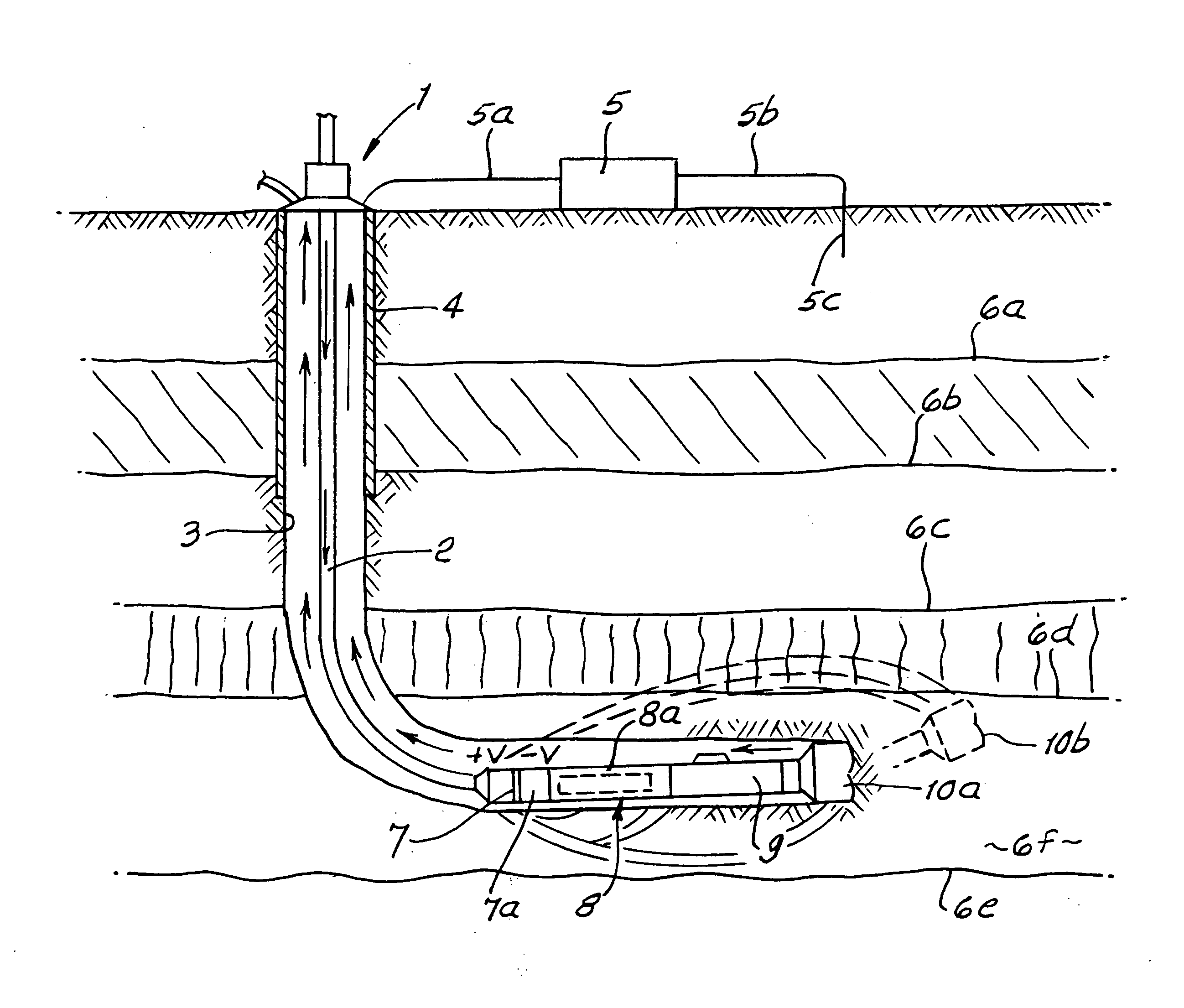
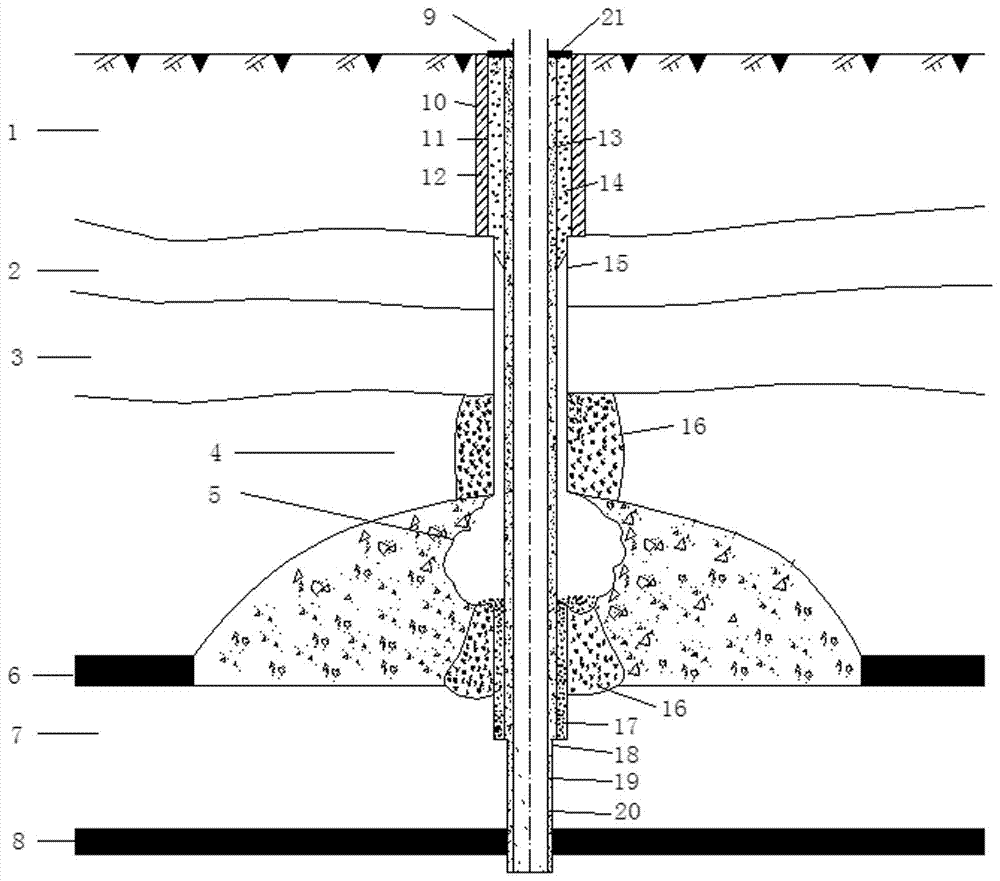
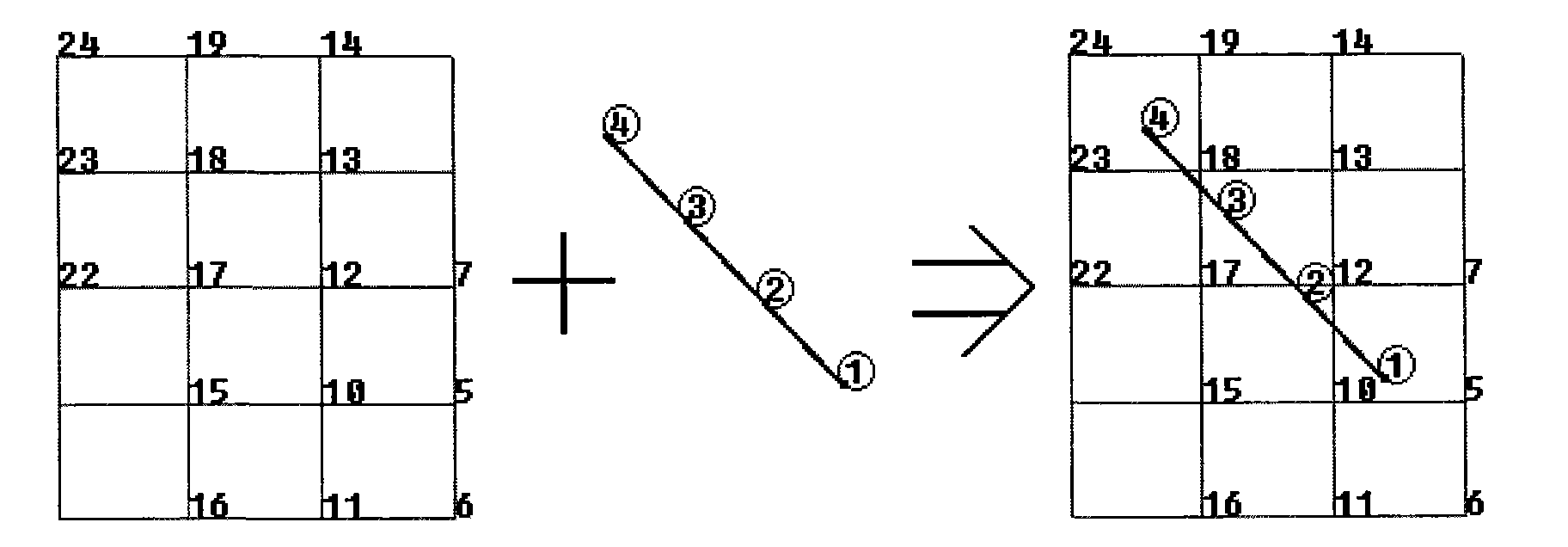Patents
Literature
243 results about "Bed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
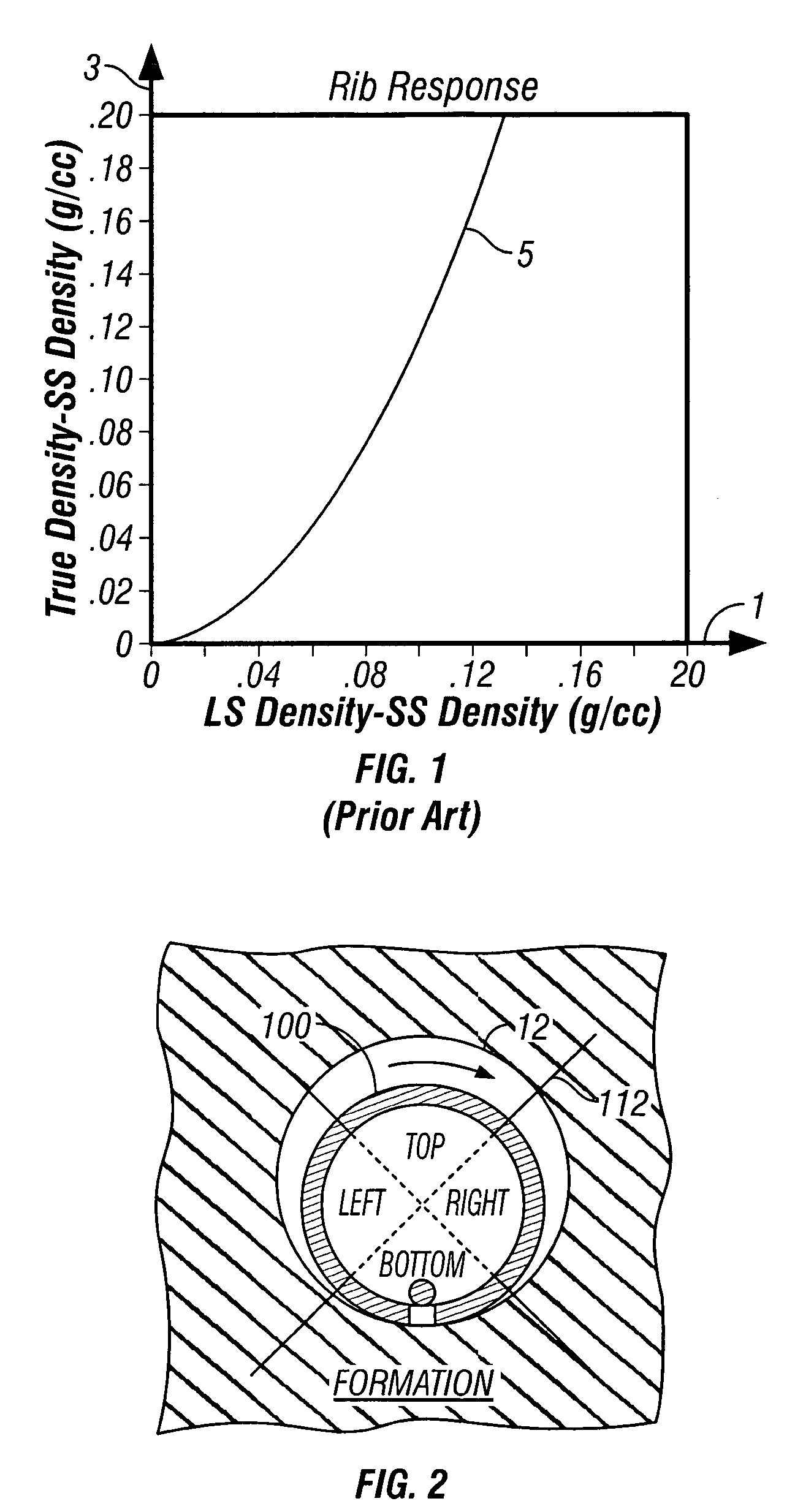
Beds are the layers of sedimentary rocks that are distinctly different from overlying and underlying subsequent beds of different sedimentary rocks. Layers of beds are called stratigraphy or strata. They are formed from sedimentary rocks being deposited on the Earth's solid surface over a long periods of time. The stratigraphy are layered in the same order that they were deposited, allowing a differentiation of which beds are younger and which ones are older (the Law of Superposition). The structure of a bed is determined by its bedding plane. Beds can be differentiated in various ways, including rock or mineral type and particle size. The term is generally applied to sedimentary strata, but may also be used for volcanic flows or ash layers.
