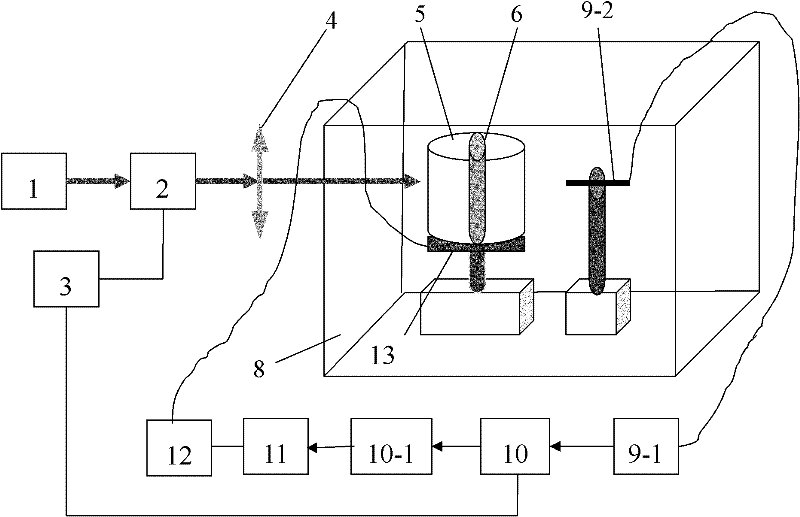
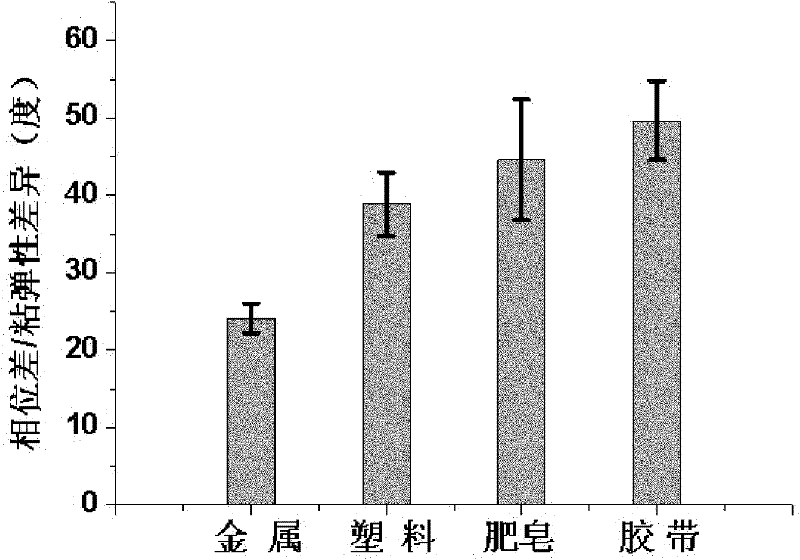
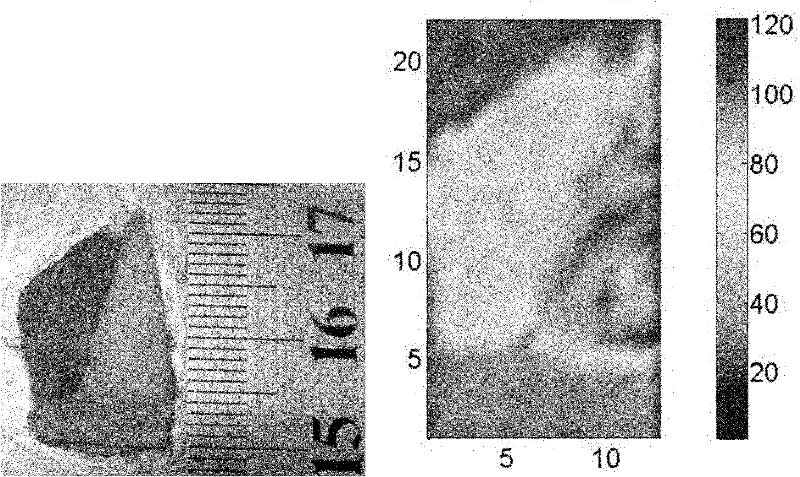
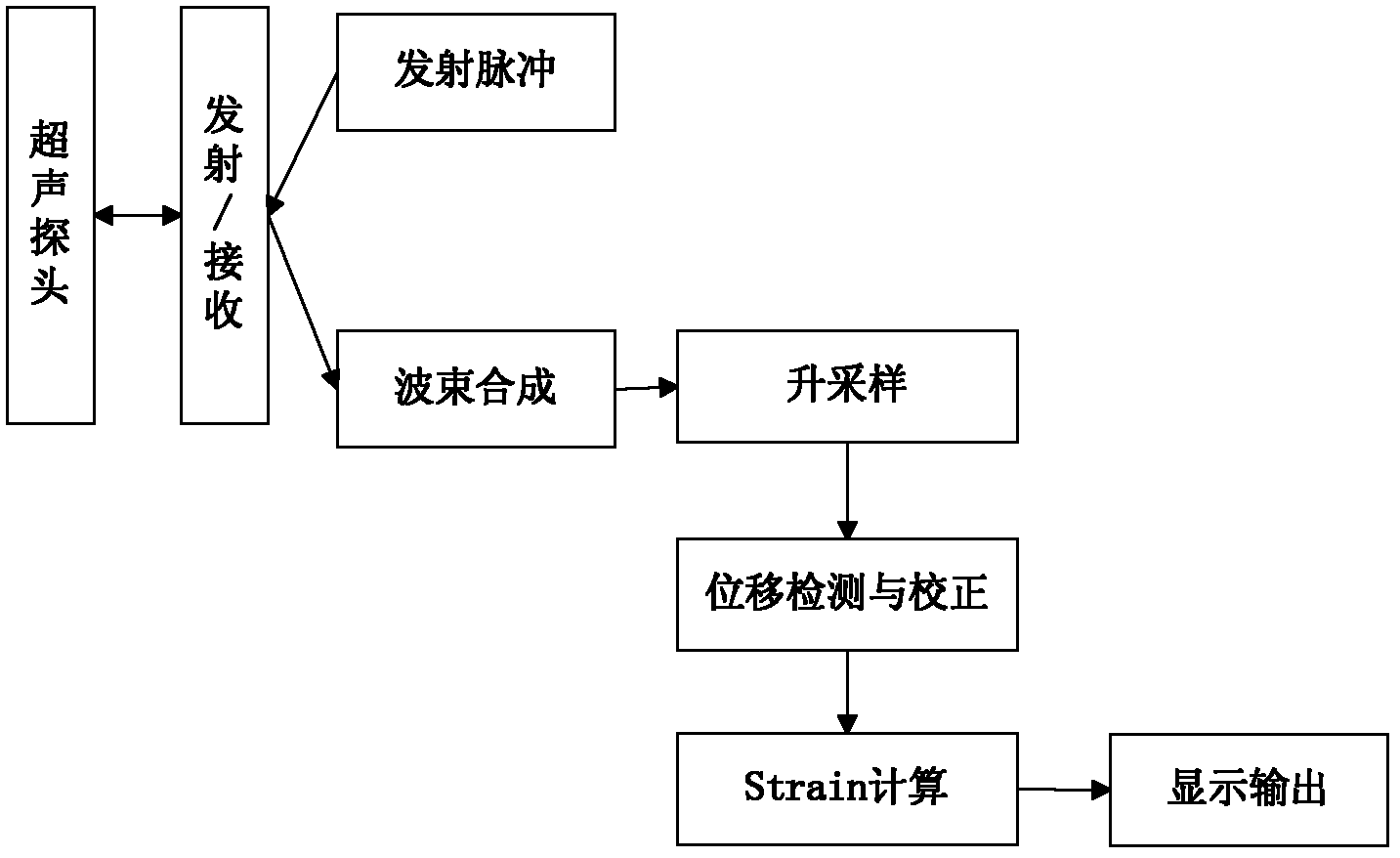
Patents
Literature
105 results about "Elastography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
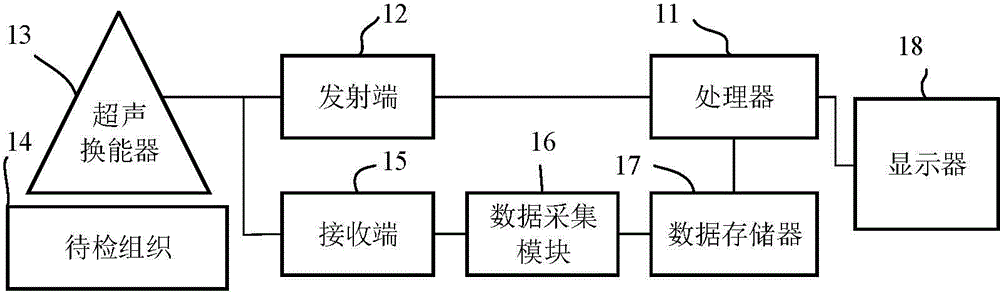
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>Transient elastography helps in identifying the level of risk of cirrhosis in patients who belong to the high-risk category</li><li>It also helps in the improved identification of cirrhosis in patients who attend the OPD (Out Patient Departments) of infectious diseases, gastroenterology, and hepatology departments</li></ul><p>Patients who are diagnosed with Hepatitis B should undergo this test to assess the condition of the liver. A score of less than 6 kPa, indicates that there is no significant fibrosis</p><ul><li>If the score is between 6 to 10 kPa, there may be a need for a liver biopsy to assess the extent of fibrosis</li><li>A score of 10 to 11 kPa is suggestive of cirrhosis</li></ul><p>This procedure cannot be performed:</p><ul><li>In patients having a large amount of chest fat</li><li>In morbidly obese patients</li><li>In patients having ascites</li></ul><p>The results of this test are not reliable in the above group. Liver biopsy may be advisable in such cases</p>
Tomography-Based and MRI-Based Imaging Systems
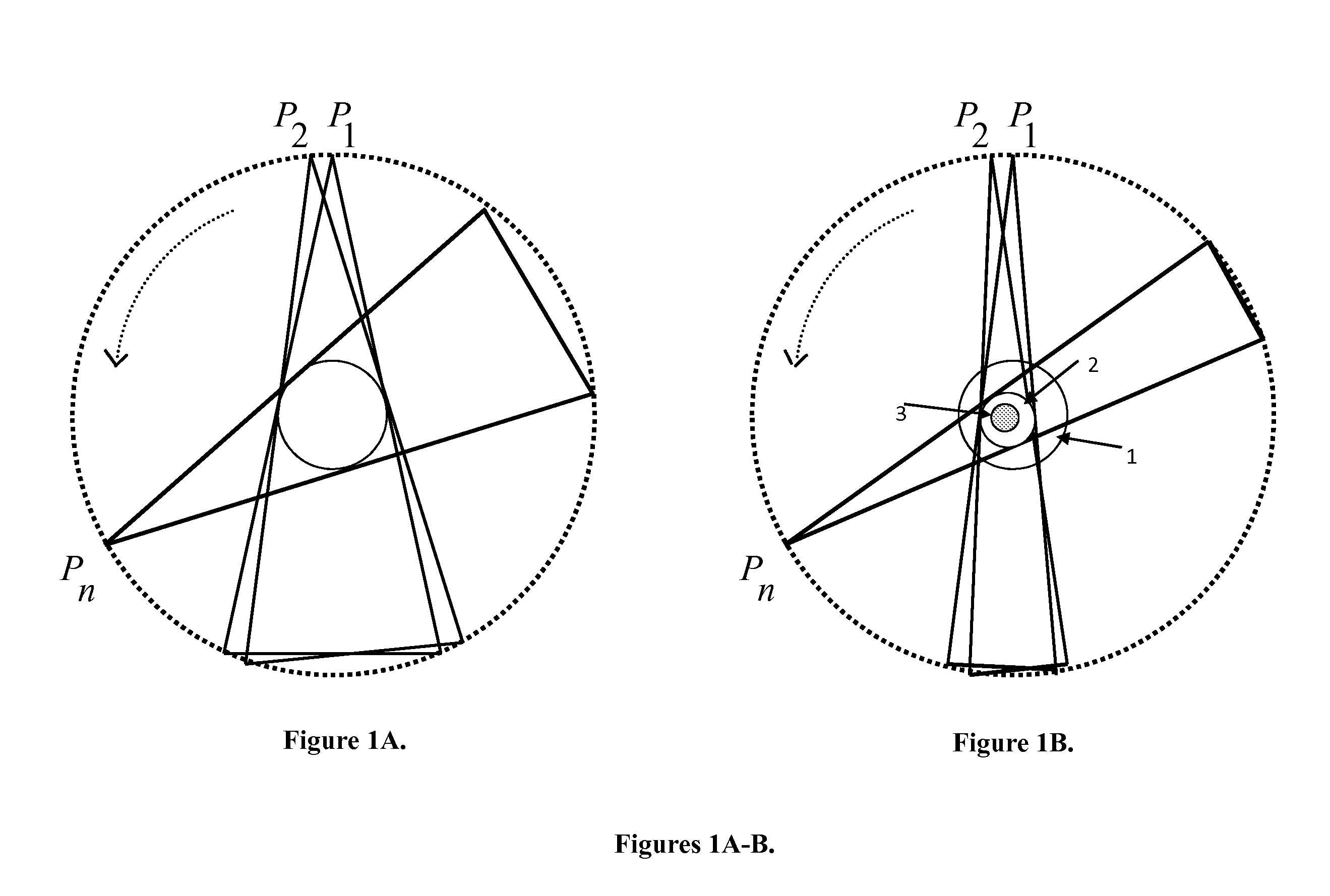
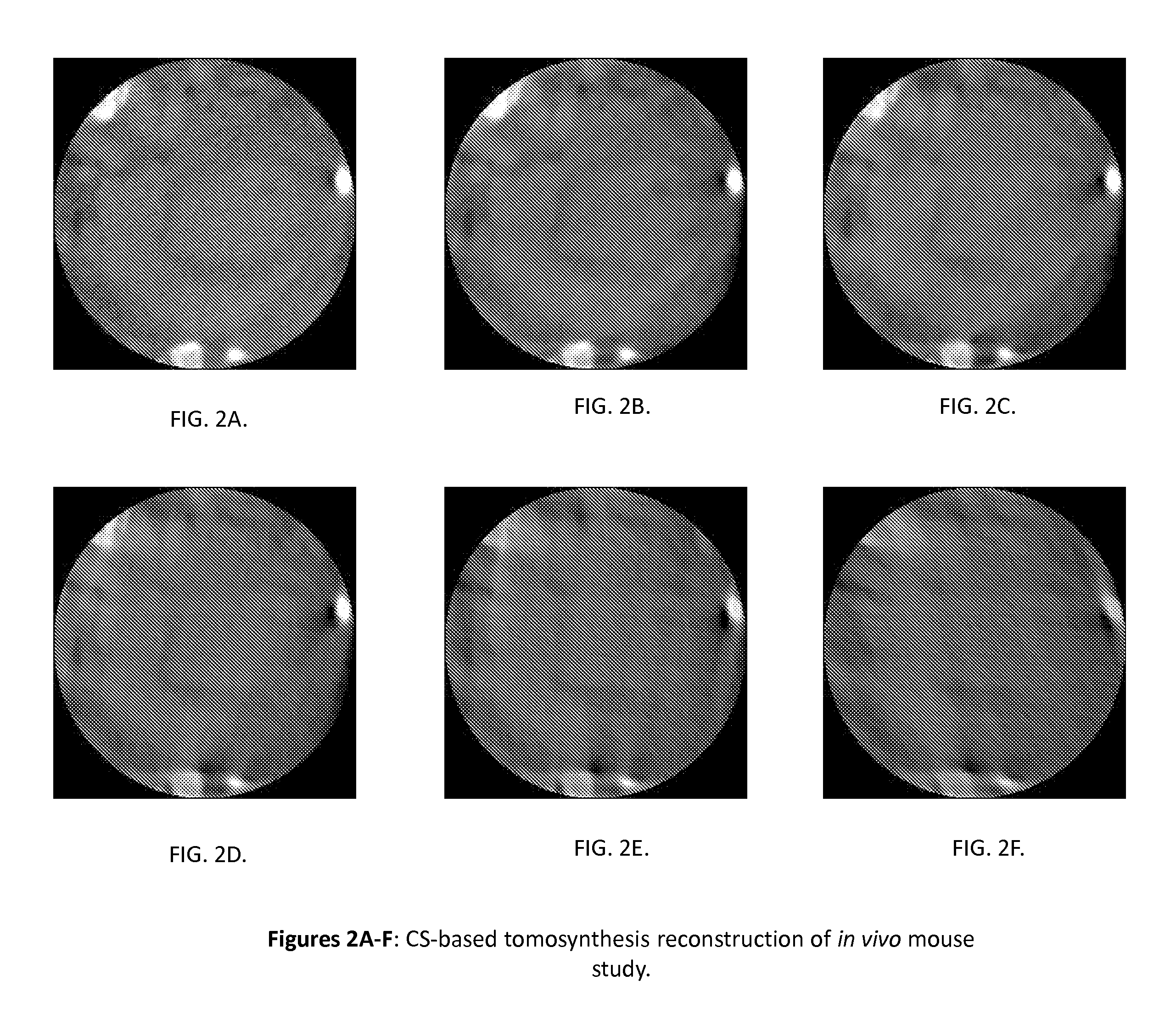
InactiveUS20110142316A1Comparable image qualityImproved temporalReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesisElastography
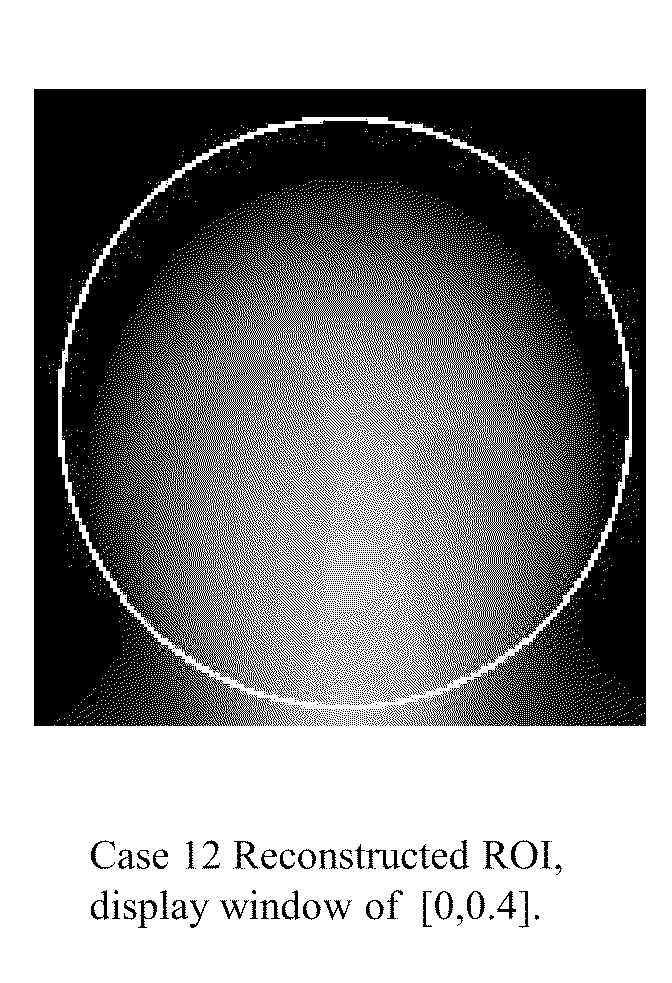
Tomography limitations in vivo due to incomplete, inconsistent and intricate measurements require solution of inverse problems. The new strategies disclosed in this application are capable of providing faster data acquisition, higher image quality, lower radiation dose, greater flexibility, and lower system cost. Such benefits can be used to advance research in cardiovascular diseases, regenerative medicine, inflammation, and nanotechnology. The present invention relates to the field of medical imaging. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to methods, systems, and devices for imaging, including tomography-based and MRI-based applications. For example, included in embodiments of the invention are compressive sampling based tomosynthesis methods, which have great potential to reduce the overall x-ray radiation dose for a patient. To name a few, compressive sensing based carbon nano-tube based interior tomosynthesis systems, tomography-based dynamic cardiac elastography systems, cardiac elastodynamic biomarkers from interior MR imaging, exact and stable interior ROI reconstructions for radial MRI, and interior reconstruction based ultrafast tomography systems are provided.
