Patents
Literature
13044 results about "Composite structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
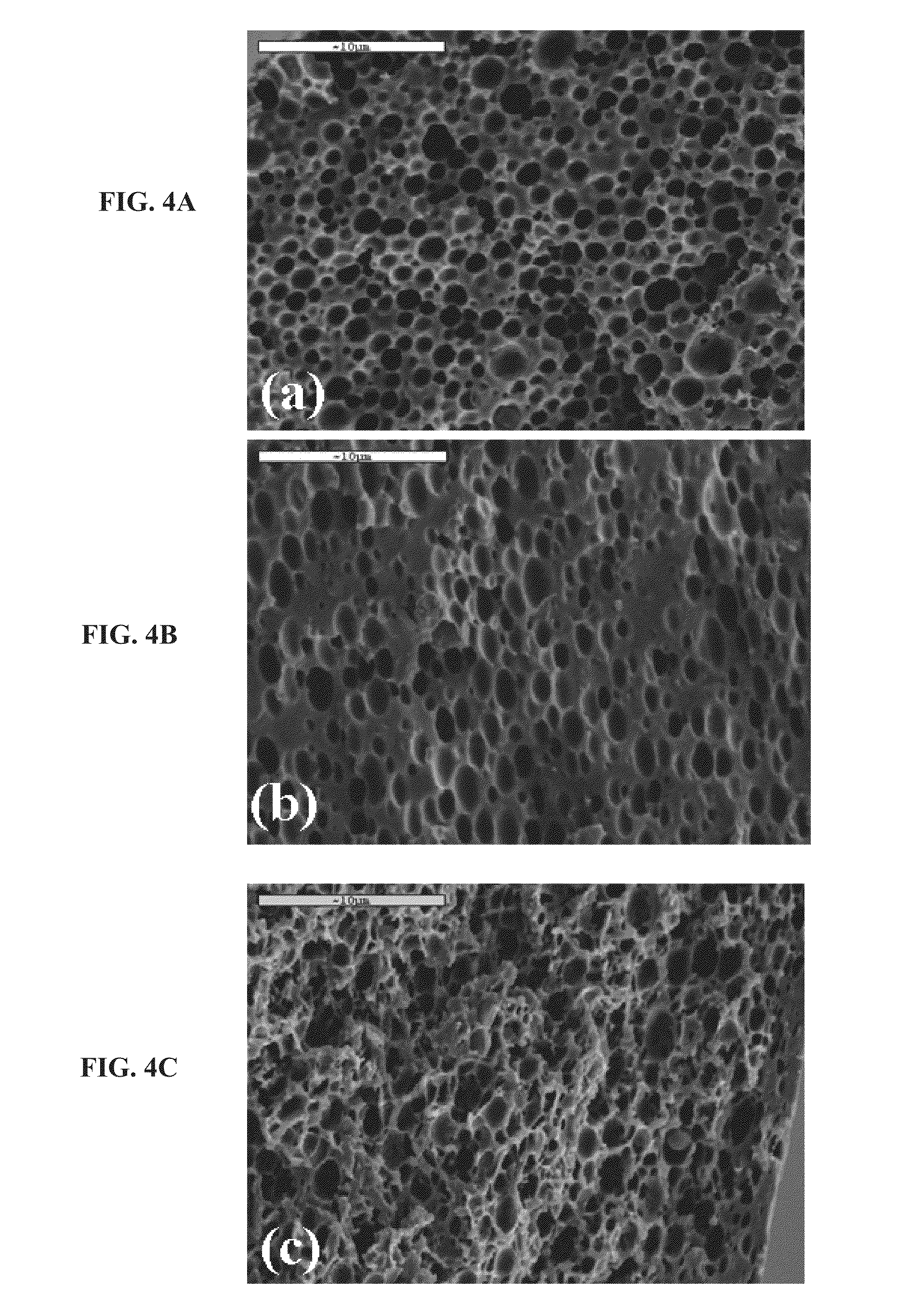
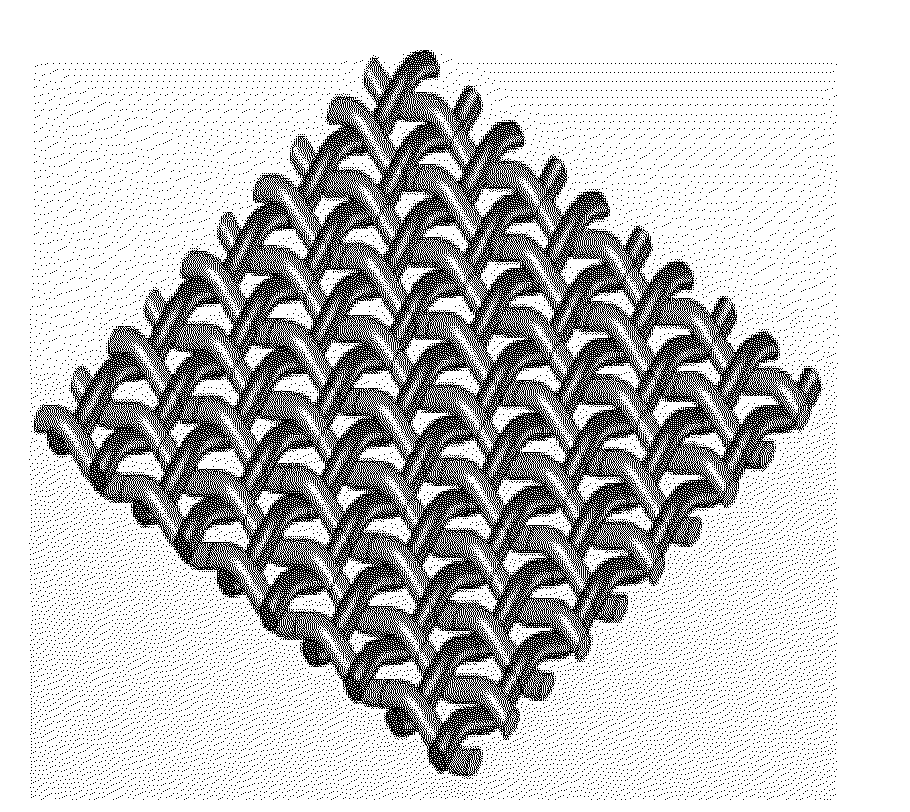
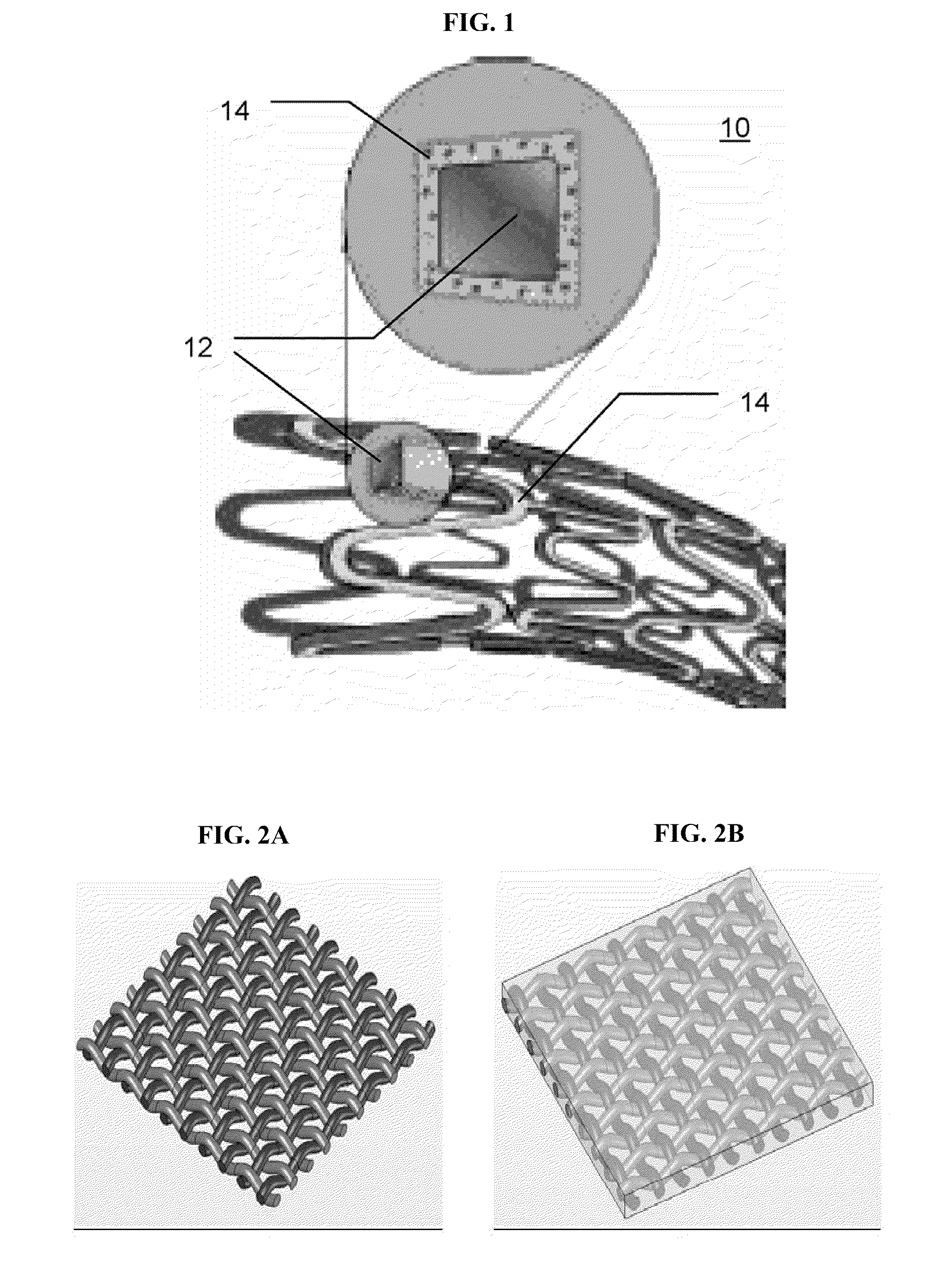
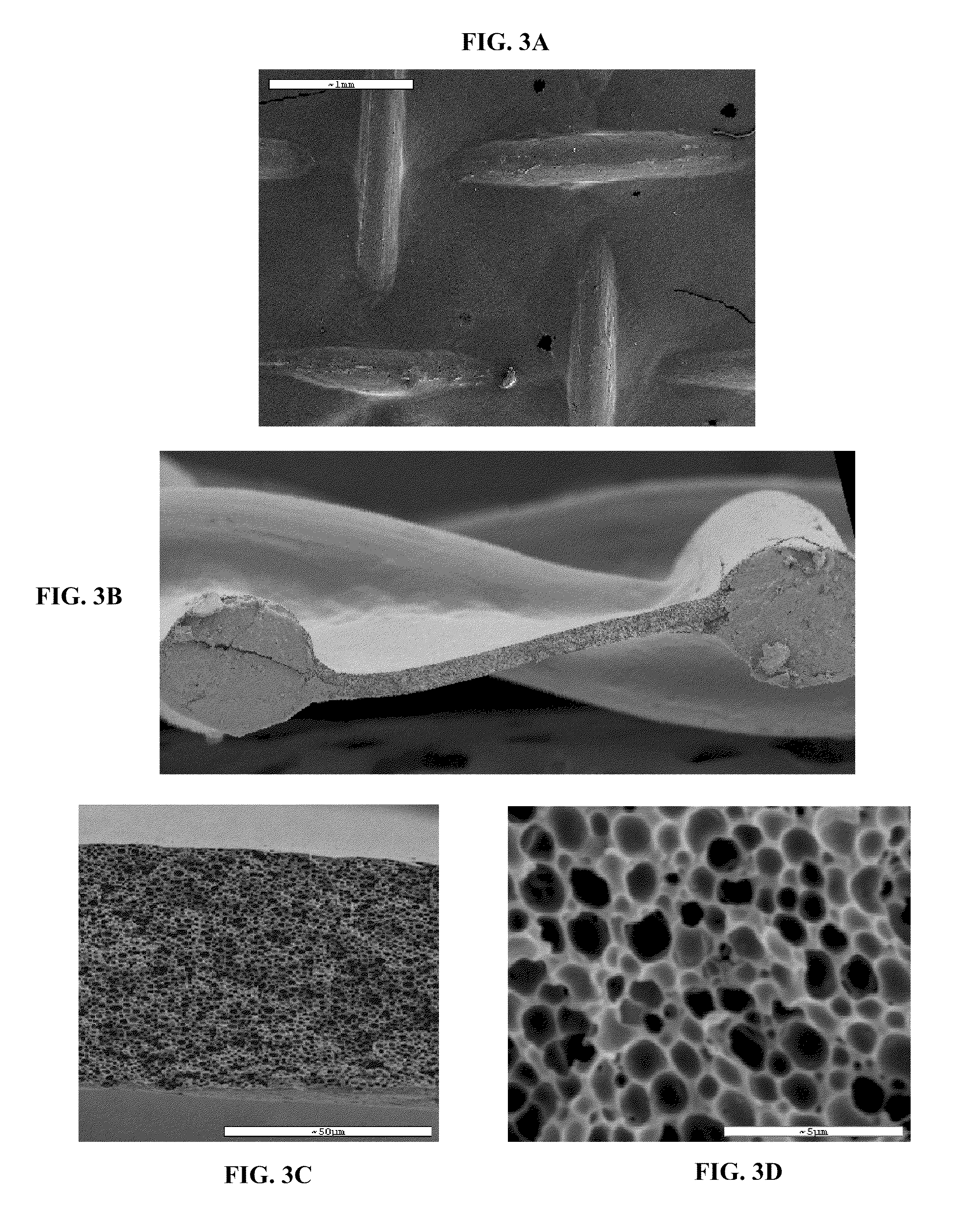
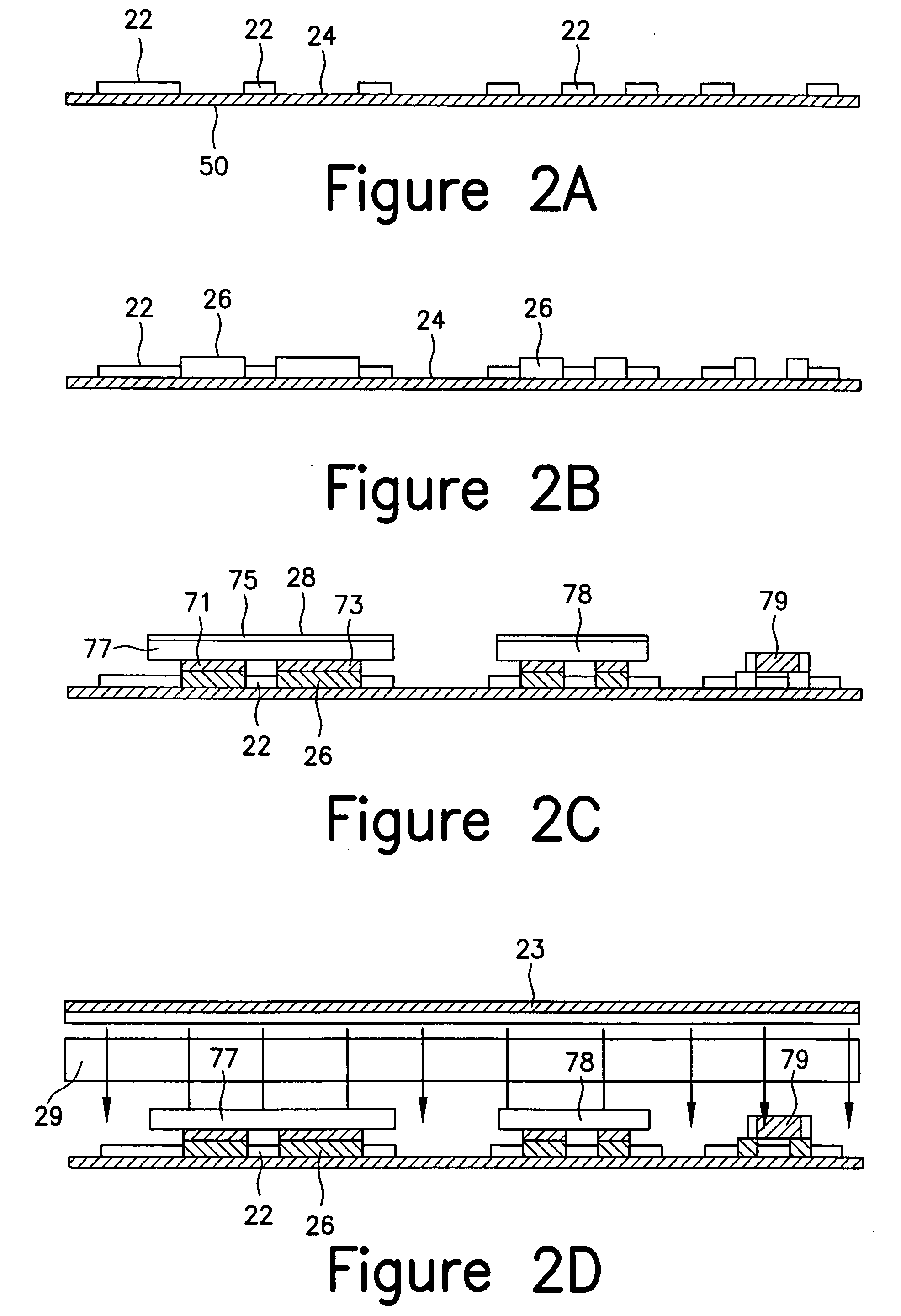
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
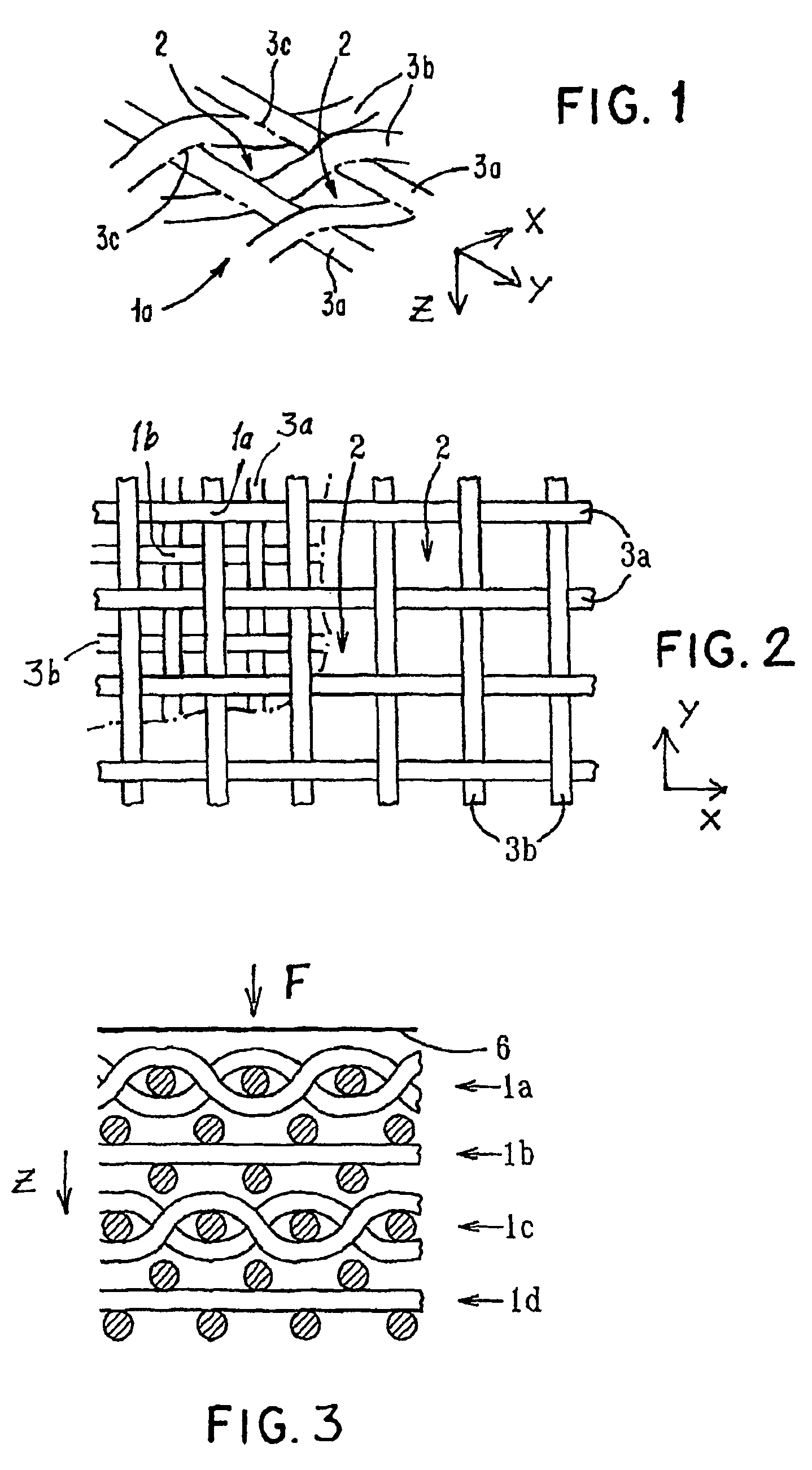
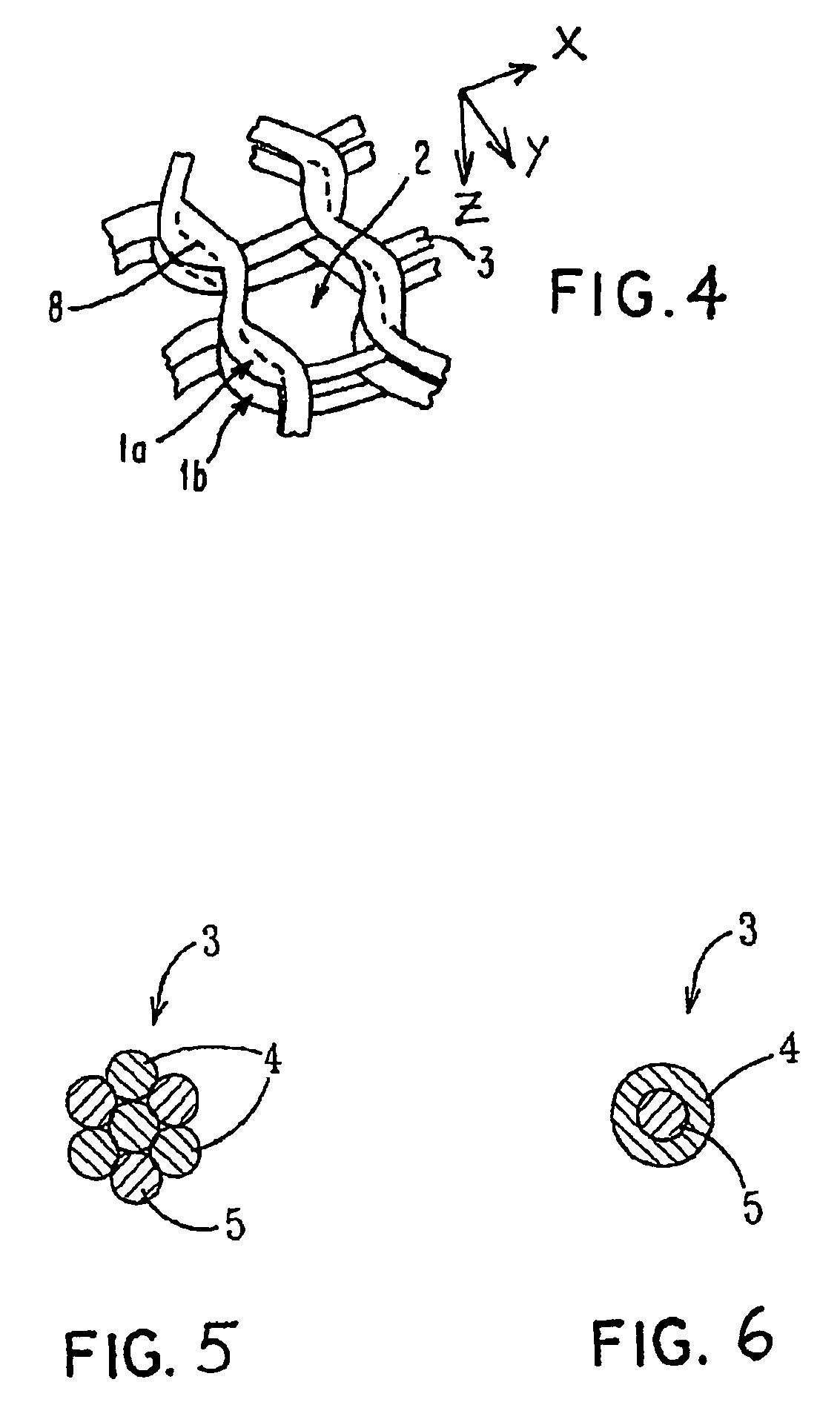
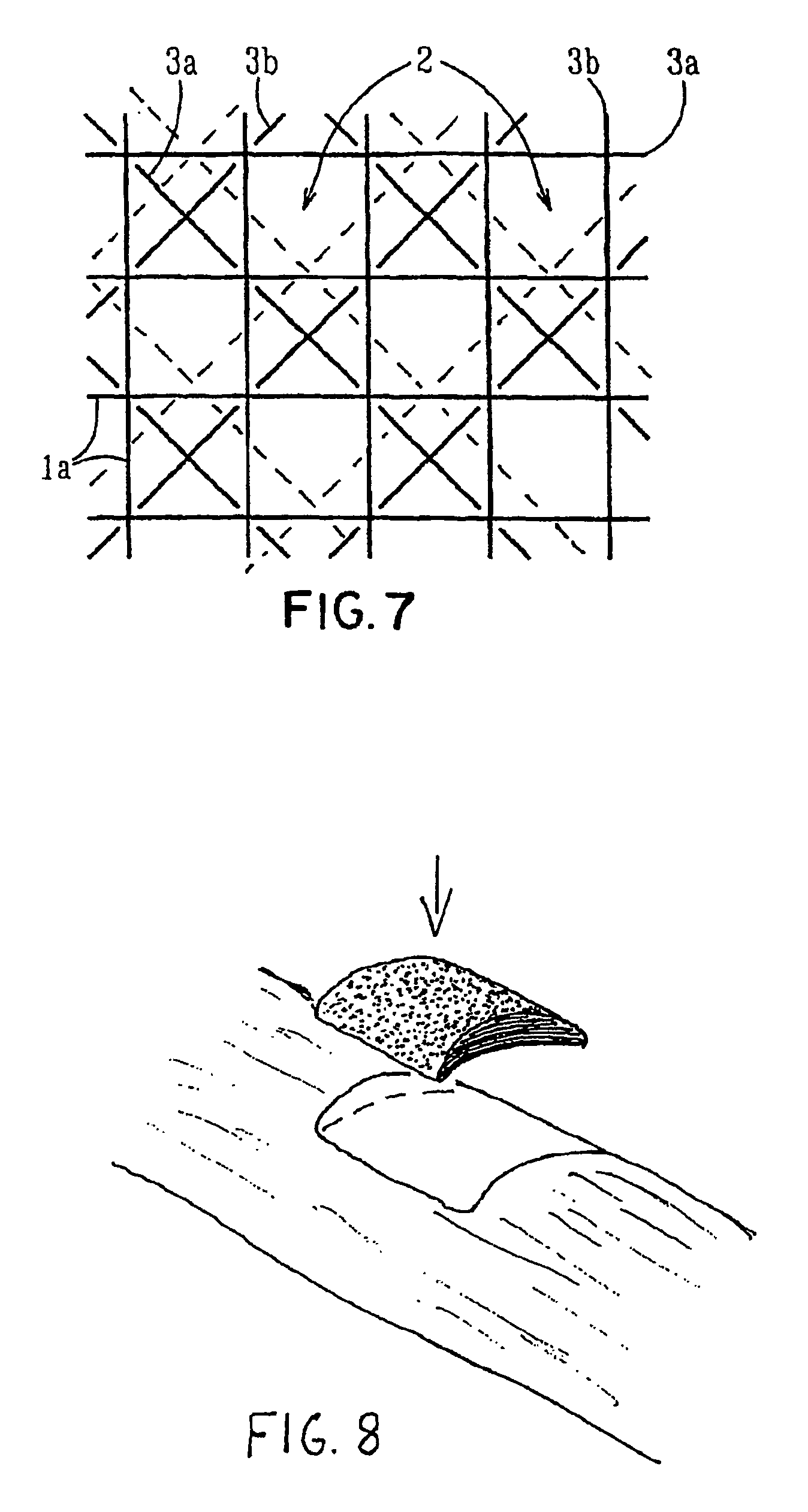
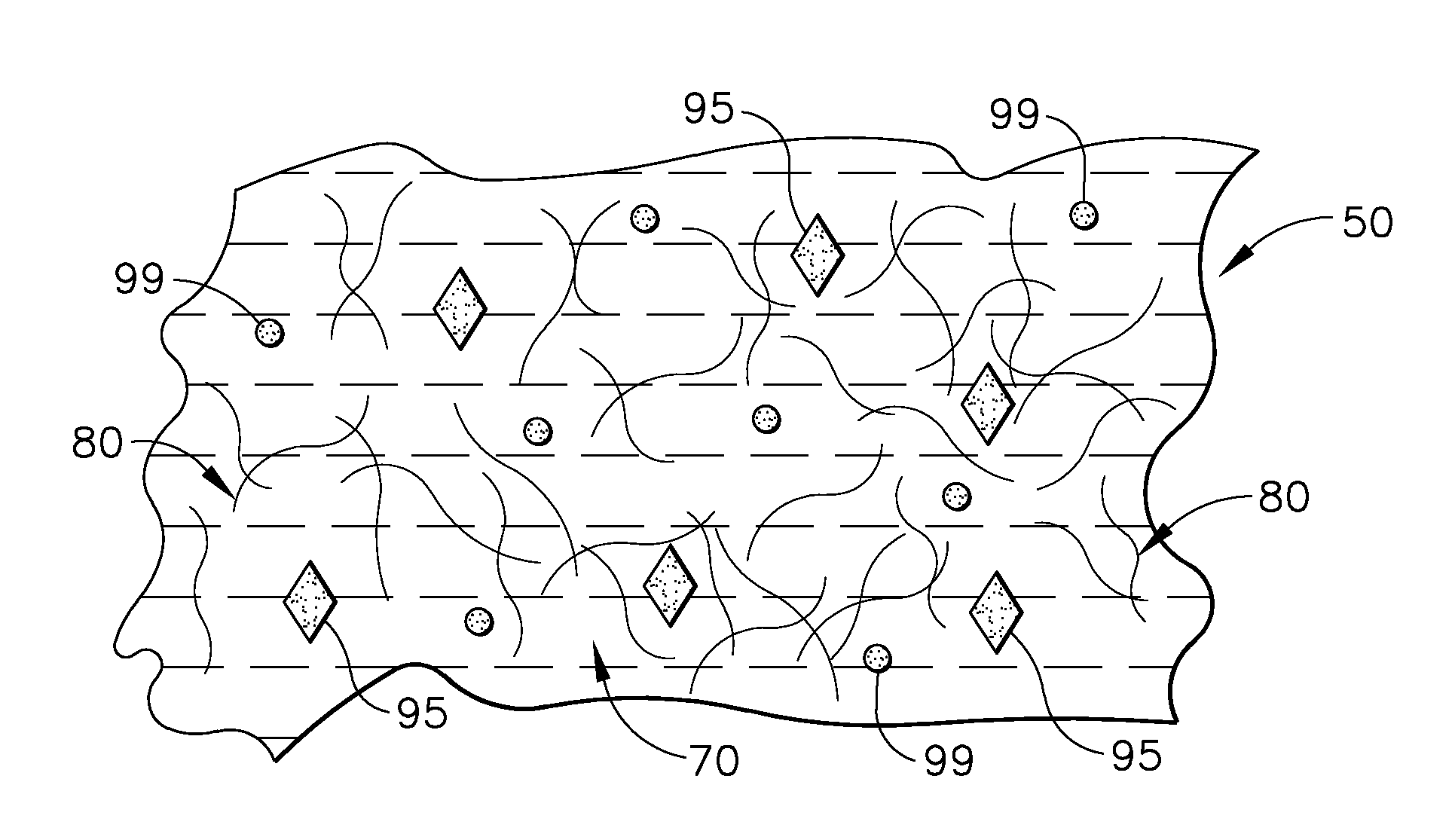
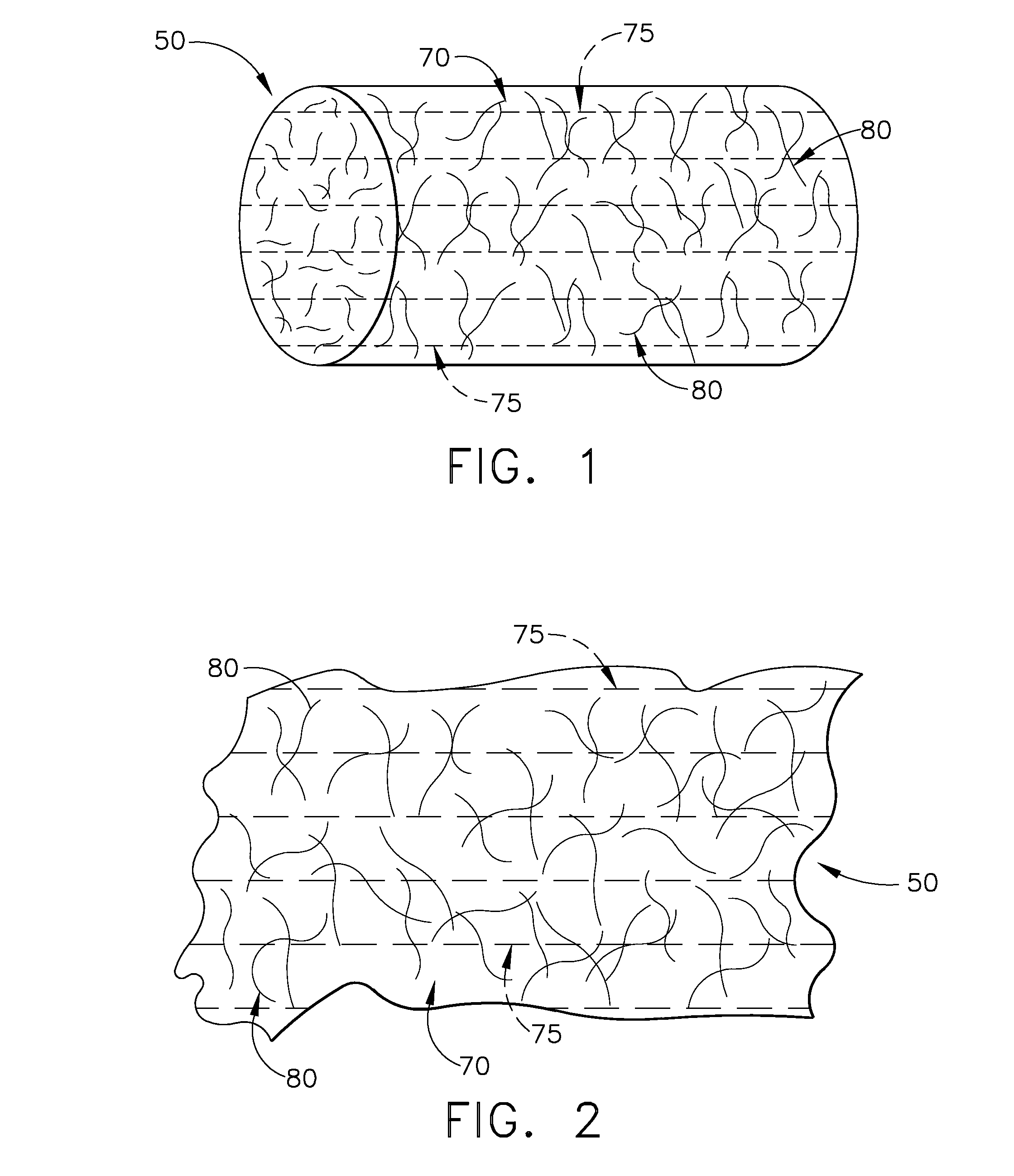
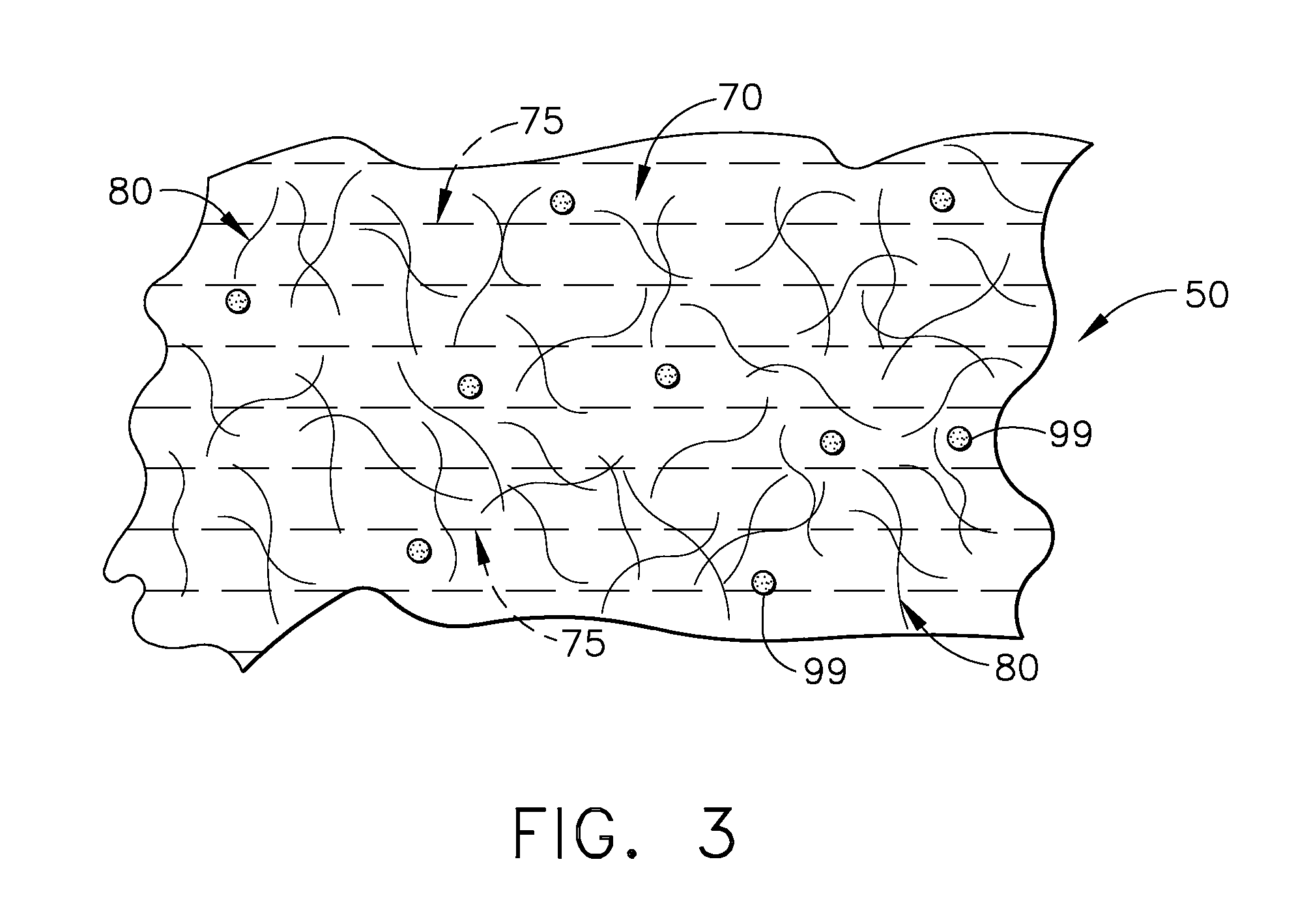
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Drug-eluting medical devices
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
Drug-eluting medical devices
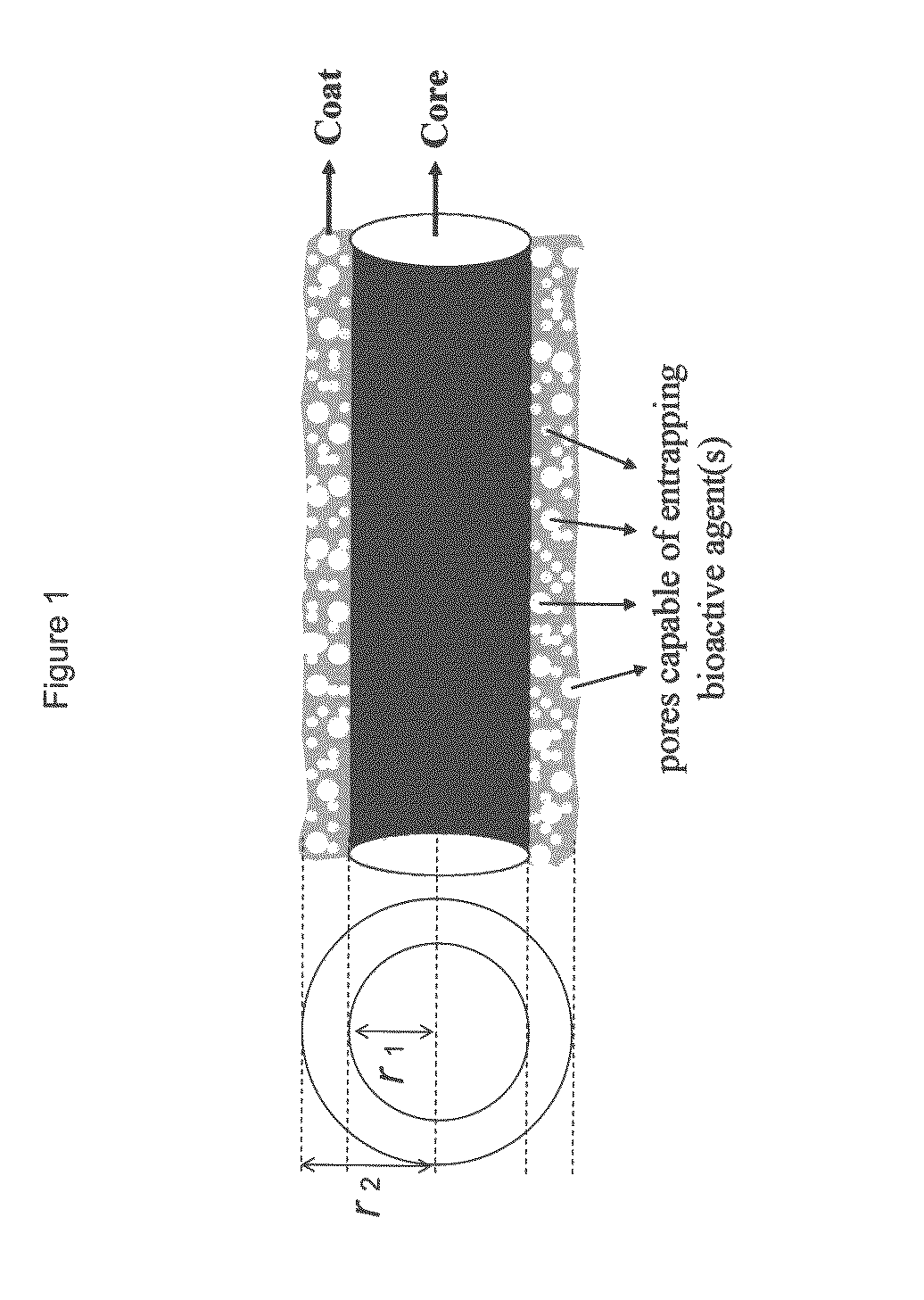
