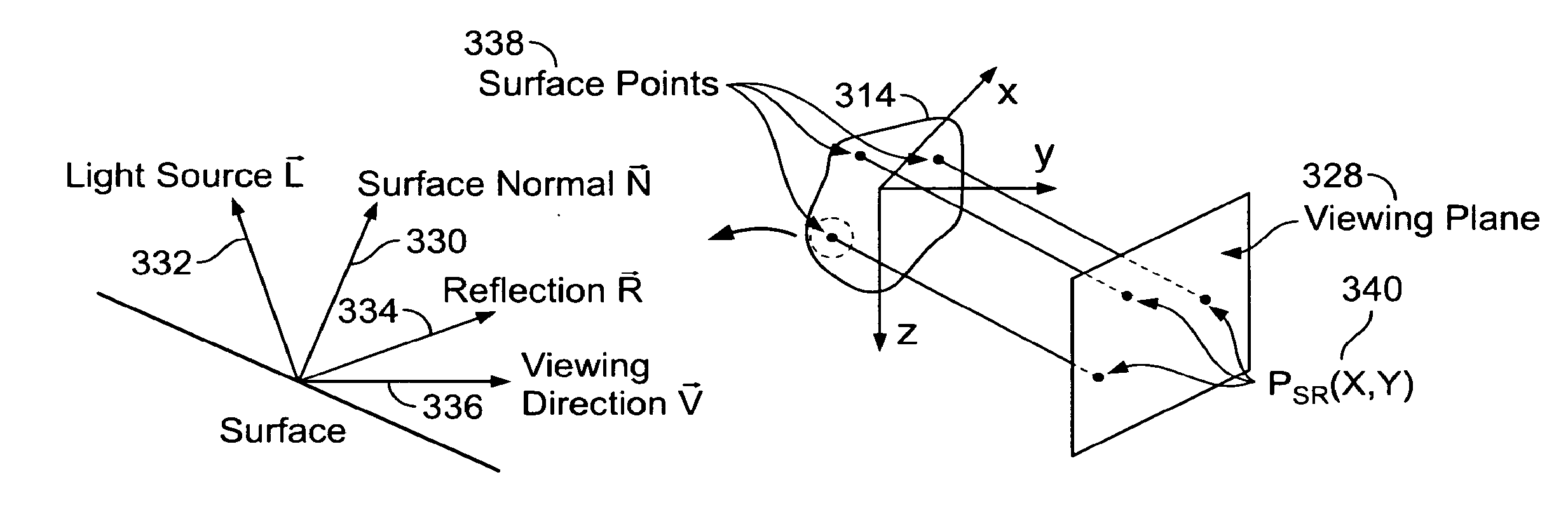
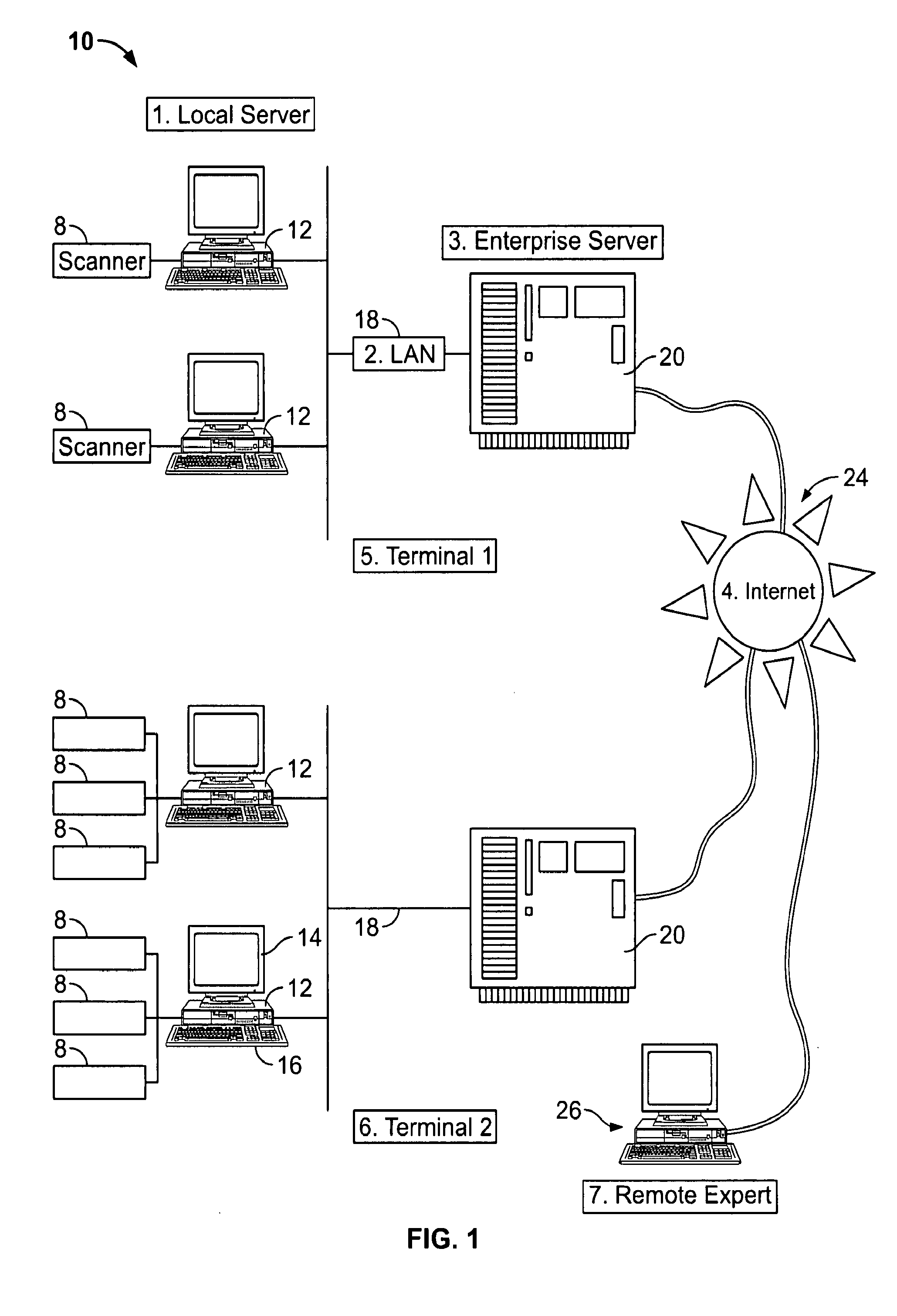
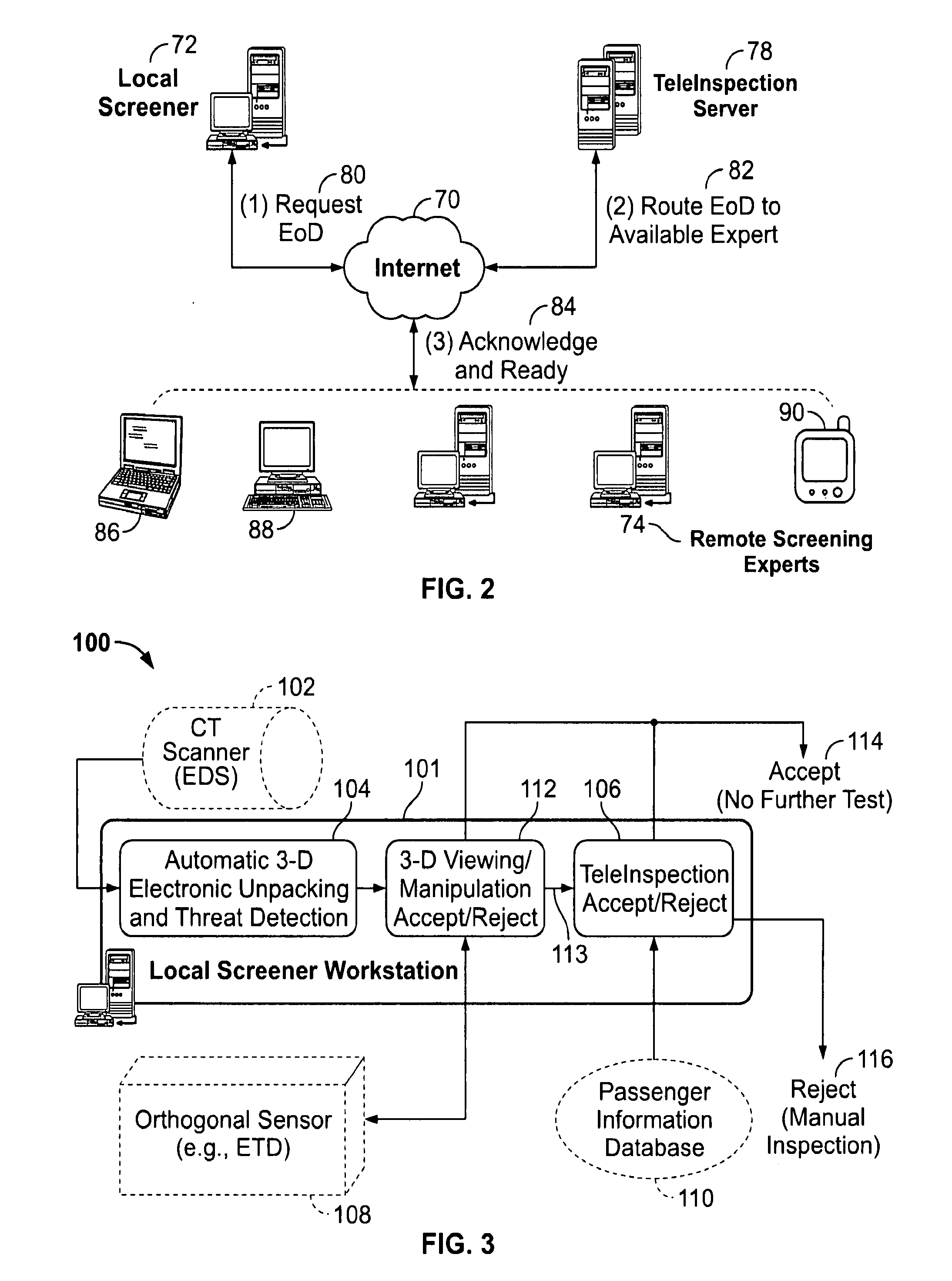
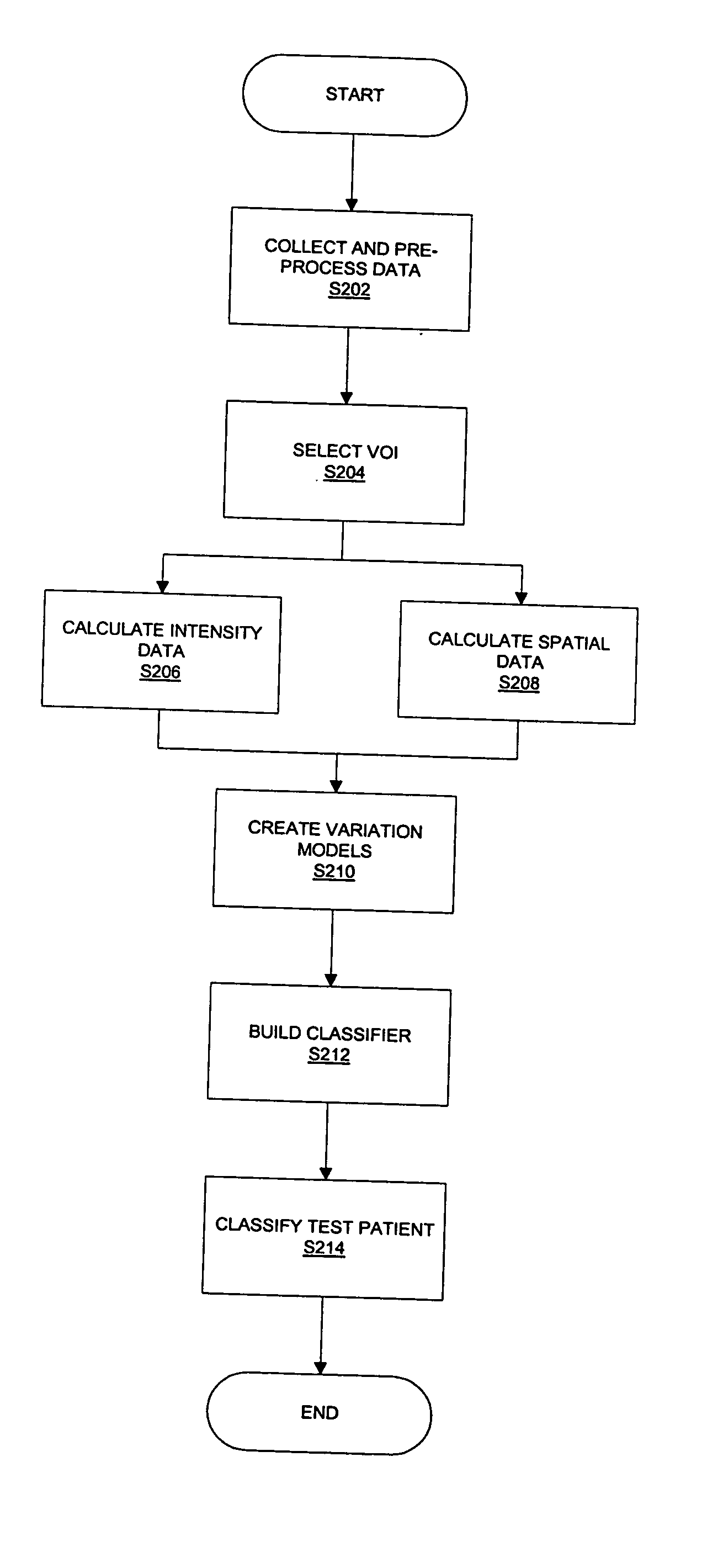
Patents
Literature
386 results about "Volume of interest" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
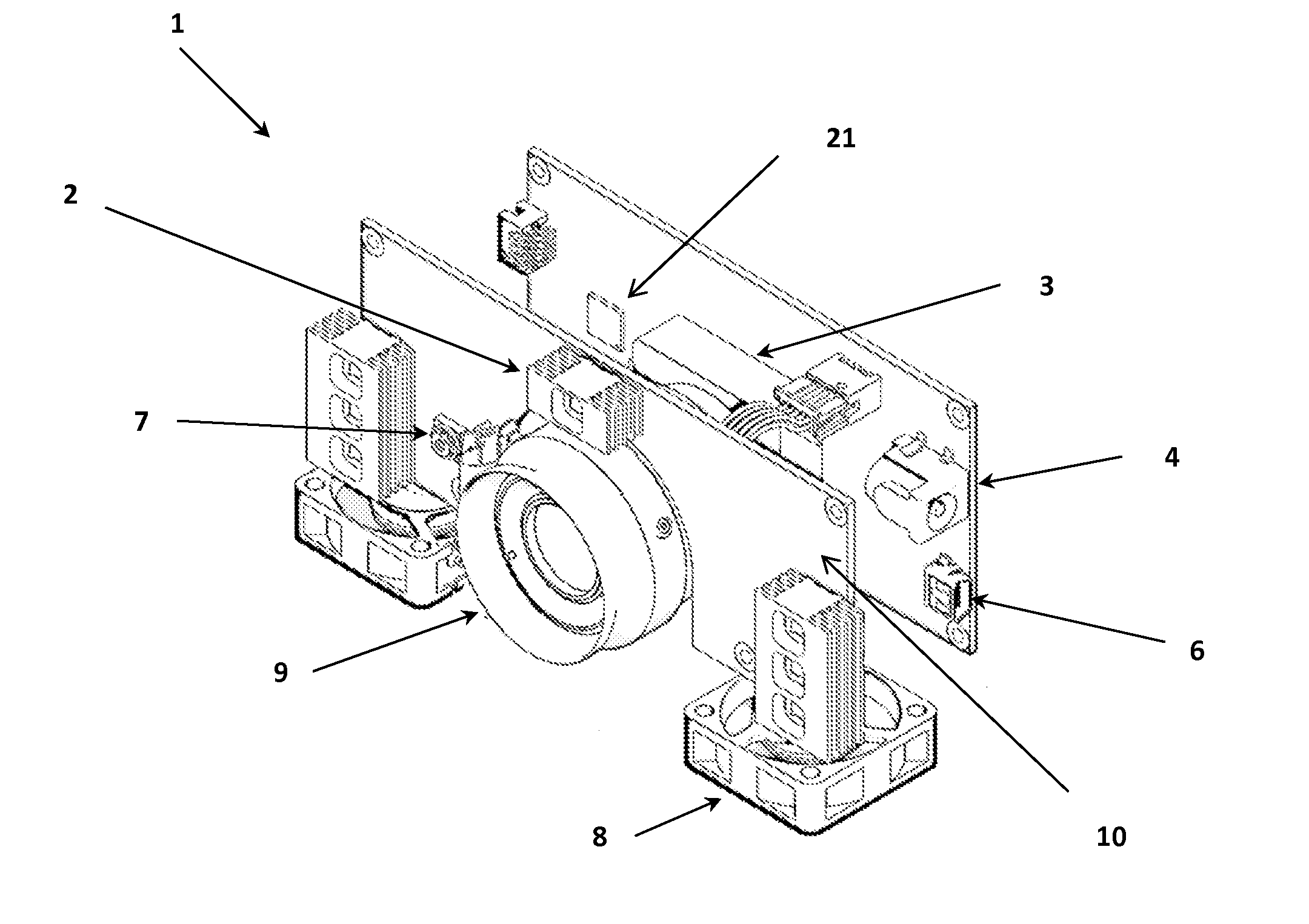
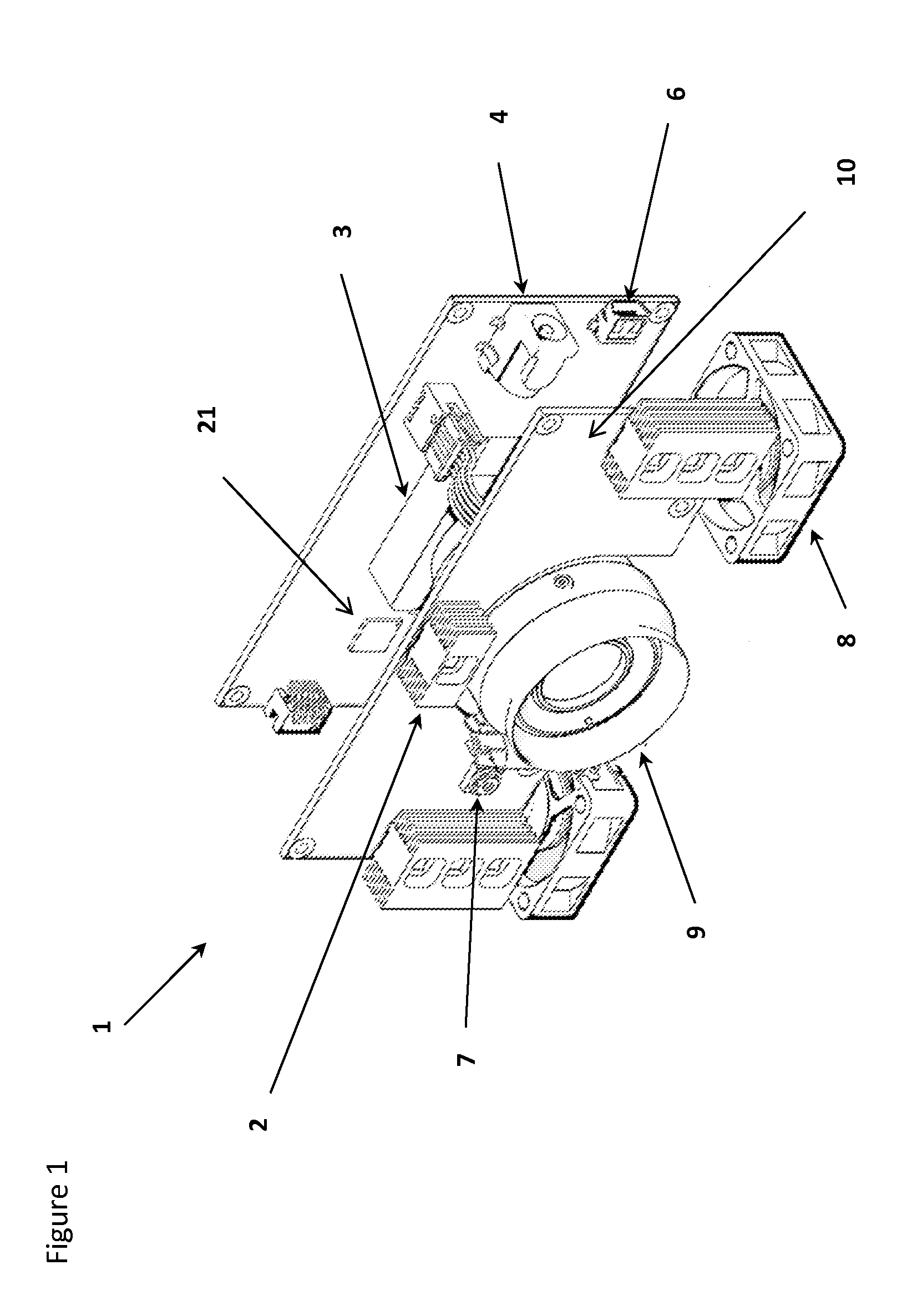
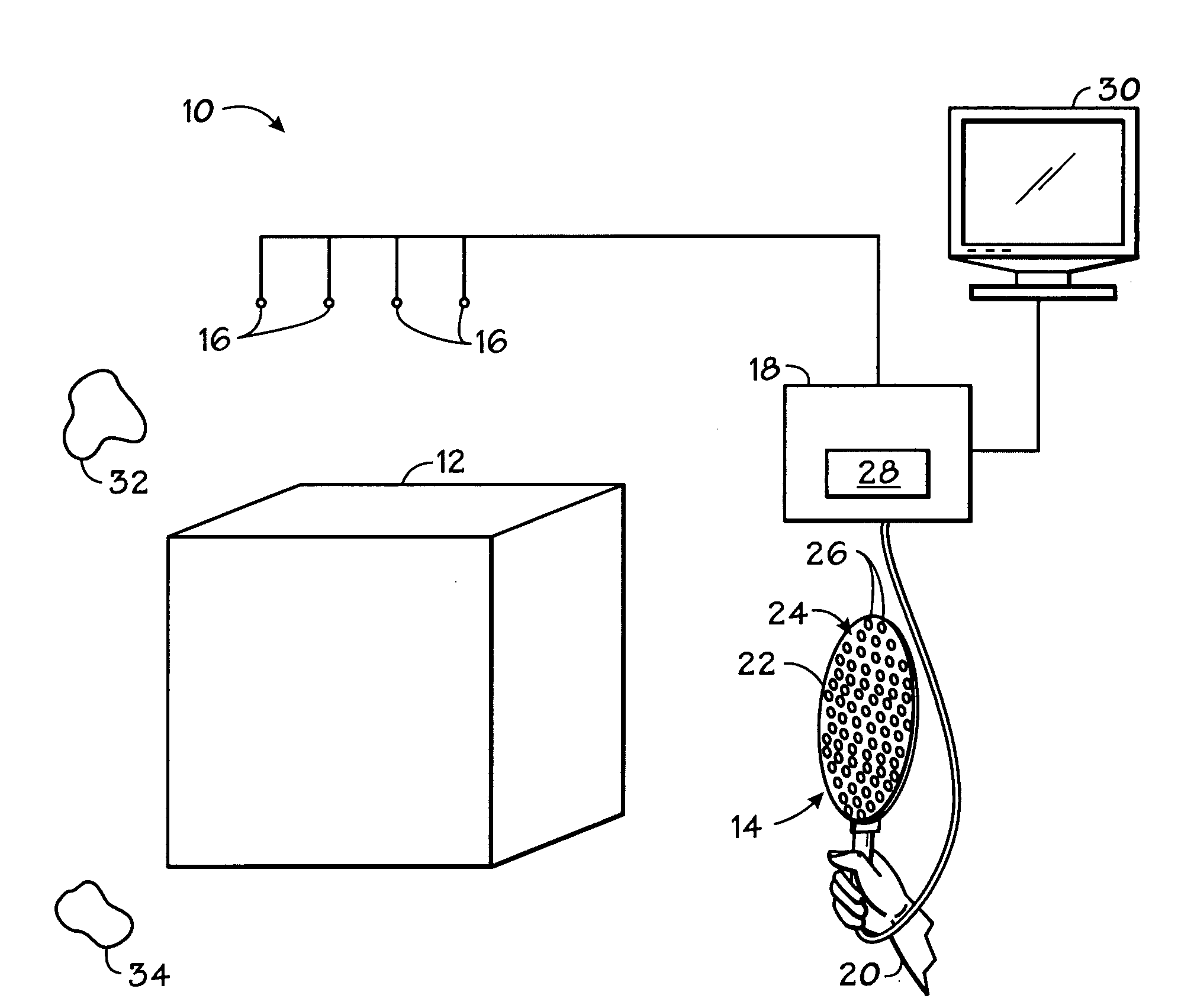
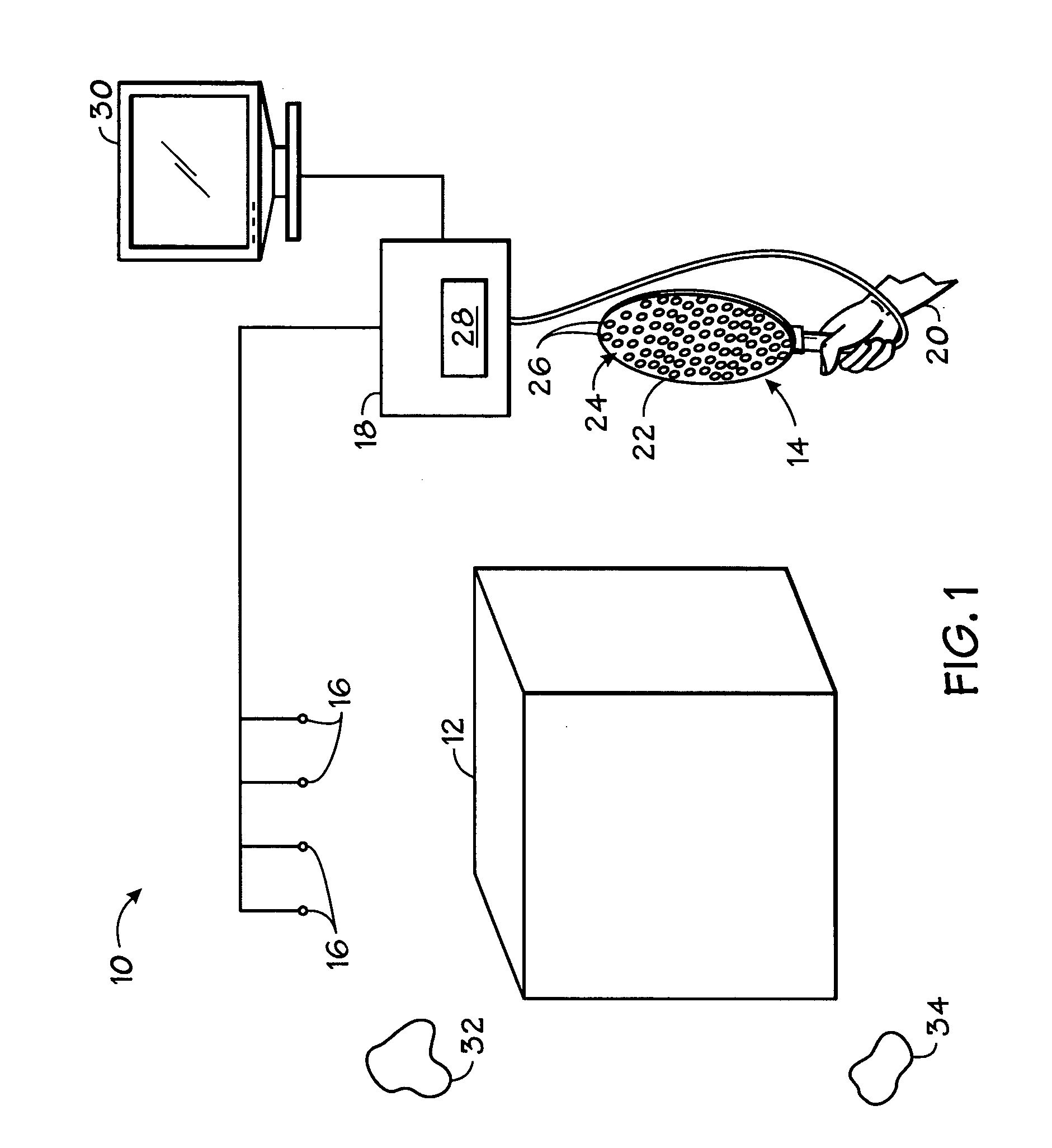
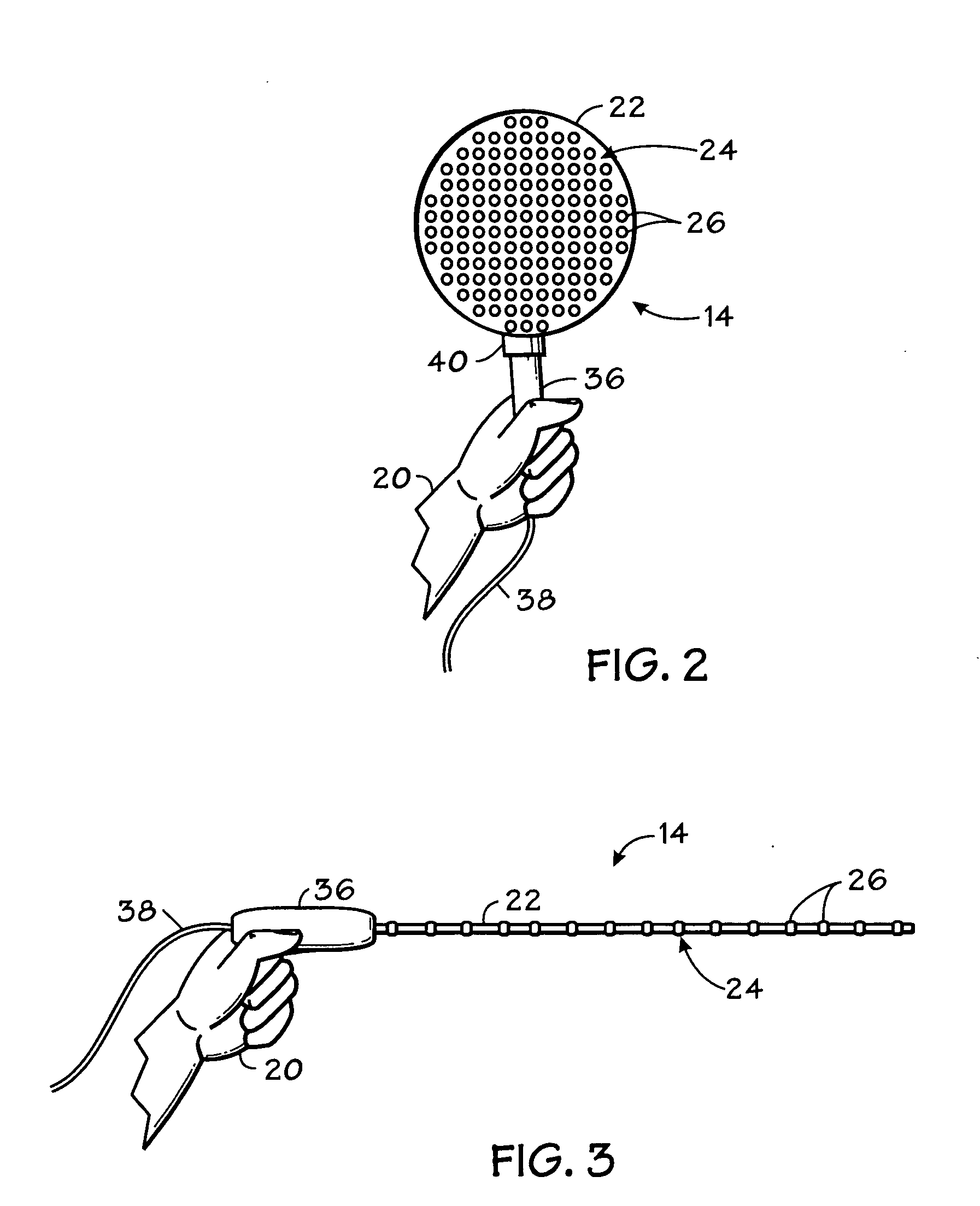
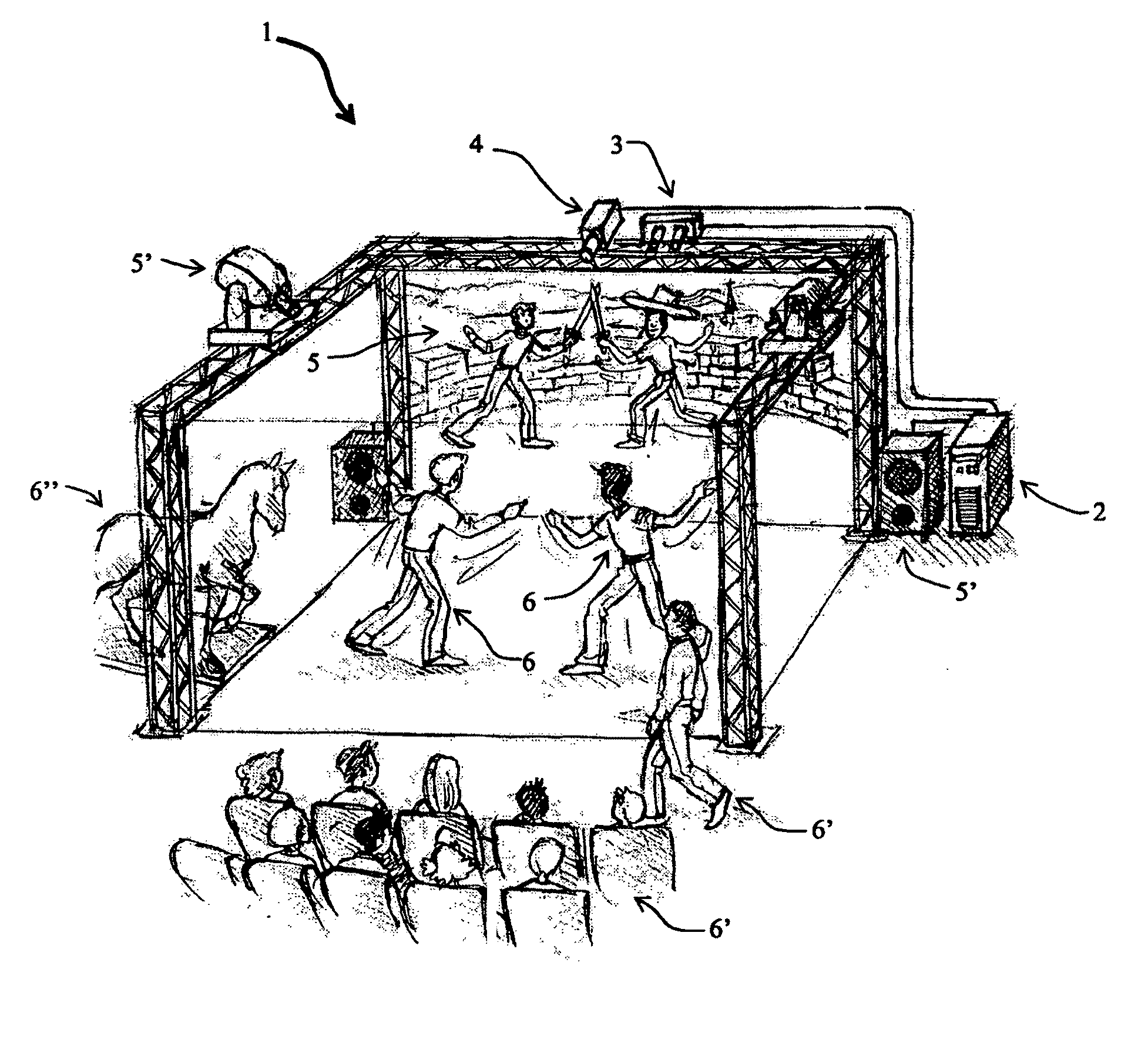
Method and Device for Identifying and Extracting Images of multiple Users, and for Recognizing User Gestures
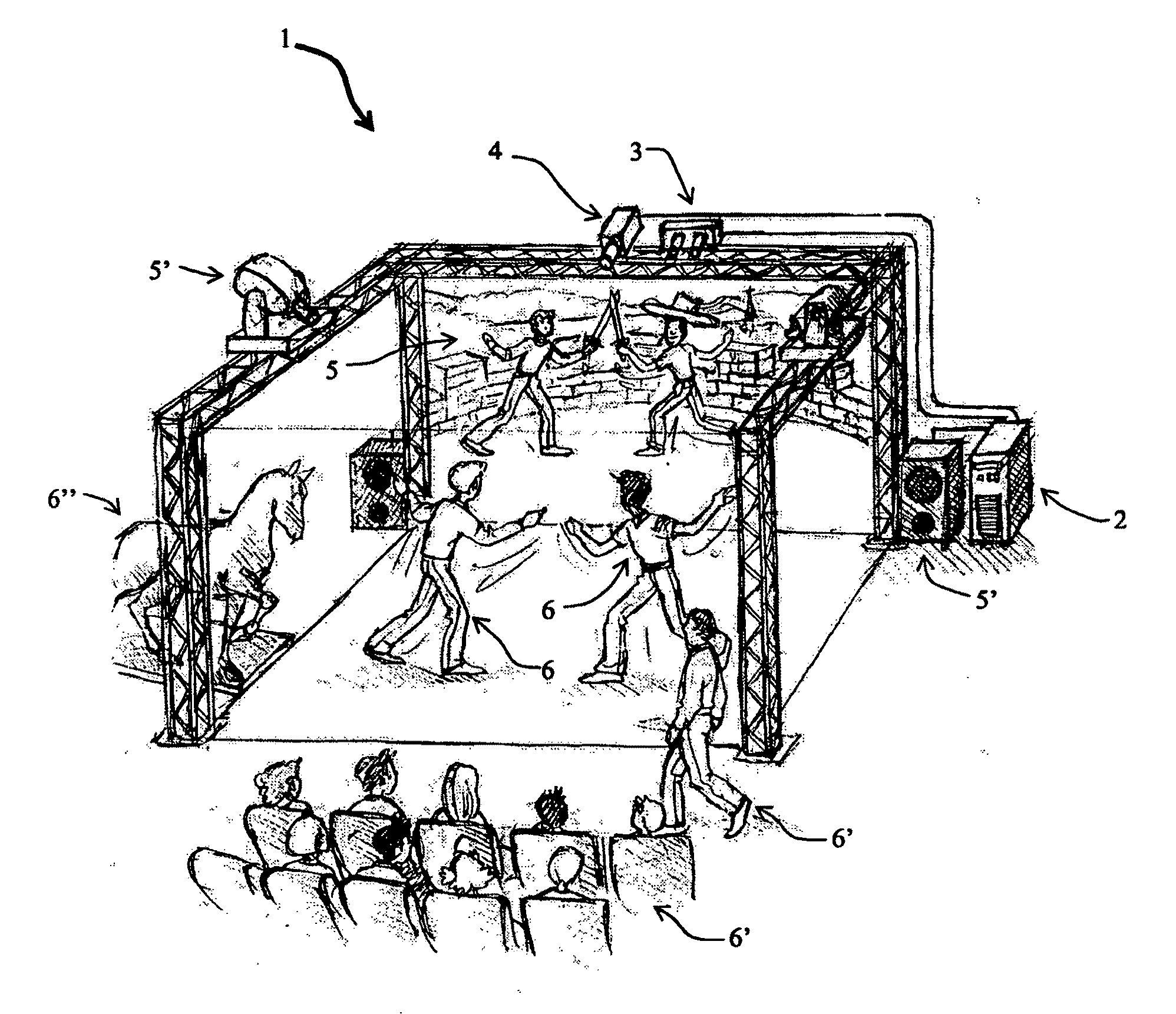
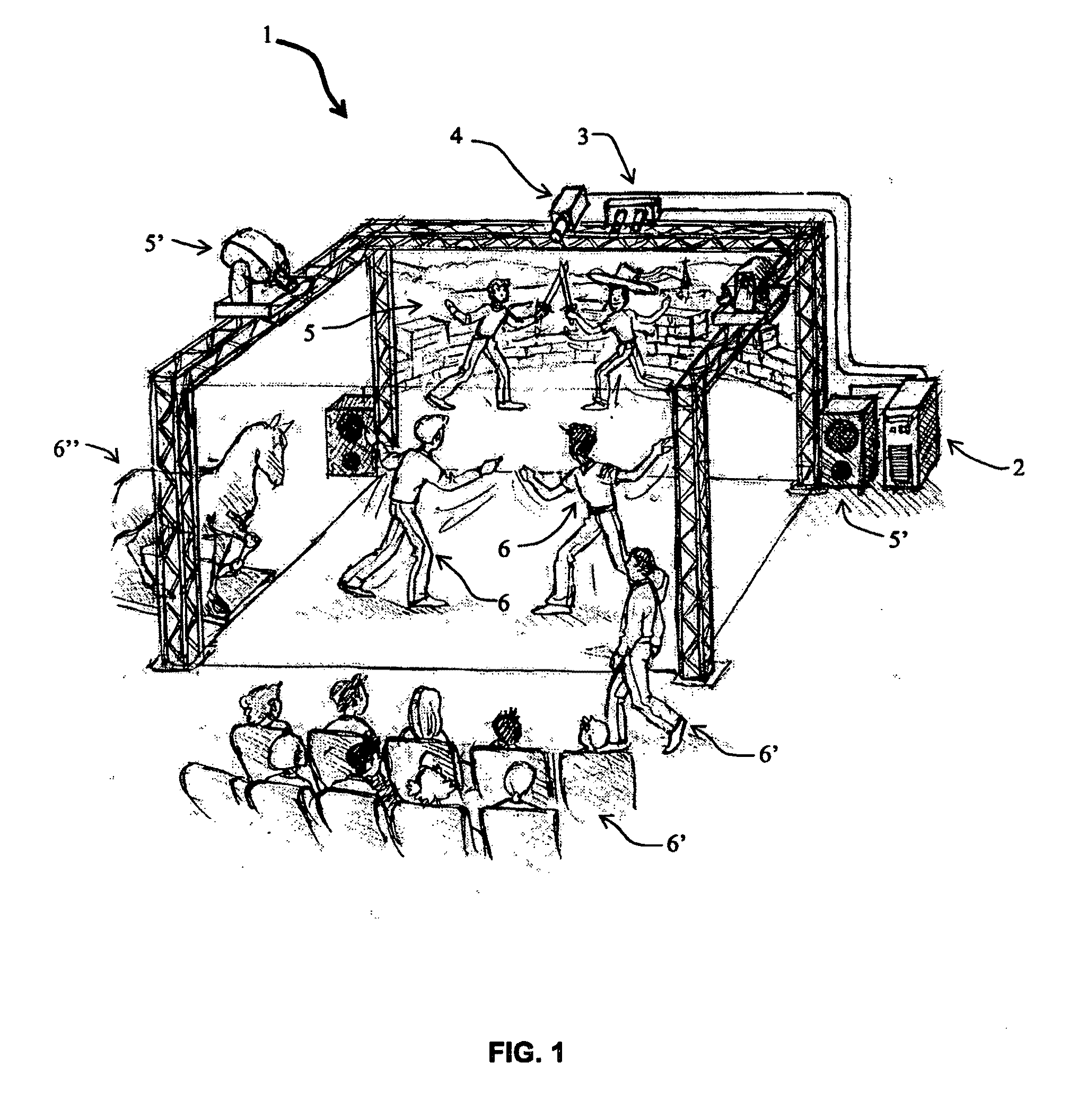
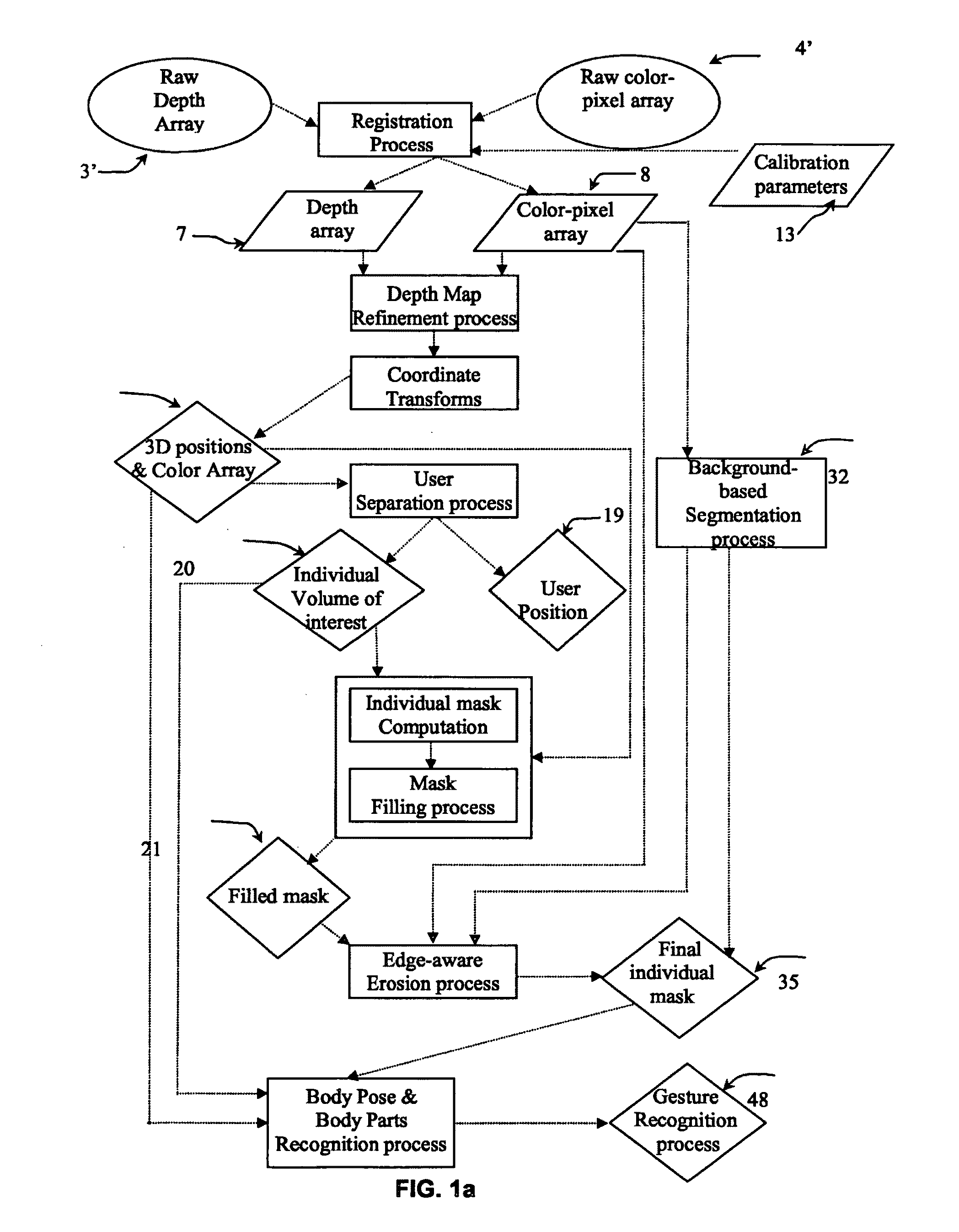
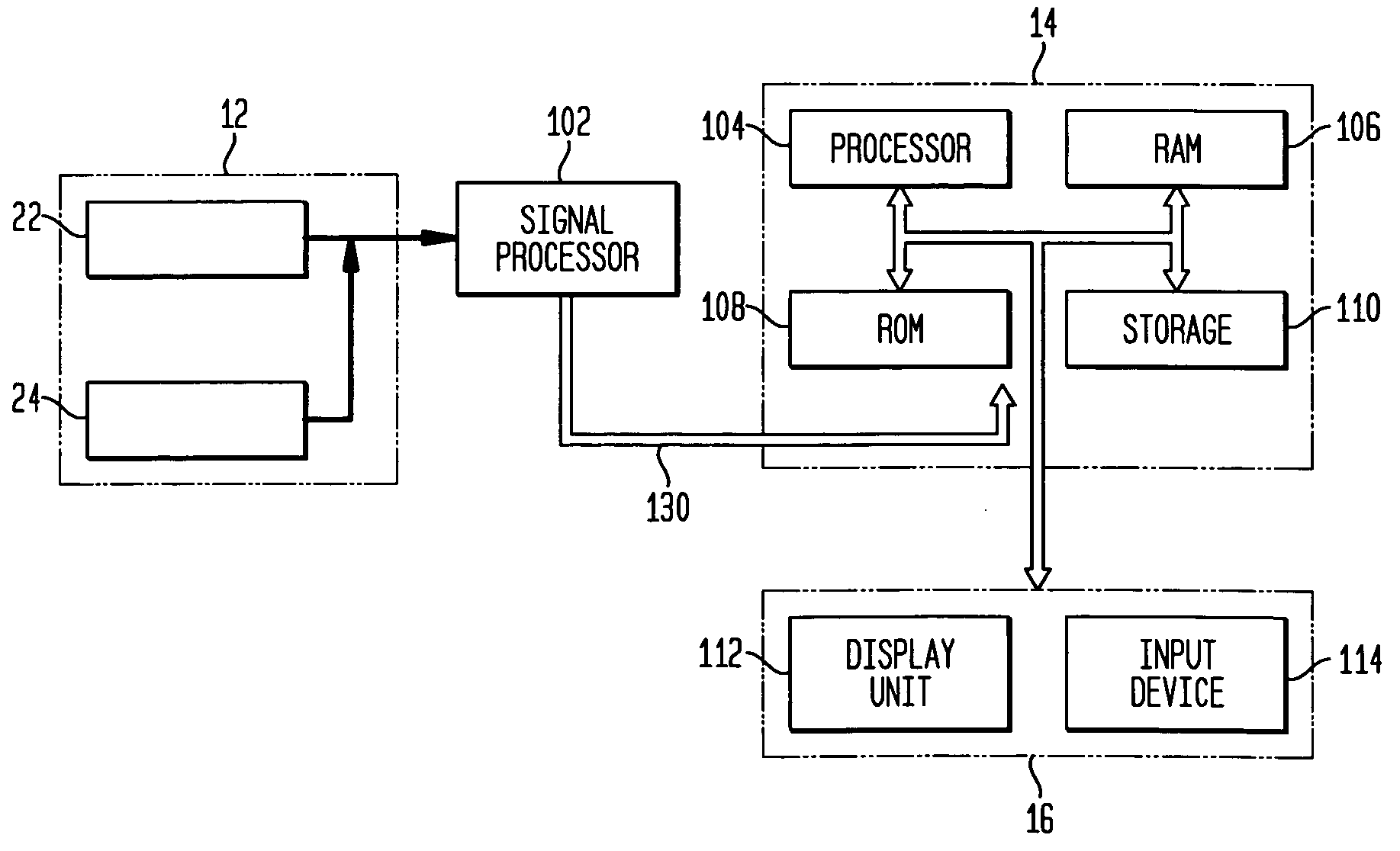
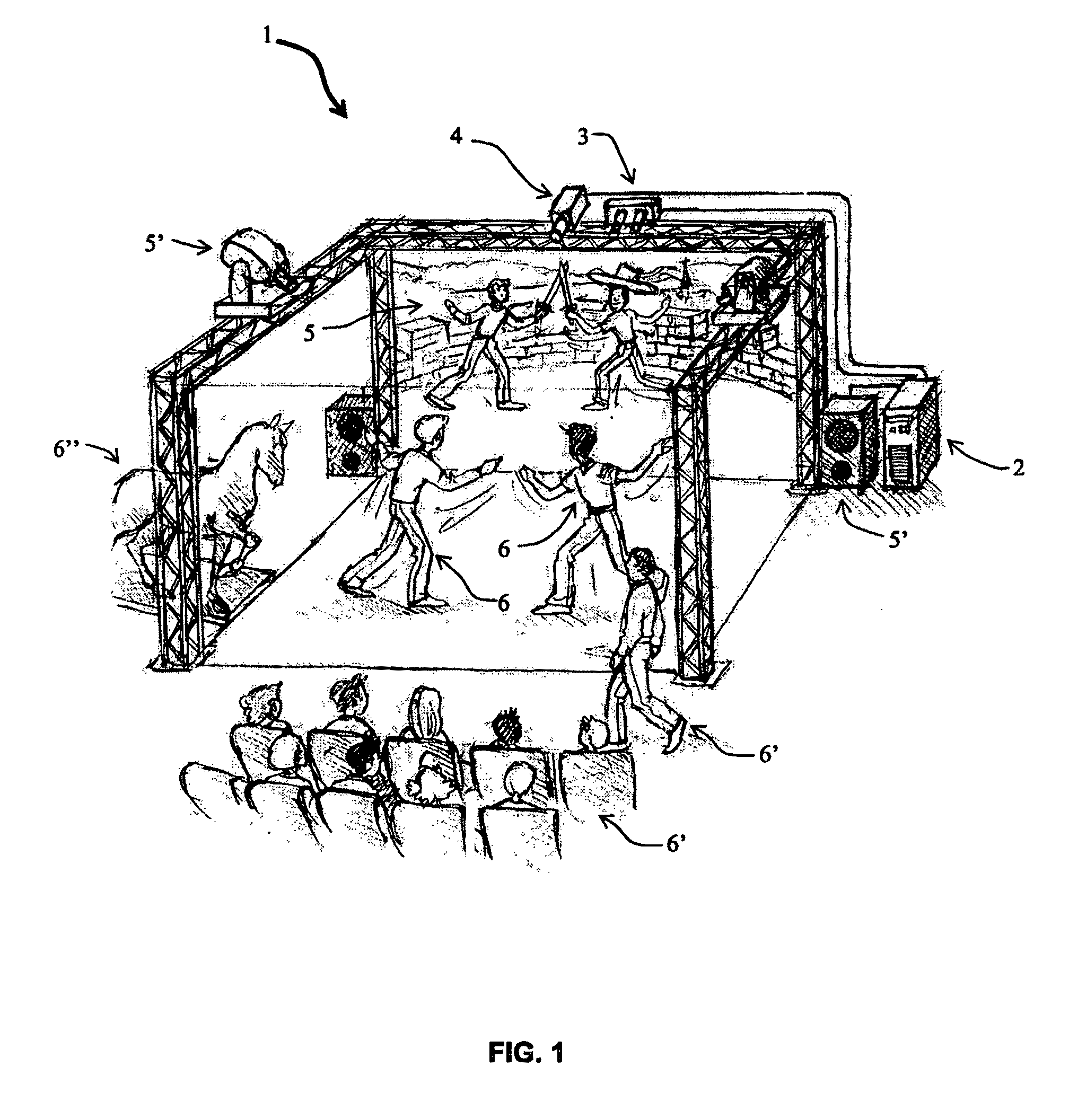
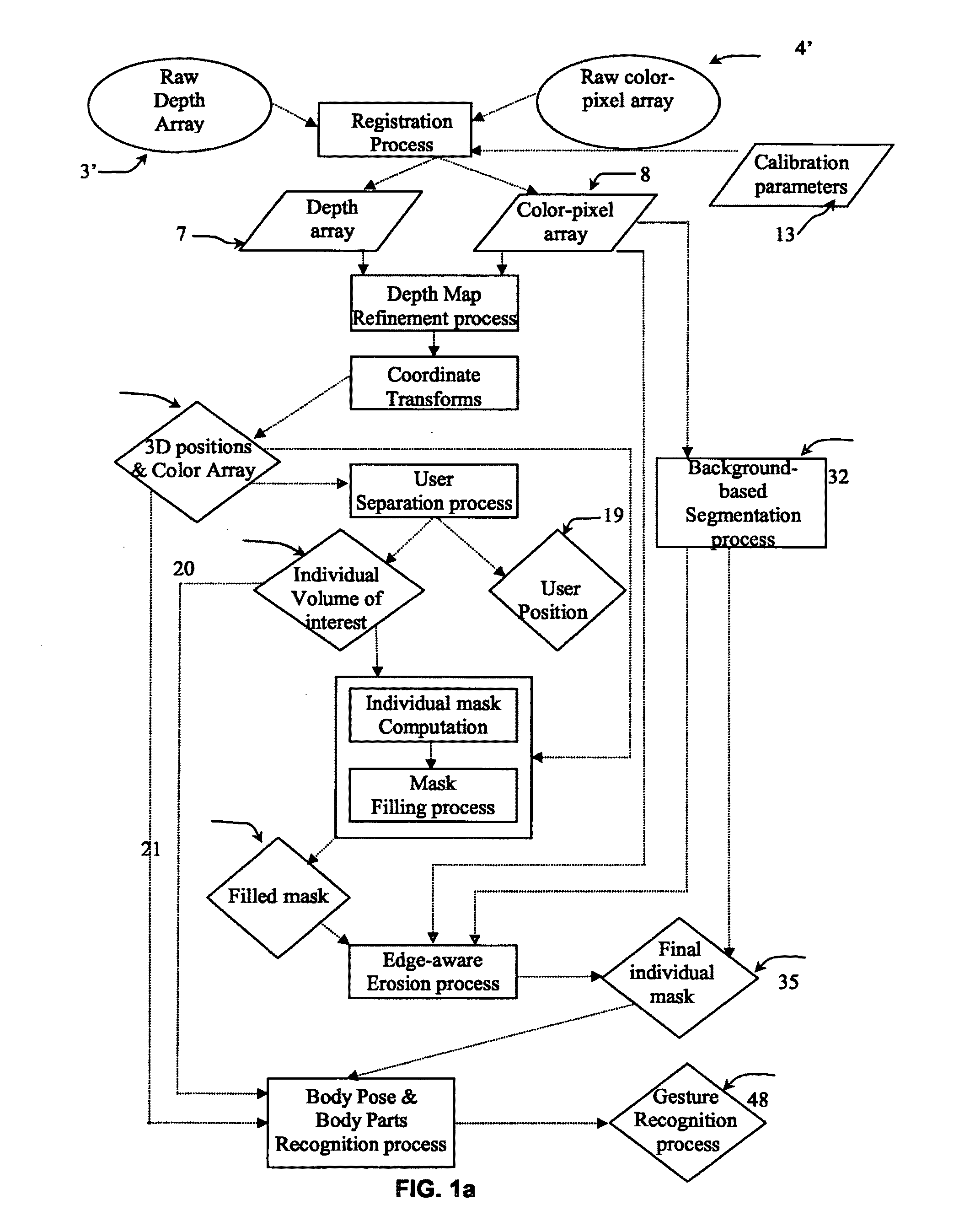
The invention relates to a method for identifying and extracting images of one or more users in an interactive environment comprising the steps of: —obtaining a depth map (7) of a scene in the form of an array of depth values, and an image (8) of said scene in the form of a corresponding array of pixel values, said depth map (7) and said image (8) being registered; applying a coordinate transformation to said depth map (7) and said image (8) for obtaining a corresponding array (15) containing the 3D positions in a real-world coordinates system and pixel values points; —grouping said points according to their relative positions, by using a clustering process (18) so that each group contains points that are in the same region of space and correspond to a user location (19); —defining individual volumes of interest (20) each corresponding to one of said user locations (19); —selecting, from said array (15) containing the 3D positions and pixel values, the points located in said volumes of interest for obtaining segmentation masks (35) for each user; —applying said segmentation masks (35) to said image (8) for extracting images of said users. The invention also relates to a method for recognizing gestures of said users.
Owner:ALTERFACE
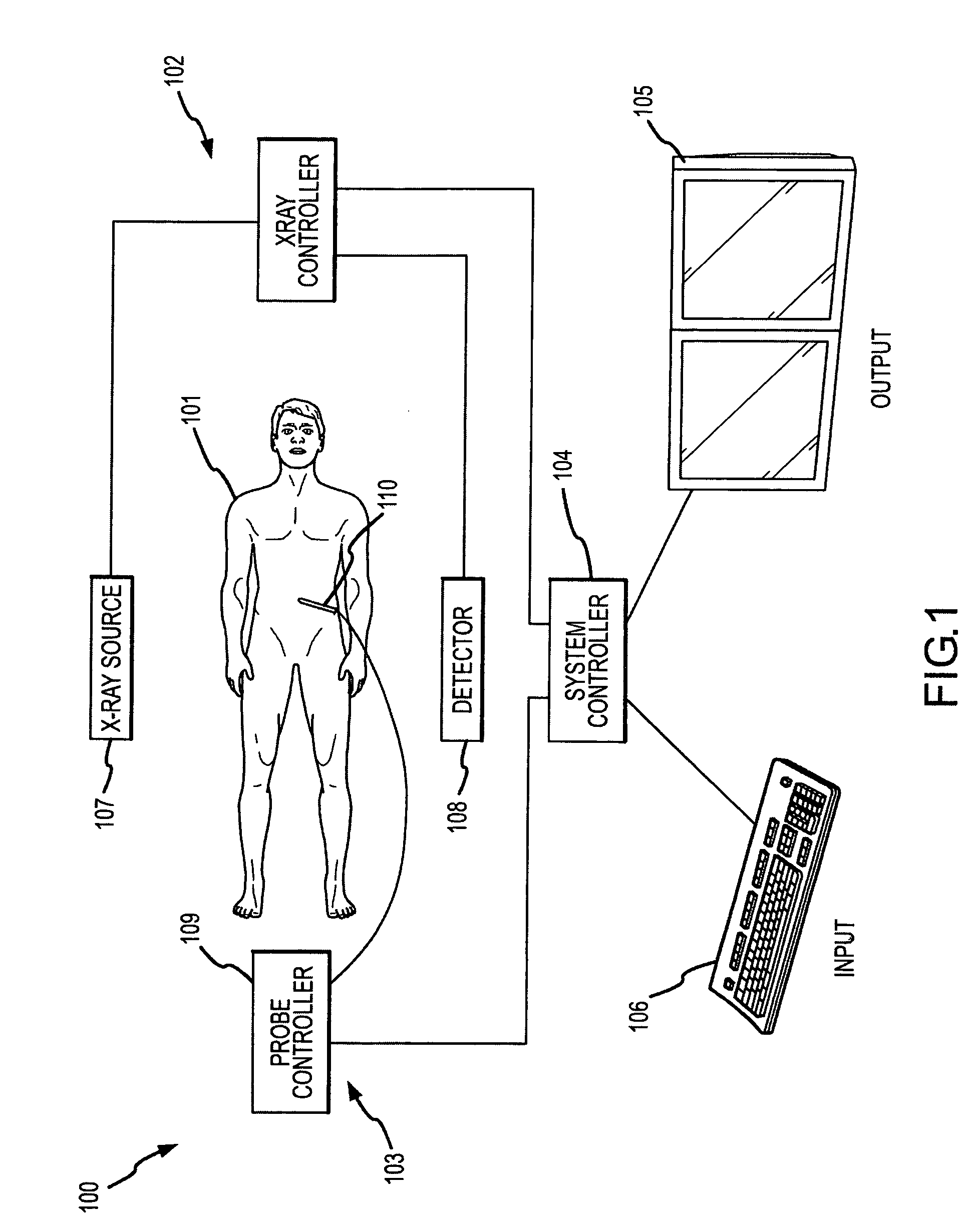
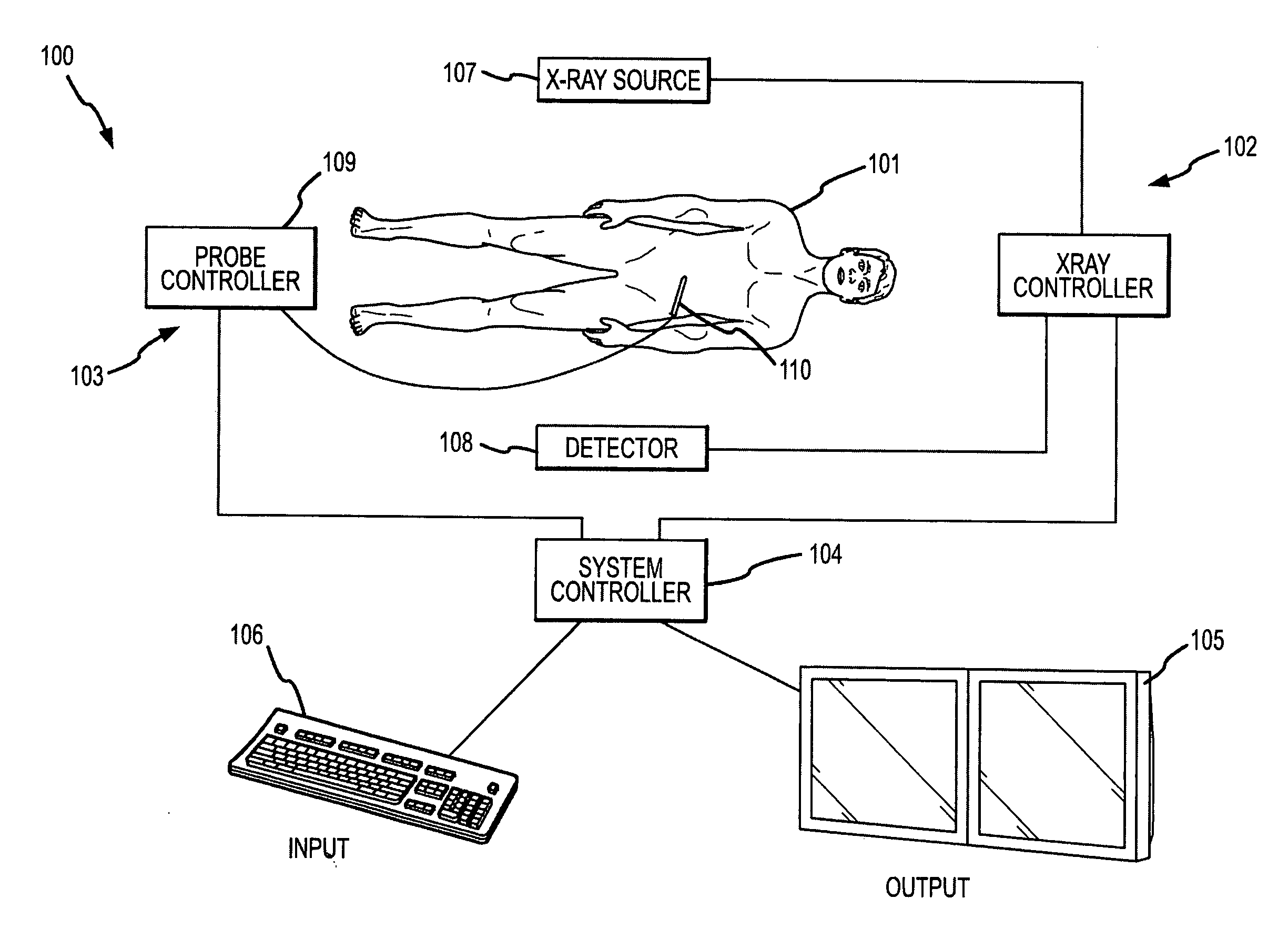
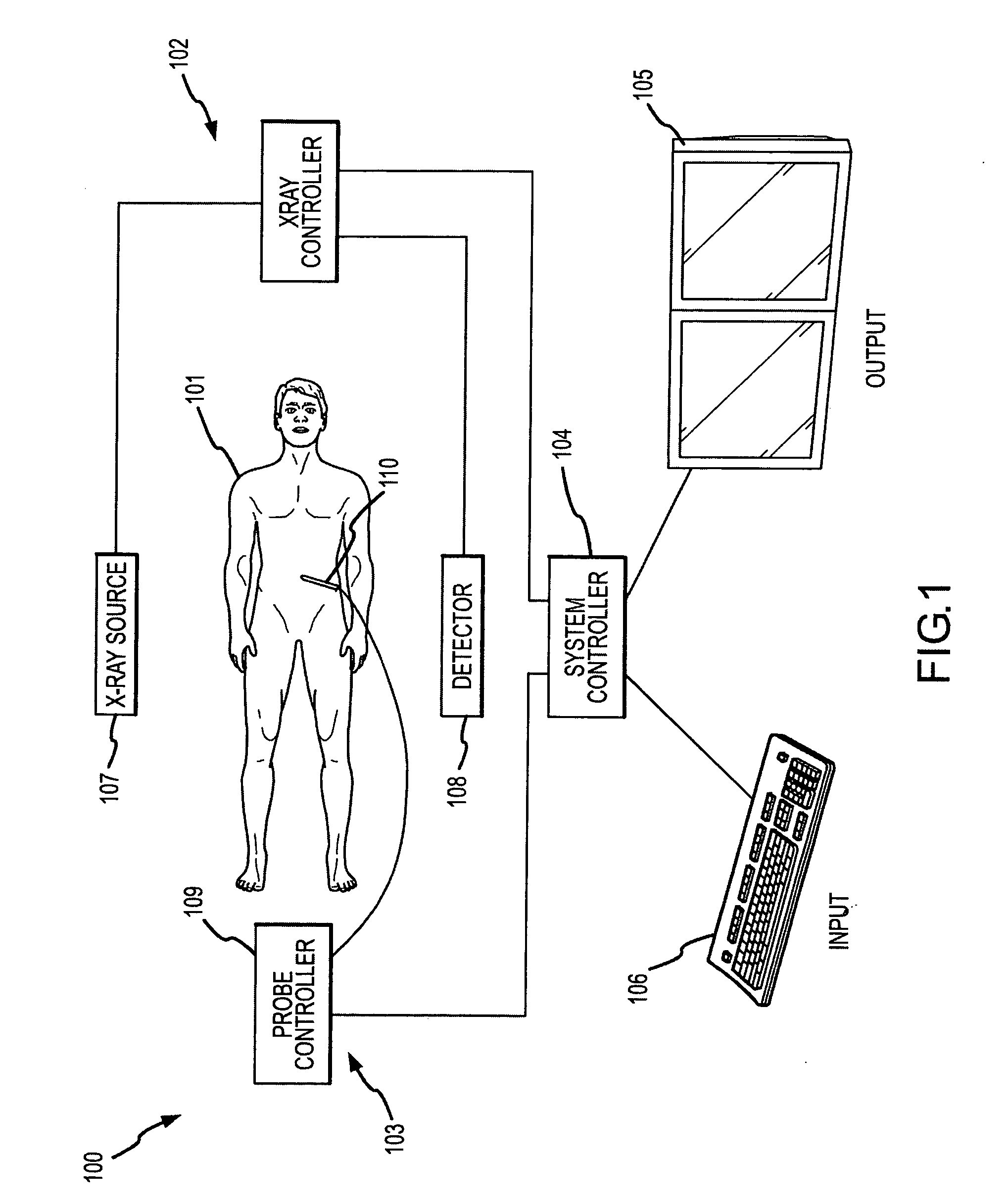
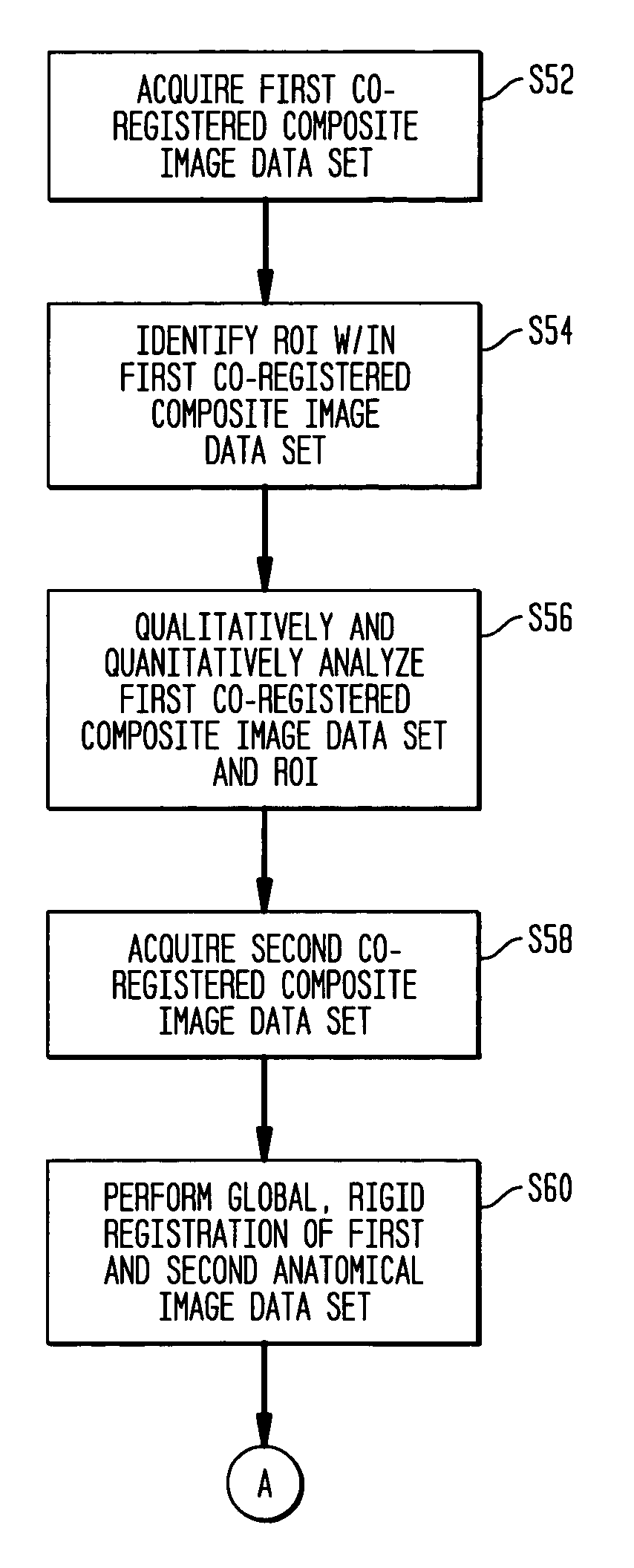
System and method of measuring disease severity of a patient before, during and after treatment
ActiveUS20050065421A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisData setImaging data