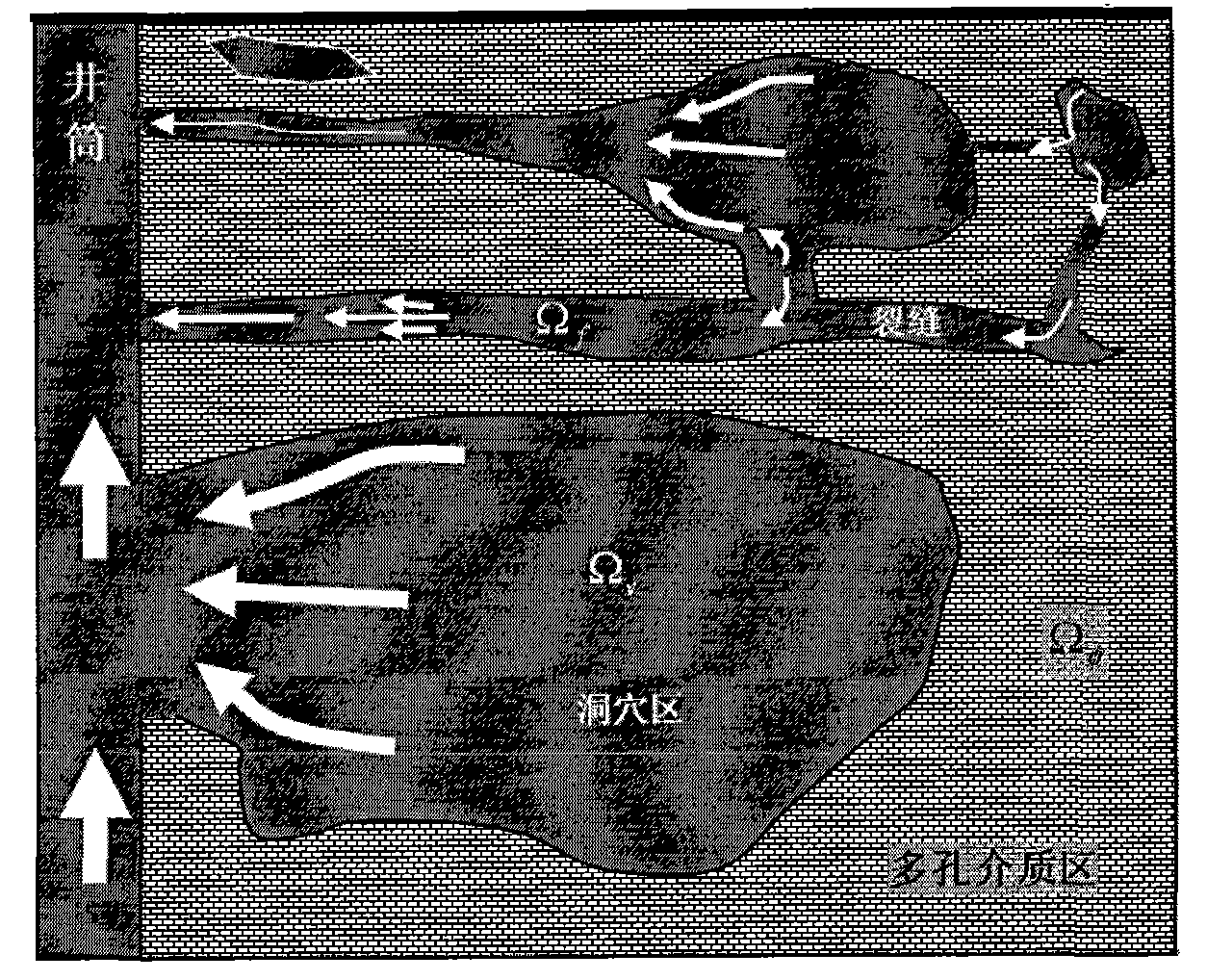
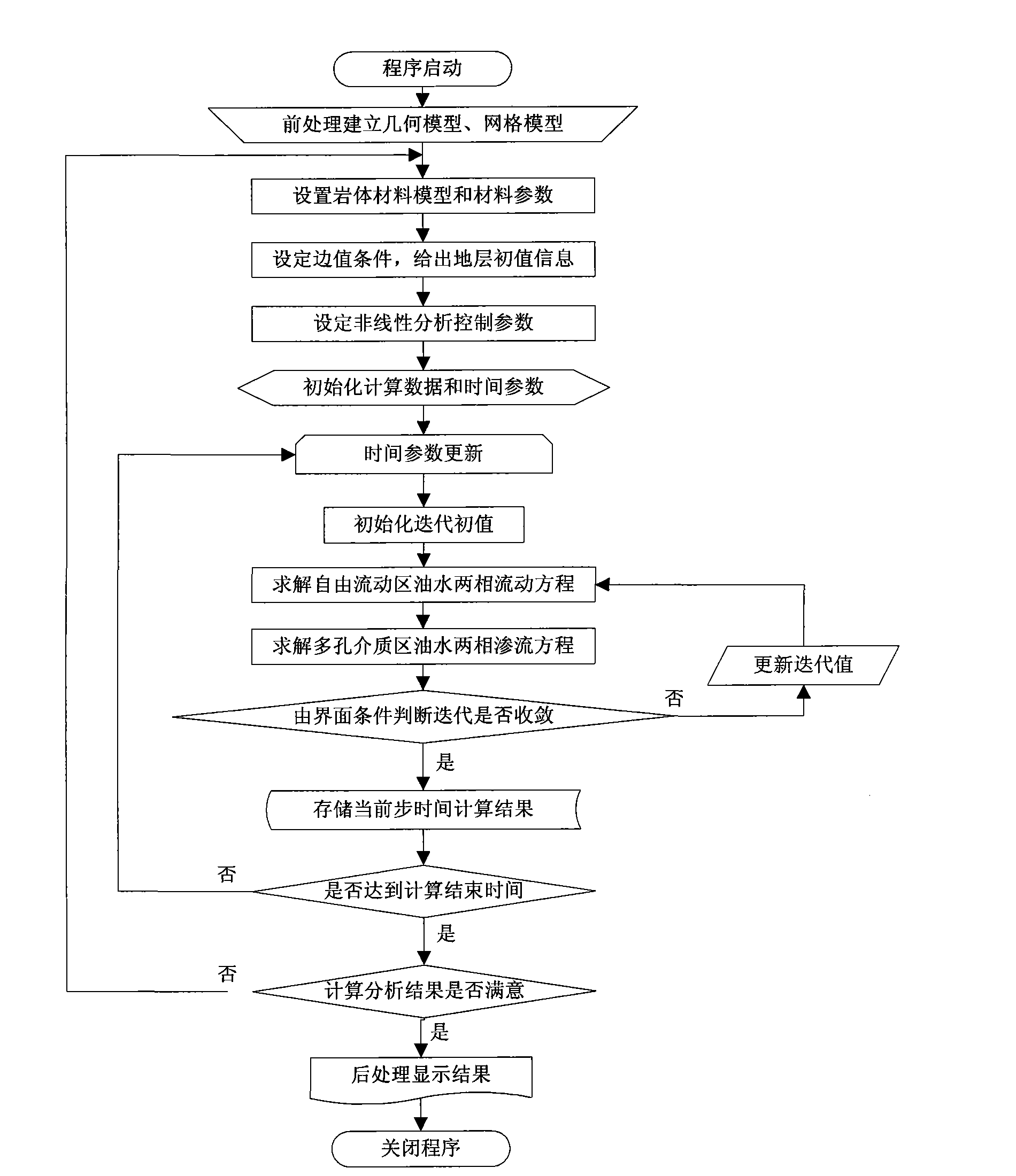
Method for analyzing and simulating fluid flow of fracture-cavity oil reservoir
ActiveCN102339326ARealize simulationEasy 3D workSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelMechanics
The invention provides a method for simulating the fluid flow of a fracture-cavity oil reservoir, belonging to the field of numerical simulation of the oil reservoir. The method provides a numerical simulation method of an oil reservoir based on the coupling of a Navier-Stokes equation and a Darcy equation and mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing a complex medium Navier-Stokes and Darcy coupling mathematical model; (2) using a numerical computing method of the Navier-Stokes and Darcy coupling model; and (3) respectively modeling a rock mass and fractures, wherein the respective modeling is easy, the description for the fractures is clear and easy, the quantity and the space of the fractures are not limited, and particularly, nodes on the fractures are not requested to be completely coincided with nodes of bed rocks so that the three-dimensional work is easier. A numerical simulation program is complied for realizing the method; and the method develops a numerical simulation theory and method of the fracture-cavity oil reservoir and scientifically realizes the simulation on the fracture-cavity oil reservoir.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
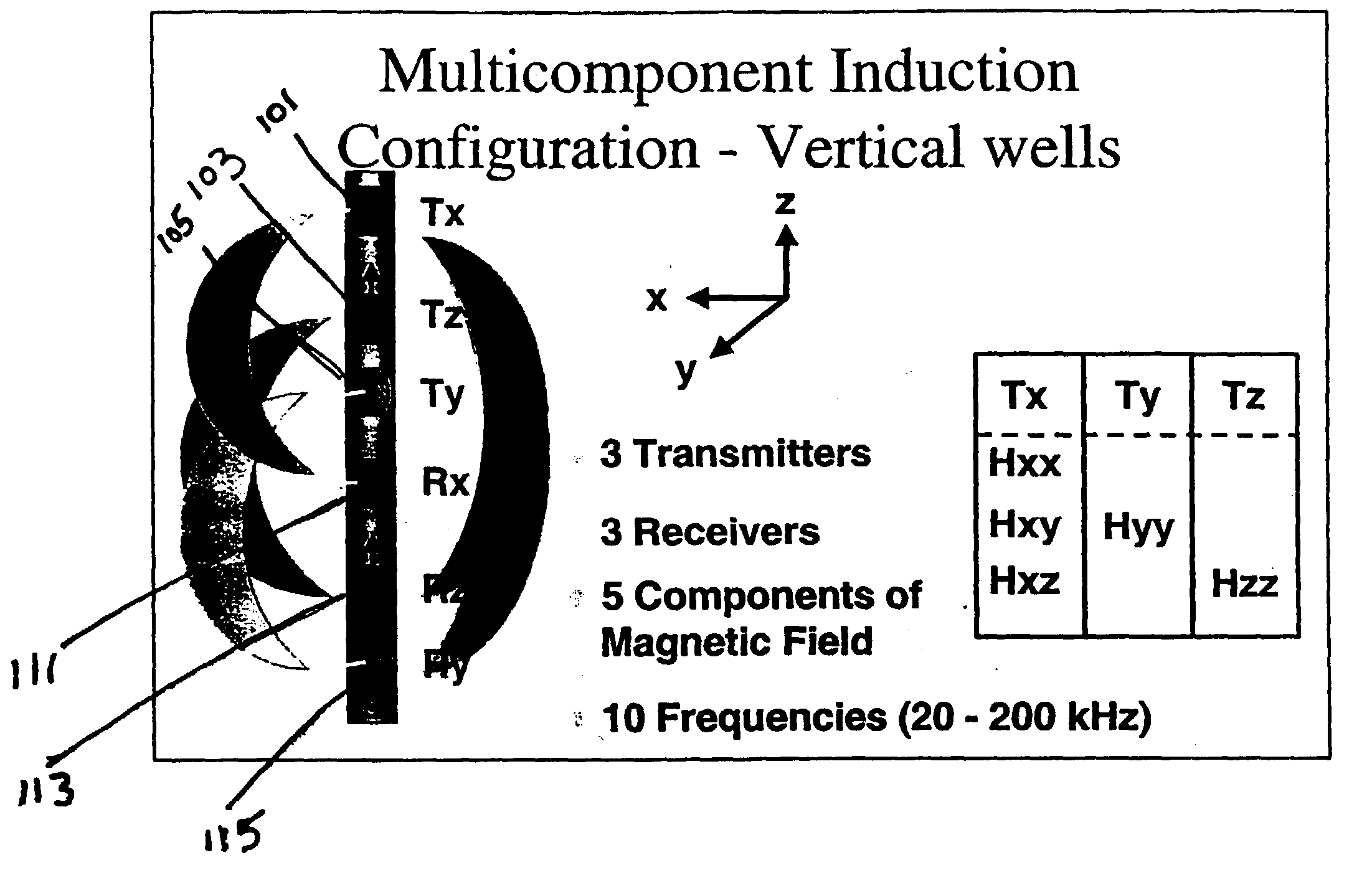
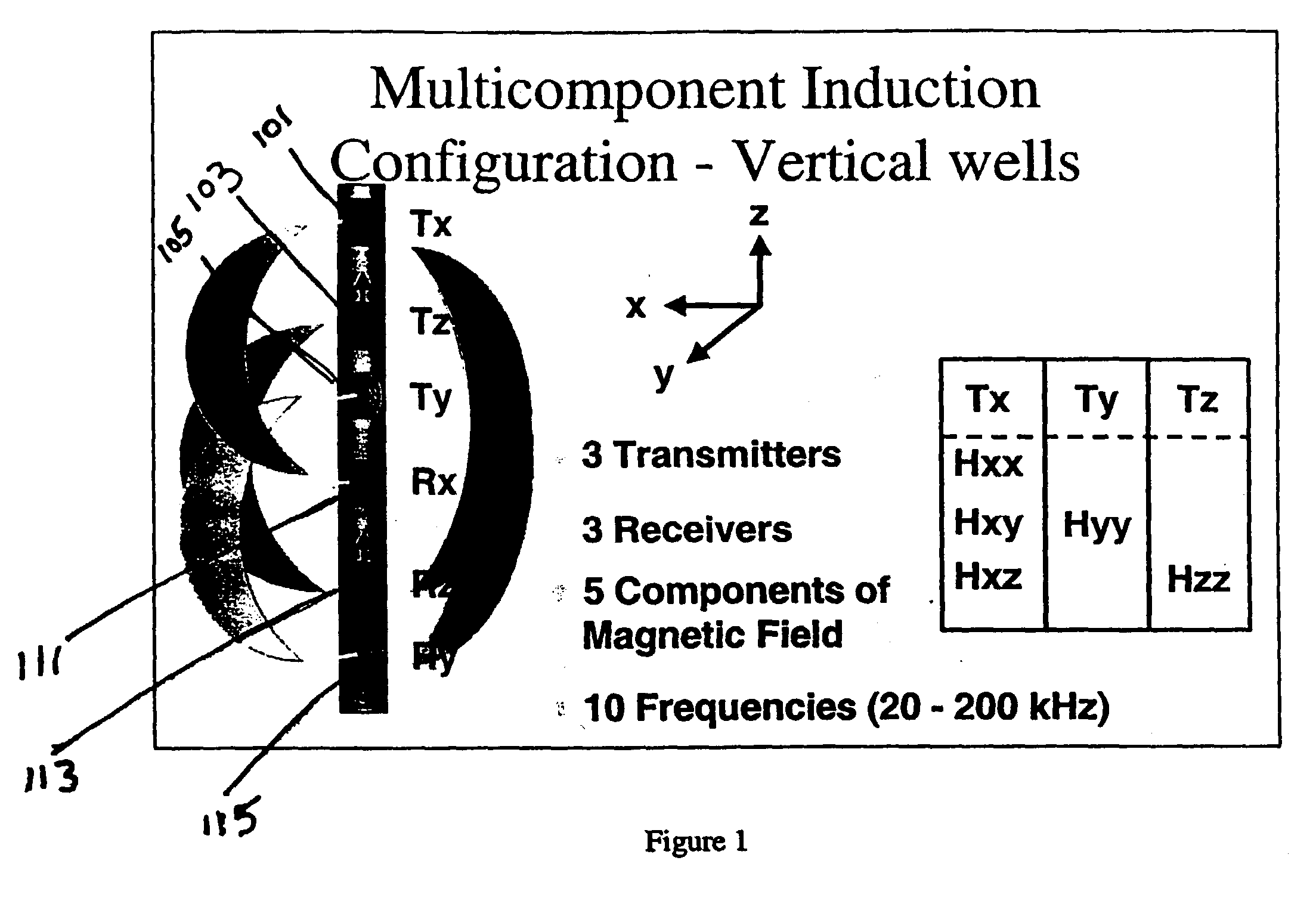
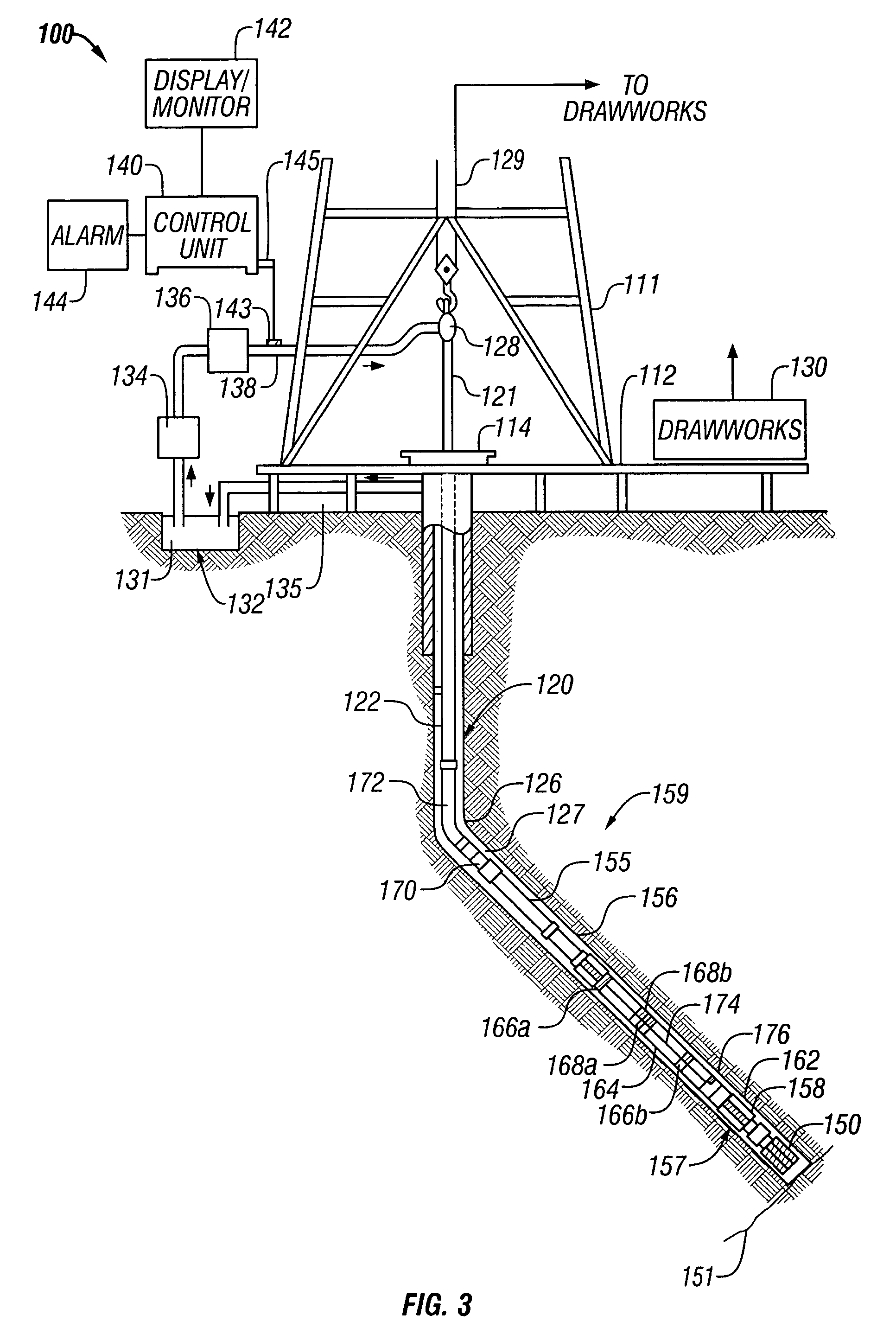
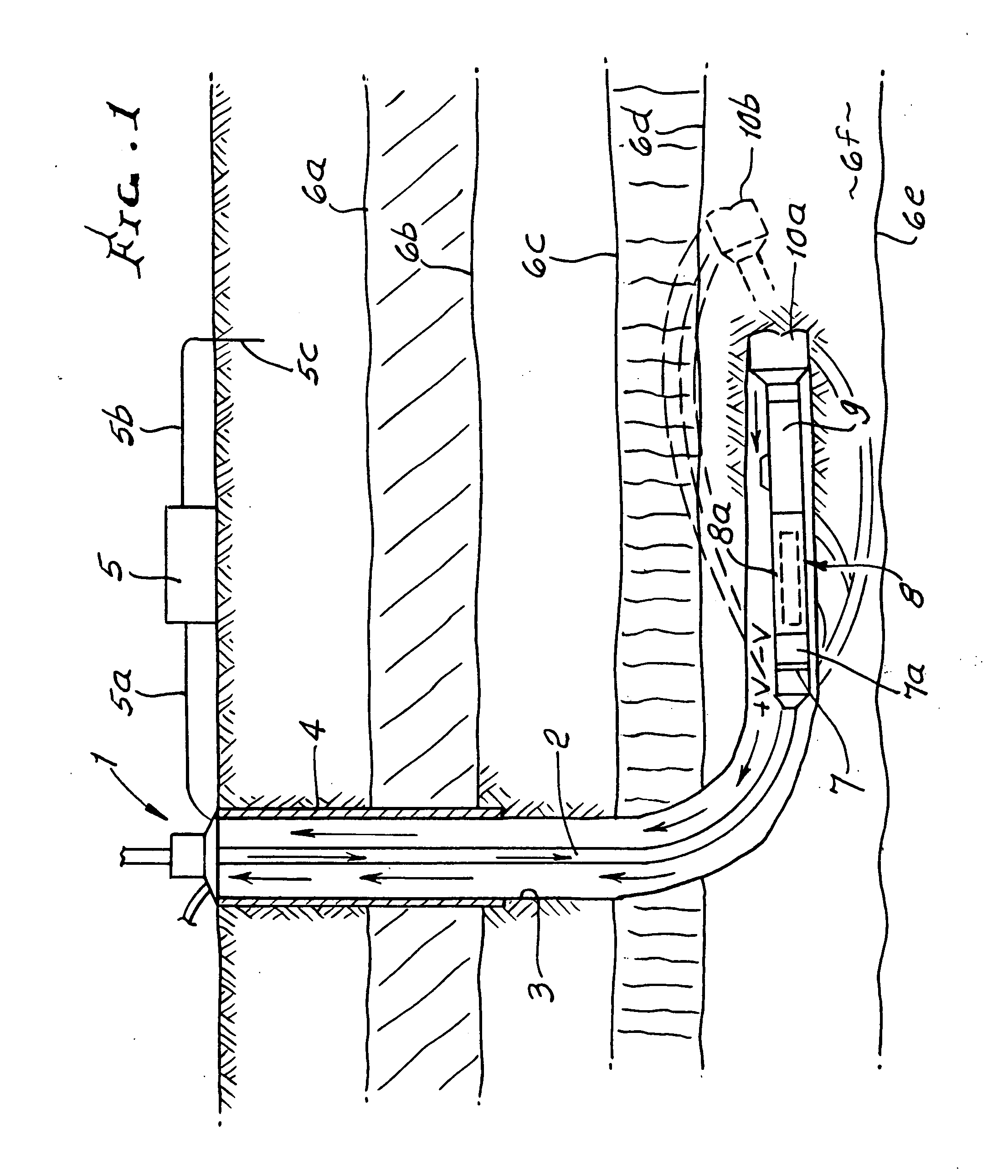
Method and apparatus for the use of multicomponent induction tool for geosteering and formation resistivity data interpretation in horizontal wells
InactiveUS20030229449A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyGeosteeringHorizontal wells
Measurements made with a multicomponent logging instrument when used in a substantially horizontal borehole in earth formations are diagnostic of the direction of beds relative to the position of the borehole. When the logging instrument is conveyed on a drilling assembly, the drilling trajectory may be maintained to follow a predetermined trajectory or to maintain a desired distance from a boundary such as an oil-water contact.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Electromagnetic and Magnetostatic Shield To Perform Measurements Ahead of the Drill Bit
InactiveUS20070216416A1Highly conductive materialReduce the impactElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
A transmitter on a bottomhole assembly (BHA) is used for generating a transient electromagnetic signal in an earth formation. A receiver on the BHA receives signals that are indicative of formation resistivity and distances to bed boundaries. A combination of electromagnetic shielding and magnetostatic shielding enables determination of distance to an interface ahead of the drillbit.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
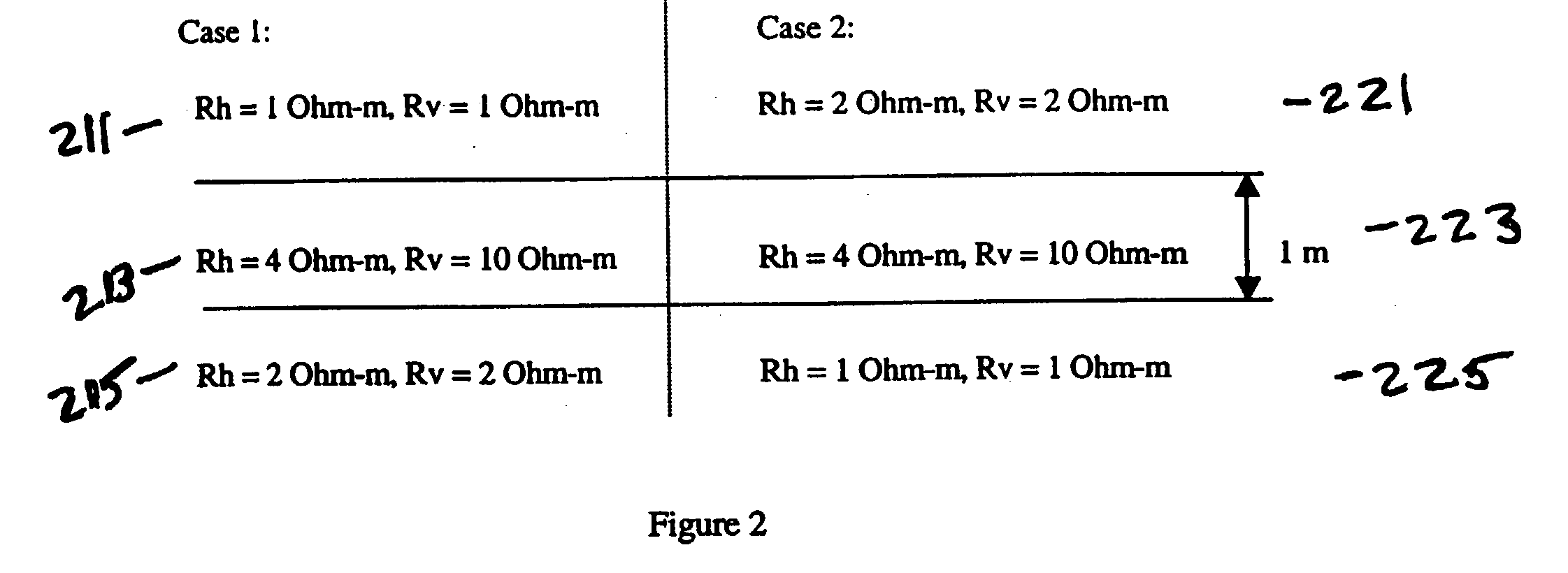
Method for joint interpretation of multi-array induction and multi-component induction measurements with joint dip angle estimation
InactiveUS20030028324A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingCorrelation coefficientClassical mechanics
Data are acquired using multi-array logging tool in a borehole having an angle of inclination to a normal to the bedding plane of earth formations. The multi-array measurements are filtered using angle dependent filters to give a filtered curve corresponding to a target one of the multi-array measurements using angle dependent filters. Correlation coefficients are determined for a set of possible dip angles and a relative dip angle is estimated from the correlation coefficients. This dip angle estimate together with bed boundaries obtained from the multi-array measurements are used for inverting multi-component measurements alone or jointly with multi-array measurements to refine the relative dip angle interpretation and give horizontal and vertical formation resistivity.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