Owner:WANG GE +5
Tactile sensor using elastomeric imaging
ActiveUS20090315989A1Television conference systemsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationElastomerElastography
A tactile sensor includes a photosensing structure, a volume of elastomer capable of transmitting an image, and a reflective skin covering the volume of elastomer. The reflective skin is illuminated through the volume of elastomer by one or more light sources, and has particles that reflect light incident on the reflective skin from within the volume of elastomer. The reflective skin is geometrically altered in response to pressure applied by an entity touching the reflective skin, the geometrical alteration causing localized changes in the surface normal of the skin and associated localized changes in the amount of light reflected from the reflective skin in the direction of the photosensing structure. The photosensing structure receives a portion of the reflected light in the form of an image, the image indicating one or more features of the entity producing the pressure.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
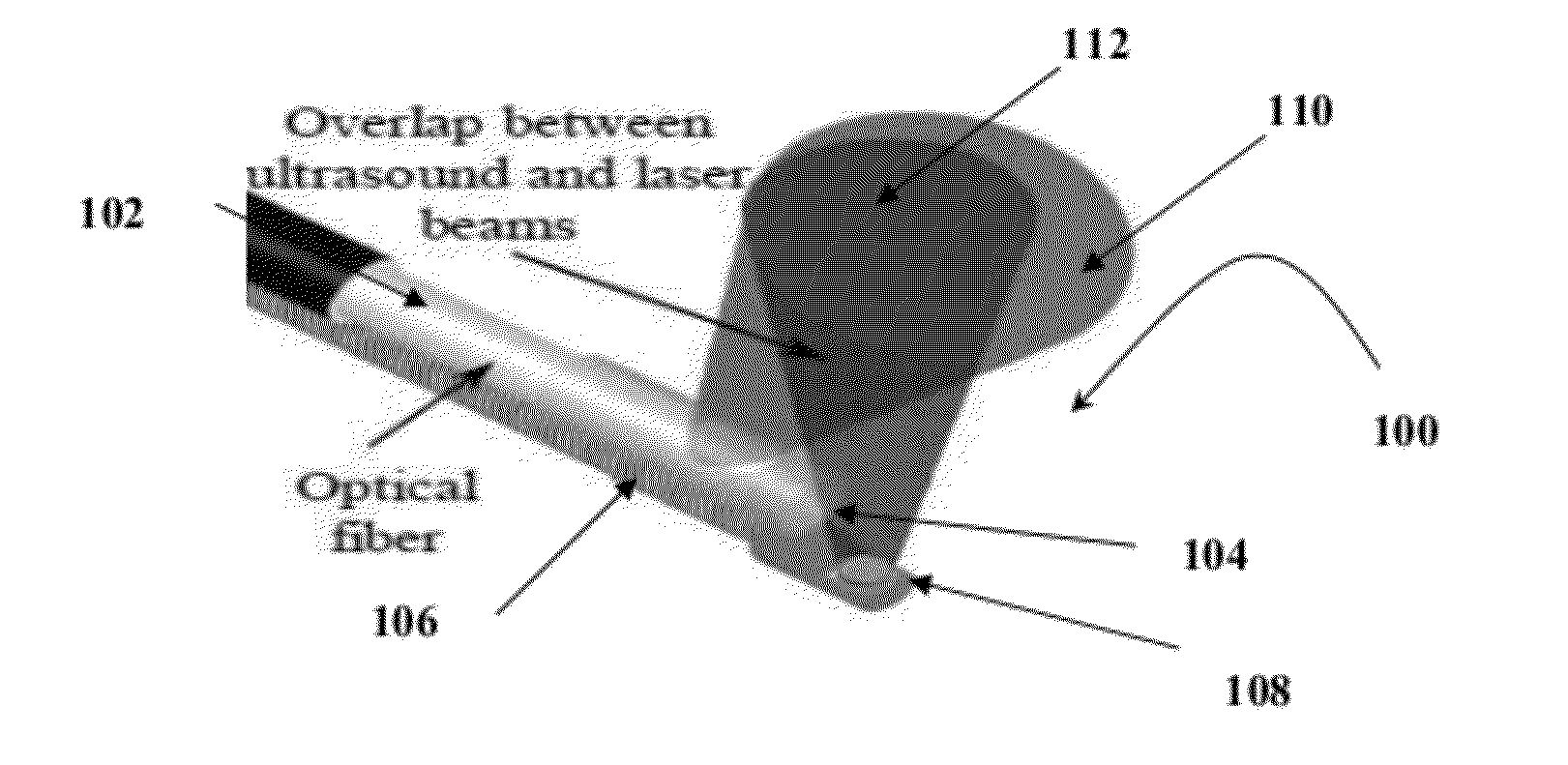
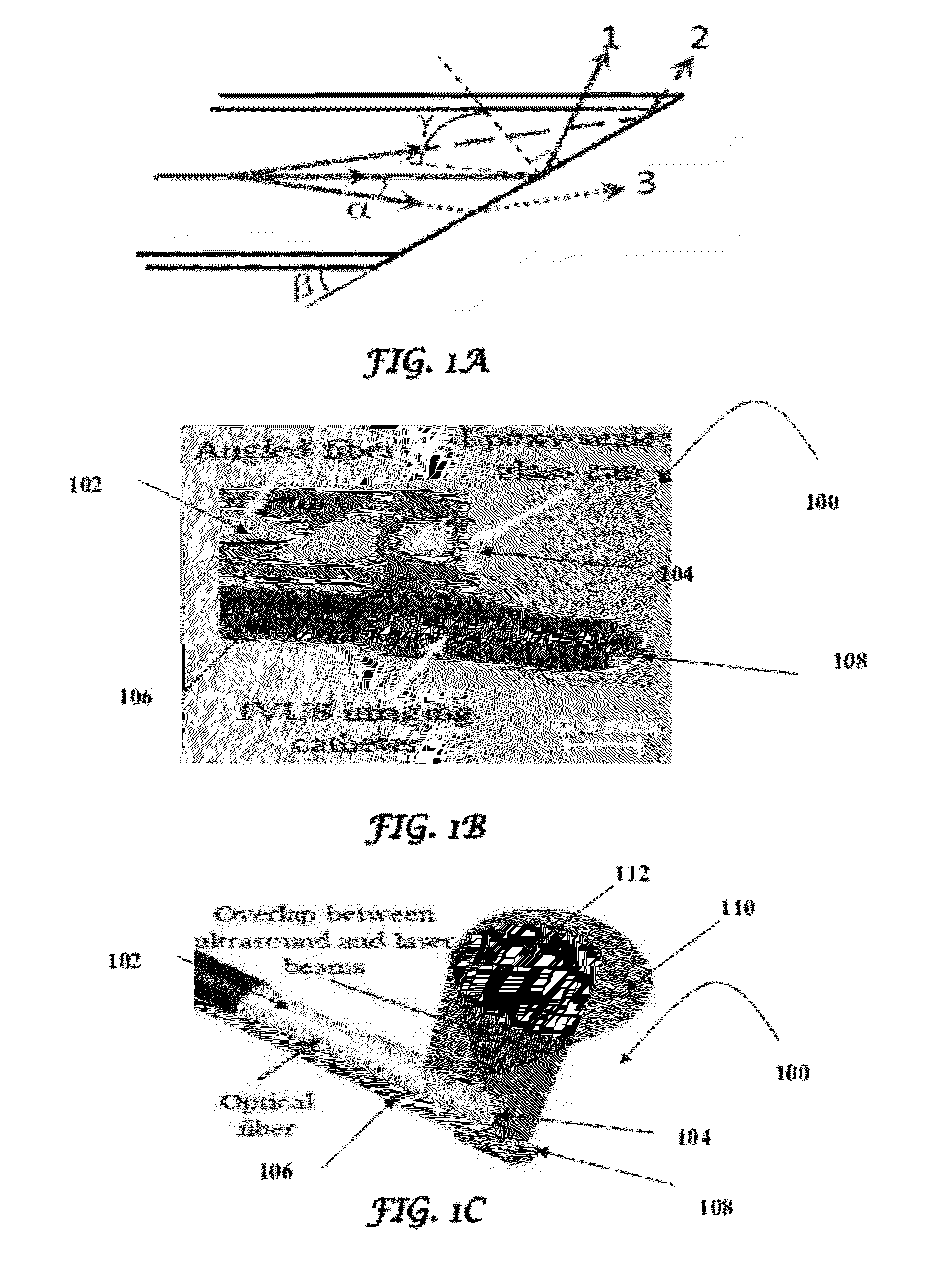
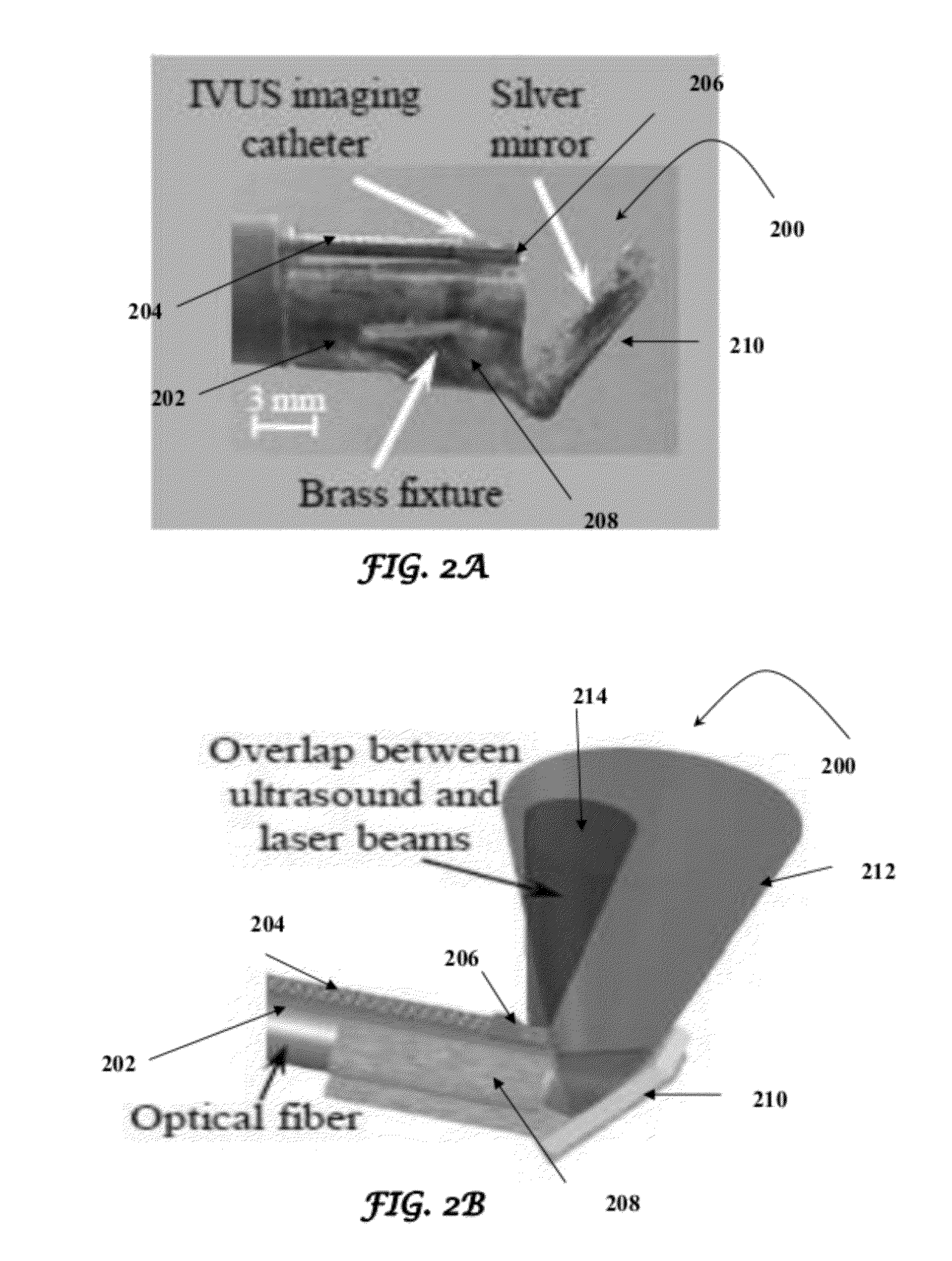
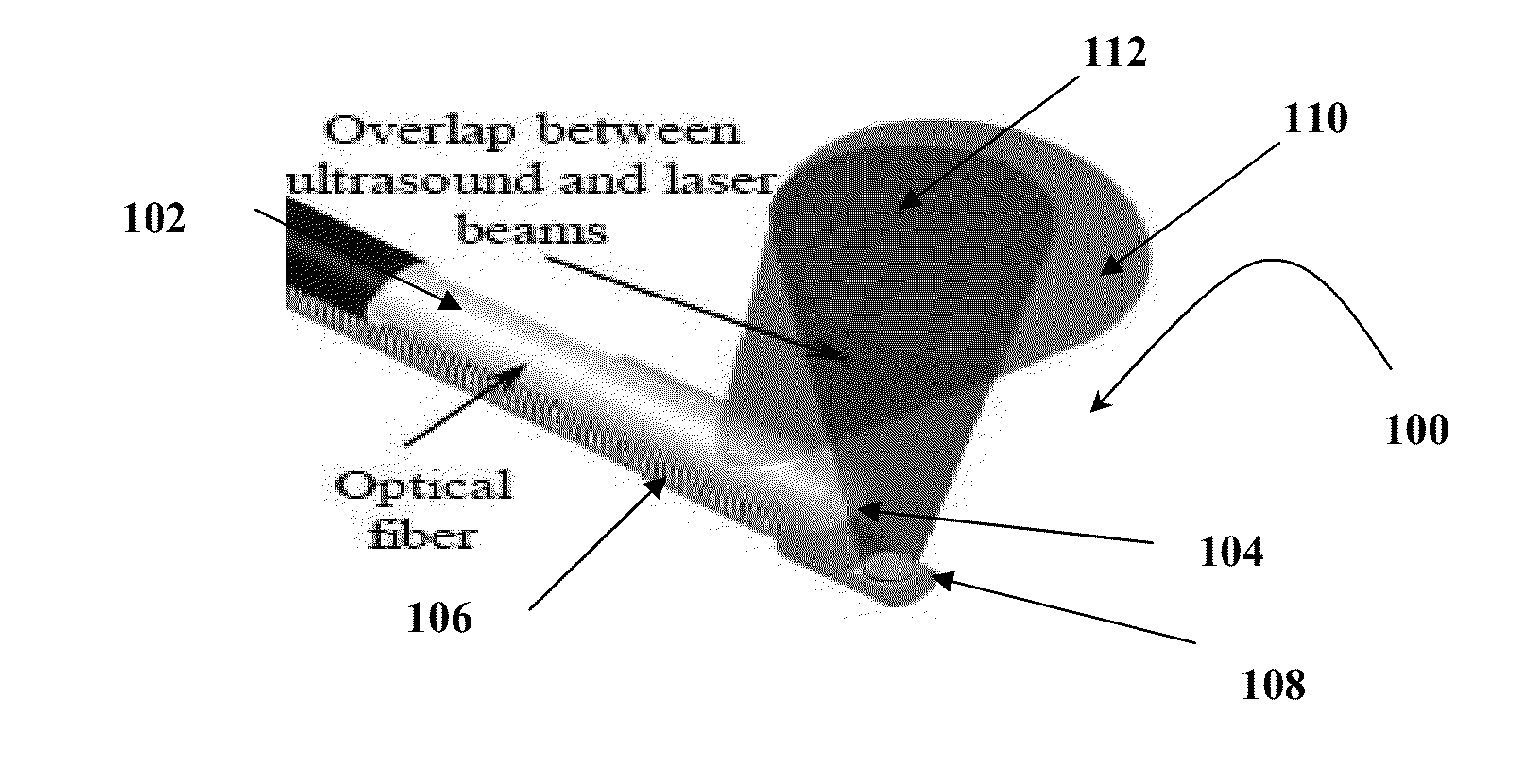
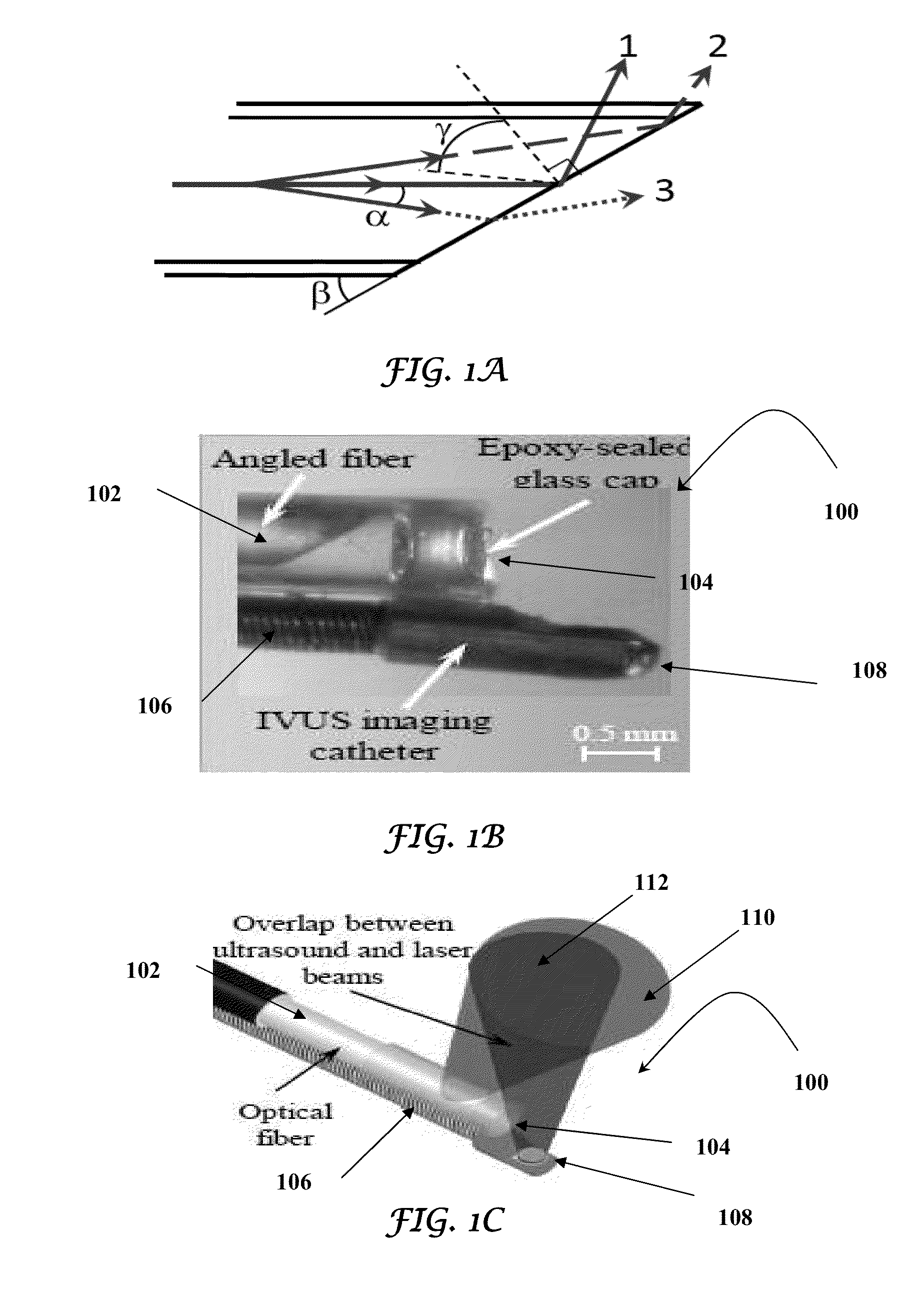
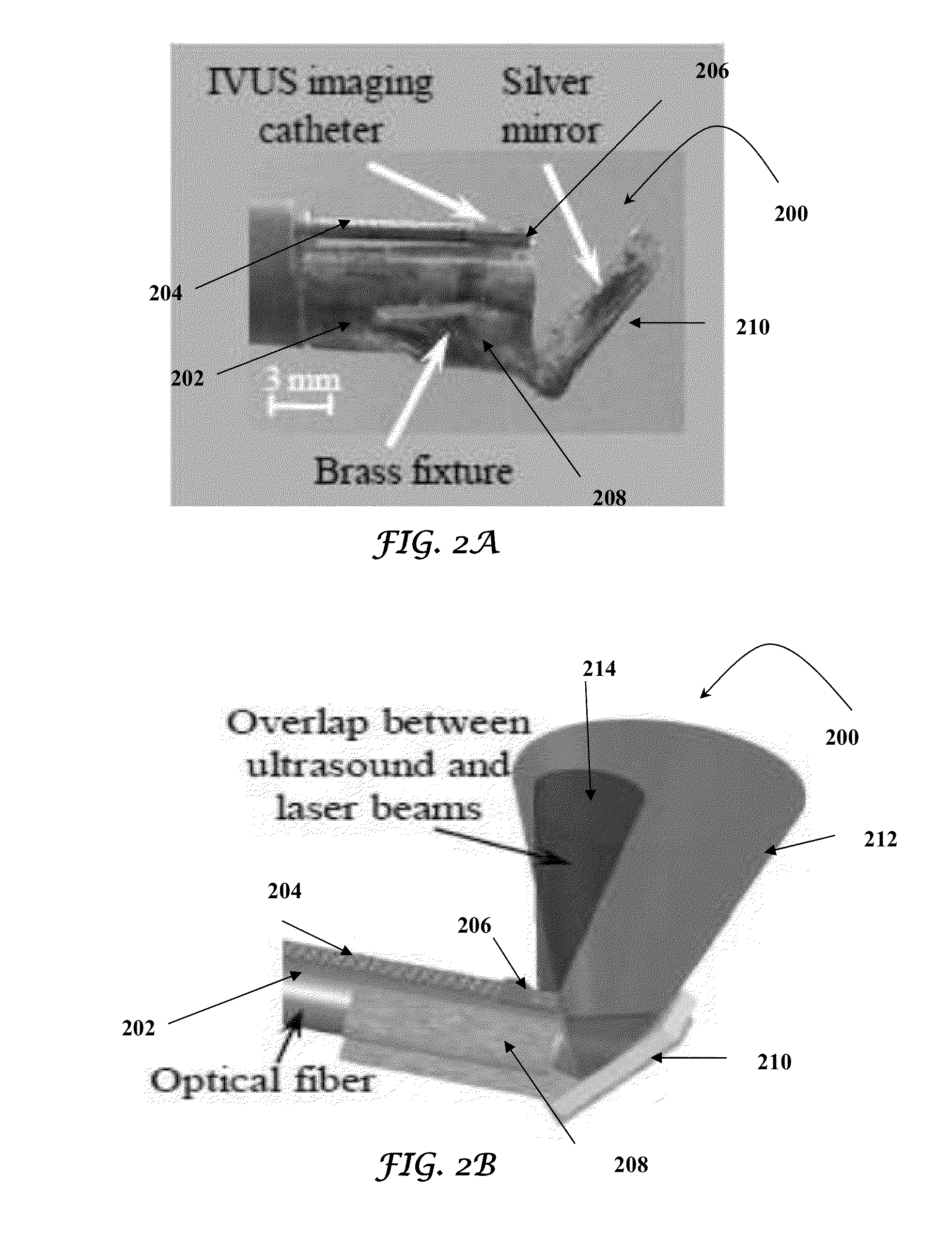
Catheter for intravascular ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
InactiveUS20120271170A1Protect partsAvoid mechanical damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorElastography
A design and a fabrication method for an intravascular imaging and therapeutic catheters for combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and for optical and / or acoustic therapy of hollow organs and diseased blood vessels and tissues are disclosed in the present invention. The invention comprises both a device—optical fiber-based intravascular catheter designs for combined IVUS / IVPA, and elasticity imaging and for acoustic and / or optical therapy—and a method of combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and optical and / or acoustic therapy. The designs of the catheters are based on single-element catheter-based ultrasound transducers or on ultrasound array-based units coupled with optical fiber, fiber bundles or a combination thereof with specially designed light delivery systems. One approach uses the side fire fiber, similar to the one utilized for biomedical optical spectroscopy. The second catheter design uses the micro-optics in the manner of a probe for optical coherent tomography.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Biopsy device with acoustic element
InactiveUS20110066073A1Continuous measurementStrong absorption capacitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsRadiologyTransducer
The invention relates to a biopsy device, particularly a biopsy device comprising a shaft with a transducer element for providing information about acoustic properties of a material to be analysed, a system of positioning a biopsy device and a method for positioning a biopsy device. The biopsy device may be adapted to take biopsies of different regions of the 5 human body for excluding or detecting abnormalities as cancerous lesions. The biopsy device may be used to measure acoustic properties of the material while inserting the tip portion of the biopsy device into the material to be analysed. The biopsy device may further allow measurement based on elastography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
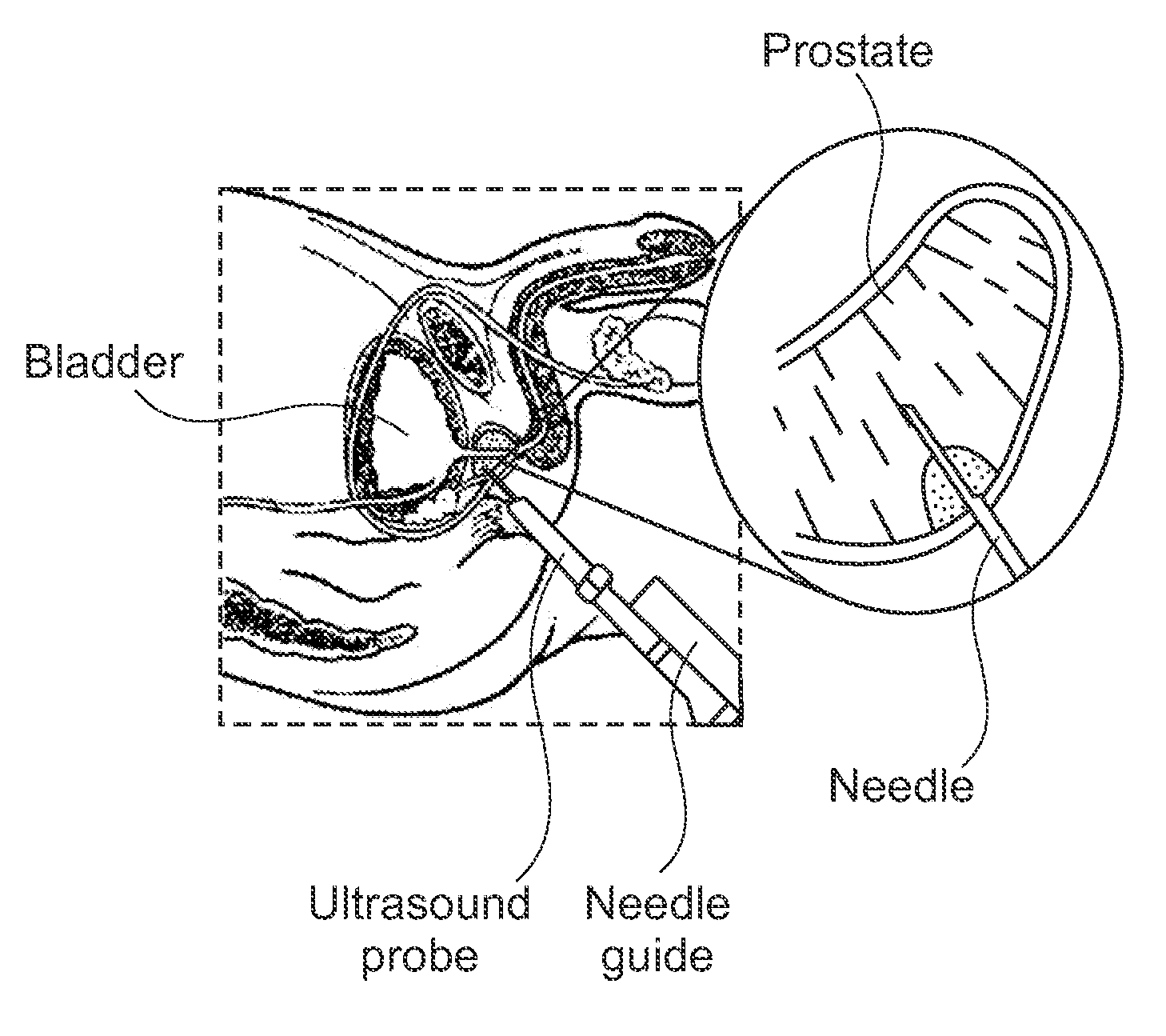
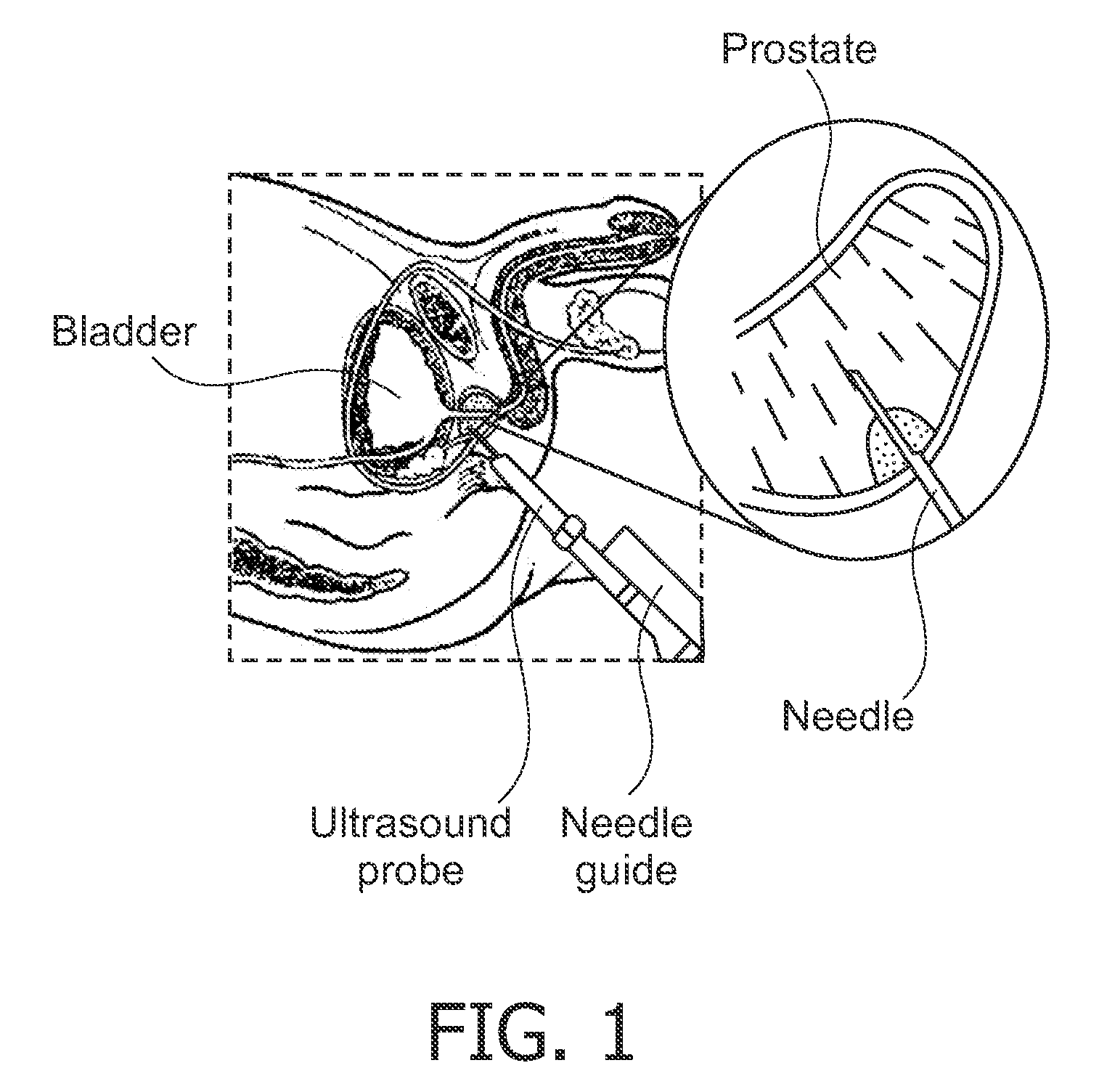
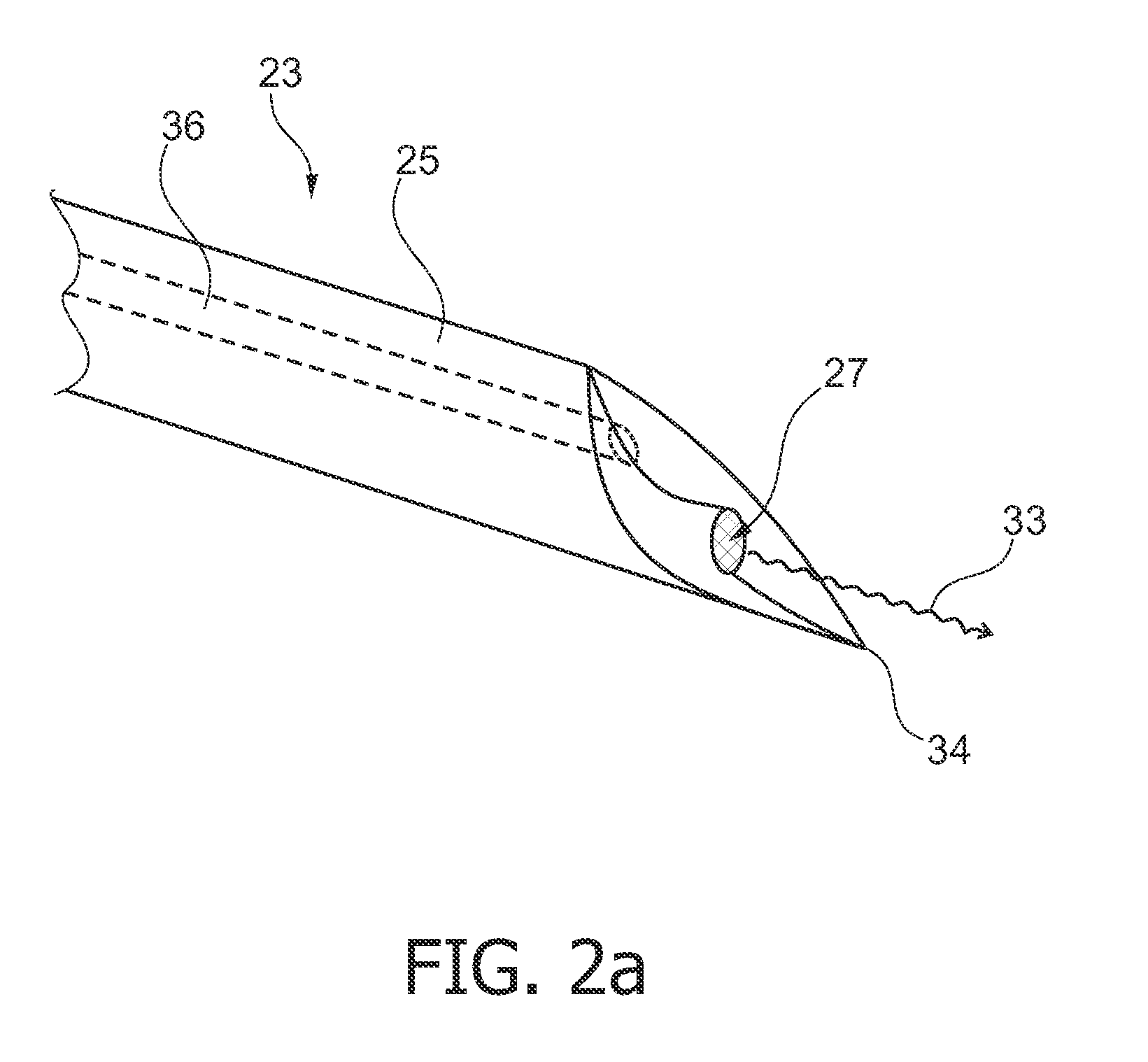
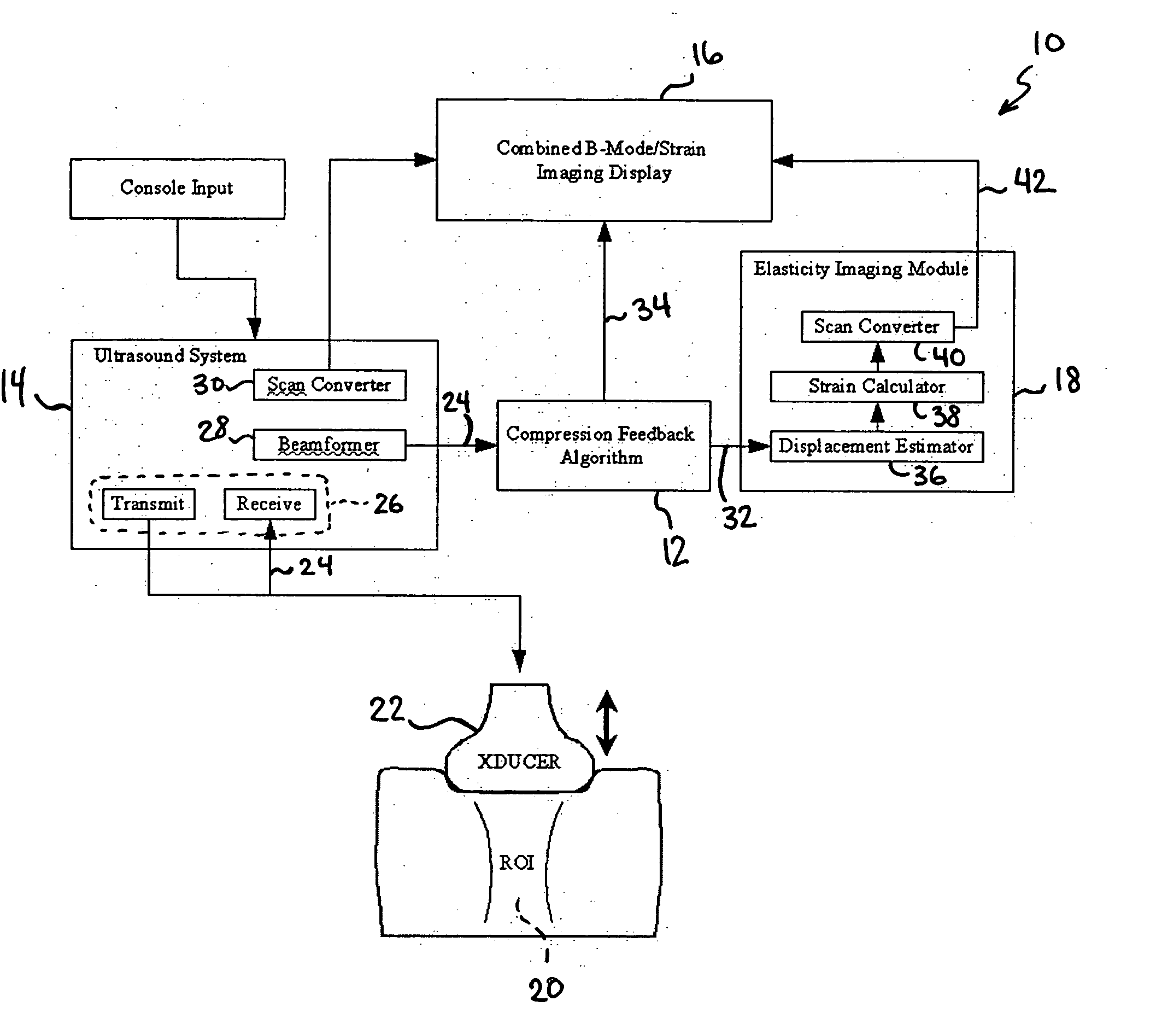
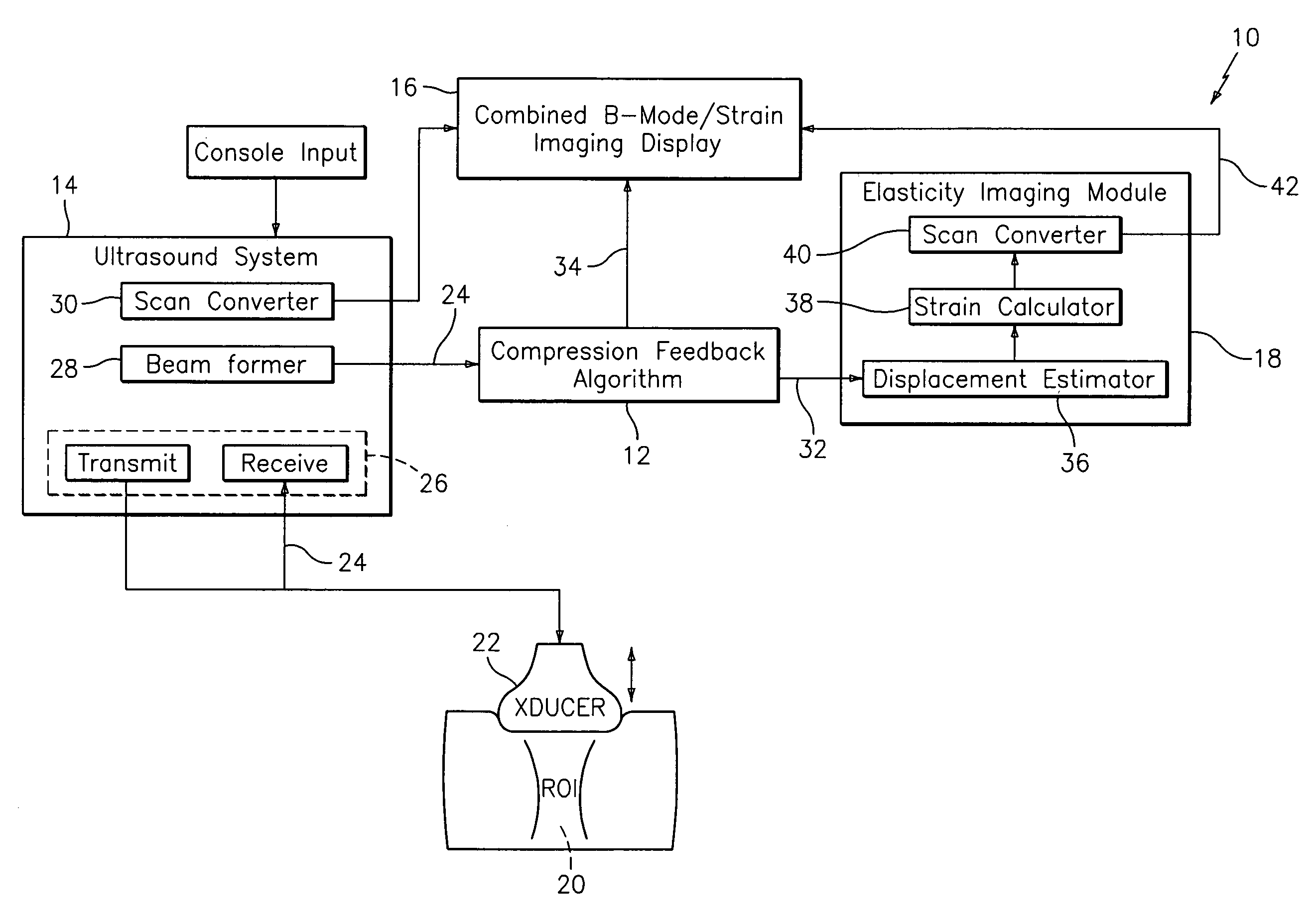
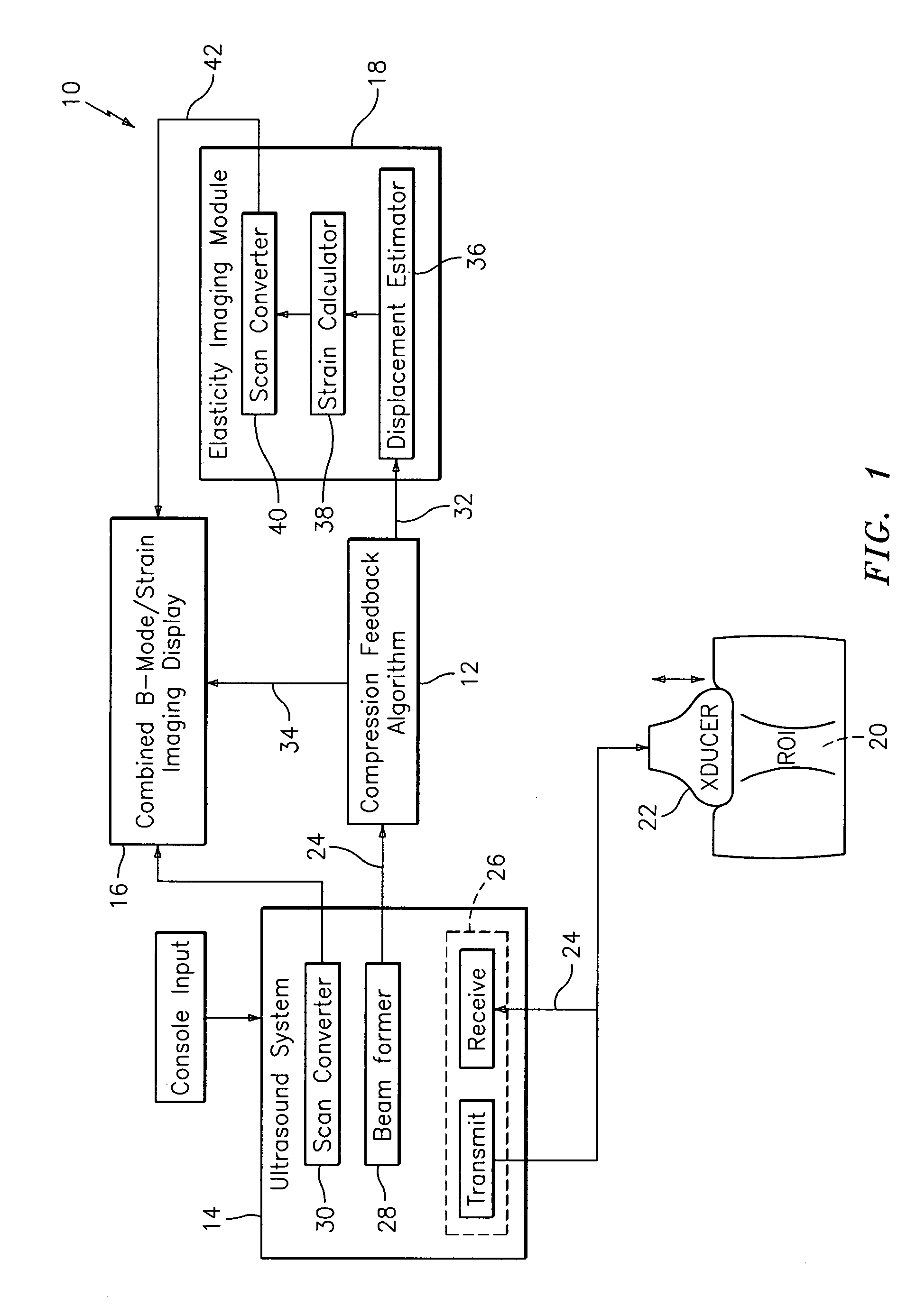
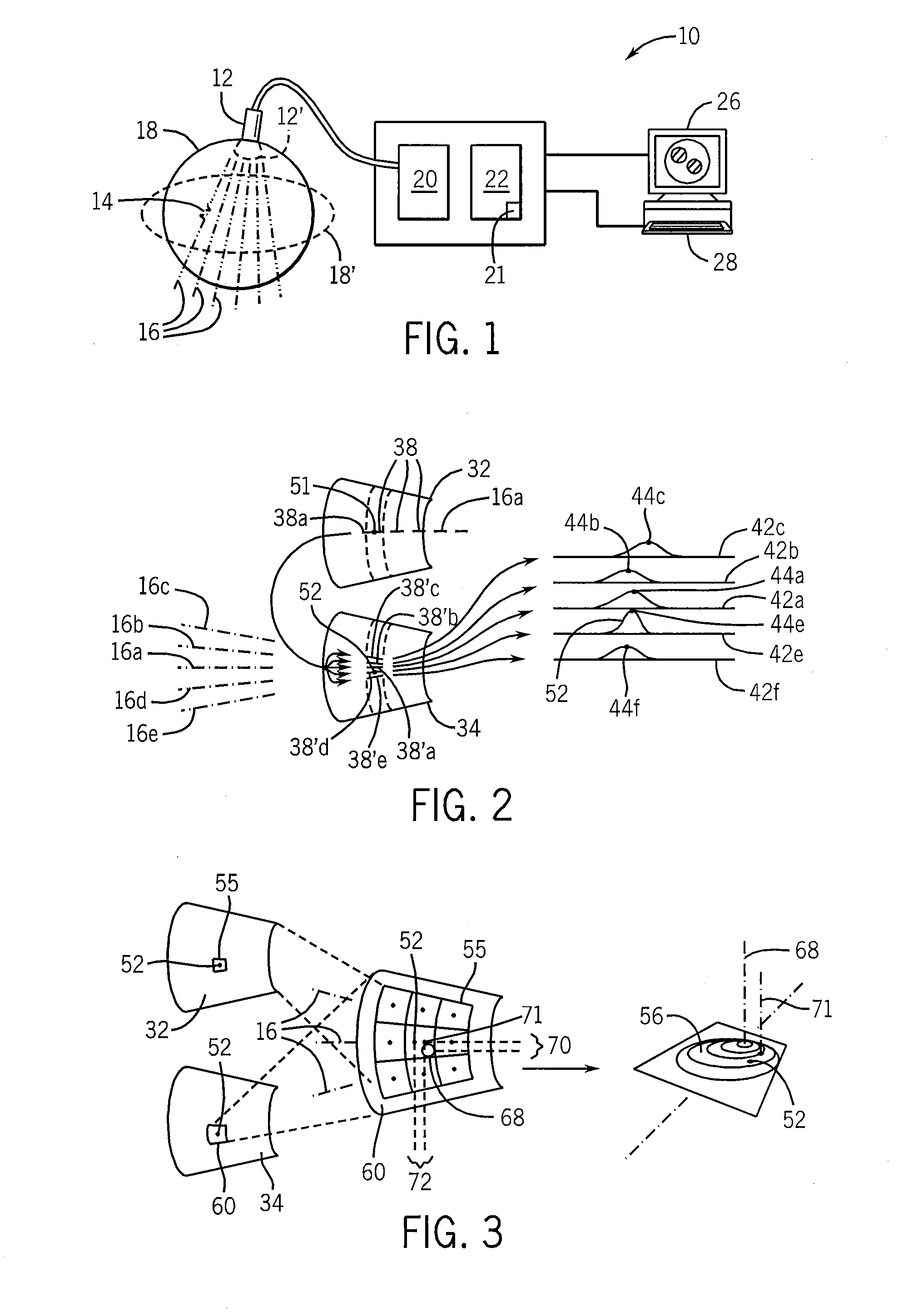
Method and apparatus for elasticity imaging
InactiveUS20060173320A1Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingElastography
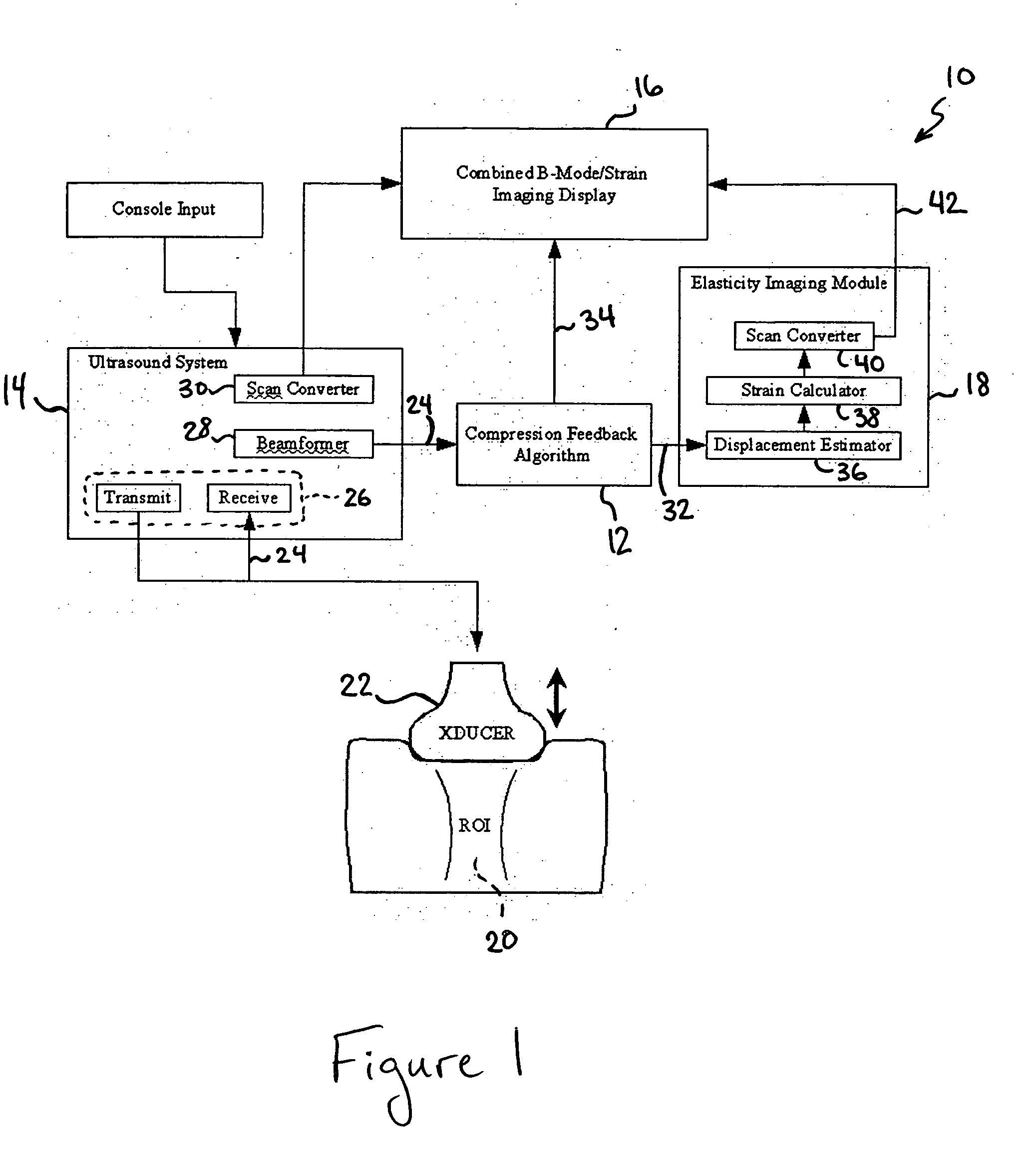
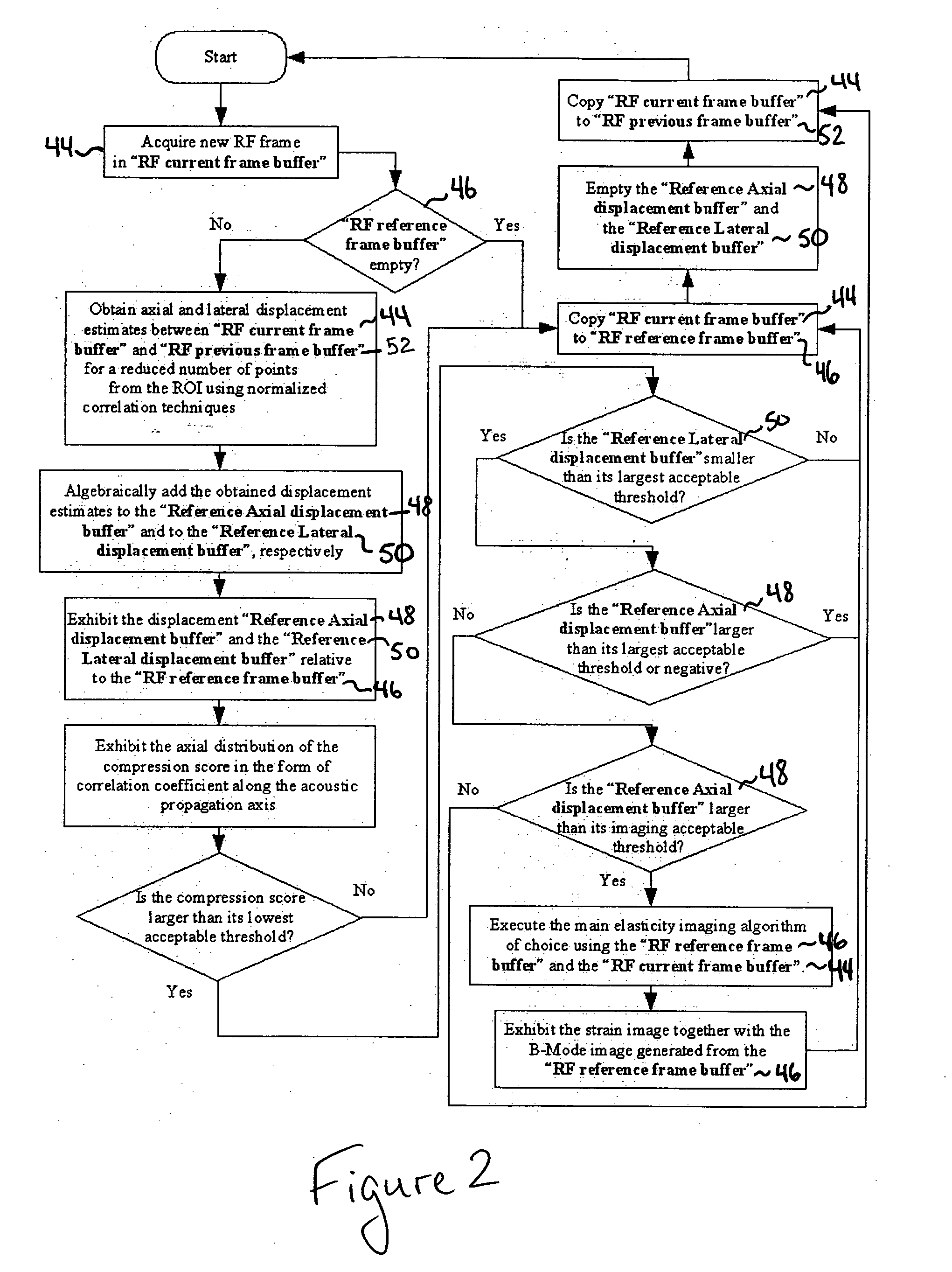
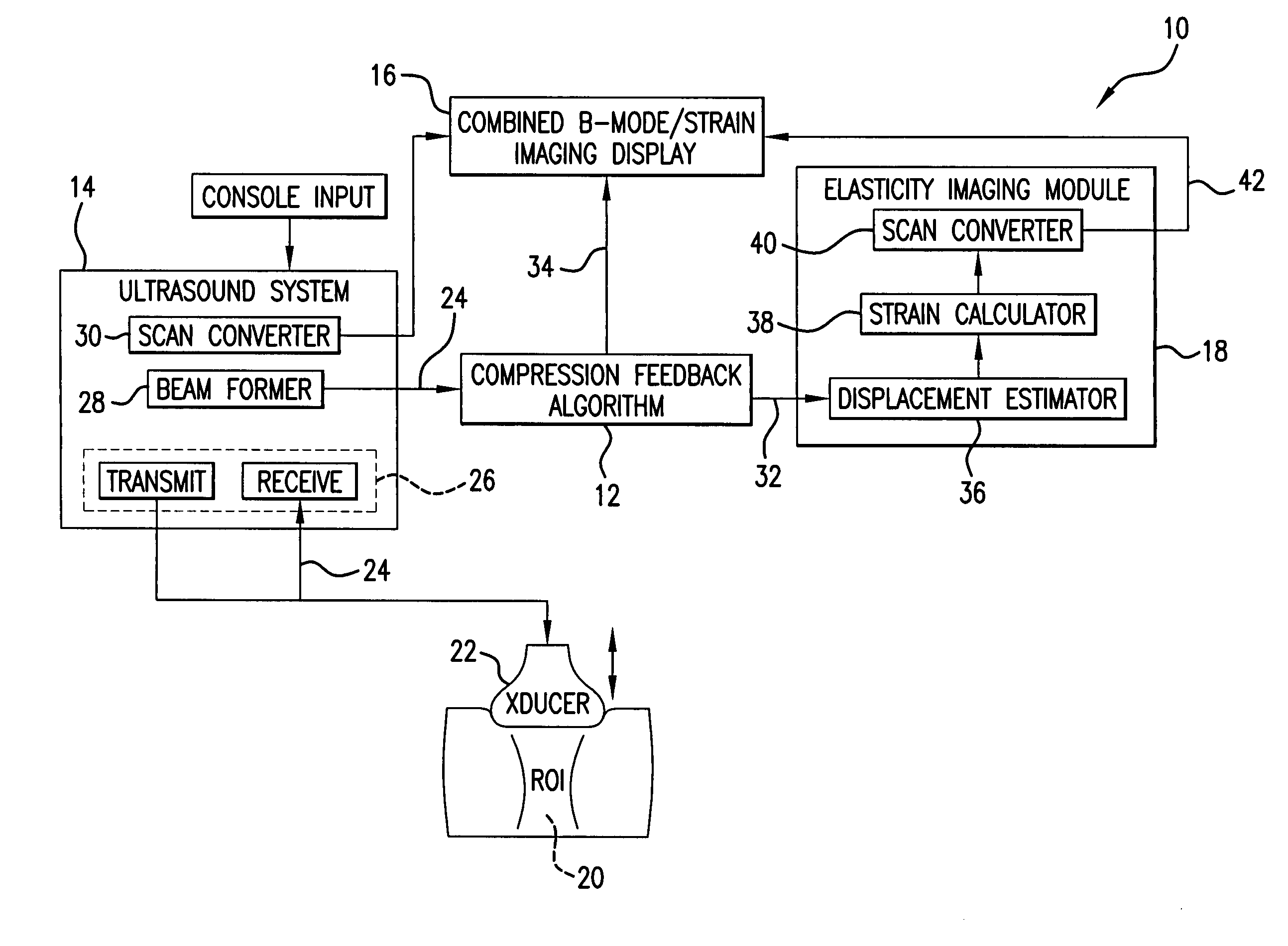
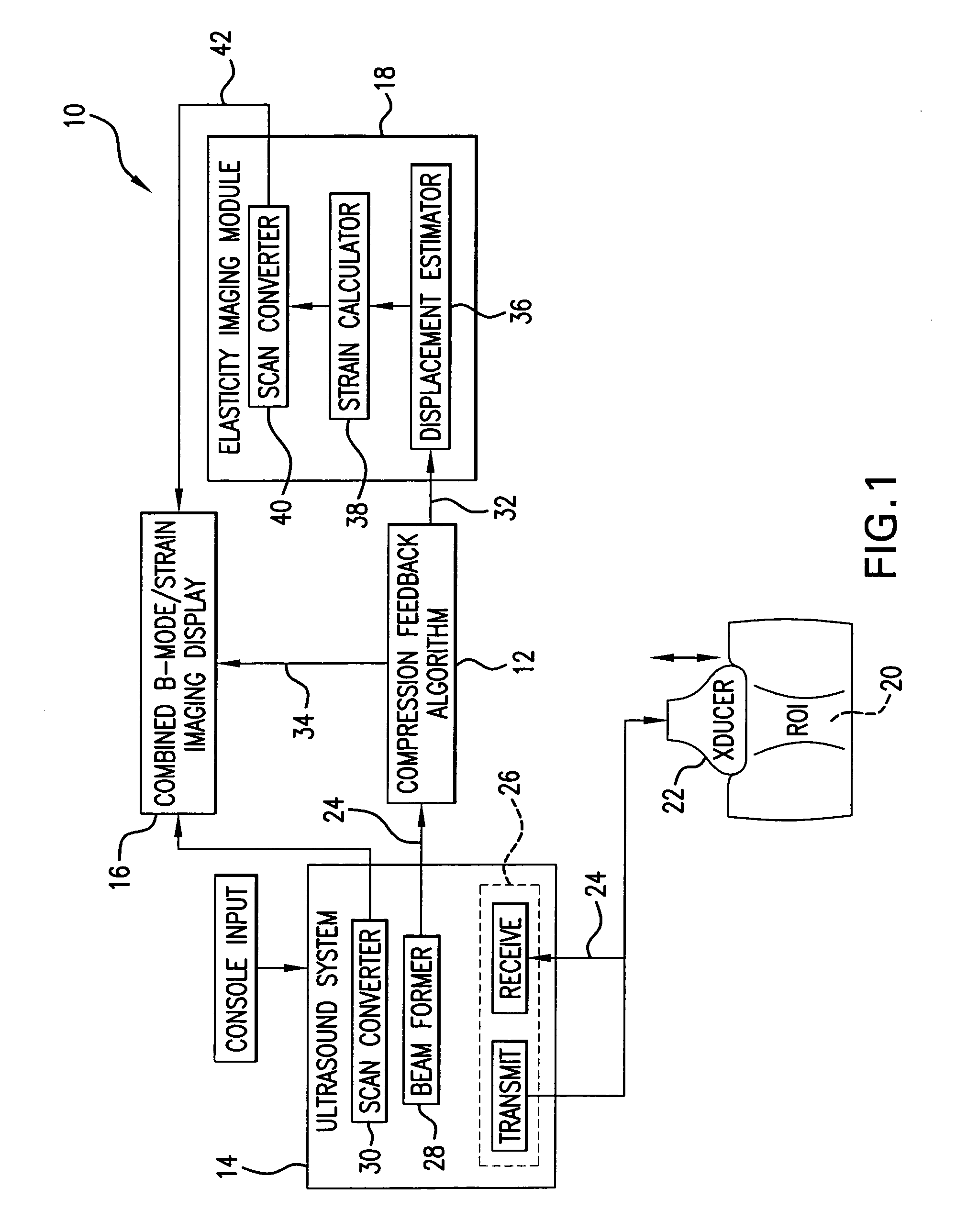
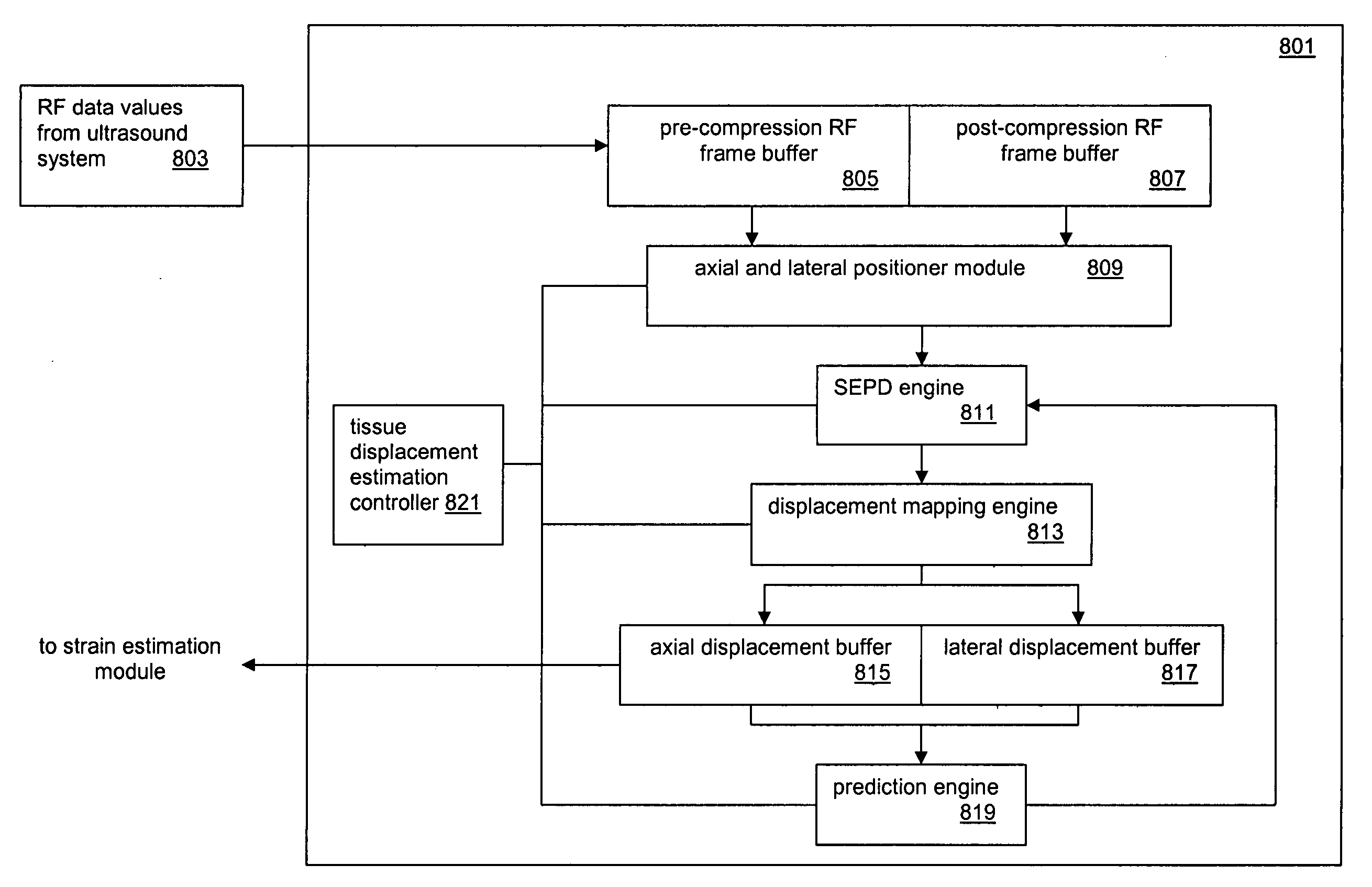
A computational efficient algorithm for compression analysis of free-hand static elasticity imaging performed using medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging equipment offers tissue compression quality and quantity feedback to the operator. The algorithm includes a criterion for automatic selection of the most advantageous pre- and post- compression frame pairs delivering elasticity images of optimal dynamic ranges (DR) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). The use of the algorithm in real time eases operator training and reduces significantly the amount of artifact in the elasticity images while lowering the computational burden.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for elasticity imaging
InactiveUS20070093716A1Wave based measurement systemsDiagnostics using vibrationsUltrasound imagingElastography
A computational efficient algorithm for compression analysis of free-hand static elasticity imaging performed using medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging equipment offers tissue compression quality and quantity feedback to the operator. The algorithm includes a criterion for automatic selection of the most advantageous pre- and post-compression frame pairs delivering elasticity images of optimal dynamic ranges (DR) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). The use of the algorithm in real time eases operator training and reduces significantly the amount of artifact in the elasticity images while lowering the computational burden.
Owner:ALOKA CO LTD
Tactile sensor using elastomeric imaging
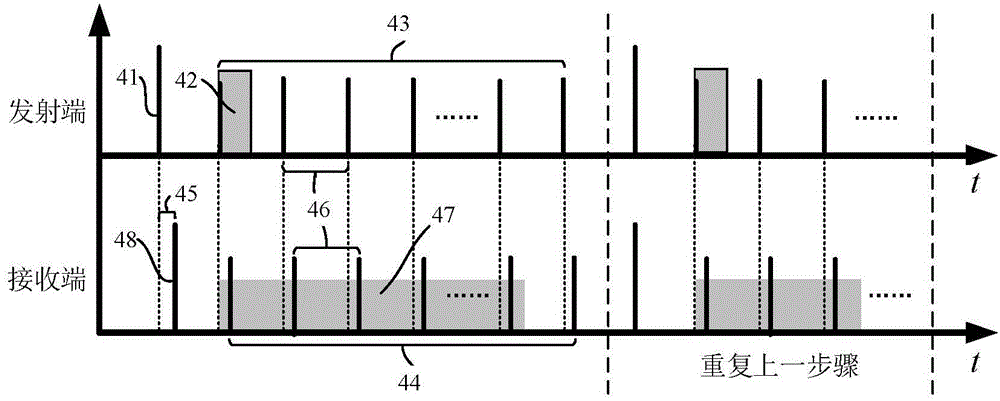
ActiveUS8411140B2Television conference systemsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationElastomerElastography
A tactile sensor includes a photosensing structure, a volume of elastomer capable of transmitting an image, and a reflective skin covering the volume of elastomer. The reflective skin is illuminated through the volume of elastomer by one or more light sources, and has particles that reflect light incident on the reflective skin from within the volume of elastomer. The reflective skin is geometrically altered in response to pressure applied by an entity touching the reflective skin, the geometrical alteration causing localized changes in the surface normal of the skin and associated localized changes in the amount of light reflected from the reflective skin in the direction of the photosensing structure. The photosensing structure receives a portion of the reflected light in the form of an image, the image indicating one or more features of the entity producing the pressure.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for elasticity imaging
InactiveUS7223241B2Organ movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingElastography
A computational efficient algorithm for compression analysis of free-hand static elasticity imaging performed using medical diagnostic ultrasound imaging equipment offers tissue compression quality and quantity feedback to the operator. The algorithm includes a criterion for automatic selection of the most advantageous pre- and post-compression frame pairs delivering elasticity images of optimal dynamic ranges (DR) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). The use of the algorithm in real time eases operator training and reduces significantly the amount of artifact in the elasticity images while lowering the computational burden.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
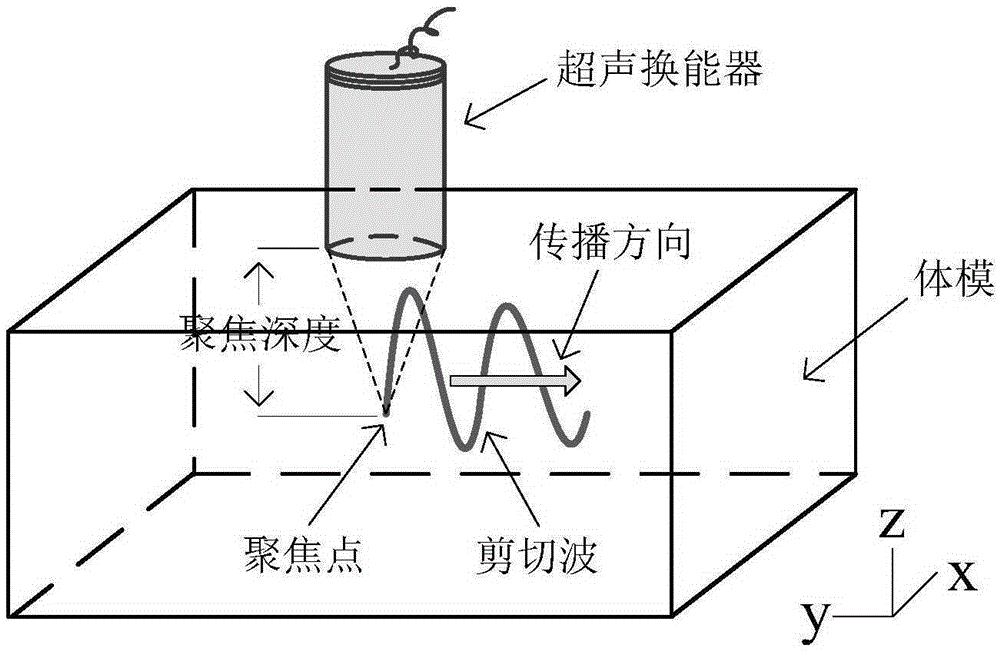
Ultrasound dynamic elastic imaging probe and method
InactiveCN101912278ALarge sound fieldIncrease field strengthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsElastographyWave equation
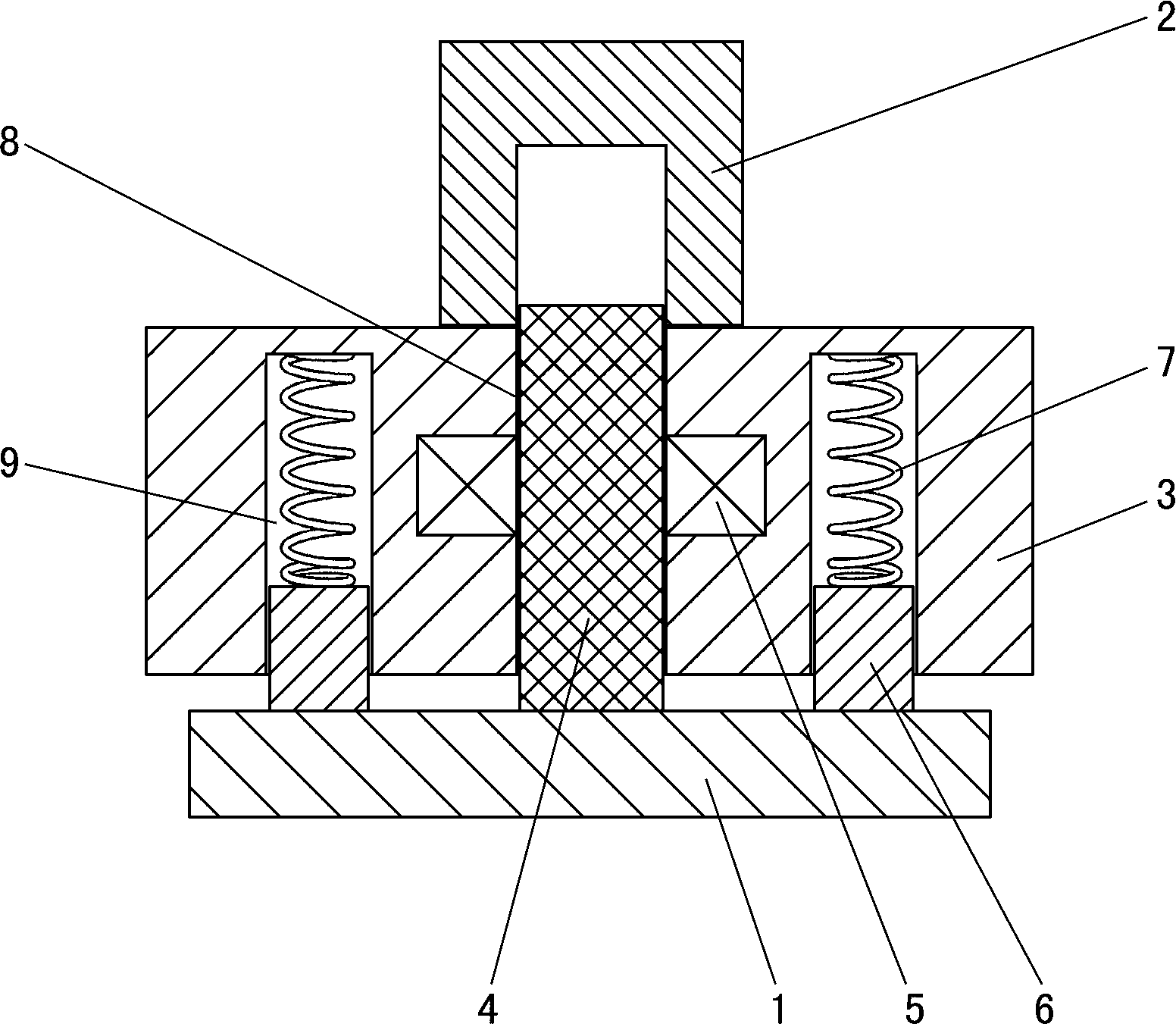
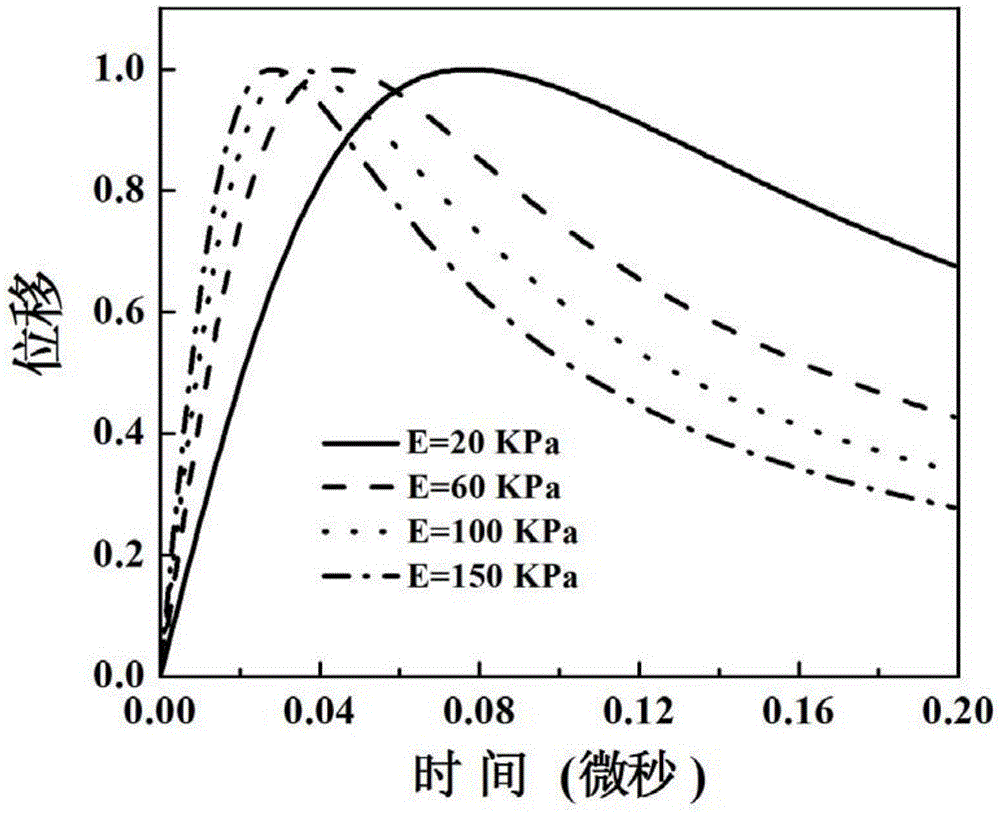
The invention discloses ultrasound dynamic elastic imaging probe and method. The probe internally comprises an imaging transducer with higher frequency and exciting transducers with lower frequency, wherein the imaging transducer is arranged in the middle, and the exciting transducers are arranged at both sides of the imaging transducer; the imaging transducer and the exciting transducers synchronously work in a coupling mode; ultrasonic radiometric force generated by the exciting transducers generates shear waves in a tissue, and the transverse propagation of the shear waves causes the longitudinal displacement of the tissue; and the imaging transducer transmits ultrasonic waves to detect the longitudinal displacement of the tissue and then reconstructs an elastic physical quantity according to a wave equation so as to acquire an elastic image of the tissue. In the invention, the transducers with lower frequency are used for exciting the tissue to generate the shear waves, and the generated shear waves have strong intensity and wider effective exciting range; and meanwhile, the traditional transducer with higher frequency is used for imaging the shear waves, and the elastic image has high signal to noise ratio and high image quality and conforms to the standard of national acoustic power.