A system and method of obtaining serial biochemical, anatomical or physiological in vivo measurements of disease from one or more medical images of a patient before, during and after treatment, and measuring extent and severity of the disease is provided. First anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a first co-registered composite image data set. At least a volume of interest (ROI) within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. The first co-registered composite image data set including the ROI is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine extent and severity of the disease. Second anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a second co-registered composite image data set. A global, rigid registration is performed on the first and second anatomical image data sets, such that the first and second functional image data sets are also globally registered. At least a ROI within the globally registered image data set using the identified ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. A local, non-rigid registration is performed on the ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set and the ROI within the globally registered image data set, thereby producing a first co-registered serial image data set. The first co-registered serial image data set including the ROIs is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine severity of the disease and / or response to treatment of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
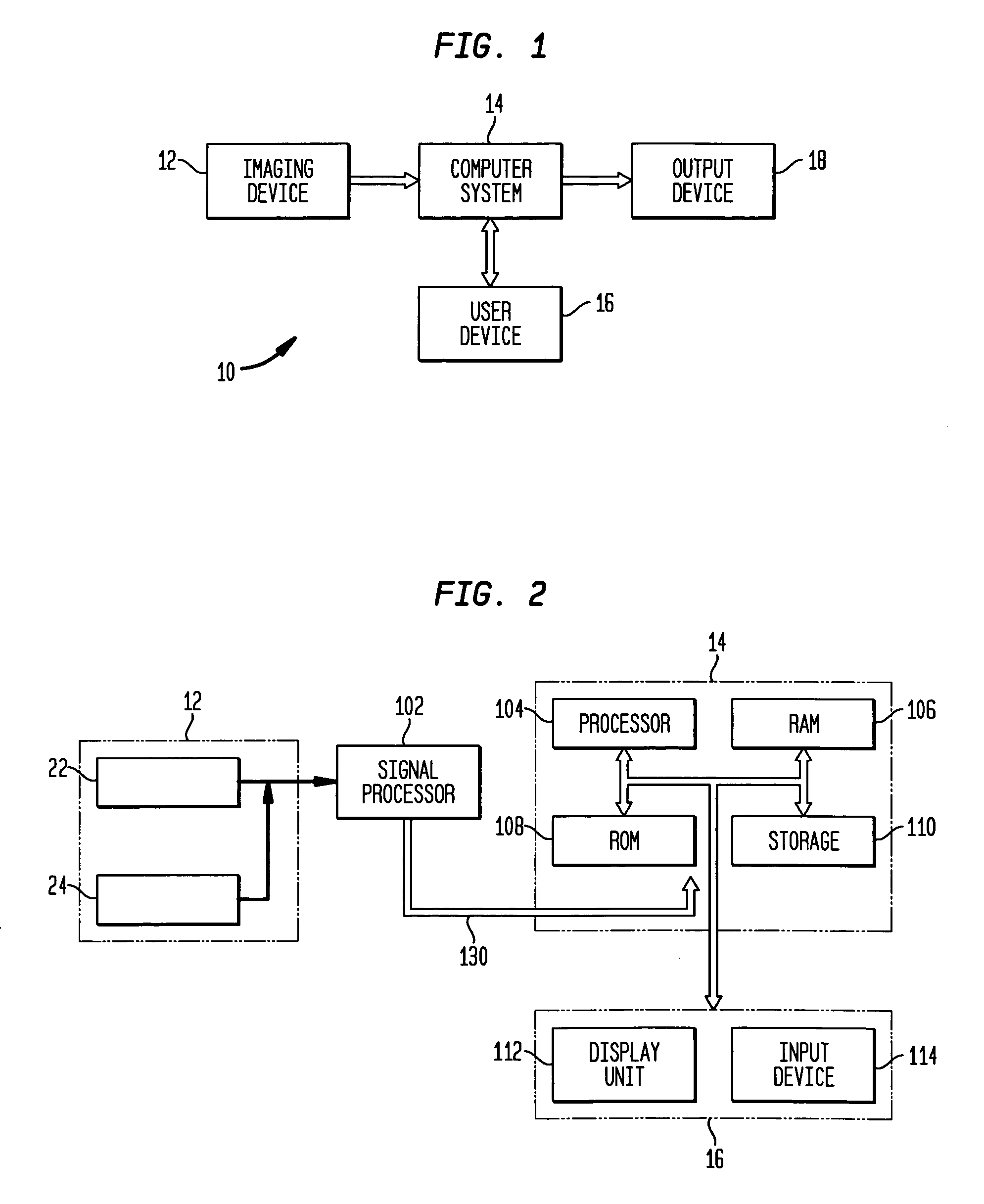
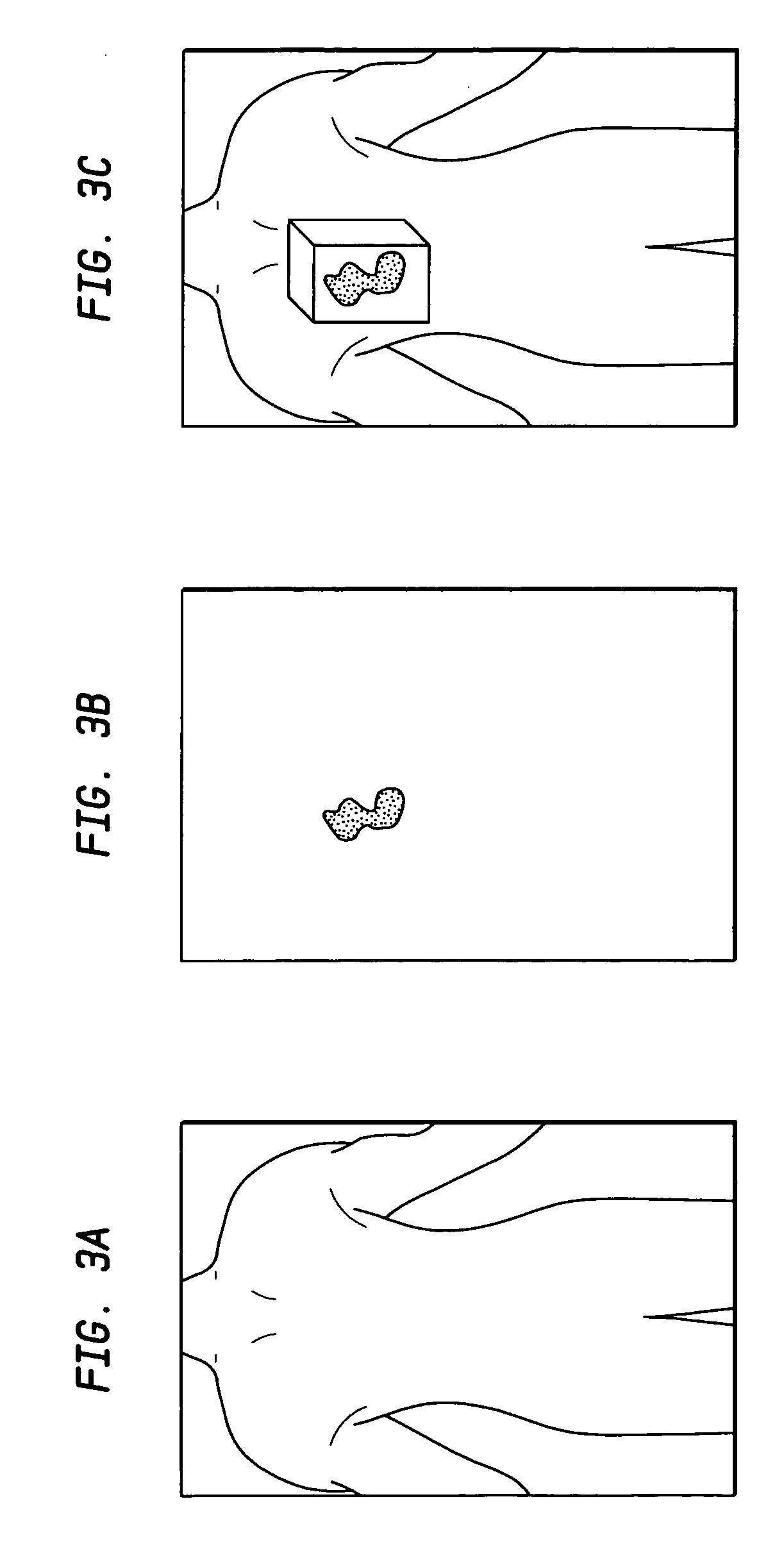
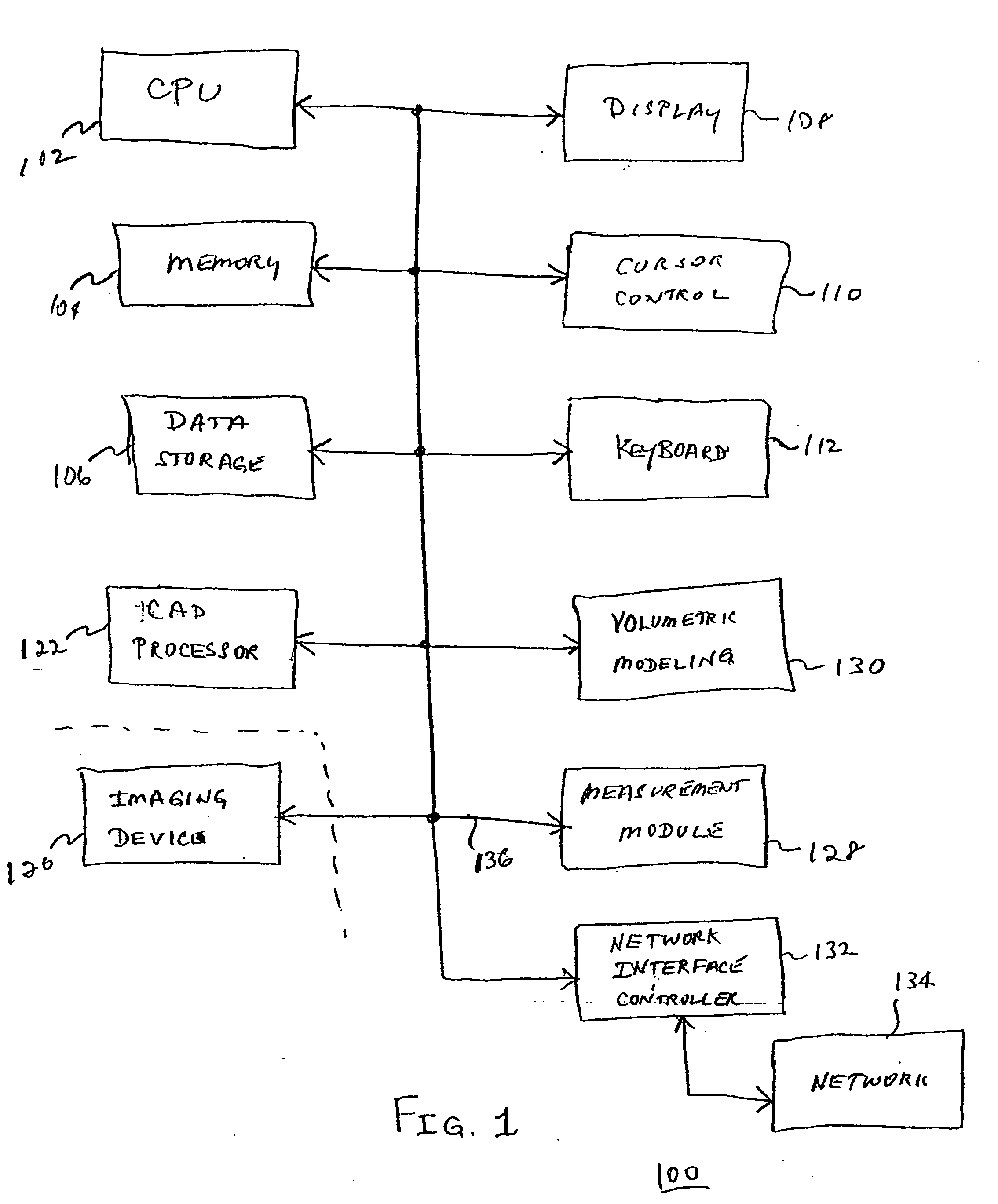
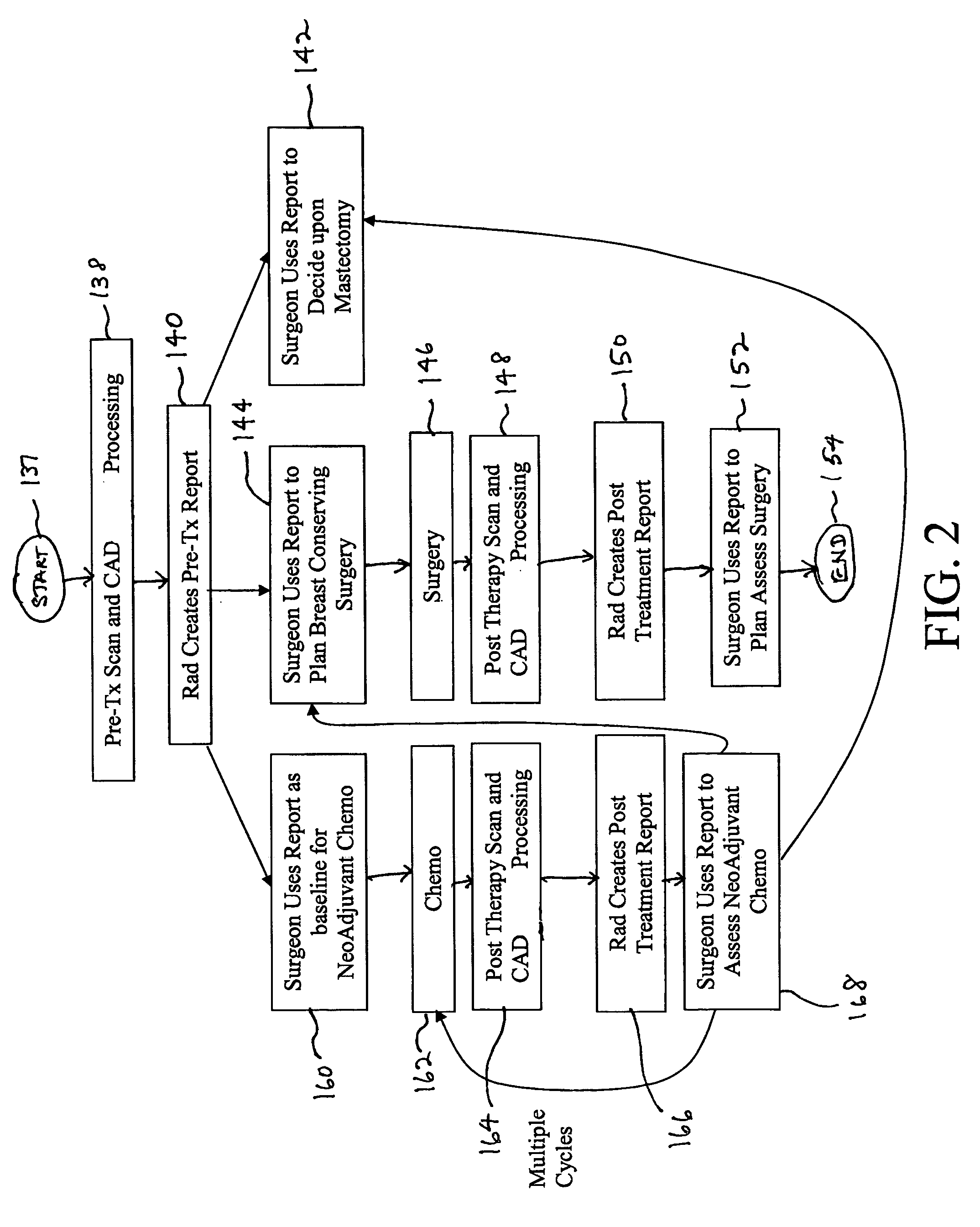
Apparatus and method for surgical planning and treatment monitoring
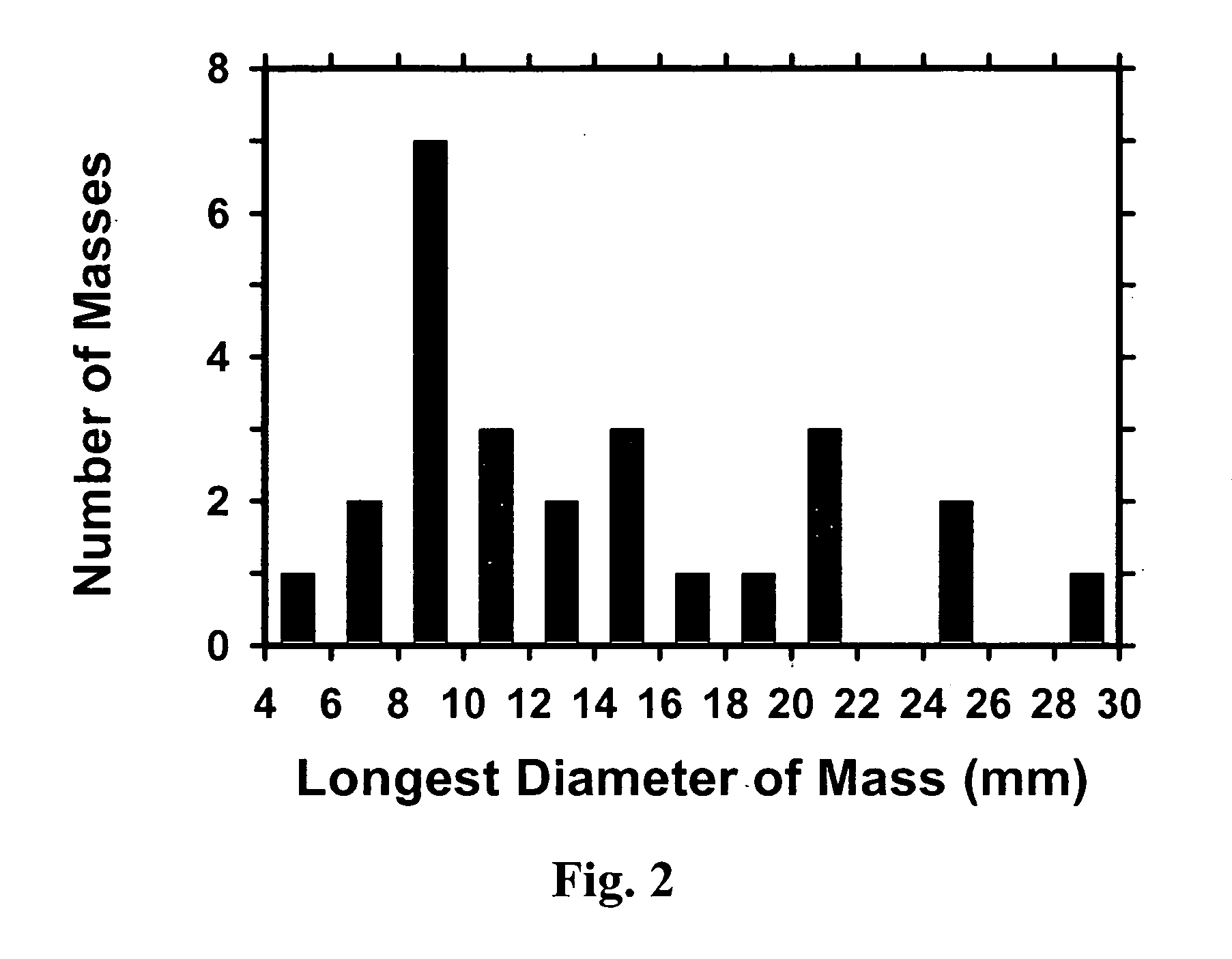
A system for surgical planning and therapeutic monitoring utilizes imaging data and computer-aided detection (CAD) technology to identify cancerous tumors. A pre-treatment report identifies all volumes of interest (VOIs) and provides data regarding the size and location of each VOI as well as volumetric data for use in surgical planning. The system can be used to monitor the progress of adjuvant chemotherapy or other non-surgical treatment and measures changes in tumor size and location. Post-treatment reports provide data regarding changes in tumor size and location as well as trend data to provide guidance to the physician.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP +1
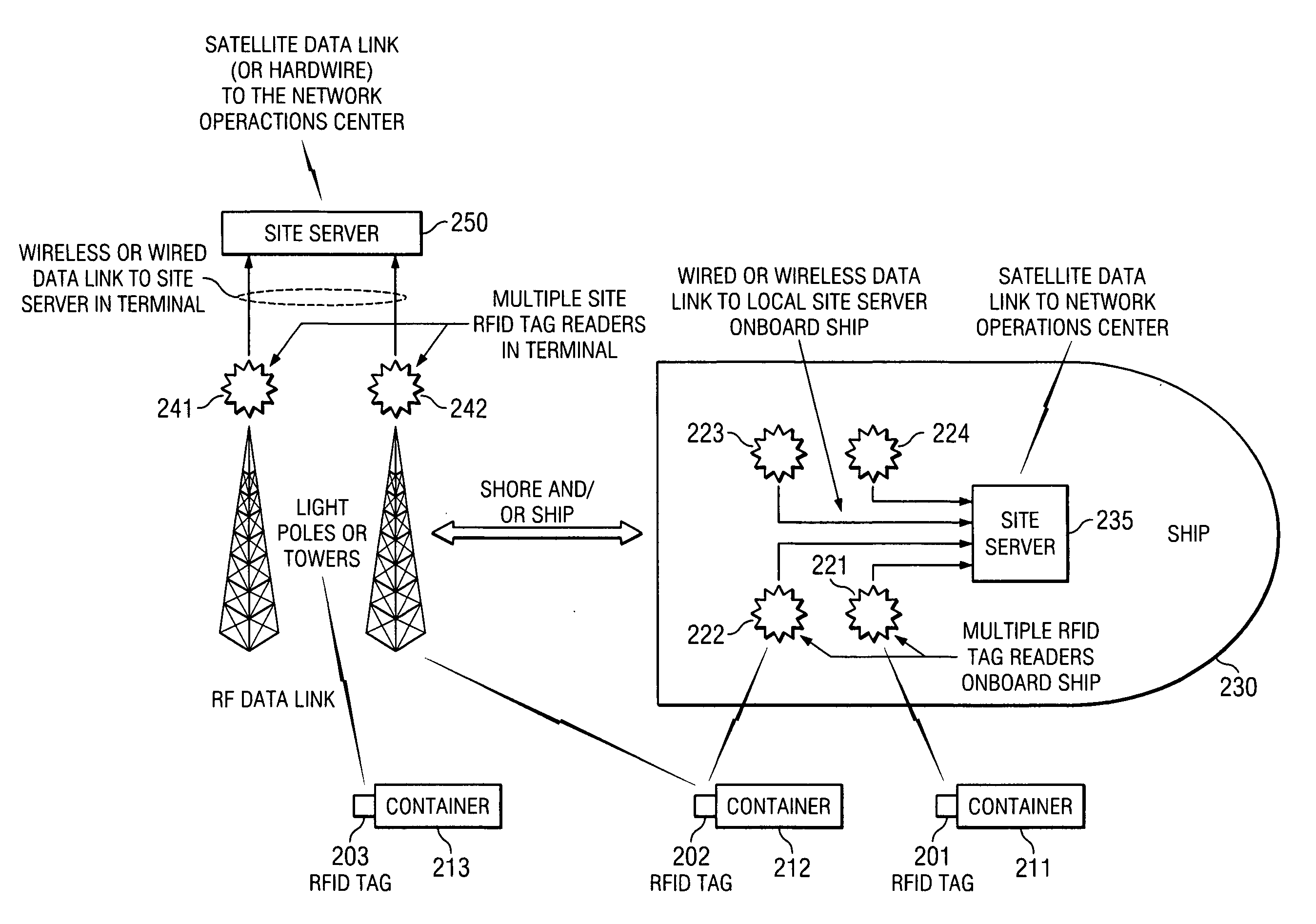
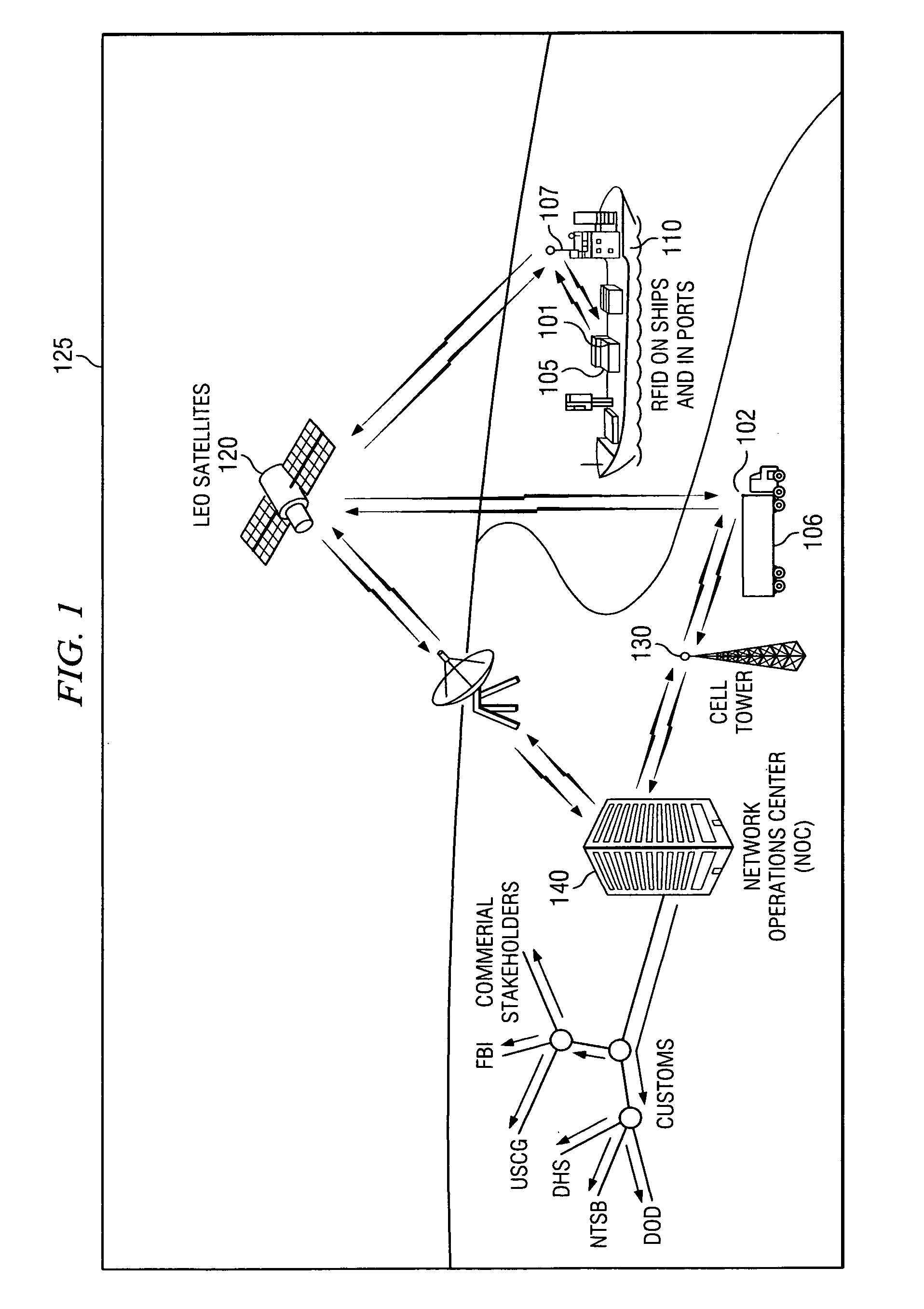
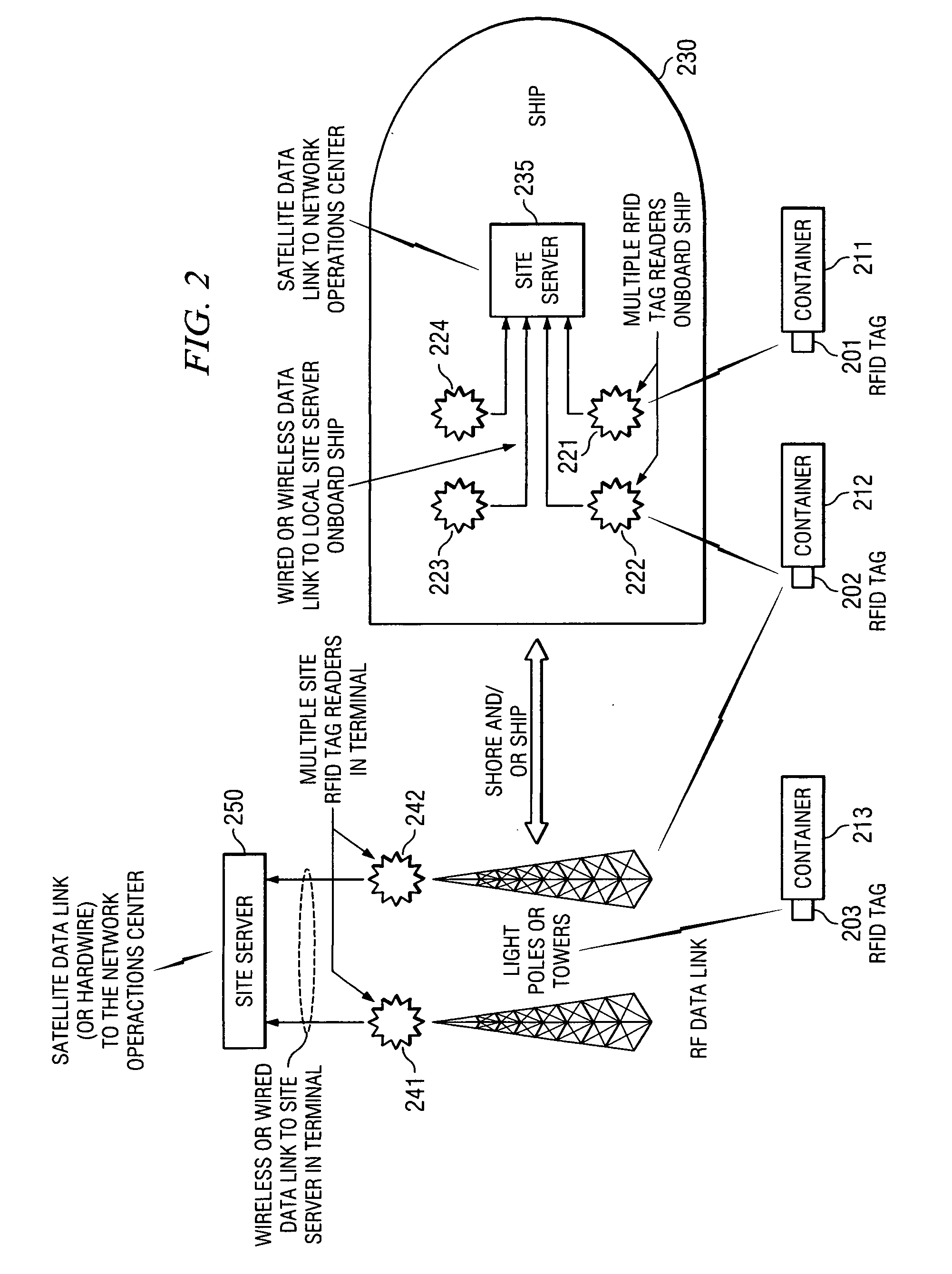
Space charge dosimeters for extremely low power measurements of radiation in shipping containers
