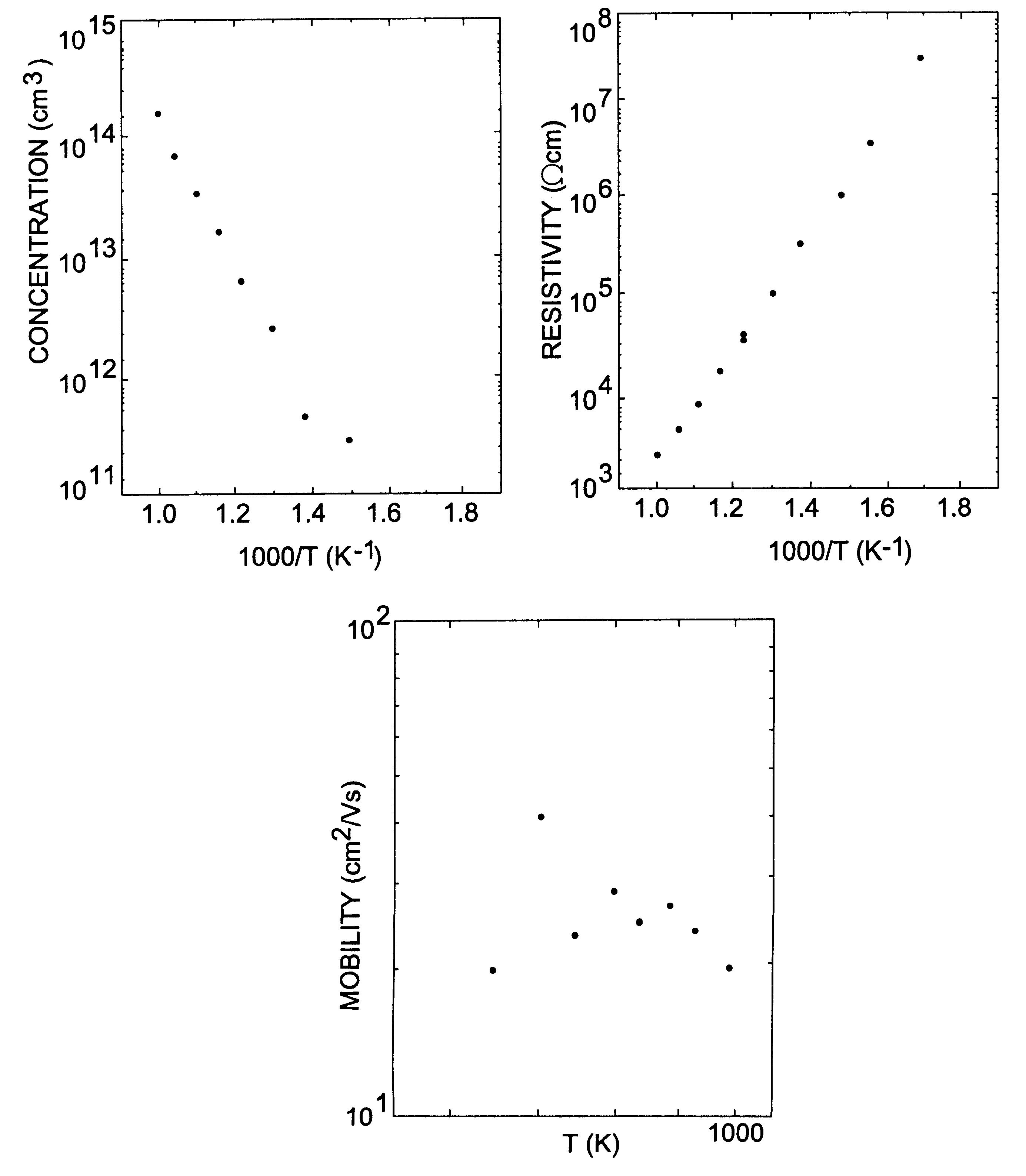
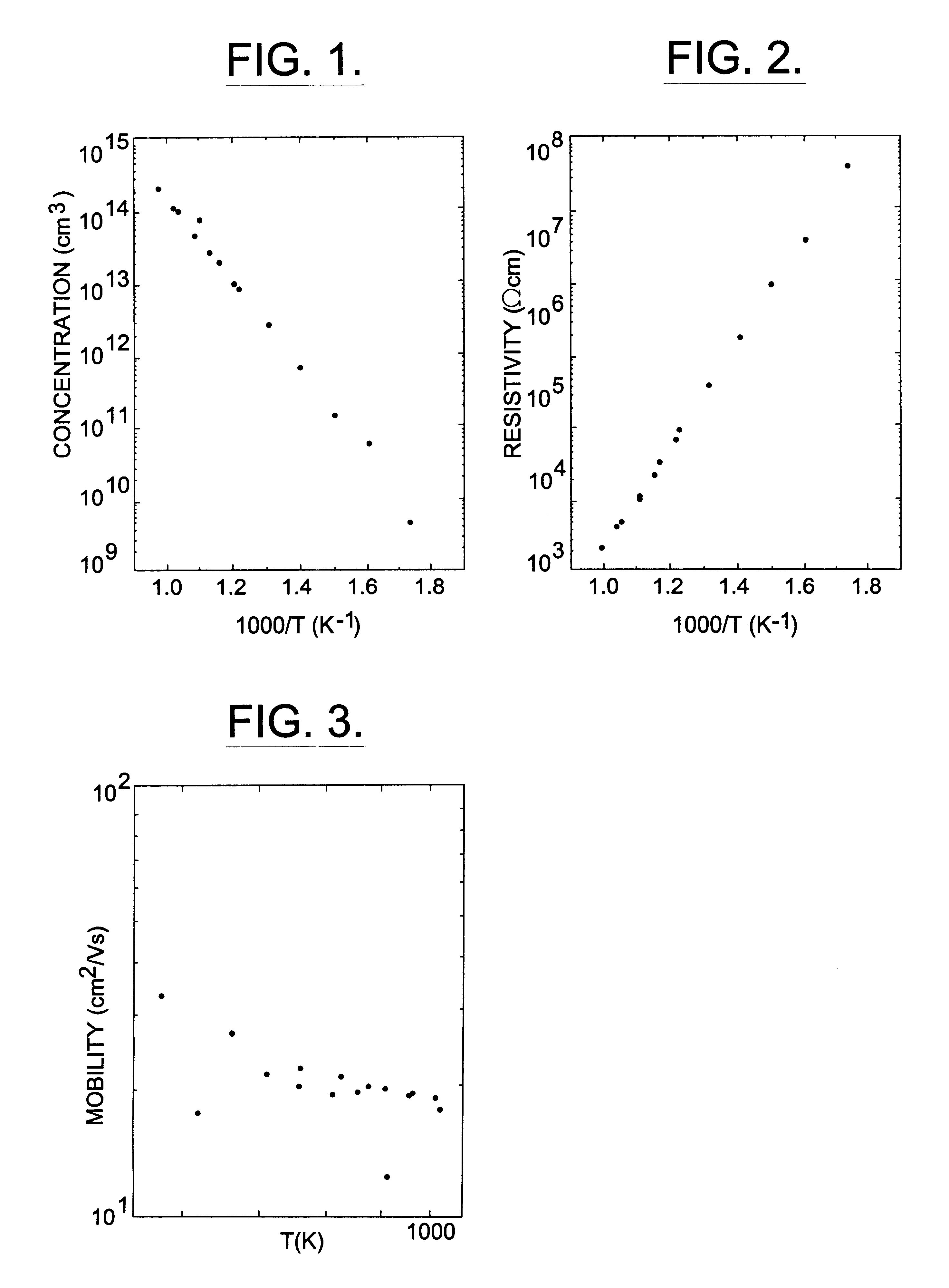
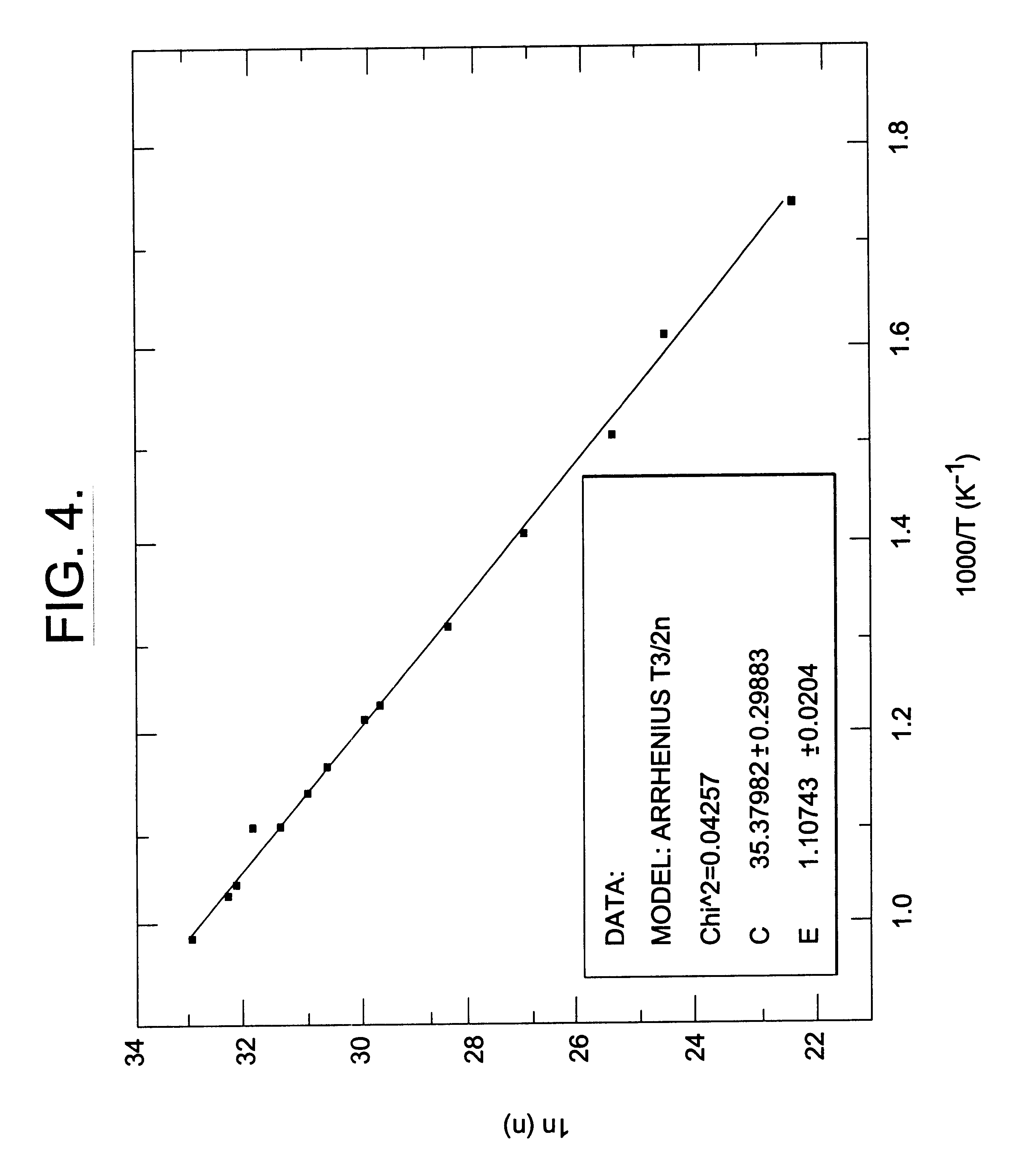
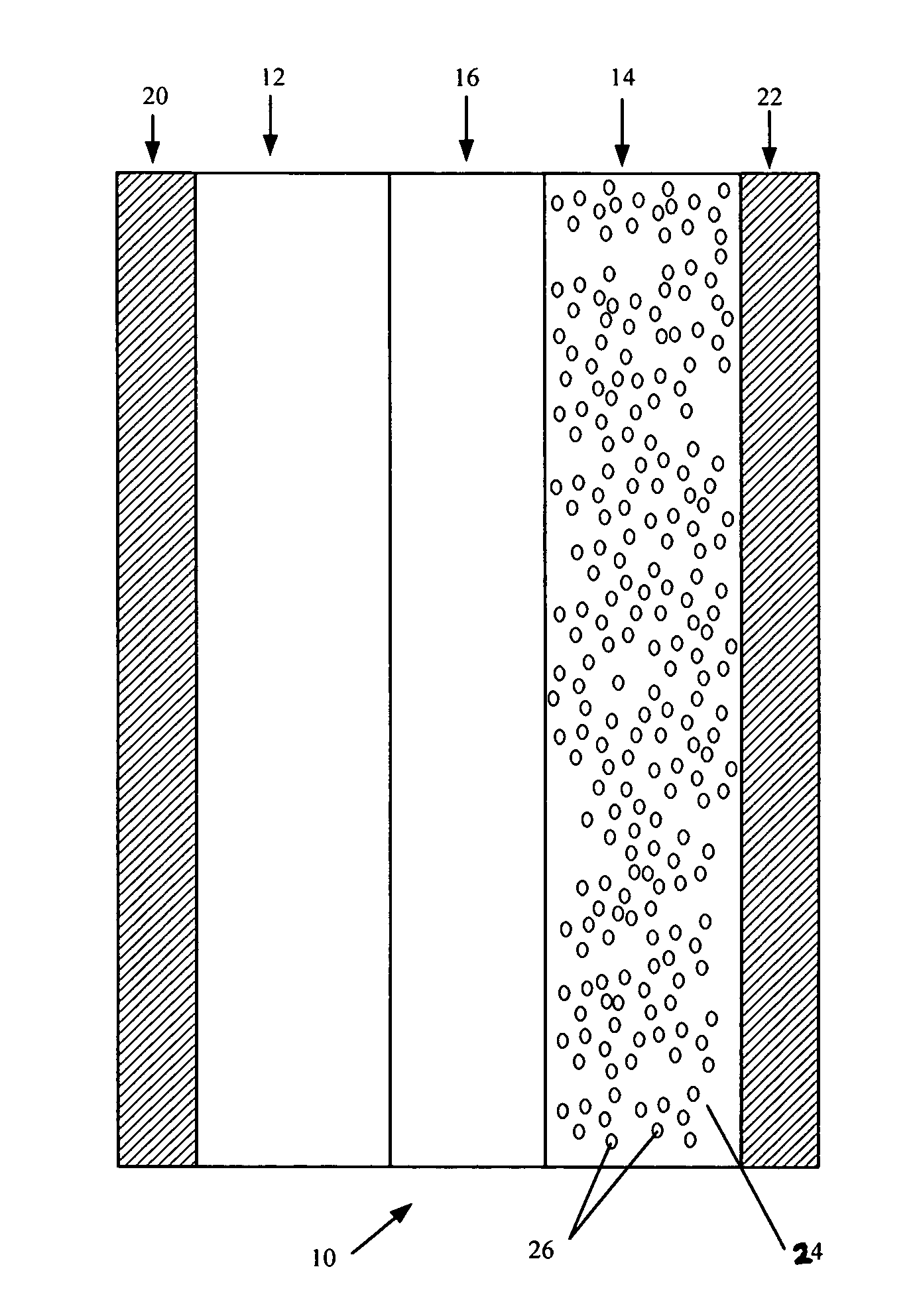
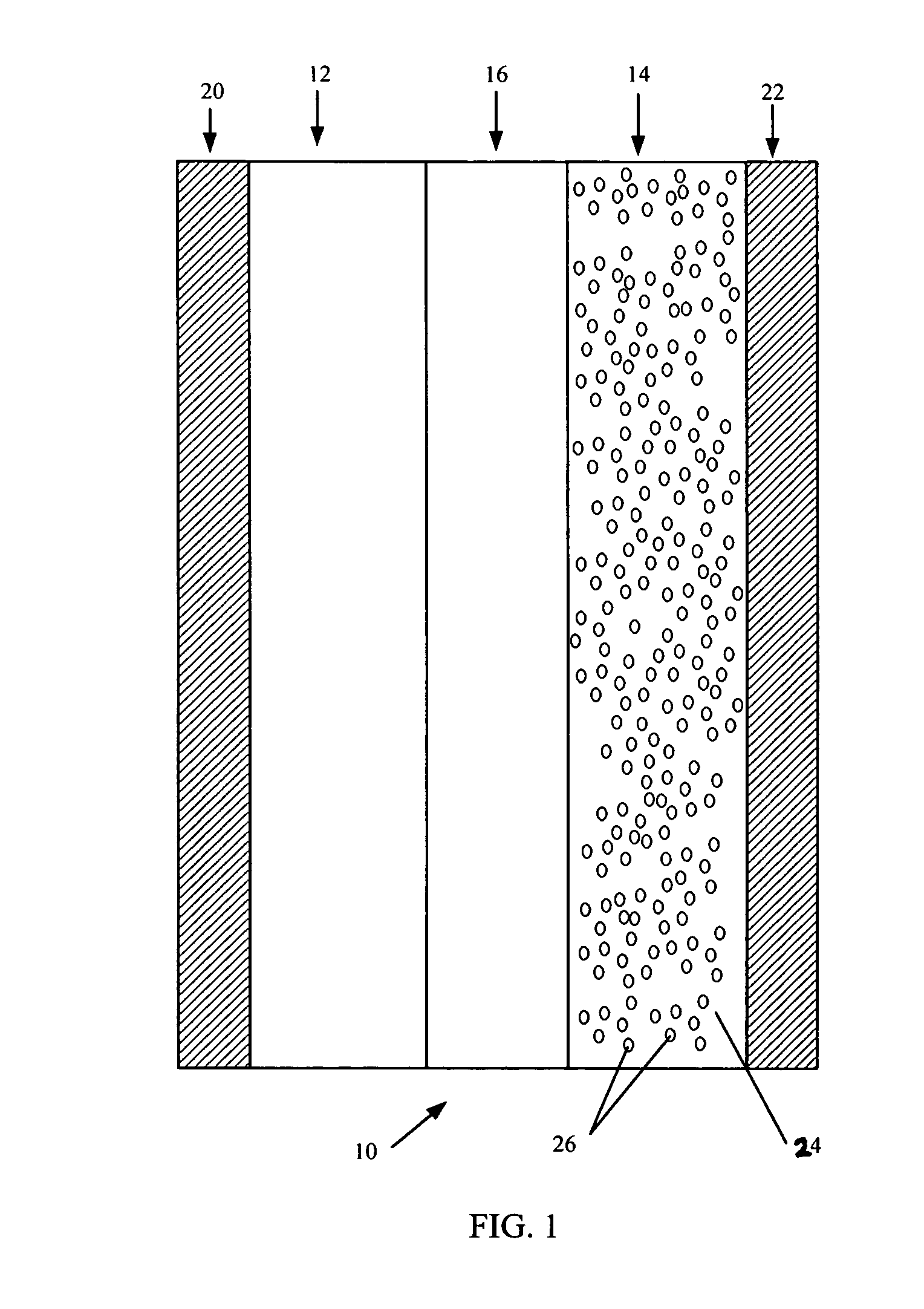
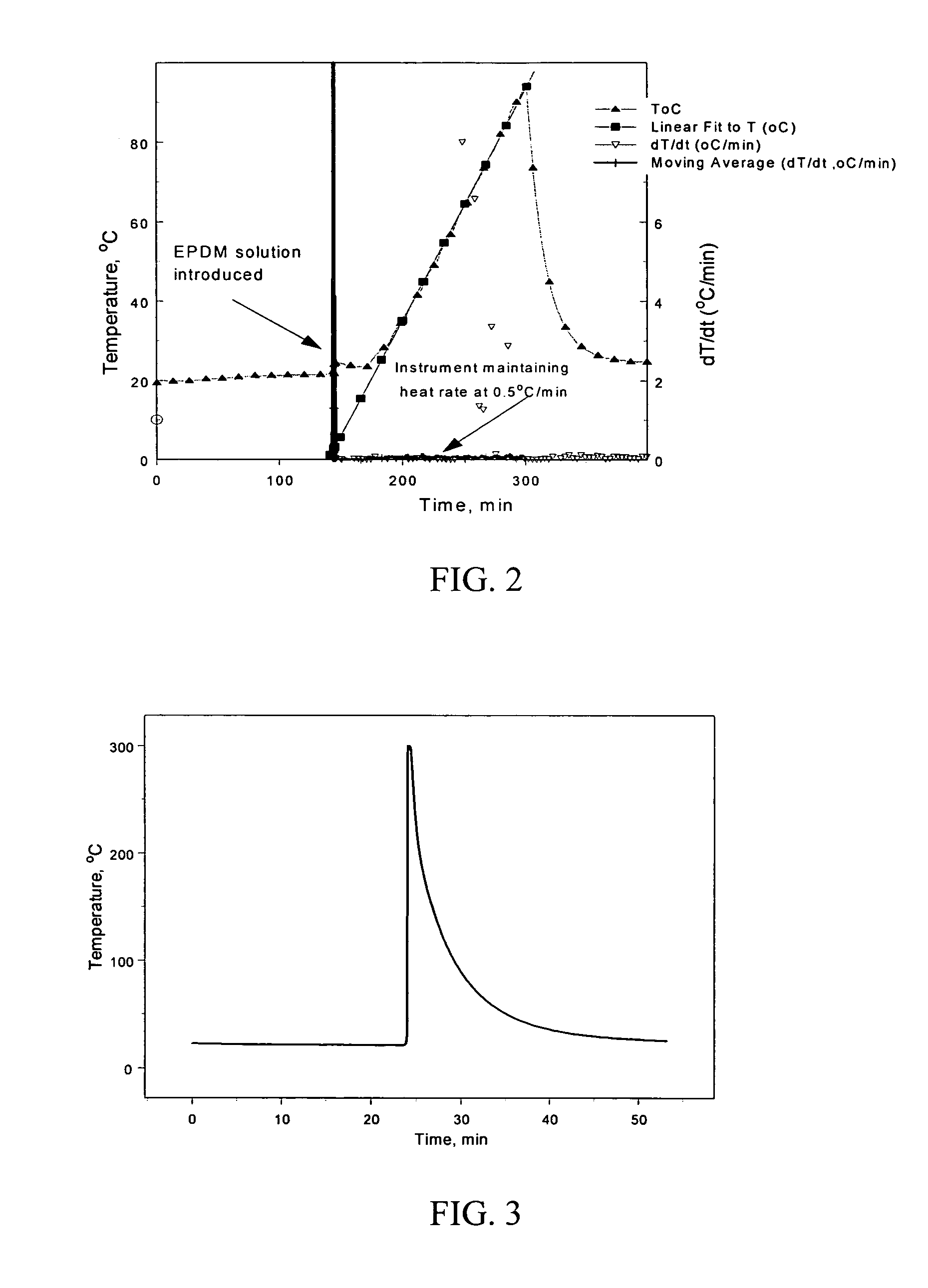
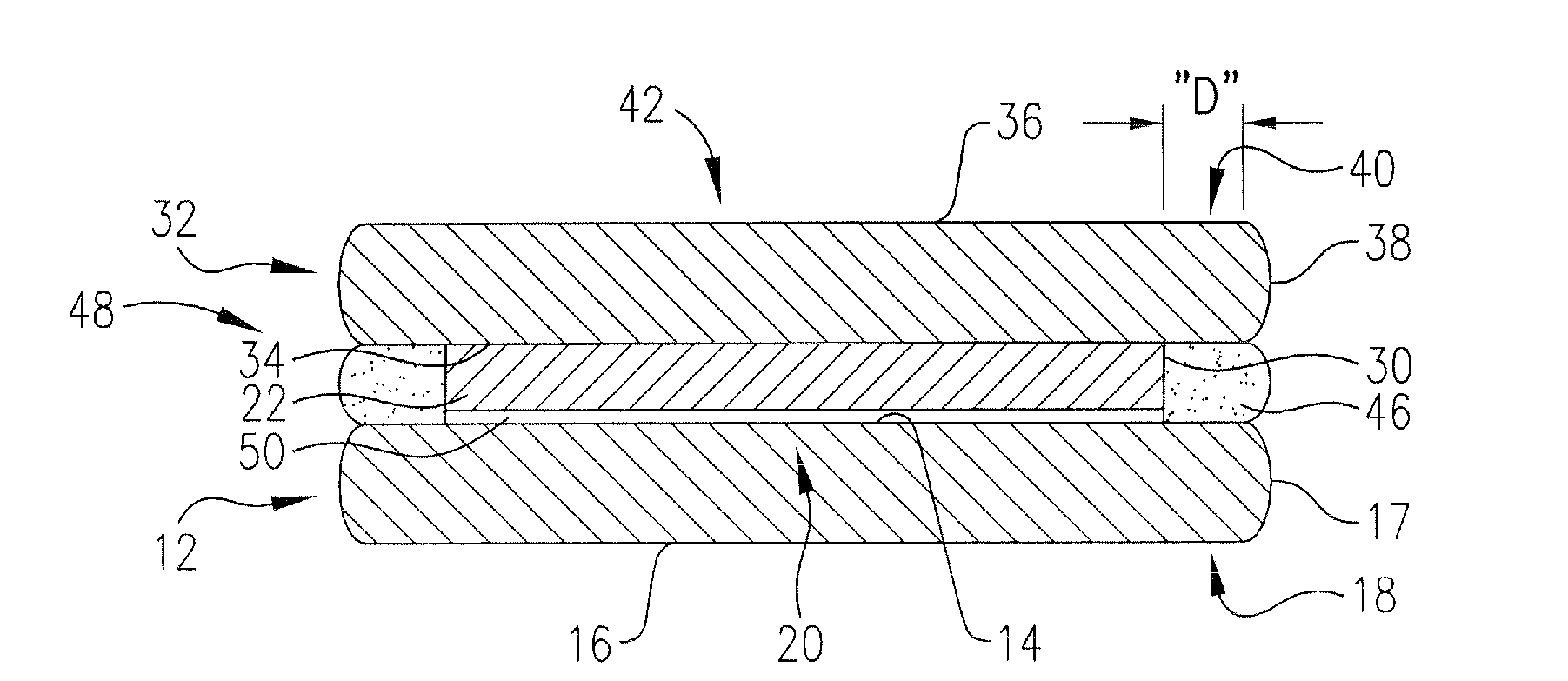
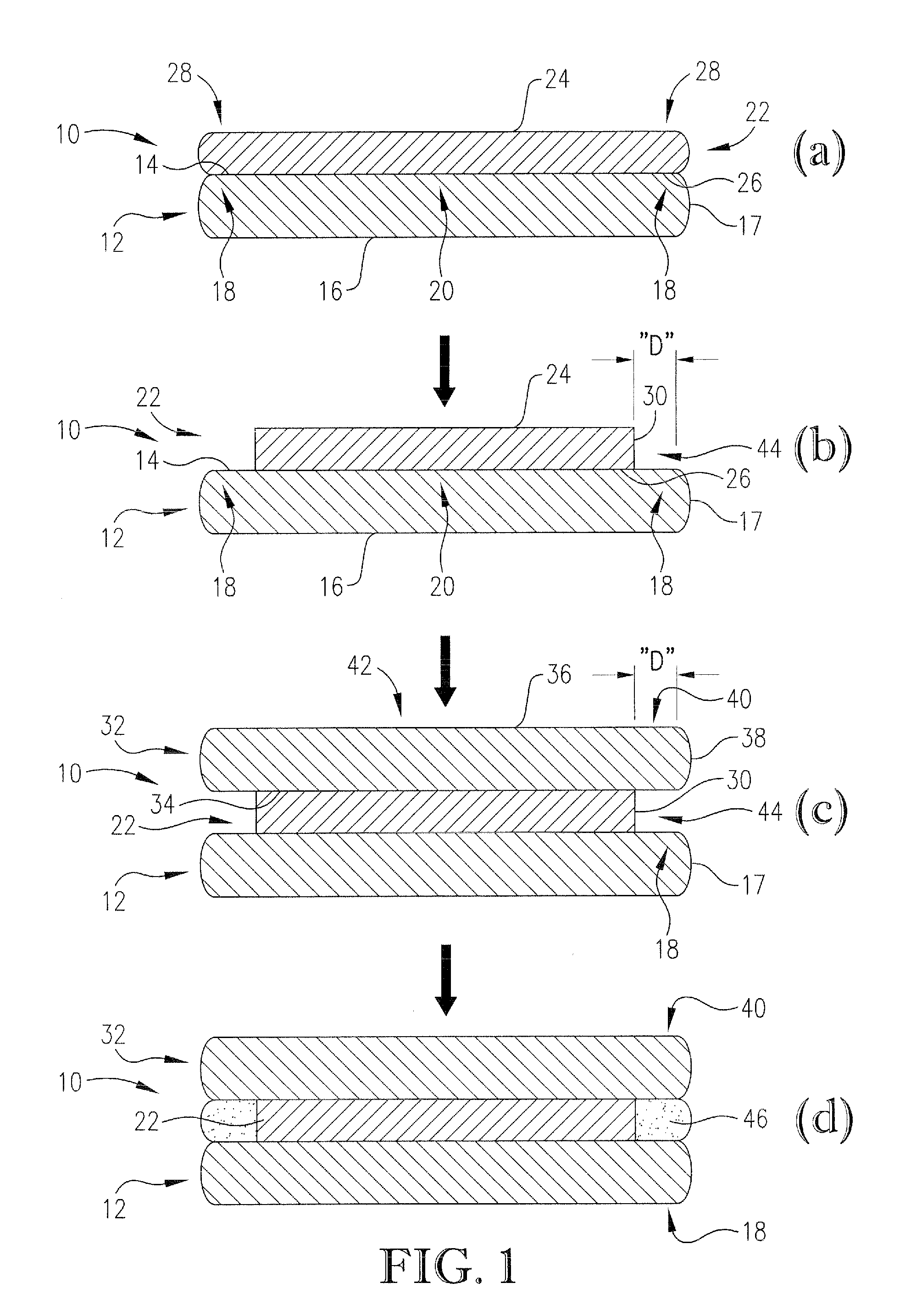
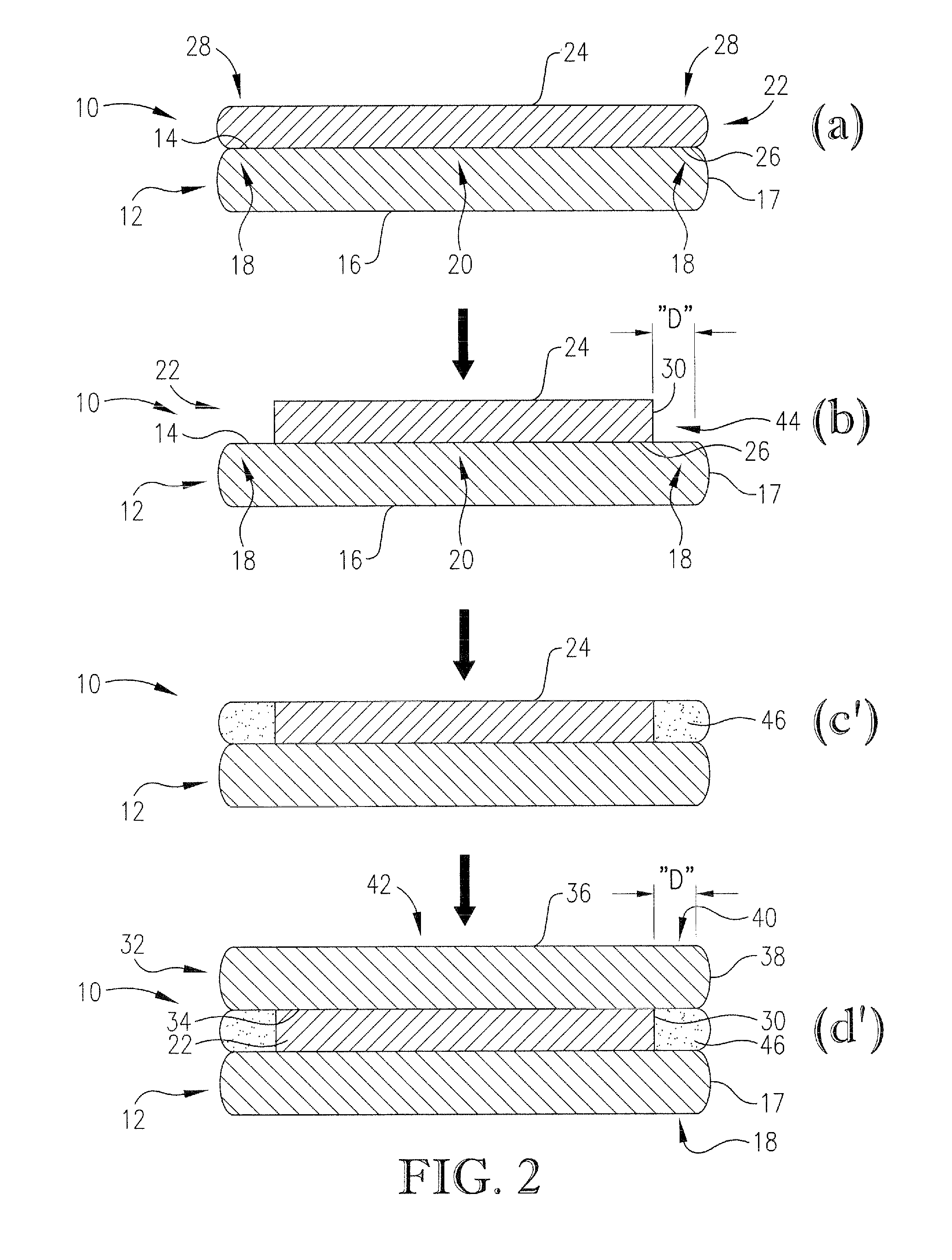
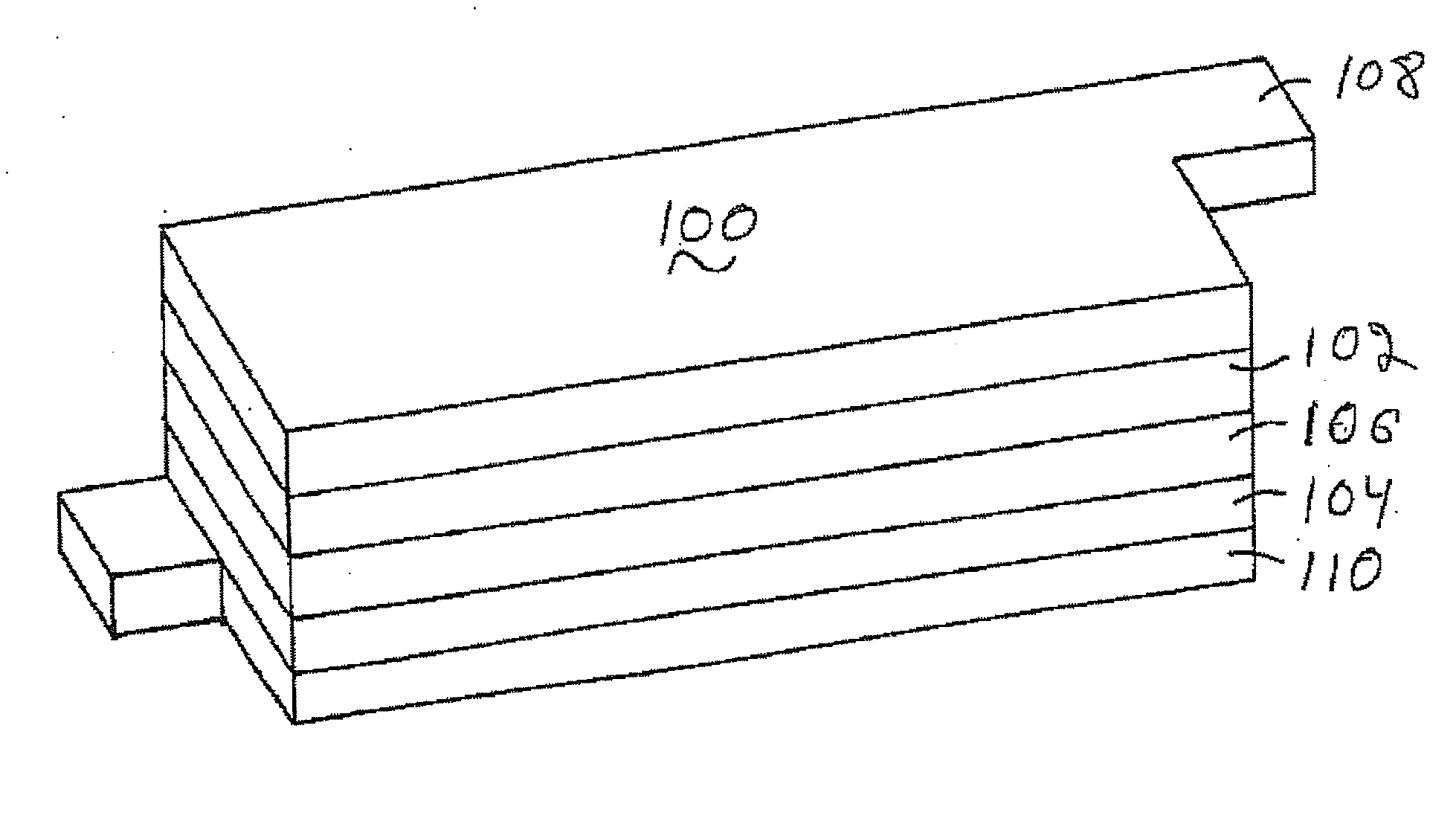
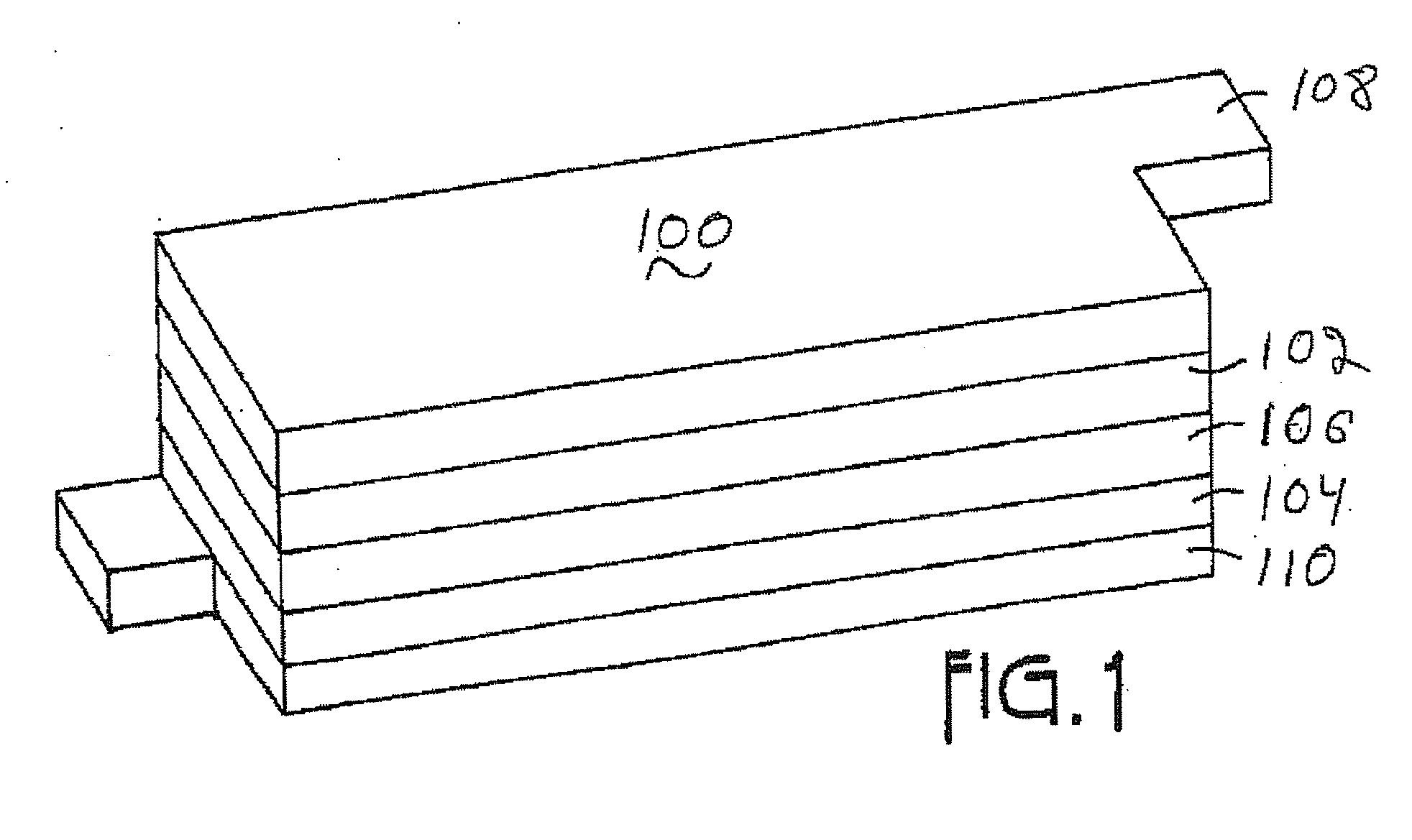
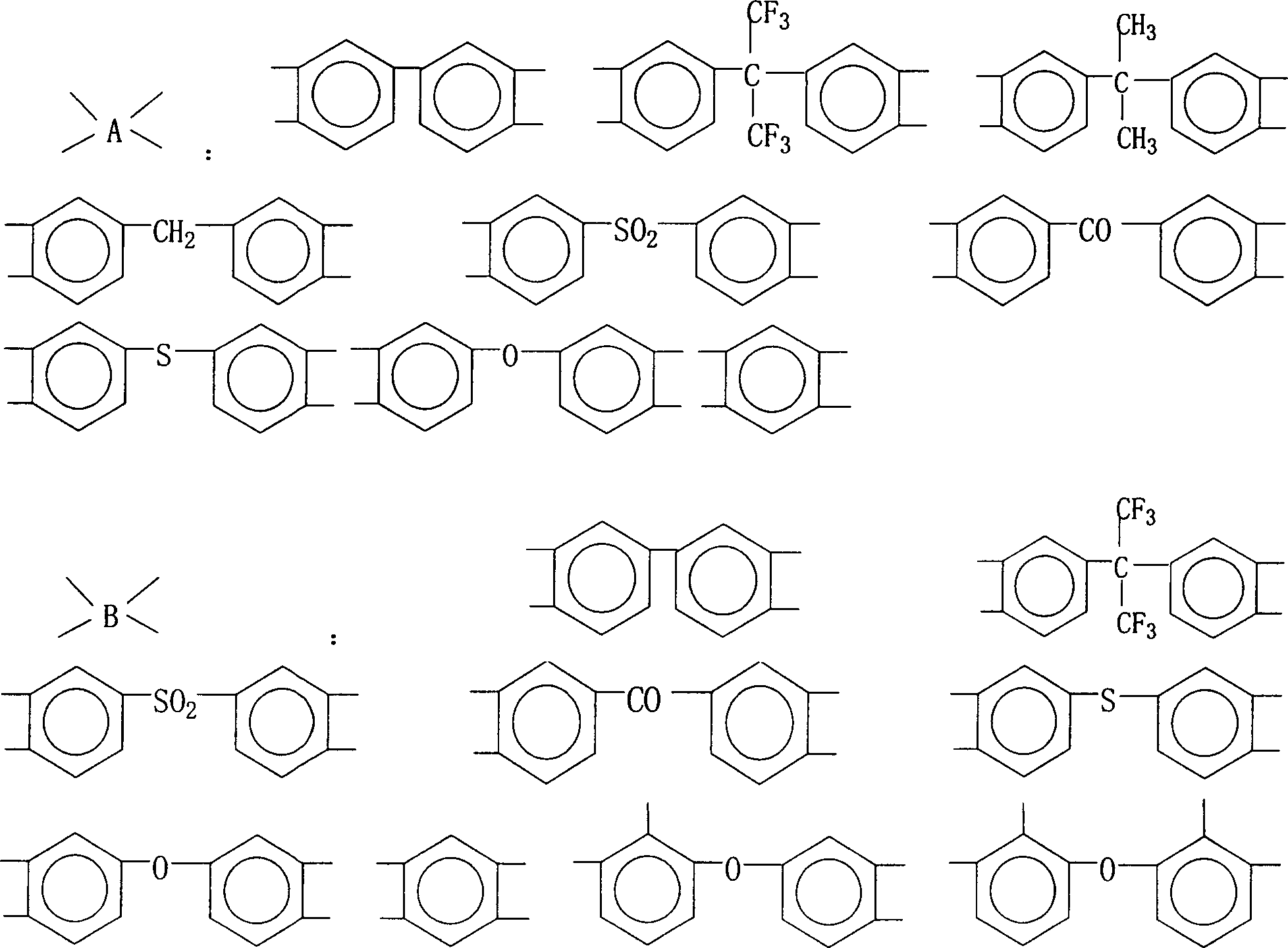Patents
Literature
83301 results about "Room temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Colloquially, room temperature is the range of air temperatures that most people prefer for indoor settings, which feel comfortable when wearing typical indoor clothing. Human comfort can extend beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation and other factors. In certain fields, like science and engineering, and within a particular context, room temperature can mean different agreed-on ranges. In contrast, ambient temperature is the actual temperature of the air (or other medium and surroundings) in any particular place, as measured by a thermometer. It may be very different from usual room temperature, for example an unheated room in winter.
