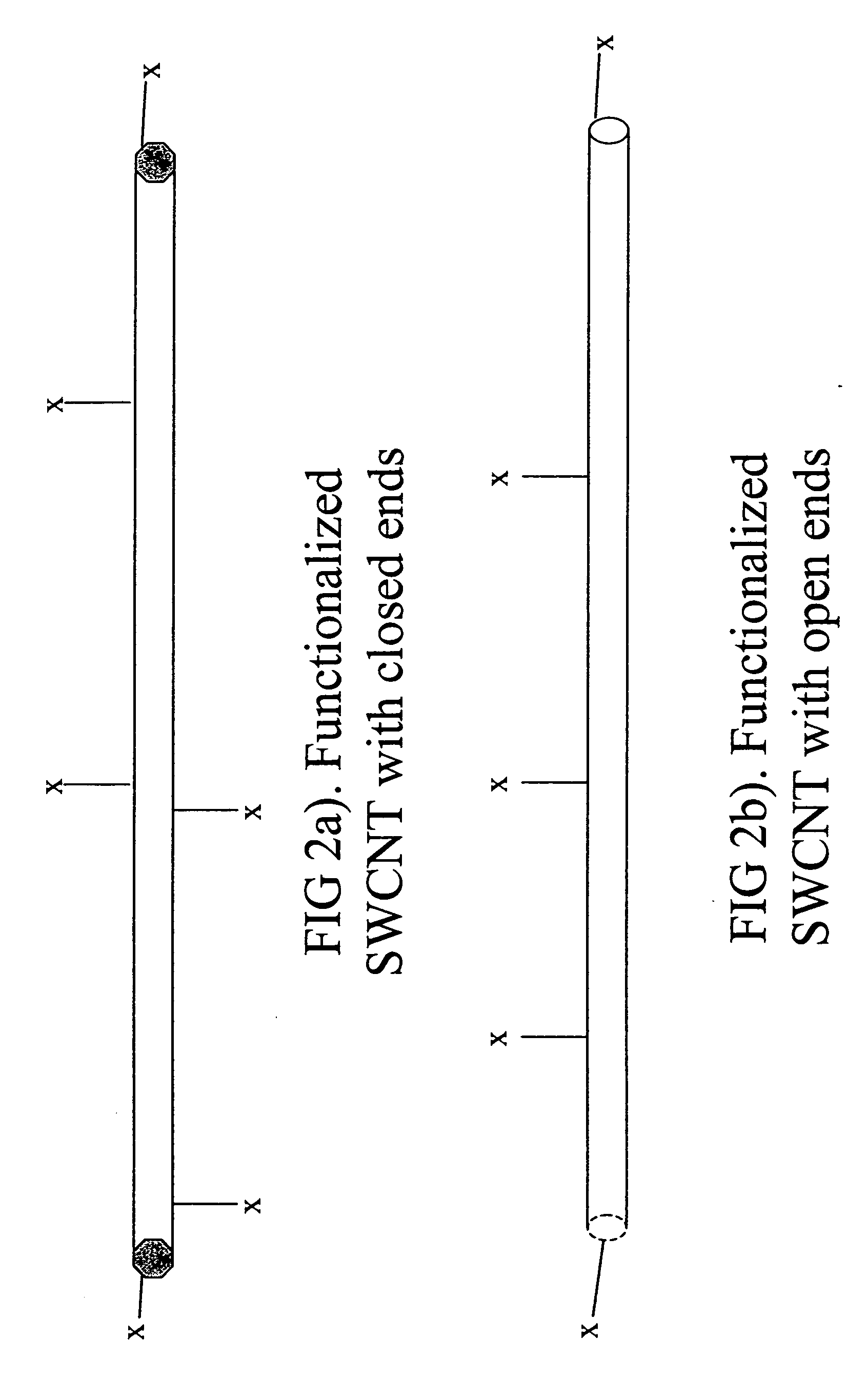
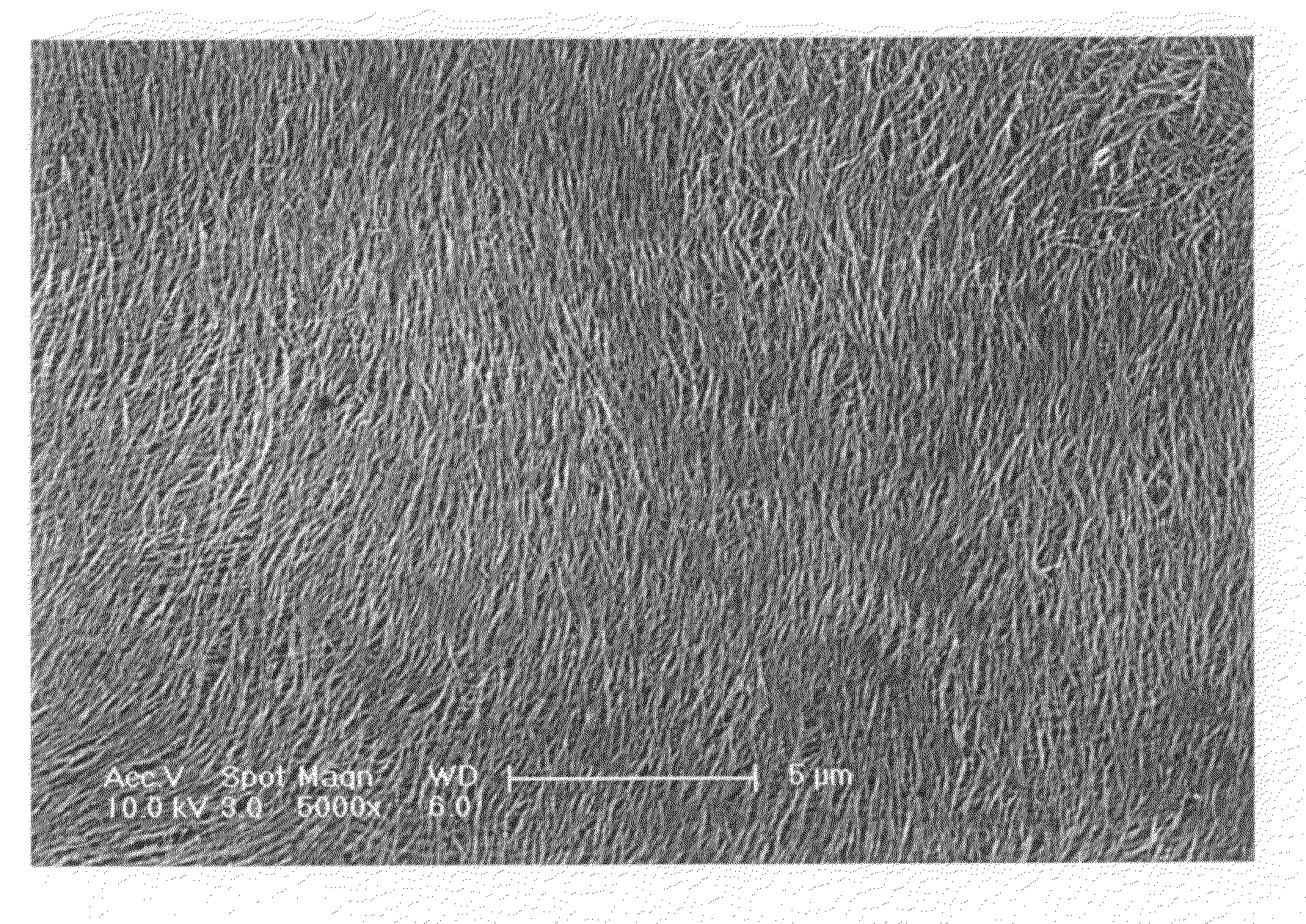Patents
Literature
25310 results about "Carbon nanotube" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are tubes made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. Carbon nanotubes often refers to single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) with diameters in the range of a nanometer. They were discovered independently by Iijima and Ichihashi and Bethune et al. In carbon arc chambers similar to those used to produce fullerenes. Single-wall carbon nanotubes are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene.
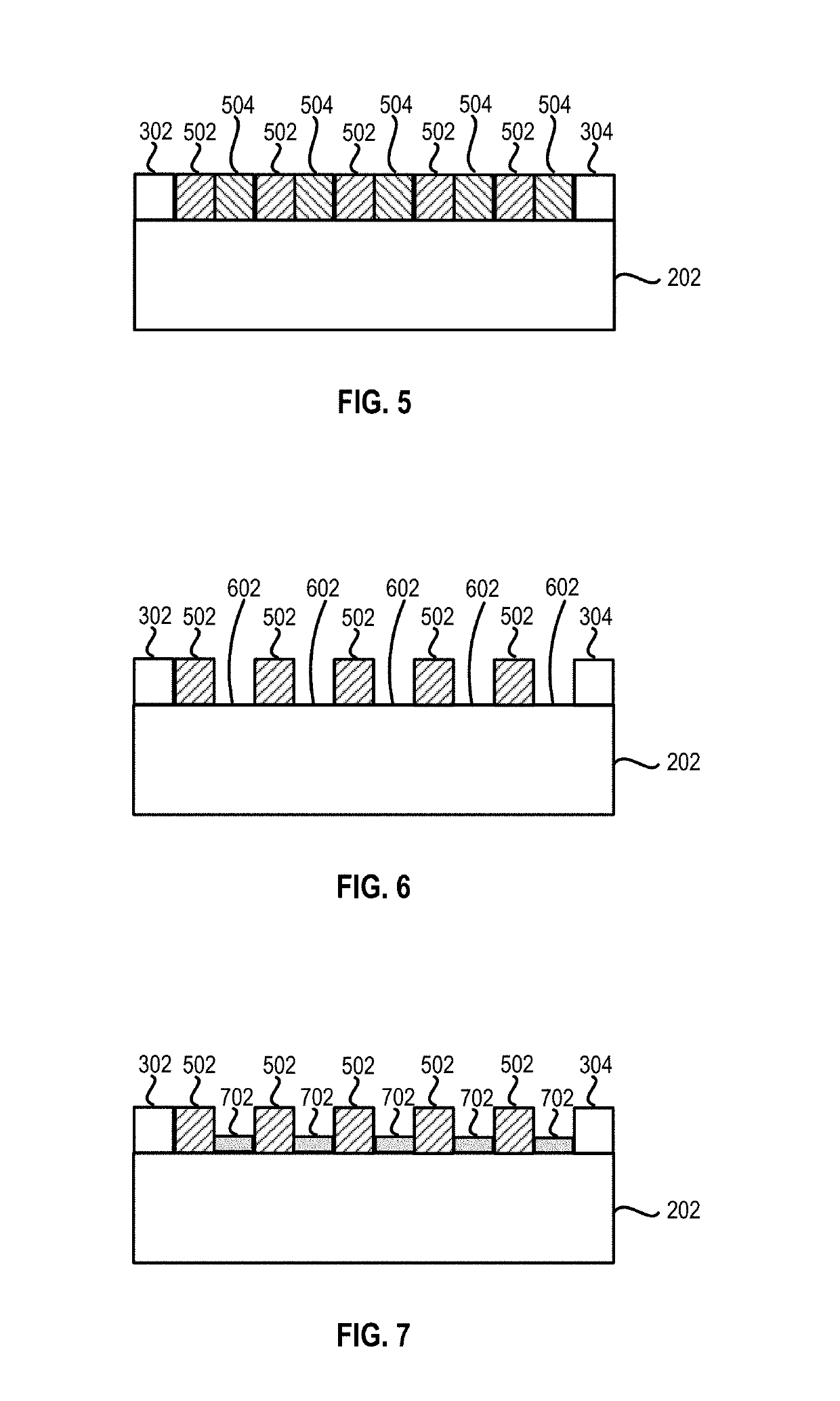
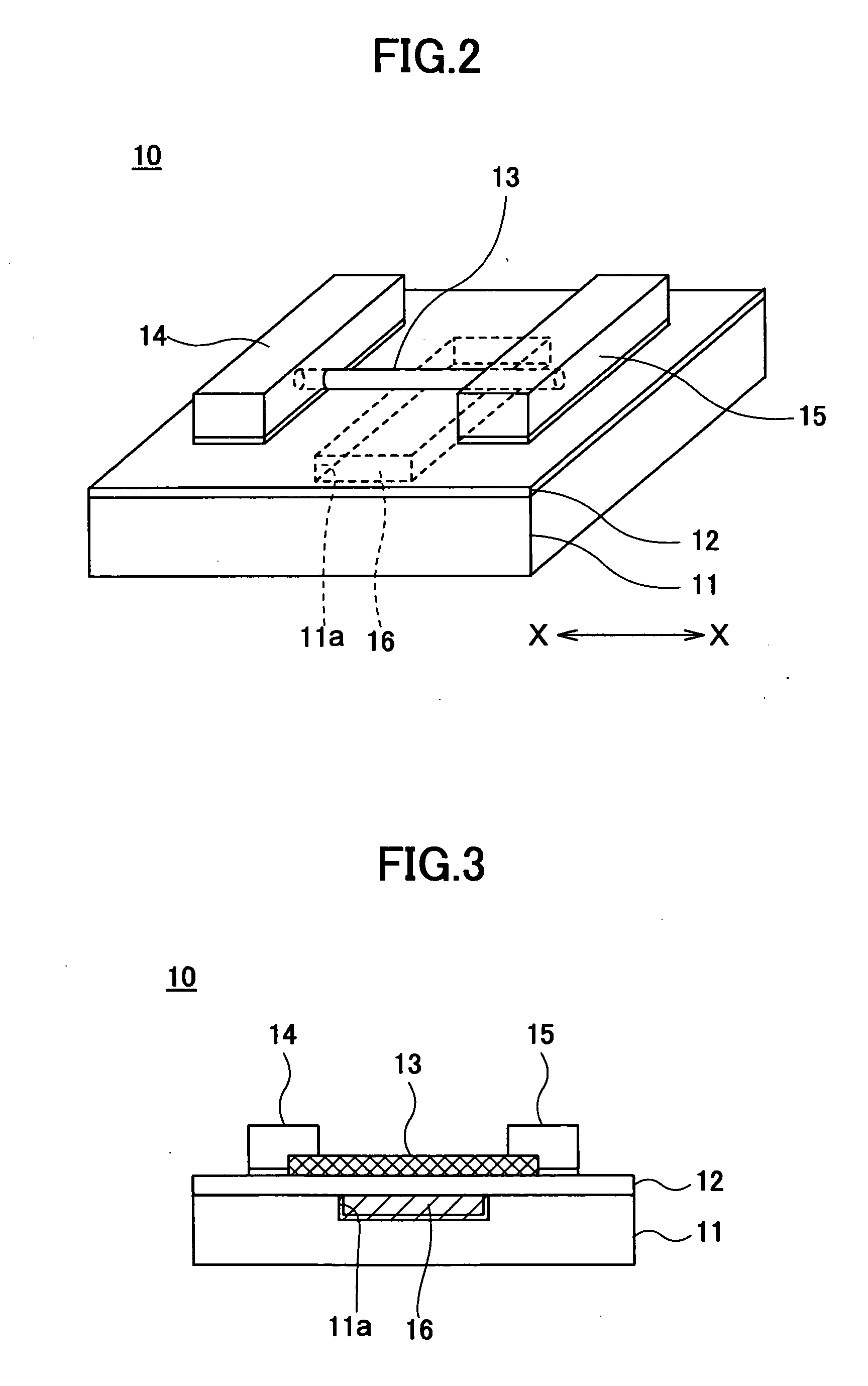
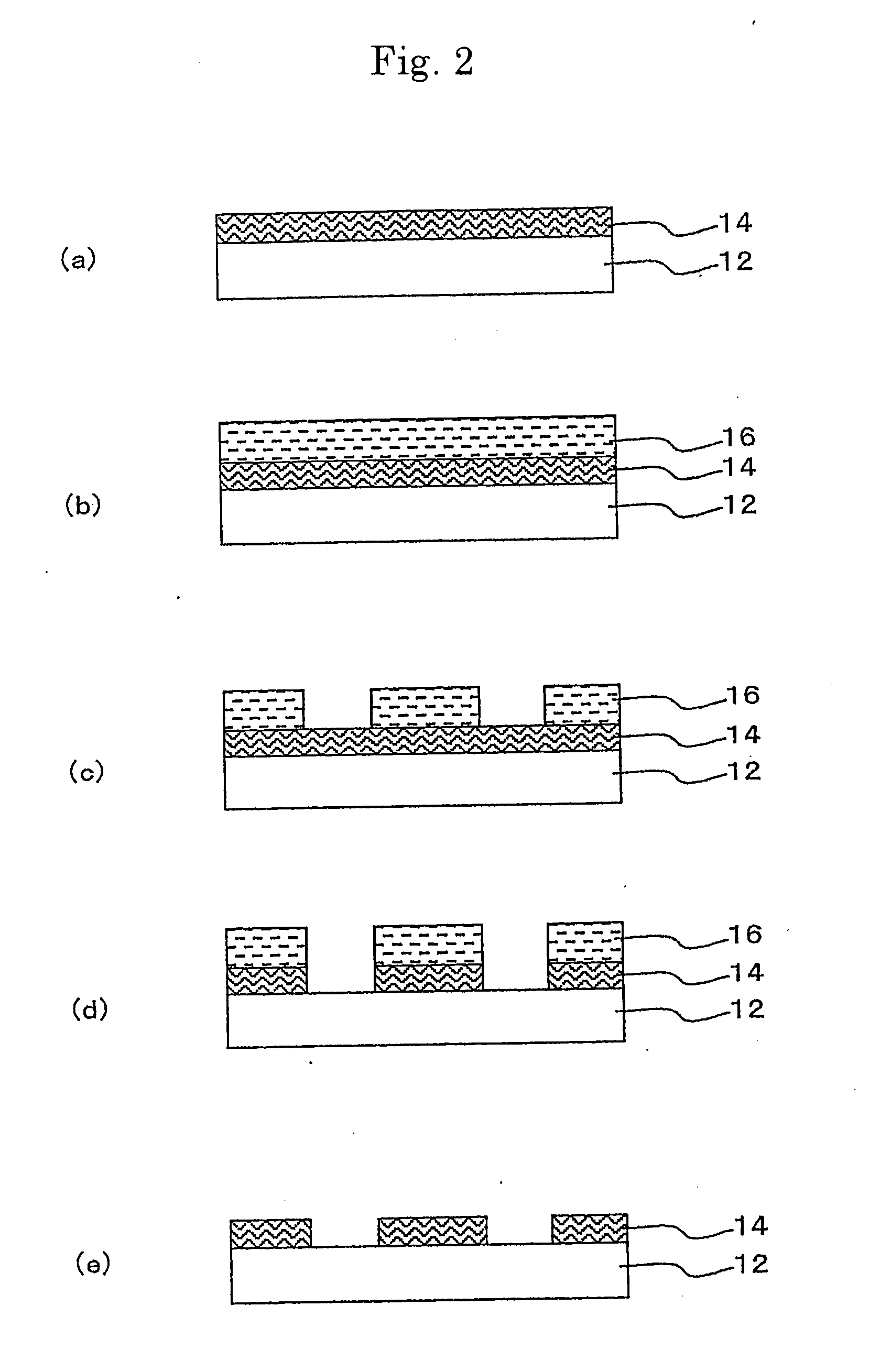
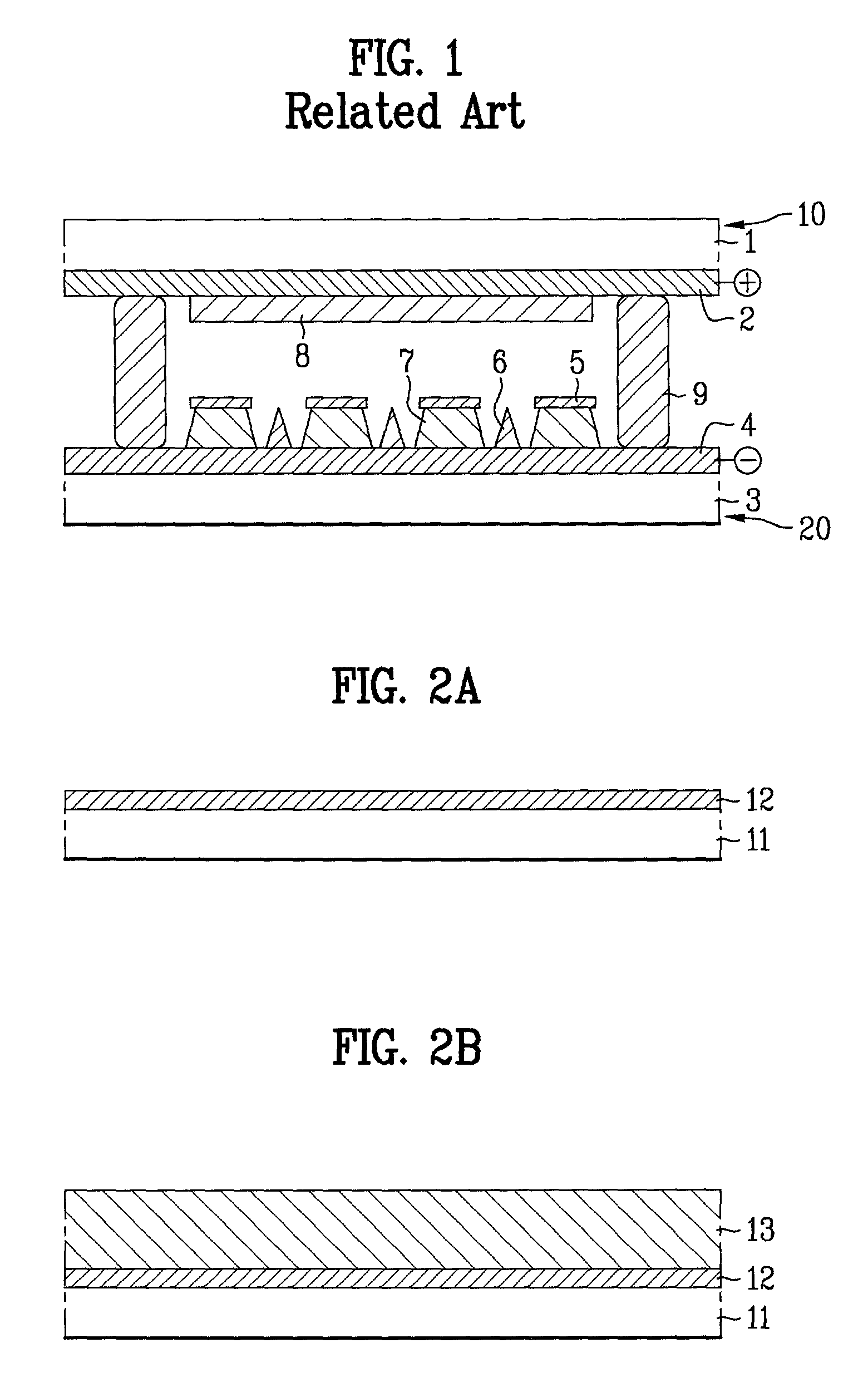
Carbon nano-tube thin film structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101239712ASmall surface to volume ratioNon stickyMaterial nanotechnologyLamination ancillary operationsOrganic solventFixed frame
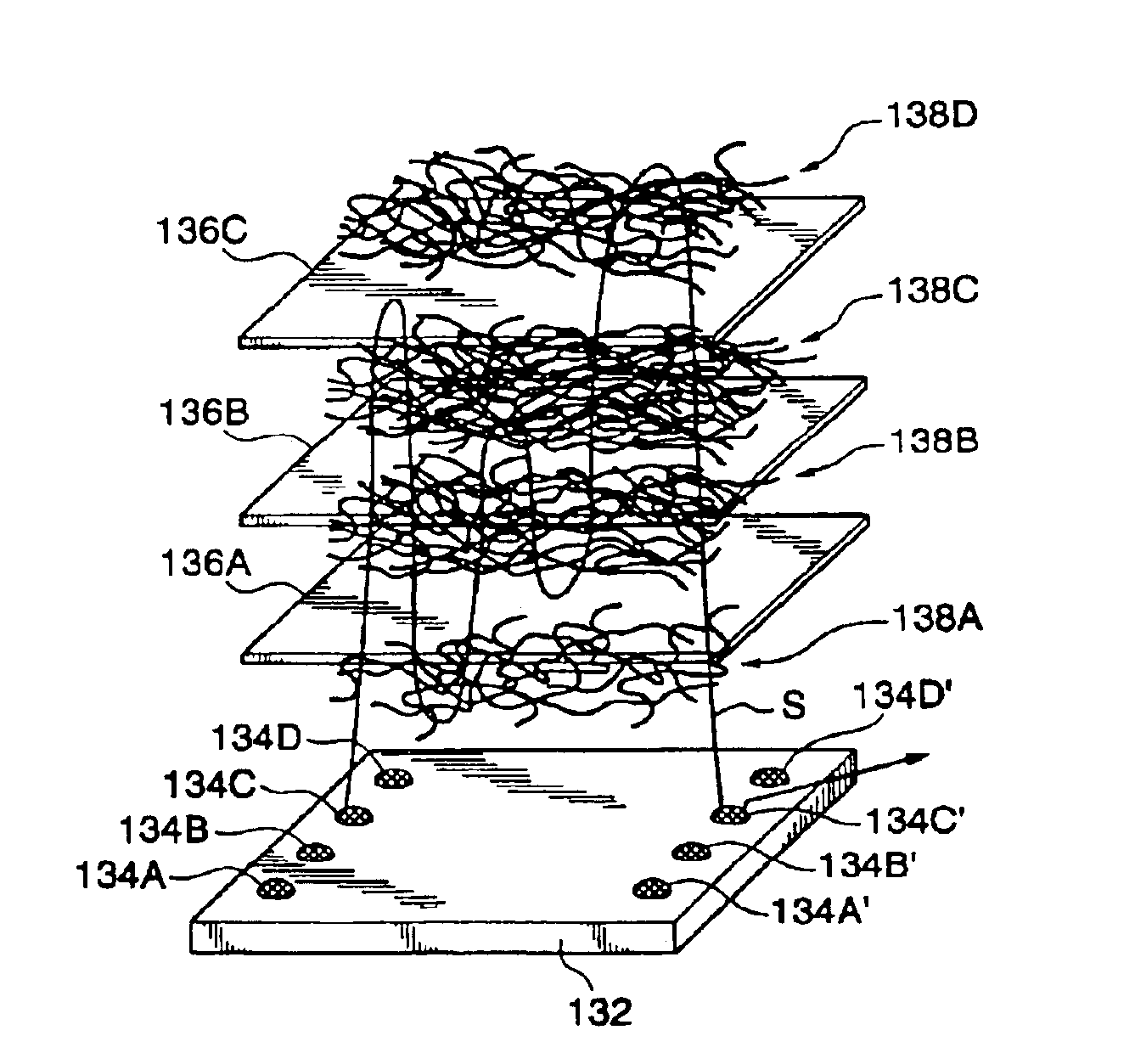
The present invention provides a preparing method of carbon nanotube film structure, including following steps: providing a carbon nanotube array; adopting a pulling tool to acquire at least two carbon nanotube films from the carbon nanotube array; providing a fixed frame, forming a multiple-layer carbon nanotube film structure by overlap adhereing the carbon nanotube film in the fixed frame; and treating the multiple-layer carbon nanotube film by an organic solvent. The carbon nanotube film structure prepared by the method includes at least two layers overlapped and cross-over installed carbon nanotube film, which includes multiple carbon nanotube bundle end to end and arranged in the direction, the multiple-layer carbon nanotube film further includes millipore crosswise formed by multiple carbon nanotube bundles.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Free-standing and aligned carbon nanotubes and synthesis thereof
One or more highly-oriented, multi-walled carbon nanotubes are grown on an outer surface of a substrate initially disposed with a catalyst film or catalyst nano-dot by plasma enhanced hot filament chemical vapor deposition of a carbon source gas and a catalyst gas at temperatures between 300° C. and 3000° C. The carbon nanotubes range from 4 to 500 nm in diameter and 0.1 to 50 μm in length depending on growth conditions. Carbon nanotube density can exceed 104 nanotubes / mm2. Acetylene is used as