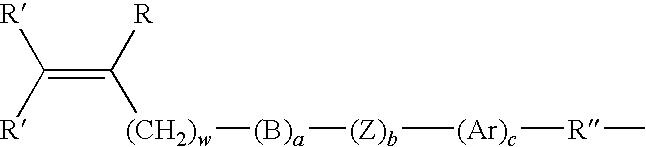Patents
Literature
210results about How to "Guaranteed preservation quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
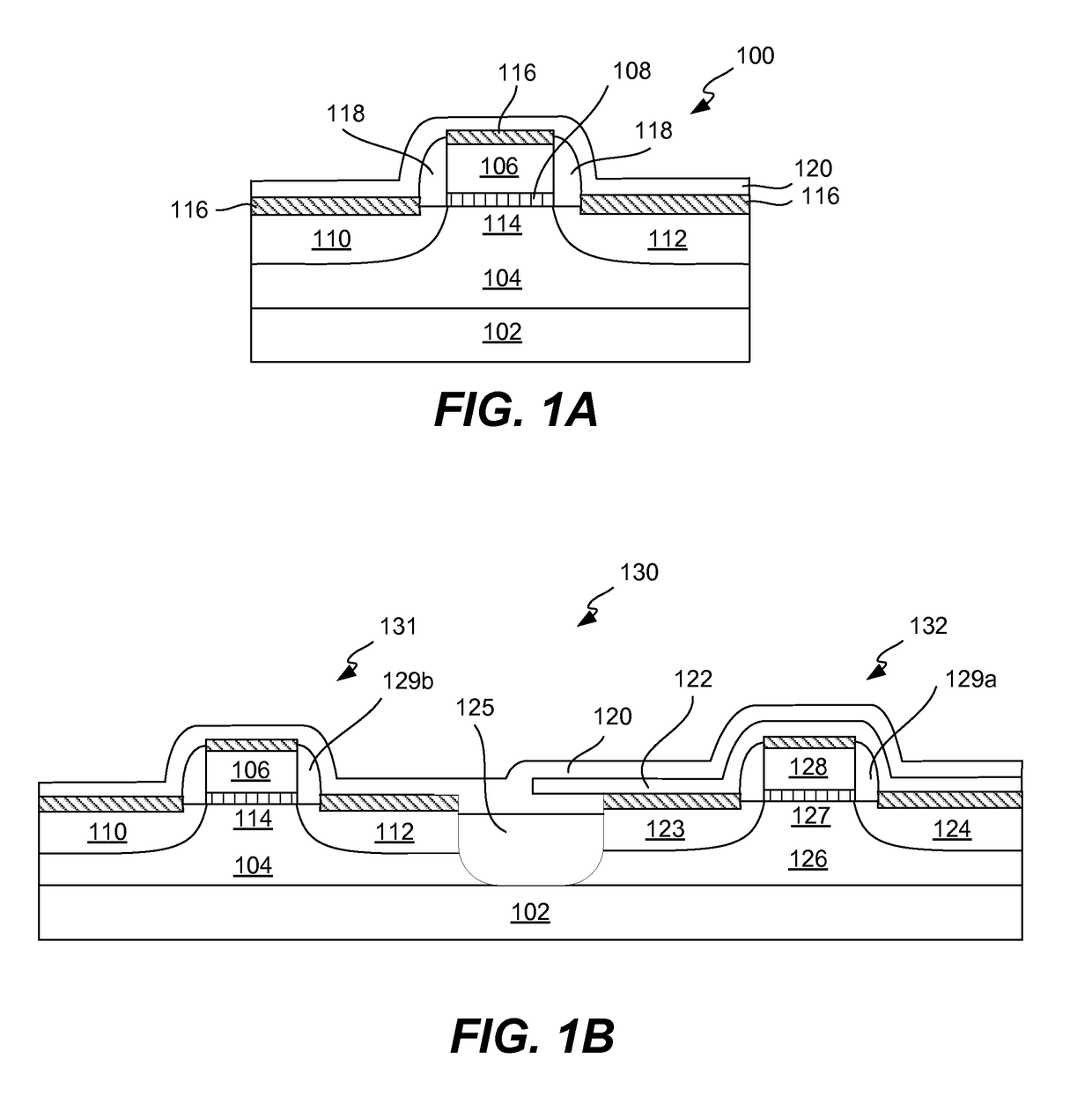
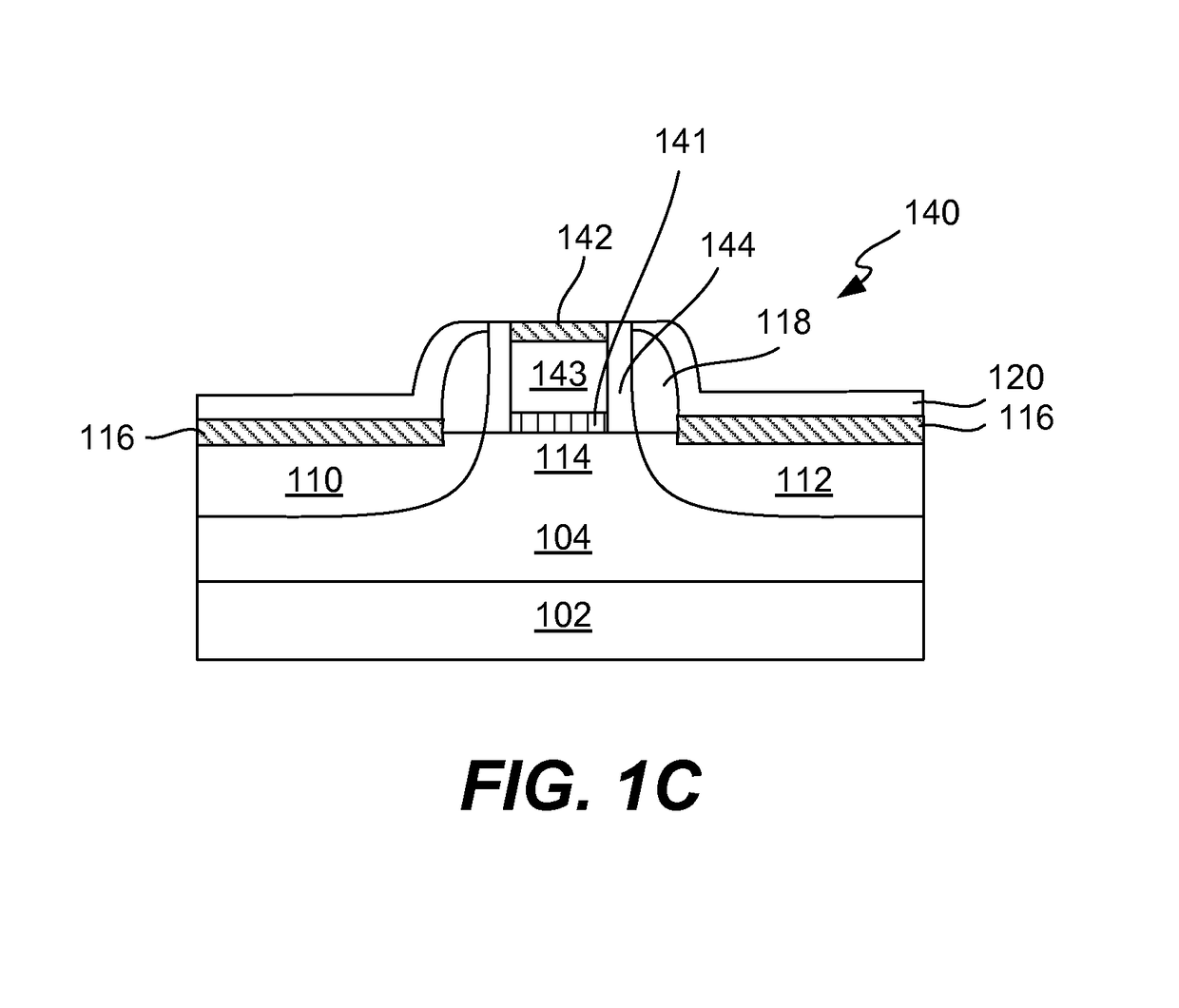
PMOS transistor with compressive dielectric capping layer
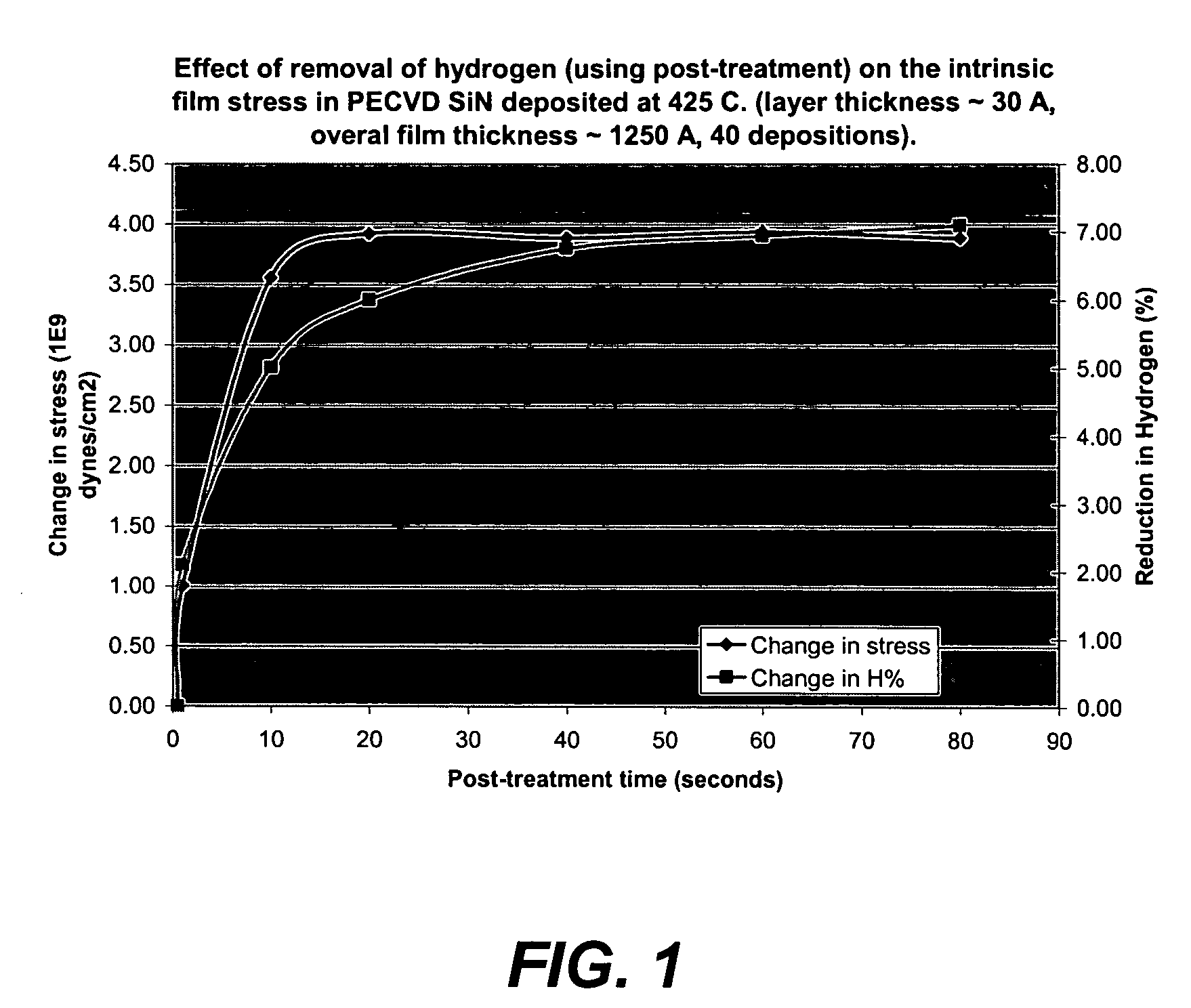
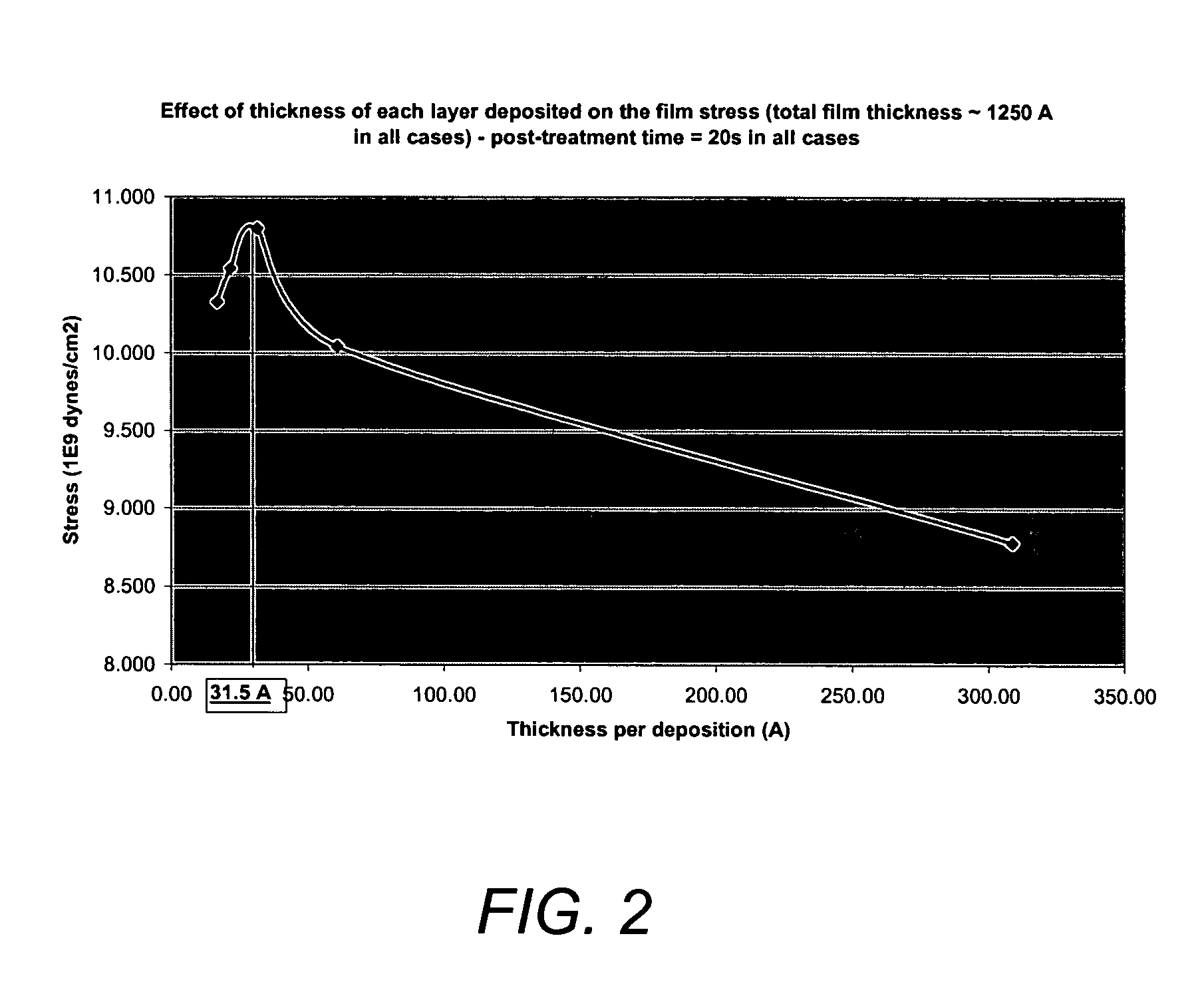
ActiveUS7214630B1Preserving material qualityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSalicideOxidation state
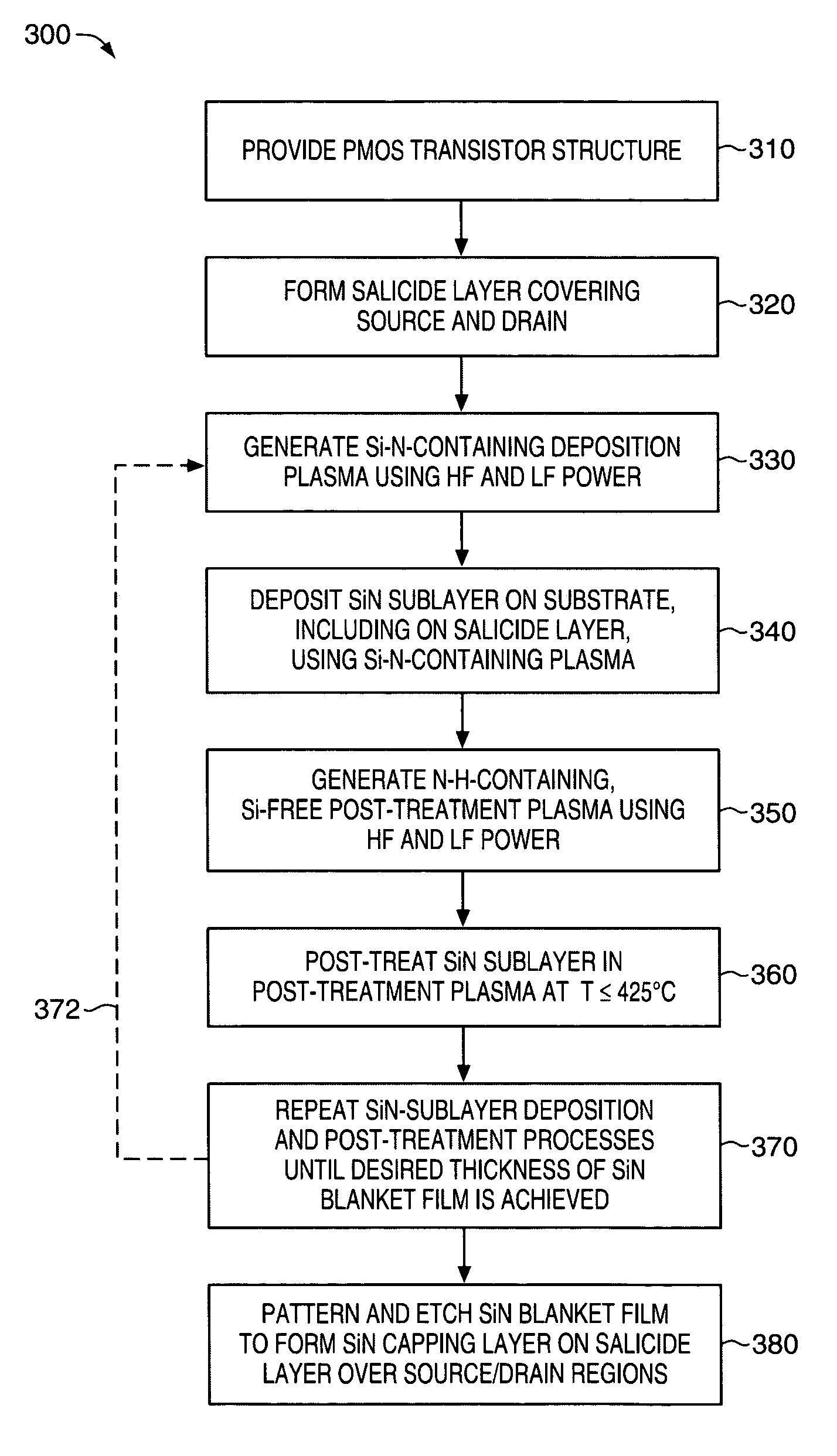
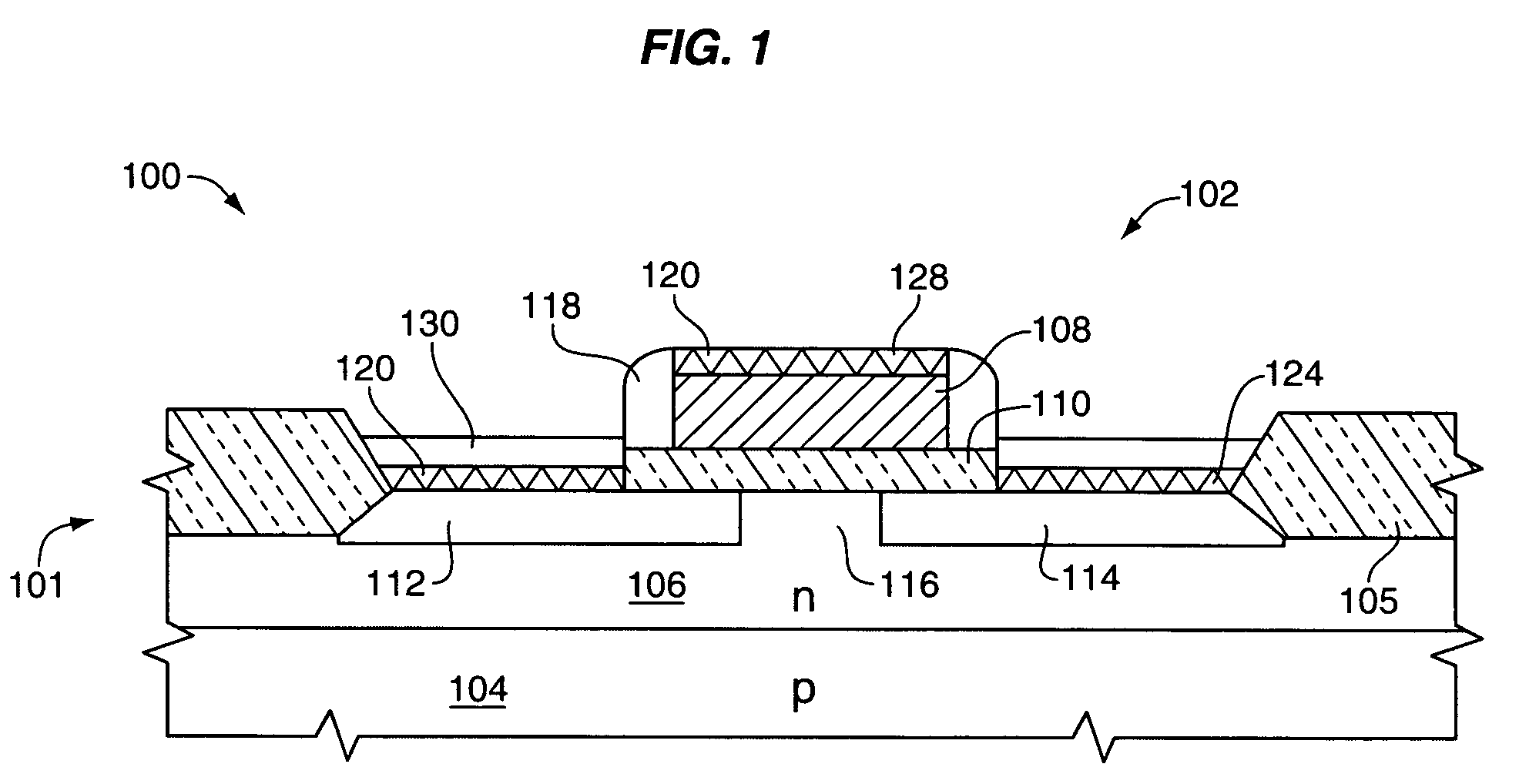
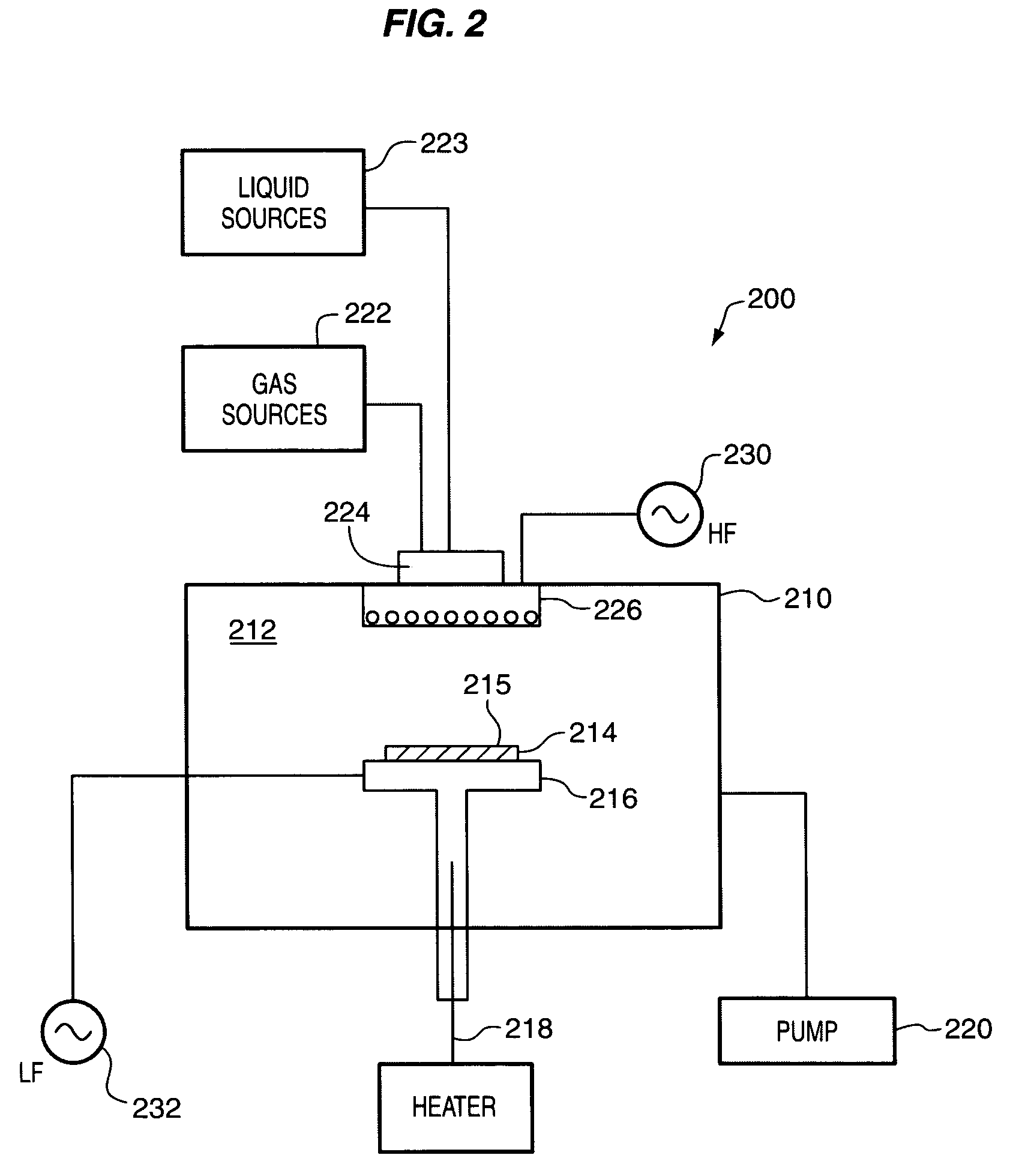
A salicide layer is deposited on the source / drain regions of a PMOS transistor. A dielectric capping layer having residual compressive stress is formed on the salicide layer by depositing a plurality of PECVD dielectric sublayers and plasma-treating each sublayer. Compressive stress from the dielectric capping layer is uniaxially transferred to the PMOS channel through the source-drain regions to create compressive strain in the PMOS channel. To form a compressive dielectric layer, a deposition reactant mixture containing A1 atoms and A2 atoms is provided in a vacuum chamber. Element A2 is more electronegative than element A1, and A1 atoms have a positive oxidation state and A2 atoms have a negative oxidation state when A1 atoms are bonded with A2 atoms. A deposition plasma is generated by applying HF and LF radio-frequency power to the deposition reactant mixture, and a sublayer of compressive dielectric material is deposited. A post-treatment plasma is generated by applying HF and LF radio-frequency power to a post-treatment gas that does not contain at least one of A1 atoms and A2 atoms. Compressive stress in the dielectric sublayer is increased by treating the sublayer in the post-treatment plasma. Processes of depositing a dielectric sublayer and post-treating the sublayer in plasma are repeated until a desired thickness is achieved. The resulting dielectric layer has residual compressive stress.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Magnetic resonance imaging having patient video, microphone and motion tracking
ActiveUS20050283068A1Minimize patient movementEfficient removalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDigital videoBody area
