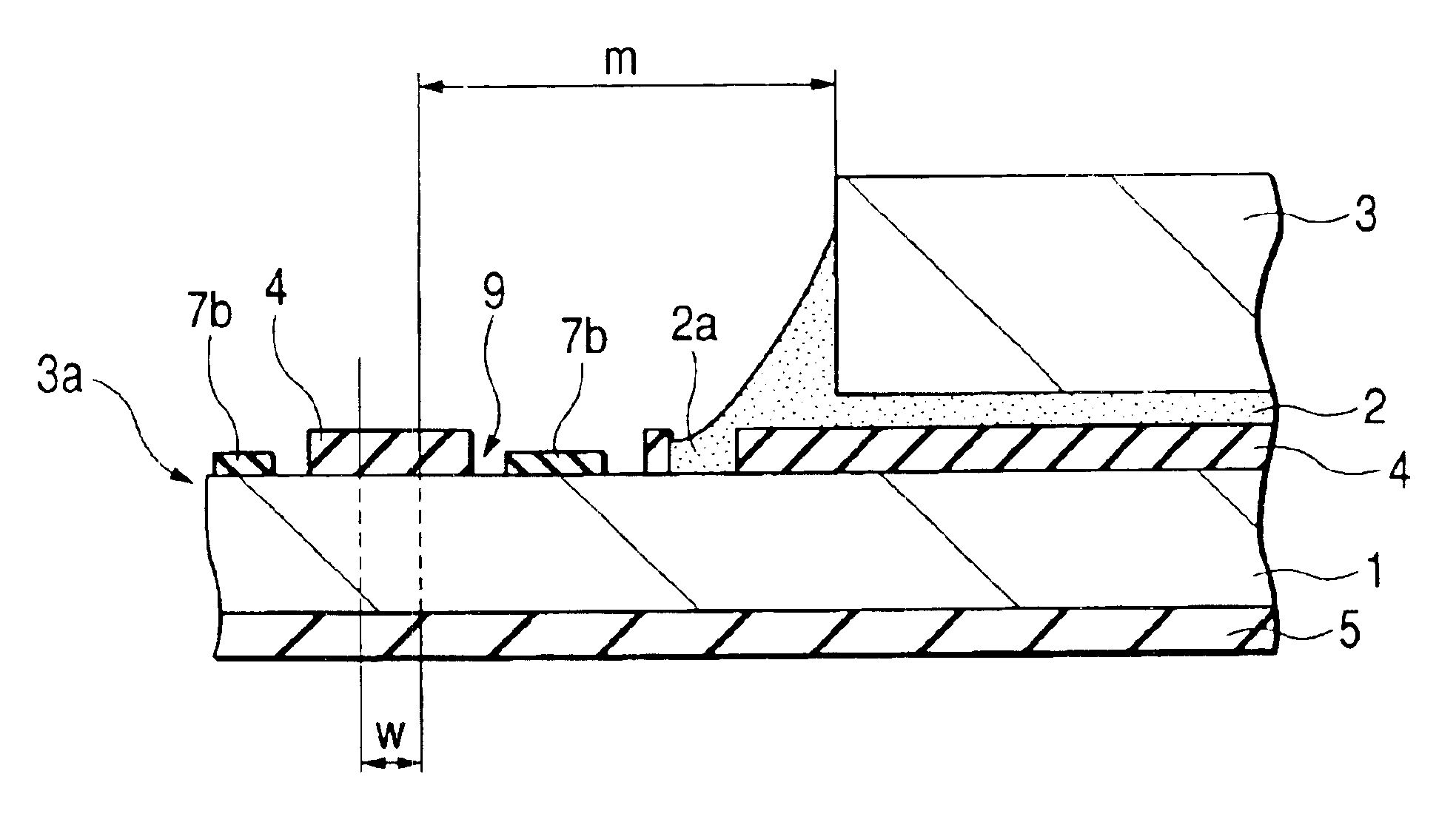
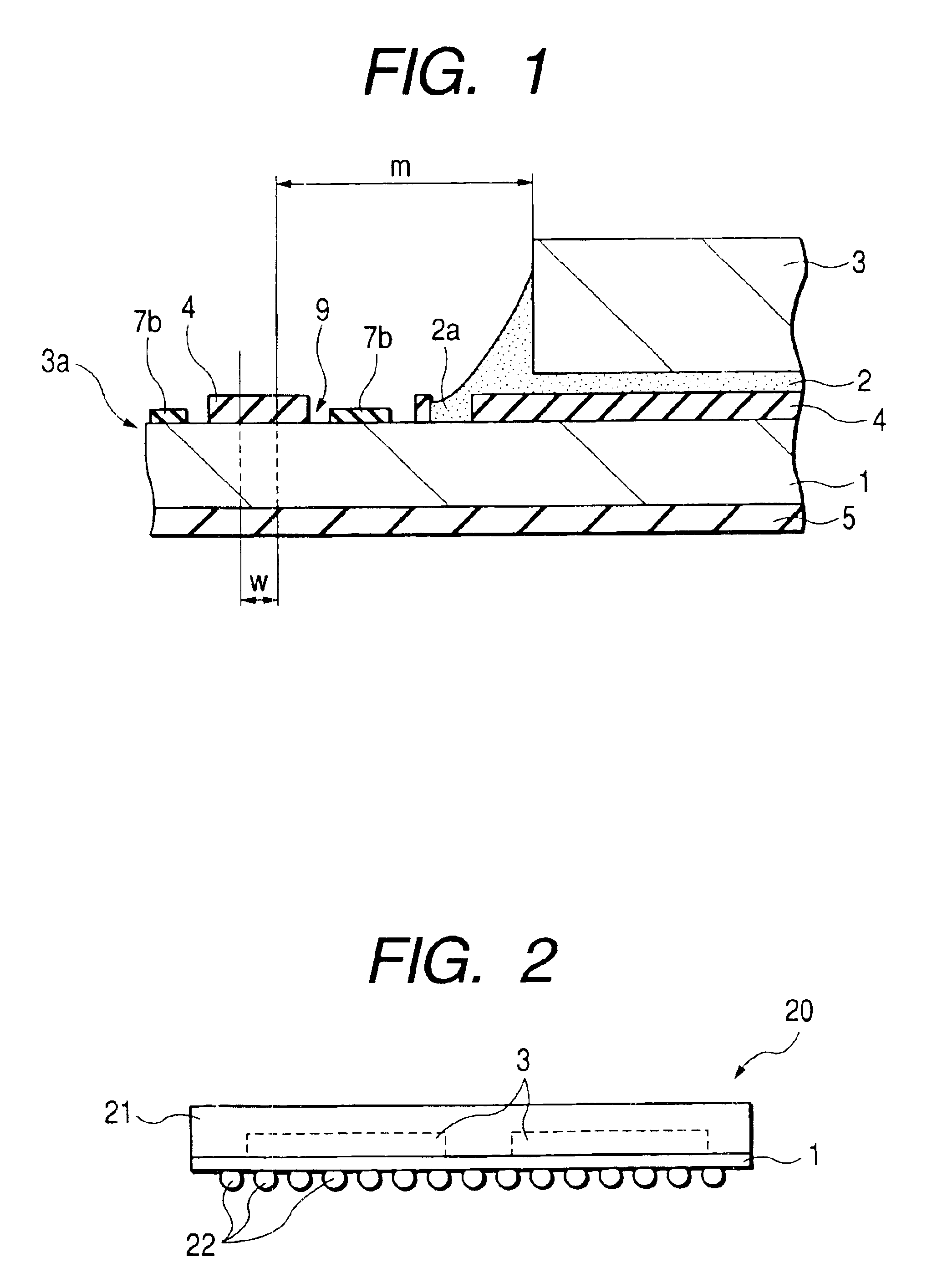
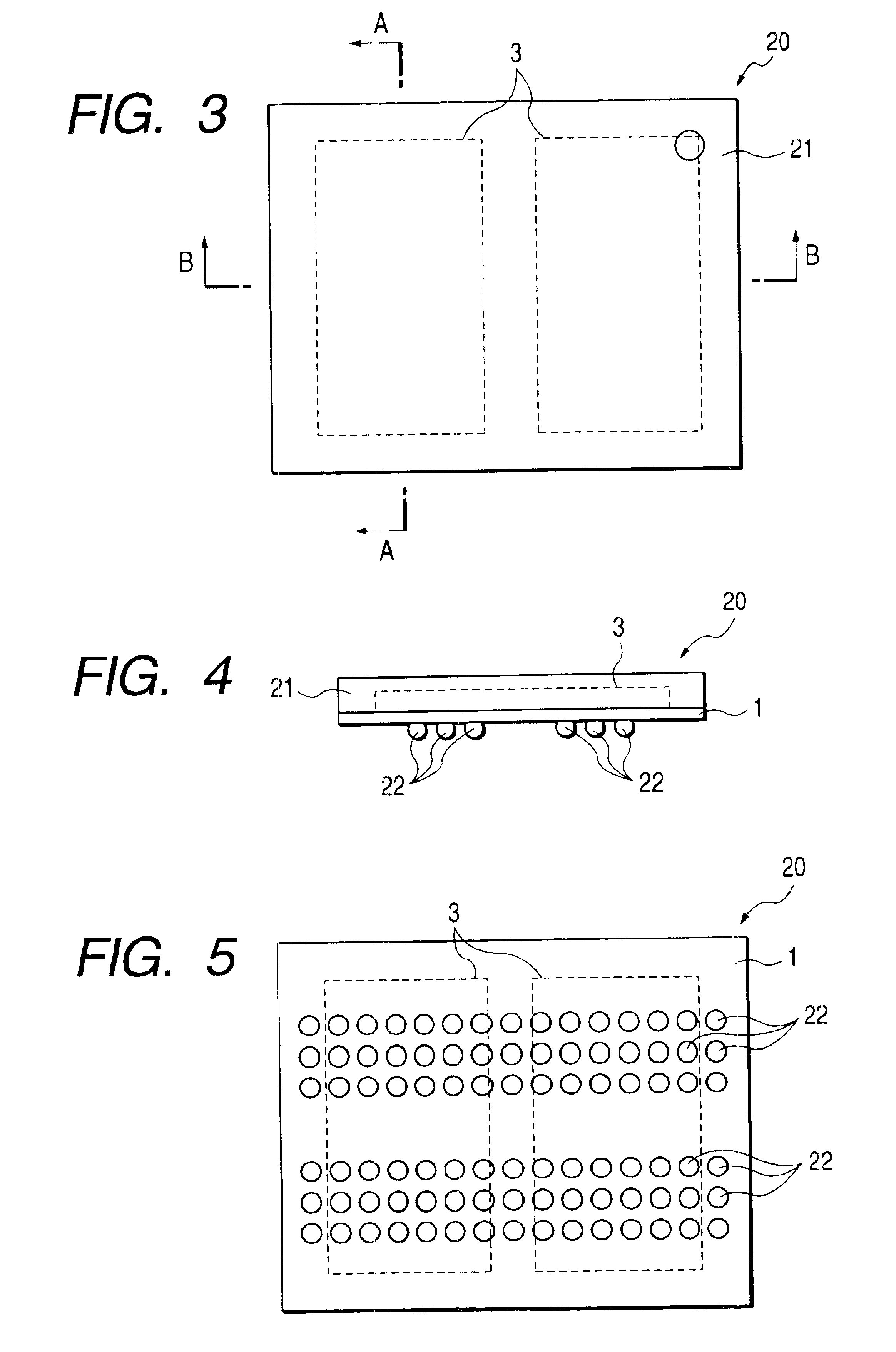
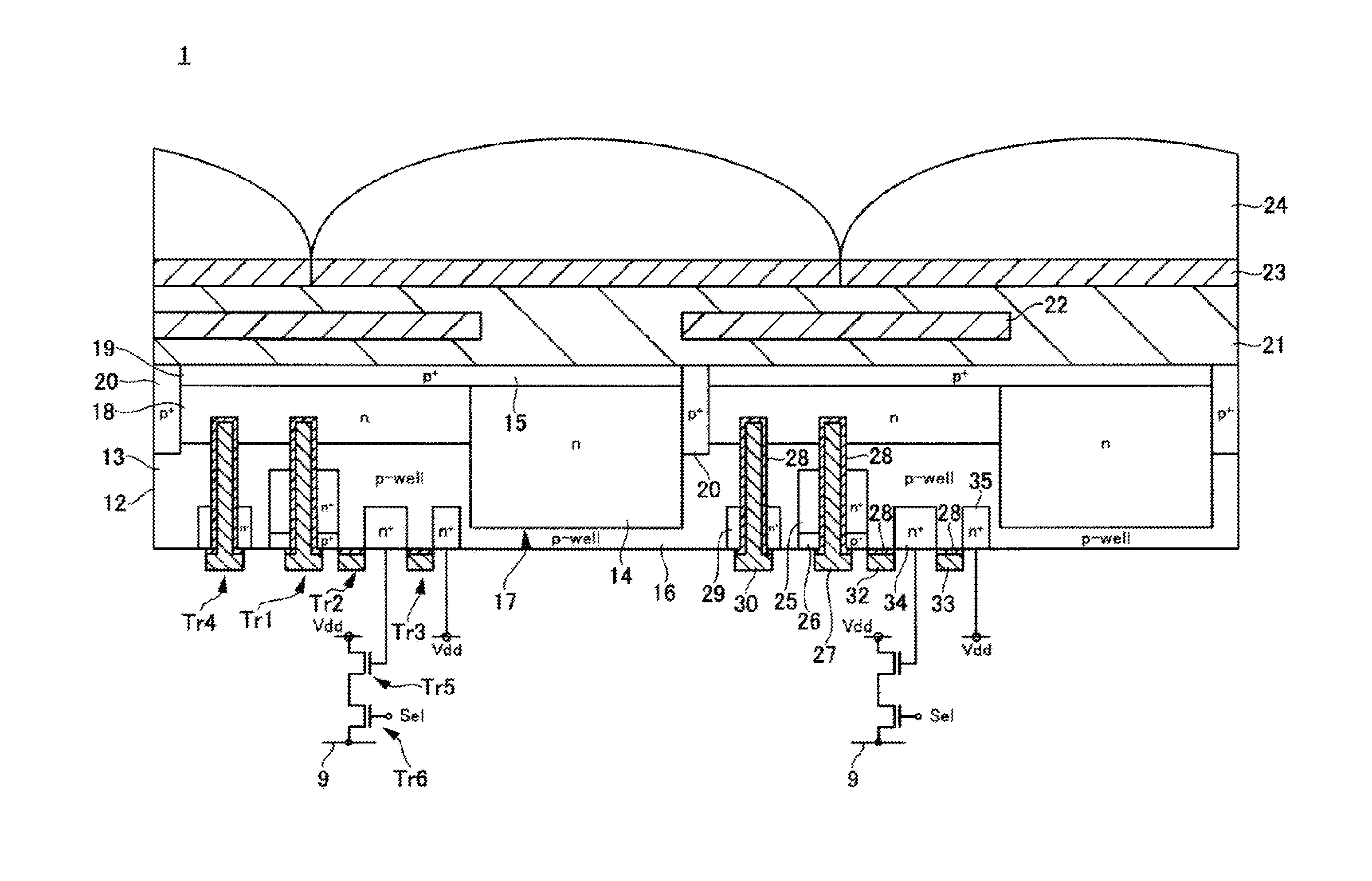
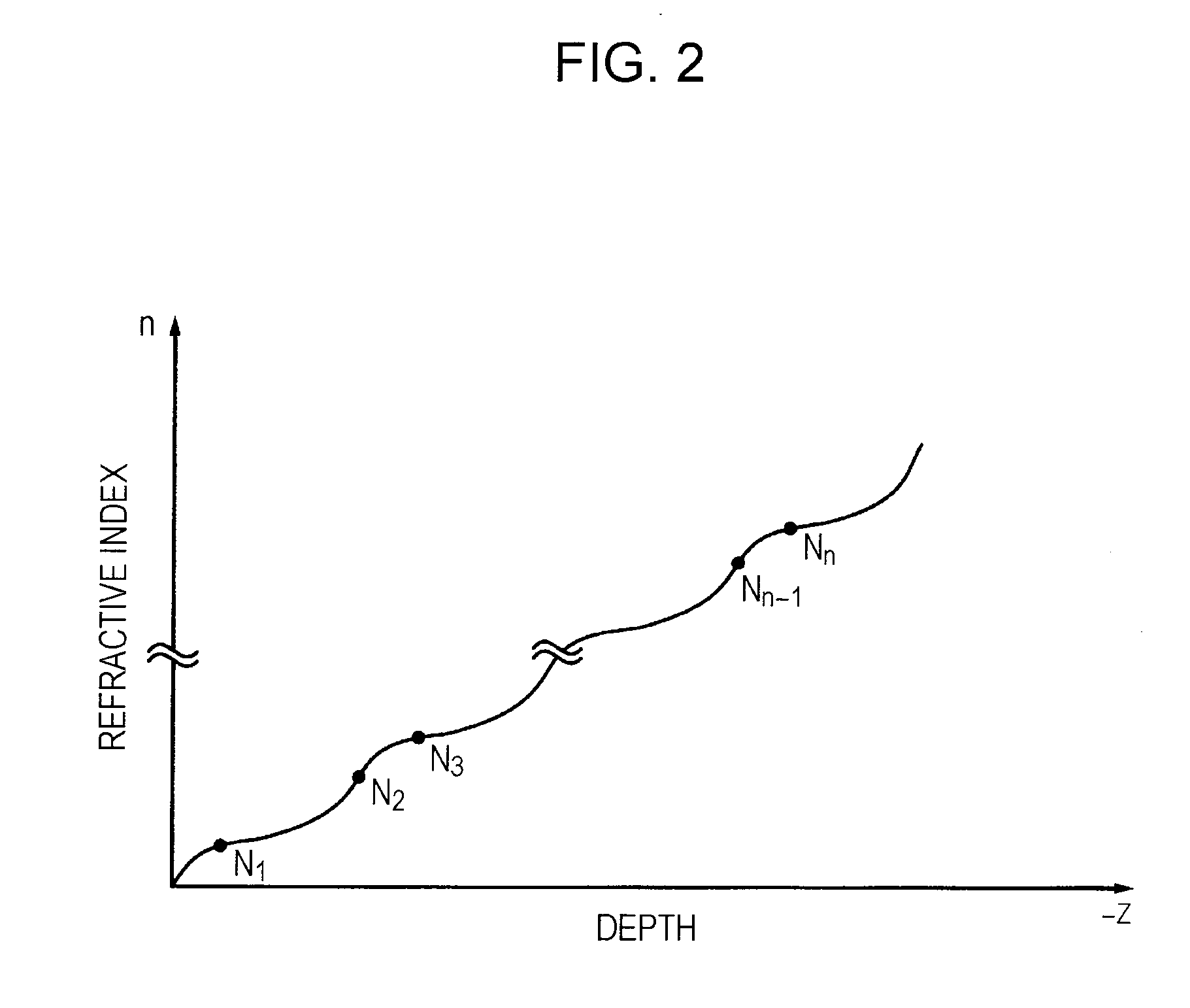
Patents
Literature
2831 results about "Depth direction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
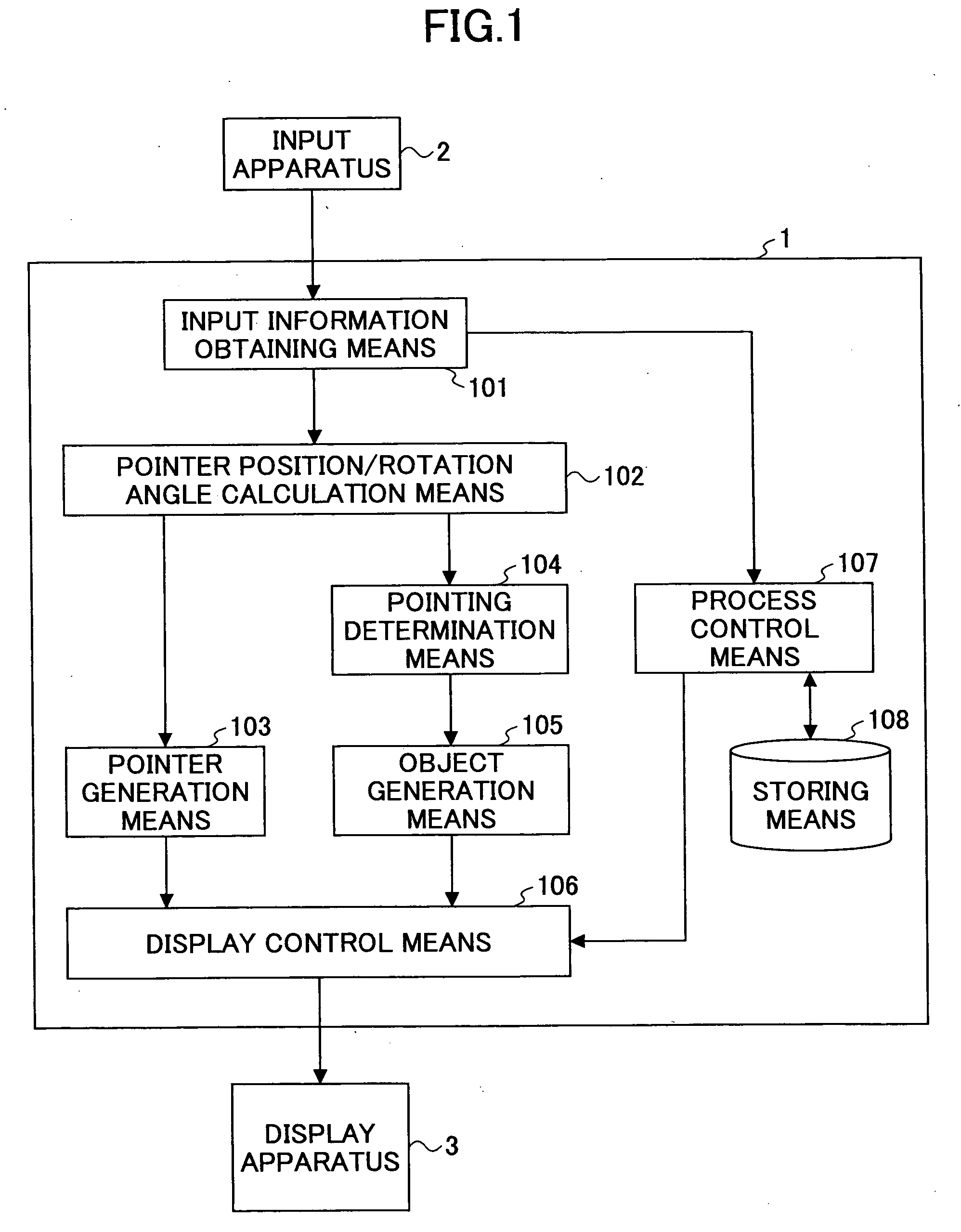
3D Pointing Method, 3D Display Control Method, 3D Pointing Device, 3D Display Control Device, 3D Pointing Program, and 3D Display Control Program
InactiveUS20080225007A1Easy to operateReduce fatigueInput/output processes for data processing3D modellingThree-dimensional spacePointing device
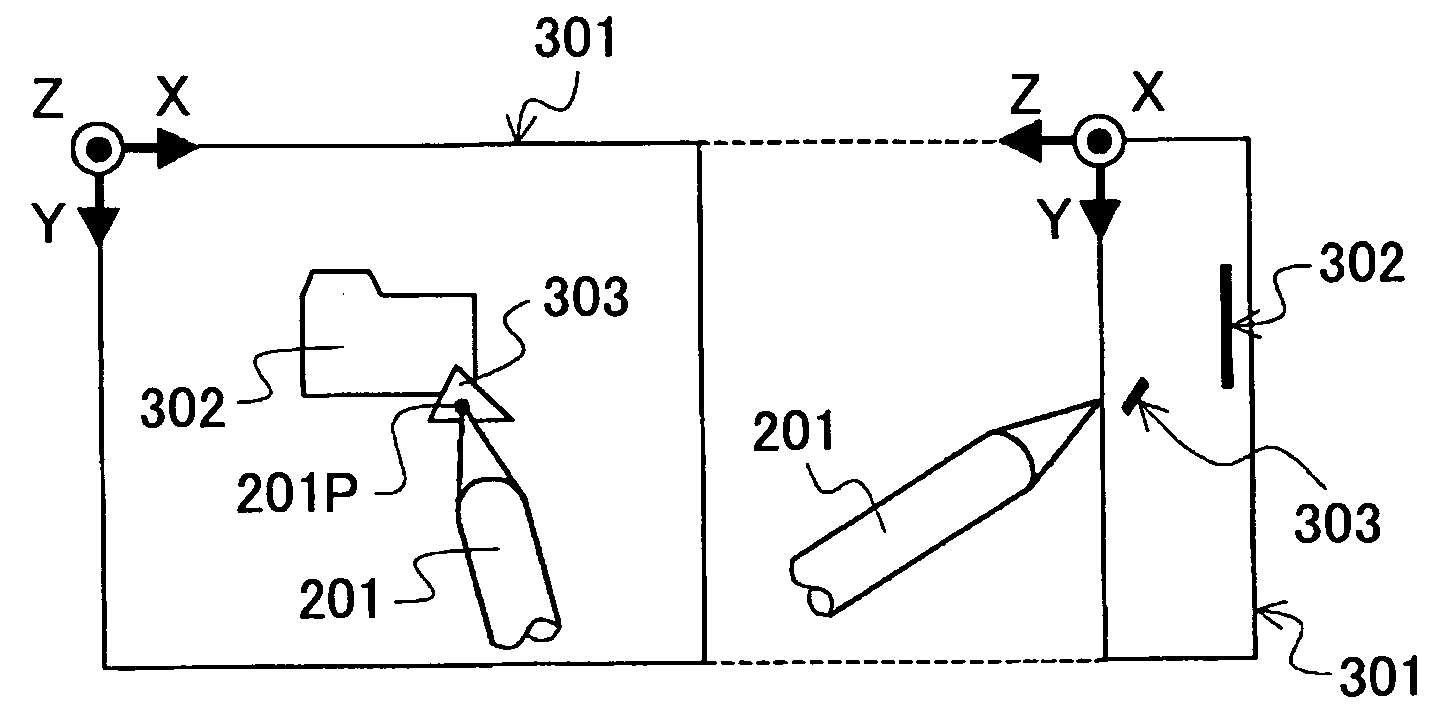
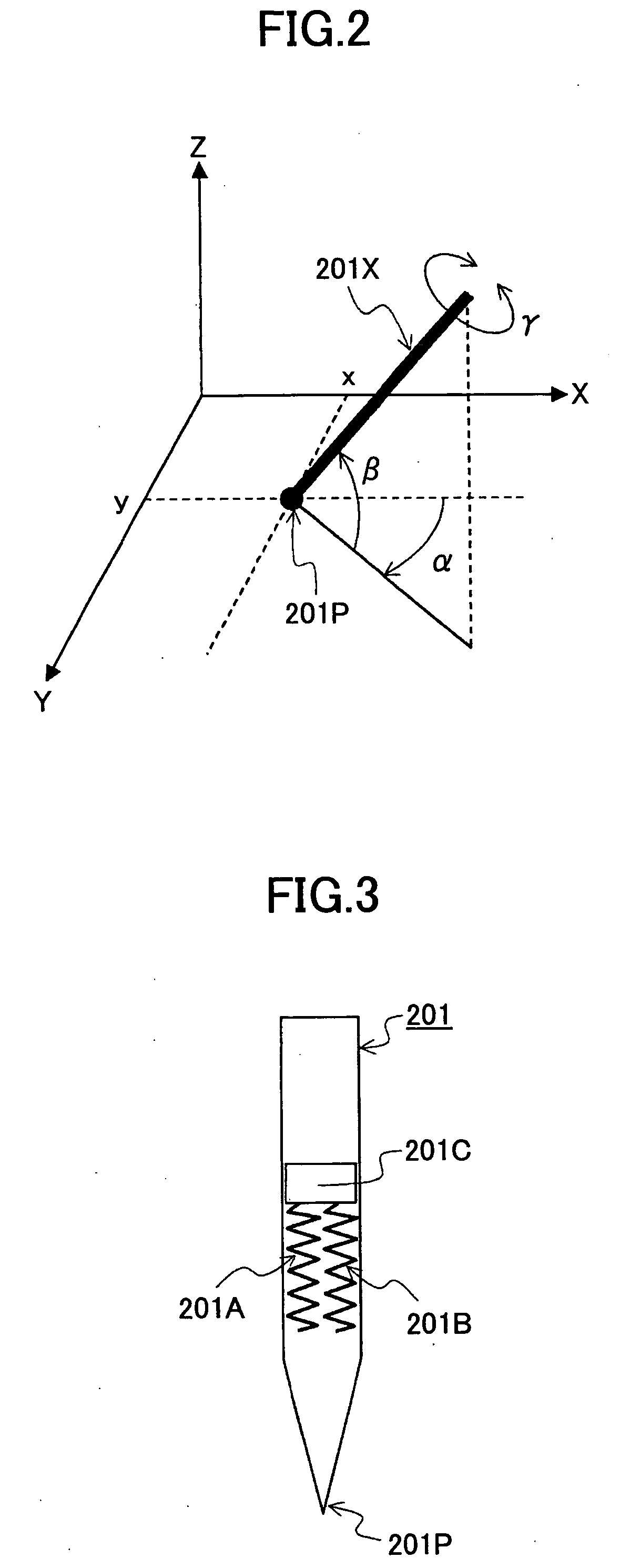
A three-dimensional pointing method is disclosed. In the three-dimensional pointing method of the present invention, a desired point in a three-dimensional space represented on a display apparatus is pointed at based on two-dimensional coordinates of a position that is pointed at by a pen tip of an input pen on a predetermined detection plane, and, based on pen pressure that is pressure applied to the pen tip of the input pen, time for continuing to point or operation of an operation means provided in the input pen. In addition, in the three-dimensional pointing method of the present invention, a depth direction coordinate of a three-dimensional pointer to be displayed in the three-dimensional space is changed according to the pen pressure of the input pen, the time for continuing to point or the operation of the operation means provided in the input pen, and the three-dimensional pointer is displayed.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
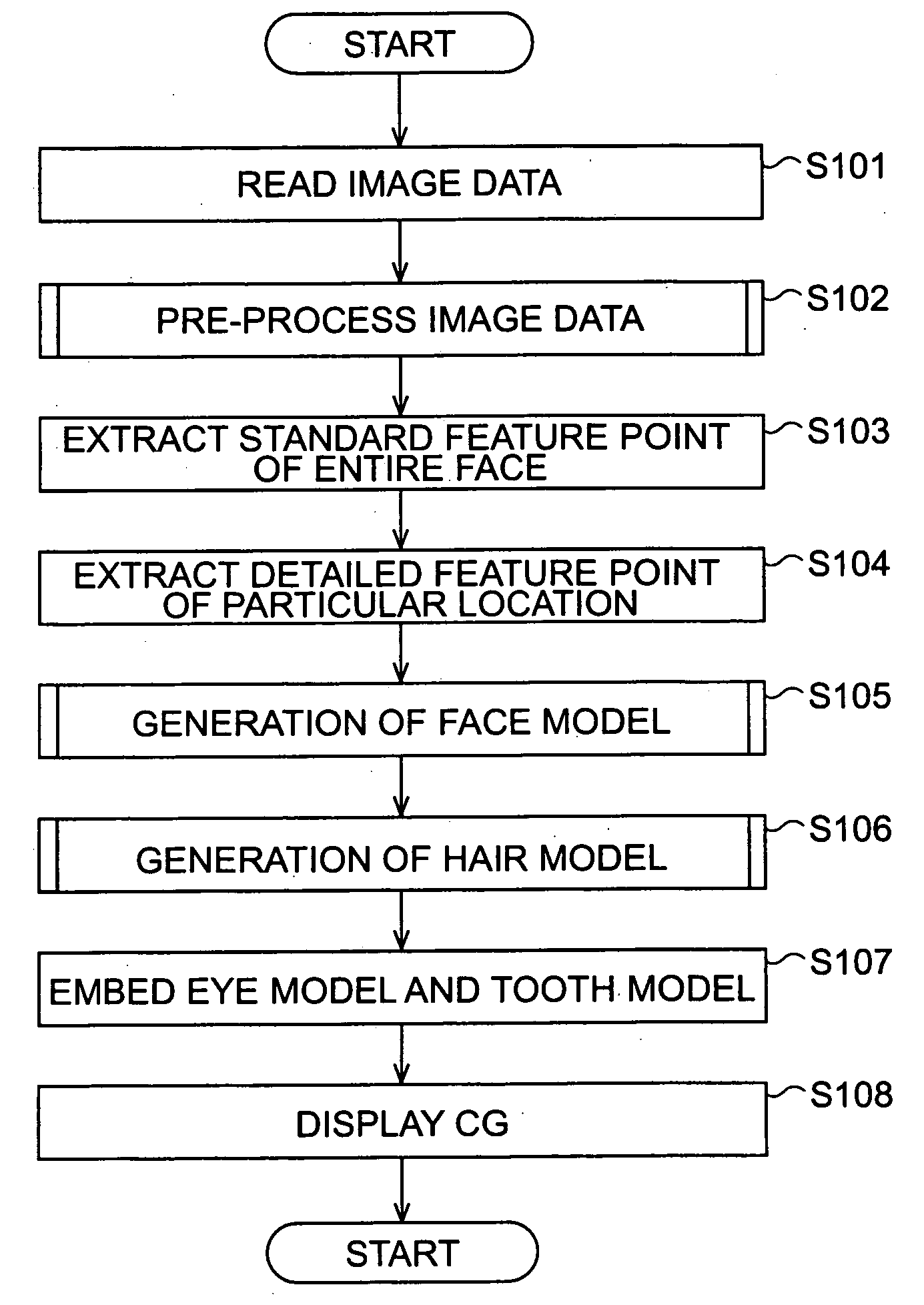
Method, apparatus, and computer program for processing image
ActiveUS20060188144A1Easy to getRealistic animationCharacter and pattern recognitionAnimationImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus for generating a three-dimensional model of a three-dimensional object from an image displaying the object in two dimensions includes a three-dimensional model generator operable to generate the three-dimensional model of the object from the image, and an extender operable to extend a lateral region of the three-dimensional model in a depth direction orthogonal to the two dimensions.
