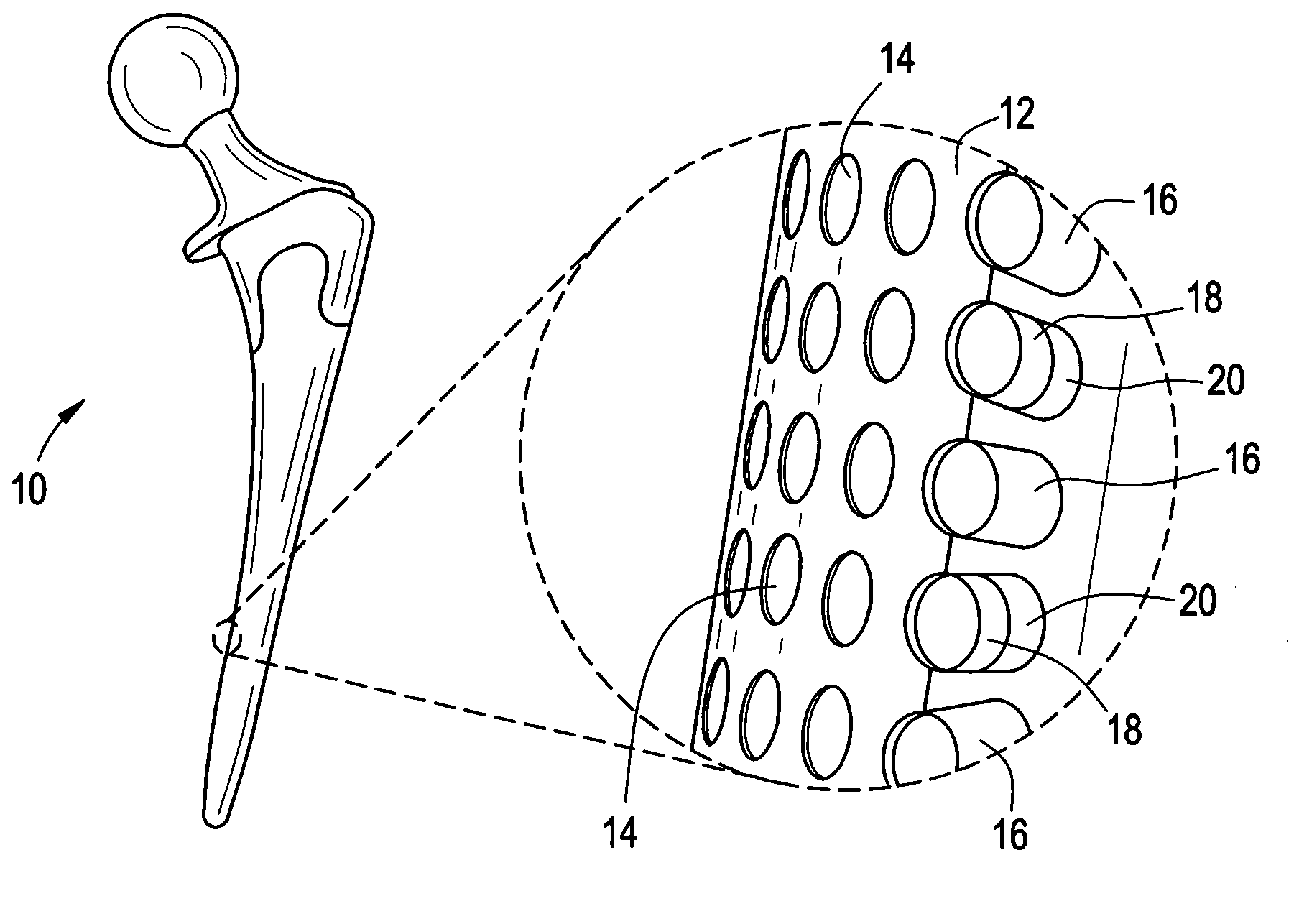
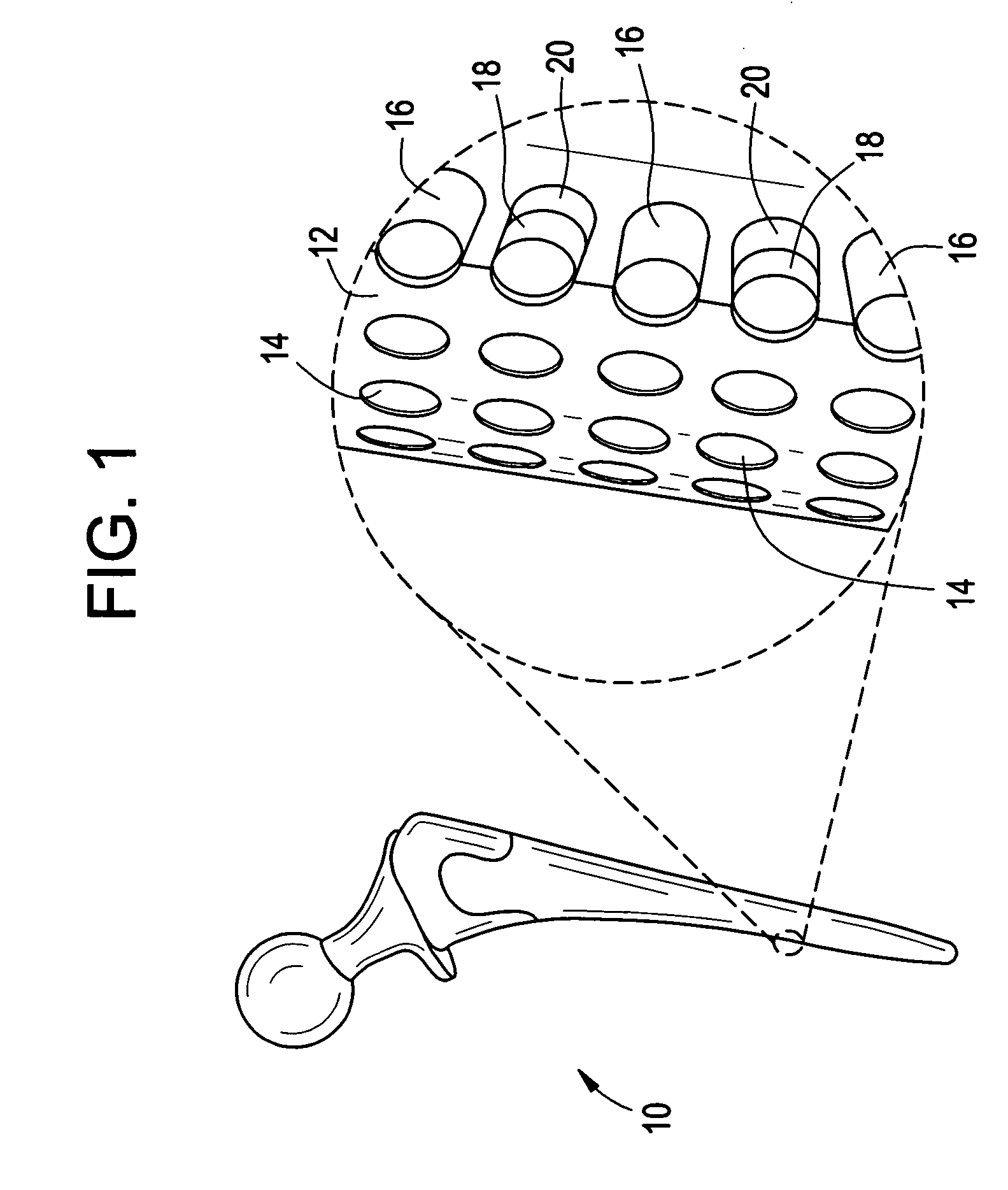
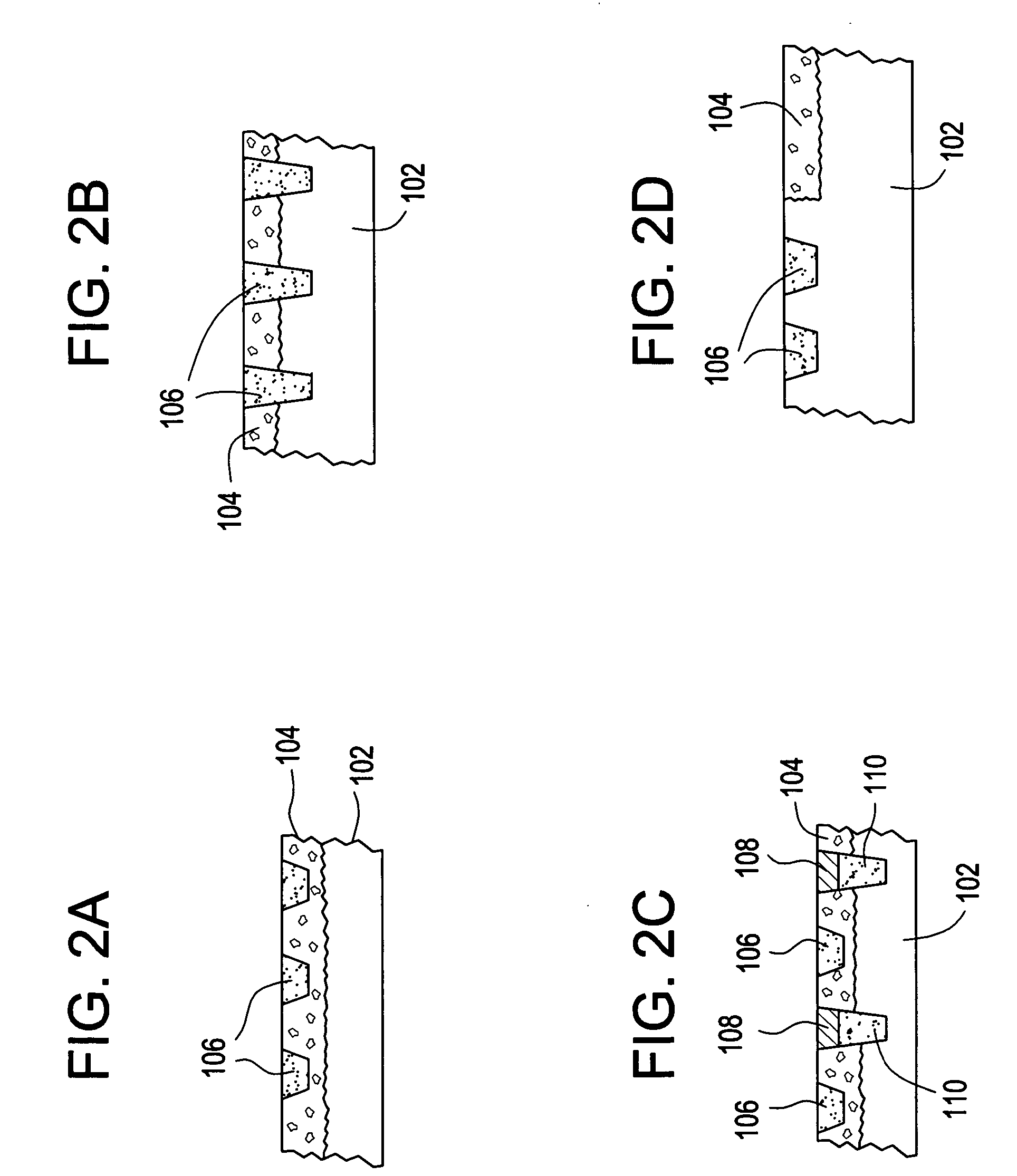
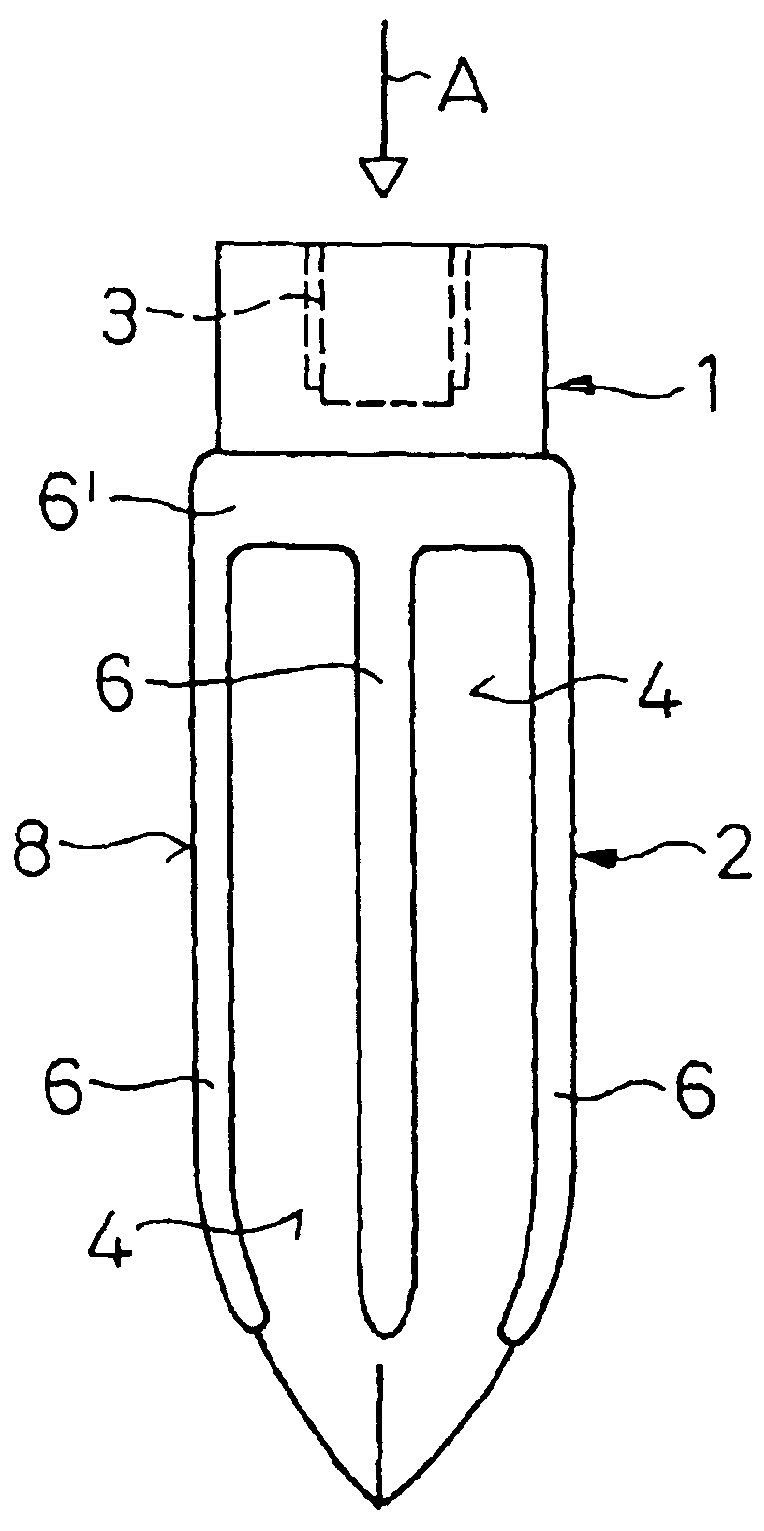
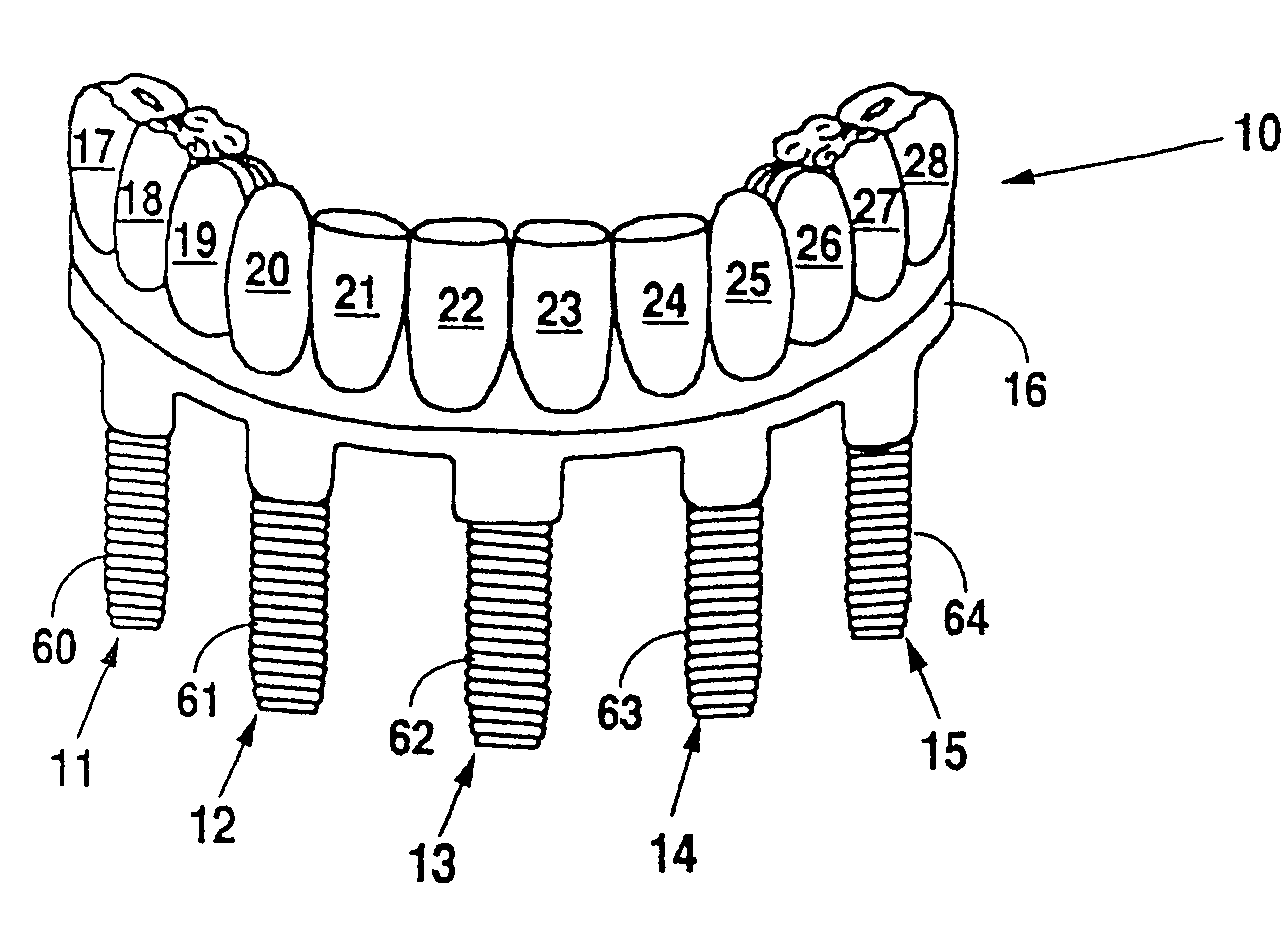
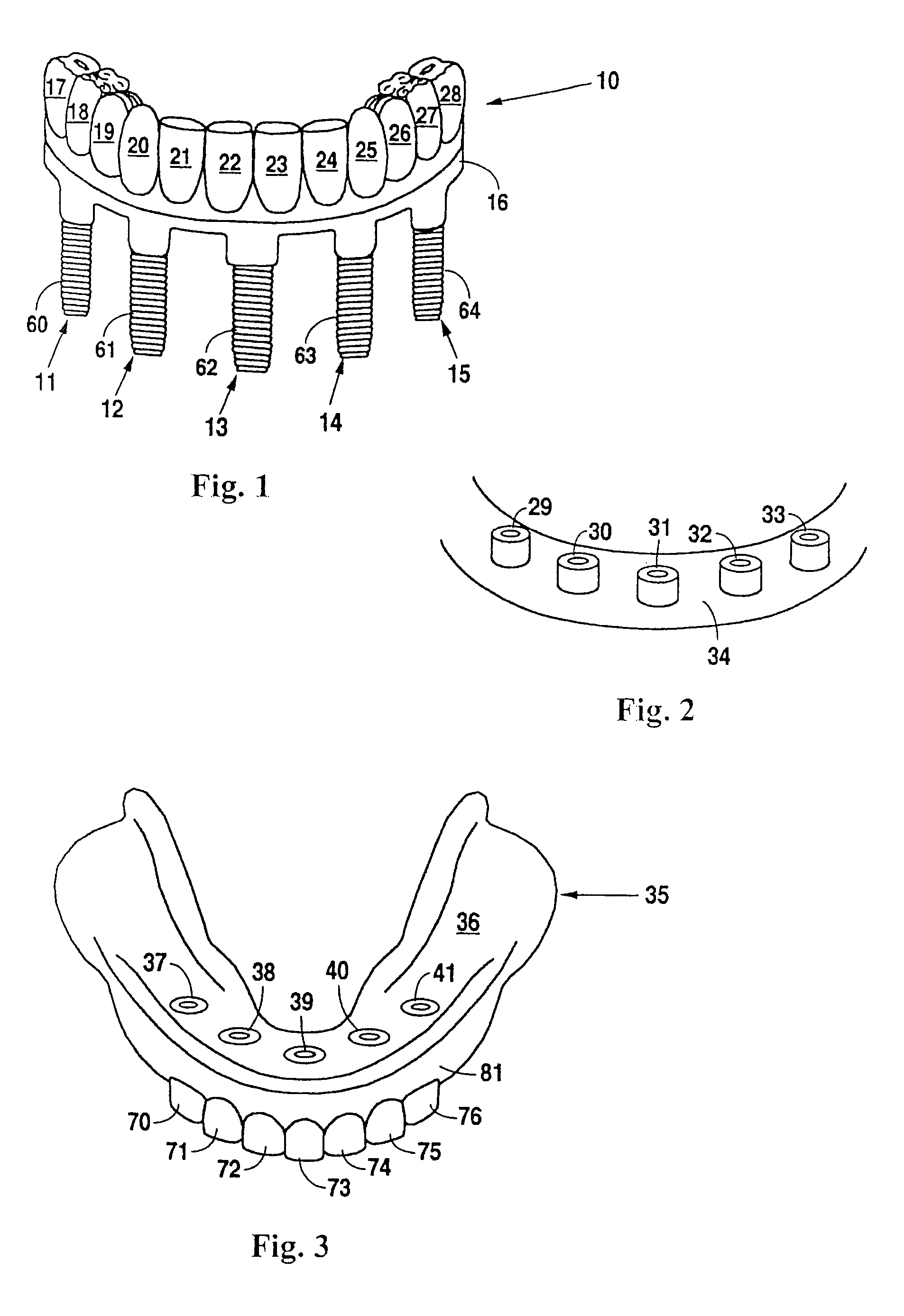
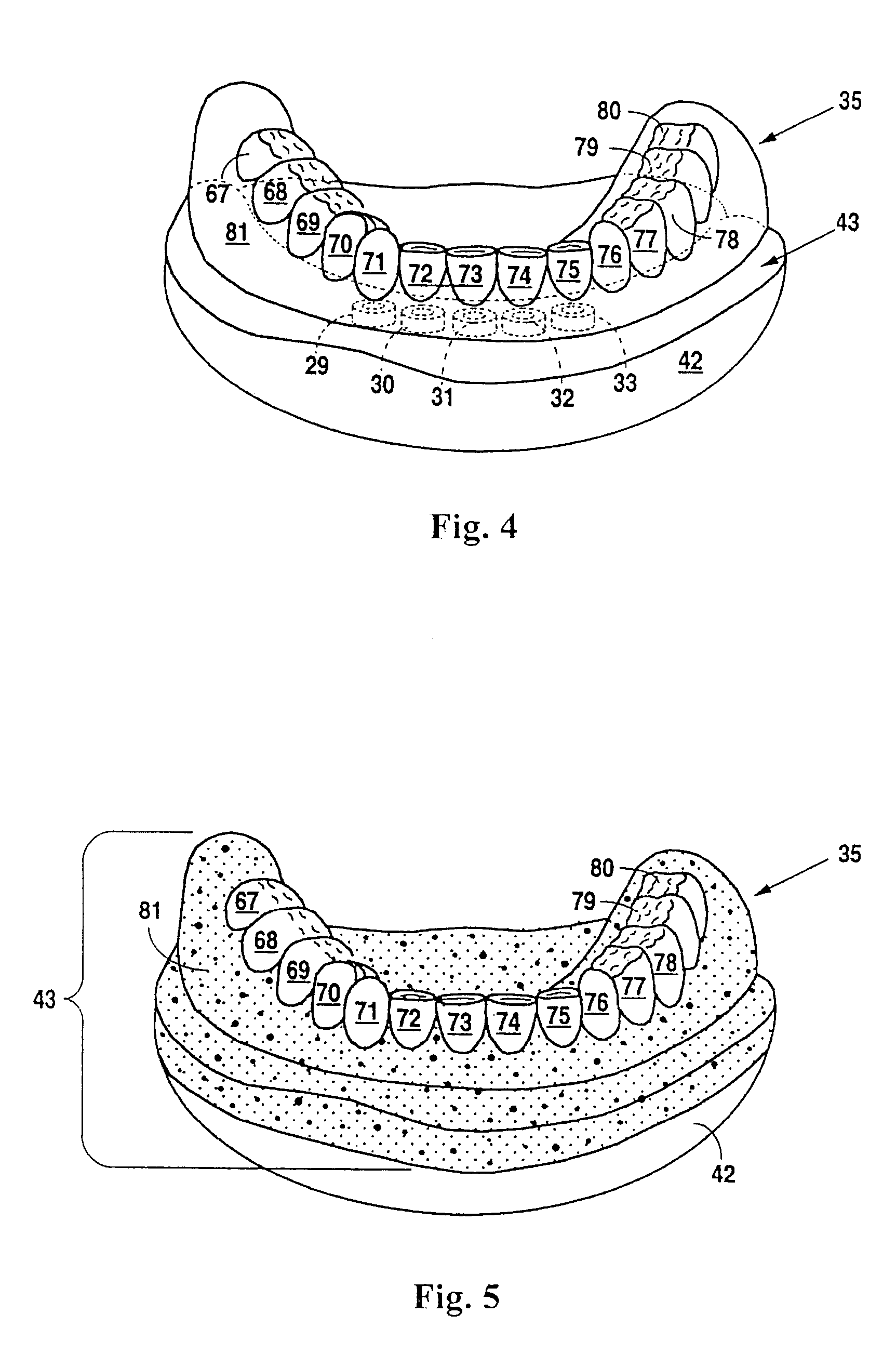
Patents
Literature
2579 results about "Dental implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
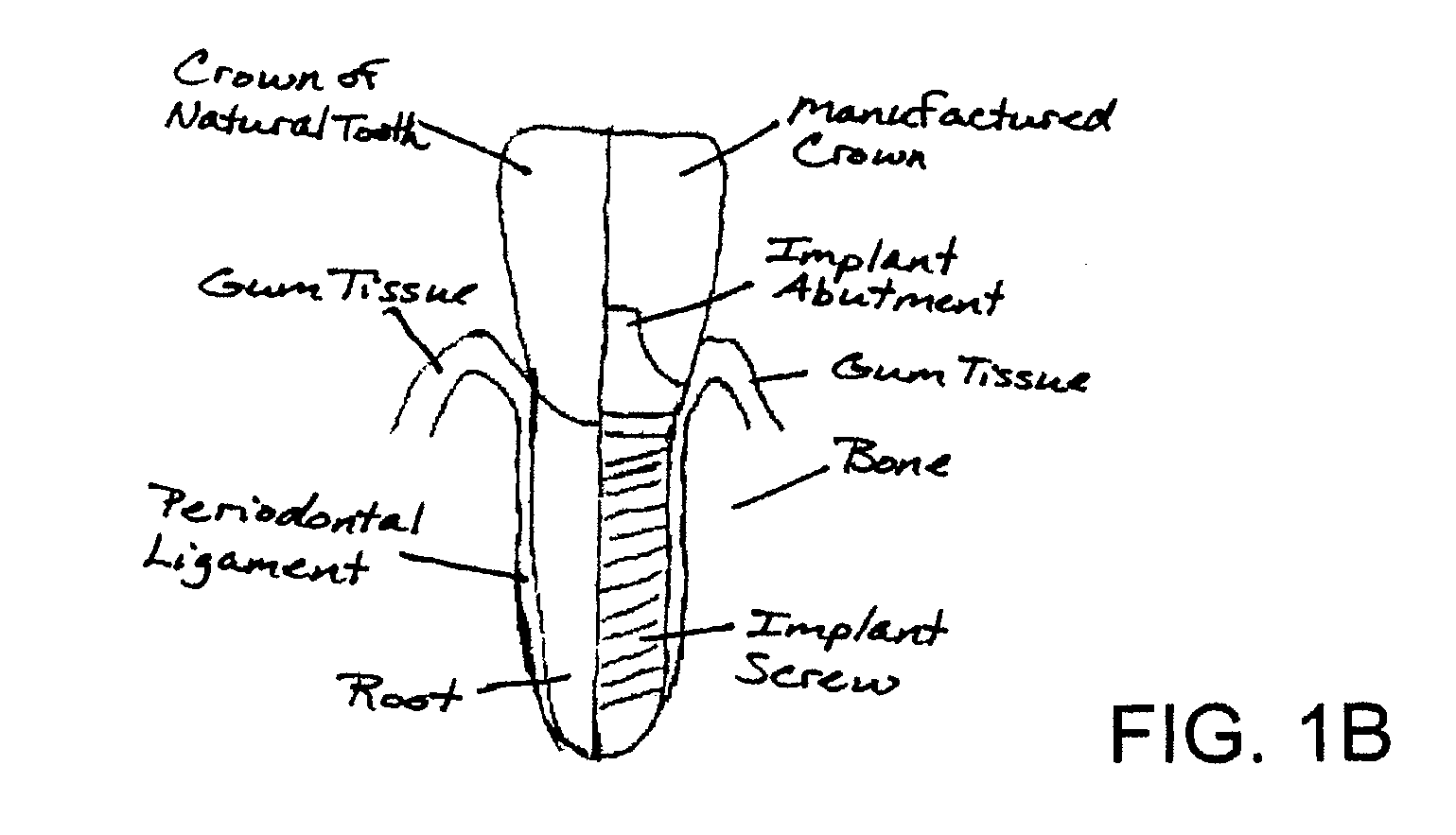
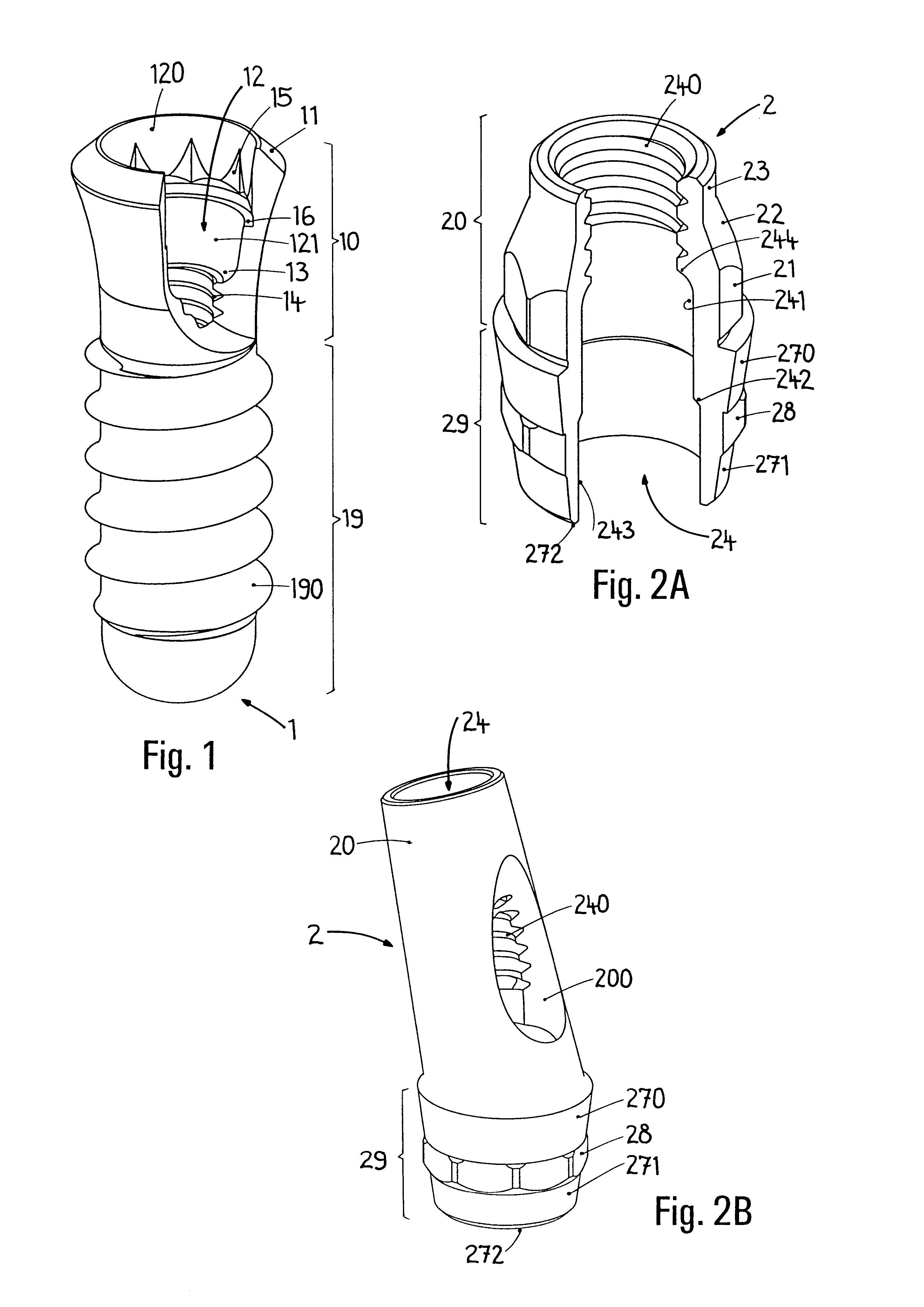
A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a surgical component that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic.
