Patents
Literature
9611 results about "Erosion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In earth science, erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location (not to be confused with weathering which involves no movement). This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, air (wind), plants, animals, and humans. In accordance with these agents, erosion is sometimes divided into water erosion, glacial erosion, snow erosion, wind (aeolic) erosion, zoogenic erosion, and anthropogenic erosion. The particulate breakdown of rock or soil into clastic sediment is referred to as physical or mechanical erosion; this contrasts with chemical erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by its dissolving into a solvent (typically water), followed by the flow away of that solution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.
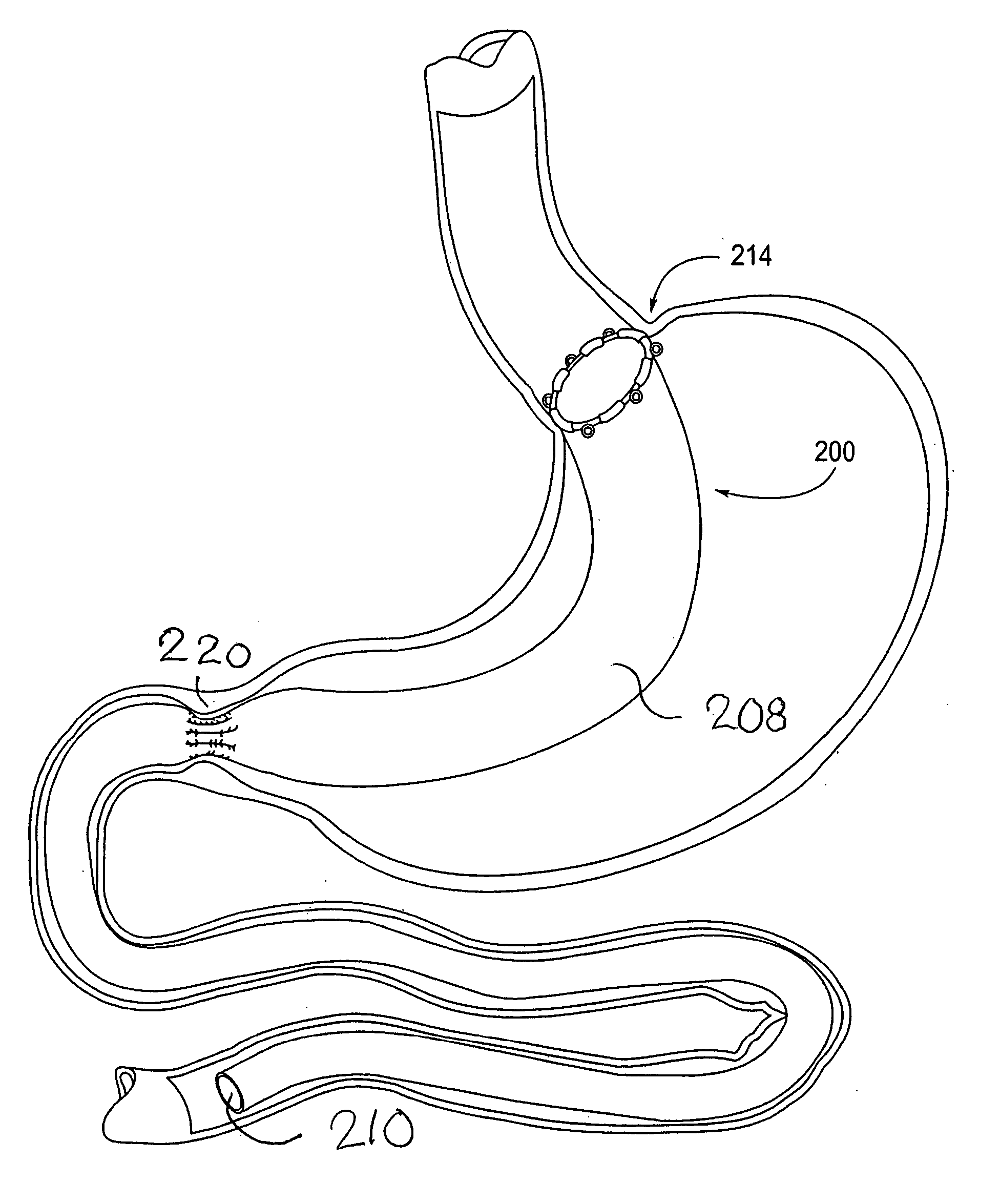
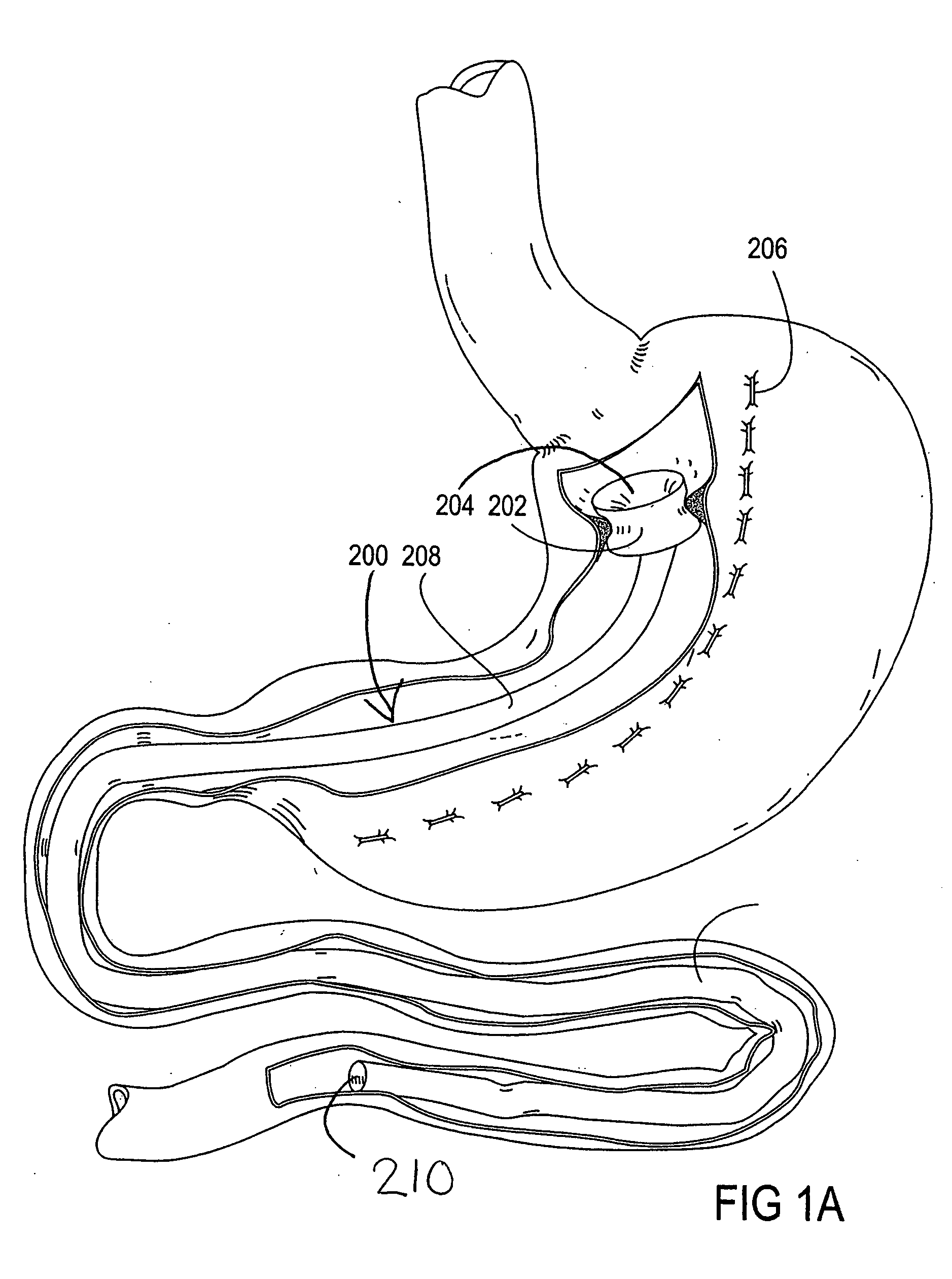
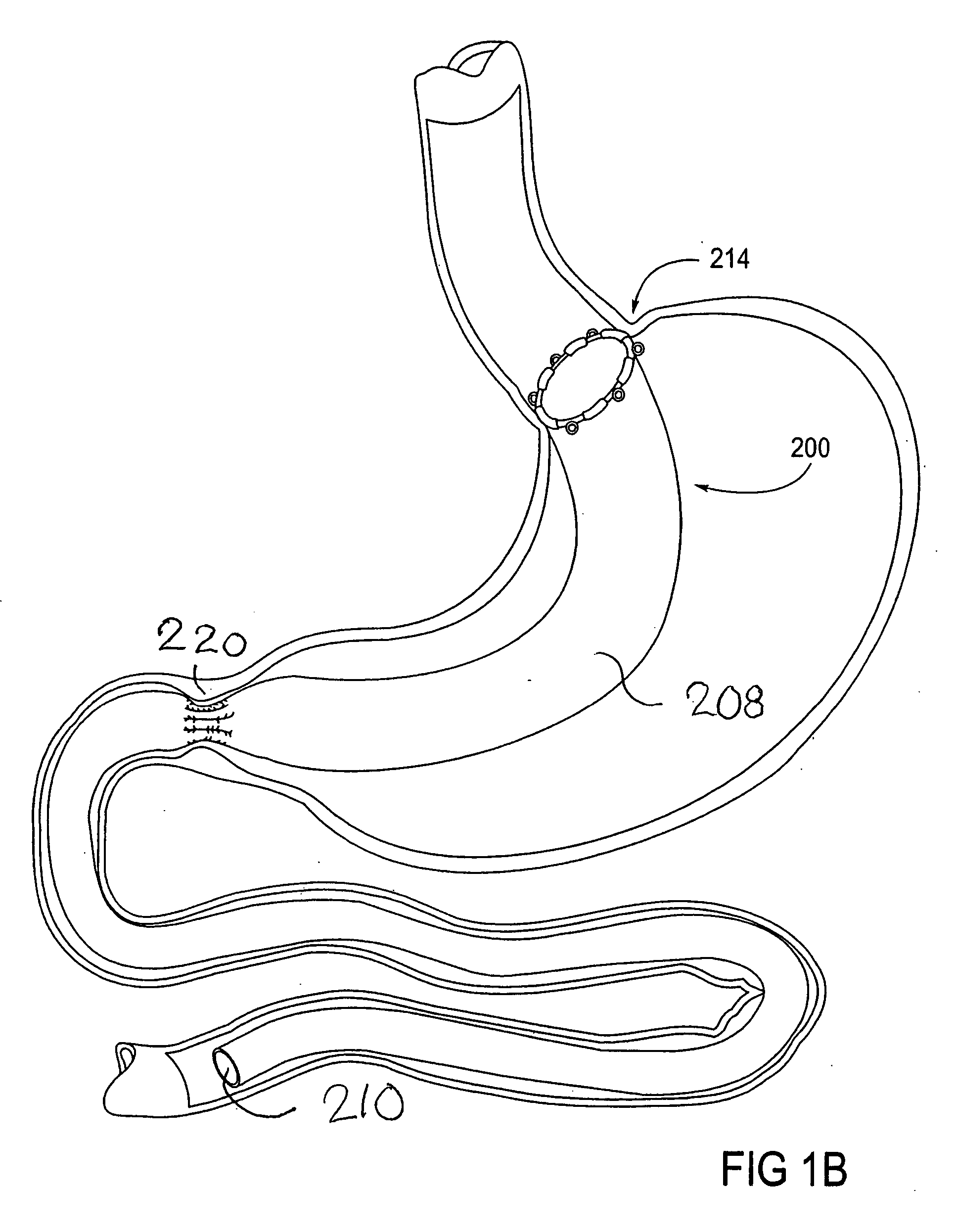
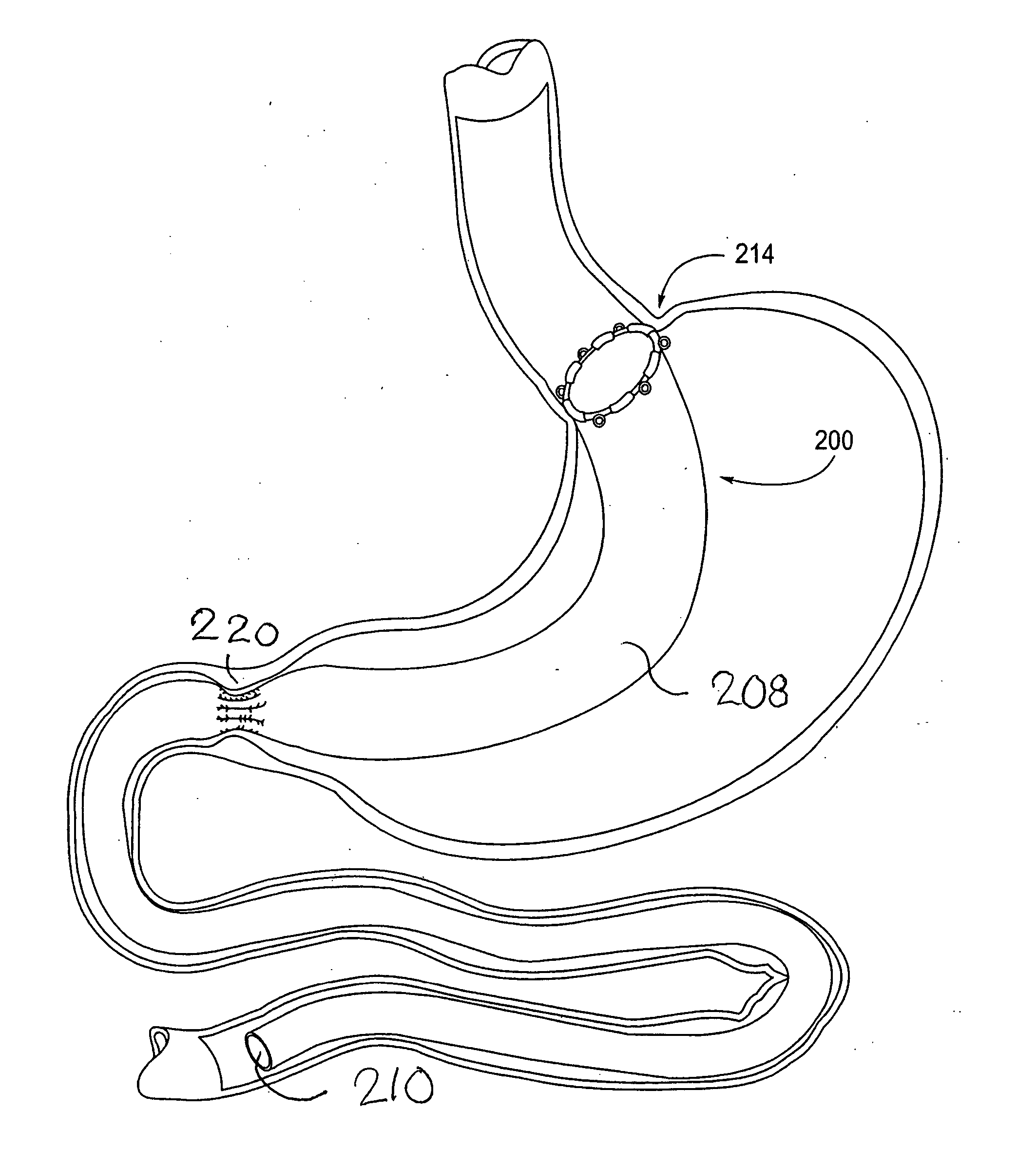
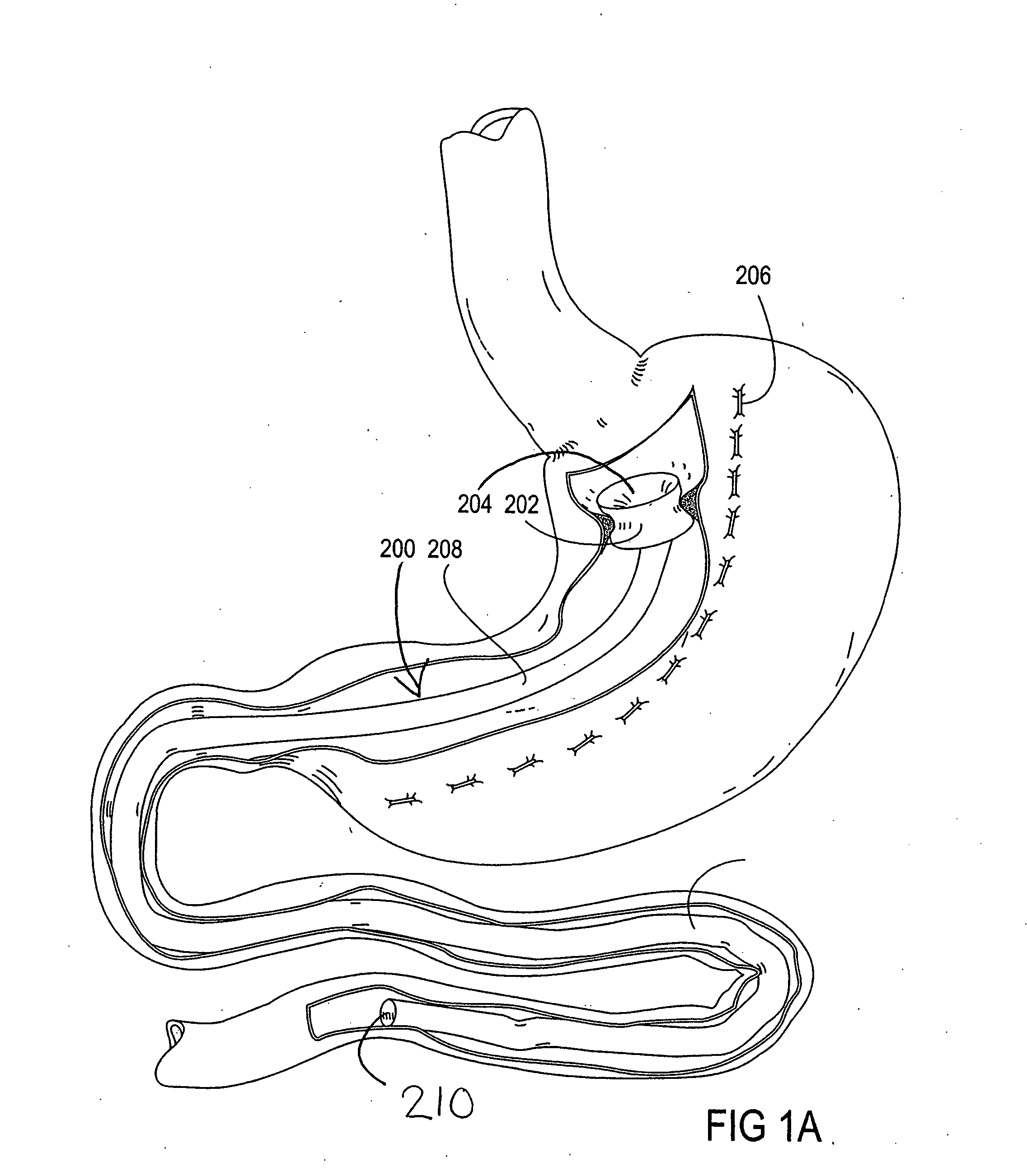
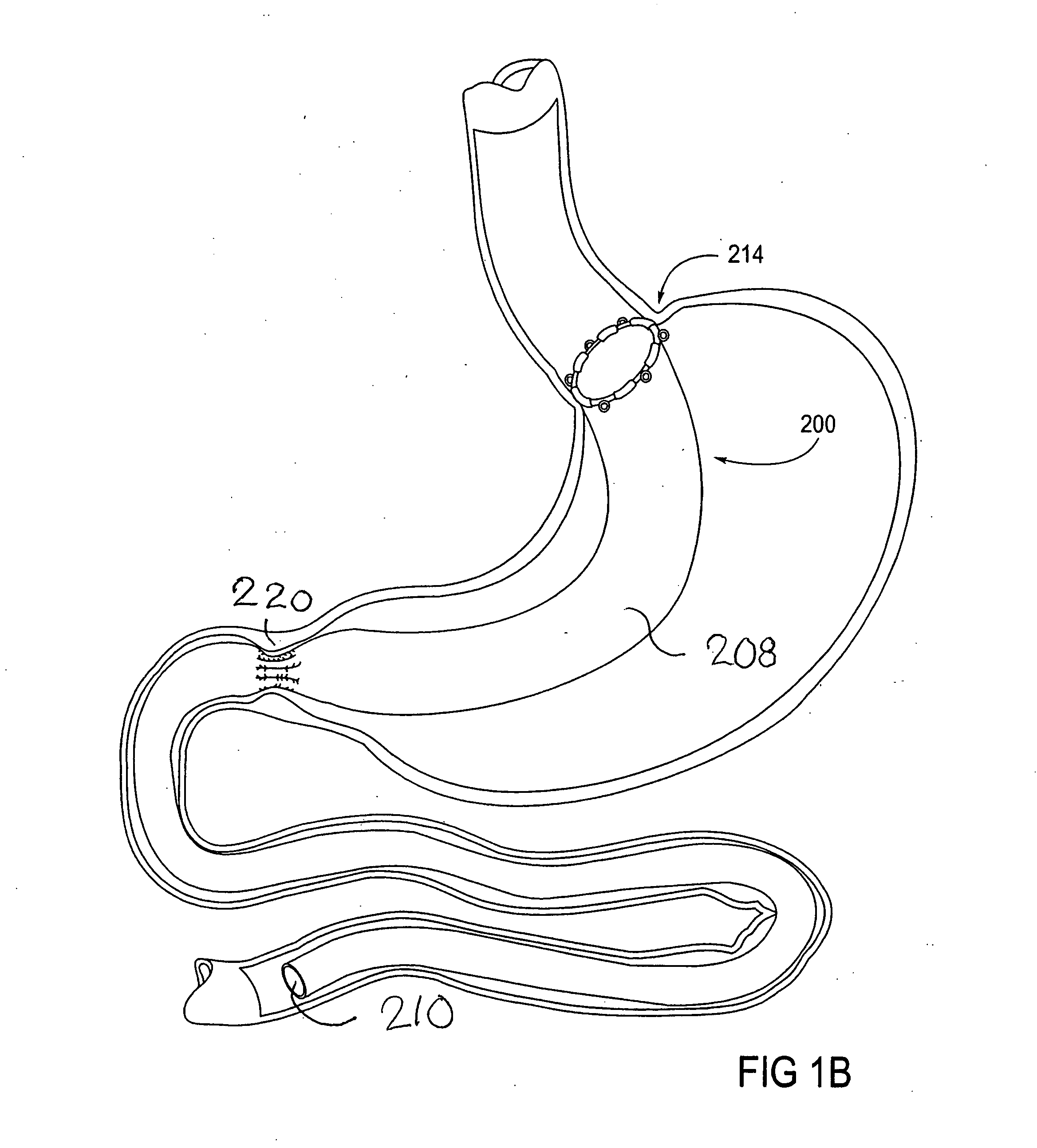
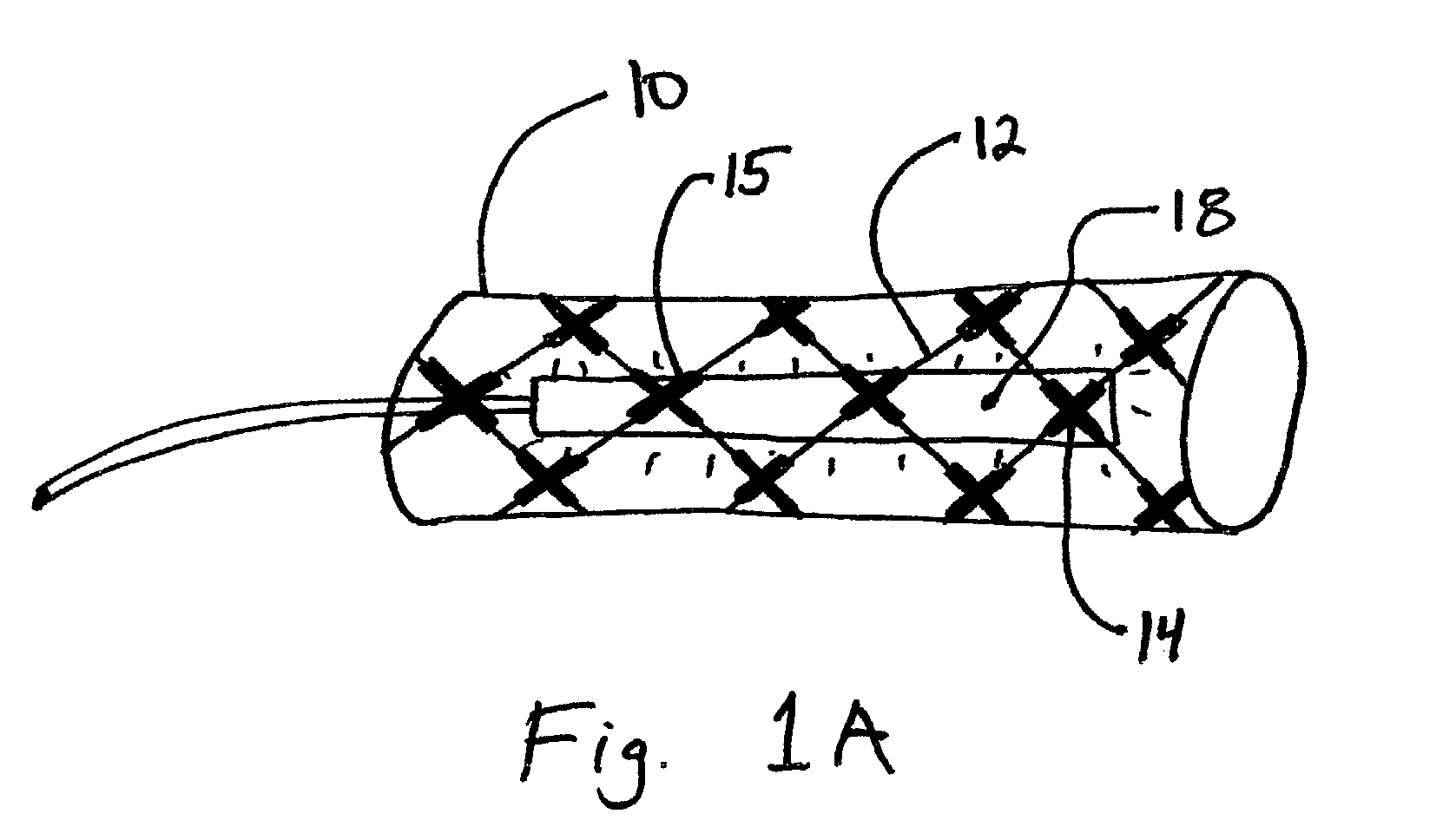
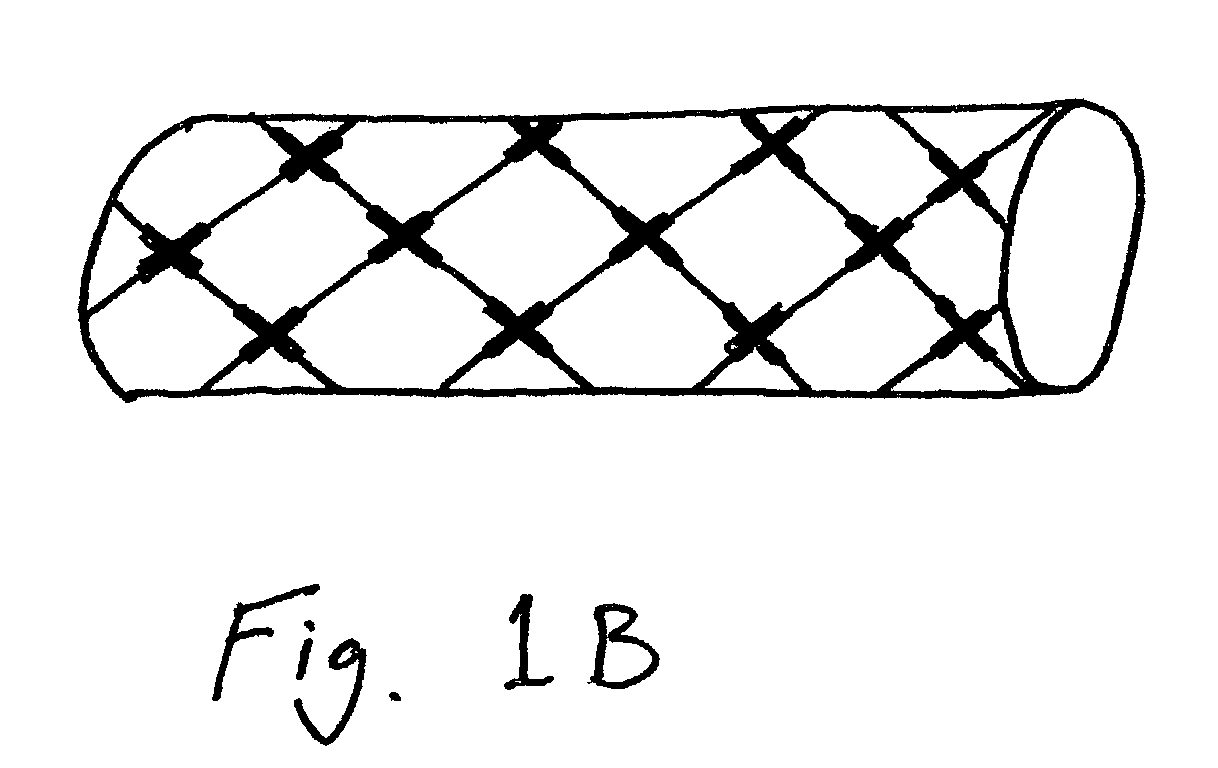
Devices and methods for treating morbid obesity
The present invention provides devices and methods for attachment of an implanted device, such as an artificial stoma device, a gastrointestinal sleeve device or an attachment cuff, within a patient's digestive tract for treatment of obesity. Special surgical fasteners provide a lasting and durable attachment to the gastrointestinal tissue without causing excessive pressure that could result in tissue erosion and detachment of the implanted device. Fastener delivery devices that facilitate peroral placement and deployment of fasteners and secondary devices are also provided. Also described are implantable devices and attachment means that avoid causing excessive pressure within the tissue by having compliance that is compatible with the gastrointestinal tissues where it is attached.
Owner:VALENTX
Devices and methods for treating morbid obesity