InactiveUS20050248456A1Electric signal transmission systemsSolid-state devicesDosimeterRadiation sensor
Methods and apparatus are described for space charge dosimeters for extremely low power measurements of radiation in shipping containers. A method includes insitu polling a suite of passive integrating ionizing radiation sensors including reading-out dosimetric data from a first passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor and a second passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor, where the first passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor and the second passive integrating ionizing radiation sensor remain situated where the dosimetric data was integrated while reading-out. Another method includes arranging a plurality of ionizing radiation sensors in a spatially dispersed array; determining a relative position of each of the plurality of ionizing radiation sensors to define a volume of interest; collecting ionizing radiation data from at least a subset of the plurality of ionizing radiation sensors; and triggering an alarm condition when a dose level of an ionizing radiation source is calculated to exceed a threshold.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
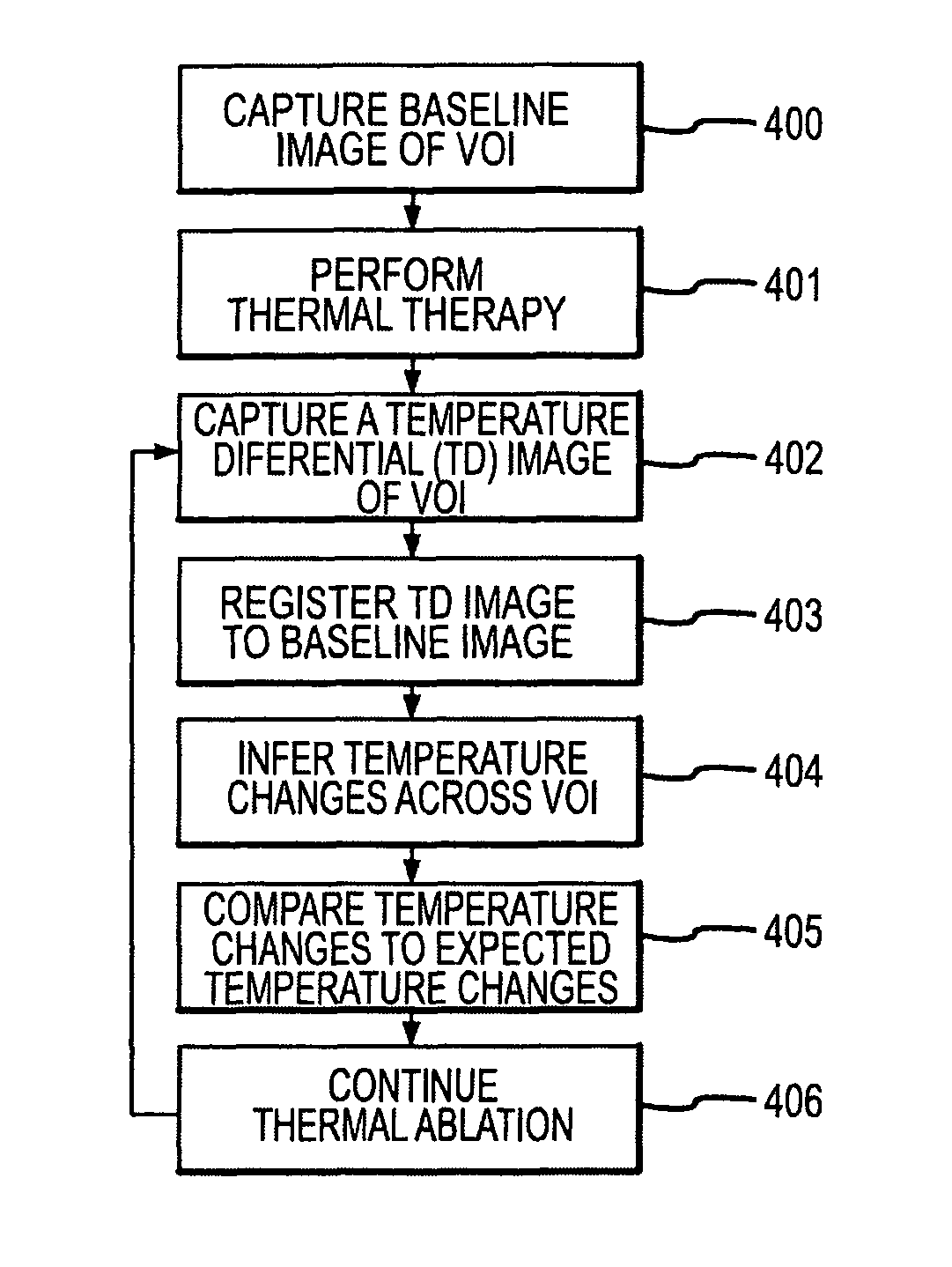
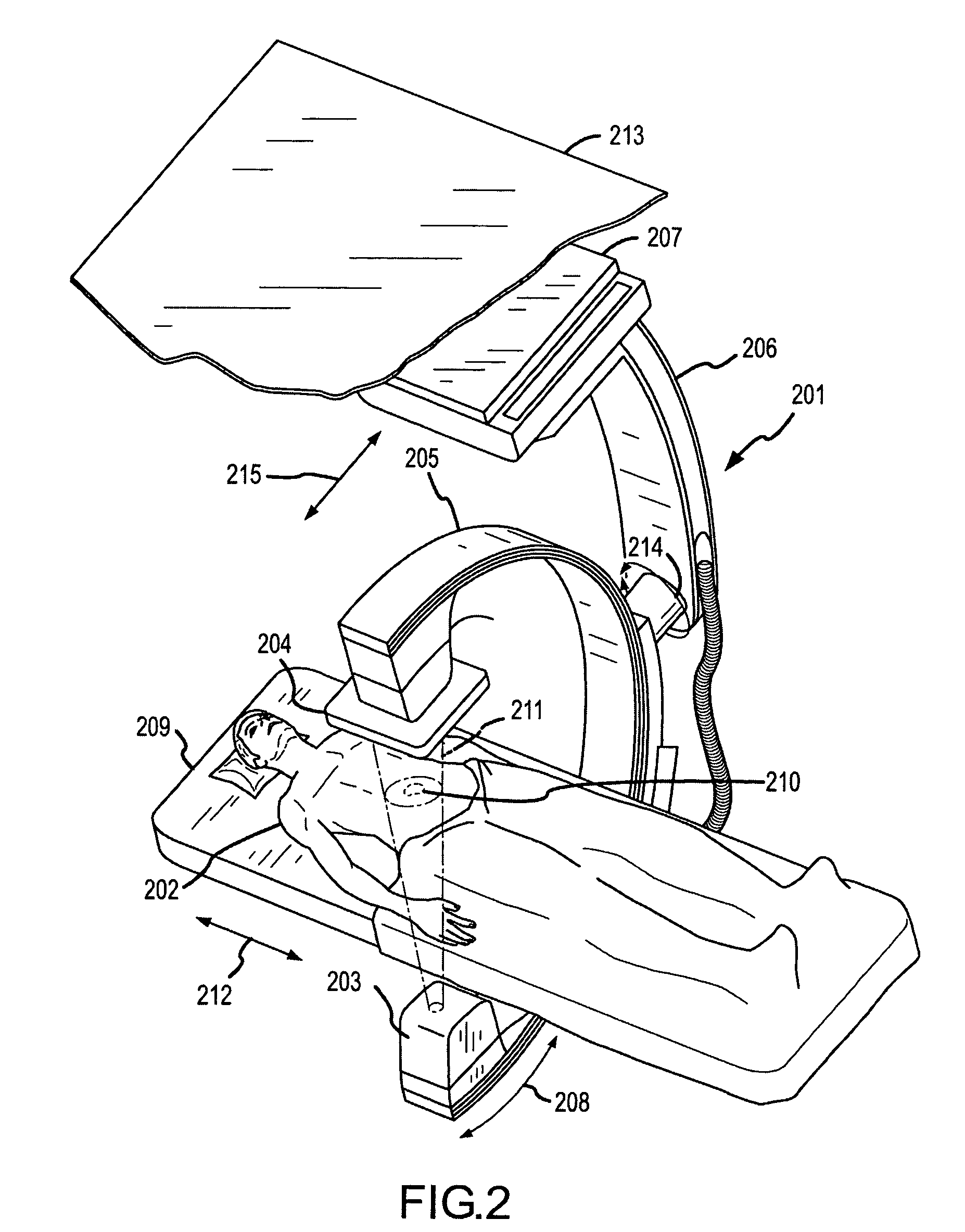
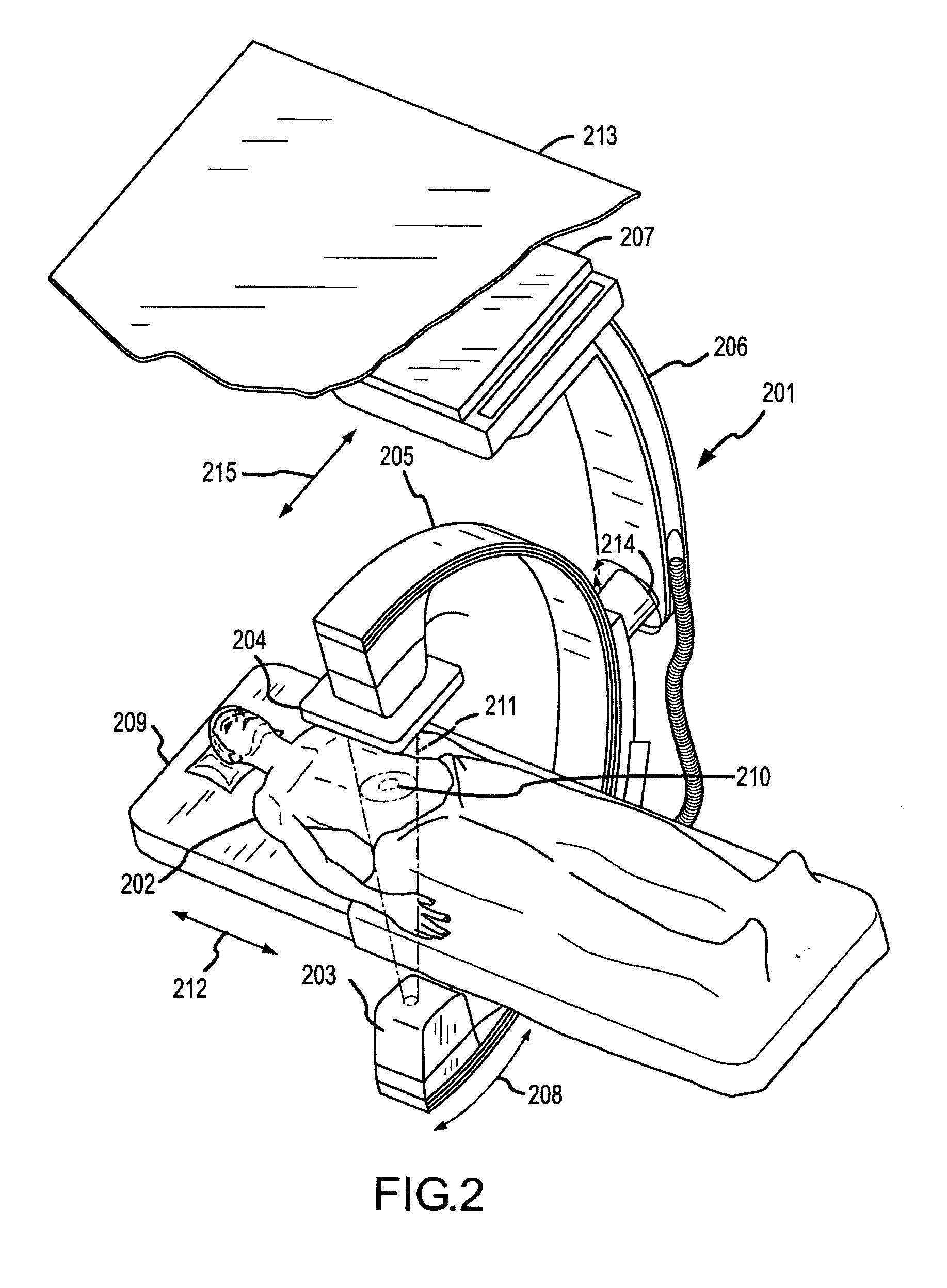
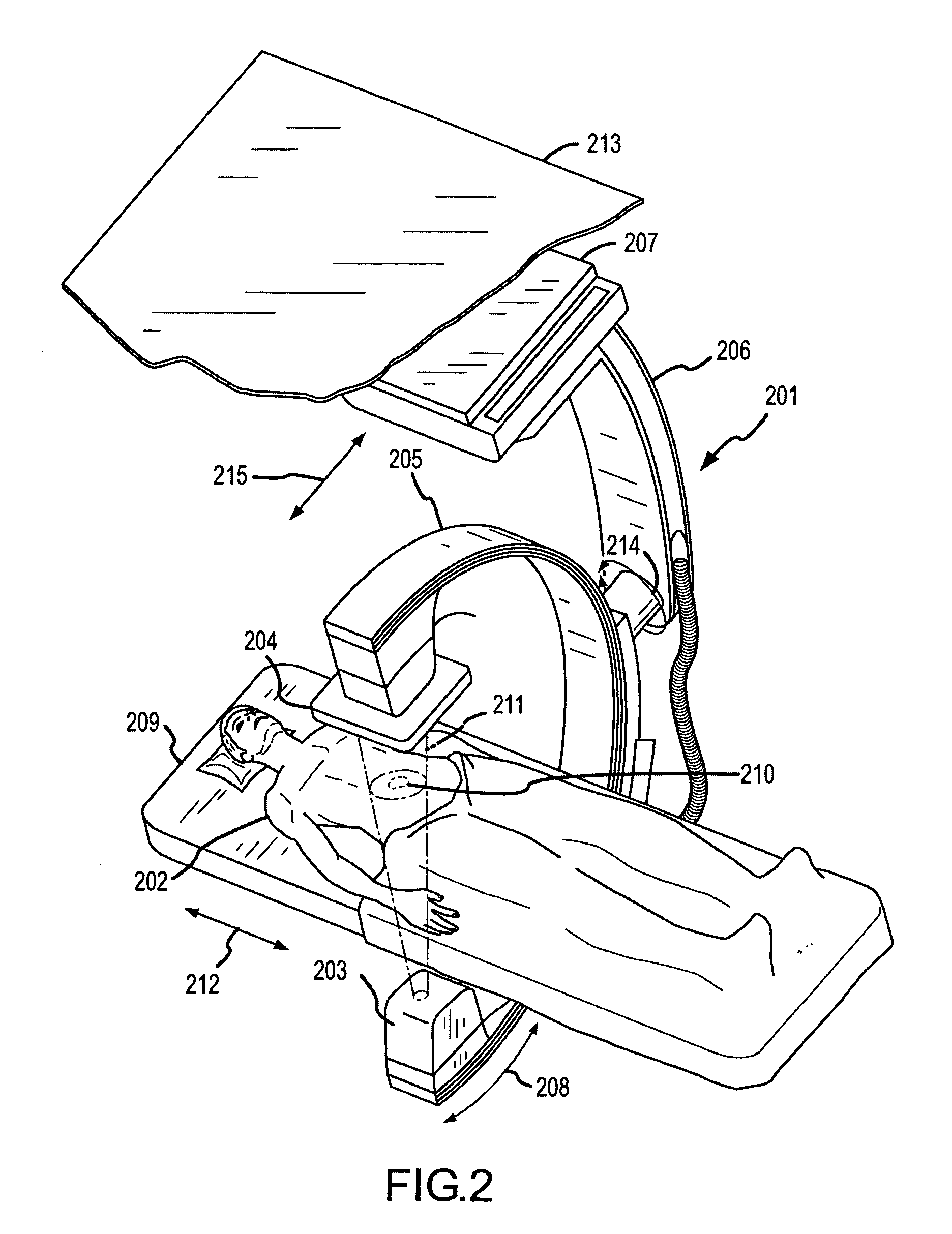
Methods for planning and performing thermal ablation
ActiveUS7871406B2Shorten the timeMovement is minimized and eliminatedUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingIntermediate imageRadiofrequency ablation
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC
High dynamic range & depth of field depth camera
ActiveUS20130201288A1Add depthImprove dynamic rangeElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteroscopic systemsObject motionFrame time
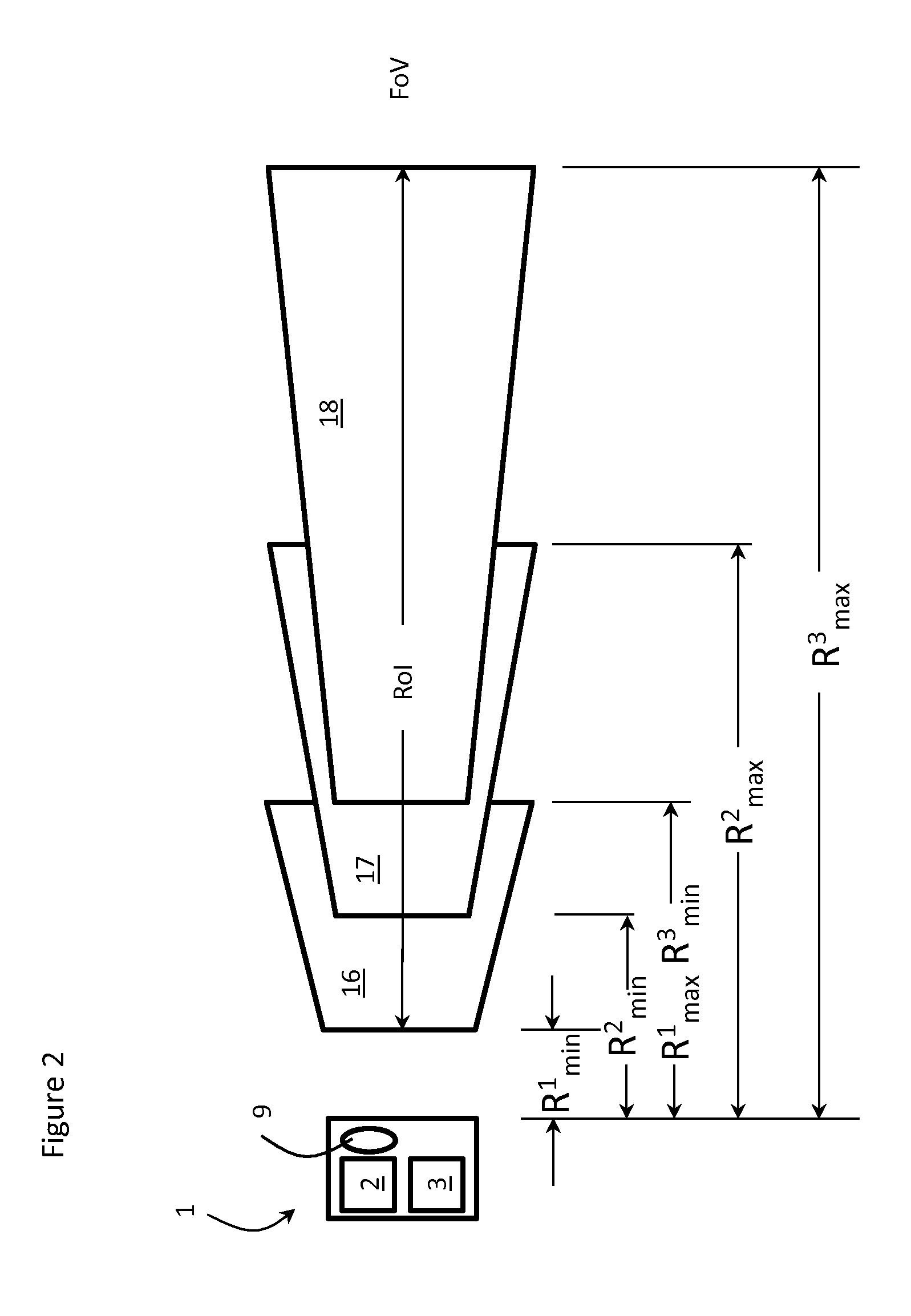
In order to maximize the dynamic range and depth of field for a depth camera used in a time of flight system, the light source is modulated at a plurality of different frequencies, a plurality of different peak optical powers, a plurality of integration subperiods, a plurality of lens foci, aperture and zoom settings during each camera frame time. The different sets of settings effectively create subrange volumes of interest within a larger aggregate volume of interest, each having their own frequency, peak optical power, lens aperture, lens zoom and lens focus products consistent with the distance, object reflectivity, object motion, field of view, etc. requirements of various ranging applications.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS20060177125A1Improve breast cancer detectionExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
