Patents
Literature
215212 results about "Fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fiber (or fibre in British English, see spelling differences; from the Latin fibra) is a natural or synthetic substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene.
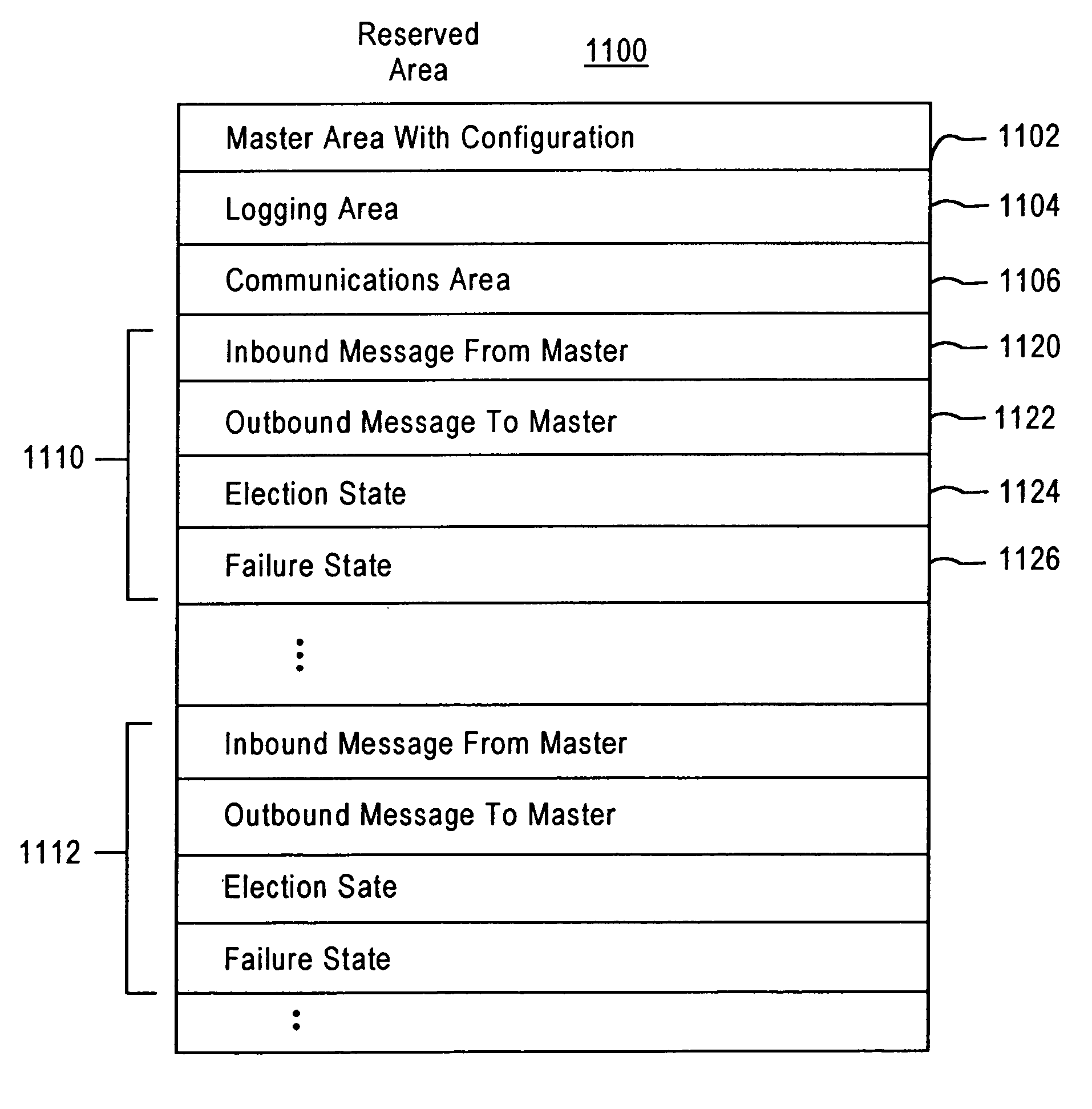
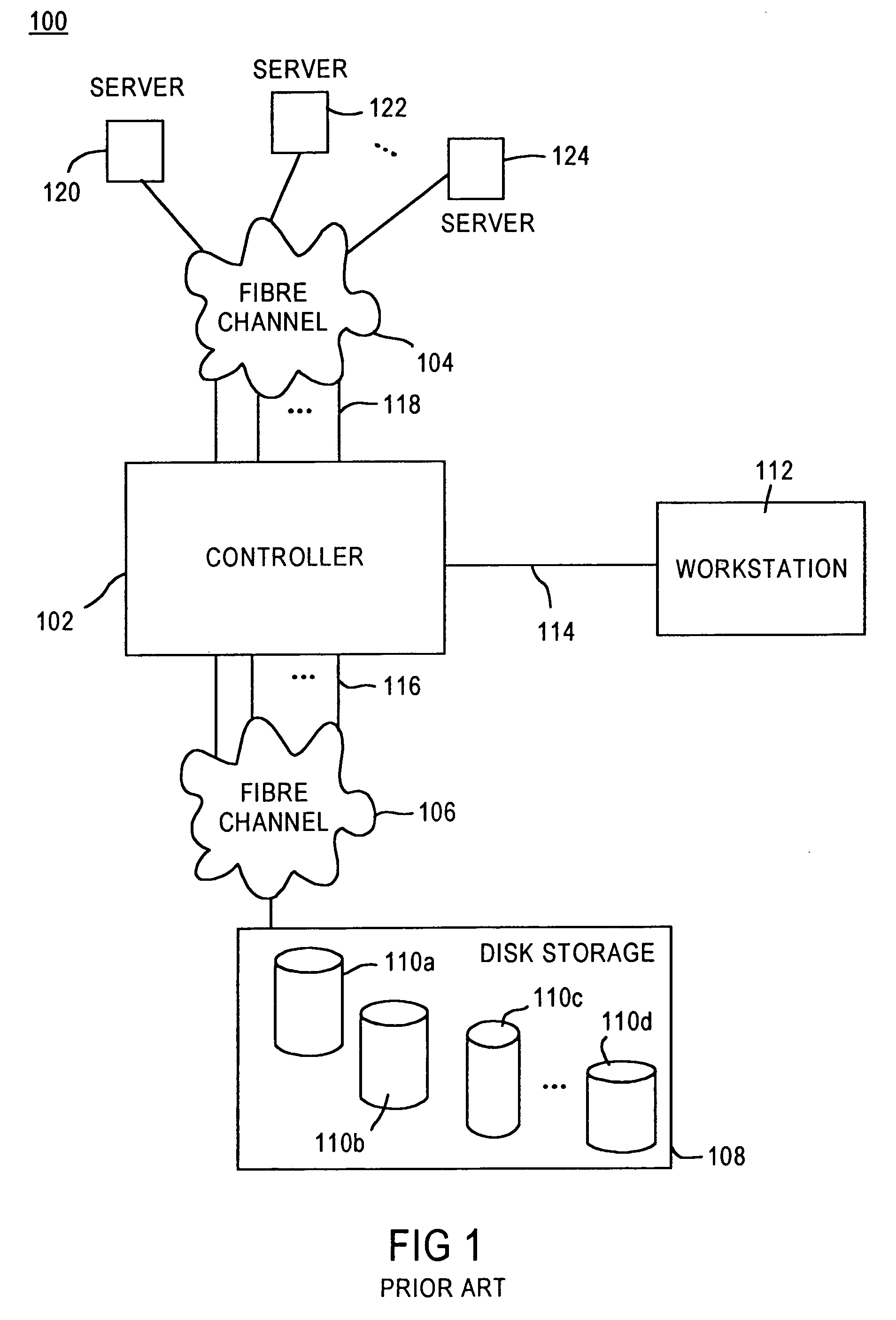
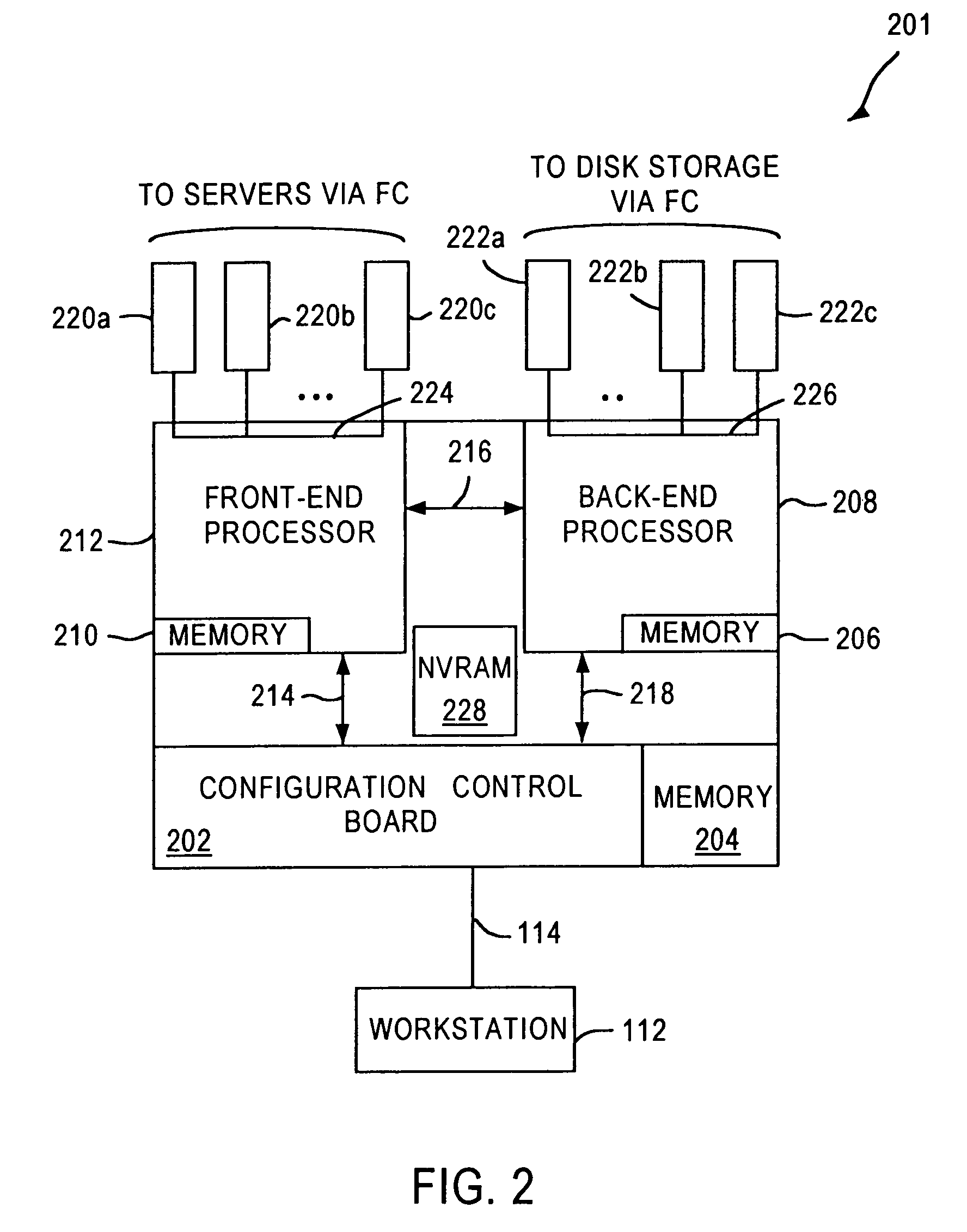
System and method for a reserved memory area shared by all redundant storage controllers
A fibre channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability. In particular, a common memory storage device is connected to the back-ends of every controller to provide a storage area. In this manner, the common memory storage device can be accessed via operations similar to those a controller already uses to presently access the physical disks which are connected to the back-end of the controllers.
Owner:VSIP HLDG LLC
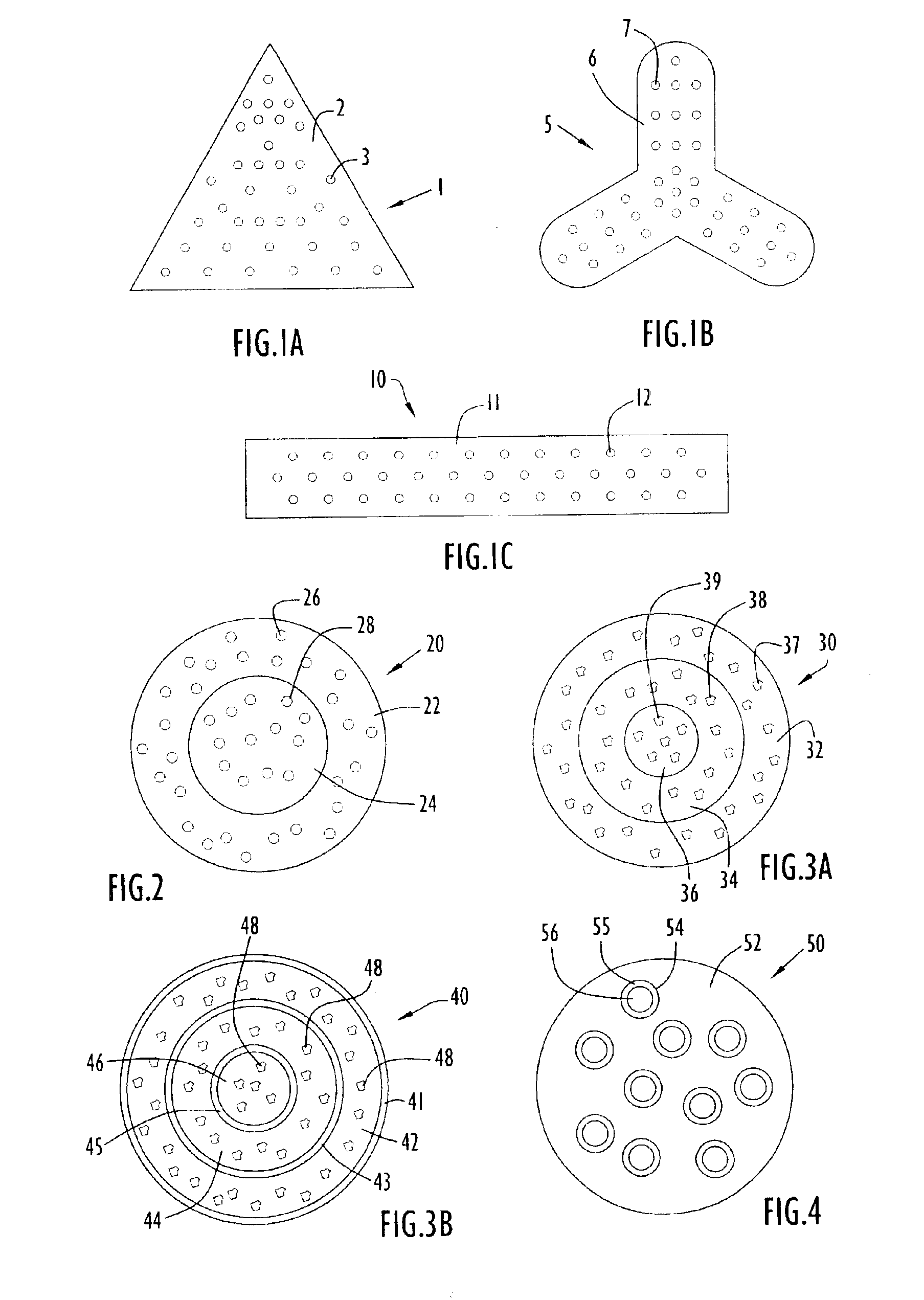
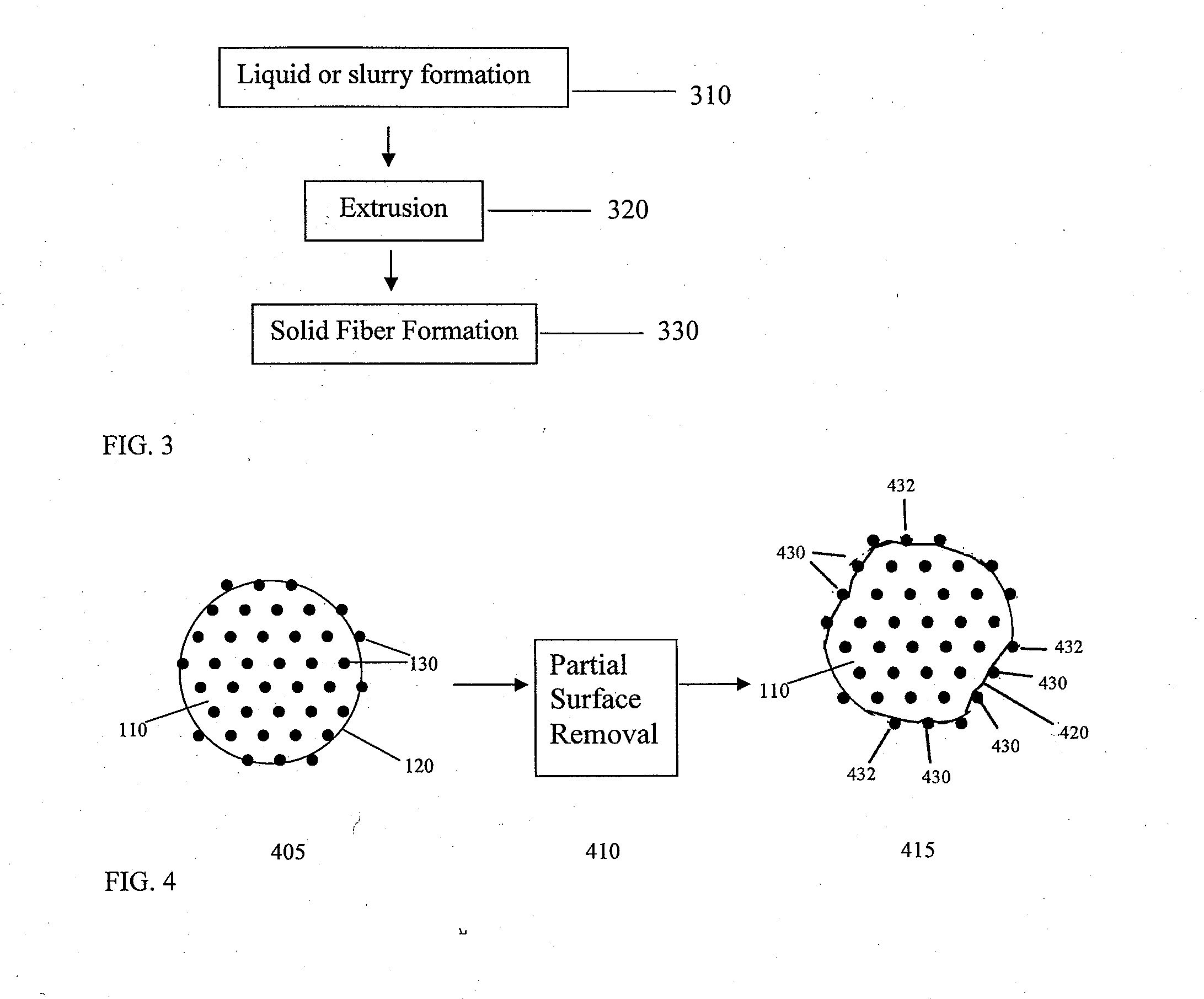
Controlling the dissolution of dissolvable polymer components in plural component fibers
The dissolution of dissolvable components in plural component polymer fibers is achieved by providing a polymer fiber including at least two sections, where at least one fiber section includes a dissolvable component. The rate at which at least part of the fiber dissolves is controlled by at least one of a fiber section having a non-round cross-sectional geometry, and at least two fiber sections including two different dissolvable components. In an exemplary embodiment, island-in-the-sea fibers are formed with non-round and elongated cross-sectional geometries. In another embodiment, sheath-core fibers are formed in which the sheath and core include different dissolvable components.
Owner:HILLS CO
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional biopolymeric materials and methods
Self-supporting, shaped, three-dimensional cross-linked proteinaceous biopolymeric materials that may be implanted in vivo, and methods of making such materials are disclosed. The biopolymeric materials most preferably include reinforcing media, such as biocompatible fibrous or particulate materials. In use, the preformed, shaped biopolymeric materials may be applied to tissue in need of repair and then sealed around its edges with a liquid bioadhesive. In such a manner, repaired tissue which is capable of withstanding physiological pressures may be provided.