Low voltage flexible organic/transparent transistor for selective gas sensing, photodetecting and CMOS device applications
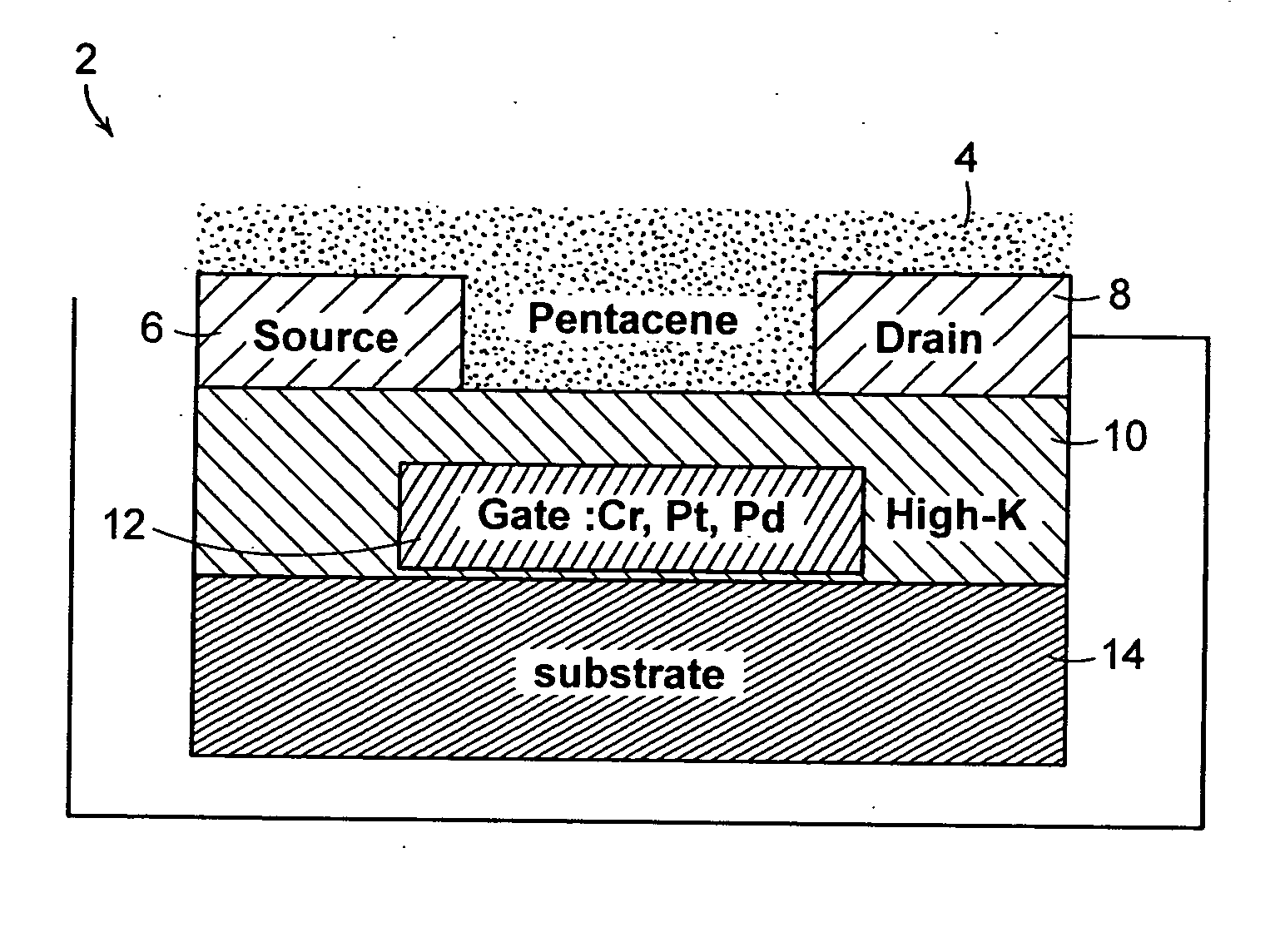
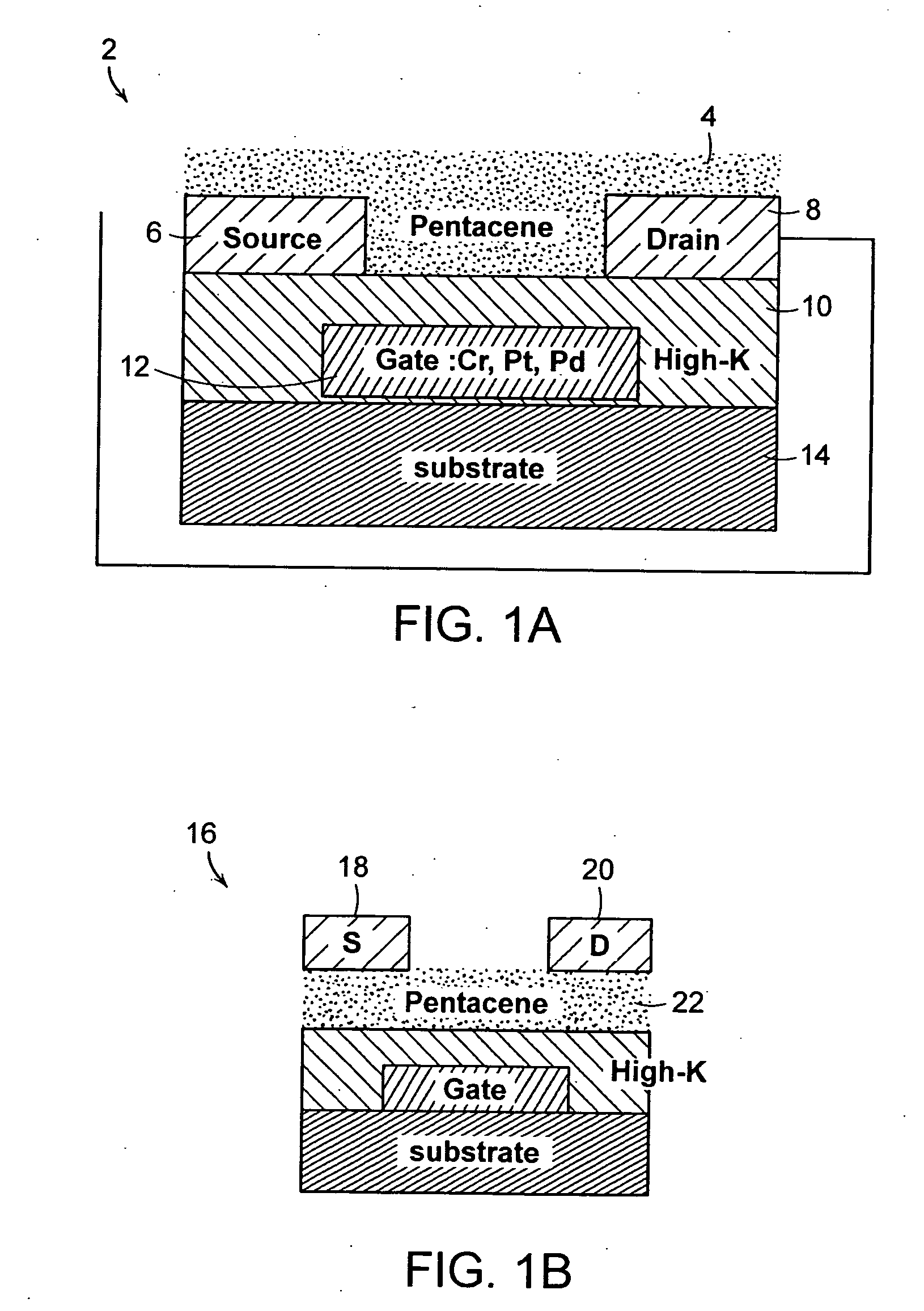
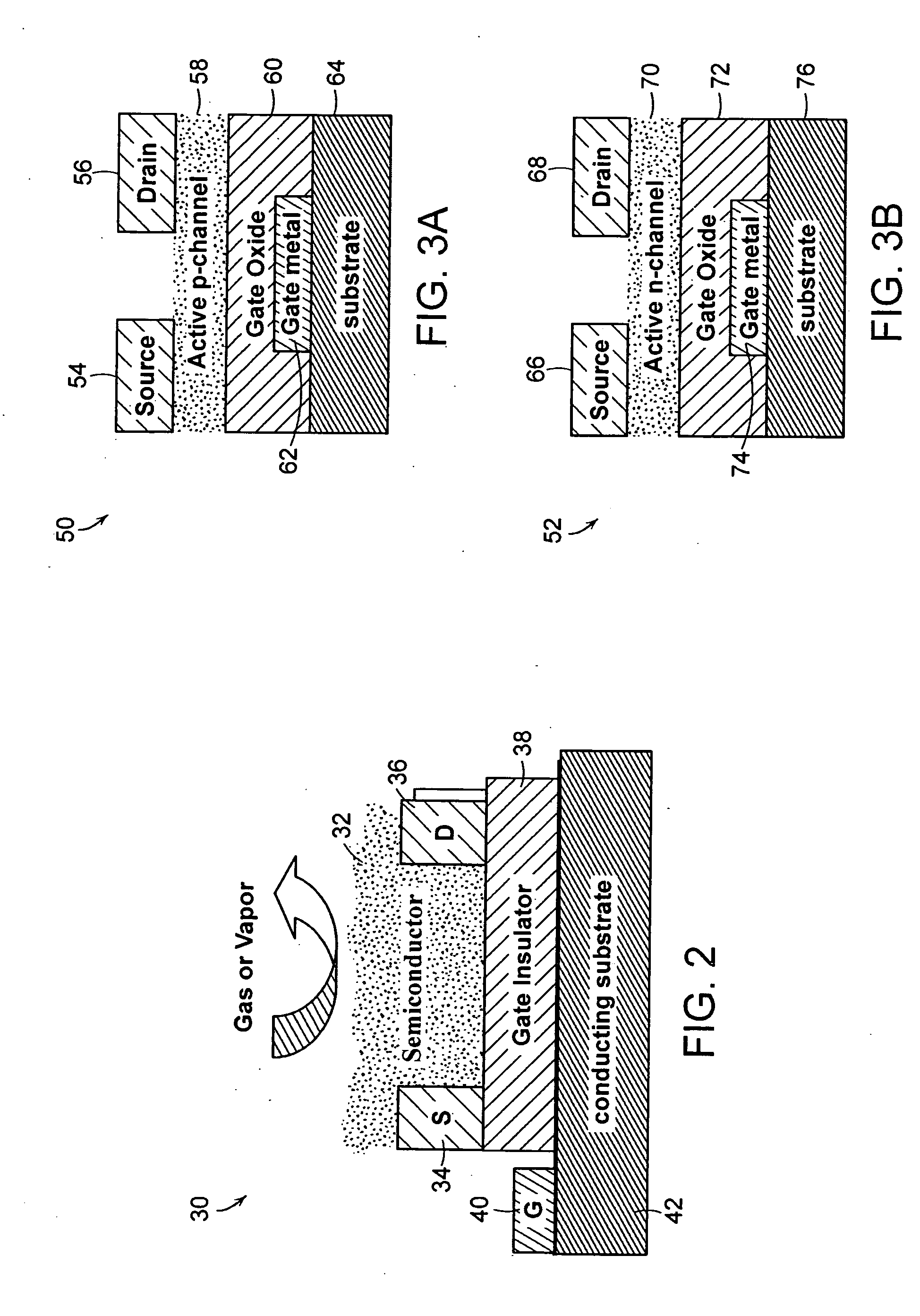
A thin film transistor (TFT) includes a source electrode, a drain electrode, and a gate electrode. A gate insulator is coupled to the source electrode, drain electrode, and gate electrode. The gate insulator includes room temperature deposited high-K materials so as to allow said thin film transistor to operate at low operating voltage.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for sterilizing medical appliance
InactiveCN1634601AAvoid influenceImprove sterilization effectDiagnosticsSurgeryVacuum pressureMicrowave
A medical instrument sterilization method is disclosed, which characterizes in following process: pending medical instrument for sterilization treatment being placed in a closed container, then being vacuum pumped, the vacuum pressure of the container being controlled between 1 Pa to 1500 Pa, air and / or oxygen and / or inert gases are charged to closed container and the vacuum pressure being between 1 Pa to 1500 Pa, microwave is fed, the favorable power of which should make the gas charged into the container to generate ionization, the microwave be cut after the sterilization, then air being charged to release vacuum to finish the whole process.
Owner:吉林省中立实业有限公司
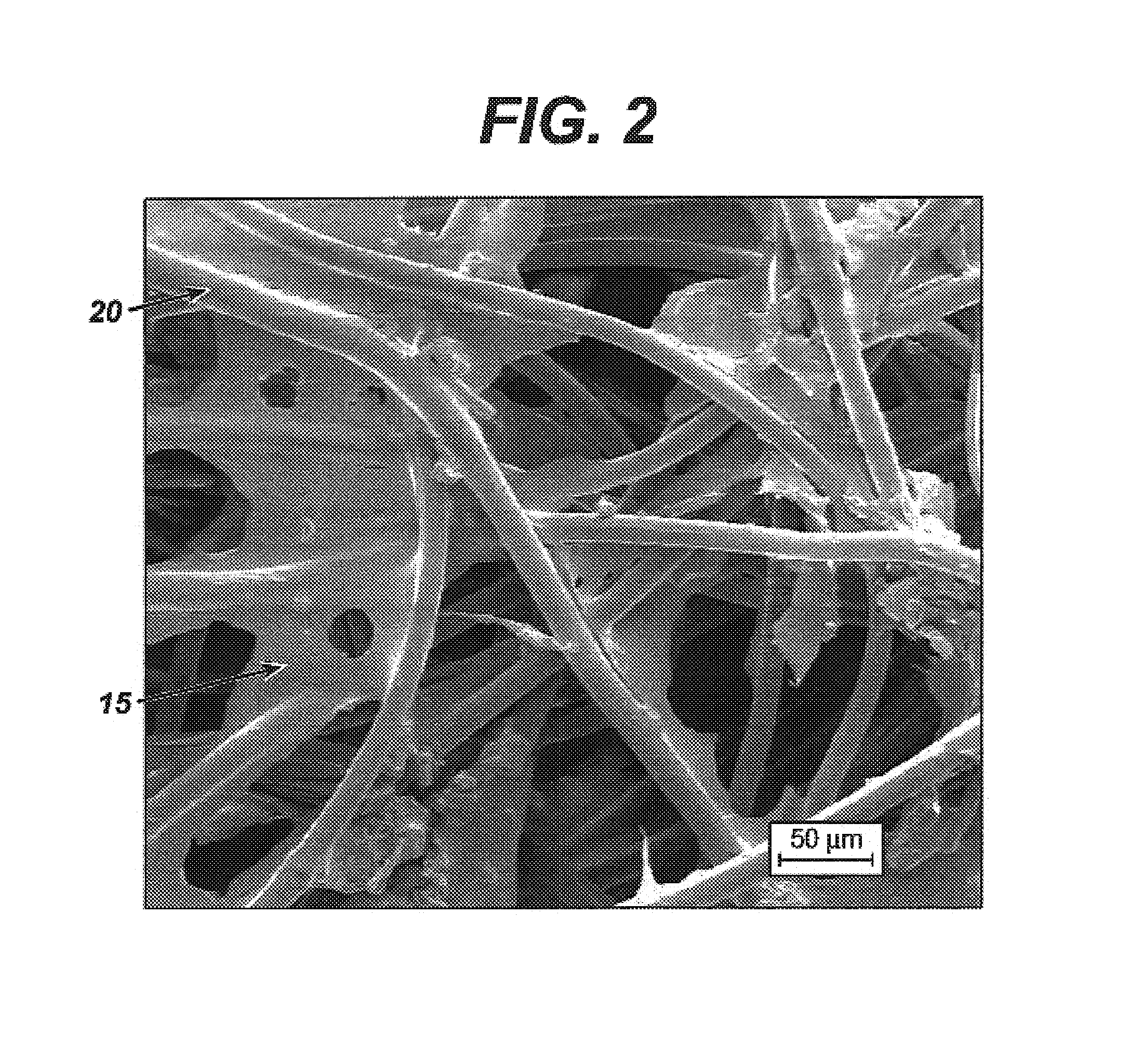
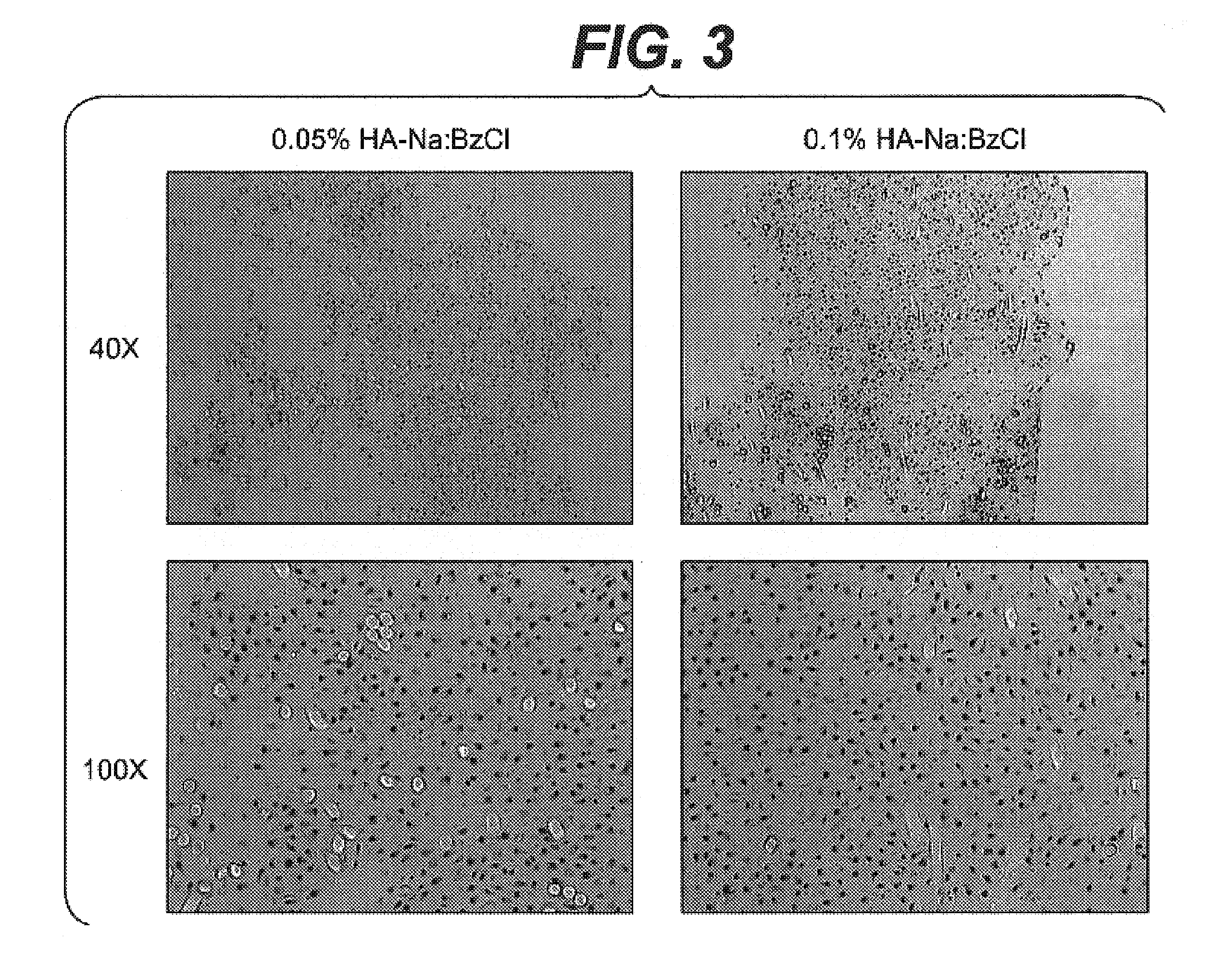
Modified hyaluronic acid for use in musculoskeletal tissue repair
The present invention includes hyaluronic acid complexes of a monovalent alkali metal salt of hyaluronic acid and a tetra alkyl ammonium halide that are suitable for incorporation with tissue scaffolds that are suitable for use in repair and / or regeneration of muscoloskeletal tissue and that include a biodegradable, porous substrate made from a biodegradable, hydrophobic polymer, where the hyaluronic acid complex is substantially insoluble in water at room temperature, yet soluble in mixtures of organic and aqueous solvents in which the selected hydrophobic polymer is soluble.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Optical fiber with quantum dots
Holey optical fibers (e.g. photonic fibers, random-hole fibers) are fabricated with quantum dots disposed in the holes. The quantum dots can provide light amplification and sensing functions, for example. When used for sensing, the dots will experience altered optical properties (e.g. altered fluorescence or absorption wavelength) in response to certain chemicals, biological elements, radiation, high energy particles, electrical or magnetic fields, or thermal / mechanical deformations. Since the dots are disposed in the holes, the dots interact with the evanescent field of core-confined light. Quantum dots can be damaged by high heat, and so typically cannot be embedded within conventional silica optical fibers. In the present invention, dots can be carried into the holes by a solvent at room temperature. The present invention also includes solid glass fibers made of low melting point materials (e.g. phosphate glass, lead oxide glass) with embedded quantum dots.
Owner:LAMBDA LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS +1
Semi-insulating silicon carbide without vanadium domination
InactiveUS6218680B1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease the number ofPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsDevice formTrapping
Owner:CREE INC
Precursors for CVD silicon carbo-nitride films
ActiveUS20060258173A1Easy to movePromote formationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesRoom temperature
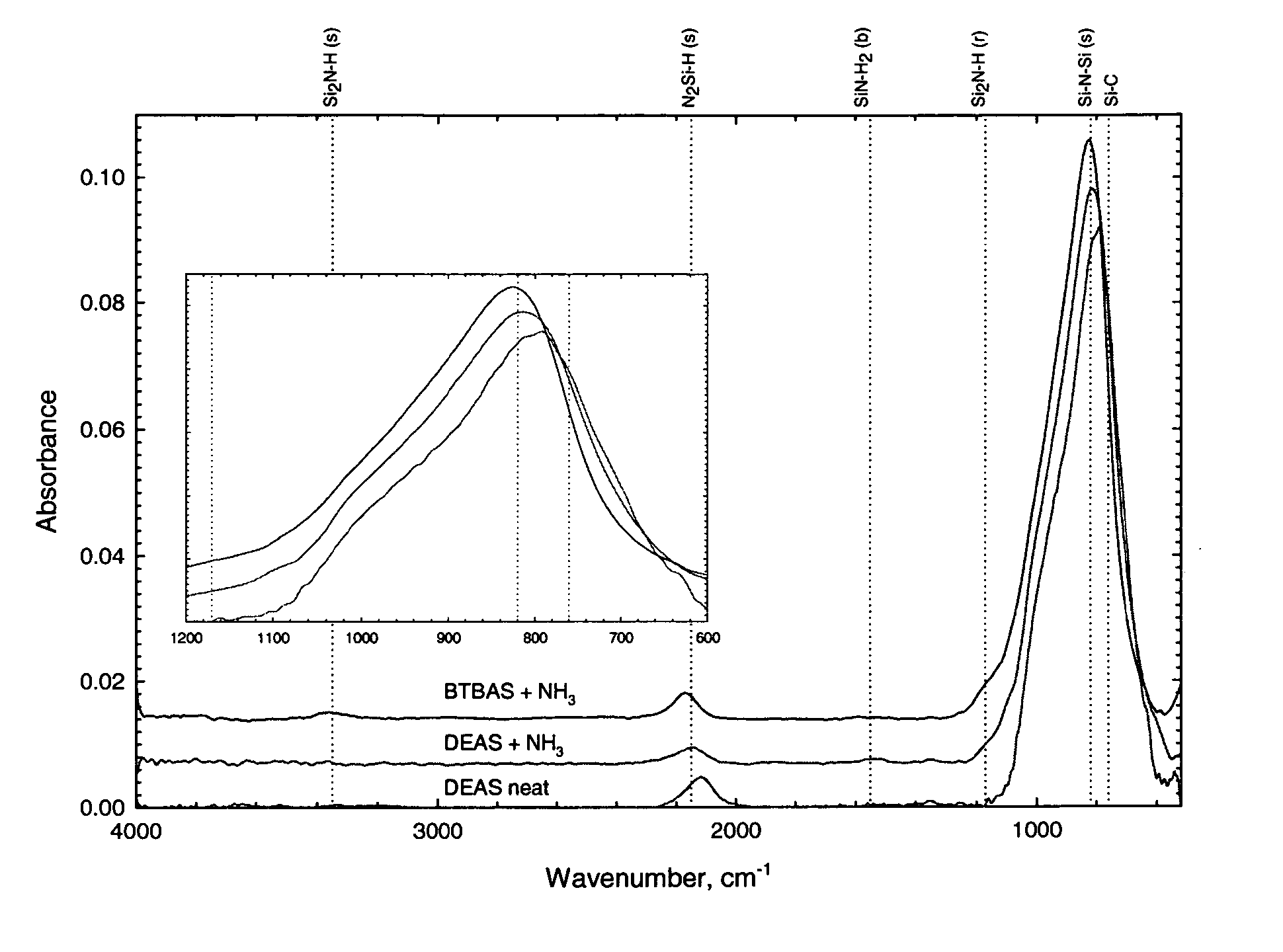
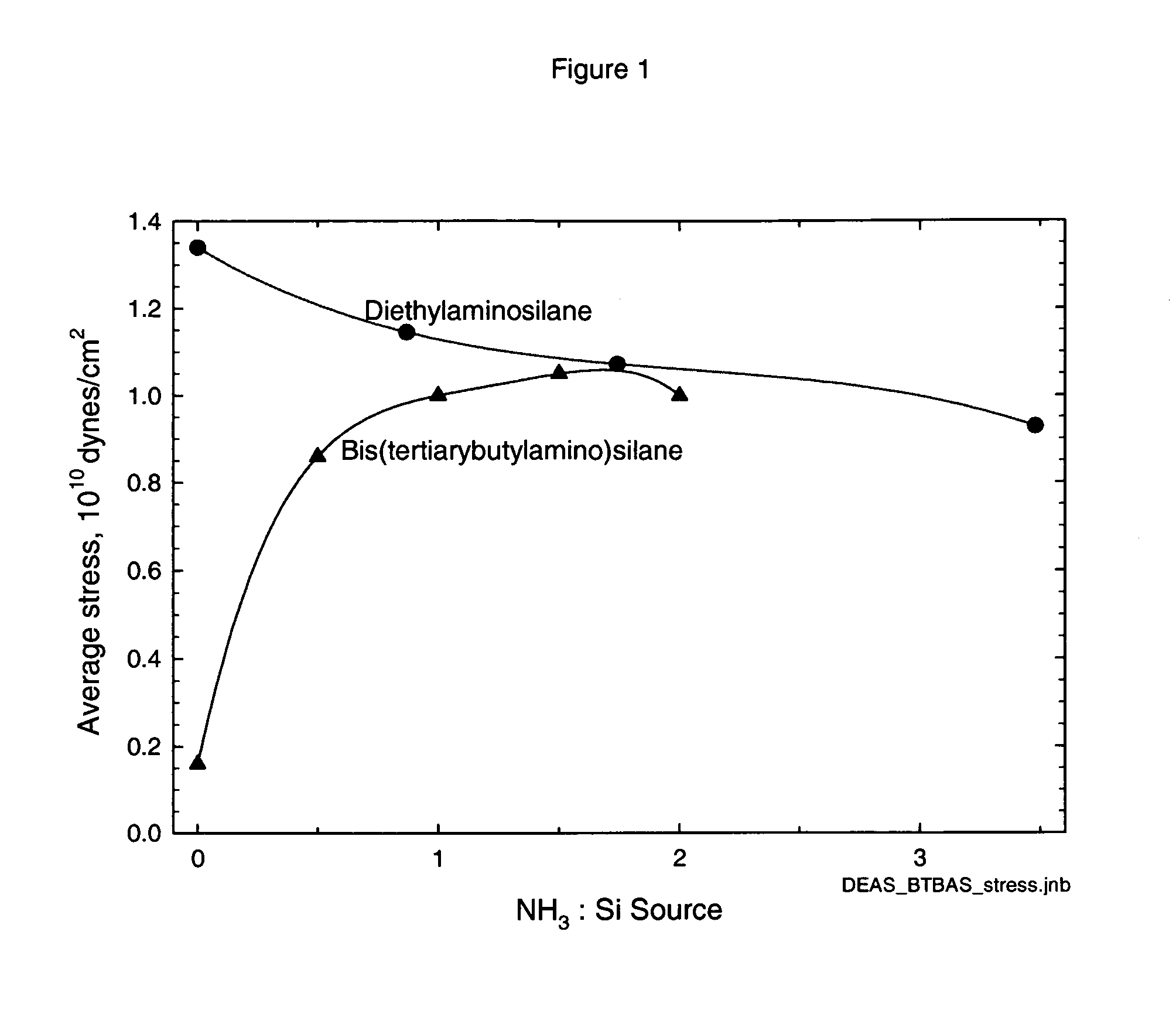
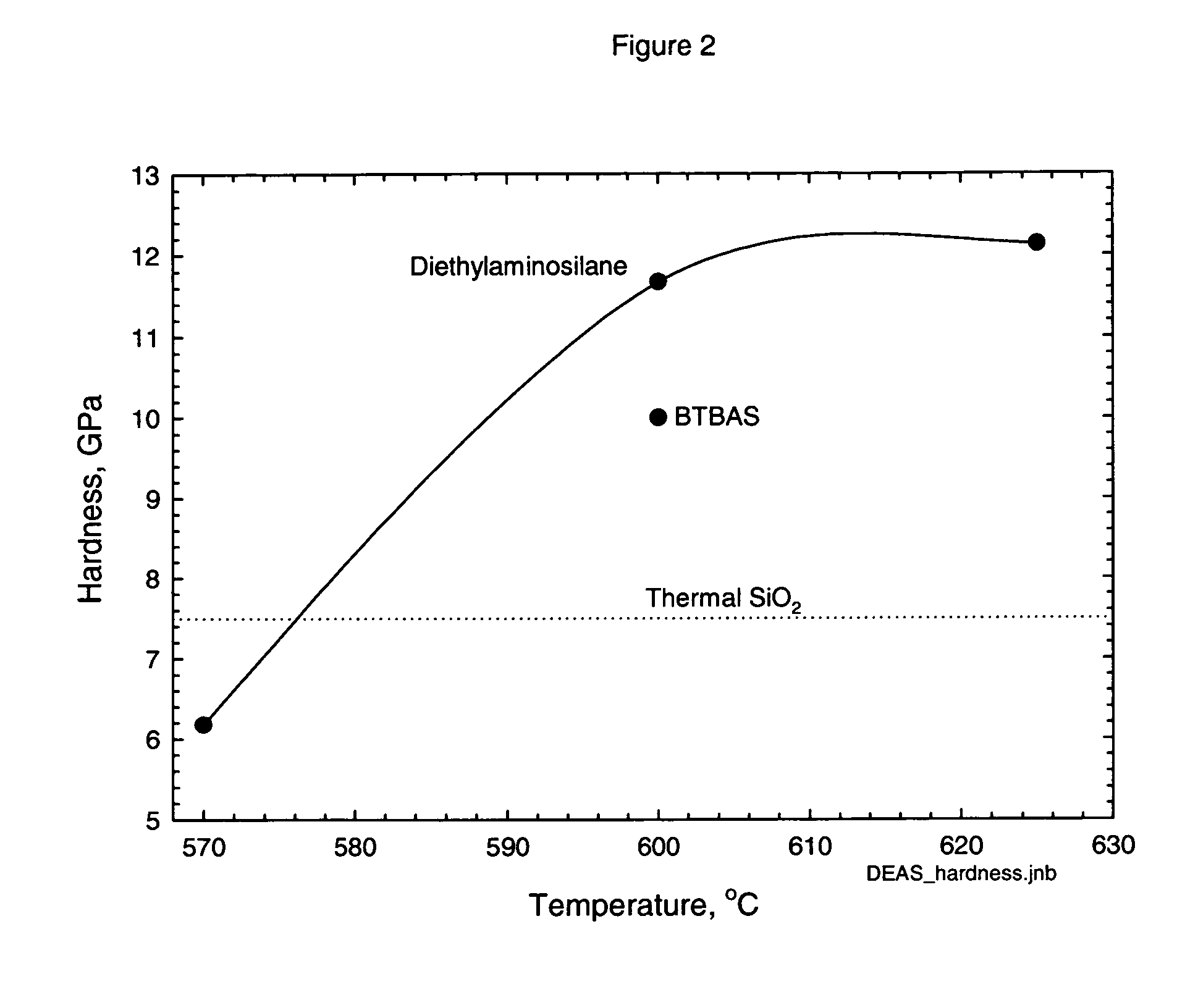
Classes of liquid aminosilanes have been found which allow for the production of silicon carbo-nitride films of the general formula SixCyNz. These aminosilanes, in contrast, to some of the precursors employed heretofore, are liquid at room temperature and pressure allowing for convenient handling. In addition, the invention relates to a process for producing such films. The classes of compounds are generally represented by the formulas: and mixtures thereof, wherein R and R1 in the formulas represent aliphatic groups typically having from 2 to about 10 carbon atoms, e.g., alkyl, cycloalkyl with R and R1 in formula A also being combinable into a cyclic group, and R2 representing a single bond, (CH2)n, a ring, or SiH2.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Non-uniformly-rigid barrier wall spacers used to correct problems caused by thermal contraction of smectic liquid crystal material
InactiveUS6337730B1Relieve stressRelieve pressureLiquid crystal compositionsStatic indicating devicesRoom temperatureEngineering
According to this liquid crystal cell, a vacuum to be established between two electrode substrates as a result of the volume shrinkage of a liquid crystal having a high viscosity at the room temperature can be damped by communicating between two of a plurality of filling portions formed between two electrode substrates by a plurality of barrier walls through the intervening barrier walls. An anti-ferroelectric liquid crystal (AFLC) is used as the liquid crystal. The liquid crystal cell has a lower electrode substrate and an upper electrode substrate, between which a smectic liquid crystal is disposed together with a plurality of barrier walls on the inner side of a band seal. Each barrier wall has through holes to communicate between the two filling portions located on the two sides of the barrier walls.
