Patents
Literature
6261 results about "Depth map" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
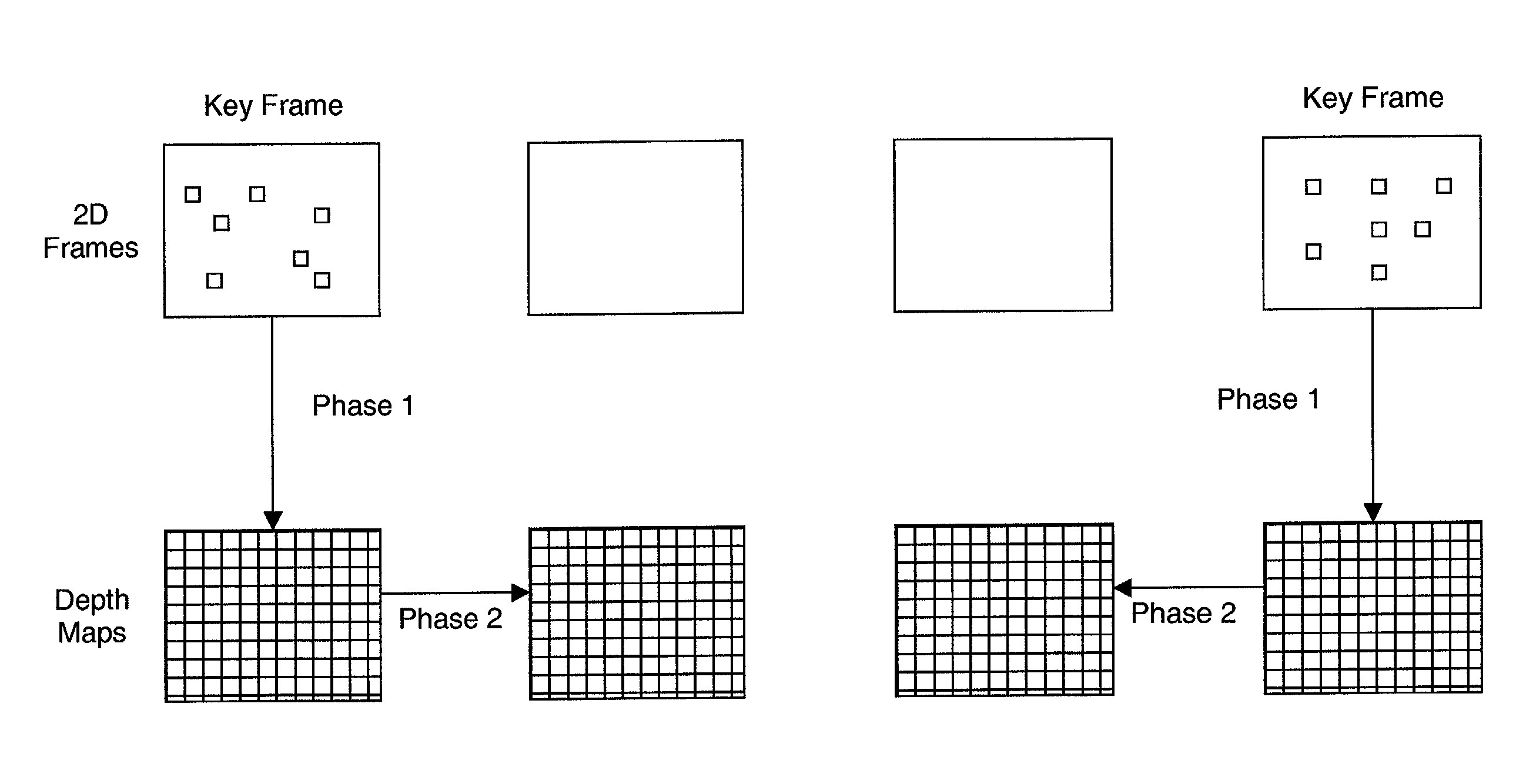
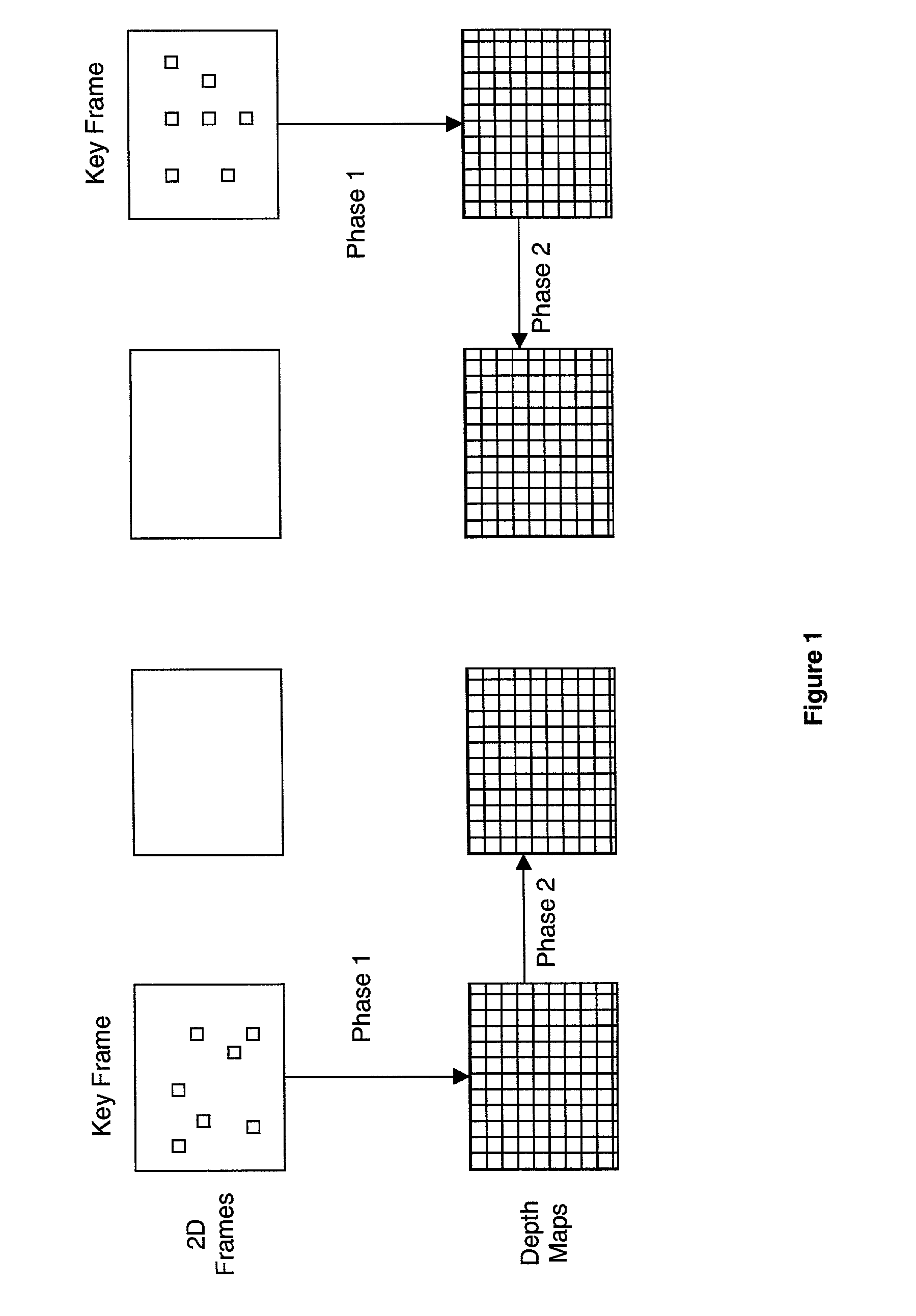
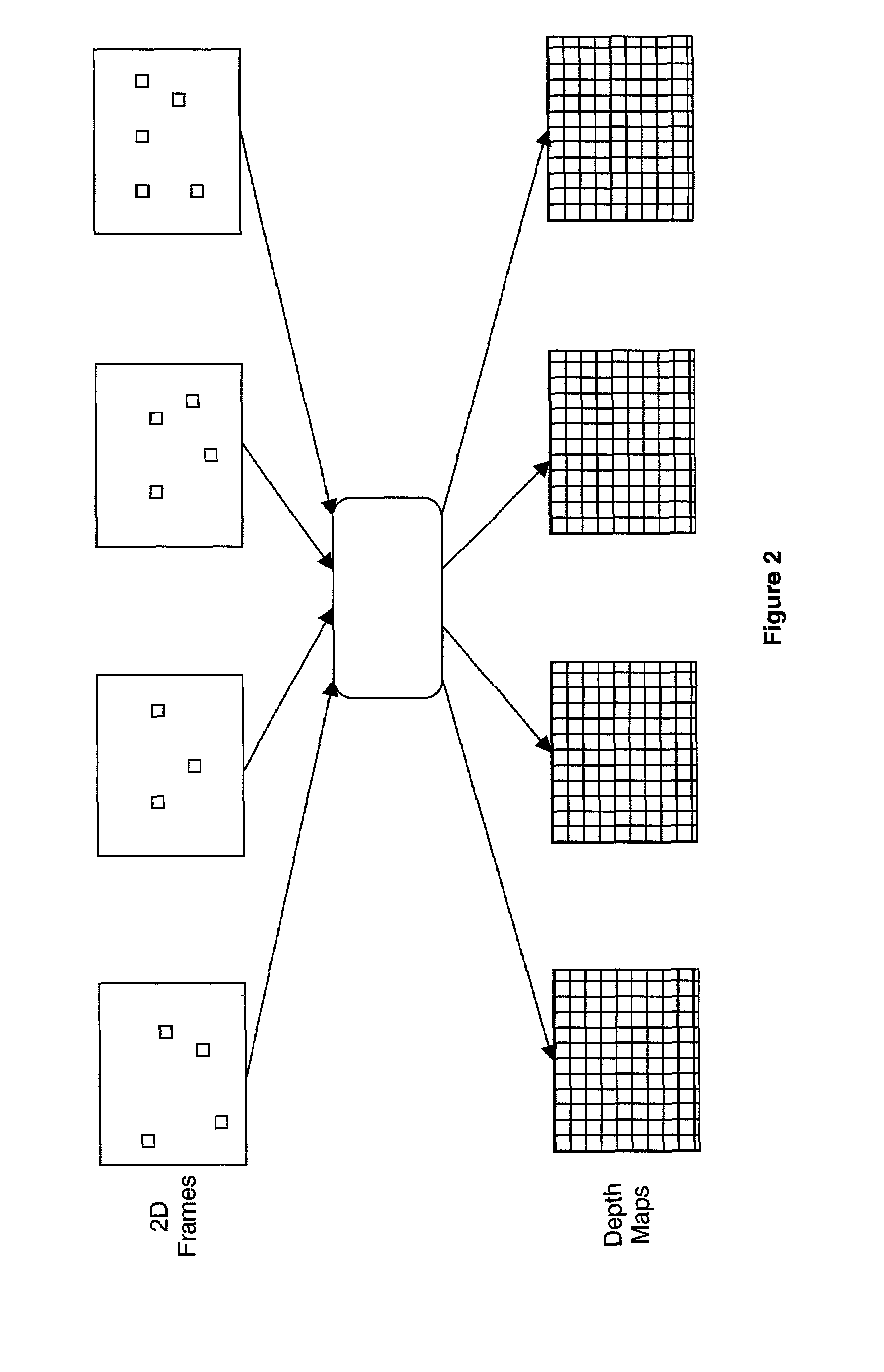
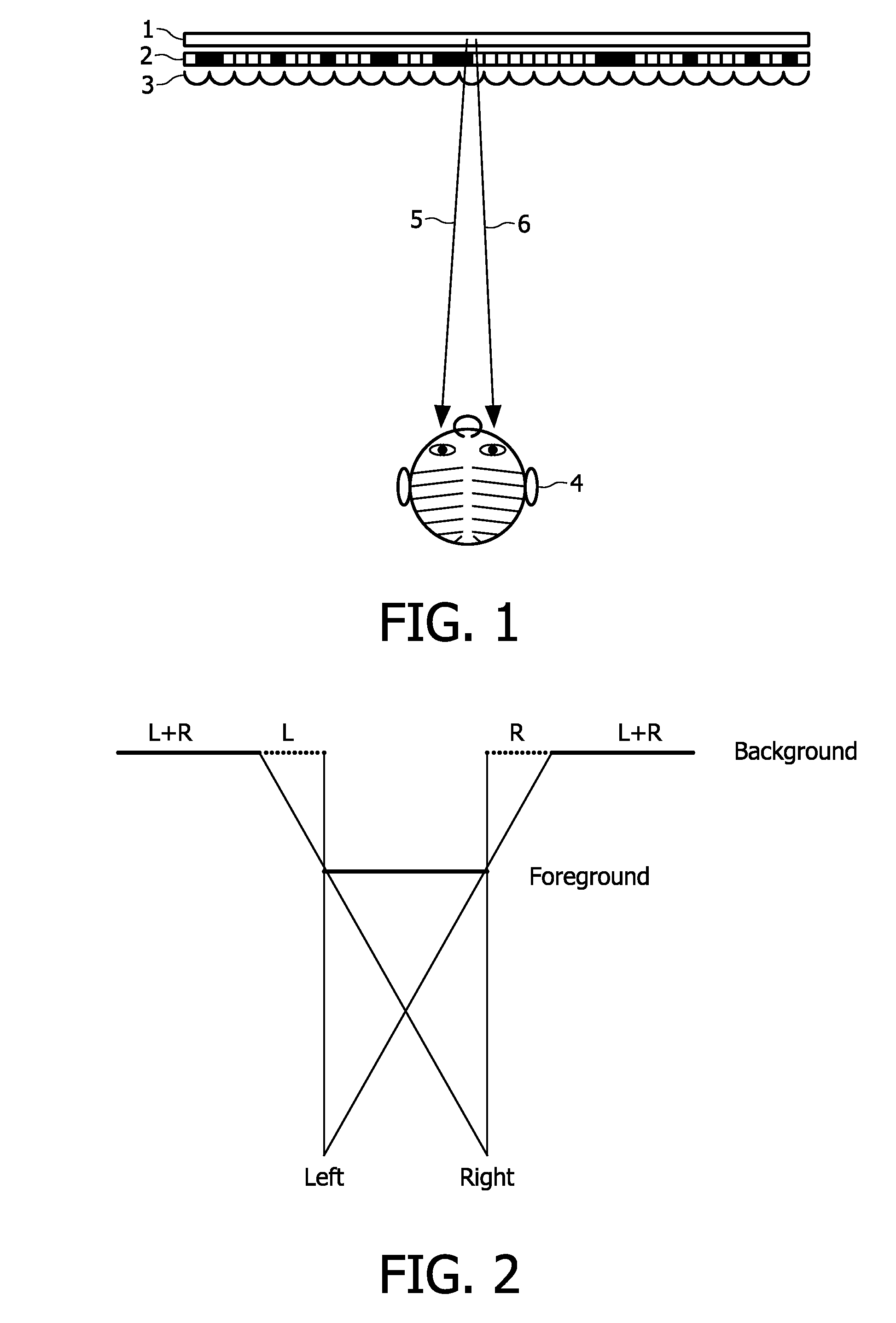
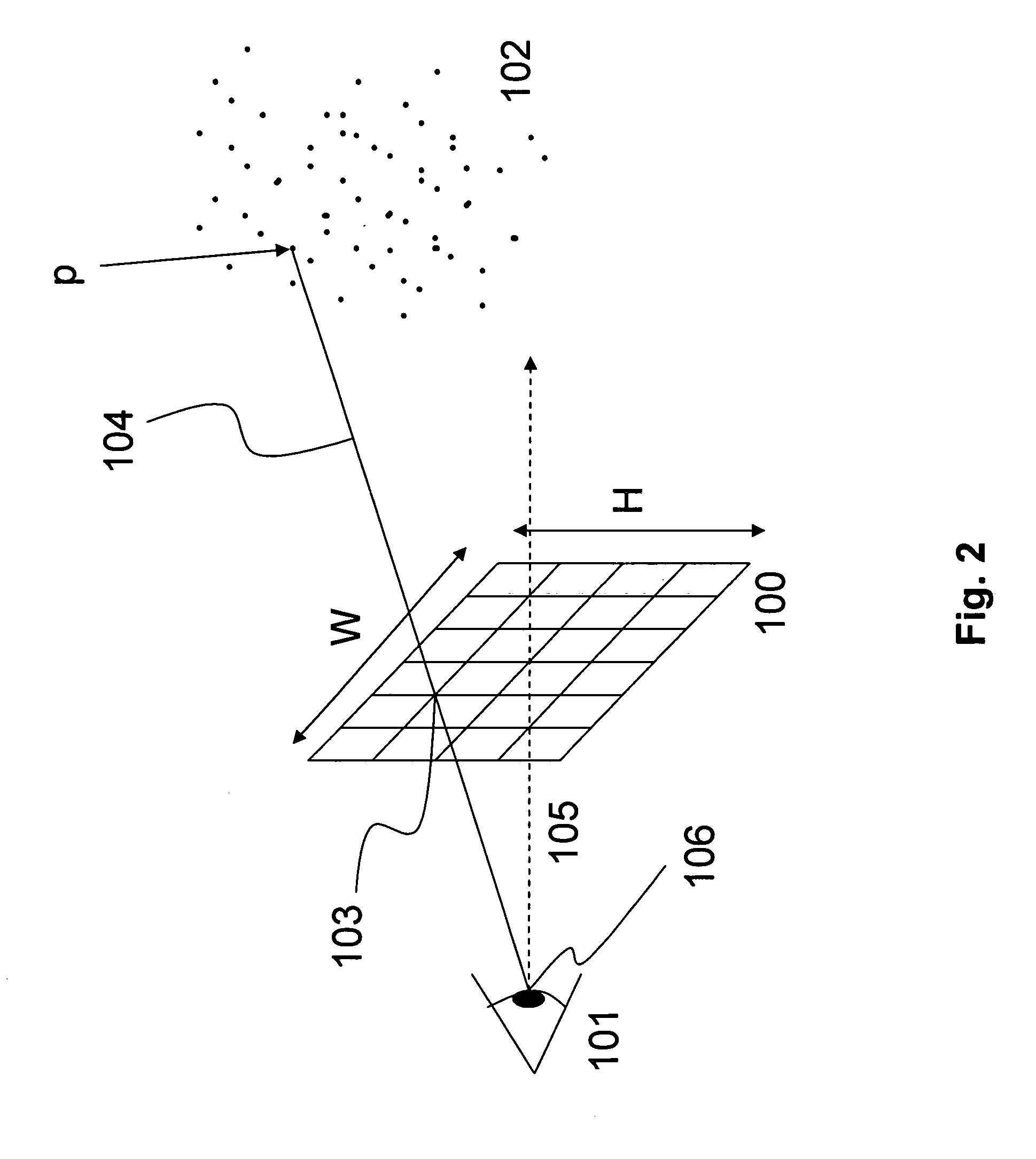
In 3D computer graphics a depth map is an image or image channel that contains information relating to the distance of the surfaces of scene objects from a viewpoint. The term is related to and may be analogous to depth buffer, Z-buffer, Z-buffering and Z-depth. The "Z" in these latter terms relates to a convention that the central axis of view of a camera is in the direction of the camera's Z axis, and not to the absolute Z axis of a scene.
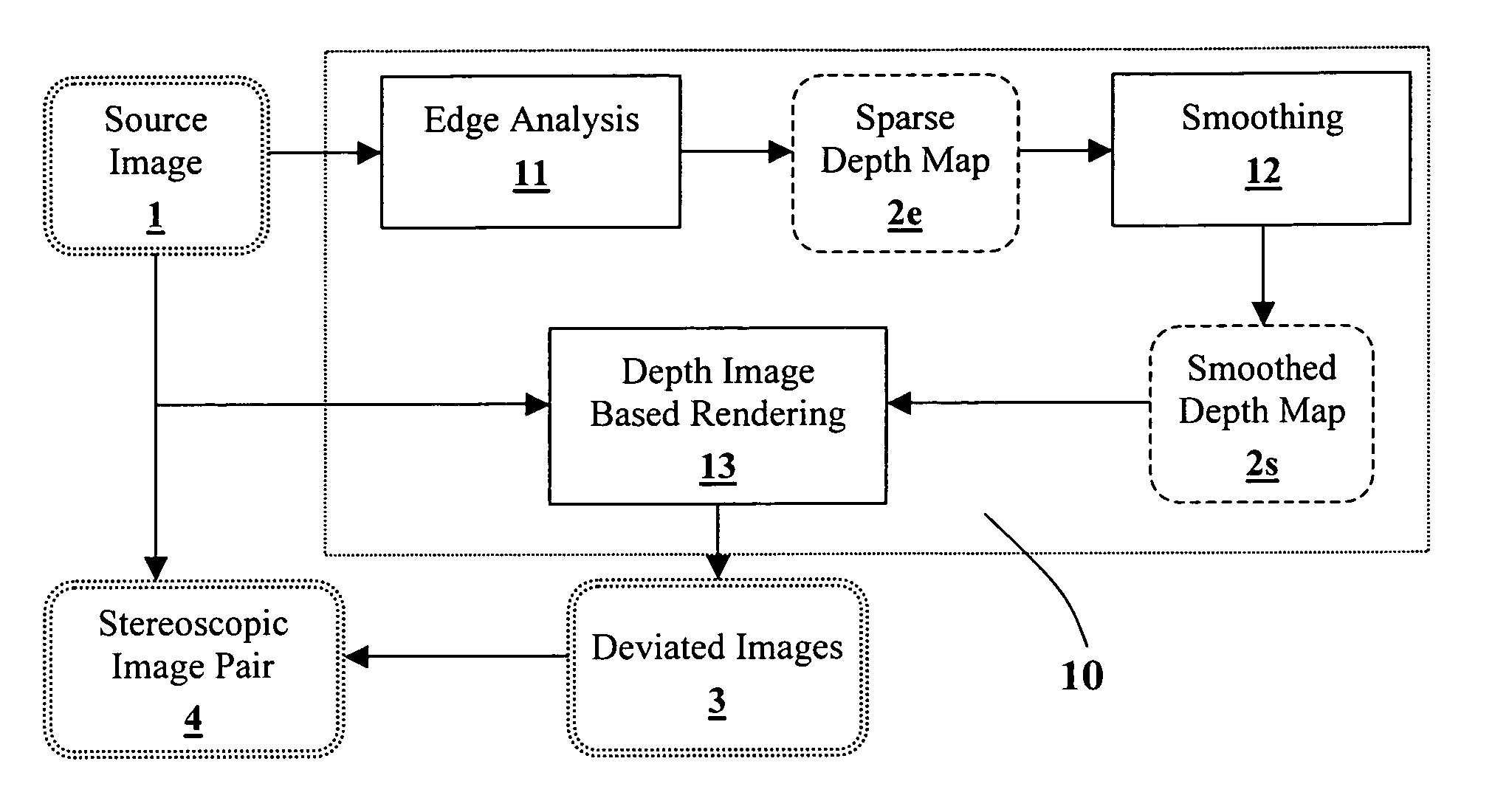
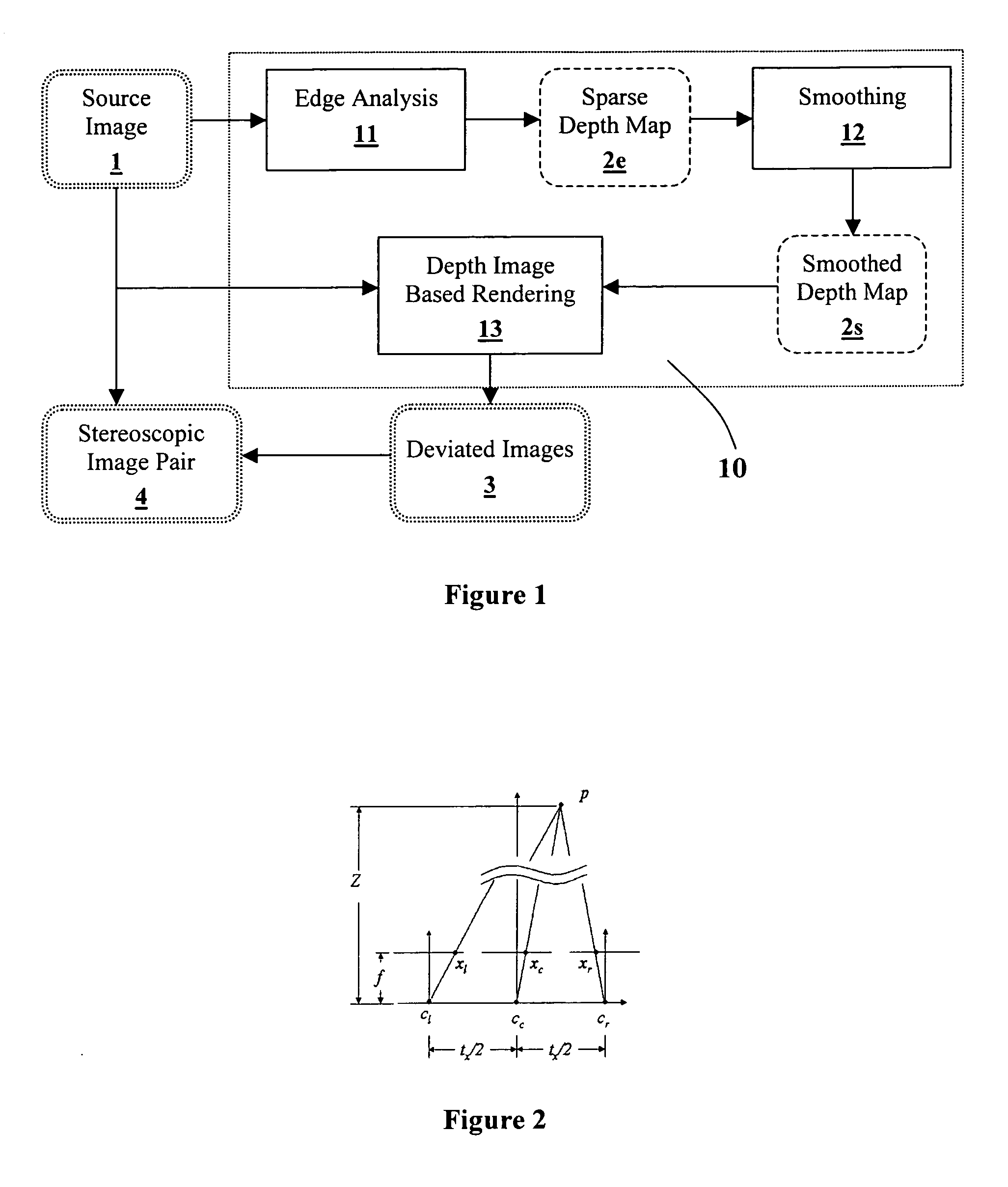
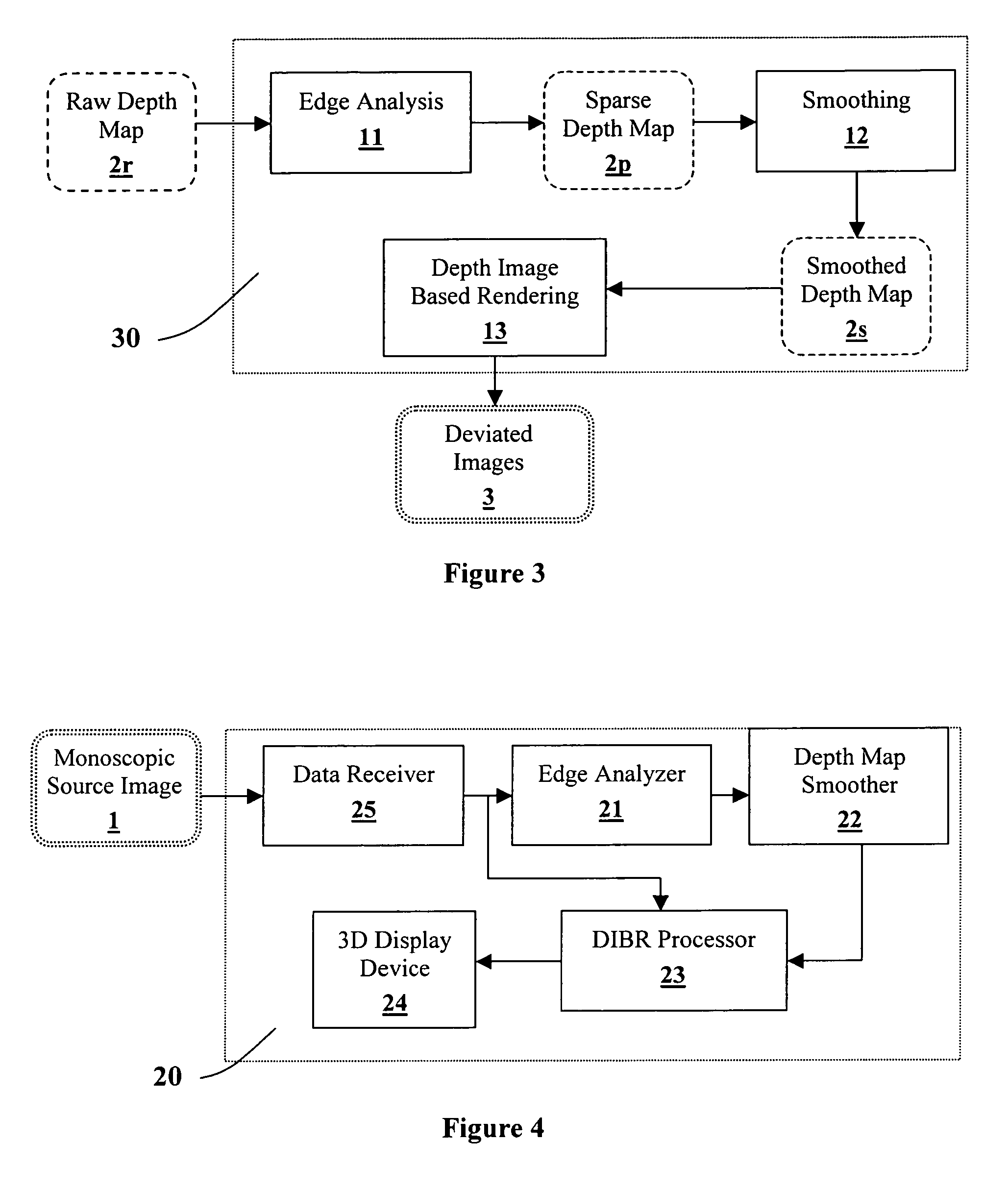
Generating a depth map from a two-dimensional source image for stereoscopic and multiview imaging
InactiveUS20070024614A1Saving in bandwidth requirementIncrease widthImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsImage pair
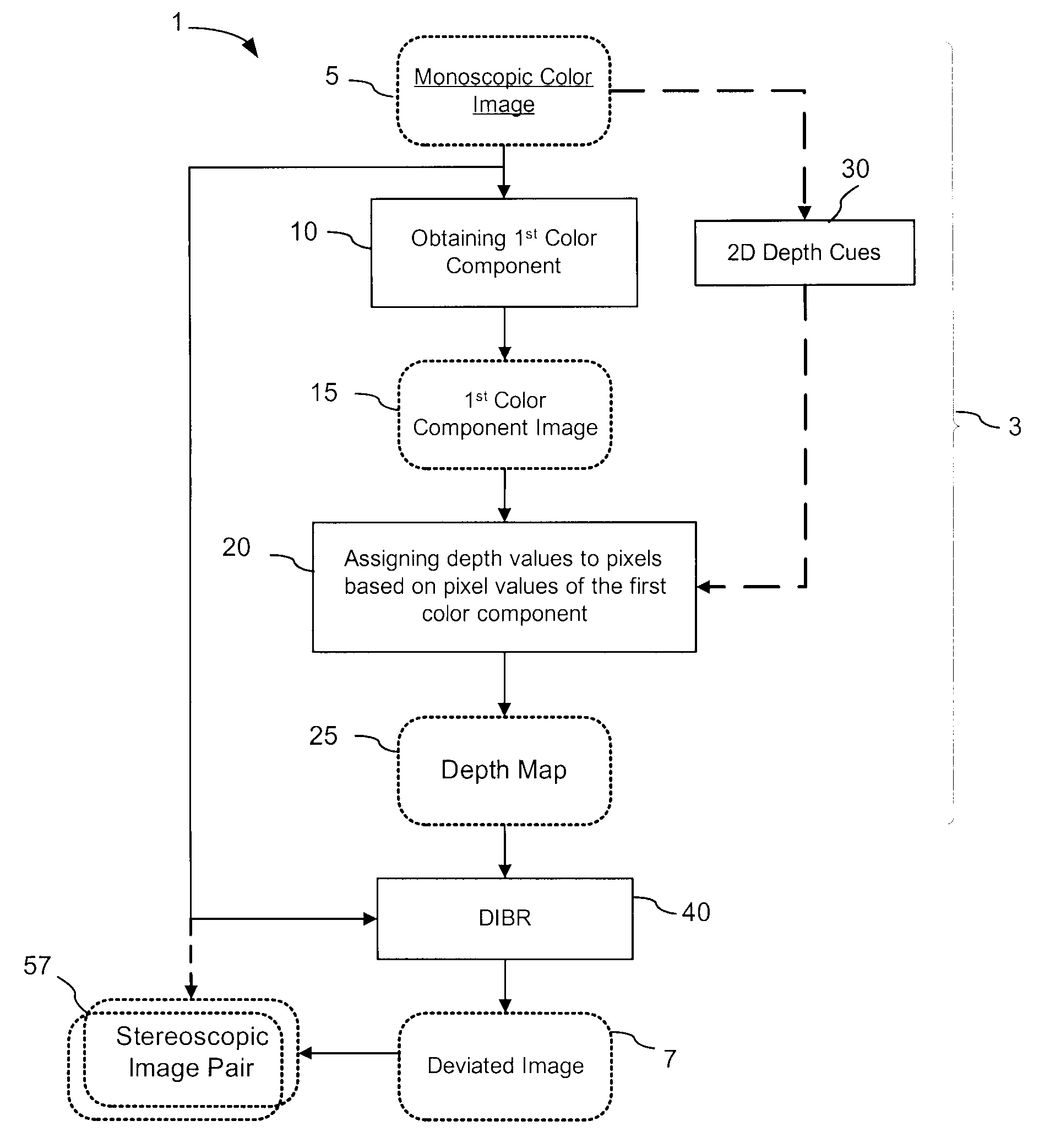
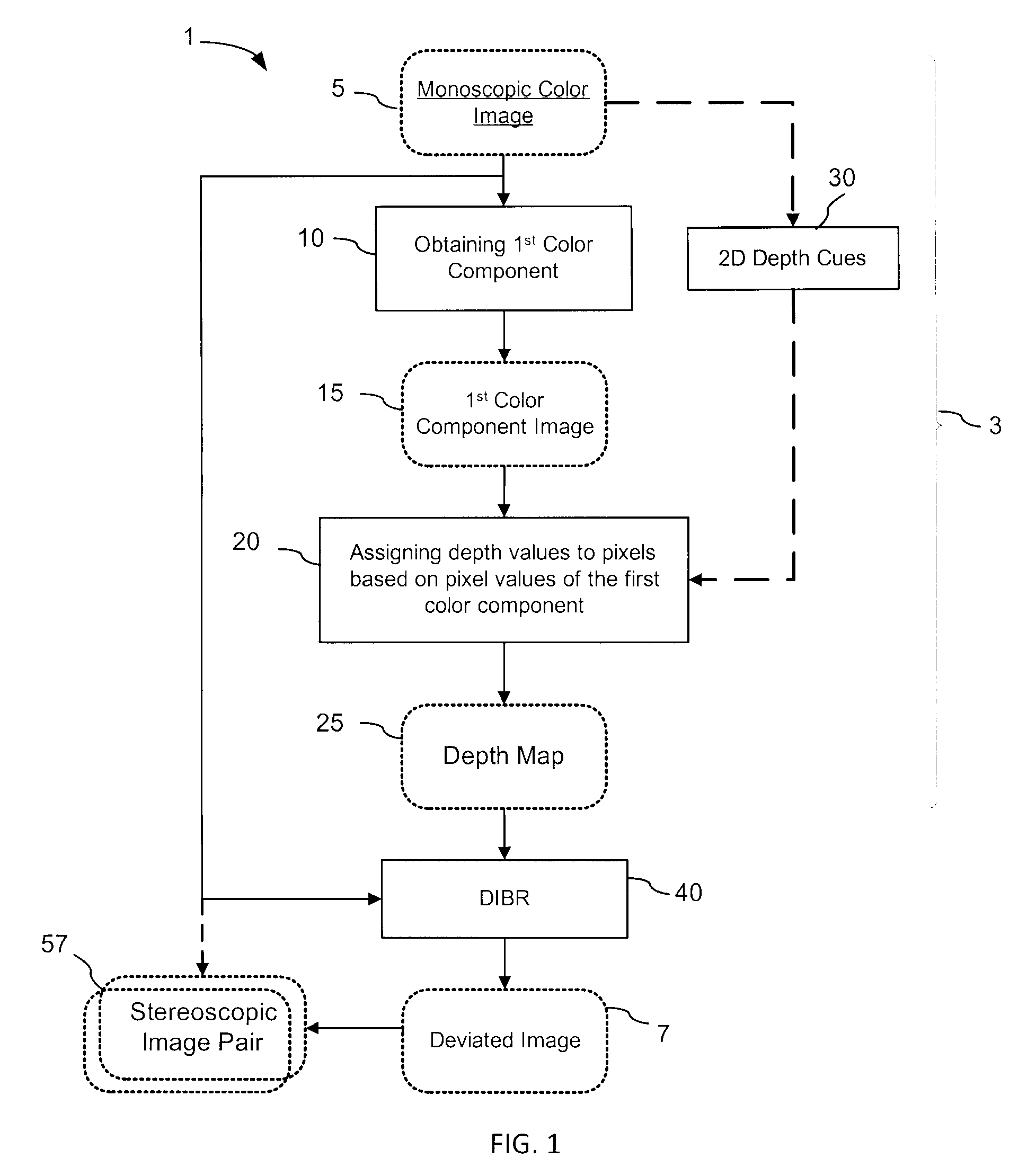
Depth maps are generated from a monoscopic source images and asymmetrically smoothed to a near-saturation level. Each depth map contains depth values focused on edges of local regions in the source image. Each edge is defined by a predetermined image parameter having an estimated value exceeding a predefined threshold. The depth values are based on the corresponding estimated values of the image parameter. The depth map is used to process the source image by a depth image based rendering algorithm to create at least one deviated image, which forms with the source image a set of monoscopic images. At least one stereoscopic image pair is selected from such a set for use in generating different viewpoints for multiview and stereoscopic purposes, including still and moving images.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Systems and Methods for Synthesizing Images from Image Data Captured by an Array Camera Using Restricted Depth of Field Depth Maps in which Depth Estimation Precision Varies
ActiveUS20140267243A1Great depth estimation precisionHigh depth estimateImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingViewpoints
Systems and methods are described for generating restricted depth of field depth maps. In one embodiment, an image processing pipeline application configures a processor to: determine a desired focal plane distance and a range of distances corresponding to a restricted depth of field for an image rendered from a reference viewpoint; generate a restricted depth of field depth map from the reference viewpoint using the set of images captured from different viewpoints, where depth estimation precision is higher for pixels with depth estimates within the range of distances corresponding to the restricted depth of field and lower for pixels with depth estimates outside of the range of distances corresponding to the restricted depth of field; and render a restricted depth of field image from the reference viewpoint using the set of images captured from different viewpoints and the restricted depth of field depth map.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
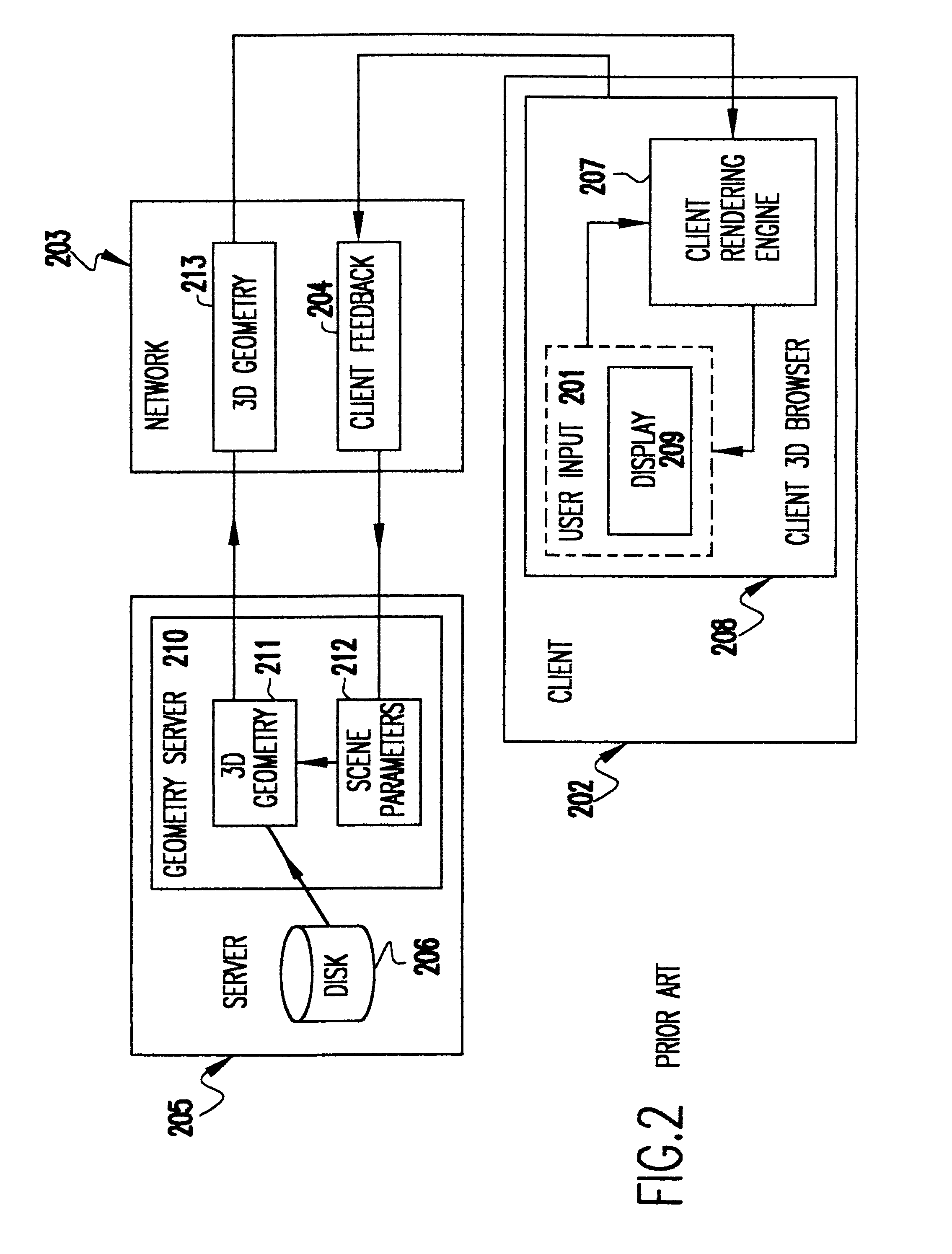
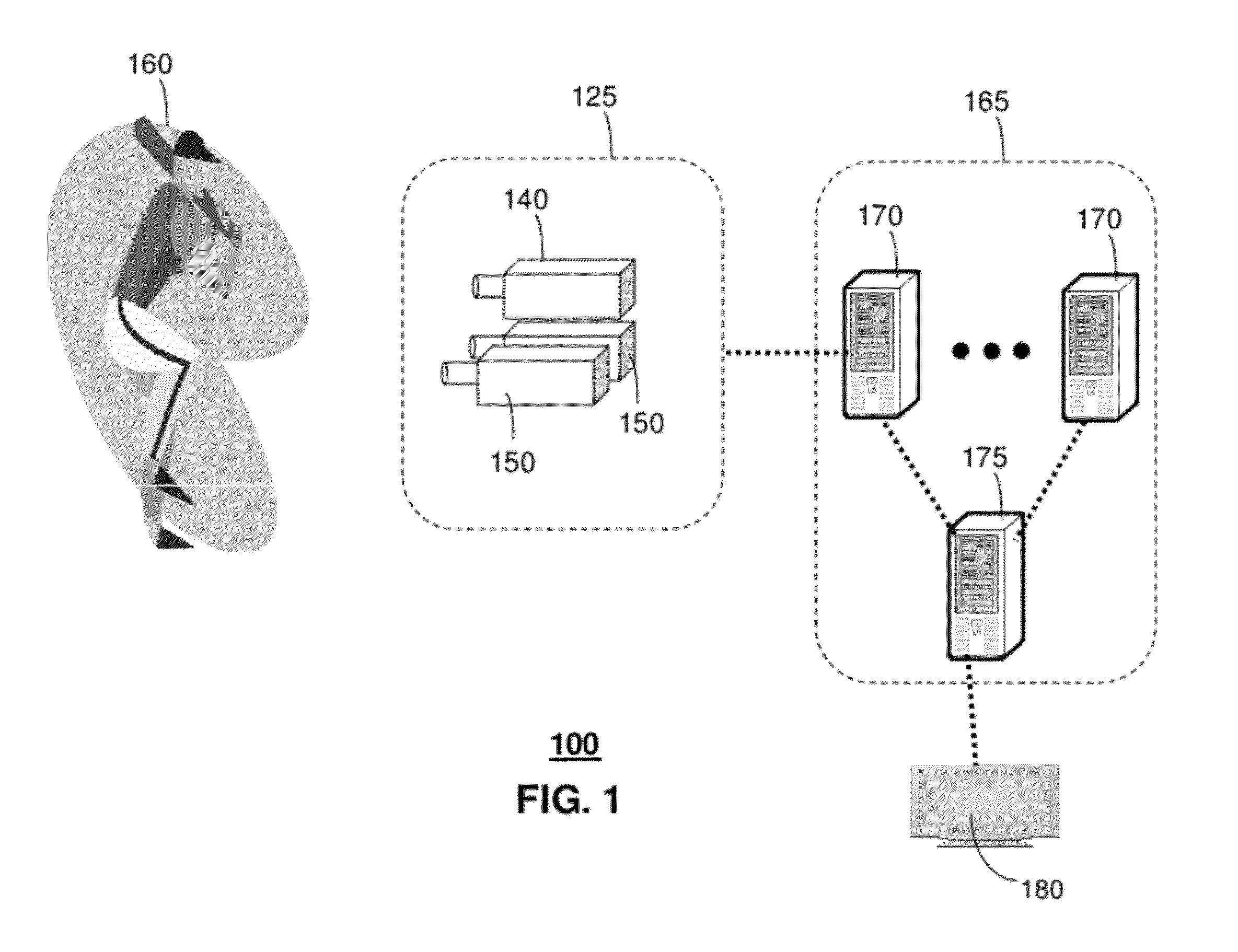
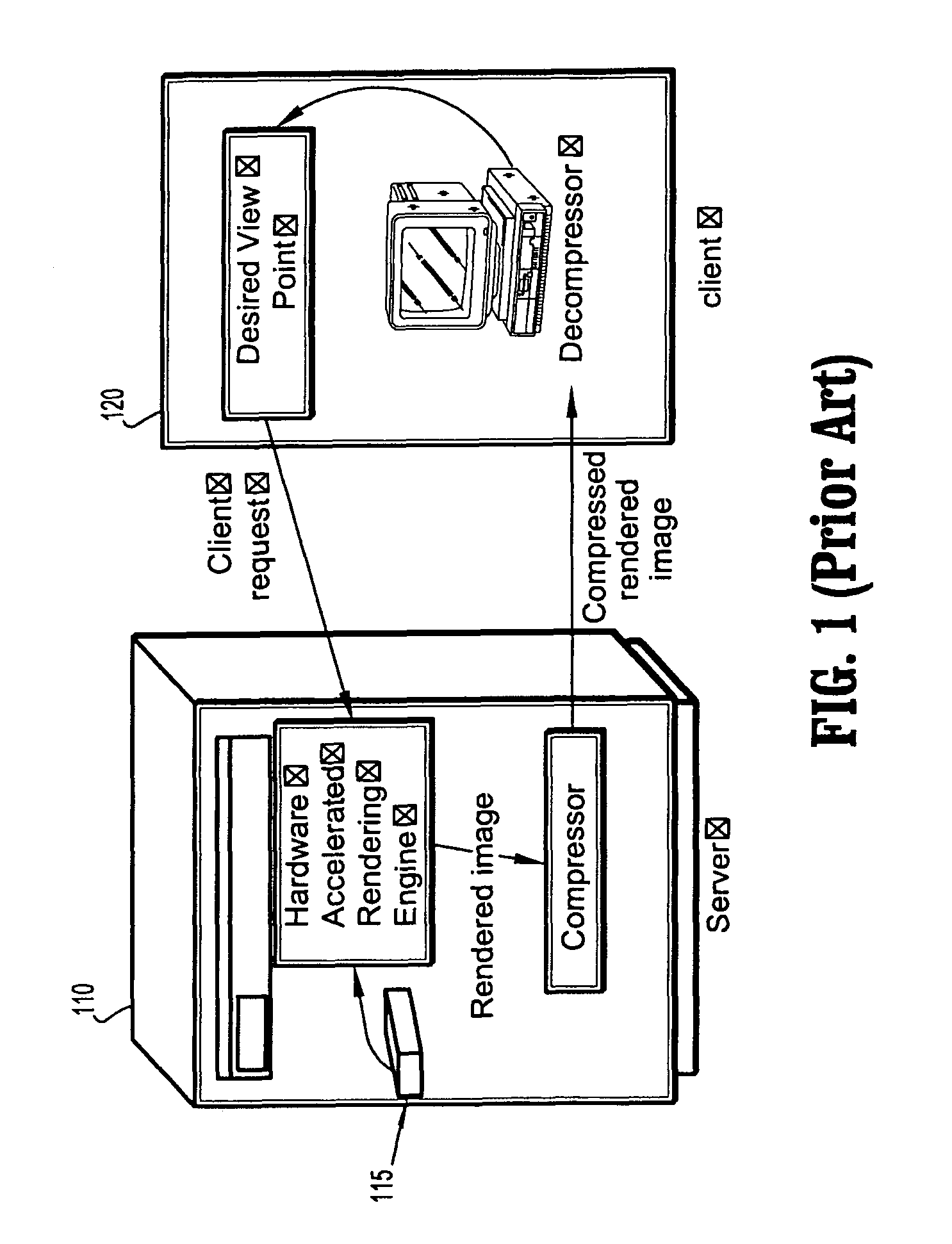
Methods and apparatus for delivering 3D graphics in a networked environment
InactiveUS6377257B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionSelective content distributionImage resolutionThree dimensional graphics