the carbon source gas, and ammonia is used as the catalyst gas. Plasma intensity, carbon source gas to catalyst gas ratio and their flow rates, catalyst film thickness, and temperature of chemical vapor deposition affect the lengths, diameters, density, and uniformity of the carbon nanotubes. The carbon nanotubes of the present invention are useful in electrochemical applications as well as in electron emission, structural composite, material storage, and microelectrode applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Single-wall carbon nanotube-polymer composites
This invention relates to single-wall carbon nanotube / polymer composites, a process for the production of such, and their use as fibers, films and articles.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Carbon nanotube hybrid system using carbide-derived carbon, a method of making the same, an electron emitter comprising the same, and an electron emission device comprising the electron emitter
InactiveUS20080248310A1Improve uniformityLong life-timeMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureHybrid systemHalogen
A carbon nanotube hybrid system includes: a carbide-derived carbon prepared by reacting a carbide compound and a halogen group containing gas to extract elements of the carbide compound except carbons; metals supported on the carbide-derived carbon or remaining in the carbide-derived carbon; and carbon sources from which carbon nanotubes are grown from the carbide-derived carbon. A method of preparing the carbon nanotube hybrid system includes preparing the carbide-derived carbon, extracting elements therefrom, and growing carbon nanotubes from the carbide-derived carbon. The carbon nanotube hybrid system has excellent uniformity and a long lifetime. An electron emitter having improved electron emitting properties can be inexpensively prepared using the carbon nanotube hybrid system compared to conventional carbon nanotubes. An electron emission device having excellent electron emitting properties can be prepared using the electron emitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Carbon nanotube structures, carbon nanotube devices using the same and method for manufacturing carbon nanotube structures
InactiveUS6921575B2Easy to manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsElectricityCarbon nanotube
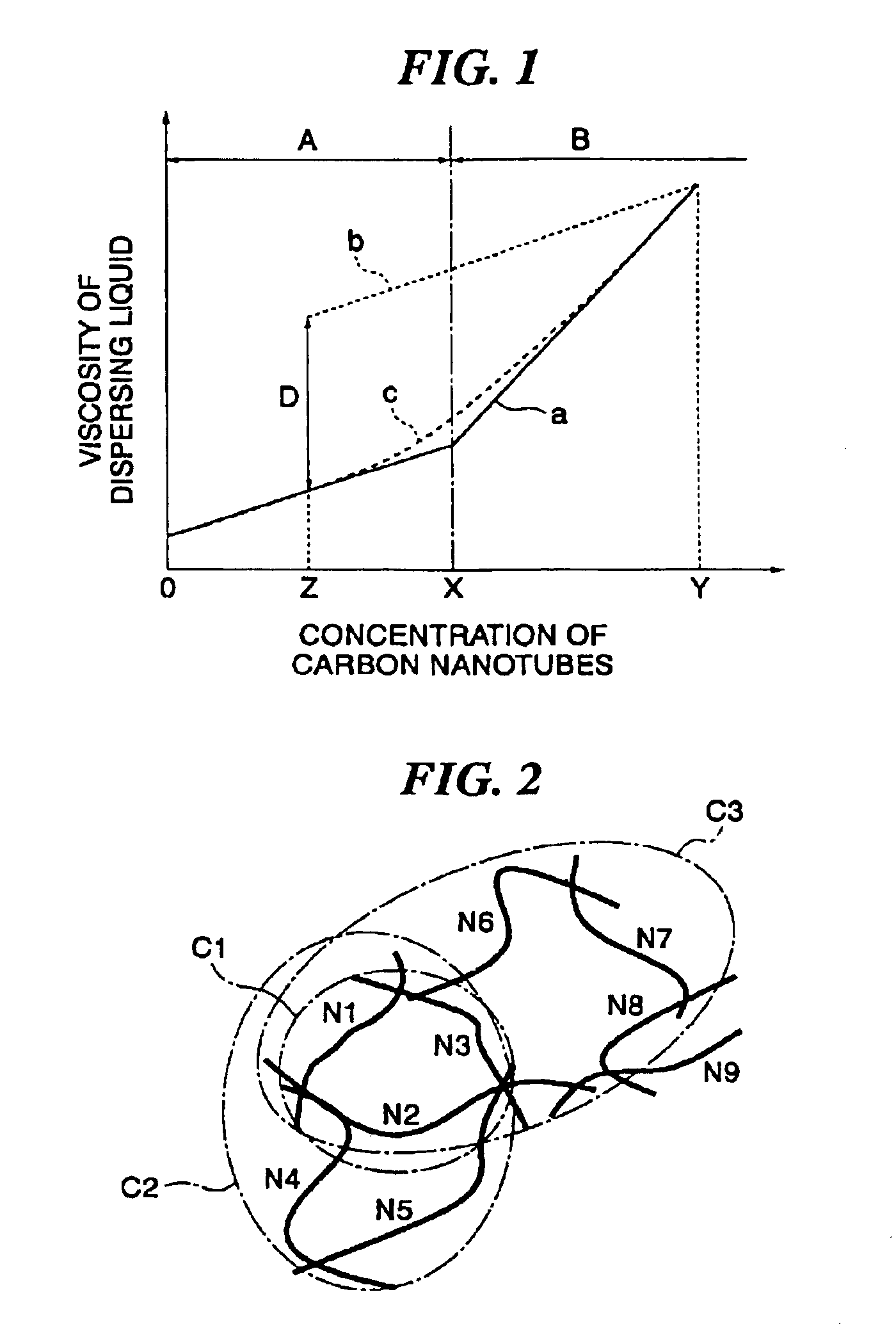