Owner:DENSO CORP
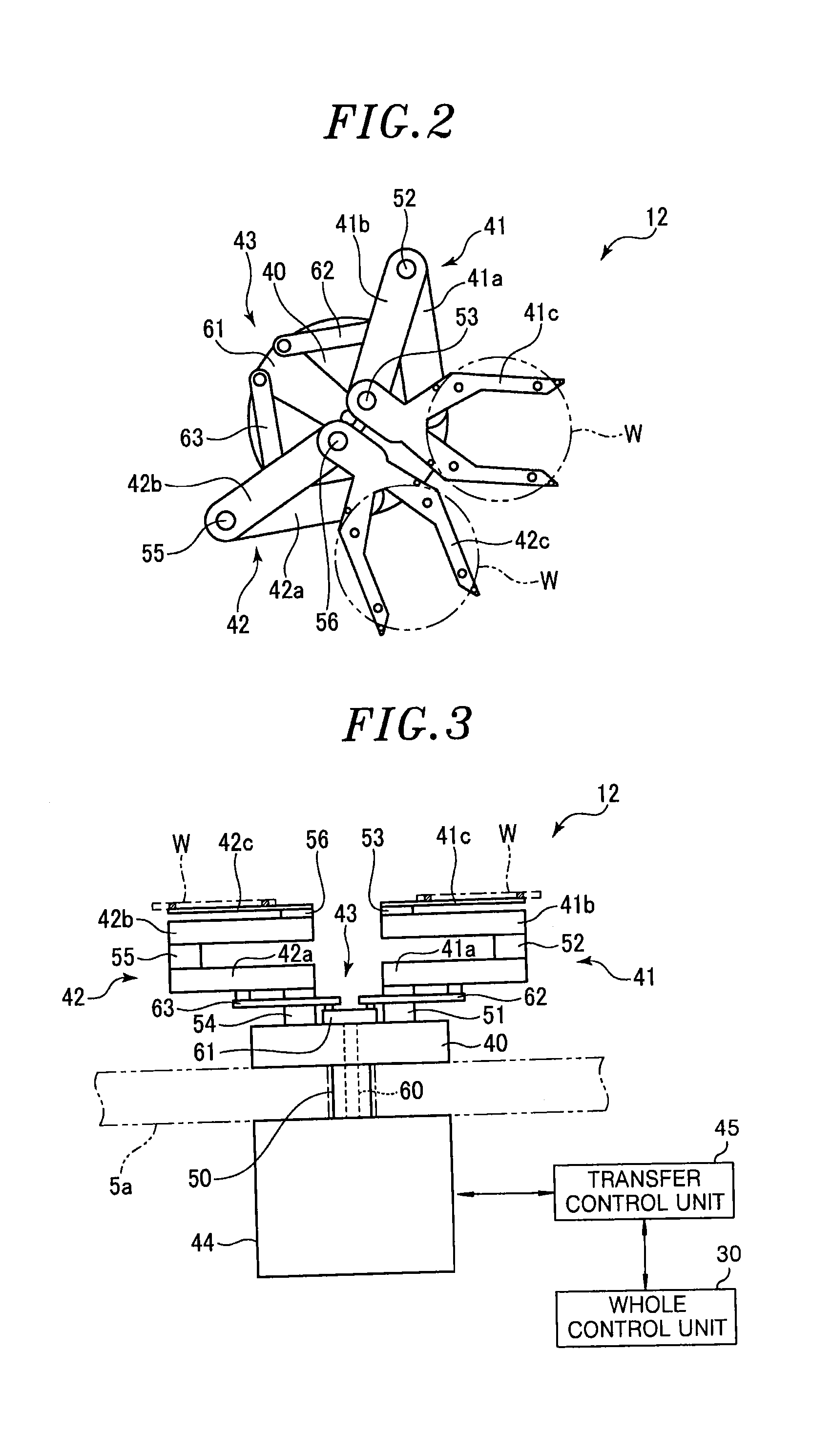
Substrate transfer device and substrate processing system
InactiveUS20130180448A1Suppress position deviationHigh positioning accuracyLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRoom temperatureProcessing element
A substrate transfer device includes a pick which has positioning pins to position a substrate and holds a positioned substrate; a drive unit which drives the pick such that the substrate is loaded / unloaded to / from a vacuum processing unit by using a pick; and a transfer control unit which controls a transfer operation of the substrate using the pick. The transfer control unit obtains in advance information on a reference position of the substrate at room temperature when the substrate is loaded into the vacuum processing unit, calculates a positional deviation from the reference position of the substrate when the substrate is loaded into the vacuum processing unit in actual processing, and controls a drive unit such that the substrate is loaded into the vacuum processing unit by correcting the positional deviation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
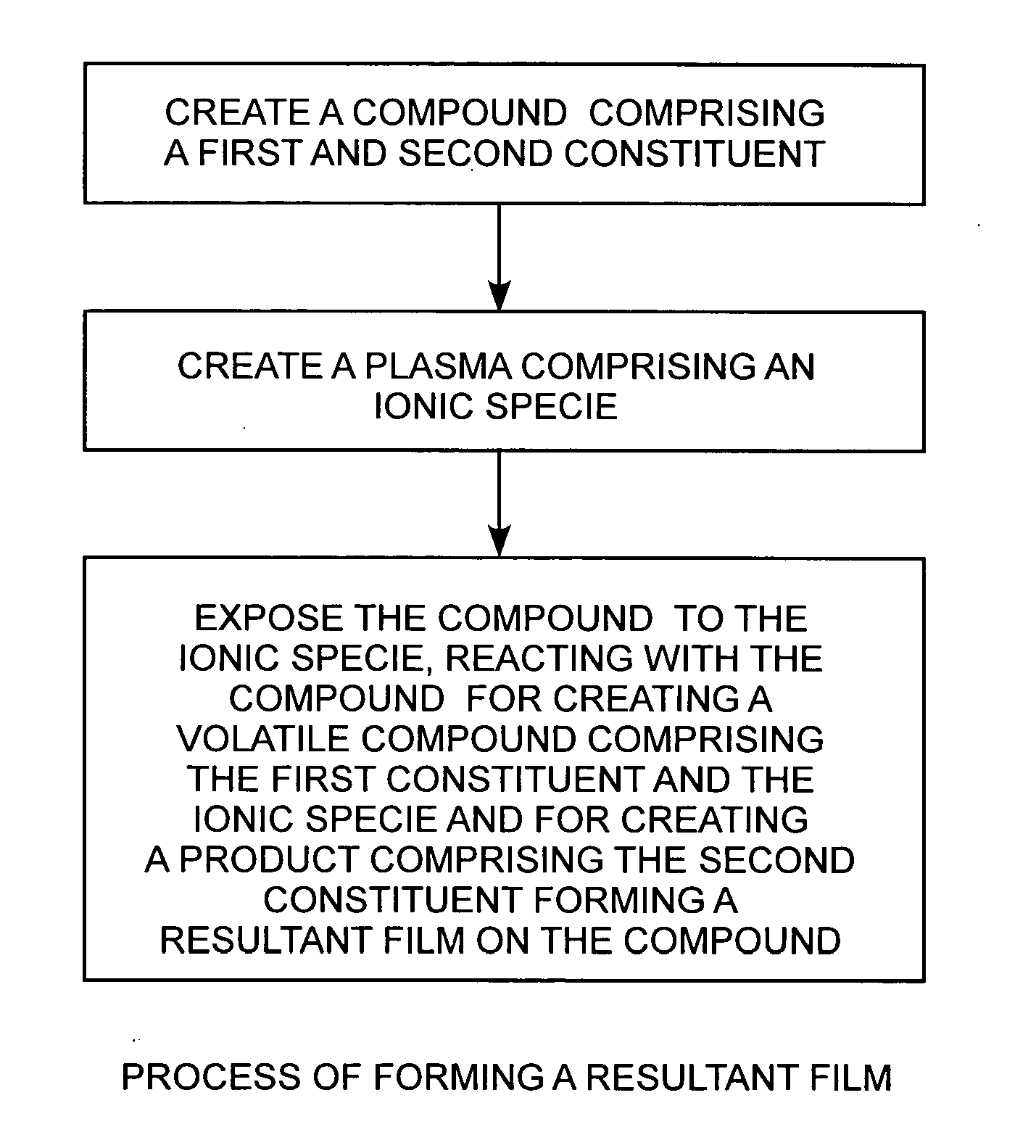
Method for producing carbon surface films by plasma exposure of a carbide compound
InactiveUS20060068125A1Reduce frictionEasy to controlChemical vapor deposition coatingFlexible microstructural devicesCarbon filmCarbon coating
Reactive halogen-ion plasmas, having for example, generating chloride ions, generated from low-pressure halogen gases using a radio-frequency plasma are employed for producing low-friction carbon coatings, such as a pure carbon film, at or near room temperature on a bulk or thin film of a compound, such as titanium carbide.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Wafer holder for wafer prober and wafer prober equipped with same
InactiveUS20090045829A1Improve rigidityGood effectHot plates heating arrangementsIndividual semiconductor device testingRoom temperatureEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a wafer prober wafer holder that is highly rigid and increases the heat insulating effect, thereby improving positional accuracy, thermal uniformity, and chip temperature ramp-up and cooling rates, as well as a wafer prober device equipped therewith.A wafer holder of the present invention includes a chuck top that mounts a wafer, and a support member that supports the chuck top, wherein, a restricting member is provided that covers an interface between the chuck top and the support member. By covering the gap between the chuck top and the support member with the restricting member, the heat insulating effect can be increased by preventing the flow of outside air through the gap into the support member, and the cooling rate can be particularly improved if cooling to a temperature below room temperature.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Room temperature-setting compositions
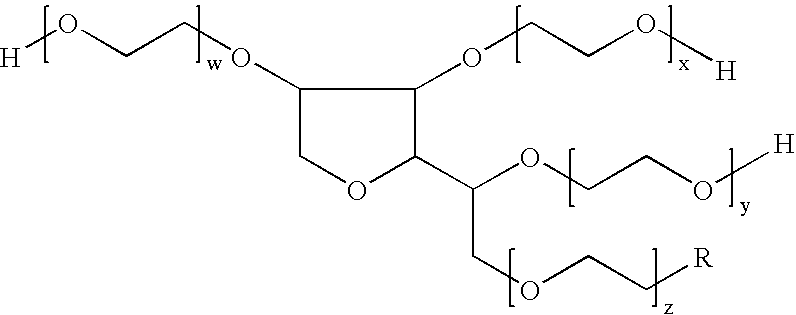
The present invention provides a room temperature-setting composition containing a polyoxyalkylene polymer (A), having a molecular weight of from 8000 to 50000 and having hydrolyzable silicon groups of the following formula (1), which comprises, as an essential component, the polyoxyalkylene polymer, having a molecular weight of from 8000 to 50000 and having hydrolyzable silicon groups of the formula (1), wherein a is 3 and a room temperature-setting composition containing a polyoxyalkylene polymer (A) having a molecular weight of from 8000 to 50000 and having hydrolyzable silicon groups of the formula (1), which comprises, as essential components, the polyoxyalkylene polymer having a molecular weight of from 8000 to 50000 and having hydrolyzable silicon groups of the formula (1) wherein a is 3, and a polymer (B) made by polymerization of a polymerizable unsaturated group-containing monomer (C):wherein R1 is a C1-20 substituted or unsubstituted monovalent organic group, X is a hydroxyl group or a hydrolyzable group, a is 1, 2 or 3, provided that when more than one R1 exist, the plurality of R1 may be the same or different, and when more than one X exist, the plurality of X may be the same or different.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Single-electron floating-gate MOS memory
A Single Electron MOS Memory (SEMM), in which one bit of information is represented by storing only one electron, has been demonstrated at room temperature. The SEMM is a floating gate Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) transistor in silicon with a channel width (about 10 nanometers) which is smaller than the Debye screening length of a single electron stored on the floating gate, and a nanoscale polysilicon dot (about 7 nanometers by 7 nanometers by 2 nanometers) as the floating gate which is positioned between the channel and the control gate. An electron stored on the floating gate can screen the entire channel from the potential on the control gate, and lead to: (i) a discrete shift in the threshold voltage; (ii) a staircase relation between the charging voltage and the shift; and (iii) a self-limiting charging process. The structure and fabrication of the SEMM is well adapted to the manufacture of ultra large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