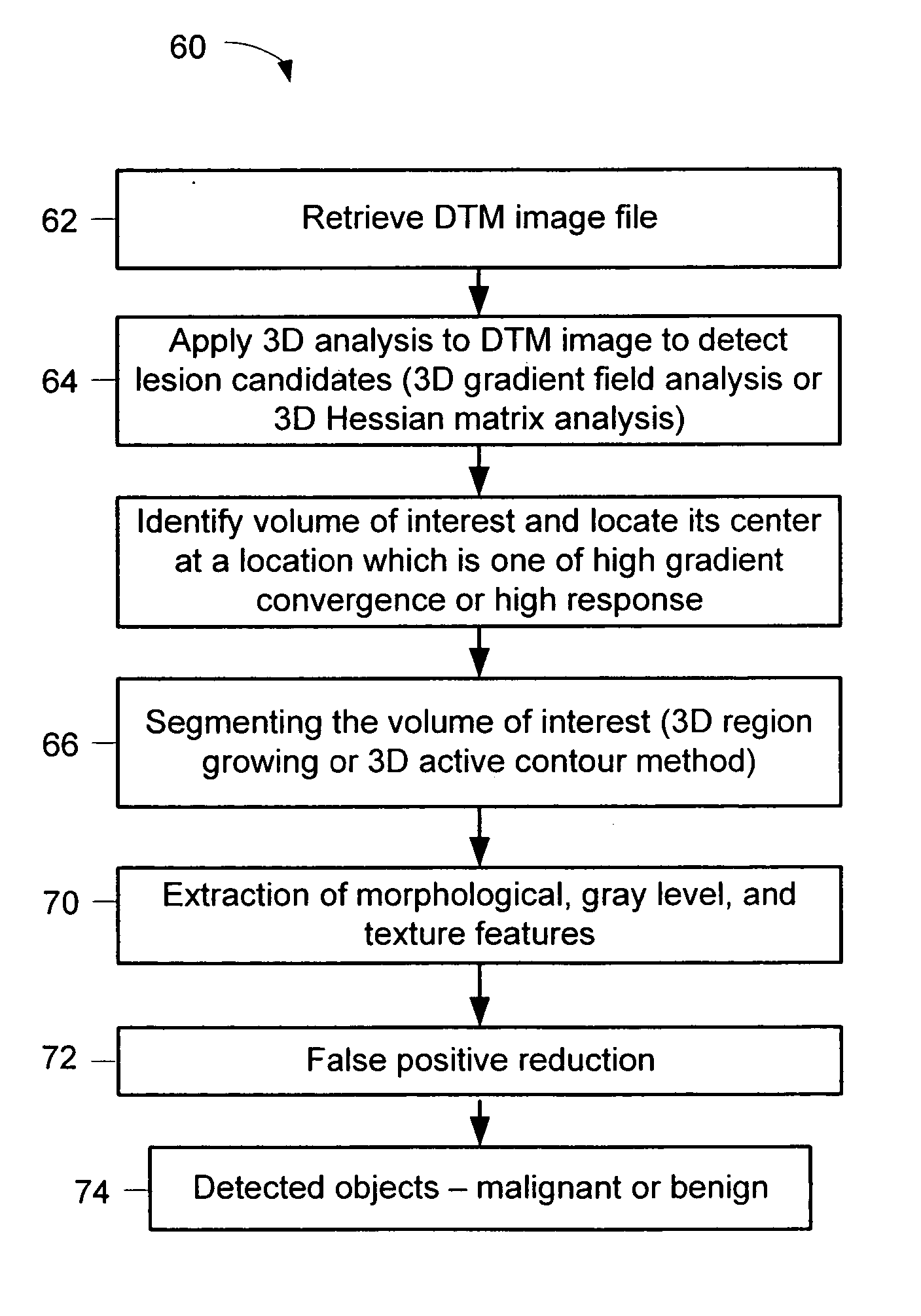
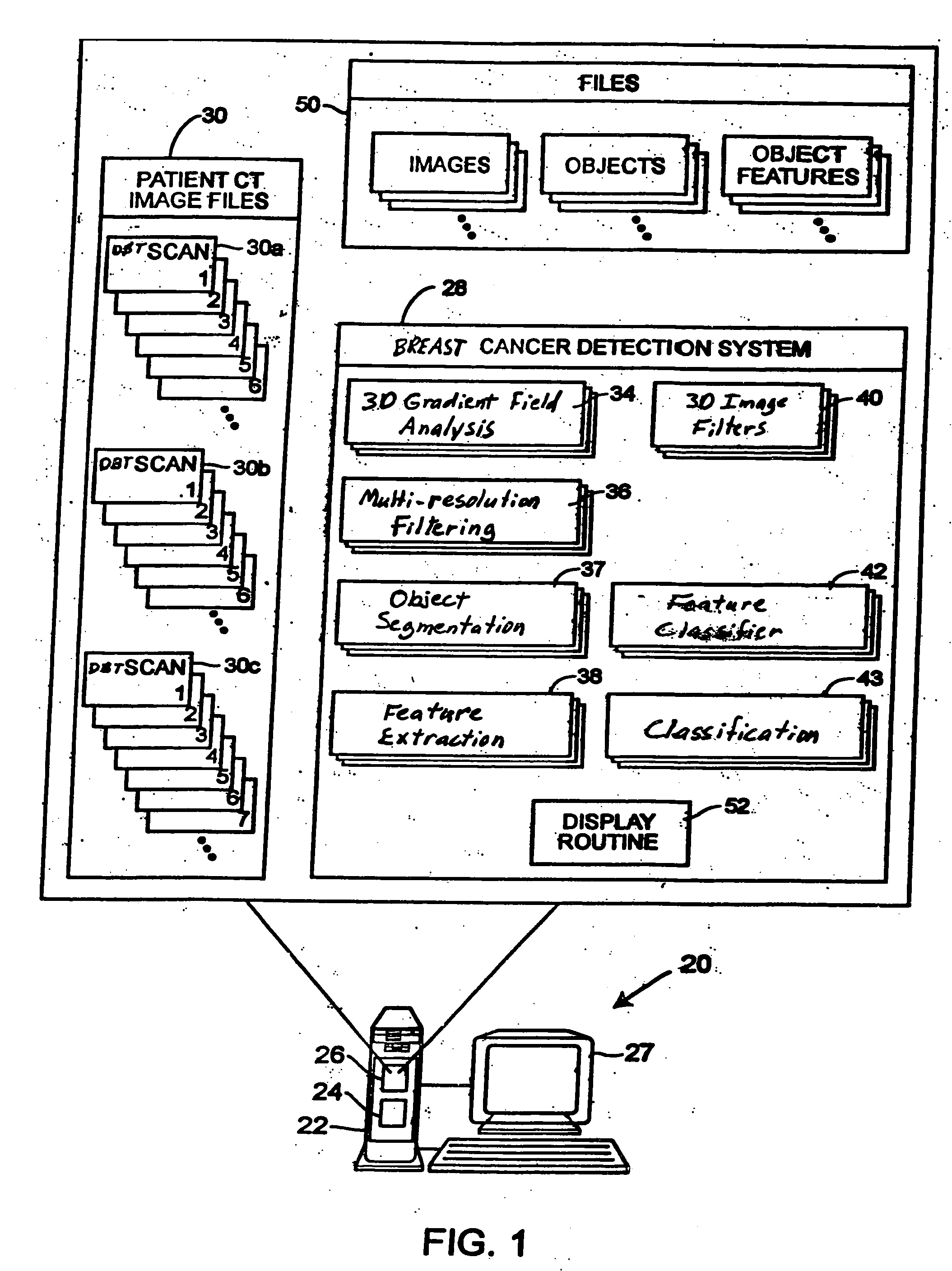
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
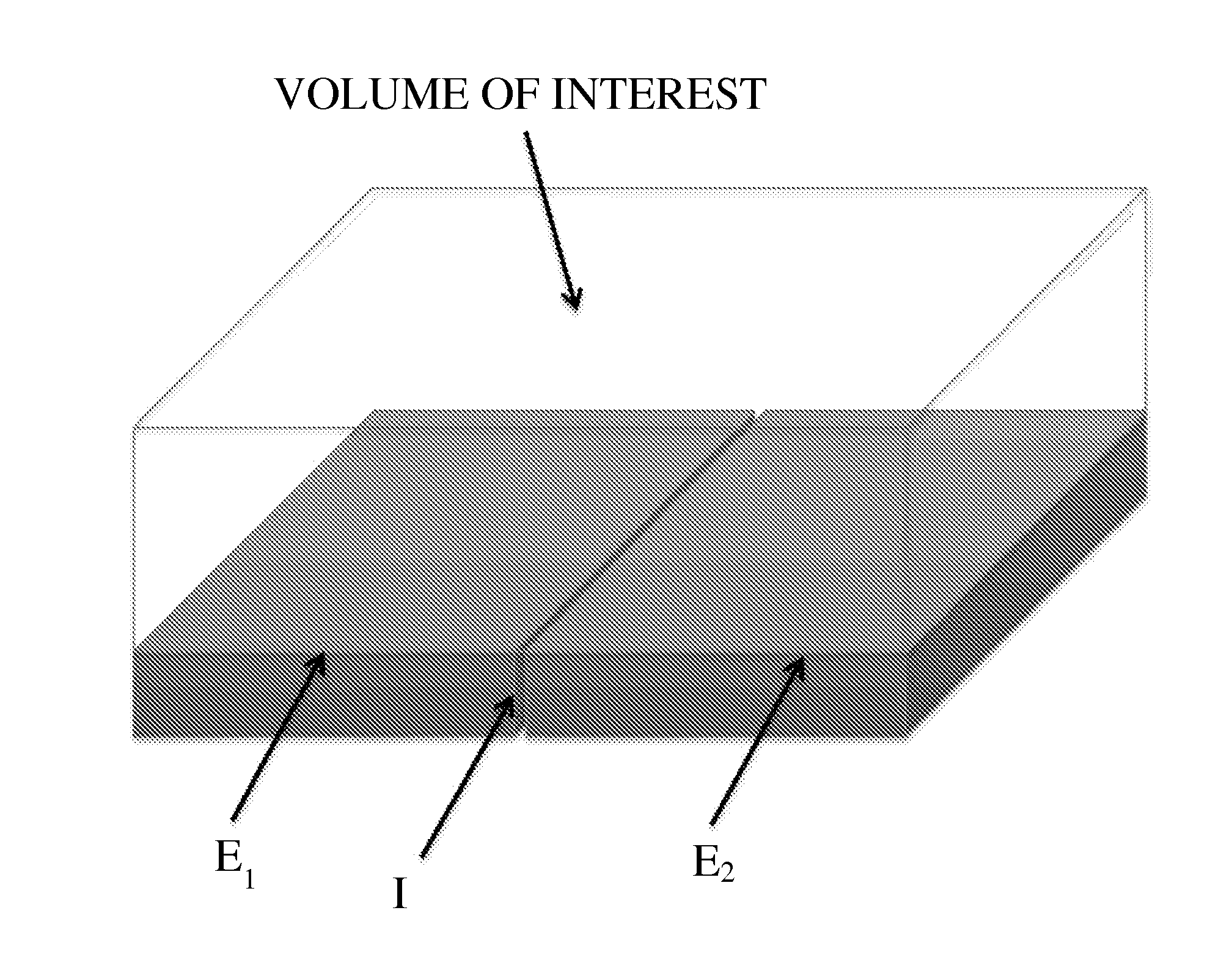
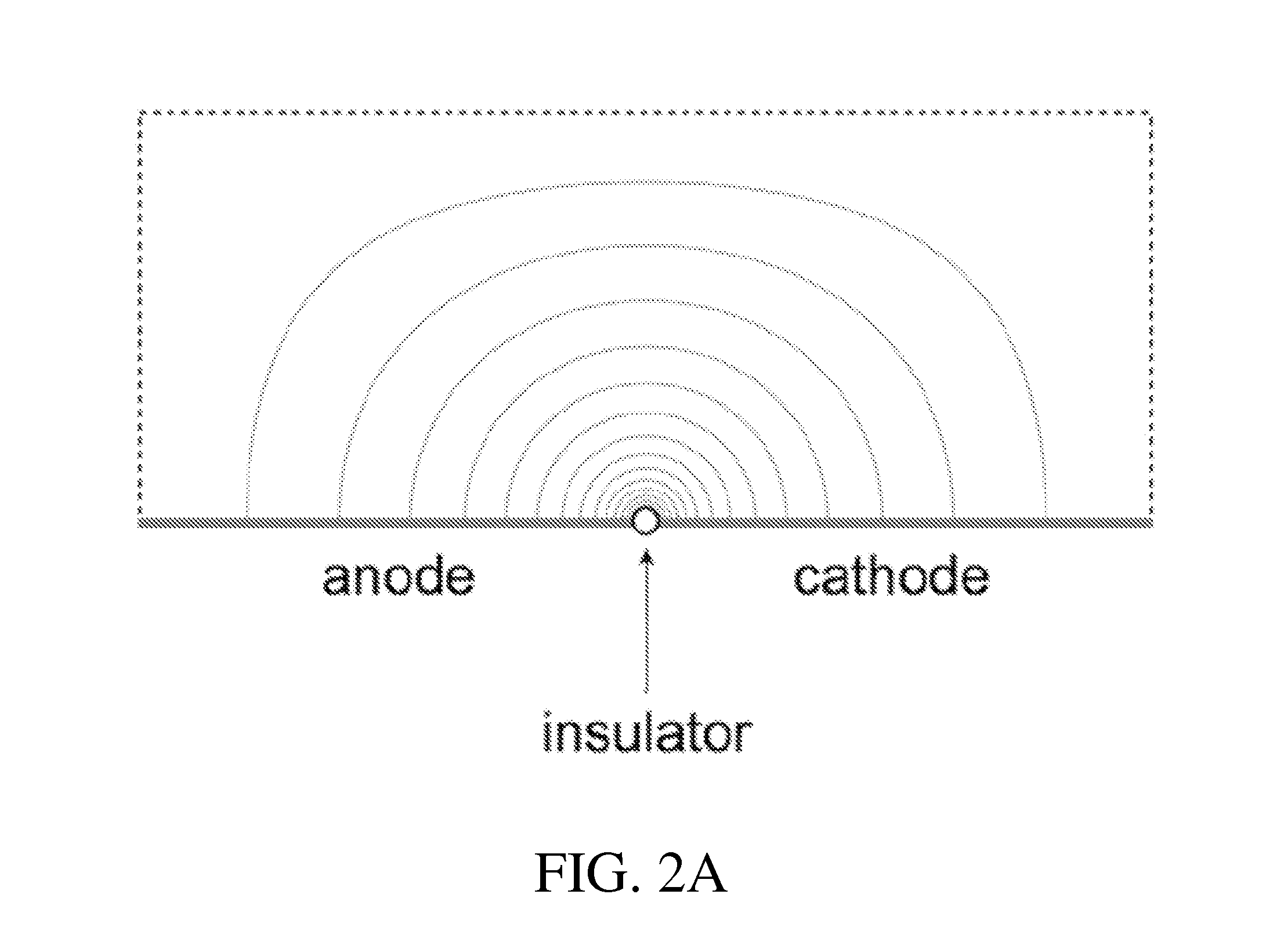
Electroporation electrode configuration and methods
InactiveUS20130196441A1High electric fieldReduce potential differenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLiquid separation by electricityPotential differenceElectroporation
Provided herein are the concept that “singularity-based configuration” electrodes design and method can produce in an ionic substance local high electric fields with low potential differences between electrodes. The singularity-based configuration described here includes: an anode electrode; a cathode electrode; and an insulator disposed between the anode electrode and the cathode electrode. The singularity-based electrode design concept refers to electrodes in which the anode and cathode are adjacent to each other, placed essentially co-planar and are separated by an insulator. The essentially co-planar anode / insulator / cathode configuration bound one surface of the volume of interest and produce desired electric fields locally, i.e., in the vicinity of the interface between the anode and cathode. In an ideal configuration, the interface dimension between the anode and the cathode tends to zero and becomes a point of singularity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus for planning and performing thermal ablation
InactiveUS20080033417A1Maintain positionShorten the timeUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsData setRadiofrequency ablation
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:ABLA TX +1
Object detection system
InactiveUS20070019181A1Wide field of viewHigh resolutionOptical rangefindersRoad vehicles traffic controlTriangulationHome robot
An object detection system utilizing one or more thin, planar structured light patterns projected into a volume of interest, along with digital processing hardware and one or more electronic imagers looking into the volume of interest. Triangulation is used to determine the intersection of the structured light pattern with objects in the volume of interest. Applications include navigation and obstacle avoidance systems for autonomous vehicles (including agricultural vehicles and domestic robots), security systems, and pet training systems.