Owner:AX INC +1
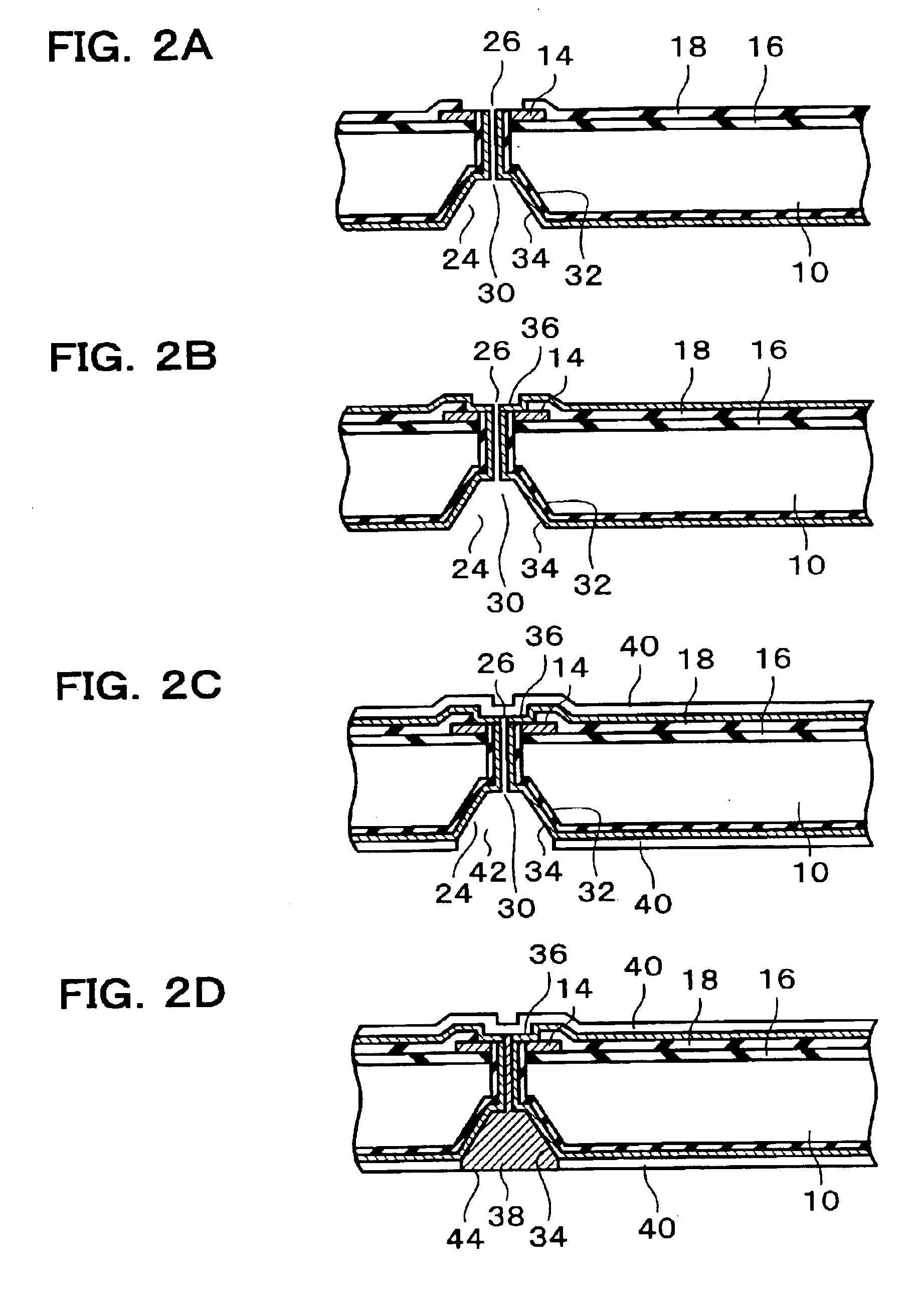
Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same, a circuit board and an electronic apparatus
InactiveUS6873054B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A through hole tapered from an opening to the in-depth direction is formed in a semiconductor substrate provided with an integrated circuit. An insulating material is supplied to the through hole through the opening so as to form an insulating layer on the inner surface of the through hole. A conductive material is supplied through the opening to the through hole provided with the insulating layer so as to form a conductive portion inside the insulating layer.
Owner:ADVANCED INTERCONNECT SYST LTD
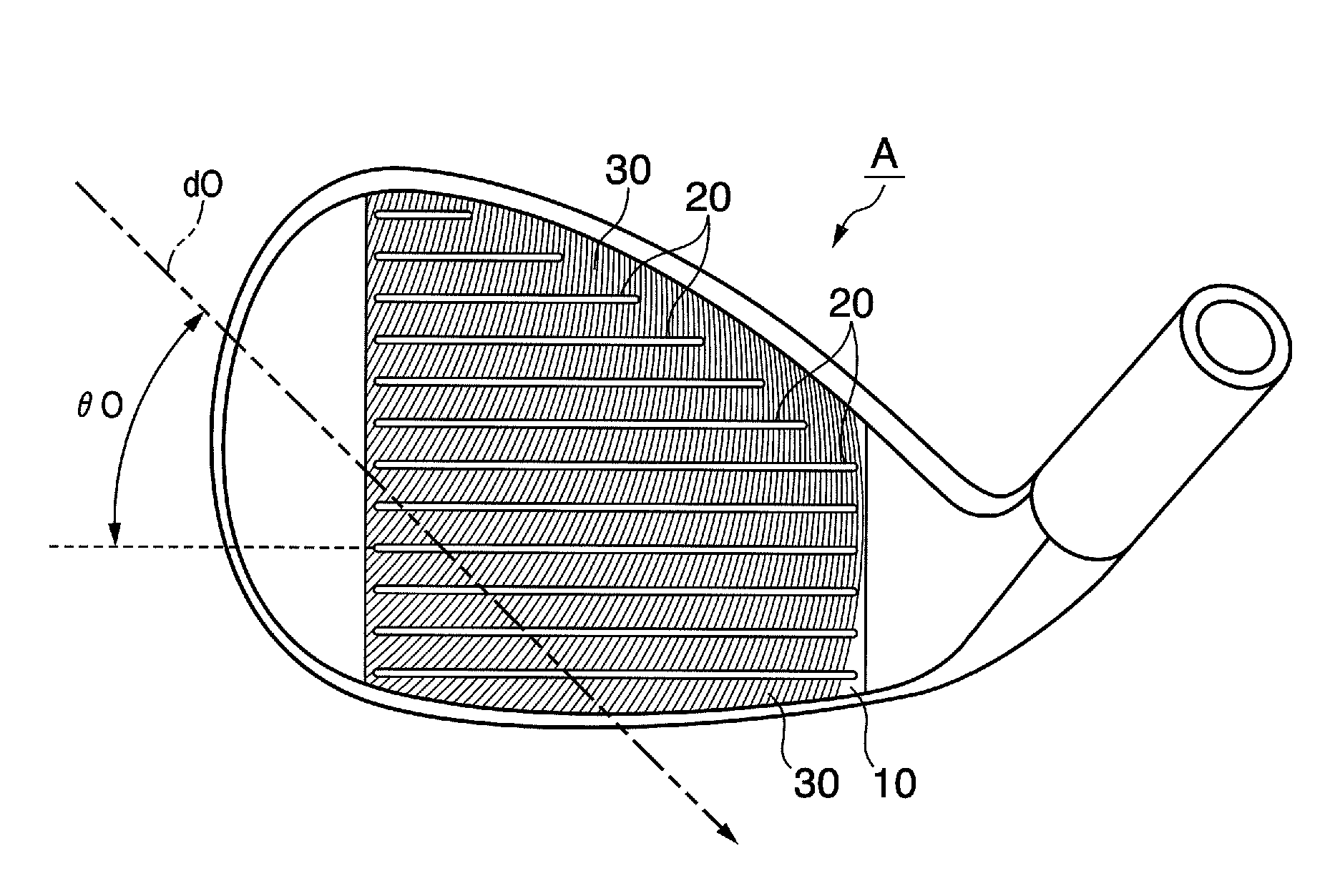
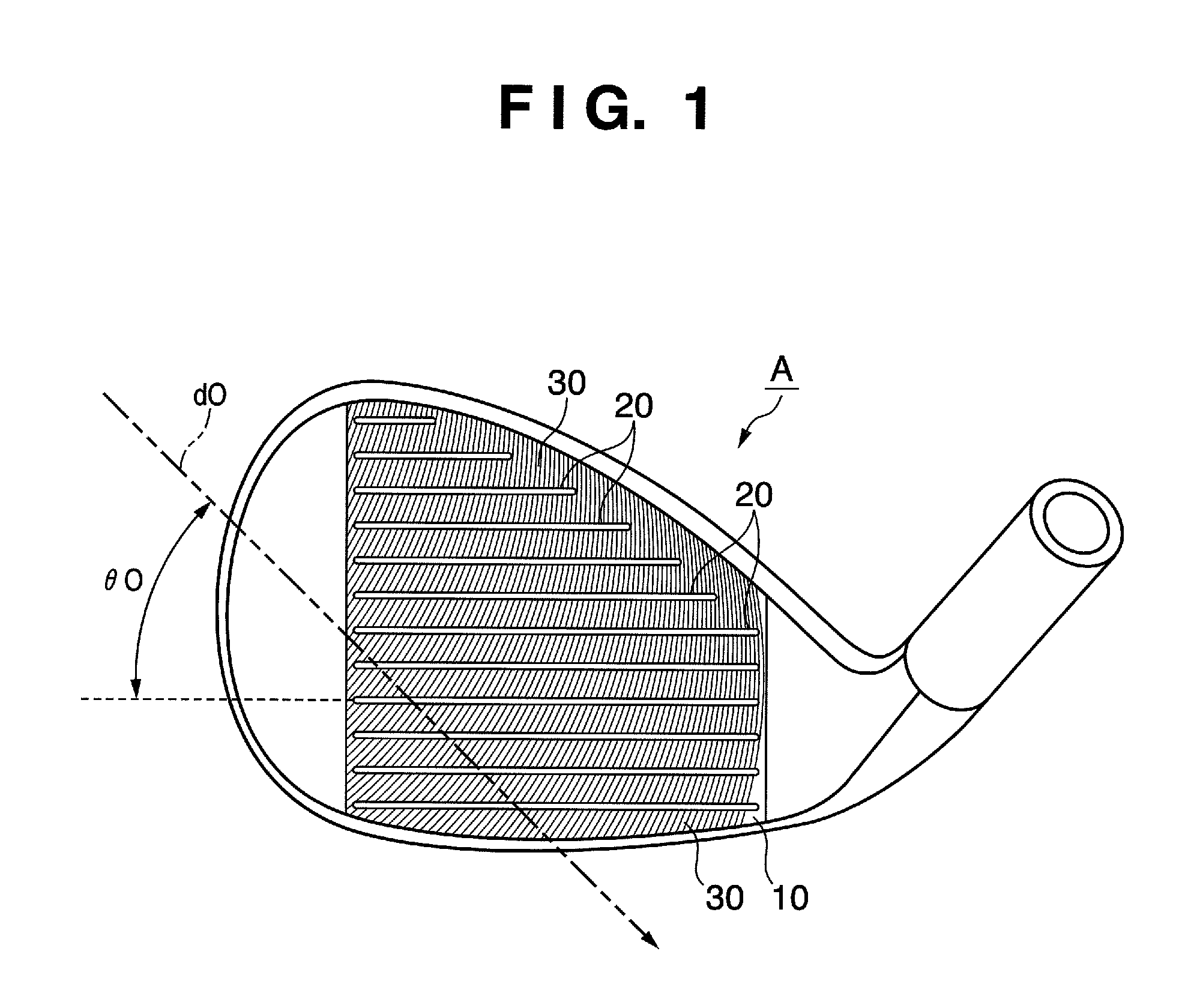
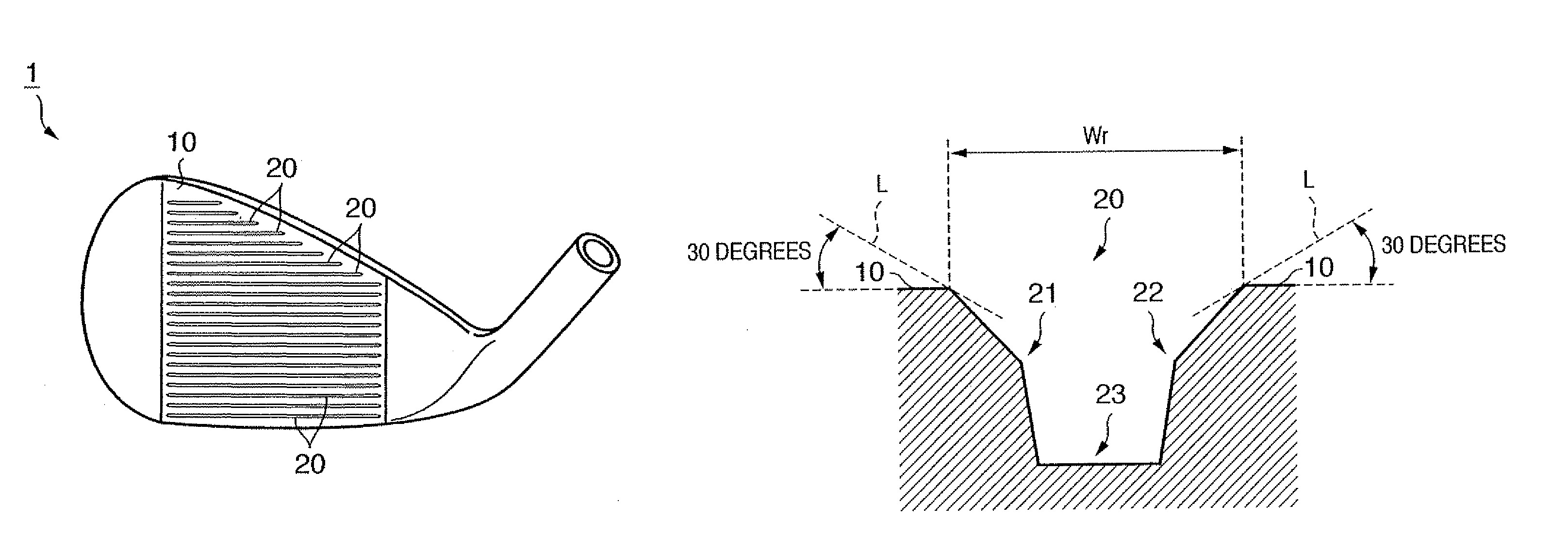
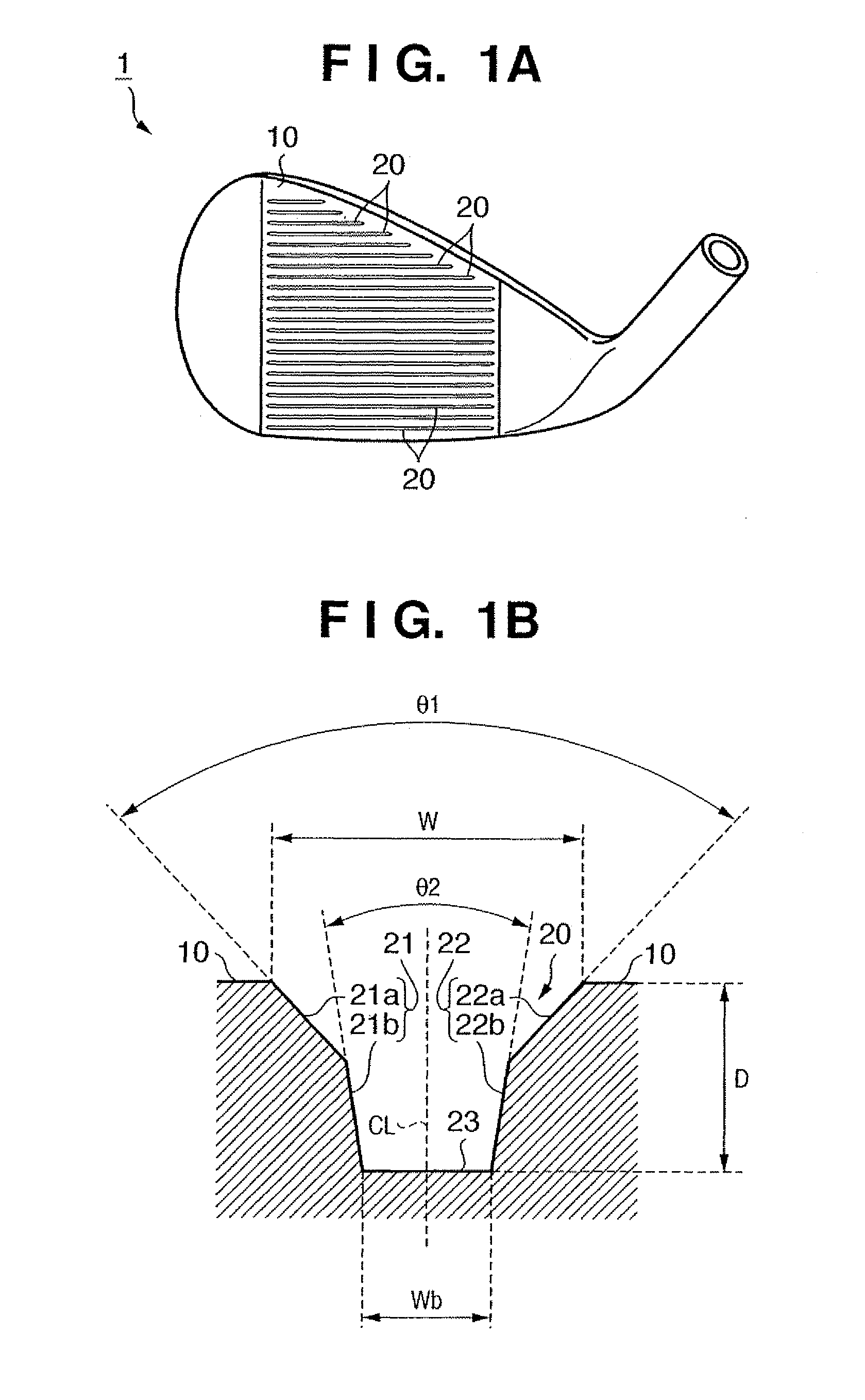
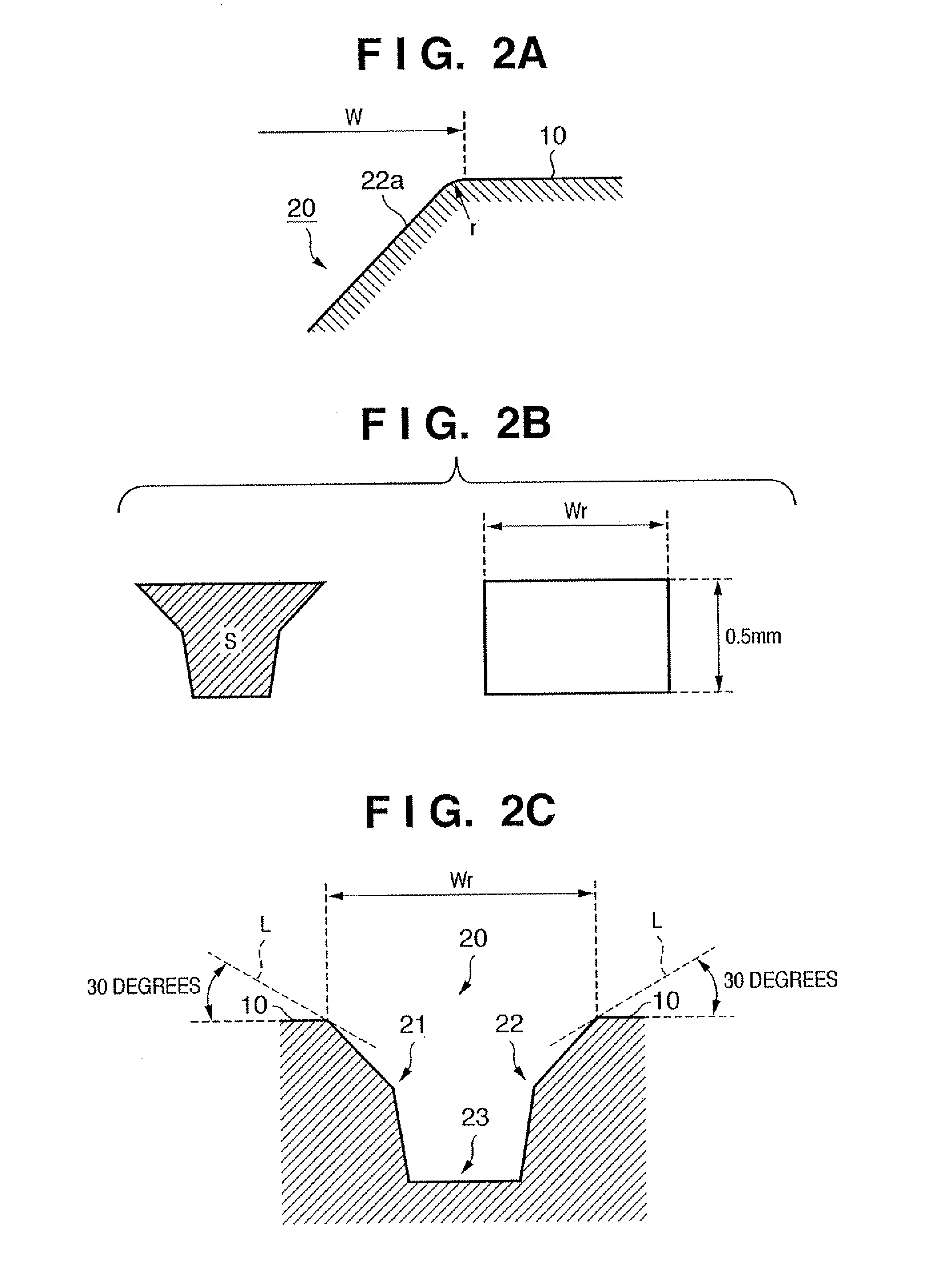
Golf club head
InactiveUS7815521B2Avoid damageAvoid significant declines in spinGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringGolf Ball
The present invention provides a golf club head comprising, a face, a plurality of score line grooves formed in the face, traces formed in the face by milling; and a pair of side surfaces of the score line groove including a first surface that is contiguous with the face and a second surface that is contiguous with the first surface in the depth direction of the score line groove. A first angle that is formed by each first surface of the pair of side surfaces is larger than a second angle that is formed by each second surface of the pair of surfaces. The face in which the traces are formed has the arithmetic mean deviation of the profile (Ra) of not less than 4.00 μm.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
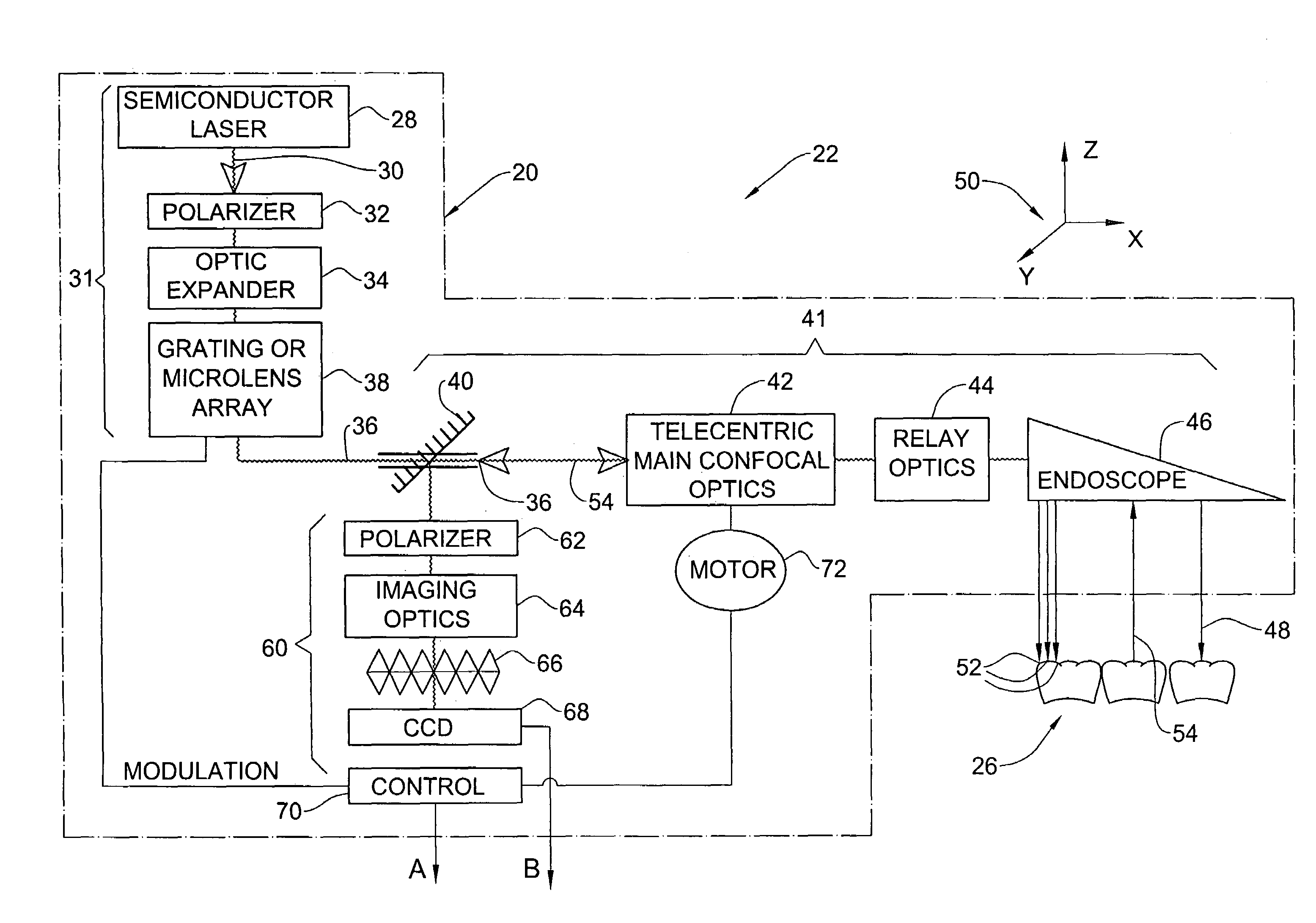
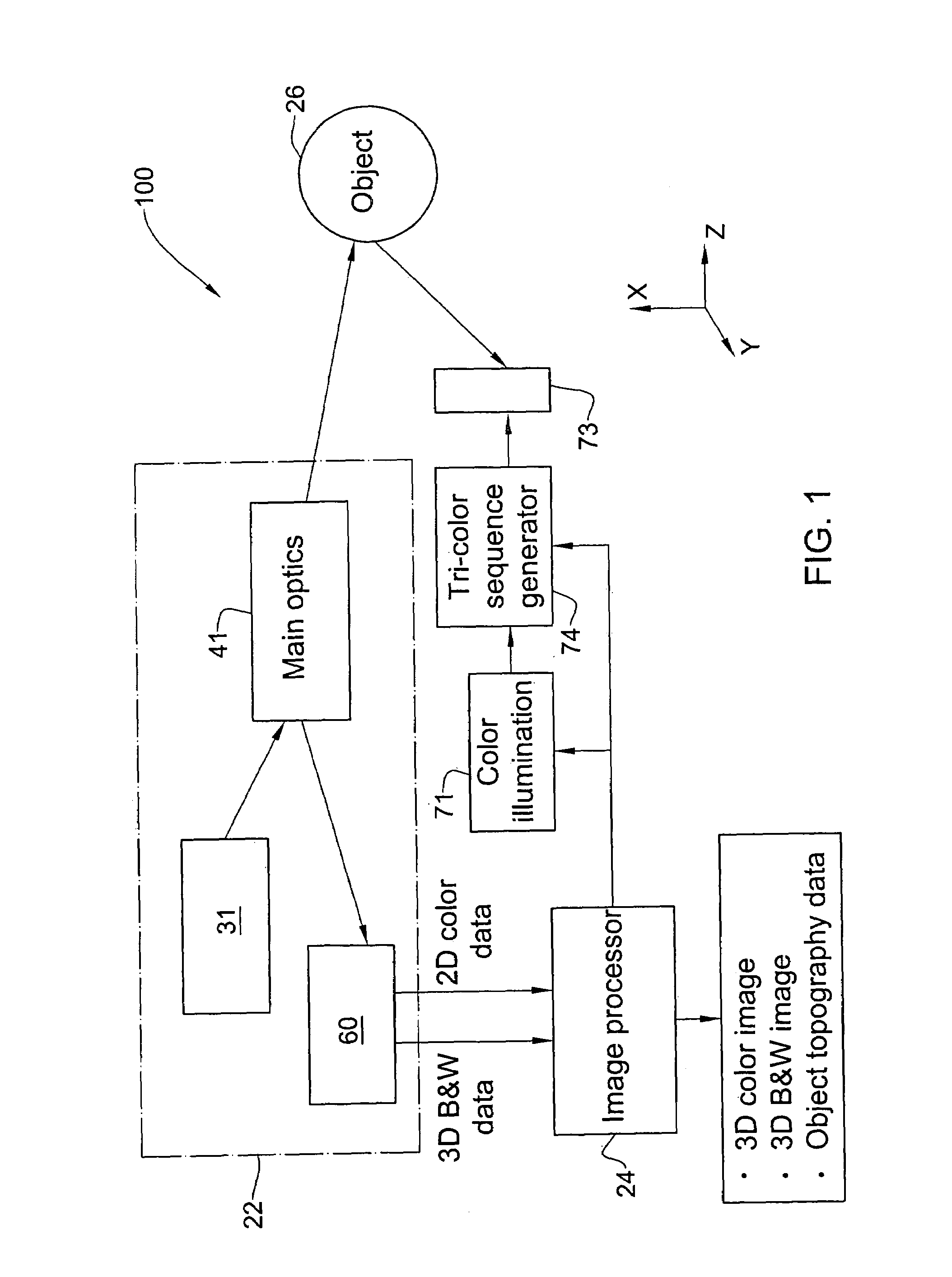
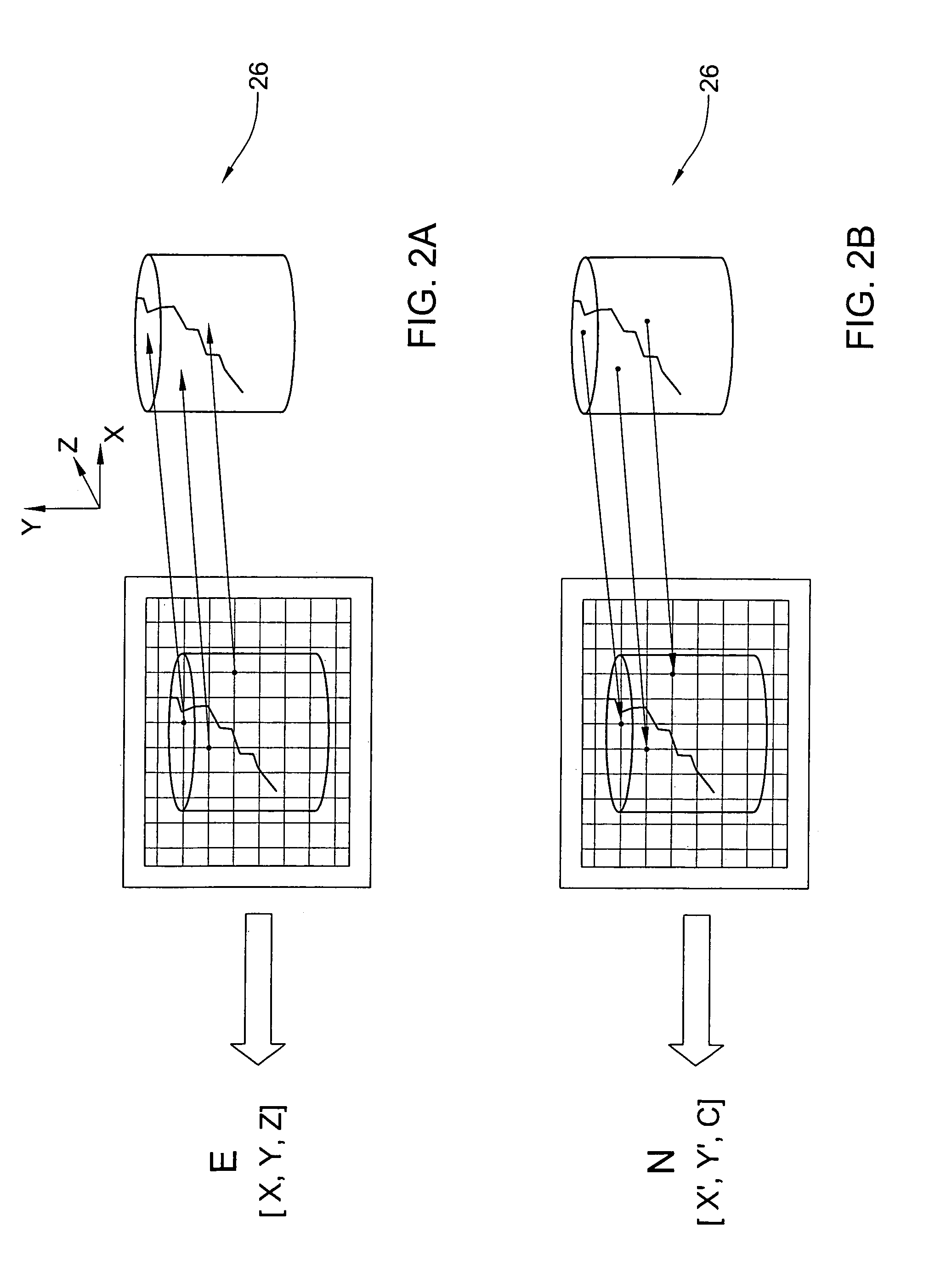
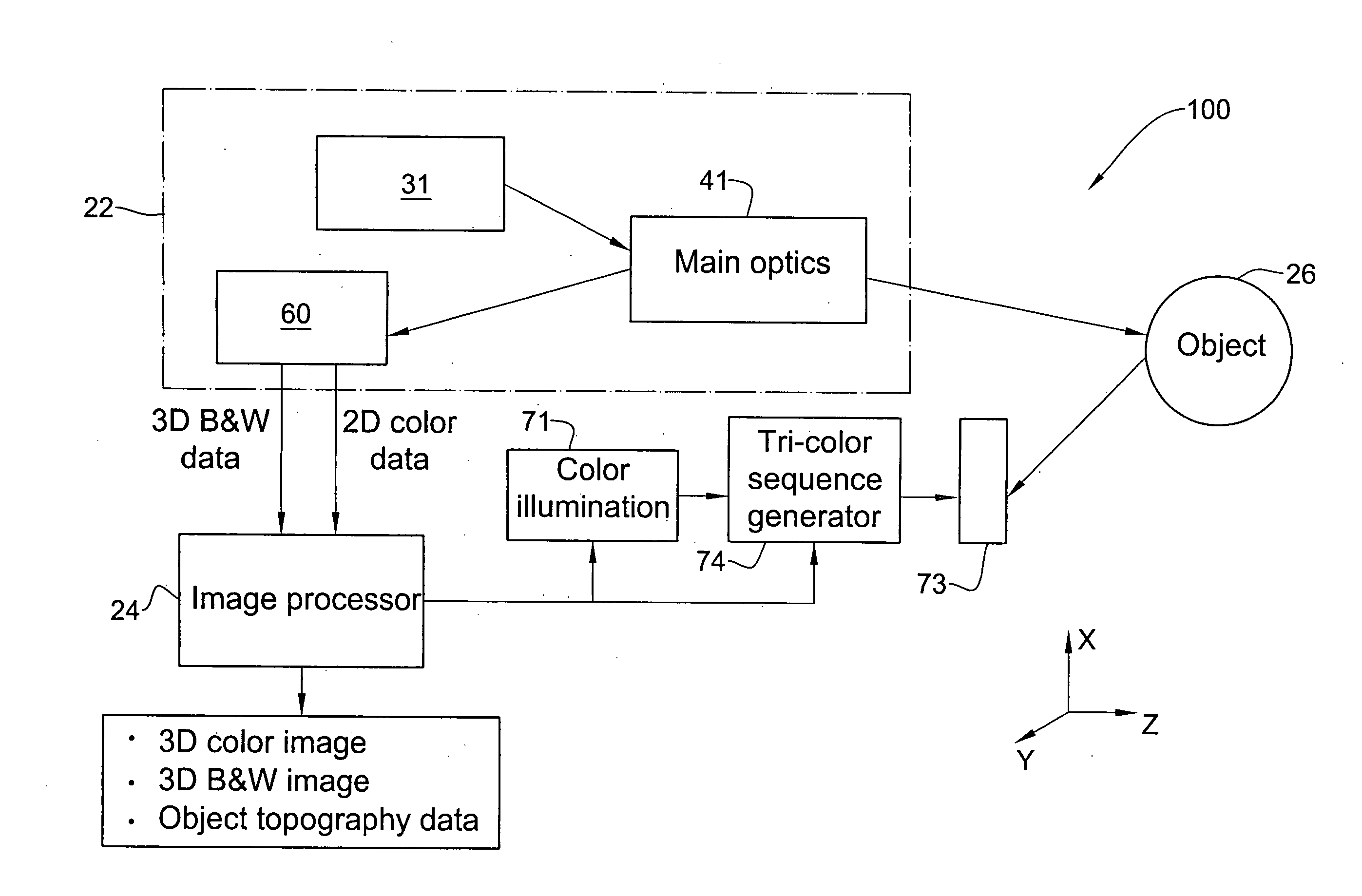
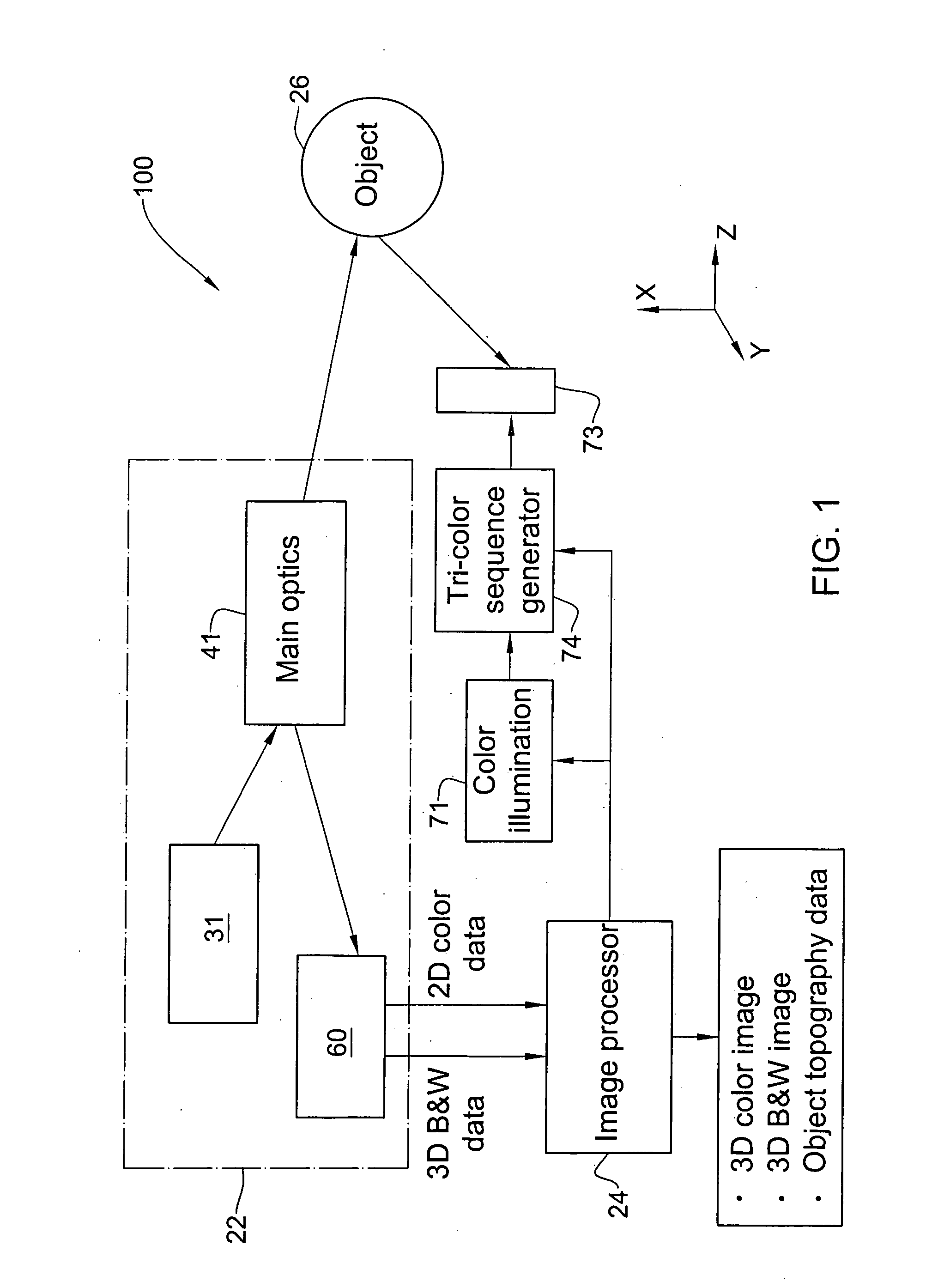
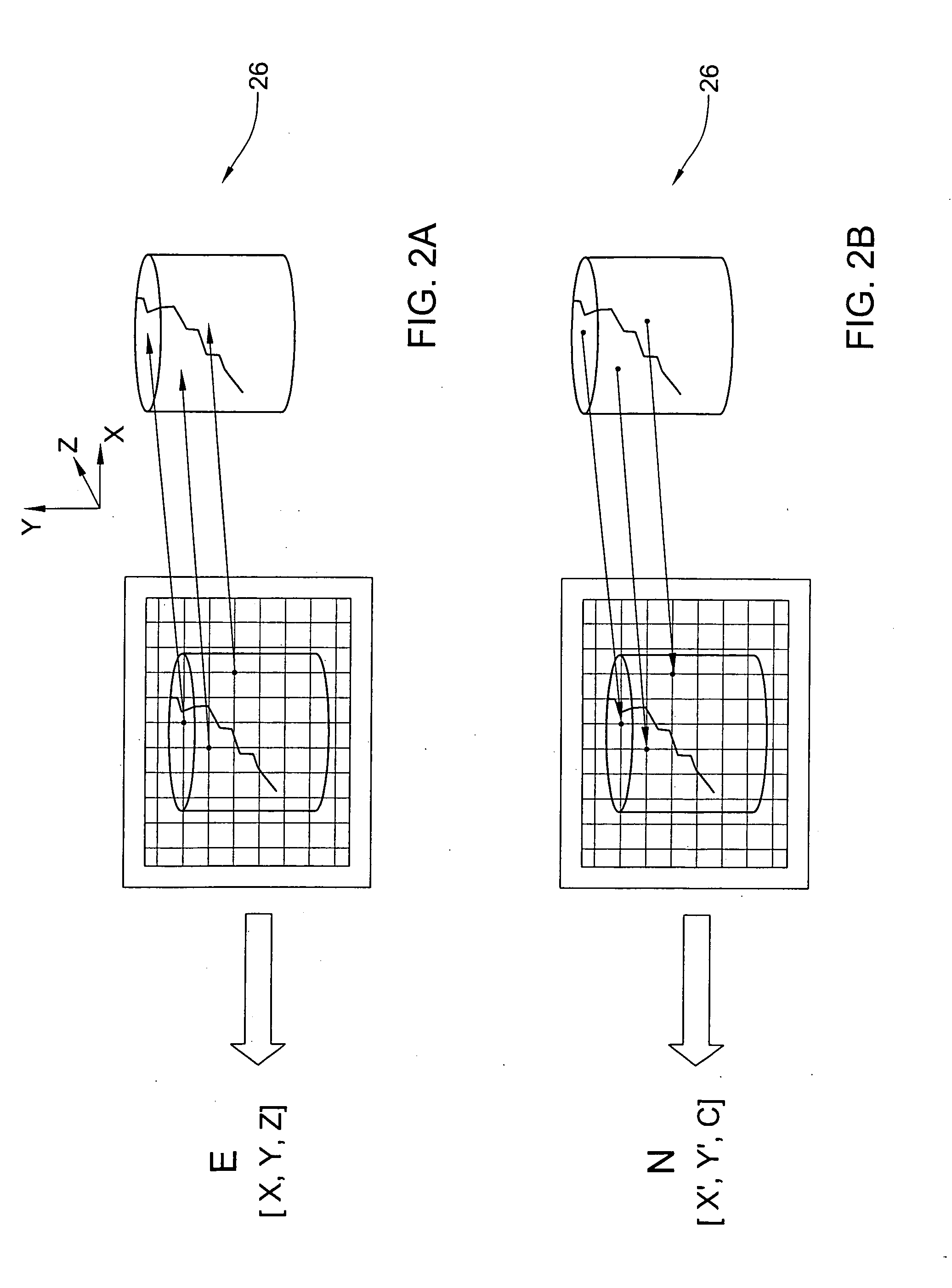
Method and apparatus for colour imaging a three-dimensional structure
A device for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure, such as a teeth segment, includes a scanner for providing depth data for points along a two-dimensional array substantially orthogonal to the depth direction, and an image acquisition means for providing color data for each of the points of the array, while the spatial disposition of the device with respect to the structure is maintained substantially unchanged. A processor combines the color data and depth data for each point in the array, thereby providing a three-dimensional color virtual model of the surface of the structure. A corresponding method for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure is also provided.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