Conformal thermal interface material for electronic components
InactiveUS6054198AOptimize allocationReadily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRoom temperatureConductive materials
A thermally-conductive interface for conductively cooling a heat-generating electronic component having an associated thermal dissipation member such as a heat sink. The interface is formed as a self-supporting layer of a thermally-conductive material which is form-stable at normal room temperature in a first phase and substantially conformable in a second phase to the interface surfaces of the electronic component and thermal dissipation member. The material has a transition temperature from the first phase to the second phase which is within the operating temperature range of the electronic component.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
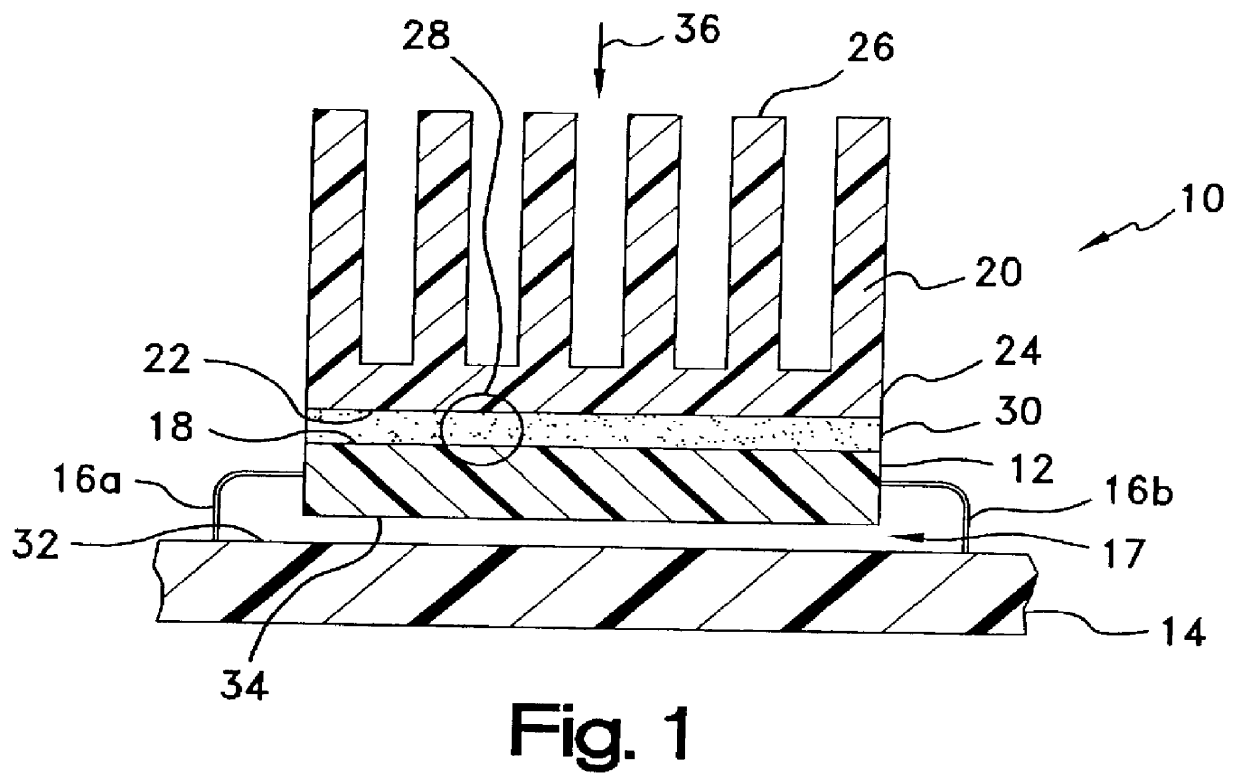
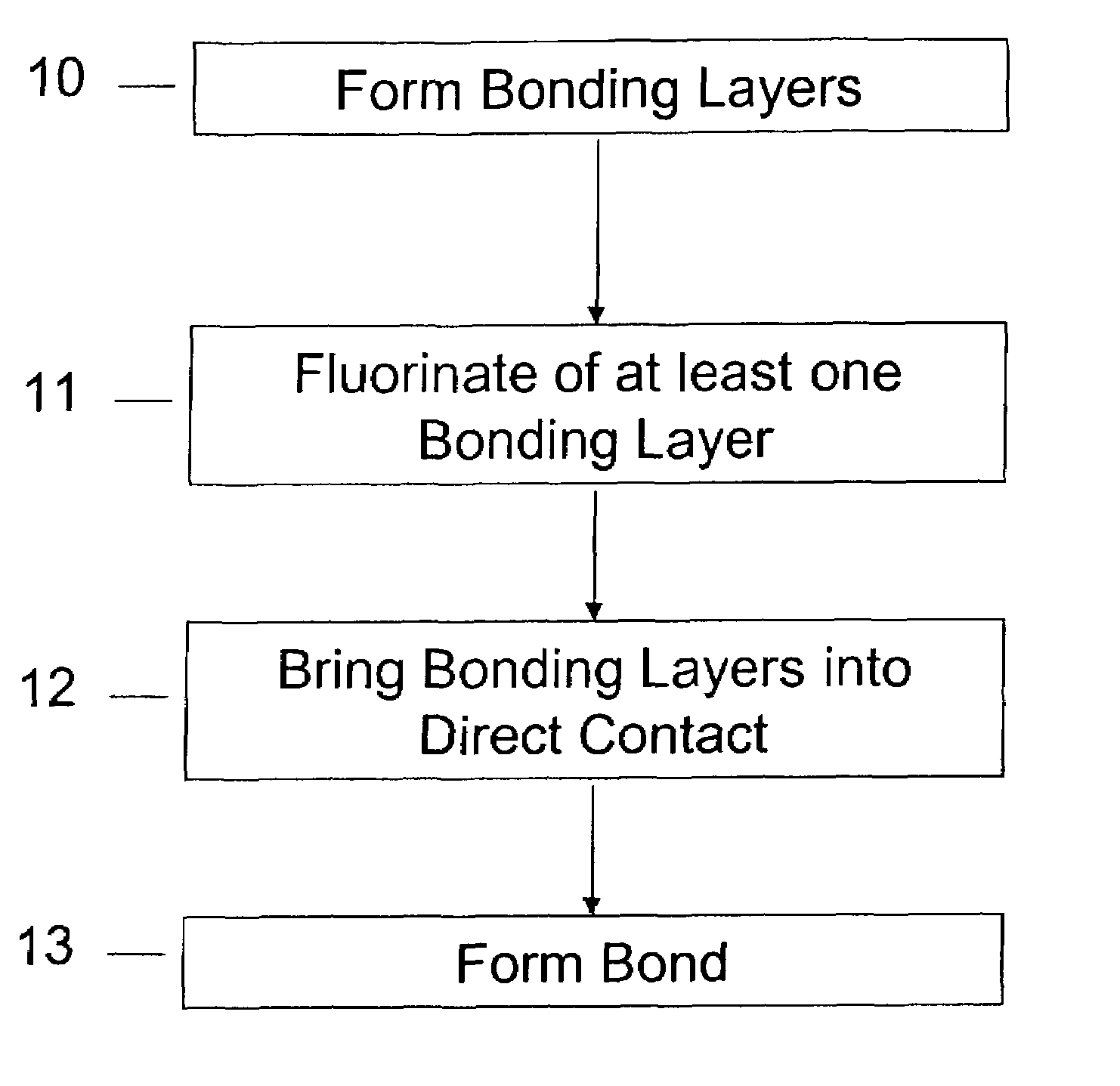
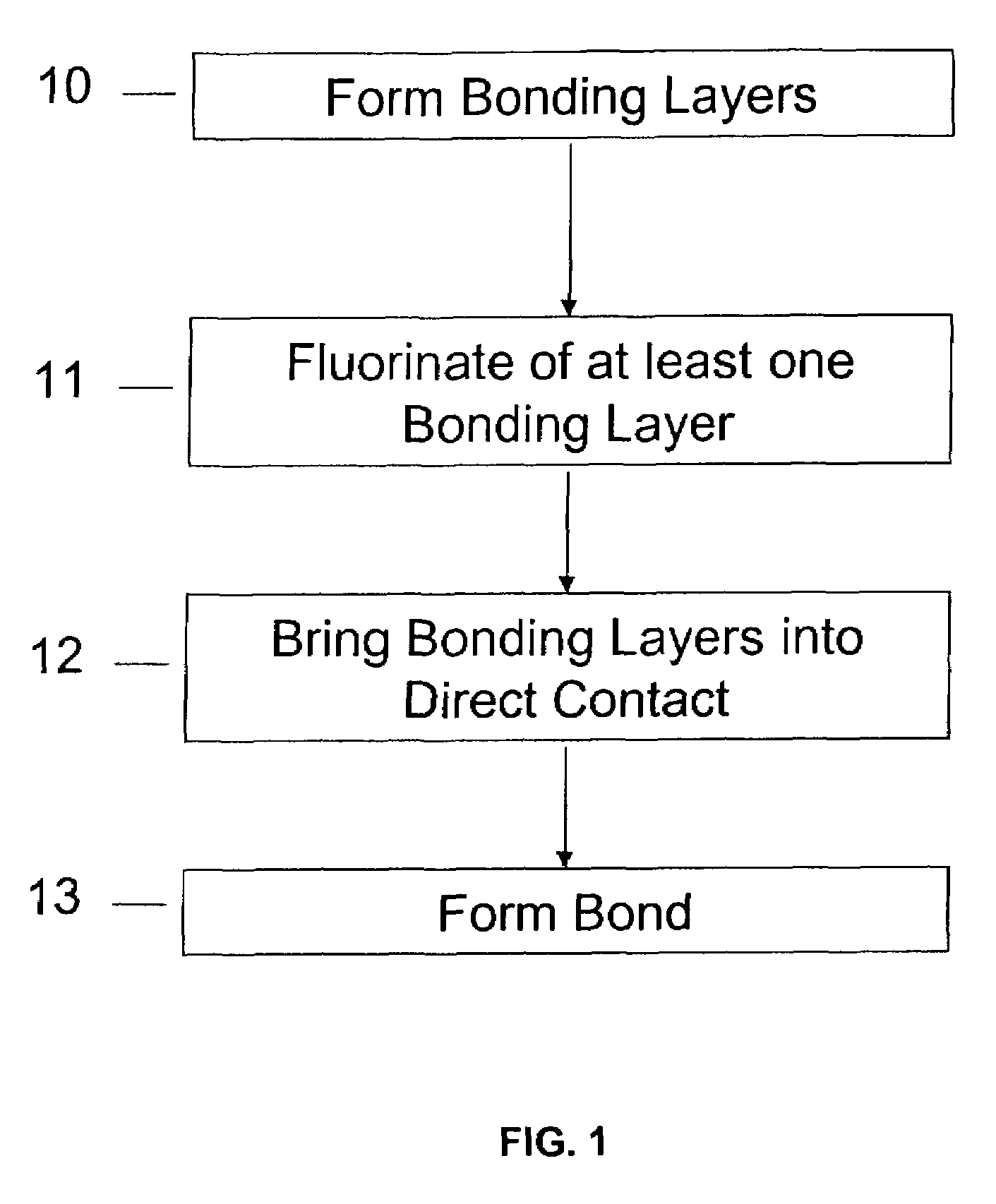
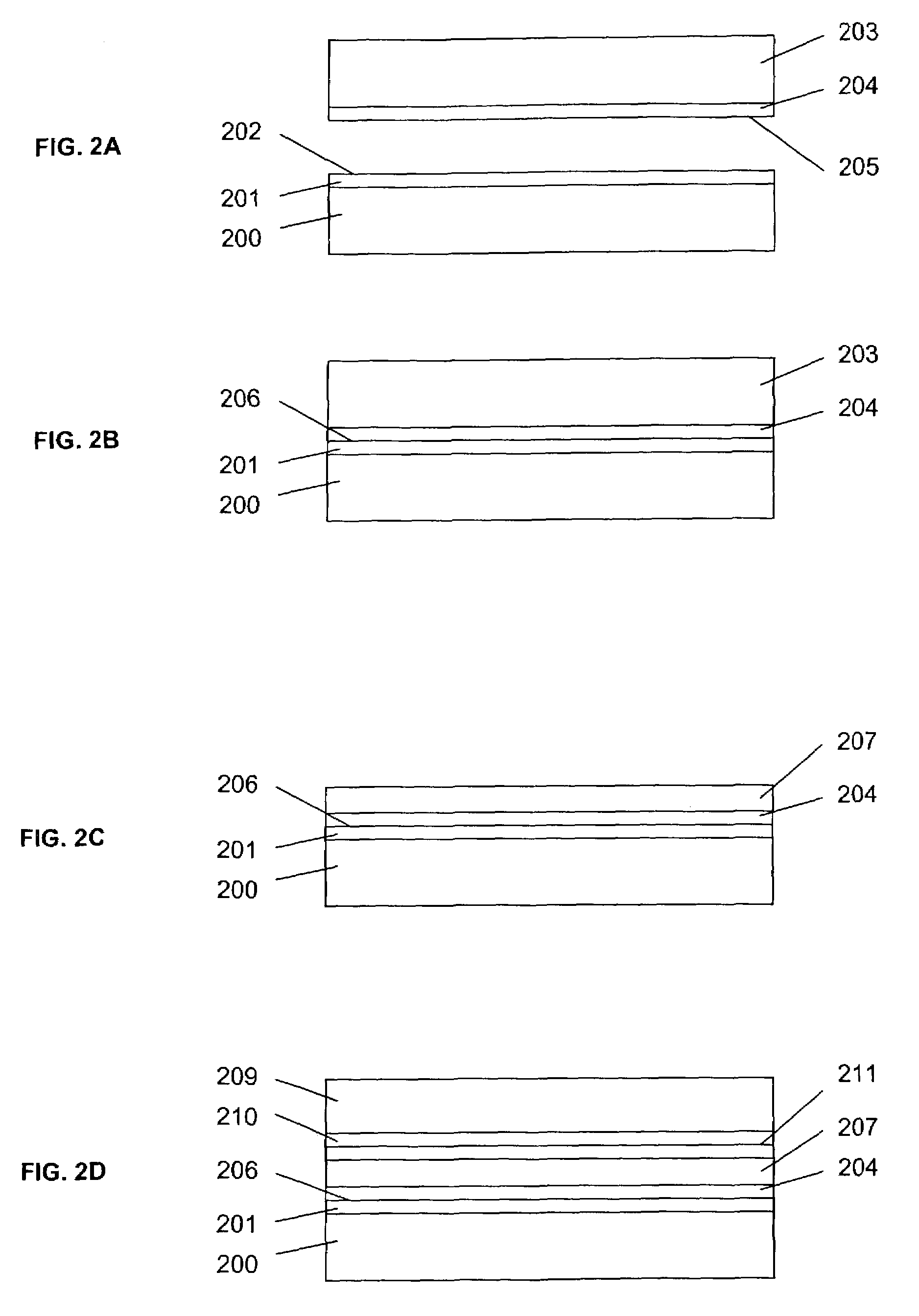
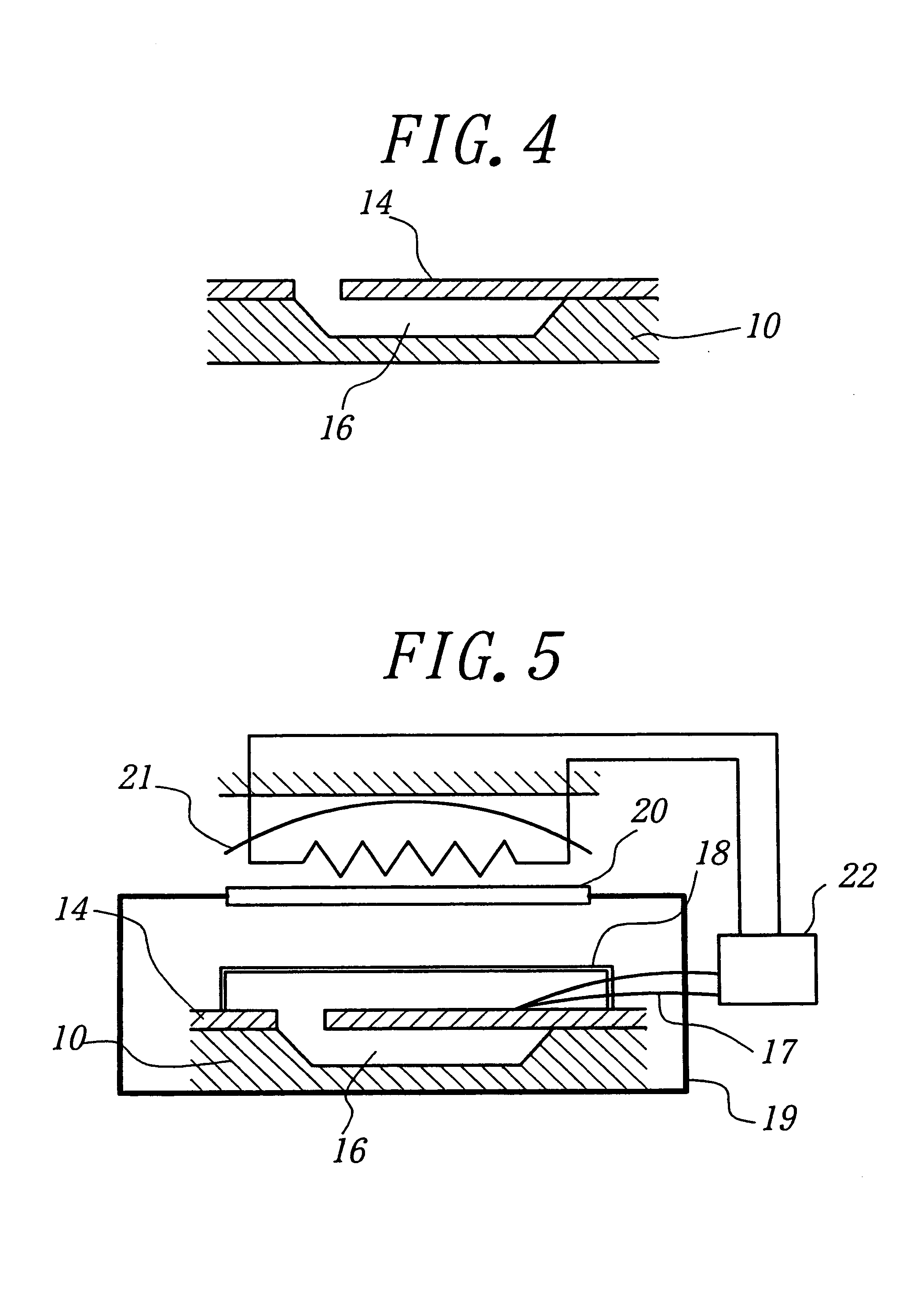
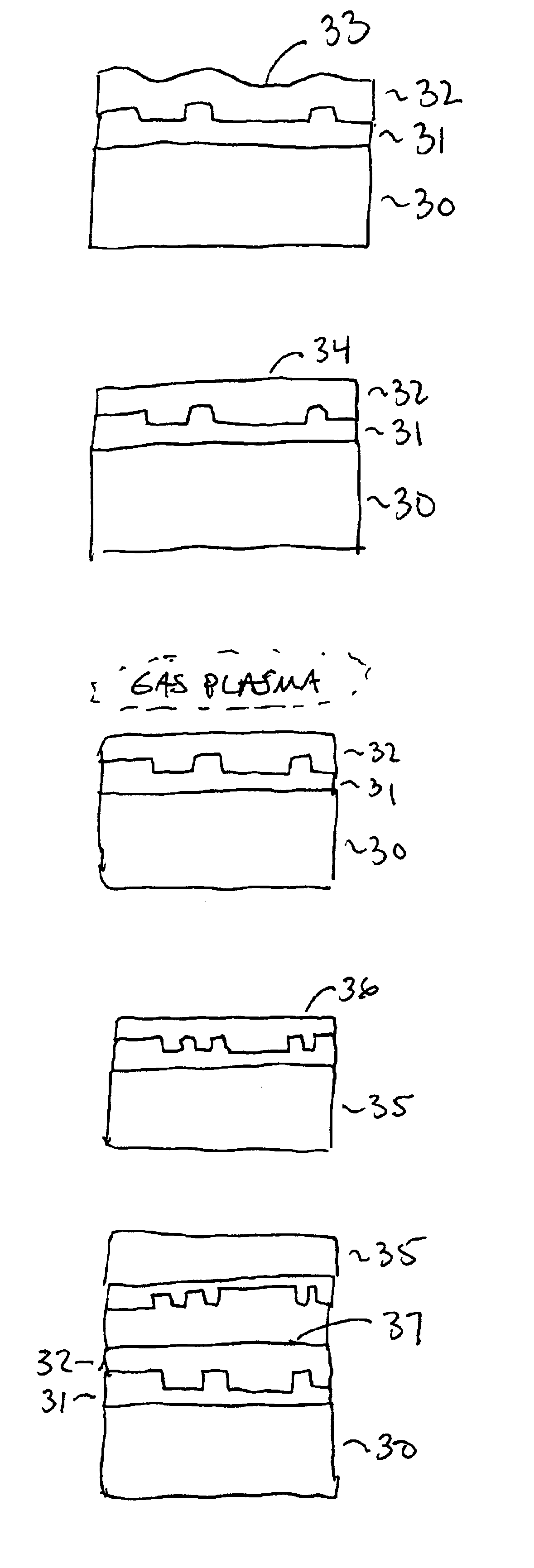
Method of room temperature covalent bonding
InactiveUS7109092B2High densityLow densityLayered productsDecorative surface effectsRoom temperatureFluorine containing
A method of bonding includes using a bonding layer having a fluorinated oxide. Fluorine may be introduced into the bonding layer by exposure to a fluorine-containing solution, vapor or gas or by implantation. The bonding layer may also be formed using a method where fluorine is introduced into the layer during its formation. The surface of the bonding layer is terminated with a desired species, preferably an NH2 species. This may be accomplished by exposing the bonding layer to an NH4OH solution. High bonding strength is obtained at room temperature. The method may also include bonding two bonding layers together and creating a fluorine distribution having a peak in the vicinity of the interface between the bonding layers. One of the bonding layers may include two oxide layers formed on each other. The fluorine concentration may also have a second peak at the interface between the two oxide layers.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Thin film-structure and a method for producing the same
InactiveUS6759261B2Increase productivityGood reproducibilityLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthElectrical measurement instrument detailsRoom temperatureCooling down
A thin film made of an amorphous material having supercooled liquid phase region is formed on a substrate. Then, the thin film is heated to a temperature within the supercooled liquid phase region and is deformed by its weight, mechanical external force, electrostatic external force or the like, thereby to form a thin film-structure. Thereafter, the thin film-structure is cooled down to room temperature, which results in the prevention of the thin film's deformation.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
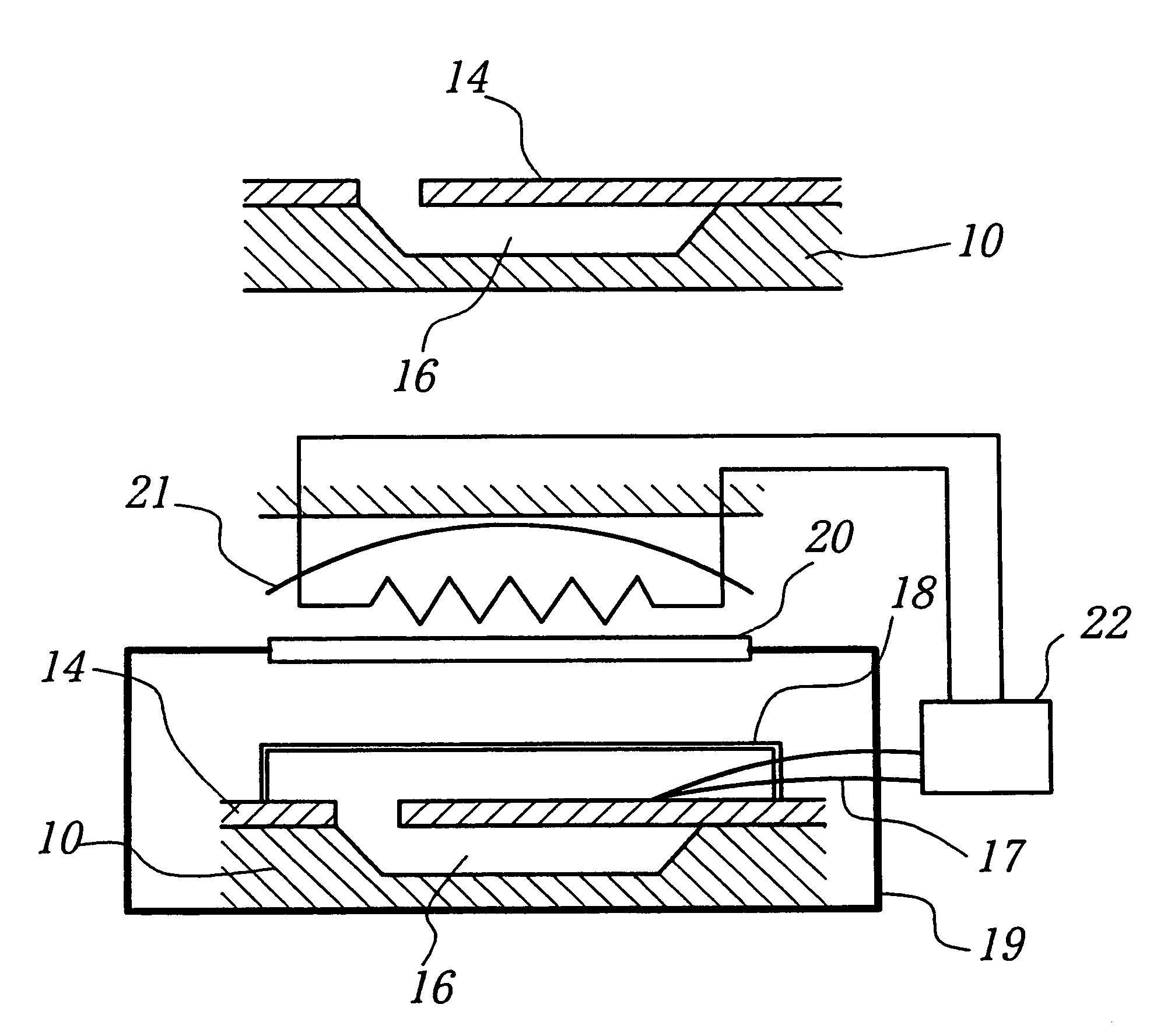
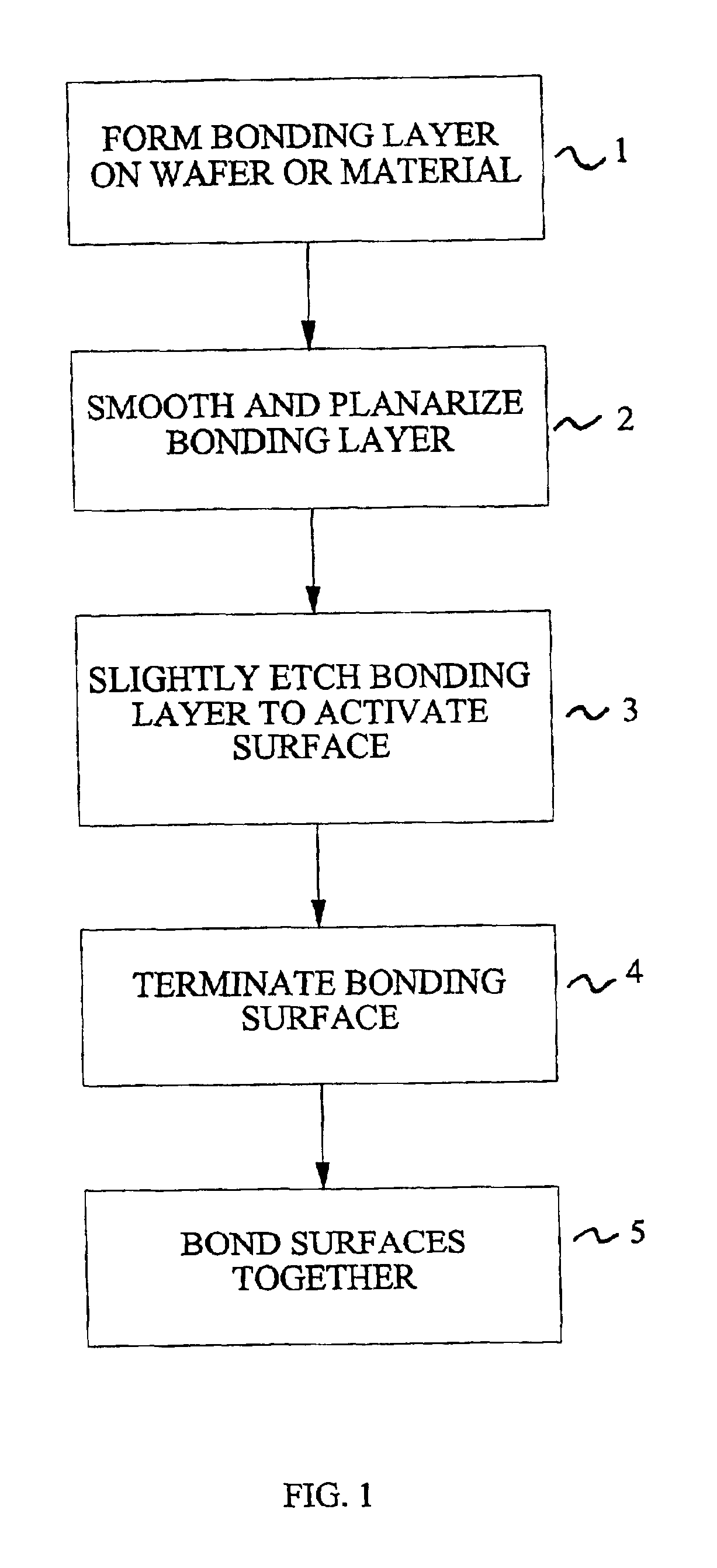
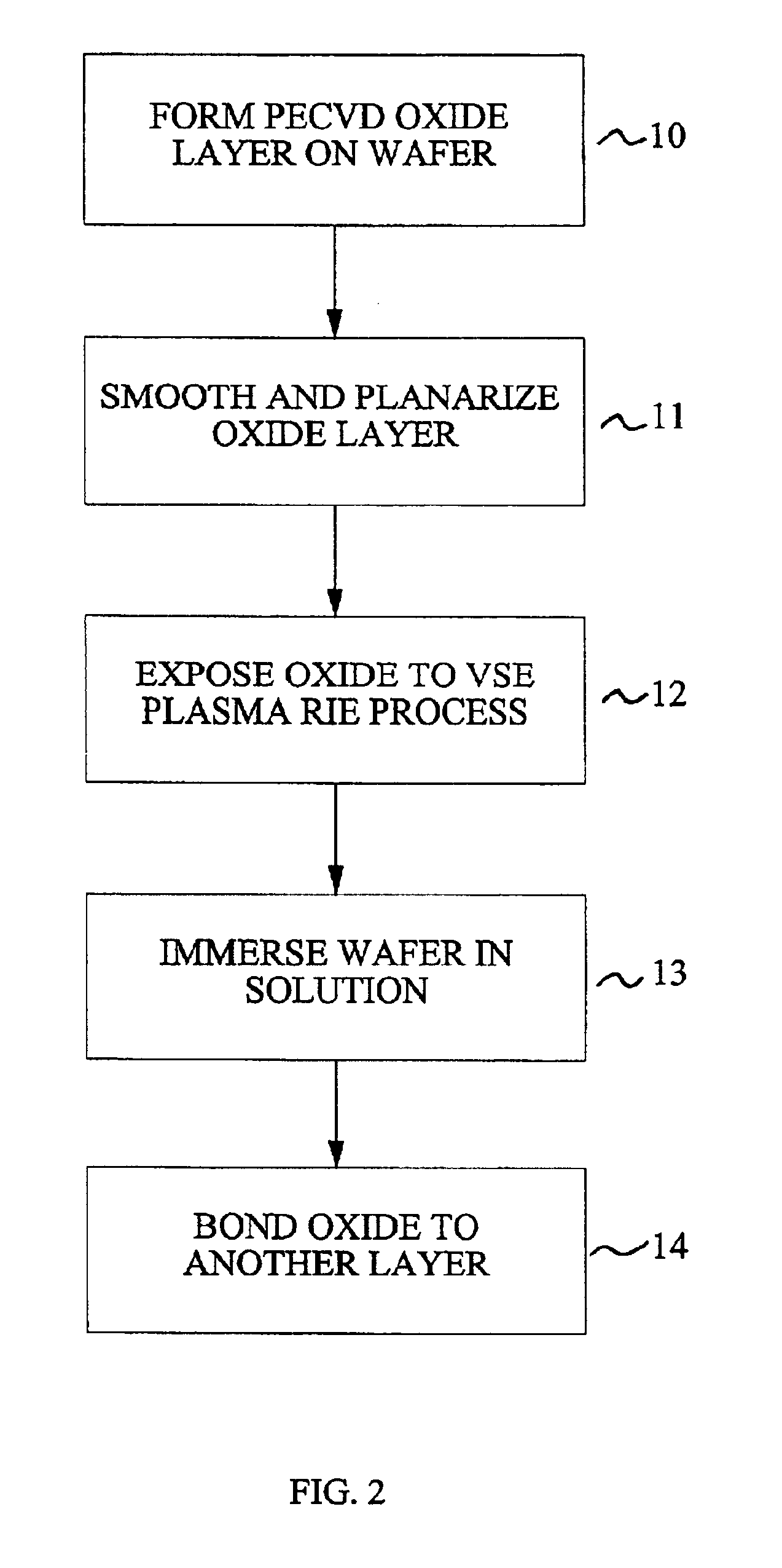
Method for low temperature bonding and bonded structure
InactiveUS6902987B1High bonding strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface cleaningBiological activation
A method for bonding at low or room temperature includes steps of surface cleaning and activation by cleaning or etching. One etching process the method may also include removing by-products of interface polymerization to prevent a reverse polymerization reaction to allow room temperature chemical bonding of materials such as silicon, silicon nitride and SiO2. The surfaces to be bonded are polished to a high degree of smoothness and planarity. VSE may use reactive ion etching or wet etching to slightly etch the surfaces being bonded. The surface roughness and planarity are not degraded and may be enhanced by the VSE process. The etched surfaces may be rinsed in solutions such as ammonium hydroxide or ammonium fluoride to promote the formation of desired bonding species on the surfaces.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Lithium metal dispersion in electrodes
InactiveUS20050130043A1High specific capacityPromote circulationElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrode thermal treatmentLithium metalHost material
Electrodes, such as anodes and cathodes, can include a host material that is prelithiated or undergoes lithiation upon electrolyte introduction into a battery. Lithiation of the host material can occur by the agitation of lithium metal and a host material, the agitation of a lithium metal powder and a host material at a temperature greater than room temperature, the application of pressure to a lithium metal and host material mixture, contact of the host material with molten lithium metal, the lamination of lithium foil or lithium mesh onto an electrode containing the host material, or by lamination of lithium metal or mesh onto an electrode at elevated temperatures.
