Patents
Literature
7916results about How to "Increase width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
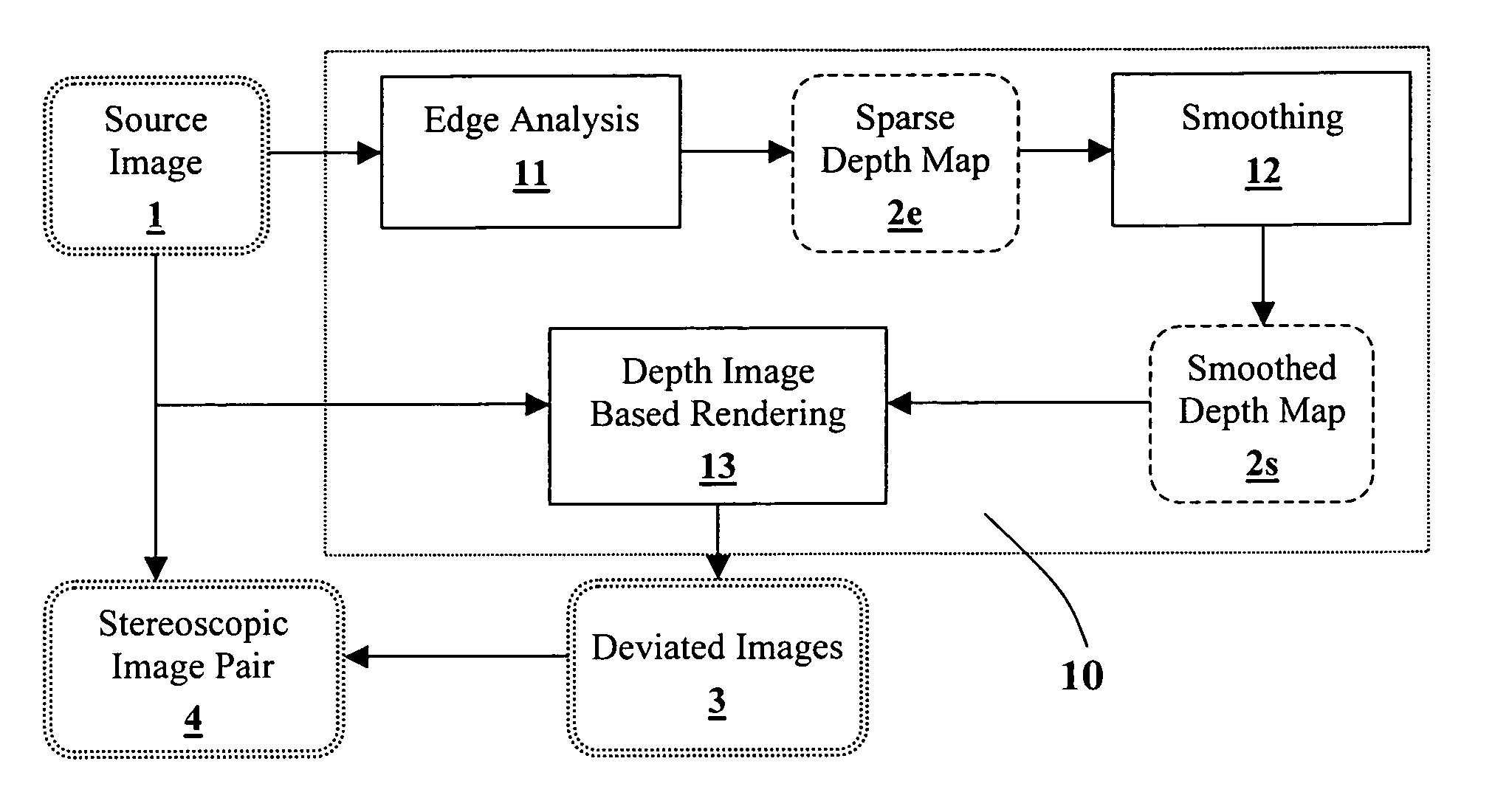
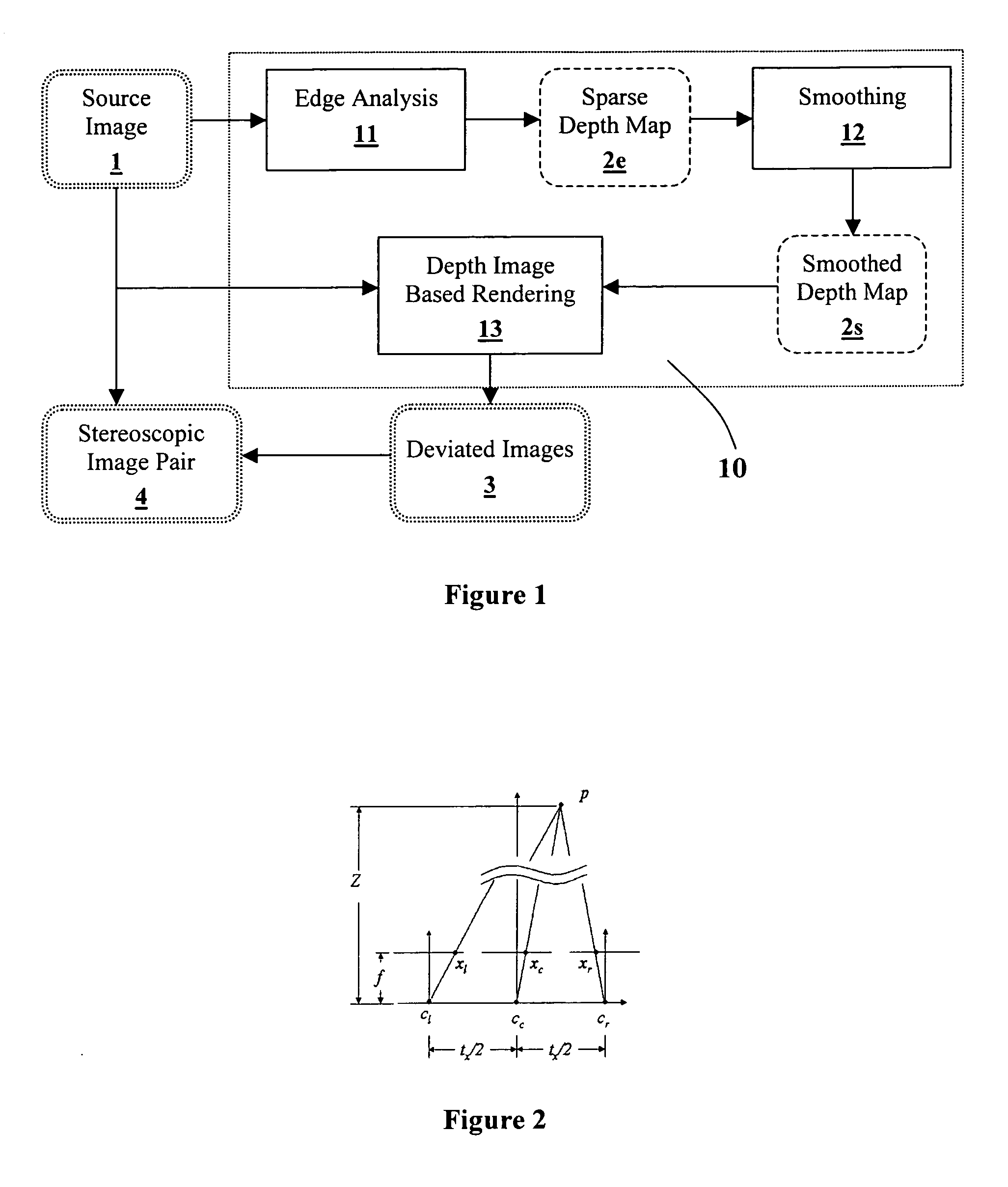
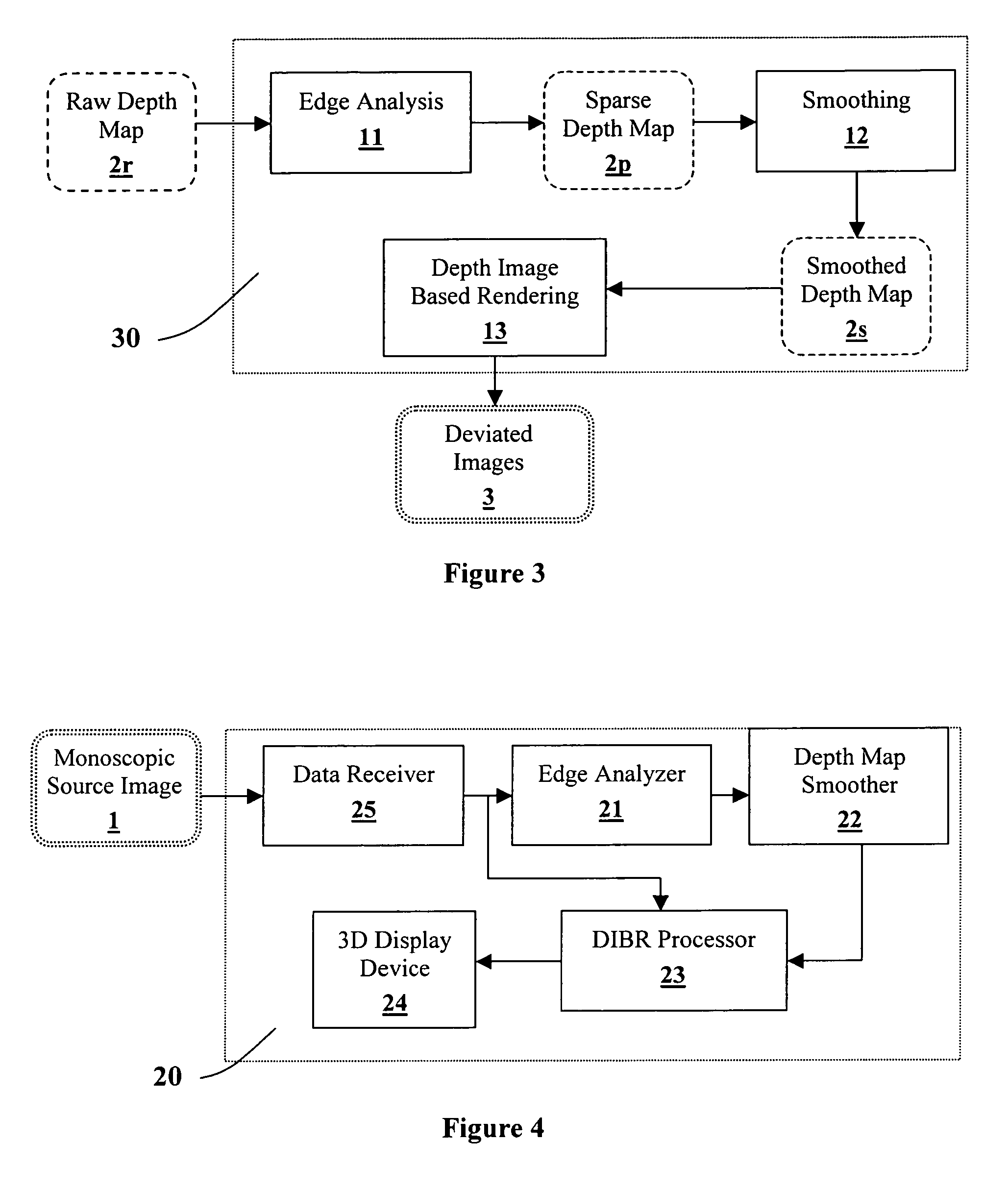
Generating a depth map from a two-dimensional source image for stereoscopic and multiview imaging
InactiveUS20070024614A1Saving in bandwidth requirementIncrease widthImage enhancementImage analysisViewpointsImage pair
Depth maps are generated from a monoscopic source images and asymmetrically smoothed to a near-saturation level. Each depth map contains depth values focused on edges of local regions in the source image. Each edge is defined by a predetermined image parameter having an estimated value exceeding a predefined threshold. The depth values are based on the corresponding estimated values of the image parameter. The depth map is used to process the source image by a depth image based rendering algorithm to create at least one deviated image, which forms with the source image a set of monoscopic images. At least one stereoscopic image pair is selected from such a set for use in generating different viewpoints for multiview and stereoscopic purposes, including still and moving images.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
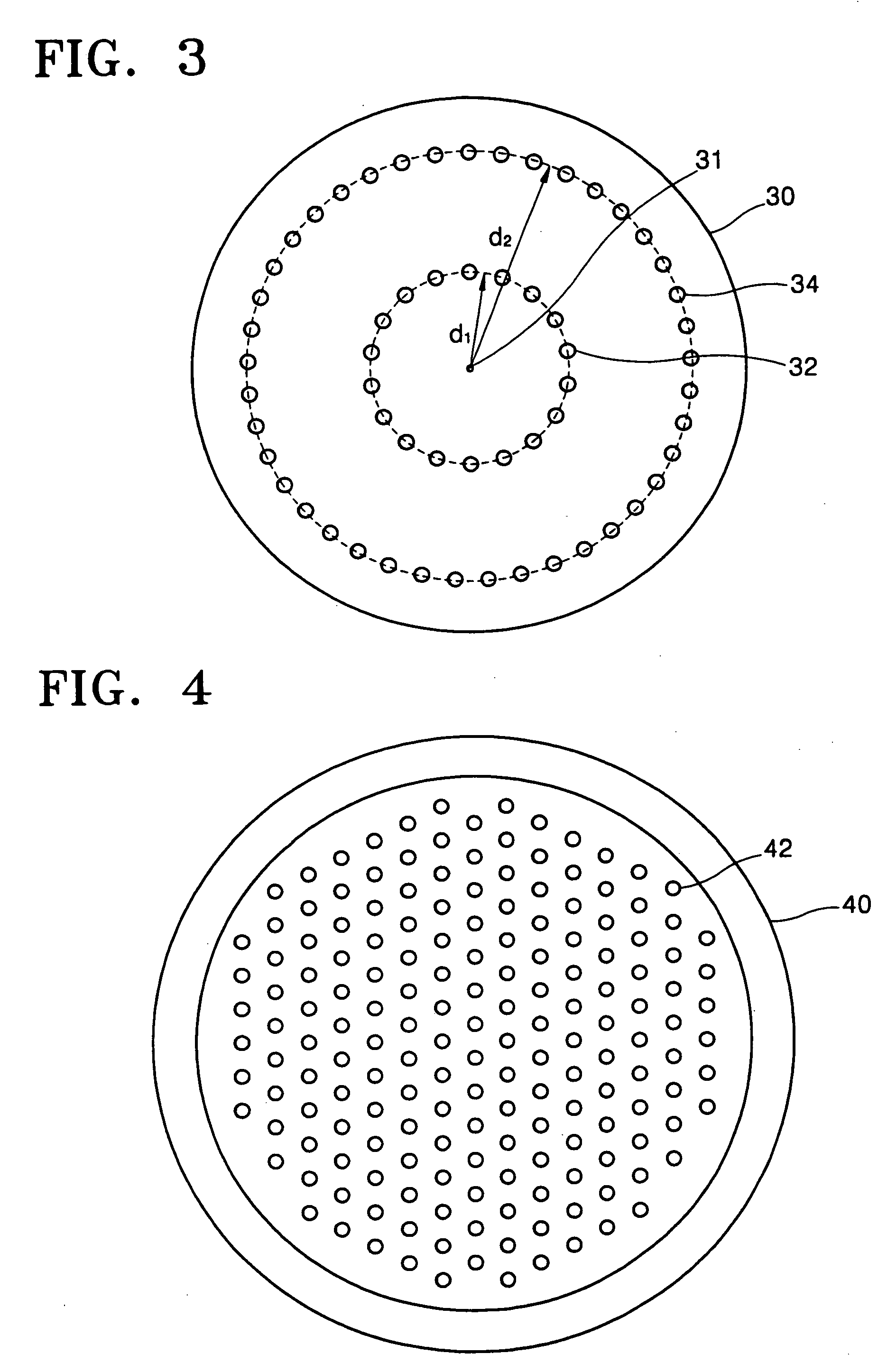
Shower head of a wafer treatment apparatus having a gap controller
InactiveUS6872258B2Improve uniformityEtch rate be optimizedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingProcess regionSemiconductor
A shower head for adjusting distribution of a reactant gas in a process region of a semiconductor manufacturing reaction chamber, wherein a top plate has a gas port for introducing the reactant gas into the reaction chamber; a face plate, having through holes, disposed opposite the process region; a first baffle plate, having through holes, disposed between the top plate and the face plate and capable of moving up or down, wherein the first baffle plate has a top surface that defines a first gap for forming a first lateral flow passage; a second baffle plate, having through holes, disposed between the first baffle plate and the face plate and capable of moving up or down, wherein the second baffle plate has a top surface that defines a second gap for forming a second lateral flow passage; and a gap controller for determining widths of the first and second gaps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Shower head of a wafer treatment apparatus having a gap controller
InactiveUS20050145338A1Improve uniformityIncrease widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingProcess regionEngineering