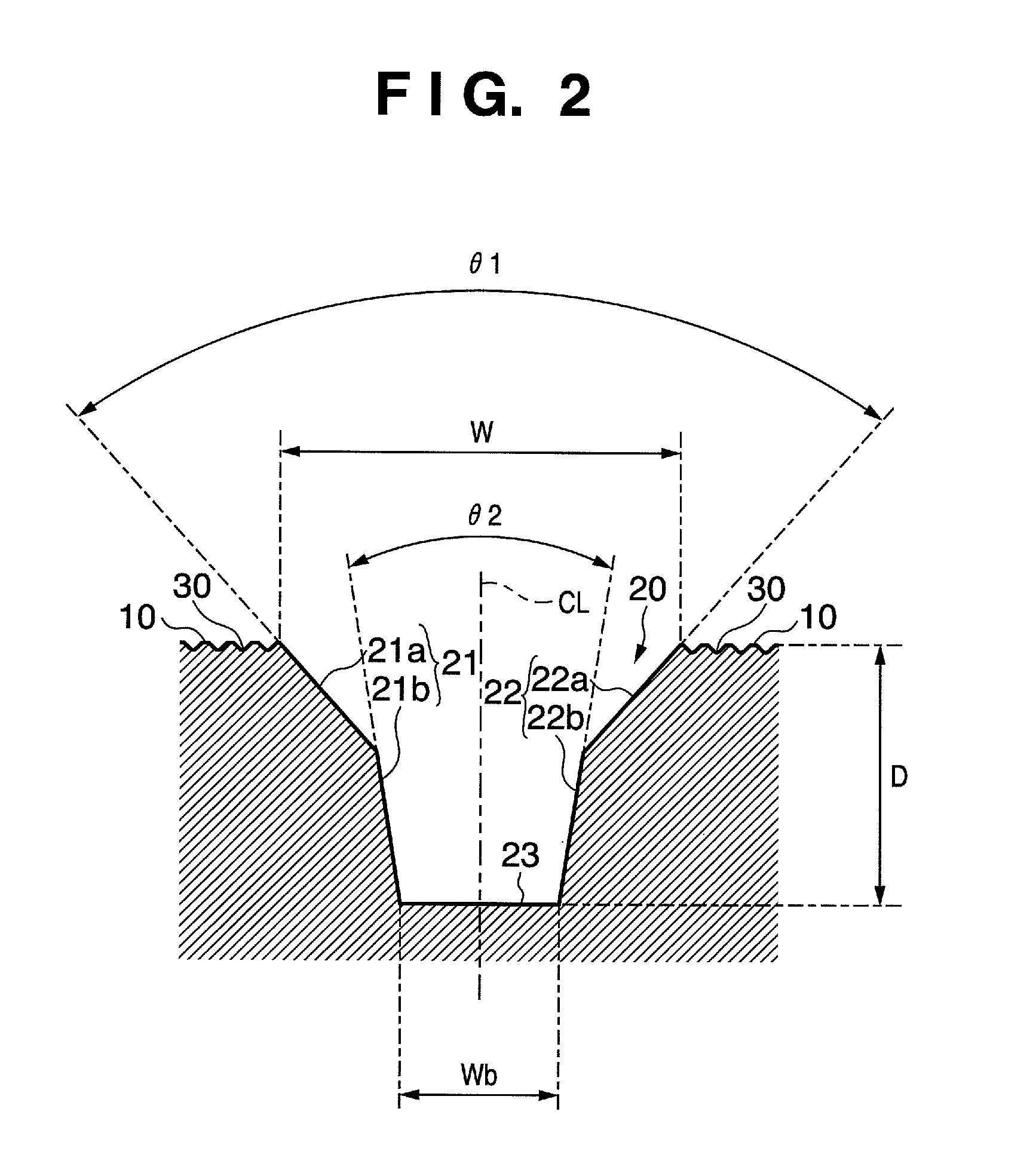
Golf club head
This invention provides a golf club head having a groove formed on a face of the golf club head. Each of a pair of side surfaces of the groove has a first surface leading to the face and a second surface leading to the first surface in the depth direction of the groove. A first angle between the first surfaces of each of the pair of the side surfaces is larger than a second angle between the second surfaces of each of the pair of the side surfaces.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060205182A1Reduce widthRate of the processing for providing the trenched portion can beSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialDevice form
A method of dicing a semiconductor wafer includes providing an interconnect layer providing a protective film on the interconnect layer on the side of a device-forming surface of a silicon wafer, irradiating the protective film with a laser beam to provide a trenched portion that extends through the interconnect layer from the protective film and reaches to an inside of the silicon wafer, removing a portion of the silicon wafer selectively in a depth direction from a bottom of the trenched portion, after irradiating with the laser beam to provide the trenched portion and dividing the silicon wafer along the portion where the trenched portion is provided into respective pieces of the silicon wafer, after removing a portion of the silicon wafer 101 selectively in the depth direction.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus with thumbnail display
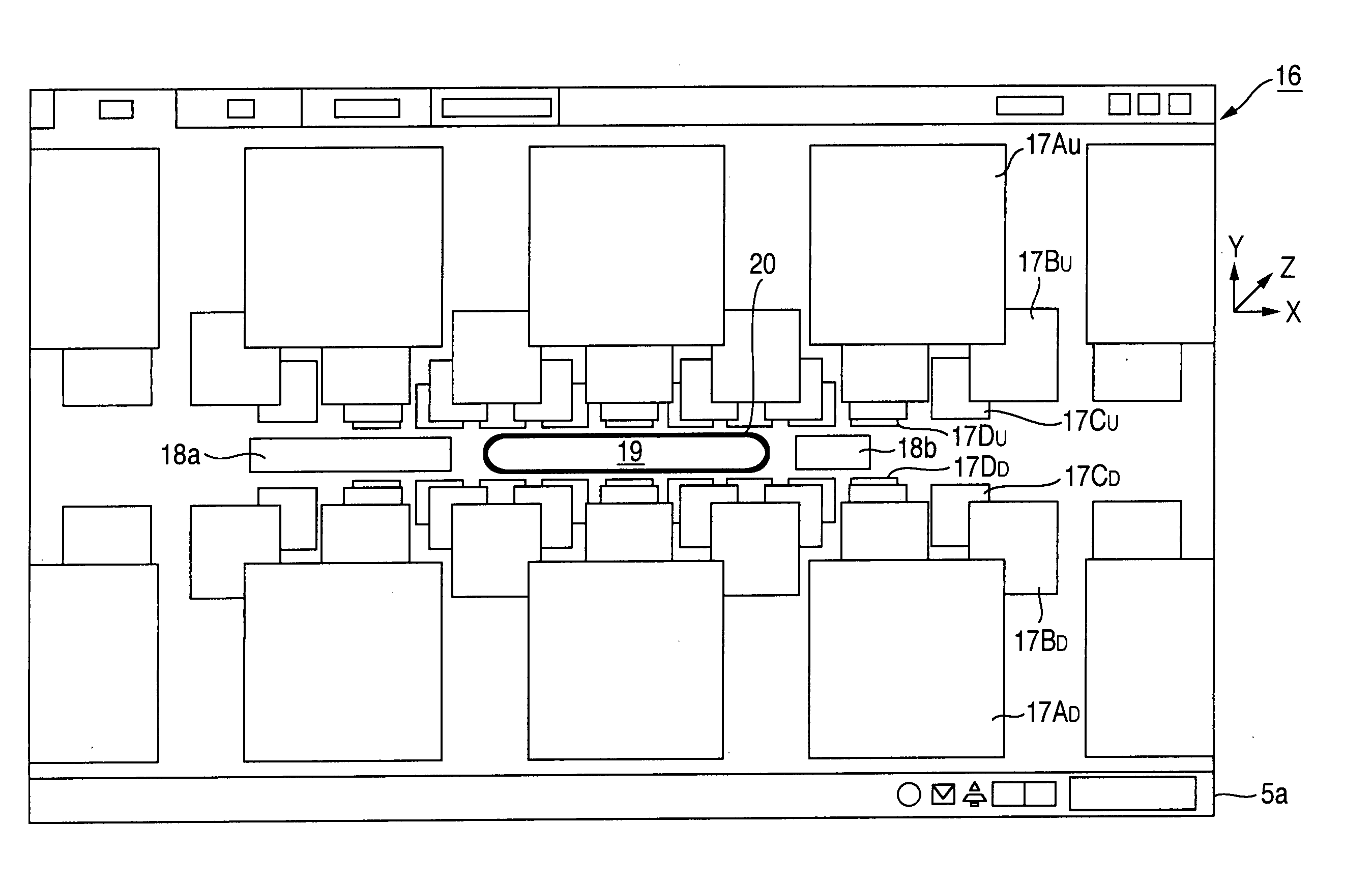
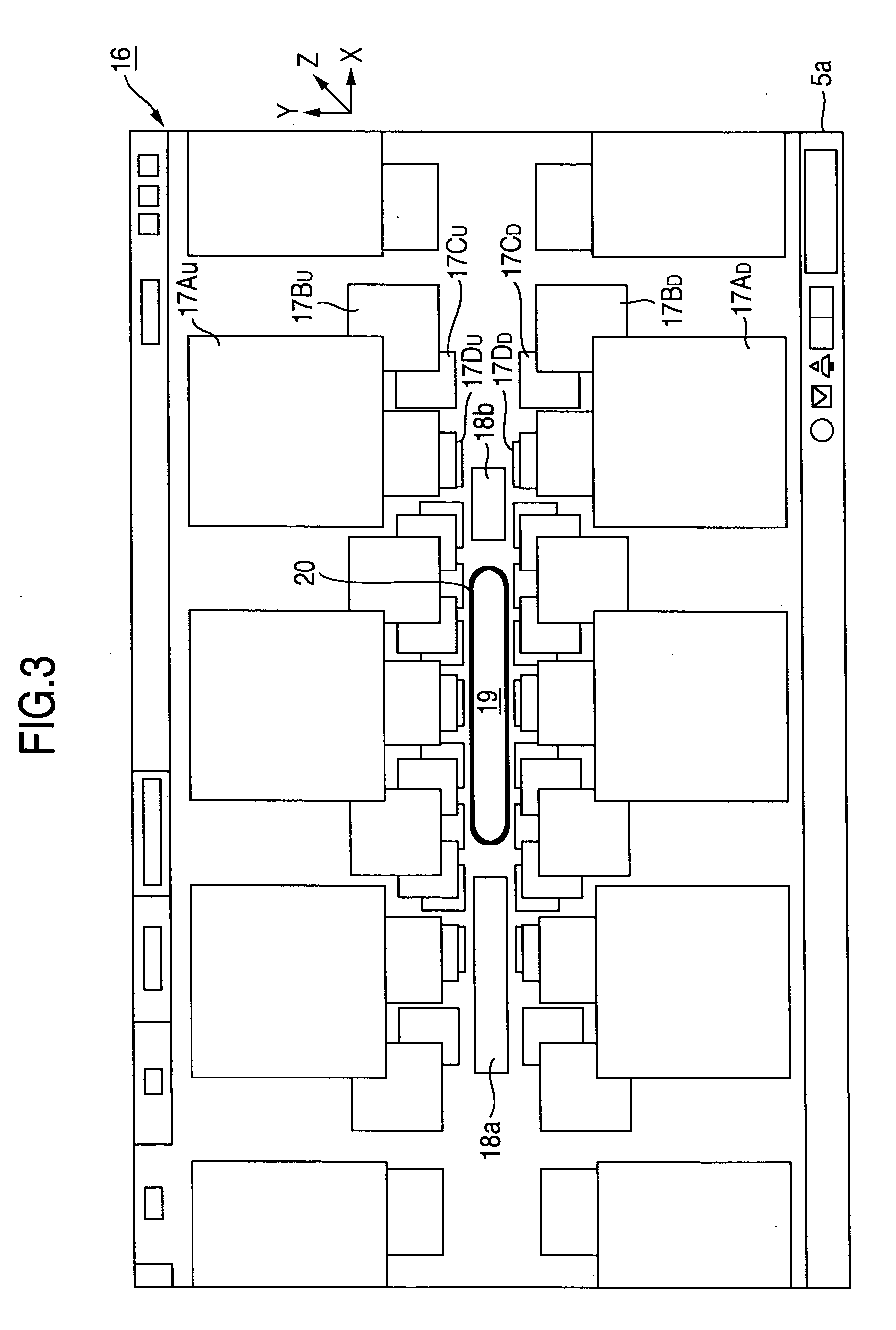
ActiveUS20060236251A1Easy to identifyEasy to search contentTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLeft directionThumbnail
In a thumbnail screen, categories and category thumbnails are disposed and displayed in the depth (Z-axis) direction and in the horizontal (X axis) direction, respectively. When focus is given by a focus to any of upper and lower category thumbnails, which are displayed on the most front side, and a category name display part, the row (layers) of the thumbnails scrolls in the horizontal direction. When the right and left direction keys of a remote controller are operated while the category name display has focus, the scroll in the depth direction is performed, thus enabling the specification of a desired category. This three-dimensionally displays the thumbnails and facilitates the operation for viewing information.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Method and apparatus for colour imaging a three-dimensional structure