A system and method for seamlessly combining client-only rendering techniques with server-only rendering techniques. The approach uses a composite stream containing three distinct streams. Two of the streams are synchronized and transmit camera definition, video of server-rendered objects, and a time dependent depth map for the server-rendered object. The third stream is available to send geometry from the server to the client, for local rendering if appropriate. The invention can satisfy a number of viewing applications. For example, initially the most relevant geometry can stream to the client for high quality local rendering while the server delivers renderings of less relevant geometry at lower resolutions. After the most relevant geometry has been delivered to the client, the less important geometry can be optionally streamed to the client to increase the fidelity of the entire scene. In the limit, all of the geometry is transferred to the client and the situation corresponds to client-only rendering system where local graphics hardware is used to improve fidelity and reduce bandwidth. Alternatively, if a client does not have local three-dimensional graphics capability then the server can transmit only the video of the server-rendered object and drop the other two streams. In either case, the approach also permits for a progressive improvement in the server-rendered image whenever the scene becomes static. Bandwidth that was previously used to represent changing images is allocated to improving the fidelity of the server-rendered image whenever the scene becomes static.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Conversion and encoding techniques
A method of creating at least one depth map for an image sequence including the steps of receiving depth data for a plurality of points in the image sequence, utilising the depth data and a classifier to ascertain depth characteristics as a function of image characteristics and relative position and creating a depth map for at least one frame of the image sequence utilising the image characteristics.
Owner:HOMEWAV
Method and apparatus for synthesizing new video and/or still imagery from a collection of real video and/or still imagery
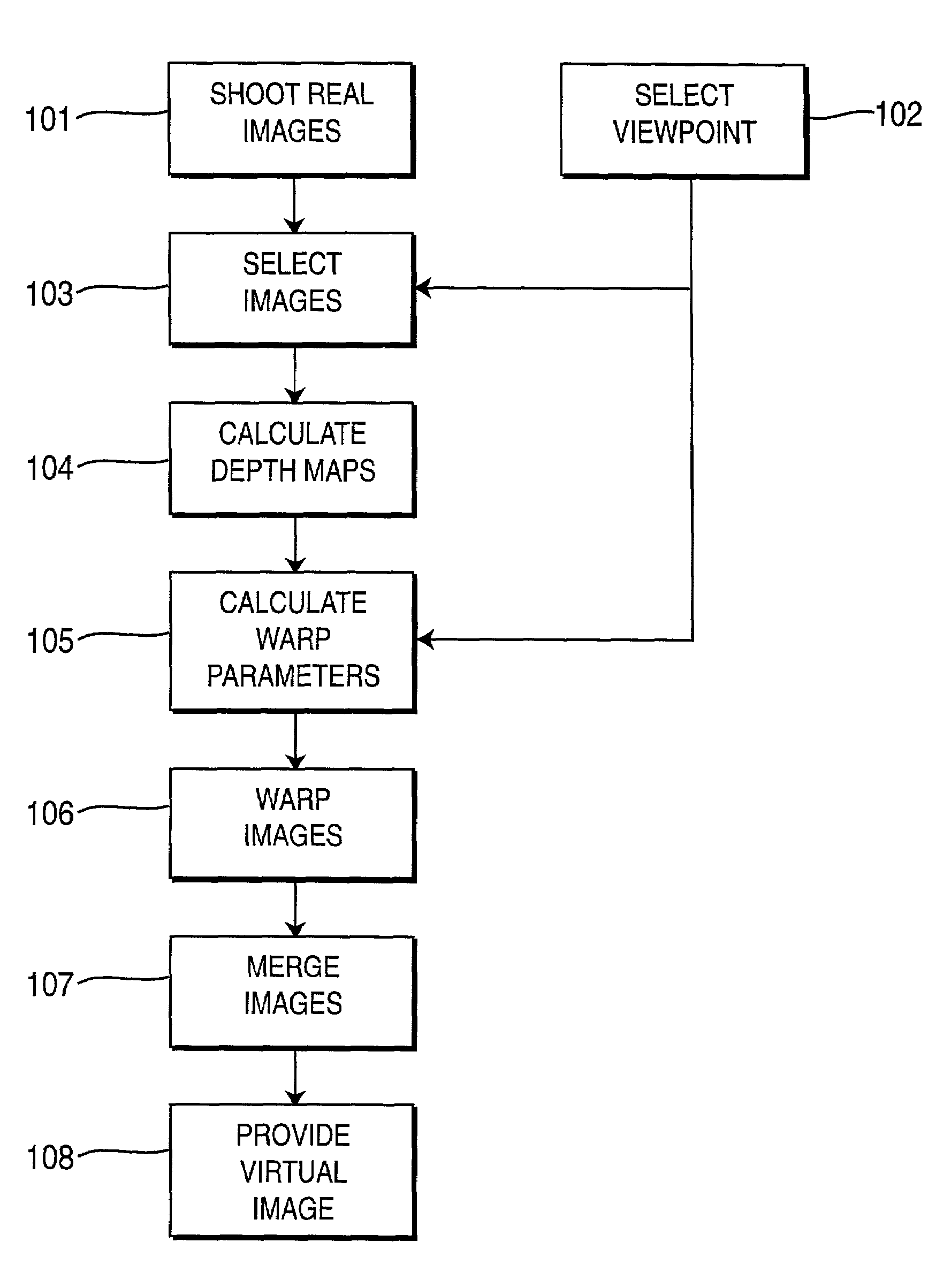
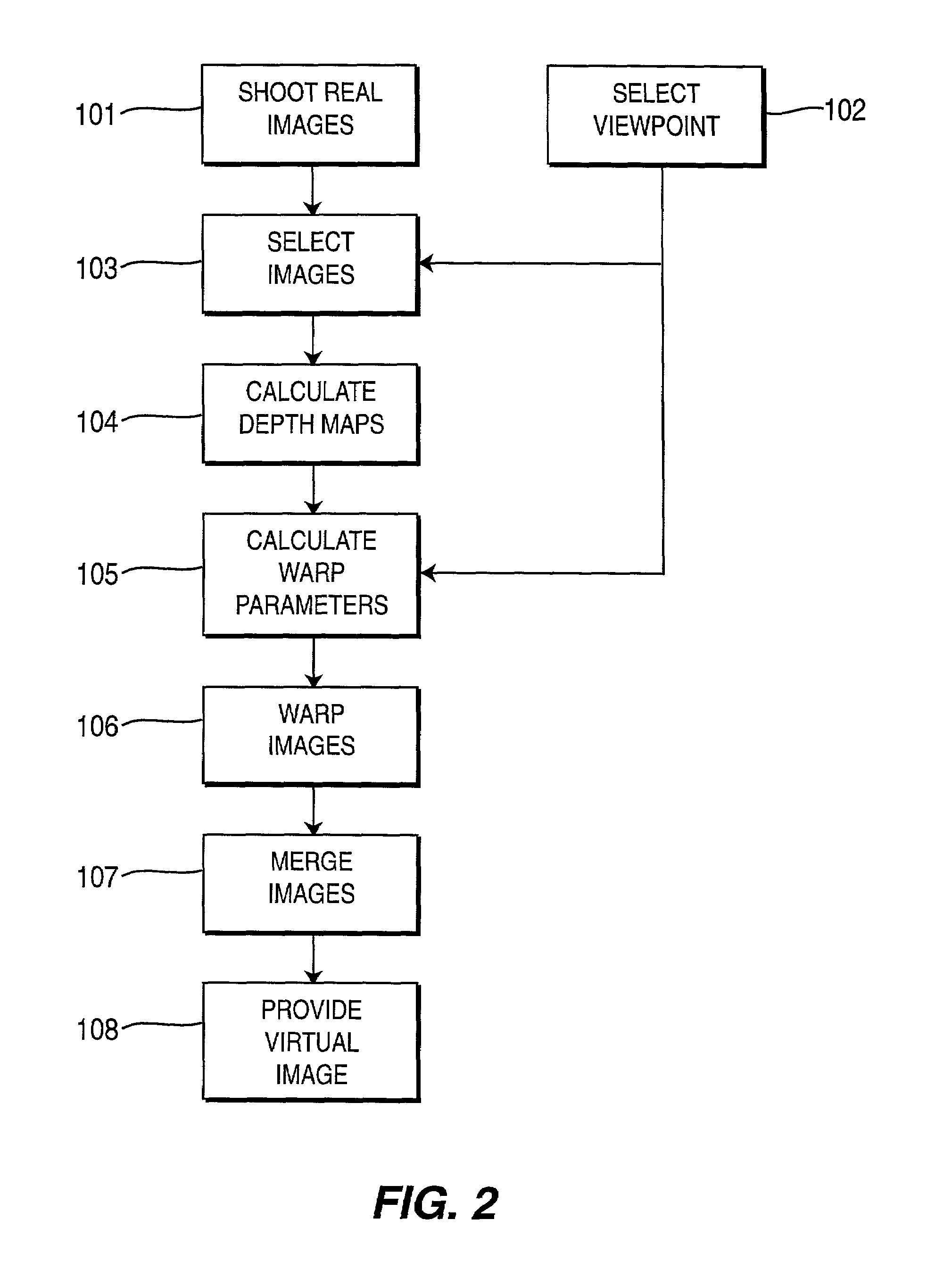
ActiveUS7085409B2Quality improvementIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsVirtual position
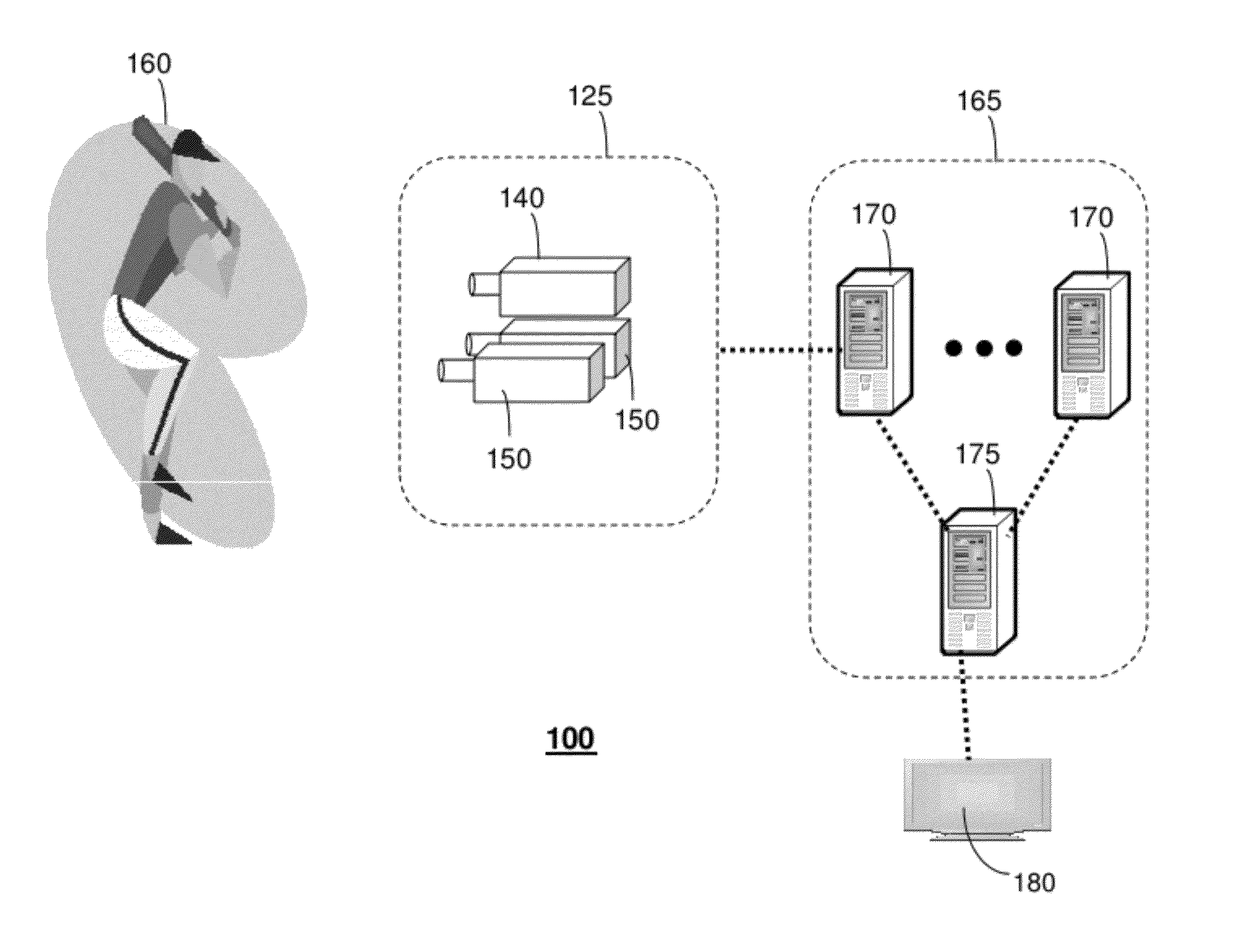
An image-based tele-presence system forward warps video images selected from a plurality fixed imagers using local depth maps and merges the warped images to form high quality images that appear as seen from a virtual position. At least two images, from the images produced by the imagers, are selected for creating a virtual image. Depth maps are generated corresponding to each of the selected images. Selected images are warped to the virtual viewpoint using warp parameters calculated using corresponding depth maps. Finally the warped images are merged to create the high quality virtual image as seen from the selected viewpoint. The system employs a video blanket of imagers, which helps both optimize the number of imagers and attain higher resolution. In an exemplary video blanket, cameras are deployed in a geometric pattern on a surface.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
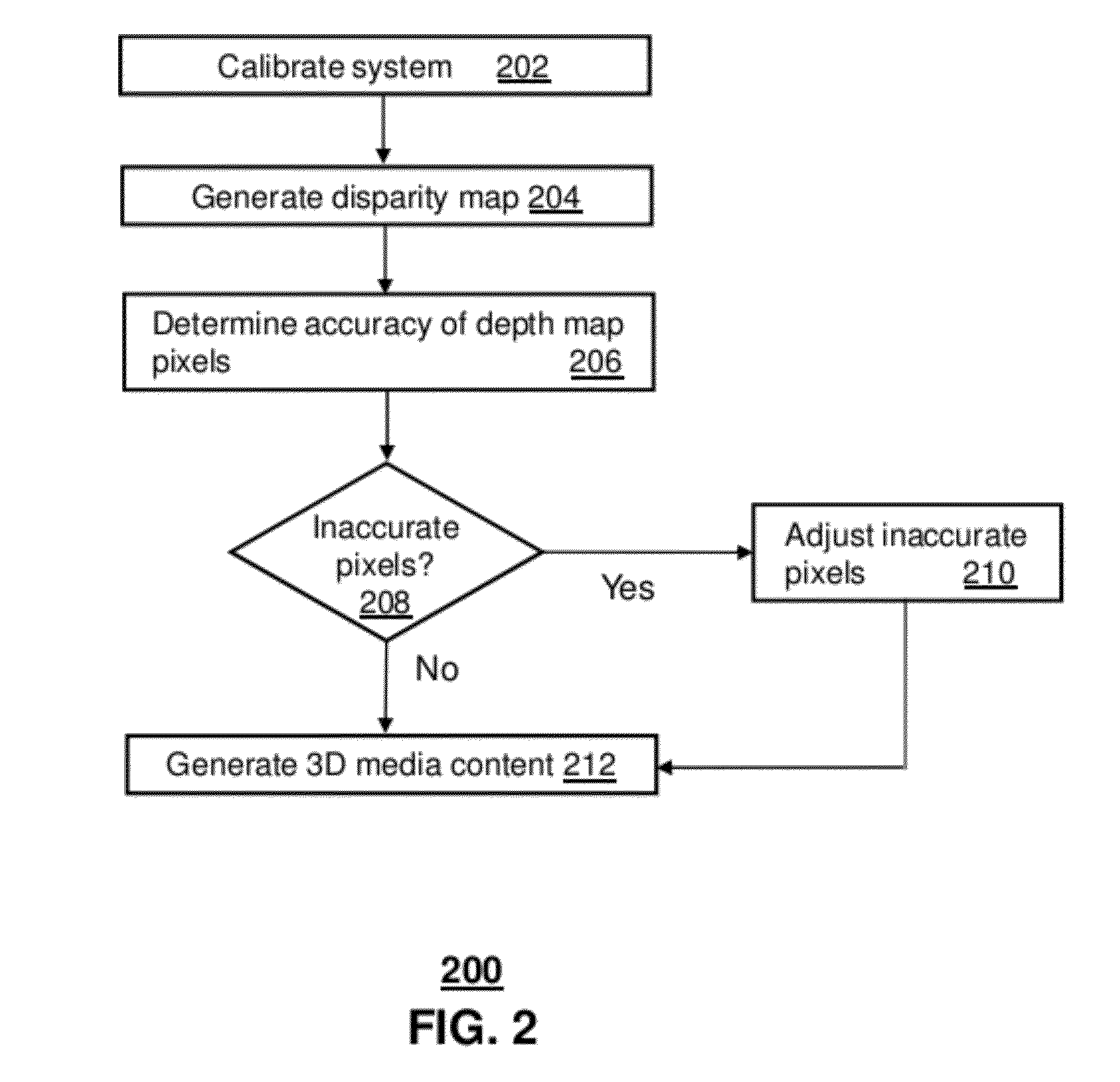
Apparatus and method for providing three dimensional media content
A system that incorporates teachings of the exemplary embodiments may include, for example, means for generating a disparity map based on a depth map, means for determining accuracy of pixels in the depth map where the determining means identifies the pixels as either accurate or inaccurate based on a confidence map and the disparity map, and means for providing an adjusted depth map where the providing means adjusts inaccurate pixels of the depth map using a cost function associated with the inaccurate pixels. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
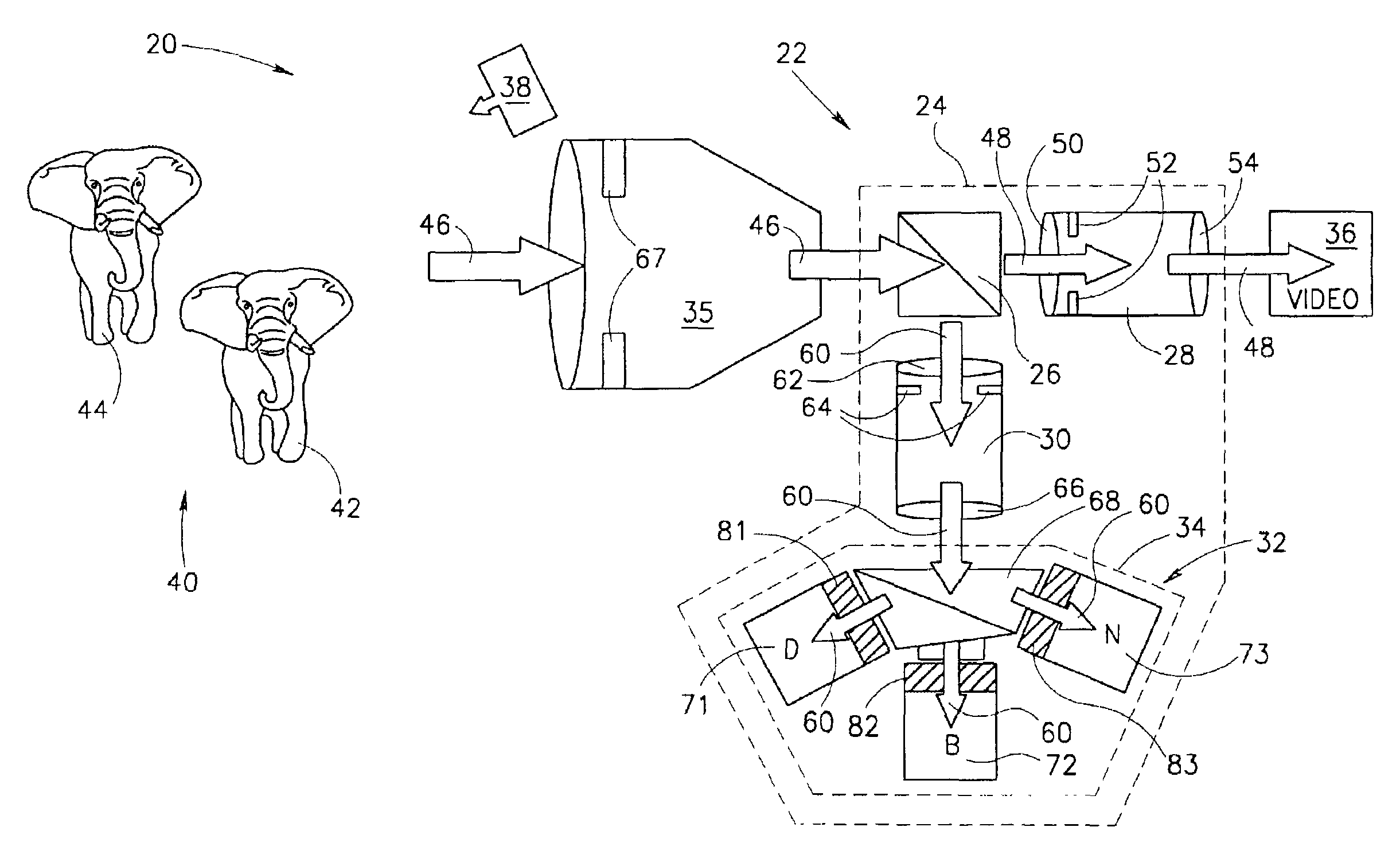
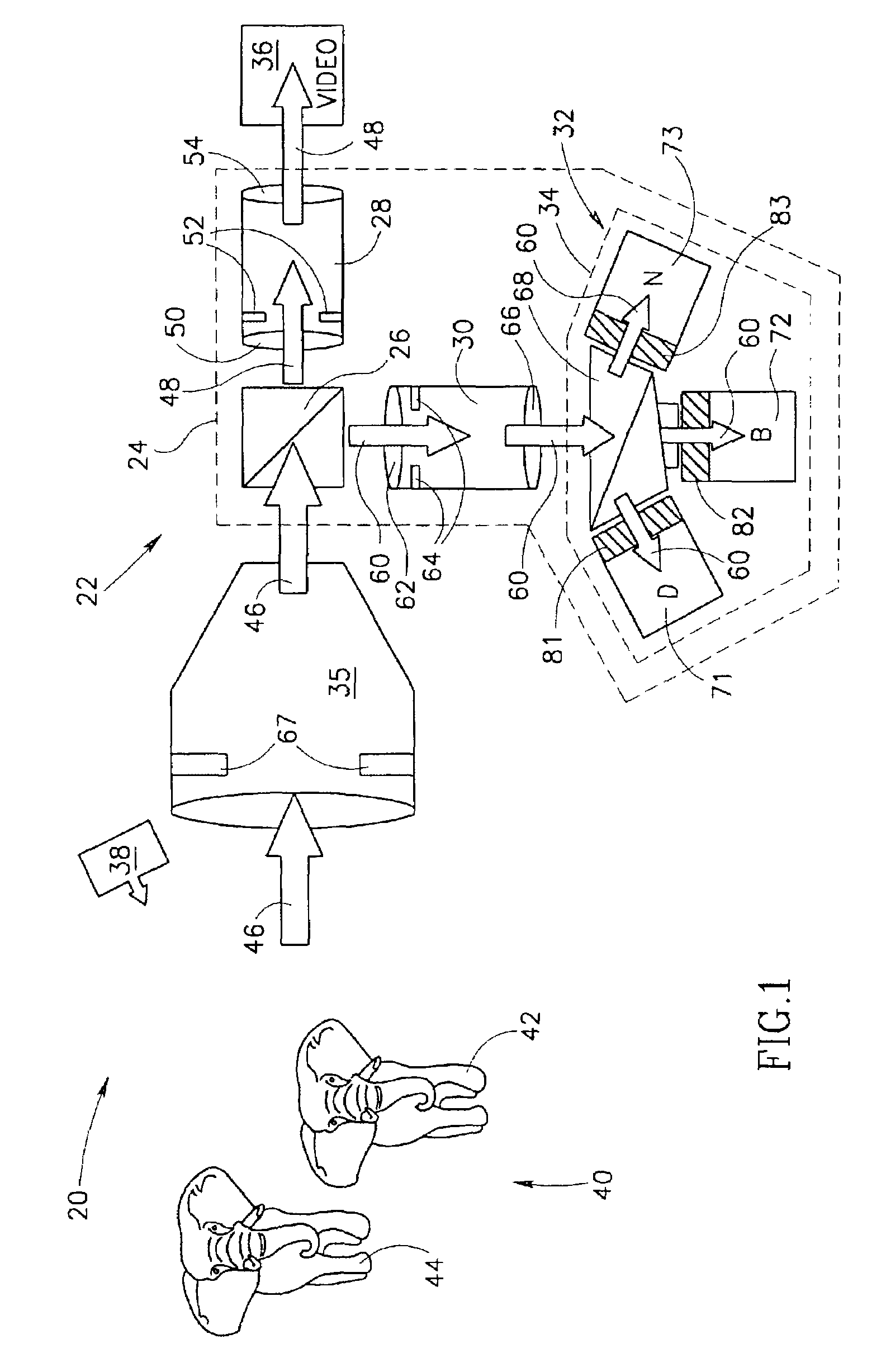
3D imaging system
InactiveUS7224384B1Easy to controlConvenient amountTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsCamera lens3d image
An optical imaging system comprising: a taking lens system that collects light from a scene being imaged with the optical imaging system; a 3D camera comprising at least one photosurface that receives light from the taking lens system simultaneously from all points in the scene and provides data for generating a depth map of the scene responsive to the light; and an imaging camera comprising at least one photosurface that receives light from the taking lens system and provides a picture of the scene responsive to the light.
Owner:MICROSOFT INT HLDG BV
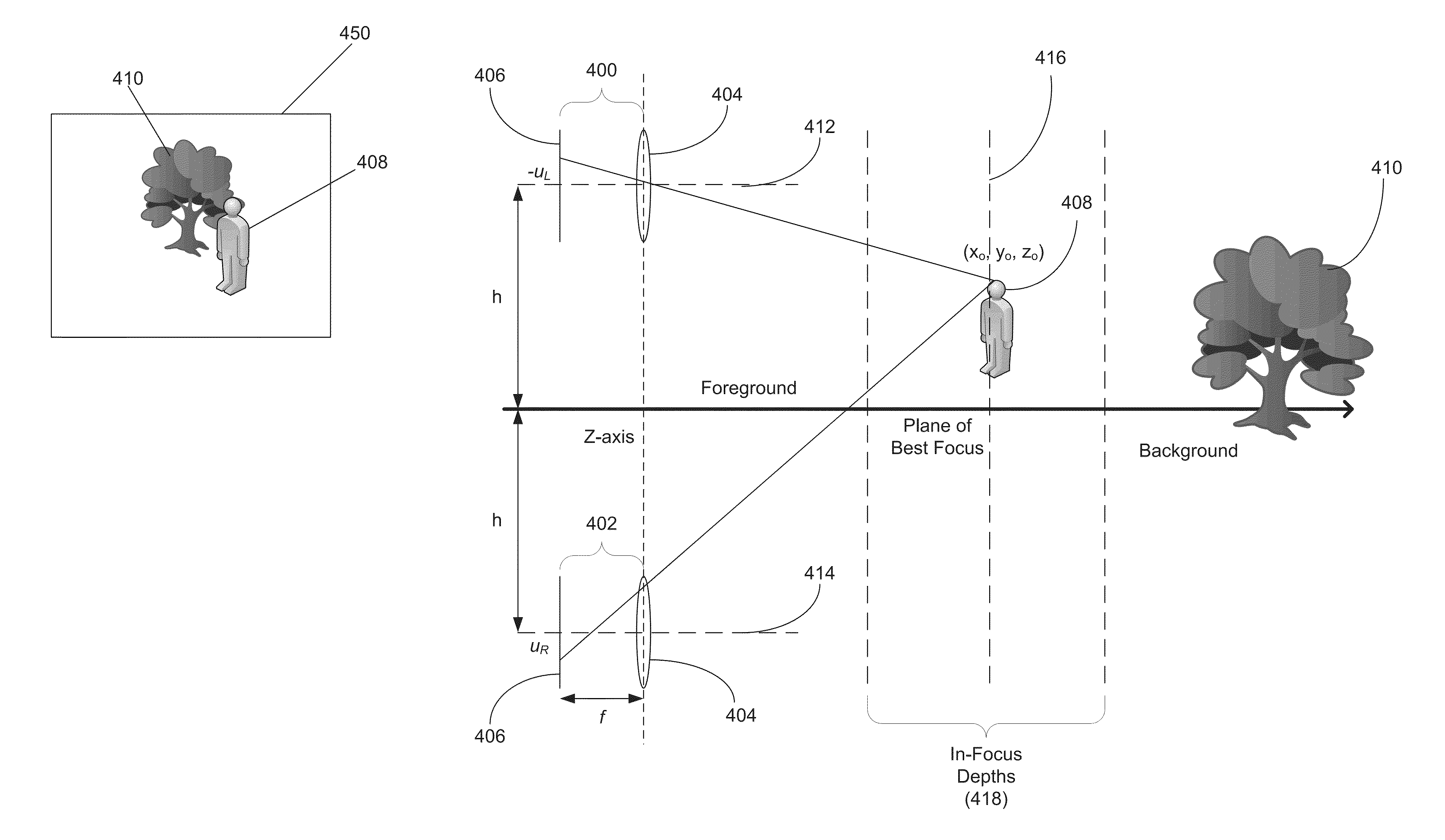
