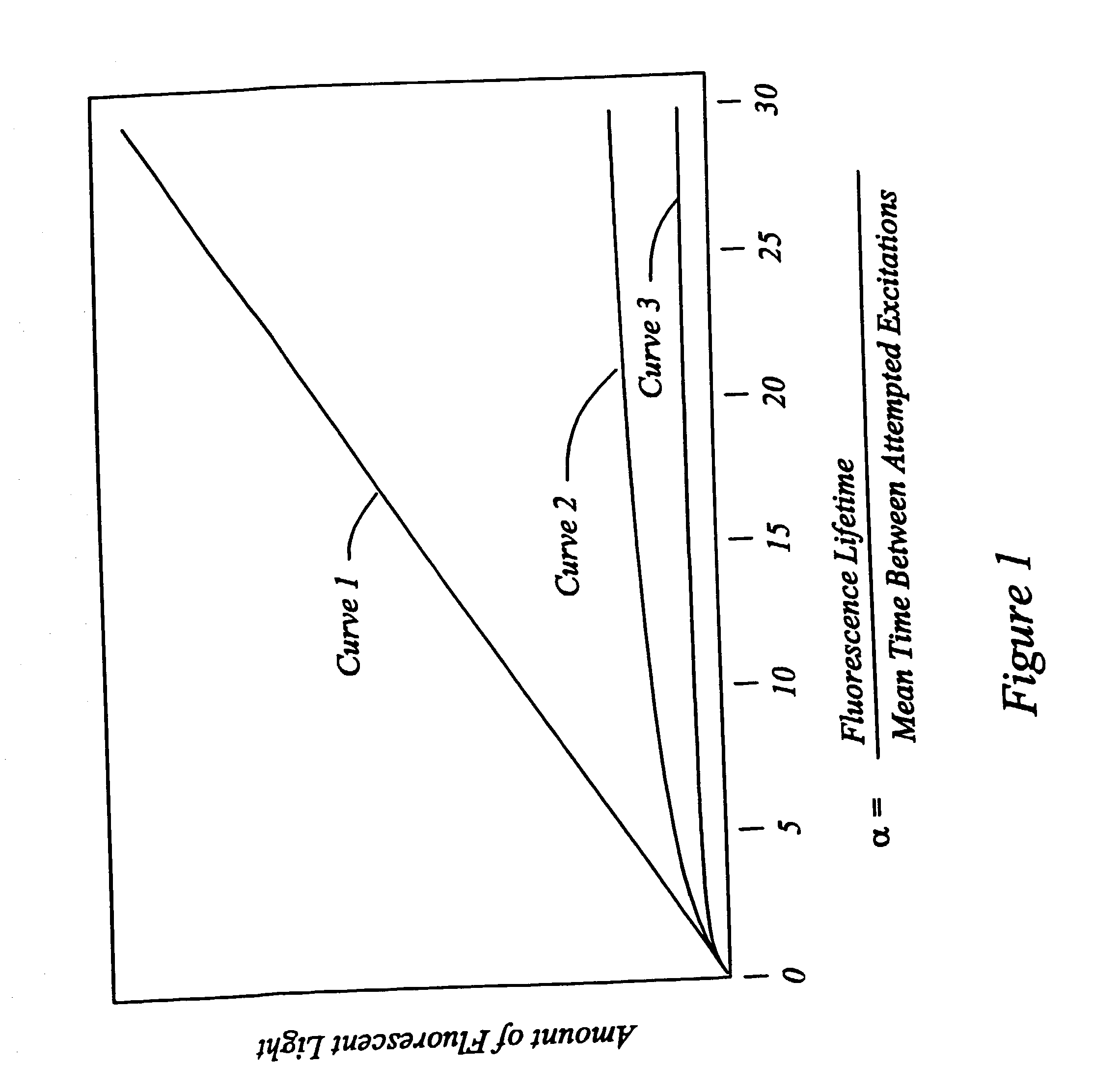
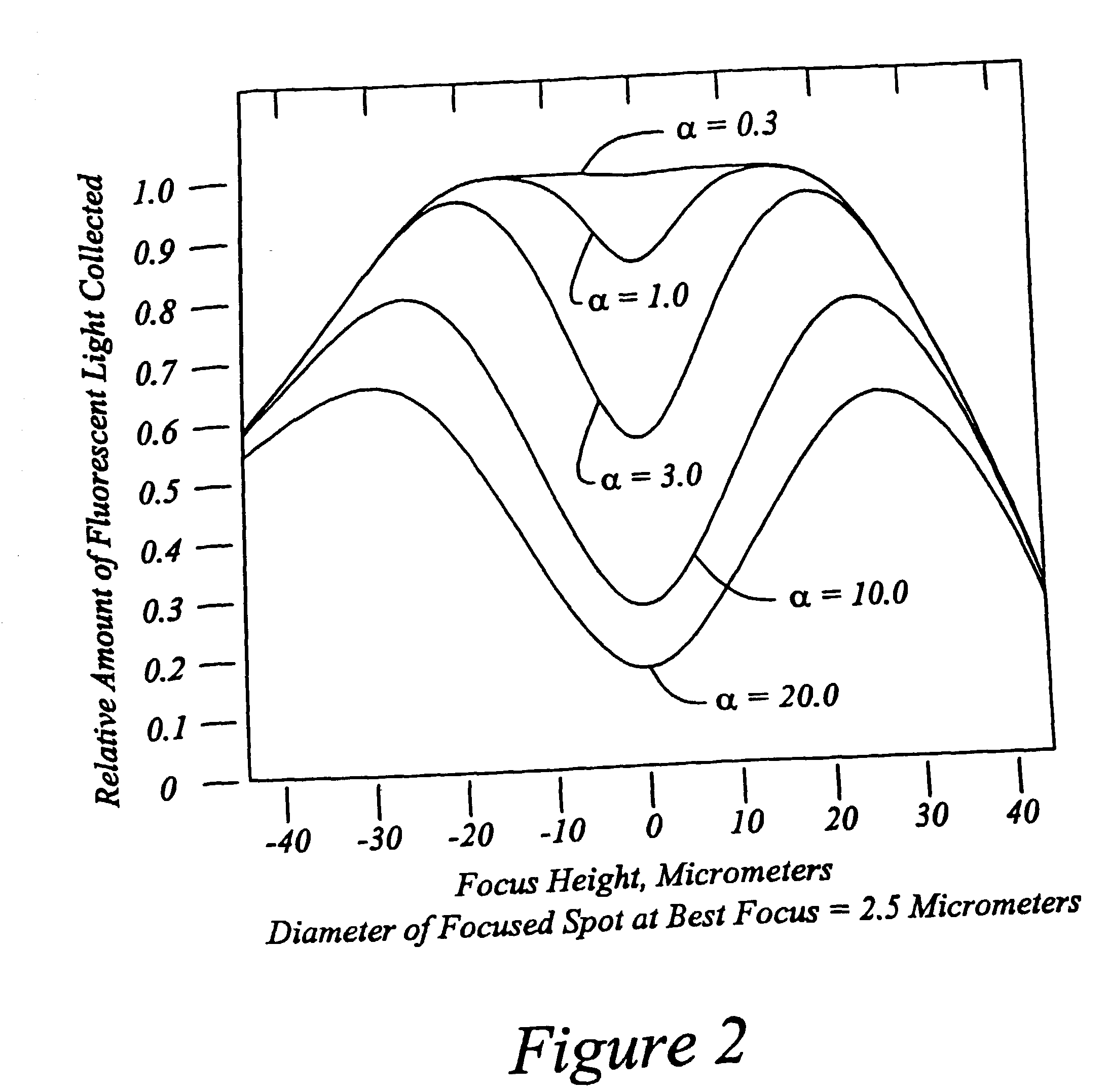
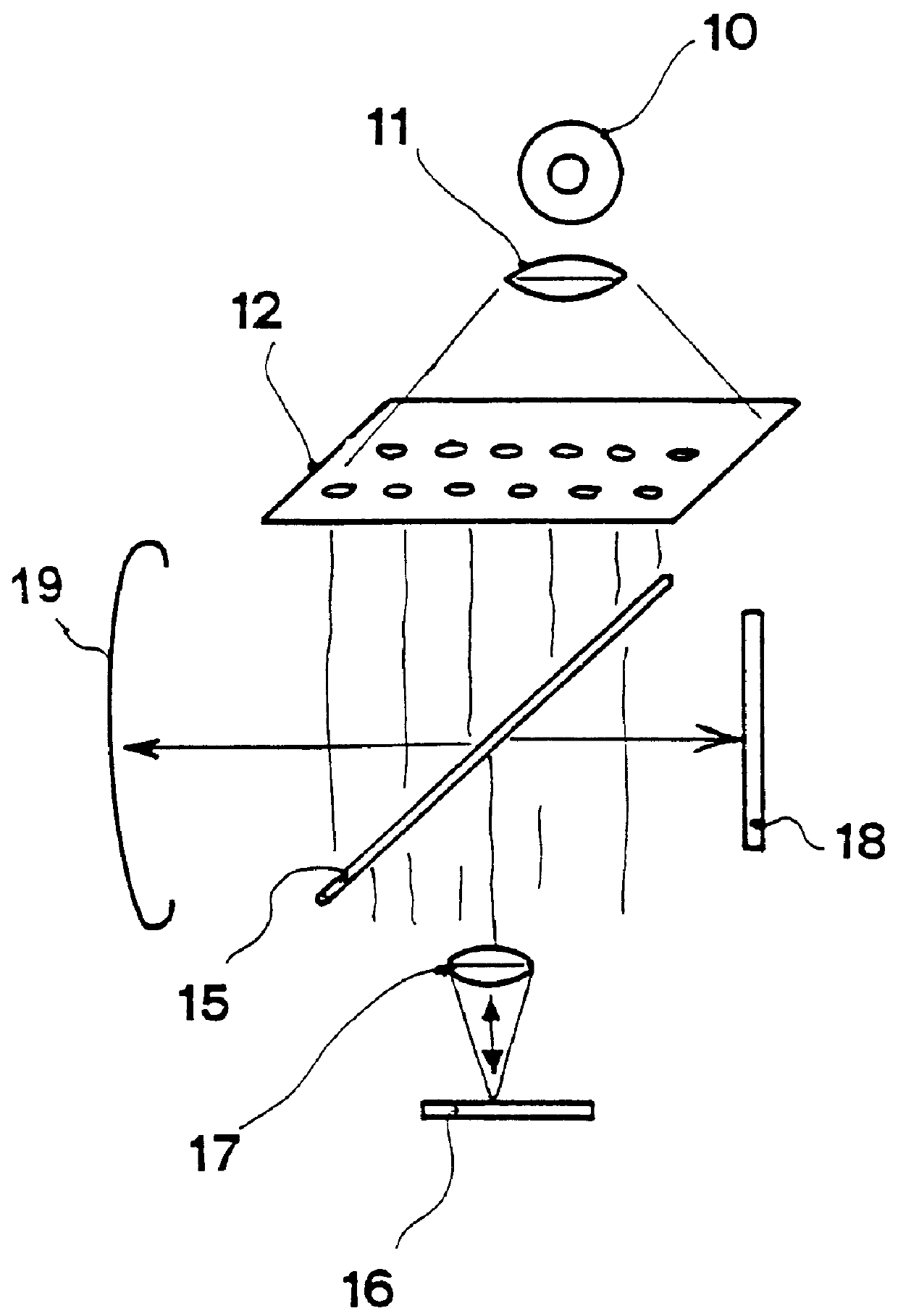
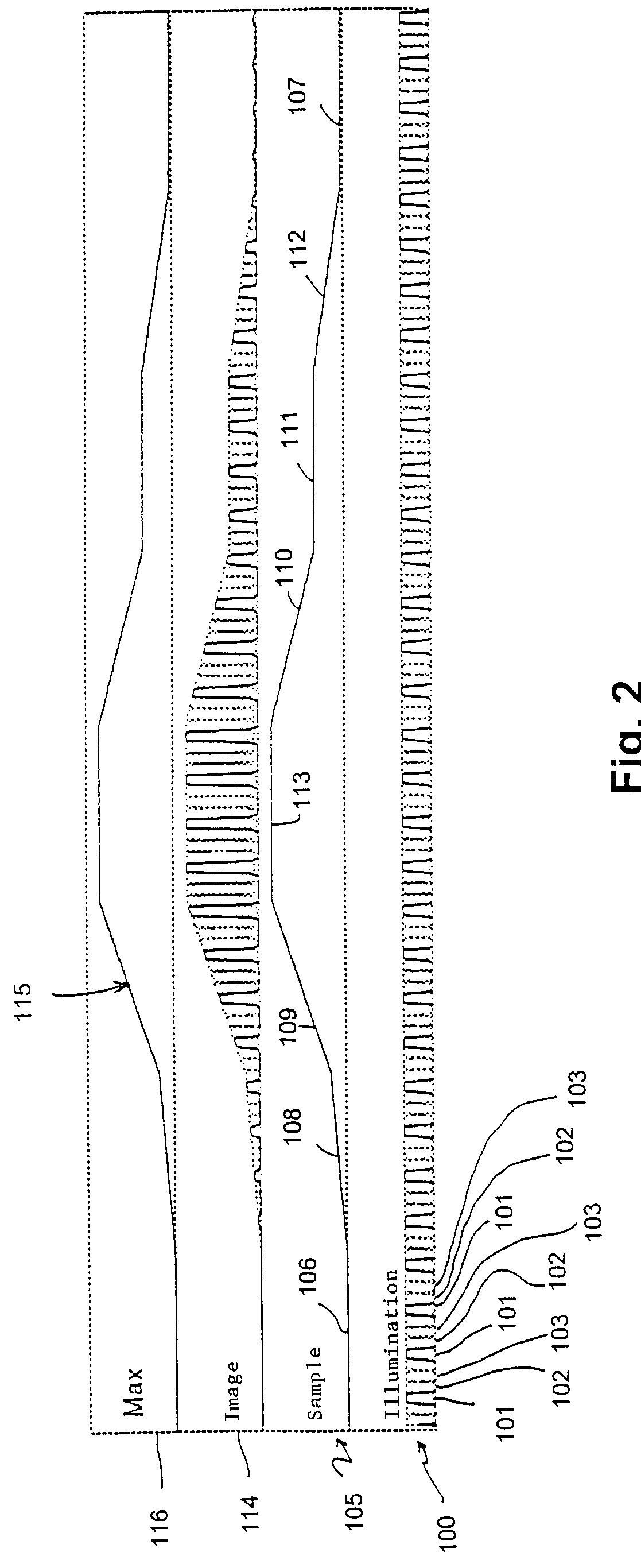
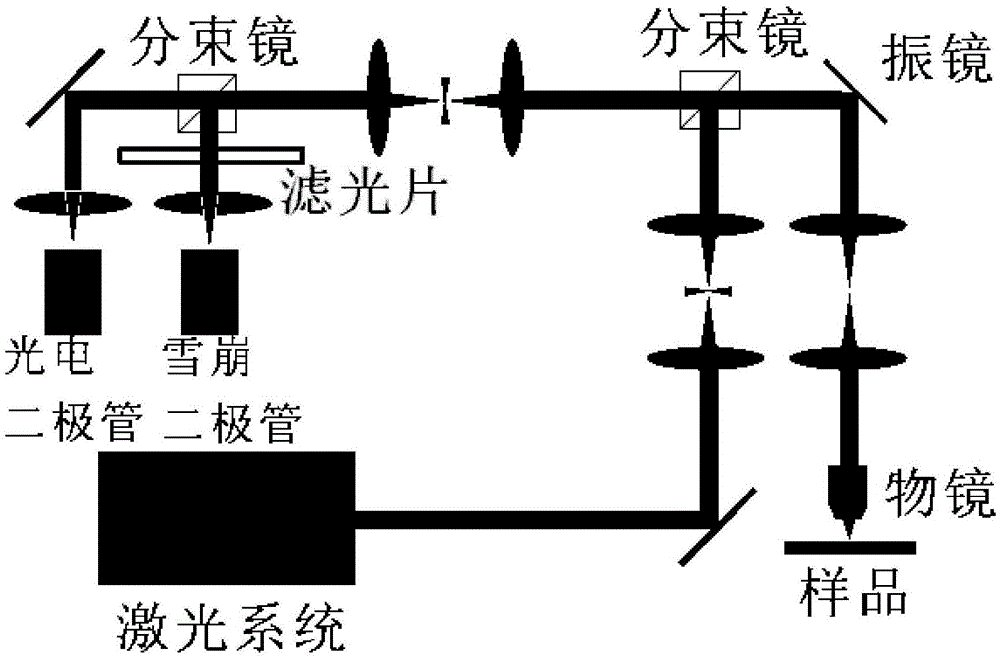
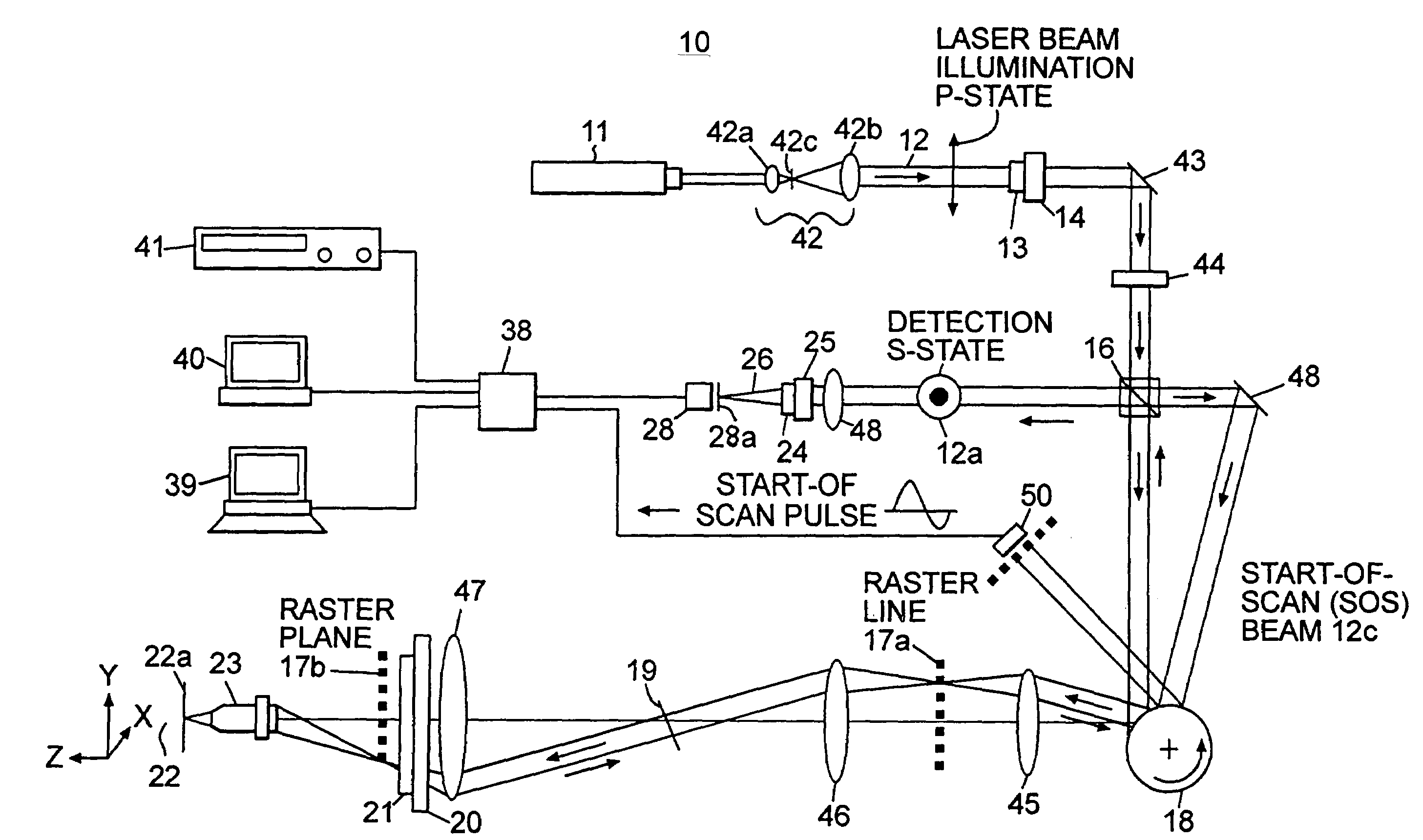
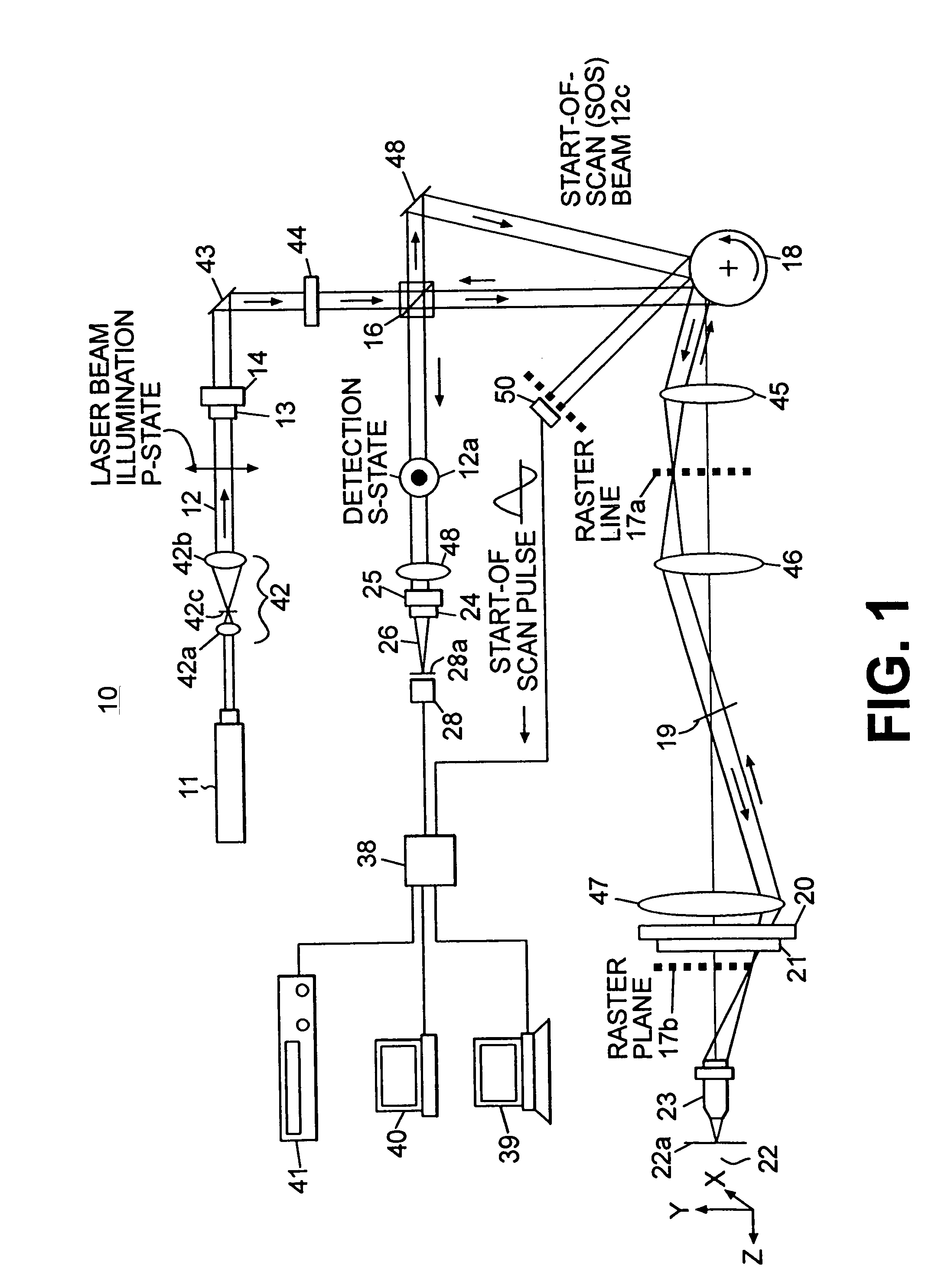
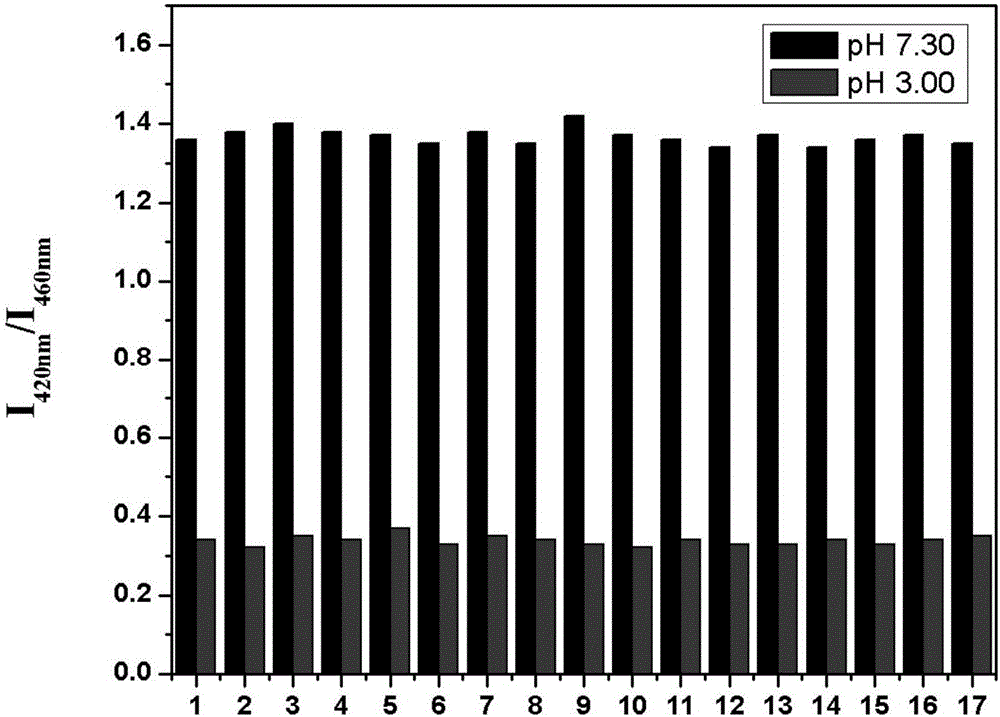
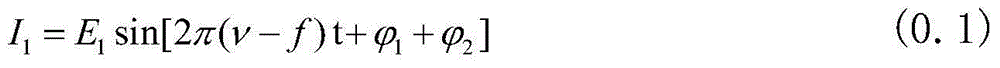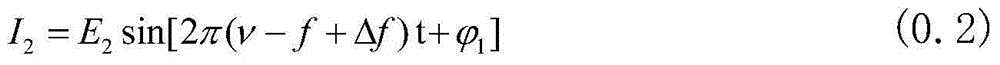Patents
Literature
62 results about "Confocal scanning microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Indirect imaging technique which uses a sharply focused light source (typically a laser) to excite fluors or otherwise visualize the specimen one point at a time; 2 or 3 dimensional likenesses are then reconstructed by computer; relatively noninvasive, applicable to thick sections and living tissue.