Degradable implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20060229711A1Reduce probabilityLower resistanceStentsBlood vesselsVascular implantBlood vessel
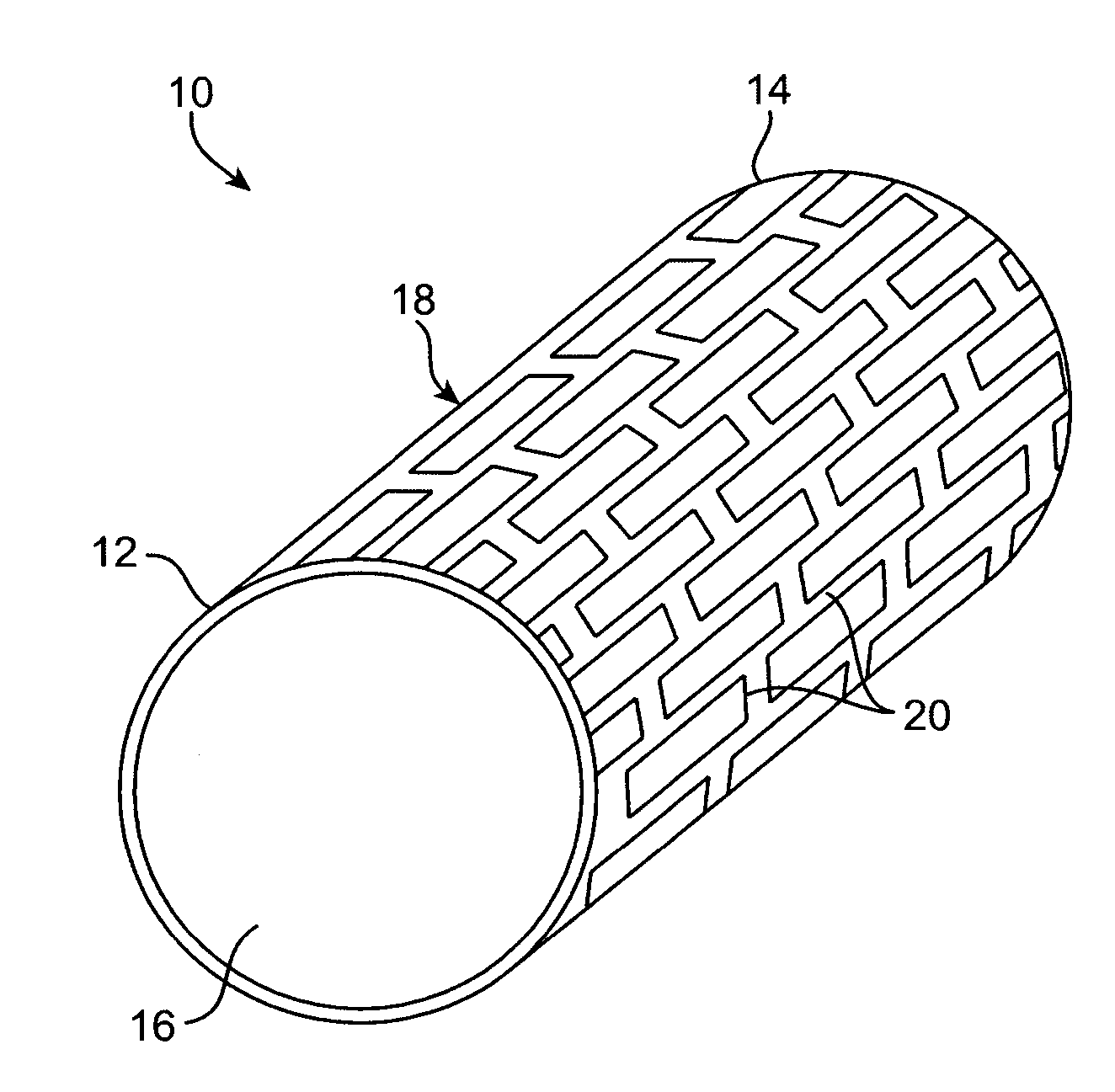
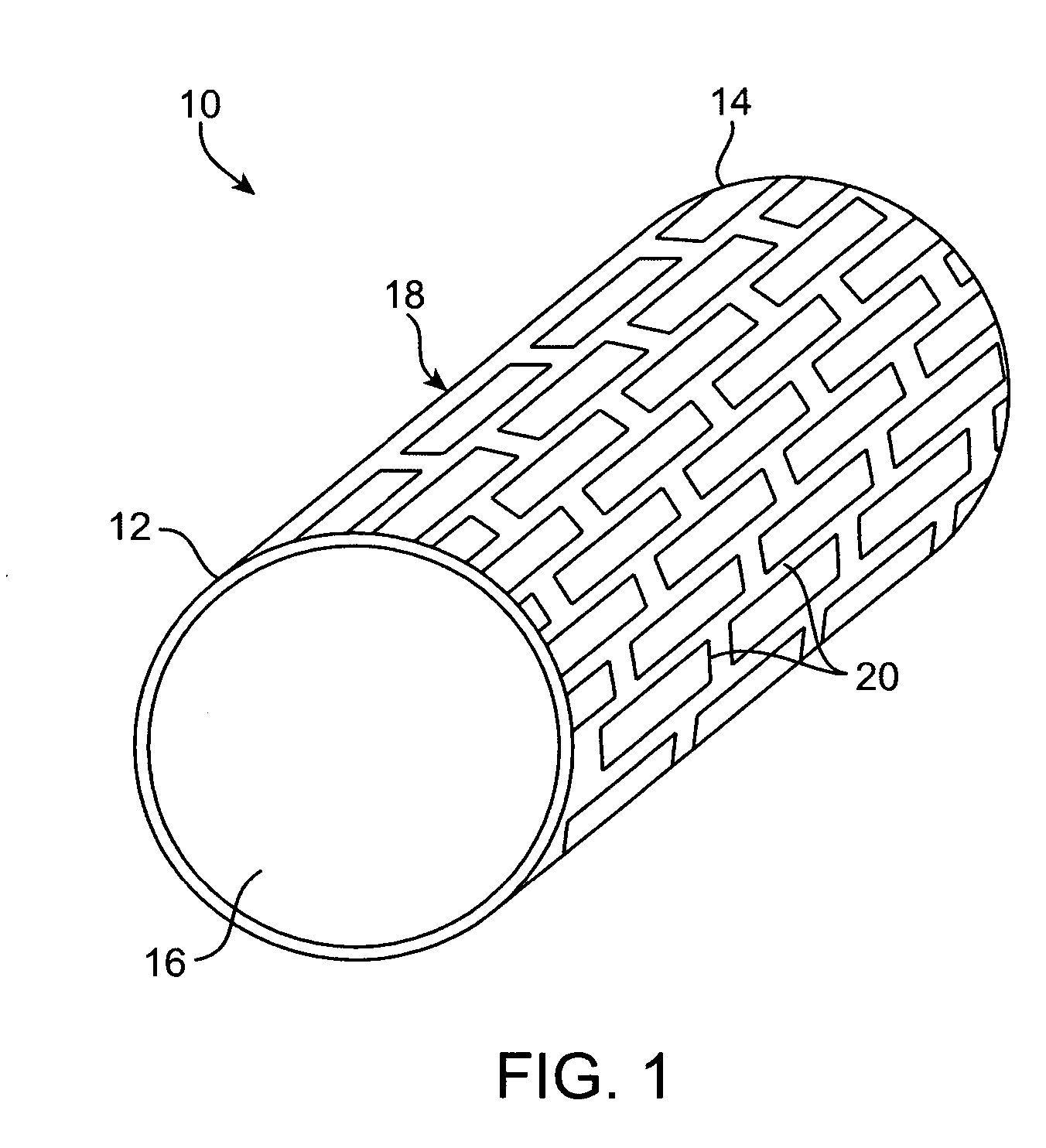
Devices and methods are provided for an implantable medical device which is degradable over a clinically relevant period of time. The medical devices may have the form of implants, graft implants, vascular implants, non vascular implants, wound closure implants, sutures, drug delivery implants, biologic delivery implants, urinary tract implants, inter-uterine implants, organ implants, bone implants including bone plates, bone screws, dental implants, spinal disks, or the like. In preferred embodiments, the implantable medical device comprises an implantable luminal prosthesis, such as vascular and non-vascular stents and stents grafts.
Owner:ELIXIR MEDICAL CORP
Medical and dental implant devices for controlled drug delivery
Implantable devices and methods for use in the treatment of osteonecrosisare provided. The device includes at least one implant device body adapted for insertion into one or more channels or voids in bone tissue; a plurality of discrete reservoirs, which may preferably be microreservoirs, located in the surface of the at least one implant device body; and at least one release system disposed in one or more of the plurality of reservoirs, wherein the release system includes at least one drug selected from the group consisting of bone growth promoters, angiogenesis promoters, analgesics, anesthetics, antibiotics, and combinations thereof. The device body may be formed of a bone graft material, a polymer, a metal, a ceramic, or a combination thereof. The device body may be a monolithic structure, such as one having a cylindrical shape, or it may be in the form of multiple units, such as a plurality of beads.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
System, Method And Apparatus For Tooth Implant Planning And Tooth Implant Kits
InactiveUS20100105011A1Improve the level ofFacilitate proper fixture placementDental implantsDispensing apparatusPatient dataDental implant
Systems and methods support dental implant patient scheduling and treatment process relating to packaging one or more dental appliances as a kit which is readily used by dental professional during surgery, by communicating manufacturing progress information with a doctor over a network and performing patient scheduling and treatment when the dental appliances reach a certain manufacturing progress. A network-based service may also provide a doctor with a treatment solution including a surgical kit derived from patient data.
Owner:INPRONTO
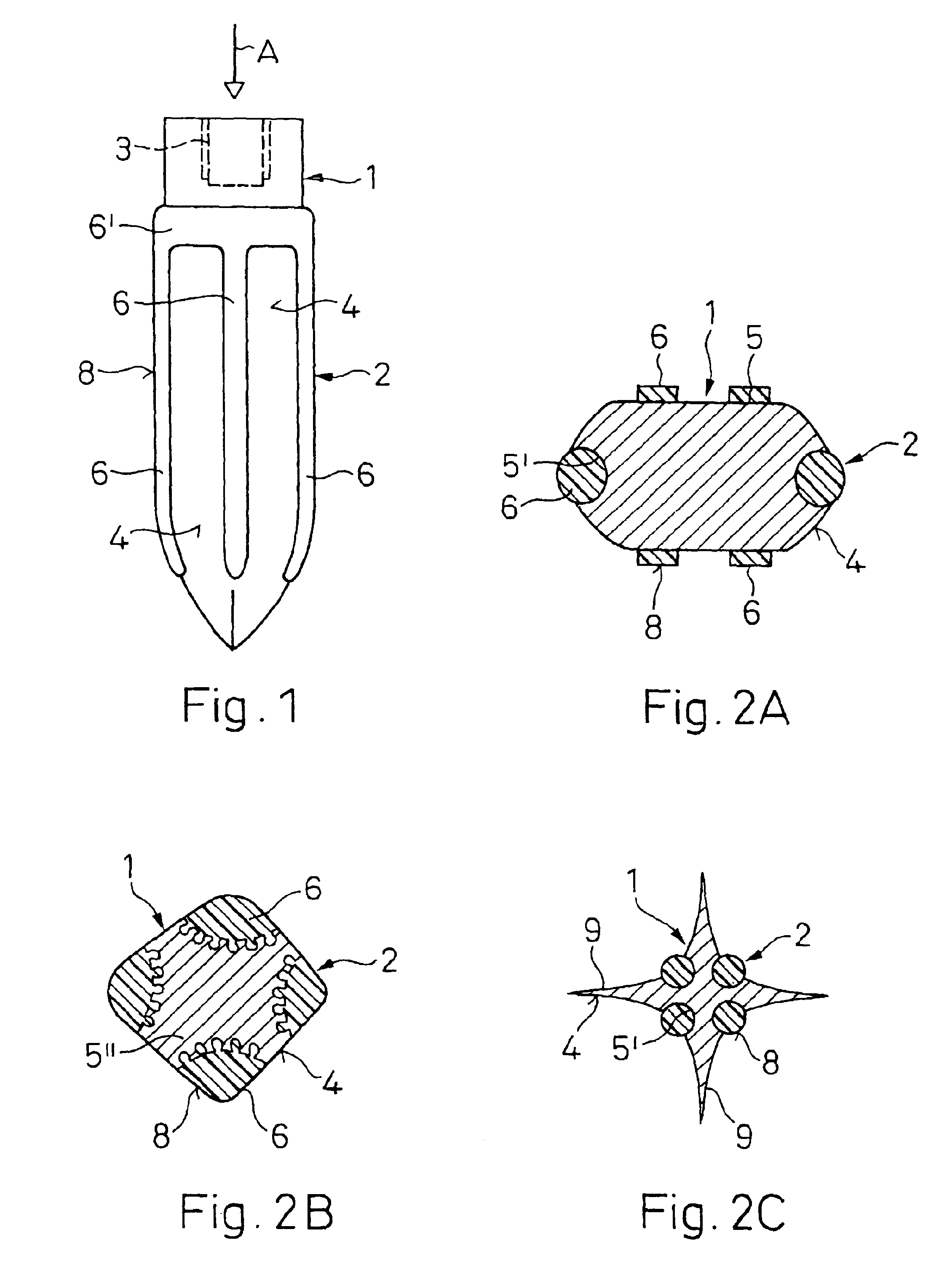
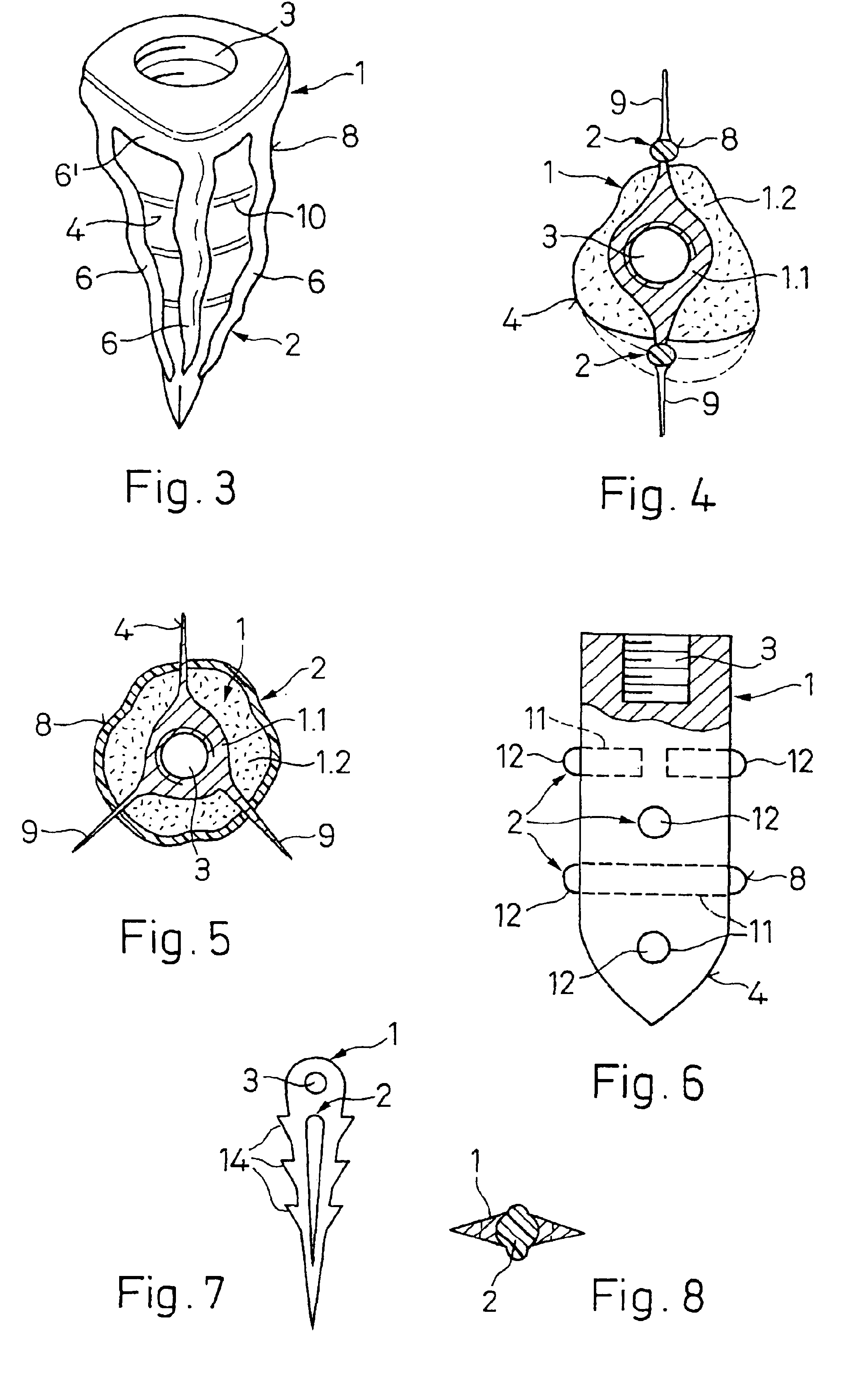
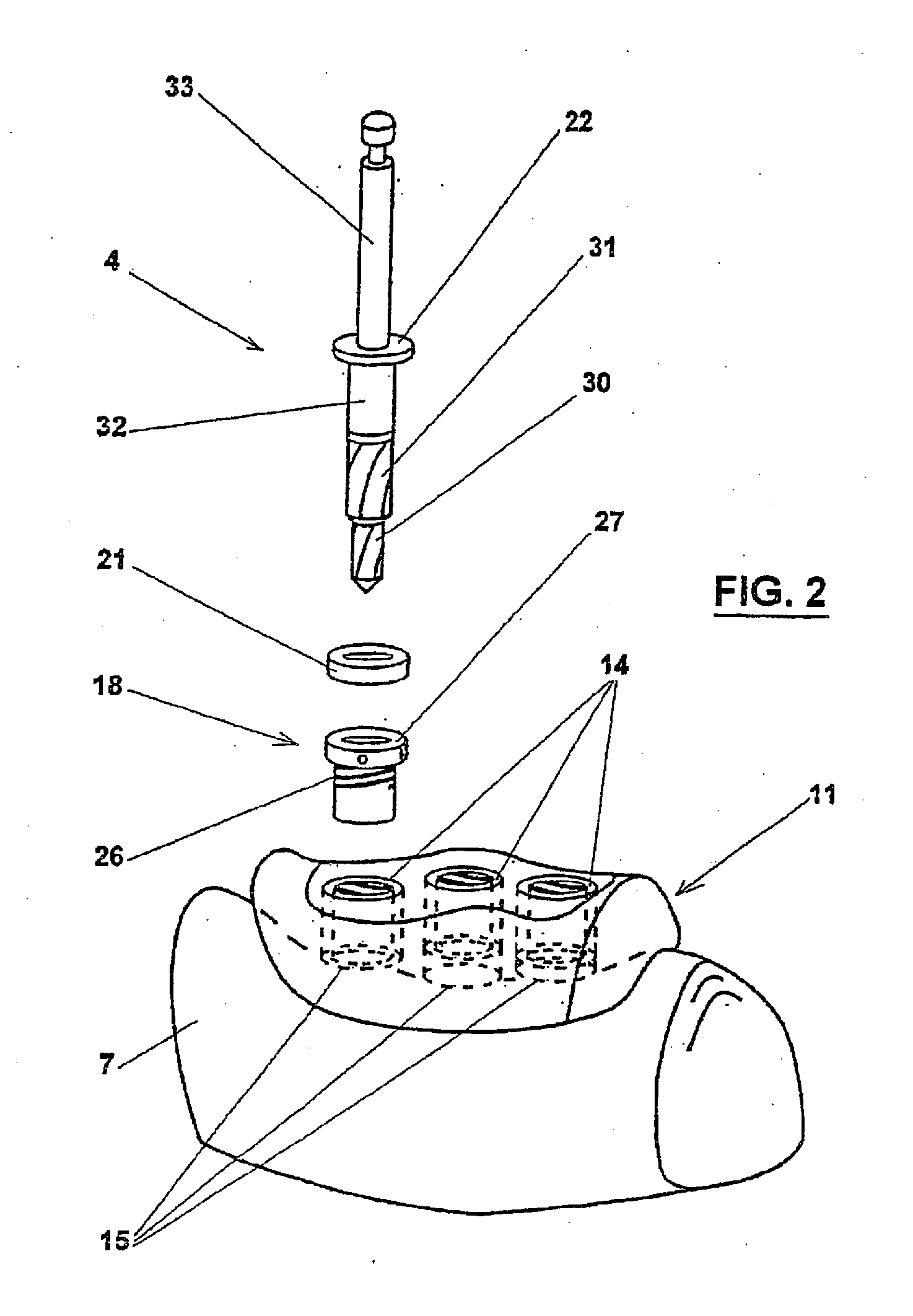
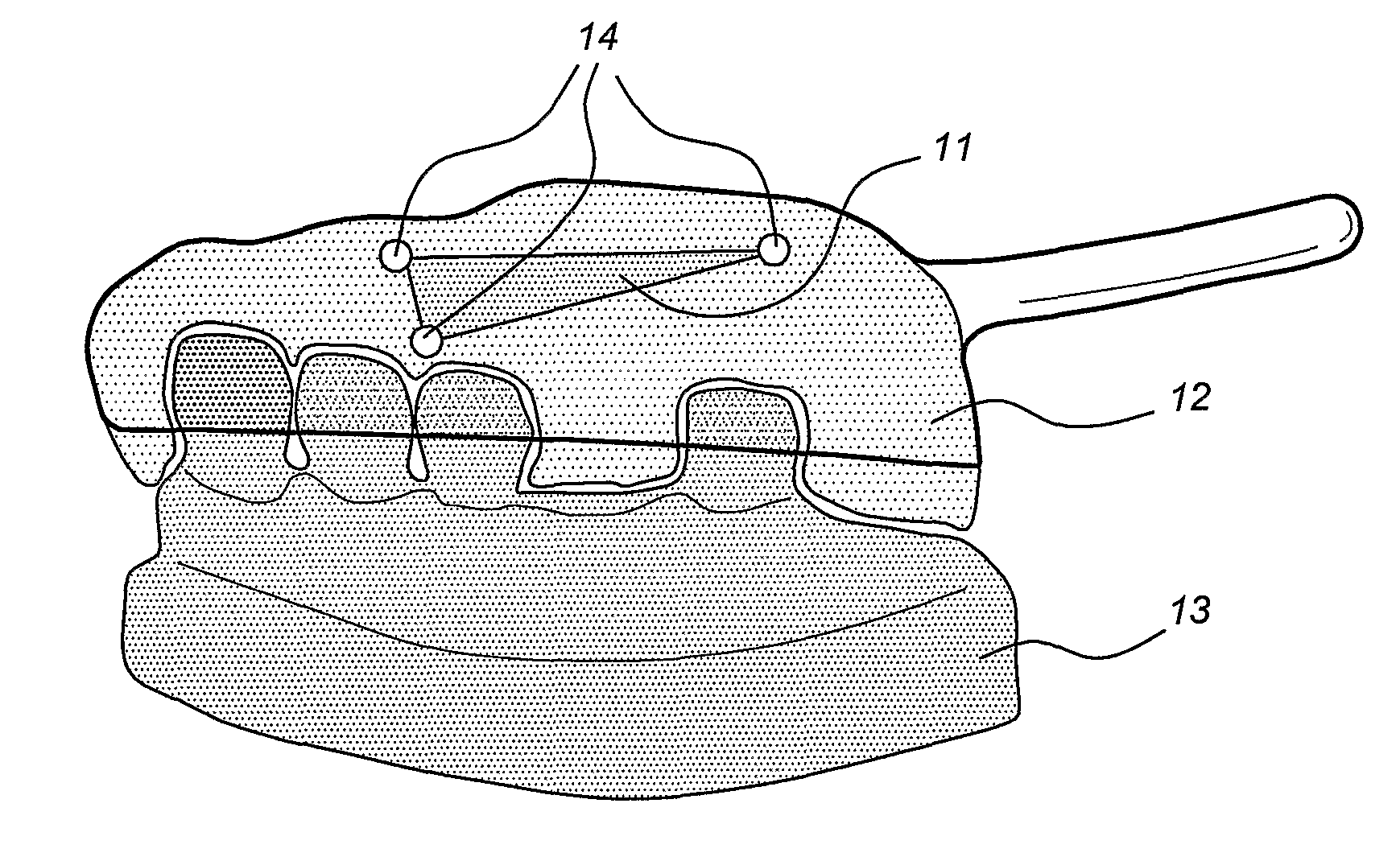
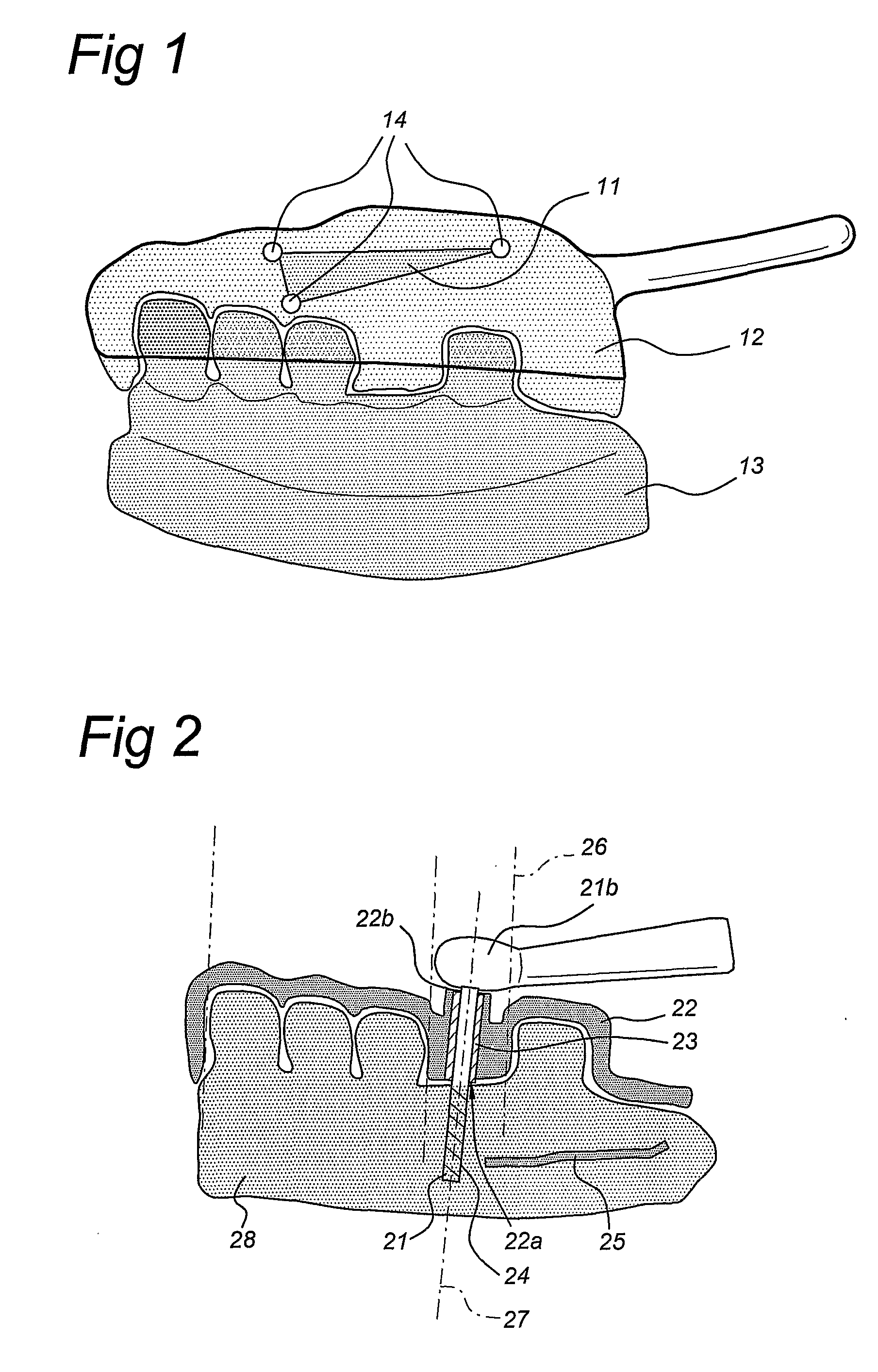
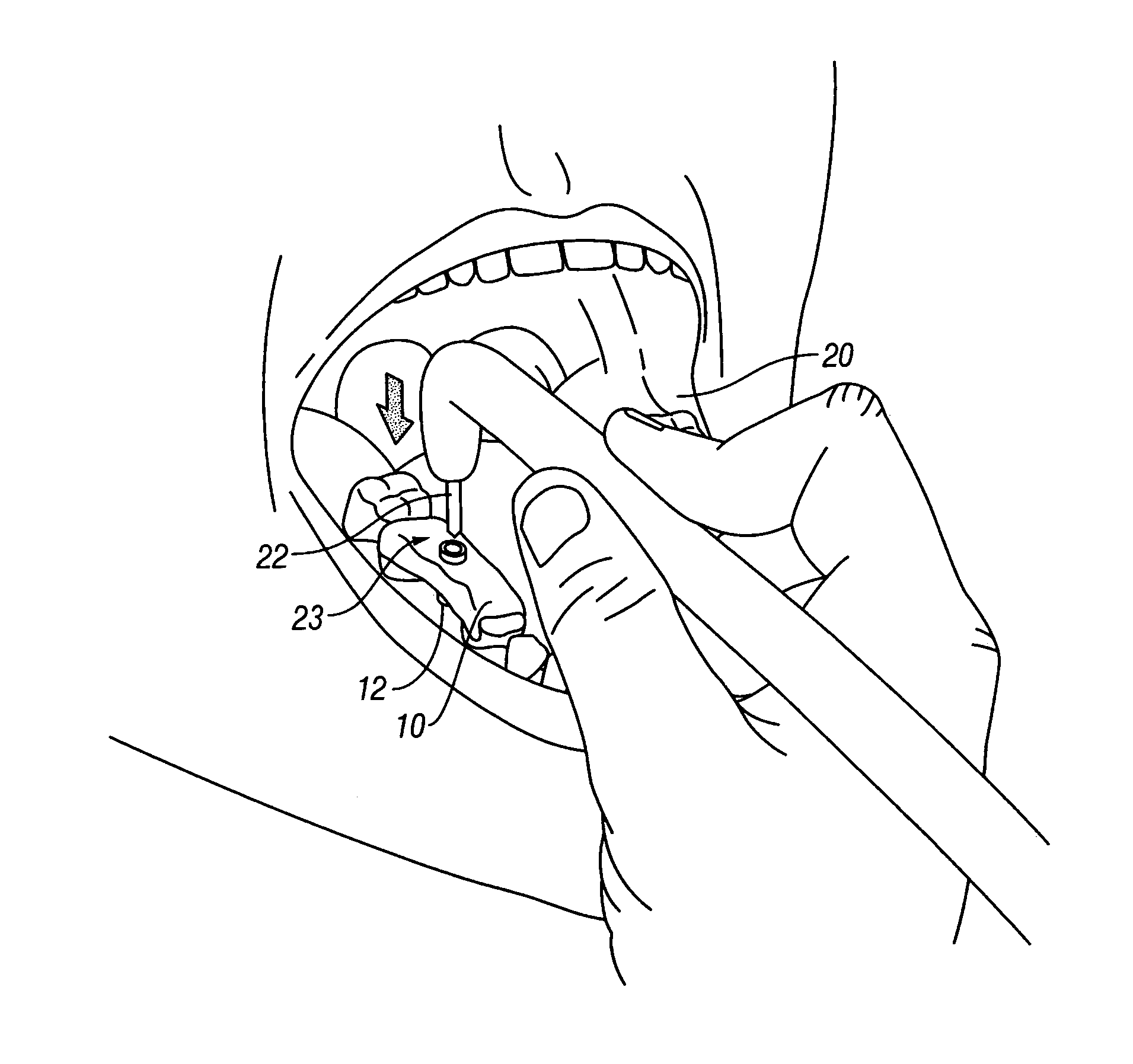
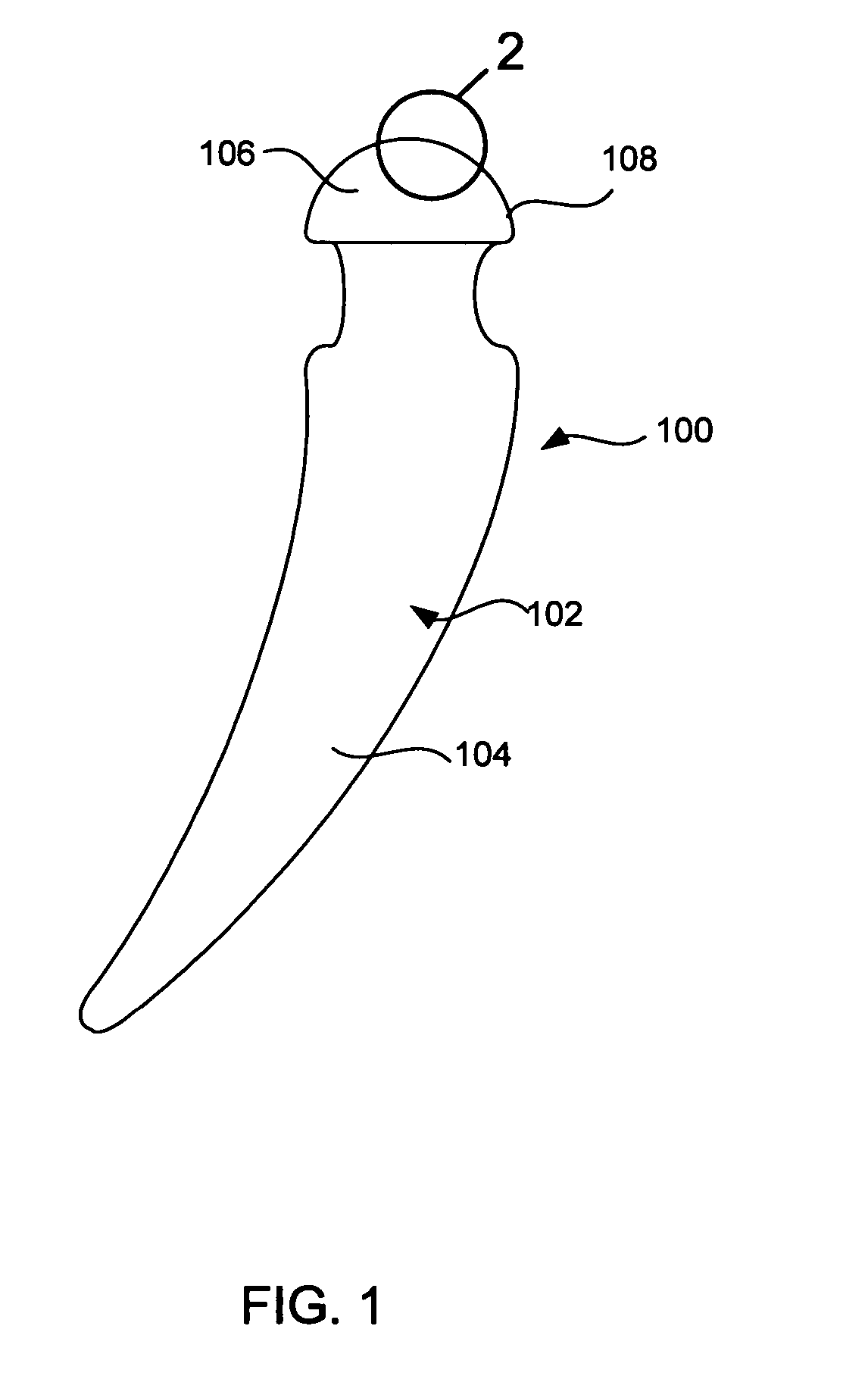
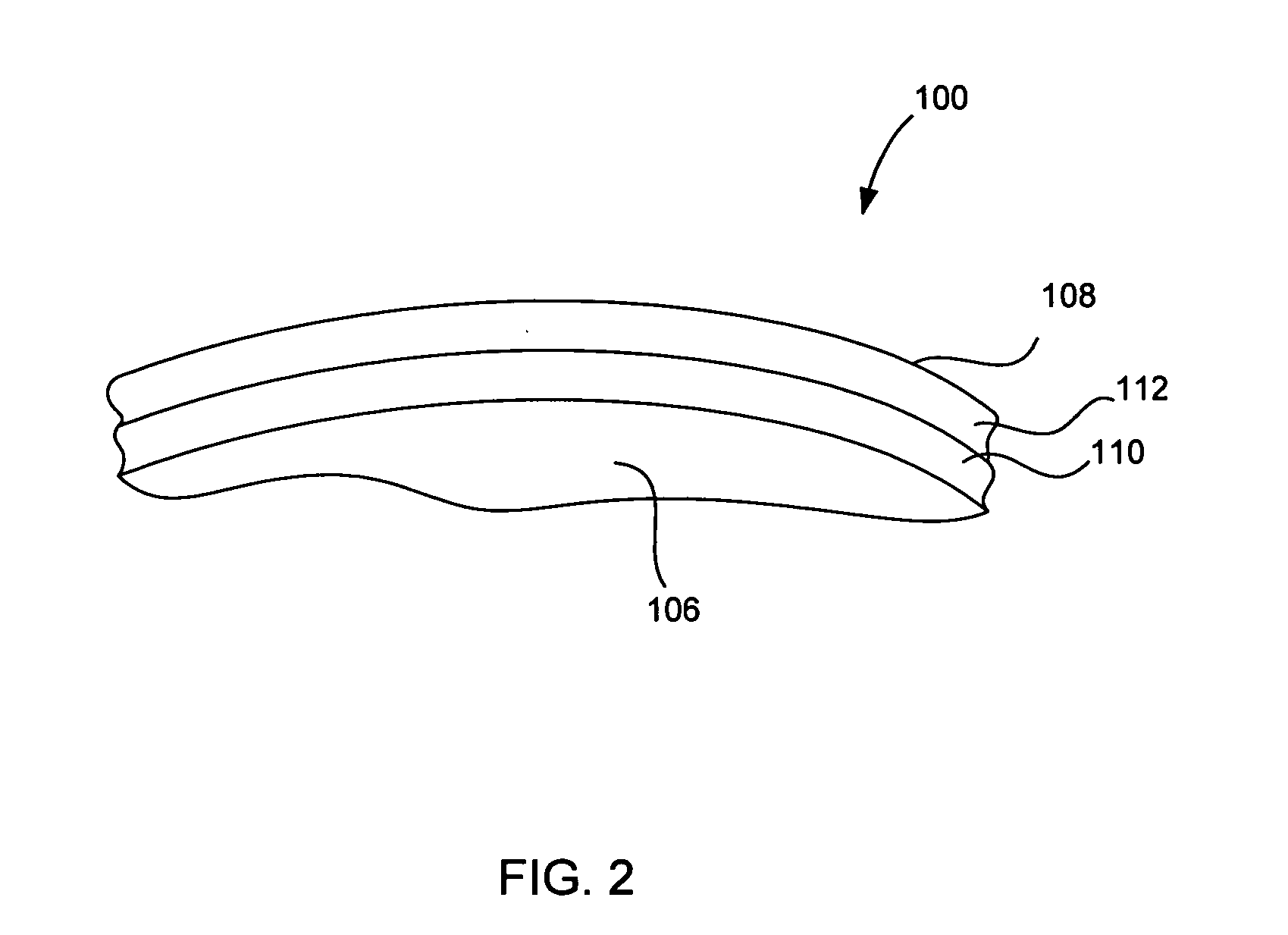
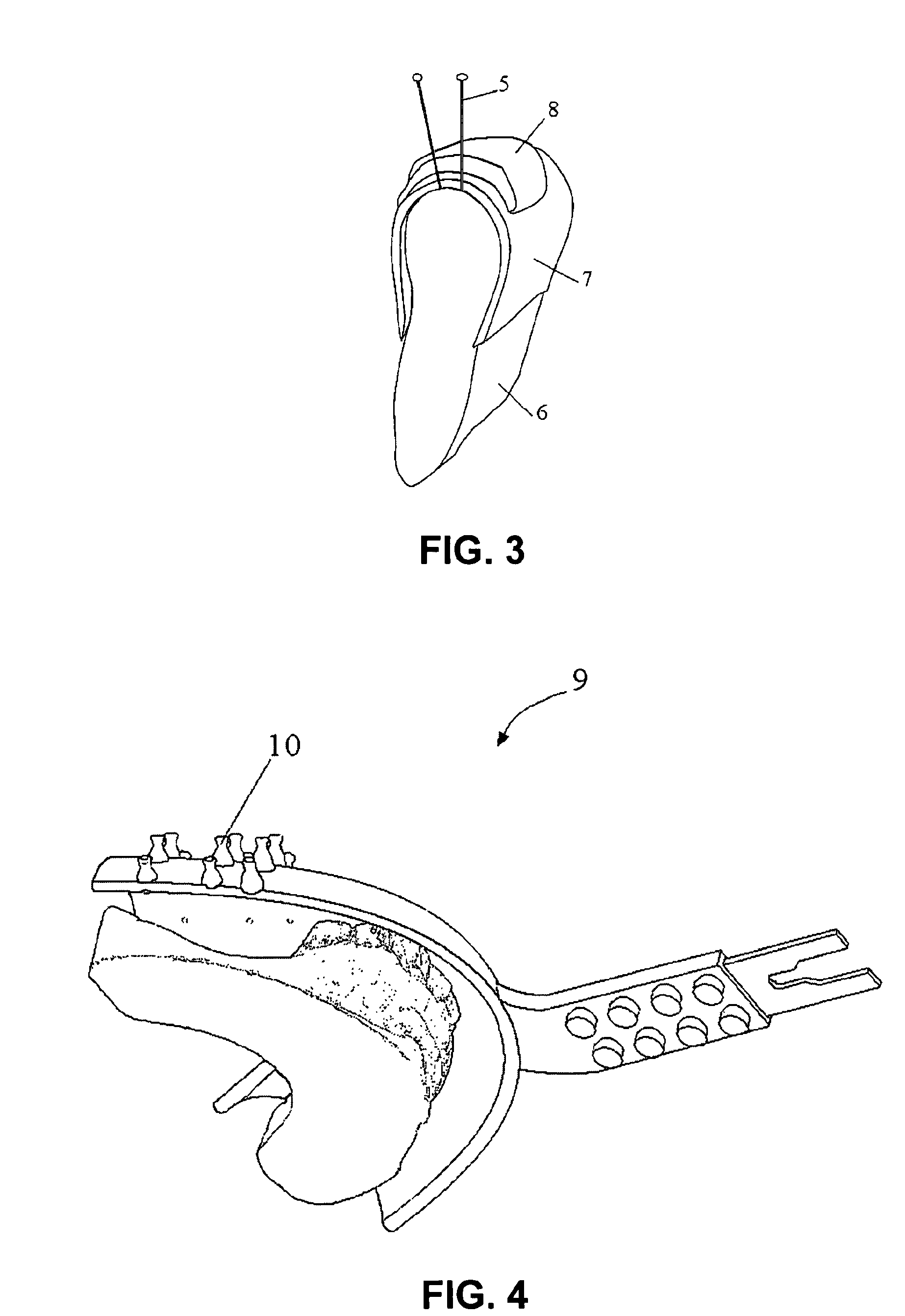
Method and device for placing dental implants
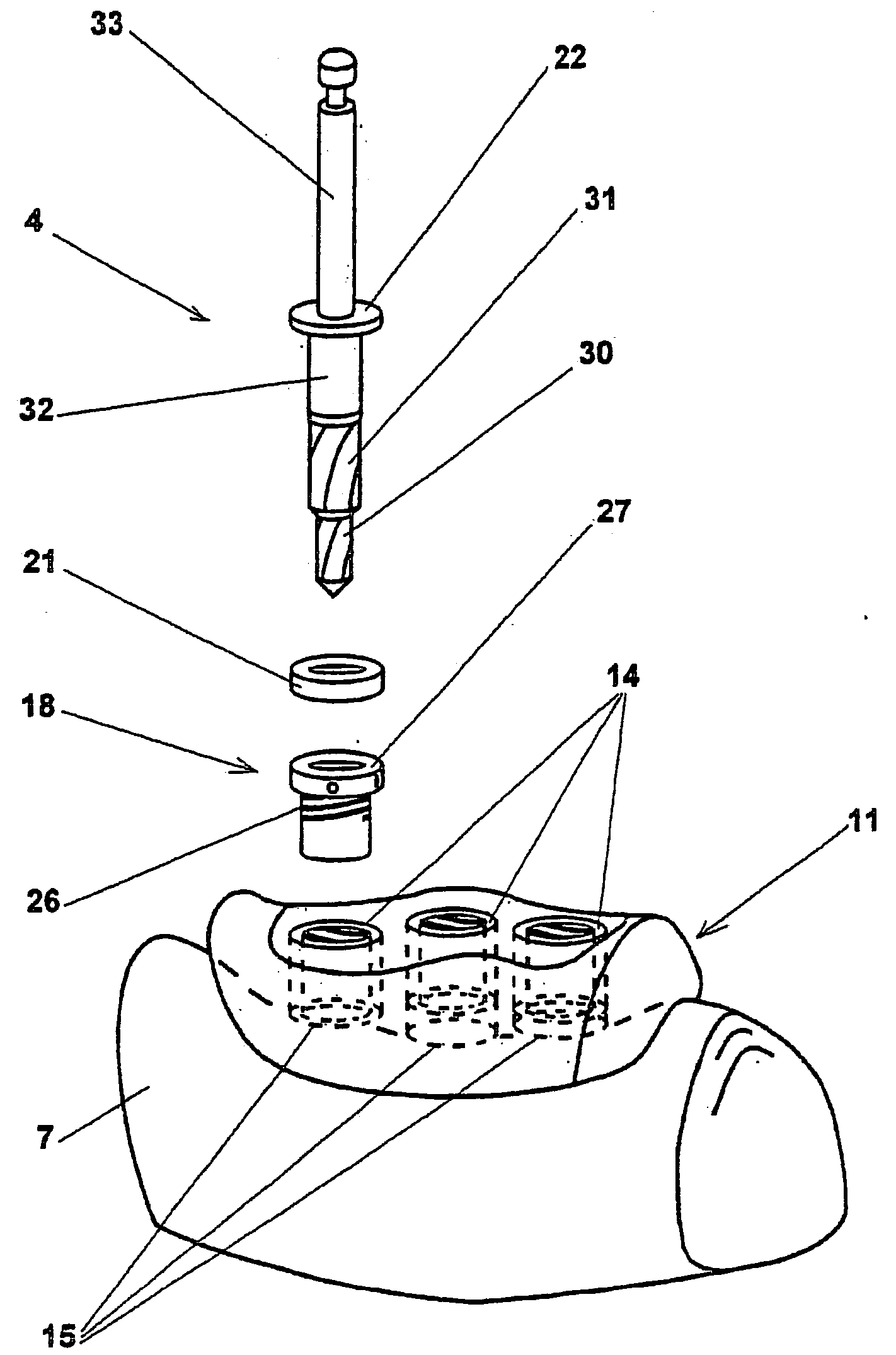
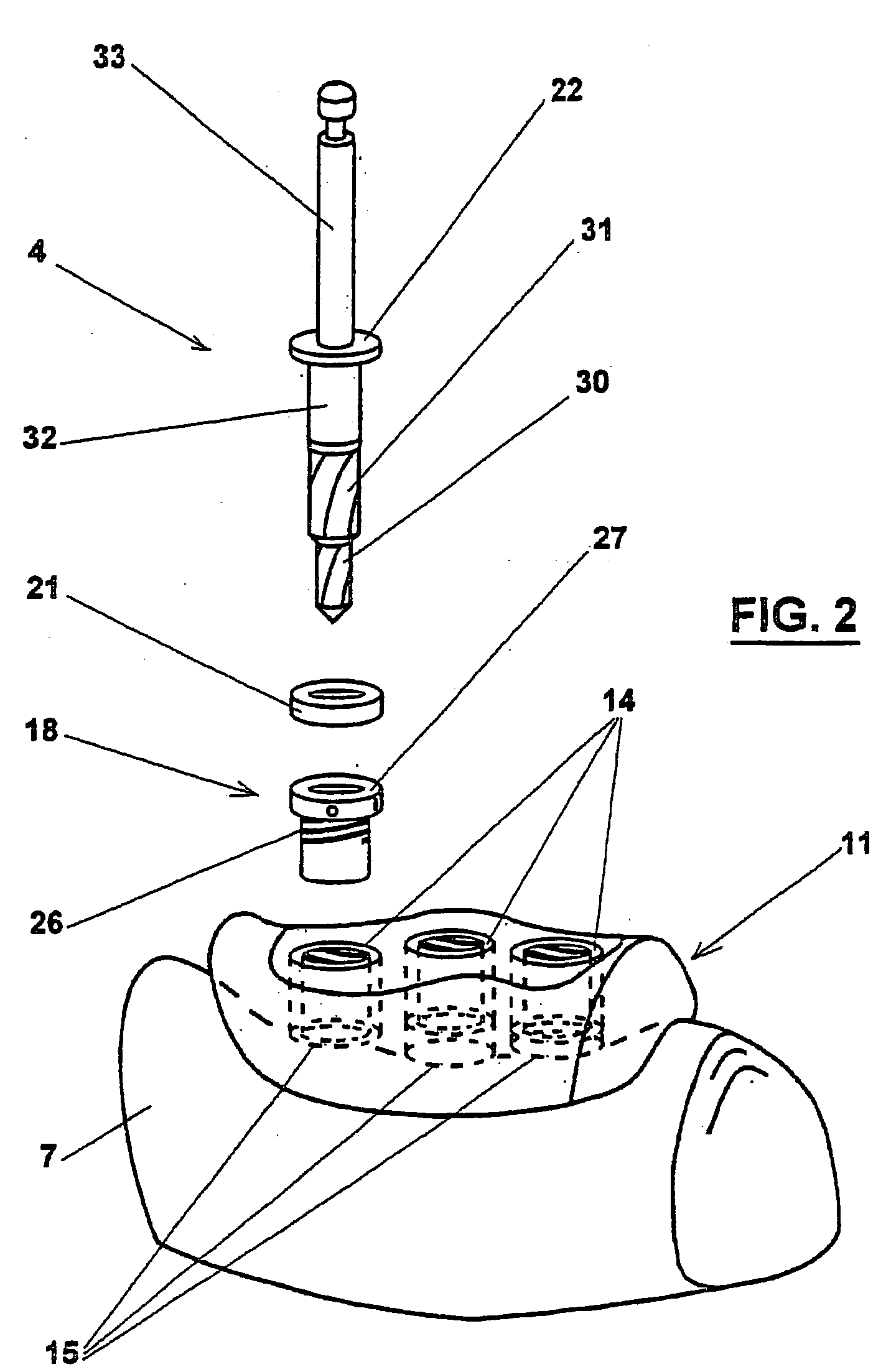
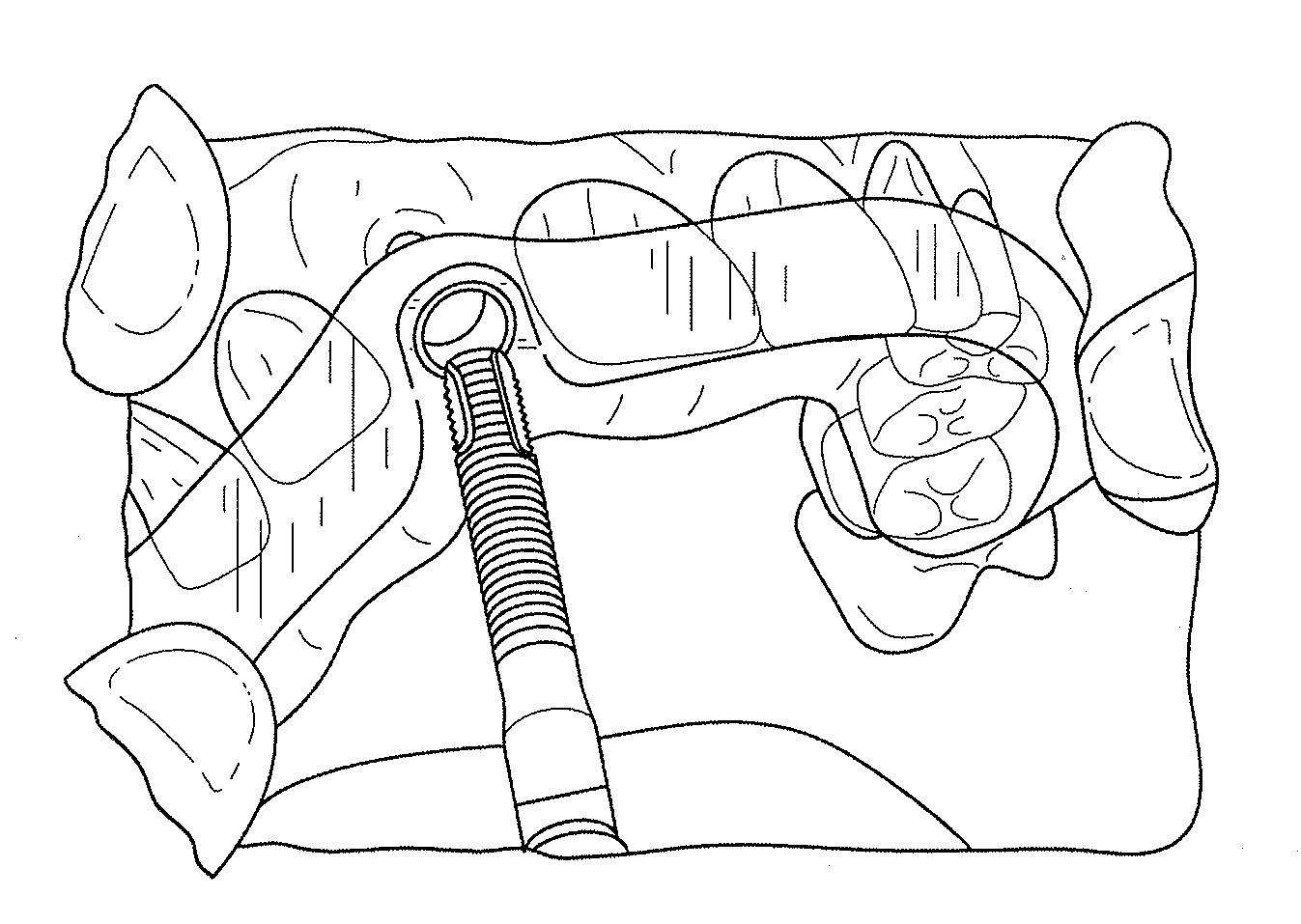
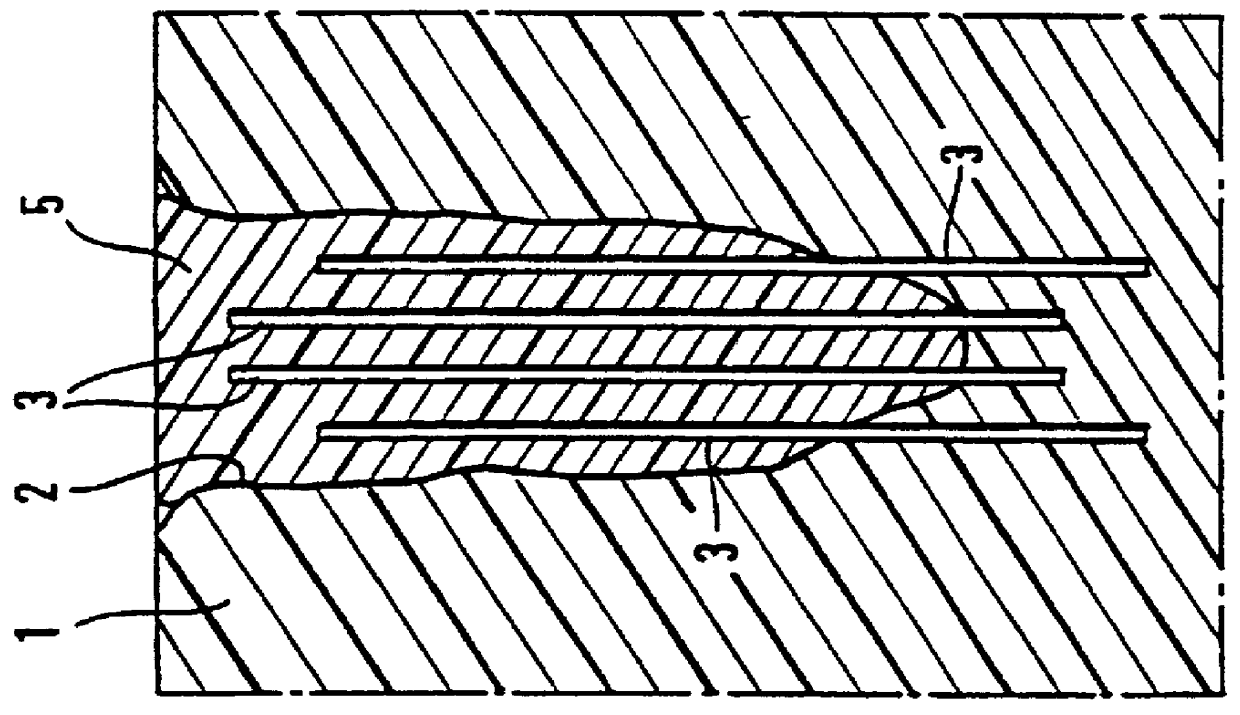
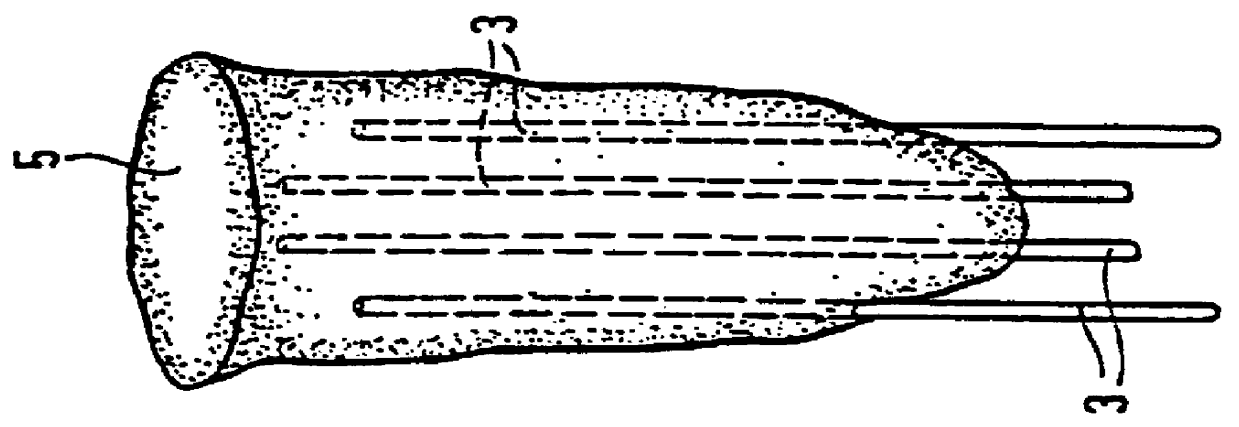
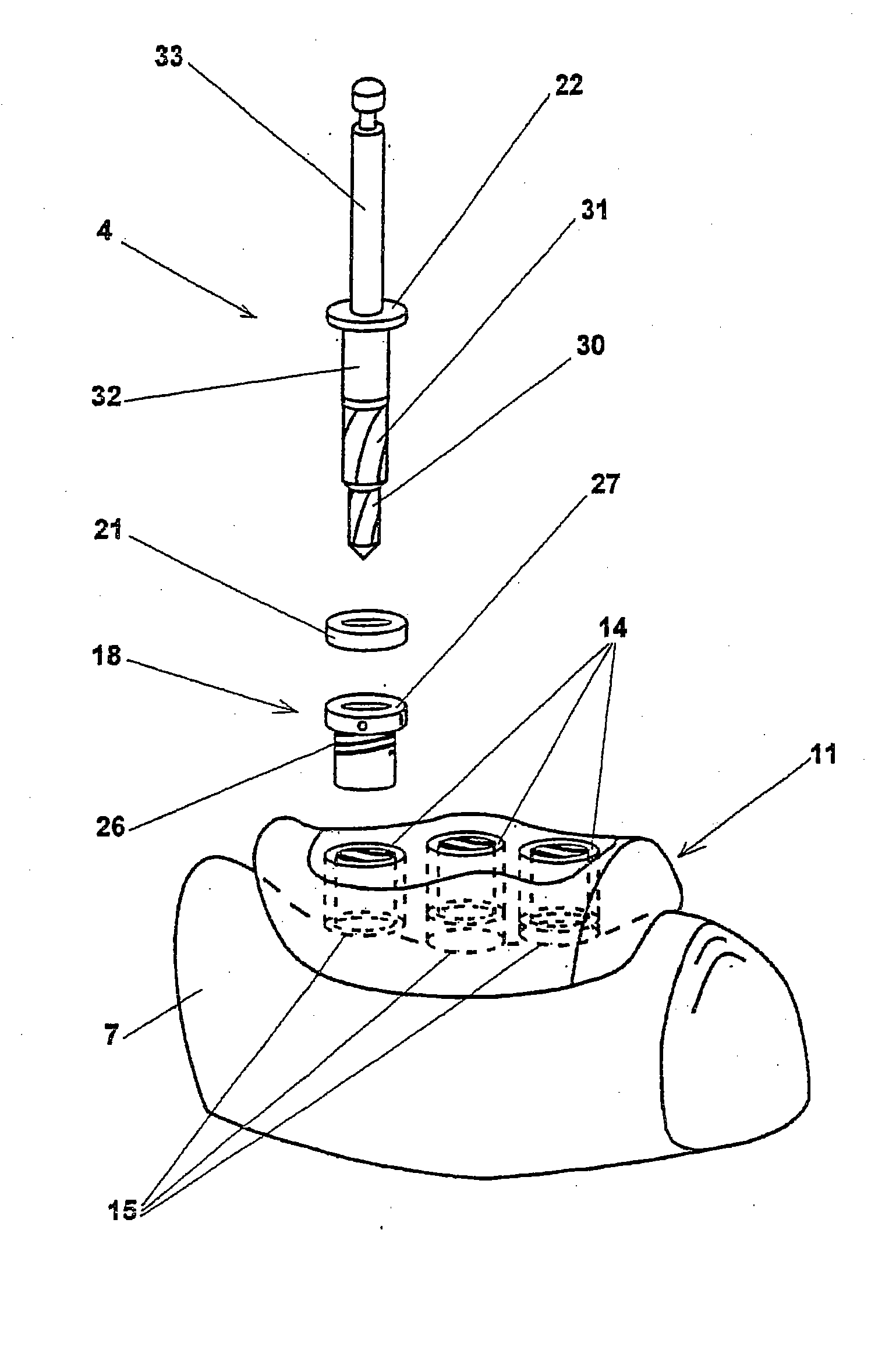