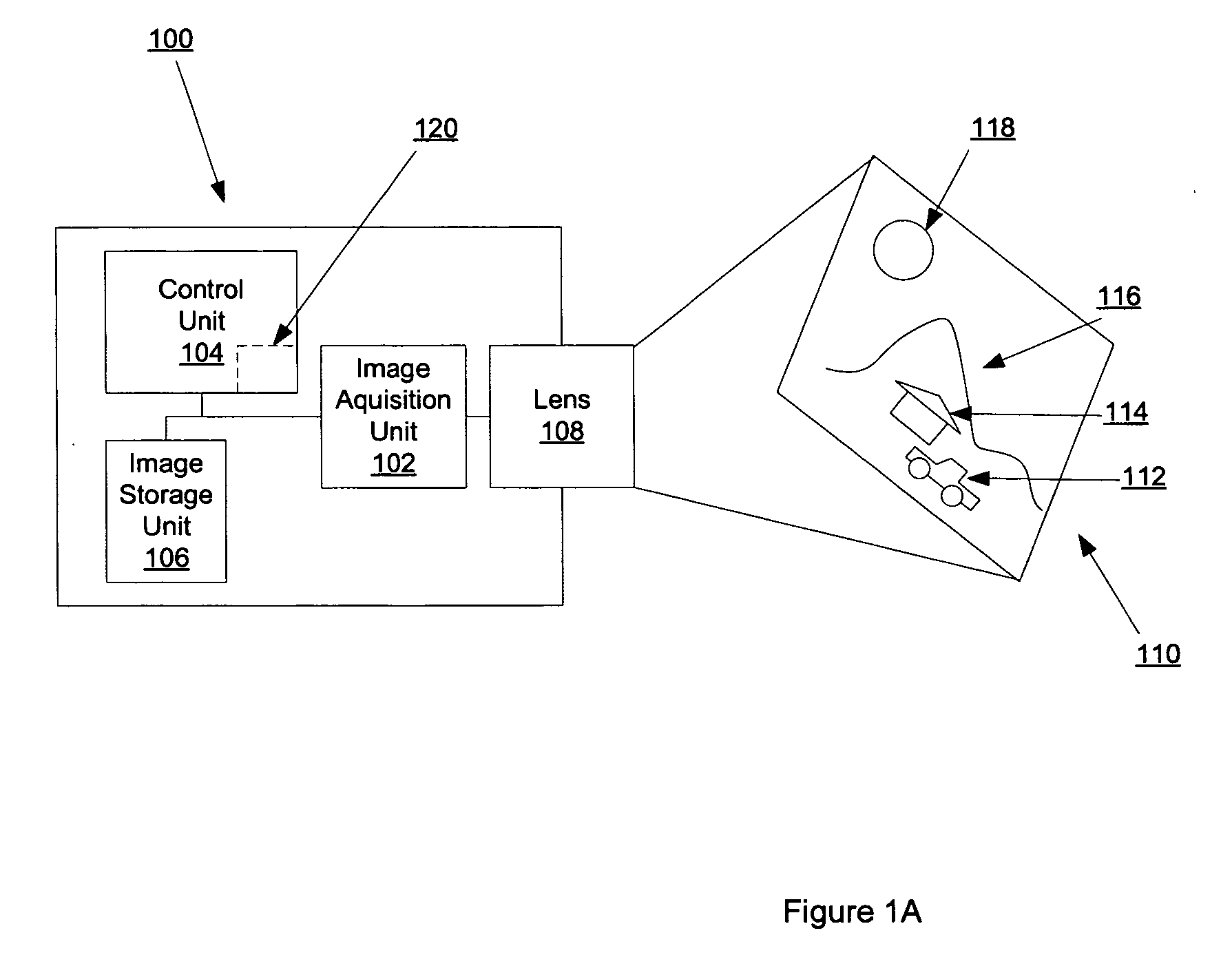
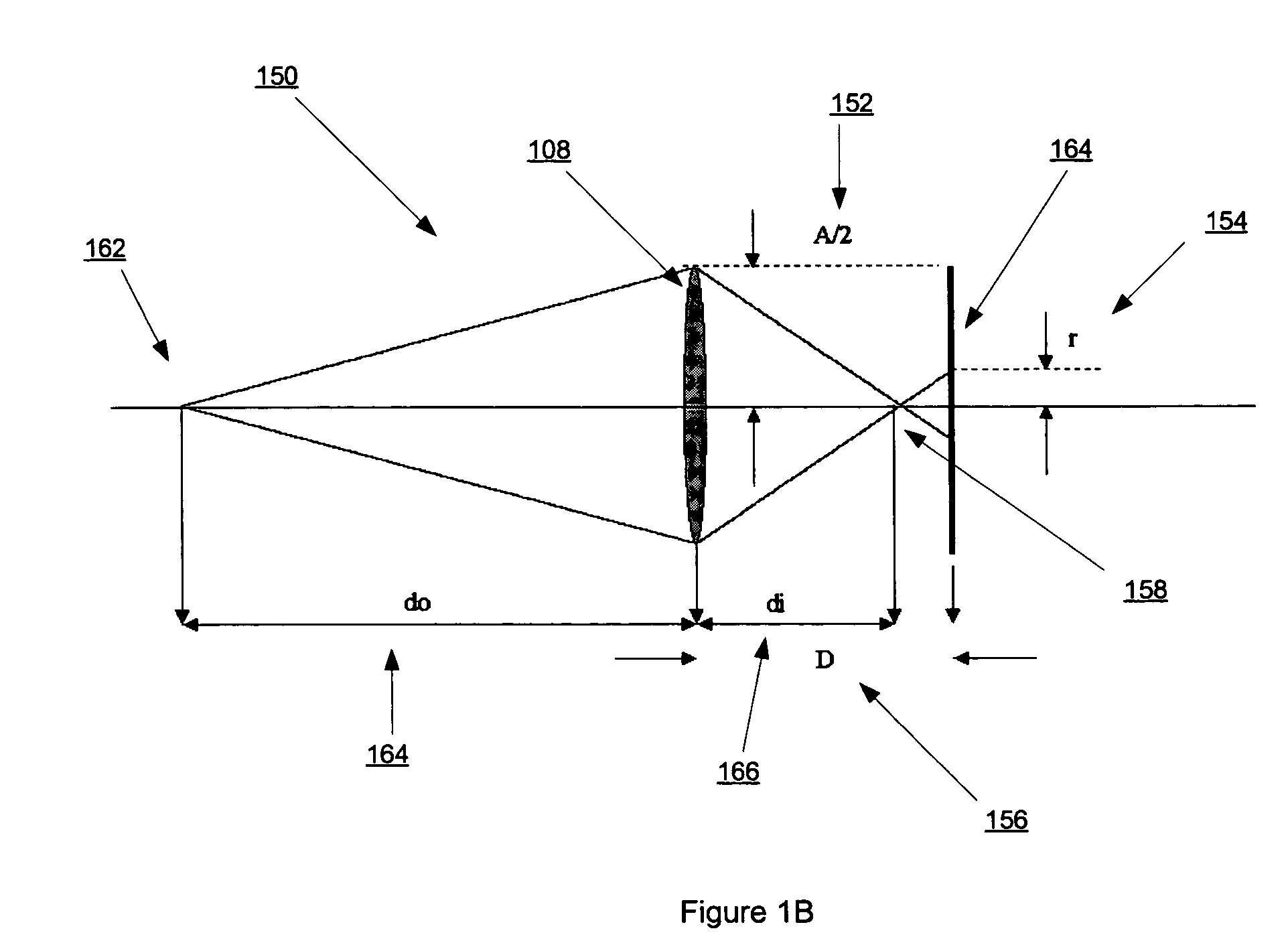
Depth information for auto focus using two pictures and two-dimensional gaussian scale space theory
InactiveUS20070036427A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree-dimensional spaceAutofocus
An imaging acquisition system that generates a depth map from two pictures of a three dimensional spatial scene is described. According to one aspect of the invention, the system generates the depth map based on the relative blur between the two pictures and the absolute blur contributed by the system. According to another aspect of the invention, the system calculates the depth map directly from the relative blur between the two pictures.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
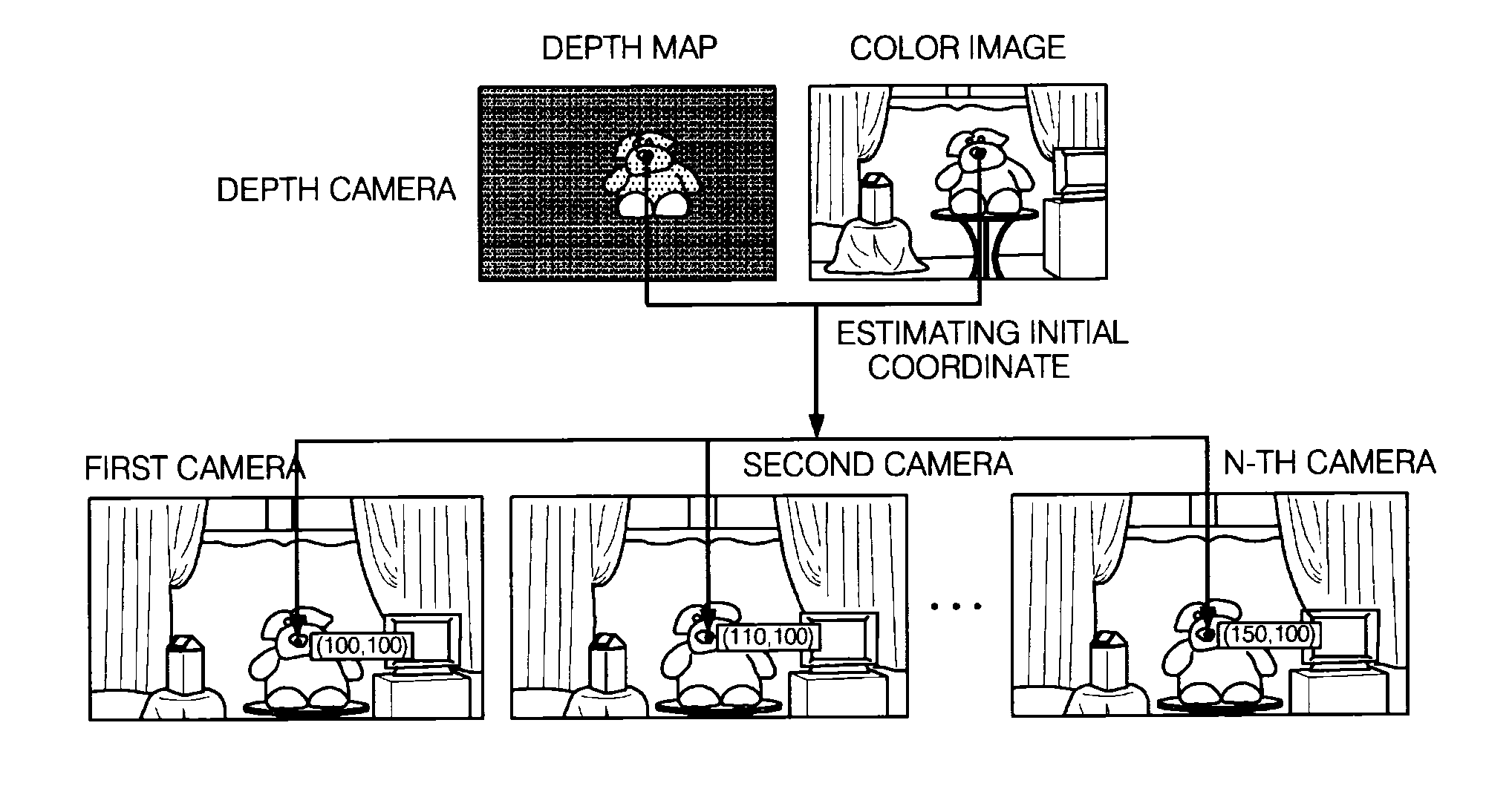
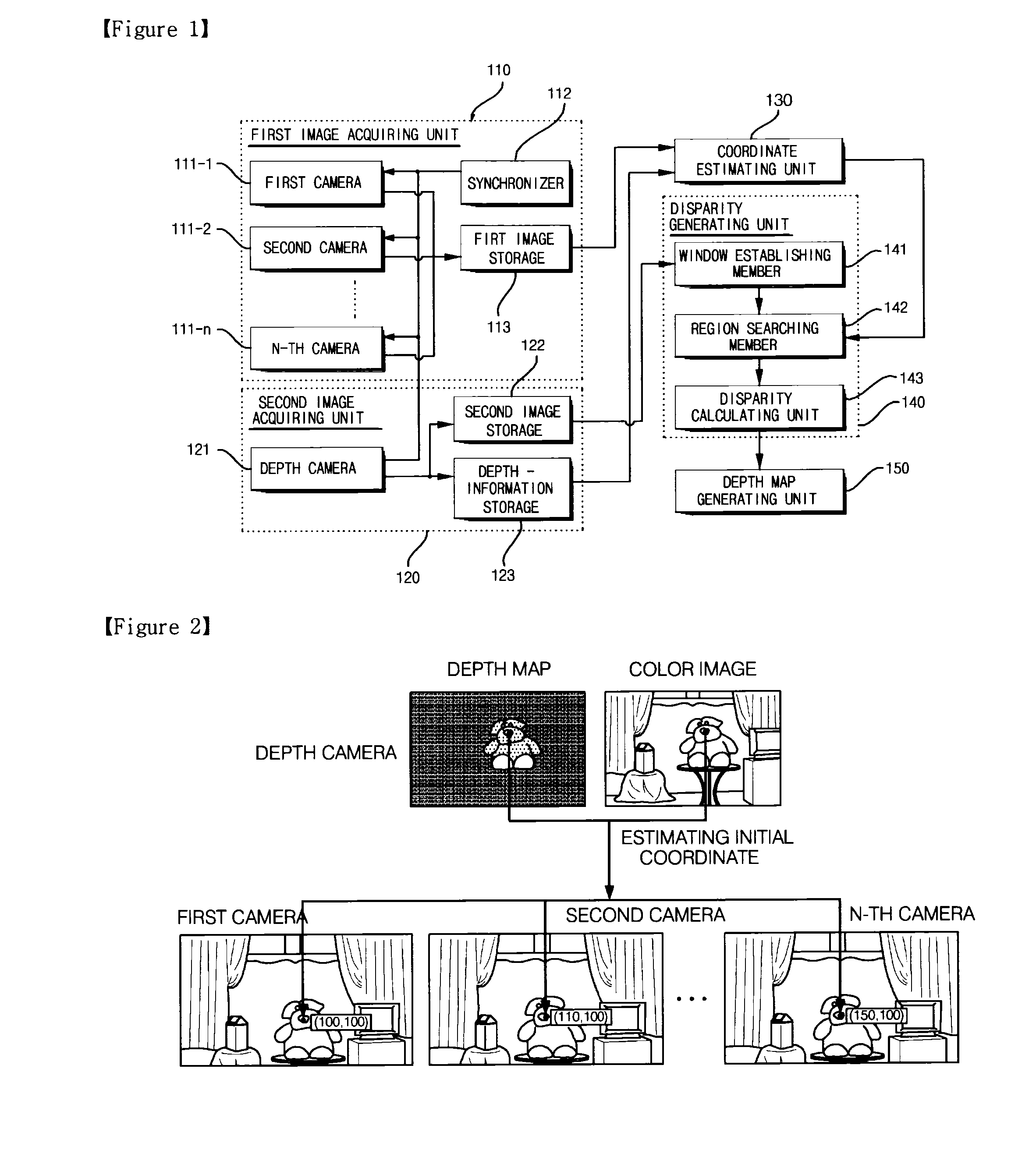
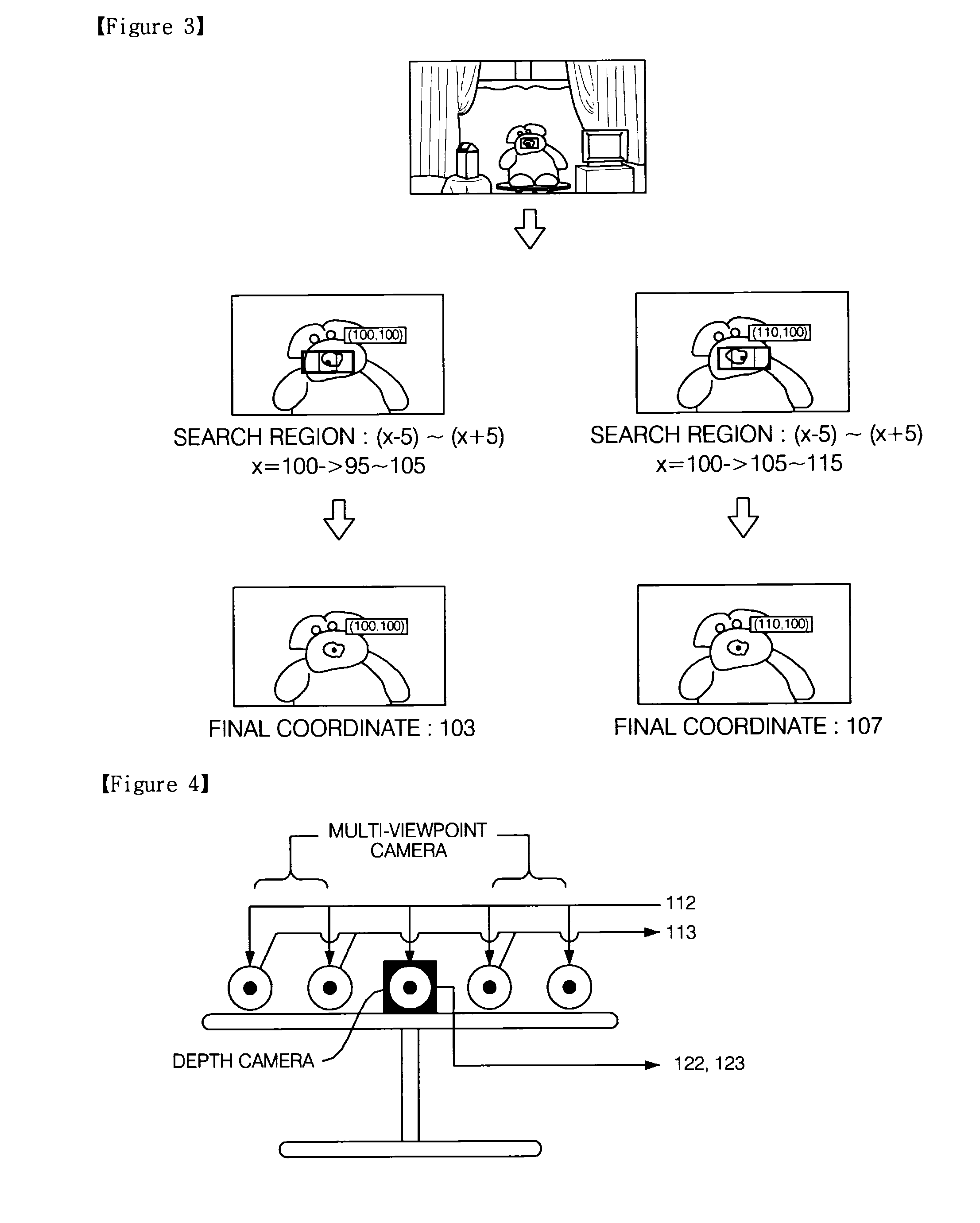
Method and apparatus for generating multi-viewpoint depth map, method for generating disparity of multi-viewpoint image
InactiveUS20100309292A1Short timeQuality improvementImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxStereo matching
There are provided a method and an apparatus for generating a multi-viewpoint depth map, and a method for generating a disparity of a multi-viewpoint image. A method for generating a multi-viewpoint depth map according to the present invention includes the steps of: (a) acquiring a multi-viewpoint image constituted by a plurality of images by using a plurality of cameras (b) acquiring an image and depth information by using a depth camera; (c) estimating coordinates of the same point in a space in the plurality of images by using the acquired depth information; (d) determining disparities in the plurality of images with respect to in the same point by searching a predetermined region around the estimated coordinates; and (e) generating a multi-viewpoint depth map by using the determined disparities. According to the above-mentioned present invention, it is possible to generate a multi-viewpoint depth map within a shorter time and generate a multi-viewpoint depth map having higher quality than a multi-viewpoint depth map generated by using known stereo matching.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH +1
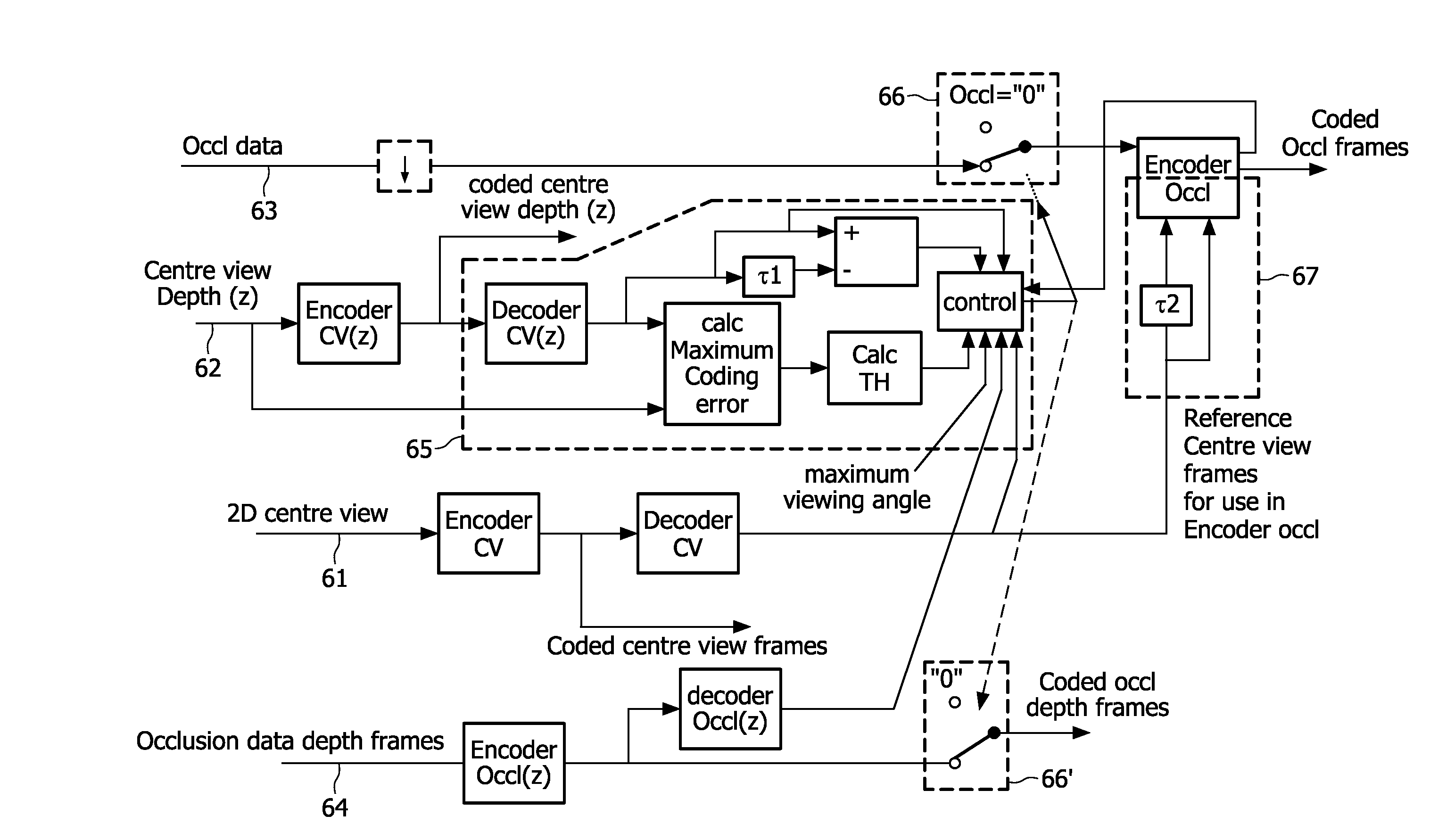
Method and system for encoding a 3D video signal, enclosed 3D video signal, method and system for decoder for a 3D video signal
ActiveUS20100195716A1Improve coding efficiencyReduce in quantityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamDepth map
In a method for encoding and an encoder for a 3D video signal, centre view frames, a depth map for centre view frames and an occlusion data frame are encoded. On the basis of the depth map for the centre view frame a distinction is made between functional and non-functional data in an occlusion data frame. This allows a strong reduction in bits needed for the encoded occlusion data frame. In the decoder a combined data stream is made of functional data in the encoded occlusion data frames and the centre view frames. Preferably the centre view frames are used as reference frames in encoding the occlusion data frames.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Systems and methods for 2D image and spatial data capture for 3D stereo imaging
InactiveUS20110222757A1Facilitate post-productionLarge separationImage enhancementImage analysisVirtual cameraMovie camera
Systems and methods for 2D image and spatial data capture for 3D stereo imaging are disclosed. The system utilizes a cinematography camera and at least one reference or “witness” camera spaced apart from the cinematography camera at a distance much greater that the interocular separation to capture 2D images over an overlapping volume associated with a scene having one or more objects. The captured image date is post-processed to create a depth map, and a point cloud is created form the depth map. The robustness of the depth map and the point cloud allows for dual virtual cameras to be placed substantially arbitrarily in the resulting virtual 3D space, which greatly simplifies the addition of computer-generated graphics, animation and other special effects in cinemagraphic post-processing.