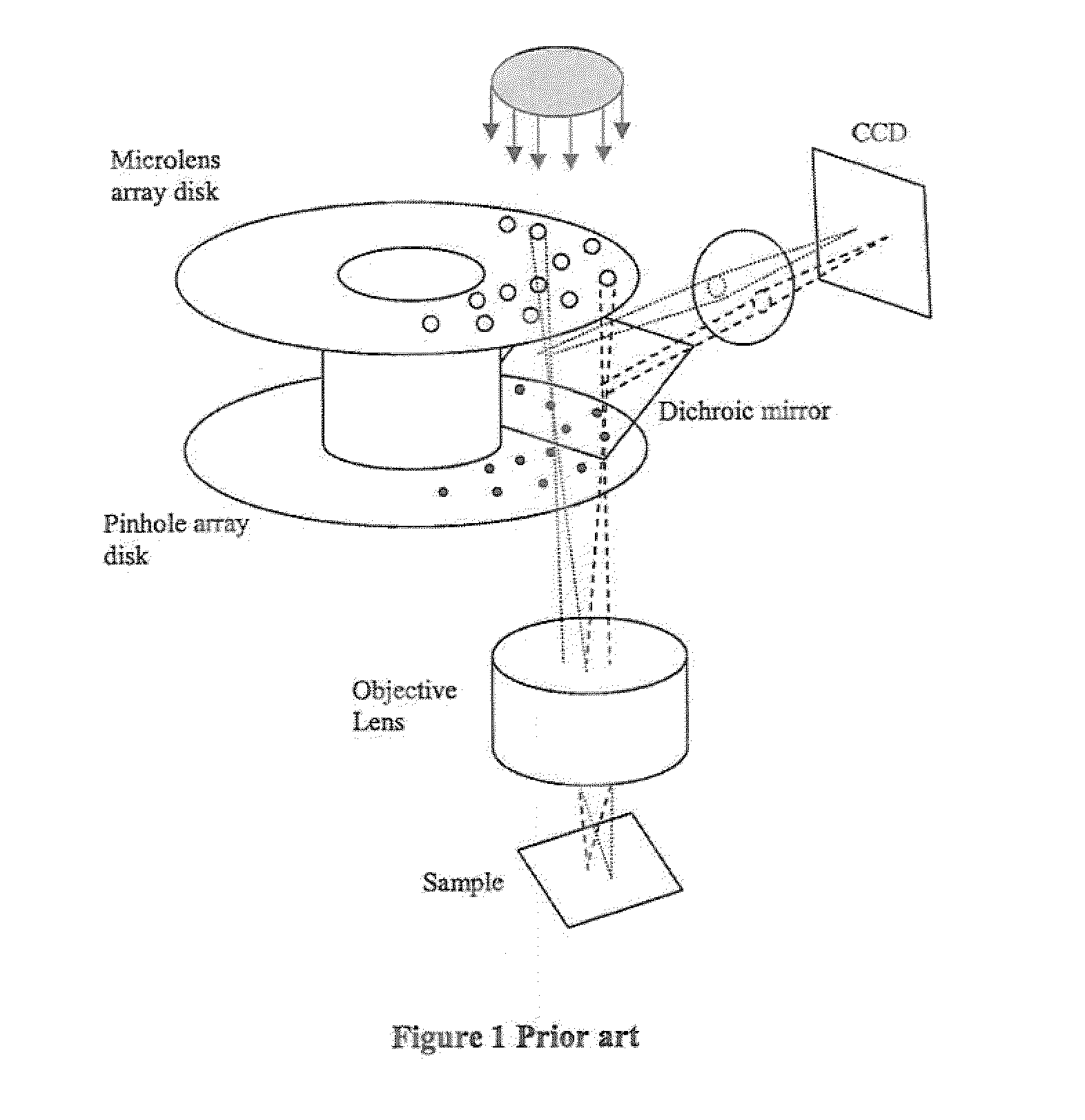
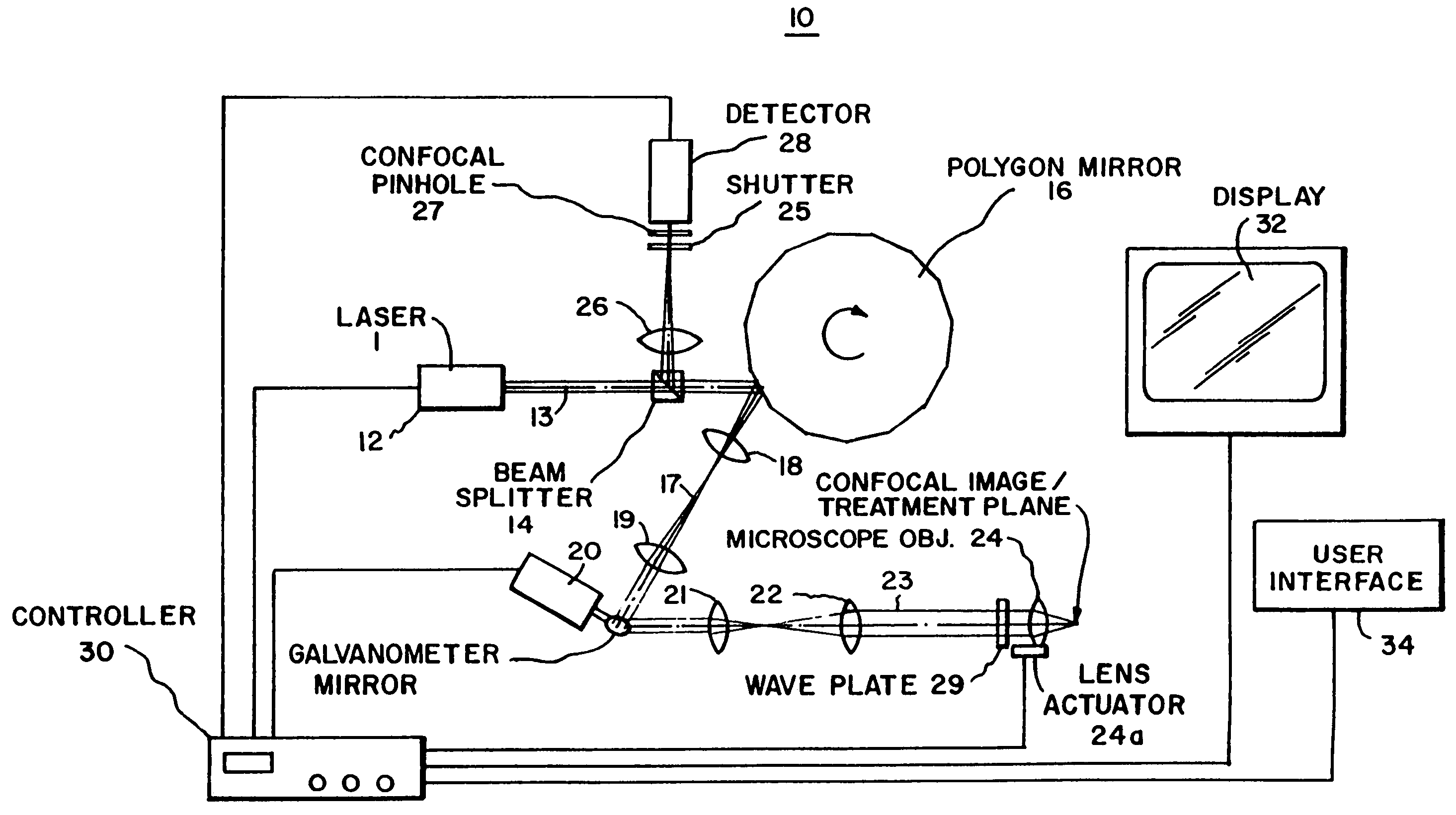
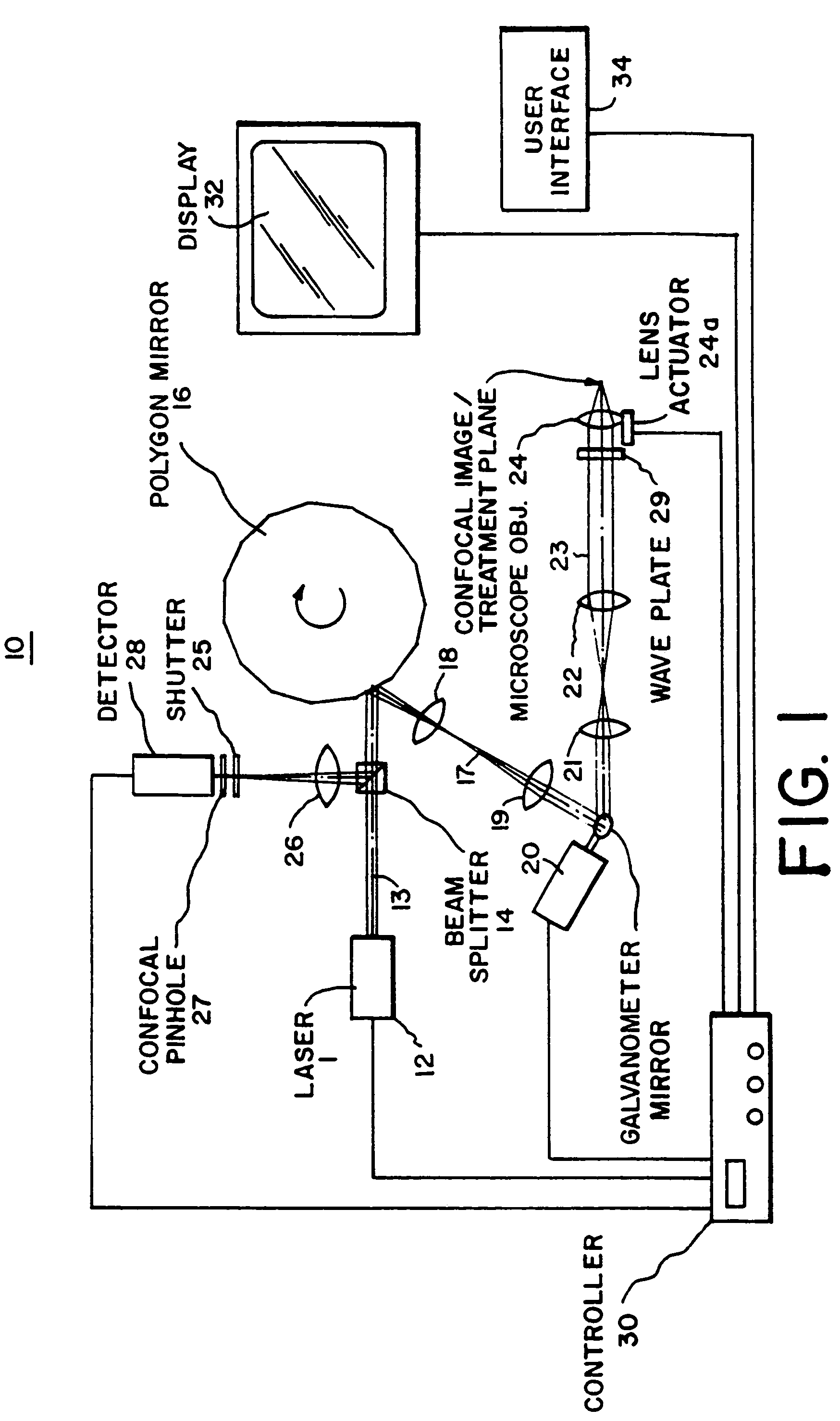
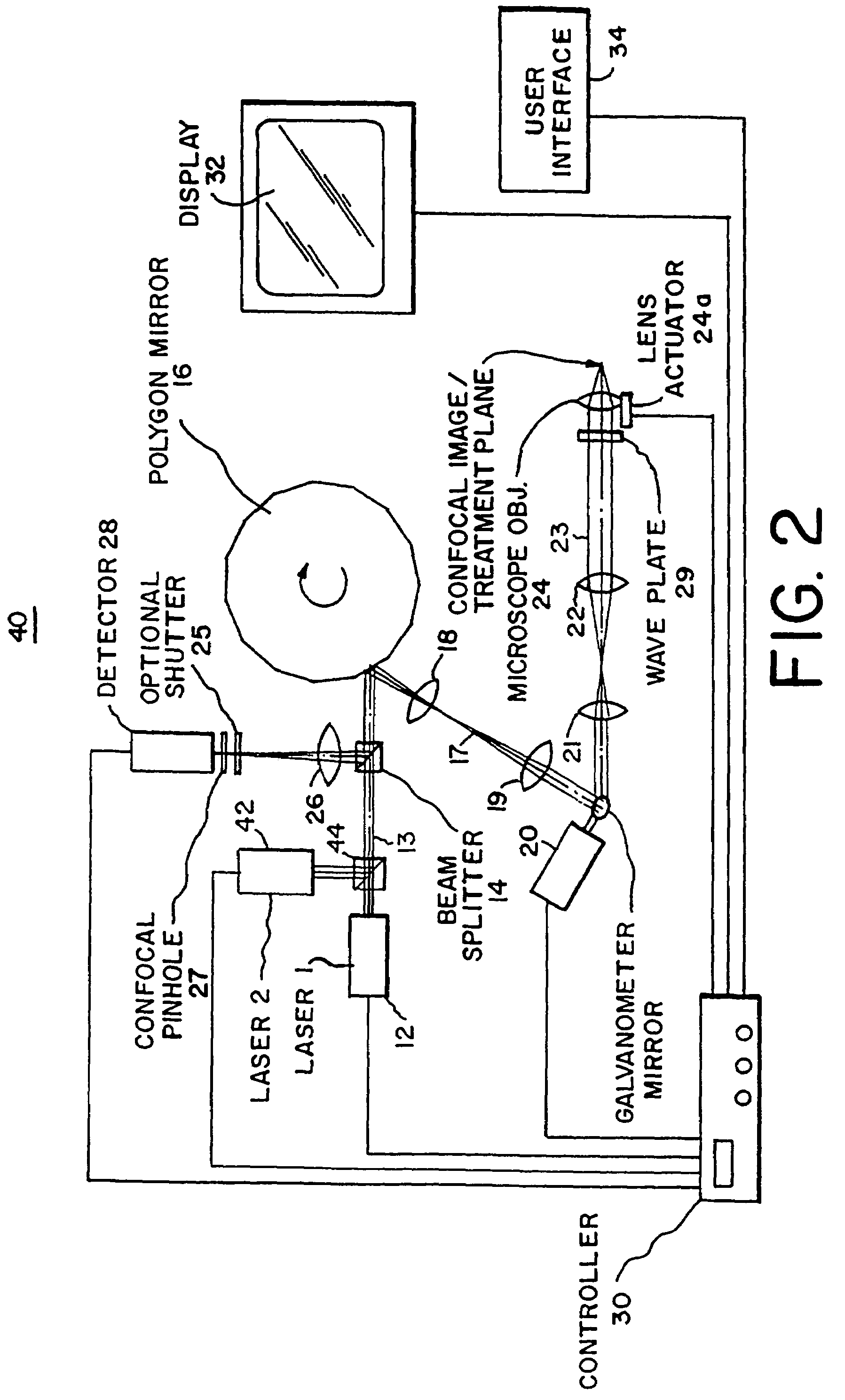
Confocal scanning microscope
ActiveUS20050122579A1Spectrum investigationLuminescent dosimetersConfocal scanning microscopyExcitation beam
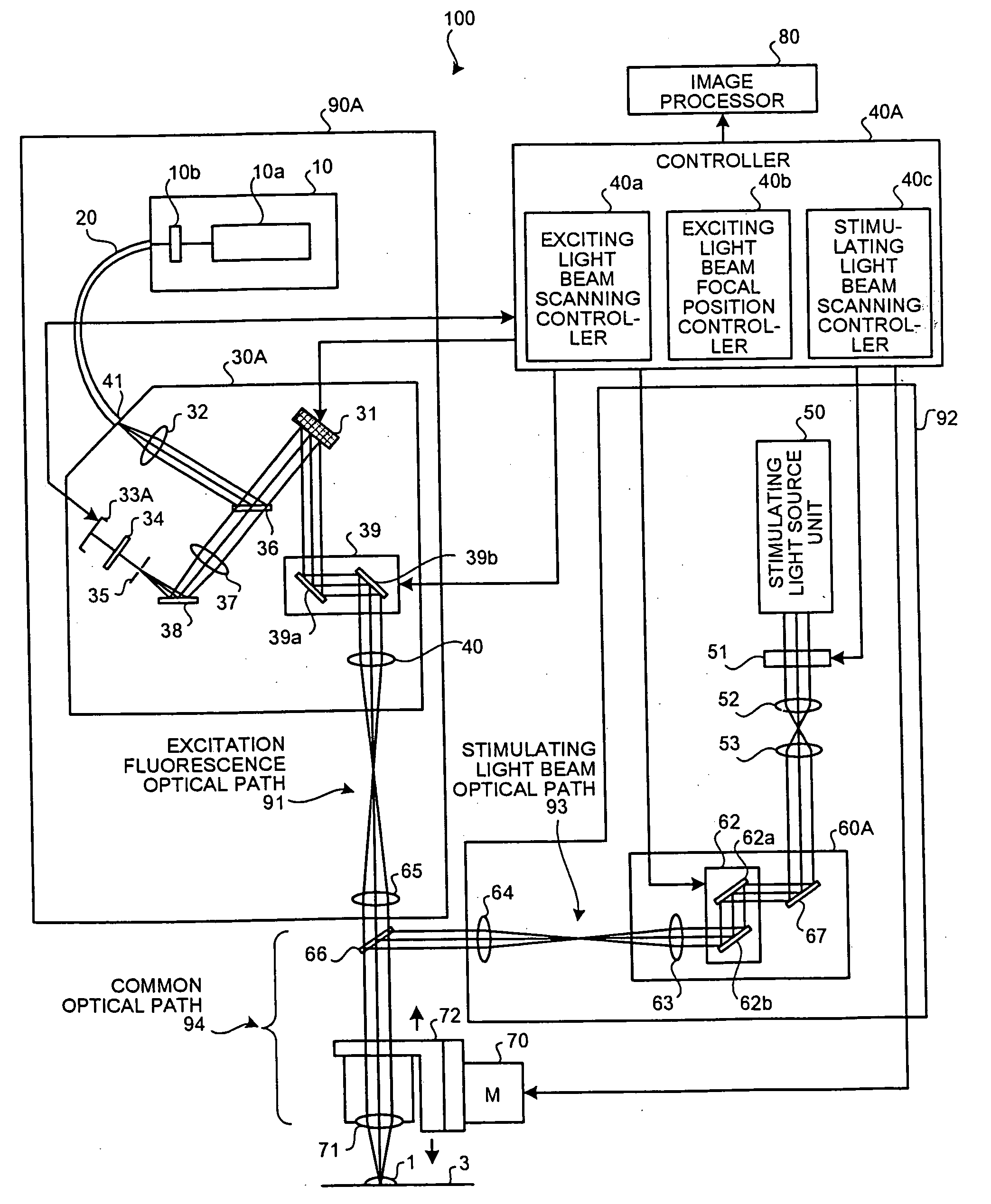
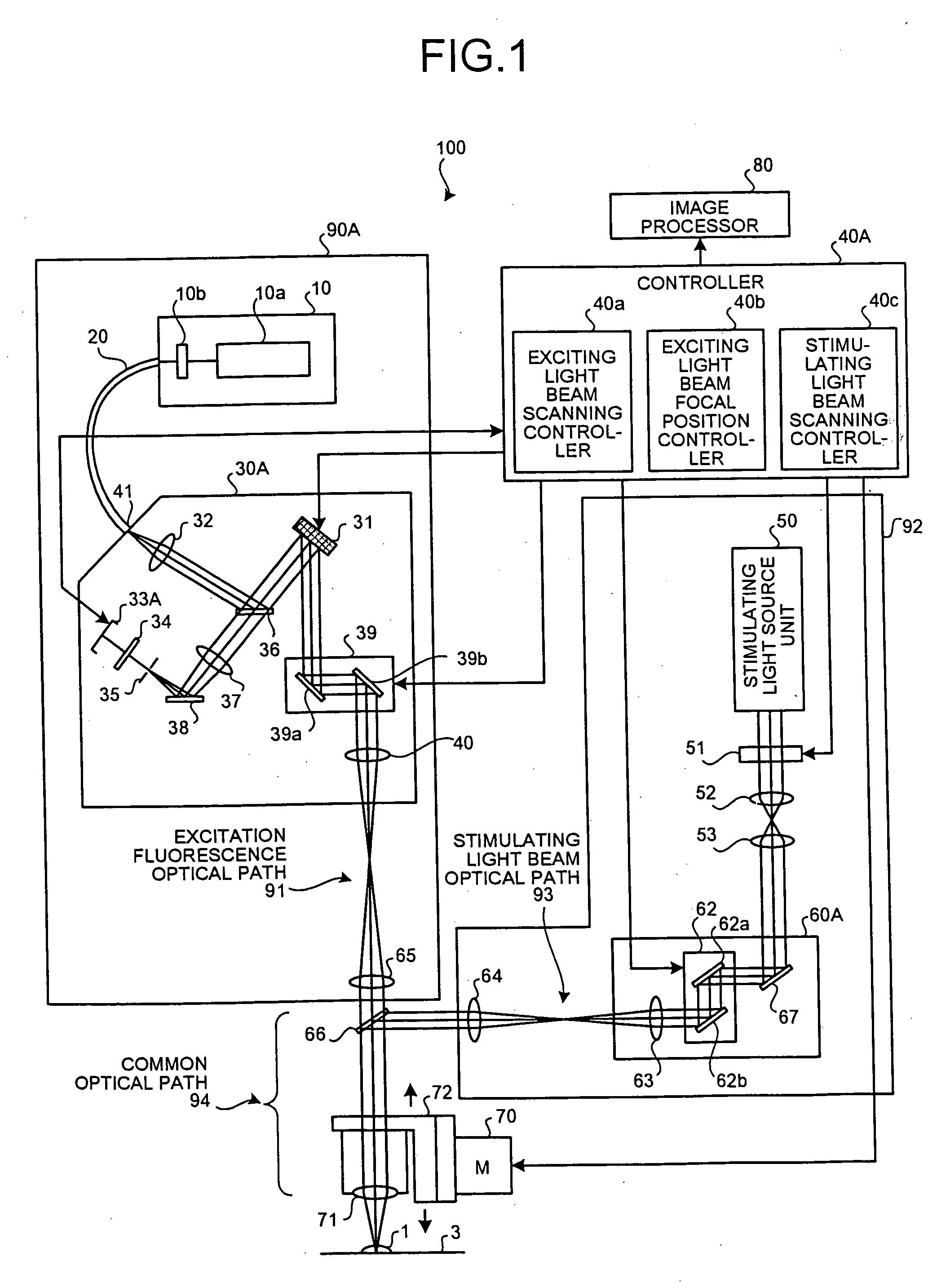
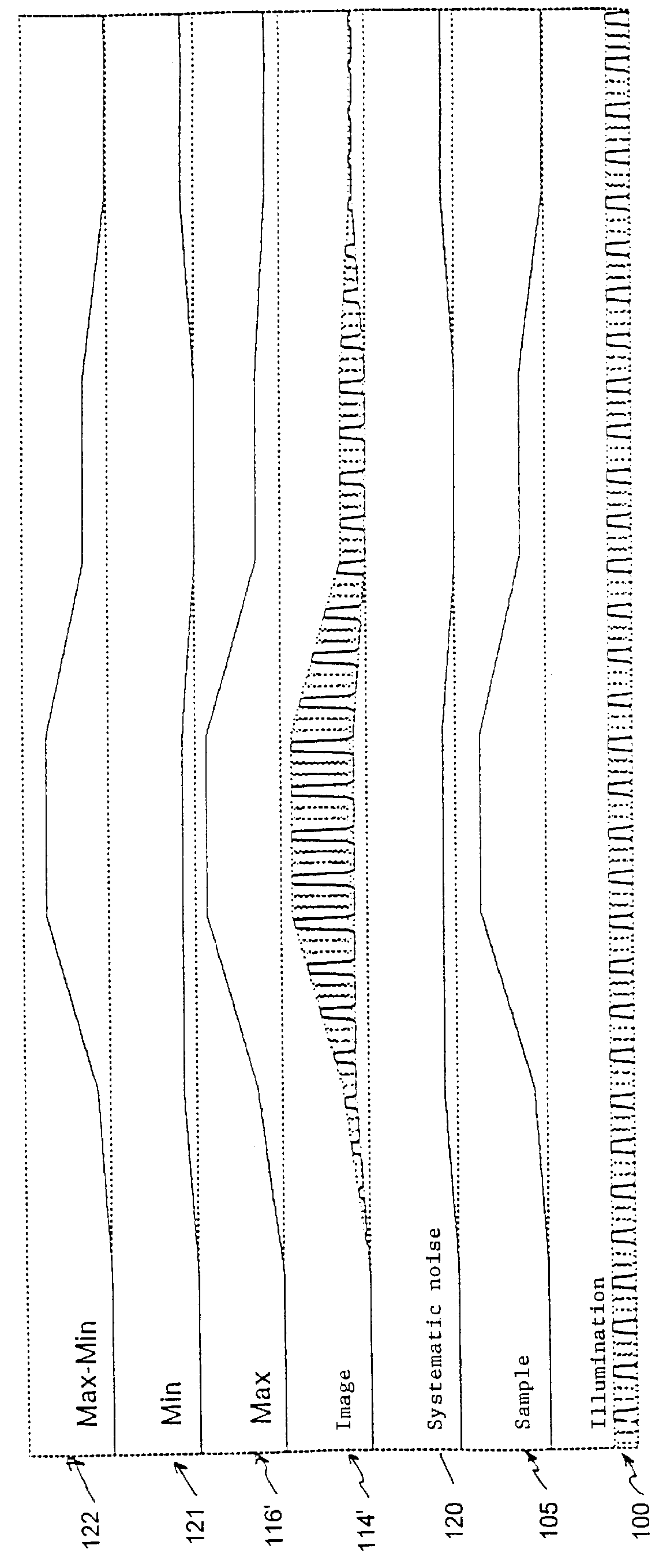
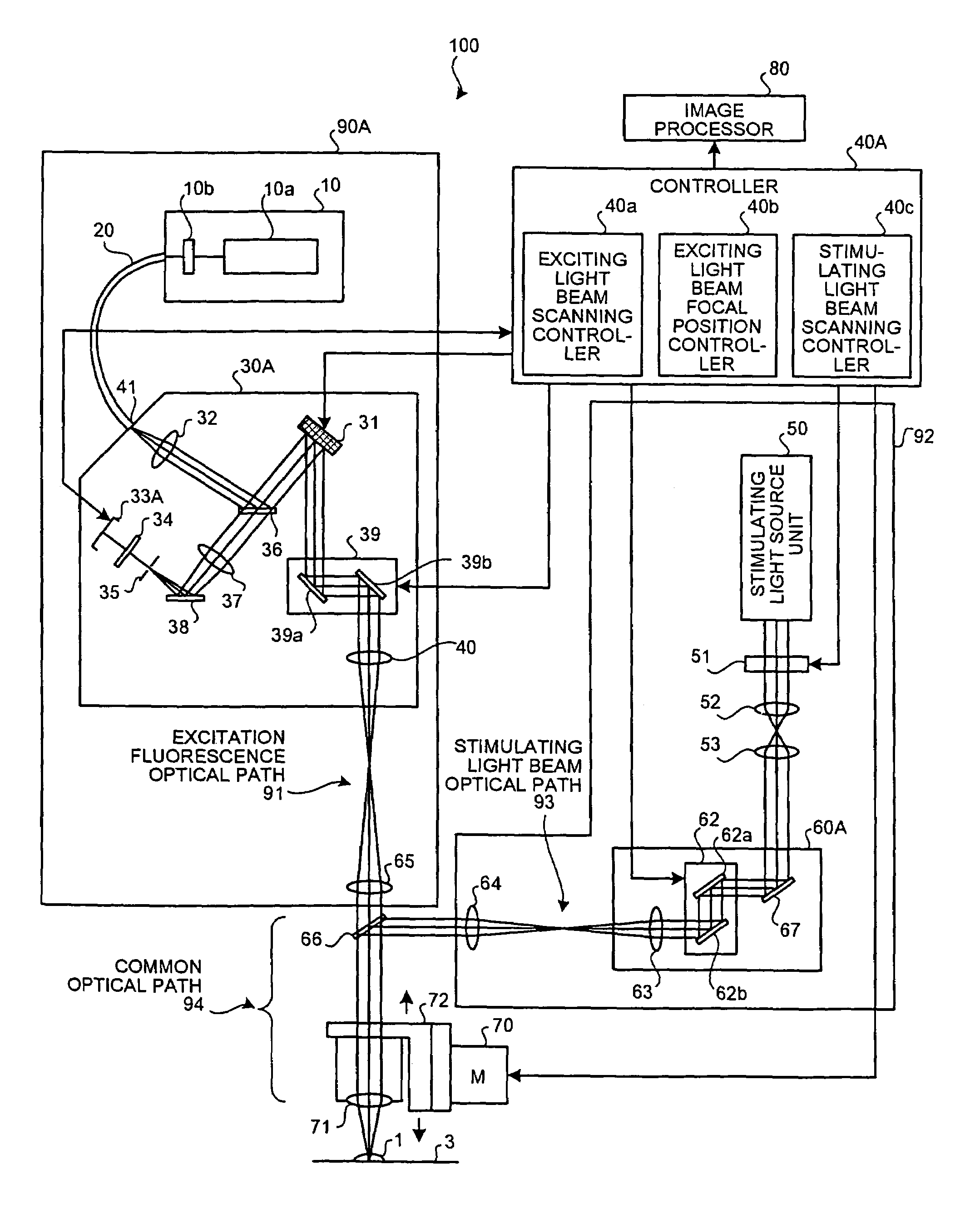
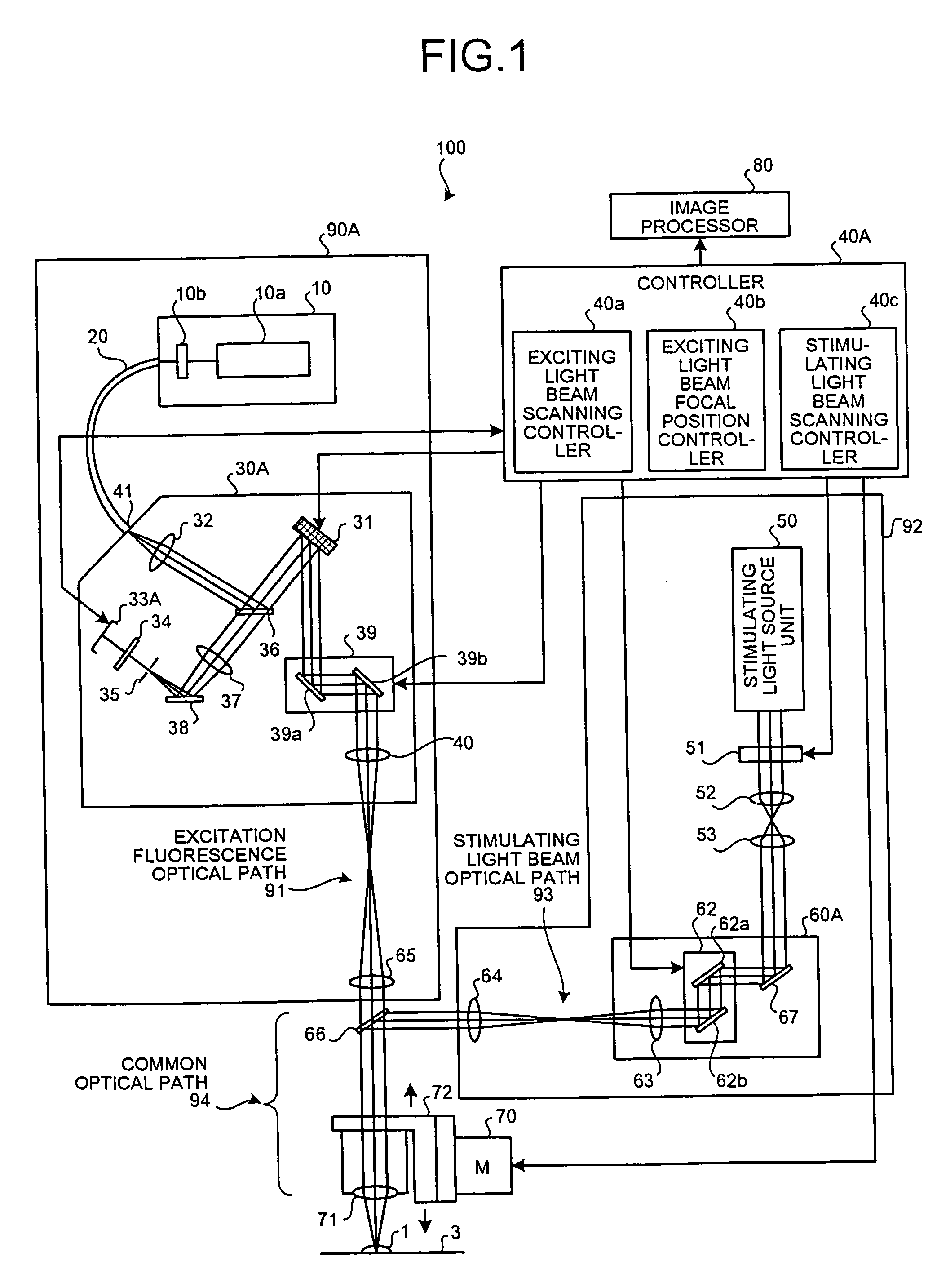
A confocal scanning microscope includes a stimulating light beam scanning unit that scans at least a predetermined plane perpendicular to the depth direction of the stimulating light beam focal position, a stimulating light beam scanning control unit that controls the scanning area of the stimulating light beam to a desired area, an exciting light beam scanning control unit that controls the scanning area of the exciting light beam to a desired area, an exciting light beam focal position changing unit, provided in an excitation fluorescence optical path, which is a portion of an optical path where the exciting light beam and the fluorescence pass and located outside a common optical path where the exciting light beam, the fluorescence, and the stimulating light beam pass, that changes at least the exciting light beam focal position in the depth direction, and an exciting light beam control unit that controls the exciting light beam focal position variably to a desired position.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning
InactiveUS20030156323A1Diameter of to varyEnsure high efficiency and accuracyMirrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansWide areaGrating
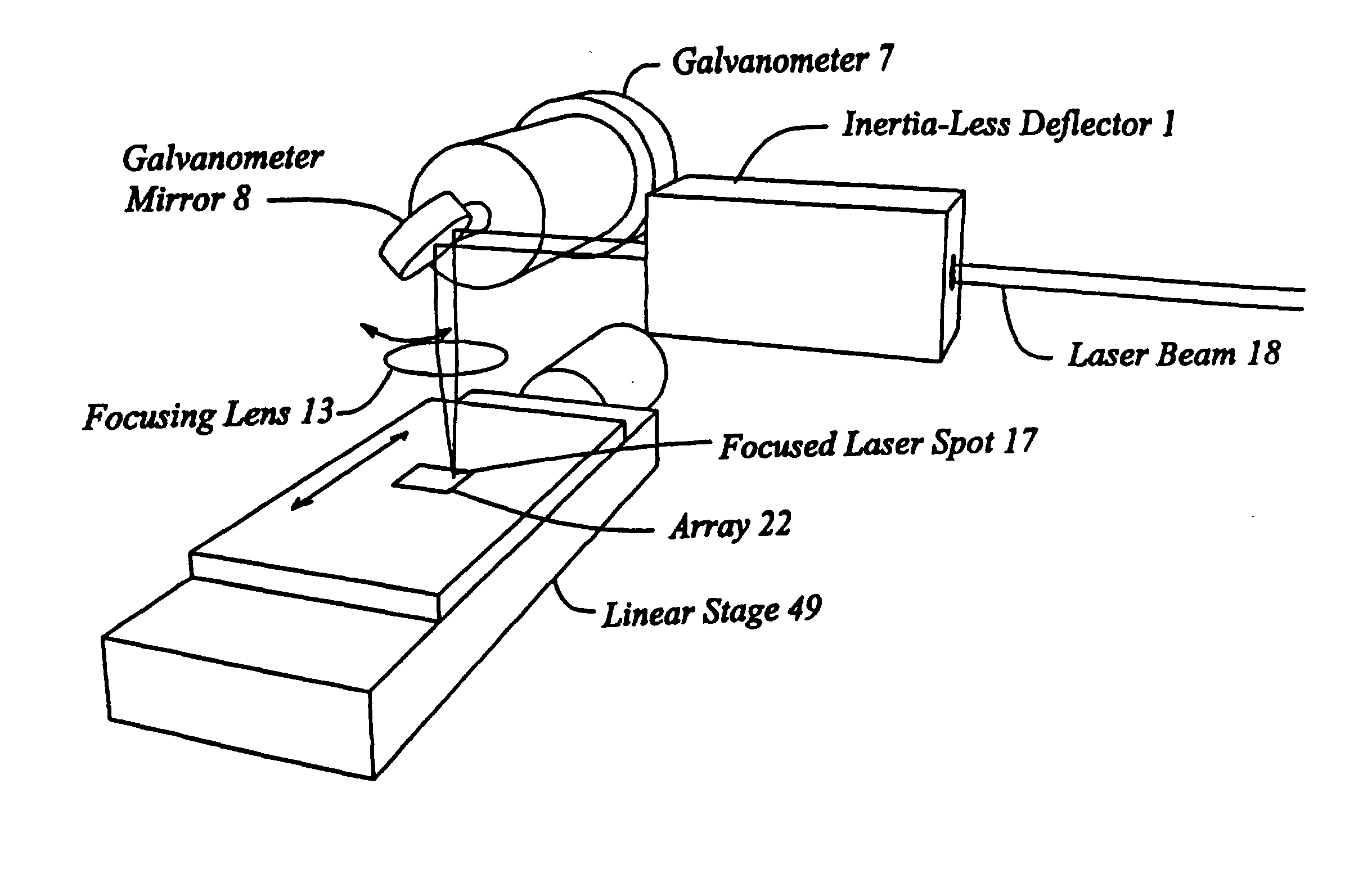
High speed, wide area microscopic scanning or laser positioning is accomplished with an inertia-less deflector (for example an acousto-optic or electro-optic deflector) combined with a high speed wide area microscopic scanning mechanism or laser positioner mechanism that has inertia, the motion of the inertia-less deflector specially controlled to enable a focused spot to stabilize, for example to stop and dwell or be quickly aimed. It leads to improved data acquisition from extremely small objects and higher speed operation. In the case of fluorescence reading of micro-array elements, dwelling of fluorophore-exciting radiation in a spot that is relatively large enables obtaining the most fluorescent photons per array element, per unit time, a winning criterion for reducing fluorophore saturation effects. The same inertia-less deflector performs stop and dwell scanning, edge detection and raster scans. Automated mechanism for changing laser spot size enables selection of spot size optimal for the action being performed.
Owner:OVERBECK JAMES W
Method for the acquisition of images by confocal microscopy