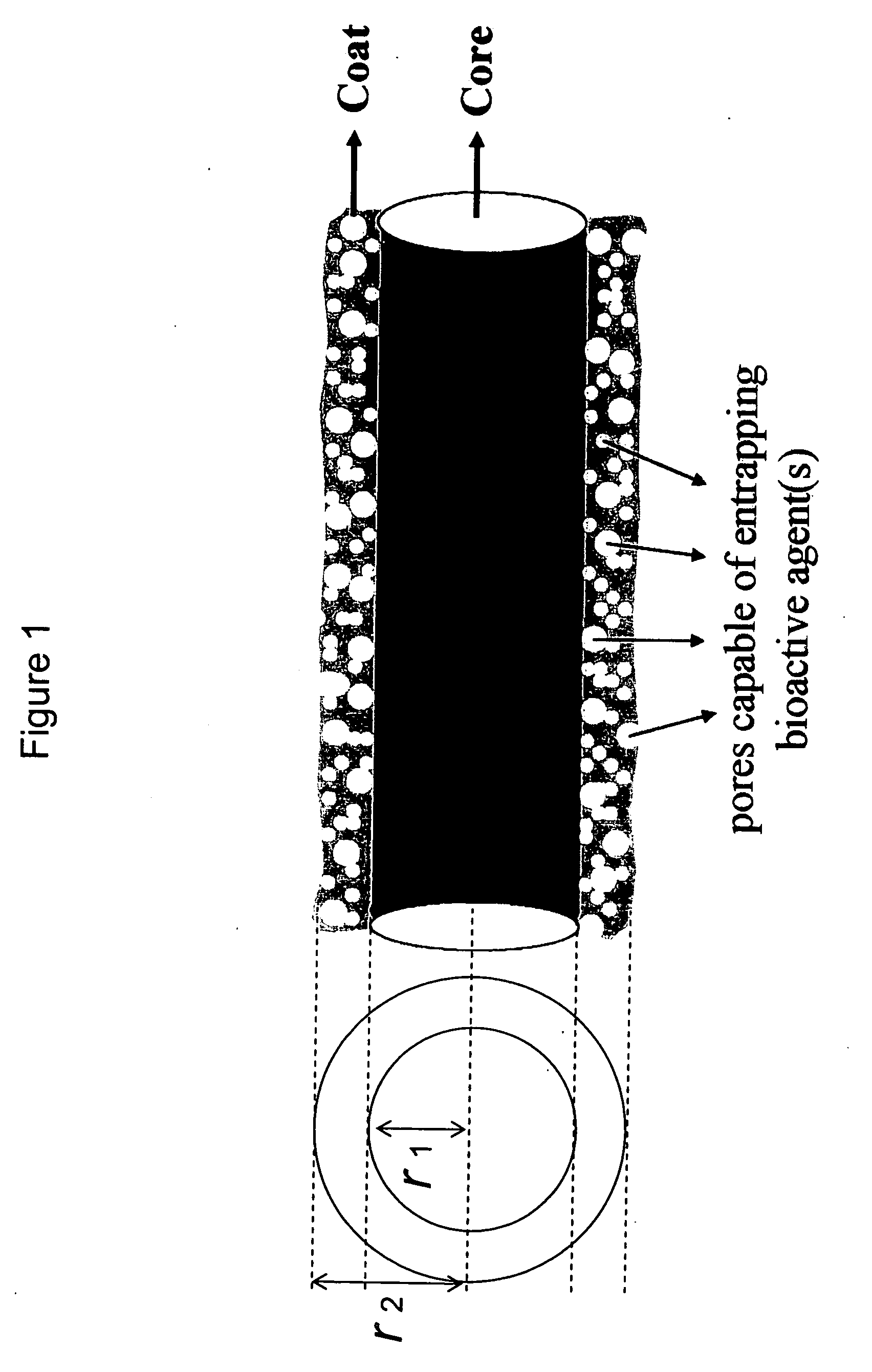
Composite structures composed of a device as a core structure, being a medical device or article, and a porous polymeric coat and designed capable of encapsulating bioactive agents while retaining the activity of these agents are disclosed. Further disclosed are processes of preparing such composite structures.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Drug-delivering composite structures
Composite structures composed of a fibril core and a polymeric coat and designed capable of encapsulating both hydrophobic and hydrophilic bioactive agents while retaining the activity of these agents are disclosed. Further disclosed are processes of preparing such composite structures, and medical devices and disposable articles made therefrom.
