Patents
Literature
388results about How to "Reduce edge effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
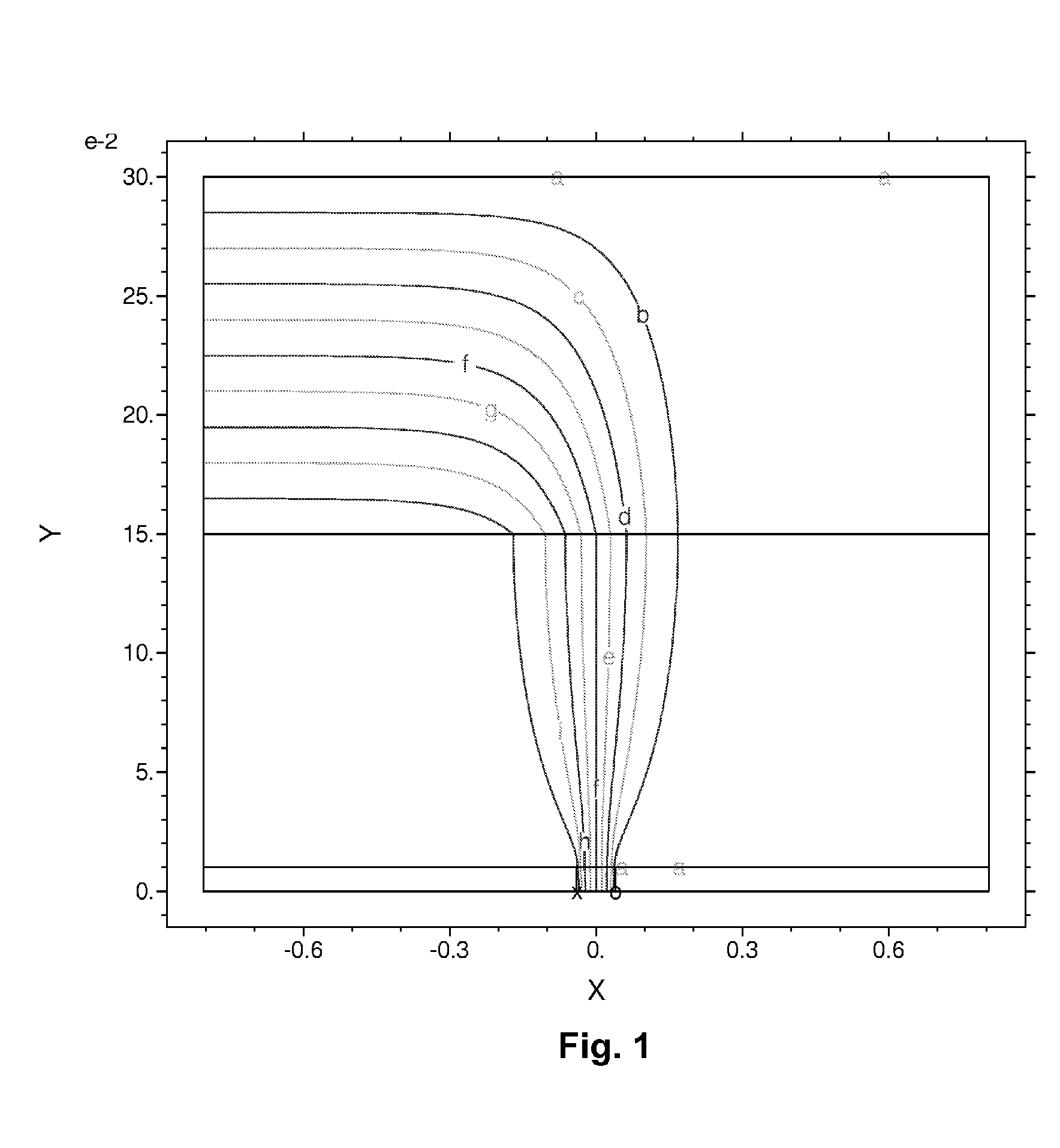
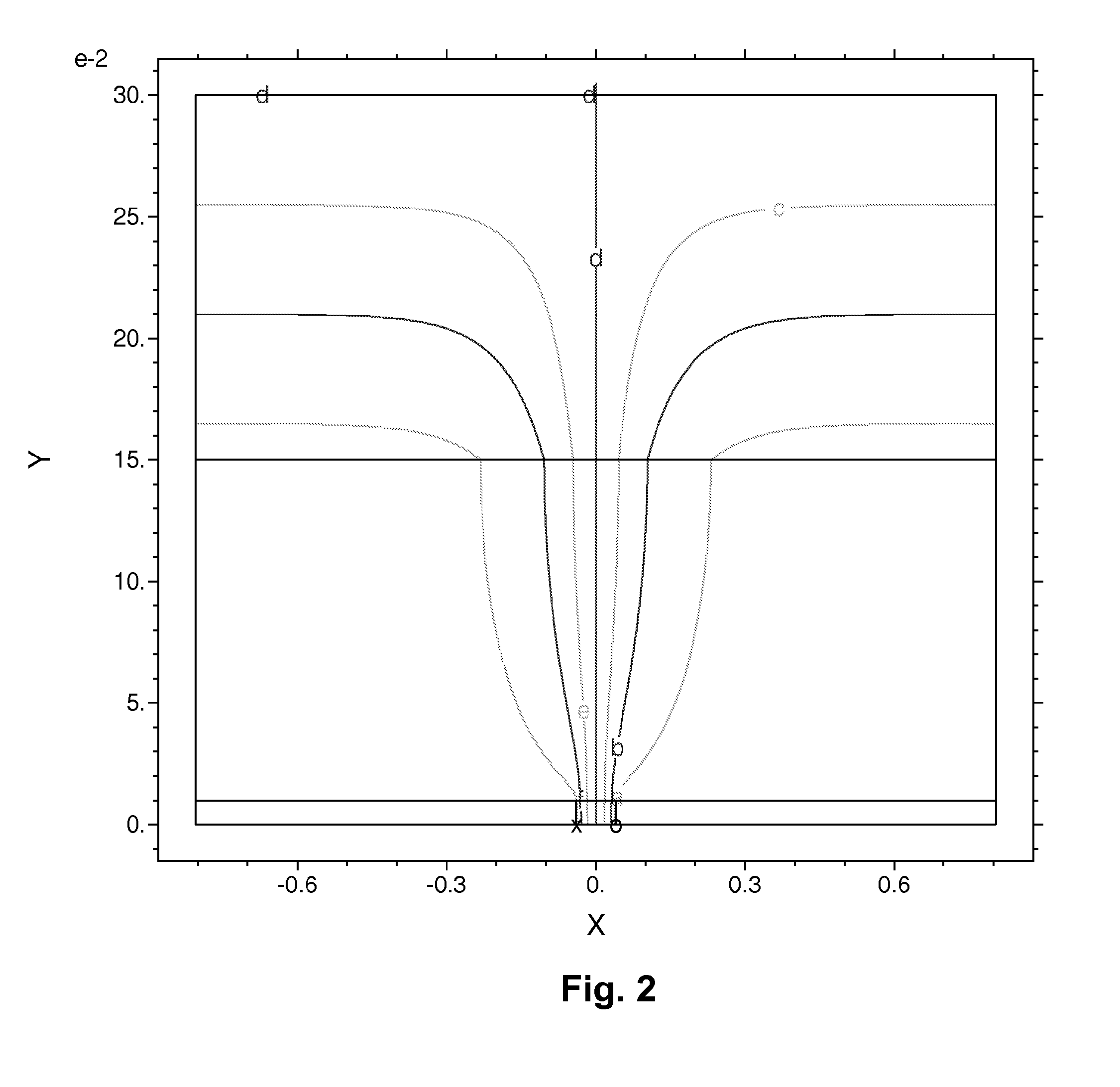
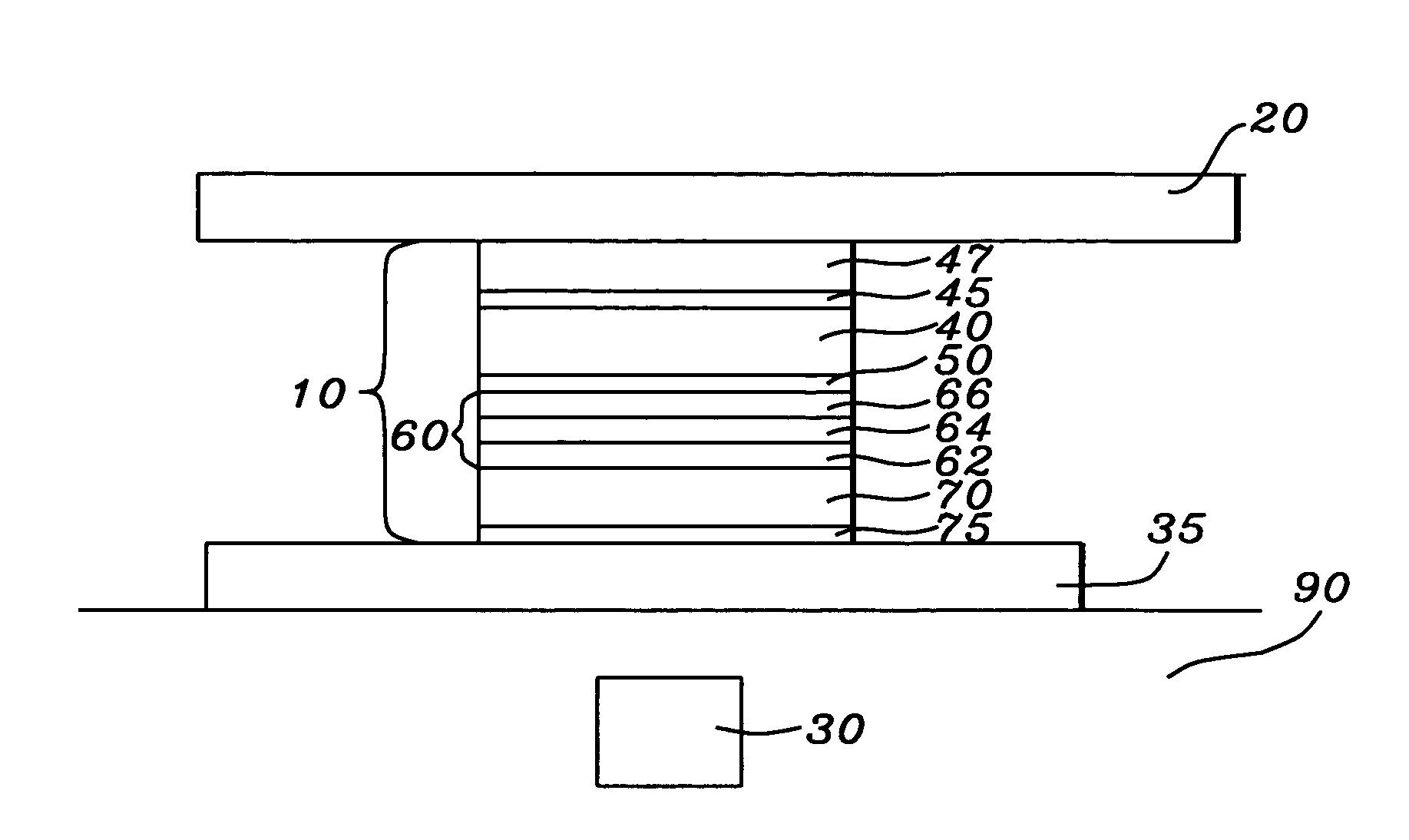
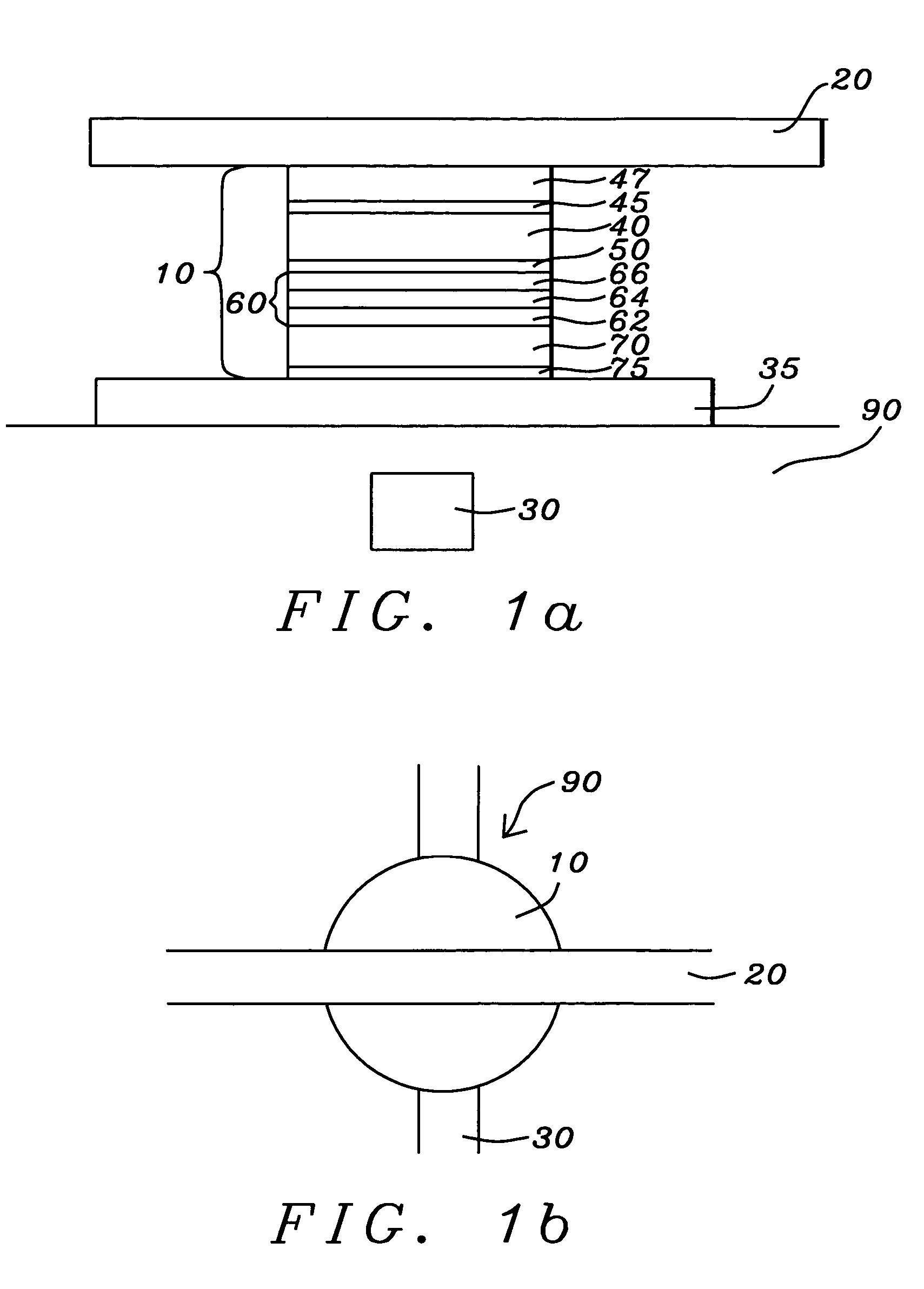
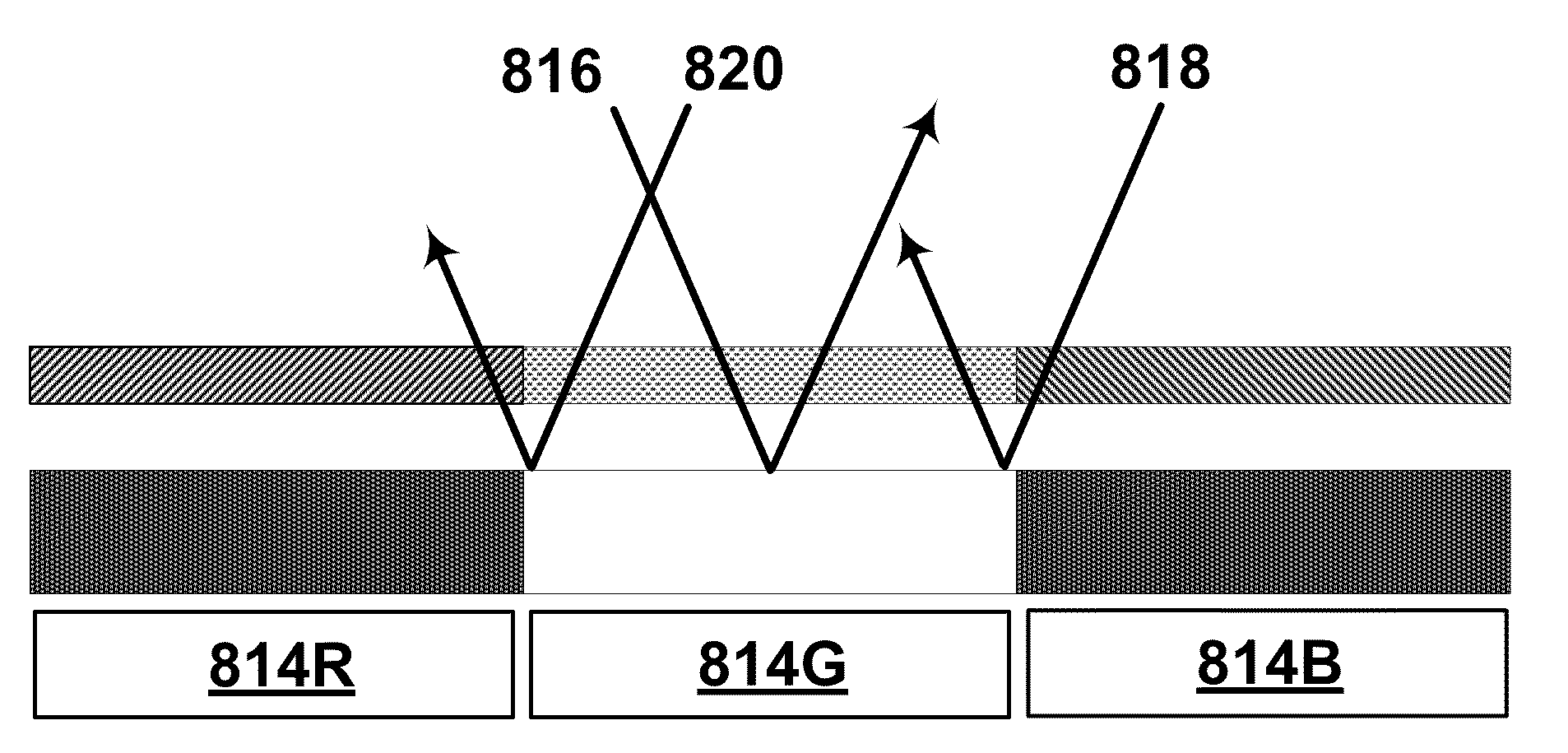
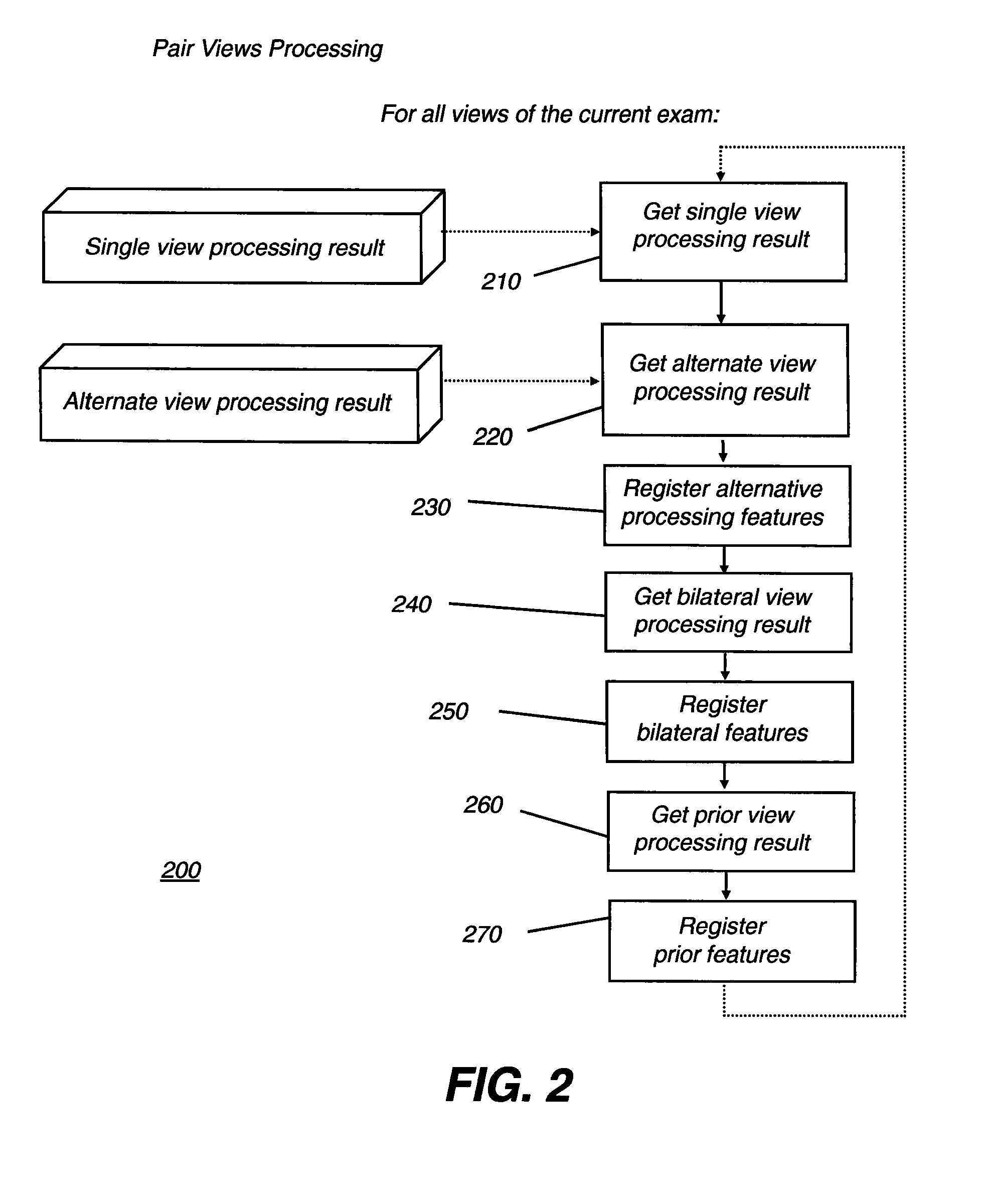
Methods for reducing edge effects in electro-optic displays
InactiveUS20050062714A1Improve scanning rateReduce edge effectsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEdge effectsDisplay device
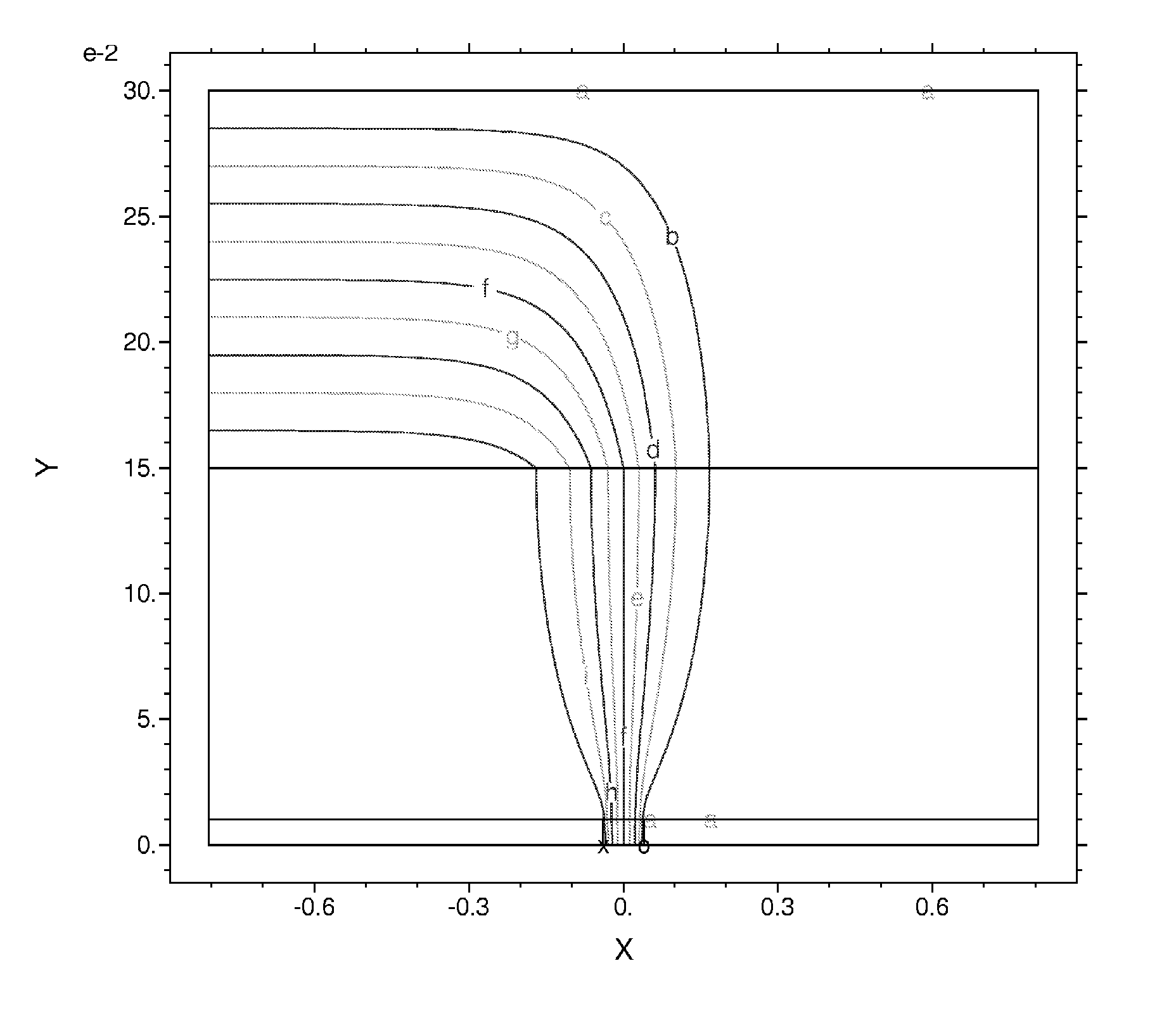
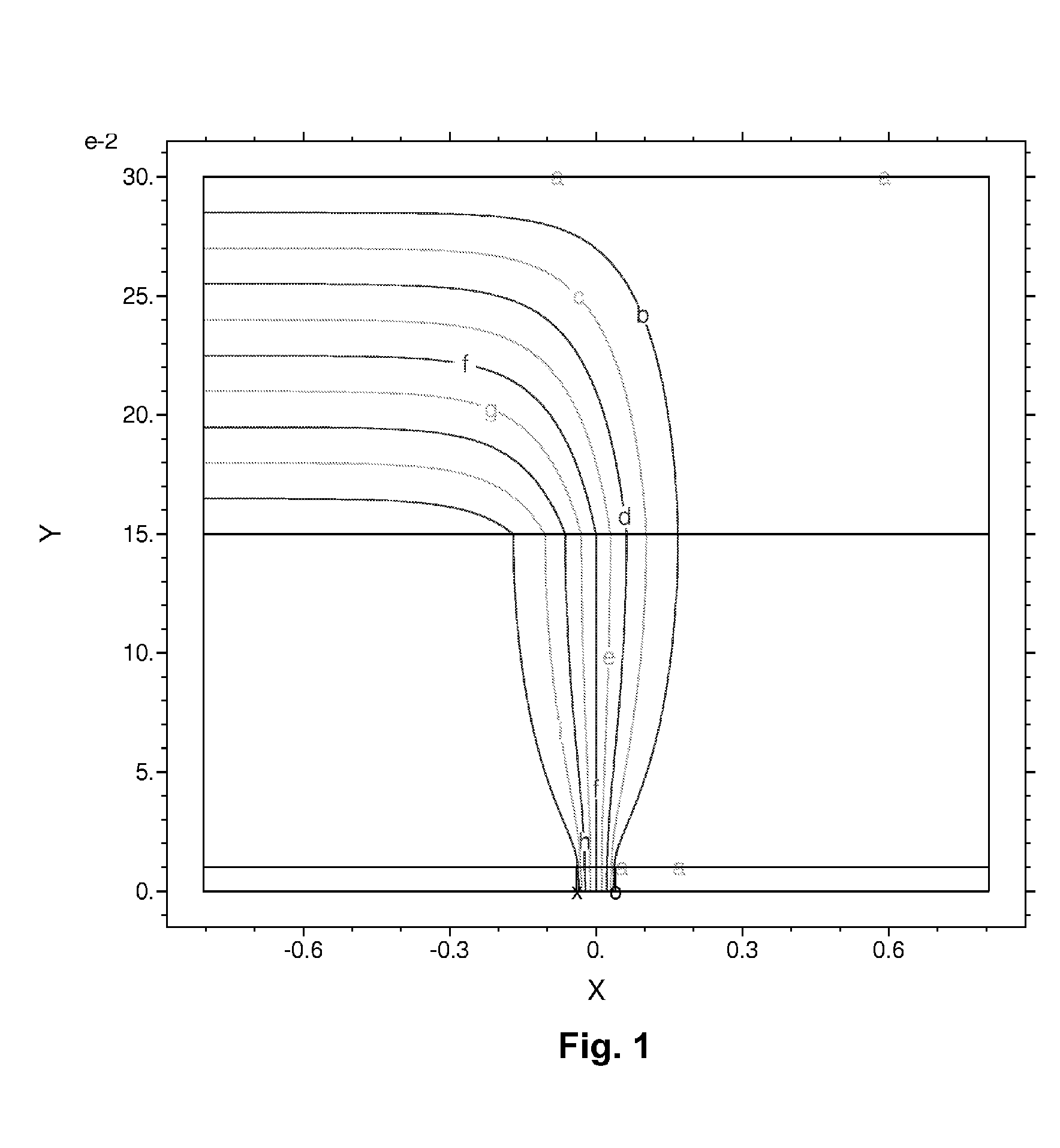
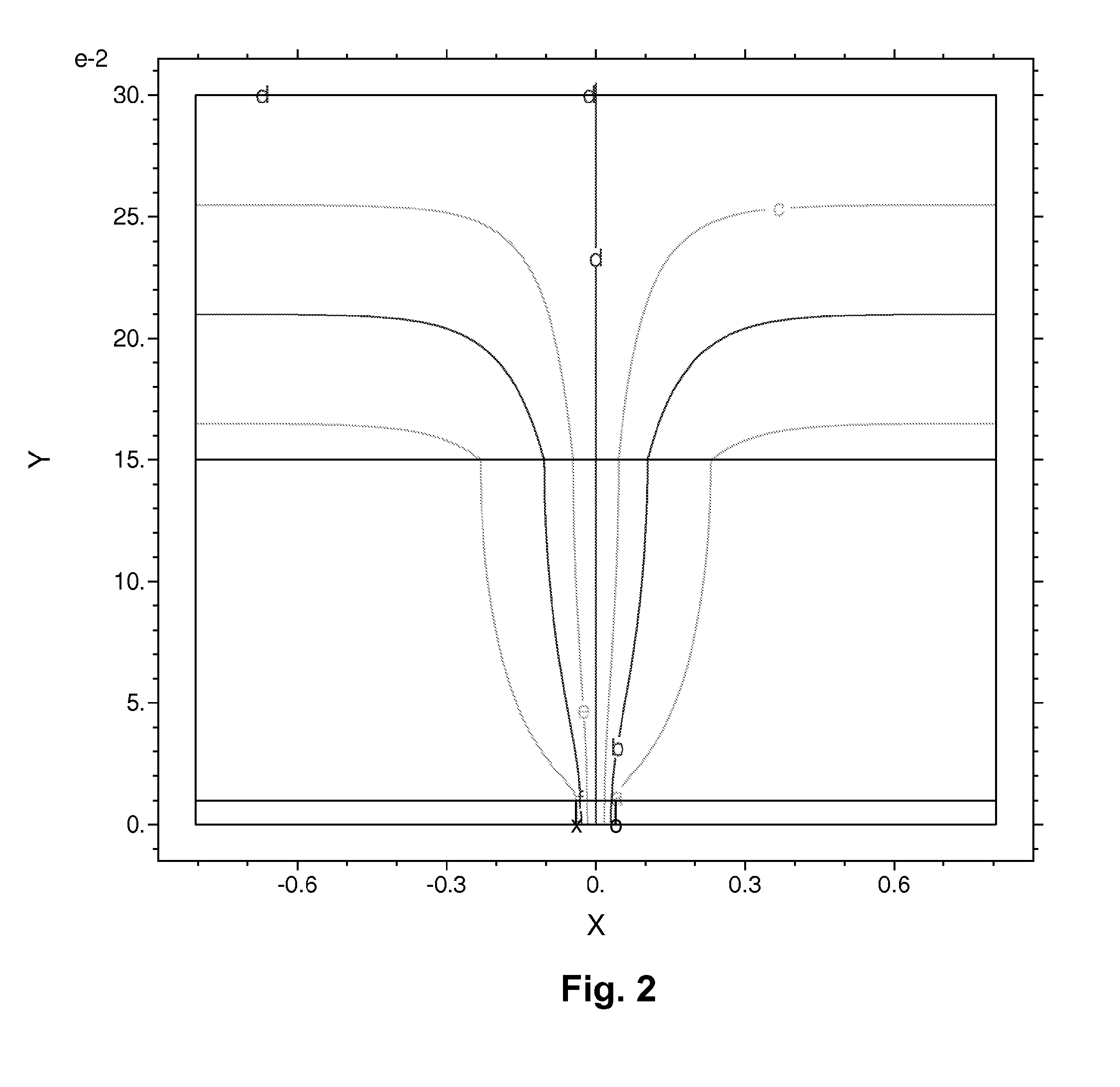
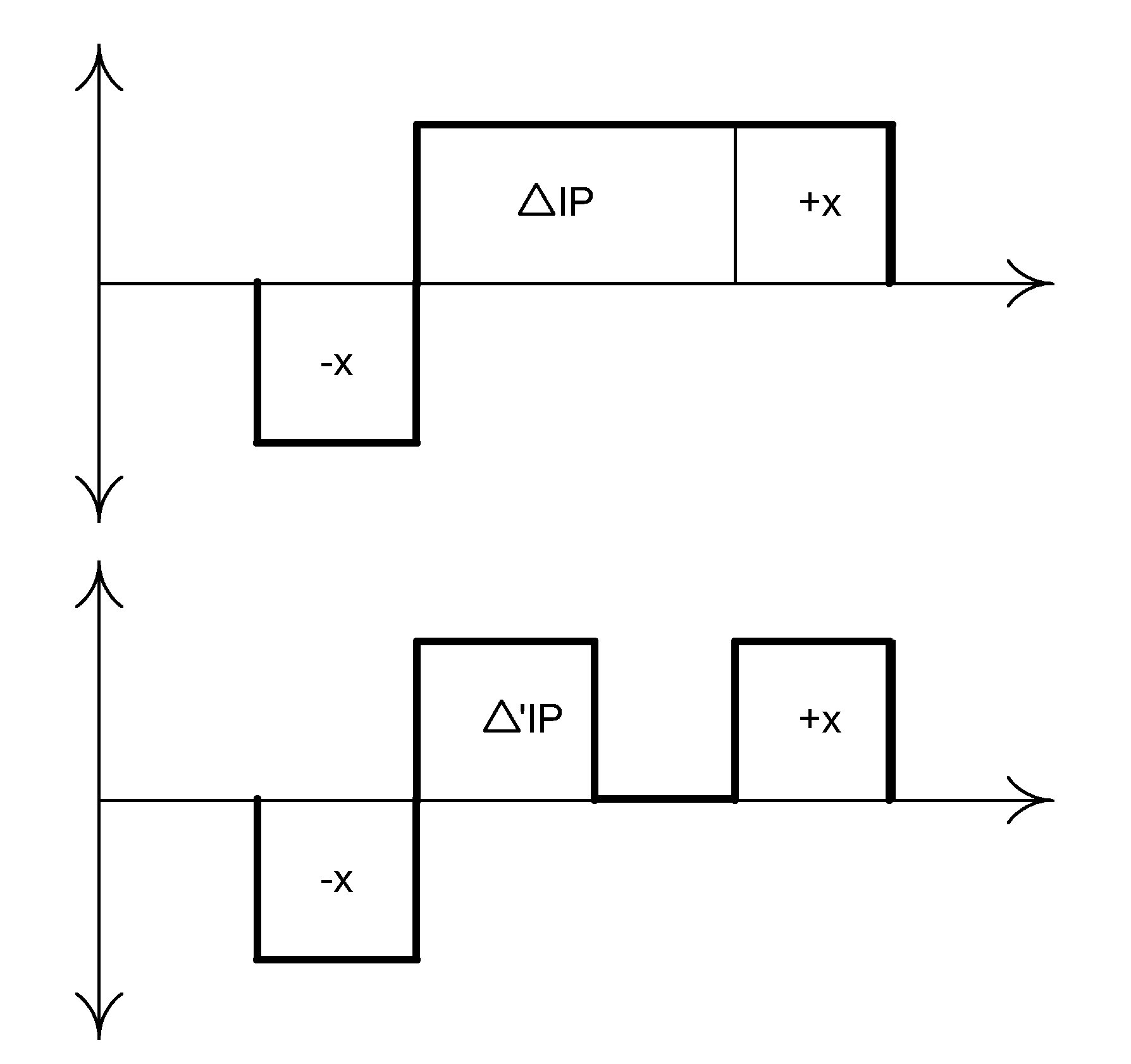
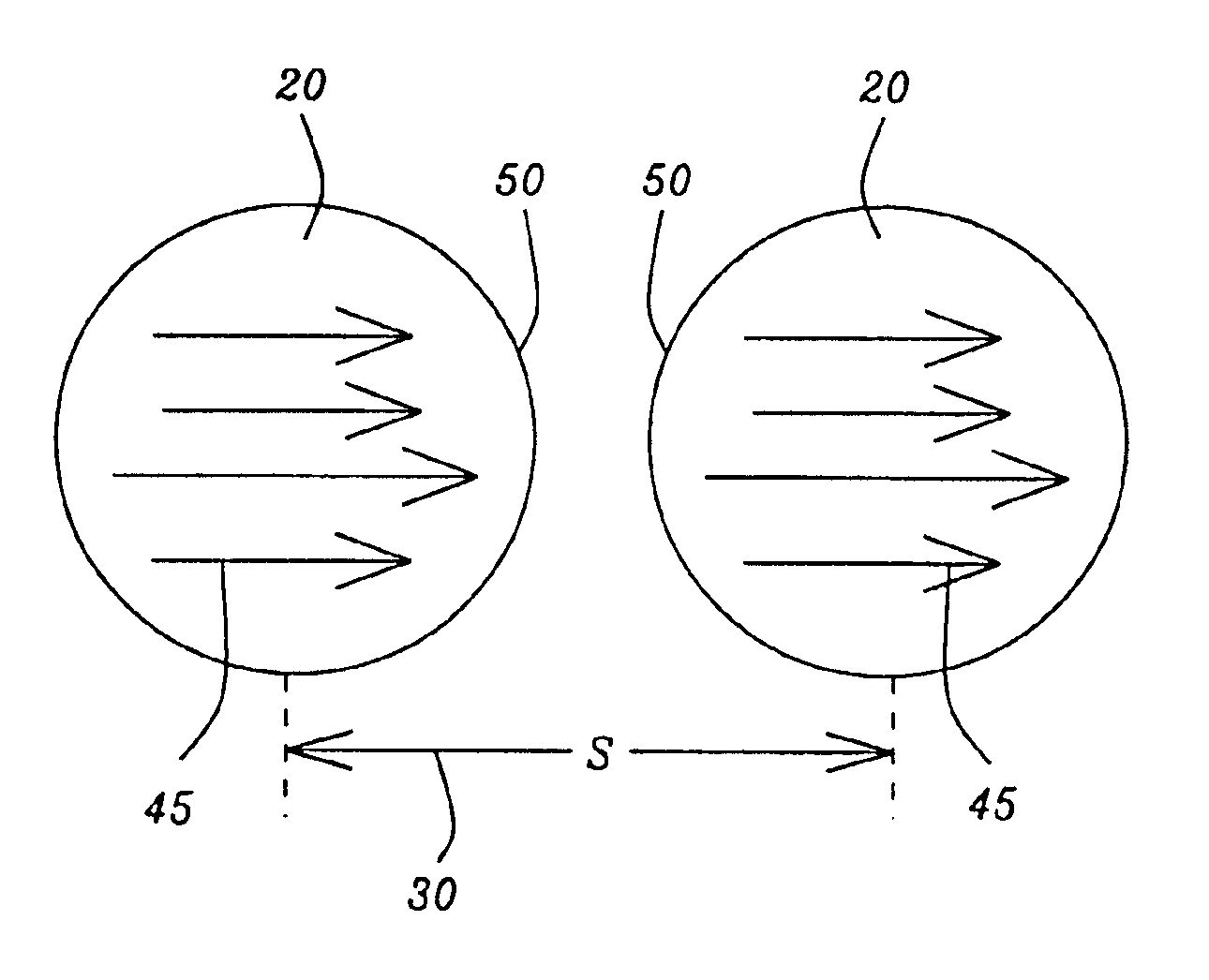
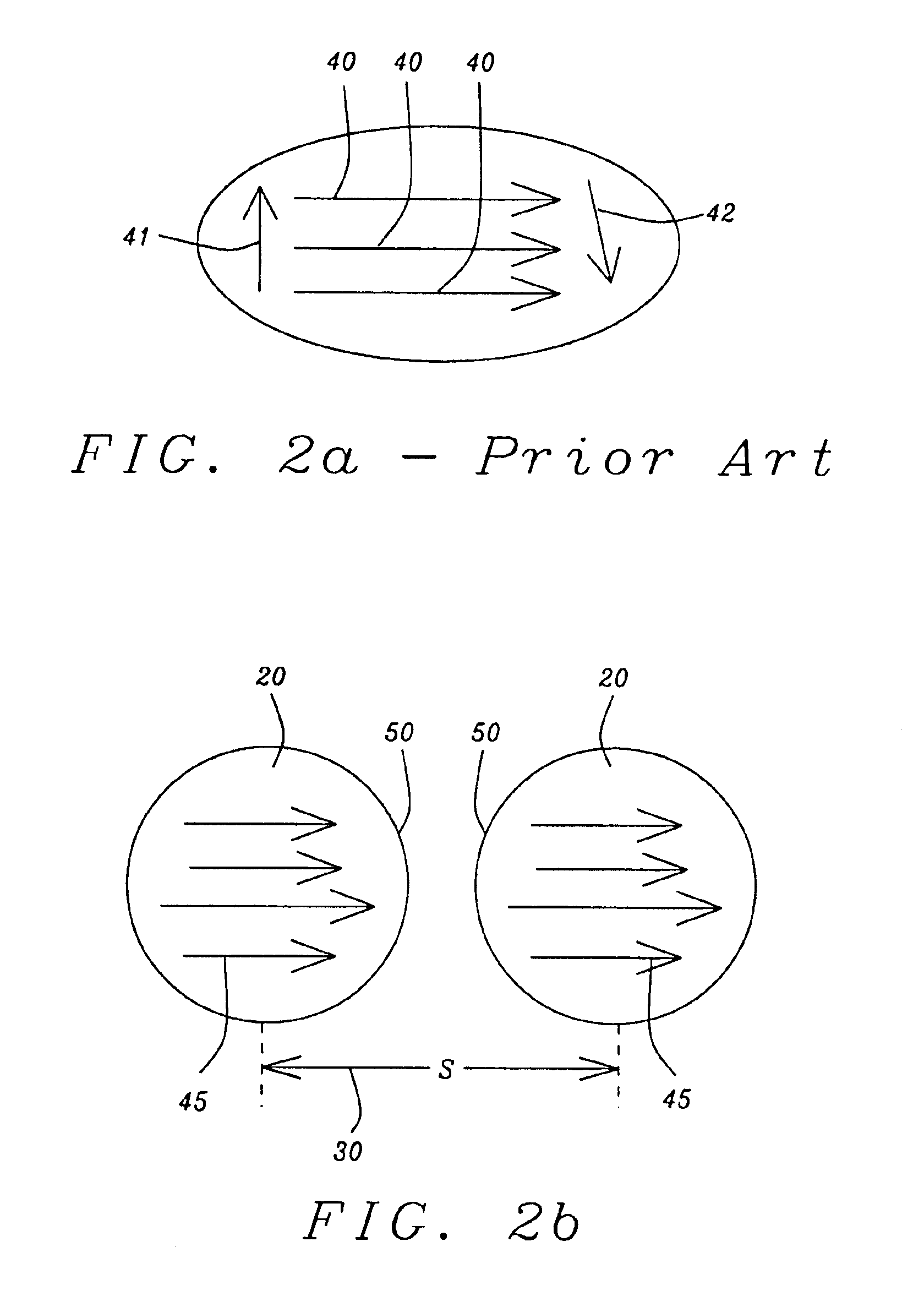
Edge effects in electro-optic displays are reduced by (a) ensuring that during rewriting of the display, the last period of non-zero voltage applied all pixels terminates at substantially the same time; and (b) scanning the display at a scan rate of at least 50 Hz.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Methods for reducing edge effects in electro-optic displays
InactiveUS7602374B2Reduce edge effectsCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEdge effectsDisplay device
Edge effects in electro-optic displays are reduced by (a) ensuring that during rewriting of the display, the last period of non-zero voltage applied all pixels terminates at substantially the same time; and (b) scanning the display at a scan rate of at least 50 Hz.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
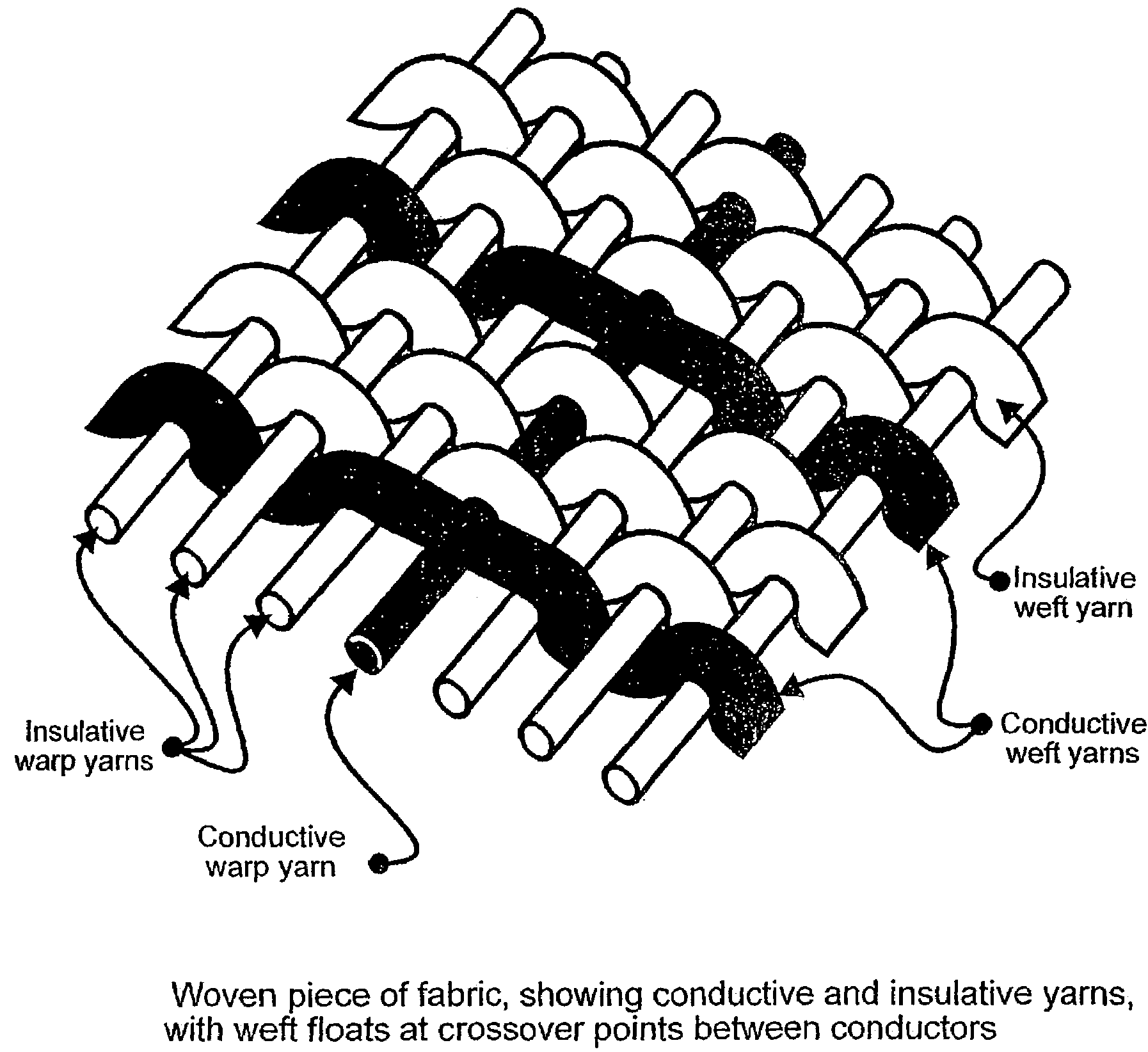
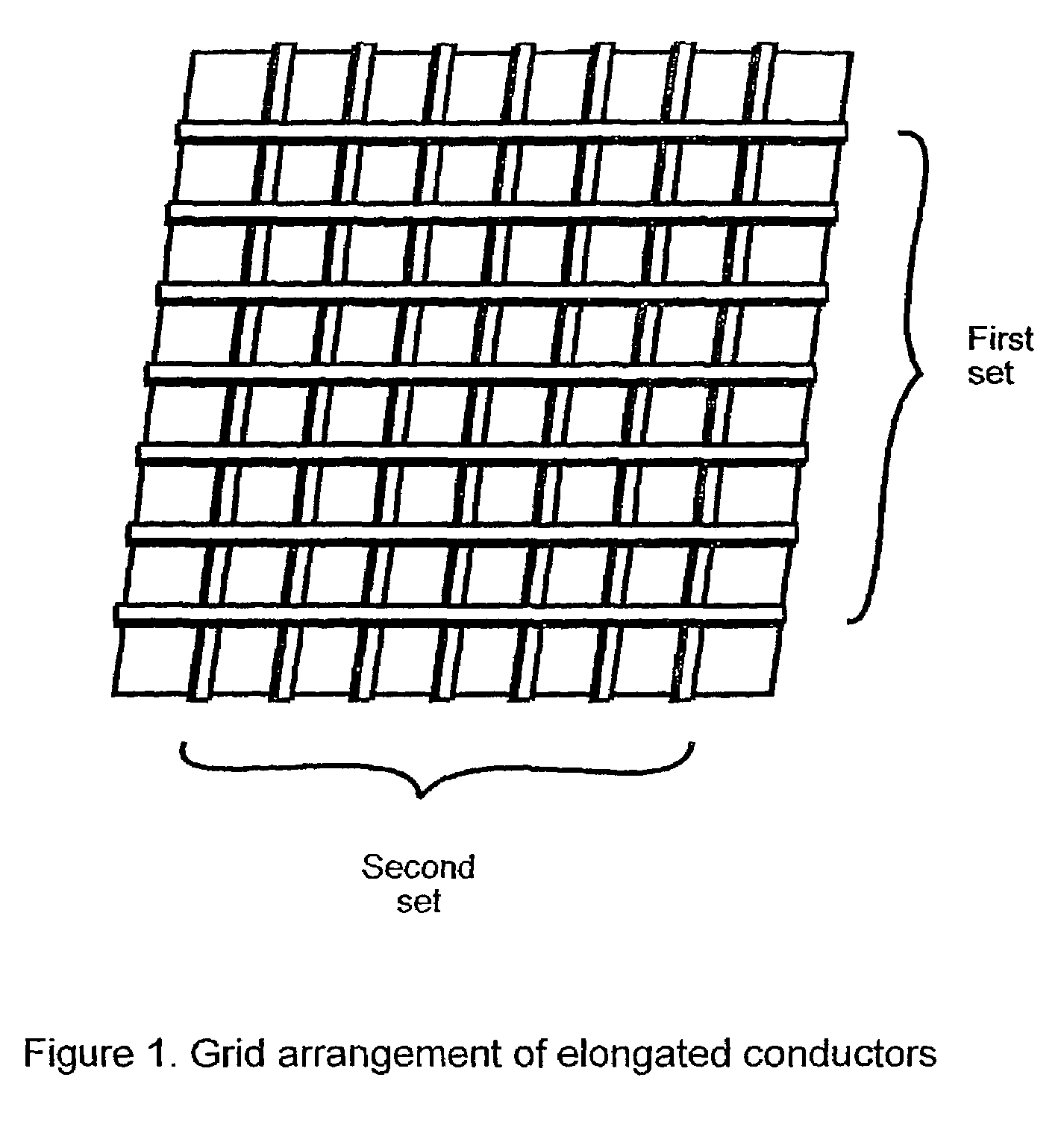
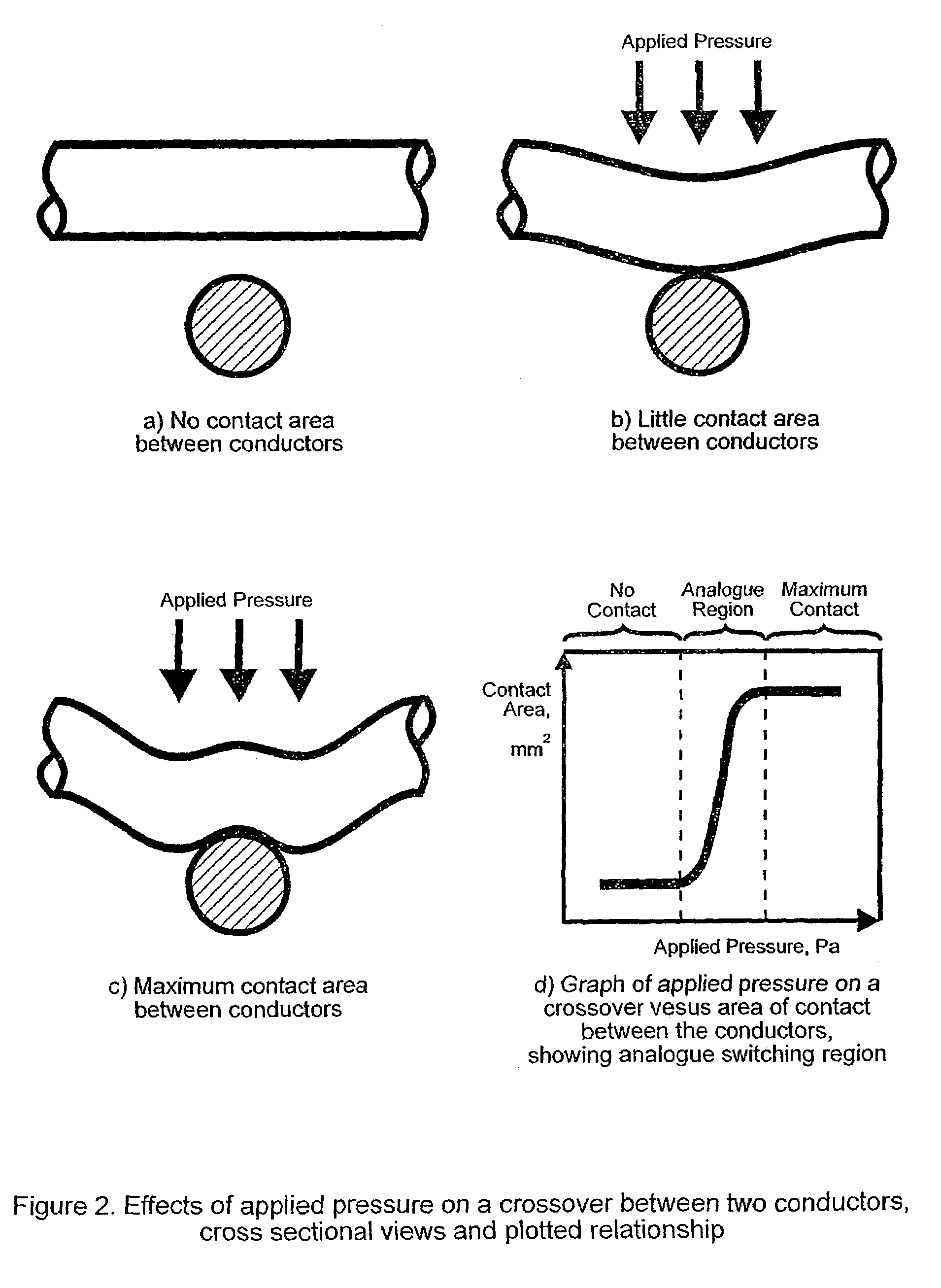
Conductive pressure sensitive textile
InactiveUS7365031B2Low production costReduce edge effectsForce measurementInsulated cablesElectrical conductorEngineering
A fabric including within its construction a first elongated electrical conductor crossed by a second elongated electrical conductor, the conductors being normally biased apart at a crossover point of said fibres with an air gap between them, whereby application of pressure in a direction substantially normal to a plane of the fabric causes the conductors to make contact. The fabric may be woven, knitted, non-woven or plaited. The fabric can be used as a pressure sensor, switch or other sensor.
Owner:INTELLIGENT TEXTILES
High efficiency, inductive vibration energy harvester
InactiveUS7569952B1Reducing magnetic field fringing effectHigh materialMagnetsMechanical energy handlingHigh fluxThin layer