Owner:SHAPEQUEST
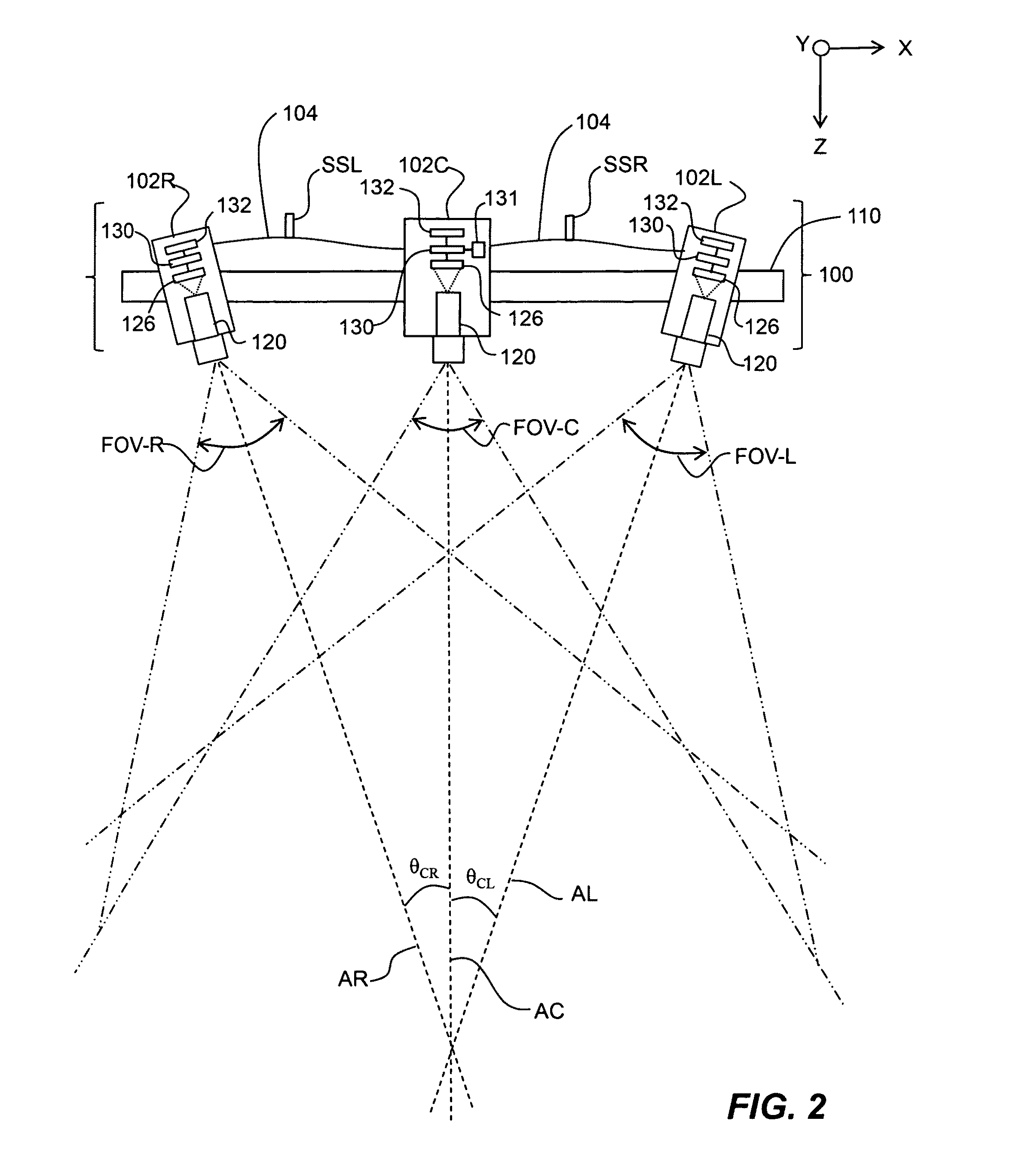
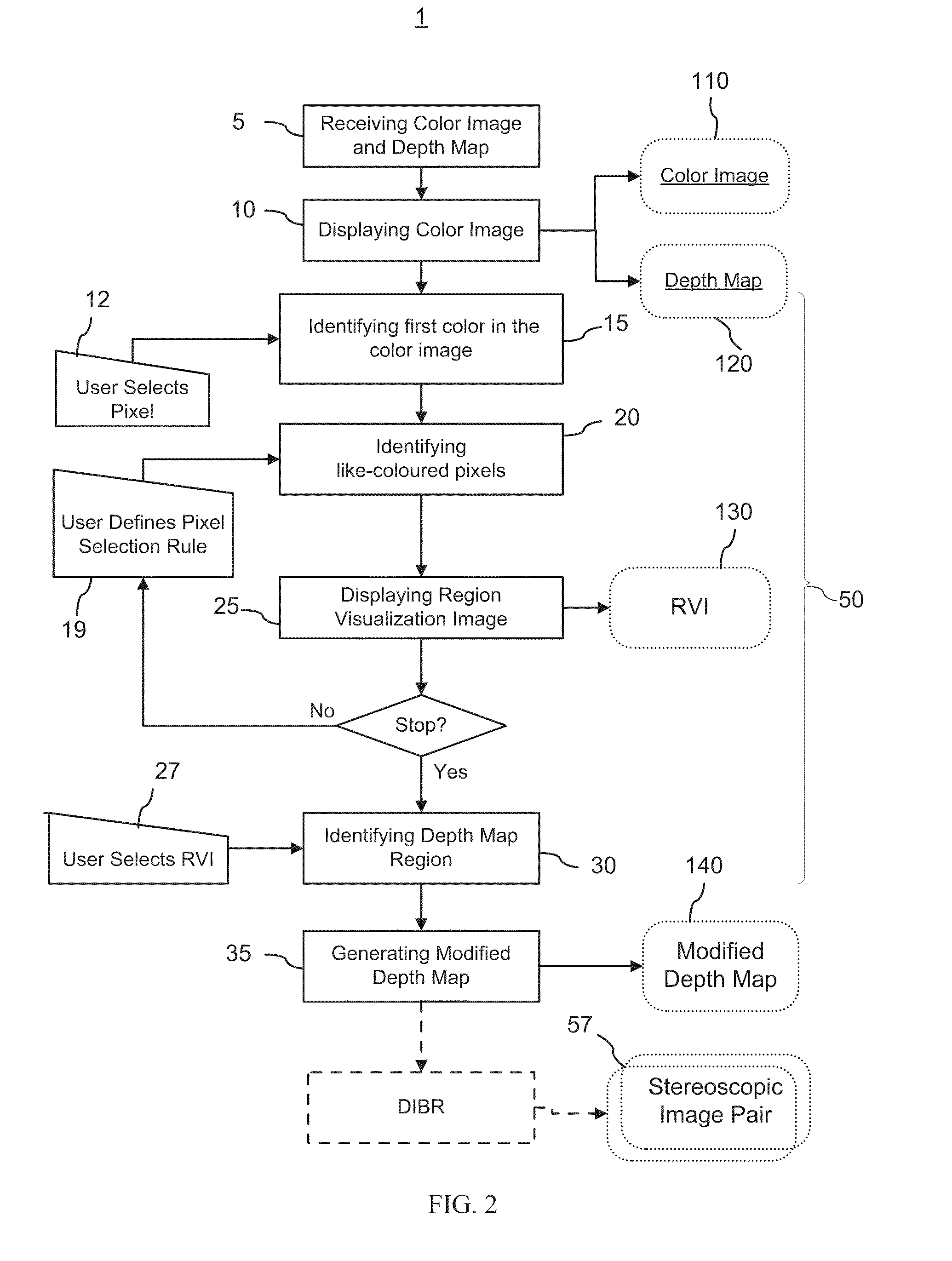
Method and graphical user interface for modifying depth maps
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
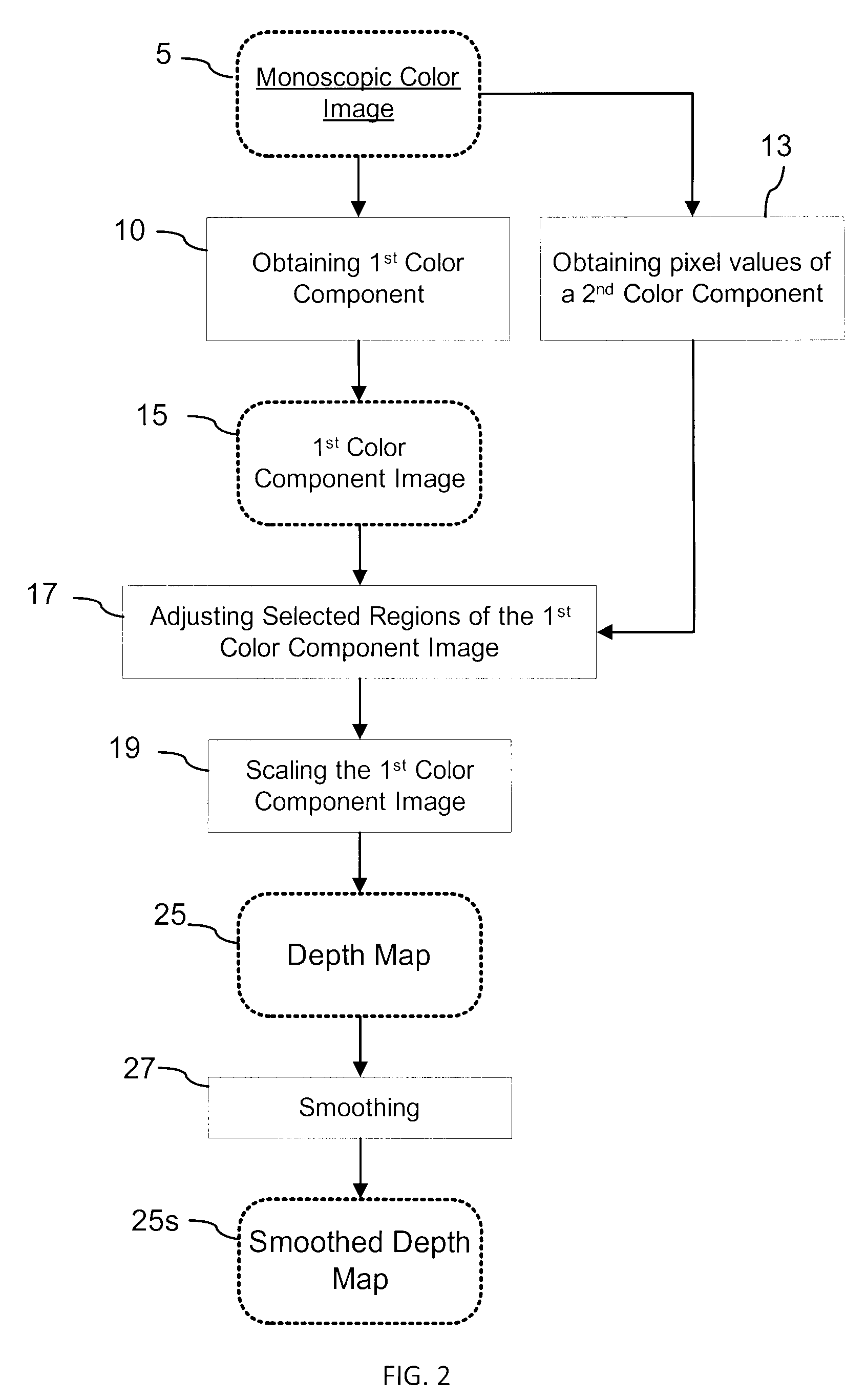
Generation of a depth map from a monoscopic color image for rendering stereoscopic still and video images
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for generating a depth map from a digital monoscopic color image. The method includes the following general steps: a) obtaining a first color component of the MCI, said first color component corresponding to partial color information of the MCI; and, b) assigning depth values to pixels of the MCI based on values of the first color component of respective pixels for forming the depth map for the MCI. In one embodiment, the depth values are generated by adjusting and / or scaling of pixel values of the Cr chroma component of the monoscopic source color image in the Y′CbCr color system.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Method and system to segment depth images and to detect shapes in three-dimensionally acquired data
ActiveUS20060239558A1Rapidly correctly characterizeQuick identificationImage enhancementImage analysisSystems analysisHistogram
A method and system analyzes data acquired by image systems to more rapidly identify objects of interest in the data. In one embodiment, z-depth data are segmented such that neighboring image pixels having similar z-depths are given a common label. Blobs, or groups of pixels with a same label, may be defined to correspond to different objects. Blobs preferably are modeled as primitives to more rapidly identify objects in the acquired image. In some embodiments, a modified connected component analysis is carried out where image pixels are pre-grouped into regions of different depth values preferably using a depth value histogram. The histogram is divided into regions and image cluster centers are determined. A depth group value image containing blobs is obtained, with each pixel being assigned to one of the depth groups.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
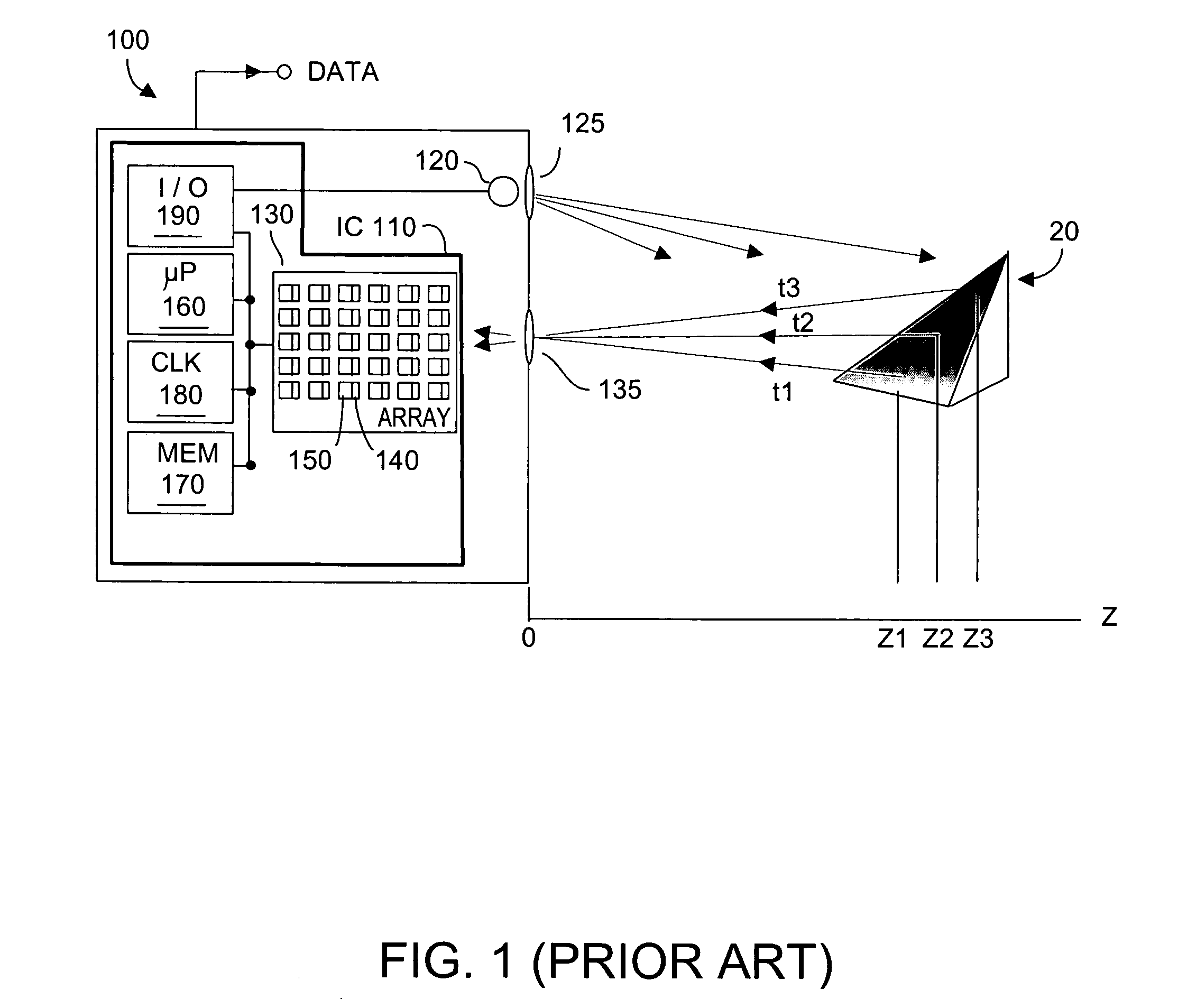
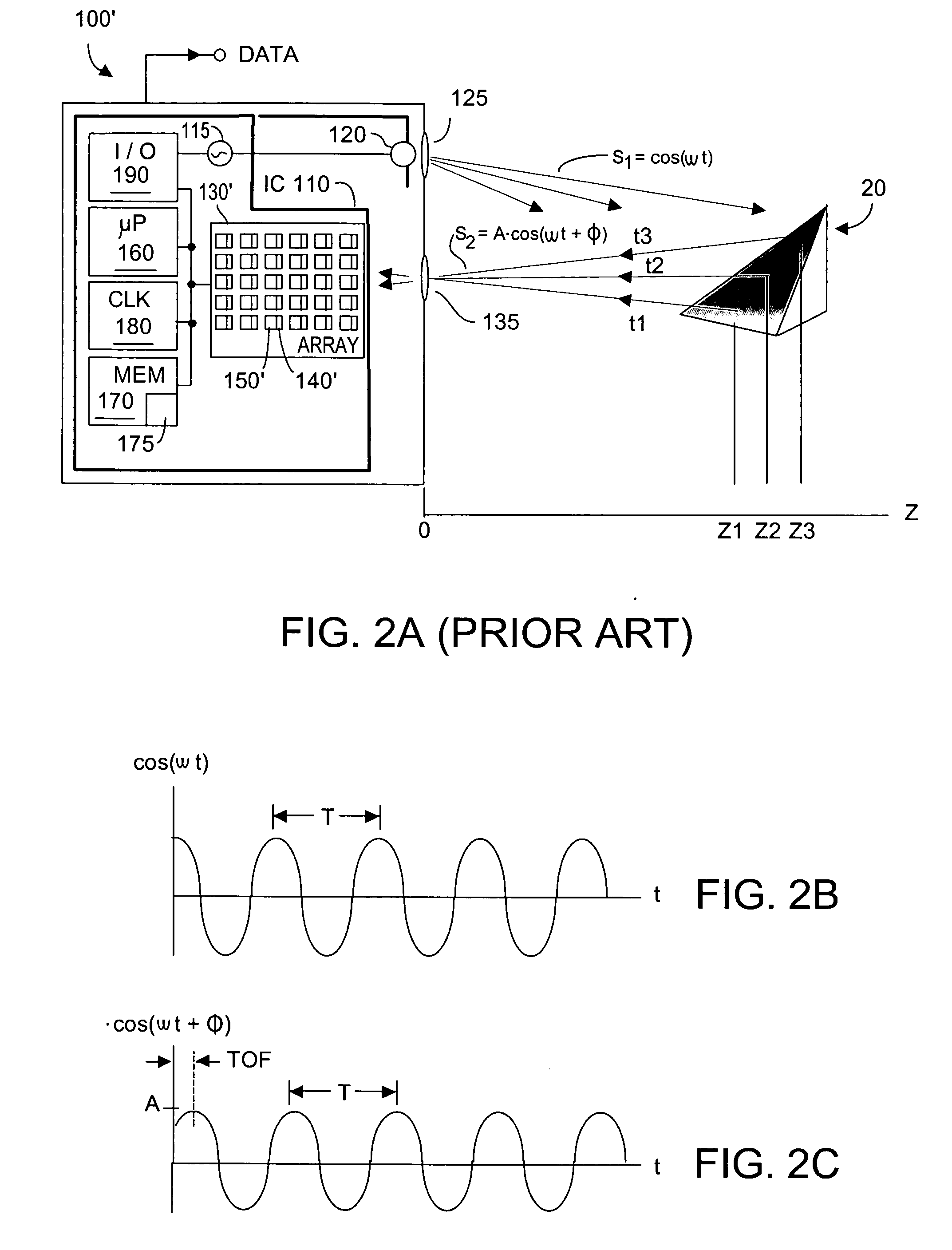
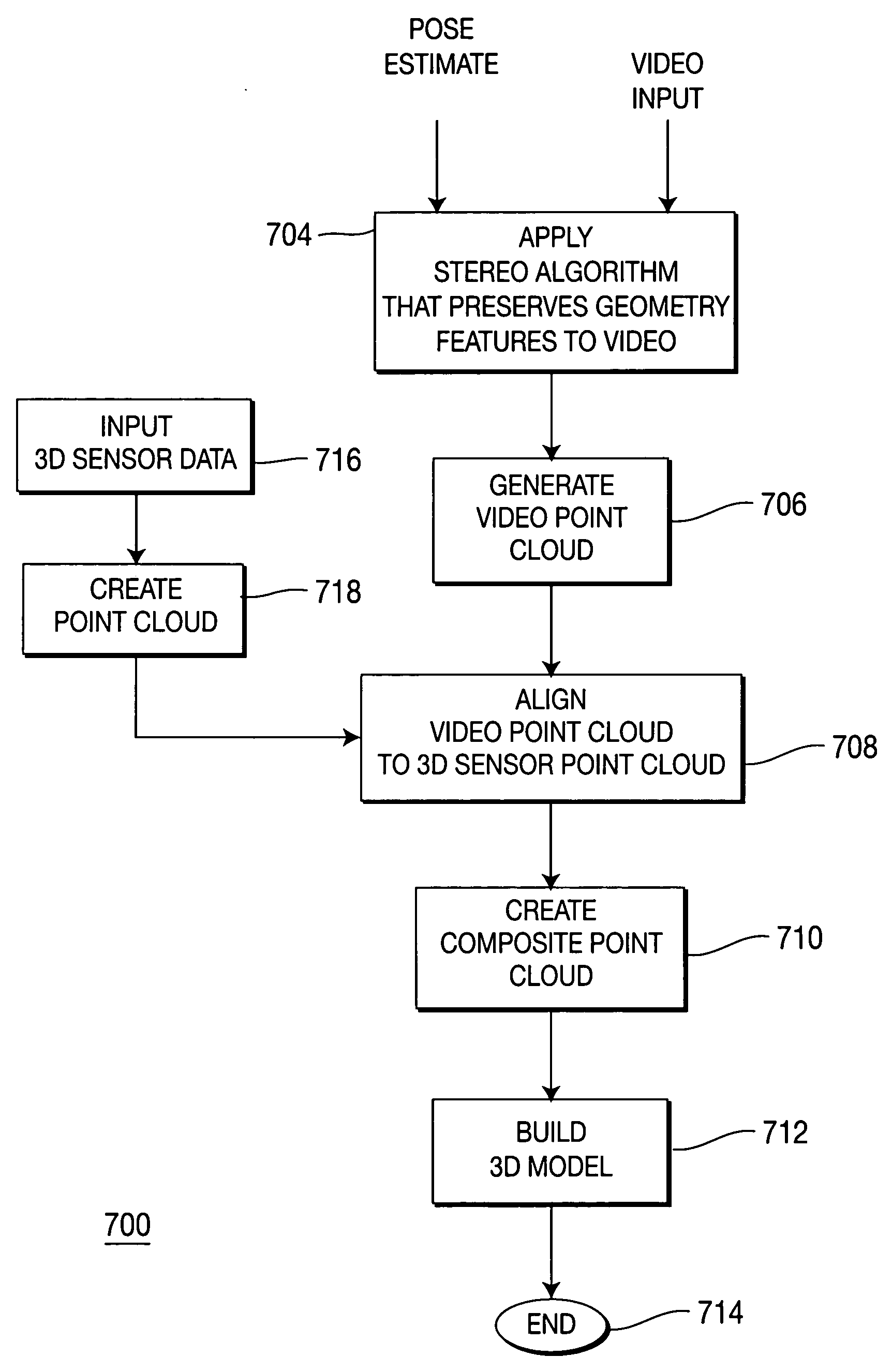
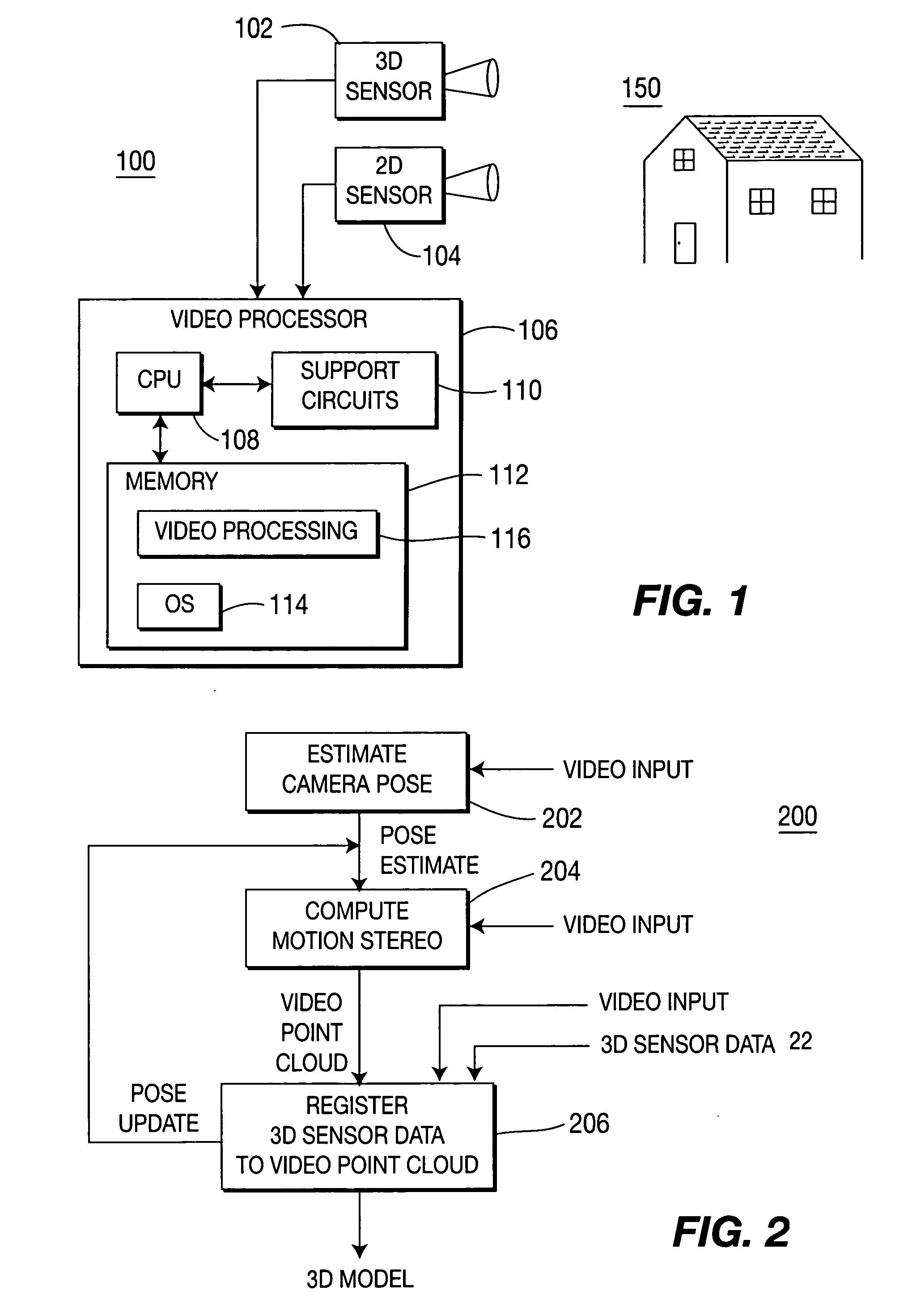
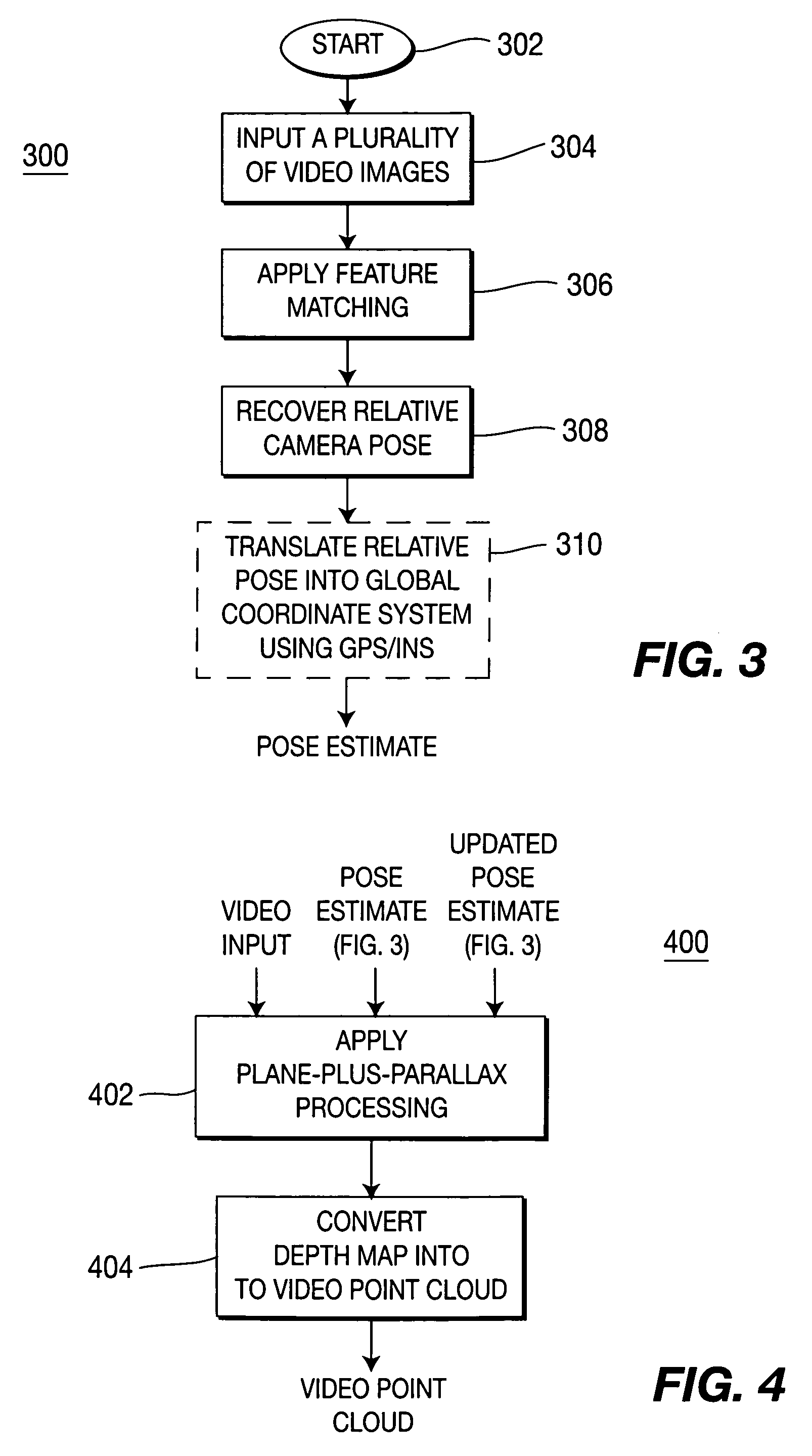
Method and apparatus for aligning video to three-dimensional point clouds
A method and apparatus for performing two-dimensional video alignment onto three-dimensional point clouds. The system recovers camera pose from camera video, determines a depth map, converts the depth map to a Euclidean video point cloud, and registers two-dimensional video to the three-dimensional point clouds.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
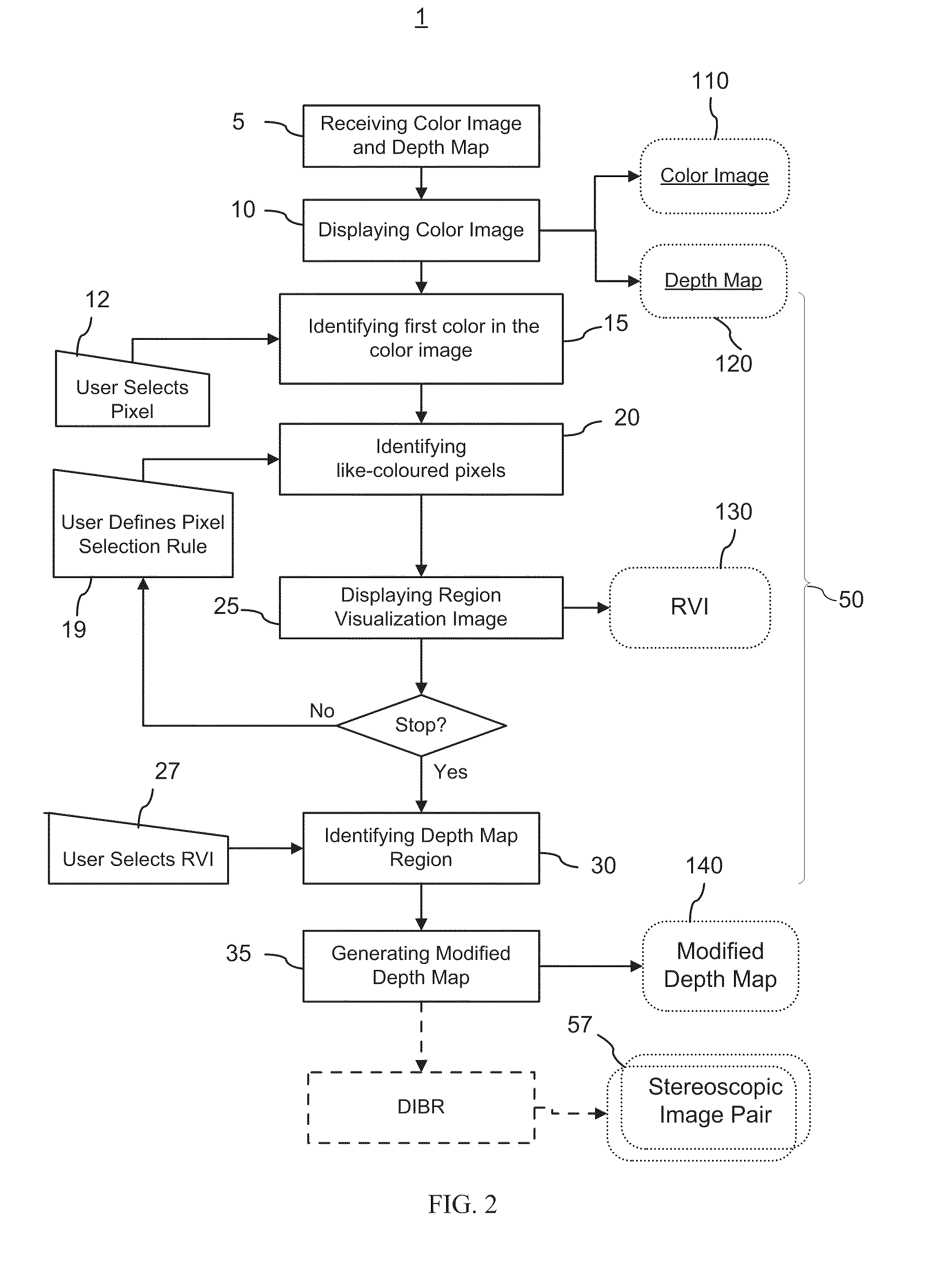
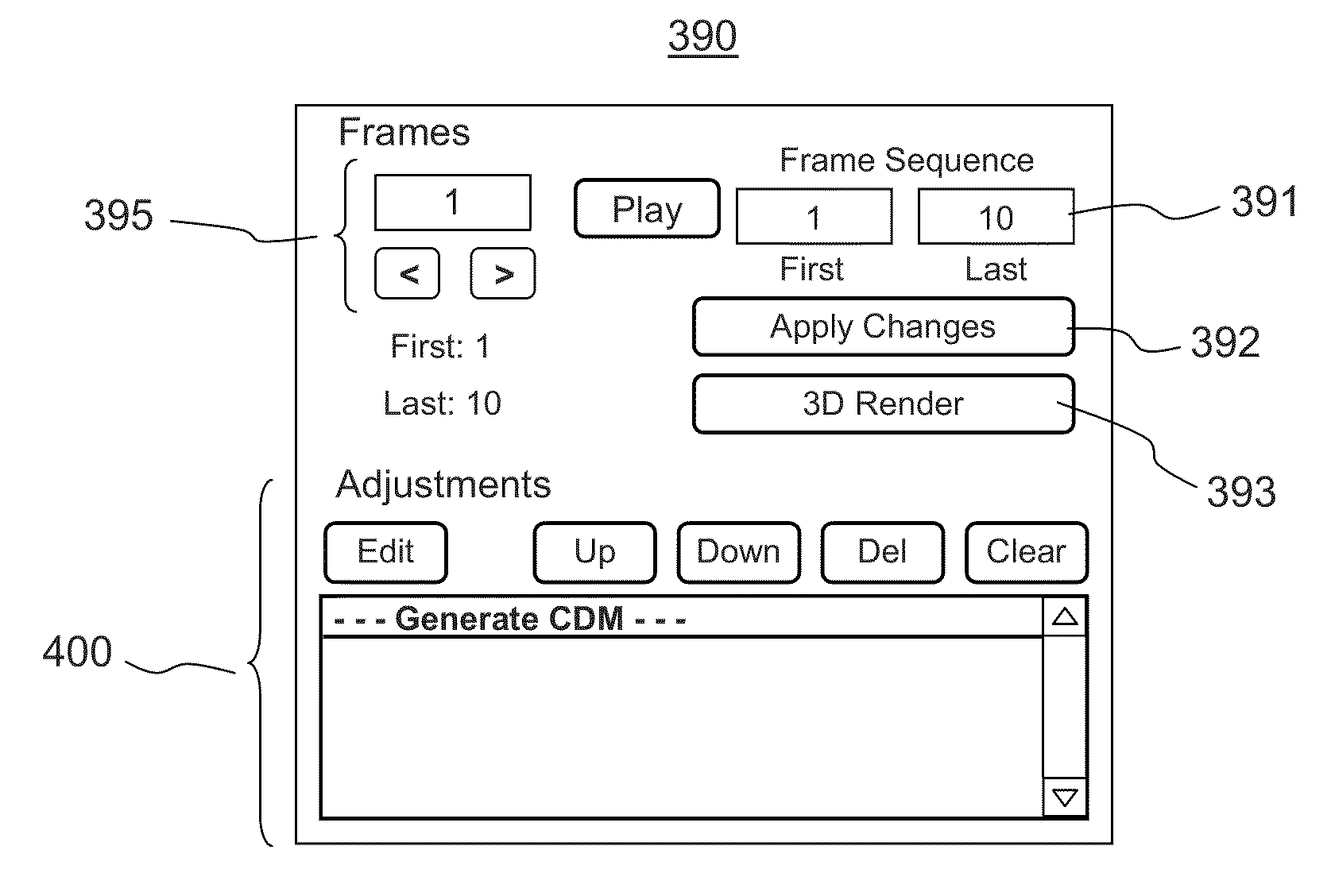
Method and graphical user interface for modifying depth maps
The invention relates to a method and a graphical user interface for modifying a depth map for a digital monoscopic color image. The method includes interactively selecting a region of the depth map based on color of a target region in the color image, and modifying depth values in the thereby selected region of the depth map using a depth modification rule. The color-based pixel selection rules for the depth map and the depth modification rule selected based on one color image from a video sequence may be saved and applied to automatically modify depths maps of other color images from the same sequence.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