A shower head for adjusting distribution of a reactant gas in a process region of a semiconductor manufacturing reaction chamber, wherein a top plate has a gas port for introducing the reactant gas into the reaction chamber; a face plate, having through holes, disposed opposite the process region; a first baffle plate, having through holes, disposed between the top plate and the face plate and capable of moving up or down, wherein the first baffle plate has a top surface that defines a first gap for forming a first lateral flow passage; a second baffle plate, having through holes, disposed between the first baffle plate and the face plate and capable of moving up or down, wherein the second baffle plate has a top surface that defines a second gap for forming a second lateral flow passage; and a gap controller for determining widths of the first and second gaps.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
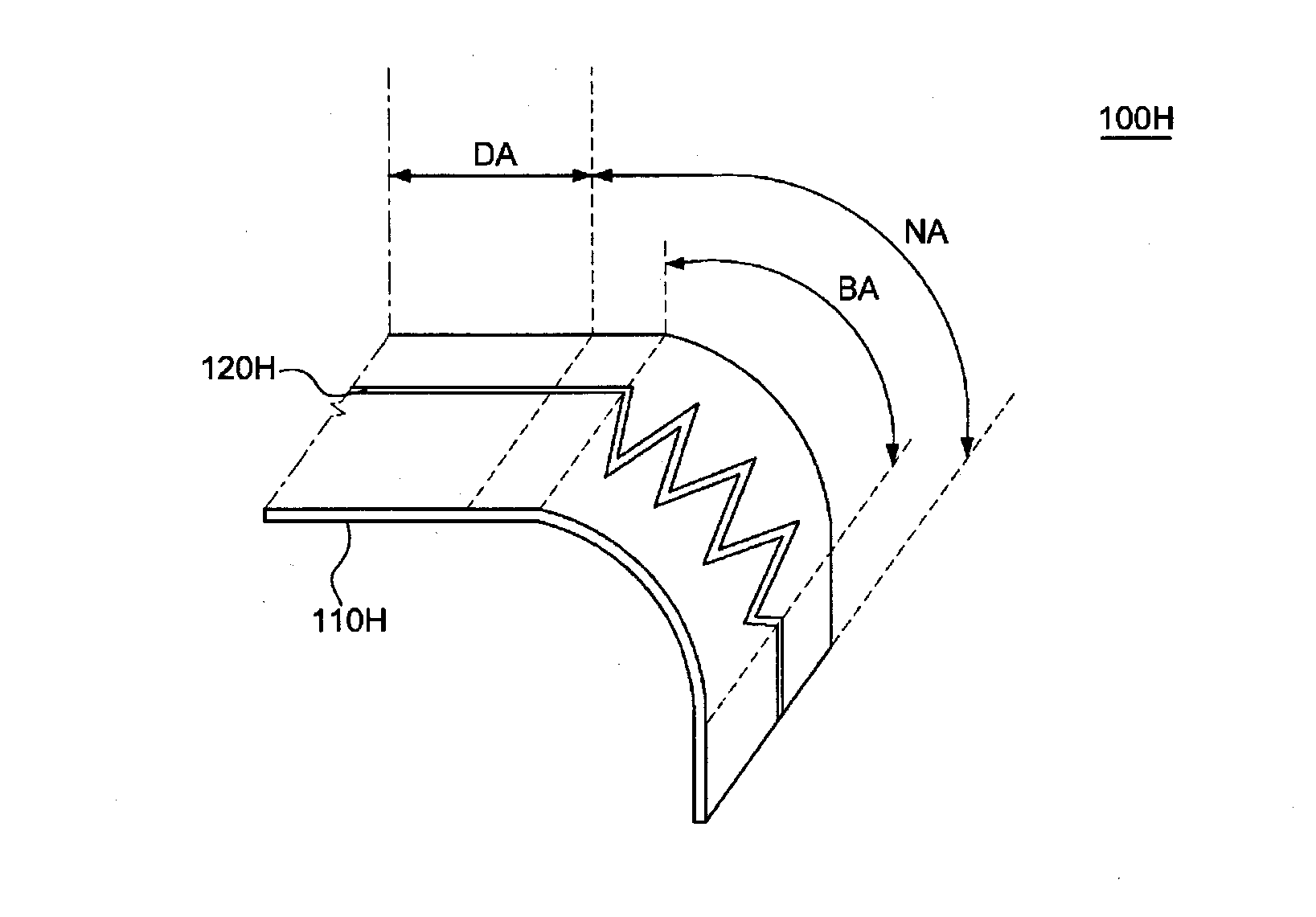
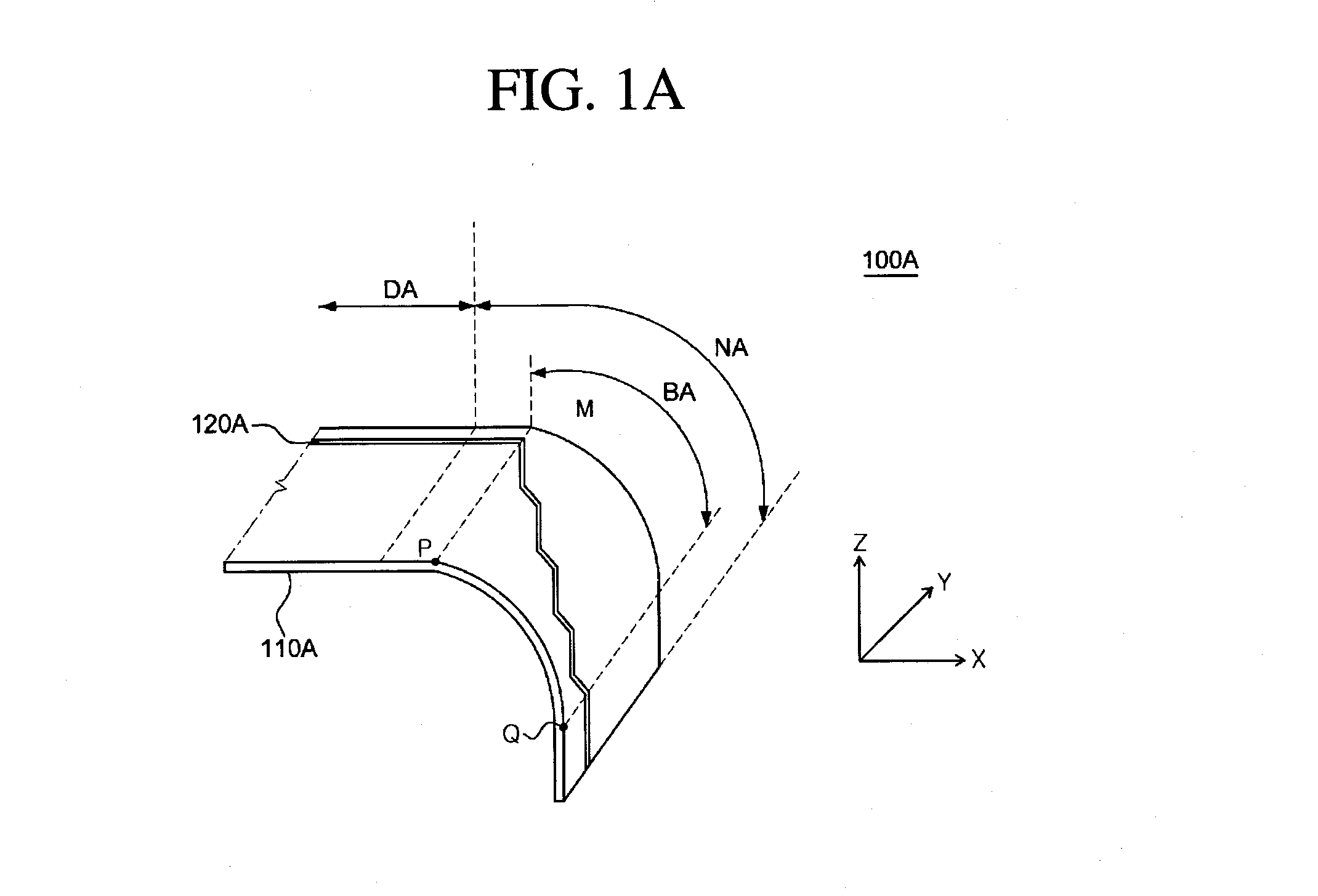
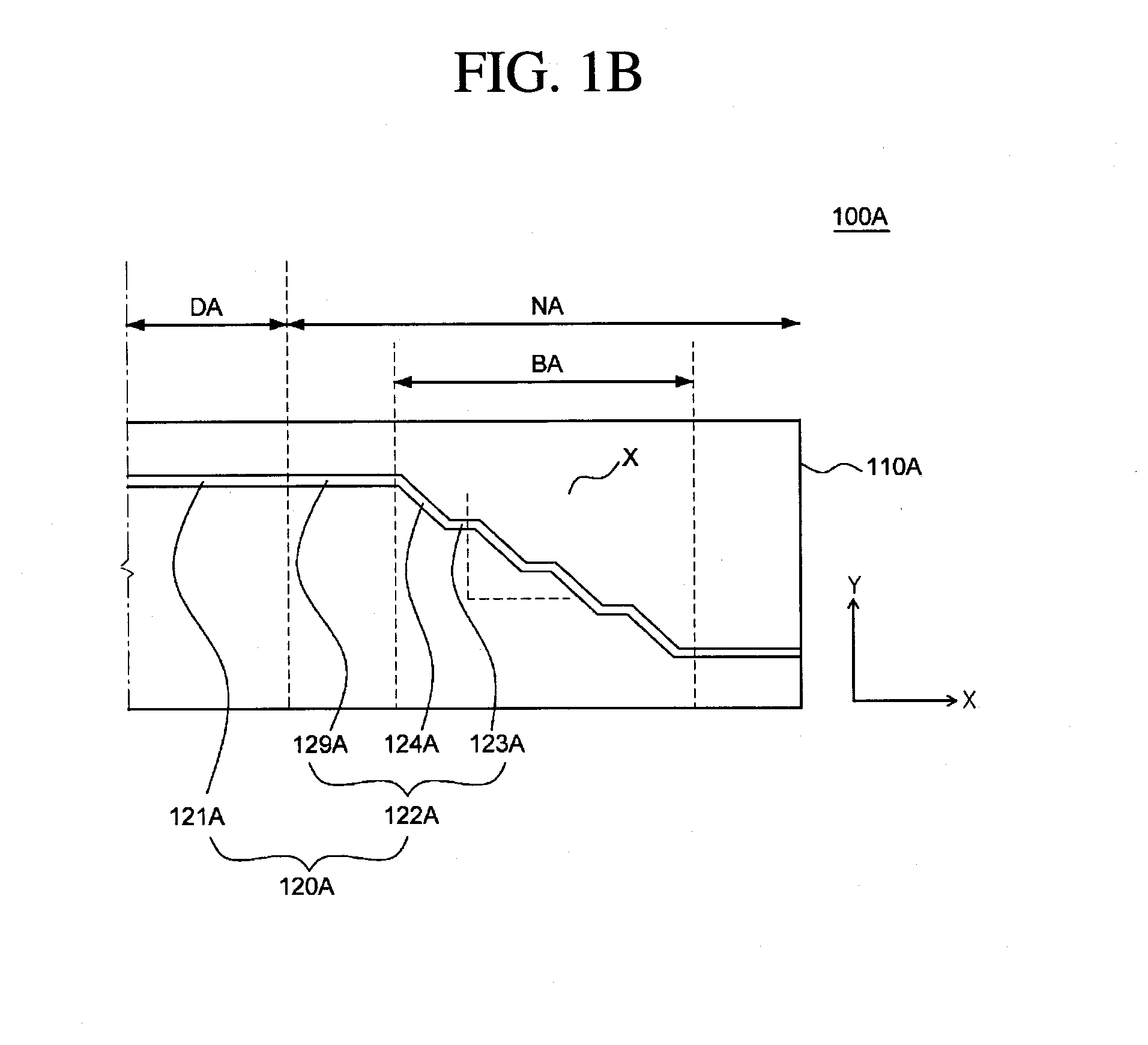
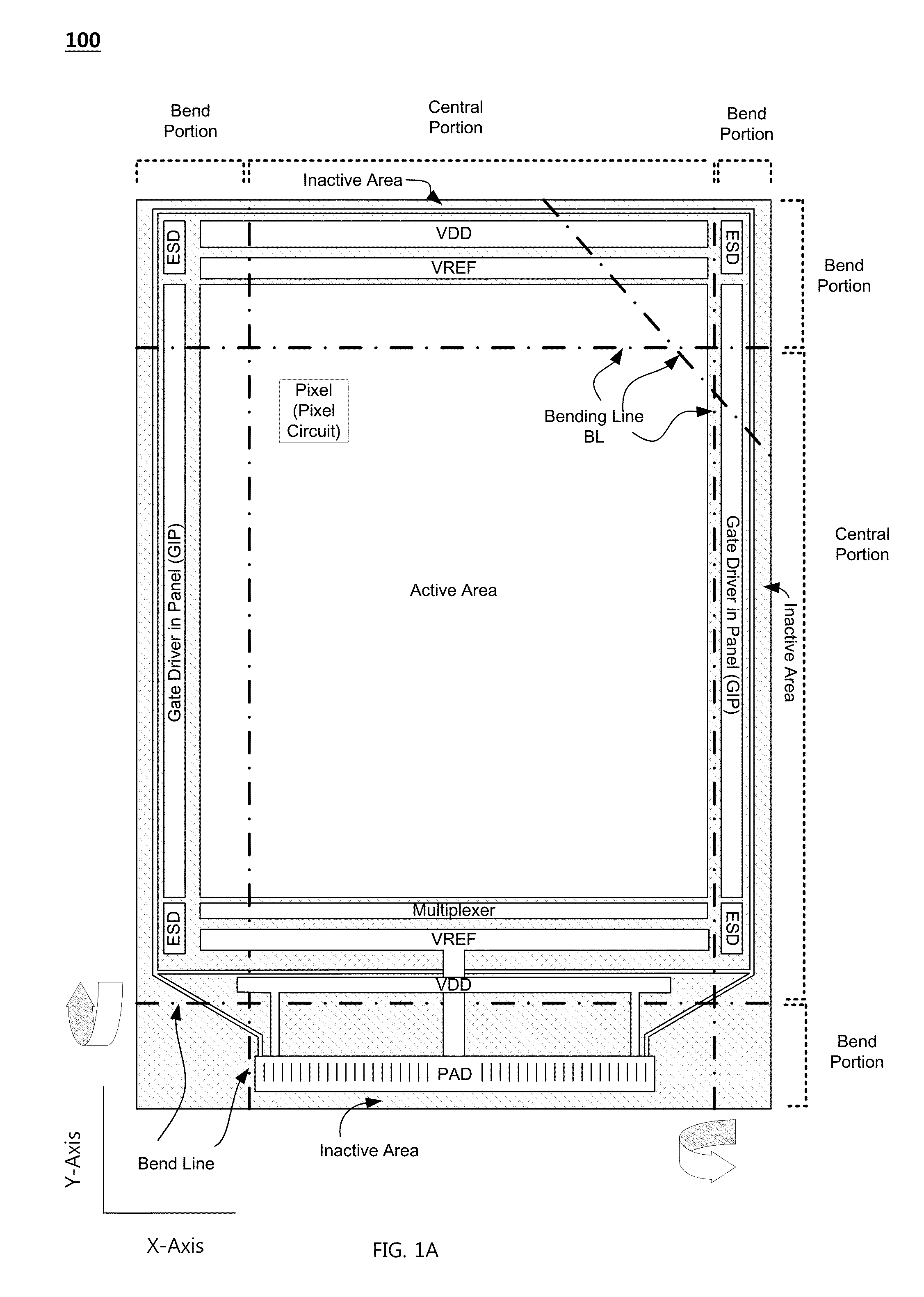
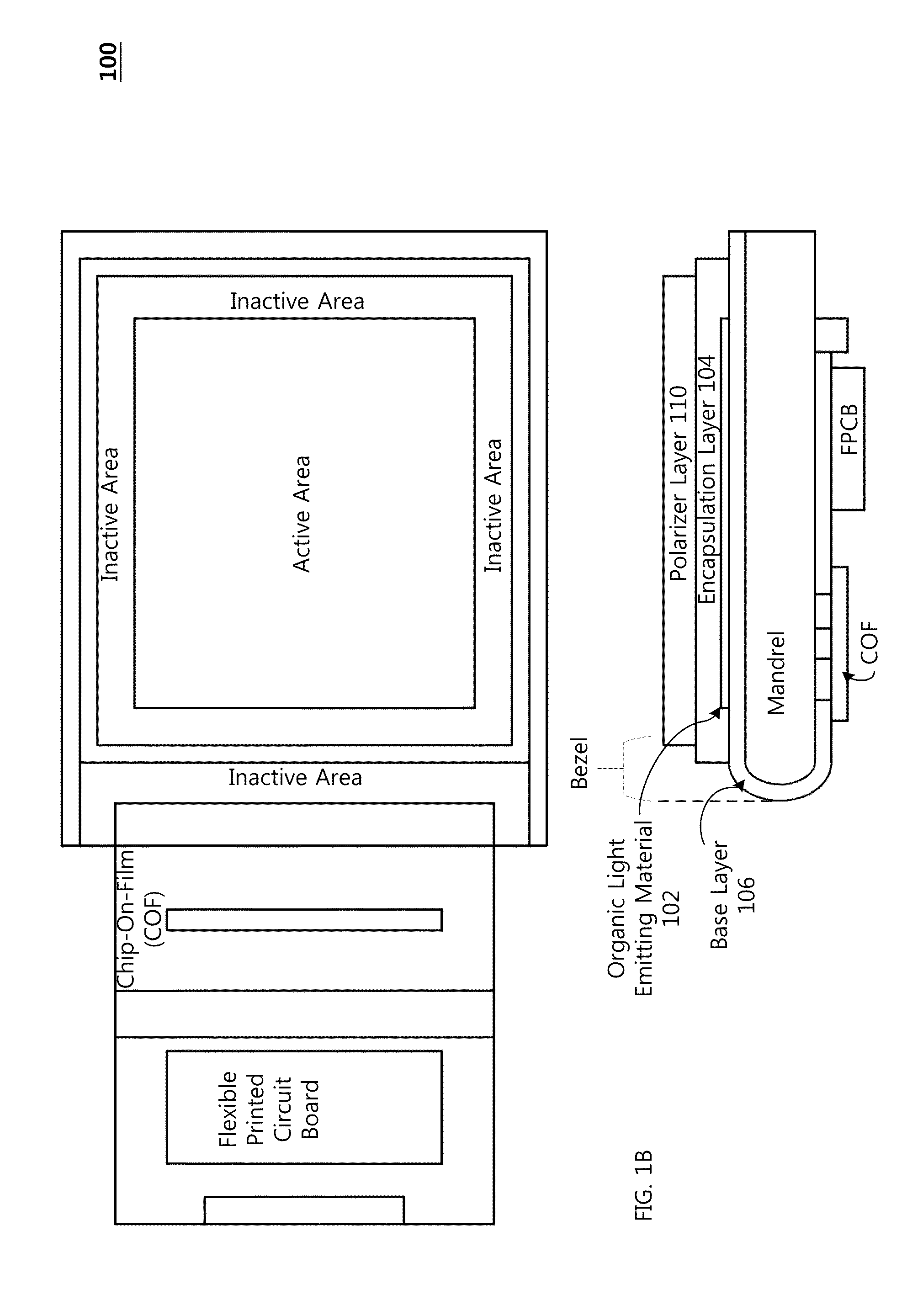
Flexible display substrate, flexible organic light emitting display device and method for manufacturing the same
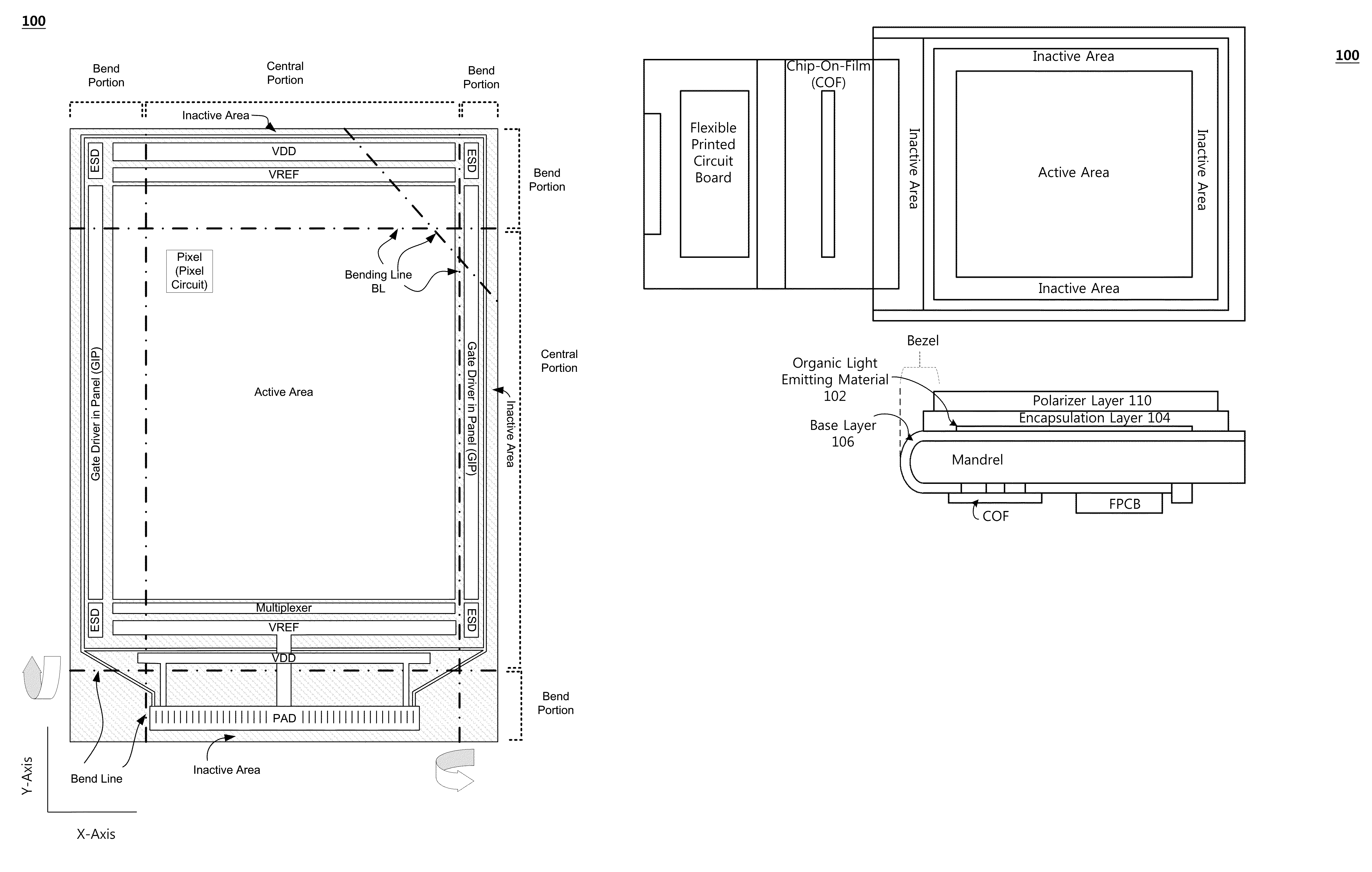
ActiveUS20140217373A1Relieve pressureIncrease widthCircuit bendability/stretchabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDisplay deviceEngineering
A flexible display substrate, a flexible organic light emitting display device, and a method of manufacturing the same are provided. The flexible display substrate comprises a flexible substrate including a display area and a non-display area extending from the display area, a first wire formed on the display area of the flexible substrate, and a second wire formed on the non-display area of the flexible substrate, wherein at least a part of the non-display area of the flexible substrate is curved in a bending direction, and the second wire formed on at least a part of the non-display area of the flexible substrate includes a first portion formed to extend in a first direction and a second portion formed to extend in a second direction.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
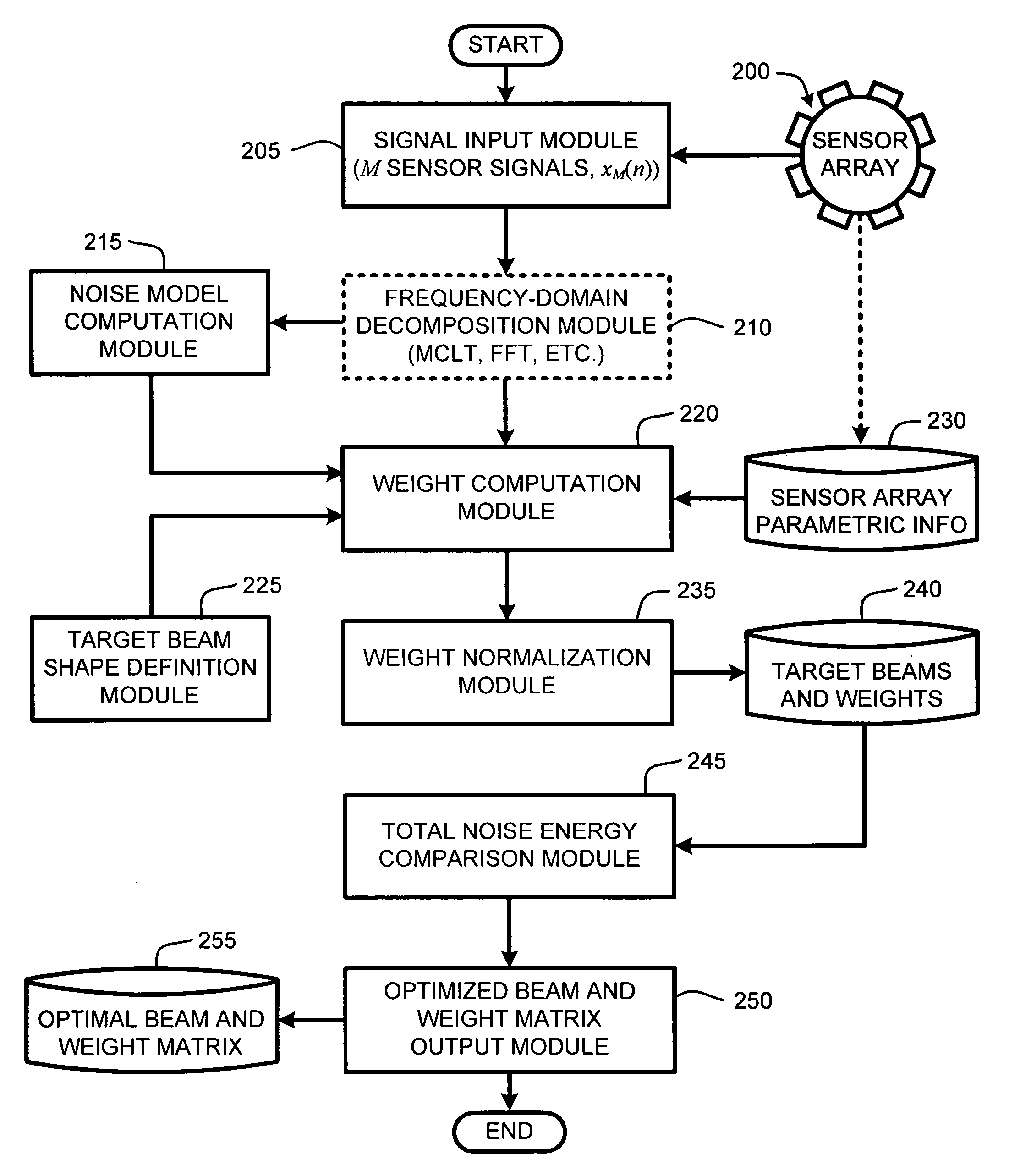
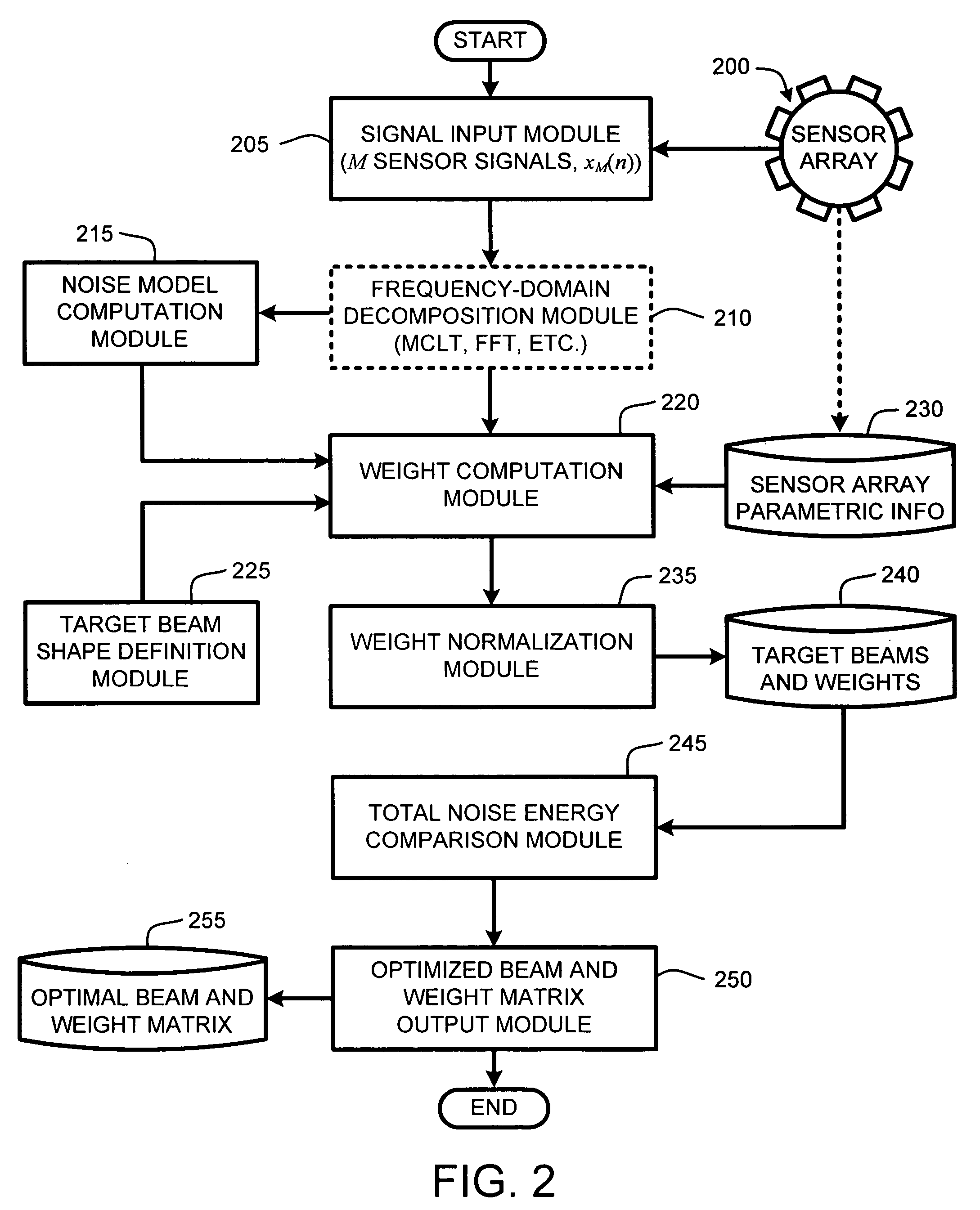
System and method for beamforming using a microphone array
InactiveUS20050195988A1Maximal noise suppressionIncrease widthPosition fixationMicrophones signal combinationEnvironmental noiseSound sources
The ability to combine multiple audio signals captured from the microphones in a microphone array is frequently used in beamforming systems. Typically, beamforming involves processing the output audio signals of the microphone array in such a way as to make the microphone array act as a highly directional microphone. In other words, beamforming provides a “listening beam” which points to a particular sound source while often filtering out other sounds. A “generic beamformer,” as described herein automatically designs a set of beams (i.e., beamforming) that cover a desired angular space range within a prescribed search area. Beam design is a function of microphone geometry and operational characteristics, and also of noise models of the environment around the microphone array. One advantage of the generic beamformer is that it is applicable to any microphone array geometry and microphone type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