An inductive energy harvester comprises a permanent magnet magnetic field source attached by a pair of compact spiral disk springs to an induction coil. The springs position the magnet so that the induction coil surrounds one end of the magnet where the flux density is greatest. In addition, the magnetic flux emerging from that end of the magnet is enhanced by a disk of magnetic material having high permeability and high flux density. In another embodiment, the magnetic field source comprises two dipole magnets arranged in opposing flux relationship with a thin layer of high flux density, high magnetic permeability material located in a gap between the magnets.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
Electro-optic displays, and processes for their production
ActiveUS8902153B2Reduce edge effectsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDisplay deviceComputer science
A color display has continuous areas of a single color covering a plurality of sub-pixel electrodes. Each sub-pixel of a given color has sub-pixels of the same given color disposed along at least two of its adjacent edges. Each area of a single color may cover a 2×2 array of sub-pixel electrodes. The colors used may be red / green / blue / white (RGBW), red / green / blue / yellow (RGBY), or orange / lime / purple / white.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Process and system for laser crystallization processing of film regions on a substrate to minimize edge areas, and a structure of such film regions
InactiveUS20060030164A1Increase speedSmall sizeTransistorLaser detailsLaser crystallizationCrystallization
A process and system for processing a thin film sample are provided. In particular, a beam generator can be controlled to emit at least one beam pulse. The beam pulse is then masked to produce at least one masked beam pulse, which is used to irradiate at least one portion of the thin film sample. With the at least one masked beam pulse, the portion of the film sample is irradiated with sufficient intensity for such portion to later crystallize. This portion of the film sample is allowed to crystallize so as to be composed of a first area and a second area. Upon the crystallization thereof, the first area includes a first set of grains, and the second area includes a second set of grains whose at least one characteristic is different from at least one characteristic of the second set of grains. The first area surrounds the second area, and is configured to allow an active region of a thin-film transistor (“TFT”) to be provided at a distance therefrom.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
System and method for varying wafer surface temperature via wafer-carrier temperature offset
InactiveUS20070186853A1Reducing mass-transport edge effectReduce edge effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical vapor depositionTreatment system