Owner:SINCLAIR KENNETHH +2
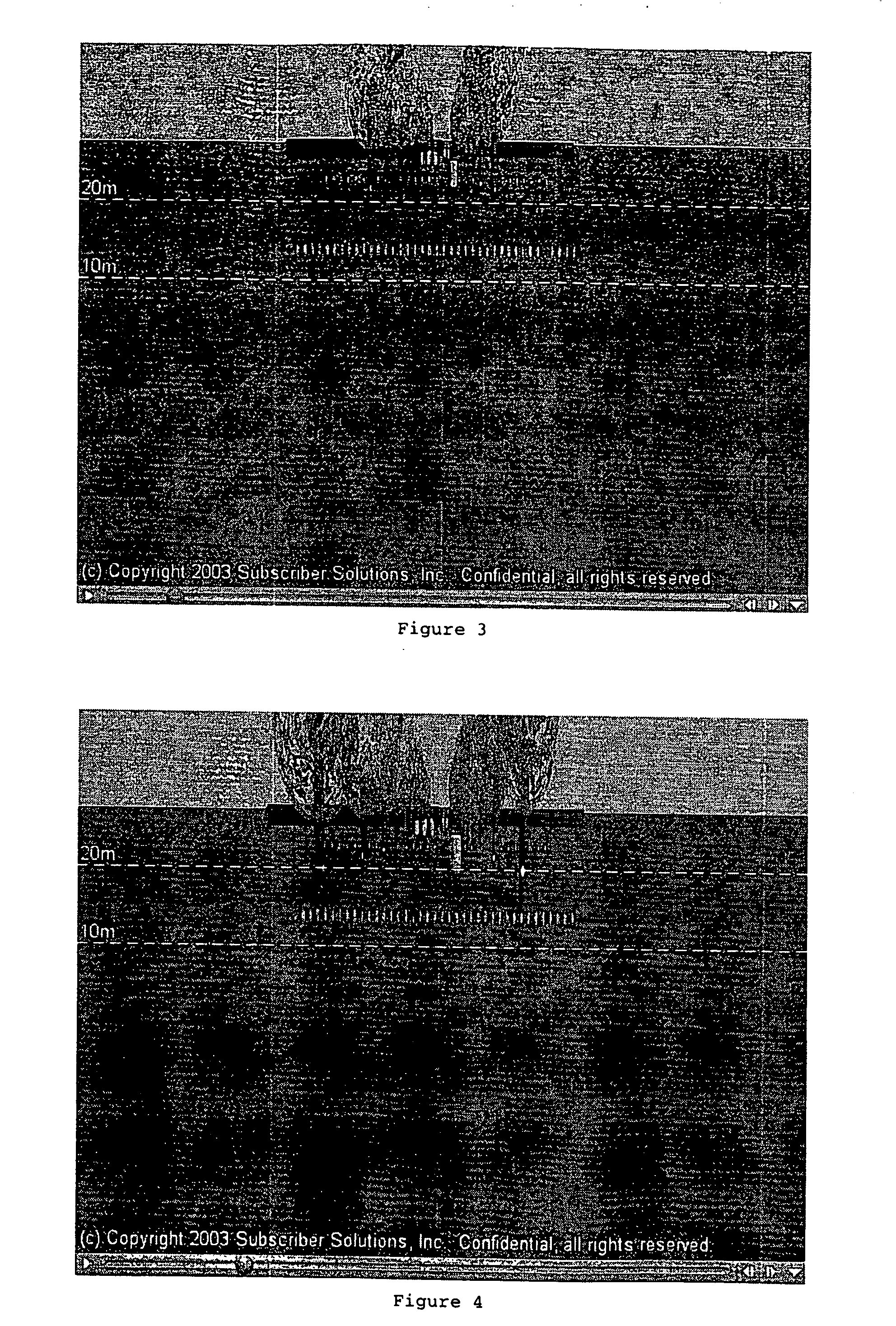
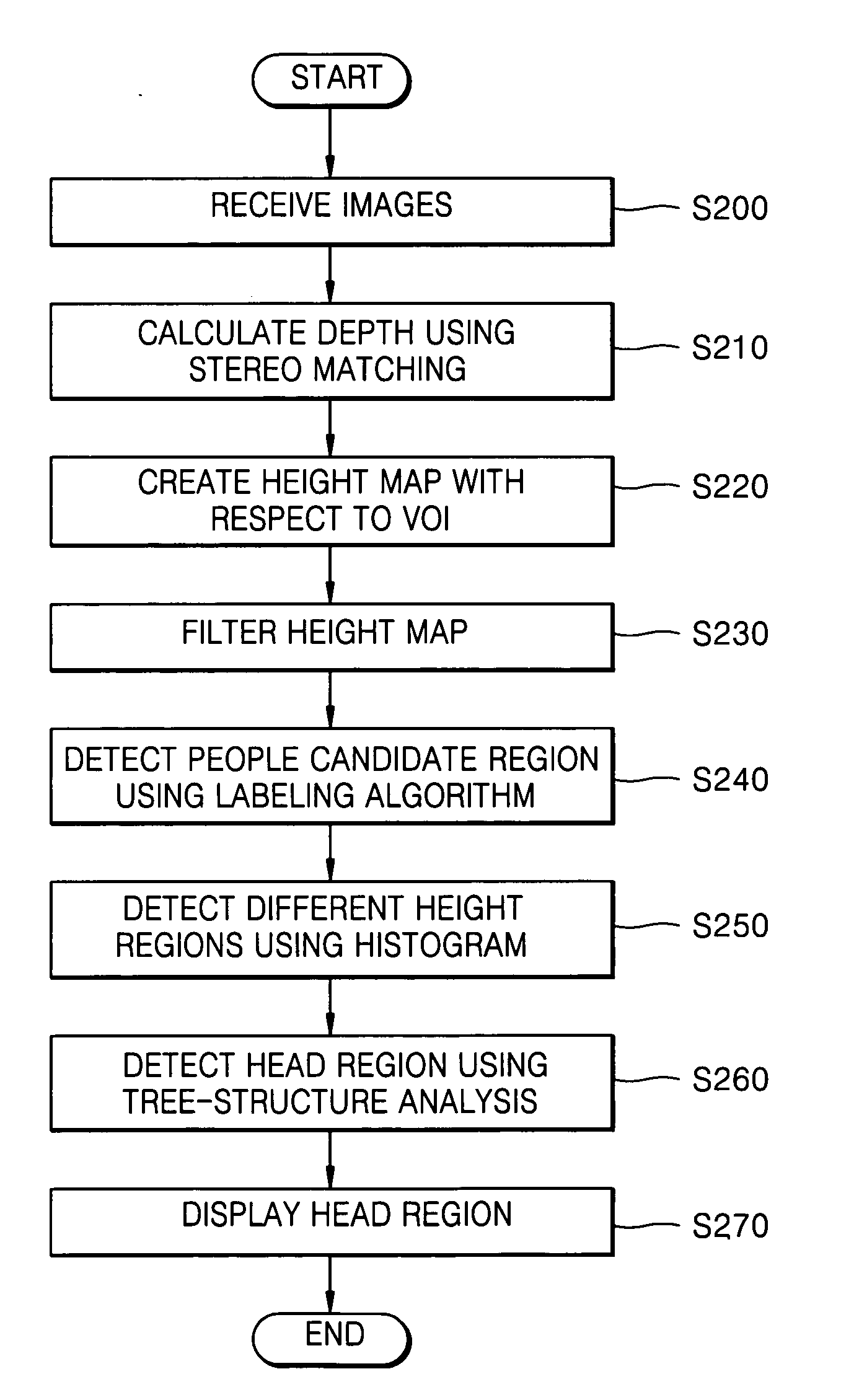
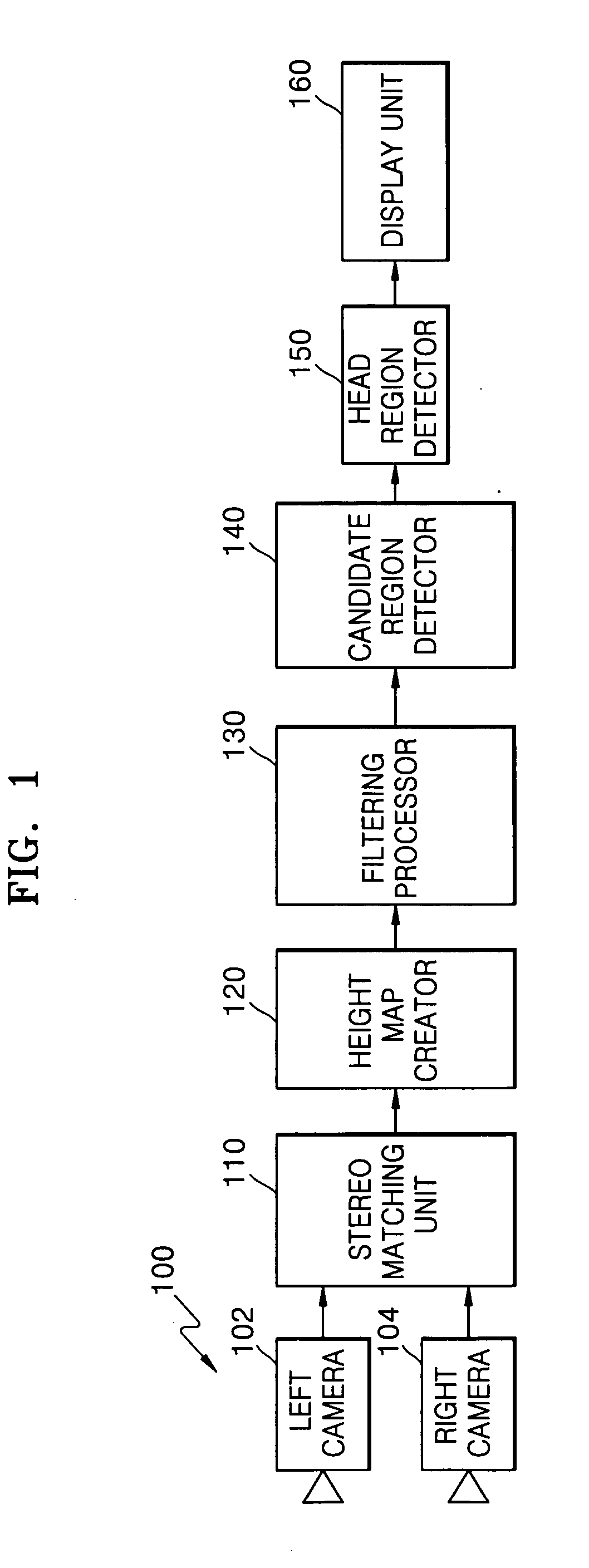
Method and apparatus for detecting people using stereo camera
InactiveUS20050201612A1Accurate detectionWide viewing angleFish sortingCharacter and pattern recognitionHeight mapStereo matching
A method of and apparatus for detecting people using a stereo camera. The method includes: calculating three-dimensional information regarding a moving object from a pair of image signals received from the stereo camera using stereo matching and creating a height map for a specified discrete volume of interest (VOI) using the three-dimensional information; detecting a people candidate region estimated as including one or more persons by finding connected components from the height map using a predetermined algorithm; and generating a histogram with respect to the people candidate region, detecting different height regions using the histogram, and detecting a head region by analyzing the different height regions using a tree structure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for planning, performing and monitoring thermal ablation
InactiveUS20080033419A1Shorten the timeMovement is minimized and eliminatedUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsRadiofrequency ablationData set
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC +1
Multi-sensor distortion mapping method and system
ActiveUS20080079421A1Surgical navigation systemsUsing electrical meansSensor arrayElectromagnetic field
In one aspect of the present technique, an array of electromagnetic sensors is positioned within a volume of interest. In the presence of an electromagnetic field, the array of electromagnetic sensors is sampled to acquire signals representative of the location of the electromagnetic sensors in the array. The electromagnetic field distortion within the volume of interest is determined based on the acquired signals. In another aspect of the present technique, a system for detecting electromagnetic field distortions includes an electromagnetic sensor assembly for positioning within a volume of interest, a plurality of electromagnetic sensors for transmitting or receiving signals representative of the location of the electromagnetic sensors on the sensor assembly; and a tracker. In another aspect of the present technique, an electromagnetic sensor assembly for detecting electromagnetic field distortion includes a body, and an array of electromagnetic sensors positioned on the body.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
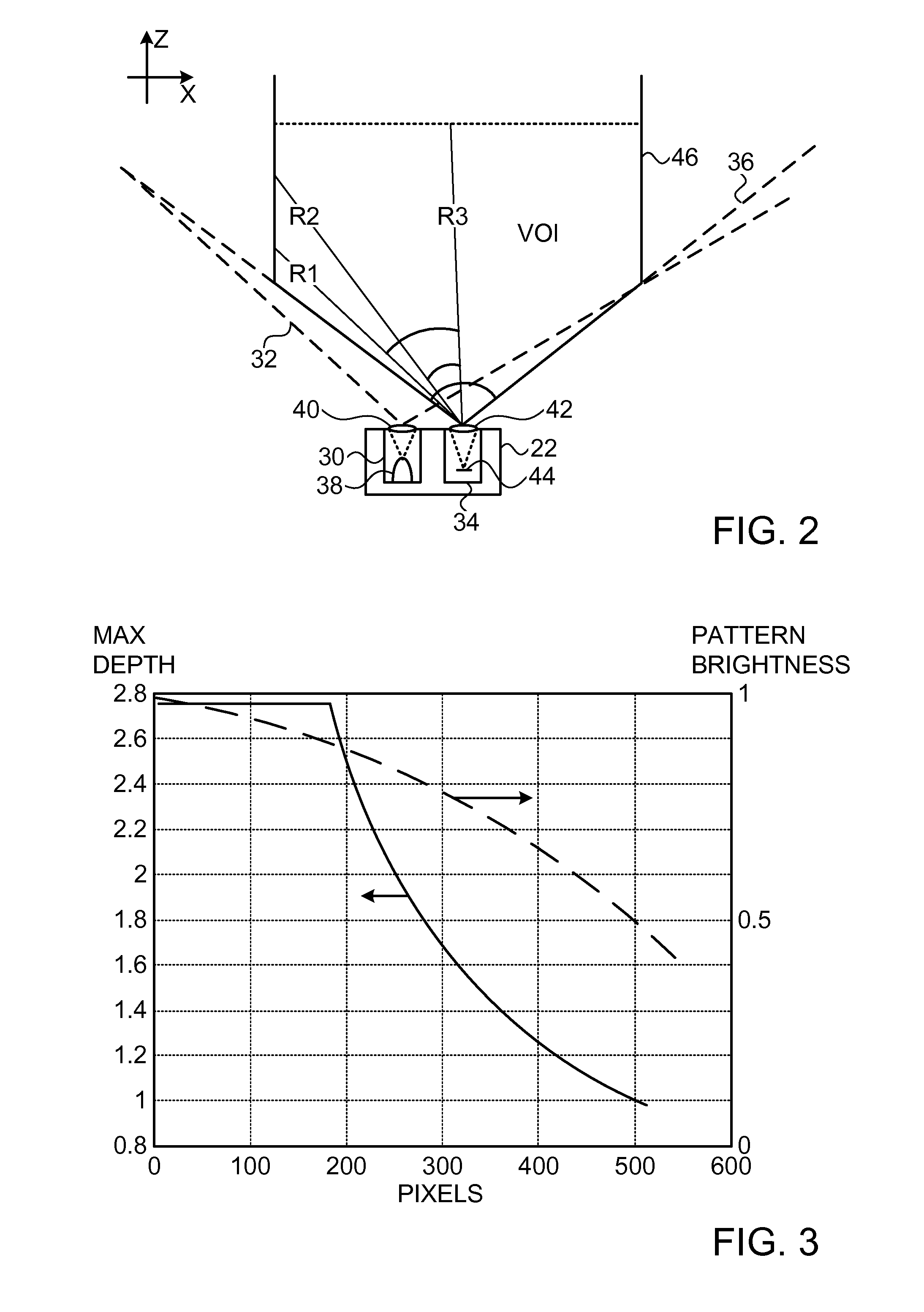
Non-Uniform Spatial Resource Allocation for Depth Mapping
ActiveUS20110211044A1Limited resourceImprove system performanceImage enhancementImage analysisOptical radiationDepth mapping
A method for depth mapping includes providing depth mapping resources including an illumination module, which is configured to project patterned optical radiation into a volume of interest containing the object, and an image capture module, which is configured to capture an image of the pattern reflected from the object. A depth map of the object is generated using the resources while applying at least one of the resources non-uniformly over the volume of interest.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for displaying tomosynthesis images
ActiveUS20090034684A1Character and pattern recognitionX-ray apparatusTomosynthesisComputer graphics (images)
An embodiment of a method for displaying a volume obtained by tomosynthesis includes displaying a two-dimensional image. It further includes receiving user input that defines on the displayed image at least one volume of interest associated with a two-dimensional region of interest located in a plane of the image. The method further includes displaying in the region of interest, according to a practitioner's wishes: (a) images of slices of the volume of interest; (b) three-dimensional images of the volume of interest; and / or (c) slabs obtained from the volume of interest.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multi-sensor distortion detection method and system
InactiveUS20080183064A1Electric/magnetic position measurementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringFixed position
A method for detecting EM field distorting includes sampling a sensor assembly positioned within a volume of interest to acquire measurements of EM fields within the volume of interest, and monitoring the measurements to detect EM field distortion within the volume of interest. The sensor assembly includes a set of EM transmitters and a set of EM receivers fixed thereon. A system for detecting EM field distorting includes a sensor assembly for positioning within a volume of interest, wherein the EM sensor assembly comprises a set of EM receivers, and a set of EM transmitters, wherein the EM receivers and the EM transmitters are disposed at fixed locations on the sensor assembly. The system further includes a tracker configured to sample the sensor assembly to acquire measurements of EM fields generated by the EM transmitters, and monitor the measurements to detect EM field distortion within the volume of interest.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
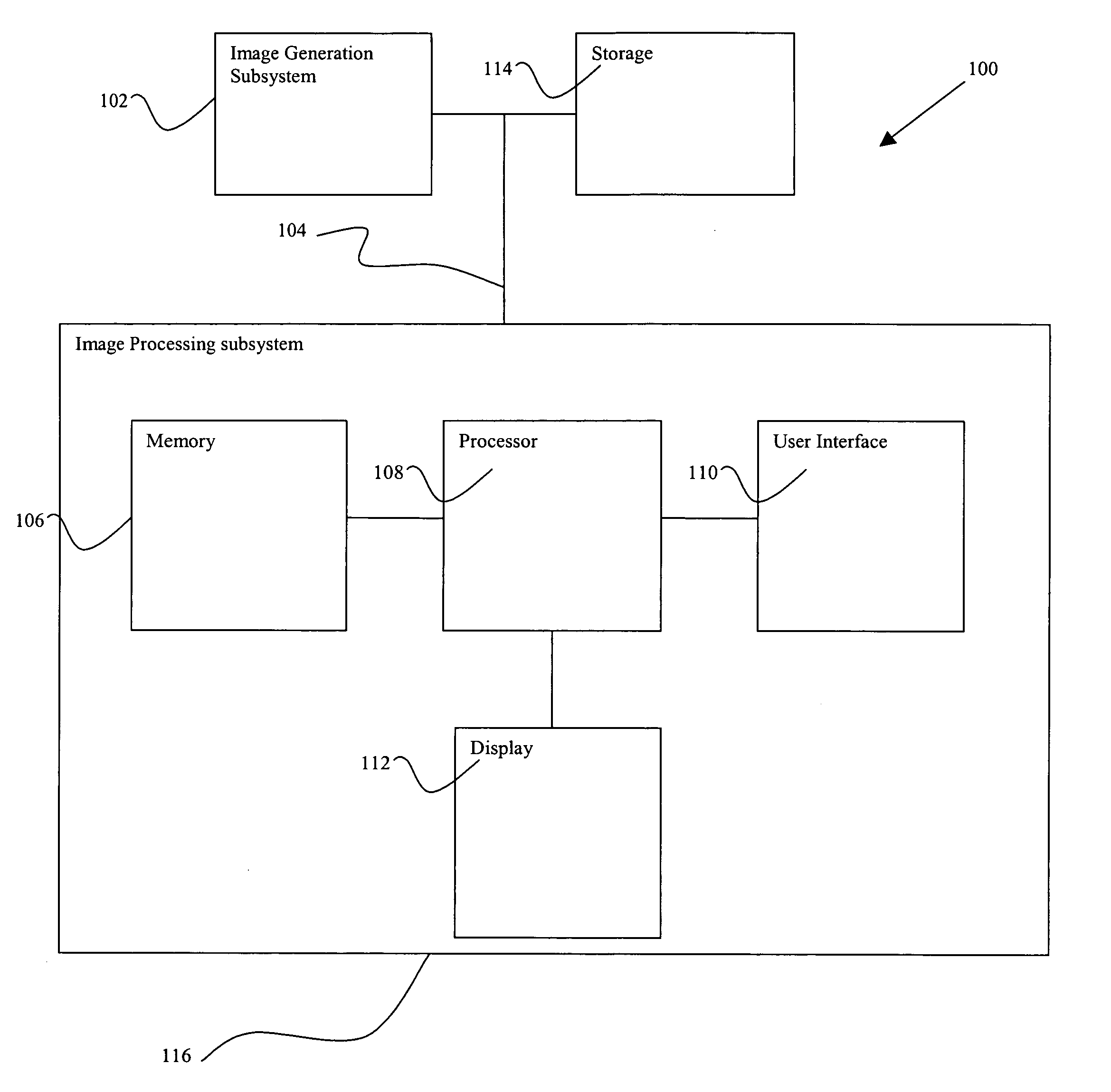
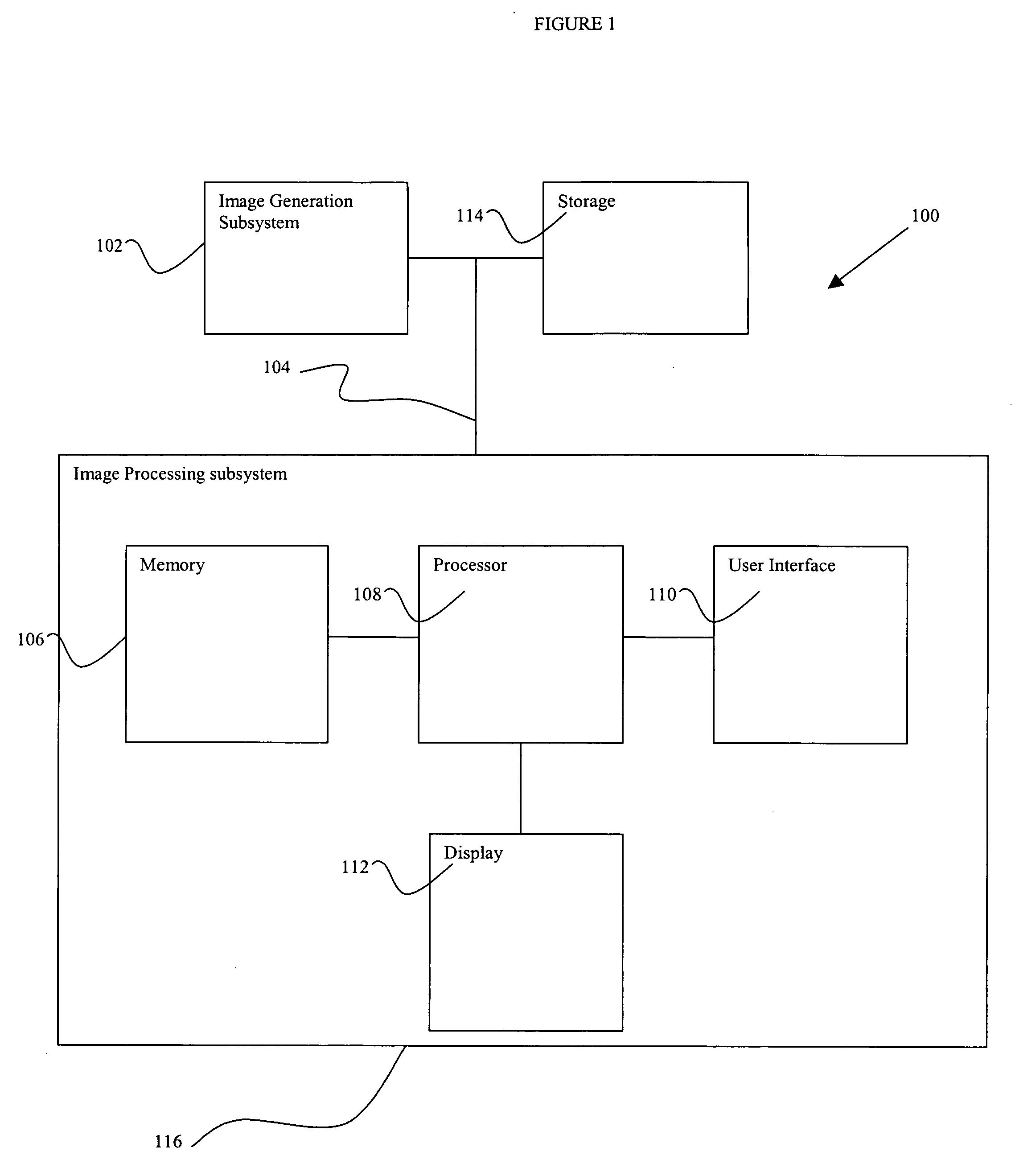
System and method for improved multiple-dimension image displays
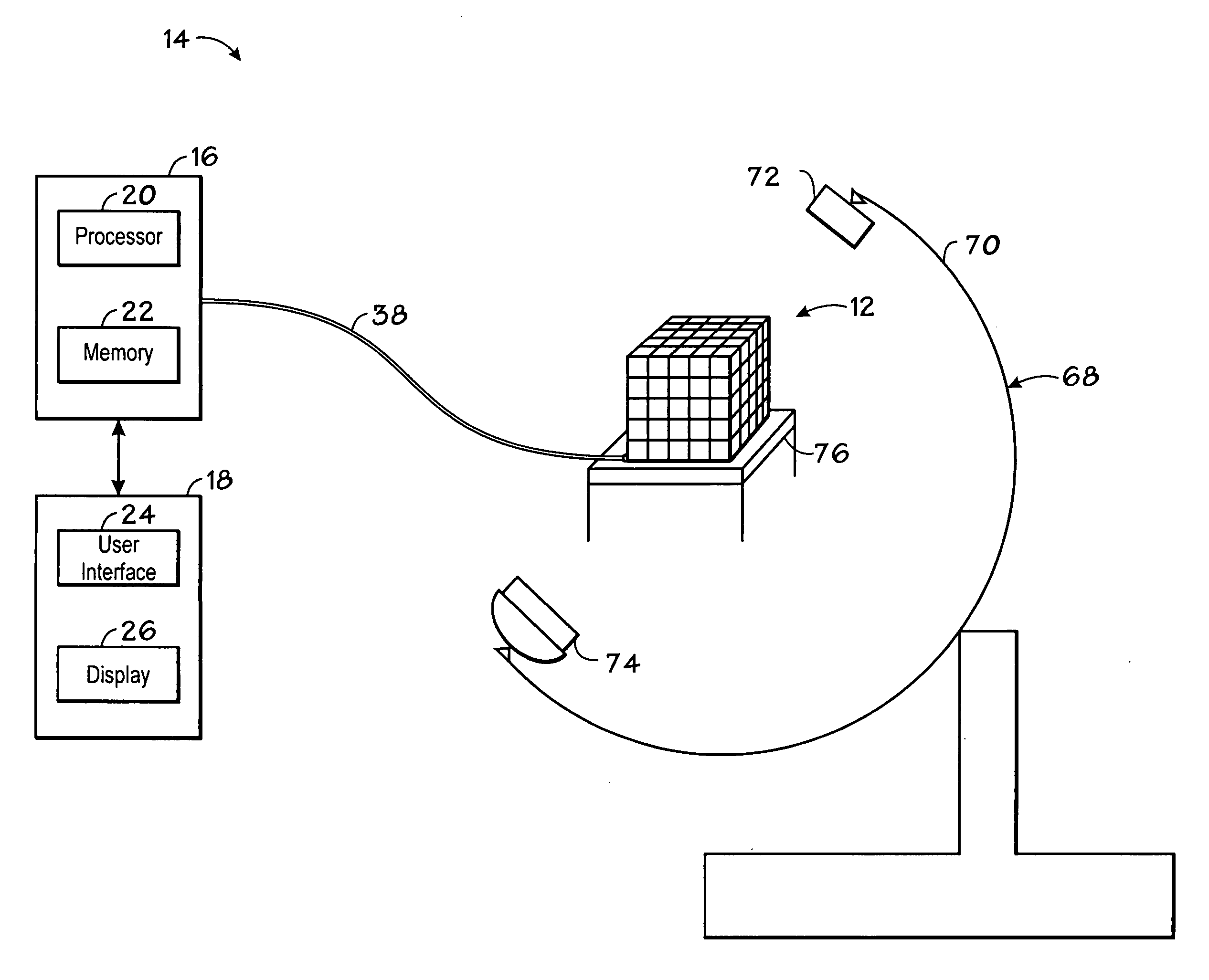
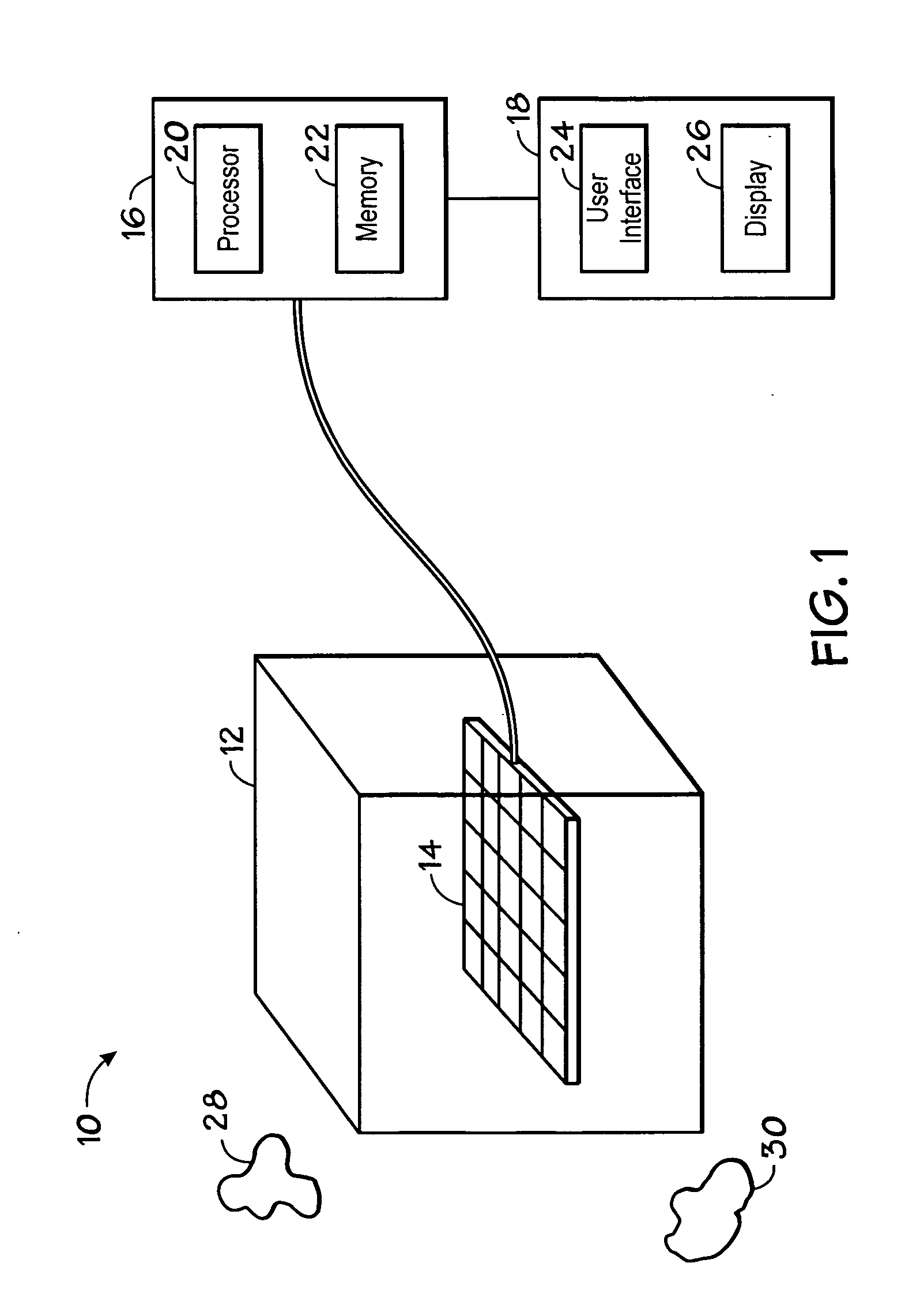
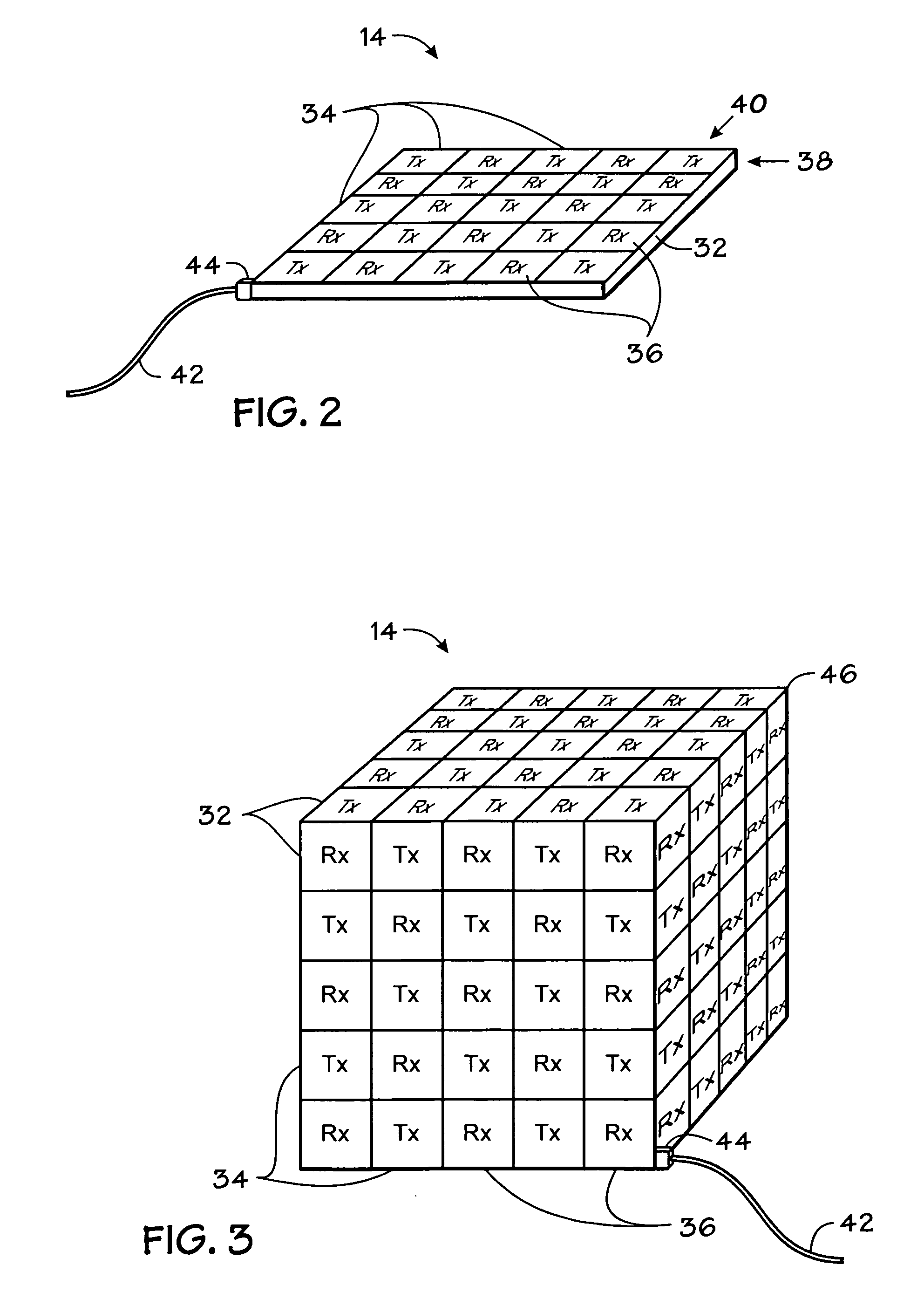
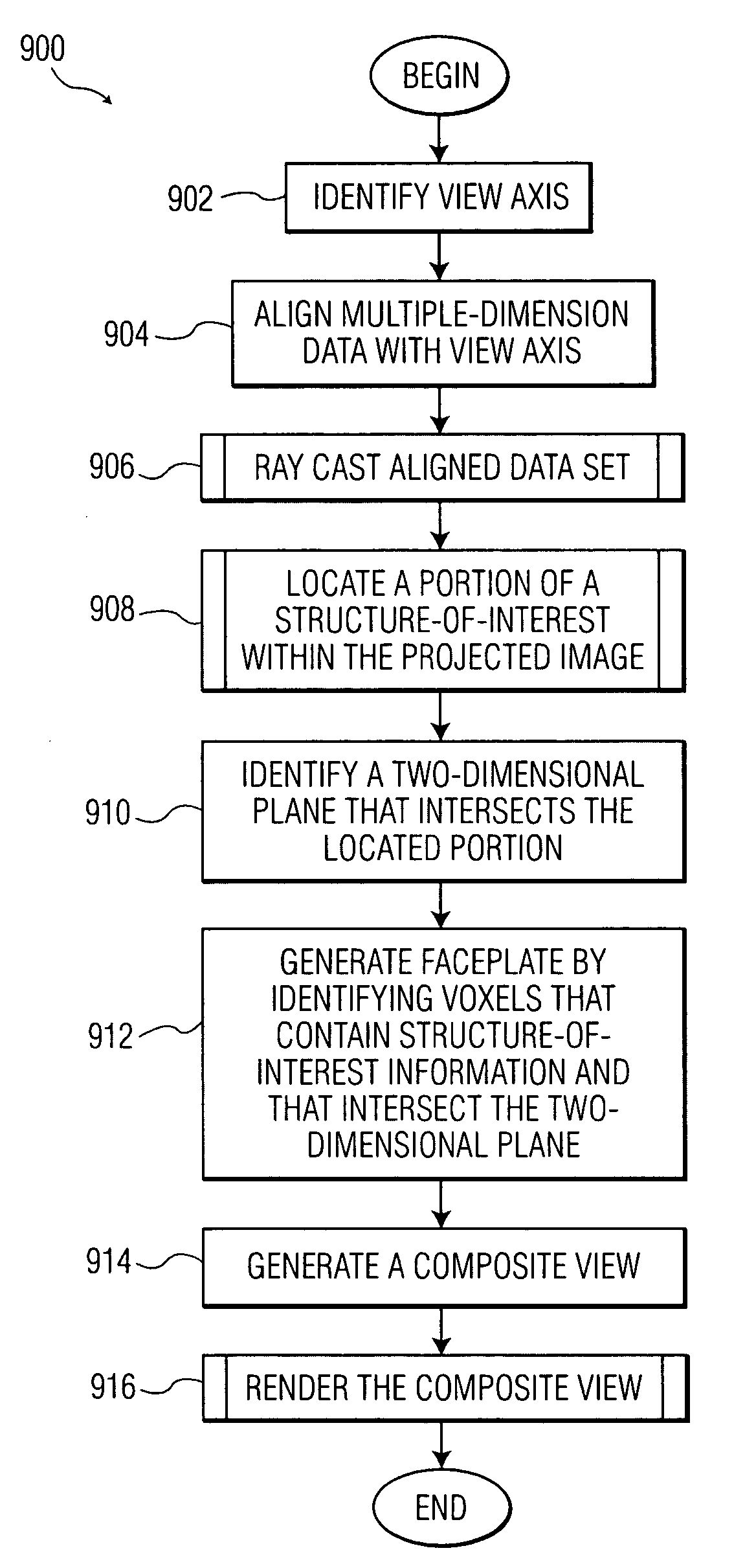
ActiveUS7356178B2Character and pattern recognition3D-image renderingData setComputer graphics (images)