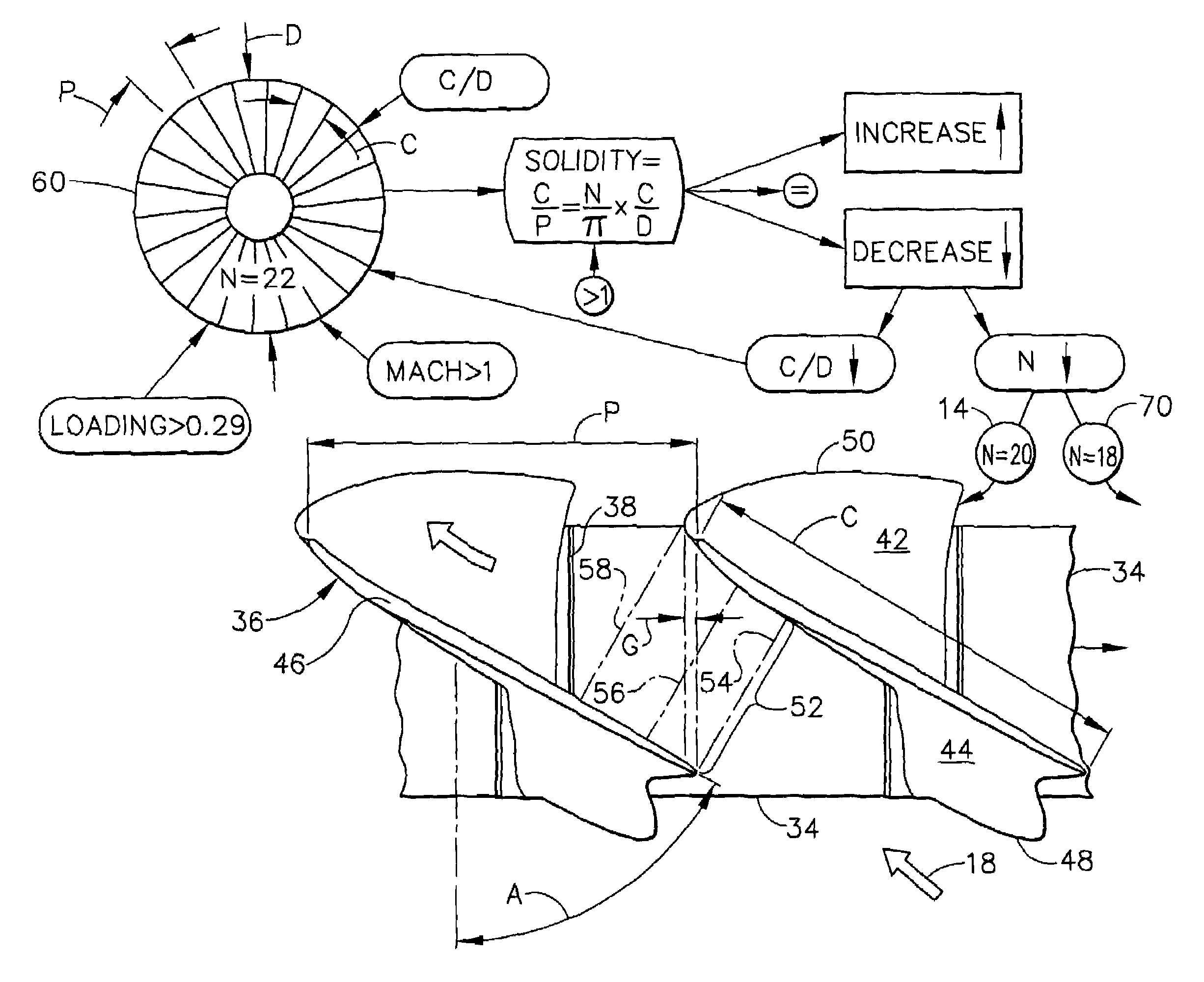
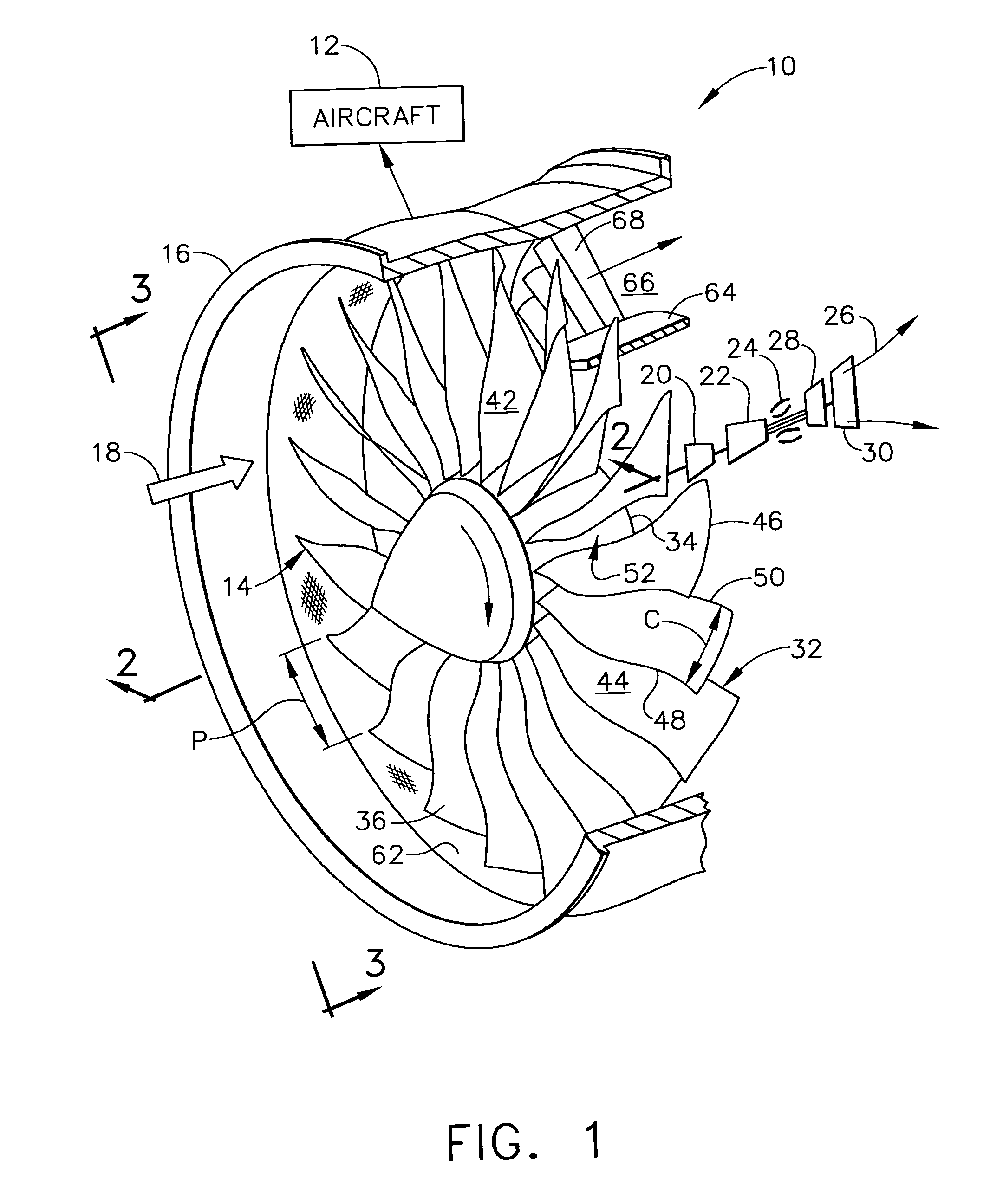
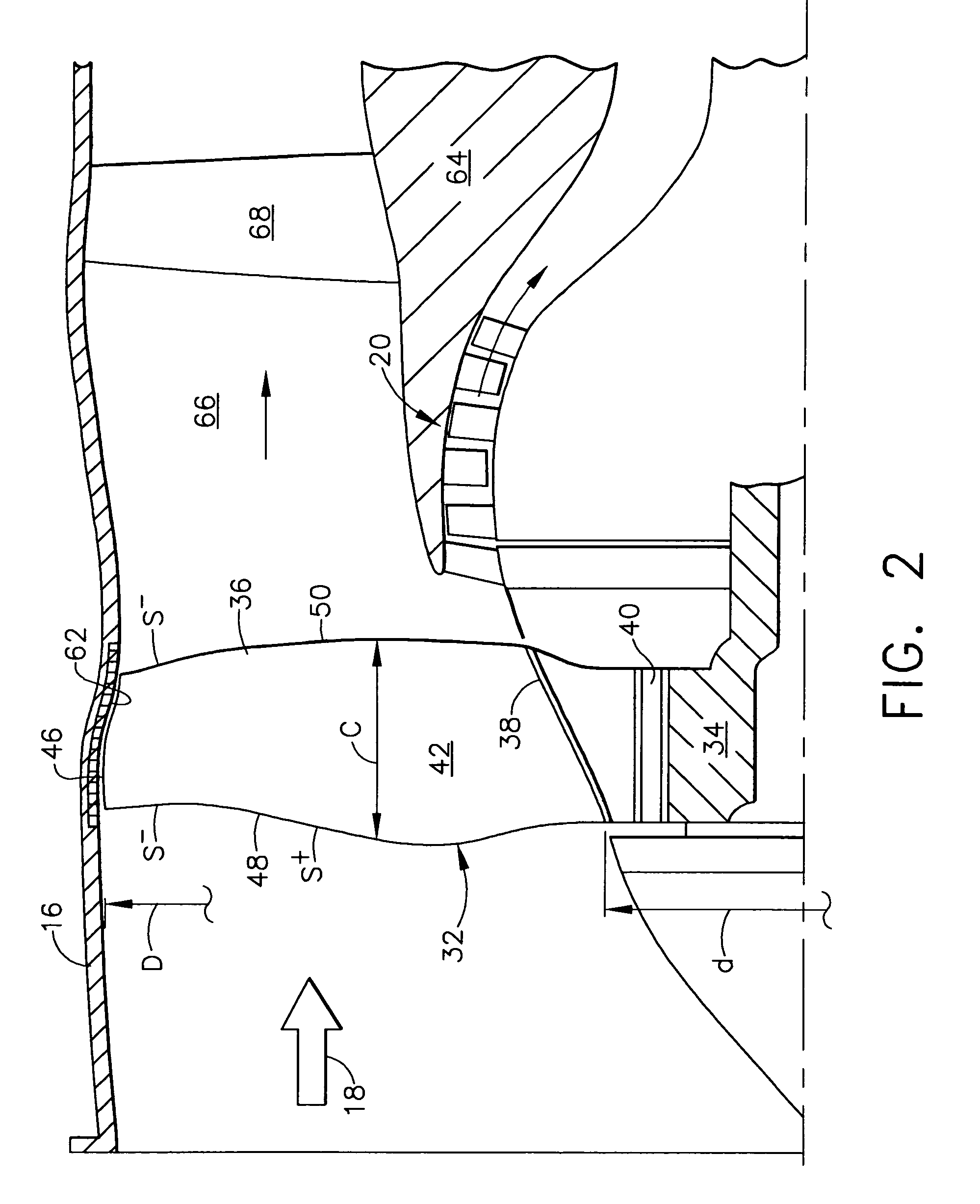
Low solidity turbofan
A turbofan includes a row of fan blades extending from a supporting disk inside an annular casing. Each blade includes an airfoil having opposite pressure and suction sides extending radially in span between a root and tip and axially in chord between leading and trailing edges. Adjacent airfoils define corresponding flow passages therebetween for pressurizing air. Each airfoil includes stagger increasing between the root and tip, and the flow passage has a mouth between the airfoil leading edge and the suction side of an adjacent airfoil and converges to a throat aft from the mouth. The row includes no more than twenty fan blades having low tip solidity for increasing the width of the passage throat.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electro-magneto volume tomography system and methodology for non-invasive volume tomography
InactiveUS20180325414A1Maximize surface areaMaximize number of turnReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCapacitanceImage resolution
A system and method capable of performing multiple types of non-invasive tomographic techniques. The system is capable, via electronic control, of detecting and imaging materials within a volume using electrical capacitance, displacement phase current, magnetic inductance, and magnetic pressure sensing. The system is also able to control the amplitude, phase, and frequency of individual electrode excitation to increase imaging resolution and phase detection. This allows many dimensions of non-invasive data to be captured without the need for multiple instruments or moving parts, at a high data capture rate.
Owner:TECH4IMAGING
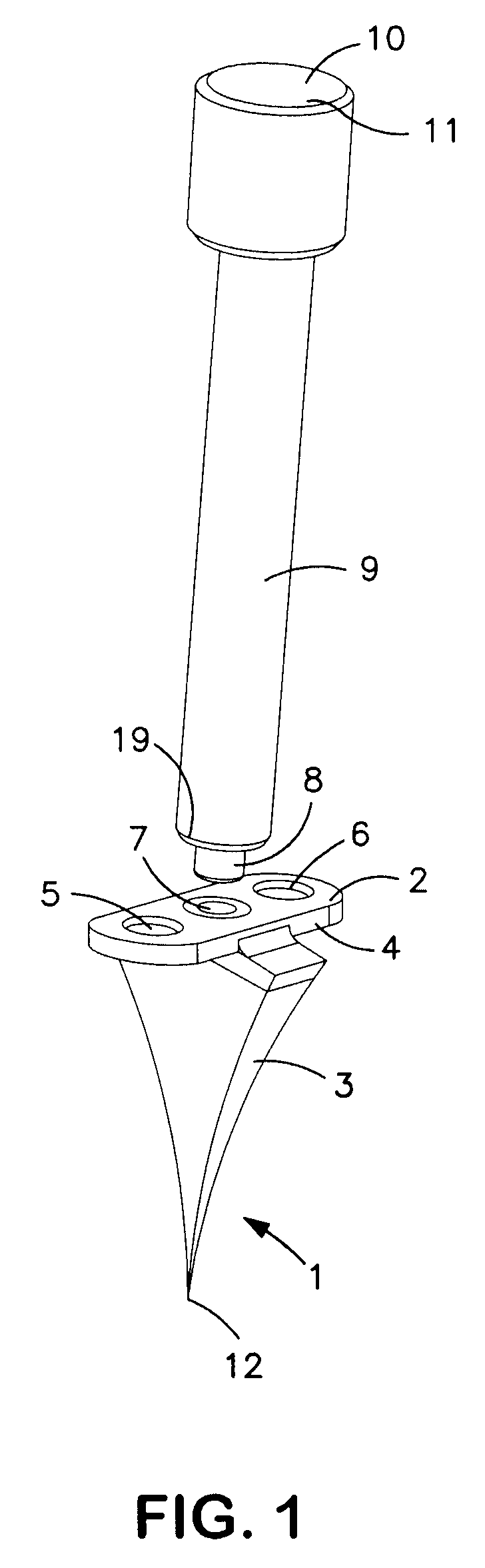
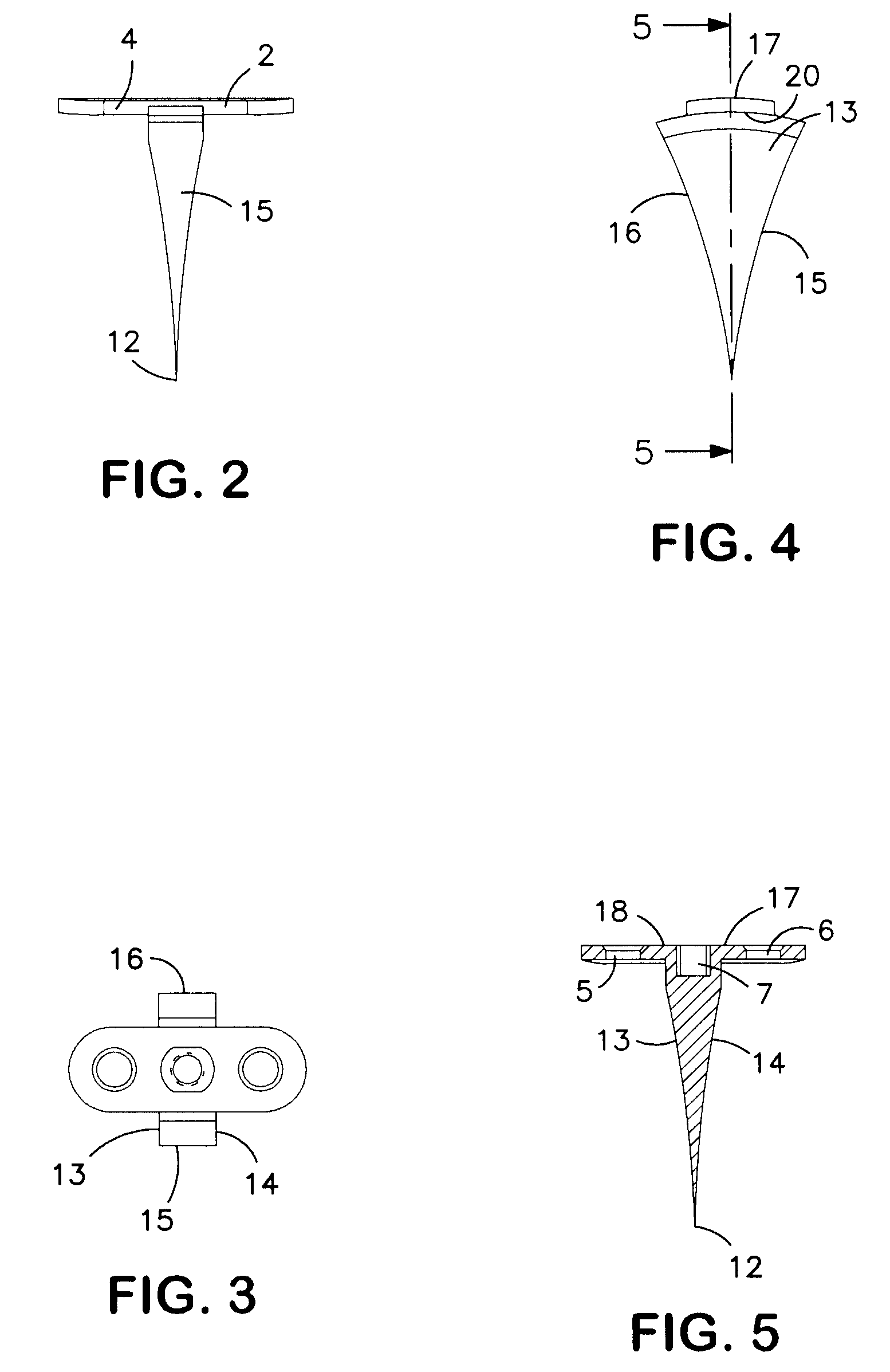
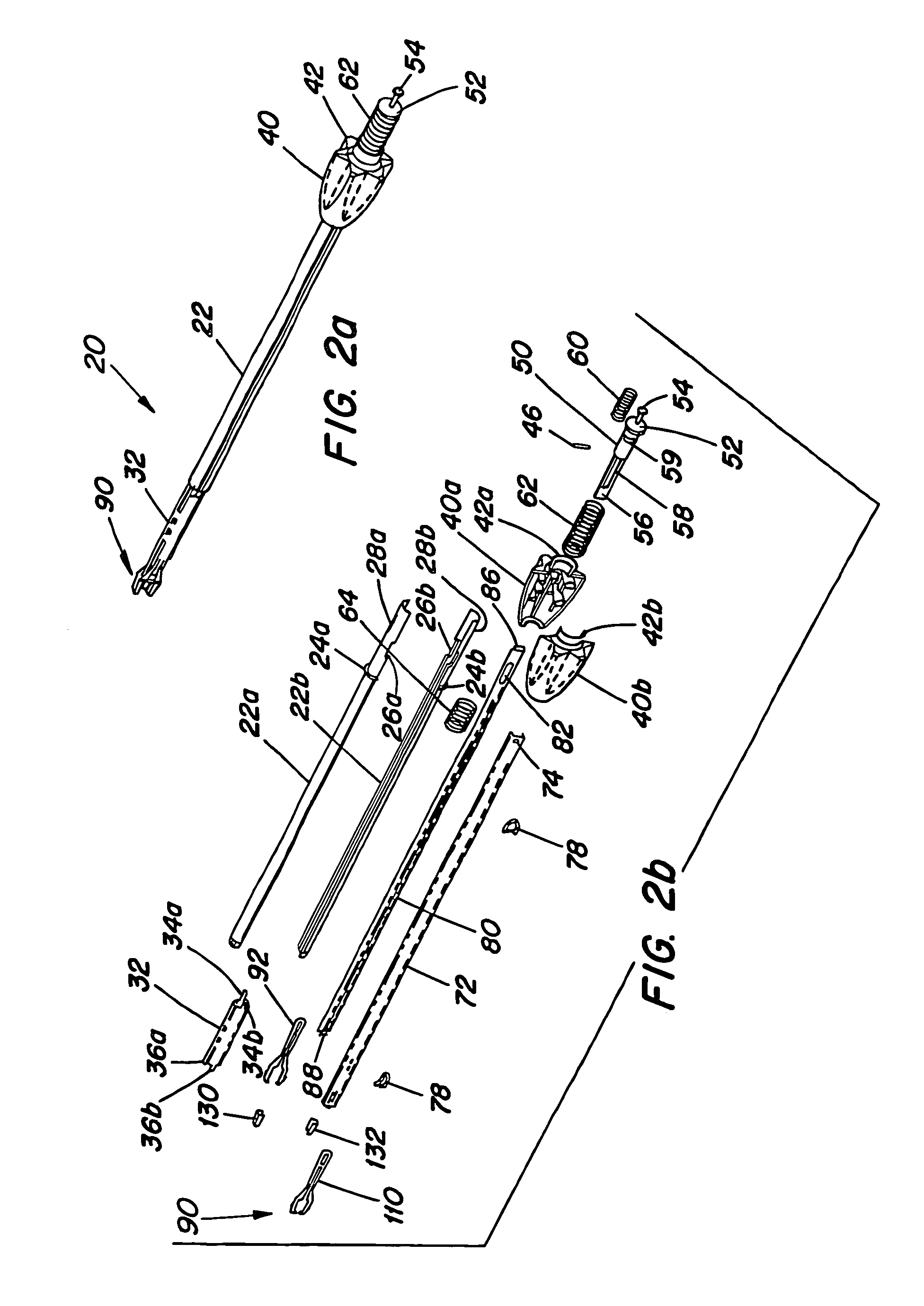
Method and apparatus for bone fracture fixation
InactiveUS20050065521A1Easy to separateEases engagementFastenersBone platesOrthodonticsBone fixation
A plate for coupling severed bone regions comprising at least one bridge region, the at least one bridge region terminating in at least two bone fixation regions. The at least two bone fixation regions each contain at least one aperture for receiving a suitable fastening device for securing the plate to the bone regions to be coupled. The bridge region may be configured so as to be easily severed by a suitable severing device such as surgical scissors. The plate and fastening device may be formed from a bio-compatible or bio-resorbable material.