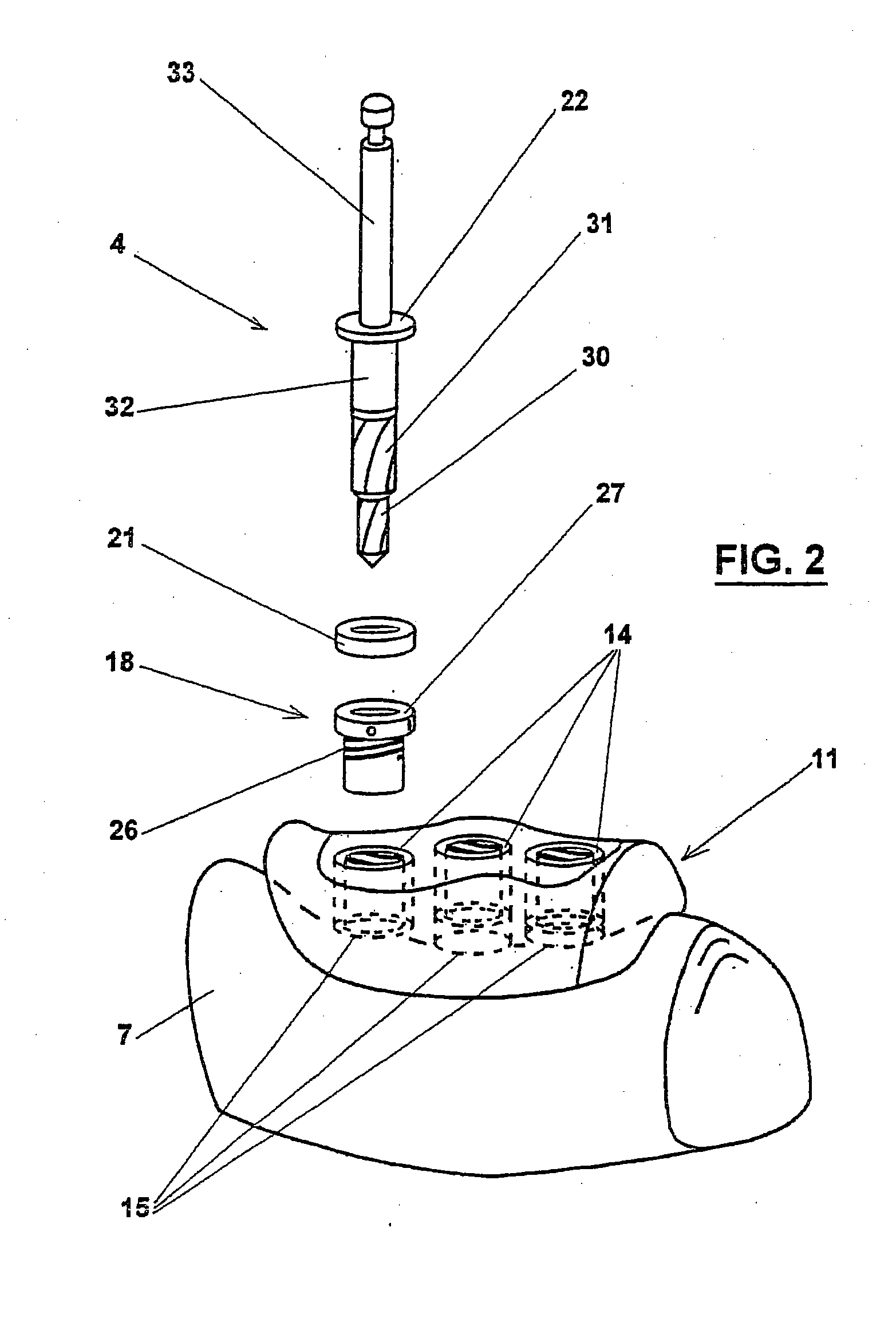
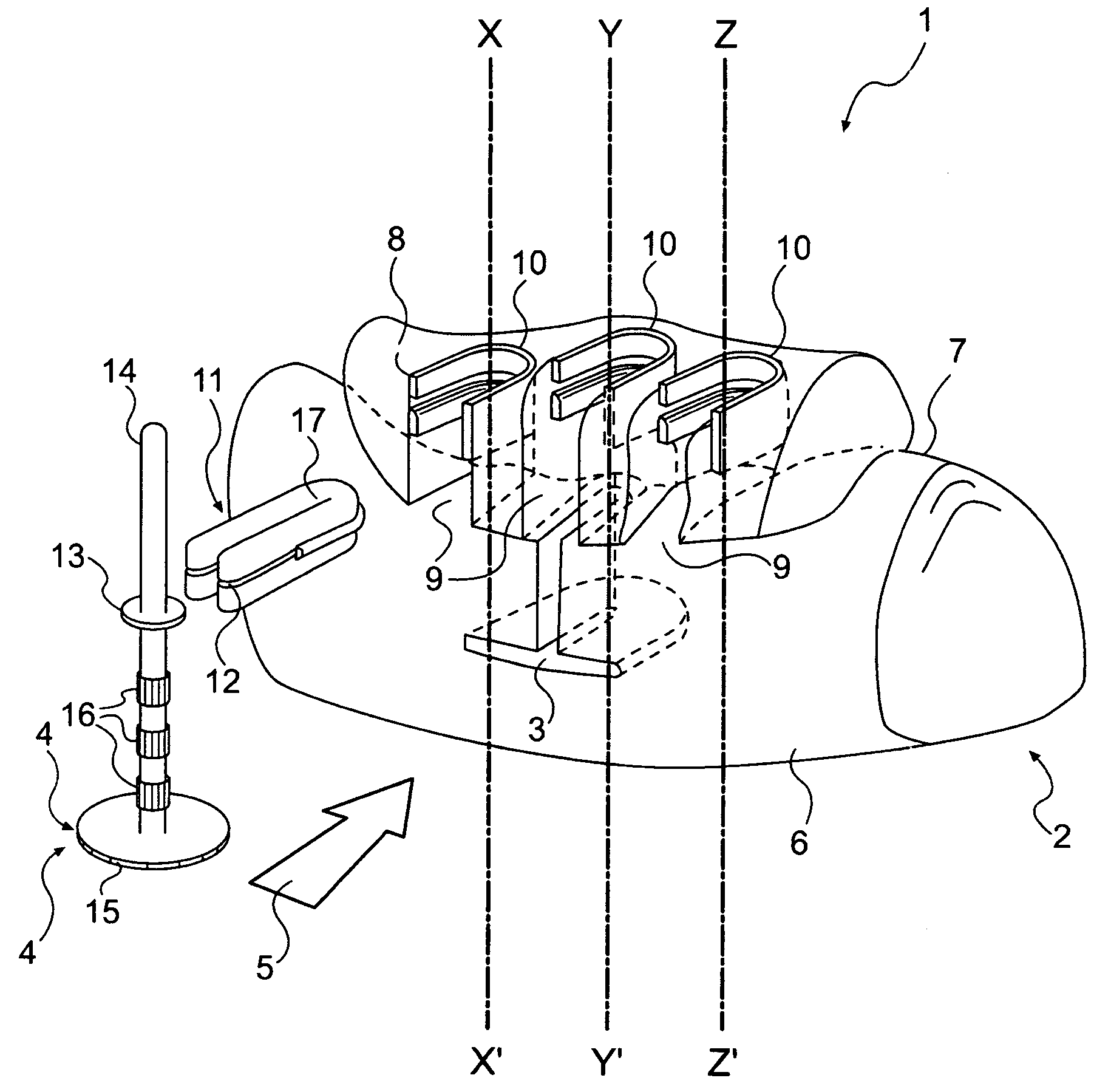
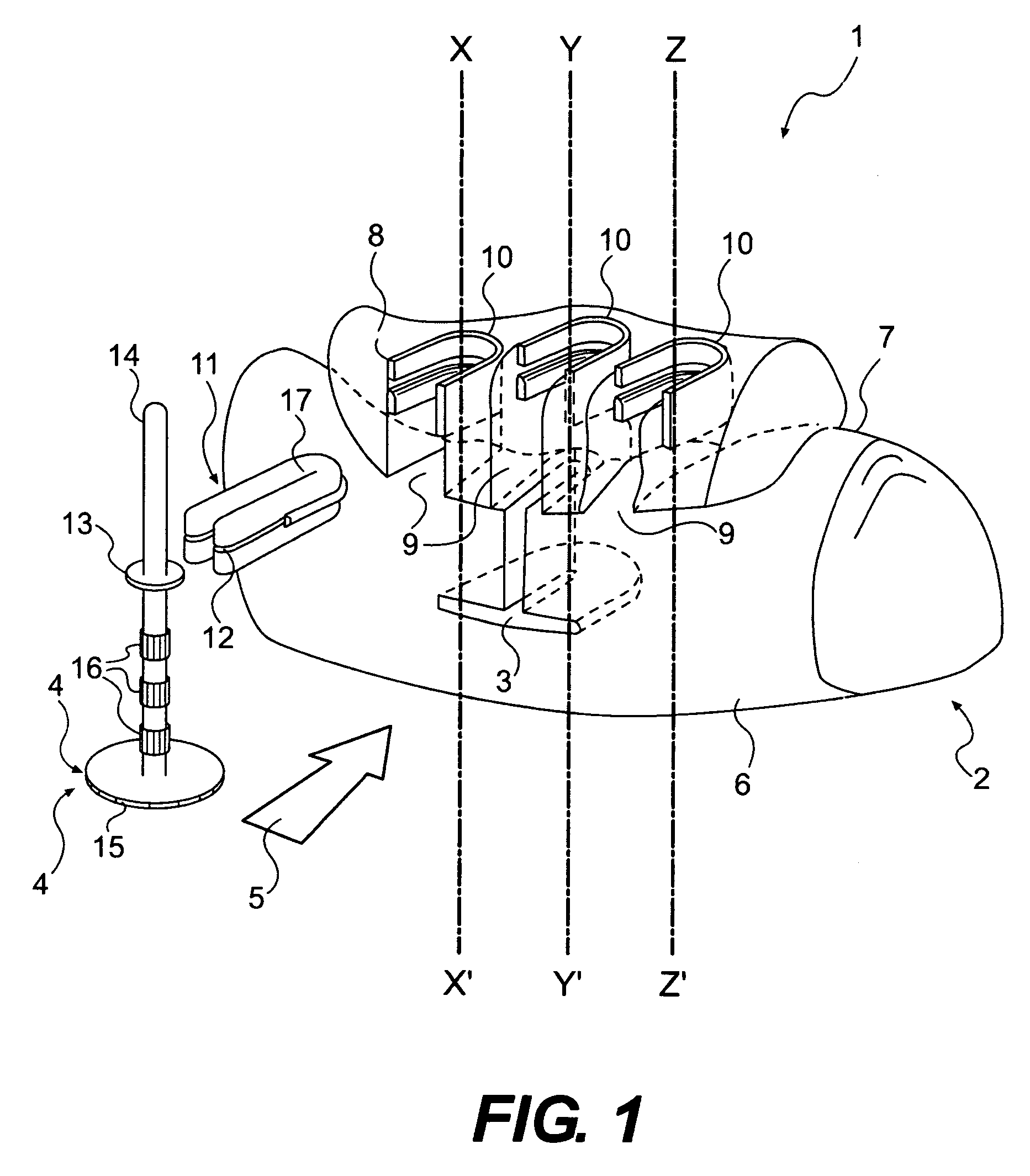
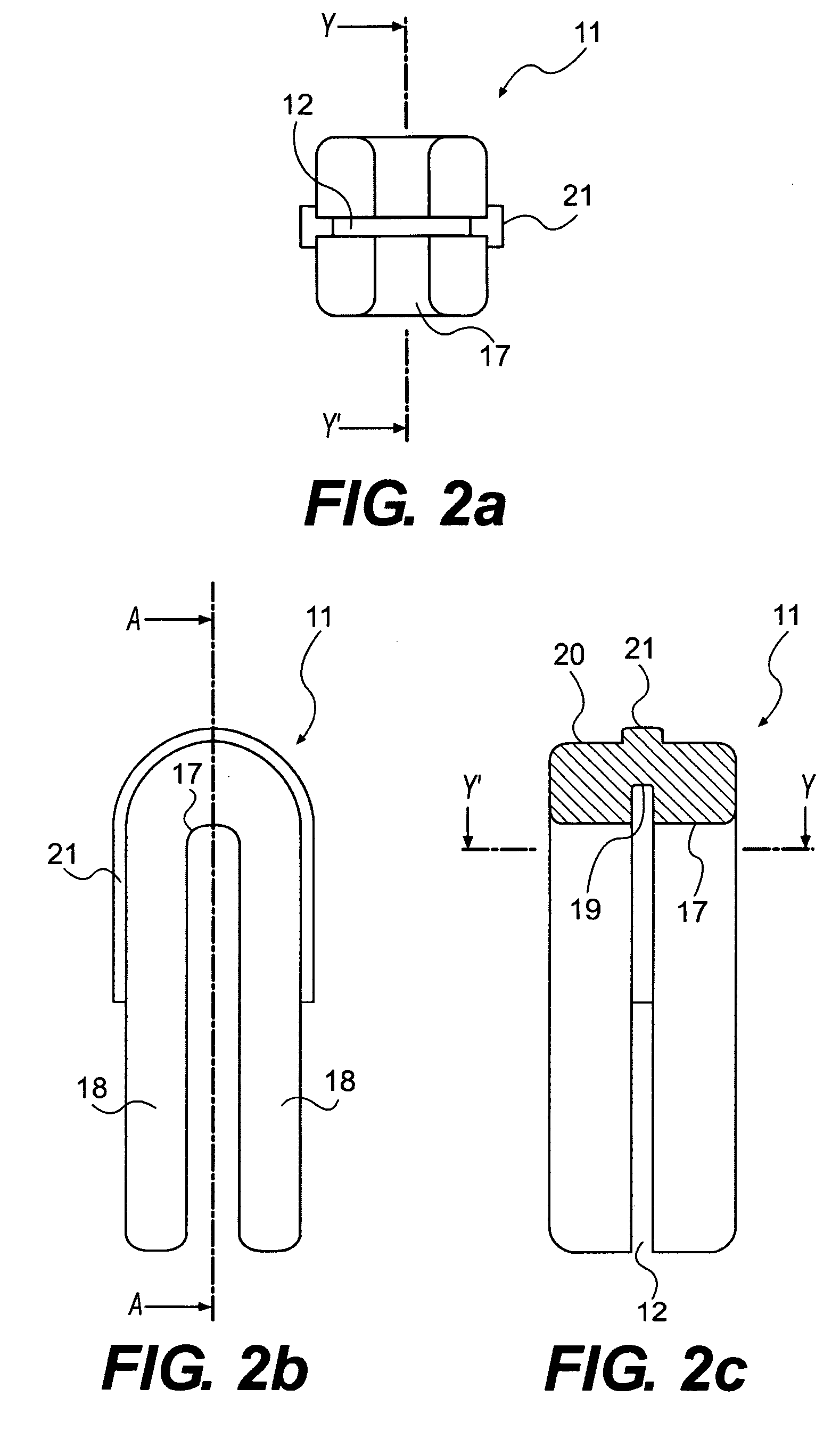
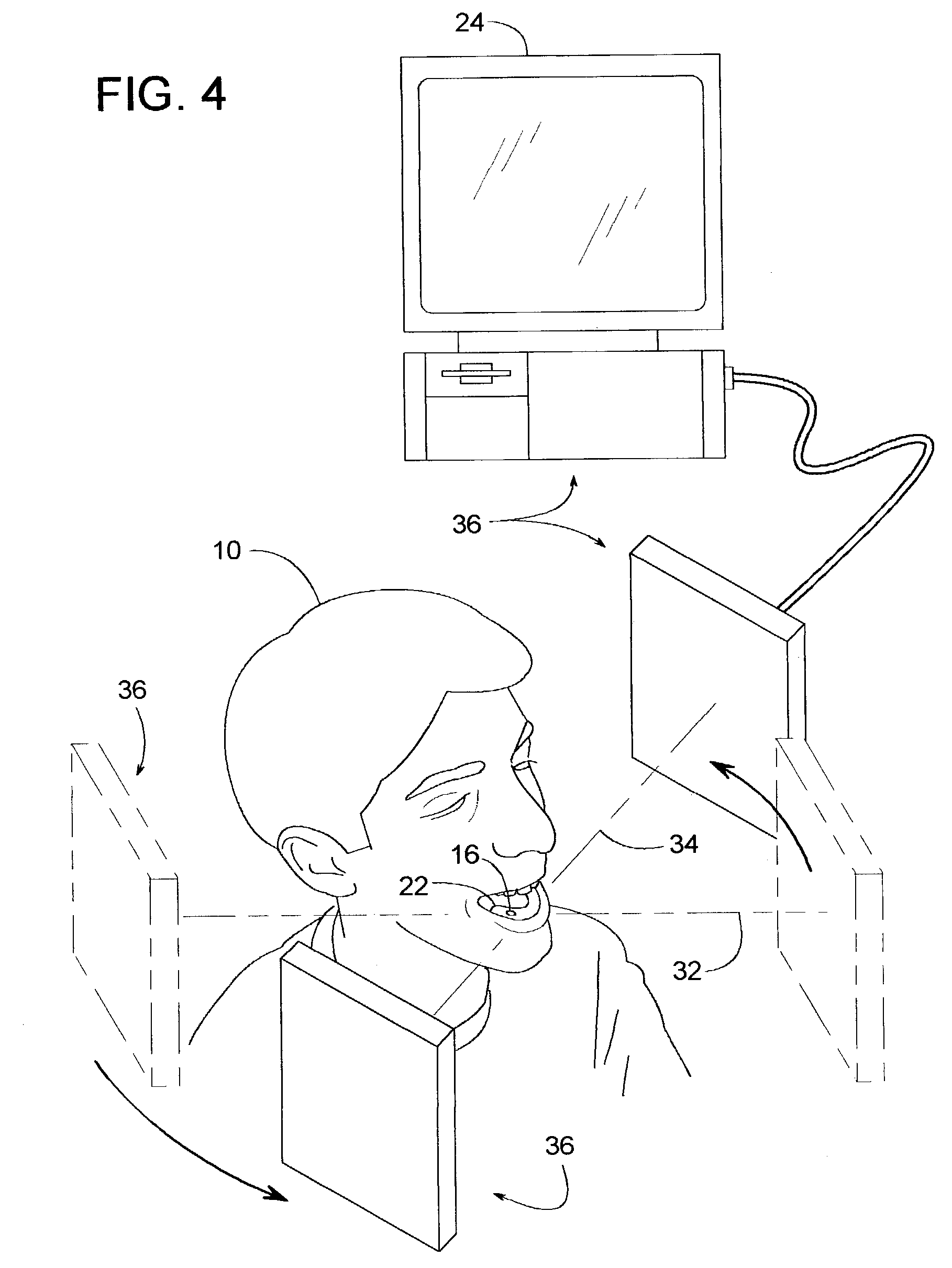
The invention relates to a method and device for placing implants (1) using a surgical template (11) which is made from tomographic cuts in the patient's jawbone (7). According to the invention, step drills (4) and calibrating drills (5), having a single standard diameter for each type of implant (1), are guided through drill bushings (18) which are inserted into bores (15) in the template (11) in order to produce any drilling sequence corresponding to an implant plan. The penetration depth of the drills (4, 5) is controlled by the height of the bores (15) or by the drill rings (21). The aforementioned template (11) bores (15) serve as a guide for the precise placement of the implants (1) owing to the adapted implant supports (3). Moreover, washers (23), which are mounted around the implant supports (3), limit compression in relation to the implants (1) while said implants are being placed (20). The above-mentioned characteristics serve to limit the required number of drills (4, 5) and implant supports (3) to the longest models only. The inventive method and device are particularly suitable for computer-assisted implantology systems.
Owner:MATERIALISE DENTAL NV
Orthopedic and dental implant devices providing controlled drug delivery
Implantable prosthetic devices are provided for controlled drug delivery, for orthopedic and dental applications. The device may include a prosthetic device body having at least one outer surface area; two or more discrete reservoirs located in spaced apart positions across at least a portion of the outer surface area, the reservoirs formed with an opening at the surface of the device body and extending into the device body; and a release system disposed in the reservoirs which comprises at least one therapeutic or prophylactic agent, wherein following implantation into a patient the therapeutic or prophylactic agent is released in a controlled manner from the reservoirs. The prosthetic device body preferably is a joint prosthesis or part thereof, such as a hip prosthesis, a knee prosthesis, a vertebral or spinal disc prosthesis, or part thereof. Optional reservoir caps may further control release kinetics.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
Implant to be implanted in bone tissue or in bone tissue supplemented with bone substitute material
InactiveUS6921264B2High softening temperatureLow softening temperatureDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBone tissueGrowth promoting
An implant (1) to be implanted in bone tissue, e.g. a dental implant or an implant for an orthopedic application, comprises surface regions (4) of a first type which have e.g. osseo-integrative, inflammation-inhibiting, infection-combating and / or growth-promoting properties, and surface regions (8) of a second type which consist of a material being liquefiable by mechanical oscillation. The implant is positioned in an opening of e.g. a jawbone and then mechanical oscillations, e.g. ultrasound is applied to it while it is pressed against the bone. The liquefiable material is such liquefied at least partly and is pressed into unevennesses and pores of the surrounding bone tissue where after resolidification it