Owner:陈庆武
Two-dimension displacement estimation method of elasticity imaging
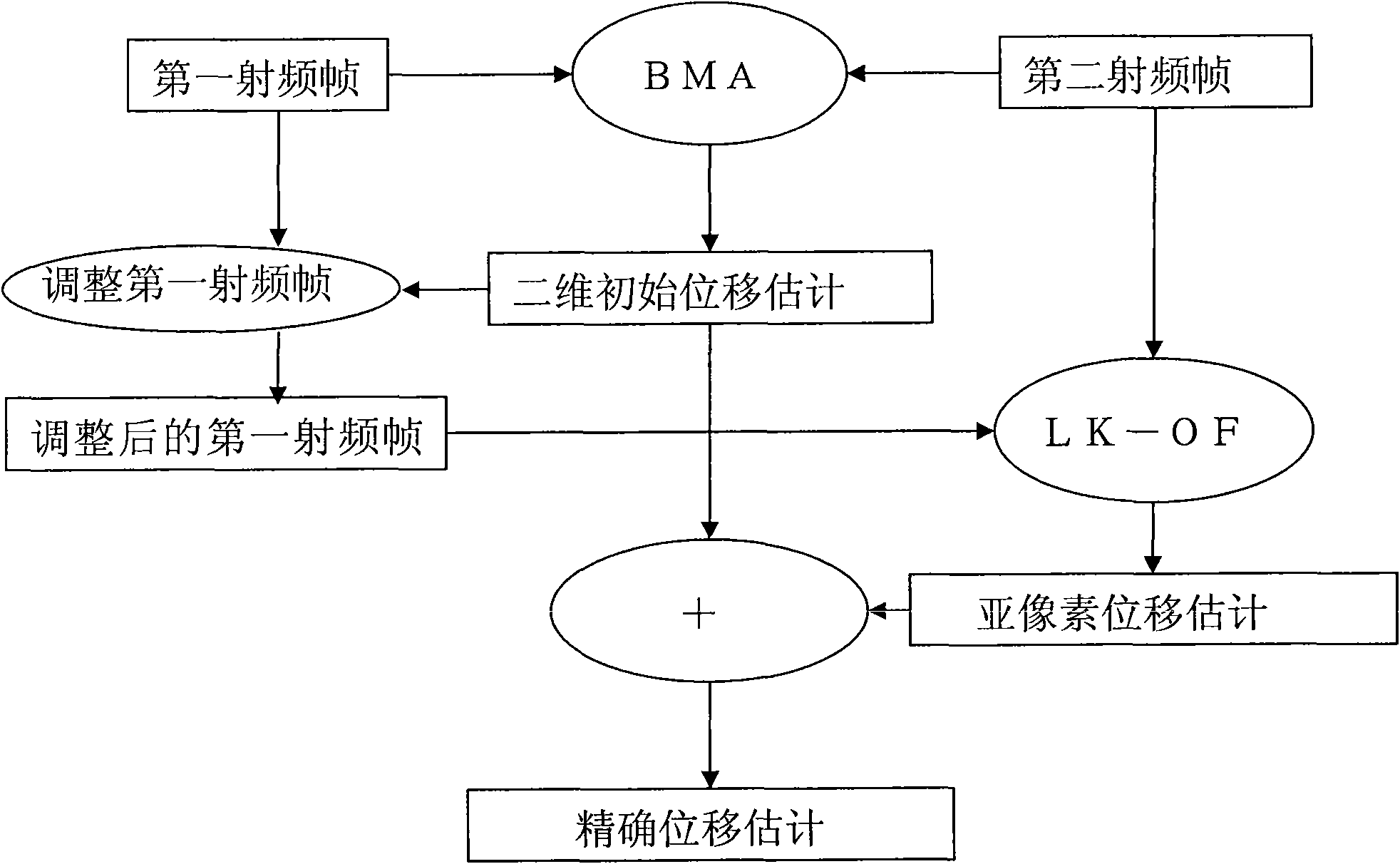
ActiveCN101569543AMeet real-time requirementsOptimizing anamorphic imagesImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionElastographySonification
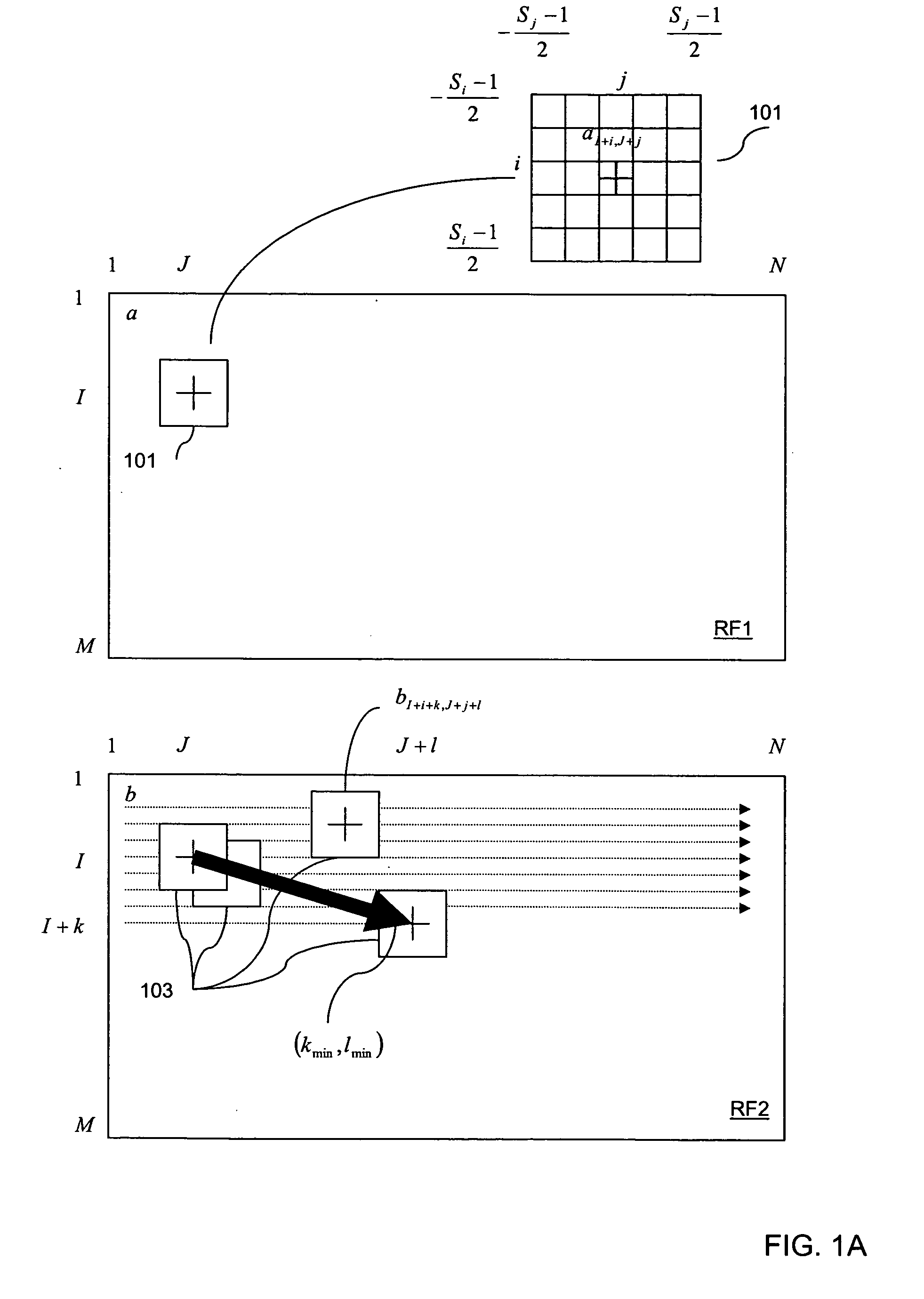
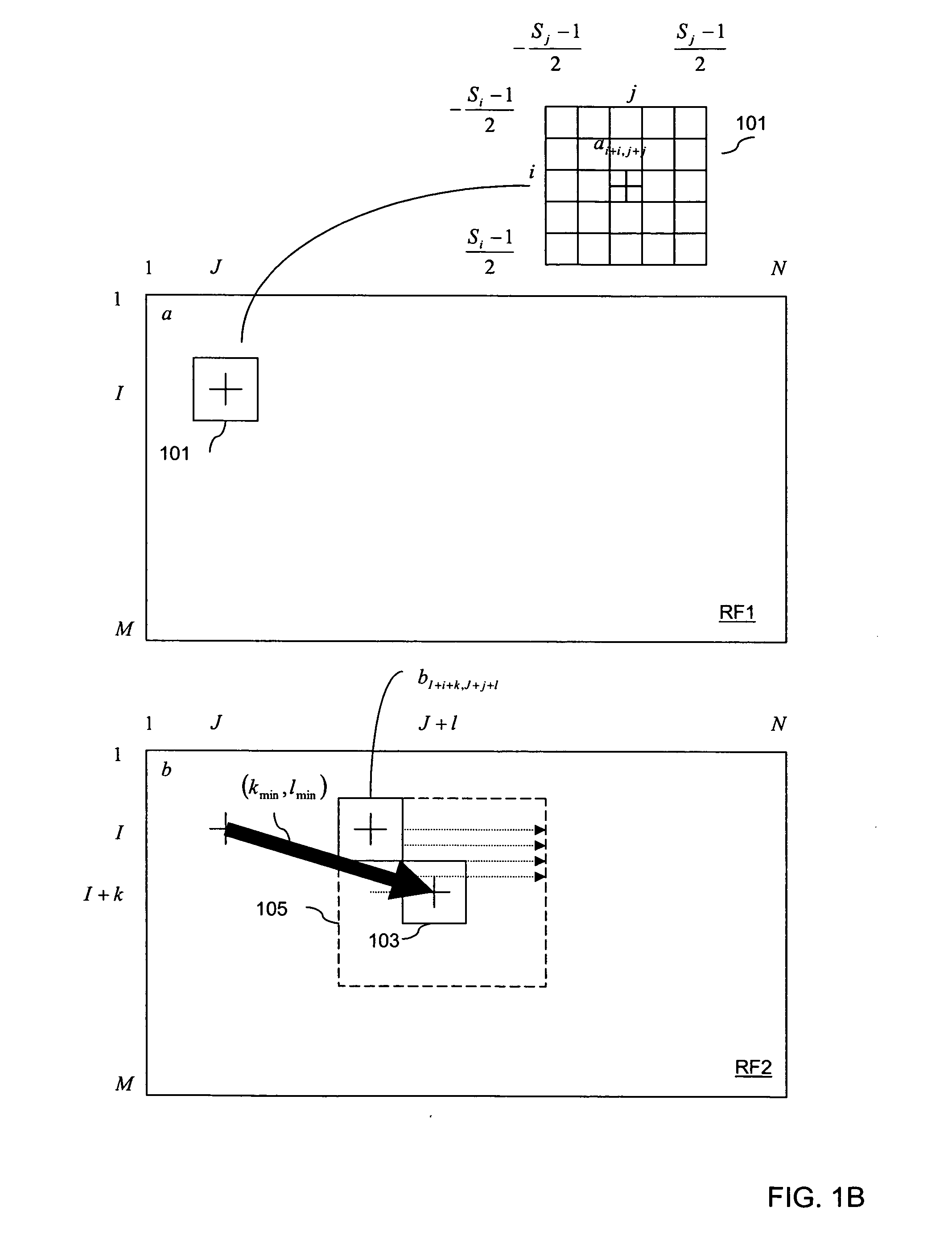
The invention relates to a two-dimension displacement estimation method of elasticity imaging, which comprises the following steps: carrying out two-dimension initial displacement estimation on a first radio frequency frame and a second radio frequency frame of an ultrasonic pattern to be treated by a matching algorithm with robustness; using the obtained two-dimension initial displacement estimation to adjust the image of the first radio frequency frame to cause that the relativity between the regulated first frame and the original second frame is higher compared with the original first frame; and carrying out the displacement estimation on the original second frame and the regulated first frame by a sub-pixel displacement estimation algorithm; synthesizing the obtained two-dimension initial displacement estimation result with the displacement estimation result obtained by the sub-pixel displacement estimation algorithm and obtaining the total two-dimension displacement estimation. The two-dimension displacement estimation method of elasticity imaging adopts an initial estimation step which is rough but robust and a fine searching step which is accurate but needs the image with higher relativity so as to simultaneously achieve high speed and accuracy.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Photoacoustic elastic imaging method and device
ActiveCN102175776AHigh resolutionHigh precisionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationContinuous lightElastography
The invention discloses a photoacoustic elastic imaging method, wherein the photoacoustic elastic imaging method comprises the following steps: exciting and generating a photoinduced thermal elastic ultrasound signal by an intensity modulated continuous light source, and reconstructing an elastic distribution image of a sample to be detected via measuring the phase difference between the signal and a modulation signal and scanning point by point. The invention further discloses a photoacoustic elastic imaging device, wherein the photoacoustic elastic imaging device comprises a photoacoustic excitation light source generating assembly, a photoacoustic signal collecting assembly and a photoacoustic signal processing assembly; and the photoacoustic excitation light source generating assembly, the photoacoustic signal collecting assembly and the photoacoustic signal processing assembly are electrically connected in sequence. In the invention, the detects such as the traditional elastic imaging method is influenced by the tissues around the area to be detected, and the like are overcome; the images reflecting the tissue elastic distribution with new principle can be provided; the location is accurate; and the resolution ratio is high. The device disclosed by the invention is low in cost, and is easy to be popularized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Displacement detecting method and device thereof in elasticity imaging
ActiveCN102824194AQuality improvementSmall amount of calculationMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImage analysisElastographyMutual correlation
The invention discloses a displacement detecting method and a device thereof in elasticity imaging; the displacement detecting method comprises the following steps: acquiring a target point; acquiring the mutual-correlation phase counting position of the target point in a second frame image; counting a mutual-correlation phase according to the mutual-correlation phase counting position; counting a longitudinal displacement result according to the mutual-correlation phase; and working out a gradient for the displacement result so as to acquire a strain result. According to an elasticity imaging method and a device disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, an two paths of I / Q echo baseband signals which are down-sampled in two frames before and after compression are acquired; displacement information between two frames is detected quickly by guide-type phase estimation; an axial gradient is counted so as to obtain strain information; therefore, a strain image in relatively high quality can be acquired; in addition, counting quantity is reduced greatly; and clinical real-time demands are satisfied.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for detecting transmission speed of shear wave in biological tissue, method for detecting elasticity of biological tissue and method for biological tissue elasticity imaging
ActiveCN104605891AHigh resolutionAchieve early diagnosisOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsShape changeElastography
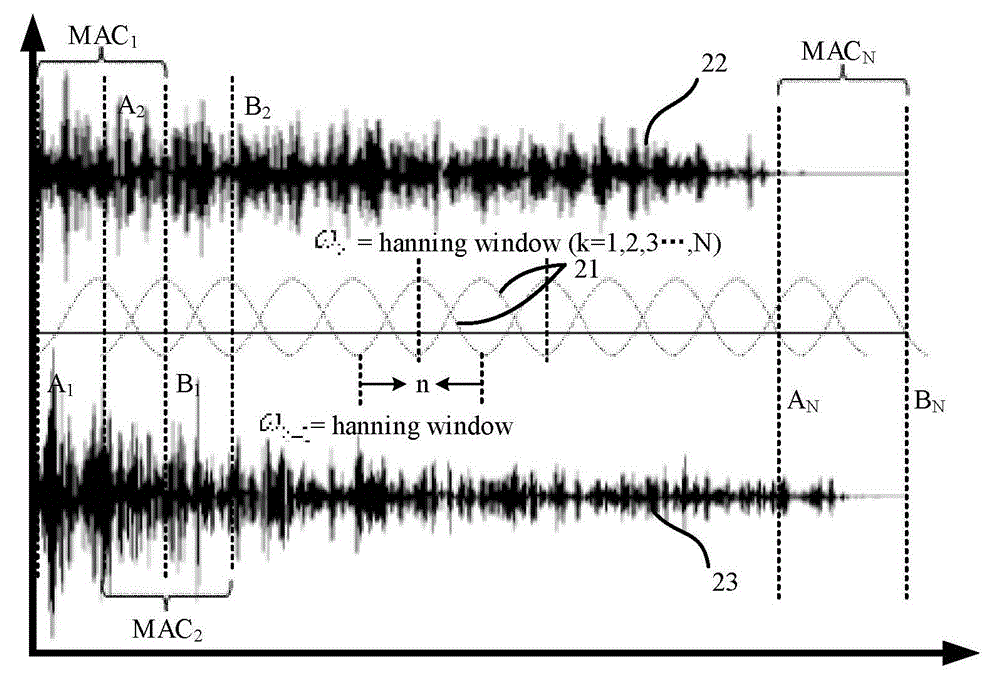
The invention discloses a method for detecting transmission speed of a shear wave in biological tissue, a method for detecting elasticity of the biological tissue and a method for biological tissue elasticity imaging. The method for detecting the transmission speed of the shear wave in the biological tissue is characterized in that the distance of any two positions in the to-be-detected tissue in the shear wave transmission direction and time difference of MAC values of real-time echo signals and original echo signals changing on the two positions respectively are used for calculating the transmission speed of the shear wave between the two positions. The modal assurance criterion is used for tracking the shear wave, a fine shape change estimation of the issue under the action of the shear wave can be achieved, and the signal to noise ratio, the resolution ratio and the contrast degree of an image can be improved. The sensitivity is high. The modal assurance criterion serves as a time domain calculation method for ultrasound echo radio frequency signals, the consistency of calculating processes is better, multi-term continuous modality confidence divisor calculating tasks can be permitted to be concurrently operated in the same time, and that is, parallel calculating is performed to enable complex calculating operation of the whole elastic image to obtain a higher speed-up ratio. Accordingly, the method can effectively improve the calculating speed of an elastic imaging algorithm, and achieve real-time tracking of the shear wave in the transmission process.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Shear wave viscoelasticity imaging method and system
InactiveCN104825195AAccurate measurementEasy to detectOrgan movement/changes detectionComputerised tomographsElastographyUltrasonic sensor
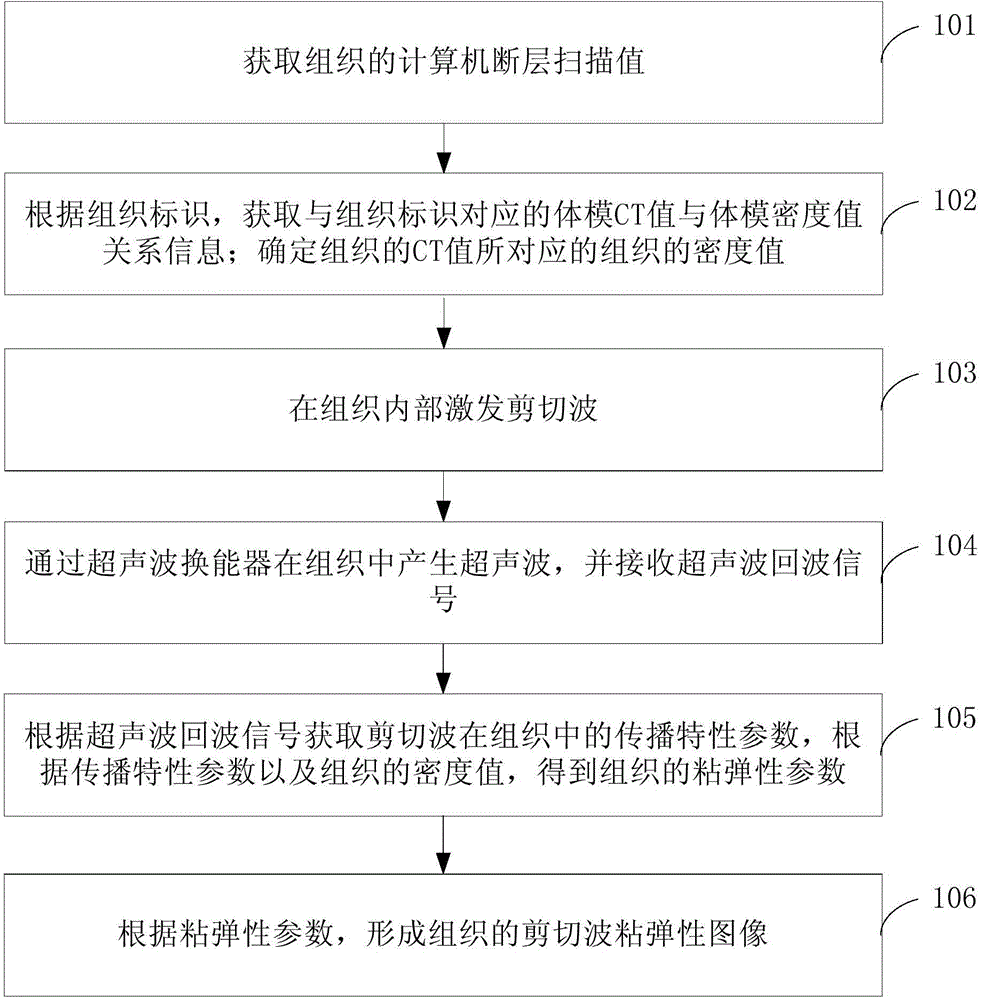
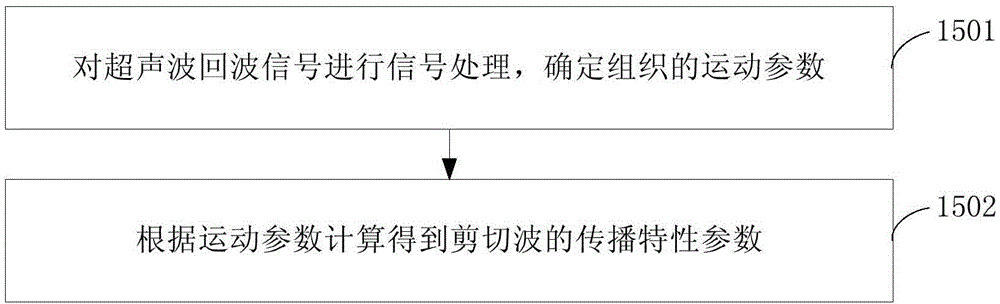
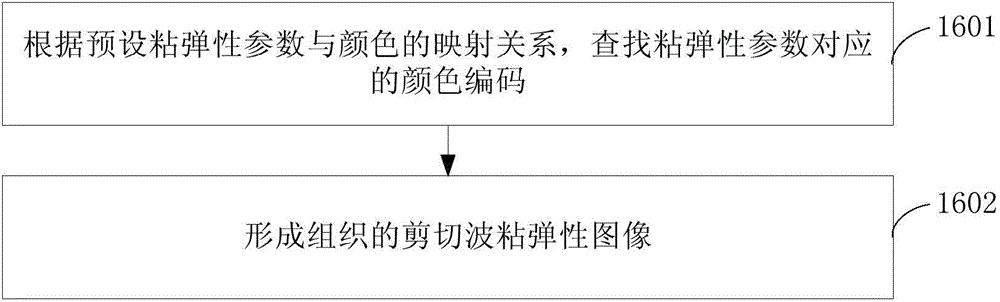
The invention provides a shear wave viscoelasticity imaging method and system. The method includes the steps that a CT value of tissue is obtained; according to a tissue mark, body model CT value and body model density value relation information corresponding to the tissue mark is obtained; a tissue density value corresponding to the CT value of the tissue is determined; shear waves are stimulated inside the tissue, ultrasonic waves are generated in the tissue through an ultrasonic transducer, and an ultrasonic wave return signal is received; according to the ultrasonic wave return signal, a propagation characteristic parameter of the shear waves in the tissue is obtained, and according to the propagation characteristic parameter and the tissue density value, the viscoelasticity parameter of the tissue is obtained; according to the viscoelasticity parameter, a shear wave viscoelasticity image of the tissue is formed. In this way, the effect of viscoelasticity parameter detection is improved, and more reliable references are provided for pathology judgment on the tissue by a doctor according to the shear wave viscoelasticity image of the tissue.