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
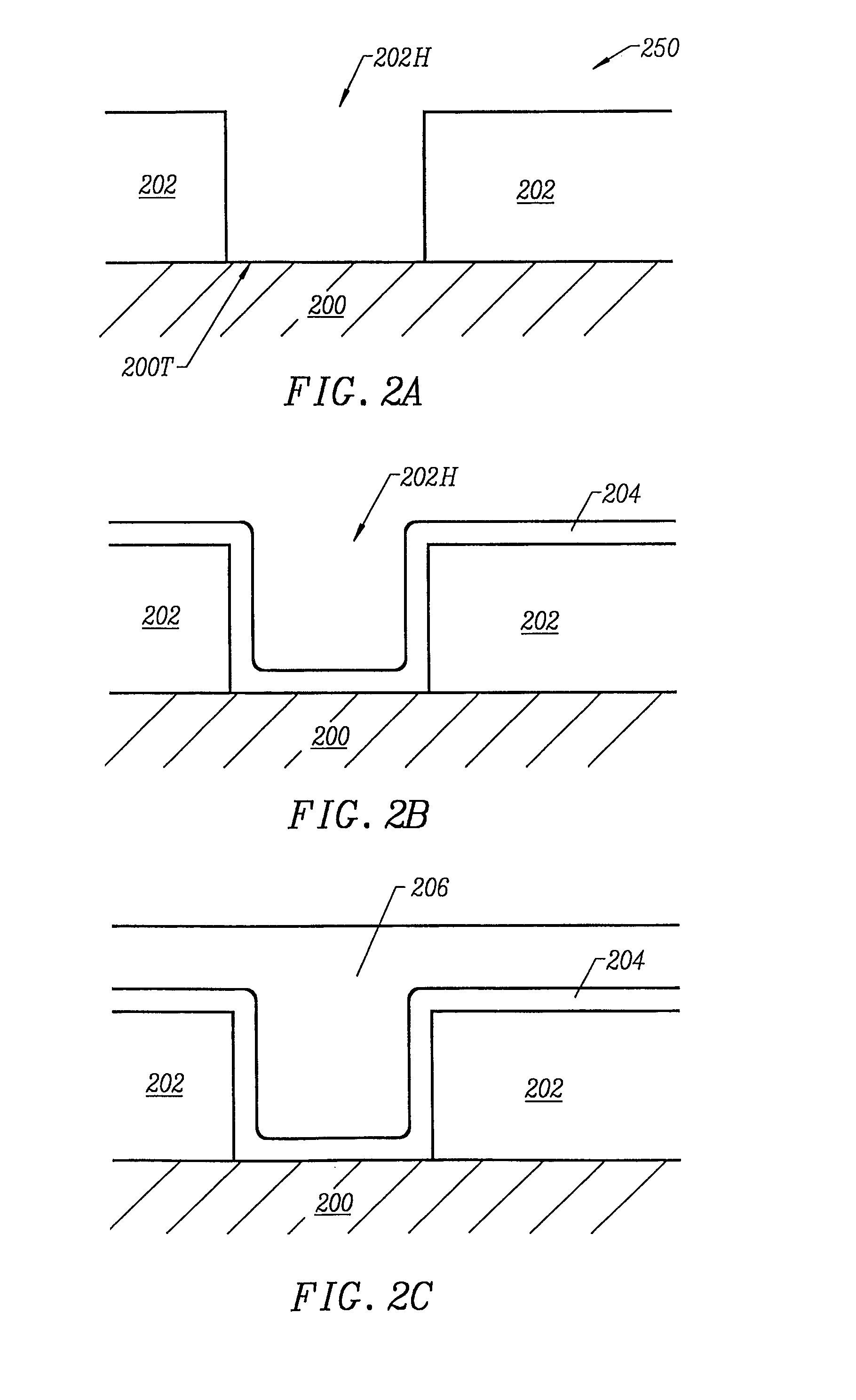
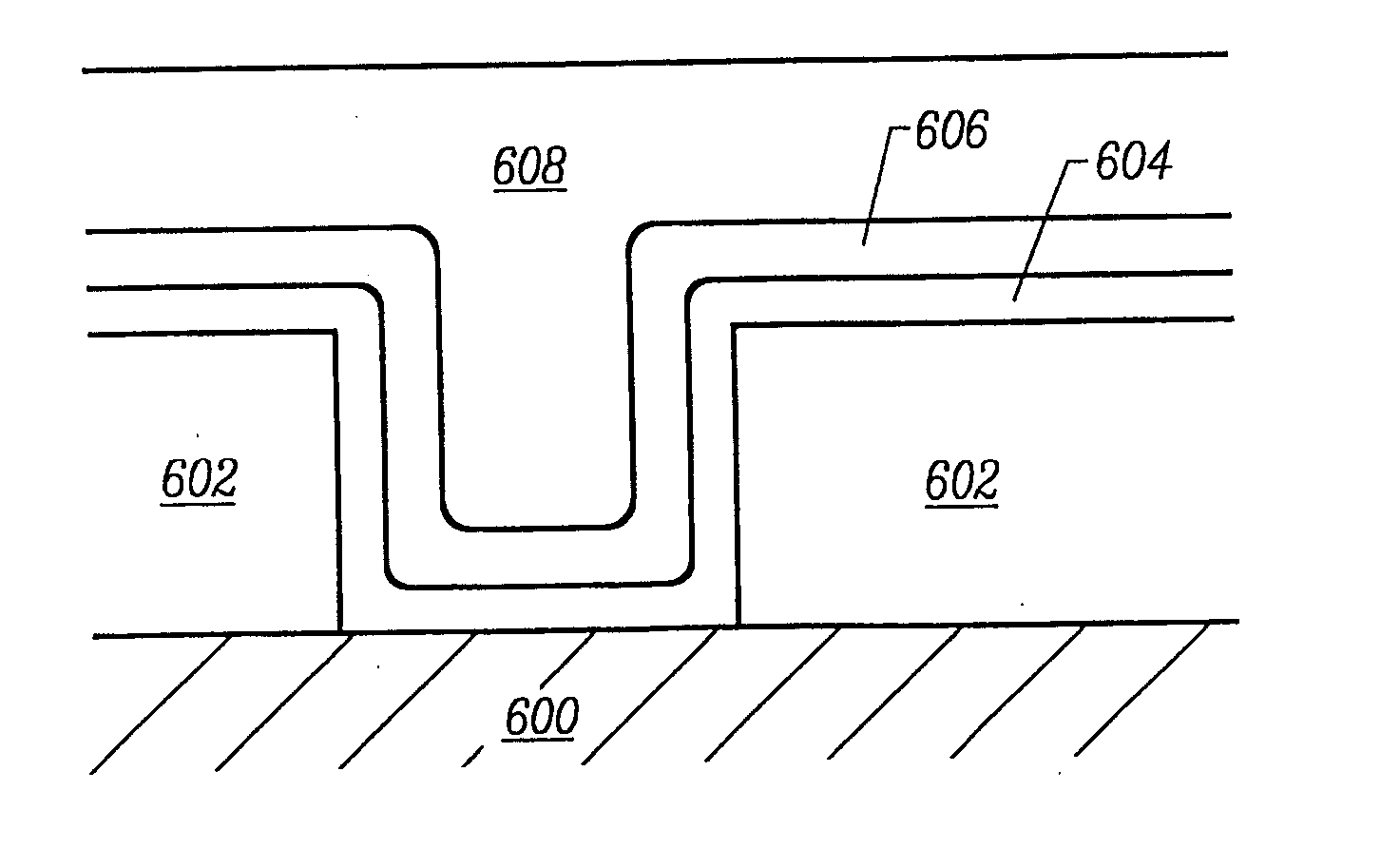
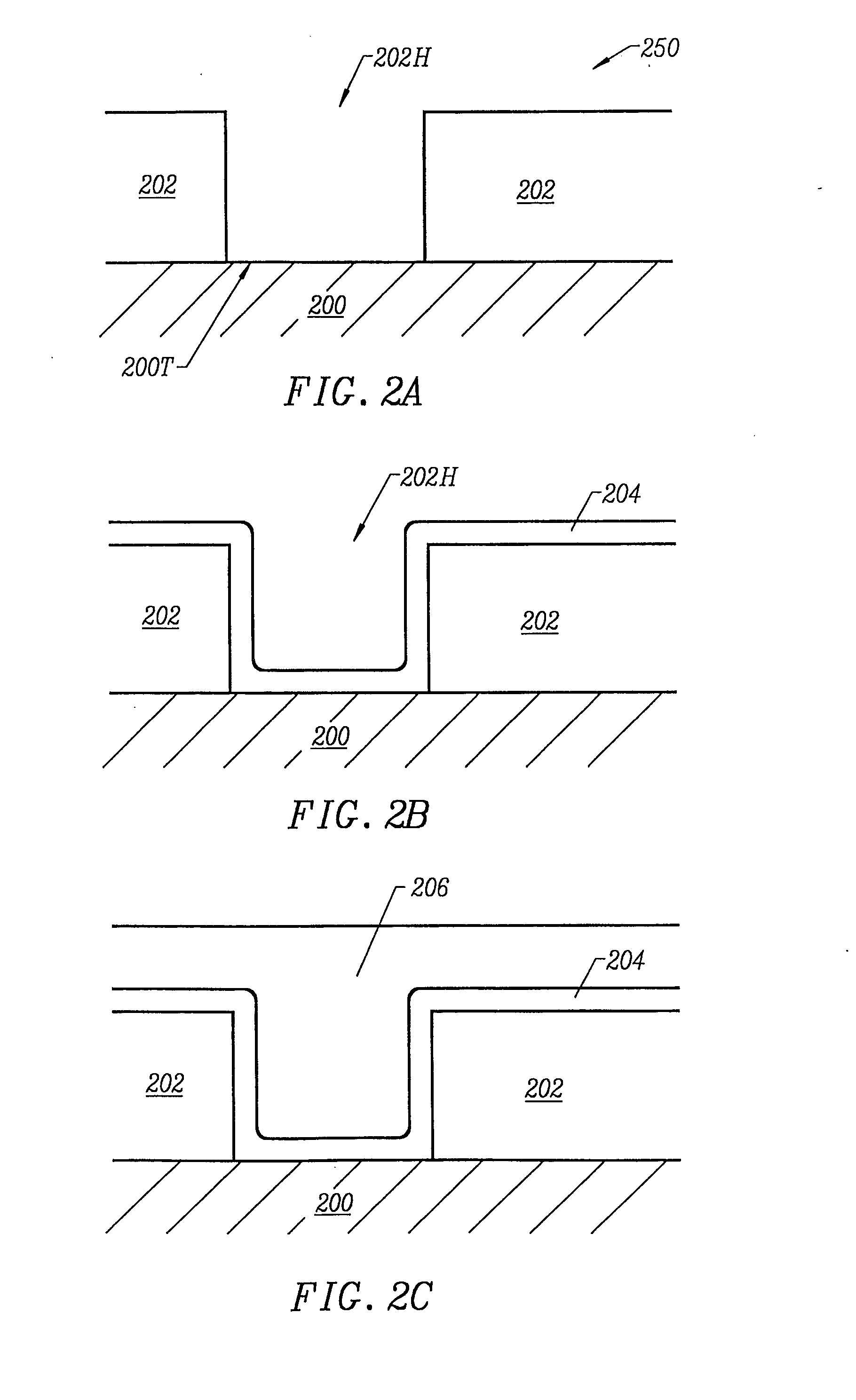
Formation of boride barrier layers using chemisorption techniques
InactiveUS7208413B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBorideBoron containing
A method of forming a boride layer for integrated circuit fabrication is disclosed. In one embodiment, the boride layer is formed by chemisorbing monolayers of a boron-containing compound and one refractory metal compound onto a substrate. In an alternate embodiment, the boride layer has a composite structure. The composite boride layer structure comprises two or more refractory metals. The composite boride layer is formed by sequentially chemisorbing monolayers of a boron compound and two or more refractory metal compounds on a substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Formation of boride barrier layers using chemisorption techniques
InactiveUS20050118804A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingBorideChemisorption
A method of forming a boride layer for integrated circuit fabrication is disclosed. In one embodiment, the boride layer is formed by chemisorbing monolayers of a boron-containing compound and one refractory metal compound onto a substrate. In an alternate embodiment, the boride layer has a composite structure. The composite boride layer structure comprises two or more refractory metals. The composite boride layer is formed by sequentially chemisorbing monolayers of a boron compound and two or more refractory metal compounds on a substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
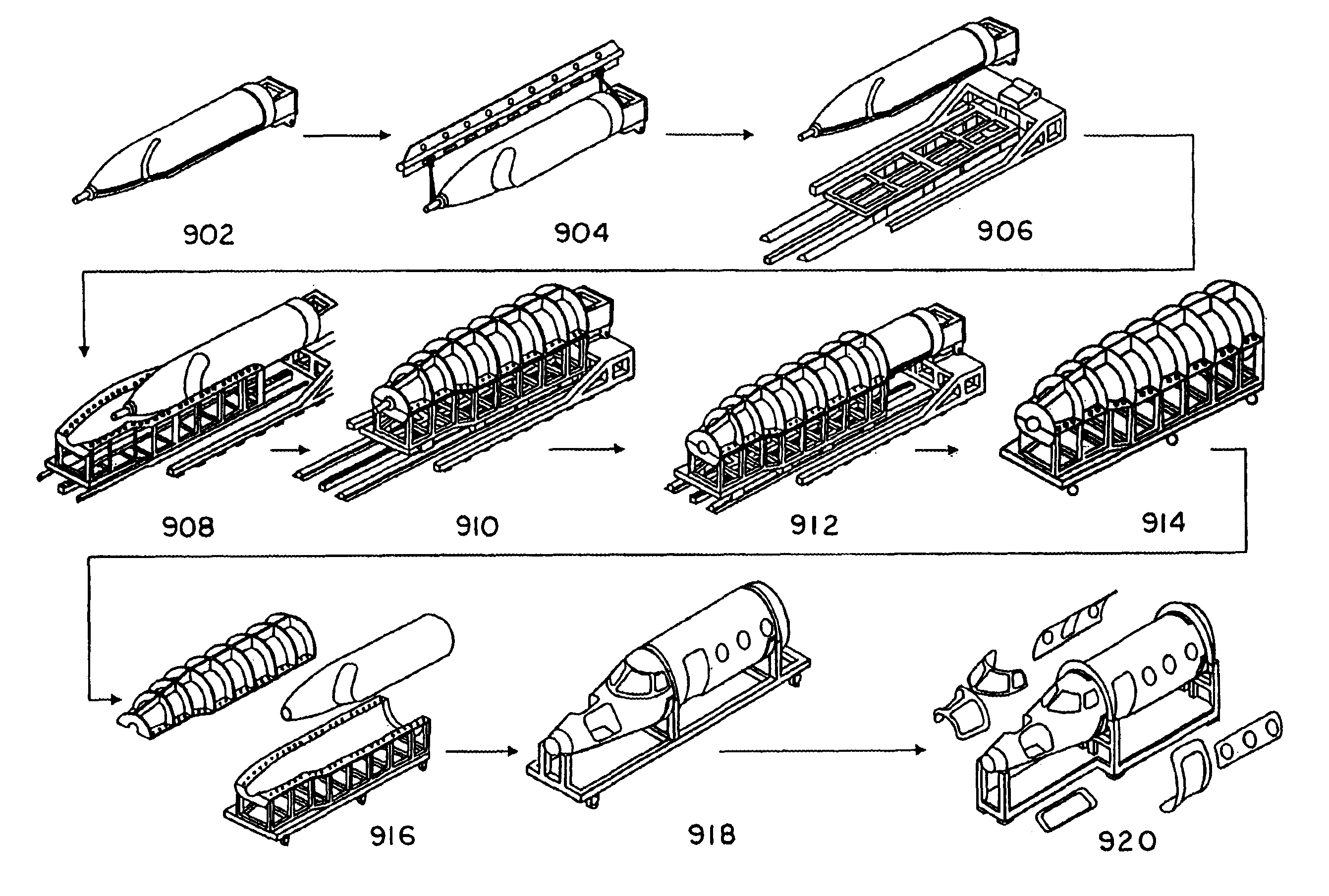
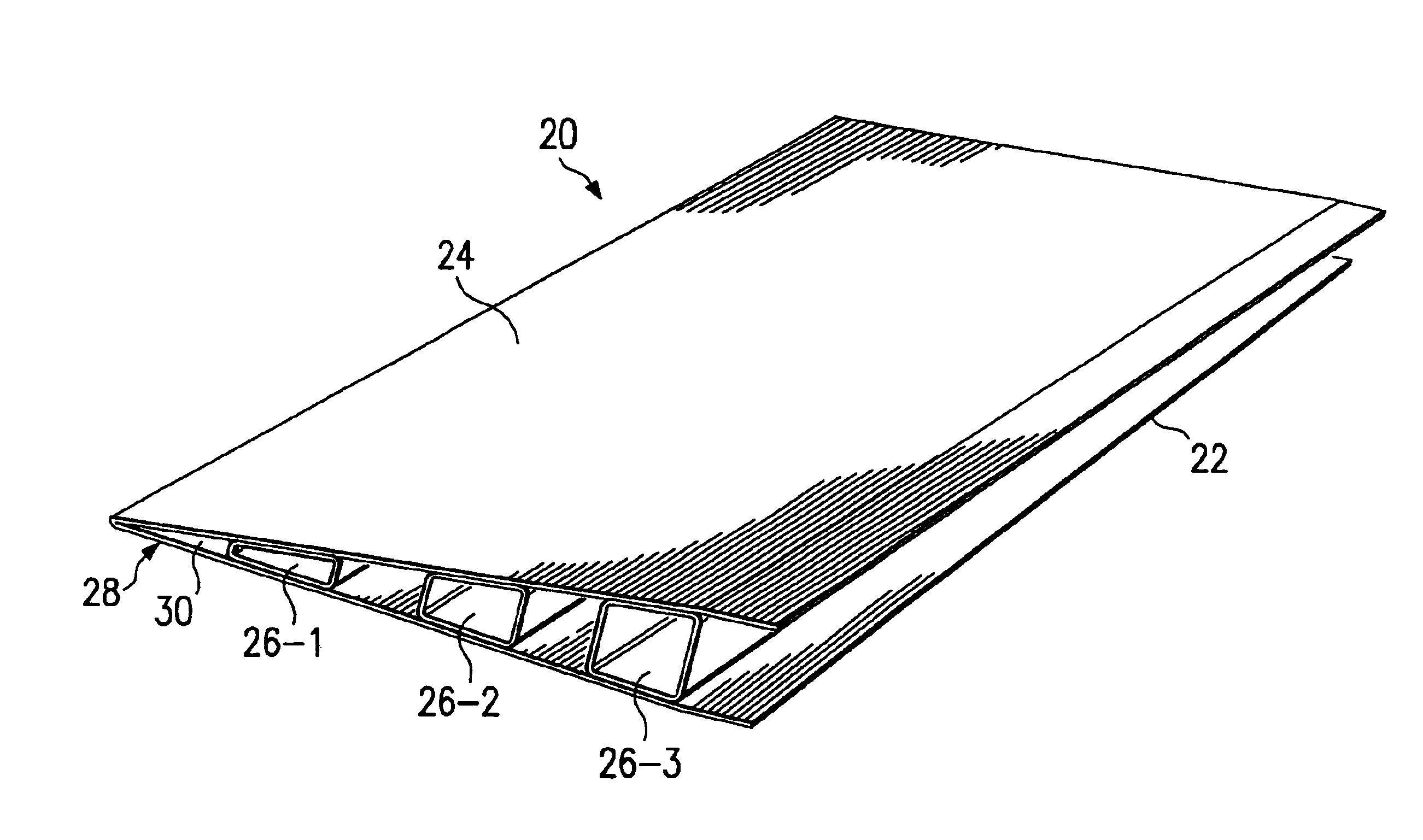
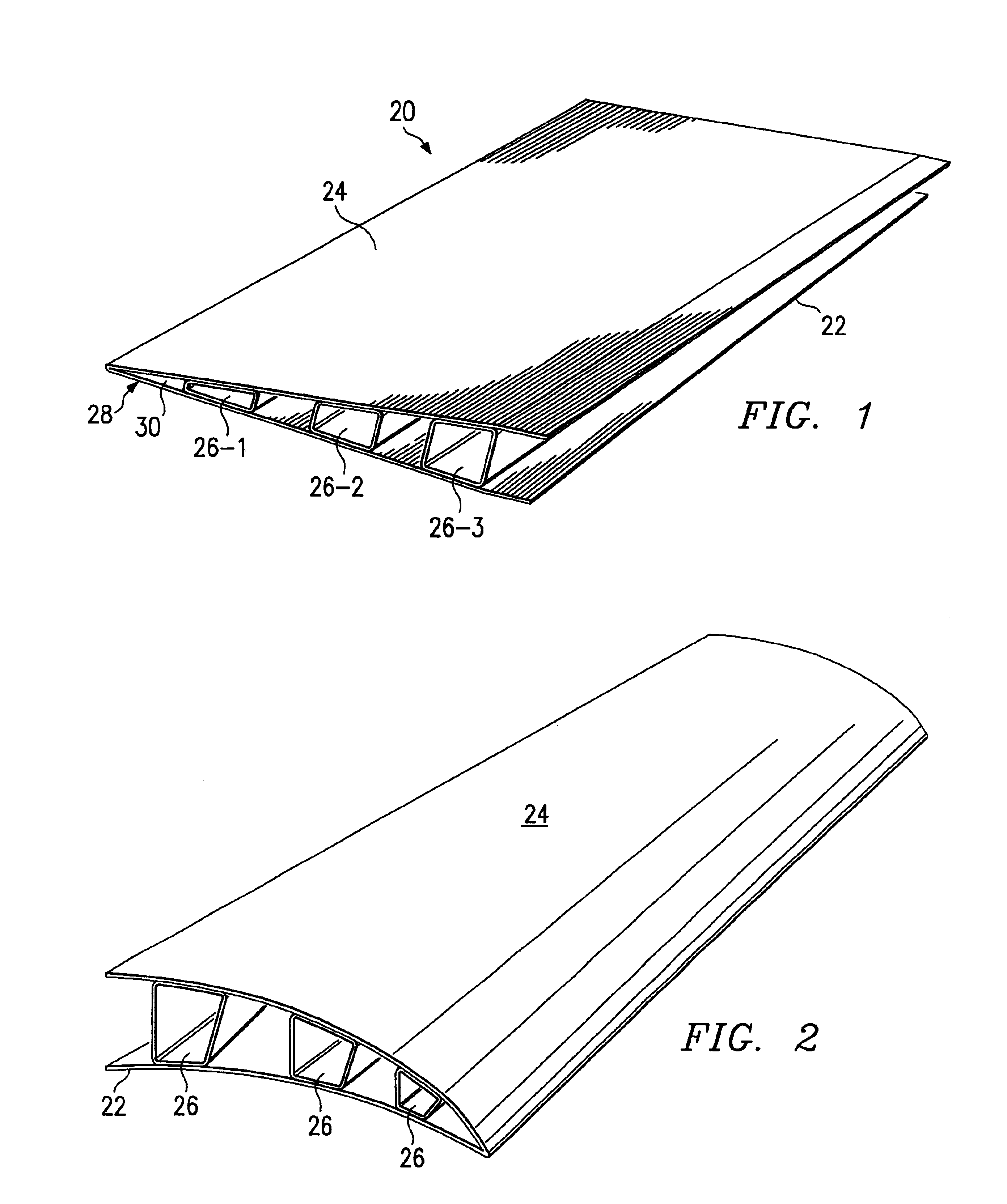
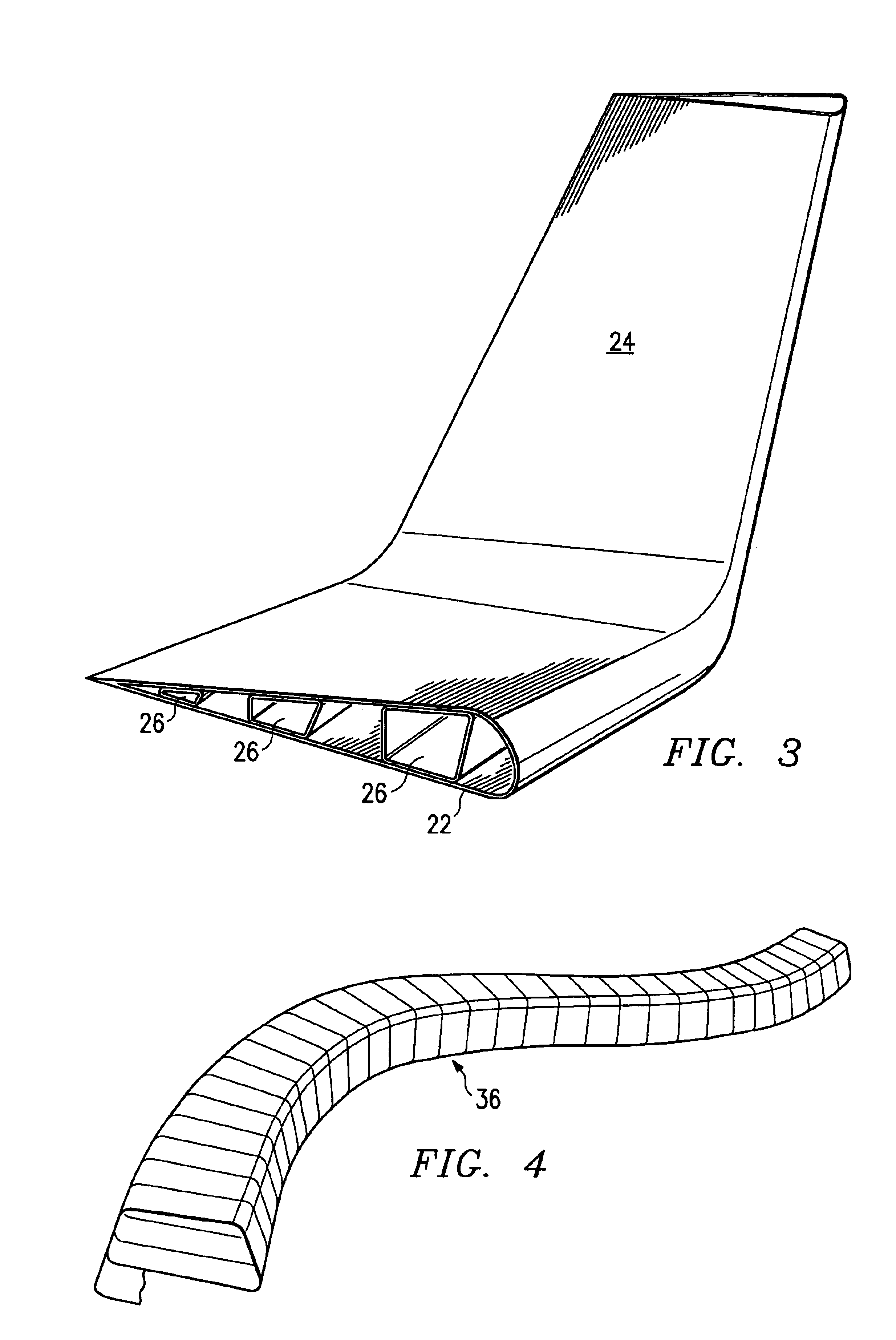
Method and apparatus for manufacturing composite structures
Composite structures having a single continuous skin may be formed using automated fiber placement methods. These composite structures include frameless aircraft fuselage components offering an increased interior cabin width over conventional fuselage components. The composite structures may be constructed of multiple layers of fibers and other materials placed on a fiber placement tool that includes a mandrel body surrounded by a bladder or an integral bladder / caul sheet having expansion spaces created within the caul sheet section. Uncured composite structures may be created by placing fibers around the fiber placement tool in a plurality of discontinuous segments that are capable of moving or sliding in relation to each other so that the uncured composite structure is expandable from within. Fluid openings may be provided in the outer surface of the mandrel body for the application of vacuum and / or fluid pressure to secure the bladder to the mandrel body and to assist in the removal of the bladder from the mandrel body, respectively. Uncured composite structures may be sealed between the bladder and is clam shell molds. The uncured structures may be expanded against the inner surface of the molds by creating a vacuum between the bladder and molds.