Owner:BIOMET MICROFIXATION
Catheter with cryogenic and heating ablation
InactiveUS7097641B1Improve versatilityEnhancing speed and placement lesionCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingTissue remodelingCelsius Degree
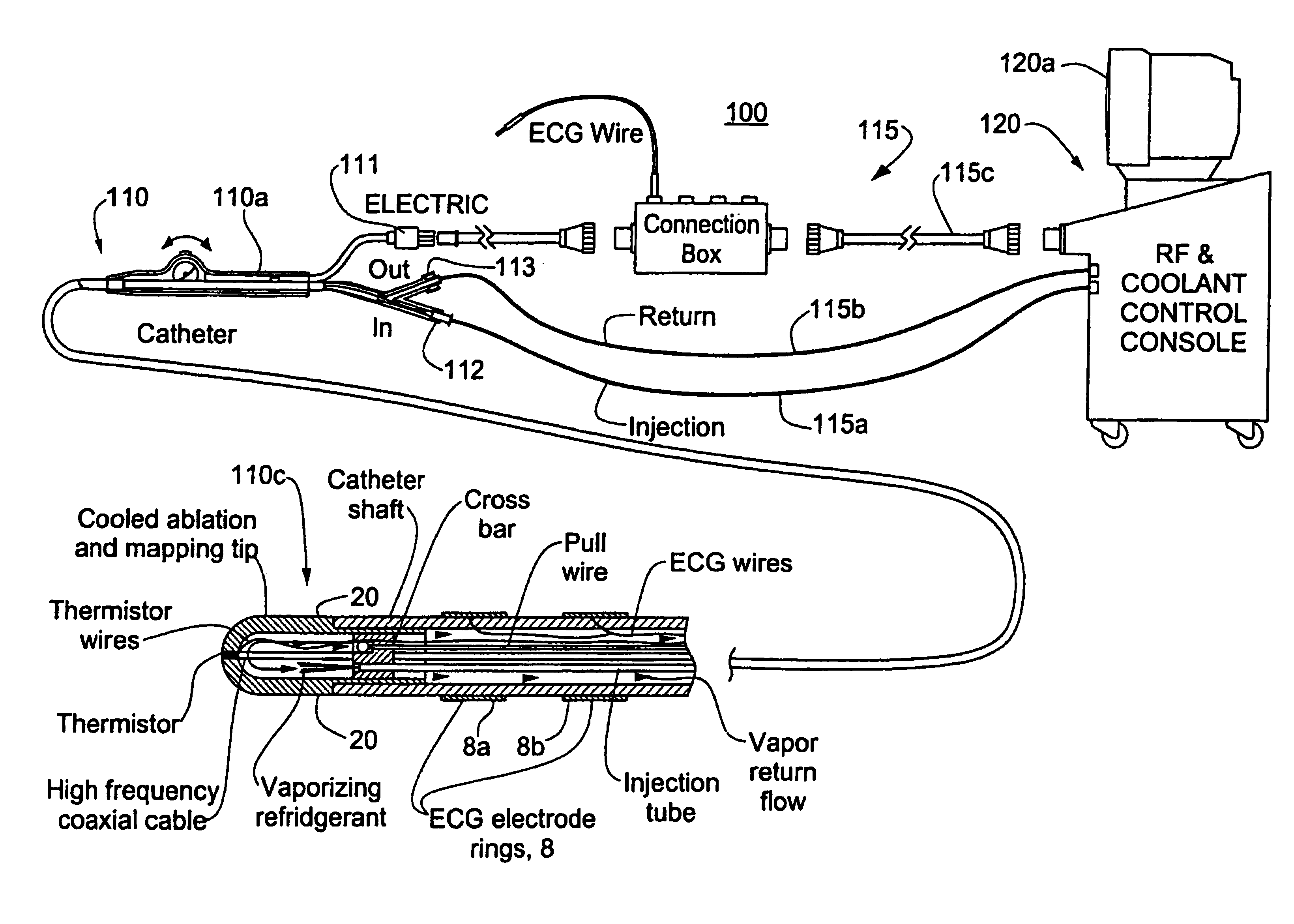
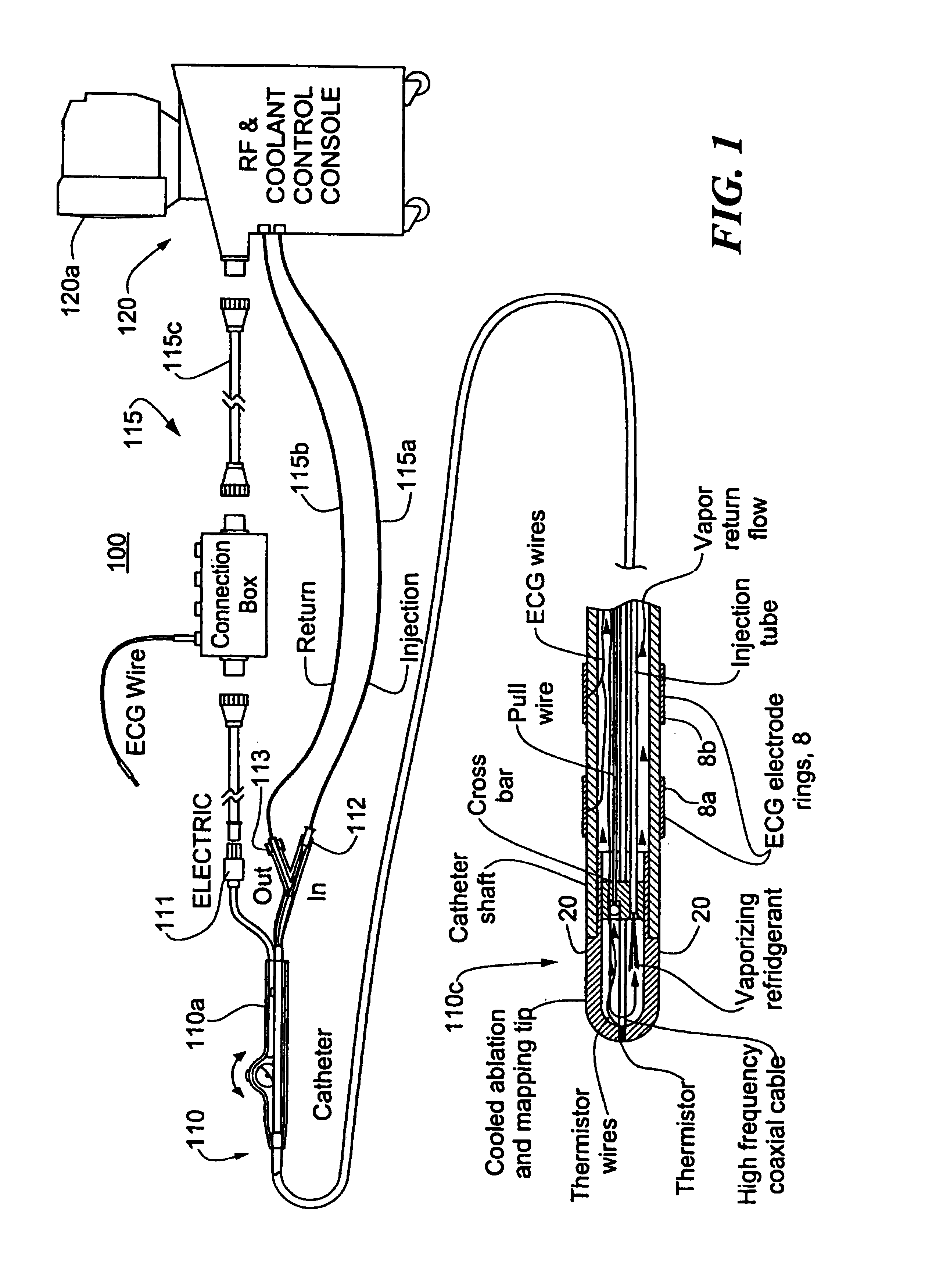
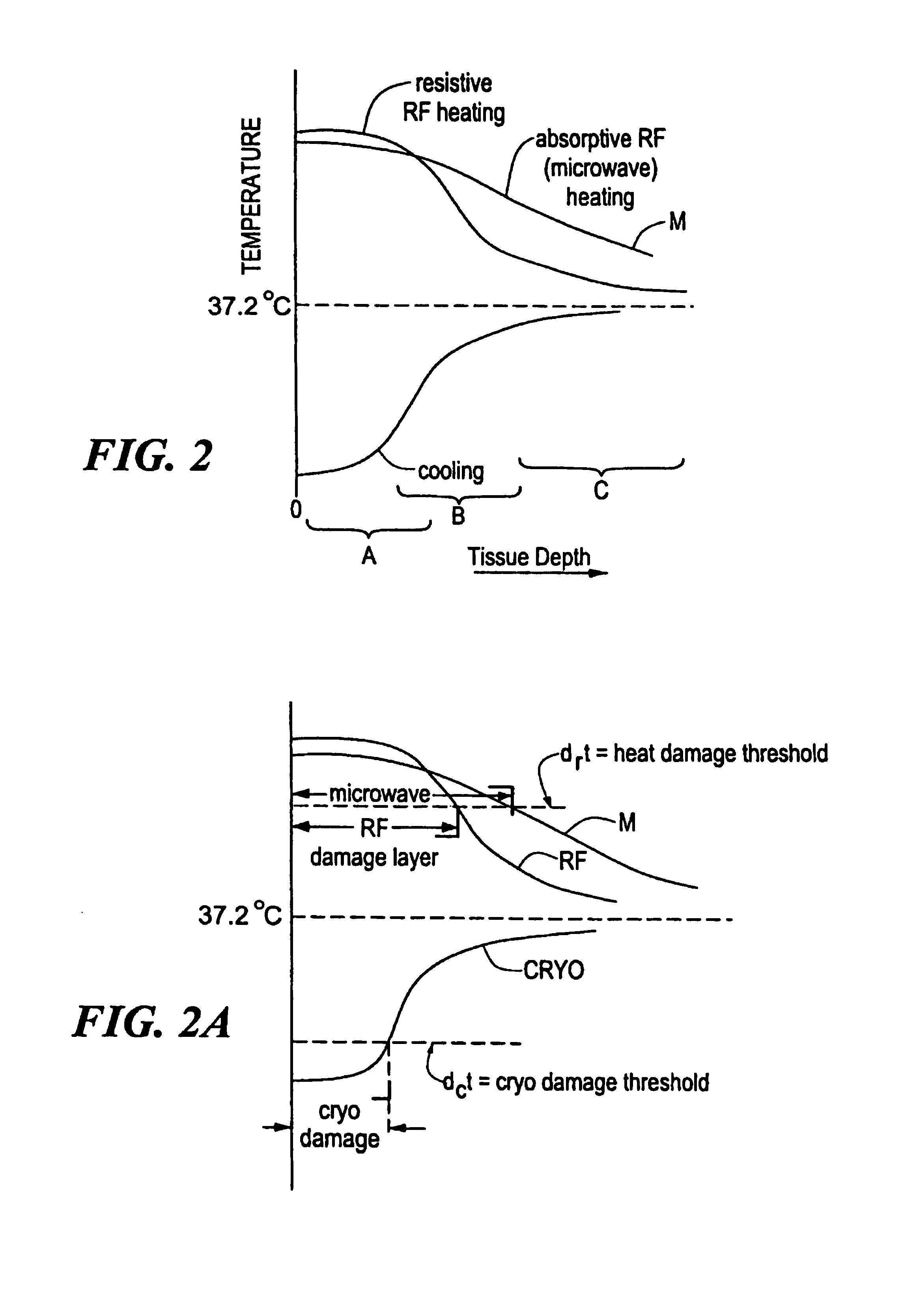
A catheter includes a cryoablation tip with an electrically-driven ablation assembly for heating tissue. The cryoablation tip may be implemented with a cooling chamber through which a controllably injected coolant circulates to lower the tip temperature, and having an RF electrode at its distal end. The RF electrode may be operated to warm cryogenically-cooled tissue, or the coolant may be controlled to conductively cool the tissue in coordination with an RF treatment regimen, allowing greater versatility of operation and enhancing the lesion size, speed or placement of multi-lesion treatment or single lesion re-treatment cycles. In one embodiment a microwave energy source operates at a frequency to extend beyond the thermal conduction depth, or to penetrate the cryogenic ice ball and be absorbed in tissue beyond an ice boundary, thus extending the depth and / or width of a single treatment locus. In another embodiment, the cooling and the application of RF energy are both controlled to position the ablation region away from the surface contacted by the electrode, for example to leave surface tissue unharmed while ablating at depth or to provide an ablation band of greater uniformity with increasing depth. The driver or RF energy source may supply microwave energy at a frequency effective to penetrate the ice ball which develops on a cryocatheter, and different frequencies may be selected for preferential absorption in a layer of defined thickness at depth in the nearby tissue. The catheter may operate between 70 and minus 70 degrees Celsius for different tissue applications, such as angioplasty, cardiac ablation and tissue remodeling, and may preset the temperature of the tip or adjacent tissue, and otherwise overlay or delay the two different profiles to tailor the shape or position where ablation occurs or to speed up a treatment cycle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Flexible display device with reduced bend stress wires and manufacturing method for the same
ActiveUS20150382446A1Guaranteed uptimeIncrease widthCircuit bendability/stretchabilityDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceFlexible display
There is provided a flexible display having a plurality of innovations configured to allow bending of a portion or portions to reduce apparent border size and / or utilize the side surface of an assembled flexible display.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Horn antenna device and step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus thereof
ActiveUS20150029065A1Sure easyAssembly precisionWaveguide hornsAntennas earthing switches associationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Noise rate
The present invention relates to a horn antenna device. The horn antenna device has a step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus and a conical horn antenna. The step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus has a stepped body having multiple stairs and a connecting pin. The stepped body is adapted to radiate electromagnetic waves and receive a reflection of the electromagnetic waves. According to the structure of the step-shaped signal feed-in apparatus of the invention, the resonating modes are easy to be determined. The directivity and the signal-to-noise rate are improved. In addition, the connecting pin is directly connected to the stairs for improving the signal stability of the horn antenna device.
Owner:FINETEK CO LTD
Surface cleaning apparatus
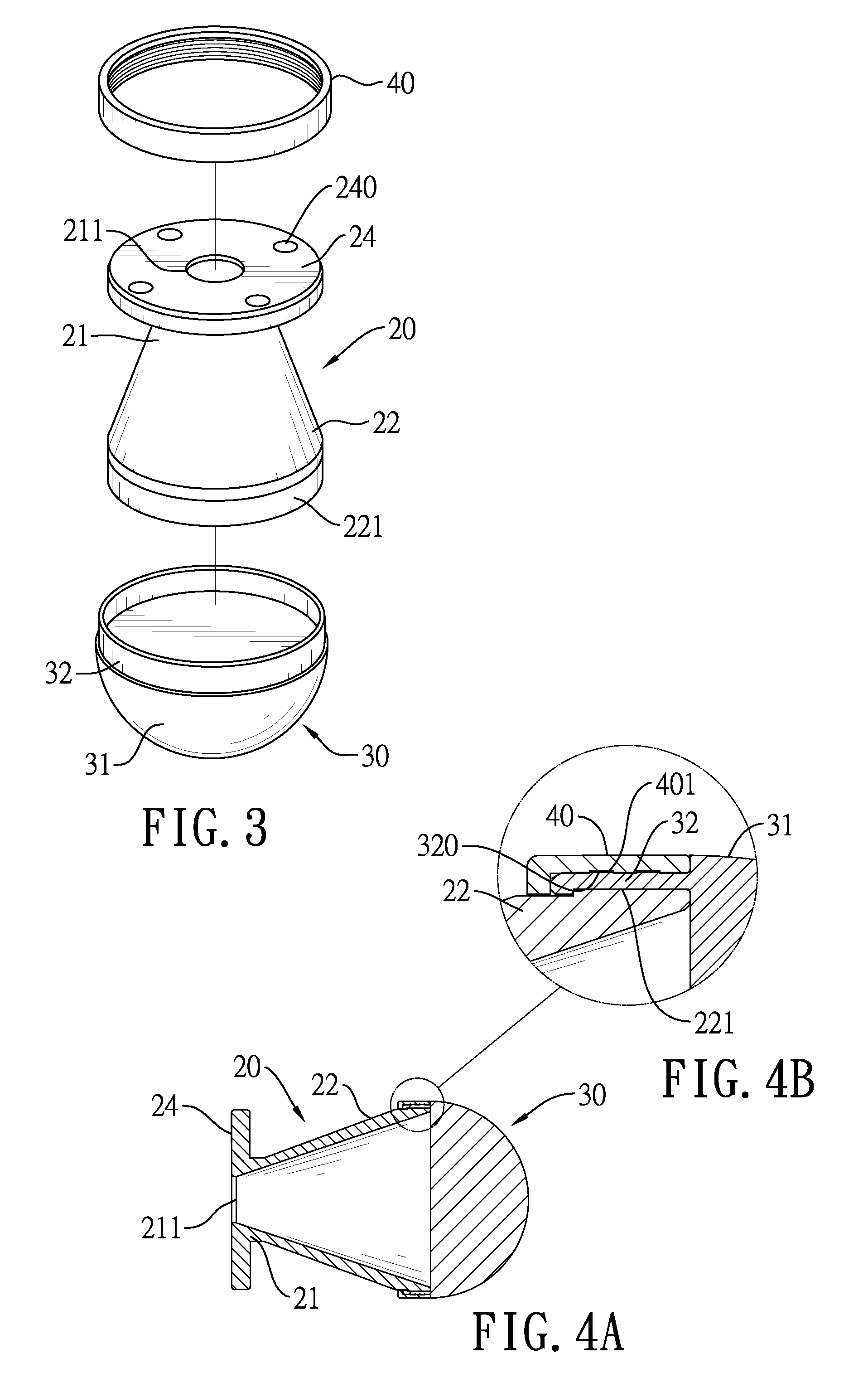
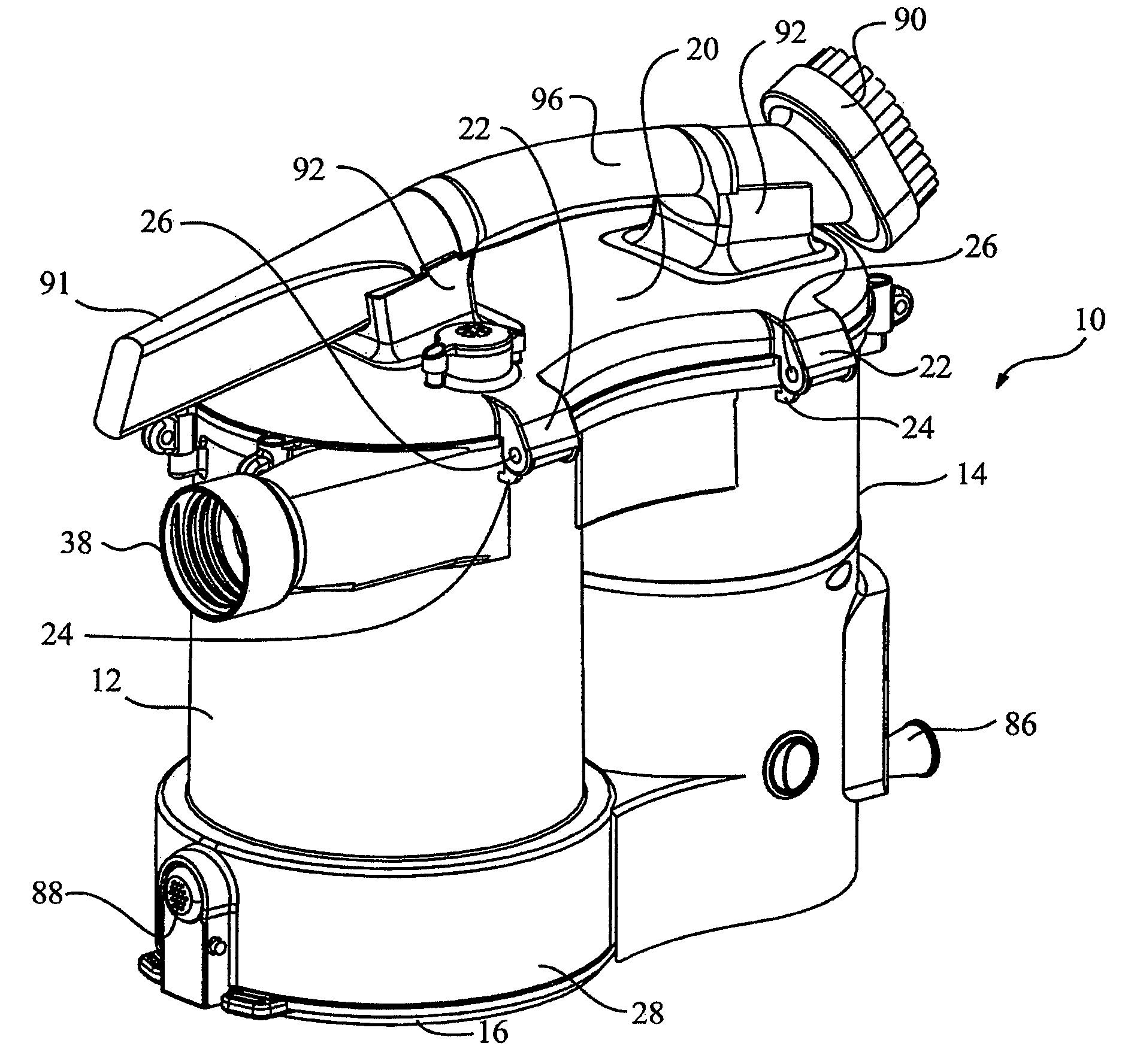
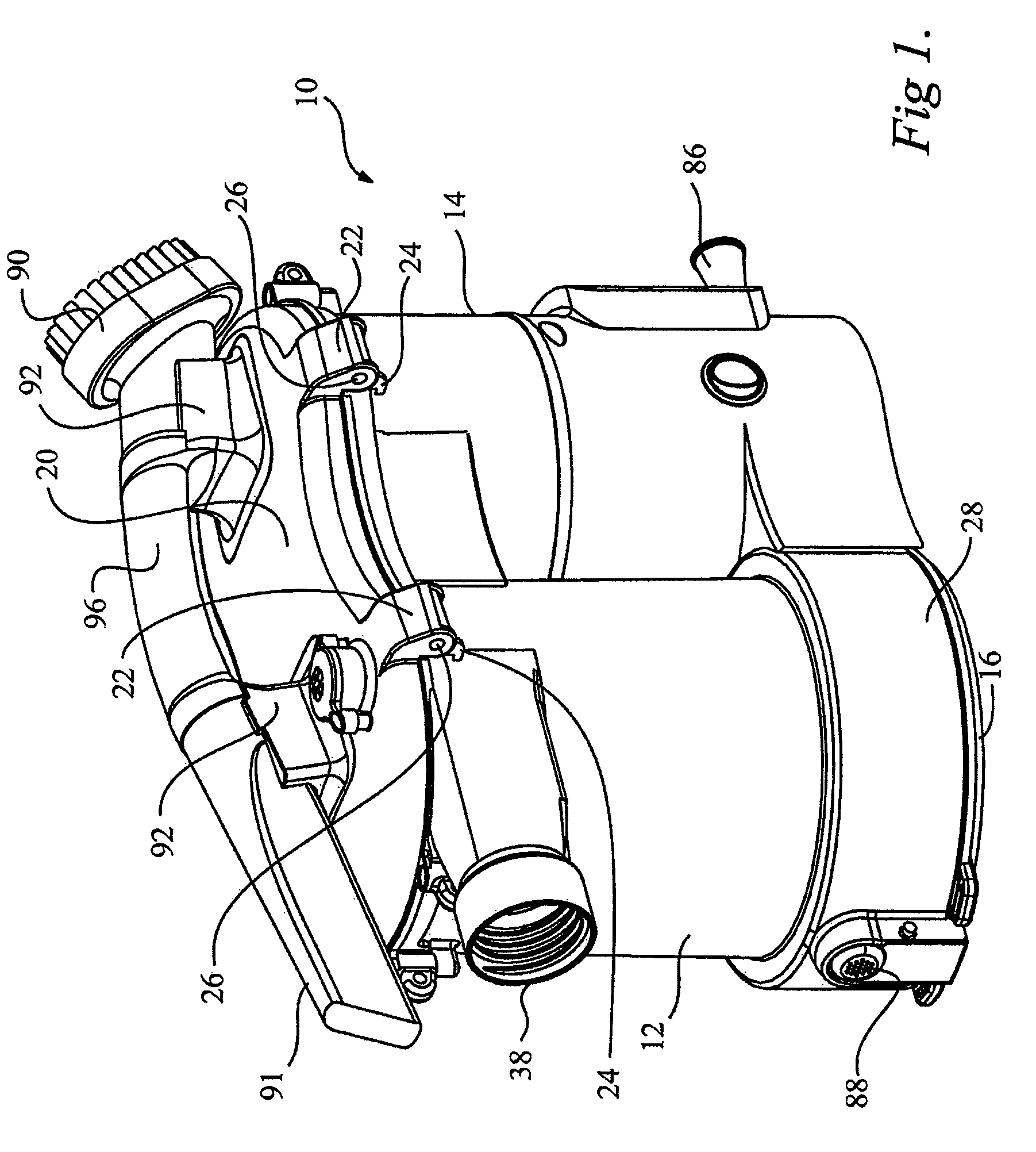
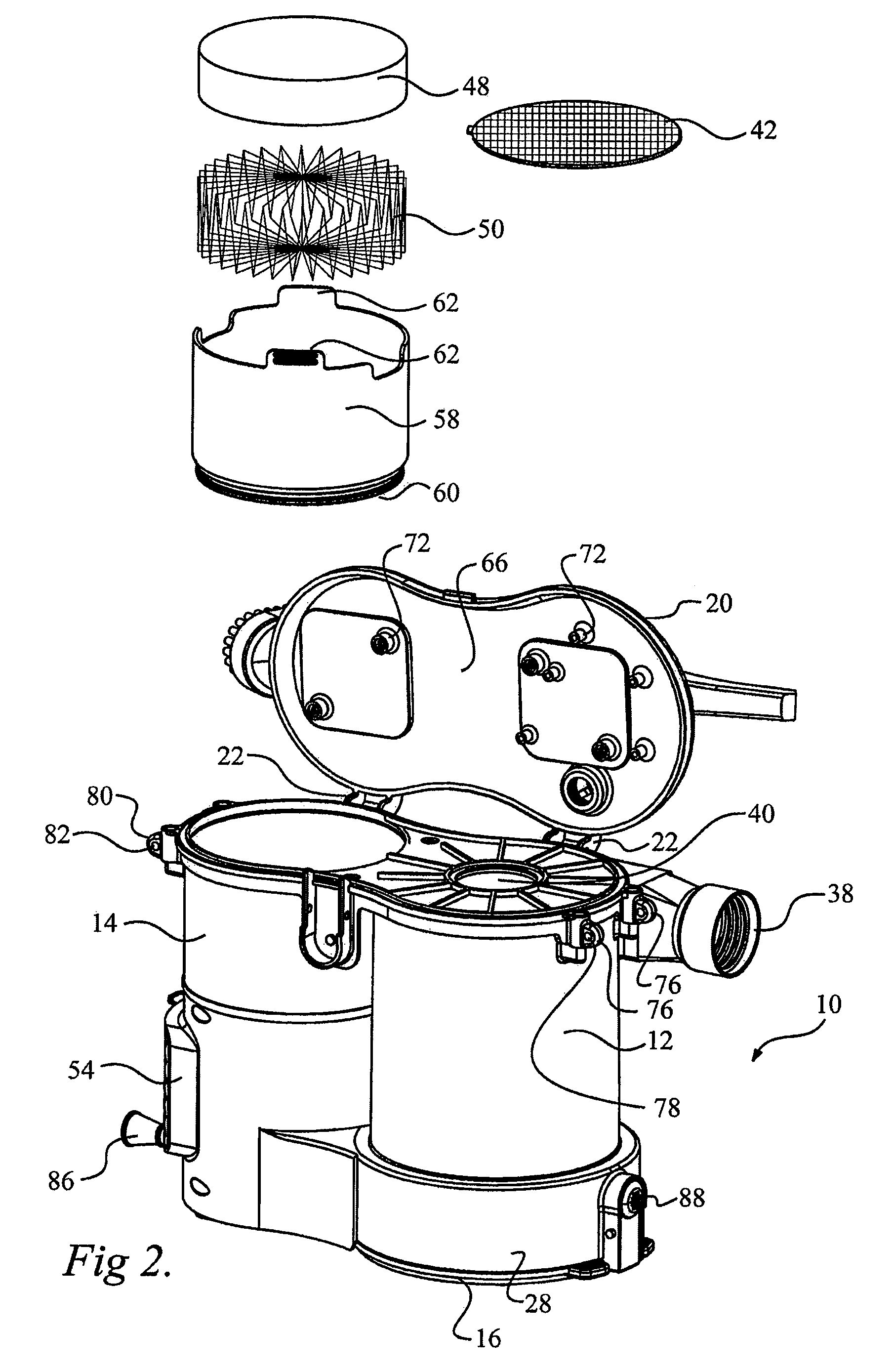
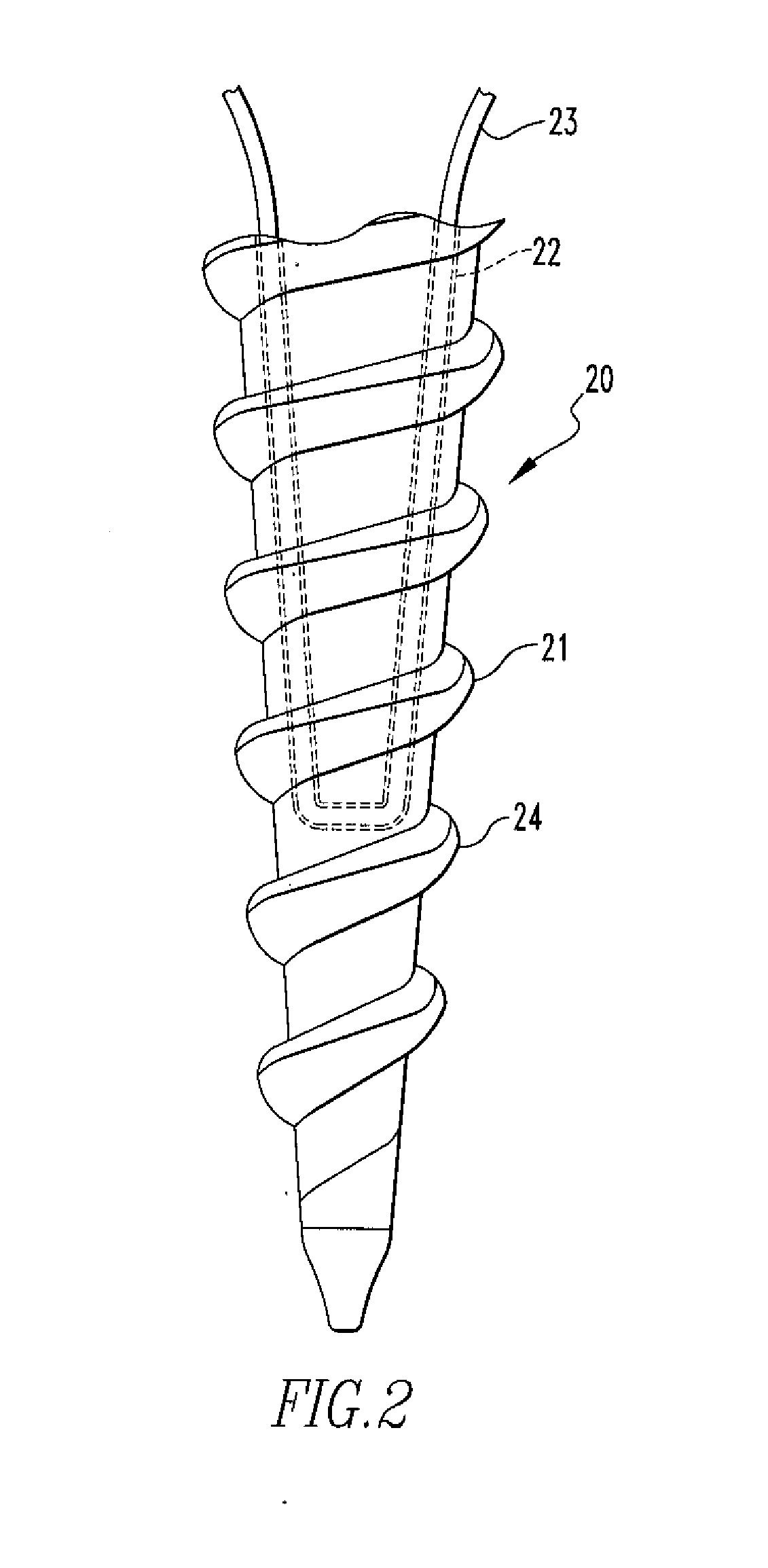
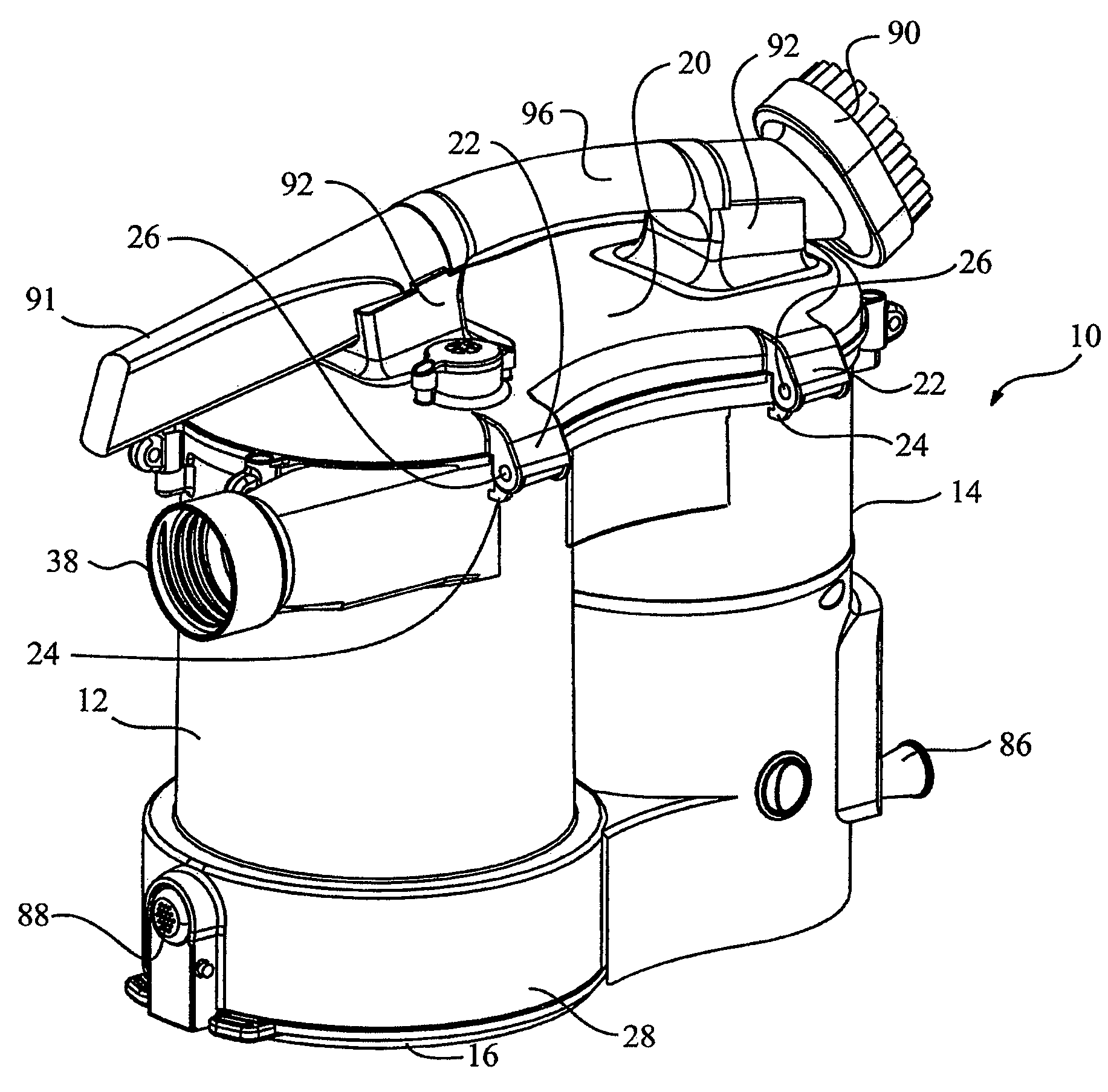
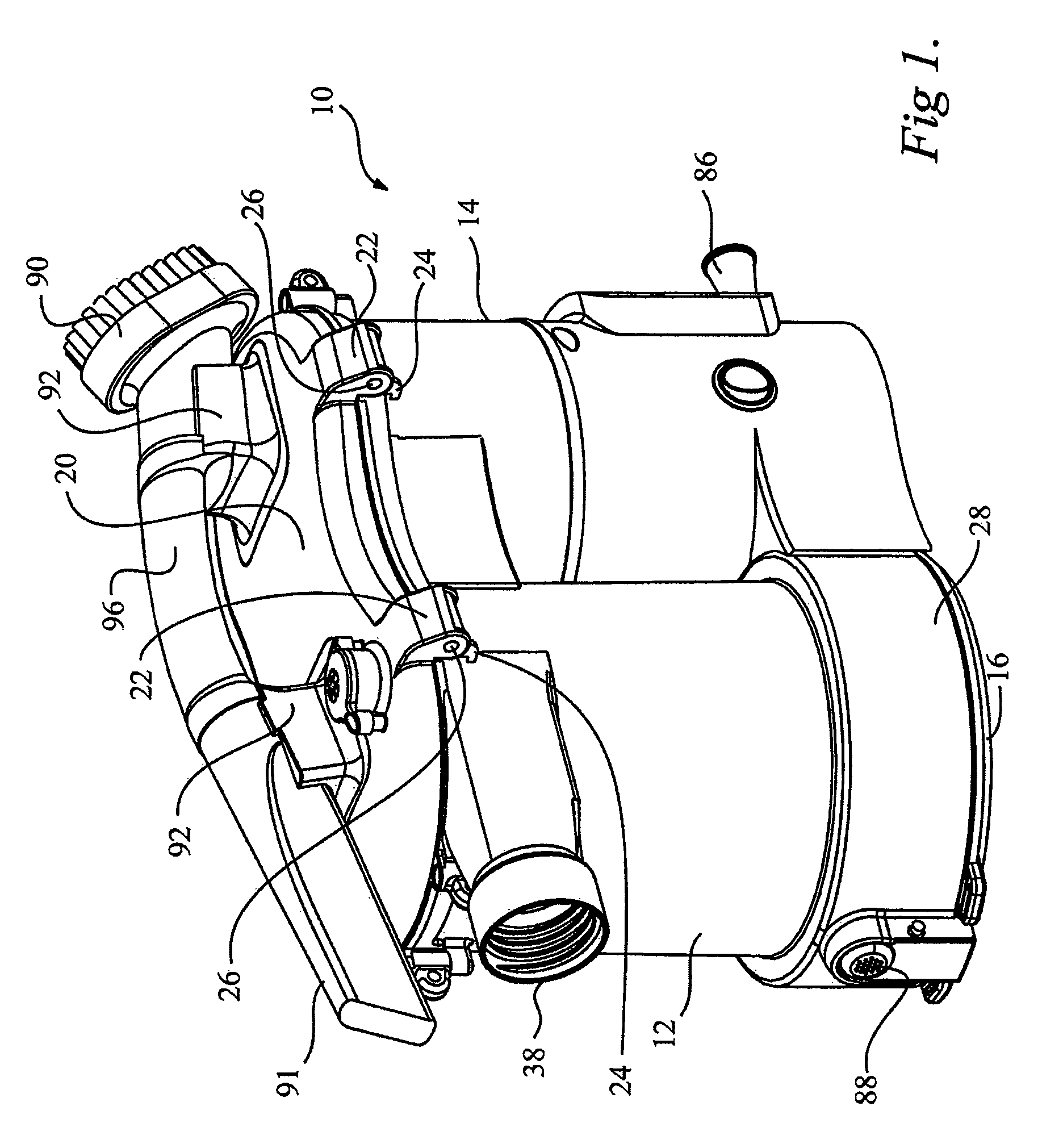
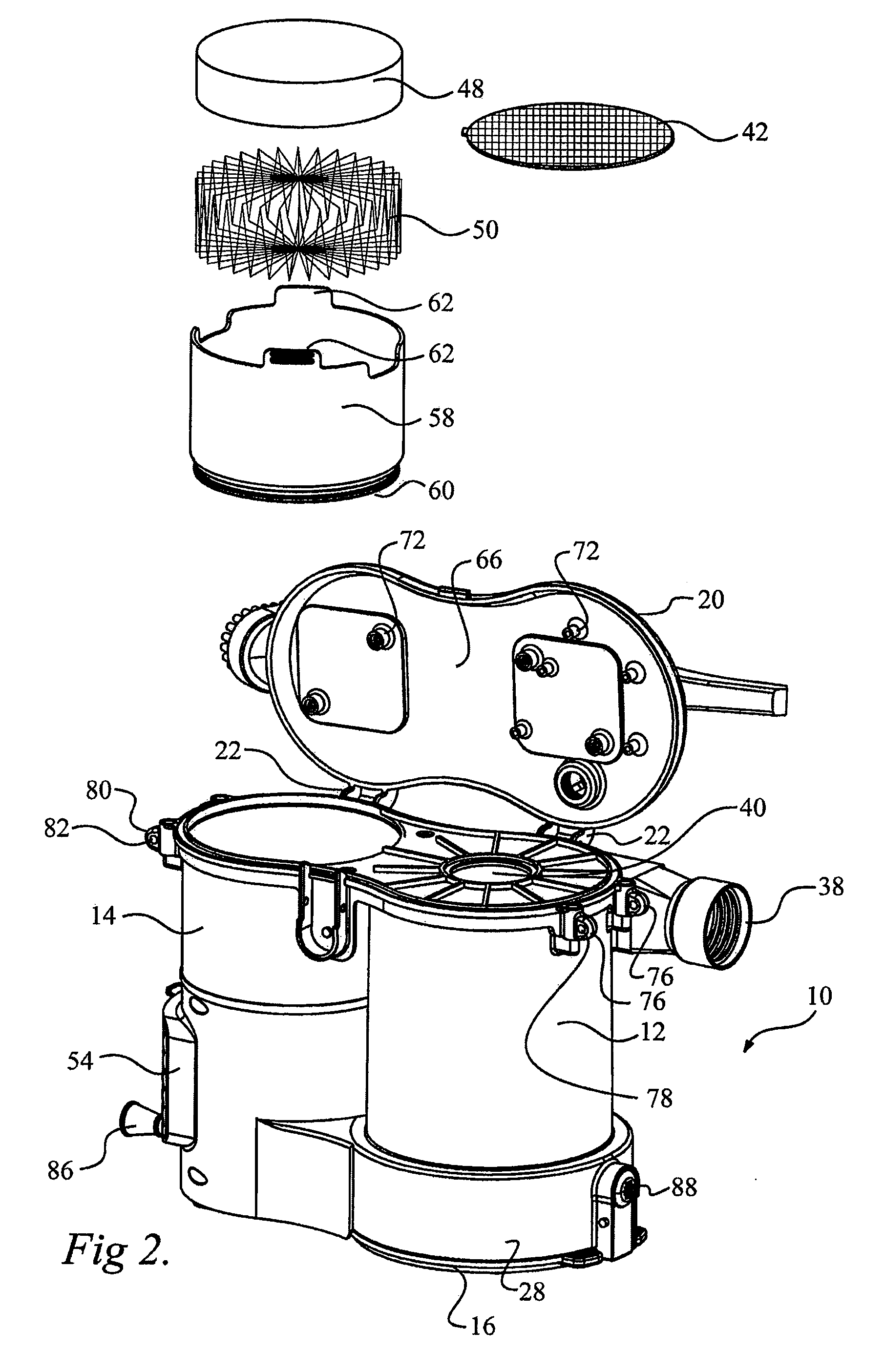
