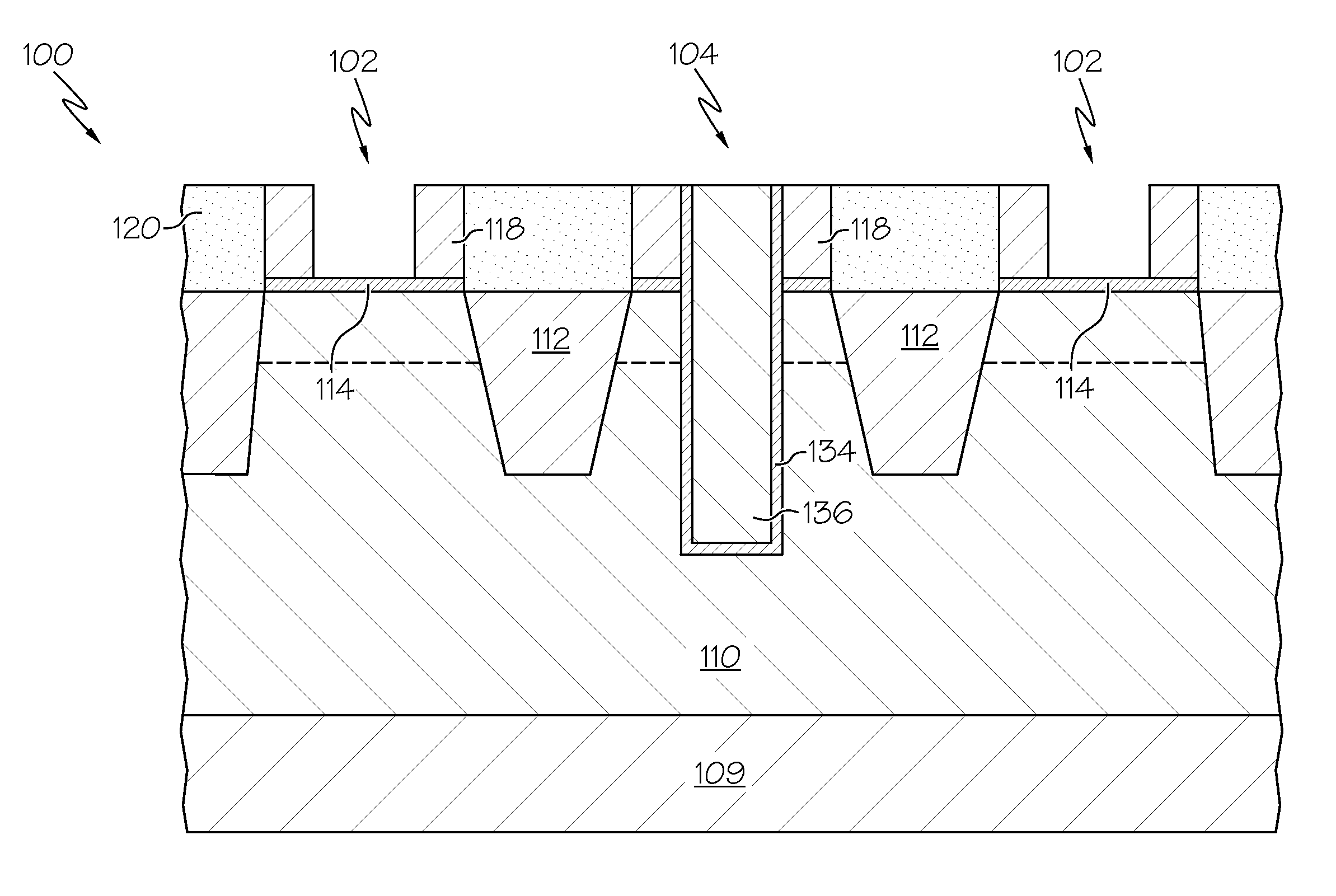
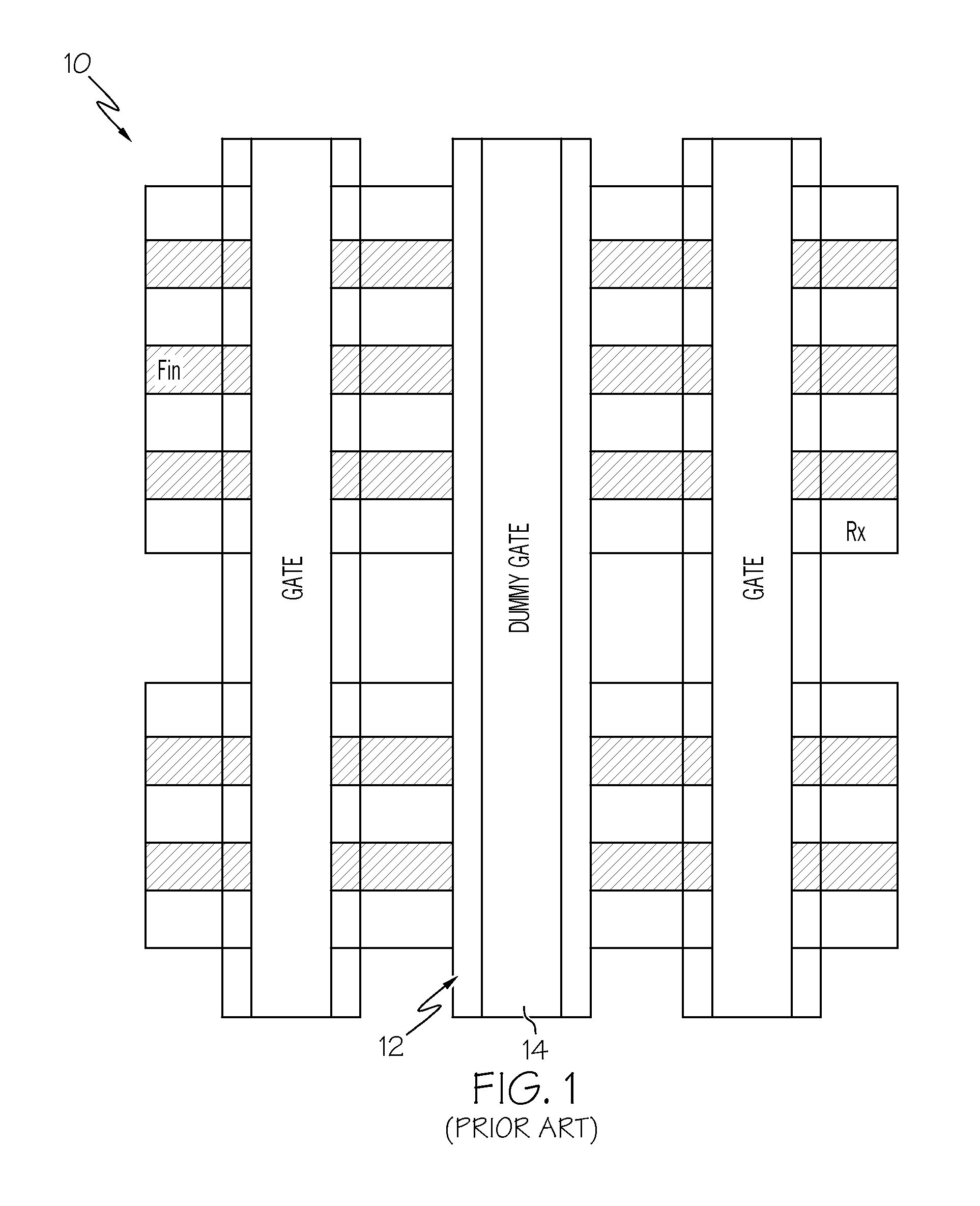
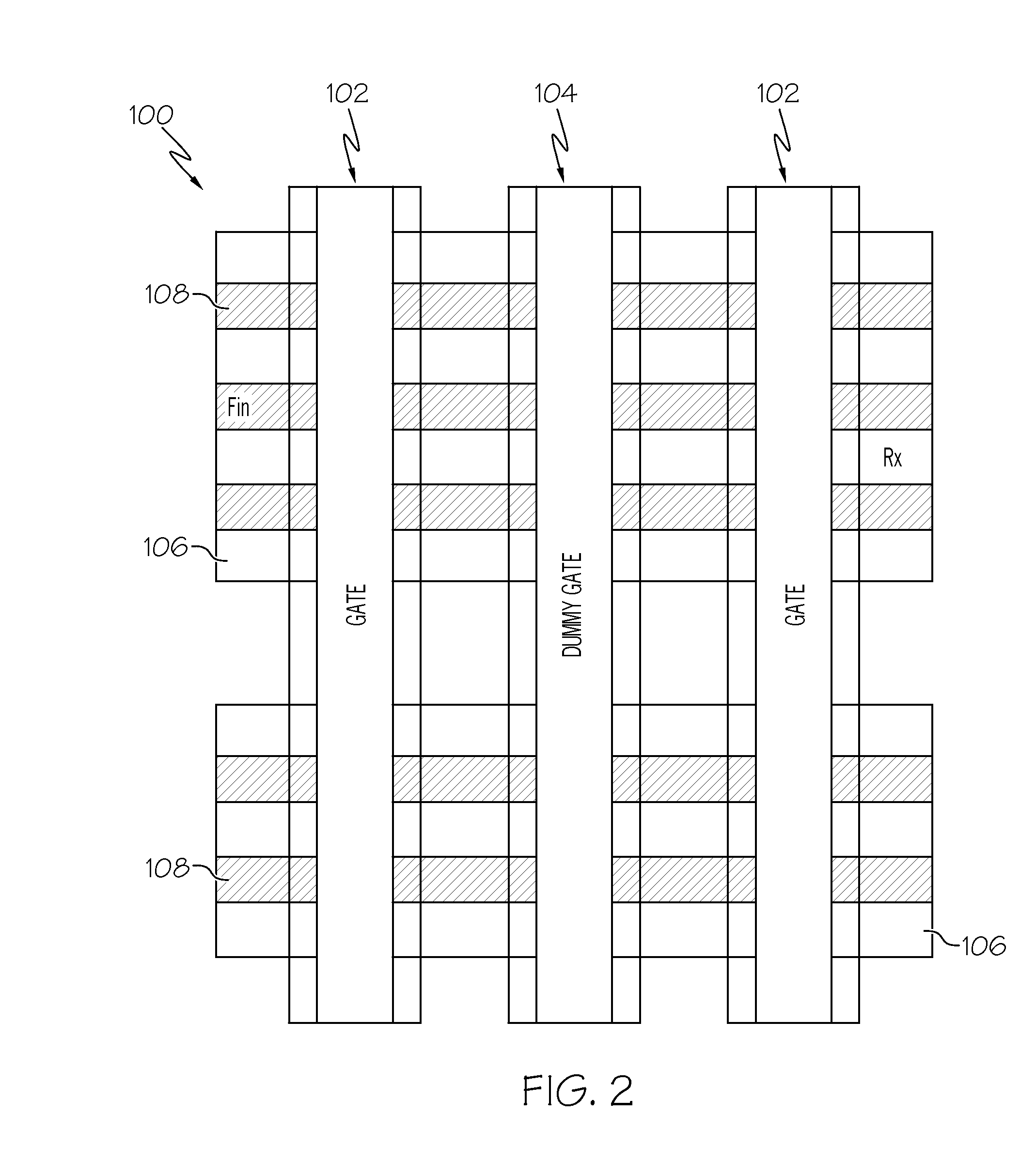
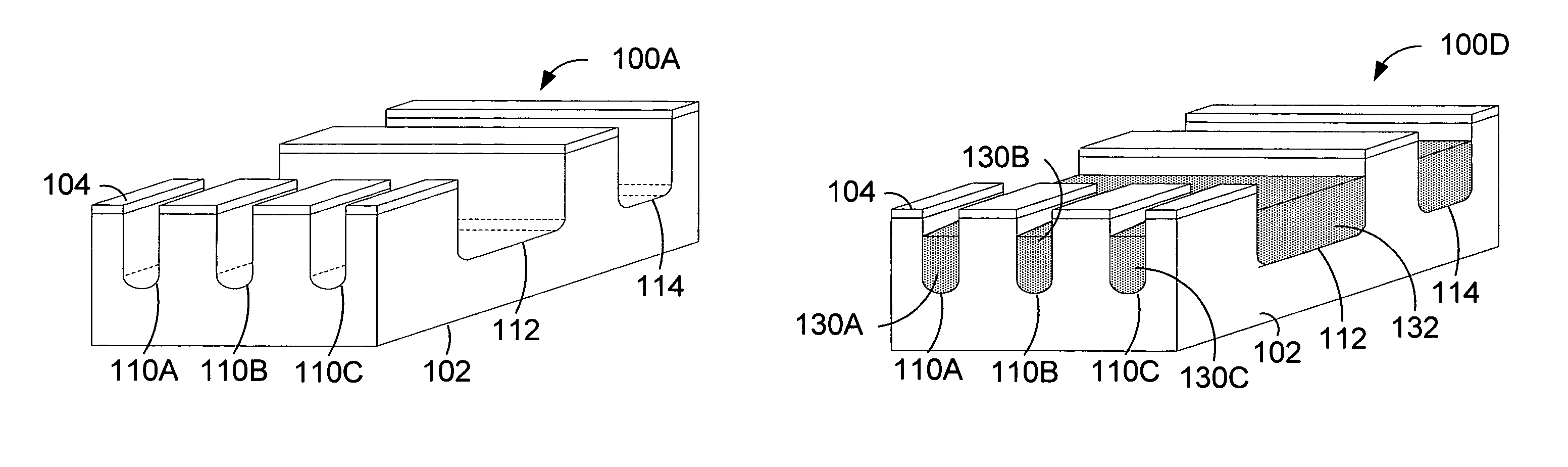
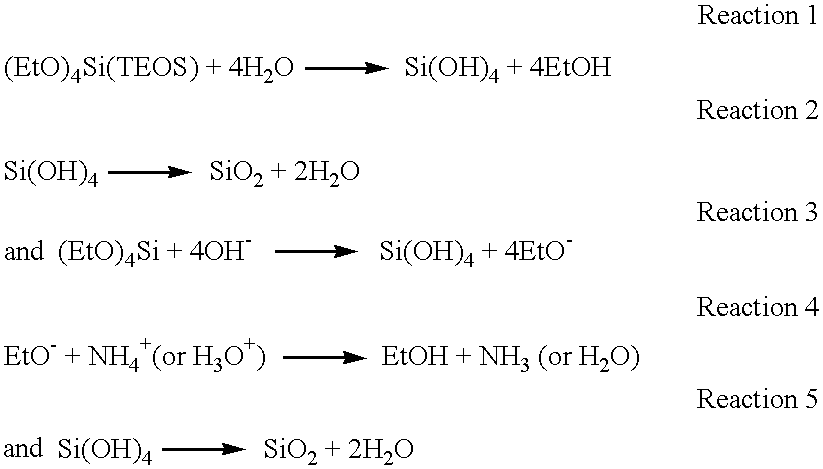Patents
Literature
1286 results about "Chemical-mechanical planarization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
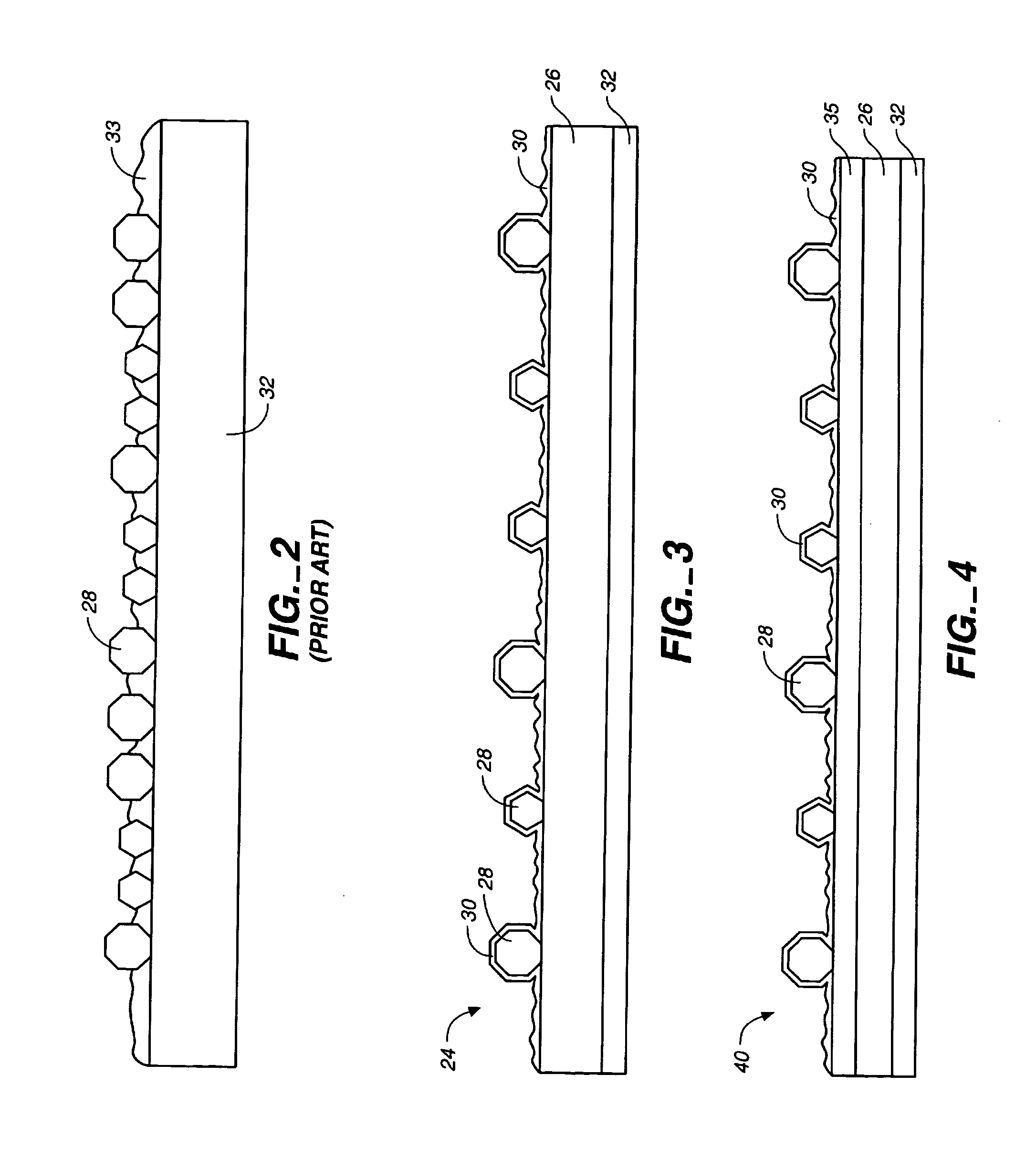
Chemical mechanical polishing or planarization is a process of smoothing surfaces with the combination of chemical and mechanical forces. It can be thought of as a hybrid of chemical etching and free abrasive polishing.