The present invention provides devices and methods for attachment of an implanted device, such as an artificial stoma device, a gastrointestinal sleeve device or an attachment cuff, within a patient's digestive tract for treatment of obesity. Special surgical fasteners provide a lasting and durable attachment to the gastrointestinal tissue without causing excessive pressure that could result in tissue erosion and detachment of the implanted device. Fastener delivery devices that facilitate peroral placement and deployment of fasteners and secondary devices are also provided. Also described are implantable devices and attachment means that avoid causing excessive pressure within the tissue by having compliance that is compatible with the gastrointestinal tissues where it is attached.
Owner:VALENTX
Pulsed cavitational ultrasound therapy
ActiveUS20080319356A1Improve drug deliveryEasy to transportOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgerySonificationMicrobubbles
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
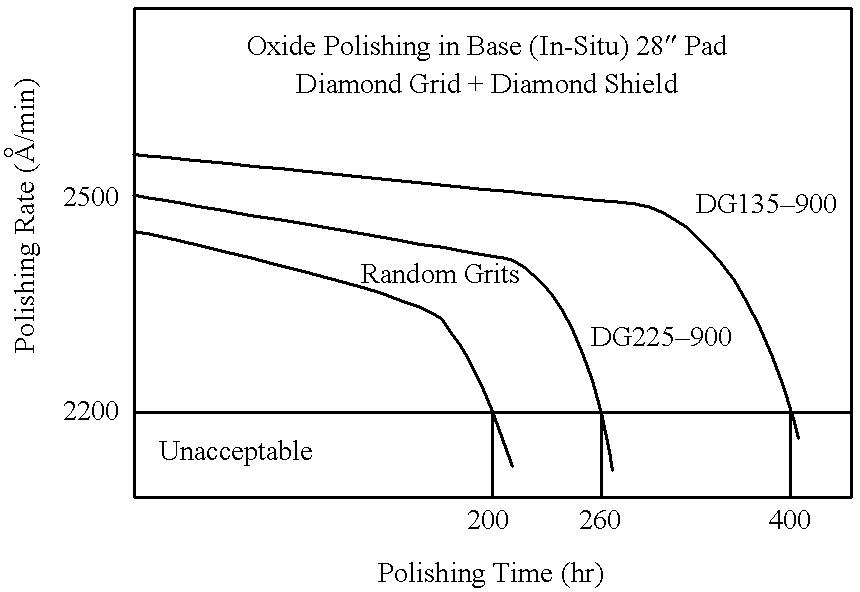
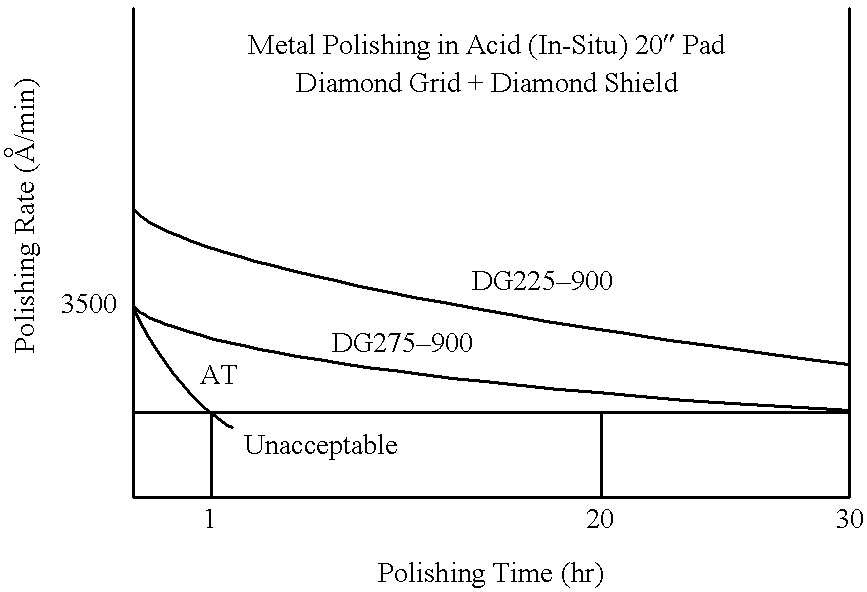
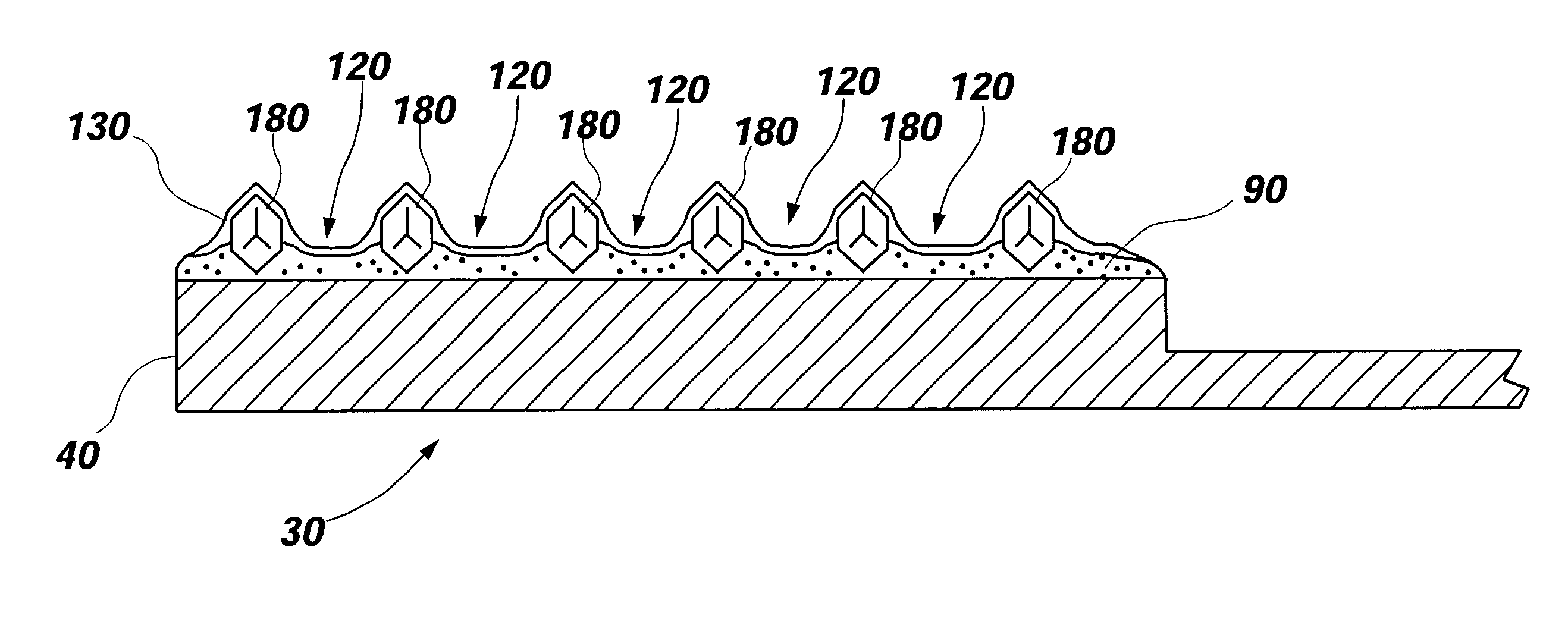
Diamond grid CMP pad dresser
InactiveUS6368198B1Improve polishing efficiencyExtended service lifePolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesSuperhard materialDiamond-like carbon
The present invention discloses a CMP pad dresser which has a plurality of uniformly spaced abrasive particles protruding therefrom. The abrasive particles are super hard materials, and are typically diamond, polycrystalline diamond (PCD), cubic boron nitride (cBN), or polycrystalline cubic boron nitride(PcBN). The abrasive particles are brazed to a substrate which may be then coated with an additional anti-corrosive layer. The anti-corrosive layer is usually a diamond or diamond-like carbon which is coated over the surface of the disk to prevent erosion of the brazing alloy by the chemical slurry used in conjunction with the CMP pad. This immunity to chemical attack allows the CMP pad dresser to dress the pad while it is polishing a workpiece. In addition to even spacing on the substrate, the abrasive particles extend for a uniform distance away from the substrate, allowing for even grooming or dressing of a CMP pad both in vertical and horizontal directions. A method of producing such a CMP pad dresser is also disclosed.