ActiveUS20060001739A1Accurate mappingImage enhancementImpression capsComputer graphics (images)Tooth segment
A device for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure, such as a teeth segment, includes a scanner for providing depth data for points along a two-dimensional array substantially orthogonal to the depth direction, and an image acquisition means for providing color data for each of the points of the array, while the spatial disposition of the device with respect to the structure is maintained substantially unchanged. A processor combines the color data and depth data for each point in the array, thereby providing a three-dimensional color virtual model of the surface of the structure. A corresponding method for determining the surface topology and associated color of a structure is also provided.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Disk array apparatus
InactiveUS20070053154A1Improve cooling effectEasy to controlReducing temperature influence on carrierCarrier constructional parts dispositionDisk enclosureDisk array
A disk array apparatus including a rack-shaped basic frame, and a plurality of disk boxes that can be inserted into and pulled out of the basic frame depth-wise. Each disk box has: disk drive connectors for connecting a plurality of disk drives arranged in a matrix on a platter substrate, which is the bottom face of the disk box, roughly parallel to the depth direction of the basic frame; and a cooling module for cooling the disk drives. The disk box is a hermetically sealed structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
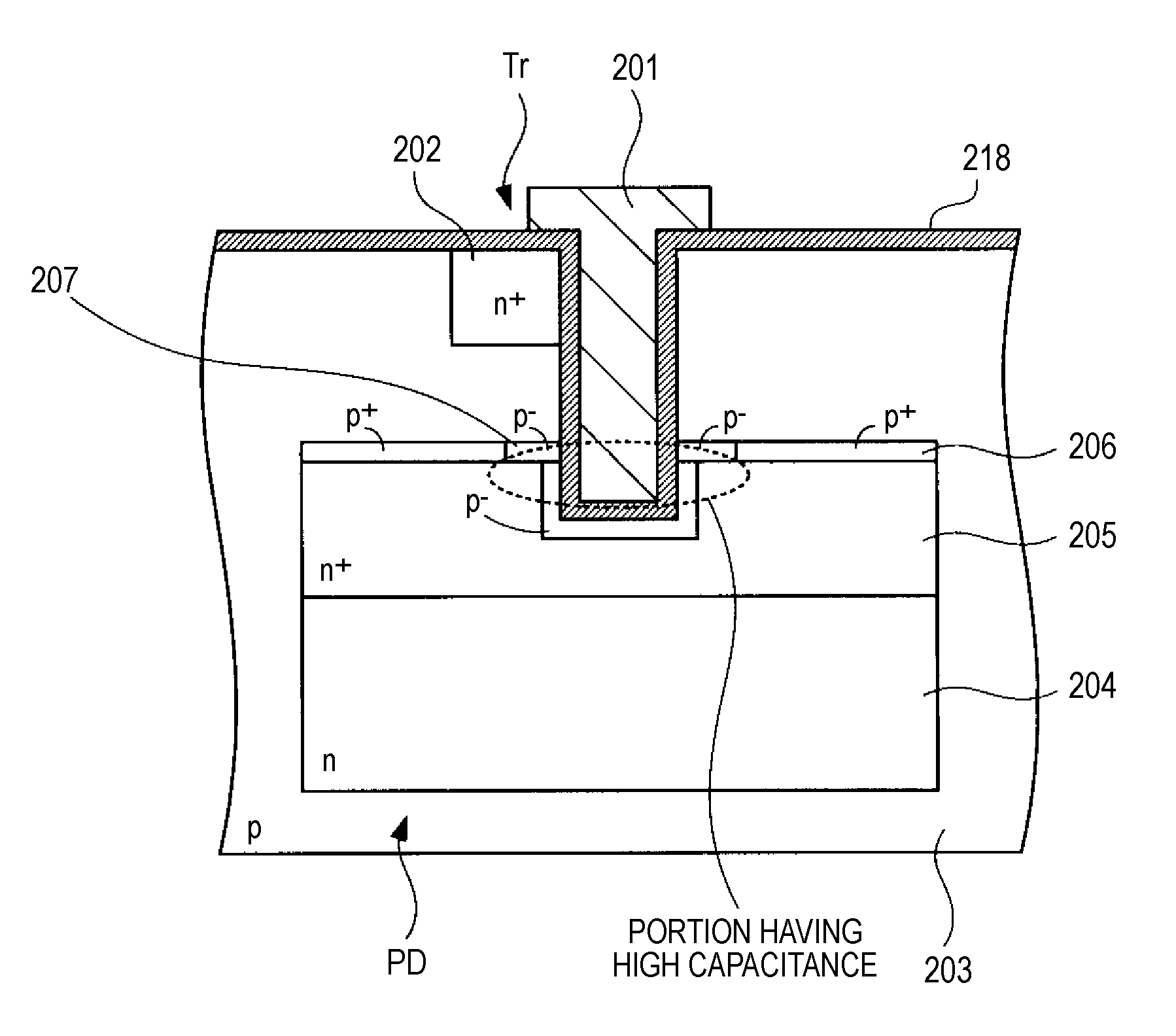
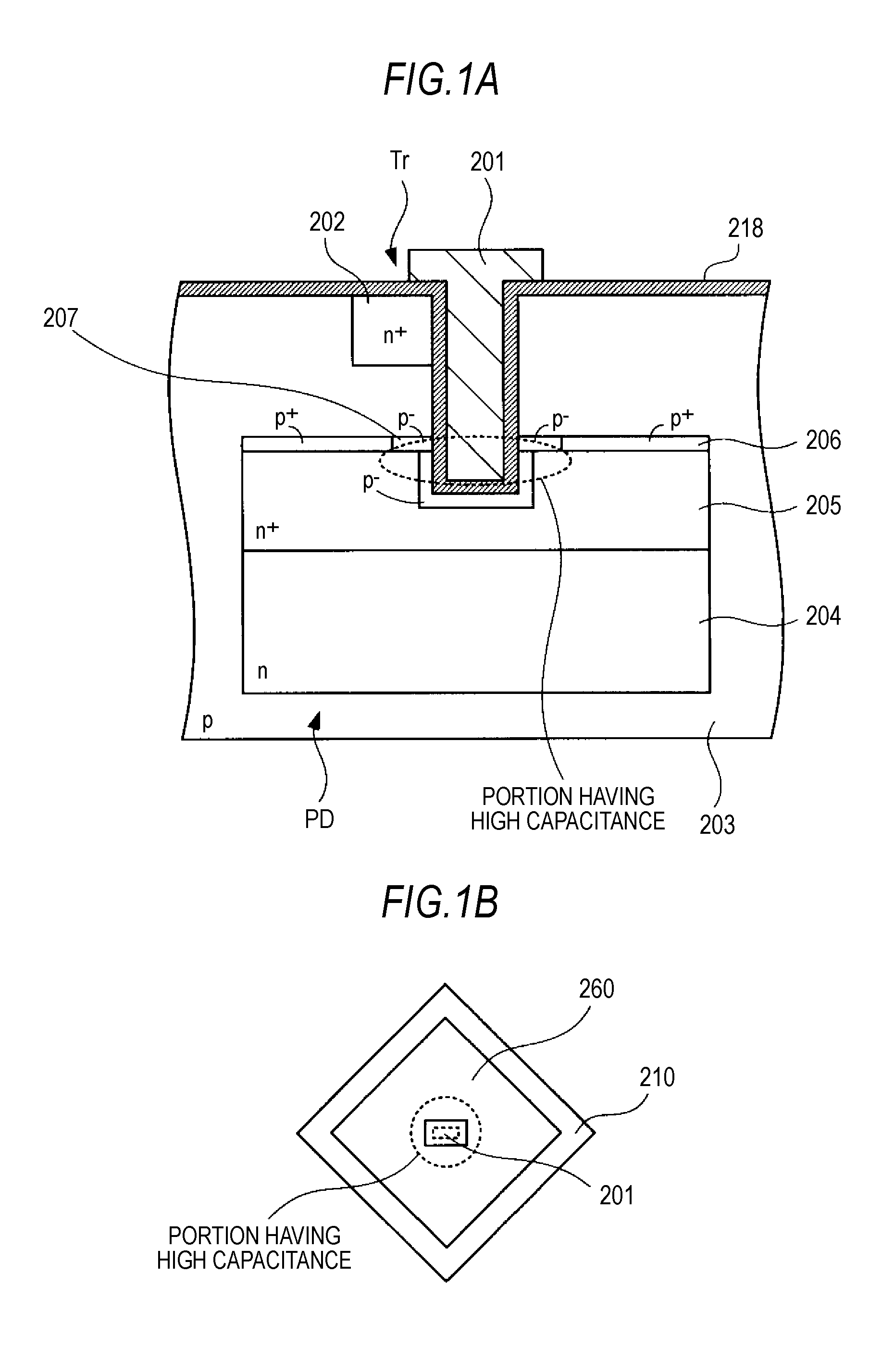
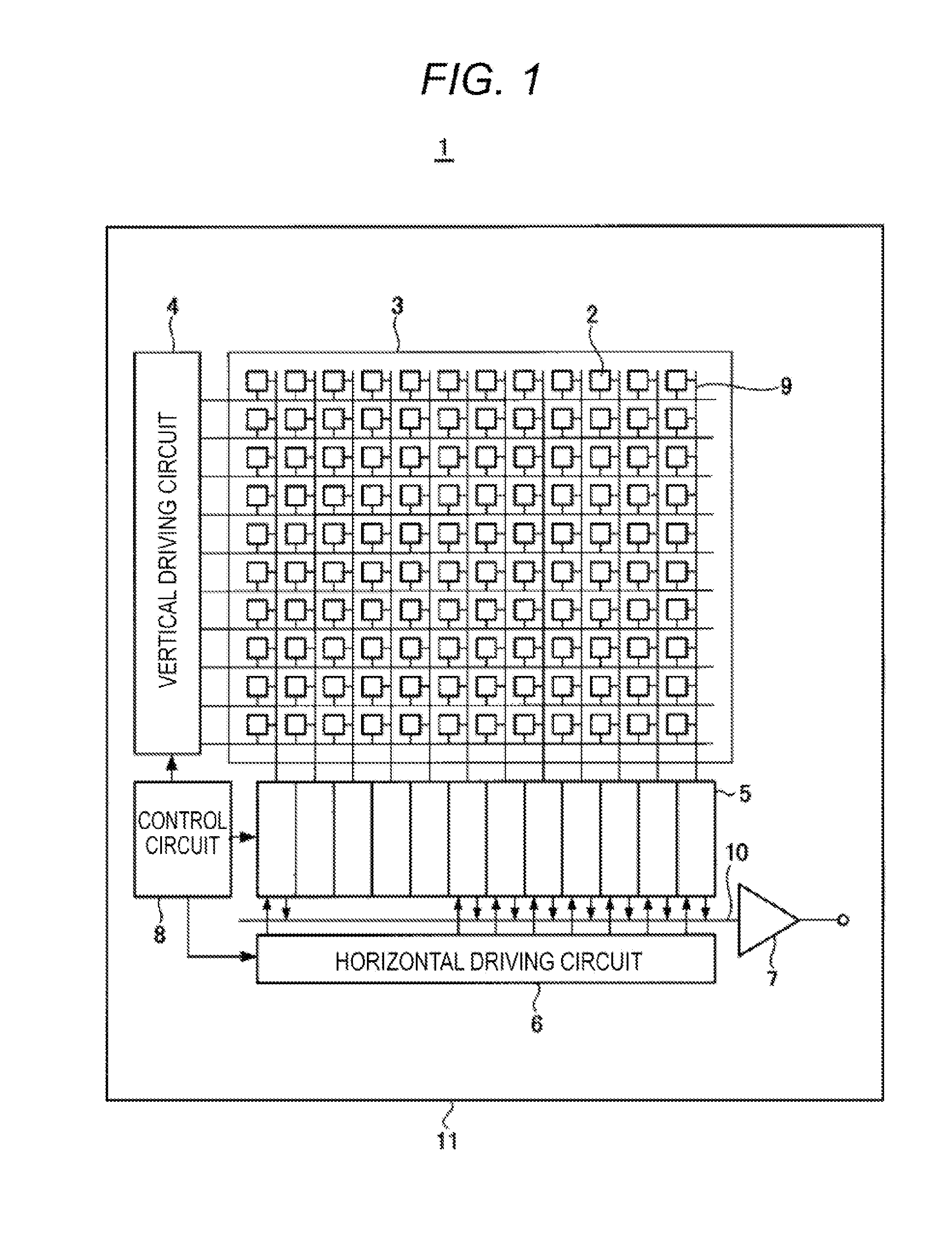
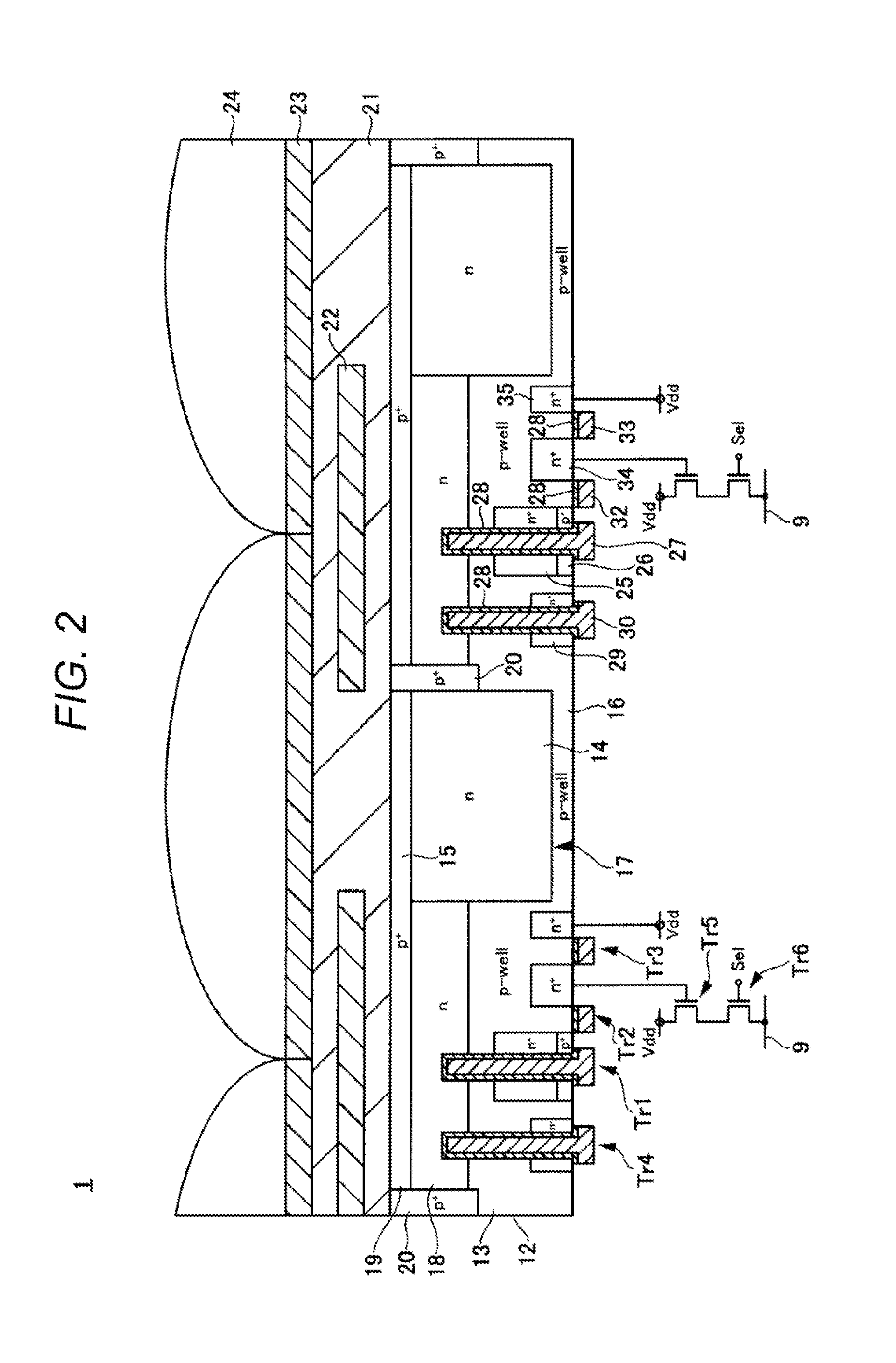
Solid-state imaging device, drive method thereof and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20090303371A1Improve charging capacityHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
A solid-state imaging device includes: plural photodiodes formed in different depths in a unit pixel area of a substrate; and plural vertical transistors formed in the depth direction from one face side of the substrate so that gate portions for reading signal charges obtained by photoelectric conversion in the plural photodiodes are formed in depths corresponding to the respective photodiodes.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
