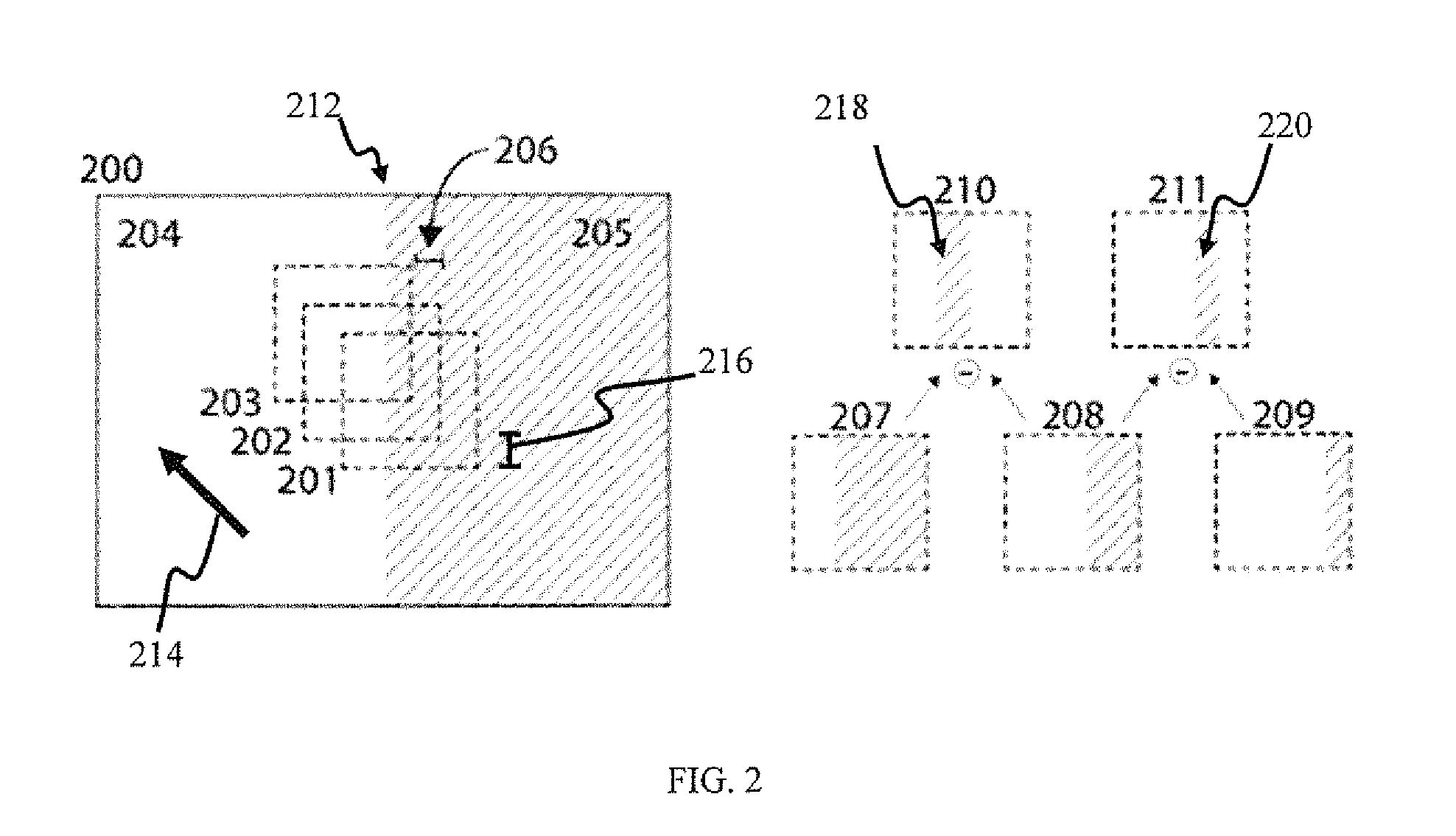
A video frame arithmetical context adaptive encoding and decoding scheme is presented which is based on the finding, that, for sake of a better definition of neighborhood between blocks of picture samples, i.e. the neighboring block which the syntax element to be coded or decoded relates to and the current block based on the attribute of which the assignment of a context model is conducted, and when the neighboring block lies beyond the borders or circumference of the current macroblock containing the current block, it is important to make the determination of the macroblock containing the neighboring block dependent upon as to whether the current macroblock pair region containing the current block is of a first or a second distribution type, i.e., frame or field coded.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
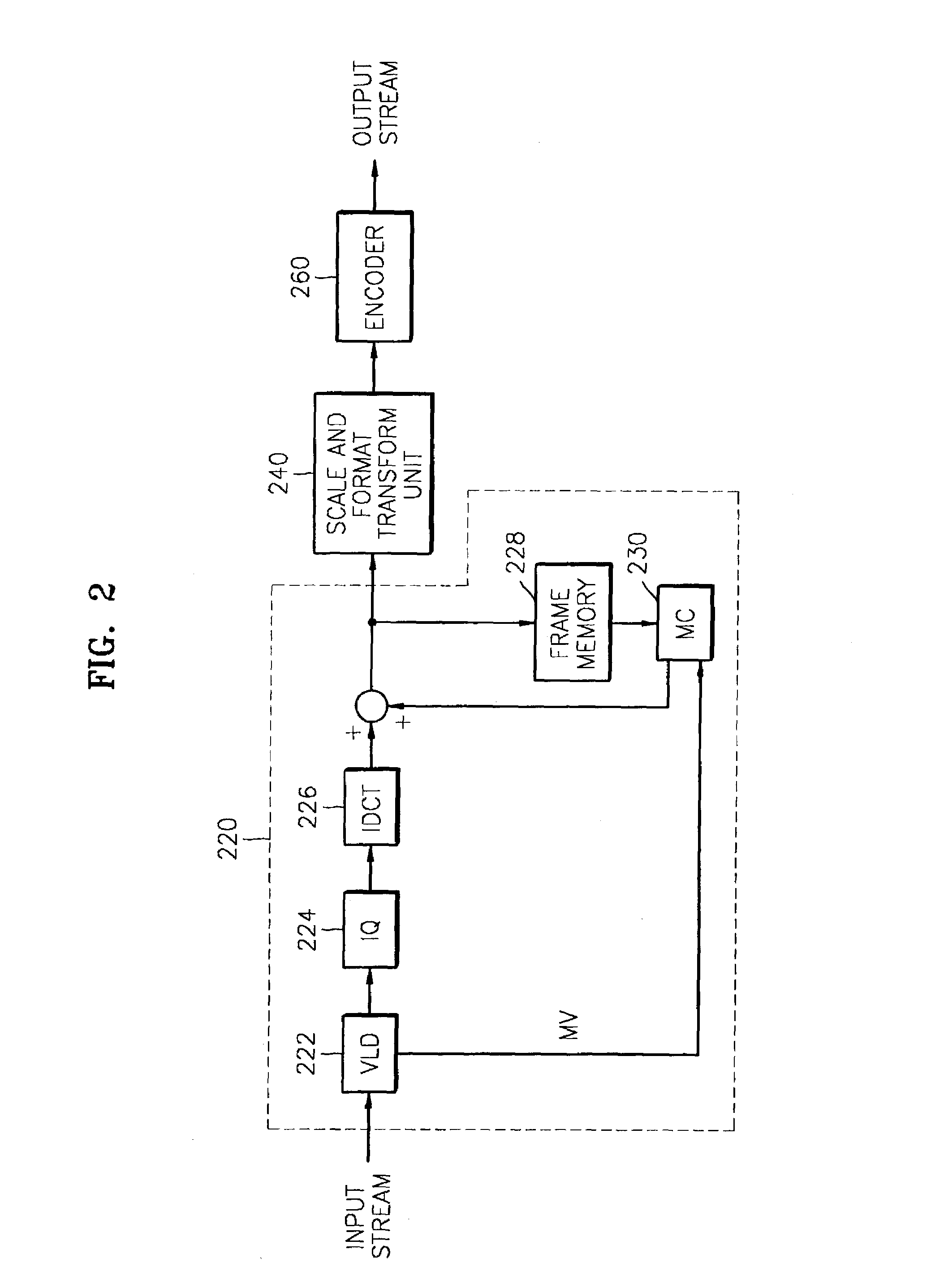
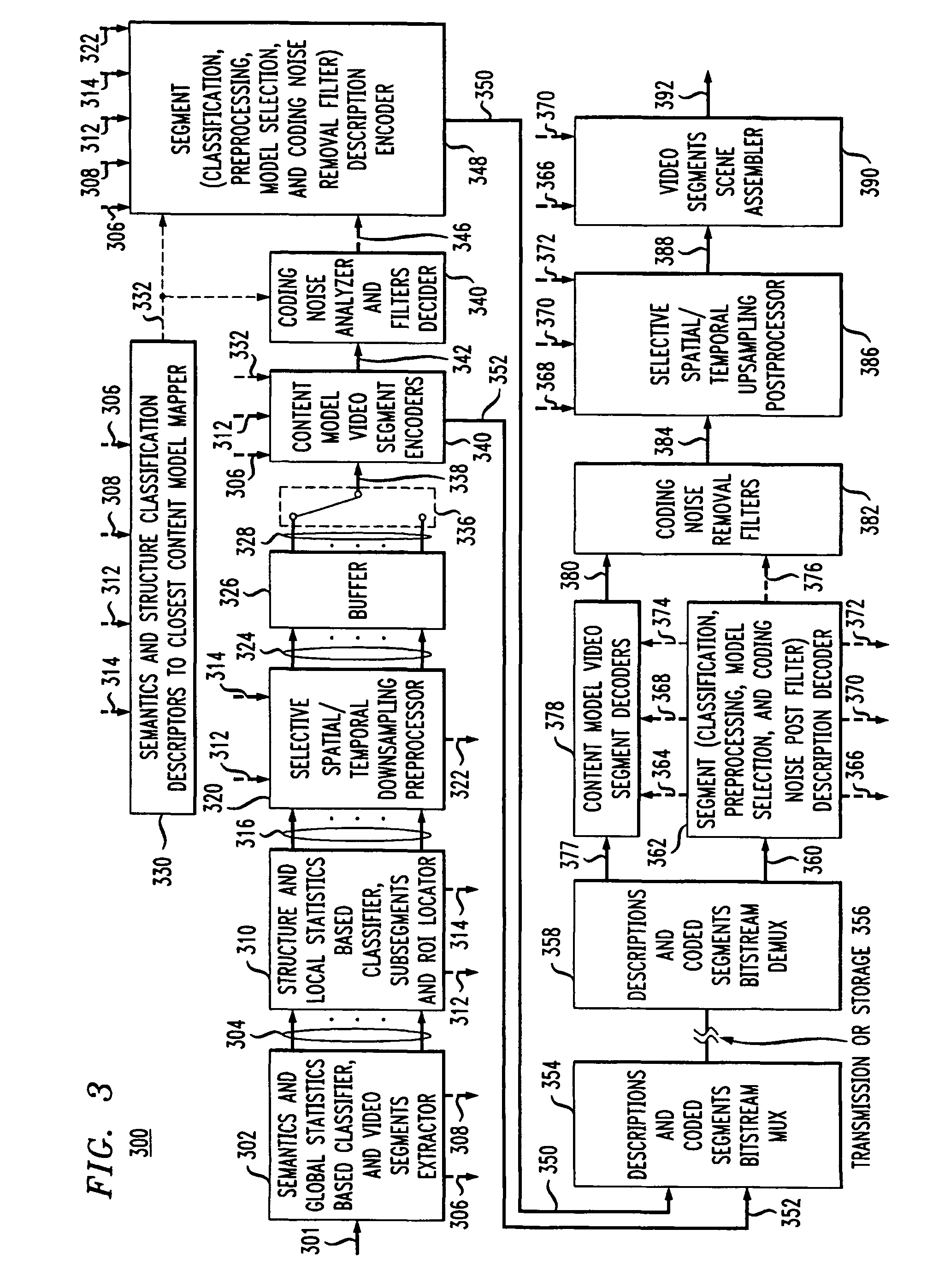
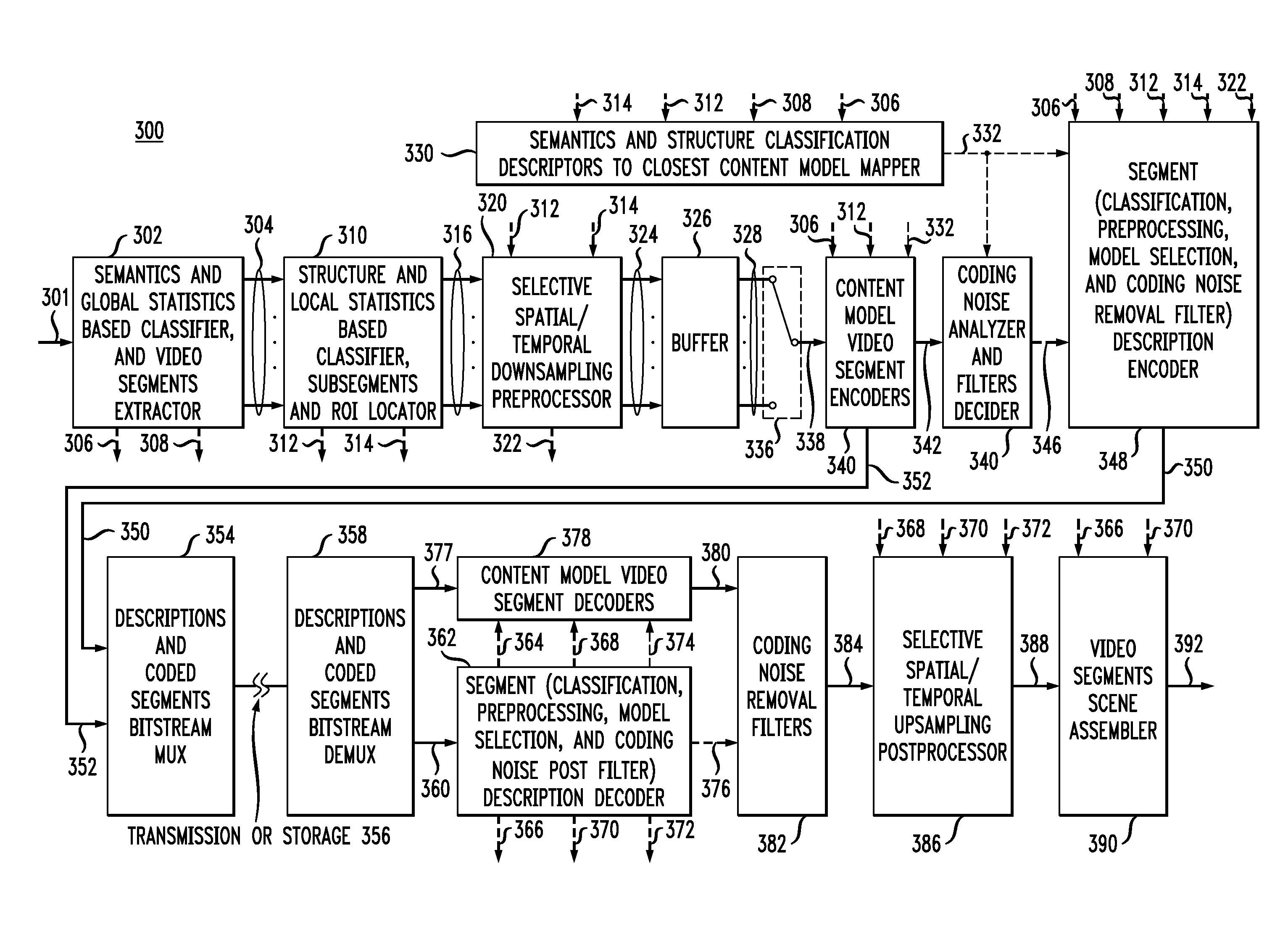
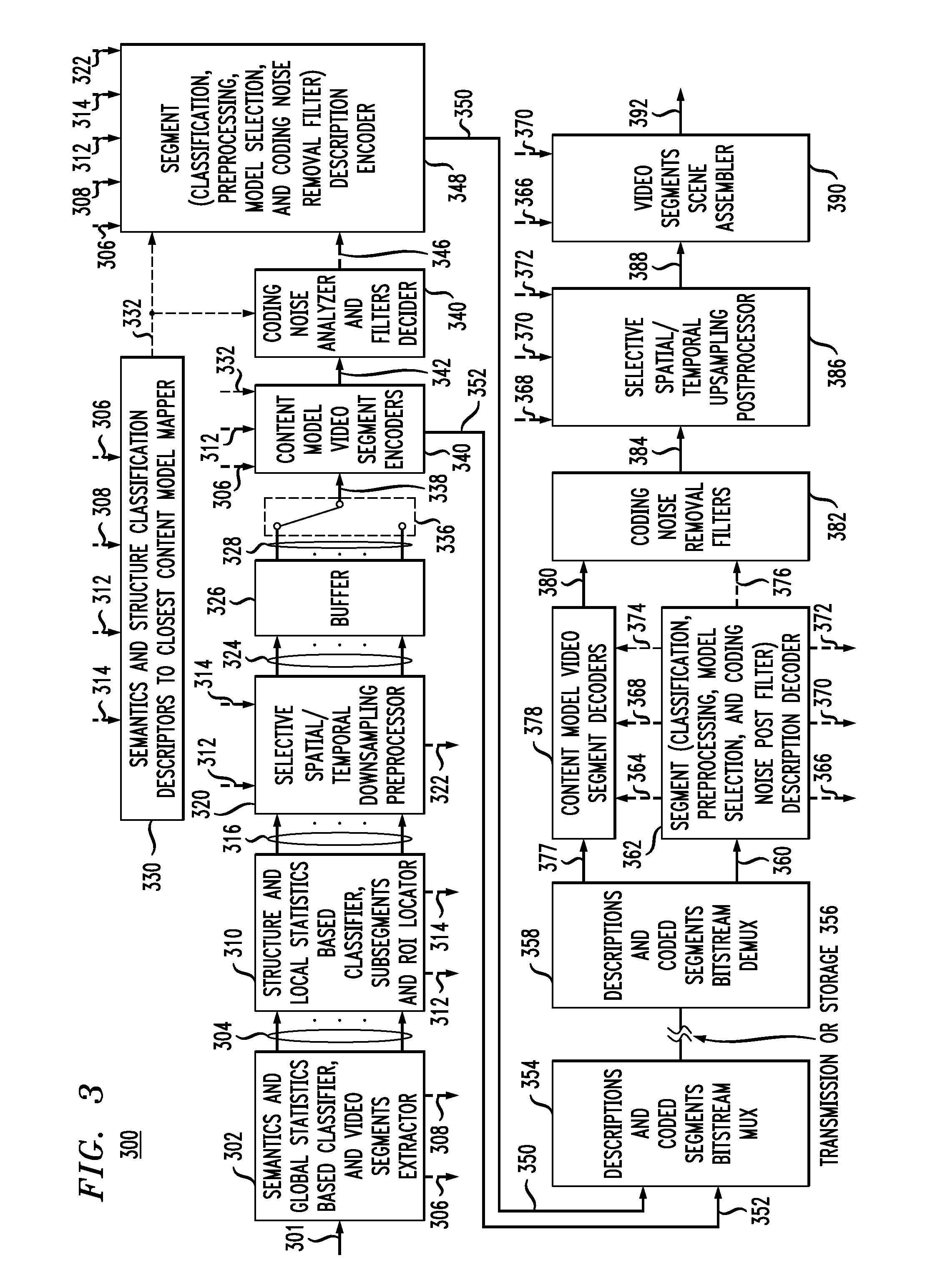
Content adaptive video encoder
InactiveUS6909745B1Improve efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAdaptive encodingSubject matter
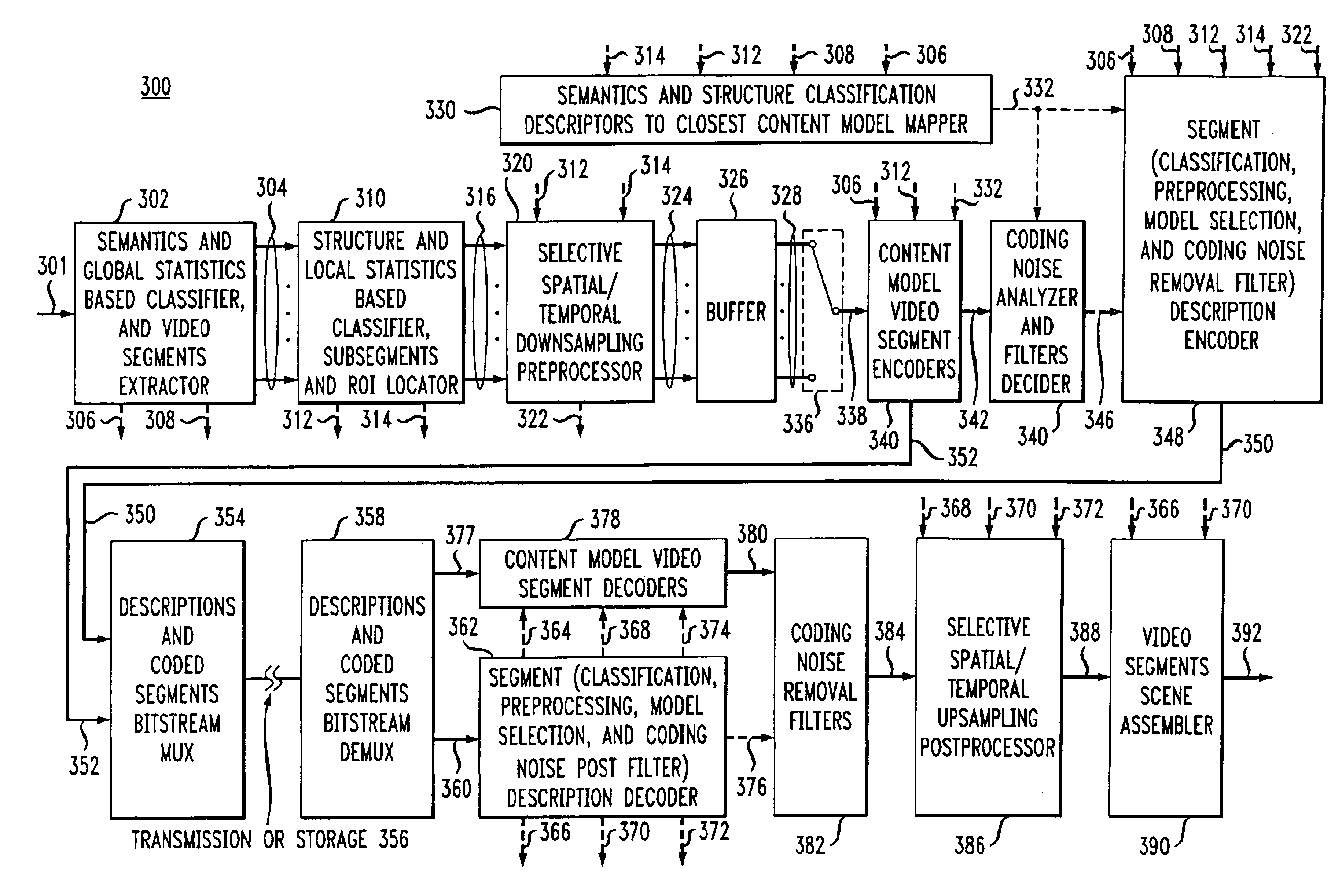
A system for content adaptive encoding and decoding video is disclosed. The system comprises modules for segmenting video content into segments based on predefined classifications or models. Examples of such classifications comprise action scenes, slow scenes, low or high detail scenes, and brightness of the scenes. Based on the segment classifications, each segment is encoded with a different encoder chosen from a plurality of encoders. Each encoder is associated with a model. The chosen encoder is particularly suited to encoding the unique subject matter of the segment. The coded bit-stream for each segment includes information regarding which encoder was used to encode that segment. A matching decoder of a plurality of decoders is chosen using the information in the coded bitstream to decode each segment using a decoder suited for the classification or model of the segment. If scenes exist which do not fall in a predefined classification, or where classification is more difficult based on the scene content, these scenes are segmented, coded and decoded using a generic coder and decoder.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
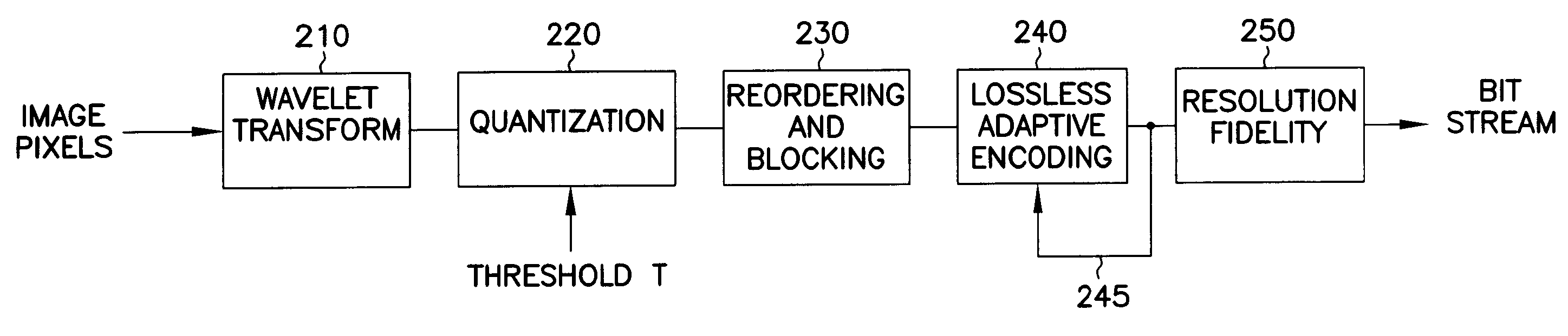
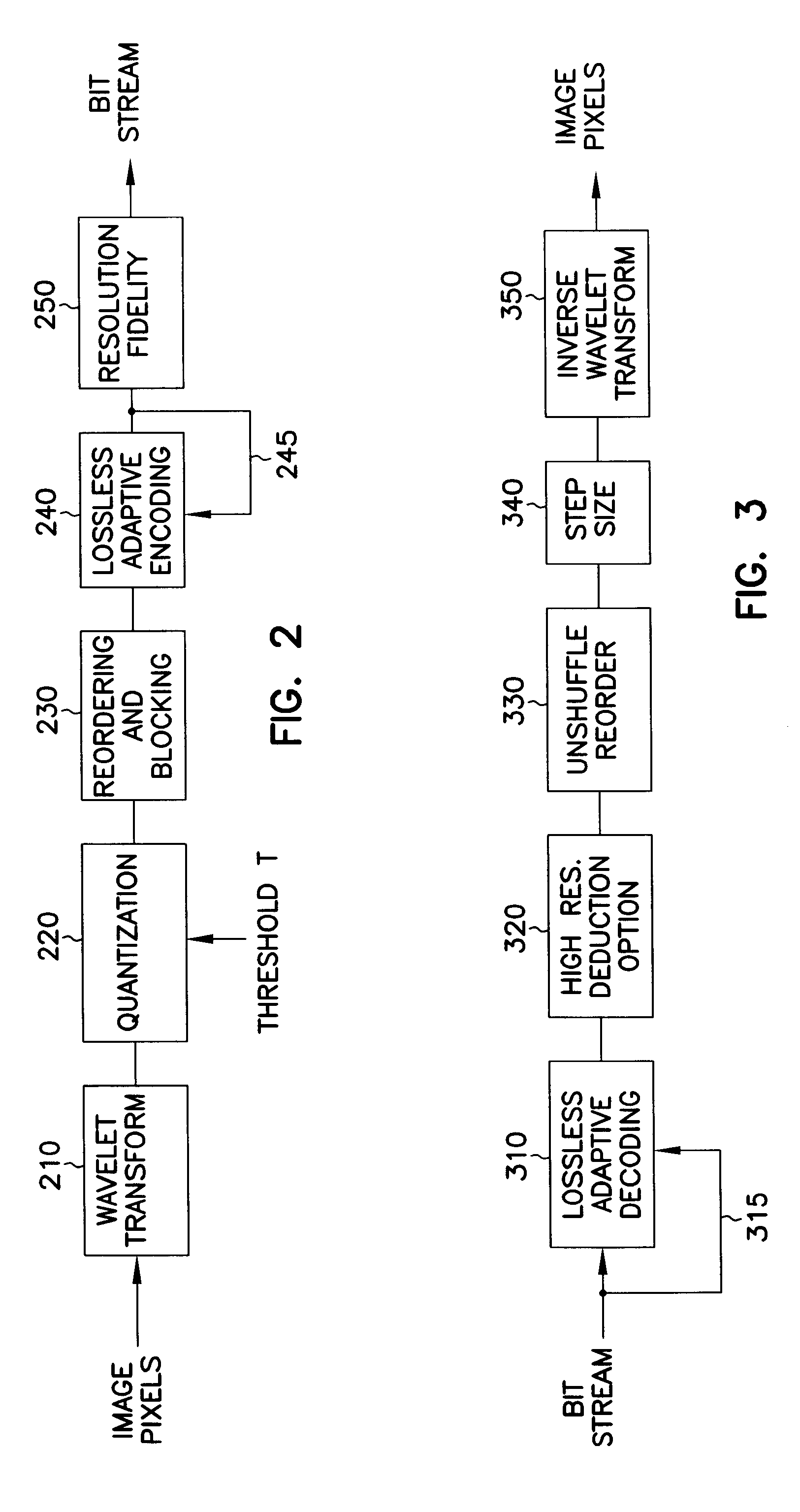
Image encoding using reordering and blocking of wavelet coefficients combined with adaptive encoding
InactiveUS6850649B1Increase the compression ratioEasy to buildCode conversionImage codingReverse orderAdaptive encoding
An encoder reorders quantized wavelet coefficients to cluster large and small wavelet coefficients into separate groups without requiring the use of data-dependent data structures. The coefficients are then adaptively encoded based on a run-length code which continuously modifies a parameter that controls the codewords uses to represent strings of quantized coefficients, seeking to minimize the number of bits spent in the codewords. A matrix of indices contains the coarsest coefficients in the upper left corner, and filling in low high and high low sub bands in larger and larger blocks in an alternating manner, such that low high sub bands comprise the top of the matrix and the high low sub bands comprise the left side of the matrix. The shortest codewords are assigned to represent a run of the most likely character having length of 2k, where k is a parameter. k is adjusted based on successive characters being encountered. k is increased when the character is the same, and decreased when the character is different. A decoder applies the above in reverse order. Decoding of the encoded coefficients is first performed, followed by an unshuffling of the coefficients. The unshuffled coefficients are then subjected to an inverse wavelet transform to recover the transformed and compressed data, such as image pixels.
Owner:DYNADEX DATA LLC