ActiveUS8146201B2Increasing overall height and linear extentMore compactCleaning filter meansBowling gamesSurface cleaningFiltration
A vacuum cleaner comprises adjacent housings, which contain the filtration and suction fan motor assembly of the vacuum cleaner.
Owner:OMACHRON INTPROP
Integrated circuits with substrate protrusions, including (but not limited to) floating gate memories
ActiveUS20080265305A1Enhanced couplingIncrease currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricPhotonic integrated circuit
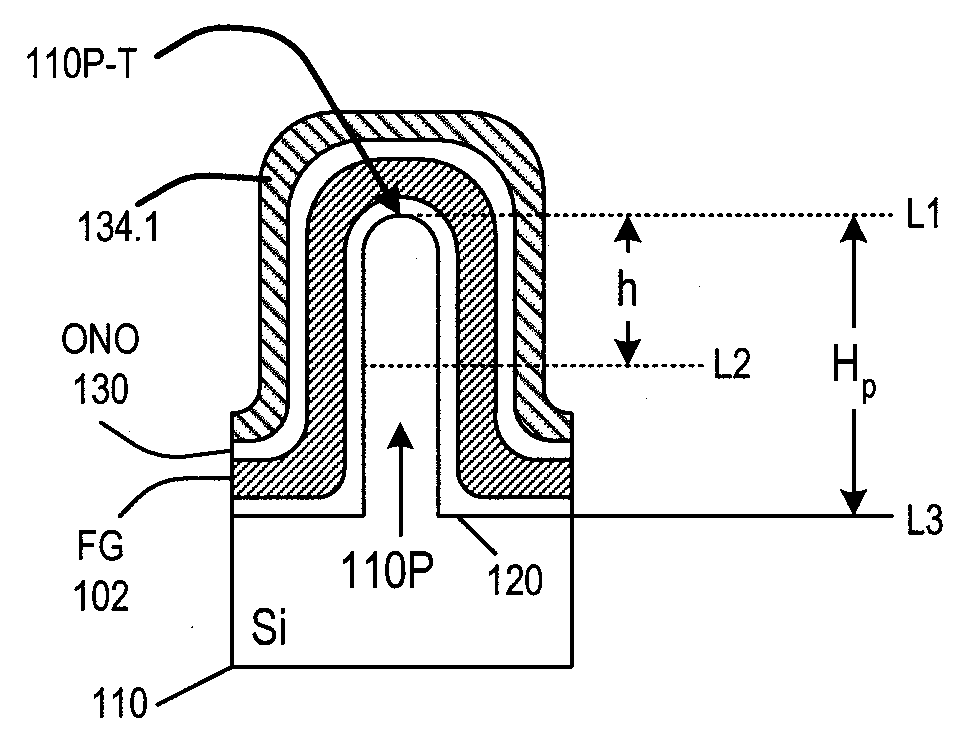
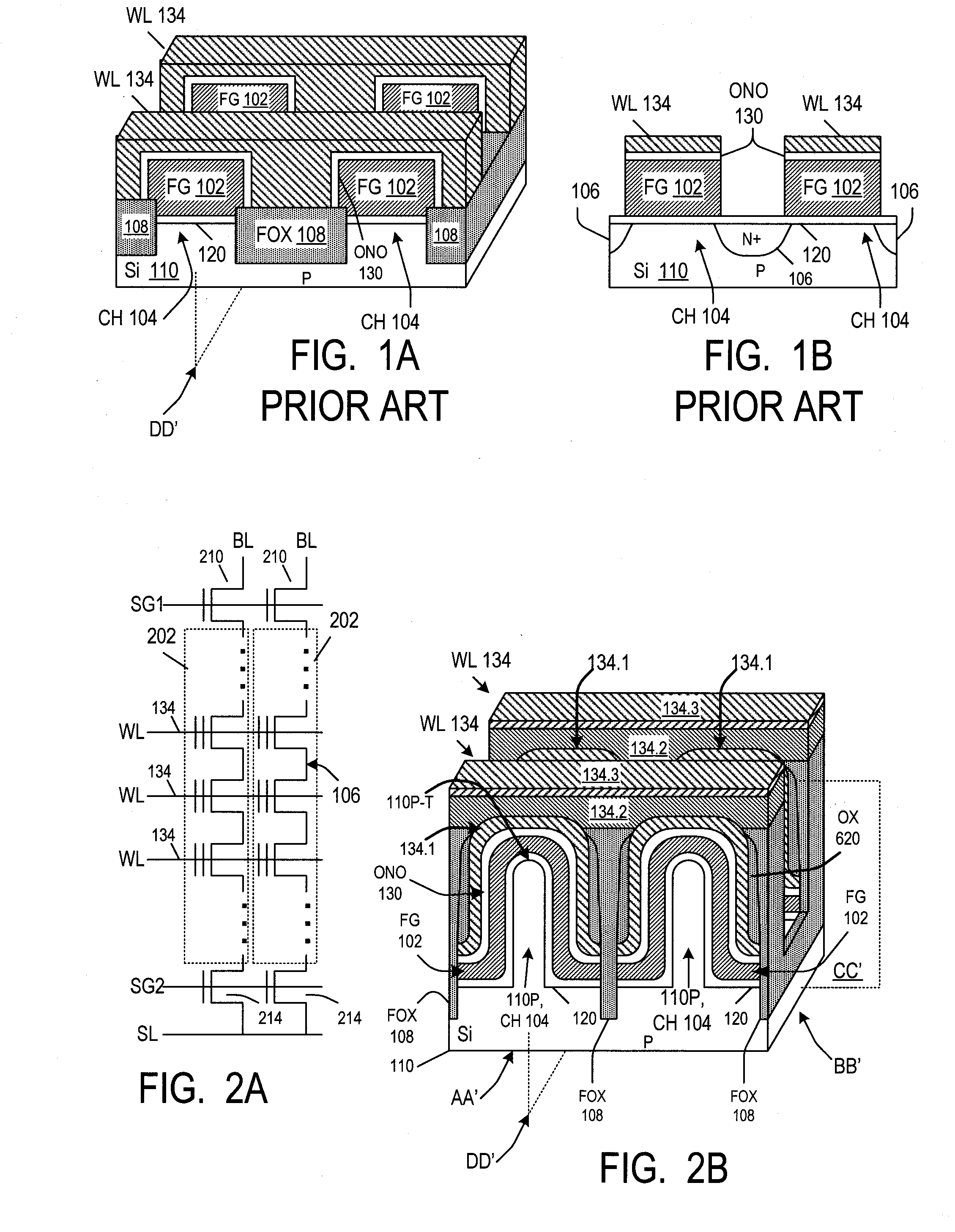
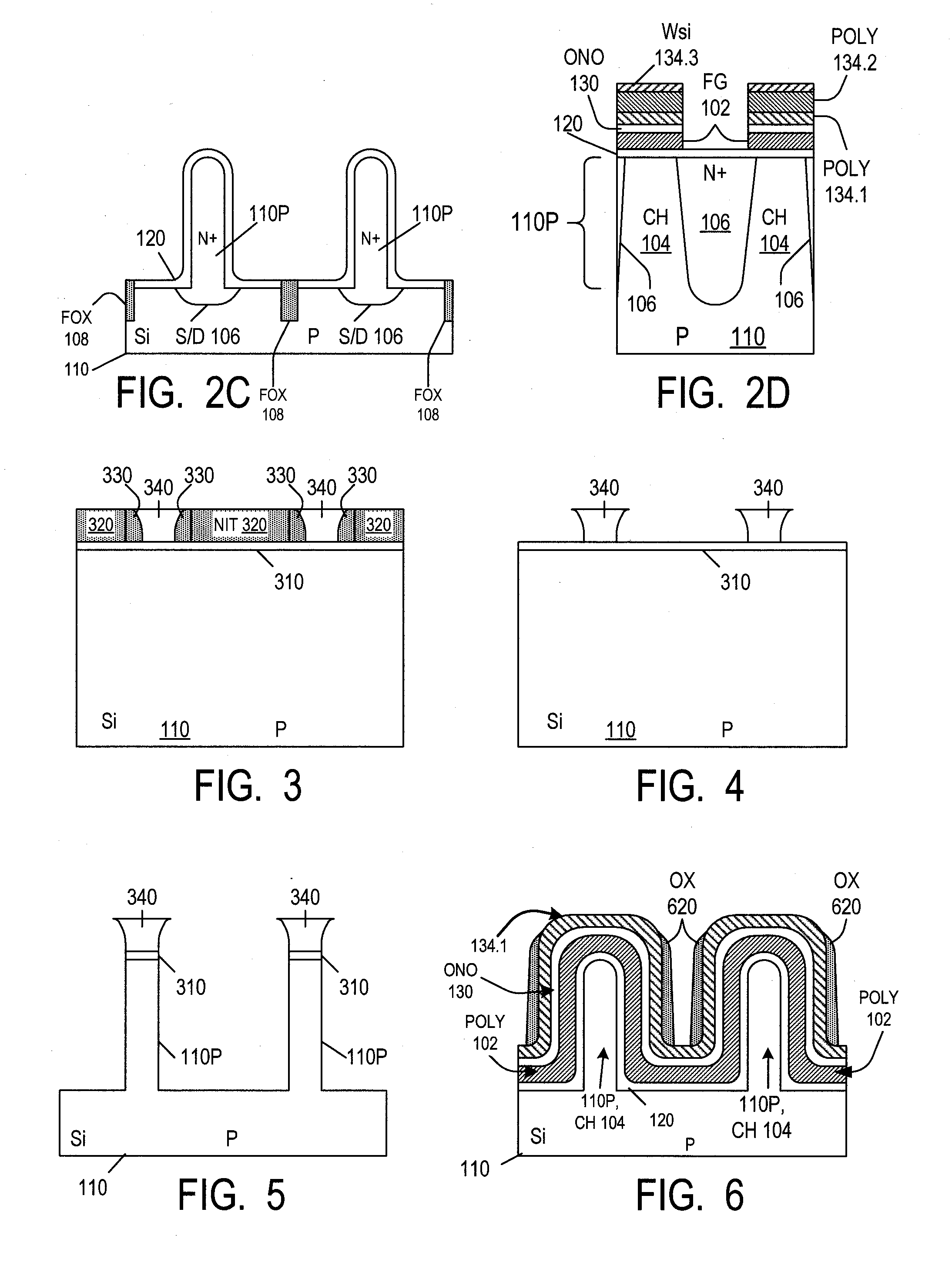
A floating gate memory cell's channel region (104) is at least partially located in a fin-like protrusion (110P) of a semiconductor substrate. The floating gate's top surface may come down along at least two sides of the protrusion to a level below the top (110P-T) of the protrusion. The control gate's bottom surface may also comes down to a level below the top of the protrusion. The floating gate's bottom surface may comes down to a level below the top of the protrusion by at least 50% of the protrusion's height. The dielectric (120) separating the floating gate from the protrusion can be at least as thick at the top of the protrusion as at a level (L2) which is below the top of the protrusion by at least 50% of the protrusion's height. A very narrow fin or other narrow feature in memory and non-memory integrated circuits can be formed by providing a first layer (320) and then forming spacers (330) from a second layer without photolithography on sidewalls of features made from the first layer. The narrow fin or other feature are then formed without further photolithography in areas between the adjacent spacers. More particularly, a third layer (340) is formed in these areas, and the first layer and the spacers are removed selectively to the third layer. The third layer is used as a mask to form the narrow features.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
Methods to mitigate plasma damage in organosilicate dielectrics using a protective sidewall spacer
InactiveUS20090072401A1Reduce plasma damageIncrease line widthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectEngineering
Plasma damage in ultra low k dielectric materials during formation of a dual damascene metal interconnect structure is reduced by providing a protective spacer on sidewalls of a line trench. A densified trench bottom region may be additionally formed directly beneath an exposed horizontal surface of the line trench. The protective spacer and / or the densified trench bottom region protects an ultra low k intermetal dielectric layer from plasma damage during a plasma strip process that is used to remove a disposable via fill plug employed in the dual damascene metal interconnect structure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Fixation Devices and Method of Repair
InactiveUS20080234730A1Easy to fixShorten the lengthSuture equipmentsLigamentsRepair methodSurgical device
In one aspect, the present disclosure relates to a surgical device including an anchor body having an opening, the anchor body having a copolymer composition including polylactide-co-glycolide and calcium carbonate, wherein the calcium carbonate comprises more than 30% but less than 40% of the weight of the composition; and a flexible member passing through the opening, wherein deformation of the device occurs at body temperature. The present disclosure also relates to an oriented polymer material having a copolymer composition including a polylactide-co-glycolide and calcium carbonate, the calcium carbonate comprising more than 30% but less than 40% of the weight of the composition, wherein the material changes shape upon introduction to an environment having a temperature that is lower than a relaxation temperature of the material. A method of repairing soft tissue and other surgical devices are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Surface cleaning apparatus
ActiveUS20080134460A1Increasing heightIncreasing linear extentCleaning filter meansBowling gamesSurface cleaningFiltration
A vacuum cleaner comprises adjacent housings, which contain the filtration and suction fan motor assembly of the vacuum cleaner.