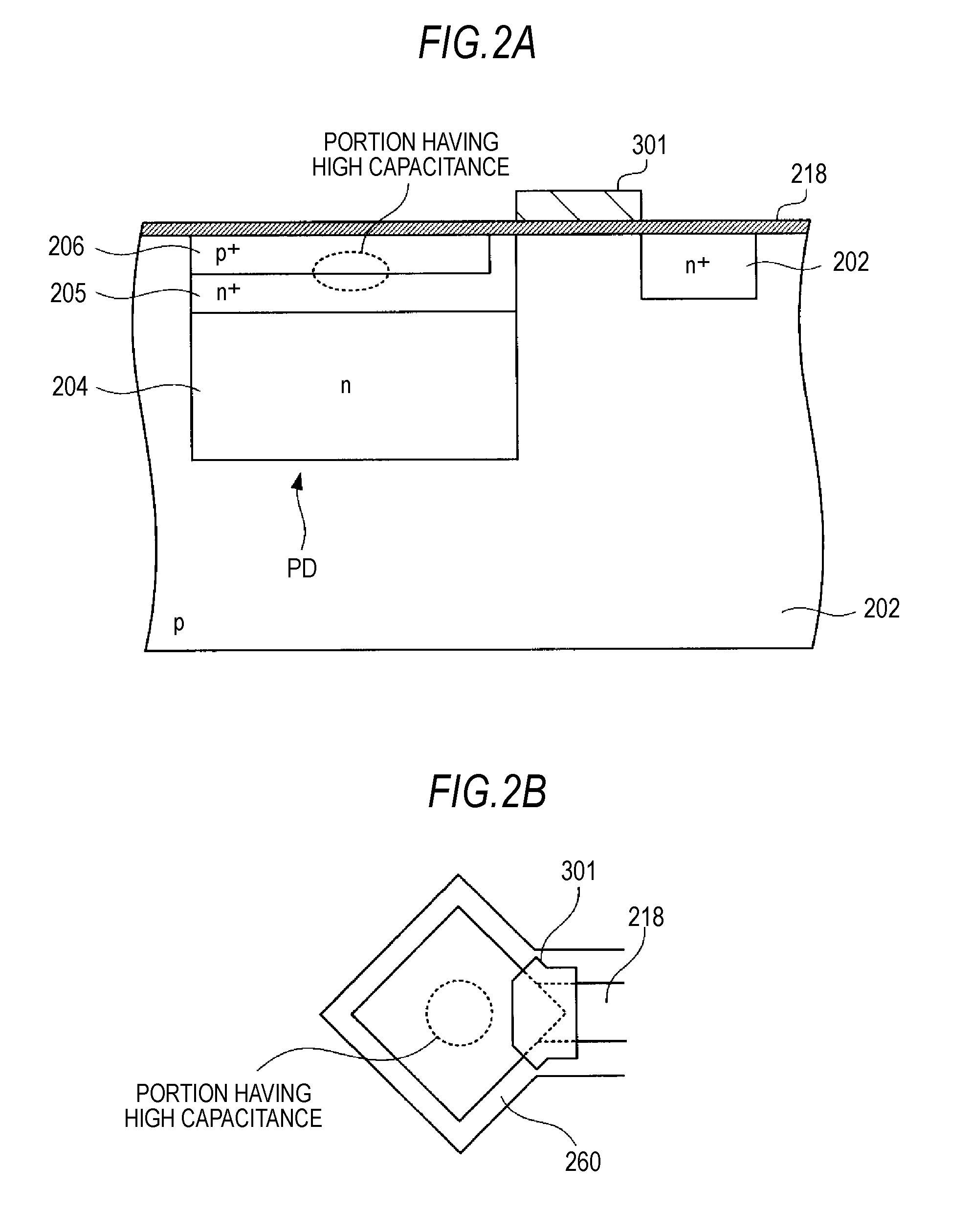
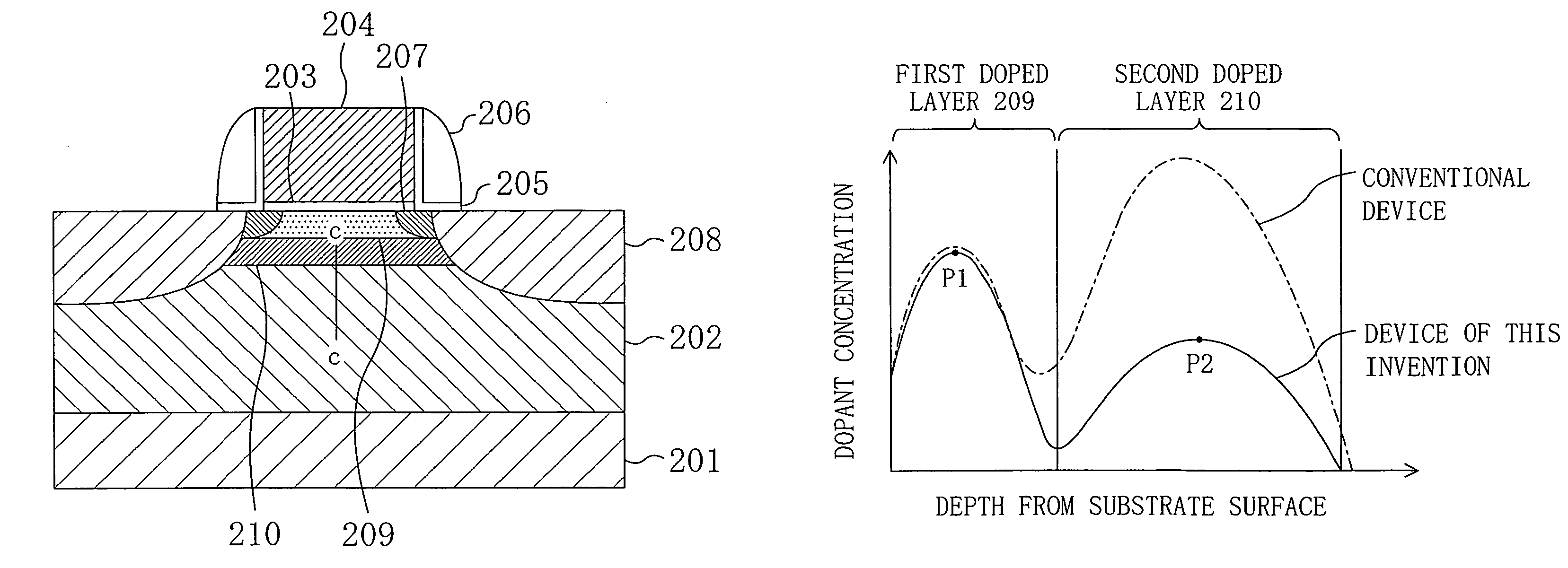
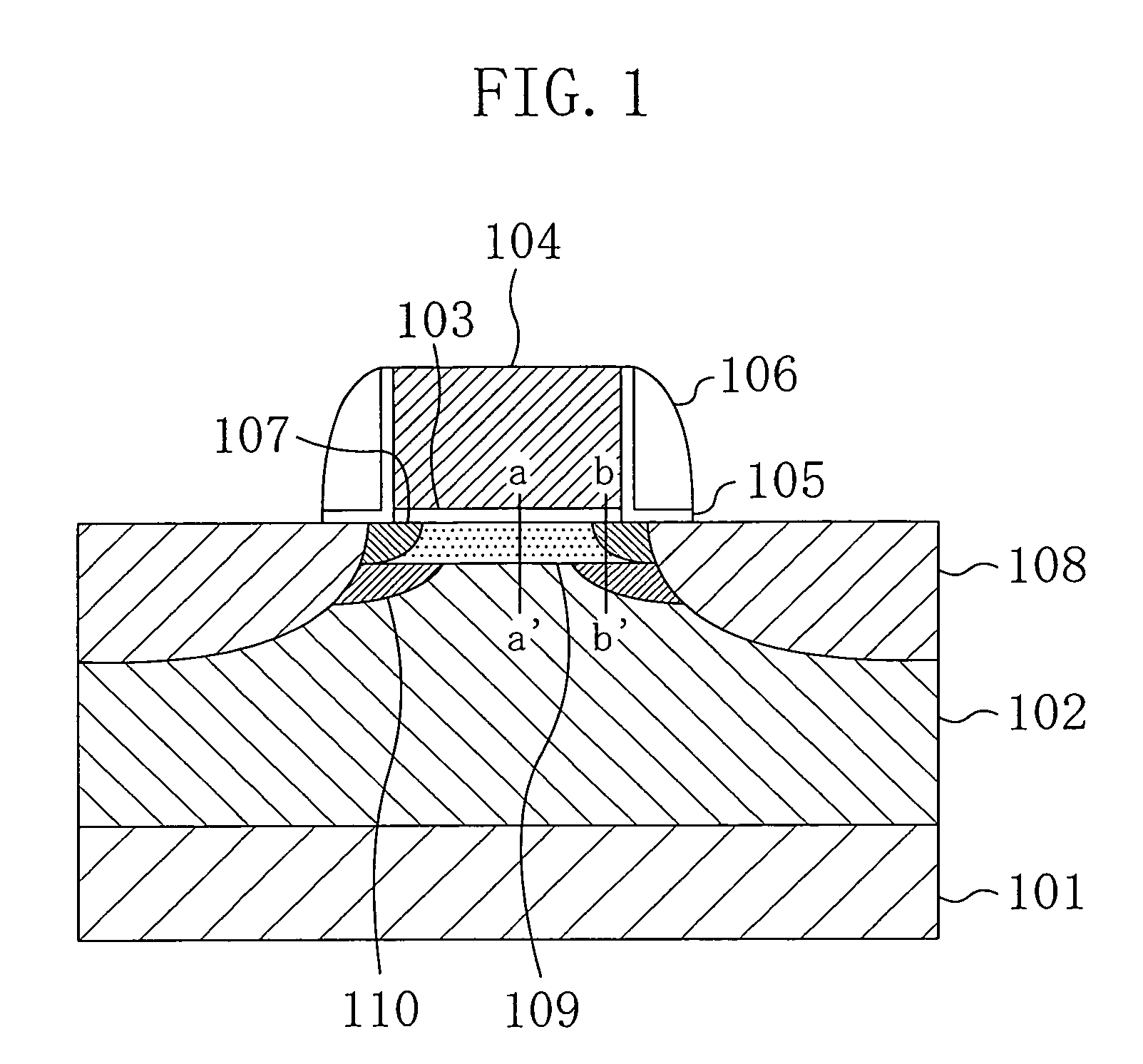
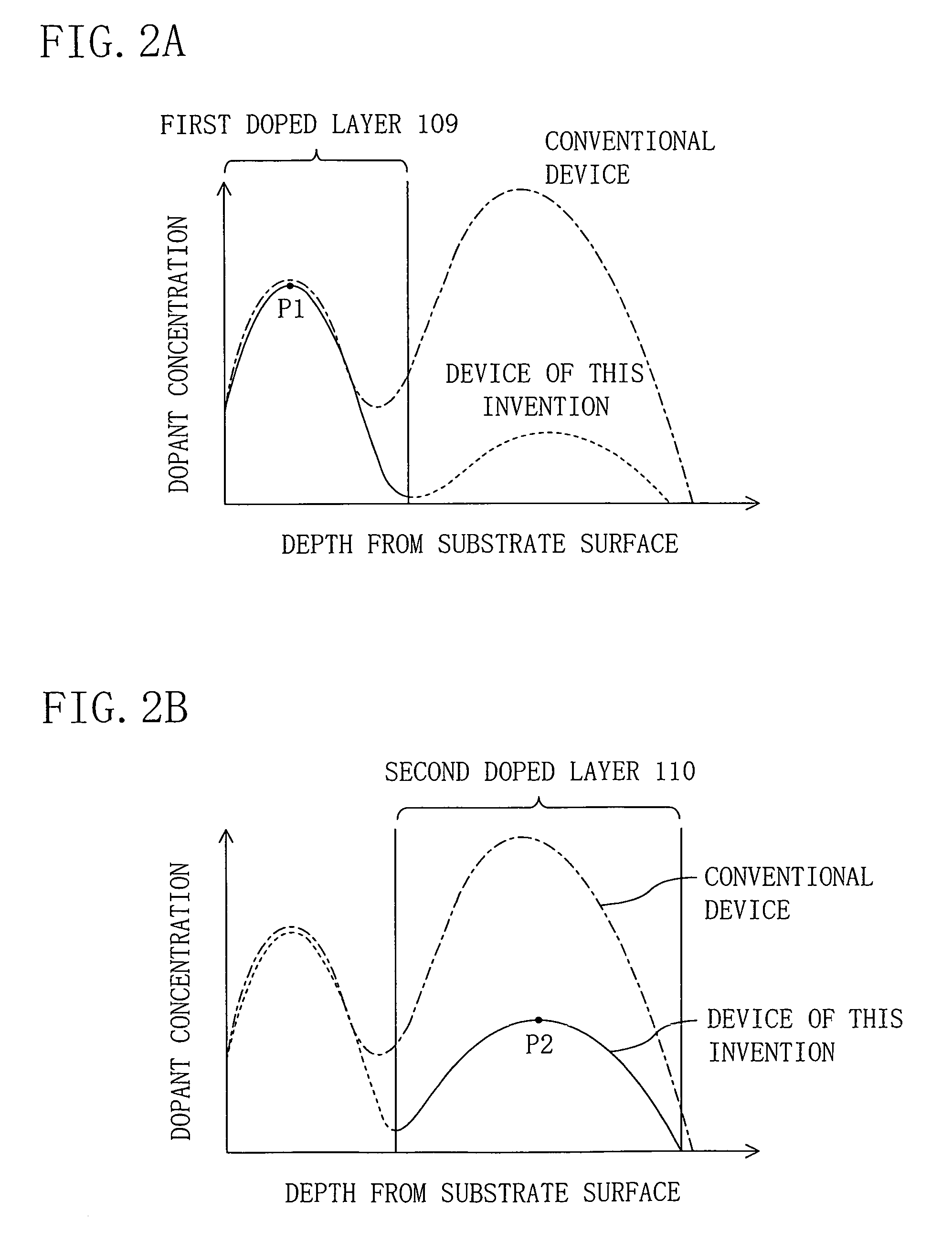
ActiveUS7301208B2Increase powerImprove leakage currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantPeak value
A first doped layer of a conductivity type opposite to that of source / drain regions is formed in a semiconductor substrate under a gate electrode. A second doped layer of the conductivity type opposite to that of the source / drain regions is formed in the semiconductor substrate below the first doped layer. The first doped layer has a first peak in dopant concentration distribution in the depth direction. The first peak is located at a position shallower than the junction depth of the source / drain regions. The second doped layer has a second peak in dopant concentration distribution in the depth direction. The second peak is located at a position deeper than the first peak and shallower than the junction depth of the source / drain regions. The dopant concentration at the first peak is higher than that at the second peak.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
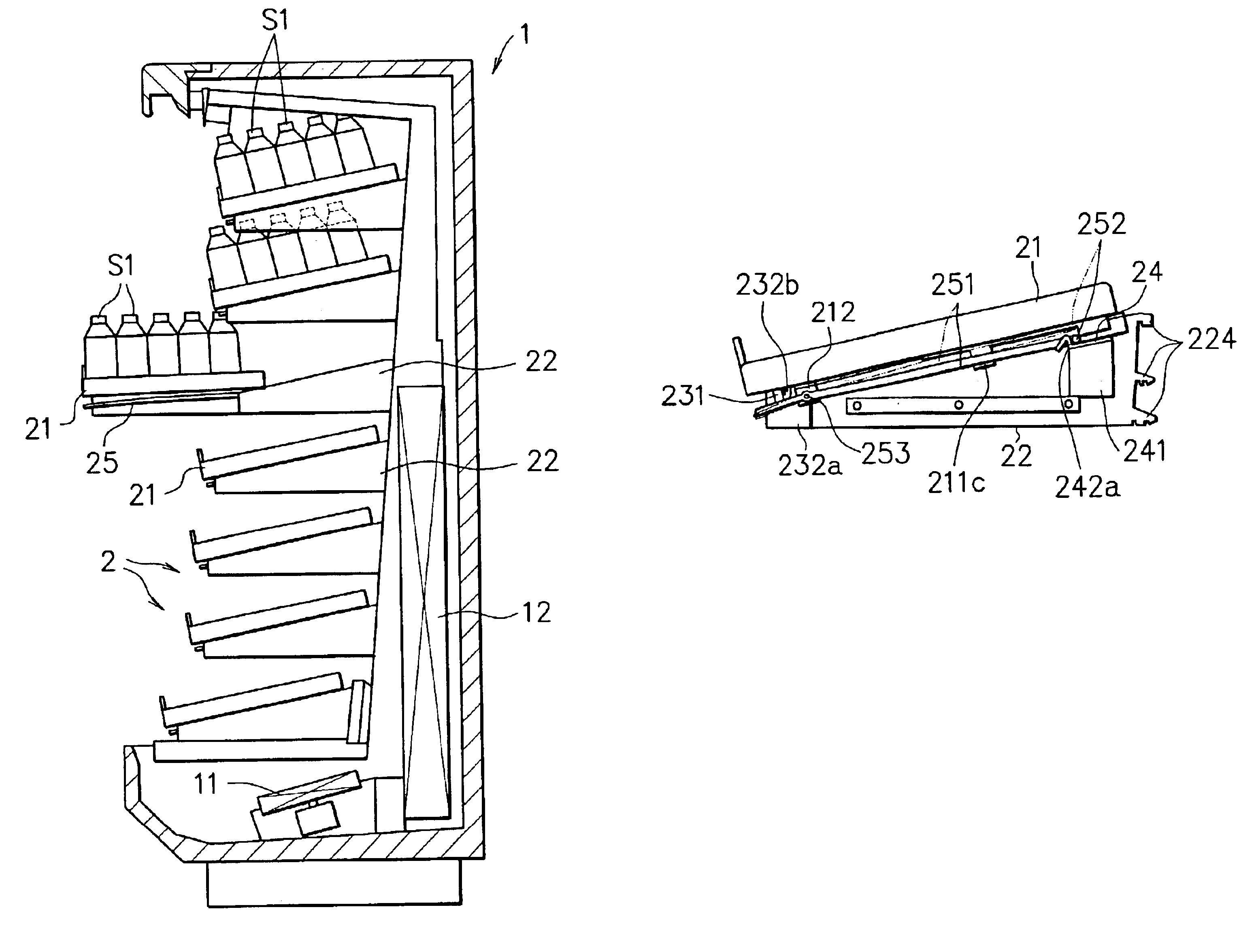
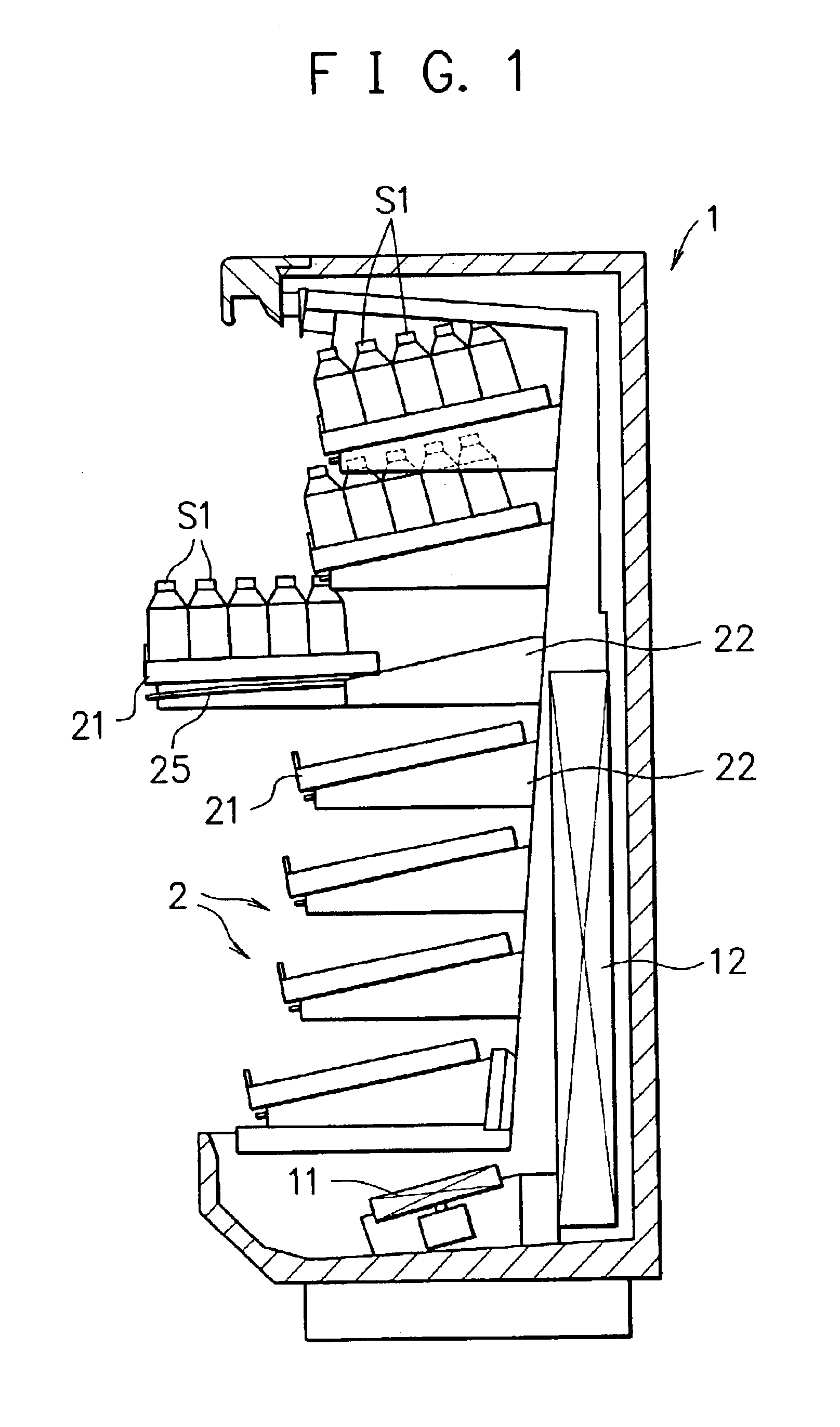
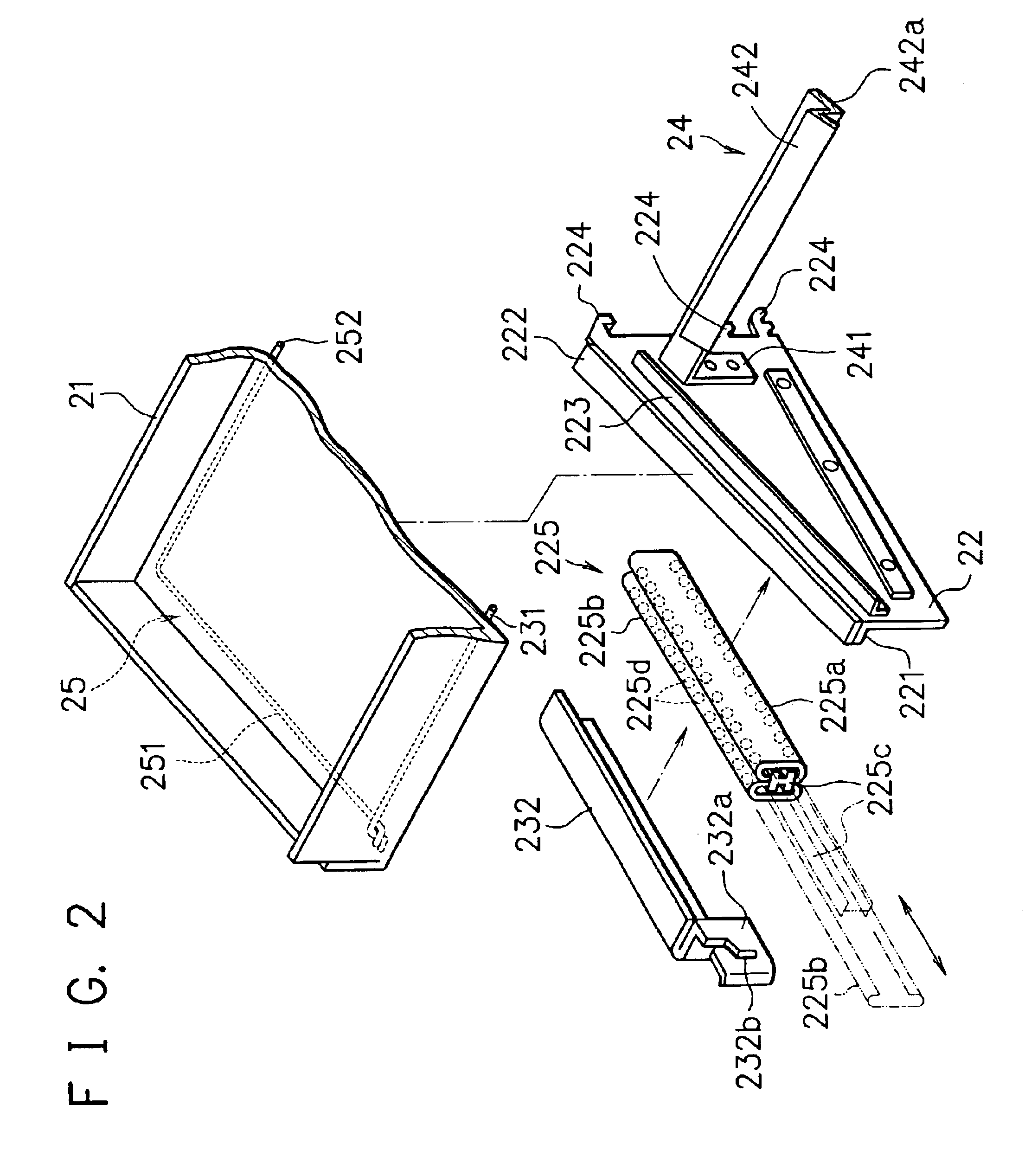
Shelf apparatus for showcase
In a shelf apparatus for a showcase, which is provided with a shelf support for supporting a shelf plate on which commodities are placed so as to be slidable in a depth direction, the shelf apparatus is constructed so that the shelf support is provided with a locking plate extending in a width direction of the shelf plate, and the shelf plate is provided with a hooking member which is formed with a steel rod member which extends in the depth direction and whose rear portion further extends along the locking plate on a back surface side of the shelf plate, and also which enables the rear portion to be locked to and unlocked from the locking plate by being swayed vertically. When the shelf plate is held on the shelf supports, the rear portion of the hooking member is locked to the locking plate. By doing this, the shelf plate does not slide forward. When the shelf plate is pulled out forward, the hooking member is unlocked from the locking plate by being swayed vertically. By doing this, the shelf plate can be pulled out forward.