Critical needs for MRI patient instruction, testing, comfort, motion control, and speech communication are provided for better imaging which leads to more effective medical care. An MRI Digital Video Projection System is disclosed which provides better quality display to the patient to better inform, instruct, test, and comfort the patient plus the potential to stimulate the brain with microsecond onset times to better diagnose brain function. An MRI Motion Tracker and Patient Augmented Visual Feedback System enables monitoring patient body part motion, providing real time feedback to the patient and / or technician to substantially improve diagnostic yield of scanning sessions, particularly for children and mentally challenged individuals. An MR Forward Predictive Noise Canceling Microphone System removes the intense MRI acoustic noise improving patient communication, patient safety and enabling coding of speech output. These systems can be used individually but maximum benefit is from providing all three.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF +1
Method to control point spread function of an image
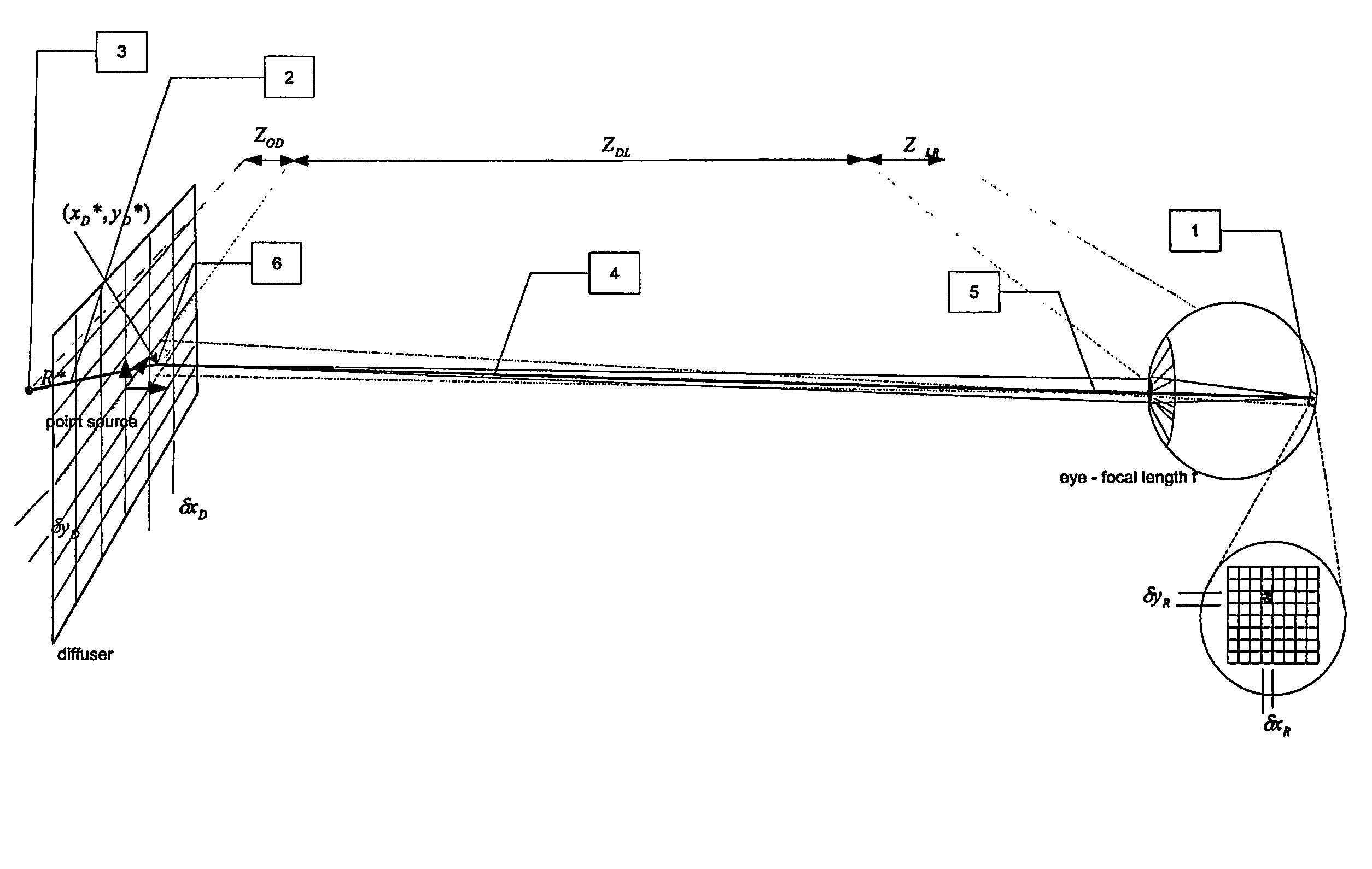
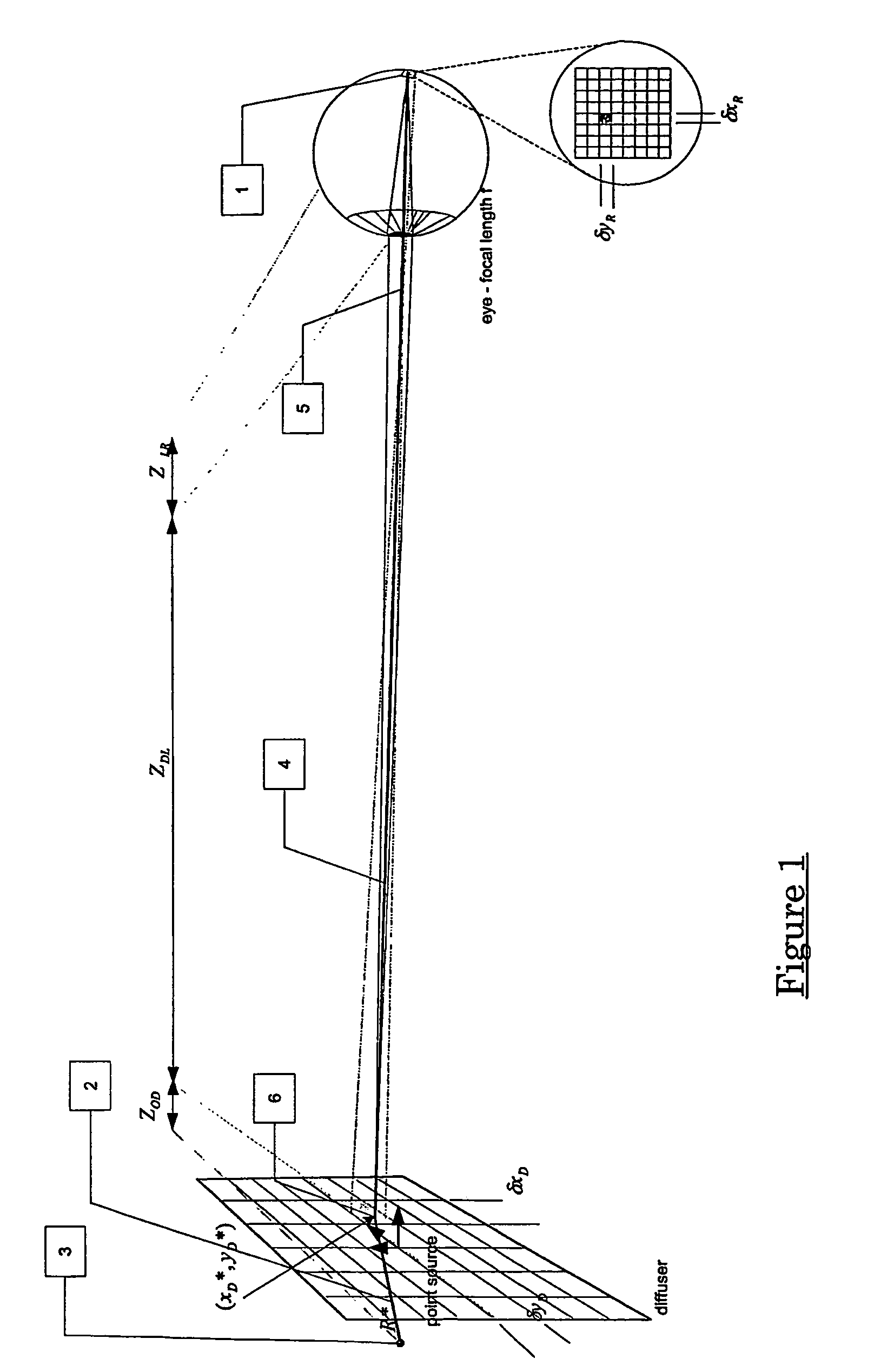
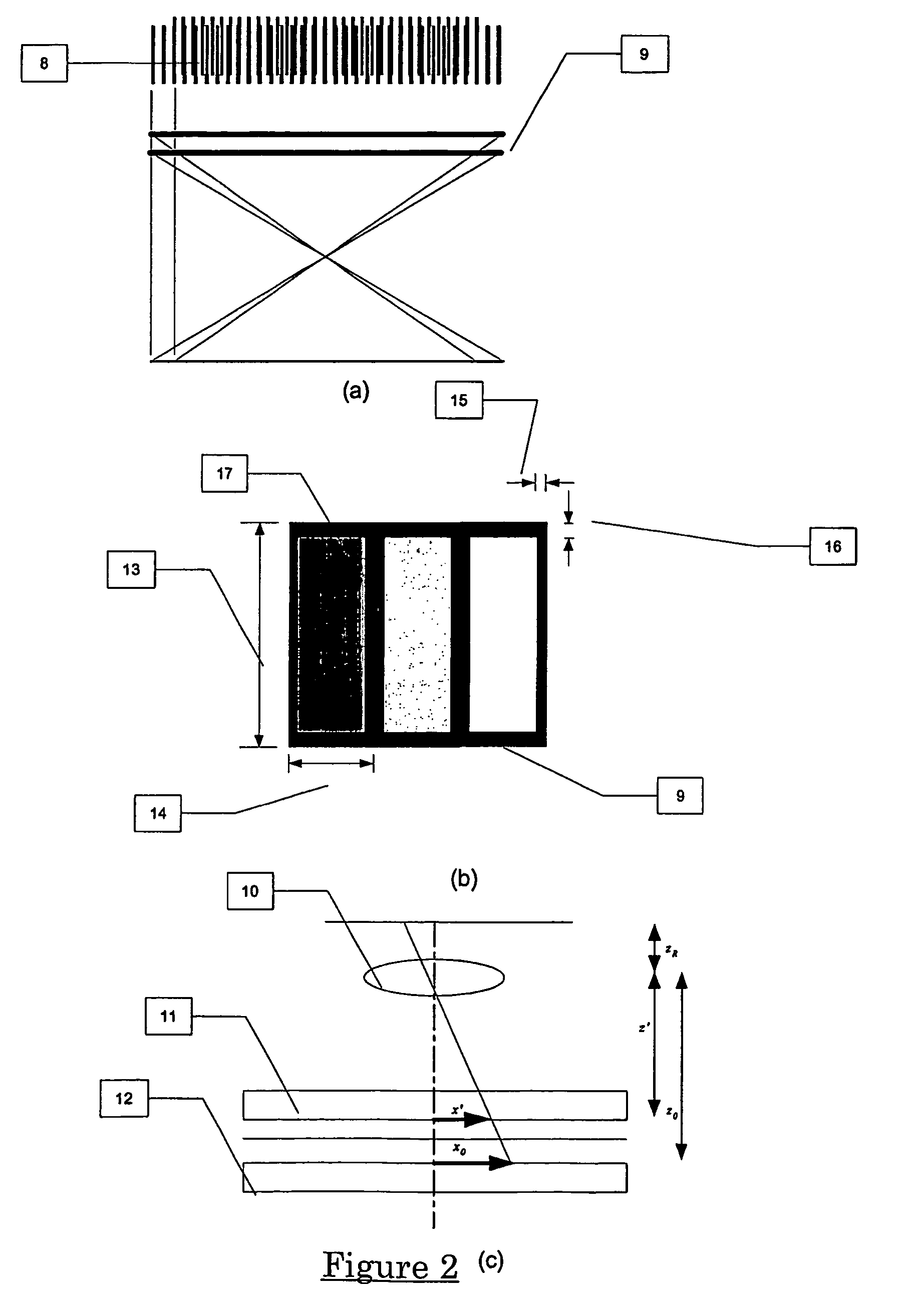
ActiveUS20060103951A1Guaranteed preservation qualityMore interferenceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityPoint spread function
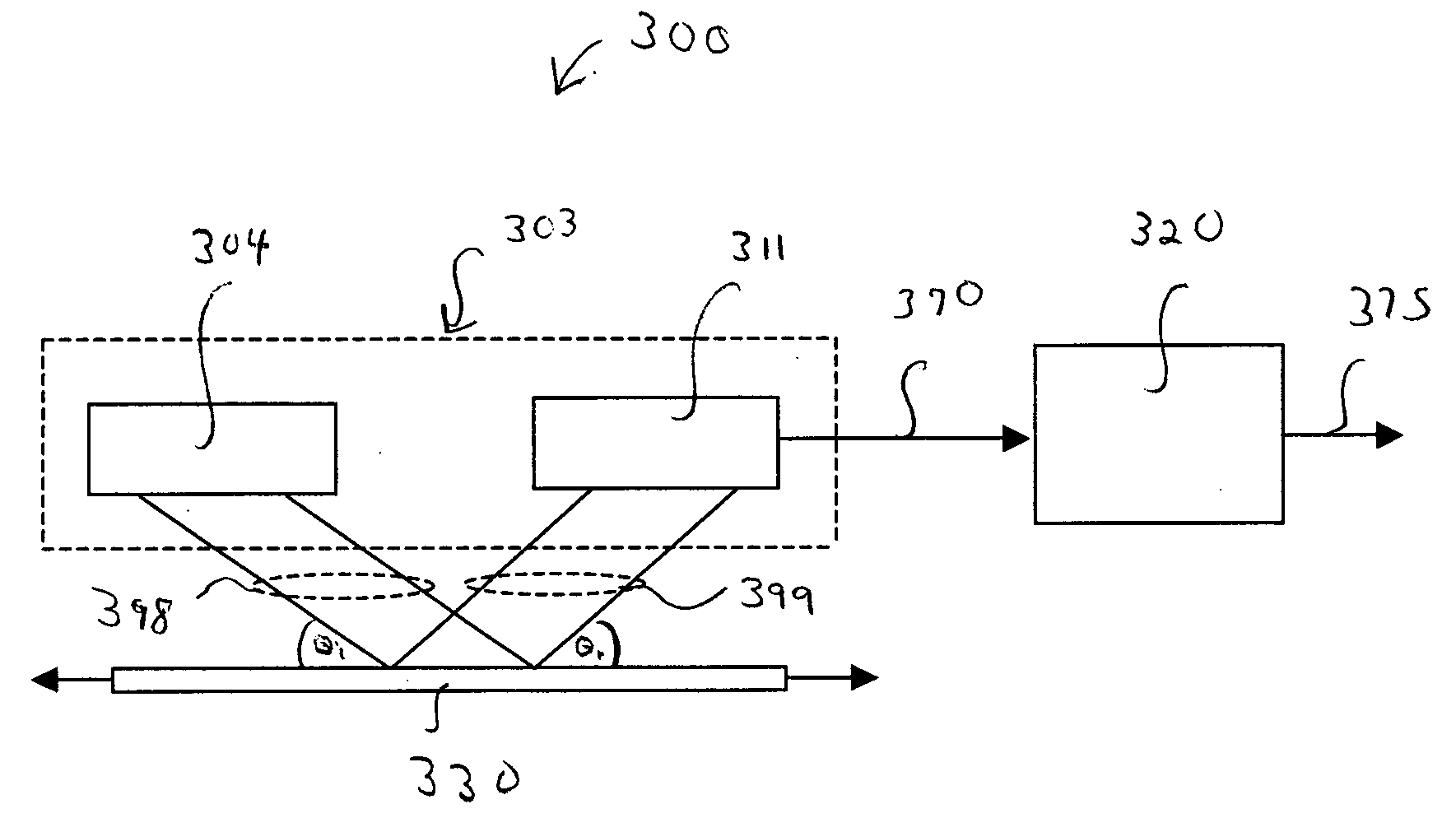
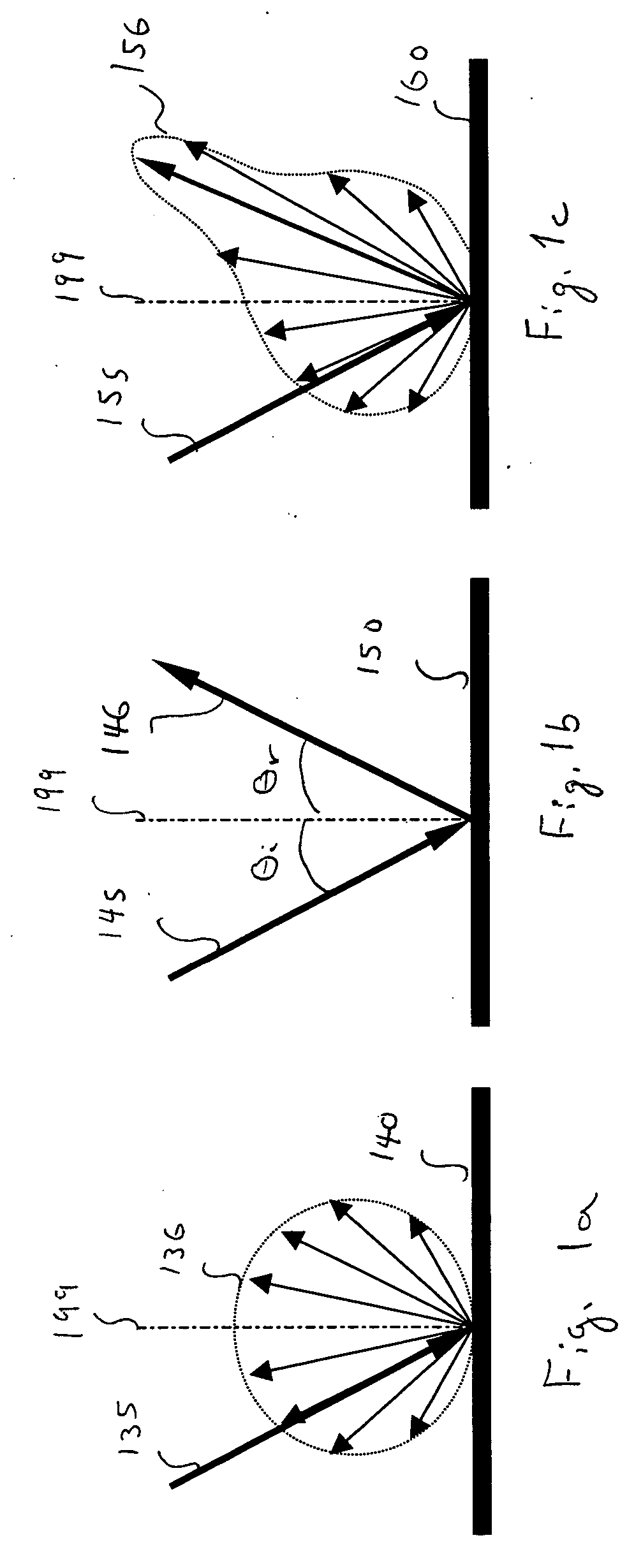
A method of controlling the point spread function of an image projected with said image being diffused by a filter; said point spread function is a result of the application of spatial filter(s) on said image; with said control of the point spread function effected by varying the distance between such image and said spatial filter(s) and varying the bidirectional scattering transmission function of the spatial filter(s). Said spatial filter may be a holographic diffuser, which by method of manufacture has a ell defined bi-directional scattering transmission spread function. Control of said spread function is particularly useful to maintain image quality while abating moiré interference in situations where two periodic patterns are layered causing moiré interference.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Method and device for optical navigation
InactiveUS20050024336A1Good signalHigh contrast imageInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsRelative motionSpecular reflection
An method and device suitable for navigation on a wide variety of surfaces is introduced. Specular reflection is used to determine relative motion over typical surfaces. A specific application is a computer mouse.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Method and device for optical navigation
ActiveUS20050024623A1Good signalHigh contrast imageInput/output for user-computer interactionOptical rangefindersRelative motionSpecular reflection
