Patents
Literature
1749 results about "Intermediate image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
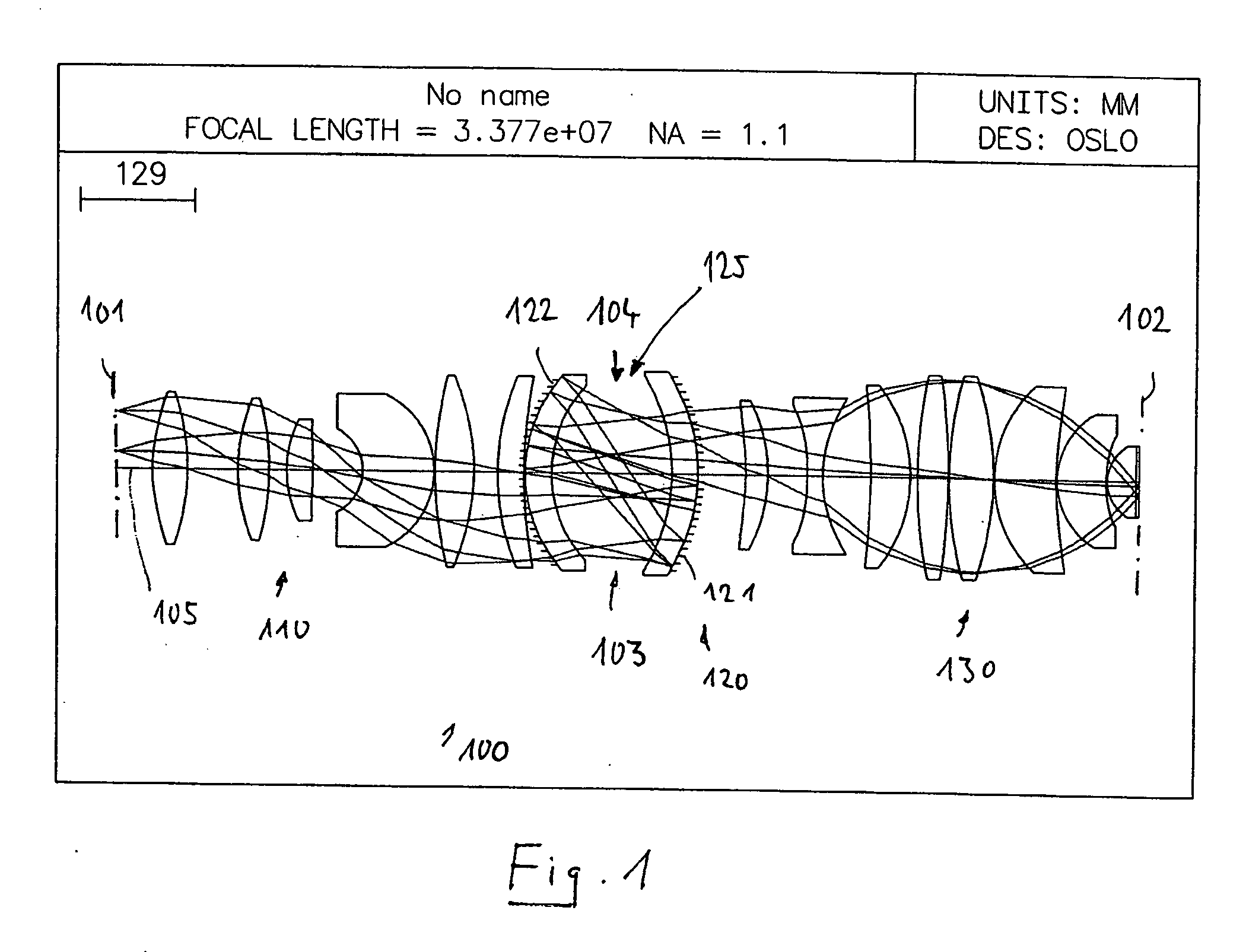