Owner:SANDEN RETAIL SYST CORP
Laser processing apparatus and laser processing method
InactiveUS20070202619A1Reliable formingLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser processingOptoelectronics
A laser processing apparatus has one laser light source that simultaneously radiates laser beams with two wavelengths. Depth positions of focusing points for laser beams are gradually changed in a wafer. Three sets of modifying region groups, i.e., six layers of modifying region groups, are successively formed. One set of modifying region groups constitutes two layers and is formed at a time. The modifying region groups are separated, adjoined, or overlapped with each other along an estimated cut line of the wafer in a depth direction from a surface thereof.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Oxide semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same and active matrix substrate
InactiveUS20100140614A1High content ratioImprove contact effectTransistorSolid-state devicesActive matrixThreshold potential
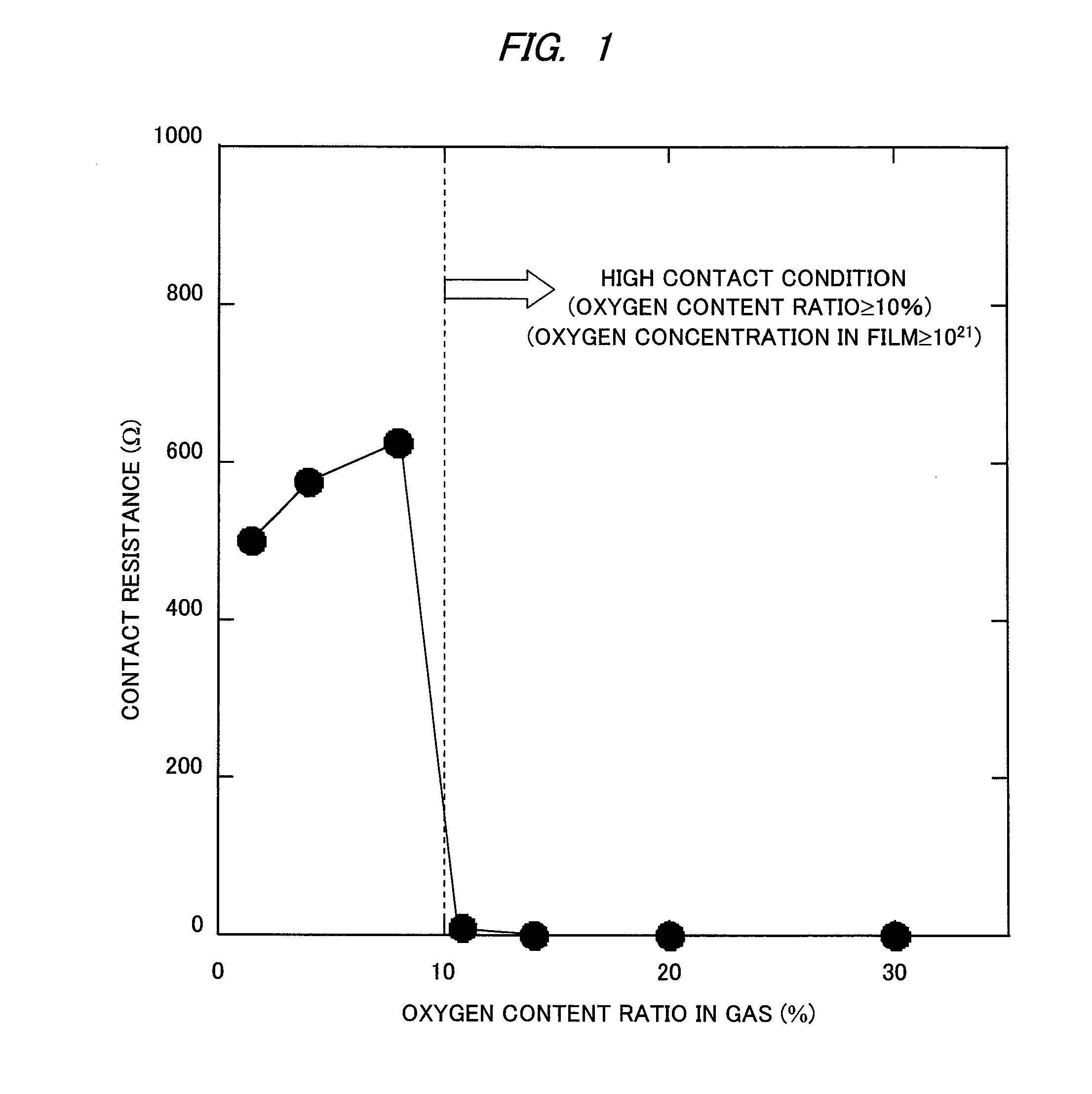
A phenomenon of change of a contact resistance between an oxide semiconductor and a metal depending on an oxygen content ratio in introduced gas upon depositing an oxide semiconductor film made of indium gallium zinc oxide, zinc tin oxide, or others in an oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor. A contact layer is formed with an oxygen content ratio of 10% or higher in a region from a surface, where the metal and the oxide semiconductor are contacted, down to at least 3 nm deep in depth direction, and a region to be a main channel layer is further formed with an oxygen content ratio of 10% or lower, so that a multilayered structure is formed, and both of ohmic characteristics to the electrode metal and reliability such as the suppression of threshold potential shift are achieved.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Disk array apparatus
InactiveUS7457112B2Improve cooling effectEasy to controlReducing temperature influence on carrierCarrier constructional parts dispositionDisk enclosureComputer module
A disk array apparatus including a rack-shaped basic frame, and a plurality of disk boxes that can be inserted into and pulled out of the basic frame depth-wise. Each disk box has: disk drive connectors for connecting a plurality of disk drives arranged in a matrix on a platter substrate, which is the bottom face of the disk box, roughly parallel to the depth direction of the basic frame; and a cooling module for cooling the disk drives. The disk box is a hermetically sealed structure.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6853089B2Low costHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialAdhesive
In the manufacture of a semiconductor device by adopting a block molding method wherein a semiconductor chip is fixed onto a wiring substrate through an adhesive, the occurrence of a defect caused by flowing-out of the adhesive is to be prevented. The semiconductor device according to the present invention comprises a wiring substrate, the wiring substrate having a main surface, an insulating film formed on the main surface, and electrodes formed on the main surface so as to be exposed from the insulating film, a semiconductor chip fixed through an adhesive onto the insulating film formed on the main surface of the wiring substrate, conductive wires for connecting the electrodes on the main surface of the wiring substrate and electrodes on the semiconductor chip with each other, and a seal member, i.e., a package, which covers the semiconductor chip, the main surface of the wiring substrate and the electrodes, wherein a groove is formed between the semiconductor chip and the electrodes and the seal member and the wiring substrate have side faces cut by dicing. A protruding portion of the adhesive (an insulating resin) stays within the groove without getting over the groove and does not reach the electrodes. The groove is formed by removing the insulating film partially in the full depth direction of the film so as to extend through the film.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
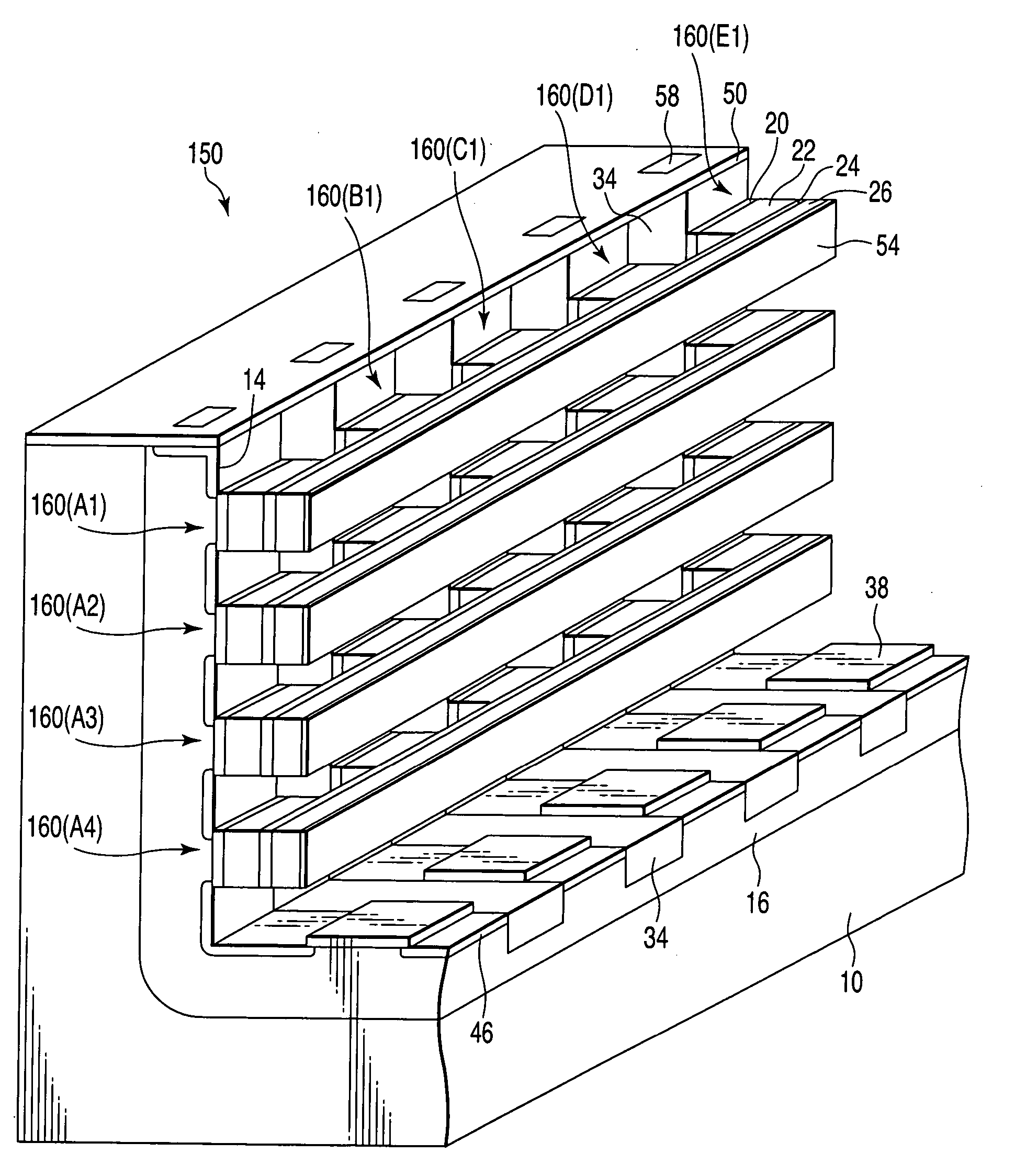
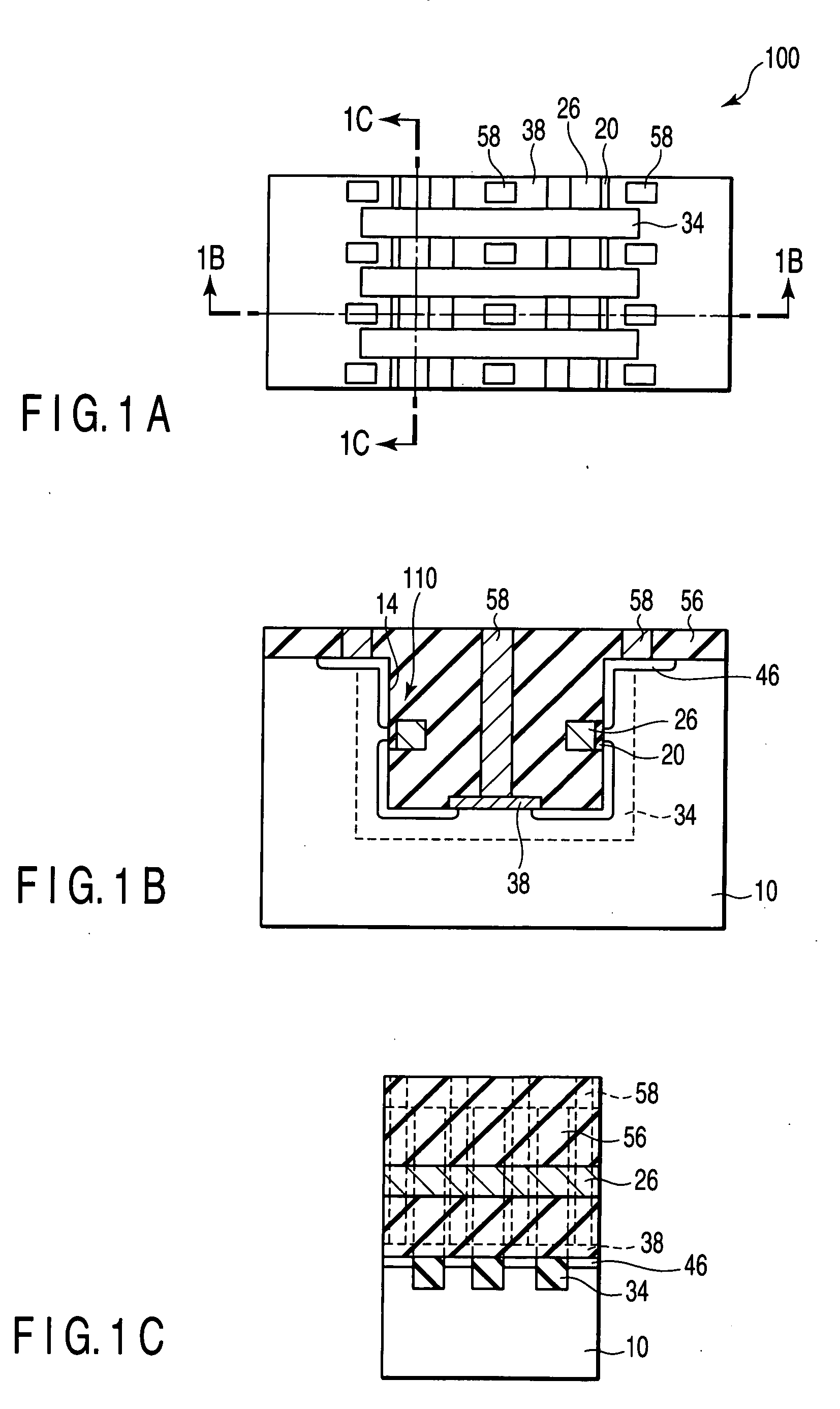
Solid-state imaging device, driving method for solid-state imaging device, and electronic appliance
ActiveUS20140347538A1Improve image qualityImprove charging capacityTransistorTelevision system detailsMiniaturizationEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a solid-state imaging device, a driving method for the same, and an electronic appliance, and an object is to provide a solid-state imaging device that can achieve the pixel miniaturization and the global shutter function with higher sensitivity and saturated charge amount. Another object is to provide an electronic appliance including the solid-state imaging device. In a solid-state imaging device 1 having the global shutter function, a first charge accumulation unit 18 and a second charge accumulation unit 25 are stacked in the depth direction of a substrate 12, and the transfer of the signal charges from the first charge accumulation unit 12 to the second charge accumulation unit 25 is conducted by a vertical first transfer transistor Tr1. Thus, the pixel miniaturization can be achieved.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060091556A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A semiconductor device with a new three-dimensional structure comprises a semiconductor substrate including a trench vertically formed to a surface of the semiconductor substrate, a plurality of isolations formed in side and bottom surfaces of the trench in a depth direction of the trench, a plurality of functional elements formed on the side surfaces of the trench separated be the isolation and including an insulator, an electrode formed on the insulator and a pair of source / drain formed in the both sides of the electrode in the depth direction, and a wiring connected to the electrodes located in both sides of the isolation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Apparatus and method for interferometric measurement of a sample