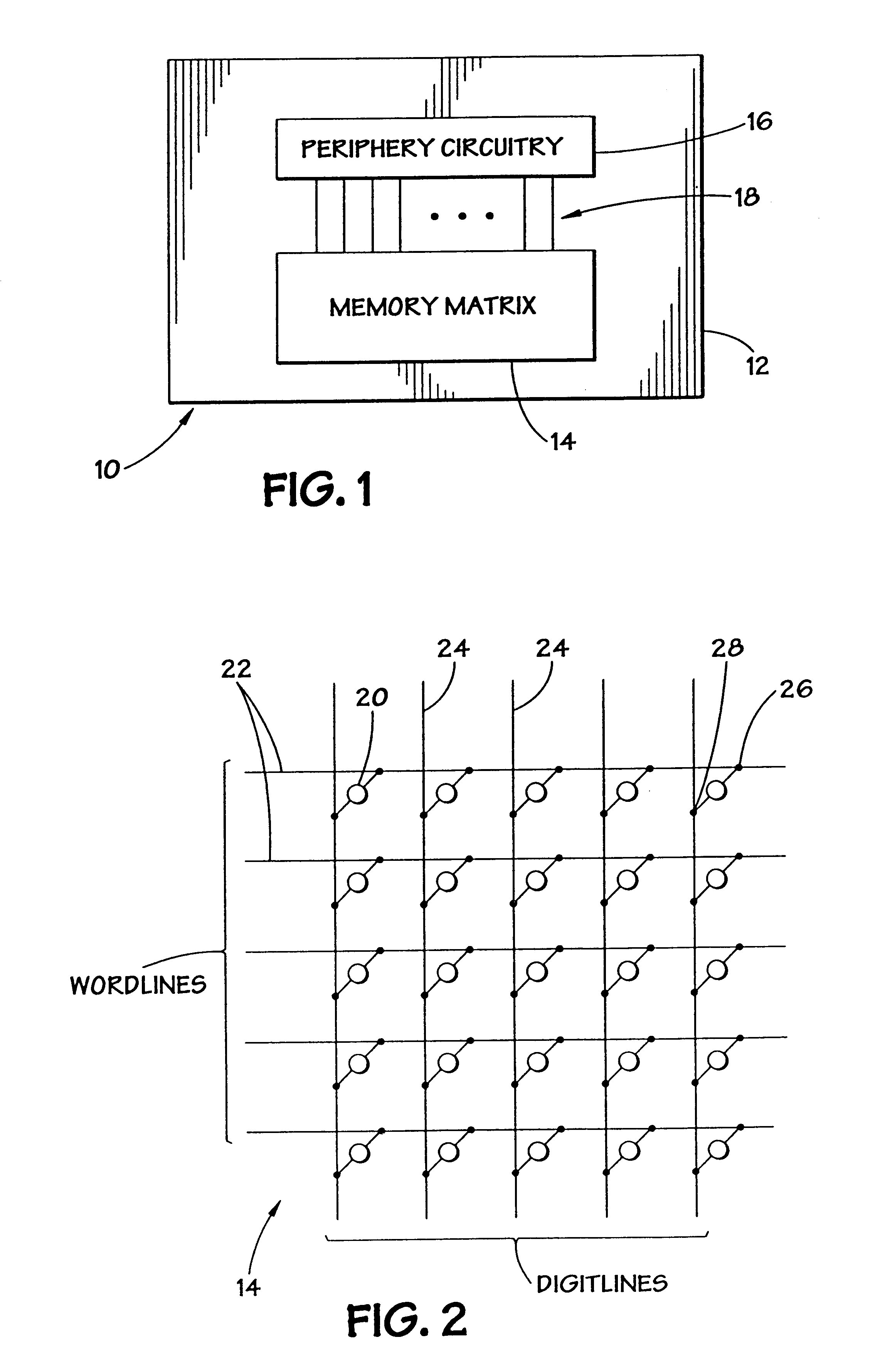
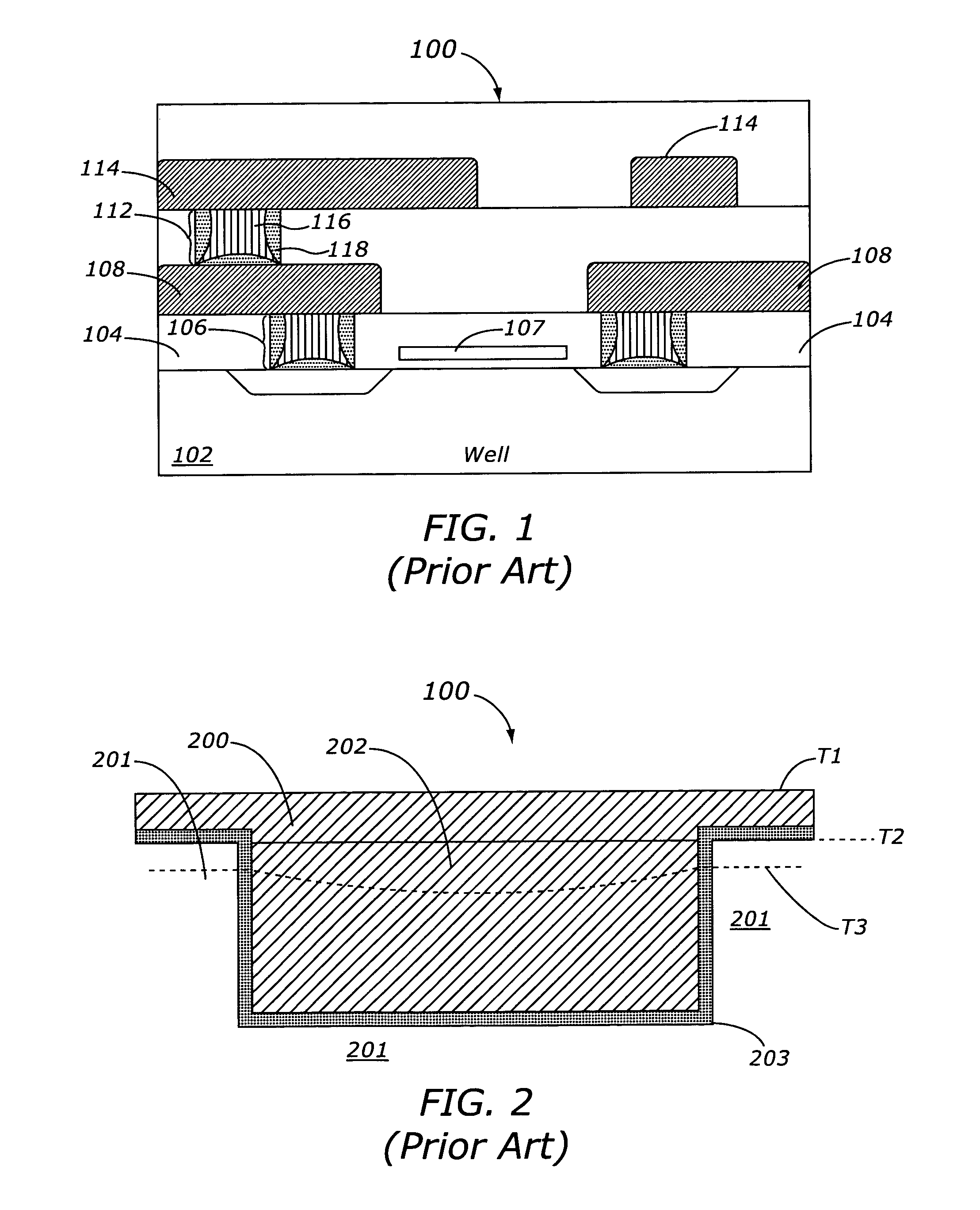
Contact structure and memory element incorporating the same
InactiveUS6031287ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesChemical-mechanical planarizationEtching
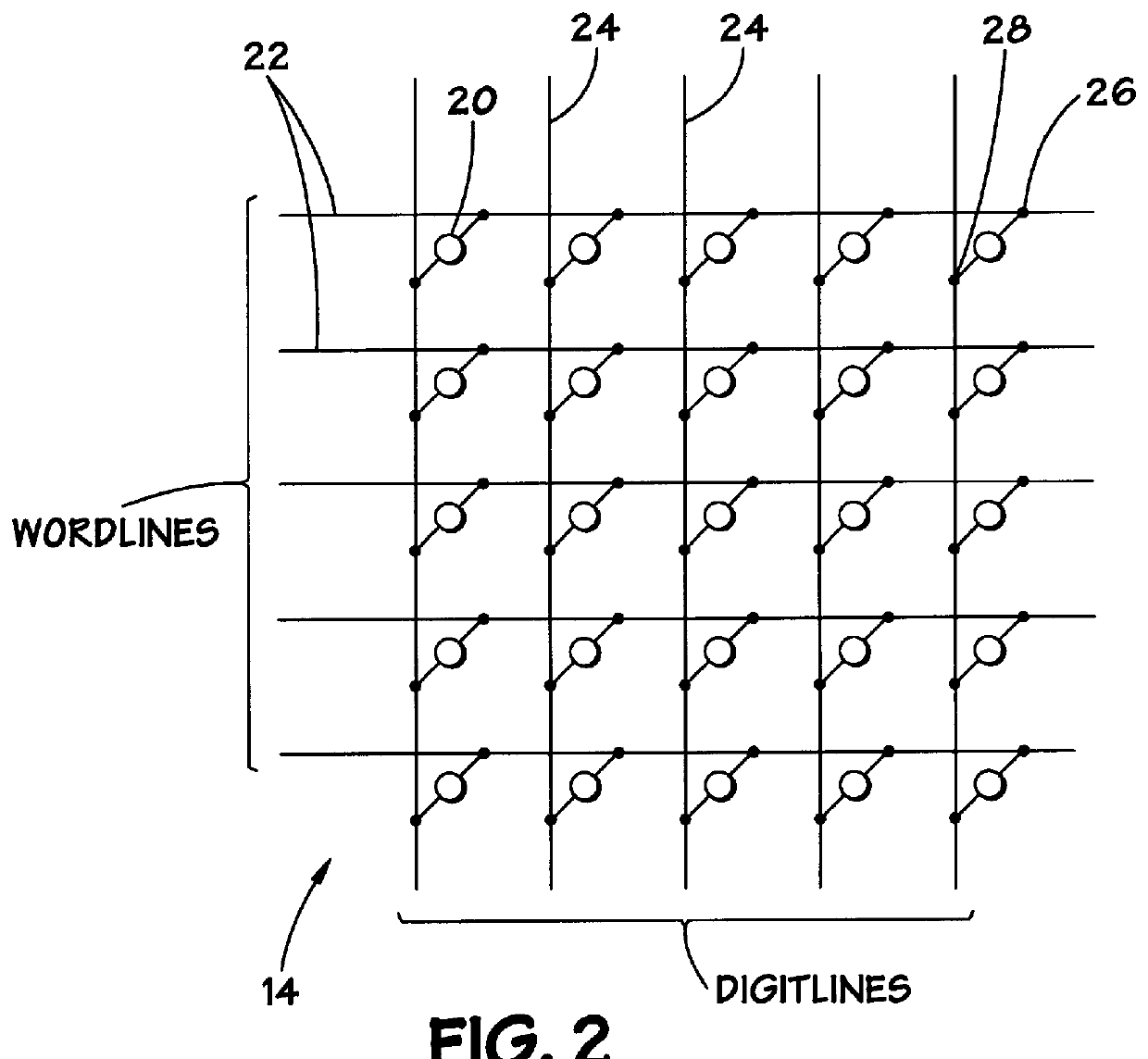
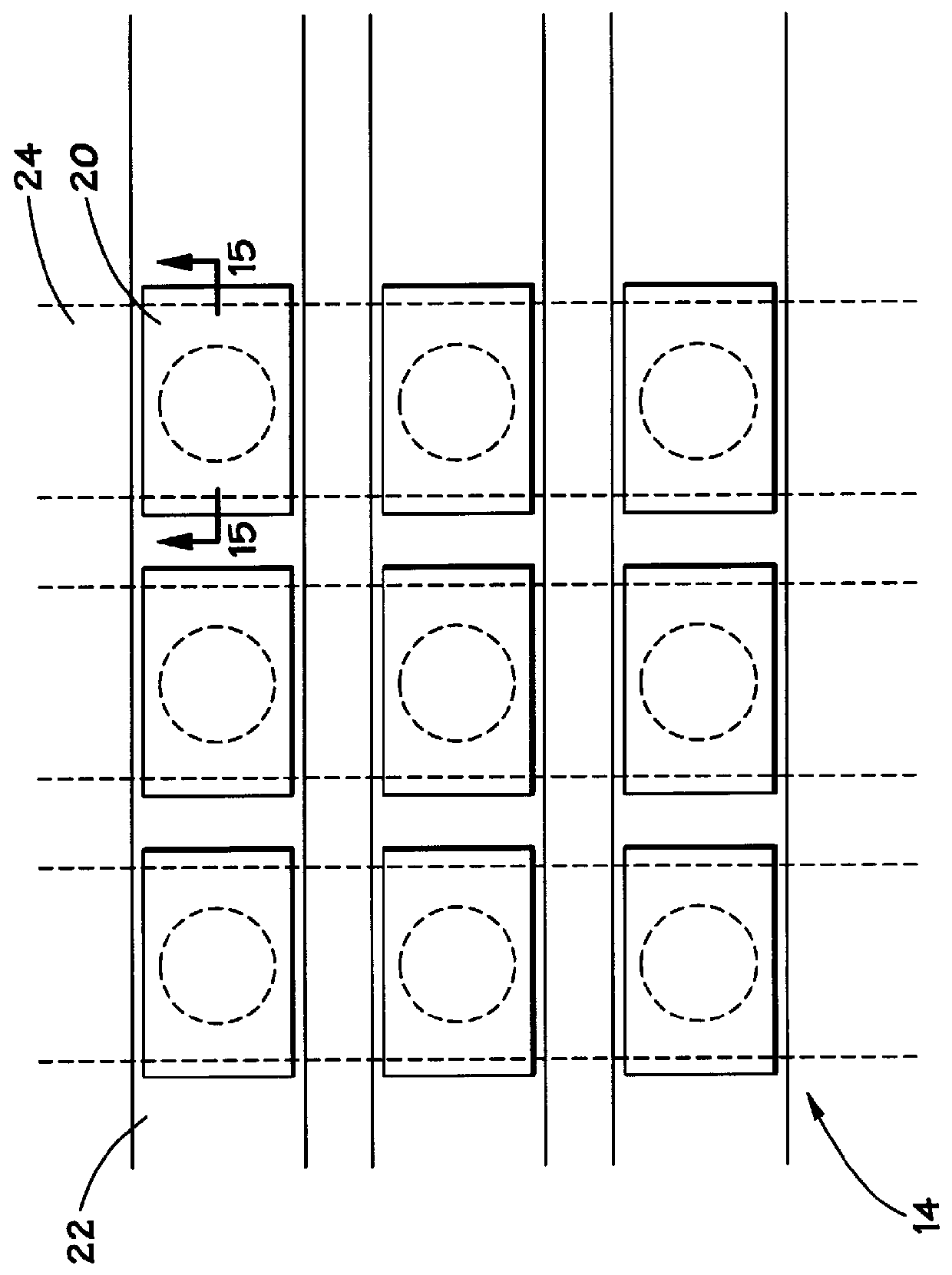
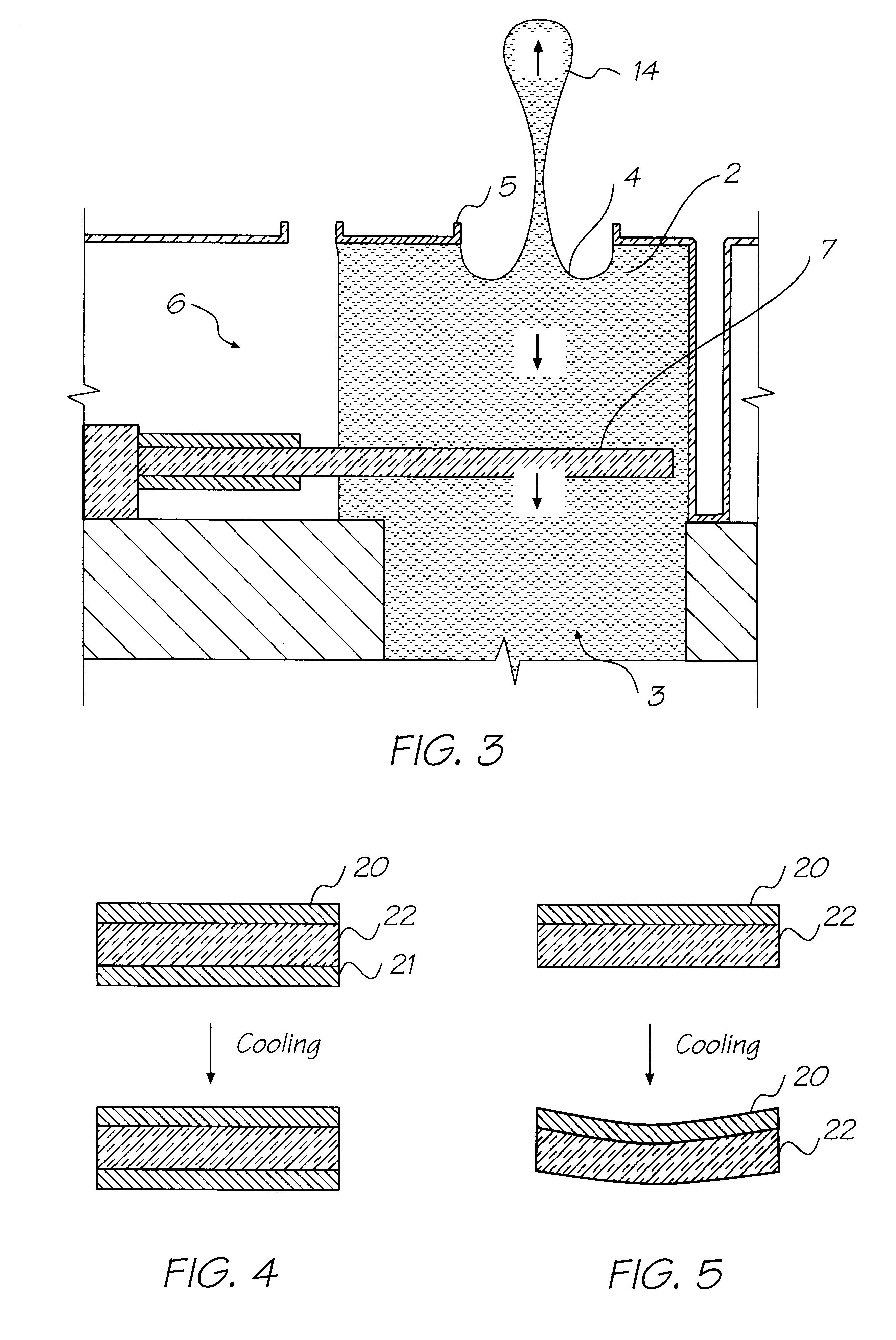
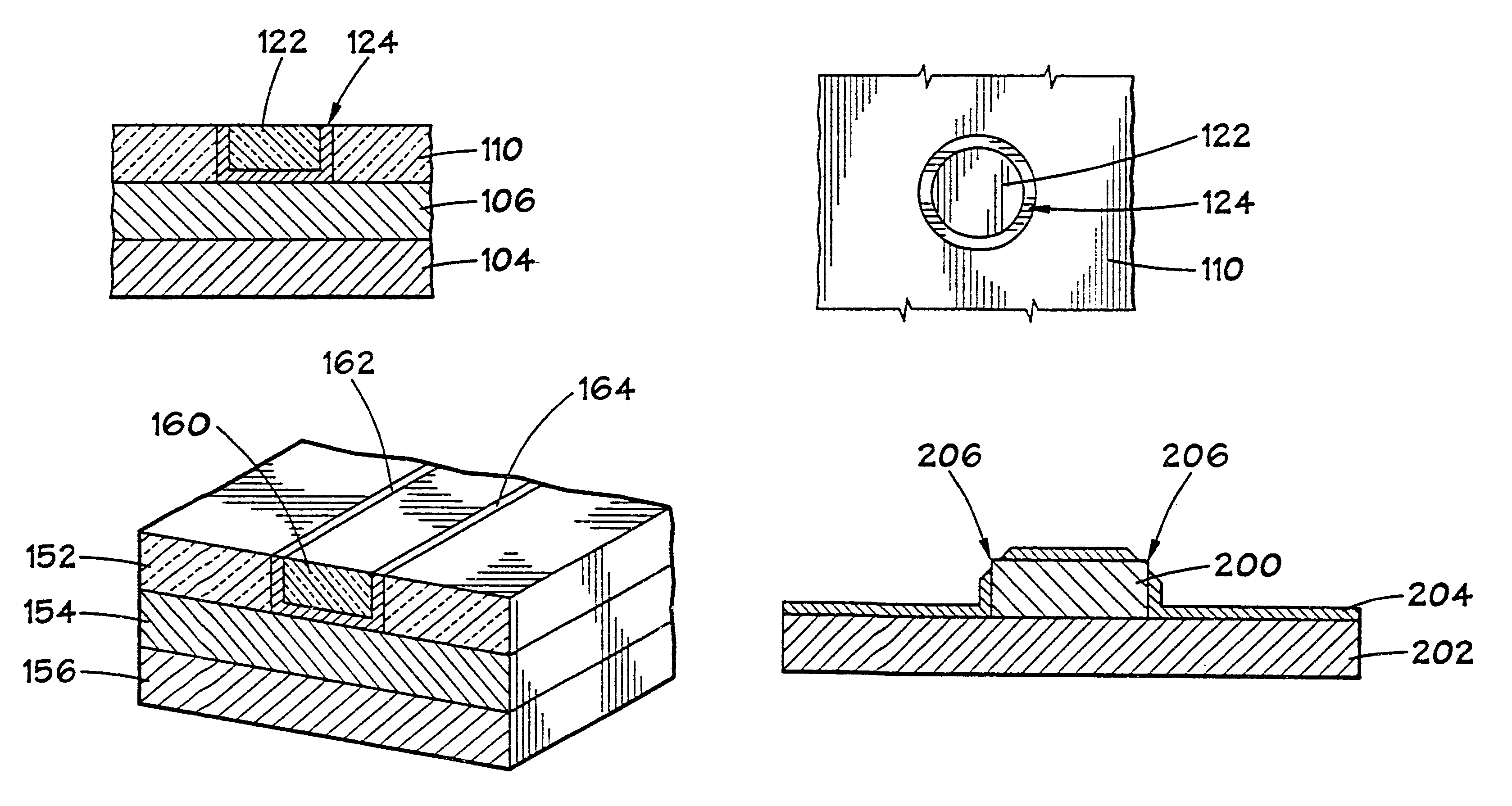
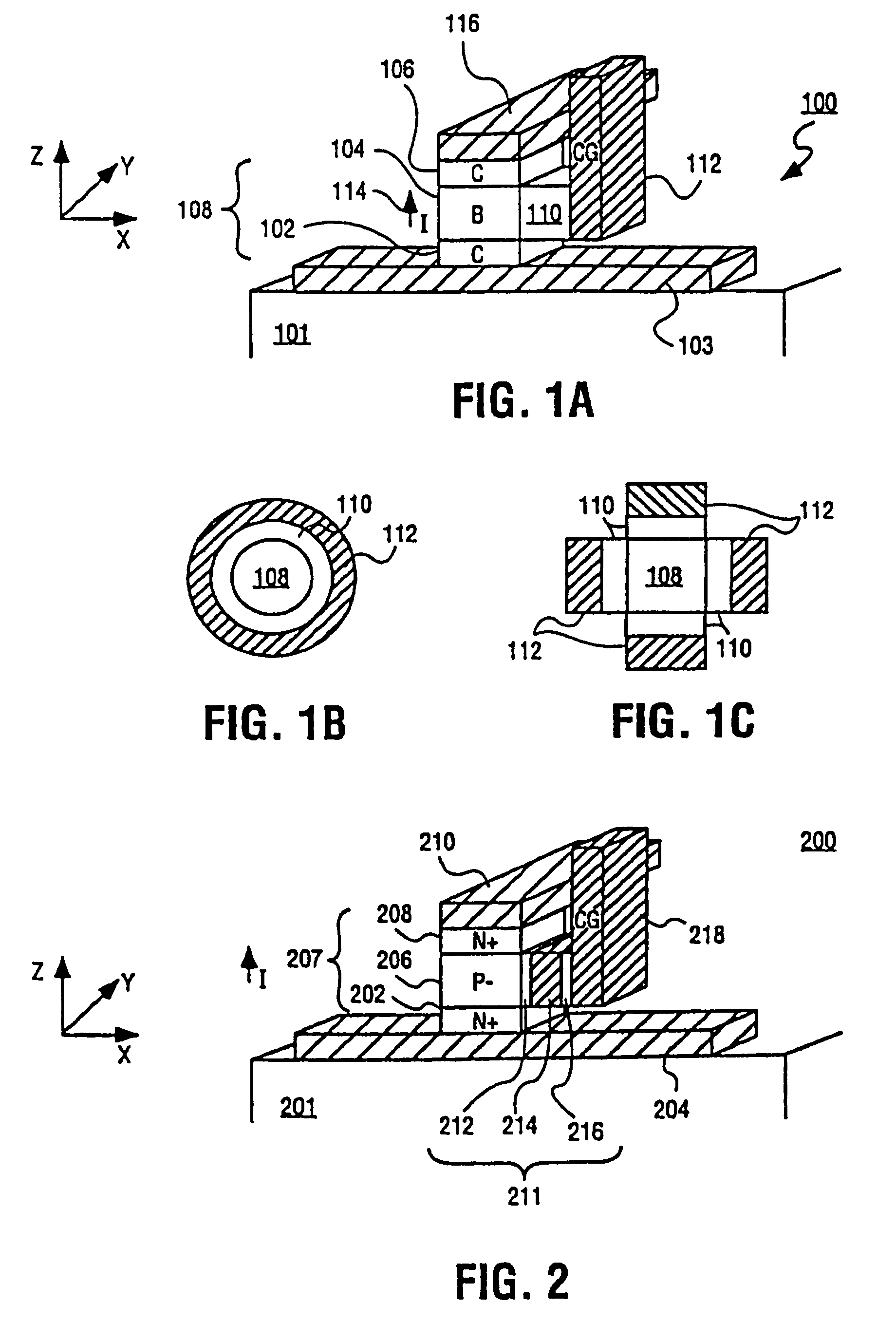
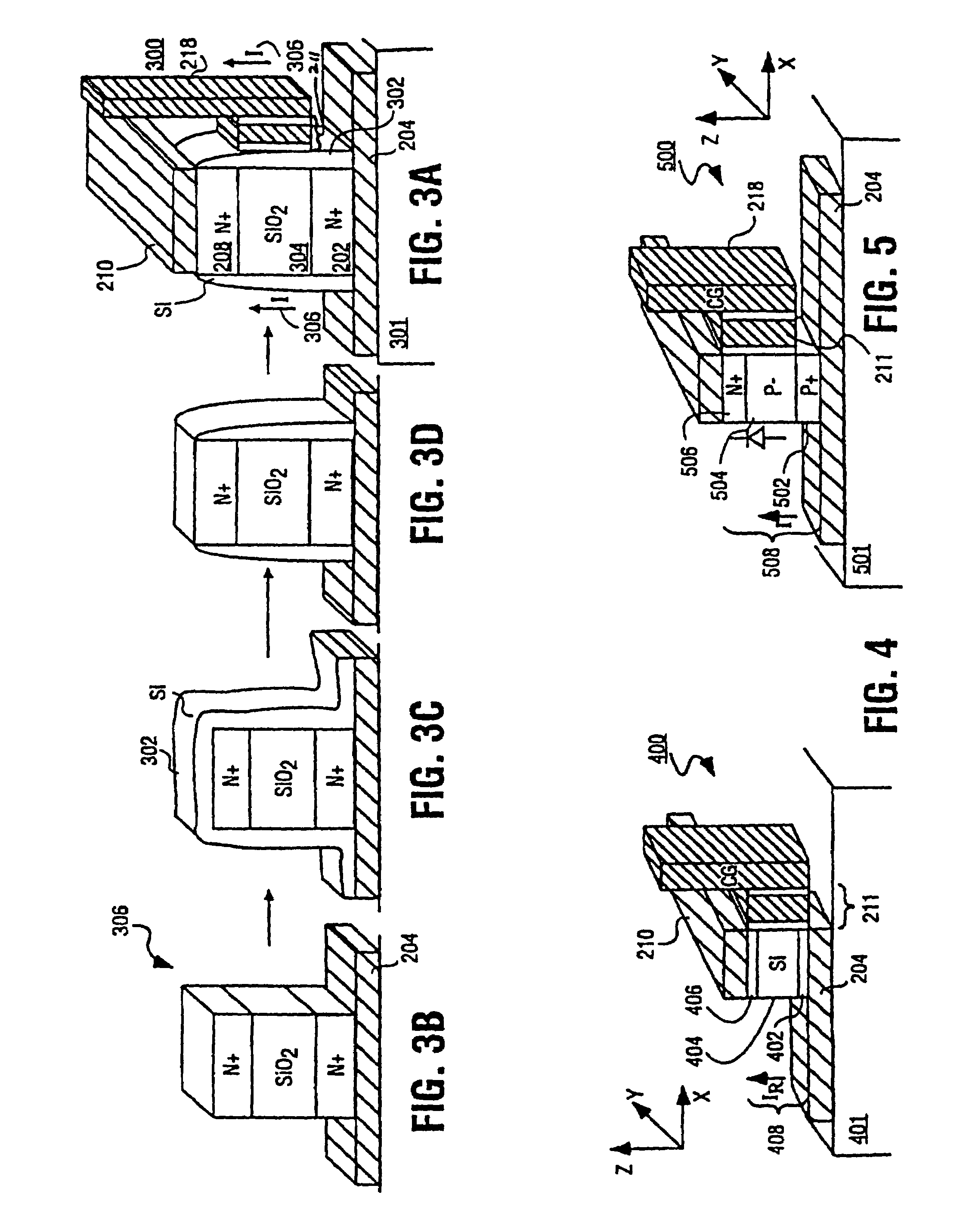
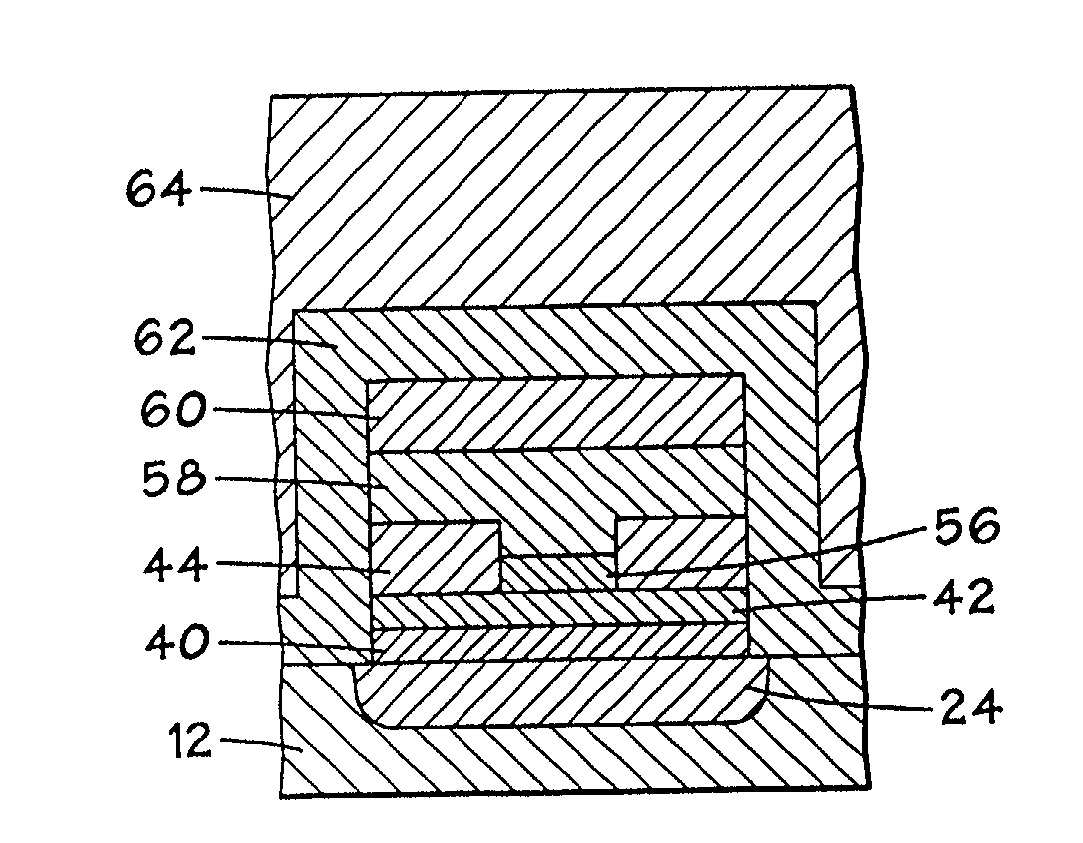
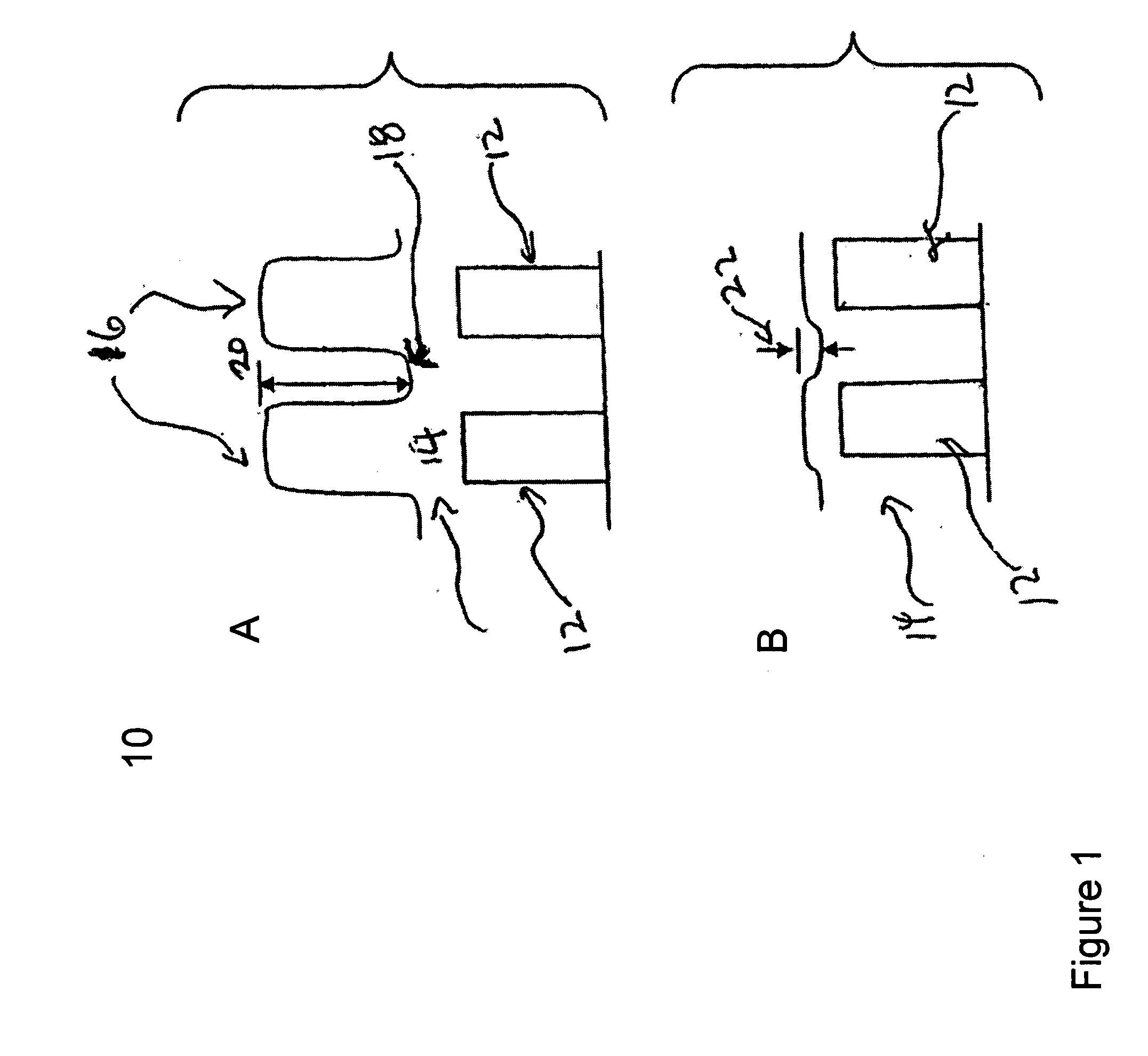
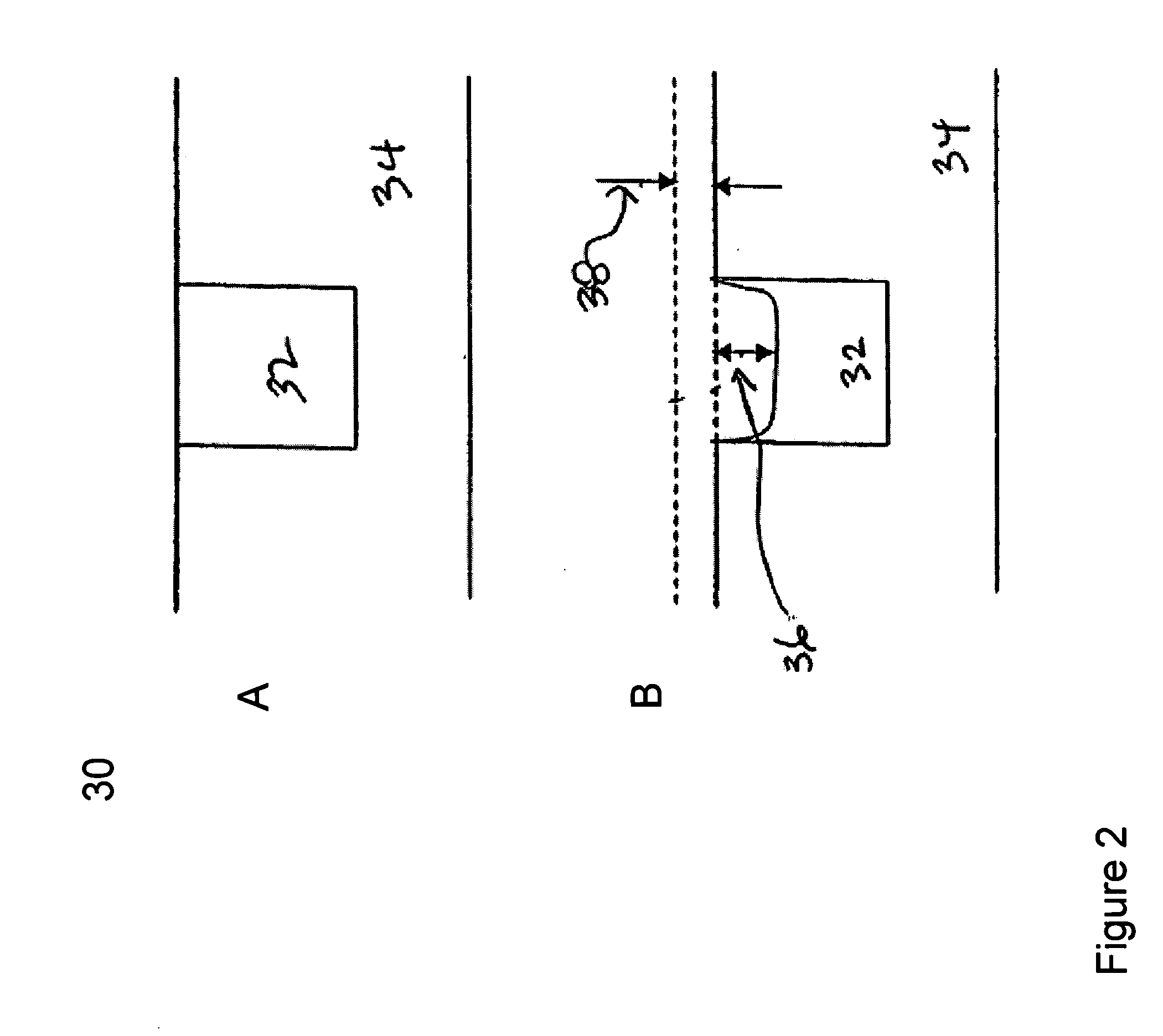
Annular and linear contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