A system and method for evenly heating a substrate placed in a wafer carrier used in wafer treatment systems such as chemical vapor deposition reactors, wherein a first pattern of wafer compartments is provided on the top of the wafer carrier, such as one or more rings of wafer carriers, and a second pattern of inlaid material dissimilar to the wafer carrier material is inlaid on the bottom of the wafer carrier, and the second pattern of inlaid material is substantially the opposite of the first pattern of wafer compartments, such that there are at least as many material interfaces in intermediate regions without wafer compartments as there are in wafer carrying regions with wafers and wafer compartments.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
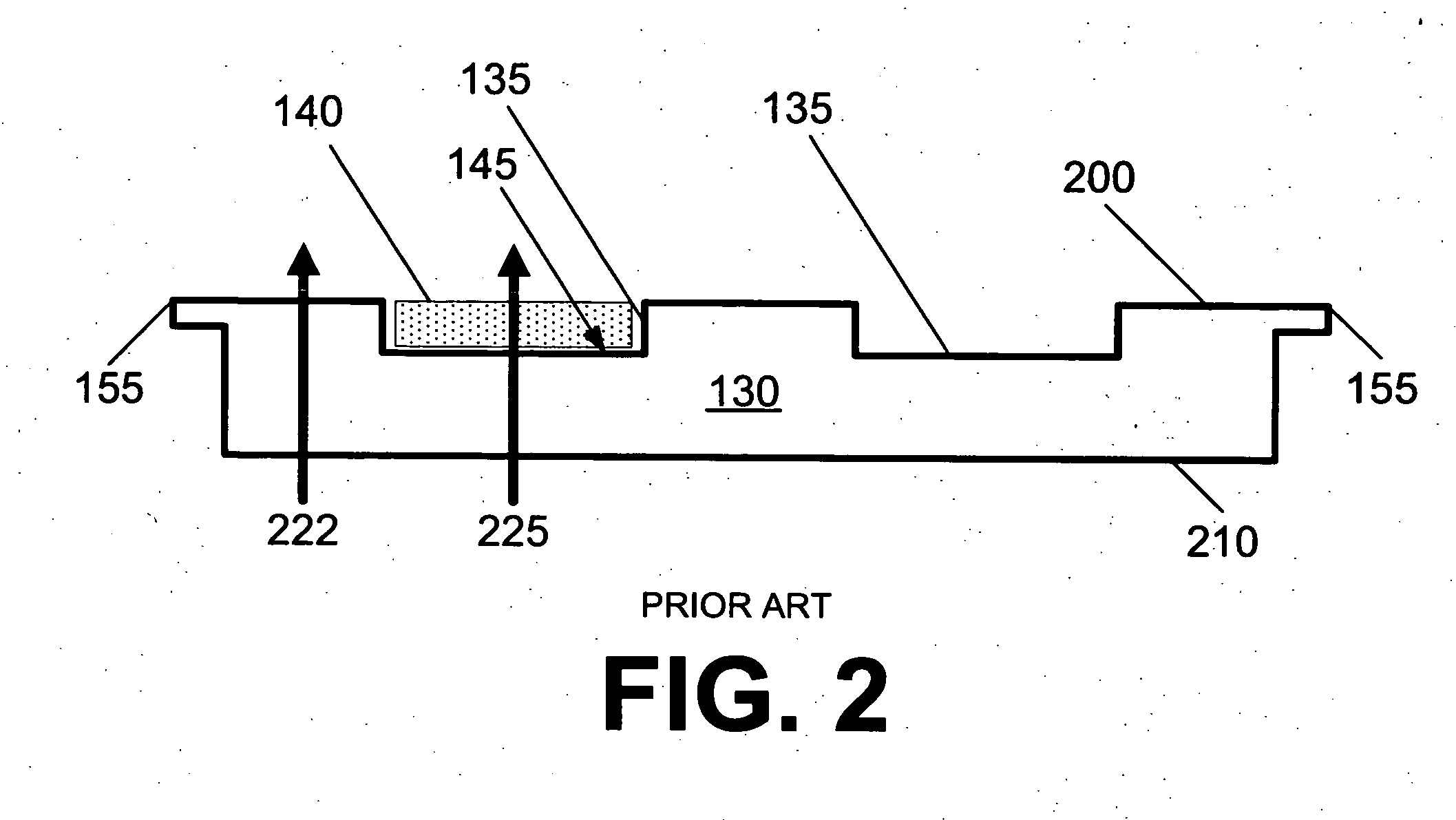
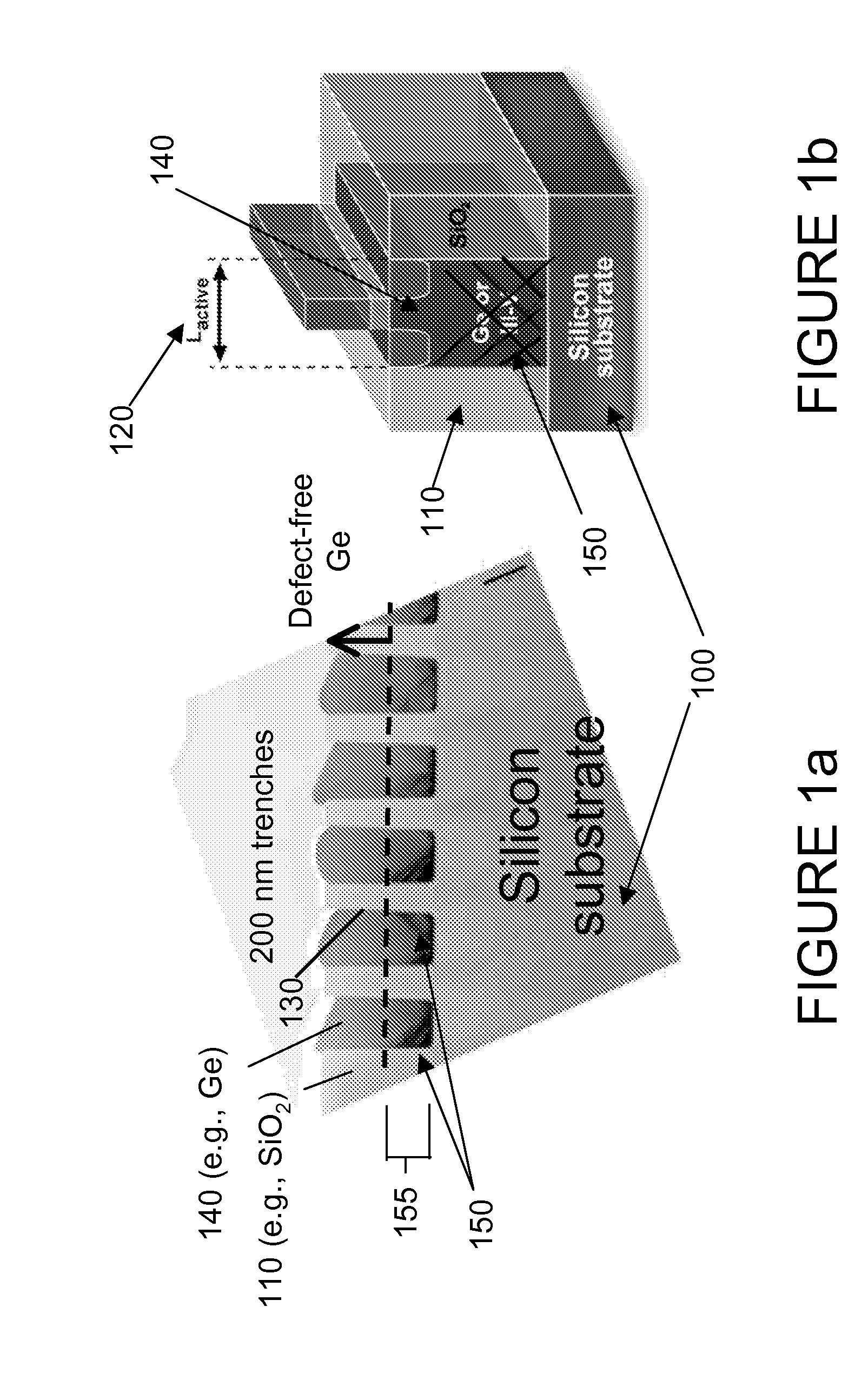
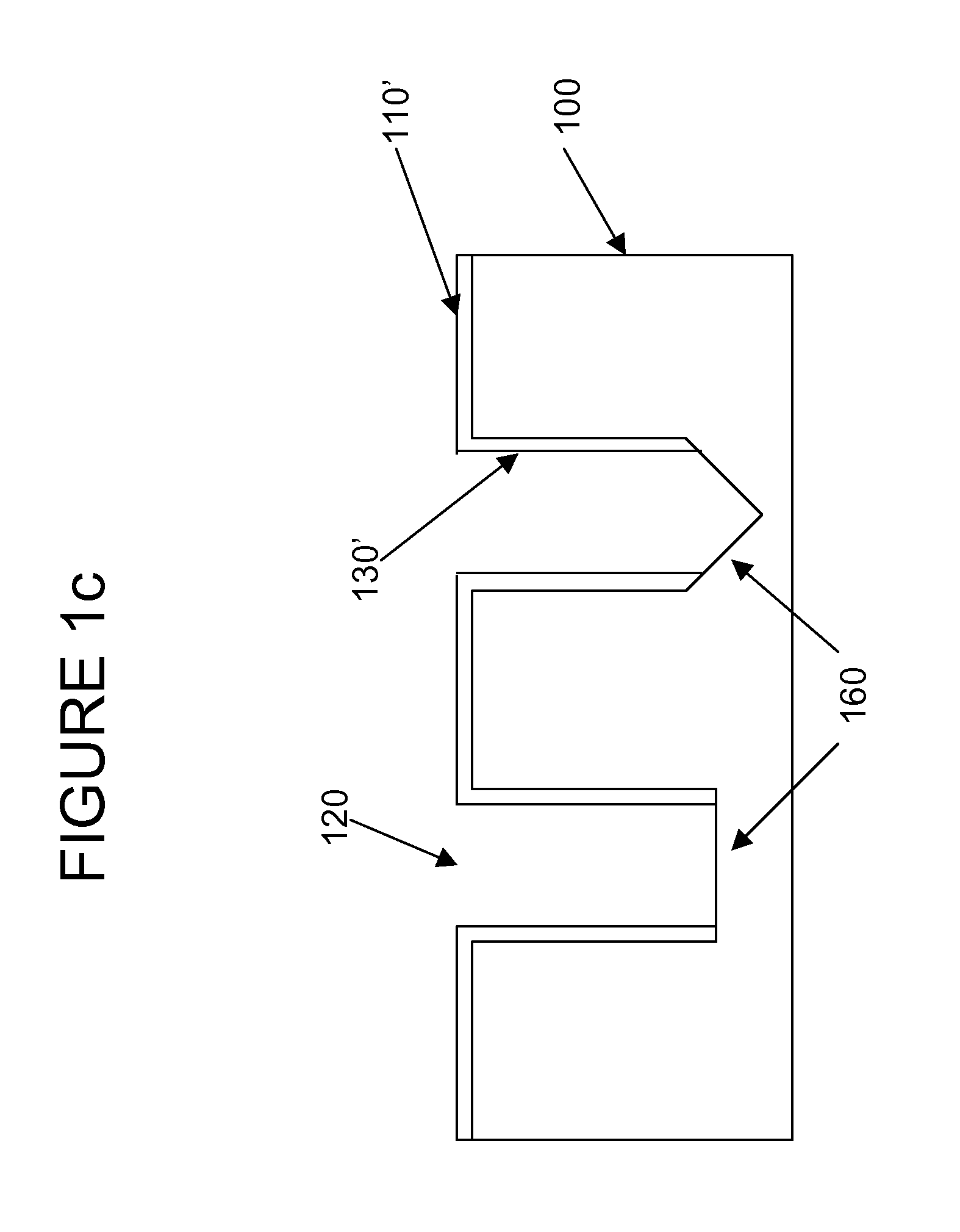
Reduction of edge effects from aspect ratio trapping
ActiveUS8274097B2Reduce edge effectsReduce disadvantagesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEdge effectsTrapping
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetic tunneling junction film structure with process determined in-plane magnetic anisotropy
ActiveUS7105372B2Data efficientSmall sizeNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeMagnetic anisotropy
A method of forming an MTJ memory cell and / or an array of such cells is provided wherein each such cell has a small circular horizontal cross-section of 1.0 microns or less in diameter and wherein the ferromagnetic free layer of each such cell has a magnetic anisotropy produced by a magnetic coupling with a thin antiferromagnetic layer that is formed on the free layer. The MTJ memory cell so provided is far less sensitive to shape irregularities and edge defects than cells of the prior art.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
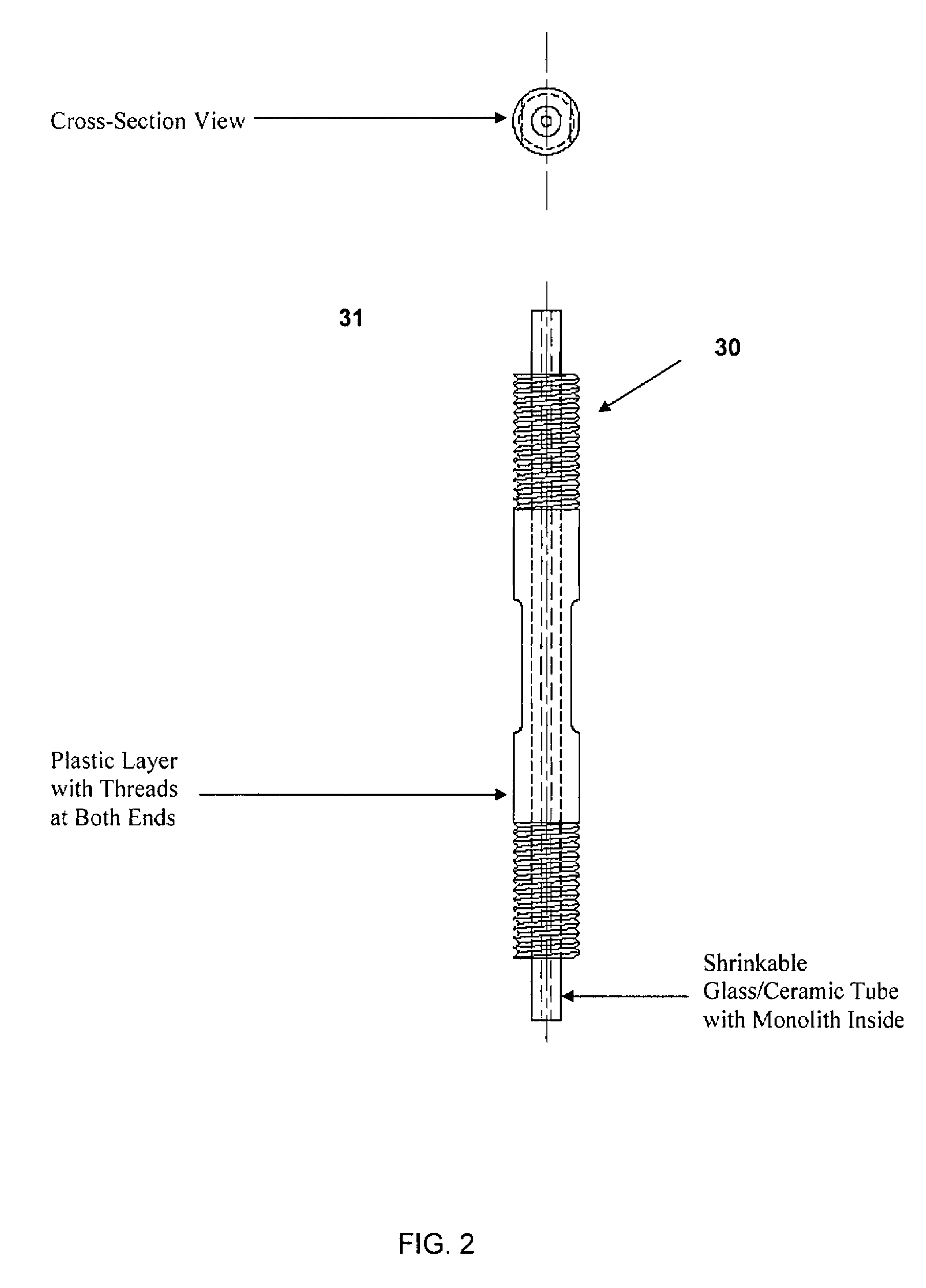
Methods and devices using a shrinkable support for porous monolithic materials
ActiveUS7651762B2Smooth inner surfacePromote resultsIon-exchange process apparatusPhysical/chemical process catalystsPorous substrateFiltration
Articles of manufacture and devices and methods of forming and using the same are provided, wherein the article comprises a porous inorganic substrate contained in or bounded by a support made from an inorganic material are provided, wherein said porous substrate and support are heated to a temperature effective to shrink the support onto the porous substrate such that liquid tight contact is formed between the porous substrate and the support. In a preferred aspect, the porous inorganic substrate has a porosity of at least 5%, and is a porous monolith formed using a sol-gel method. The articles thus formed provide a confined fluid flow through the porous substrate, providing superior performance in separations, catalysis, filtration, and the like.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