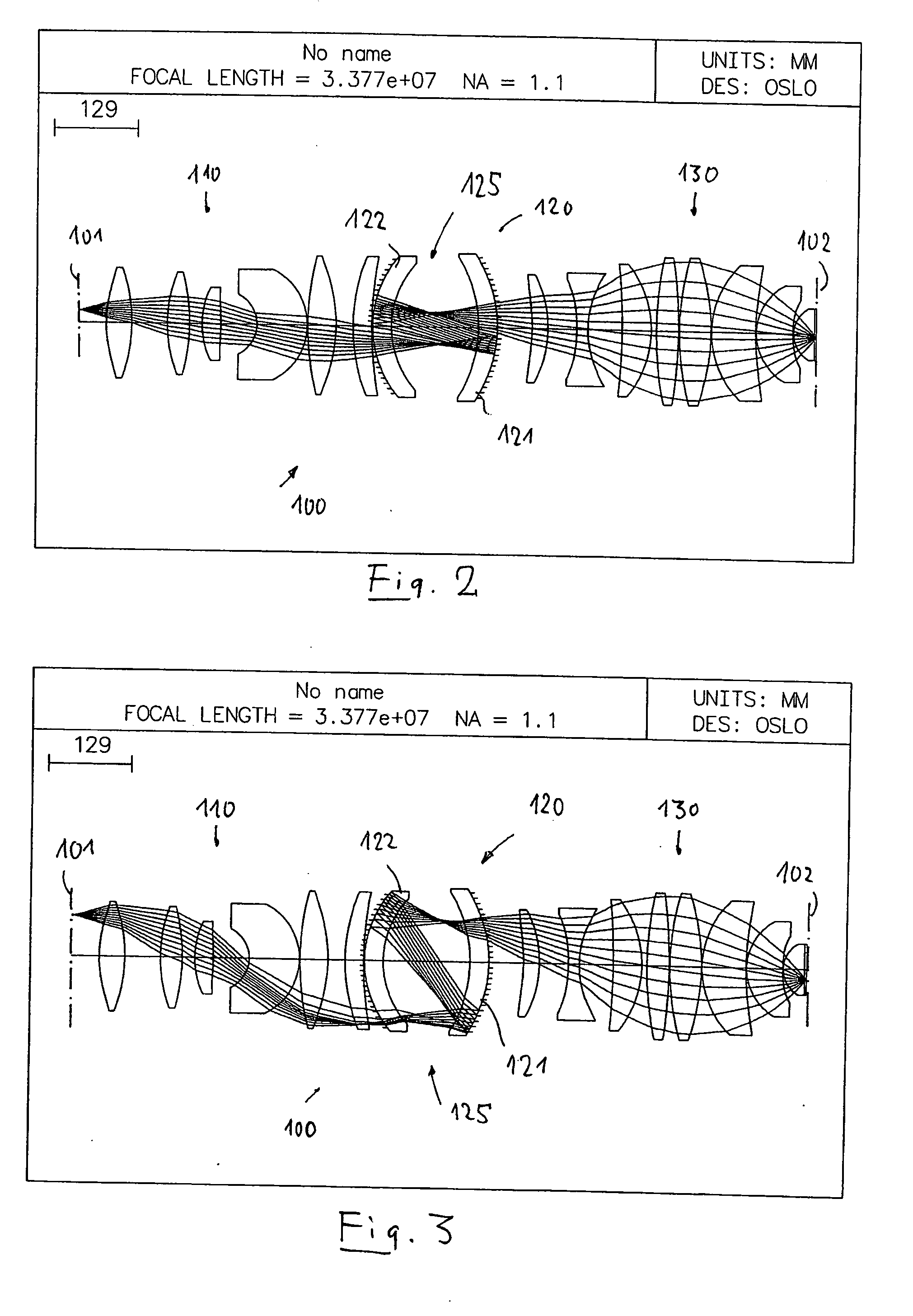
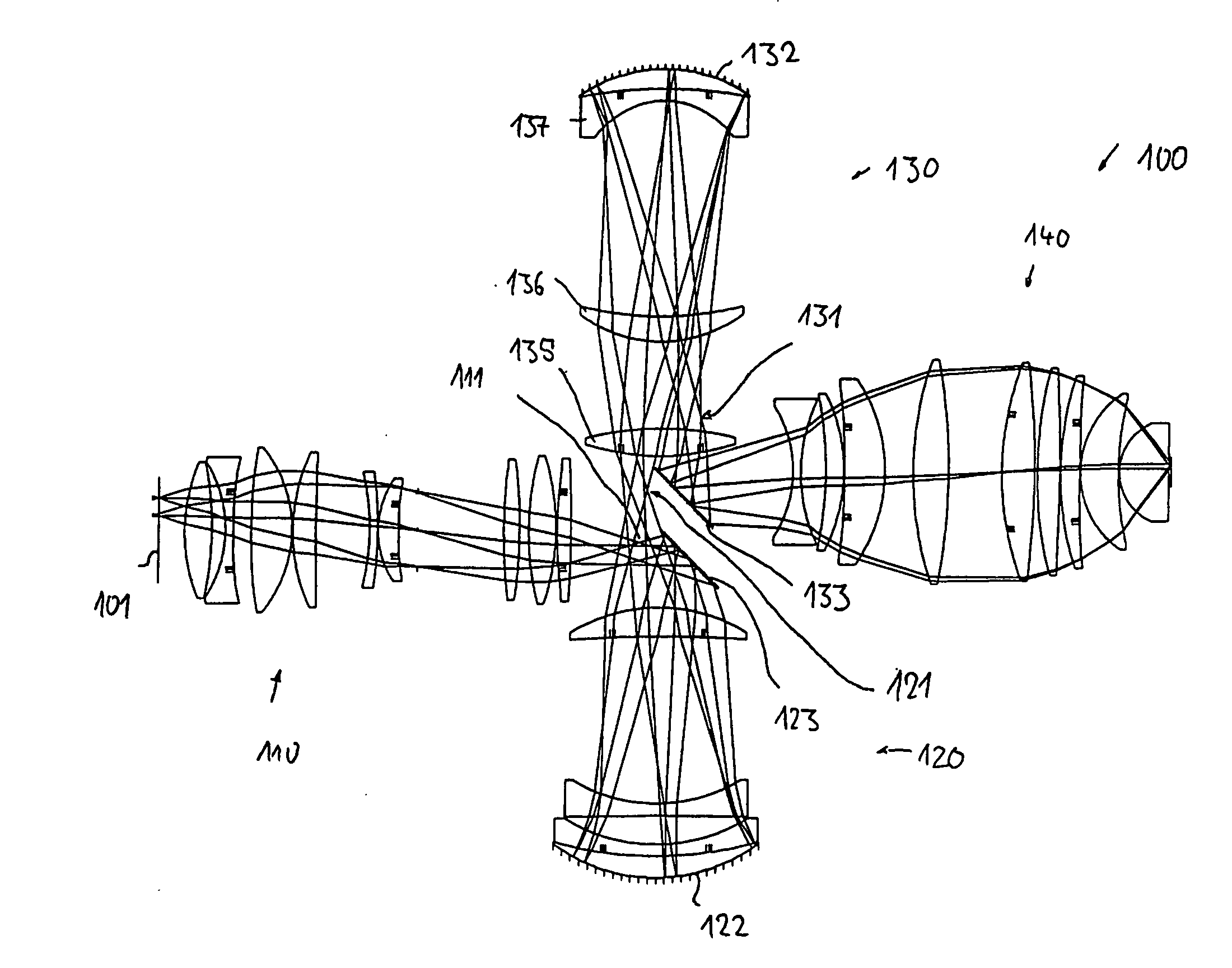