Owner:AEA TECH BATTERY SYST +1
Method for reversibly mounting a device wafer to a carrier substrate
ActiveUS20090218560A1Reduced adhesion strengthLamination ancillary operationsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHeat resistanceRoom temperature
New temporary bonding methods and articles formed from those methods are provided. The methods comprise bonding a device wafer to a carrier wafer or substrate only at their outer perimeters in order to assist in protecting the device wafer and its device sites during subsequent processing and handling. The edge bonds formed by this method are chemically and thermally resistant, but can also be softened, dissolved, or mechanically disrupted to allow the wafers to be easily separated with very low forces and at or near room temperature at the appropriate stage in the fabrication process.
Owner:BREWER SCI
Positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries having a high specific discharge capacity and processes for the synthesis of these materials
ActiveUS20100086853A1Electrode manufacturing processesAlkali metal oxidesDischarge rateLithium-ion battery
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Tungsten deposition sequence
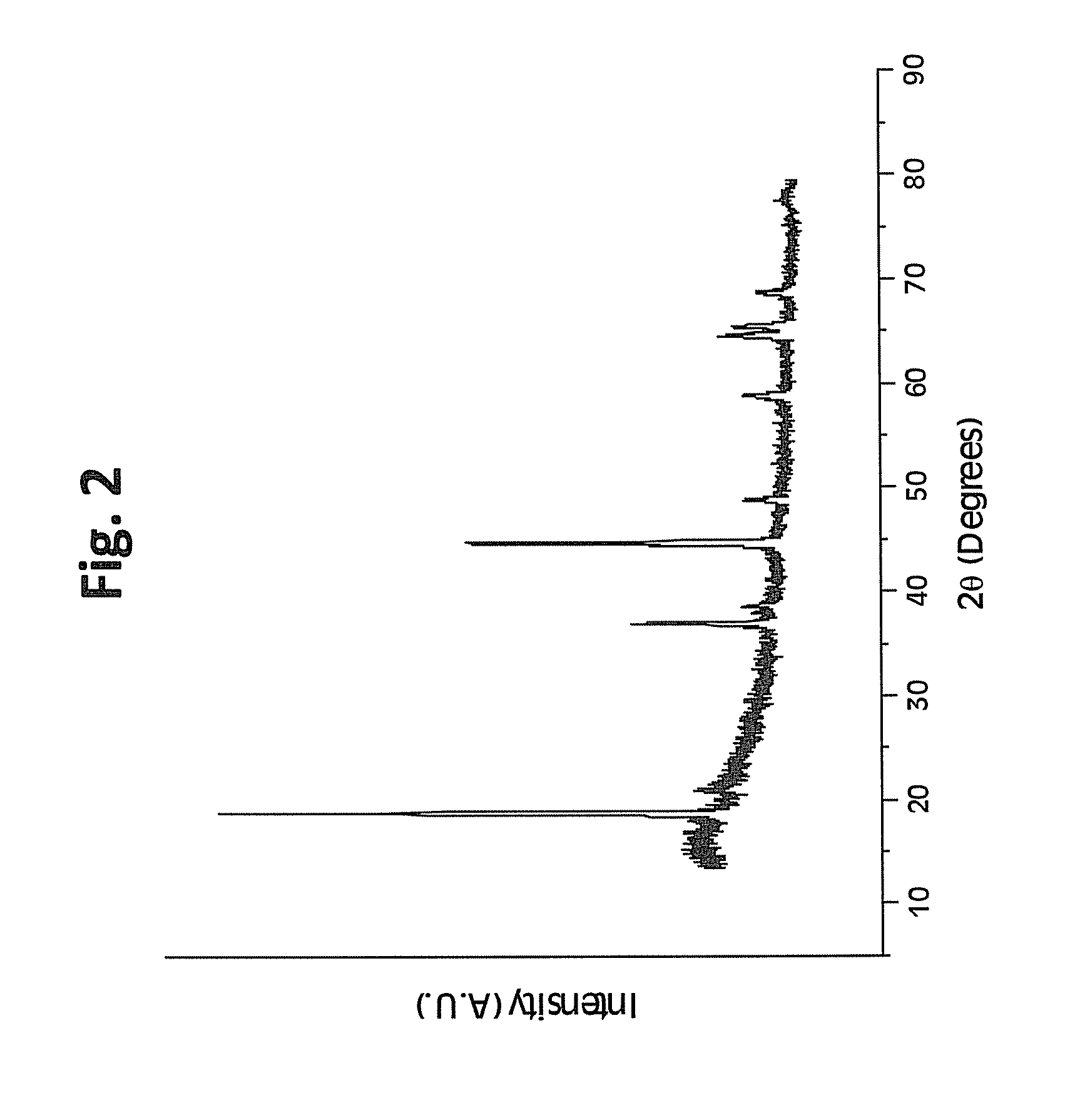
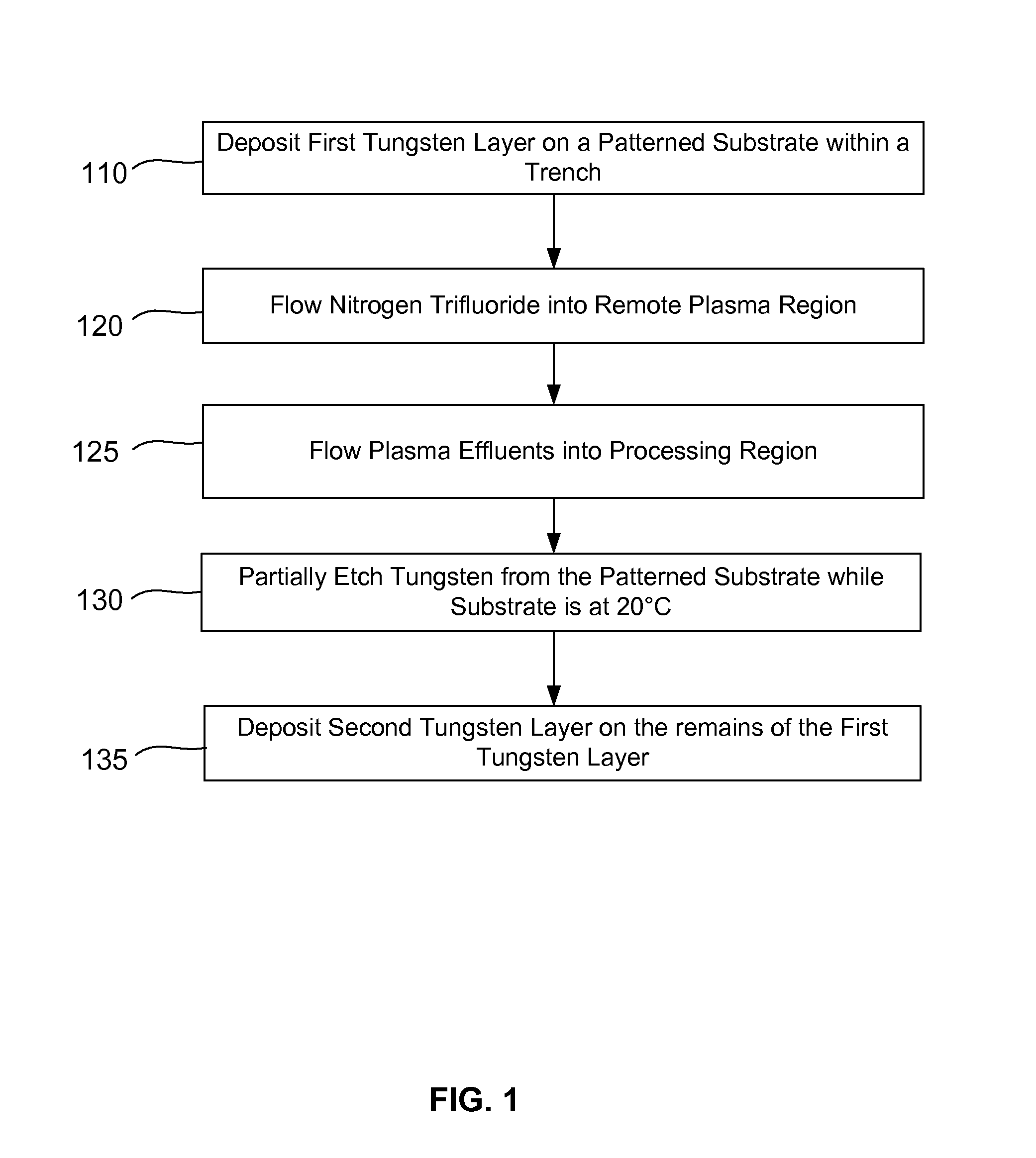
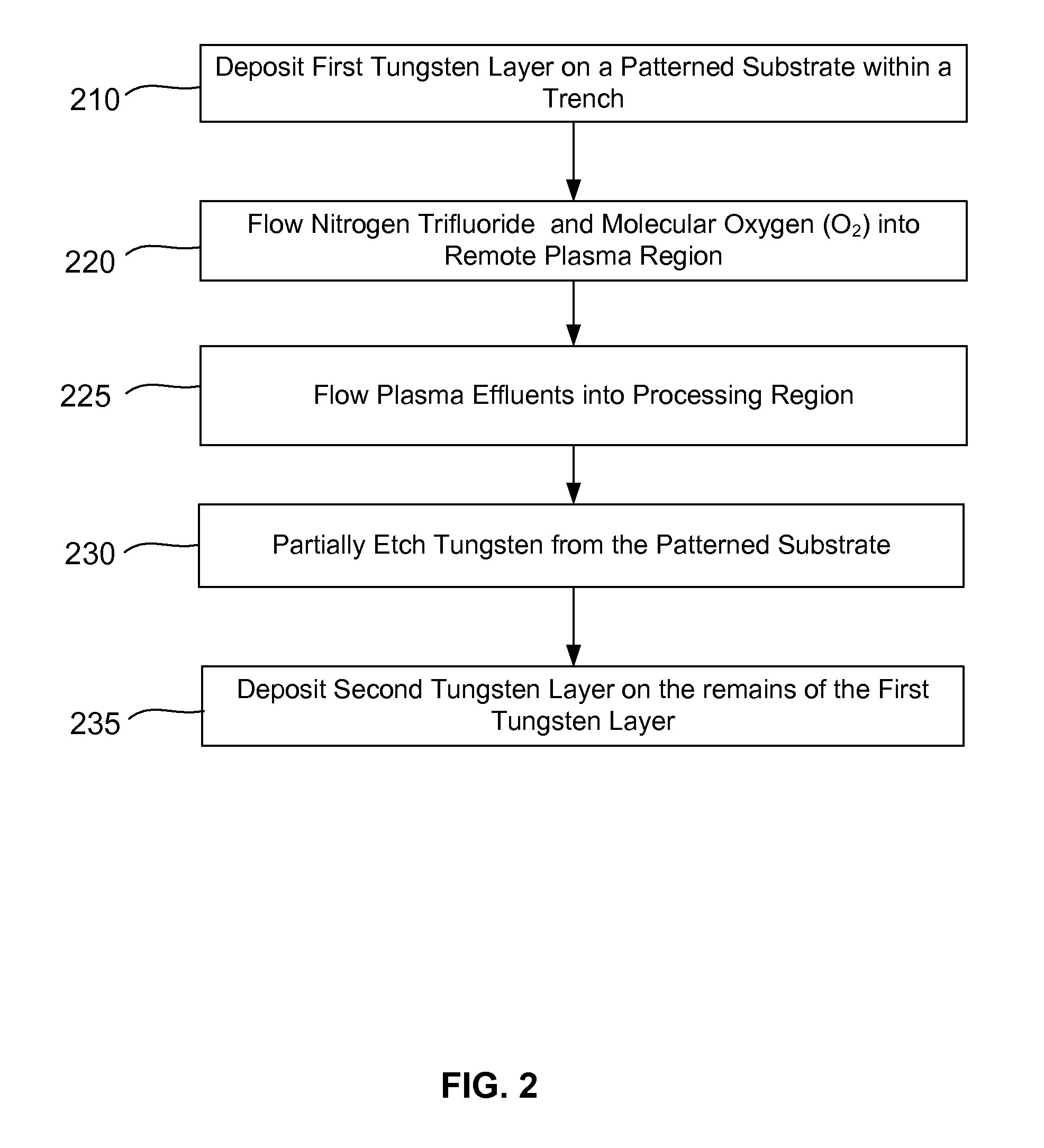
InactiveUS20140273451A1Enhance gapfillingAvoid difficultySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHalogenRoom temperature
Methods of filling gaps with tungsten are described. The methods include a tungsten dep-etch-dep sequence to enhance gapfilling yet avoid difficulty in restarting deposition after the intervening etch. The first tungsten deposition may have a nucleation layer or seeding layer to assist growth of the first tungsten deposition. Restarting deposition with a less-than-conductive nucleation layer would impact function of an integrated circuit, and therefore avoiding tungsten “poisoning” during the etch is desirable. The etching step may be performed using a plasma to excite a halogen-containing precursor while the substrate at relatively low temperature (near room temperature or less). The plasma may be local or remote. Another method may be used in combination or separately and involves the introduction of a source of oxygen into the plasma in combination with the halogen-containing precursor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for room temperature metal direct bonding
InactiveUS6962835B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBond interfaceRoom temperature
A bonded device structure including a first substrate having a first set of metallic bonding pads, preferably connected to a device or circuit, and having a first non-metallic region adjacent to the metallic bonding pads on the first substrate, a second substrate having a second set of metallic bonding pads aligned with the first set of metallic bonding pads, preferably connected to a device or circuit, and having a second non-metallic region adjacent to the metallic bonding pads on the second substrate, and a contact-bonded interface between the first and second set of metallic bonding pads formed by contact bonding of the first non-metallic region to the second non-metallic region. At least one of the first and second substrates may be elastically deformed.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
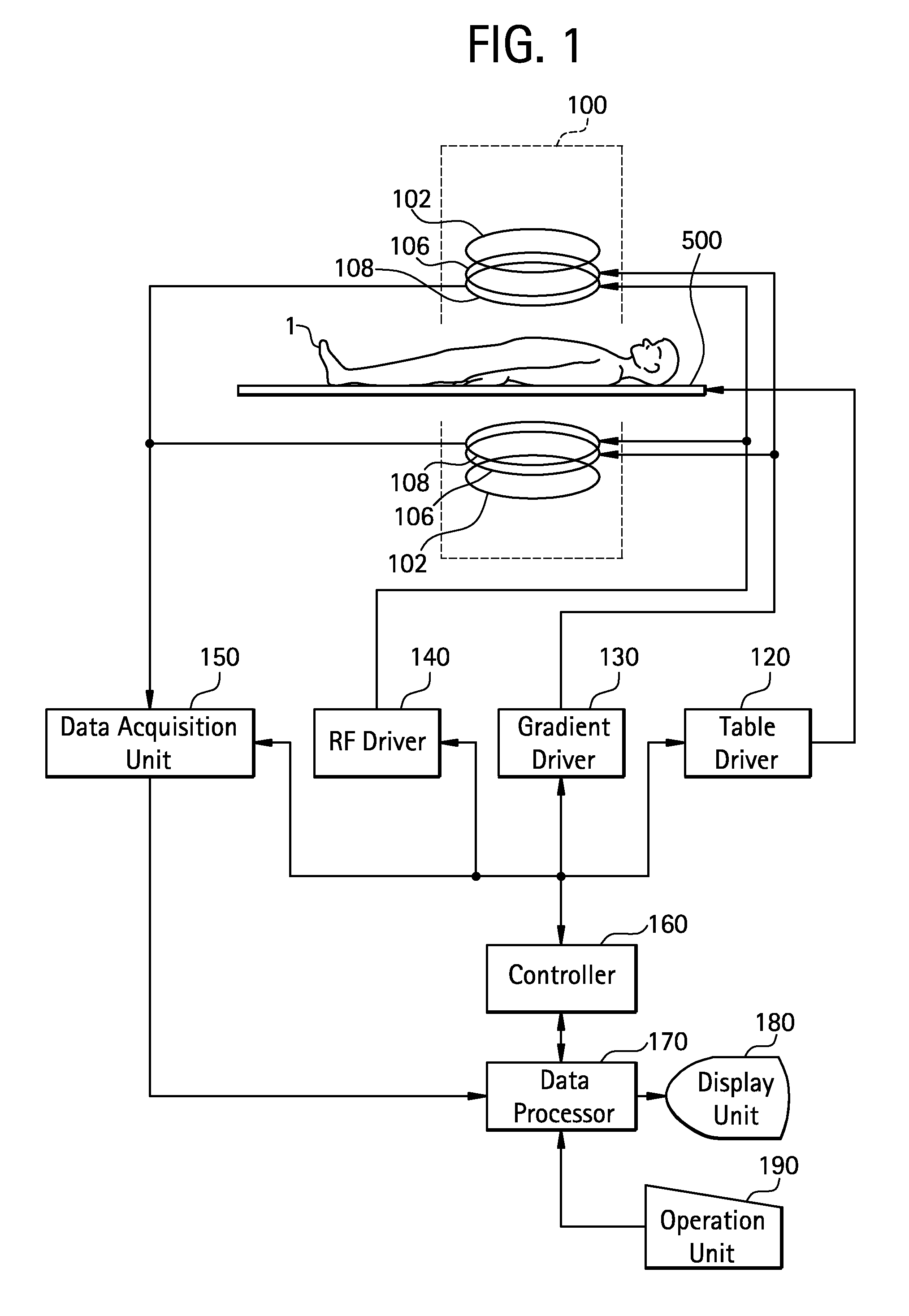
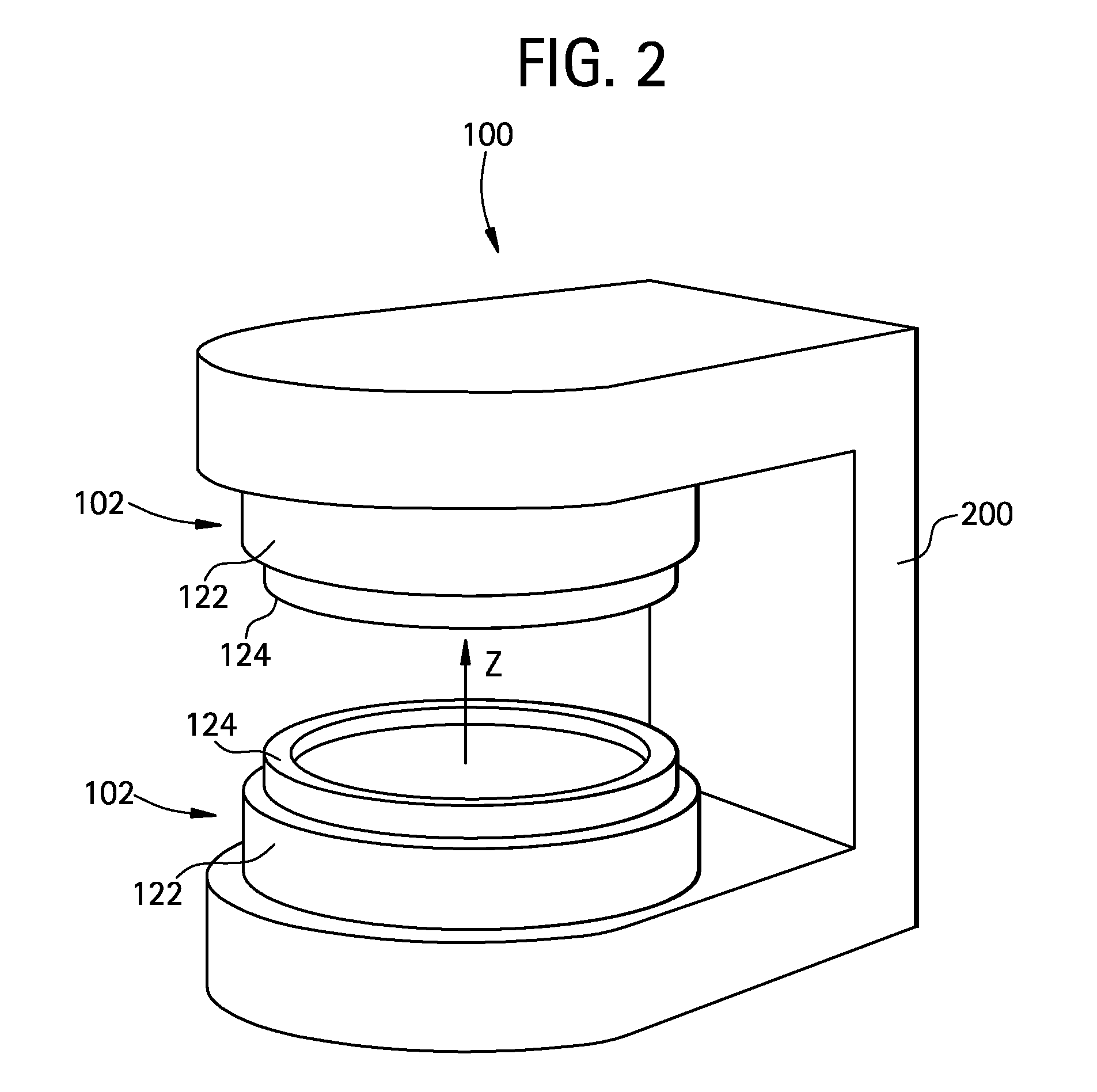
Thermal controlling method, magnetic field generator and MRI apparatus
InactiveUS20080048656A1Permanent magnetsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic polesRoom temperature
With a view toward implementing a thermal controlling method for making reversible a temperature characteristic of a magnetic field generator using permanent magnets small in Hcj, a magnetic field generator whose temperature characteristic is reversible, using permanent magnets small in Hcj, and an MRI apparatus provided with such a magnetic field generator, there is provided a method for controlling the temperature of a magnetic field generator having a pair of disc-shaped permanent magnets whose magnetic poles opposite in polarity to each other are opposed to each other with spacing defined therebetween, and a yoke that forms return passes for magnetic fluxes of the permanent magnets, comprising the steps of raising the temperature from room temperature to a temperature higher than the room temperature, maintaining the temperature higher than the room temperature, and lowering the temperature from the temperature higher than the room temperature to the room temperature, whereby the temperature characteristics of the permanent magnets are made reversible.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
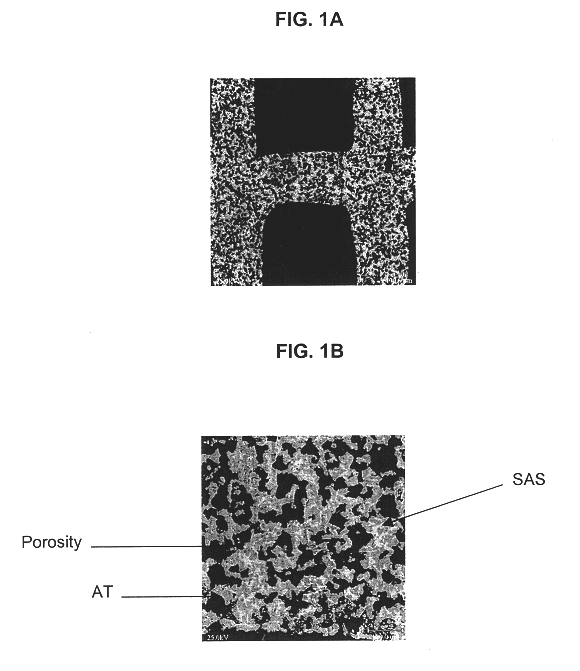
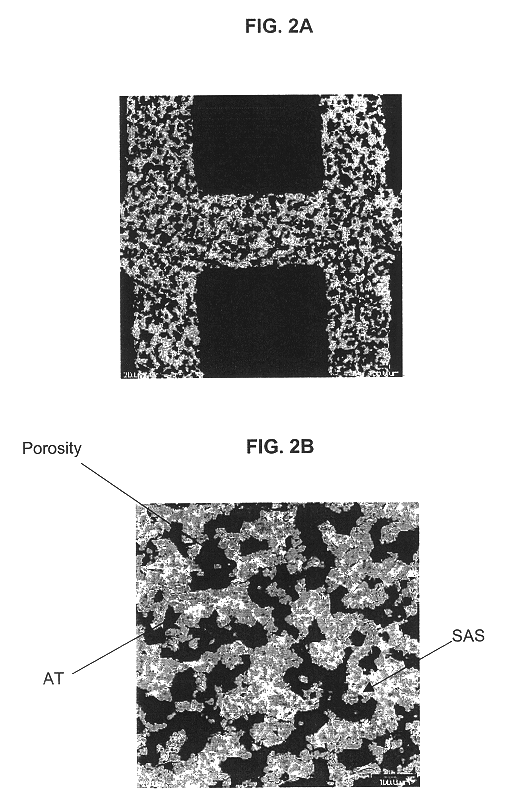
Strontium feldspar aluminum titanate for high temperature applications
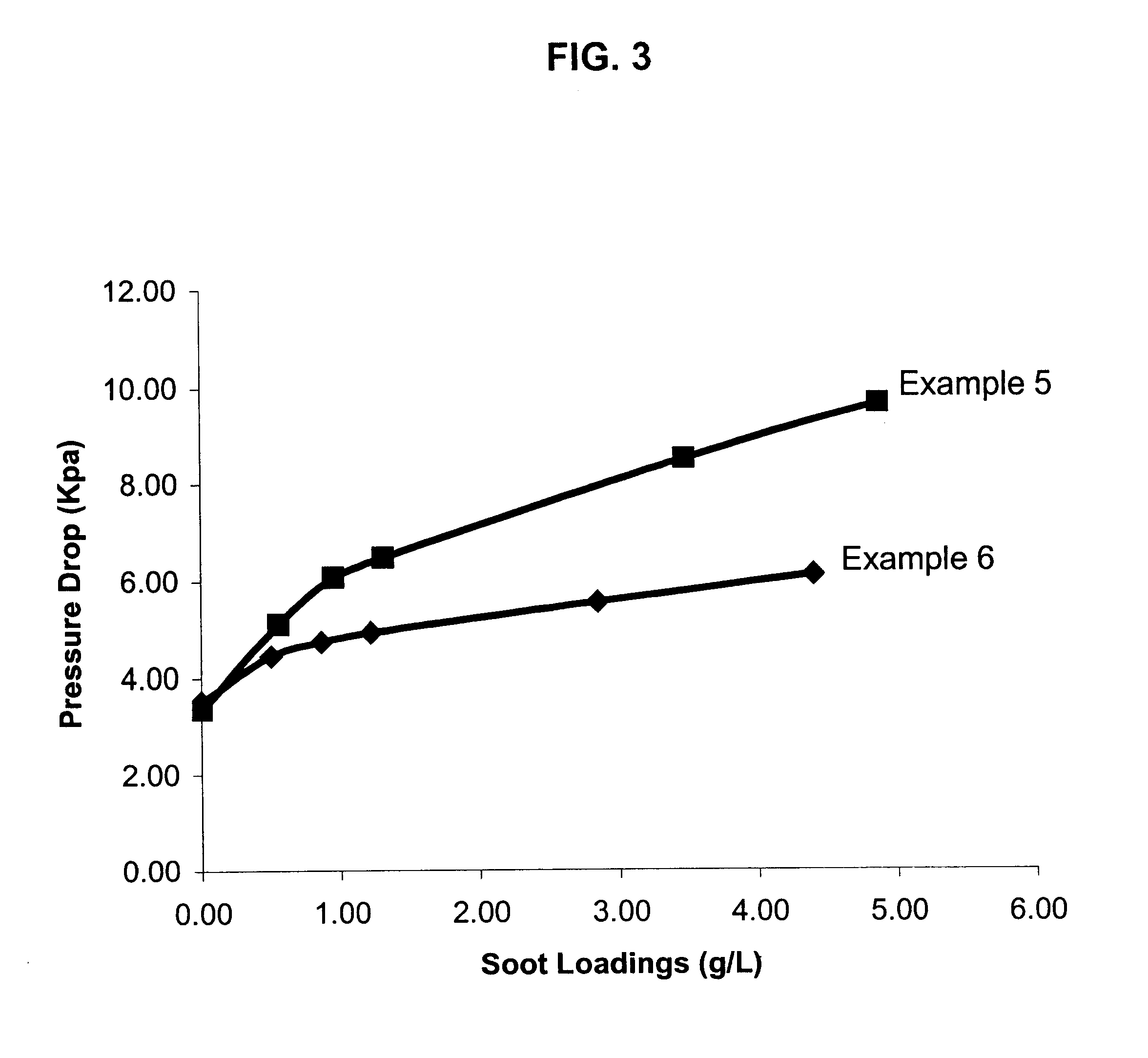
InactiveUS6620751B1Improve stabilityReduce bloatInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationMicrometerRoom temperature