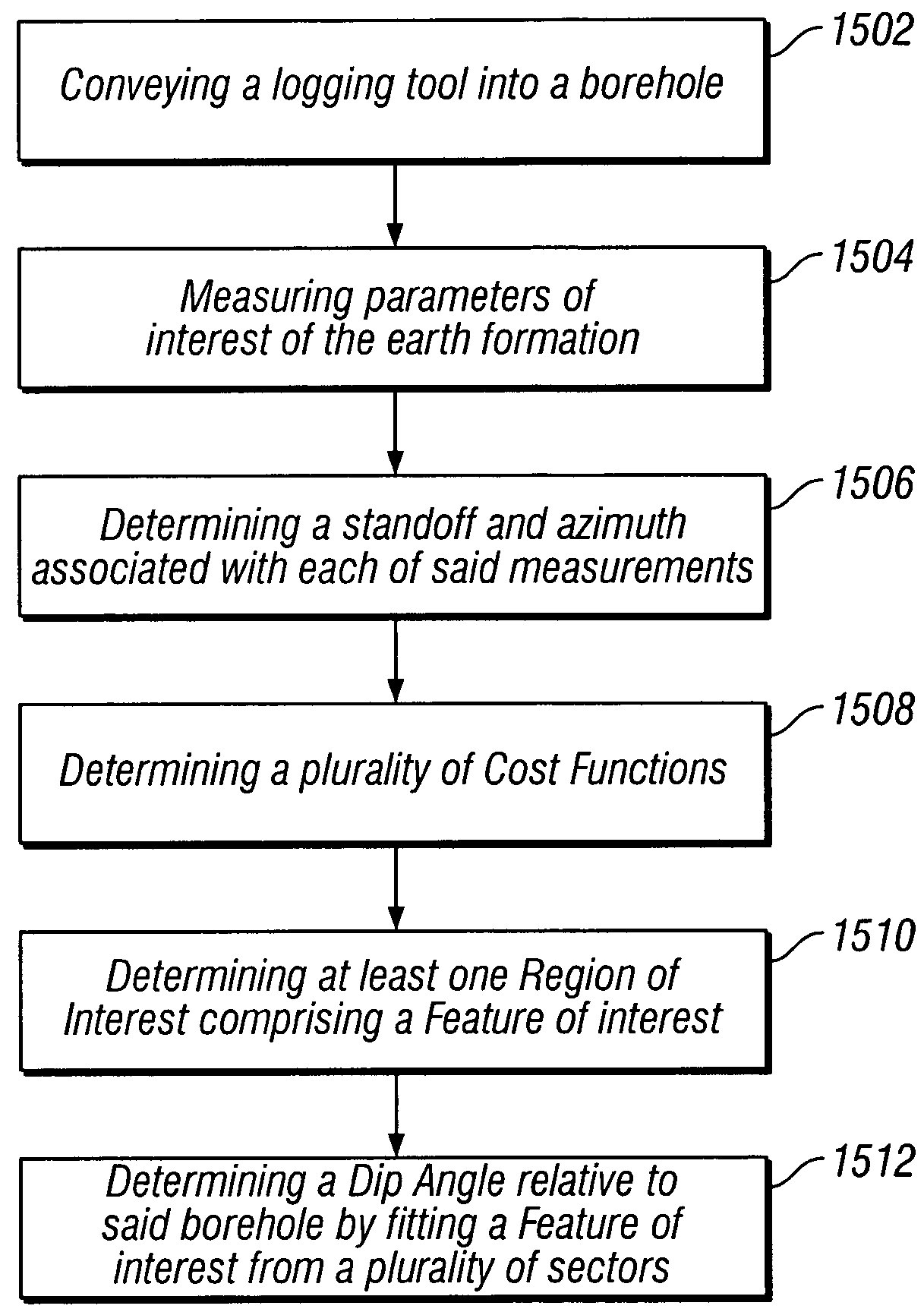
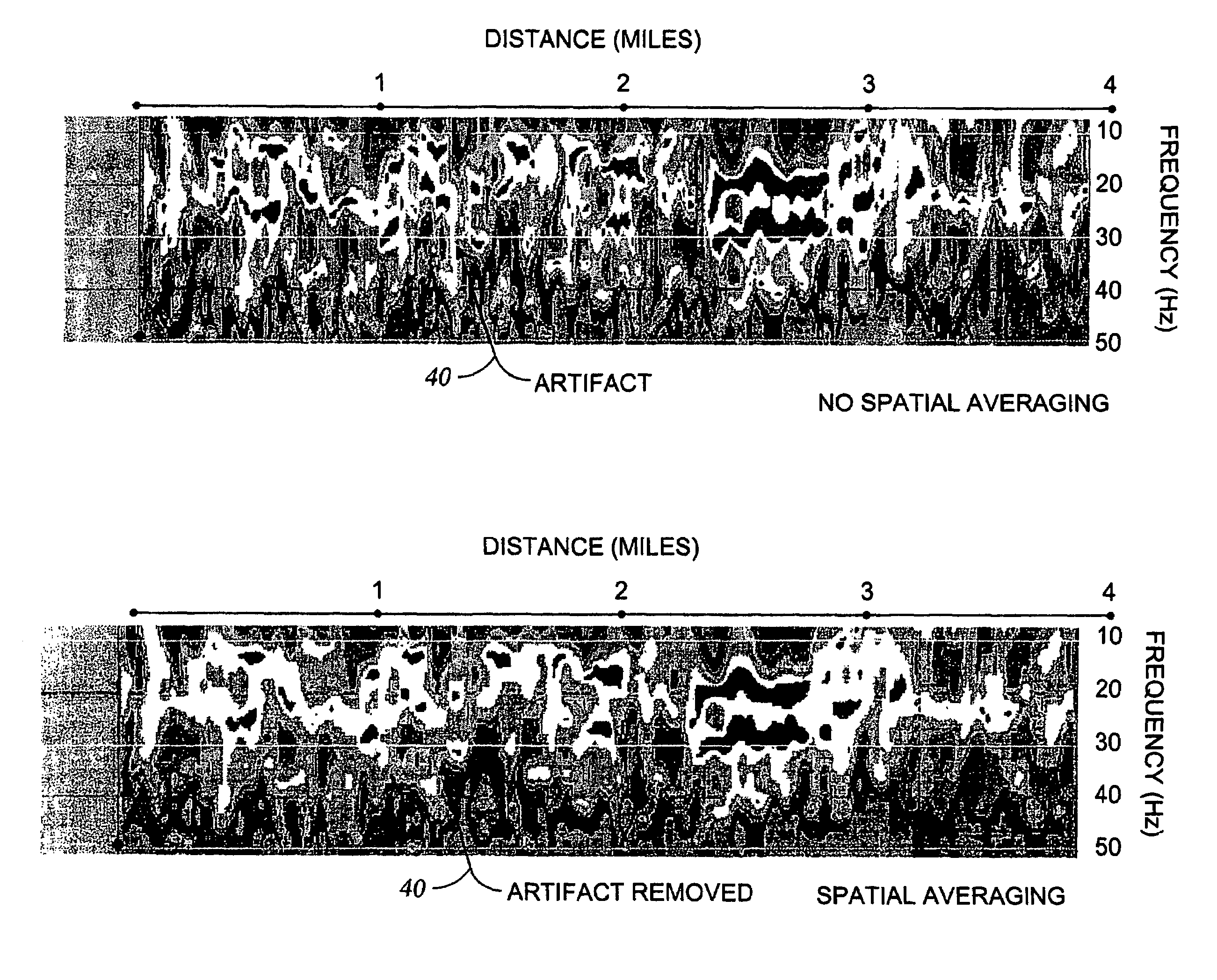
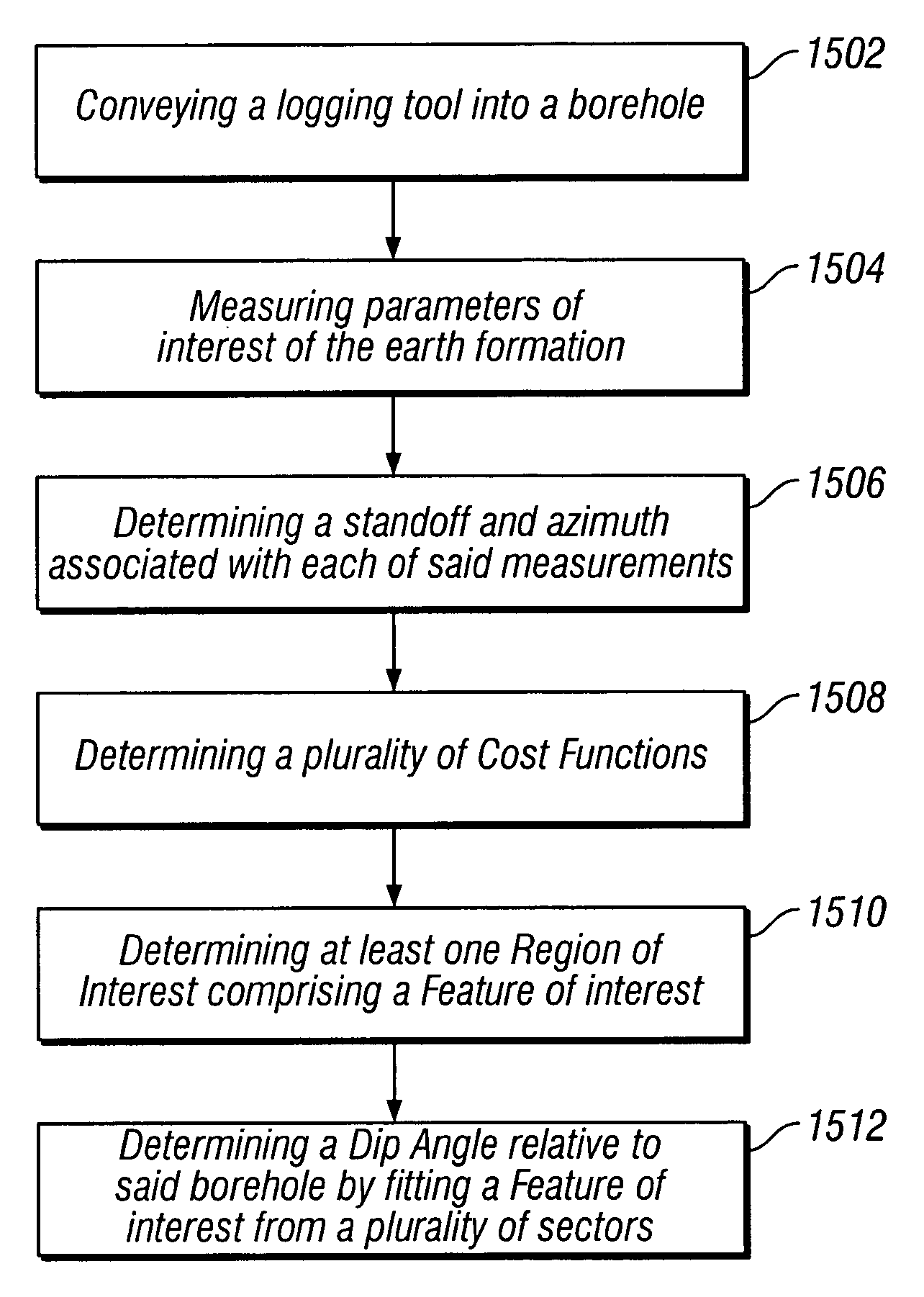
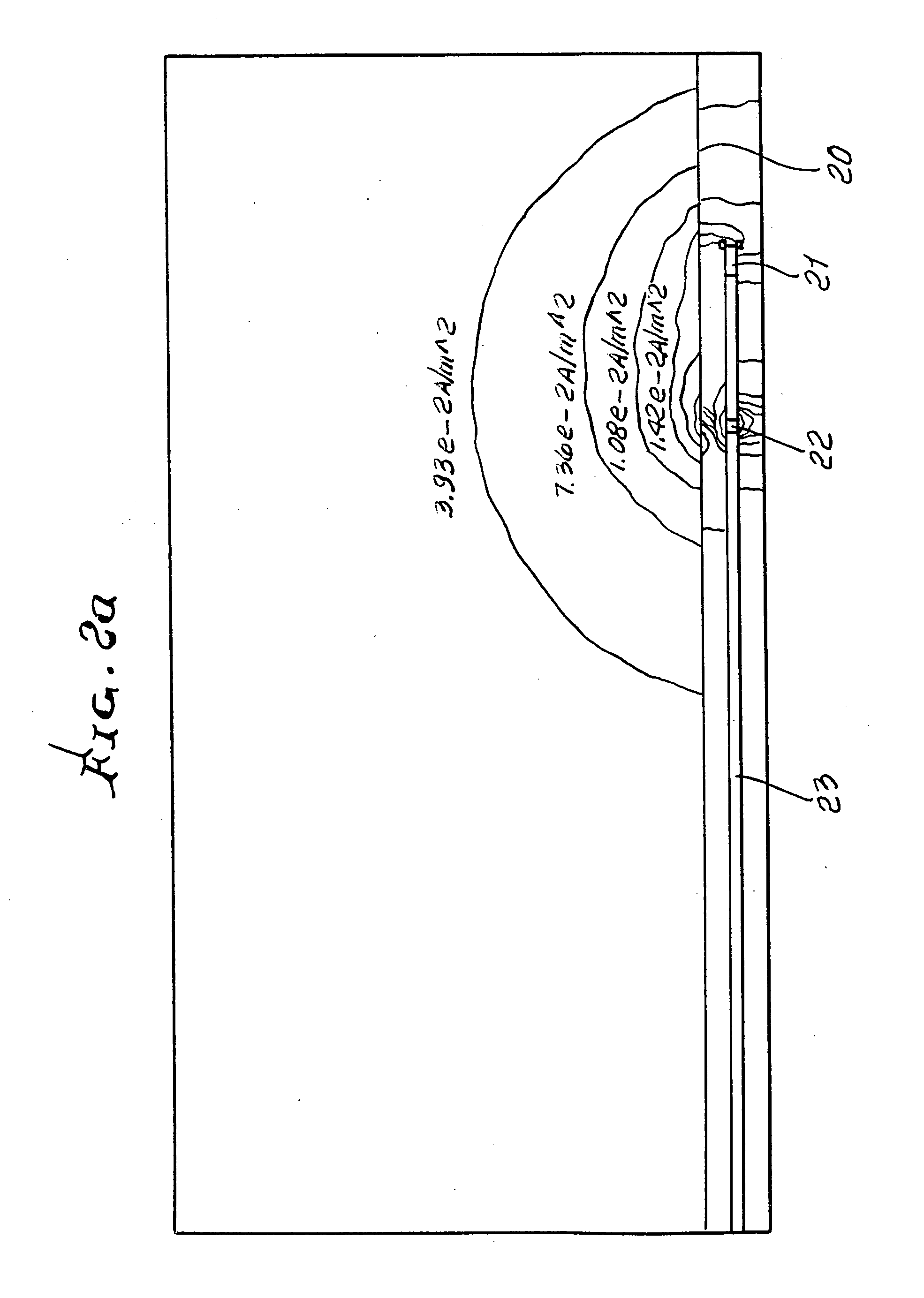
Apparent dip angle calculation and image compression based on region of interest
ActiveUS20060015256A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingComputational scienceLithology
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for logging an earth formation and acquiring subsurface information wherein a logging tool is conveyed in borehole to obtain parameters of interest. The parameters of interest obtained may be density, acoustic, magnetic or electrical values as known in the art. The parameters of interest may be transmitted to the surface at a plurality of resolutions using a multi-resolution image compression method. Parameters of interest are formed into a plurality of Cost Functions from which Regions of Interest are determined to resolve characteristics of the Features of interest within the Regions. Feature characteristics may be determined to obtain time or depth positions of bed boundaries and borehole Dip Angle relative to subsurface structures, as well borehole and subsurface structure orientation. Characteristics of the Features include time, depth, and geometries of the subsurface such as structural dip, thickness, and lithologies.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Deep resistivity transient method for MWD applications using asymptotic filtering
ActiveUS7027922B2Reduce impactExclude influenceElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveySeries expansionEnvironmental geology
A method is discussed of obtaining a parameter of interest of an earth formation, typically a formation resistivity or a distance to a bed boundary, in conditions where an induction tool is using having a body with finite, non-zero conductivity. The method substantially removes the effects of the conductivity of the tool from the signal received from the earth formation. A Taylor series expansion in one half of odd integer powers of time is used to represent the received signal. At least one leading term of the Taylor series expansion can be subtracted from the second signal. A filtering operation is applied to the second signal to remove the terms most dominated by pipe effects. Typical filtering operations can be a differential filtering operation or an integral filtering operation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
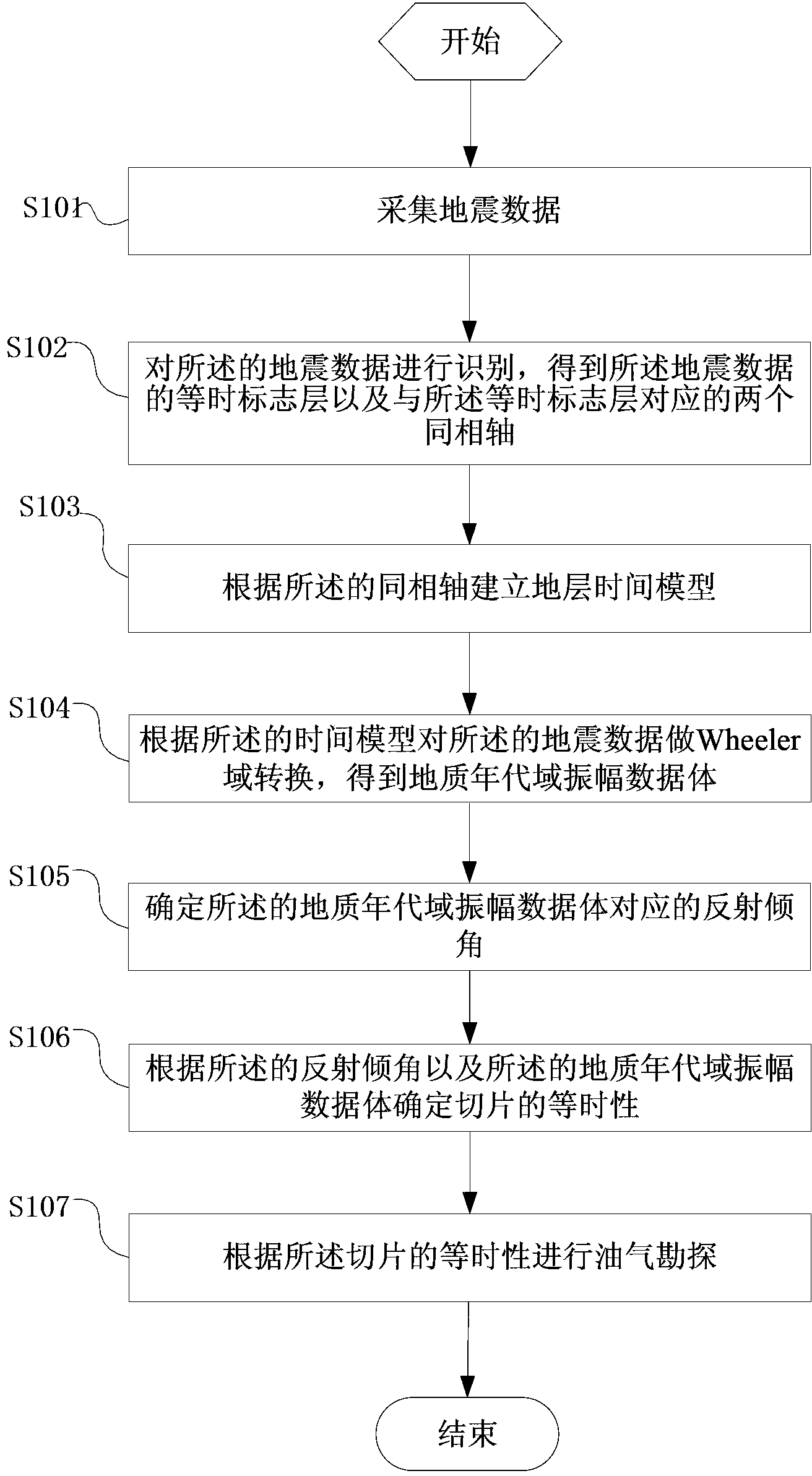
Method and system for determining seismic slice isochronism
ActiveCN103454678AIsochronous Efficient PredictionSolving the difficult problem of determining whether seismic slices are isochronousSeismic signal processingGeophysicsGeologic time scale
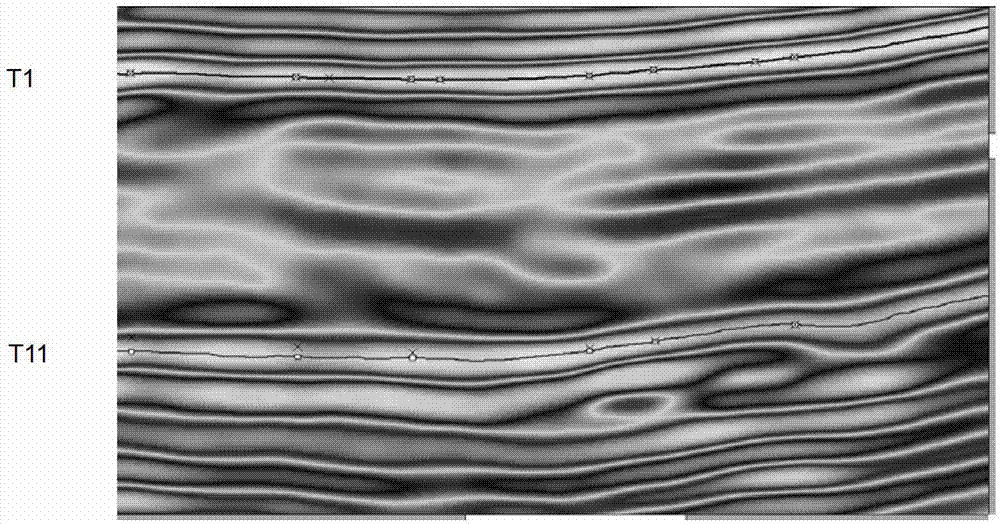
The invention provides a method and system for determining seismic slice isochronism. The method includes the steps that seismic data are collected; the seismic data are identified to obtain the isochronal maker bed of the seismic data and two events corresponding to the isochronal maker bed; according to the events, a stratum time model is established; according to the time model, Wheeler domain conversion is performed on the seismic data to obtain a geologic age domain amplitude data cube; reflection inclination angles corresponding to the geologic age domain amplitude data cube are determined; according to the reflection inclination angle and the geologic age domain amplitude data cube, the slice isochronism is determined; according to the slice isochronism, oil and gas exploration is performed. The problem that because the stratum deposition rate changes, whether seismic slices are isochronal or not is difficult to determine is solved, and the seismic slice isochronism is effectively judged.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method of constructing a geological model