Owner:KINIK
Abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical compositions of opioids and other drugs
ActiveUS7399488B2Good treatment effectSmall dosePowder deliveryNervous disorderAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, a drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity. In preferred embodiments the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble, but enzymatically degradable by enzymes present in the human gastrointestinal tract. The abuse-deterrent composition retards the release of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Morphine controlled release system
InactiveUS20070003617A1Low administration frequencyAffecting extent of drug bioavailabilityBiocideNervous disorderMorphineDissolution
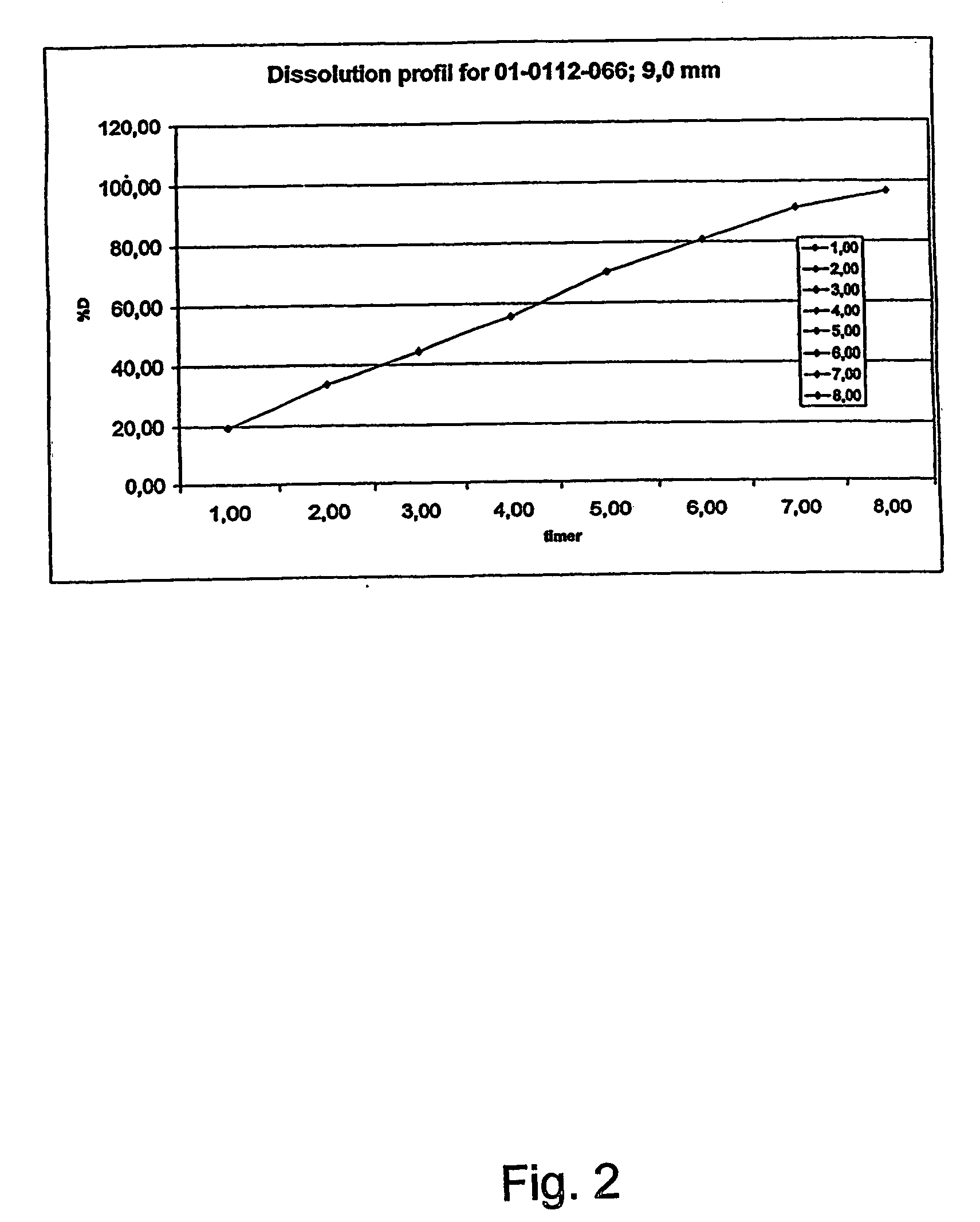
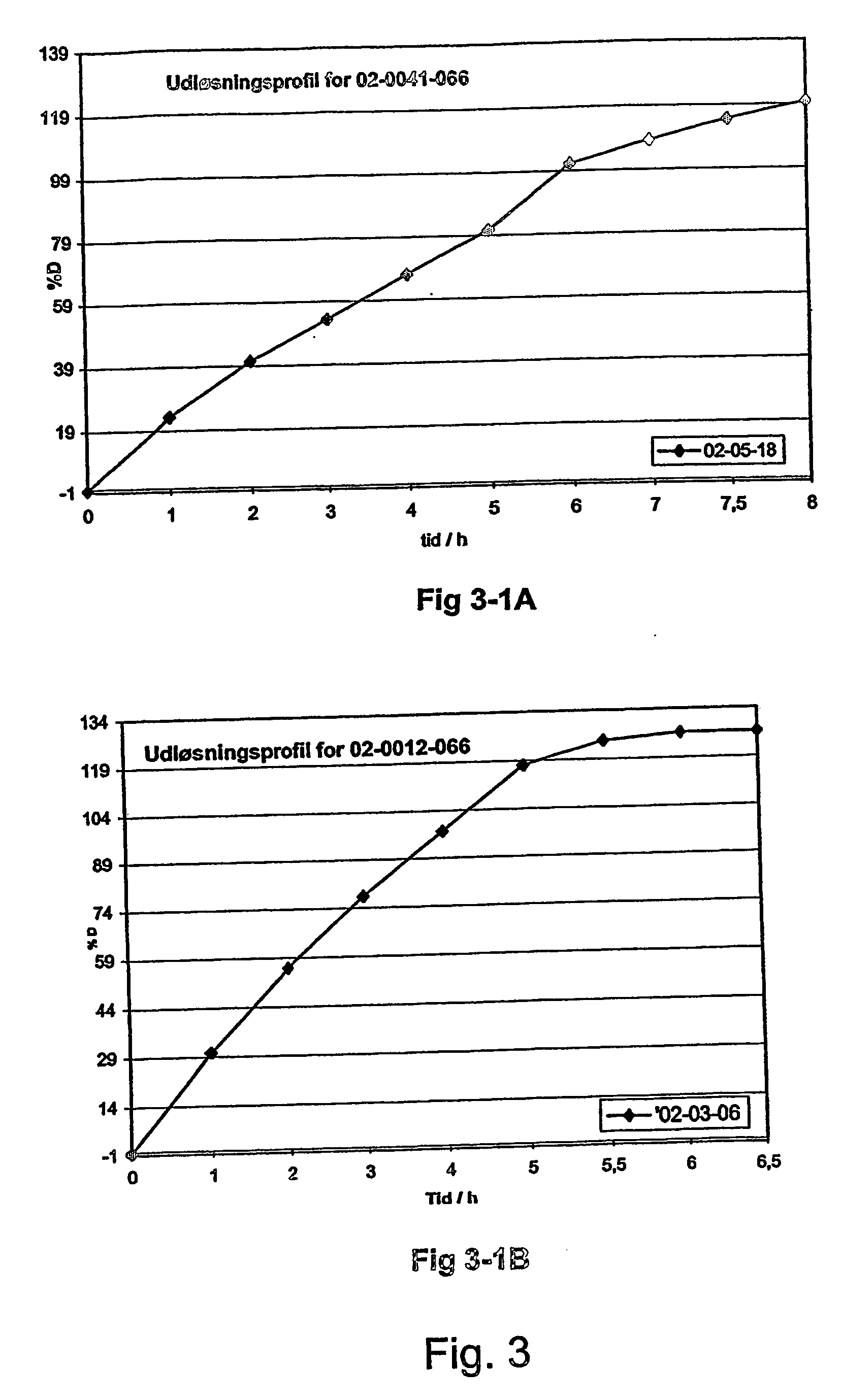
A composition for controlled release of an opioid from a pharmaceutical composition, the method comprises controlling the release of at least one opioid into an aqueous medium by erosion of at least one surface of a pharmaceutical composition comprising I) a matrix composition comprising a) polymer or a mixture of polymers, b) an opioid and, optionally, c) one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, and (i) a coating. The matrix composition has a conus-like shape so the surface area exposed to the aqueous medium increases at least during initial erosion of the matrix composition, and the dissolution of the opioid-when tested in a Dissolution Test as described herein with or without application of sinkers-results in a zero order release of at least 80% of the opioid contained in the composition. Such compositions are especially suitable for controlled release of an opioid to obtain a delayed pead concentration and a prolonged therapeutically effective plasma concentration upon oral administration. Once or twice daily administration is possible. The matrix typically comprises PEO and the active substance is typically an opioid such as morphine or a glucuronide thereof.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Acoustic nacelle inlet lip having composite construction and an integral electric ice protection heater disposed therein
An engine nacelle inlet lip includes both acoustic treatment and electric heating for ice protection. The inlet lip has a composite outer skin and a composite inner skin, with the composite outer skin having at least one integrated heater element embedded in the composite material. An acoustic cellular core positioned between the outer and inner skin acts to attenuate fan noise from the engine. Covering the outer skin and overlying the acoustic core is a perforated erosion shield having a first set of openings that pass entirely thorough its thickness. The composite outer skin includes a second set of openings such that sound waves can pass from an inner barrel portion of the inlet lip through the erosion shield, outer skin, and heater element to the underlying acoustic cellular core.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO +1
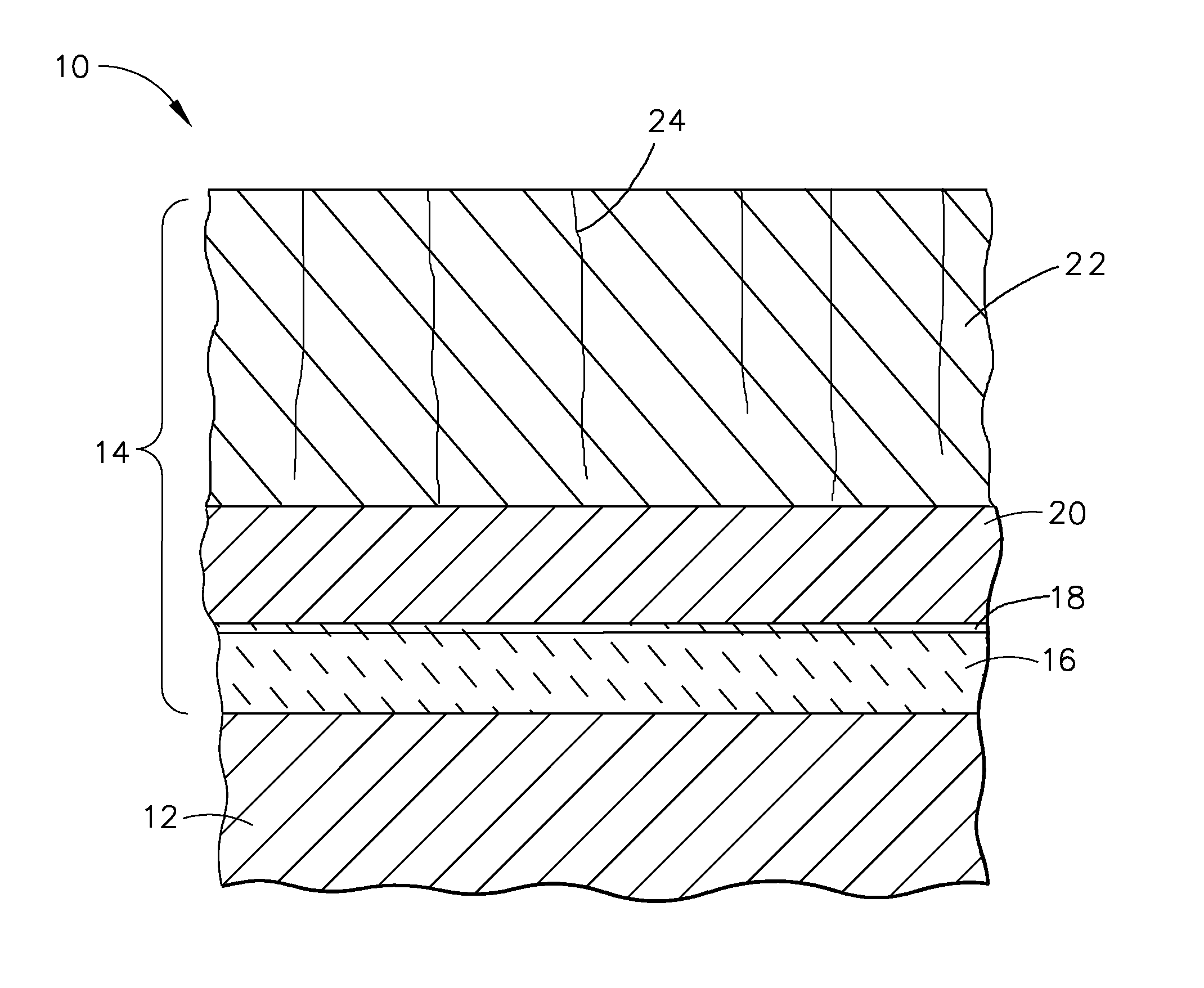
Coatings for controlling erosion of a substrate of an implantable medical device
InactiveUS20050283229A1Reduce and inhibit and delay erosionReduce erosion rateStentsSurgeryInsertion stentMedical device
An implantable medical device, such as a stent, with a coating region for controlling erosion of the substrate region is disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
High temperature erosion resistant coating and material containing compacted hollow geometric shapes
InactiveUS6641907B1Improve corrosion resistanceReduce void volumeEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesPorosityMetallurgy
A material system (60) contains close packed hollow shapes (50, 70) having a dense wall structure (52, 66), which are bonded together and which may contain a matrix binder material (56) between the shapes, where the system has a stable porosity, and is abradable and thermally stable at temperatures up to possibly 1700° C., where such systems are useful in turbine apparatus.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
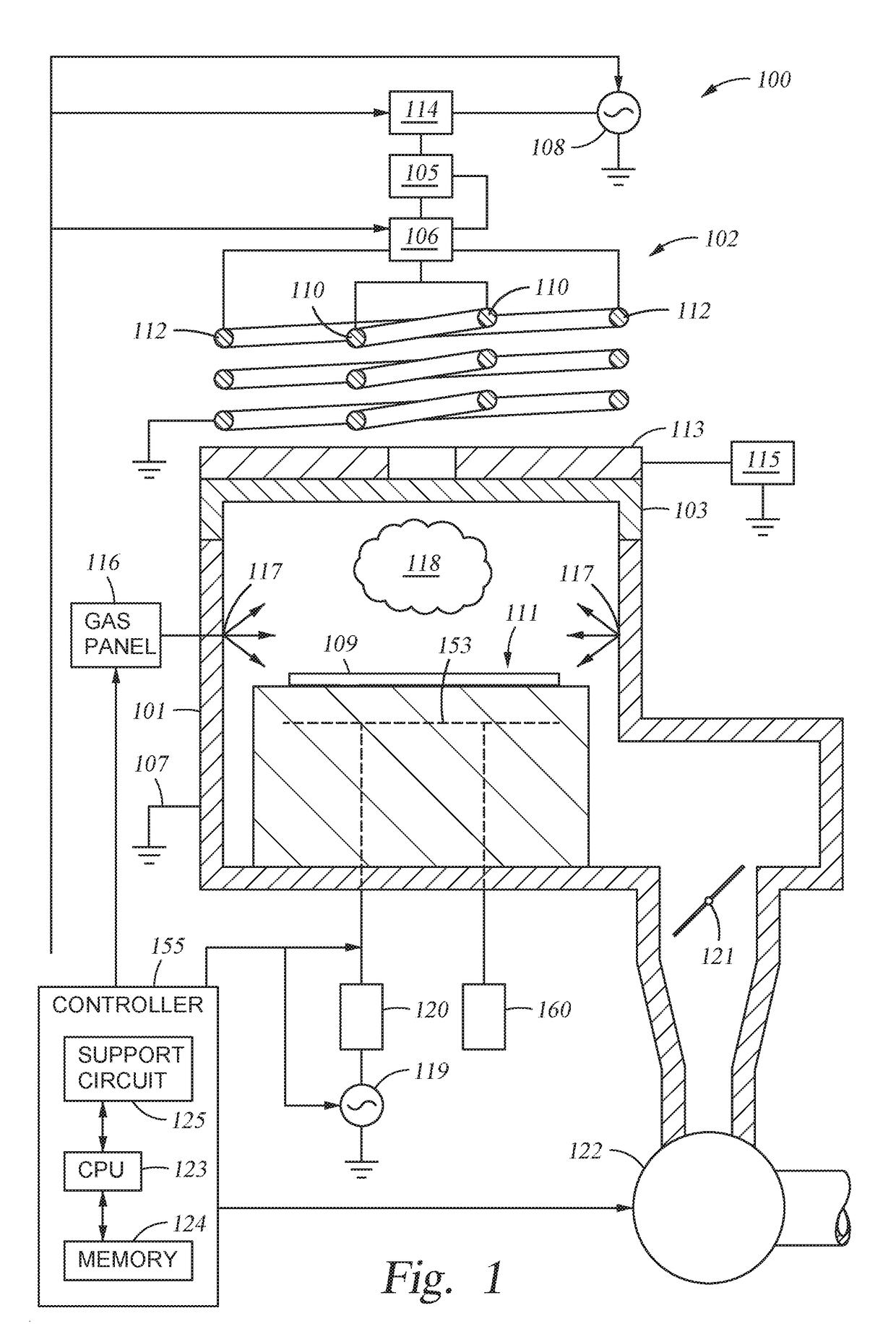
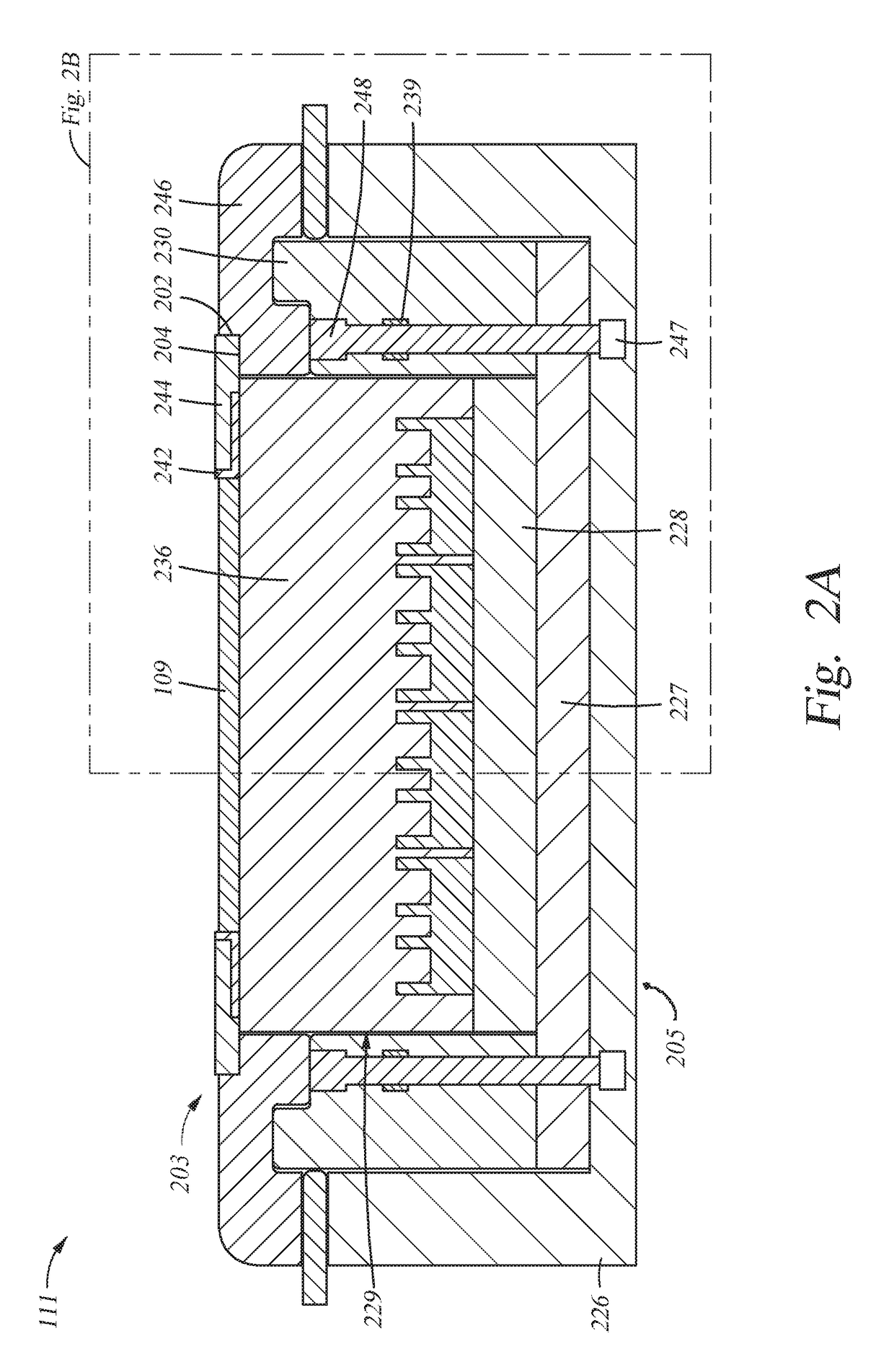
Methods and apparatus toward preventing esc bonding adhesive erosion
Embodiments of the present invention provide chamber components having a protective element for shielding bonding material from processing environments in a processing environment. The protective element may include protective seals, protective structures, erosion resistive fillers, or combinations thereof. Embodiments of the present invention reduce erosion of bonding material used in a processing chamber, thus, improving processing quality and reducing maintenance costs.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Polishing pads for chemical mechanical planarization
An improved pad and process for polishing metal damascene structures on a semiconductor wafer. The process includes the steps of pressing the wafer against the surface of a polymer sheet in combination with an aqueous-based liquid that optionally contains sub-micron particles and providing a means for relative motion of wafer and polishing pad under pressure so that the moving pressurized contact results in planar removal of the surface of said wafer, wherein the polishing pad has a low elastic recovery when said load is removed, so that the mechanical response of the sheet is largely anelastic. The improved pad is characterized by a high energy dissipation coupled with a high pad stiffness. The pad exhibits a stable morphology that can be reproduced easily and consistently. The pad surface resists glazing, thereby requiring less frequent and less aggressive conditioning. The benefits of such a polishing pad are low dishing of metal features, low oxide erosion, reduced pad conditioning, longer pad life, high metal removal rates, good planarization, and lower defectivity (scratches and Light Point Defects).