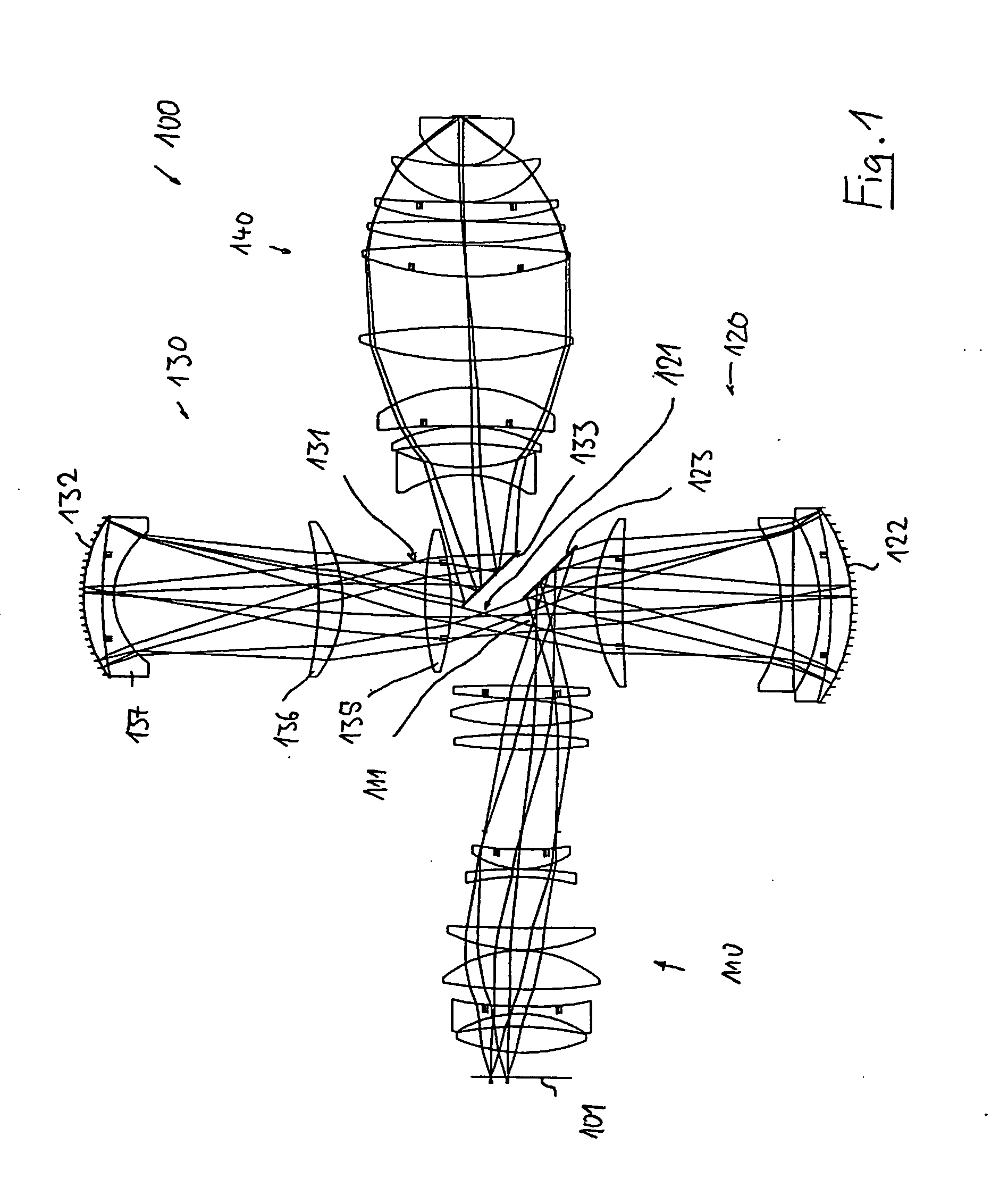