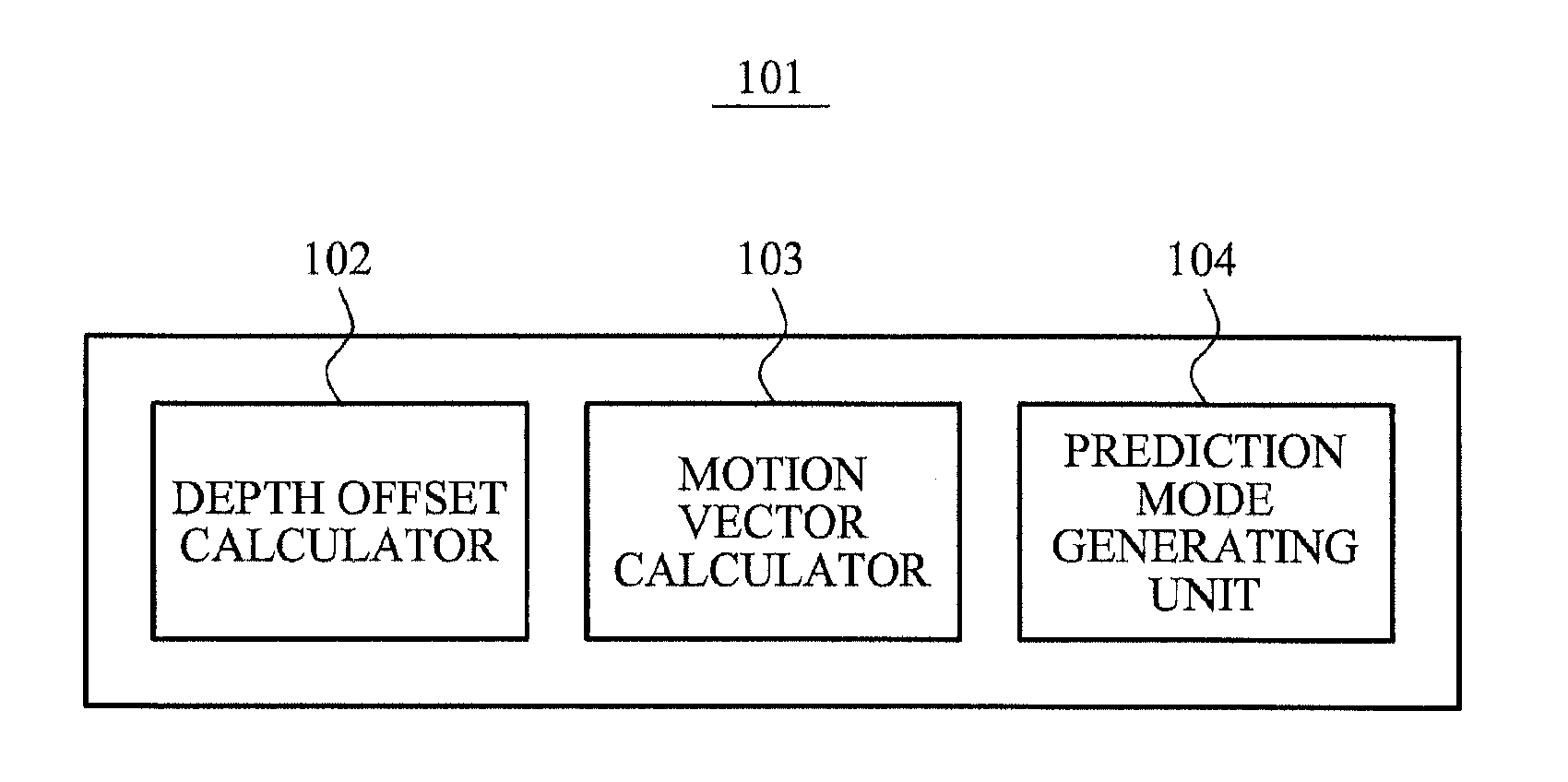
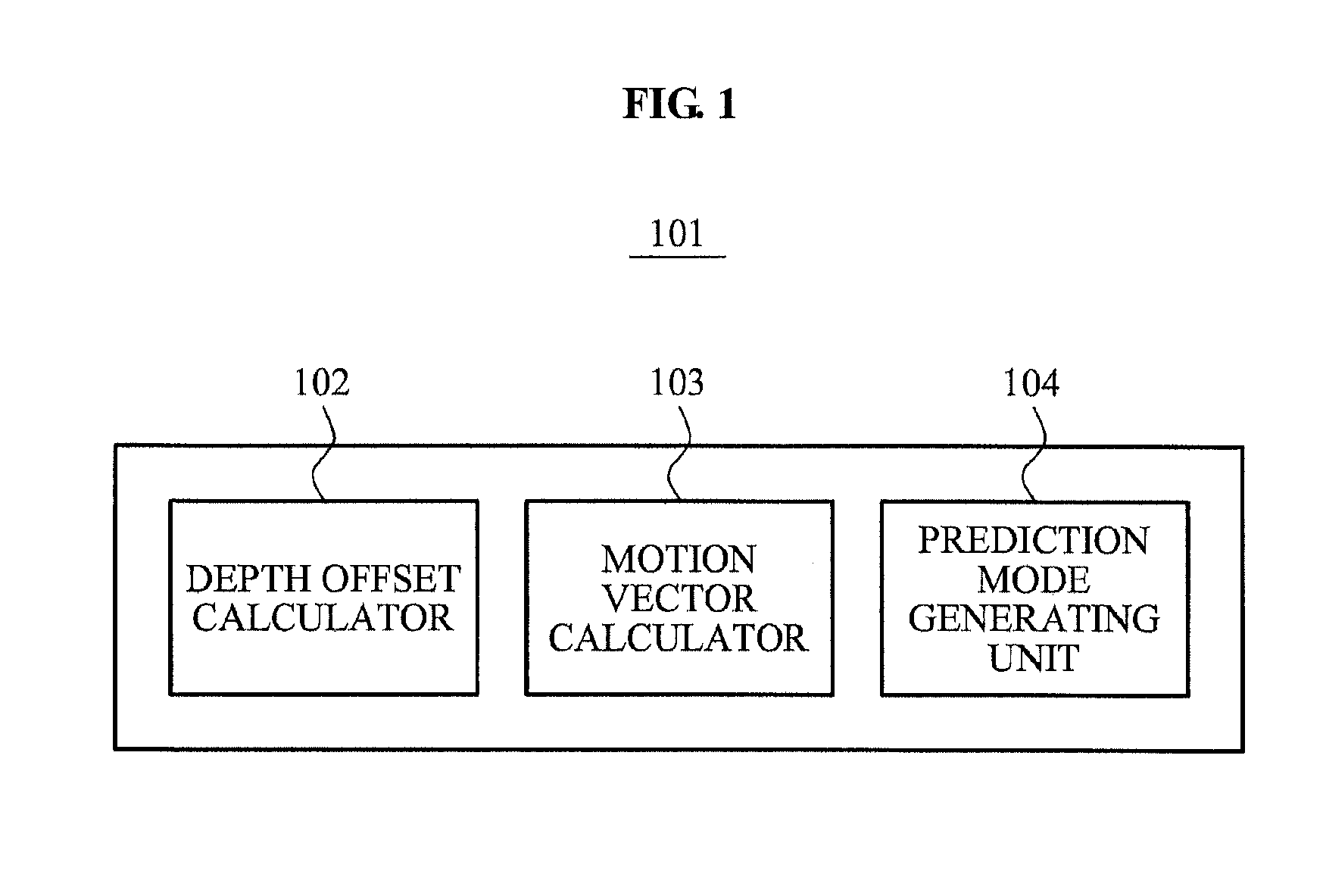
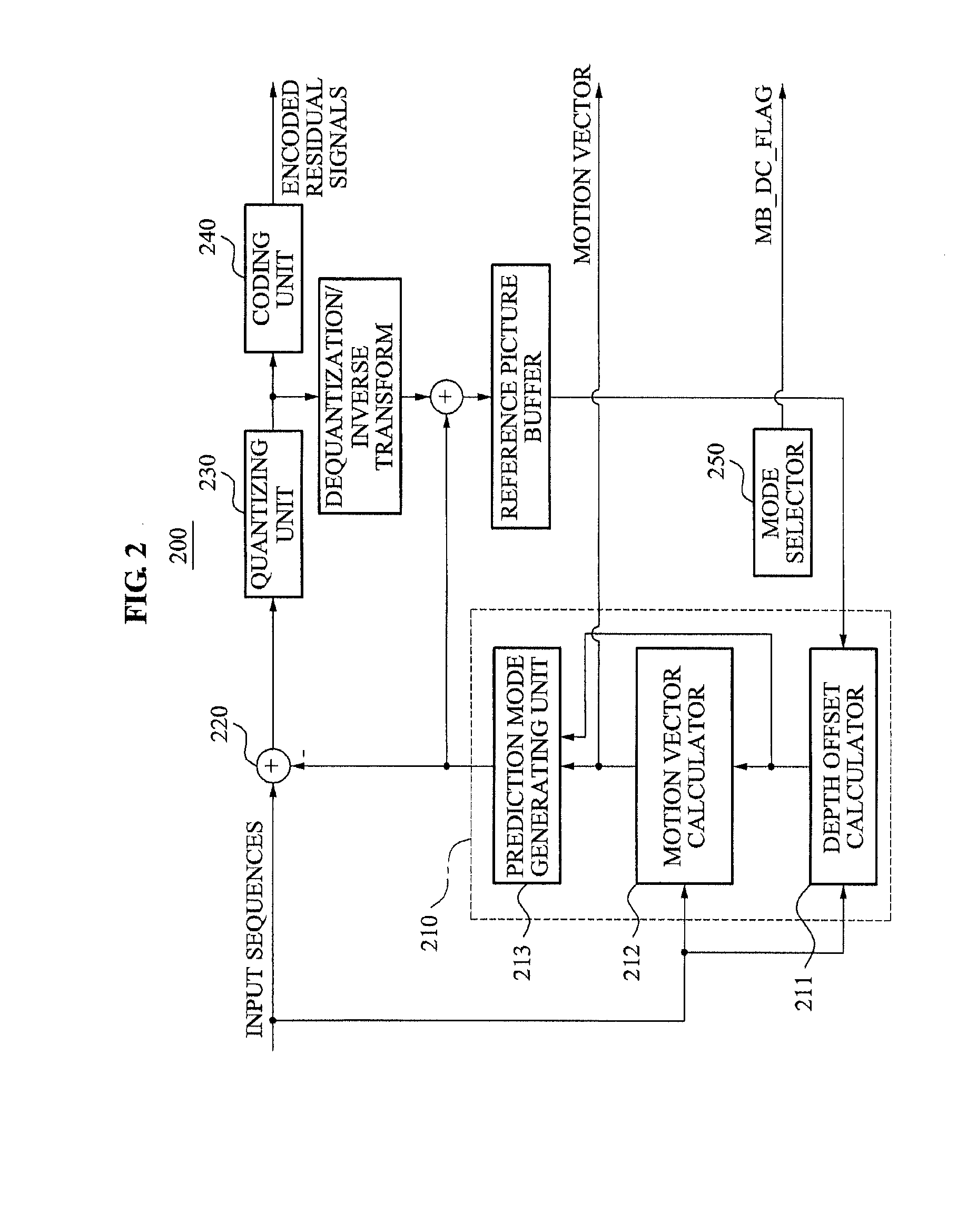
Apparatus and method of depth coding using prediction mode
InactiveUS20110317766A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorTemporal correlation
A depth image coding method may calculate a depth offset of a depth image, may generate a prediction mode based on the depth offset, may minimize a prediction error of the depth image having a low correlation between adjacent points of view and a low temporal correlation and may enhance a compression rate. The depth offset may be calculated based on a representative value of adjacent pixels included in a template as opposed to using a depth representative value of pixels in a block and header information may not be needed to encode an offset and the offset may be generated by a depth image decoding apparatus. When a plurality of objects is included in a block, a depth offset is calculated for each of the plurality of objects and a motion vector is calculated for each of the plurality of objects and the depth image may be accurately predicted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
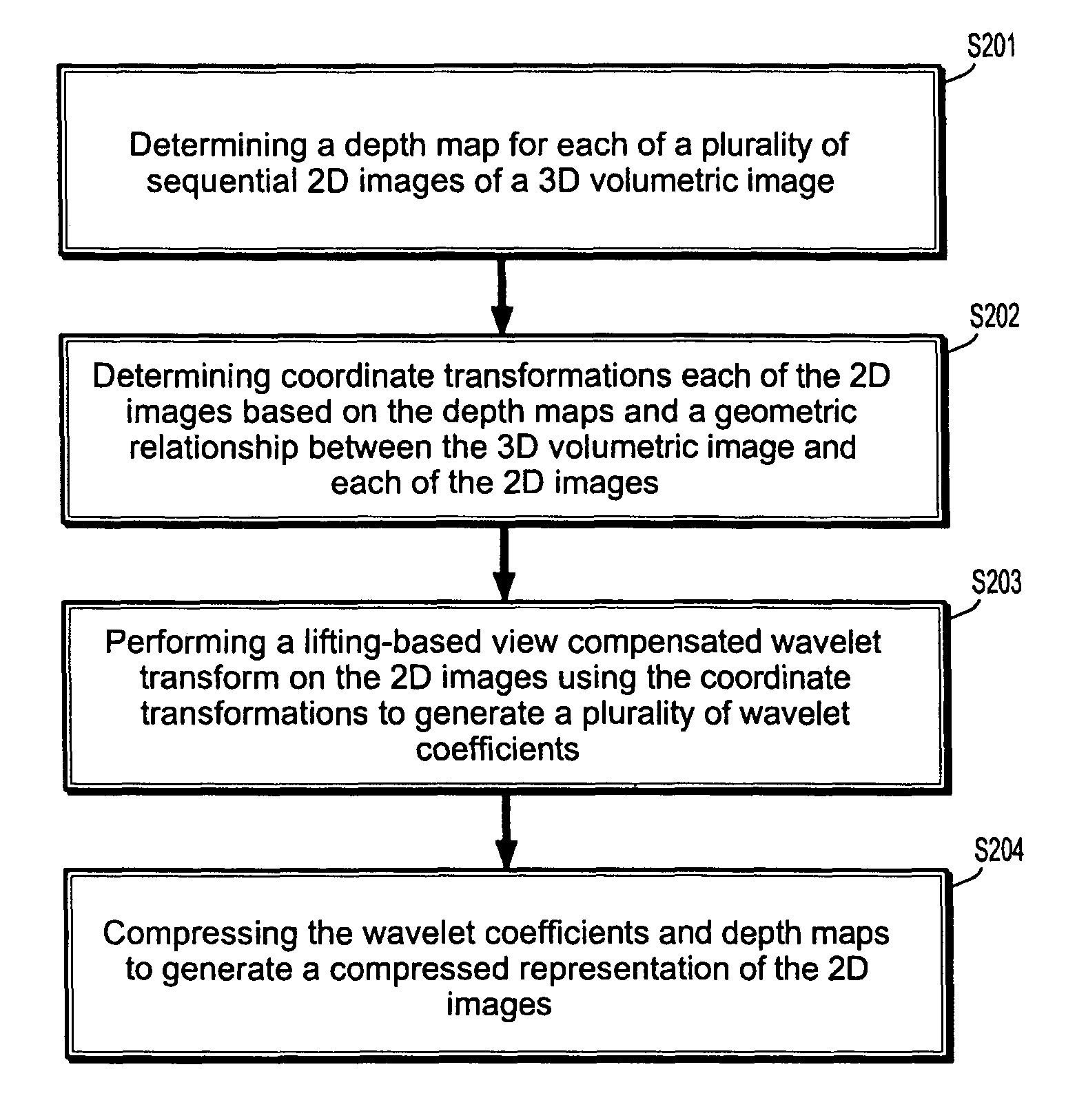
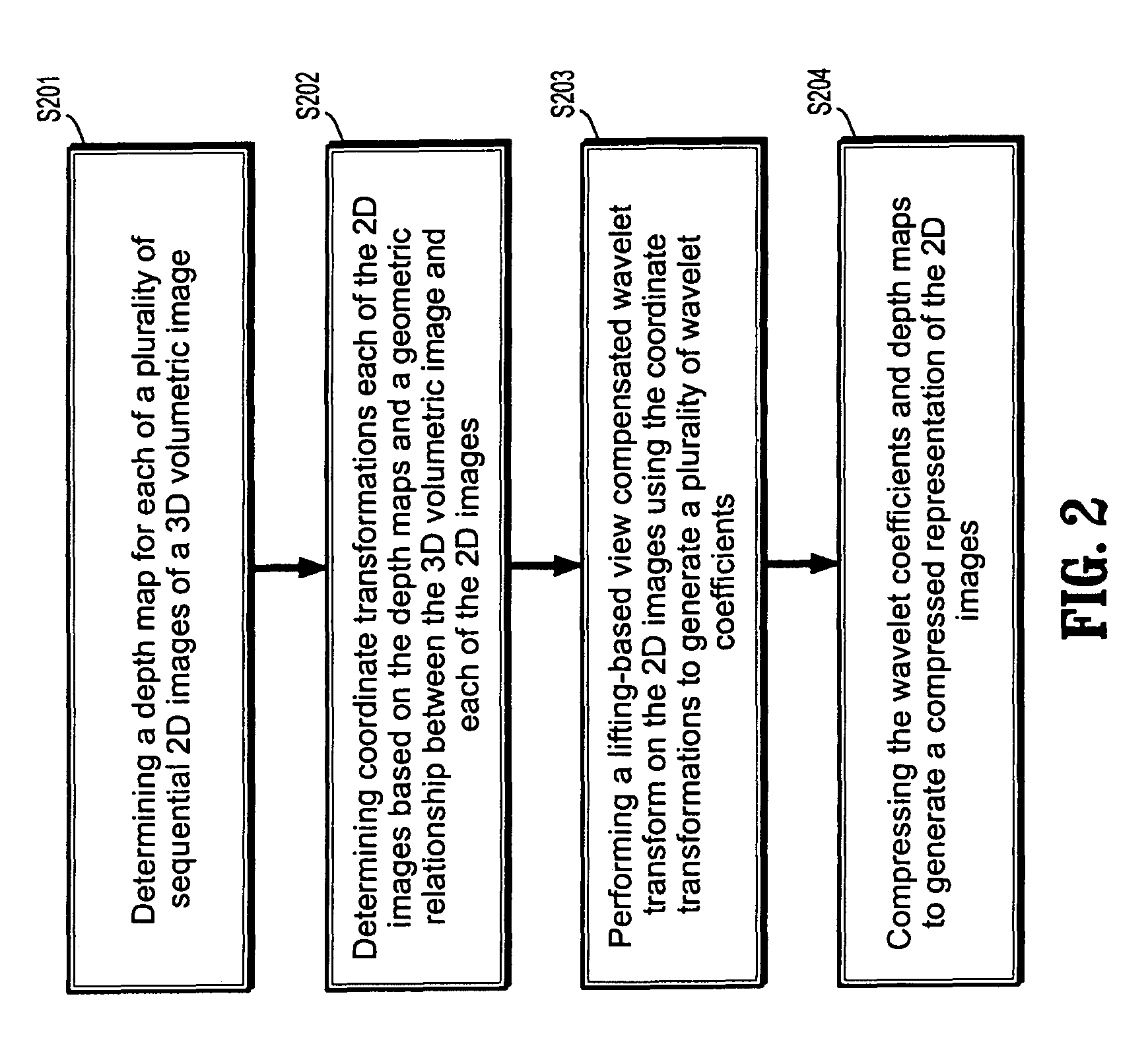
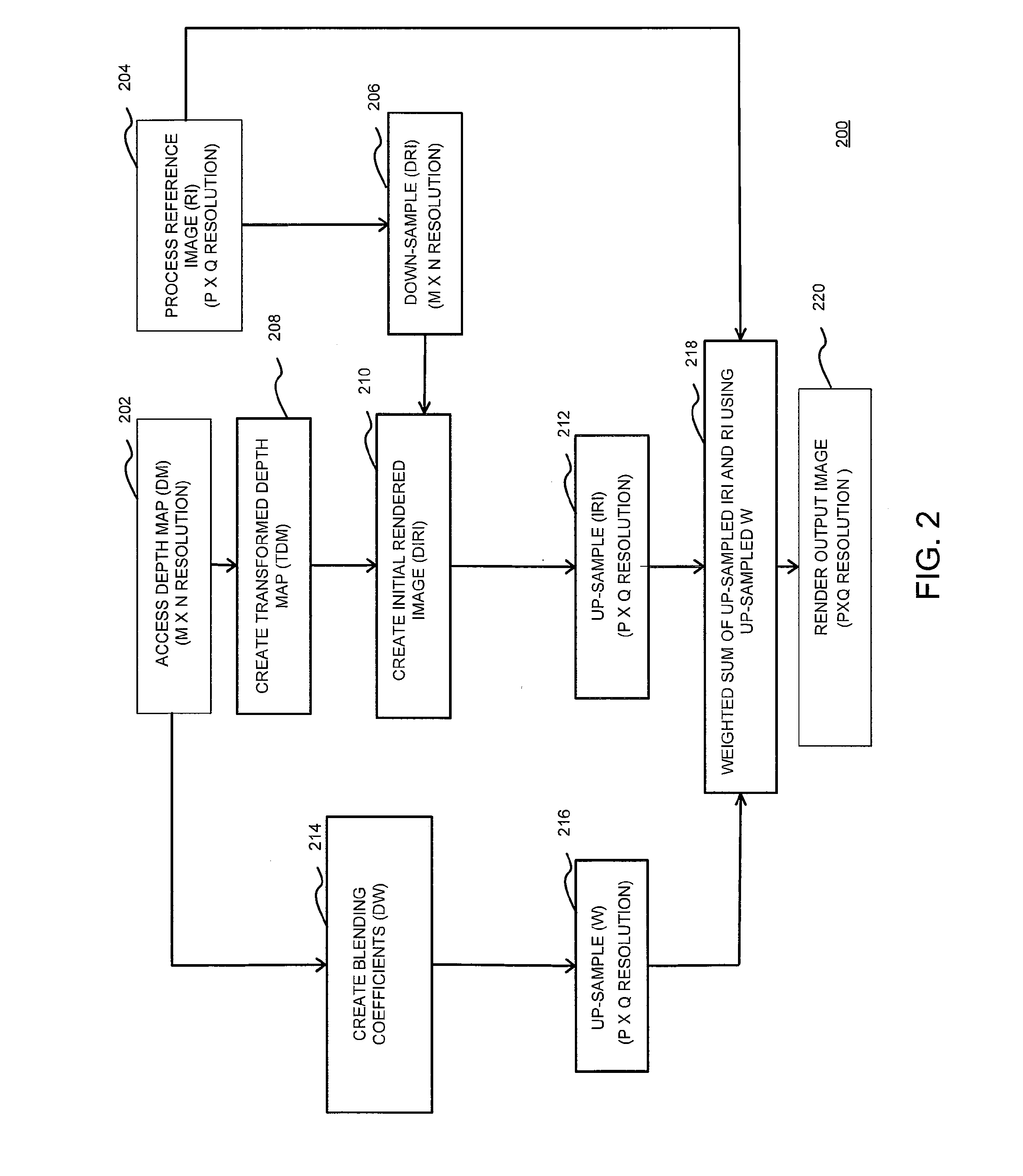
Lifting-based view compensated compression and remote visualization of volume rendered images
ActiveUS8126279B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationWavelet transformDepth map
A method for compressing 2D images includes determining a depth map for each of a plurality of sequential 2D images of a 3D volumetric image, determining coordinate transformations the 2D images based on the depth maps and a geometric relationship between the 3D volumetric image and each of the 2D image, performing a lifting-based view compensated wavelet transform on the 2D images using the coordinate transformations to generate a plurality of wavelet coefficients and compressing the wavelet coefficients and depth maps to generate a compressed representation of the 2D images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
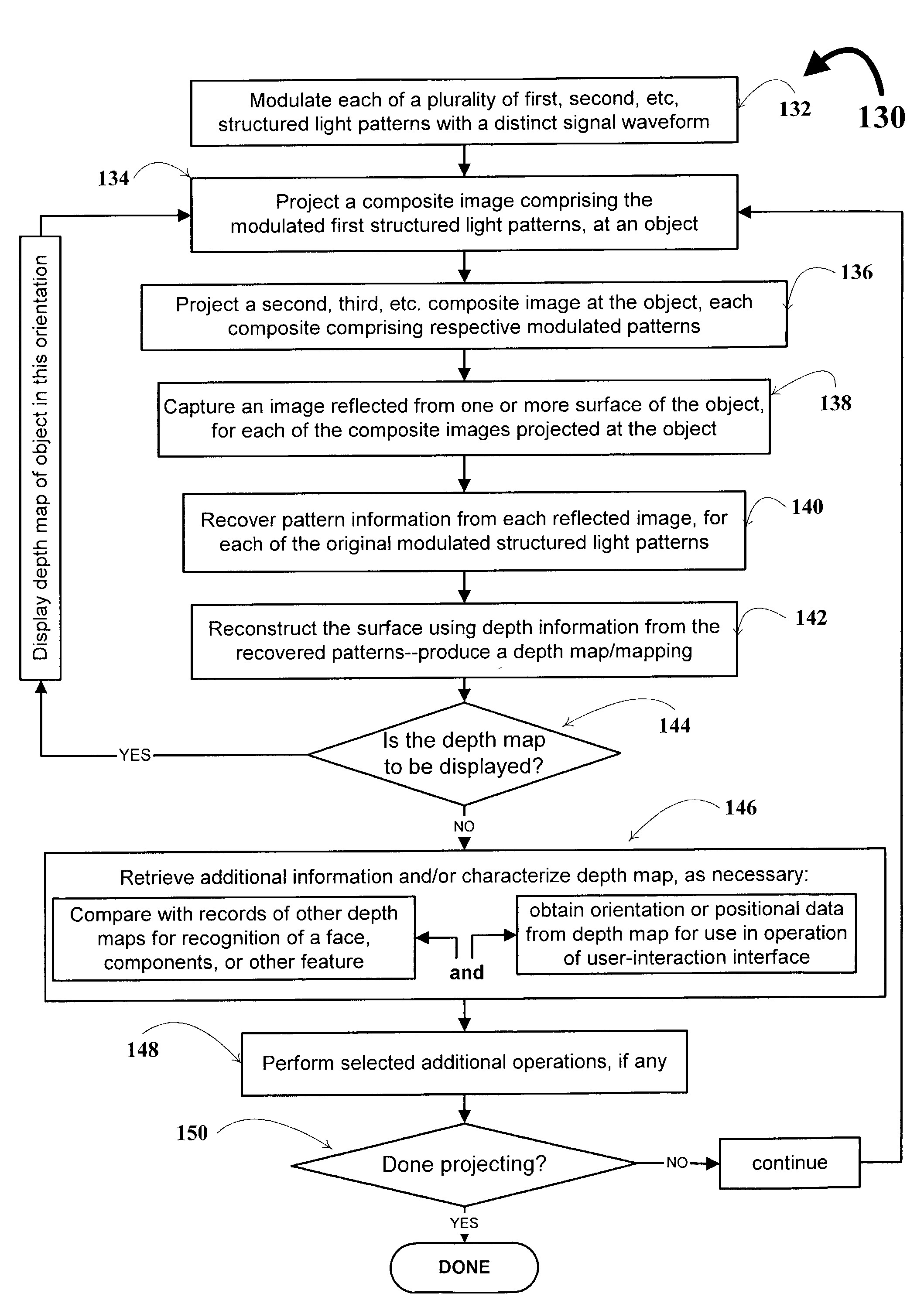
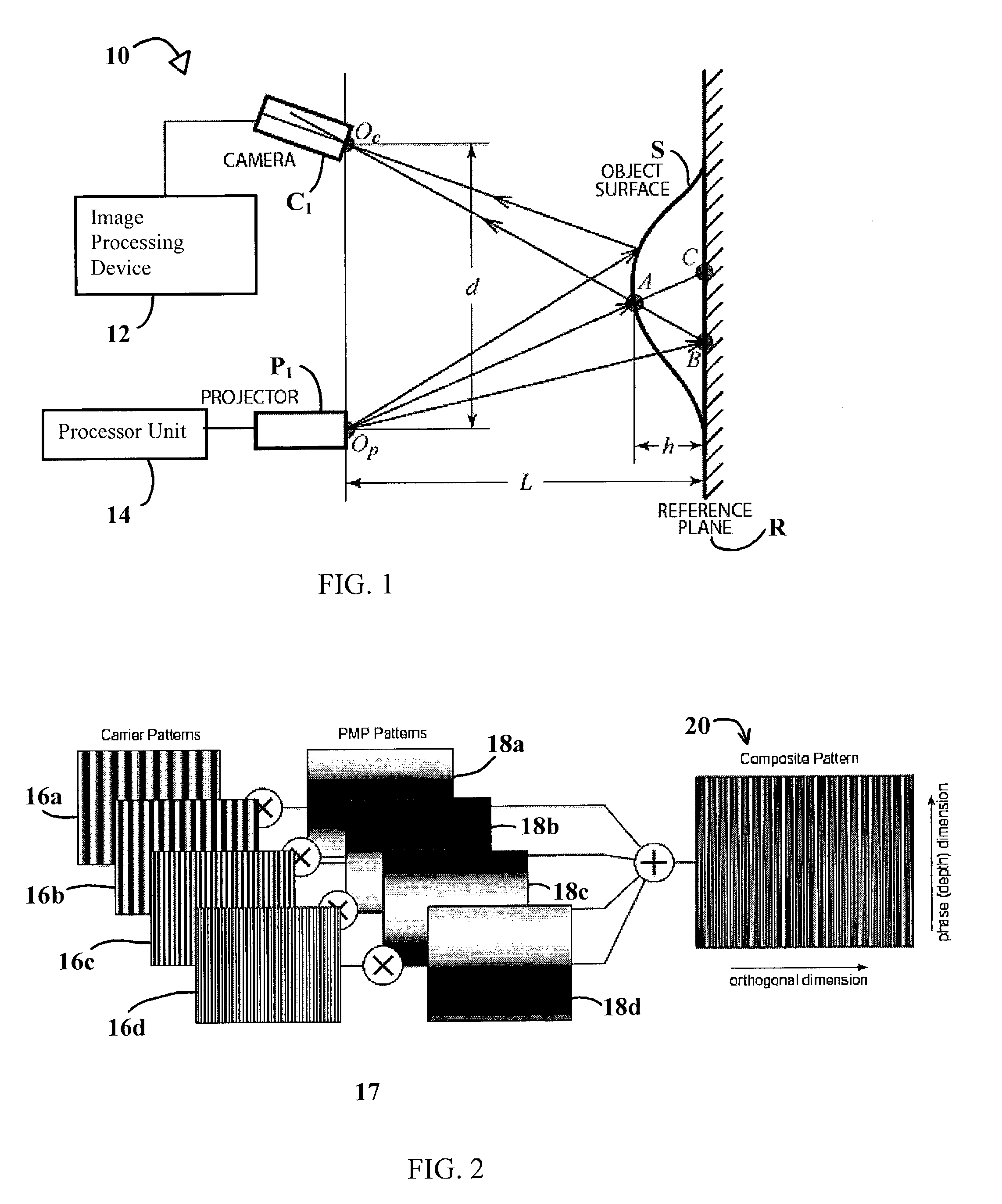
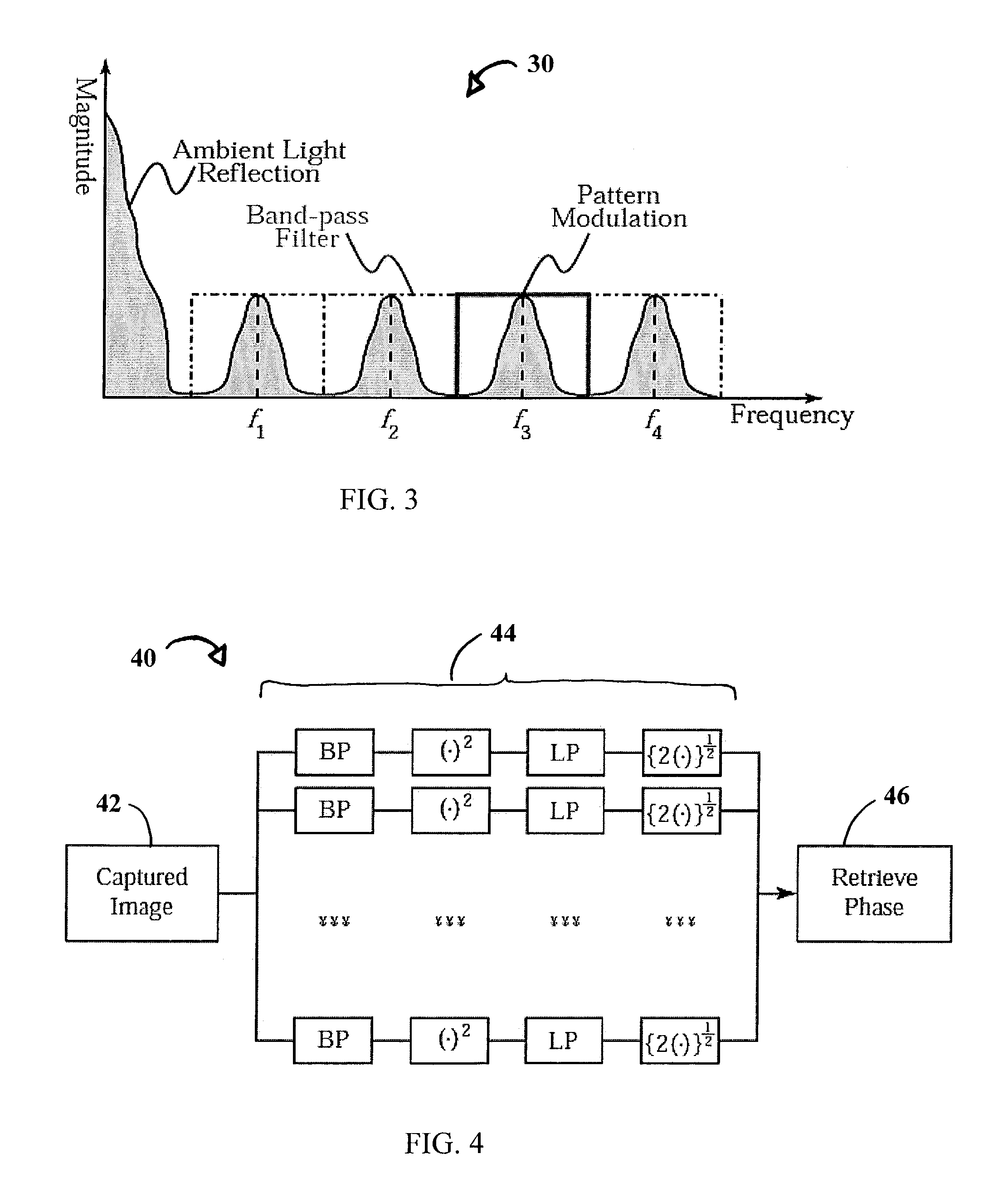
System and technique for retrieving depth information about a surface by projecting a composite image of modulated light patterns
InactiveUS7440590B1More detailed and large depth mappingLimited bandwidthProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInteraction interfaceTelecollaboration
A technique, associated system and program code, for retrieving depth information about at least one surface of an object. Core features include: projecting a composite image comprising a plurality of modulated structured light patterns, at the object; capturing an image reflected from the surface; and recovering pattern information from the reflected image, for each of the modulated structured light patterns. Pattern information is preferably recovered for each modulated structured light pattern used to create the composite, by performing a demodulation of the reflected image. Reconstruction of the surface can be accomplished by using depth information from the recovered patterns to produce a depth map / mapping