Method of constructing a geological model of a subterranean formation formed of at least two sedimentary beds.On the basis of sparse measurements of the geometry of boundaries of beds of a subterranean formation carried out on a grid, values of the geometry of each bed at any point of the grid are calculated according to at least the following steps: a succession of coarser and coarser grids is defined, constructed on the basis of the grid of interest; then, proceeding from the coarsest grid to the grid of interest, the geometry of the boundaries of each bed is determined by solving an inverse problem initialized with the result obtained for the previous coarser grid. Next, on the basis of the completed geometry of each boundary of beds on the grid of interest, the geological model of the formation is constructed.Application especially to the exploration and exploitation of oilfields.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
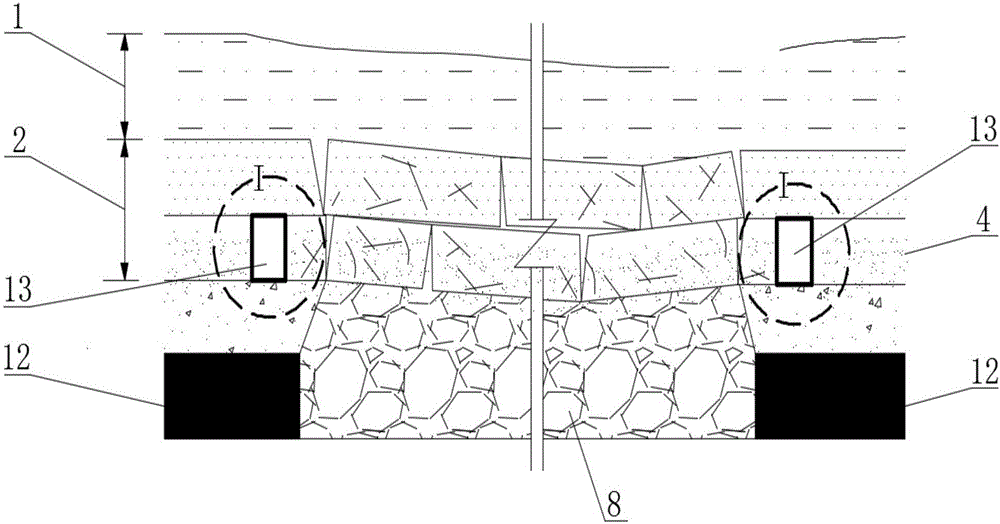
None-full-depth freezing method for penetrating through ultra-thick water-rich bed rock in shaft deepening
The invention discloses a none-full-depth freezing method for penetrating through ultra-thick water-rich bed rock in shaft deepening. According to the method, a shaft penetrates through surface soil, the water-rich bed rock, a water-resisting layer and low-permeability bed rock sequentially from top to bottom, and main freezing pipes penetrate through the surface soil and the water-rich bed rock sequentially from top to bottom, penetrate into the water-resisting layer by 10m-20m and stop in a low-permeability rock stratum; a none-full-depth freezing depth is 240m-260m and a wall-caving-preventing freezing depth is 40m-45m; the main freezing pipes are annularly arranged with the circle center of the shaft as a circle center and the distance between the main freezing pipes and the outer wall of the shaft is 2m; wall-caving-preventing freezing pipes penetrate into the surface soil only by 43m and are annularly arranged with the circle center of the shaft as a circle center, and the distance between the wall-caving-preventing freezing pipes and the outer wall of the shaft is 1m. The method is fast in construction, safe and efficient and capable of preventing water damage caused when underground water damages a horsehead and related chamber rock mass along annular water diversion channels during construction of the horsehead after a full-depth freezing shaft is frozen, wherein the annular water diversion channels are formed by the freezing pipes and temperature measuring pipes; therefore, cost for treating water burst is saved, and safety construction of the horsehead and a chamber is guaranteed.
Owner:陕西彬长矿业集团有限公司 +1
System for Extracting Hydrocarbons From Underground Geological Formations and Methods Thereof
InactiveUS20130220598A1Improve efficiencyReduce and eliminate needFluid removalVibration devicesElectricityTectonics
An ultrasonic fracking system and methods of using the same to extract hydrocarbons from underground geological formations (e.g., oil shale, coal beds, etc.) are disclosed. The system includes piezoelectric devices that are used to produce ultrasonic mechanical vibrations and induce fractures in the geological formations. In one embodiment, a system for extracting underground hydrocarbons comprises a plurality of piezoelectric devices capable of producing mechanical waves sufficient to fracture oil shale and other geological formations, a system of delivery for innocuous proppants to create a path of least resistance for enhanced hydrocarbon flow, and a vacuum pump connected to the fractures created by the piezoelectric devices to assist in removing the hydrocarbons.