A structure for use in high temperature applications and including a porous ceramic material consisting essentially of about 50-90 percent by weight iron or magnesium stabilized aluminum titanate (AlTiO5) and about 10-50 percent by weight strontium feldspar (SrO.Al2O3.2SiO2), and having a coefficient of thermal expansion over a temperature range from room temperature to 1000° C. of about -10x10-7 / ° C. to +15x10-7 / ° C., a heat capacity at 500° C. greater than 3.2 J / cm3K, a porosity of about 15-50 percent by volume, preferably 40-50 percent by volume, and a median pore size of about 5-50 micrometers, preferably 8-15 micrometers. The structure is especially useful as a diesel exhaust particulate filter.
Owner:CORNING INC
Thermoplastic surgical template for performing dental implant osteotomies and method thereof
A surgical template for performing dental implant osteotomies comprises a malleable, resinous, thermoplastic base, at least one non-thermoplastic, rigid drill guide attached to the base, and a securing mechanism between the base and the drill guide. The template may reversibly melt to a malleable state and can be handled by hand without additional tools so as to conform to the adjacent teeth of the edentulous ridge, either directly in the patient's mouth or on a cast model. Dental osteotomies using the template can then be performed. The surgical template may be manufactured of a thermoplastic material having a sharp and low melting point but high rigidity in the solid state at room temperature.
Owner:TANG BRIAN
Fluoropolymer dispersion containing no or little low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant
ActiveUS6861466B2Good film formingTransportation and packagingFibre treatmentPolymer scienceRoom temperature
In an aspect of the invention, a fluoropolymer dispersion, preferably a PTFE dispersion, is provided that comprises fluoropolymer particles having an average particle size of 10 to 400 nm dispersed in water whereby the dispersion has an amount of solids between 35 and 70% by weight. The dispersion is free of fluorinated surfactant having a molecular weight of less than 1000 g / mol (hereinafter called low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant) or contains the low molecular weight fluorinated surfactant in an amount of not more than 0.05% by weight based on the total weight solids of the dispersion. The dispersion further comprises a non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactant or mixture of non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactants and one or more non-fluorinated anionic surfactants. Through the use of a non-fluorinated anionic surfactant, a dispersion is obtained that has a low viscosity at room temperature (20° C.). The dispersion is further free of aromatic group containing non-ionic surfactants and is accordingly environmentally more friendly and can yield coatings that are less susceptible of discoloration. The amount and nature of the non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactant or mixture of non-ionic non-fluorinated surfactants is selected such that the Viscosity Transition Temperature (VTT) (measured as set forth in the examples) of the fluoropolymer dispersion is at least 26, preferably at least 28° C. In a further aspect of the invention, a method is provided to obtain the aforementioned dispersion.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
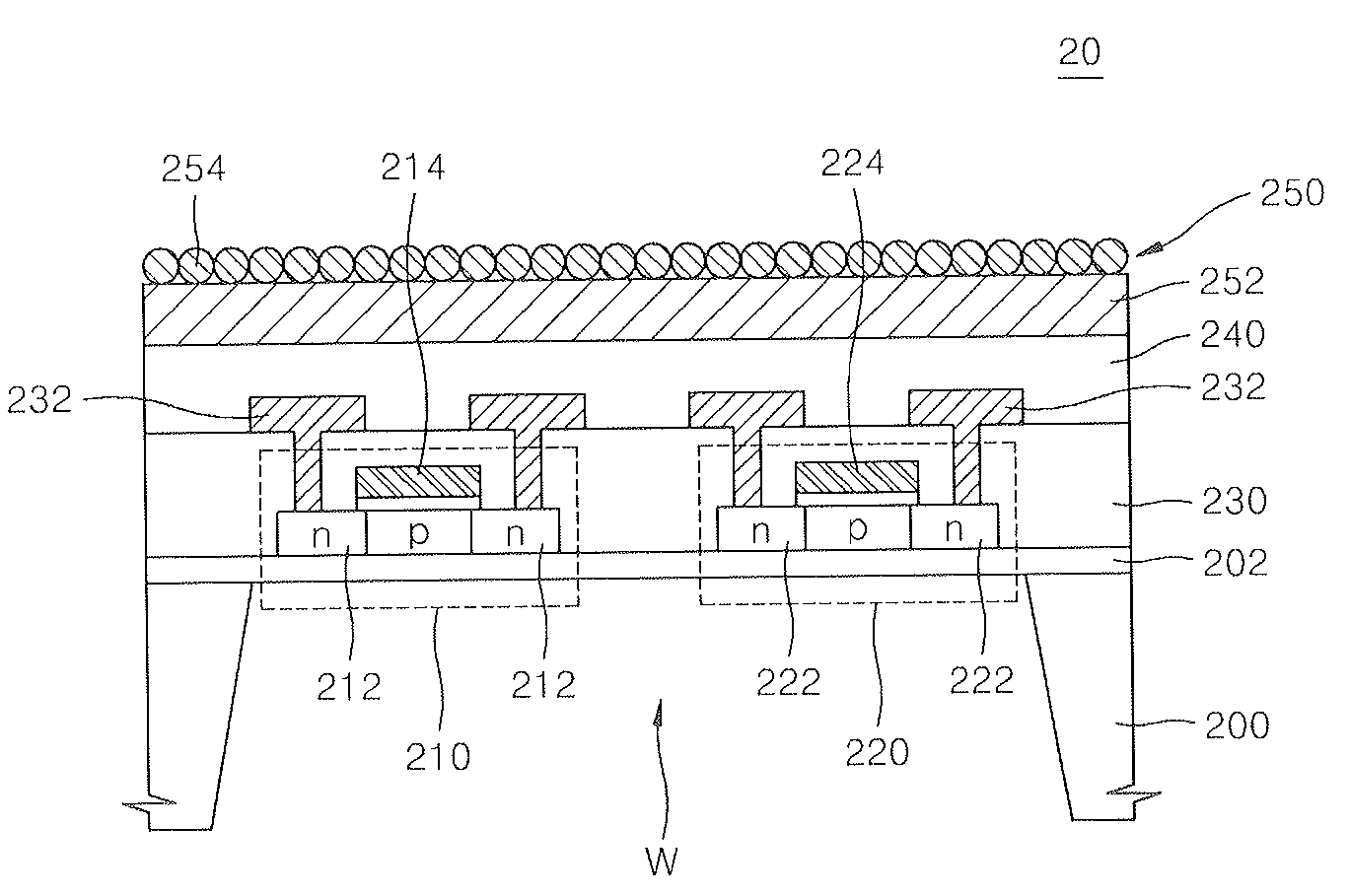
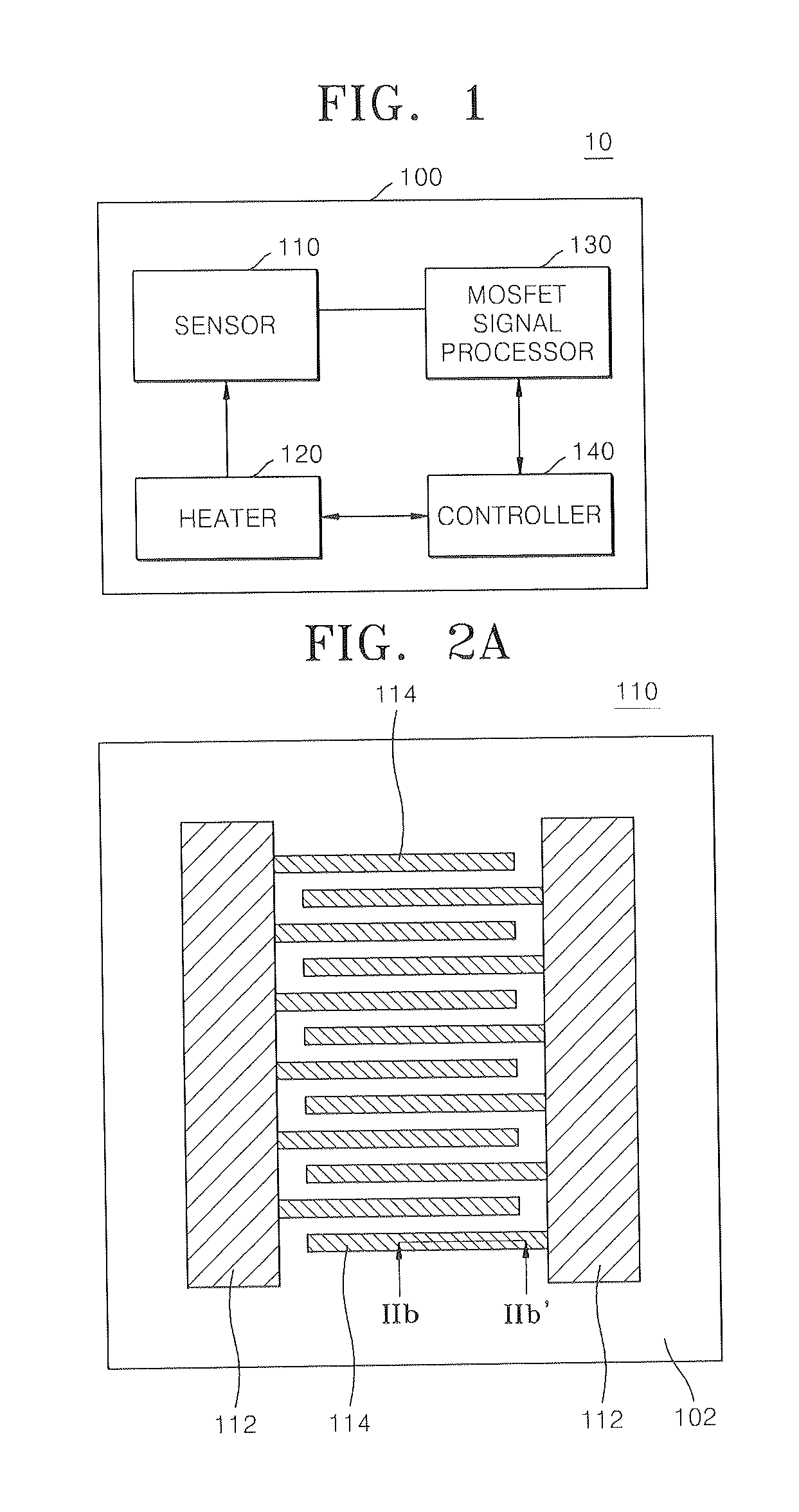
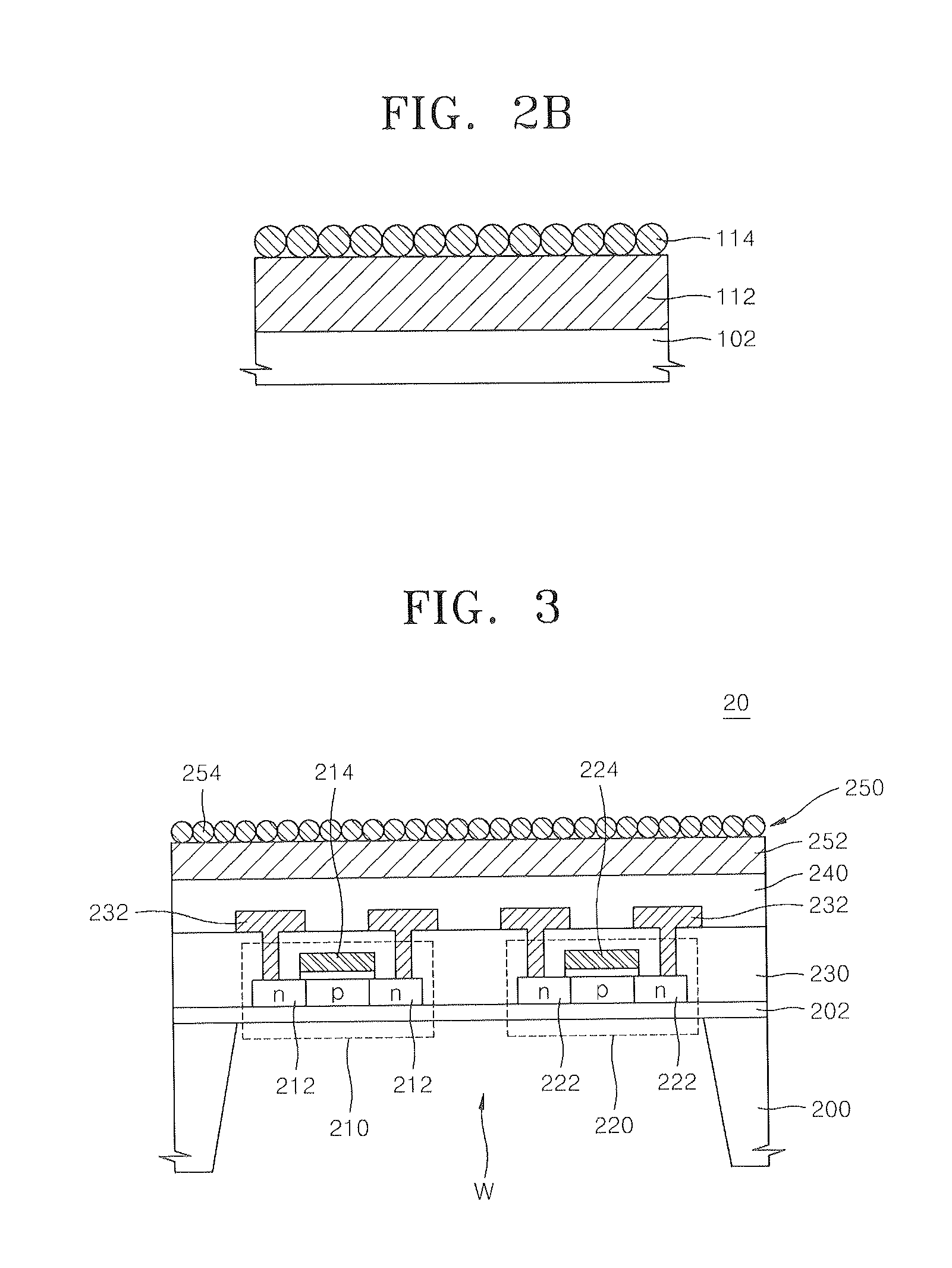
Method of forming sensor for detecting gases and biochemical materials, integrated circuit having the sensor, and method of manufacturing the integrated circuit
InactiveUS20080121946A1Characteristics degradation of an integrated circuit caused by heating the unit devices when forming the sensor can be preventedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanosensorsMOSFETNano structuring
A method of forming a sensor for detecting gases and biochemical materials that can be fabricated at a temperature in a range from room temperature to 400° C., a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET)-based integrated circuit including the sensor, and a method of manufacturing the integrated circuit are provided. The integrated circuit includes a semiconductor substrate. The sensor for detecting gases and biochemical materials includes a pair of electrodes formed on a first region of the semiconductor substrate, and a metal oxide nano structure layer formed on surfaces of the pair electrodes. A heater is formed to perform thermal treatment to re-use the material detected in the metal oxide nano structure layer. Also, a signal processor is formed by a MOSFET to process a predetermined signal obtained from a quantity change of a current flowing through the pair of electrodes of the sensor. To form the sensor, the metal oxide nano structure layer is formed on surfaces of the pair of electrodes at a temperature in a range from room temperature to 400° C.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
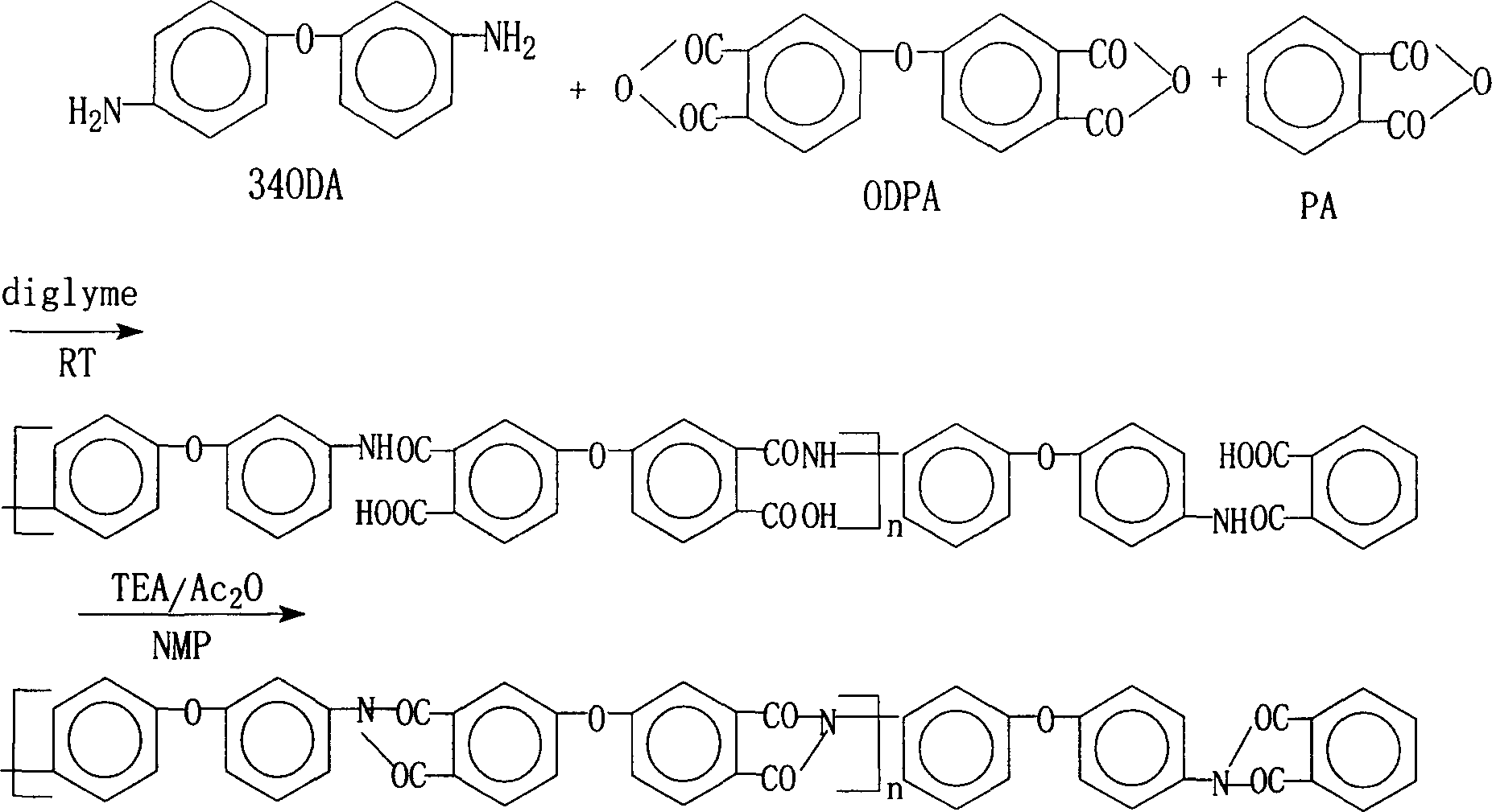
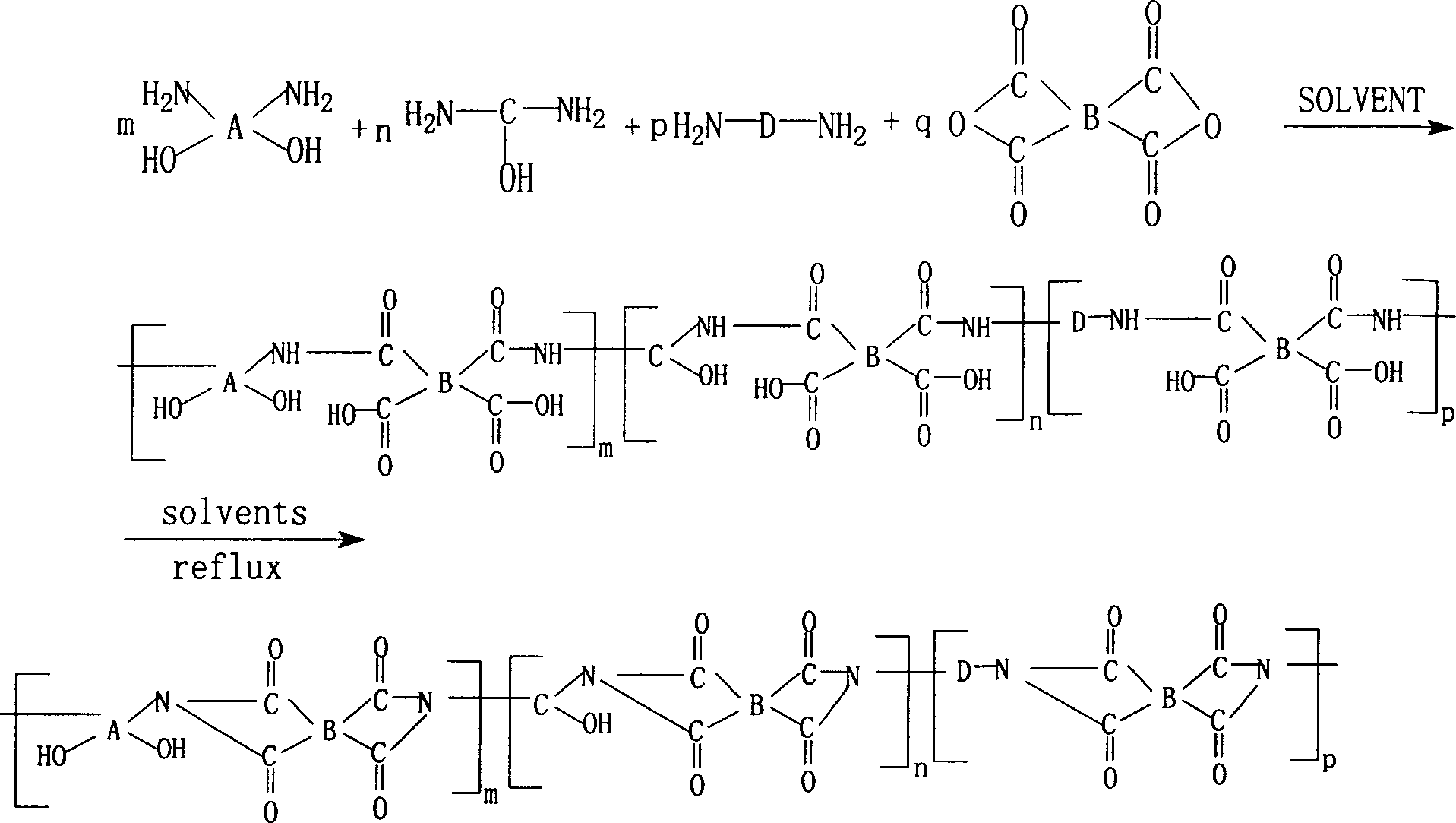
Preparation method of phenolic hydroxyl group containing polyimide powder