An method and device suitable for navigation on a wide variety of surfaces is introduced. Specular reflection is used to determine relative motion over typical surfaces. A specific application is a computer mouse.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
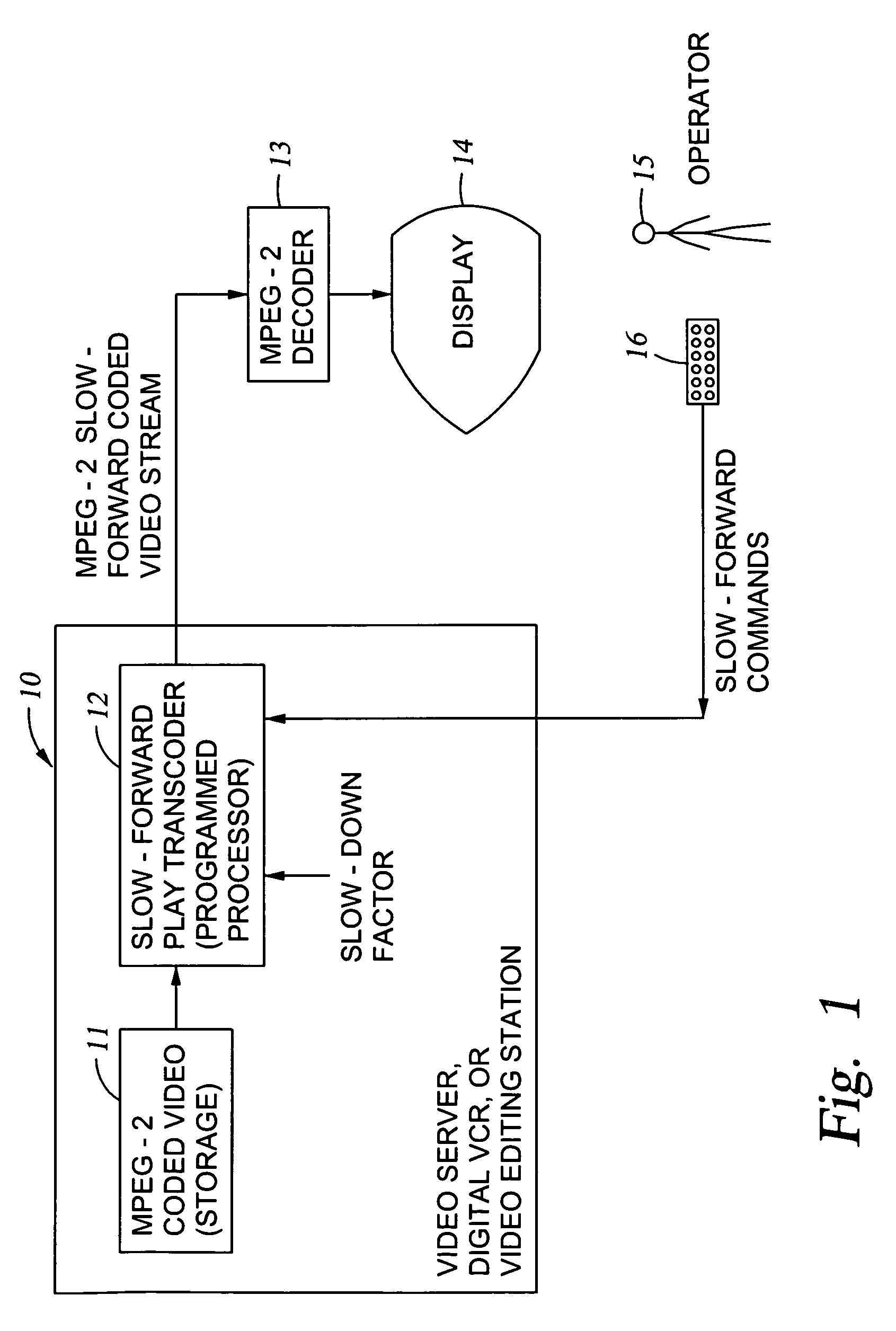
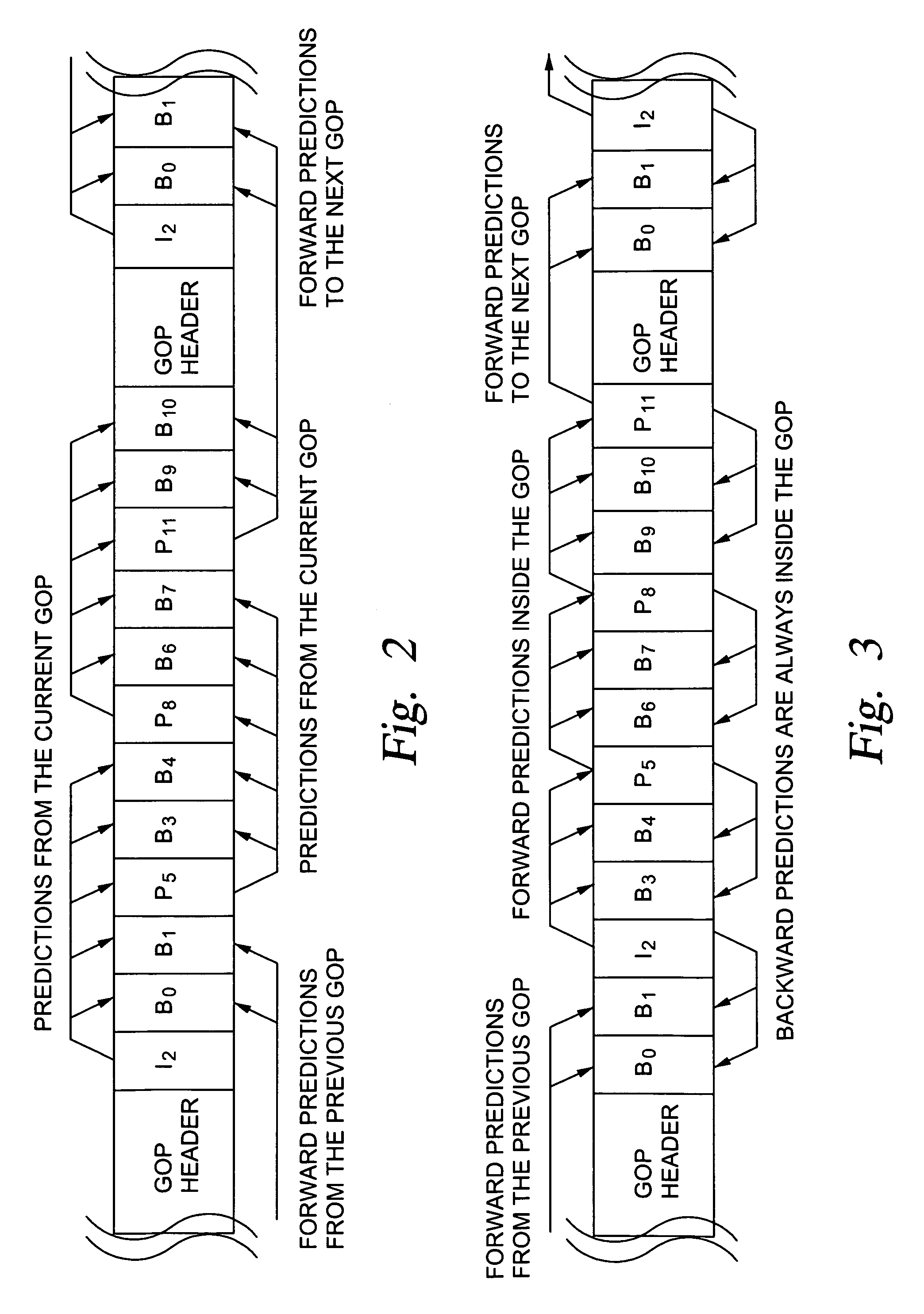
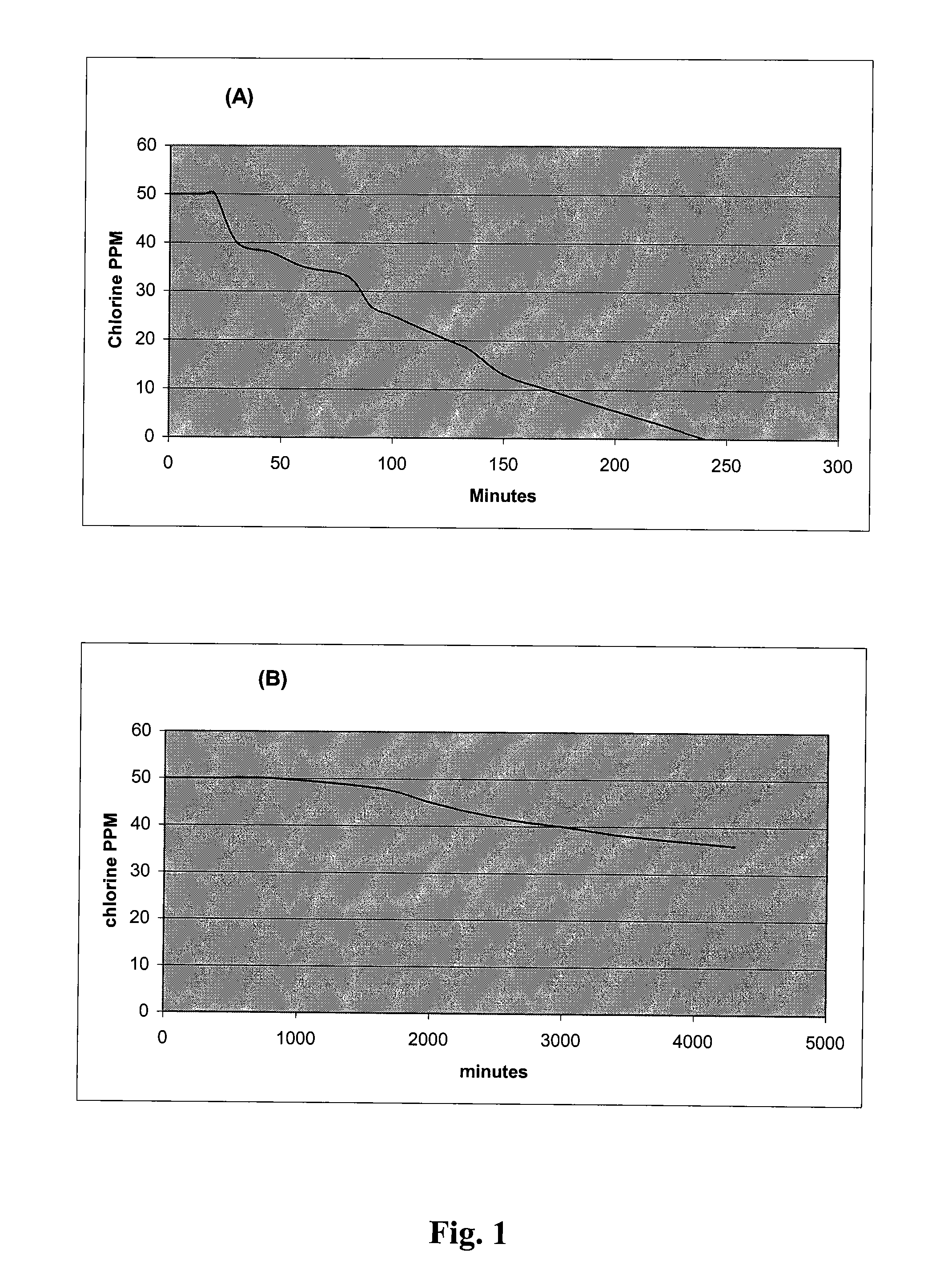
Generation of MPEG slow motion playout
InactiveUS6980594B2Minimal costGuaranteed preservation qualityTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersGroup of picturesComputer graphics (images)
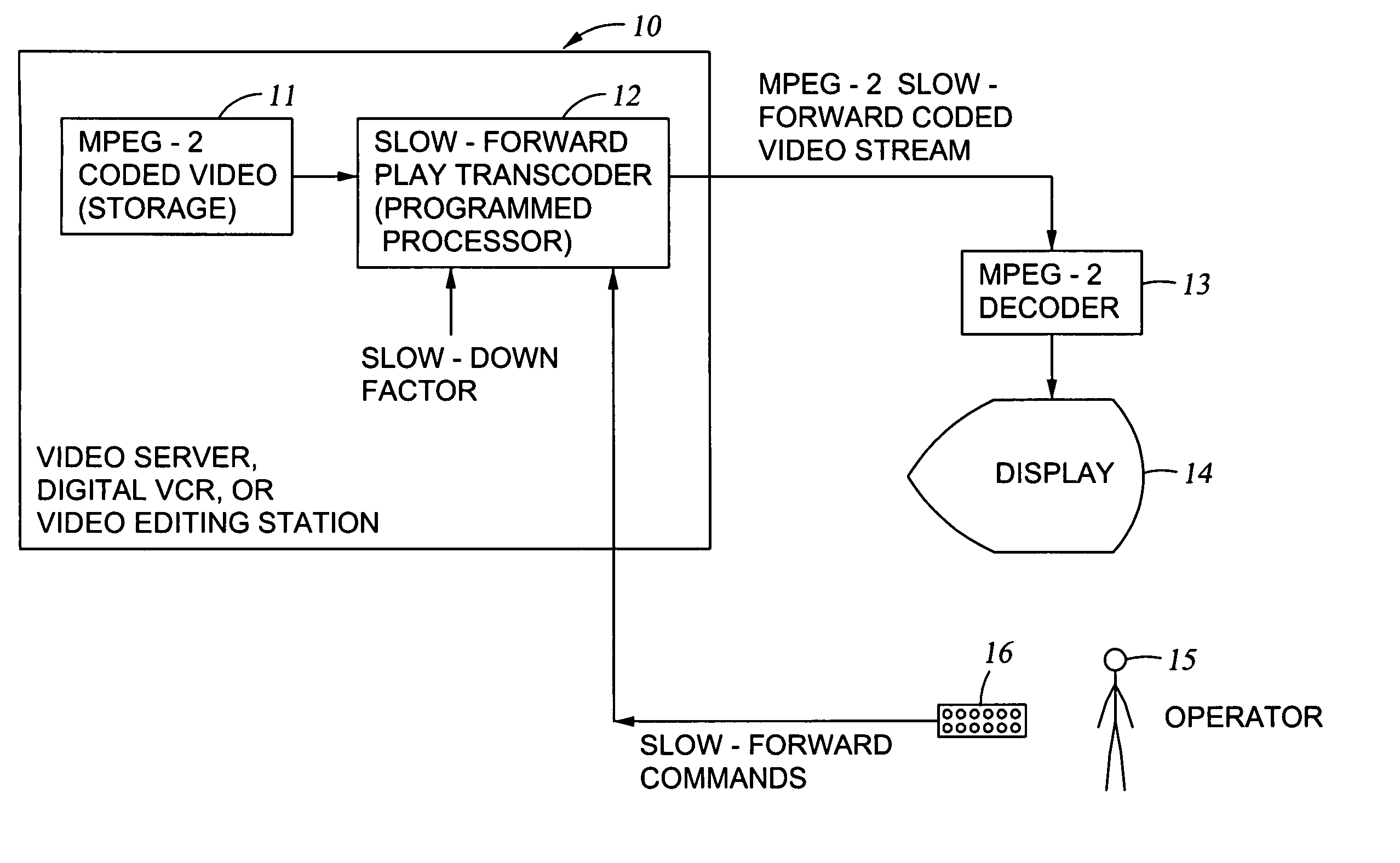
MPEG coded video data includes groups of pictures (GOPs). Each group of pictures includes one or more I-frames and a plurality of B- or P-frames. To produce an MPEG slow-forward coded video stream, the coding type of each frame in the MPEG coded video data is identified, and freeze frames are inserted as a predefined function of the identified coding type and as a predefined function of a desired slow down factor. In a preferred implementation, for a slow-down factor of n, for each original I- or P-frame, (n−1) backward-predicted freeze frames are inserted, and for each original B-frame, (n−1) copies of the original B-frames are added, and a selected amount of padding is added to each copy of each original B-frame in order to obtain a normal play bit rate and avoid video buffer overflow or underflow.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
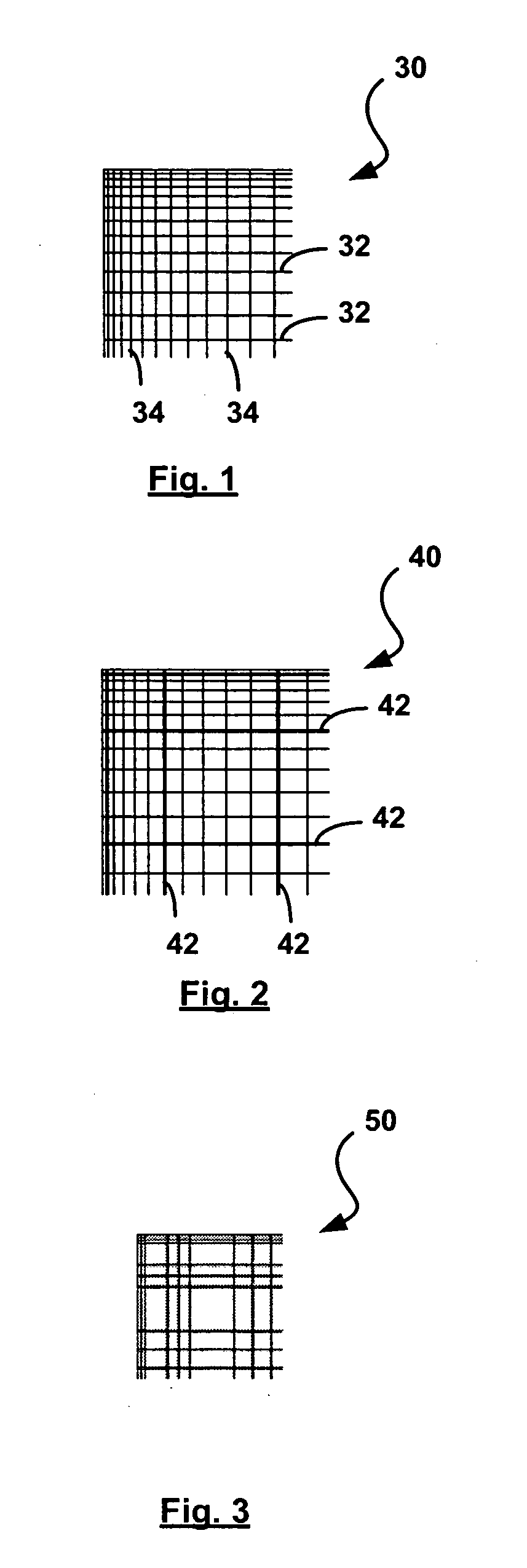
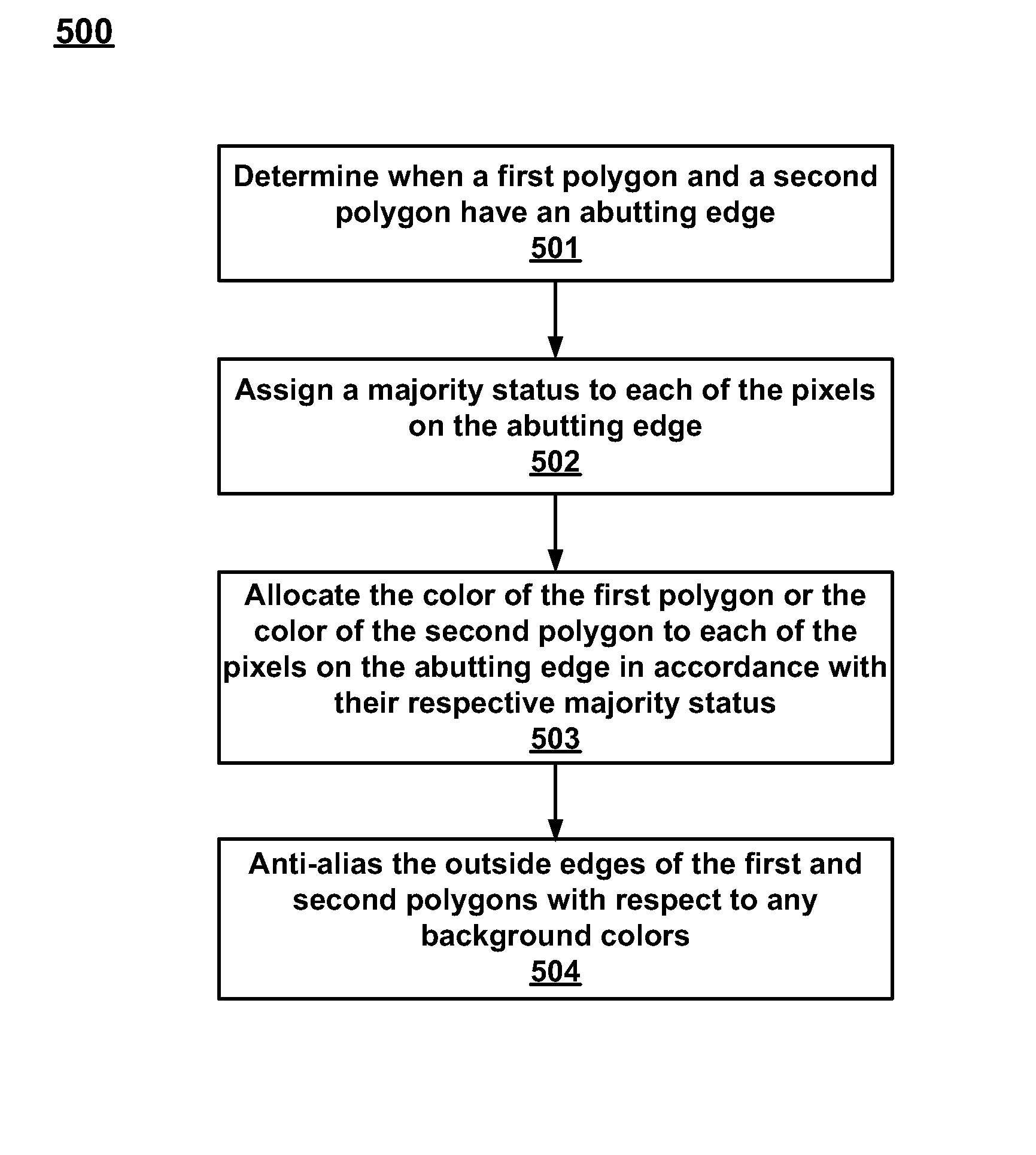
Method and system for rendering polygons having abutting edges
ActiveUS20070139440A1Fast and efficient real-timeImage quality is preservedTexturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and device for optical navigation
InactiveUS7161682B2Good signalHigh contrast imageInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsRelative motionSpecular reflection
An method and device suitable for navigation on a wide variety of surfaces is introduced. Specular reflection is used to determine relative motion over typical surfaces. A specific application is a computer mouse.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
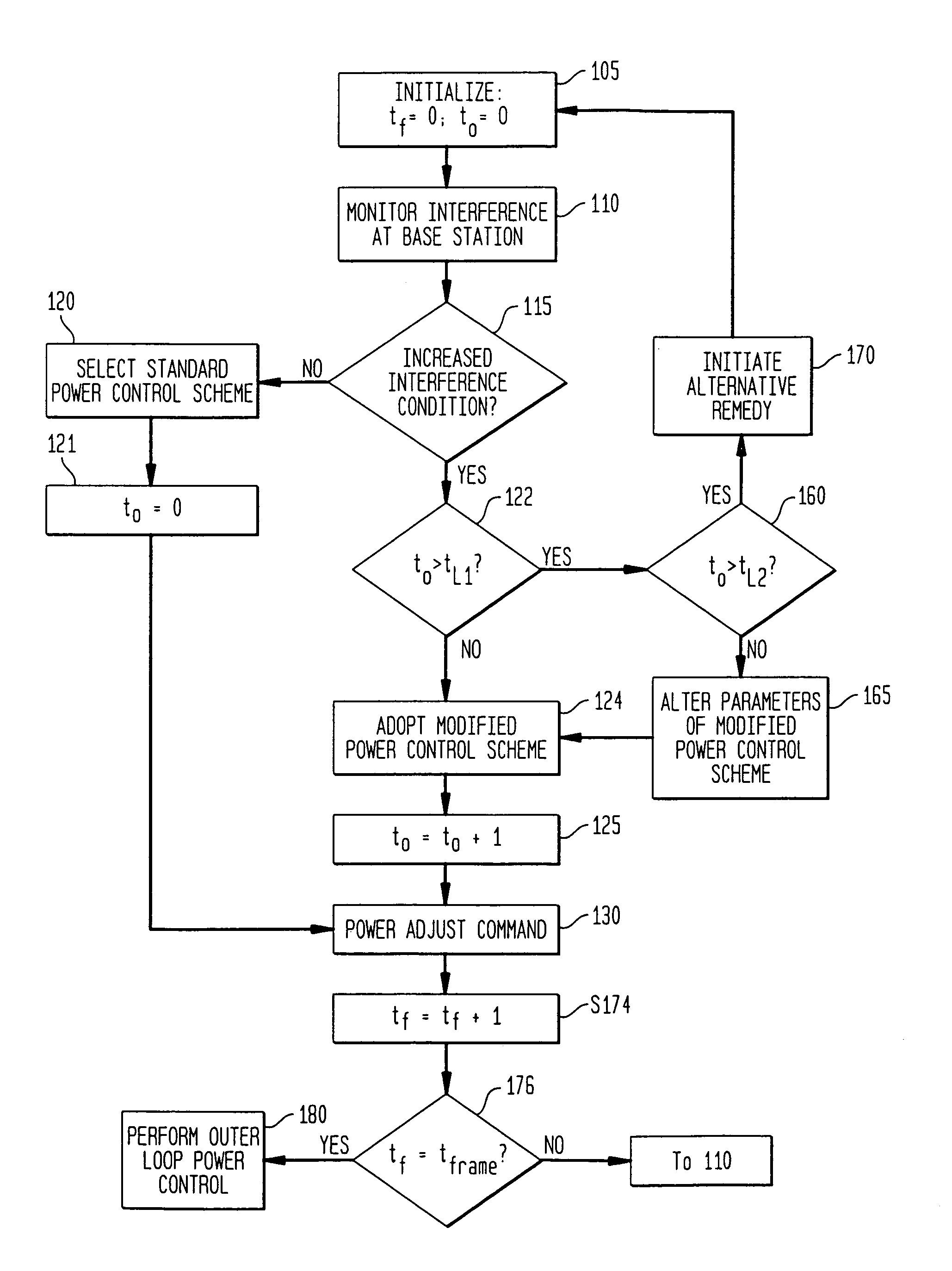
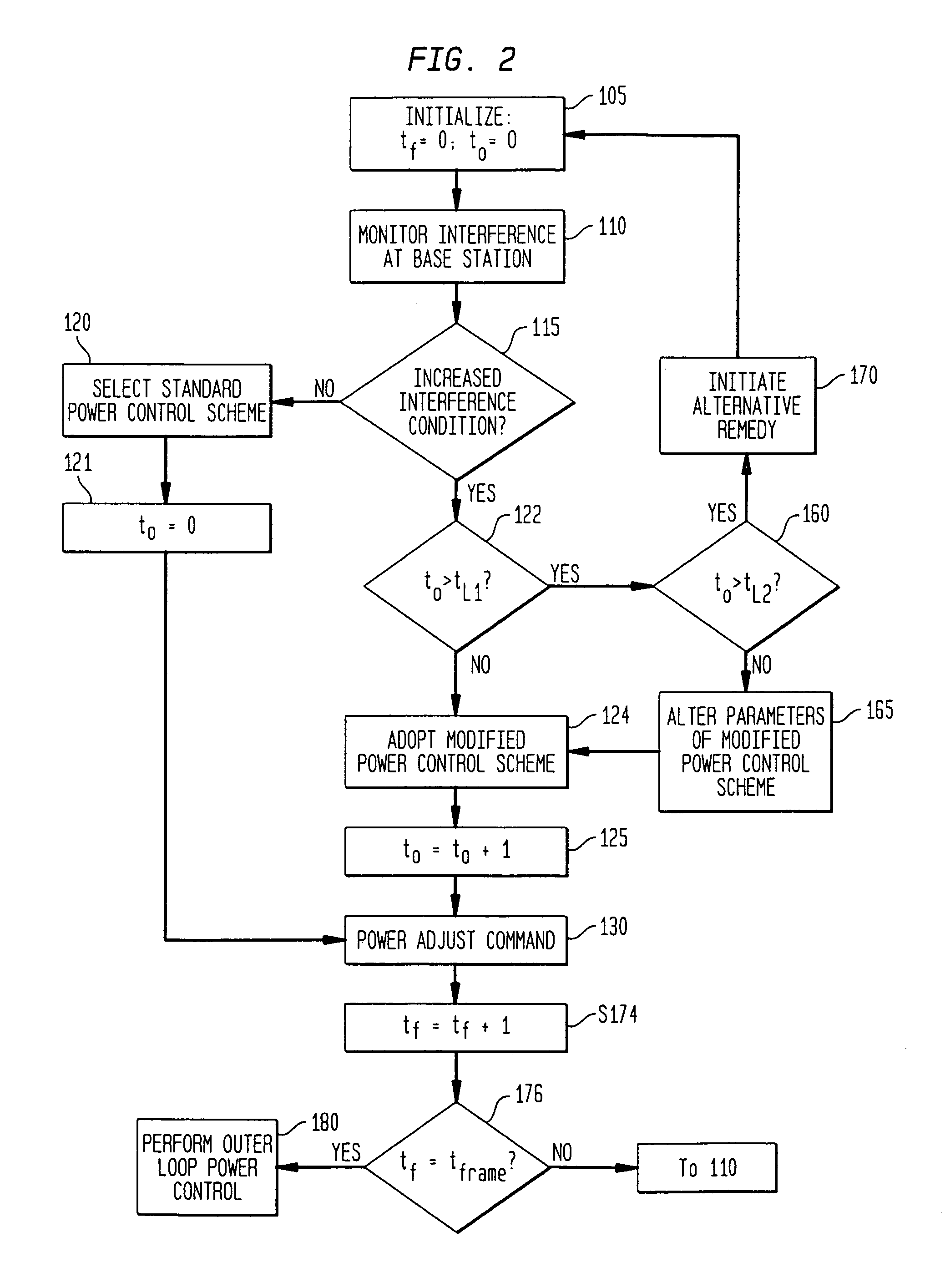
Method and apparatus for controlling reverse link interference rise and power control instability in a wireless system
InactiveUS6968201B1Call quality will deterioratePreserve quality of serviceEnergy efficient ICTPower managementInterference (communication)Transmitted power