InactiveUS6016367AEnhanced confocal characteristicReduced scattering effectImage enhancementBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsConfocal scanning microscopyComputer vision
A method for the acquisition of images by means of confocal microscopy in which a new image is calculated which is constituted by the "maxima" among the corresponding elements of each captured image. The new image contains mainly the signal coming from the most luminous and in focus areas and even the signal coming from the less luminous areas, as being out of focus or laterally displaced with respect to the grid positions. A further image is then calculated which is constituted by the "minima" among the corresponding elements of each captured image and the requested confocal image is then obtained by calculating the difference between the "maxima" image and the "minima" image.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Confocal scanning microscope
A confocal scanning microscope includes a stimulating light beam scanning unit that scans at least a predetermined plane perpendicular to the depth direction of the stimulating light beam focal position, a stimulating light beam scanning control unit that controls the scanning area of the stimulating light beam to a desired area, an exciting light beam scanning control unit that controls the scanning area of the exciting light beam to a desired area, an exciting light beam focal position changing unit, provided in an excitation fluorescence optical path, which is a portion of an optical path where the exciting light beam and the fluorescence pass and located outside a common optical path where the exciting light beam, the fluorescence, and the stimulating light beam pass, that changes at least the exciting light beam focal position in the depth direction, and an exciting light beam control unit that controls the exciting light beam focal position variably to a desired position.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
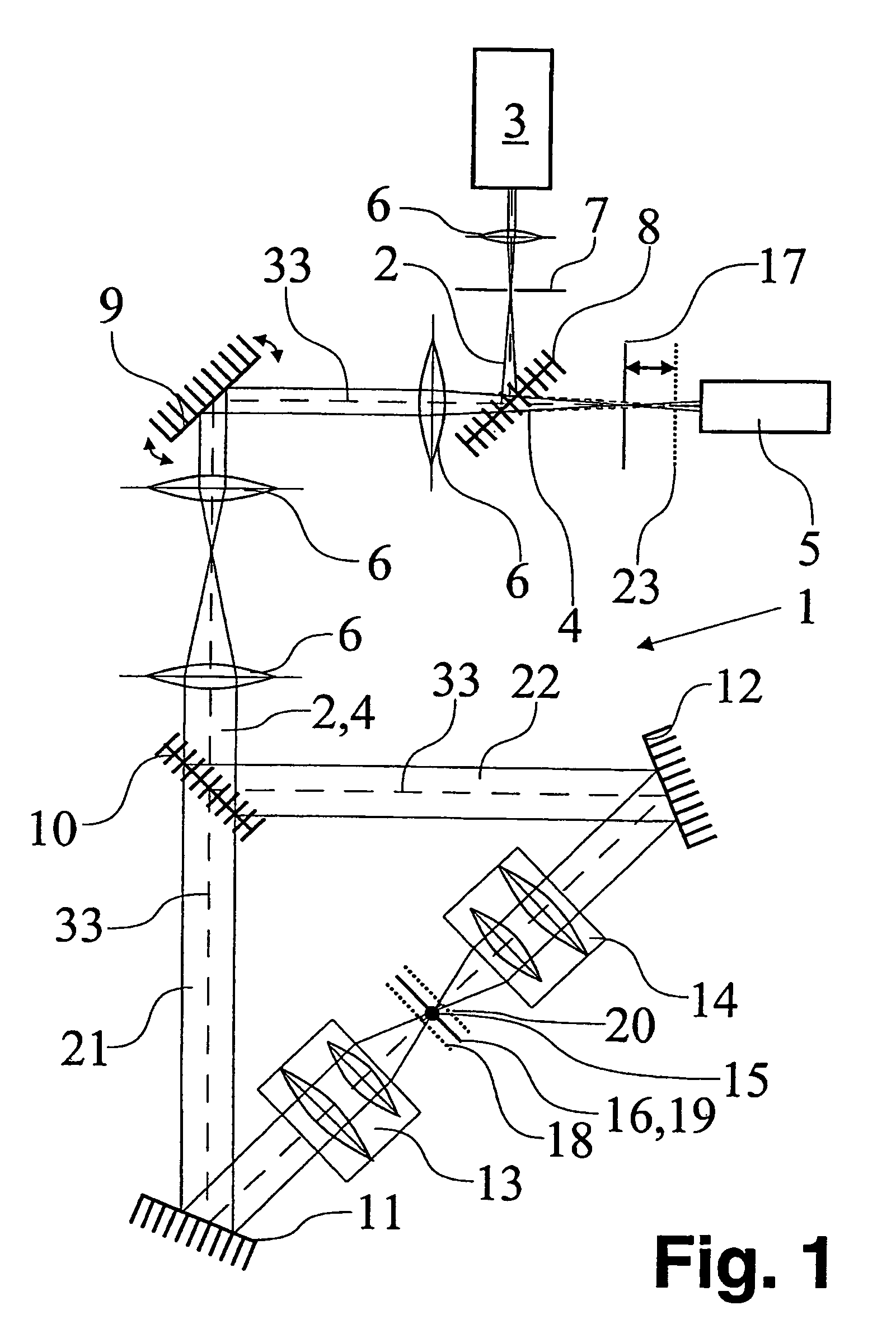
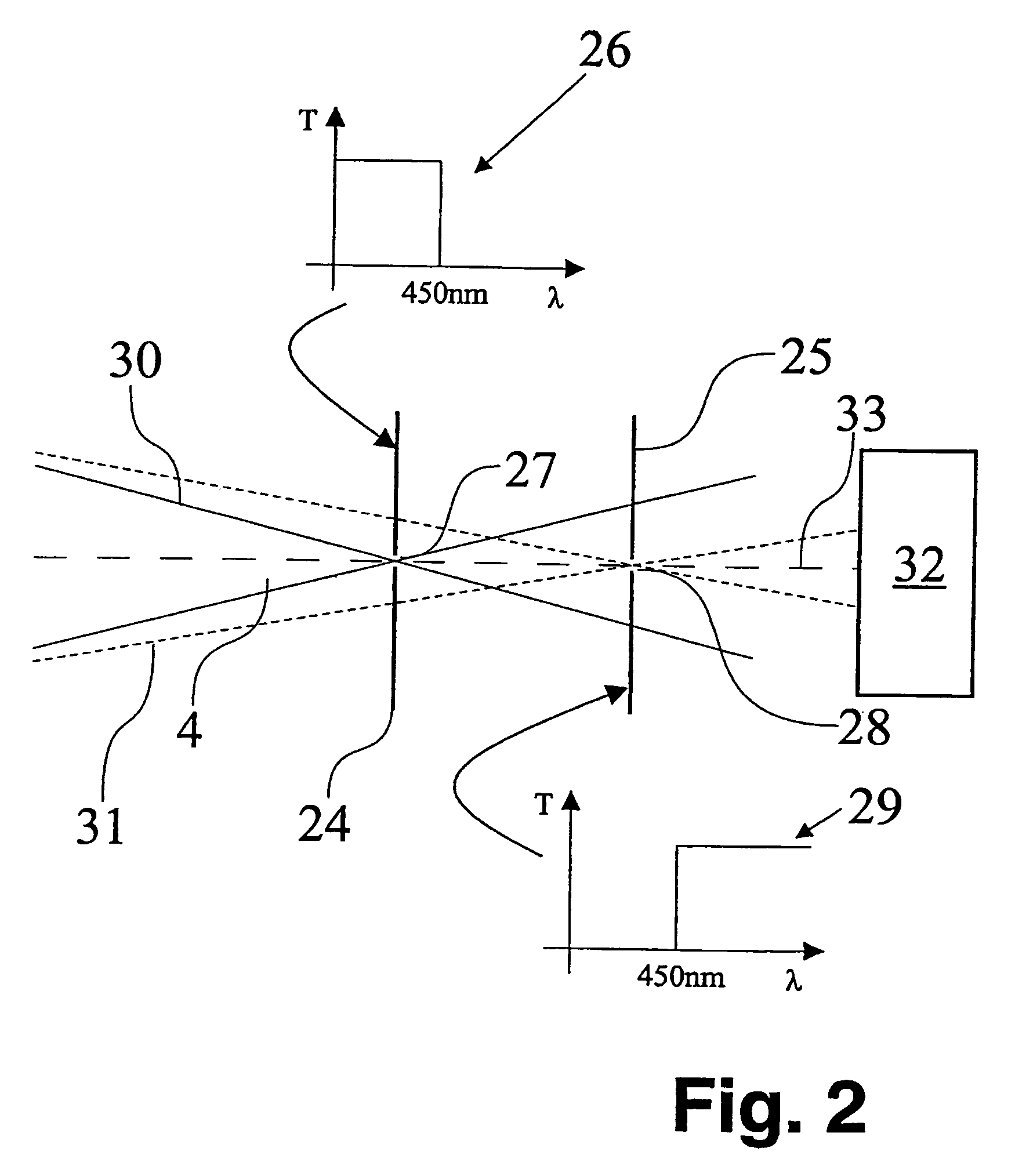
Confocal laser scanning microscope, calibration unit for a confocal laser scanning microscope and method for calibrating a confocal laser scanning microscope
InactiveUS6355919B1Simple configurationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInvestigating moving sheetsConfocal laser scanning microscopeConfocal scanning microscopy
For the purpose of calibration which is simple and can also be carried out as often as desired, an arrangement and a method for calibrating a preferably confocal laser scanning microscope, it being possible for an object (1) to be scanned by a scanning beam (2), are defined by calibration means (12) which are arranged in the plane of an intermediate image (11) and can likewise be scanned by the scanning beam (2).