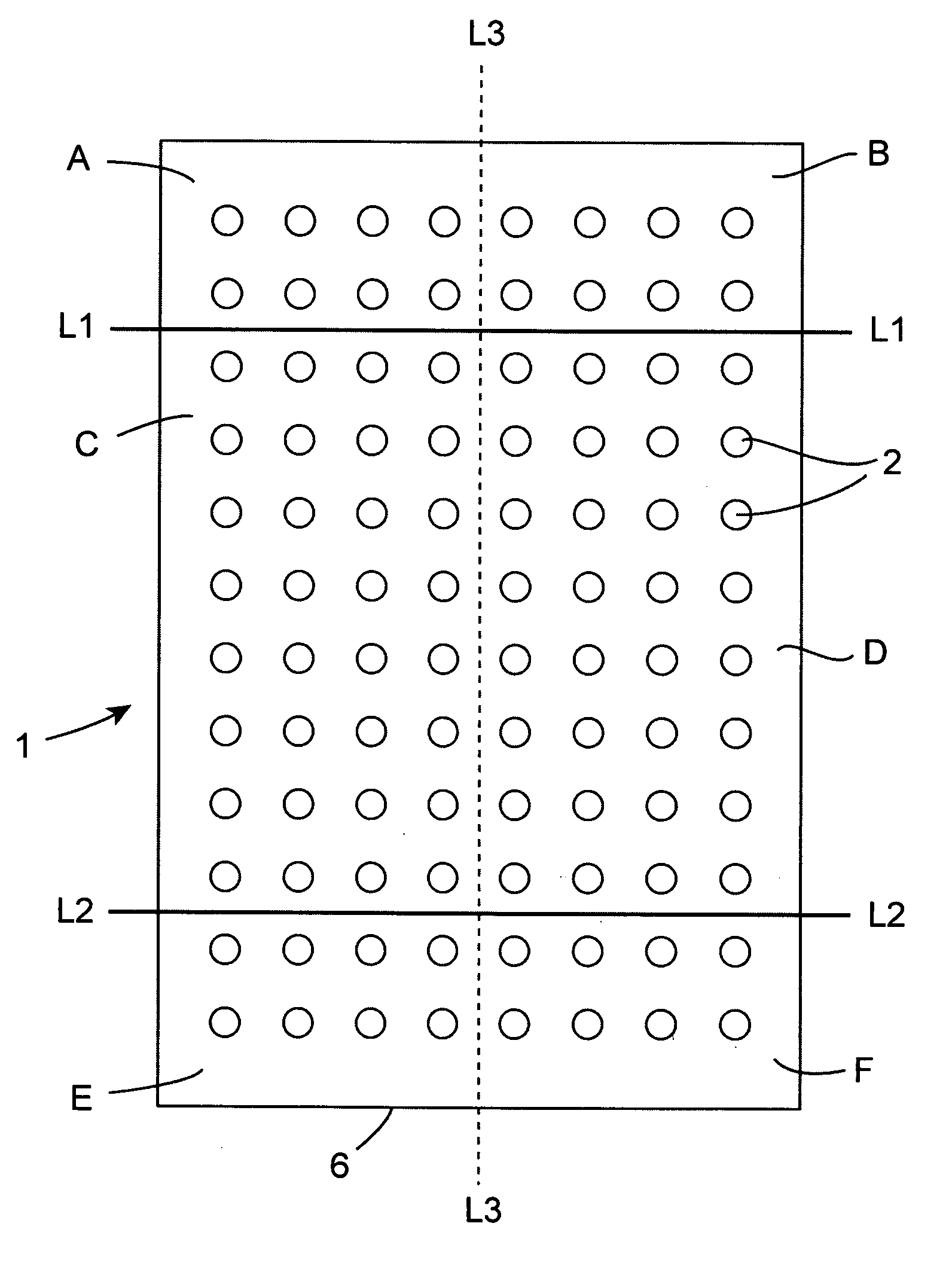
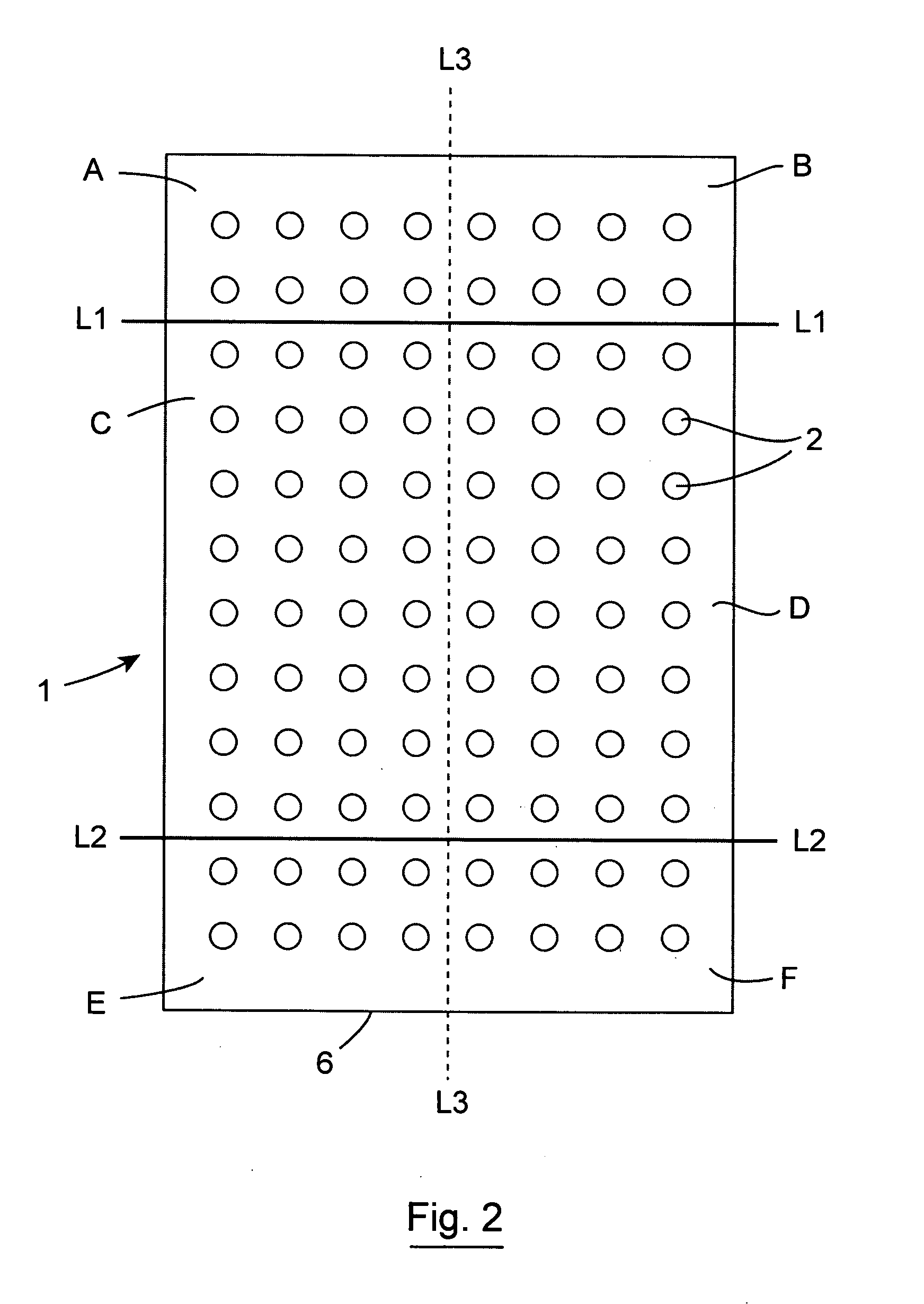
Multi-well device
InactiveUS20110172128A1Fluctuating levelReduce edge effectsLaboratory glasswaresLibraries apparatusBiomedical engineering
A device comprising a plurality of sample wells wherein the device has a plurality of compartments, each compartment surrounding at least one well. The compartments are defined by compartment wall means. The compartment wall means may be associated with at least one well or the compartment wall means may be associated with a group of wells. The compartment may house an environmental buffering system.
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
Electro-optic displays, and processes for their production
ActiveUS20110310461A1Reduce edge effectsNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDisplay deviceComputer science
A color display has continuous areas of a single color covering a plurality of sub-pixel electrodes. Each sub-pixel of a given color has sub-pixels of the same given color disposed along at least two of its adjacent edges. Each area of a single color may cover a 2×2 array of sub-pixel electrodes. The colors used may be red / green / blue / white (RGBW), red / green / blue / yellow (RGBY), or orange / lime / purple / white
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Wafer carrier with pressurized membrane and retaining ring actuator
ActiveUS20050215182A1Reduce edge effectReduce edge effectsPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesChemical-mechanical planarizationRetaining ring
A wafer carrier for controlling downward force and edge effect during chemical mechanical planarization. A retaining ring actuator is disposed within the retaining ring to control the height of the retaining ring relative to the bottom surface of the wafer carrier. An inflatable membrane is disposed across the bottom surface of the wafer carrier such that pressure in the bladder is independently regulated to control the downward force acting on the wafer during CMP. In addition, an edge control bladder may also be disposed within the carrier such that if the pressure in the bladder is also regulated, the amount of force on the edge of the wafer changes. By regulating retaining ring actuator pressure, inflatable membrane pressure, and edge control bladder pressure, non-uniformities in the wafer surface and edge effect may be addressed during CMP.