Owner:OMACHRON INTPROP
Mitral and tricuspid annuloplasty rings
ActiveUS20080086203A1Minimize the possibilityStay in shapeBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsMitral annuloplasty ringPosterior region
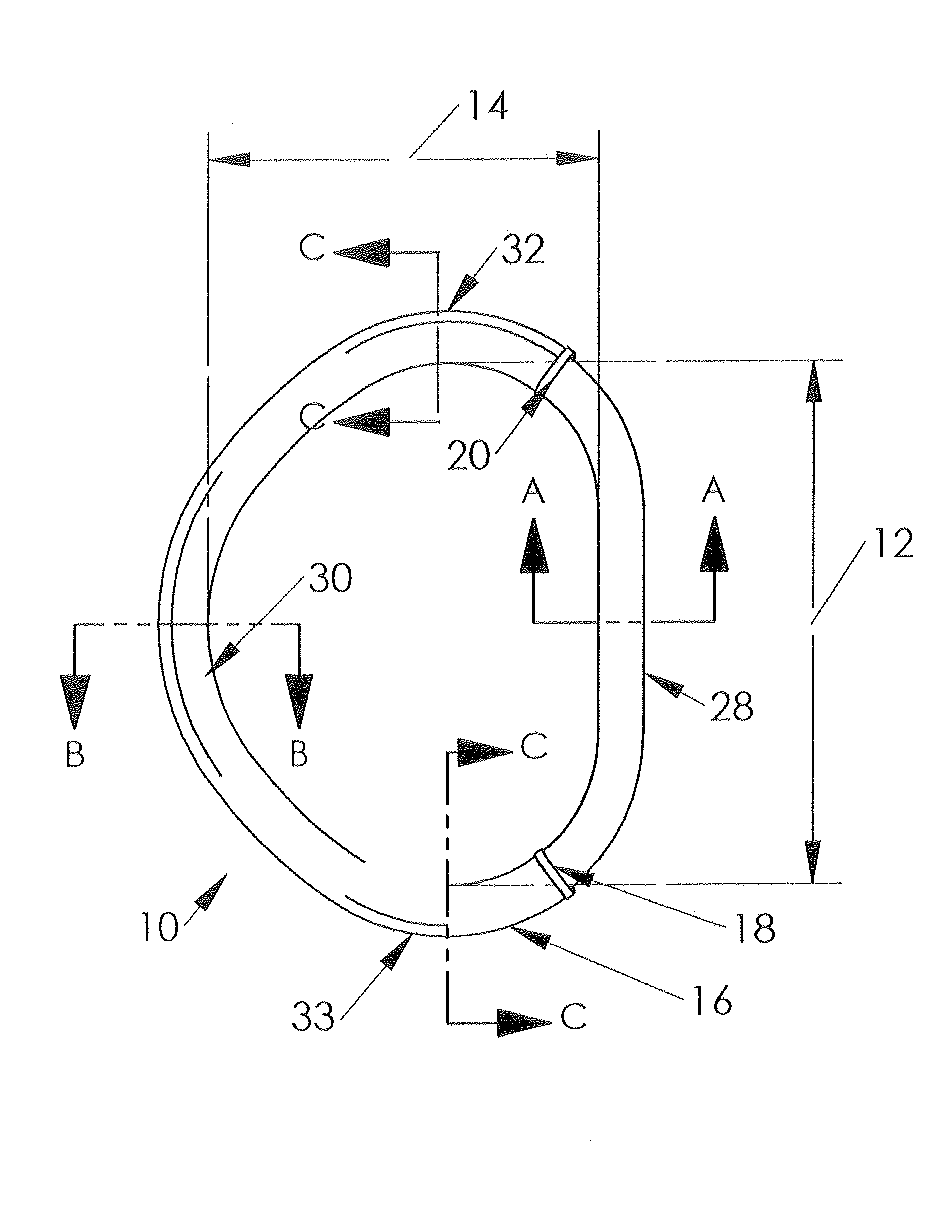
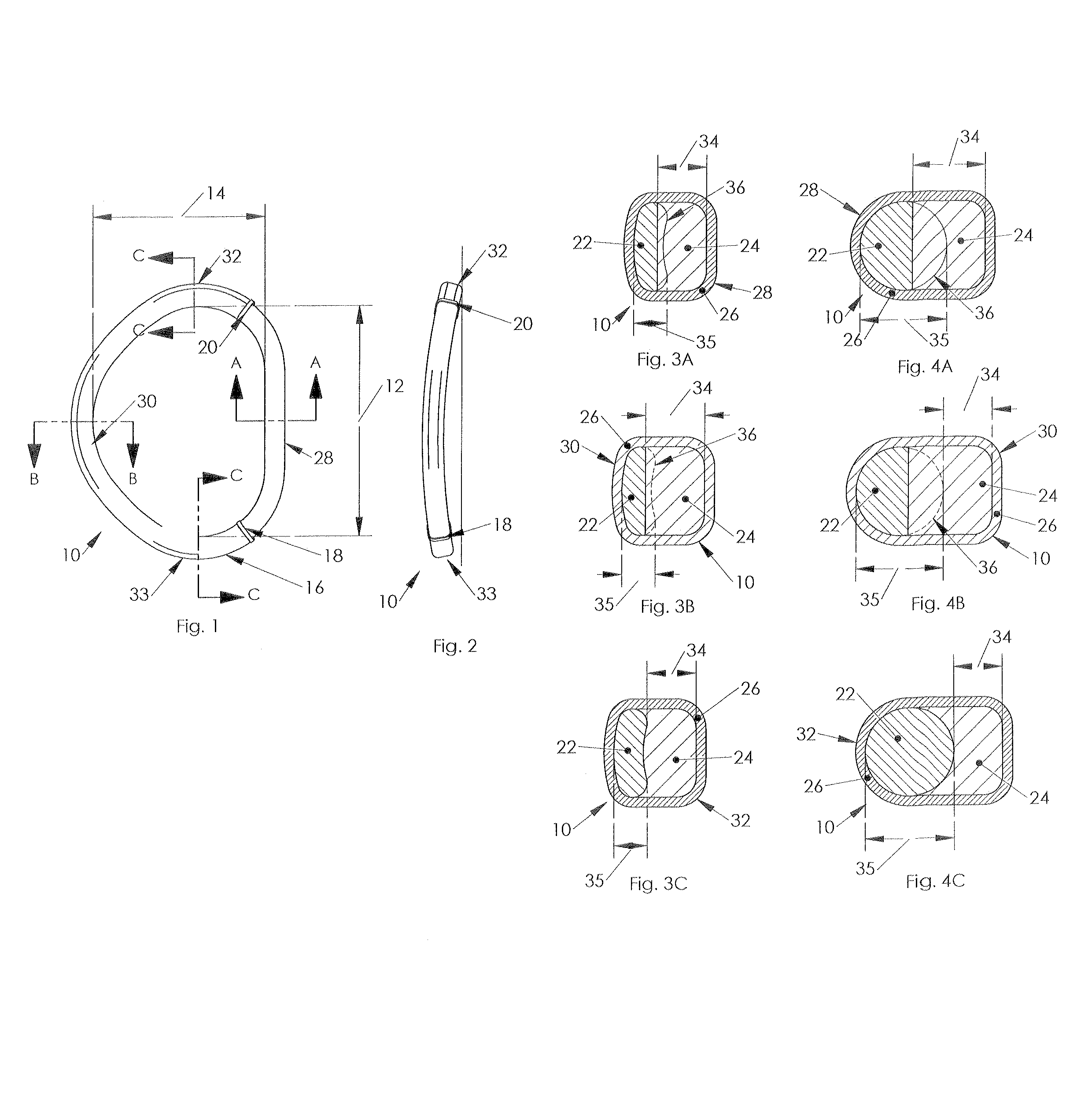
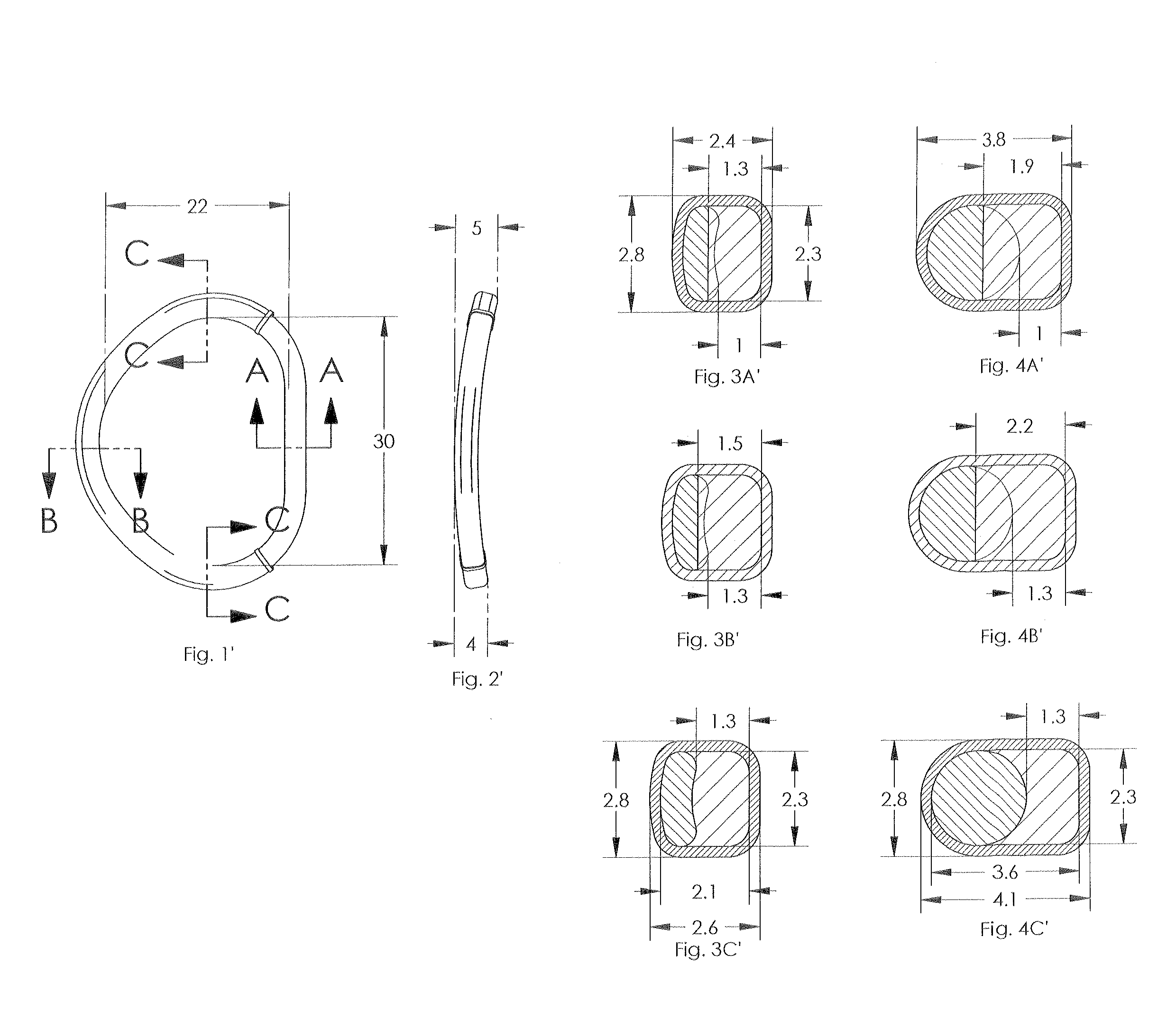
A mitral annuloplasty ring with an inner core and an outer band located therearound is disclosed. The ring has an anterior region, a posterior region opposite the anterior region, and two side regions therebetween. A cross-sectional width dimension of the outer band is greater in the posterior region of the ring than in the anterior region. A cross-sectional width dimension of a semi-flexible core is thinner in the anterior and posterior regions than in the side regions so that the mitral ring is more rigid in the anterior-posterior direction. A tricuspid annuloplasty ring of the invention has an inner core and an outer band located therearound. The inner core has an anterior region separated across a gap from a septal region, and a posterior region. A cross-sectional width dimension of the outer band is greater in the septal region than either the anterior or posterior regions.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Medical foot implant and system
InactiveUS20090082770A1Easy to introduceMinimizes strainJoint implantsArtificial legsFirst tarsometatarsal jointSacroiliac joint
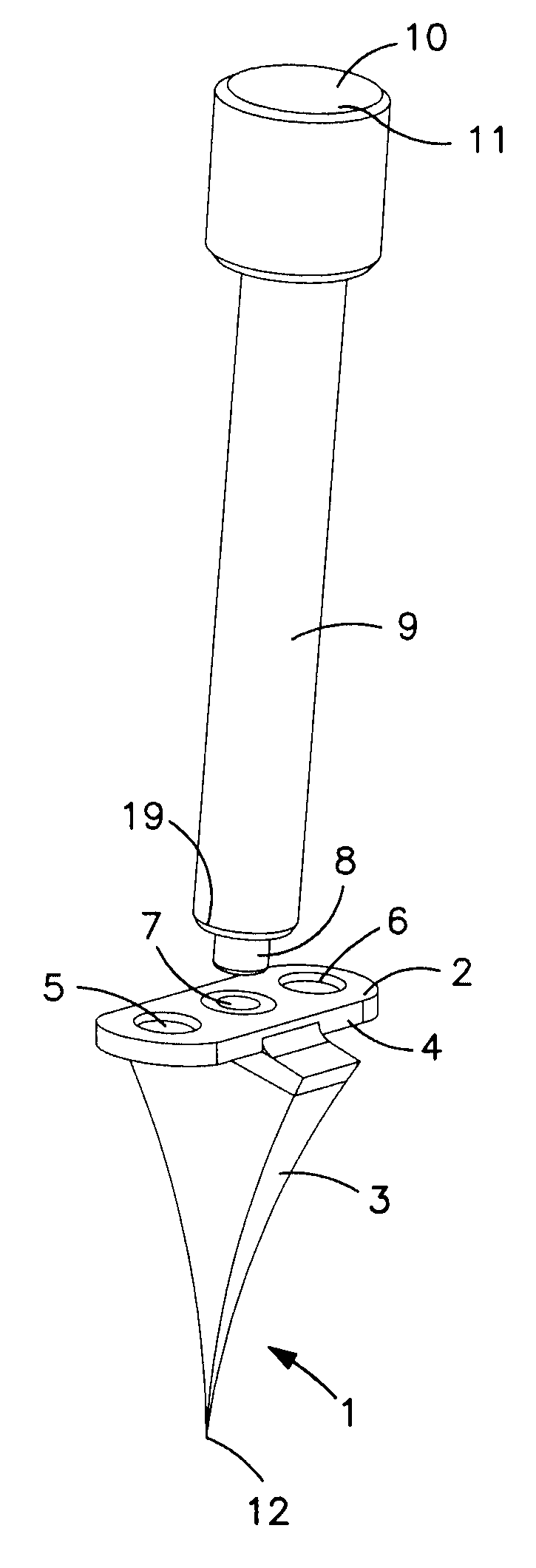
A medical foot implant (1) with a fastening section (2) for fixing the foot implant (1) to two adjacent bones or bone segments and with a wedge section (3). The wedge section (3) has an end-side tip (12), in a plan view at least approximately punctiform, for easier introduction of the foot implant (1) into bone or into tarsometatarsal joint.