Carbon nanotube structures are provided, in which the networks with a desired area and volume, where the carbon nanotubes are electrically or magnetically connected, are formed and the method for easily manufacturing the carbon nanotube structures with less carbon nanotube structures. Carbon nanotube devices are also provided, to which the useful carbon nanotube structures mentioned above are applied. A method for manufacturing carbon nanotube structures includes the steps of applying carbon nanotubes to a low-viscosity dispersion medium to obtain a high-viscosity dispersing liquid which includes carbon nanotubes, and forming a network of the carbon nanotubes having electrical and / or magnetic connections therebetween by removing the low-viscosity dispersion medium from the high-viscosity dispersed liquid.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Method of preparing catalyst for manufacturing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20070020167A1Improve uniformityMinimize agglomerationMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureFreeze-dryingCarbon nanotube
A novel method of forming catalyst particles, on which carbon nanotubes grow based, on a substrate with increased uniformity, and a method of synthesizing carbon nanotubes having improved uniformity are provided. A catalytic metal precursor solution is applied to a substrate. The applied catalytic metal precursor solution is freeze-dried, and then reduced to catalytic metal. The method of forming catalyst particles can minimize agglomeration and / or recrystallization of catalyst particles when forming the catalyst particles by freeze-drying the catalyst metal precursor solution. The catalyst particles formed by the method has a very uniform particle size and are very uniformly distributed on the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
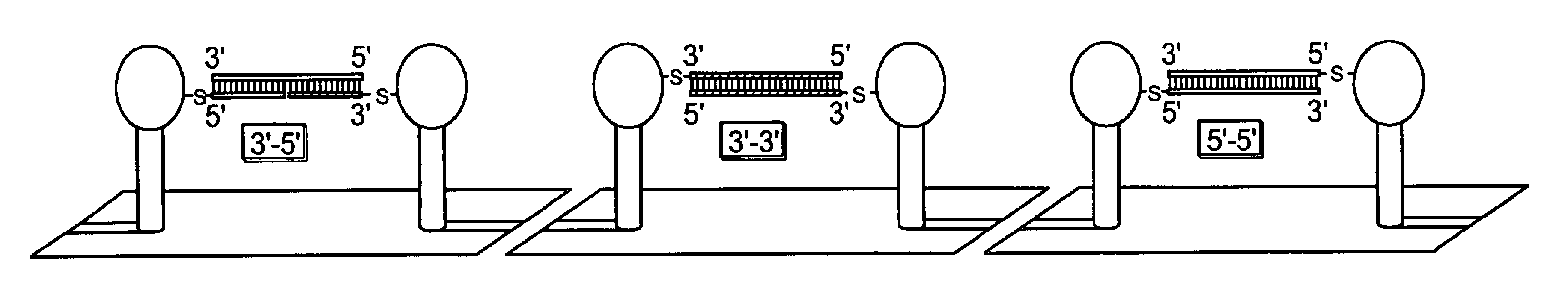
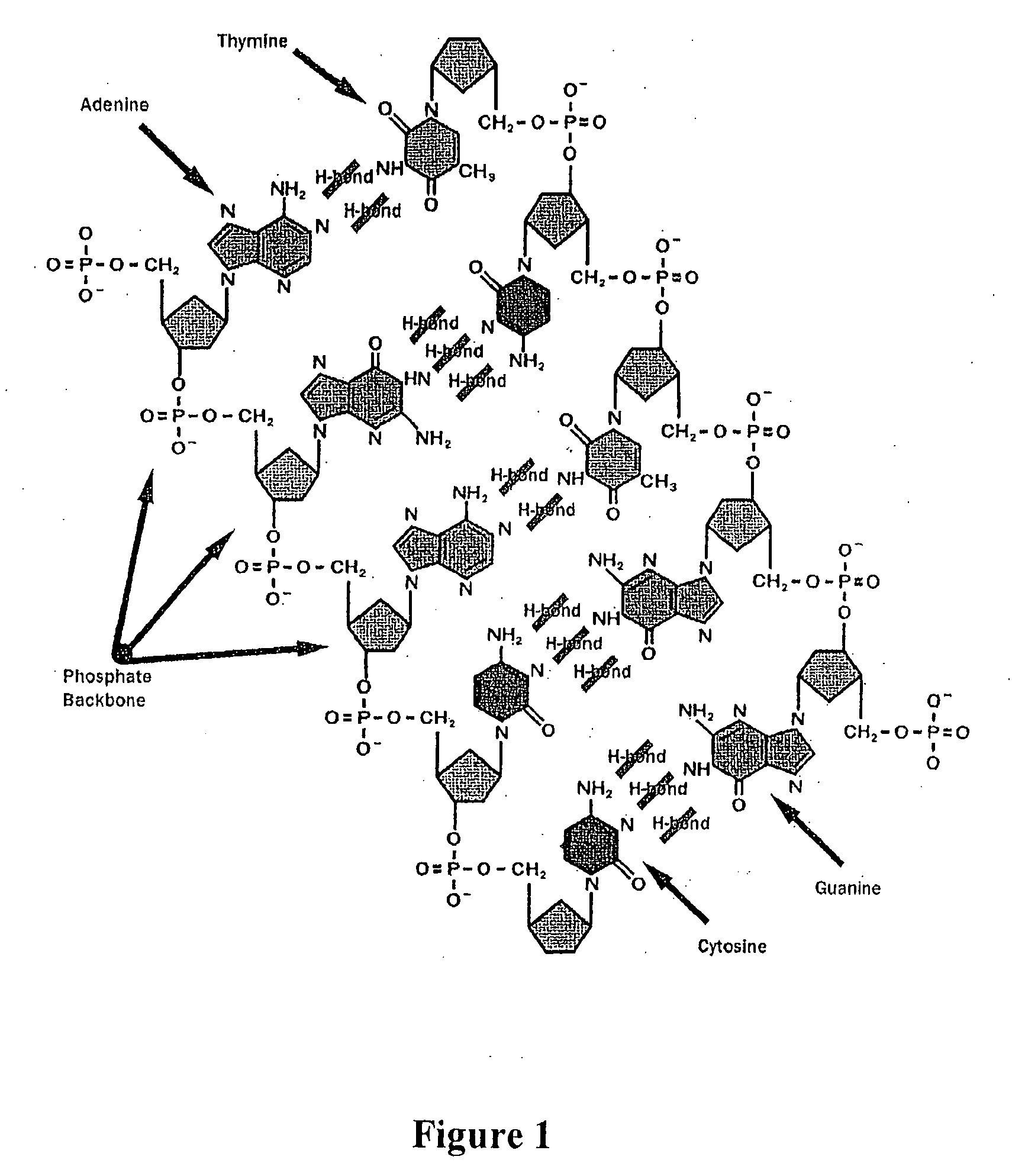
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS20020172963A1High precisionHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
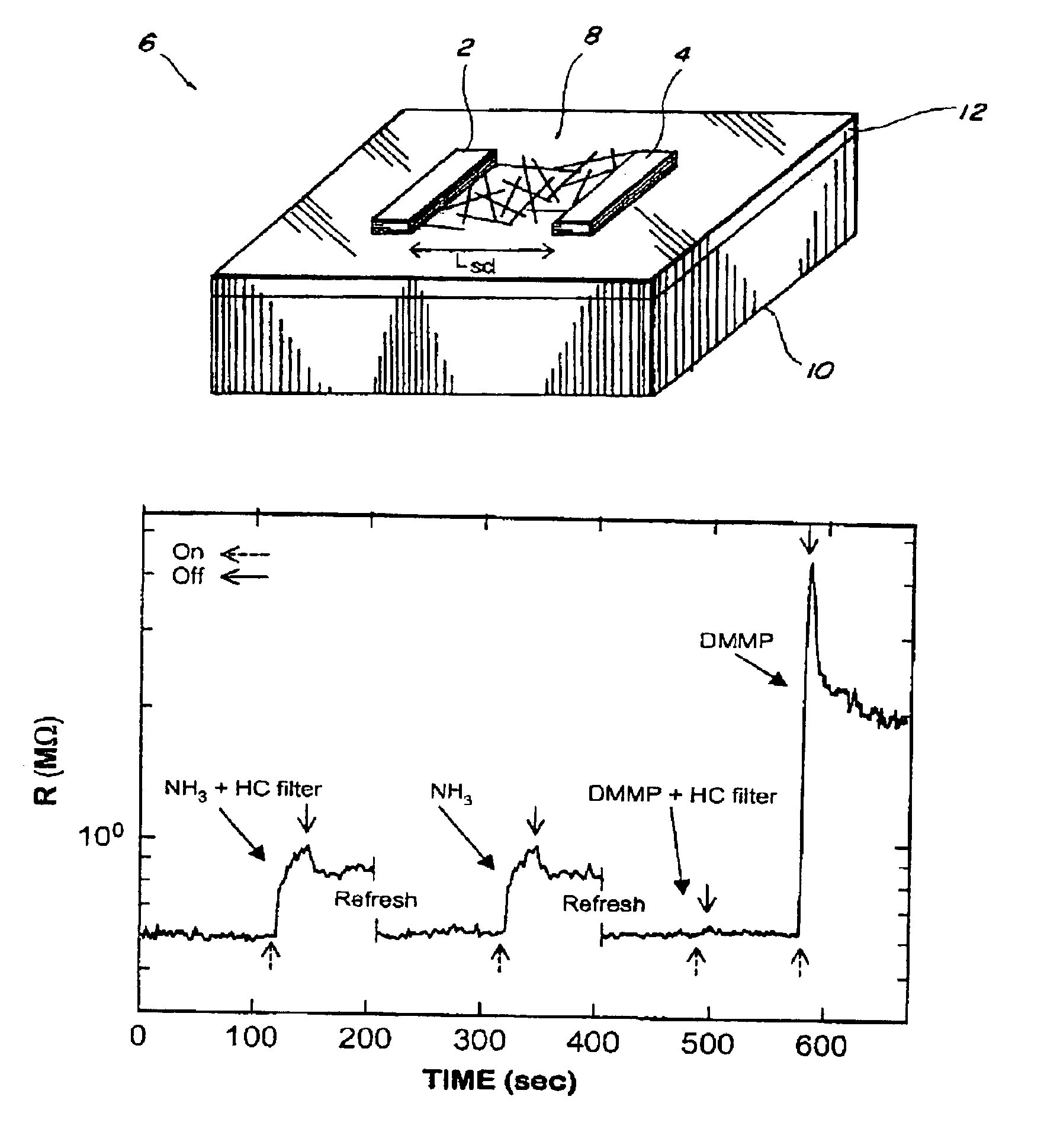
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
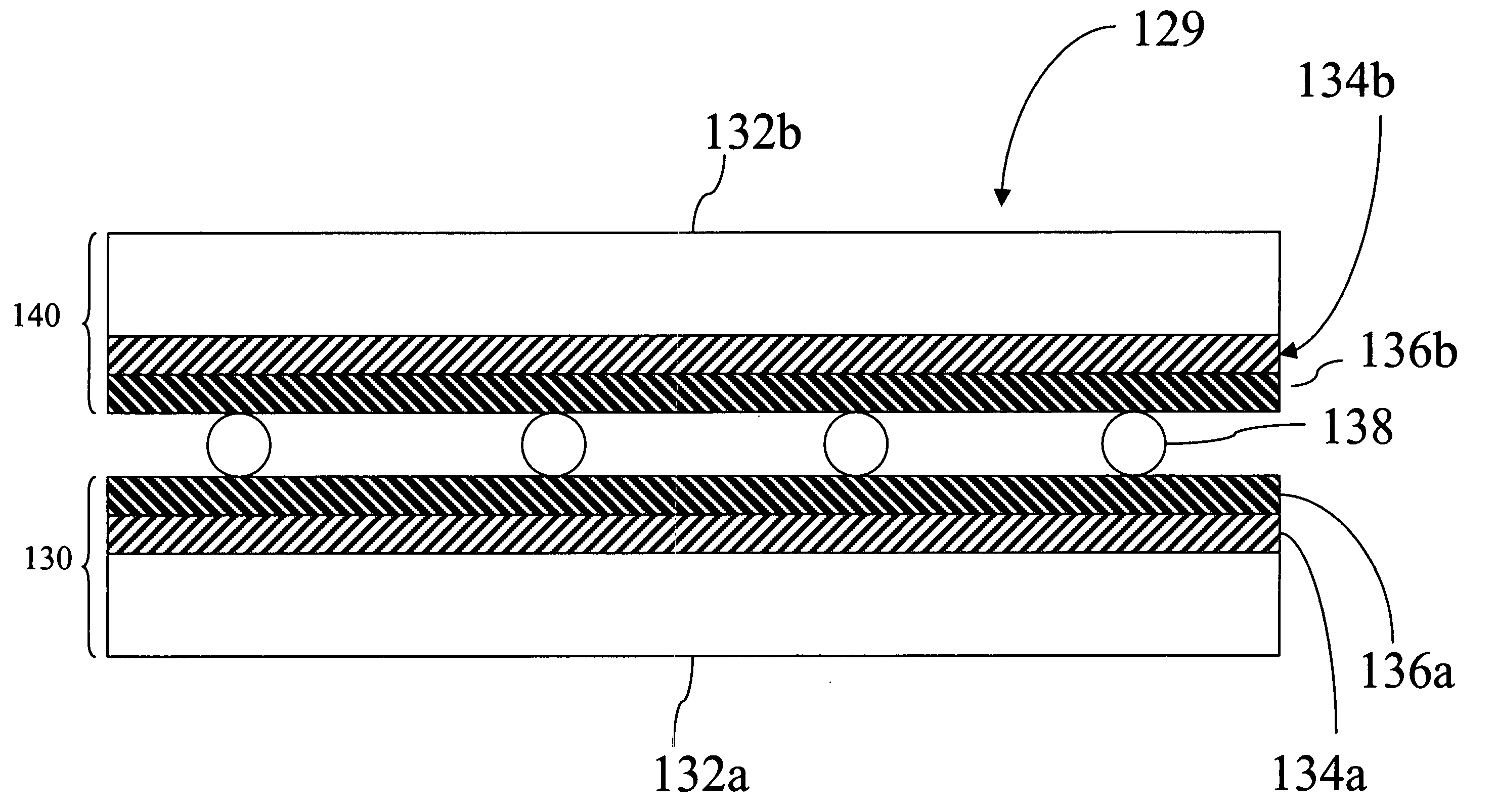
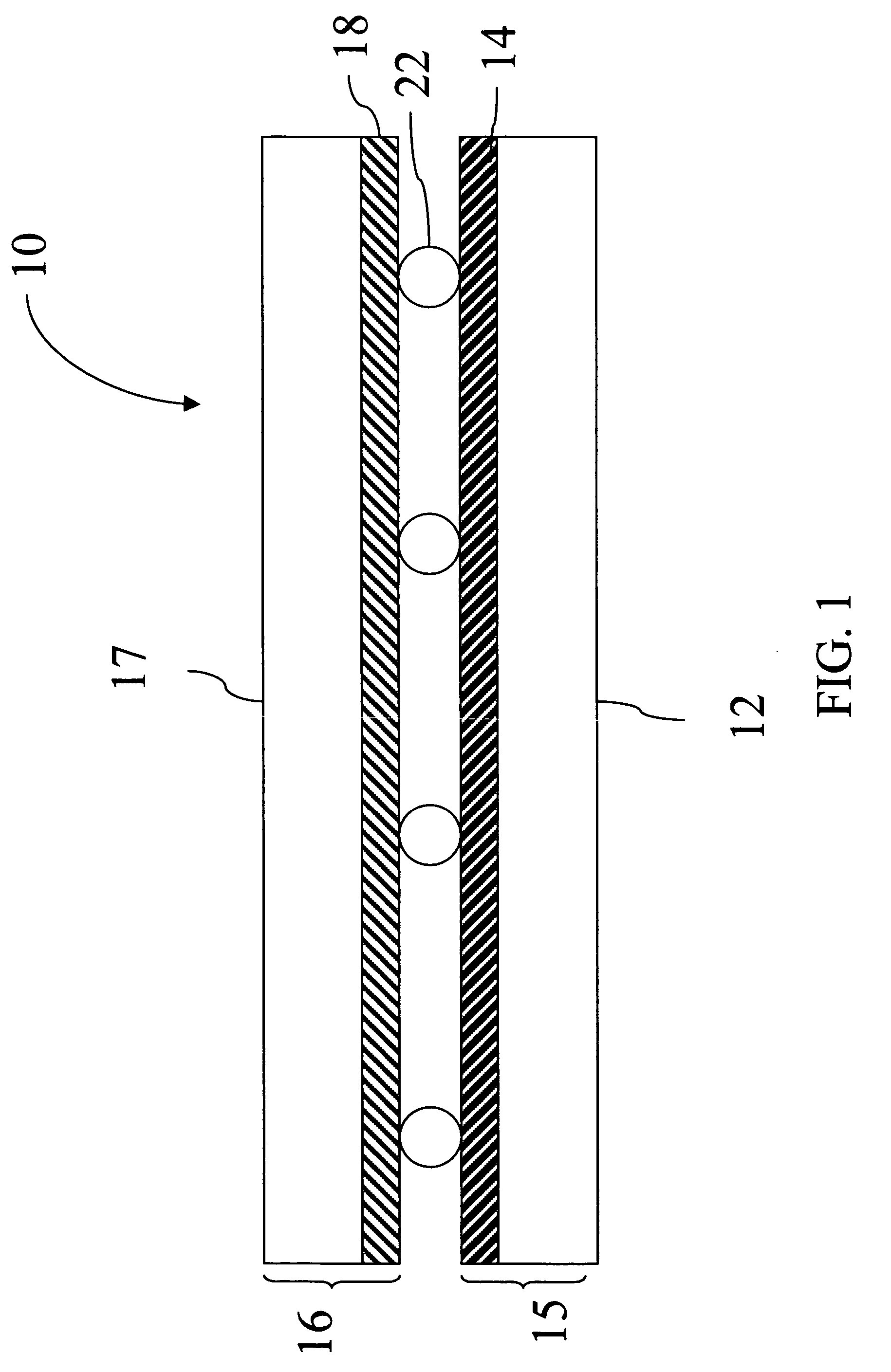
Multi-layer conductor with carbon nanotubes
The present invention is directed to an electronically conductive article comprising at least one conductive carbon nanotube layer in contact with at least one conductive layer comprising electronically conductive polymer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Aligned carbon nanotubes