Owner:WUXI HISKY MEDICAL TECH
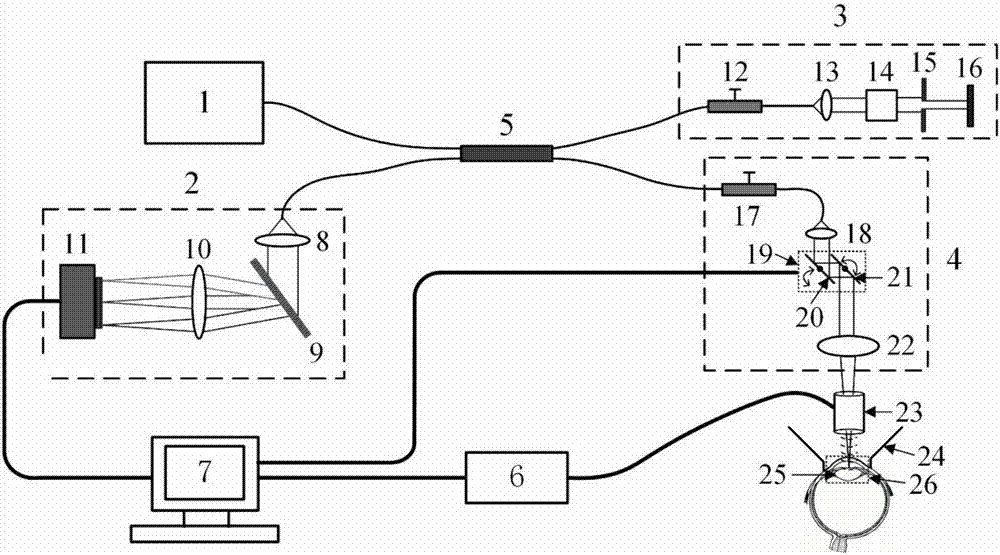
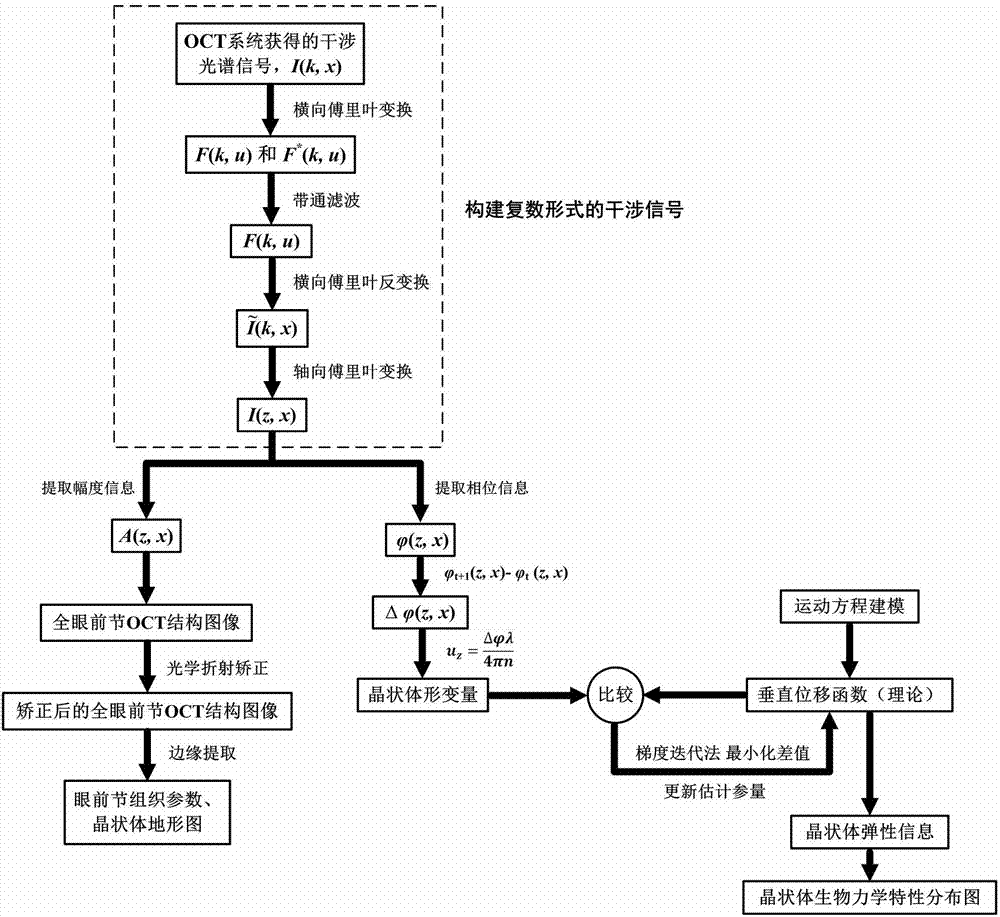
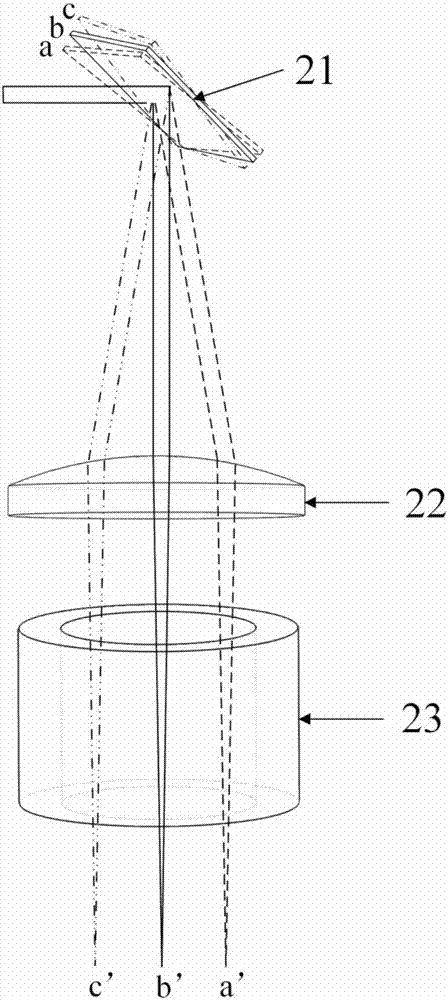
Crystalline lens biomechanics and optical property noninvasive in-vivo imaging system and measuring method
The invention discloses a crystalline lens biomechanics and optical property noninvasive in-vivo imaging system and a measuring method. The ultrasonic load system provides mechanical waves capable of enabling a crystalline lens to deform, a spectral domain OCT system achieves the structure and elastic imaging of the crystalline lens; on the basis of the yoke eliminating technology, OCT full-range imaging is achieved, full anterior segment two-dimensional or three-dimensional structure images from the anterior corneal surface to the retrolental surface, morphological and optical characteristic parameters of the crystalline lens are obtained through calculation, and a crystalline lens topographic map is constructed. Meanwhile, the phase sensitive OCT technology is utilized, strain distribution in the depth direction of the crystalline lens is obtained, and a two-dimensional or three-dimensional biomechanical characteristic distribution diagram of the crystalline lens is obtained through rebuilding. High-resolution imaging and precision measurement of biomechanics and optical properties of the crystalline lens provide the more comprehensive and complete imaging surveying basis for fundamental research, early diagnosis, operation plan formulating and postoperation result evaluation of cataract and other crystalline lens diseases, and the important practical significance and clinical significance are achieved.
Owner:浙江瑞瞳生物科技有限公司
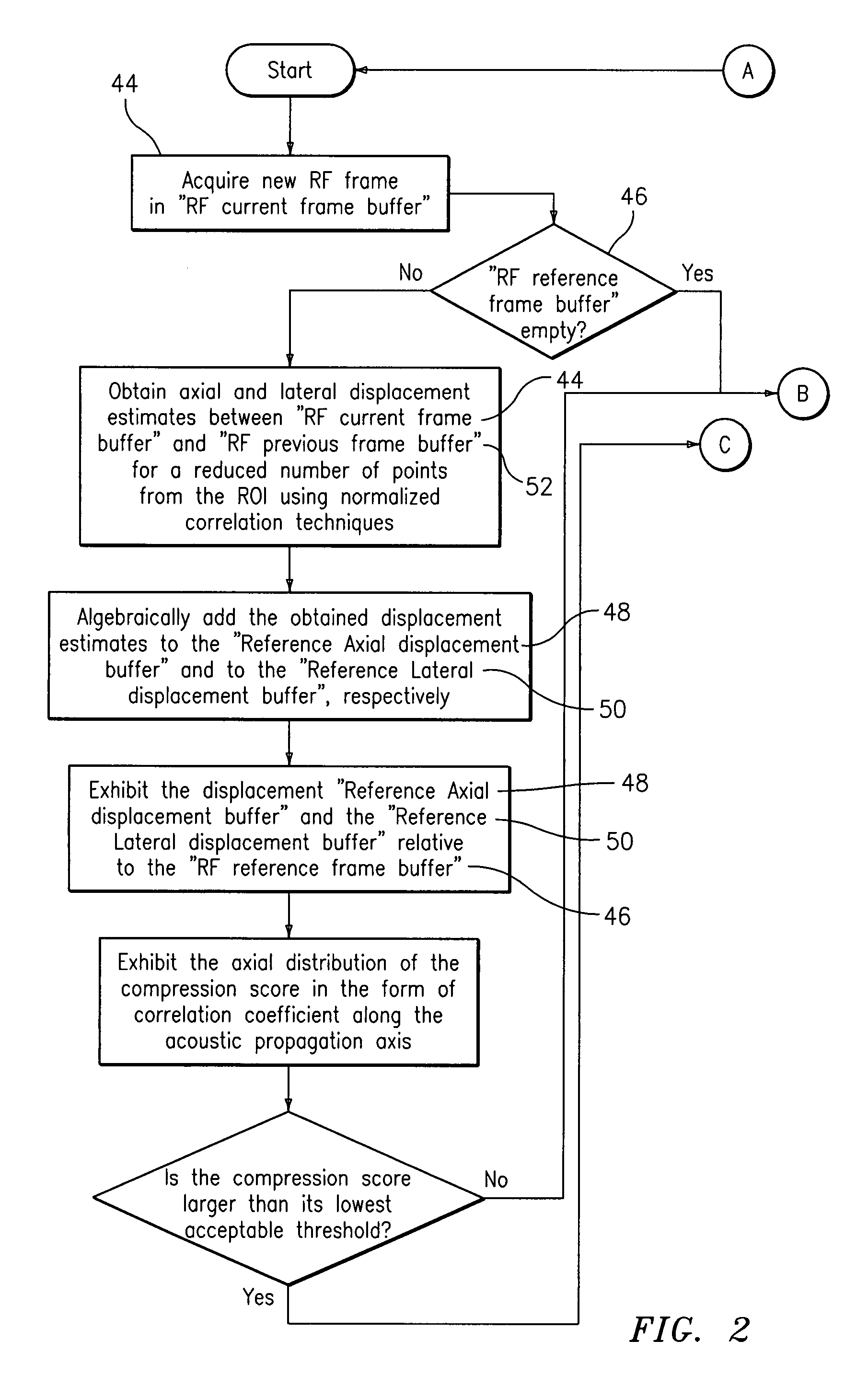
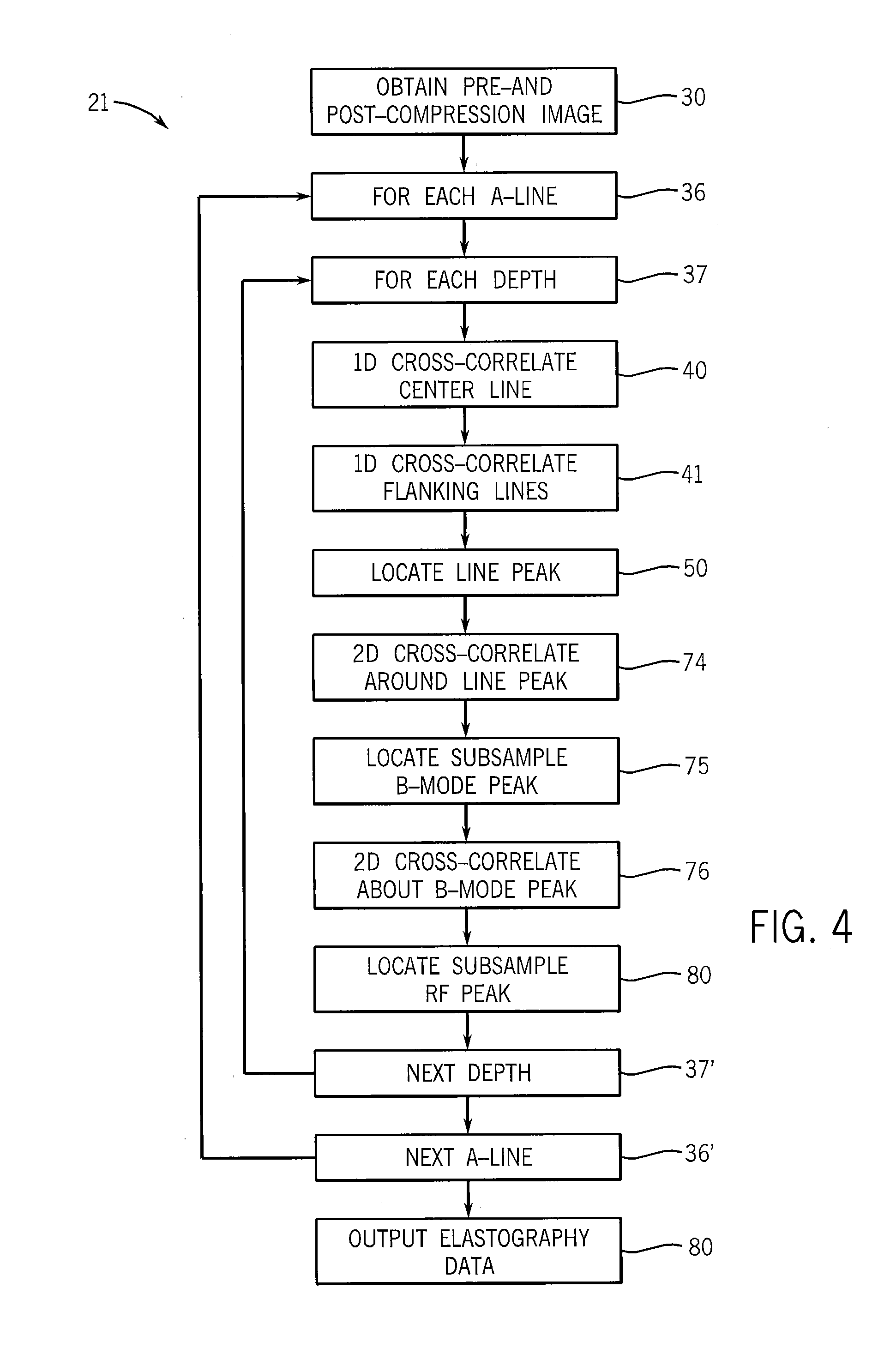
Apparatus and method for optimized search for displacement estimation in elasticity imaging
InactiveUS20070167772A1Efficient processingImage enhancementImage analysisElastographyEstimation methods
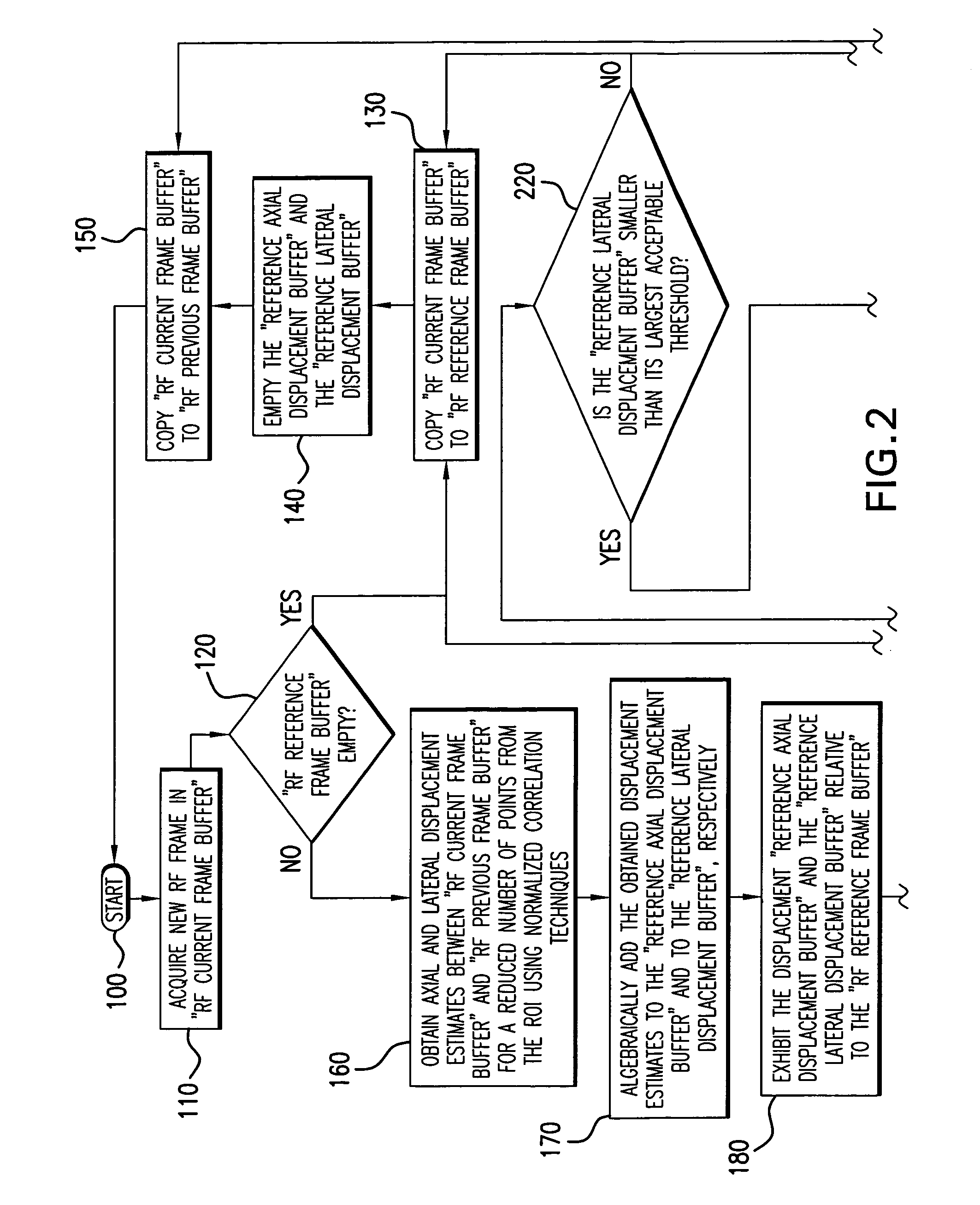
A displacement estimation method is described that limits the exhaustive search for all points in a region of interest of a biological tissue by delivering the axial and lateral displacement maps in two phases. During the first phase, the method executes a limited search to determine axial and lateral displacement estimates for a plurality of locations on at least one axial reference line positioned in the ROI. Non-zero estimates form transition points along the axial reference line where one non-zero transition point value differs from another. During the second phase, the method laterally tracks each transition point throughout the ROI using block-matching algorithms or correlation methods. The displacement estimations identify a trajectory of the transition point through the ROI and form a displacement map. The plurality of transition point displacement maps are assembled as a complete displacement map. The resultant displacement map is used to form a tissue strain display.