Owner:BEECHCRAFT
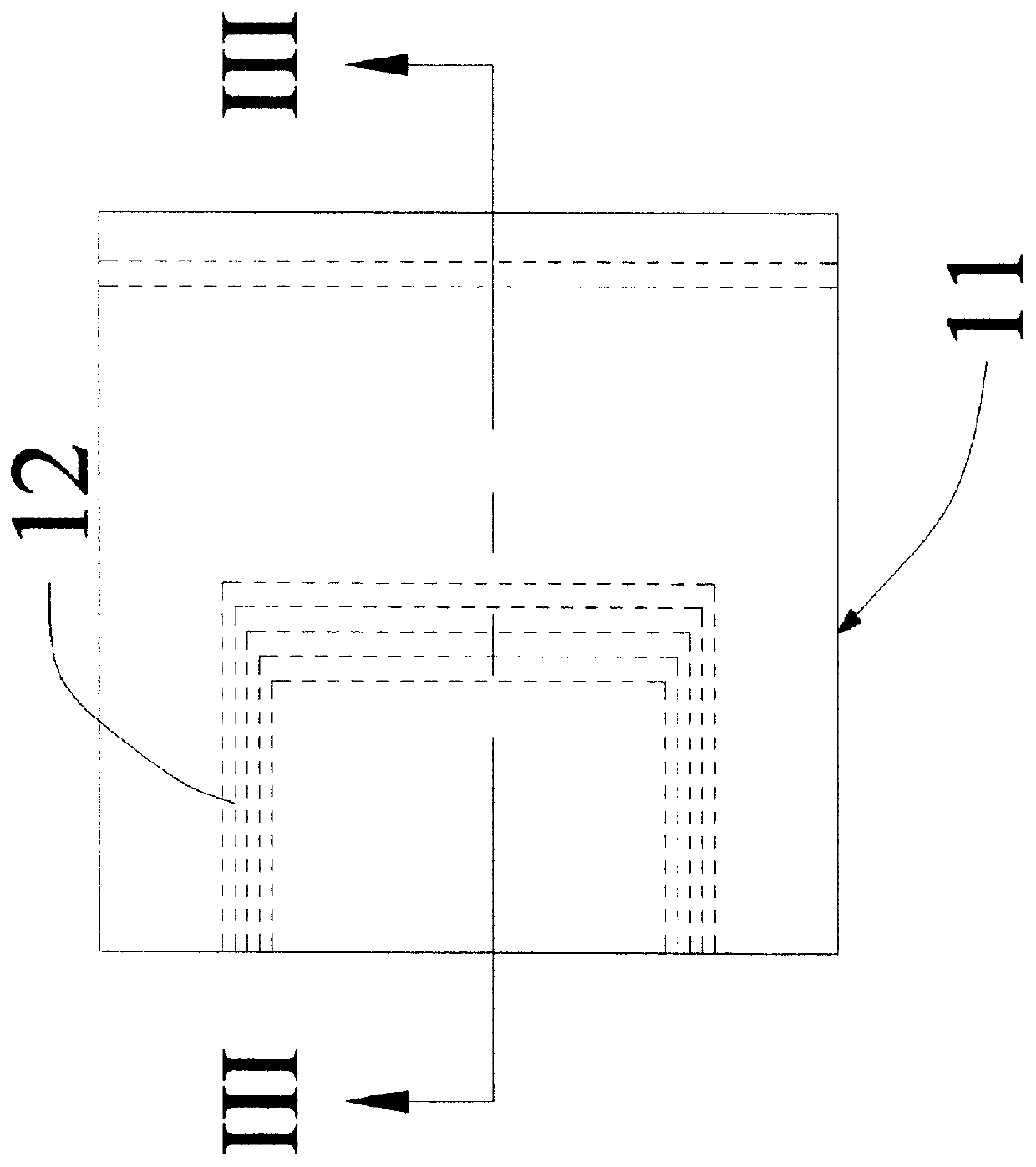
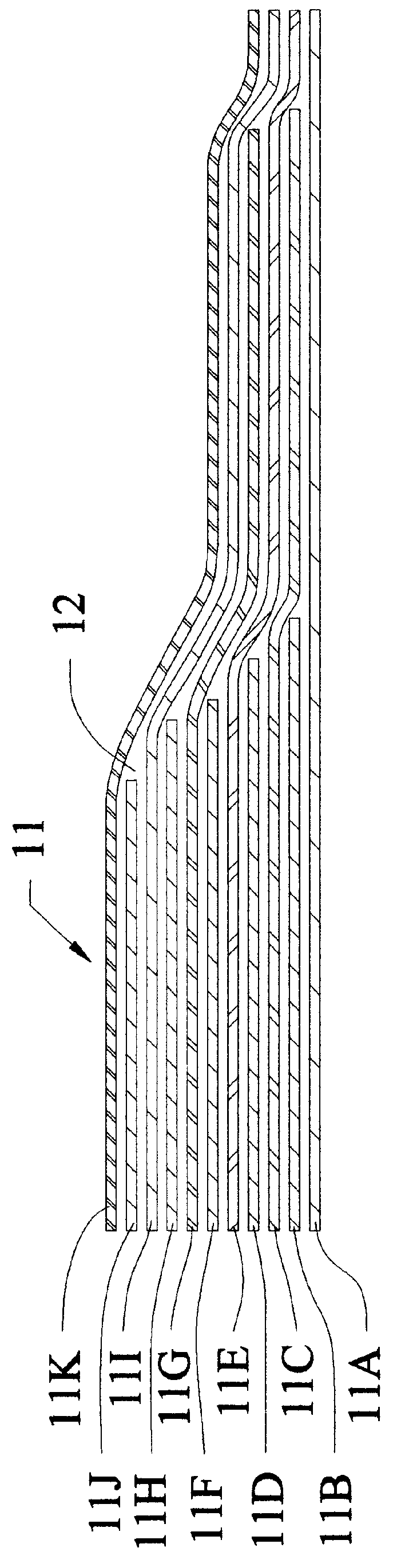
Intravascular deliverable stent for reinforcement of vascular abnormalities
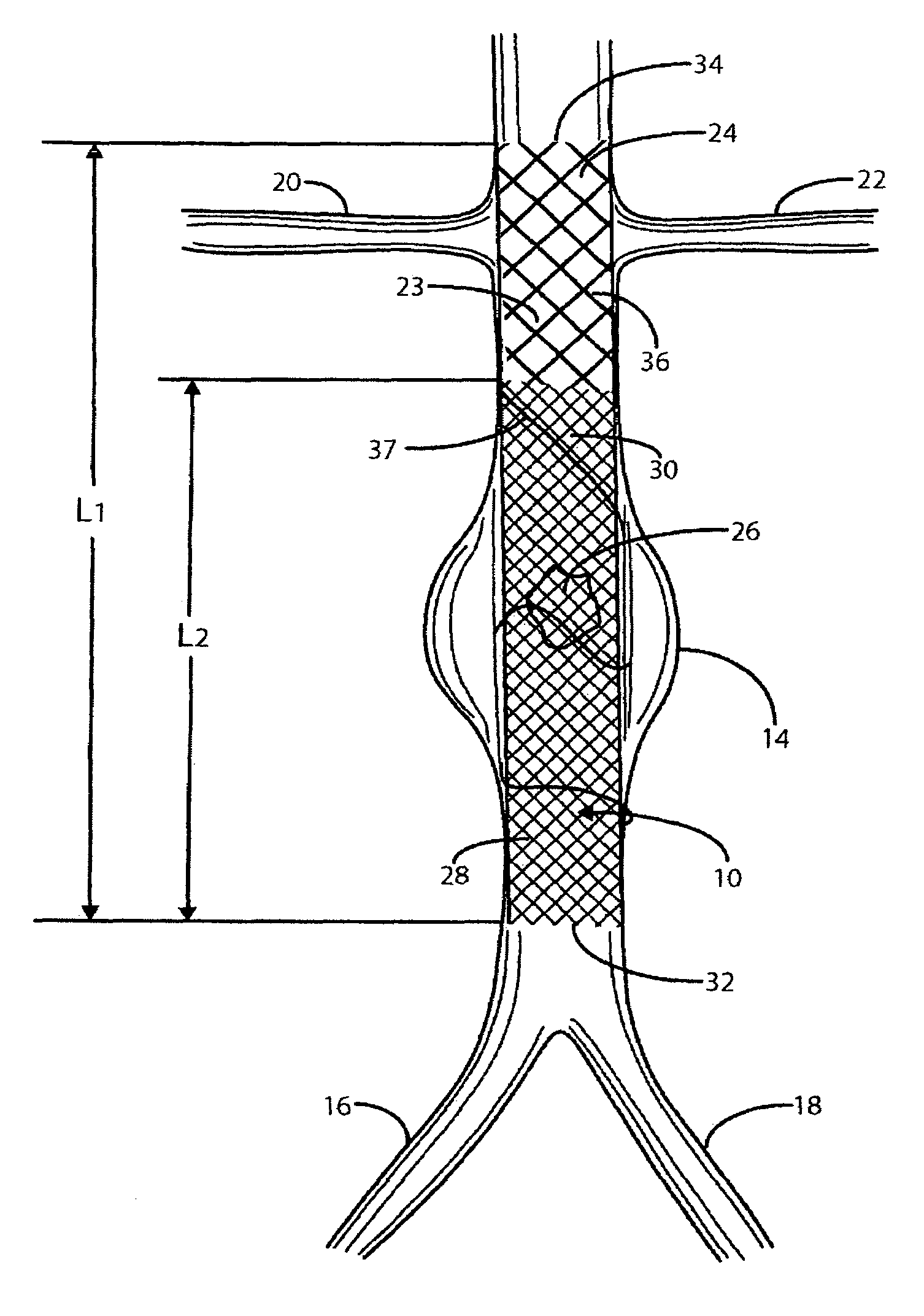
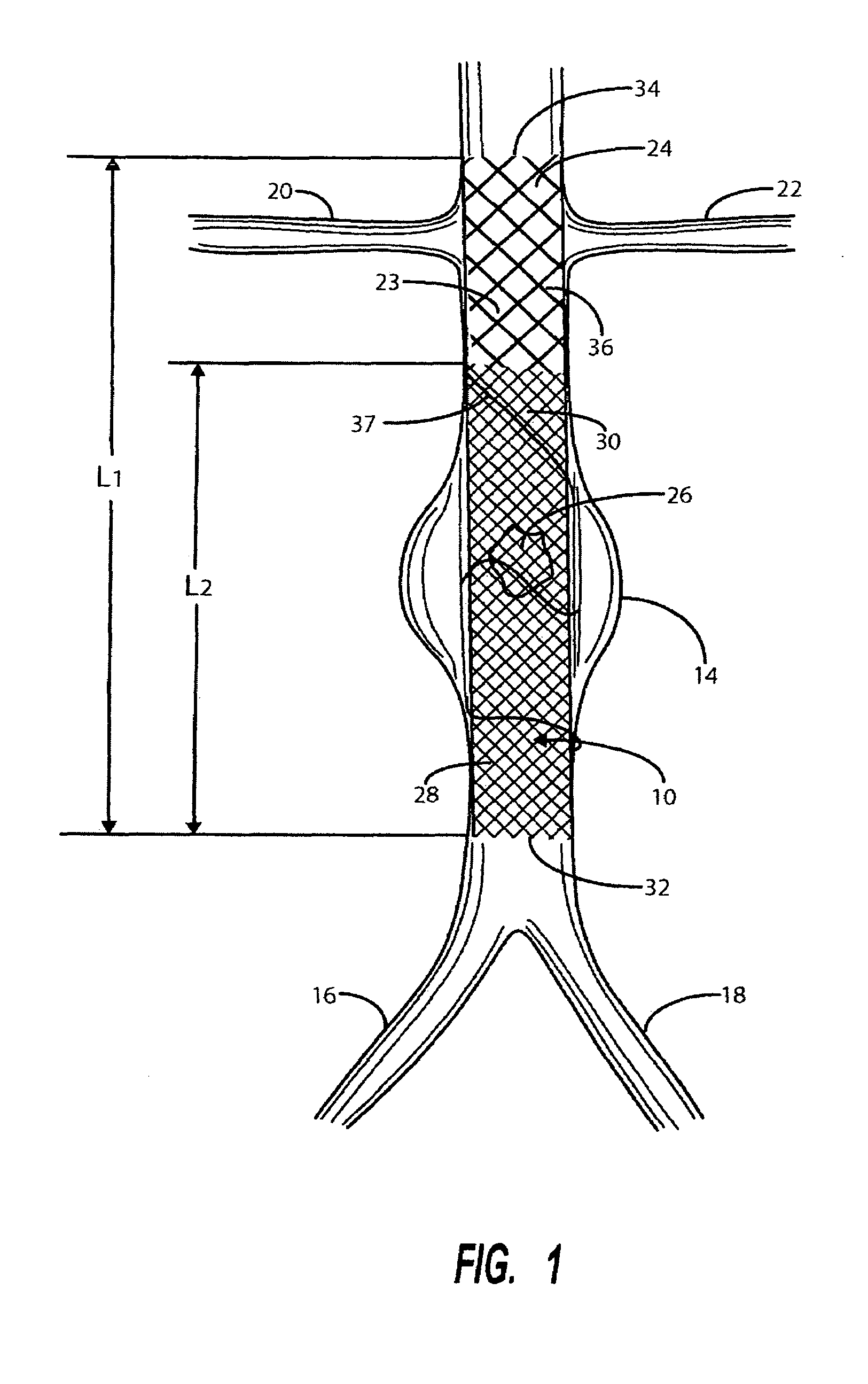
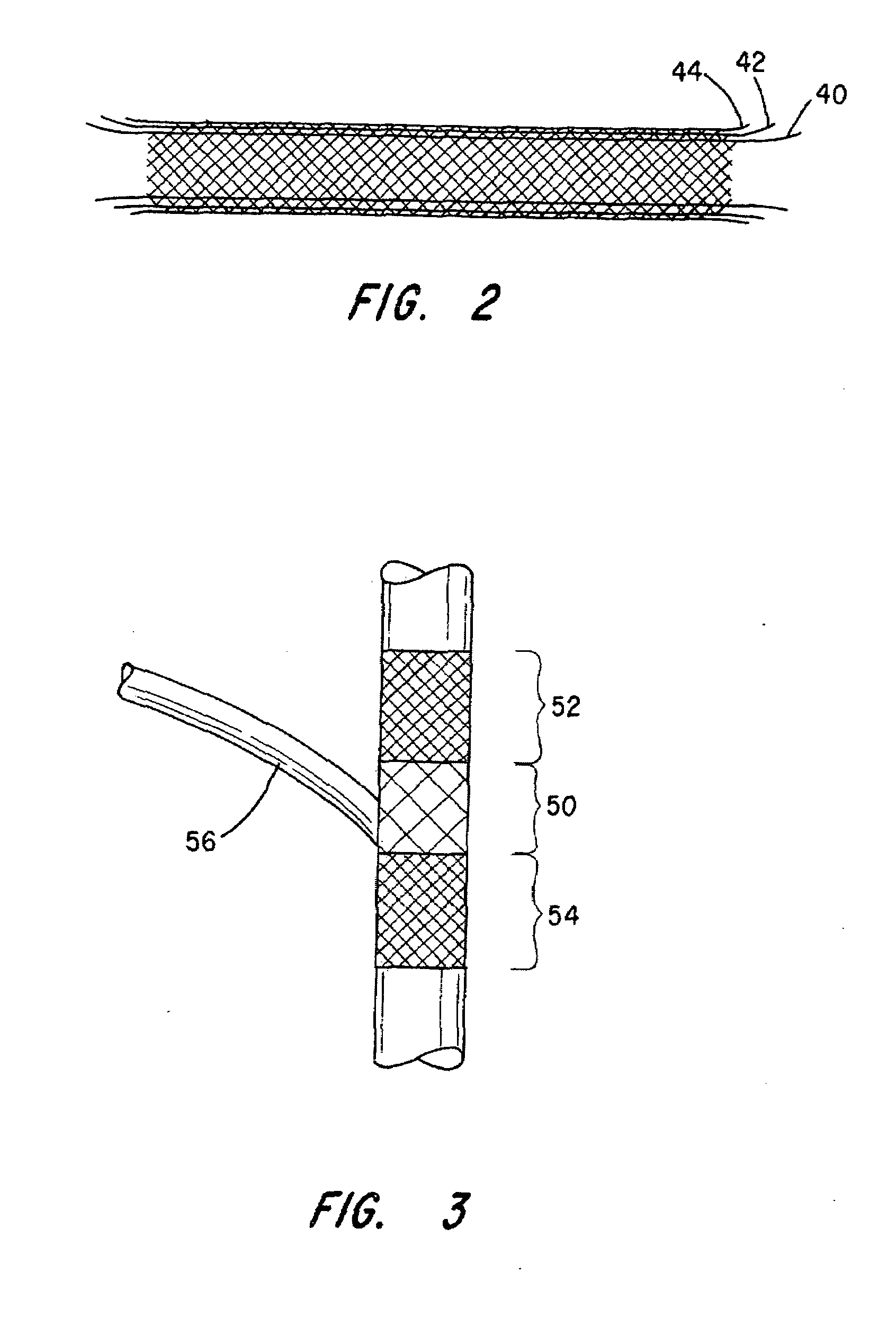
InactiveUS20070168019A1Avoid interactionReduce overall outer diameterStentsCatheterVascular Skin TumorSaphenous veins
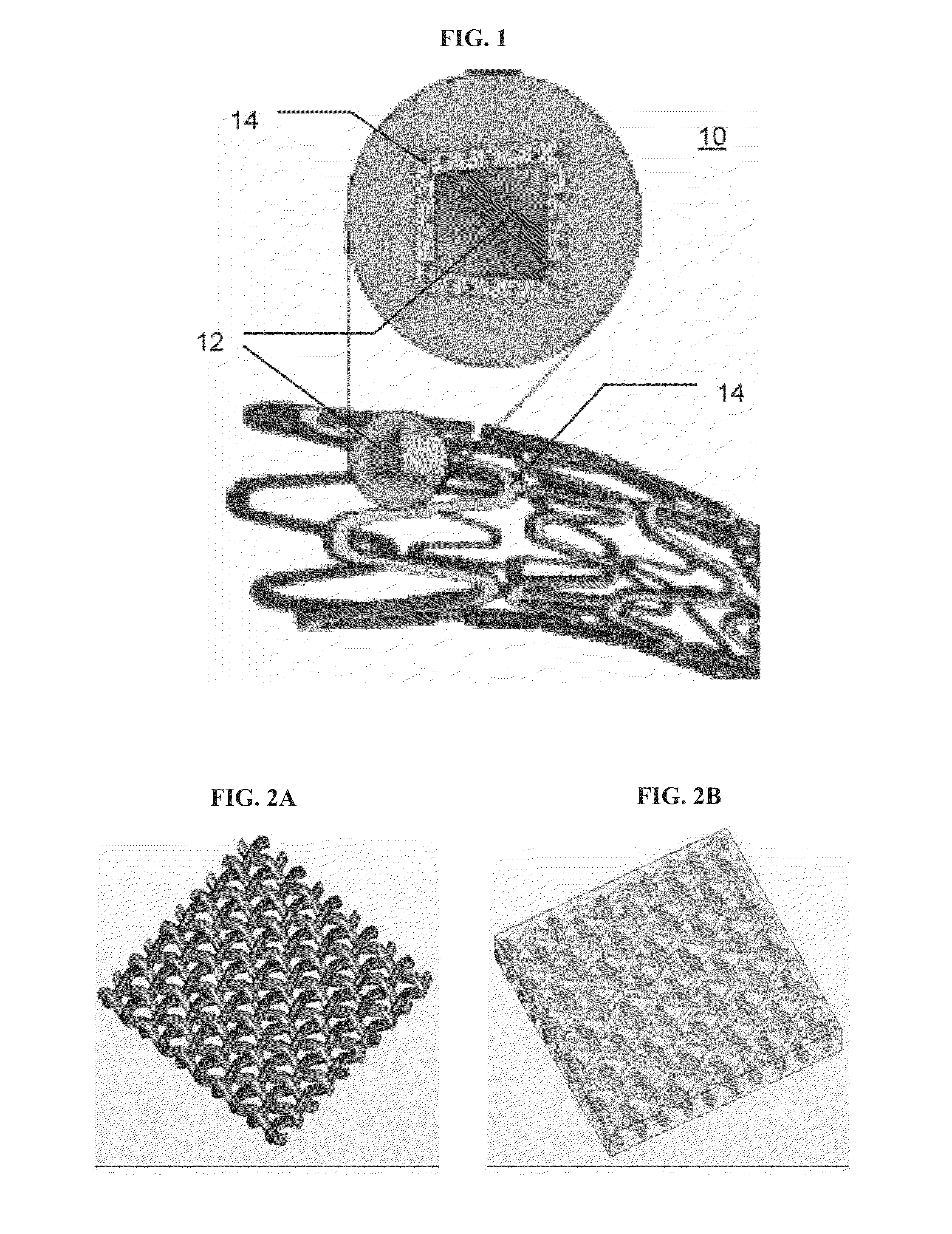
A catheter deliverable stent / graft especially designed to be used in a minimally invasive surgical procedure for treating a variety of vascular conditions such as aneurysms, stenotic lesions and saphenous vein grafts, comprises an innermost tubular structure and at least one further tubular member in coaxial arrangement. In one embodiment, the innermost tubular structure is of a length (L1) and is formed by braiding a relatively few strands of highly elastic metallic alloy. The pick and pitch of the braid are such as to provide relative large fenestrations in the tubular wall that permit blood flow through the wall and provide the primary radial support structure. A portion of the innermost tubular structure of a length L1 is surrounded by a further braided tubular structure having relatively many strands that substantially inhibit blood flow through the fenestrations of the innermost tubular structure. The composite structure can be stretched to reduce the outer diameter of the stent / graft, allowing it to be drawn into a lumen of a delivery catheter. The catheter can then be advanced through the vascular system to the site of treatment and then released, allowing it to self-expand against the vessel wall. Various optional embodiments are disclosed that allow one skilled in the art to tailor the design to the specific application.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