An improved imaging system includes a memory-storage unit, a multiple-dimensional image processor configured to convert information within a multiple-dimensional data set to a two-dimensional representation in a plane orthogonal to an operator-identified view axis, and an image-rendering device configured to display the two-dimensional representation of a volume-of-interest contained within the three-dimensional data set, wherein the two-dimensional representation is responsive to pixel values associated with a faceplate orthogonal to the view axis. A method for viewing information includes identifying a view axis that intersects a multiple-dimensional data set, modifying the multiple-dimensional data set to align the multiple-dimension data set responsive to the view axis, locating a portion of a structure-of-interest along a vector parallel to view axis, associating a set of pixels with a faceplate, and generating a composite view in accordance with the faceplate.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
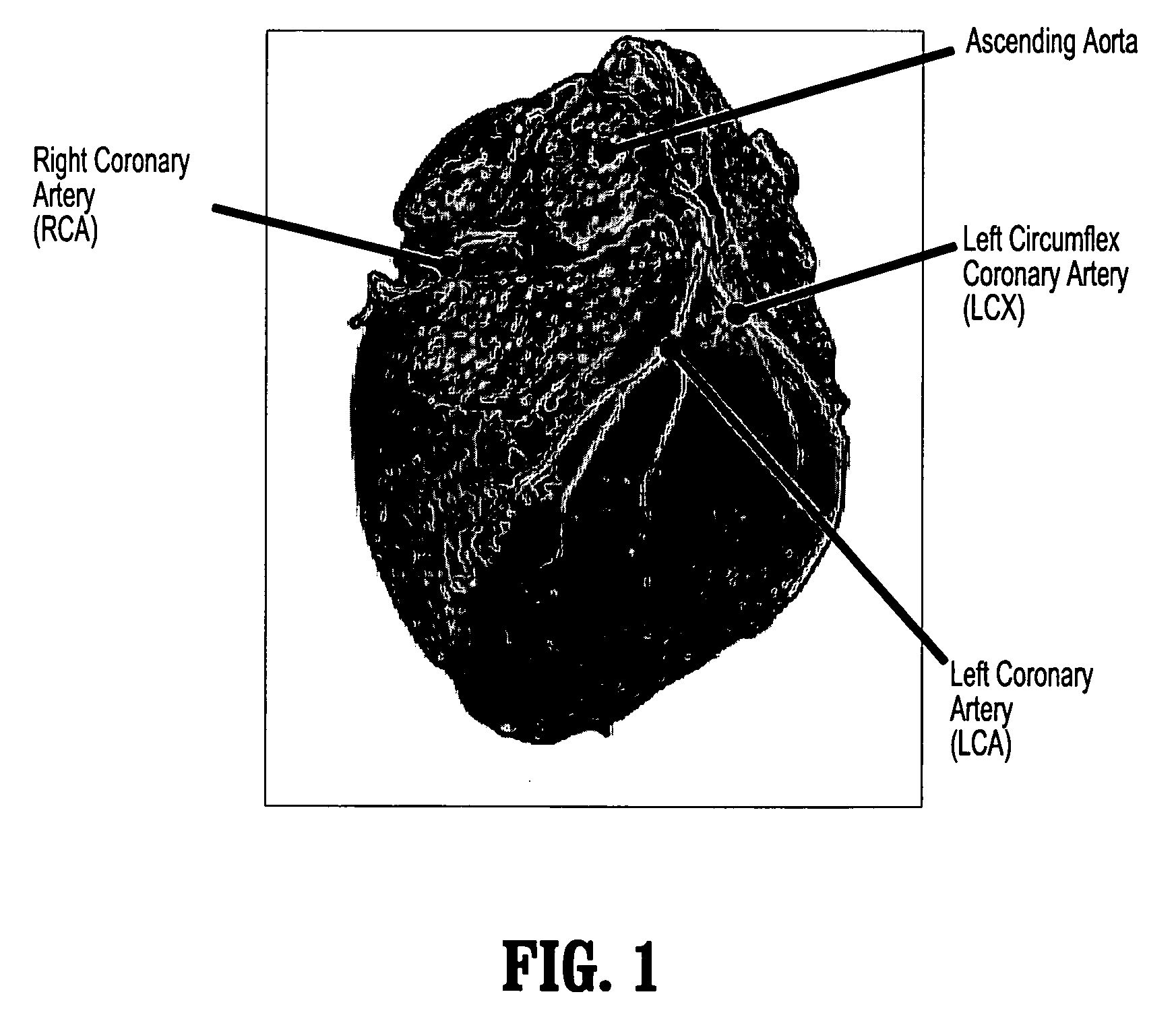
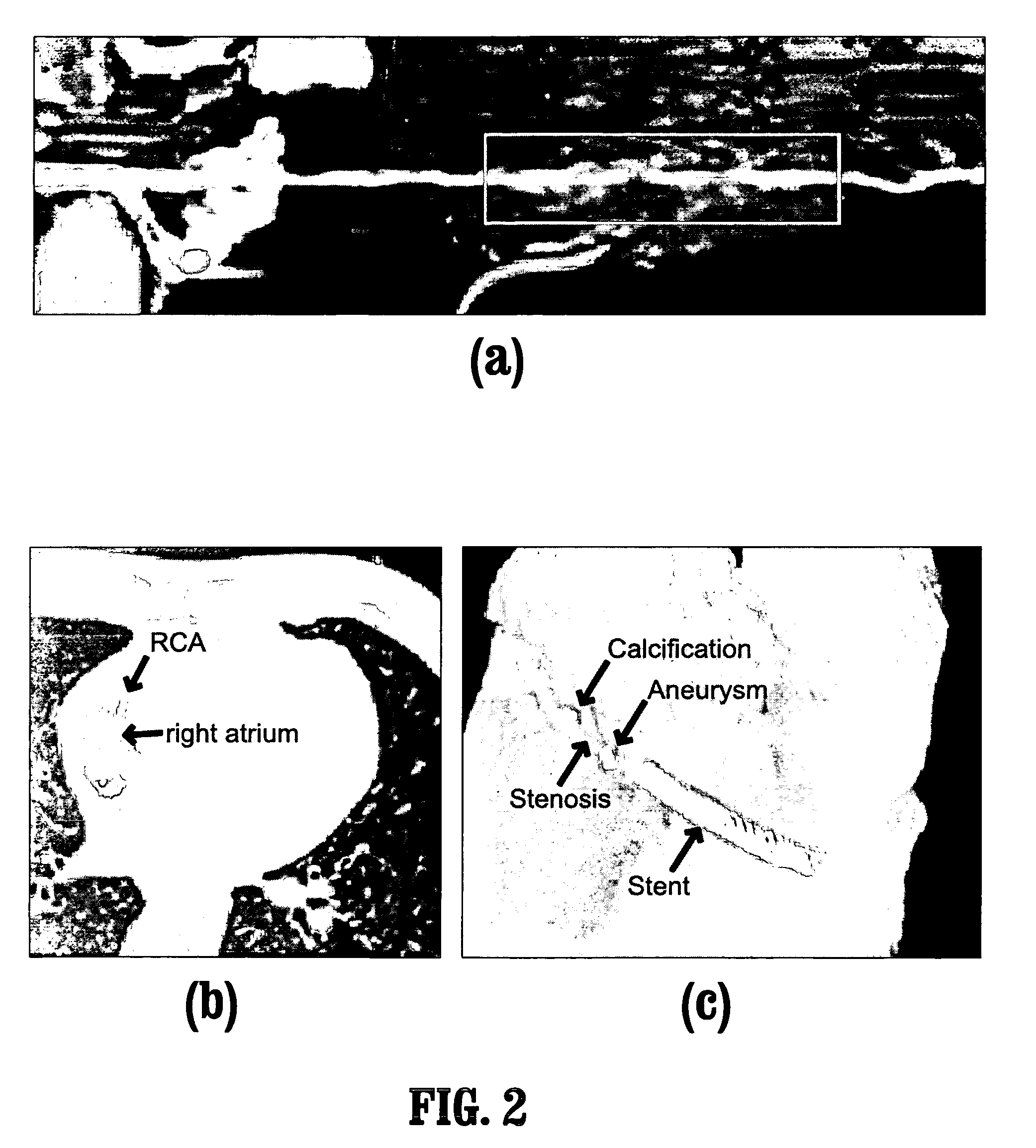
System and method for coronary artery segmentation of cardiac CT volumes
InactiveUS20070031019A1Easy to implementRobust and accurate segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCoronary arteries
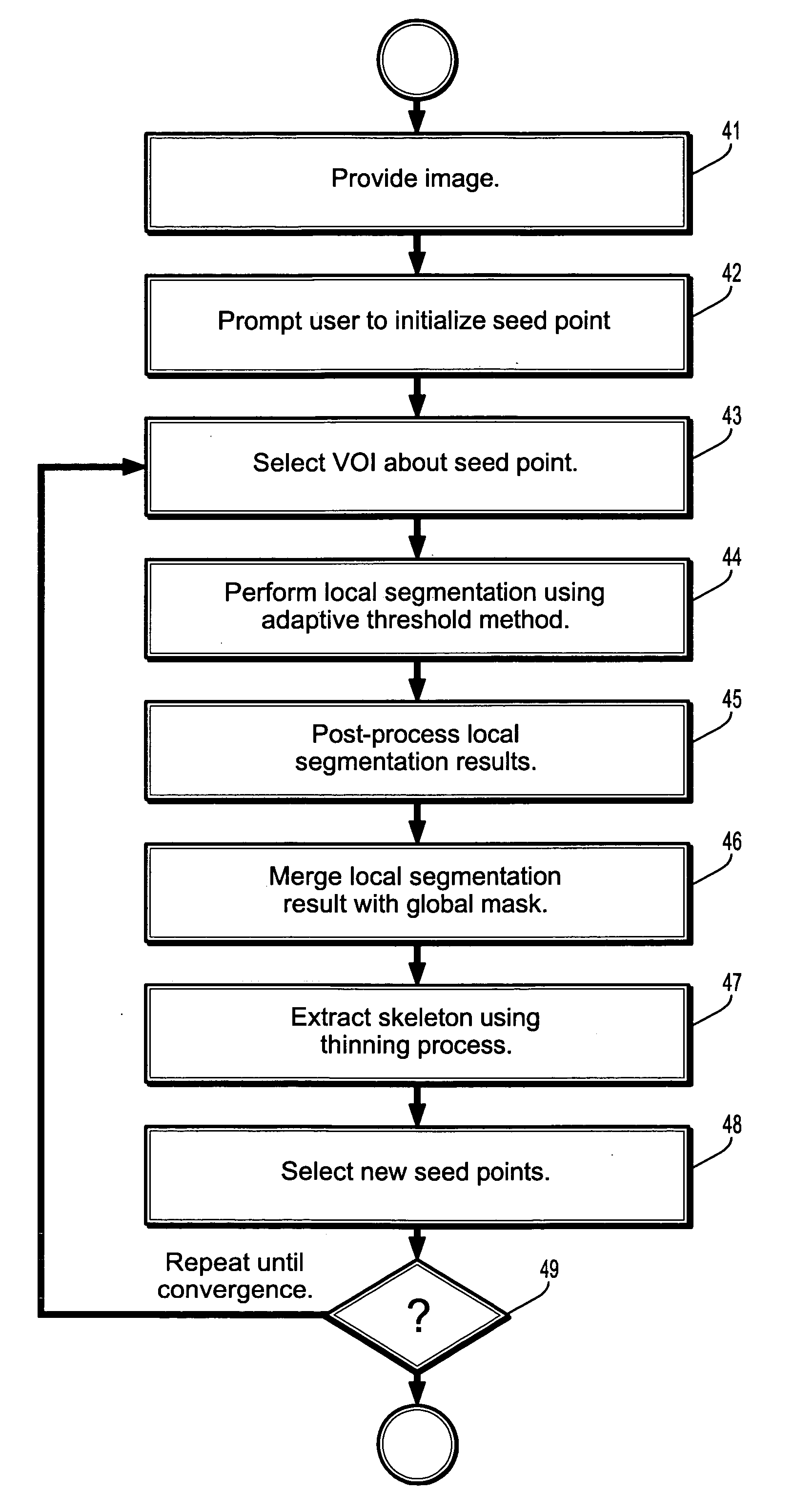
A method for segmenting coronary vessels in digitized cardiac images includes providing a digitized cardiac image, providing a seed point in the image, selecting a volume-of-interest about the seed point, performing a local segmentation in the volume-of-interest, including initializing a connected component with the seed point and a threshold intensity value to the intensity of the seed point, adding a point to the connected component if the point is adjacent to the connected component and if the intensity of the point is greater than or equal to the threshold value, lowering the threshold intensity value, and computing an attribute value of the connected component, wherein if a discontinuity in the attribute value is detected, the local segmentation is terminated, wherein a local segmentation mask of a vessel is obtained.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
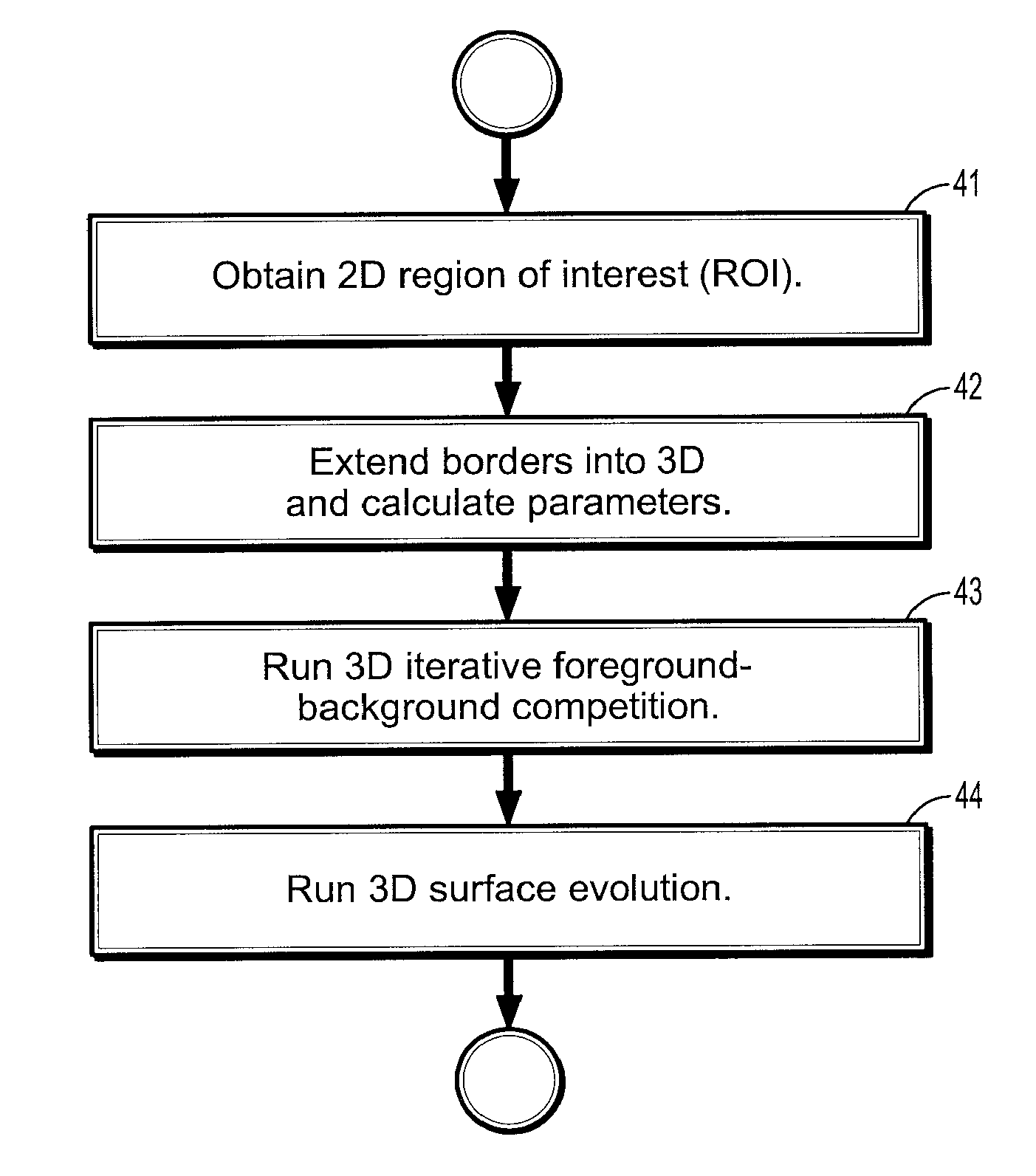
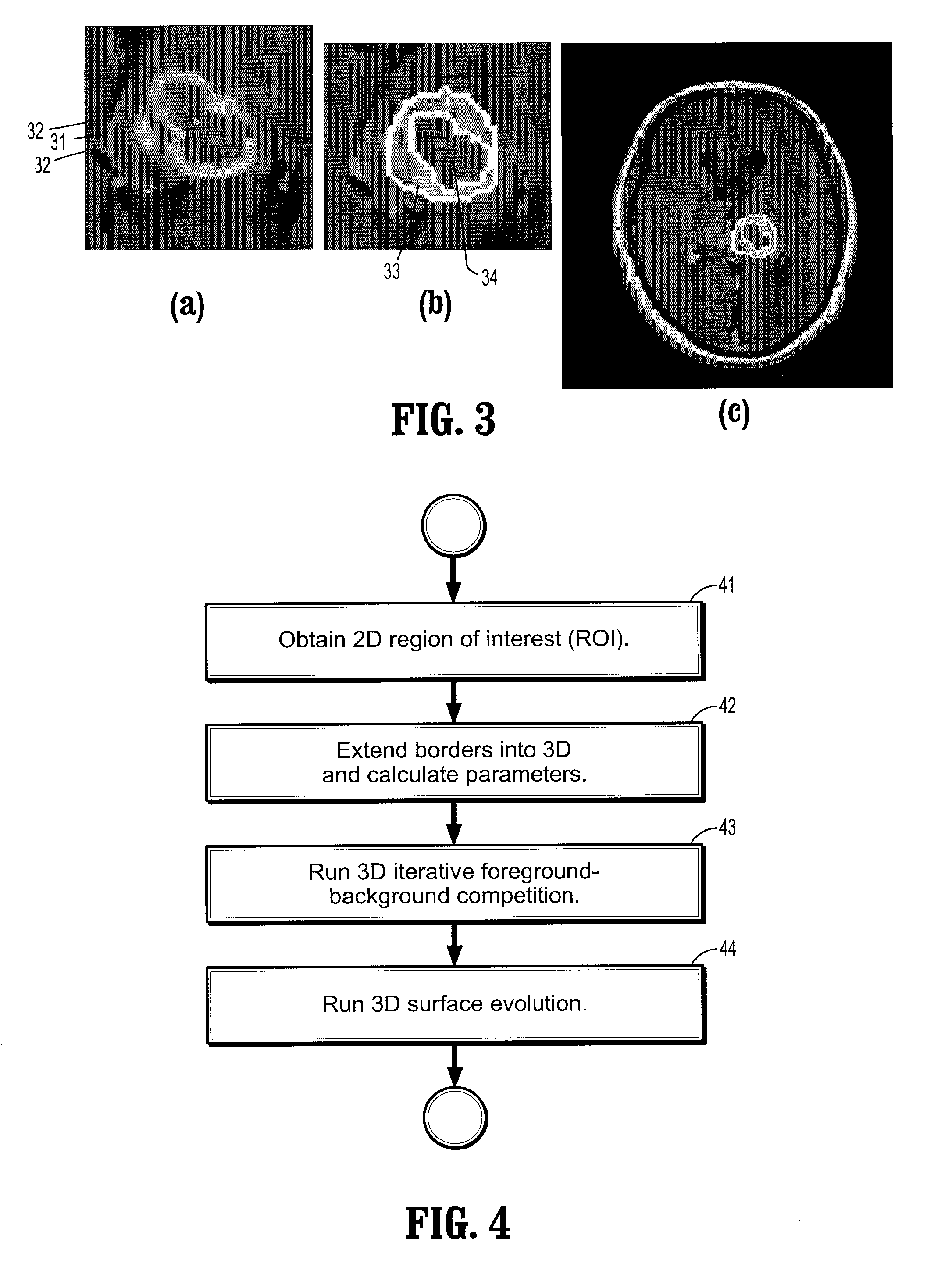
System and Method for Lesion Segmentation in Whole Body Magnetic Resonance Images
InactiveUS20080260221A1The result is accurateMinimal user interactionImage enhancementImage analysisWhole body mriVoxel
A method for lesion segmentation in 3-dimensional (3D) digital images, includes selecting a 2D region of interest (ROI) from a 3D image, the ROI containing a suspected lesion, extending borders of the ROI to 3D forming a volume of interest (VOI), where voxels on the borders of the VOI are initialized as background voxels and voxels in an interior of the VOI are initialized as foreground voxels, propagating a foreground and background voxel competition where for each voxel in the VOI, having each neighbor voxel in a neighborhood of the voxel attack the voxel, and, if the attack is successful, updating a label and strength of the voxel with that of the successful attacking voxel, and evolving a surface between the foreground and background voxels in 3D until an energy functional associated with the surface converges in value, where the surface segments the suspected lesion from the image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
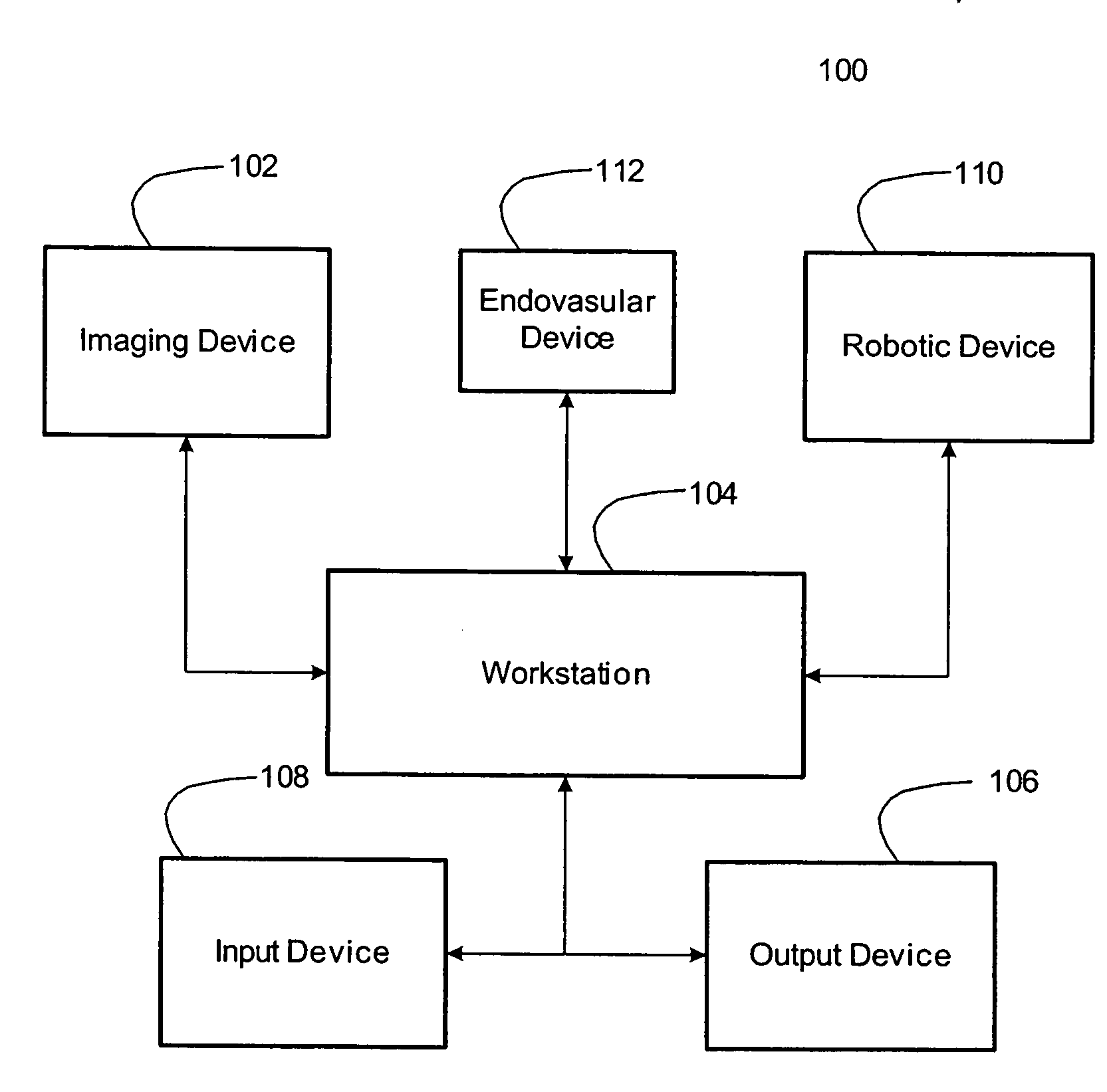
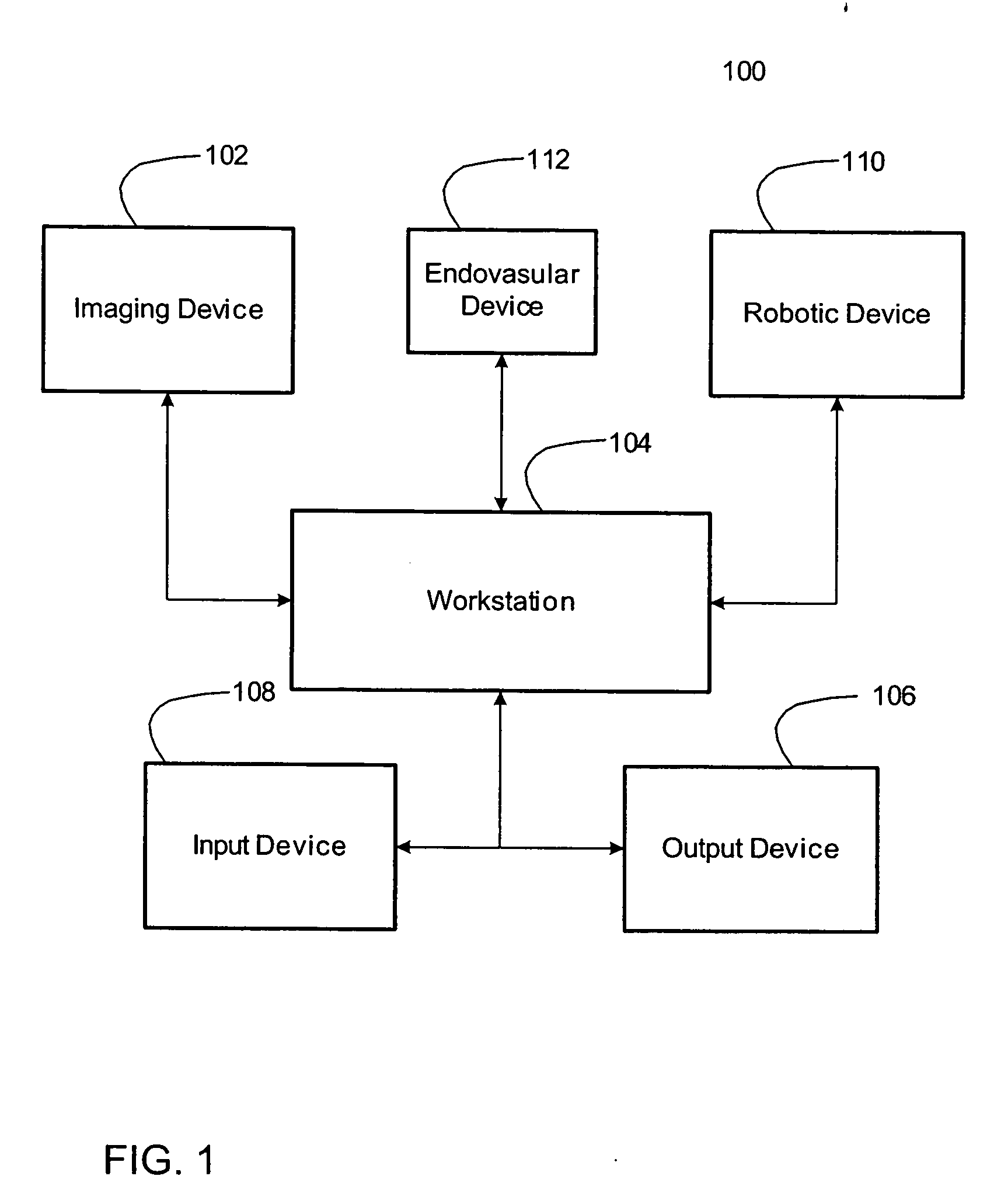
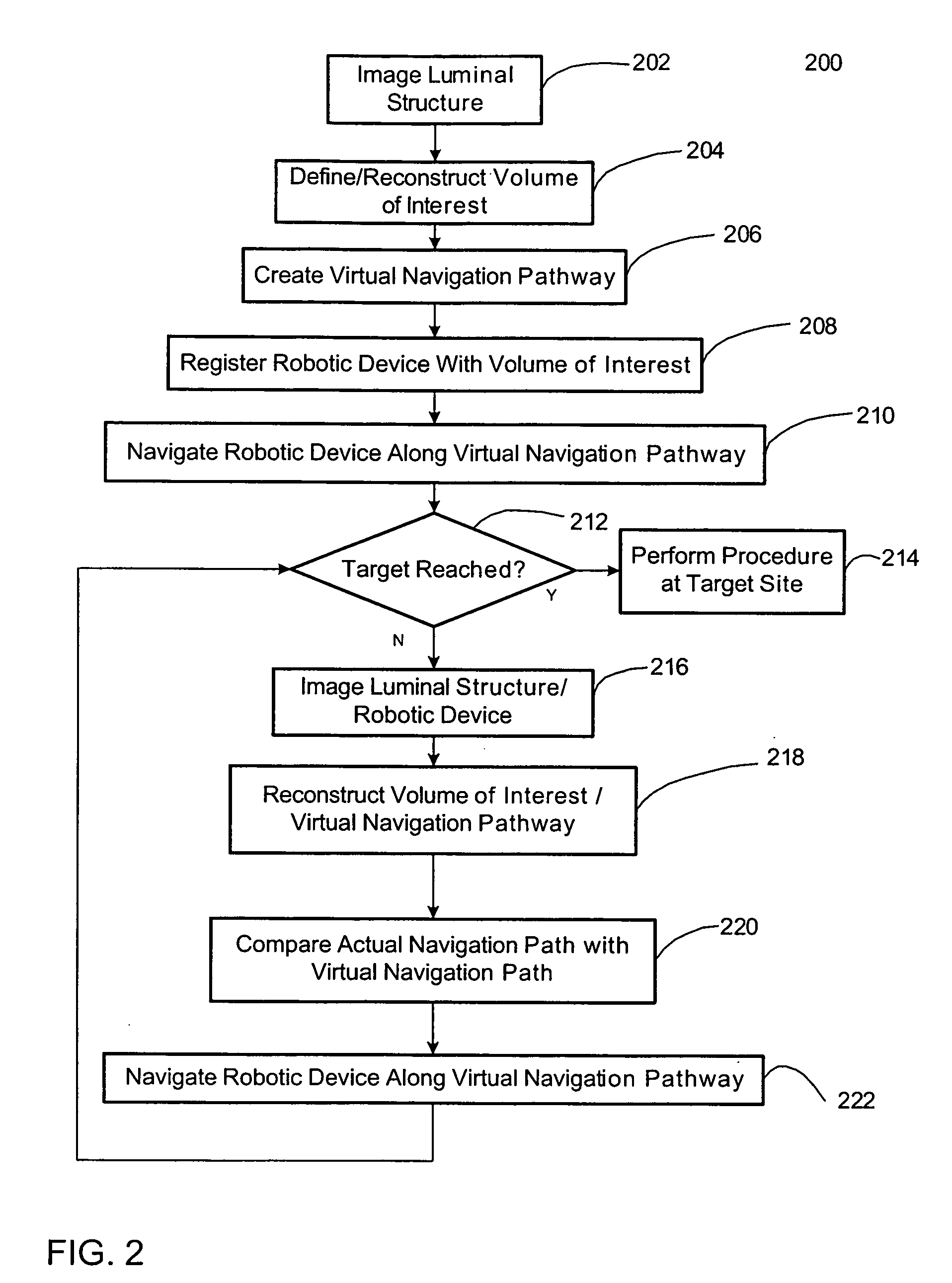
System for autonomous robotic navigation
The present invention provides systems and corresponding methods for autonomous robotic navigation that are capable of obtaining a volumetric image data set of the structure having a lumen, defining a volume of interest between a first point within the structure having a lumen and a second point within the structure having a lumen, creating a virtual navigation pathway for navigating a navigable device with a robotic device between the first and second points, registering the navigable device within the volume of interest, and navigating the navigable device iteratively along the virtual navigation path with the robotic device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
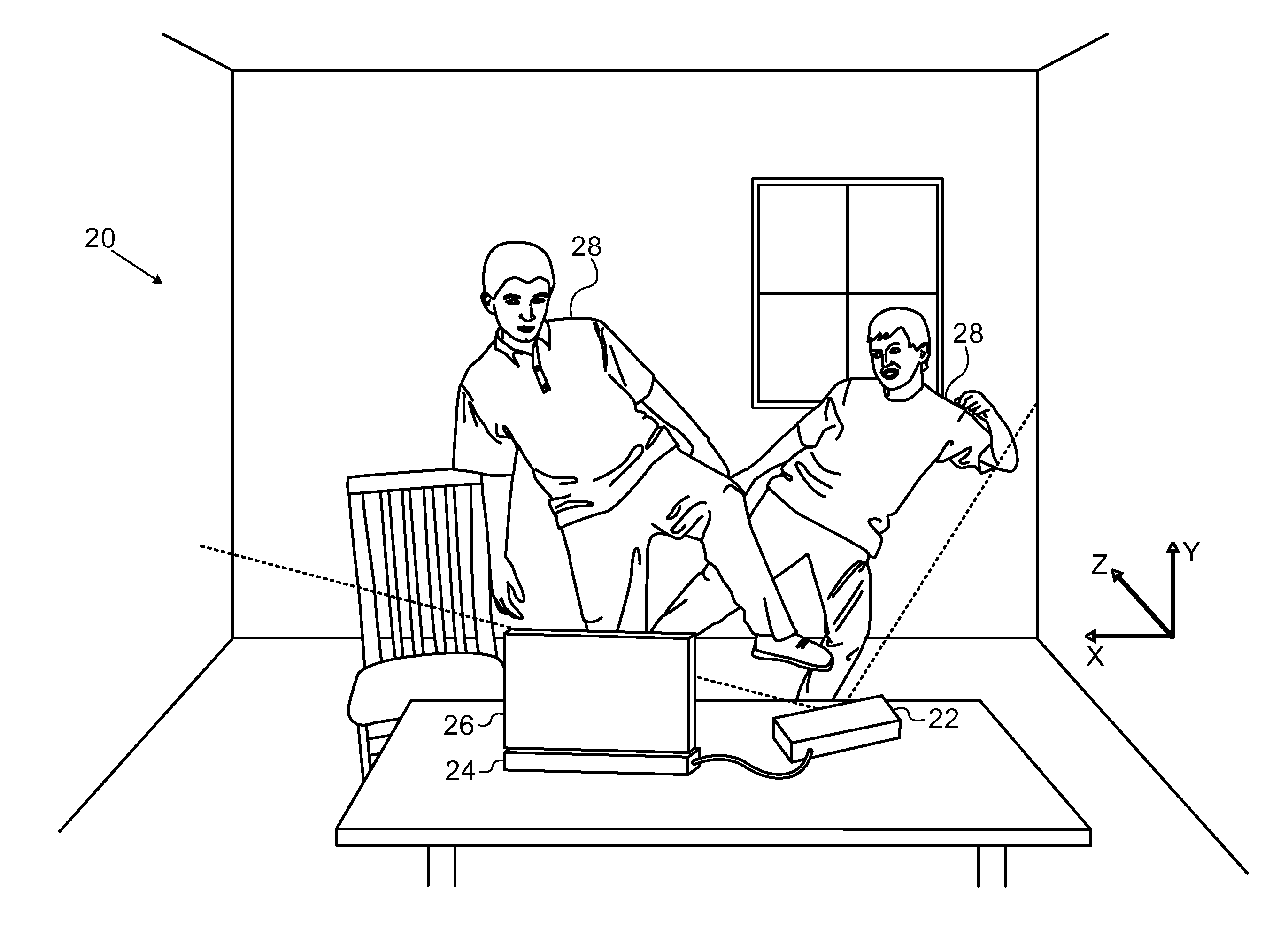
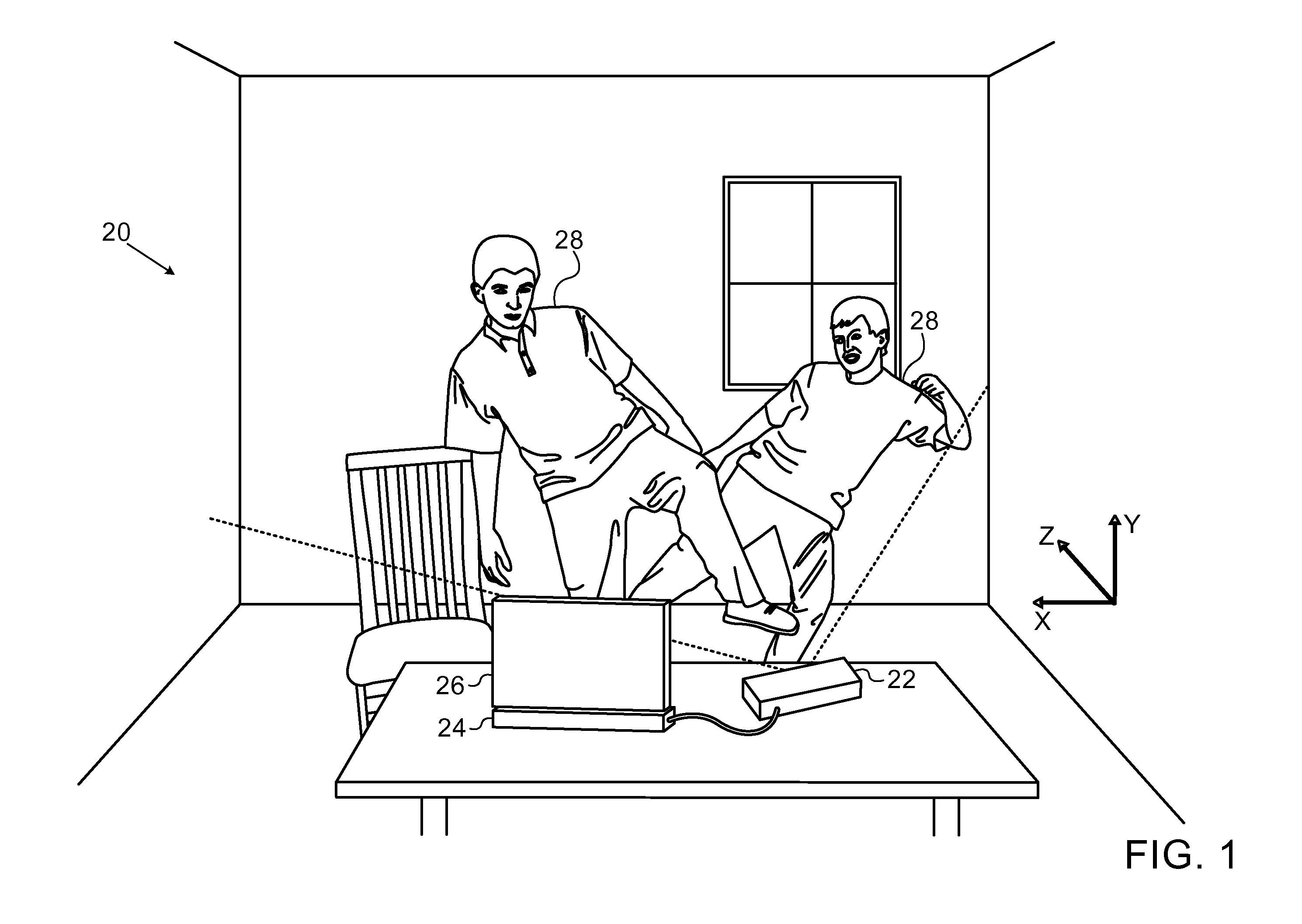
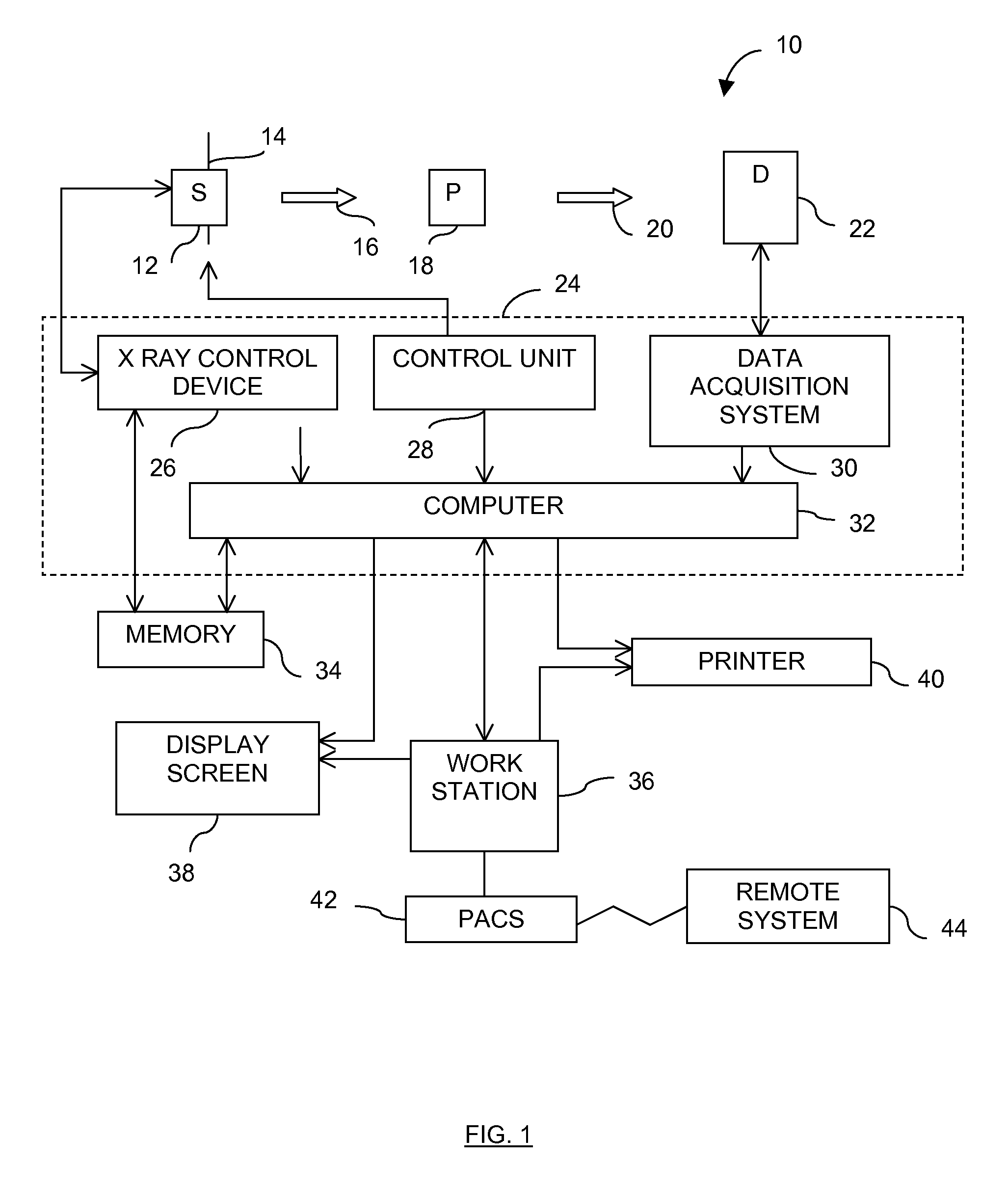
Method and device for identifying and extracting images of multiple users, and for recognizing user gestures
The invention relates to a method for identifying and extracting images of one or more users in an interactive environment comprising the steps of: —obtaining a depth map (7) of a scene in the form of an array of depth values, and an image (8) of said scene in the form of a corresponding array of pixel values, said depth map (7) and said image (8) being registered; applying a coordinate transformation to said depth map (7) and said image (8) for obtaining a corresponding array (15) containing the 3D positions in a real-world coordinates system and pixel values points; —grouping said points according to their relative positions, by using a clustering process (18) so that each group contains points that are in the same region of space and correspond to a user location (19); —defining individual volumes of interest (20) each corresponding to one of said user locations (19); —selecting, from said array (15) containing the 3D positions and pixel values, the points located in said volumes of interest for obtaining segmentation masks (35) for each user; —applying said segmentation masks (35) to said image (8) for extracting images of said users. The invention also relates to a method for recognizing gestures of said users.