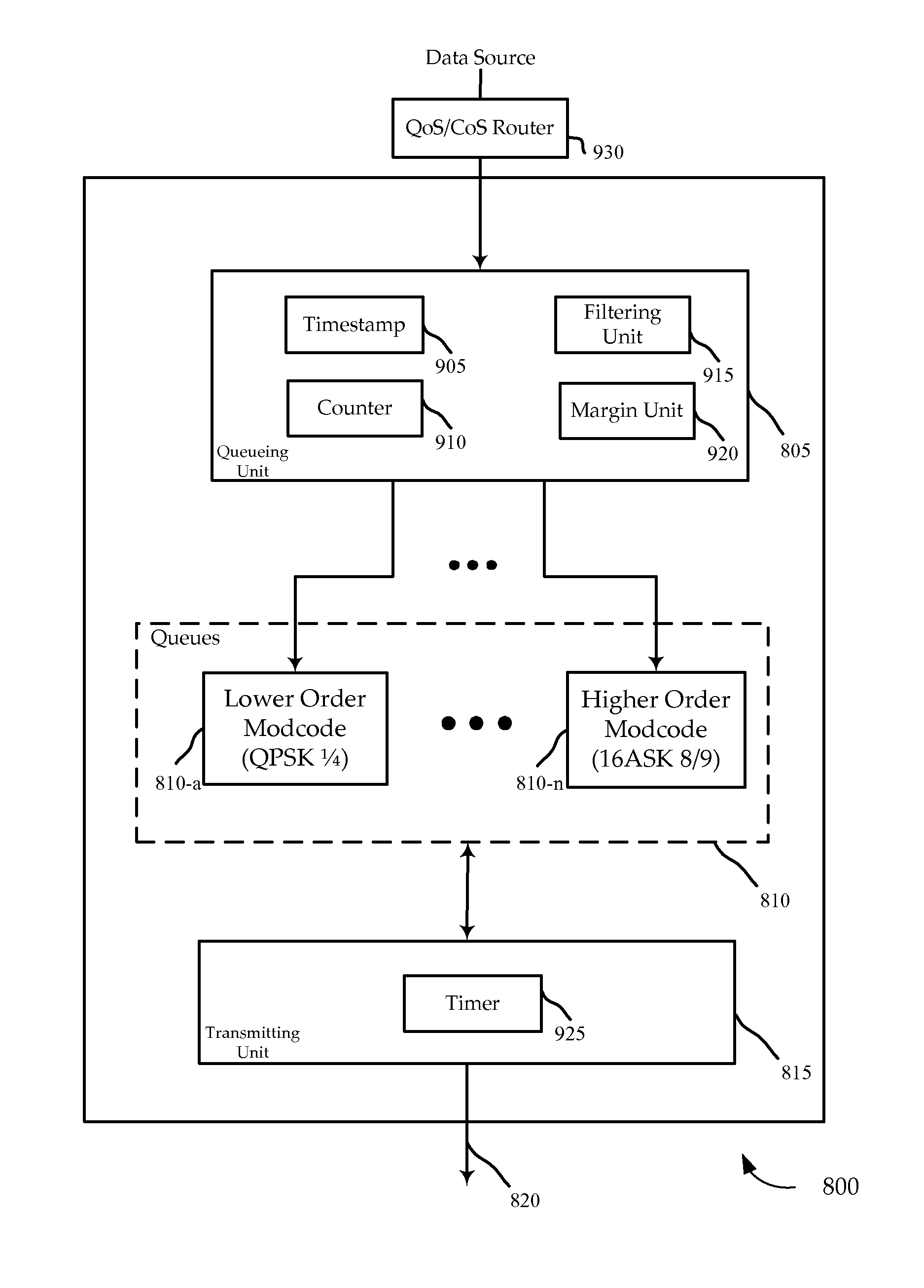
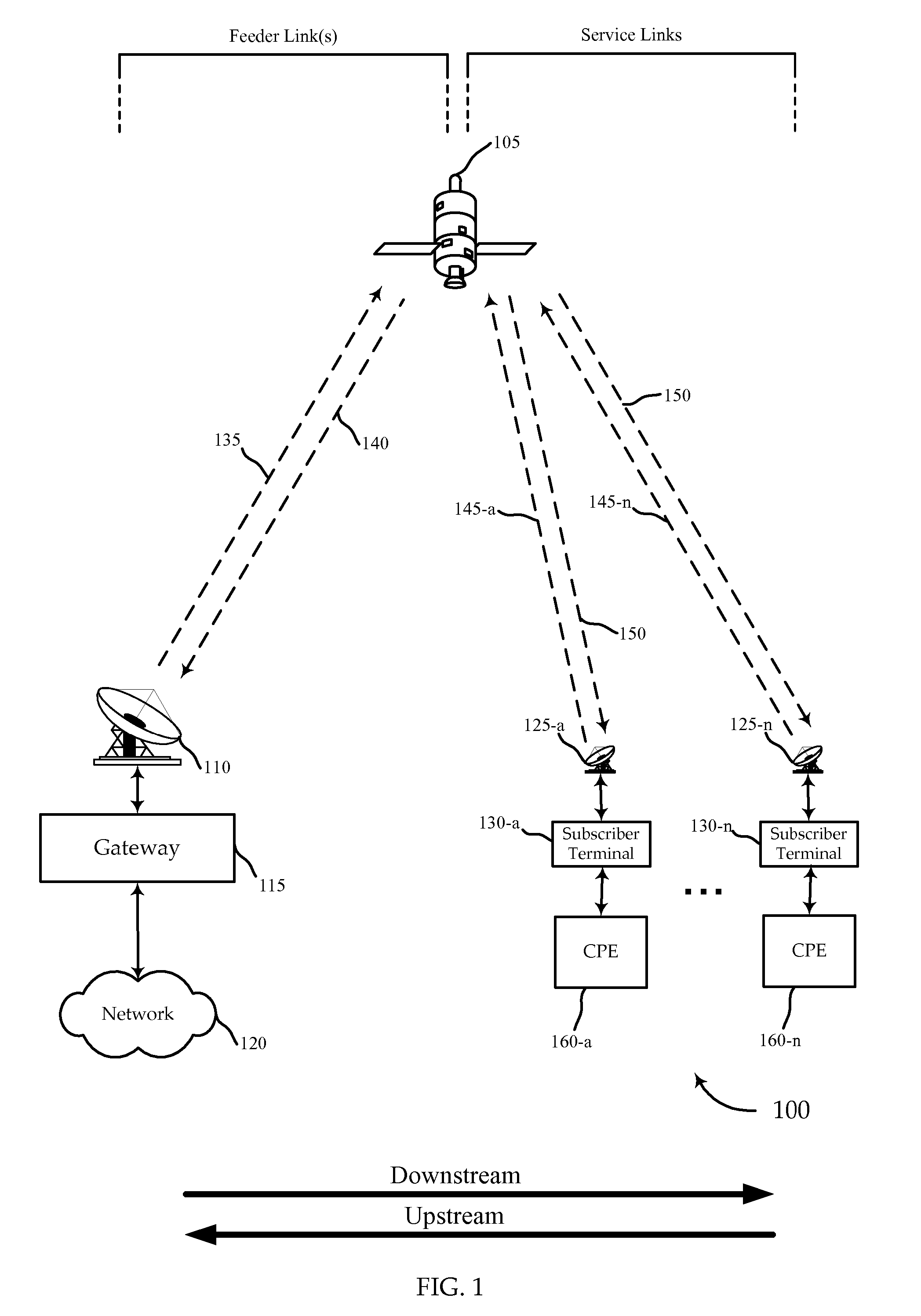
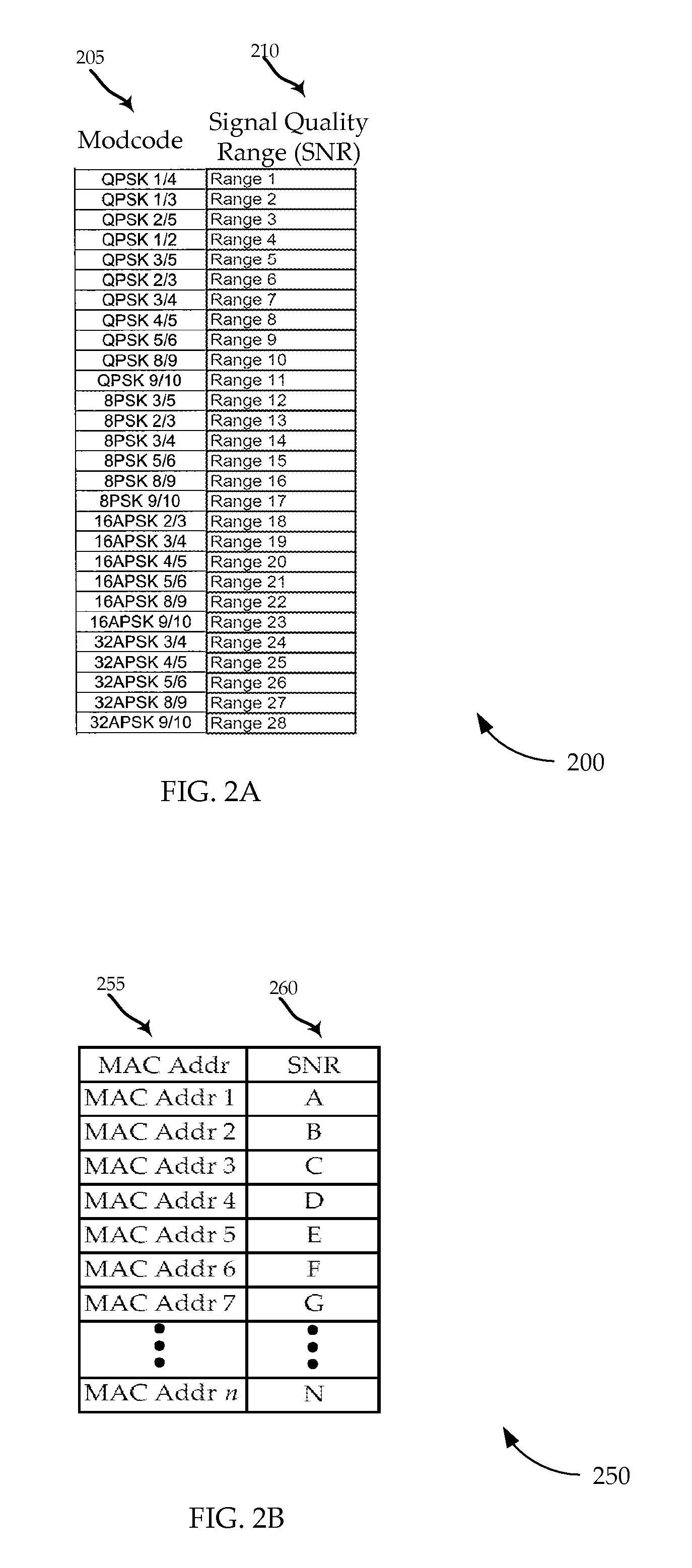
Adaptive coding and modulation queuing methods and devices
ActiveUS20070116152A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTraffic capacitySignal quality
A process is described to build physical layer frames with a modcode adapted to the signal quality of a destination terminal. Data packets assigned to the same modcode may be sent in the same frame, although packets associated with higher modcodes may be used to complete a frame before switching to the applicable higher modcode for construction of subsequent frames. After an interval, the order of progression is restarted with an out of order packet above a threshold age. Flow control filtering mechanisms and a variable reliability margin may be used to adapt dynamically to the current data traffic conditions.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Video frame encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20090074057A1Improve compression efficiencyImprove effectivenessColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithmAdaptive encoding
A video frame arithmetical context adaptive encoding and decoding scheme is presented which is based on the finding, that, for sake of a better definition of neighborhood between blocks of picture samples, i.e. the neighboring block which the syntax element to be coded or decoded relates to and the current block based on the attribute of which the assignment of a context model is conducted, and when the neighboring block lies beyond the borders or circumference of the current macroblock containing the current block, it is important to make the determination of the macroblock containing the neighboring block dependent upon as to whether the current macroblock pair region containing the current block is of a first or a second distribution type, i.e., frame or field coded.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Sensory input processing apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20140064609A1Easy to detectCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFrame sequenceAdaptive encoding
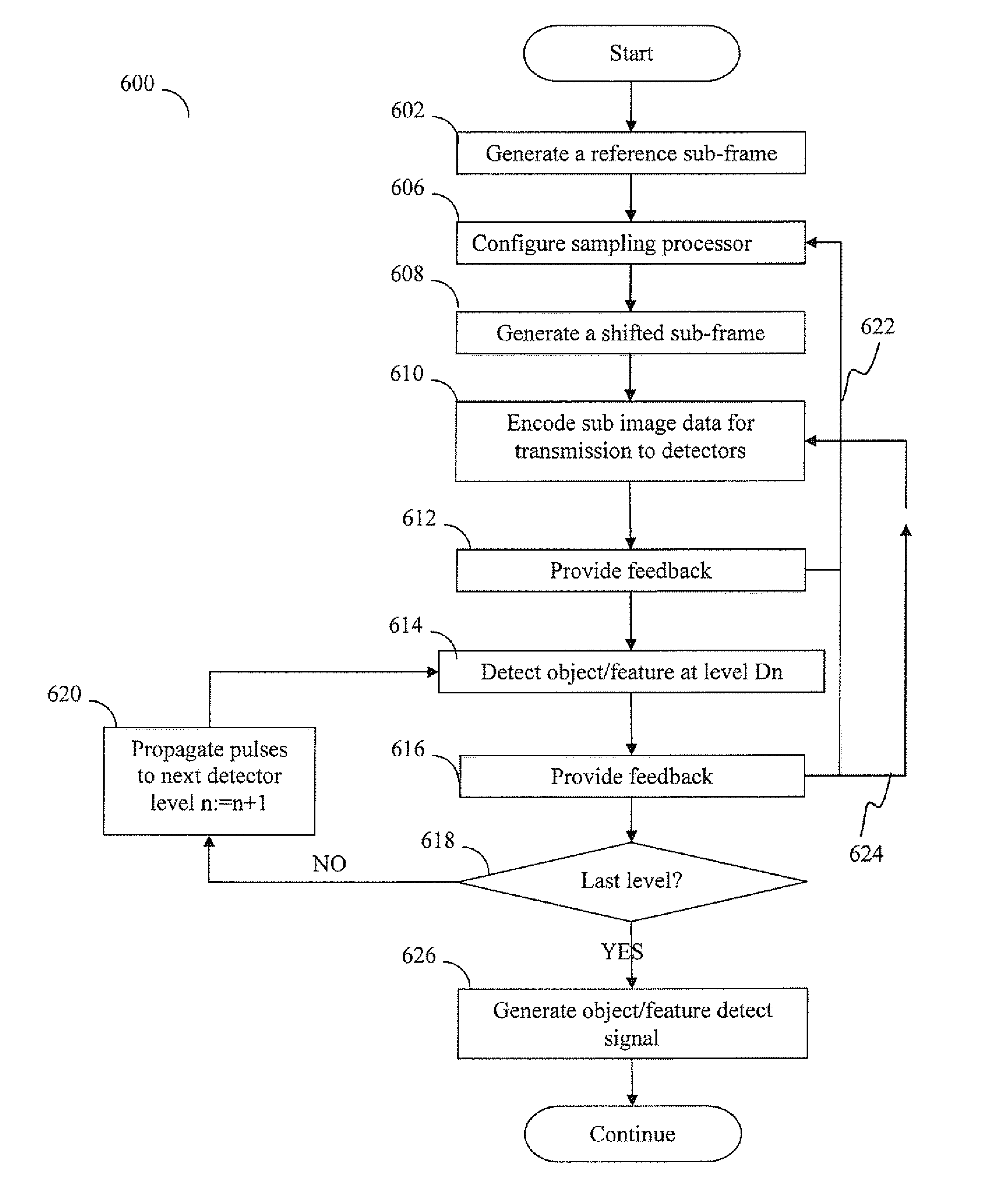
Sensory input processing apparatus and methods useful for adaptive encoding and decoding of features. In one embodiment, the apparatus receives an input frame having a representation of the object feature, generates a sequence of sub-frames that are displaced from one another (and correspond to different areas within the frame), and encodes the sub-frame sequence into groups of pulses. The patterns of pulses are directed via transmission channels to detection apparatus configured to generate an output pulse upon detecting a predetermined pattern within received groups of pulses that is associated with the feature. Upon detecting a particular pattern, the detection apparatus provides feedback to the displacement module in order to optimize sub-frame displacement for detecting the feature of interest. In another embodiment, the detections apparatus elevates its sensitivity (and / or channel characteristics) to that particular pulse pattern when processing subsequent pulse group inputs, thereby increasing the likelihood of feature detection.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
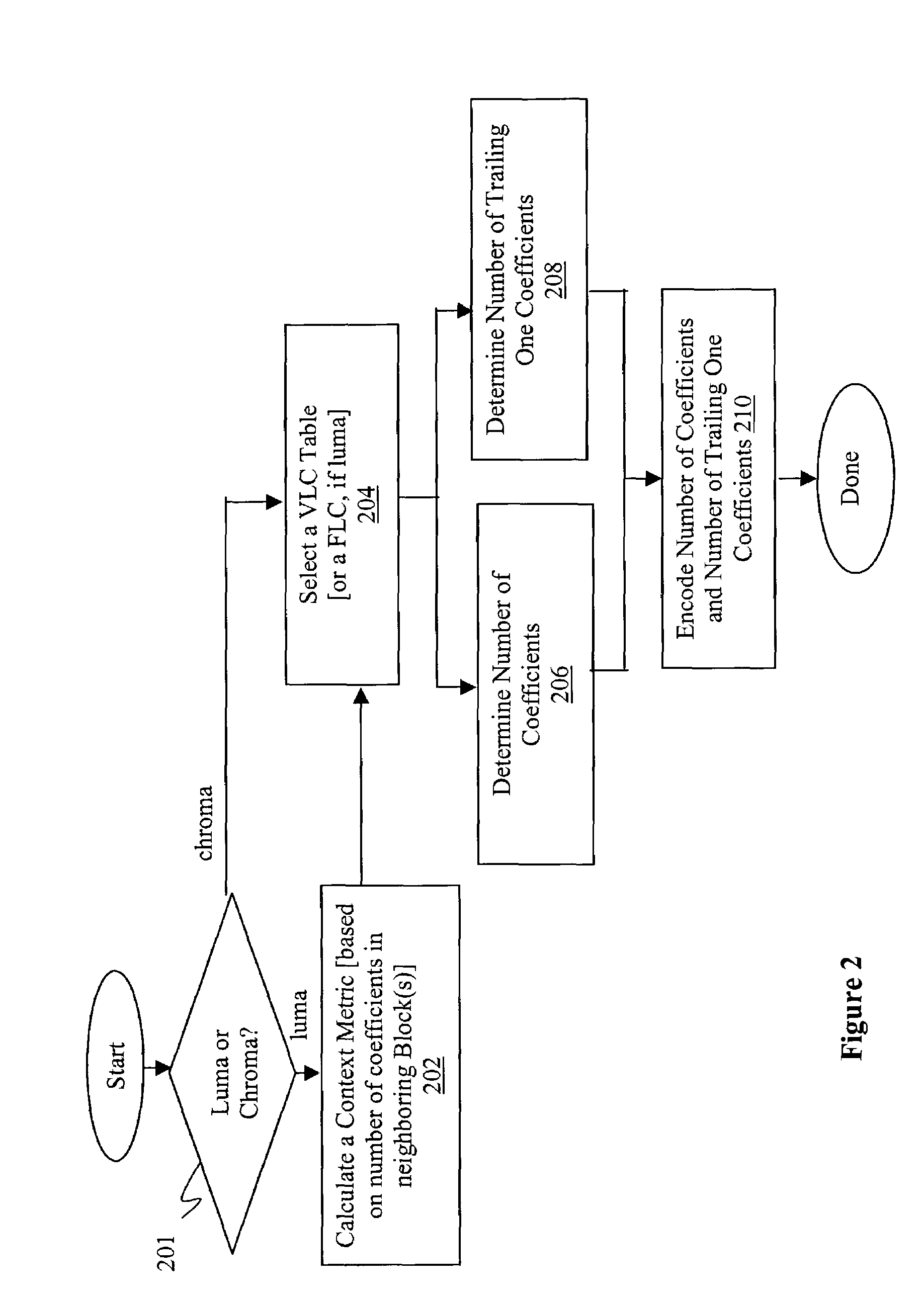
Context-adaptive VLC video transform coefficients encoding/decoding methods and apparatuses
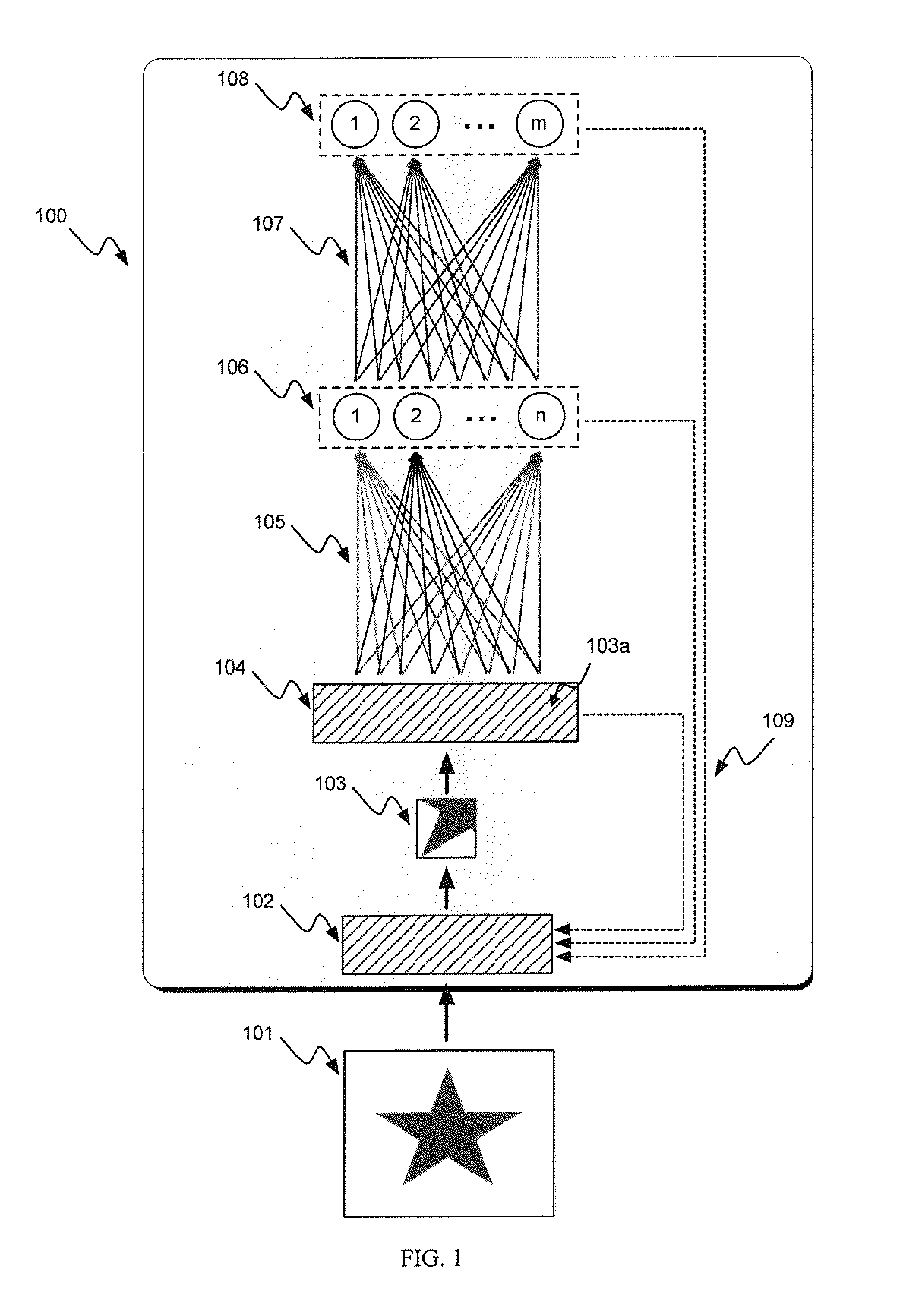
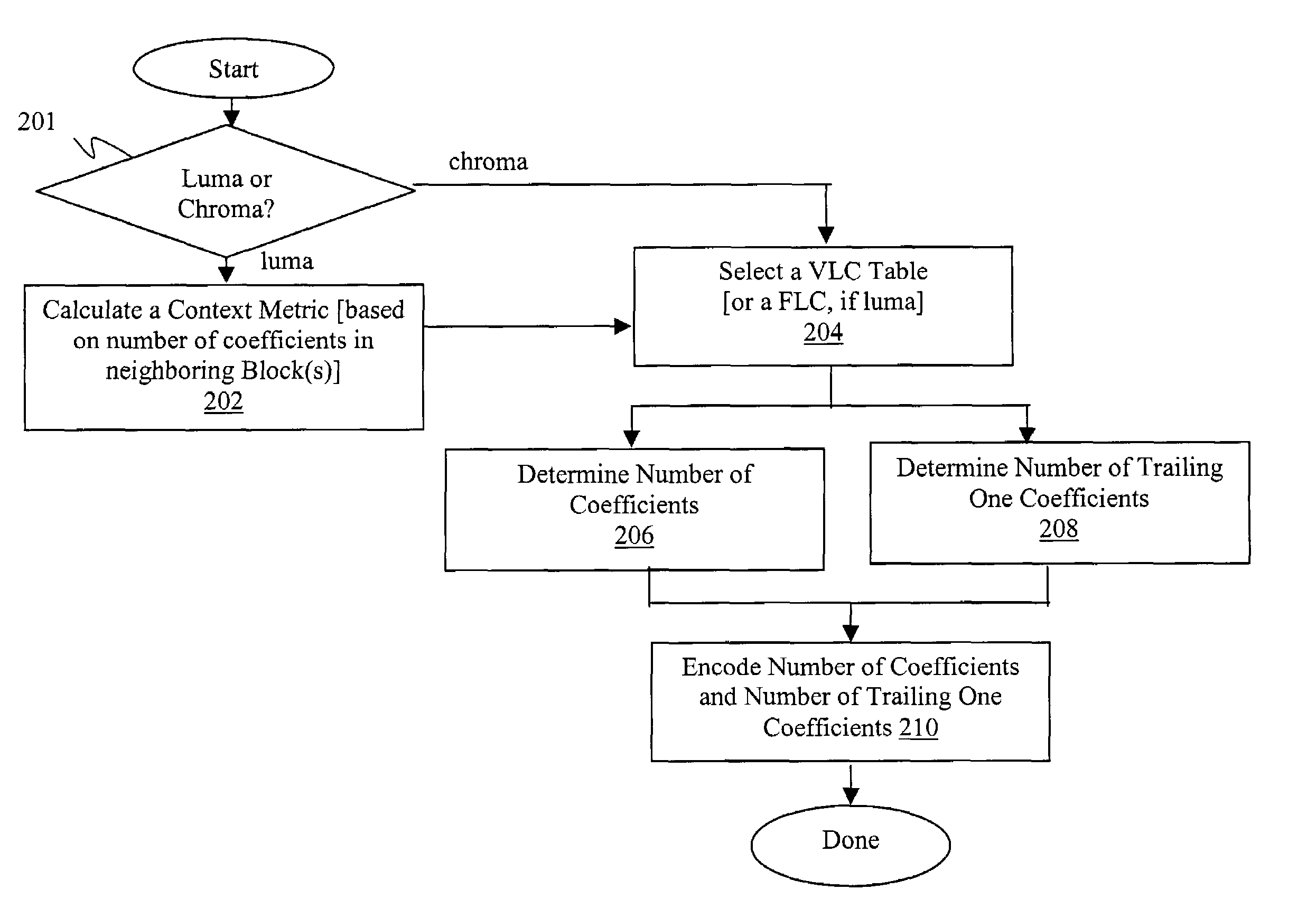
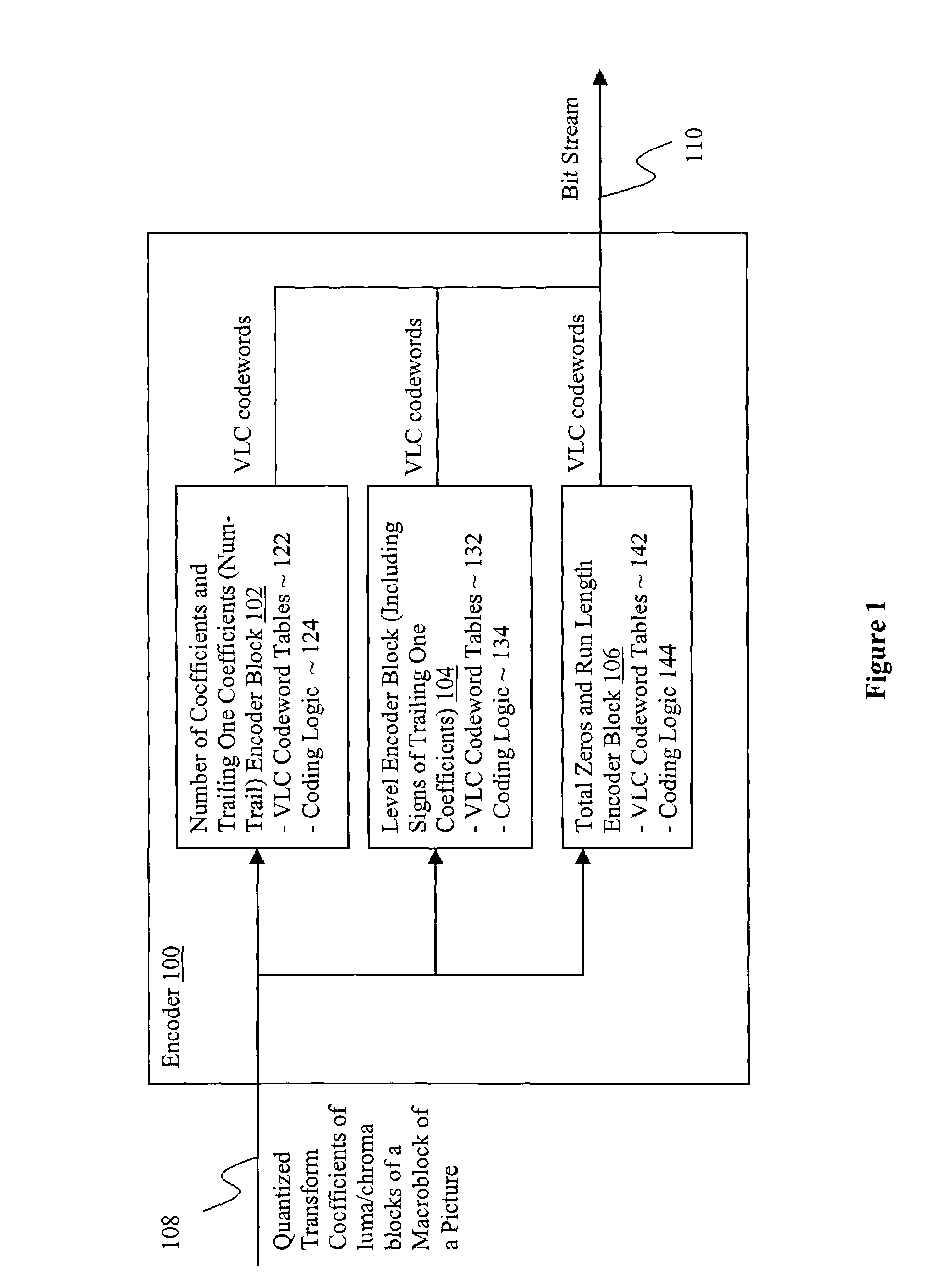
ActiveUS7099387B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionNonzero coefficientsComputer architecture