thereof. Each signal waveform used for the modulation of a respective structured light pattern, is distinct from each of the other signal waveforms used for the modulation of other structured light patterns of a composite image; these signal waveforms may be selected from suitable types in any combination of distinct signal waveforms, provided the waveforms used are uncorrelated with respect to each other. The depth map / mapping to be utilized in a host of applications, for example: displaying a 3-D view of the object; virtual reality user-interaction interface with a computerized device; face—or other animal feature or inanimate object—recognition and comparison techniques for security or identification purposes; and 3-D video teleconferencing / telecollaboration.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
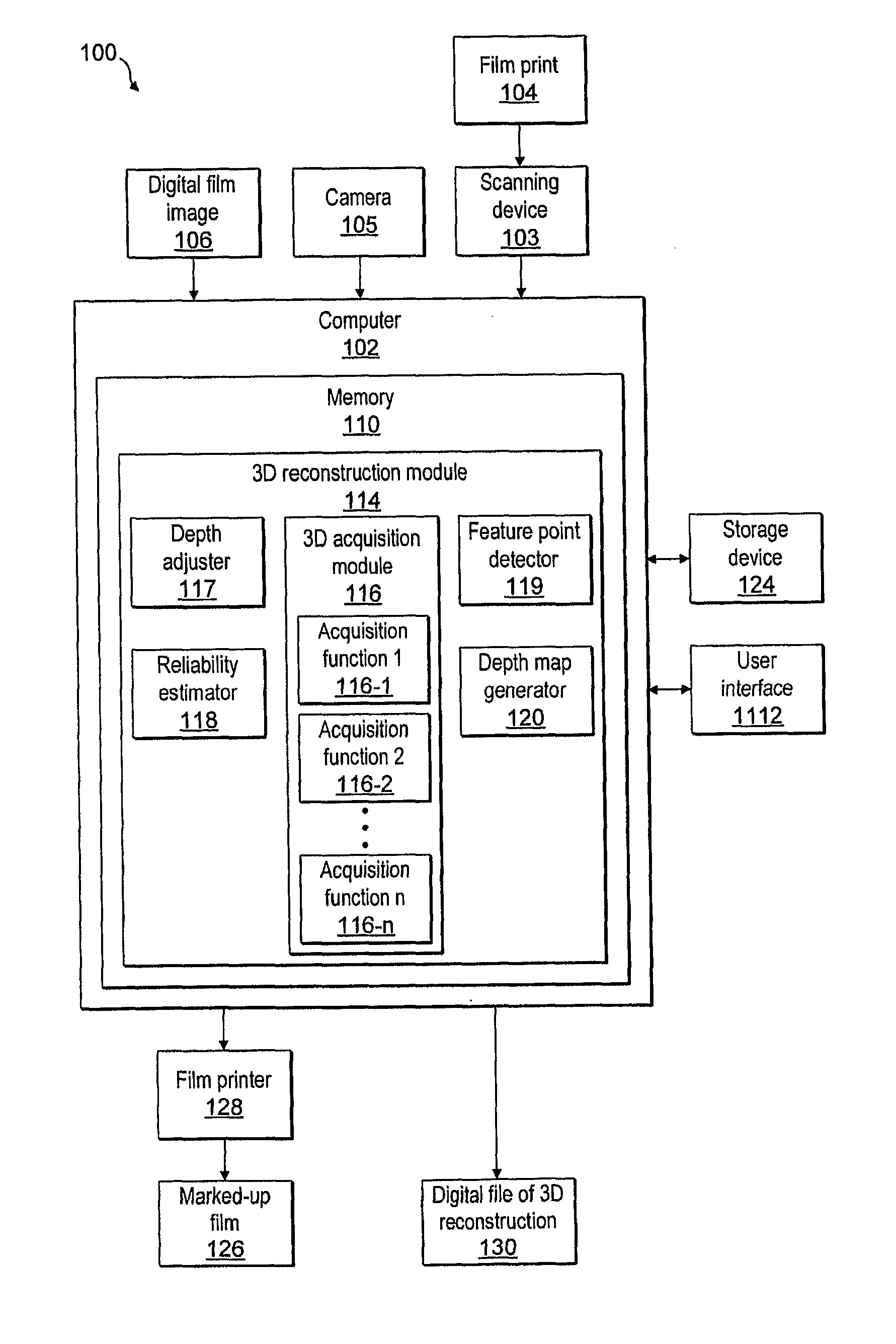
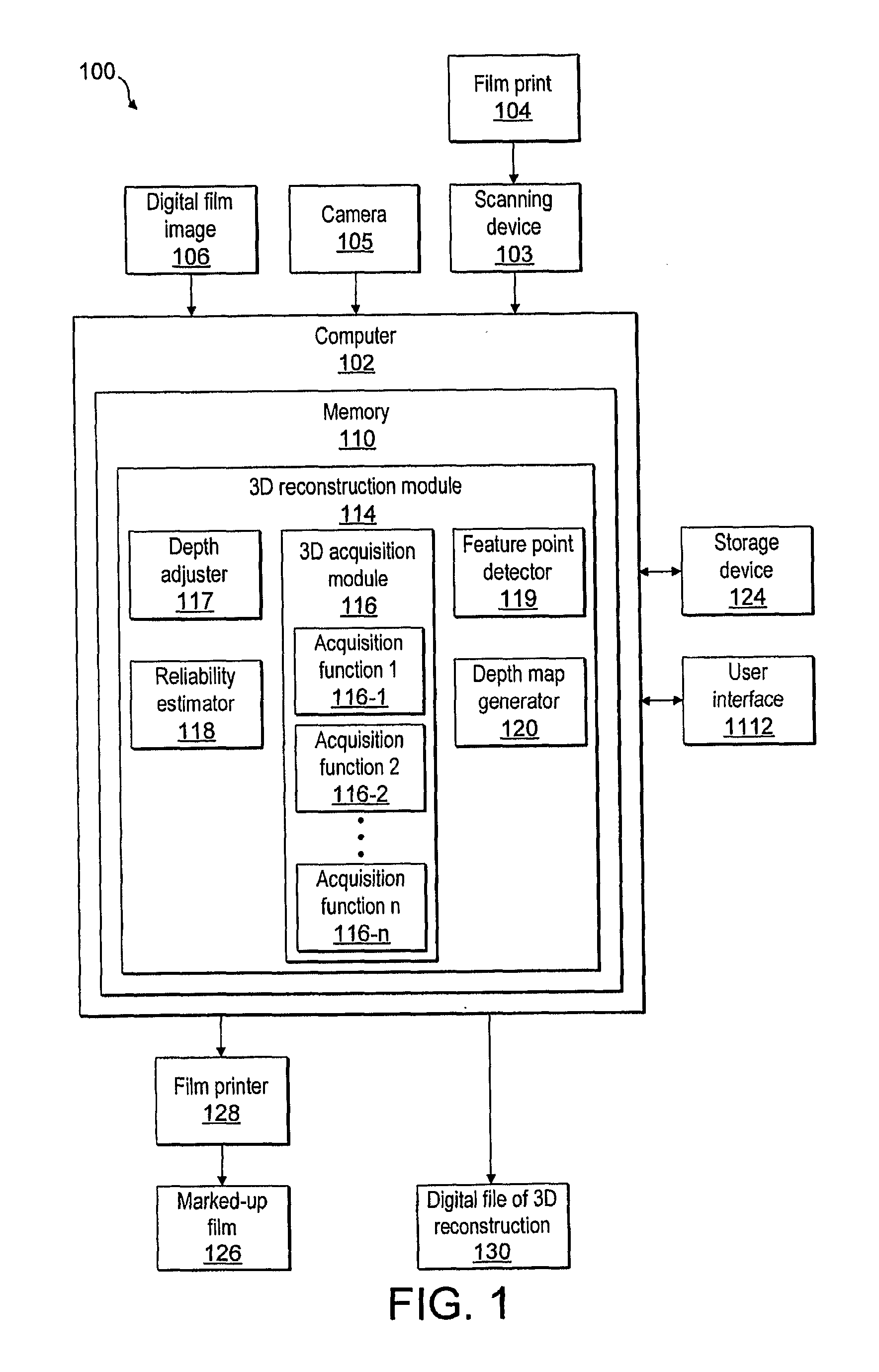
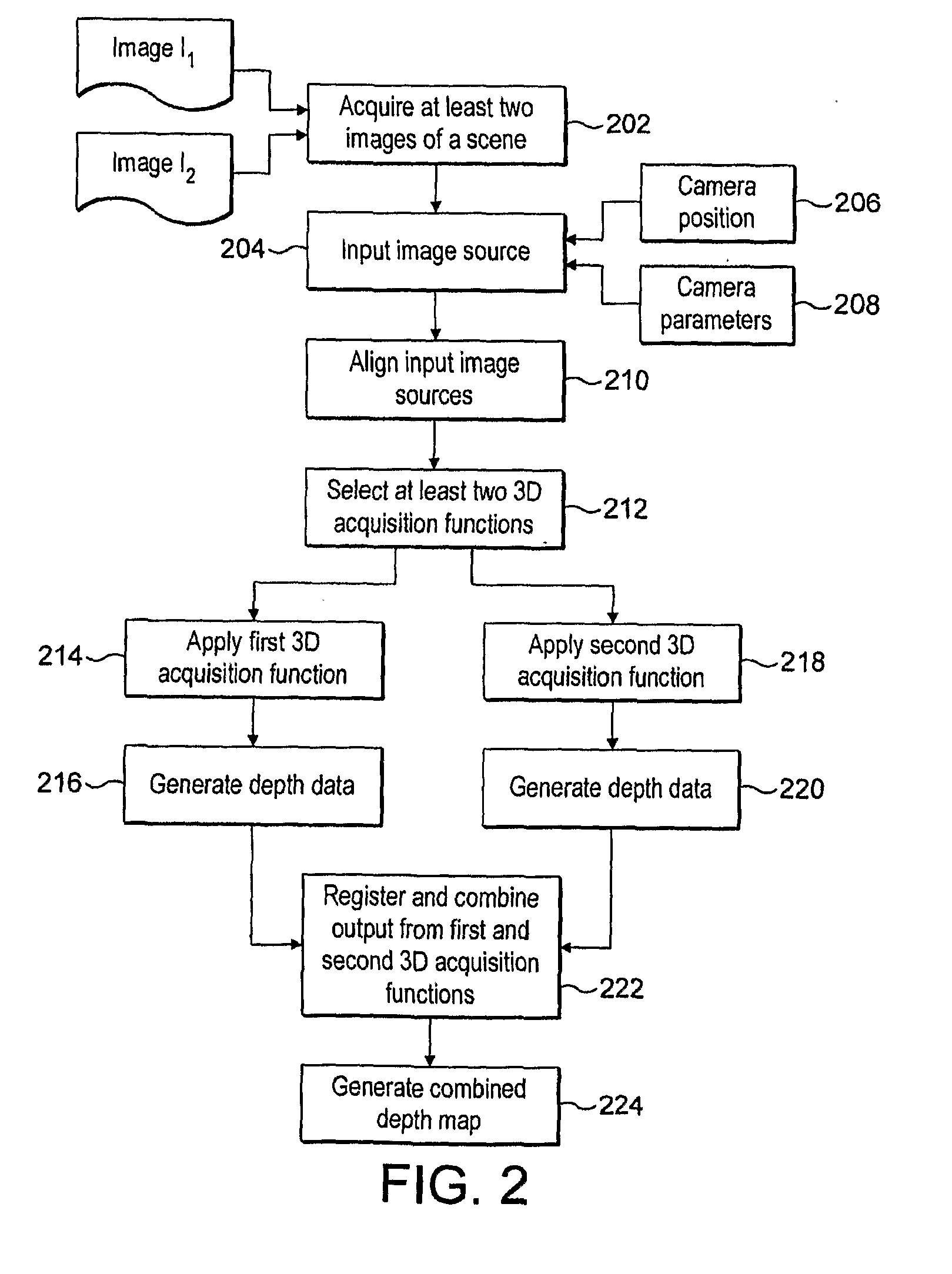
System and method for three-dimensional object reconstruction from two-dimensional images
InactiveUS20100182406A1Precise processImprove accuracyImage analysisSteroscopic systemsParallaxAcquisition technique
A system and method for three-dimensional acquisition and modeling of a scene using two-dimensional images are provided. The present disclosure provides a system and method for selecting and combining the three-dimensional acquisition techniques that best fit the capture environment and conditions under consideration, and hence produce more accurate three-dimensional models. The system and method provide for acquiring at least two two-dimensional images of a scene, applying a first depth acquisition function to the at least two two-dimensional images, applying a second depth acquisition function to the at least two two-dimensional images, combining an output of the first depth acquisition function with an output of the second depth acquisition function, and generating a disparity or depth map from the combined output. The system and method also provide for reconstructing a three-dimensional model of the scene from the generated disparity or depth map.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING INC
Method and apparatus for automatically generating a site model
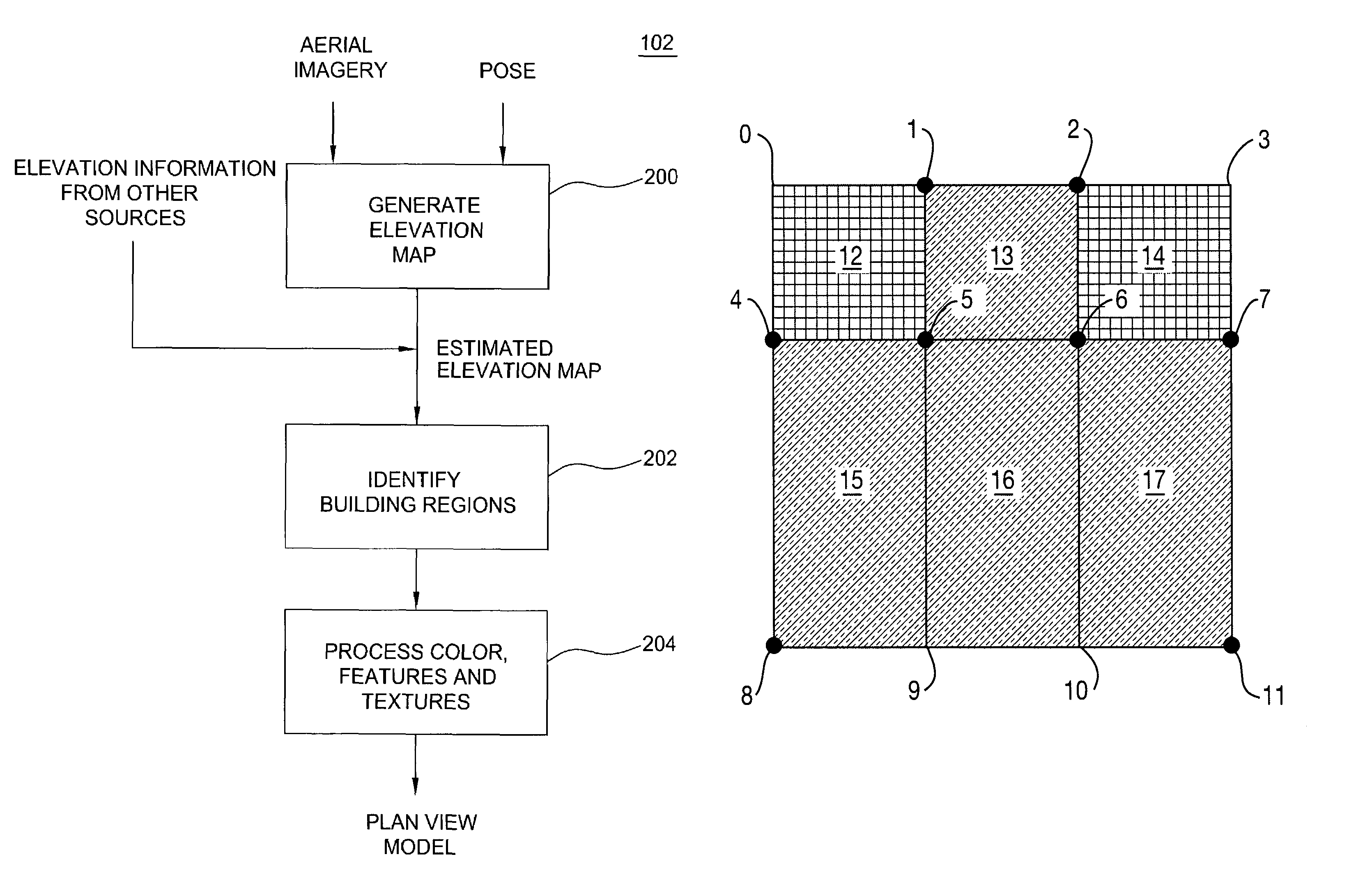
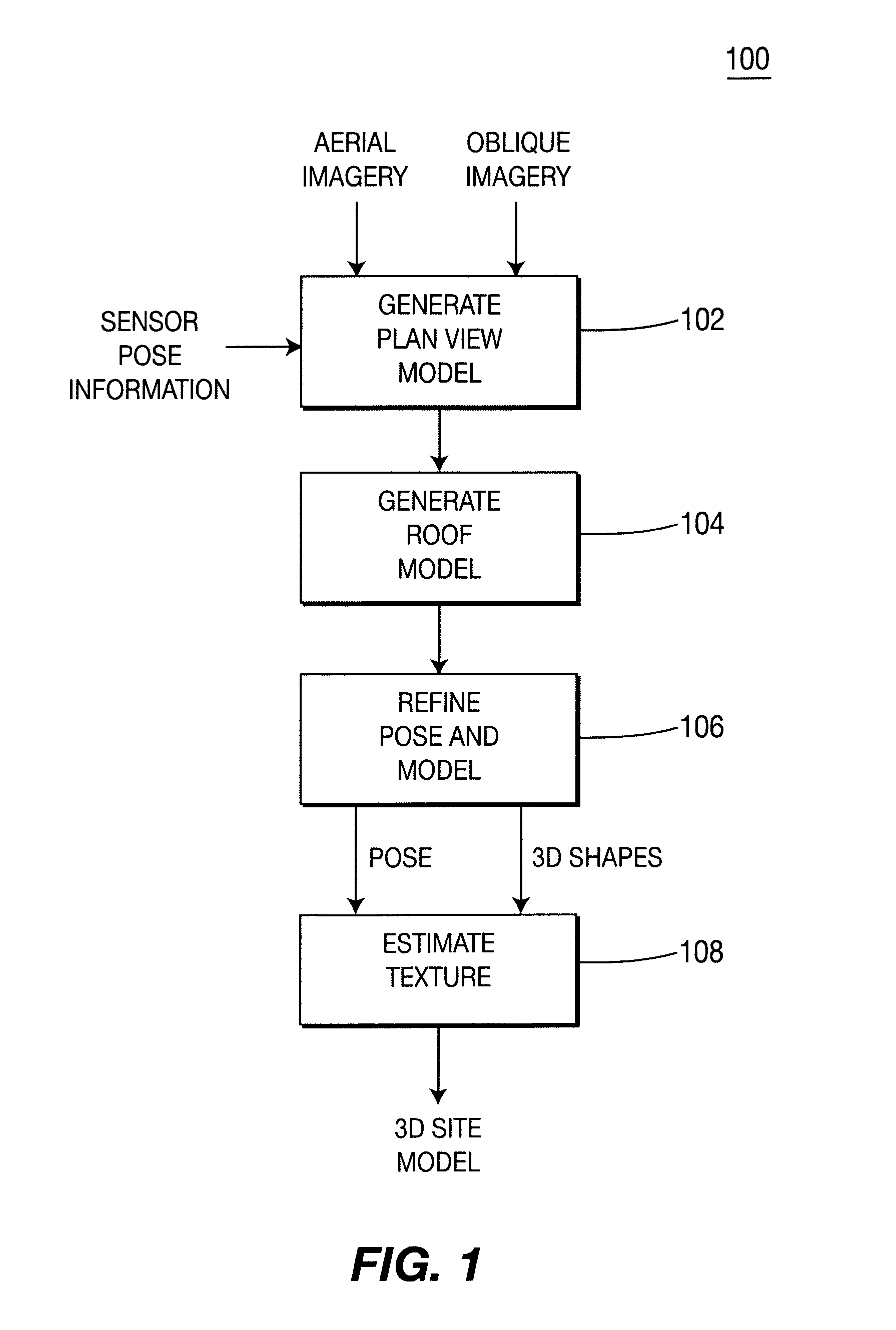
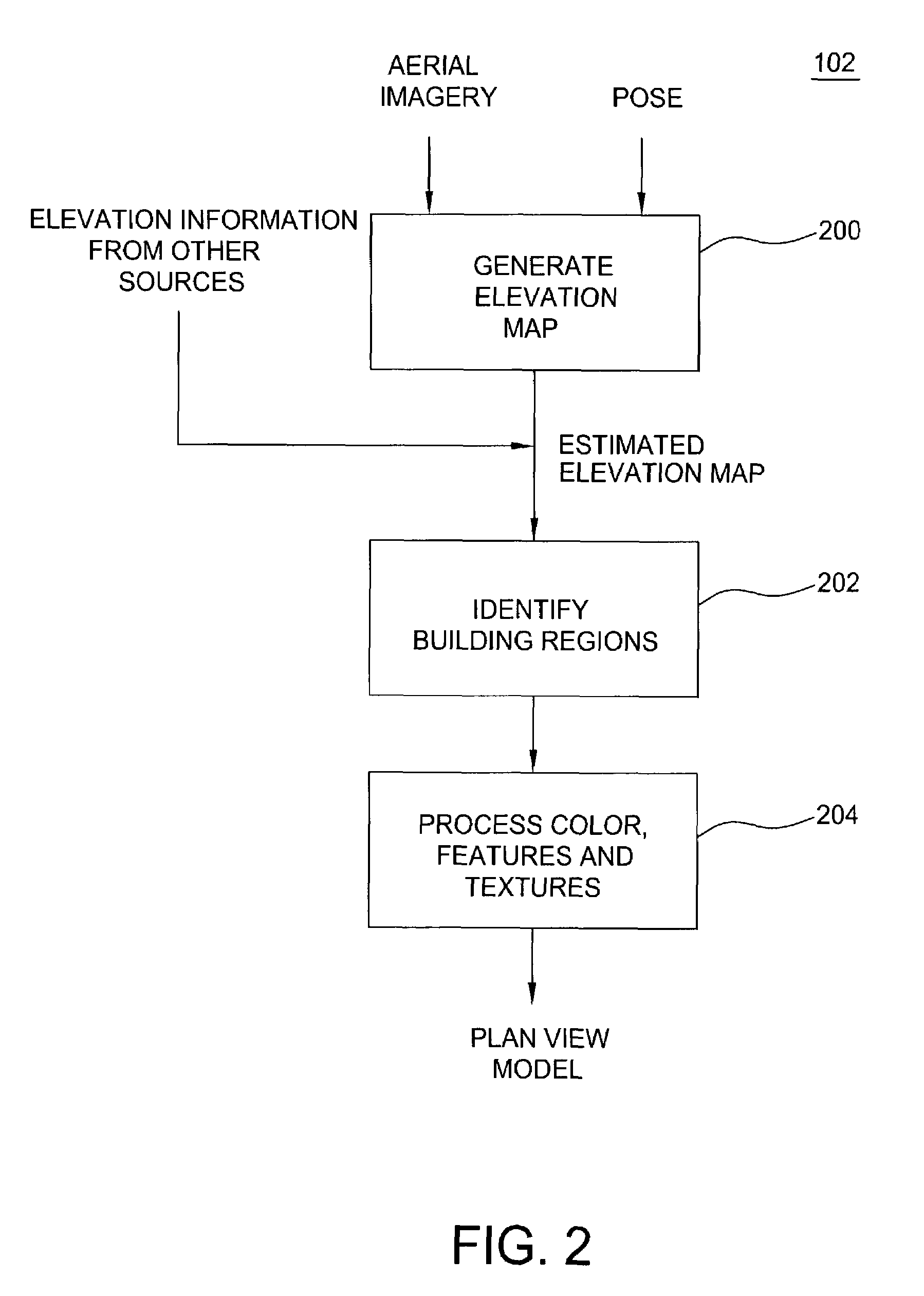
ActiveUS7509241B2Overcome disadvantagesPrecise definitionGeometric CADDetails involving processing stepsSite modelView model
A method and apparatus for automatically combining aerial images and oblique images to form a three-dimensional (3D) site model. The apparatus or method is supplied with aerial and oblique imagery. The imagery is processed to identify building boundaries and outlines as well as to produce a depth map. The building boundaries and the depth map may be combined to form a 3D plan view model or used separately as a 2D plan view model. The imagery and plan view model is further processed to determine roof models for the buildings in the scene. The result is a 3D site model having buildings represented rectangular boxes with accurately defined roof shapes.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Systems and Methods for Depth-Assisted Perspective Distortion Correction
ActiveUS20150091900A1Reduce Perspective DistortionDistortion in appearanceImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsAngle of view