Owner:REVASUM INC +1
Magnetic tunneling junction film structure with process determined in-plane magnetic anisotropy
ActiveUS20050157544A1Data efficientSmall sizeNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeMagnetic anisotropy
A method of forming an MTJ memory cell and / or an array of such cells is provided wherein each such cell has a small circular horizontal cross-section of 1.0 microns or less in diameter and wherein the ferromagnetic free layer of each such cell has a magnetic anisotropy produced by a magnetic coupling with a thin antiferromagnetic layer that is formed on the free layer. The MTJ memory cell so provided is far less sensitive to shape irregularities and edge defects than cells of the prior art.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
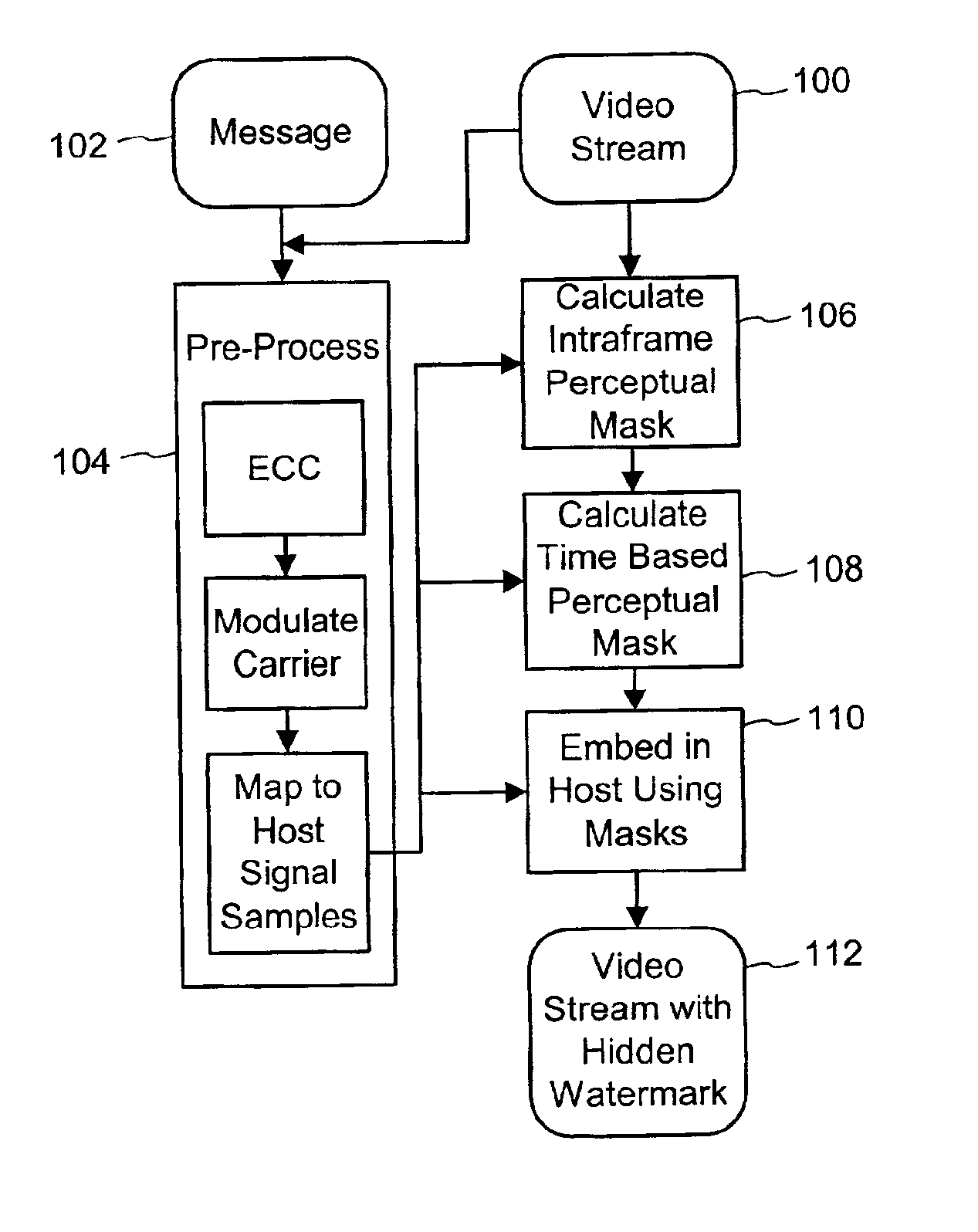
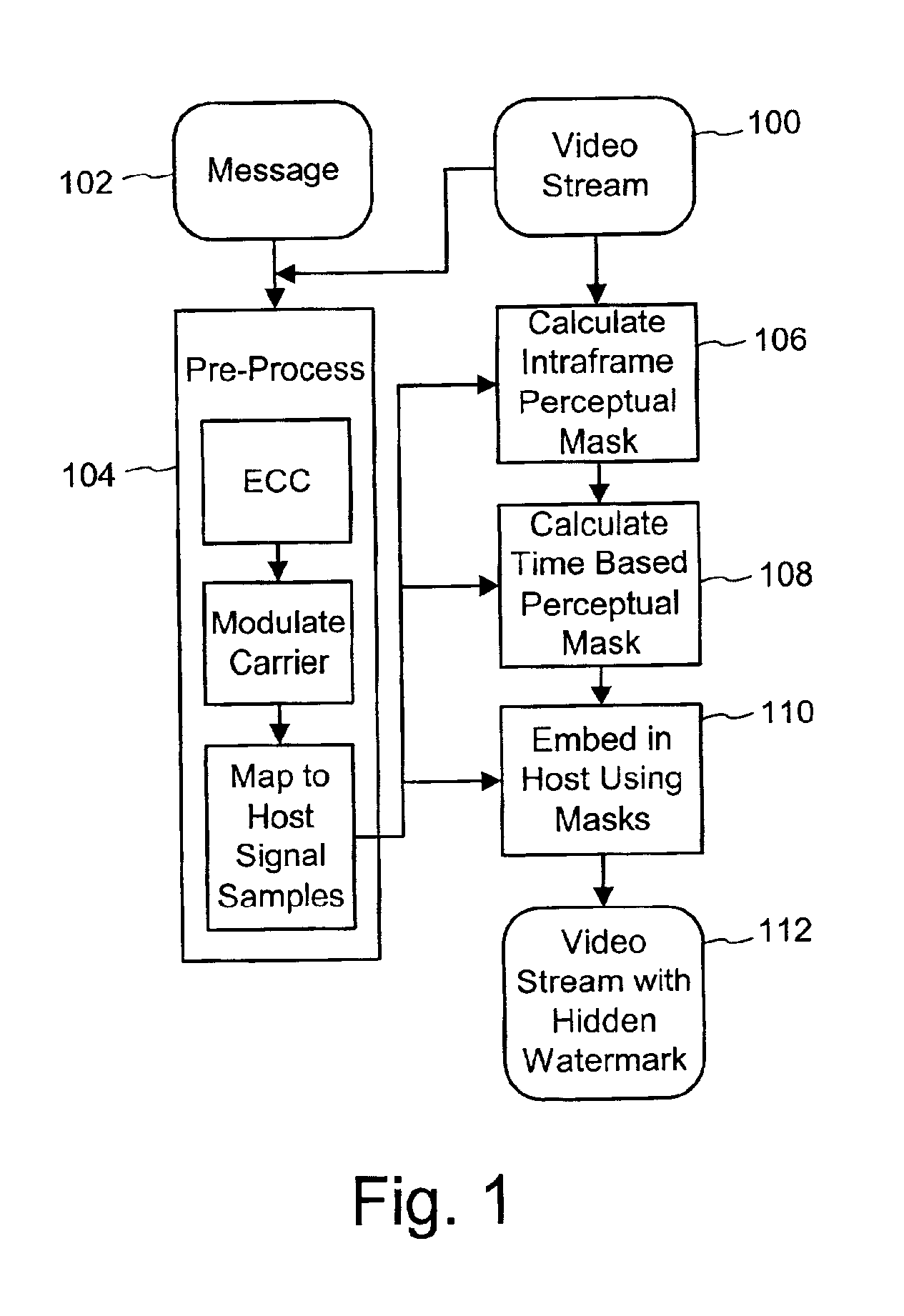
Time and object based masking for video watermarking
InactiveUS6961444B2Remove distortionReduce the valuePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningObject basedComputer science
The disclosure describes a method of embedding a digital watermark into a video signal using a time based perceptual mask such that the digital watermark is substantially imperceptible in the video signal. A digital watermark embedder computes a time based perceptual mask comprising gain values corresponding to locations within a frame. The gain value for a location in the frame is changed as a function of the change in one or more pixel values at the location over time. The embedder uses the gain values of the time based perceptual mask to control embedding of corresponding elements of a digital watermark signal such that the perceptibility of the elements of the digital watermark signal is reduced in time varying locations of the video signal.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Method and apparatus for improving film deposition uniformity on a substrate
InactiveUS20020020358A1Reduce edge effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingReaction layerSusceptor
A method and apparatus for depositing a film on a substrate. According to the present invention a prewafer reaction layer is deposited onto a susceptor placed in the reaction chamber to form a prewafer reaction layer coated susceptor prior to film deposition. A deposition gas is then fed into the reaction chamber so that it flows over the prewafer reaction layer coated susceptor and the substrate to form a film on the prewafer reaction layer coated susceptor and the substrate.
Owner:HEY H PETER W +2
Universally functional biomedical electrode
InactiveUS20020072664A1Reduce edge effectsDecrease stockHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesBiomedicineBiomedical engineering
A universally functional biomedical electrode is disclosed, where the electrode has a resistive element that reduces edge effect by a redistribution of current within the electrode and in mammalian tissue contacting the electrode. In one embodiment, the electrode has at its perimeter in one layer the resistive element that provides a cross-sectional area to reduce edge effect regardless of the type of biomedical instrumentation connected thereto. With the construction of other layers suitable for multifunctional electrode usage, this electrode can serve as a single item in inventory at health facilities.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
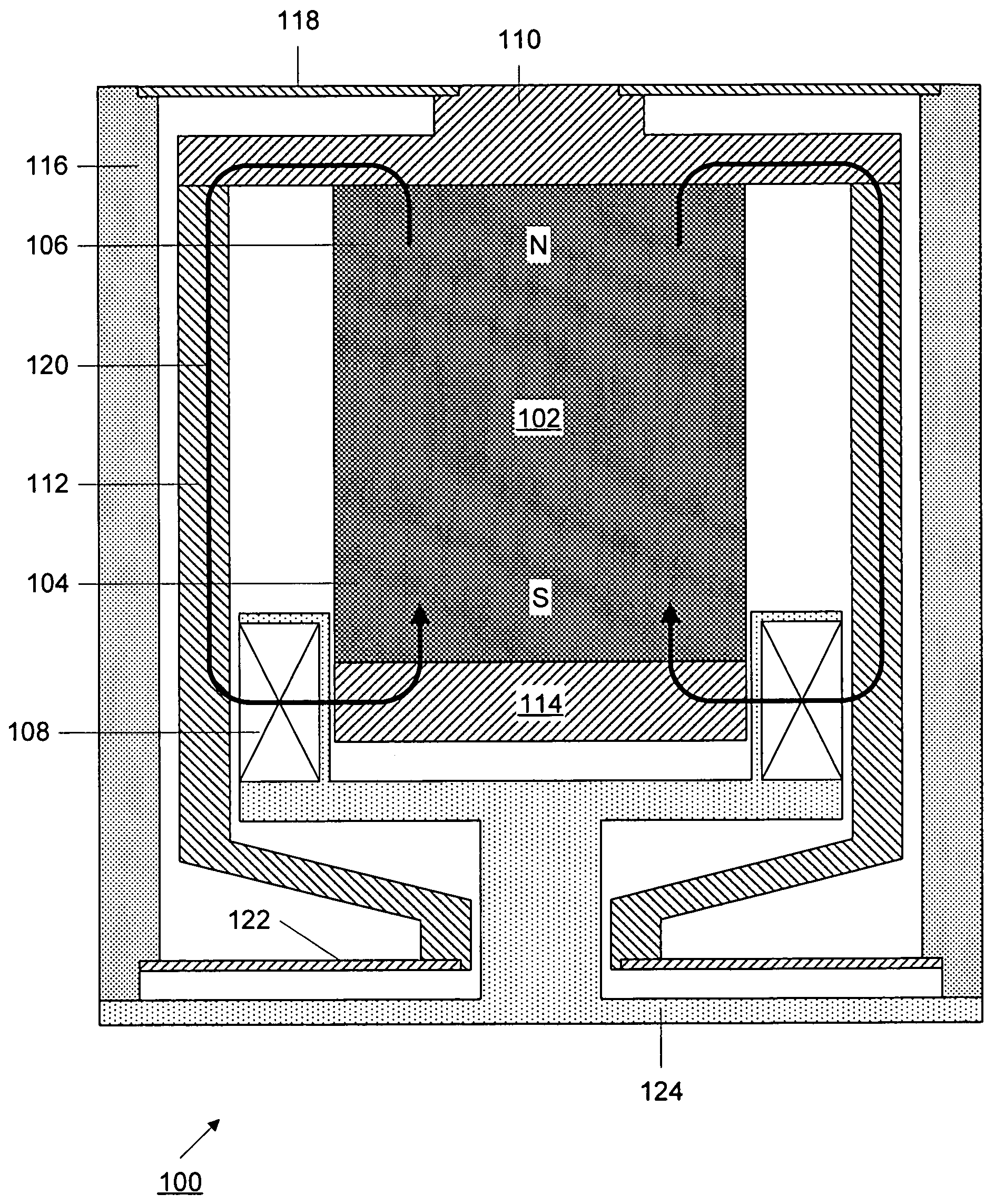
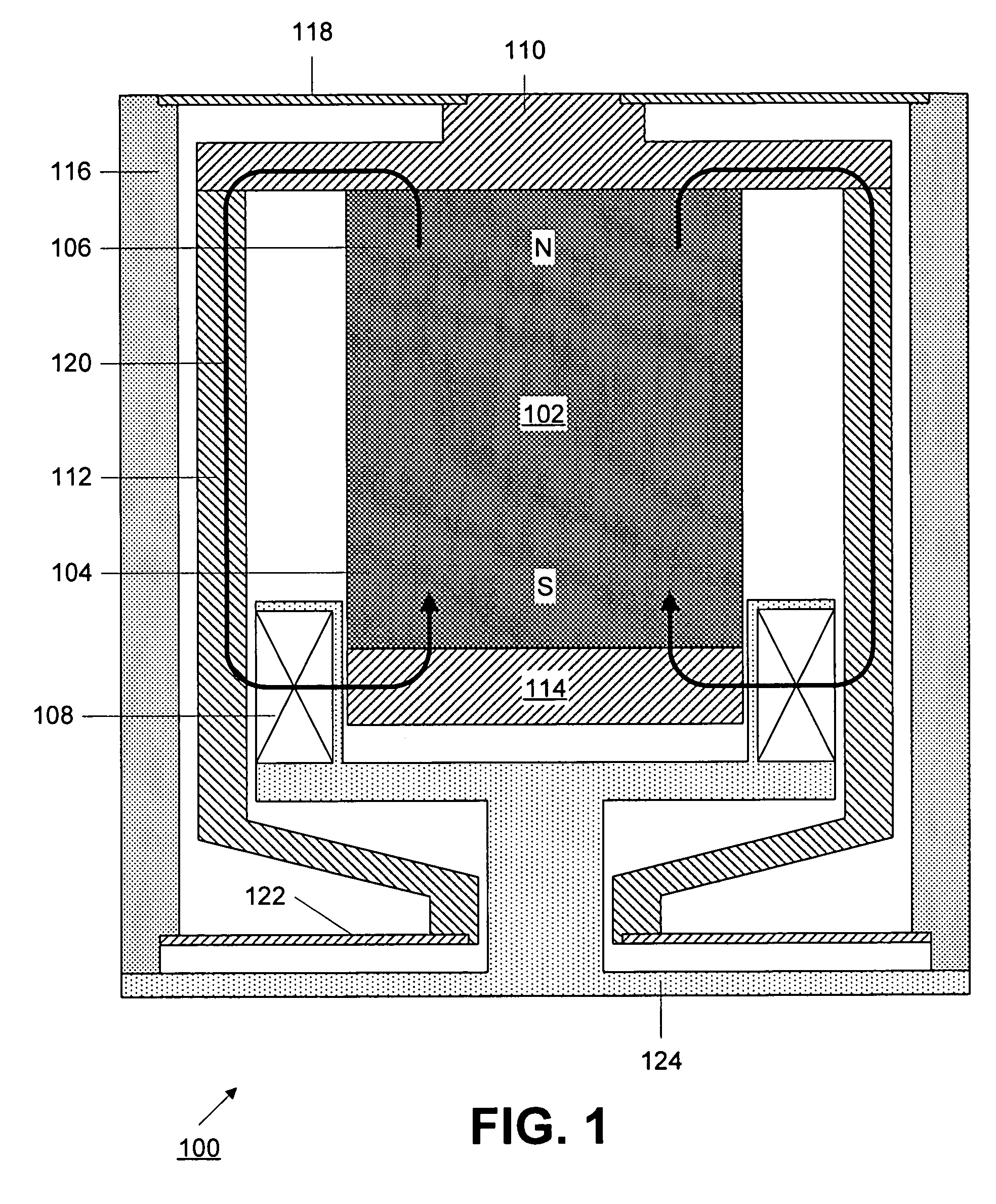
Magnetic random access memory designs with controlled magnetic switching mechanism by magnetostatic coupling
InactiveUS6943040B2Adverse effect storage and readingDisadvantageous effectNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismStatic random-access memoryCoupling
A magnetic tunneling junction (MTJ) memory cell for a magnetic random access memory (MRAM) array is formed as a chain of magnetostatically coupled segments. The segments can be circular, elliptical, lozenge shaped or shaped in other geometrical forms. Unlike the isolated cells of typical MTJ designs which exhibit curling of the magnetization at the cell ends and uncompensated pole structures, the present multi-segmented design, with the segments being magnetostatically coupled, undergoes magnetization switching at controlled nucleation sites by the fanning mode. As a result, the multi-segmented cells of the present invention are not subject to variations in switching fields due to shape irregularities and structural defects.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Method for the determination of local similitude from seismic 3d measured data