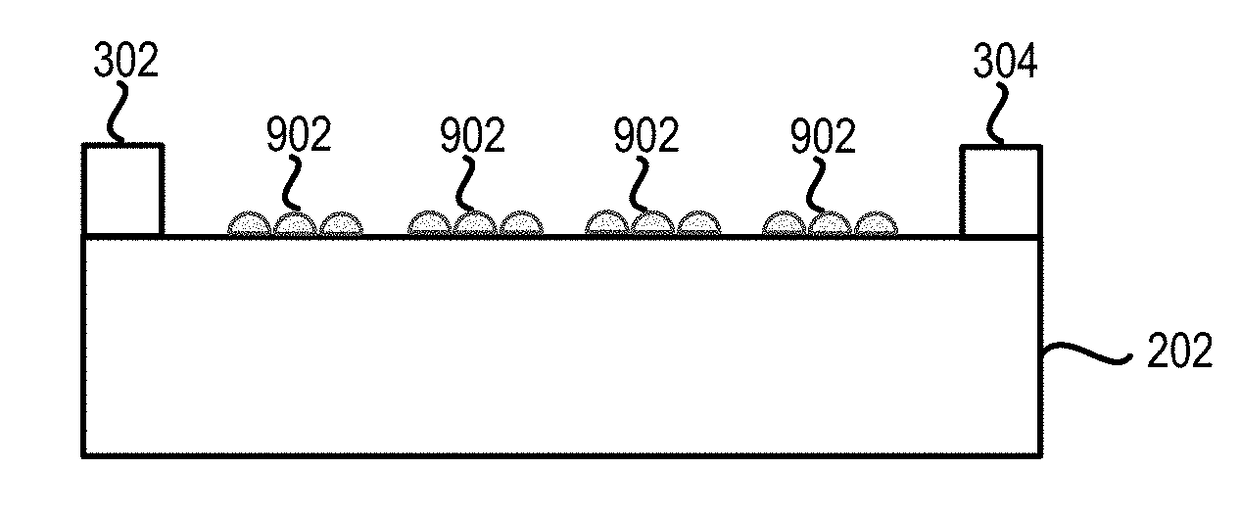
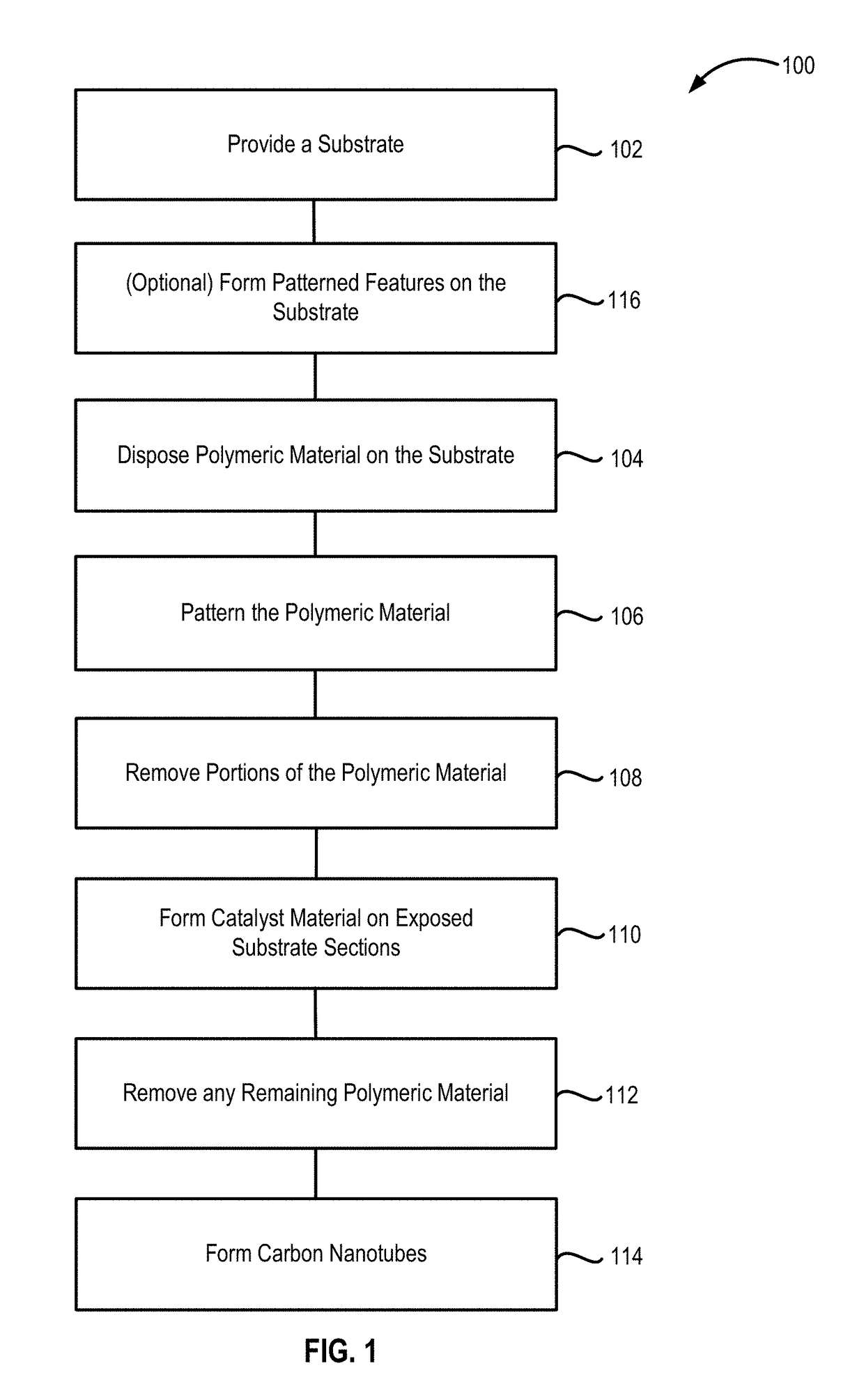
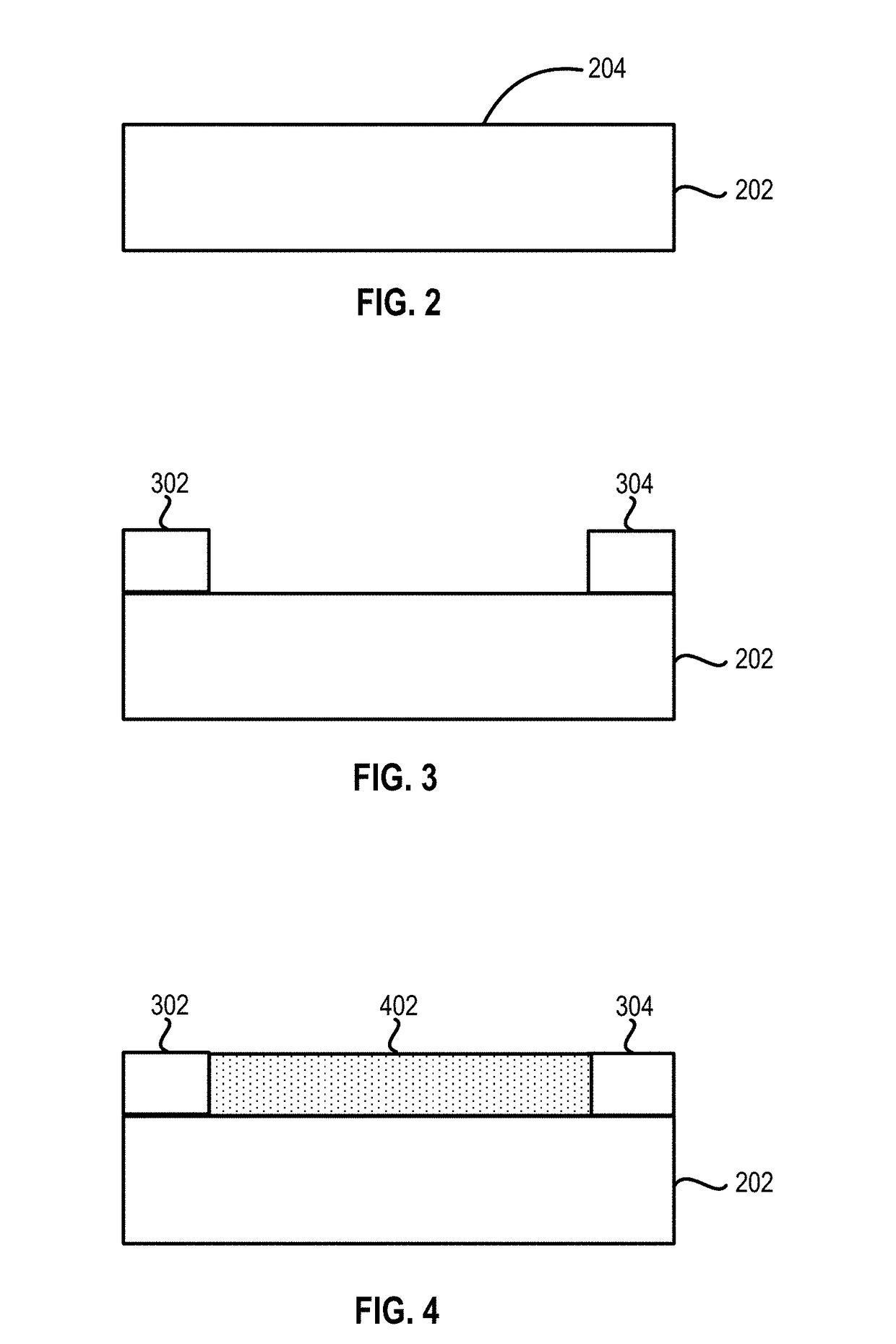
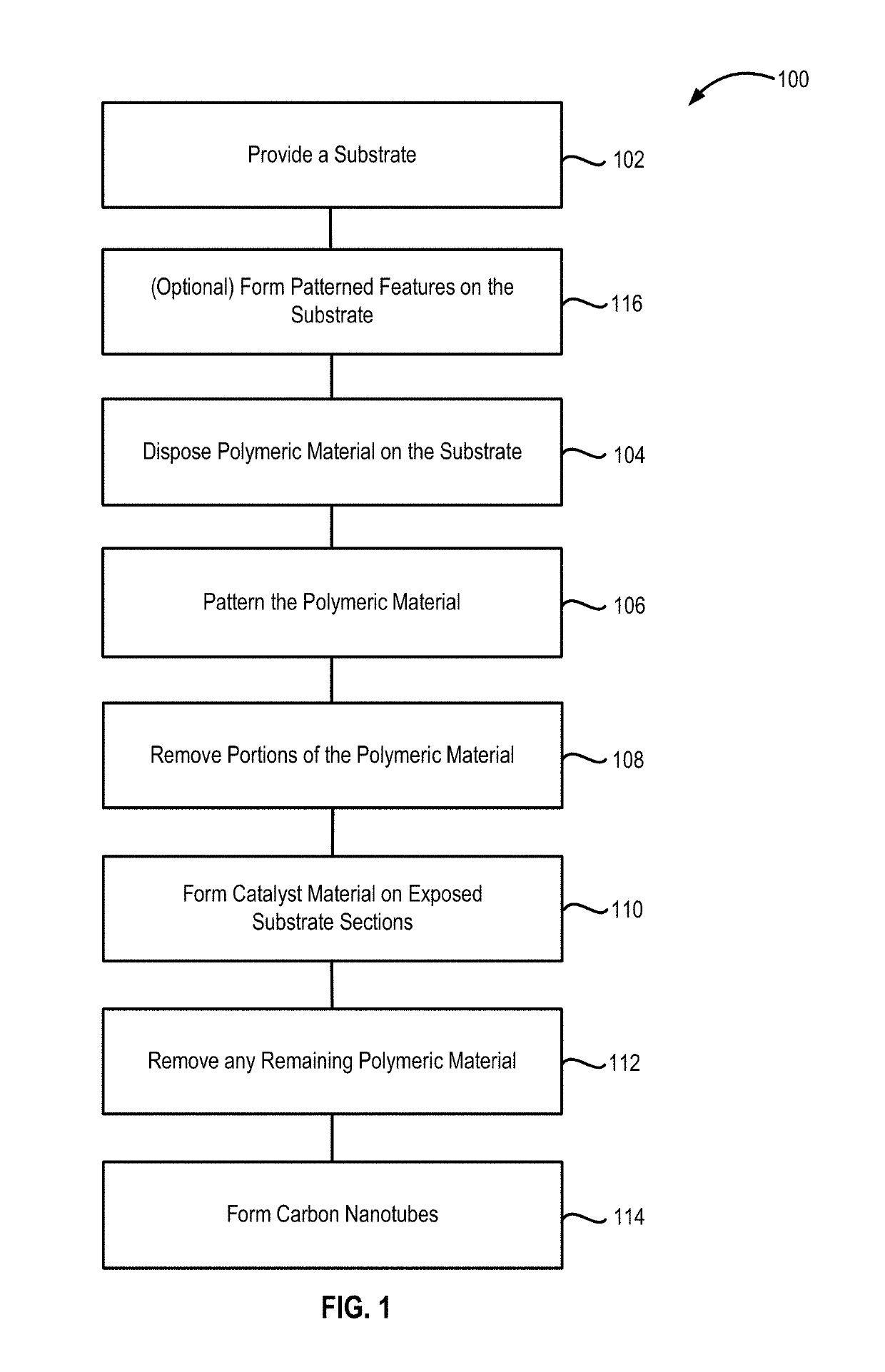
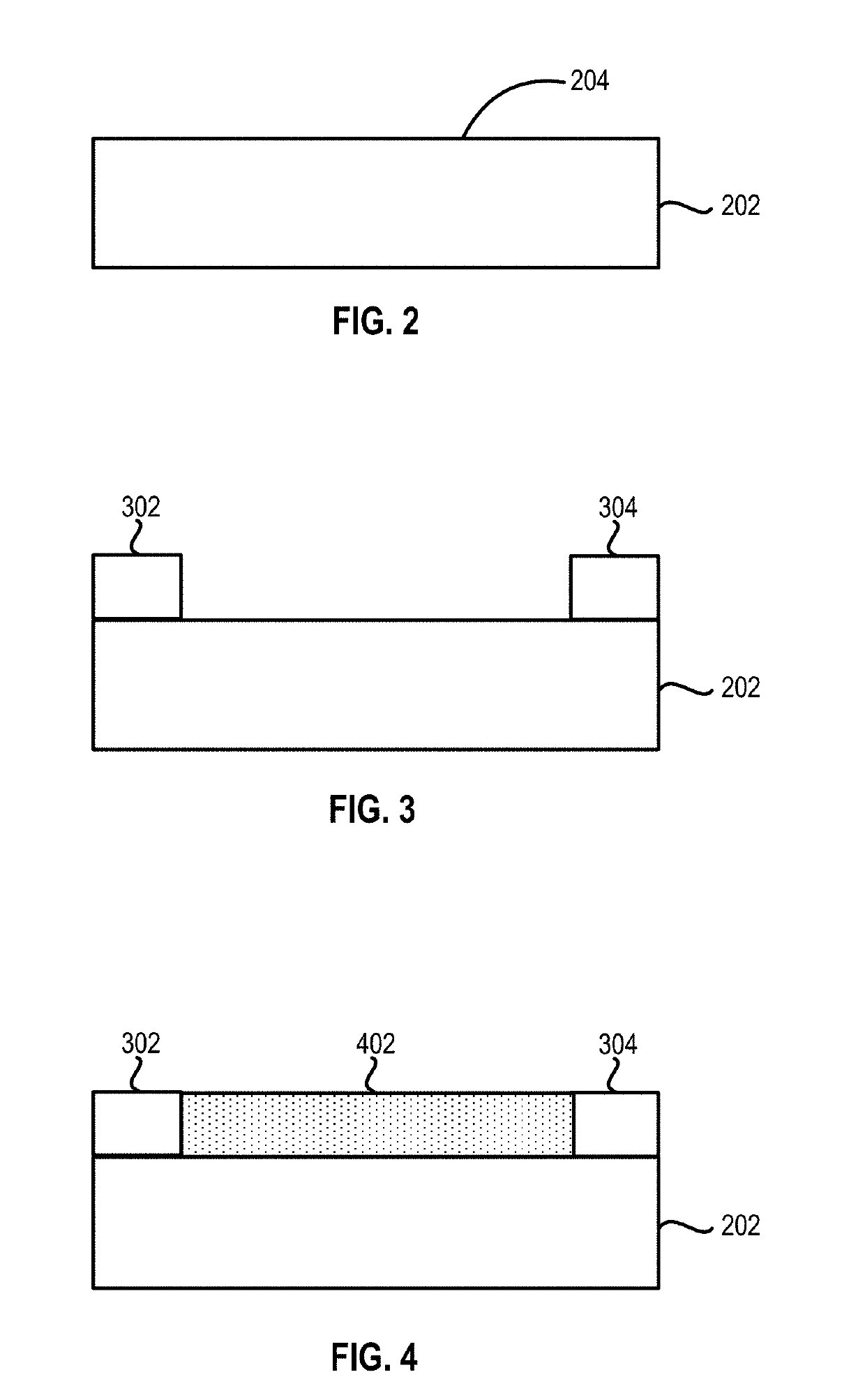
Methods of forming carbon nanotubes and structures and devices including carbon nanotubes are disclosed. Methods of forming the carbon nanotubes include patterning a surface of a substrate with polymeric material, removing portions of the polymeric material to form exposed substrate surface sections, and forming the carbon nanotubes on the exposed substrate sections.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
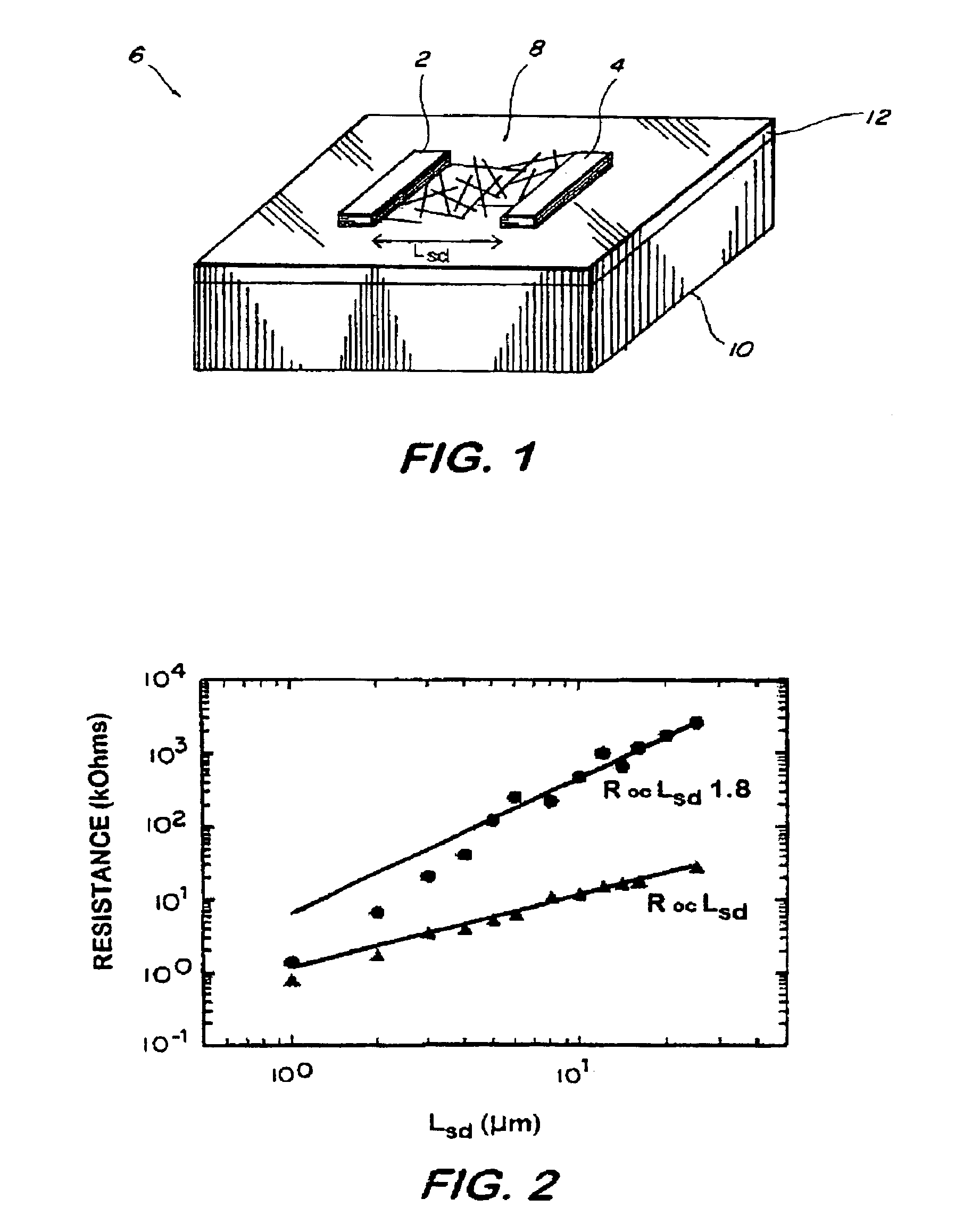
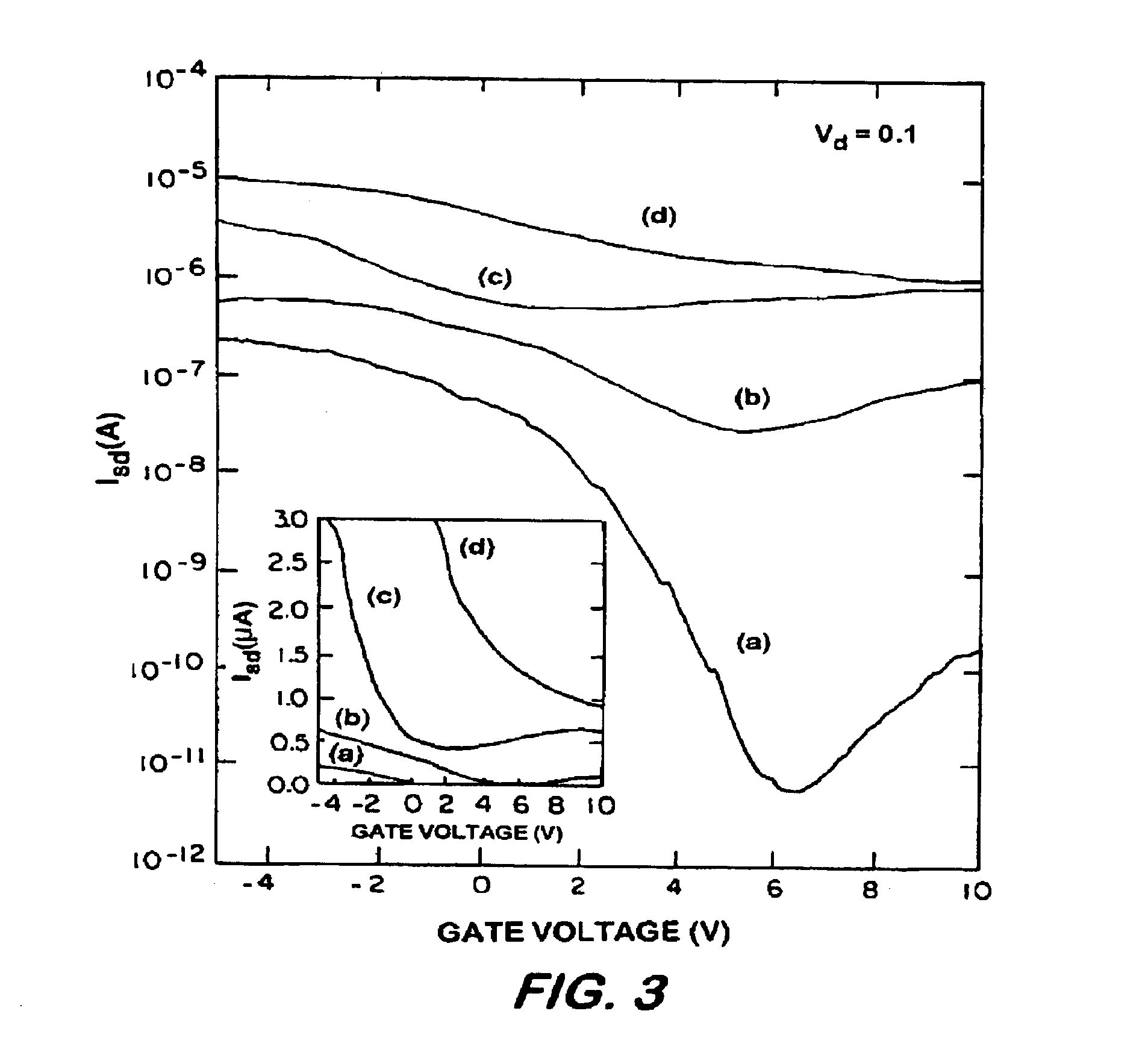
Interconnected networks of single-walled carbon nanotubes
An electronic device having an interconnected network of carbon nanotubes on the surface of a substrate, and two or more electrical leads. The network forms an electrical connection between the leads.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Aligned carbon nanotubes
Methods of forming carbon nanotubes and structures and devices including carbon nanotubes are disclosed. Methods of forming the carbon nanotubes include patterning a surface of a substrate with polymeric material, removing portions of the polymeric material to form exposed substrate surface sections, and forming the carbon nanotubes on the exposed substrate sections.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Polymer binders for flexible and transparent conductive coatings containing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050209392A1Decrease in optical transparencyDecrease in surface conductivityMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresThermoplasticCarbon nanotube
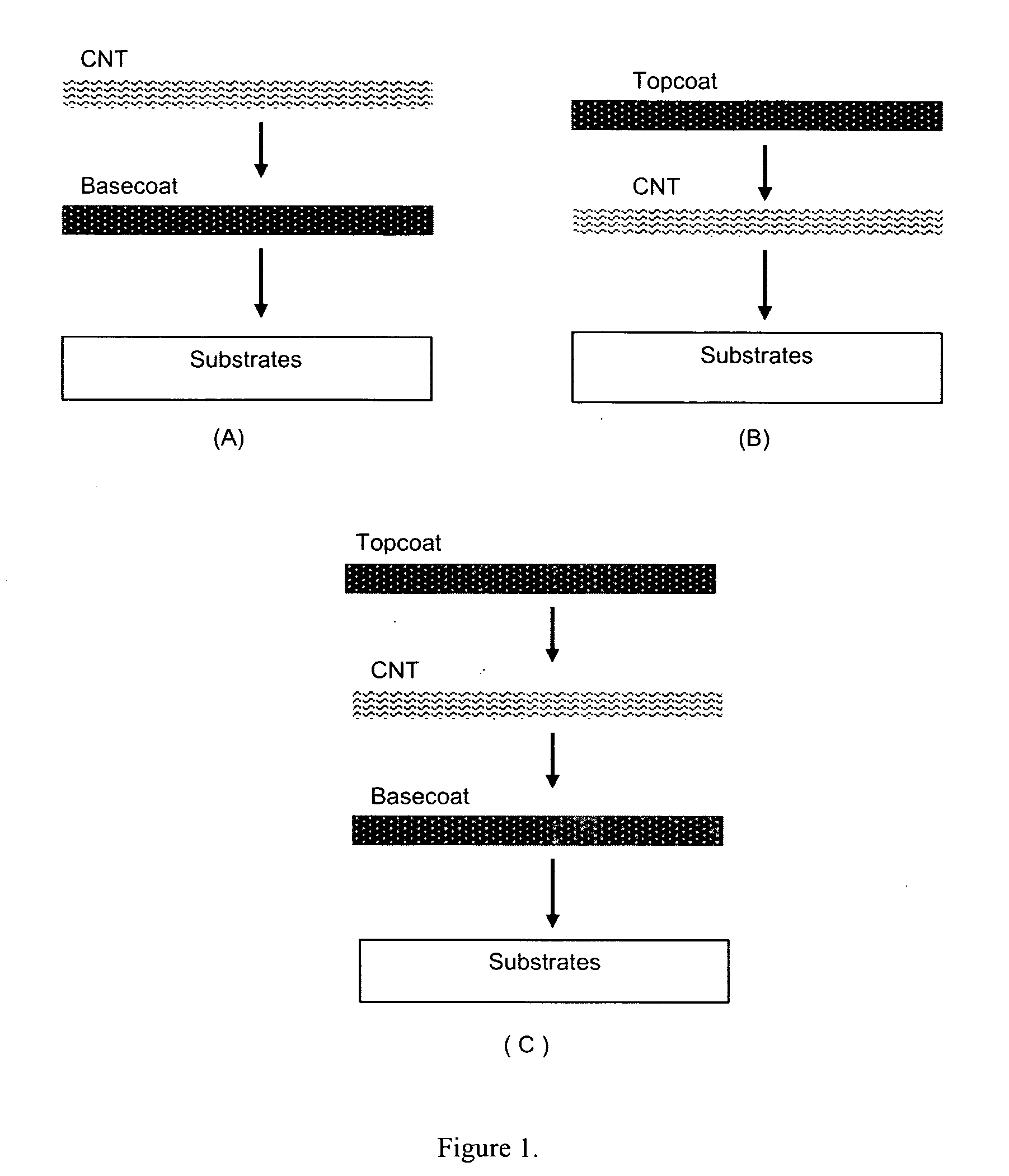
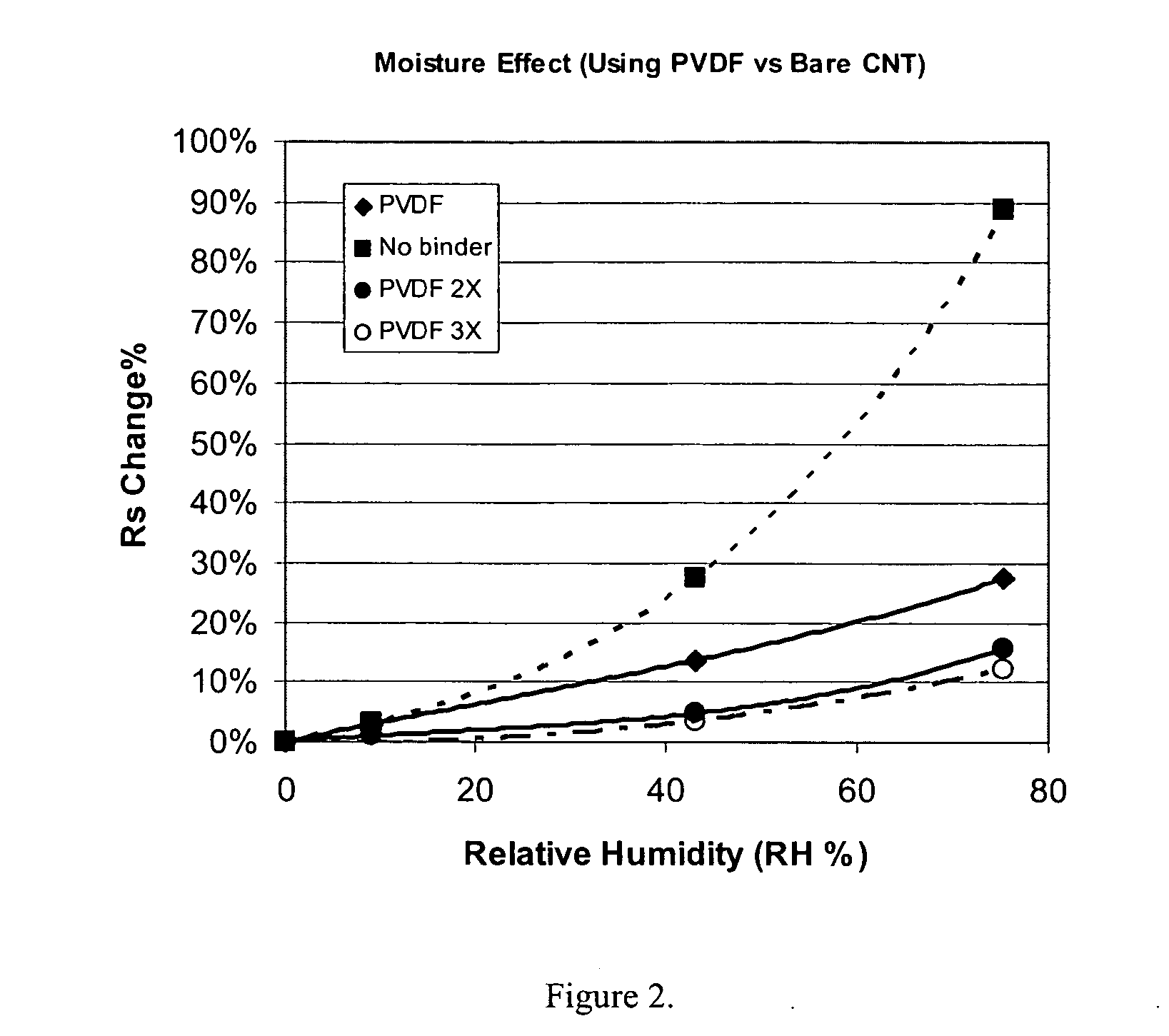
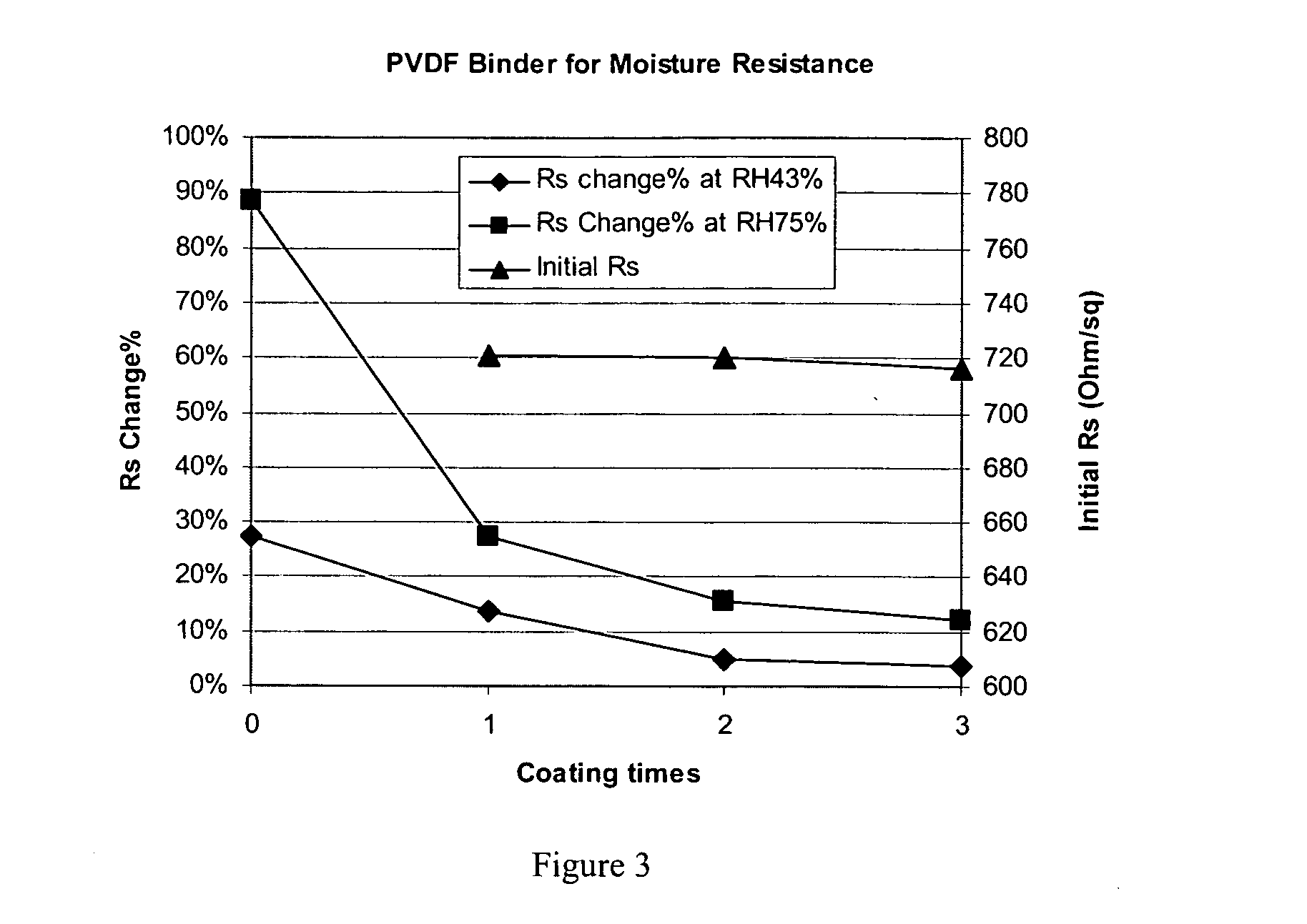
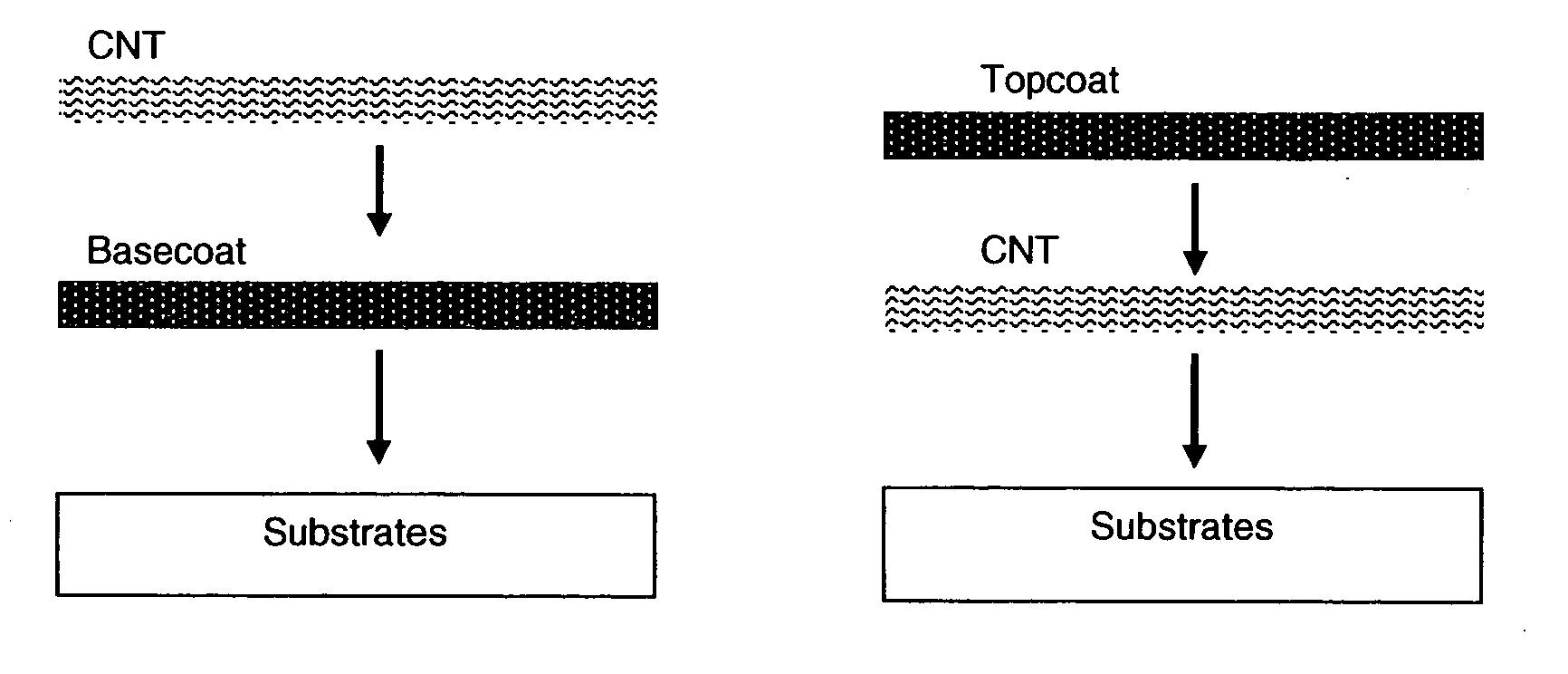
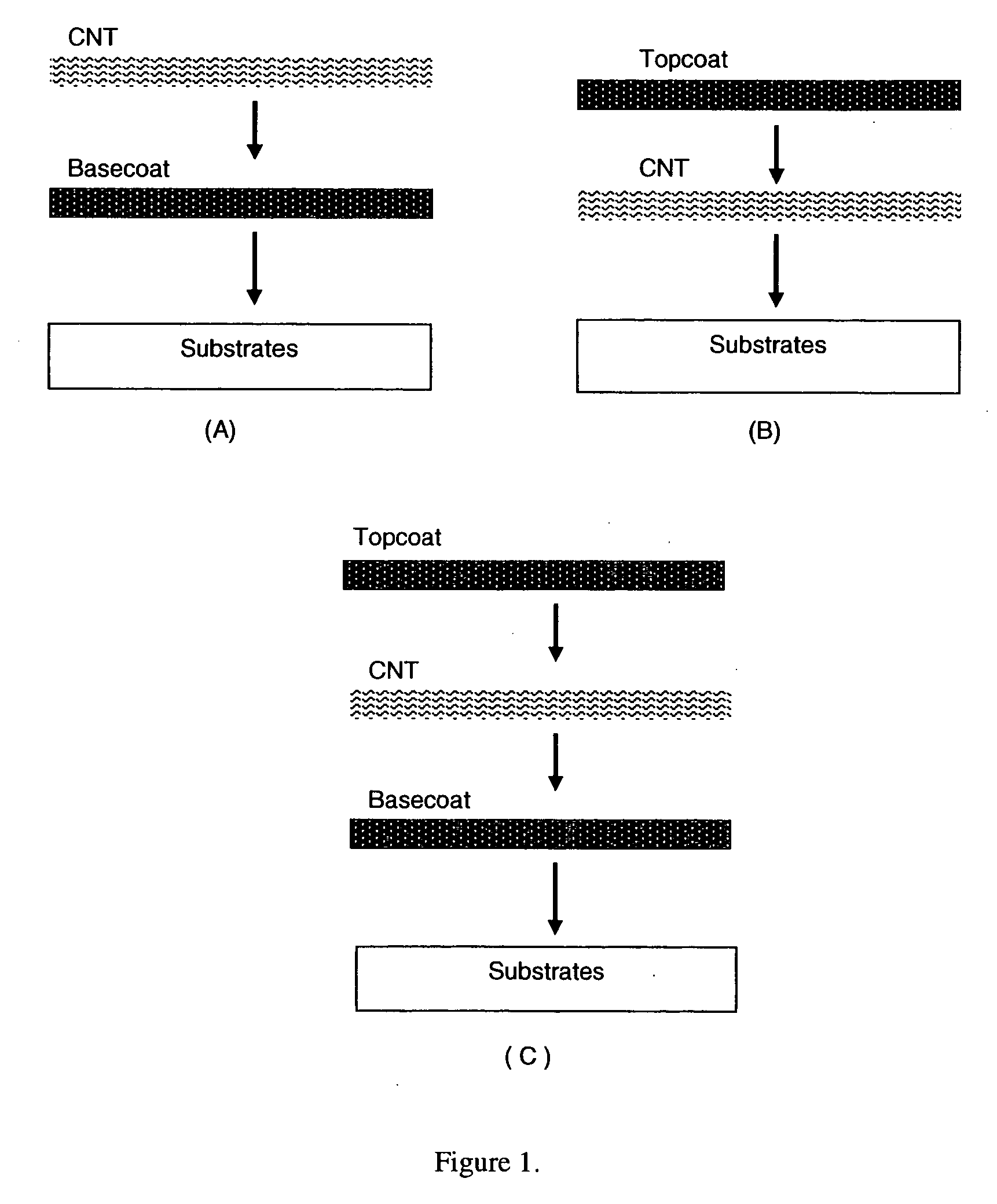
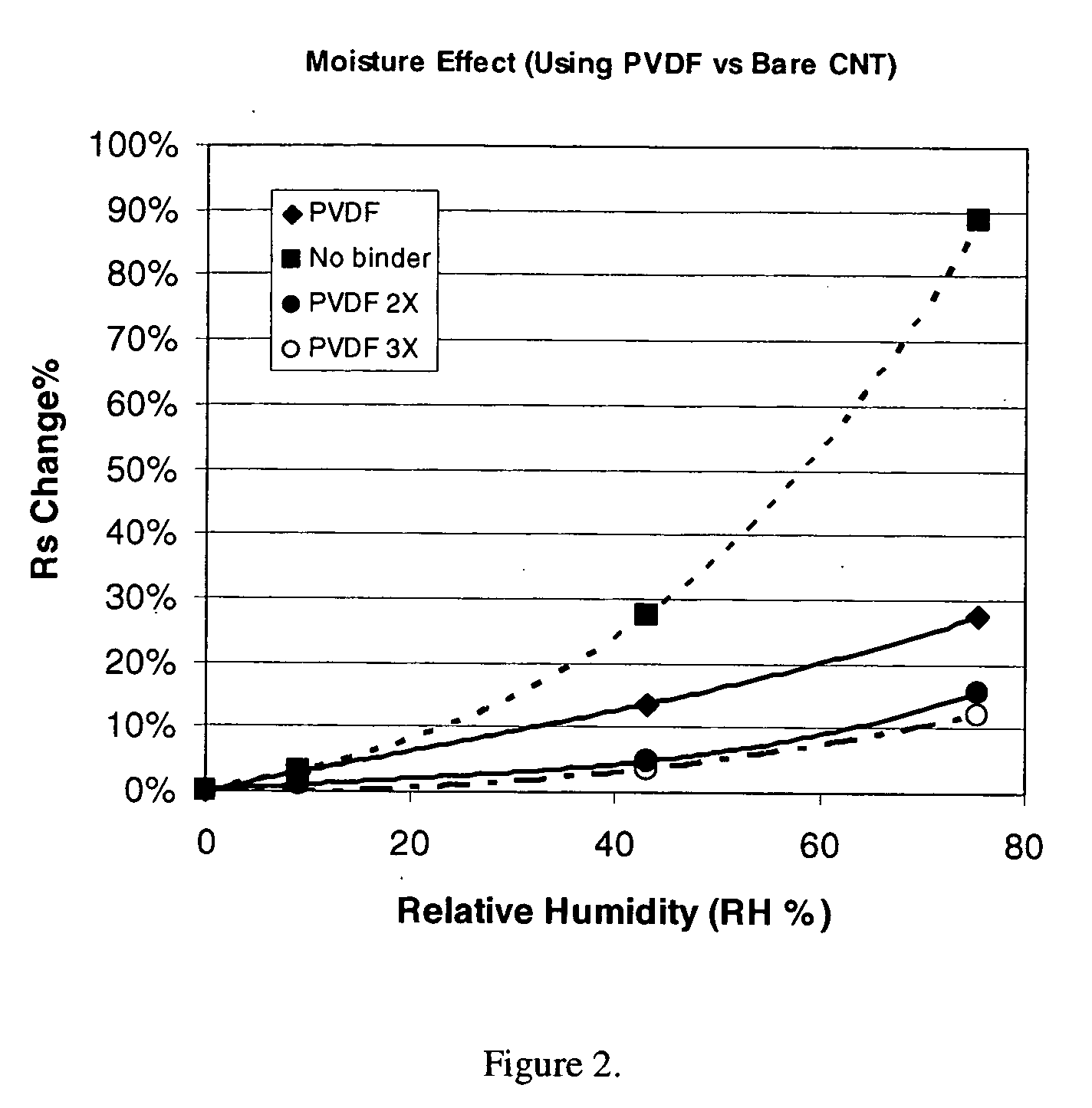
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using single wall carbon nanotubes and polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes (CNT) applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for the enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or any combination of both. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. Resulting films and articles can be used as transparent conductors for flat panel display, touch screen and other electronic devices.