Systems and methods for automatically correcting apparent distortions in close range photographs that are captured using an imaging system capable of capturing images and depth maps are disclosed. In many embodiments, faces are automatically detected and segmented from images using a depth-assisted alpha matting. The detected faces can then be re-rendered from a more distant viewpoint and composited with the background to create a new image in which apparent perspective distortion is reduced.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
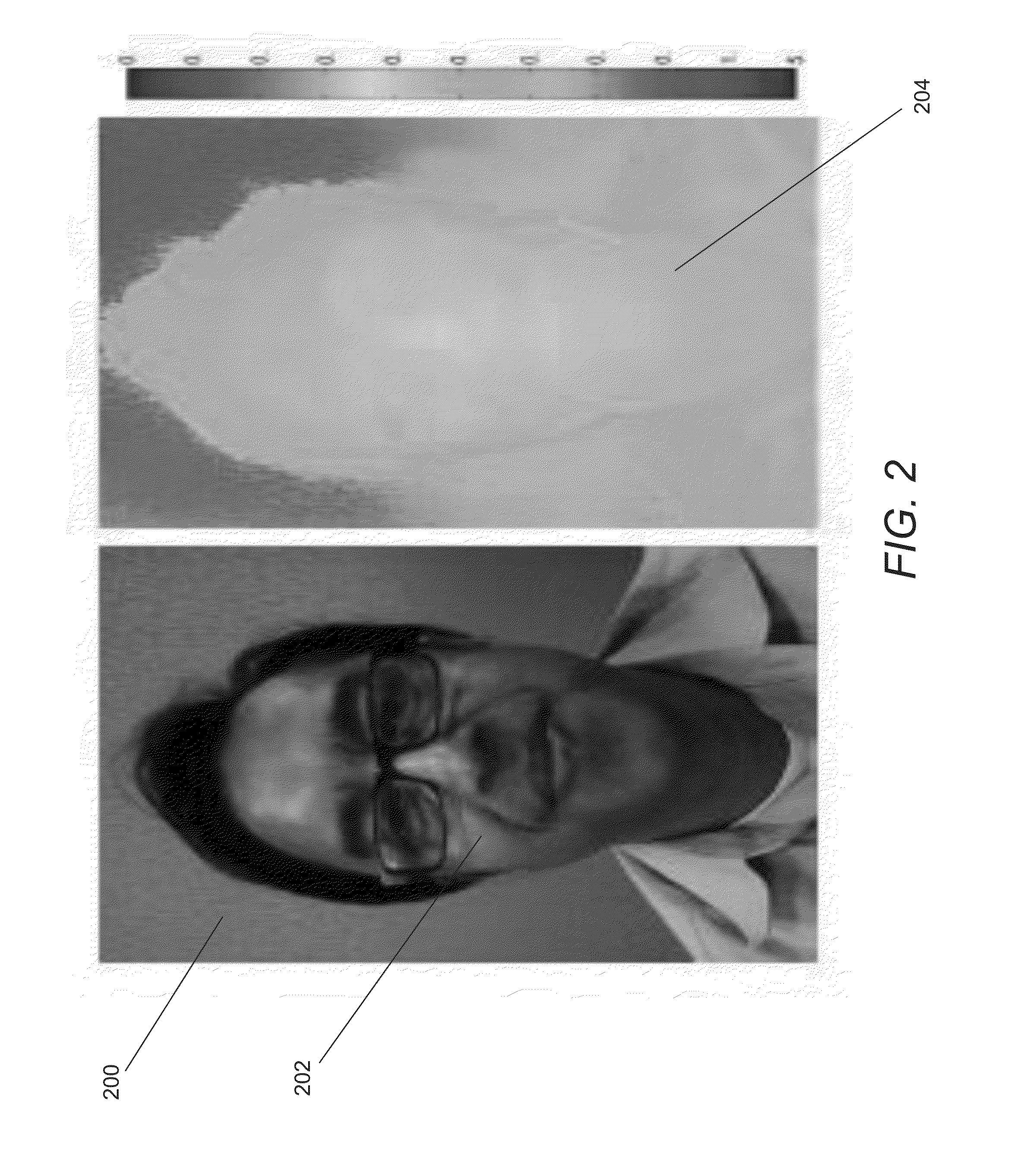
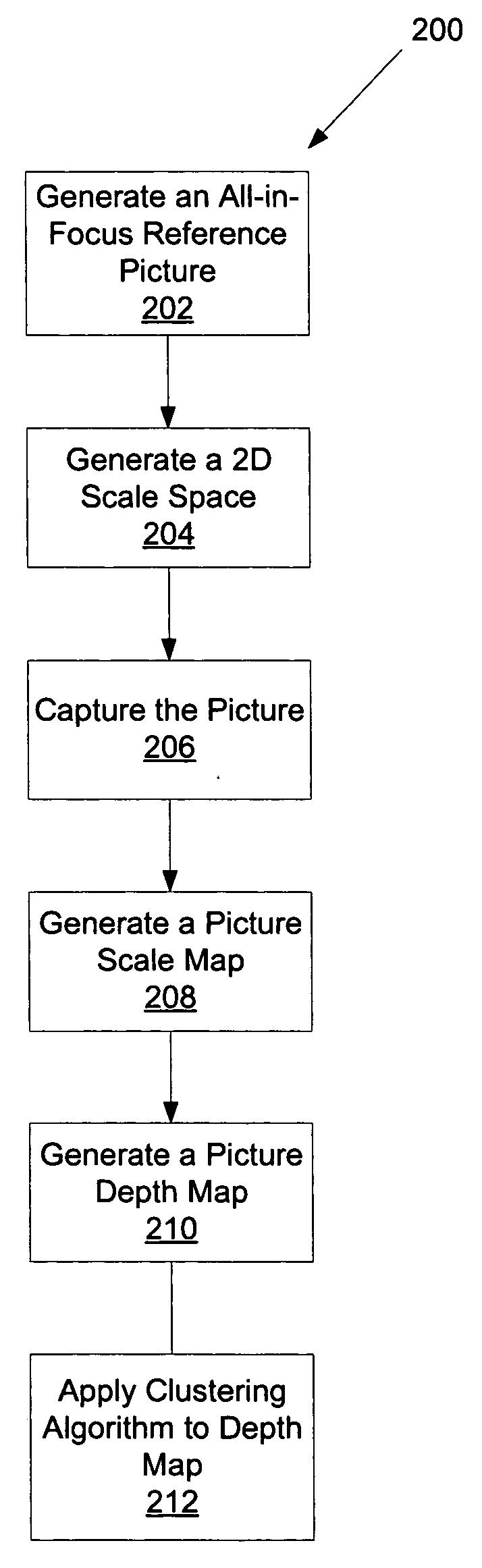
Method for creating a depth map for auto focus using an all-in-focus picture and two-dimensional scale space matching
InactiveUS20070019883A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree-dimensional spaceDepth of field
An imaging acquisition system that generates a depth map for a picture of a three dimension spatial scene from the estimated blur radius of the picture is described. The system generates an all-in-focus reference picture of the three dimension spatial scene. The system uses the all-in-focus reference picture to generate a two-dimensional scale space representation. The system computes the picture depth map for a finite depth of field using the two-dimensional scale space representation.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
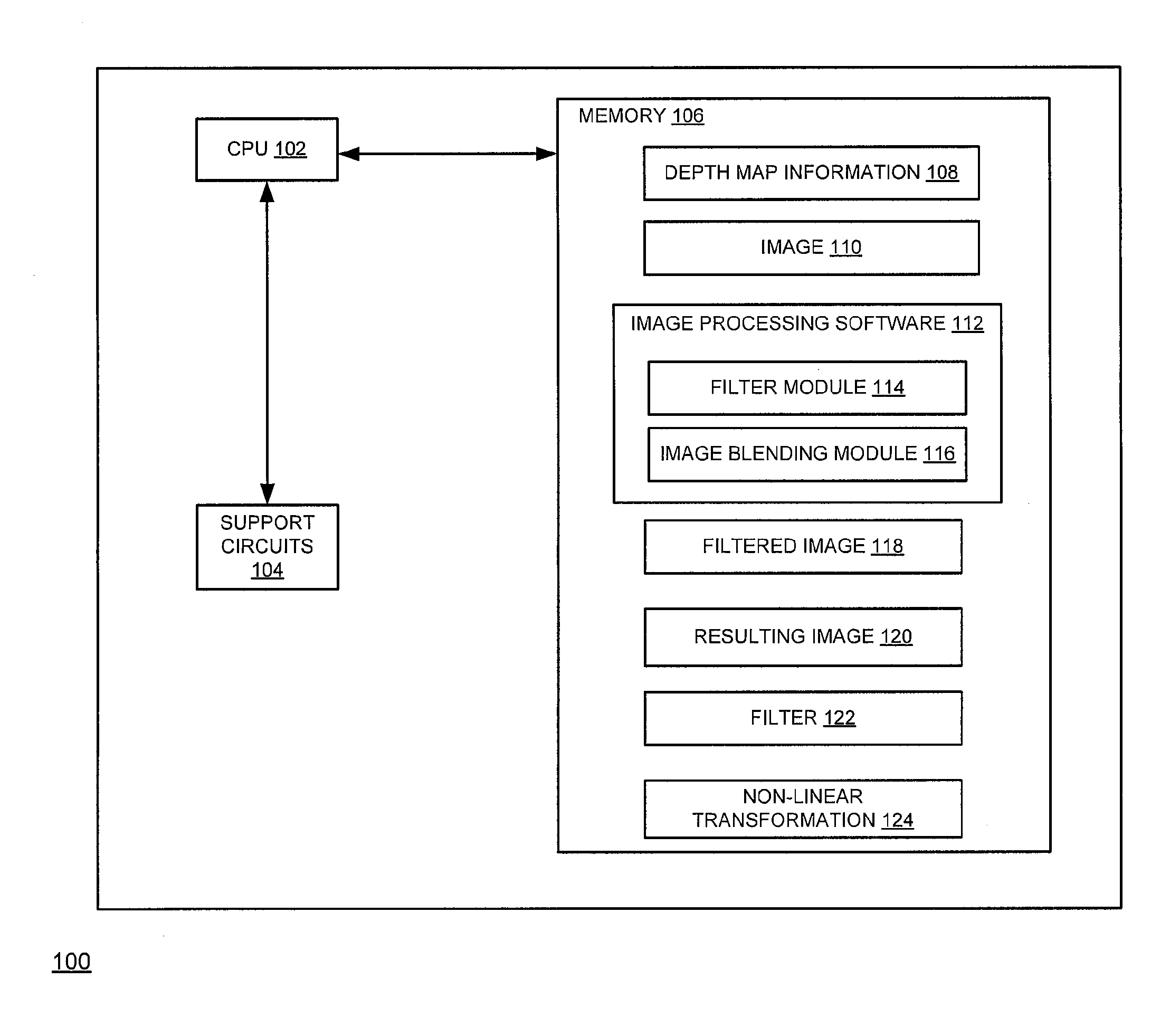
Method and apparatus for performing a blur rendering process on an image
A method and apparatus for performing a blur rendering process on an image is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method of performing a blur rendering process includes accessing a filtered image and depth map information, determining a plurality of blending coefficients for computing a weighted sum for the image and filtered image, wherein the plurality of blending coefficients define a substantially smooth transition from at least one first depth class to at least one second depth class and a substantially sharp transition from the at least one second depth class and the at least one first depth class, wherein the at least one first depth class and the at least one second depth class form at least a portion of a plurality of depth classes and combining the image and the filtered image into a resulting image using the plurality of coefficients.
Owner:SONY CORP
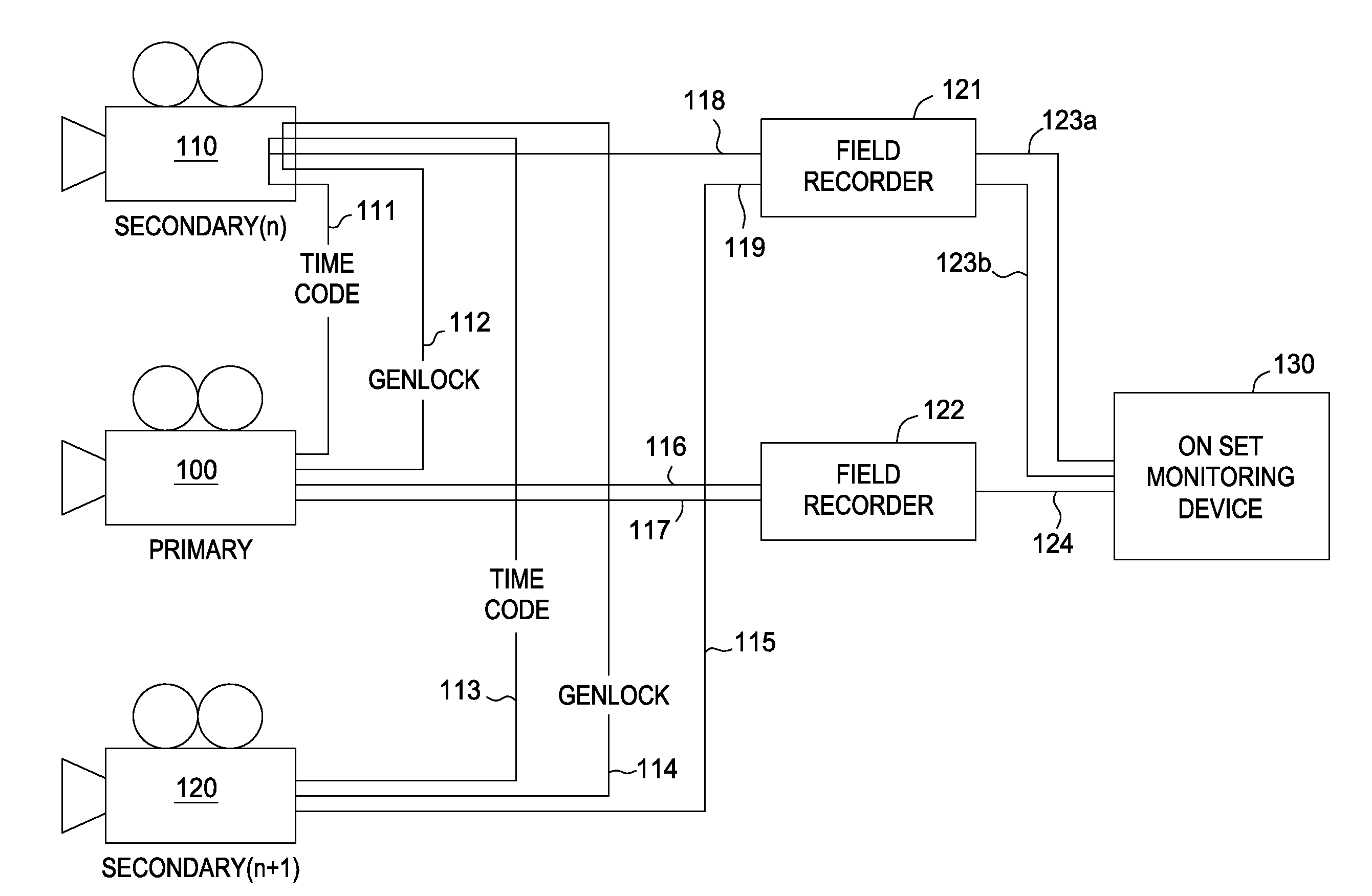
Processing image data from multiple cameras for motion pictures
An approach is disclosed for generating stereoscopic image sequences. The approach includes receiving a plurality of image sequences, each image sequence captured from a distinct camera or other capture device in a multi-camera array. One image sequence is a primary image sequence and the other image sequences are secondary image sequences. The approach further includes generating, from the primary and at least one or more of the secondary image sequences, depth maps corresponding to images of the primary image sequence and generating, for each image in the primary image sequence, based on at least the depth maps and the corresponding images of the primary image sequence, stereoscopic images of a stereoscopic image sequence.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
Method of generating surface defined by boundary of three-dimensional point cloud