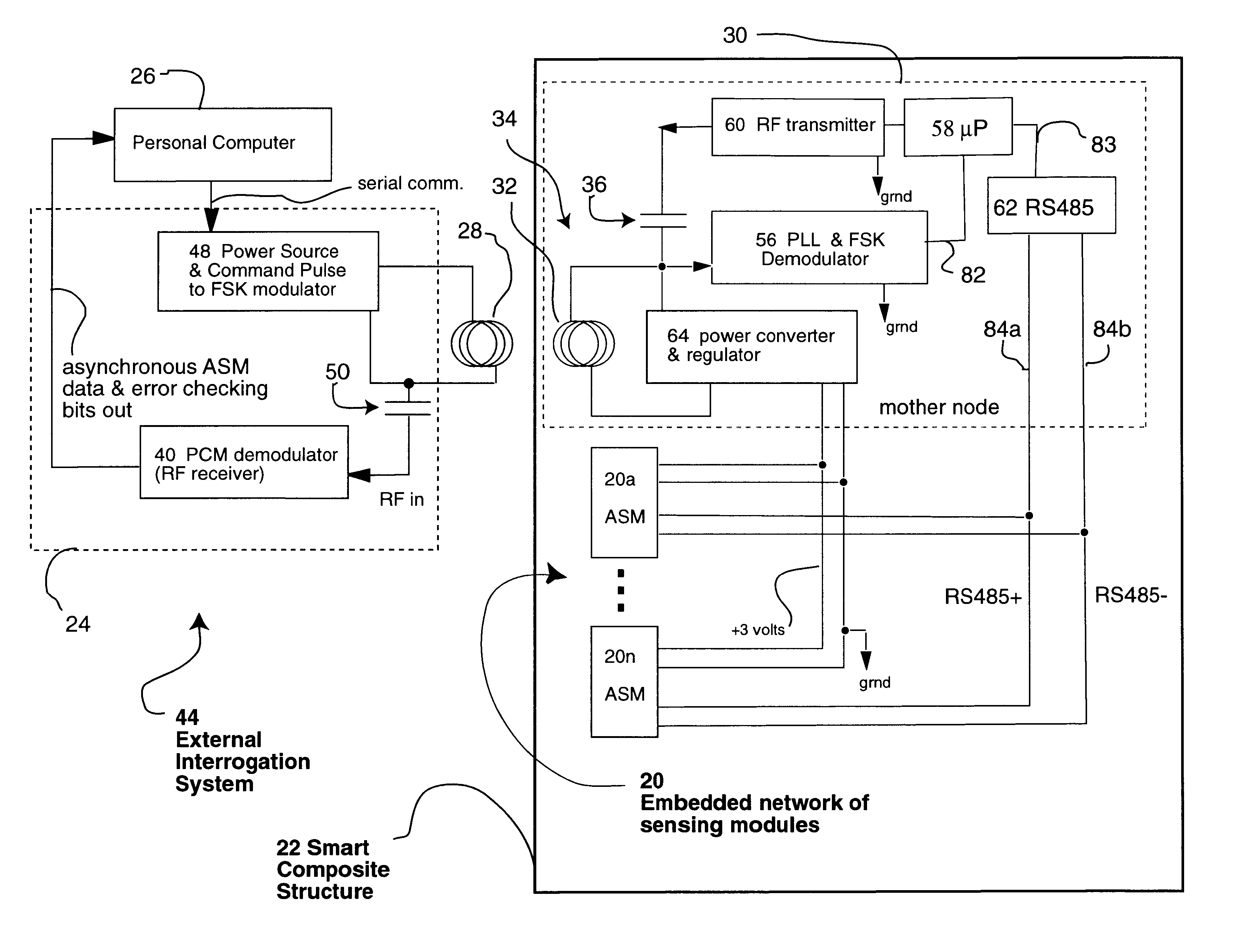
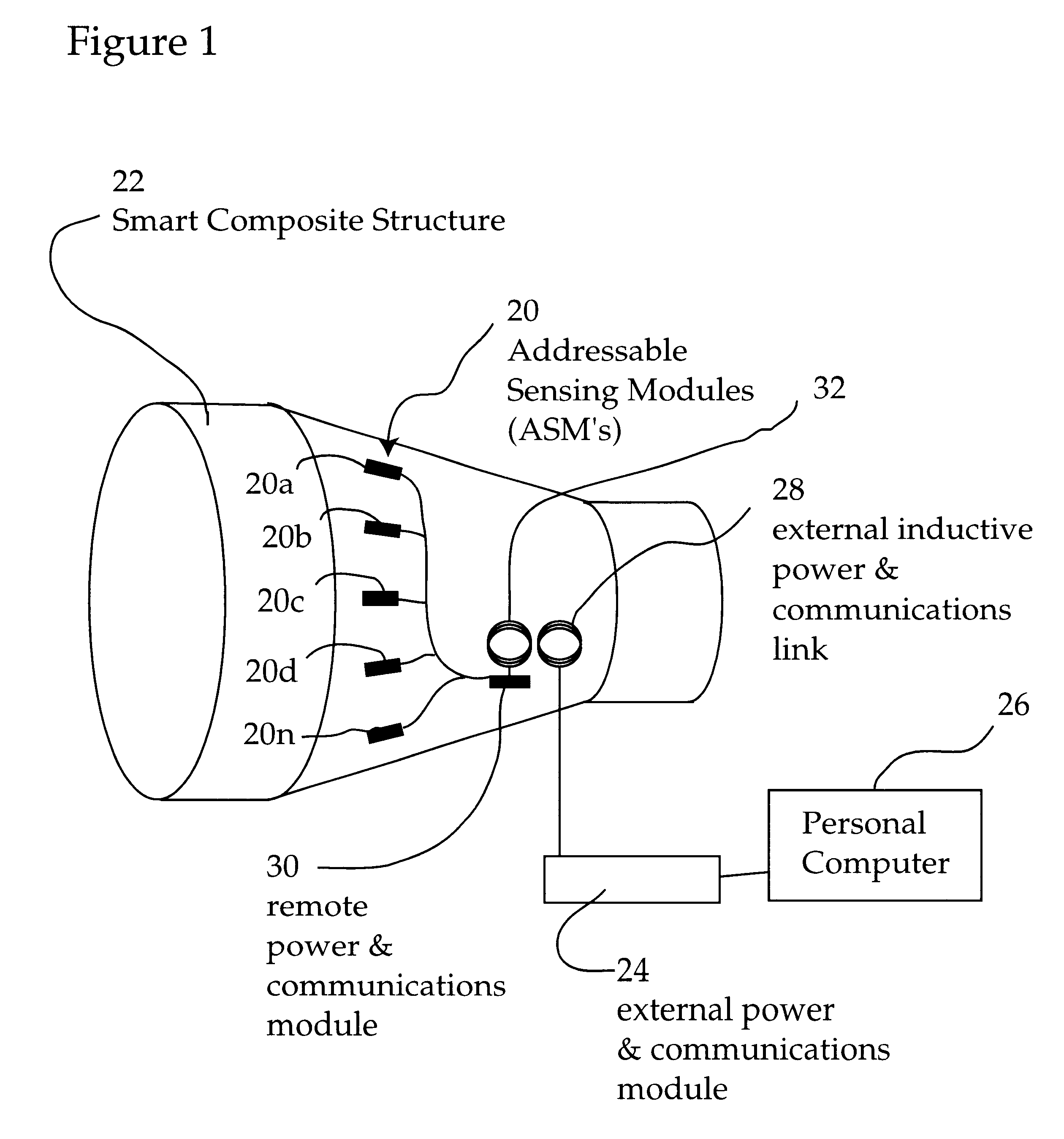
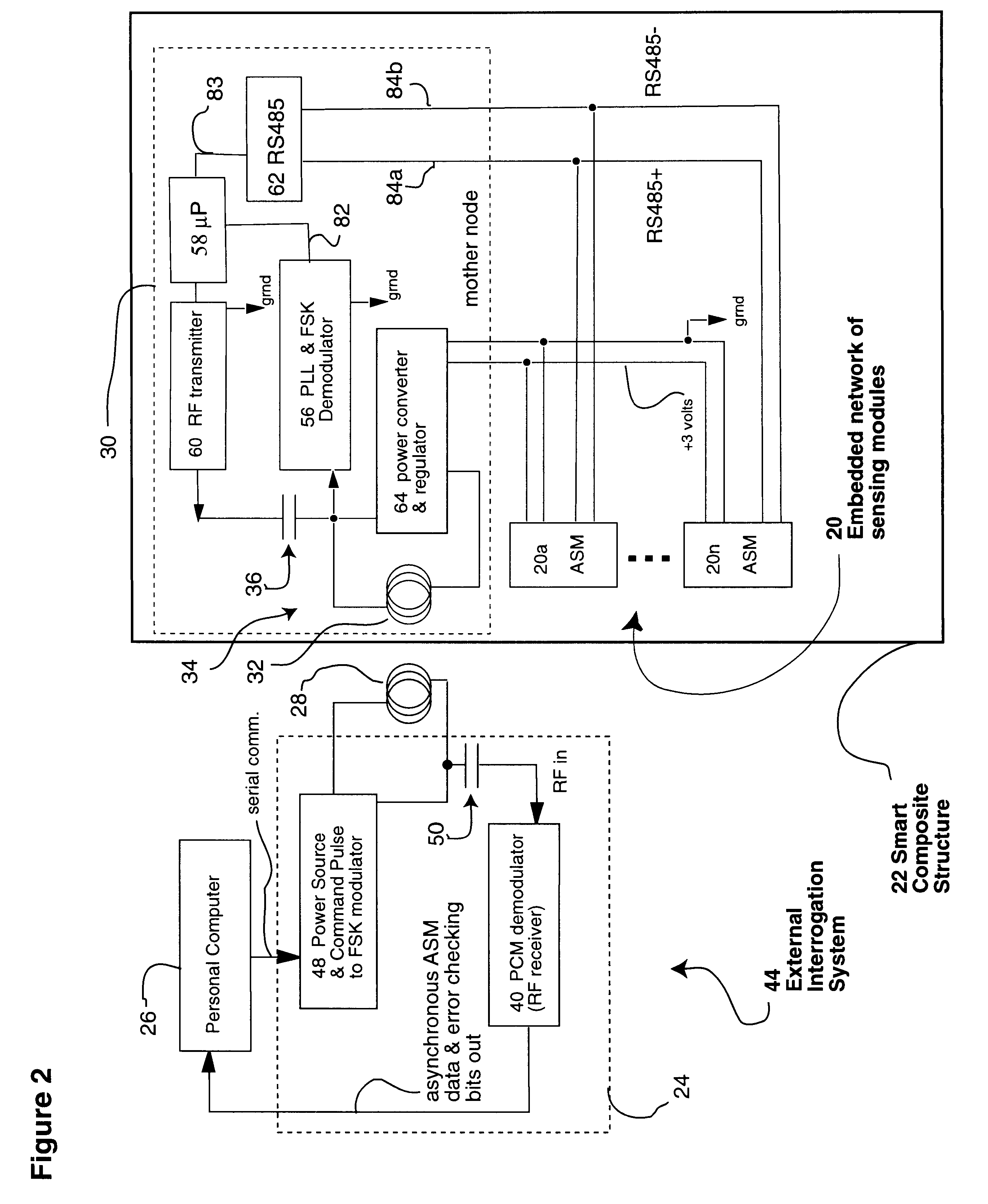
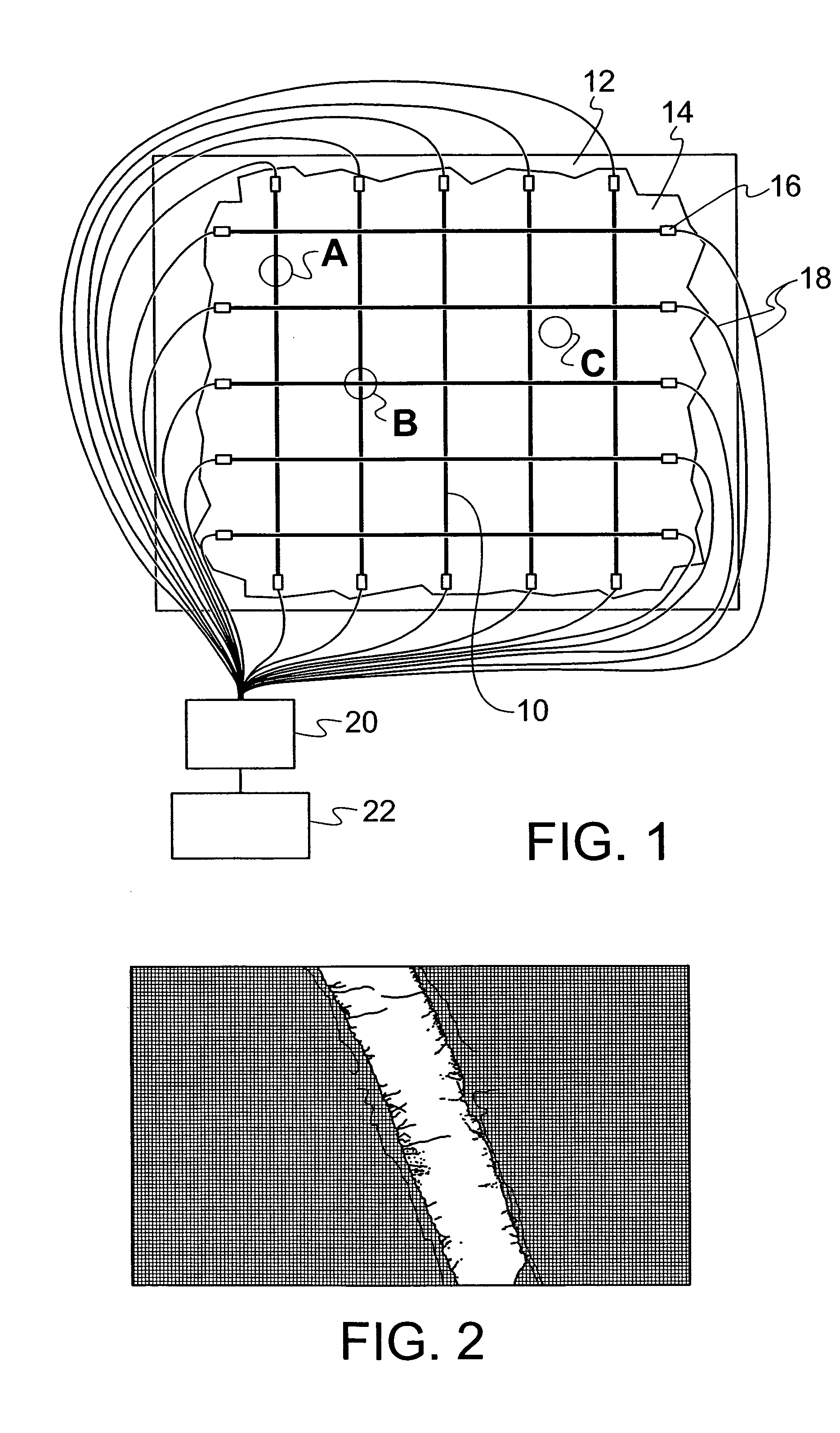
System for remote powering and communication with a network of addressable, multichannel sensing modules
InactiveUS6529127B2Low costElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsError checkingInstrumentation amplifier
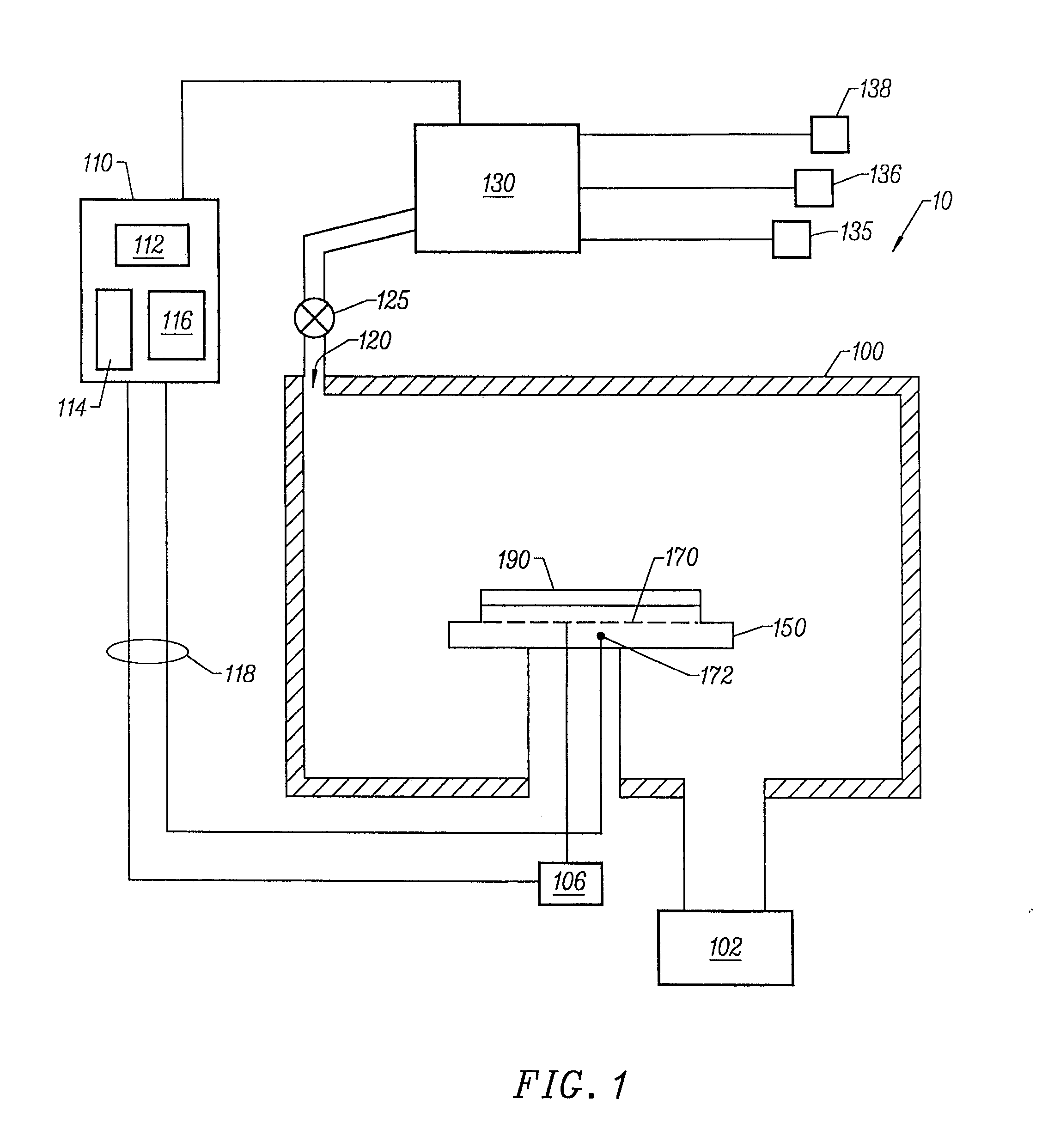
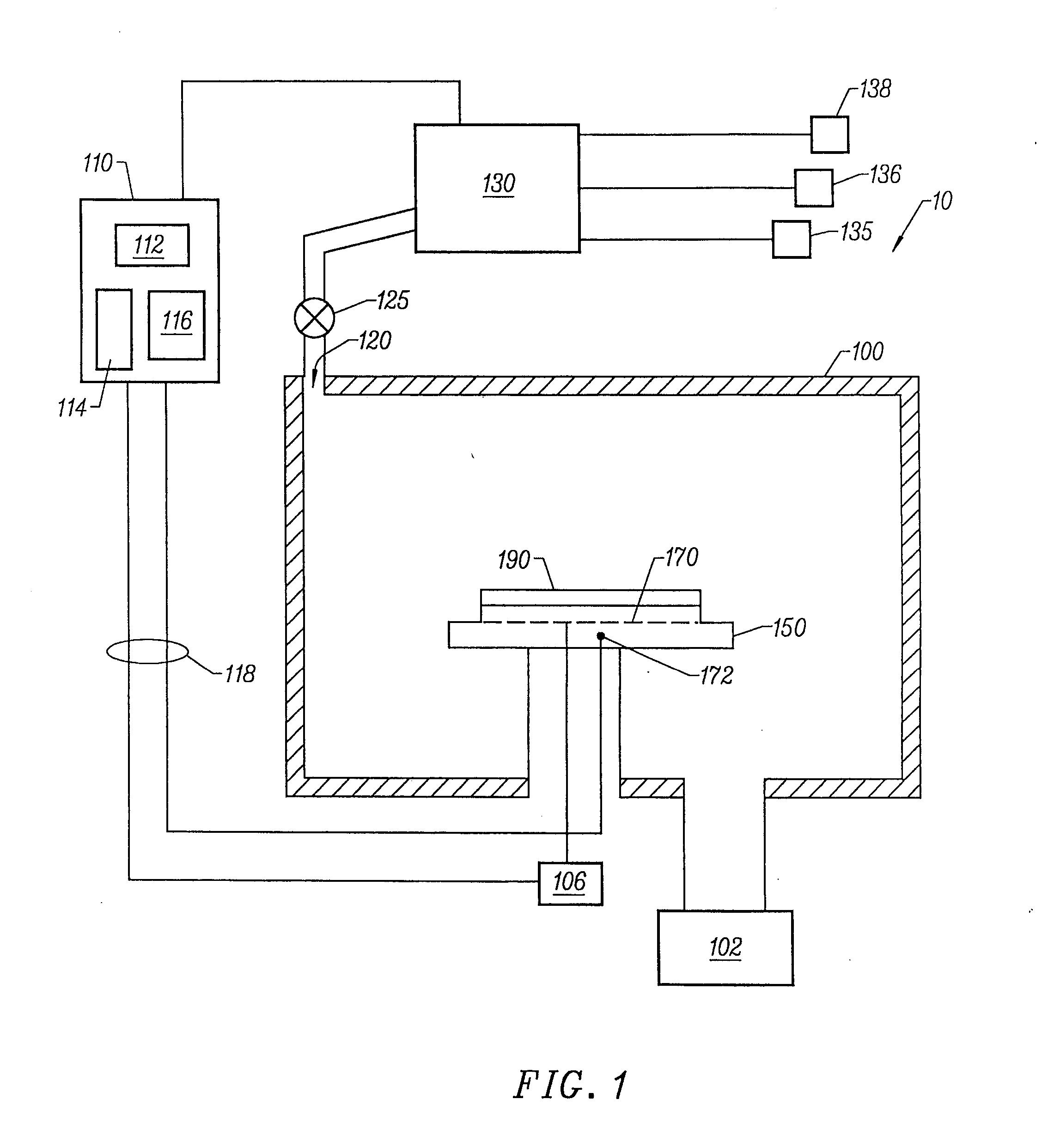
A multidrop network of multichannel, addressable sensing modules (ASM's), to be embedded within a composite structure, remotely powered, and interrogated by a personal computer through a non-contacting inductive link. Each ASM contains a microprocessor with non-volatile memory, multiplexer, programmable gain and filter instrumentation amplifier, and sigma delta analog to digital converter (all housed in two thin surface mount packages). An embedded mothernode includes circuitry for power and data reception (into the structure), and data transmission (back out of the structure). The external interrogation system communicates into the network of ASM's by modulating the AC waveform that delivers power to the embedded electronics. Once addressed, each ASM powers up its programmable (gain & filter) sensing channels (3 full differential or 5 pseudo differential) and data conversion elements. Sensed data are pulse code modulated, including error checking, which serially modulate an RF carrier for wireless transmission out of the composite to the interrogating computer. These advanced, micro-miniature sensing networks may be applied to a wide variety of military, medical, & civil structures.