InactiveUS6988038B2Reduce edge effectsWithout deteriorating resolutionSeismic signal processingComplex mathematical operationsData setSeries data
The invention concerns a method for the determination of local similarity values for geological units in the subsurface from a seismic 3-D dataset, which consists of a multitude of traces, each of which being formed by a sequence of data points that carry amplitude values, and especially a method for the determination of local dip-dependent similarity values, in each weighted environment of an analysis point, determining the maximum similarity value, which is assigned, together with the corresponding dip angle and dip azimuth, to the respective analysis point.
Owner:TRAPPE HENNING
Near-field plume mass-spectroscopic diagnostic E*B probe based on Faraday cup
InactiveCN104730066AGuaranteed OrthogonalityGuaranteed collimationAnalysis by thermal excitationMass spectrometryDrift tube
The invention discloses a near-field plume mass-spectroscopic diagnostic E*B probe based on the Faraday cup and belongs to the technical field of plasma mass-spectroscopic diagnosis. The probe mainly applied to measuring near-field plumes of an ion thruster and of a Hall thruster comprises a central frame, ferrite permanent magnets, a flat electrode plate, an electrode plate holder, a collimator tube, a drift tube, a Faraday cup, six carbon steel shells and an anti-sputtering heat-insulating layer. According to the connectional relation, the central frame is used as a core part, the ferrite permanent magnets are distributed on upper and lower surfaces of the central frame, the electrode plate is fixed in the central frame, and an orthogonal electromagnetic field area is formed. The six carbon steel shells are used for packaging, and the front ends of the shells are coated with an anti-sputtering heat-insulating layer. The collimator tube of stainless steel and the drift tube are fitly fixed to the centers of two ends of the central frame through shaft holes. Ions different in valence are screened by adjusting voltage among the electrode plates, univalent and bivalent ion currents are acquired with the Faraday cup of aluminum, and the ratio of near-field plum bivalent ions is acquired by analytical computing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
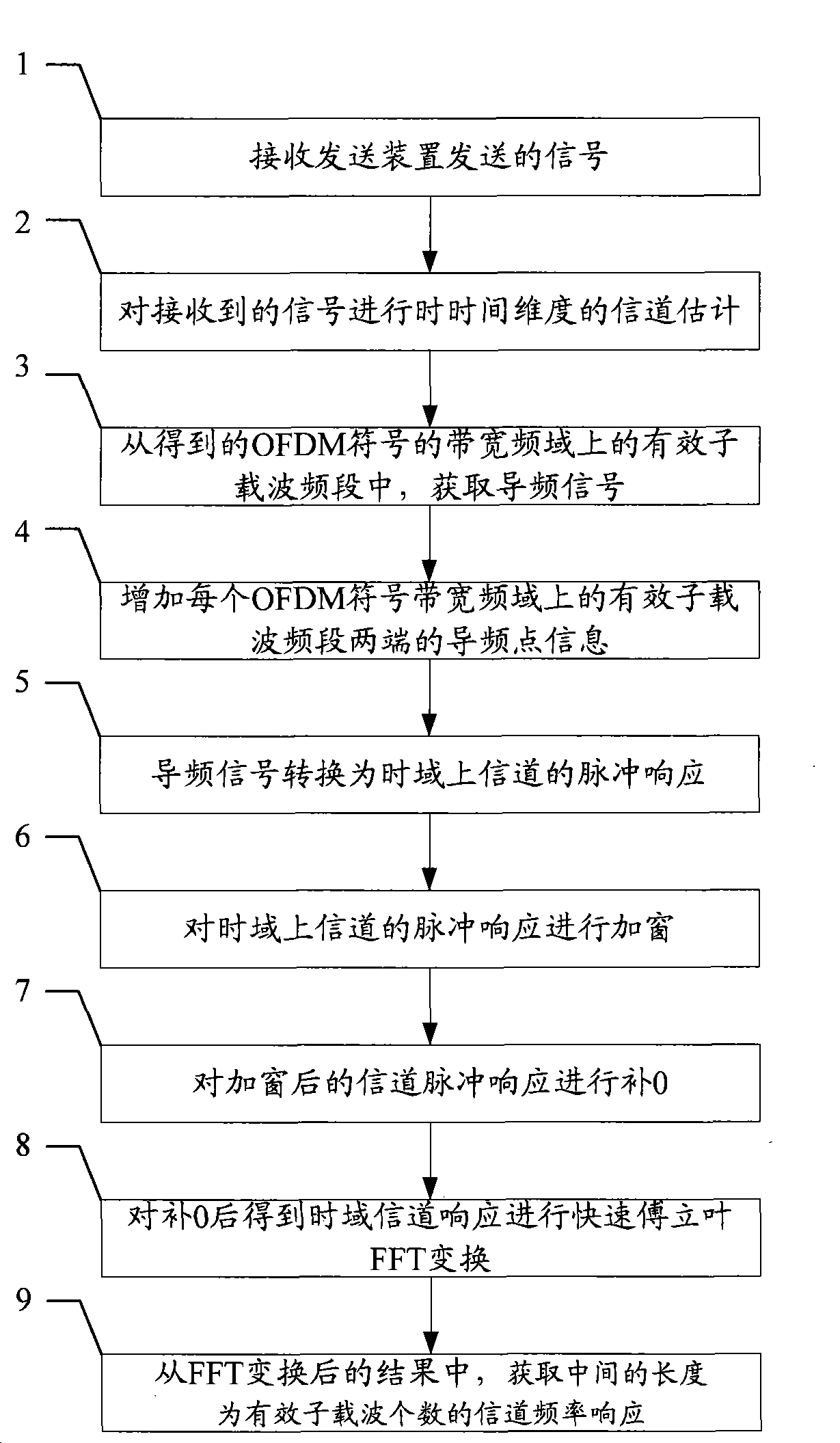
Method and apparatus for estimating OFDM system channel
ActiveCN101437010AImprove estimation accuracyIncrease the number of pilot pointsChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsEstimation methodsSubcarrier
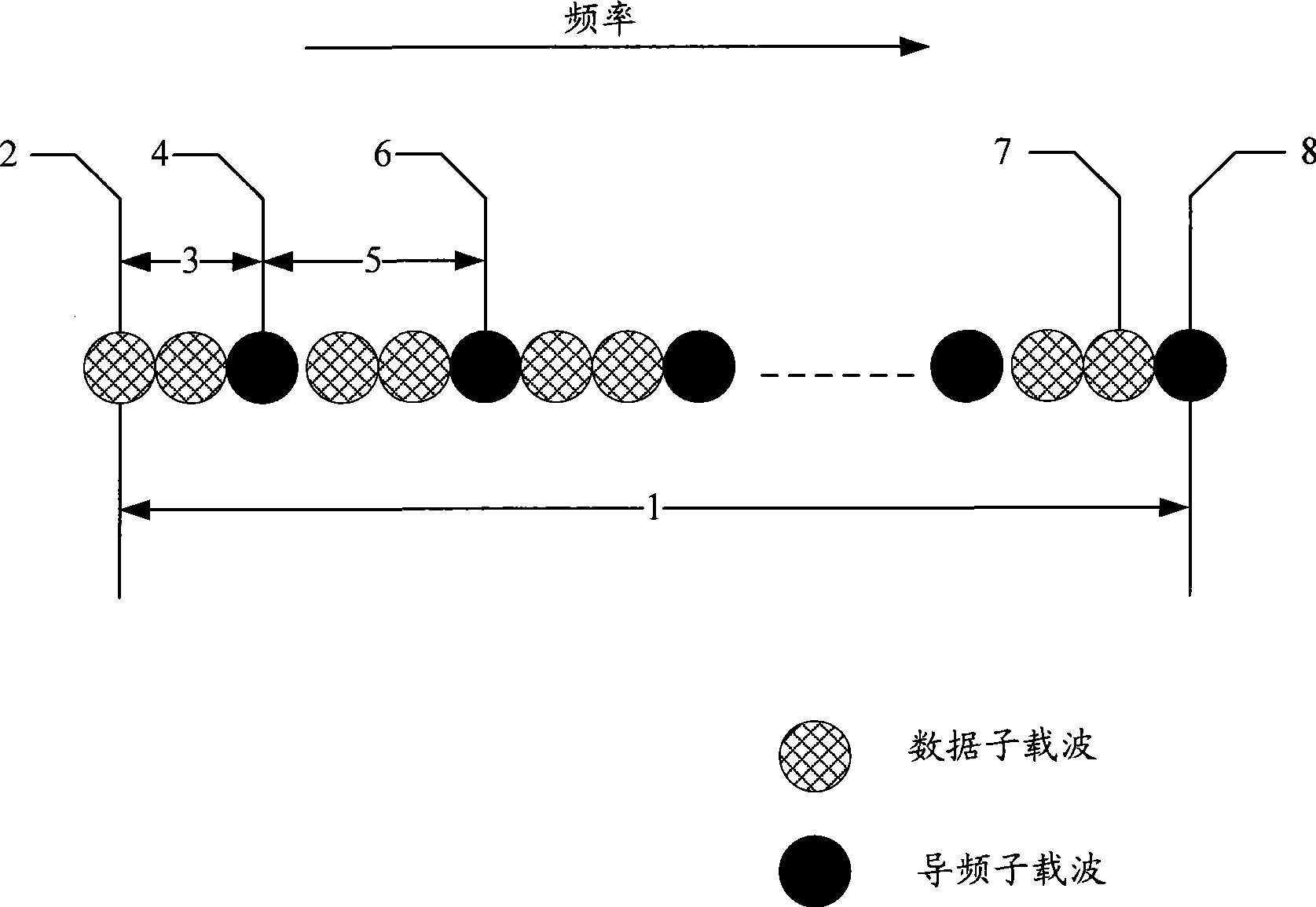
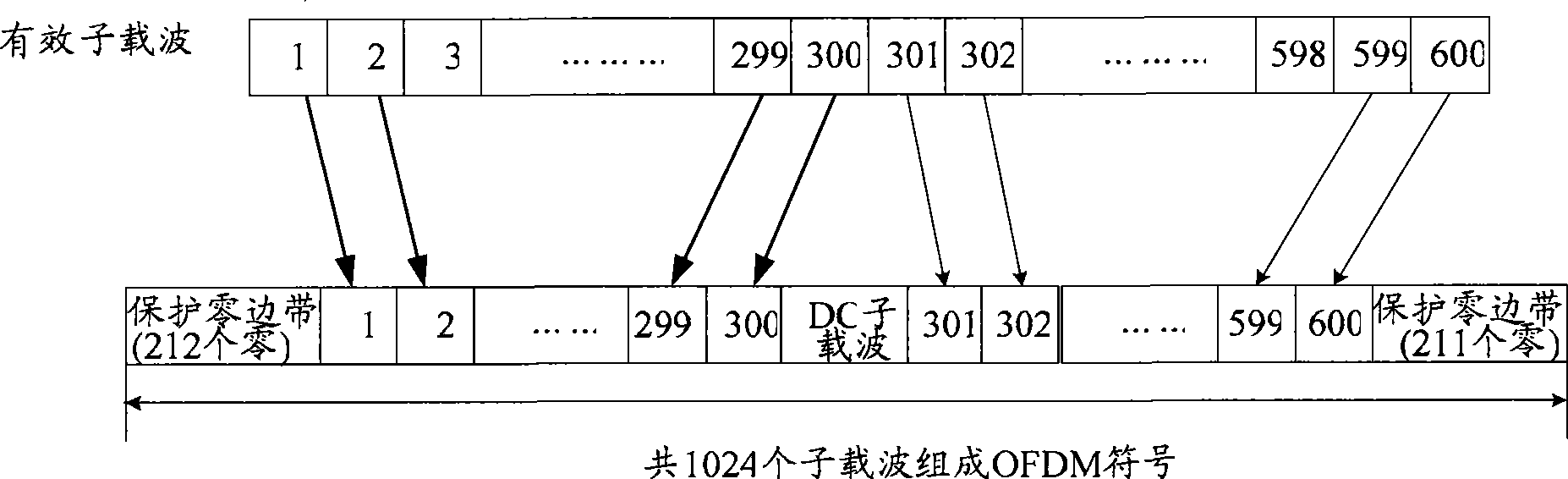
The invention discloses an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system channel estimation method. The embodiment of the invention also provides a corresponding receiving device. The technical proposal of the invention adopts the receiving device to perform channel estimation of time dimension to a received signal first, channel information of pilot points is obtained in an effective subcarrier frequency point on a frequency domain of each OFDM symbol, information of pilot points except for an effective subcarrier frequency band can be obtained by adding the information of the pilot points, and then the frequency response of a channel is obtained through IFFT conversion, window adding, zero complement and FFT conversion, namely an estimation result to the channel is obtained. The number of the pilot points is increased, thereby achieving the aims of inhibiting the edge effect and improving the accuracy of channel estimation.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Magnetic random access memory designs with patterned and stabilized magnetic shields
InactiveUS6929957B2Minimizing overall magnetic energyAdverse effect storage and readingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesRandom access memoryDirect coupling
A magnetic tunneling junction (MTJ) memory cell and an MRAM array of such cells, is shielded by magnetic shields of ferromagnetic material or by ferromagnetic shields that are stabilized by patterned layers of antiferromagnetic material or permanent magnetic material. The ferromagnetic portions of the shields surround the MTJ cells substantially conformally and thereby can compensate the poles of the free layers of MTJ cells of various geometric cross-sectional shapes and also protect the cells from the adverse effects of extraneous fields. The additional antiferromagnetic and permanent magnetic materials stabilize the shields by exchange or direct coupling.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