Owner:MINDCAKE LLC
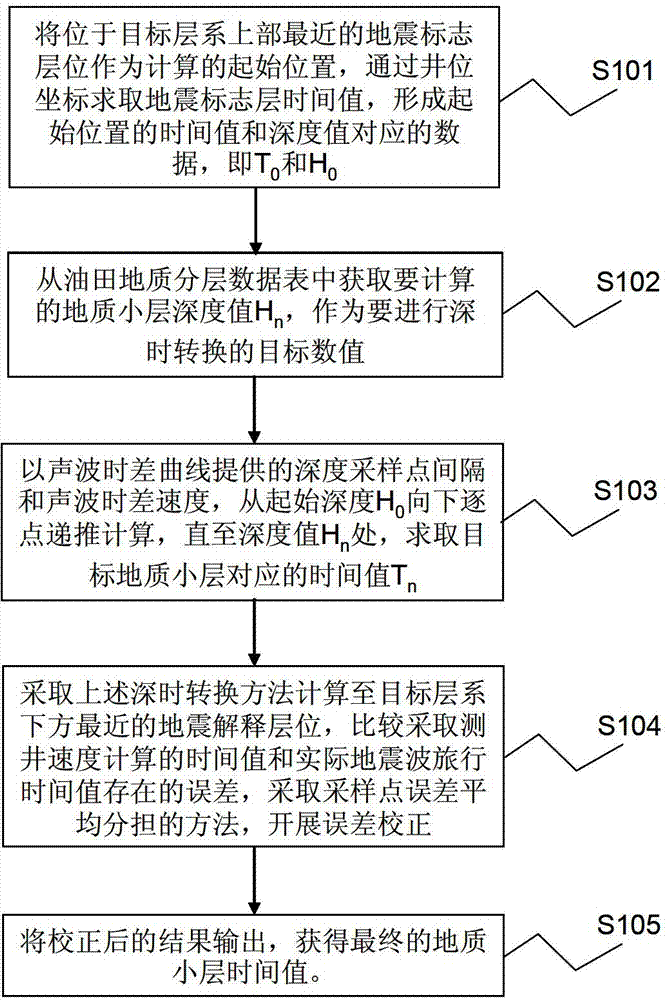
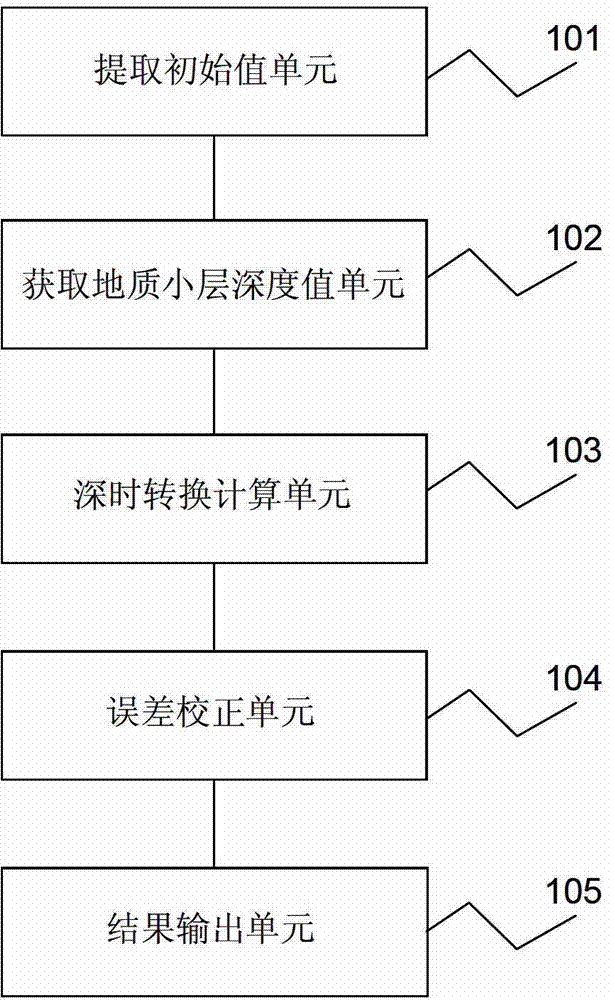
Geology single-layer data depth time conversion method and device for seismic data explanation
ActiveCN102967881ARealize automatic batch processingExplanation is validSeismic signal processingDifferential space timeWell logging
The invention provides a geology single-layer data depth time conversion method and device for seismic data explanation. The geology single-layer data depth time conversion method includes: using a seismic marker bed position nearest to the upper portion of a target series of strata as the initial position of calculating to extract time and depth initial values; obtaining the geology single-layer depth values to be calculated from an oil filed geology stratified data table to serve as the target depth values in deep time conversion; adopting an interval transit time curve, performing depth time conversion calculation from the initial depth downwards in a point-by-point recurrence mode until reaching the target depth, and solving the time value corresponding to the target geology single layer; and using the seismic data explanation layer position under the target series of strata as the reference, comparing errors between time values of well logging speed calculation and actual seismic wave travel time values, performing error correction in an error averaging method, and outputting the rectified results to obtain the final geology single-layer time values.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Apparent dip angle calculation and image compression based on region of interest
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for logging an earth formation and acquiring subsurface information wherein a logging tool is conveyed in borehole to obtain parameters of interest. The parameters of interest obtained may be density, acoustic, magnetic or electrical values as known in the art. The parameters of interest may be transmitted to the surface at a plurality of resolutions using a multi-resolution image compression method. Parameters of interest are formed into a plurality of Cost Functions from which Regions of Interest are determined to resolve characteristics of the Features of interest within the Regions. Feature characteristics may be determined to obtain time or depth positions of bed boundaries and borehole Dip Angle relative to subsurface structures, as well borehole and subsurface structure orientation. Characteristics of the Features include time, depth, and geometries of the subsurface such as structural dip, thickness, and lithologies.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
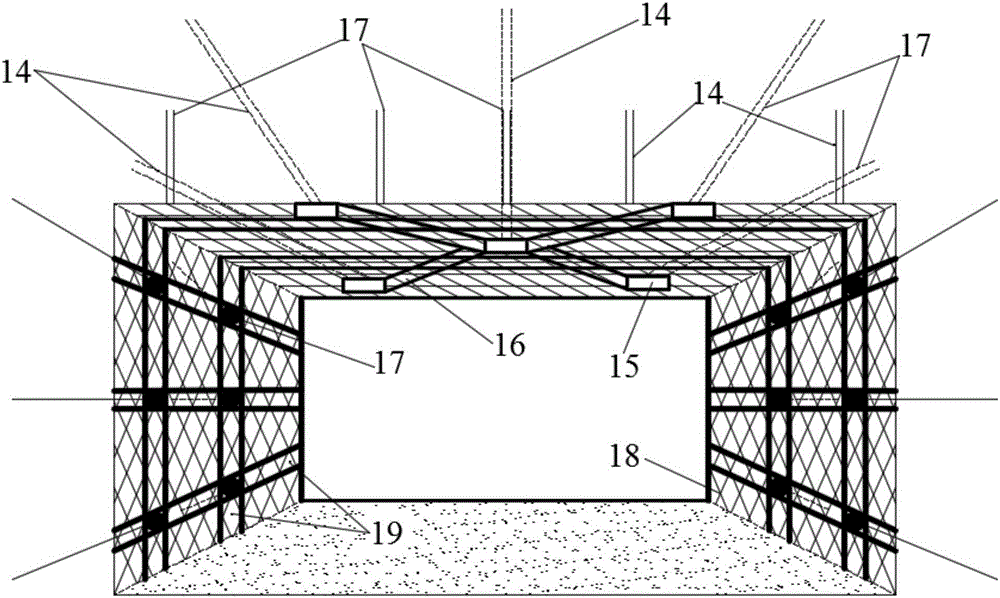
Construction method for weakening zone of floor plate wall rock
InactiveCN1865660AReduce swellingReduce concentrationUnderground chambersTunnelsEngineeringStress reduction
The invention relates to a construction method in weak wall rock area. Wherein, it arranges stress transfer channel in the channel bottom plate, and loosing explodes at the bottom corner of said stress transfer channel to form one weak wall rock area; via said area, the high developing stress in the upper coal bed can be transmitted into the deep part of wall rock, and the developing stress in the bottom plate can be reduced, to effectively control the bottom drum. The invention has simple process and significant stress reduction effect, with wider application.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
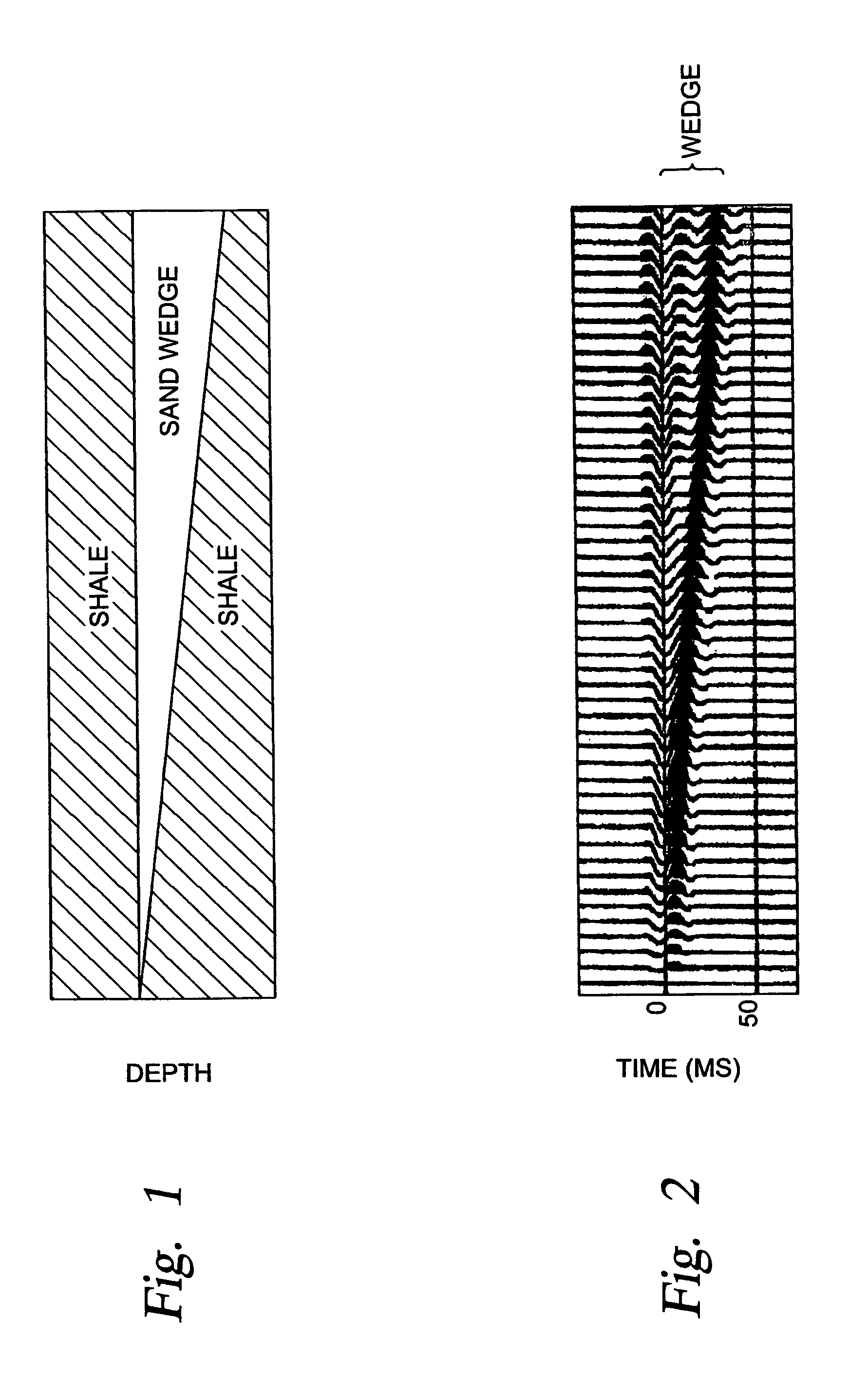
System for estimating thickness of thin subsurface strata
InactiveUS6965830B1Seismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowSpatial correlationFrequency spectrum
A system is disclosed for processing a group of spatially related seismic data traces in which seismic data windows extending over selected portions of said group of spatially related seismic data traces are defined, and a transform is applied to the successively selected windows to convert the seismic data within the successively selected widows to the frequency domain thereby generating a frequency spectrum of the seismic data within said successively selected windows. Selected frequency spectra are then combined to generate an average of the selected frequency spectra, thereby generating averaged frequency spectra, ane the averaged frequency spectra are utilized to generate data related to the location of thin beds in the earth's subsurface.
Owner:APACHE CORPORATION
Apparent dip angle calculation and image compression based on region of interest
ActiveUS20080120035A1Efficiently obtainedElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyLithologyImage resolution
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for logging an earth formation and acquiring subsurface information wherein a logging tool is conveyed in borehole to obtain parameters of interest. The parameters of interest obtained may be density, acoustic, magnetic or electrical values as known in the art. The parameters of interest may be transmitted to the surface at a plurality of resolutions using a multi-resolution image compression method. Parameters of interest are formed into a plurality of Cost Functions from which Regions of Interest are determined to resolve characteristics of the Features of interest within the Regions. Feature characteristics may be determined to obtain time or depth positions of bed boundaries and borehole Dip Angle relative to subsurface structures, as well borehole and subsurface structure orientation. Characteristics of the Features include time, depth, and geometries of the subsurface such as structural dip, thickness, and lithologies.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
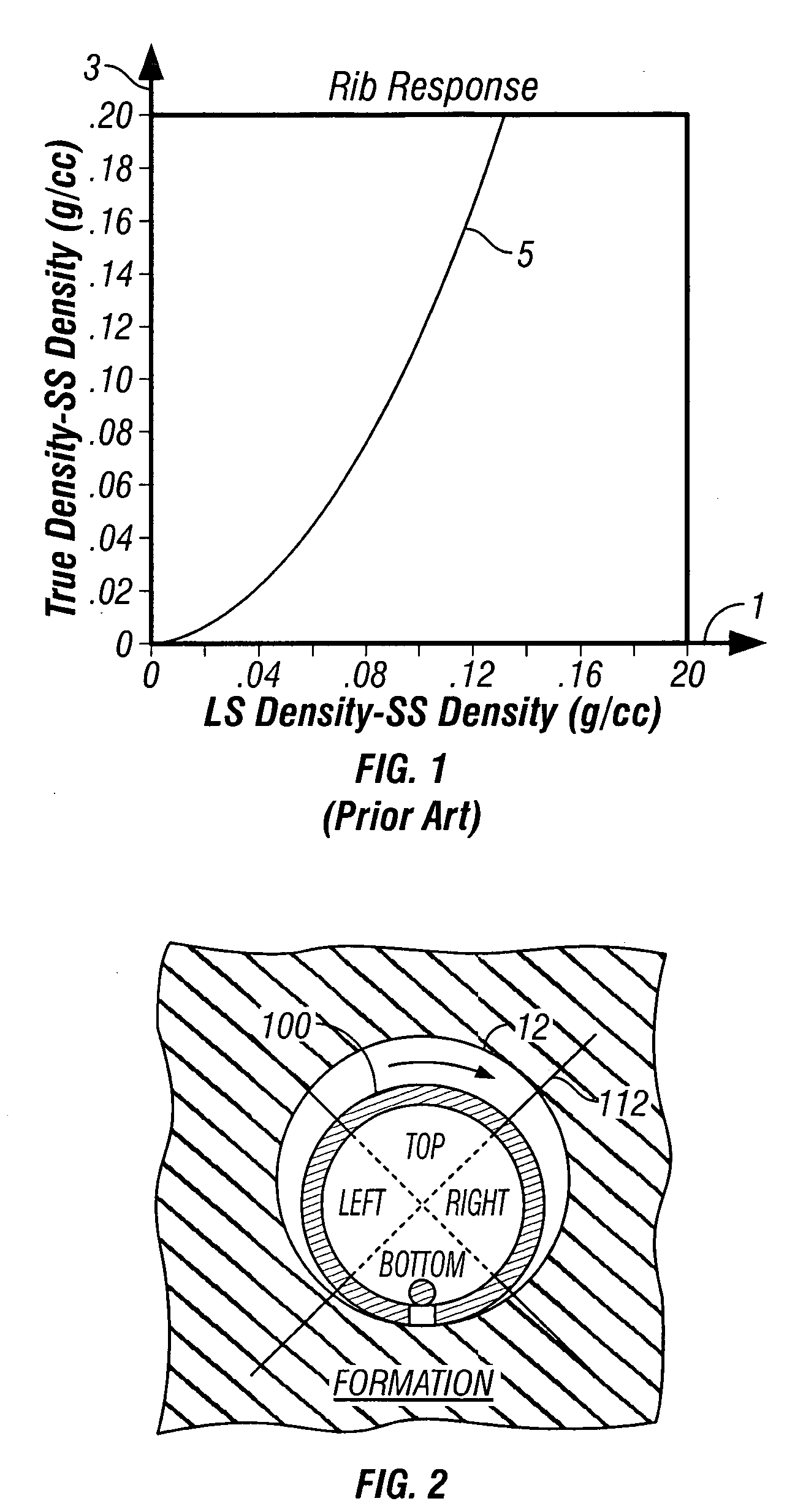
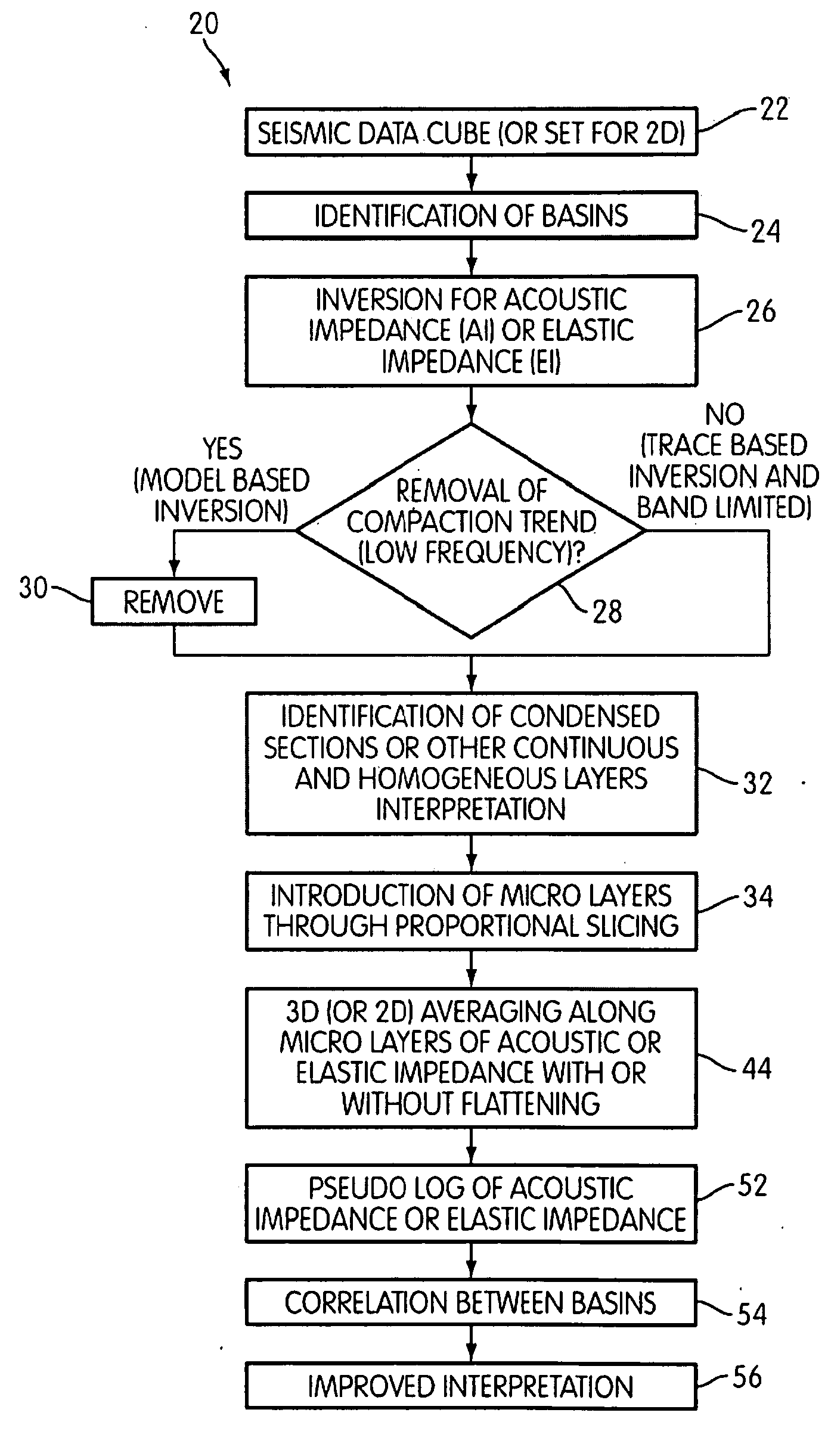
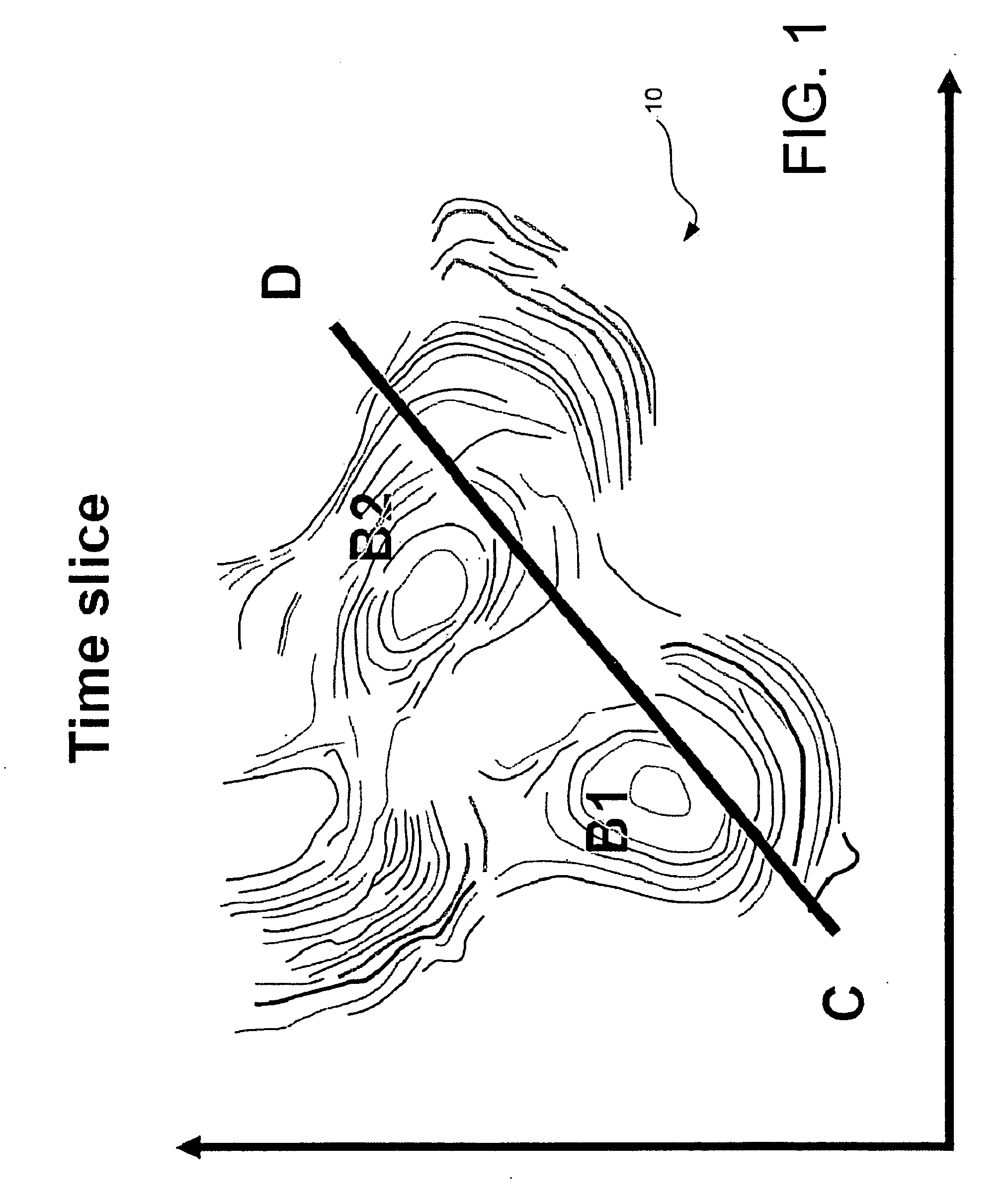
Pseudo logs to improve stratigraphic correlation between sedimentary basins
InactiveUS20100094559A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsGeomorphologySedimentary basin