A system and a method for reverse link power control in a wireless communications network generates power adjust commands for mobiles being served by a network base station in a centralized manner by considering overall system performance when an increased interference condition is detected. In one implementation, a base station power control processor adopts a modified reverse inner loop power control (RILPC) and / or a reverse outer loop power control (ROLPC) algorithm when an increased interference condition is detected. According to the modified RILPC algorithm, a percentage of power-up adjust commands which would normally be generated when Eb / No measurements for served mobiles do not meet target Eb / No levels are converted to power down-adjust commands, thereby forcing some mobiles to reduce transmit power, at least temporarily, to constrain interference. When the increased interference condition persists, the percentage of power-up adjust commands which are converted to power-down commands may be changed. According to the modified ROLPC algorithm, the power control processor adjusts target Eb / No levels in a centralized manner based on an overall system state so that only a limited number of target Eb / No levels are allowed to increase when frame erasures occur. By preventing a percentage of target Eb / No level increases, at least temporarily, when frame erasures occur, a percentage of power up-adjust commands are avoided. Therefore, a similar effect to that achieved by the modified RILPC is achieved. In accordance with still a further implementation of the present invention, the modified RILPC algorithm may be used in combination with the modified ROLPC algorithm to provide greater resistance to increased interference conditions.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS +1
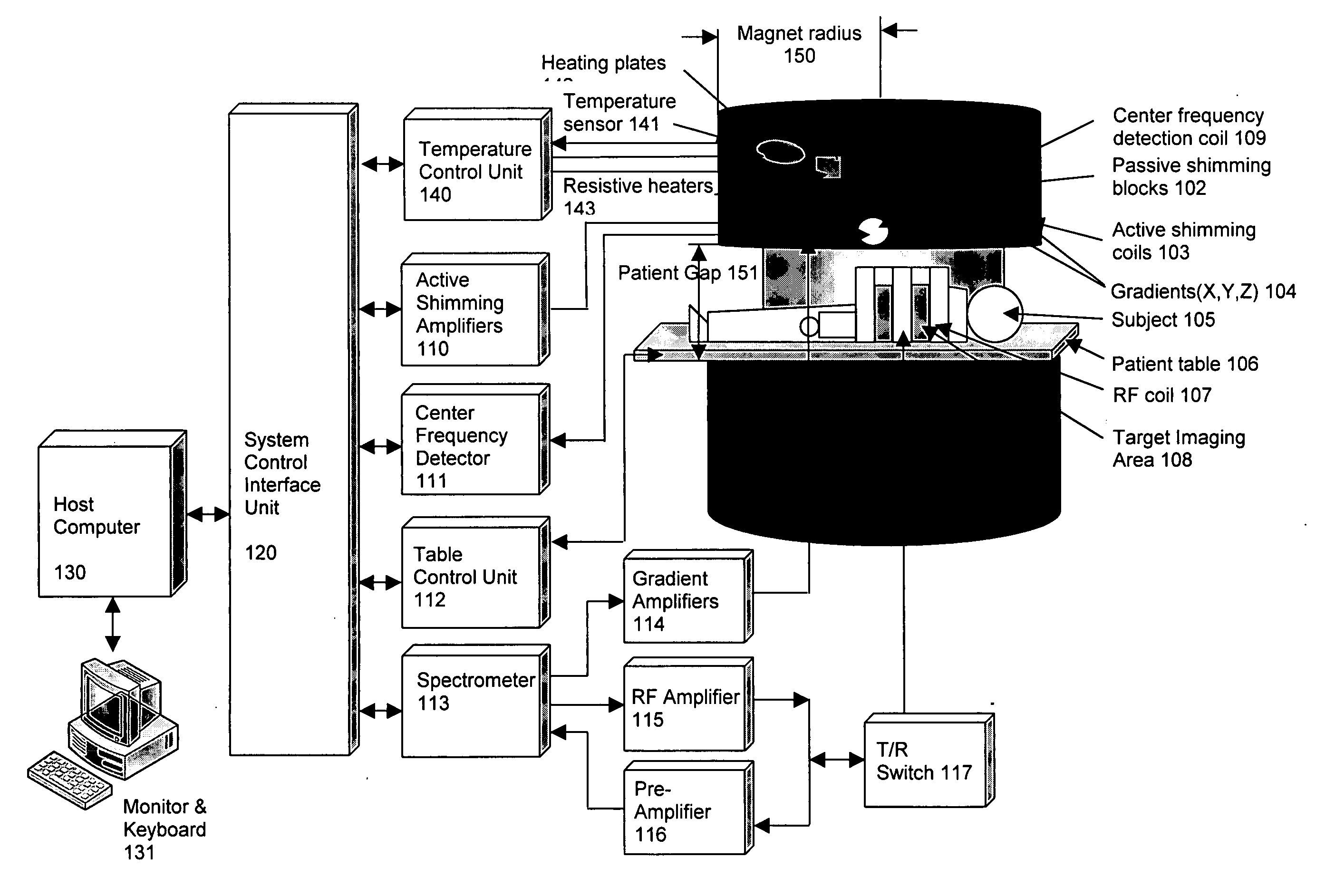
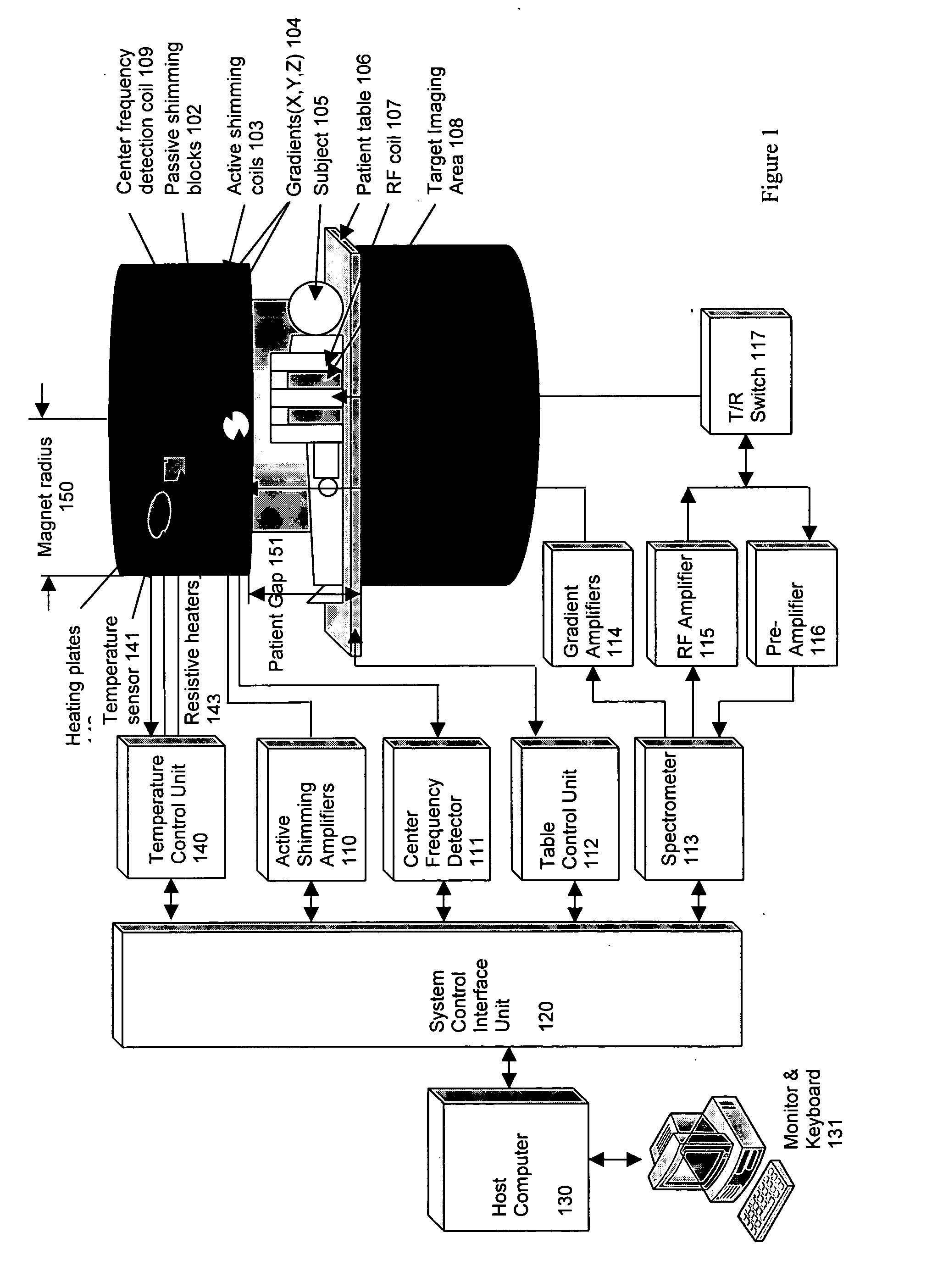
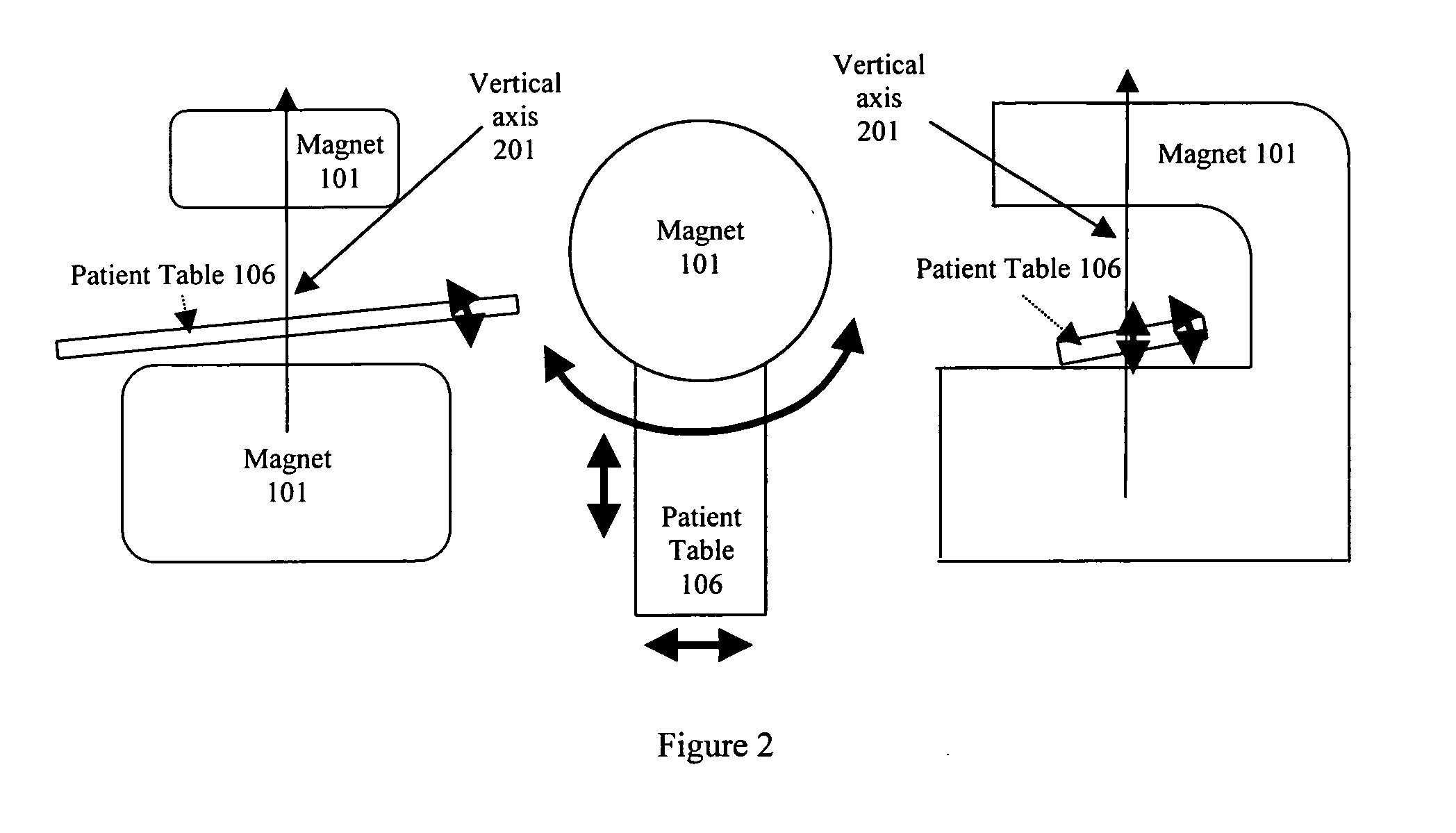
Method of using a small MRI scanner
InactiveUS20050154291A1Close accessMore accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCost effectivenessWhole body
Multiple methods of performing whole body scans using a cost-effective small magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system are disclosed. High magnetic field homogeneity of an open, small MRI is obtained by a combination of passive shimming and high order active shimming. A dynamic shimming while imaging (DSWI) method is provided to dynamically optimize field homogeneity for each scanned slab (slice) during imaging. Also provided is a method that scan a large subject volume only using a limited optimal imaging region of a magnet by continuously adjusting patient position and orientations with a 6 degrees of freedom patient table.