Owner:EIKOS
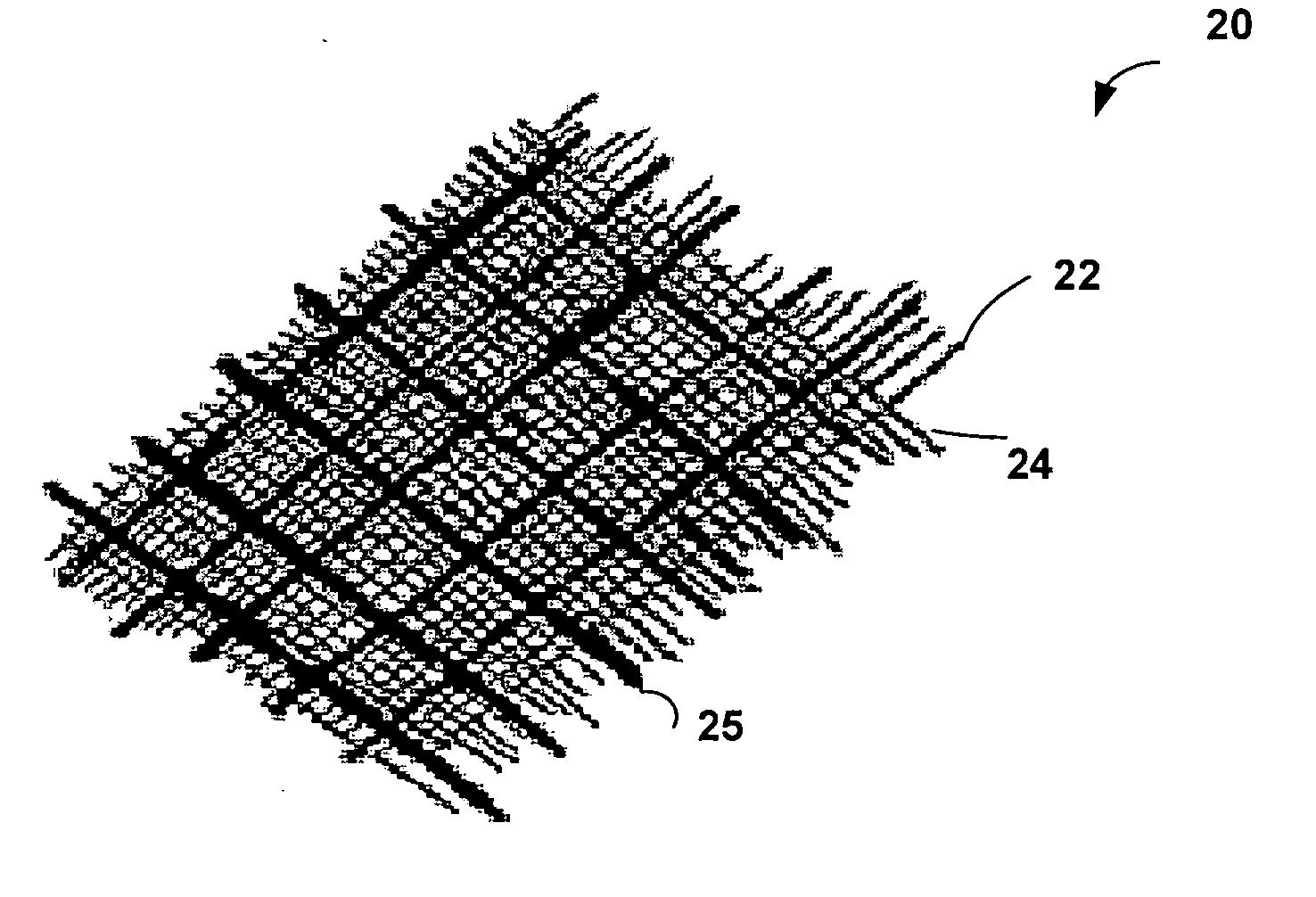
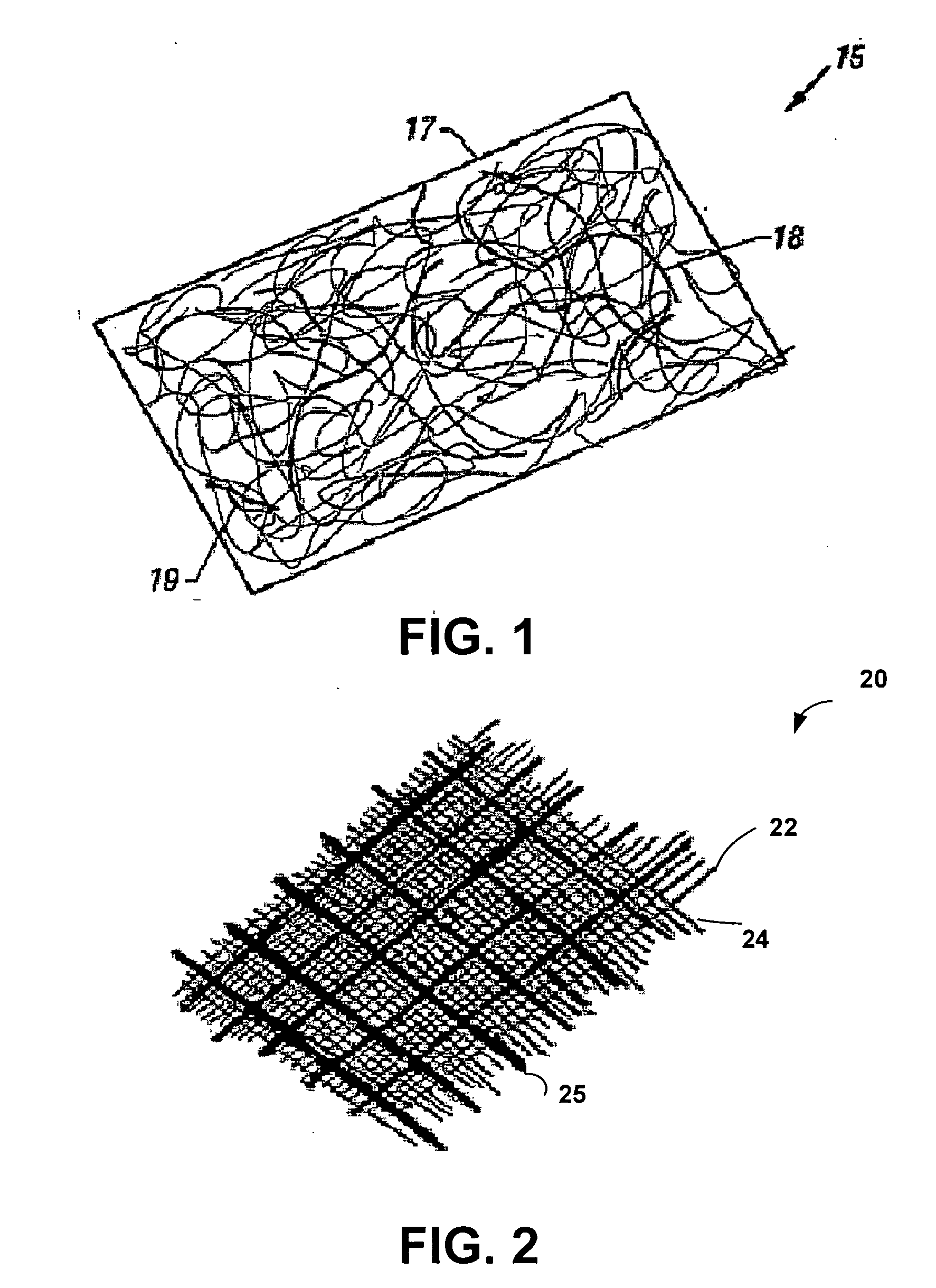
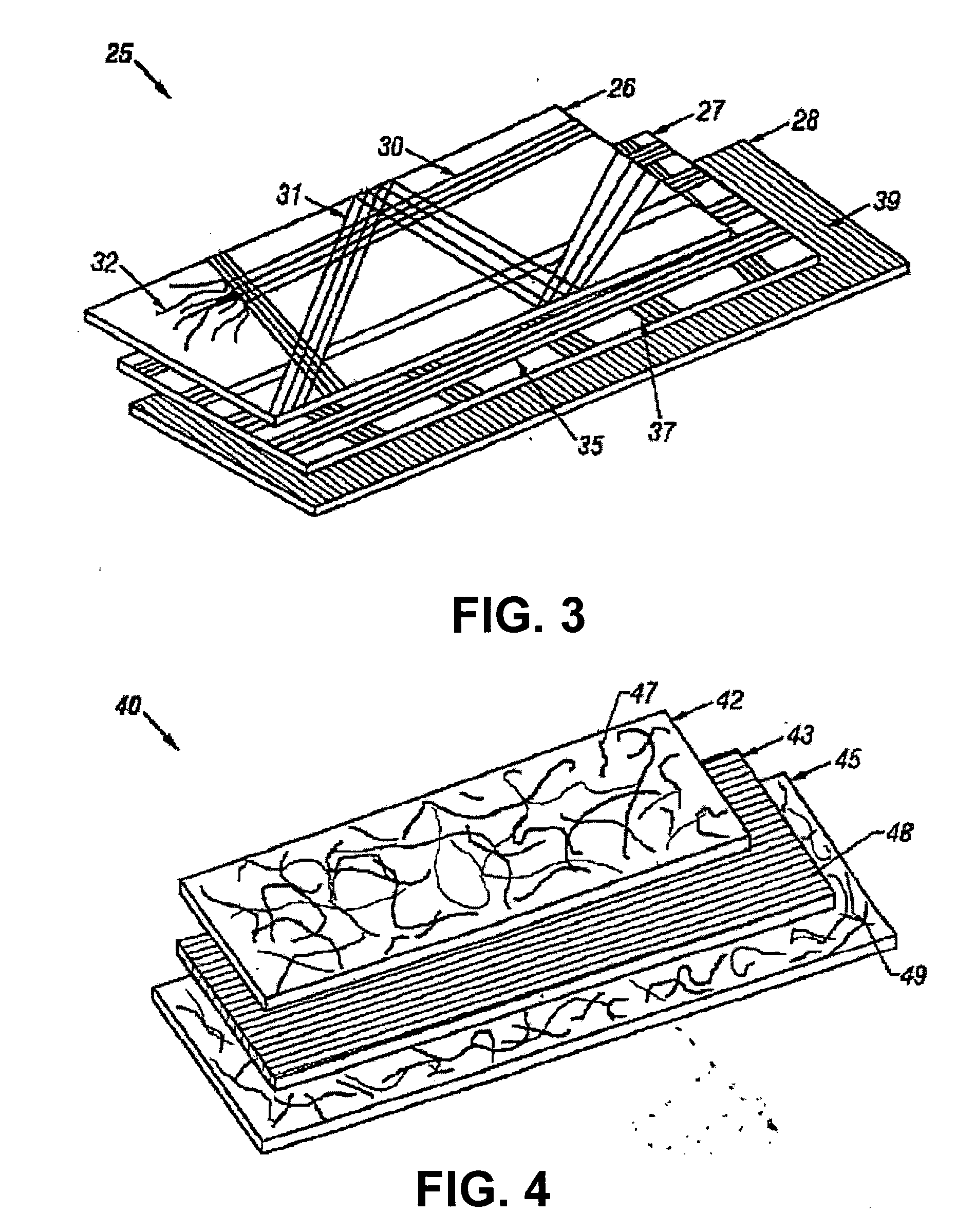
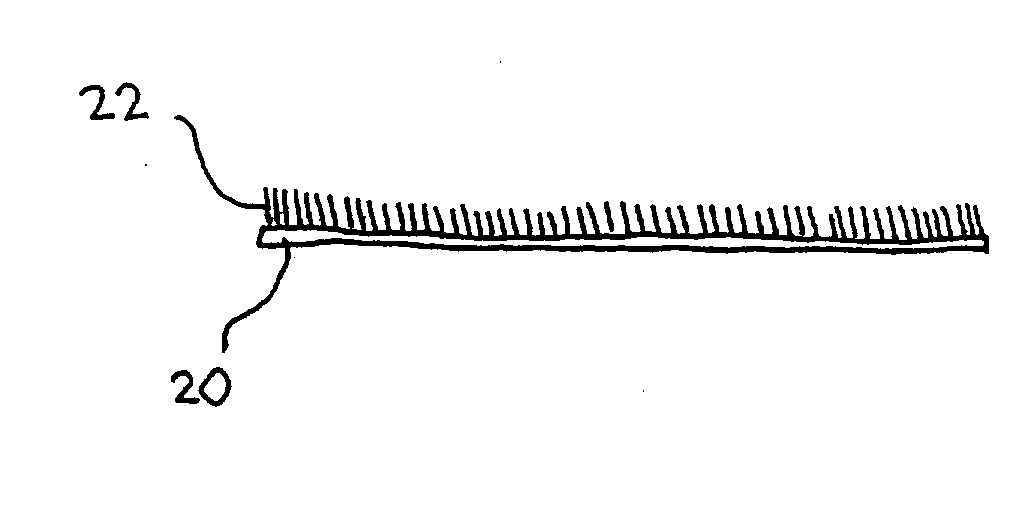
Carbon nanotube fabrics
The present invention provides fabrics that have unique chemical, electrical, and thermal properties. The fabrics comprise layers of yarns woven together wherein the yarns further comprise carbon nanotube fibers. These carbon nanotube fibers may be either single-walled or multi-walled carbon nanotubes. The use of carbon nanotube fibers allows the fabrics to insulate, semi-conduct or super-conduct electrical charges. Additionally, the thermal properties of carbon nanotubes allow thermal energy to flow efficiently between the fabric and a heat sink or source. Additional yarns of materials other than carbon nanotubes can be integrated or woven into the fabric to provide other unique properties for the fabric. These fabrics can be layered to form unique garments or structures.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Fiber adhesive material
InactiveUS20040071870A1Improve adhesion performanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDielectricFiber
A fiber velvet comprising nano-size fibers or nanofibrils attached to micro-size fibers is disclosed. Methods of manufacturing the velvet as well as various uses of the velvet are also described. For example, the fiber velvet can be used as a thermal interface or as an adhesive material. The nanofibrils may be attached to a flat base or membrane, or may be attached to the tip portions of the micro-size or larger diameter fibers. Various attributes of the micro-size fibers and of the nano-size fibers, for example, geometry (e.g. size, length, packing density) material type (e.g. carbon, metal, polymer, or ceramic) and properties (e.g. conductivity, modulus, surface energy, dielectric constant, surface roughness) can be selected depending on the desired attributes of the fiber velvet. The nanofibrils have a diameter of less than about 1 micron, and may advantageously be formed from single walled and / or multi-walled carbon nanotubes.