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Device and method for supporting a substrate
ActiveUS8528889B2Prevent abnormal supportingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusTectorial membraneEngineering
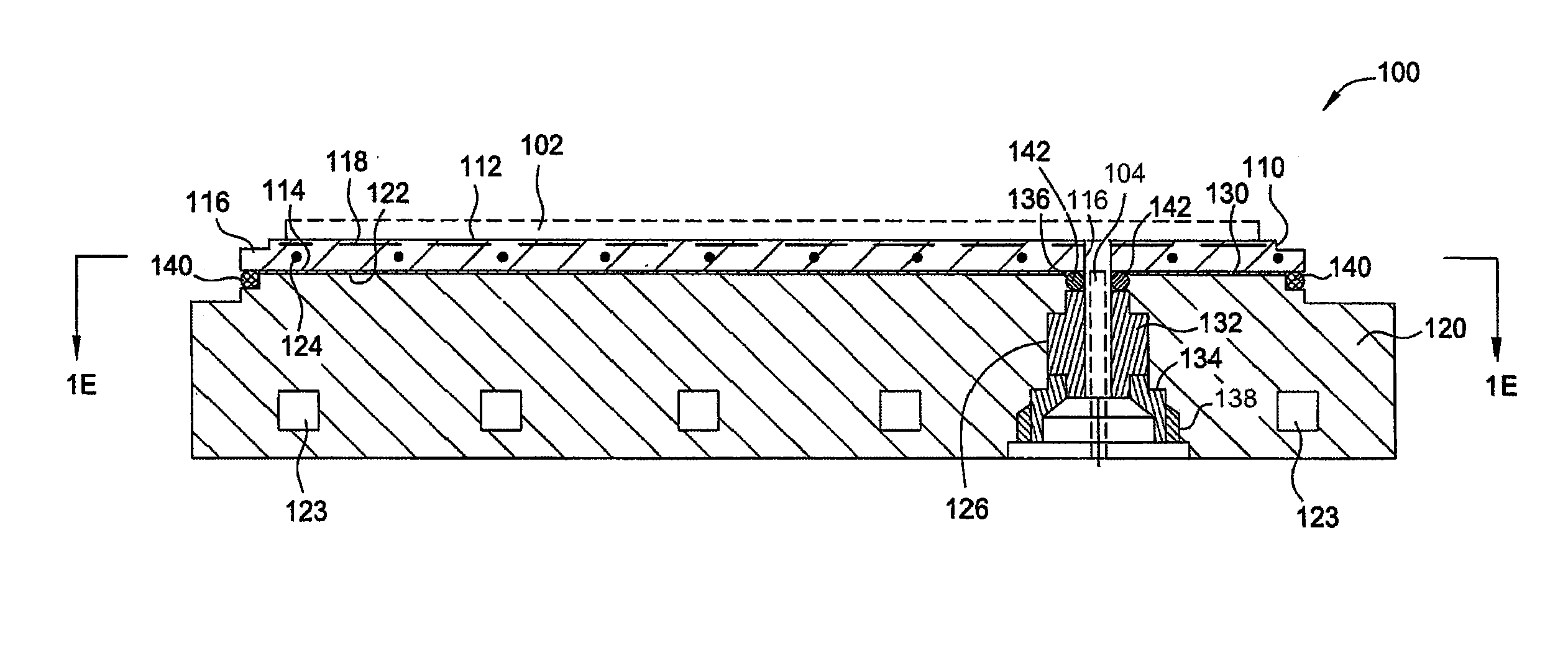
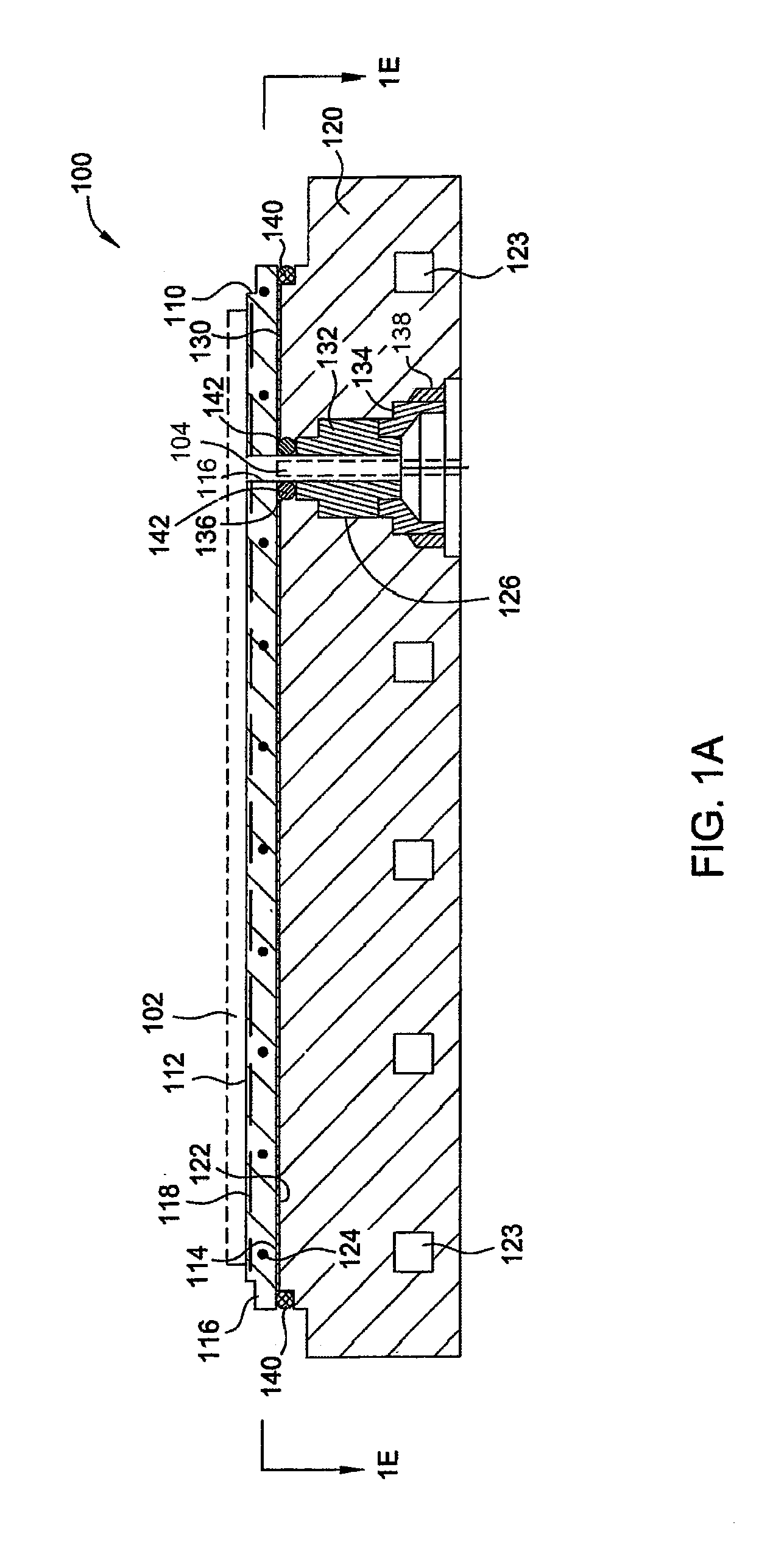
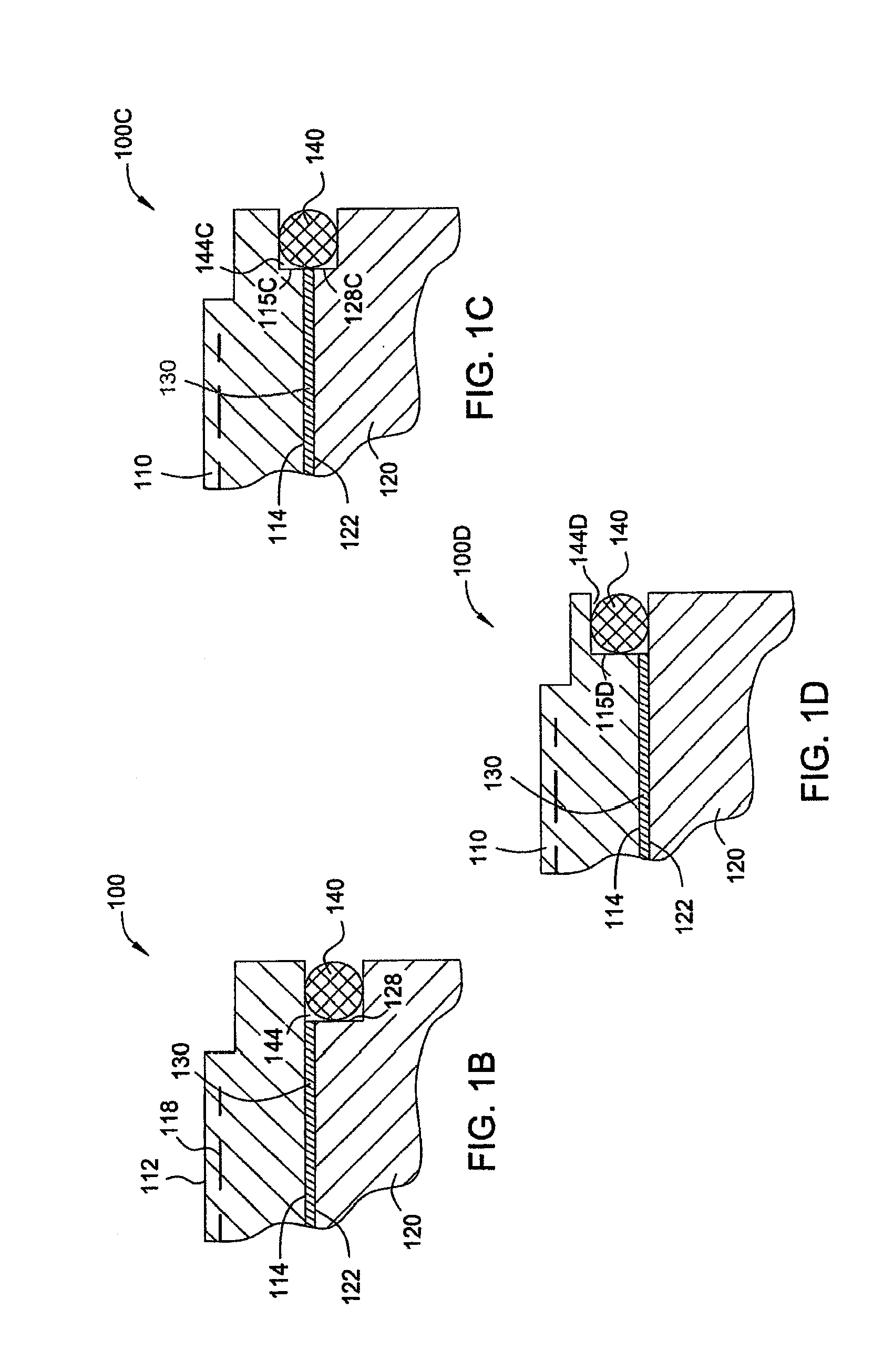
A substrate support device including a support member having a lower-surface support section to support a lower surface of a substrate; and a position restriction section provided on the lower-surface support section, the position restriction section being formed to surround a periphery of the substrate supported on the lower-surface support section and restrict a position of the substrate. At least one of the lower-surface support section and the position restriction section includes a base material and a protective film formed to cover the base material and prevent at least one of wear and chemical erosion to which the base material will be subject. The substrate support device further includes, for example, a base that supports the support member, and a driving structure that moves the support member in a relative fashion with respect to the base, and is constructed as a substrate transport device.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Drillable drill bit nozzle
InactiveUS6848517B2Thin structureImprove corrosion resistanceDrill bitsDrilling rodsHigh resistanceRubber material
A drill bit nozzle providing a through bore for the passage of drilling fluid through a drill bit. The nozzle is made of a material or materials which can be drilled through by standard well bore drilling equipment. The material(s) are selected to provide a surface to the through bore which has a relatively high resistance to erosion to withstand the abrasive and corrosive impact of jetted drilling fluid. Embodiments are described using a hard chrome / copper combination and a single rubber material.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
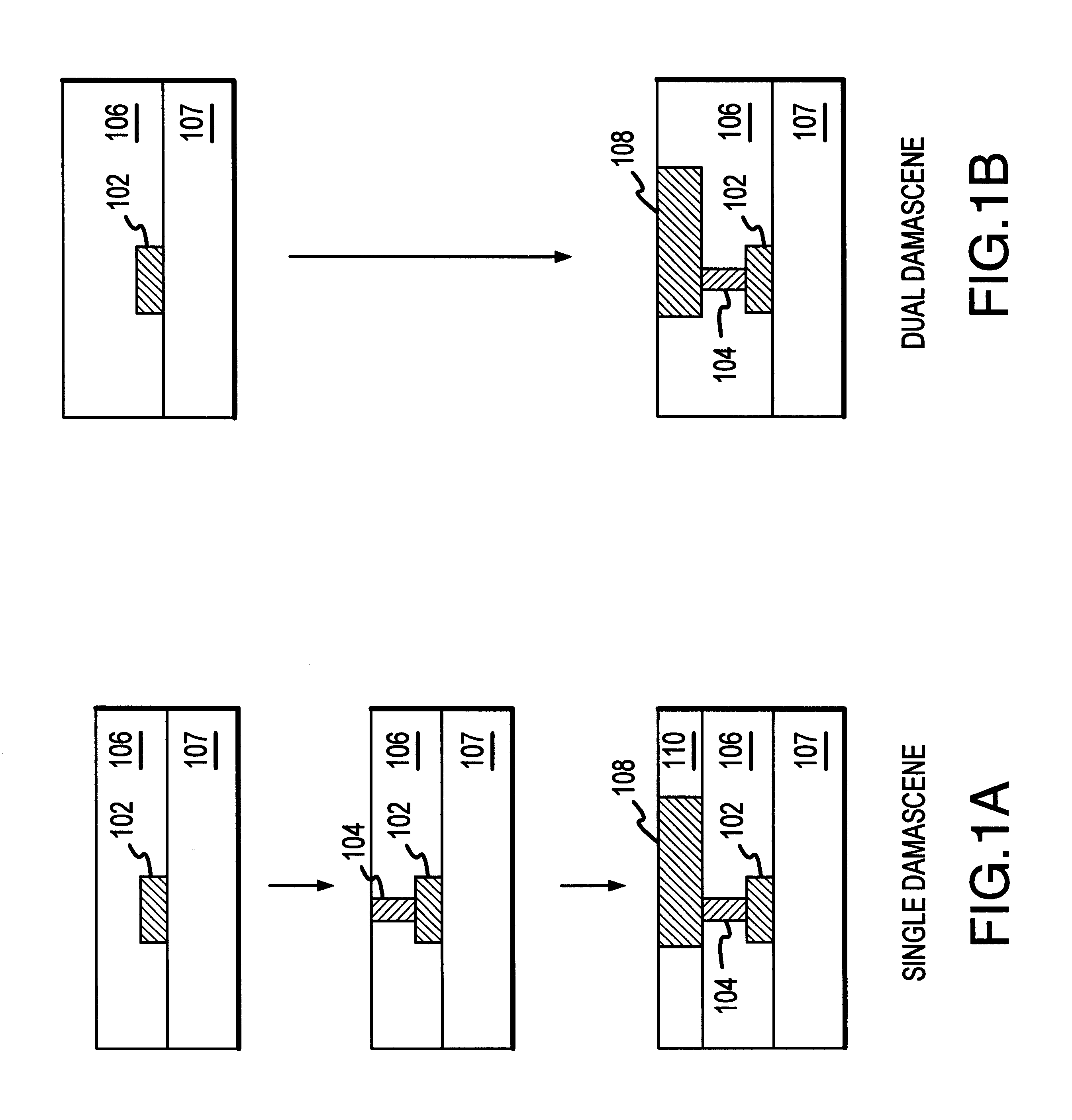
IC interconnect structures and methods for making same
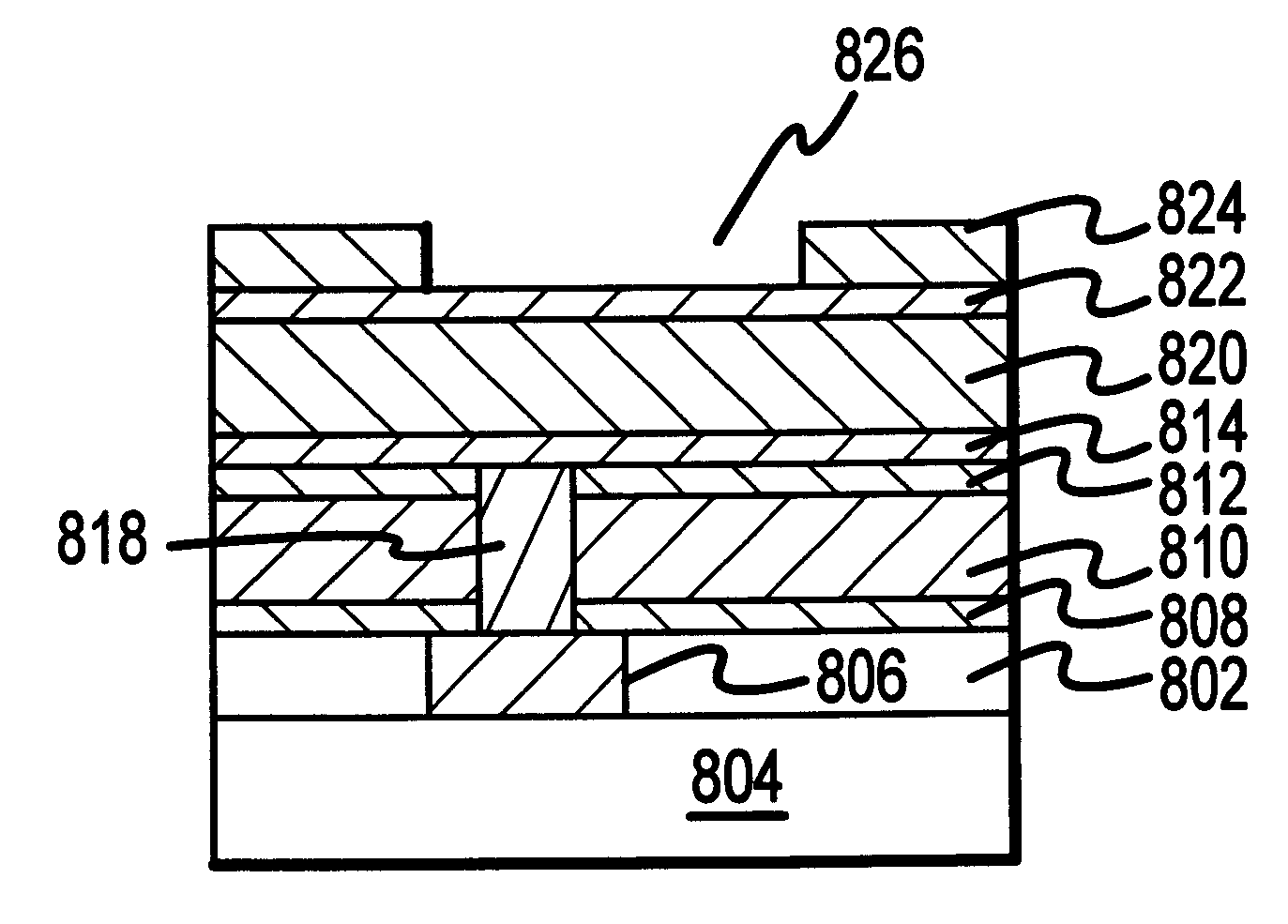
Methods and structures are disclosed for advanced interconnects in sub-micron and sub-half-micron integrated circuit devices fabricated using a single damascene process. a dielectric etch-stop layer (e.g., silicon nitride) is deposited subsequent to rather than prior to CMP processing of the previous metallization layer (e.g., the conductive plug). This scheme effectively eliminates the effect of CMP-induced erosion on the etch-stop layer and therefore allows an extremely thin etch stop to be used. Moreover, a high etch-selectivity can be obtained for the trench etch, and all etch-stop material is removed from beneath the interconnect metal, thereby reducing parasitic effects. A patterned dielectric layer is used as a metal cap in place of the standard blanket silicon nitride layer, thus preventing the formation of blisters and bubbles associated with trapped moisture and gasses, and reducing interconnect capacitance.