In order to improve the tie between depositionally equivalent beds relative to two or more basins detected within a multi dimensional seismic volume of interest, pseudo logs based on the average of attributes derived from seismic impedance where the compaction trend is not present are created for each basin. The mean is taken over all available azimuths, following the structural variations of introduced micro layers. The correlation between the pseudo log relative to each basin enable a more reliable interpretation between the different basins from which sound exploration decision can be made. Such a process has been successfully applied to seismic data acquired in deep water environment.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
High-strength mining rock stratum migration grouting control and grouting amount calculation method
The invention provides a shallow-buried high-strength mining rock stratum migration grouting control and grouting amount calculation method, and belongs to a coal mine high-strength mining damage control and surface damage reduction method. Aiming at a shallow-buried high-strength overlying strata large-damage two-zone development structure of a western mining area, the invention provides a low-damage three-zone overlying strata structure formed by grouting and filling a caving zone and a bed-separated fissure zone, so that the surface damage is greatly reduced. The shallow-buried high-strength mining rock stratum migration grouting control and grouting amount calculation method mainly comprises the steps of determining the position of an overlying strata key layer; calculating maximum deflection w of the key layer before breaking; calculating a grouting amount calculation formula Vg=piwLd / 3 required by the bed-separated fissure zone, and determining the height H1 of the caving zone according to the mining height of the coal seam working face and the properties of a roof and a floor; and further giving a calculation formula Vk = dH1L-Vg-(H1-M)bdL of the grouting amount of the caving zone for ensuring that the key layer is not broken; according to a calculation result, after a lower main roof of the working face is fractured for the first time, drilling a well from the ground and grouting into the caving zone; and when the working face is pushed to one square, beginning to grout the bed-separated fracture body. The shallow-buried high-strength mining rock stratum migration grouting control and grouting amount calculation method is as shown in the drawing of the abstract. By implementing the shallow-buried high-strength mining rock stratum migration grouting control and grouting amount calculation method, the surface damage degree of shallow-buried high-strength mining can be greatly reduced, and green mining of ecologically fragile regions of western mining areas isrealized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Seismic-resistant-columned rock bolt foundation with enlarged toe and construction method of seismic-resistant-columned rock bolt foundation with enlarged toe
InactiveCN102561377AReduce excavationSolve the large amount of engineeringBulkheads/pilesEarthquake resistanceEarthquake intensity
The invention provides a seismic-resistant-columned rock bolt foundation with an enlarged toe and a construction method of the seismic-resistant-columned rock bolt foundation with the enlarged toe. The seismic-resistant-columned rock bolt foundation comprises a vertical cylindrical foundation body, the vertical cylindrical foundation body is equal to an upper seismic-resistance column in cross sectional size, and the cylindrical foundation body is inlaid in bed rock and provided with an enlarged bottom. The enlarged bottom is provided with a plurality of radial anchor bolts, and the cylindrical foundation body and the bed rock are anchored integrally with concrete by in-trench placement. Excavated volume of the rock foundation can be reduced effectively, the problems of large project amount, high manpower and material consumption and high cost are solved, and excavation cost is lowered greatly. The foundation is reliably connected with the bed rock by bottom enlargement and radial distribution of anchor bolts, connection of the column with the bed rock is enhanced effectively, extraction resistance, shear resistance, compression resistance and antidumping bearing capacity of the foundation are enhanced, horizontal or vertical displacement or separation between the column bottom and the bed rock in a high earthquake intensity area under the action of earthquake when an earthquake occurs is avoided, and seismic resistance of a building on the rock foundation is improved effectively.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
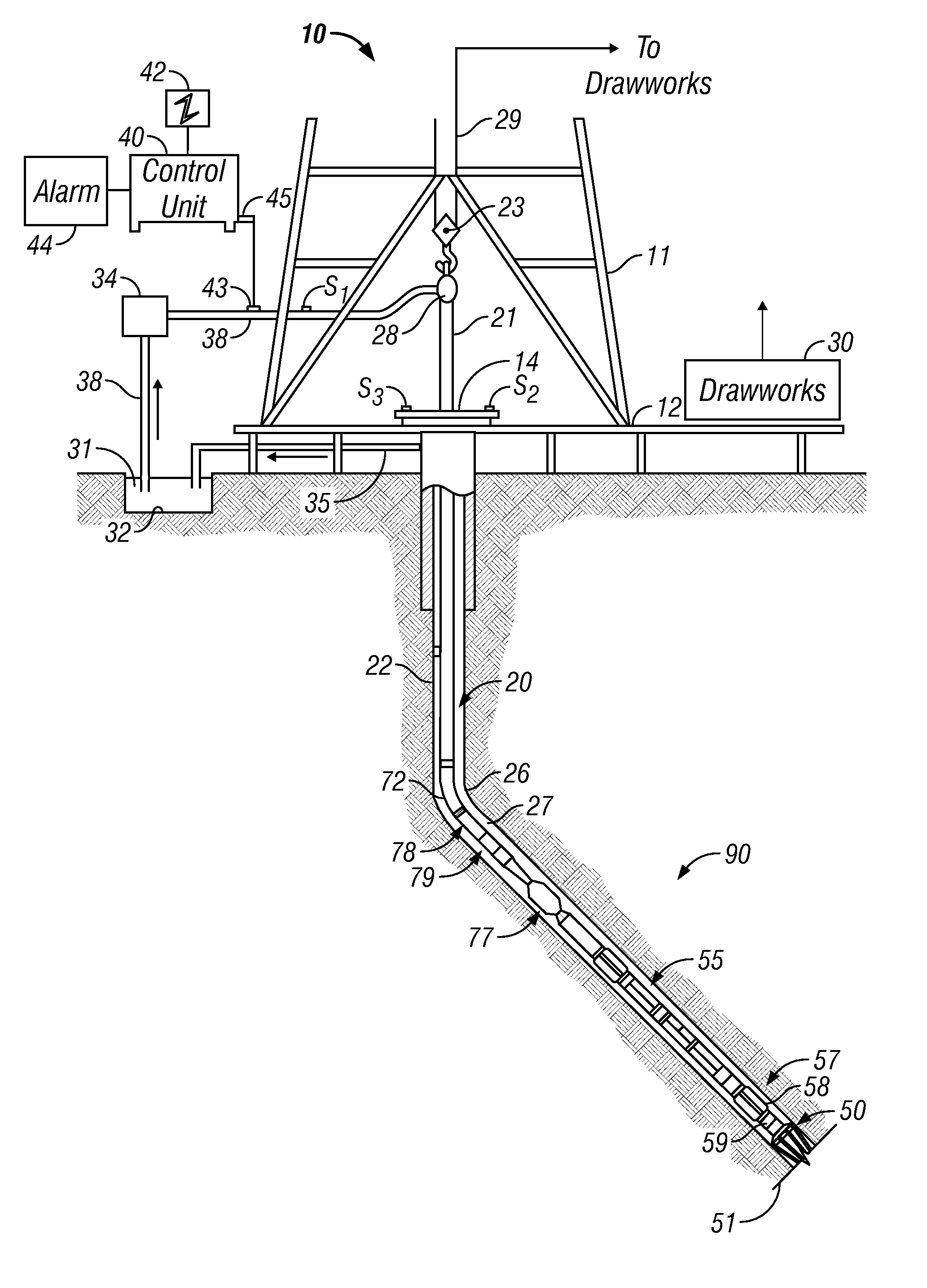
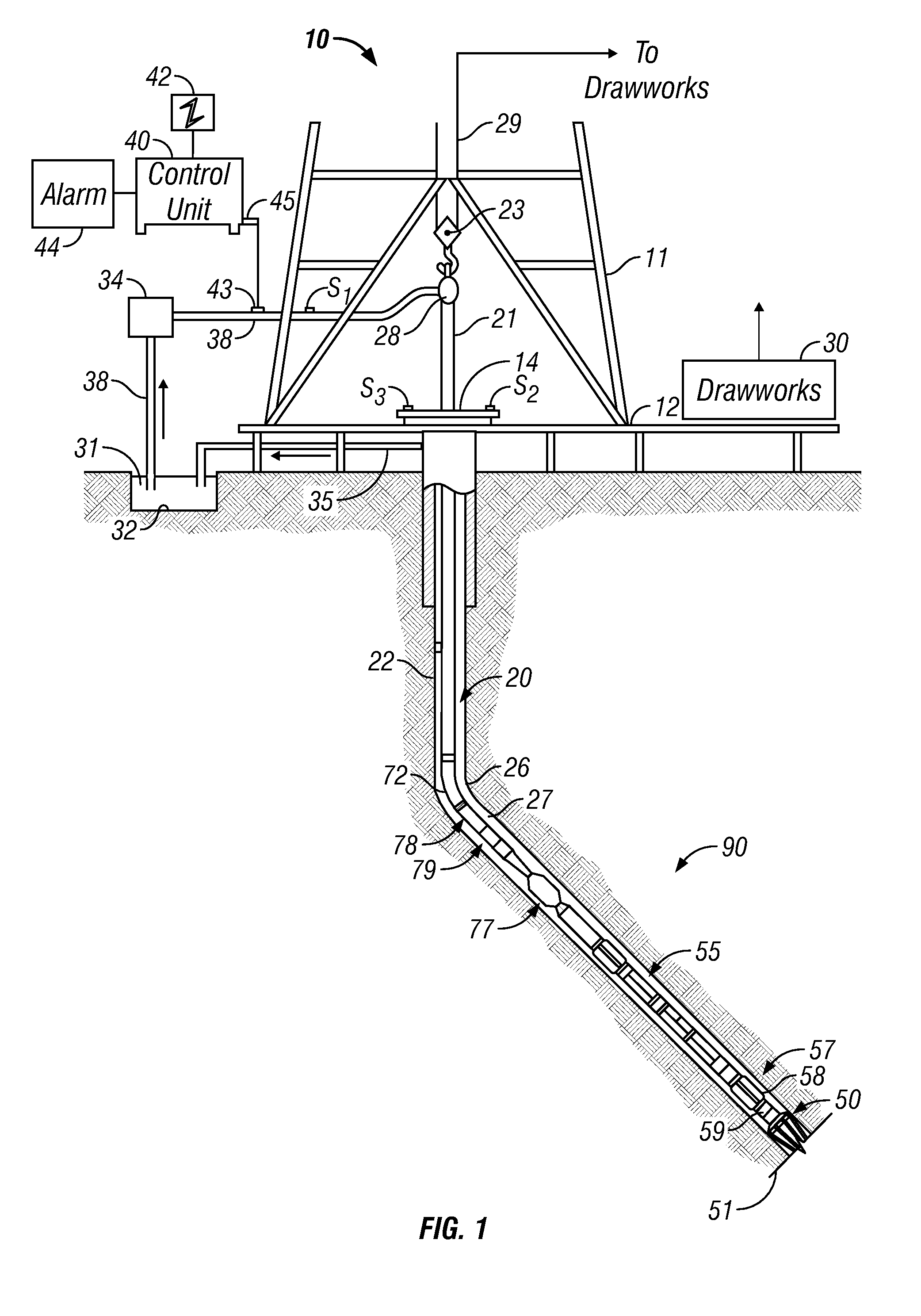
Sub-surface formation boundary detection using an electric-field borehole telemetry apparatus
InactiveUS20150101817A1Easy to controlEasy procedureSurveyConstructionsWell drillingBoundary detection
The method of maintaining drill bit advancement in an underground formation that contains shale, including providing an electrical signal from an insulated gap location in a drill string substantially directly behind the bit in the formation, detecting substantial change in a signal as the bit advances, and changing the direction of drilling of the bit as a function of a signal change, to thereby maintain the direction of bit advancement in the formation.A method is disclosed for detecting the existence and direction of adjacent bed boundaries. A short hop transmitter assembly generates a signal that is detected by an associated receiver assembly. The received signal(s) are tied to the azimuthal orientation of the transmitter or receiver and processed to yield the direction and / or the distance of the bed boundary. This information is transmitted to the surface via surface telemetry for real-time control of the drilling assembly to stay within, or to enter, a pay zone.