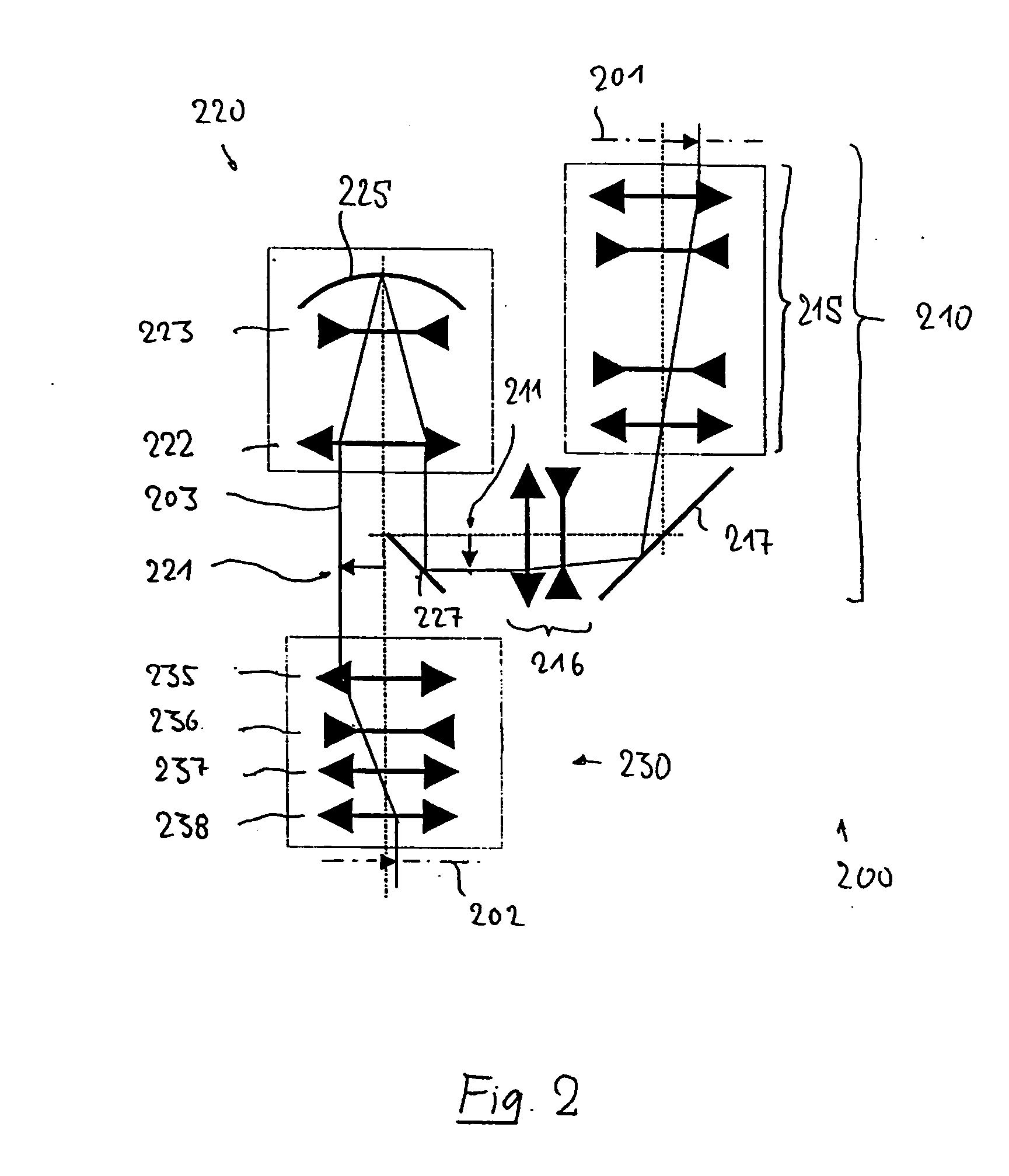
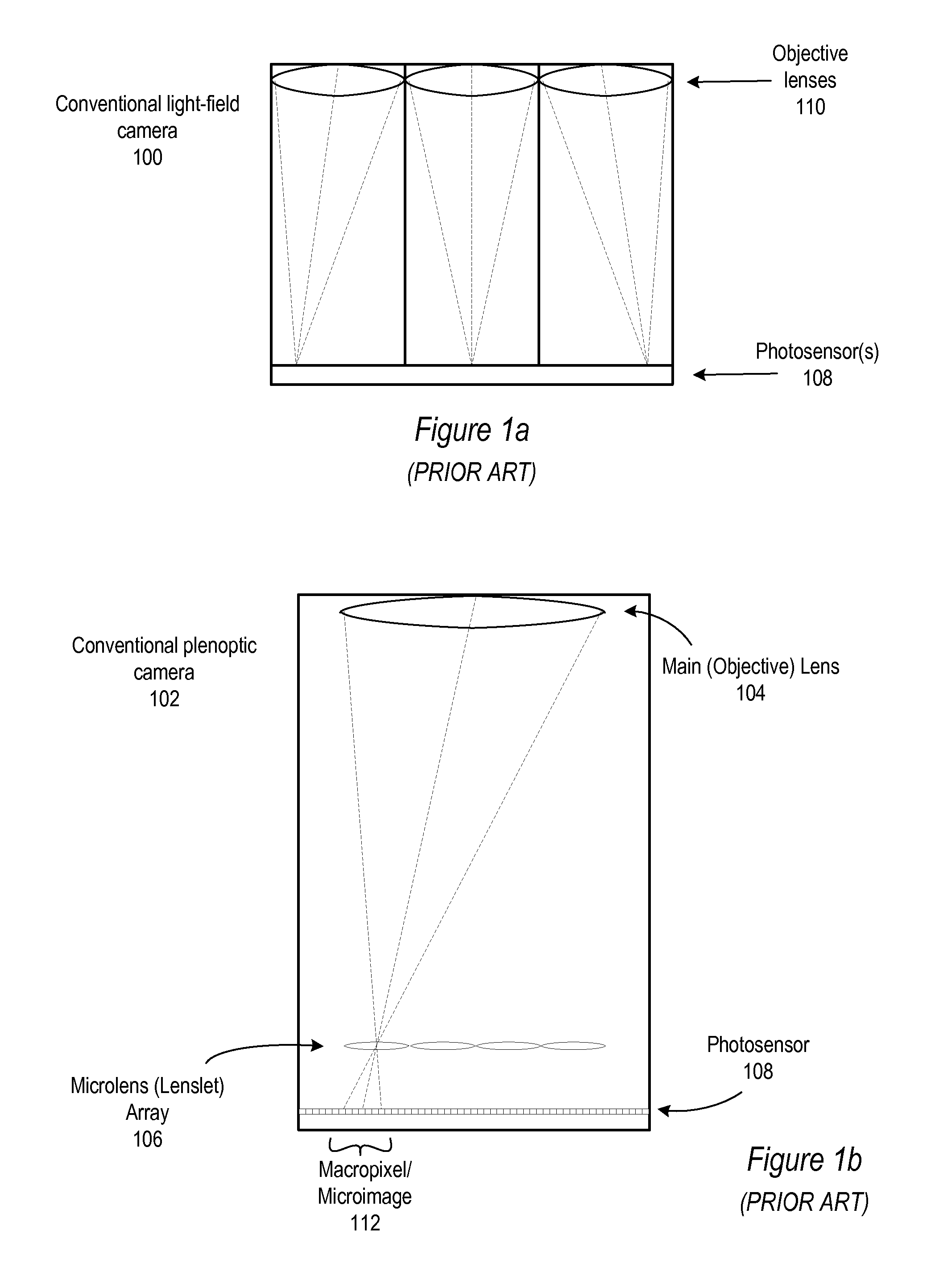