Transform coefficients of sample blocks of a macroblock of a video picture are encoded by adaptively encoding in combination, the number of non-zero coefficients before the trailing one coefficients and the number of trailing one coefficients. The transform coefficients may be further encoded by adaptively encoding one or more of the signs of the trailing one coefficients, the level measures of the non-zero coefficients, the total number of zero coefficients interposed in the non-zero coefficients, and the respective run lengths of the zero coefficients. Adaptive encoding of the number and trailing one coefficients may be performed in view of one or more neighboring sample blocks, whereas adaptive encoding of level measures may be performed in view of quantization parameters of a macroblock and previously encoded level measures. Decoding may be performed in an inverse manner.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Code compression algorithms and architectures for embedded systems
InactiveUS7095343B2Increase the compression ratioSimple designCode conversionProbit modelAdaptive coding
Code compression techniques and decompression architectures for embedded systems are disclosed, providing good compression ratio while improving decompression time for VLIW instructions and reducing bus power consumption. The invention includes two fixed-to-variable (F2V) length code compression schemes based on a reduced arithmetic code compression algorithm combining arithmetic coding with probability models; a static probability model using static coding and semi-adaptive coding using a Markov model. Multi-bit decompression methods for the F2V techniques are presented, together with a parallel decompression scheme that tags and divides a compressed block into smaller sub-blocks. The Markov model provides better compression ratio, but the static model has a less complicated decompression unit design. The invention also includes two variable-to-fixed (V2F) length coding algorithms, one based on Tunstall coding and another on arithmetic coding. The V2F algorithms are also combined with a static model and a Markov model.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Method and Transmission Unit for Adaptive Coding, Modulation and Transmittion of Data Words in a Wireless Communication System
InactiveUS20080232340A1Improve throughputLarge quality variationEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemAdaptive coding
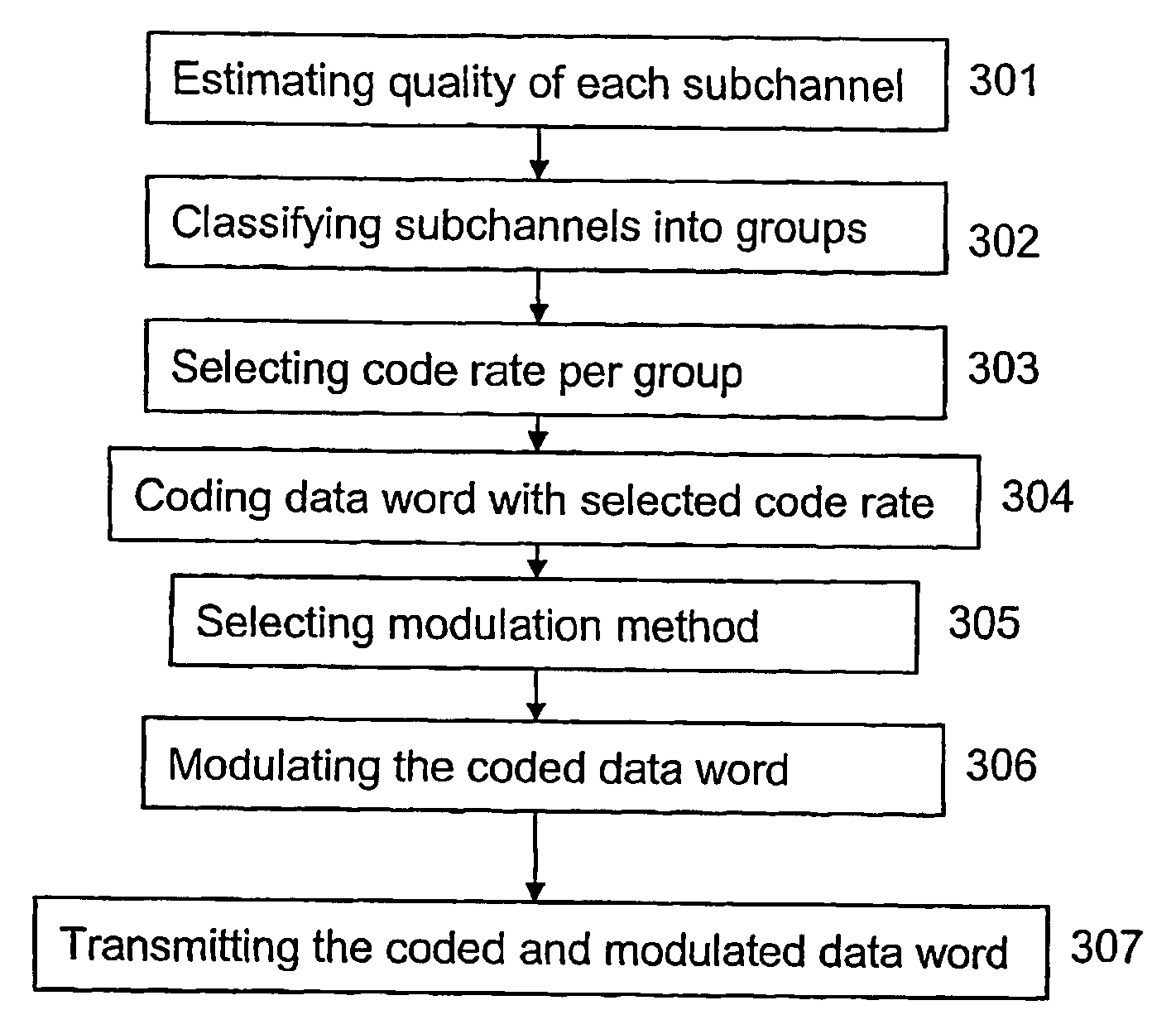
When transmitting data from a transmission unit to a reception unit over a channel in a wireless communication system, it has been observed that there are inherent losses in throughput, especially for a channel experiencing high channel quality variations over its frequency range. To improve the throughput over such a channel, it is proposed to: estimate the quality of each subchannel of a channel, classify the subchannels into a number of quality groups based on the estimated quality, and select a code rate per quality group. This selected code rate per quality group is then used when a data word to be transmitted is coded. Simulations have shown that by grouping the subchannels into a limited number of groups, for example one to four groups depending on the channel quality variation, a high throughput could be achieved with a minimum of signaling cost in the form of extra overhead.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method, device, and module for improved encoding mode control in video encoding
InactiveUS20070030894A1Improve robustnessImproved end user experienceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAdaptive encodingMode control
In general the present invention provides a video encoder, which is arranged for adaptive encoding mode selection. The video encoder is operable with a plurality of encoding modes for encoding a current macroblock of a video sequence. The video sequence is preferably intended for being transmitted by a communication network, e.g. any circuit-switched or packet-switched communication network. A distortion estimator is arranged for estimating expected distortion values due to potential erroneous transmission of the current macroblock in dependence of the encoding modes. A decision module is arranged for selecting a final encoding mode from the plurality of encoding modes on the basis of the distortion values and encoding parameters. Further, a table is provided, which is referenced by the spatial position of the macroblock and which is updated with an accumulated distortion value. The video encoder is arranged for applying the final encoding mode for encoding the current macroblock.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