Owner:NORMED MEDIZIN TECHN VERTRIEBS
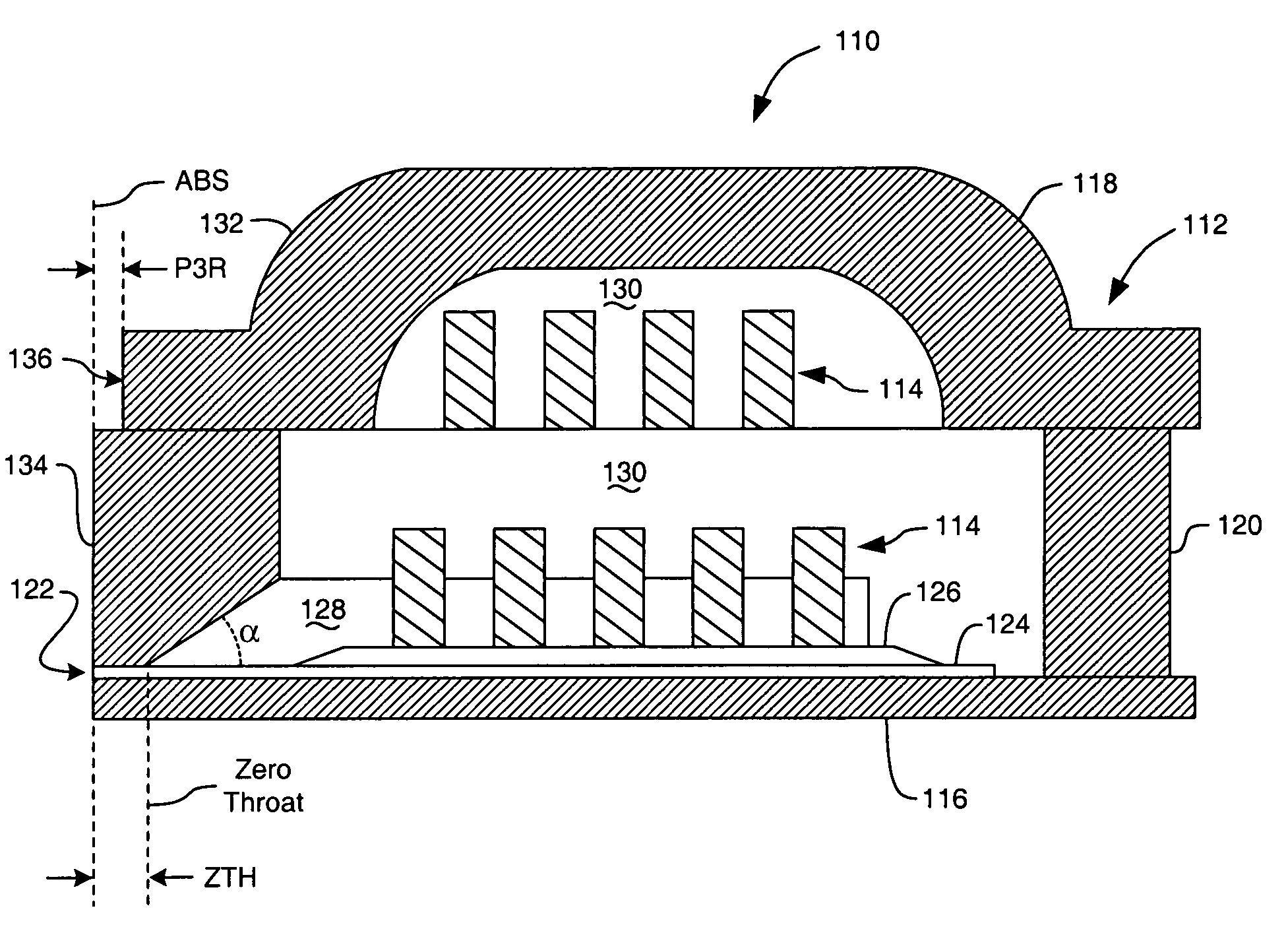
Stitched pole write element with a T-shaped pole tip portion
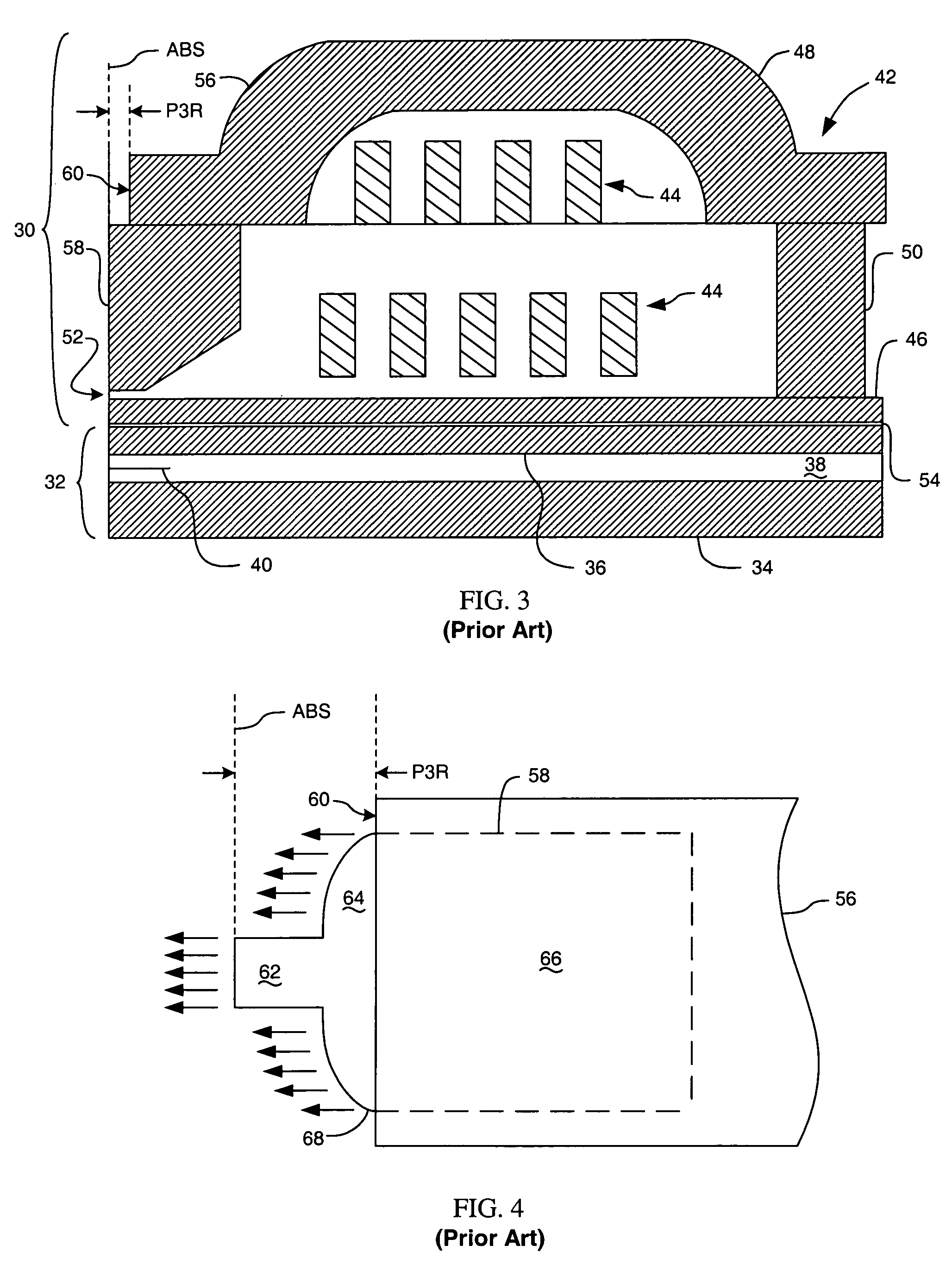
InactiveUS7116517B1Less lengthIncrease widthRecord information storageHeads with metal sheet coresNarrow noseMagnetic disks
A T-shaped pole tip portion of an upper pole of a write element for a magnetic disk drive is provided. One end of the pole tip portion, constituting the bottom of the “T,” forms a narrow nose segment at an air bearing surface, while a wing segment at the opposite end of the pole tip portion constitutes the cross-bar top of the “T.” A transition segment extends between the nose segment and the wing segment. A yoke portion of the upper pole includes a surface that is parallel to the air bearing surface and recessed therefrom by a P3R depth. The transition segment does not widen significantly until after the P3R depth, accordingly, the wing segment is recessed from the air bearing surface by more than the P3R depth.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Elastic wave device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130285768A1Recover piezoelectricityImprove featuresImpedence networksSpeed of soundElectrode
An elastic wave device includes a supporting substrate, a high-acoustic-velocity film stacked on the supporting substrate and in which an acoustic velocity of a bulk wave propagating therein is higher than an acoustic velocity of an elastic wave propagating in a piezoelectric film, a low-acoustic-velocity film stacked on the high-acoustic-velocity film and in which an acoustic velocity of a bulk wave propagating therein is lower than an acoustic velocity of a bulk wave propagating in the piezoelectric film, the piezoelectric film is stacked on the low-acoustic-velocity film, and an IDT electrode stacked on a surface of the piezoelectric film.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
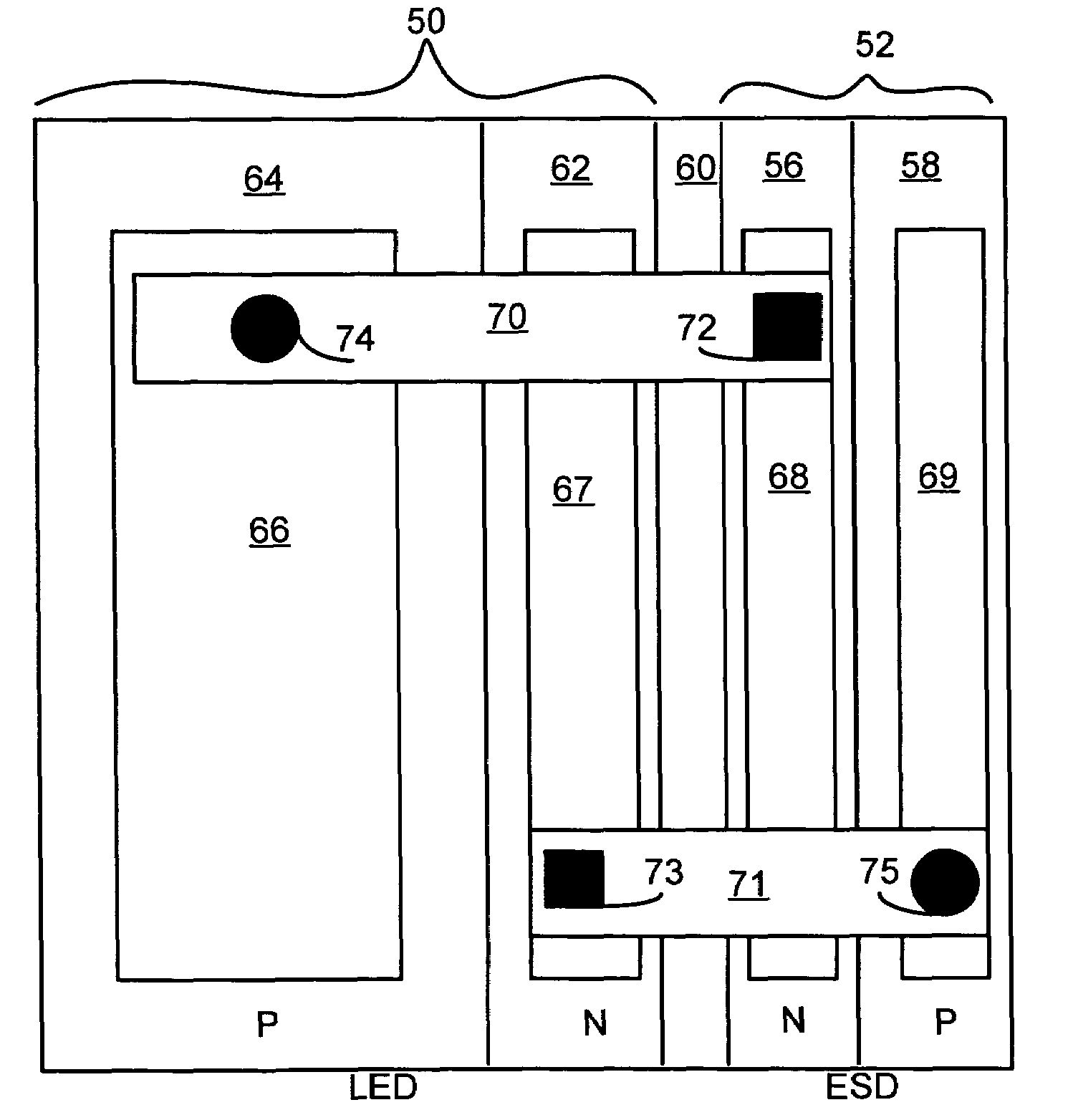
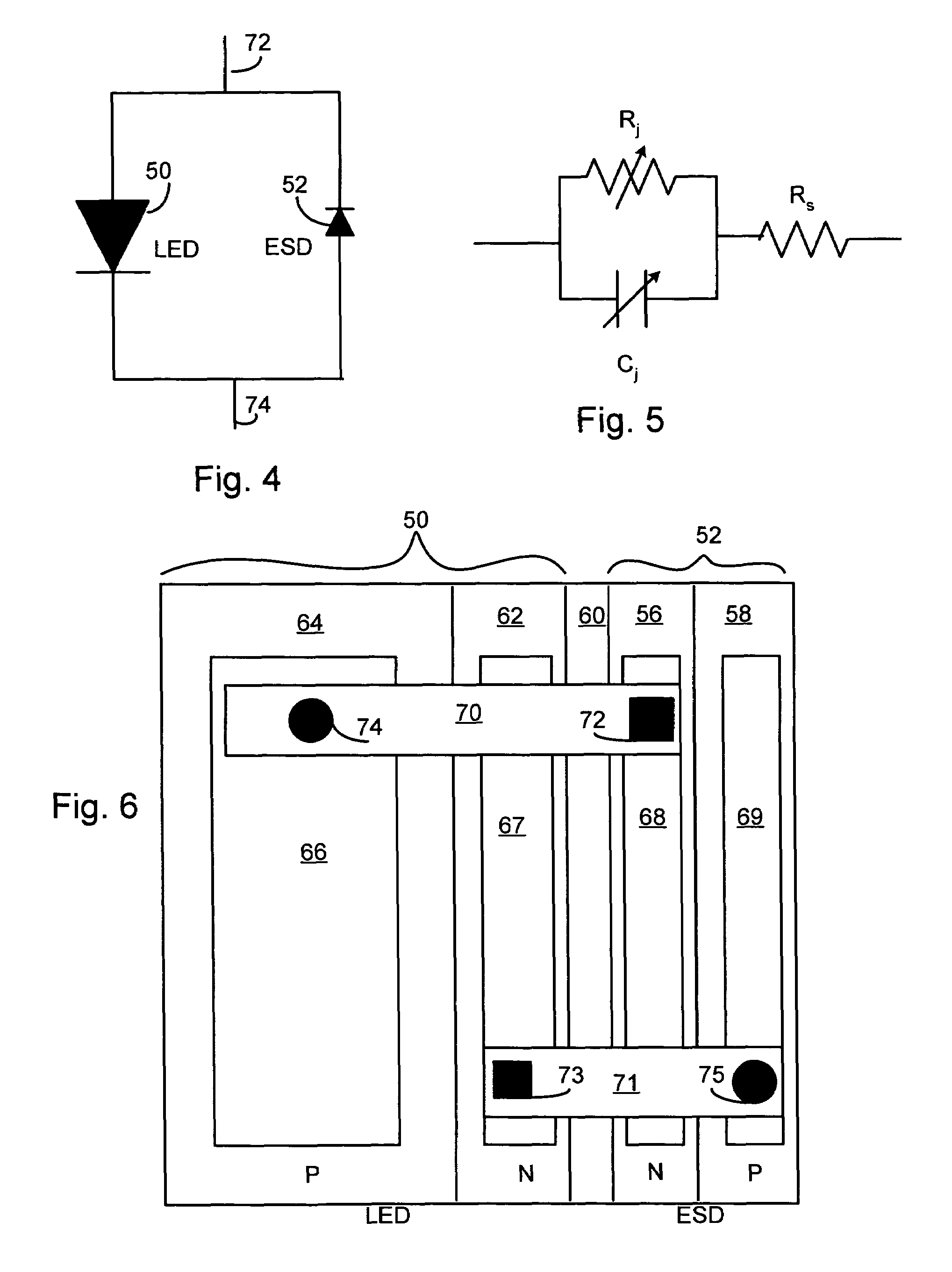
LED chip with integrated fast switching diode for ESD protection
ActiveUS7064353B2Reduced series resistanceIncrease widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsP–n junction
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV +1
Subsonic aircraft with backswept wings and movable wing tip winglets
InactiveUS6345790B1Optimized aerodynamic streamline contourRaise the ratioInfluencers by generating vorticesAircraft stabilisationWingspanAirplane
A subsonic aircraft having backswept lifting wings is equipped with individually rotatable winglets at the wing tips thereof, in order to reduce drag during cruise flight, to minimize the dangers posed by wing tip vortices to following aircraft during take-off and landing, and to minimize the total wingspan during ground operations, with respective different positions of the winglets. A streamline-shaped rotation body made up of at least two individually rotatably supported rotation segments is mounted on the wing tip of each lifting wing. A respective winglet is mounted on each respective rotation segment. Each rotation segment with its associated winglet is individually rotatable about a rotation axis of the rotation body extending substantially parallel to the aircraft lengthwise axis. Thereby, each winglet is individually pivotable to any selected pivot angle relative to a horizontal plane extending through the rotation axis. Each winglet and its associated rotation segment is rotatable through an angular range between maximum end limits of at least +90° (vertically upward) and at least -90° (vertically downward) relative to the horizontal plane.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
Endoscopic clip applying apparatus with improved aperture for clip release and related method
ActiveUS7585304B2Increase widthFacilitated releaseSurgical forcepsWound clampsEndoscopic clippingSurgical Clips
An apparatus for applying surgical clips includes a jaw assembly and a jaw opening member. The jaw assembly includes first and second opposing pivotable jaw members that define a variable-width jaw aperture therebetween for receiving a clip. The jaw opening member is movable into engagement with the first and second jaw members for increasing the width of the jaw aperture, thereby improving the release of a clip from the jaw assembly.
Owner:TELEFLEX MEDICAL INC
Method for manufacturing wafer level chip scale package using redistribution substrate
InactiveUS20060079019A1Increase widthIncrease flexibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringChip-scale package
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a wafer level chip scale package using a redistribution substrate, which has patterned bump pairs connected by redistribution lines and formed on a transparent insulating substrate. The redistribution substrate is produced separately from a wafer and then bonded to the wafer. One part of each bump pair is in contact with a chip pad on the active surface of the wafer, and the other part coincides with one of holes formed in the wafer. Conductive lines are formed in the holes and on the non-active surface of the wafer. External connection terminals are formed on the conductive lines at the non-active surface.
Owner:EPWORKS
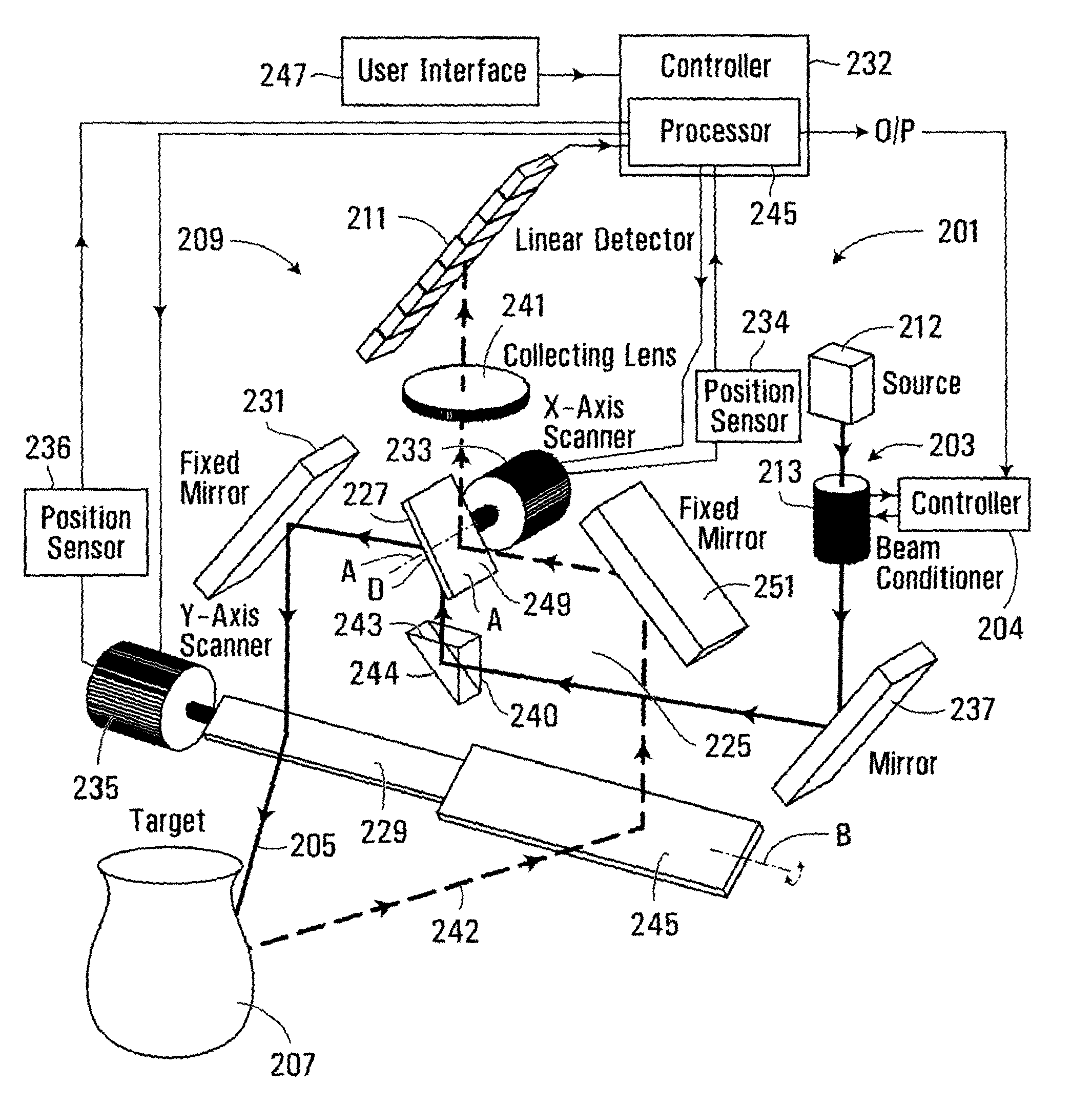
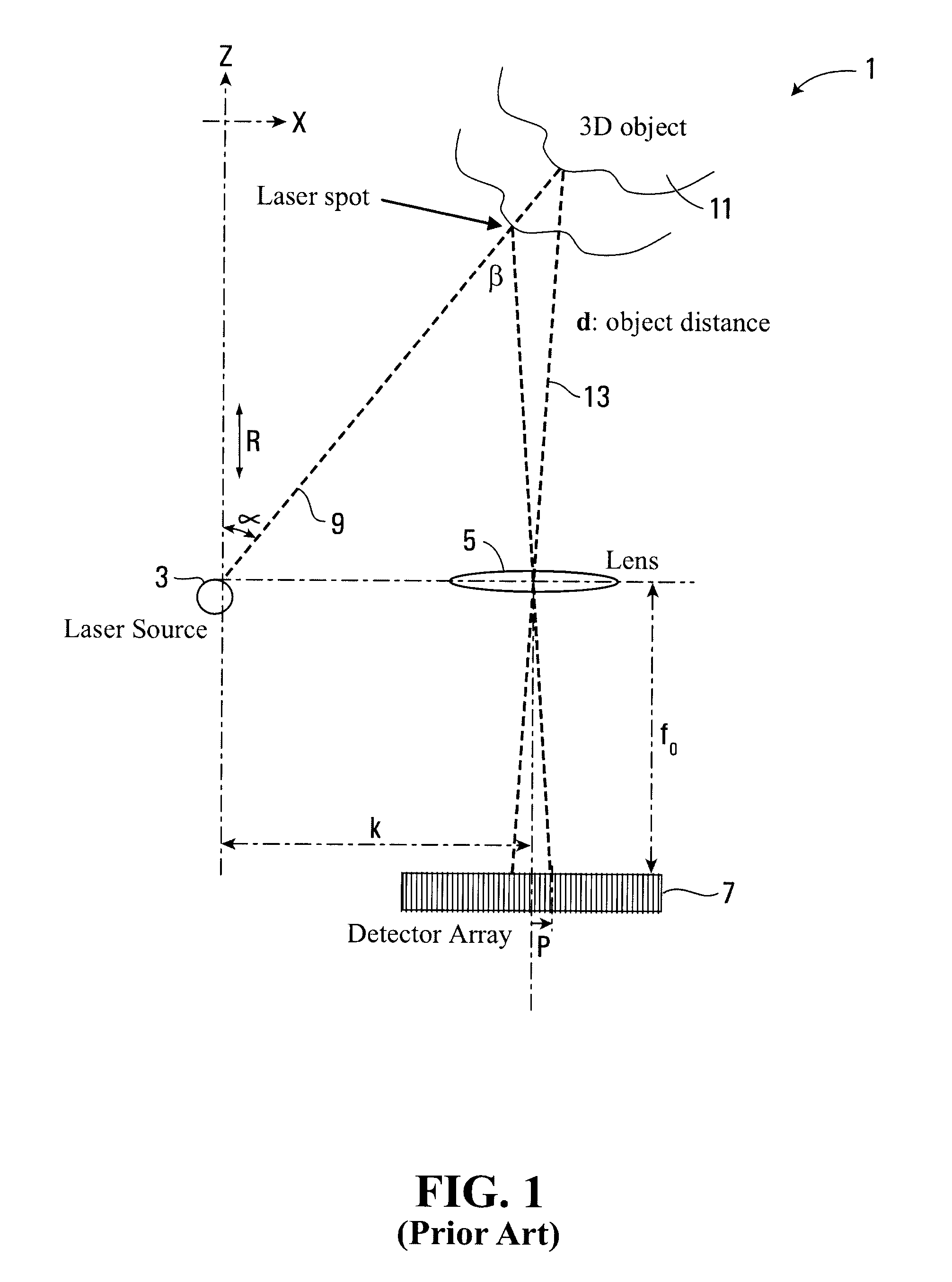
Imaging system and method
InactiveUS20090195790A1Reduce edge effectsReduce errorsUsing optical meansBeam expanderTarget surface
An apparatus for measuring the coordinates of a point on the surface of an object comprises a projection system for projecting a beam of energy onto the surface of the object, a receiving system for receiving reflected beam energy from the target surface, and a detector for detecting the received energy. The projection system comprises a beam expander for expanding the width of the beam, and a focussing device for focussing the projected beam. The position of the reflected beam energy at the detector provides a measure of the range of the point on the target surface using triangulation and the direction of the projected beam provides the x and y coordinates. The focussing device can be controlled to vary the focal length of the projected beam and to control the beam size at the target object to vary the area of the target surface illuminated by the beam and thereby to control the resolution of the measurements.