Owner:NEWPORT FAB
Wafer edge ring lifting solution
ActiveUS20170213758A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActuatorValve opening
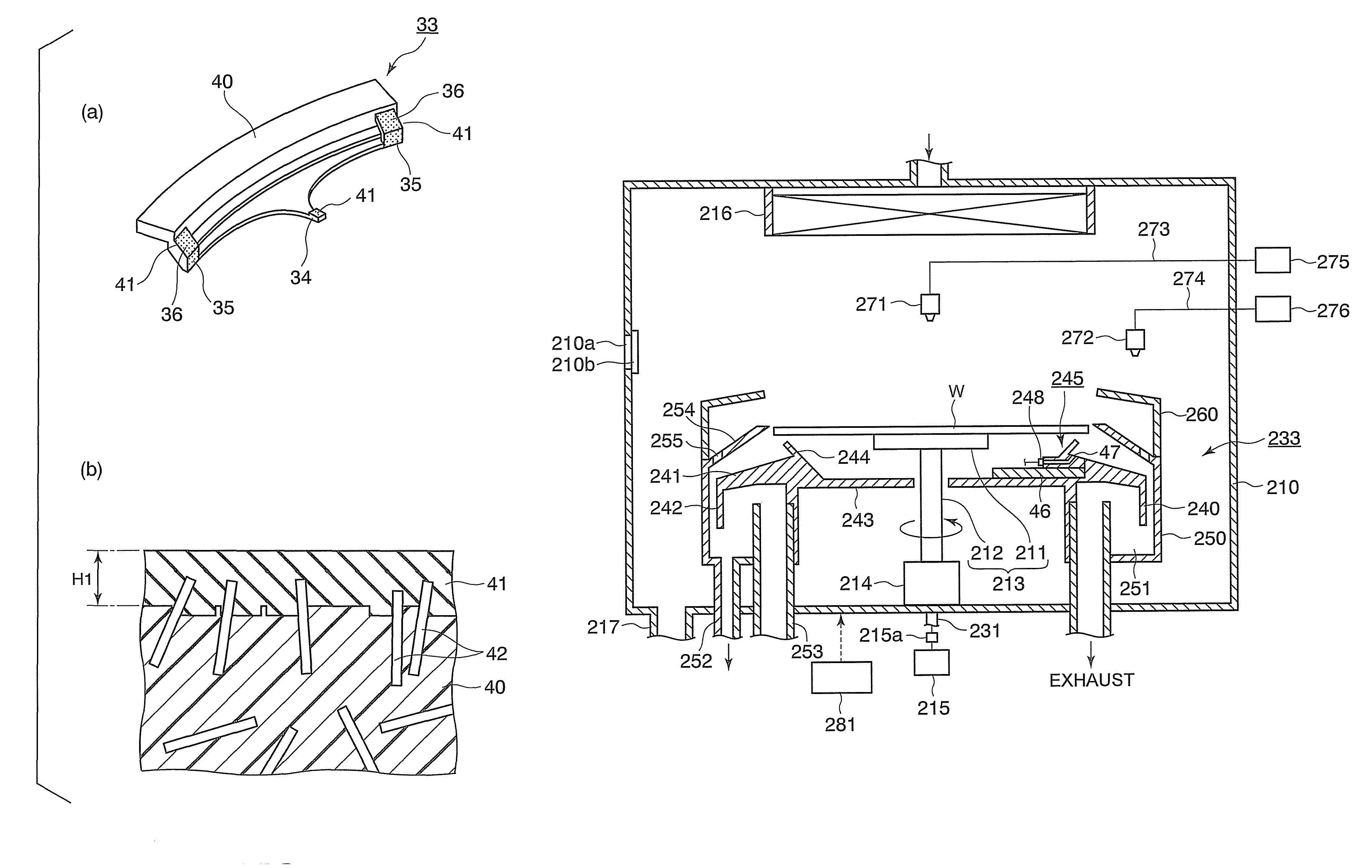
Apparatuses including a height-adjustable edge ring, and methods for use thereof are described herein. In one example, a substrate support assembly includes a height-adjustable edge ring, and the substrate support assembly is located within a process chamber. The substrate support assembly includes an electrostatic chuck, an edge ring positioned on a portion of the electrostatic chuck, and one or more actuators to adjust the height of the edge ring via one or more push pins. The height-adjustable edge ring can be used to compensate for erosion of the edge ring over time. In addition, the height-adjustable edge ring can be removed from the process chamber via a slit valve opening without venting and opening the process chamber. The height-adjustable edge ring can be tilted by the one or more actuators in order to improve azimuthal uniformity at the edge of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
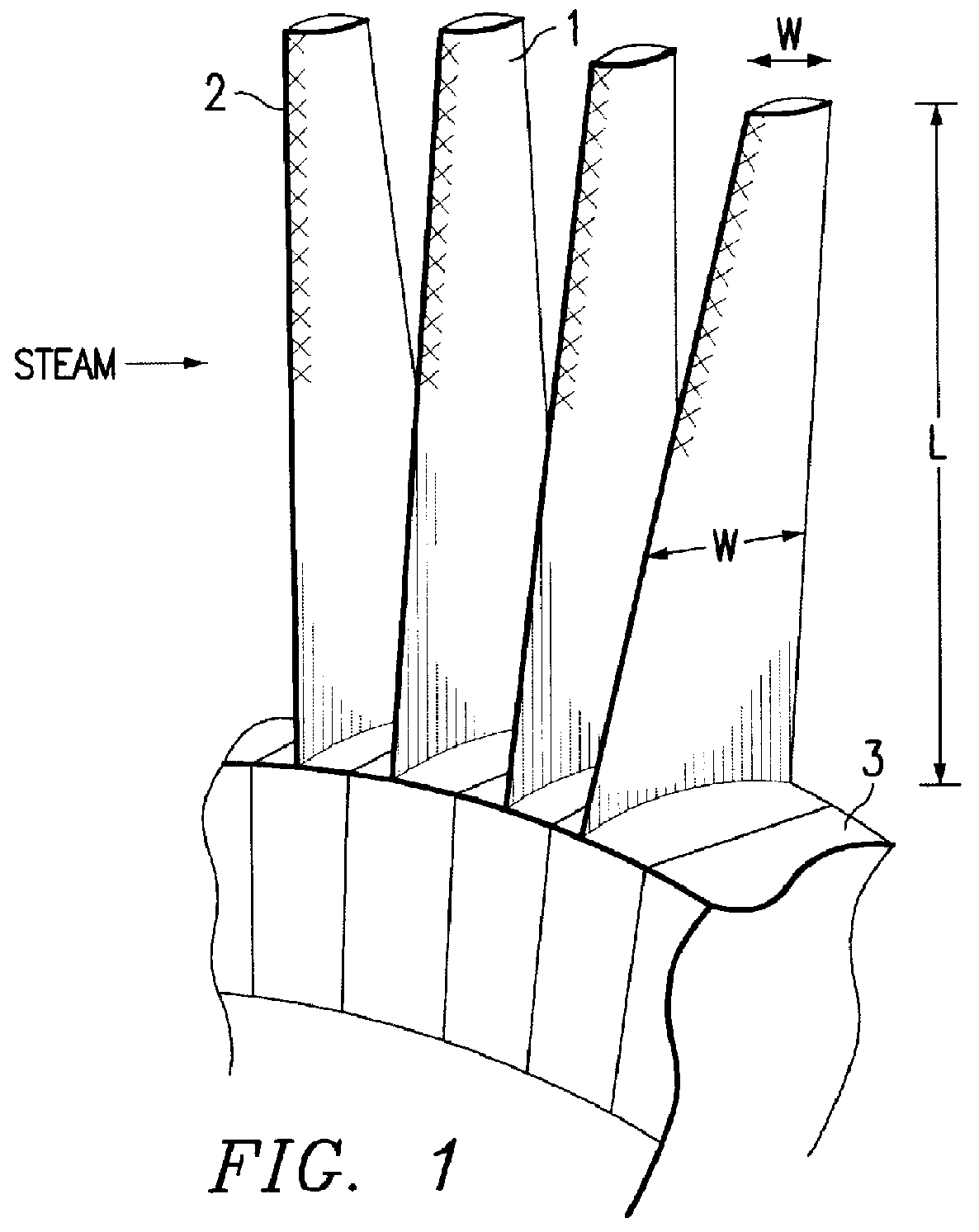
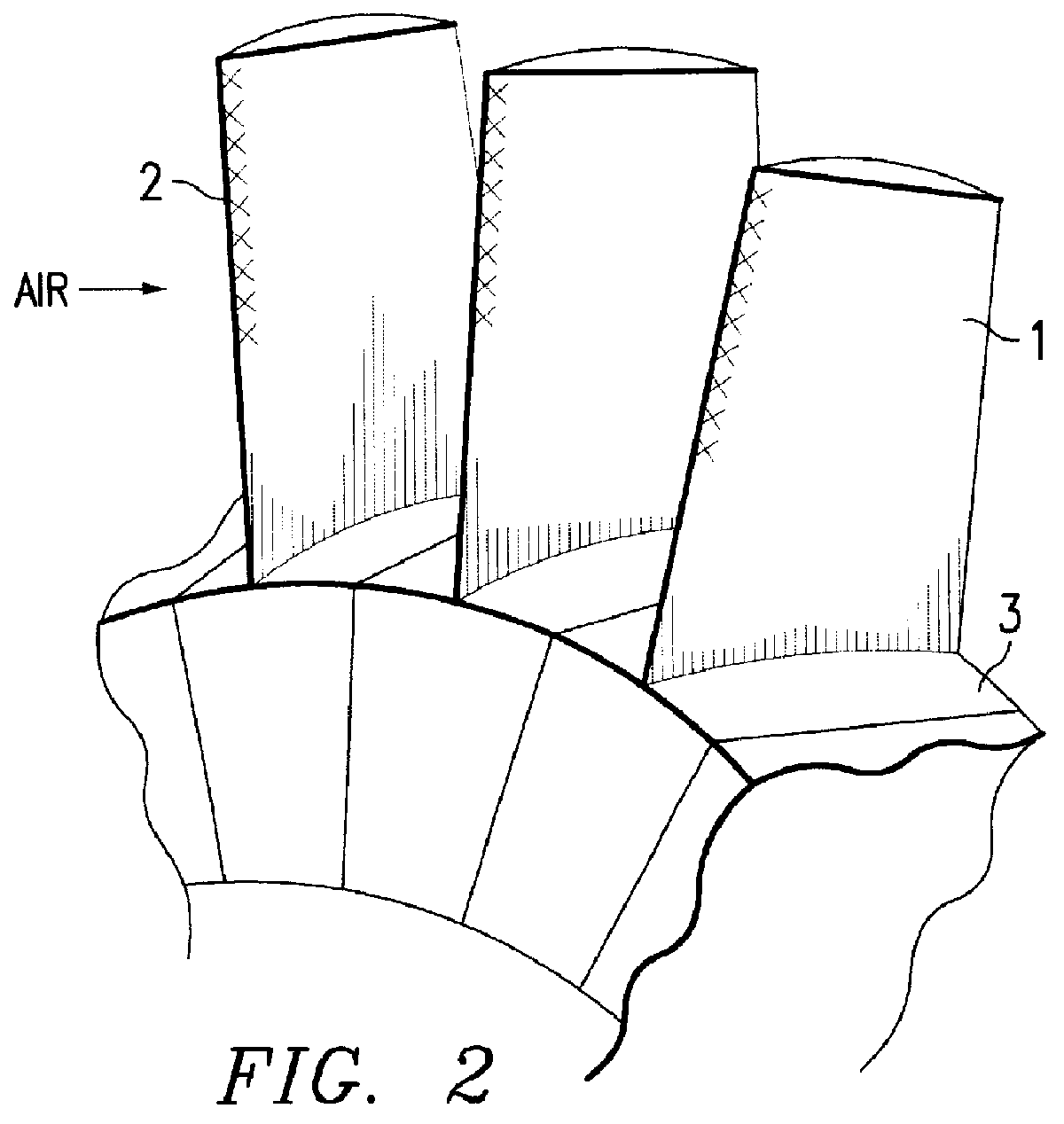
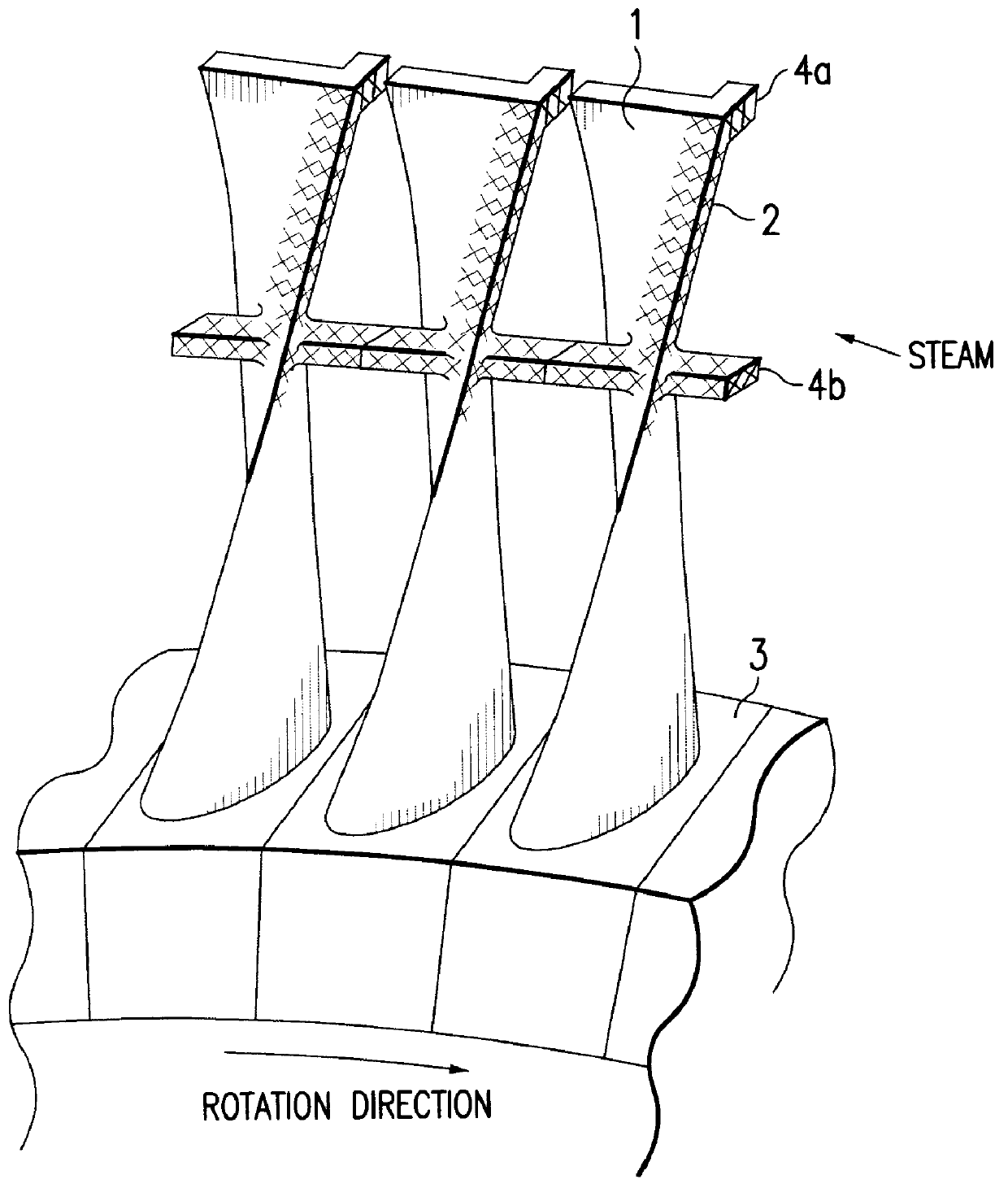
Method for producing titanium alloy turbine blades and titanium alloy turbine blades
InactiveUS6127044ALess abrasionSuperior in water droplet erosion resistancePropellersEngine manufactureLeading edgeTurbine blade
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 01817 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 13, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 10066 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1997A method for producing titanium alloy turbine blades comprising the steps of (a) forming turbine blades of titanium alloy through hot forging or machining, (b) cooling leading edges on tip portions of the turbine blades including covers thereof formed through hot forging or machining faster than blade main body after final hot forging or solid solution treatment, and (c) heat treating the cooled turbine blades. With this method, it is possible to manufacture titanium turbine blades in an economical fashion and obtain titanium alloy turbine blades superior in reliability by preventing erosion.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
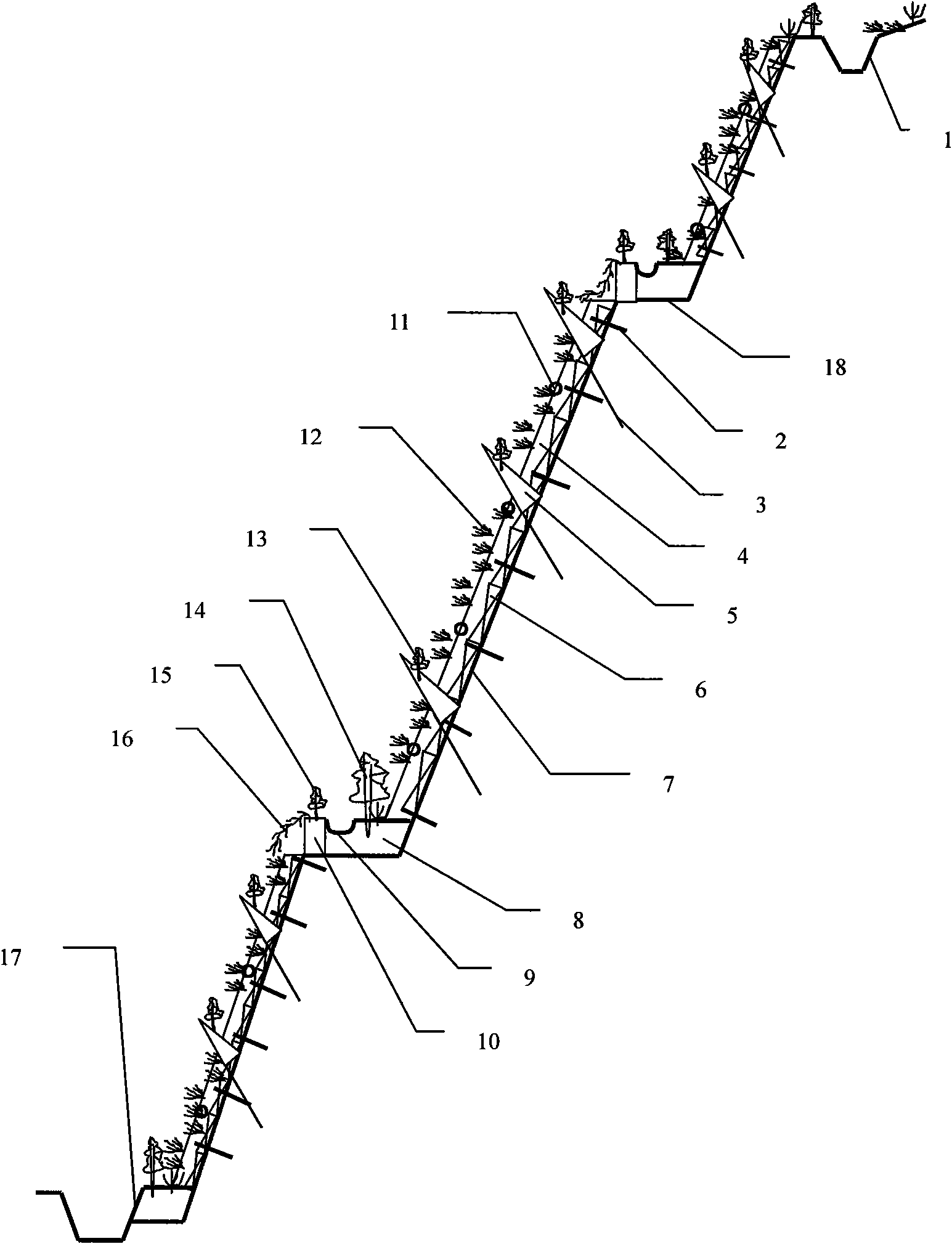
Revegetation system on steep rocky slopes and implementing method thereof
The invention discloses a revegetation system on steep rocky slopes and an implementing method thereof, which are suitable for surface vegetalization of steep rocky uncover slopes with the gradient of 60 degrees above. A slope drainage system is arranged in the system to prevent the vegetalization layer from being flushed by rainwater and reduce water loss and soil erosion; a mix-sprayed vegetalization layer plastic-covered with iron wire corrugated meshes and consisting of continuous fiber is arranged on the slopes and has stable structure, rich nutrition and functions of water conservation and ventilation. The casting separator prevents the mix-sprayed vegetalization layer from sliding downwards; and a drop irrigation facility is distributed to make sure that the vegetalization layer is moist. After maintenance of mix-sprayed construction on the slopes, the vegetable layer with herbaceous plants and shrubs can be effectively formed, thereby reconstructing the destructed vegetables on the slopes and recovering the natural landscapes on the uncover slopes.