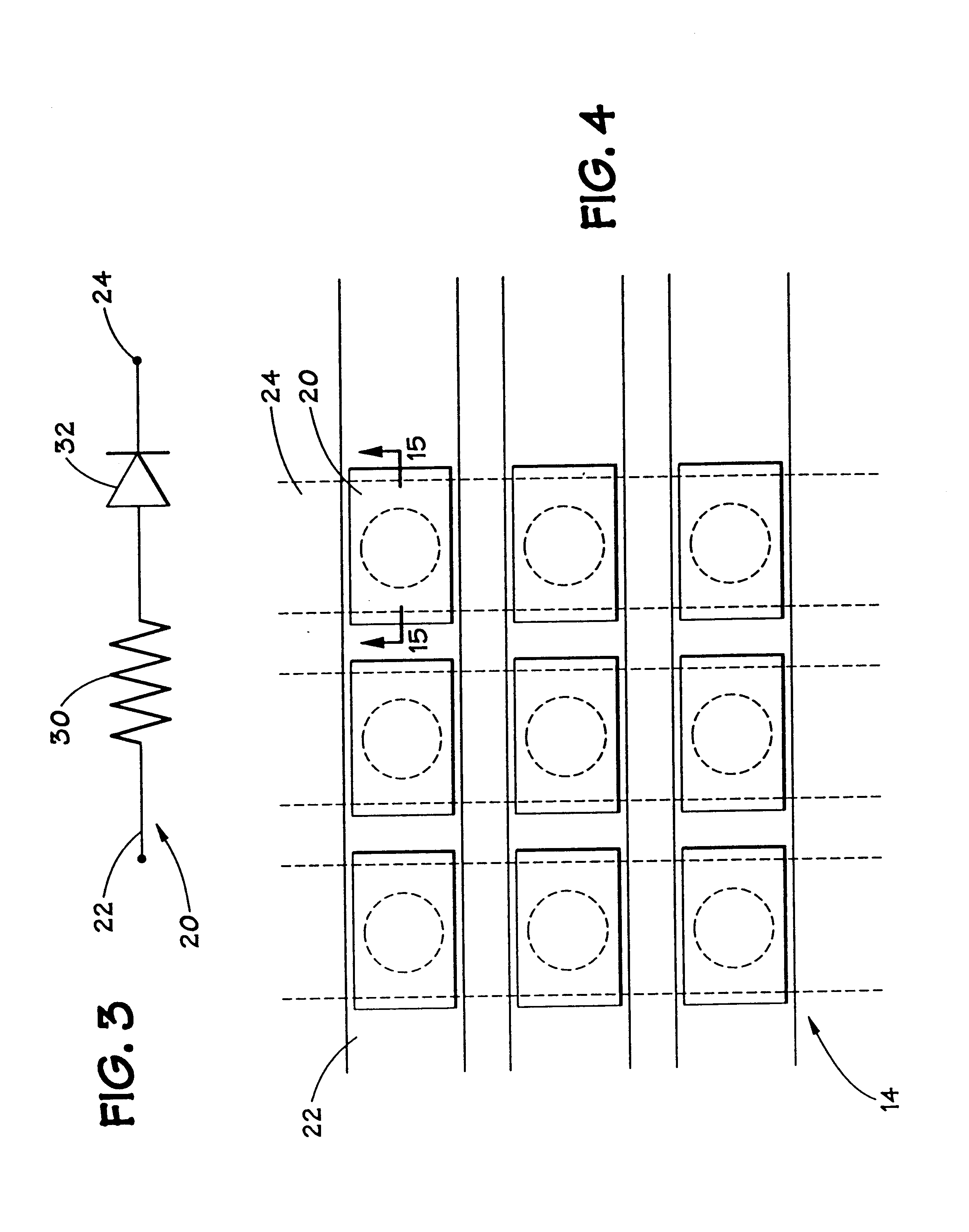
Memory elements and methods for making same
Annular, linear, and point contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
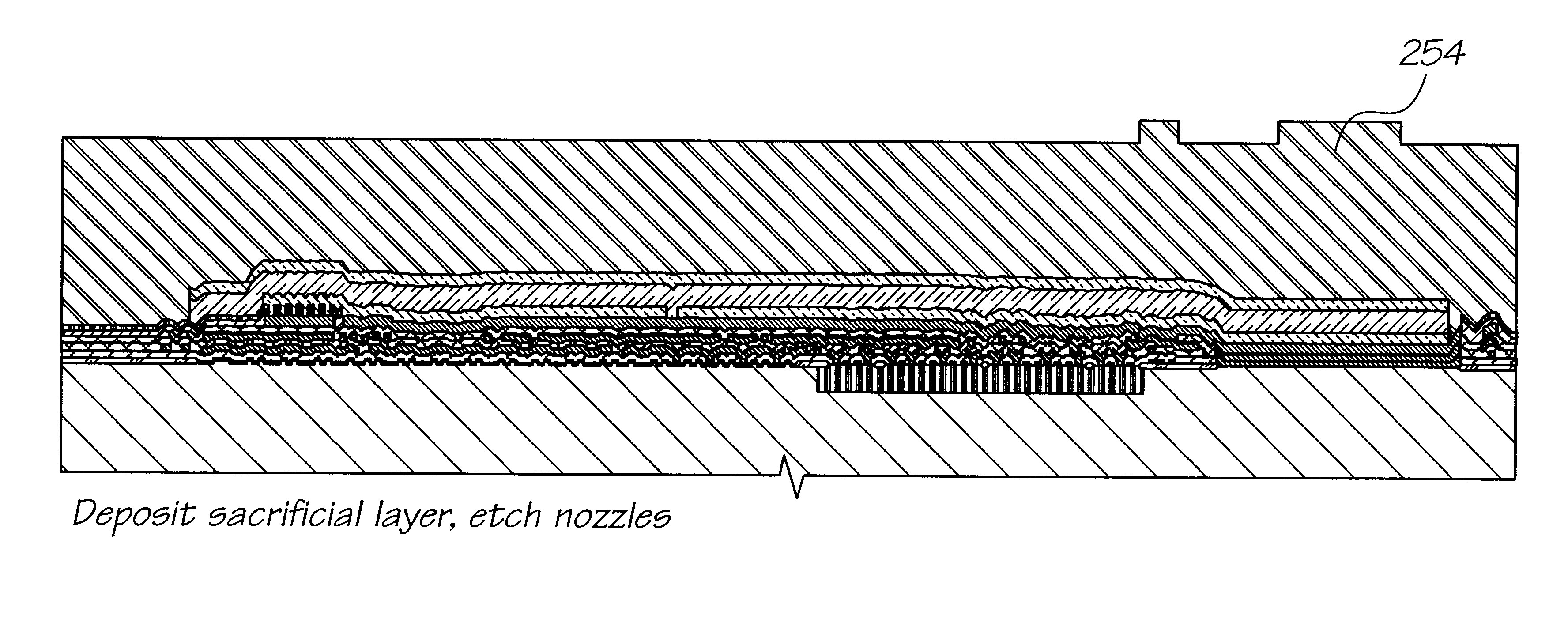
Inkjet printhead having a self aligned nozzle
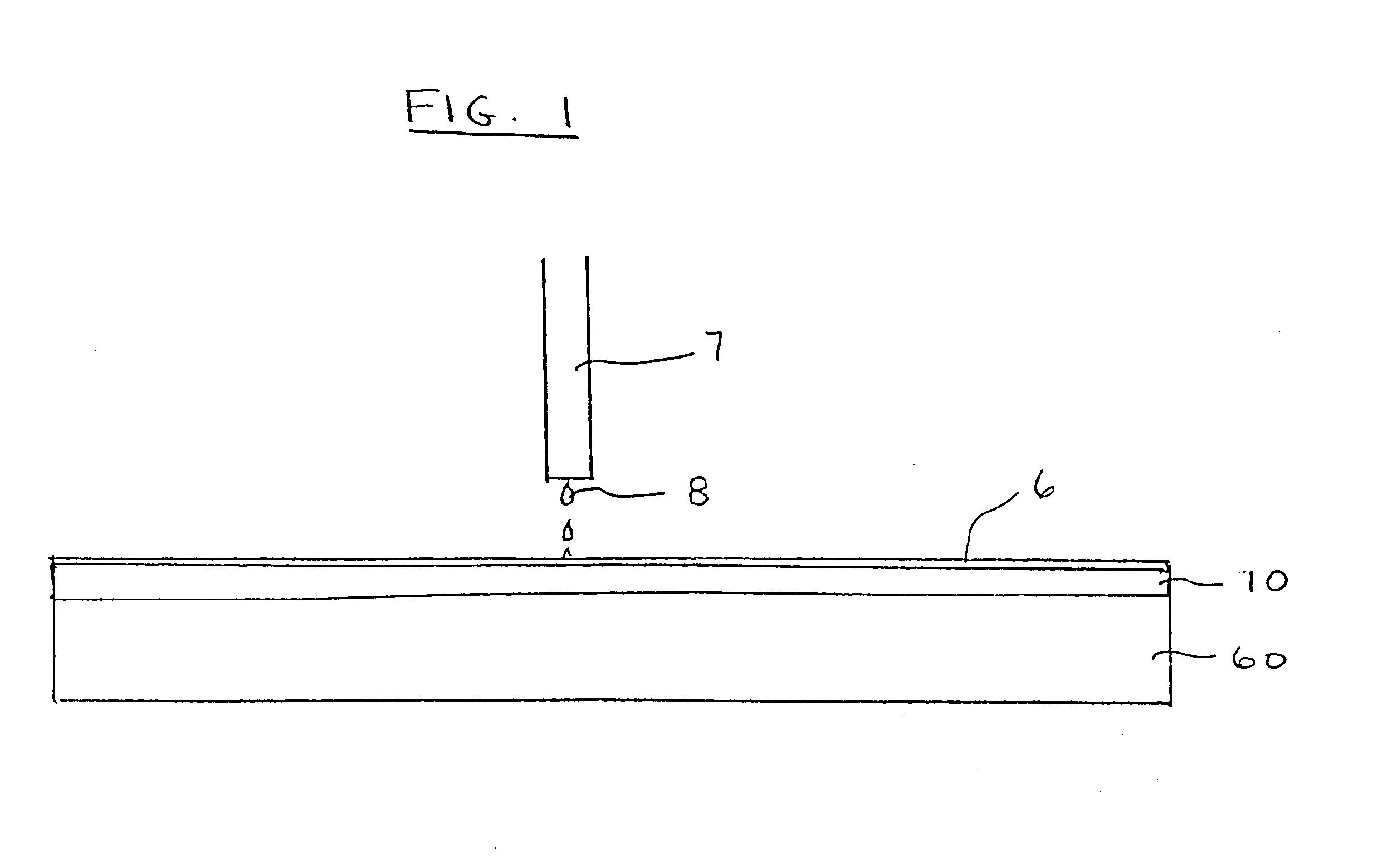
An inkjet printing arrangement having a series of nozzles for the ejection of ink wherein the nozzle rims are formed as a result of the deposition of a rim material layer and a subsequent planar etching of the material layer so as to form the nozzle rim. The planar etching can comprise chemical-mechanical planarization of the rim material layer and any associated sacrificial layers.