forms a positive-fit connection between the implant and the bone tissue. The surface regions of the two types are arranged and dimensioned such that, during implantation, the liquefied material does not flow or flows only to a clinically irrelevant degree over the surface regions of the first type such enabling the biologically integrative properties of these surface regions to start acting directly after implantation. The implant achieves with the help of the named positive fit a very good (primary) stability, i.e. it can be loaded immediately after implantation. By this, negative effects of non-loading are prevented and relative movements between implant and bone tissue are reduced to physiological measures and therefore have an osseo-integration promoting effect.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Method and device for placing dental implants
The invention relates to a method and device for placing implants using a surgical template which is made from tomographic cuts in the patient's jawbone. Step drills and calibrating drills, having a single standard diameter for each type of implant, are guided through drill bushings which are inserted into bores in the template in order to produce any drilling sequence corresponding to an implant plan. The penetration depth of the drills is controlled by the height of the bores or by the drill rings. The method limits the required number of drills and implant supports to the longest models only. The inventive method and device are particularly suitable for computer-assisted implantology systems.
Owner:DENTSPLY IMPLANTS NV
Method of Manufacturing and Installing a Ceramic Dental Implant with an Aesthetic Implant Abutment
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a tooth prosthesis, for insertion in a jawbone, including an implant and an abutment on top of the implant. The method includes: defining a shape of the prosthesis and its location in the jawbone by using first data from a first CT scan image of the jawbone and second data from a second image of a gypsum cast, correlating first and second data by extracting from the first data first position reference data of a first reference in the first image, and from the second data second position reference data of a second reference in the second image, the second reference being identical to the first reference; performing a geometric transformation on the second data and / or the first data to have a coincidence of the second image with the first image and to combine the first and second data into composite scan data.
Owner:ORATIO
Thermoplastic surgical template for performing dental implant osteotomies and method thereof
A surgical template for performing dental implant osteotomies comprises a malleable, resinous, thermoplastic base, at least one non-thermoplastic, rigid drill guide attached to the base, and a securing mechanism between the base and the drill guide. The template may reversibly melt to a malleable state and can be handled by hand without additional tools so as to conform to the adjacent teeth of the edentulous ridge, either directly in the patient's mouth or on a cast model. Dental osteotomies using the template can then be performed. The surgical template may be manufactured of a thermoplastic material having a sharp and low melting point but high rigidity in the solid state at room temperature.