Owner:ALOKA CO LTD
Optical coherence tomography catheter for elastographic property mapping of lumens utilizing micropalpation
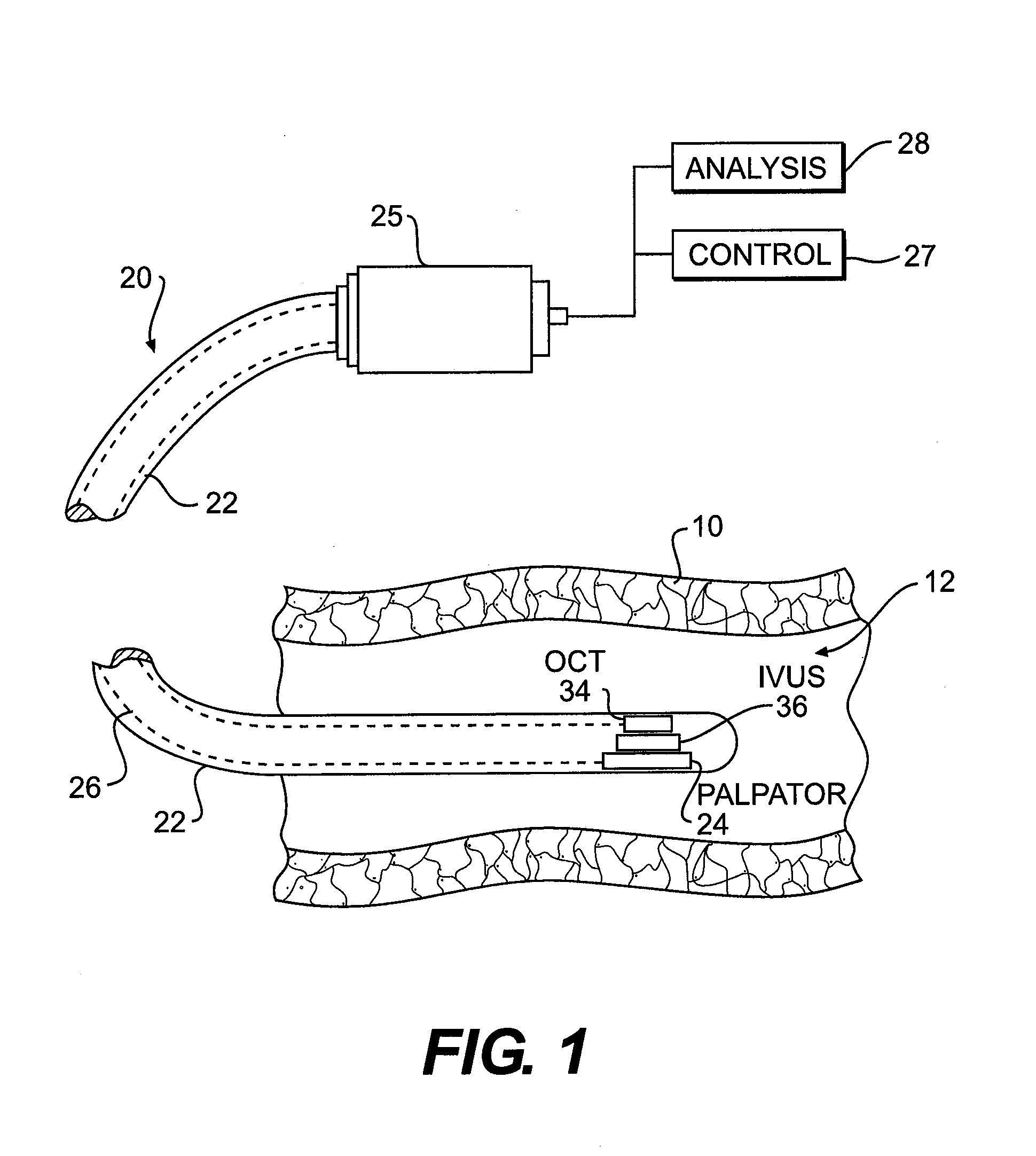
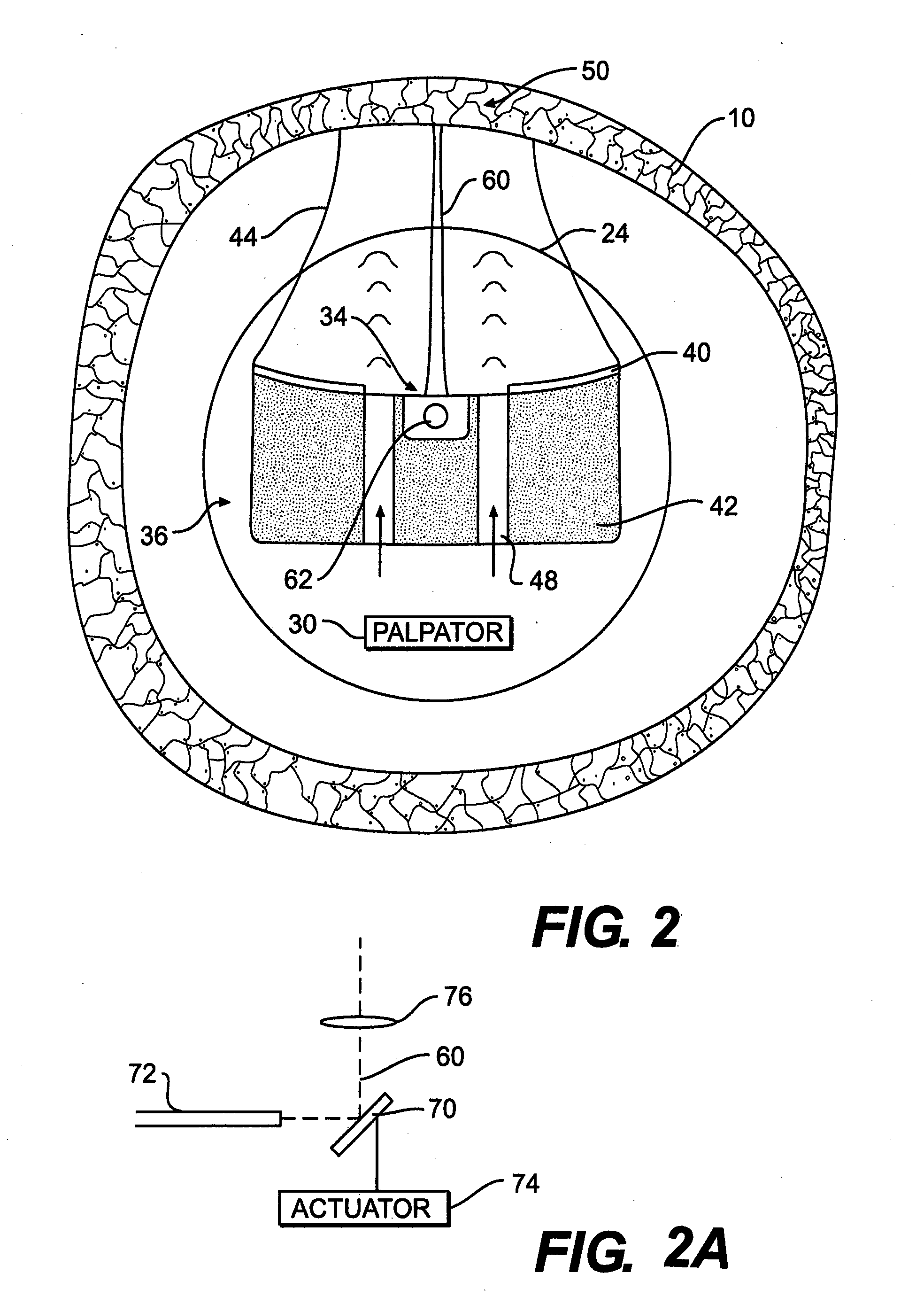
InactiveUS20120265062A1High speed elastographic property mappingHigh propertyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using pressurePalpationElastography
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) catheter, for performing high performance elastographic deformation mapping of tissues and plaques, comprises: a catheter having elongated catheter body extending longitudinally between a proximal end and a distal end along a longitudinal axis, the catheter body including a distal portion at the distal end and a catheter lumen; a palpator, disposed in the distal portion, to apply one of a directed fluid or a mechanical indenter to produce a surface-applied palpation force to a target area of the interior body to mechanically displace the interior body and cause elastographic deformation of the target area of one or more surface and subsurface tissues and plaques; and OCT imaging sensor, disposed in the distal portion, to direct and deliver OCT beam for OCT deformation detection including elastographic deformation measurement to provide elastographic mapping of the target area.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Ultrasonic shearing wave elastic imaging method based on dynamic aperture control
InactiveCN105232085AEliminate spurious displacementsImprove measurement accuracyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsElastographyAcoustic radiation force
The invention provides an ultrasonic shearing wave elastic imaging method based on dynamic aperture control. Array elements of which the number corresponds to different focus depths are started, the aperture is set up, grating lobe phenomena and false displacement in a displacement field can be effectively eliminated, an obtained mass point displacement-time curve relatively well meets the rule that a single point triggered shearing wave is attenuated along with time, and the shearing wave transmission speed measurement accuracy can be improved. By using the ultrasonic shearing wave elastic imaging method, the technical problems that in the prior art in shallow focus depth, because of the influence of acoustic radiation force grating lobe, a mark point displacement-time curve is deformed and the shearing wave transmission speed measurement accuracy is degraded can be solved.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Optimal block searching algorithm for tissue displacement estimation in elasticity imaging
InactiveUS20080144902A1Efficient processingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage analysisElastographySonification
Disclosed is a method and system that efficiently compares data from two ultrasound images and derives a tissue displacement map for real-time diagnostic imaging applications.
Owner:ALOKA CO LTD
Motor-type automatic ultrasonic probe for elasticity imaging
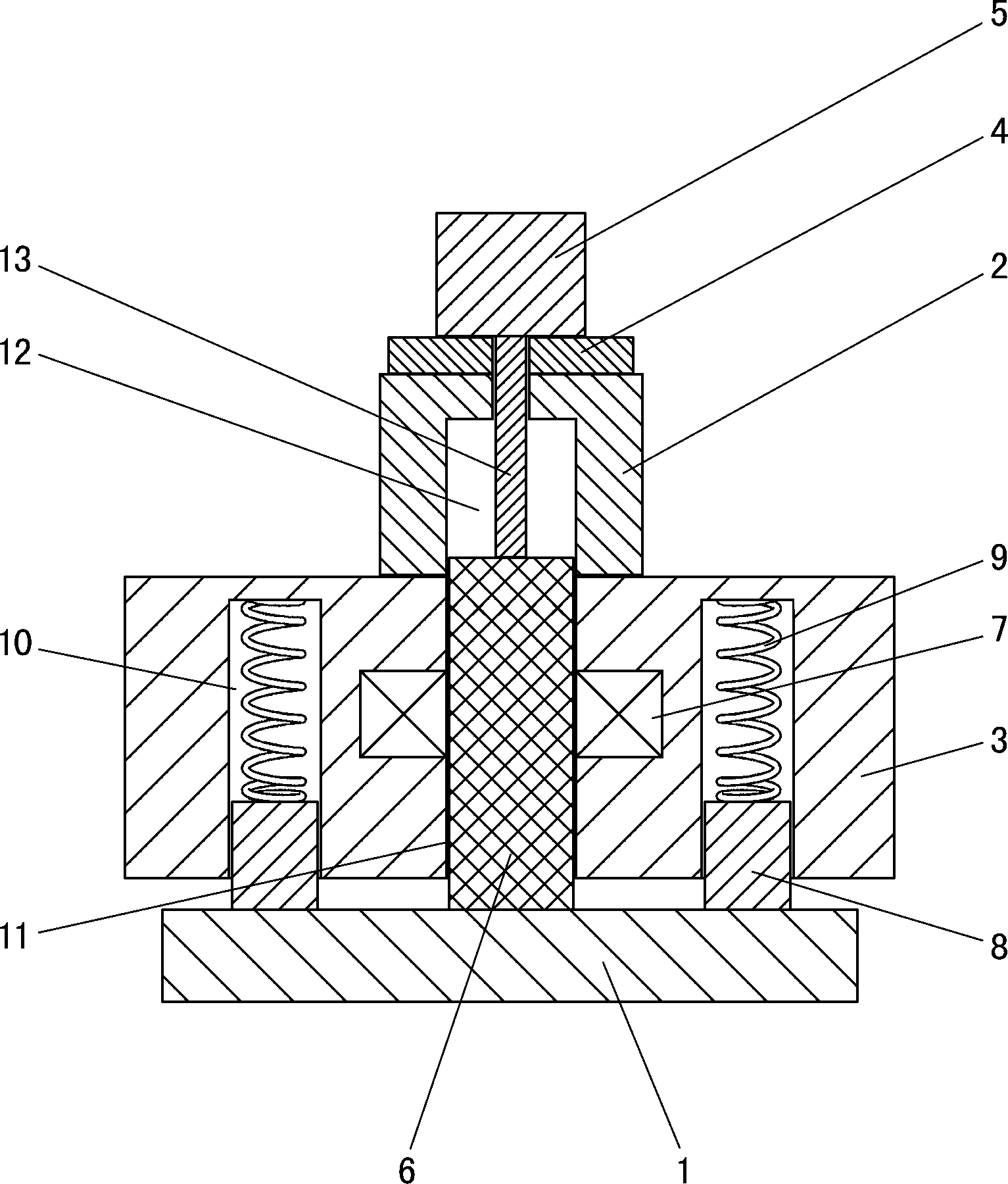
ActiveCN103006268AQuality improvementAccurate force situationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsStress conditionsElastography
The invention relates to a motor-type automatic ultrasonic probe for elasticity imaging, which comprises a probe core part, a handle, a probe seat, a connection base, a linear motor, a sliding shaft, a sliding bearing, a pressure sensor and a spring. The probe core part is connected with an output shaft of the linear motor by the sliding shaft; both ends of the spring are respectively connected with the probe seat and the upper end of the pressure sensor; and the lower end of the pressure sensor is connected with the probe core part. A user only needs to hold the handle with a hand and the probe core part is very easy to keep always in contact with a checked part, so that working intensity of a checking doctor is reduced and the problem of interruption of elasticity imaging, which is caused by the case that the probe core part is separated from the checked part, is avoided; an acting force applied by the linear motor is perpendicular to the surface of the probe core part, so that quality of elasticity imaging is improved; and moreover, the pressure sensor is arranged at the back of the probe core part, so that the stress condition of the checked part is more accurately detected and the elastic modulus of the checked part is better reflected, and thus, elasticity difference of the checked part and the surroundings thereof is more accurately judged.
Owner:SHANTOU INST OF UITRASONIC INSTR CO LTD
Mechanical pressure sensing ultrasonic probe for elasticity imaging
ActiveCN103006267AReflect elastic modulusQuality improvementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsElastographyStress conditions
The invention relates to a mechanical pressure sensing ultrasonic probe for elasticity imaging, which comprises a probe core part, a handle, a probe seat, a sliding shaft, a sliding bearing, a pressure sensor and a spring. The lower end of the sliding shaft is connected with the probe core part; both ends of the spring are respectively connected with the probe seat and the upper end of the pressure sensor; the lower end of the pressure sensor is connected with the probe core part; and the handle is arranged at the top of the probe seat. The spring is arranged between the probe core part and the handle for carrying out buffering, so that the probe core part is always adhered to a checked part to carry out low-amplitude vibration, and thus, the problem of interruption of elasticity imaging, which is caused by the case that the probe core part is separated from the checked part, is avoided; the force application direction is more easily kept perpendicular to the surface of the probe core part, so that quality of elasticity imaging is improved; and moreover, the pressure sensor is arranged at the back of the probe core part, so that the stress condition of the checked part is more accurately detected and the elastic modulus of the checked part is better reflected, and thus, elasticity difference of the checked part and the surroundings thereof is more accurately judged.
Owner:SHANTOU INST OF UITRASONIC INSTR CO LTD
Elastography method, elastography system, and biological tissue displacement estimation method and biological tissue displacement estimation system in elastography
ActiveCN102764141AImprove stabilityProcessing speedOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesElastographyEstimation methods
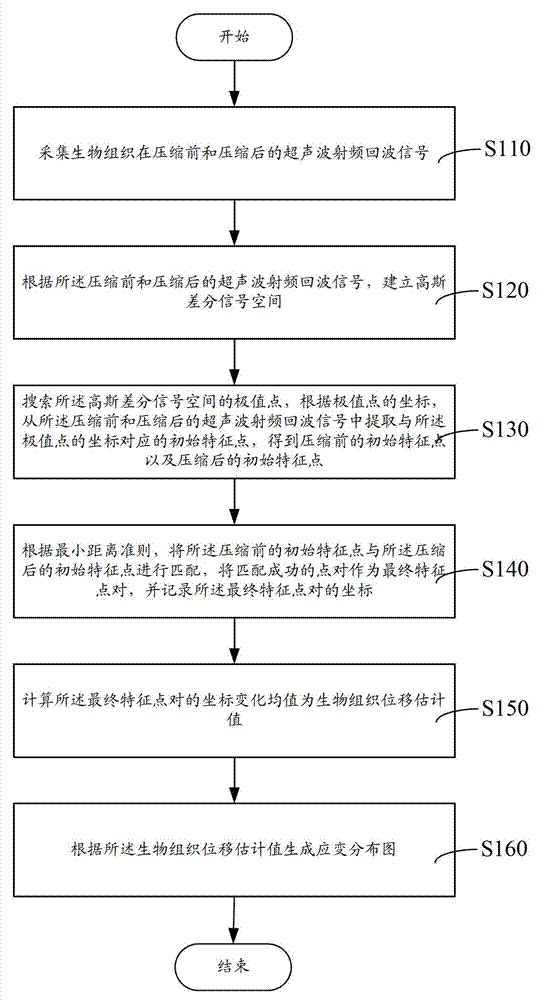
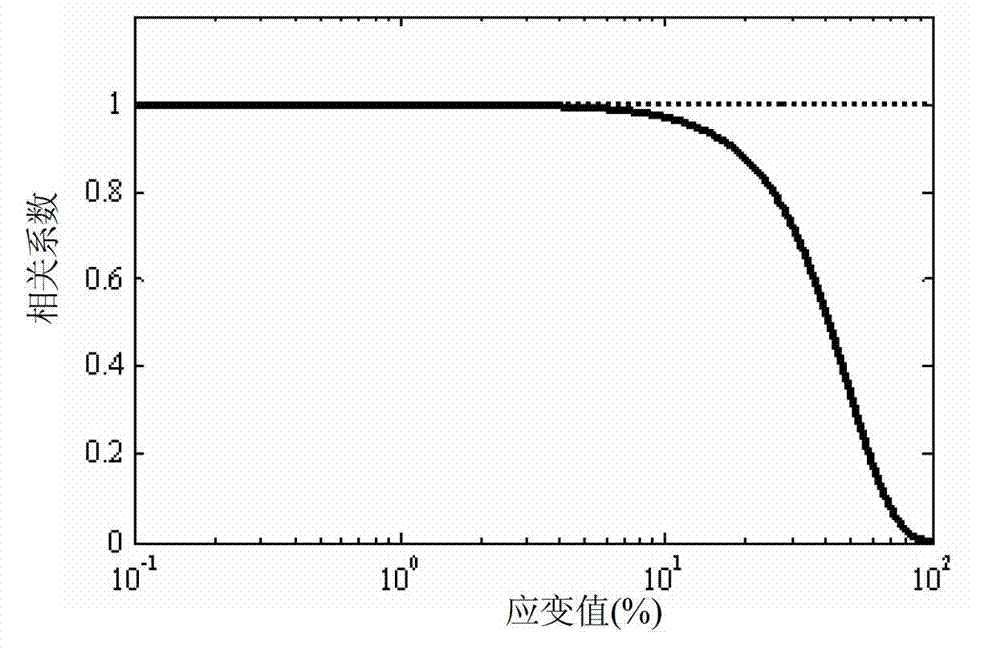
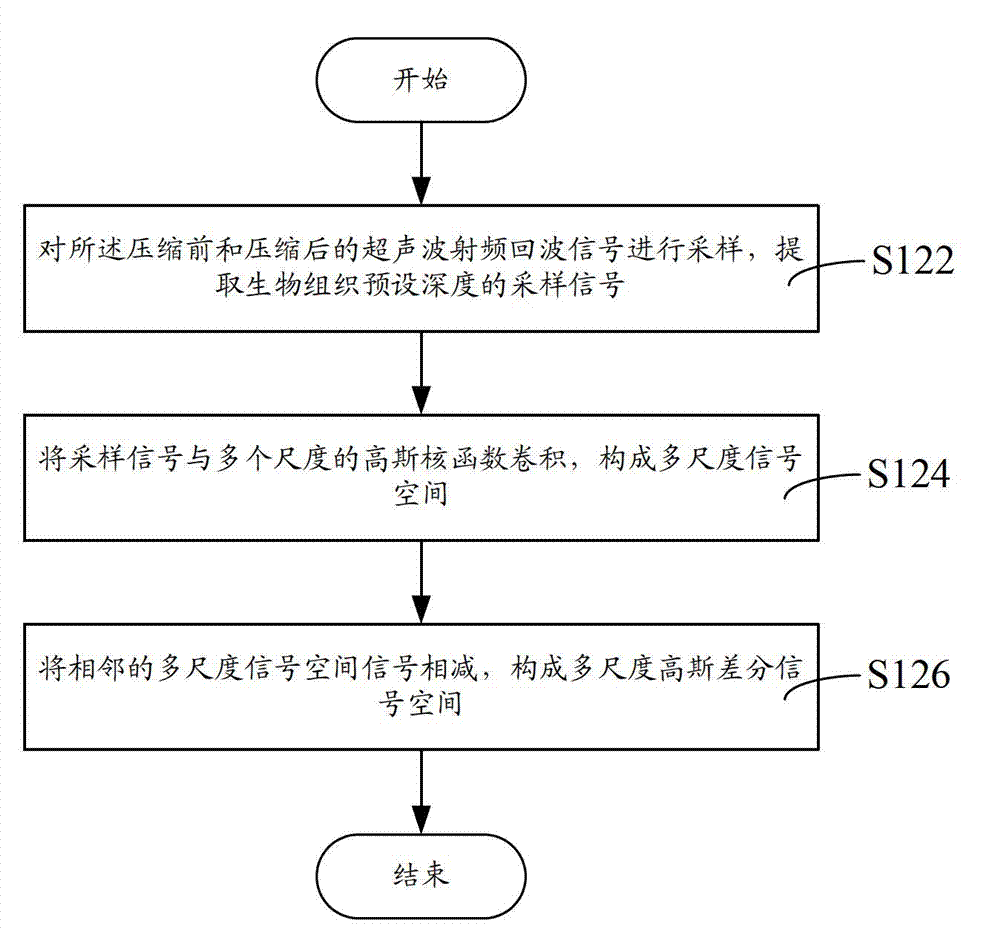
The invention discloses an elastography method, an elastography system, and a biological tissue displacement estimation method and a biological tissue displacement estimation system in elastography. The biological tissue displacement estimation method in the elastography comprises the following steps of: acquiring ultrasonic radio frequency echo signals of biological tissues before and after compression; establishing a Gaussian differential signal space according to the ultrasonic radio frequency echo signals before and after compression; searching extreme points of the Gaussian differential signal space, and extracting initial feature points which correspond to coordinates of the extreme points from the ultrasonic radio frequency echo signals before and after compression according to the coordinates of the extreme points so as to obtain initial feature points before the compression and initial feature points after compression; matching the initial feature points before the compression with the initial feature points after compression according to the minimum distance criterion, and recording coordinates of a successfully matched point pair which is taken as a final feature point pair; and calculating a mean value of coordinate transformation of the final feature point pair to obtain a biological tissue displacement estimation value. By the method, the processing accuracy can also be ensured while the processing speed is greatly improved.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
Ultrasonic viscoelasticity measurement method and system
InactiveCN106037816AImprove detection depthOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsElastographySonification
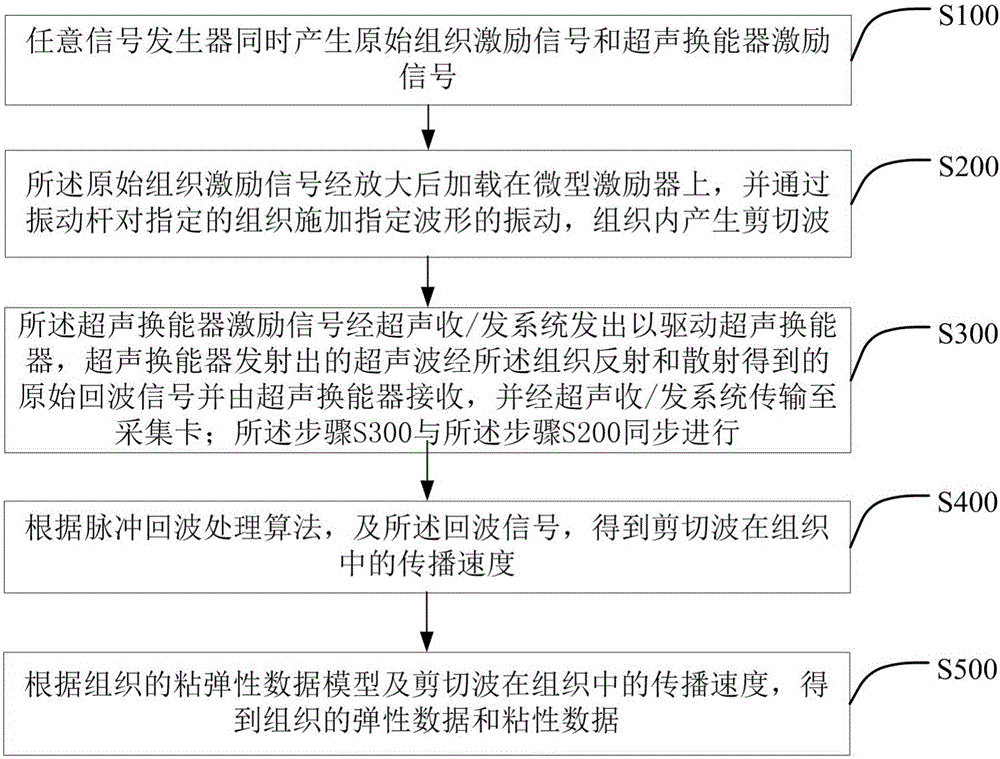
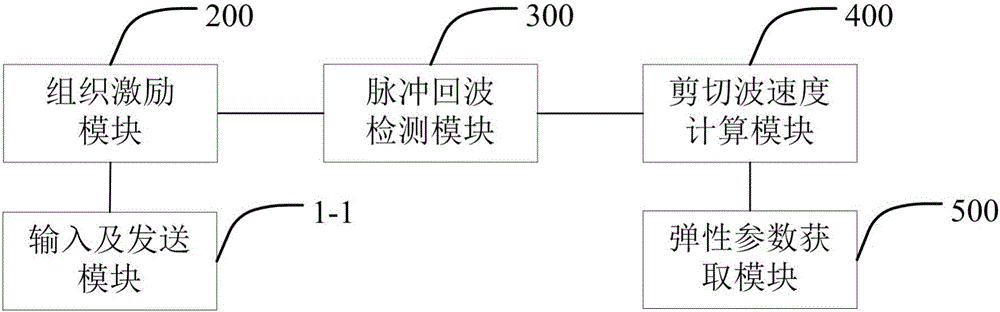
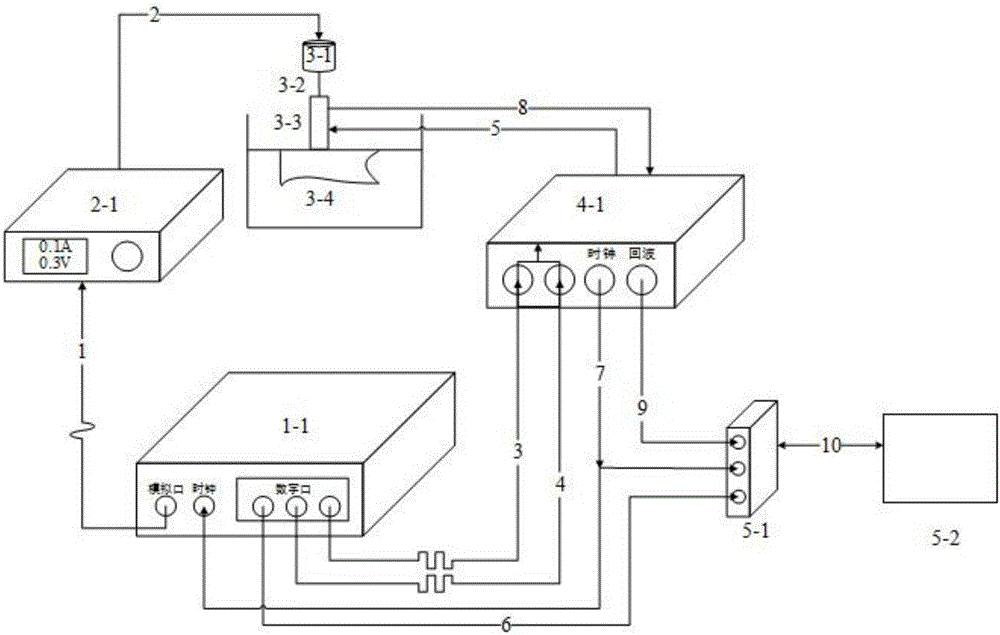
The invention provides a method and system for measuring ultrasonic viscoelasticity. The method includes: an arbitrary signal generator simultaneously generates an original tissue excitation signal and an ultrasonic transducer excitation signal; the original tissue excitation signal is amplified and then loaded on a micro-actuator , and apply the vibration of the specified waveform to the specified tissue through the vibrating rod, so that shear waves are generated in the tissue; the ultrasonic transducer excitation signal is sent by the ultrasonic receiving / transmitting system to drive the ultrasonic transducer, and the ultrasonic transducer emits The original echo signal obtained by the ultrasonic wave reflected and scattered by the tissue is received by the ultrasonic transducer, and transmitted to the acquisition card through the ultrasonic receiving / transmitting system; according to the pulse echo processing algorithm, and the echo signal, The propagation velocity of the shear wave in the tissue is obtained; according to the viscoelastic data model of the tissue and the propagation velocity of the shear wave in the tissue, the elastic data and viscous data of the tissue are obtained. The invention applies the coding detection technology to the ultrasonic transient elasticity imaging system to increase the detection depth.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Rapid two/three-dimensional sector strain imaging
ActiveUS20090247871A1Processing speedHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisElastographyImage resolution
An elastographic imaging system providing for axial, lateral and elevational strain measurements employs a series of one-dimensional axial measurements to deduce a coarse axial, lateral and / or elevational displacement that is used to guide one or more two or three-dimensional cross-correlations of smaller kernels providing improved image resolution.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Device and Method for Performing Blood Thromboelastographic Assays by Magnetic Sensing
ActiveUS20150024473A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrocontrollerMotion detector
A magnetic sensor elastometry device (MSED) and a method to perform the whole blood thromboelastography assay. It contains key components, including sample cuvette, detecting head, rotating disc, optical motion detector, and etc; and measures viscoelasticity of whole blood samples. The device optically monitors the physical motion of the magnetically driven rotating disc immersed in the blood sample. The thromboelastograph is recorded by the optical motion detector reading high pulse counts through a gated time window passing through the rotating disc. The device also includes a microcontroller and its embedded firmware to perform the functions of driving the rotating magnetic disc, generating high-frequency pulses, controlling the data pulse time window, as well as handling the user's interface, data analysis, and maintaining communication with an external computer.