Owner:CRYOLIFE
Scaffold for connective tissue repair
A connective tissue scaffold including opposed first and second anchoring segments formed from a plurality of bioresorbable polymeric fibers oriented in a direction substantially parallel to a longitudinal axis of the scaffold and a plurality of bioresorbable polymeric fibers oriented in a direction substantially transverse to a longitudinal axis of the scaffold. A central segment joins the first and second anchoring segments and includes a plurality of bioresorbable polymeric fibers oriented in a direction substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the scaffold. The scaffold can also a tissue particle and / or biological component.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
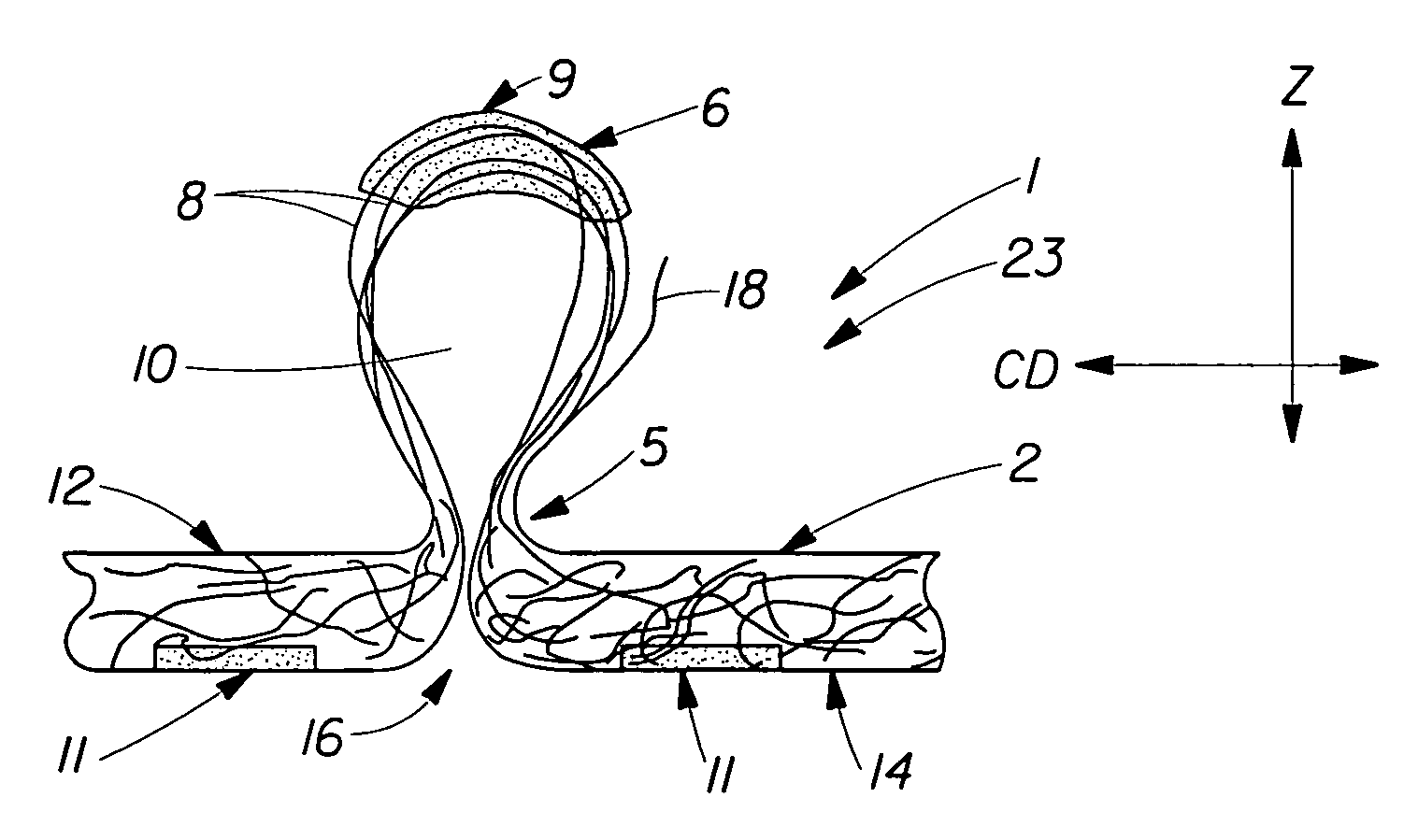
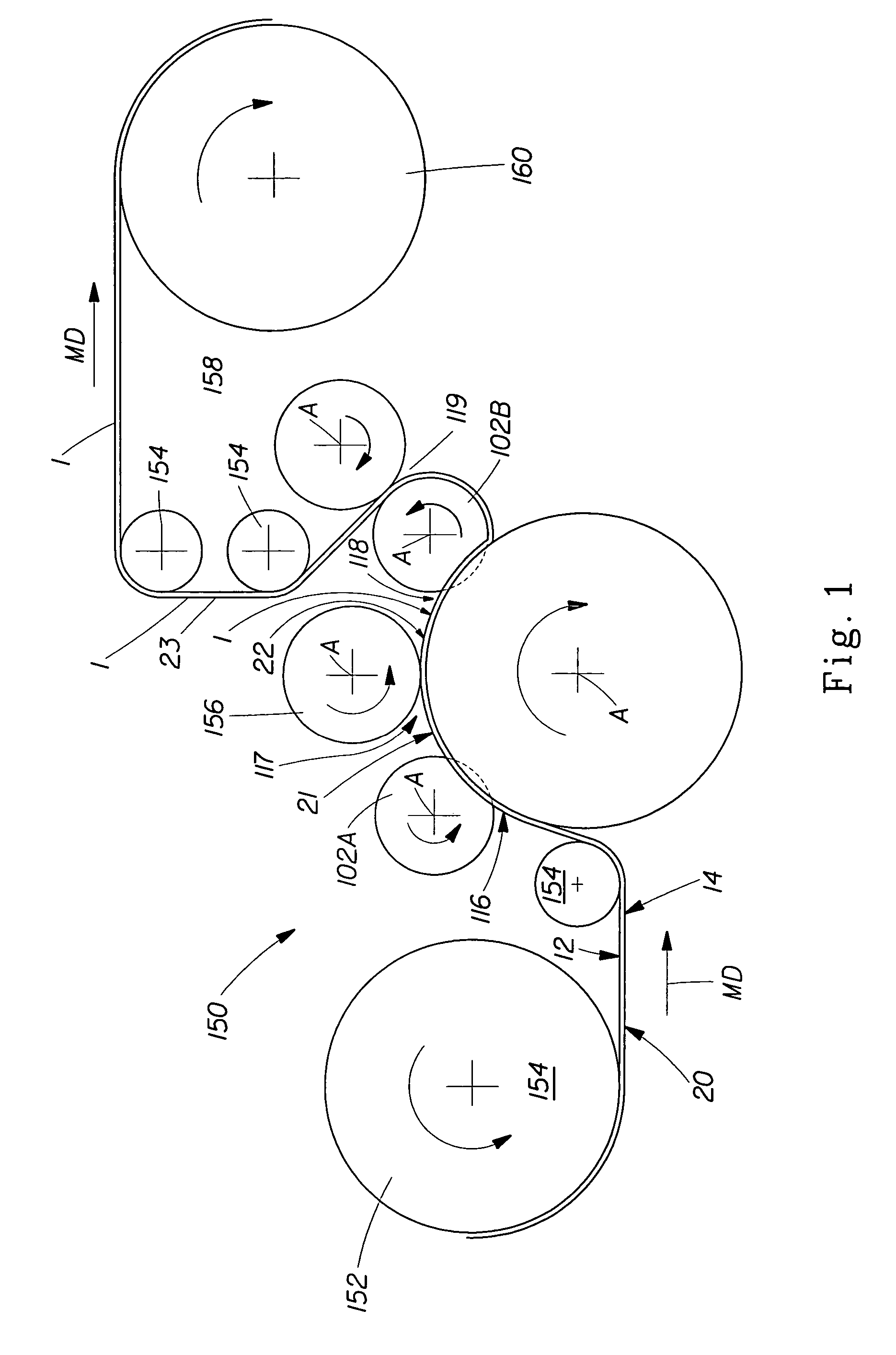
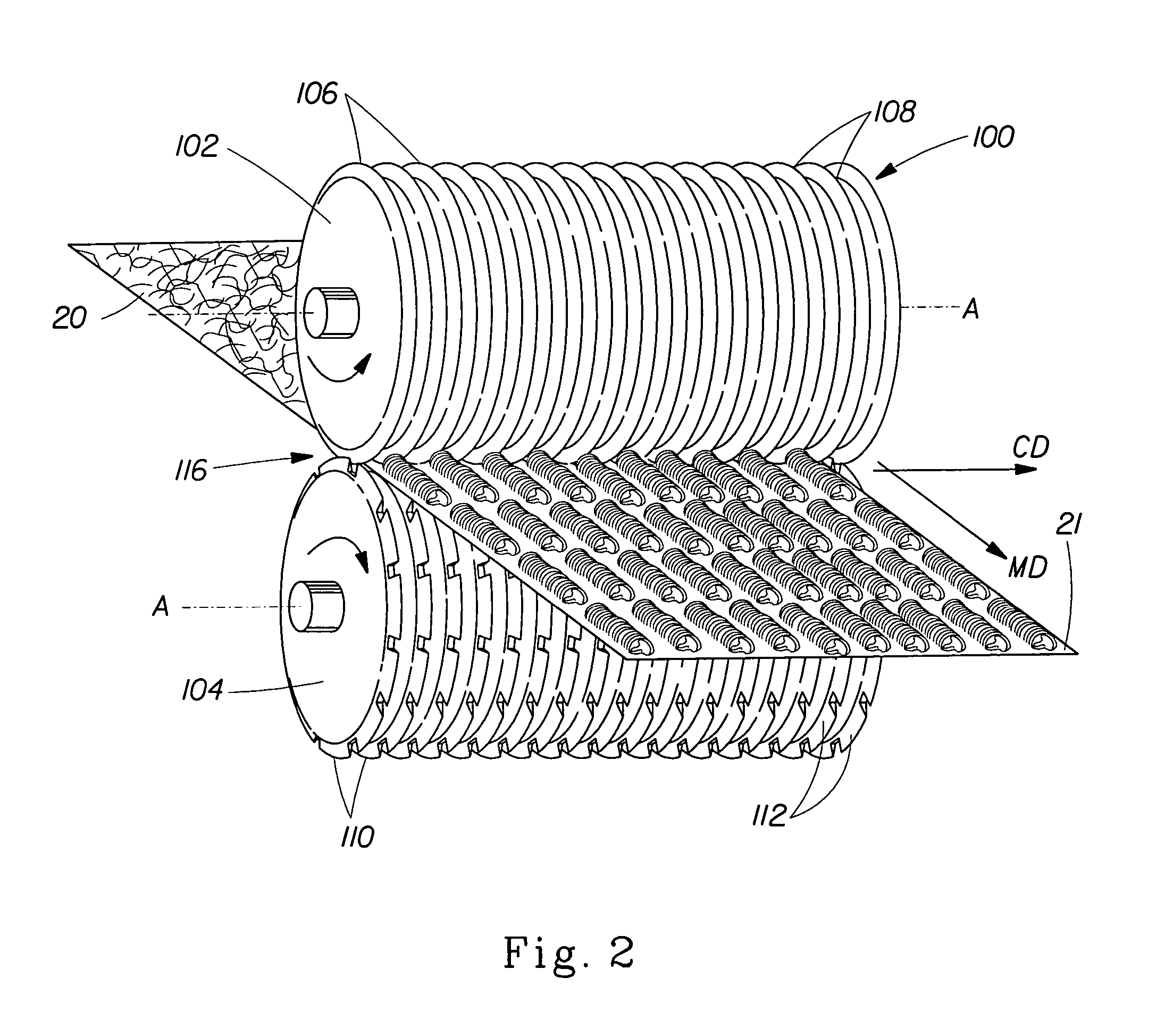
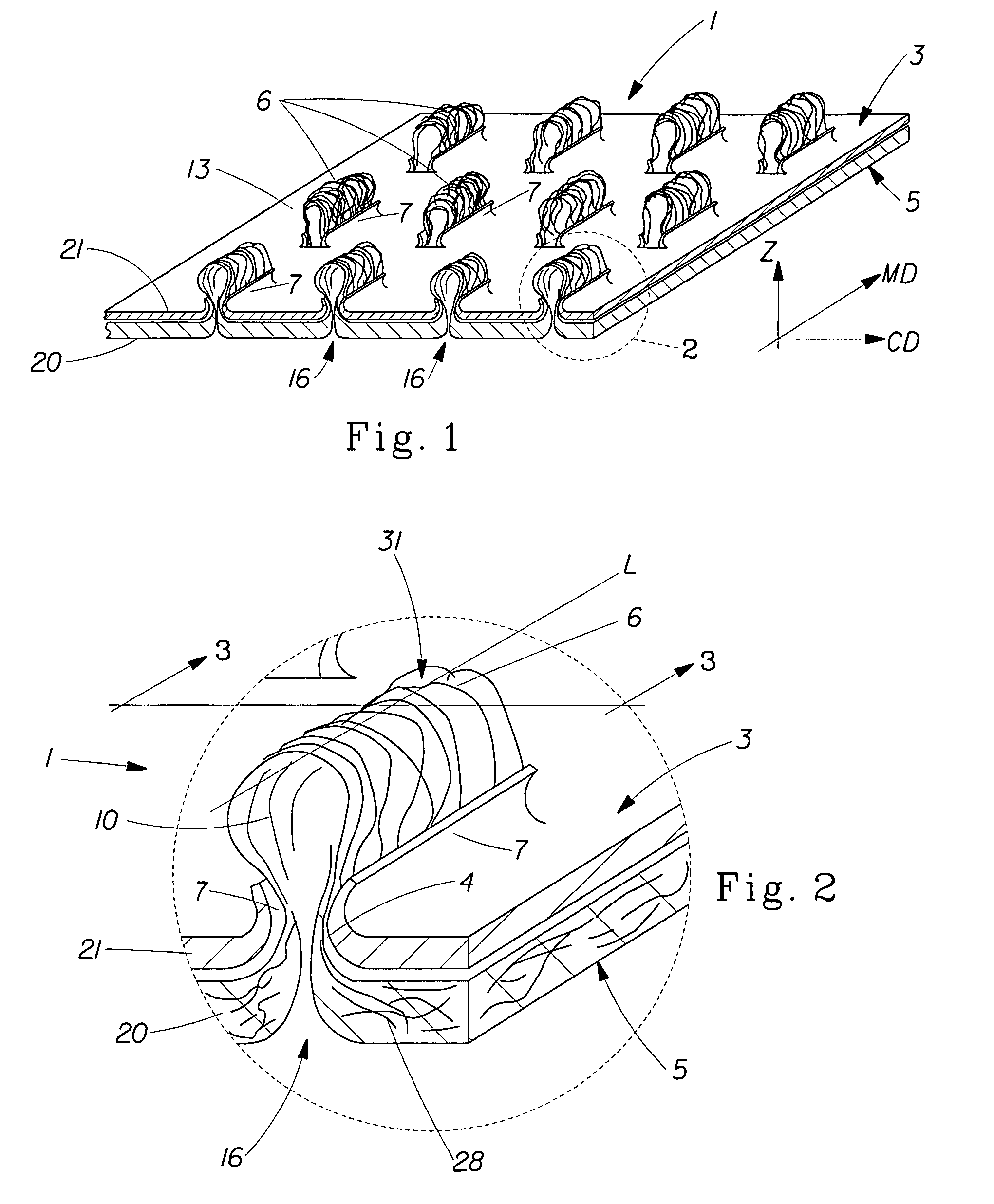
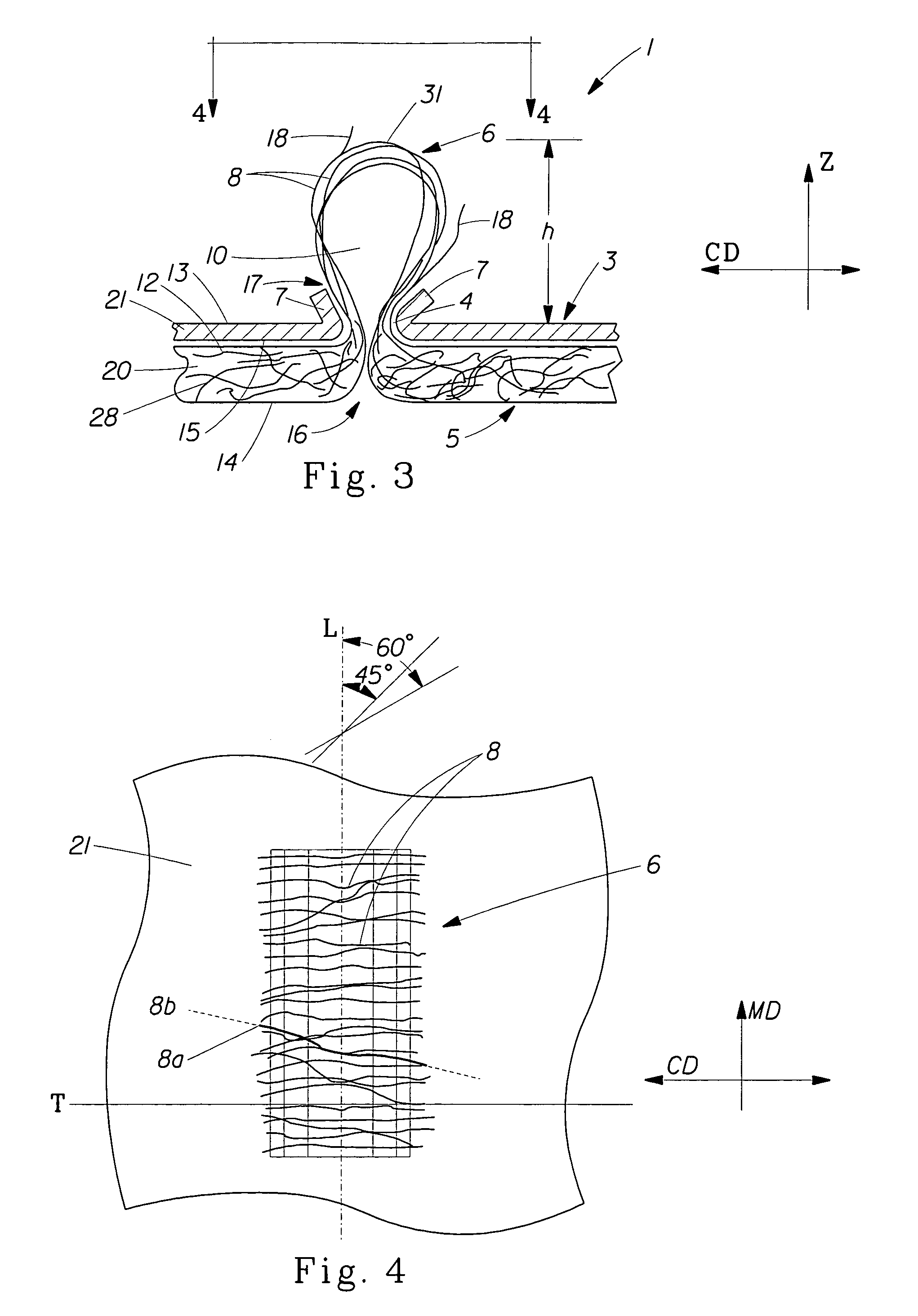
Tufted fibrous web
A fibrous web having a first surface and a second surface. The fibrous web has a first region and at least one discrete second region, the second region being a discontinuity on the second surface and being a tuft comprising a plurality of tufted fibers extending from the first surface. The tufted fibers define a distal portion, the distal portion comprising portions of the tufted fibers being bonded together. Bonding can be thermal melt-bonding. In another embodiment the second surface of the web can have non-intersecting or substantially continuous bonded regions, which also can be thermal melt-bonding.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Hemostatic fibrous material
InactiveUS20120004636A1Promote blood clottingPromoting blood clottingBiocideDiagnosticsFiberMolecular materials
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
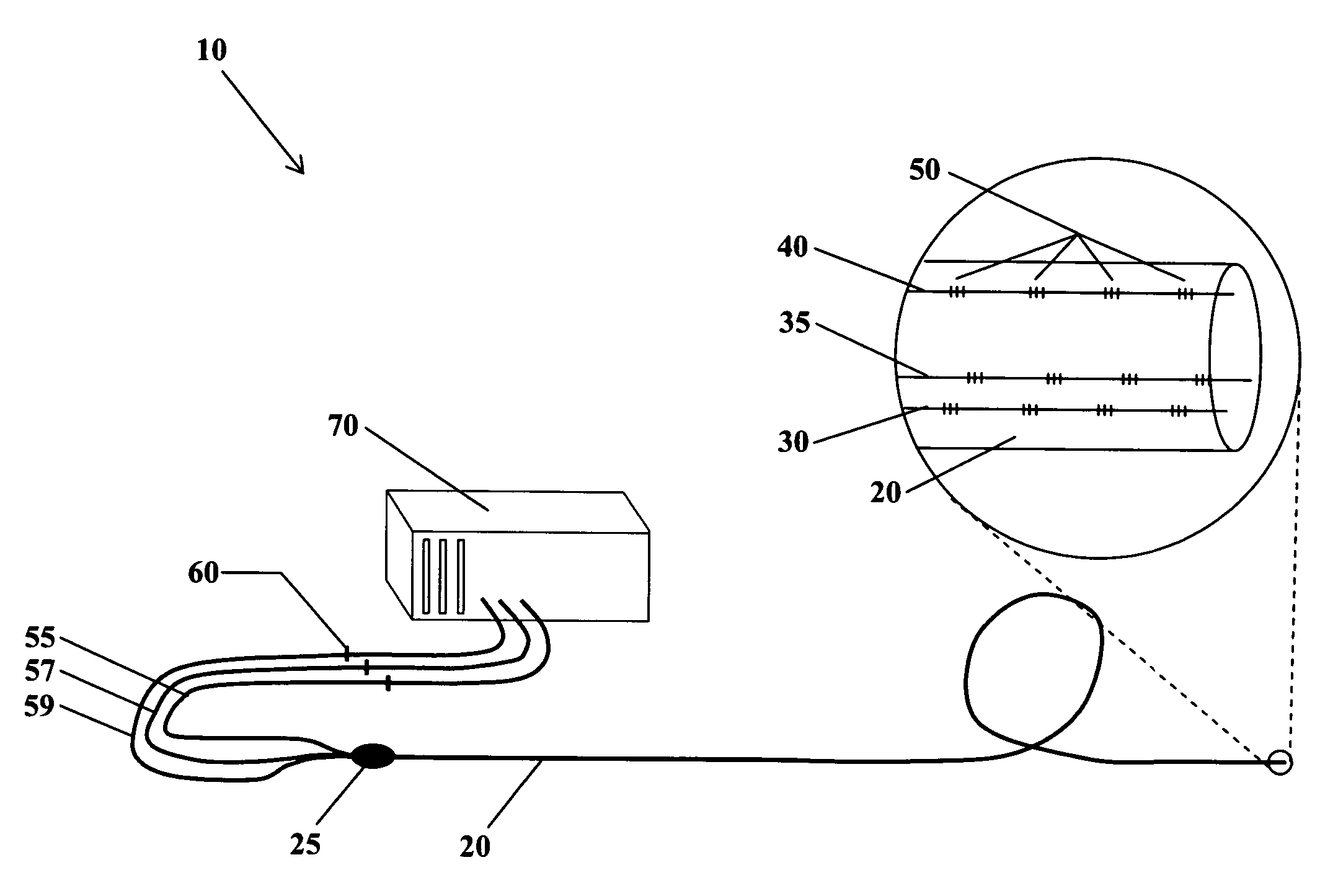
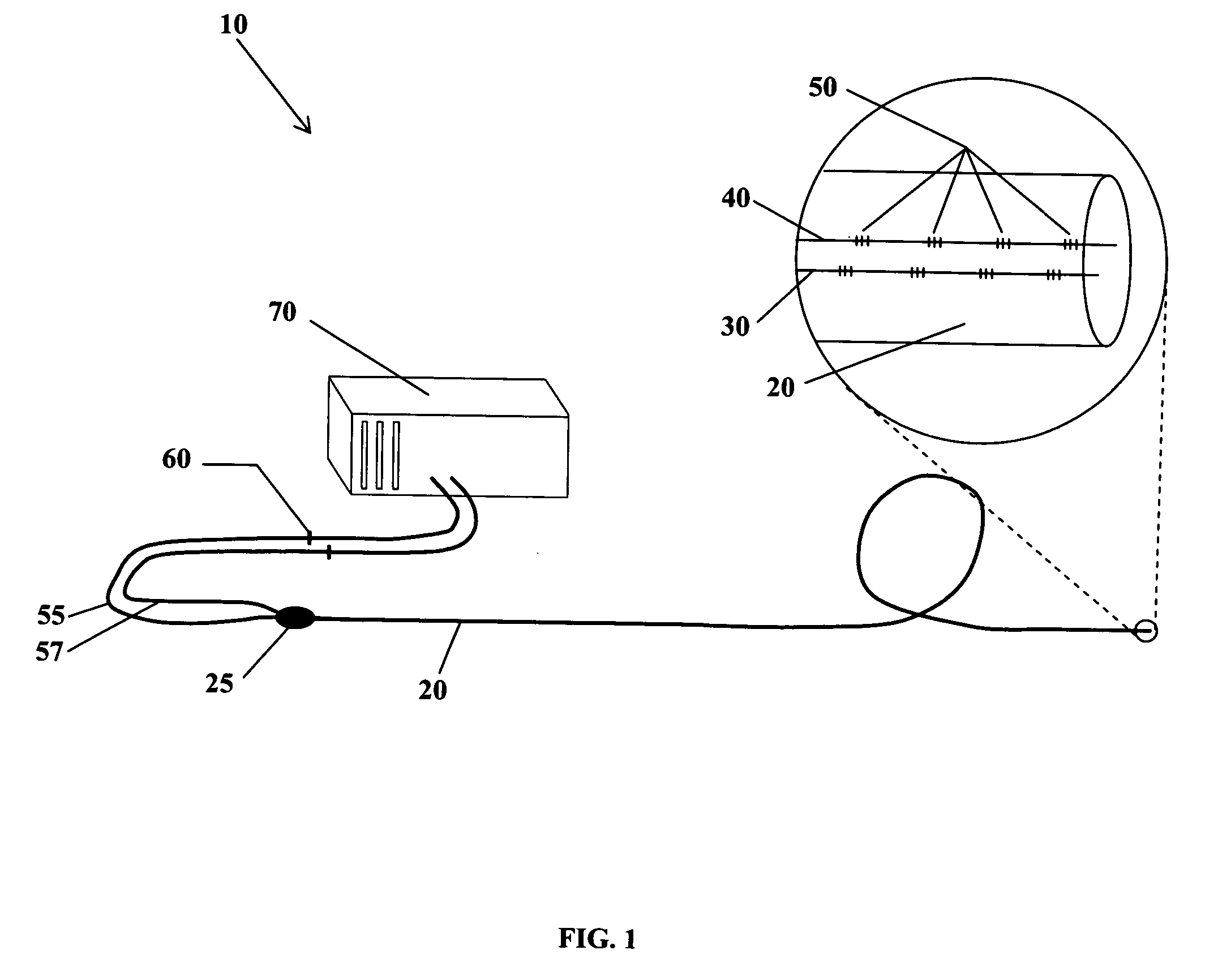
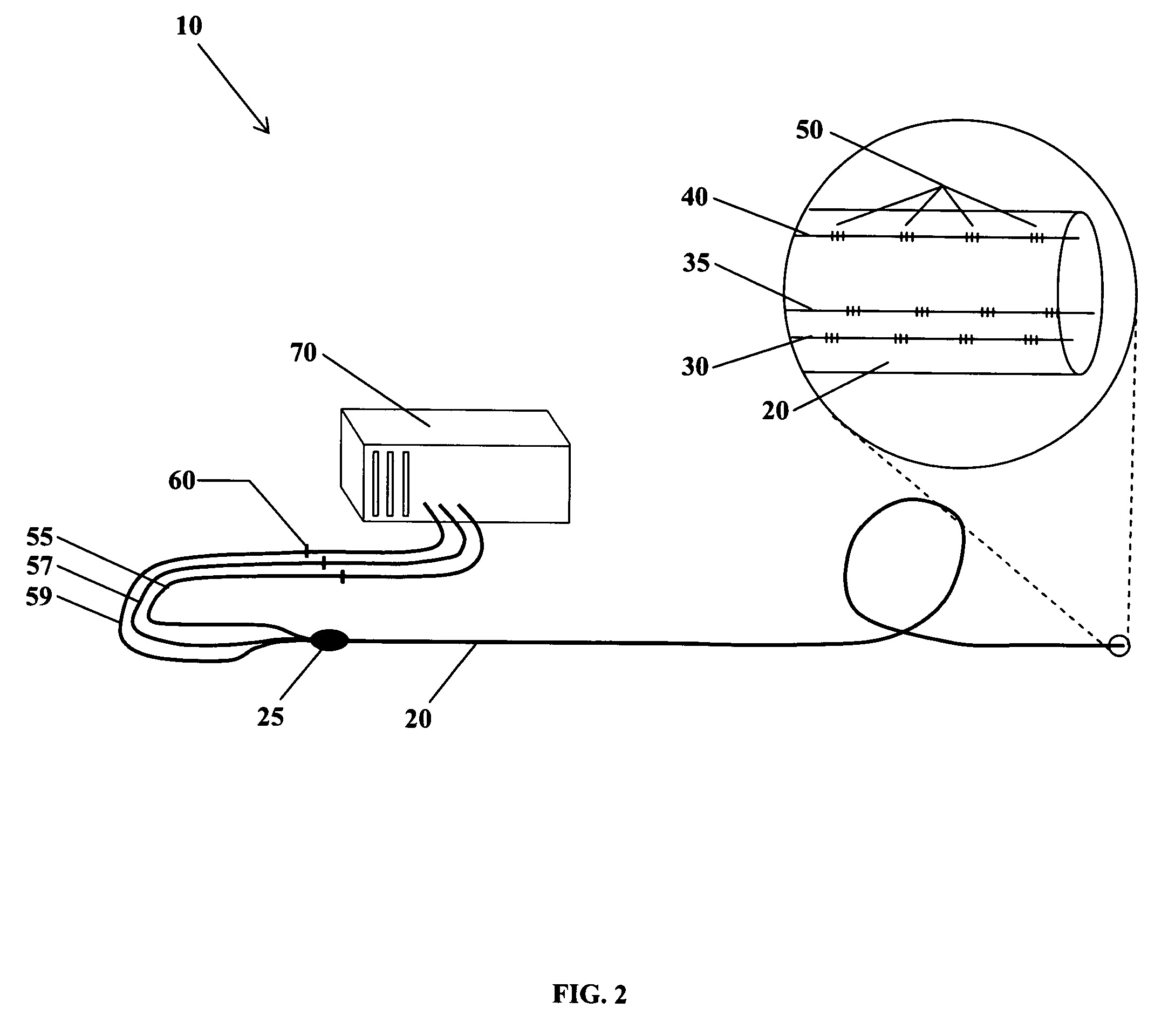
Fiber optic position and shape sensing device and method relating thereto
The present invention is directed toward a fiber optic position and shape sensing device and the method of use. The device comprises an optical fiber means. The optical fiber means comprises either at least two single core optical fibers or a multicore optical fiber having at least two fiber cores. In either case, the fiber cores are spaced apart such that mode coupling between the fiber cores is minimized. An array of fiber Bragg gratings are disposed within each fiber core. A broadband reference reflector is positioned in an operable relationship to each fiber Bragg grating wherein an optical path