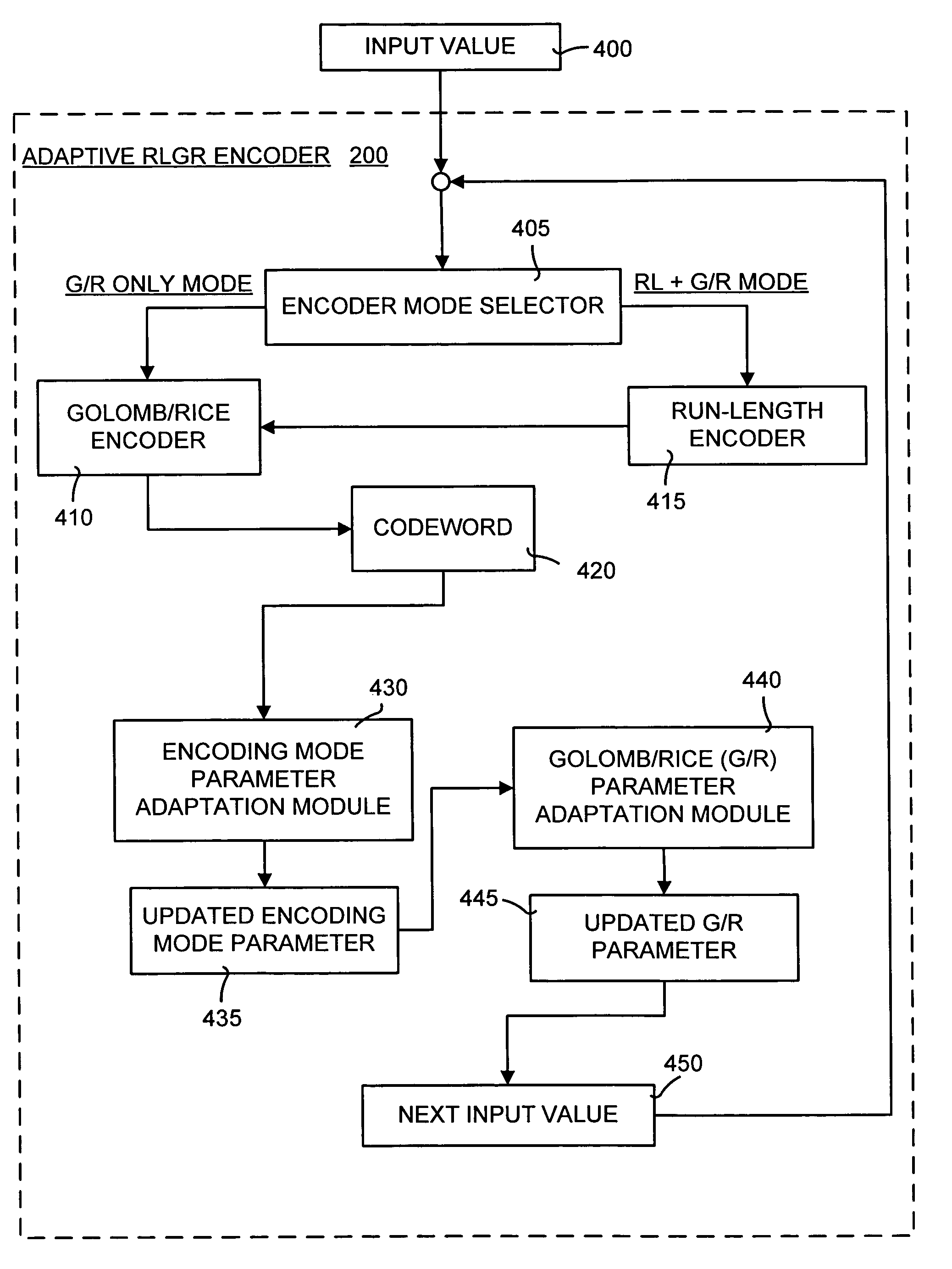
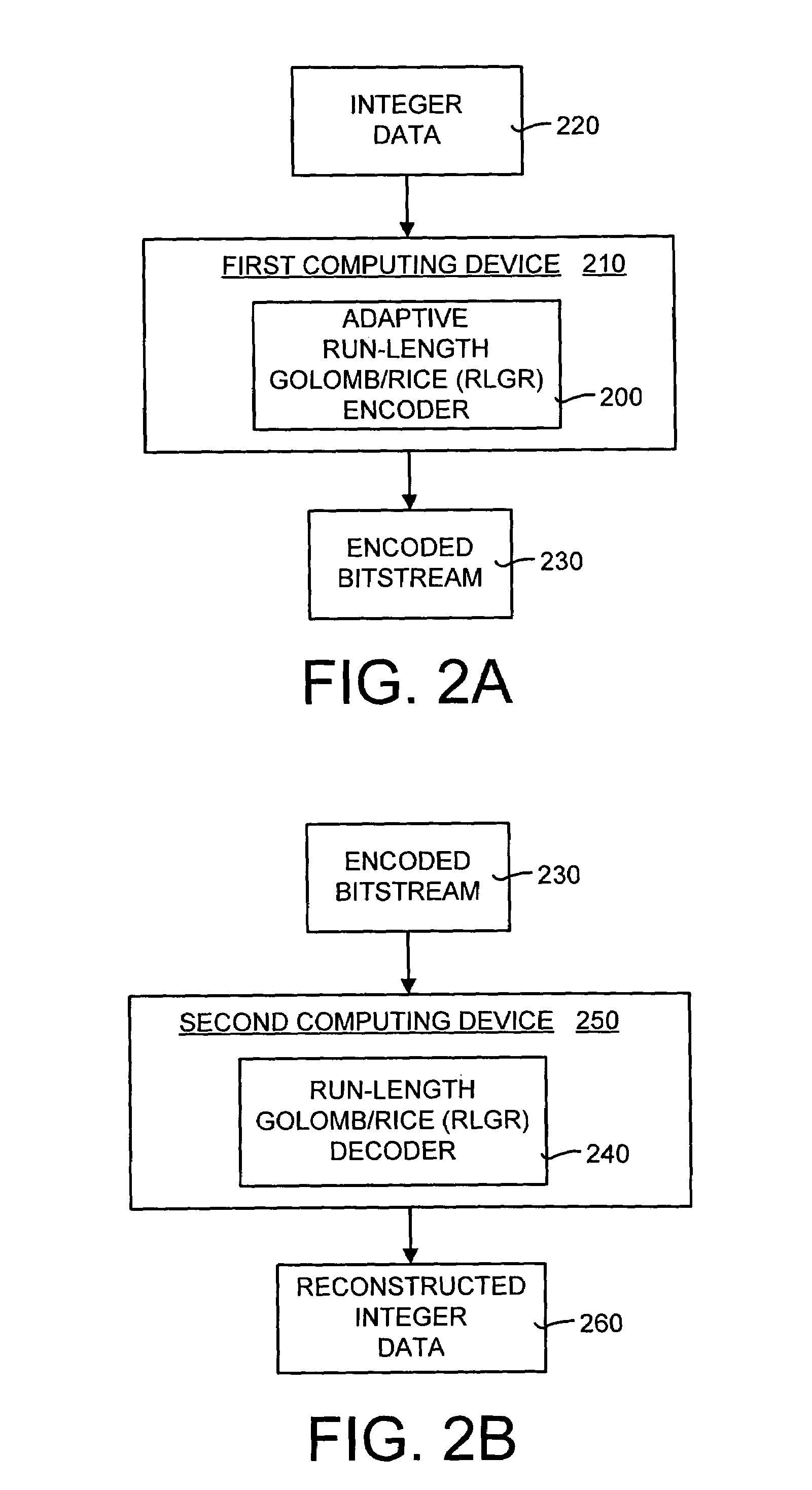
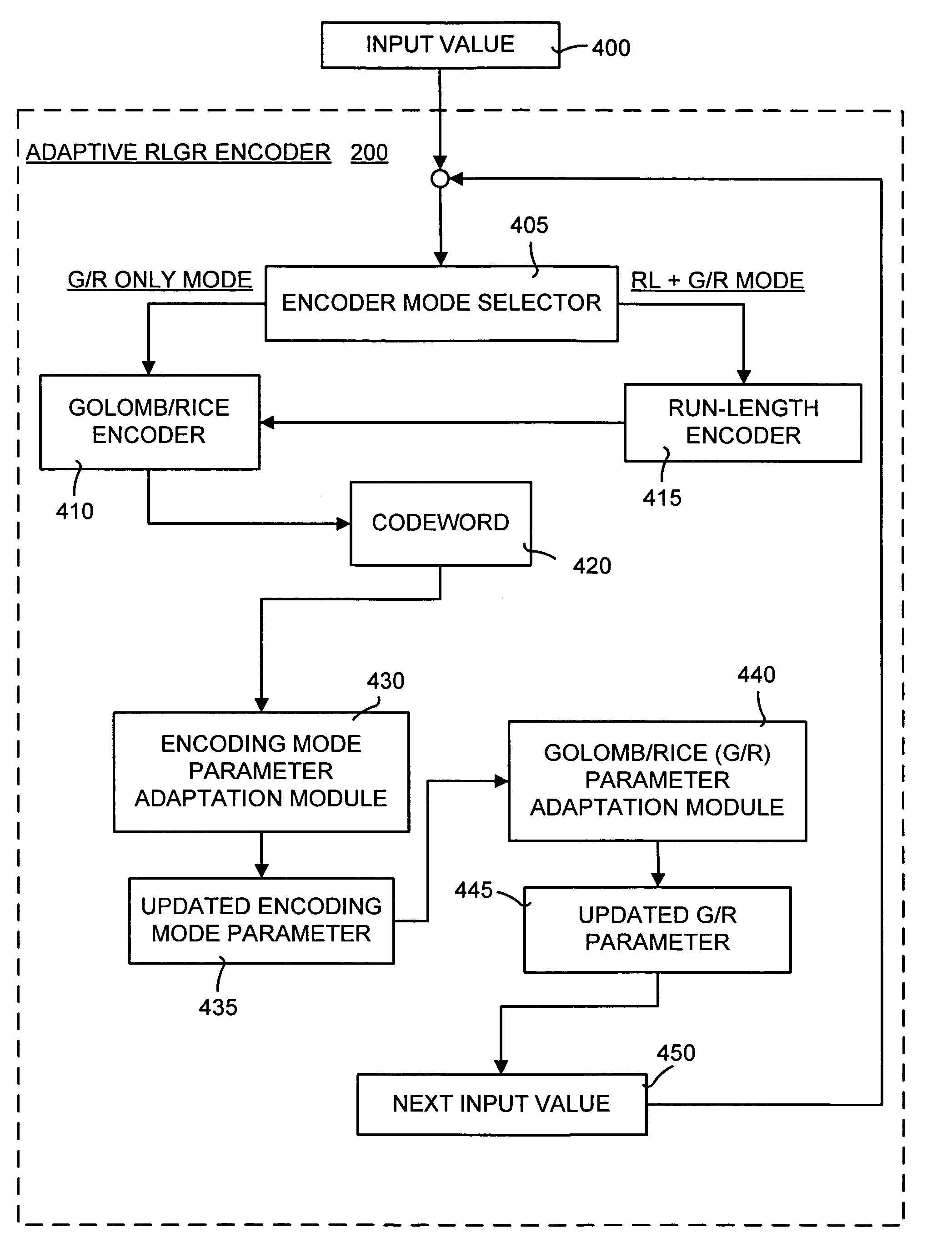
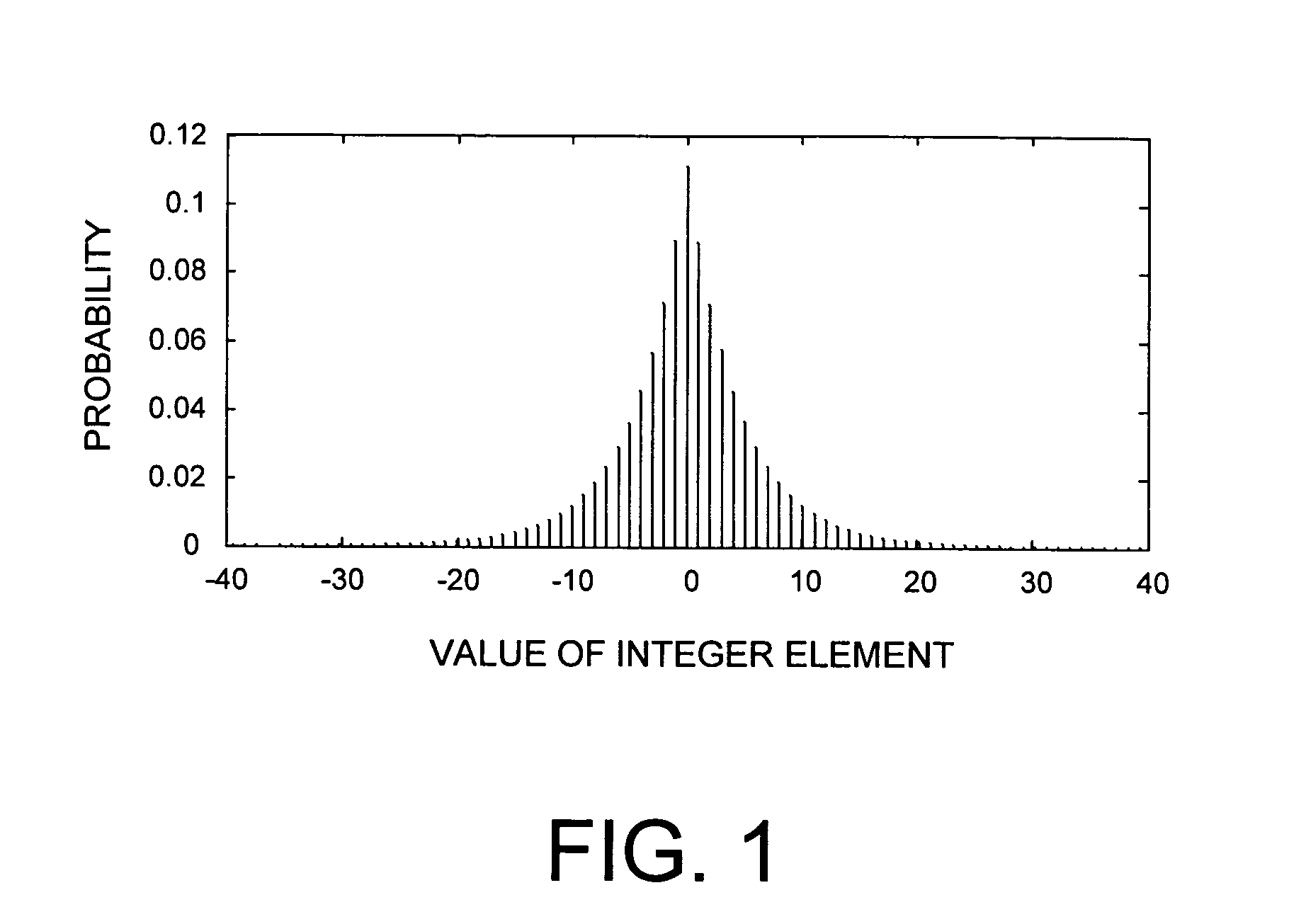
Lossless adaptive encoding and decoding of integer data
ActiveUS6987468B1Lossless encodingFast trackCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive encodingLossless compression
A method and system of lossless compression of integer data using a novel backward-adaptive technique. The adaptive Run-Length and Golomb / Rice (RLGR) encoder and decoder (codec) and method switches between a Golomb / Rice (G / R) encoder mode only and using the G / R encoder combined with a Run-Length encoder. The backward-adaptive technique includes novel adaptation rules that adjust the encoder parameters after each encoded symbol. An encoder mode parameter and a G / R parameter are adapted. The encoding mode parameter controls whether the adaptive RLGR encoder and method uses Run-Length encoding and, if so, it is used. The G / R parameter is used in both modes to encode every input value (in the G / R only mode) or to encode the number or value after an incomplete run of zeros (in the RLGR mode). The adaptive RLGR codec and method also includes a decoder that can be precisely implemented based on the inverse of the encoder rules.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Lossless adaptive encoding and decoding of integer data
A method and system of lossless compression of integer data using a novel backward-adaptive technique. The adaptive Run-Length and Golomb / Rice (RLGR) encoder and decoder (codec) and method switches between a Golomb / Rice (G / R) encoder mode only and using the G / R encoder combined with a Run-Length encoder. The backward-adaptive technique includes novel adaptation rules that adjust the encoder parameters after each encoded symbol. An encoder mode parameter and a G / R parameter are adapted. The encoding mode parameter controls whether the adaptive RLGR encoder and method uses Run-Length encoding and, if so, it is used. The G / R parameter is used in both modes to encode every input value (in the G / R only mode) or to encode the number or value after an incomplete run of zeros (in the RLGR mode). The adaptive RLGR codec and method also includes a decoder that can be precisely implemented based on the inverse of the encoder rules.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Data transmission apparatus, system and method
InactiveUS20150101003A1Minimize transmissionMinimize receptionTwo-way working systemsChannel coding adaptationLow distortionAdaptive encoding
This invention relates to a method and system of transmitting video data and data to a plurality of client radio receivers over an air interface using an adaptive encoding / transcoding scheme and updating the adaptive encoding / transcoding scheme in dependence upon received feedback data. The invention further describes estimating channel states and distortion levels for a plurality of transmission modes, then selecting that transmission mode for subsequent data transmission that has the lowest distortion level. Control data items can be extracted from the first data stream to produce a multimedia data stream and a control data stream and the multimedia data stream is transmitted over a first channel; the control data stream is transmitted over a second channel. The received data stream may be put into a plurality of multimedia slices having a predetermined slice size; and encoded into first data packets of a first predetermined size; which are divided into respective integral second data packets of a second predetermined size and are aggregated into a stream of third data packets of a third predetermined size.