ActiveUS7982881B2Quick measurementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryLight beamWavelength
A device for the interferometric measurement of a sample, in particular the eye, including an interferometer arrangement with a first measurement beam path, through which a measurement beam falls onto the sample, and a first reference beam path, through which a reference beam runs, which is applied to the measuring beam for interference. The interferometer arrangement includes a second measuring beam path and / or second reference beam path. The optical path lengths of the second measuring beam path and / or second reference beam path are different from one of the first beam paths. The wave length difference is selected according to a distance of two measuring areas which are arranged at a distance in the depth direction of the sample.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Apparatus with thumbnail display
ActiveUS7716604B2Select the thumbnail of the desired content easily and without failTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLeft directionThumbnail
In a thumbnail screen, categories and category thumbnails are disposed and displayed in the depth (Z-axis) direction and in the horizontal (X axis) direction, respectively. When focus is given by a focus to any of upper and lower category thumbnails, which are displayed on the most front side, and a category name display part, the row (layers) of the thumbnails scrolls in the horizontal direction. When the right and left direction keys of a remote controller are operated while the category name display has focus, the scroll in the depth direction is performed, thus enabling the specification of a desired category. This three-dimensionally displays the thumbnails and facilitates the operation for viewing information.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
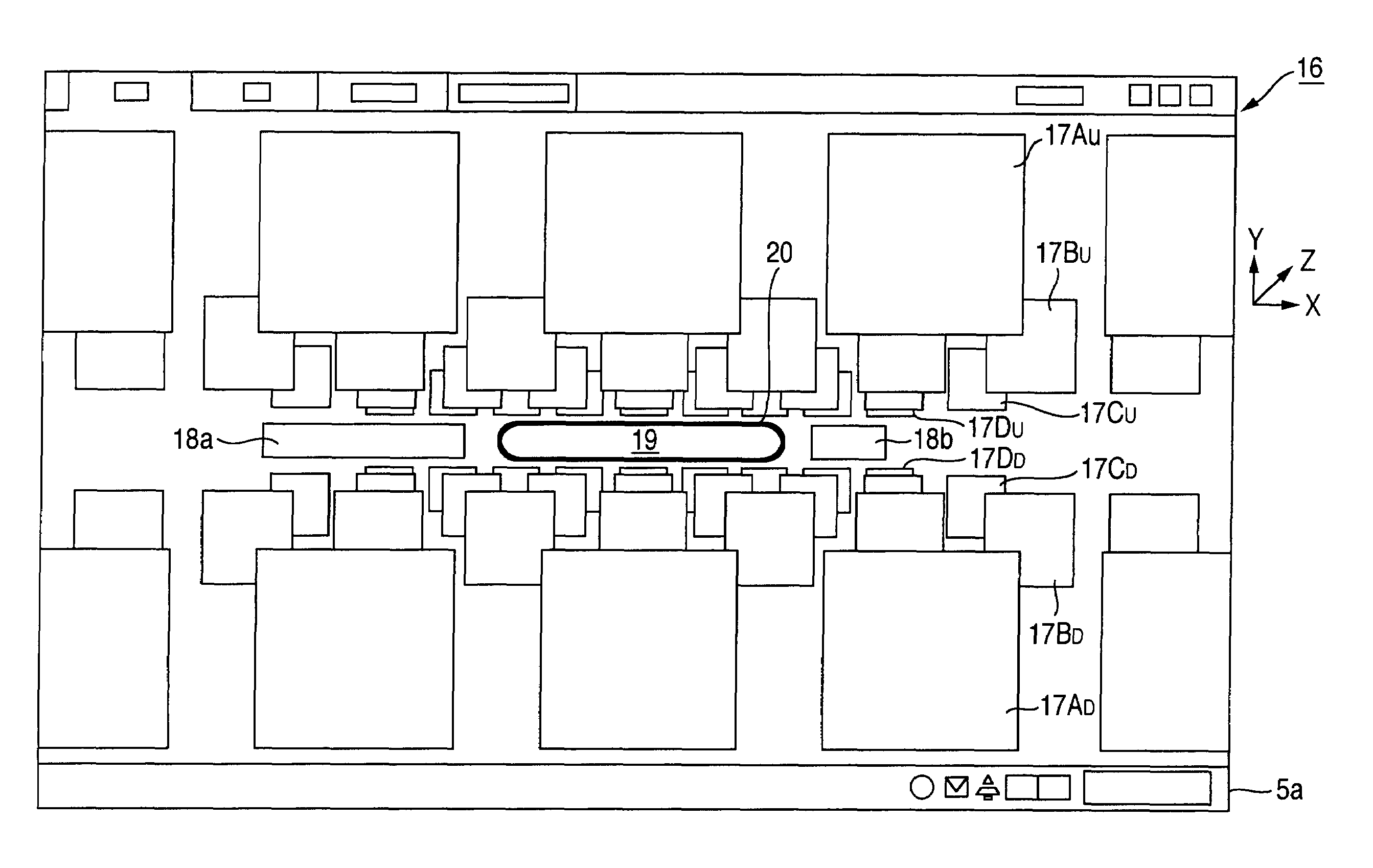
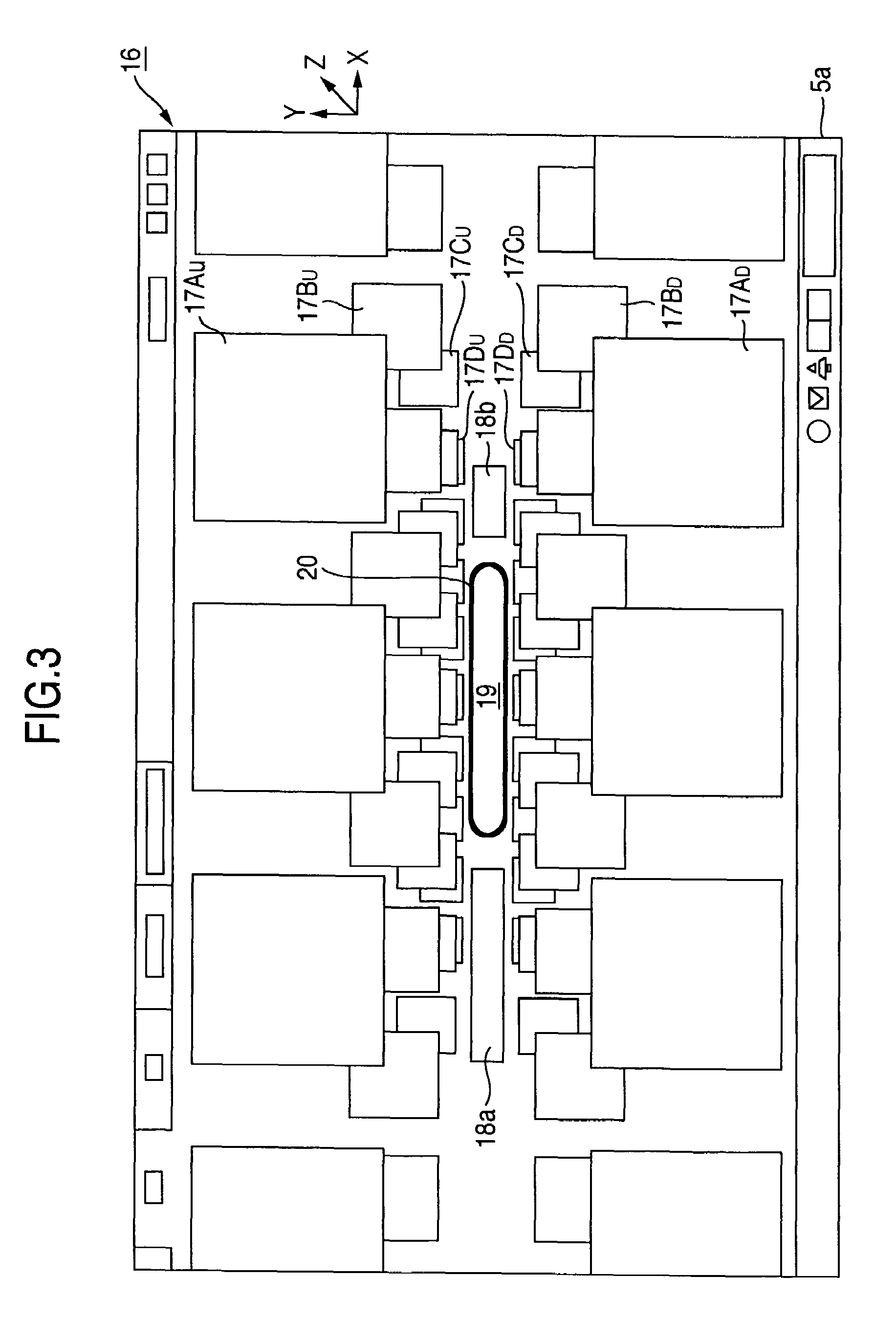
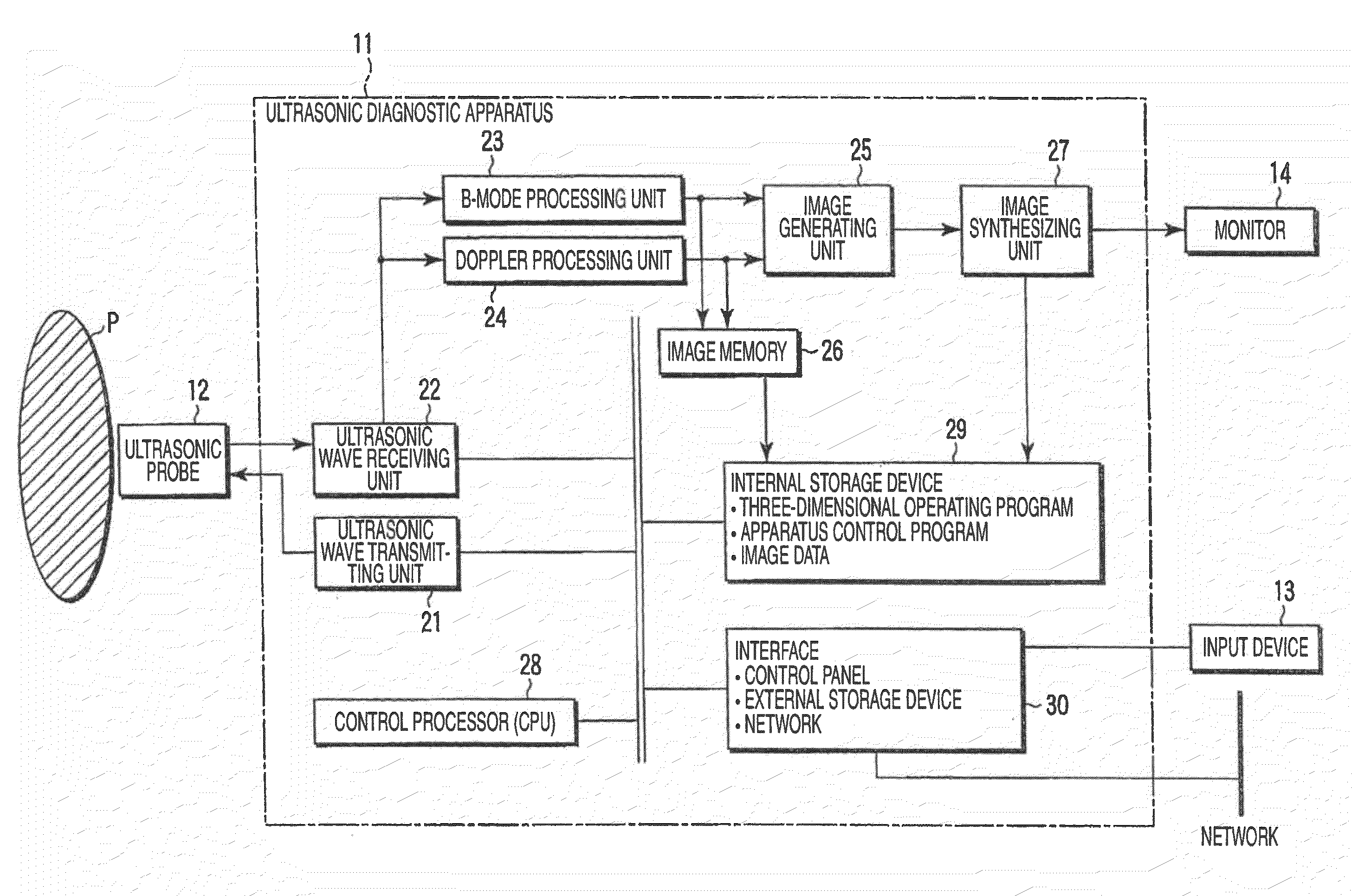
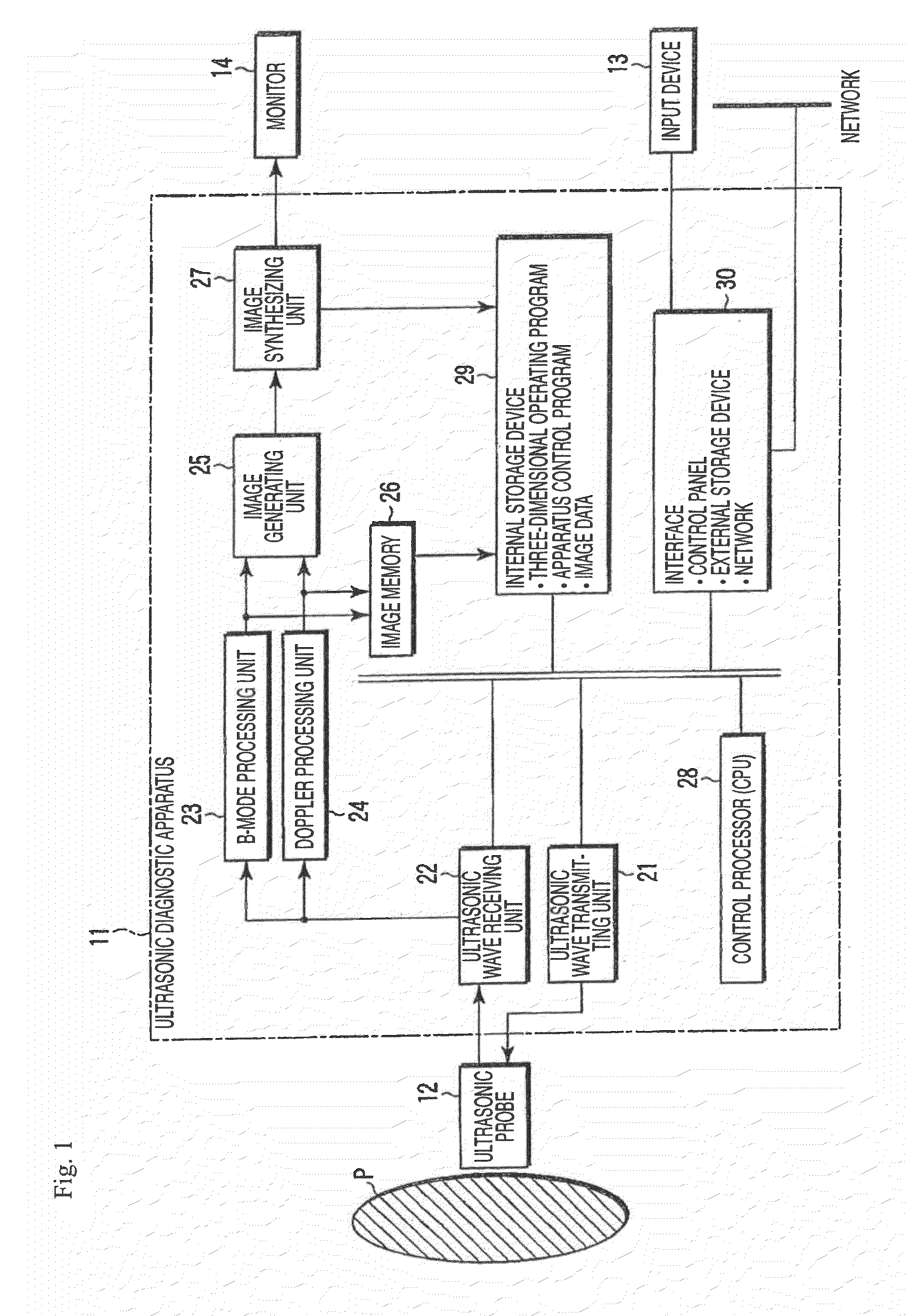
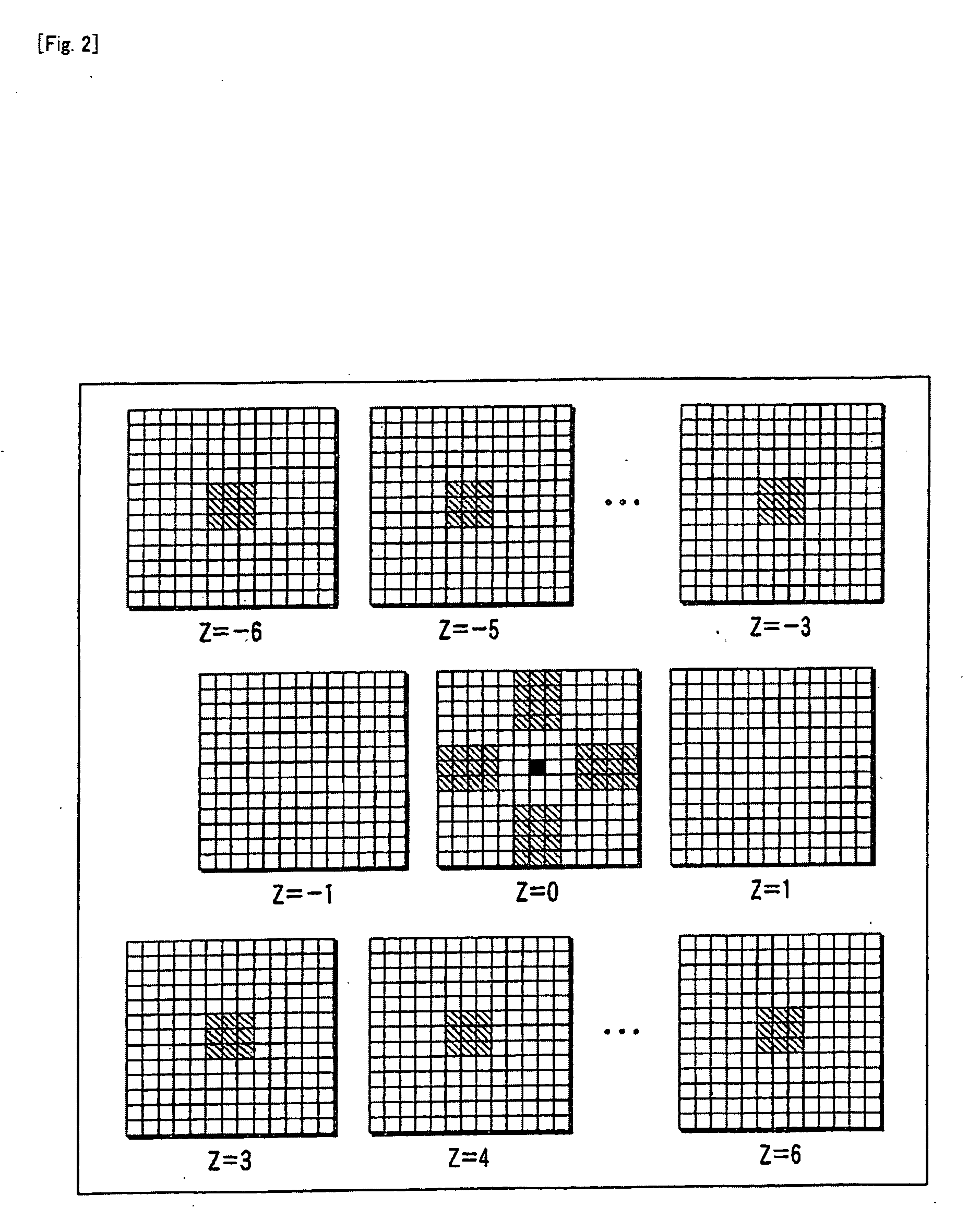
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20080319317A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognition3d imageSpeckle pattern
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
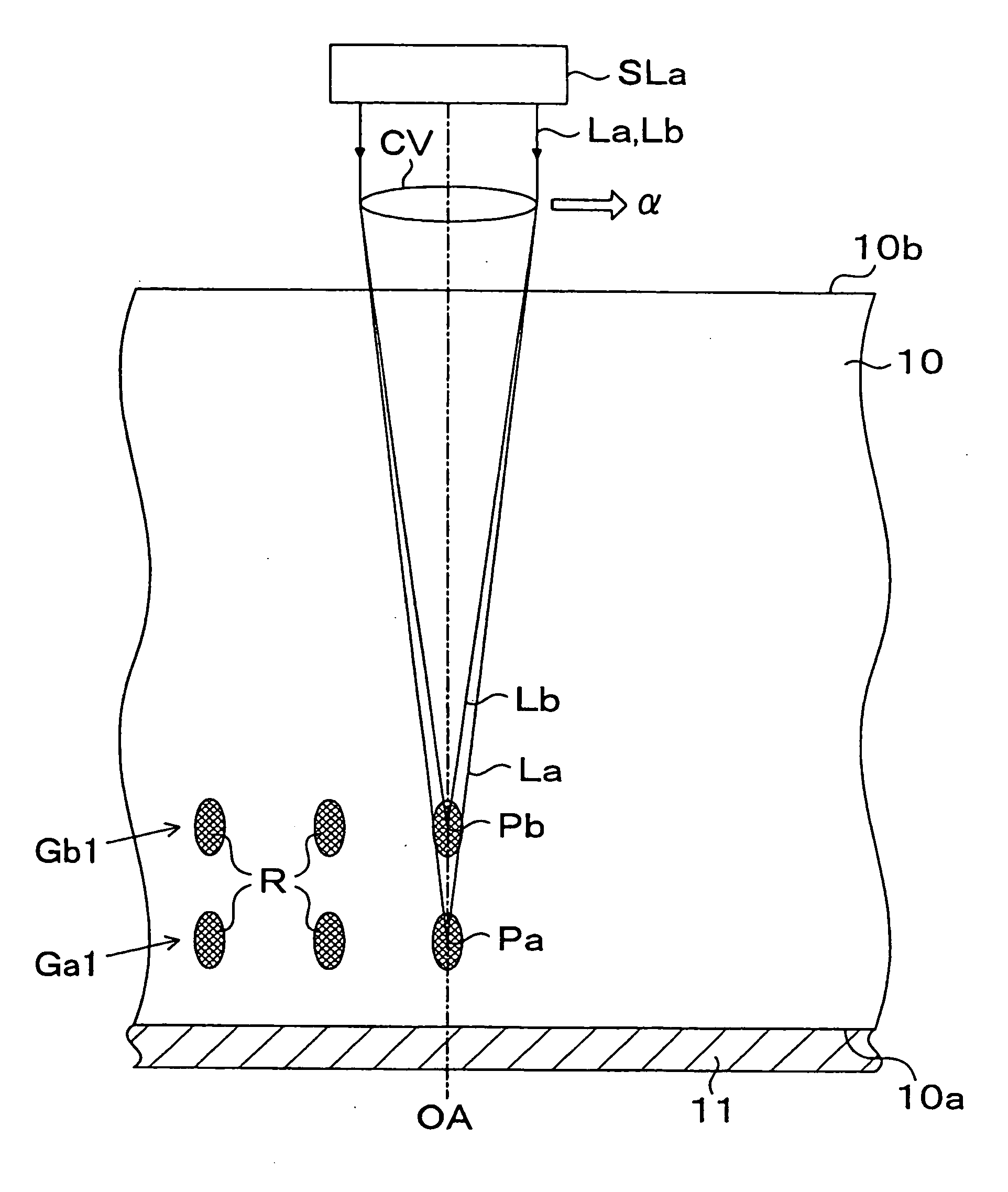
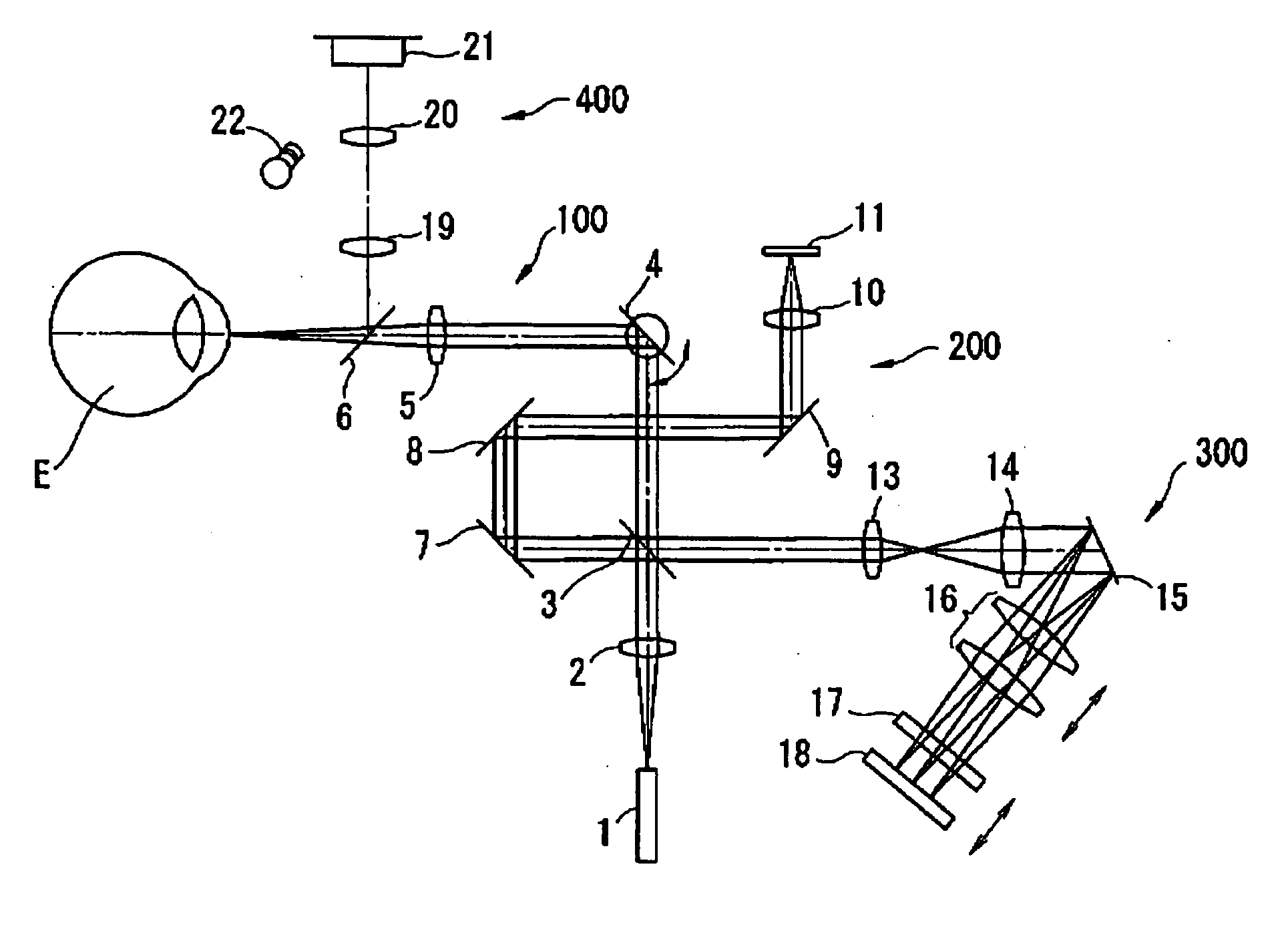
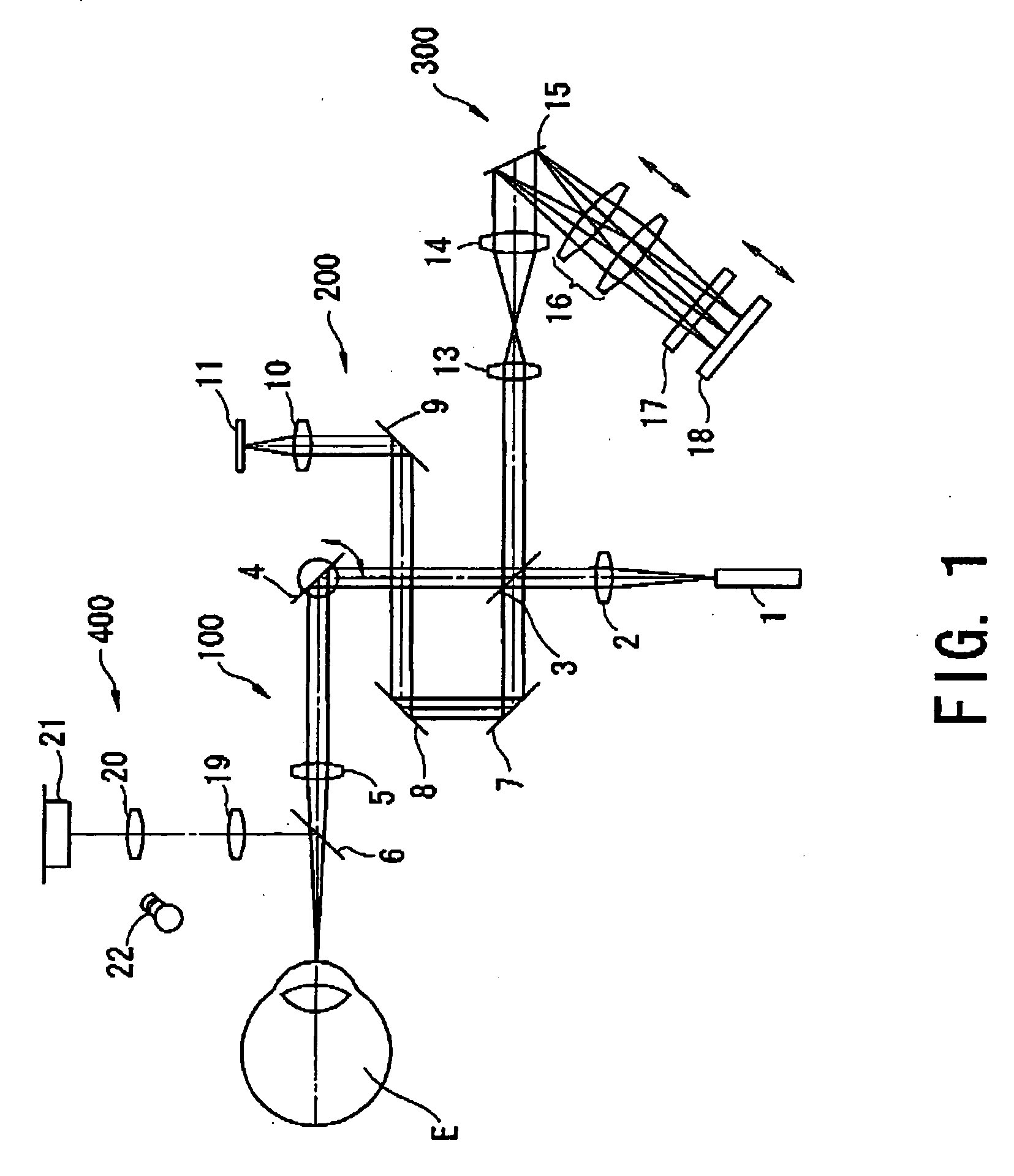
Optical coherence tomography apparatus based on spectral interference and an ophthalmic apparatus
InactiveUS20060066869A1Information acquisition range in a depth direction can be enlargedEye diagnosticsUsing optical meansOphthalmological devicePhotovoltaic detectors
An optical coherence tomography apparatus based on spectral interference where object information can be speedily obtained and an information acquisition range in a depth direction can be enlarged, and an ophthalmic apparatus. The apparatus includes a first optical system for projecting light with short coherence length onto an object to form object light which is reflection light from the object, a second optical system for projecting light with short coherence length onto a reference surface to form reference light which is reflection light from the surface, an optical system for synthesizing the object light and the reference light to be interference light, dispersing the interference light into predetermined frequency components and photo-receiving the dispersed light with a photodetector, a device varying a spectral characteristic when the interference light is dispersed by the interference / dispersion / photo-receiving optical system, and a calculation part obtaining the information based on an output signal from the photodetector.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Mesa-type bipolar transistor
InactiveUS20070241427A1Good repeatabilityImprove controllabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densityPower switching
In conventional mesa-type npn bipolar transistors, the improvement of a current gain and the miniaturization of the transistor have been unachievable simultaneously as a result of a trade-off being present between lateral diffusion and recombination of the electrons which have been injected from an emitter layer into a base layer, and a high-density base contact region—emitter mesa distance. In contrast to the above, the present invention is provided as follows:The gradient of acceptor density in the depth direction of a base layer is greater at the edge of an emitter layer than at the edge of a collector layer. Also, the distance between a first mesa structure including the emitter layer and the base layer, and a second mesa structure including the base layer and the collector layer, is controlled to range from 3 μm to 9 μm. In addition, in order for the above to be implemented with high controllability, the base layer is formed of a first p-type base layer having an acceptor of uniform density, and a second p-type base layer whose density is greater than the uniform acceptor density of the first base layer while having a gradient in the depth direction of the second base layer. These features produce the advantageous effect that it is possible to provide a high-temperature adaptable, power-switching bipolar transistor that ensures a current gain high enough for practical use and is suitable for miniaturization.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