length is established for each reflector / grating relationship. A frequency domain reflectometer is positioned in an operable relationship to the optical fiber means. In use, the device is affixed to an object. Strain on the optical fiber is measured and the strain measurements correlated to local bend measurements. Local bend measurements are integrated to determine position or shape of the object.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
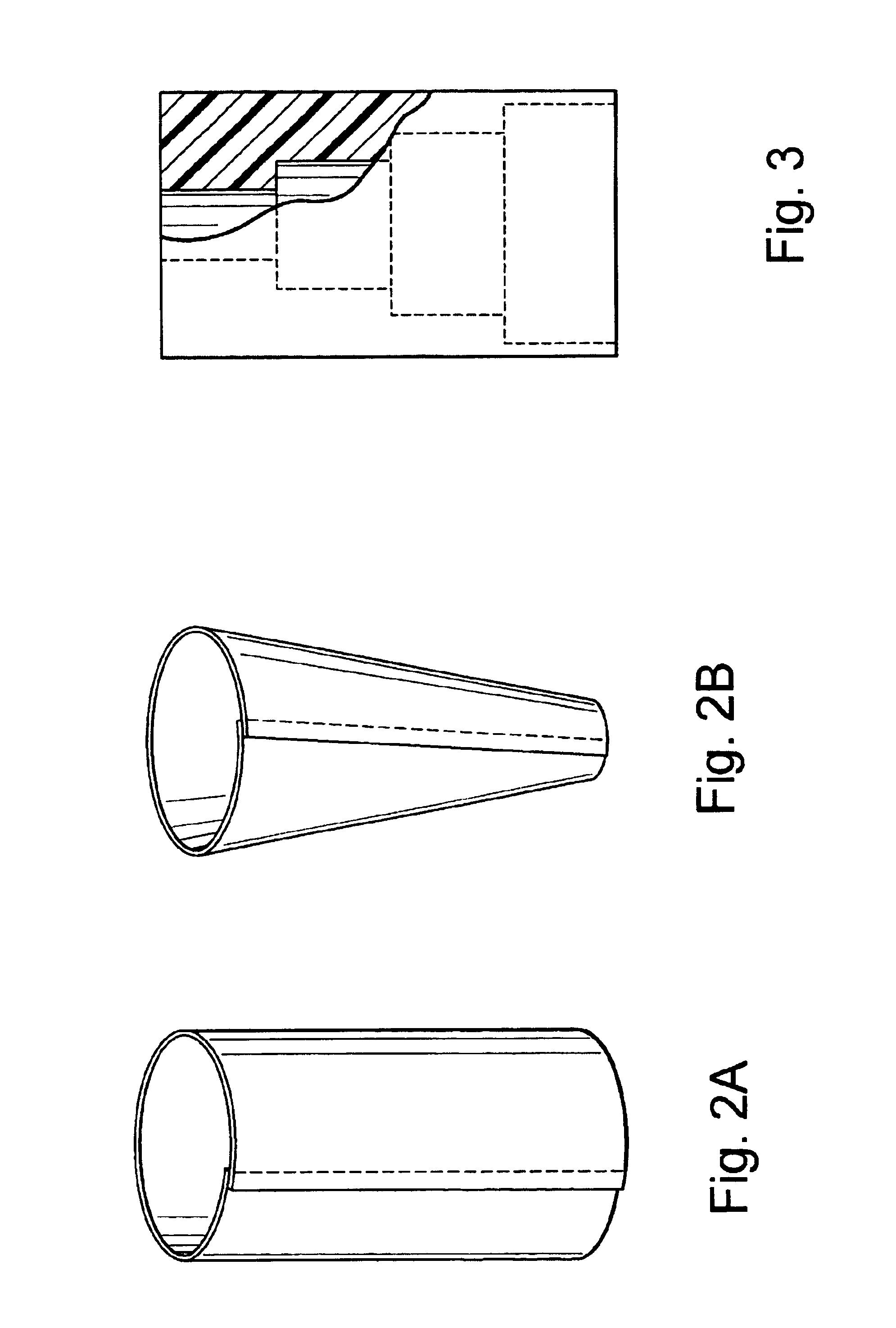
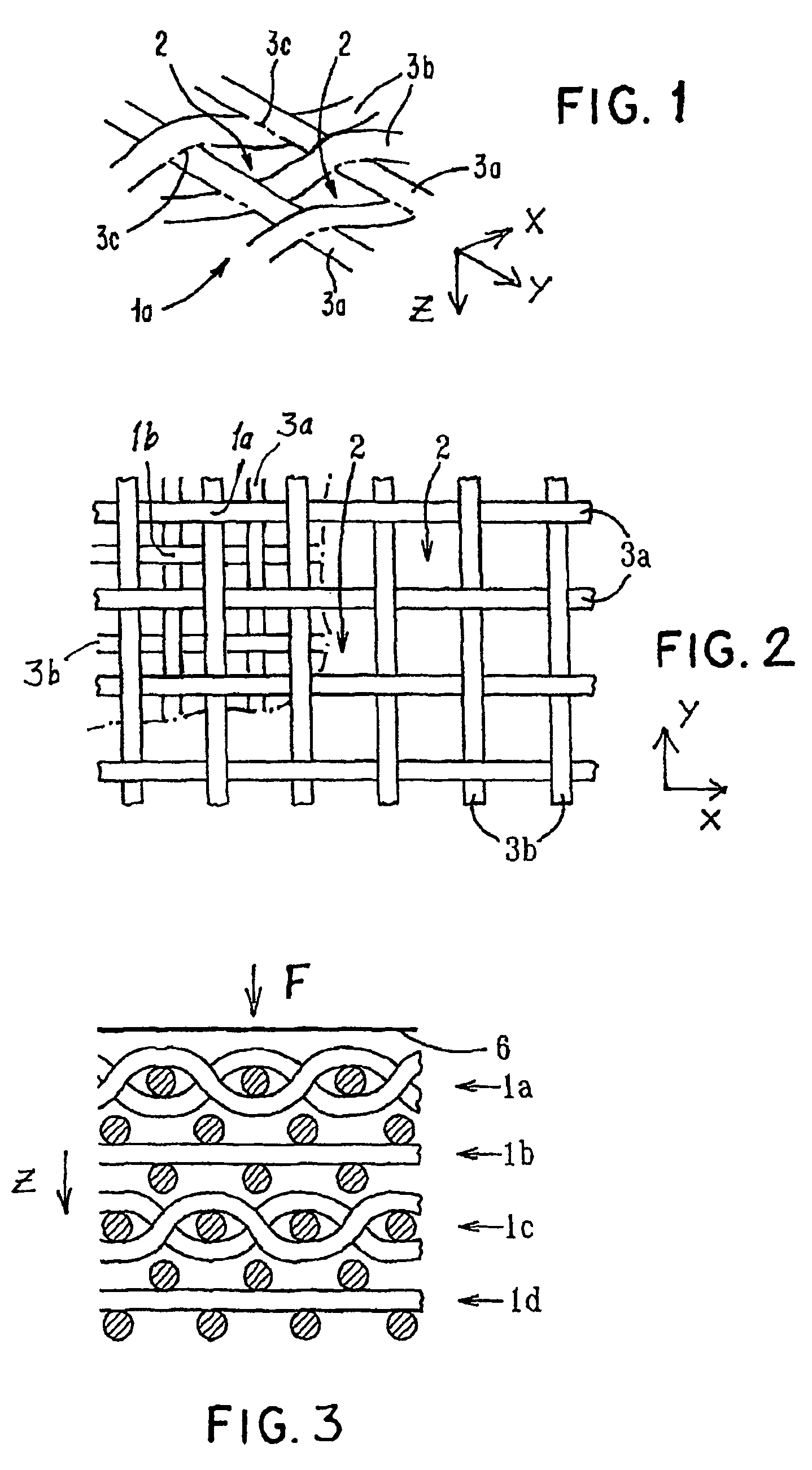
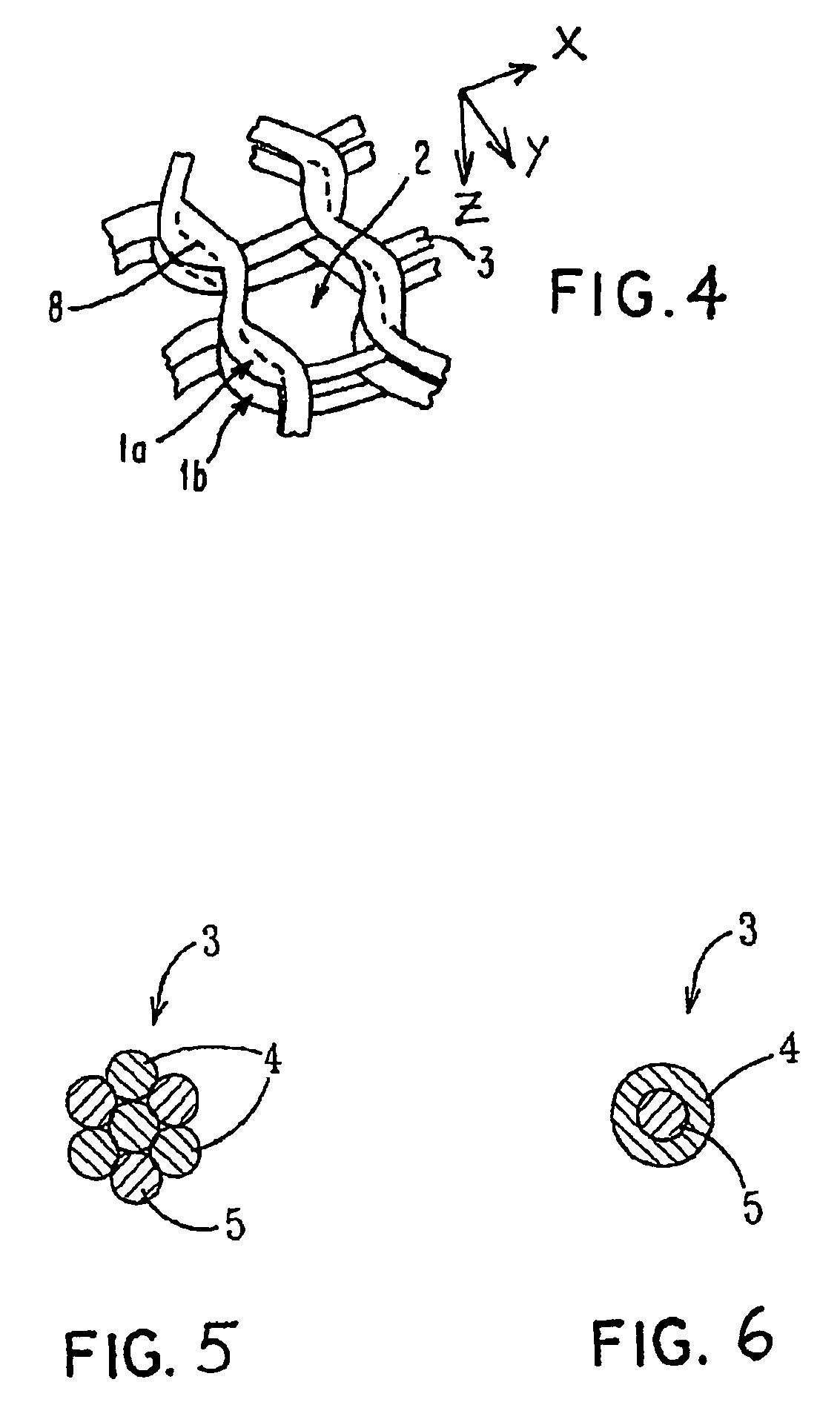
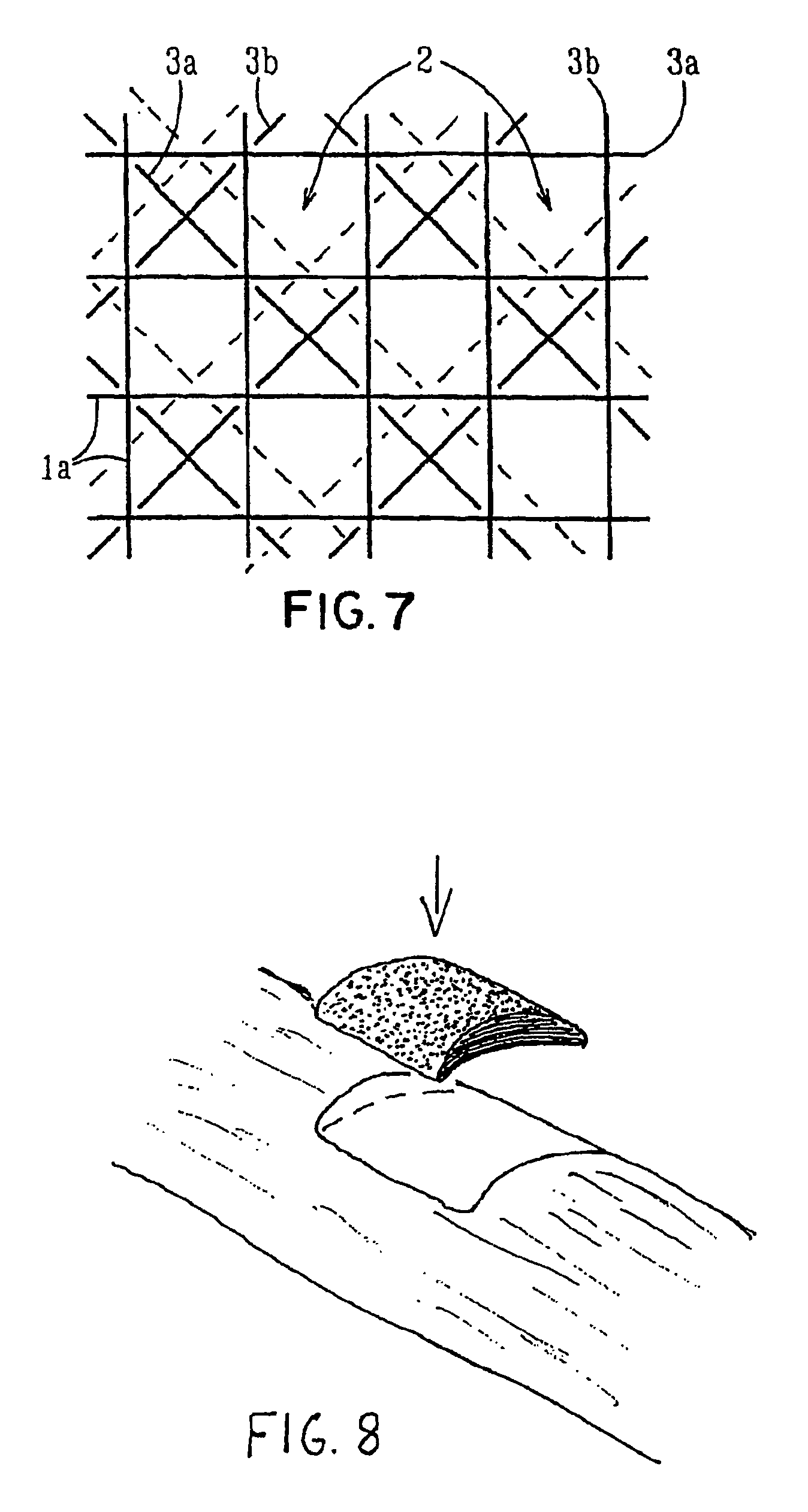
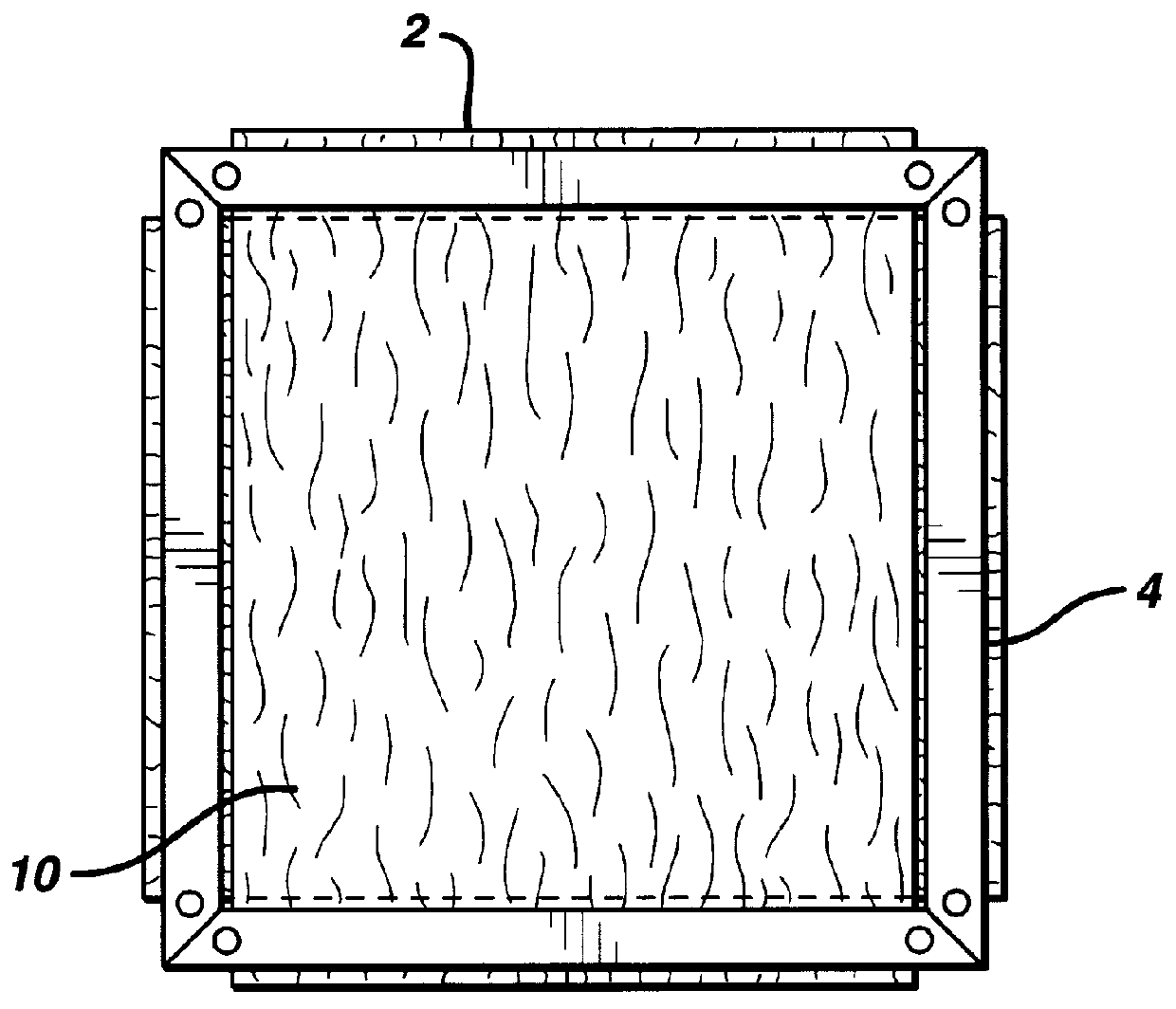
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Fabrication of biocompatible polymeric composites
InactiveUS6147135ASure easyImprove performanceSuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsFiberPolymer science
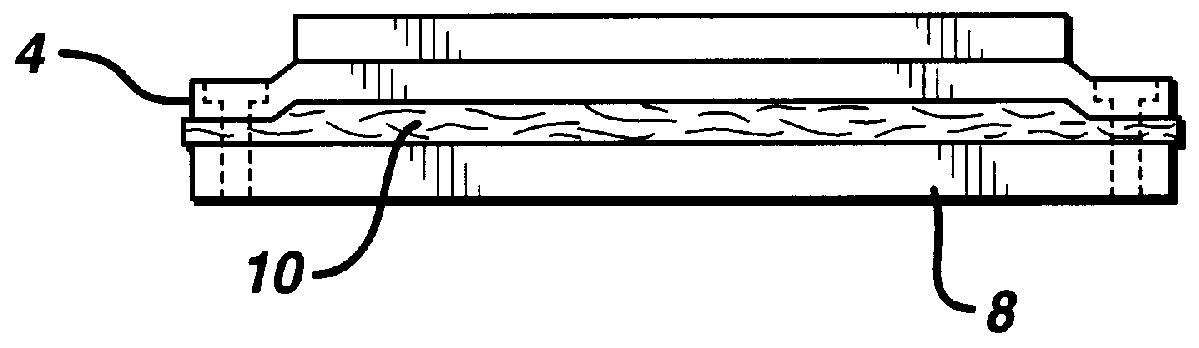
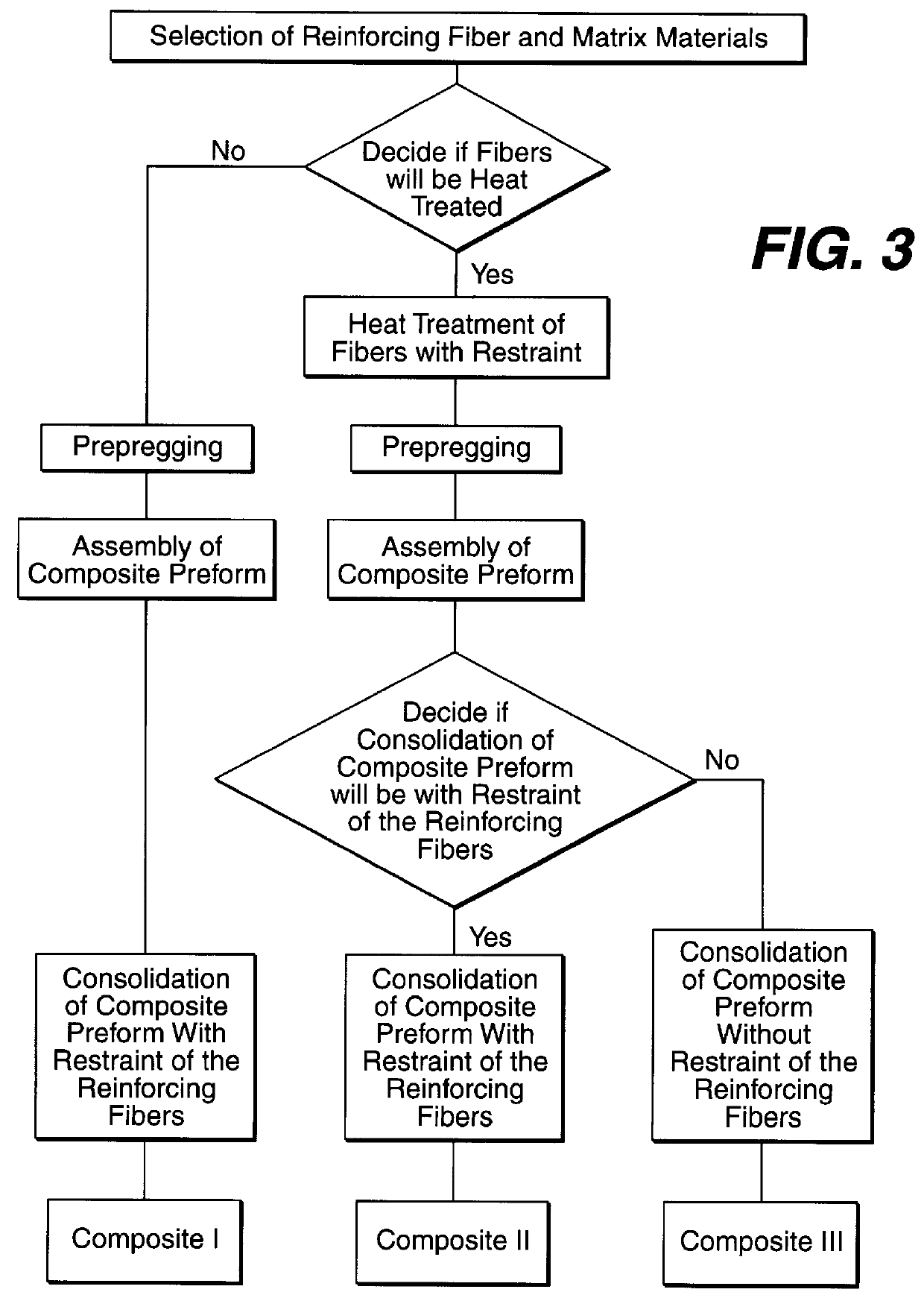
Composite materials formed from biocompatible polymer fibers and biodegradable polymers are disclosed. The heat treatment conditions for the reinforcing fibers are described so that the mechanical properties of the fibers can be retained during composite consolidation process. The processing conditions and set-ups to consolidations are constrained to the temperatures lower than fiber heat treatment temperatures. The reinforcing fibers are restrained under tension so that the minimum relaxation occurs during consolidation process.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Ultraviolet laser apparatus and exposure apparatus using same
InactiveUS7023610B2Easy to getReduce spatial coherenceLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberUltraviolet lights
An ultraviolet laser apparatus having a single-wavelength oscillating laser generating laser light between an infrared band and a visible band, an optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, and a wavelength converting portion converting the amplified laser light into ultraviolet light using a non-linear optical crystal. An exposure apparatus transfers a pattern image of a mask onto a substrate and includes a light source having a laser apparatus emitting laser light having a single wavelength, a first fiber optical amplifier for amplifying the laser light, a light dividing device for dividing or branching the amplified laser light into plural lights, and second fiber optical amplifiers for amplifying the plural divided or branched lights, respectively, and a transmission optical system for transmitting the laser light emitted from the light source to the exposure apparatus.