Owner:KULR TECH
Semiconductor device and semiconductor sensor
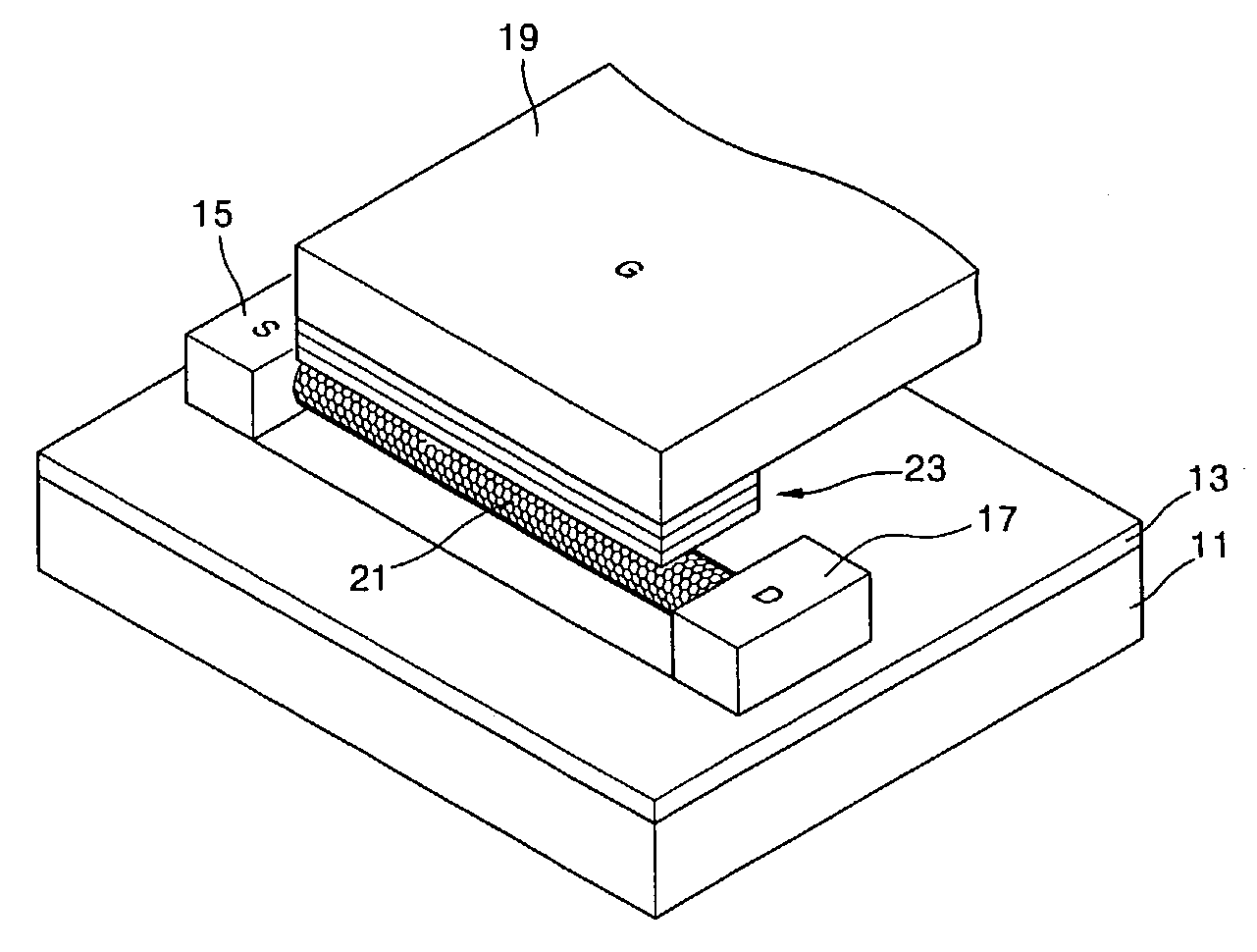
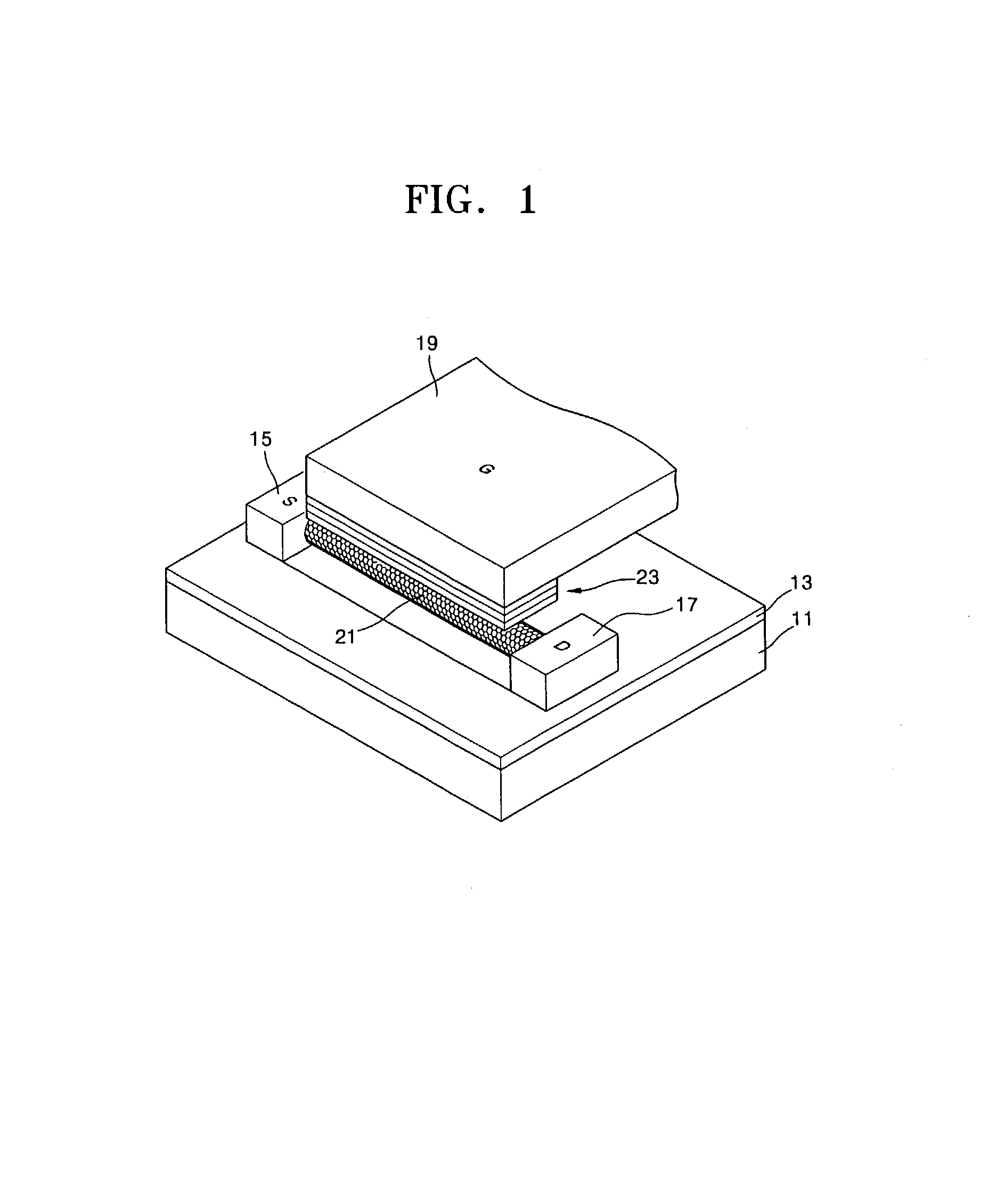
InactiveUS20050212014A1Improve featuresReduce harmTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationDevice materialCarbon nanotube
A semiconductor device includes a substrate; a gate electrode formed on the substrate; a gate insulating film covering the gate electrode; a carbon nanotube disposed above the gate electrode and coming in contact with the gate insulating film; and a source electrode and a drain electrode formed apart from one another in a longitudinal direction of the carbon nanotube.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
DNA-bridged carbon nanotube arrays
InactiveUS6958216B2High sensitivityImprove portabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical ligationElectron transfer reactions
A class of biological sensing devices that include a substrate comprising an array of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to which are chemically attached biological molecules is disclosed. The attached biological molecules are capable of electrical conductivity that is responsive to chemical changes occurring as a result of their interaction with target species. A means for means for using DNA as a material of potential in molecular electronic sensor devices, being primarily based on molecular electron-transfer reaction processes between DNA-binding donors and acceptors is also disclosed, including composition, method of manufacture and their use are described.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON COLLEGE THE
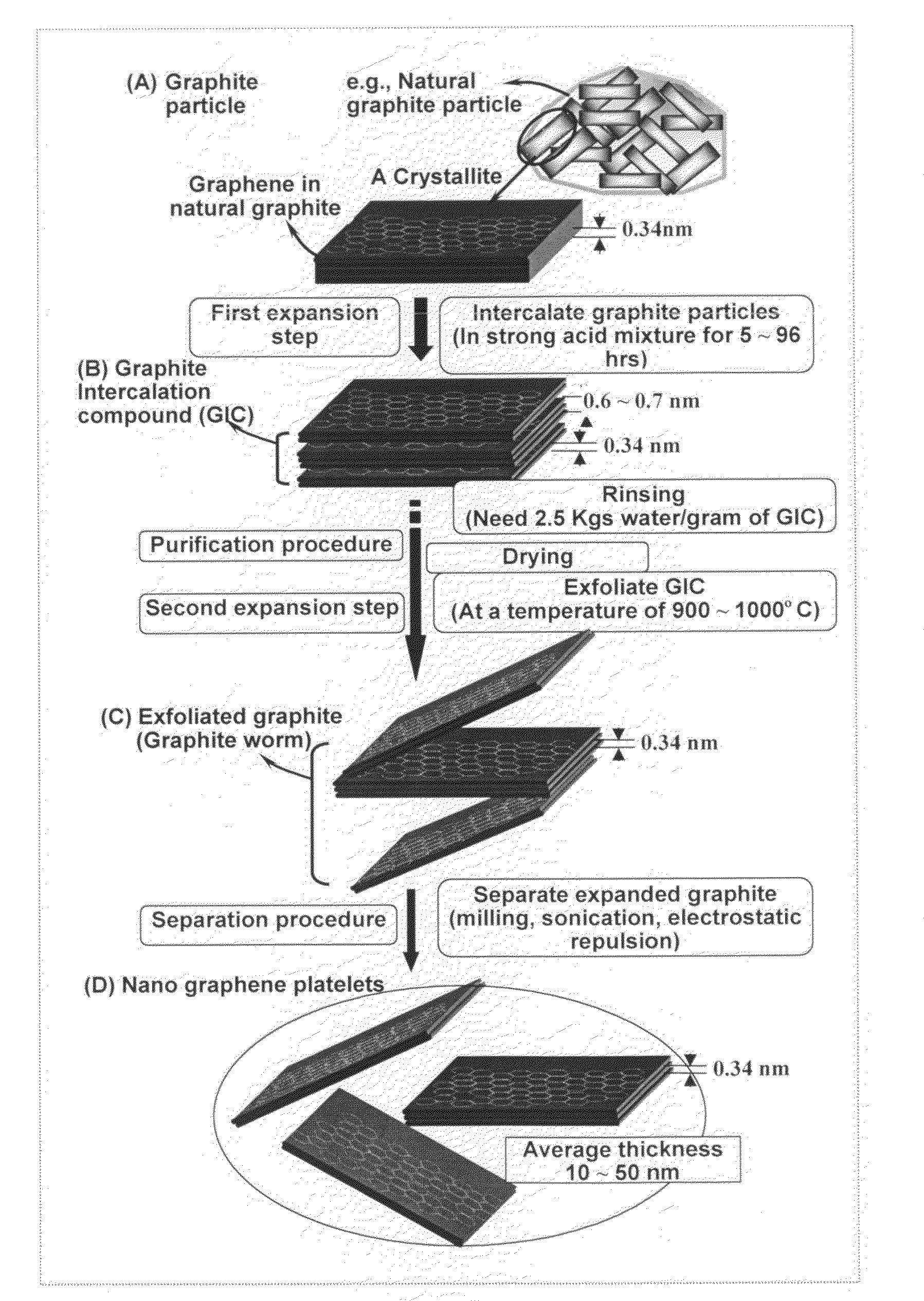
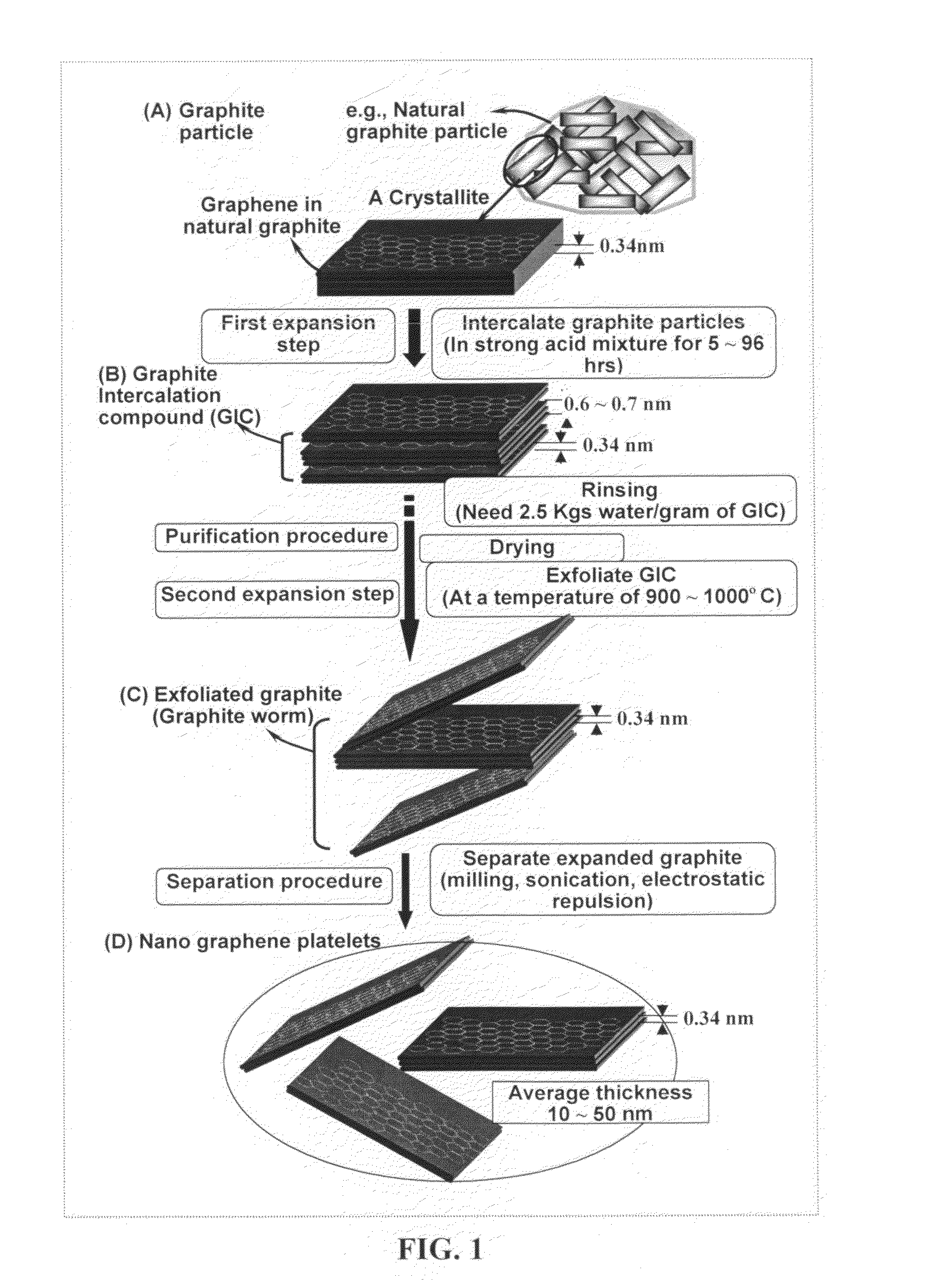
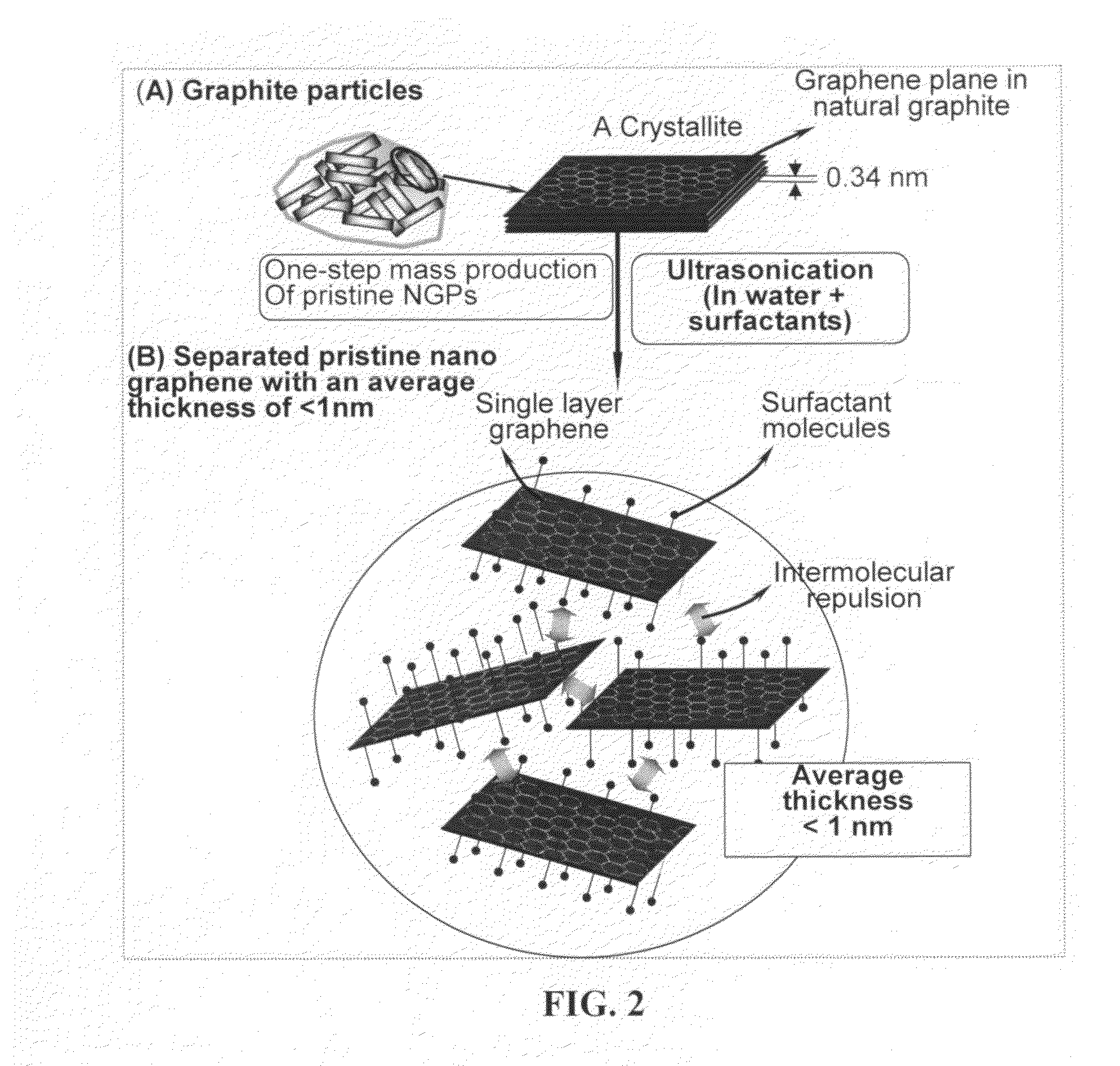
Method of producing exfoliated graphite, flexible graphite, and nano-scaled graphene platelets
ActiveUS20080279756A1Good dispersionImprove conductivityCarbon compoundsFibre chemical featuresFiberLiquid medium
The present invention provides a method of exfoliating a layered material (e.g., graphite and graphite oxide) to produce nano-scaled platelets having a thickness smaller than 100 nm, typically smaller than 10 nm. The method comprises (a) dispersing particles of graphite, graphite oxide, or a non-graphite laminar compound in a liquid medium containing therein a surfactant or dispersing agent to obtain a stable suspension or slurry; and (b) exposing the suspension or slurry to ultrasonic waves at an energy level for a sufficient length of time to produce separated nano-scaled platelets. The nano-scaled platelets are candidate reinforcement fillers for polymer nanocomposites. Nano-scaled graphene platelets are much lower-cost alternatives to carbon nano-tubes or carbon nano-fibers.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Fluoropolymer binders for carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coatings
InactiveUS20060113510A1Reduce conductivityFunction increaseNanoinformaticsConductive materialThermoplasticOptical transparency
This invention relates to flexible, transparent and conductive coatings and films formed using carbon nanotubes (CNT) and, in particular, single wall carbon nanotubes, with polymer binders. Preferably, coatings and films are formed from carbon nanotubes applied to transparent substrates forming one or multiple conductive layers at nanometer level of thickness. Polymer binders are applied to the CNT network coating having an open structure to provide protection through infiltration. This provides for enhancement of properties such as moisture resistance, thermal resistance, abrasion resistance and interfacial adhesion. Polymers may be thermoplastics or thermosets, or a combination thereof. Polymers may also be insulative or inherently electrical conductive, or any combination of both. Polymers may comprise single or multiple layers as a basecoat underneath a CNT coating, or a topcoat above a CNT coating, or combination of the basecoat and the topcoat forming a sandwich structure. A fluoropolymer containing binder, which is a solution of one fluoropolymer or a blend of fluoropolymers, which may be formulated with additives, is applied onto a carbon nanotube-based transparent conductive coating at nanometer level of thickness on a clear substrate such as PET and glass. The fluoropolymers or blend can be either semi-crystalline (with low level of crystallinity) or amorphous, preferably to be amorphous with low refraction index. Binder coating thickness can be adjusted by changing binder concentration, coating speed and / or other process conditions. This binder coating significantly improves optical transparency, and also maintain or increases conductivity of the CNT-based coating. With other benefits such as abrasion, thermal and moisture resistance, this binder coating and the resulting products is used for display and electronic applications.
Owner:EIKOS
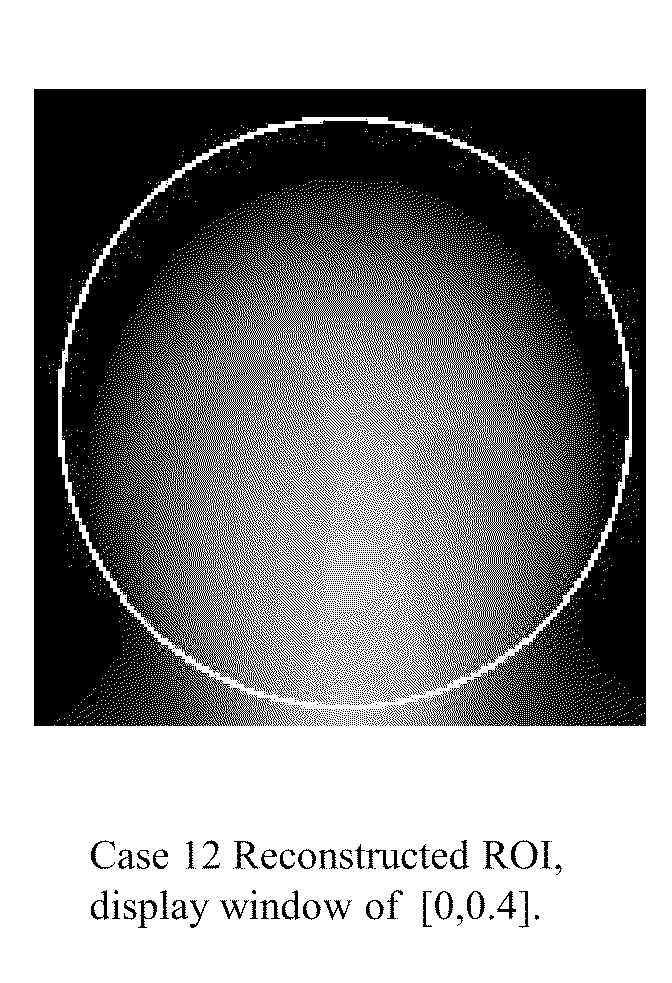
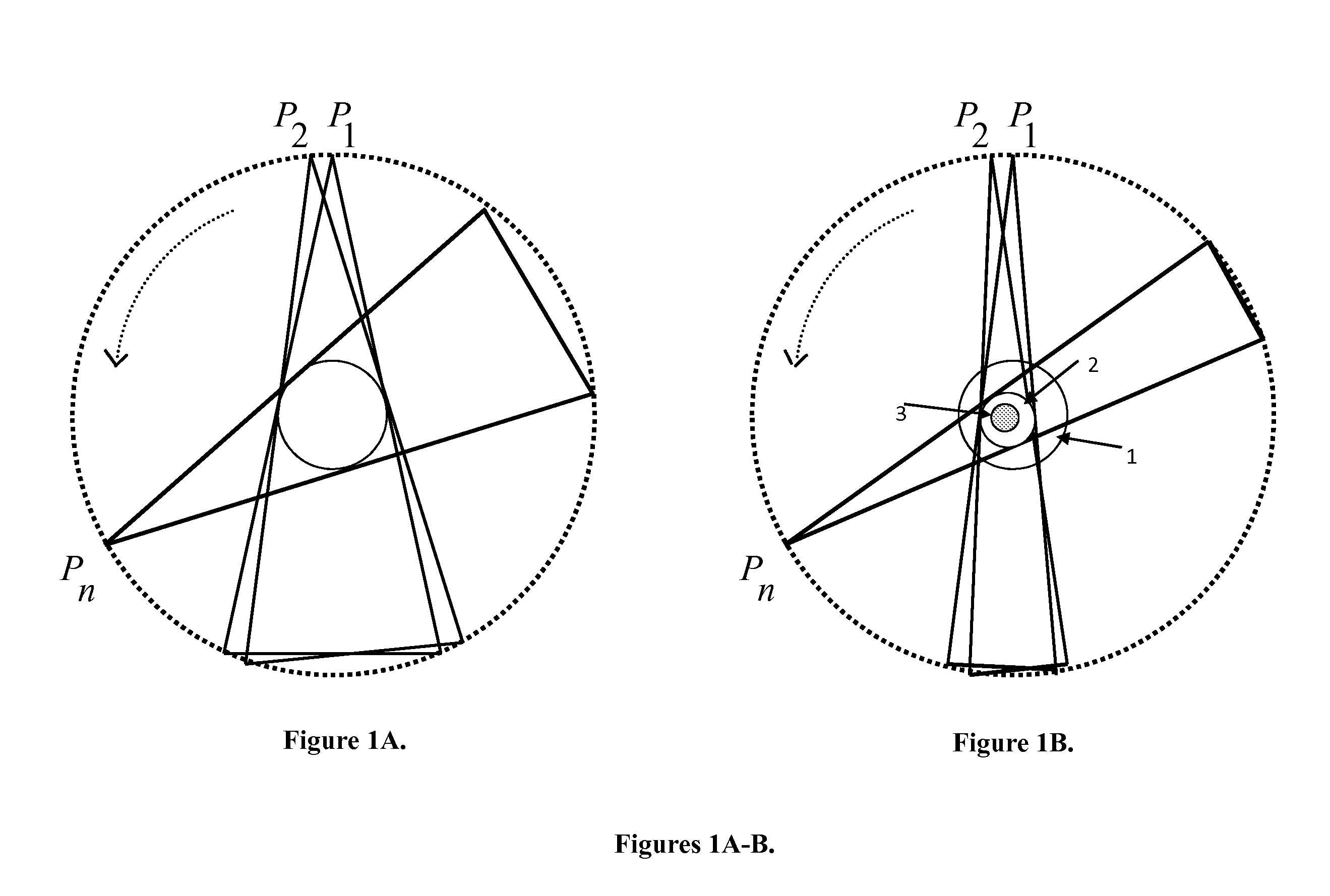
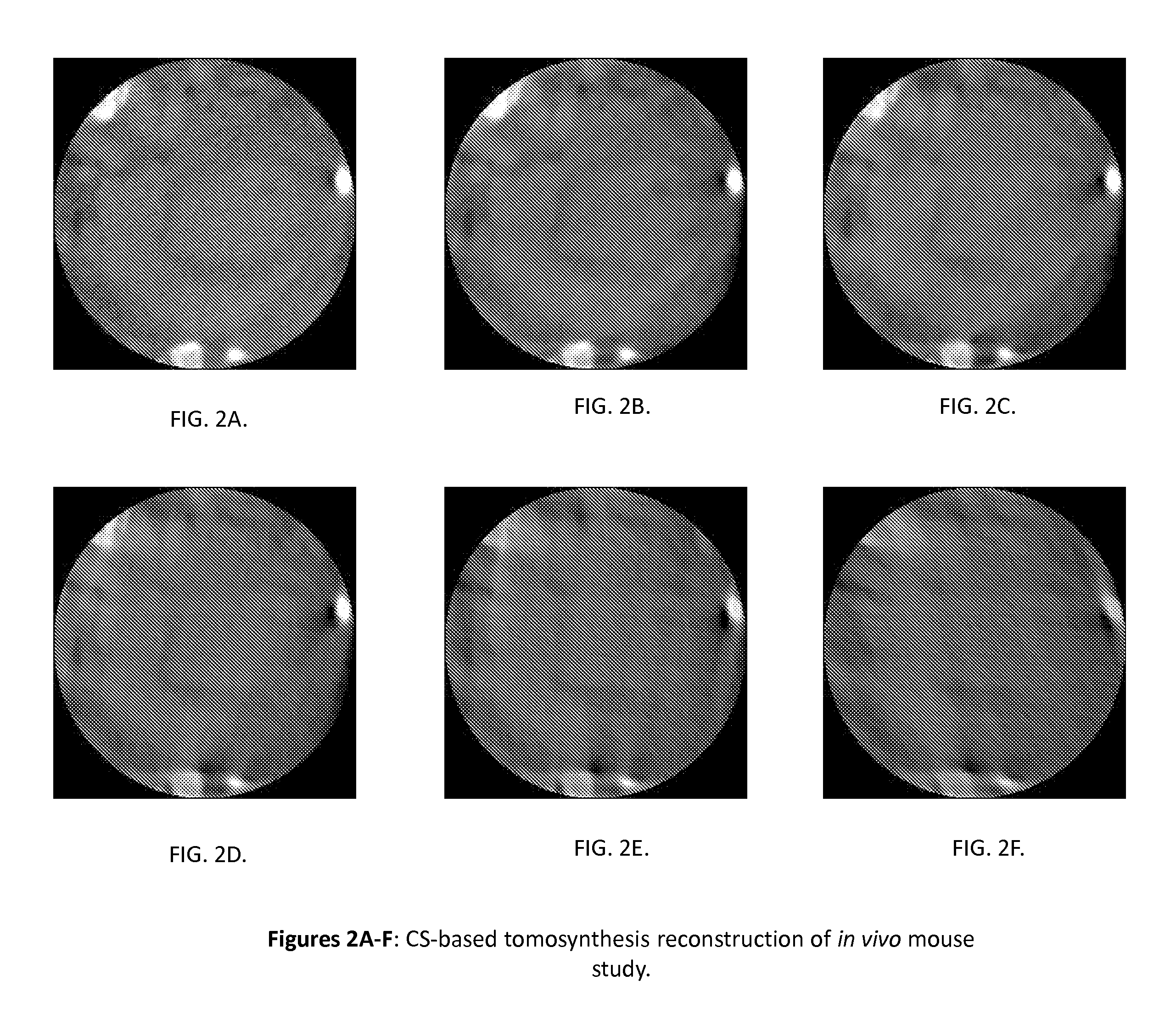
Tomography-Based and MRI-Based Imaging Systems
InactiveUS20110142316A1Comparable image qualityImproved temporalReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesisElastography
Tomography limitations in vivo due to incomplete, inconsistent and intricate measurements require solution of inverse problems. The new strategies disclosed in this application are capable of providing faster data acquisition, higher image quality, lower radiation dose, greater flexibility, and lower system cost. Such benefits can be used to advance research in cardiovascular diseases, regenerative medicine, inflammation, and nanotechnology. The present invention relates to the field of medical imaging. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to methods, systems, and devices for imaging, including tomography-based and MRI-based applications. For example, included in embodiments of the invention are compressive sampling based tomosynthesis methods, which have great potential to reduce the overall x-ray radiation dose for a patient. To name a few, compressive sensing based carbon nano-tube based interior tomosynthesis systems, tomography-based dynamic cardiac elastography systems, cardiac elastodynamic biomarkers from interior MR imaging, exact and stable interior ROI reconstructions for radial MRI, and interior reconstruction based ultrafast tomography systems are provided.