Owner:LORD CORP
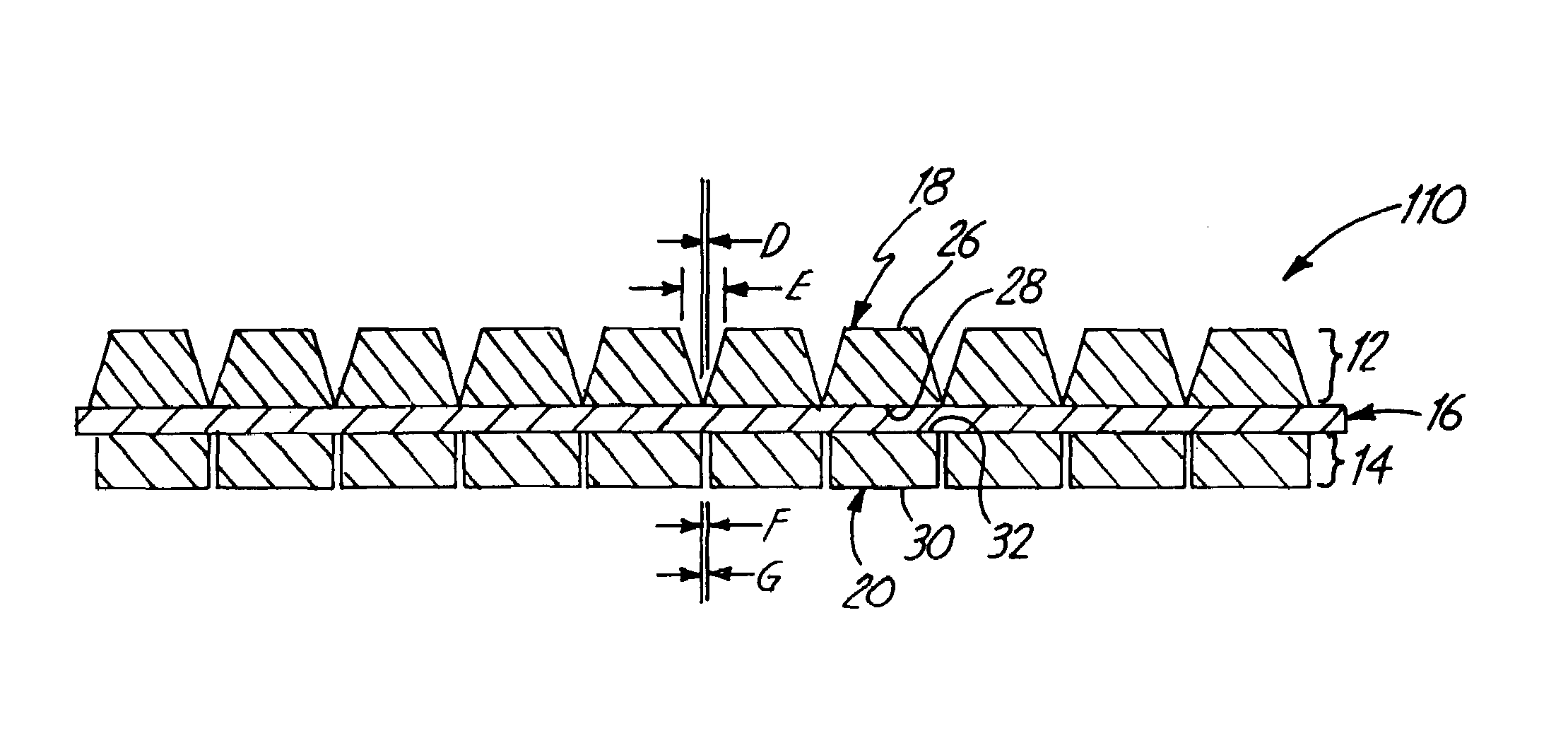
Impact absorbing composite
An impact absorbing composite structure (10), the impact absorbing composite structure including a plurality of impact absorbing members (18) and a flexible layer (16), each impact absorbing member (18) integral with the flexible layer (16).
Owner:GOLDFINE ANDREW A
Carbon/silicon/carbon nano composite structure cathode material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carbon / silicon / carbon nano composite structure cathode material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of electrochemical power supply technologies. The cathode material consists of a carbon-based conductive substrate, nano silicon and a nano carbon coating layer, wherein the nano silicon is uniformly distributed on the carbon-based conductive substrate; the nano carbon coating layer is arranged on the surface of the nano silicon; the carbon-based conductive substrate is porous carbon, a carbon nanotube or graphene; the nano silicon exists in the state of nanoparticles or nano films; the weight percentage of the nano silicon in the cathode material is 10-90 percent; and the thickness of the nano carbon coating layer is 0.1-10 nanometers. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: depositing nano silicon on the carbon substrate in a reaction space in oxygen-free atmosphere by adopting a chemical vapor deposition process; and coating nano carbon on the surface of the nano silicon by adopting the chemical vapor deposition process. In the obtained carbon / silicon / carbon composite cathode material, the volume change of a silicon electrode material is controlled effectively in the charging and discharging processes, the electrode structure is kept complete, the circulation volume is large, the circulation service life is long, and the electrochemical performance is high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
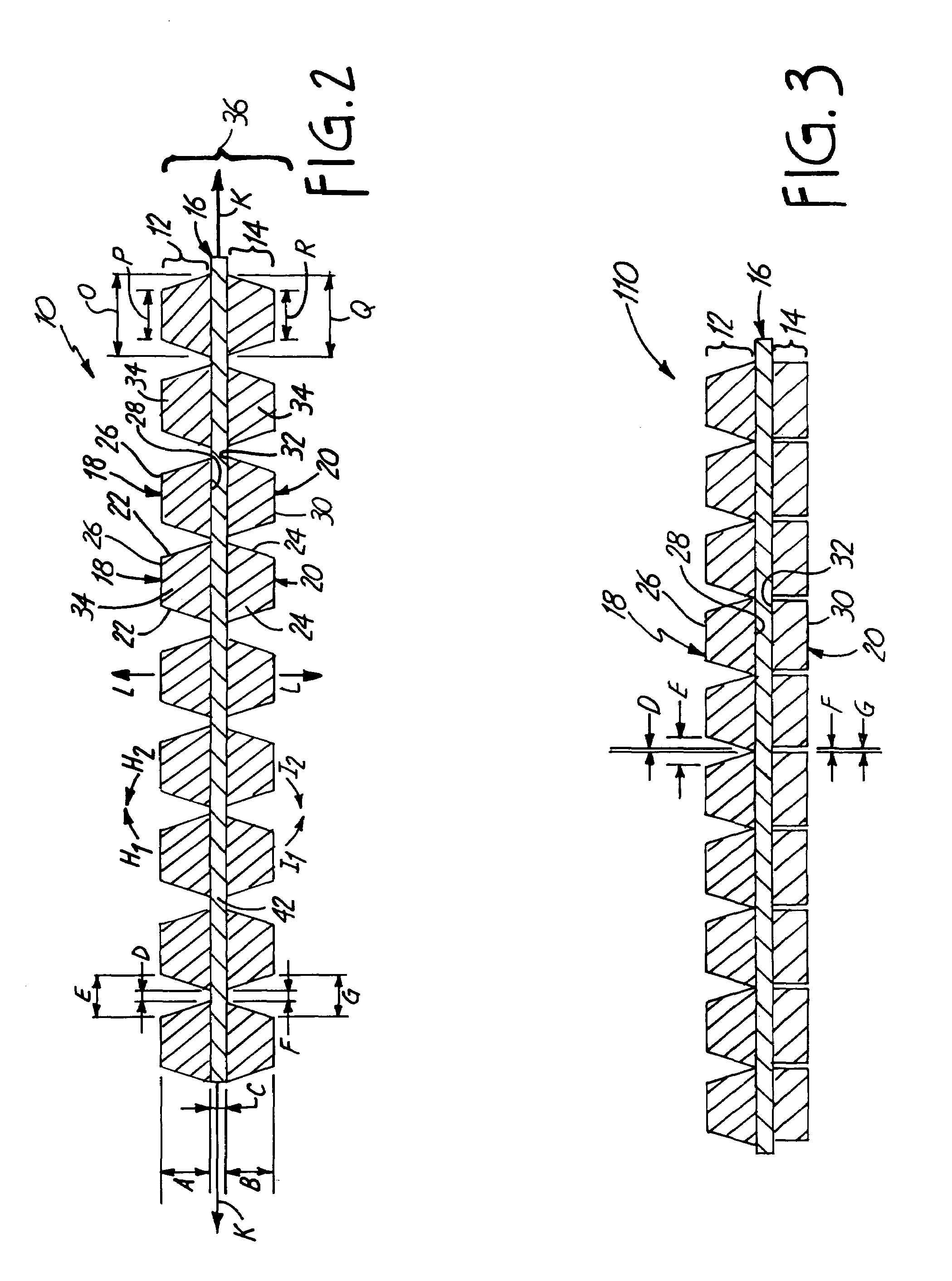
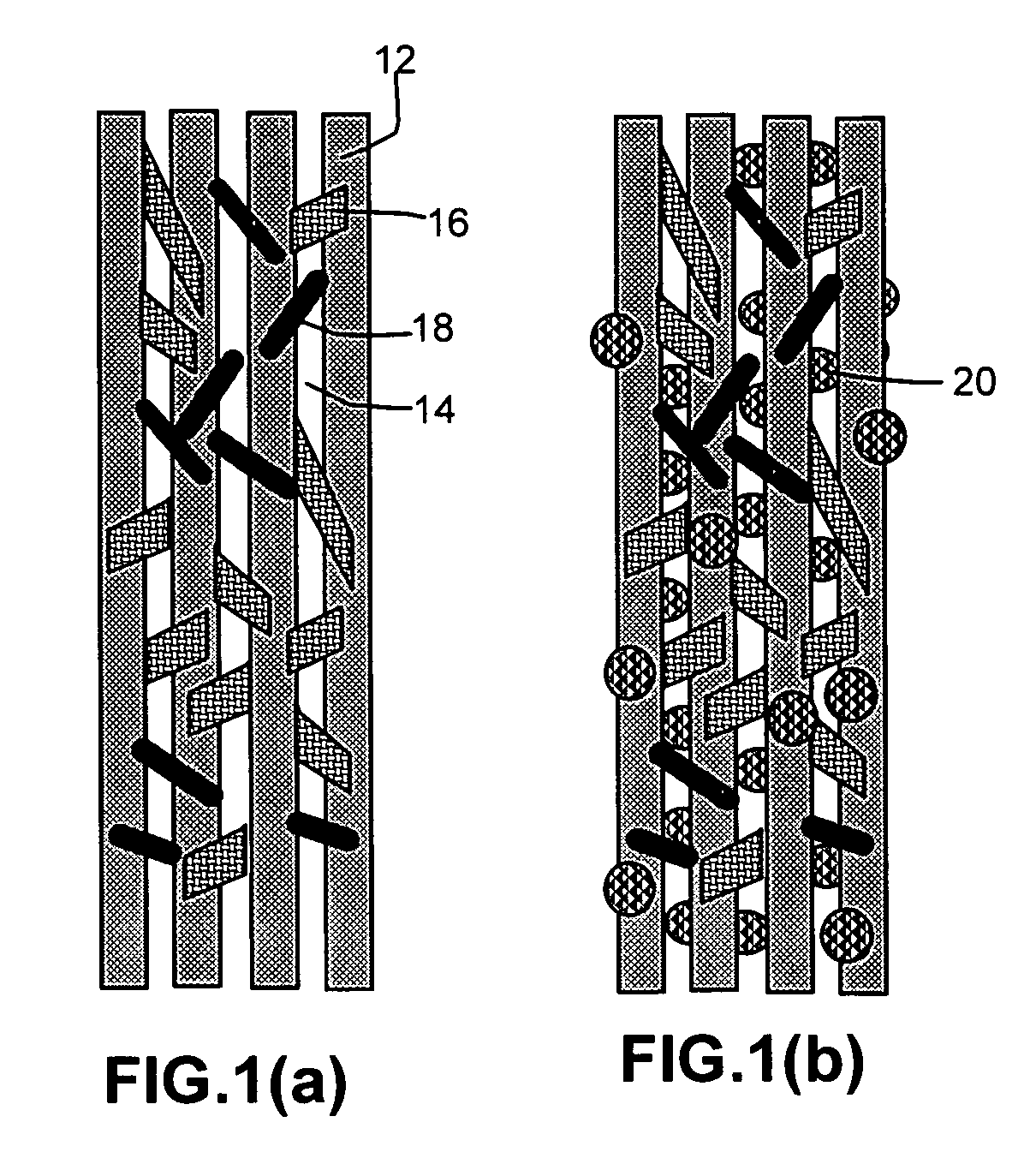
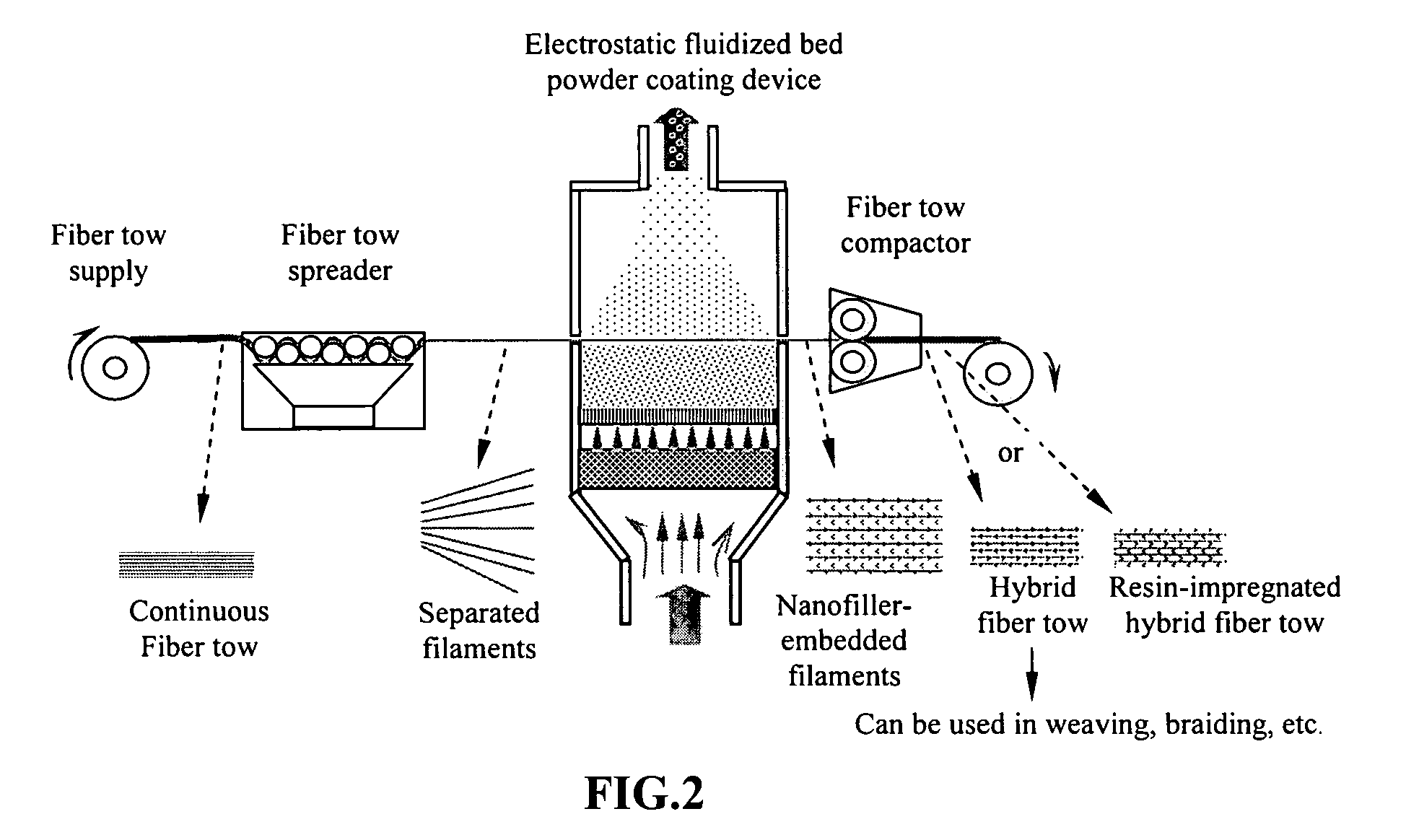
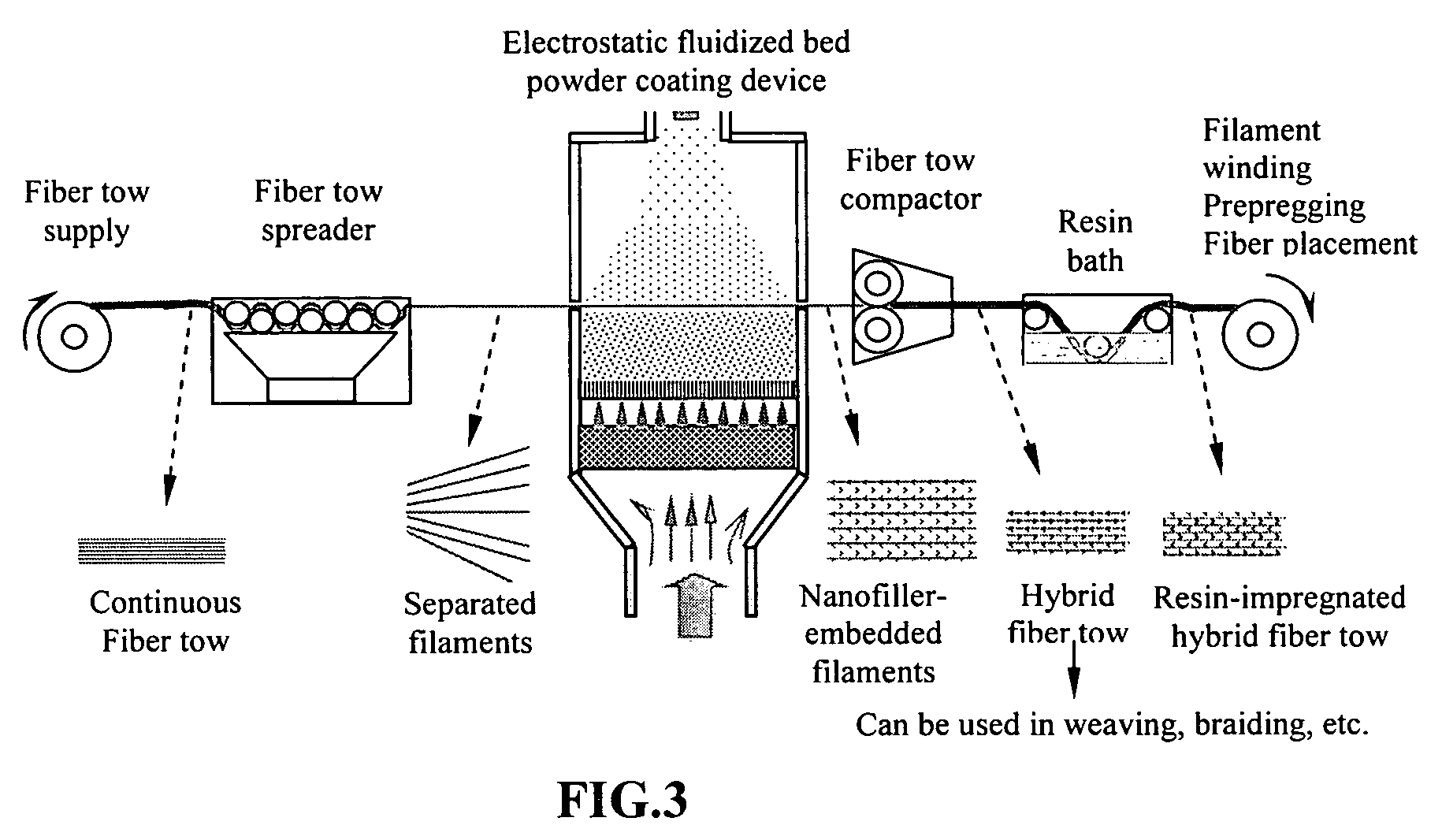
Hybrid fiber tows containning both nano-fillers and continuous fibers, hybrid composites, and their production processes
Disclosed is a hybrid fiber tow that comprises multiple continuous filaments and nanoscale fillers embedded in the interstitial spaces between continuous filaments. Nanoscale fillers may be selected from a nanoscale graphene plate, non-graphite platelet, carbon nano-tube, nano-rod, carbon nano-fiber, non-carbon nano-fiber, or a combination thereof. Also disclosed are a hybrid fiber tow impregnated with a matrix material and a composite structure fabricated from a hybrid fiber tow. The composite exhibits improved physical properties (e.g., thermal conductivity) in a direction transverse to the continuous fiber axis. A roll-to-roll process for producing a continuous fiber tow or matrix-impregnated fiber tow and an automated process for producing composite structures containing both continuous filaments and nanoscale fillers are also provided.