Owner:NIKON CORP
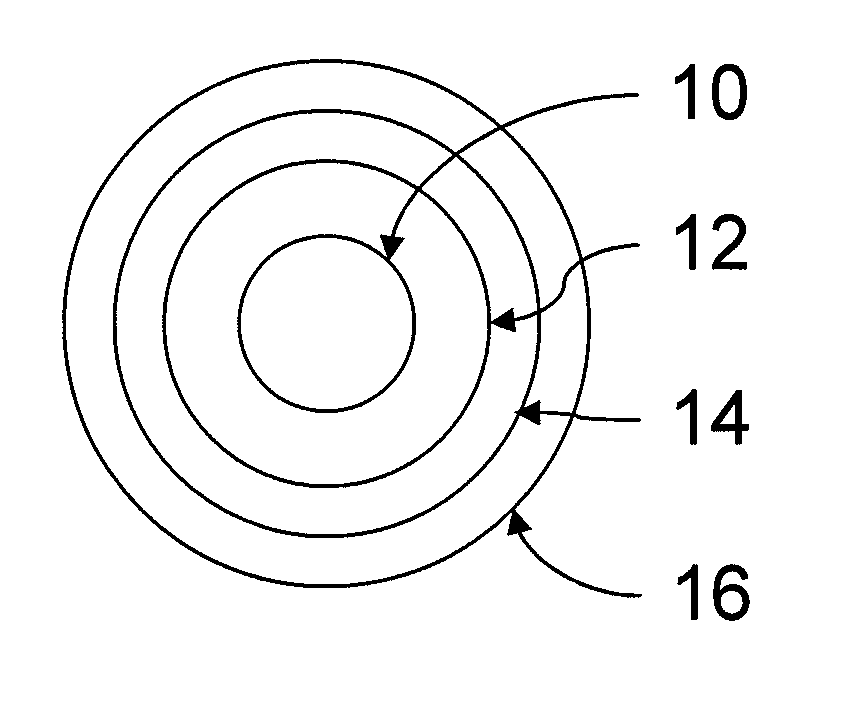
Fiber strand and implantable supporting body having a fiber strand
InactiveUS7997054B2Desired mechanical properties can be adjusted especially easilySignificant positive effectPowder deliveryStentsFiberBiomedical engineering
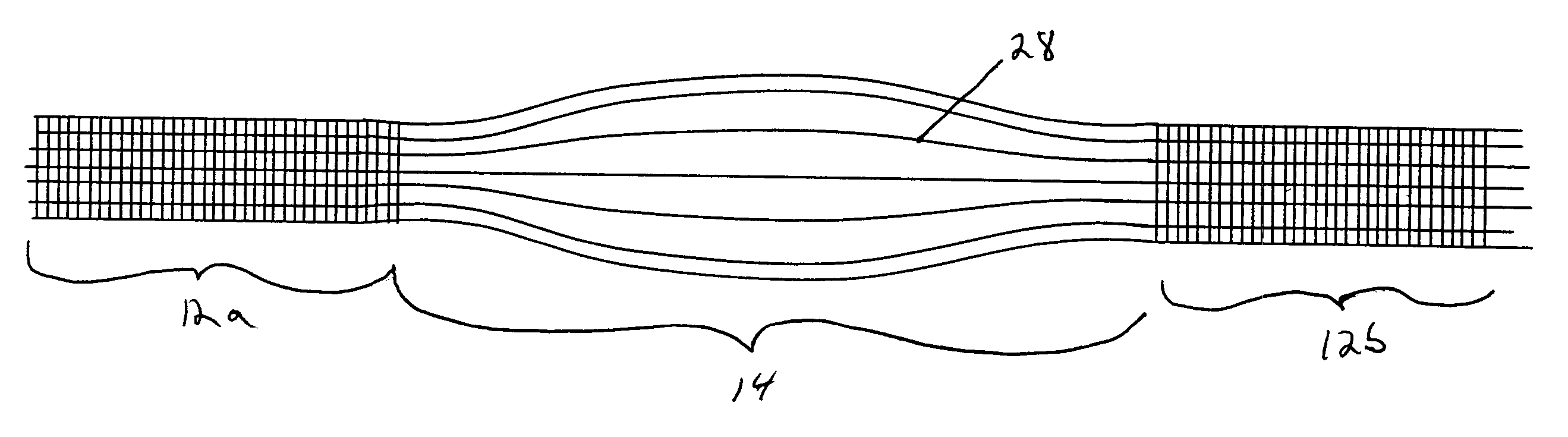
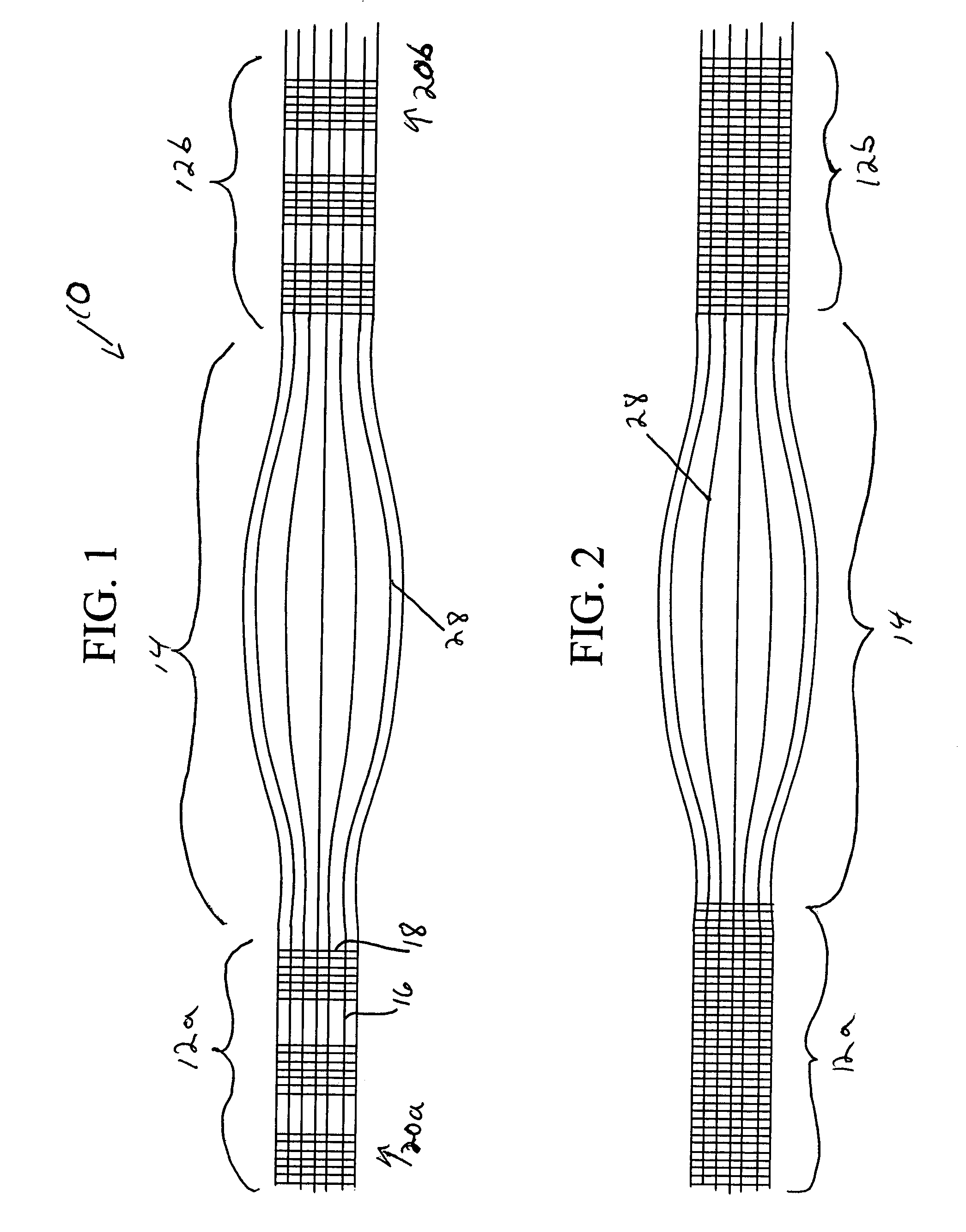
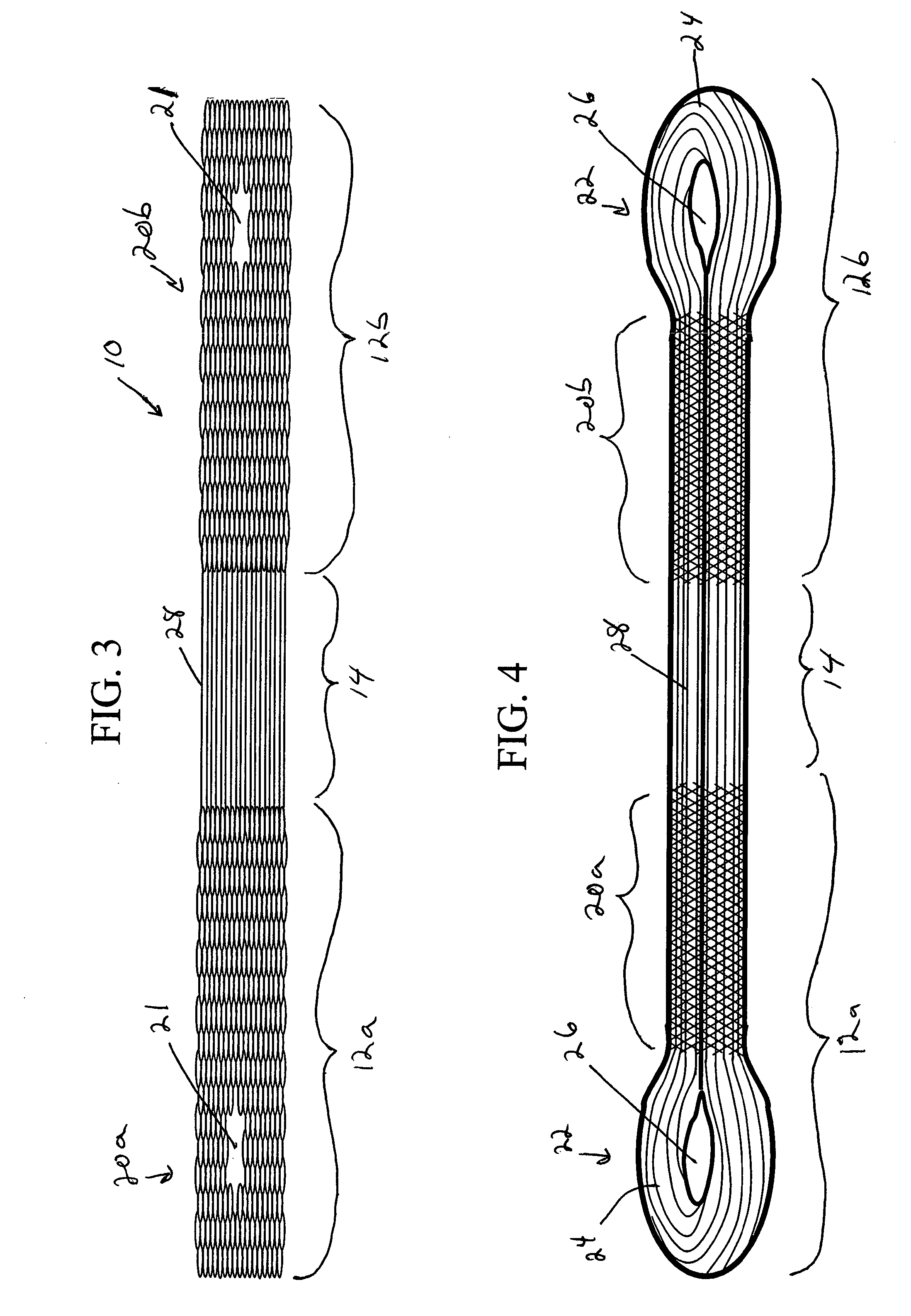
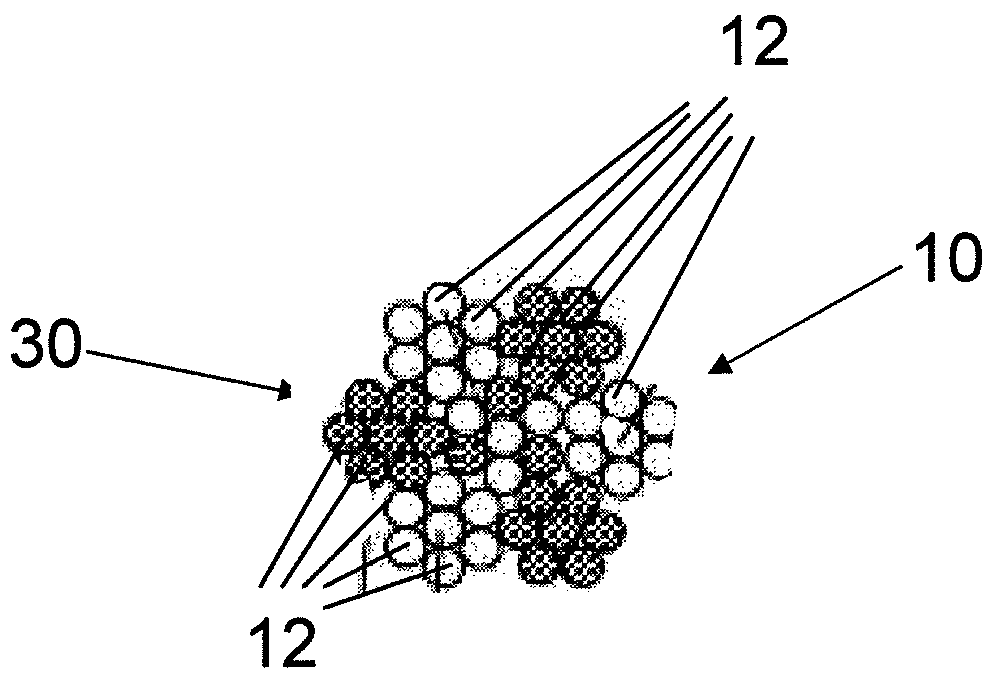
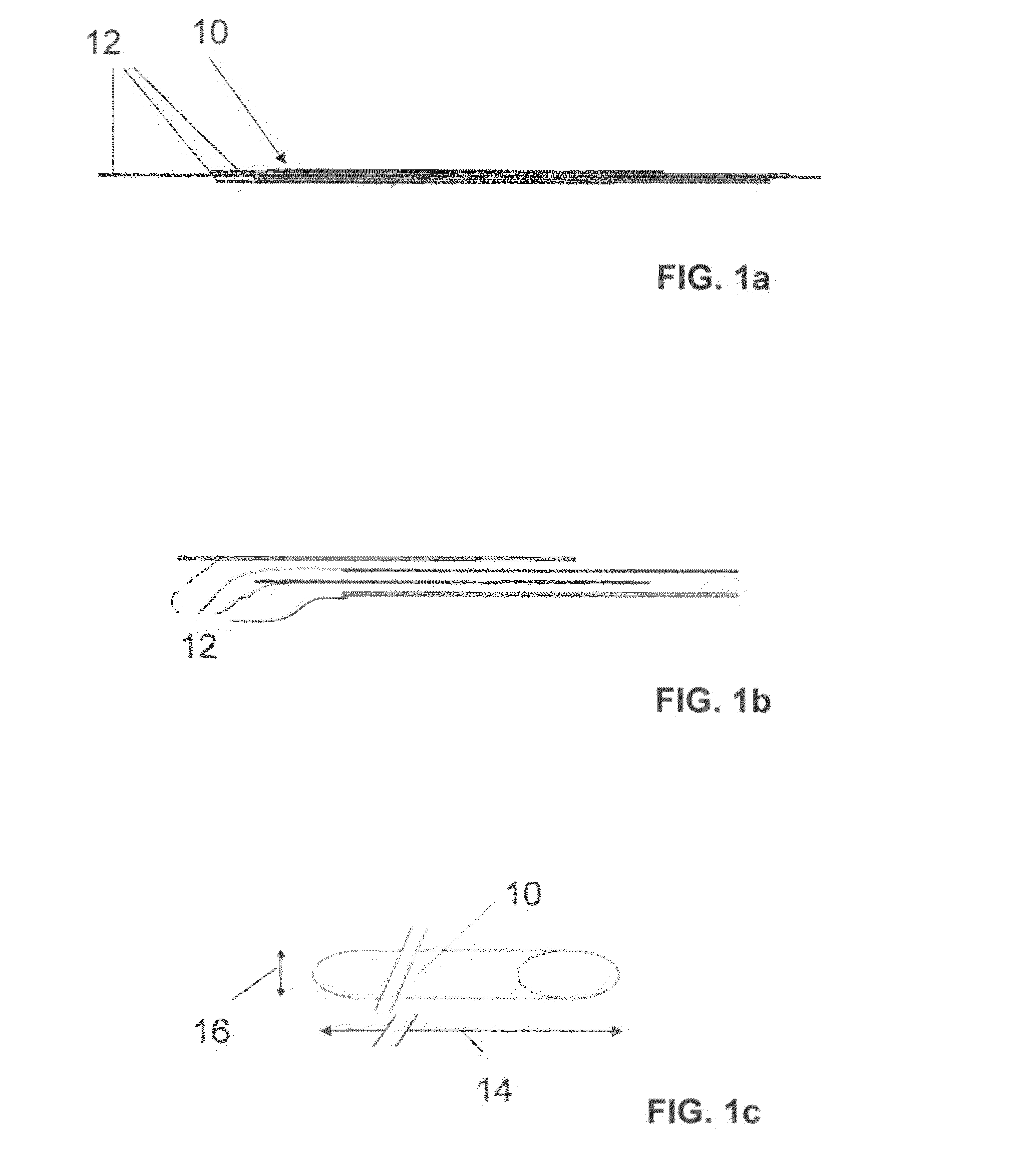
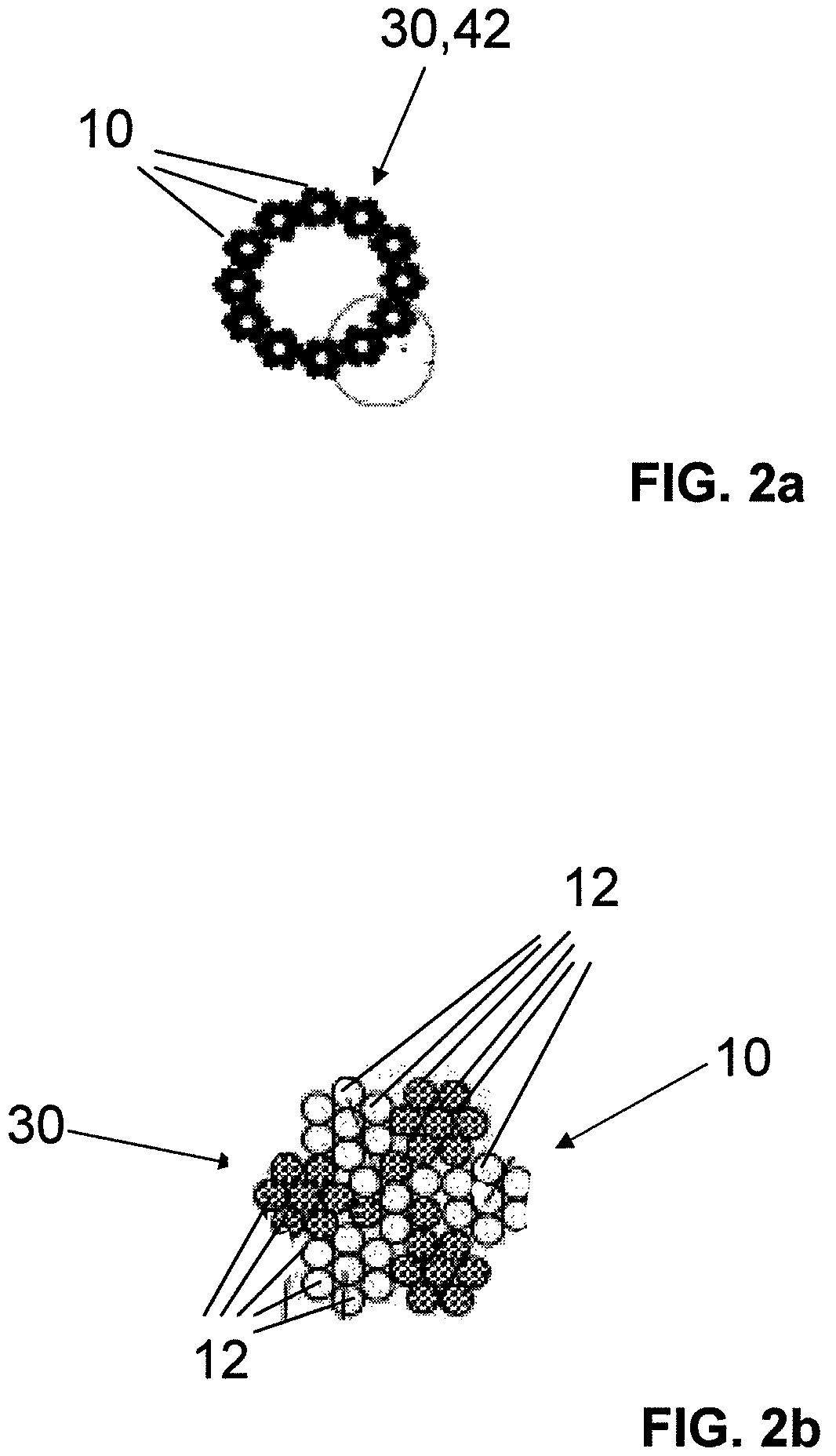
The invention relates to a fiber strand (10) for an implantable supporting body (100) comprising at least two individual fibers (12). The at least two individual fibers (12) are each shorter in their longitudinal extent than the longitudinal extent (14) of the fiber strand, and in their transverse extent they are each thinner than the transverse extent (16) of the fiber strand.