Disclosed is a method of generating a three-dimensional (3D) surface defined by a boundary of a 3D point cloud. The method comprises generating density and depth maps from the 3D point cloud, constructing a 2D mesh from the depth and density maps, transforming the 2D mesh into a 3D mesh, and rendering 3D polygons defined by the 3D mesh.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method and system to transform stereo content
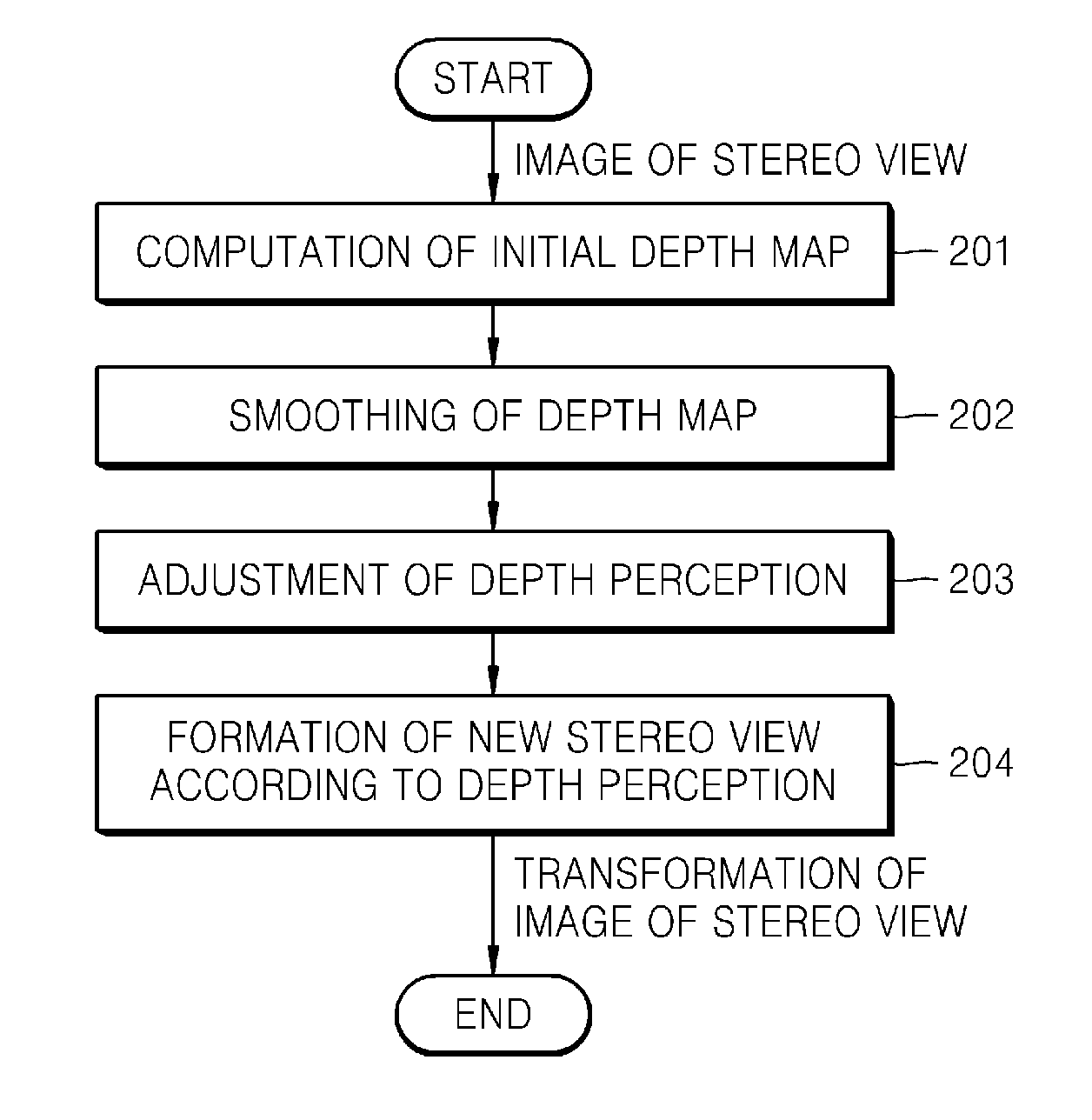
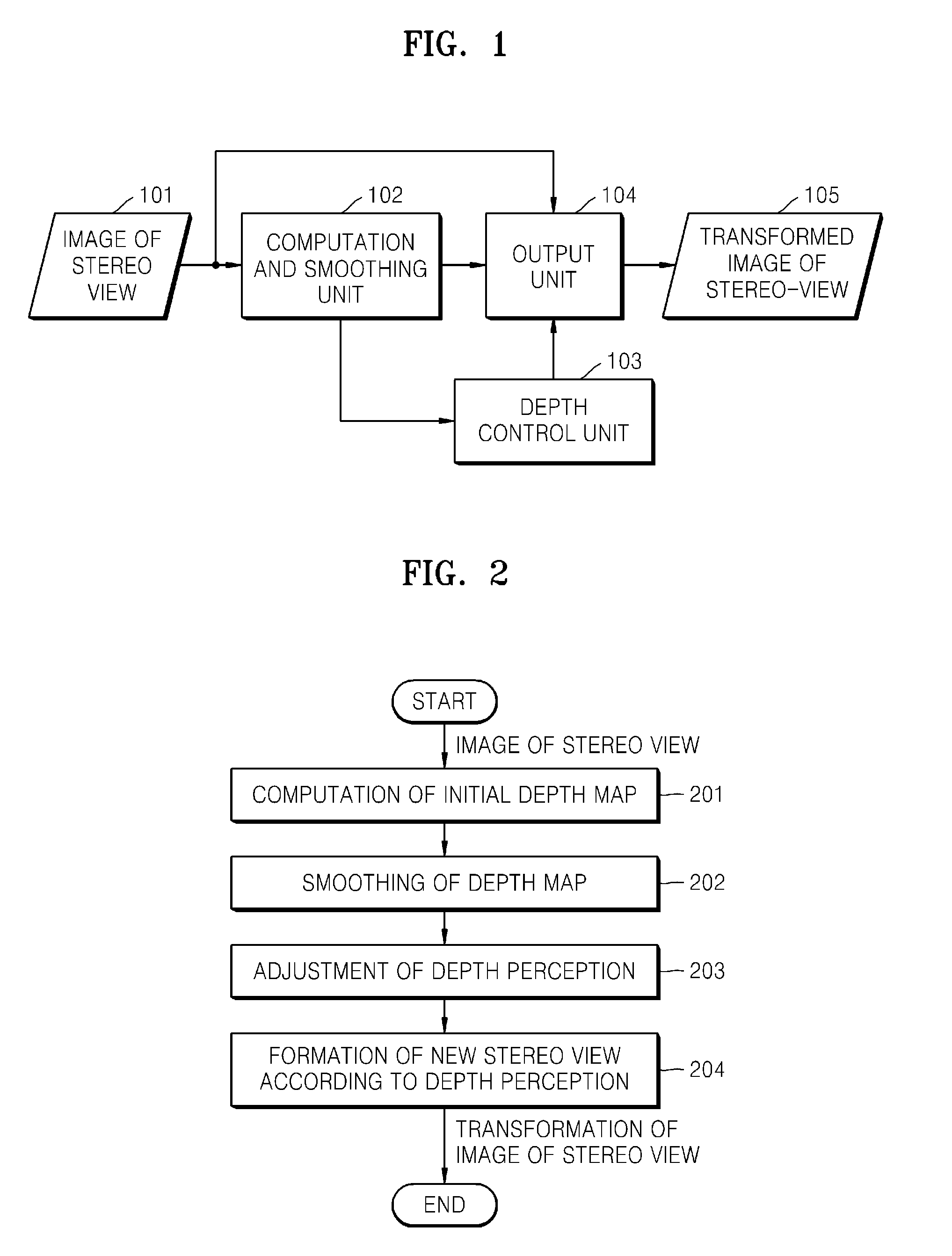
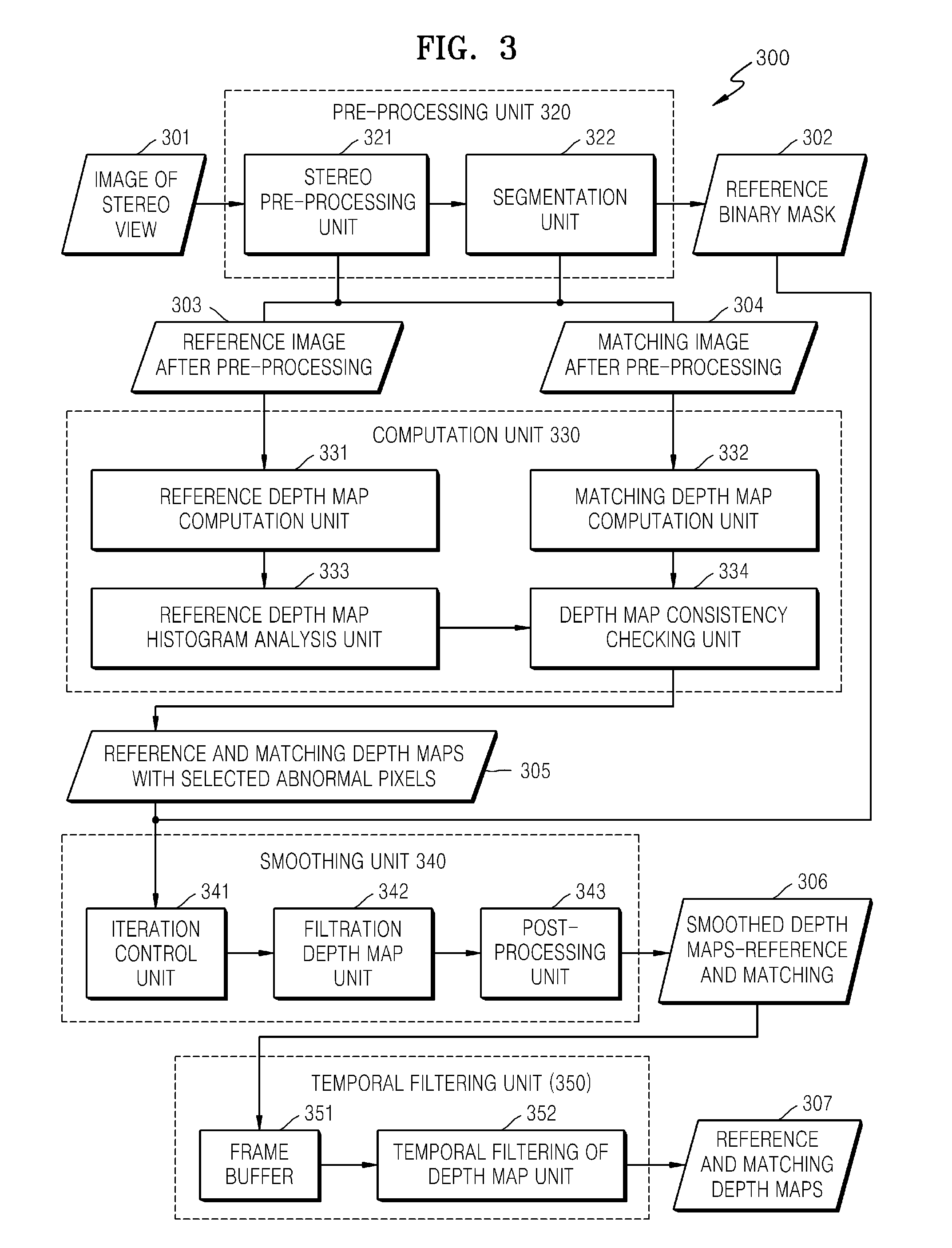
Methods and systems to process stereo images and video information, and, in particular, to methods and devices to transfer and / or transform stereo content to decrease eye fatigue of a user during viewing of 3D video. The methods and systems can compute an initial map of disparity / depth for stereo images from 3D video, smooth a depth map, change depth perception parameters according to the estimation of eye fatigue, and generate new stereo image according to the depth perception parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Time-of-Flight (TOF) Assisted Structured Light Imaging
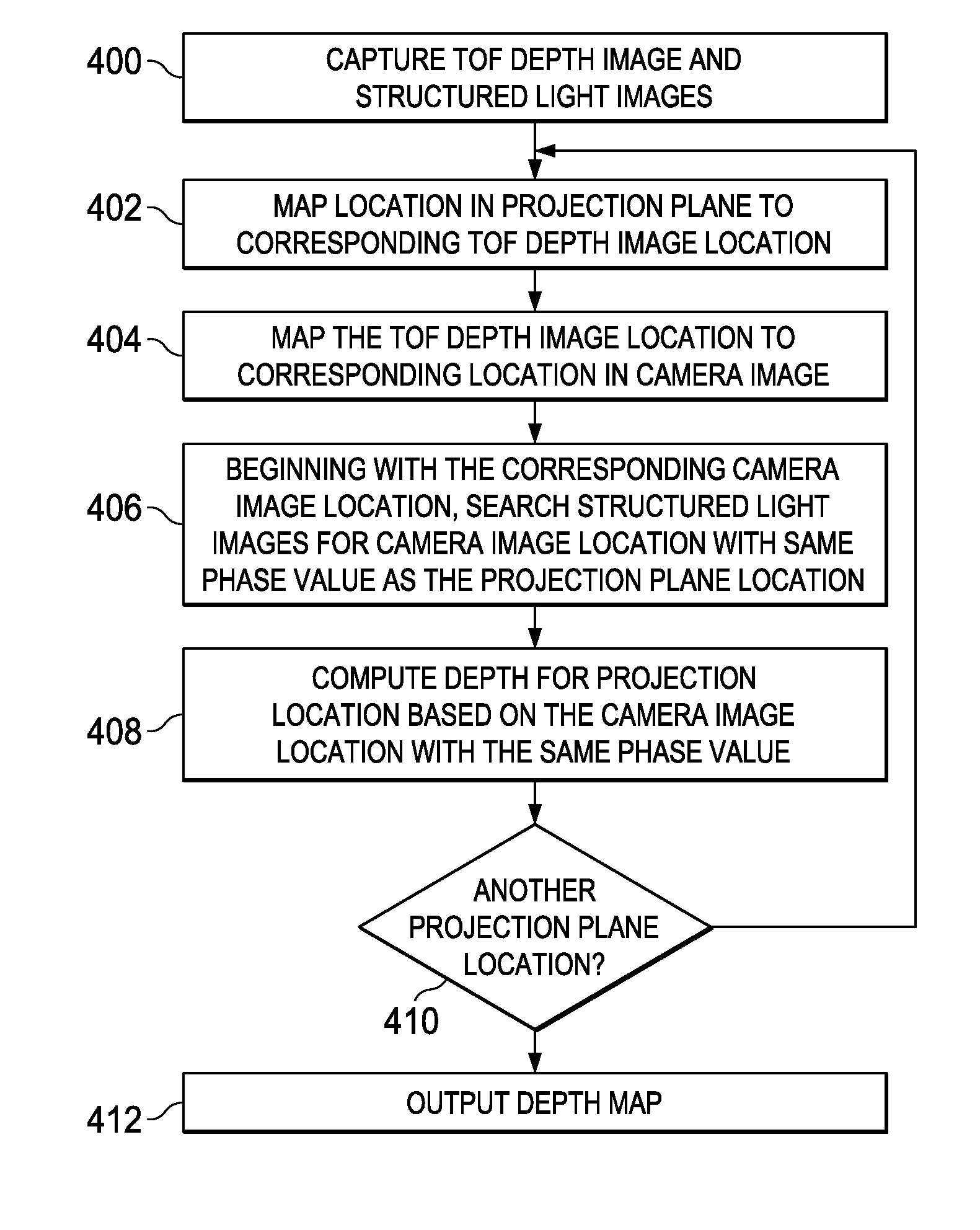
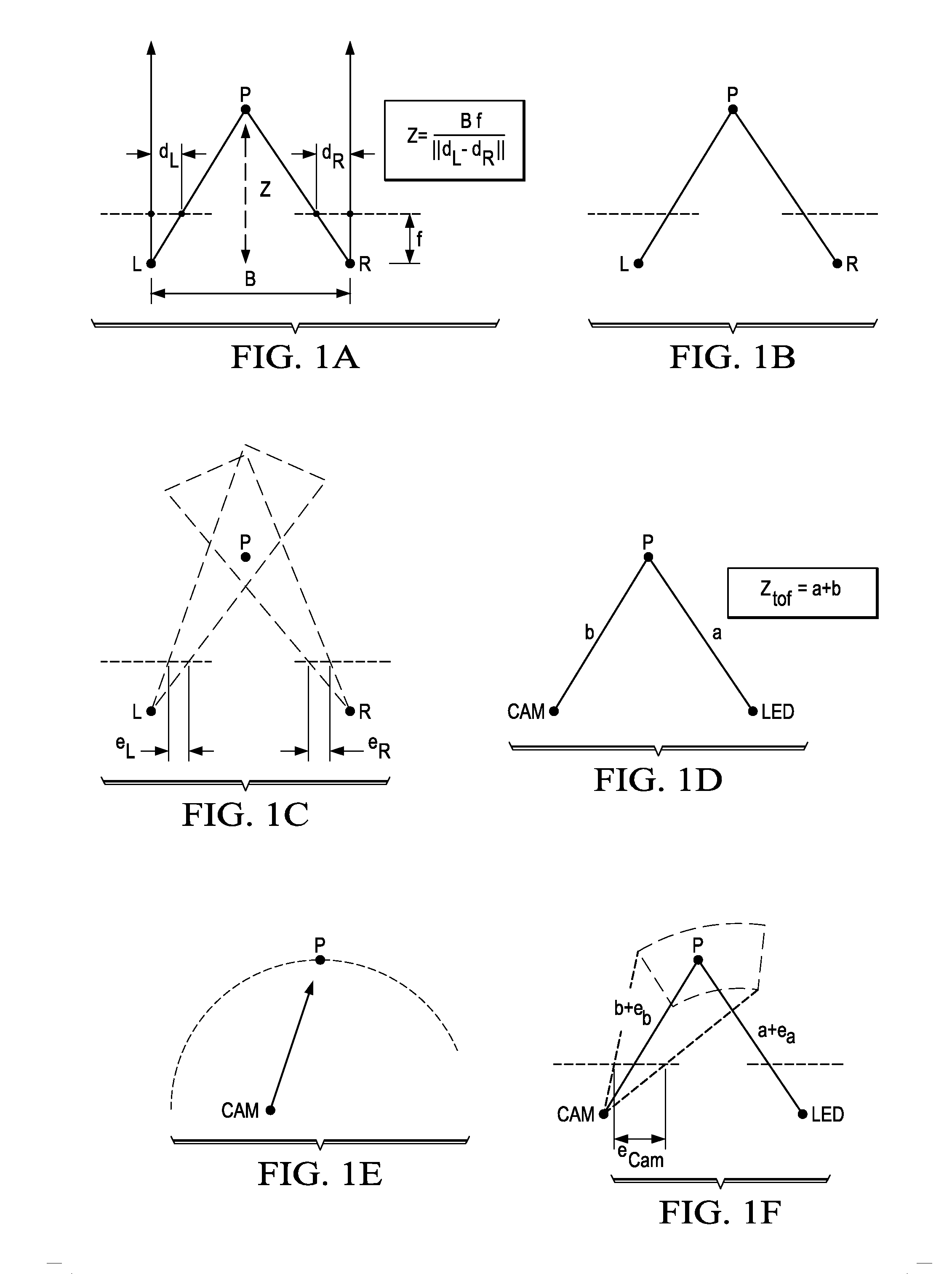
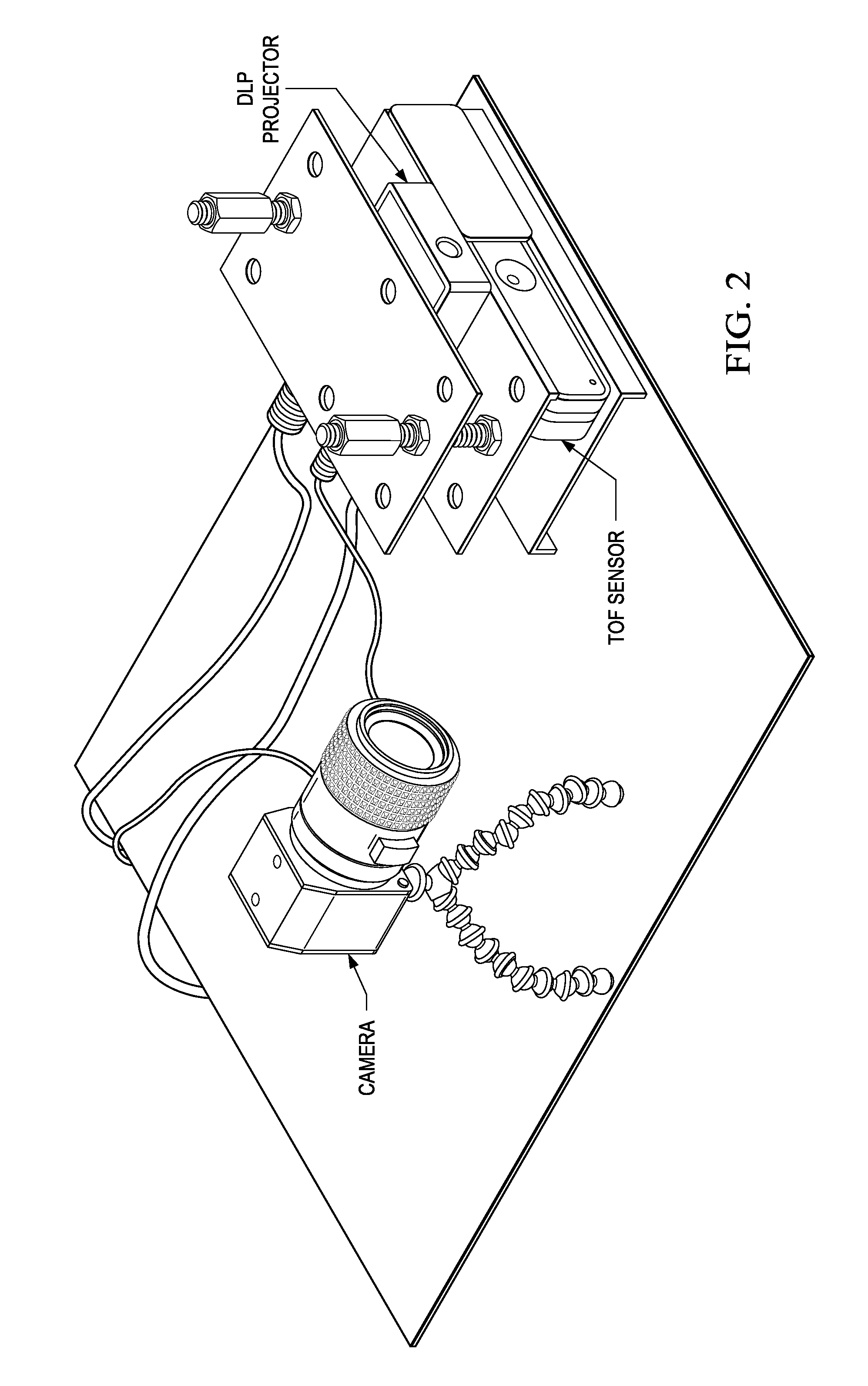
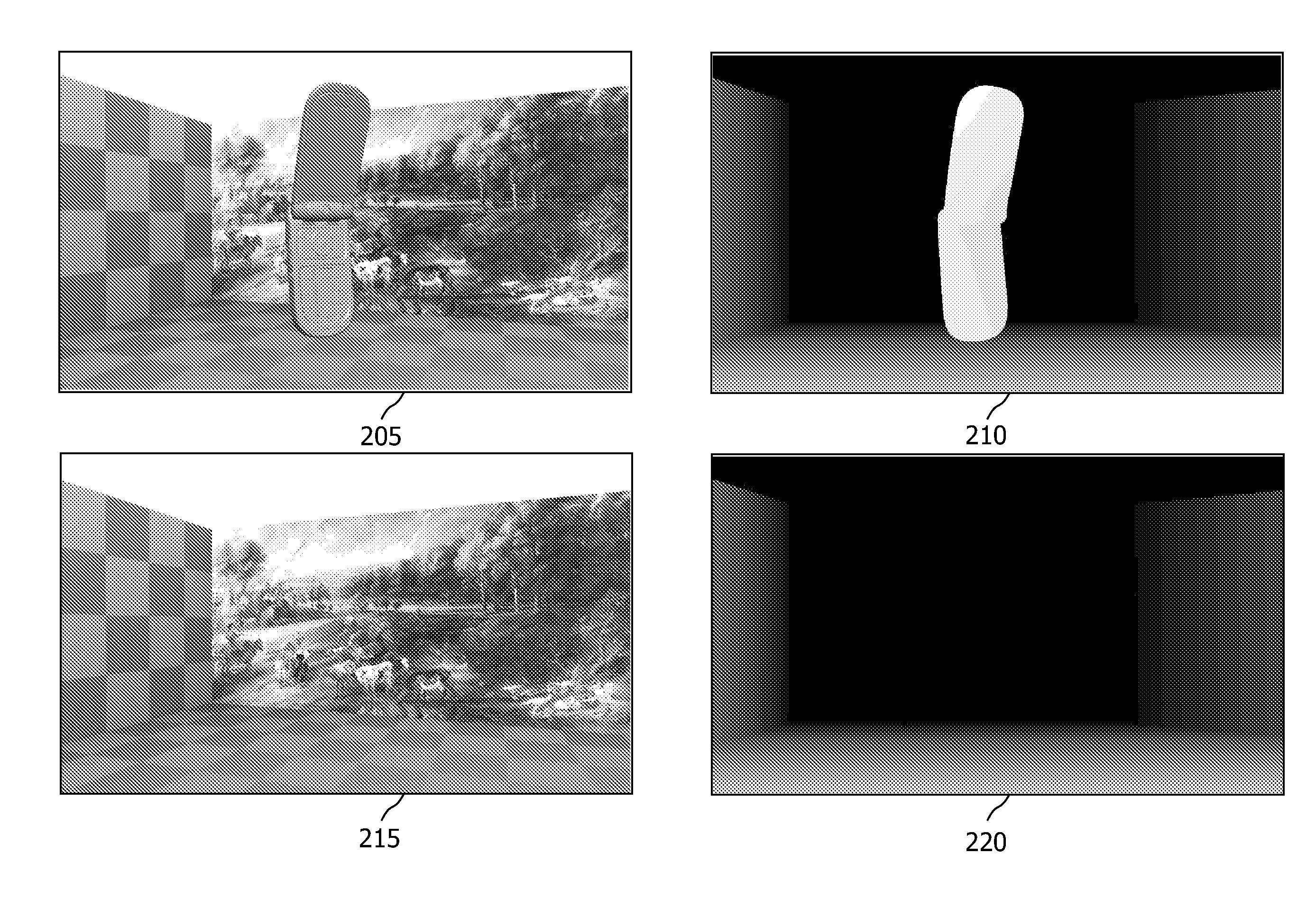
A method for computing a depth map of a scene in a structured light imaging system including a time-of-flight (TOF) sensor and a projector is provided that includes capturing a plurality of high frequency phase-shifted structured light images of the scene using a camera in the structured light imaging system, generating, concurrently with the capturing of the plurality of high frequency phase-shifted structured light images, a time-of-flight (TOF) depth image of the scene using the TOF sensor, and computing the depth map from the plurality of high frequency phase-shifted structured light images wherein the TOF depth image is used for phase unwrapping.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and device for processing a depth-map
InactiveUS20100215251A1Reduce the impact of noiseReduce compression artifactTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionViewpointsCompression artifact
The present invention relates to a device and apparatus for processing a depth-map 710, the method comprising obtaining a depth-map 710 based on a lossy compressed depth-map, the depth-map 710 comprising depth information of a scene from a viewpoint, the scene comprising an object, obtaining occlusion information for the scene from the viewpoint, the occlusion information comprising information occluded by the object in the depth-map 710, and processing at least part of the depth information using at least part of the occlusion information in order to reduce compression artifacts in the depth-map 710.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Three dimensional image generating system and method accomodating multi-view imaging
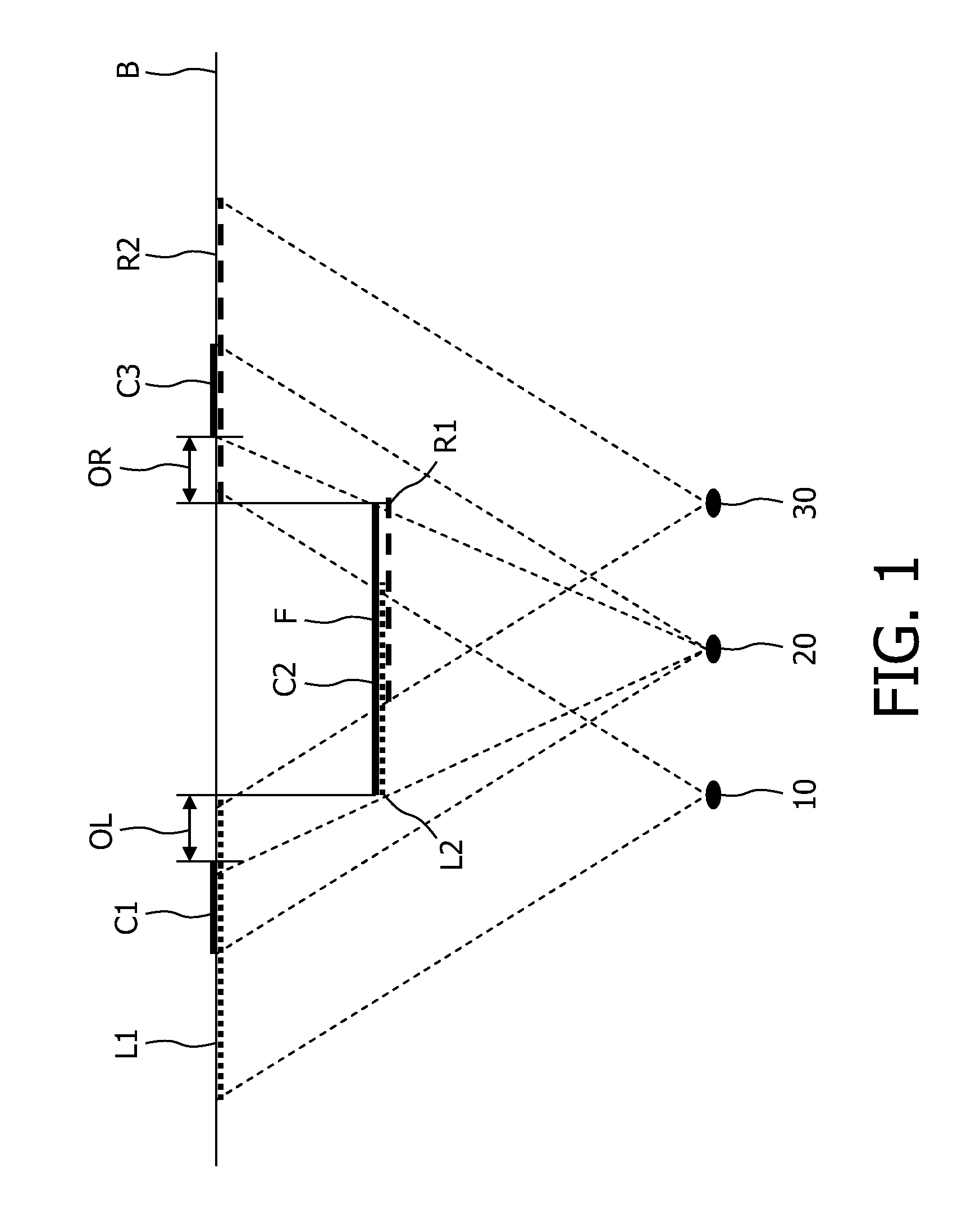
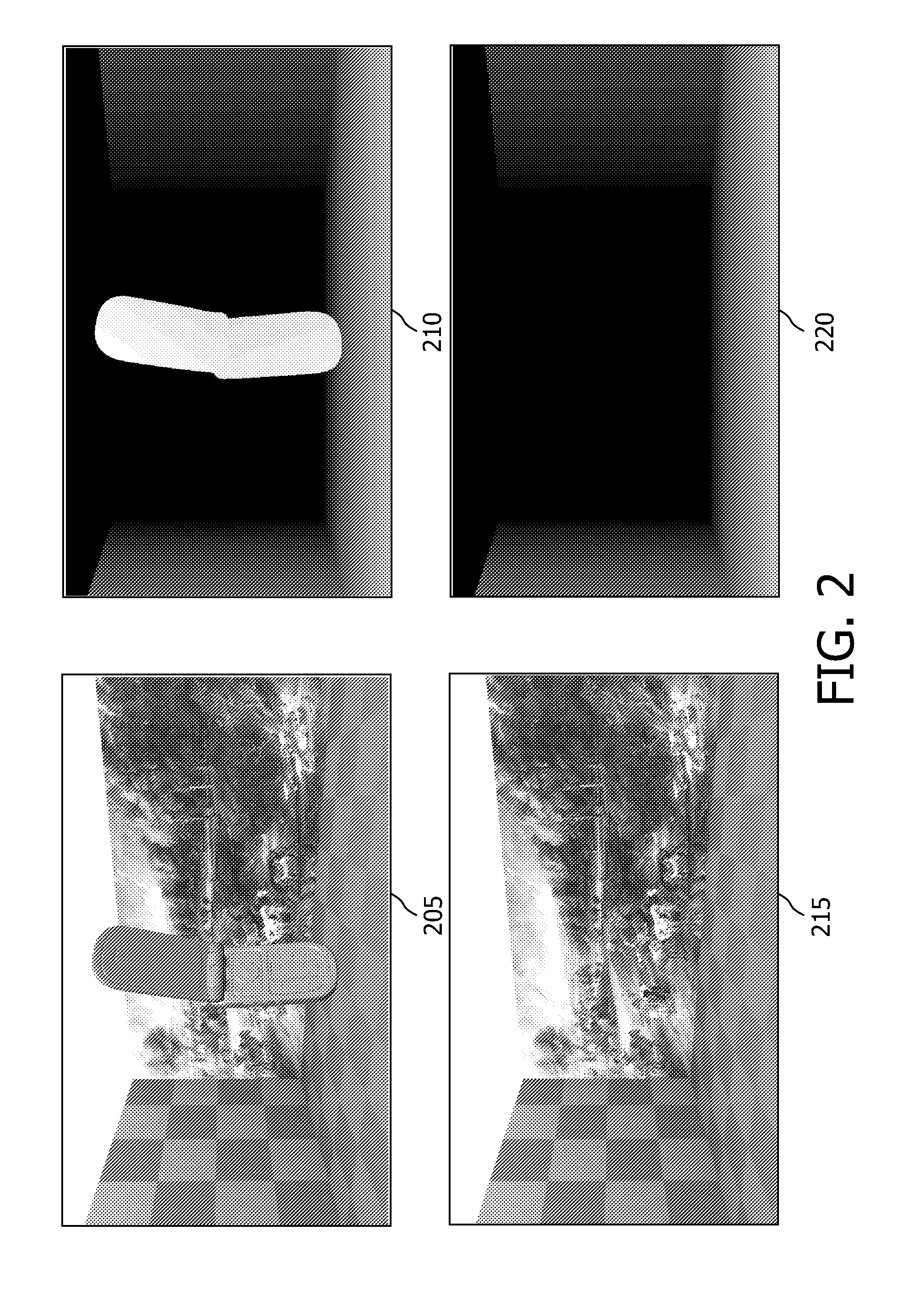
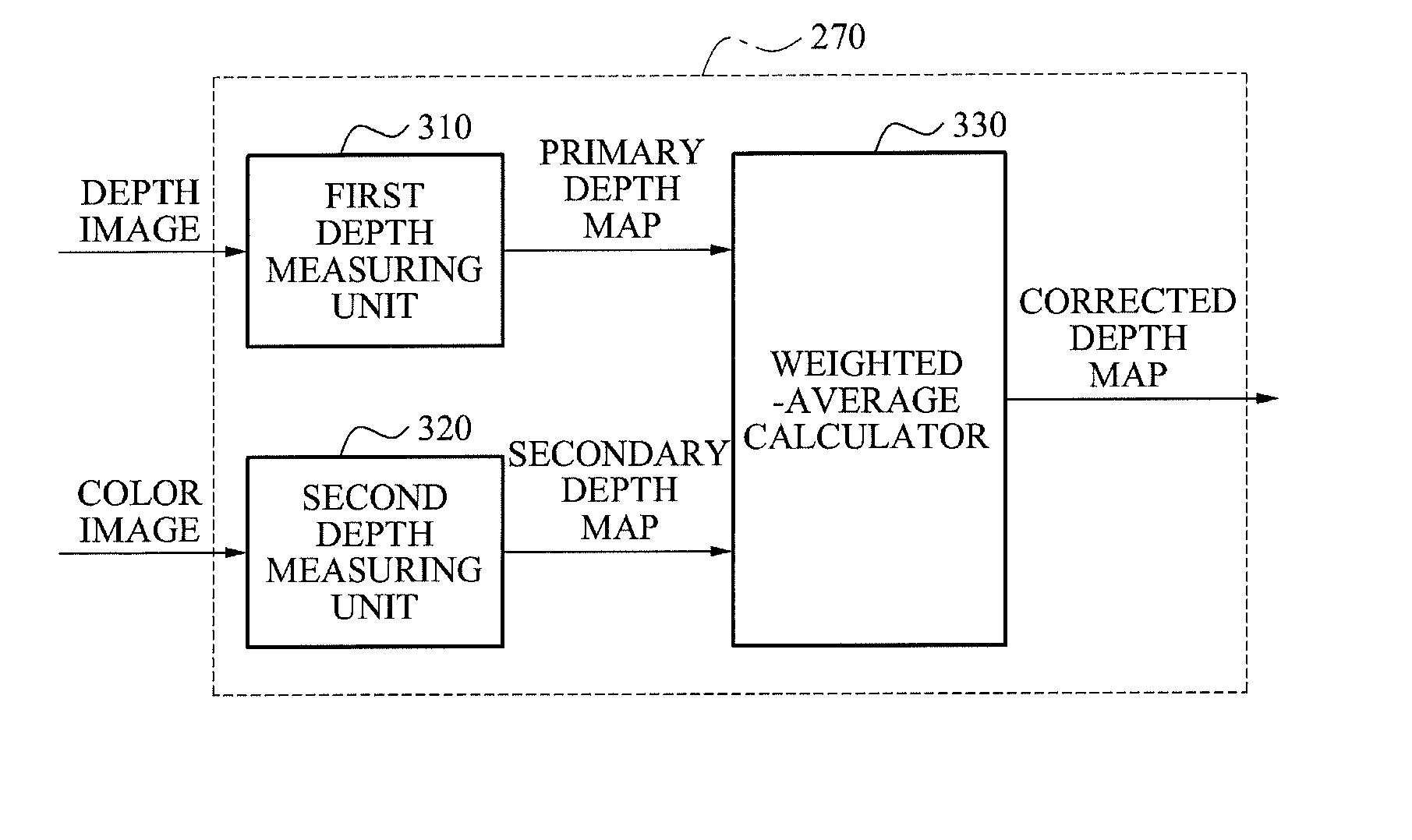
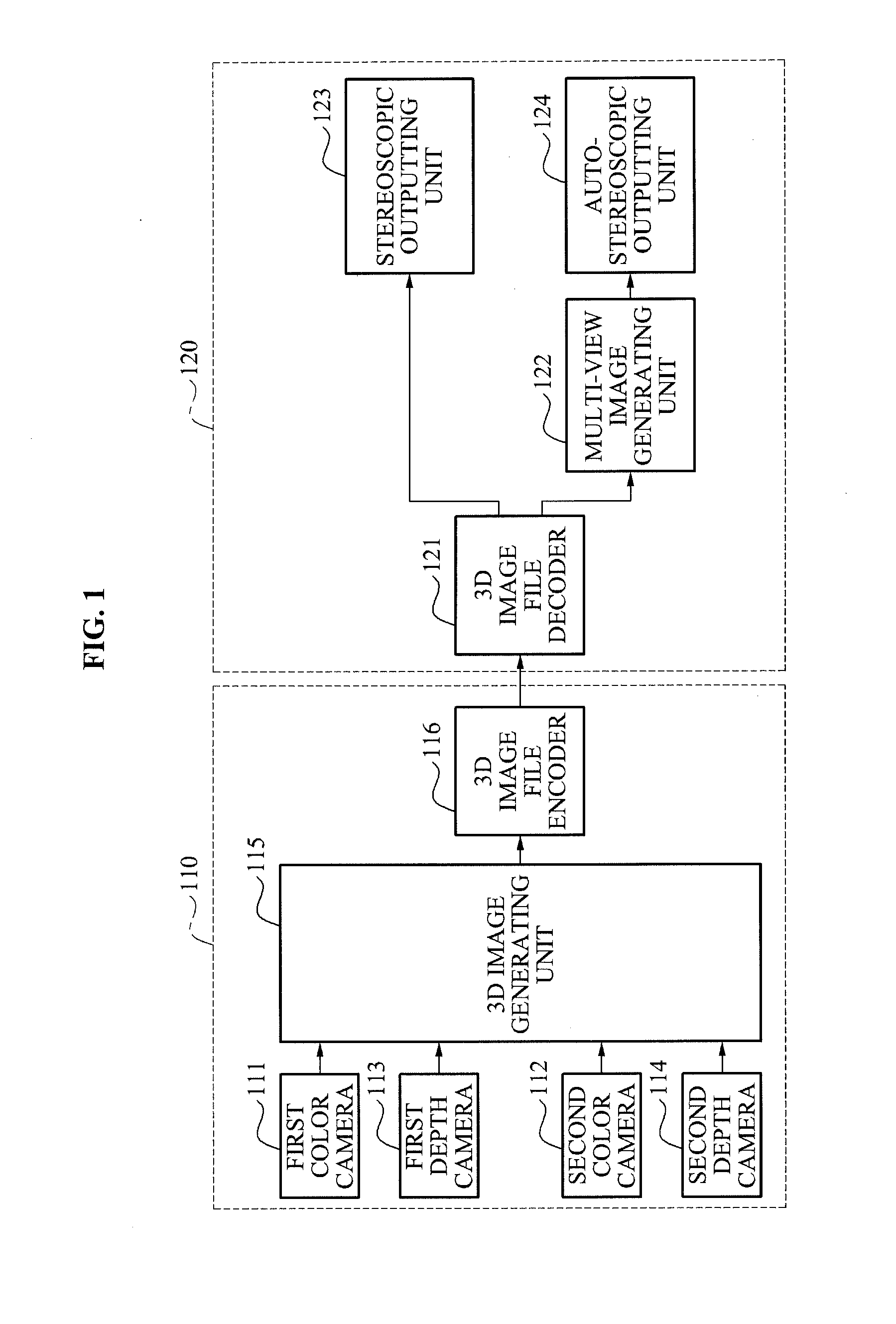
Provided is a three-dimensional (3D) image generating system and method accommodating multi-view imaging. The 3D image generating system and method may generate corrected depth maps respectively corresponding to color images by merging disparity information associated with a disparity between color images and depth maps generated respectively from depth images.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com