Owner:GLOBAL INVACOM
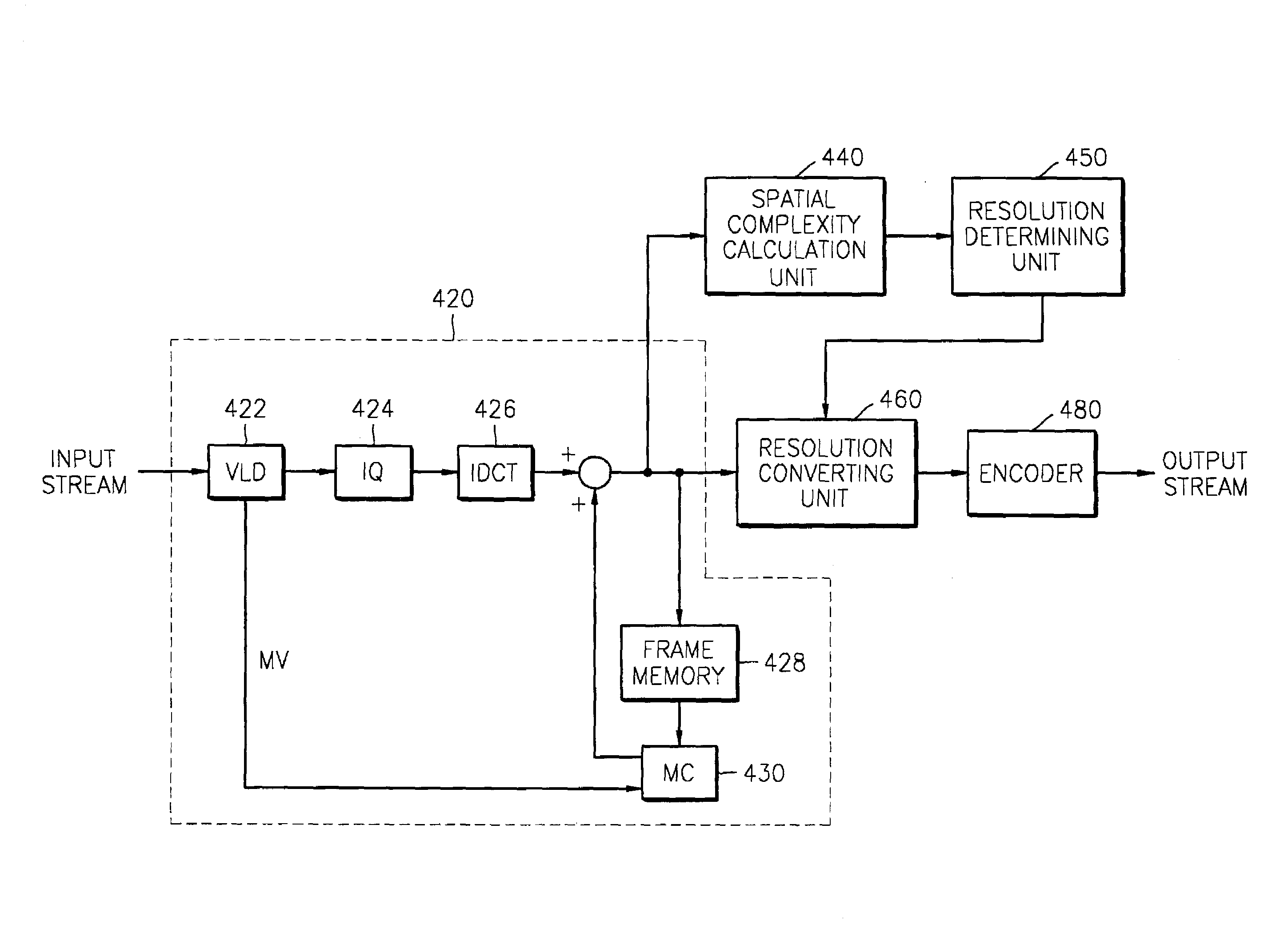
Method for adaptively encoding motion image based on temporal and spatial complexity and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7280708B2Improve efficiencyMaximize efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionImage resolutionSelf adaptive
A method and an apparatus adaptively encode a motion image based on temporal and / or spatial complexity. In the method, encoding is performed with different temporal and spatial resolutions at frame rates based on the temporal and / or spatial complexity of an input image so that image data is stored with high efficiency. The method includes calculating a spatial complexity of input image data, determining a resolution by comparing the calculated spatial complexity with a predetermined threshold, and converting the resolution of the input image data based on the resolution.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
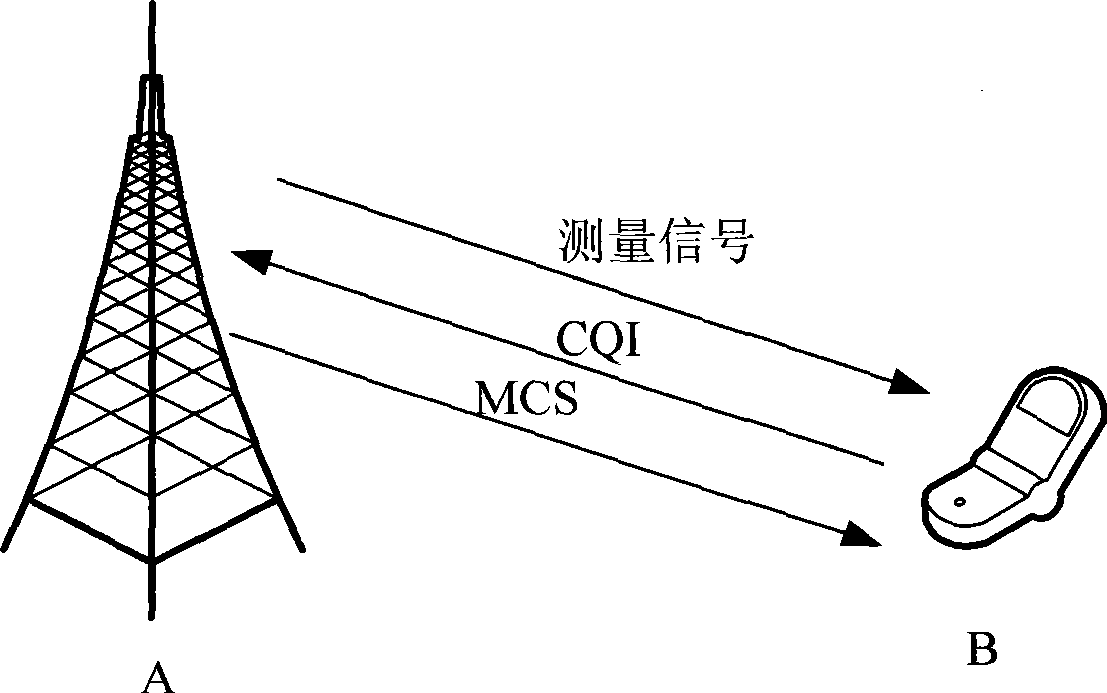
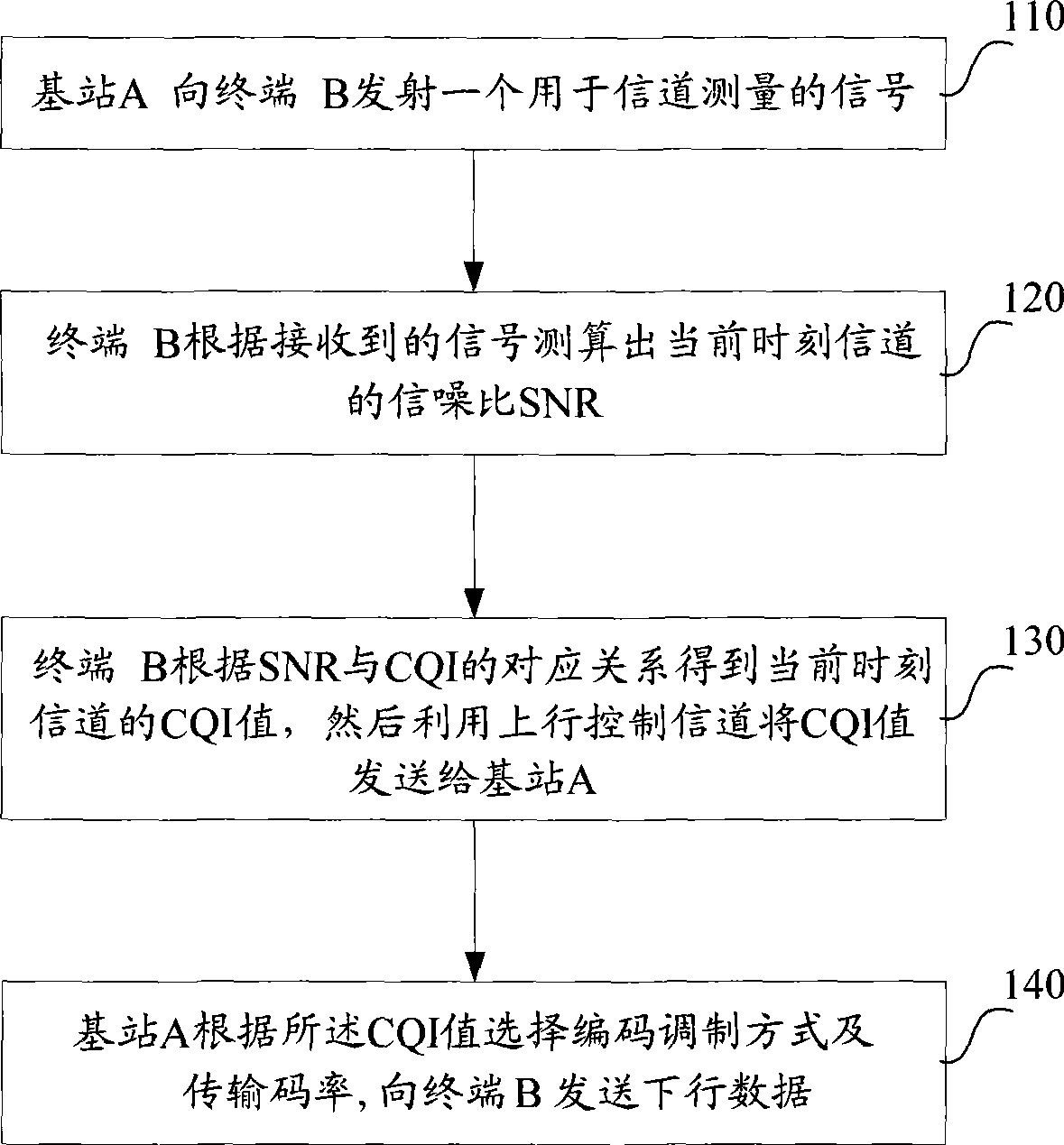
Adaptive encoding modulation method
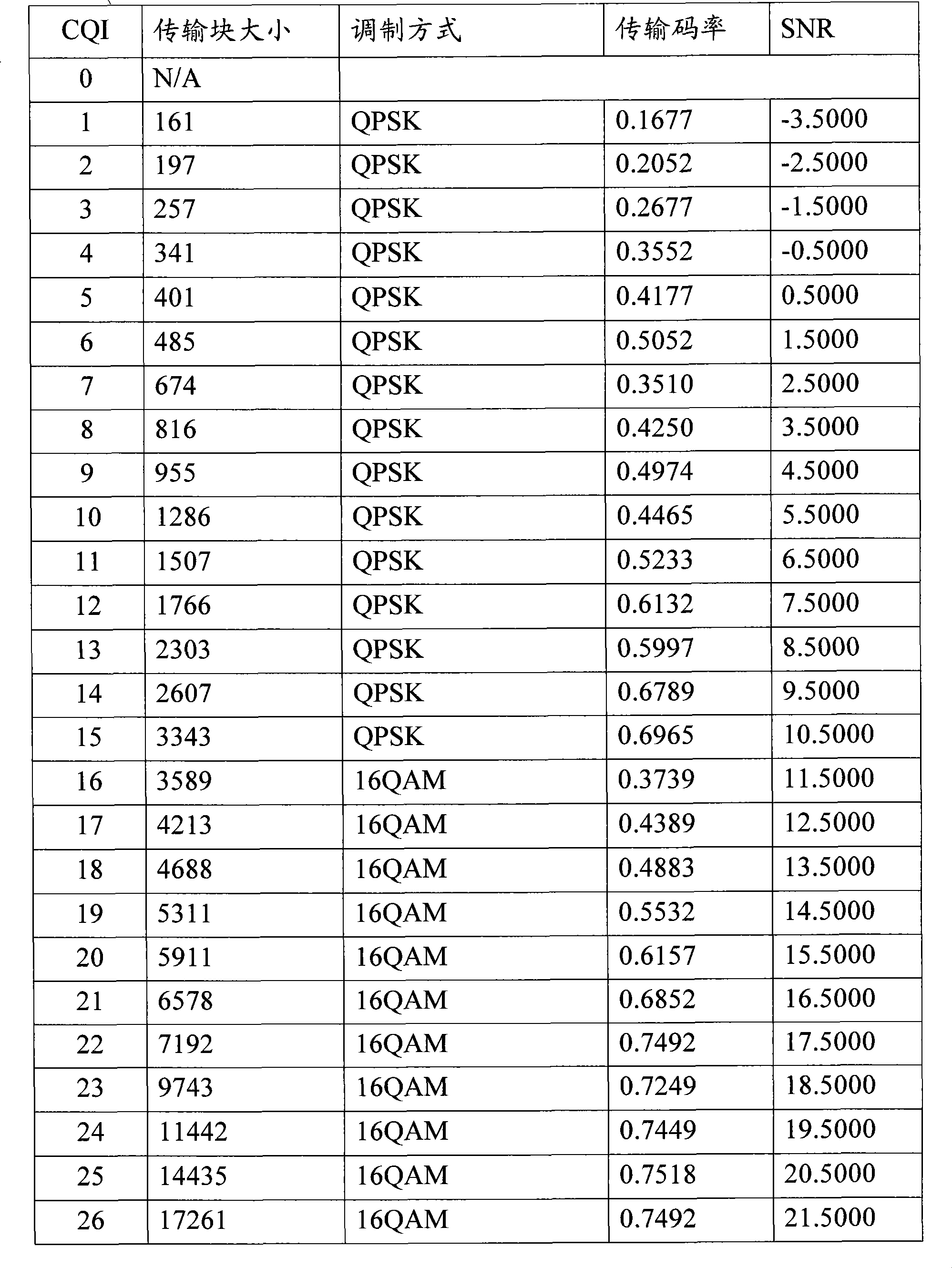
ActiveCN101388744AImprove throughputGood coding performanceError preventionMultiple carrier systemsAdaptive encodingPulse-code modulation
The invention relates to a self-adapting pulse code modulation method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, locally allocating the corresponding relationship between the indicated value, the modulation mode and the transmission code rate of the communication channel quality by a base station, secondly, transmitting down-bound data to a mobile terminal according the locally allocated corresponding relationship to select the corresponding modulation method and the transmission code rate after the base station receives the indicated value of the communication channel quality of the current time of the communication channel, namely the indicated value is transmitted by the mobile terminal. The self-adapting pulse code modulation method of the invention correspondingly selects the appropriate transmission code rate when selecting the appropriate modulation mode through the CQI, thereby the throughput of the system can reach the maximum value and the coding performance can be better.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Adaptive coding for lidar systems
ActiveUS10466342B1Avoid cross-talk across different channels and/or interferenceImproved resistance to environmental noiseOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationAdaptive encodingAtmospheric sciences
A Lidar system is provided. The Lidar system comprise: a light source configured to emit a multi-pulse sequence to measure a distance between the Lidar system and a location in a three-dimensional environment, and the multi-pulse sequence comprises multiple pulses having a temporal profile; a photosensitive detector configured to detect light pulses from the three-dimensional environment; and one or more processors configured to: determine a coding scheme comprising the temporal profile, wherein the coding scheme is determined dynamically based on one or more real-time conditions including an environment condition, a condition of the Lidar system or a signal environment condition; and calculate the distance based on a time of flight of a sequence of detected light pulses, wherein the time of flight is determined by determining a match between the sequence of detected light pulses and the temporal profile.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
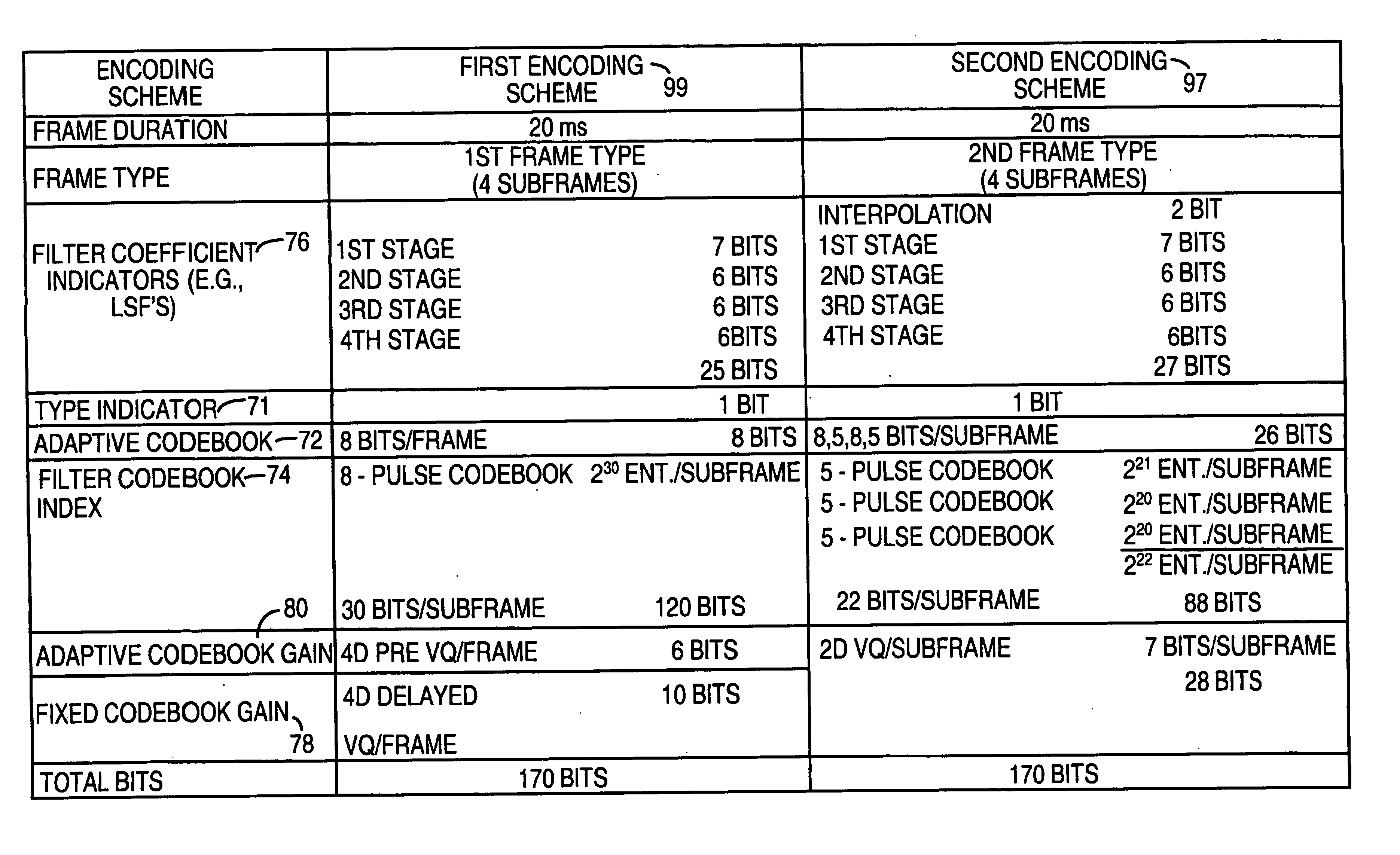
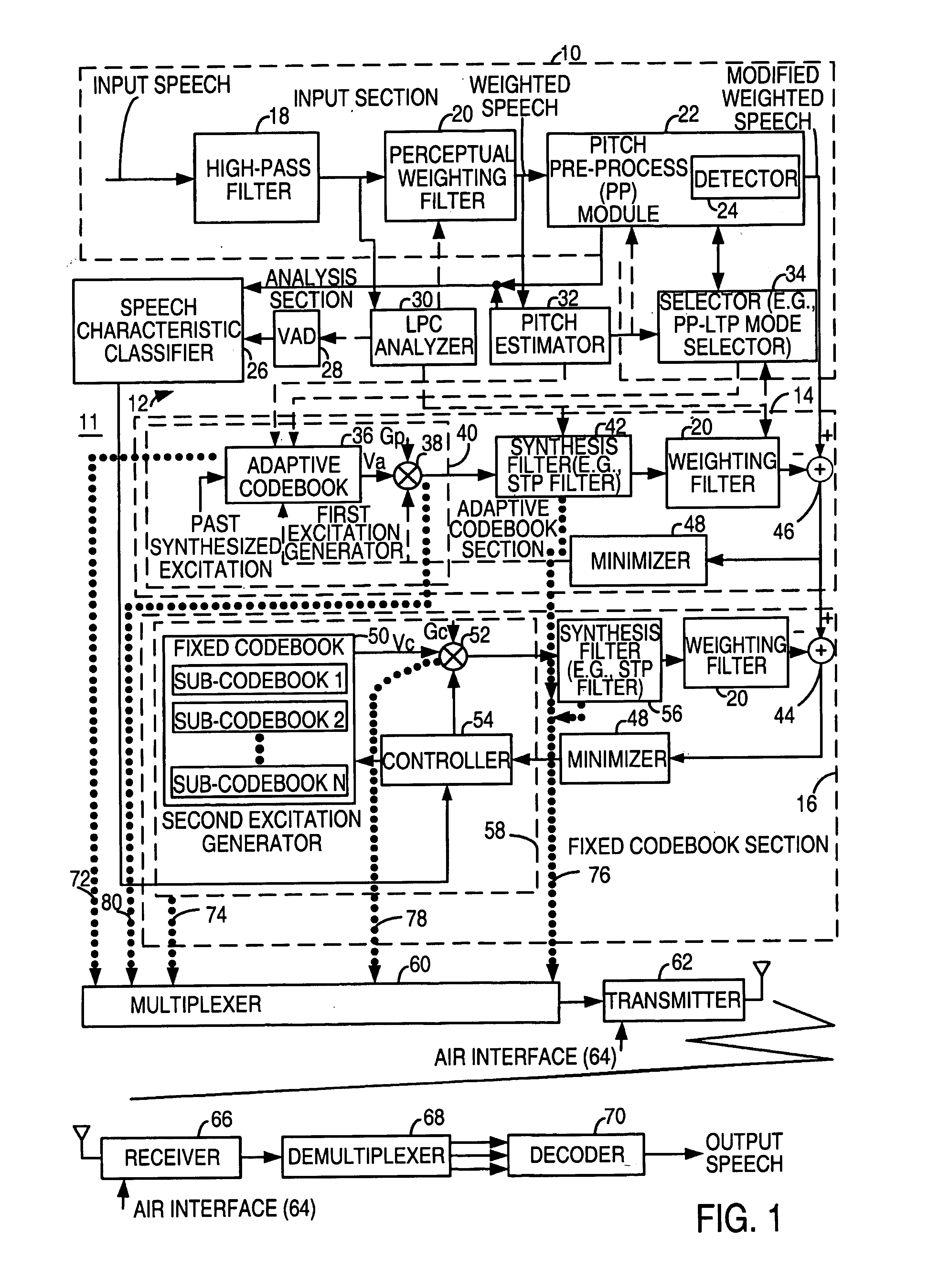
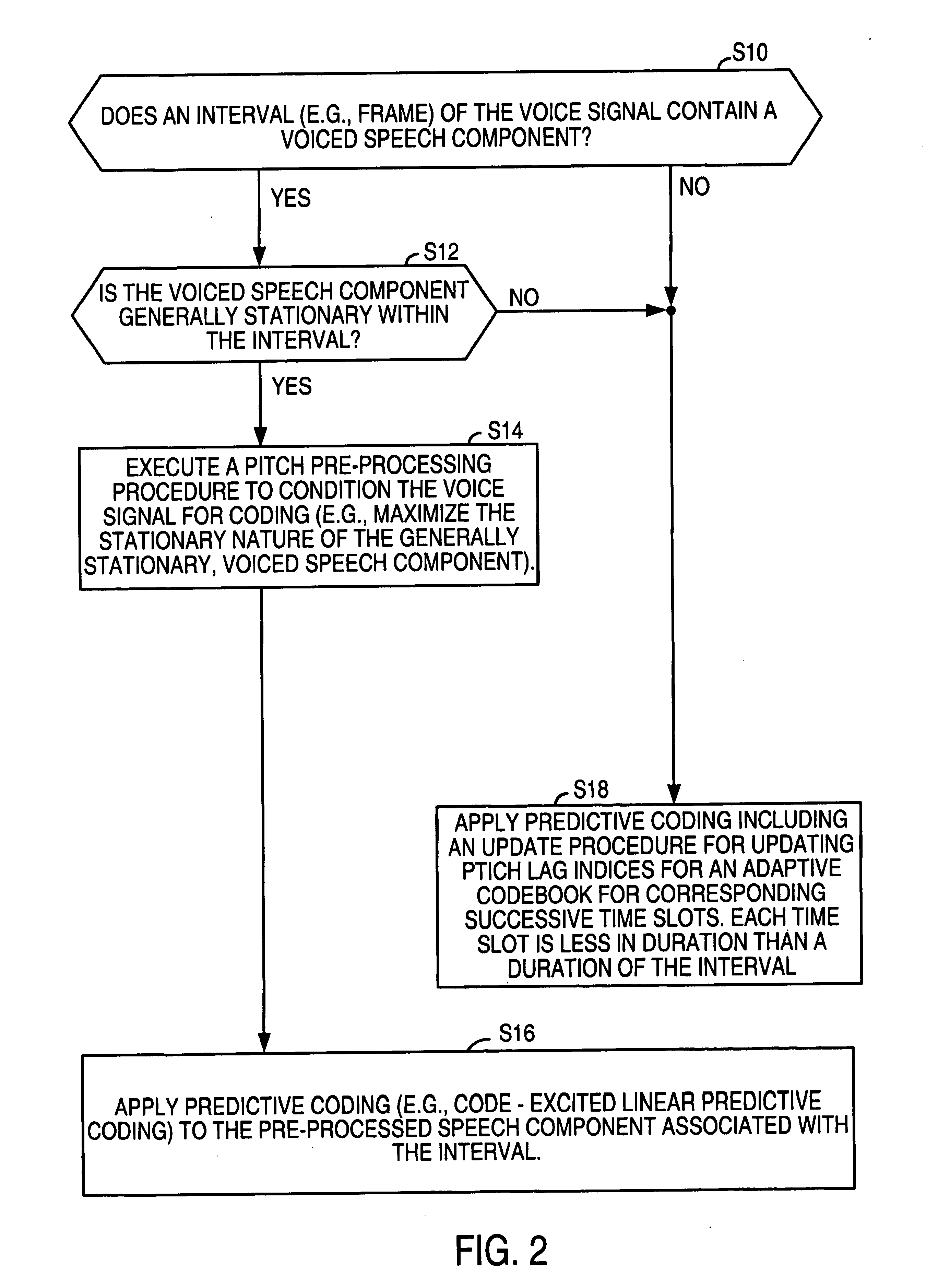
System for speech encoding having an adaptive encoding arrangement
InactiveUS7072832B1Facilitates the efficient bit-usage per frameGuaranteed preservation qualitySpeech analysisAdaptive encodingSpeech sound