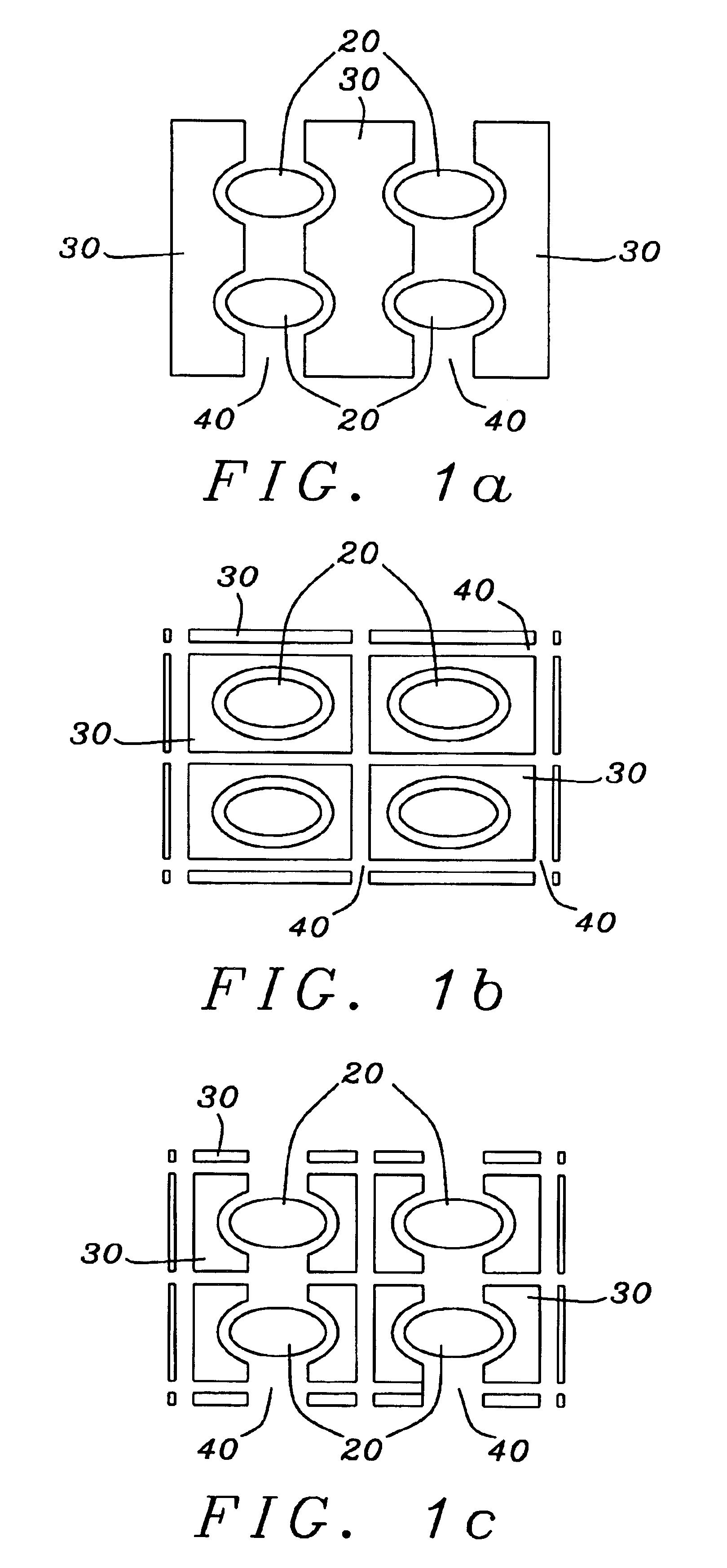
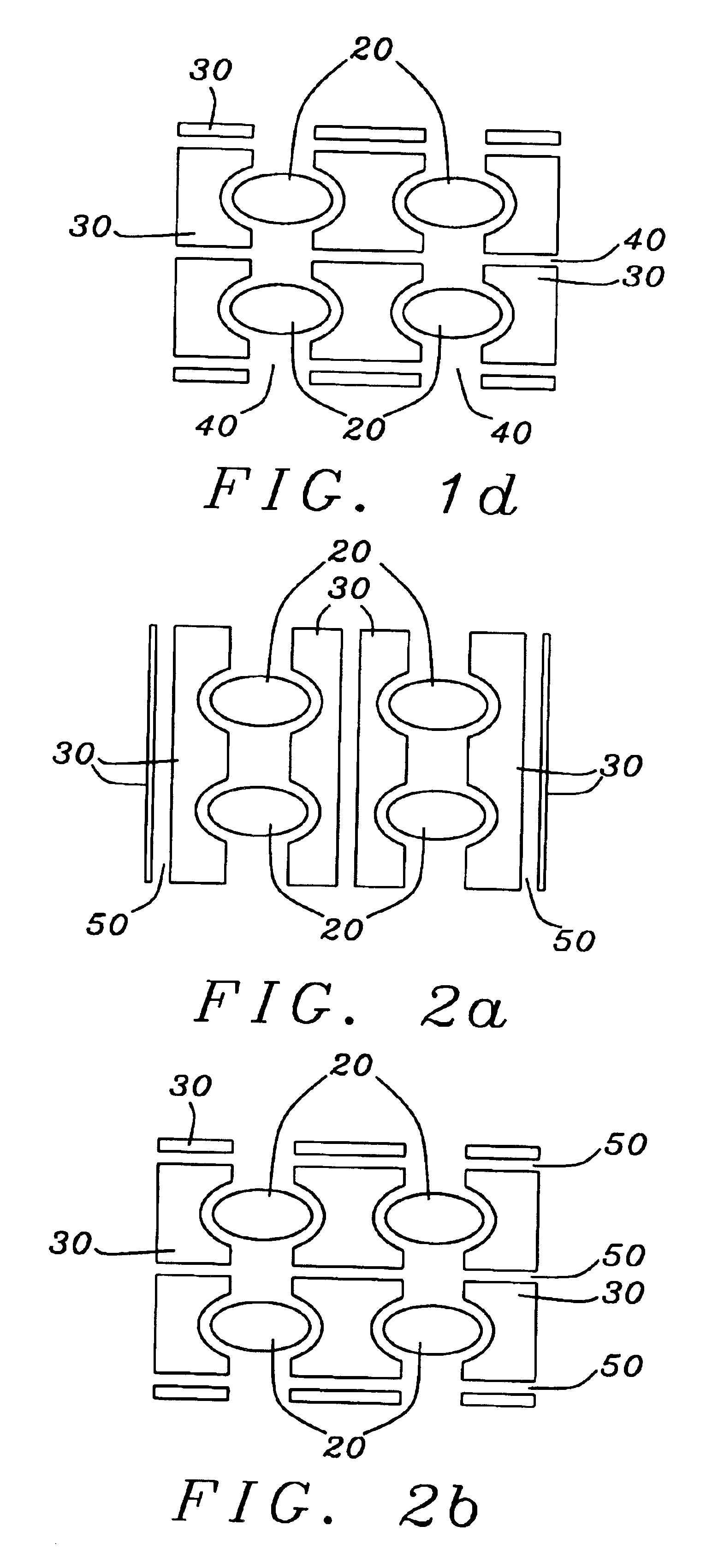
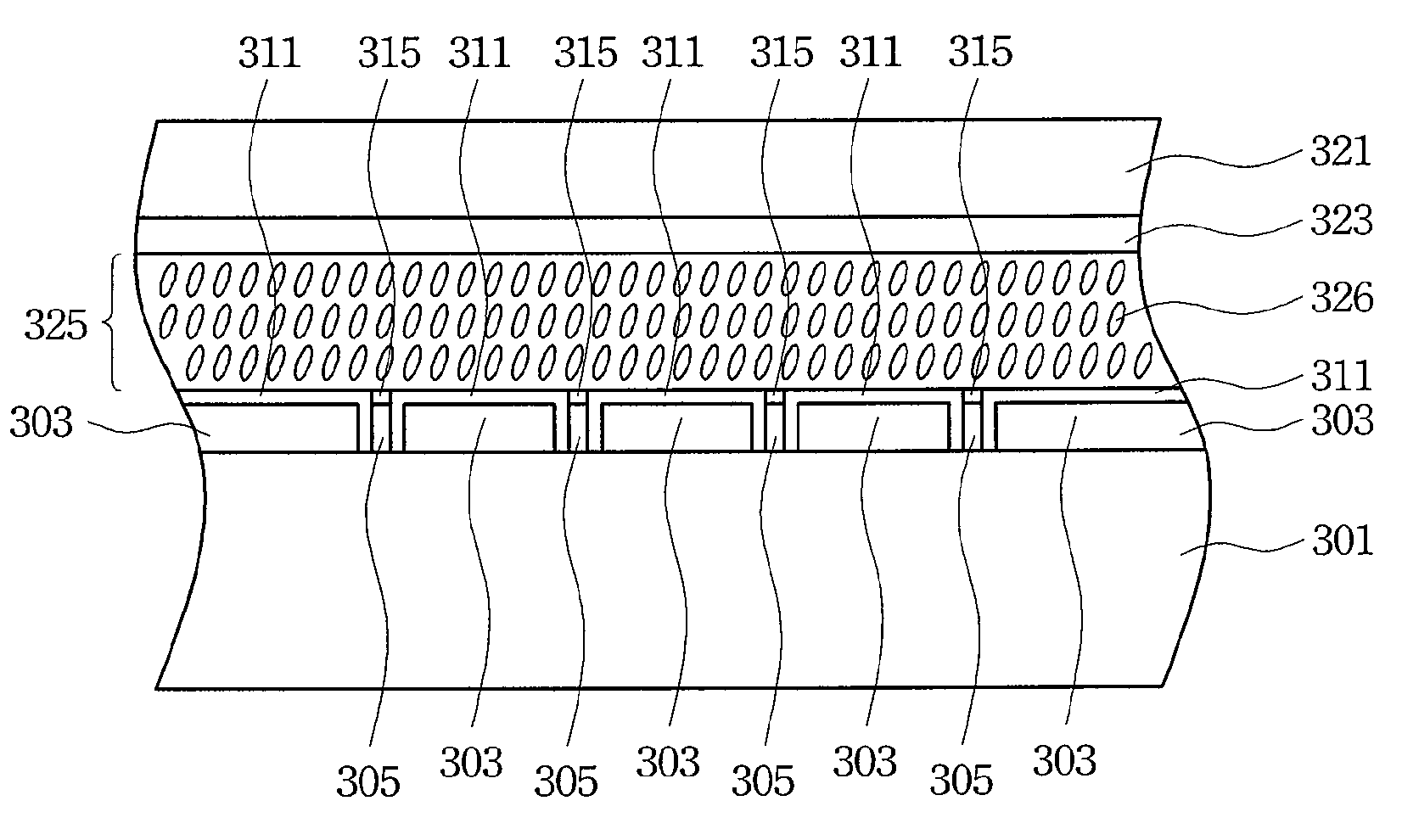
Liquid Crystal on Silicon Display Panel with Reducing Fringe Effect
ActiveUS20090015742A1Reduce edge effectsIncrease production costStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsSiliconLiquid crystal on silicon
A liquid crystal on silicon (LCOS) display panel with reducing fringe effect is provided herein. The liquid crystal on silicon display panel includes a common electrode, a semiconductor substrate having a plurality of pixel electrodes and control electrodes, a passivation layer on the pixel electrodes and a part of the semiconductor substrate, an anti-reflection coating (ARC) layers on the control electrodes, a transparent substrate on the semiconductor substrate, and a liquid crystal layer between the transparent substrate and the semiconductor substrate, wherein each of the control electrodes is disposed between and isolated with two adjacent ones of the pixel electrodes.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
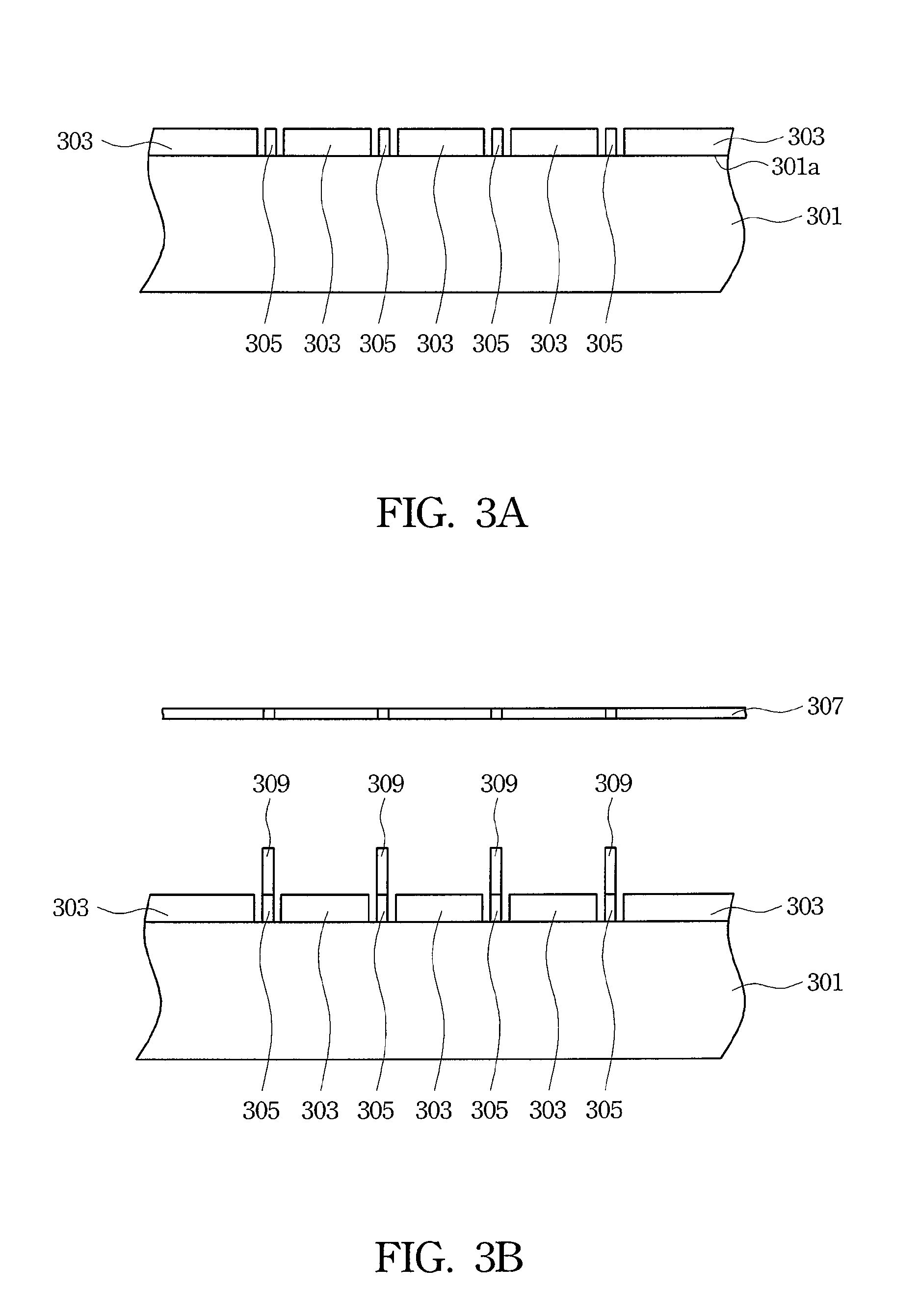
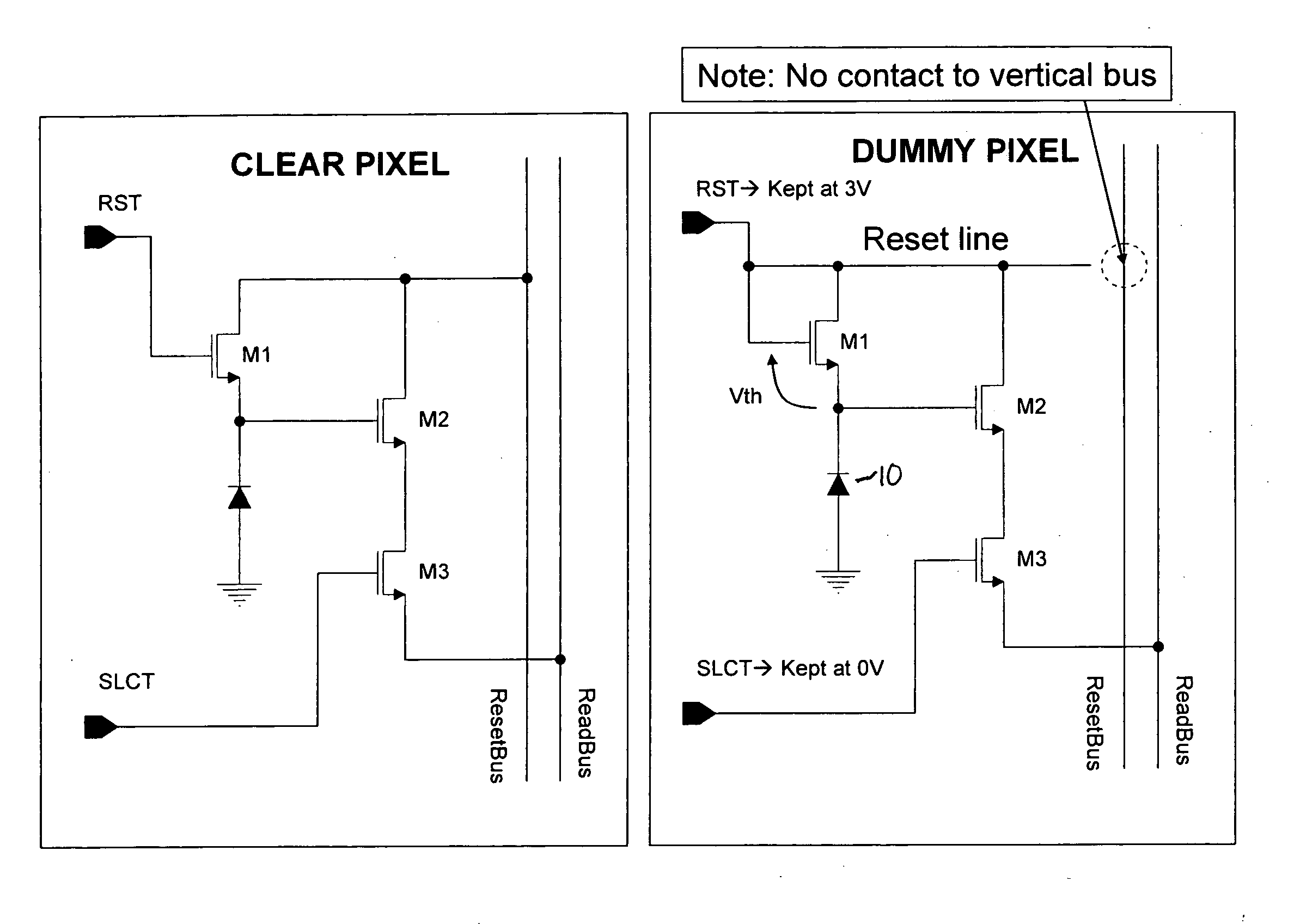
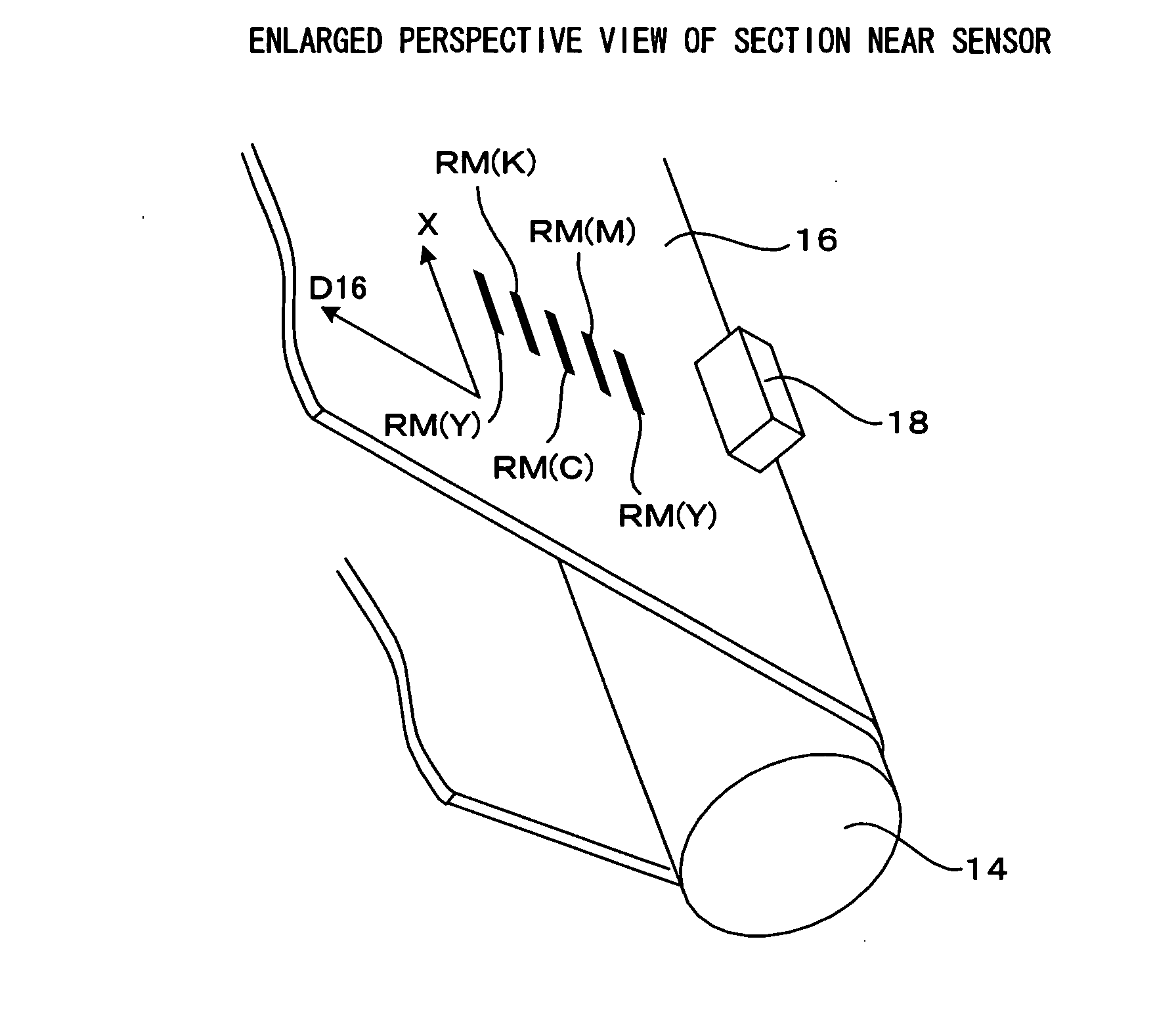
Apparatus and method for reducing edge effect in an image sensor
ActiveUS20080218608A1Prevent discontinuity stemmingEliminate edge effectsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEdge effectsImage sensor
A method and apparatus for forming dummy pixels exhibiting electrical characteristics virtually identical to the clear pixels of the imaging array. Arrays of such dummy pixels are used to form regions that isolate the main imaging array and sub-arrays of optical black pixels while preventing edge effects. The dummy pixels are preferably clear but can also be covered with optical black. By setting quiescent operation in soft reset, the dummy pixels exhibit the diode ideality and RoA product that are typical of any of the pixels in the entire array.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
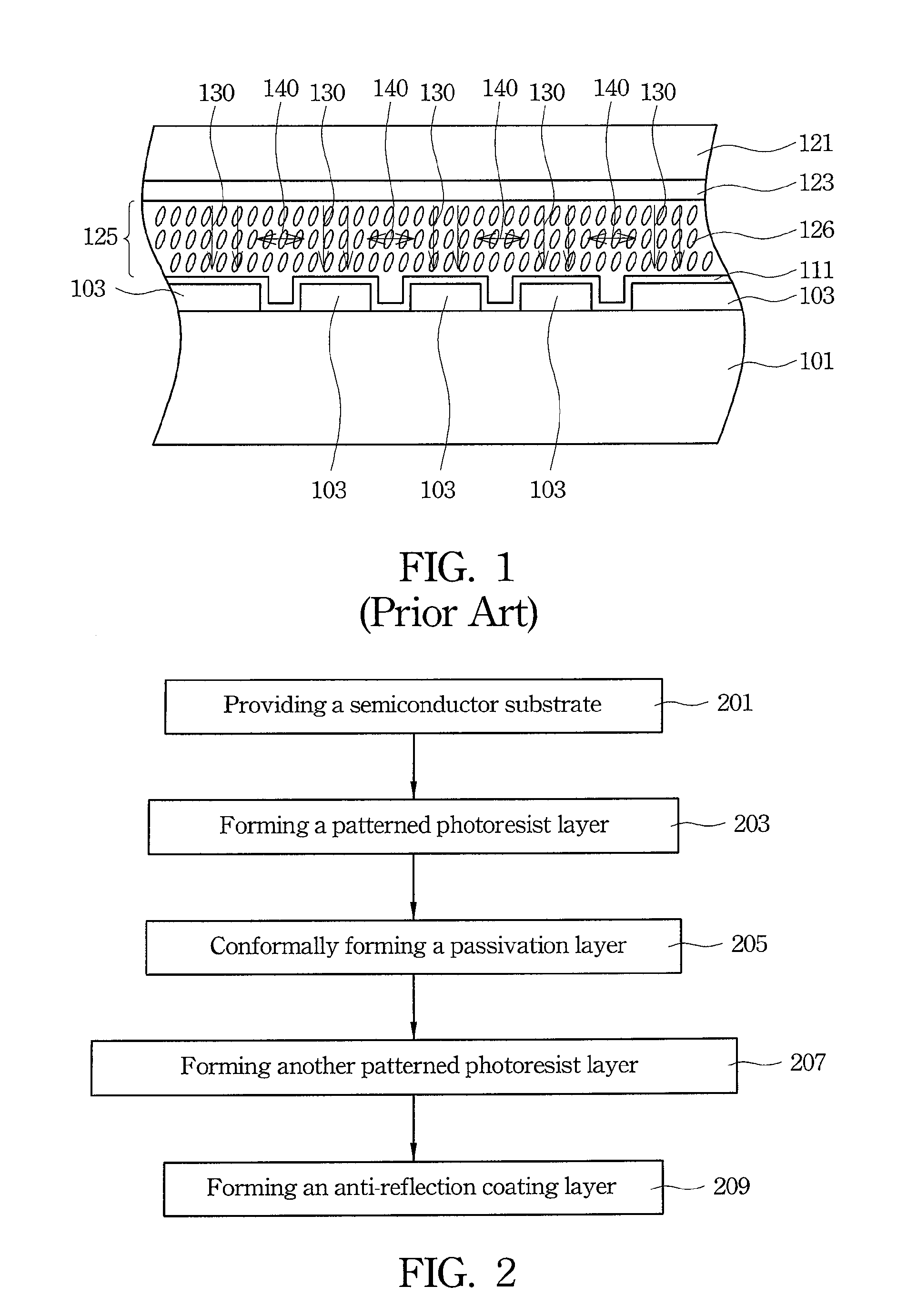
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060177246A1Detection accuracy be deteriorateEnhance density of tonerRecording apparatusElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringImage formation
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
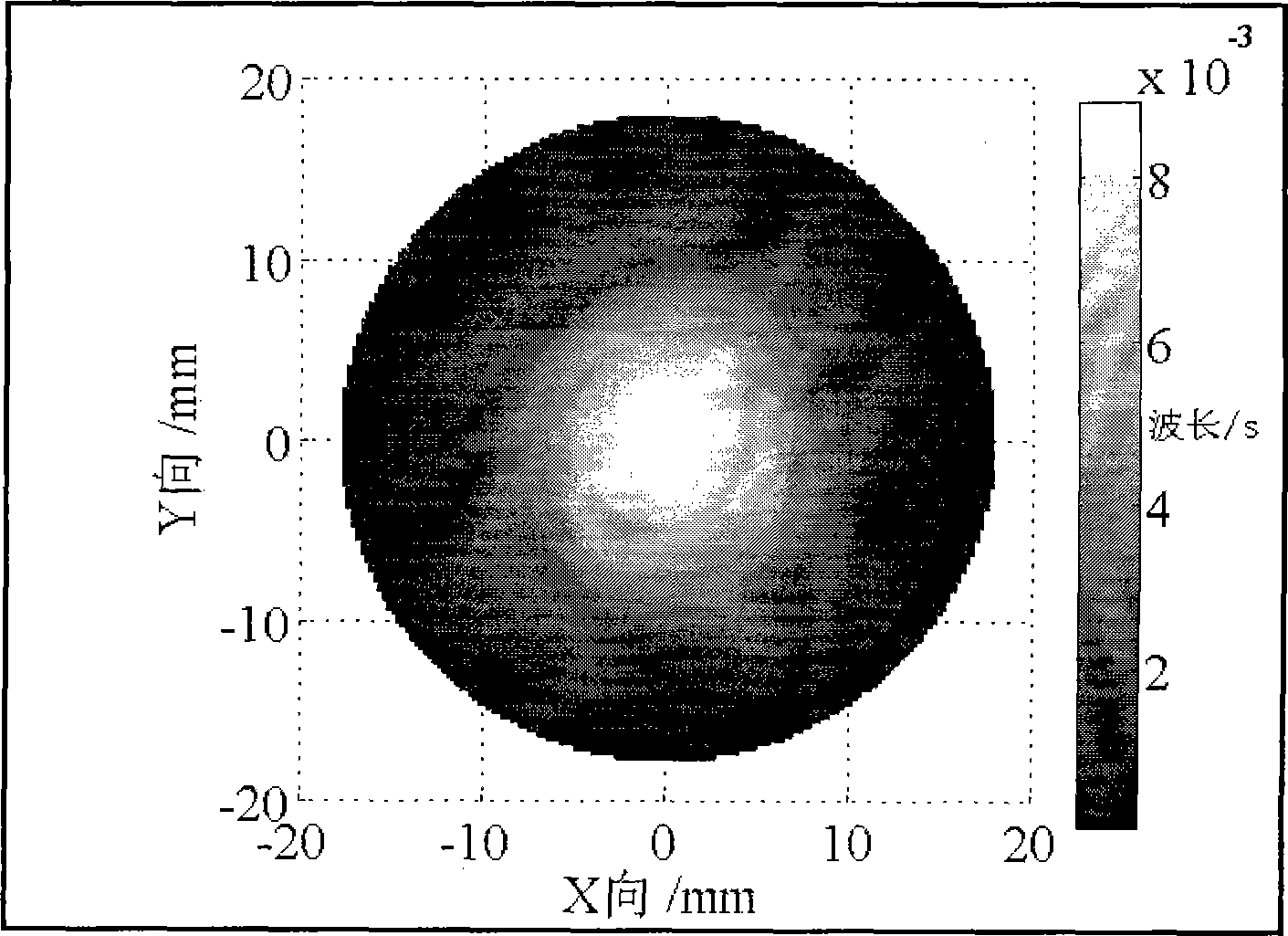
Processing method for correcting low steepness optical mirror surface error
The invention discloses a processing method for correcting error of a low-gradient optical mirror surface, which comprises the following steps: firstly acquiring a removal function through experiment, then using a wave surface interferometer to acquire a surface shape error function of an element, dispersing the surface shape error function, programming a processing path at the same time, extending the surface shape error function, establishing a model and solving processing residence time, carrying out numerical control processing by using the solved residence time, identifying error and controlling accuracy for the processed result, so as to finish processing. The processing method has the advantages of high process efficiency, low processing cost and good error correction effect, and can effectively correct the surface shape error of the low-gradient optical mirror surface.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Computer-aided detection of microcalcification clusters
InactiveUS7593561B2Reduce edge effectsReduce image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisEdge effectsImaging processing
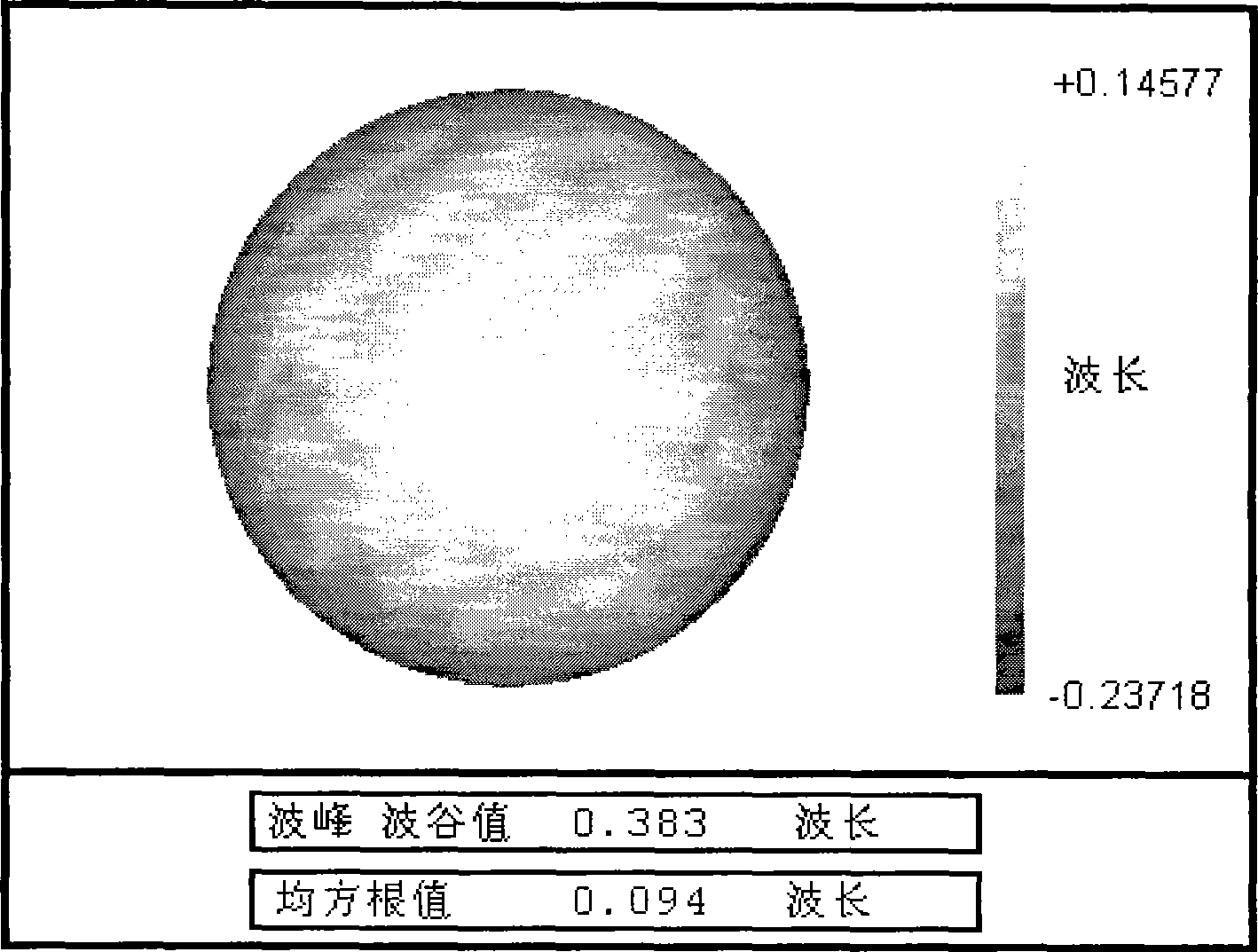
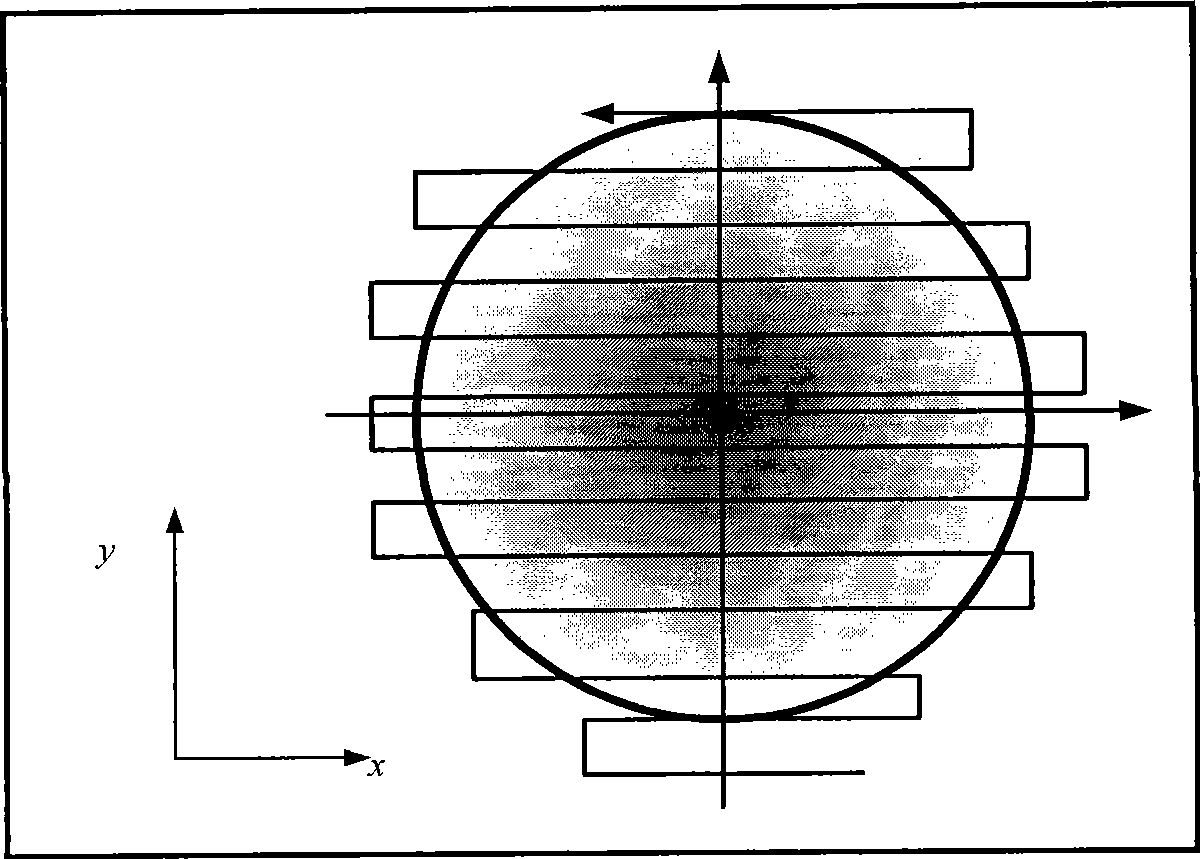
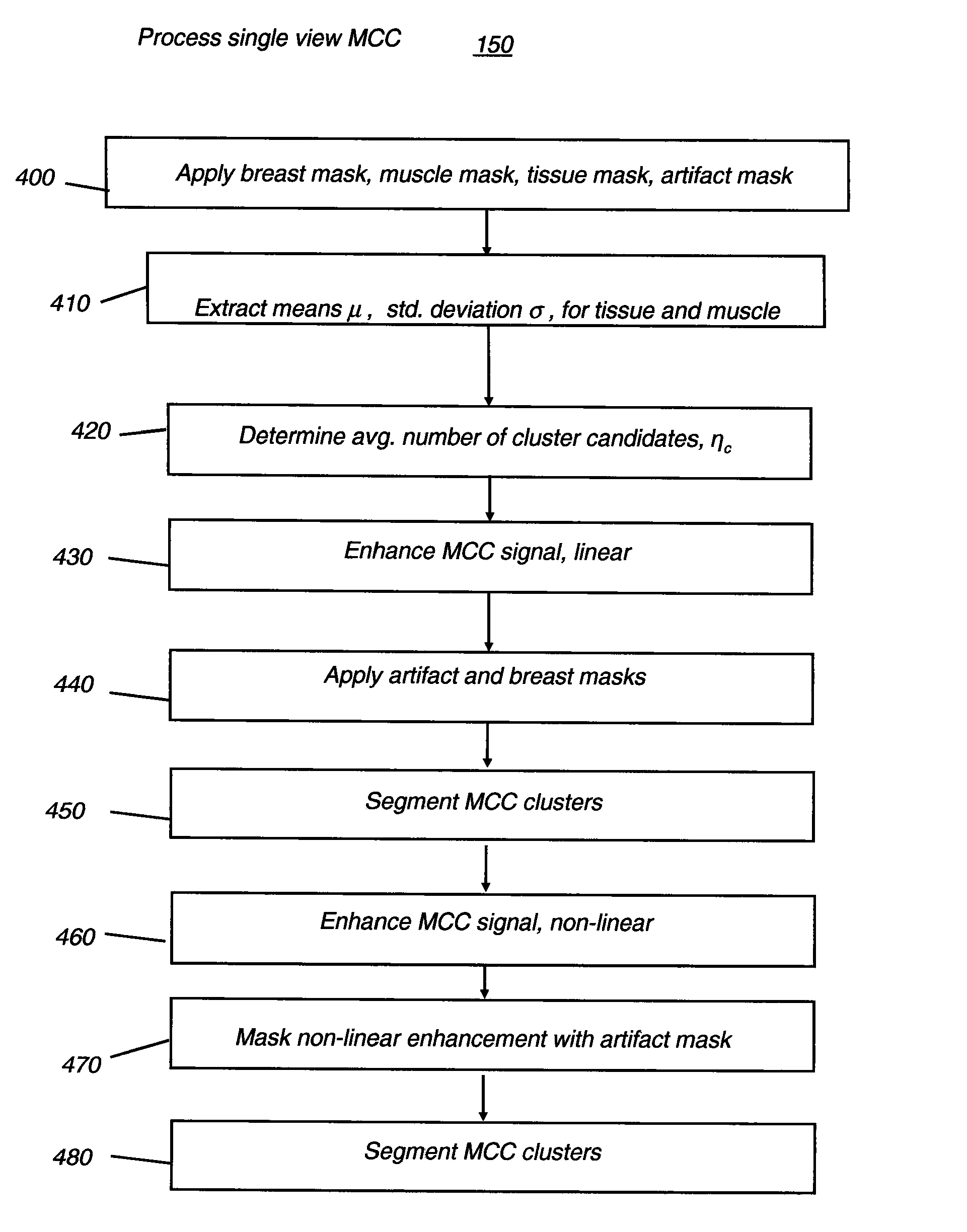
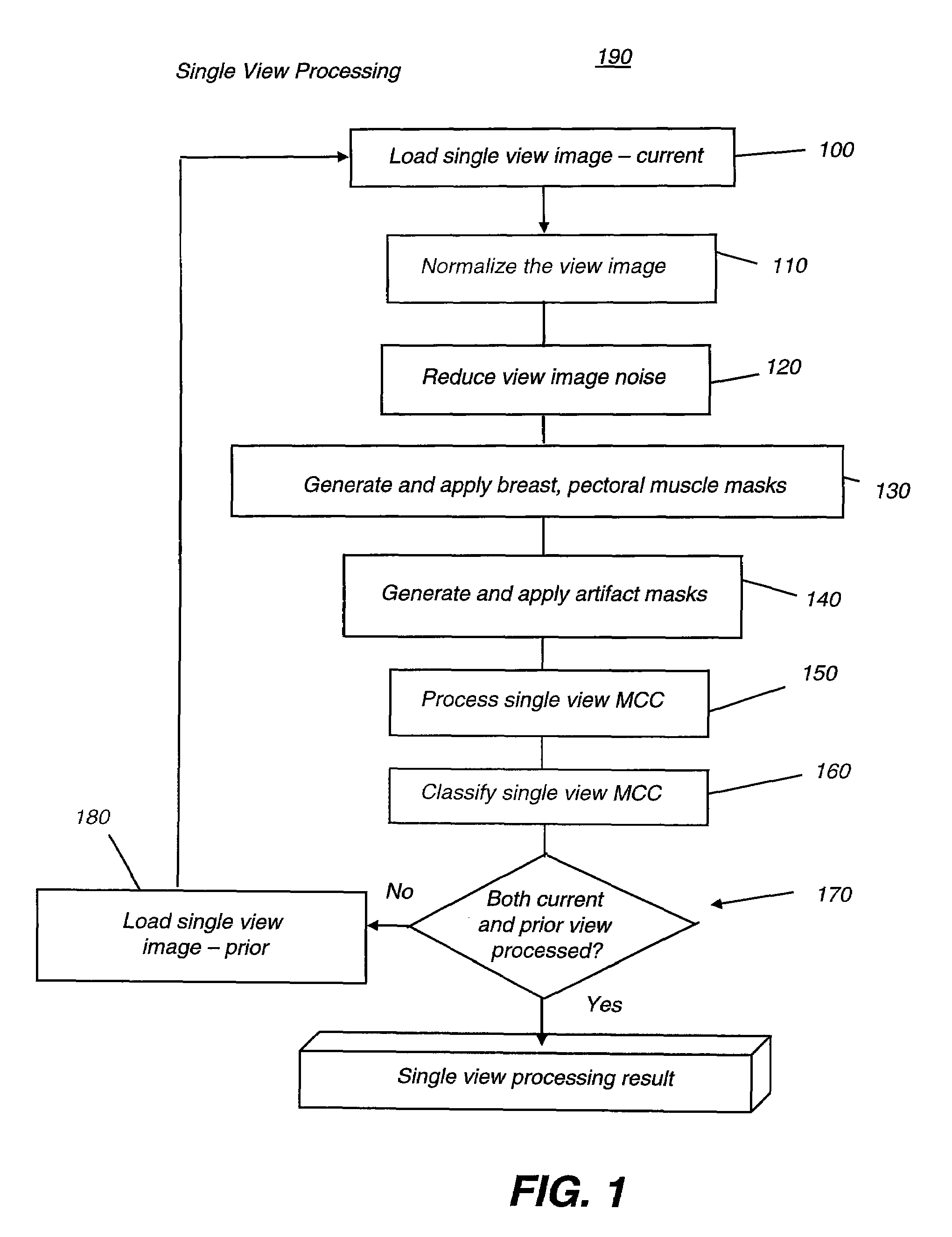
A method for computer-aided detection of microcalcification clusters using a digital computer obtains digital mammography data for a single view image and normalizes and filters the image data to reduce noise. A first mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining the breast structure, forming a first cropped image. A second mask is generated and applied to the image data for defining muscle structure, forming a second cropped image. An artifact mask corresponding to vascular calcifications and known imaging artifacts is generated and applied to the first and second cropped images, defining first and second artifact-masked cropped images. In a repeated sequence, portions of each artifact-masked cropped image are processed using an enhancement algorithm and reducing edge effects to obtain a set of microcalcification cluster candidates and suspected microcalcification clusters. Image processing algorithms remove false positives from the listing of microcalcification clusters and classify candidate microcalcification clusters to identify true positives.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