Owner:TANG BRIAN
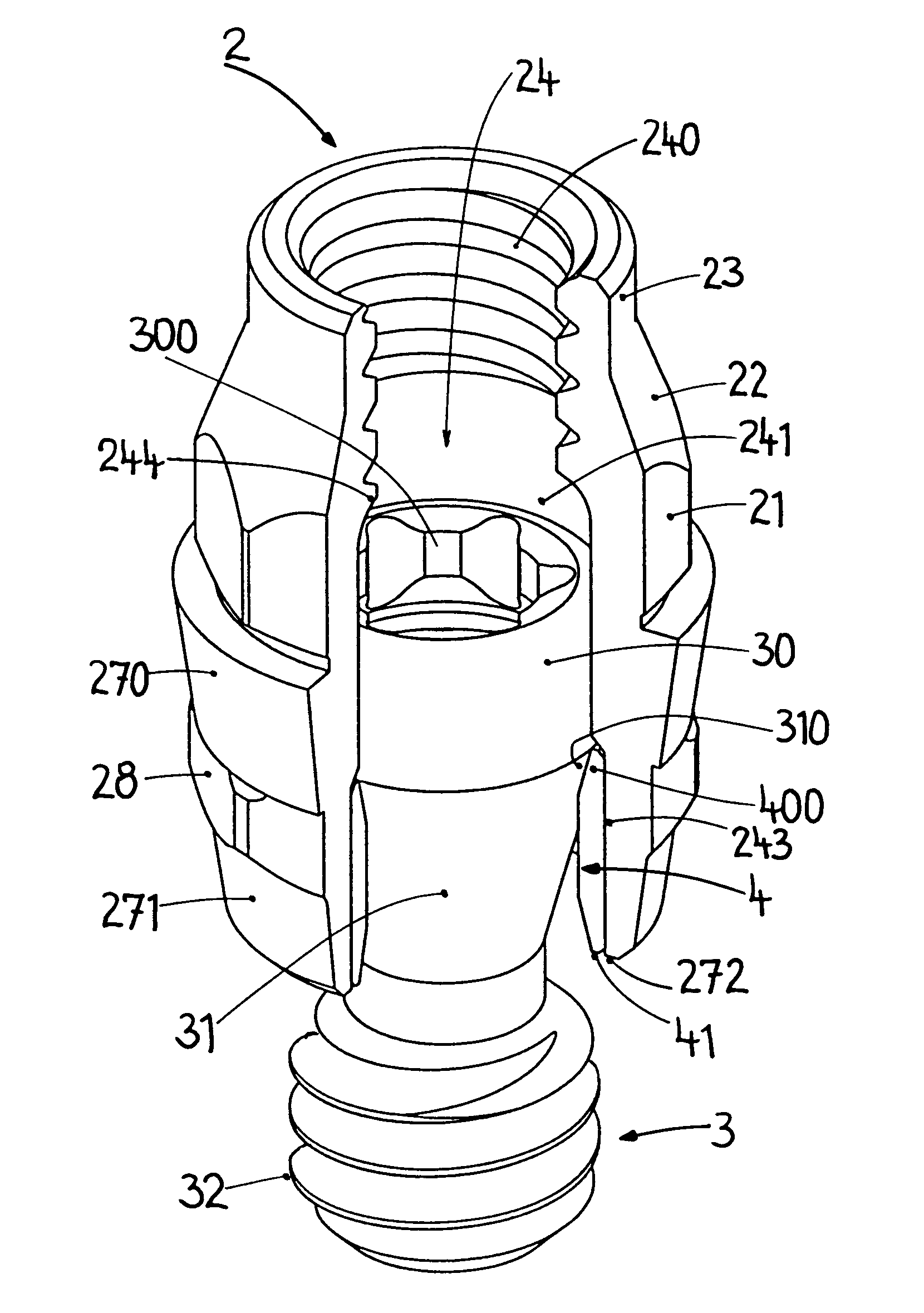
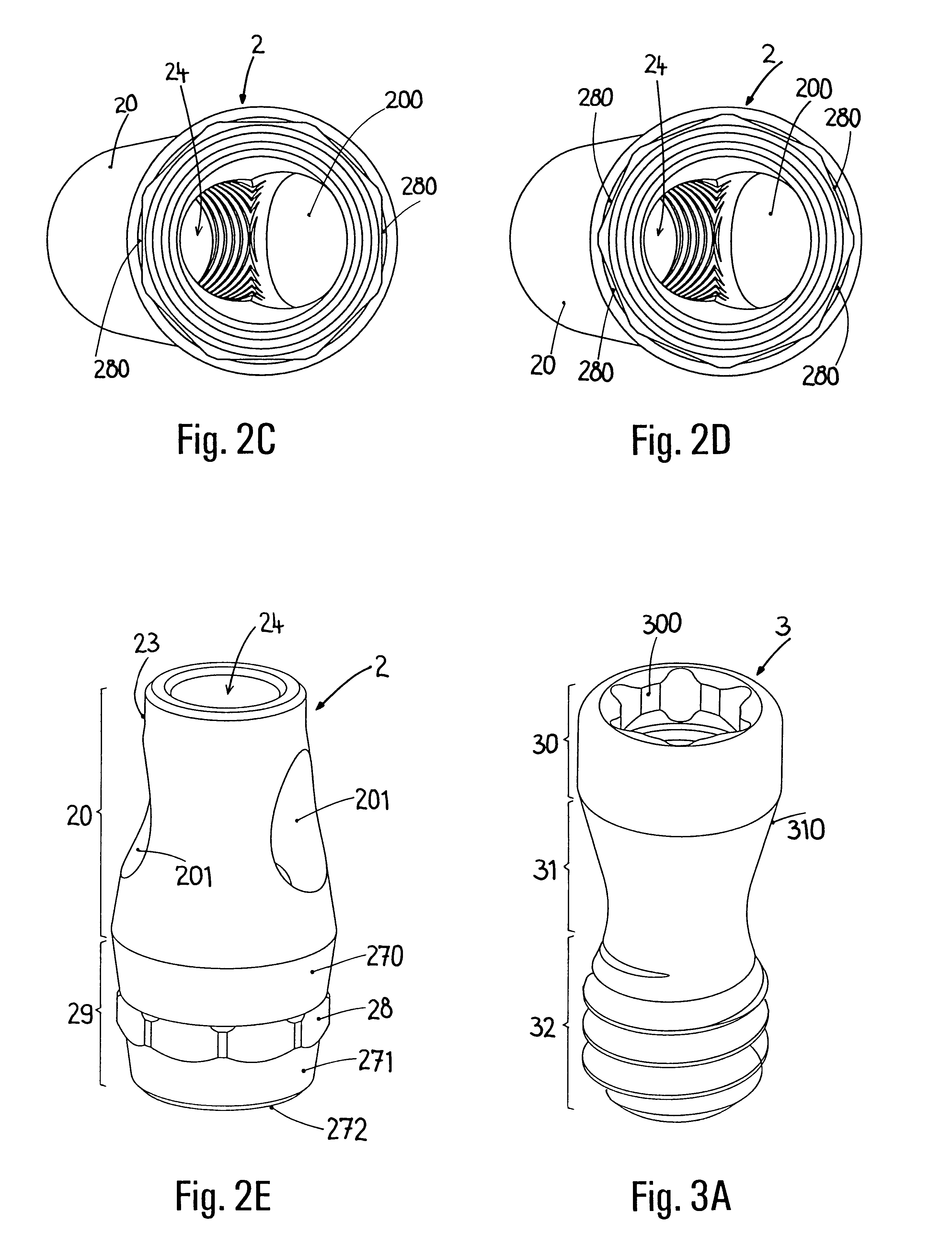
Dental implant and device with a dental implant
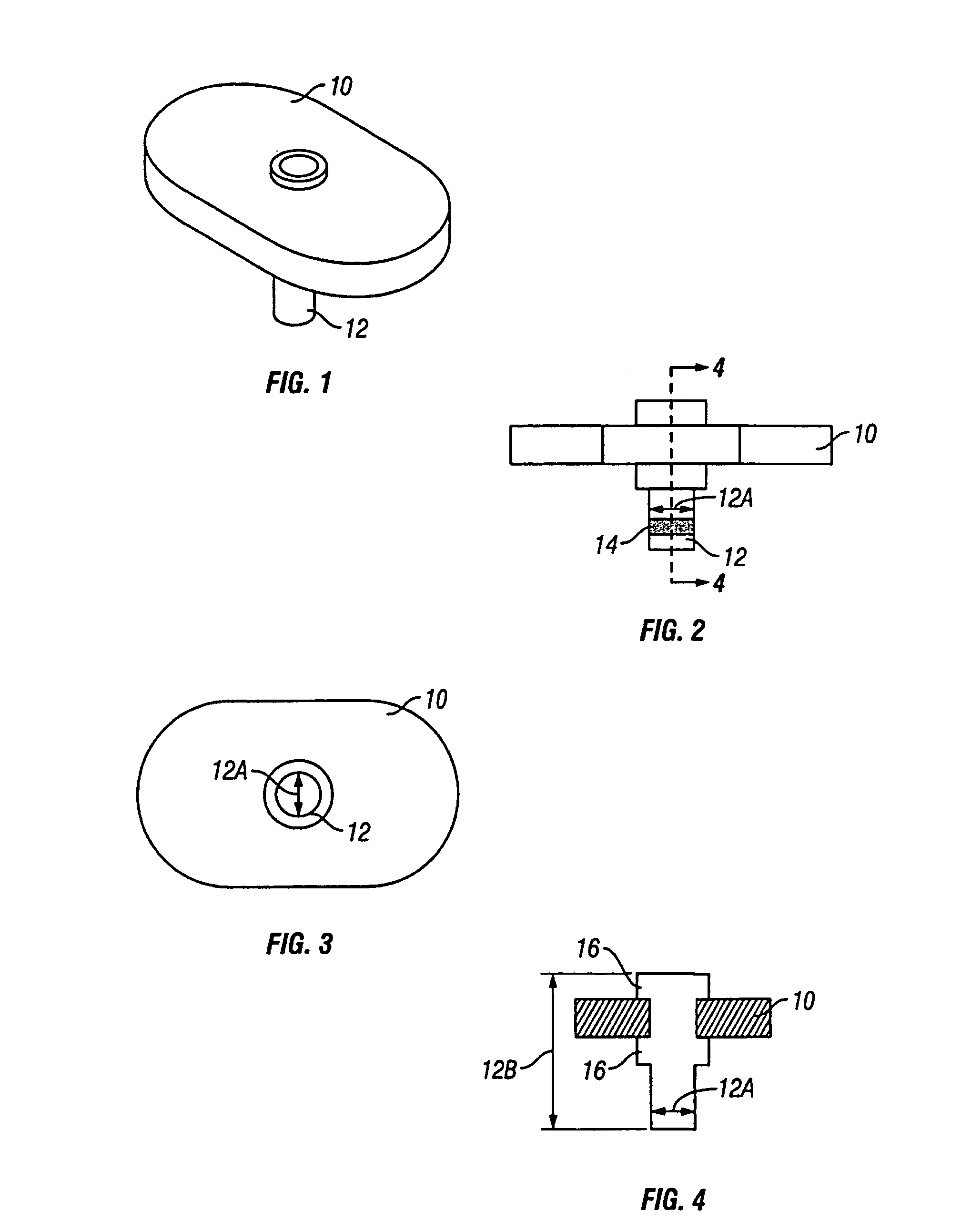
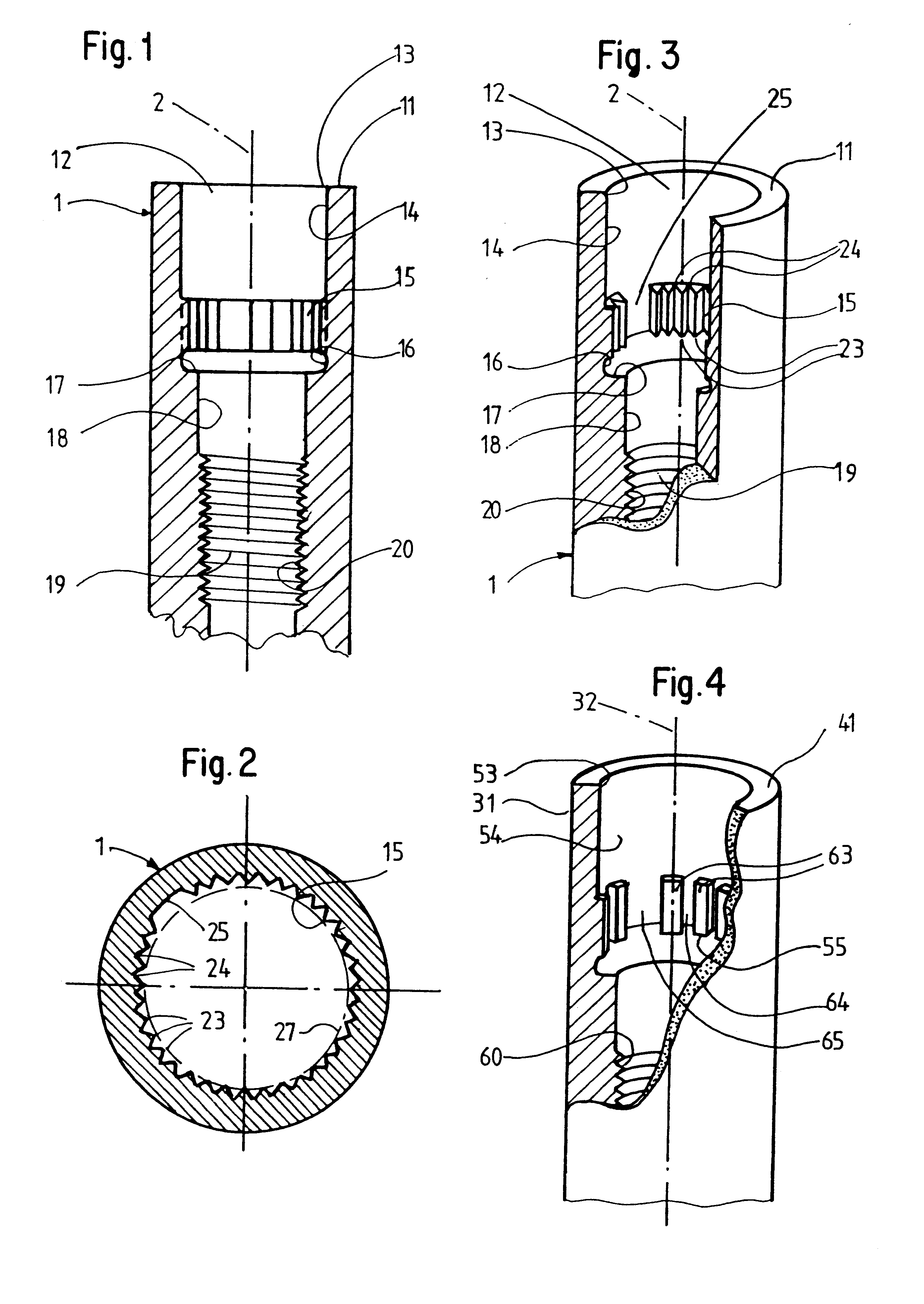
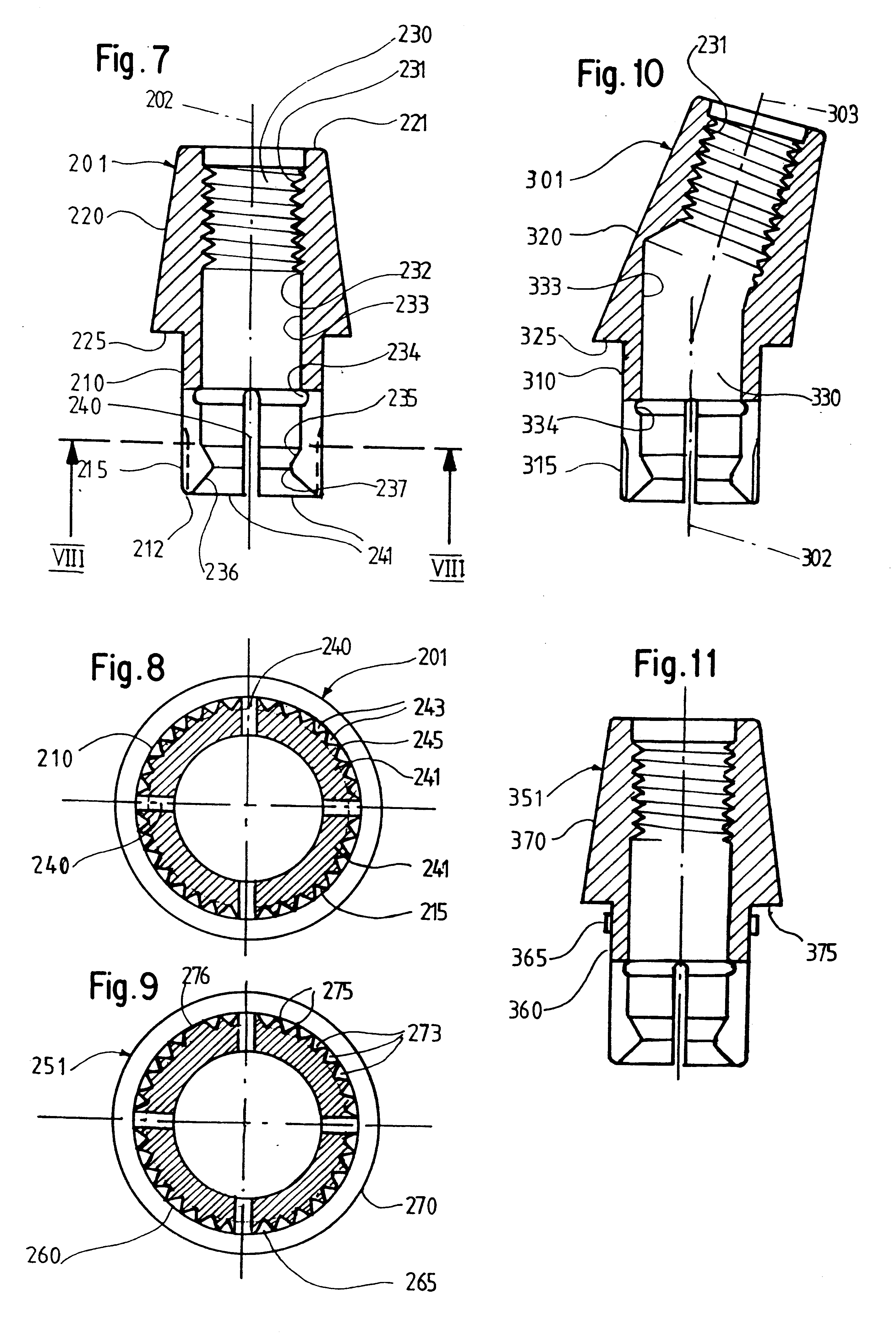
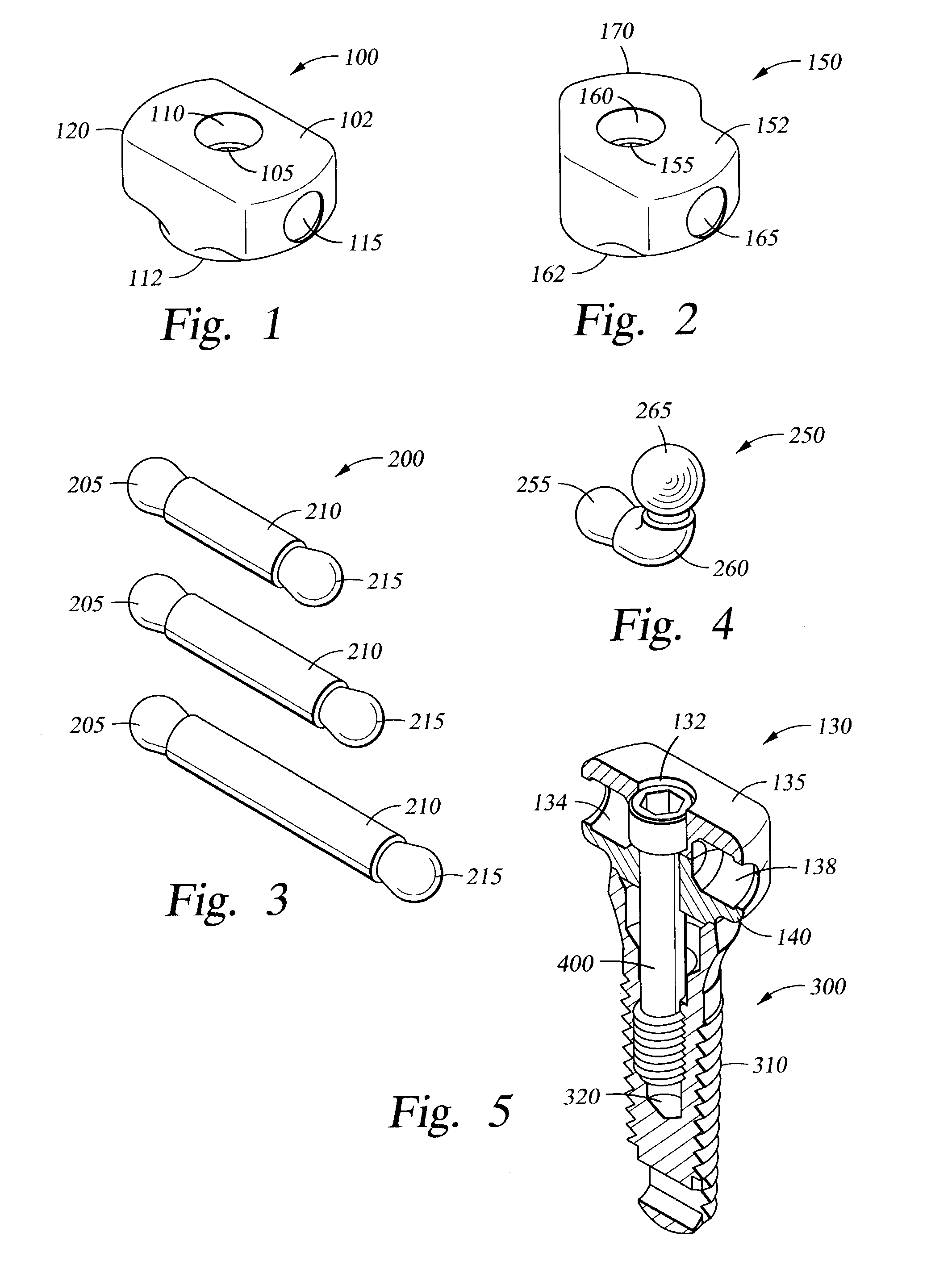
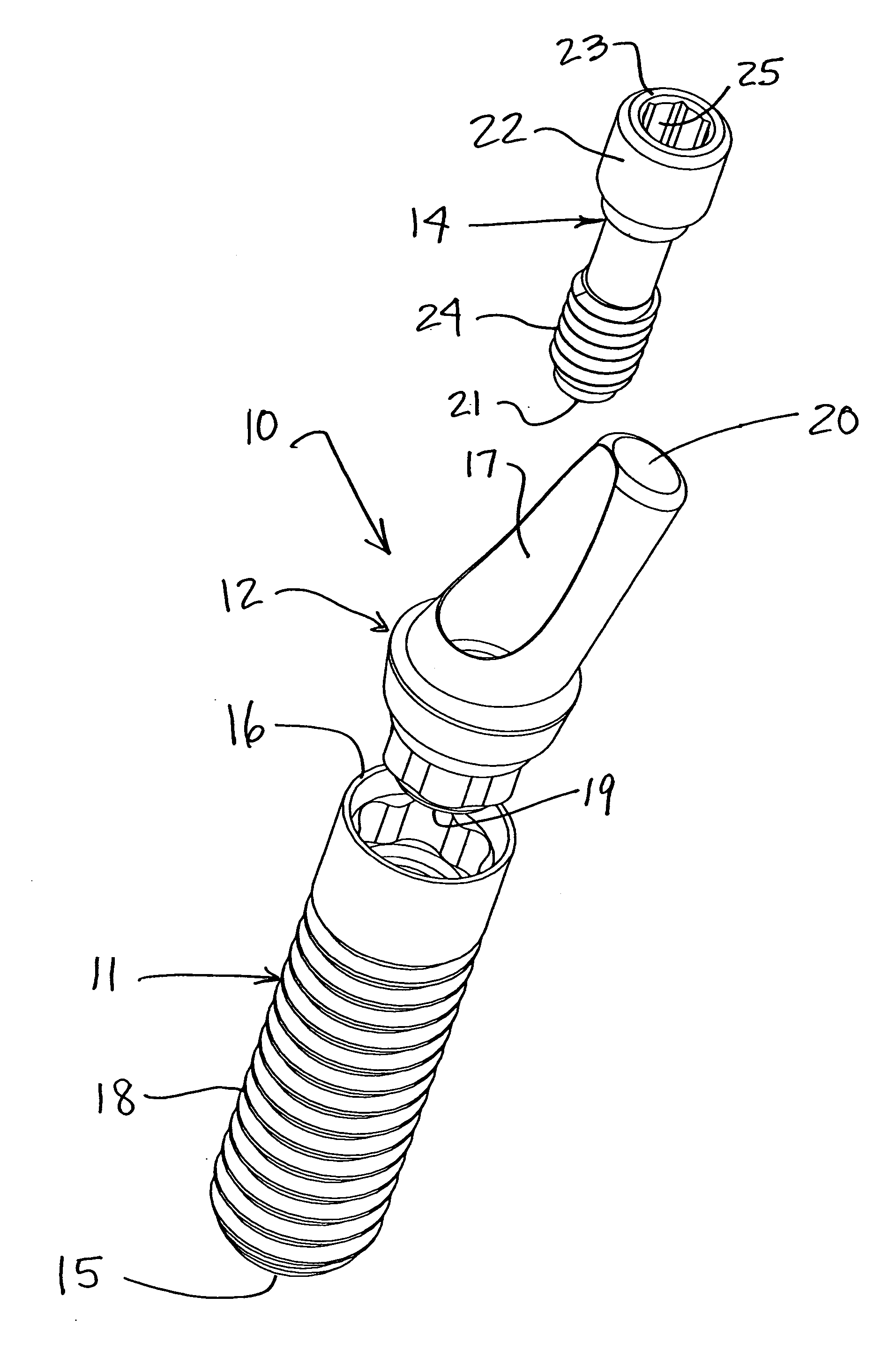
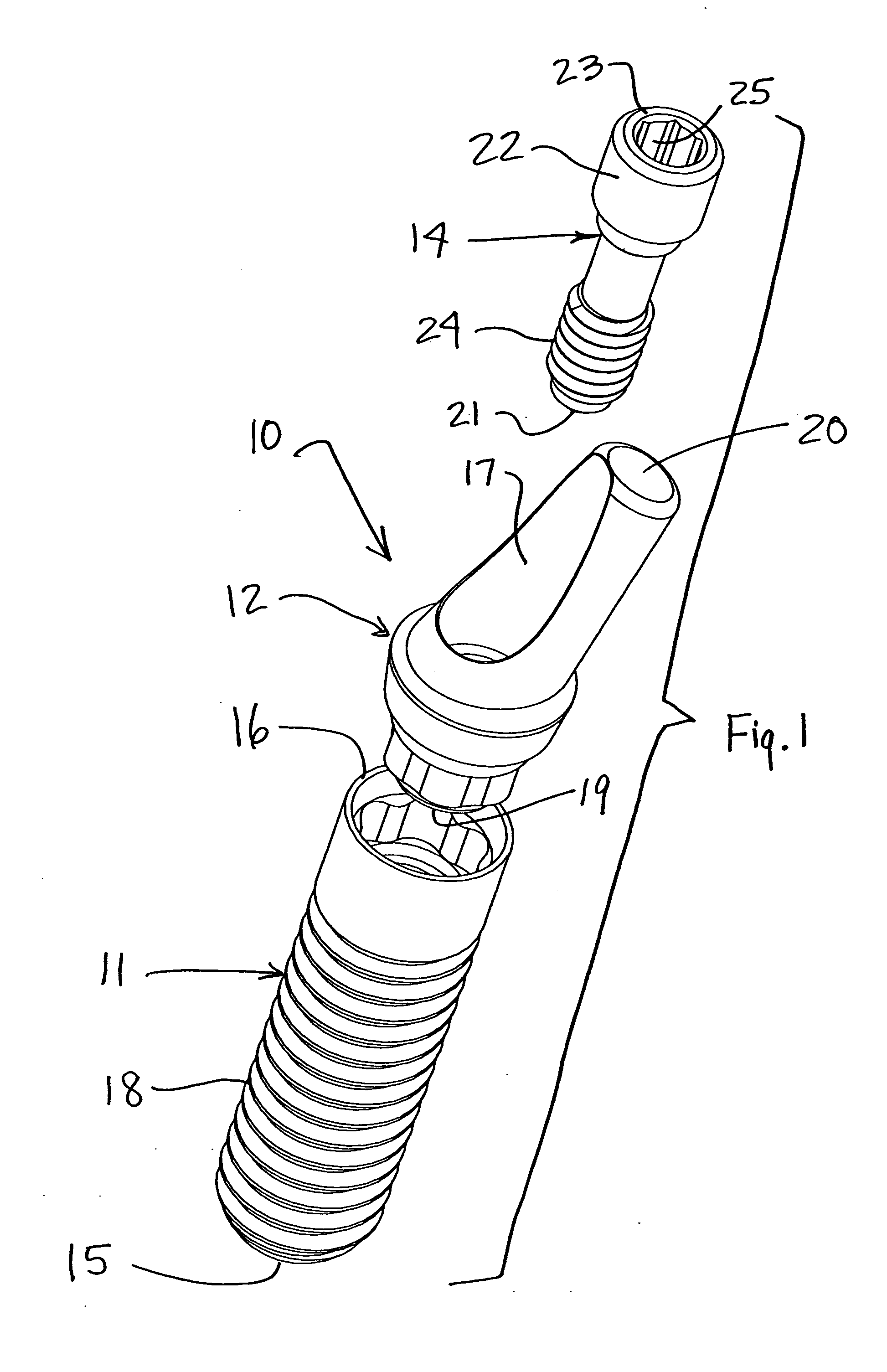
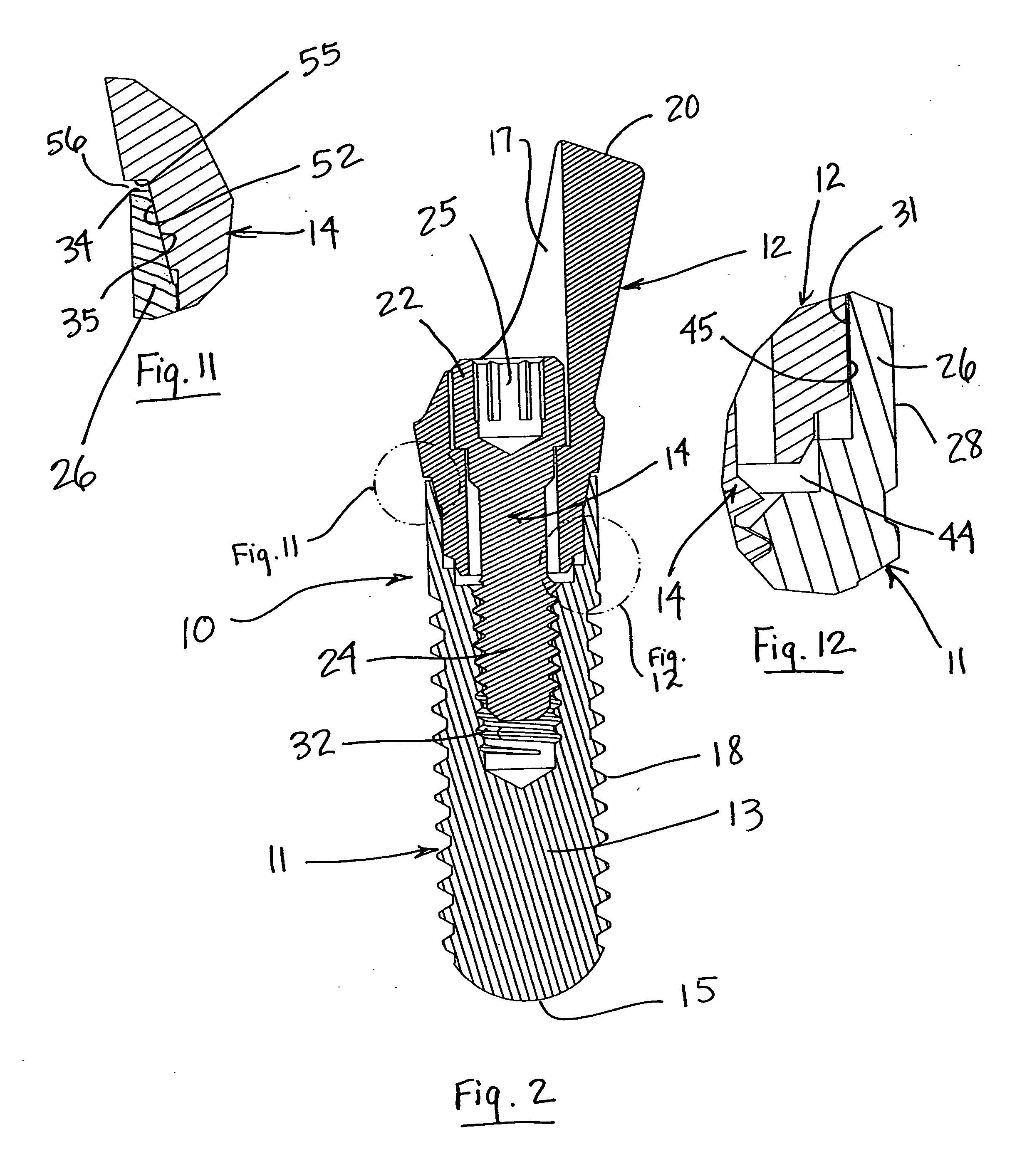
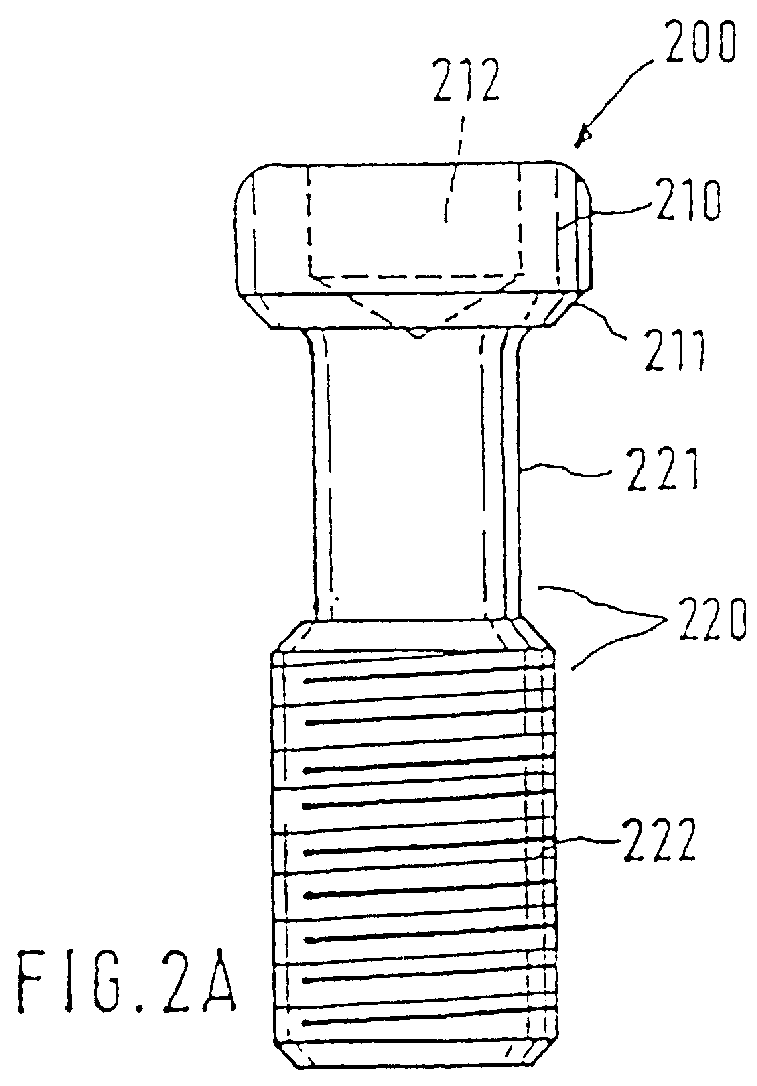
The invention relates to a dental implant which has an axis and a hole with a positioning section. Said positioning section has projecting parts and intermediate spaces distributed alternately, one after the other, along the periphery. Said intermediate spaces comprise several first intermediate spaces which create a division, and a second, wider intermediate space. A secondary and / or supplementary structural part can be attached in the implant, said part having a connecting section which extends into the hole. Said connecting section can have projecting parts for engaging in the intermediate spaces of the implant, and can be configured in such a way that it can be fixed to the implant in several different rotated positions or a single rotated position. The secondary and / or supplementary structural part can also be produced without projecting parts of the type mentioned, so that it can be screwed into the implant.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG +1
Intraoral apparatus for non-invasive blood and saliva monitoring & sensing
Controlled-specimen-sampling oral devices are described, implanted or inserted into an oral cavity, built onto a prosthetic tooth crown, a denture plate, braces, a dental implant, or the like. The devices are replaced as needed. The controlled specimen sampling may be passive, based on a dosage form, or electro-mechanically controlled, for a high-precision, intelligent, specimen sampling. Additionally, the controlled sampling may be any one of the following: sampling in accordance with a preprogrammed regimen, sampling at a controlled rate, delayed sampling, pulsatile sampling, chronotherapeutic sampling, closed-loop sampling, responsive to a sensor's input, sampling on demand from a personal extracorporeal system, sampling regimen specified by a personal extracorporeal system, sampling on demand from a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system, and sampling regimen specified by a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system. Specimen collection in the oral cavity may be assisted or induced by a transport mechanism, such as any one of, or a combination of iontophoresis, electroosmosis, electrophoresis, electroporation, sonophoresis, and ablation. The oral devices require replacement at relatively long intervals of weeks or months. The oral devices and methods for controlled specimen sampling apply to humans and animals.