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
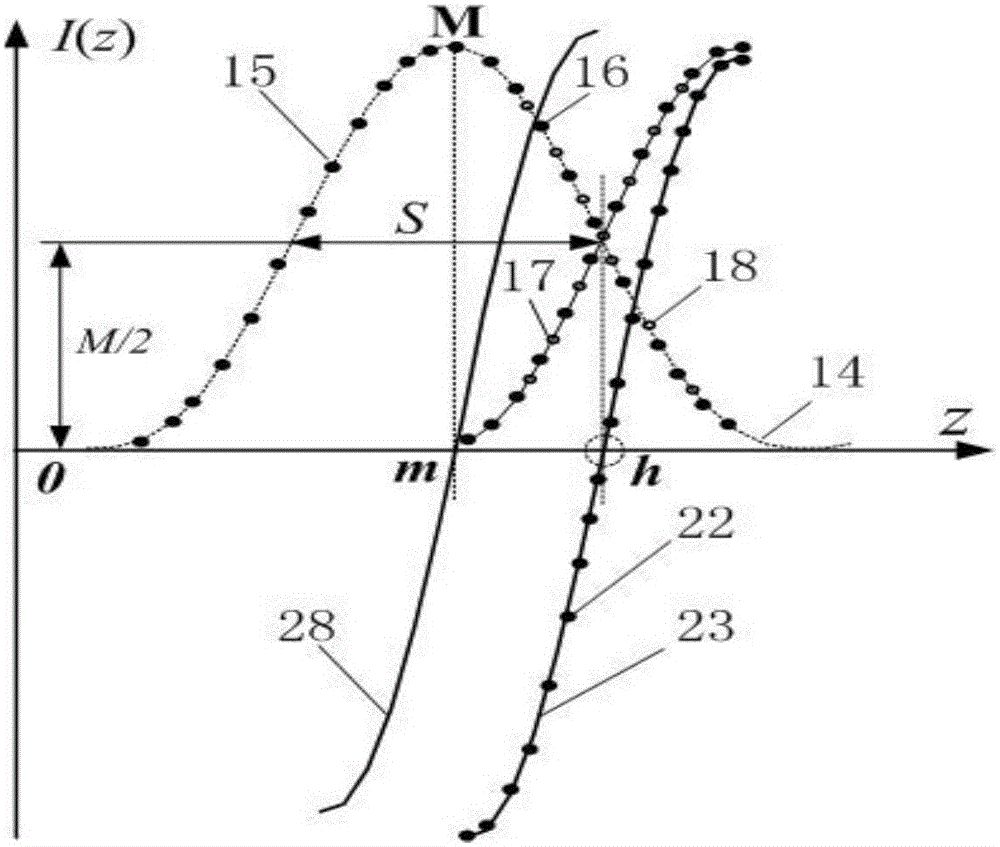
Bilateral dislocation differential confocal measuring method
ActiveCN104568390AImprove axial resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioTesting optical propertiesAxial displacementConfocal scanning microscopy
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical imaging and detecting and relates to a bilateral dislocation differential confocal measuring method. According to the method, due to the dislocation differential subtracting process on data sets on the two sides of the confocal axial characteristic curve, the position of the extreme point of a confocal system characteristic curve is accurately obtained. Due to the fact that two sections of data, close to the position of the full width at half maximum and very sensitive to axial displacement, of the cofocal characteristic curve are used for conducting the dislocation differential subtracting processing, the position, calculated by the data sections, of the extreme point of the confocal characteristic curve is more sensitive than that the position, calculated through an existing confocal characteristic curve top fitting method, of the extreme point of the confocal characteristic curve, according to the result of the bilateral dislocation differential confocal measuring method, under the condition that the structure of a confocal microscopy system is not changed, the axial resolving power, the signal-to-noise ratio and the like of the existing confocal microscopy system can be obviously improve, and a new technological approach is provided for the field of confocal imaging or detecting.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
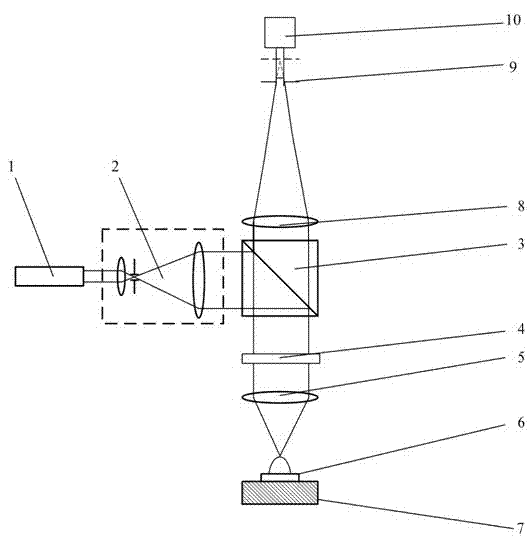
Confocal microscopy measuring device based on measured surface fluorescence excitation
The invention provides a confocal microscopy measuring device based on measured surface fluorescence excitation, and belongs to the technical field of surface topography measurement. The confocal microscopy measuring device comprises a laser device, a collimation beam expander, a polarizing beam splitter, a quarter-wave plate, a detection objective lens, a tested part, a collection objective lens, a pinhole and a detector, wherein the collimation beam expander and the polarizing beam splitter are configured on a collineation light path of the laser device along the light propagation direction; the quarter-wave plate, the detection objective lens and the tested part are configured on the reflection light path of the polarizing beam splitter; the collection objective lens, the pinhole and the detector are configured on the transmission light path of the polarizing beam splitter; a narrow band filter is contained inside the detector; and the tested part is borne by a micrometric displacement objective table, and the surface of the tested part is coated with a film in a vacuum evaporating coating method. By means of the design that surface characteristics of the tested surface are changed through film coating, the fact that measurement light can return back to a detection system after being reflected by the tested surface is guaranteed, the difficult problems of detection of a large numerical aperture (NA) and high gradient surface are resolved, and the confocal microscopy measuring device is suitable for ultra precise measurement of three-dimensional shapes with large NA and high gradient spherical surfaces, aspheric surfaces and free-form surfaces.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
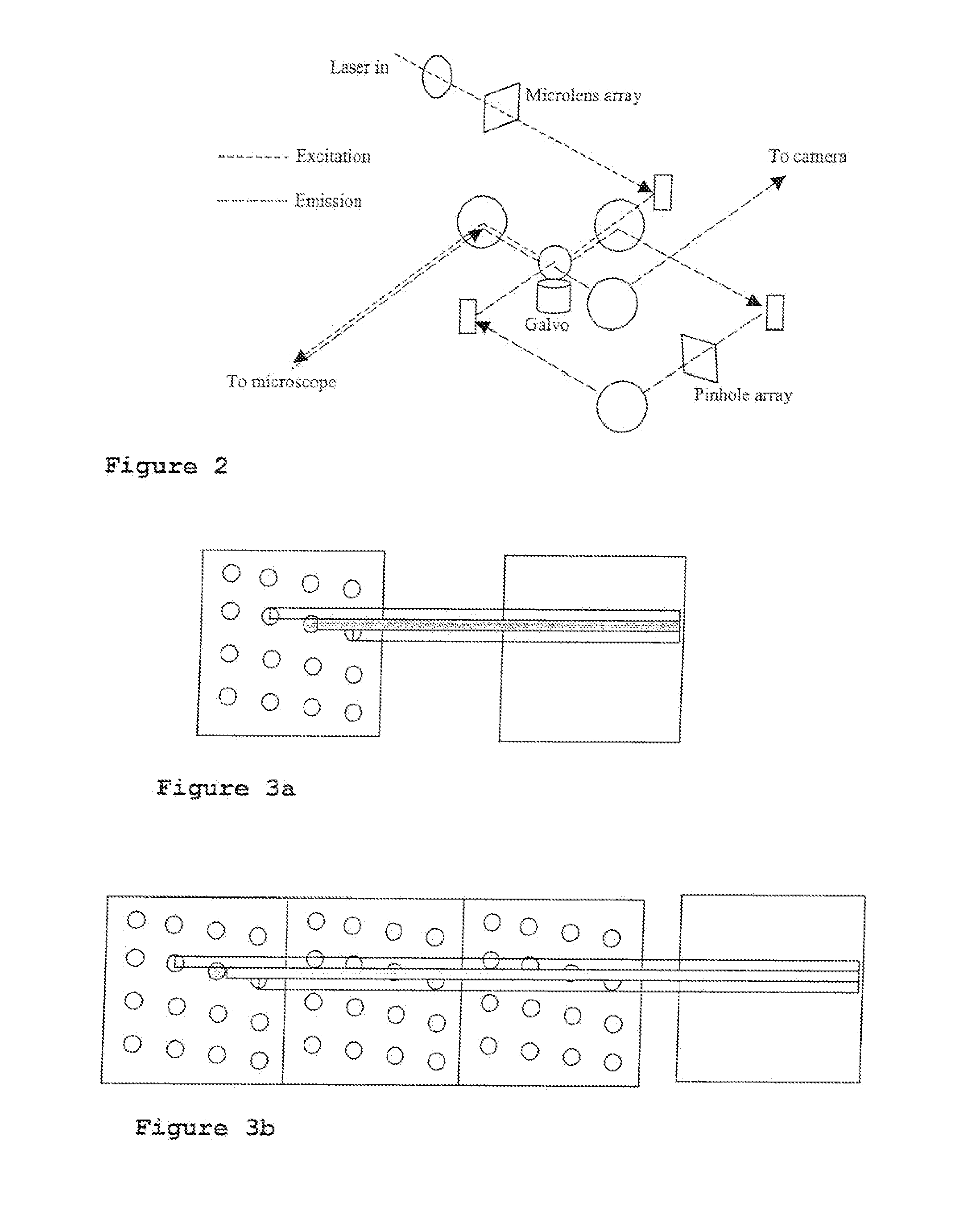
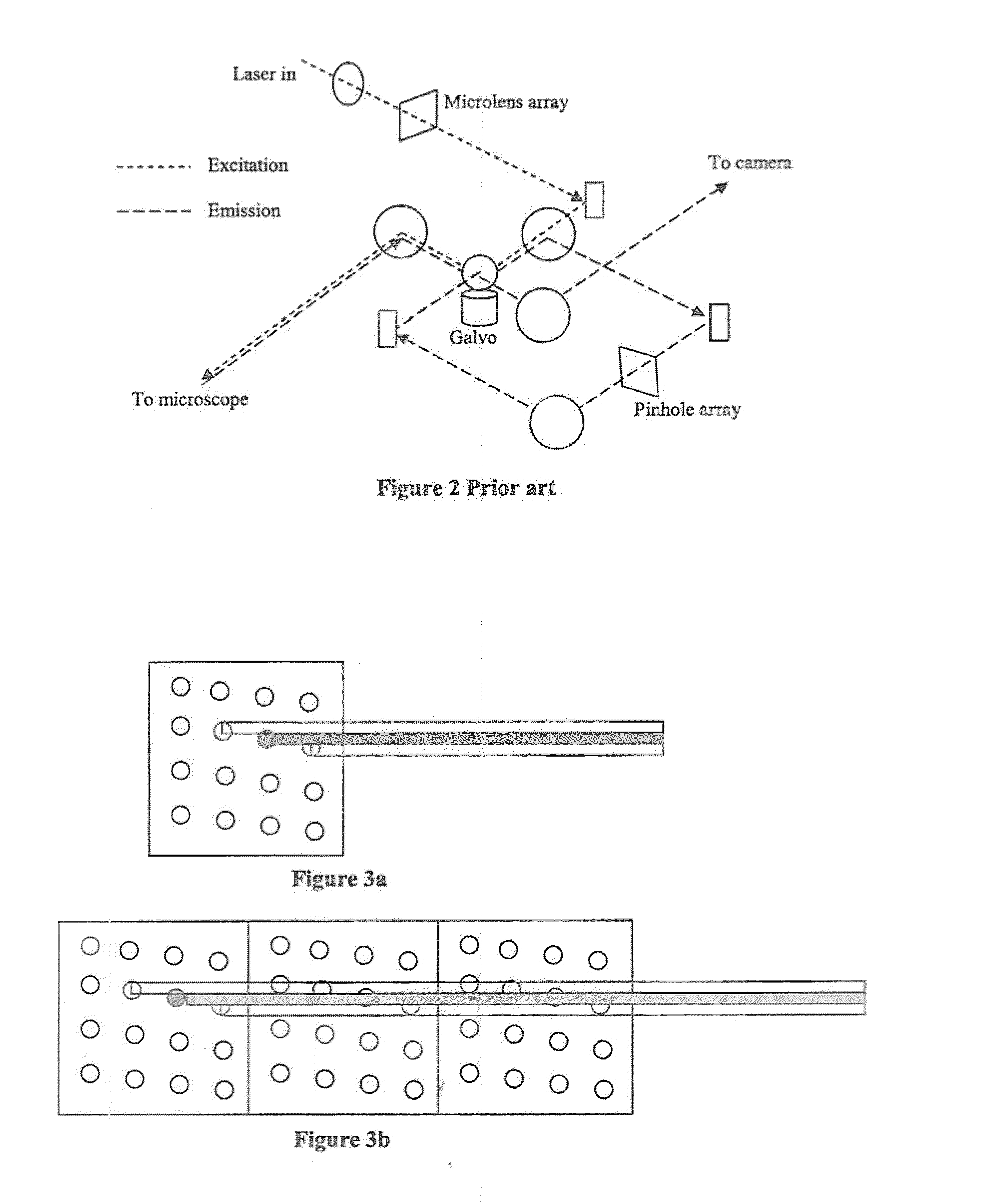
Laser confocal scanning microscope and methods of improving image quality in such microscope
InactiveUS20080037114A1High strengthReduce appearance problemsMicroscopesModulation functionImaging quality
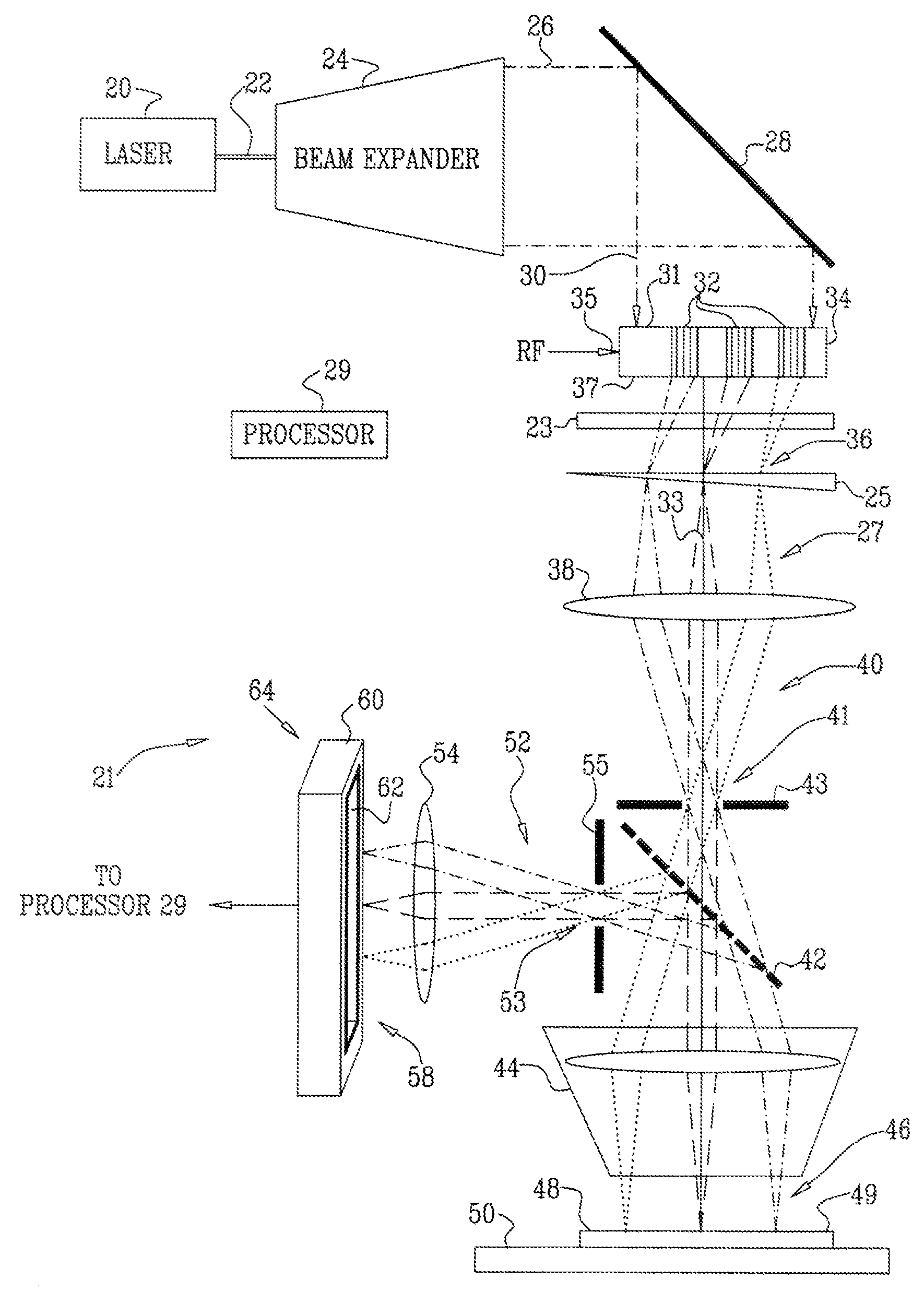
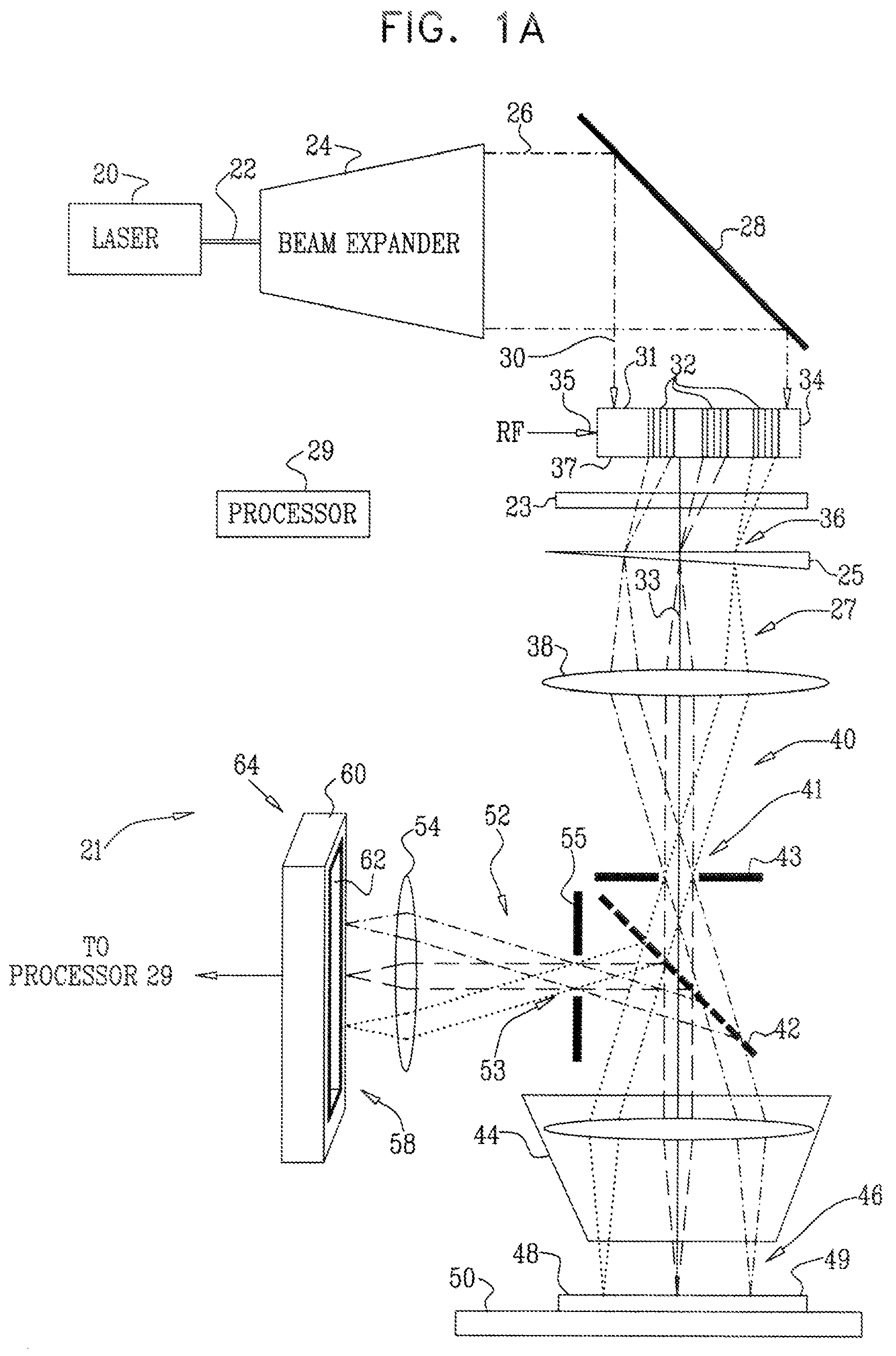
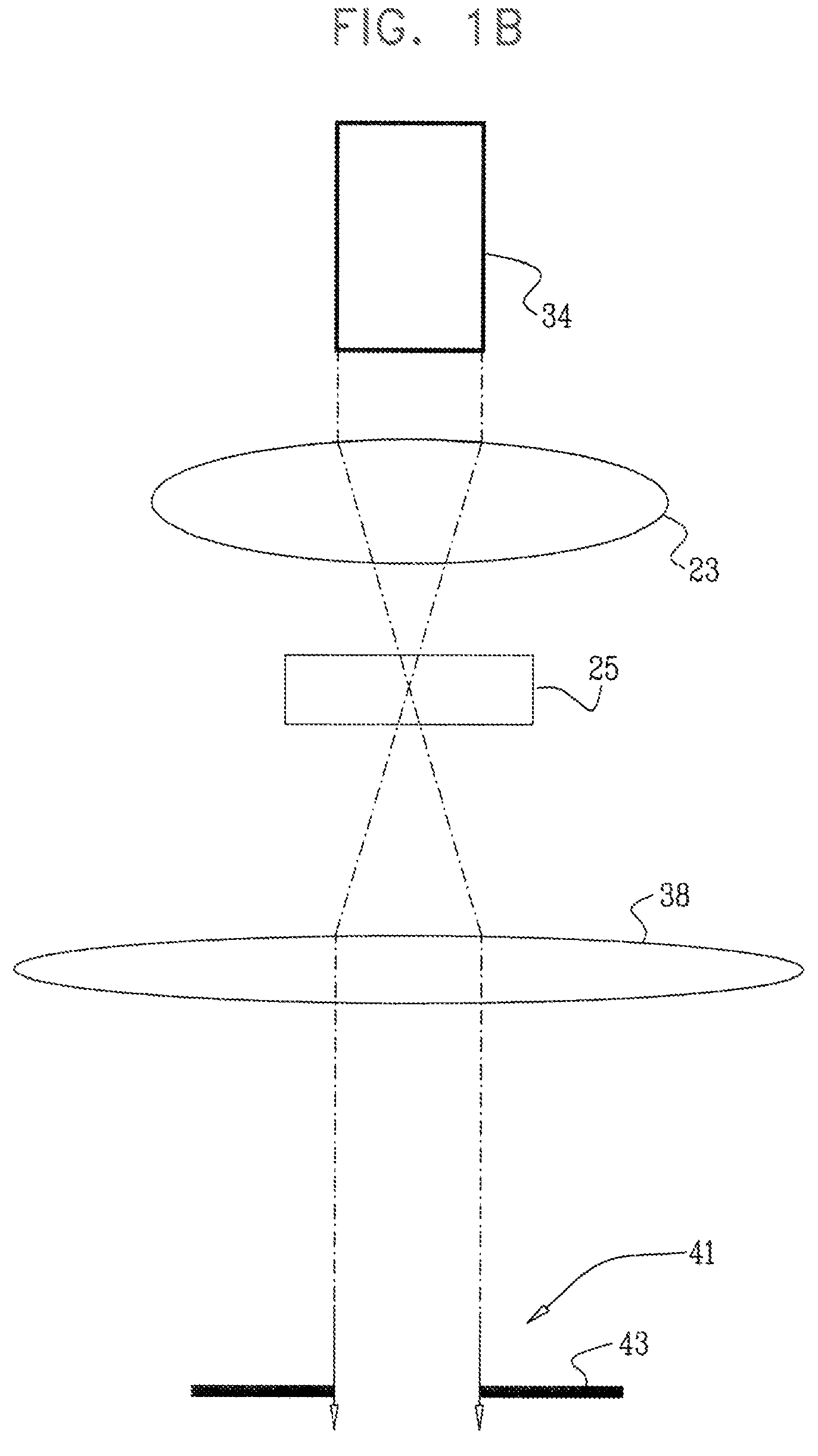
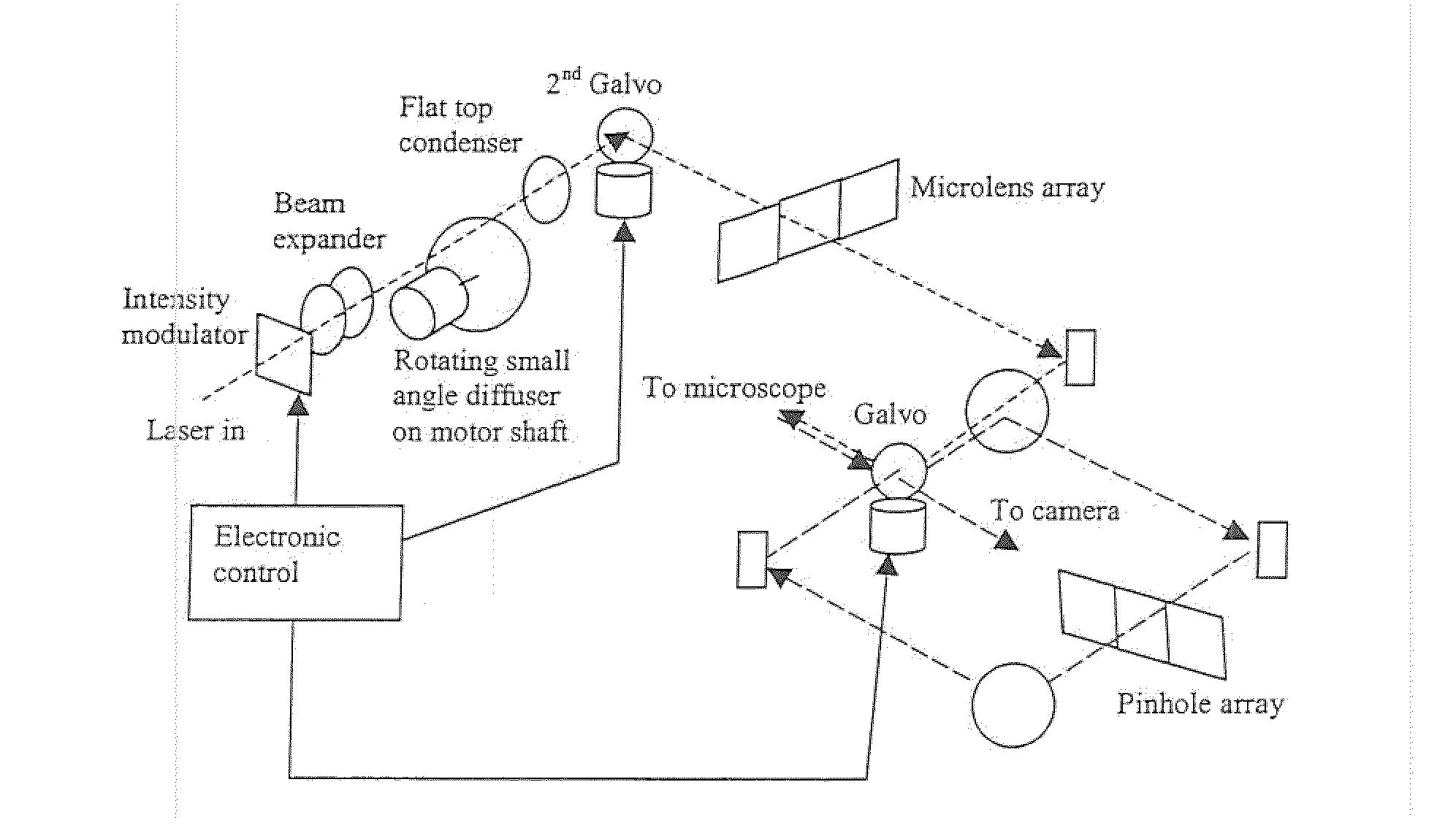
According to a first embodiment the invention provides for increasing the throughput and reducing the striping due to imperfections in the microlens and / or confocal aperture arrays of a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope by increasing the number of repeat patterns in the microlens and confocal aperture arrays to more than one, and incorporating an intensity modulation function that ensures constant integrated image intensities at the image detector independent of the instantaneous speed of scanning. According to a second embodiment the invention provides for reducing the striping in a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope by introducing a second galvanometer mirror such that the emitted laser light beam is descanned at the image (sample) plane. According to embodiments three to five, striping in a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope is also reduced by destroying coherency in the emitted light beam by insertion of a small angle diffuser, by flattening the Gaussian intensity distribution of the emitted laser light beam and changing the characteristics of the beam expander. According to embodiment six the invention provides for changing the degree of confocality of a Laser Confocal Scanning Microscope by inserting a mechanism that offers a range of selectable confocal aperture sizes.