Owner:ZHAO LEI +2
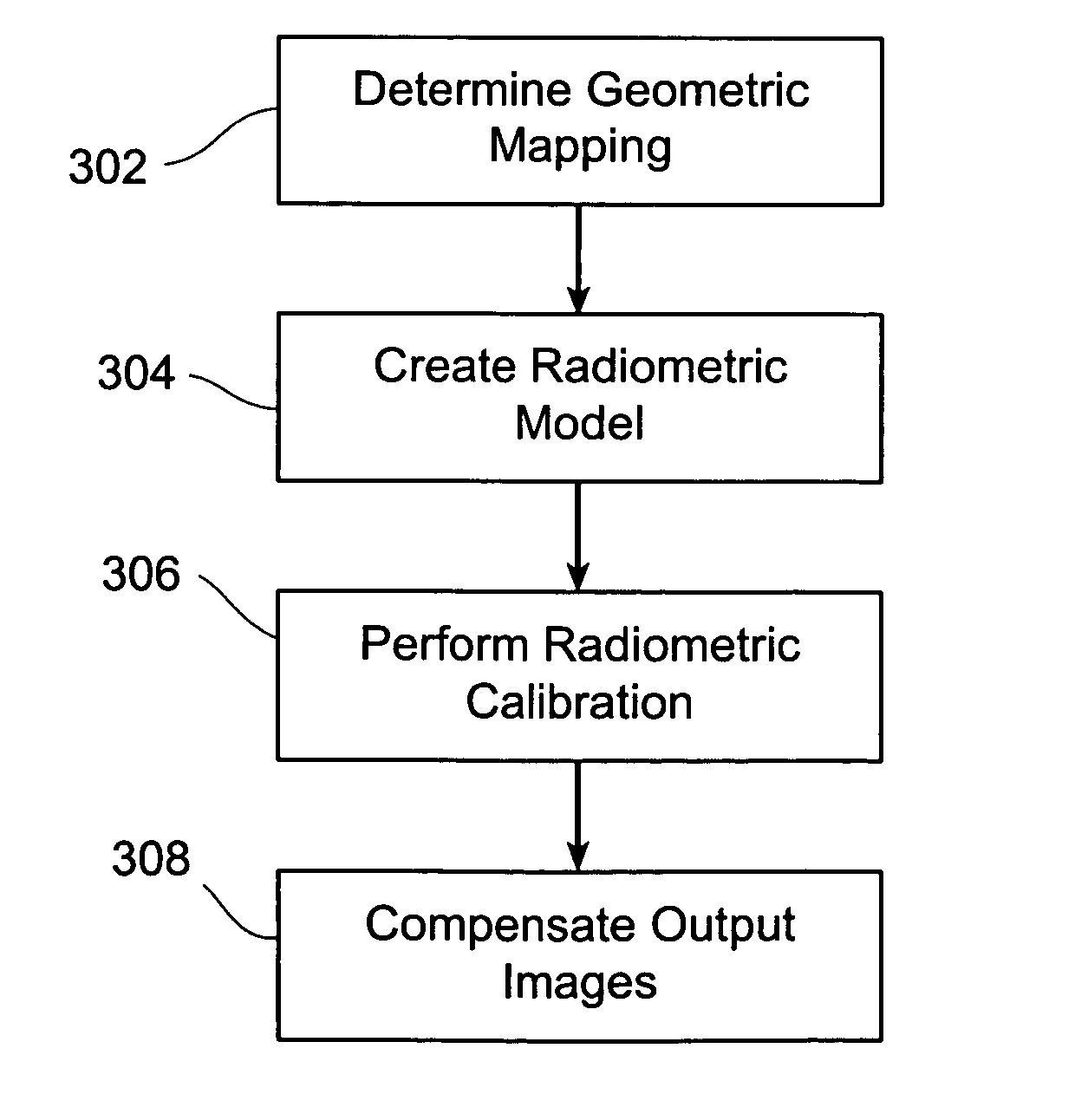
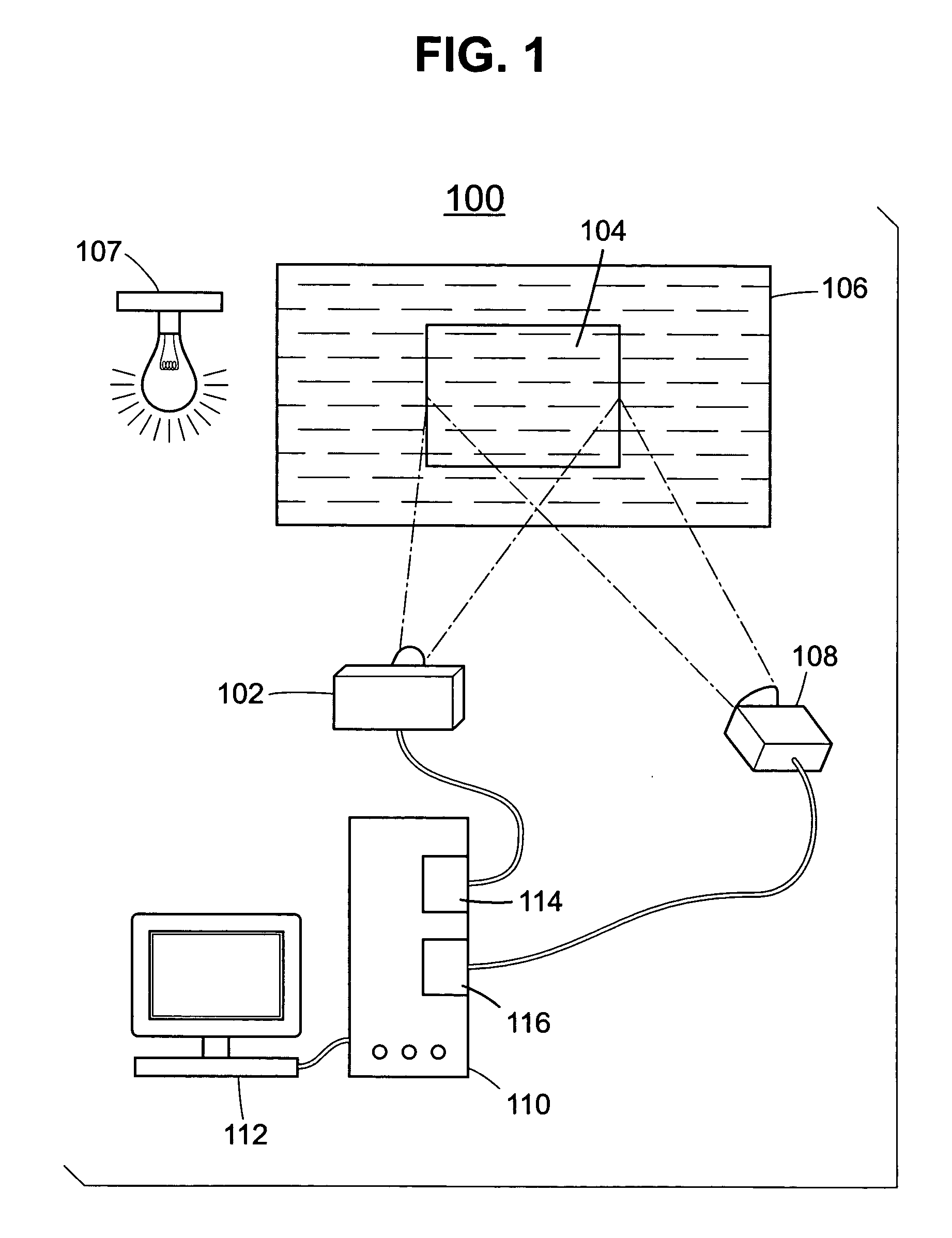
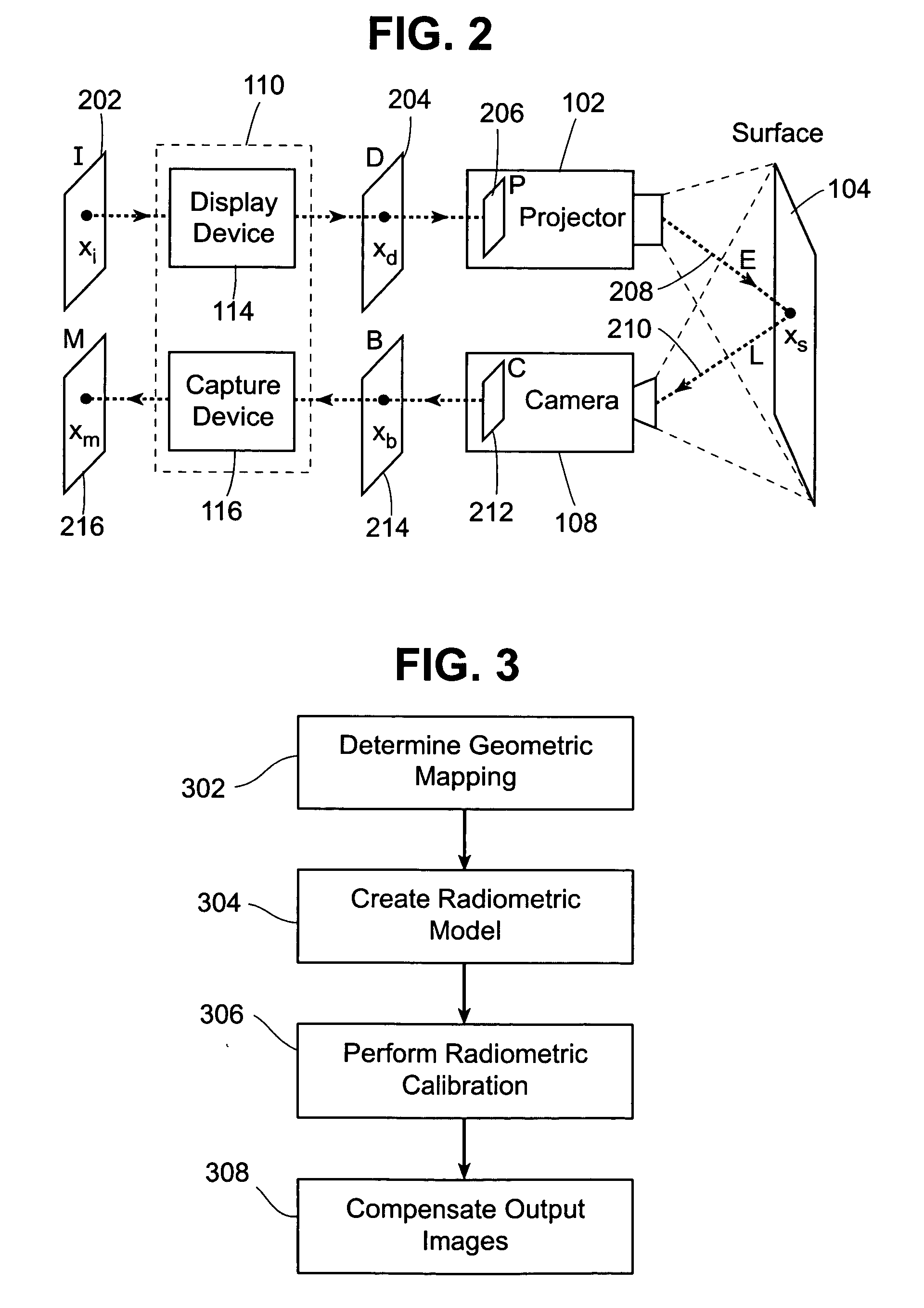
Methods and systems for compensating an image projected onto a surface having spatially varying photometric properties
ActiveUS20050134599A1Guaranteed preservation qualityMaintain qualityGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsCompensation algorithmRadiation model
Methods and systems are provided for displaying images onto an arbitrary surface, using a projector, such that the quality of the images is preserved despite surface imperfections or color variations. Methods and systems are also provided for controlling the appearance of a projection surface. Various embodiments use a detailed radiometric model and a calibration method to determine the pixel values required to be projected by a projector in order for a camera to observe a desired image. Other embodiments use a compensation algorithm that uses a feedback approach to provide the desired image compensation. Geometric mapping may be used to establish a correspondence between points in the images to be displayed by the projector and the corresponding points in the images that are captured by the camera.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for producing paper pulp, lignins, sugars and acetic acid by frantionation of lignocellulosic vegetable material in formic/acetic acid medium
InactiveUS7402224B1Low hydrationPromote dissociationWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsDigestersVegetable materialChemistry
A method for producing paper pulp from a lignocellulosie vegetable raw material. The method includes contacting the raw material with a mixture of formic acid and acetic acid (in an amount more than 5 wt. % of the mixture) at a temperature and for a suitable reaction time, the whole being performed at room temperature. The paper pulp is separated from the organic phase and optionally bleached with ozone. The organic phase is treated to enable the recycling of the formic and acetic acids and the extraction of lignins, sugars and excess acetic acid.
Owner:CIE IND DE LA MATIERE VEGETALE
Antimicrobial Compositions And Methods Of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20090192231A1Reduce discolorationReduce turbidityBiocideDead plant preservationBiotechnologyActive agent
The invention provides antimicrobial compositions comprising one or more acid and one or more organic diol. In one embodiment, the invention's compositions have an acidic pH. The compositions may optionally further contain one or more oxidizing agent (including stabilized oxidizing agent and / or unstabilized oxidizing agent), and / or one or more surfactant. In particular embodiments, the acid lacks one or both of —NH group and —NH2 group. The invention's compositions are useful in all stages of handling agricultural products, in hospitals, and in commercial and household applications.
Owner:SMARTWASH SOLUTIONS
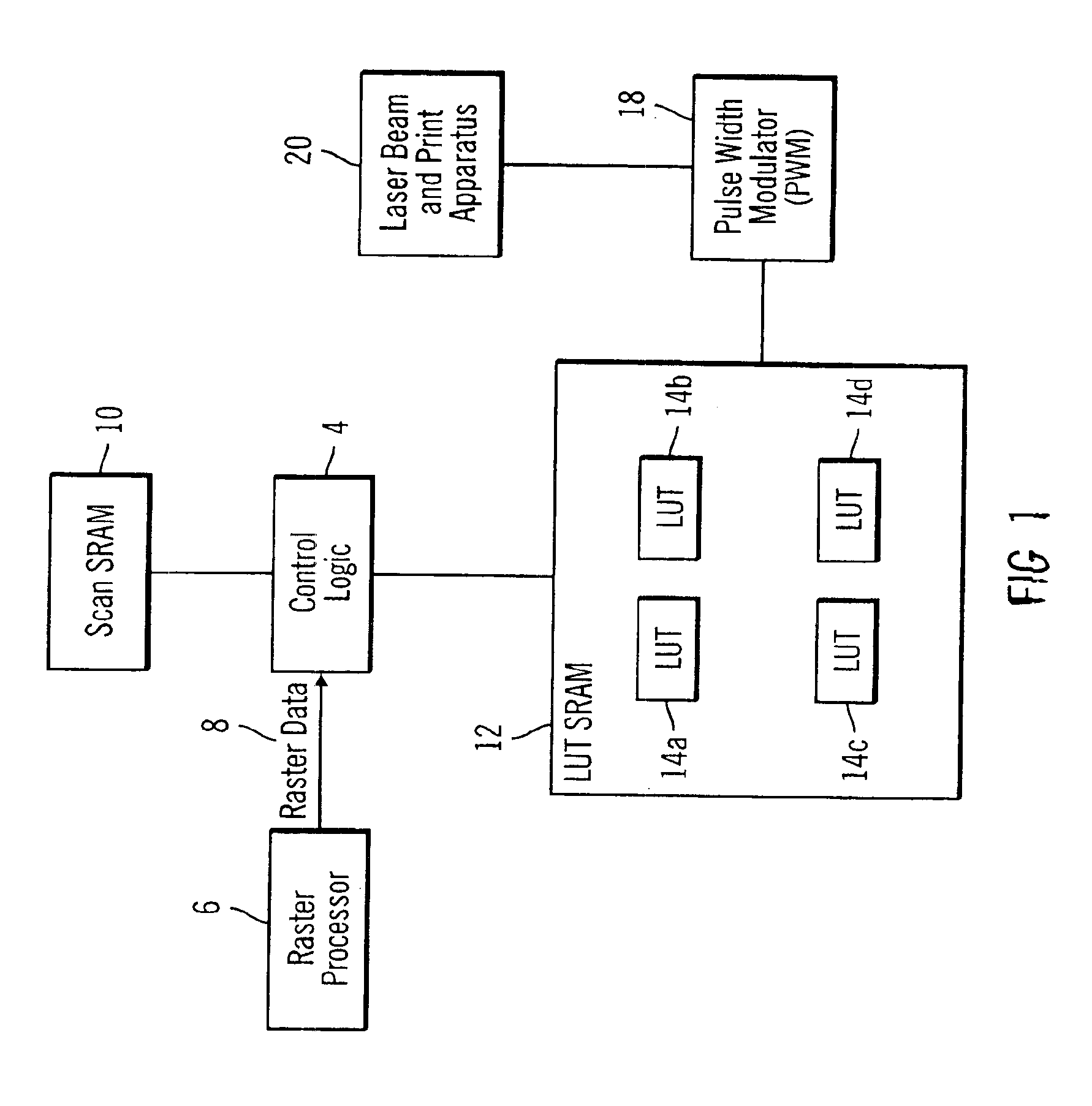
Method, system, and program for reducing toner usage in print output
InactiveUS6975428B1Reduce toner usageMinimizes EMI radiationDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGratingSubject matter
Disclosed is a method, system, and program for reducing toner in an image comprised of raster pel data. A determination is made of pels surrounding subject pels. For each subject pel, a sub-pulse width power is generated to charge a sub-pel region within the subject pel based on a pattern of the surrounding pels of the subject pel. Further, for each subject pel, position information is generated indicating an alignment of the sub-pel region in the pel. The position information is used to position the sub-pel region produced by the sub-pulse width power in the pel.