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, a selector supports the selection of a first encoding scheme or the second encoding scheme based upon the detection or absence of the triggering characteristic in the interval of the input speech signal. The first encoding scheme has a pitch pre-processing procedure for processing the input speech signal to form a revised speech signal biased toward an ideal voiced and stationary characteristic. The pre-processing procedure allows the encoder to fully capture the benefits of a bandwidth-efficient, long-term predictive procedure for a greater amount of speech components of an input speech signal than would otherwise be possible. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, the second encoding scheme entails a long-term prediction mode for encoding the pitch on a sub-frame by sub-frame basis. The long-term prediction mode is tailored to where the generally periodic component of the speech is generally not stationary or less than completely periodic and requires greater frequency of updates from the adaptive codebook to achieve a desired perceptual quality of the reproduced speech under a long-term predictive procedure.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Content adaptive video encoder
InactiveUS7715475B1Improve efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision signal transmission by single/parallel channelsAdaptive encodingSubject matter
A system for content adaptive encoding and decoding video is disclosed. The system comprises modules for segmenting video content into segments based on predefined classifications or models. Examples of such classifications comprise action scenes, slow scenes, low or high detail scenes, and brightness of the scenes. Based on the segment classifications, each segment is encoded with a different encoder chosen from a plurality of encoders. Each encoder is associated with a model. The chosen encoder is particularly suited to encoding the unique subject matter of the segment. The coded bit-stream for each segment includes information regarding which encoder was used to encode that segment. A matching decoder of a plurality of decoders is chosen using the information in the coded bitstream to decode each segment using a decoder suited for the classification or model of the segment. If scenes exist which do not fall in a predefined classification, or where classification is more difficult based on the scene content, these scenes are segmented, coded and decoded using a generic coder and decoder.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
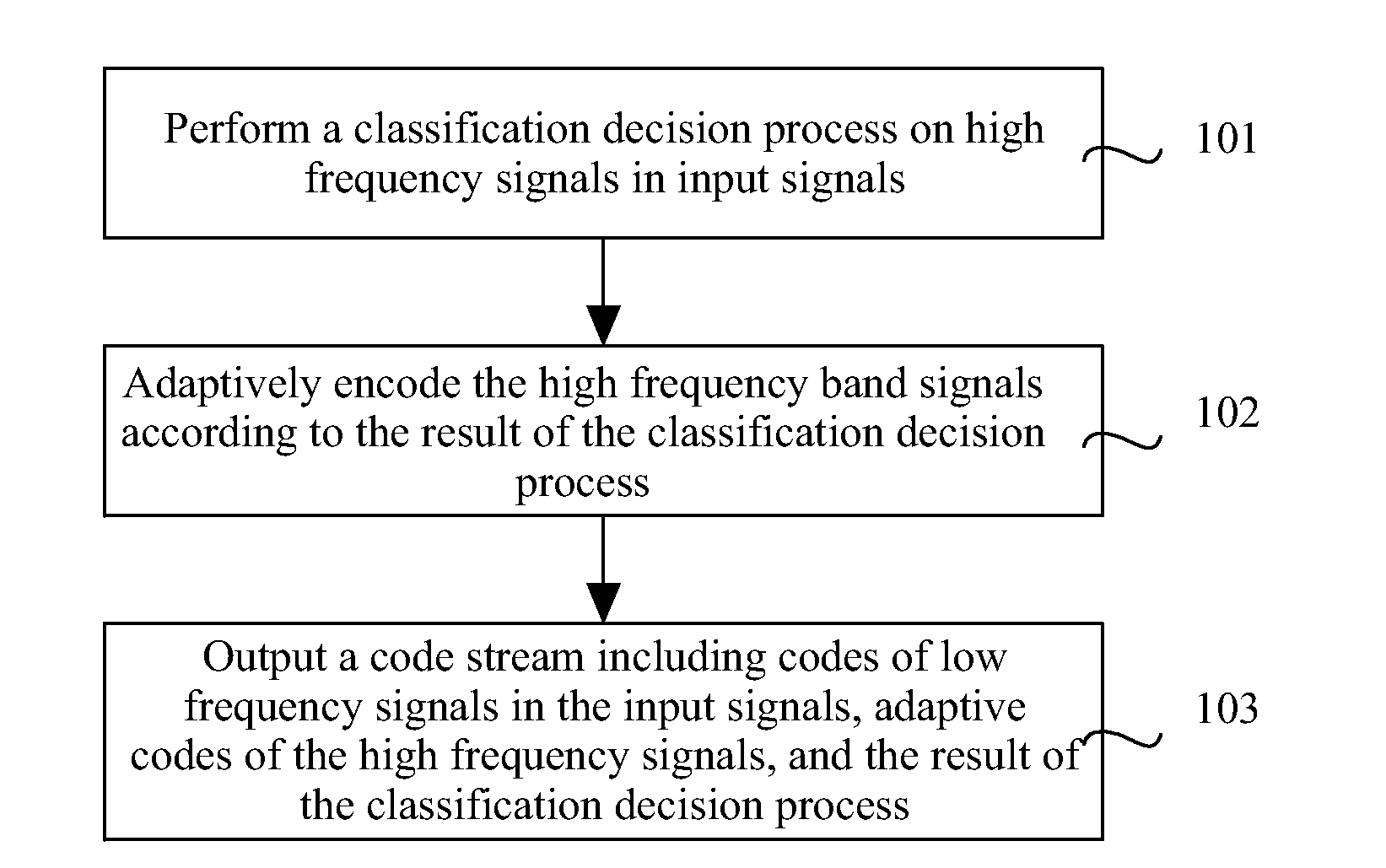
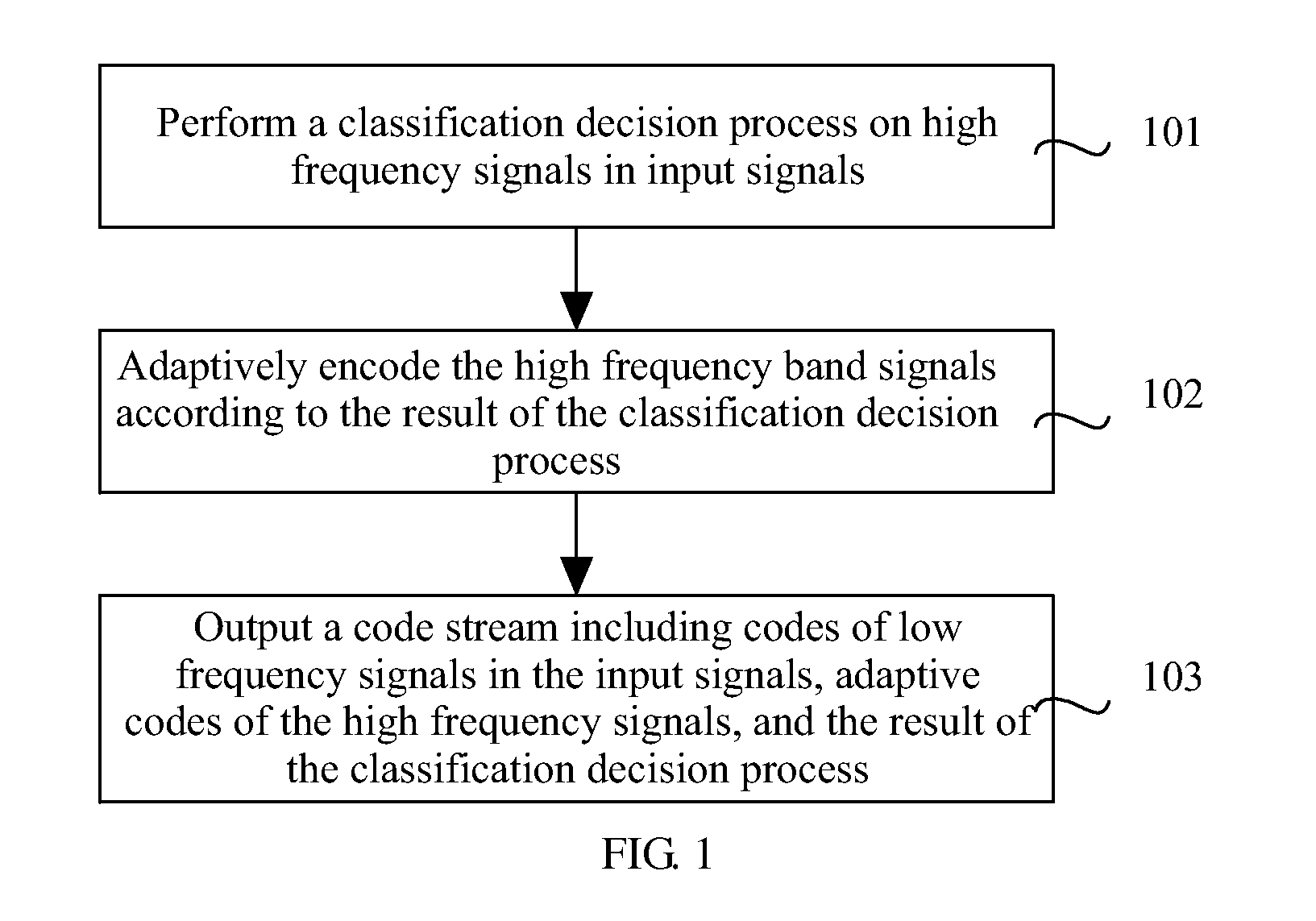
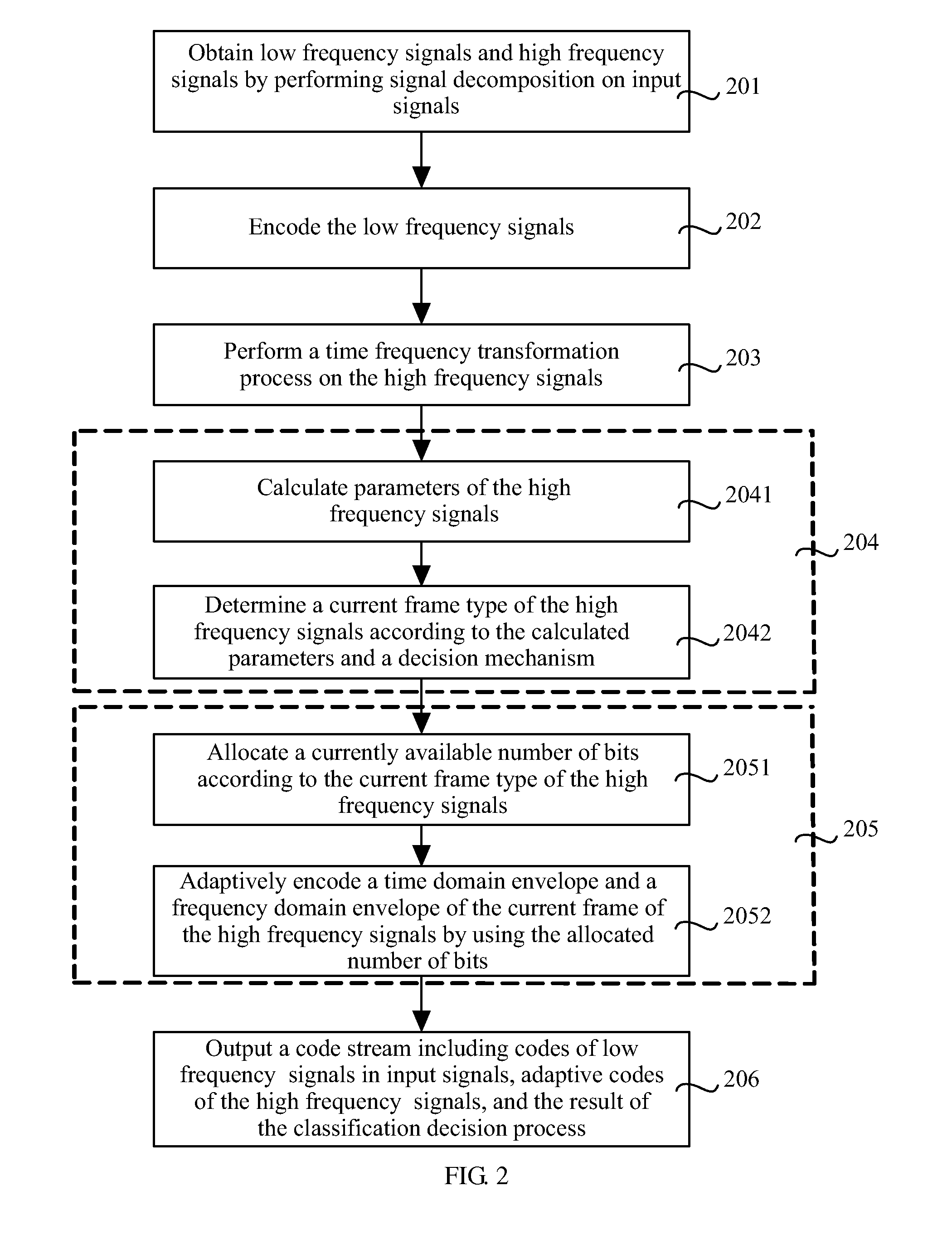
Methods, Apparatuses and System for Encoding and Decoding Signal
ActiveUS20110194598A1Improve audio qualityAudio signal improvedSpeech analysisTransmissionAdaptive encodingSelf adaptive
Methods and apparatuses for encoding a signal and decoding a signal and a system for encoding and decoding are provided. The method for encoding a signal includes performing a classification decision process on high frequency signals of input signals, adaptively encoding the high frequency signals according to the result of the classification decision process, and outputting a bitstream including codes of low frequency signals of the input signals, adaptive codes of the high frequency signals, and the result of the classification decision process. The classification decision process is performed on the high frequency signals, and adaptive encoding or adaptive decoding is performed according to the result of the classification decision process, so the quality of voice and audio output signals is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
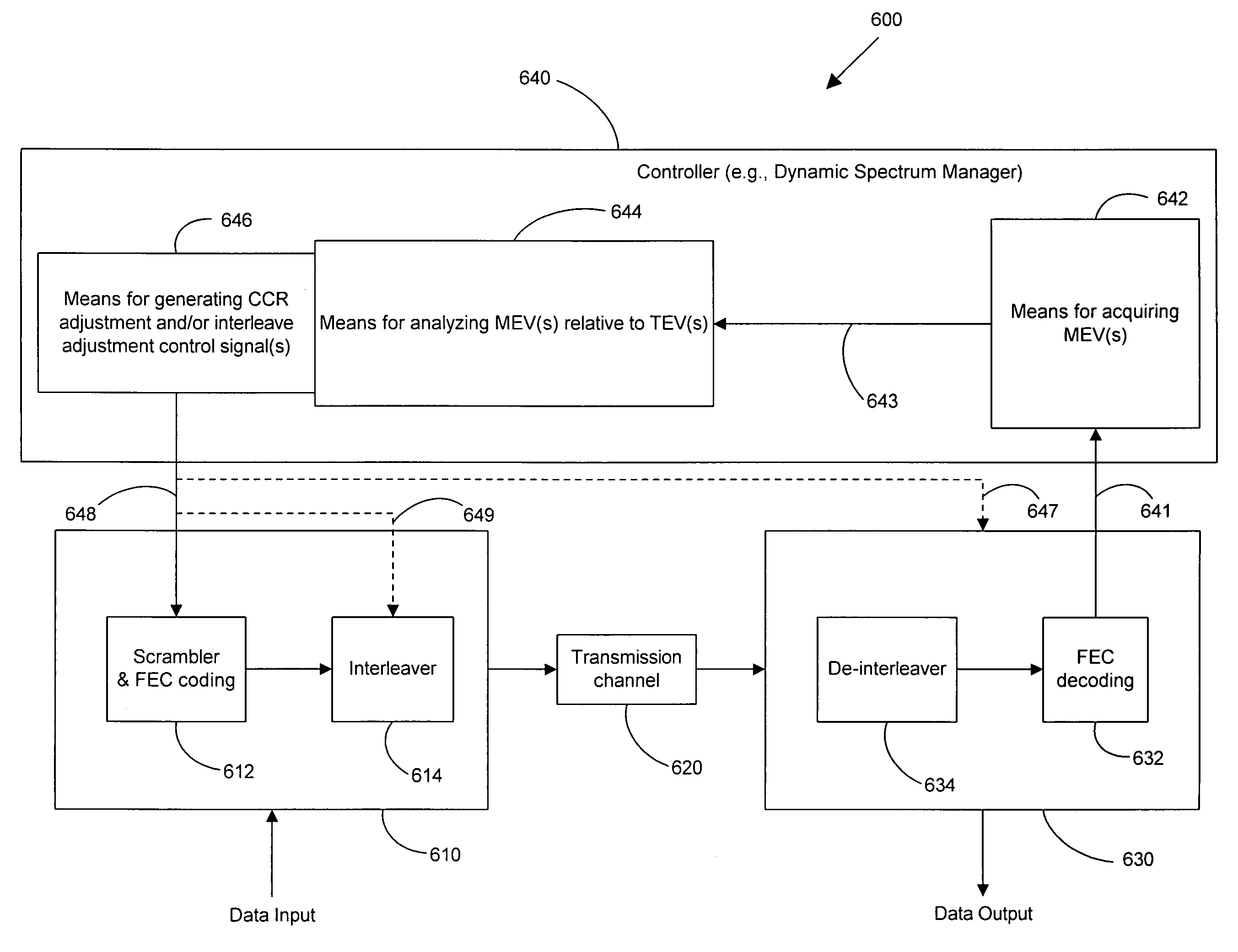
Adaptive FEC codeword management
Adaptive FEC coding is used to adjust the codeword composition of FEC codewords in a communication system. A codeword composition ratio may be adjusted in response to variance of a measured transmission error value from a target transmission error value in the system. The codeword composition ratio may be any quantity or value that represents the relation between the payload and parity bytes in the applicable FEC coding scheme. Adjustment of the codeword composition ratio may be adjusting parameters such as the N, K and / or R values in ADSL1 systems or the INP and / or maximum interleaving delay values in ADSL2 systems. A controller may be used to monitor, analyze and adjust the various values used in adaptively managing FEC coding. The present invention may be implemented in a transmission system in which a transmitter transmits data to a receiver via a transmission channel, such as a DSL system.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
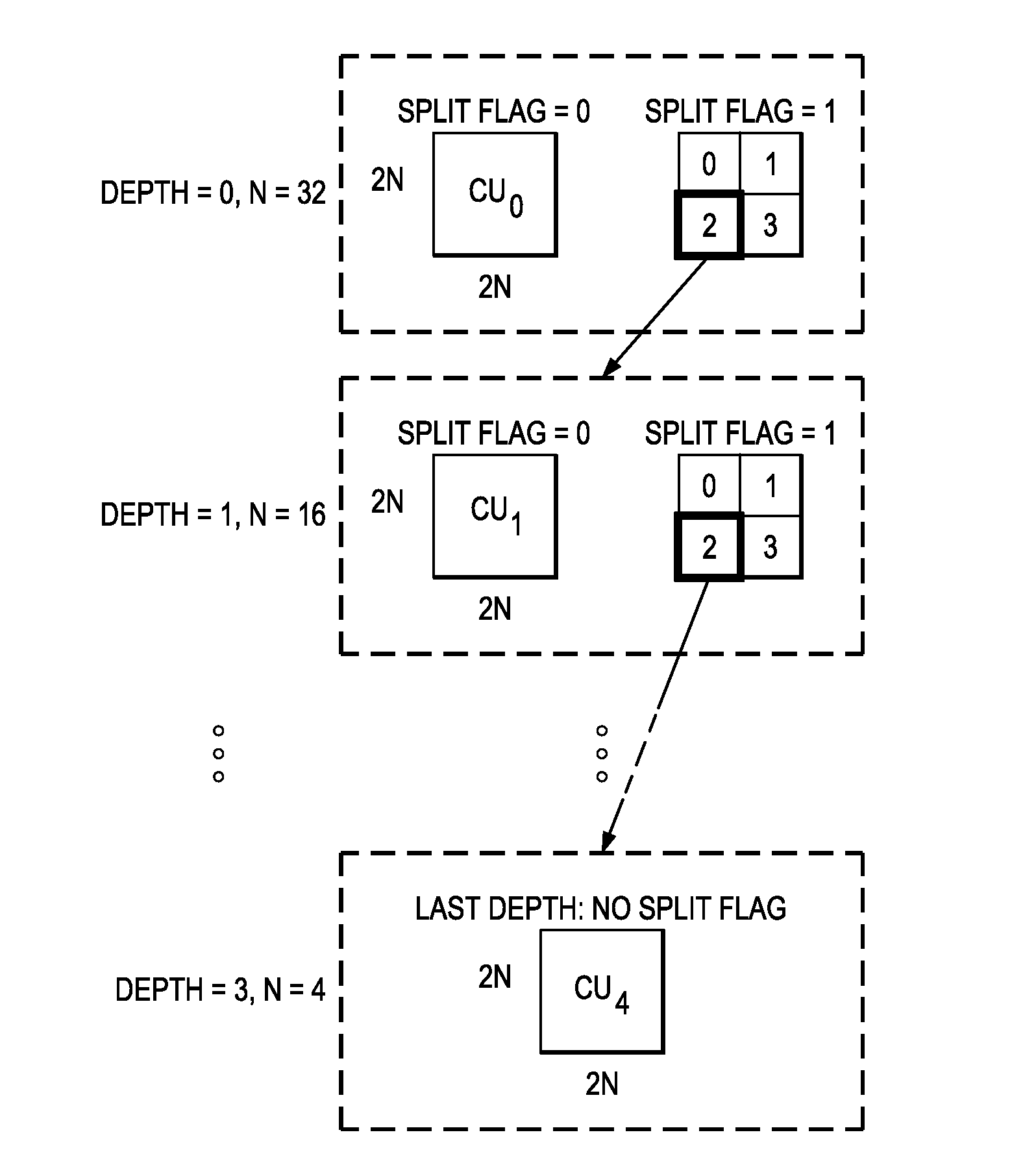
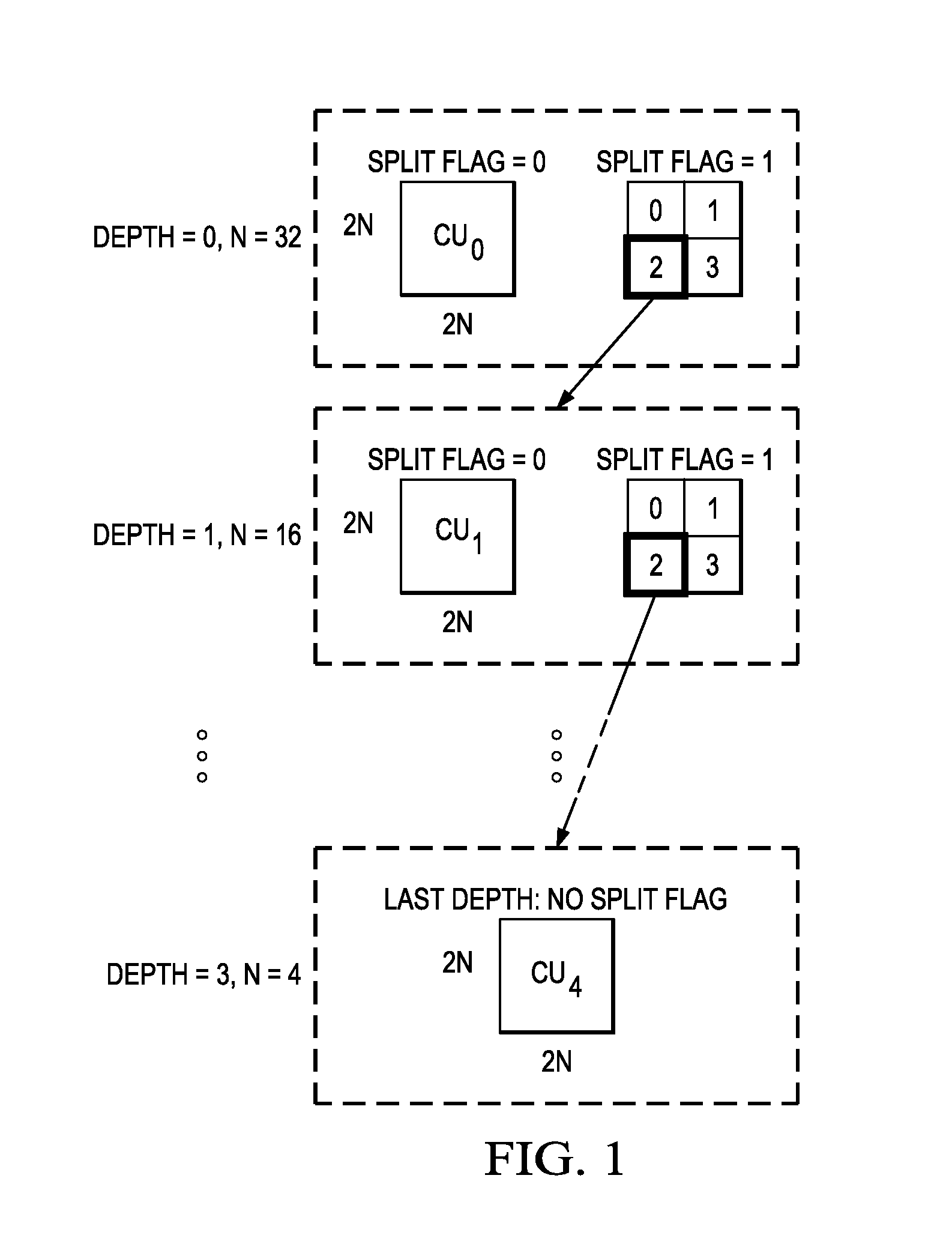
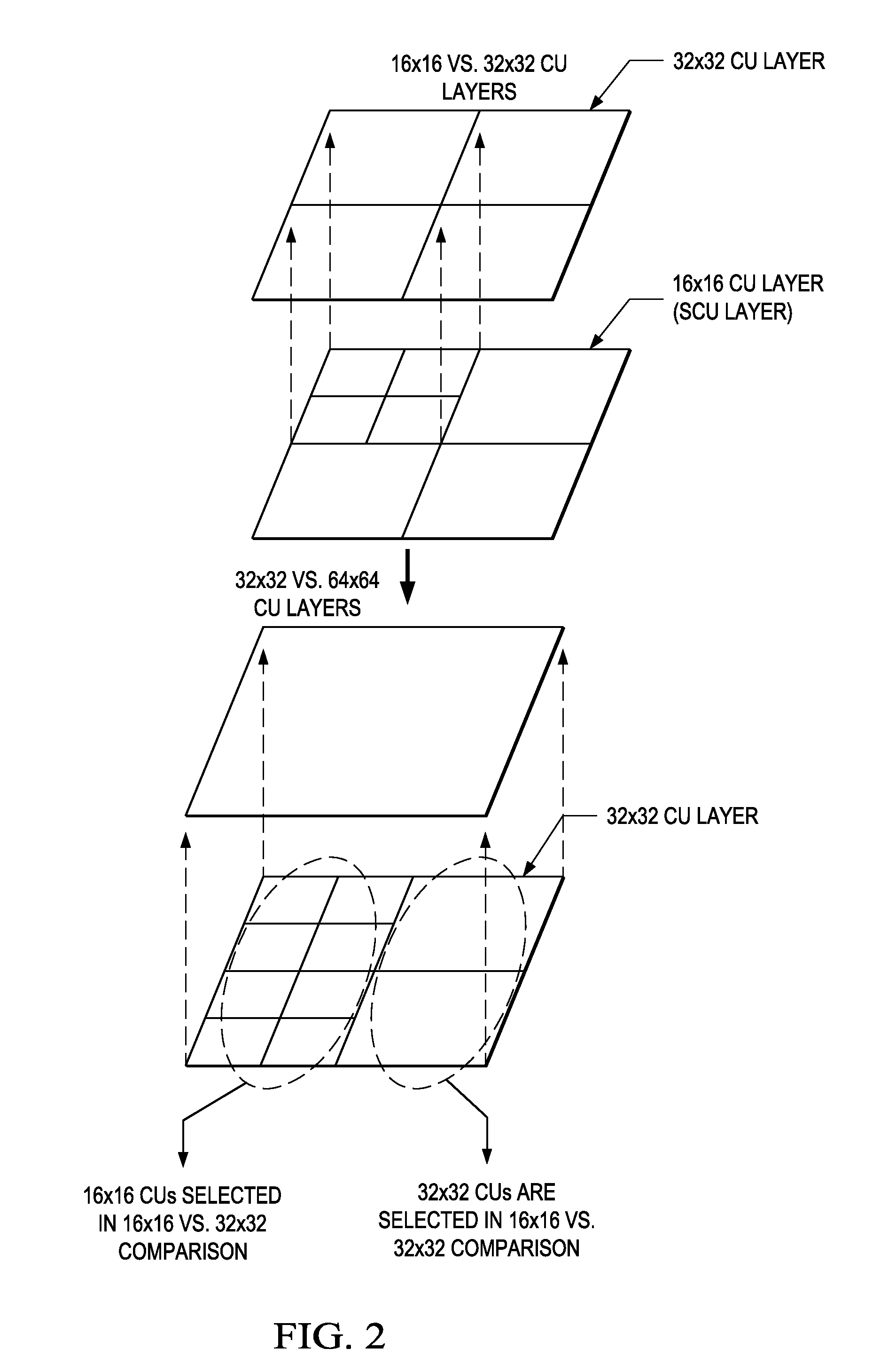
Adaptive Coding Unit (CU) Partitioning Based on Image Statistics
ActiveUS20140140395A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionAdaptive coding