Owner:BEISKI BEN ZION +1
Surgical guides and methods for positioning artificial teeth and dental implants
InactiveUS20080085489A1Eliminate radiographic scatterMedical simulationDental implantsDigital dataNatural tooth
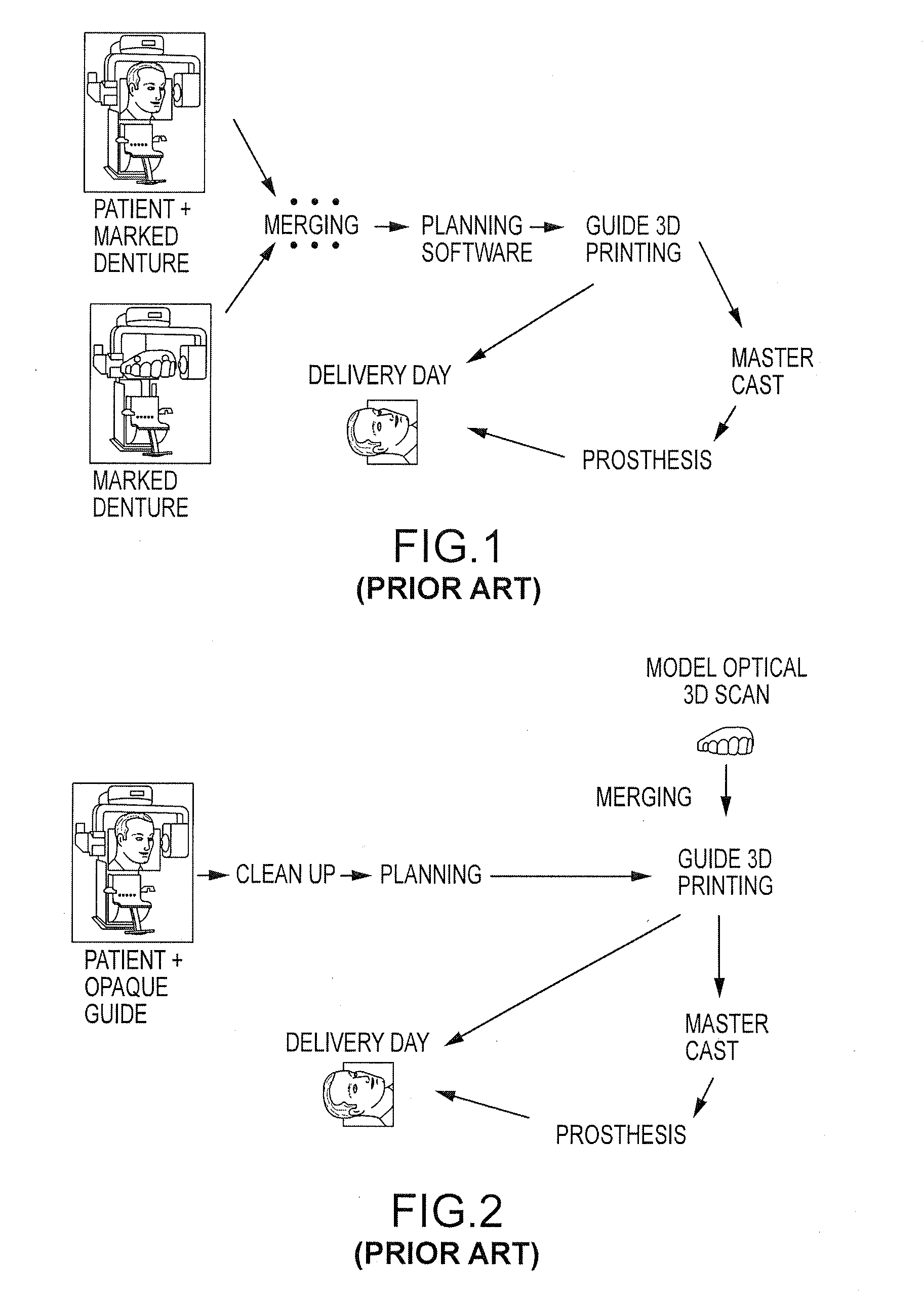
A method is set forth for making a computer model of patient's jaws on the basis of digital information. Digital data about the jaws, teeth, soft tissues and artificial teeth is joined in computer space to create aesthetic and functional plans for the removal of teeth, shaping of supporting bone and placement of dental implants. Artificial teeth and pre-manufactured prosthetic devices are made and attached to the dental implants at the time of surgery. The aesthetic and functional position of artificial teeth is determined prior to surgical removal of natural teeth and the ideal position of implants and the proper form of the remaining bone are determined prior to surgery. Surgical guides used to shape bone, record occlusal orientation and position dental implants are manufactured using computer milling or layered manufacturing.
Owner:VOXELOGIX CORP
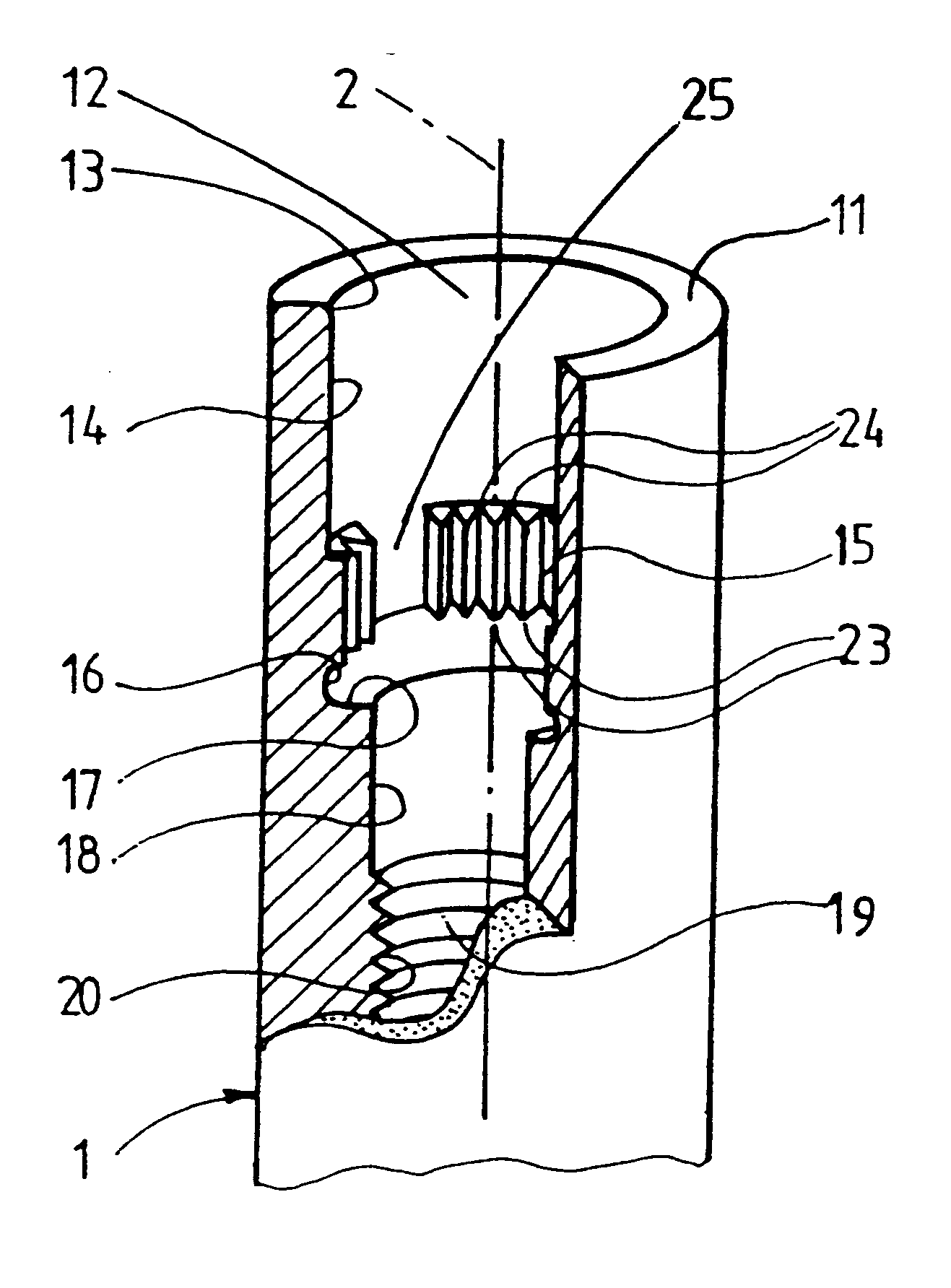
Connection between a dental implant and an abutment
InactiveUS6663388B1Increased functional reliabilityImprove reliabilityDental implantsAbutmentWeld seam
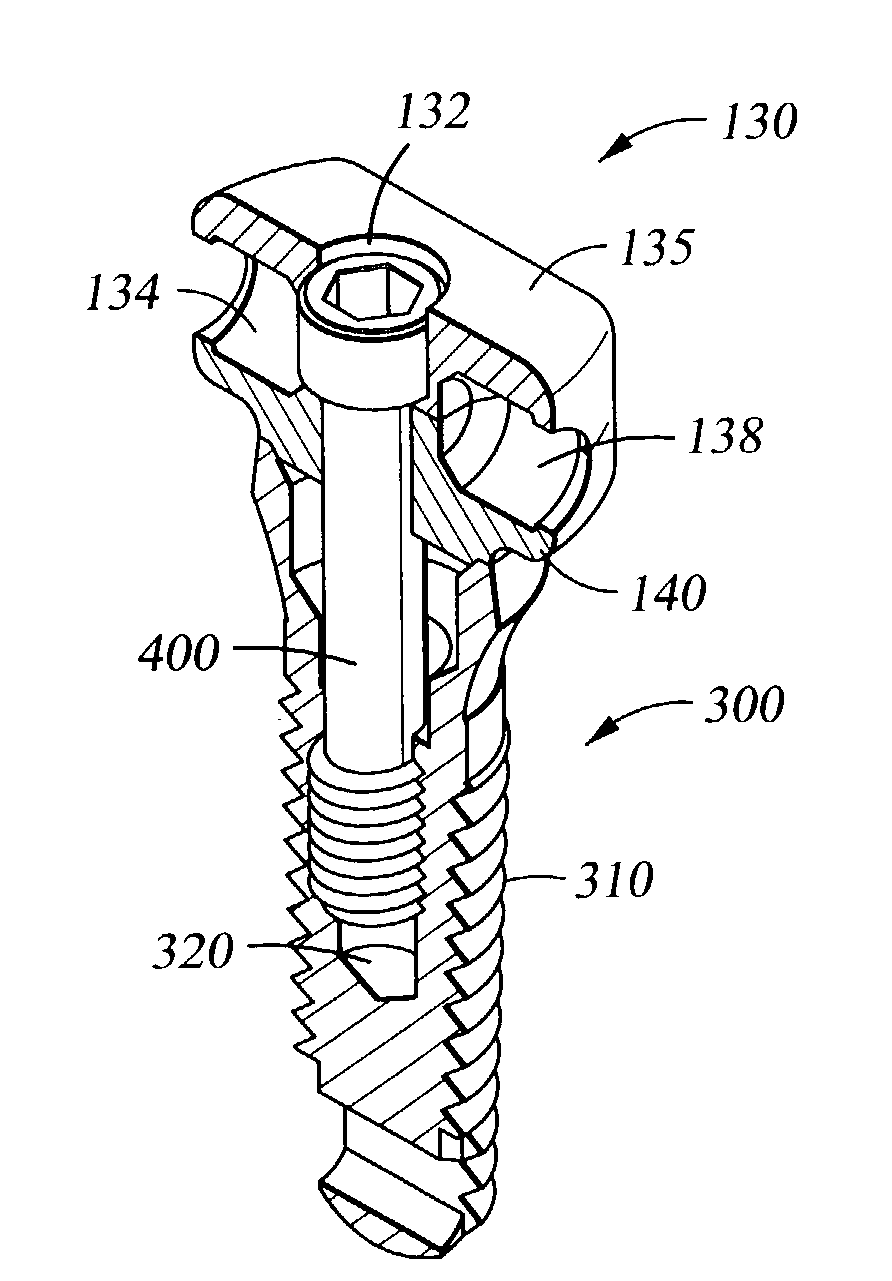
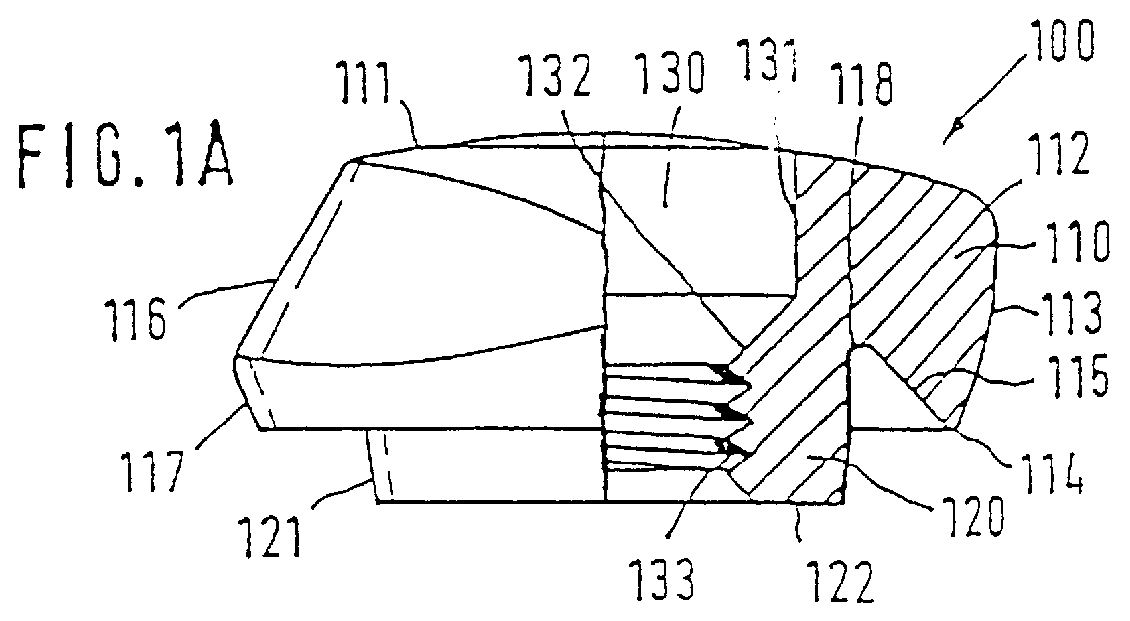
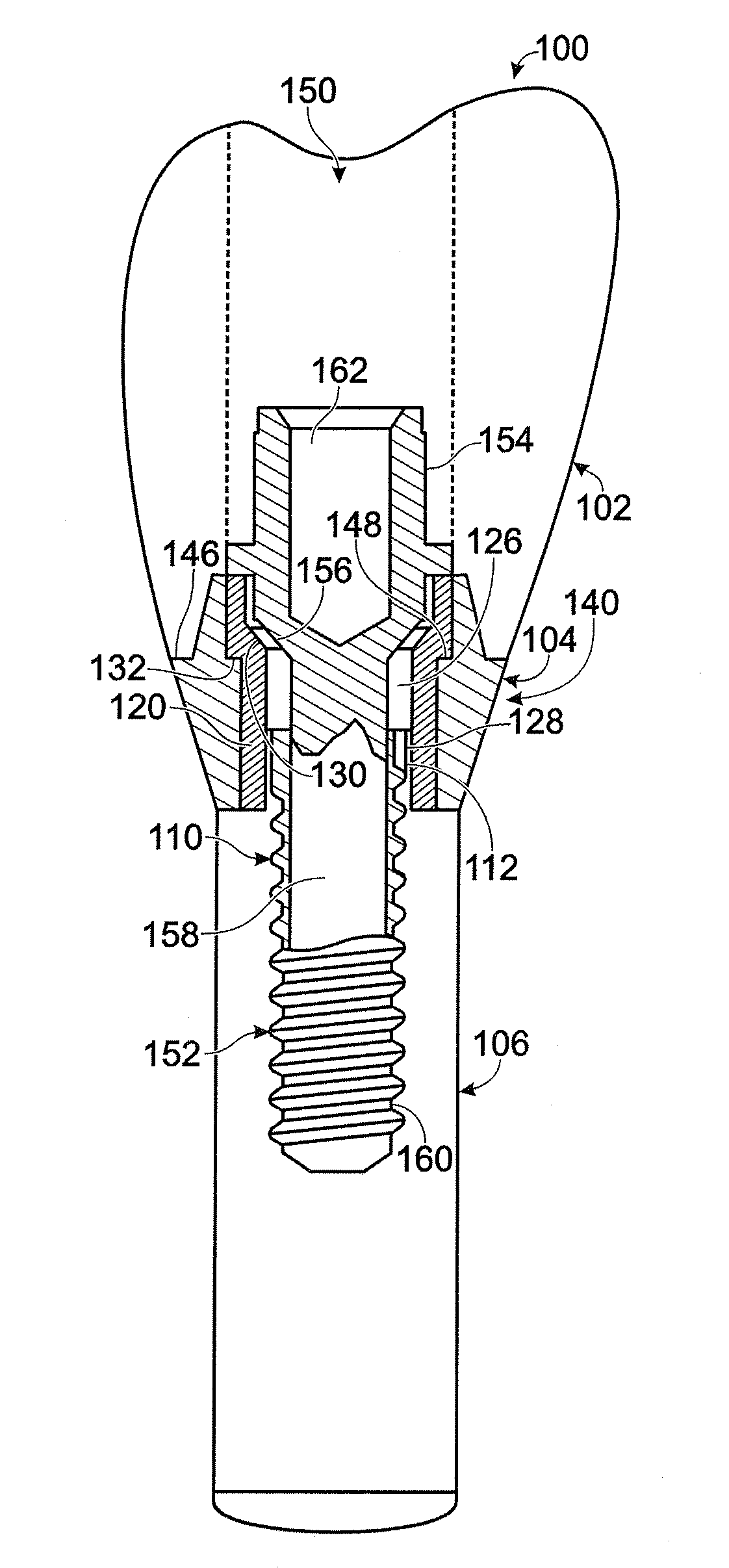
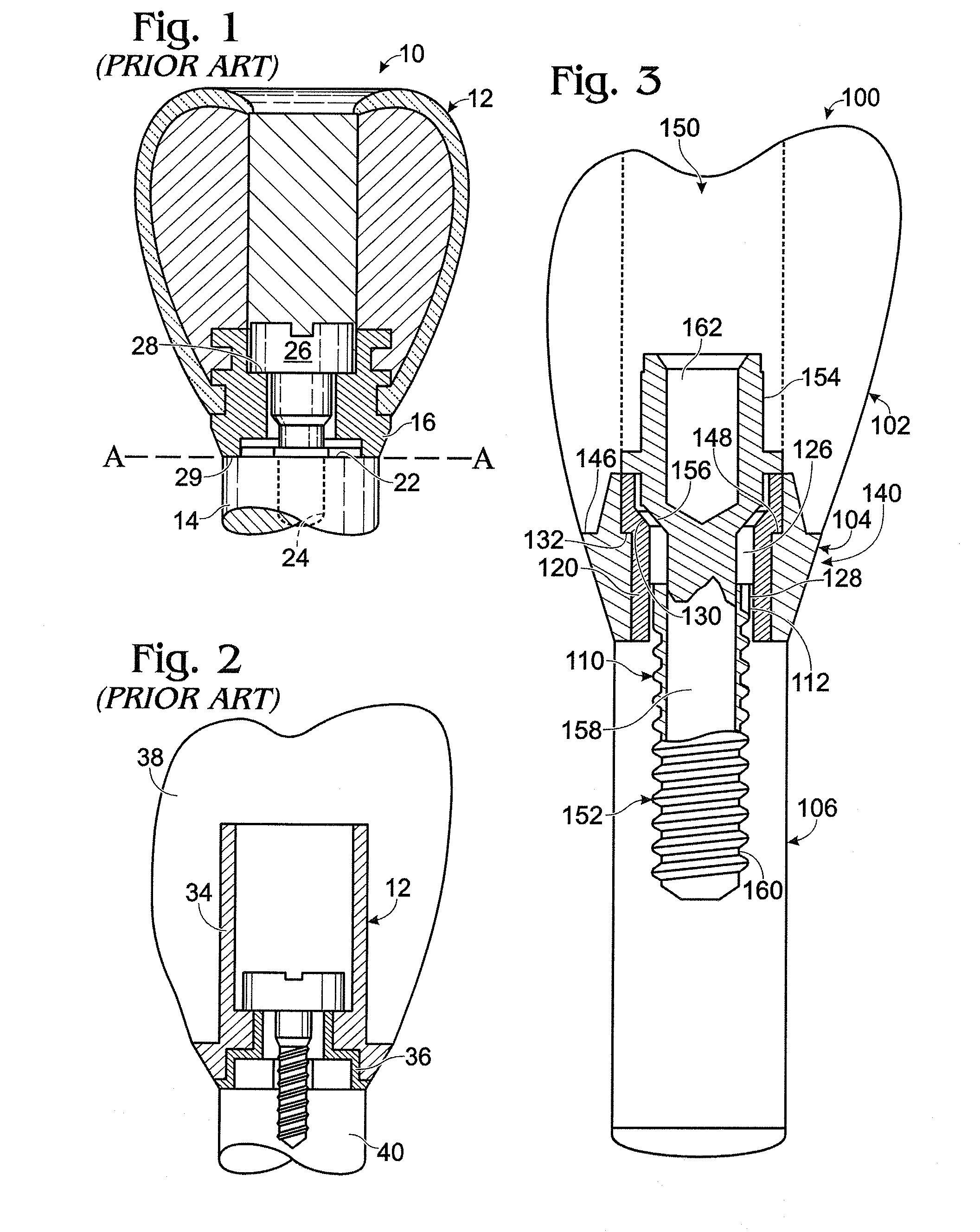
The invention relates to a connection between a known dental implant (1) and a straight or angular abutment (2) which can be established by means of a base screw (3) and a support ring (4). The support ring (4) is fixedly introduced into the inlet of the abutment (2) near the lower edge of same, preferably by welding or by bending over of the lower edge of the abutment (2). Before insertion of the support ring (4) the base screw (3) is introduced head first into the inlet (24) from the side of the root part of the abutment. The base screw is held in the abutment (2) by the support ring (4) on which the base screw (3) rests. The threaded shank (32) of the base screw (3) engages the inner thread (14) provided for in the implant (1) and draws the abutment (2) into the receiving hole (12) of the implant (1). An angled surface of the base screw (3) and a beveled surface of the support ring (4) contact each other so that the welding seam or bent over lower edge of the abutment (2) are relieved of axial stress. The above connection system is designed especially for implants (1) with a conical receiving hole (12) and internal polygon as well as abutments (2) having a complementary external conical shape and external polygon.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
Laser based metal deposition of implant structures
InactiveUS20050123672A1Improved bearing propertyIncrease bone ingrowth propertyDental implantsFinger jointsArtificial jointsBone ingrowth
Owner:MEDICINELODGE
Polymer nanocomposite implants with enhanced transparency and mechanical properties for administration within humans or animals
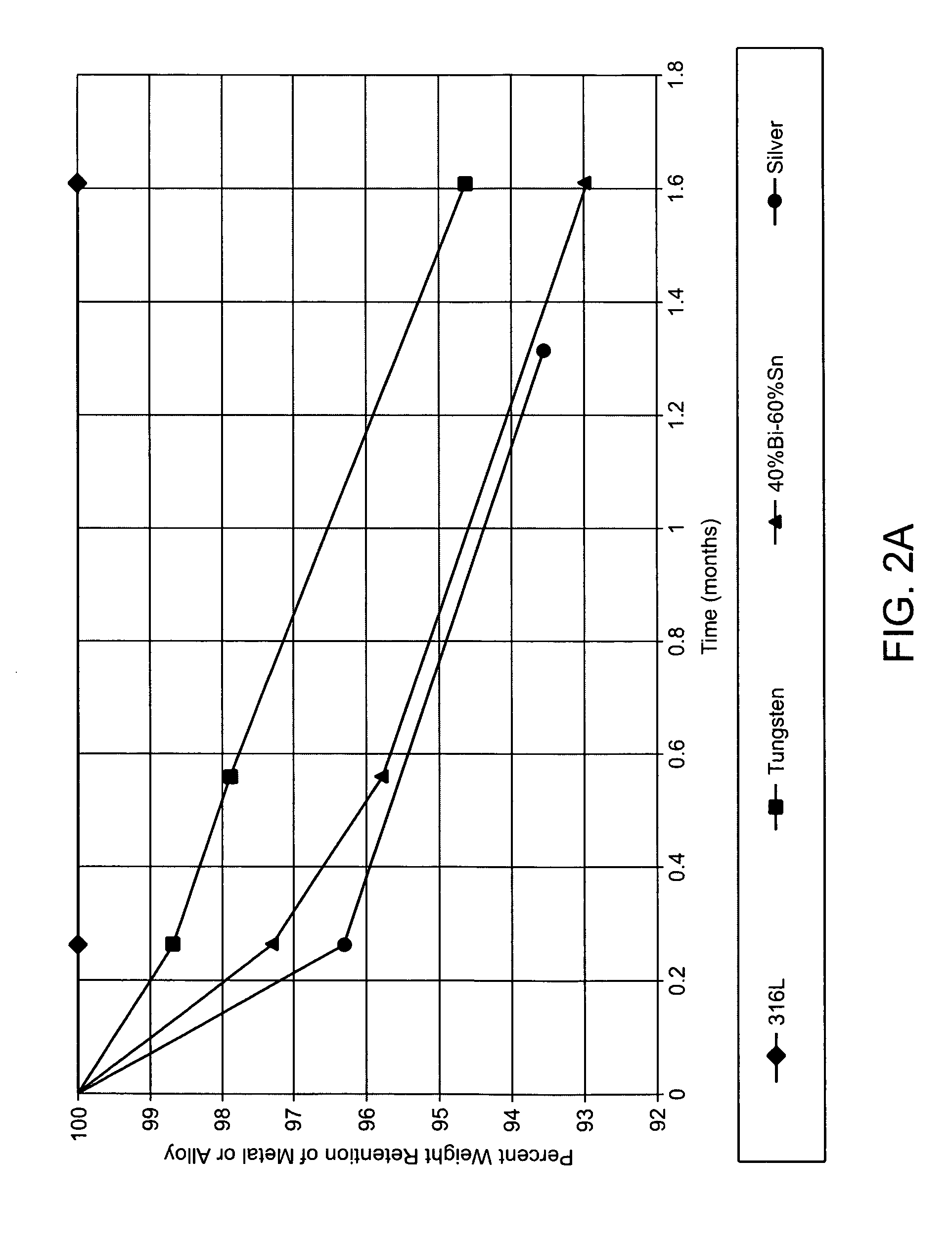
Polymer nanocomposite implants with nanofillers and additives are described. The nanofillers described can be any composition with the preferred composition being those composing barium, bismuth, cerium, dysprosium, europium, gadolinium, hafnium, indium, lanthanum, neodymium, niobium, praseodymium, strontium, tantalum, tin, tungsten, ytterbium, yttrium, zinc, and zirconium. The additives can be of any composition with the preferred form being inorganic nanopowders comprising aluminum, calcium, gallium, iron, lithium, magnesium, silicon, sodium, strontium, titanium. Such nanocomposites are particularly useful as materials for biological use in applications such as drug delivery, biomed devices, bone or dental implants.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Assisted dental implant treatment
InactiveUS20090092948A1Diminished attractivenessEase of productionDental implantsImpression capsPhysical modelComputer module
Embodiments of systems and methods for planning and / or delivering an oral or facial endosseous implantation in a patient are described. In certain embodiments, systems according to the invention include a processing module; a bone imaging module that communicates bone data about the patient to the processing module; a surface imaging module that communicates surface data about the patient to the processing module; and the processing module processes the bone data and the surface data into an output that includes three-dimensional (3-D) representation data indicative of at least one of an oral structure and a facial structure of the patient. In certain embodiments, a system includes a fabrication module that produces a physical model based on the 3-D representation data and indicating a planned location of an endosseous implant. In certain embodiments, a system includes a surgical module that guides implantation of an endosseous implant based on the 3-D representation data.