Owner:ZAMTEC +1
Method of forming a contact structure in a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6440837B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess deviationsEtching
Annular and linear contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
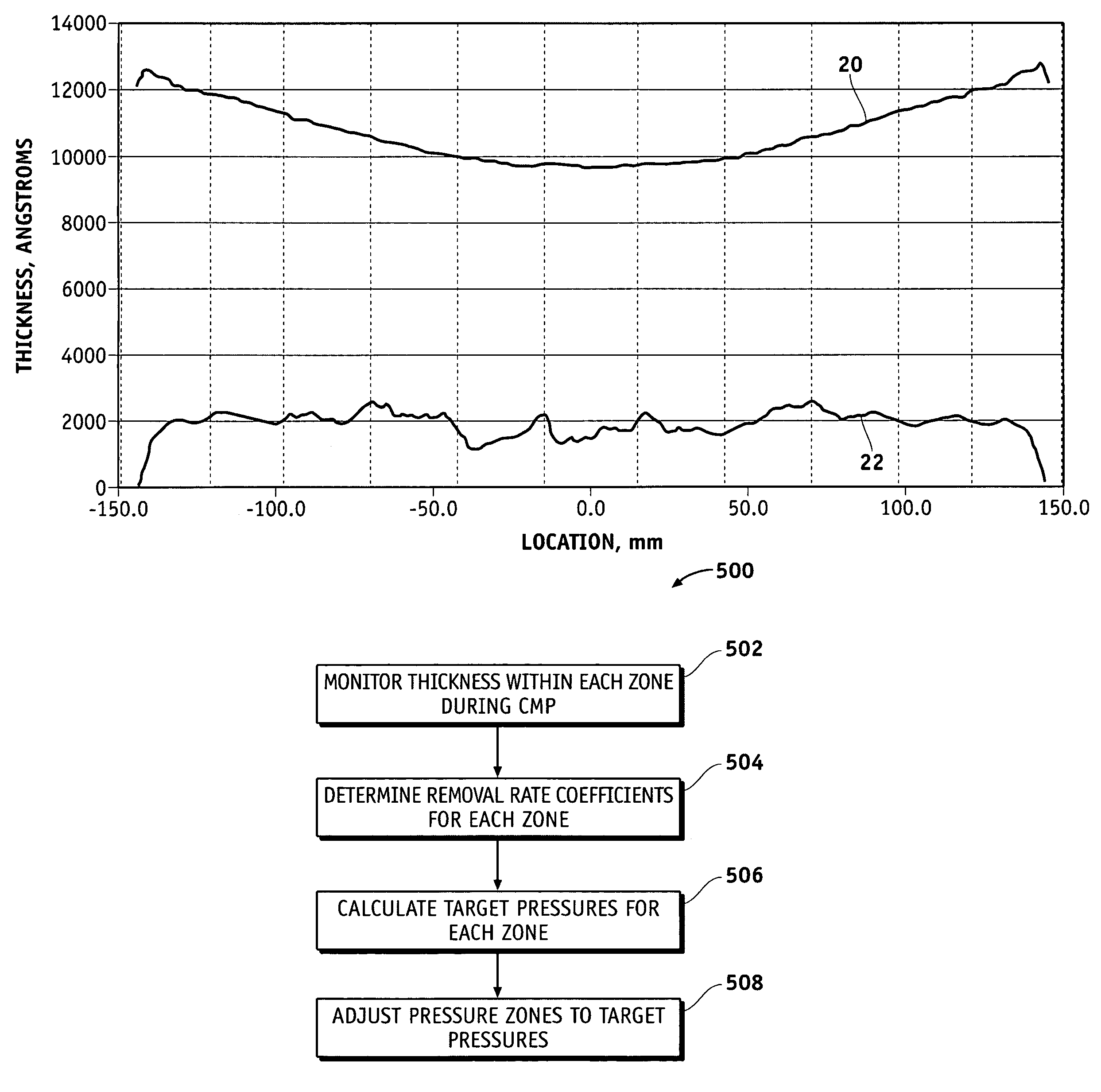
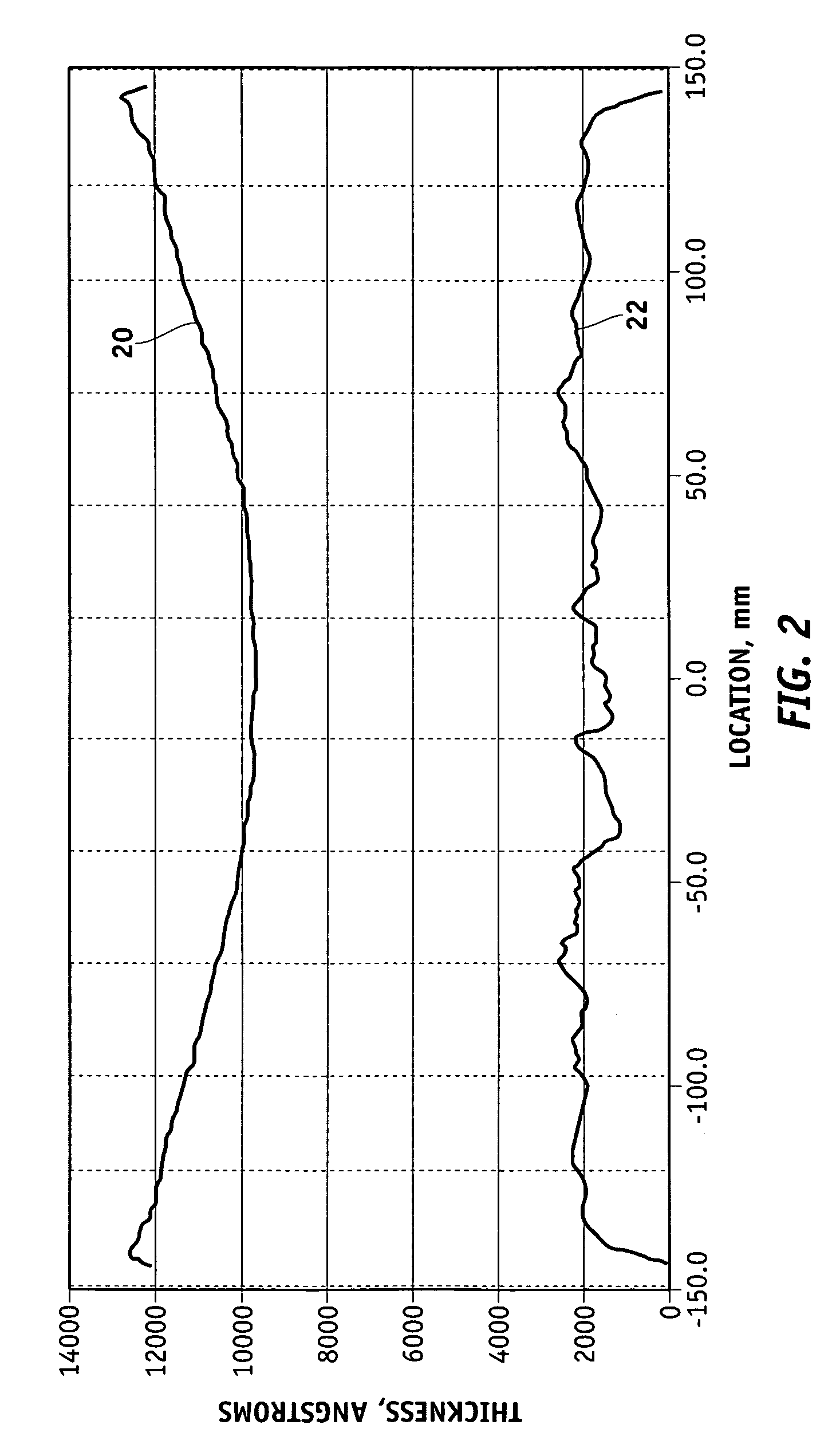
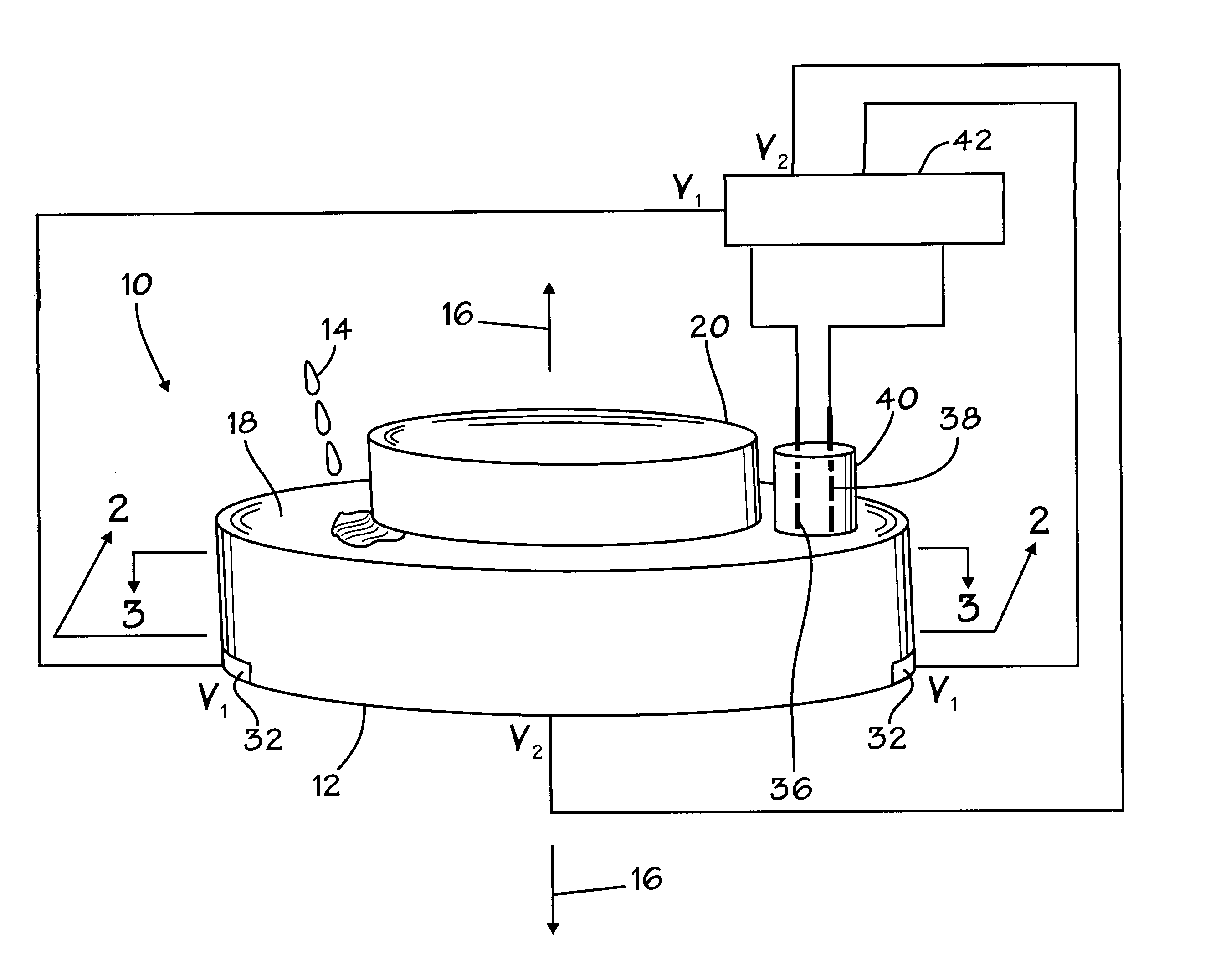
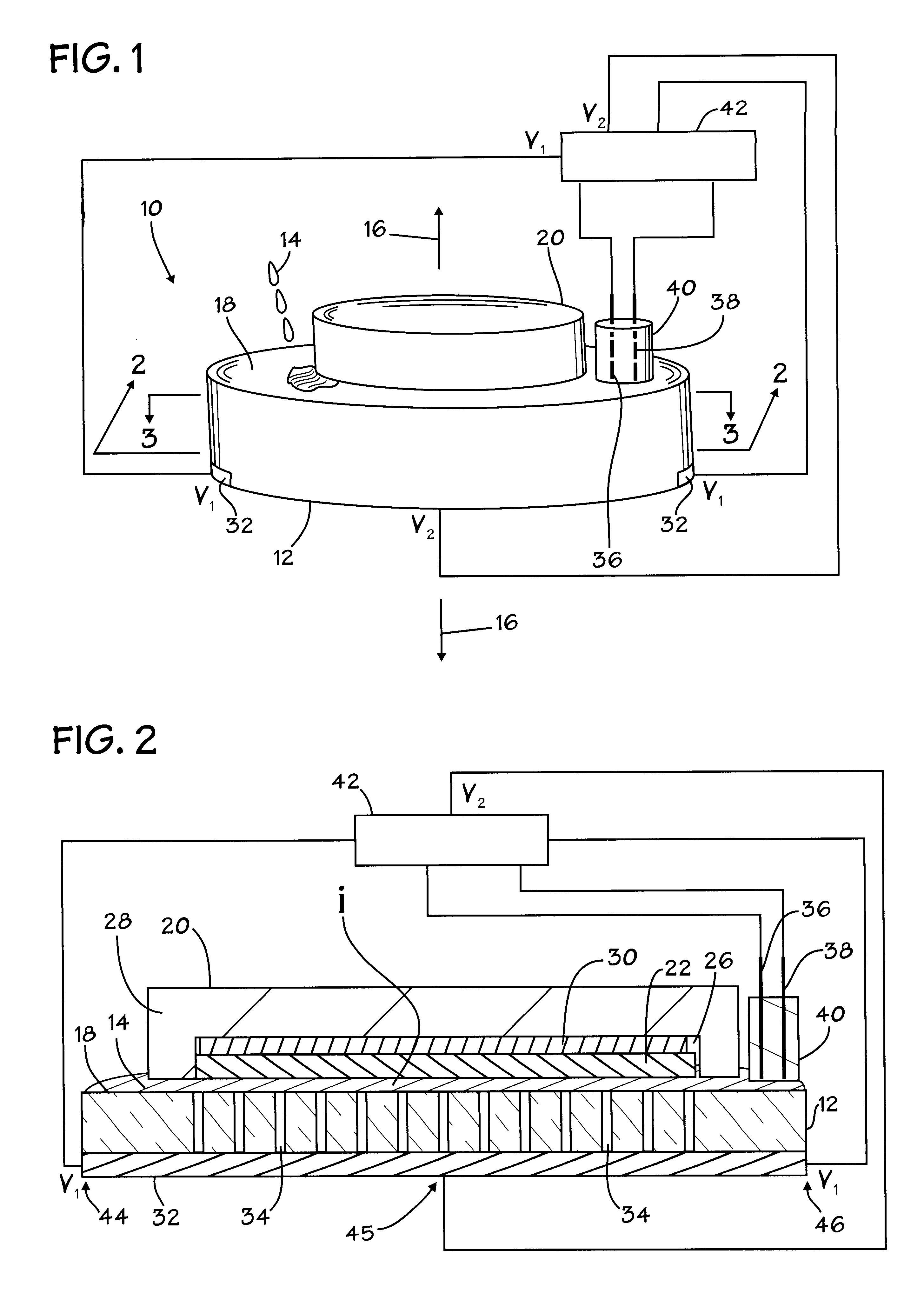
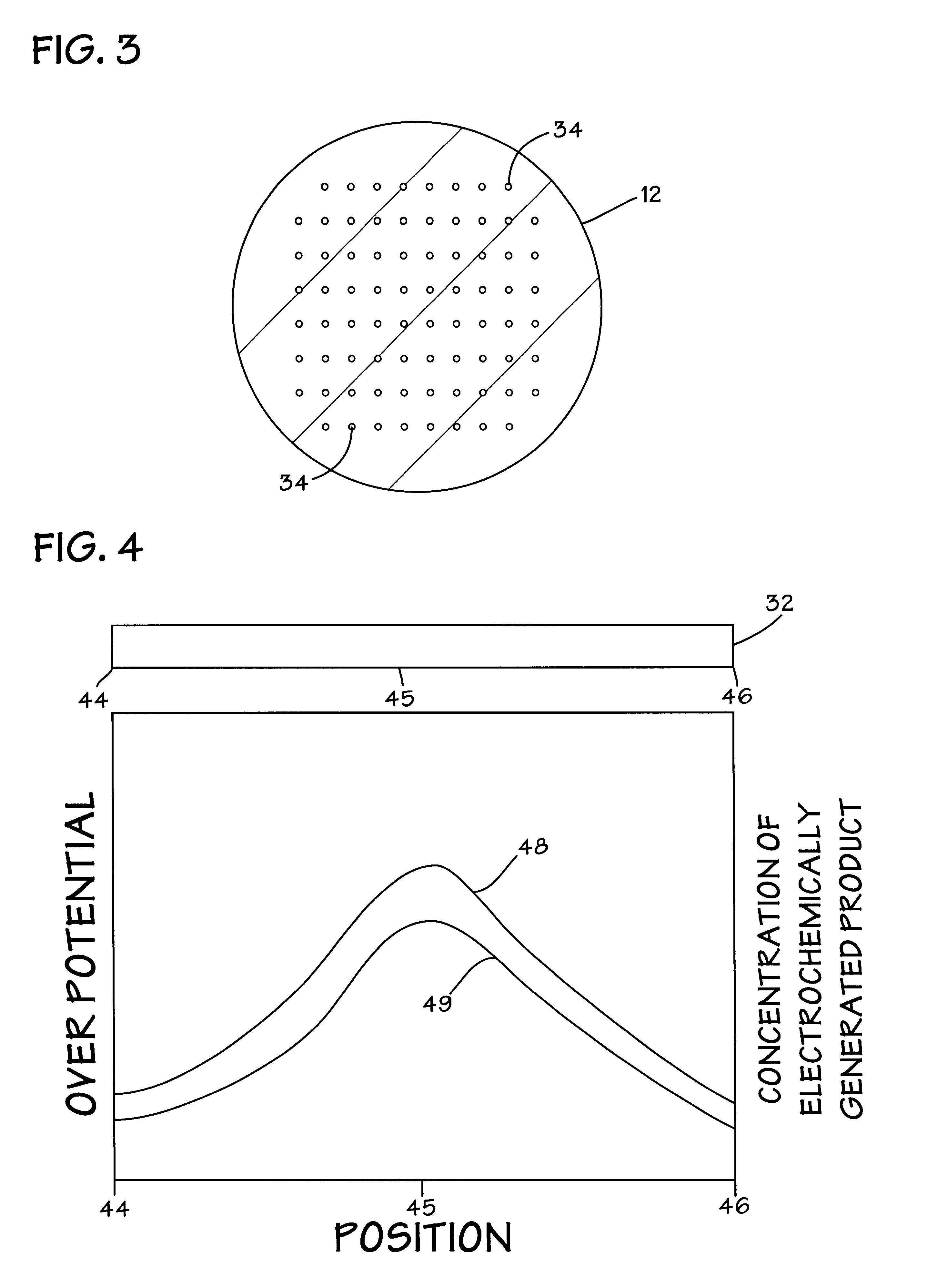
Methods for controlling the pressures of adjustable pressure zones of a work piece carrier during chemical mechanical planarization
ActiveUS7115017B1Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringChemical-mechanical planarization
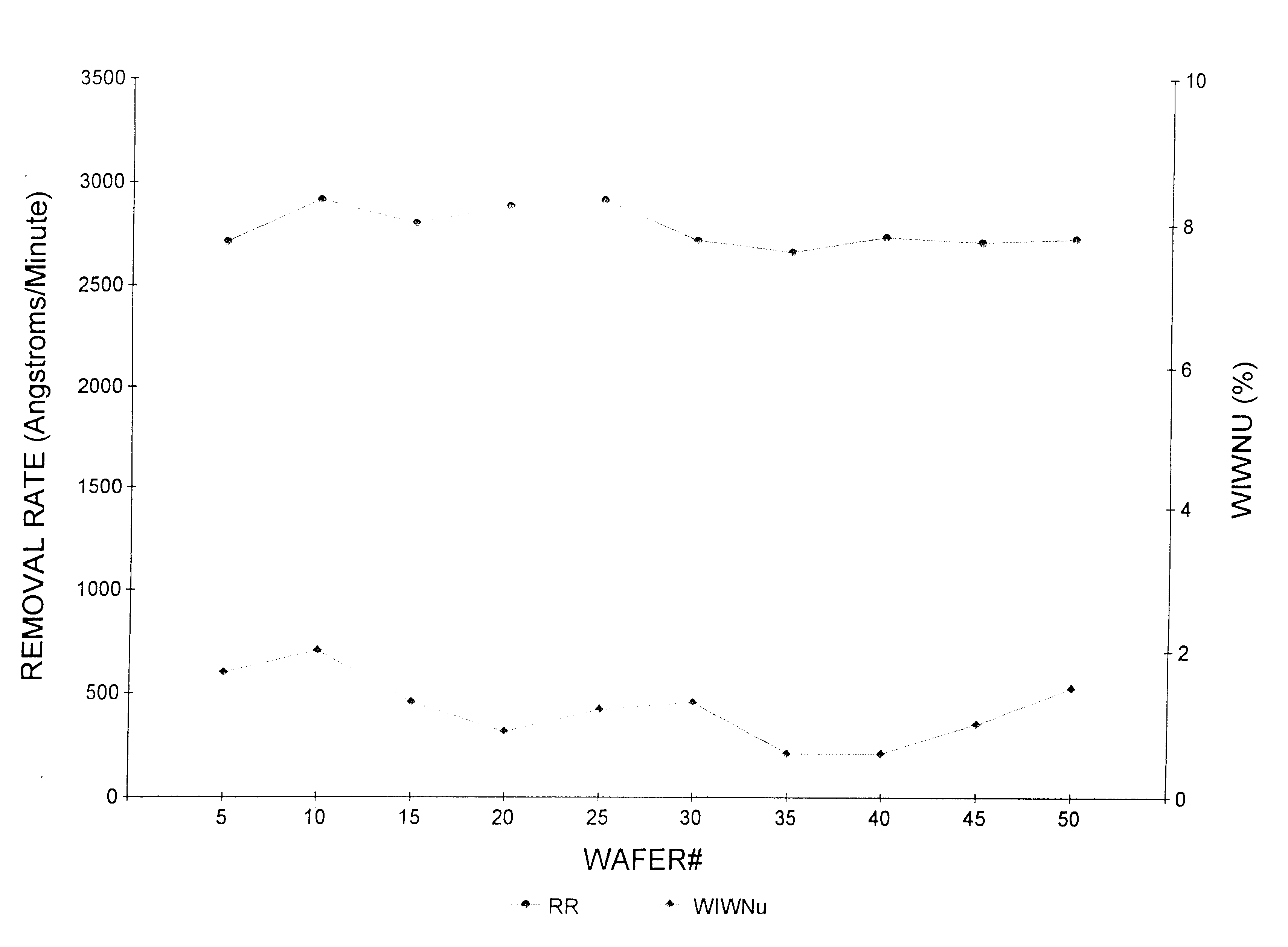
Methods are provided for controlling adjustable pressure zones of a CMP carrier. A method comprises determining a first thickness of a layer on a wafer underlying a first zone of the carrier. A first portion of the layer underlying the first zone is removed. The first zone is configured to exert a first pressure against the second surface of the wafer. A second thickness of the layer underlying the first zone is determined and a target thickness corresponding to a predetermined thickness profile is selected. A second pressure for the first zone is calculated using the first thickness, the second thickness, the first pressure, and the target thickness. The pressure exerted by the first zone against the second surface of the wafer is adjusted to the second pressure and the steps are repeated for a second zone.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Slurry compositions for chemical mechanical polishing of copper and barrier films
InactiveUS20050090104A1High selectivityShorten the counting processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolishing compositions with abrasivesSlurryPolymer
Owner:INNOVATIUM TECH
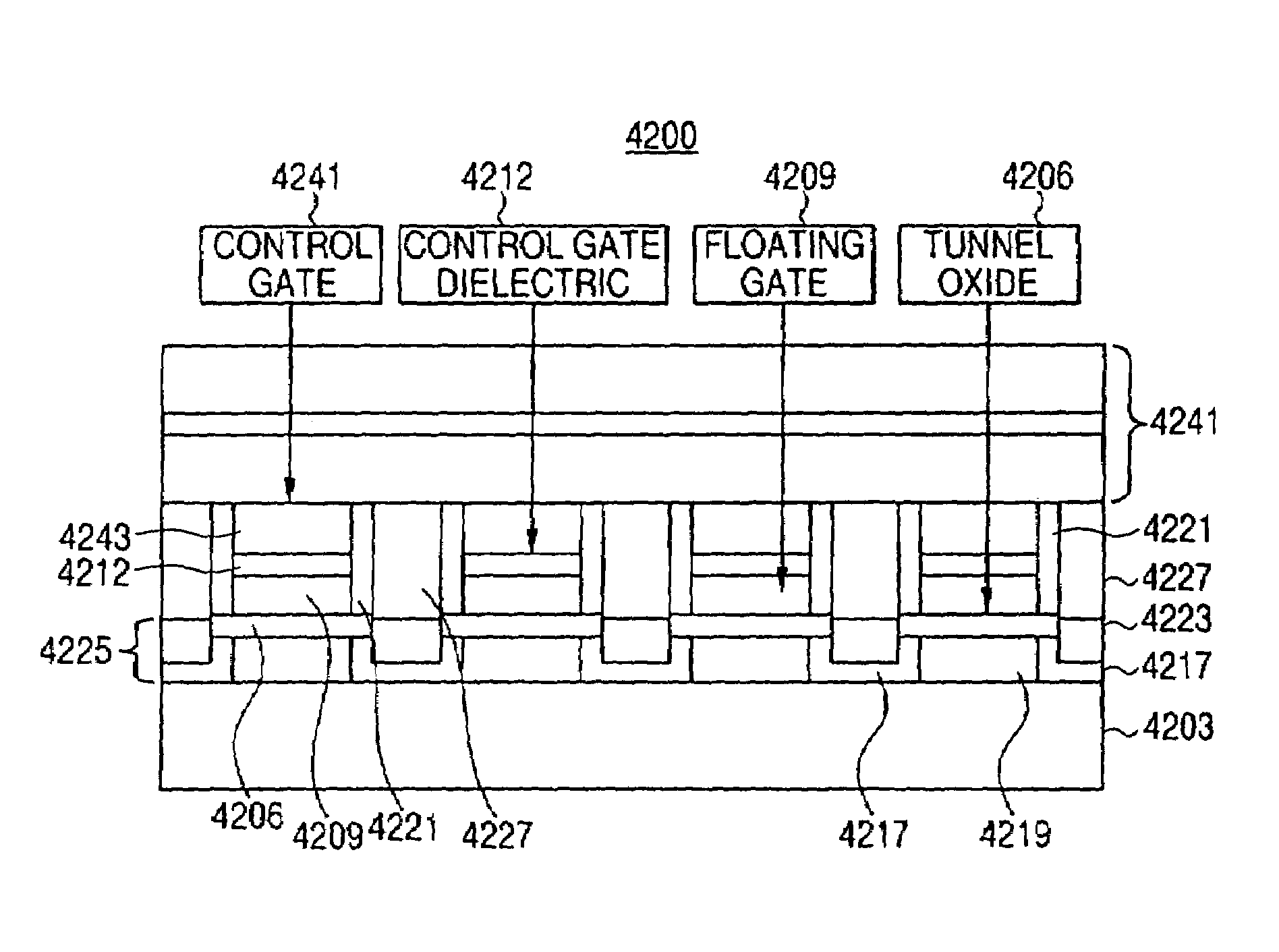
Dense arrays and charge storage devices
Owner:WODEN TECH INC
Memory elements and methods for making same
InactiveUS20020160551A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess deviationsEtching
Annular, linear, and point contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
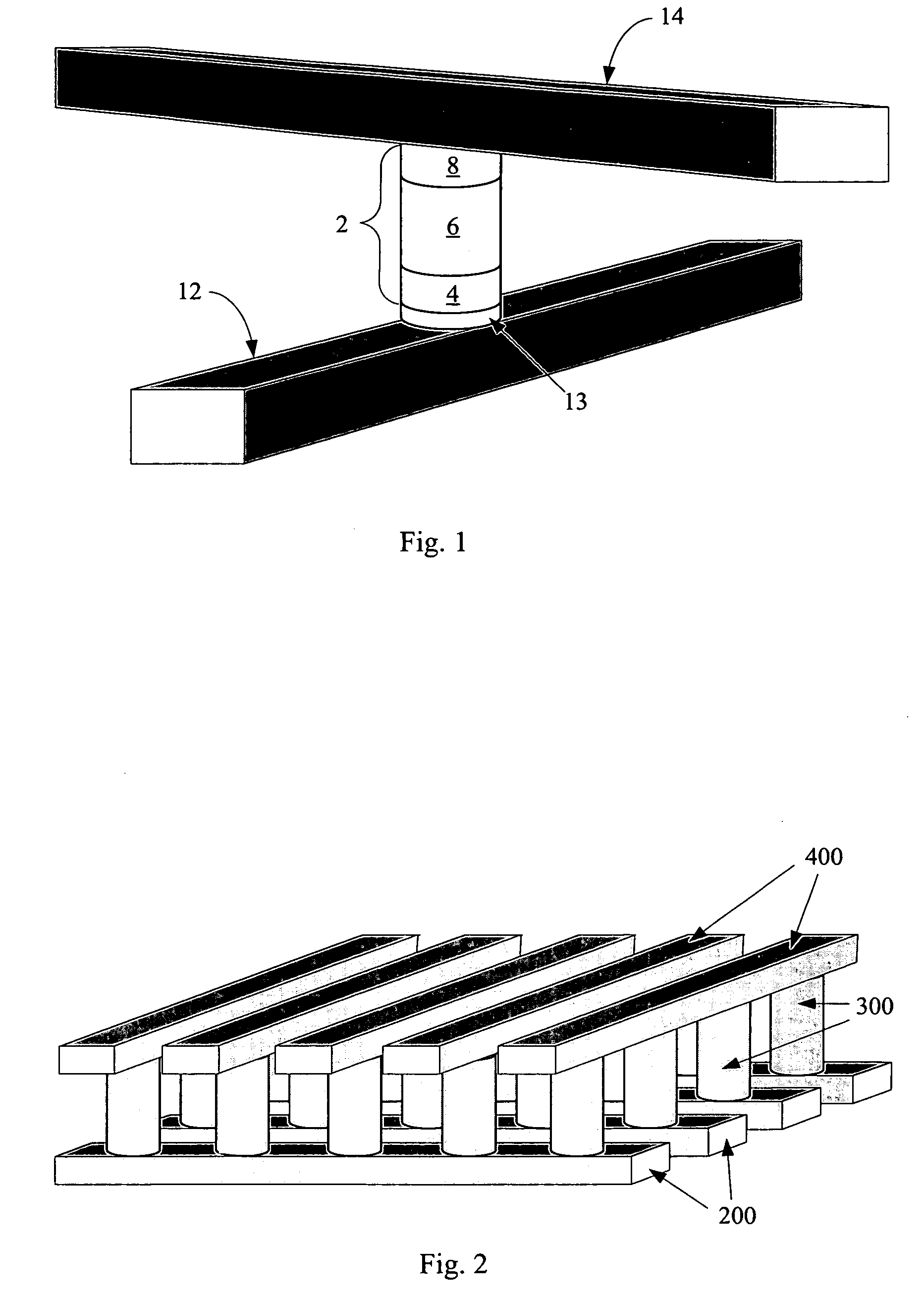
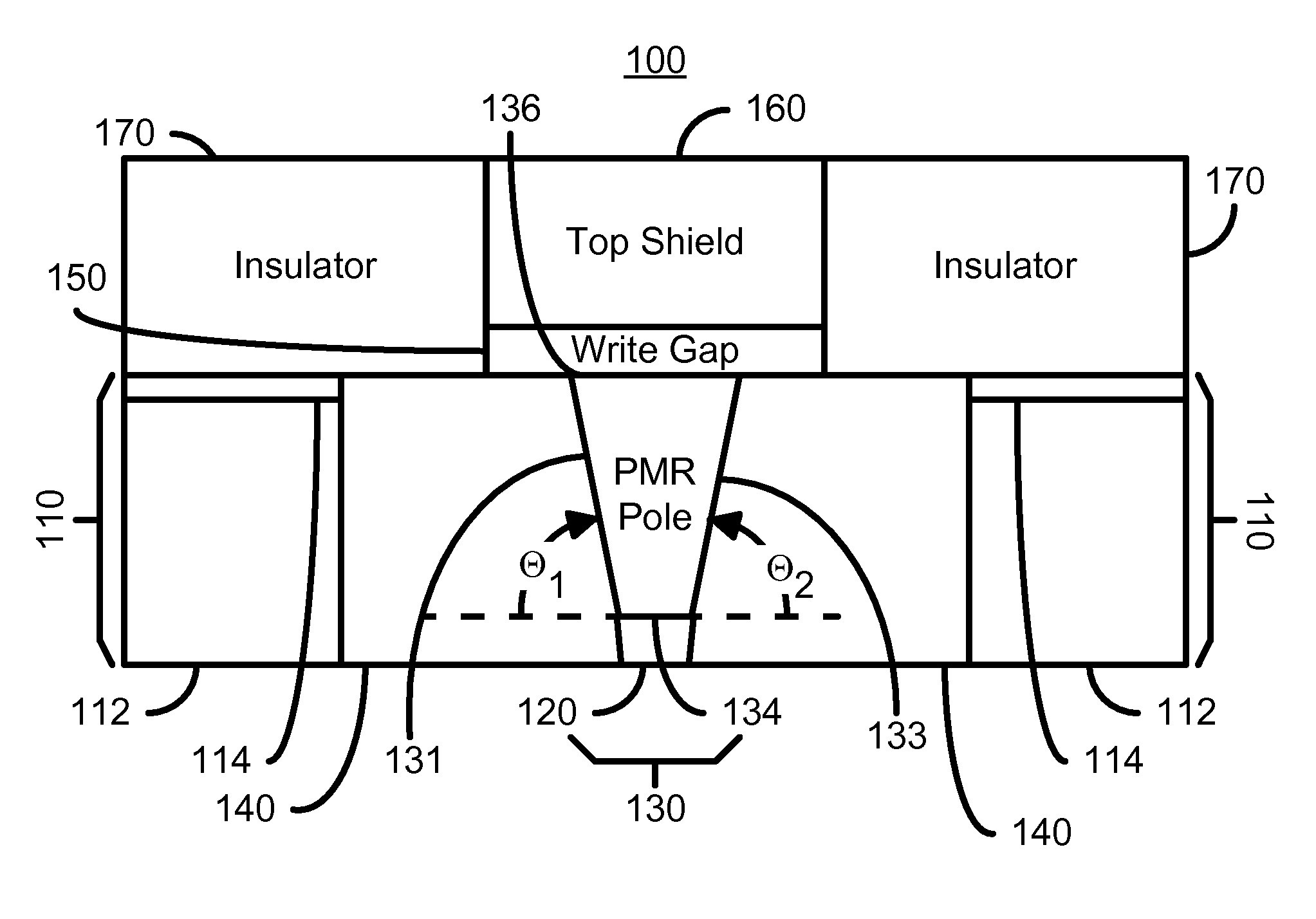
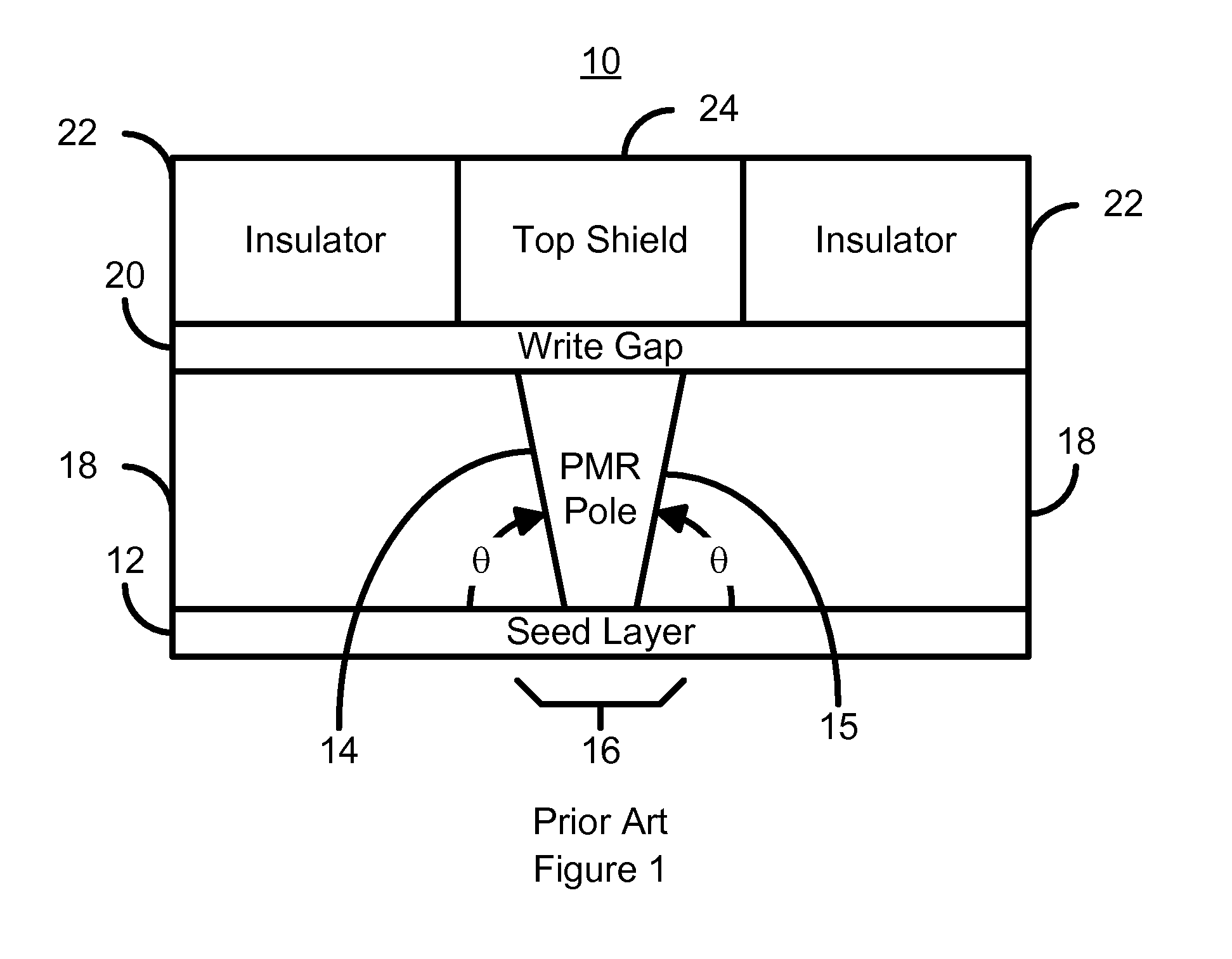
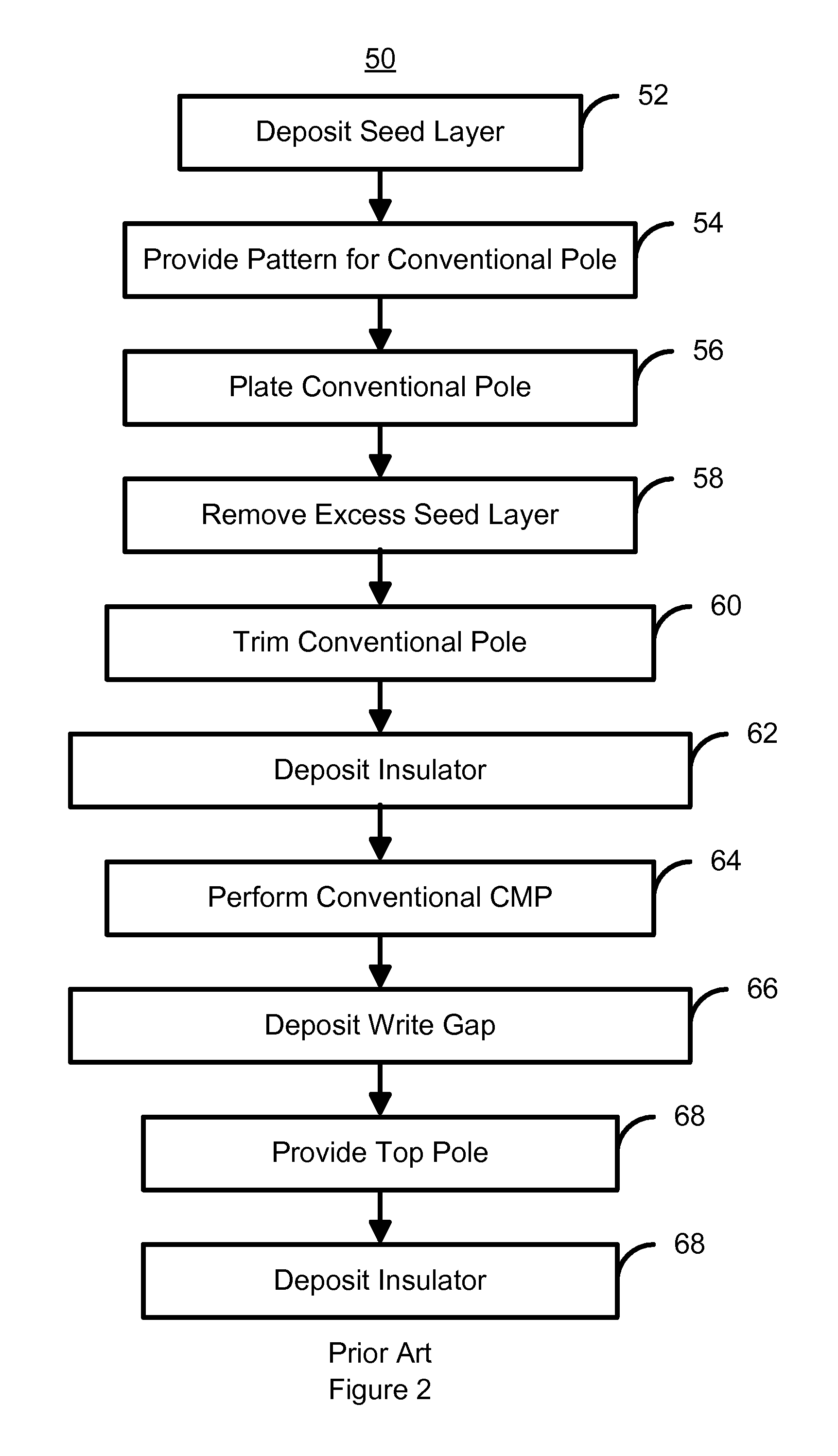
Method for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording head
InactiveUS7296339B1Construction of head windingsElectrical transducersEngineeringChemical-mechanical planarization
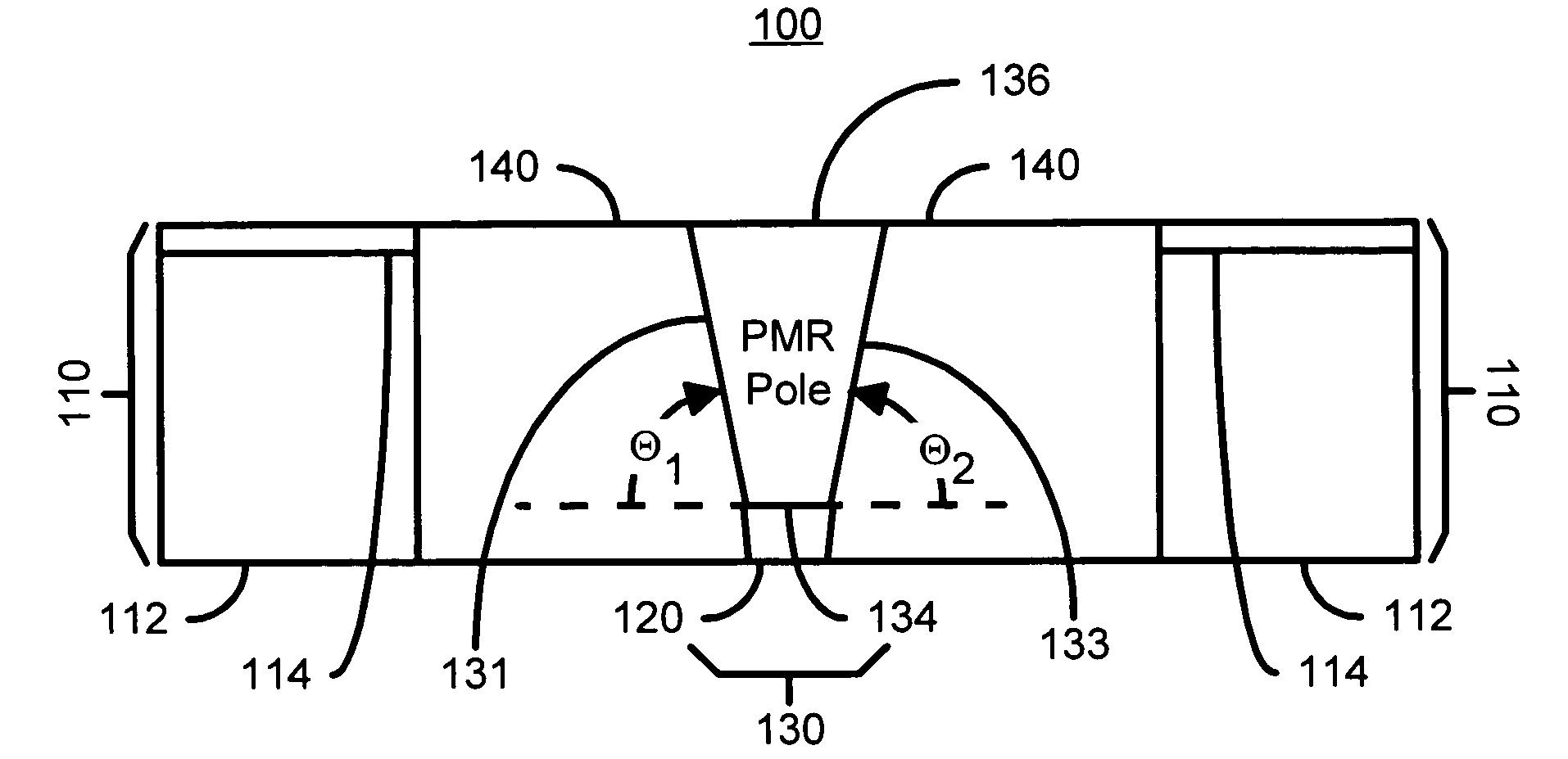
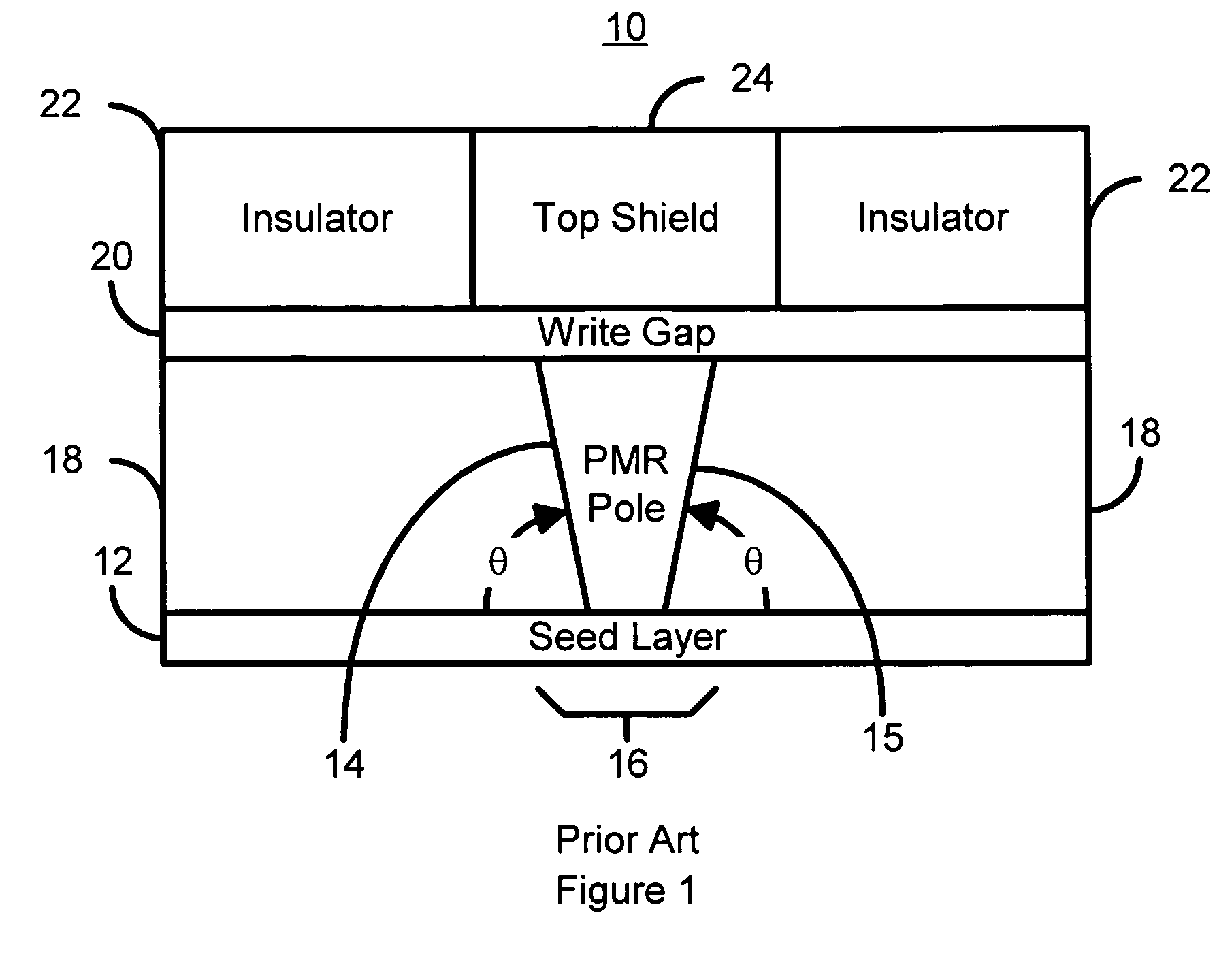
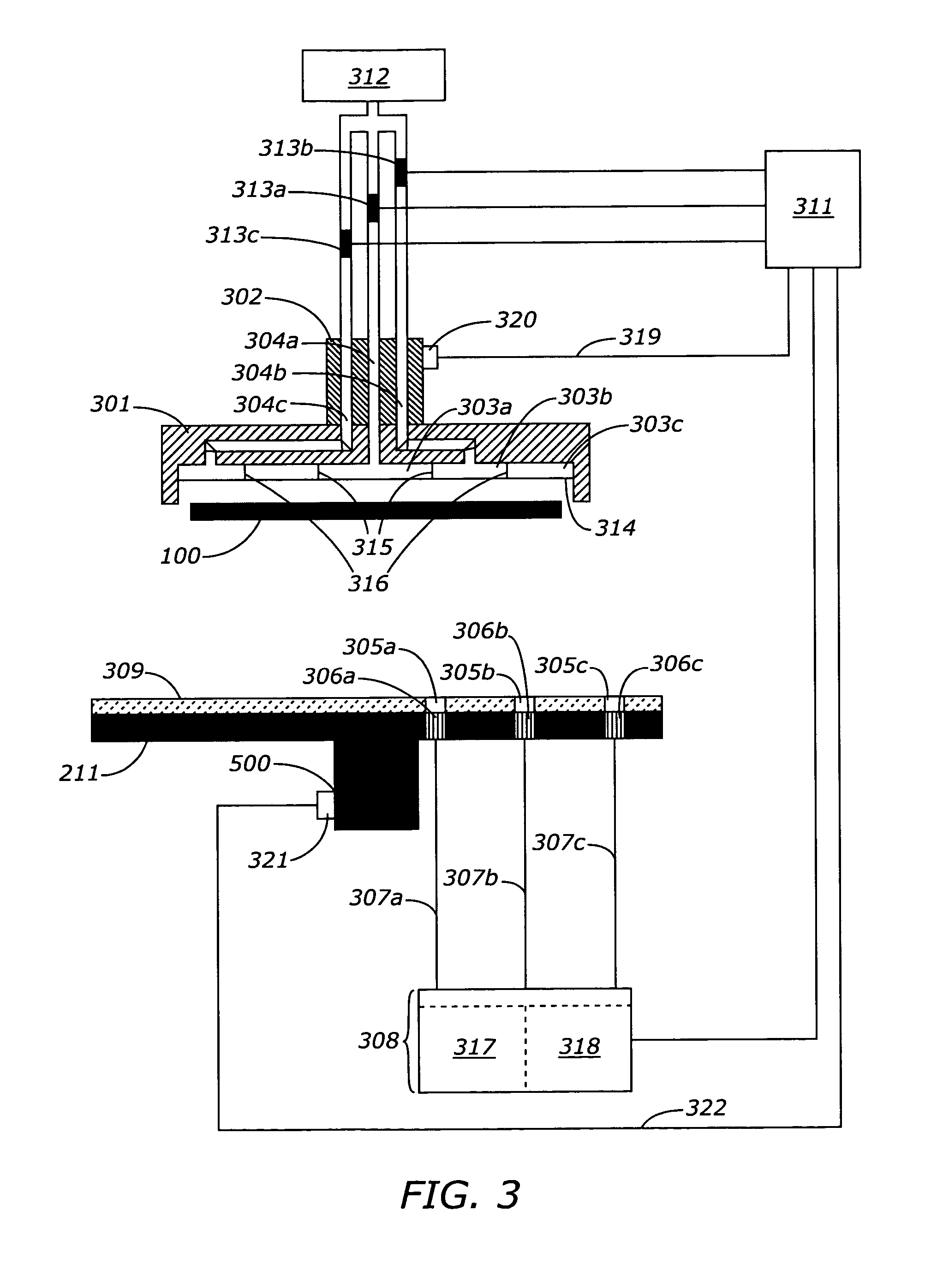
A method and system for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording head is disclosed. The method and system include providing a chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) uniformity structure having an aperture therein and forming a perpendicular magnetic recording pole within the aperture. The CMP uniformity structure may include a CMP barrier layer. The method and system further include fabricating an insulator after formation of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and performing a CMP to remove a portion of the insulator, expose a portion of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and planarize an exposed surface of the perpendicular magnetic recording head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method to minimize formation of recess at surface planarized by chemical mechanical planarization
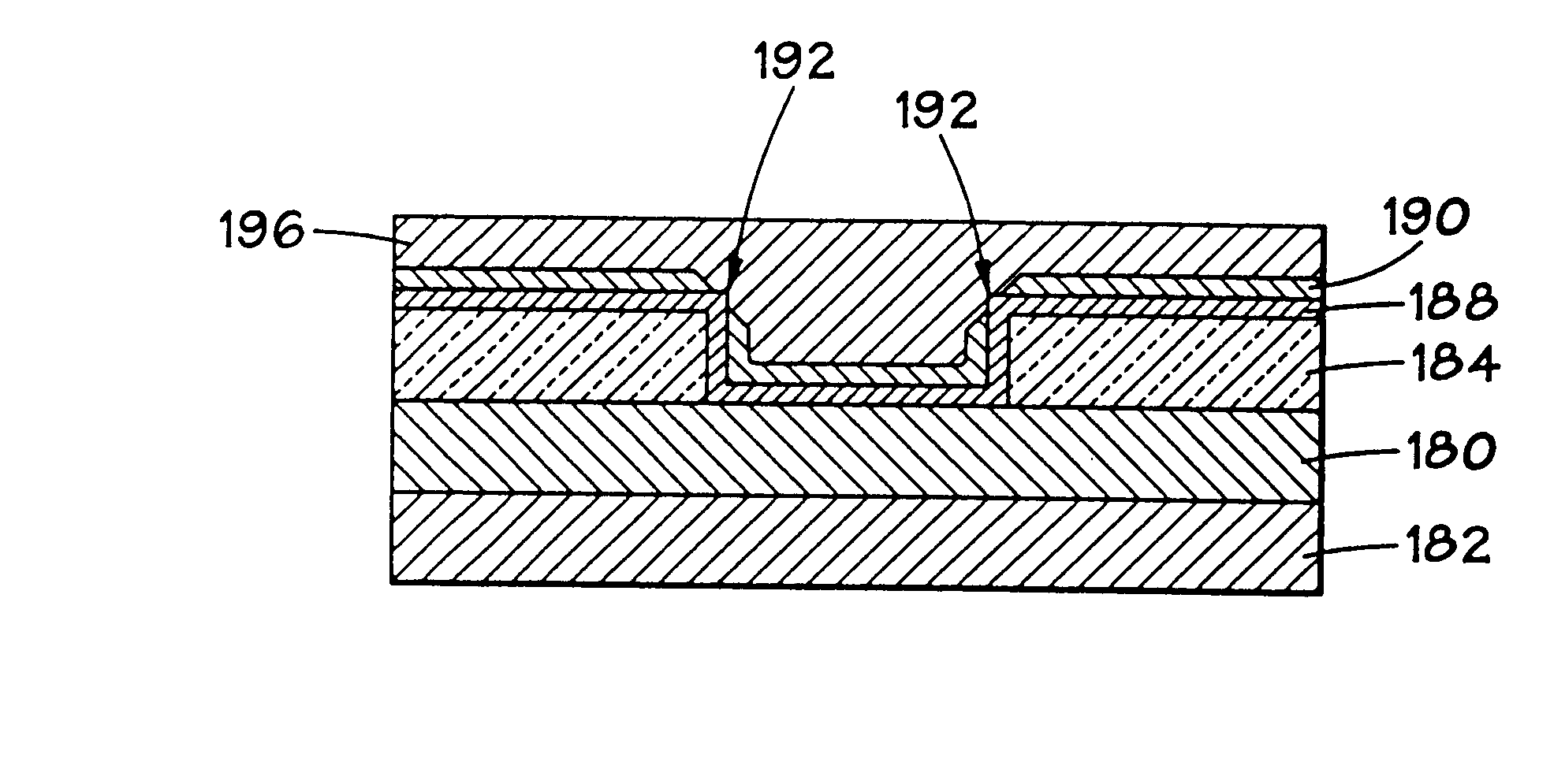
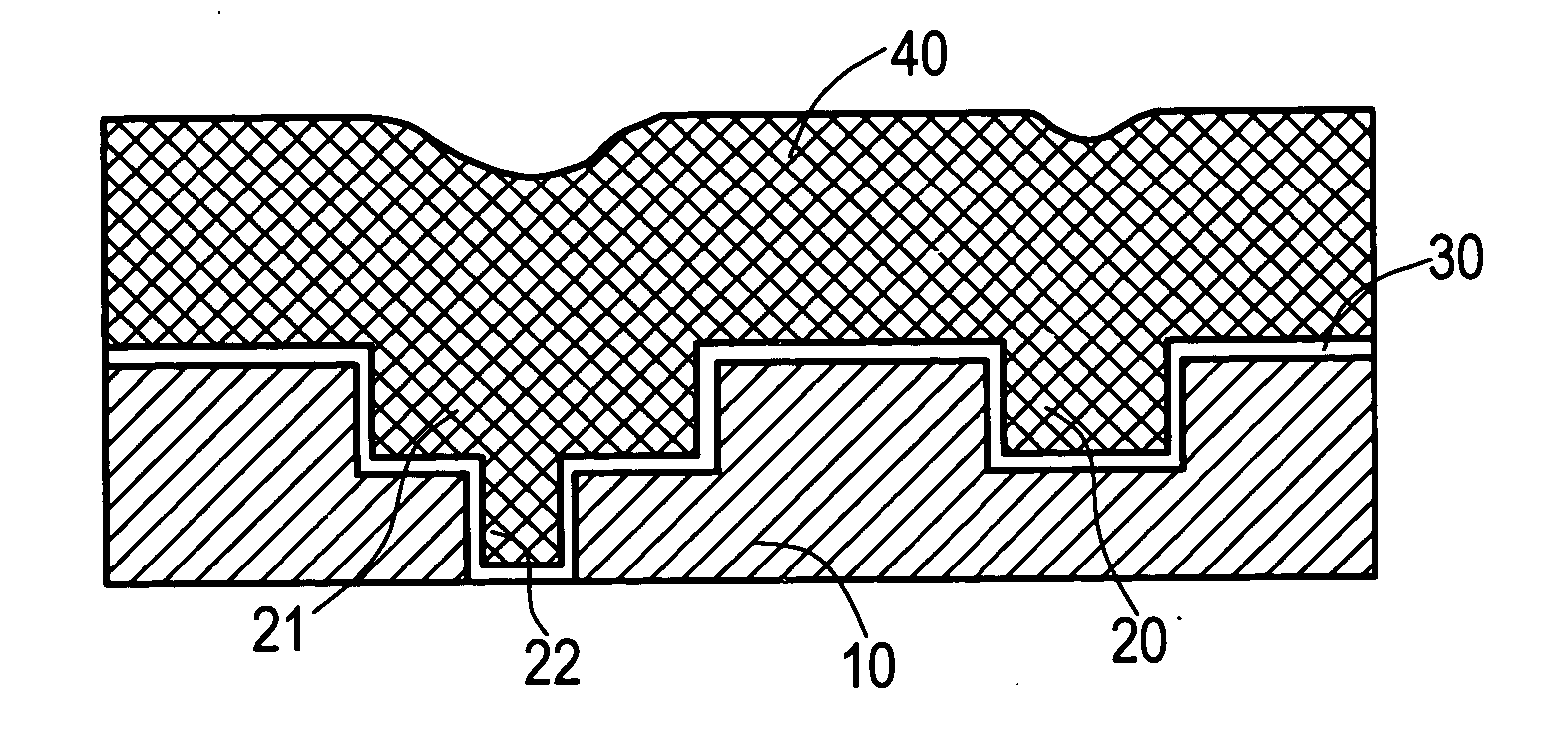
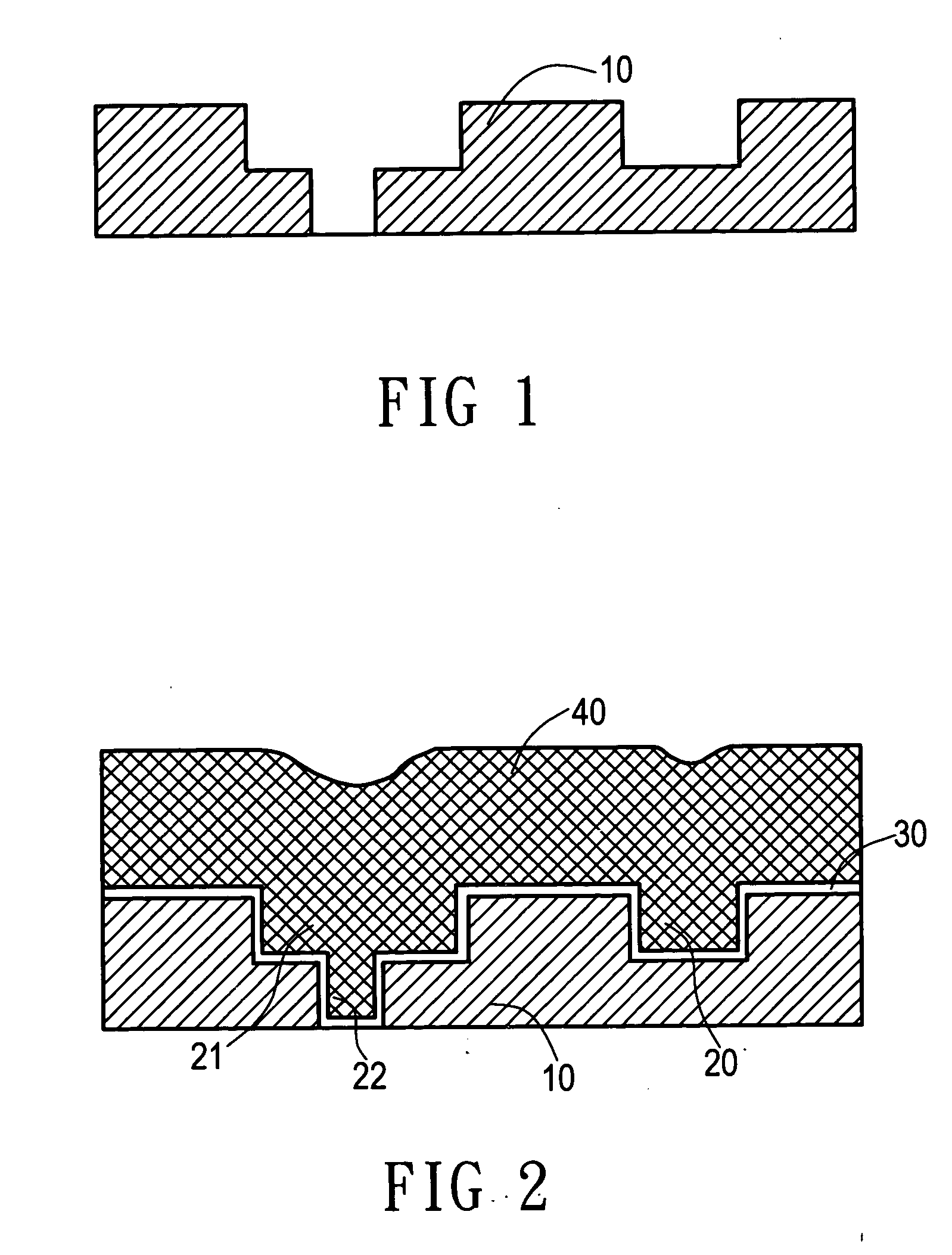
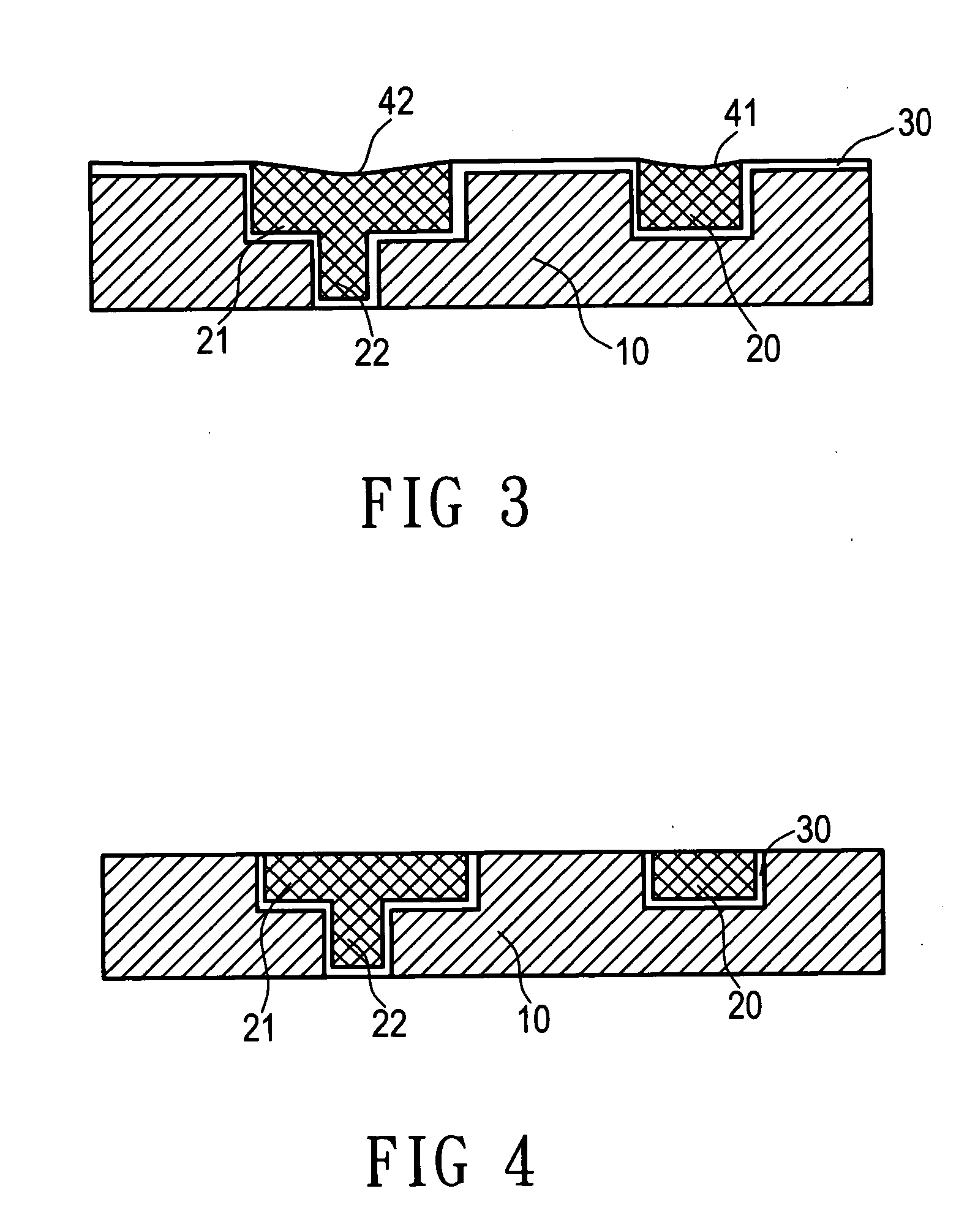
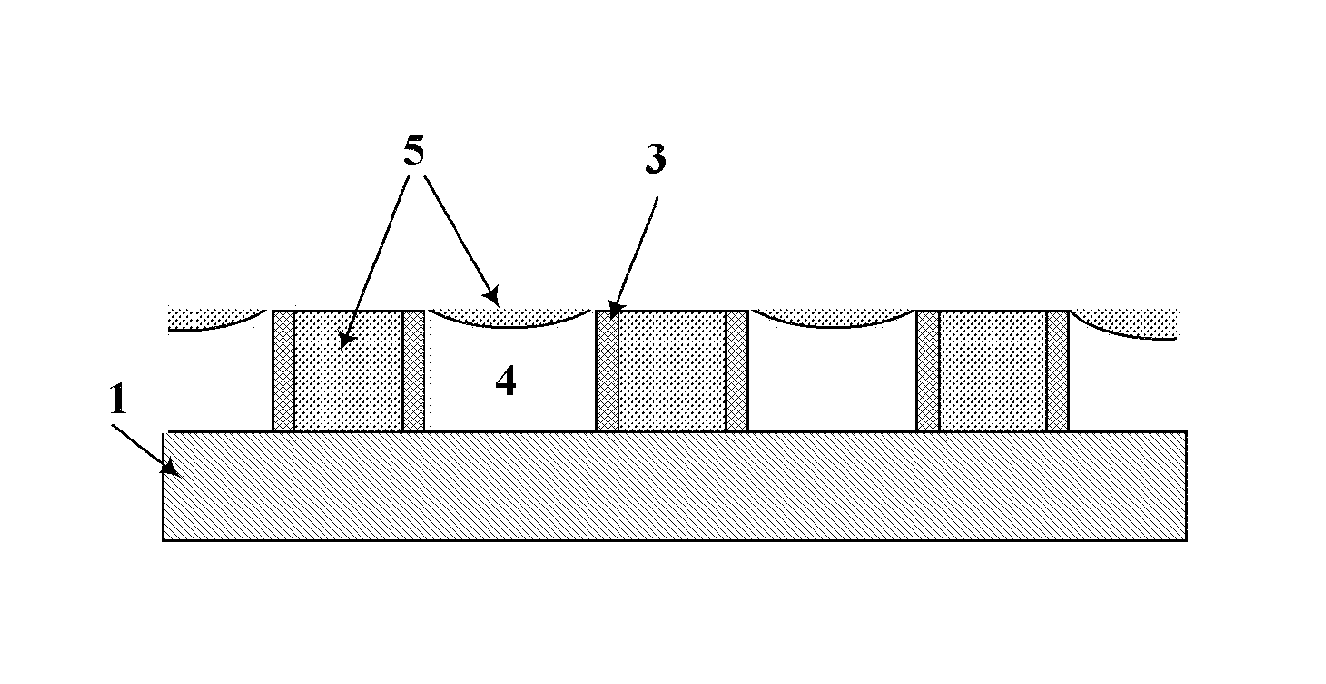
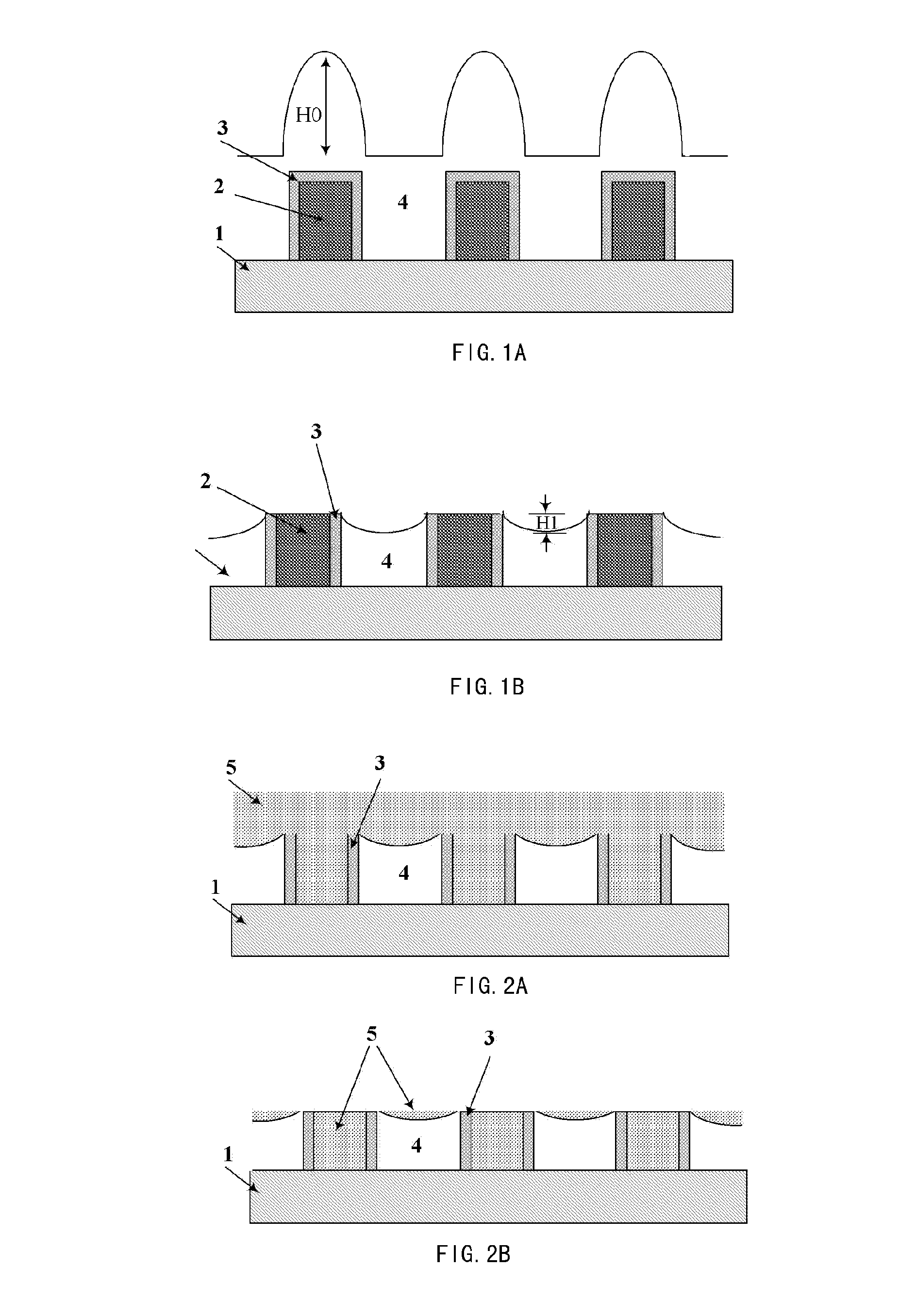
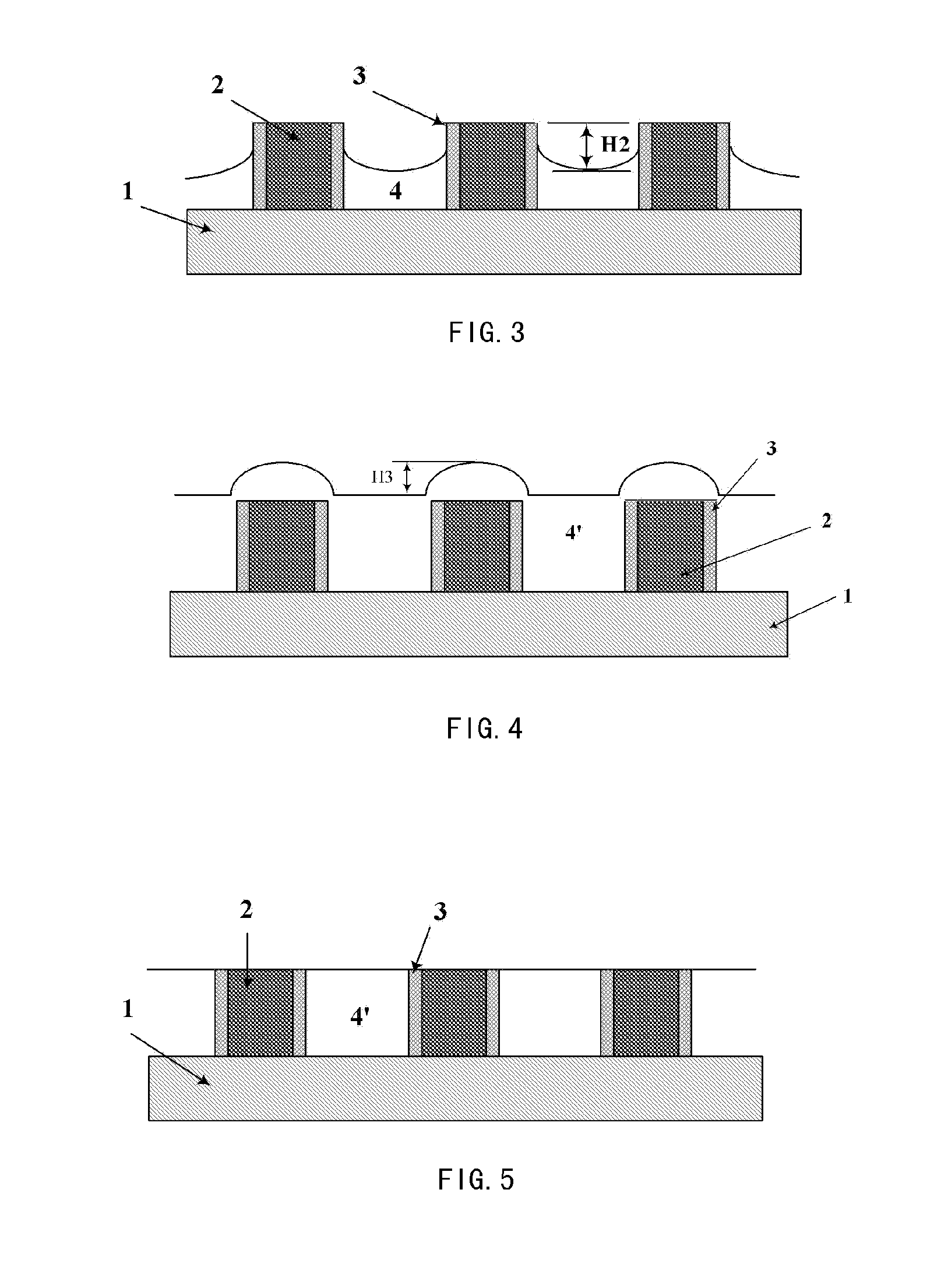
When chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) is used to planarize a surface coexposing patterned features and dielectric fill, where patterned features and the fill are formed of materials having very different CMP removal rates or characteristics, the planarized surface may have excessively rough, dishing or recessing may take place, or one or more or the materials may be damaged. In structures in which planarity is important, these problems can be prevented by forming a capping layer on the patterned features, wherein the CMP removal rate of the material forming the capping layer is similar to the CMP removal rate of the dielectric fill.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Perpendicular magnetic recording head having a pole tip formed with a CMP uniformity structure
InactiveUS8149536B1Record information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsChemical-mechanical planarizationElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method and system for manufacturing a perpendicular magnetic recording head is disclosed. The method and system include providing a chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) uniformity structure having an aperture therein and forming a perpendicular magnetic recording pole within the aperture. The CMP uniformity structure may include a CMP barrier layer. The method and system further include fabricating an insulator after formation of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and performing a CMP to remove a portion of the insulator, expose a portion of the perpendicular magnetic recording pole and planarize an exposed surface of the perpendicular magnetic recording head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
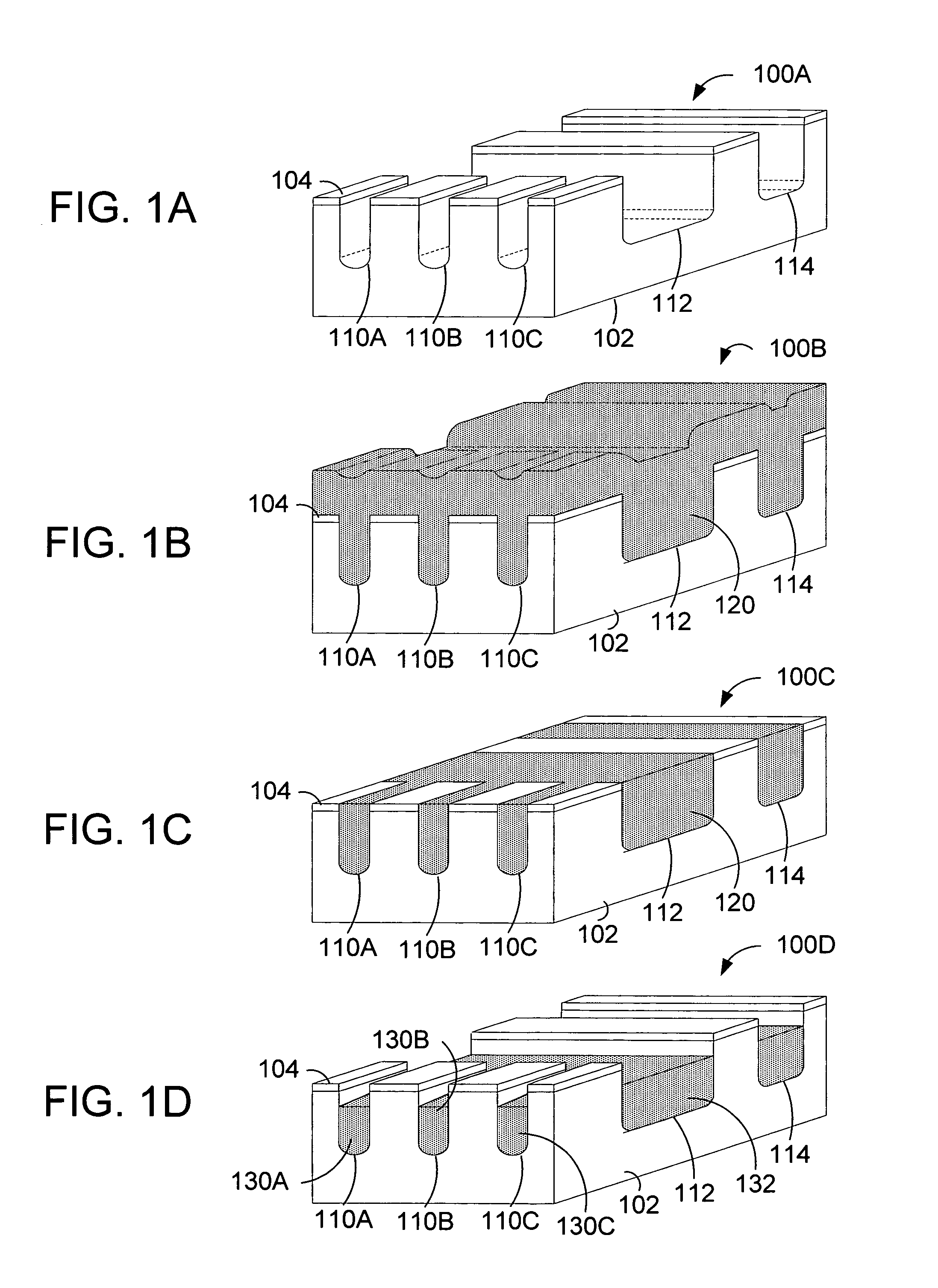
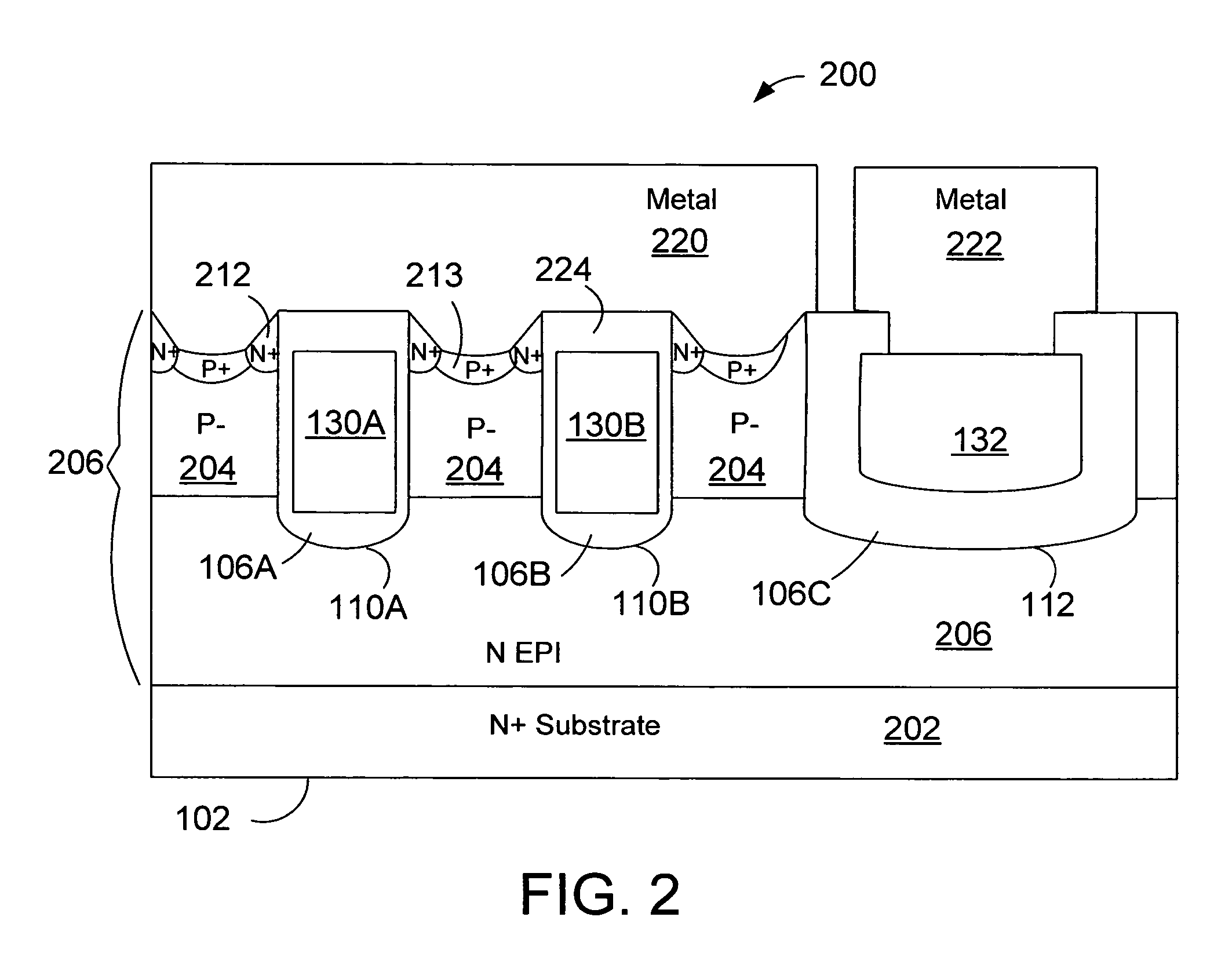
Power device utilizing chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS20070155104A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorTrench gate
A trench-gated field effect transistor (FET) is formed as follows. Using one mask, a plurality of active gate trenches and at least one gate runner trench are defined and simultaneously formed in a silicon region such that (i) the at least one gate runner trench has a width greater than a width of each of the plurality of active gate trenches, and (ii) the plurality of active gate trenches are contiguous with the at least one gate runner trench.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Polishing pads for chemical mechanical planarization
An improved pad and process for polishing metal damascene structures on a semiconductor wafer. The process includes the steps of pressing the wafer against the surface of a polymer sheet in combination with an aqueous-based liquid that optionally contains sub-micron particles and providing a means for relative motion of wafer and polishing pad under pressure so that the moving pressurized contact results in planar removal of the surface of said wafer, wherein the polishing pad has a low elastic recovery when said load is removed, so that the mechanical response of the sheet is largely anelastic. The improved pad is characterized by a high energy dissipation coupled with a high pad stiffness. The pad exhibits a stable morphology that can be reproduced easily and consistently. The pad surface resists glazing, thereby requiring less frequent and less aggressive conditioning. The benefits of such a polishing pad are low dishing of metal features, low oxide erosion, reduced pad conditioning, longer pad life, high metal removal rates, good planarization, and lower defectivity (scratches and Light Point Defects).
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Post clean treatment
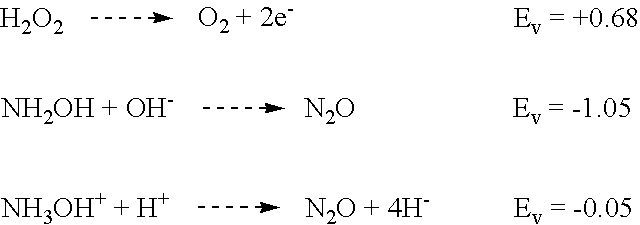
InactiveUS6546939B1Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsHydroxylamineHydrazine compound
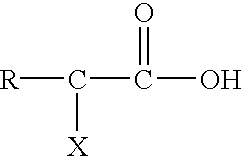
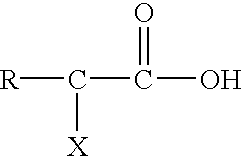
A composition for removal of chemical residues from metal or dielectric surfaces or for chemical mechanical polishing of a copper or aluminum surface is an aqueous solution with a pH between about 3.5 and about 7. The composition contains a monofunctional, difunctional or trifunctional organic acid and a buffering amount of a quaternary amine, ammonium hydroxide, hydroxylamine, hydroxylamine salt, hydrazine or hydrazine salt base. A method in accordance with the invention for removal of chemical residues from a metal or dielectric surface comprises contacting the metal or dielectric surface with the above composition for a time sufficient to remove the chemical residues. A method in accordance with the invention for chemical mechanical polishing of a copper or aluminum surface comprises applying the above composition to the copper or aluminum surface, and polishing the surface in the presence of the composition.