Owner:VISITECH INT LTD
Confocal-scanning microscopic imaging method and system based on laser heterodyne interferometry
ActiveCN104359862ASame polarization directionImprove beat frequency efficiencyPhase-affecting property measurementsConfocal scanning microscopyFluorescence
The invention discloses a confocal microscopic imaging system based on the laser heterodyne interferometry. The confocal microscopic imaging system is characterized in that on the basis of a microscope optical system and a scanning part of the existing laser confocal microscope, a frequency-shifting part is added, and accurate measurement is realized by combination of the optical heterodyne interferometry. The confocal microscopic imaging system disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the ultrahigh lateral resolution of a confocal scanning microscope is fully utilized, and simultaneously accurate phase information is acquired for replacing intensity information, so that not only is the axial resolution increased, but also a series of problems brought by use of a fluorescent dye are avoided; and a transparent phase object can be measured under the condition without marks.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPTO MEDIC TECH CO LTD
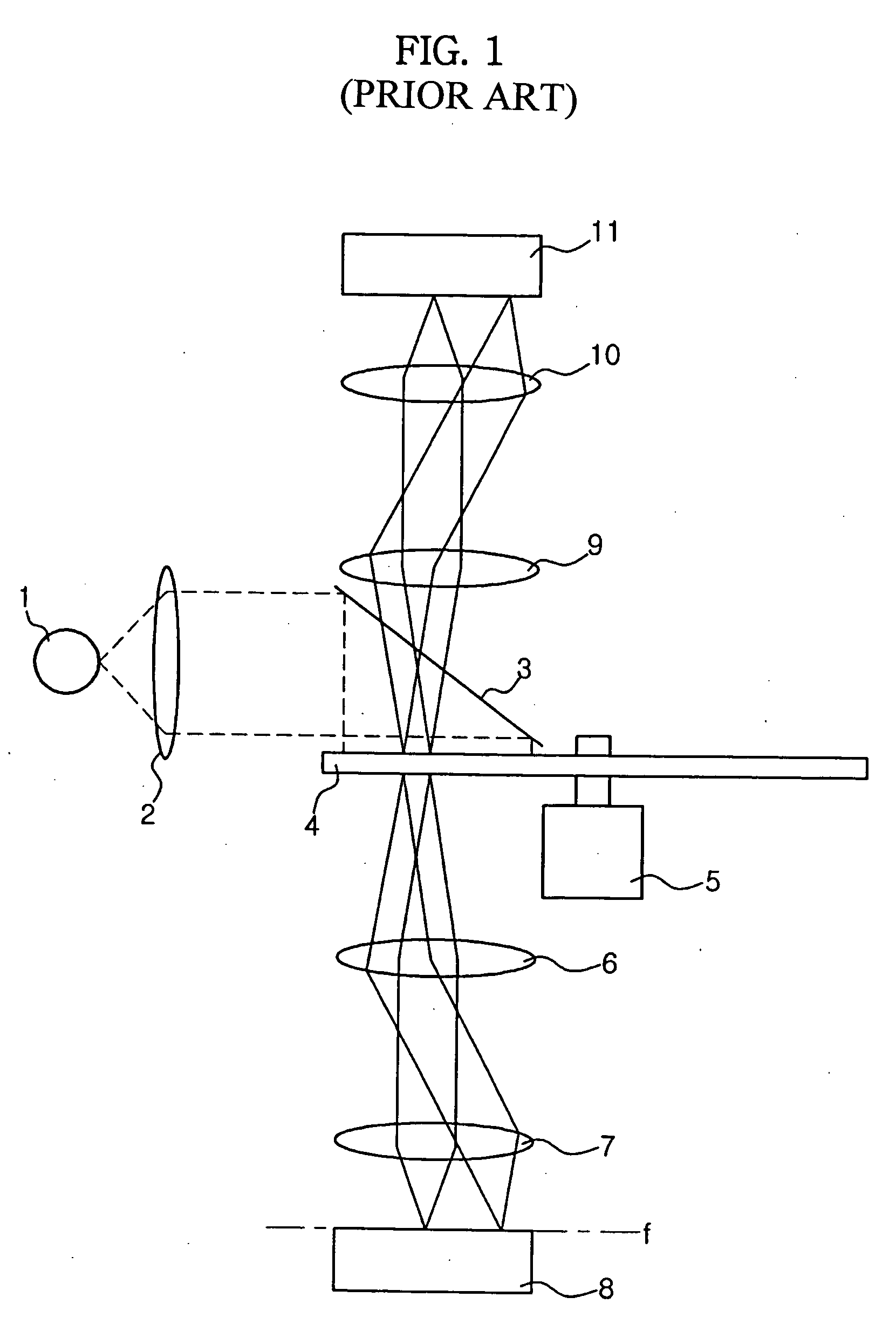
Laser microscope and confocal laser scanning microscope
InactiveUS6621628B1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansConfocal laser scanning microscopeConfocal scanning microscopy
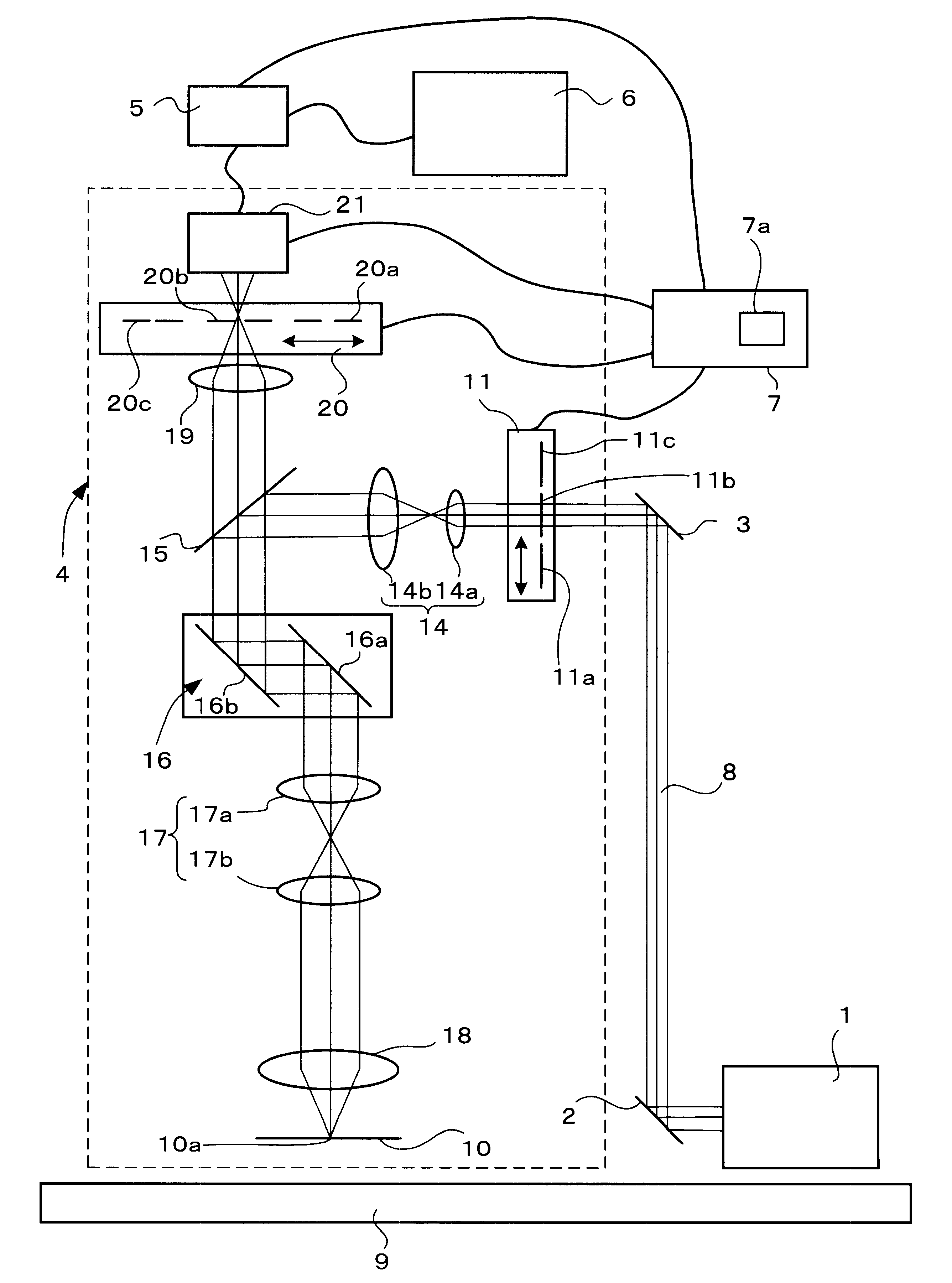
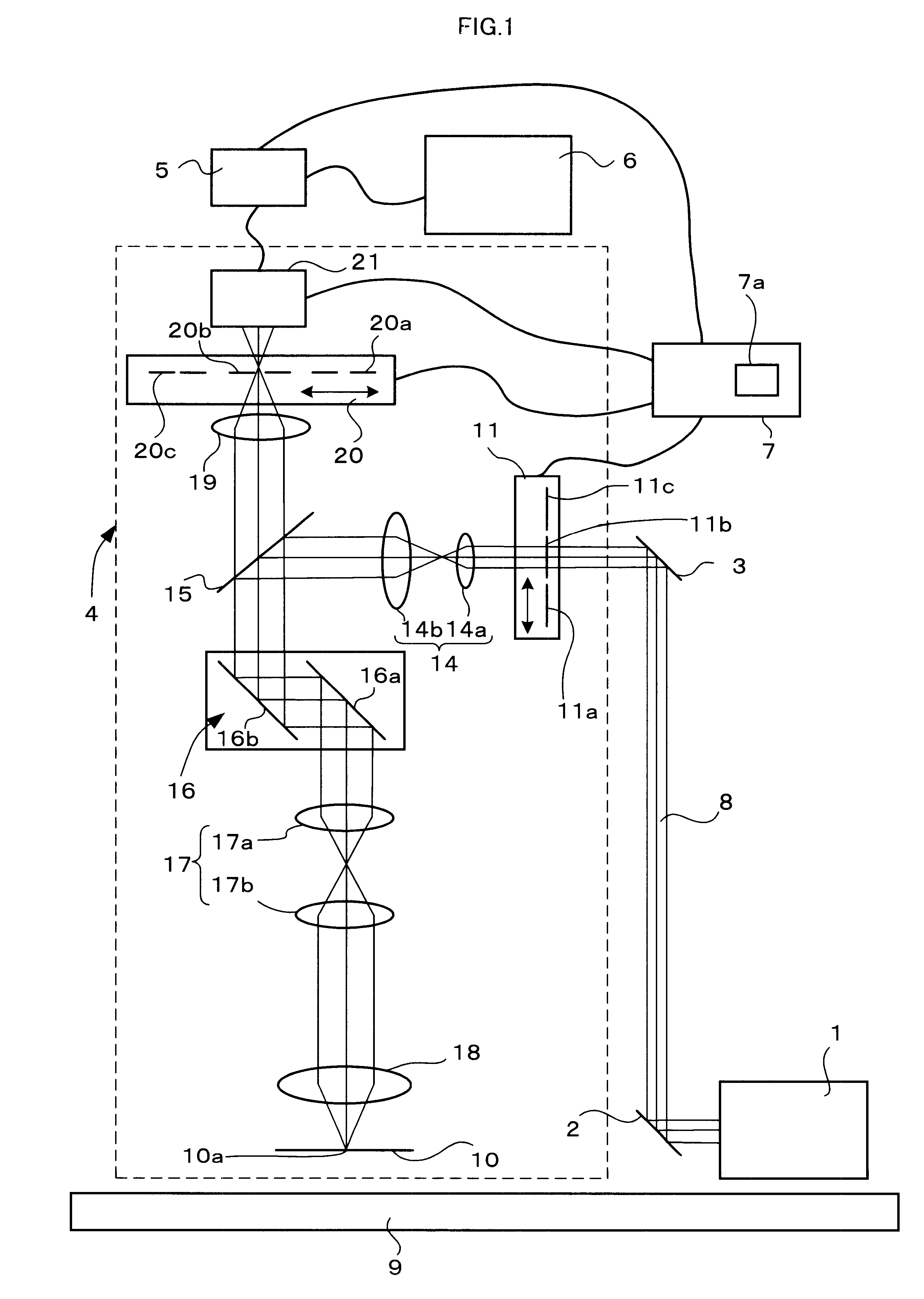
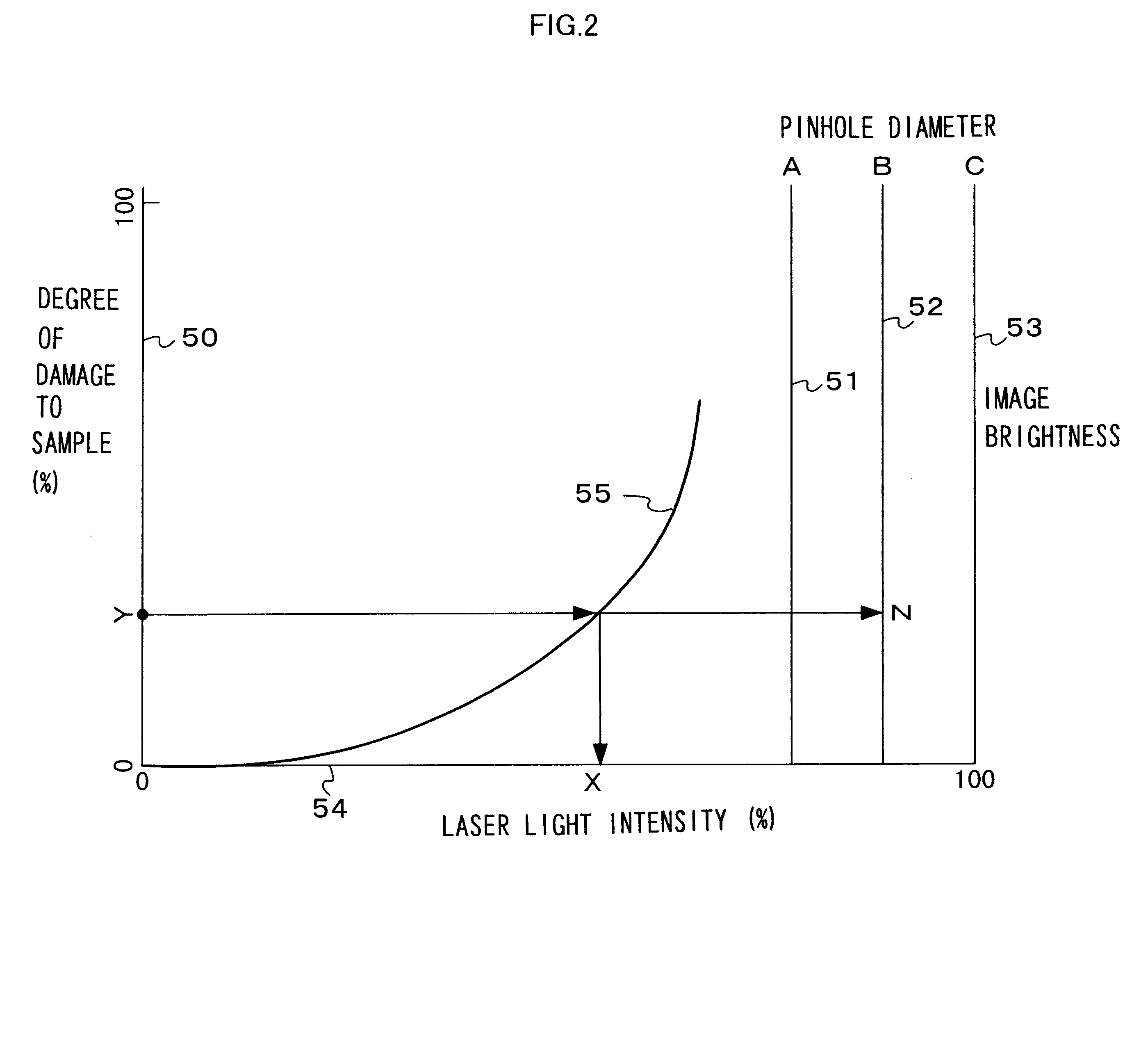
A laser microscope includes: a light source that emits deep ultraviolet laser light to be irradiated on a sample; a limiting device that sets a limit to an intensity of the deep ultraviolet laser light irradiated on the sample; a detection device that detects the deep ultraviolet laser light having been reflected from the sample; a storage device that stores first information related to damage to the sample corresponding to the intensity of the deep ultraviolet laser light; and a control device that controls the limiting device based upon the first information when a sample damage limit is input from outside.