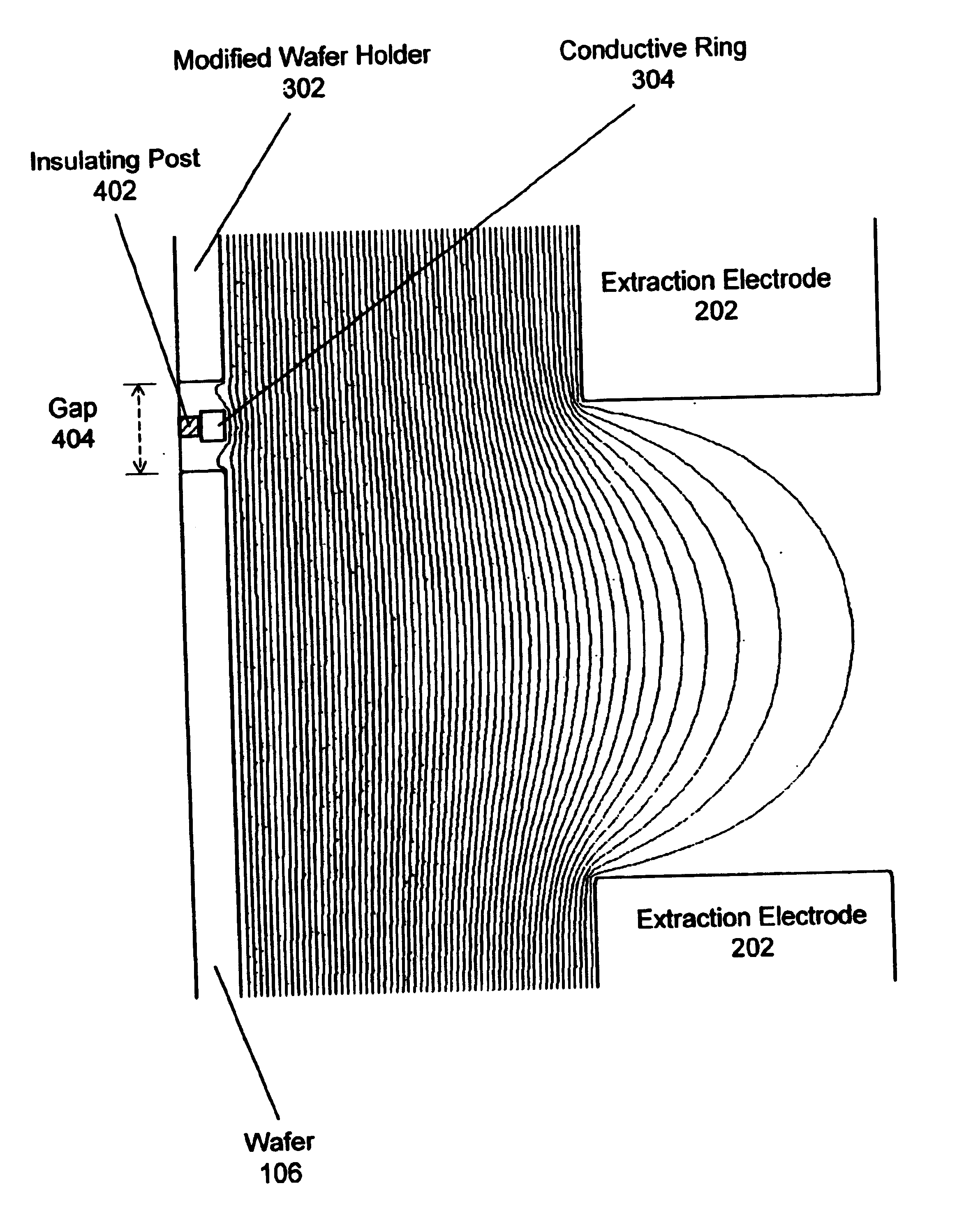
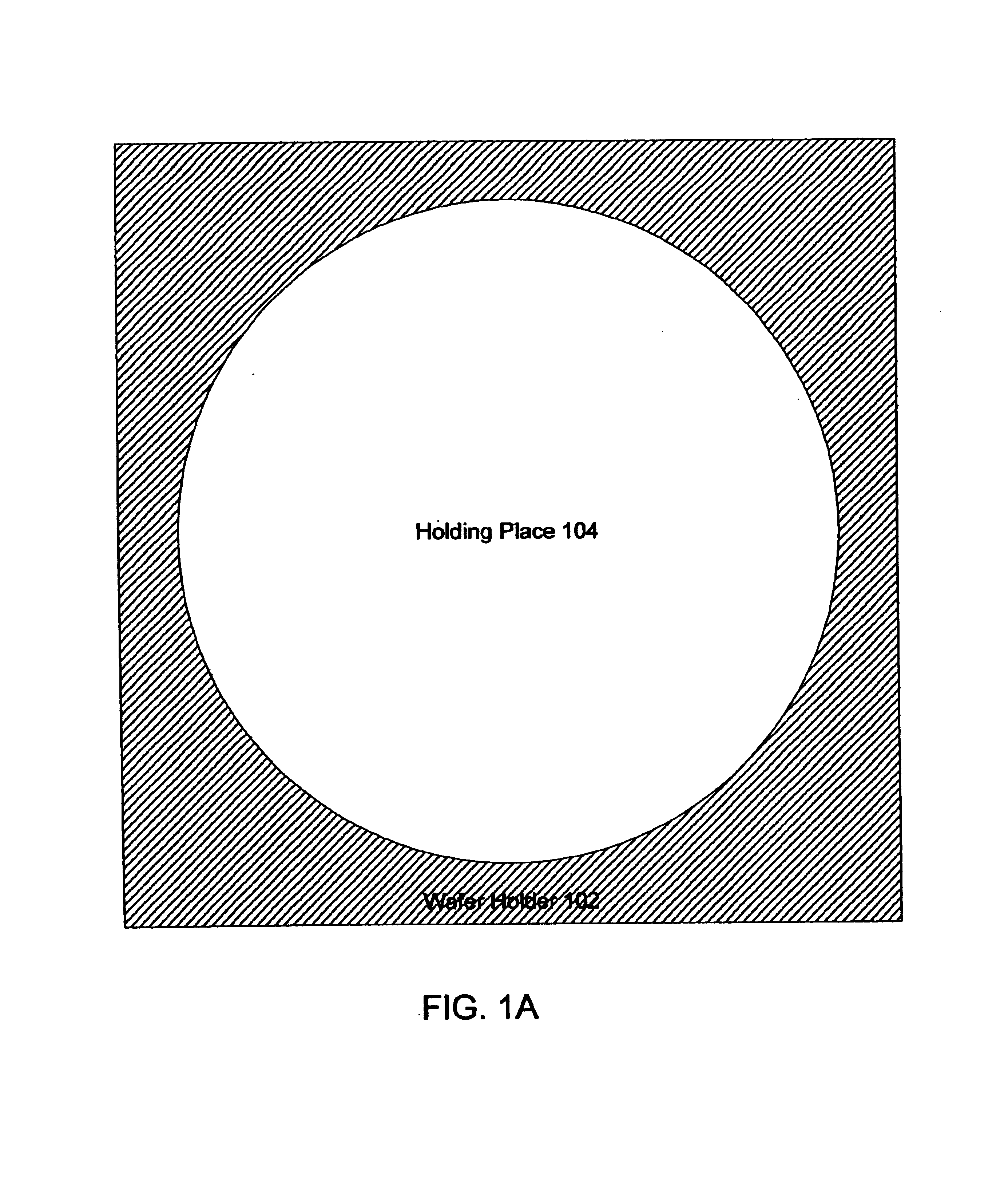
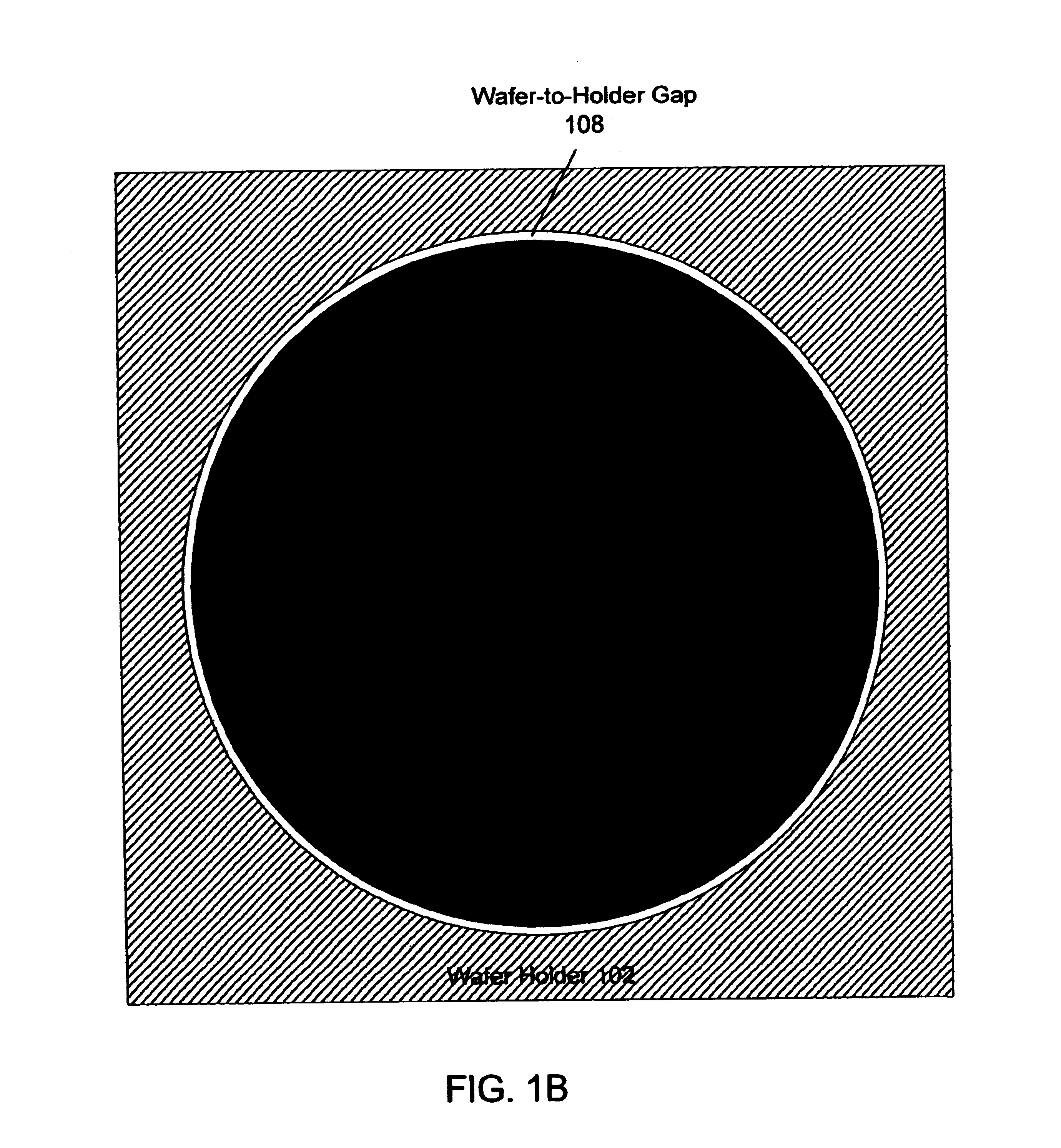
Method and apparatus for reducing substrate edge effects in electron lenses
ActiveUS6903338B2Reduce edge effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesEdge effectsElectron lenses
One embodiment disclosed pertains to a method for inspecting a substrate. The method includes inserting the substrate into a holding place of a substrate holder, moving the substrate holder under an electron beam, and applying a voltage to a conductive element of the substrate holder. The voltage applied to the conductive element reduces a substrate edge effect. Another embodiment disclosed relates to an apparatus for holding a substrate that reduces a substrate edge effect. The apparatus includes a holding place for insertion of the substrate and a conductive element. The conductive element is positioned so as to be located within a gap between an edge of the holding place and an edge of the substrate.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Differential D-dot voltage sensor
ActiveCN103235170AReduce volumeWill not affect the input sideCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical conductorSmart grid
The invention discloses a differential D-dot voltage sensor, which comprises a measuring module, an electrode plate, a signal modulation module and a collection transmission module, wherein the measuring module is provided with a first input end and a second input end, the electrode plate is provided with a first electrode and a second electrode, the measuring module is a differential amplification module, the differential amplification module is used for measuring the differential voltage between conducting layers, the sensor is not in grounding contact and is also not in direct contact with a tested conductor, and the output is floating potential difference, so the sensor can reduce the size of an insulation structure. Because the differential structure carries out non-contact measurement on the same potential, no direct energy transmission exists between the tested conductor and the sensor, and the influence cannot be generated on the input side when the sensor generates fault such as insulation breakthrough or output short circuit. The differential D-dot voltage sensor can solve the non-contact electrodeless voltage measurement problem of an intelligent electric network and can be used for 10kV to 35kV voltage measurement.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for the determination of local similitude from seismic 3d measured data
InactiveUS20040210394A1Reduce edge effectsWithout deteriorating resolutionSeismic signal processingComplex mathematical operationsSpatial OrientationsData set
The invention concerns a method for the determination of local similarity values for geological units in the subsurface from a seismic 3-D dataset, which consists of a multitude of traces, each of which being formed by a sequence of data points that carry amplitude values, or seismic attributes derived thereof, with the following steps: Assigning a weighted environment to a respective analysis point, whereby weight factors according to a weight function are assigned to the data points in the environment of the analysis point, and calculating similarity values in each weighted environment, whereby the weight function is included in the similarity measure; and especially a method for the determination of local dip-dependent similarity values with the steps: Assigning a weighted environment to a respective analysis point, whereby weight factors according to a weight function are assigned to the data points in the environment of the analysis point, calculating similarity values in each weighted environment, whereby the weight function is included in the similarity measure, and similarity values are determined for discrete spatial orientation, and the similarity values are represented at least as a function of a dip angle and a dip azimuth; and, in each weighted environment of an analysis point, determining the maximum similarity value, which is assigned, together with the corresponding dip angle and dip azimuth, to the respective analysis point.
Owner:TRAPPE HENNING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com