The preparation process of phenolic hydroxyl group-containing polyimide powder includes the following steps: 1. reaction of phenolic hydroxyl group-containing aromatic diamine compound or its mixture with other diamine compound and aromatic binary anhydride in the molar ratio of 1 to 1 in strong polar non-protonic organic solvent under protection of nitrogen at 0-30 deg.c for 3-12 hr to obtain transparent ropy polyhydroxy amido acid solution; and 2. adding azeotropic dewatering agent in nitrogen atmosphere and heating to 120-160 deg.c to reflux, azeotropically dewater and imidize for 5-18 hr, cooling to room temperature, washing and vacuum drying to obtain phenolic hydroxyl group-containing polyimide powder. The industrial production process has environment friendship, simple operation, low cost and easy solvent recovery.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Large area optical quality synthetic polycrystalline diaond window
ActiveUS20140349068A1Improve optical qualityPrecise design toleranceSynthetic resin layered productsDiamondDielectric lossRoom temperature
A polycrystalline chemical vapour deposited (CVD) diamond wafer comprising: a largest linear dimension equal to or greater than 70 mm; a thickness equal to or greater than 1.3 mm; and one or both of the following characteristics measured at room temperature (nominally 298 K) over at least a central area of the polycrystalline CVD diamond wafer, said central area being circular, centred on a central point of the polycrystalline CVD diamond wafer, and having a diameter of at least 70% of the largest linear dimension of the polycrystalline CVD diamond wafer: an absorption coefficient ≦0.2 cm−1 at 10.6 μm; and a dielectric loss coefficient at 145 GHz, of tan δ≦2×10−4.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX TECH LTD
Sealed, edible film strip packets and methods of making and using them
The invention provides, in one aspect, a method of making a confectionery packet or sachet formed with an edible film and enclosing a center composition. The packet or sachet can be designed to be placed in the mouth, where the film dissolves and the center composition is released. In preferred embodiments, the center composition comprises a sugar alcohol, such as xylitol, that creates a cooling sensation. Many other flavors and / or colors or sensates can also be used in the center composition, and some embodiments include breath-freshening, anti-bacterial, nutriceutical, or pharmaceutical compositions in the center composition. The invention also comprises the edible packets or sachets, especially those composed of film with a desired retained water level suitable for producing a self-sealing film and / or an edible film packet that is stable at room temperature for at least six to twelve months.
Owner:CARROLL THOMAS J +5
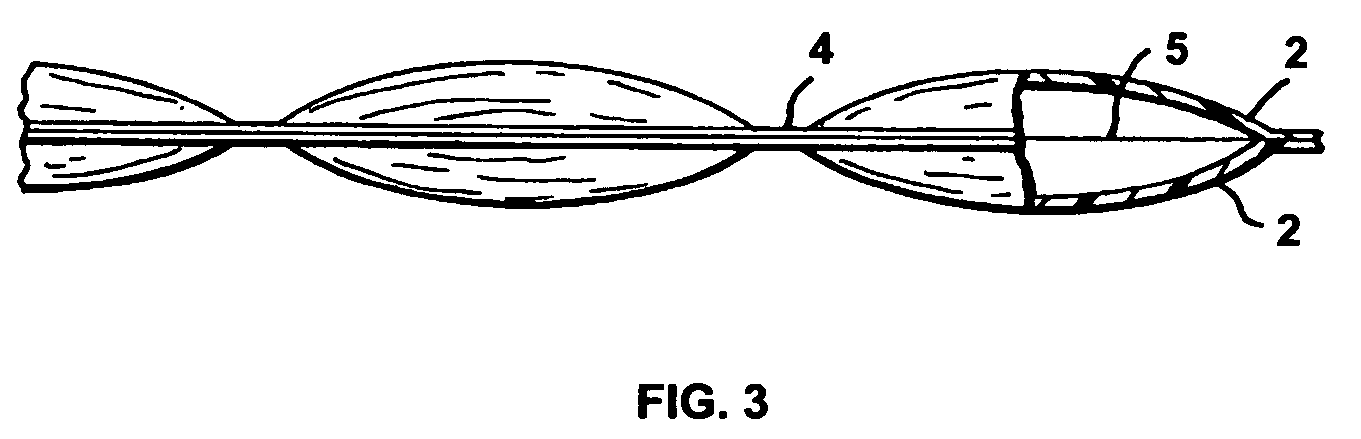
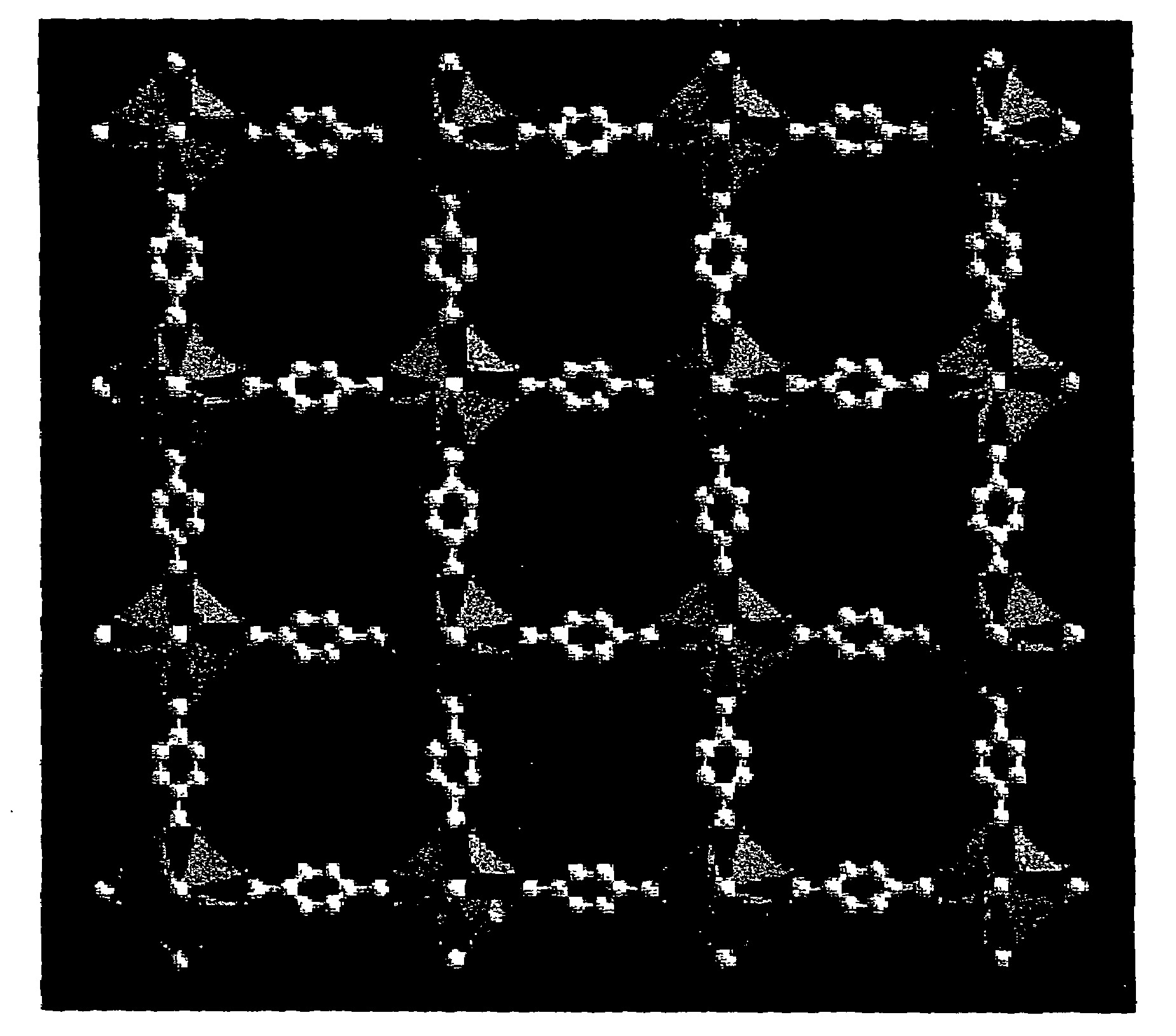
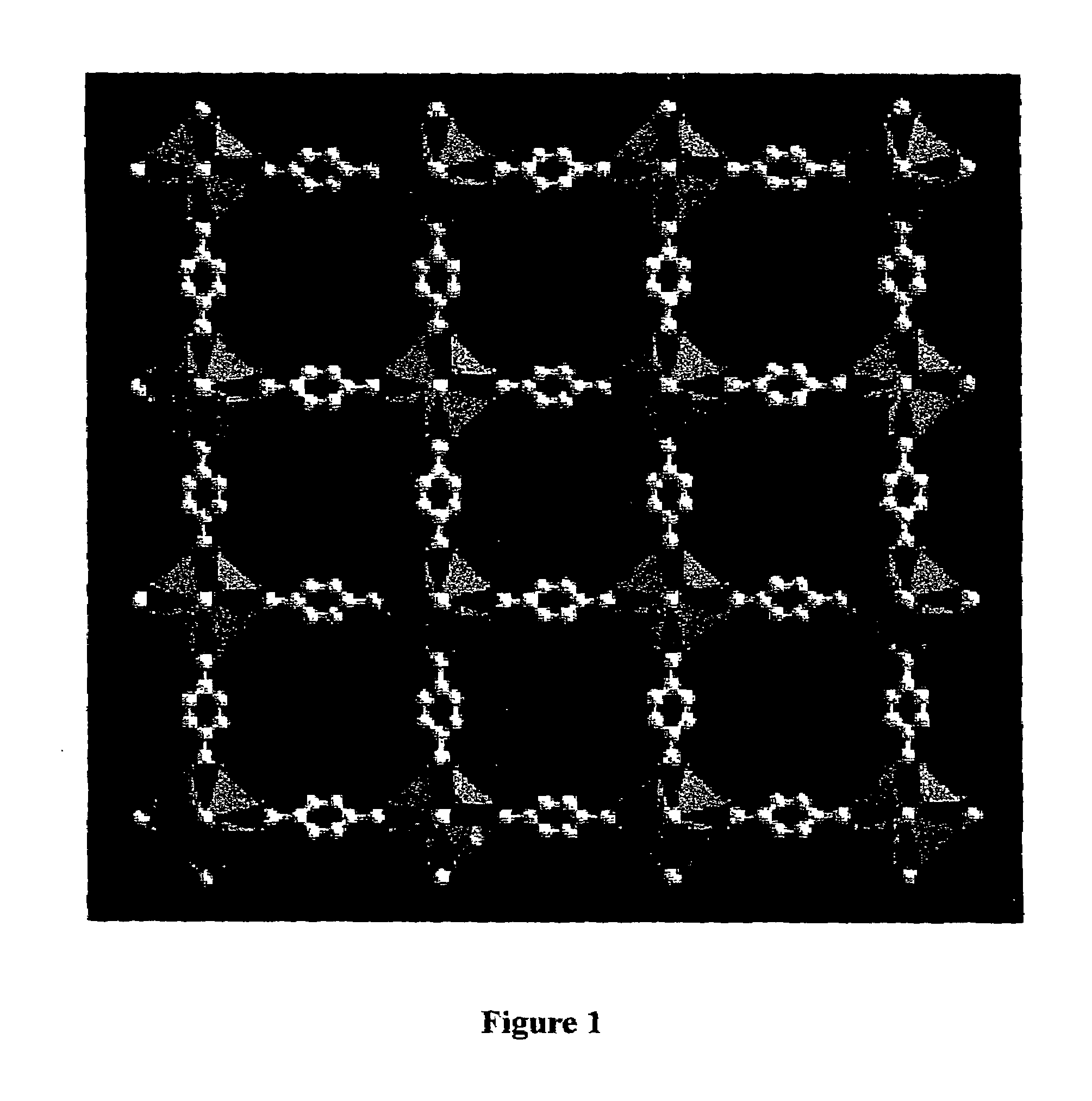
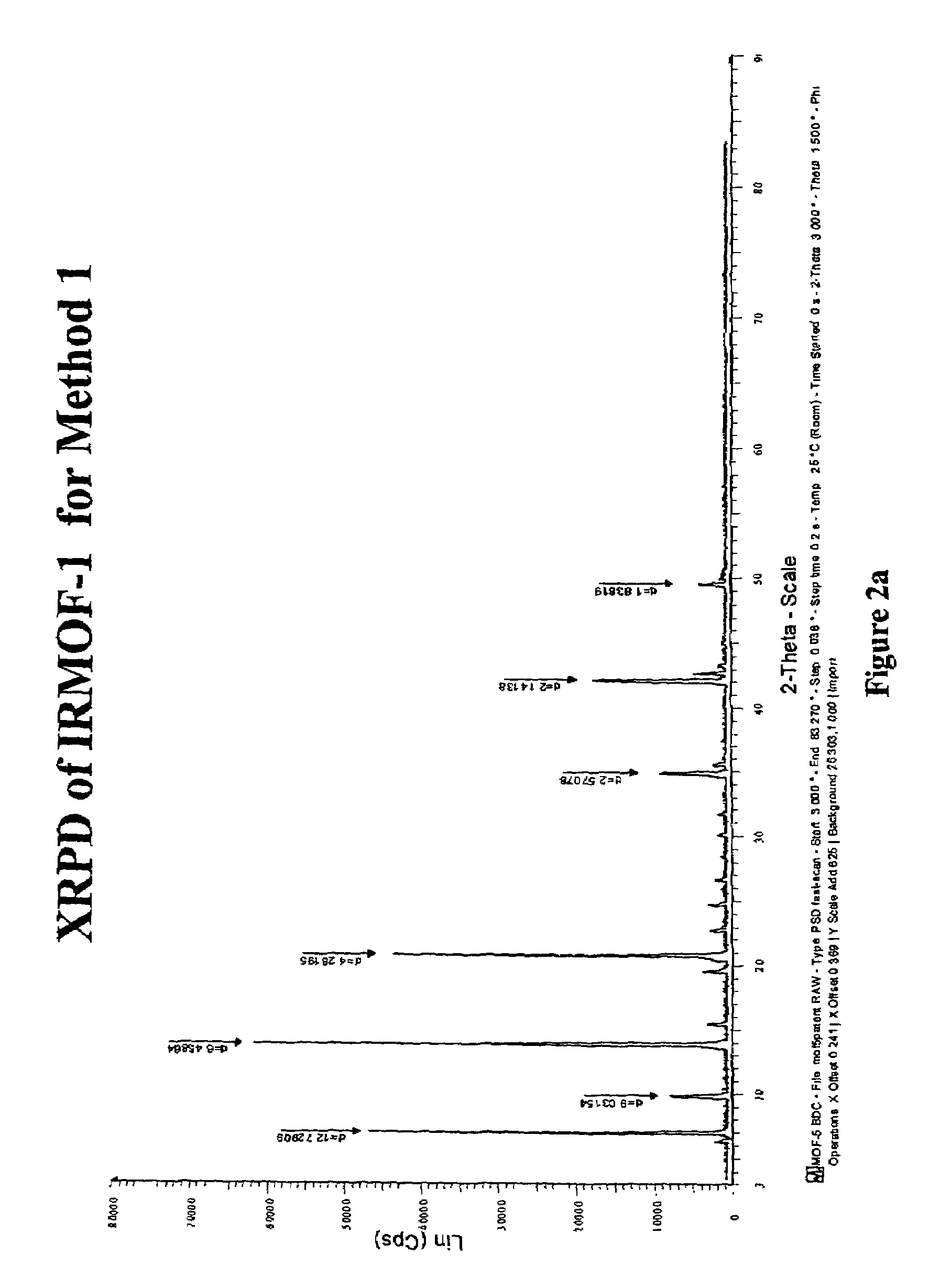
Isoreticular metal-organic frameworks, process for forming the same, and systematic design of pore size and functionality therein, with application for gas storage
InactiveUS7196210B2Group 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSystems designMetal-organic framework
The ability to design and construct solid-state materials with pre-determined structures is a grand challenge in chemistry. An inventive strategy based on reticulating metal ions and organic carboxylate links into extended networks has been advanced to a point that has allowed the design of porous structures in which pore size and functionality can be varied systematically. MOF-5, a prototype of a new class of porous materials and one that is constructed from octahedral Zn—O—C clusters and benzene links, was used to demonstrate that its 3-D porous system can be functionalized with the organic groups, —Br, —NH2, —OC3H7, —OC5H11, —H4C2, and —H4C4, and its pore size expanded with the long molecular struts biphenyl, tetrahydropyrene, pyrene, and terphenyl. The ability to direct the formation of the octahedral clusters in the presence of a desired carboxylate link is an essential feature of this strategy, which resulted in the design of an isoreticular (having the same framework topology) series of sixteen well-defined materials whose crystals have open space representing up to 91.1% of the crystal volume, and homogeneous periodic pores that can be incrementally varied from 3.8 to 28.8 angstroms. Unlike the unpredictable nature of zeolite and other molecular sieve syntheses, the deliberate control exercised at the molecular level in the design of these crystals is expected to have tremendous implications on materials properties and future technologies. Indeed, data indicate that members of this series represent the first monocrystalline mesoporous organic / inorganic frameworks, and exhibit the highest capacity for methane storage (155 cm3 / cm3 at 36 atm) and the lowest densities (0.41 to 0.21 g / cm3) attained to date for any crystalline material at room temperature.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com