Owner:NIKON CORP
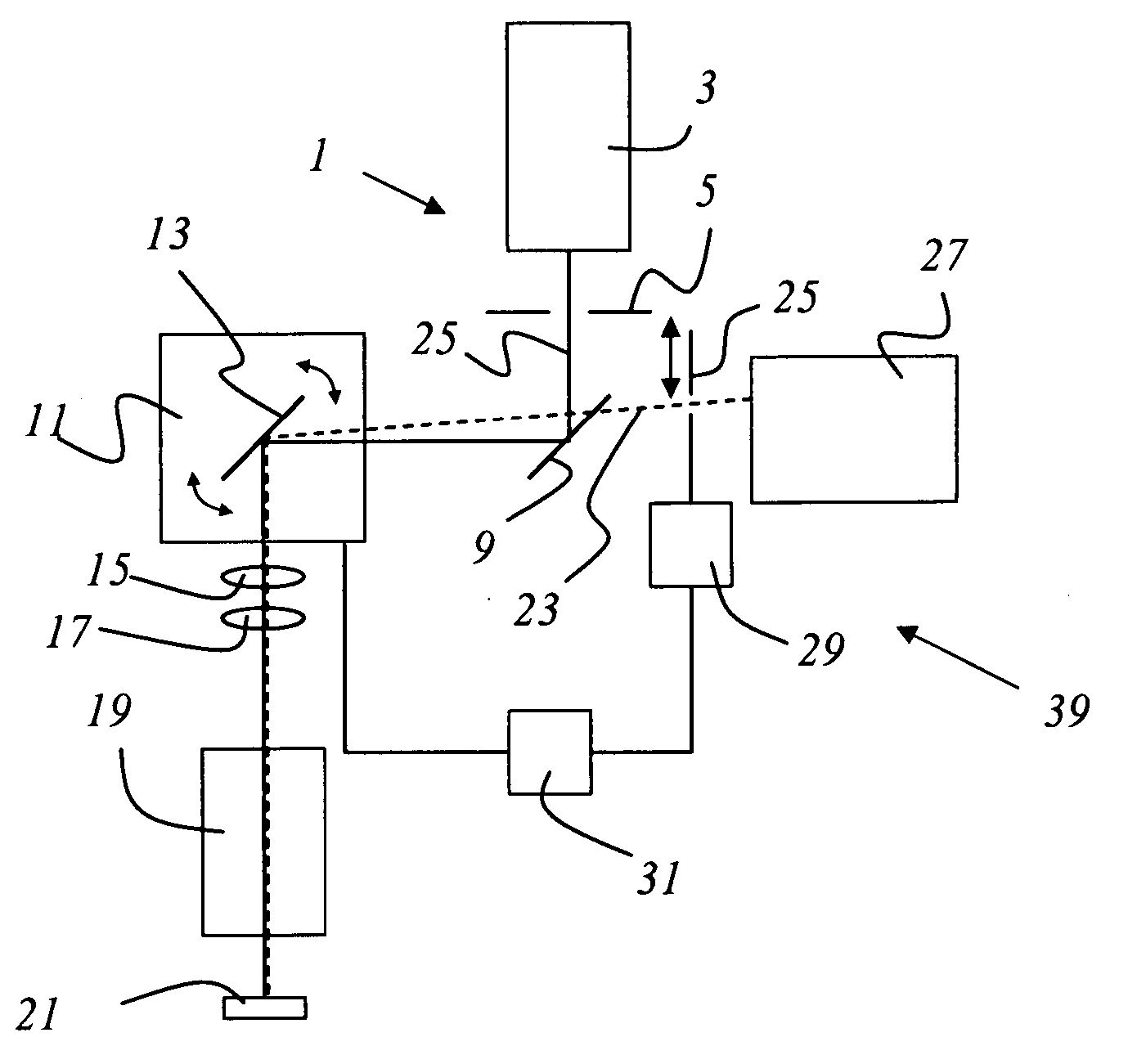
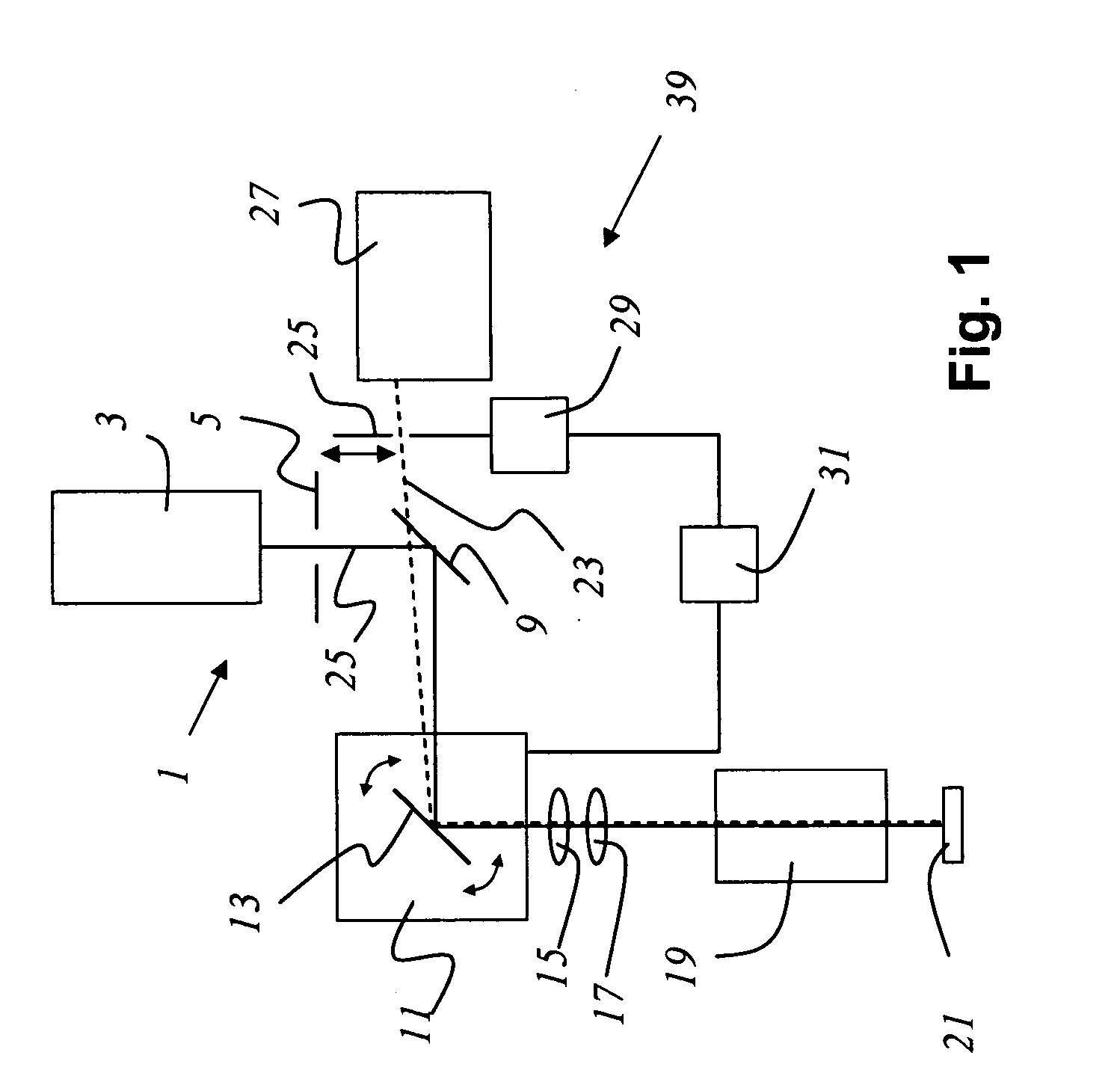
Double confocal scanning microscope
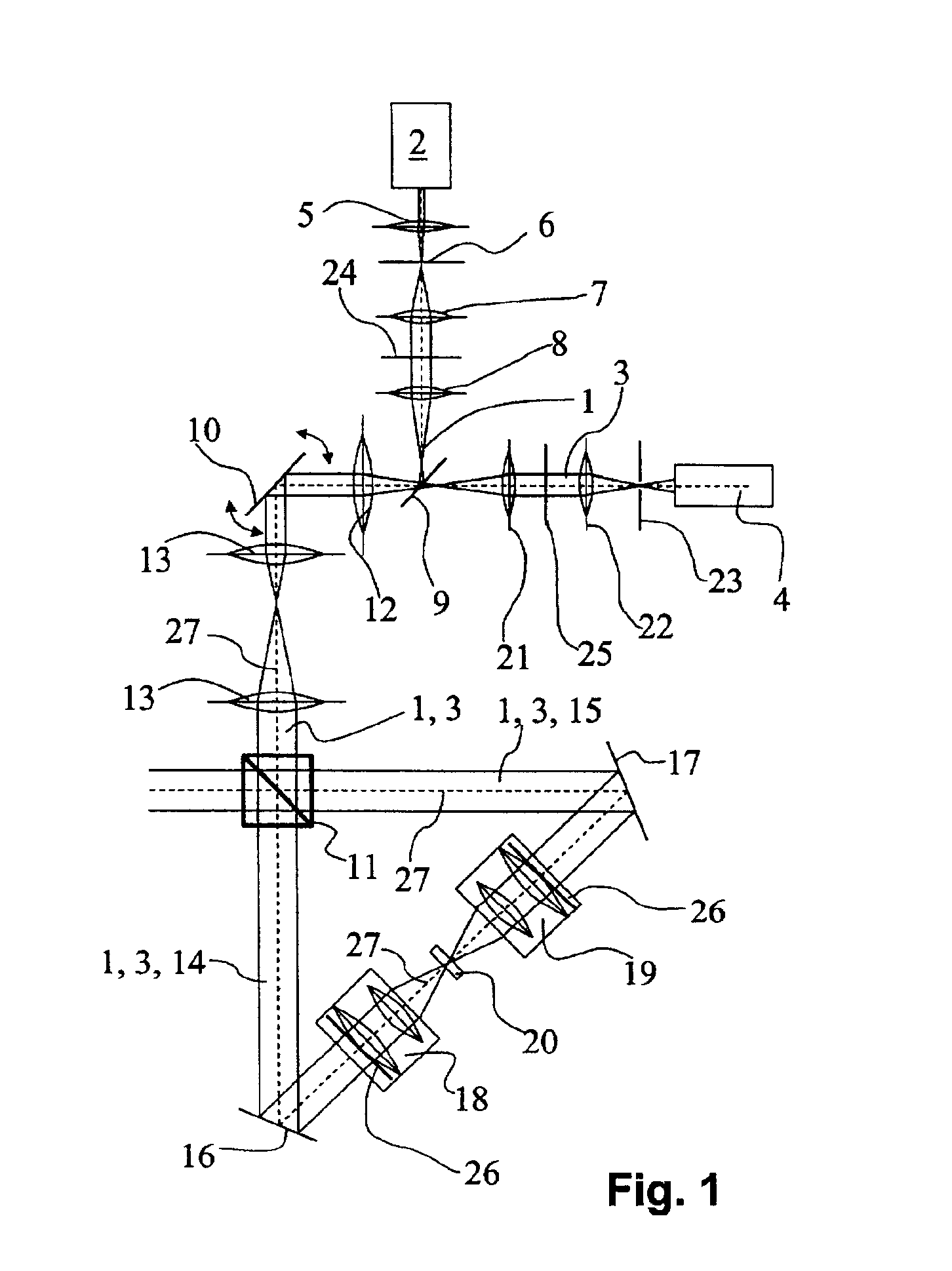
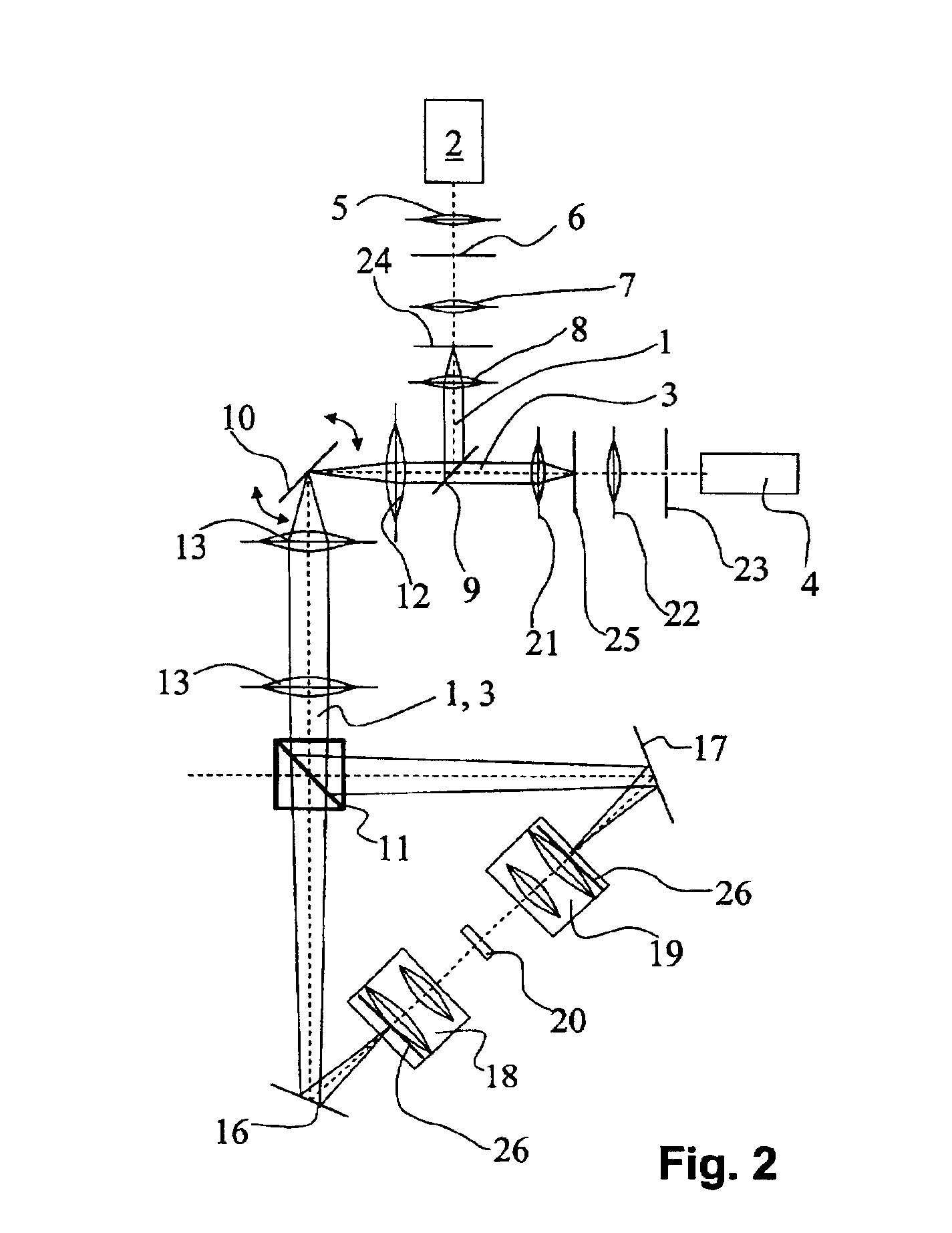
InactiveUS6891670B2Eliminate the problemPromote resultsMicroscopesConfocal scanning microscopyLight beam
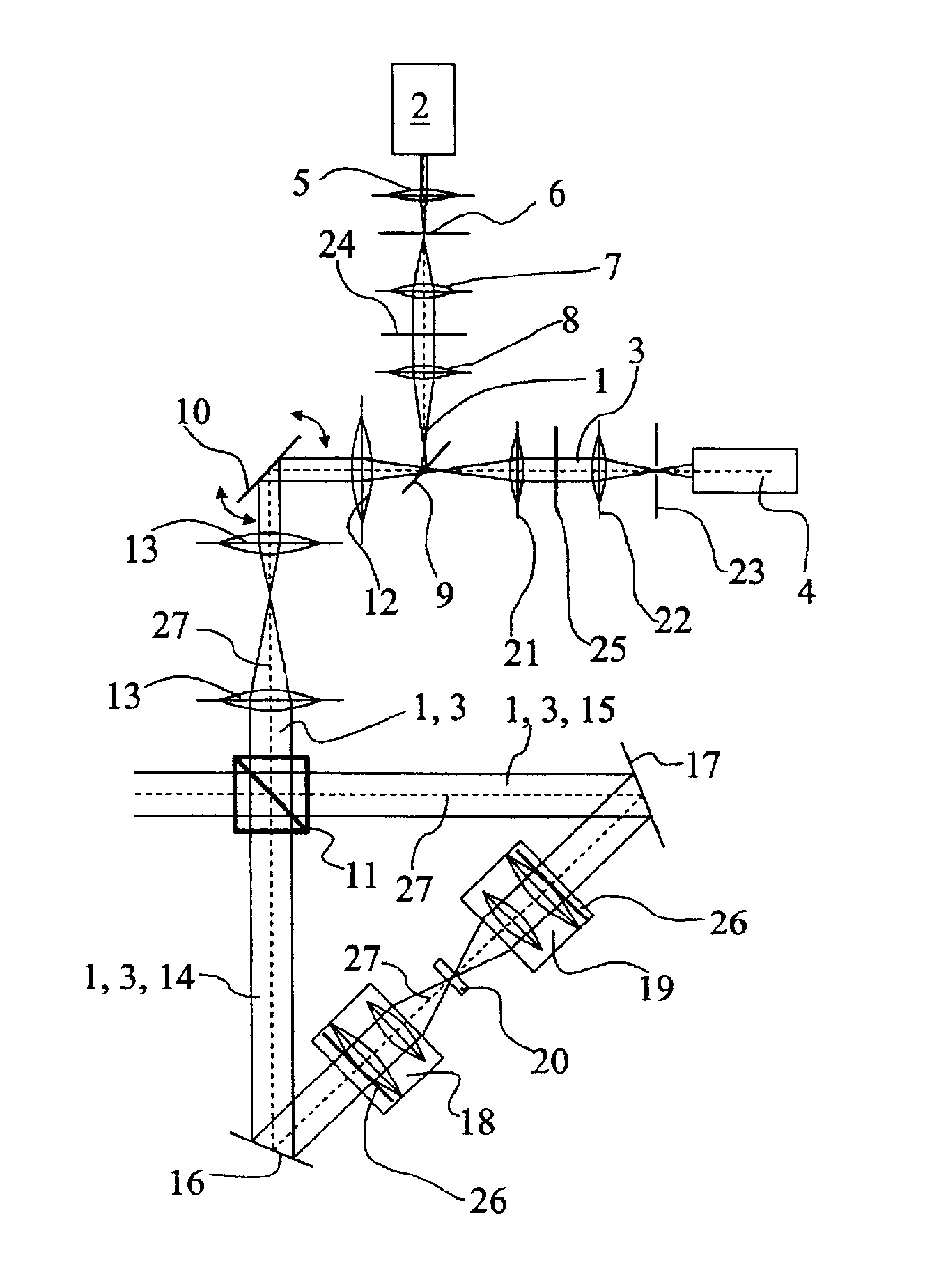
The present invention concerns a double confocal scanning microscope having an illuminating beam path (1) of a light source (2) and a detection beam path (3) of a detector (4), and in order to eliminate at their cause the problems of reconstruction methods. To do so, at least one optical component (24, 25) acting on the illuminating and / or detection beam path (1, 3) is provided, and is configured in such a way that it influences the amplitude and / or phase and / or polarization of the light; and the characteristics of the double confocal illumination and / or detection are thereby modifiable.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Fluorescence labeling method for cotton pollen tube microfilament framework
InactiveCN101477000AOmit the step of enzymatic digestionHigh fluorescence staining efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationZoologyRefrigerated temperature
The invention relates to a method for carrying out fluorescence labeling on an actin filament framework of a cotton pollen tube, which belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises: perforating a glass slide to make a chamber for cultivating the pollen tube; cultivating pollen in the chamber to bourgeon the pollen tube; fixing the cultivated pollen tube by 50mm Pipes buffer solution (pH6.9) containing 4 percent of paraformaldehyde for 1 to 2 h; washing the pollen tube, and putting the pollen tube into 0.1 to 0.2 percent glycerin (or 0.1 to 0.2 percent Triton X-100) for 3 to 4 h at a room temperature (or over night in a 4 DEG C refrigerator); washing the pollen tube, and staining the pollen tube through a phalloidine labeled by TRITC(rhodamine) with the concentration of 1 to 2.5 mu g / ml; and washing the pollen tube, and then observing the pollen tube under a confocal scanning microspope. The method has the advantages of simple operation, good labeling effect and important practical application value, and can play an important part in researching the framework of a cotton pollen tube cell and fertilization reproduction.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
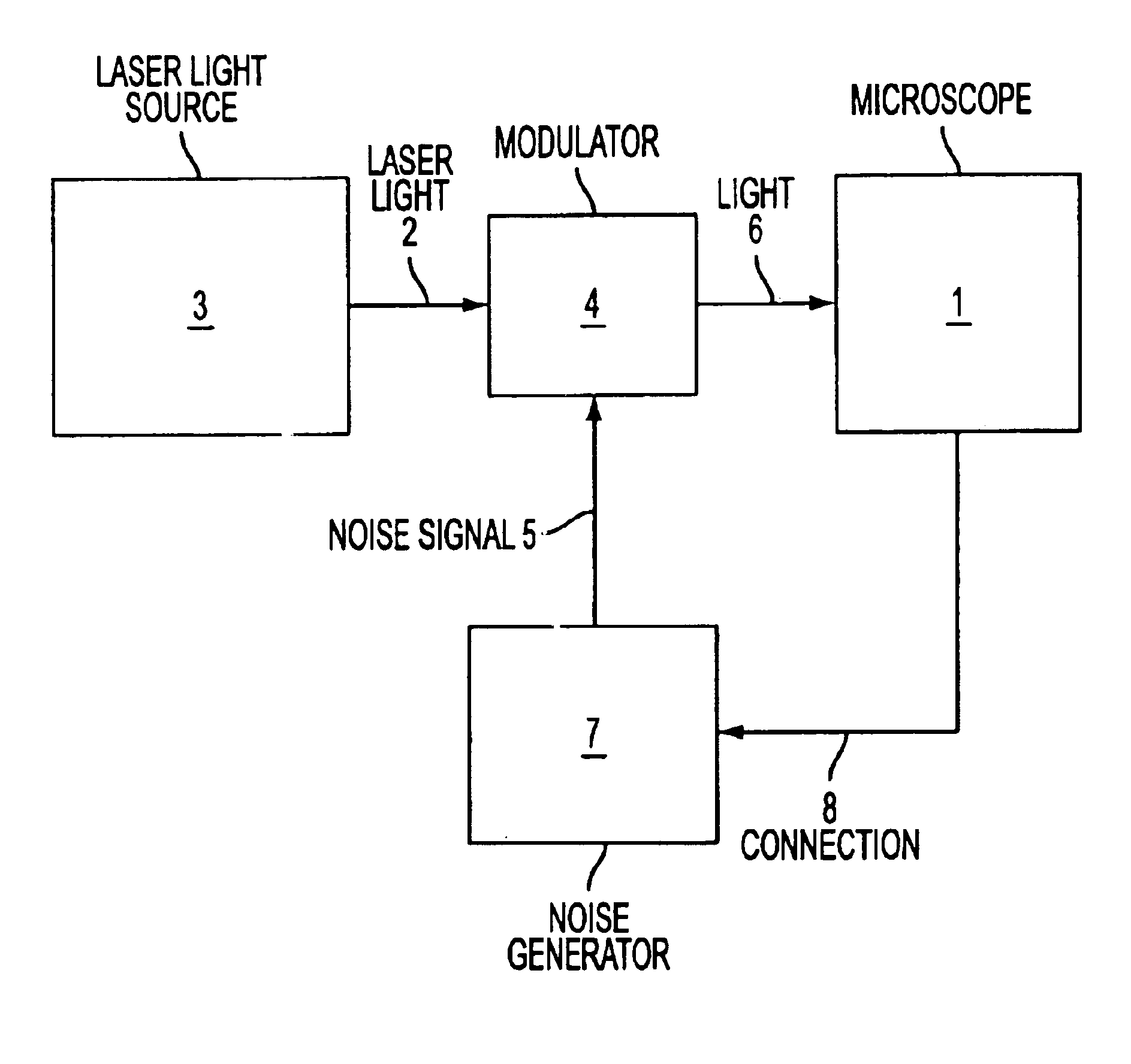
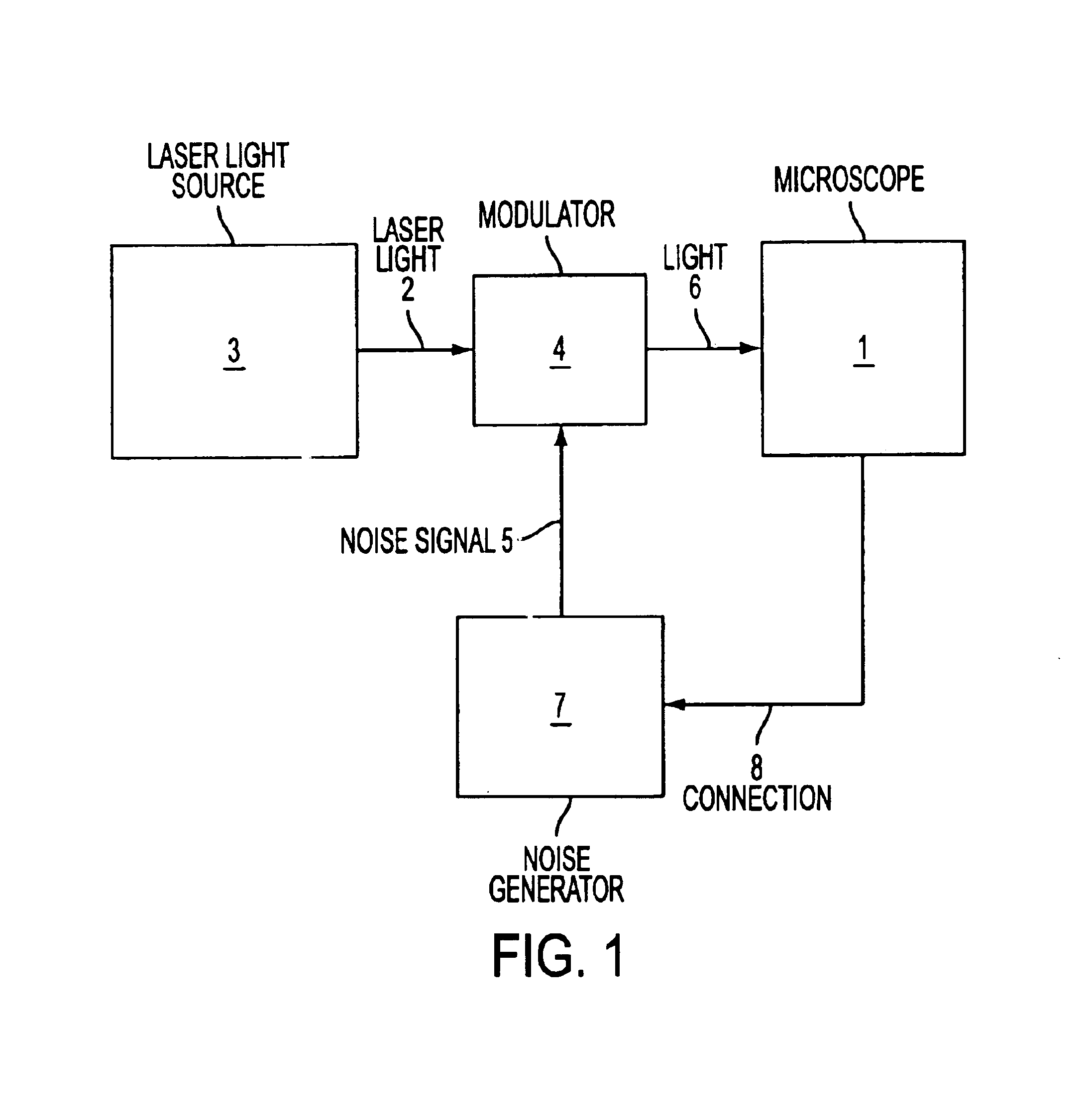
Method for illuminating an object with light from a laser light source
InactiveUS6864989B2Laser detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsConfocal scanning microscopyInterference phenomenon
A method for illuminating an object with light (2) from a laser light source (3), preferably in a confocal scanning microscope (1). With the method according to the invention, it is possible to reduce the coherence length of the laser light, so that disruptive interference phenomena can be substantially eliminated. Should interference phenomena nevertheless be formed, these are to be influenced in such a way that they have no effect on the detection. The method according to the invention is characterized in that the phase angle of the light field is varied by a modulator in such a way that interference phenomena do not occur in the optical beam path, or occur only to an undetectable extent, within a predeterminable time interval.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Confocal scanning microscope
A confocal scanning microscope for scanning a sample has an illumination beam path that encompasses at least one point light source and a beam deflection device, and has further a detection beam path that encompasses at least one detection pinhole and the beam deflection device. The routing of the illumination beam path and / or of the detection beam path is adaptable to the scanning speed.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
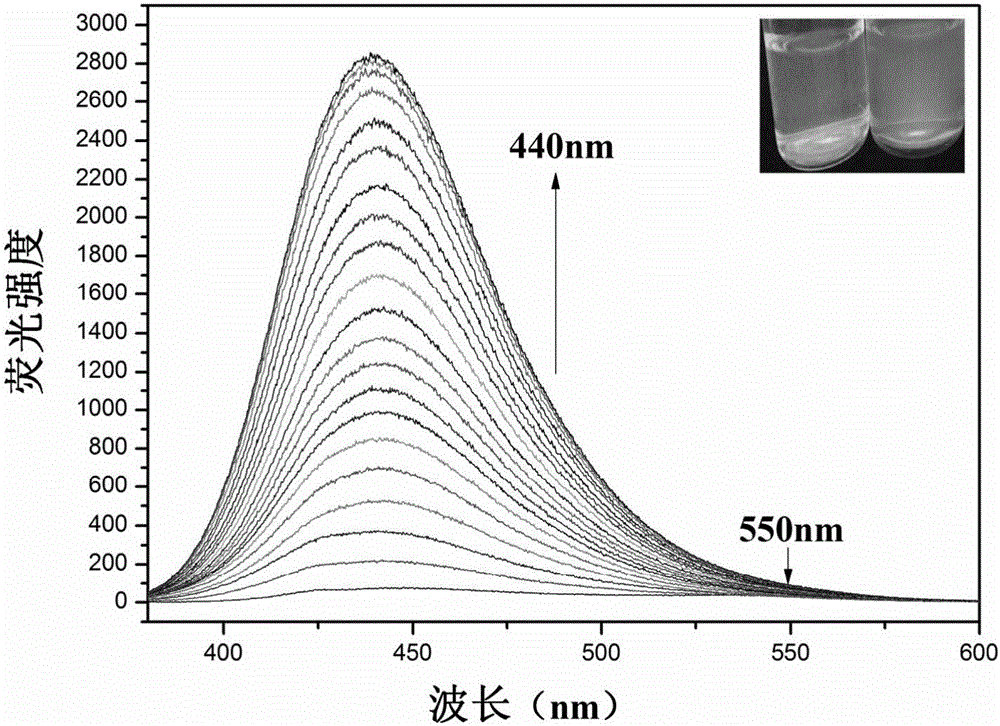
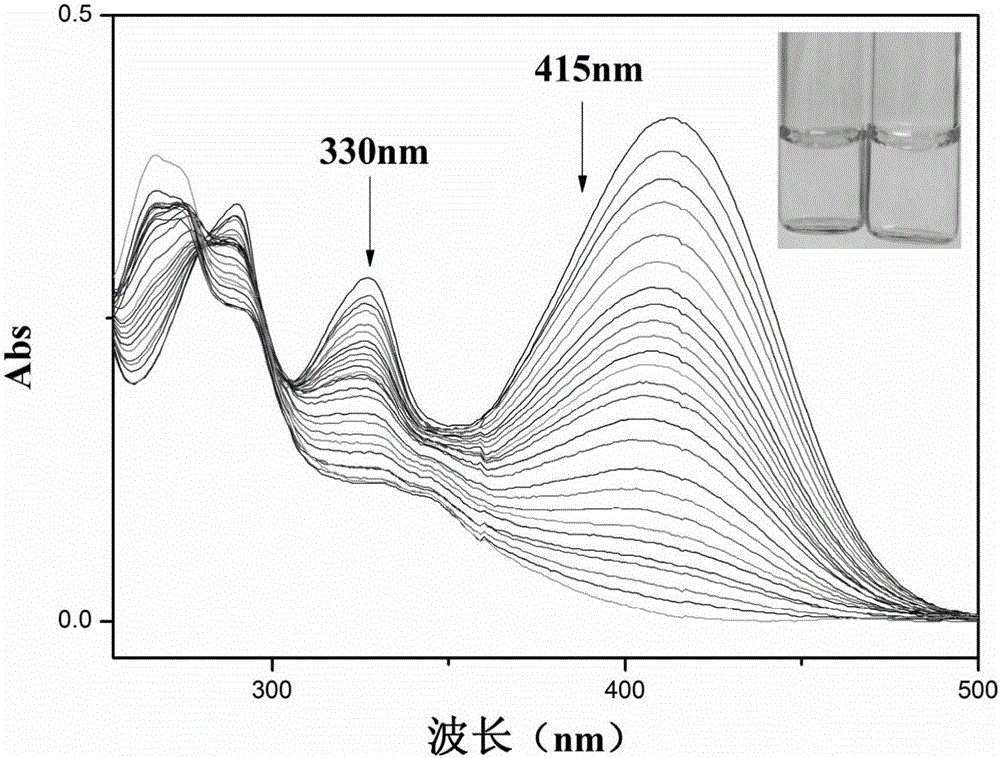
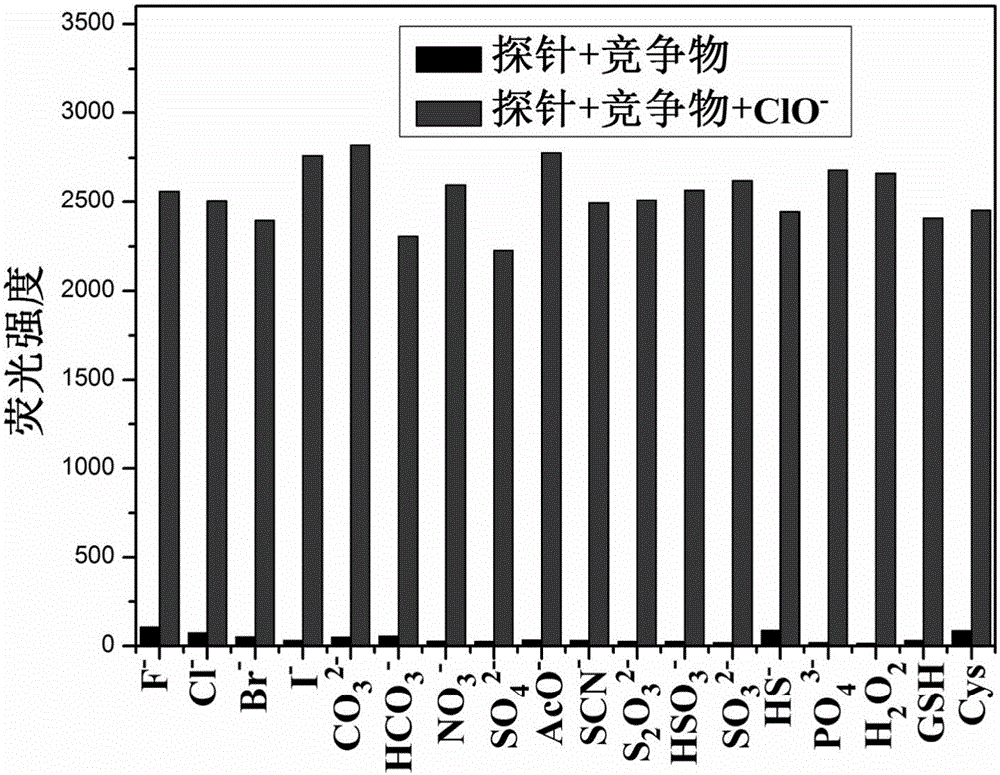
Carbazole fluorescent probe for detecting ClO- and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105968094ACell membrane penetration is goodSimple reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationSolvent
The invention discloses a carbazole fluorescent probe for detecting ClO- and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the fluorescent probe comprises the steps that carbazole and bromobutane are dissolved in a DMSO / KOH mixed solution, stirred and heated, and 9-butyl carbazole is generated; a DMF is used as a solvent, POC13 reacts with the product, and 3-formoxyl-9-butyl carbazole is obtained; the 3-formoxyl-9-butylcarbazole and 3-pyridine acetonitrile are mixed in methyl alcohol, potassium tert-butoxide is added, and 1-methyl-3-(9-butylcarbazole-3-cyanogen vinyl)pyridine is generated; the product is dissolved in HCC13, CH3I is added, suction filtration and drying are carried out, and a saffron yellow solid product is obtained. The probe displays high sensitivity and selectivity for CIO- and displays large Stocks displacement when detecting CIO- ions, the detection process is easy and convenient, and the detection result is accurate. By means of laser confocal scanning microscopy, a fluorescence image of the novel fluorescent probe in living cells can be obtained.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Scanning microscopy
ActiveUS7684048B2Good imaging propertiesImprove featuresPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsConfocal scanning microscopyLight beam
Apparatus for imaging a surface, including scanning optics, which are configured to scan and focus one or more traveling beams onto the surface so as to form one or more traveling spots thereon. The apparatus also includes collection optics, which are arranged to collect radiation scattered from the one or more traveling spots and to focus the radiation to form one or more image spots traveling along a line. The apparatus also has a detecting assembly, which consists of a detector which is configured to generate a signal in response to the one or more traveling image spots, and a detector entry port interposed between the collection optics and the detector, which is coincident with the line. The apparatus also includes phase and / or polarization altering elements for the traveling beams.
Owner:APPL MATERIALS ISRAEL LTD
Laser confocal scanning microscope and methods of improving image quality in such microscope
InactiveUS20110002024A1Selectable degreeImprove throughputMicroscopesModulation functionImaging quality
Owner:VISITECH INT LTD
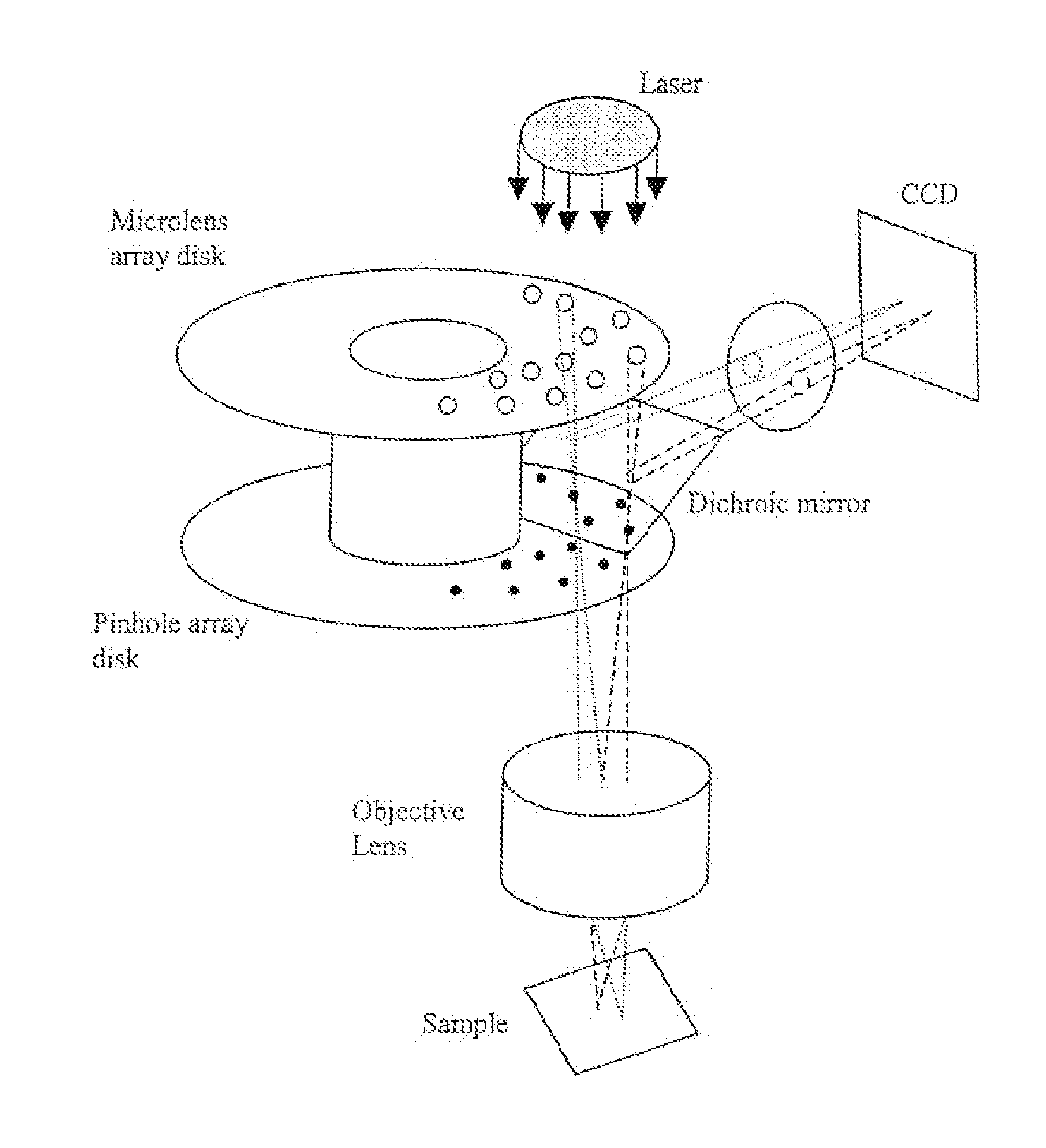
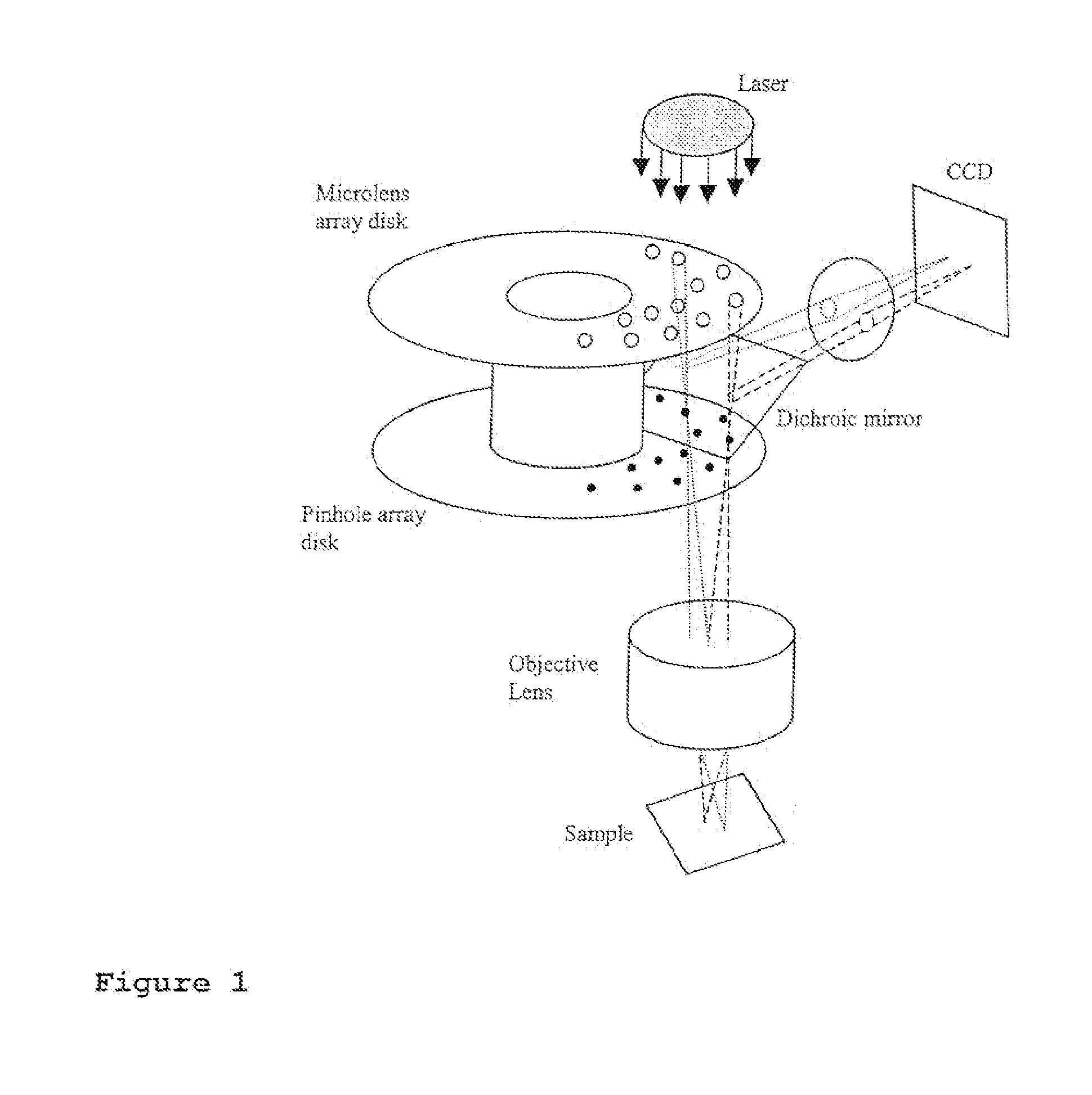
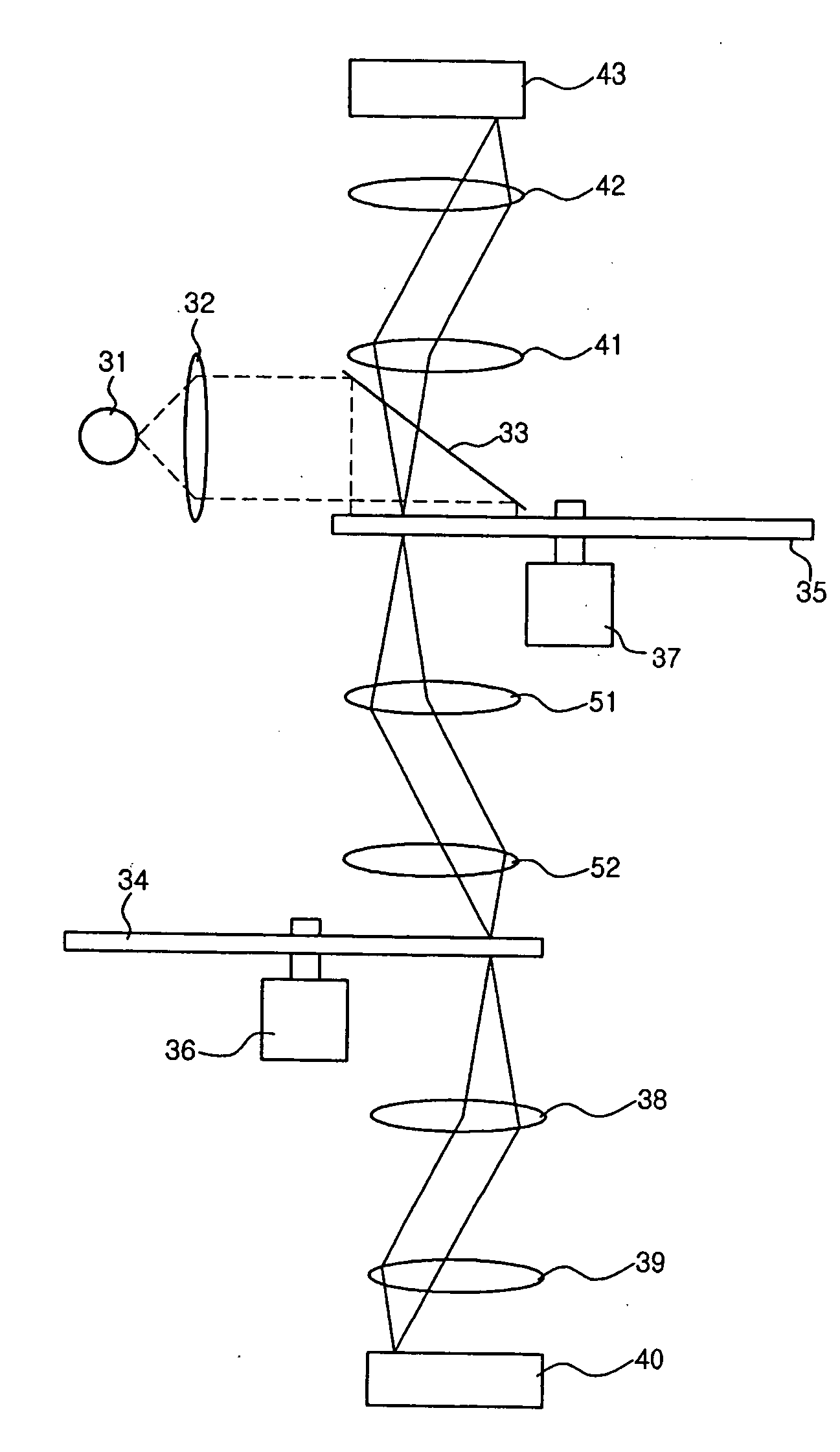
Confocal scanning microscope using two nipkow disks
ActiveUS20060061857A1Avoid performance degradationFast measurement speedMicroscopesConfocal scanning microscopyCircular disc
A confocal scanning microscope using a Nipkow disk prevents deterioration of performance in an optical axis direction while maintaining a high measurement speed. The confocal scanning microscope includes a light source, an illuminating device to pass the light from the light source toward a certain direction, and two Nipkow disks each having slit-shaped apertures formed thereon such that the light incident from the illuminating device travels in a form of light which passed through a single aperture. In addition, the confocal scanning microscope includes a first optical system to form an image on a sample by the light passed through the Nipkow disks, and a second optical system to form a second image by the light reflected from the sample and passed through the Nipkow disks.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and methods for optical coherence tomography and confocal microscopy
InactiveUS20120218558A1Reduce the overall diameterAvoid interferenceMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringConfocal scanning microscopyLight beam
An optical imaging device which receives an optical collimated input beam, the device having a pair of axicon lenses through which a beam is directed to generate a collimated ring beam, wherein the ring beam is scattered from a substance to generate a return beam, and to bypass a reflector that redirects the return beam to prevent the return beam from interfering with the input beam; and a detector which detects an image projected by the return beam.