Owner:NEOTEK BIOSCI
A-mode ultrasonic elastic imaging system based on mechanical scanning and method thereof
InactiveCN102908168AMechanical positioning with high scanning accuracyImprove imaging effectTomographyElastographySonification
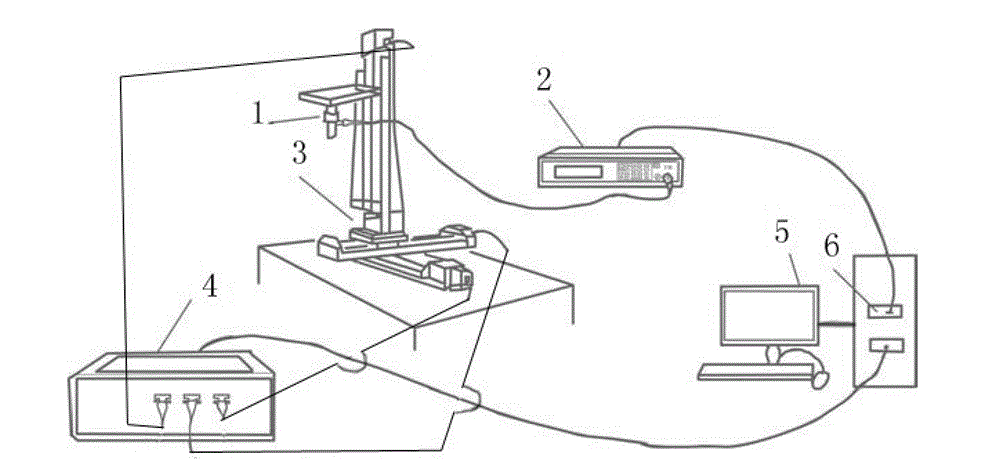
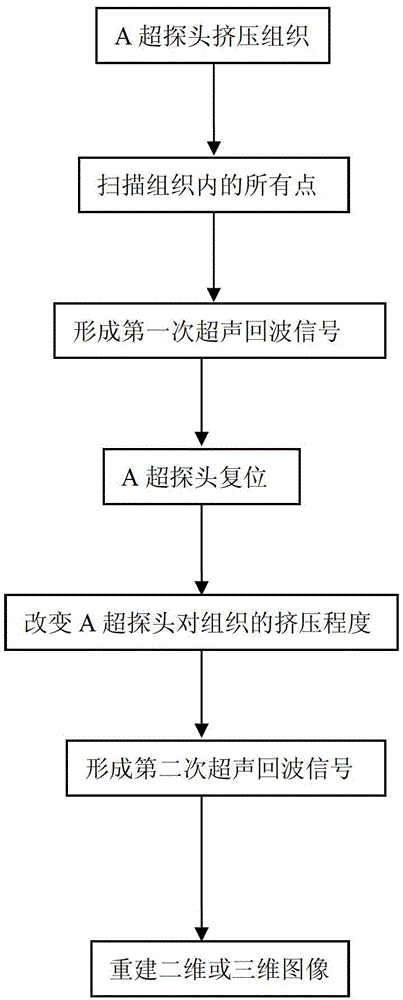
The invention provides an A-mode ultrasonic elastic imaging system based on mechanical scanning. The A-mode ultrasonic elastic imaging system comprises a three-dimensional motion control device, an A-mode ultrasonic probe, an A-mode ultrasonic instrument and an ultrasonic imaging device, wherein the A-mode ultrasonic instrument controls the A-mode ultrasonic probe to generate ultrasonic signals and receive ultrasonic echo signals; the three-dimensional motion control device drives the A-mode ultrasonic probe to mechanically scan an interesting tissue; and the ultrasonic imaging device re-establishes a two-dimensional or three-dimensional thromboelastogram. An imaging method of the A-mode ultrasonic elastic imaging system based on the mechanical scanning comprises the following steps of: step 1, squeezing the interesting tissue by the A-mode ultrasonic probe under different pressures, sending the ultrasonic signals, and mechanically scanning each point inside the interesting tissue twice, so as to form secondary ultrasonic echo signals; and step 2, re-establishing the two-dimensional or three-dimensional thromboelastogram of the interesting tissue by the ultrasonic imaging device according to elastic deformation amounts of the interesting tissue under the different pressures twice. The A-mode ultrasonic elastic imaging system has the advantages of high positioning precision, high sensitivity, high image resolution, strong practical applicability, wide application range and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Catheter for intravascular ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
InactiveUS8932223B2Protect partsAvoid mechanical damageOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryElastographyUltrasonic sensor
A design and a fabrication method for an intravascular imaging and therapeutic catheters for combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and for optical and / or acoustic therapy of hollow organs and diseased blood vessels and tissues are disclosed in the present invention. The invention comprises both a device—optical fiber-based intravascular catheter designs for combined IVUS / IVPA, and elasticity imaging and for acoustic and / or optical therapy—and a method of combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and optical and / or acoustic therapy. The designs of the catheters are based on single-element catheter-based ultrasound transducers or on ultrasound array-based units coupled with optical fiber, fiber bundles or a combination thereof with specially designed light delivery systems. One approach uses the side fire fiber, similar to the one utilized for biomedical optical spectroscopy. The second catheter design uses the micro-optics in the manner of a probe for optical coherent tomography.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
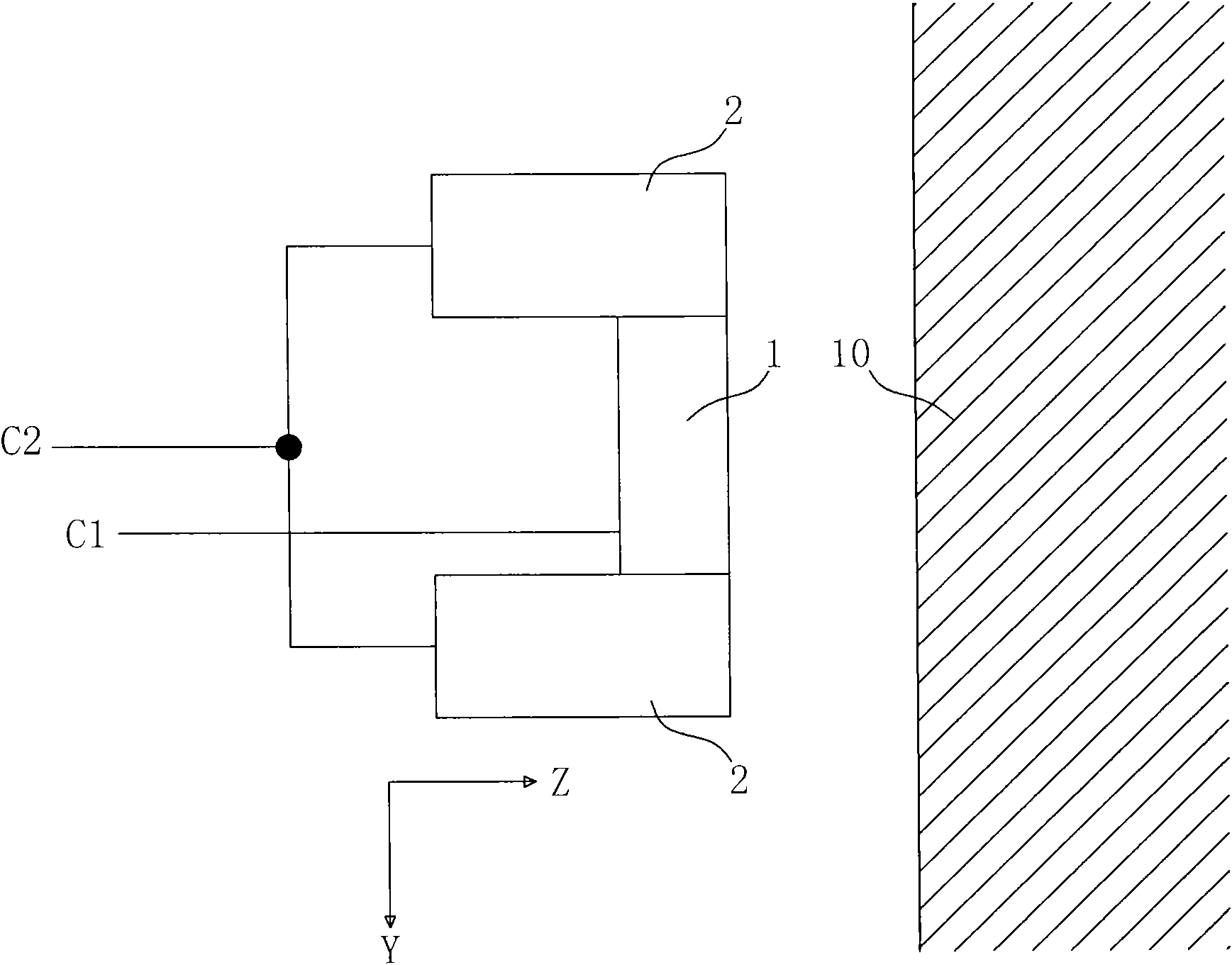
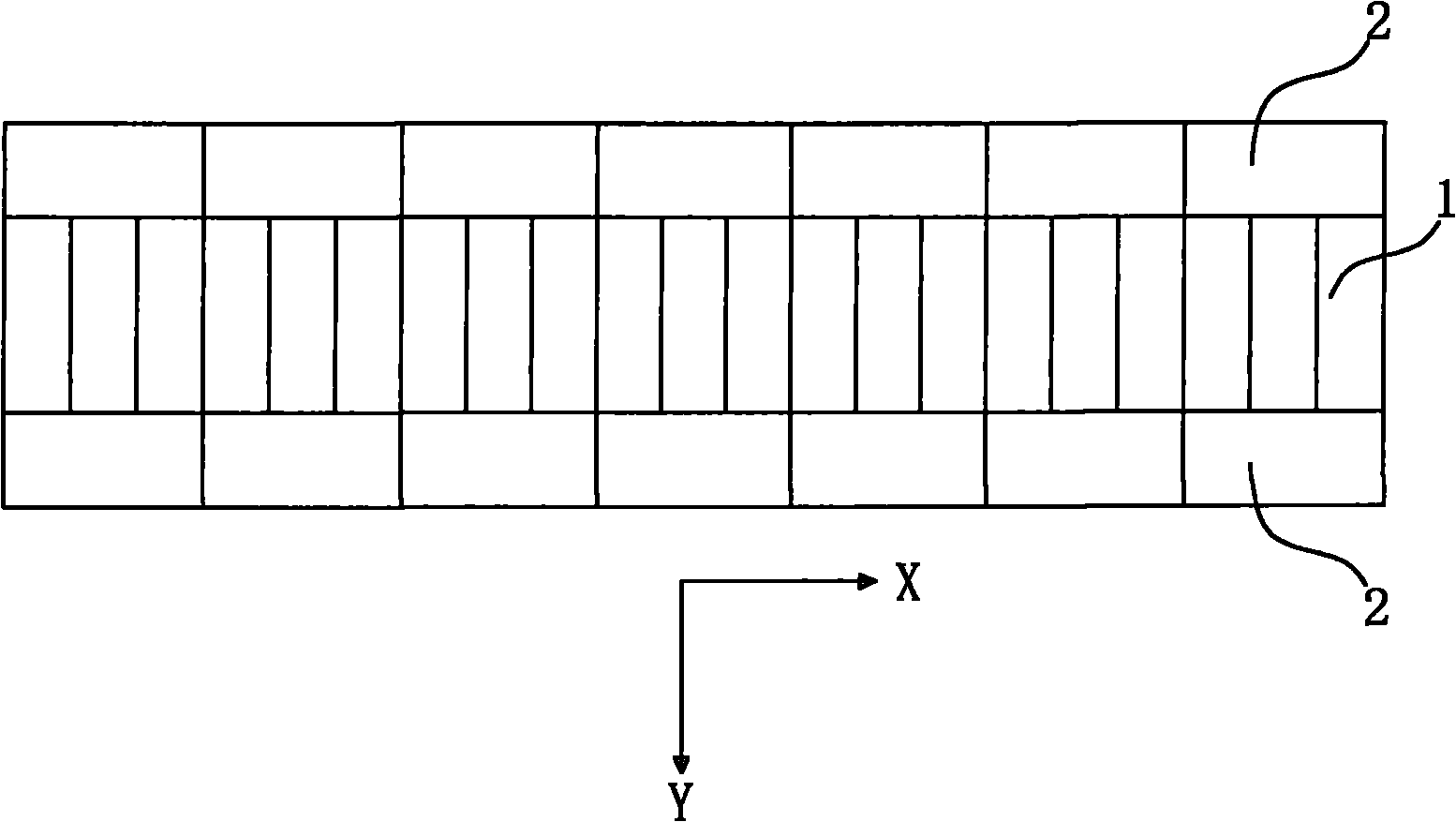
Transducer arrangement and method for acquiring sono-elastographical data and ultrasonic data of a material
InactiveUS20110137166A1Low cost productionImprove accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFrequency spectrumElastography
The present invention relates to a transducer arrangement, particularly a transducer arrangement for acquiring tissue information, a method for using a transducer arrangement for acquiring tissue information and a glove which comprises a transducer arrangement. The transducer arrangement 21 for analysing material 40 comprises: a first transducer element 51 for inducing and receiving mechanical displacements in the material to be analysed 40; and an analysing unit 30. The transducer arrangement is arranged such as to be flexible in order to conform with a curved surface of the material to be analysed 40; and the transducer arrangement 21 is adapted to derive a first signal from a low frequency spectrum of mechanical displacements which first signal correlates to sono-elastographical properties of a material to be analysed 40; and the transducer arrangement 21 is adapted to derive a second signal from a high frequency spectrum of mechanical displacements received by the first transducer element 51 which second signal correlates to ultrasonic properties of a material to be analysed 40. With a transducer arrangement according to the invention it may be possible to generate information about the topographical anatomy and information about elastical properties of the material to be analyzed in parallel, whereby the transducer arrangement may be adapted to the unevenness of the material's surface optimally due to its flexibility which may allow the examiner or user of the transducer arrangement to analyze regions which normally may have an uneven surface profile, which may only be reached with difficulty or whose examination may cause inconvenience to the examiner as well as to the person that is being examined.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Ultrasonic probe and ultrasonic detection equipment with same
ActiveCN105748106AImprove imaging effectReduce data processingBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionElastographyUltrasonic imaging
Owner:毛军卫
Opto-acoustic quantitative elasticity imaging method and device
ActiveCN105572049AImprove accuracyTissue specificMaterial analysis by optical meansNon destructiveElastography
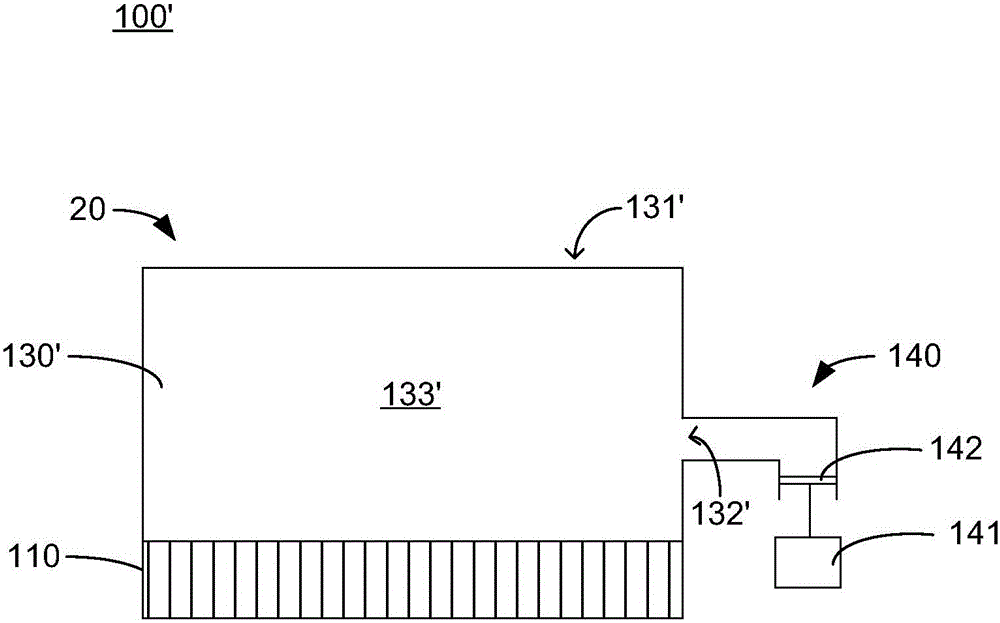
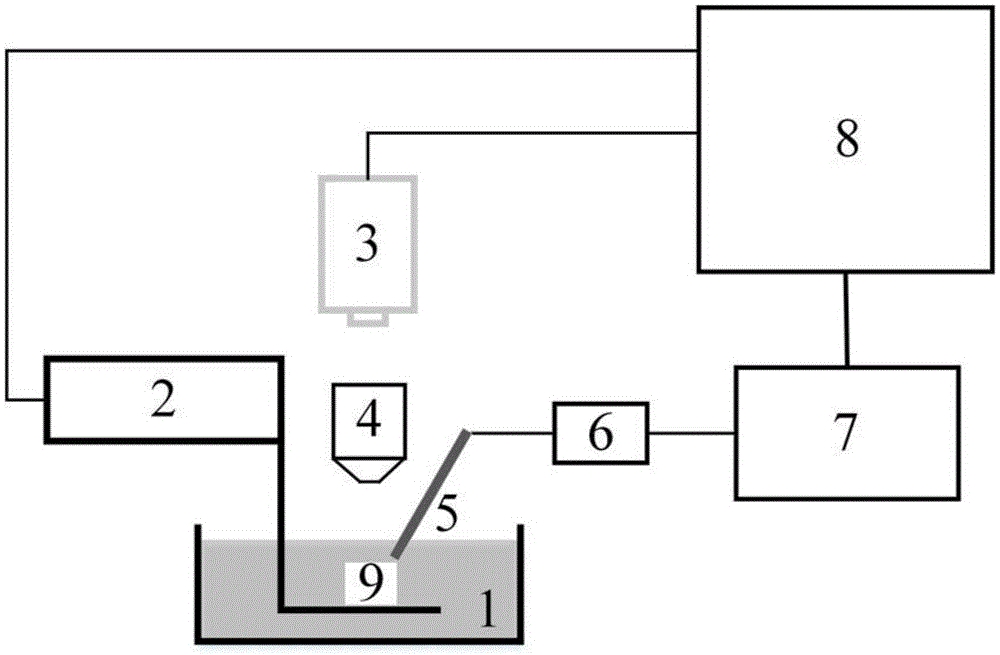
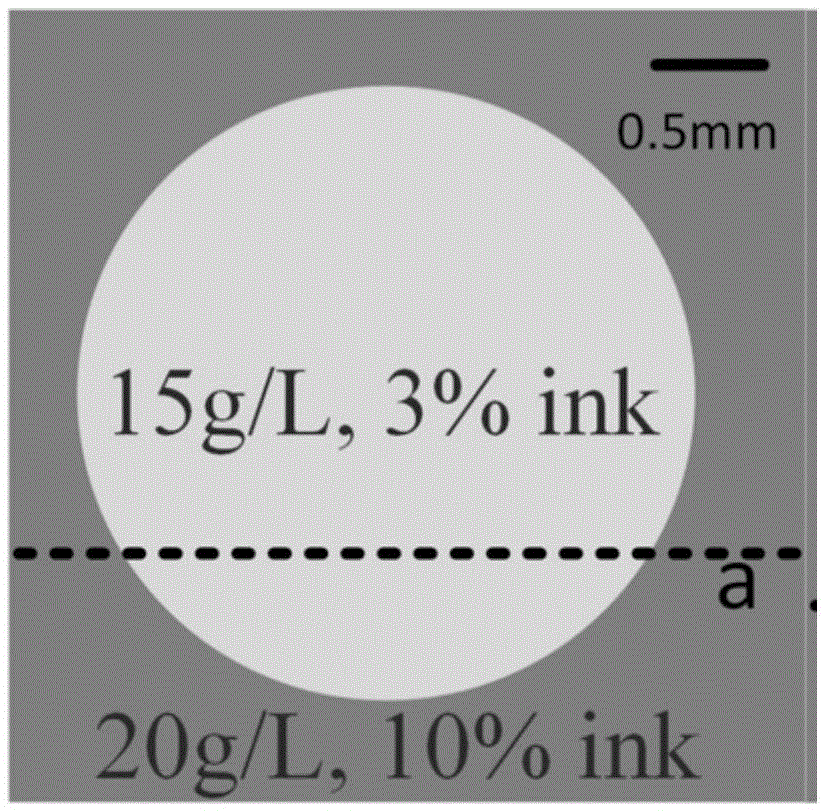
The invention discloses an opto-acoustic quantitative elasticity imaging method and device. The method comprises the following steps: a laser device emits pulse laser which is focused by a focusing lens and irradiates a tissue sample so as to excite an opto-acoustic signal, and the opto-acoustic signal is received by an ultrasonic detector through a coupling solution in a coupling trough; the opto-acoustic received by the ultrasonic detector is collected by an oscilloscope after being amplified by an amplifier, and signal information is stored into a computer; the computer controls a stepping motor to move the tissue sample point by point, so that an X-Y two-dimensional planar scanning region is formed on the corresponding tissue sample; after the oscilloscope collects all the signals, the computer calculates a quantitative elastic modulus of the tissue sample of each point; and a quantitative elastic two-dimensional image of the tissue sample is reconstructed according to the calculated quantitative elastic modulus. The device comprises an opto-acoustic exciting source, a signal collection / transmission / reconstruction assembly, the coupling trough, the stepping motor and an X-Y two-dimensional scanning platform. The opto-acoustic quantitative elasticity imaging method and device can realize non-destructive and high-resolution elastic and quantitative tissue measurement and imaging.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com