Owner:NEPTEC
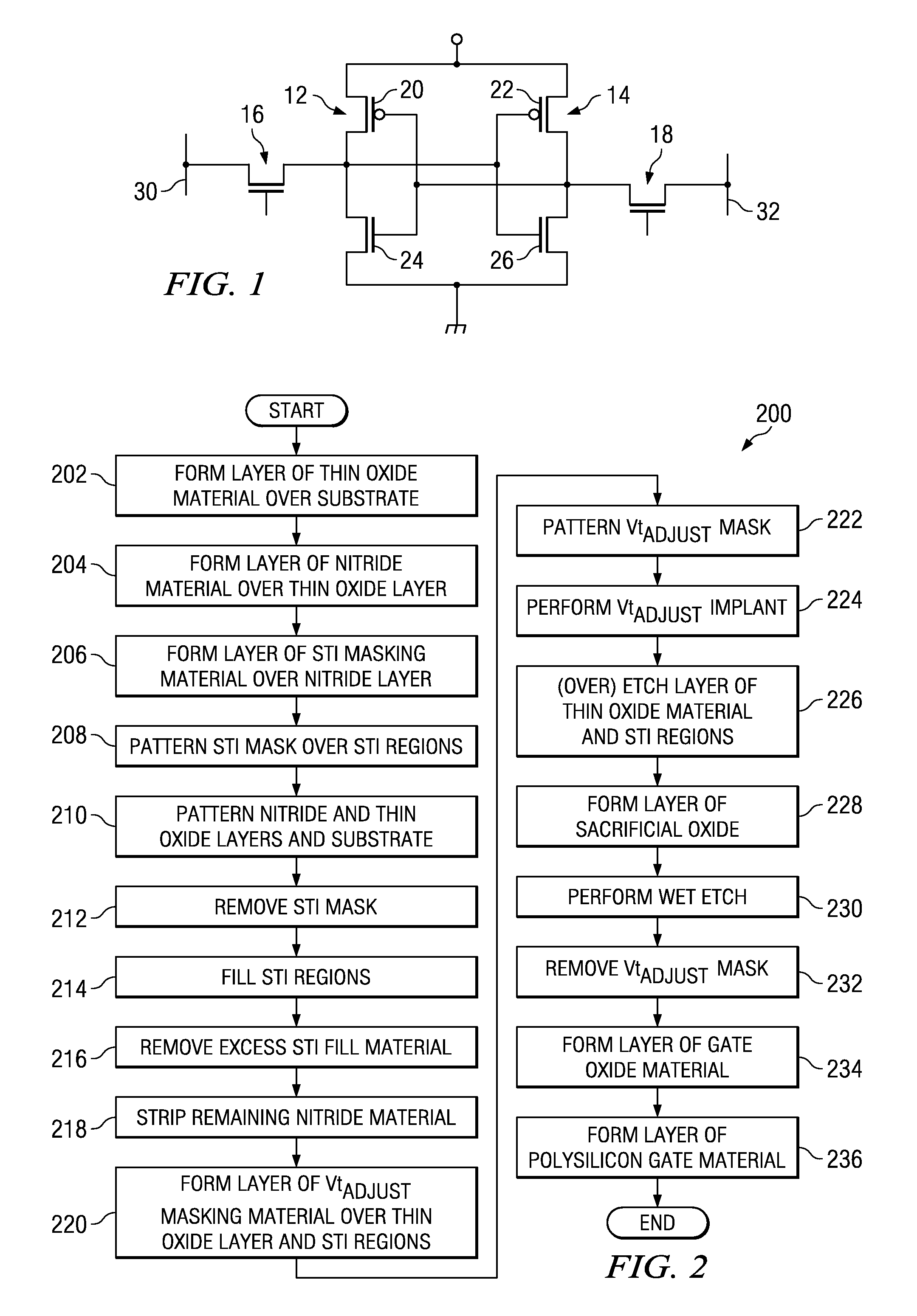
Method to improve SRAM performance and stability
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and systems using prediction of outcome for launched objects
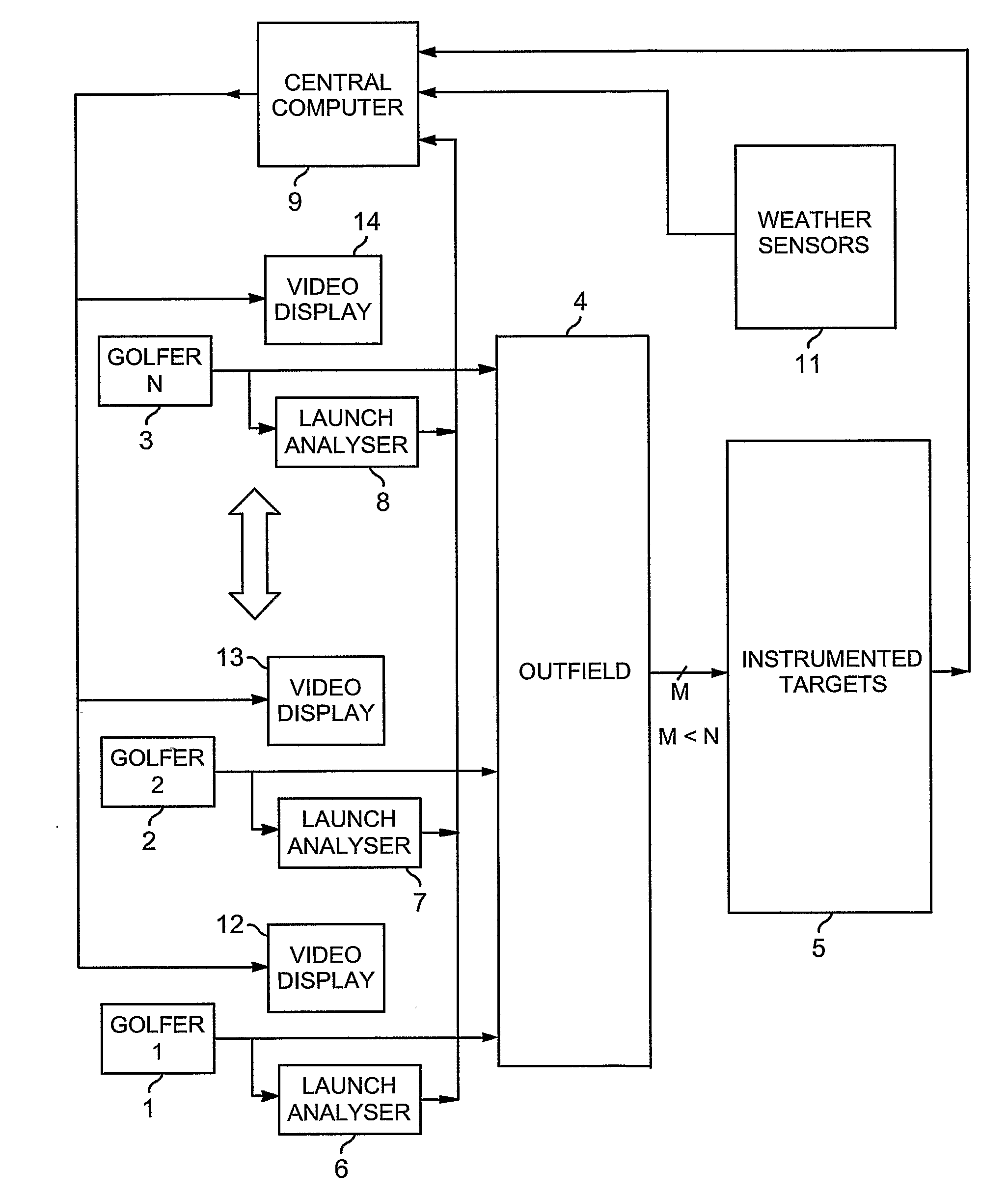
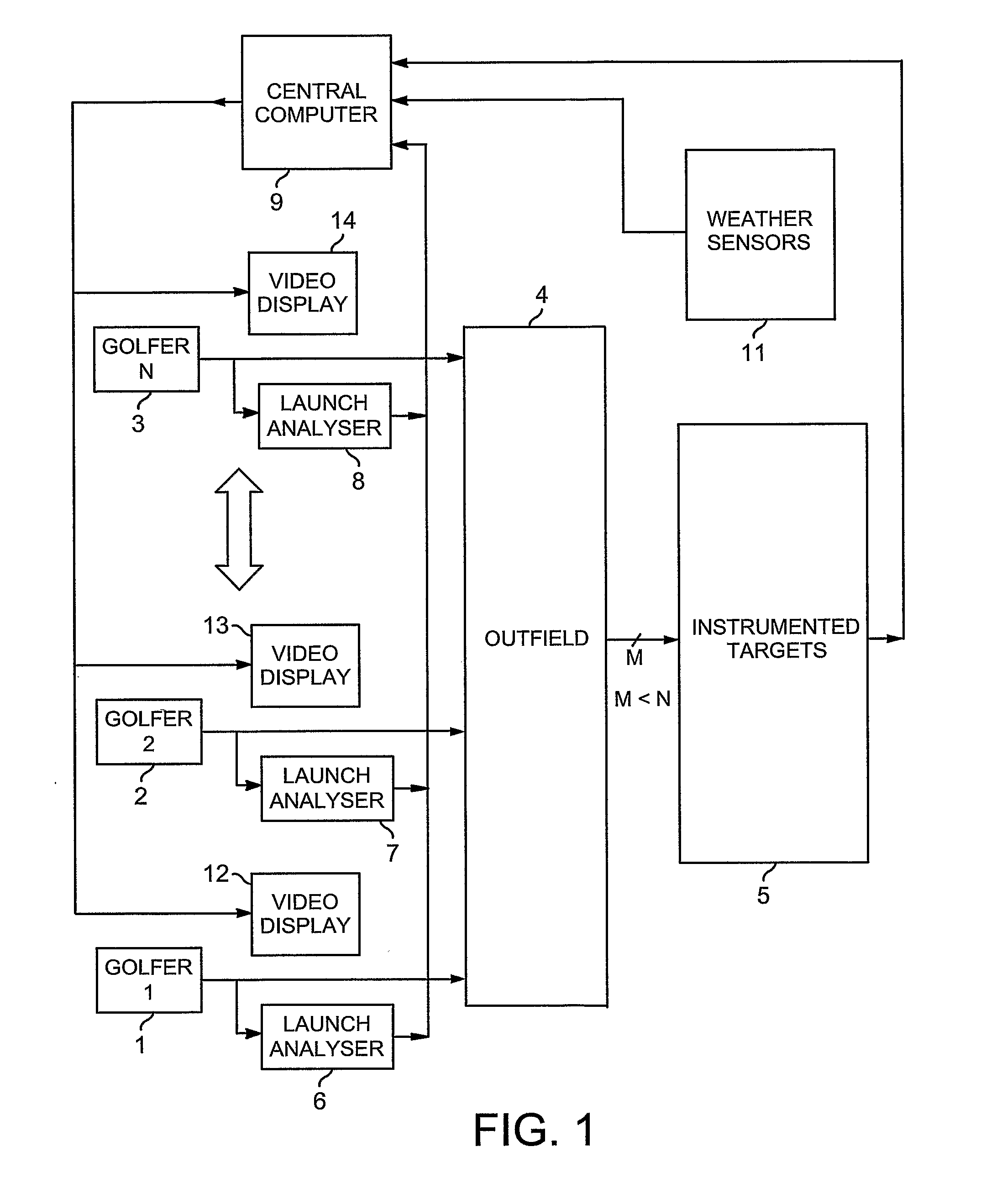
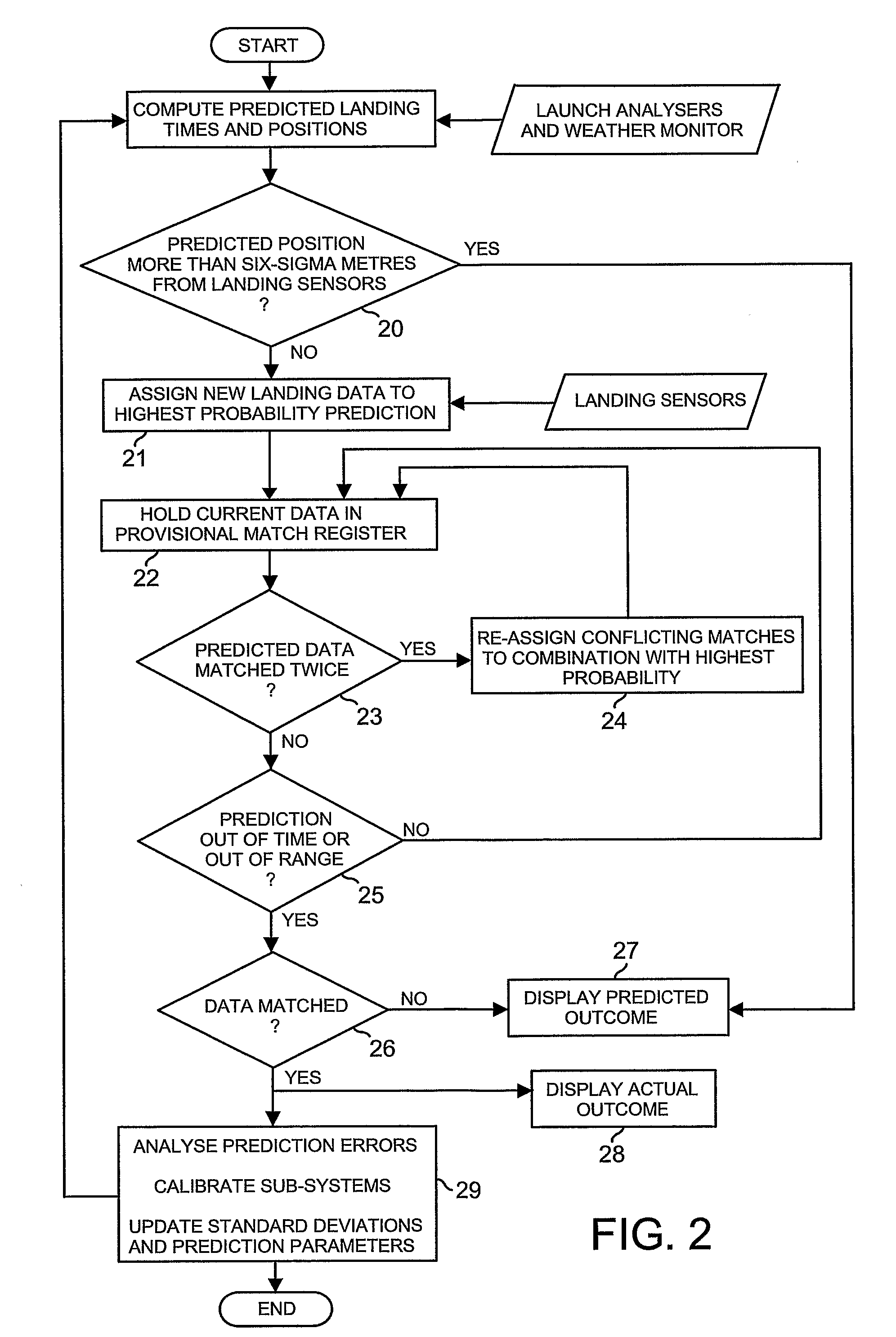
InactiveUS20070167247A1Improve forecast accuracyReduce errorsGymnastic exercisingBall sportsElectricityDisplay device
Each golfer (1-3) on a golf range (4) has an individual display (12-14) showing at least a predicted outcome of each of his / her shots, and a launch-analyser (6-8) to measure velocity vectors of the ball and / or club at strike for central-computation (9) of the prediction. Vibration and piezo-cable sensors (54,55;68,69) at instrumented targets (5;41-45,47) distributed throughout the range (4), detect the presence of balls arriving in their respective locations for matching with launched balls using the computed predictions and probability; active or passive radio-frequency identification and location of balls may also be used. Where a match is found, error between predicted and actual outcome is applied to adaptive correction of the prediction-computing process, and the actual outcome is displayed to the golfer instead of the prediction. Ball and / or club velocity vectors, and ball spin, at launch are measured from light changes occurring in detection planes (96,97;105;114-117;134;144-146) defined by slit apertures (94,95;104), and resulting from retro-reflection from ball (91;110;131) and / or club (130).
Owner:LINDSAY LTD
Dielectric lens cone radiator sub-reflector assembly
ActiveUS9105981B2Reduction of sub-reflector spill-overIncrease widthOptical articlesCoupling light guidesWaveguidePhysics
A dielectric cone radiator sub-reflector assembly for a reflector antenna with a waveguide supported sub-reflector is provided as a unitary dielectric block with a sub-reflector at a distal end. A waveguide transition portion of the dielectric block is dimensioned for insertion coupling into an end of the waveguide. A dielectric radiator portion is provided between the waveguide transition portion and a sub-reflector support portion. An outer diameter of the dielectric radiator portion is provided with a plurality of radially inward grooves extending radially inward to a diameter less than an inner diameter of the end of the waveguide and a lens bore extends from a proximal end of the dielectric block towards the distal end of the dielectric block at least to the sub-reflector support portion. The unitary dielectric block may be manufactured as a single contiguous monolithic portion of dielectric material via injection molding.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Fabrication method of semiconductor wafer
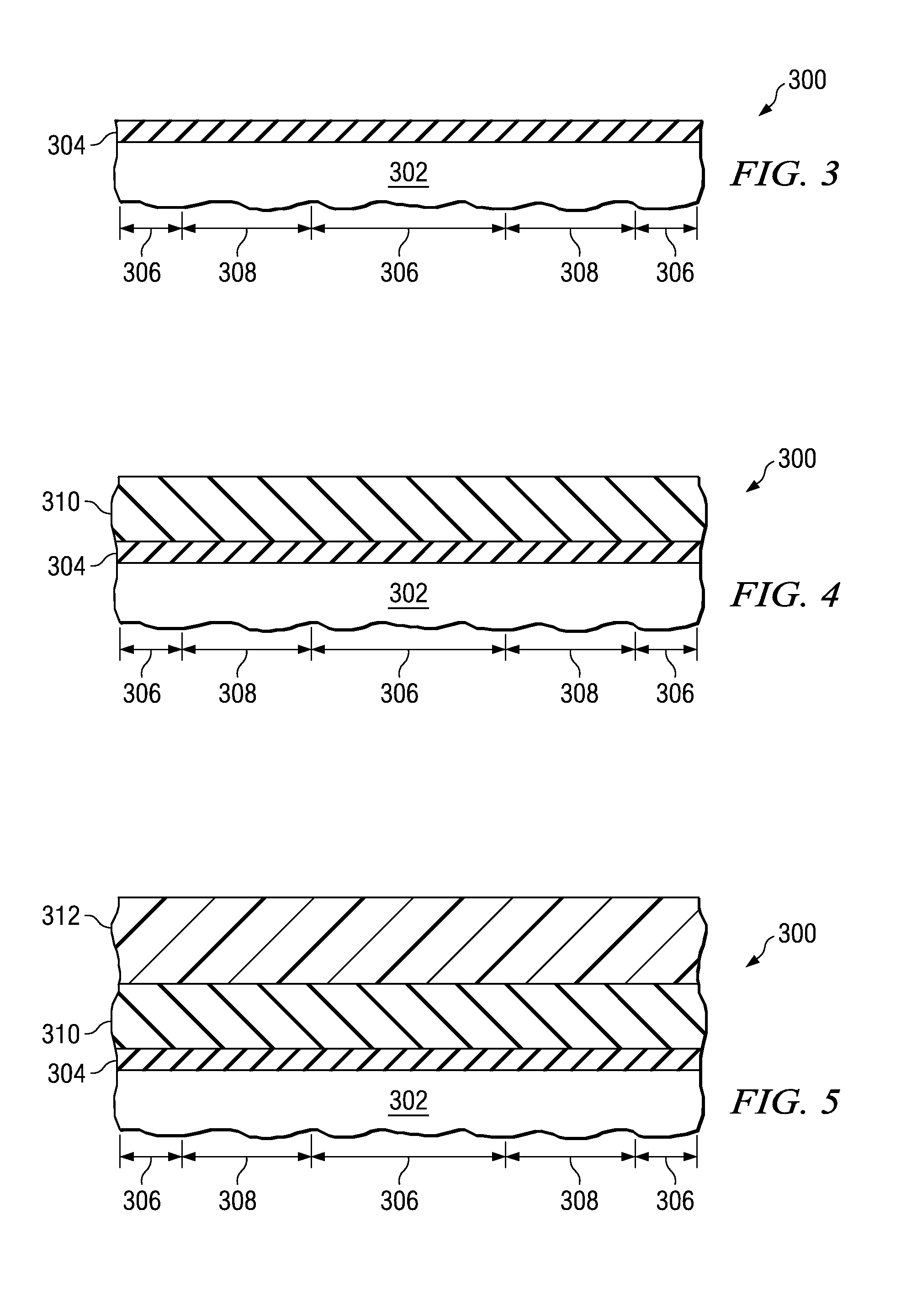
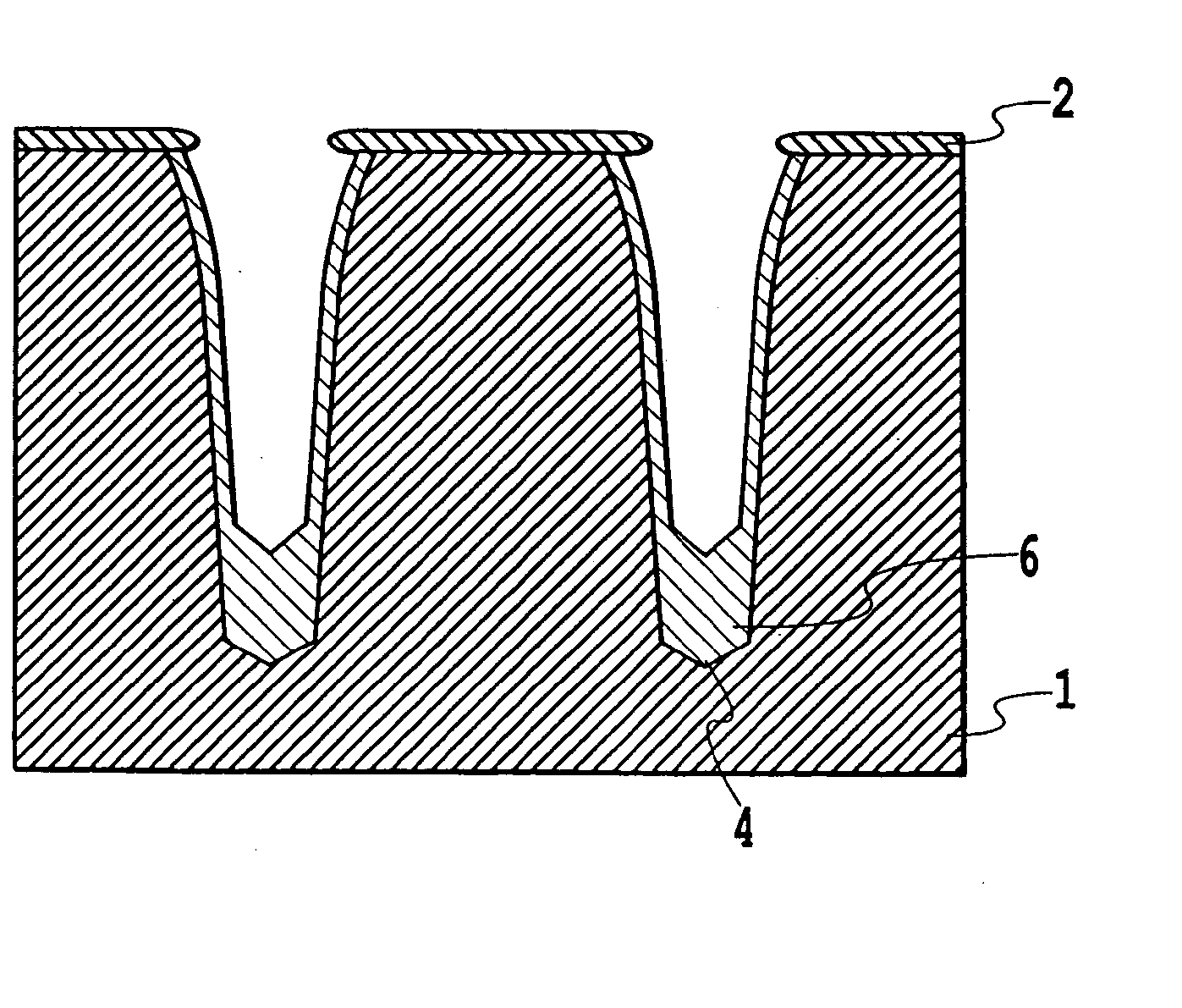
ActiveUS20040185665A1Little contaminationImprove crystal qualityTransistorPolycrystalline material growthMicrometerEtching
A fabrication method of a semiconductor wafer can fill trenches formed in a semiconductor substrate with an epitaxial film with high crystal quality without leaving cavities in the trenches. The trenches are formed in the first conductivity type semiconductor substrate. Planes exposed inside the trenches are made clean surfaces by placing the substrate in a gas furnace, followed by supplying the furnace with an etching gas and carrier gas, and by performing etching on the exposed planes inside the trenches by a thickness from about a few nanometers to one micrometer. The trenches have a geometry opening upward through the etching. Following the etching, a second conductivity type semiconductor is epitaxially grown in the trenches by supplying the furnace with a growth gas, etching gas, doping gas and carrier gas, thereby filling the trenches. Instead of making the trenches slightly-opened upward, their sidewalls may be made planes enabling facet formation.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com