Owner:NANOTEK INSTR
Co-cured composite structures and method of making them
InactiveUS6743504B1Fully understandEasy to installPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSynthetic resin layered productsComposite structureFiber
A composite structure has composite skin layers and at least two elongated stiffener / spacer composite members interposed between the skin layers. The stiffener / spacer composite members are arranged generally longitudinally of the skin layers in spaced-apart relation laterally. Each of the skin layers is formed by assembling a layer of an uncured resin-impregnated fiber material on a forming surface of a jig. Each stiffener / spacer composite member is formed of an uncured resin-impregnated fiber material that is laid up over an elongated hollow mandrel of a stiffened fabric and is assembled to one of the uncured skin layers. The jigs are juxtaposed to form a sandwich with the assembled uncured composite layers, which are then vacuum-bagged and co-cured under a predetermined pressure and a predetermined temperature to render the structure unitary.
Owner:ROHR INC
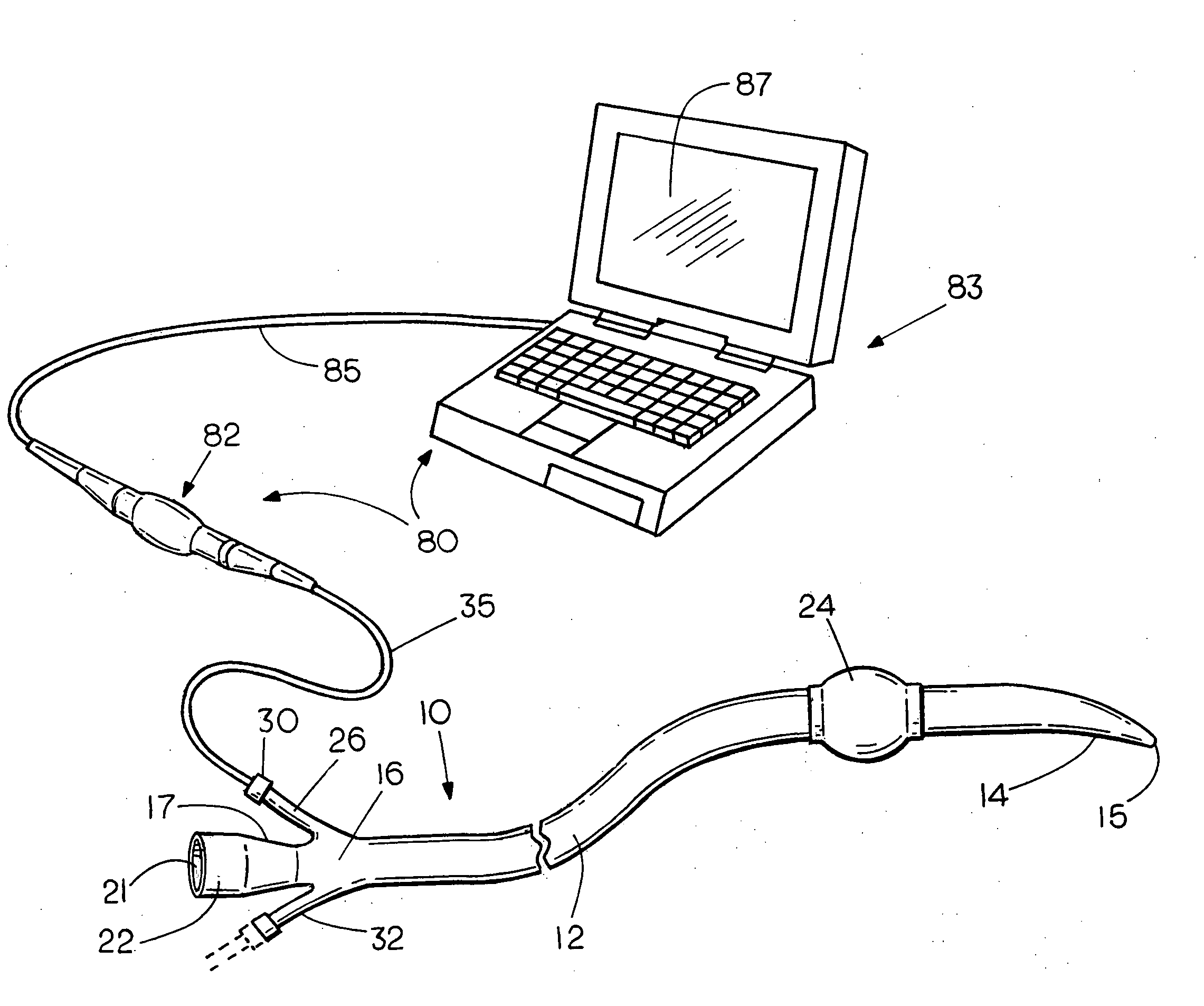
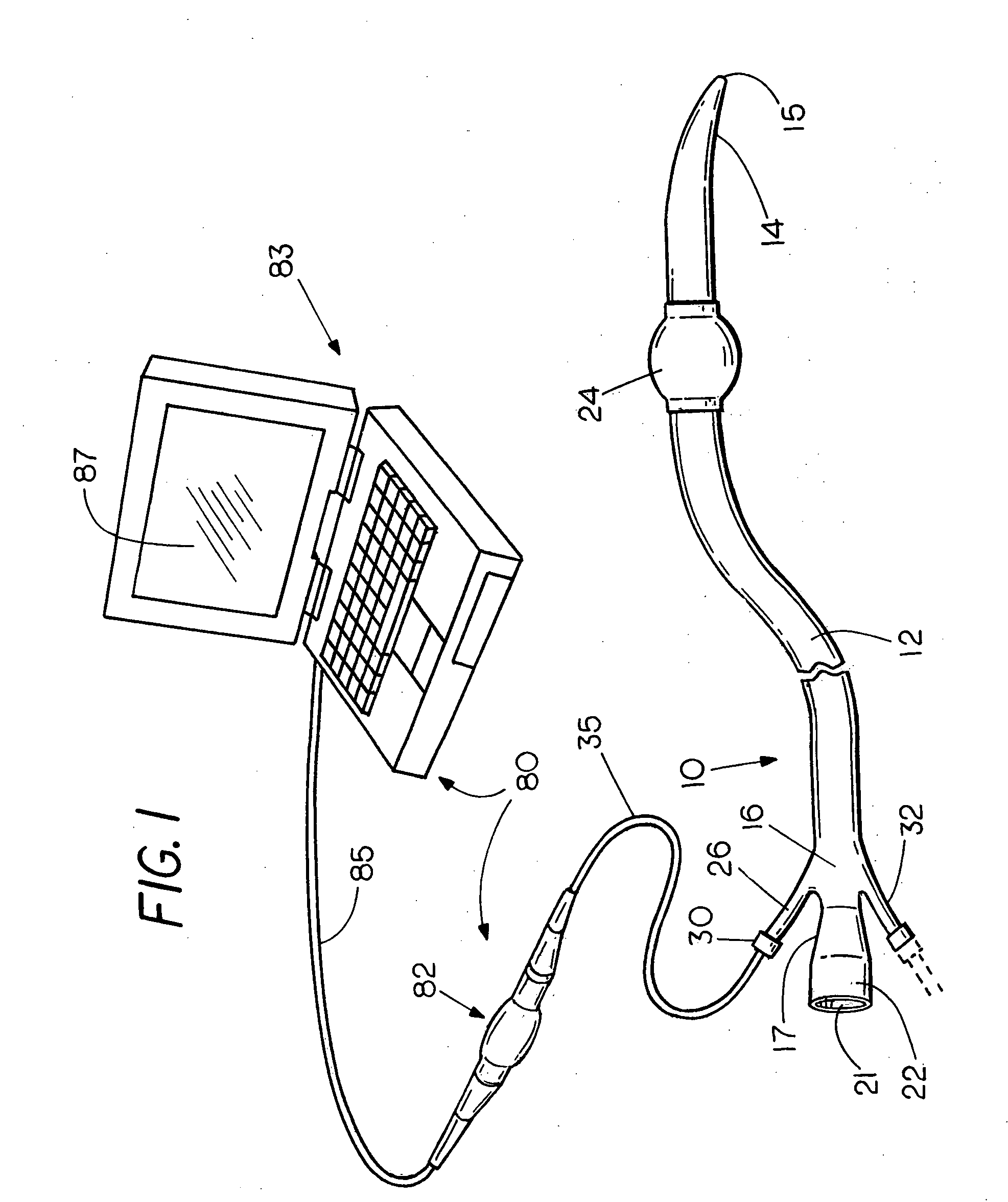
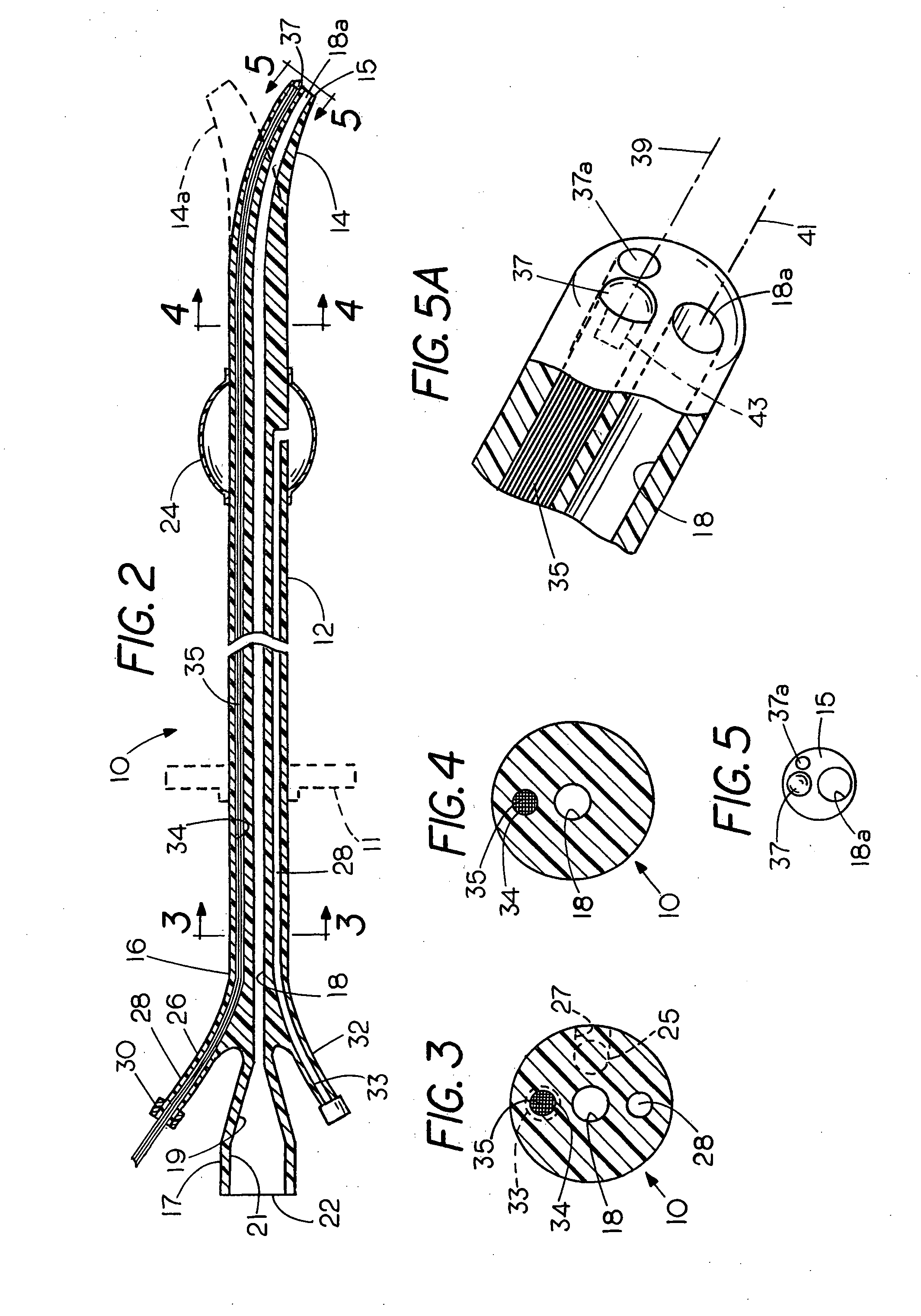
Flexible visually directed medical intubation instrument and method
Owner:PERCUVISION
Drug-delivering composite structures
Composite structures composed of a fibril core and a polymeric coat and designed capable of encapsulating both hydrophobic and hydrophilic bioactive agents while retaining the activity of these agents are disclosed. Further disclosed are processes of preparing such composite structures, and medical devices and disposable articles made therefrom.
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
Bioabsorbable device having composite structure for accelerating degradation
A medical device has a structure made of a first biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable material and a second biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable material. The first biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable material has a degradation rate that is faster than a degradation rate of the second biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable material. And, the structure experiences a period of accelerated degradation upon exposure of the first biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable material.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Method for manufacture of minimum porosity, wrinkle free composite parts
A process and associated apparatus used to prepare a thermoplastic composite from a plurality of plies of thermoplastic resin prepregs. The prepregs are formed into a composite structure under two chambers; a rigid outer chamber (of any convenient size or shape) and a second flexible inner chamber containing a prepreg lay-up. The absolute pressures are reduced concurrently in a stepwise method in both chambers. This concurrent, stepped pressure reduction is accomplished at a rate which prevents the vacuum bag from moving far from the prepregs, and prevents wrinkles from forming in the prepregs. Pinching off the diffusion paths required for the removal of unwanted gases is eliminated. The lay-up is then heated and the absolute pressure in the outer rigid chamber is increased. This pressure constrains the flexible inner chamber during out-gassing of the thermoplastic resin, preventing wrinkles from forming in the prepregs. The absolute pressure in the outer rigid chamber is increased to atmospheric pressure or greater causing the prepregs to consolidate. A low absolute pressure is maintained in the flexible inner chamber. The temperature is then increased to the cure temperature of the resin and held for a time sufficient for the resin to cure. The resulting consolidated thermoplastic resin is substantially void free and detectable wrinkles are absent.
Owner:HALE HAROLD P
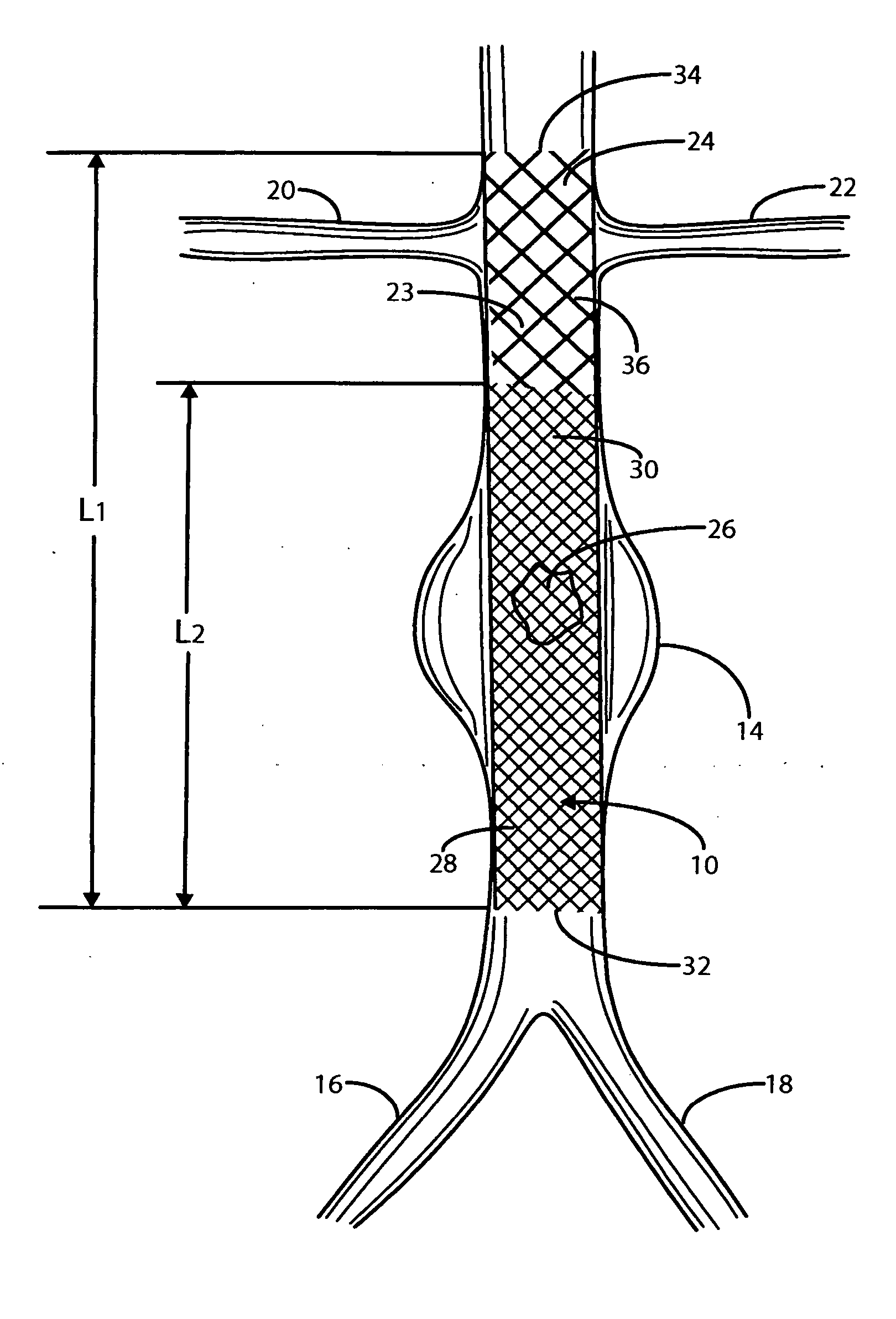
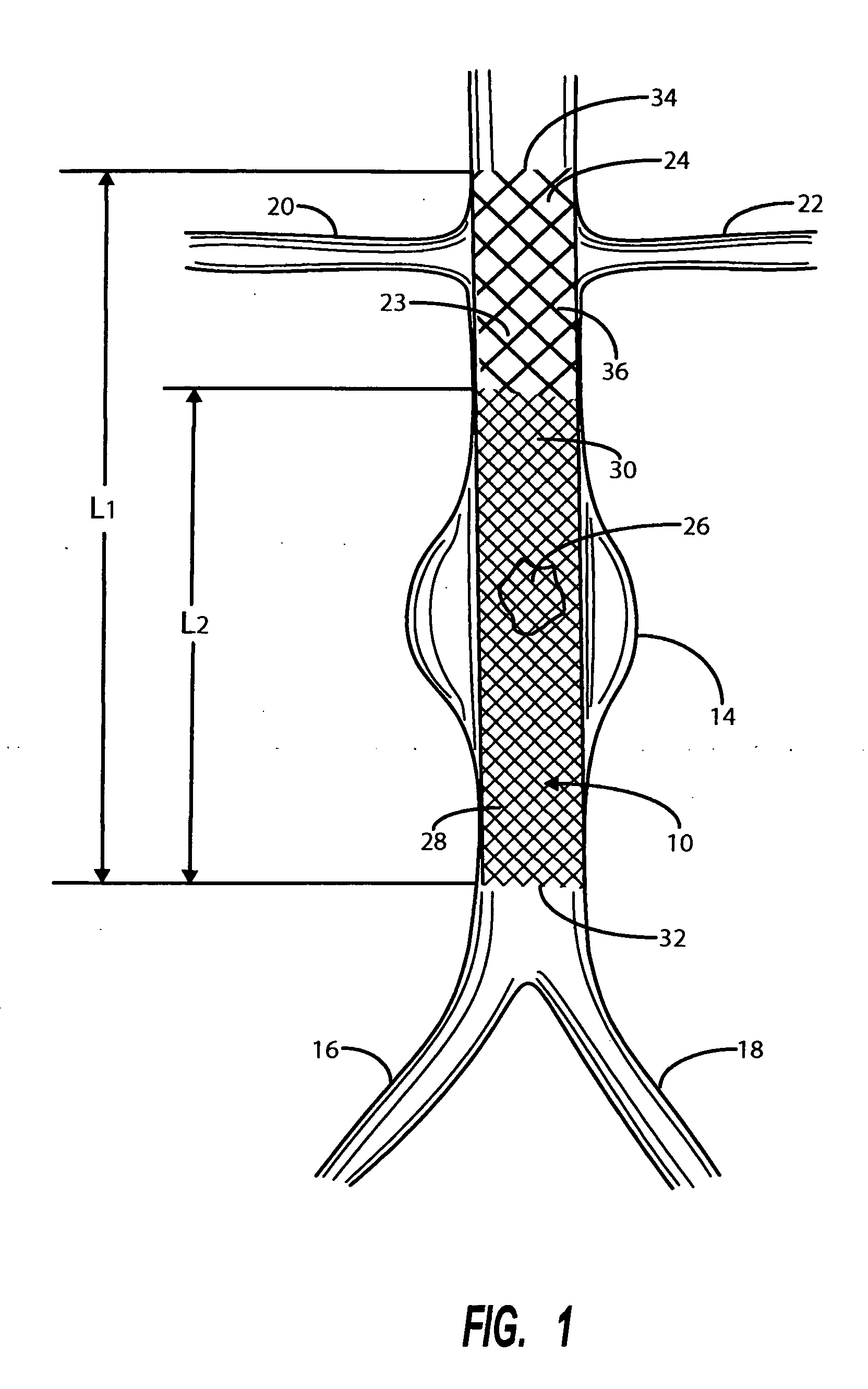
Intravascular deliverable stent for reinforcement of abdominal aortic aneurysm
A stent / graft especially designed to be used in a minimally invasive surgical procedure for treating an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) comprises an innermost tubular structure of a length (L1) formed by braiding a relatively few strands of shape memory alloy wire. The pick and pitch of the braid are such as to provide relative large fenestrations in the tubular wall. A portion of the innermost tubular structure of a length L2<L1 is surrounded by a further braided tubular structure having relatively many strands that occlude the fenestrations of the innermost tubular structure. The composite structure can be stretched to reduce the outer diameter of the stent / graft, allowing it to be drawn into a lumen of a delivery catheter. The catheter can then be advanced through the vascular system to the site of the AAA and then ejected, allowing it to self-expand with the portion L2 bridging the aneurysm. The portion L1>L2 does not block blood flow to the renal arteries while the portion L2 prevents the aneurysm to grown and burst.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Thin film wound cover, suction assisted wound treatment system using the same, method of using the thin film wound cover and method of making the same
A composite structure, a suction-assisted wound treatment system including the composite structure and a method of making the same is disclosed. The composite structure includes a cover, a stiffener, and a releasable liner. The cover is a thin flexible film having an, upper surface, an undersurface, a principal portion, a pair of marginal edges and an adhesive on the undersurface. The stiffener is releasably secured to the upper surface of the principal portion of the cover and includes a handle which is more rigid than the principal portion of the stiffener. The handle, forms a portion of the undersurface of the stiffener and defines a finger space between it and portion of the cover disposed therebelow. The liner includes at least one section releasably secured to the adhesive of the cover. The stiffener and the handle are removable as a unit from the cover.