Owner:CYBER IMPLANTS
Medical implant
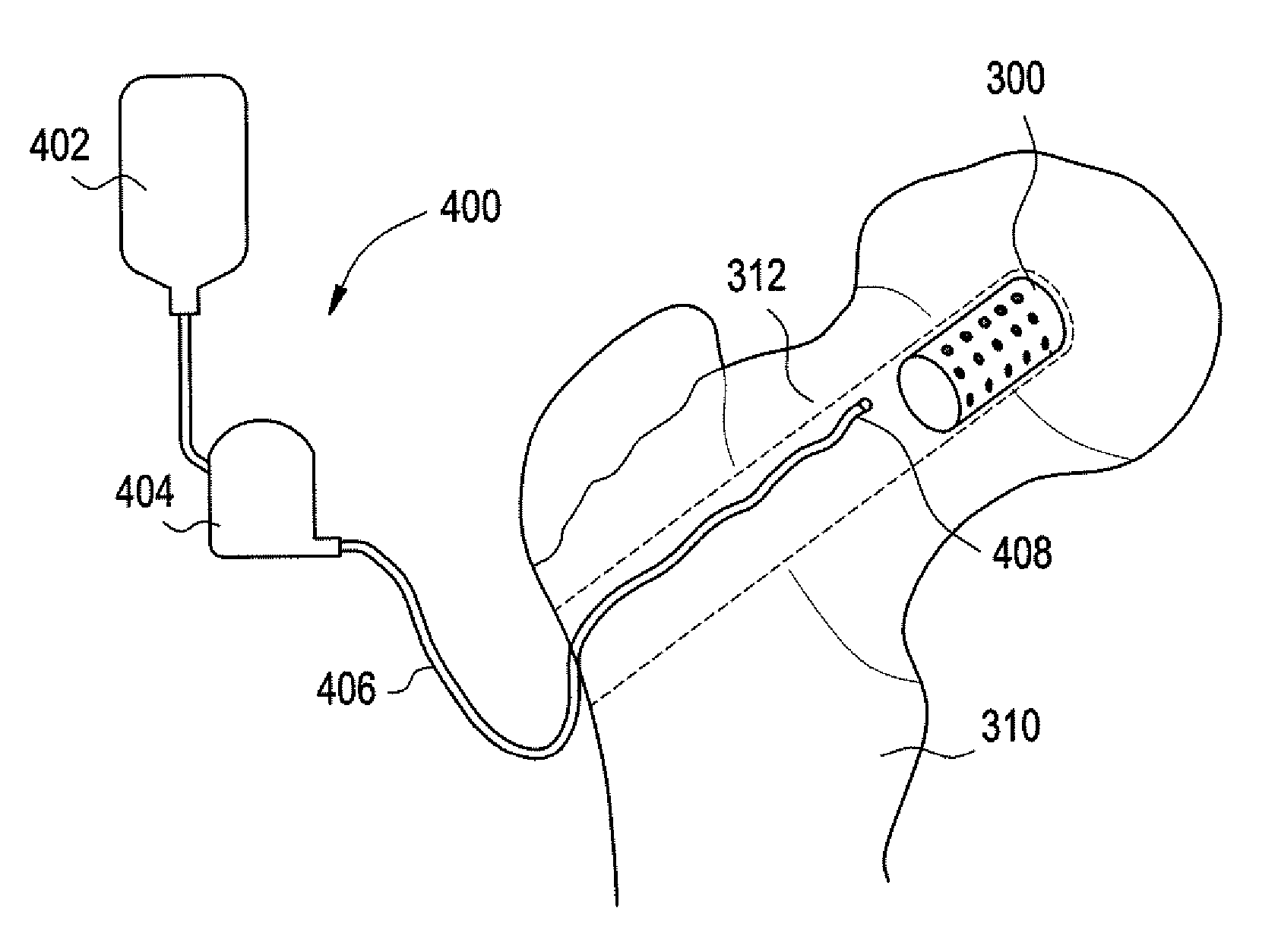
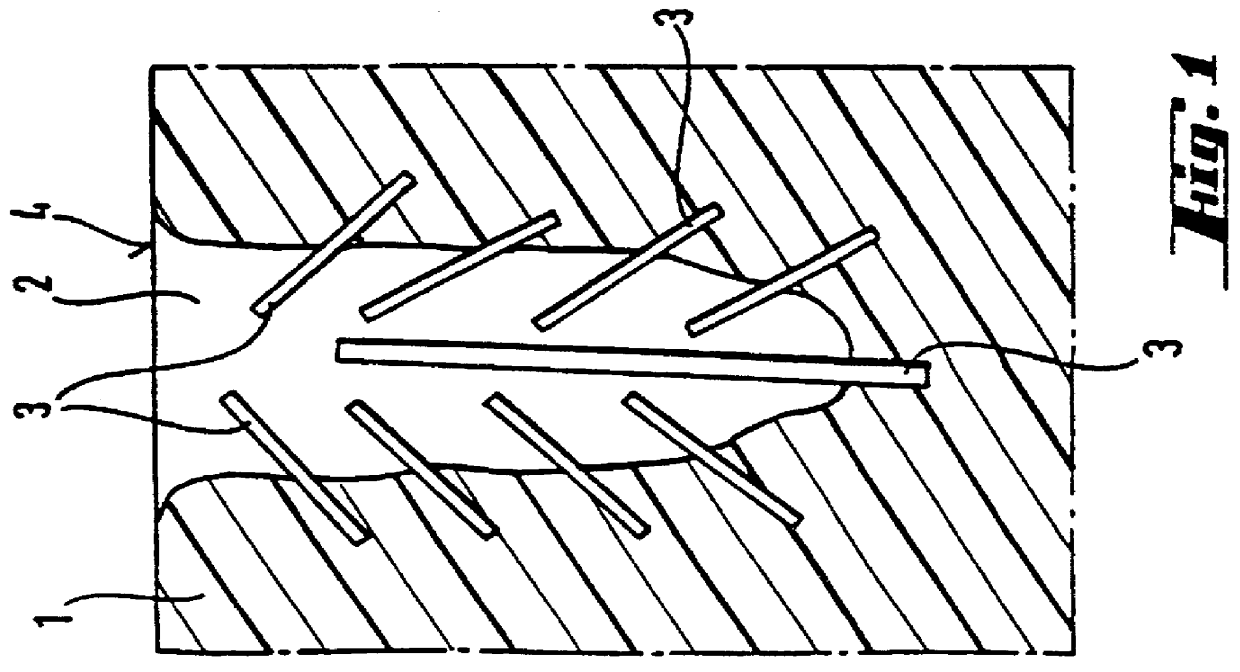
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 05506 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 12, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 12, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 10, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 22308 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 26, 1997The invention relates to a medical implant, in particular a dental implant, intended for implantation in available cavities. Dental implants are implanted in extraction sockets. The implant is provided with reservoirs for a biologically active substance. An advantage of the implant is that, for dental procedures, it can be manufactured and implanted as part of a single therapeutic treatment. However, the implant can also be used as a release system for biologically active substances.
Owner:DR JOUKO SUHONEN +1
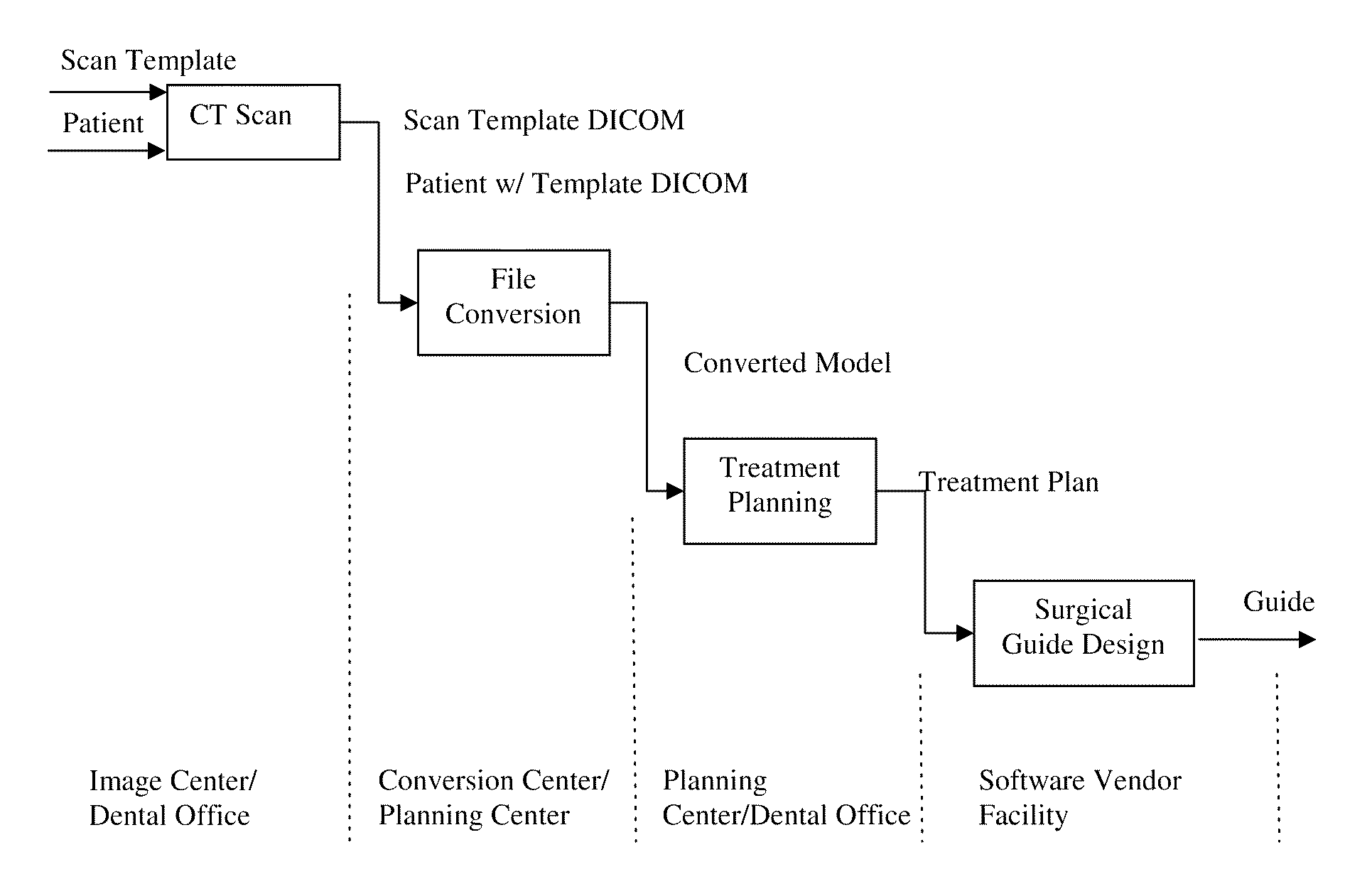
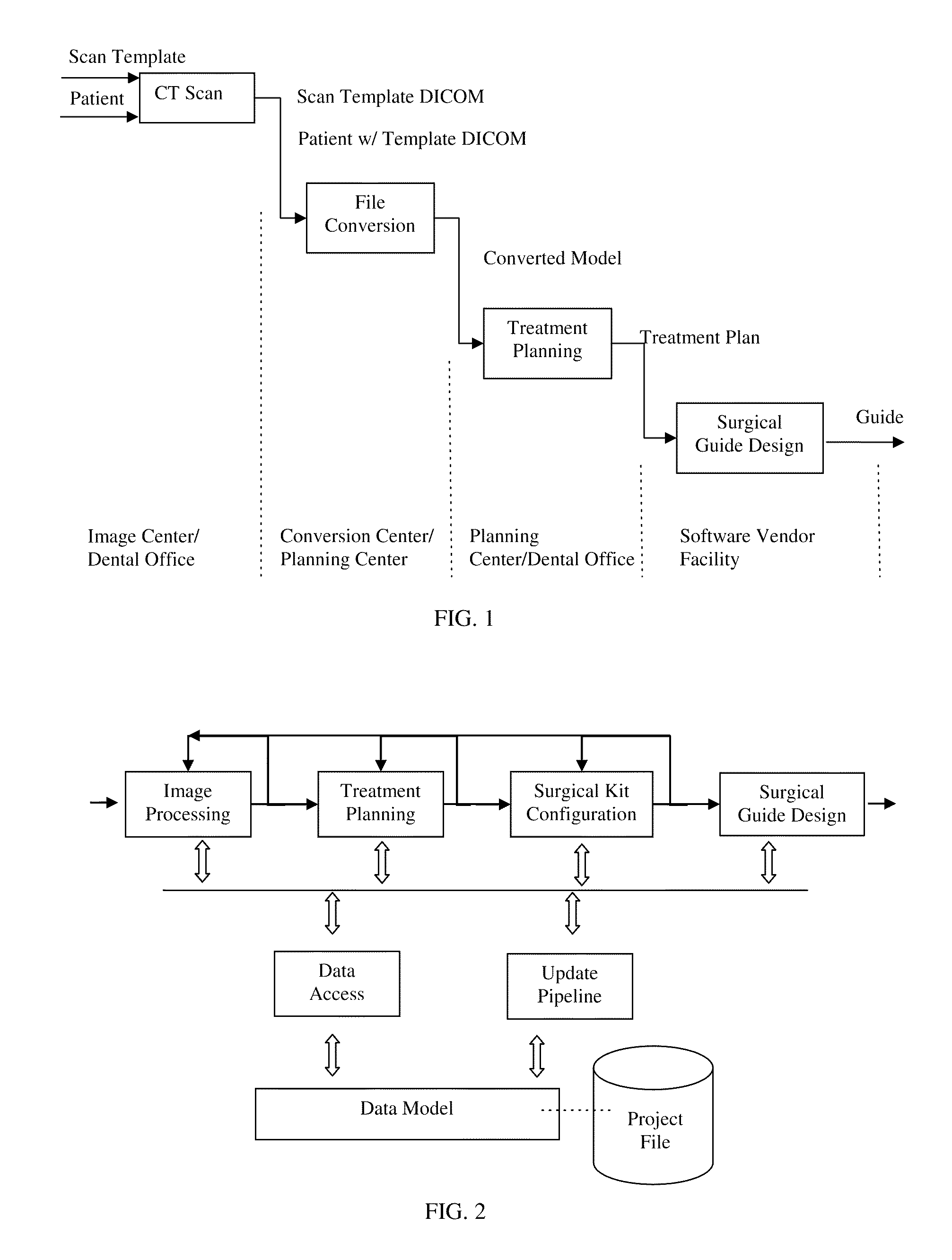
Method and software system for treatment planning and surgical guide CAD/CAM
ActiveUS8543234B2Process controlMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusImaging processingSoftware system
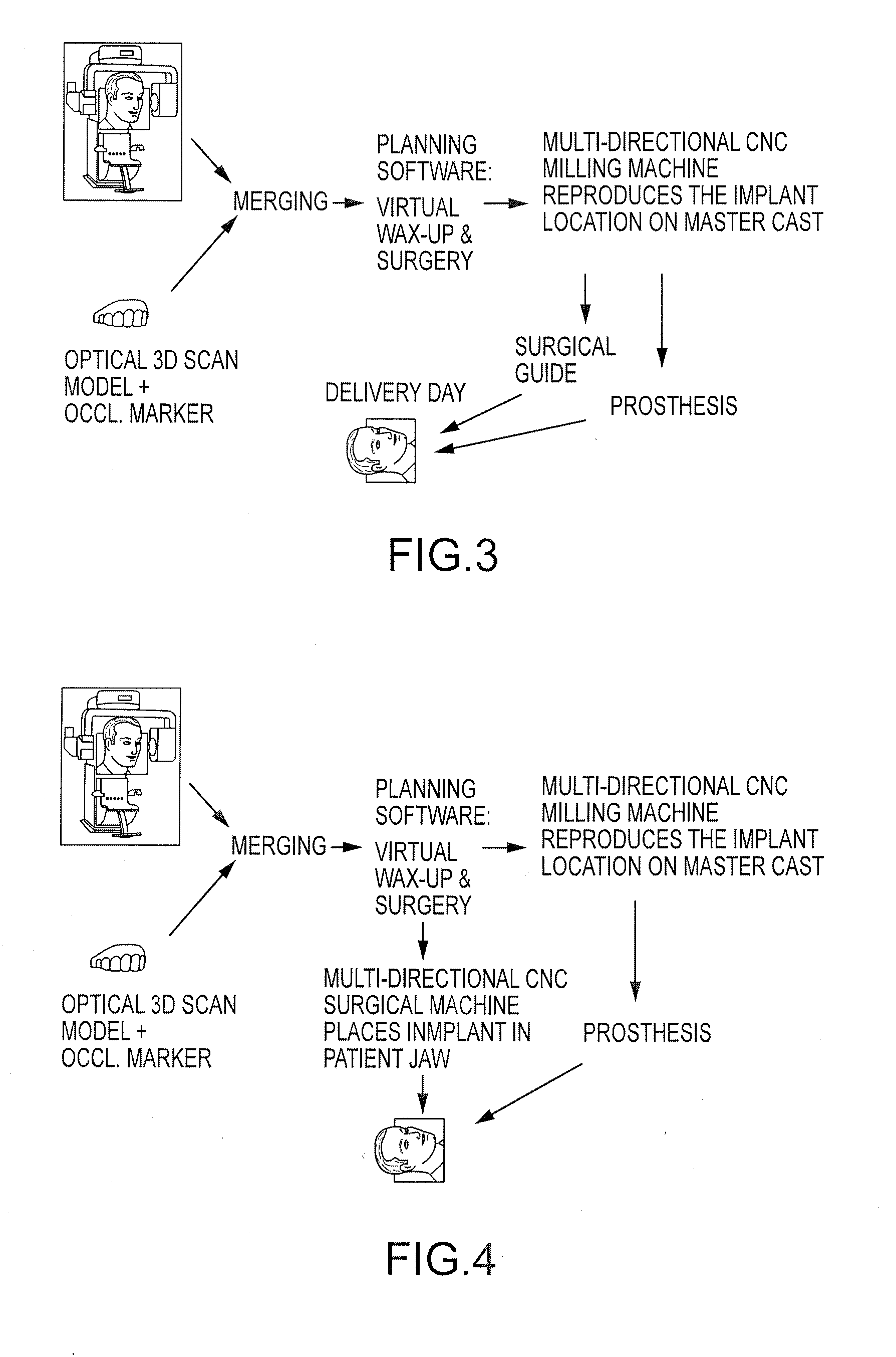
A method and interactive computer system for dental implant treatment planning, surgical guide design and manufacturing. In the heart of the method is a fully associative workflow integrating image processing, treatment planning, surgical kit configuration and surgical guide CAD / CAM in one single computer system. In this workflow, any changes of image processing parameters and implant information in the earlier stage are automatically propagated to the downstream. This characteristic is referred as associativity. The software aspect of the system is built upon this concept and its corresponding data model. This invention also includes an image processing and geometric modeling approach that is characterized as design for manufacturability and applicability. The integration of treatment planning and surgical guide CAD is further on integrated with manufacturing equipment to constitute a complete CAD / CAM solution, which is also fully associative.
Owner:GUIDEMIA TECH
Dental implant placement locator and method of use
The present invention provides a device and method for facilitating the placement of dental implants by use of an implant placement locator and a sequentially sized drill orientation tube series. The implant placement locator disclosed herein comprises a visible radiolucent moldable grid, a set of radiopaque markers located at known intervals within the moldable grid, and a plastic sheeting encasing the visible radiolucent moldable grid and the radiopaque markers. The method of the present invention comprises obtaining a radiograph of a patient's mouth with the implant placement locator overlaying the patient's dental ridge and then transferring reference points as indicated by the location of the radiopaque markers relative to existing teeth and other oral structures to a dental stone model. In a preferred embodiment, drill bits are directed in the desired trajectory into the patient's available lower or upper jaw bone by use of drill orientation tubes in combination with the implant placement locator. A sequentially sized set of spacers is provided having sequentially sized inside diameters to direct varying diameter drills. Drill guide parallelism is thus provided by the invention.
Owner:SHELTON ROBERT
Method and device for placing dental implants
The invention relates to a method and device for placing implants (1) using a surgical template (11) which is made from tomographic cuts in the patient's jawbone (7). According to the invention, step drills (4) and calibrating drills (5), having a single standard diameter for each type of implant (1), are guided through drill bushings (18) which are inserted into bores (15) in the template (11) in order to produce any drilling sequence corresponding to an implant plan. The penetration depth of the drills (4, 5) is controlled by the height of the bores (15) or by the drill rings (21). The aforementioned template (11) bores (15) serve as a guide for the precise placement of the implants (1) owing to the adapted implant supports (3). Moreover, washers (23), which are mounted around the implant supports (3), limit compression in relation to the implants (1) while said implants are being placed (20). The above-mentioned characteristics serve to limit the required number of drills (4, 5) and implant supports (3) to the longest models only. The inventive method and device are particularly suitable for computer-assisted implantology systems.
Owner:MATERIALISE DENTAL NV
Custom-fit implant surgery guide and associated milling cutter, method for their production, and their use
InactiveUS7824181B2Ensure total axial stabilityEnsure stabilityDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusMilling cutterEngineering
The invention relates to a custom-fit implantable surgical guide (1) and an associated milling tool (4), which is positioned in straddling on the alveolar ridge (7) of a maxillary or mandible arch (2) and comprises at least one drilling barrel (11) for axially guiding said milling tool (4), wherein said barrel (11) is laterally open and at least one part of the internal surface thereof (17) and at least one part of the external surface of the milling tool (4) interact and axially maintain the entire milling tool (4) with respect to the barrel (11). Said invention makes it possible to carry out high precision osteotomies for lateral insertion dental implants.
Owner:MATERIALISE DENTAL NV
Method of installing a dental implant
InactiveUS7044735B2Simple methodBetter method of installing a dental implantDental implantsImpression capsTomographyCatheter
A method of installing a dental implant includes positioning a drill guide tube adjacent to a jawbone and taking a tomographical scan of the two. Based on the scan, a computer-generated image is created and analyzed to confirm whether the drill guide tube is properly aligned. If the drill guide tube is in the correct position, that same tube to used to guide a drill bit into the jawbone. In some cases, the tube also helps guide a biopsy punch in cutting just a small, round opening into the gum tissue, which minimizes the time needed for healing.