Owner:深圳市如茵生态环境建设有限公司
Thermal barrier coating system
ActiveUS20050170200A1Avoid low surface temperaturesInferior erosion resistancePropellersMolten spray coatingThermal sprayingMetallurgy
A TBC system suitable for protecting the surface of a substrate subjected to a hostile thermal environment. The TBC system comprises a bond coat on the substrate surface, an alumina scale on the bond coat, and a multilayer TBC comprising a thermal-sprayed first ceramic layer on the alumina scale and a thermal-sprayed second ceramic layer overlying the first ceramic layer. The first ceramic layer consists essentially of partially stabilized zirconia so as to comprise the tetragonal and cubic phases of zirconia. The second ceramic layer consists essentially of fully stabilized zirconia so as to consist essentially of the cubic phase of zirconia. The second ceramic layer is also characterized by having vertical microcracks that extend through the thickness thereof. The second ceramic layer is thicker and more erosion resistant than the first ceramic layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
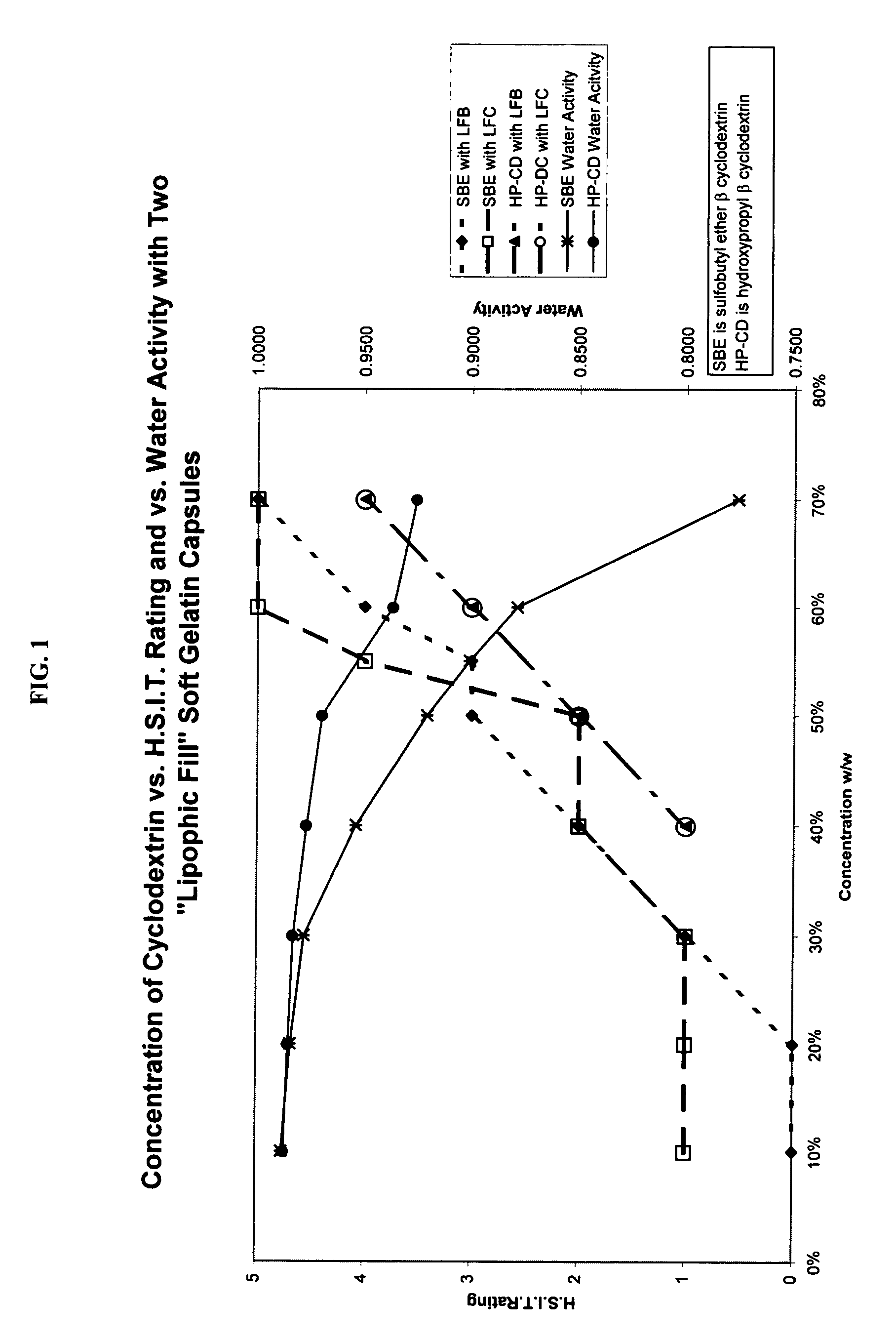
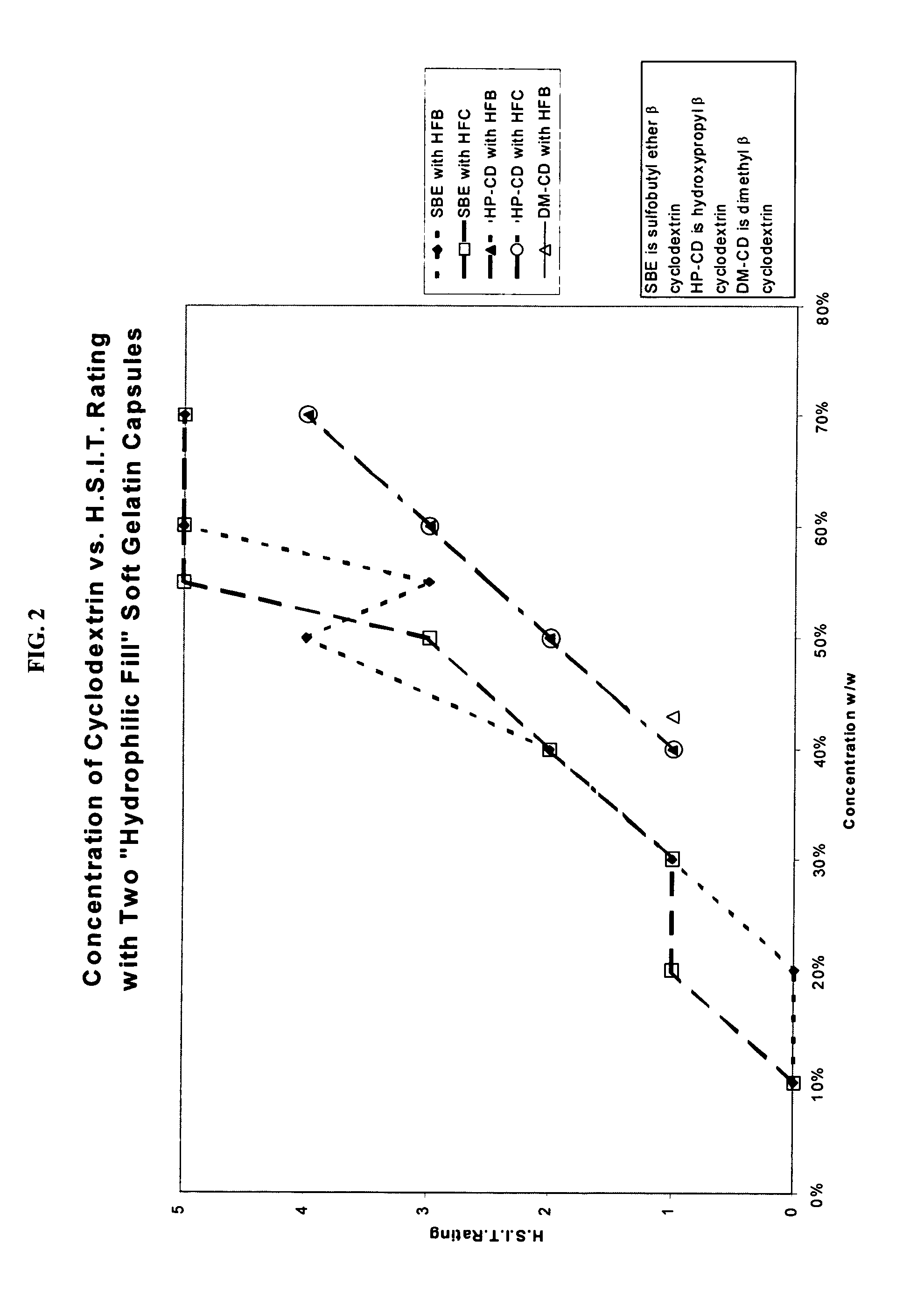
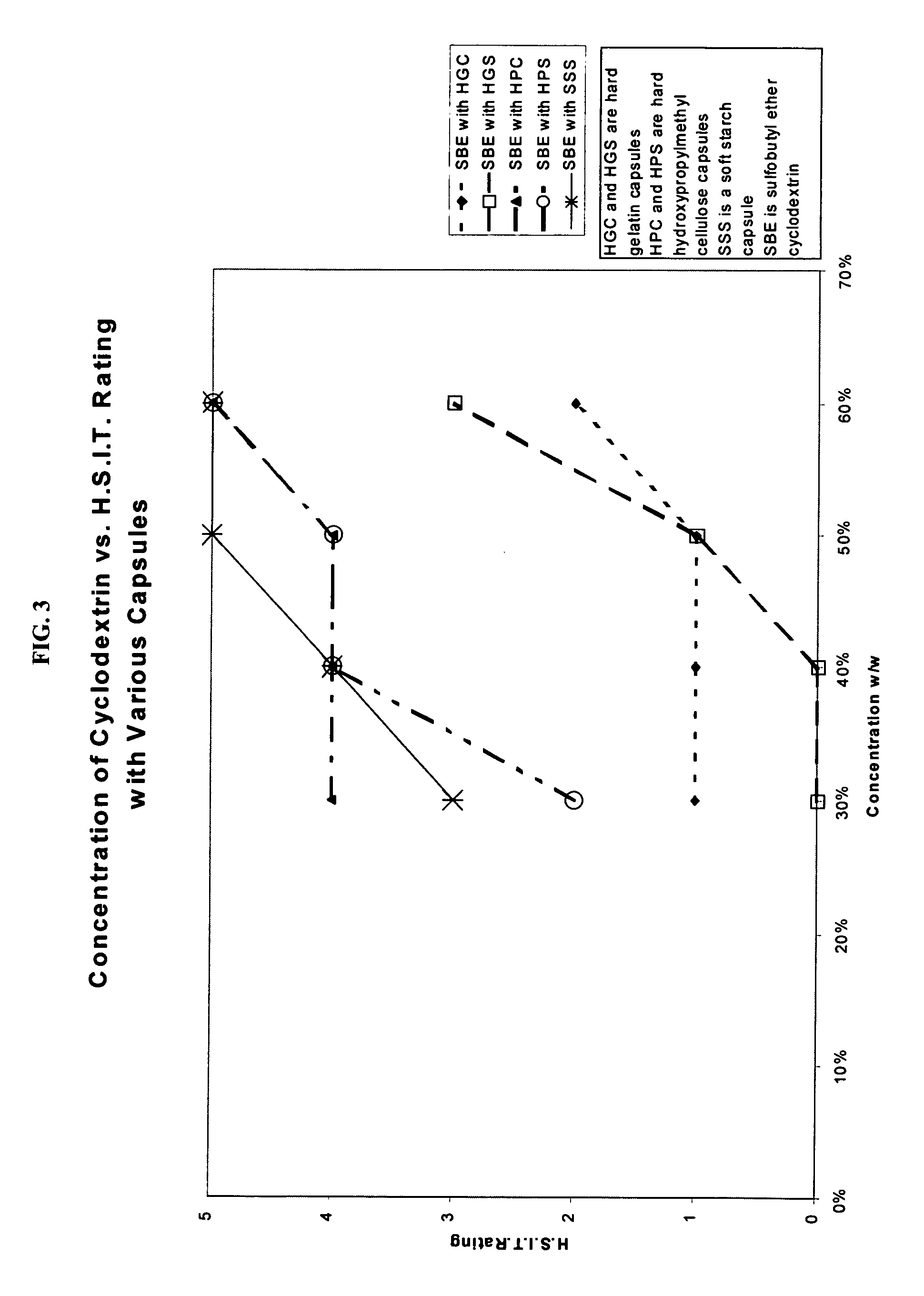
Capsules containing aqueous fill compositions stabilized with derivatized cyclodextrin
ActiveUS20050186267A1Reduce and stop dissolutionReduce and stop and erosionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsActive agentWater activity
A capsule containing an aqueous fill composition that comprises water, a derivatized cyclodextrin, such as sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin (SAE-CD) or hydroxypropyl cyclodextrin (HPCD), optionally one or more active agents and optionally one or more excipients is stabilized from degradation, erosion, swelling or dissolution of its shell during storage. The derivatized cyclodextrin is present in an amount sufficient to reduce, eliminate or inhibit degradation, erosion, swelling and / or dissolution of the shell by water present in the fill composition. Alternatively, the derivatized cyclodextrin and another shell-stabilizing material together stabilize the shell from degradation, erosion, swelling and / or dissolution by water present in the fill composition. The derivatized cyclodextrin can reduce the water activity of the fill composition.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Anti-back-splash sand blasting perforator
The invention relates to an anti-back-splash sand blasting perforator, which comprises a body and a nozzle, wherein a groove is formed in the outer wall of the body; an installation hole is formed in the middle of the groove; the side wall of the groove is inclined; the nozzle is installed in the installation hole; the outer end of the nozzle stretches out from the bottom surface of the groove. The anti-back-splash sand blasting perforator is simple in structure, less in parts, and easy to process and assemble; through the arranged groove and a bulge on the outer end of the nozzle, a flow guide structure is formed around the nozzle, so that back-splash liquid can be timely and uniformly flown when back splashing on the perforator, can be prevented from forming vortex in the groove, and can be prevented from flowing in the groove for a long time; the erosion of the back-splash liquid on the perforator is reduced, and the service life of the perforator is improved.
Owner:JEREH ENERGY SERVICES
Compositions and Methods for Improving Overall Tooth Health and Appearance
ActiveUS20080247973A1Avoid lostSuperior anticariesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAmmonium compoundsStaining
Disclosed are oral care compositions comprising selected surface-active organophosphate compounds and methods of use to provide protection of teeth from erosion caused by the action of chemicals, such as harsh abrasives and acids. The surface-active organophosphate compounds are substantive to teeth, the phosphate groups binding the calcium in teeth and thus preventing loss of calcium from dissolution when contacted with acids. The organophosphate compound may also deposit a protective surface coating that prevents contact of teeth with erosive challenges. Selected organophosphate compounds contain one or more phosphate groups and are combined in the oral care composition with one or more of a fluoride ion agent, an antimicrobial agent preferably selected from quaternary ammonium compounds and polyvalent metal salts, an anticalculus agent and additional surfactant, to provide benefits including superior anti-erosion, anticaries, antiplaque and anti-staining as demonstrated by enhanced fluoride uptake, remineralization, resistance to acid demineralization and antimicrobial activities, resulting in improved overall tooth health, structural integrity and appearance.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
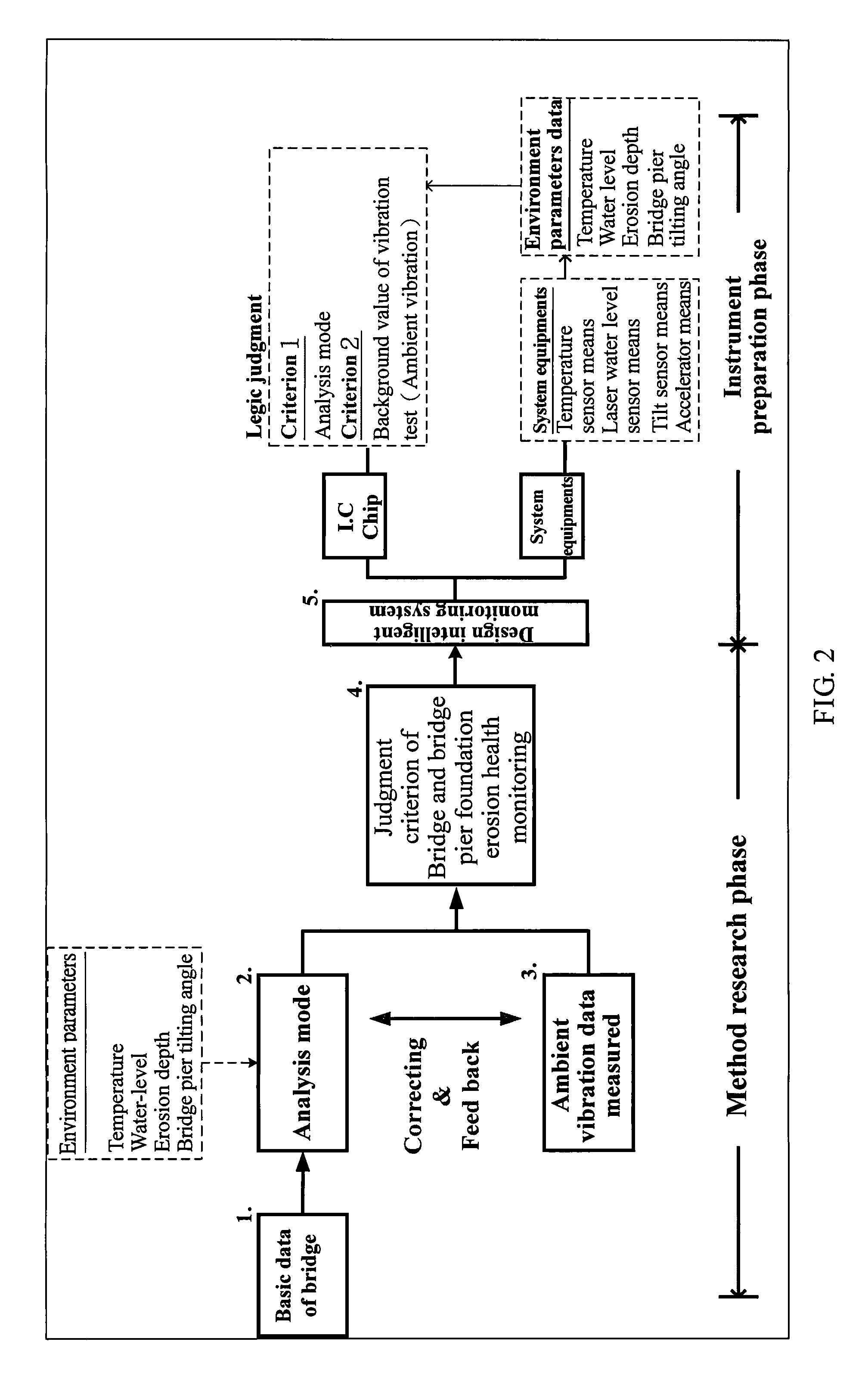
Bridge monitoring and safety evaluation method using a vibration technique
ActiveUS20100242609A1Easy system maintenanceImprove the level ofVehicle testingFluid-tightness measurementStructural monitoringEngineering
The invention relates bridge structure safety evaluation technology by means of combining vibration measuring and structural model analysis techniques for bridge erosion evaluation and pre-warning monitoring applications. This technology can also be applied for long-term bridge structure monitoring and safety evaluation as well as judgment and evaluation of rail structure abnormality.