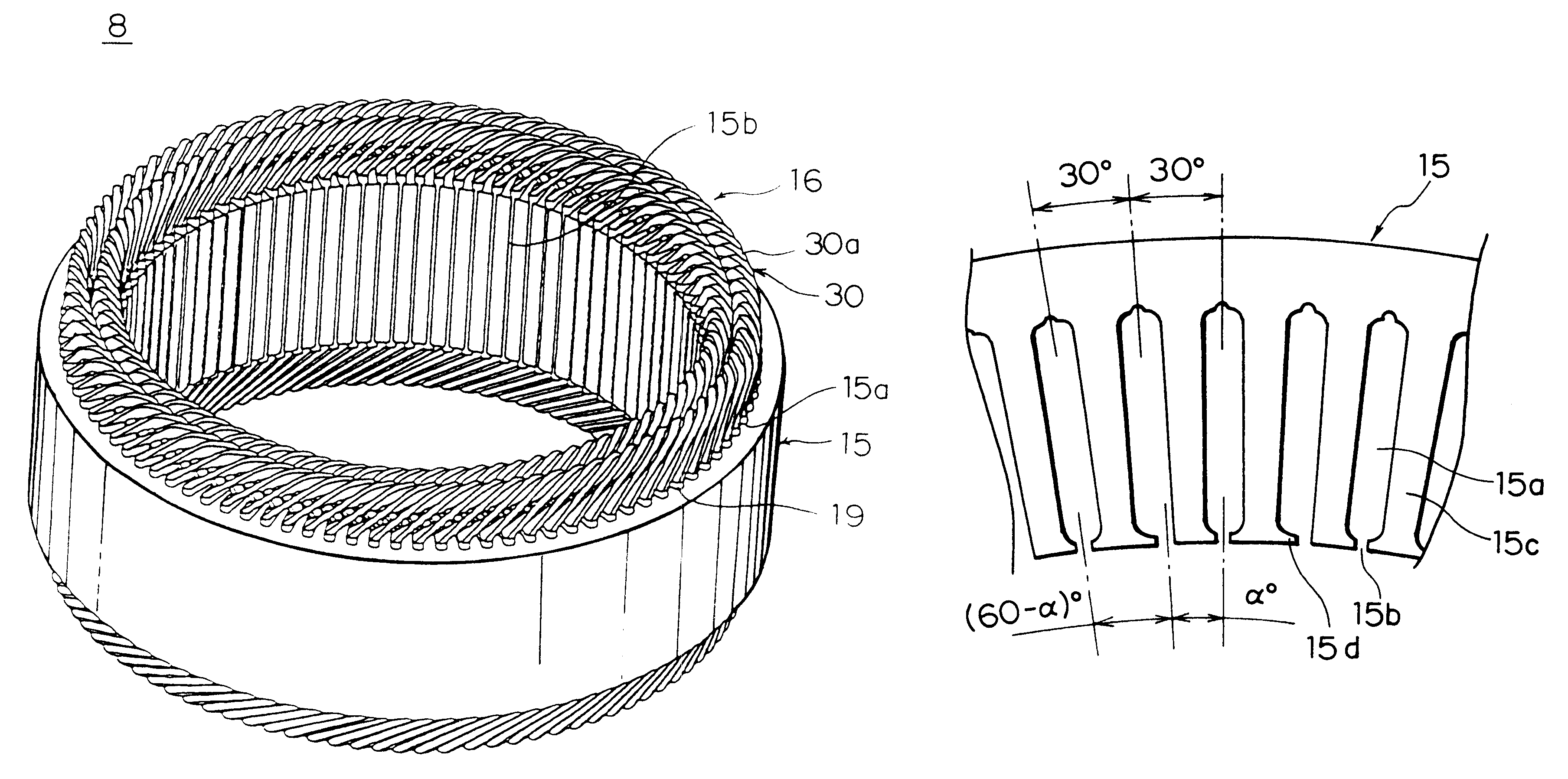
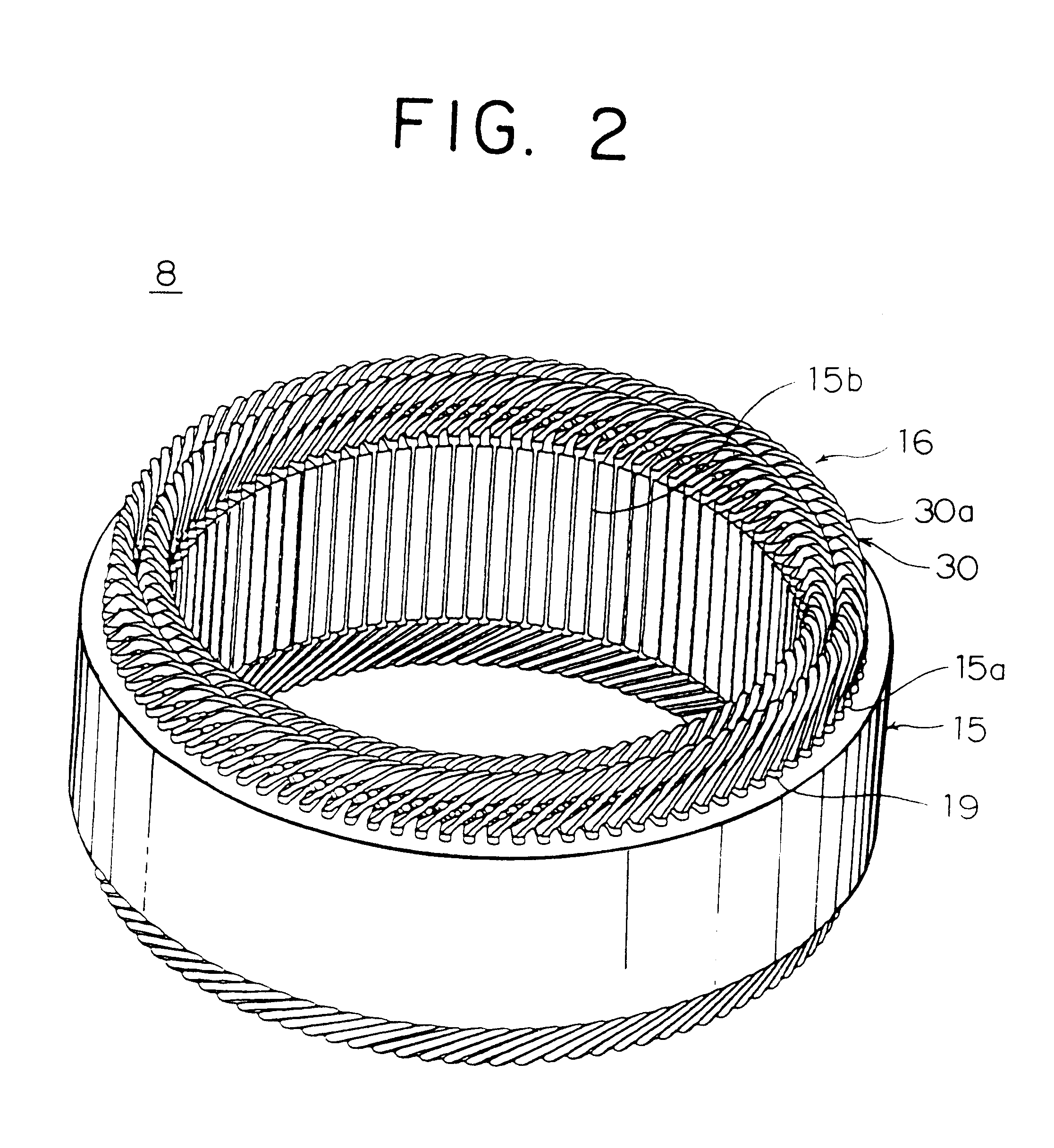
Alternator
InactiveUS6504283B1Reduce noise levelComponent with highSynchronous generatorsAsynchronous induction motorsAlternatorStator coil
An alternator includes a stator having an annular stator core provided with a number of slots extending axially disposed in lines circumferentially so as to open on an inner circumferential side and a stator coil wound into the stator core so as to be installed in the slots, a rotor having a number of claw-shaped magnetic poles for alternately forming north-seeking (N) and south-seeking (S) poles about a rotational circumference, the rotor being rotatably disposed on the inner circumferential side of the stator core, a bracket supporting the rotor and the stator, and a rectifier disposed at a first axial end of the stator and connected to end portions of the stator coil, the rectifier converting alternating current from the stator coil into direct current, wherein a number of slots is two per phase per pole, and the stator coil comprises a number of winding sub-portions in each of which a long strand of wire is wound so as to alternately occupy an inner layer and an outer layer in a slot depth direction within the slots at intervals of a predetermined number of slots by folding back the strand of wire outside the slots at axial end surfaces of the stator core.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
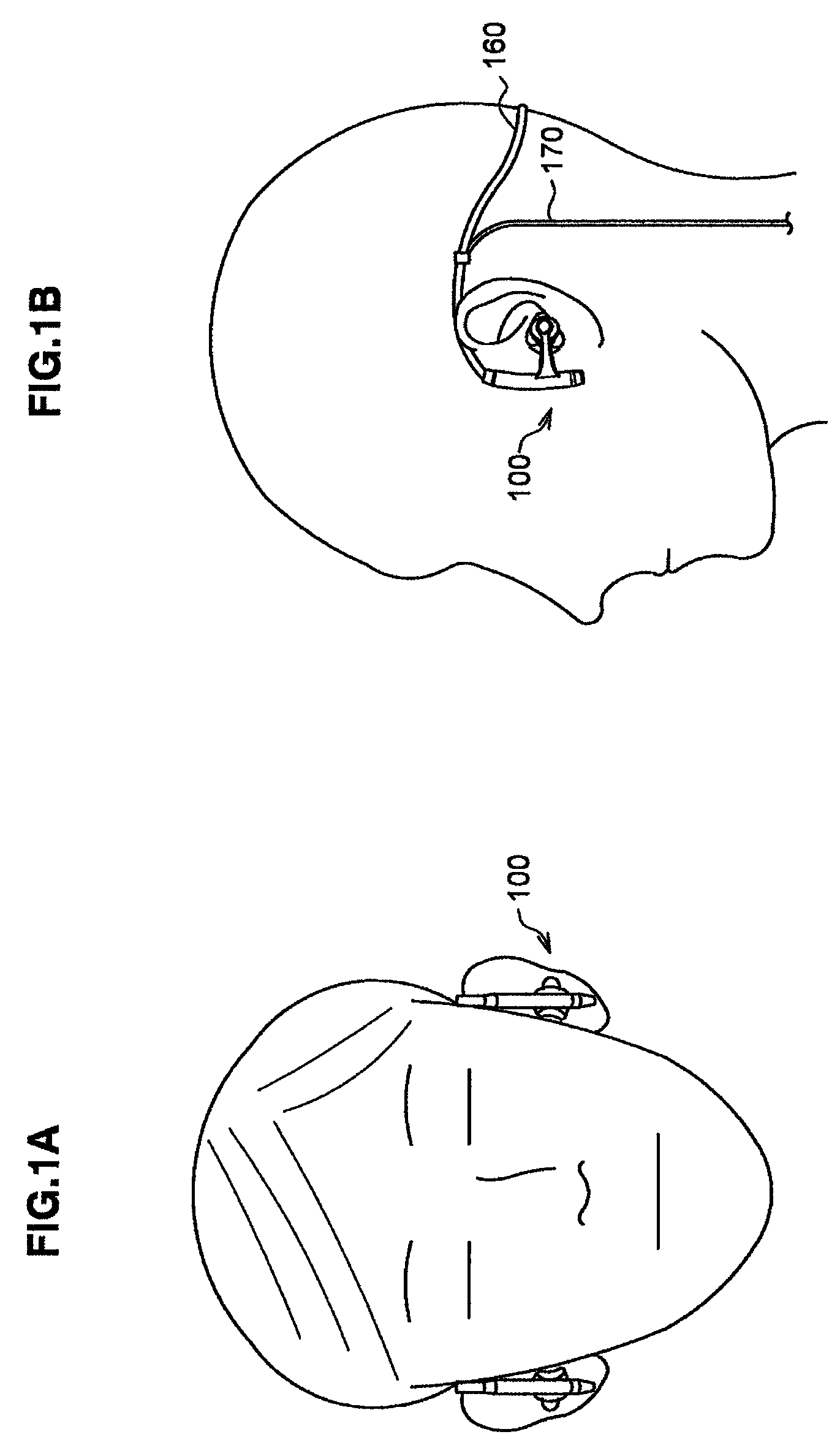
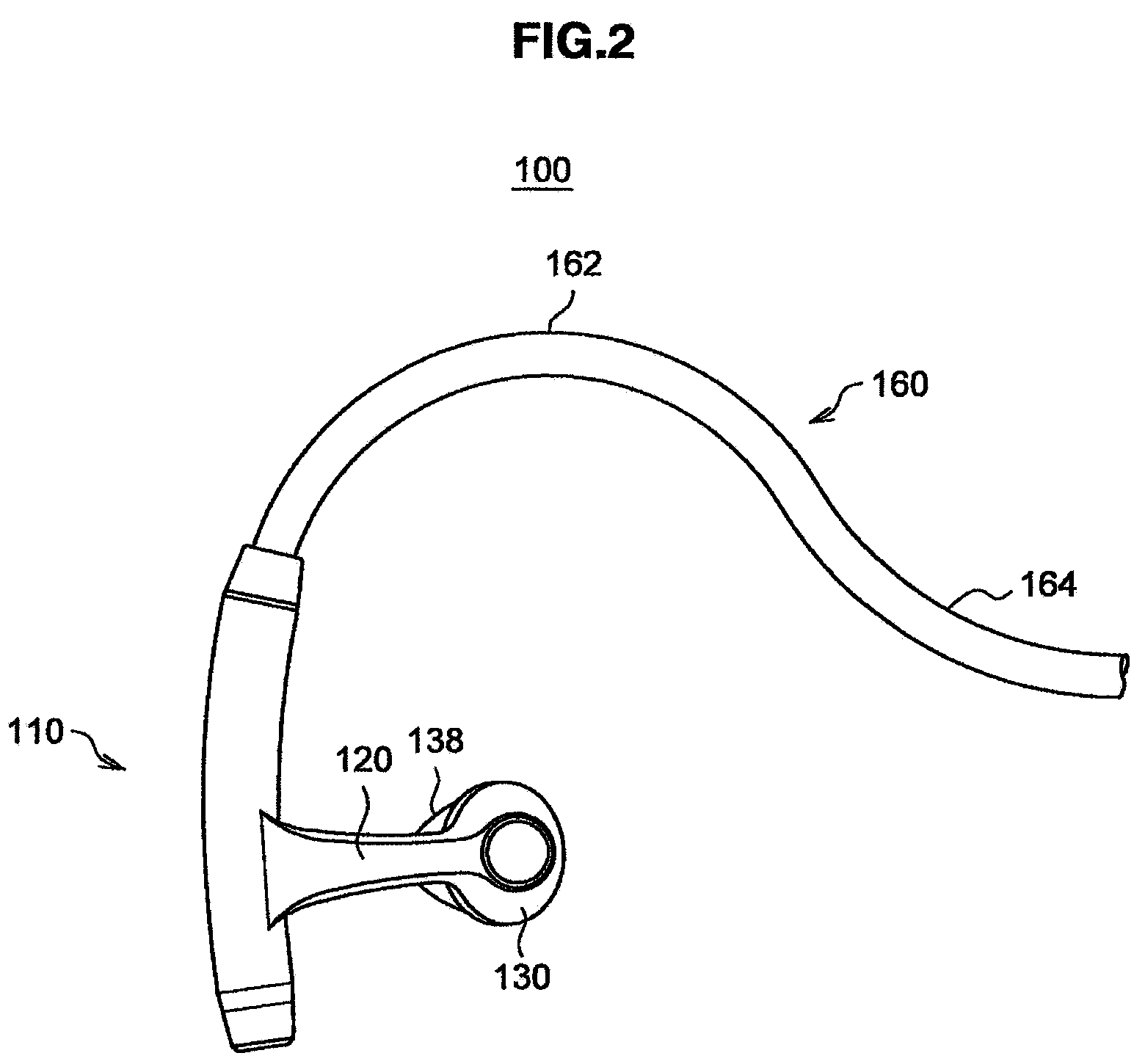
Headphone
InactiveUS8411893B2Improve wear resistanceDirection adjustableEar supported setsStethoscopeExternal Auditory CanalsEngineering
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical film, antireflection optical element and master
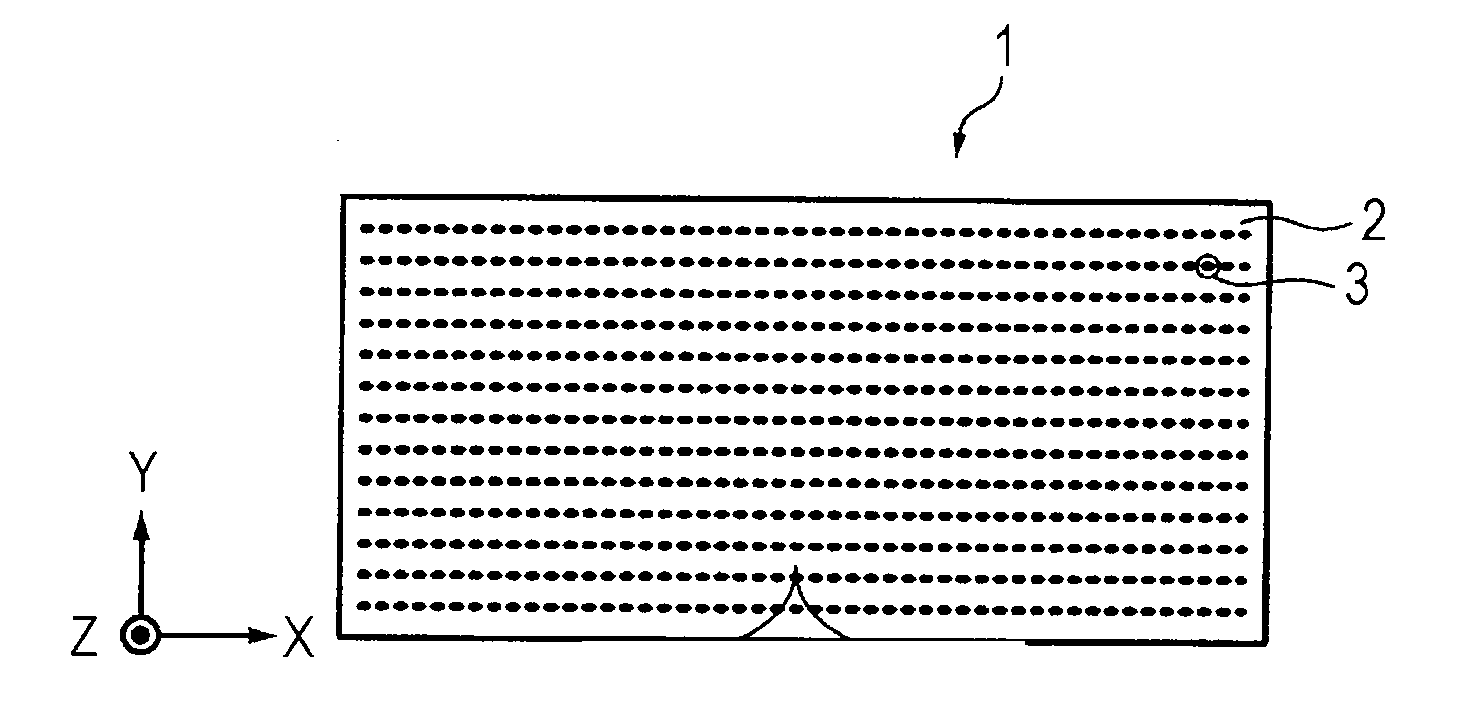
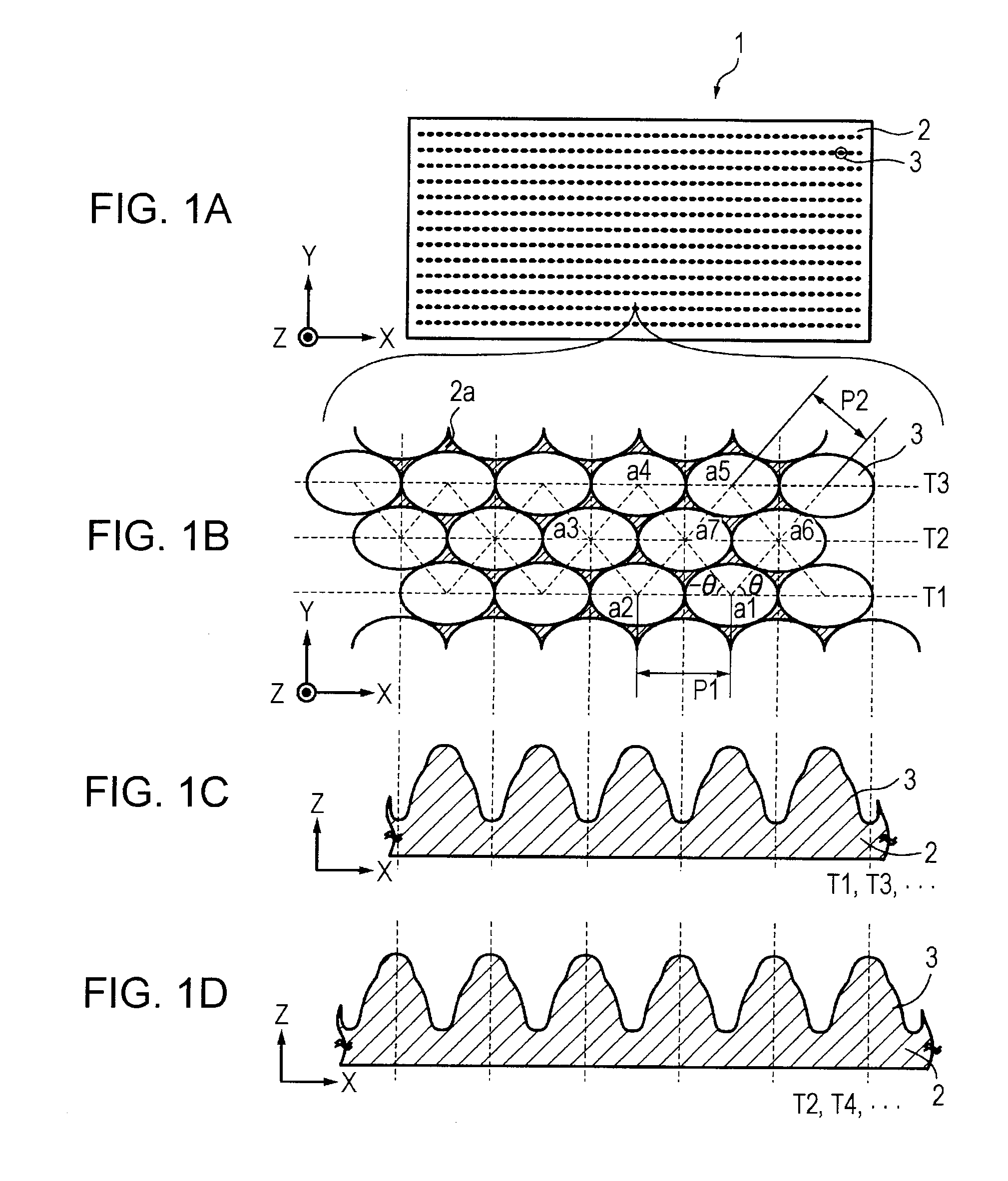
ActiveUS20110235181A1Good anti-reflection propertiesCoatingsOptical elementsLength waveDepth direction
An optical element includes a base and a large number of structures arranged on the surface of the base, the structures being projections or depressions. The structures are arranged at a pitch shorter than or equal to a wavelength of light in a use environment. An effective refractive index in the depth direction of the structures gradually increases toward the base and has two or more inflection points.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program
InactiveUS20110242098A1No fatigueFlexible performanceSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingParallaxImaging processing
When a plurality of faces are arranged in order of distance, a three-dimensional effect evaluation value r for each face is determined on the basis of a three-dimensional effect evaluation function Fl having a point A which internally divides the distance from the front side to the rear side in the depth direction at 1:2 as the vertex. A face with the maximum three-dimensional effect evaluation value r, serving as a face with the highest priority, is determined to be a main object. Then, three-dimensional processing is performed on a plurality of images such that the parallax of the determined main object is the minimum, thereby generating an image for three-dimensional display.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image processing apparatus and method
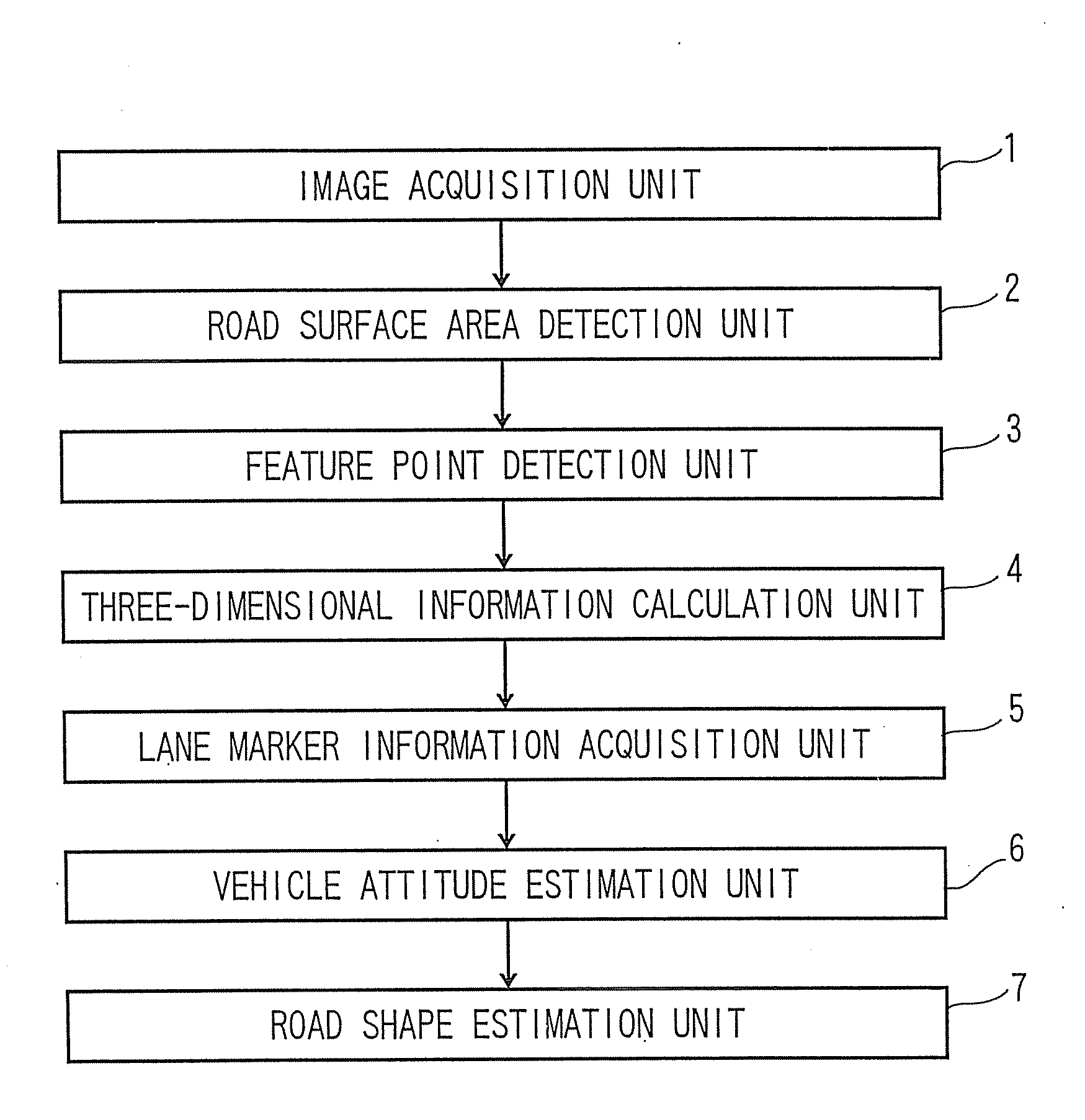
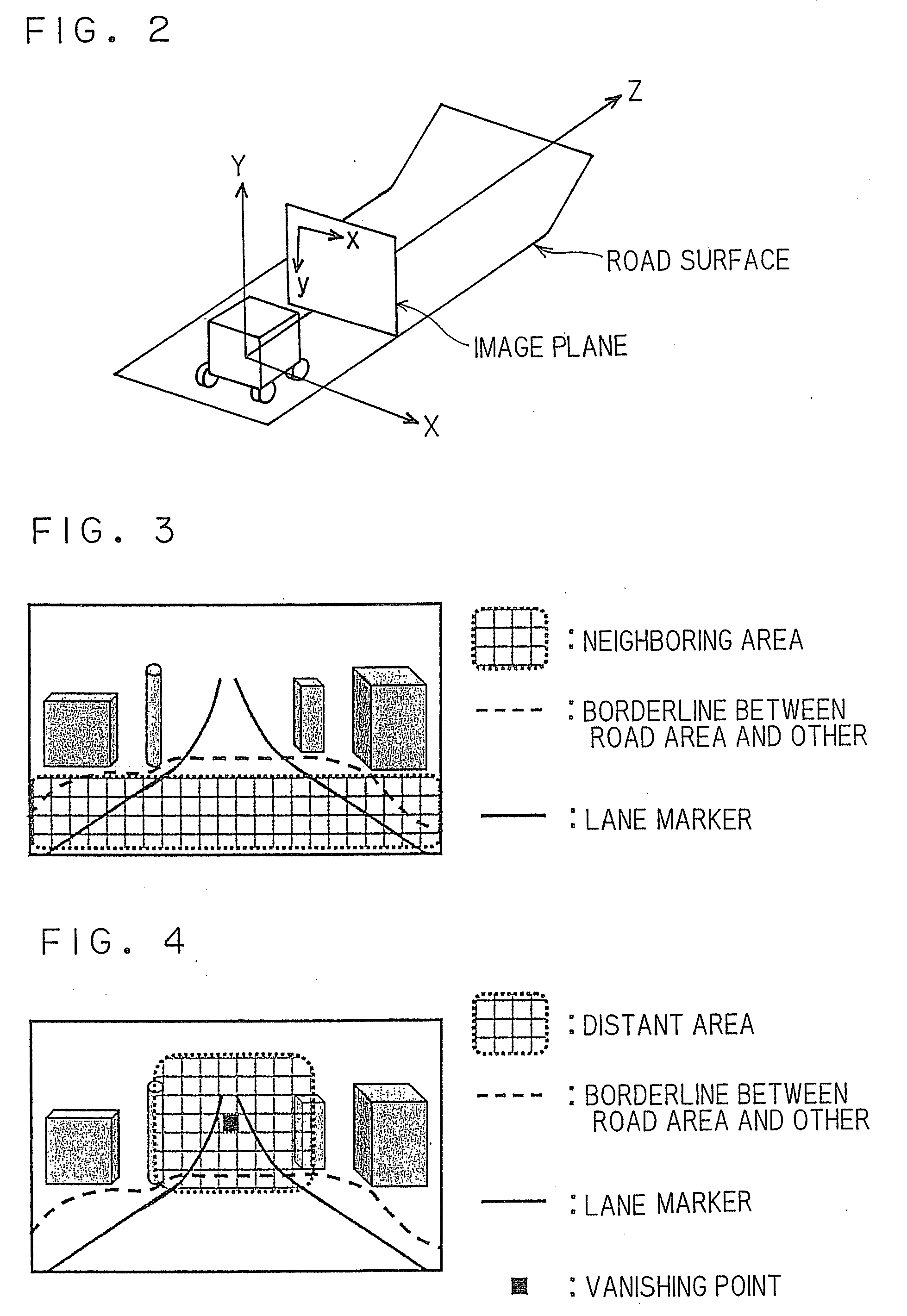
InactiveUS20090041337A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsParallaxImaging processing
Three-dimensional position information of each of feature points in a left and a right image is calculated based on a disparity between the left and right images; a lane marker existing on a road surface is detected from each of the left and right images; based on three-dimensional position information of a lane marker in a neighboring road surface area, by extending the lane marker to a distant area, a lateral direction position, and a depth direction position, of the extended lane marker in the distant area are estimated; an edge segment of a certain length or more is detected from feature points in the distant area in each of a plurality of images; three-dimensional position information of the edge segment is calculated; and, based on the three-dimensional position information of the edge segment, and on the extended lane marker information, a road incline in the distant area is estimated.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Confocal scanning microscope
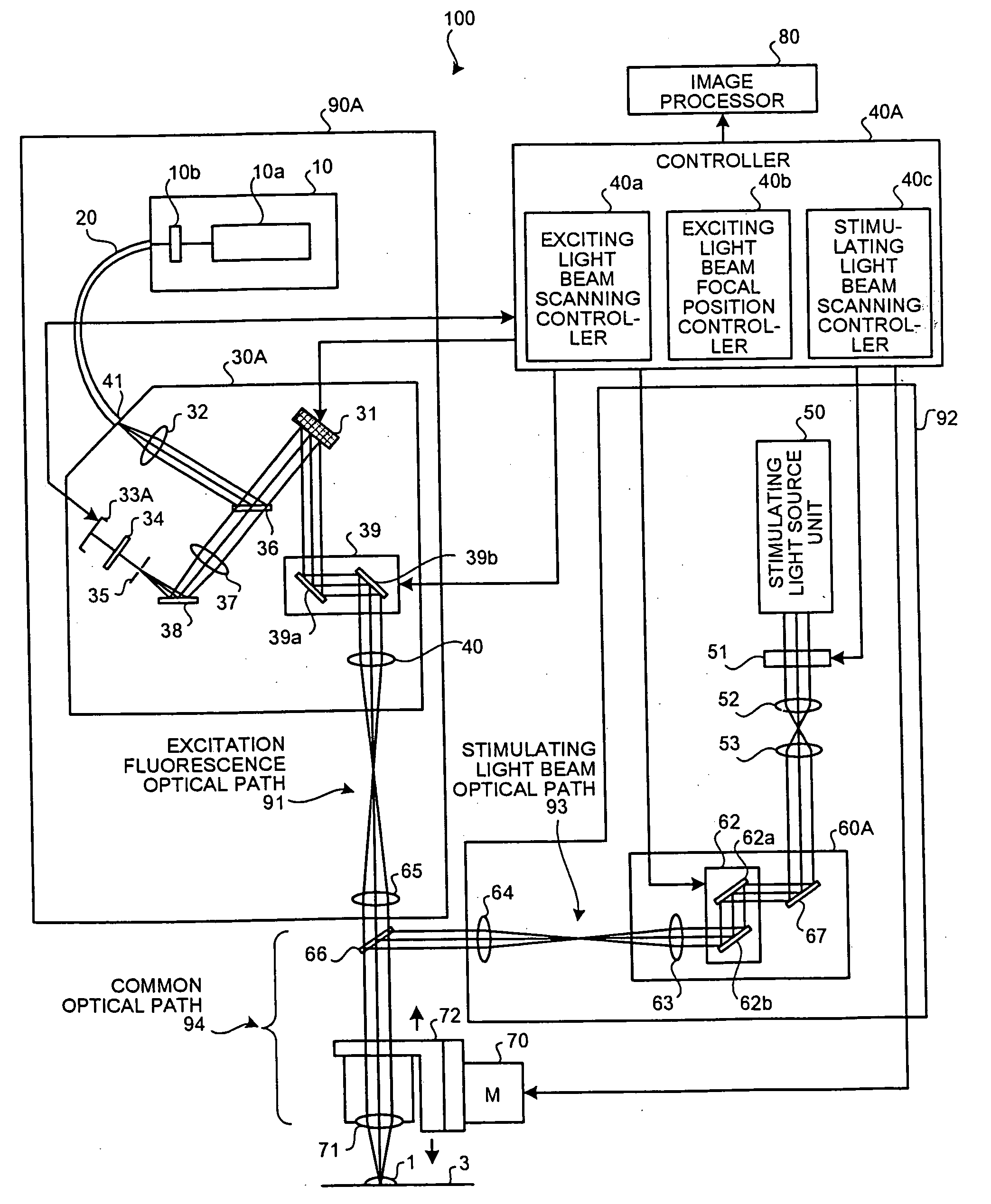
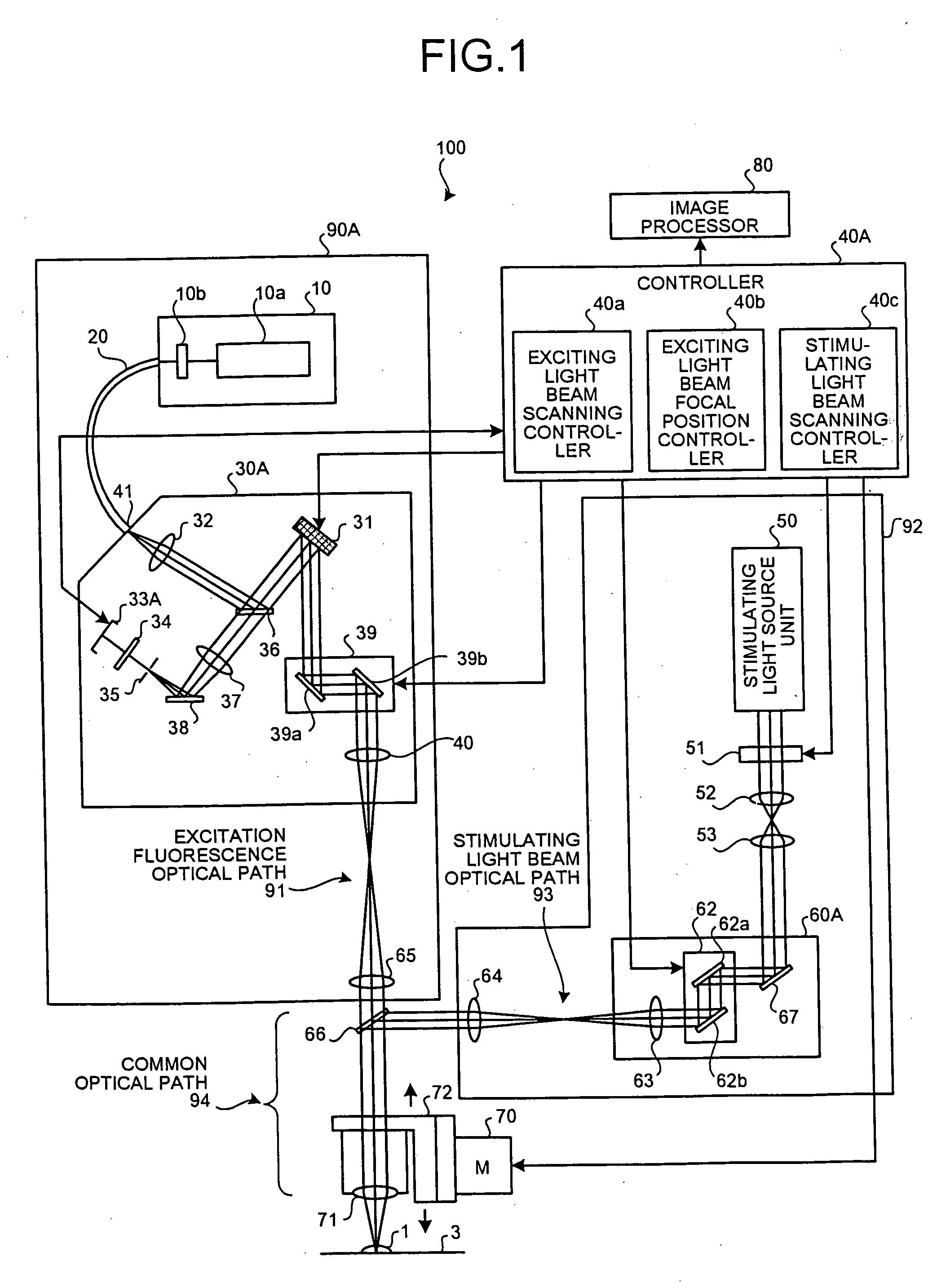
ActiveUS20050122579A1Spectrum investigationLuminescent dosimetersConfocal scanning microscopyExcitation beam
A confocal scanning microscope includes a stimulating light beam scanning unit that scans at least a predetermined plane perpendicular to the depth direction of the stimulating light beam focal position, a stimulating light beam scanning control unit that controls the scanning area of the stimulating light beam to a desired area, an exciting light beam scanning control unit that controls the scanning area of the exciting light beam to a desired area, an exciting light beam focal position changing unit, provided in an excitation fluorescence optical path, which is a portion of an optical path where the exciting light beam and the fluorescence pass and located outside a common optical path where the exciting light beam, the fluorescence, and the stimulating light beam pass, that changes at least the exciting light beam focal position in the depth direction, and an exciting light beam control unit that controls the exciting light beam focal position variably to a desired position.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com