A method for determining coding unit (CU) partitioning of a largest coding unit (LCU) of a picture is provided that includes computing a first statistical measure and a second statistical measure for the LCU, selecting the LCU as the CU partitioning when the first statistical measure does not exceed a first threshold and the second statistical measure does not exceed a second threshold, and selecting CUs in one or more lower layers of a CU hierarchy of the LCU to form the CU partitioning when the first statistical measure exceeds the first threshold and / or the second statistical measure exceeds the second threshold.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
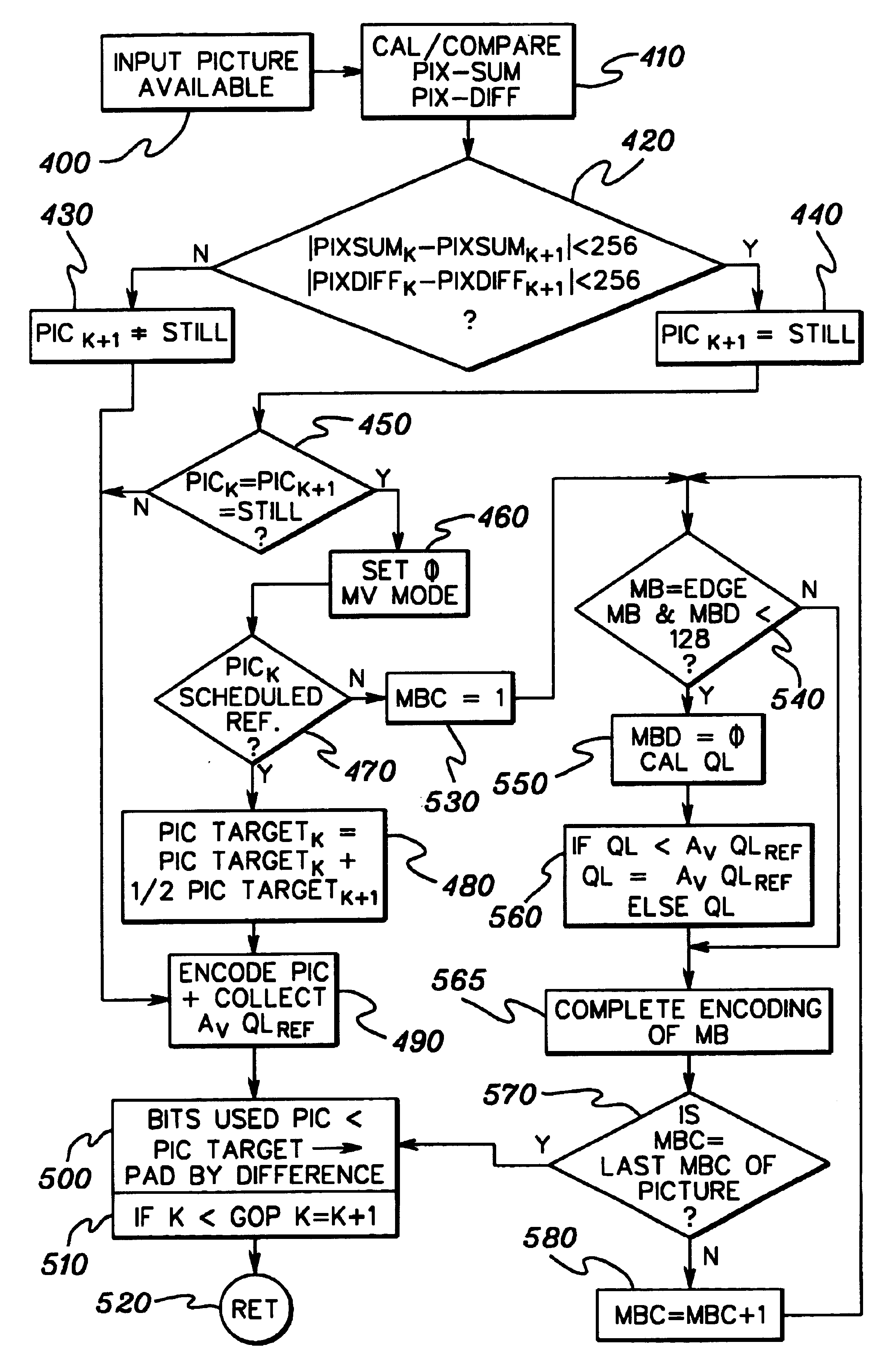
Adaptive encoding of a sequence of still frames or partially still frames within motion video
InactiveUS6895048B2Prevent pulsation artifactConstant picture qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingAdaptive encoding
Method, system and computer program product are provided for adaptively encoding in hardware, software or a combination thereof a series of still or partially still pictures using motion video encoding. A pre-encode statistics measurement unit is employed to derive statistics on each frame of the sequence of video frames to be encoded. The statistics are determinative of whether the frame comprises a still frame. If so, at least one controllable parameter to be used to encode the still frame is modified, and an encoding engine employs the at least one controllable parameter to encode the still frame so that pulsation artifacts are prevented between still frames of the series of still frames. Partial still picture encoding to prevent pulsation artifacts on a macroblock level is also addressed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Video interesting region double-stream encoding and transmitting method and system
InactiveCN102905200AEnhanced codingImprove bandwidth utilizationSelective content distributionTime domainAlgorithm
The invention discloses a video interesting region double-stream encoding and transmitting method and a video interesting region double-stream encoding and transmitting system. By the method, an interesting region is subjected to enhanced encoding by adopting a relatively high code rate, and a non-interesting region is encoded by adopting a common code rate; a generated basic stream and a generated enhanced stream can be transmitted under a condition of finite bandwidth according to distribution in a time domain. The information determination degree is determined according to the probability of a specific semantic event, and user-oriented interesting encoding is executed, so that information redundancy the user is not interested in can be effectively removed from a monitored video, and the overall encoding efficiency of the monitored video can be greatly improved. By the method, an extension-type encoding model with adaptive determination degree and an optimal channel space domain-time domain resource distribution double-stream packaging method are constructed by researching the information determination degree of the monitored video, so that adaptive encoding of interesting information of the monitored video is realized; and the monitored video encoding efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
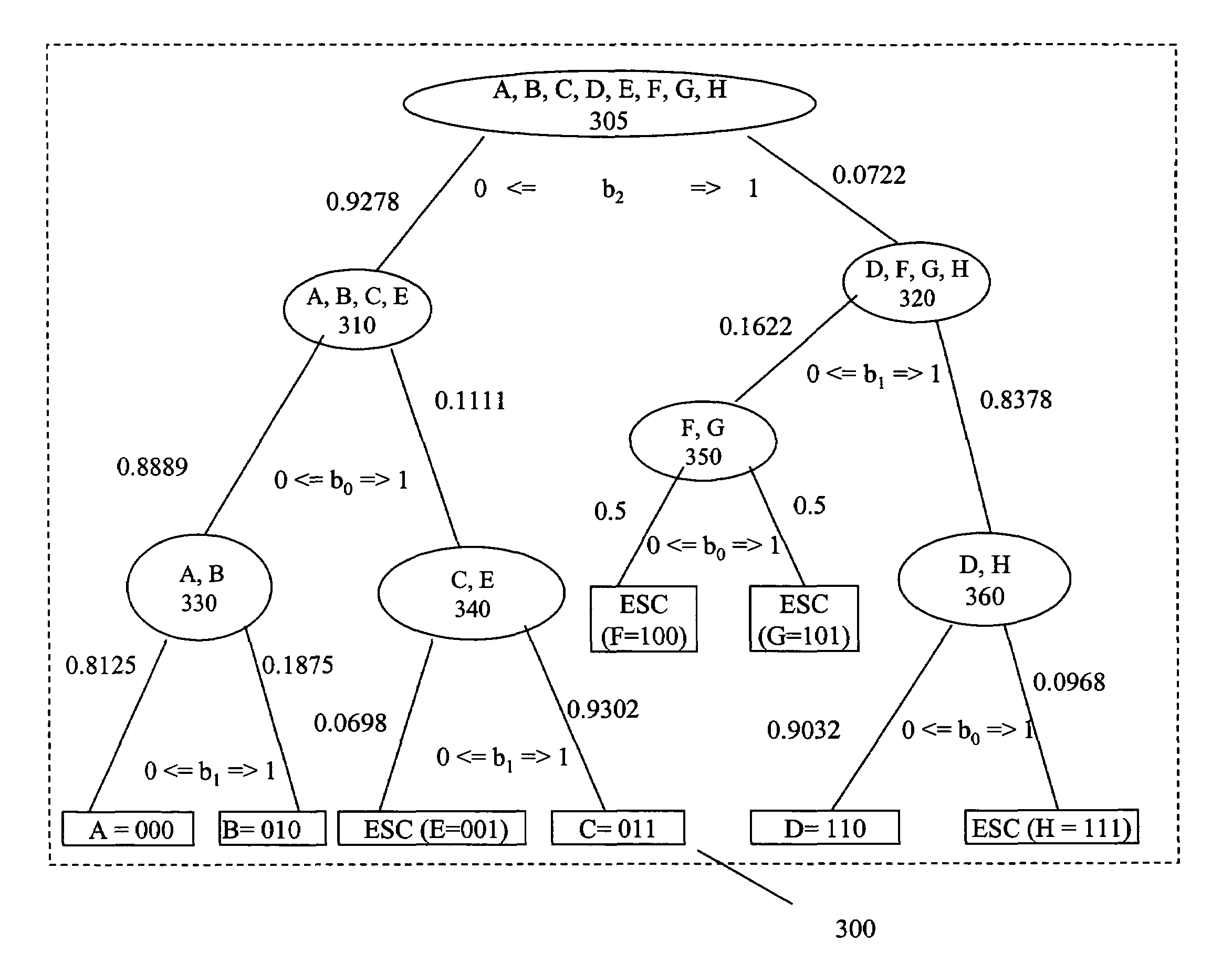
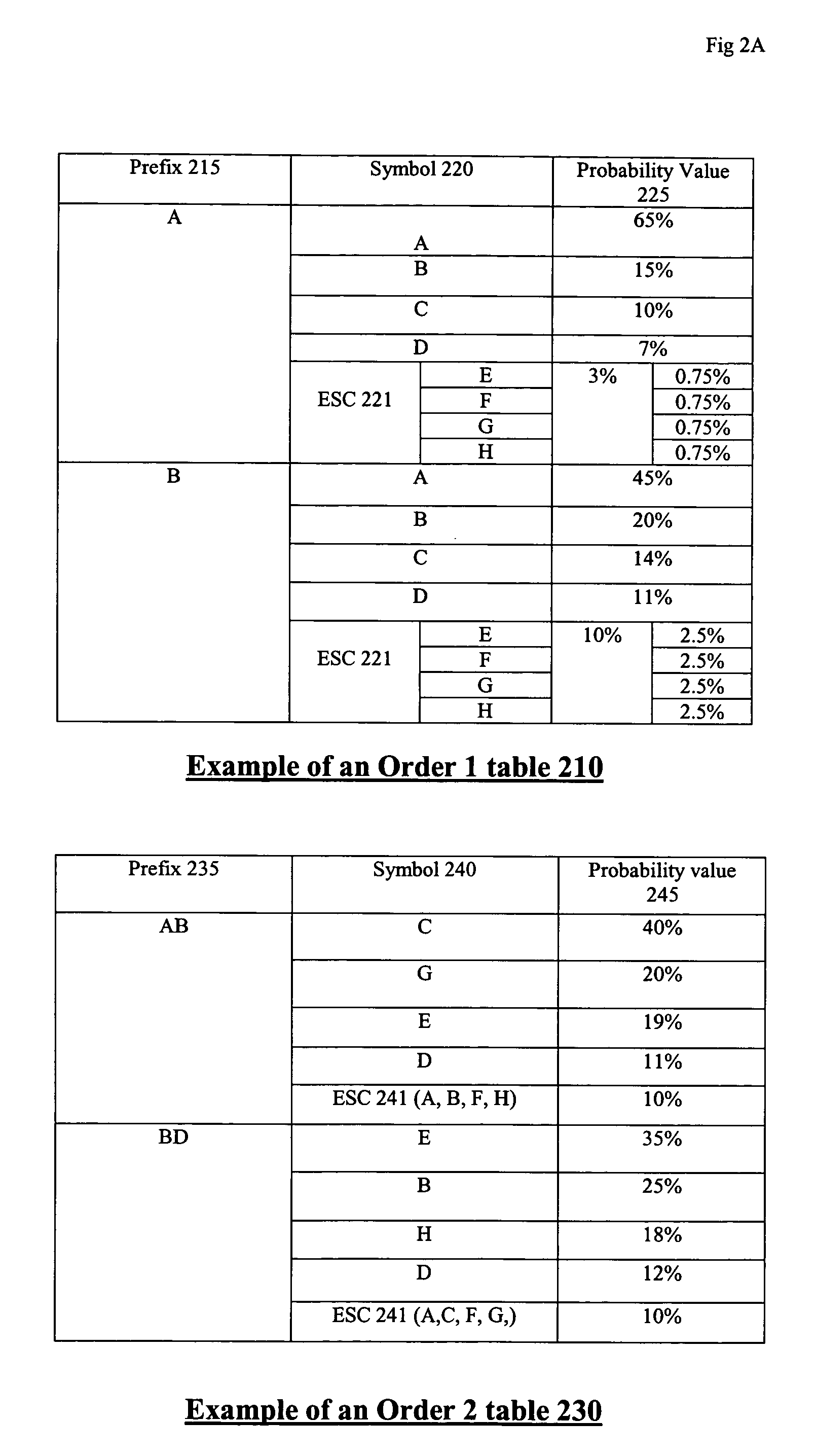
Bitwise adaptive encoding using prefix prediction
InactiveUS7274671B2Effective evaluationEfficiently encodeCode conversionData switching by path configurationAdaptive encodingAssessment data
A technique is presented for compressing data which leverages the frequency of an escape symbol for better compression. The prefix of a data string is evaluated and the probability of all characters that might succeed it is predicted in tabular form. Symbols are designated “Hit” or “Miss” based upon whether they are in the table. A binary tree is generated by partitioning nodes into Zero and One groups based on a single bit value. A partition bit is chosen to maximize the difference of probability sums of Hit symbols in Zero and One groups, with exceptions for partitions having non Hit symbols in one of the groups. A probability value is assigned to each branch, based on the probabilities of Hit and Miss symbols. Encoding or decoding a symbol is facilitated by encoding or decoding the branch probabilities on the shortest path from the root to the leaf node containing the symbol using arithmetic encoding or decoding method.