Owner:ALTERFACE
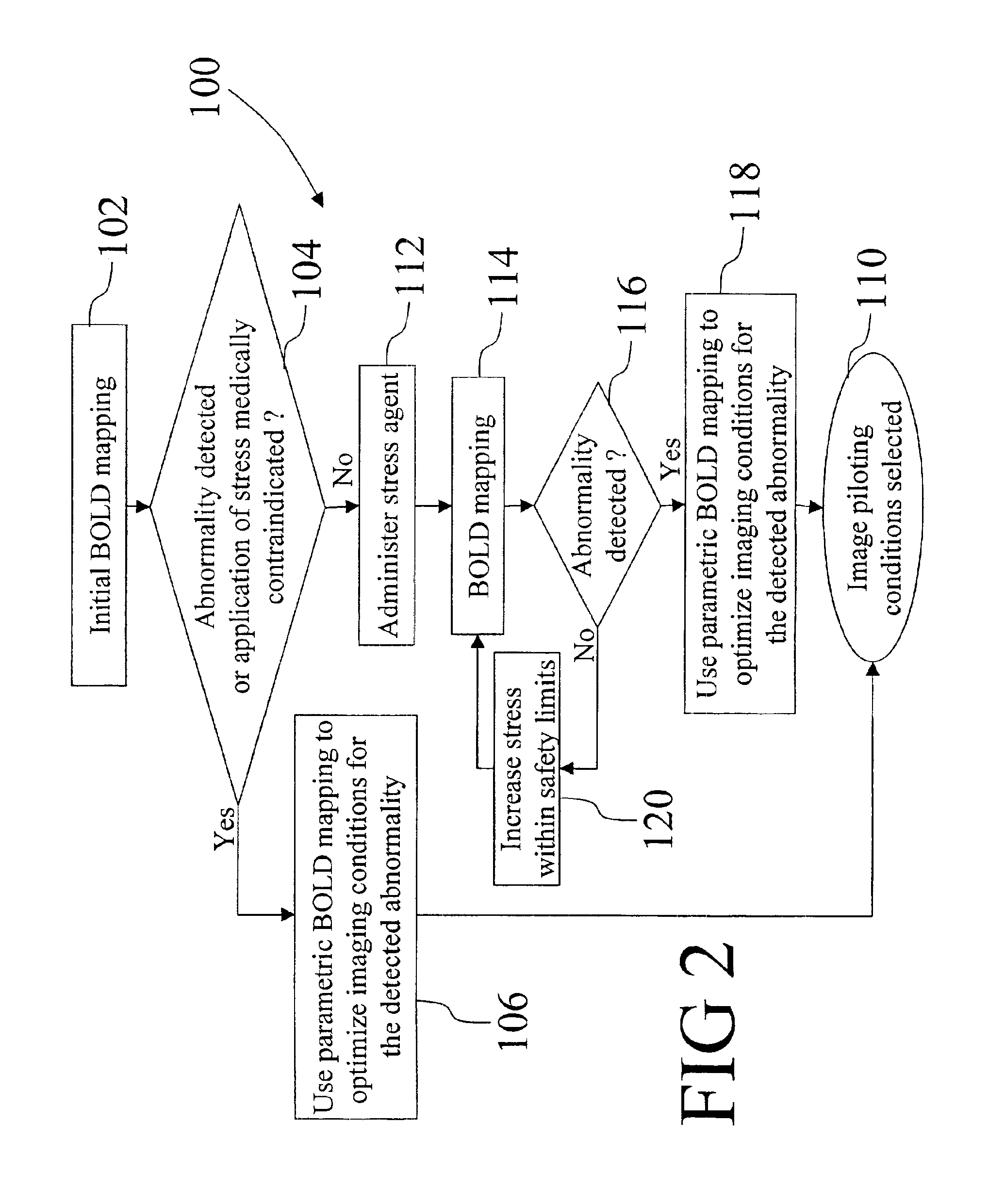
Method and apparatus for evaluation of contrast agent uptake based on derived parametric images
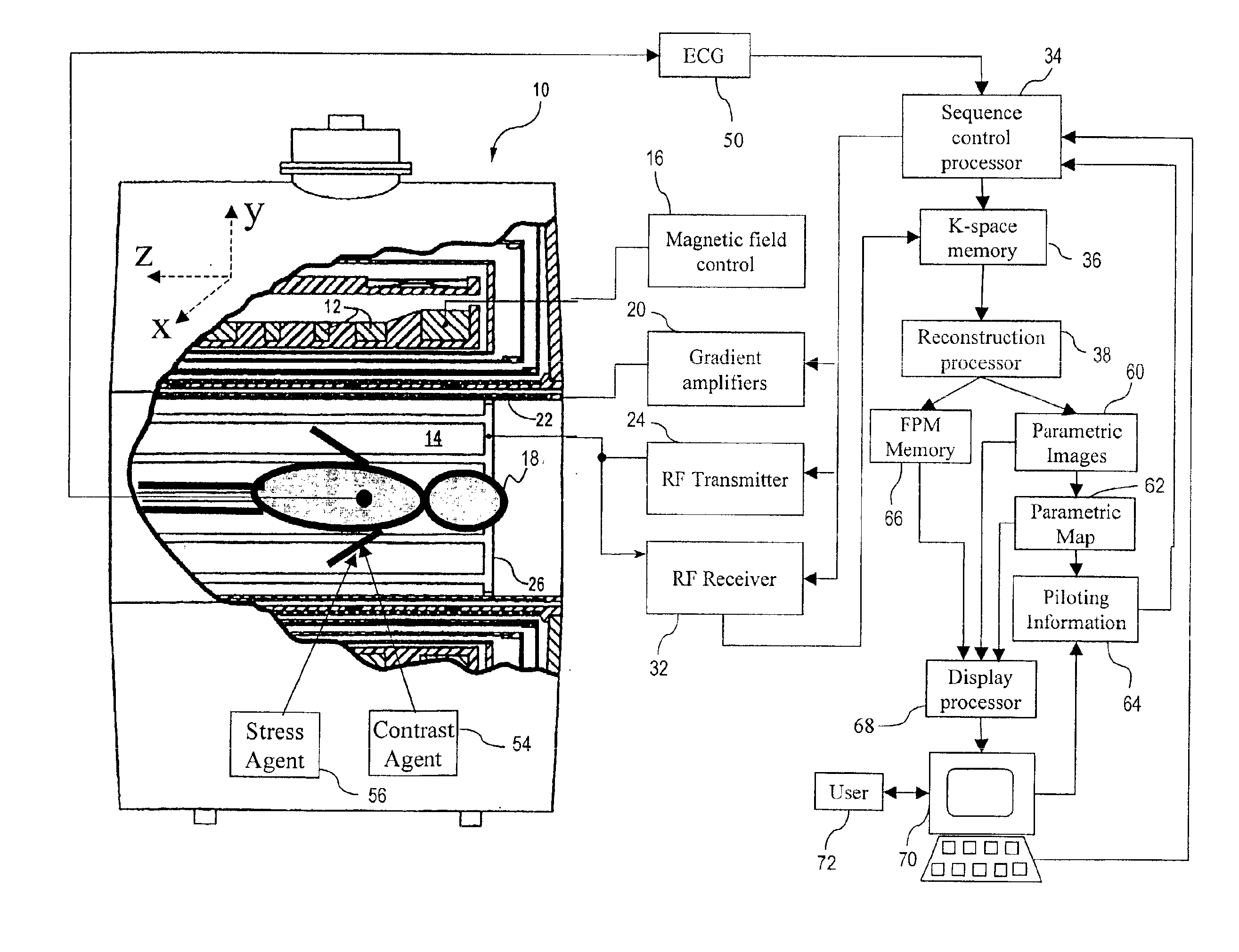
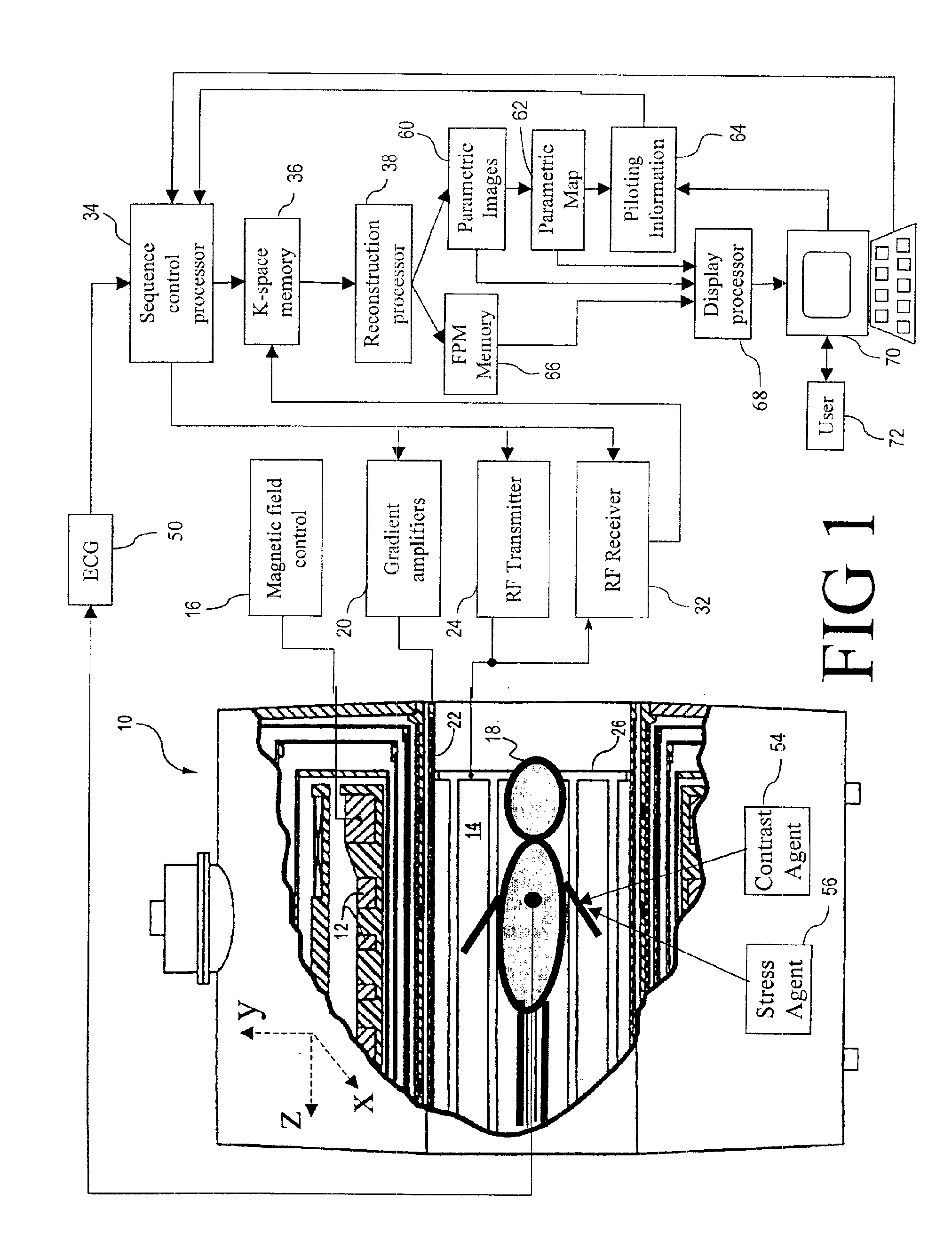
InactiveUS6904306B1Improved clinical work flowMaximize probabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsComputer scienceVolume of interest
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus (10) acquires a plurality of parametric images (60) with at least one varying imaging parameter. A parametric map (62) is constructed from the plurality of parametric images (60). At least one pilot parameter (64) is identified from at least the parametric map (62). The at least one identified pilot parameter (64) includes at least a volume of interest for a diagnostic image. A contrast agent (54) is administered to the patient (18). The identified volume of interest is imaged during influx of the administered contrast agent (54) into the identified volume of interest. The imaging uses the at least one identified pilot parameter (64).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method of measuring disease severity of a patient before, during and after treatment
ActiveUS7935055B2Image analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setAfter treatment
A system for obtaining serial biochemical, anatomical or physiological in vivo measurements of disease from one or more medical images of a patient before, during and after treatment, and measuring extent and severity of the disease is provided. First anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a first co-registered composite image data set. At least a volume of interest (VOI) within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. The first co-registered composite image data set including the VOI is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine extent and severity of the disease. Second anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a second co-registered composite image data set. A global, rigid registration is performed on the first and second anatomical image data sets, such that the first and second functional image data sets are also globally registered.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
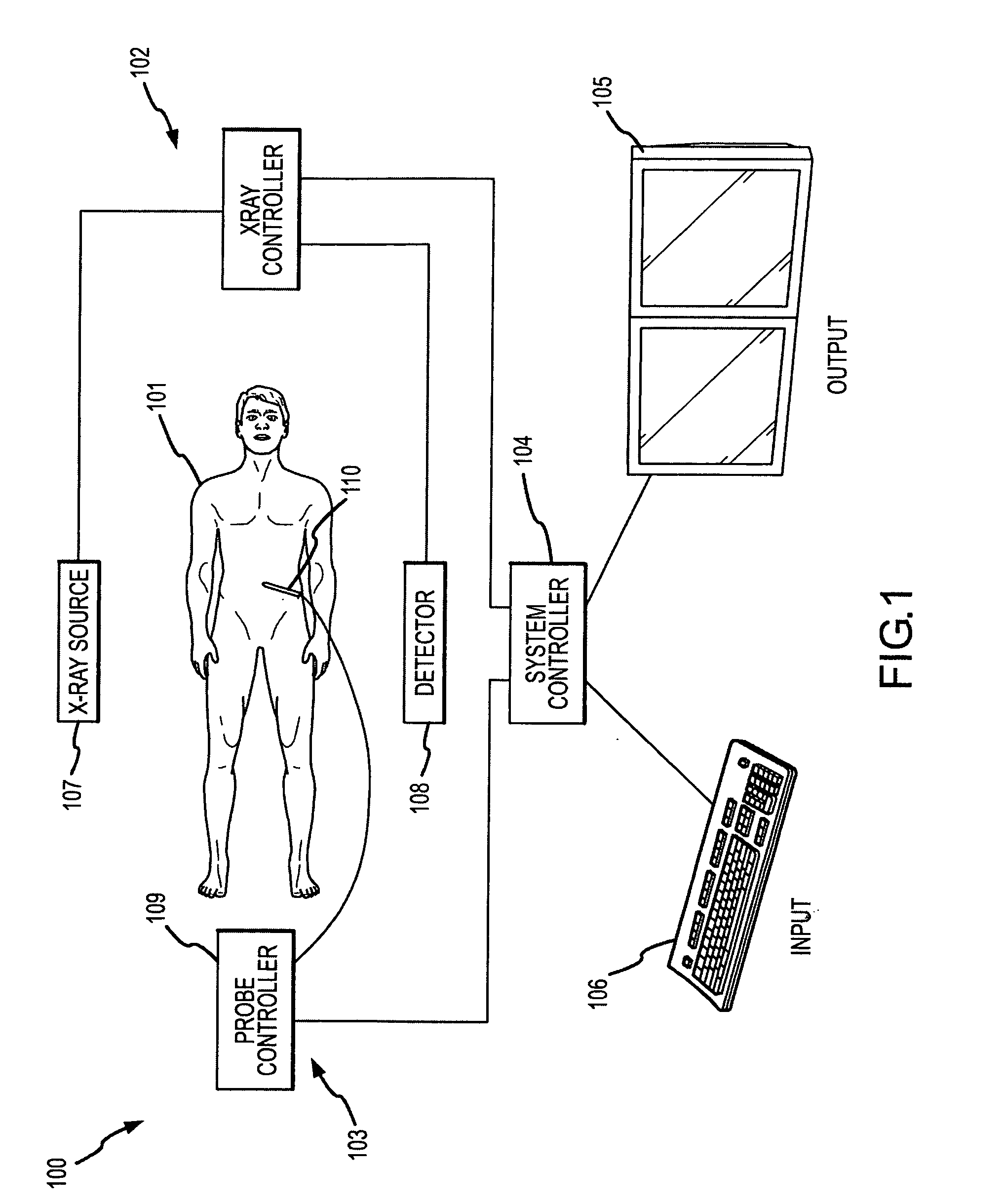
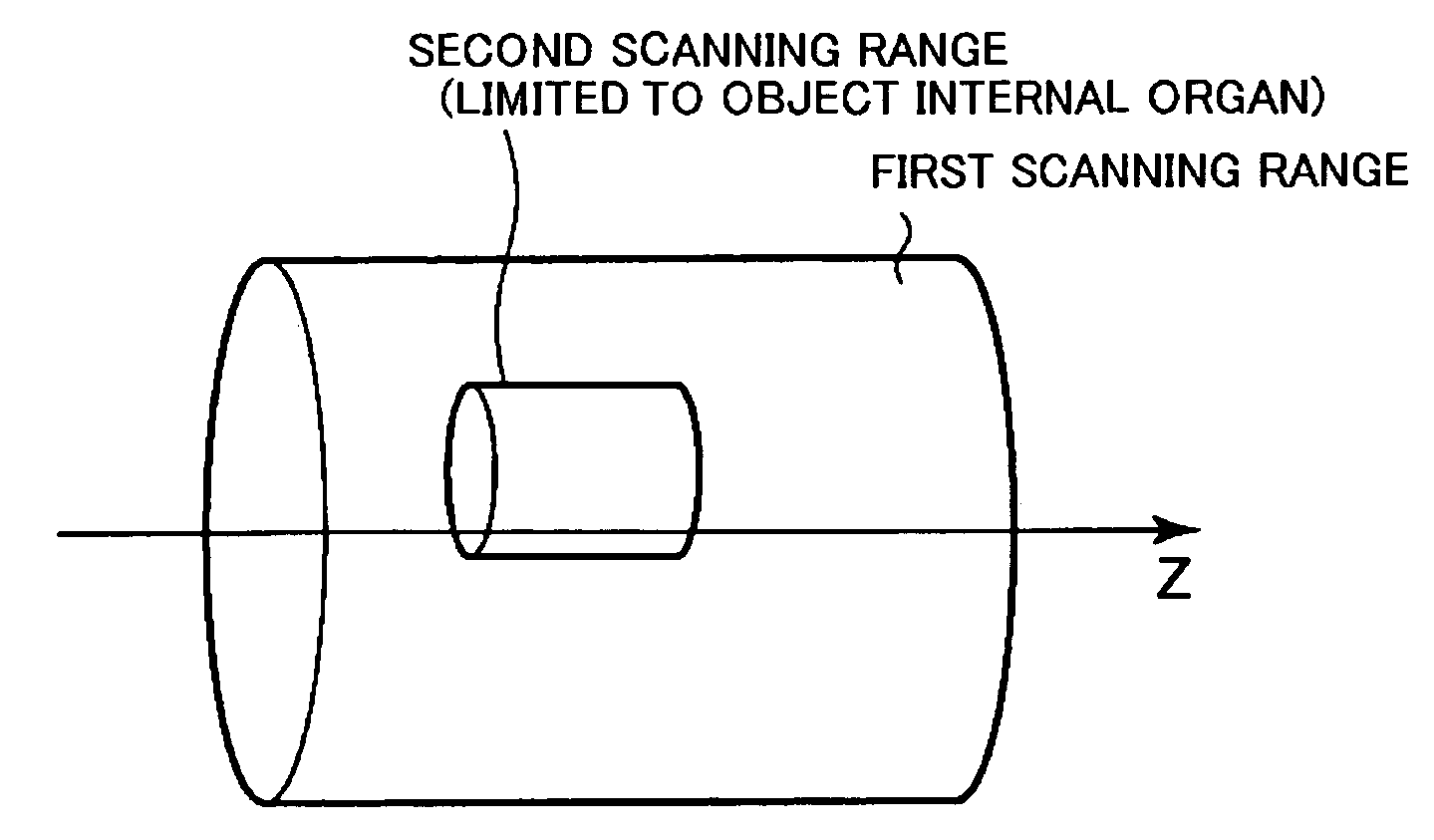
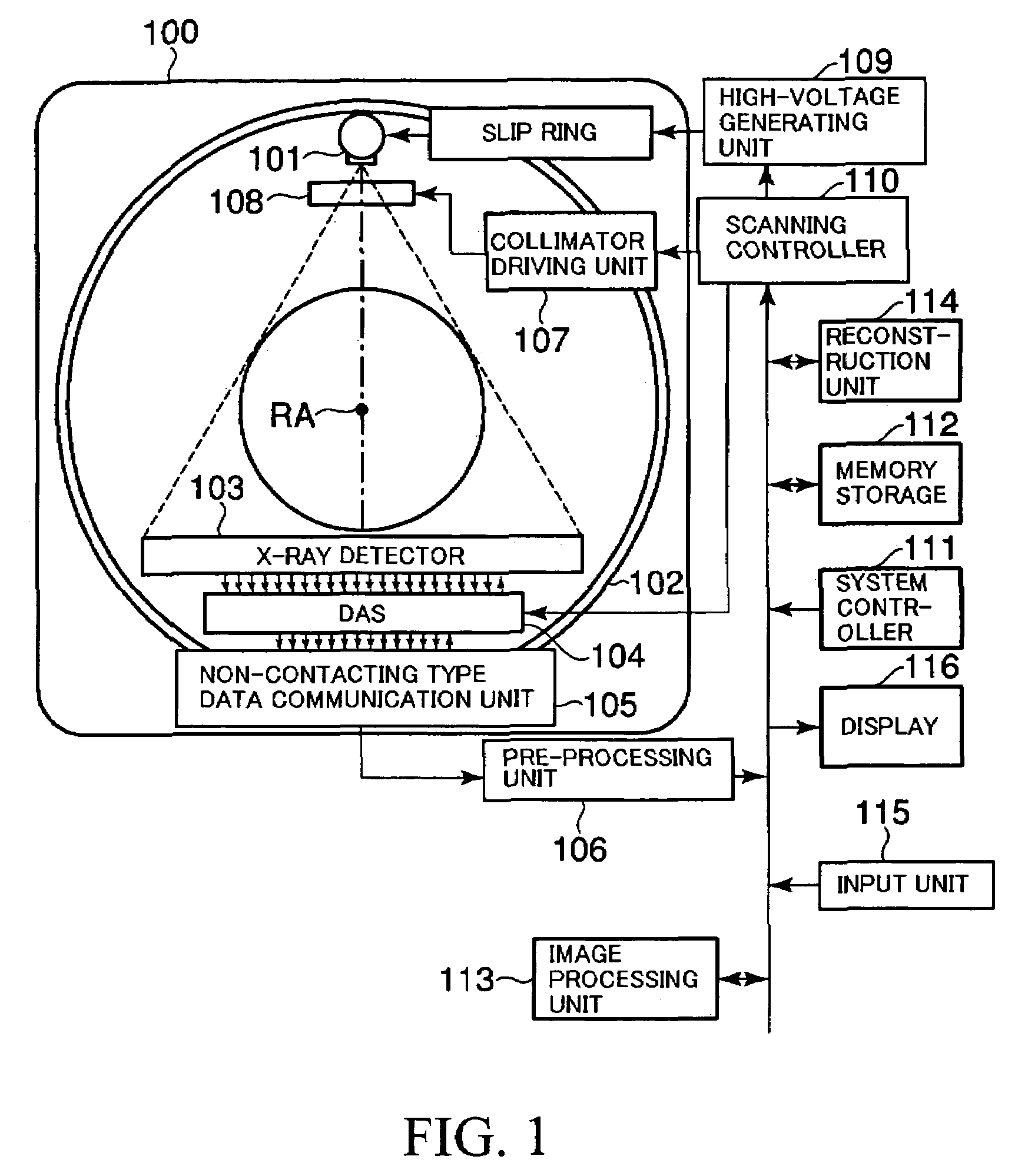
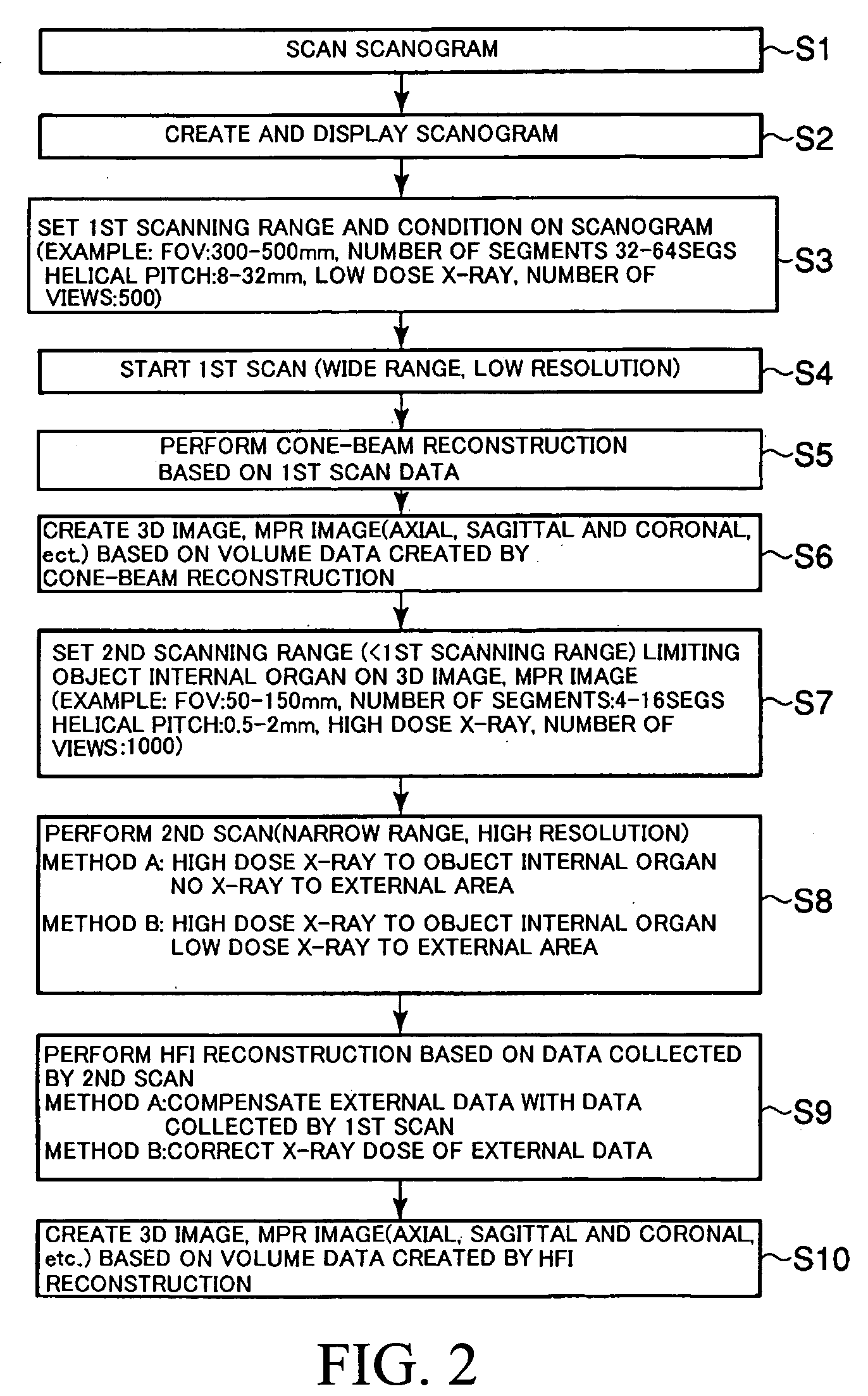
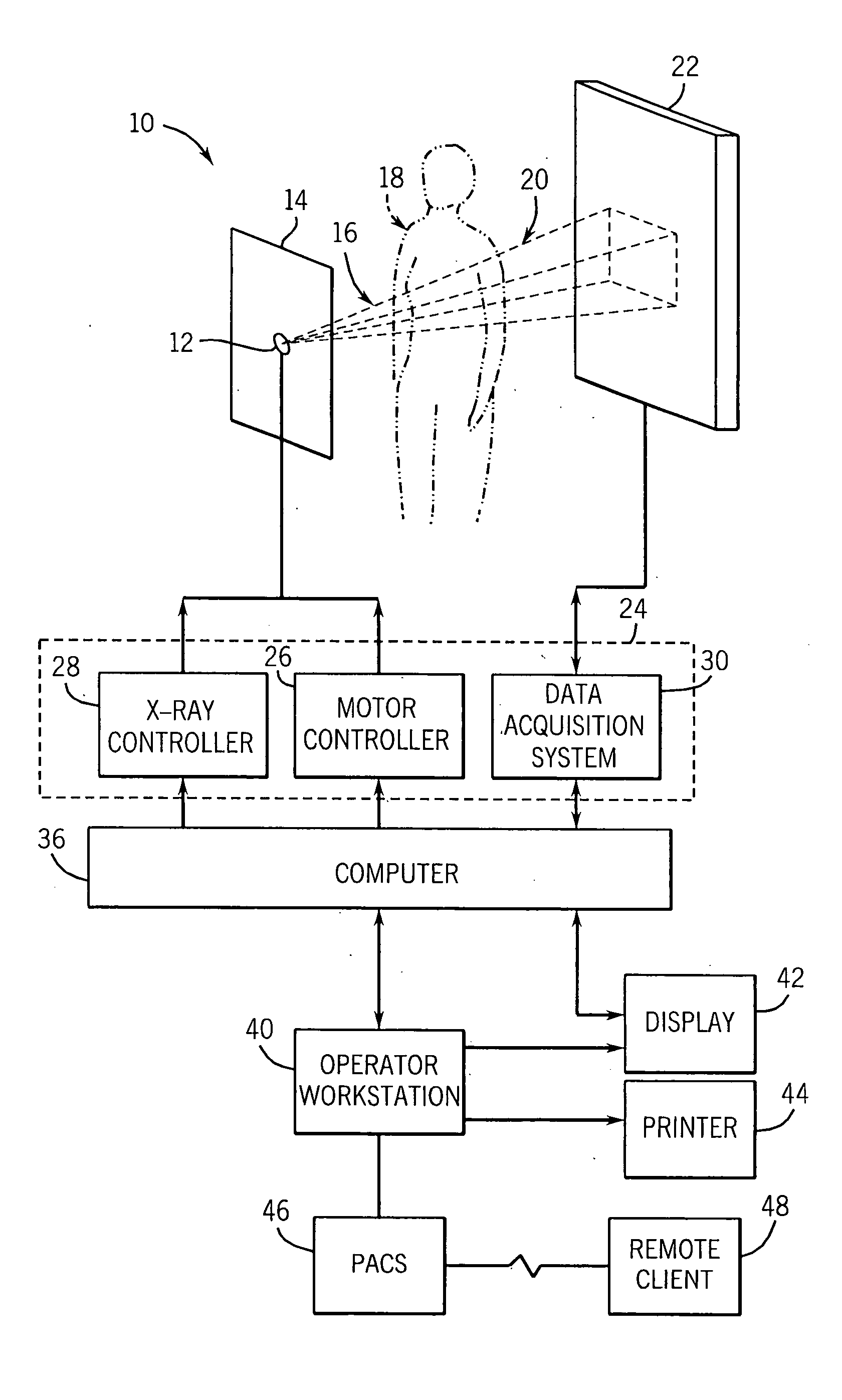
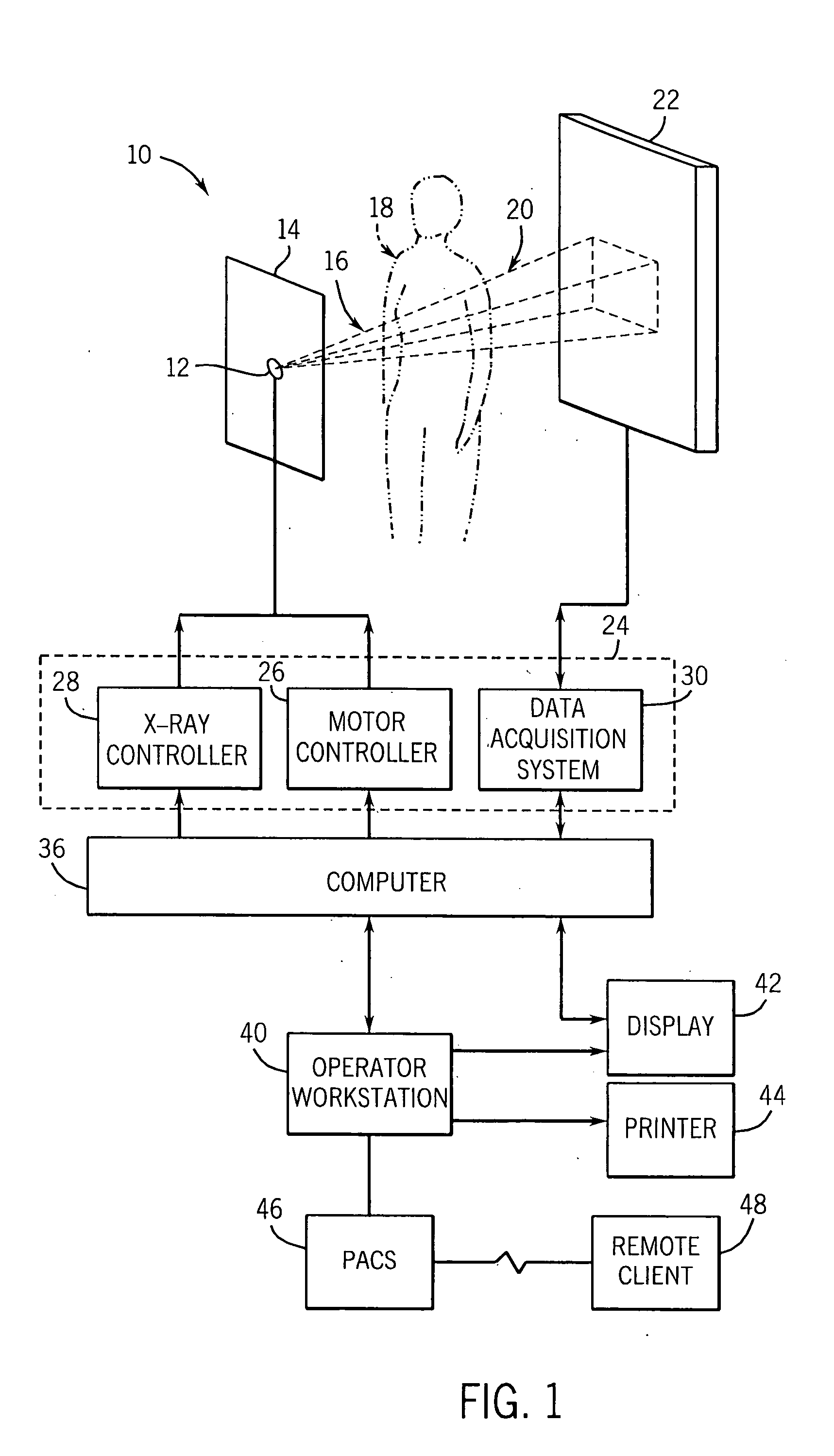
X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS7113569B2Reduce X-ray doseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSoft x rayImaging processing
An X-ray CT apparatus, as one example, includes at least one X-ray irradiation source configured to irradiate an X-ray to a volume of interest, at least one X-ray detector including a plurality of detection element segments configured to detect the X-ray penetrated through the volume of interest, at least one collimator configured to create an opening that is movable in at least one of a slice direction and a channel direction, at least one image processing part configured to extract a portion of the volume data, a controller configured to set the opening of the at least one collimator to a second opening size according to a cylinder-like second scanning range that is set to limit the volume of interest and configured to perform a second scan, and at least one reconstruction part configured to reconstruct image data based on data collected by the second scan.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
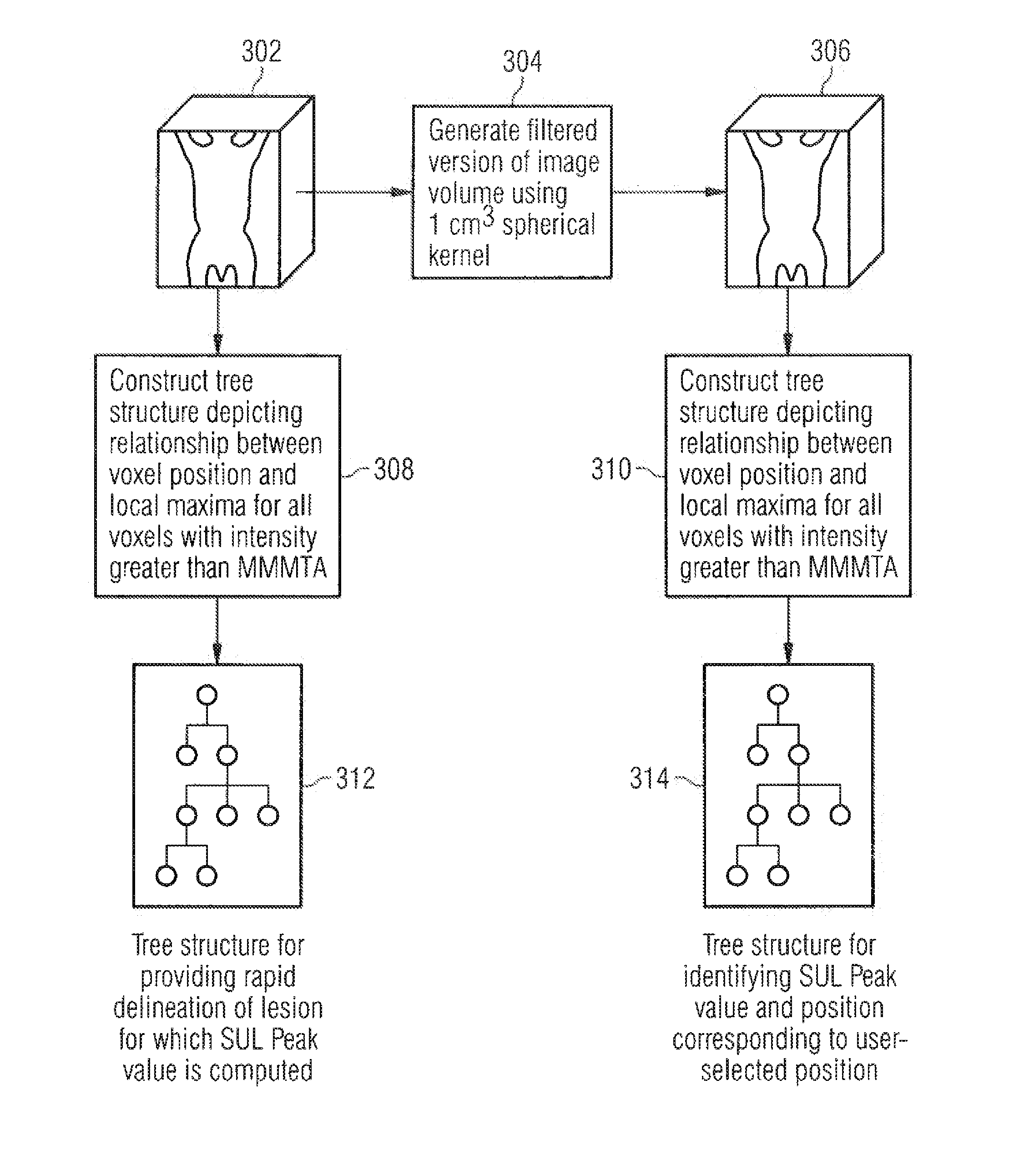
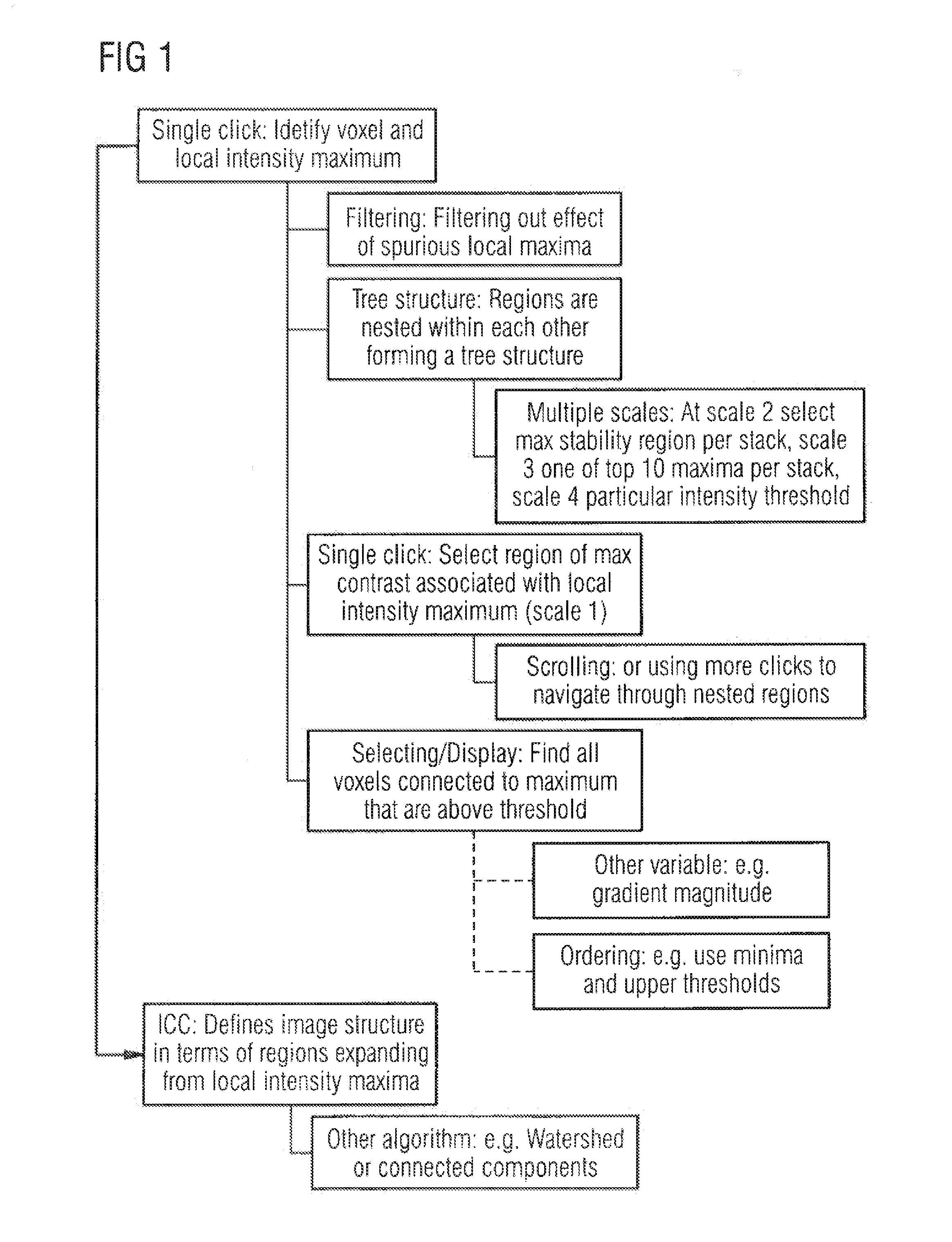
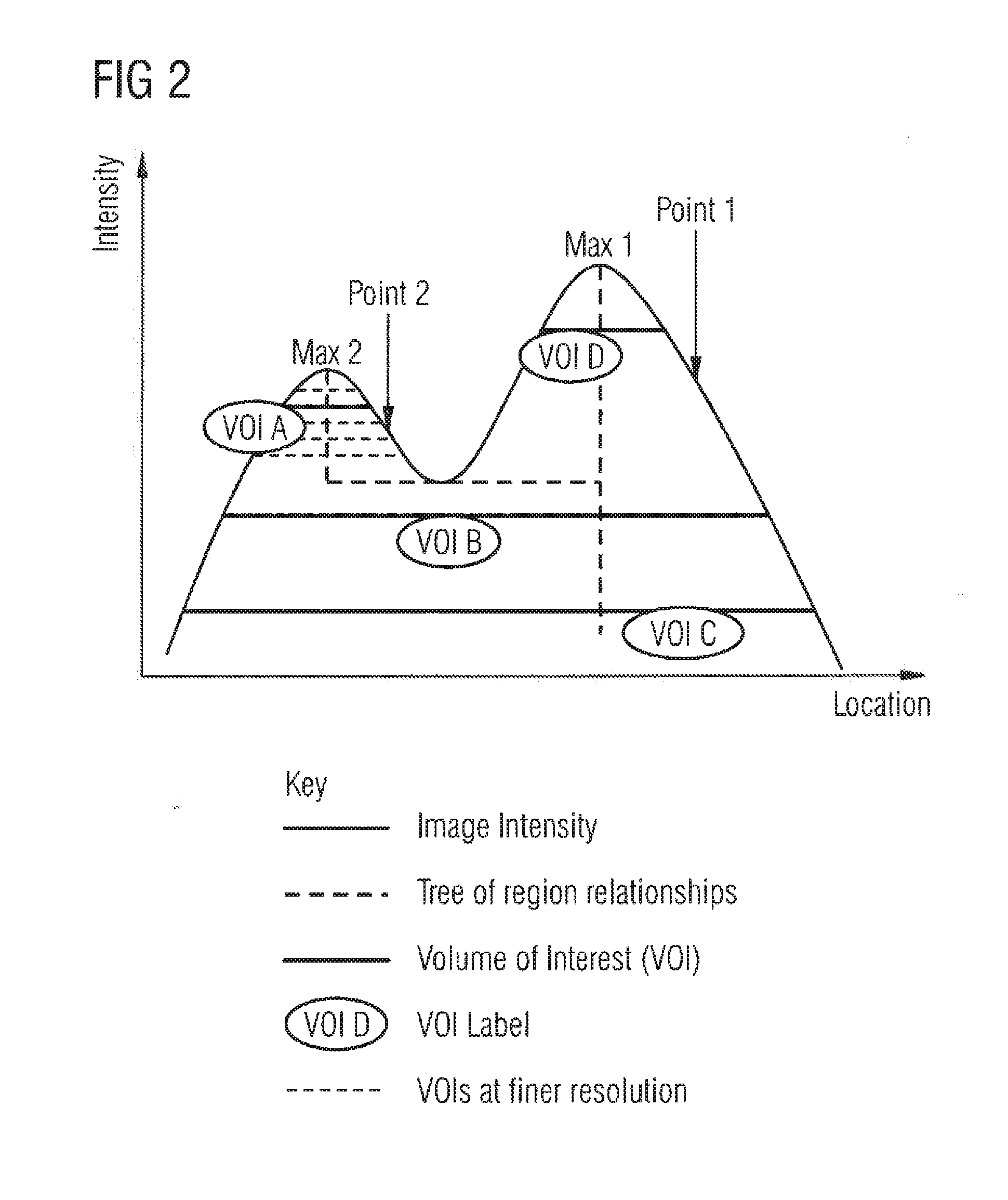
Methods of analyzing a selected region of interest in medical image data
In methods and an apparatus for analyzing a selected region of interest in medical image data of a subject, an initial image data set is obtained, and the initial image data set is filtered to generate a filtered data set. The filtering includes computing, for each voxel of the initial image data set, a value of intensity for a standardized volume of interest centered on that voxel. A user selection of a region of interest in the initial image data set is registered, and from the filtered image data set a value of intensity for the selected region of interest is computed.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
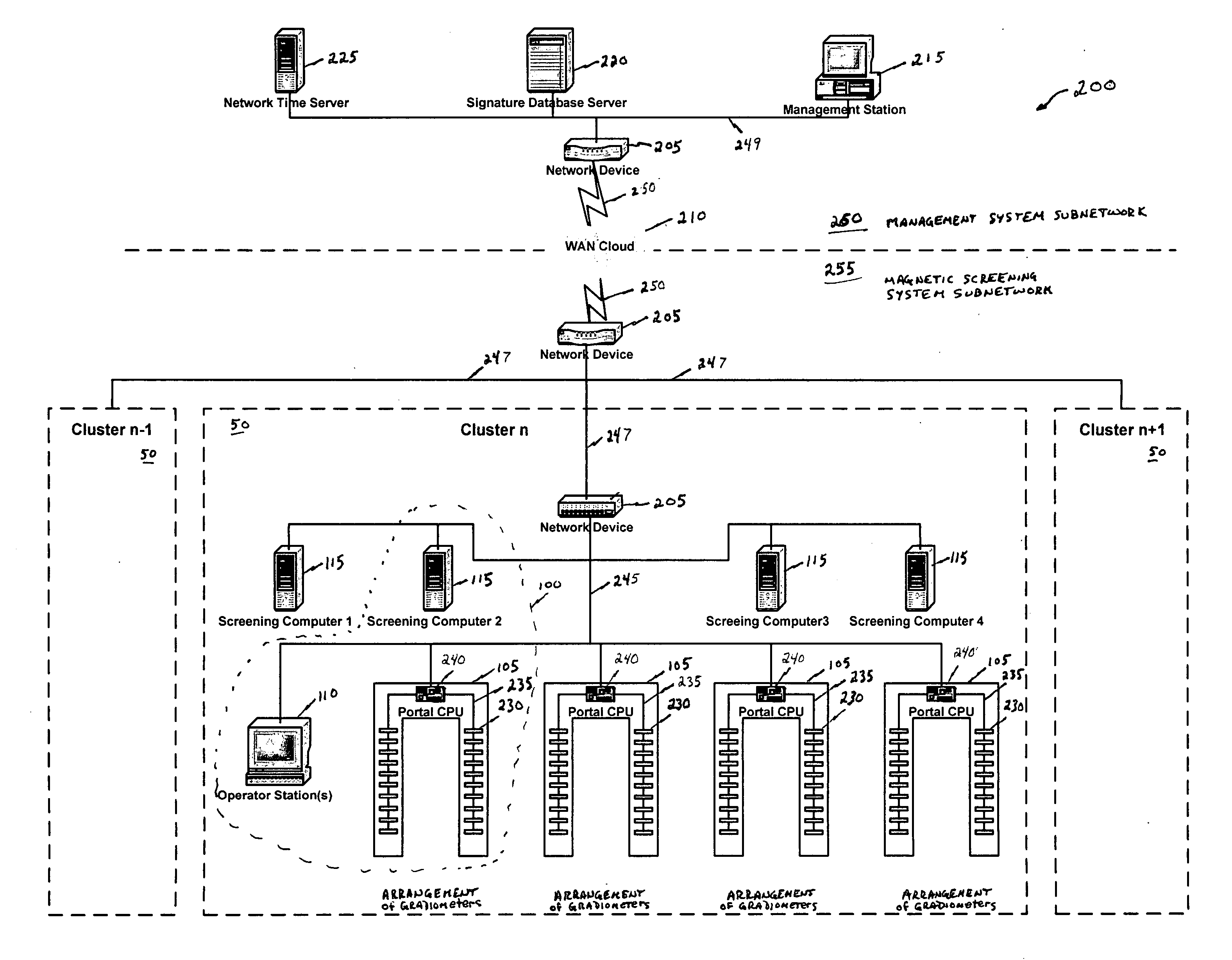
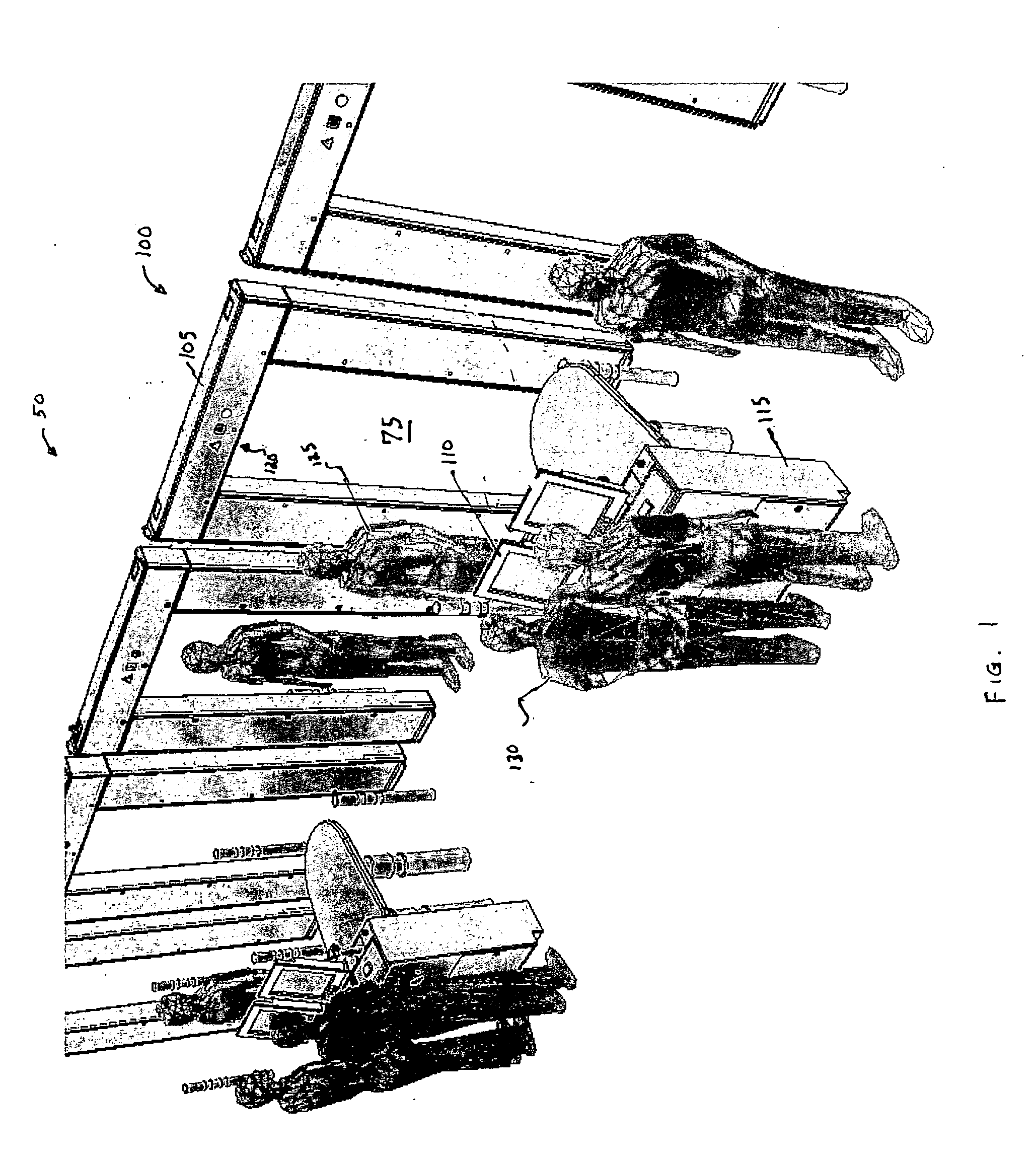
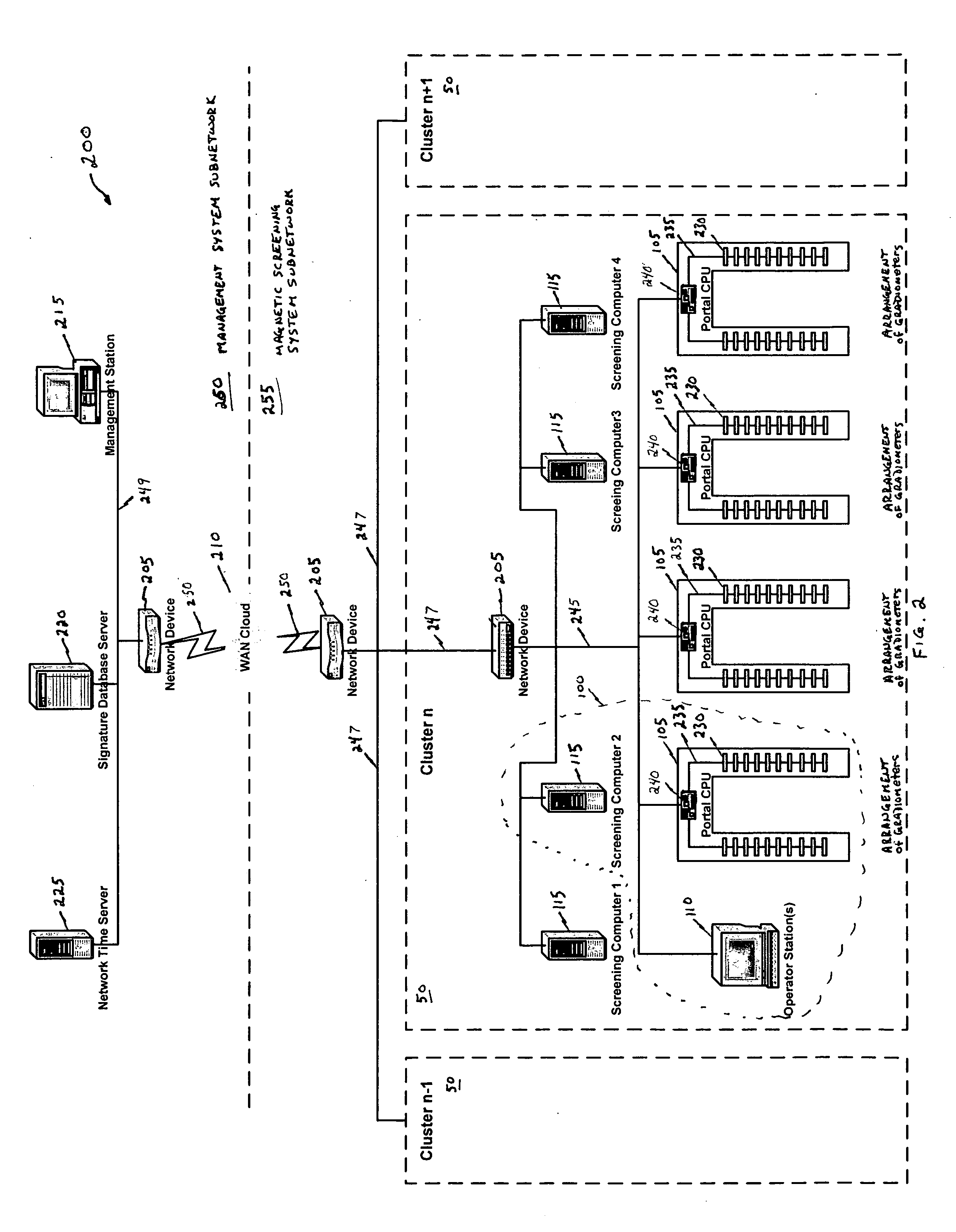
Magnetic screening system
InactiveUS20060197523A1Improve processing speedLess incidenceElectric/magnetic detectionMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsHigh rateObject store