Owner:DUPONT AIR PRODS NANOMATERIALS
Planarization compositions and methods for removing interlayer dielectric films
InactiveUS6322600B1Improve planarization qualityQuality improvementPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesThinningDielectric thin films
A planarization composition is set forth for chemical mechanical planarization of dielectric layers for semiconductor manufacture. The composition comprises spherical silica particles having an average diameter of from 30 nm to about 400 nm, and a narrow range of particle sizes, wherein about 90% of the particles is within 20% of the average particle diameter. The composition includes a liquid carrier comprising up to about 9% alcohol and an amine hydroxide in the amount of about 0.2 to about 9% by weight. The pH of the composition is in the range of about 9 to about 11.5, and the remainder of the solution is water. The composition has low amounts of metal ions, and the composition is used for thinning, polishing and planarizing interlayer dielectric thin films, shallow trench isolation structures, and isolation of gate structures. The invention also comprises methods for using the planarization composition in the manufacture of semiconductor devices.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Customized polishing pads for CMP and methods of fabrication and use thereof
ActiveUS20060276109A1Easy to controlImpact on polishing propertyAdditive manufacturing apparatusLapping machinesPorositySurface engineering
The present application relates to polishing pads for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) of substrates, and methods of fabrication and use thereof. The pads described in this invention are customized to polishing specifications where specifications include (but not limited to) to the material being polished, chip design and architecture, chip density and pattern density, equipment platform and type of slurry used. These pads can be designed with a specialized polymeric nano-structure with a long or short range order which allows for molecular level tuning achieving superior themo-mechanical characteristics. More particularly, the pads can be designed and fabricated so that there is both uniform and nonuniform spatial distribution of chemical and physical properties within the pads. In addition, these pads can be designed to tune the coefficient of friction by surface engineering, through the addition of solid lubricants, and creating low shear integral pads having multiple layers of polymeric material which form an interface parallel to the polishing surface. The pads can also have controlled porosity, embedded abrasive, novel grooves on the polishing surface, for slurry transport, which are produced in situ, and a transparent region for endpoint detection.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
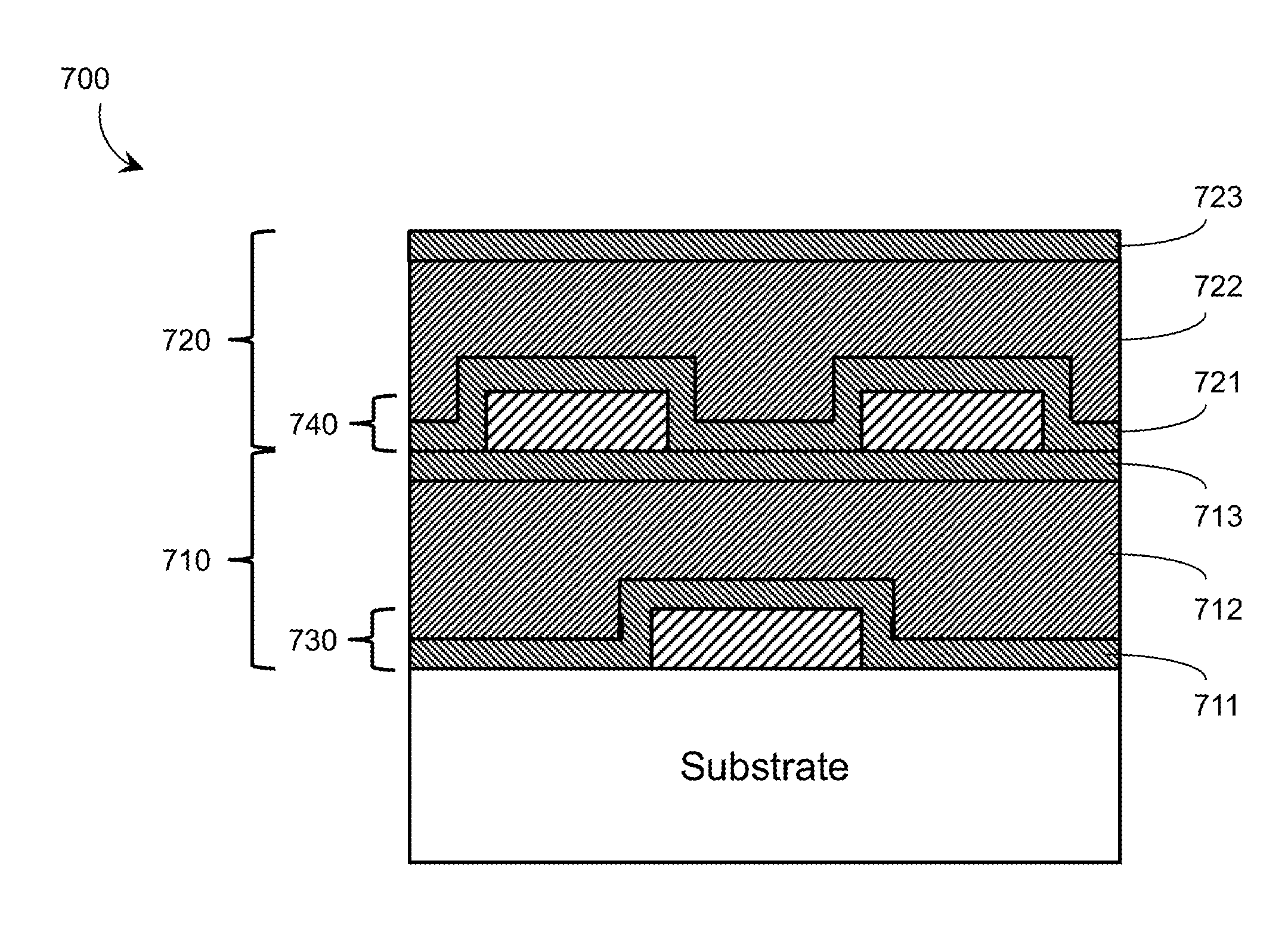
Method for improving uniformity of chemical-mechanical planarization process
ActiveUS8647987B2Improve uniformityReduce the differenceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesEngineeringDielectric layer
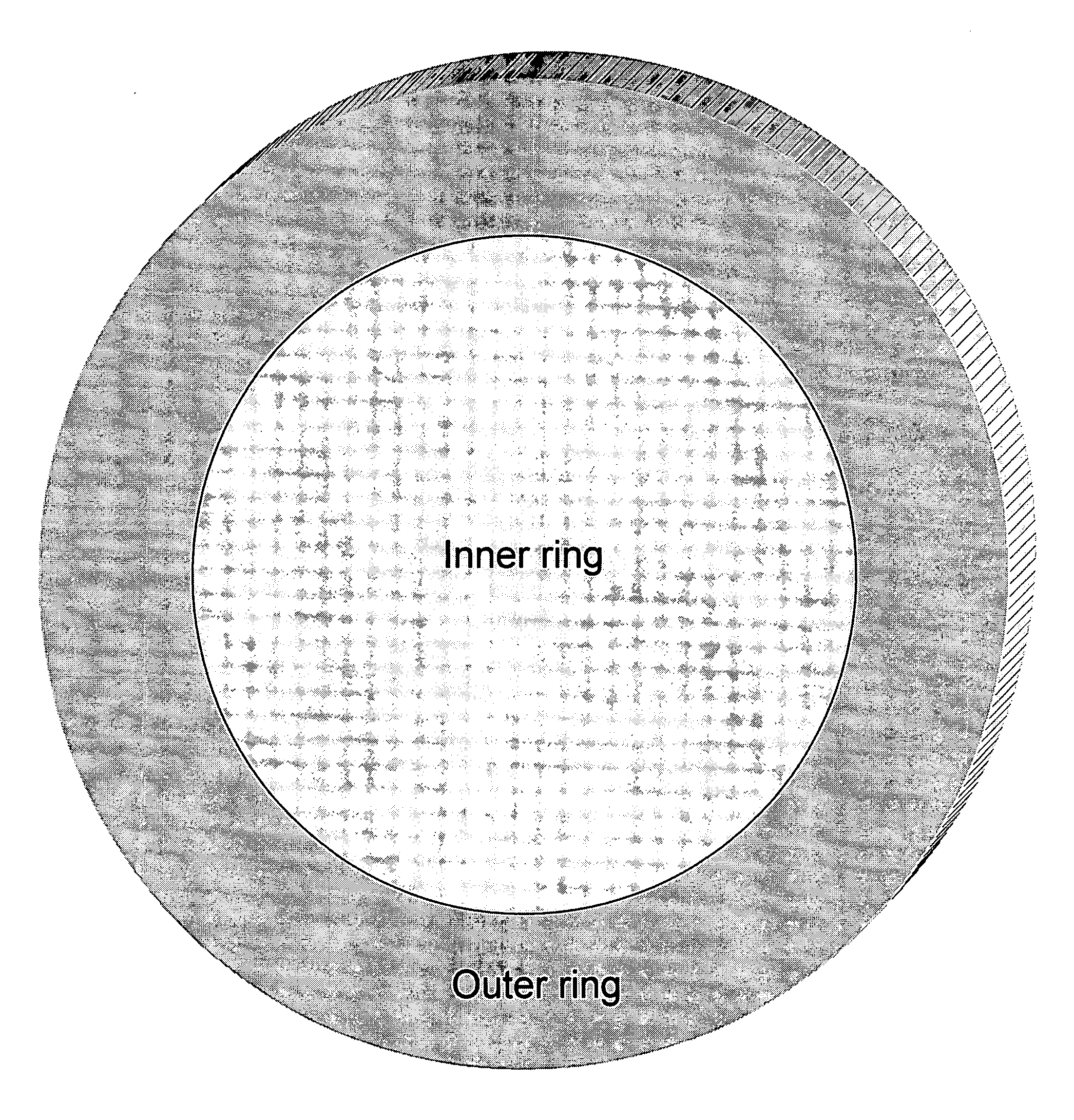