Owner:BOLY MEDIA COMM
Method and apparatus for adaptive encoding and decoding based on image quality
InactiveUS20170104993A1Reduce bitrateMinimize degradationDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionImaging quality
Disclosed herein are a method and apparatus that adaptively perform encoding and decoding based on image quality. An encoding apparatus may determine optimal Frames Per Second (FPS) for a video and may encode the video based on the determined FPS. Further, the encoding apparatus may provide improved temporal scalability. A decoding apparatus may select a frame to be displayed from among frames of a video depending on a required minimum satisfied user ratio. Through the selection of the frame, the decoding apparatus may provide improved temporal scalability.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method of content adaptive video encoding
InactiveUS20100272173A1Reduce disadvantagesColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionAdaptive encoding
A method of content adaptive encoding video is disclosed. The method comprises segmenting video content into segments based on predefined classifications or models. Examples of such classifications include action scenes, slow scenes, low or high detail scenes, and brightness of the scenes. Based on the segment classifications, each segment is encoded with a different encoder chosen from a plurality of encoders. Each encoder is associated with a model. The chosen encoder is particularly suited to encoding the unique subject matter of the segment. The coded bit-stream for each segment includes information regarding which encoder was used to encode that segment. A matching decoder of a plurality of decoders is chosen using the information in the coded bitstream to decode each segment using a decoder suited for the classification or model of the segment. If scenes exist which do not fall in a predefined classification, or where classification is more difficult based on the scene content, these scenes are segmented, coded and decoded using a generic coder and decoder.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
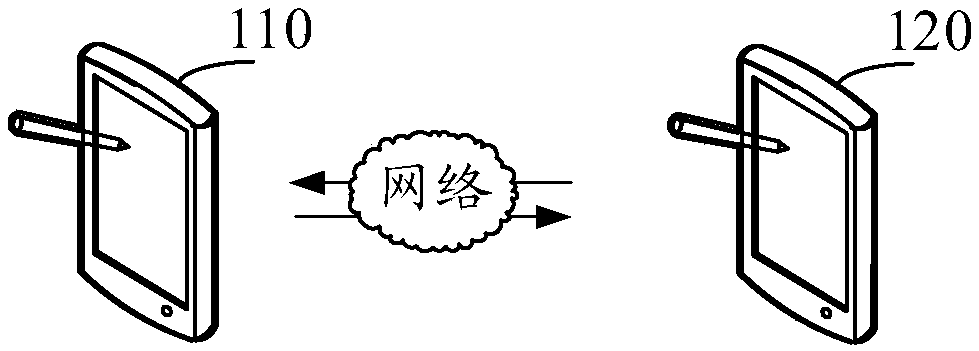
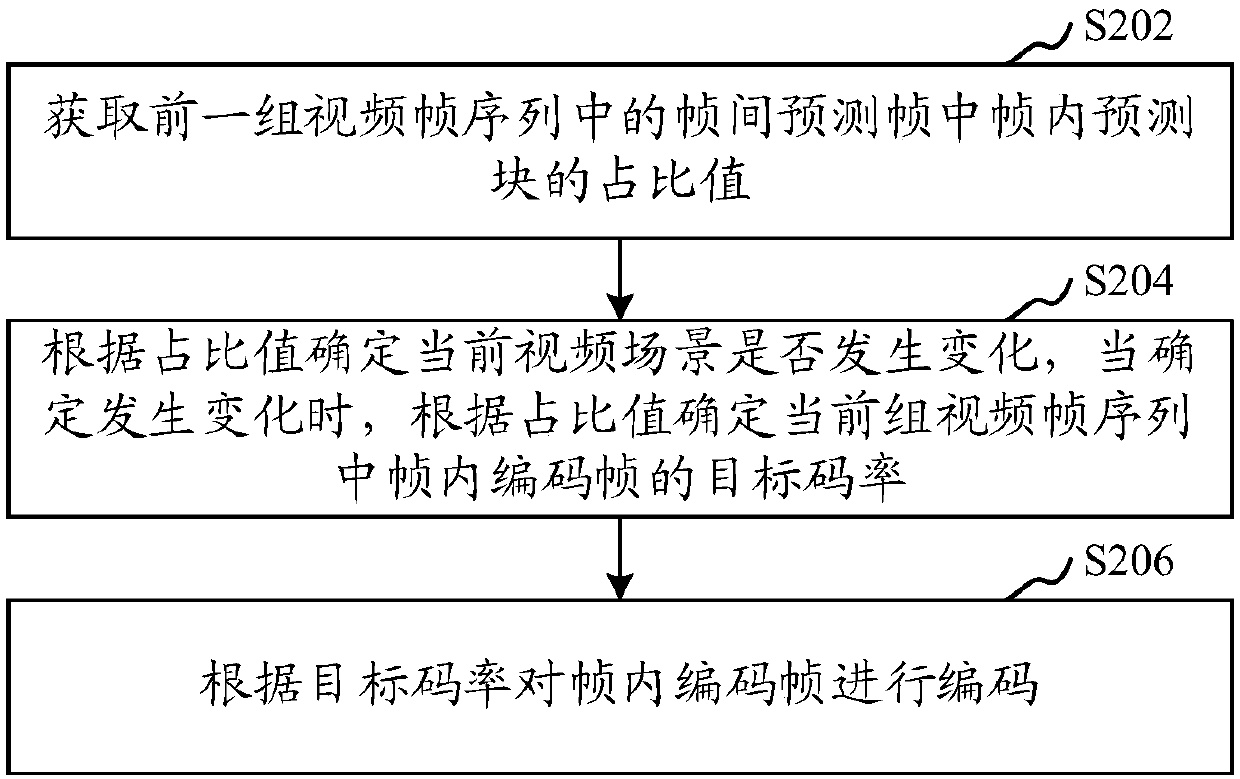
Video encoding processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN109561310AAllocation is accurateImprove Adaptive Coding CapabilitiesTwo-way working systemsDigital video signal modificationFrame sequenceVideo encoding
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
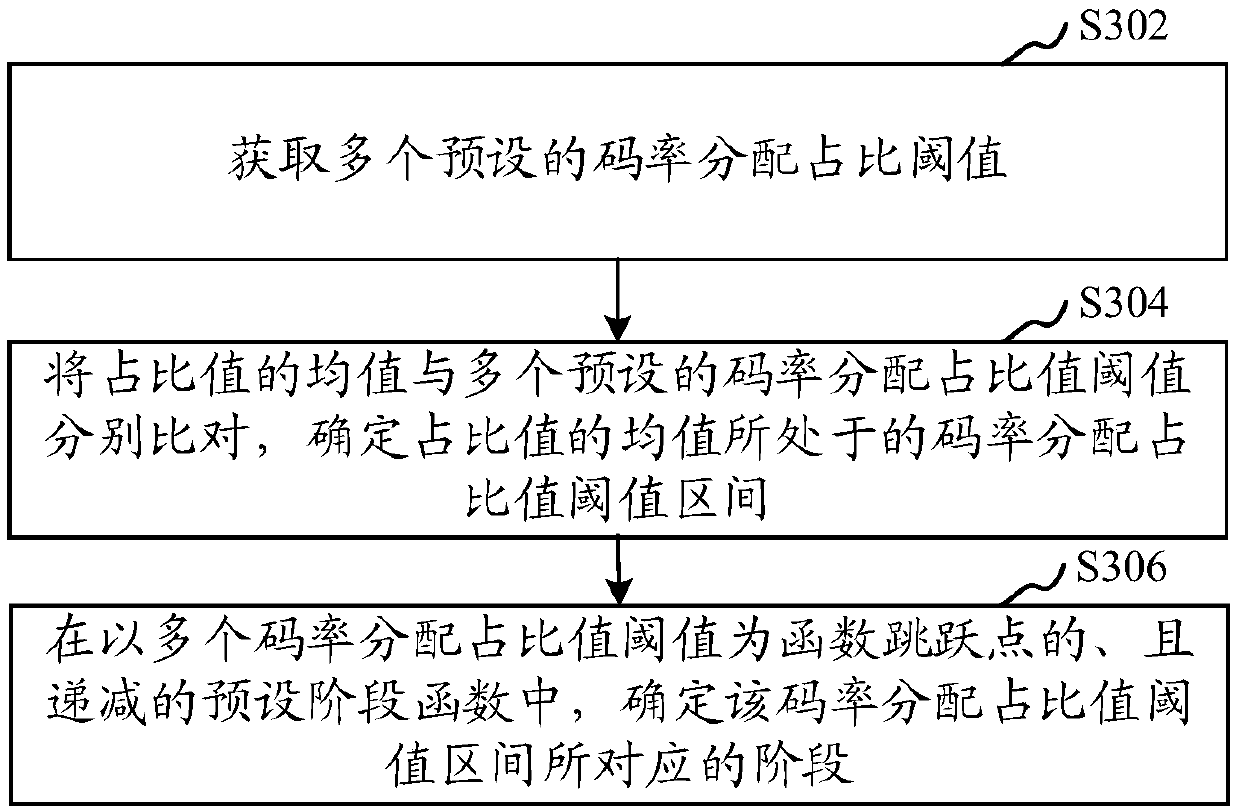
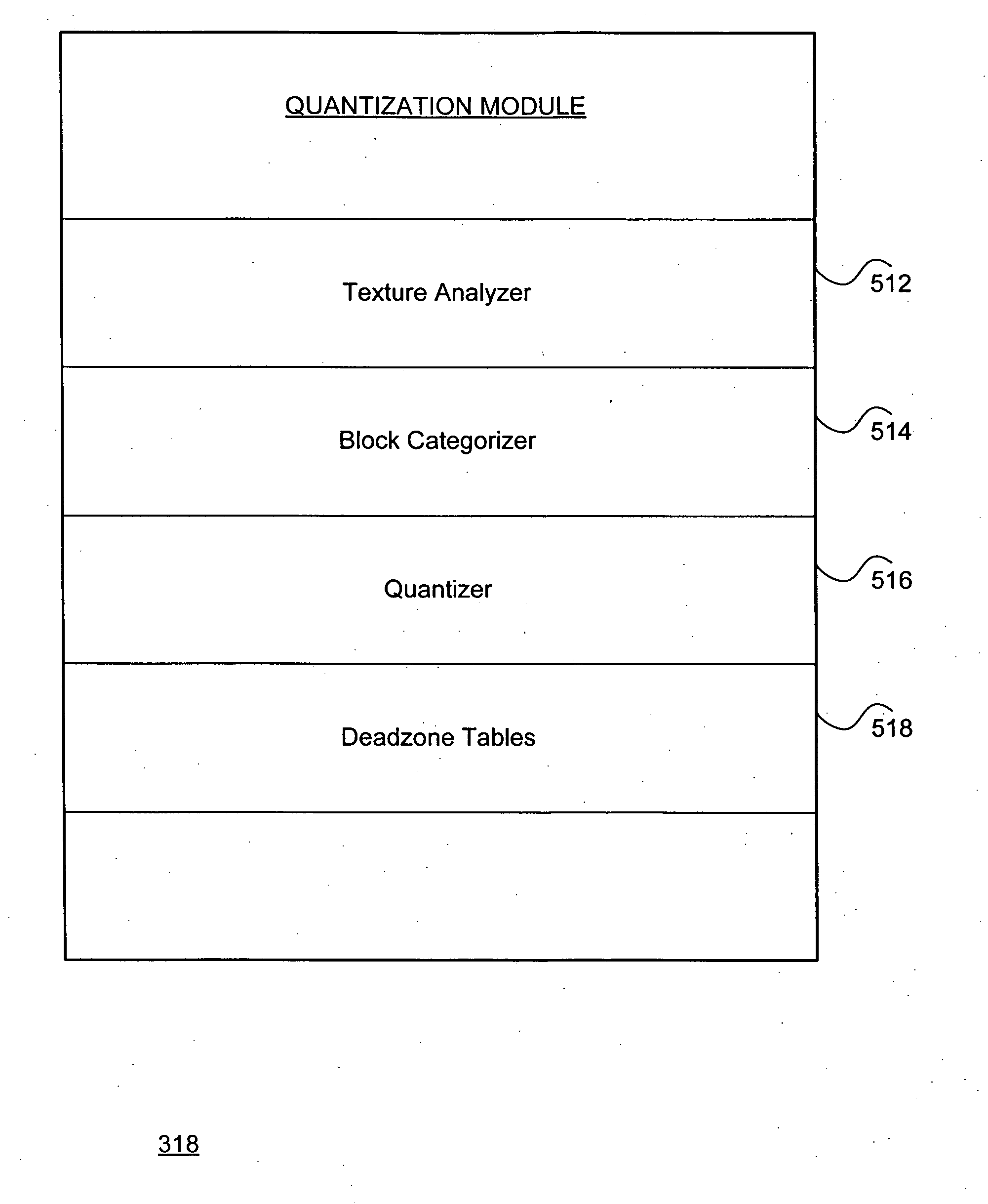
System and method for effectively performing an adaptive encoding procedure
InactiveUS20080144951A1Efficient procedureColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionTransformer
A system and method for effectively performing an adaptive encoding procedure includes a texture analyzer that initially determines texture characteristics for blocks of input image data. An image transformer converts the blocks of image data into sets of coefficients that represent the various blocks. A block categorizer utilizes the texture characteristics to associate texture categories with the sets of coefficients from the various blocks. Deadzone tables are provided for storing deadzone values that define deadzone regions for performing appropriate quantization procedures. A quantizer may then access the deadzone values from the deadzone tables to adaptively convert the coefficients into quantized coefficients according to their corresponding texture characteristics.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Method of encoding and decoding adaptive to variable code rate using LDPC code
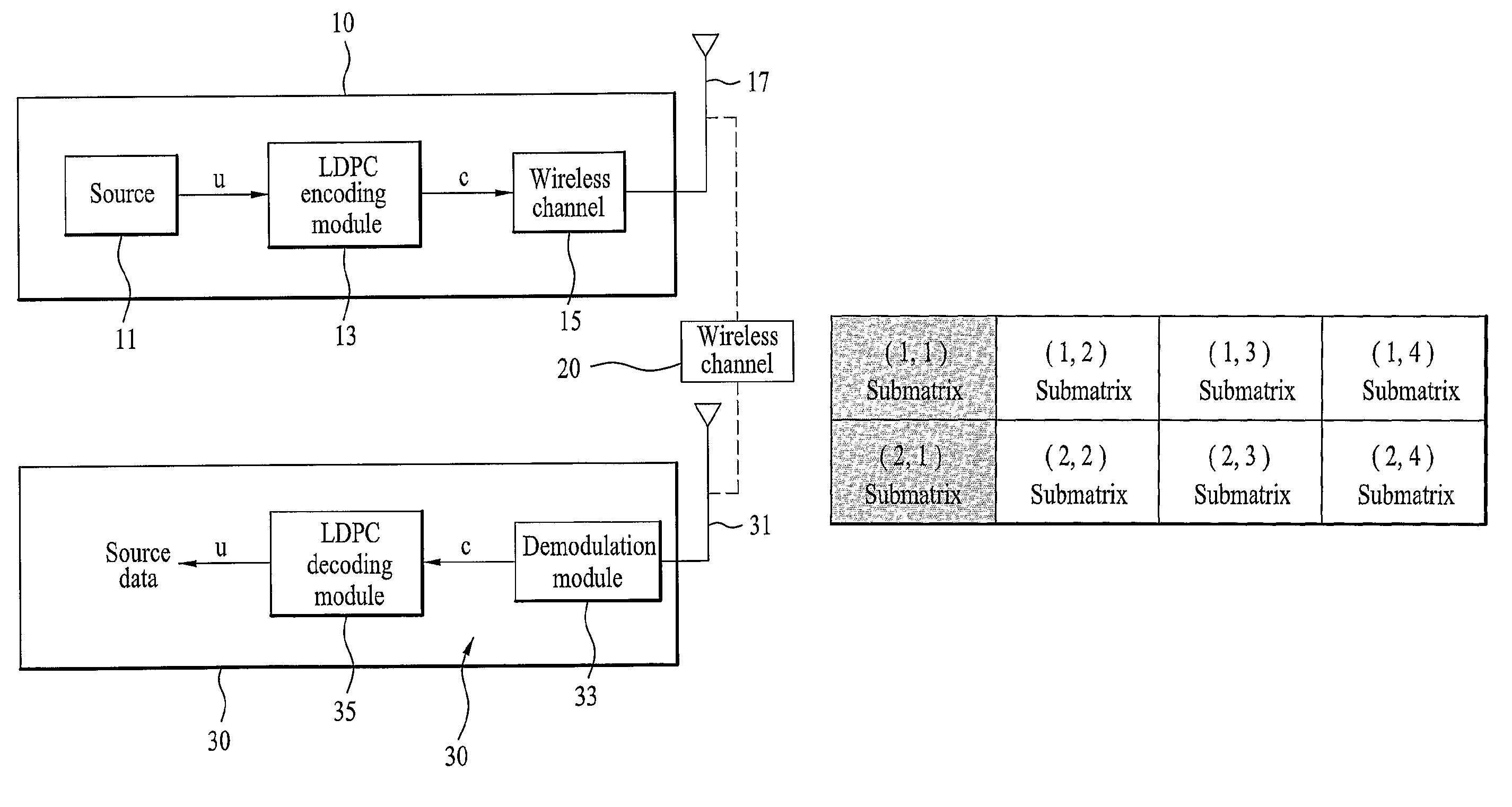
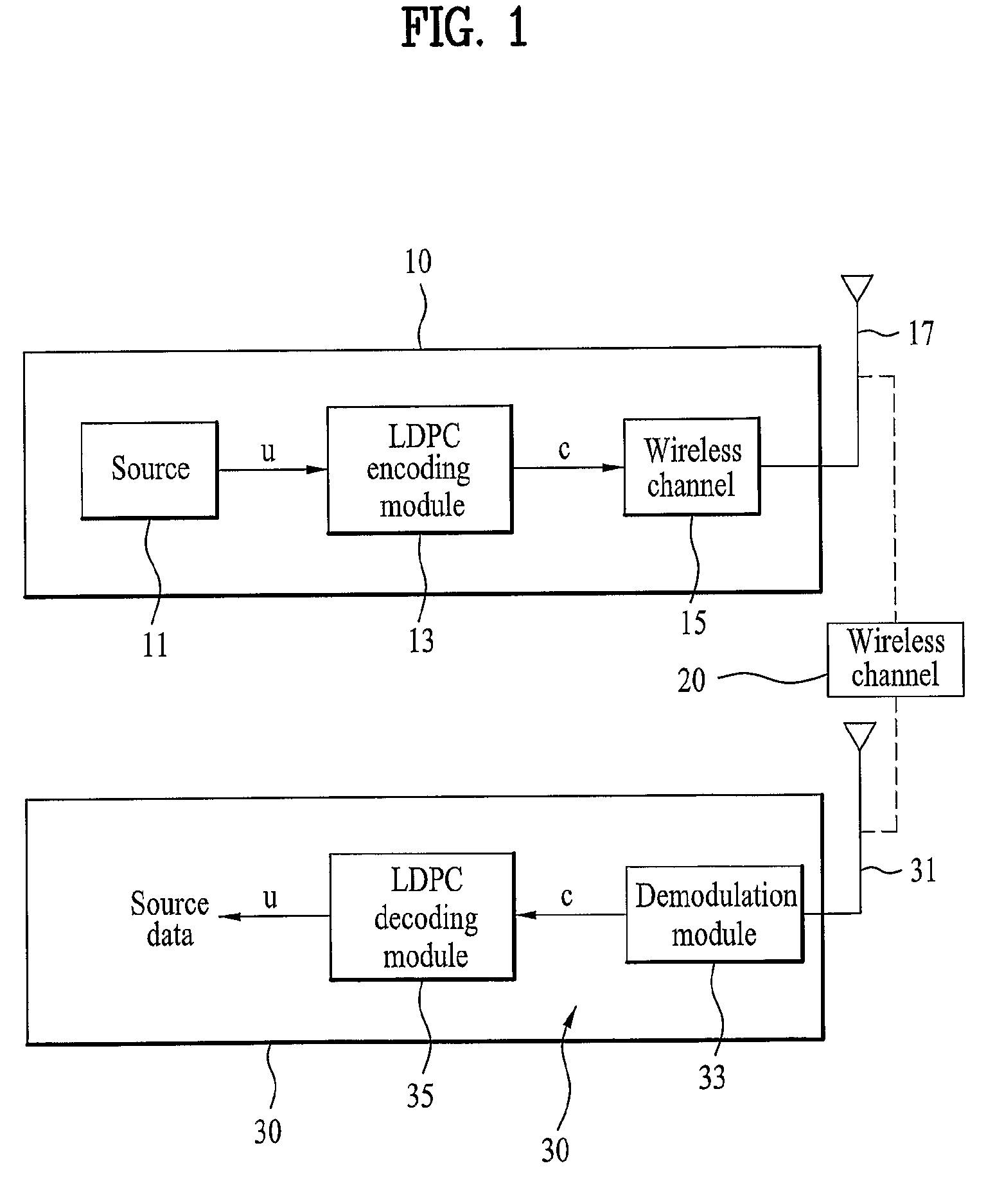
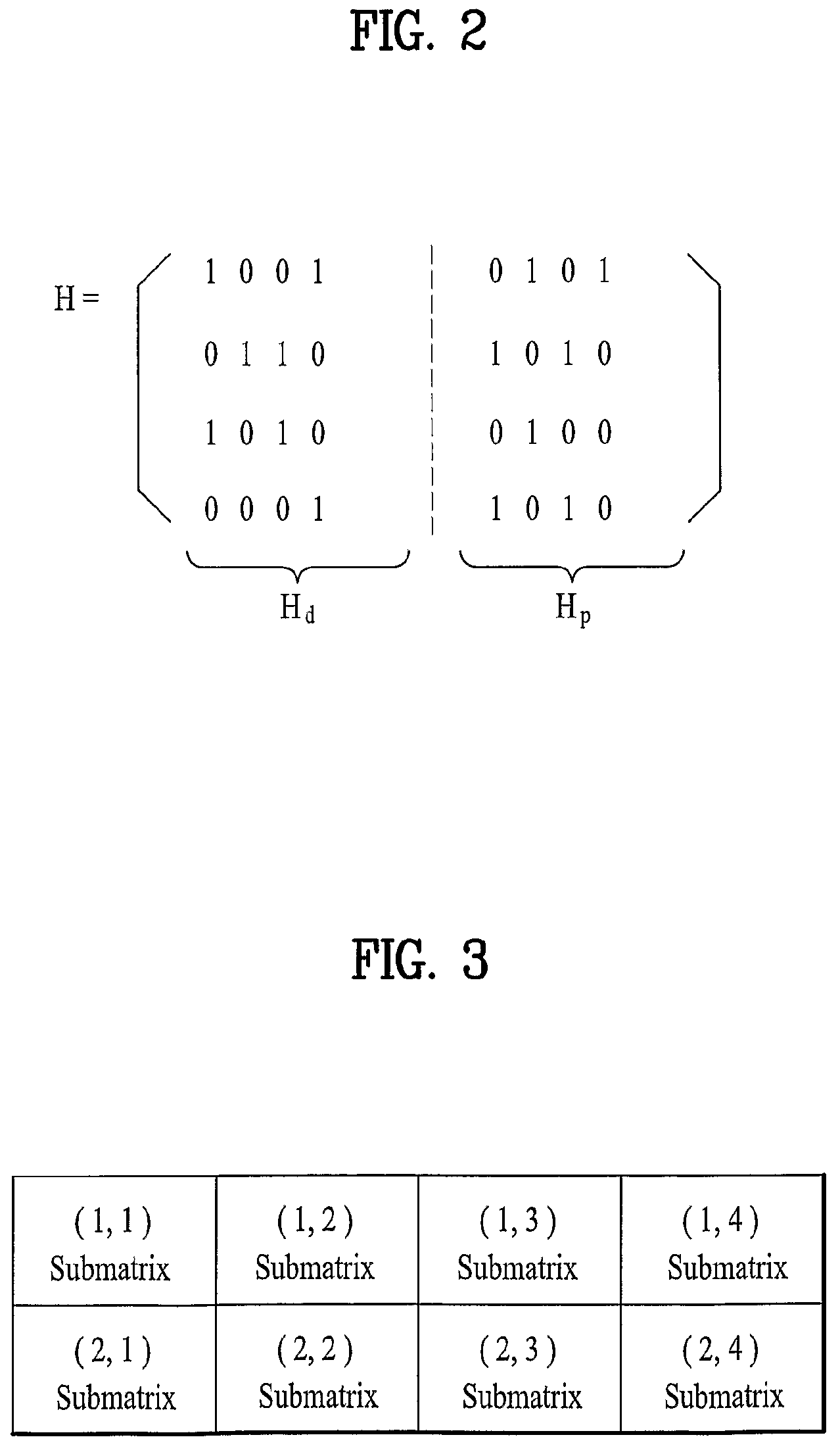
InactiveUS7930622B2Error detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsAdaptive encodingParity-check matrix
A variable code rate adaptive encoding / decoding method using LDDC code is disclosed, in which an input source data is encoded using the LDPC (low density parity check) code defined by a first parity check matrix configured with a plurality of submatrices. The present invention includes the steps of generating a second parity check matrix corresponding to a code rate by reducing a portion of a plurality of submatrices configuring a first parity check matrix according to the code rate to be applied to encoding an input source data and encoding the input source data using the second parity check matrix.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
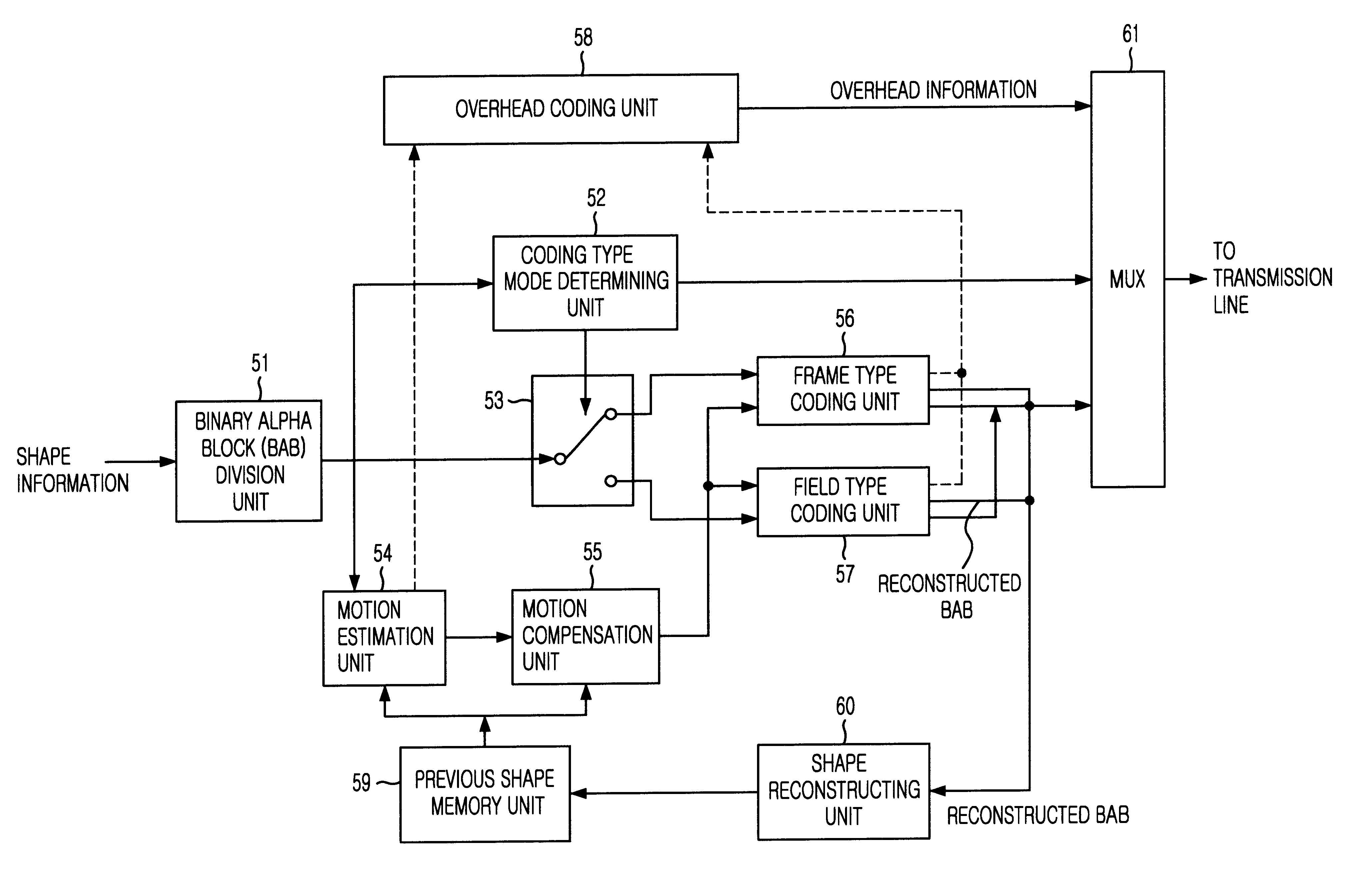
Apparatus and method of adaptively coding/decoding interlaced shaped material
An apparatus and method of adaptively coding / decoding interlace shape information estimates the amount of motion with respect to the binary alpha block (BAB). A type of the BAB is determined according to the estimated amount of motion. When the BAB falls under a type which needs coding differences between pixel pairs in each line pair comprising an odd and an adjacent even line are calculated and summed up to compute an error of the frame. Differences between pixel pairs in consecutive odd line pairs and differences between pixel pairs in consecutive even line pairs are calculated and summed up to compute an error of individual fields. When the error of the frame is larger than that of the separate fields, field type coding where coding is independently performed with respect to each field is selected. When the error of the separate fields is larger than that of the frame, frame type coding where coding is performed with respect to the frame is selected.
Owner:PANTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com