Owner:RICOH KK
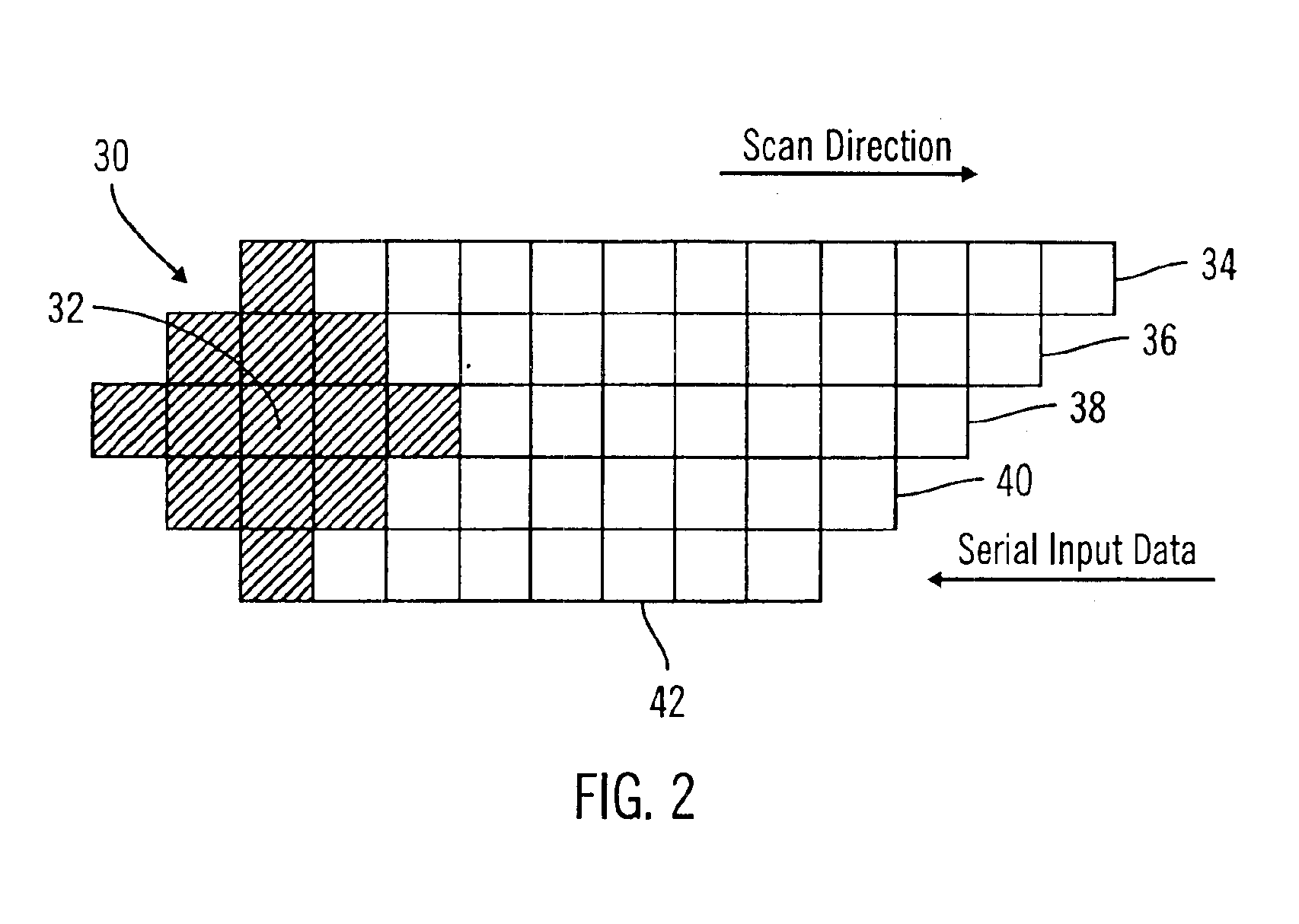
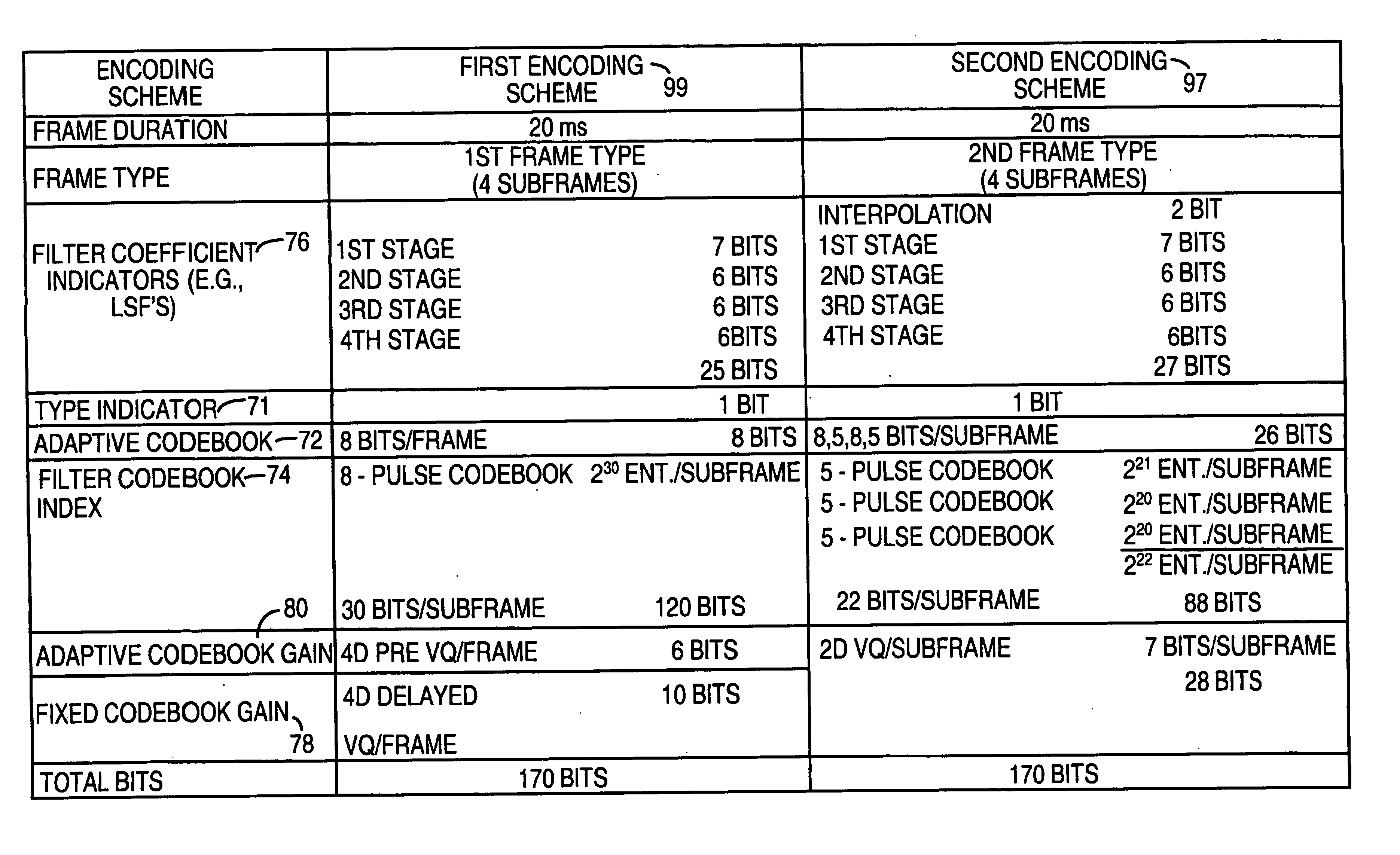
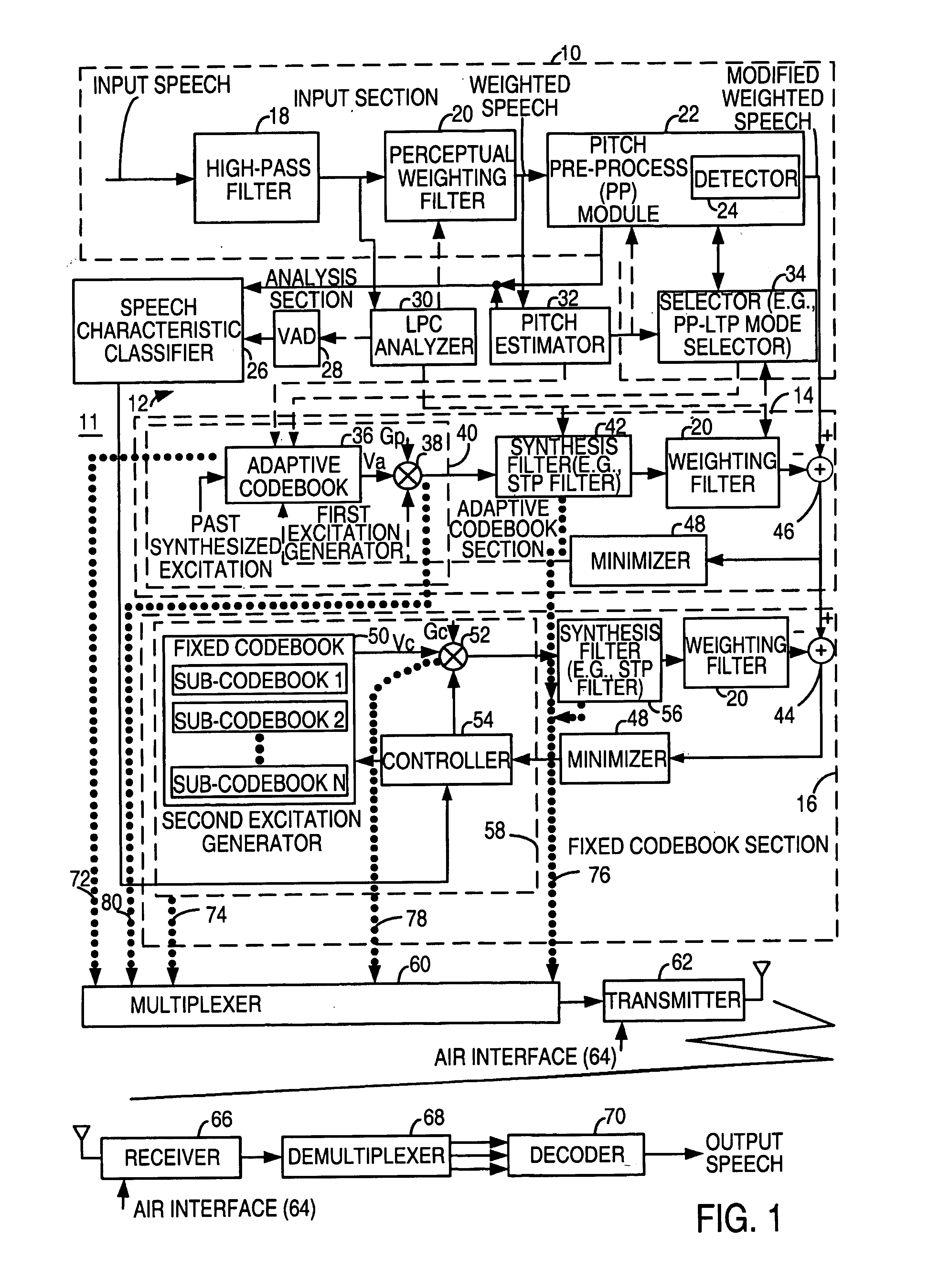
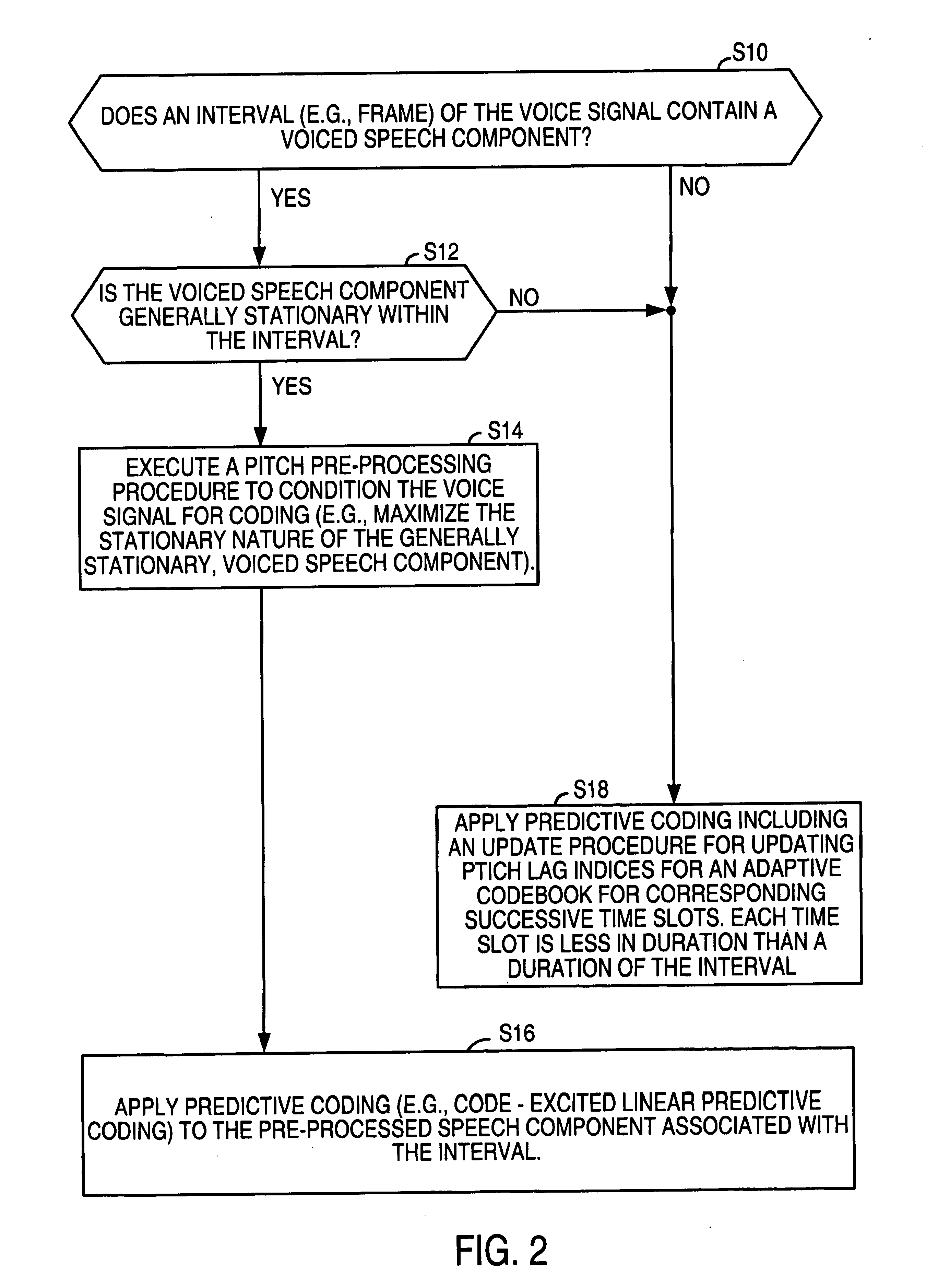
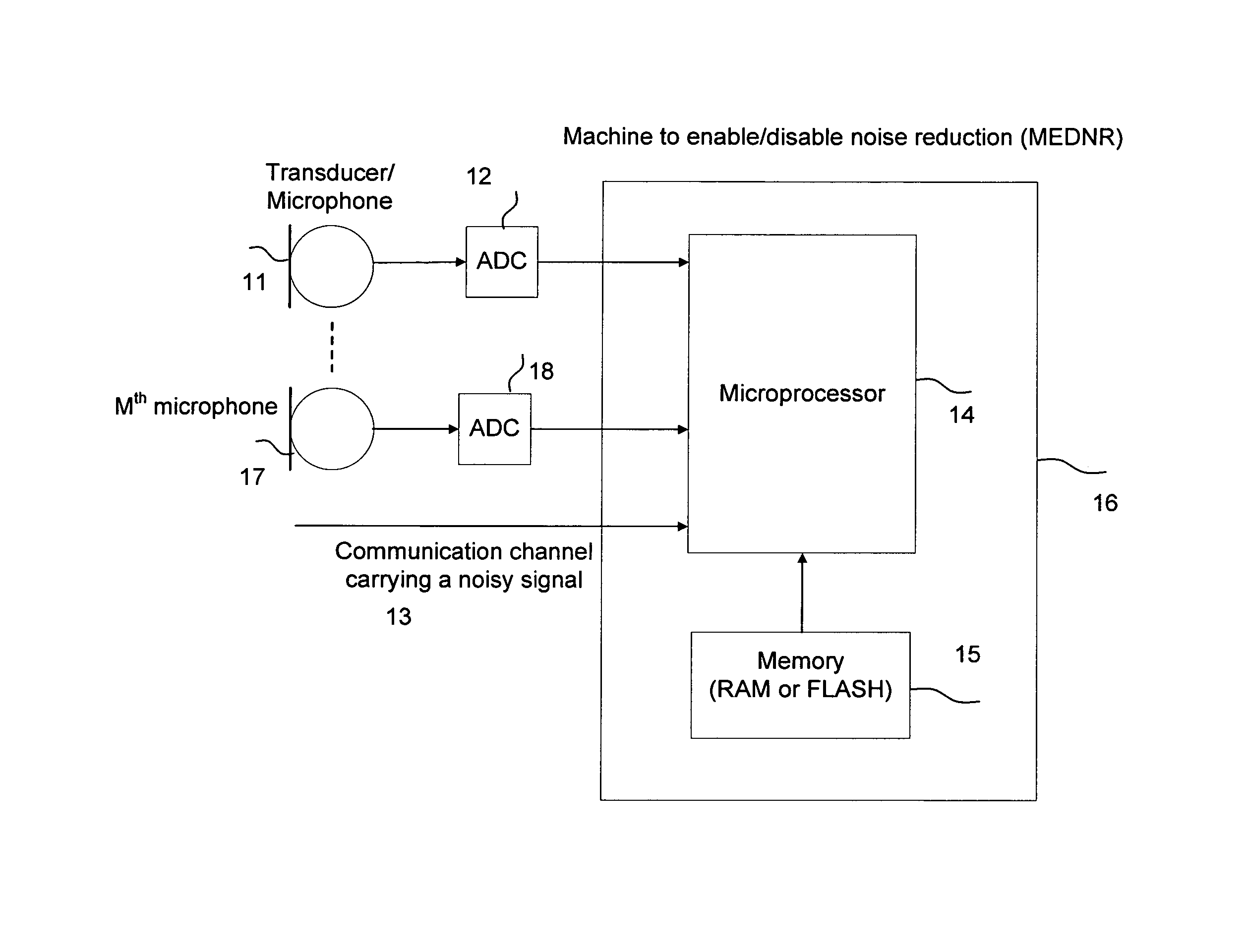
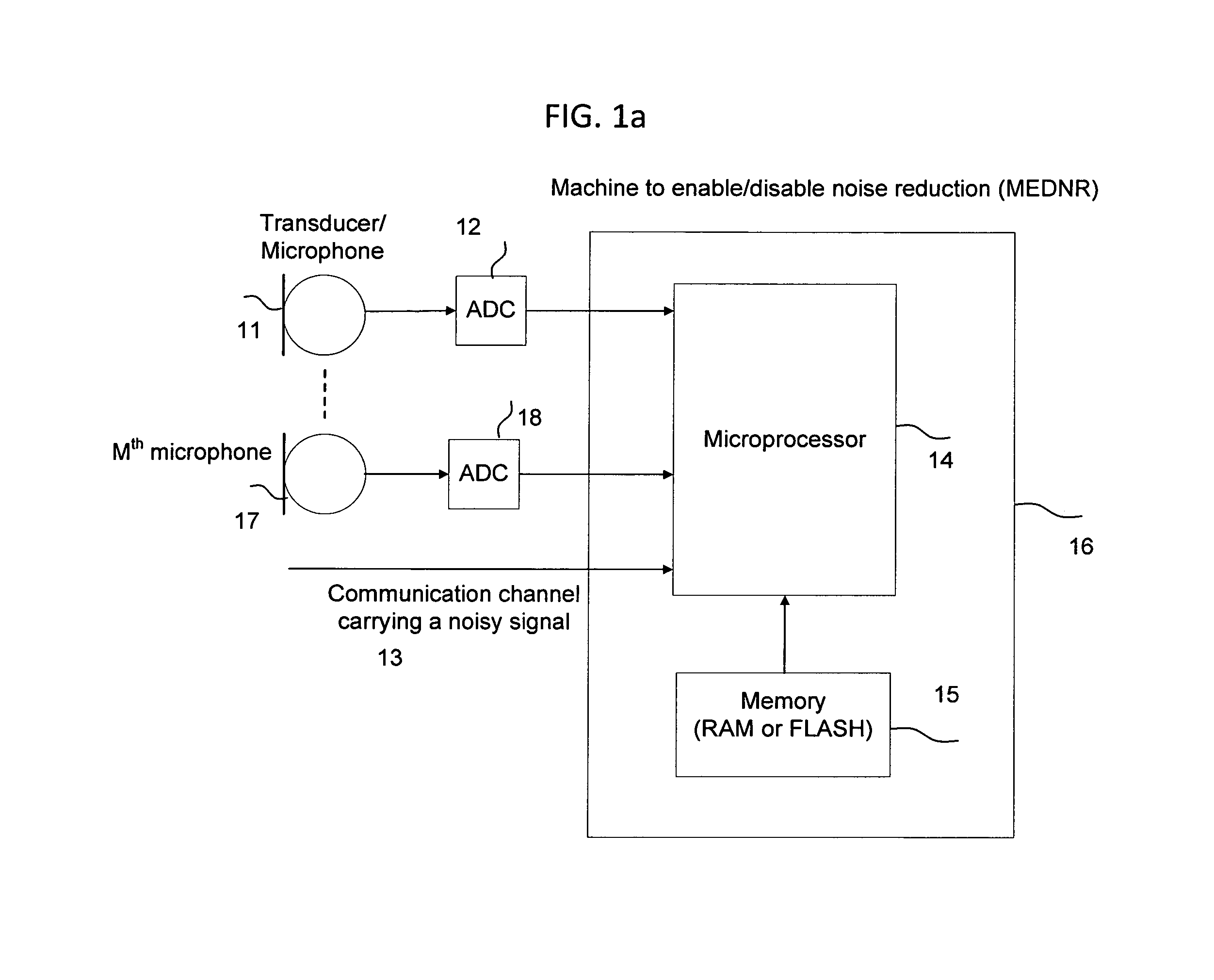
System for speech encoding having an adaptive encoding arrangement
InactiveUS7072832B1Facilitates the efficient bit-usage per frameGuaranteed preservation qualitySpeech analysisAdaptive encodingSpeech sound
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, a selector supports the selection of a first encoding scheme or the second encoding scheme based upon the detection or absence of the triggering characteristic in the interval of the input speech signal. The first encoding scheme has a pitch pre-processing procedure for processing the input speech signal to form a revised speech signal biased toward an ideal voiced and stationary characteristic. The pre-processing procedure allows the encoder to fully capture the benefits of a bandwidth-efficient, long-term predictive procedure for a greater amount of speech components of an input speech signal than would otherwise be possible. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, the second encoding scheme entails a long-term prediction mode for encoding the pitch on a sub-frame by sub-frame basis. The long-term prediction mode is tailored to where the generally periodic component of the speech is generally not stationary or less than completely periodic and requires greater frequency of updates from the adaptive codebook to achieve a desired perceptual quality of the reproduced speech under a long-term predictive procedure.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
High compressive stress carbon liners for MOS devices
InactiveUS7906817B1Improve performanceGuaranteed preservation qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideEngineering
Transistor architectures and fabrication processes generate channel strain without adversely impacting the efficiency of the transistor fabrication process while preserving the material quality and enhancing the performance of the resulting transistor. Transistor strain is generated is PMOS devices using a highly compressive post-salicide amorphous carbon capping layer applied as a blanket over on at least the source and drain regions. The stress from this capping layer is uniaxially transferred to the PMOS channel through the source-drain regions to create compressive strain in PMOS channel.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
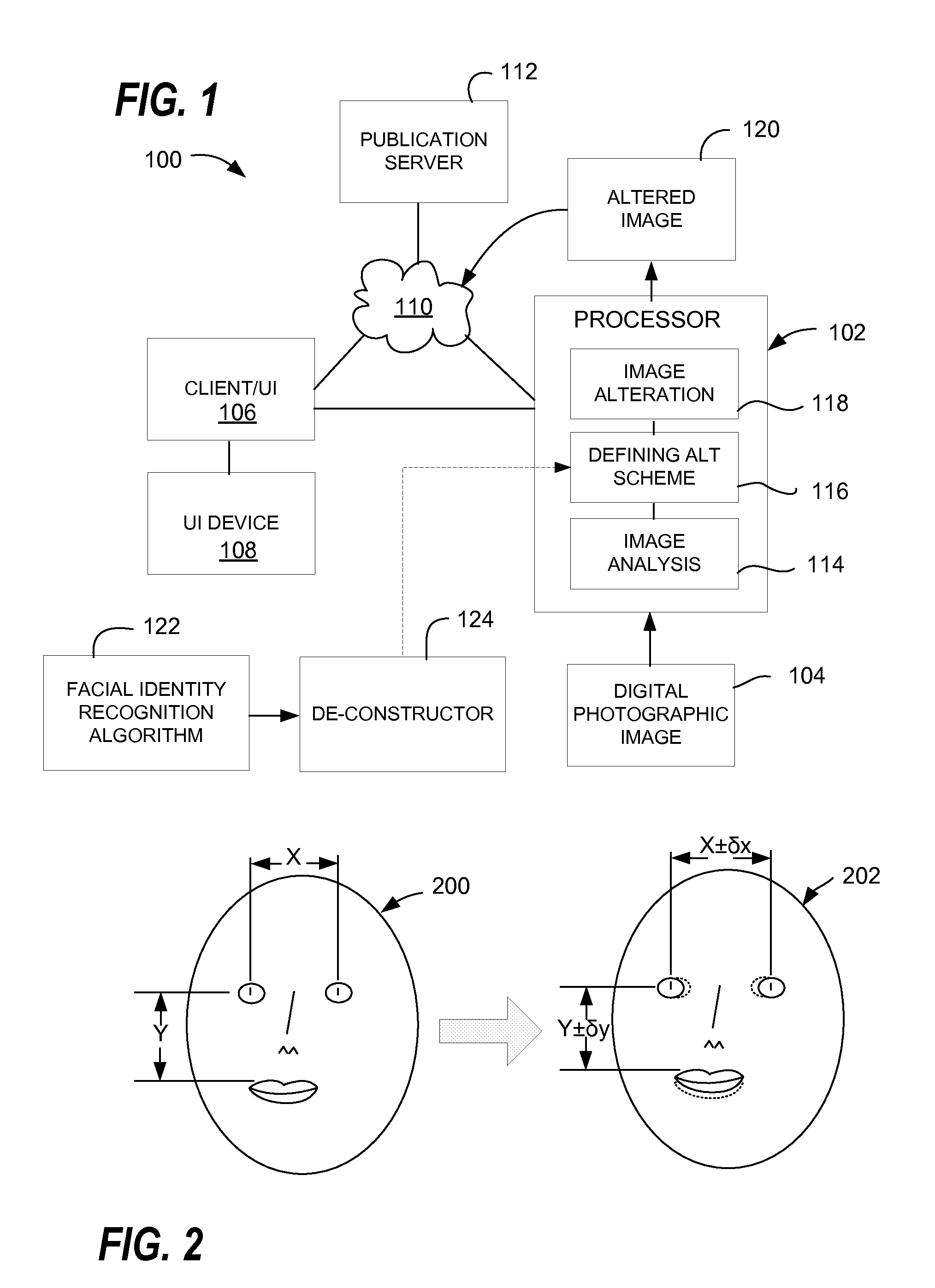
Graphic data alteration to enhance online privacy
ActiveUS20120177248A1Enhance privacyPreserve overall aesthetic qualityDigital data authenticationRegistersComputer memoryGeolocation
A computer alters at least one recognizable metric or text in a digitally-encoded photographic image by operating an alteration algorithm in response to user input data while preserving an overall aesthetic quality of the image and obscuring an identity of at least one individual or geographic location appearing in the image. An altered digitally-encoded photographic image prepared by the altering of the at least one recognizable metric or text in the image is stored in a computer memory. User feedback and / or automatic analysis may be performed to define parameter values of the alteration algorithm such that the alteration process achieves preservation of aesthetic qualities while obscuring an identity of interest.