Owner:BIOTRONIK AG
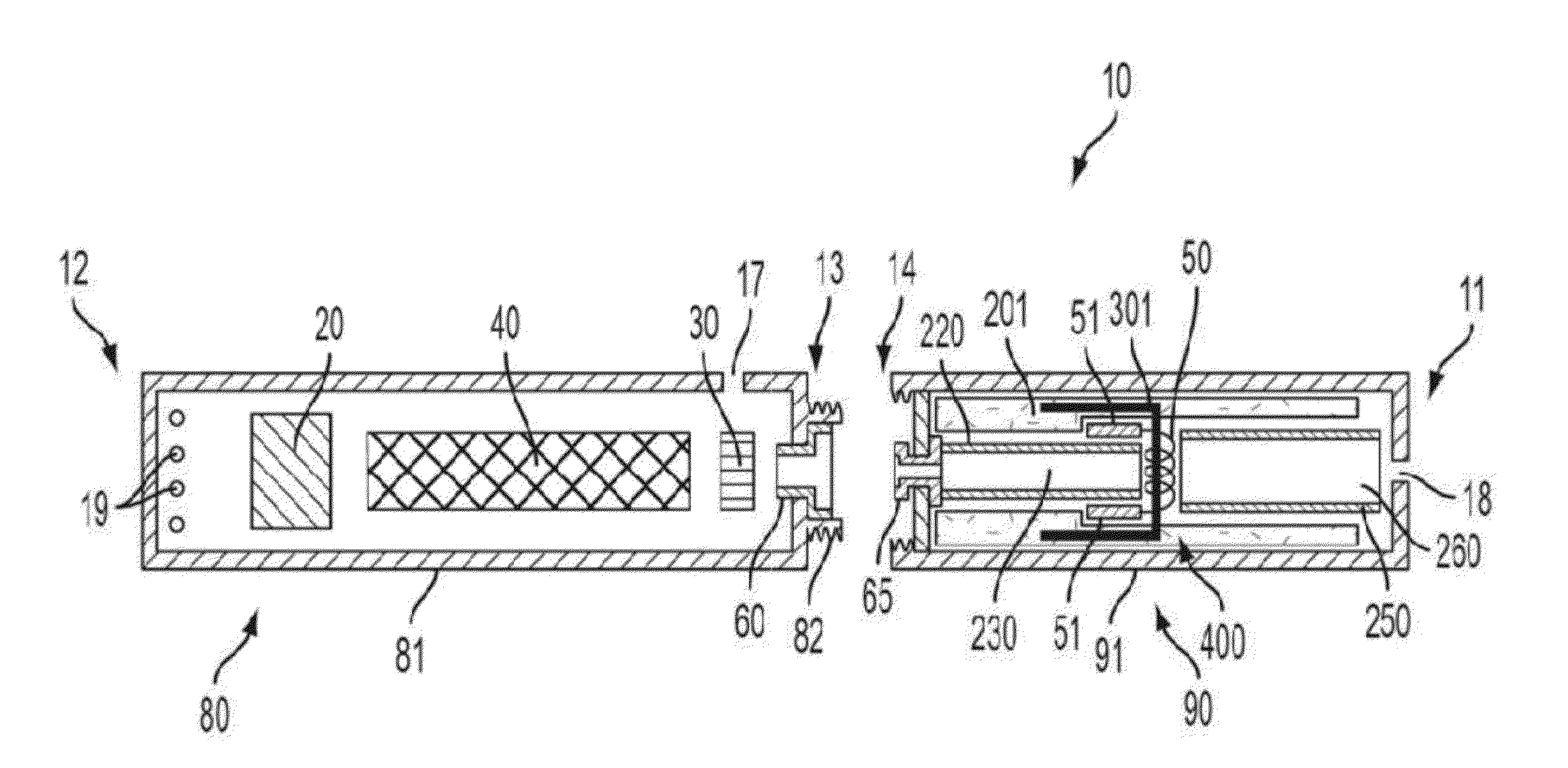
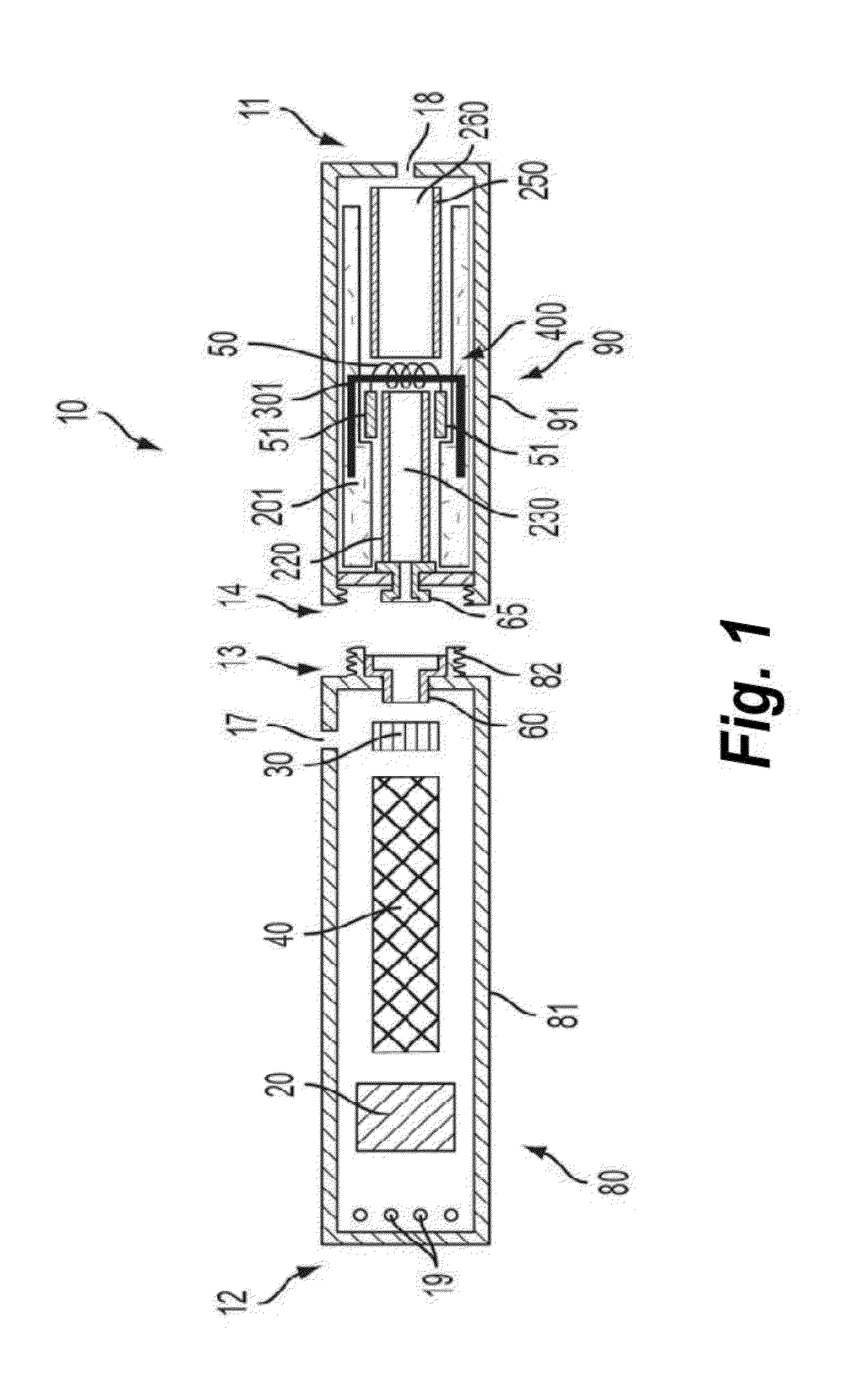
Electronic smoking article with improved storage and transport of aerosol precursor compositions
The present disclosure relates to reservoirs for storing products in electronic smoking articles. The reservoir is manufactured from cellulose acetate fiber, thermoplastic fiber, non-thermoplastic fiber, or a combination thereof. The reservoir is substantially tubular in shape and is adapted to accommodate internal components of the smoking article thereby increasing reservoir capacity. The internal components particularly can comprise an atomizer, which may include a braided wick.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC
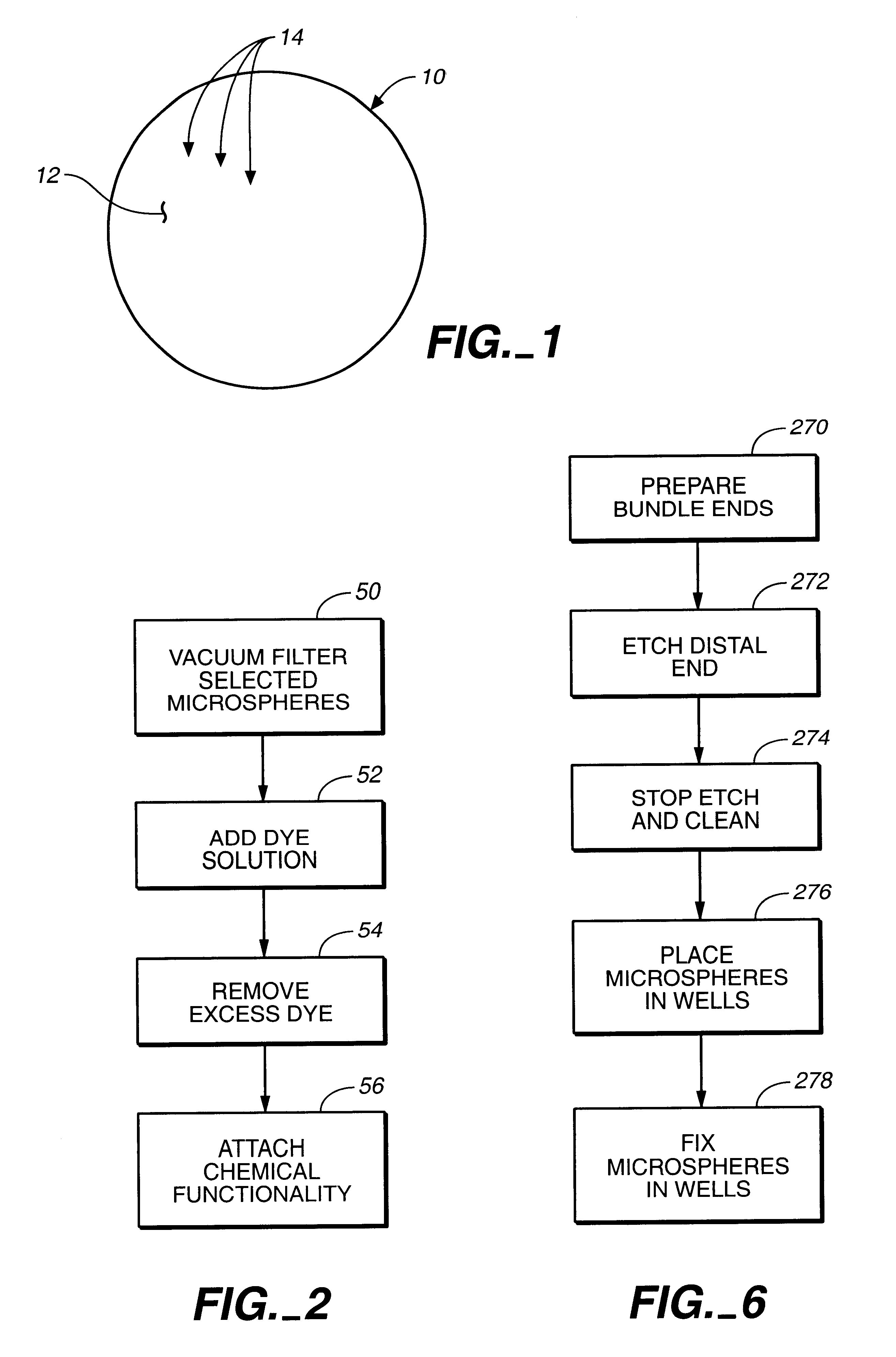
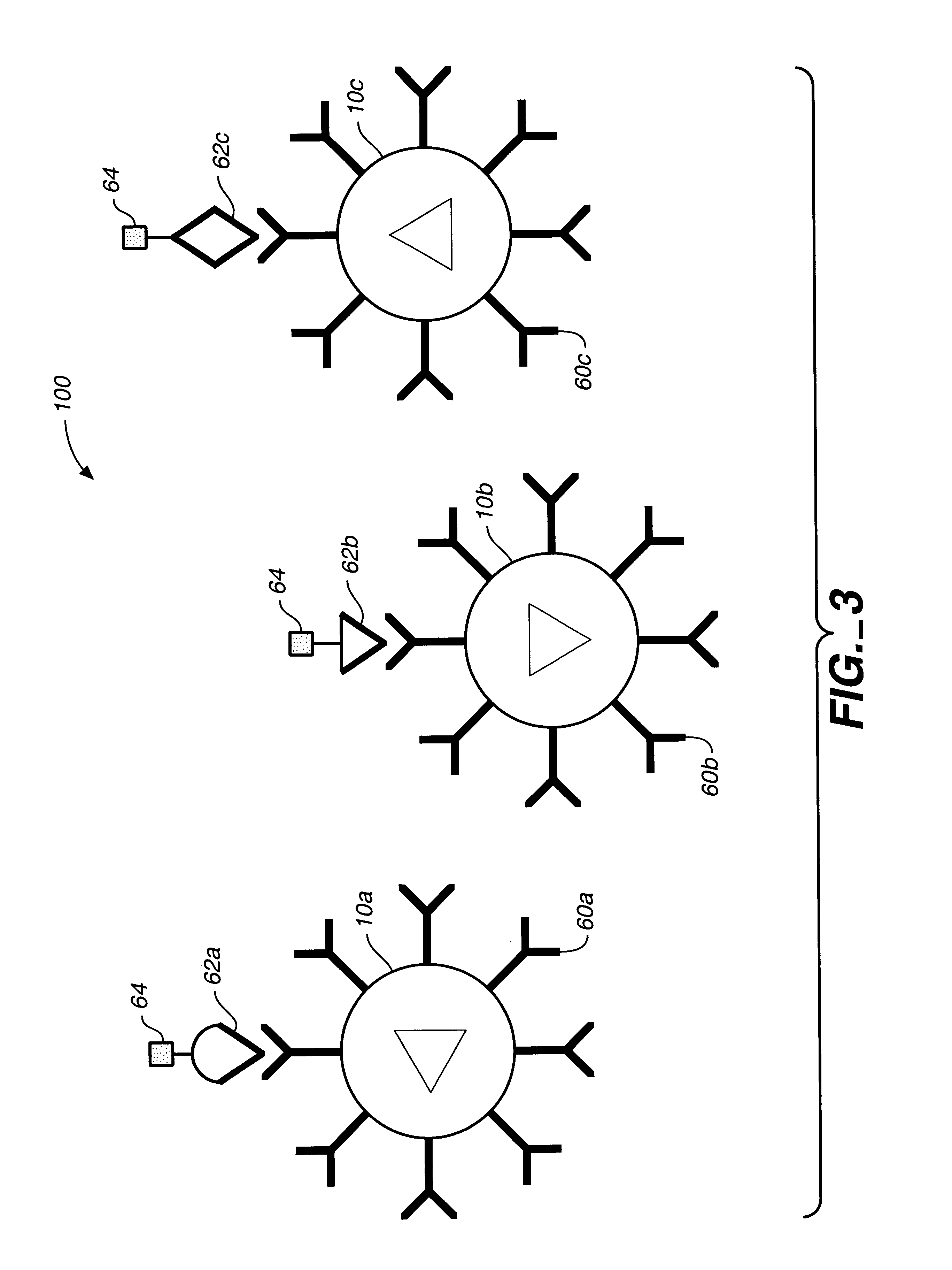
Target analyte sensors utilizing microspheres
A microsphere-based analytic chemistry system and method for making the same is disclosed in which microspheres or particles carrying bioactive agents may be combined randomly or in ordered fashion and dispersed on a substrate to form an array while maintaining the ability to identify the location of bioactive agents and particles within the array using an optically interrogatable, optical signature encoding scheme. A wide variety of modified substrates may be employed which provide either discrete or non-discrete sites for accommodating the microspheres in either random or patterned distributions. The substrates may be constructed from a variety of materials to form either two-dimensional or three-dimensional configurations. In a preferred embodiment, a modified fiber optic bundle or array is employed as a substrate to produce a high density array. The disclosed system and method have utility for detecting target analytes and screening large libraries of bioactive agents.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGETHE
Biocompatible wound dressing
InactiveUS7070584B2Promote cell growthPrevent vacuum leakageWound drainsMedical applicatorsWound dressingWound site
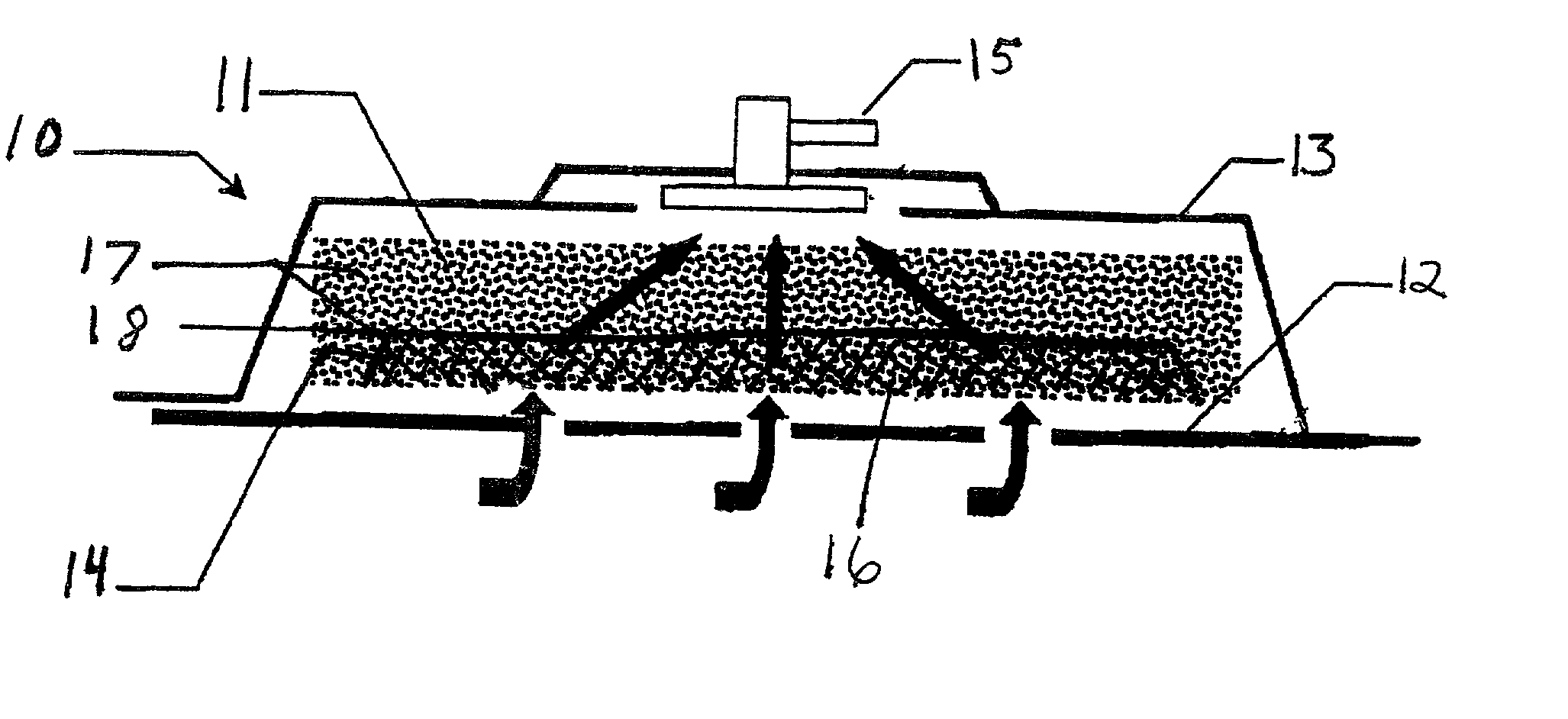
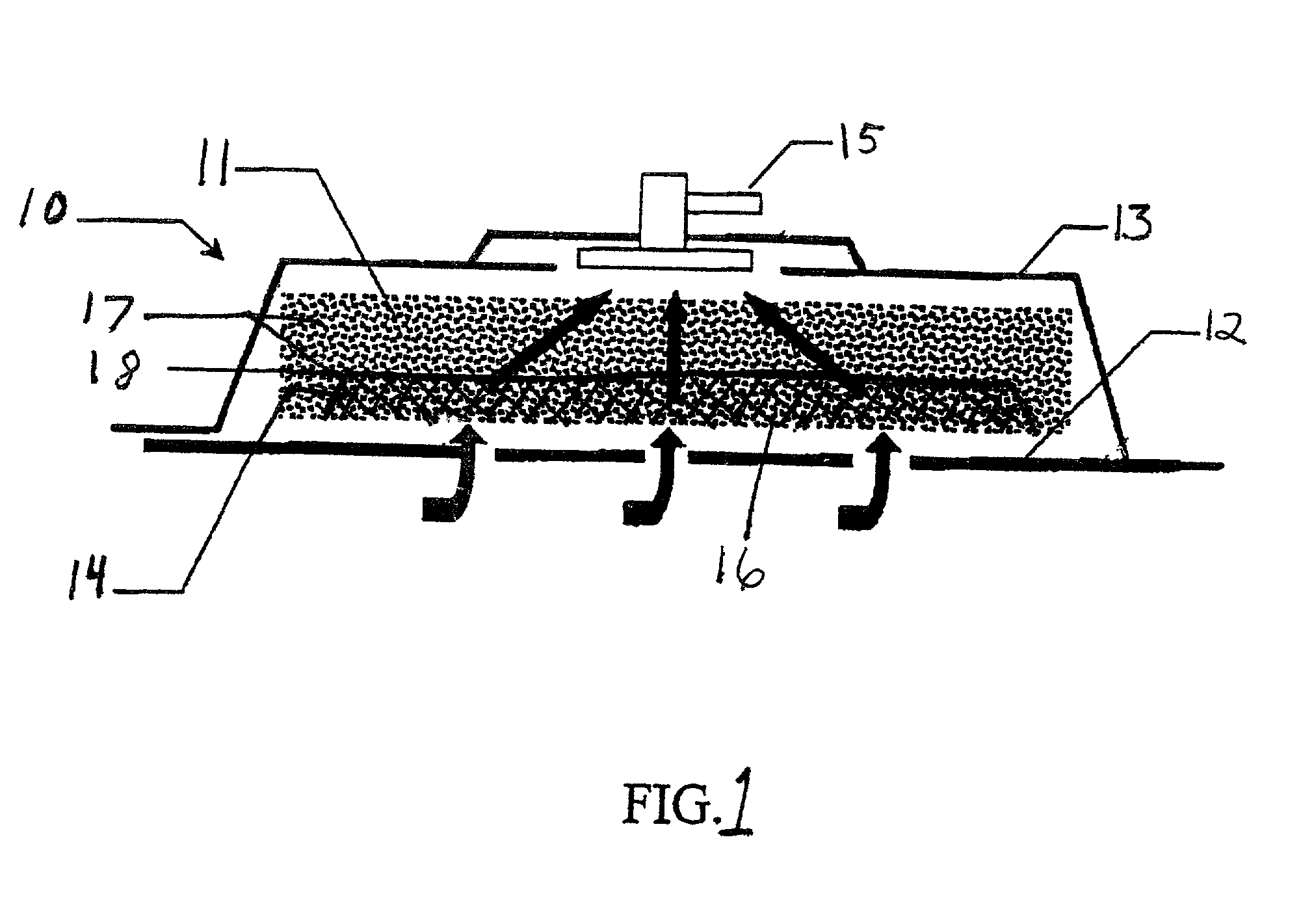
A biocompatible wound dressing comprised of a pad for insertion substantially into a wound site and a wound drape for sealing enclosure of the foam pad at the wound site. The pad, comprised of a foam or other like material having relatively few open cells in contact with the areas upon which cell growth is to be encouraged so as to avoid unwanted adhesions, but having sufficiently numerous open cells so that drainage and negative pressure therapy may continue unimpaired, is placed in fluid communication with a vacuum source for promotion of fluid drainage, as known in the art. The pad is further comprised of an ultra-low density fused-fibrous ceramic, or a bioabsorbable branched polymer, or cell growth enhancing matrix or scaffolding.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Isotactic propylene copolymers, their preparation and use
InactiveUS6960635B2Group 4/14 element organic compoundsOther chemical processesFiberZiegler–Natta catalyst
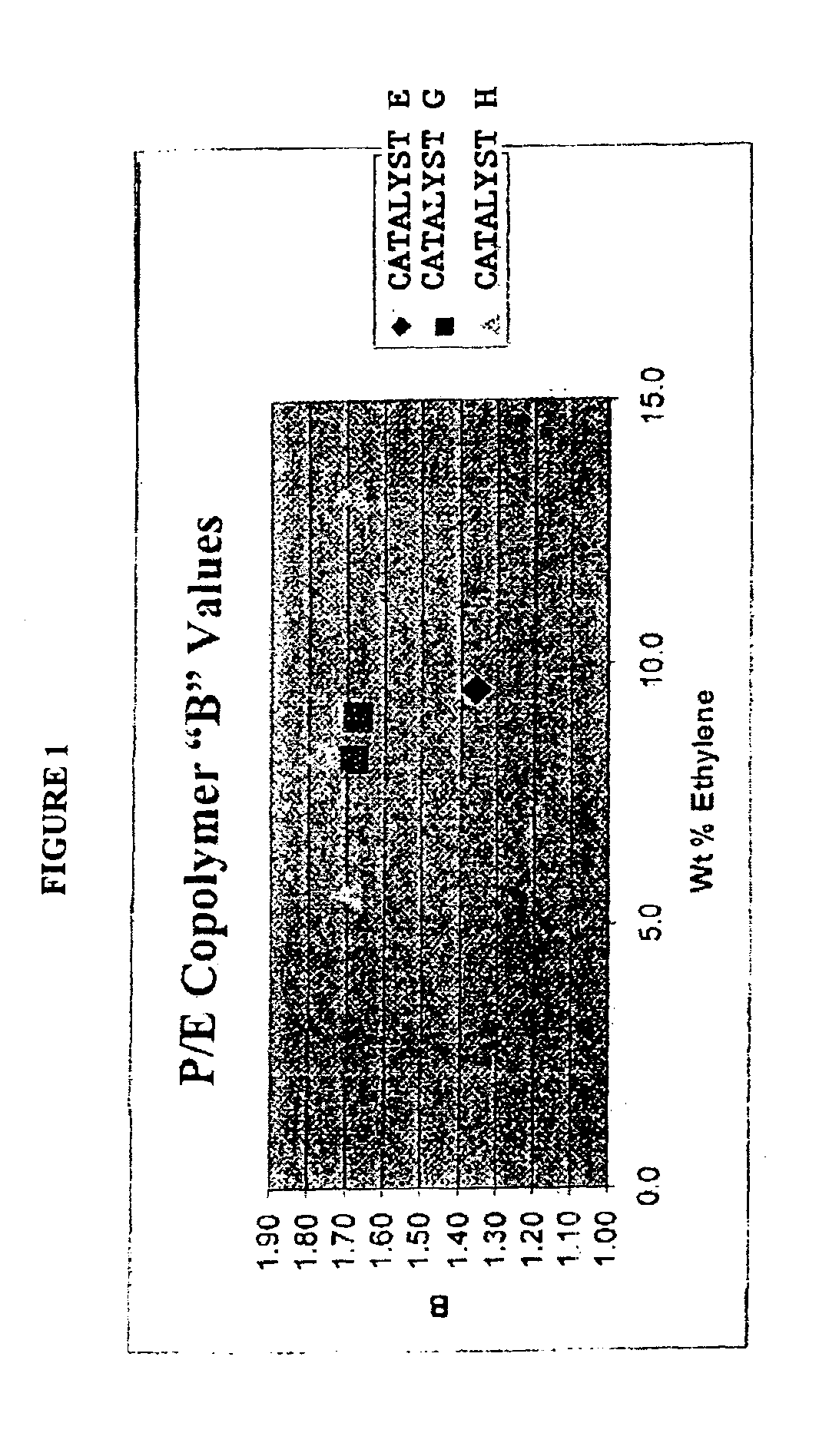
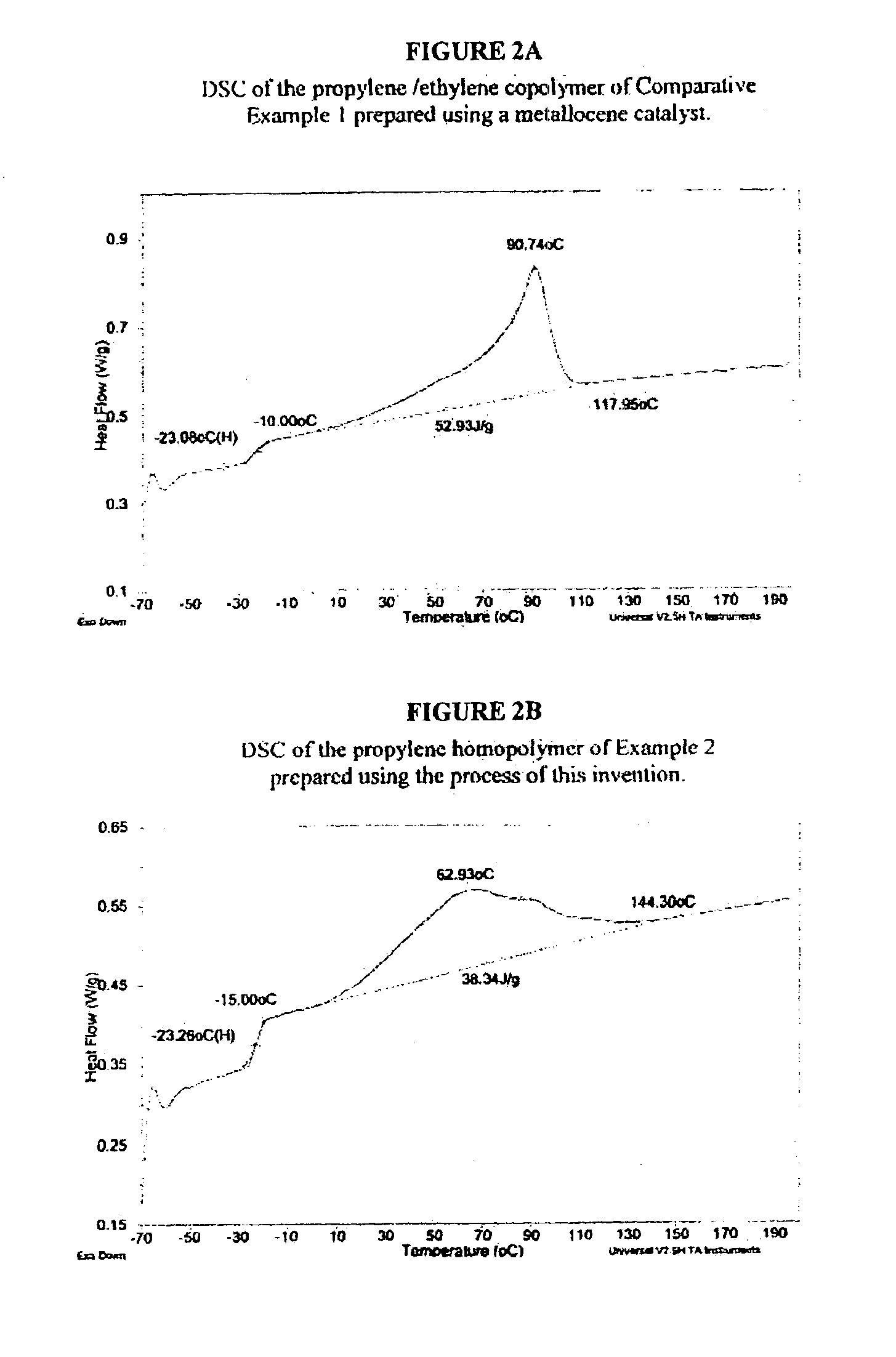
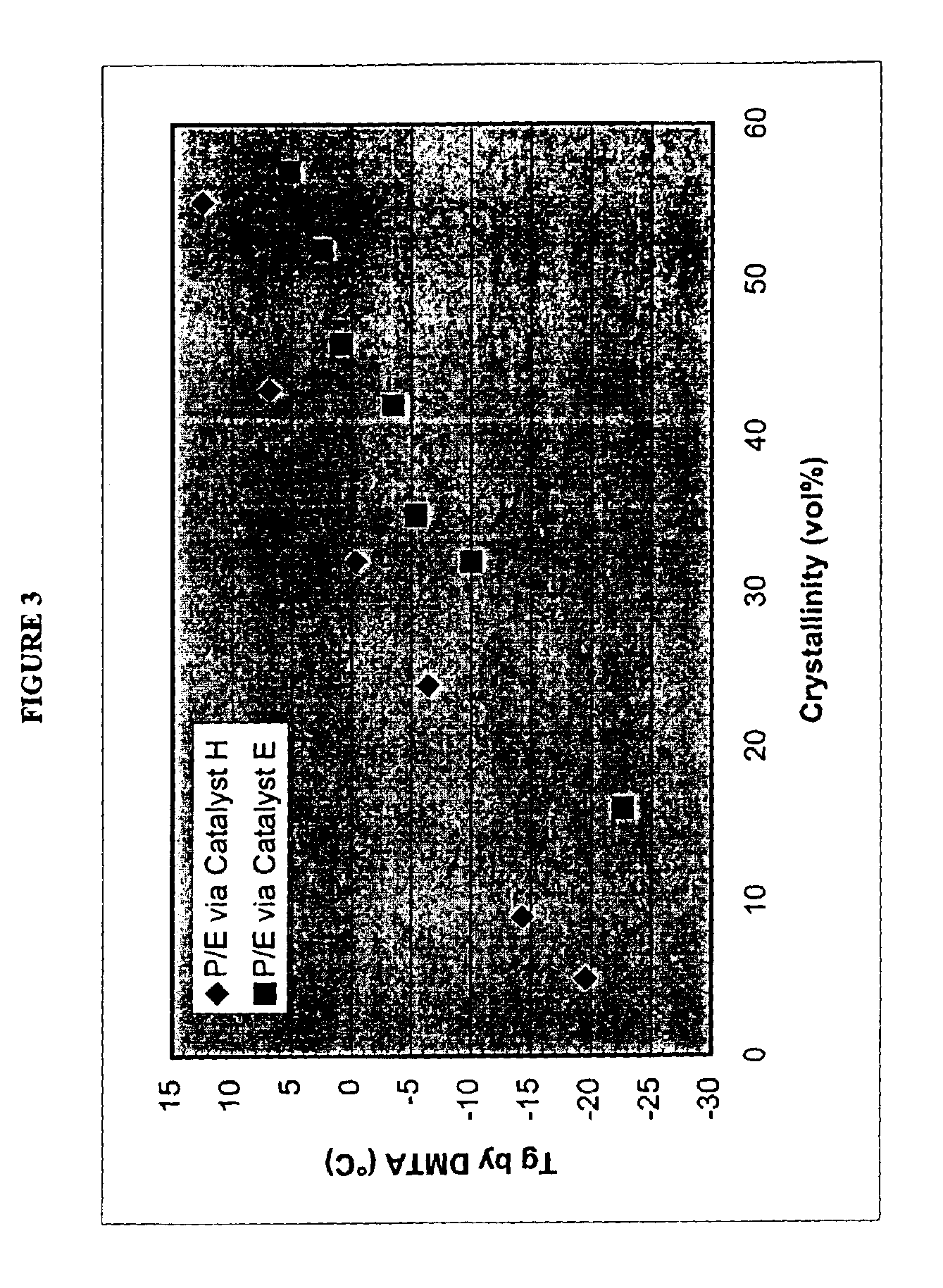
Unique copolymers comprising propylene, ethylene and / or one or more unsaturated comonomers are characterized as having: at least one, preferably more than one, of the following properties: (i) 13C NMR peaks corresponding to a regio-error at about 14.6 and about 15.7 ppm, the peaks of about equal intensity, (ii) a B-value greater than about 1.4 when the comonomer content of the copolymer is at least about 3 wt %, (iii) a skewness index, Six, greater than about −1.20, (iv) a DSC curve with a Tme that remains essentially the same and a Tmax that decreases as the amount of comonomer in the copolymer is increased, and (v) an X-ray diffraction pattern that reports more gamma-form crystals than a comparable copolymer prepared with a Ziegler-Natta catalyst. These polypropylene polymers are made using a nonmetallocene, metal-centered, heteroaryl ligand catalyst. These polymers can be blended with other polymers, and are useful in the manufacture of films, sheets, foams, fibers and molded articles.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polysaccharide fibers
This invention pertains to novel fibers made of α(1→;3) polysaccharides, and a process for their production. The fibers of the invention have “cotton-like” properties but can be produced as continuous filaments on a year-round basis. The fibers are useful in textile applications.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC
Compressed high density fibrous polymers suitable for implant
An embodiment of the present invention may be made by the following steps: providing a mixture comprising a plurality of fibers, a lubricant, and a suspension fluid, with the suspension fluid filling a void space between said fibers and subjecting said mixture to at least one compressive force. The compressive force causes the migration and alignment of said fibers; and may remove substantially all of the suspension fluid from said mixture. The mixture may further comprise a biologically active agent, or a reinforcing agent.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Medical device applications of nanostructured surfaces
InactiveUS20050038498A1Fine surfacePrevent/reduce bio-foulingAntibacterial agentsMaterial nanotechnologyFiberNanofiber
This invention provides novel nanofiber enhanced surface area substrates and structures comprising such substrates for use in various medical devices, as well as methods and uses for such substrates and medical devices.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Drug-delivering composite structures
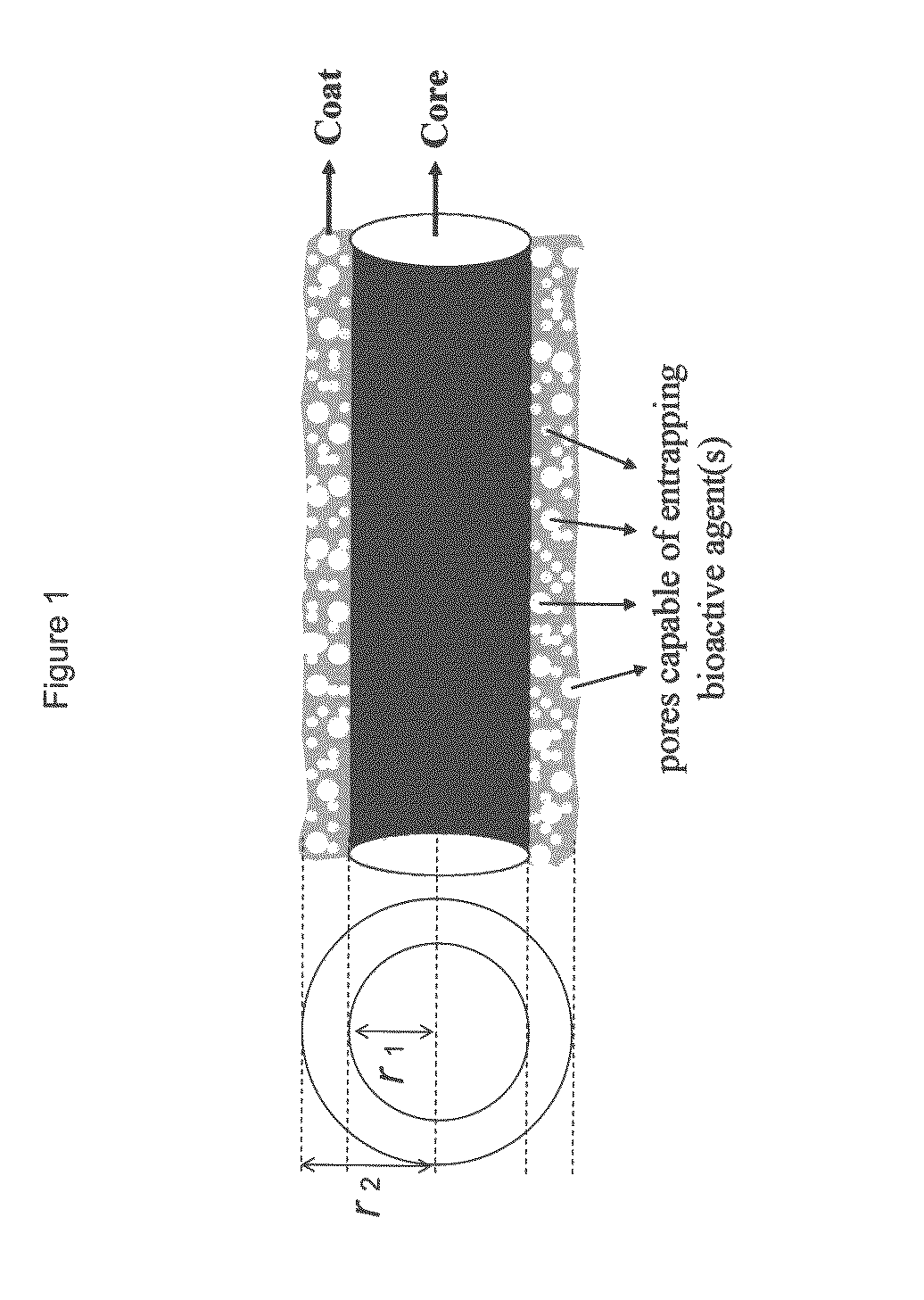
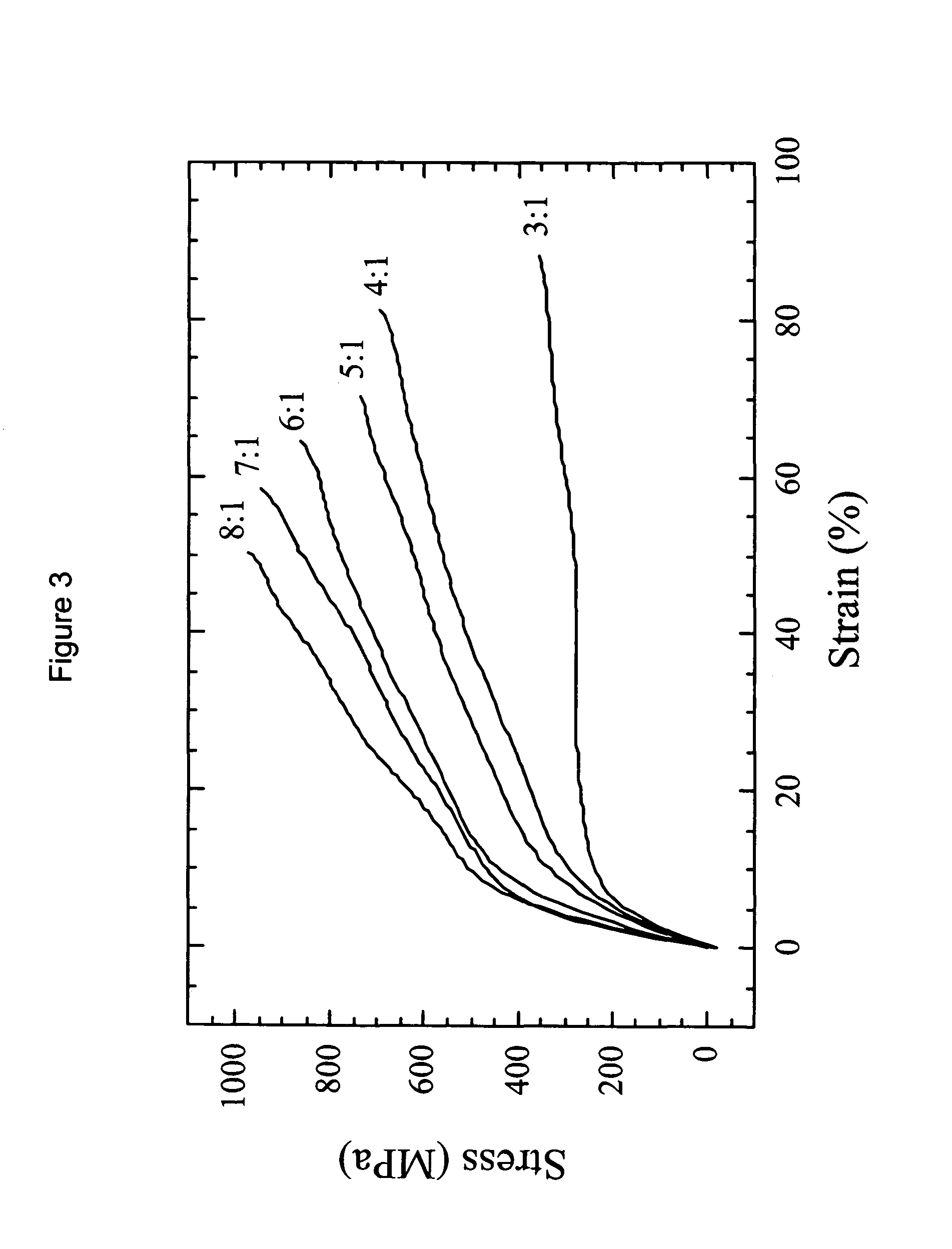
Composite structures composed of a fibril core and a polymeric coat and designed capable of encapsulating both hydrophobic and hydrophilic bioactive agents while retaining the activity of these agents are disclosed. Further disclosed are processes of preparing such composite structures, and medical devices and disposable articles made therefrom.
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
Hesperaloe tissue having improved cross-machine direction properties
ActiveUS10337148B2Satisfactory softness and strength and bulkNegatively effecting tissue product strength and stiffness and bulkPaper/cardboardTissue/absorbent paperFiberMedicine
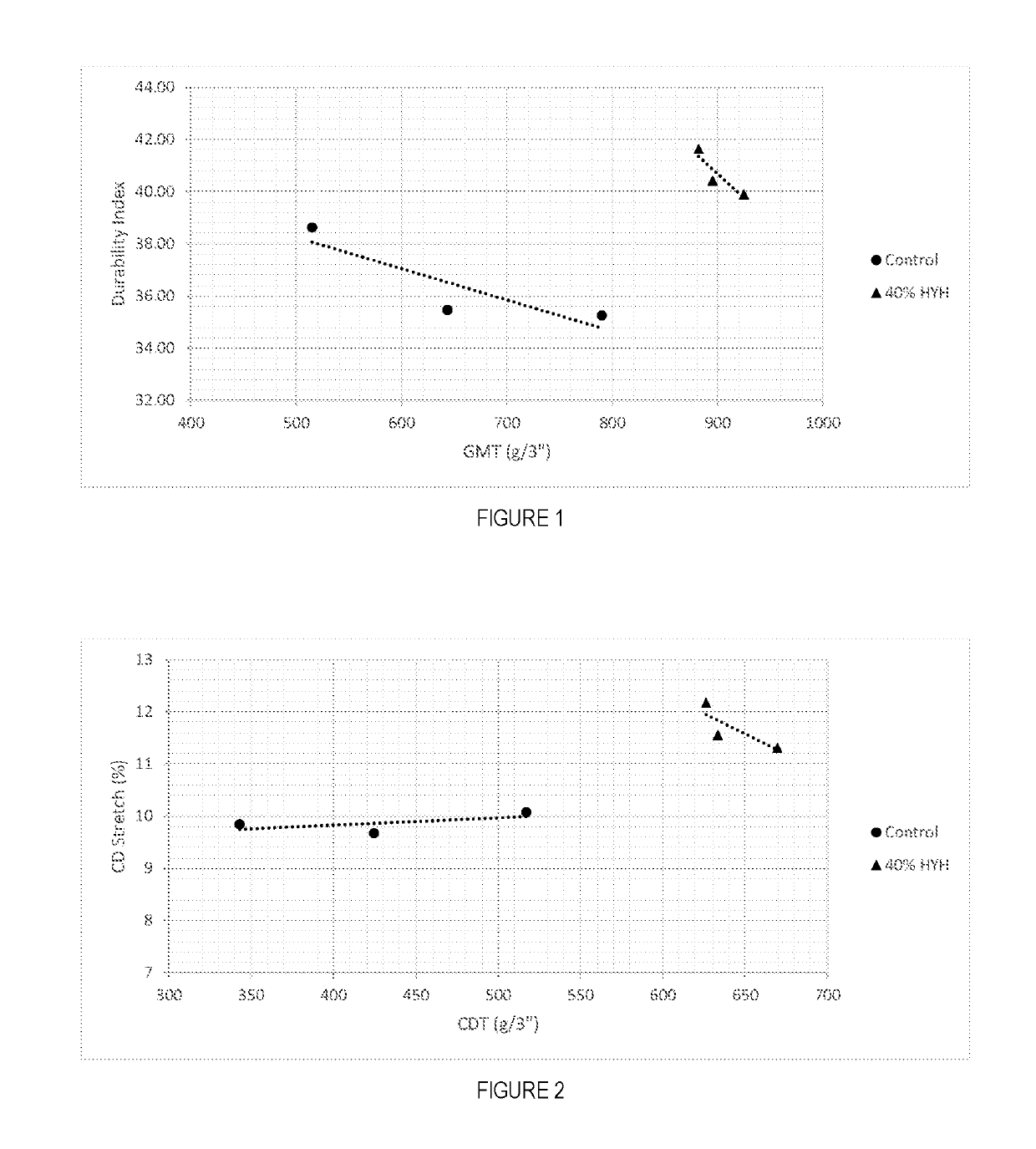
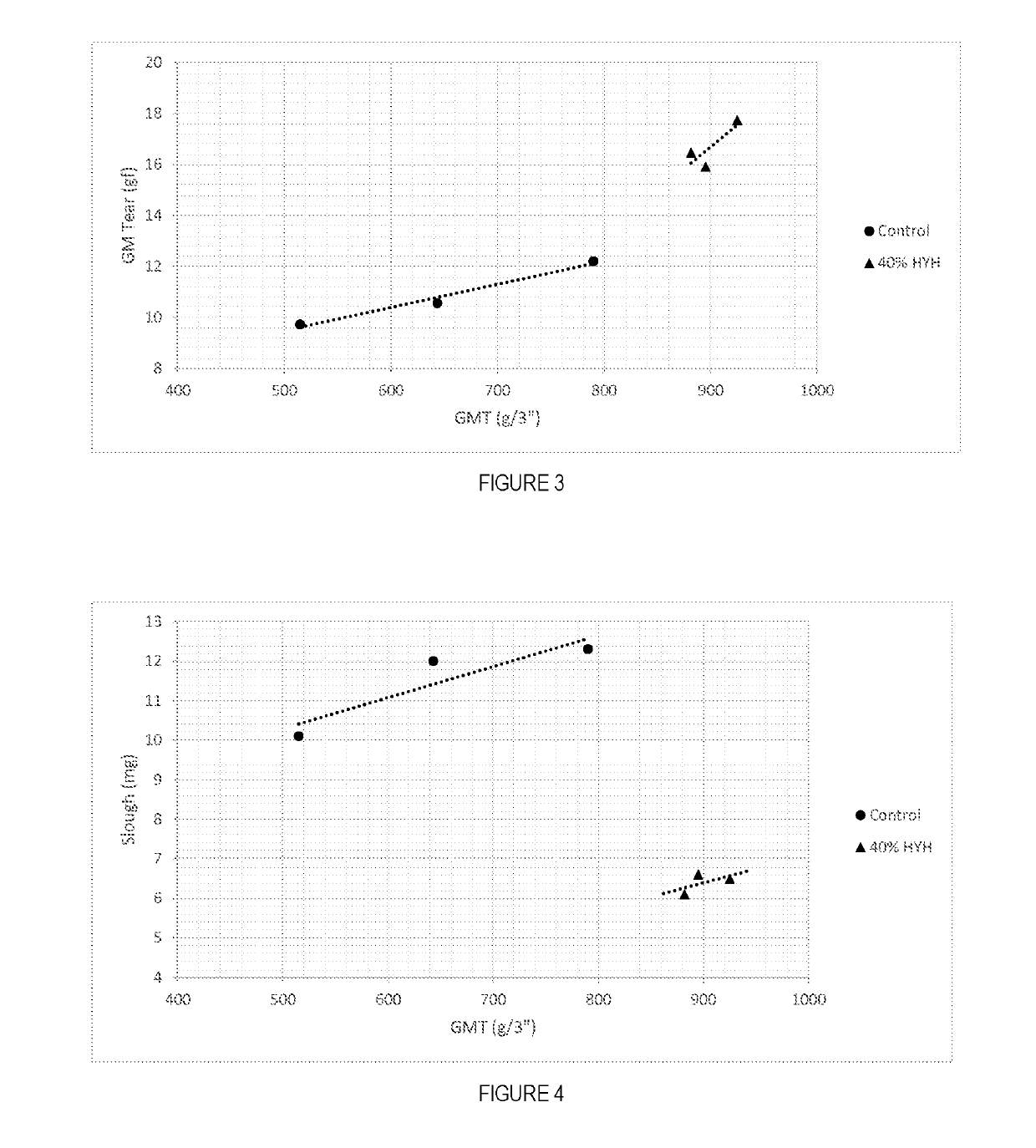
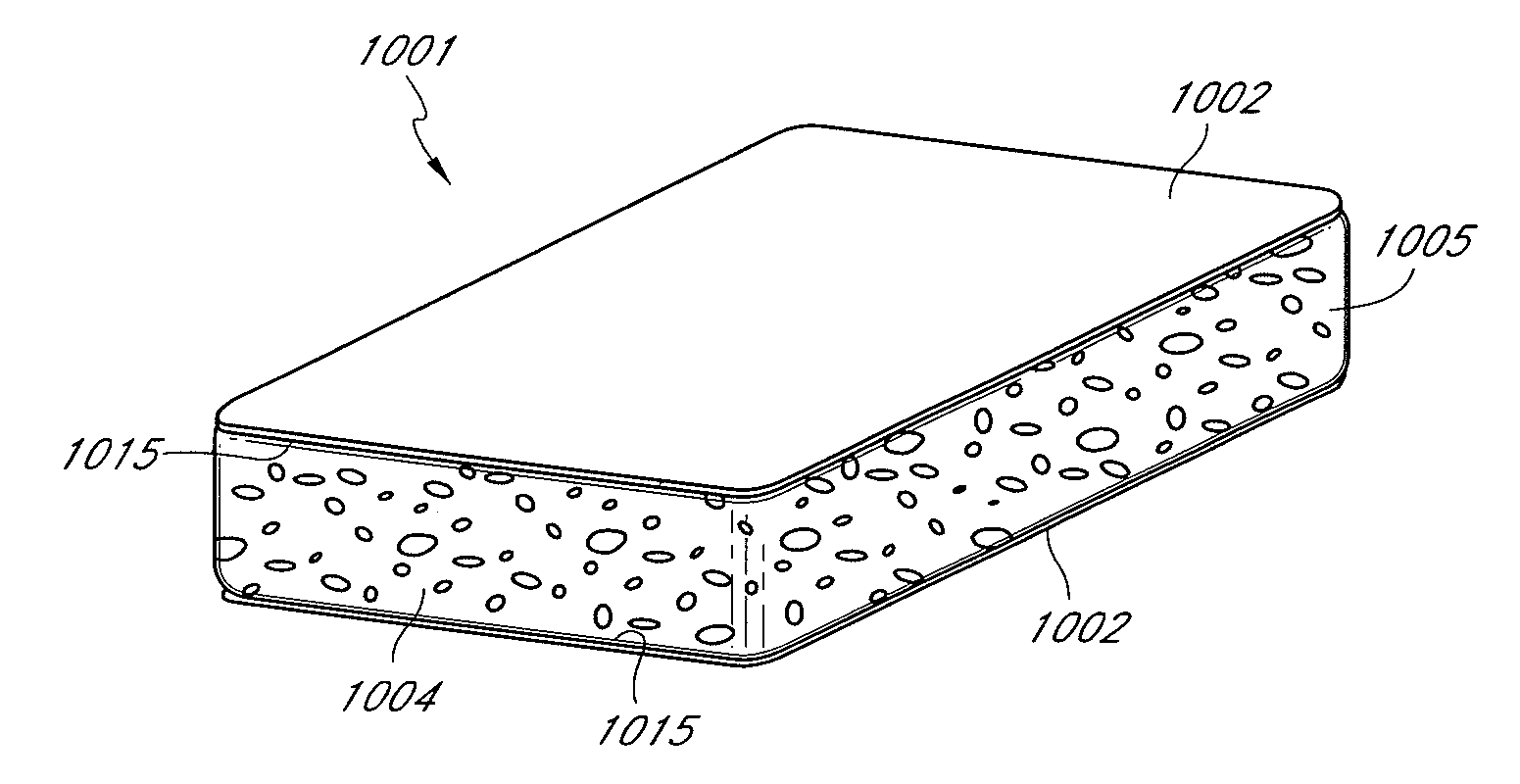
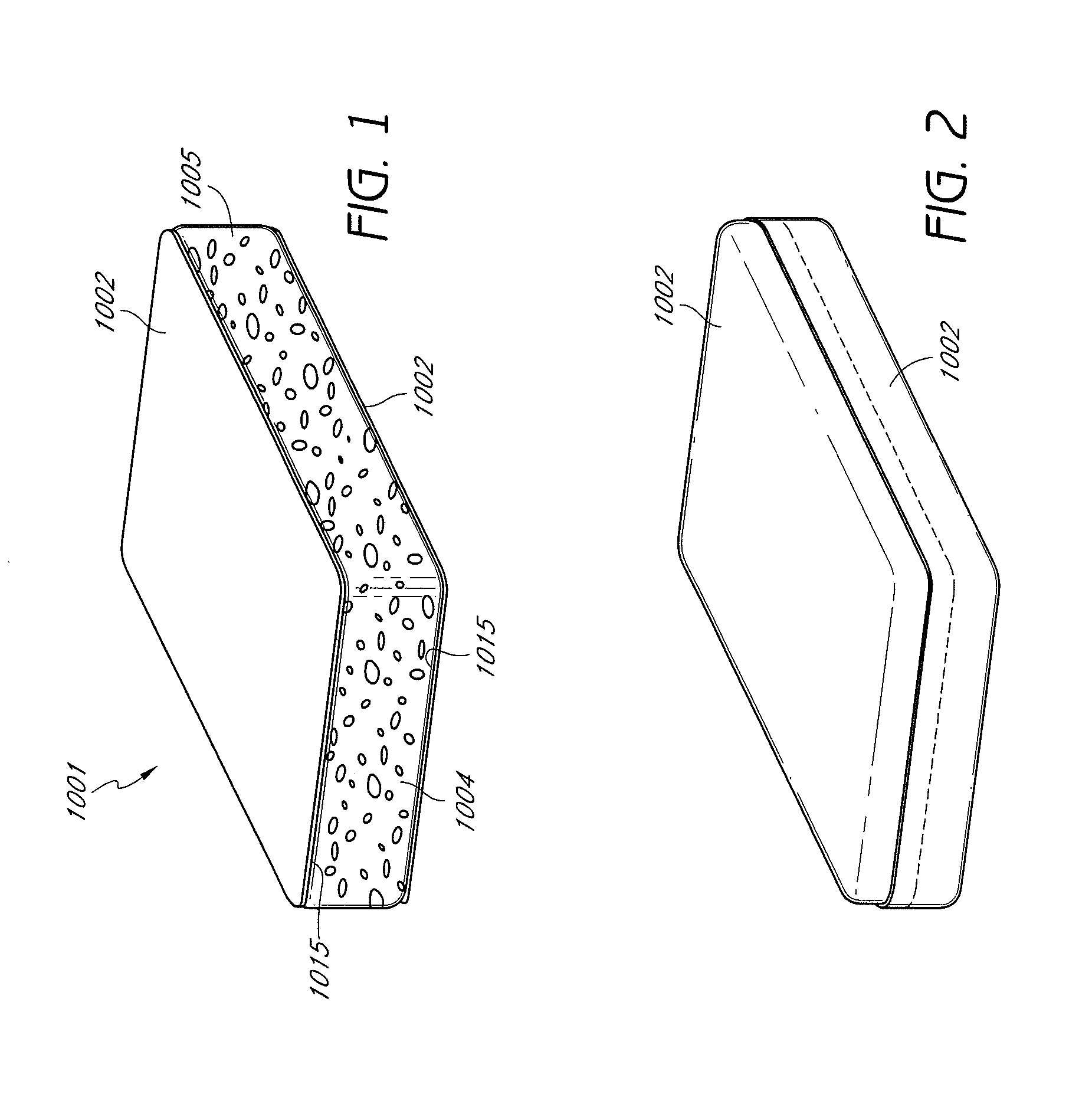
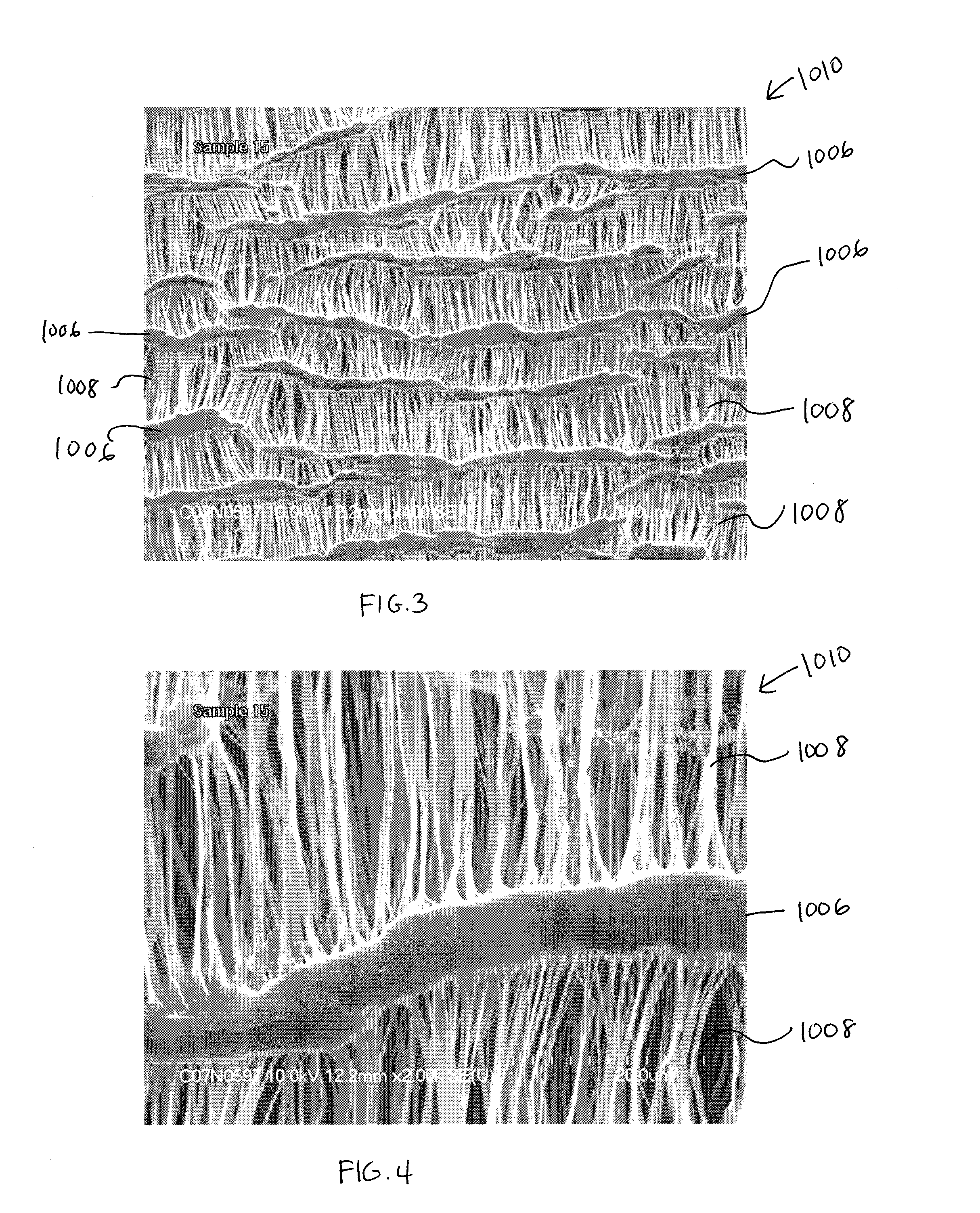
Soft, durable and bulky tissue products comprising non-wood fibers and more particularly high yield hesperaloe pulp fibers are disclosed. The tissue products preferably comprise at least about 5 percent, by weight of the product, high yield hesperaloe pulp fiber and have relatively modest tensile strengths, such as a geometric mean tensile (GMT) less than about 1,000 g / 3″, and improved durability and cross-machine direction (CD) properties, such as a CD Stretch greater than about 10 percent. Additionally, at the foregoing tensile strengths the products are not overly stiff. For example the tissue products may have a Stiffness Index less than about 10.0.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Porous implant with effective extensibility and methods of forming an implant
The implant includes an outer layer of ePTFE which exhibits extensibility normally not associated with ePTFE. The ePTFE is reduced in length by deforming the fibrils between the nodes while maintaining the nodes in a substantially flat configuration. Various implant configurations that can include the outer layer described are also disclosed.
Owner:EVERA MEDICAL
Optical fiber with quantum dots
Holey optical fibers (e.g. photonic fibers, random-hole fibers) are fabricated with quantum dots disposed in the holes. The quantum dots can provide light amplification and sensing functions, for example. When used for sensing, the dots will experience altered optical properties (e.g. altered fluorescence or absorption wavelength) in response to certain chemicals, biological elements, radiation, high energy particles, electrical or magnetic fields, or thermal / mechanical deformations. Since the dots are disposed in the holes, the dots interact with the evanescent field of core-confined light. Quantum dots can be damaged by high heat, and so typically cannot be embedded within conventional silica optical fibers. In the present invention, dots can be carried into the holes by a solvent at room temperature. The present invention also includes solid glass fibers made of low melting point materials (e.g. phosphate glass, lead oxide glass) with embedded quantum dots.
Owner:LAMBDA LABORATORY INSTRUMENTS +1
Anti-inflammatory biosensor for reduced biofouling and enhanced sensor performance