The invention provides a method for improving uniformity of chemical-mechanical planarization process, comprising the steps of: forming features on a substrate; forming a first dielectric isolation layer between the features; planarizing the first dielectric isolation layer until the features are exposed, causing the first dielectric isolation layer between the features to have a recess depth; forming a second dielectric isolation layer on the features and the first dielectric isolation layer, whereby reducing the difference in height between the second dielectric isolation layer between the features and the second dielectric isolation layer on the top of the features; planarizing the second dielectric isolation layer until the features are exposed. According to the method for improving uniformity of chemical-mechanical planarization process of the invention, a dielectric isolation layer is formed again after grinding the dielectric isolation layer on the top of the features, such that the difference in height between the dielectric layer between the features and the dielectric layer on the top of the features is effectively reduced, and the recess of the features is compensated, the within-in-die uniformity is effectively improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Replacement metal gate diffusion break formation
ActiveUS8609510B1Eliminates device variabilityQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesVolume variationMetal
Embodiments of the invention provide approaches for replacement metal gate (RMG) diffusion break formation. Specifically, a diffusion break is created after source / drain (S / D) formation, thereby allowing facet free and high quality S / D formation. A dummy gate body is removed selective to a sidewall section of a capping layer and a GOx layer formed over a substrate, and the opening is then extended through the GOx layer and into the substrate by etching the dummy gate body selective to the sidewall section of the capping layer. Retaining the capping layer during the dummy gate body etch enables the diffusion break to be self-aligned to the gate and eliminates device variability due to S / D volume variations. Processing then continues with RMG poly open chemical mechanical planarization (POC) and poly open planarization (POP).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Power device utilizing chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS7449354B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringField-effect transistor
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Surface modified colloidal abrasives, including stable bimetallic surface coated silica sols for chemical mechanical planarization
A composition and an associated method for chemical mechanical planarization (or other polishing) are described. The composition includes a surface-modified abrasive modified with at least one stabilizer and at least one catalyst differing from the at least one stabilizer. The composition can further include a medium containing the abrasive and an oxidizing agent (e.g., hydrogen peroxide), wherein the at least one catalyst is adapted to catalyze oxidation of a substrate by the oxidizing agent. Preferably, the abrasive is alumina, titania, zirconia, germania, silica, ceria and / or mixtures thereof, the stabilizer includes B, W and / or Al, and the catalyst is Cu, Fe, Mn, Ti, W and / or V. Both the stabilizer and the catalyst are immobilized on the abrasive surface. The method includes applying the composition to a substrate to be polished, such as substrates containing W, Cu and / or dielectrics.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Plug or via formation using novel slurries for chemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS6046099AOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntegrated circuit manufacturingPotassium ferricyanide
Novel slurries for the chemical mechanical polishing of thin films used in integrated circuit manufacturing. A tungsten slurry of the present invention comprises an oxidizing agent, such as potassium ferricyanide, an abrasive such as silica, and has a pH between two and four. The tungsten slurry of the present invention can be used in a chemical mechanical planarization process to polish back a blanket deposited tungsten film to form plugs or vias. The tungsten slurry can also be used to polish copper, tungsten silicide, and titanium nitride. A second slurry, which is a 9:1 dilution of the tungsten slurry is ideal for chemical mechanical polishing of titanium nitride films. A third slurry of the present invention comprises a fluoride salt, an abrasive such as silica and has a pH< / =8. The third slurry can be used to polish titanium films.