Owner:SHUSTER GARY S
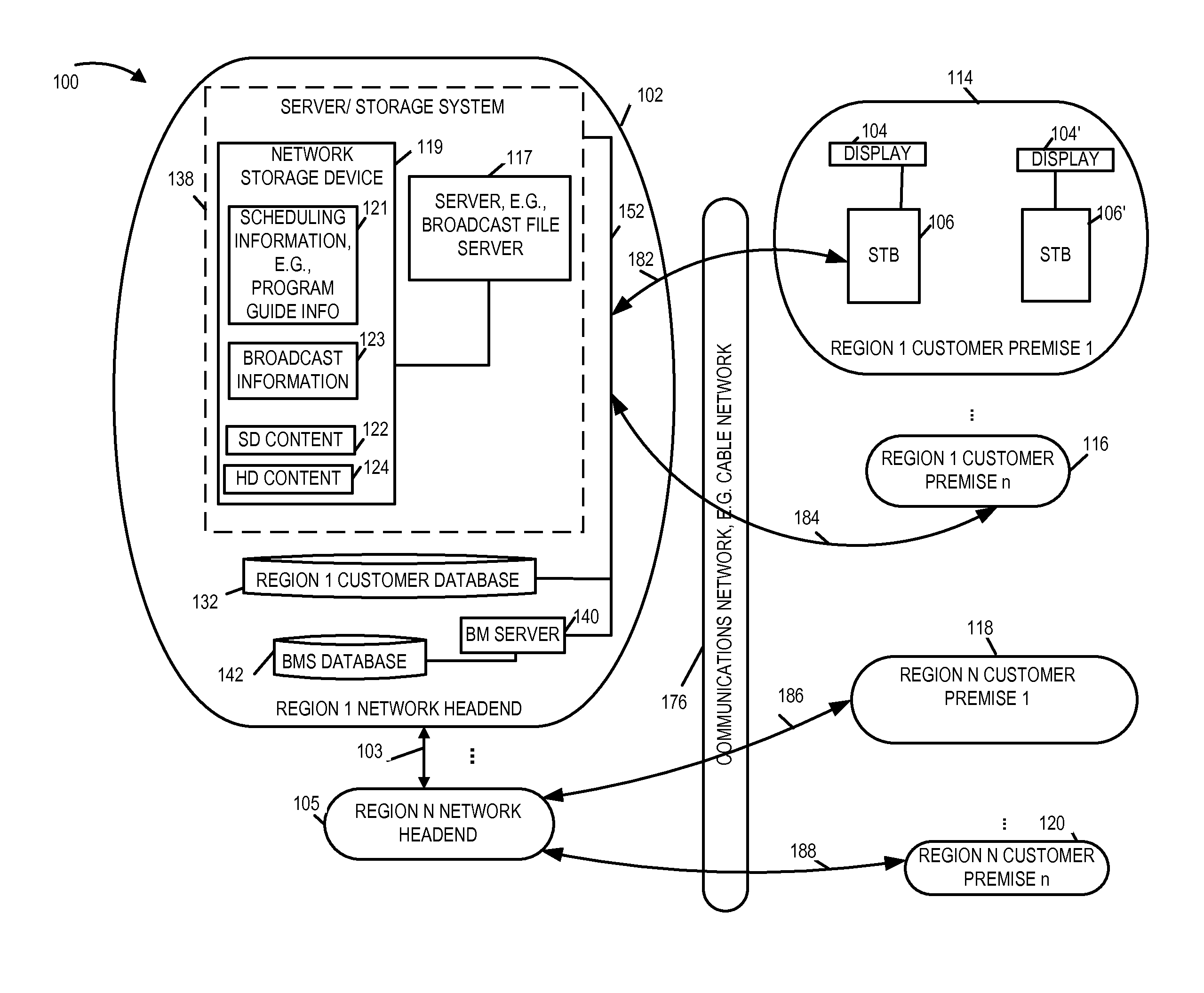
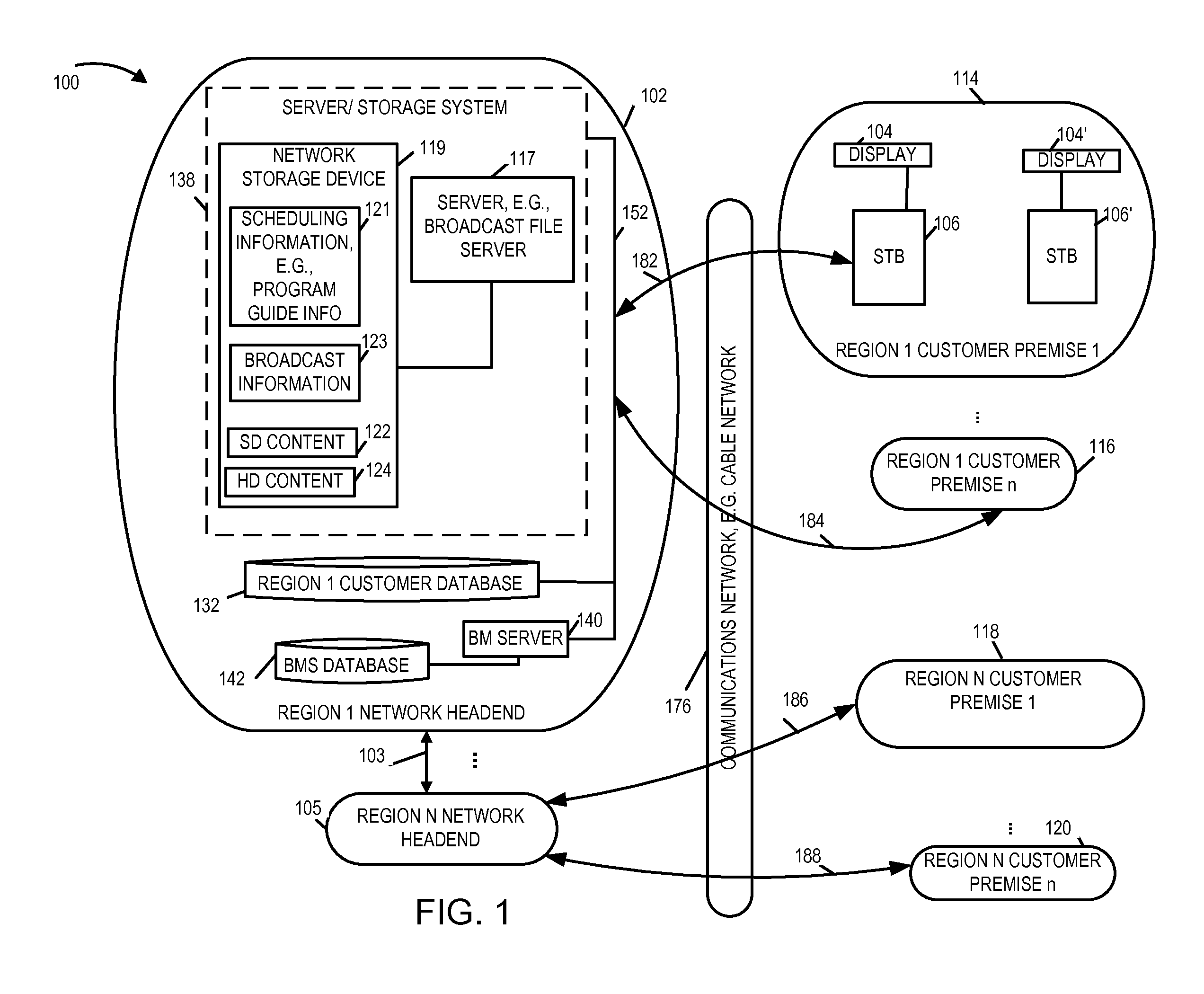
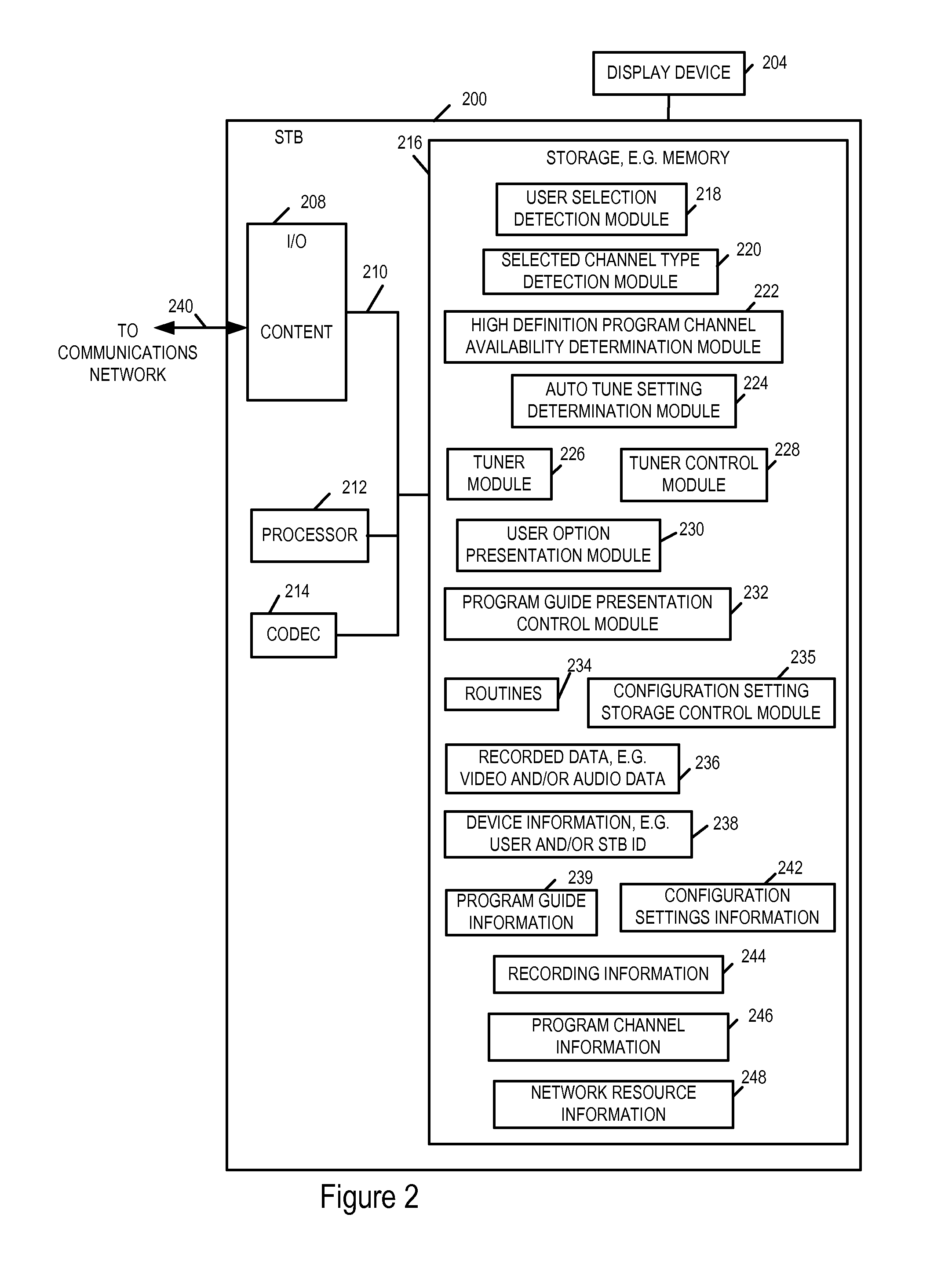
Methods and apparatus for providing access to program channels
ActiveUS20110102683A1Image quality is preservedGuaranteed preservation qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsHigh definitionStandard definition
Methods and apparatus for providing access to program channels, e.g., high definition programs and program channels which corresponding to a standard definition program and / or program channels are described. In accordance with the invention, a high definition auto tune function is supported. When enabled, in one exemplary embodiment, if a user selects a standard program definition channel, a check is automatically made to determine if a corresponding high definition program channel is available. The corresponding high definition program channel is a channel which provides the same program as on the selected standard definition channel but in high definition. When the auto tune function is enabled and a corresponding high definition channel is available, the device, e.g., set to box or tuner implementing the auto tune feature of the present invention, automatically tunes to the high definition channel instead of the standard definition channel. The content from the high definition channel is then displayed instead of the content from the user selected standard definition channel.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Magnetic resonance imaging having patient video, microphone and motion tracking
ActiveUS8214012B2Efficient removalImprove diagnostic qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDigital videoProjection system
Critical needs for MRI patient instruction, testing, comfort, motion control, and speech communication are provided for better imaging which leads to more effective medical care. An MRI Digital Video Projection System is disclosed which provides better quality display to the patient to better inform, instruct, test, and comfort the patient plus the potential to stimulate the brain with microsecond onset times to better diagnose brain function. An MRI Motion Tracker and Patient Augmented Visual Feedback System enables monitoring patient body part motion, providing real time feedback to the patient and / or technician to substantially improve diagnostic yield of scanning sessions, particularly for children and mentally challenged individuals. An MR Forward Predictive Noise Canceling Microphone System removes the intense MRI acoustic noise improving patient communication, patient safety and enabling coding of speech output. These systems can be used individually but maximum benefit is from providing all three.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF +1
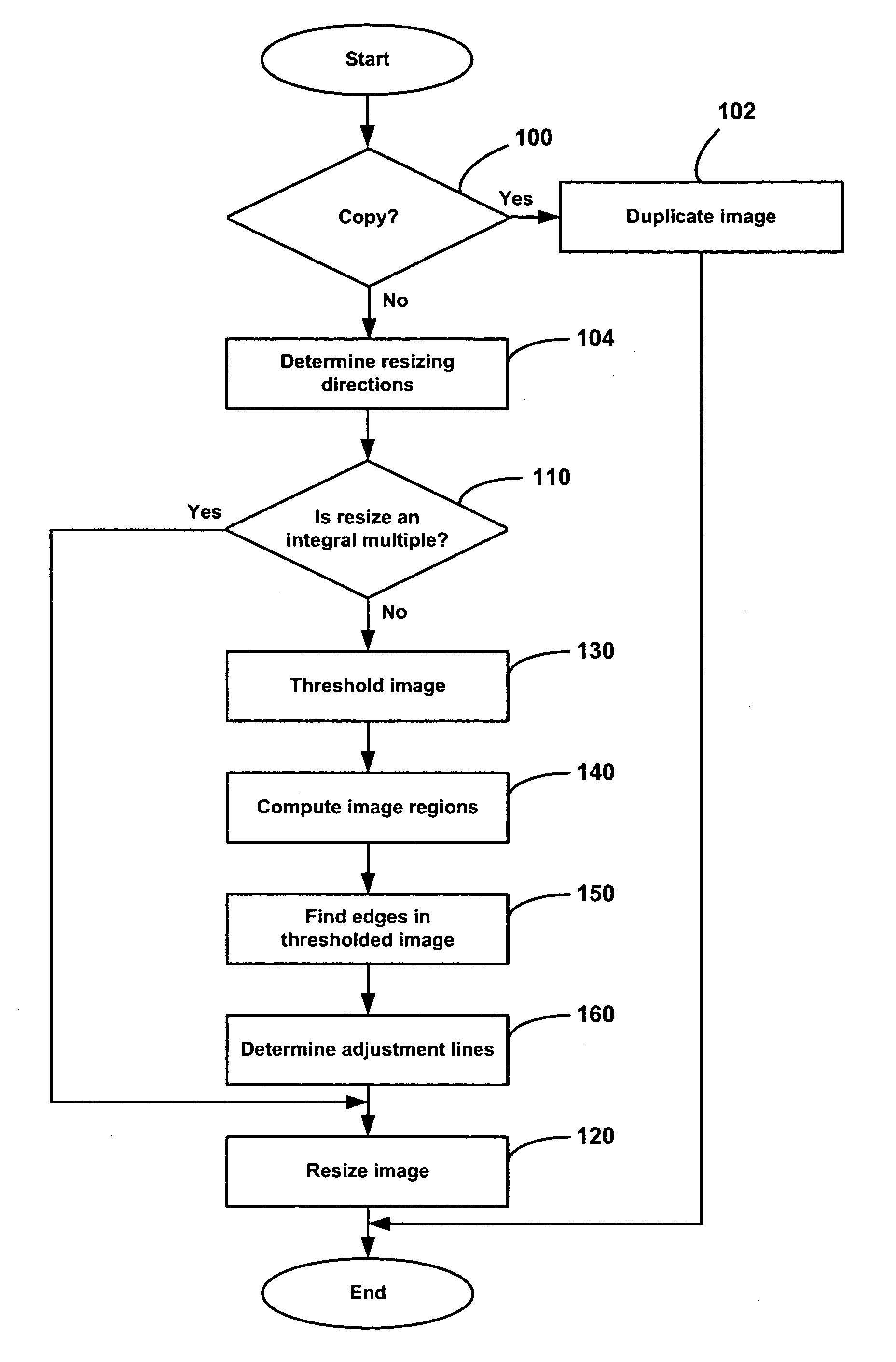
Method and apparatus for resizing images
InactiveUS20060072853A1Excessive morphingExcessive distortionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer vision
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and system for rendering polygons having abutting edges
ActiveUS7791617B2Fast and efficient real-timeGuaranteed preservation qualityDrawing from basic elementsTexturing/coloringComputer graphics (images)
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Low distortion passthrough circuit arrangement for cable television set top converter terminals
InactiveUS7039941B1Simple signal processingGuaranteed preservation qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLow distortionEngineering
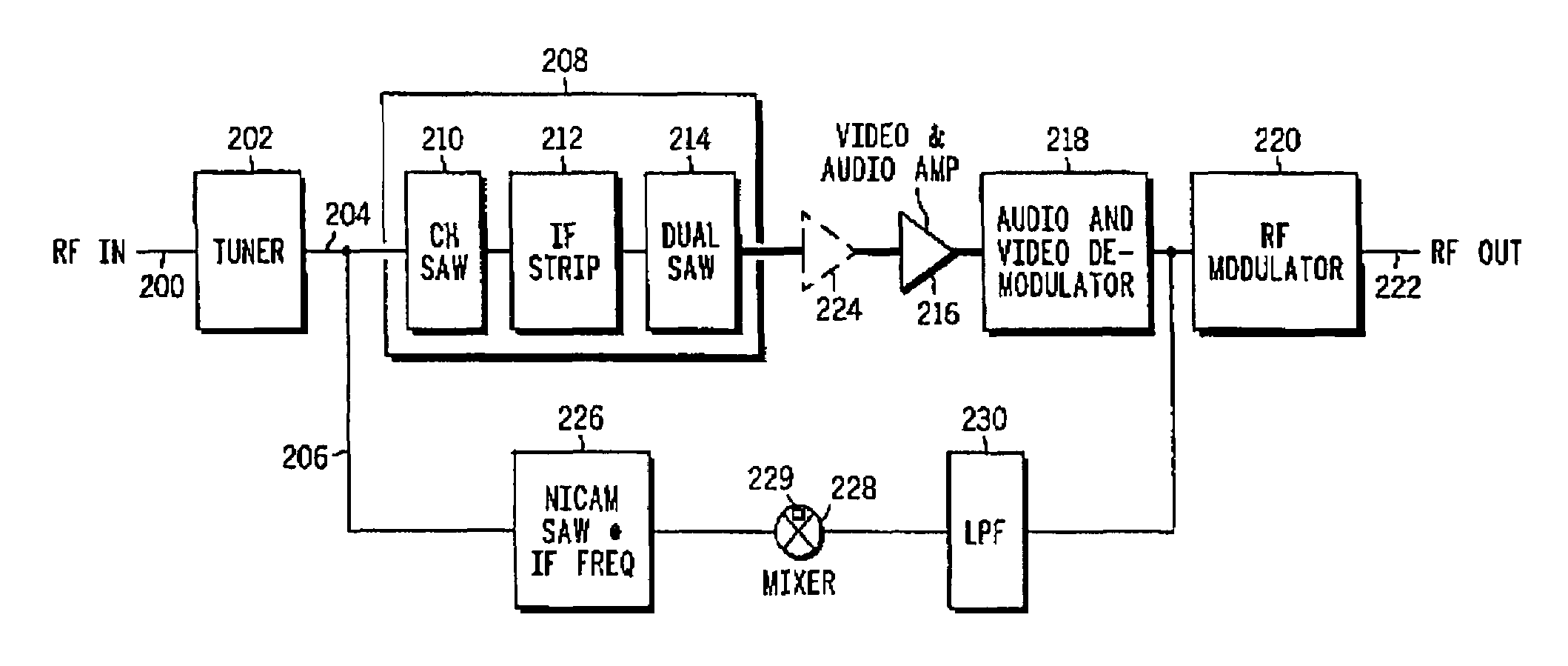
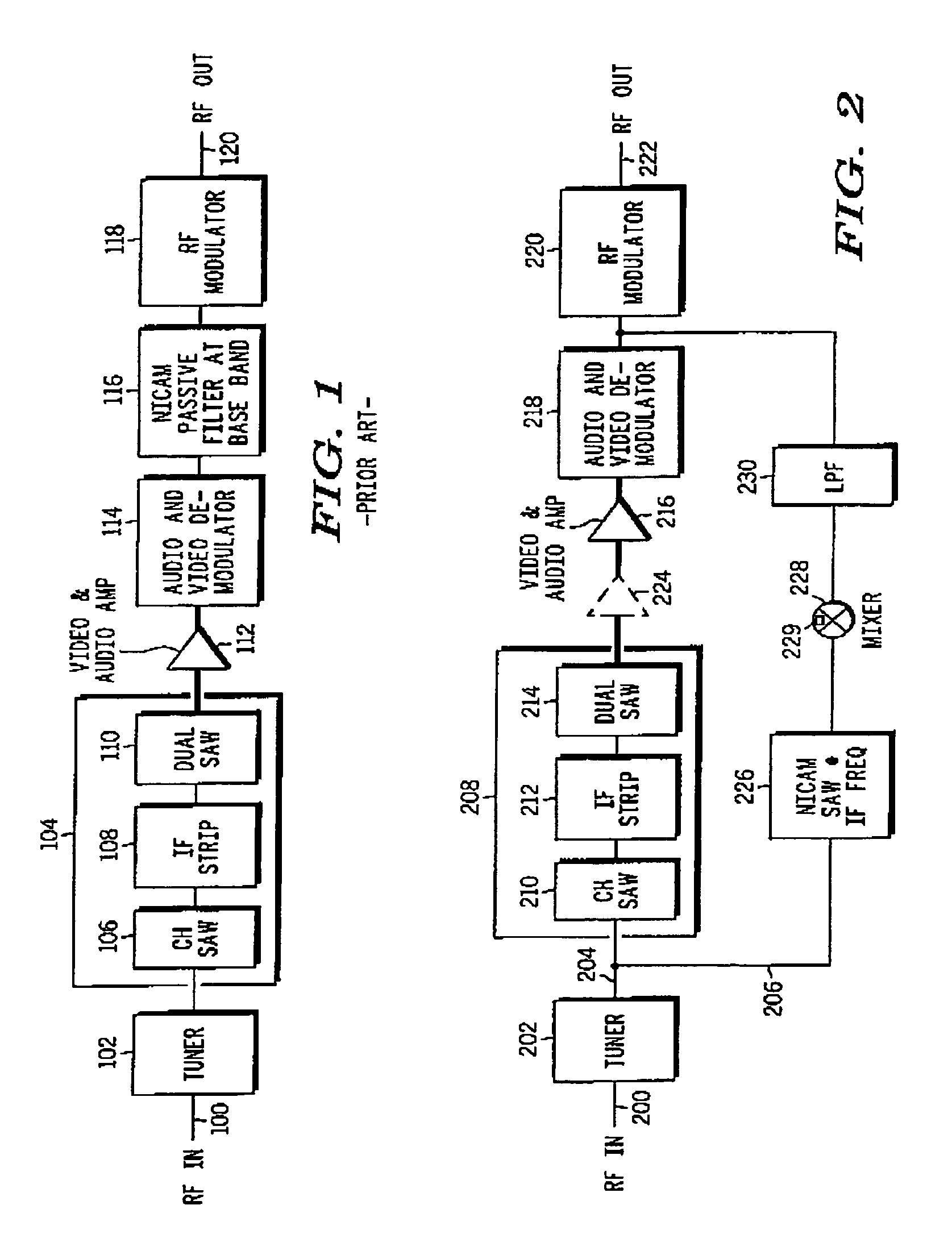
In a cable television converter terminal, NICAM signal passthrough is achieved using an alignment-free passthrough circuit including a NICAM SAW filter. The alignment-free passthrough circuit directly taps the output of the converter terminal's tuner to obtain the NICAM signal. As a result, the NICAM signal is not distorted by the components involved in obtaining the other signal components of the cable television signal. Consequently, sound quality is improved and rendered less vulnerable to degradation due to component aging, temperature fluctuations, and human error. The passthrough circuit can be implemented as a removable circuit module.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
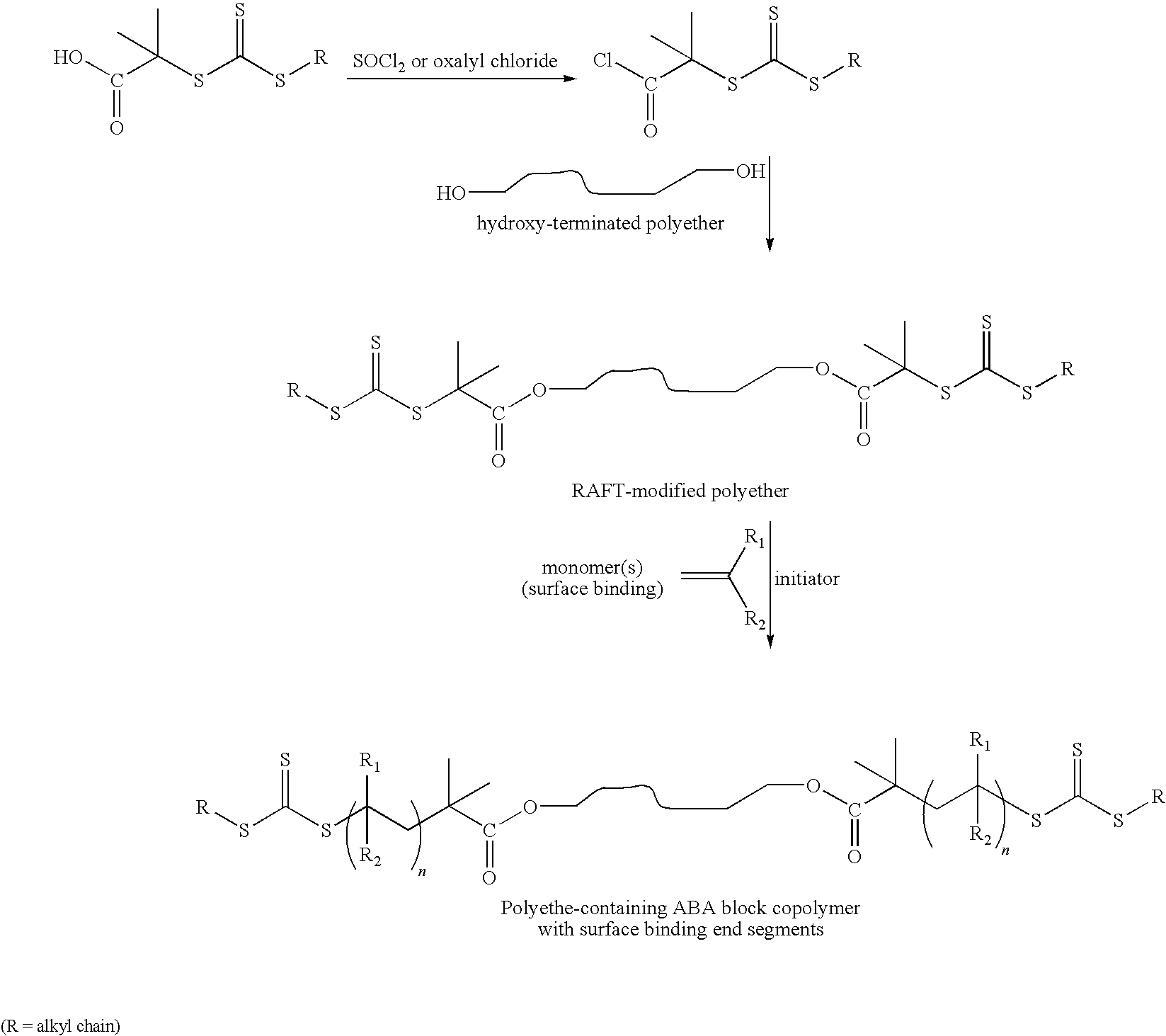
Brush Copolymers
InactiveUS20100168852A1High level of comfortHigh level of qualitySurgical adhesivesCoatingsBoric acidMacromonomer
Brush copolymers containing (a) monomeric units derived from an ethylenically unsaturated monomer containing one or more boronic acid moieties and; and (b) monomeric units derived from an ethylenically unsaturated-containing hydrophilic macromonomer are disclosed.