A biosensor including an external surface, and an accessory material in close proximity to the external surface. The accessory material includes a coating containing a hydrophilic material and / or a fiber modified to deliver a therapeutic agent. The biosensor modifies a biological response to the biosensor upon contact with a tissue, such as upon implantation into the skin of a subject, thereby reducing biofouling, inflammation and other undesirable tissue responses that interfere with biosensor performance. The biosensor can be any biocompatible sensor, suitable for short- or long-term use. Preferably, the biosensor is an enzymatic or electrochemical sensor, such as a glucose sensor. Also provided are a method of producing a biosensor and a method of delivering a biologically active substance to a subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
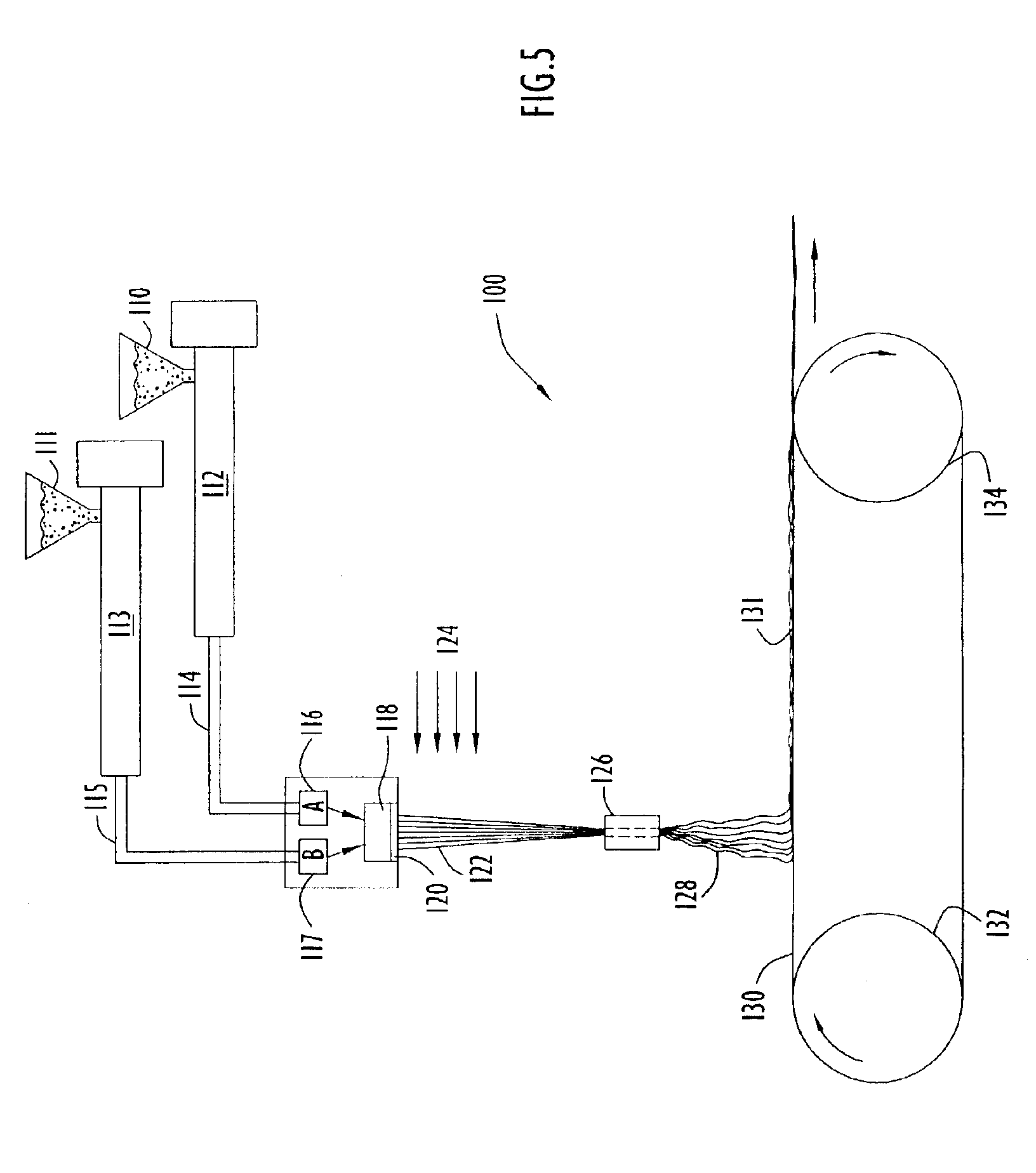
Process and apparatus for the production of nanofibers
A process for forming nanofibers comprising the steps of feeding a fiber-forming material into an annular column, the column having an exit orifice, directing the fiber-forming material into an gas jet space, thereby forming an annular film of fiber-forming material, the annular film having an inner circumference, simultaneously forcing gas through a gas column, which is concentrically positioned within the annular column, and into the gas jet space, thereby causing the gas to contact the inner circumference of the annular film, and ejects the fiber-forming material from the exit orifice of the annular column in the form of a plurality of strands of fiber-forming material that solidify and form nanofibers having a diameter up to about 3,000 nanometers.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Implants for replacing cartilage, with negatively-charged hydrogel surfaces and flexible matrix reinforcement
ActiveUS9314339B2Strong and durableStrong and secure anchoringFinger jointsWrist jointsFiberChemical agent
A permanent non-resorbable implant allows surgical replacement of cartilage in articulating joints, using a hydrogel material (such as a synthetic polyacrylonitrile polymer) reinforced by a flexible fibrous matrix. Articulating hydrogel surface(s) are chemically treated to provide a negative electrical charge that emulates the negative charge of natural cartilage, and also can be treated with halogenating, cross-linking, or other chemical agents for greater strength. For meniscal-type implants, the reinforcing matrix can extend out from the peripheral rim of the hydrogel, to allow secure anchoring to soft tissue such as a joint capsule. For bone-anchored implants, a porous anchoring layer enables tissue ingrowth, and a non-planer perforated layer can provide a supportive interface between the hard anchoring material and the softer hydrogel material.
Owner:FORMAE
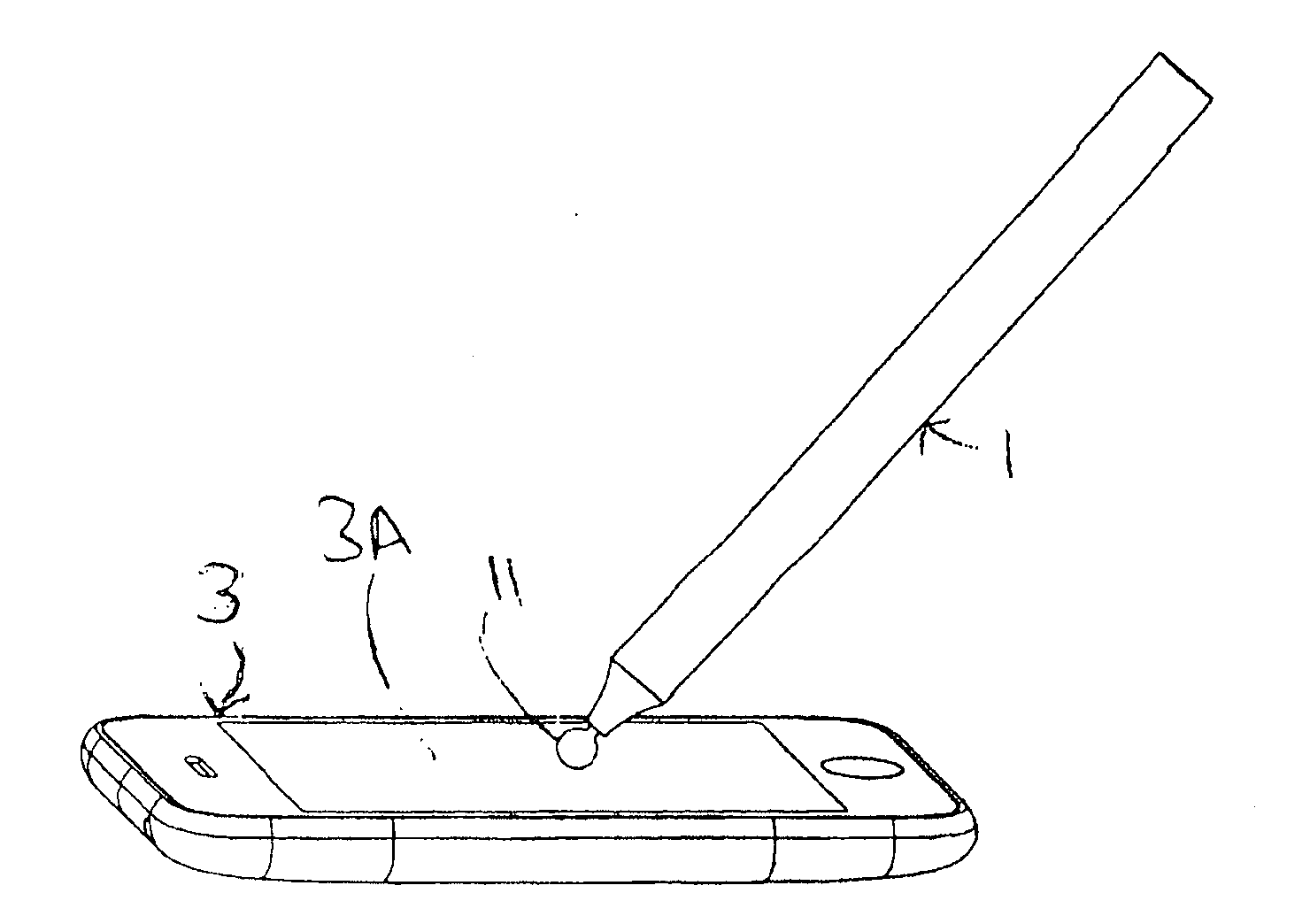
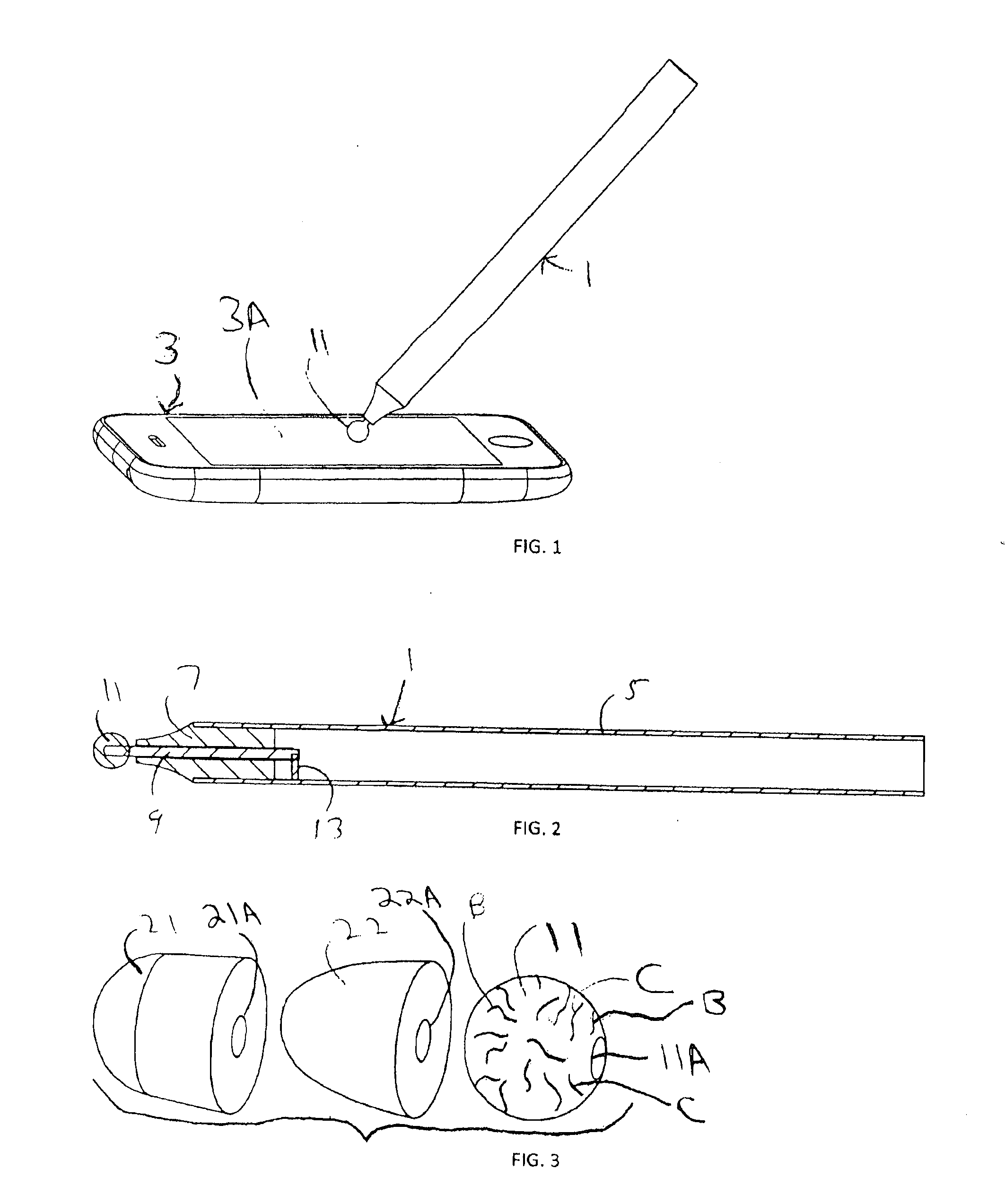
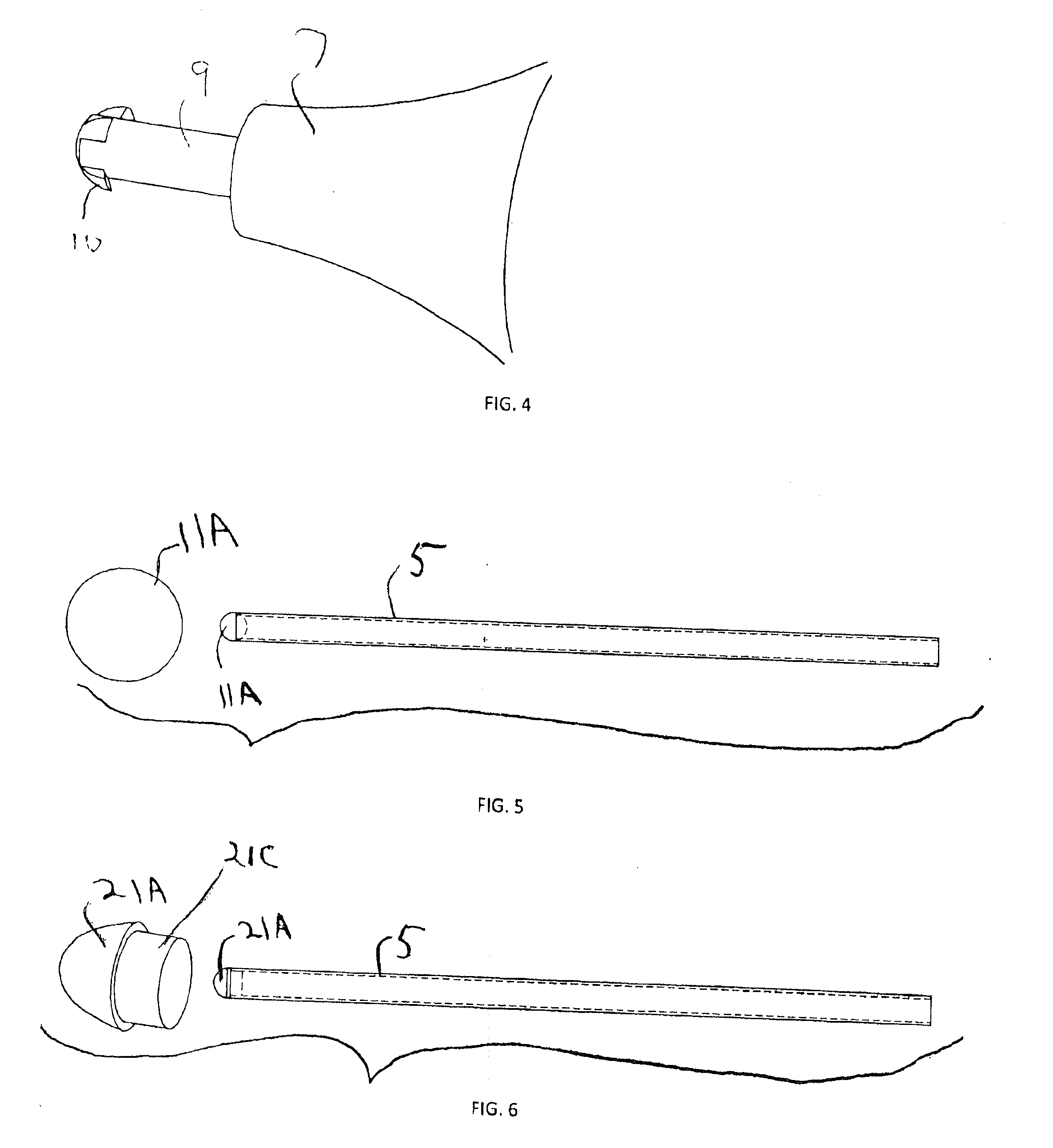
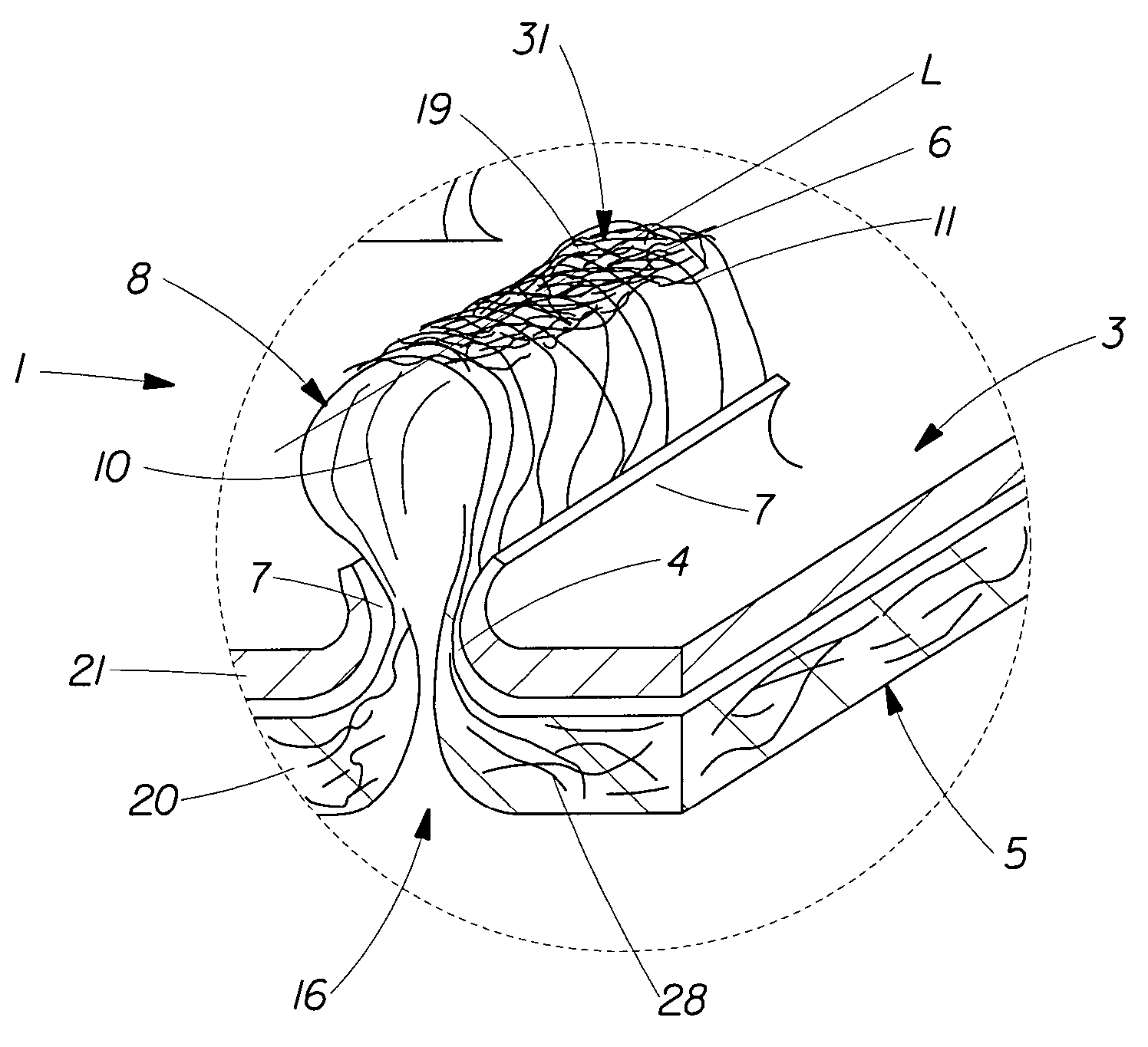
Capacitive touch screen stylus
InactiveUS20110304577A1Reduce coefficient of frictionLower impedanceInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceFiber
In some embodiments, a stylus for providing input to a capacitive touch screen, having a tip including or consisting of conductive felt, which provides a deformable conductive surface for contacting the touch screen. The tip is produced by felting base fibers (which are typically non-conductive) with conductive fibers. In other embodiments, a capacitive touch stylus having at least a first mode of operation and a second mode of operation, and including at least one conductive tip and switched circuitry (preferably, passive circuitry) including at least one switch biased in a default state indicative of the first mode of operation but switchable into a second state indicative of the second mode of operation in response to movement of the tip (typically, in response to exertion of not less than a threshold force on the tip). In some embodiments, a stylus having a conductive tip (e.g., a conductive, felted tip) and including switched circuitry (preferably, passive circuitry) having a first state which couples a capacitance to the tip, where the capacitance is sufficient to allow a capacitive touch screen device to recognize (as a touch) simple contact of the tip on the screen of the touch screen device, and a second state which decouples the capacitance from the tip, thereby preventing the touch screen device from recognizing (as a touch) simple contact of the tip on the screen.