A magnetic screening system uses directional gradiometers with high resolution and accuracy to measure magnetic field signatures of target objects (e.g., gun, knife, cell phone, keys) in a volume of interest. The measured signatures can be compared to signatures of known objects stored in a local database. Various mathematical processes may be used to identify or classify target object signatures. In a network of magnetic screening systems, the magnetic screening systems can transmit signatures to a central signature database, and a management computer can share the central signature database with all of the magnetic screening systems on the network. The magnetic screening system can operate in multiple modes, such as a tracking mode, measurement mode, and self-test mode. Through use of unique processes and designs, the magnetic screening system can achieve a high rate of processing persons for target objects.
Owner:ASSURANCE TECH CORP
Methods and systems for facilitating surgical procedures
InactiveUS20070129626A1Facilitate surgeryUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic markersAuditory feedbackSurgery procedure
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a method for facilitating surgery including: tracking a position of at least a portion of a surgical implement in a volume of interest; recognizing a surgical plan corresponding to at least a portion of the volume of interest; and providing feedback based on a correspondence between the position of the at least a portion of the surgical implement and the surgical plan. In an embodiment, the feedback is provided in real-time. In an embodiment, the feedback includes at least one of: haptic feedback, thermal feedback, optical feedback, and auditory feedback. In an embodiment, the surgical plan includes a previously generated radiological image. In an embodiment, the surgical plan includes at least one trajectory for the at least a portion of the surgical implement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for electronic unpacking of baggage and cargo
In accordance with certain embodiments a method and system to analyze the content of a packed bag utilizing a scanner is provided. The bag is scanned for a scannable characteristic to acquire scan data representative of a content of the piece of baggage. A volumetric data set is generated from the scan data, wherein the volumetric data set includes voxel values of the scannable characteristic throughout a volume of interest in the baggage. A rendered view is produced of the content of the piece of baggage based on the voxel values within a selected range from the volumetric data set. The method and system also provide identifying a threat by analyzing Hounsfield Units of the material of interest.
Owner:TELESECURITY SCI
Systems and methods of classification utilizing intensity and spatial data
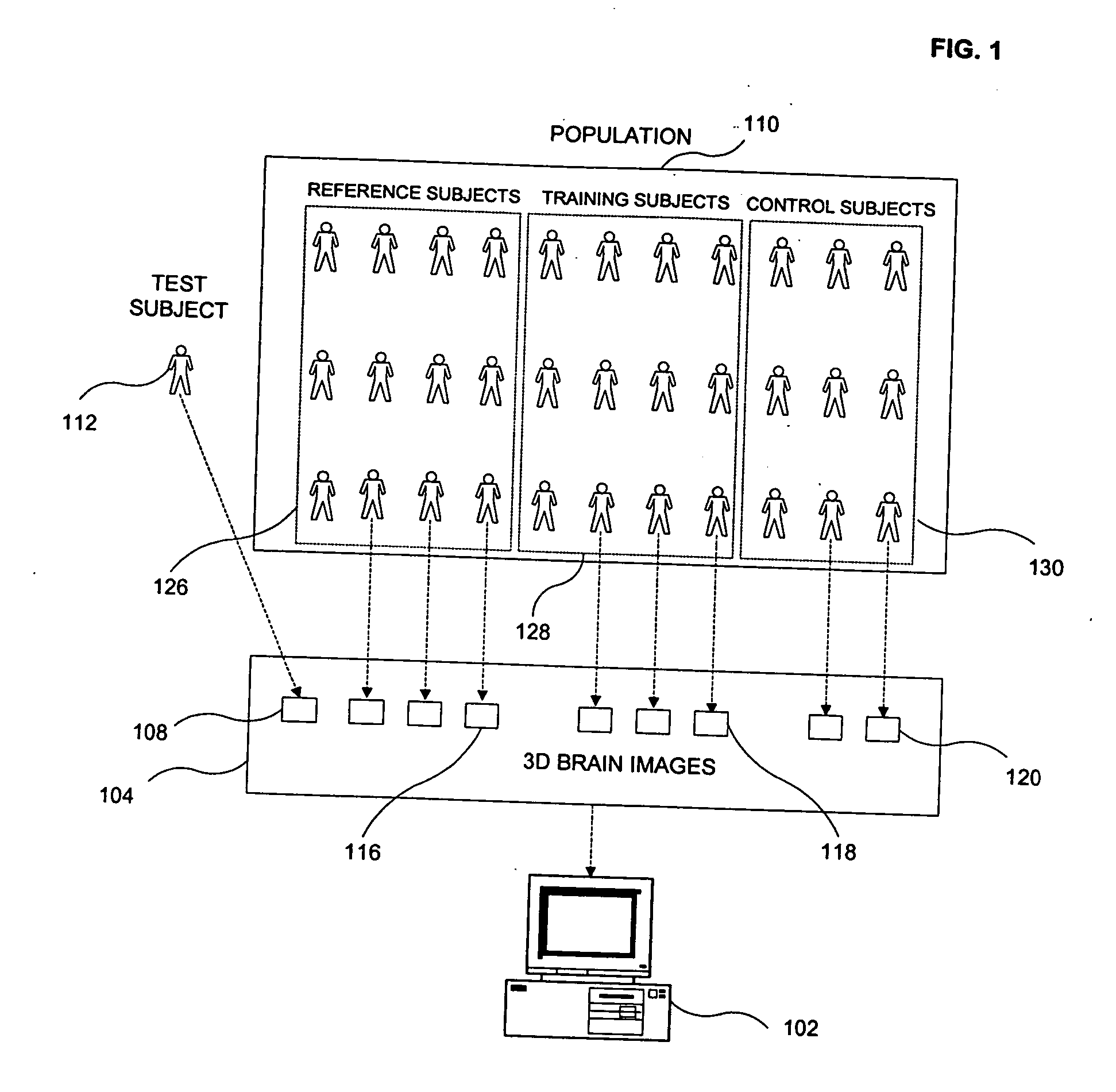
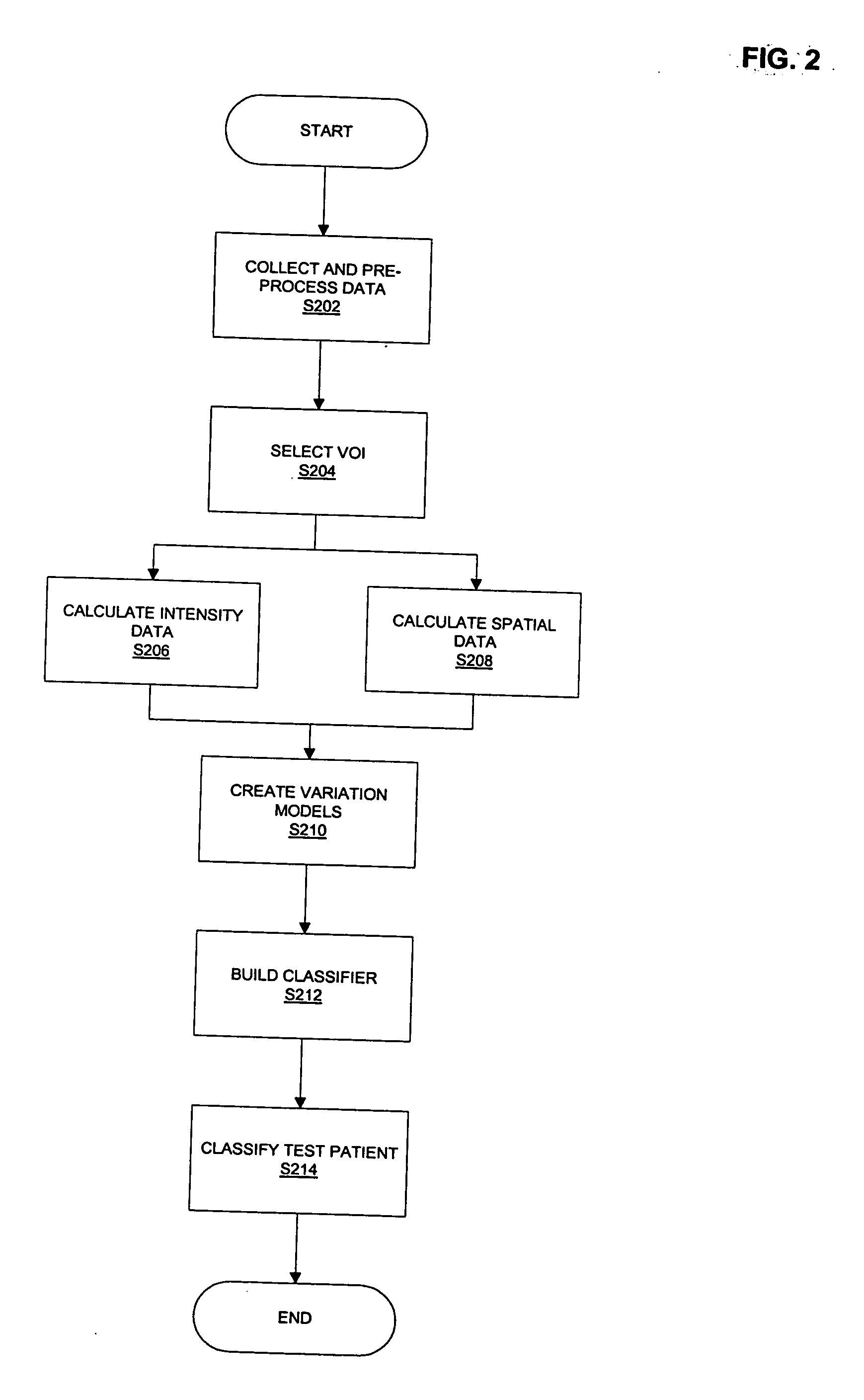
ActiveUS20060104494A1Effective classificationImage enhancementMedical data miningTest objectEpileptic disorder
A method of classifying a test subject comprises collecting imaging data for a plurality of training subjects, control subjects and a test subject. An intensity volume of interest (VOI) and a spatial VOI are selected from said imaging data. Training intensity data and spatial data are calculated for the intensity and spatial VOI. A statistical model can then be created based on the training intensity data and training spatial data to provide a universe of subjects. Control intensity data and spatial data are also calculated for the intensity and spatial VOI. A classifier can then be built dividing the universe into at least two regions. The test subject data can then be applied to the classifier to provide a determination of whether said test subject falls within the first region or the second region. The condition can be a neurological disease state such as temporal lobe epilepsy or Alzheimer's dementia.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Method and system for visualizing three-dimensional data
ActiveUS20050134582A1Reduce artifactsImage data processing detailsImage generationOcclusion effectTomosynthesis
A technique is provided for visualizing a volume of interest, such as may be acquired by a tomosynthesis imaging system. The technique provides for the use of one or more weighting functions, such as depth-dependent weighting functions, in the determination of pixel values in a volume rendering. The weighting functions may modify, for example, an intensity determination for a pixel, either directly or by modifying other contributing functions, such as for determining occlusion effects. The volume rendering may then be displayed for review by a technologist or clinician.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com