Owner:BARCLAYS BANK PLC AS SUCCESSOR AGENT
Strained transistor architecture and method
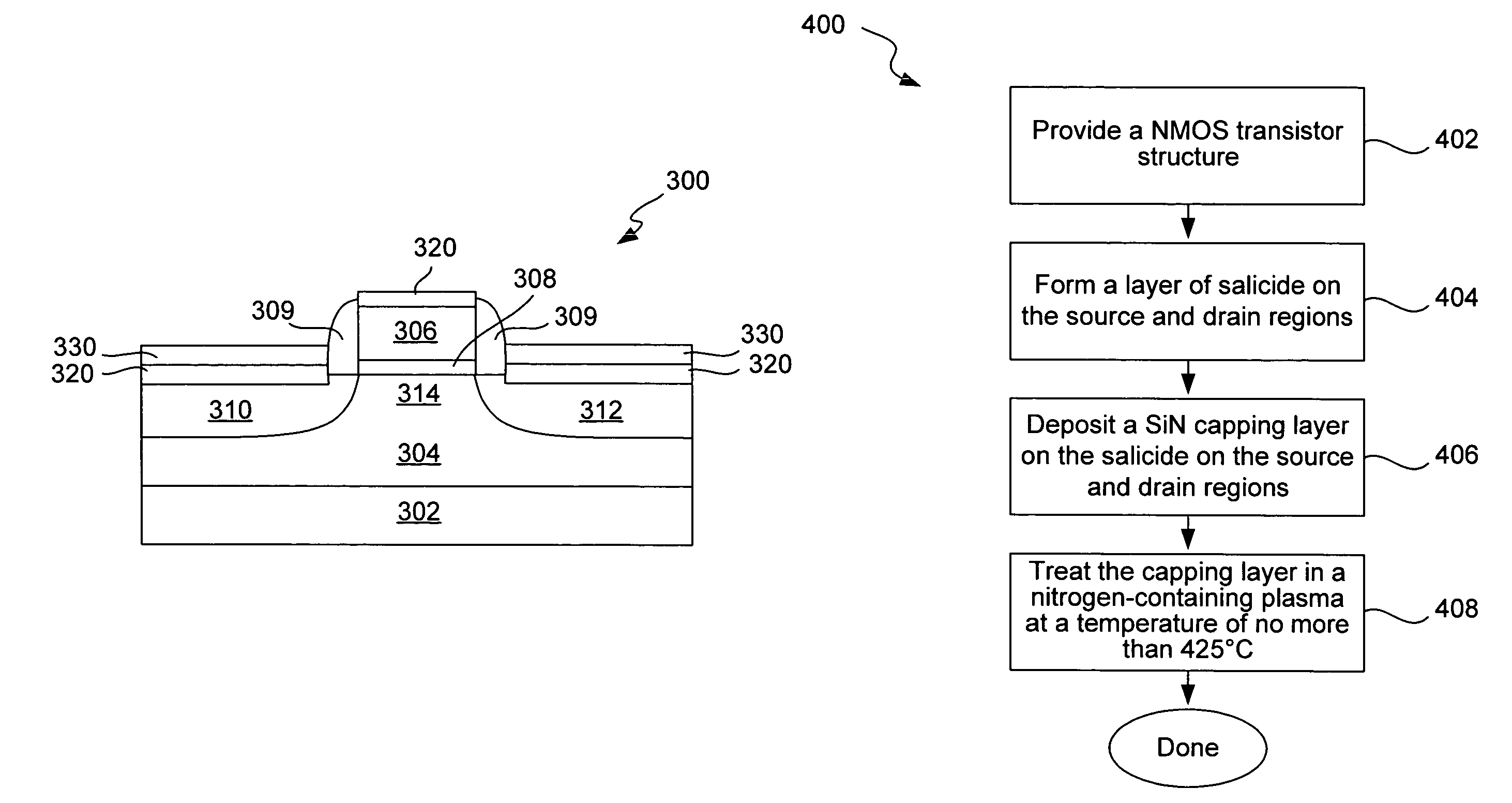
ActiveUS7041543B1Preserving material qualityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTensile strainSalicide
Transistor architectures and fabrication processes generate channel strain without adversely impacting the efficiency of the transistor fabrication process while preserving the material quality and enhancing the performance of the resulting transistor. Transistor strain is generated is NMOS devices using a highly tensile post-salicide silicon nitride capping layer on the source and drain regions. The stress from this capping layer is uniaxially transferred to the NMOS channel through the source-drain regions to create tensile strain in NMOS channel.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for producing microecological preparation of bdellovibrio bacteriourus
ActiveCN101338293AUnique production processGuaranteed preservation qualityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFreeze-dryingMicrobiology
The invention discloses a production method for a bdellovibrio micro-ecological preparation. The production method includes the following steps: A, preparing freezing-drying host bacteria powder; B, preparing the culture medium of the bdellovibrio; C, inoculating the seeds of the bdellovibrio with 2 to 5 percent into a fermentation pot loaded with the culture medium of the bdellovibrio, ventilating and culturing for 20 to 24 hours under 30 to 33 DEG C, namely obtaining the bdellovibrio micro-ecological preparation. The production technique of the host bacteria of the bdellovibrio micro-ecological preparation adopts the freezeing-drying technique to ensure the preservation quality of the host bacteria and provides a stable reliable proliferation nutrition source for the growing and proliferation of the bdellovibrio.
Owner:SHANDONG SINDER TECH
Biomedical devices
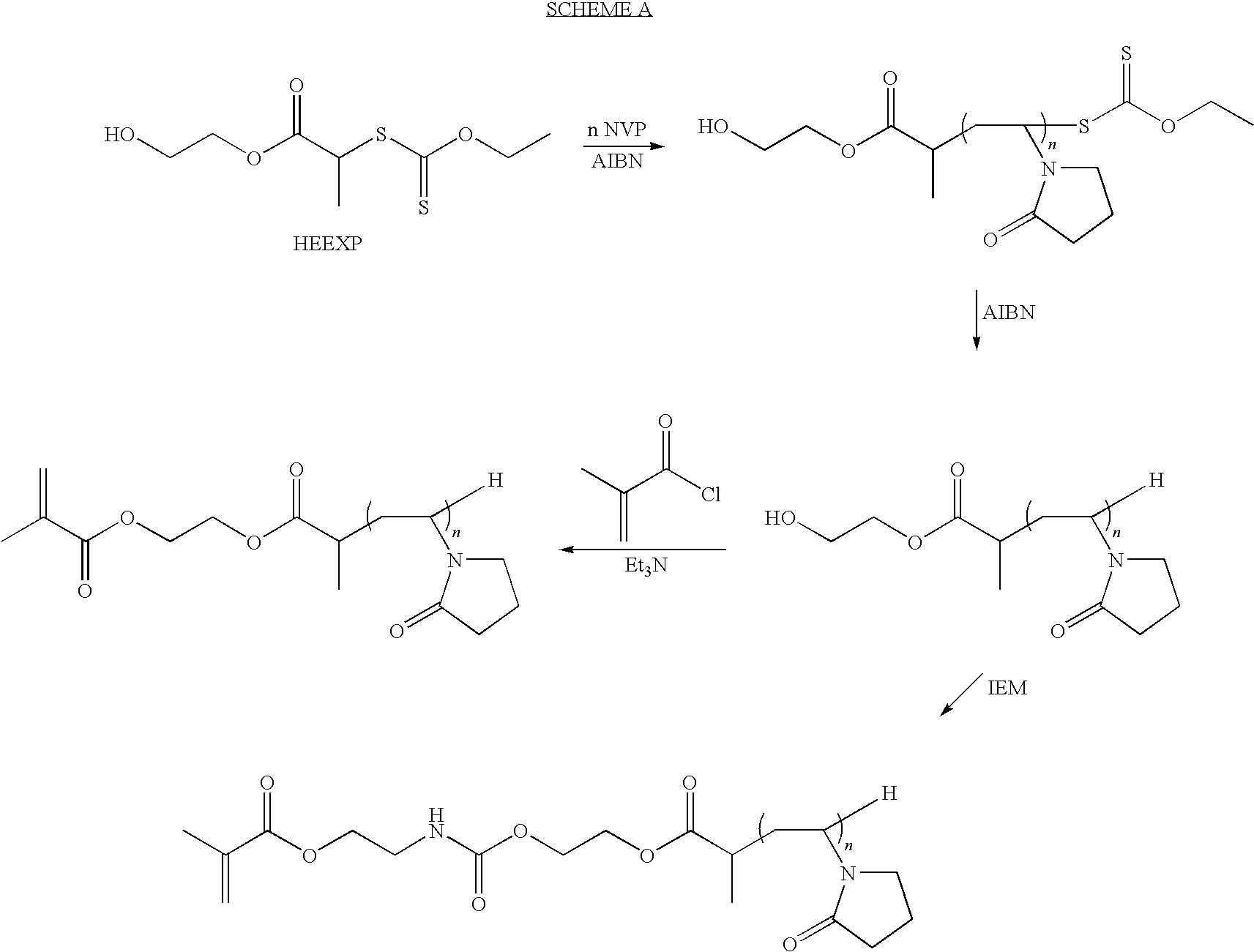
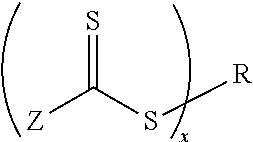
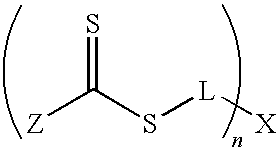
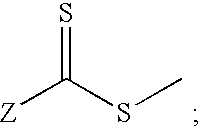
InactiveUS20100315588A1Prevent limit adsorptionMaintain clarityProsthesisOptical partsHydrophilic polymersThio-
Biomedical devices such as contact lenses formed from a polymerization product of a mixture comprising (a) a hydrophilic polymer comprising one or more hydrophilic units and one or more thio carbonyl thio fragments of a reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (“RAFT”) agent; and (b) one or more biomedical device-forming monomers are disclosed.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method to control point spread function of an image
ActiveUS7742239B2Guaranteed preservation qualityMore interferenceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityPoint spread function
A method of controlling the point spread function of an image projected with said image being diffused by a filter; said point spread function is a result of the application of spatial filter(s) on said image; with said control of the point spread function effected by varying the distance between such image and said spatial filter(s) and varying the bidirectional scattering transmission function of the spatial filter(s). Said spatial filter may be a holographic diffuser, which by method of manufacture has a well defined bi-directional scattering transmission spread function. Control of said spread function is particularly useful to maintain image quality while abating moiré interference in situations where two periodic patterns are layered causing moiré interference.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Biomedical Devices
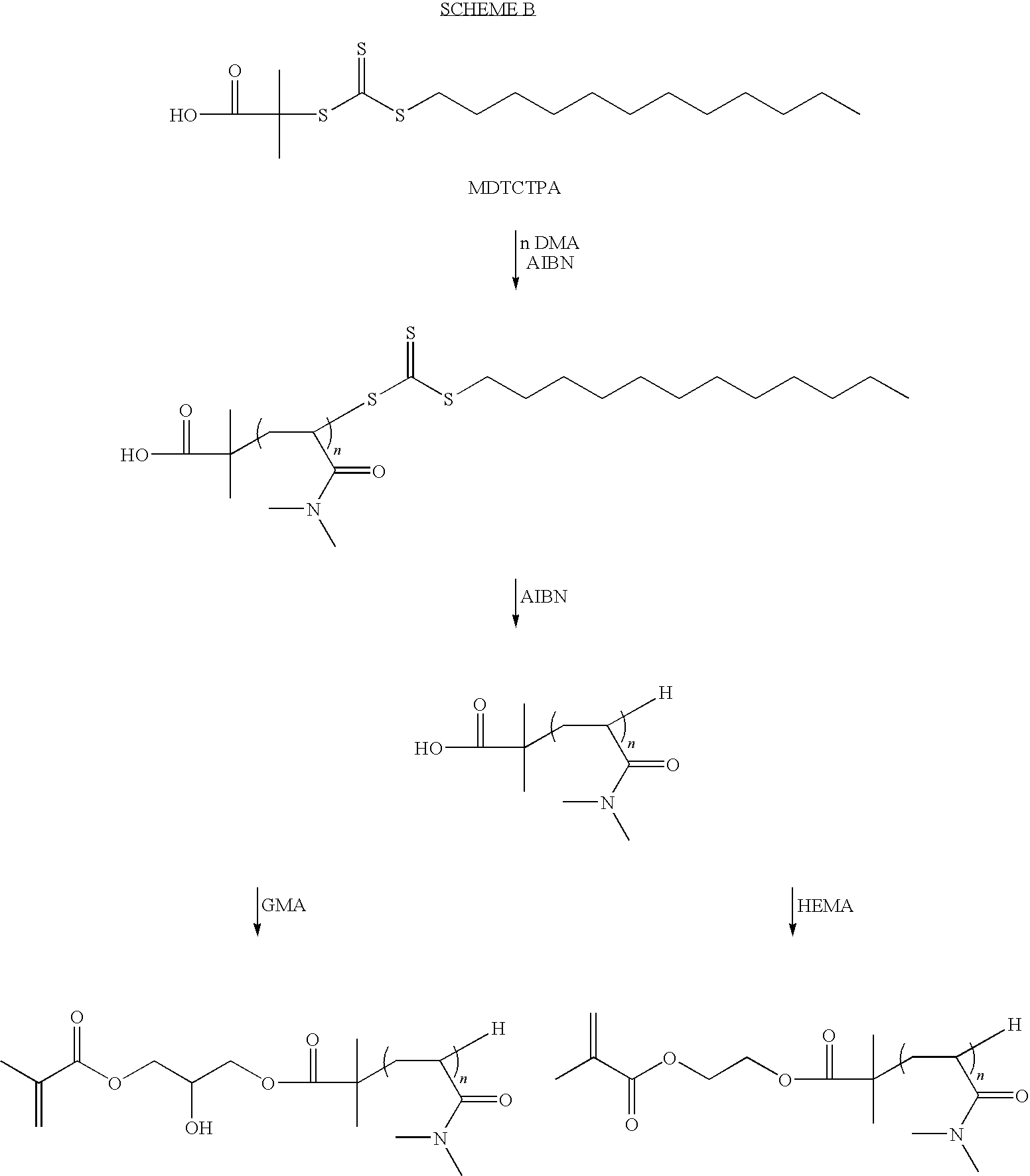
ActiveUS20100318185A1Prevent limit adsorptionMaintain clarityCatheterIntraocular lensThio-Device form
Biomedical devices such as contact lenses formed from a polymerization product of a mixture comprising (a) a multi-armed macromonomer comprising multiple side chains attached to a nucleus, wherein each side chain comprises a thio carbonyl thio fragment of the same or different reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (“RAFT”) agent; and (b) one or more biomedical device-forming monomers are disclosed.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Neutral Atmosphere and Sanitization Storage Apparatus, Method and System
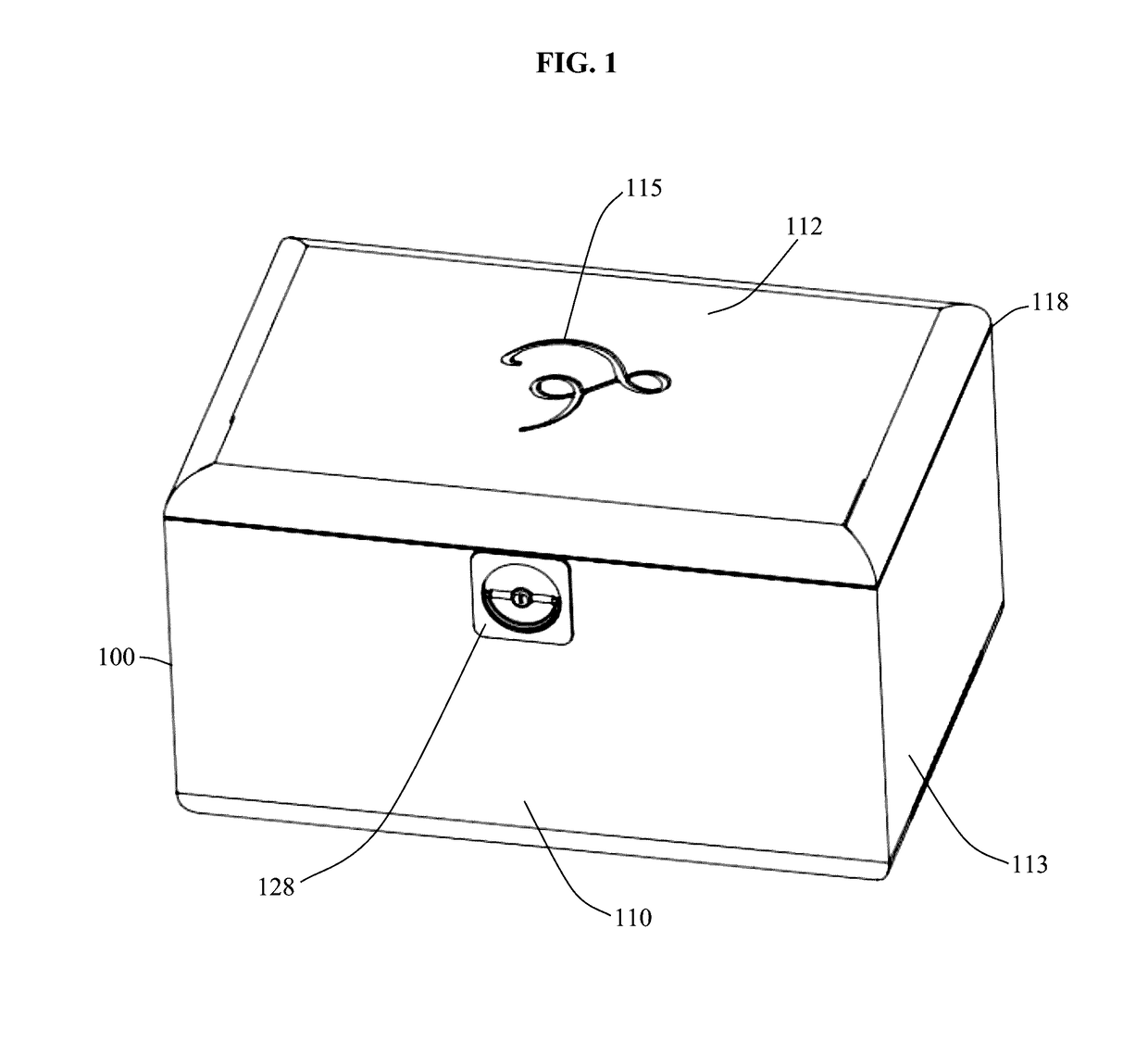
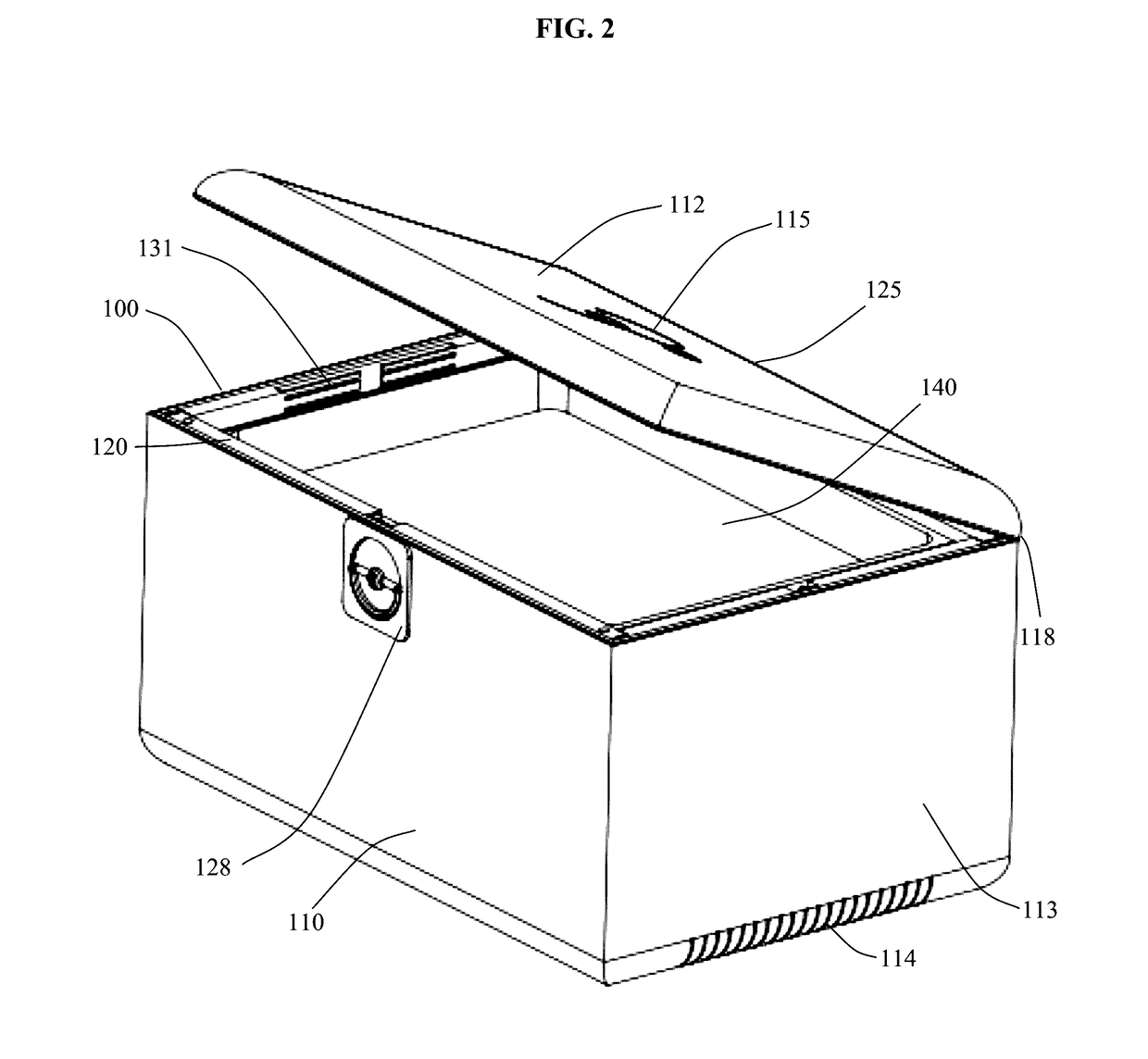
ActiveUS20170096279A1High saturationMaintain qualityLiving organism packagingNetwork topologiesWeb applicationNeutral atmosphere
Disclosed herein are an apparatus, method and system for storing perishable items that degrade in the presence of oxygen and / or humidity and that are frequently accessed by a consumer. The apparatus comprises an openable vessel, which becomes airtight when closed, and an UV light source and fan within the airtight enclosure, which converts ambient oxygen trapped within the airtight enclosure into ozone by circulating the enclosed volume of air around the UV light source after the vessel is opened and then closed. The apparatus is network connected to allow for remote control and monitoring and sends alerts to web applications or mobile applications when monitored parameters substantially vary from their settings.
Owner:CAMPALANS ALFONSO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com