Owner:WANG GE +5
Adhesive transfer method of carbon nanotube layer
InactiveUS20060188721A1Material nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsCarbon nanotubeMaterials science
The present invention relates to a donor laminate for adhesive transfer of a conductive layer comprising a substrate having thereon a conductive layer comprising carbon nanotubes, in contact with said substrate
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Memory device utilizing carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS7015500B2Increase in malfunctionIncrease resistanceTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationDevice formCarbon nanotube
A fast, reliable, highly integrated memory device formed of a carbon nanotube memory device and a method for forming the same, in which the carbon nanotube memory device includes a substrate, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a carbon nanotube having high electrical and thermal conductivity, a memory cell having excellent charge storage capability, and a gate electrode. The source electrode and drain electrode are arranged with a predetermined interval between them on the substrate and are subjected to a voltage. The carbon nanotube connects the source electrode to the drain electrode and serves as a channel for charge movement. The memory cell is located over the carbon nanotube and stores charges from the carbon nanotube. The gate electrode is formed in contact with the upper surface of the memory cell and controls the amount of charge flowing from the carbon nanotube into the memory cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Touchscreen with conductive layer comprising carbon nanotubes
The present invention is directed to a touchscreen comprising touch side and device side electrodes wherein each electrode comprises in order an insulating substrate, a first electrically conductive layer in contact with said substrate, an exposed electrically conductive layer, wherein said exposed electrically conductive layers are adjacent and separated by dielectric spacers, and wherein at least the first electrically conductive layers or the exposed electrically conductive layers comprise carbon nanotubes.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Nano graphene-modified lubricant
ActiveUS20110046027A1Modulate viscosityImprove the lubrication effectAdditivesBase-materialsCarbon nanotubeSingle layer graphene
A lubricant composition having improved lubricant properties, comprising:(a) a lubricating fluid; and (b) nano graphene platelets (NGPs) dispersed in the fluid, wherein nano graphene platelets have a proportion of 0.001% to 60% by weight based on the total weight of the fluid and the graphene platelets combined. Preferably, the composition comprises at least a single-layer graphene sheet. Preferably, the lubricating fluid contains a petroleum oil or synthetic oil and a dispersant or surfactant. With the addition of a thickener or a desired amount of NGPs, the lubricant becomes a grease composition. Compared with graphite nano particle- or carbon nanotube-modified lubricants, NGP-modified lubricants have much better thermal conductivity, friction-reducing capability, anti-wear performance, and viscosity stability.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
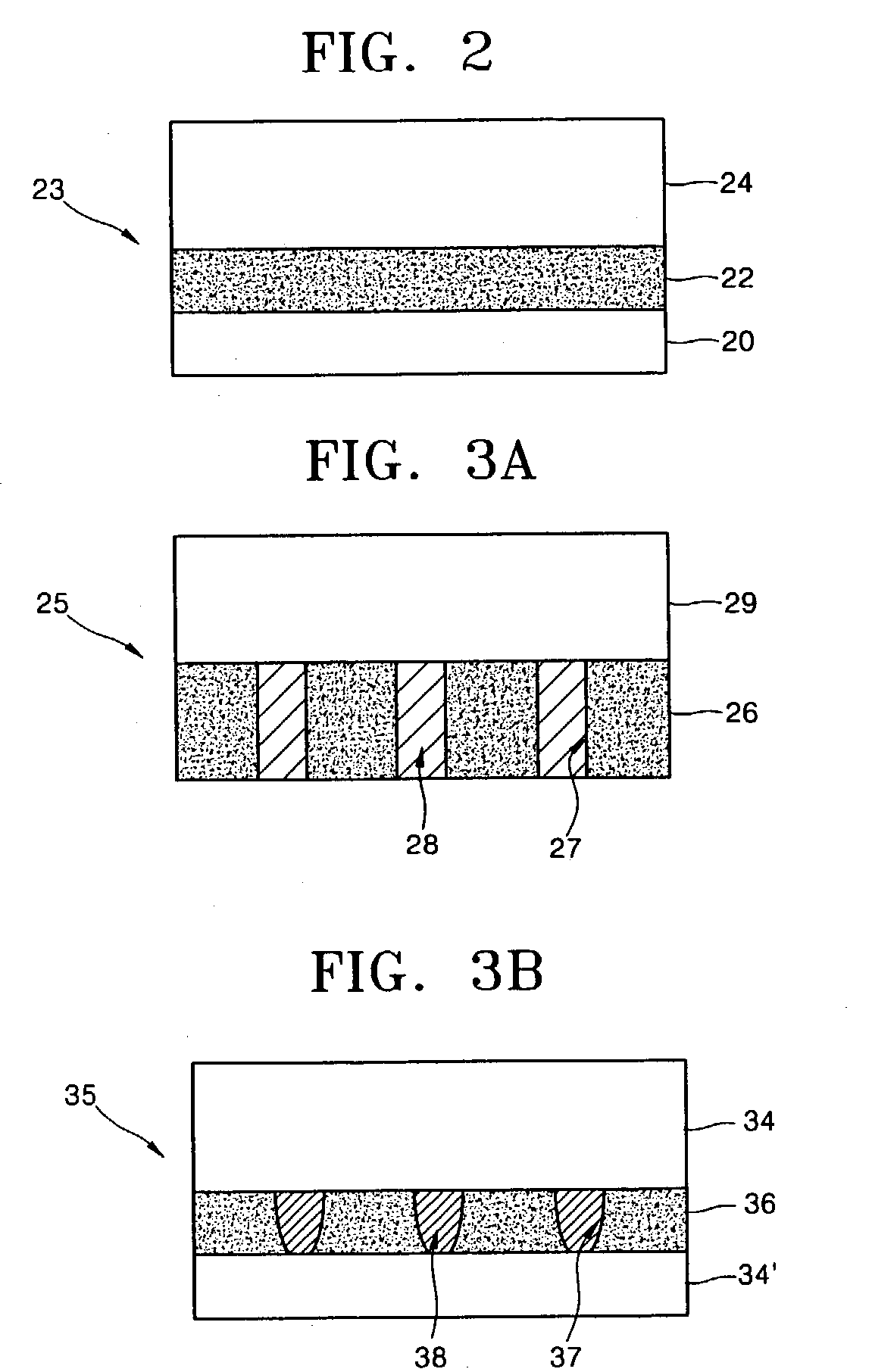
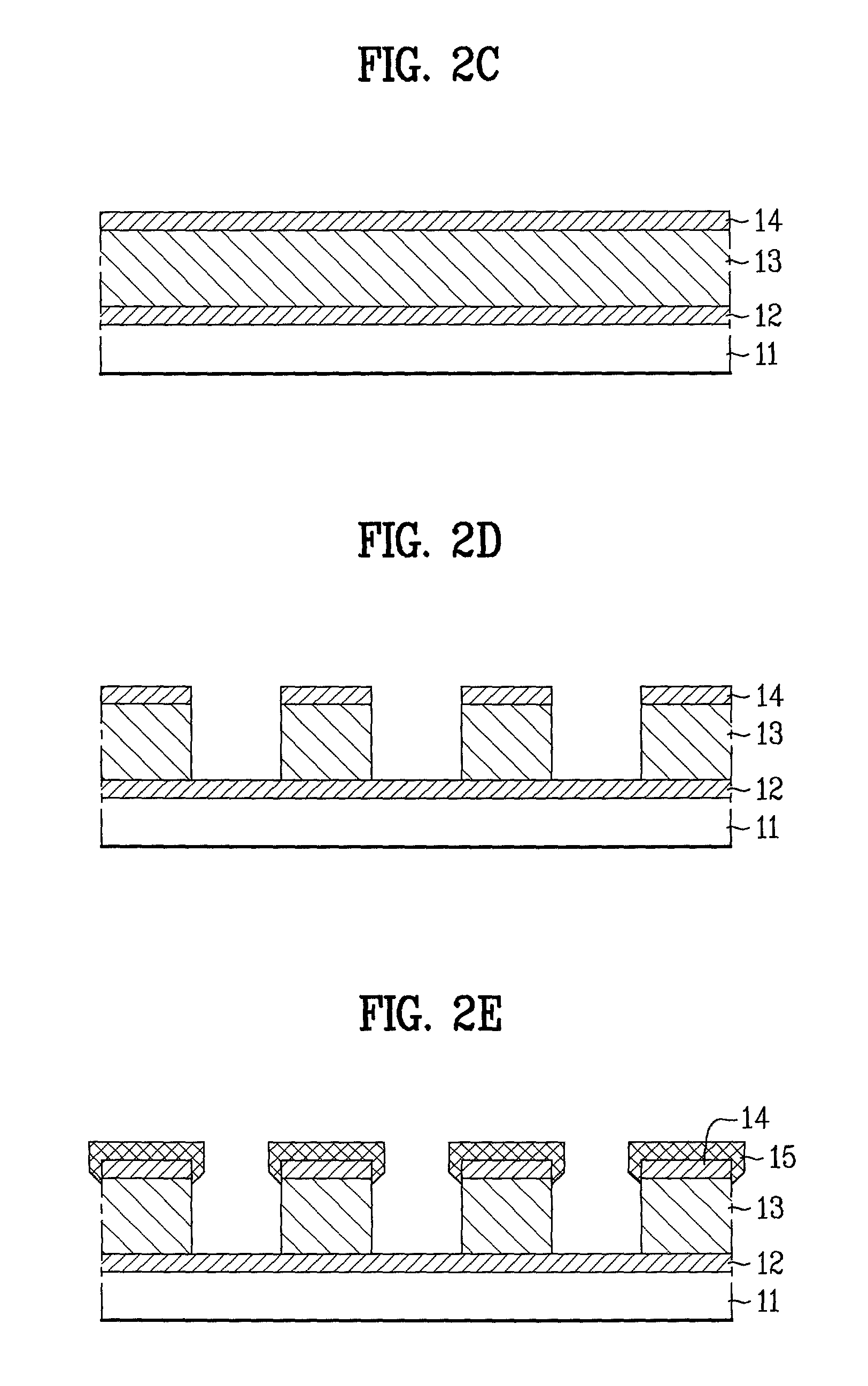
Resistance element, method of manufacturing the same, and thermistor
InactiveUS20050040371A1Easy and stable coatingLow resistivityMaterial nanotechnologyCurrent responsive resistorsResistive elementCarbon nanotube
To provide a resistance element having an electric resistance body with excellent stability and a method of manufacturing the same. The resistance element includes an electric resistance body, on a base body surface, consisting of a carbon nanotube structure layer 14, which configures a mesh structure in which at least plural carbon nanotubes are cross-linked to one another. The method of manufacturing the resistance element includes: an applying step of applying the base body surface 12 with a liquid solution containing carbon nanotubes having functional groups; and a cross-linking step of forming the carbon nanotube structure layer 14, used as an electric resistance body, that configures a mesh structure in which the plural carbon nanotubes are cross-linked to one another through curing of the liquid solution after application.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
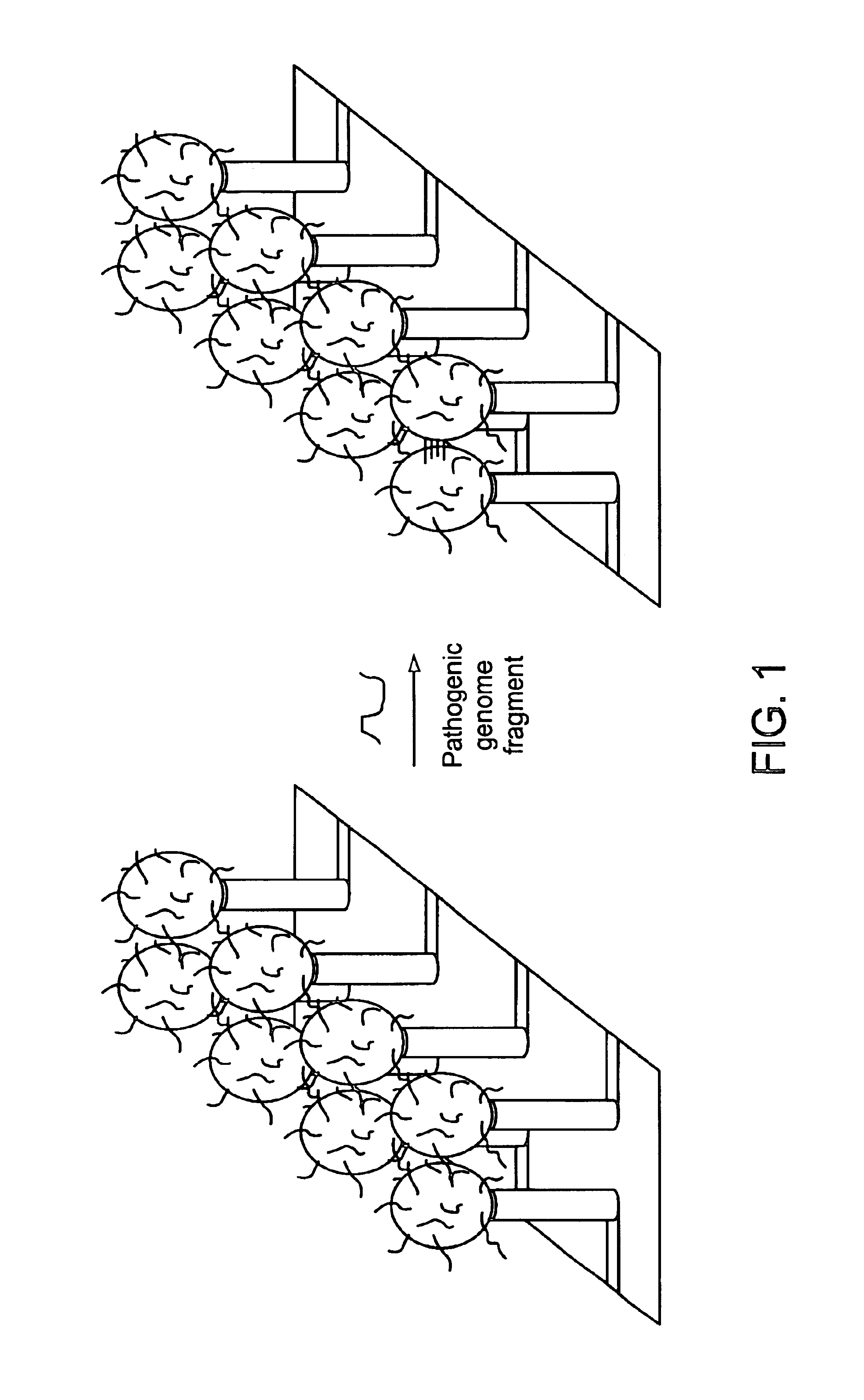
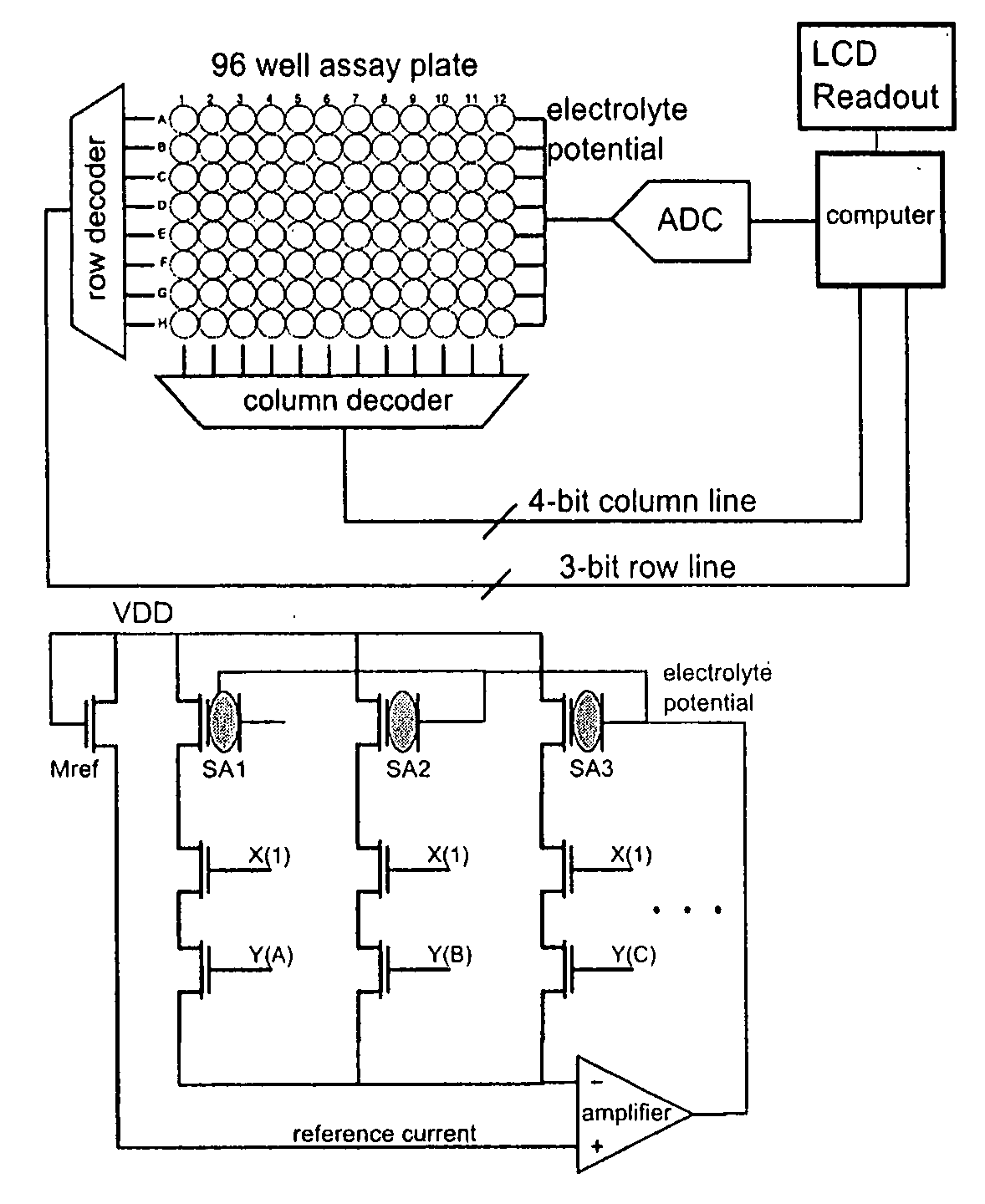
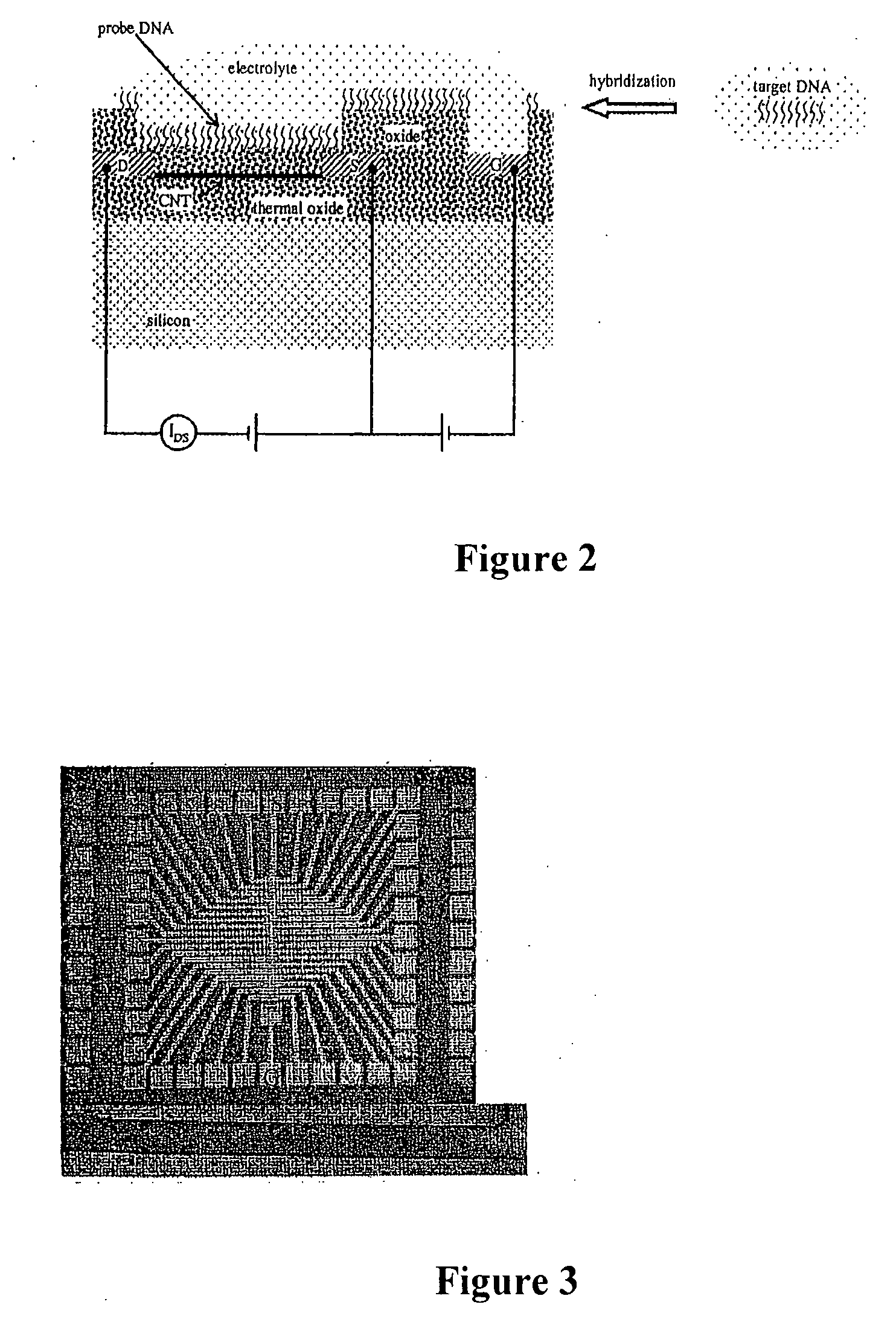
Apparatus for microarray binding sensors having biological probe materials using carbon nanotube transistors
ActiveUS20080035494A1Fast hybridizationLimited sensitivityImmobilised enzymesMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubeMiniaturization
A microarray apparatus is provided which contains at least one chip having source and drain electrodes positioned on an array of carbon nanotube transistors which allows for electronic detection of nucleic acid hybridizations, thereby affording both increased sensitivity and the capability of miniaturization.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20010004979A1Stable driving voltageUniform characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLow voltageCarbon nanotube