Owner:RB CONTROLS CO
Tufted laminate web
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
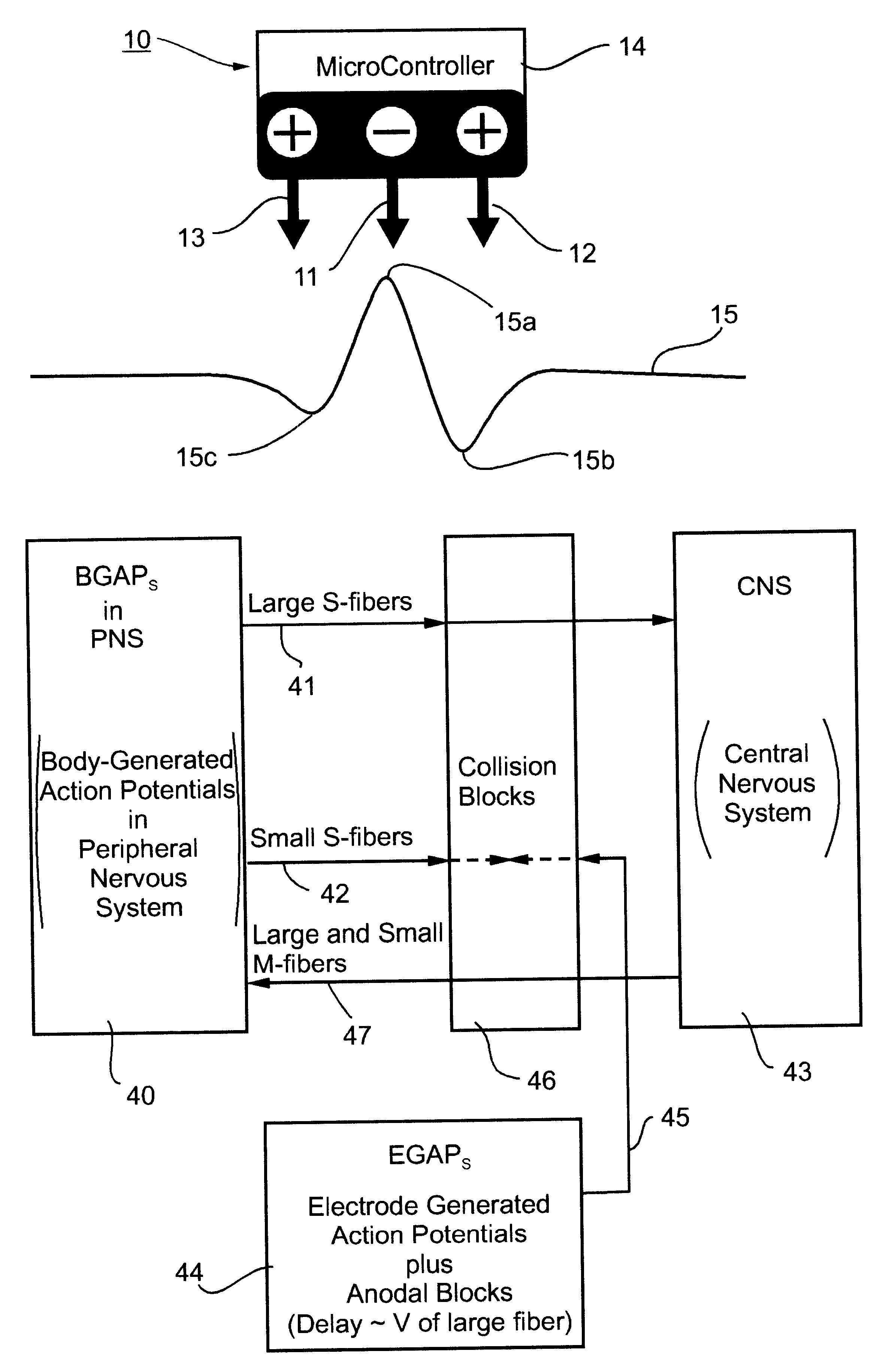
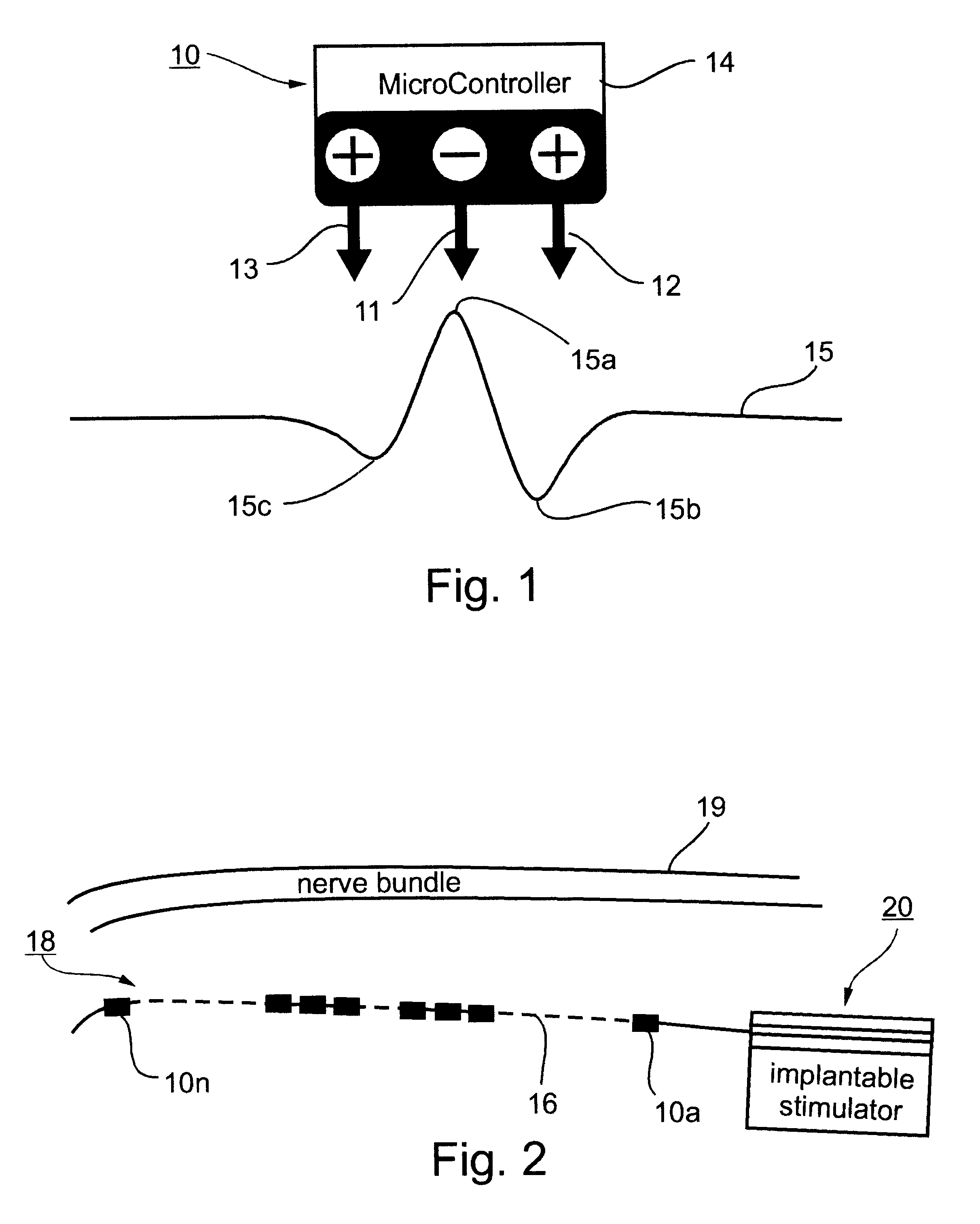
Method and apparatus for selective control of nerve fibers
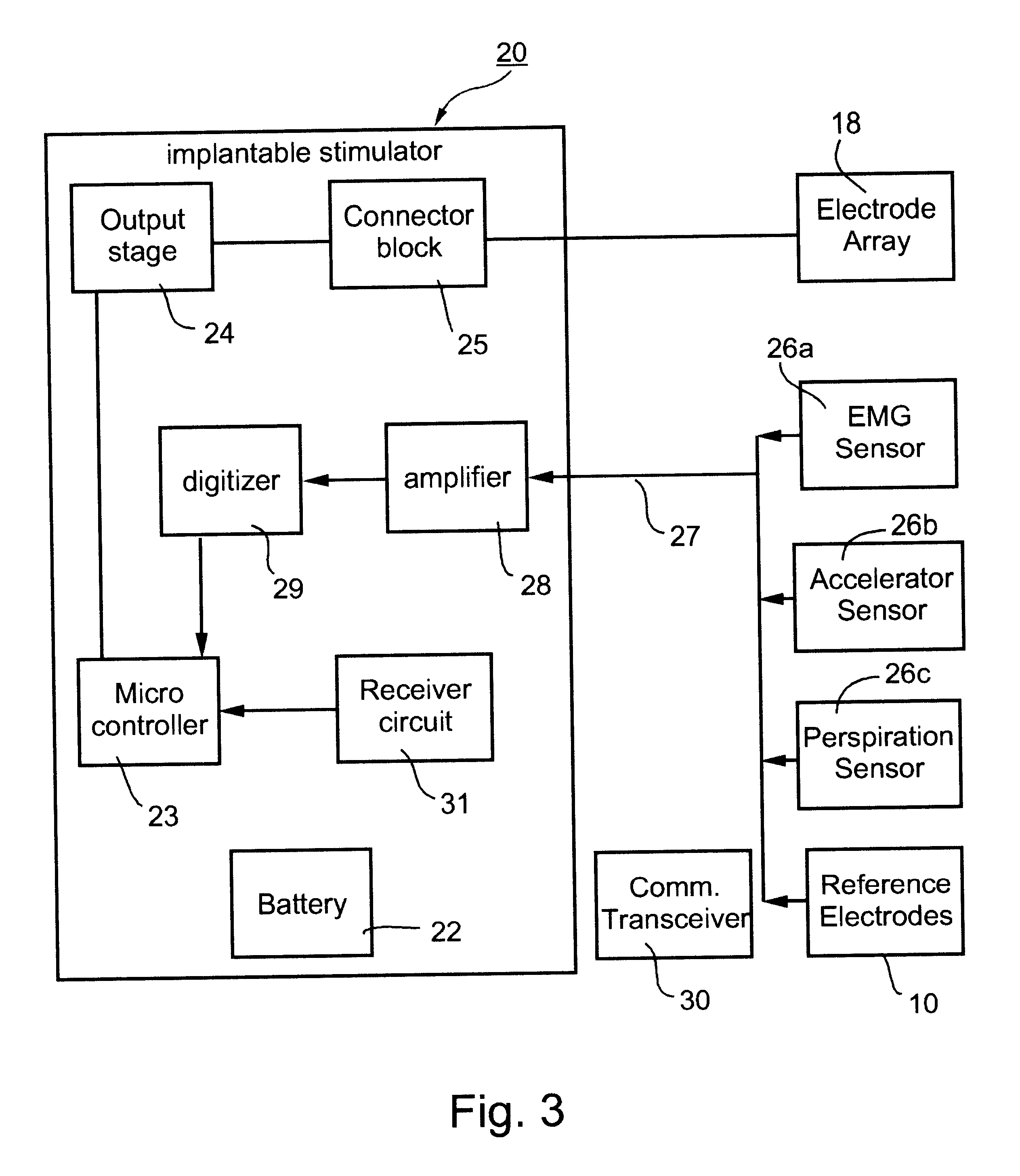
InactiveUS6600954B2Pain reliefReduced sensationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationFiberNerve fiber bundle
A method and apparatus particularly useful for pain control by selectively blocking the propagation of body-generated action potentials travelling through a nerve bundle by using a tripolar electrode device to generate unidirectional action potentials to serve as collision blocks with the body-generated action potentials representing pain sensations in the small-diameter sensory fibers. In the described preferred embodiments there are a plurality of electrode devices spaced along the length of the nerve bundle which are sequentially actuated with delays corresponding to the velocity of propagation of the body-generated action potentials through the large-diameter fibers to produce a "green wave" effect which minimizes undesired anodal blocking of the large-diameter fibers while maximizing the collision blocking of the small-diameter fibers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
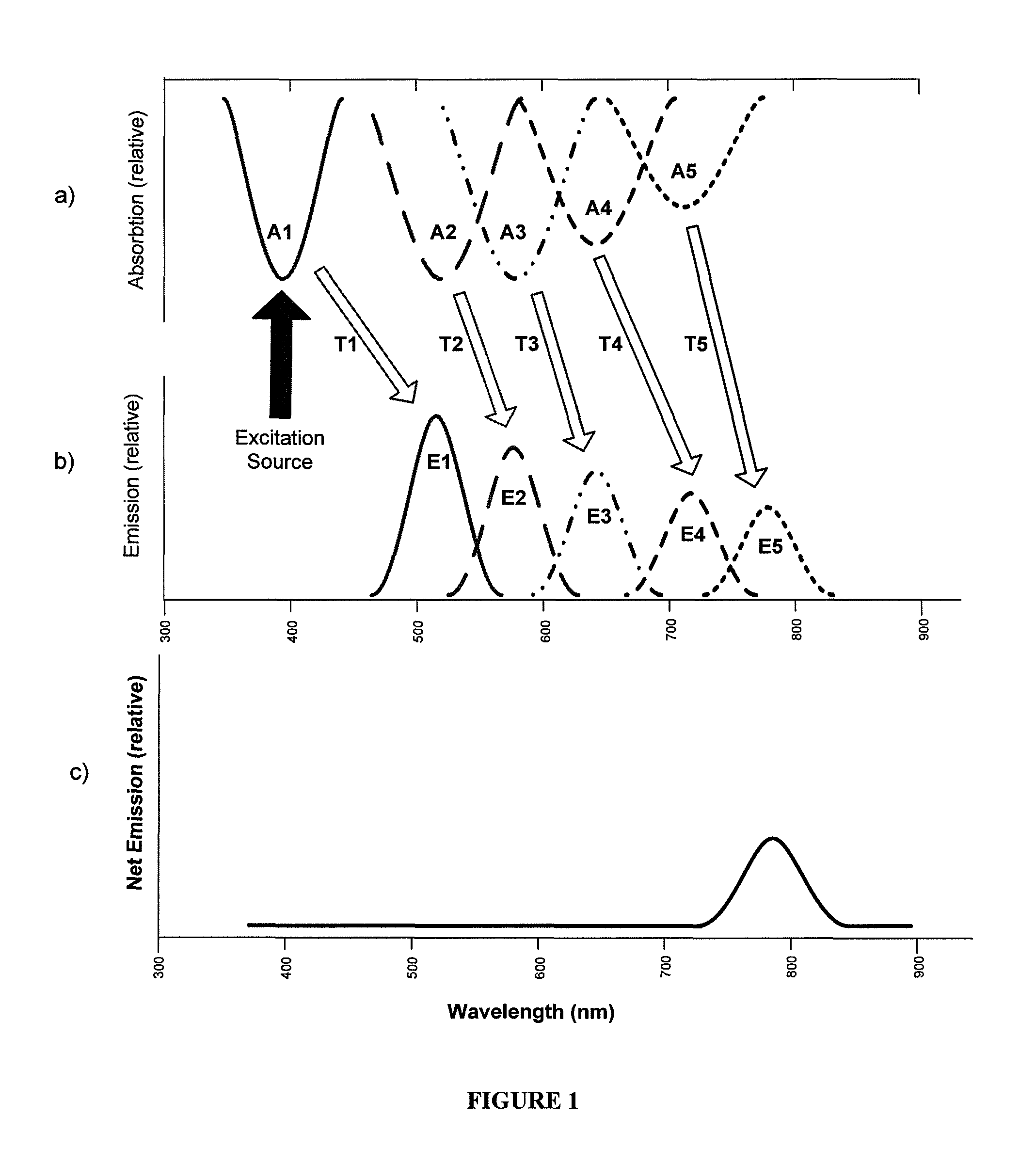
Photoluminescent fibers, compositions and fabrics made therefrom
Disclosed are photoluminescent fibers containing photoluminescent phosphorescent materials and photoluminescent fluorescent materials whose emission signature lies partly or fully in the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Also disclosed are the use of the inventive fibers, fabrics made therefrom, and objects containing the fiber.
Owner:PERFORMANCE INDICATOR LLC
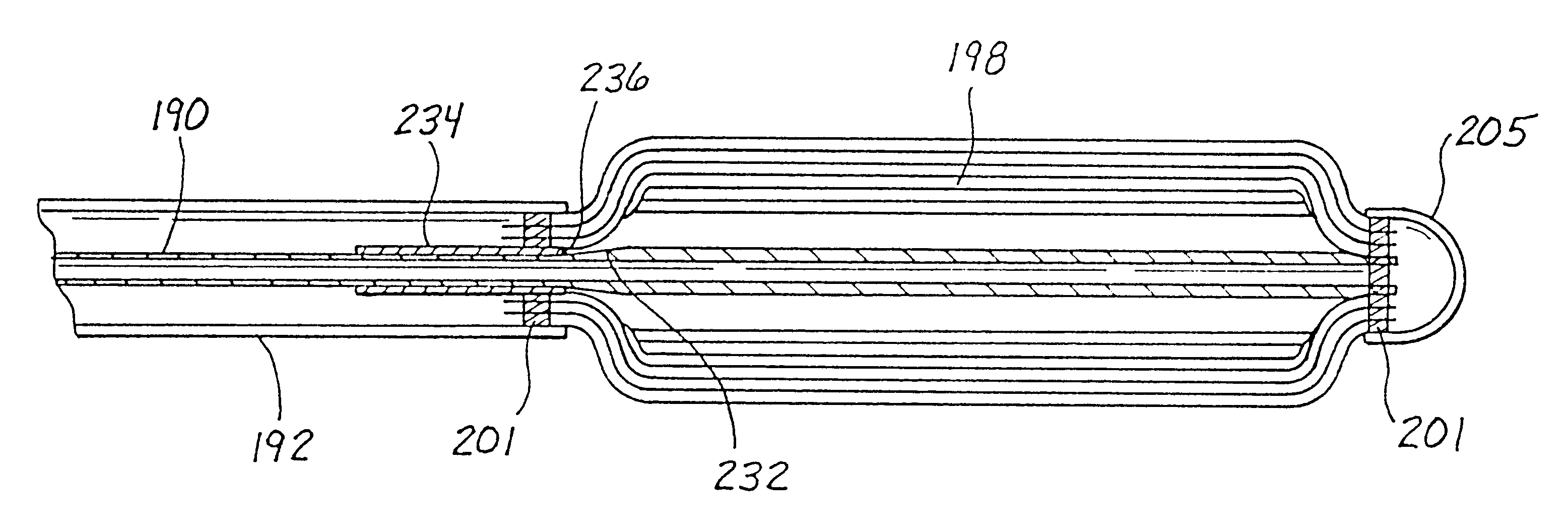
Indwelling heat exchange catheter and method of using same
A catheter is adapted to exchange heat with a body fluid, such as blood, flowing in a body conduit, such as a blood vessel. The catheter includes a shaft with a heat exchange region disposed at its distal end. This region may include hollow fibers which are adapted to receive a remotely cooled heat exchange fluid preferably flowing in a direction counter to that of the body fluid. The hollow fibers enhance the surface area of contact, as well as the mixing of both the heat exchange fluid and the body fluid. The catheter can be positioned to produce hypothermia in a selective area of the body or alternatively positioned to systemically cool the entire body system.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com