Owner:THUNDER BAY REGIONAL RES INST
Cellular surgery utilizing confocal microscopy
InactiveUS7190990B2Simple systemEvaluate effectivenessControlling energy of instrumentDiagnostic recording/measuringConfocal scanning microscopySurgical treatment
An improved system for cellular surgery which includes a laser for producing a laser beam, and confocal optics for scanning and focusing the laser beam in tissue and generating confocal images of the tissue in accordance with returned light from the tissue. The confocal images are visualized on a display. The system includes a controller for enabling the operator to select one or more cells of the tissue in the displayed confocal images for surgical treatment. The controller operates the laser and confocal optics in a first mode to treat the tissue when the confocal optics focus the laser beam at least one region associated with the selected cells in the tissue, but at all other times operates the laser and confocal optics in a second mode which does not damage the tissue. The treatment may be localized to concentrate the energy of the laser to the region including the selected cell or cells, or the treatment may be non-localized to distribute the energy of the laser to the region which includes the selected cell(s) and also the cells of the tissue surrounding such selected cell(s). In another embodiment, an apparatus is provided having a confocal imaging system, which focuses a first laser beam through confocal optics to tissue and provides confocal images of the tissue, and a treatment system which focuses a second laser beam through the confocal optics coaxial with the first laser beam for treating at one or more selected locations in the imaged tissue.
Owner:CALIBER IMAGING & DIAGNOSTICS
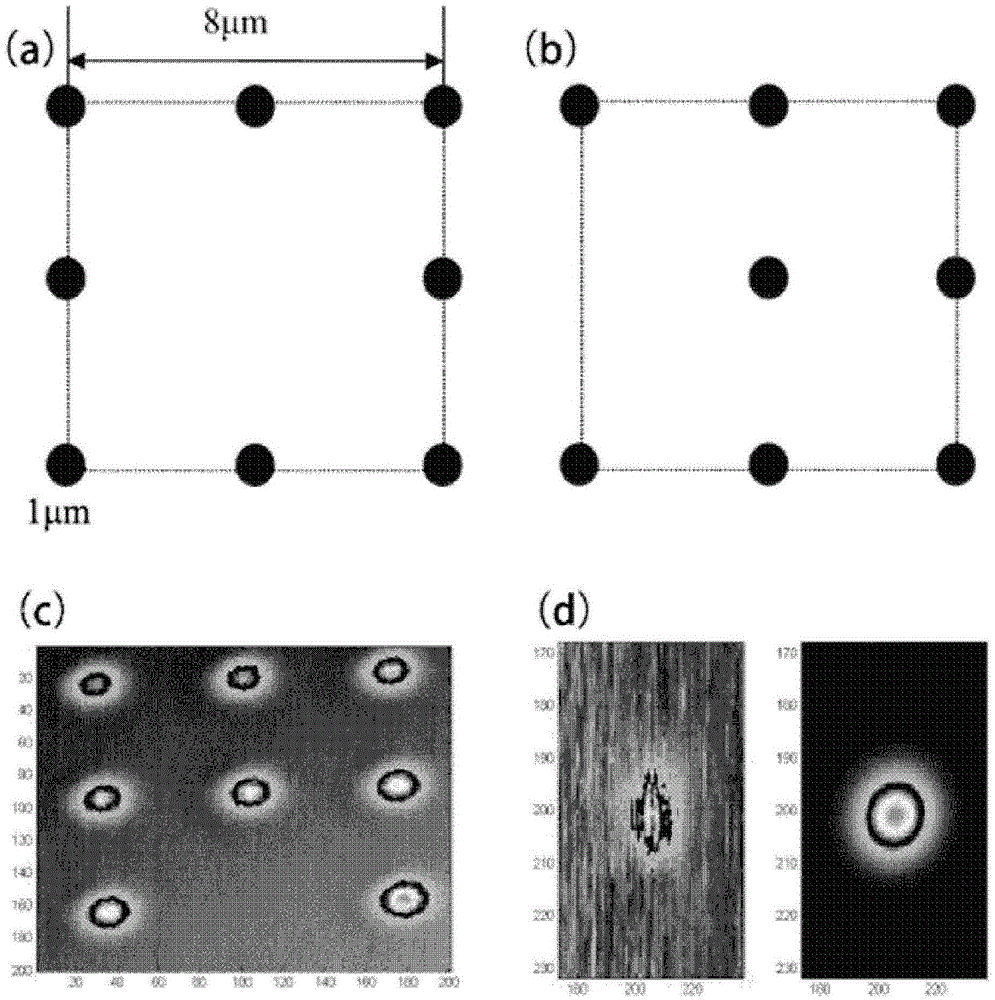
Method for precisely determining position of self-organization quantum dot by optical method
InactiveCN105572086APrecise positioningRealize automatic controlFluorescence/phosphorescenceAutomatic controlFluorescence
The invention provides a method for precisely determining the position of a self-organization quantum dot by an optical method. A metal disk is taken as a sign, a confocal scanning microscope is used for measuring a reflection signal and a fluorescence signal used for marking a sample, image data is analyzed, system errors are carefully corrected, then, the spatial position of the quantum dot relative to a metal signal is obtained, and the positioning of a single quantum dot is realized. The method has universality and can be used for various types of positioning work of a single nanometer structure with fluorescent property. Positioning accuracy is obviously improved through detailed error analysis, and requirements on the positioning accuracy in the vast majority of work can be met. An automatic control system is used for finishing measurement, a computer program is used for finishing data processing, the positioning work of a large batch of quantum dots can be realized, and the method has extremely high engineering applicability.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for enhancing confocal reflectance images of tissue specimens
InactiveUS7110114B2Easy to observeEnhance the imagePolarisation-affecting propertiesInvestigating moving sheetsAbnormal tissue growthPolarizer
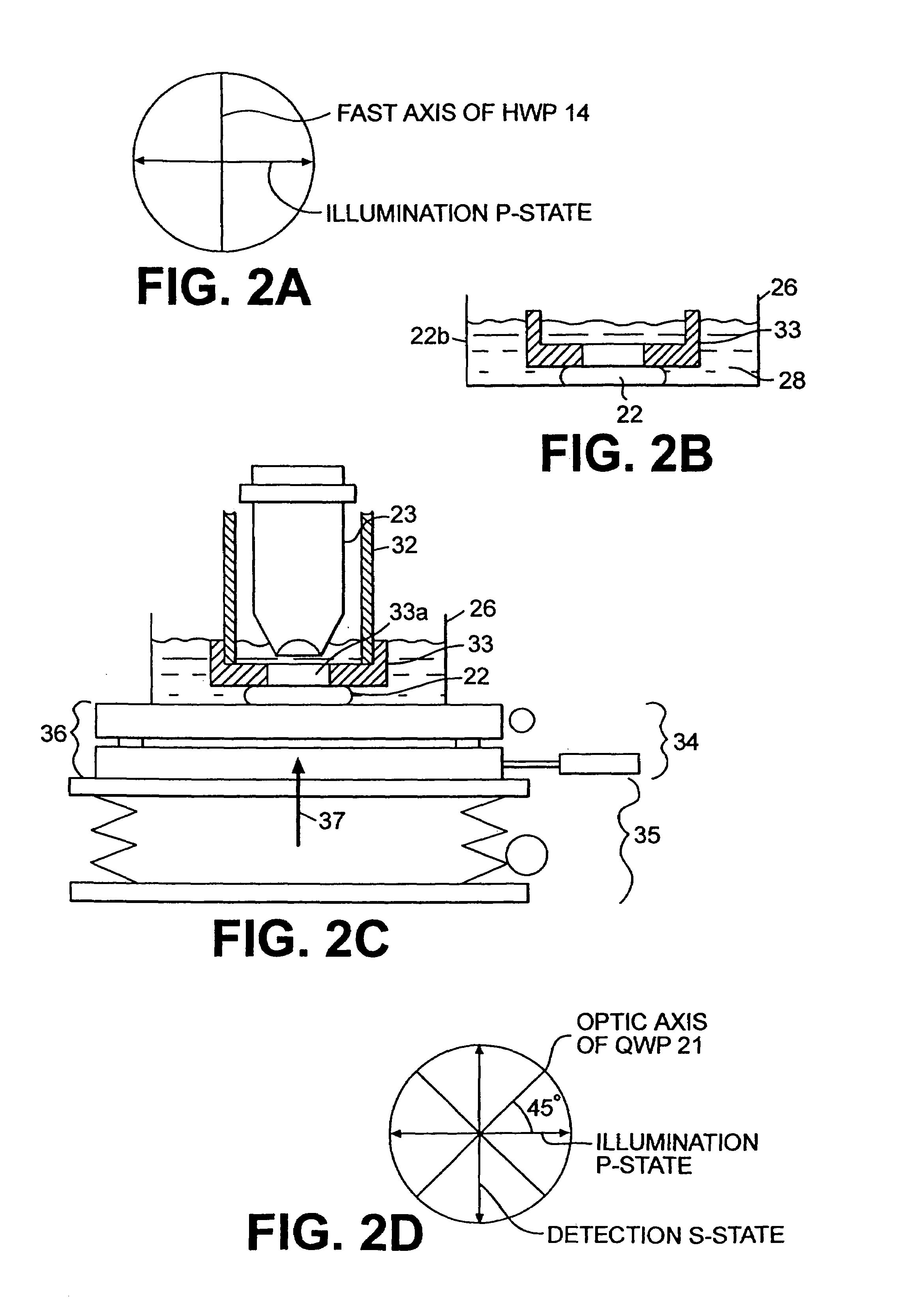
A confocal scanning microscope system (10) using cross polarization effects and an enhancement agent (acetic acid) to enhance confocal microscope reflectance images of the nuclei of BCCs (basal cell carcinomas) and SCCs (squamous call carcinomas) in the confocal reflectance images of excised tumor slices. The confocal scanning microscope system having a laser (11) for generating an illumination beam (12), a polygon mirror (18) for scanning the beam to a tissue sample (22) and for receiving a return beam from the tissue sample and detector (28) for detecting the returned beam to form an image. The system further includes a half-waveplate (13) having a rotatable stage (14) and a quarter-wave plate (21) having a rotatable stage (20) disposed in the optical path of the illumination beam and at least a linear polarizer (24) having a rotatable stage (25) disposed in the optical pat of the returned beam from the tissue sample.
Owner:CALIBER IMAGING & DIAGNOSTICS +1
Quick detection method for in-situ fluorescent staining of livestock meat spoilage bacteria
InactiveCN102866140AQuick checkExtended shelf lifeFluorescence/phosphorescencePsychological statusSpoilage bacteria
The invention relates to a quick detection method for in-situ fluorescent staining of livestock meat spoilage bacteria. Spoilage bacterium living bodies are subjected to in-situ fluorescent staining by fluorescent dye, shot images are processed by tomography through a confocal scanning laser microscope, and average fluorescent strength is calculated to represent relative cell quantity of unit area of a section of pork tissue. The quick detection method is easy to operate, high in detection speed and free of harmfulness and capable of detecting livestock spoilage bacteria within a short time on the premise of not damaging psychological status, and thus distribution and impregnation situations of spoilage bacteria in pork tissue and dynamic change of the spoilage bacteria can be observed and tracked in rail time. In addition, the quick detection method has direct practical significance in further researching spoilage mechanism of livestock meat deeply so as to control the spoilage bacteria pointedly, prolong shelf life of meat, guarantee quantity safety of meat and care health of customers.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Chlorine imaging method of central nervous system based on laser confocal scanning microscope system
ActiveCN101788484AAvoid damageLittle autofluorescencePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceNerve cellsScanning microscopy
The invention discloses a chlorine imaging method of a central nervous system based on a laser confocal scanning microscope system, comprising the following steps of: (1) together incubating a brain slice and chloridion fluorescence probe N-(ethoxycarbonylmethyl)-6-methoxyquinolinium bromide (MQAE); (2) imaging and recording by using a laser confocal microscope; and (3) correcting the fluorescent value of the MQAE in cells. The invention mainly has the advantages of quantitatively detecting the chlorine ion concentrations in nerve cells and change conditions thereof and visualizing the chlorine ion concentrations in a fluorescent form for the detected nerve cells, and having small self-emitting fluorescence and little damage on the cells because the adopted MQAE is excited in visible light.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
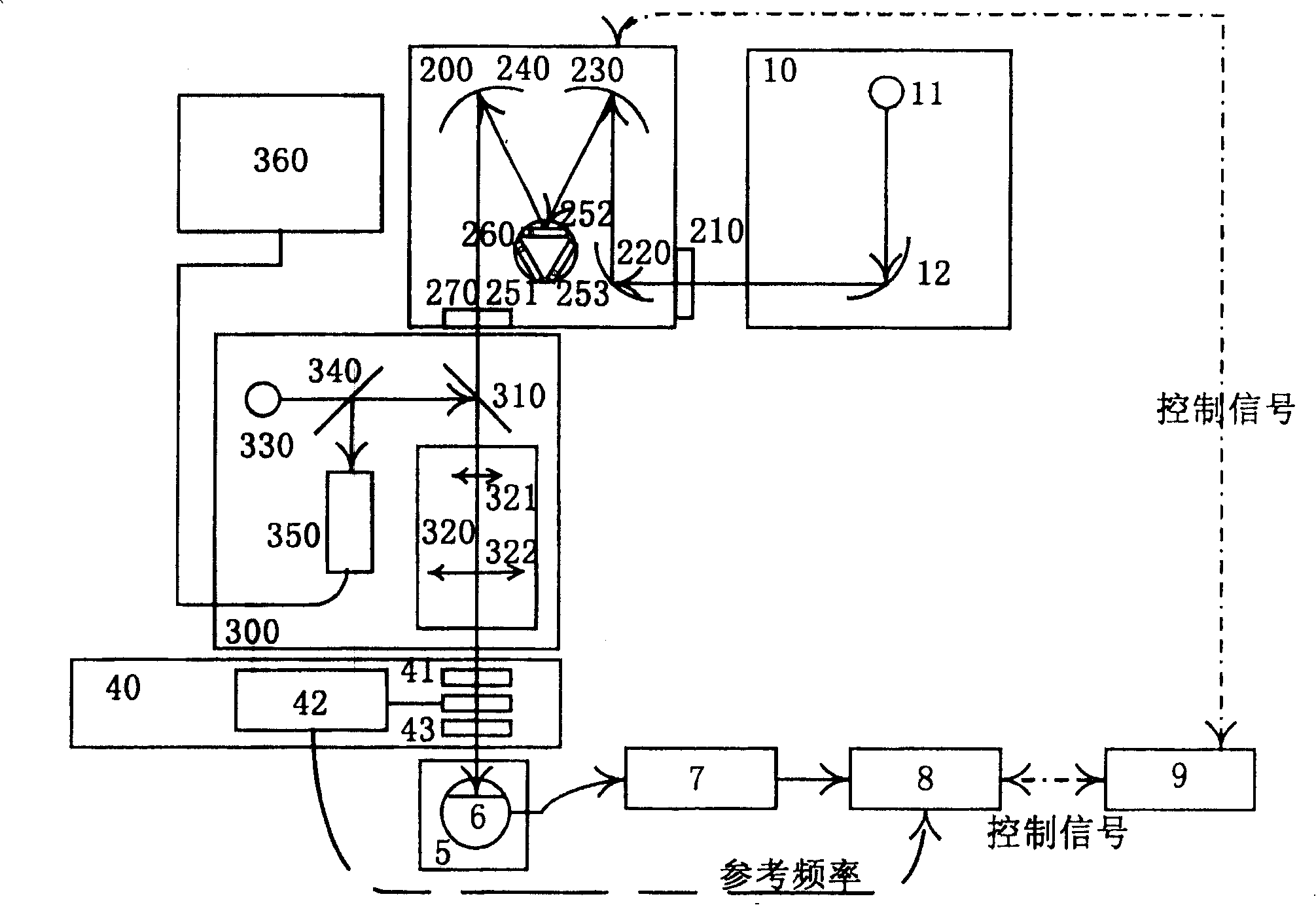
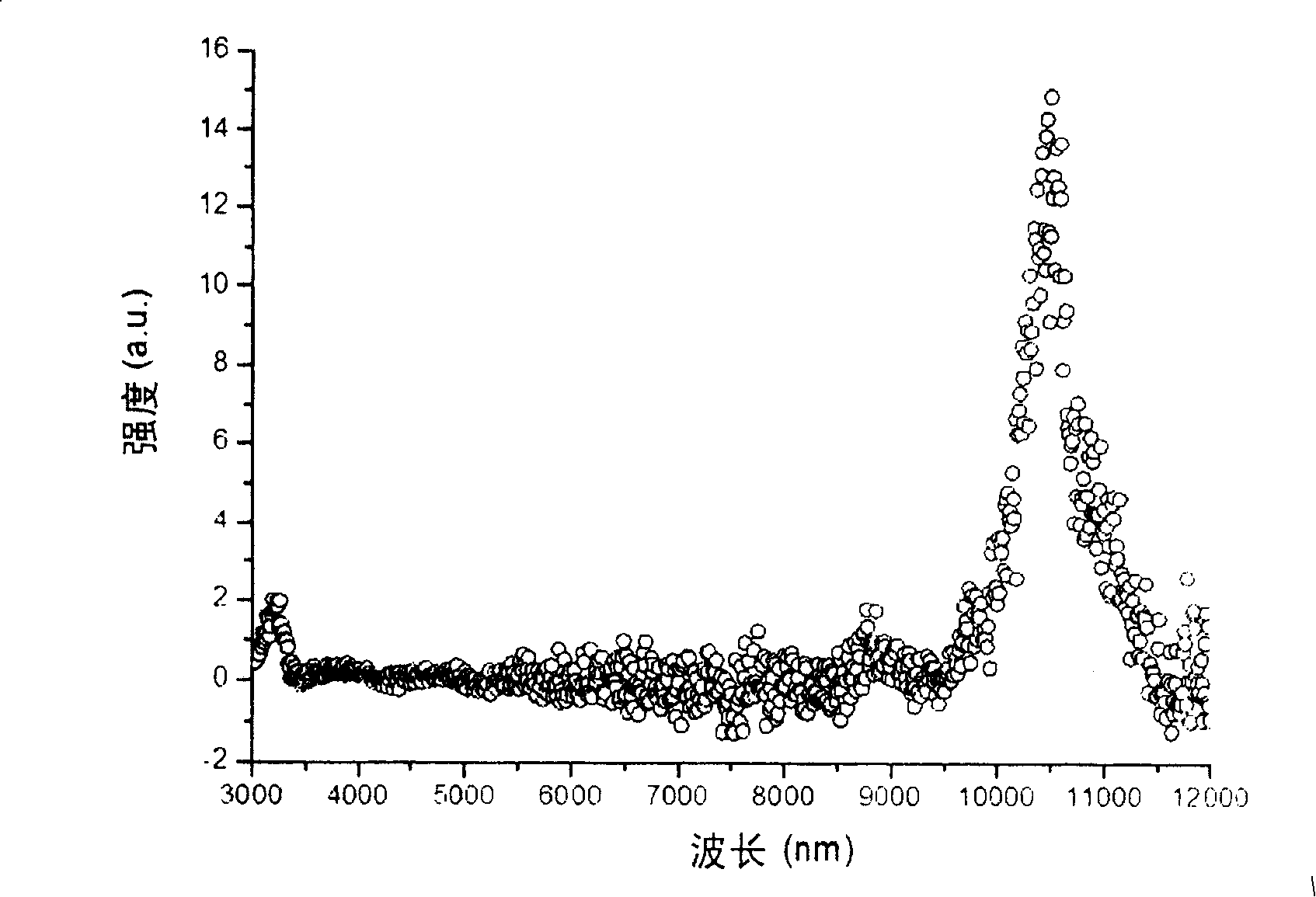
Far-infrared detector spectral response measuring system in confocal microscopy
The invention provides a confocal microscopy mid and far-infrared spectral response measurement system, which comprises an infrared source; an input end of an infrared monochrometer is connected to an output end of the infrared source; an infrared confocal microscopic system is arranged on an output light path of the infrared monochrometer; a chopper light limiting unit is arranged between the infrared confocal microscopic system and a three-dimensional micro-displacement platform and arranged on the output light path of the infrared monochrometer; the three-dimensional micro-displacement platform is arranged on the output light path of the infrared monochrometer; a sample refrigeration Dewar is fixed on the three-dimensional micro-displacement platform; a preamplifier is connected with the sample refrigeration Dewar, which plays a role of amplifying the sample electric signals; a phase-locked amplifier is connected with the preamplifier; a controlling computer is connected with the phase-locked amplifier and the infrared monochrometer to control the course of the test implemented by the phase-locked amplifier and the infrared monochrometer and collects the data signal inputted by the phase-locked amplifier and the infrared monochrometer at the same time.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Confocal microscopy imaging system for fluorescence lifetime in second near-infrared region
InactiveCN109324026AHigh sensitivityExtending Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging CapabilitiesFluorescence/phosphorescenceConfocal scanning microscopyGalvanometer
The invention discloses a confocal microscopy imaging system for the fluorescence lifetime in a second near-infrared region. A laser emitted by a femtosecond laser source is introduced into an uprightconfocal scanning microscope. The laser is focused on the sample by a near-infrared enhanced objective lens, after pass through a scanning galvanometer, a scanning lens, and a sleeve lens. The signals in the second near-infrared region of the sample are collected by a same near-infrared enhanced objective lens; are split by a long-pass dichroic mirror and then are taken out of the system, after pass through a sleeve lens, a scanning lens, and a scanning galvanometer; are collected and coupled into a large diameter fiber; and finally are converted into electrical signals by a photomultiplier tube detection. The electrical signals are converted into electrical counting signals, and input to a counting board. At the same time, the counting board receives synchronous pulse signals from an excitation light, and uses the signals as timing stop signals. The system obtains each sample of a fluorescence lifetime image in the second near-infrared region and a fluorescence intensity image in thesecond near-infrared region, after processed by the computer. According to the confocal microscopy imaging system for the fluorescence lifetime in the second near-infrared region, the system expandsa function of the fluorescence lifetime imaging in the second near-infrared region; and obtains more abundant image information.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Double confocal scanning microscope
InactiveUS7054062B2MicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceConfocal scanning microscopyOptical property
The present invention concerns a double confocal scanning microscope (1) having an illuminating beam path (2) of at least one light source (3), and a detected beam path (4) of at least one detector (5), and in order to achieve almost the theoretically possible resolution capability, in particular in the context of multi-color fluorescence applications, is characterized in that the optical properties in particular of the components (6, 10, 13, 14) arranged in the beam path are coordinated with one another in such a way that the accumulated aberrations, with respect to the optical axis (33) and / or at least one surface (18, 19, 20) in the specimen region, are at least of the order of magnitude of the theoretically achievable resolution capability.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Pyrenes fluorescent probe and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106680256ACell membrane permeability is goodEasy to prepareFluorescence/phosphorescenceEscherichia coliConfocal scanning microscopy
The invention provides a pyrenes fluorescent probe and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the probe comprises the following steps: dissolving acetyl pyrene and 2,6-dichloropyridine-3-formaldehyde with ethanol respectively, mixing, adding 10 percent by mass aqueous sodium hydroxide, and stirring with a magnetic stirrer at the normal temperature for 20 hours; filtering after a full reaction, determining whether a product is pure or not, and drying the product to obtain an orange-yellow solid. The probe has high sensitivity and high selectivity specific to CN<->, HSO3<-> and pH in different systems. In combination with a laser confocal scanning microscopy technology, the pyrene fluorescent probe can be applied to the detection of pH or HSO3<-> in cells, and can be applied to the detection of escherichia coli pH.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Microscope having a reference specimen
InactiveUS20050078361A1Easily and reliably focusedMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesConfocal scanning microscopyMicroscope
The present invention concerns a microscope, in particular a confocal or double confocal scanning microscope, as well as a method for operating a microscope, at least one specimen support unit associated with the specimen being provided, at least one reference specimen of known configuration being provided, and the reference specimen being detectable by light microscopy for calibration, alignment or adjustment of the microscope. With the microscope according to the present invention and the method according to the invention for operating a microscope, drift-related changes can be detected and compensated for. Auxiliary means with which a specimen can easily and reliably be focused are also provided.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method for preparing multilayer thin film and evaluating binding performance thereof
InactiveCN106835131AThe principle is simpleEasy to useVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingConfocal scanning microscopyIon sputtering
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multilayer thin film and evaluating binding performance thereof. The method includes: respectively depositing a Cr binding layer, a CrN transition layer and a CrMoAlN functional layer on an H13 matrix through an unbalanced ion sputtering coating process to obtain a Cr-CrN0CrMoAlN multilayer thin film; setting Cr target current to 4A, Al target current to 6A, Mo target current to 0-6A and bias voltage to -75V, and depositing the Cr binding layer for 360s, the CrN transition layer for 600s and the CrMoAlN functional layer for 3600s; conducting a scratch test through a multifunctional scratch tester; acquiring scratch shape on the surface of the thin film through an optical confocal scanning microscope to evaluate the binding performance of the thin film. The multilayer thin film prepared by the method is of a gradient structure, and the binding performance of the thin film is improved by using the Cr layer for bottoming; CrN serving as the transition layer enhances bearing capacity of the thin film; CrMoAlN serving as the functional layer can improve high-temperature resistance and friction resistance of the thin film. A scratch method is adopted to represent difference in the binding performance of the thin film due to Mo content difference.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com