Owner:BOEHRINGER TECH
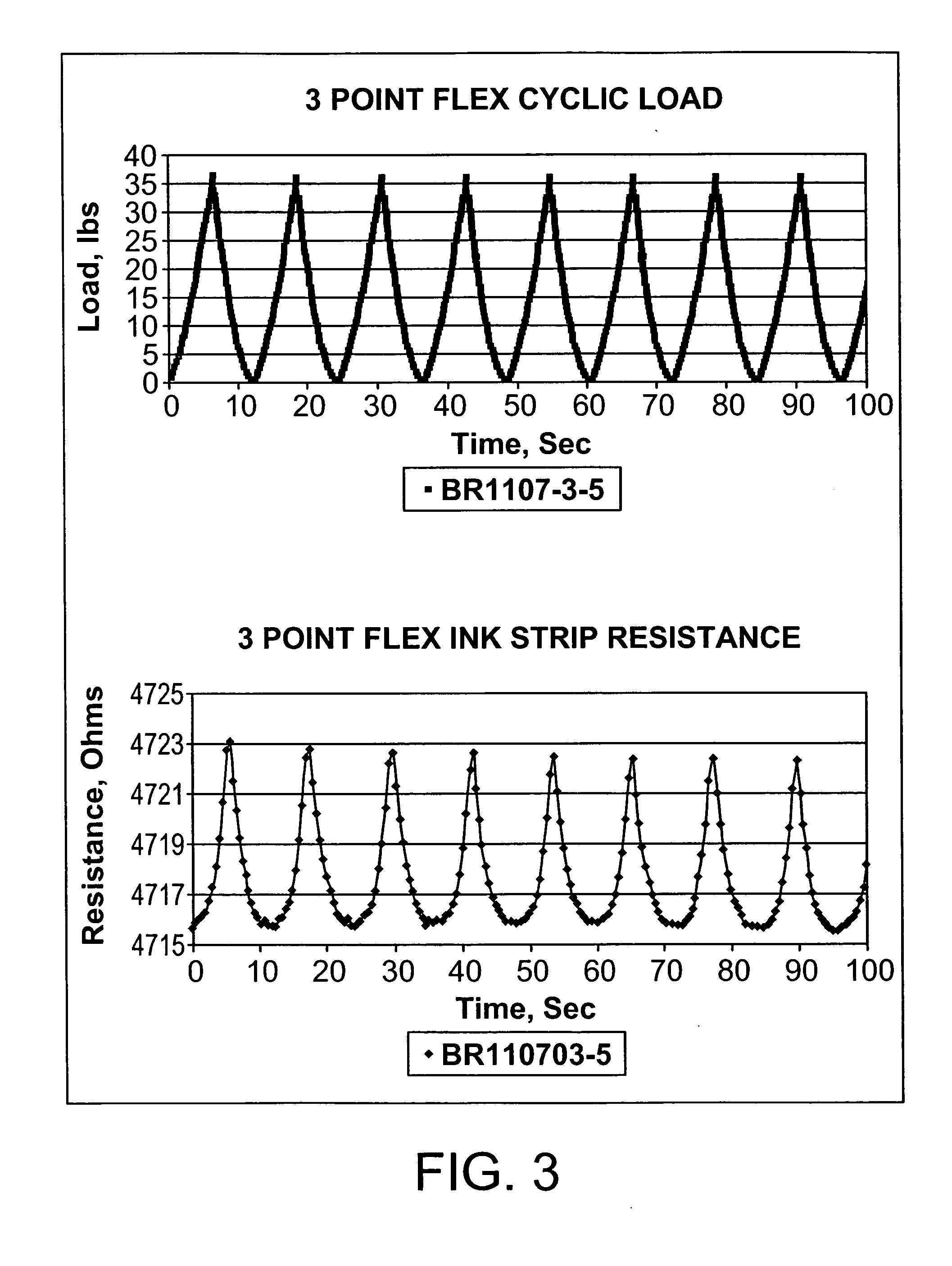
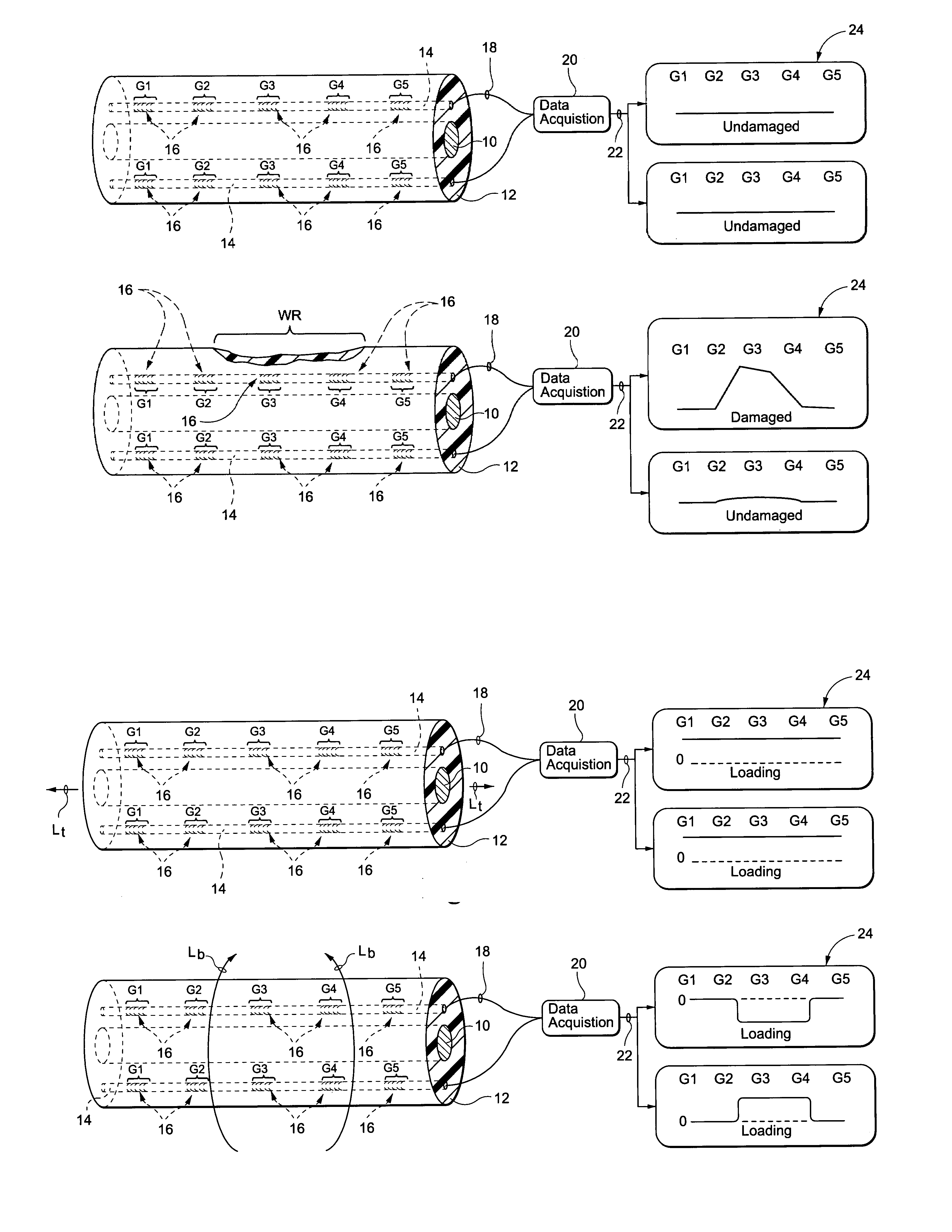
Sensing system for monitoring the structural health of composite structures
ActiveUS20050284232A1Easy to stickImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementGrid patternState of health
A sensing system for use in monitoring the structural health of a structure such as a polymeric matrix composite structure is provided. The system includes a sensor formed from a conductive ink containing carbon nanofibers and a polymeric resin, and a data acquisition system for acquiring and evaluating data from the sensor. The conductive ink may be applied directly to the structure to be monitored in the form of a grid pattern. Damage to the structure may be detected by measuring changes in resistance values detected from the sensor.
Owner:UNIV OF DAYTON
Non-expandable transluminal access sheath
InactiveUS20060253102A1Improved radiopaque characteristicMinimize potential for damageCannulasInfusion syringesFluid transportVisibility
A transluminal sheath is disclosed that permits instrumentation to be passed therethrough. The transluminal sheath comprises a composite structure with an inner layer, an outer layer, and a reinforcing layer. The materials comprising the inner and outer layer are plastically deformable and maintain their shape, once bent into a specific configuration. The reinforcing layer further has radiopacity enhancing coatings to improve visibility under fluoroscopy and a system of flutes running longitudinally, to enhance fluid transport and reduce friction.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Composite structures, such as coated wiring assemblies, having integral fiber optic-based condition detectors and systems which employ the same
InactiveUS7154081B1Weakening rangeReducing compressive strainControlRadiation pyrometryElectrical conductorGrating
Integral fiber optic-based condition sensors detect conditions of a composite structure, e.g., a coated wire assembly so as to detect damage or conditions that may damage the same. Preferably, at least one optical fiber sensor having a plurality of Bragg gratings written into the fiber at spaced-apart locations along its axial length is integrated into the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle or wiring harness. The fiber optic sensor may thus be employed to measure the environmental loads on the electrical wiring including stresses from bending, axial loading, pinch points, high temperature excursions and chemical damage. The system is capable of detecting and locating transient conditions that might cause damage to a wiring system or permanent changes in state associated with damage events. The residual stress in the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle, or wiring harness are used to monitor the evolution of damage by wear or chaffing processes. Detected stress relief on one or more Bragg gratings will thus be indicative of damage to the insulator coating on the conductor. As such, the magnitude of such stress relief may be detected and used as an alert that the wire insulation is damaged to an unsafe extent.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Nanophase multilayer barrier and process
InactiveUS20050051763A1Improve toughnessHigh fracture-resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPliabilityEngineering
A thin film barrier structure and process is disclosed, which is seen as particularly useful for use in devices that require protection from such common environmental species as oxygen and water. The disclosed barrier structure is of particular utility for such devices as implemented on flexible substrates, such as may be desirable for OLED-based or LCD-based devices. The disclosed barrier structure provides superior barrier properties, flexibility, as well as commercial-scale reproducibility, through the use of a novel organic / inorganic nanocomposite structure formed by infiltration of a porous inorganic layer by an organic material. The composite structure is produced by vacuum deposition techniques in the first preferred embodiment.
Owner:HELICON RES
Low density lightning strike protection for use in airplanes
ActiveUS20090227162A1Minimize micro-crackingWeight optimizationConductive materialWarp knittingFiberEpoxy
Surface films, paints, or primers can be used in preparing aircraft structural composites that may be exposed to lightning strikes. Methods for making and using these films, paints or primers are also disclosed. The surface film can include a thermoset resin or polymer, e.g., an epoxy resin and / or a thermoplastic polymer, which can be cured, bonded, or painted on the composite structure. Low-density electrically conductive materials are disclosed, such as carbon nanofiber, copper powder, metal coated microspheres, metal-coated carbon nanotubes, single wall carbon nanotubes, graphite nanoplatelets and the like, that can be uniformly dispersed throughout or on the film. Low density conductive materials can include metal screens, optionally in combination with carbon nanofibers.
Owner:ROHR INC +1
Carbon nanotube fiber-reinforced composite structures for EM and lightning strike protection
InactiveUS6986853B2Repaired quickly and efficientlySufficient protectionMaterial nanotechnologyShielding materialsLightning strikeFiber-reinforced composite
A method for repairing fiber-reinforced composite structures while maintaining original EM and lightning protection using carbon nanotubes, fibers, and thermoset resins is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the invention, the method comprises preparing a damaged area for repair; preparing a repair patch for the damaged area, the repair patch comprising nanotubes; applying the repair patch to the damaged area; and curing the repair patch. A repair patch for a composite structure having a conductive layer is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the repair patch includes a binder and nanotubes. A repair resin for repairing a composite structure having a conductive layer is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the repair layer includes a resin and nanotubes. A putty for repairing a composite structure having a conductive layer is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, the putty includes a base and electrically conductive carbon nanotubes.
Owner:EIKOS
Embedded power management control circuit
InactiveUS20050207133A1Save spaceImprove cooling effectPrinted circuit assemblingDigital data processing detailsElectricityElectronic systems
A peripheral electronic system for an electronic device including a motherboard having multiple individual electrically connected vertically stacked modules, at least one of which is a circuit board assembly including active and / or passive electronic components embedded therein with the components being electrically connected by conductive traces to provide desired operating function. The peripheral electronic system further includes an electrical connector array on an exposed surface of the composite structure to provide electrical connections between the peripheral electronic system and the motherboard.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL RECTIFIER COEP
Mole cular sieve with composite structure and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1552625AHigh activityHigh selectivityCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesMolecular sieveCrystallization
A composite molecular sieve with TON and MFI structures is prepared in static crystallizing condition. In the procedure of preparing gel, less crystal seeds and salt are added. The Si / Al ratio on its crystal lattice is greater than 50.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Composite structure formed by CMC-on-insulation process
ActiveUS20050076504A1Improved ceramic composite structureWood working apparatusCeramic layered productsCombustorEngineering
A method of manufacturing a composite structure uses a layer of an insulating material (22) as a mold for forming a substrate of a ceramic matrix composite (CMC) material (24). The insulating material may be formed in the shape of a cylinder (10) with the CMC material wound on an outer surface (14) of the cylinder to form a gas turbine combustor liner (20). Alternatively, the insulating material may be formed in the shape of an airfoil section (32) with the CMC material formed on an inside surface (36) of the insulating material. The airfoil section may be formed of a plurality of halves (42, 44) to facilitate the lay-up of the CMC material onto an easily accessible surface, with the halves then joined together to form the complete composite airfoil. In another embodiment, a box structure (102) defining a hot gas flow passage (98) is manufactured by forming insulating material in the shape of opposed airfoil halves (104) joined at respective opposed ends by platform members (109). A layer of CMC material (107) is then formed on an outside surface of the insulating material. A number of such composite material box structures are then joined together to form a vane ring (100) for a gas turbine engine.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Cnt-based resistive heating for deicing composite structures
ActiveUS20110024409A1Prevent freezingInhibition formationMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsFiberCarbon nanotube
A composite structure includes a matrix material and a carbon nanotube (CNT)-infused fiber material that includes a plurality of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) infused to a fiber material. The CNT-infused fiber material is disposed throughout a portion of the matrix material. The composite structure is adapted for application of a current through the CNT-infused fiber material to provide heating of the composite structure. A heating element includes a CNT-infused fiber material includes a plurality of CNTs infused to a fiber material. The CNT-infused fiber material is of sufficient proportions to provide heating to a structure in need thereof.
Owner:APPL NANOSTRUCTURED SOLUTIONS LLC
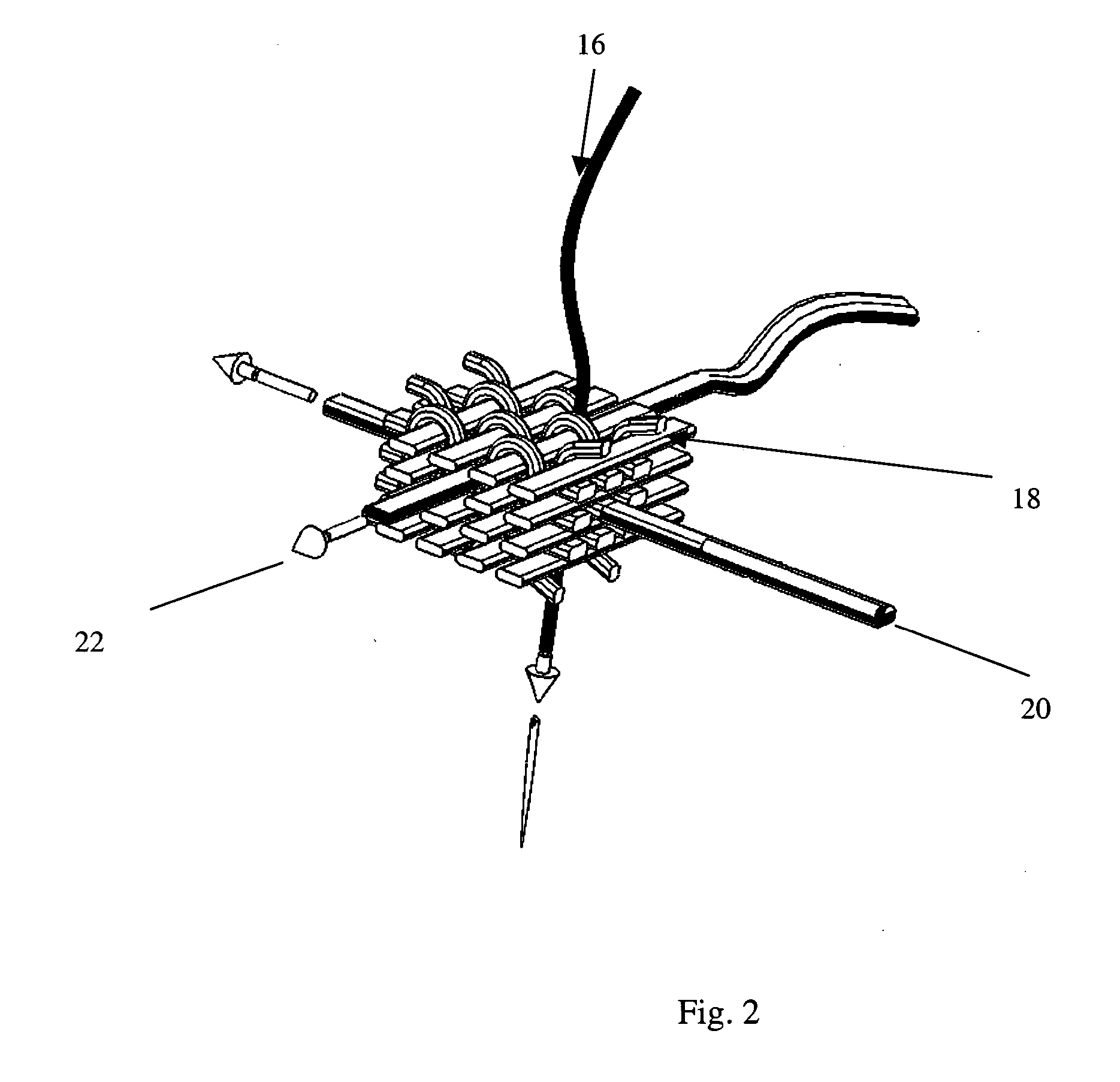
3-D fabrics and fabric preforms for composites having integrated systems, devices, and/or networks
A 3-D fabric preform for composites including a three-dimensional engineered fiber preform formed by intersecting yarn system components; and at least one system, device, and / or network integrated with the preform for providing a predetermined function, wherein the at least one system, device, and / or network is introduced prior to formation of a composite structure including the preform, thereby providing a 3-D fabric preform for composites. Also, a method for forming the 3-D fabric preform for composites including a three-dimensional engineered fiber preform formed by intersecting yarn system components; and at least one system, device, and / or network integrated with the preform for providing a predetermined function, wherein the at least one system, device, and / or network is introduced prior to formation of a composite structure including the preform, thereby providing a 3-D fabric preform for composites.
Owner:ALEXANDER BOGDANOVICH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com