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same, the field emission display including a cathode array having a cathode electrode formed on a substrate, insulating layers and carbon nanotube films for use as emitter electrodes formed alternately on the cathode electrode, and a gate electrode formed on the insulating layer, thereby permitting fabrication of a large sized cathode plate at a low cost because the film is formed by screen printing and exposure, which can reduce the cumbersome steps in fabrication of the related art Spindt emitter tip, and both a low voltage and a high voltage FEDs because the carbon nanotube film used as the emitter has a low work function, with an easy and stable electron emission capability.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
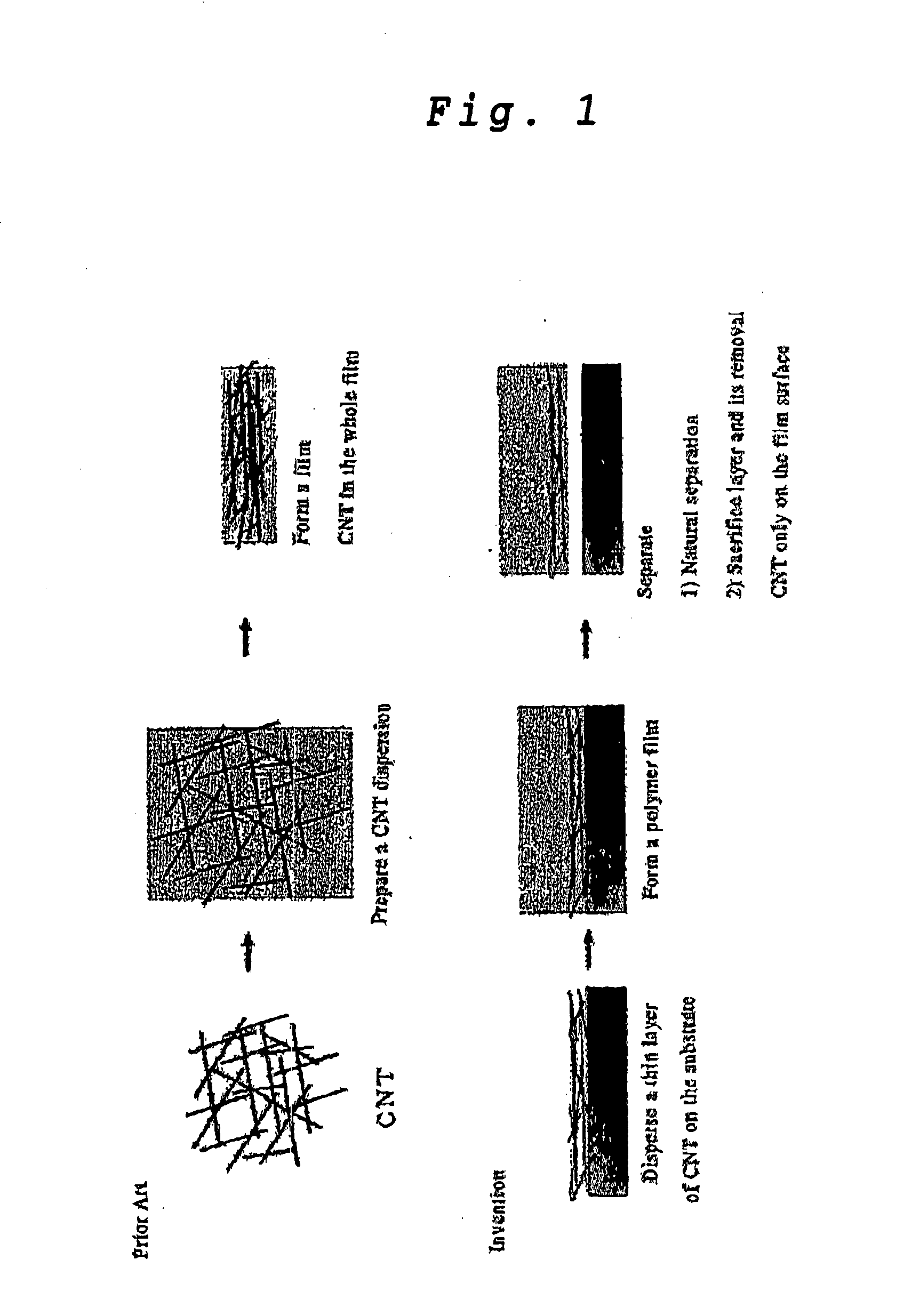
Transparent Conductive Carbon Nanotube Film and a Method for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20070298253A1Conductive and soft and flexibleImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive layers on insulating-supportsCarbon nanotubeTransparent conducting film
A transparent conductive film wherein carbon nanotubes are discursively embedded in the surface portion of a resin film is produced by (A) dispersing carbon nanotubes on a substrate surface, (B) forming a transparent resin film over the substrate on which the carbon nanotubes are dispersed, and then (C) separating the thus-formed resin film. This is a novel technique for realizing a highly transparent conductive film which is flexible and highly conductive even when amount of carbon nanotubes used therefor is small.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Carbon/silicon/carbon nano composite structure cathode material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carbon / silicon / carbon nano composite structure cathode material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of electrochemical power supply technologies. The cathode material consists of a carbon-based conductive substrate, nano silicon and a nano carbon coating layer, wherein the nano silicon is uniformly distributed on the carbon-based conductive substrate; the nano carbon coating layer is arranged on the surface of the nano silicon; the carbon-based conductive substrate is porous carbon, a carbon nanotube or graphene; the nano silicon exists in the state of nanoparticles or nano films; the weight percentage of the nano silicon in the cathode material is 10-90 percent; and the thickness of the nano carbon coating layer is 0.1-10 nanometers. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: depositing nano silicon on the carbon substrate in a reaction space in oxygen-free atmosphere by adopting a chemical vapor deposition process; and coating nano carbon on the surface of the nano silicon by adopting the chemical vapor deposition process. In the obtained carbon / silicon / carbon composite cathode material, the volume change of a silicon electrode material is controlled effectively in the charging and discharging processes, the electrode structure is kept complete, the circulation volume is large, the circulation service life is long, and the electrochemical performance is high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
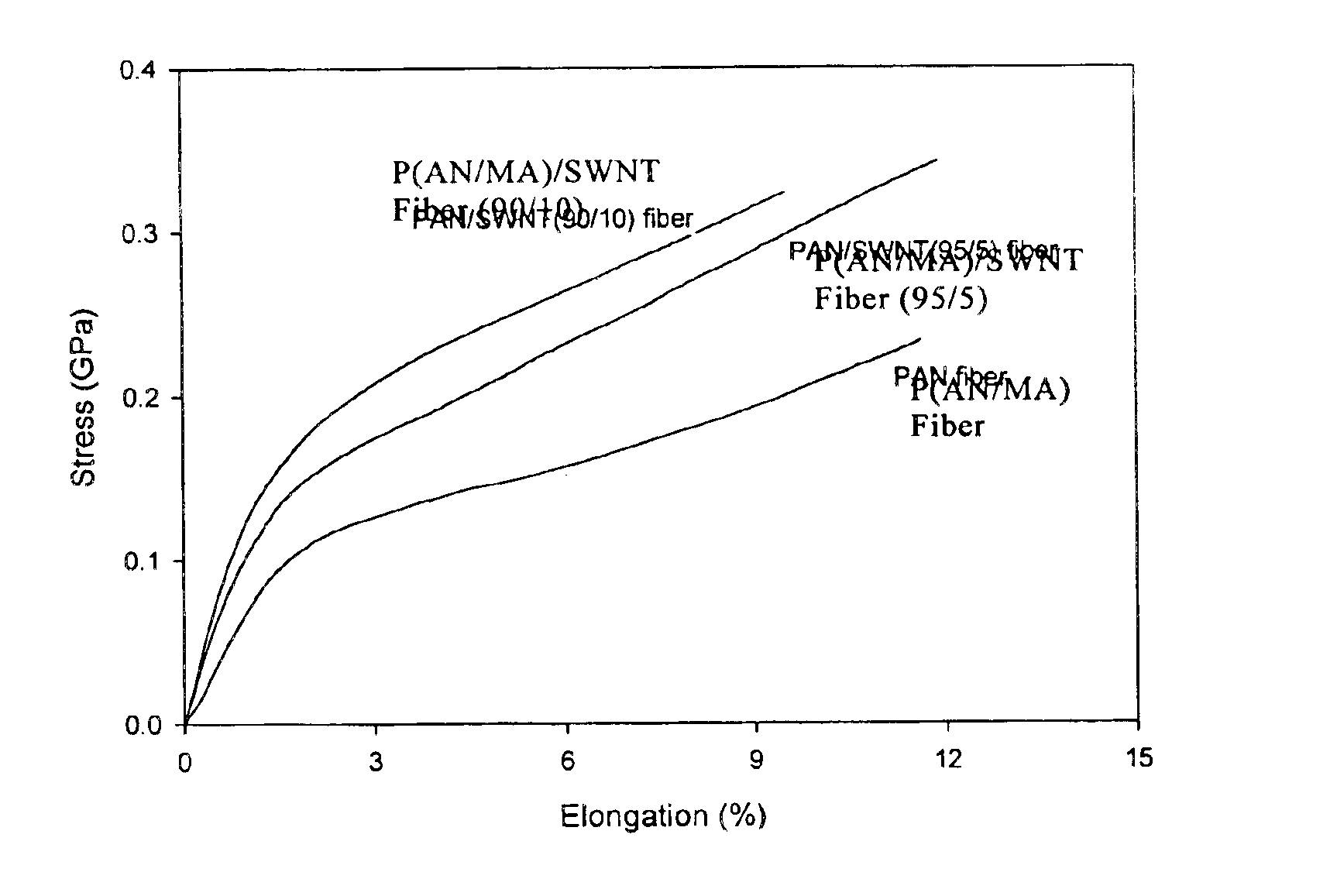
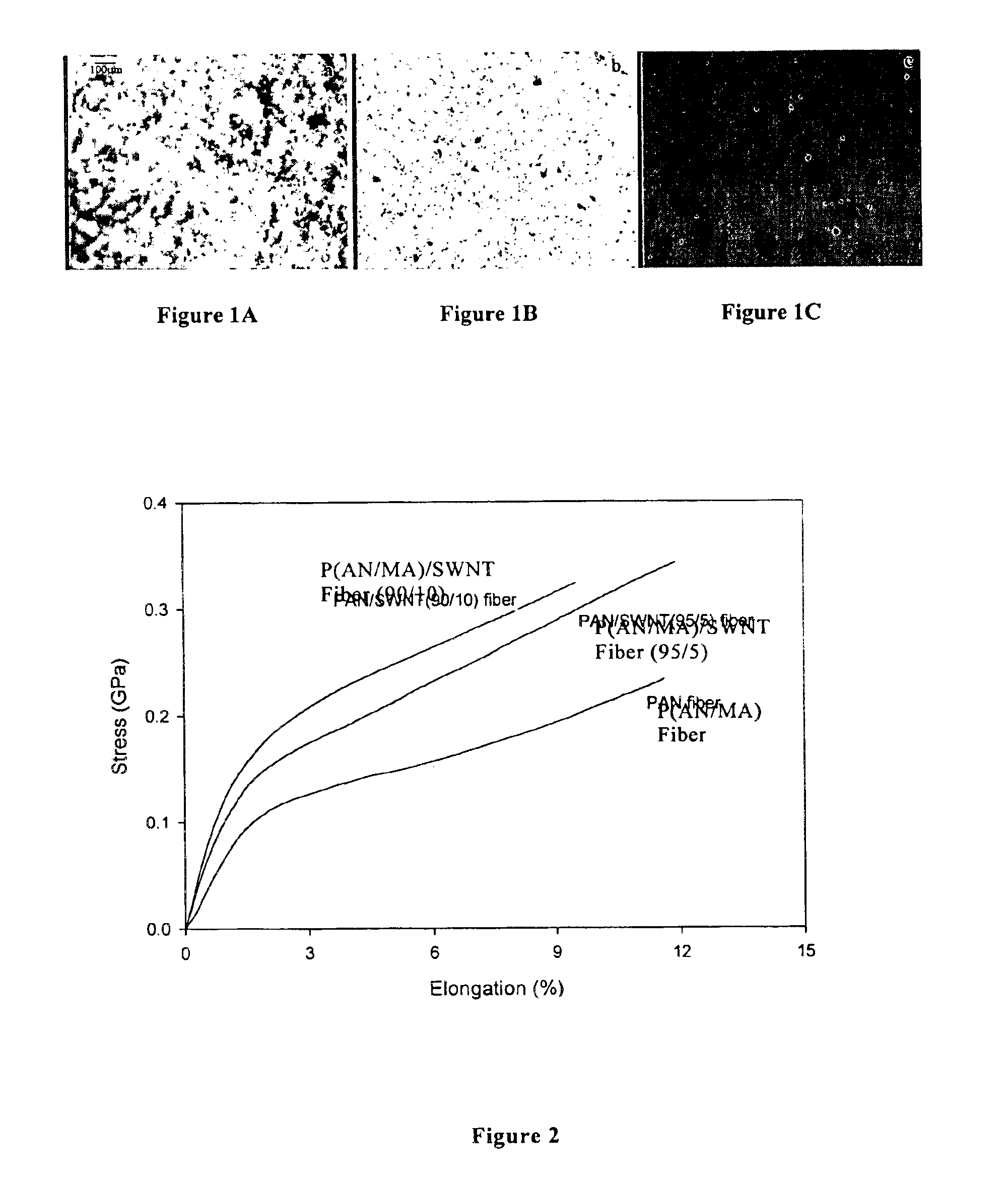
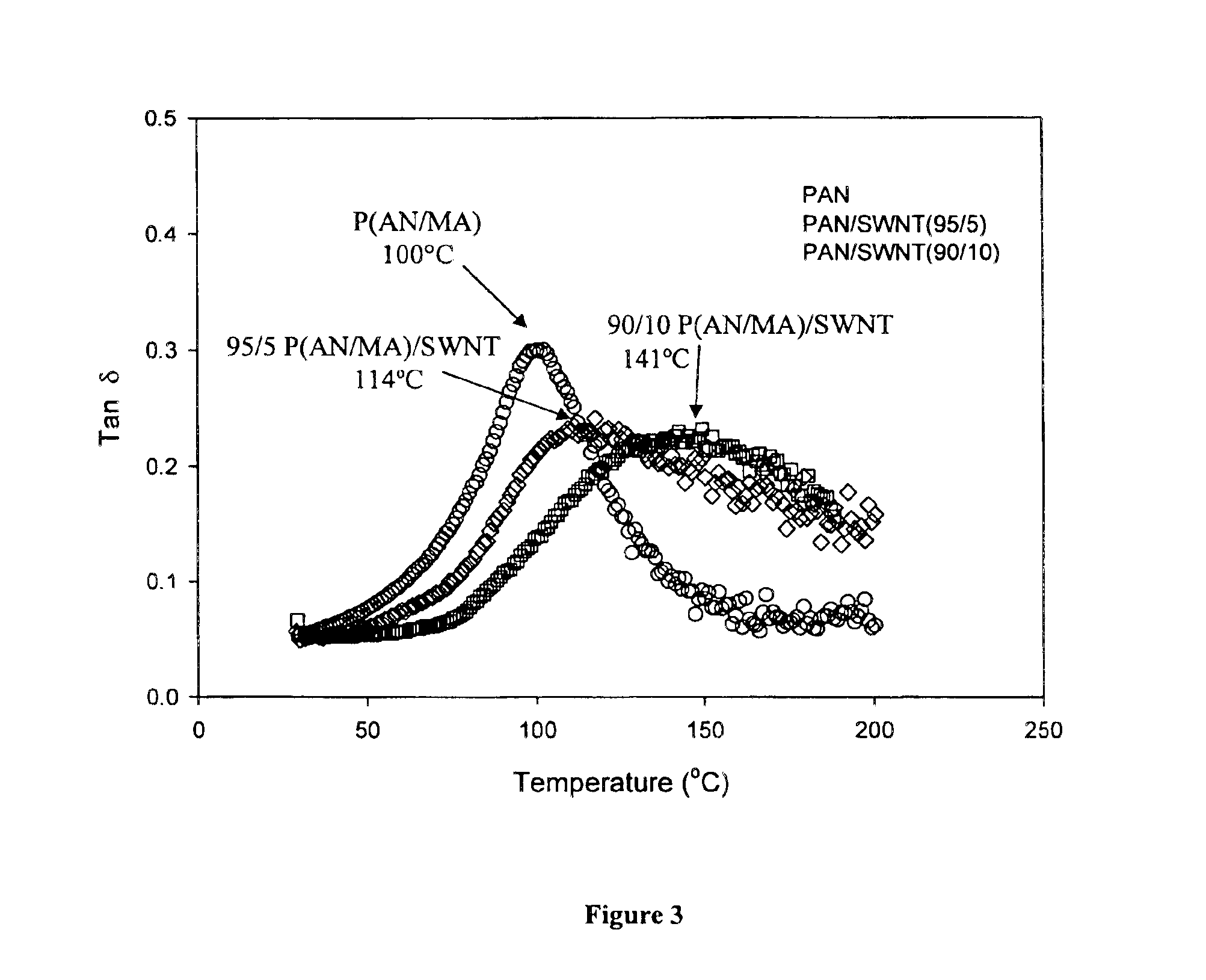
Macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes and acrylonitrile-based polymer and process for making the same
InactiveUS6852410B2Increased tensile modulusReduced thermal shrinkageMaterial nanotechnologyElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureVitrificationPolymer science
The present invention relates to a high modulus macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT) and an acrylonitrile-containing polymer. In one embodiment, the macroscopic fiber is a drawn fiber having a cross-sectional dimension of at least 1 micron. In another embodiment, the acrylonitrile polymer-SWNT composite fiber is made by dispersing SWNT in a solvent, such as dimethyl formamide or dimethyl acetamide, admixing an acrylonitrile-based polymer to form a generally optically homogeneous polyacrylonitrile polymer-SWNT dope, spinning the dope into a fiber, drawing and drying the fiber. Polyacrylonitrile / SWNT composite macroscopic fibers have substantially higher modulus and reduced shrinkage versus a polymer fiber without SWNT. A polyacrylonitrile / SWNT fiber containing 10 wt % SWNT showed over 100% increase in tensile modulus and significantly reduced thermal shrinkage compared to a control fiber without SWNT. With 10 wt % SWNT, the glass transition temperature of the polymer increased by more than 40° C.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
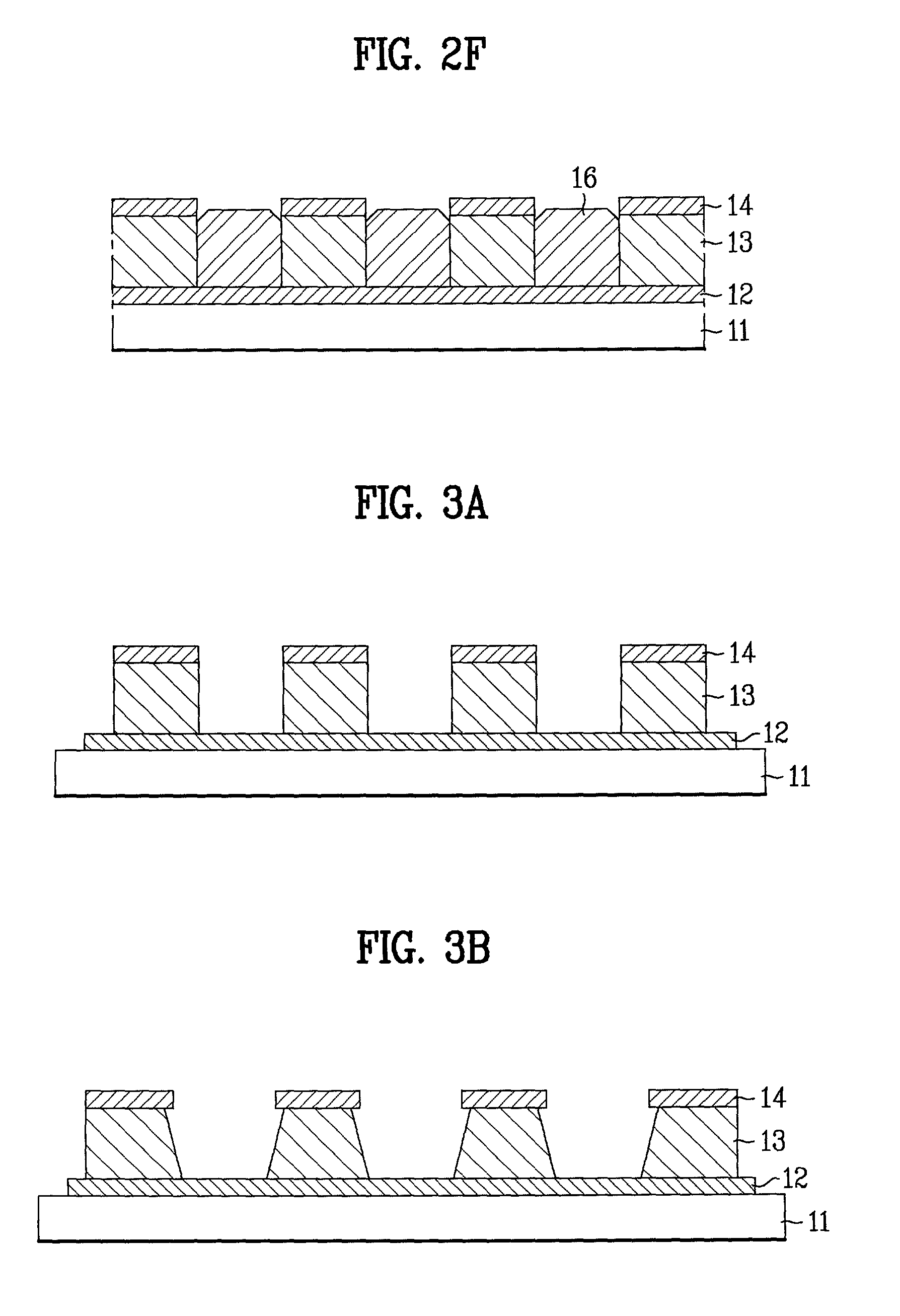
Method for making a carbon nanotube film
ActiveUS20080299031A1High strengthSimple methodMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsCarbon nanotubeNanotube array
The present invention relates to a method for making a carbon nanotube film. The method includes the steps of: (a) forming an array of carbon nanotubes on a substrate; and (b) press the array of carbon nanotubes using a compressing apparatus, thereby forming a carbon nanotube film.
Owner:BEIJING FUNATE INNOVATION TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com