Owner:INTEL CORP
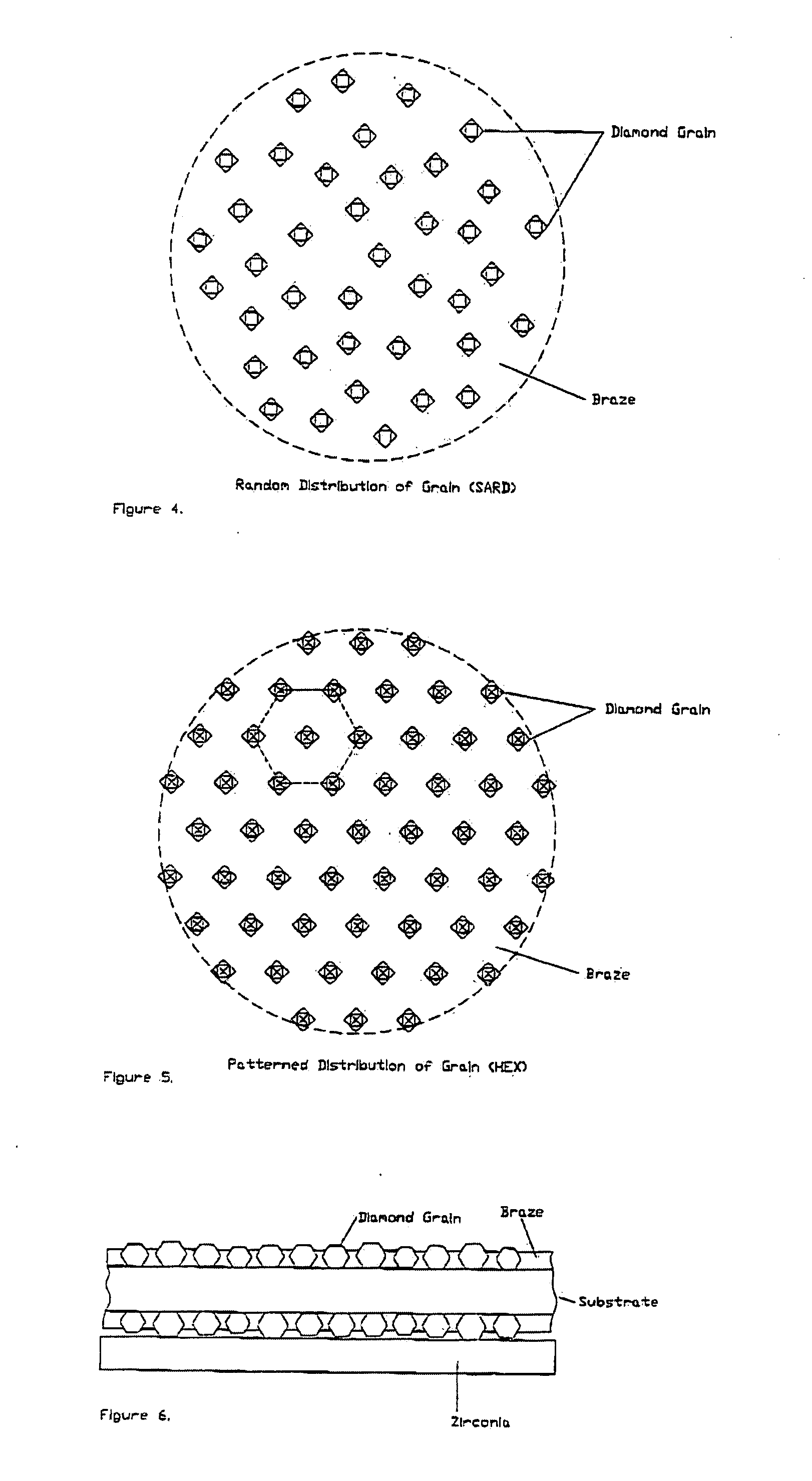
CVD diamond-coated composite substrate containing a carbide-forming material and ceramic phases and method for making same
InactiveUS20050025973A1Improve adhesionLow costPigmenting treatmentEngine sealsReaction bonded silicon carbideComposite substrate
The present invention relates to a composite material and the method of making same, which comprises a CVD diamond coating applied to a composite substrate of ceramic material and an unreacted carbide-forming material of various configurations and for a variety of applications. One example of the composite material is a composite of SiC and free silicon metal known as Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide. Several examples of applications of the invention include: 1) heads or disks for conditioning polishing pads, including pads used in Chemical-Mechanical-Planarization, 2) cutting and dressing tool inserts and tips, 3) heat spreaders for electronic devices, and 4) wear components including mechanical seals and pump seals.
Owner:MORGAN ADVANCED CERAMICS
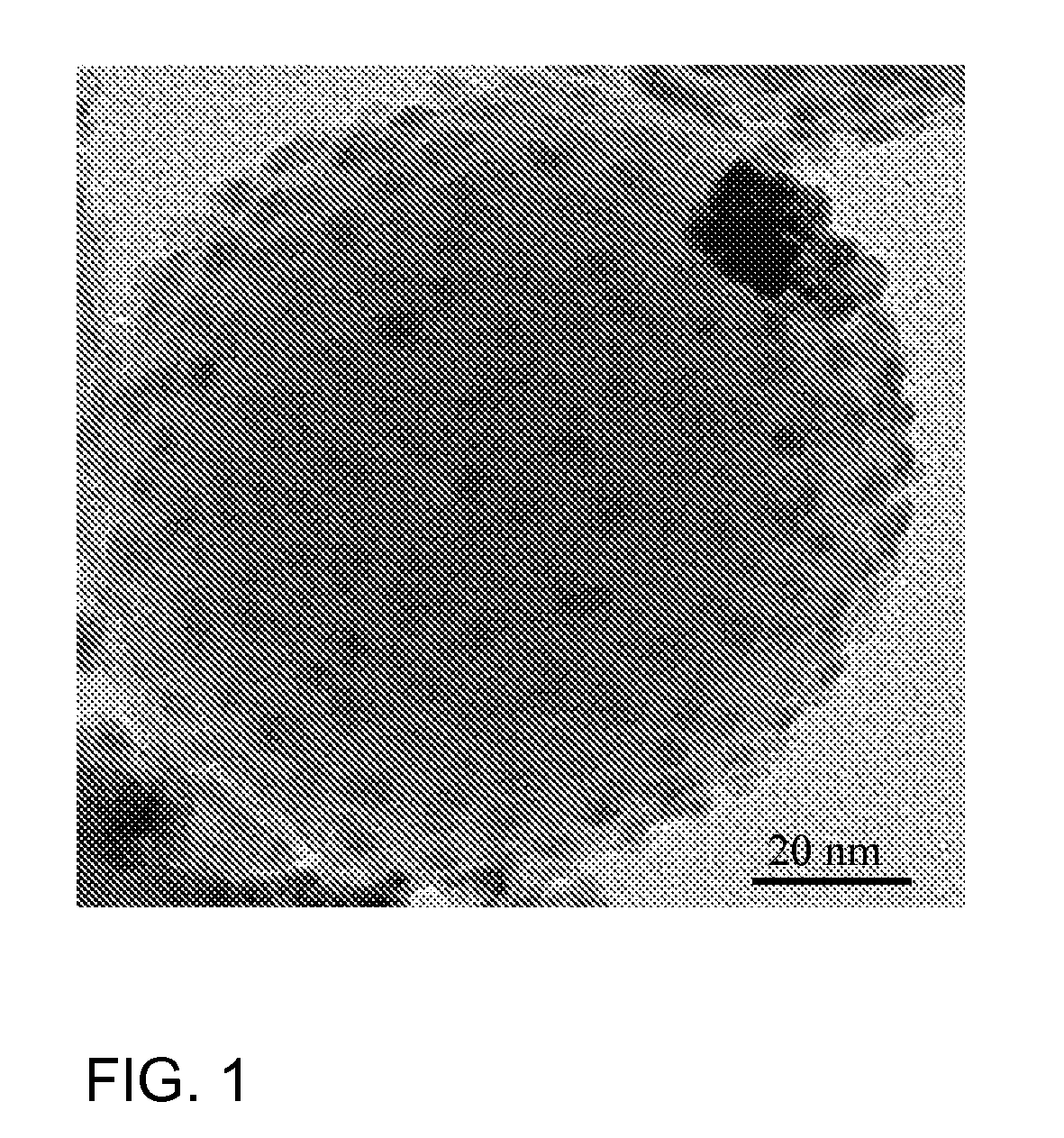
Raspberry-type metal oxide nanostructures coated with ceo2 nanoparticles for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP)
InactiveUS20120077419A1Efficient processCost-effective and convenient processMaterial nanotechnologySilicaCeo2 nanoparticlesWater soluble
Raspberry-type coated particles comprising a core selected from the group consisting of metal oxides of Si, Ti, Zr, Al, Zn and mixtures thereof with a core size of from 20 to 100 nm wherein the core is coated with CeCO2 particles having a particle size below 10 nm; process for preparing raspberry type coated particles comprising the steps of i) providing a mixture containing: a) core particles selected from the group of metal oxides of Si, Ti, Zr, Al, Zn and mixtures thereof, with a particle size of from 20 to 100 nm; b) a water soluble Ce-salt and c) water; ii) adding an organic or inorganic base to the mixture of step i) at temperatures of from 10 to 90° C. and iii) aging the mixture at temperatures of from 10 to 90° C.; and polishing agents containing the particles and their use for polishing surfaces.
Owner:BASF AG
Electrochemically generated reactants for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS6689258B1CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical speciesElectrochemistry
Various methods and apparatus for polishing semiconductor workpieces using electrochemically generated species are disclosed. In one aspect, a method of processing is provided that includes contacting a semiconductor workpiece to a solution, electrochemically generating a chemical species in the solution, and polishing the semiconductor workpiece with the aid of the solution.
Owner:FULLBRITE CAPITAL PARTNERS
Systems and methods for fabrication of superconducting integrated circuits
ActiveUS20150119252A1Avoid overall overheatingQuantum computersLiquid surface applicatorsDielectricNiobium
Various techniques and apparatus permit fabrication of superconductive circuits. A niobium / aluminum oxide / niobium trilayer may be formed and individual Josephson Junctions (JJs) formed. A protective cap may protect a JJ during fabrication. A hybrid dielectric may be formed. A superconductive integrated circuit may be formed using a subtractive patterning and / or additive patterning. A superconducting metal layer may be deposited by electroplating and / or polished by chemical-mechanical planarization. The thickness of an inner layer dielectric may be controlled by a deposition process. A substrate may include a base of silicon and top layer including aluminum oxide. Depositing of superconducting metal layer may be stopped or paused to allow cooling before completion. Multiple layers may be aligned by patterning an alignment marker in a superconducting metal layer.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Load cup for chemical mechanical polishing
ActiveUS7044832B2Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Embodiments of a load cup for transferring a substrate are provided. The load cup includes a pedestal assembly having a substrate support and a de-chucking nozzle. The de-chucking nozzle is positioned to flow a fluid between the polishing head and the back side of a substrate during transfer of the substrate from the polishing head to the substrate support.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Polishing pads for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS6860802B1Revolution surface grinding machinesFlexible-parts wheelsHigh energyRelative motion
An improved pad and process for polishing metal damascene structures on a semiconductor wafer. The process includes the steps of pressing the wafer against the surface of a polymer sheet in combination with an aqueous-based liquid that optionally contains sub-micron particles and providing a means for relative motion of wafer and polishing pad under pressure so that the moving pressurized contact results in planar removal of the surface of said wafer, wherein the polishing pad has a low elastic recovery when said load is removed, so that the mechanical response of the sheet is largely anelastic. The improved pad is characterized by a high energy dissipation coupled with a high pad stiffness. The pad exhibits a stable morphology that can be reproduced easily and consistently. The pad surface resists glazing, thereby requiring less frequent and less aggressive conditioning. The benefits of such a polishing pad are low dishing of metal features, low oxide erosion, reduced pad conditioning, longer pad life, high metal removal rates, good planarization, and lower defectivity (scratches and Light Point Defects).
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
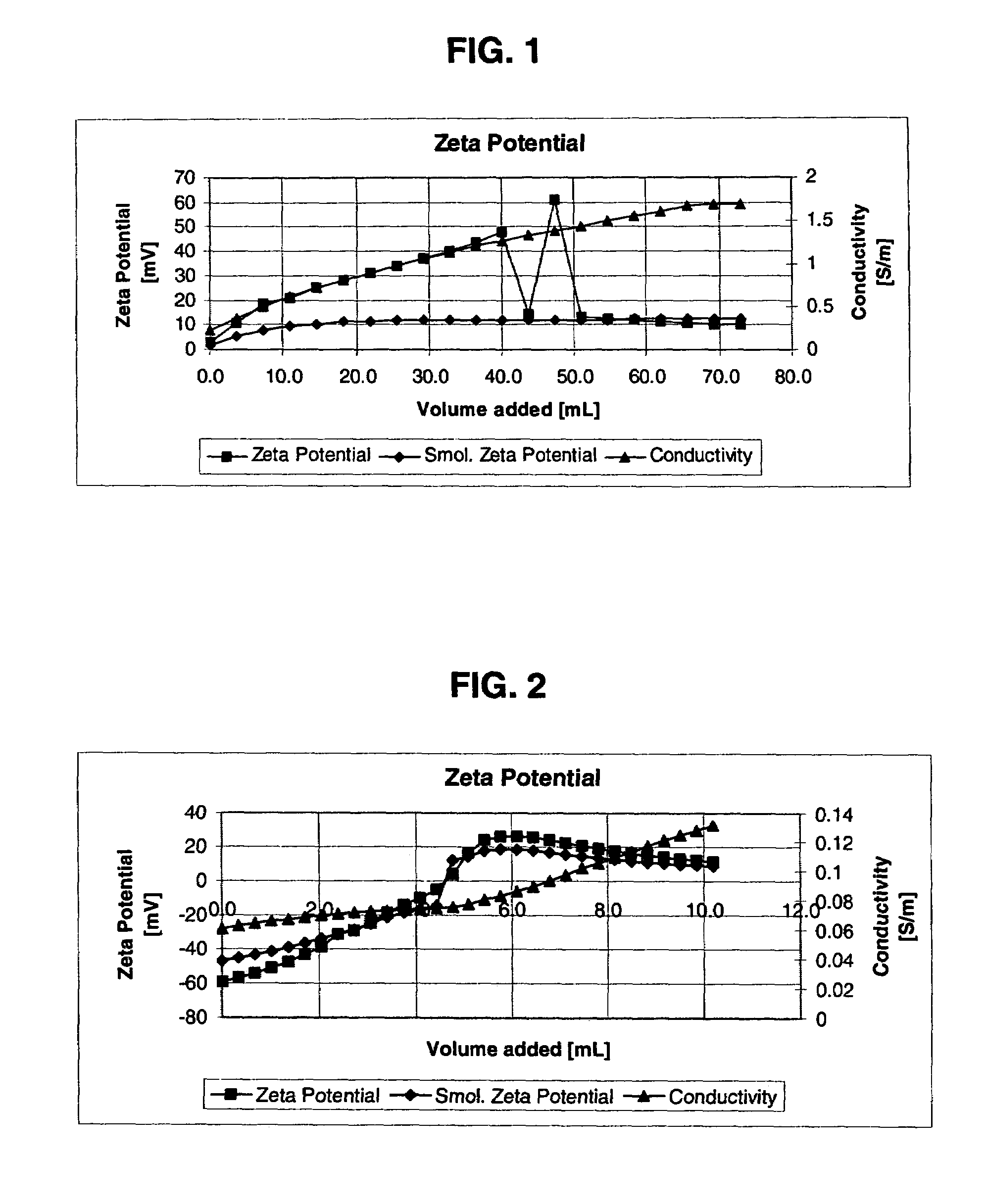
Detection system for chemical-mechanical planarization tool
InactiveUS20050026542A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLapping machinesReflectance spectroscopySemiconductor
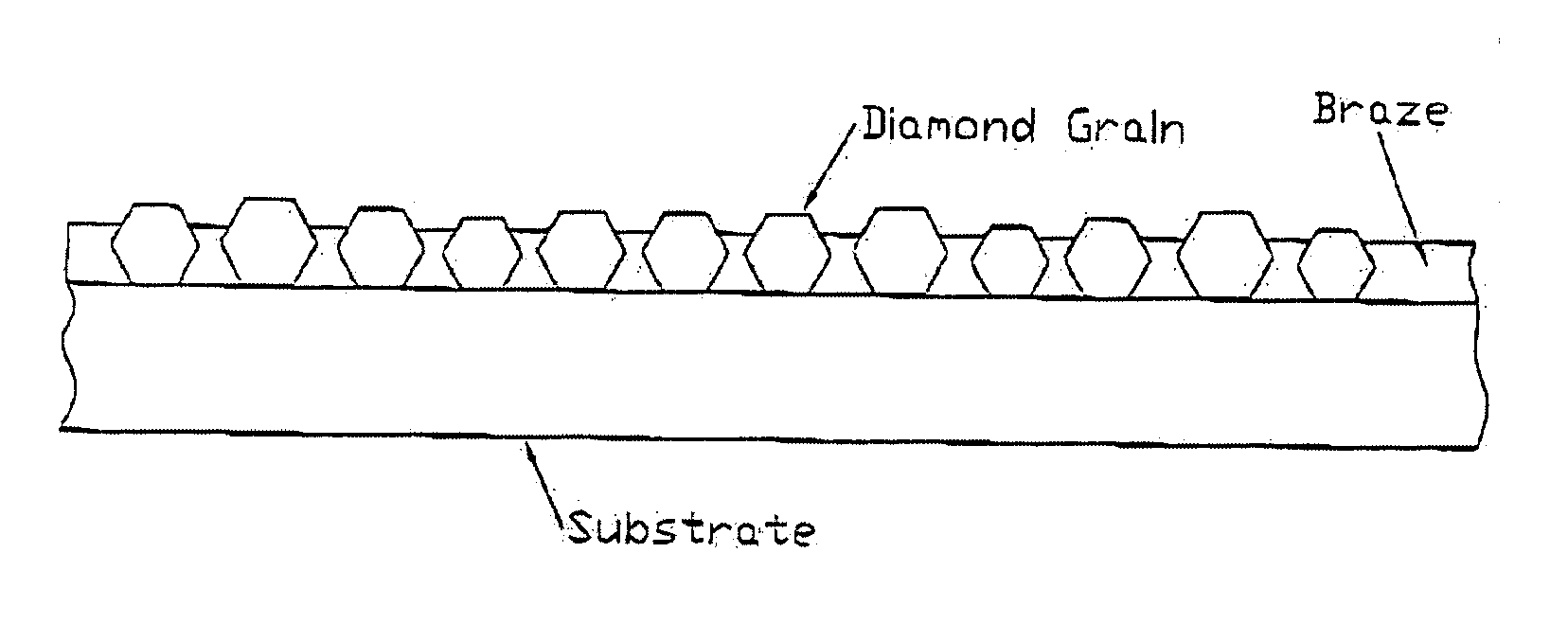
Methods and apparatus are provided for endpoint detection in a chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) process. Reflectance spectra data is taken periodically in different areas of a surface of a semiconductor wafer during a chemical mechanical planarization process. Three different reflectance spectra are identified to determine a status of the CMP process. A first reflectance spectra data corresponds to light reflected predominately from a layer of material on the surface of the semiconductor wafer. A second reflectance spectra corresponds to the layer of material being thinned such that the second reflectance spectra is modified by an underlying layer of material. A third reflectance spectra corresponds to light reflected predominately from the underlying layer of material.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Conditioning tools and techniques for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS20080271384A1Reduce the overall heightPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCopperMetal
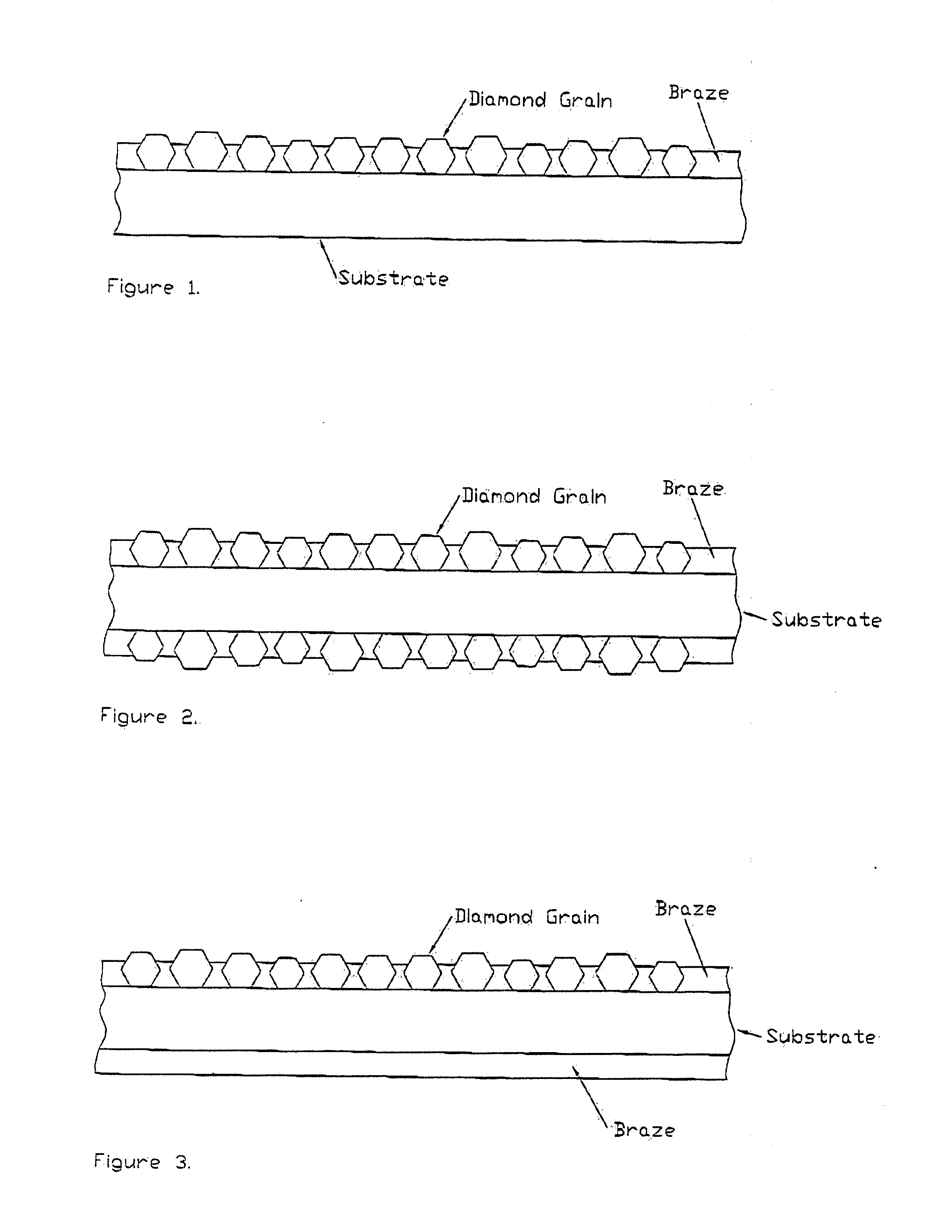
Tools for conditioning chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) pads comprise a substrate with abrasive particles coupled to at least one surface. The tools can have various particle and bond configurations. For instance, abrasive particles may be bonded (e.g., brazed or other metal bond technique) to one side, or to front and back sides. Alternatively, abrasive particles are bonded to a front side, and filler particles coupled to a back side. The abrasive particles can form a pattern (e.g., hexagonal) and have particle sizes that are sufficiently small to penetrate pores of a CMP pad during conditioning, leading to fewer defects on wafers polished with the conditioned CMP pad. Grain bonding can be accomplished using brazing films, although other metal bonds may be used as well. Also, balanced bond material (e.g., braze on both sides) allows for low out-of-flatness value.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ABRASIFS INC +1
Alkaline post-chemical mechanical planarization cleaning compositions
InactiveUS20050205835A1Organic detergent compounding agentsDetergent mixture composition preparationOrganic baseCarboxylic acid
A post-CMP cleaning composition and method comprising same are disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a composition comprising: water, an organic base, and a plurality of chelating agents comprised of a poly-amino carboxylic acid and a hydroxylcarboxylic acid wherein the pH of the composition ranges from 9.5 to 11.5.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com