Owner:LEE WEI FENG
Power distribution module(s) capable of hot connection and/or disconnection for distributed antenna systems, and related power units, components, and methods
ActiveUS20130249292A1Dc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationElectricityDistributed antenna system
Power distribution modules capable of “hot” connection and / or disconnection in distributed antenna systems (DAS), and related components, power units, and methods are disclosed. The power distribution modules are configured to distribute power to a power-consuming DAS component(s), such as a remote antenna unit(s) (RAU(s)). By “hot” connection and / or disconnection, it is meant that the power distribution modules can be connected and / or disconnected from a power unit and / or a power-consuming DAS component(s) while power is being provided to the power distribution modules. Power is not required to be disabled in the power unit before connection and / or disconnection of power distribution modules. As a non-limiting example, the power distribution modules may be configured to protect against or reduce electrical arcing or electrical contact erosion that may otherwise result from “hot” connection and / or connection of the power distribution modules.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Topography reduction and control by selective accelerator removal
ActiveUS20090280649A1Improve throughputLow costCellsDecorative surface effectsMetal interconnectEtching
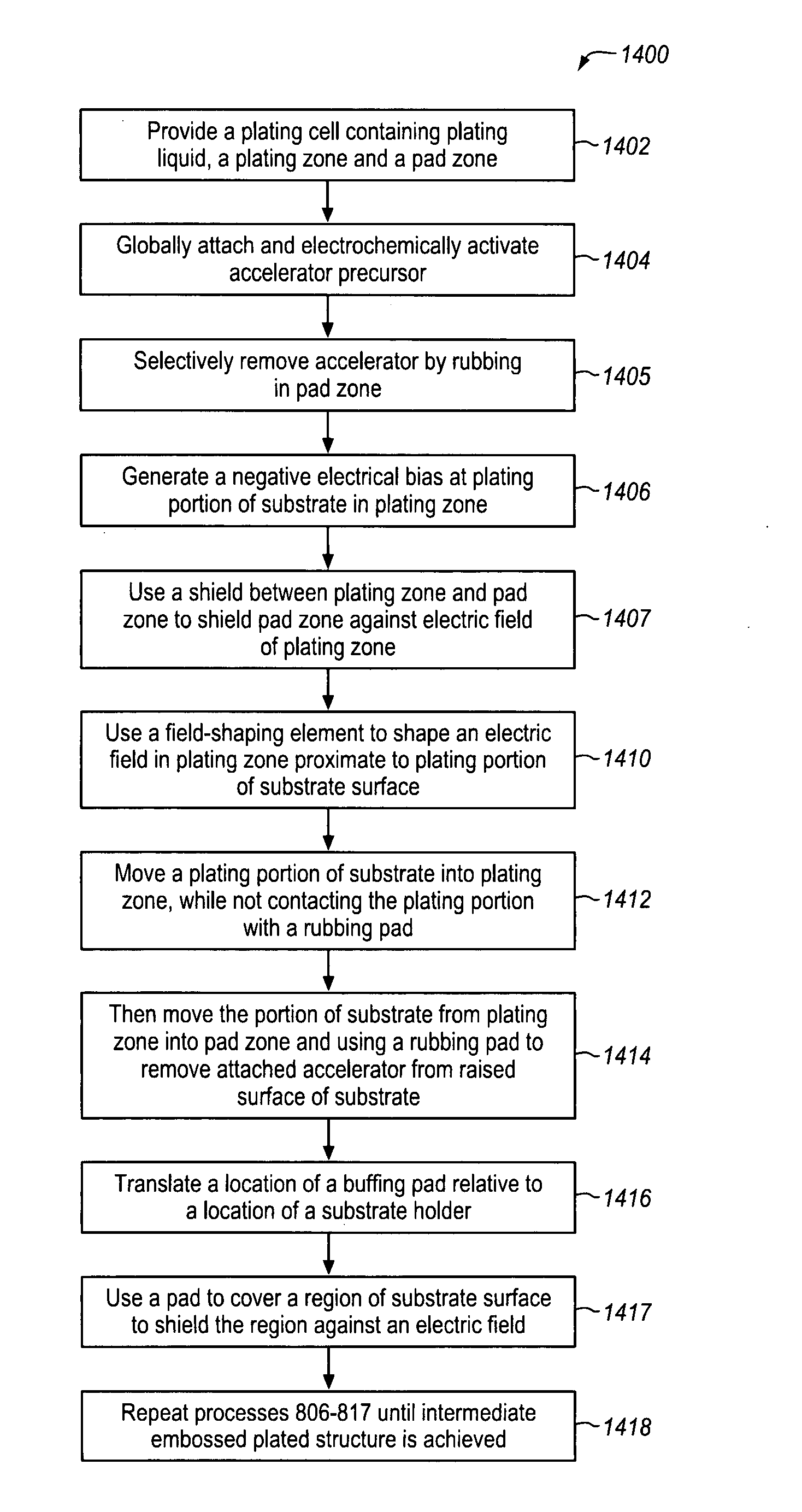
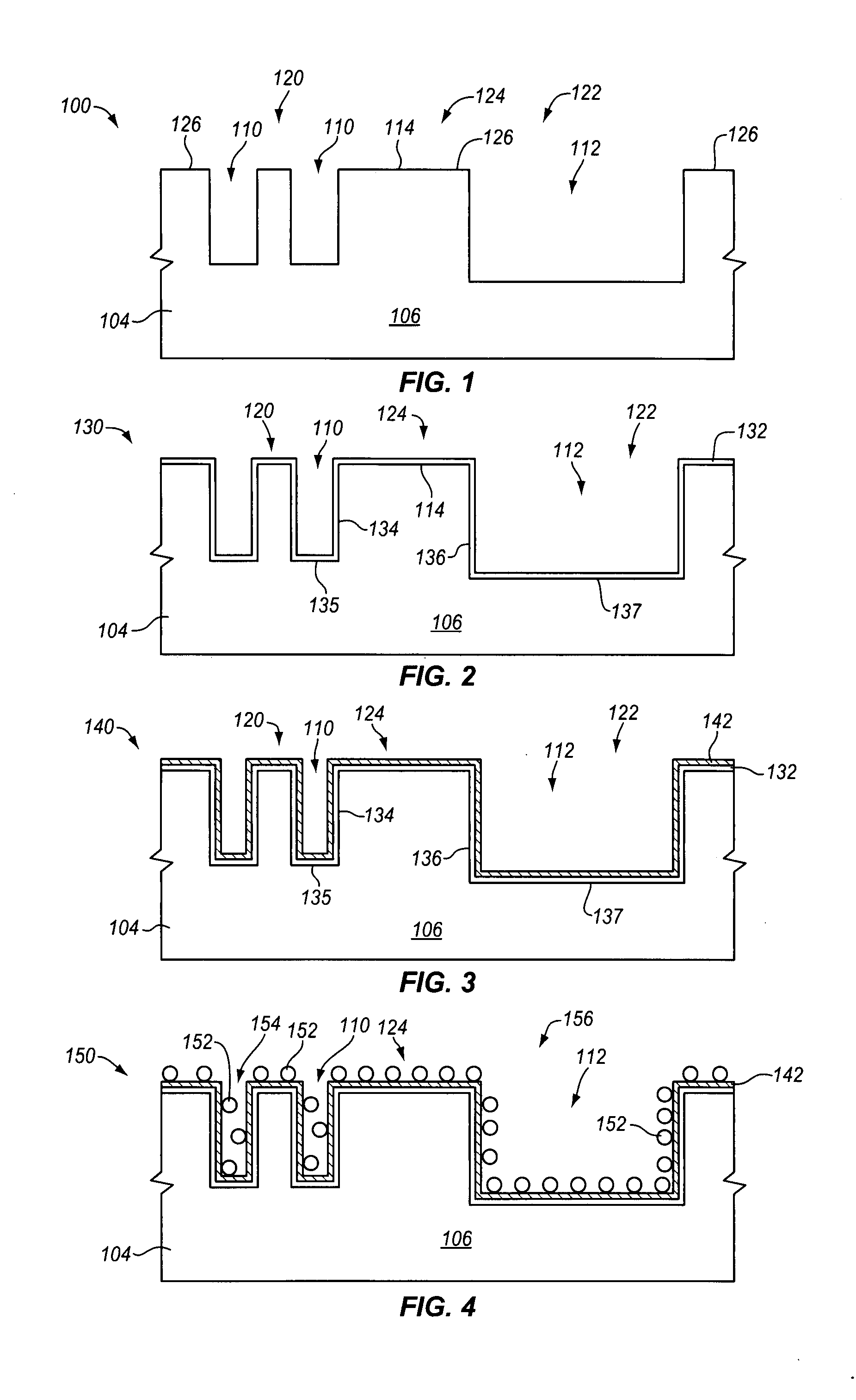
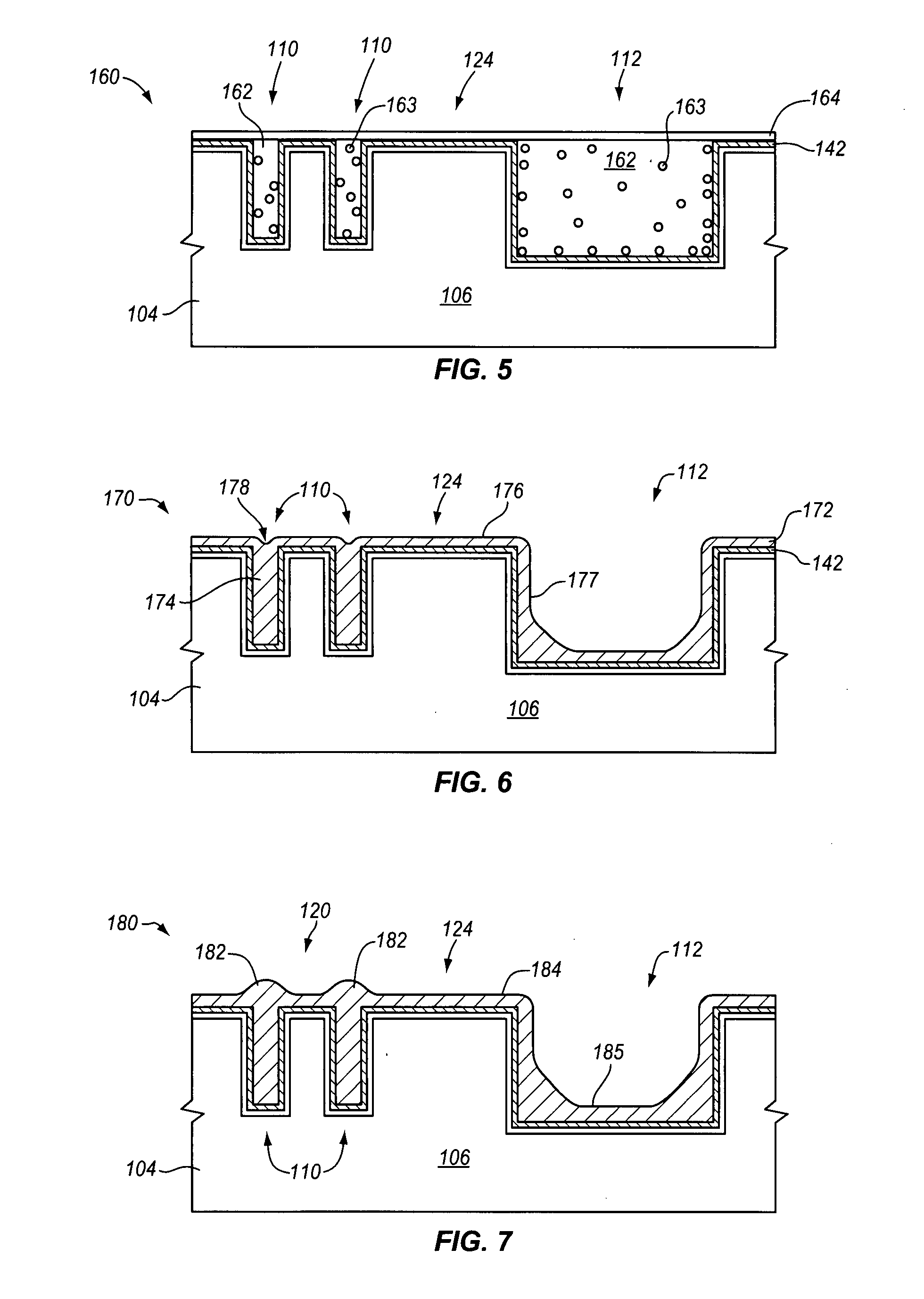
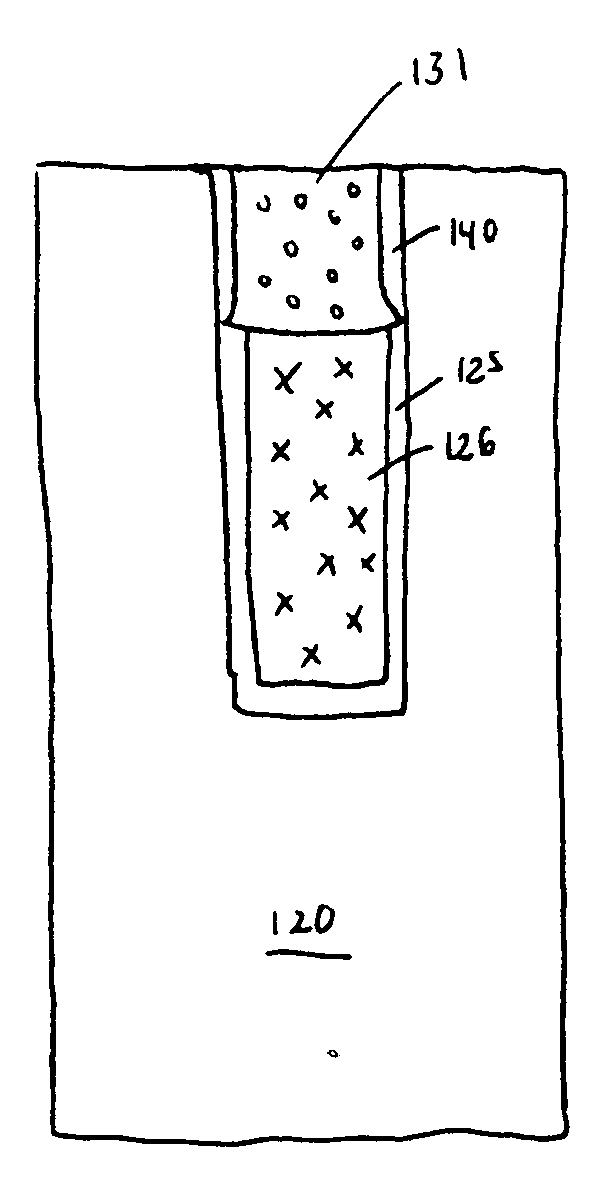
Plating accelerator is applied selectively to a substantially-unfilled wide (e.g., low-aspect-ratio feature cavity. Then, plating of metal is conducted to fill the wide feature cavity and to form an embossed structure in which the height of a wide-feature metal protrusion over the metal-filled wide-feature cavity is higher than the height of metal over field regions. Most of the overburden metal is removed using non-contact techniques, such as chemical wet etching. Metal above the wide feature cavity protects the metal-filled wide-feature interconnect against dishing, and improved planarization techniques avoid erosion of the metal interconnect and dielectric insulating layer. In some embodiments, plating of metal onto a substrate is conducted to fill narrow (e.g., high-aspect-ratio feature cavities) in the dielectric layer before selective application of plating accelerator and filling of the wide feature cavity.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Isolation structures for semiconductor integrated circuit substrates and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20070132056A1Increase flexibilityCracking can be particularly problematicSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectricCondensed matter physics
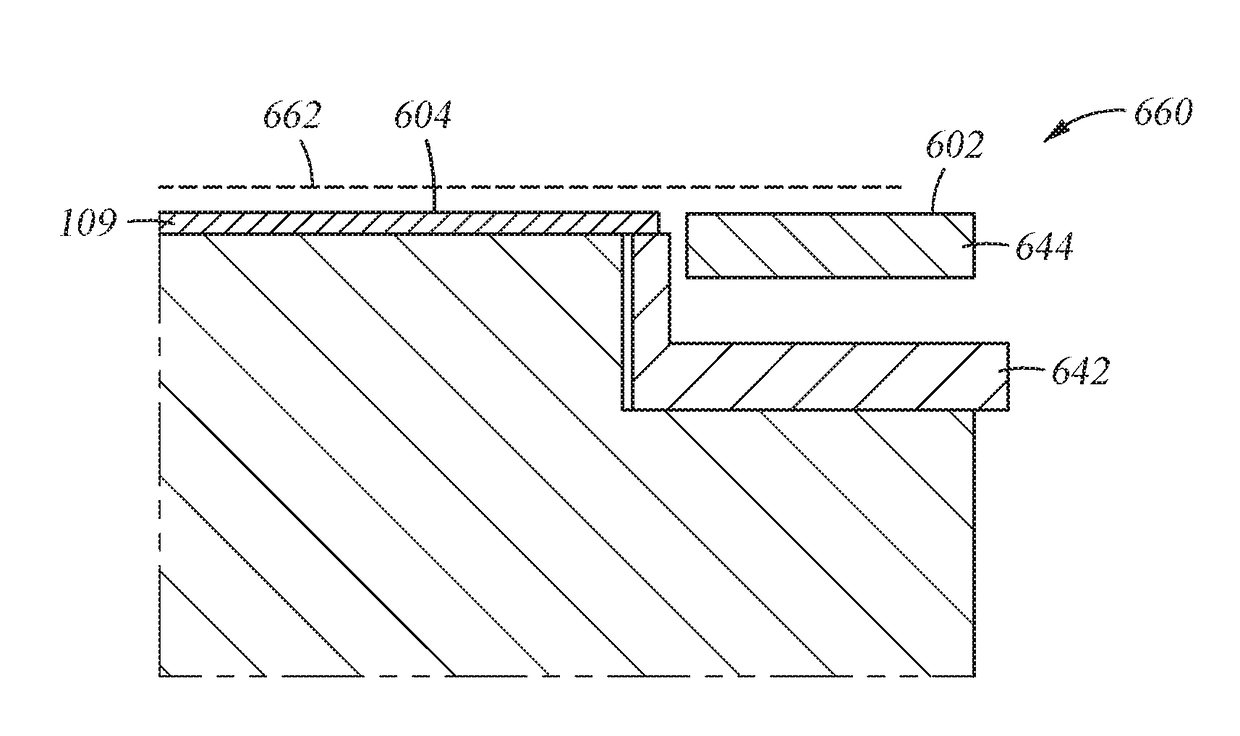
Isolation regions for semiconductor substrates include dielectric-filled trenches and field oxide regions. Protective caps of dielectric materials dissimilar from the dielectric materials in the main portions of the trenches and field oxide regions may be used to protect the structures from erosion during later process steps. The top surfaces of the isolation structures are coplanar with the surface of the substrate. Field doping regions may be formed beneath the field oxide regions. To meet the demands of different devices, the isolation structures may have varying widths and depths.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Highly convertable endolumenal prostheses and methods of manufacture
Endolumenal prostheses that readily and extensively convert from a delivery configuration to a deployed configuration are disclosed. Endolumenal prostheses may be fabricated from one or more shape memory polymers, a high modulus elastomer, a polymer that is both elastomeric and exhibits shape memory behavior, a hydrogel, or some combination thereof. Polymers used to fabricate the prostheses are selectively synthesized to exhibit desired characteristics such as crystallinity, strain fixity rate, strain recovery rate, elasticity, tensile strength, mechanical strength, cross-linking density, extent physical cross-linking, extent of covalent cross-linking, extent of interpenetrating networks, rate of erosion, heat of fusion, crystallization temperature, and acidity during erosion. The endolumenal prostheses convert to the deployed configuration following delivery to a treatment site, upon exposure to an initiator either present within the body naturally or introduced into the body.