Owner:SCIENCE DRILLING INTERNATIONAL INC
Method for drilling coal-bed gas well penetrating through goaf by means of composite blocking of hole-bottom broken rock masses
ActiveCN107313716ASimplified grouting equipmentFlushingSealing/packingSurface layerMining engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of coal-bed gas resource exploitation and provides a method for drilling a coal-bed gas well penetrating through a goaf by means of composite blocking of hole-bottom broken rock masses. According to the method, the problems that when the coal-bed gas well is constructed through the goaf, drilling is difficult, and potential safety hazards exist during drilling are solved. The second spud-in drilling stage is conducted through the goaf, and the broken rock masses of drilling surrounding rock of the coal-bed gas well are blocked in sectioned and composite modes; the broken rock masses of the drilling surrounding rock are constructed by three stages, specifically, an auxiliary measure of injecting foam liquid into a hole bottom is carried out on a medium broken rock mass section, an auxiliary measure of injecting slurry into the hole bottom is carried out on a significant broken rock mass section, and a pipe-following drilling measure is carried out on a caving zone cavity section; and accordingly safe and efficient passing-through of the broken rock mass sections and caving zone cavities is achieved. Meanwhile, through the compressive stabilizing technology of a surface layer casing, an intermediate casing and a production casing, the overall rigidity and stability of the drilled well are greatly strengthened
Owner:SHANXI JINCHENG ANTHRACITE COAL MINING GRP CO LTD +2
Coal bed methane multi-branch horizontal well system and auxiliary discharge well thereof
InactiveCN101979828ATo achieve the purpose of gas analysisReduce fluid pressureFluid removalDesorptionWell drilling
The invention discloses an auxiliary discharge well matched with a coal bed methane multi-branch horizontal well. The multi-branch horizontal well comprises a straight well section, a deflection section and a horizontal section which comprises a plurality of wellbores; and the auxiliary discharge well is arranged on the coal bed relief declination side in the horizontal section of the multi-branch horizontal well. In the invention, the auxiliary discharge well adopts a mode of arranging the drilling engineering at the tail end of the horizontal section of the horizontal well to reduce liquid pressure in branches and produces channels in a target geologic body by utilizing a newly drilled well to make the target geologic body communicated with the multi-branch horizontal well and assist the multi-branch horizontal well in draining and decompressing so as to fulfill the aim of gas desorption in the geologic body, improve the development efficiency of an assisted well and increase the well producing rate of the multi-branch horizontal well. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a coal bed methane multi-branch horizontal well system.
Owner:BEIJING ORION ENERGY TECH DEV
Method and apparatus for shale bed detection in deviated and horizontal wellbores
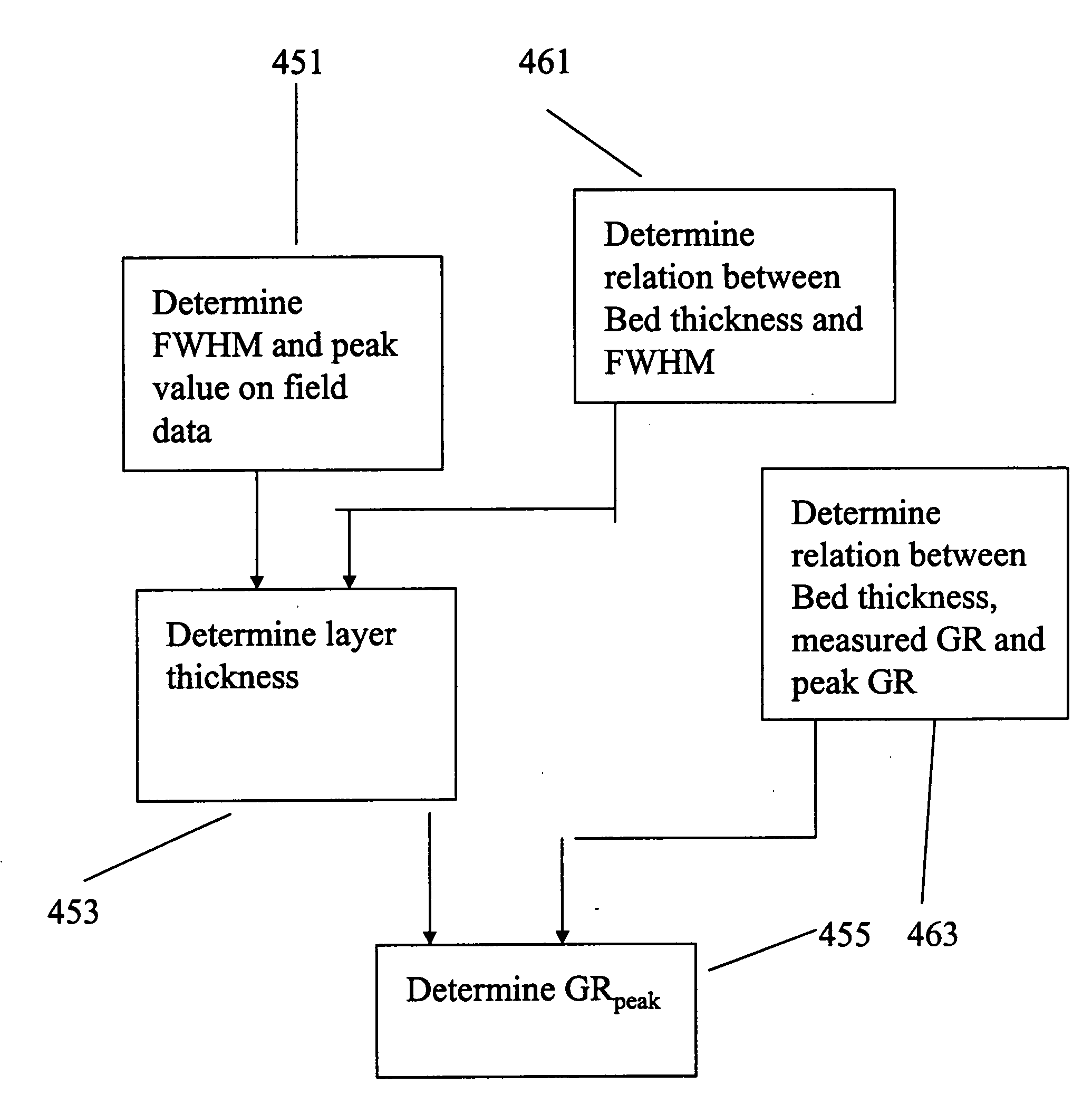
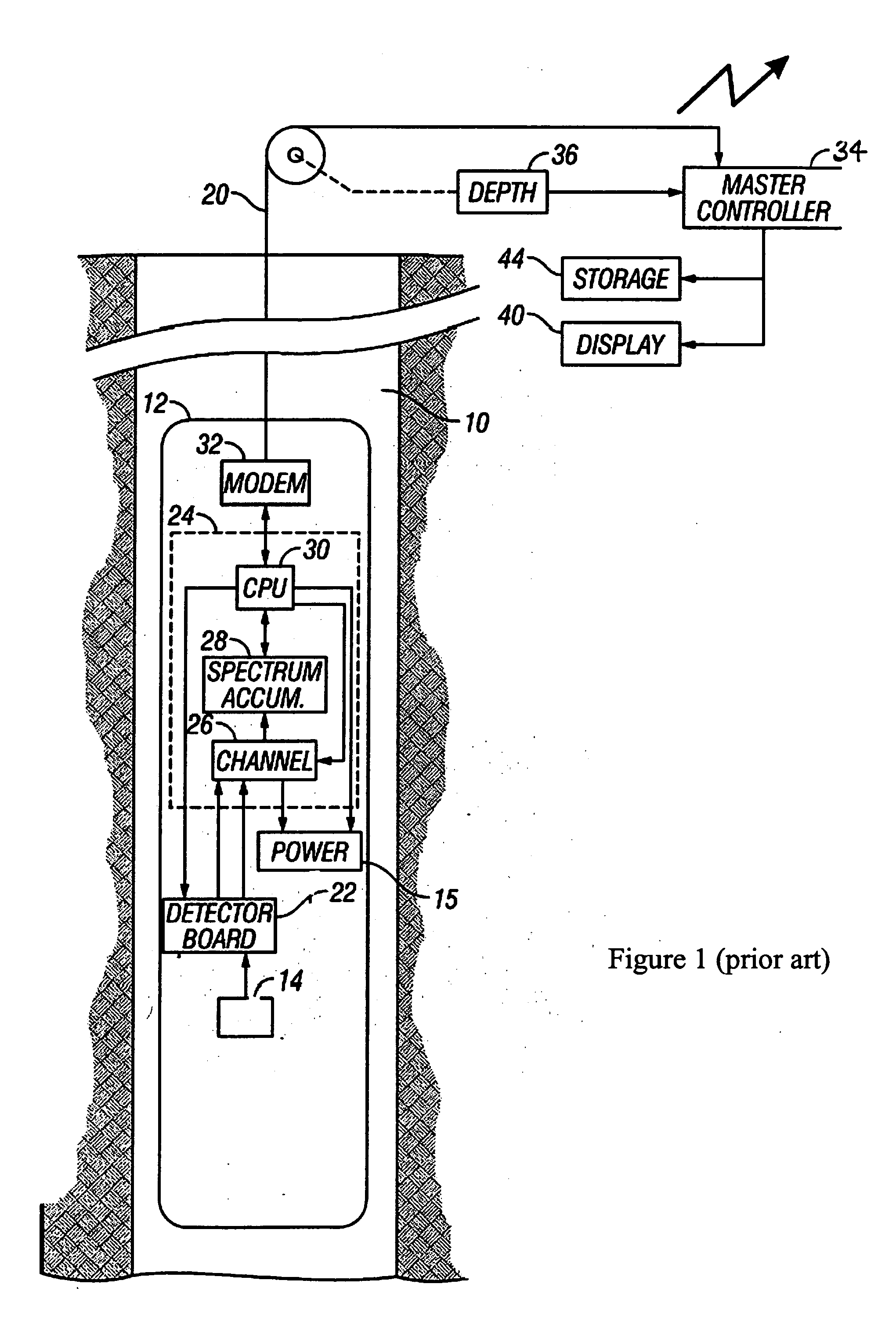
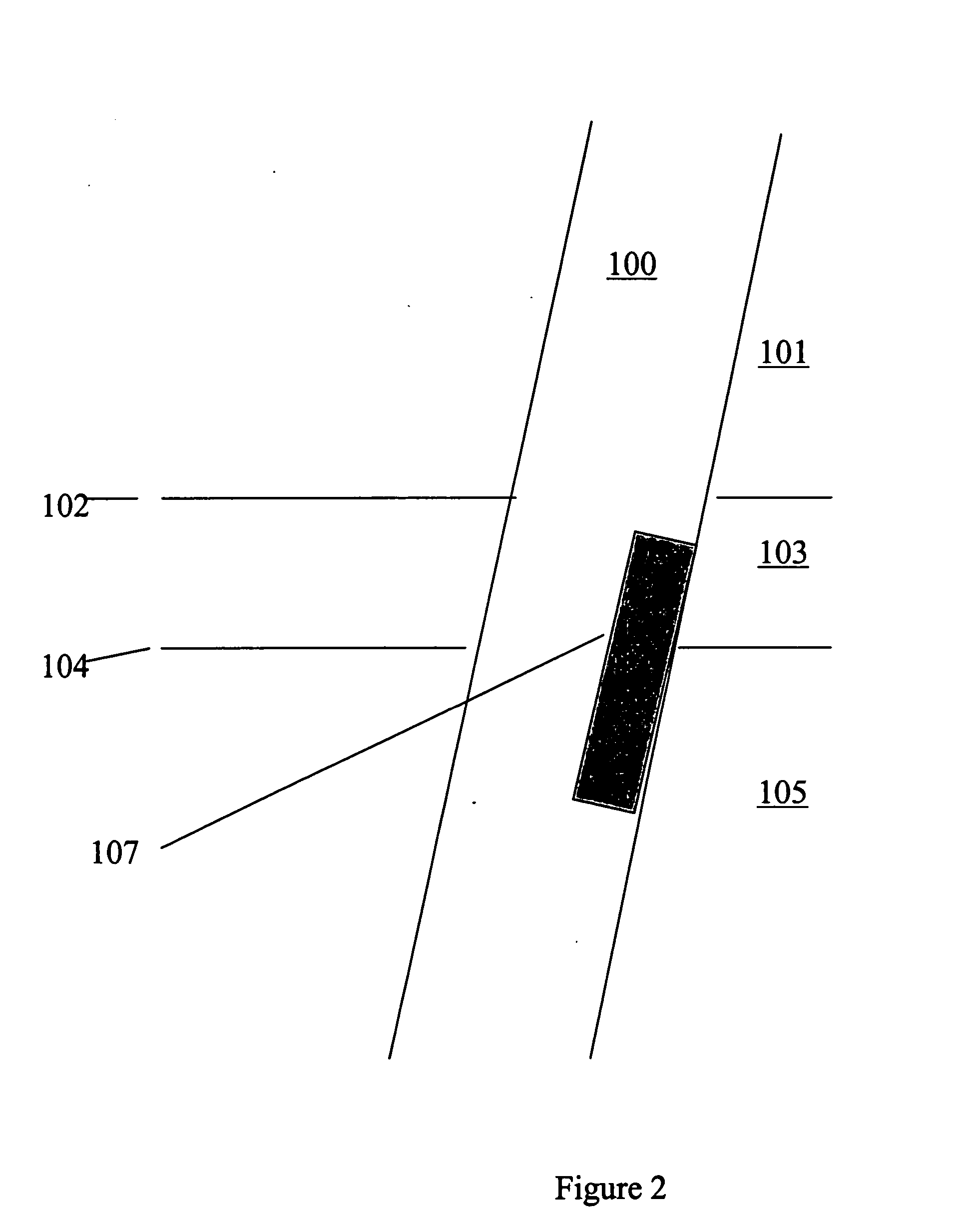
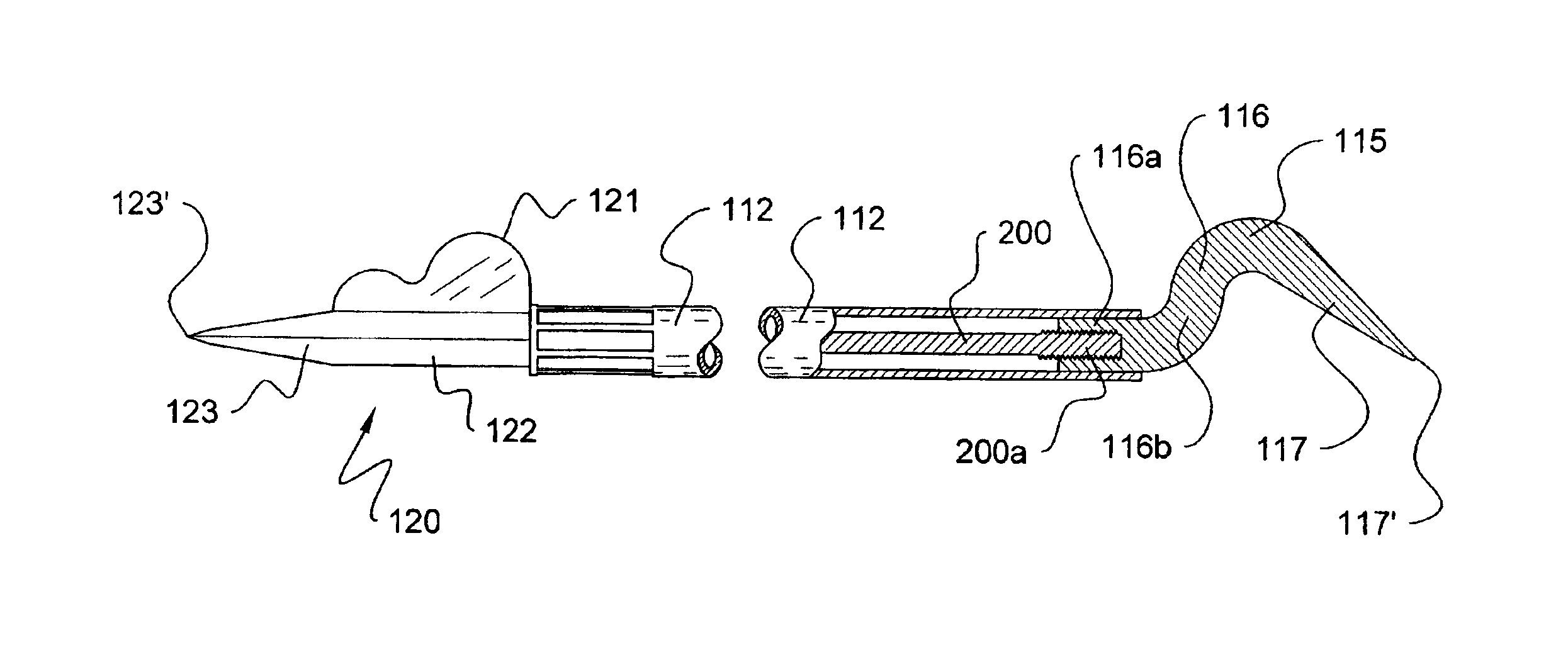
InactiveUS20060229815A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingGamma rayPeak value
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
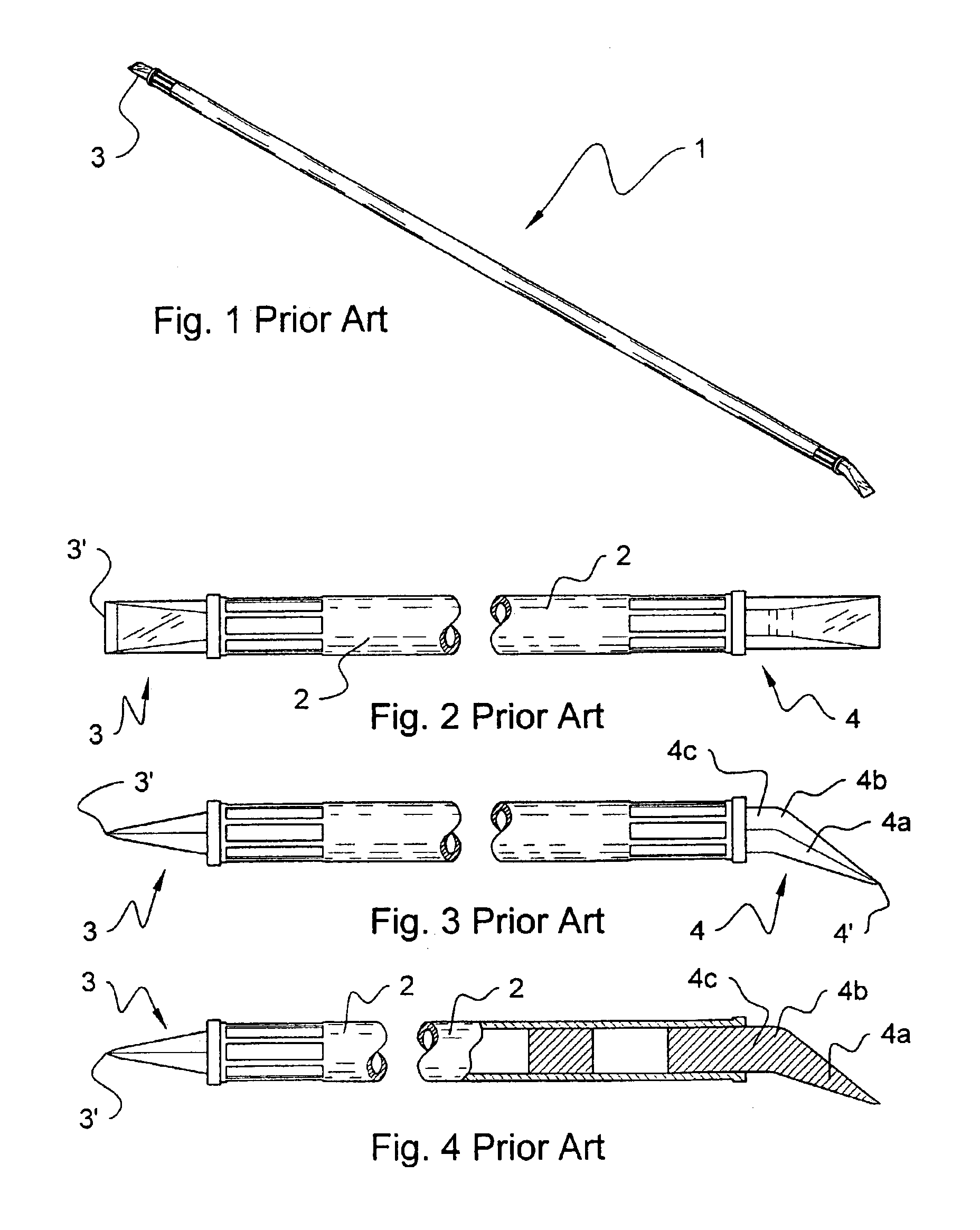
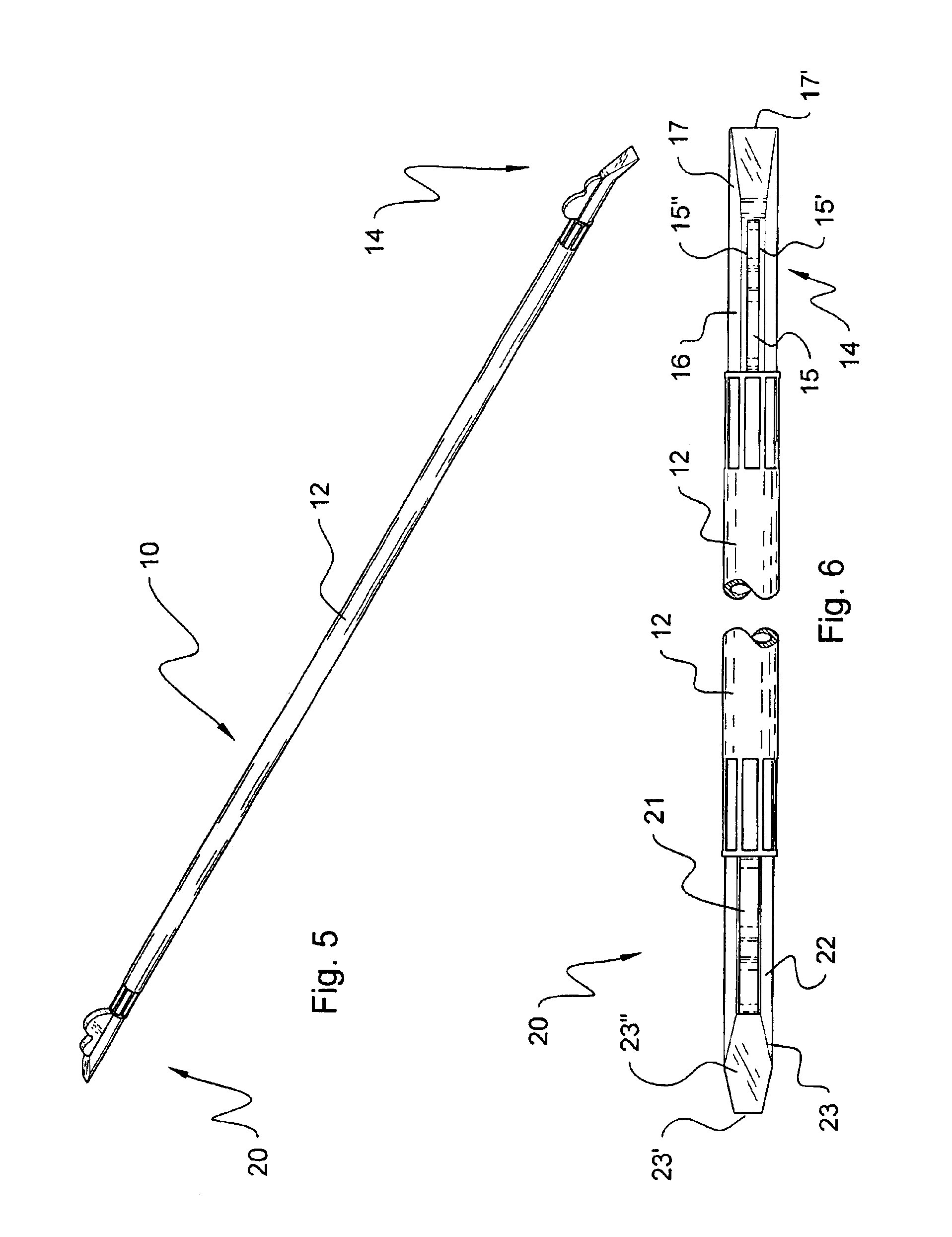
Scaling bar
A scaling bar for prying overhanging rocks from rocky wall structures. The scaling bar comprises an elongated tubular shaft and a first pick member attached to one end thereof, and, optionally, a second pick member attached to a second end thereof. At least one of the two pick members comprises an end portion closely fitted into engagement with the tubular shaft, a tip portion defining a substantially sharp leading edge for easier penetration in the rocky structure, and a cam element. The cam element comprises a first and a second leverage bulges, whereby by displacing the shaft, a lever is formed for dislodging unstable overhanging rocks with minimized physical effort from the workman. The second inner leverage bulge provides greater leverage to the tip portion than the first leverage bulge, but the size of the first leverage bulge is smaller, and can hence engage narrower clefts than the second leverage bulge. In use, a workman axially inserts the pick member of the scaling bar in a cleft adjacent to an unstable overhanging rock, and applies a transverse load by prying the unstable rock using the leverage provided by the first leverage bulge, hence widening the cleft. Subsequently, if necessary, the pick member is further axially driven into the cleft, and the workman again applies a transverse load to pry the rock away again using the leverage provided by the second leverage bulge. This procedure can be repeated so as to sink further into the rock bed, until the rock has been dislodged from its bed.
Owner:ATELIER DUSINAGE LAQUERRE & FILS
Composite seepage preventing structure for large karst cave in karst region and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a composite seepage preventing structure for a large karst cave in a karst region and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of water conservancy and hydropower engineering. The composite seepage preventing structure comprises bed rock and the karst cave. The karst cave is located in the bed rock. The lower section of the karst cave is filled to form a karst filling area. A plurality of filling-material rotary jetting holes or steel pipe piles are vertically distributed in the karst cave filling area and arranged along the seepage preventing axis at intervals in a rowed mode. A transition cushion layer is arranged on the upper surface of the karst cave filling area. A concrete seepage preventing wall is arranged on the steel pipe piles. A cavity in the upstream side of the concrete seepage preventing wall is backfilled to form a backfilling area. According to the technical scheme, due to the reasonable construction method, the concrete seepage preventing wall is built in the karst cave, and the quite good partition effect and the quite good sealing effect are achieved through a karst cave roof joining groove structure in the top and a grouting-cave-aligning-grouting method; the structure and the method are simple, the quantity of input materials is small, construction intensity is small, construction efficiency is greatly improved, and the seepage preventing aim of large karst cave in the karst region is achieved.
Owner:CHINA POWER CONSRTUCTION GRP GUIYANG SURVEY & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Method for quantitatively analyzing ultra-deep gypsum salt rock and dolomite coupling mechanism
ActiveCN111983189AImprove identification work efficiencyAccurate analysisEarth material testingGeomodellingDolostoneOutcrop
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively analyzing an ultra-deep gypsum salt rock and dolomite coupling mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) respectively acquiring geological background data, classic field geological outcrop profile measurement data, drilling and logging data and seismic data by taking a Sichuan basin carbonate rock reservoir as an object; (2) according to the data obtained in the step (1), determining the basic geological characteristics of dolomite by using sedimentology, petroleum geology theories and various geochemical test analysis, anddetermining the types of dolomite and petrology and distribution rules of various dolomites; and (3) according to the petrology and distribution rule of various dolomites, analyzing the form and formation mechanism of various dolomites and the quantitative relationship between the dolomites and gypsum salt rock, and finally determining the coupling relationship. By judging the source, the seepagedirection, the path and the like of dolomitic fluid, the coupling relation between the dolomitic fluid source and quantification of the bed series and gypsum salt rock is defined, and the method has important guiding significance for oil and gas exploration.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for combined exploitation of coal and its associated oil shales