Owner:MALIN LEO J
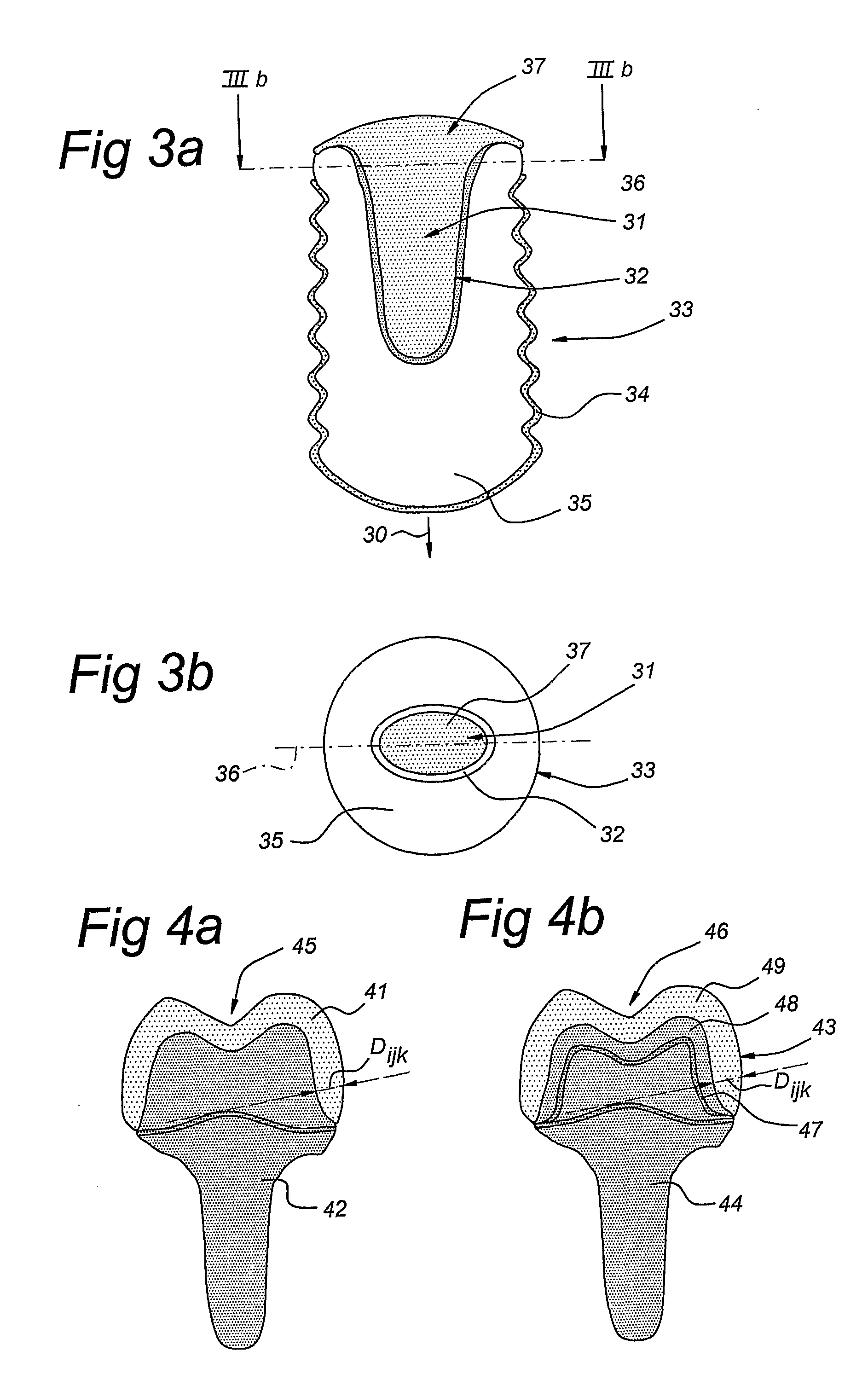
Pilot drill, step drill, and drill set for dental implant technology
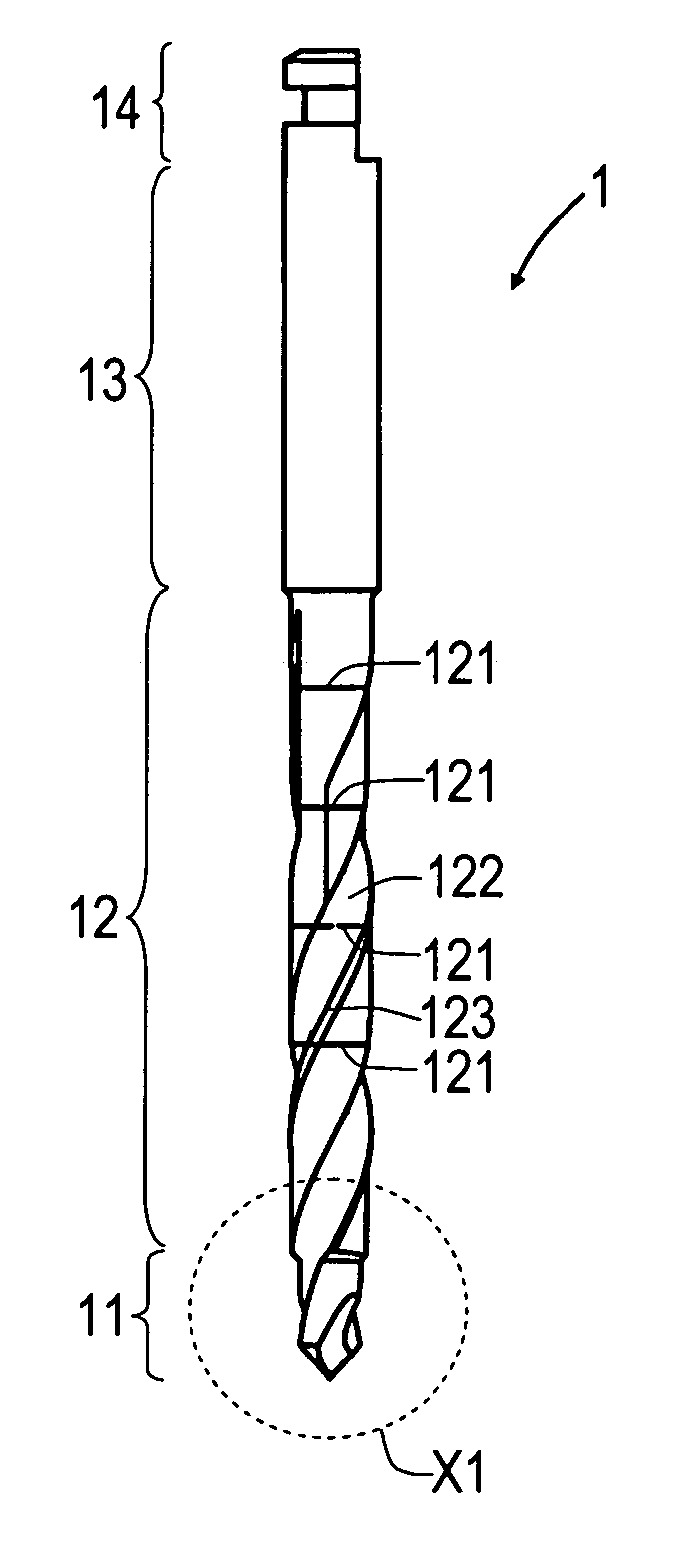
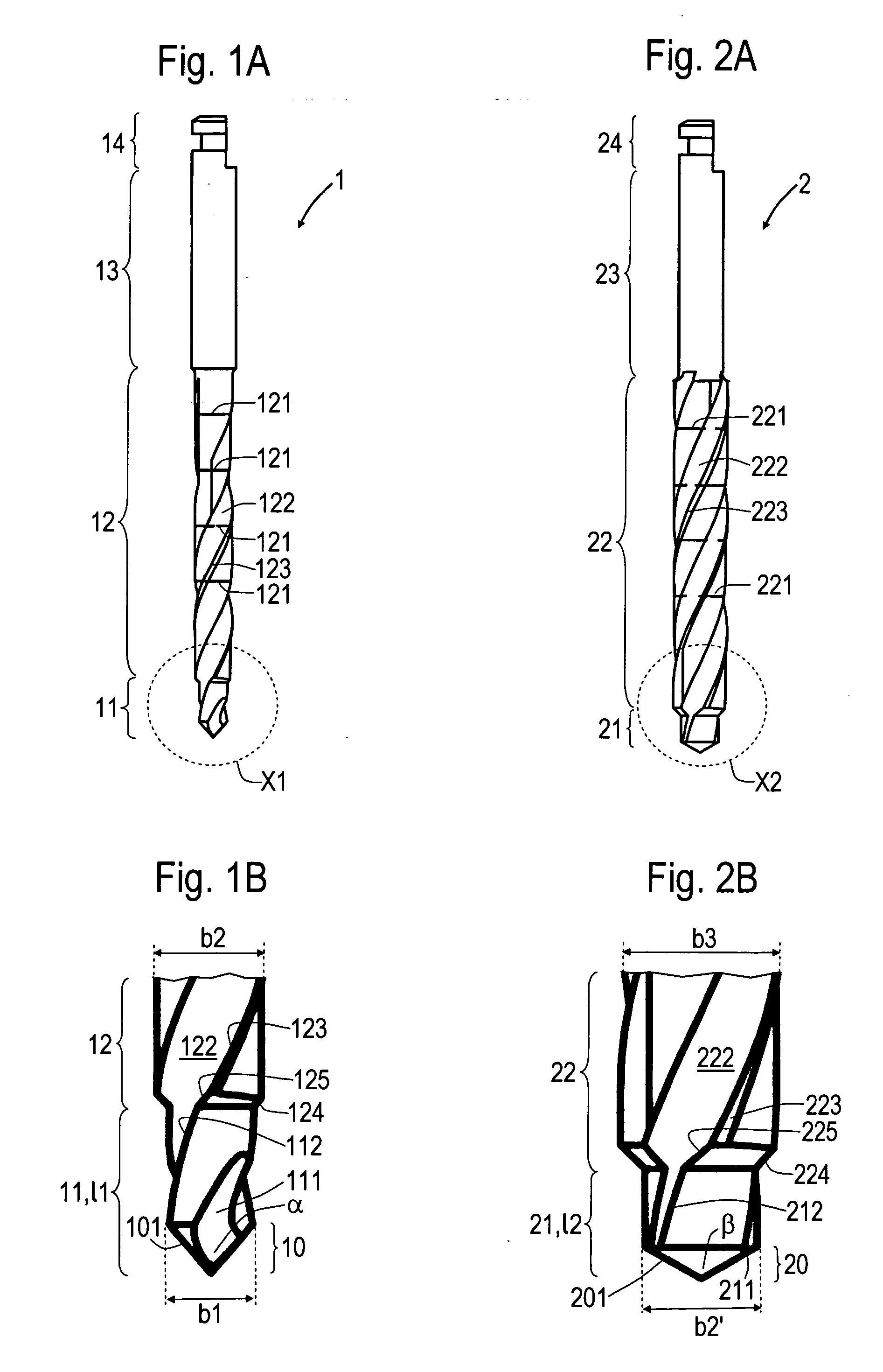
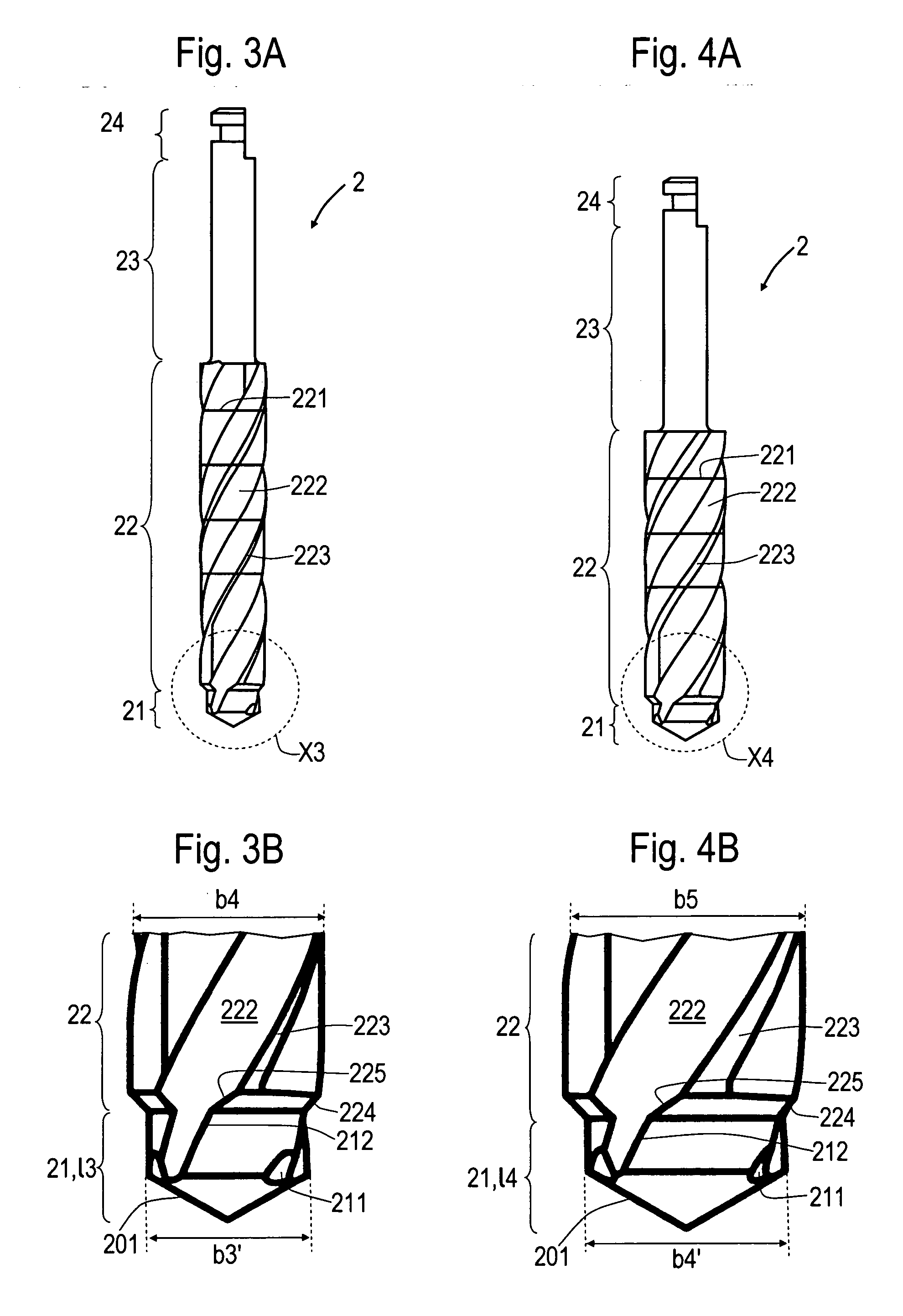
The invention relates to a pilot drill (1) for producing a pilot bore in a human jaw bone in preparation for its enlargement into a step bore, achieved by means of a first step drill (2) or if the step bore is further enlarged, by means of second and third step drills (2). The prepared step bore is designed to receive a dental implant, preferably in screw form. The pilot drill (1) and the first step drill (2) form a drill set. The pilot guide (11) on the pilot drill (1), comprising a step (124) lying in the transition region leading to the drill neck (12), positions the drill at the commencement of drilling in the corticalis, whereby the drilling direction can be corrected prior to the continued drilling down to the maximum depth of the pilot bore. The pilot guide (11) has a drill diameter (b1), whereas the step (124) leads into an enlarged drill diameter (b2). The step guide (21) of the first step drill (2) has a drill diameter (b2′) that corresponds to the drill diameter (b2). The drill diameter (b3) at the drill neck (22) of the first step drill (2) corresponds to the drill diameter at the step guide (21) of the second step drill (2). The second step drill corresponds in a similar manner to the third step drill (2). The advantages of the invention are that it requires a reduced number of drilling tools, that the implant bed can be prepared in a precise, gentle manner and that the inserted implants achieve a primary stability.
Owner:THOMMEN MEDICAL
System for producing a dental implant and method
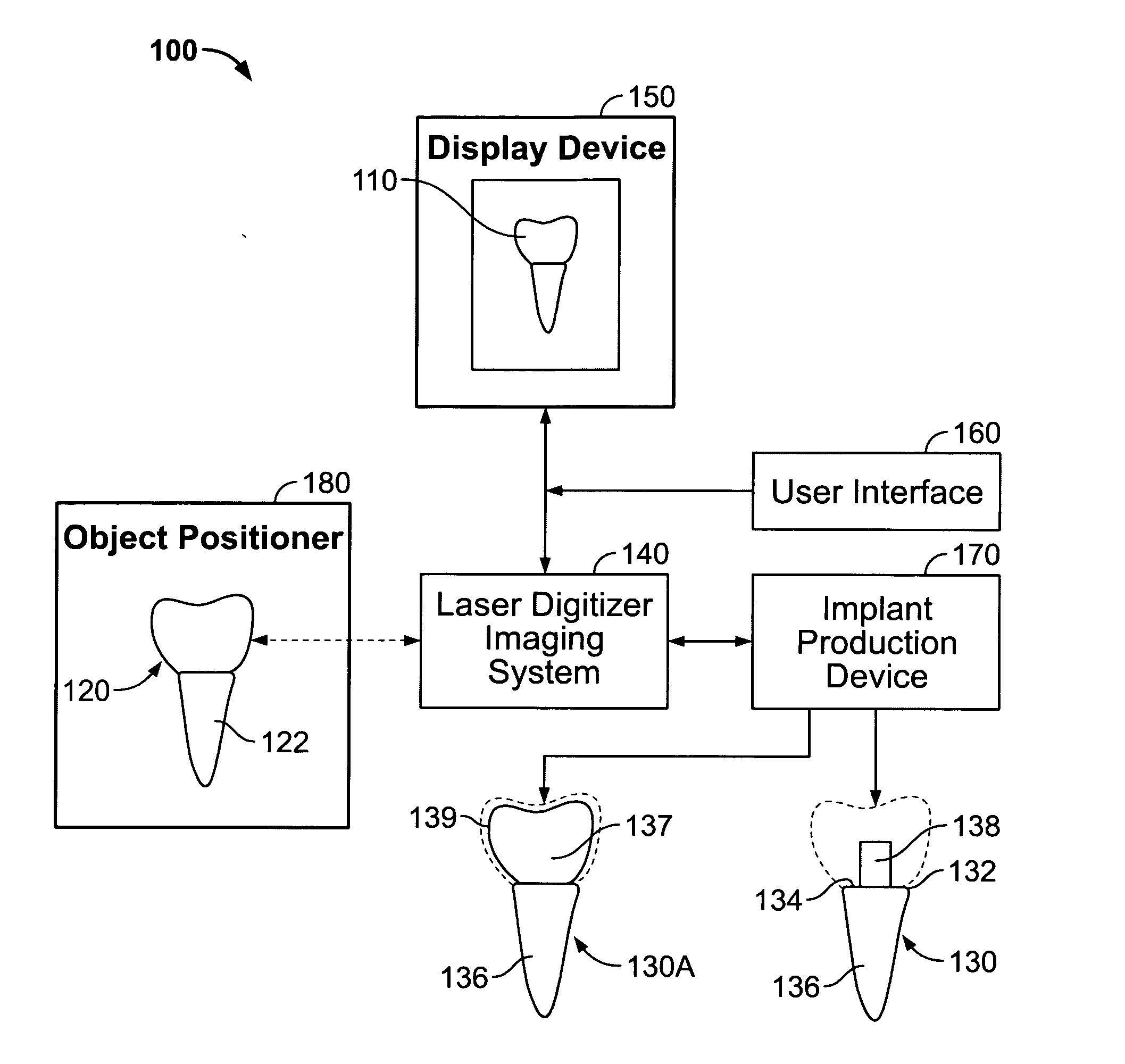
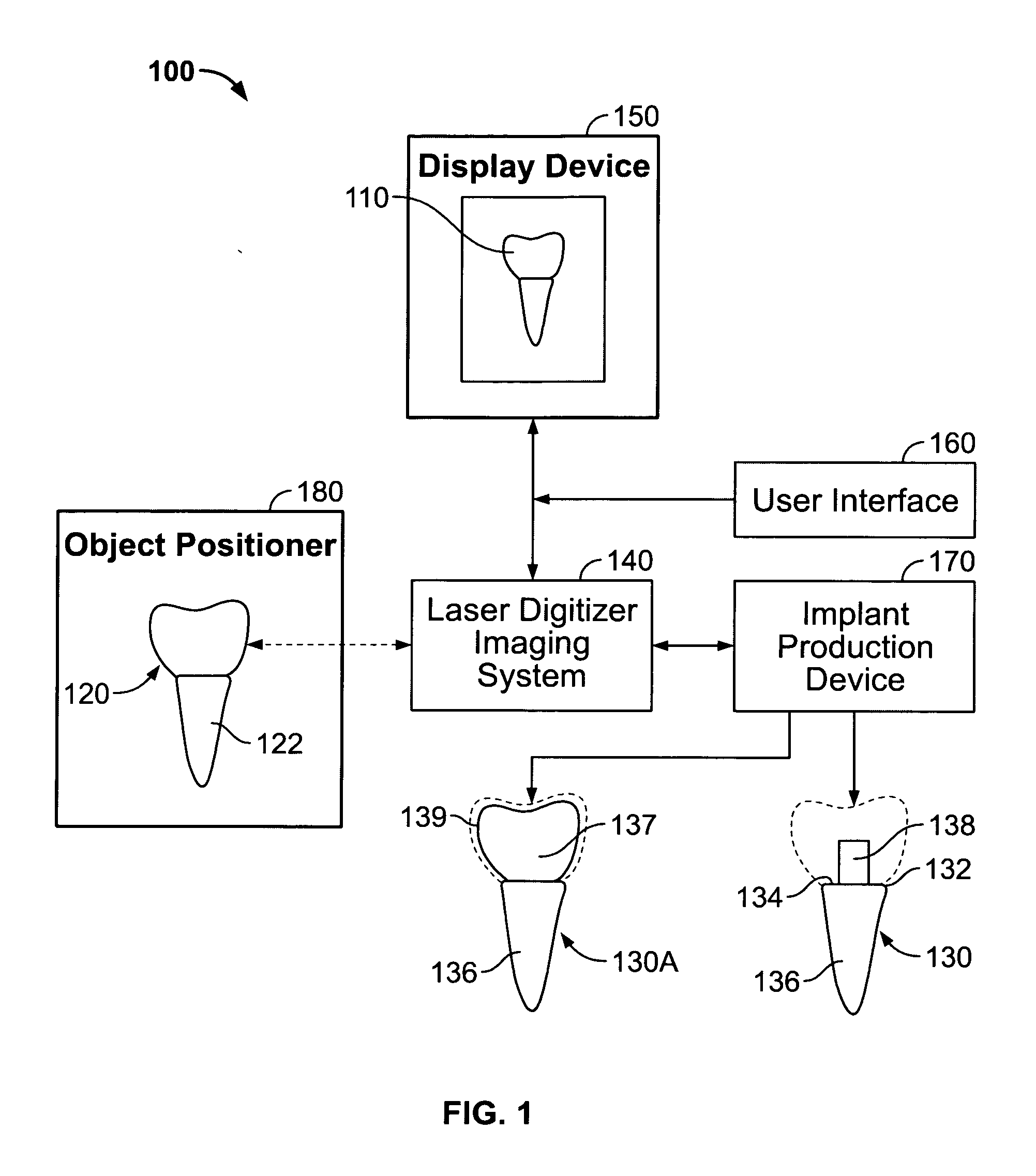
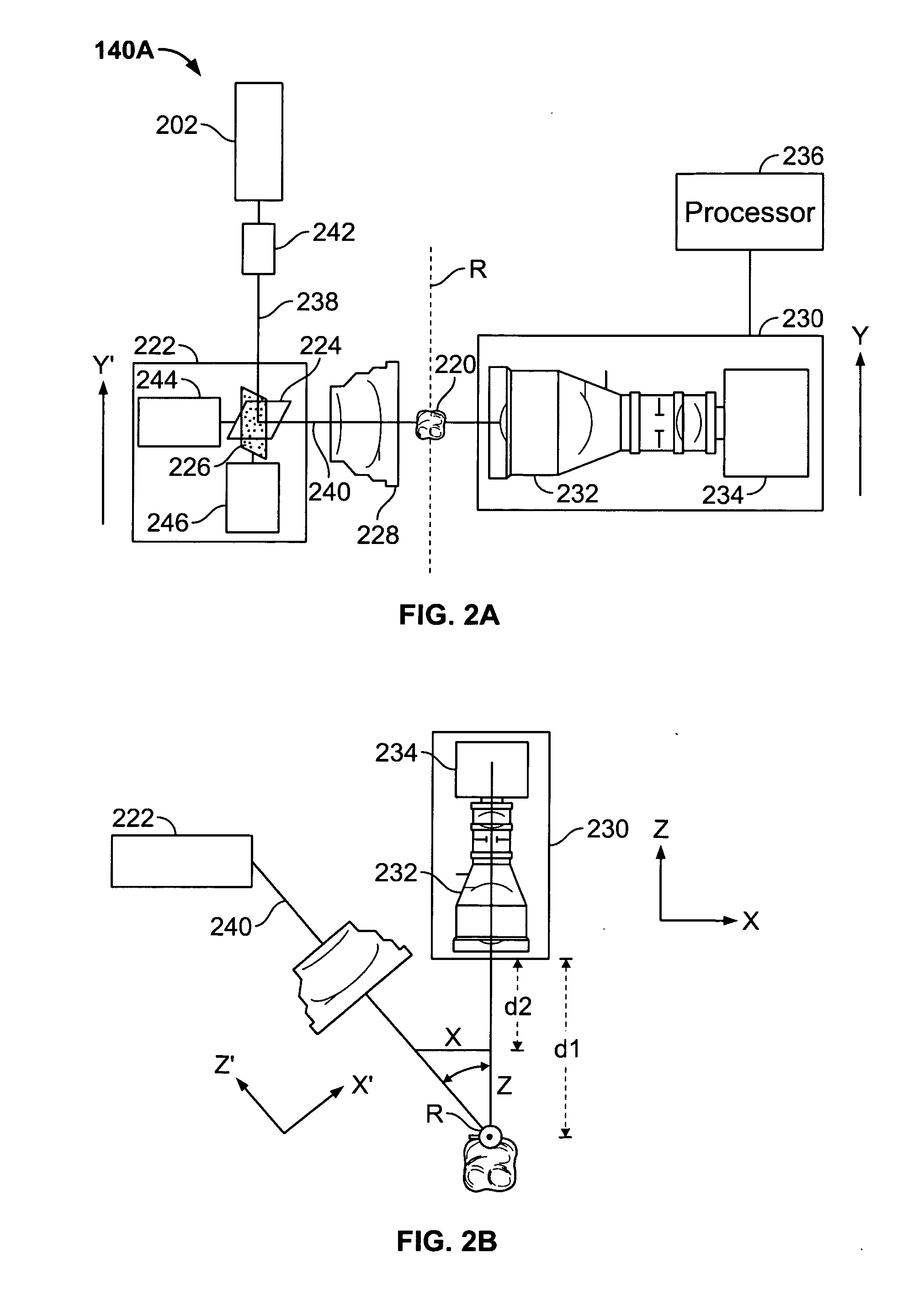
A system and method for producing a dental fixture are provided. A laser digitizer imaging system creates a visual three-dimensional image of a dental item such as a tooth or a dental impression. The three-dimensional image may be displayed and the size and shape of the image may be selectively modified by the user of the system. Digital data associated with the three-dimensional image of the dental item is sent to an implant production device. A dental implant is produced in response to receipt of the data associated with the three-dimensional image such that the implant is insertable into a socket of the jawbone from where a tooth was extracted.
Owner:D4D TECH LP
Multi-adjustable drill guide and framework system for dental prosthetics
InactiveUS7021934B2Reduce complexityLow costDental implantsDental toolsPermanent implantDental implant
In one aspect, a group of inter-connecting, prefabricated components of various shapes and sizes that can be assembled together to form a framework system directly onto dental implants installed in the patient's mouth is disclosed. In another aspect, a group of prefabricated components to form a drill guide system for drilling a properly spaced and oriented implant hole adjacent to another implant hole or adjacent to a fully-installed implant is disclosed. In yet another aspect, improved procedures for installing permanent, implant-supported dental restorations are disclosed, including an immediate loading procedure.
Owner:ZIMMER DENTAL INC
Method for creating a personalized digital planning file for simulation of dental implant placement
ActiveUS20090187393A1Provide informationAdvantageously avoidedImpression capsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPersonalizationDental implant
The present invention provides a method for creating a personalized digital planning file for simulation of dental implant placement. After planning, the digital representation in a plaster model may be used to design and produce dedicated surgical templates to assist the surgeon in transferring the implant plan to a patient during medical intervention.
Owner:MATERIALISE DENTAL NV
Design and manufacture of dental implant restorations
The present invention provides a method of making and aligning digital images from oral tissues, dental implants, healing components, and dental restorations to design and manufacture dental implant retained restorations. Image data about the space available for the planned restoration, orientation of dental implants or abutments and aesthetic contour and occlusion of the prosthesis are all integrated into a virtual three-dimensional model of the prosthesis that can be sent to the clinician or laboratory to validate design intent and to manufacture the prosthesis. The virtual model is used by either a conventional rapid prototyping machine to produce a castable pattern or a number controlled mill to machine the restoration.
Owner:VOXELOGIX CORP
Internal connection dental implant
ActiveUS20050287497A1Firmly connectedIncreased torque carrying capacityDental implantsAbutmentDental implant
An internal connection dental implant and implant assembly in which the implant includes a lobed configuration for installing the implant and a beveled surface positioned on the proximal side of the lobed configuration for providing stability between the implant and a corresponding abutment.
Owner:KEYSTONE DENTAL INC
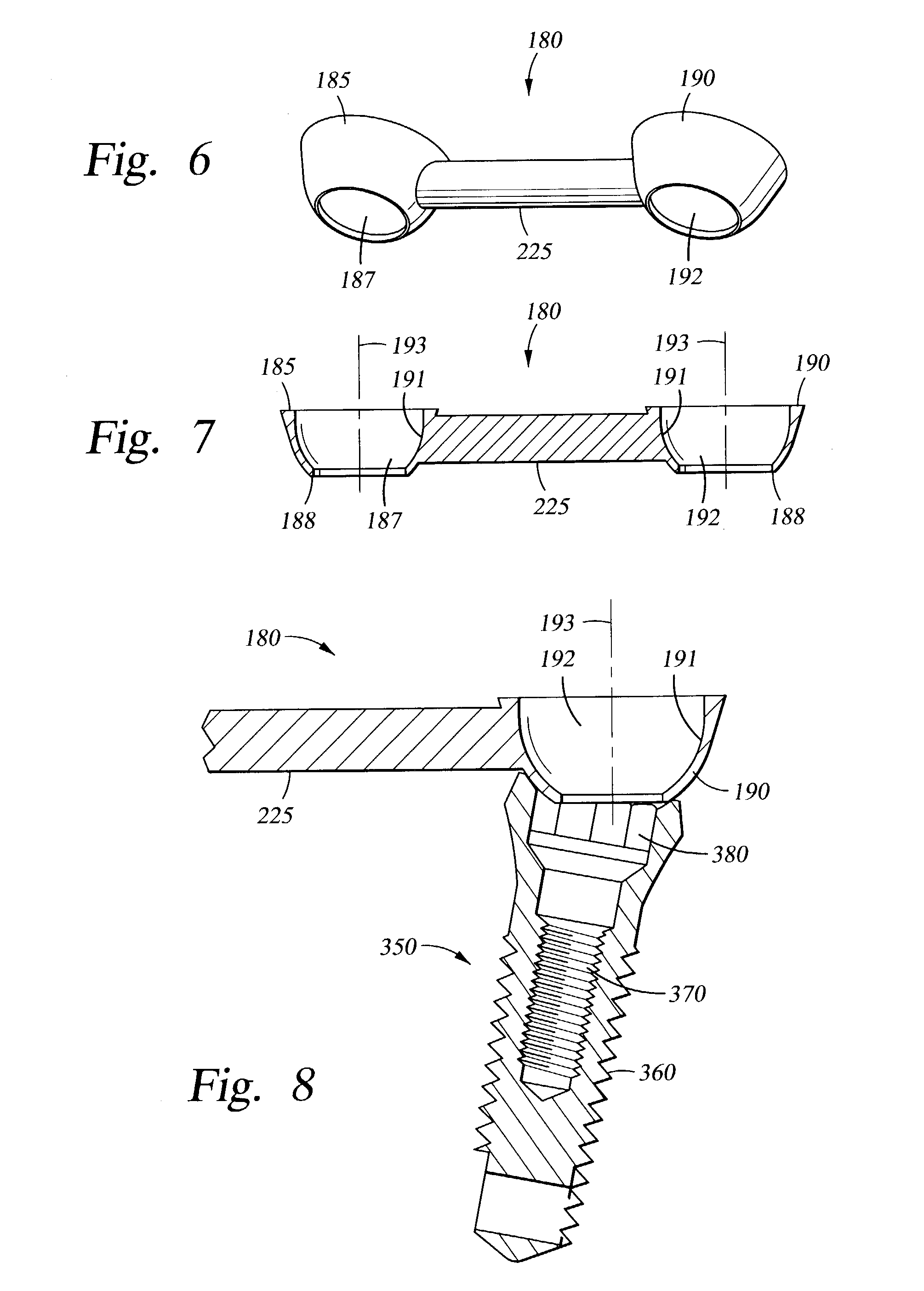
Healing cap for dental implants
PCT No. PCT / CH96 / 00426 Sec. 371 Date May 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 27, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 3, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 20518 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 12, 1997A healing cap (100) is distinguished by a bevel (116), particularly in the region to be positioned labially, the bevel being advantageous for conditioning the soft parts, as well as a firm bearing on the associated implant (1), which is achieved by means of a mating shoulder (115) and an adaptable end portion (121) of a pin (120) or a centering bead. An occlusally applicable screw (200) can be mounted in the healing cap (100) beforehand, making it easier to handle. A special protective cap is provided as an intermediate treatment and as a temporary sealing element.
Owner:STRAUMANN HLDG AG
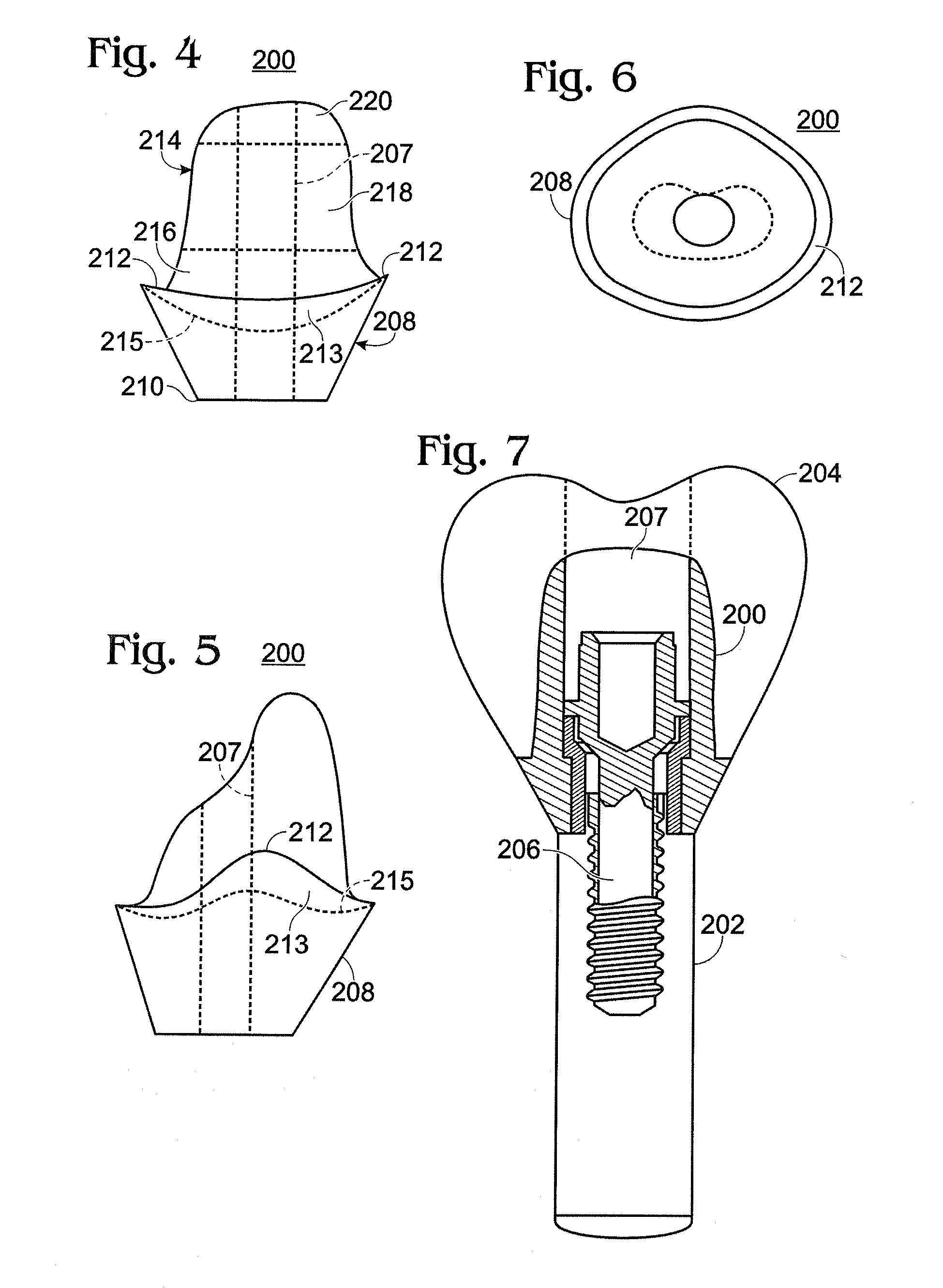
Dental Implant Abutment
A dental implant abutment for attaching a dental prosthesis within a patient's mouth. The abutment is a single unit structure fabricated of a ceramic material, multicolored throughout to match the color of the dental prosthesis, the surrounding dentition and the surrounding gingival tissue.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com