Owner:SYNECOR LLC
Multi-layer wiring structure, semiconductor apparatus having multi-layer wiring structure, and methods of manufacturing them
InactiveUS20060019485A1Low resistance contactStable, highly reliable high-density buried wiringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorInsulation layer
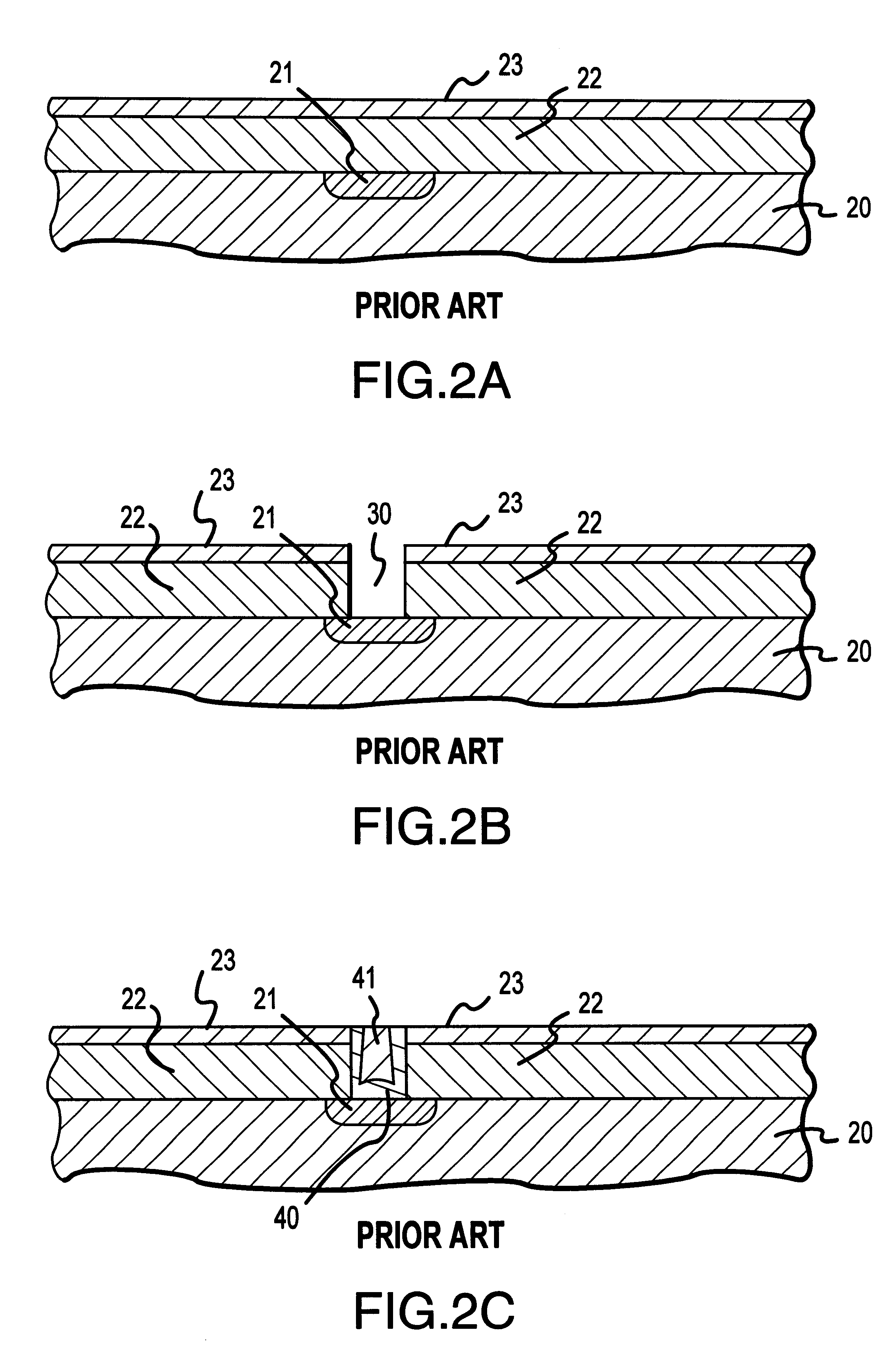
A multi-layer wiring structure including an upper layer wiring (second buried wiring) connected to a buried wiring (first buried wiring) in lower layer wiring grooves (first wiring grooves) through connection conductors, wherein a protective film capable of enduring a cleaning treatment with hydrogen radicals or hydrogen plasma applied to the surface of the first buried wiring at the time of forming the connection conductors is formed on the inside surfaces of the wiring grooves to be filled with he second buried wiring and the wiring connection holes to be filled with the connection conductors which surfaces are liable to be eroded upon exposure to the atmosphere used in the cleaning treatment, whereby erosion of the insulation layers at the time of the cleaning is obviated, sufficient cleaning can be performed, and deterioration of characteristics can be improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
Automatic motor-driven blender cup with a leak-free magnetic stirring apparatus
InactiveUS7314307B2Increase speedImprove uniformityTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersMagnetic tension forceMotor drive
An automatic motor-driven blender cup with a leakage-free stirring apparatus includes a blender cup, an internal chamber, a mounting frame, a stirring shaft, a magnetic disk and a motor with a dry battery; wherein, said mounting frame and stirring shaft are disposed at the central position of the inside base wall of said blender cup; said magnetic disk is correspondently fixed inside of the bottom space of said internal chamber with central axial line in alignment with that of said stirring shaft without any physical link or contact each other; the stirring propeller on said stirring shaft will be magnetically inducted by said corresponding magnetic disk to simultaneously rotate in said internal chamber when said magnetic disk is driven by the output shaft of said motor; thus, not only the stirring effect of liquid or fluid in said internal chamber can be achieved, but also said liquid or fluid can be prevented from leakage and seepage out of the base wall of said blender cup so as to insure said motor free from premature defectively damage due to moisture erosion.
Owner:CAI YING LIN
Photocurable endoprosthesis system
Novel endoprostheses comprising one or more photocurable materials are disclosed. Said endoprostheses may comprise regions wherein said photocurable materials are selectively disposed about said endoprosthesis and are cured according to desired parameters to achieve varying desired properties. Said properties may include but are not limited to cross-linking density, material density, modulus of elasticity, rate of erosion, extensibility, compressibility, mechanical strength, tensile strength, crystallinity, diffusion coefficient, and permeability.
Owner:SYNECOR LLC
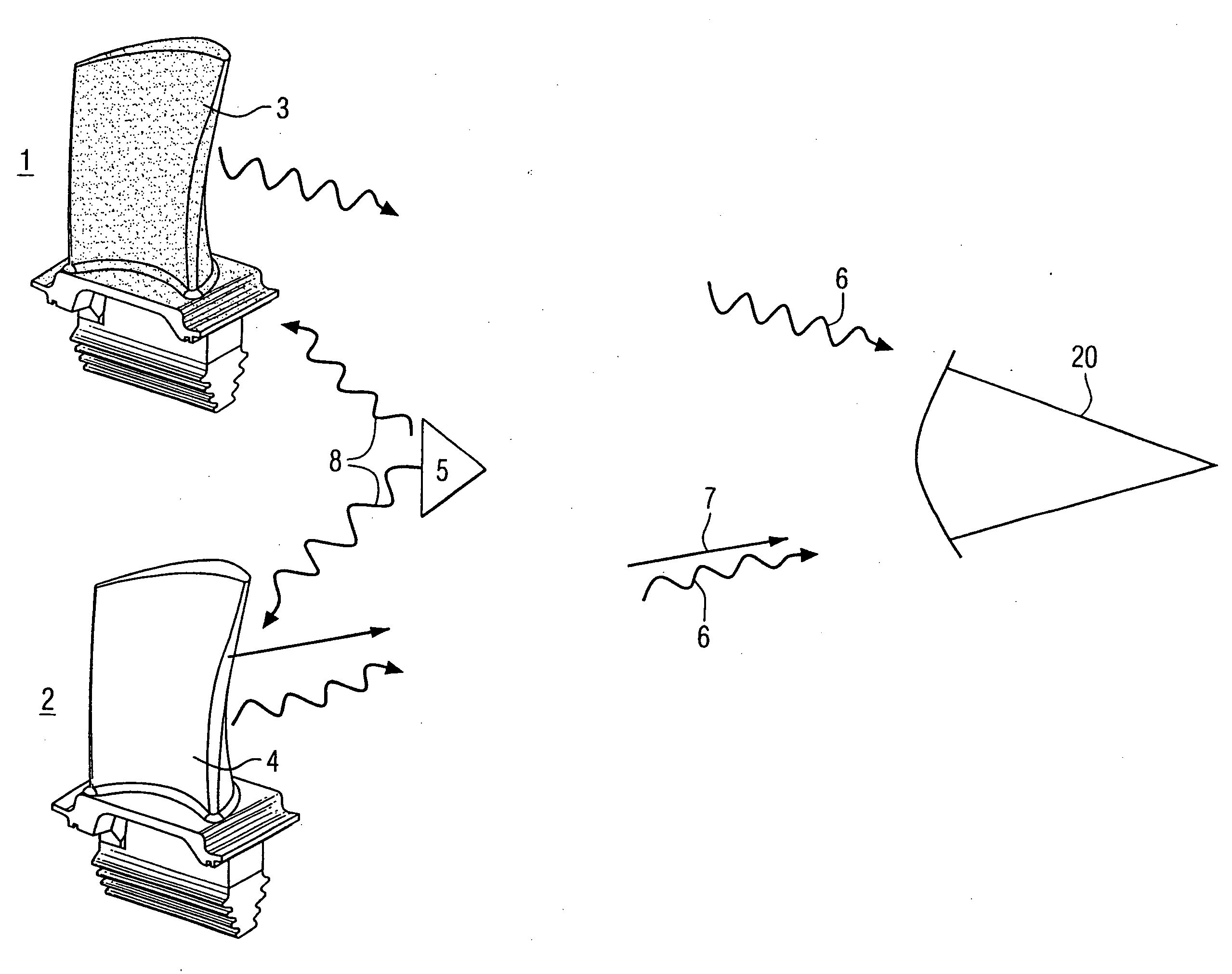
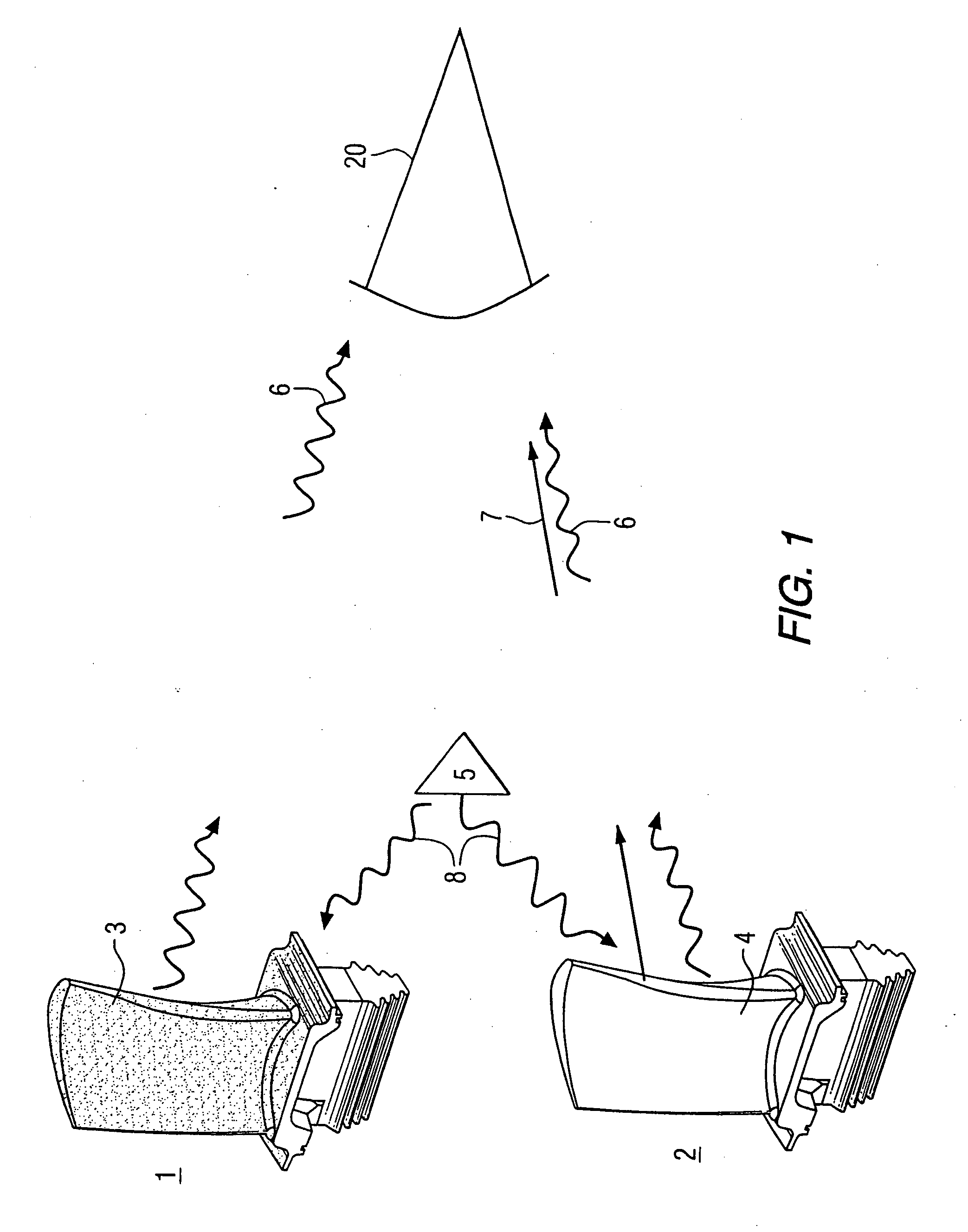
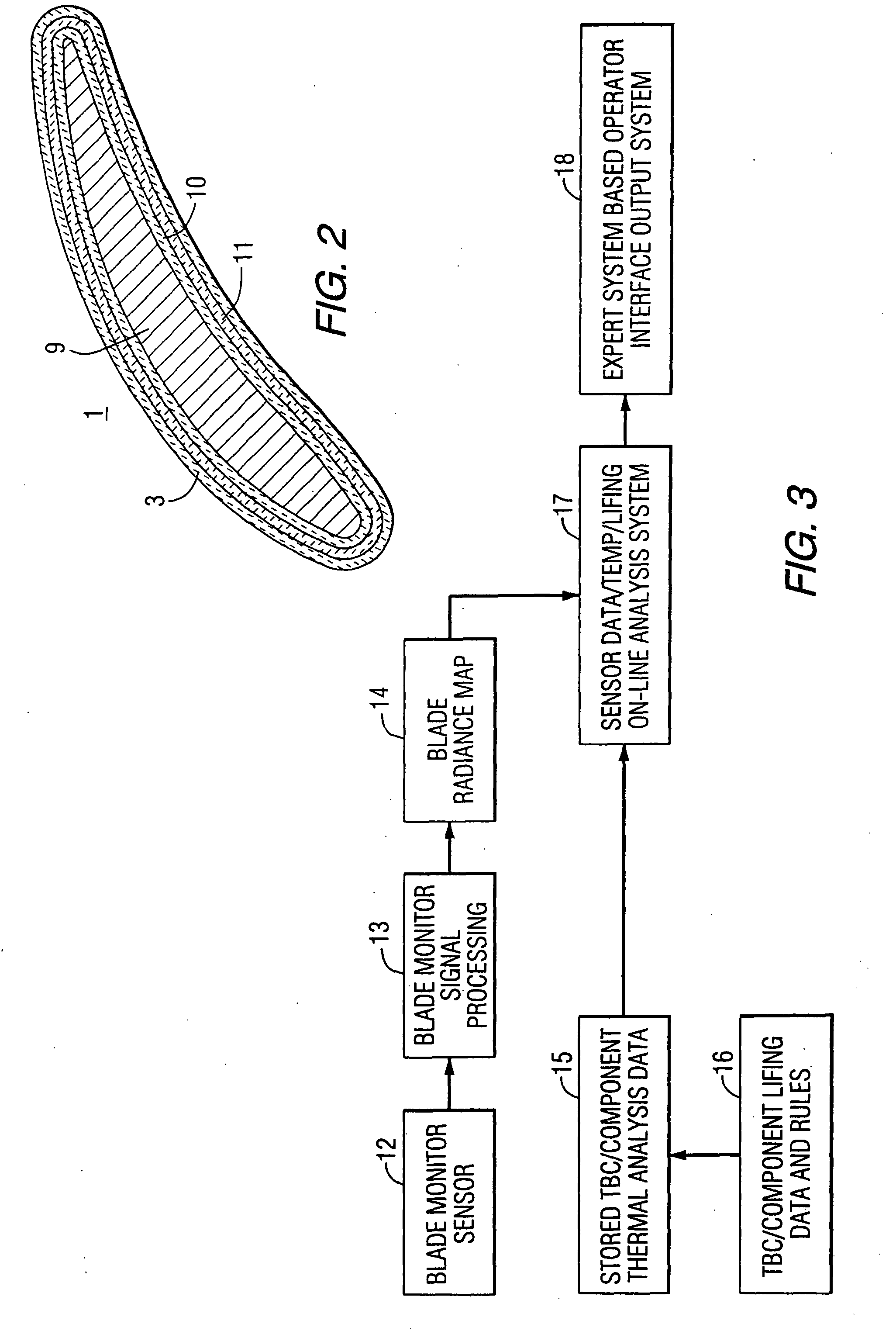
Method and apparatus for measuring on-line failure of turbine thermal barrier coatings
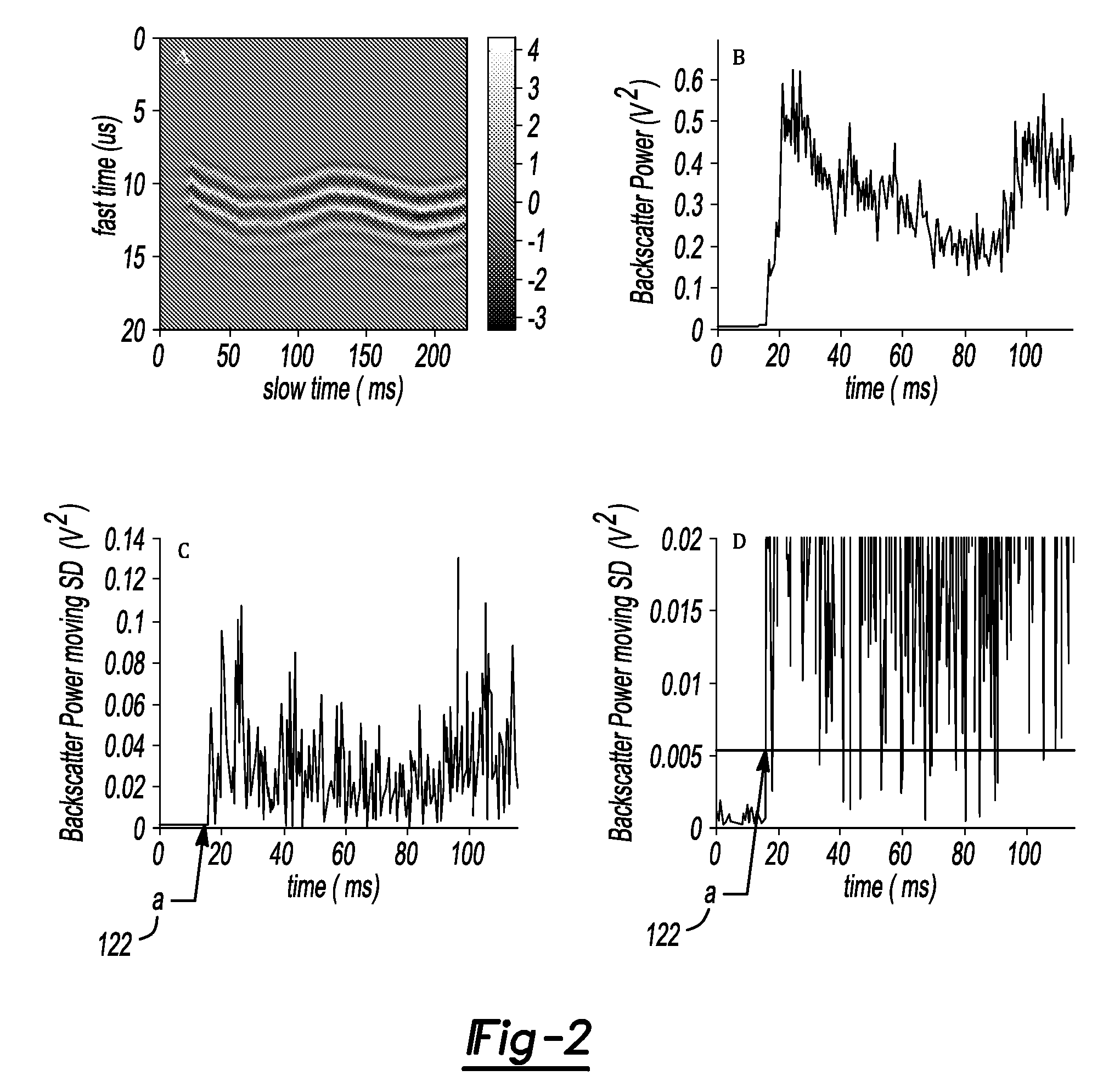
InactiveUS20090312956A1Detect degradationAvoid severe repairThermometer detailsPlug gaugesTurbine bladeEngineering
A method of remotely monitoring the radiant energy (6) emitted from a turbine component such as a turbine blade (1) having a low-reflective surface coating (3) which may be undergoing potential degradation is used to determine whether erosion, spallation, delamination, or the like, of the coating (3) is occurring.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com