ActiveCN106337685AReduce mining difficultyEnsure rock breaking efficiencyUnderground miningSurface miningResource utilizationOil shale gas
The invention provides a method for combined exploitation of coal and its associated oil shales. The method comprises the construction steps that when the coal and its associated oil shales are located in a reasonable exploitation bed separation distance range, coal resources located at the lower portion are firstly exploited, a mine bearing pressure is fully utilized to destroy associated oil shales located in an overlying rock layer and reduce the strength; then, the associated oil shales at the upper portion are exploited later to achieve combined exploitation of coal and its associated oil shales. Therefore, the shortcoming that when oil shales are independently exploited, the oil shale strength is higher and accordingly a coal cutter difficultly break rocks can be overcome. According to the exploitation method, existing infrastructures and sinking and driving engineering can be fully utilized, the roadway tunneling amount can be decreased, investment can be reduced, the costs are low, the phenomenon that the oil shales associated with coal are severely abandoned can be effectively completely eradicated or decreased, the resource utilization rate can be improved, an economic value is huge, and the method has the important practical significance on relieving of conventional energy source supply and demand pressure, energy structure adjustment and energy guaranteeing.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Whole-journey gas-proof gas content measuring instrument and method for using the same to measure residual gas of rock sample
ActiveCN104914030AAvoid exposureCompact structurePermeability/surface area analysisGraduated cylinderMeasuring instrument
The invention discloses a whole-journey gas-proof gas content measuring instrument and a method for using the same to measure residual gas of a rock sample. The measuring instrument comprises a sample smashing system, a heating system and a gas gathering and metering system, wherein the sample smashing system comprises a sample smashing tank capable of being closed, and a gas outlet is formed in the sample smashing tank; the heating system is used for heating the sample smashing tank; the gas gathering and metering system comprises a gas gathering and metering barrel used for gathering and metering the gas separated from the sample smashing tank, and the gas gathering and metering barrel is hermetically connected with the gas outlet of the sample smashing tank. The whole-journey gas-proof gas content measuring instrument uses the multi-functional integrated design, the operation is flexible, the use is facilitated, the gas-proof effect is good, the gas measuring error can be reduced, and the measuring accuracy and precision are improved; when measuring the residual gas of the rock sample, the whole-journey gas-proof gas content measuring instrument is capable of precisely and quickly measuring the residual gas content in shale, coal bed, tight sandstone and the like reservoirs, a sample tank does not need change in the whole journey of experiment, and the gas tightness is rigid; the gas measuring error is small, and the measuring precision is high.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Integrated drilling tool for crushing and cleaning drilling borehole rock debris deposit bed
InactiveCN110886582AReasonable structural designPrevent subsidenceDrilling rodsCleaning apparatusMining engineeringAlloy
The invention discloses an integrated drilling tool for crushing and cleaning a drilling borehole rock debris deposit bed, and relates to the field of drilling tools. A scraping and cleaning short joint is a columnar pipe body, more than one convex edge spiral wing is longitudinally arranged on the annular wall of the scraping and cleaning short joint, the convex edge spiral wings are longitudinally arranged in a V-shaped circumferential interval mode, hard alloy convex blocks are evenly distributed on the edge faces of the convex edge spiral wings, the two ends of each V-shaped convex edge spiral wing are connected with cutting edges which are sunken inwards and warped outwards, and columnar cutting teeth are arranged on the surfaces of the cutting edges; and a V-shaped sunken flow guidegroove is formed between every two adjacent V-shaped convex edge spiral wings, and liquid flow nozzles which communicate with the interior of a pipe are arranged at the two ends of each flow guide groove. The V-shaped sunken flow guide grooves rotate along with a drilling rod, so that drilling fluid generates severe turbulence, and sedimentation of rock debris particles in a well section is effectively prevented; and meanwhile, formed rock debris bed particles can be efficiently stirred, and the stirred rock debris particles are captured by the flow guide grooves, then brought into a suspension layer with a high annular flow rate and thrown to a high-side annulus and a farther distance.
Owner:HELI TECH ENERGY CO LTD
Rock slope slip test system
PendingCN111323561AImprove practicalityExtended cleaning cycleEarth material testingInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceSoil scienceStructural engineering
The invention discloses a rock slope slip test system which comprises a base, a mounting mechanism and a test mechanism are arranged on the base, the test mechanism comprises a bottom plate and baffles, a slope body is arranged between the two baffles, a circulating rainfall mechanism is arranged above the slope body, and a sliding groove is formed in one end of the bottom plate; the slope body sequentially comprises an overlying rock layer, a soft soil interlayer and a bed rock layer from outside to inside. A collecting groove is formed in the base, and a filtering mechanism is installed at the bottom of the collecting groove and communicated with the circulating rainfall mechanism. According to the rock slope slip test system provided by the invention, bedding rock slope slip motion in nature can be simulated in an indoor experiment, and the rock slope slip test system is used for researching a slope failure process and mechanism; bedding rock slope sliding motion of different combined structural planes in the nature can be simulated; in addition, corresponding damage test data can be obtained by adopting corresponding detection instruments, and the system is used for deep research on the damage process of the rock slope.
Owner:NEIJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Shield excavating method of tunnel containing boulder and bed rock salient stratum
InactiveCN110924956ASafe and smooth constructionEliminate the effects of tunnelingBlastingTunnelsSoil scienceBedrock
The invention discloses a shield excavating method of a tunnel containing a completely weathered granite boulder development stratum and a bed rock salient section. Pertinent excavating methods are provided for the completely weathered granite boulder development stratum and the bed rock salient section correspondingly, the construction method adopting sequential detection and treatment is adoptedfor the completely weathered granite boulder development stratum, and the method of mid-sea explosion and grouting reinforcement is adopted for the bed rock salient section for construction. The damage probability of a cutterhead and a shield main bearing are greatly reduced, the influences on shield excavating are basically eliminated, and subsea tunnel shield construction is safely and smoothlycarried out.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY TUNNEL GROUP CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com