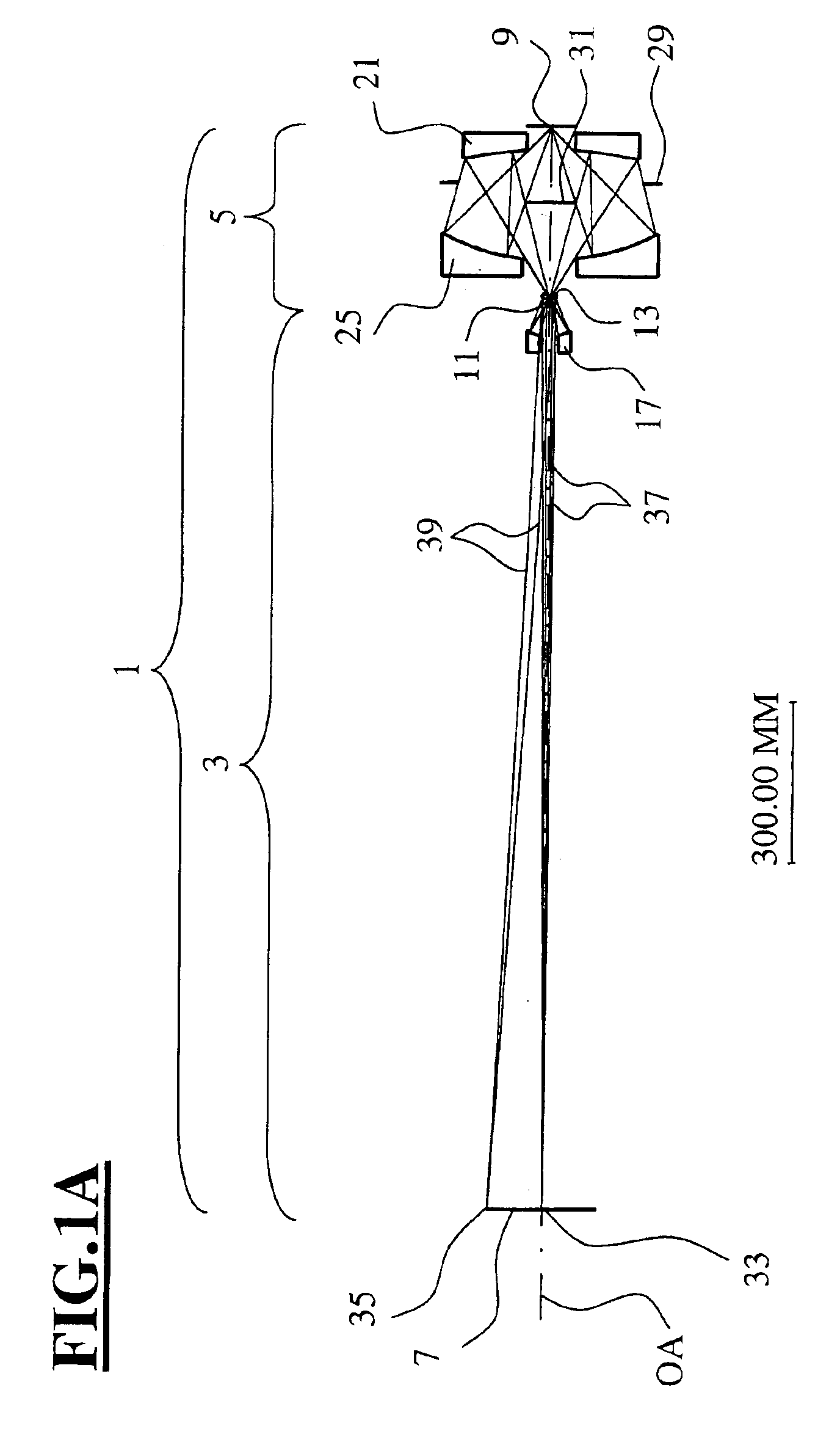
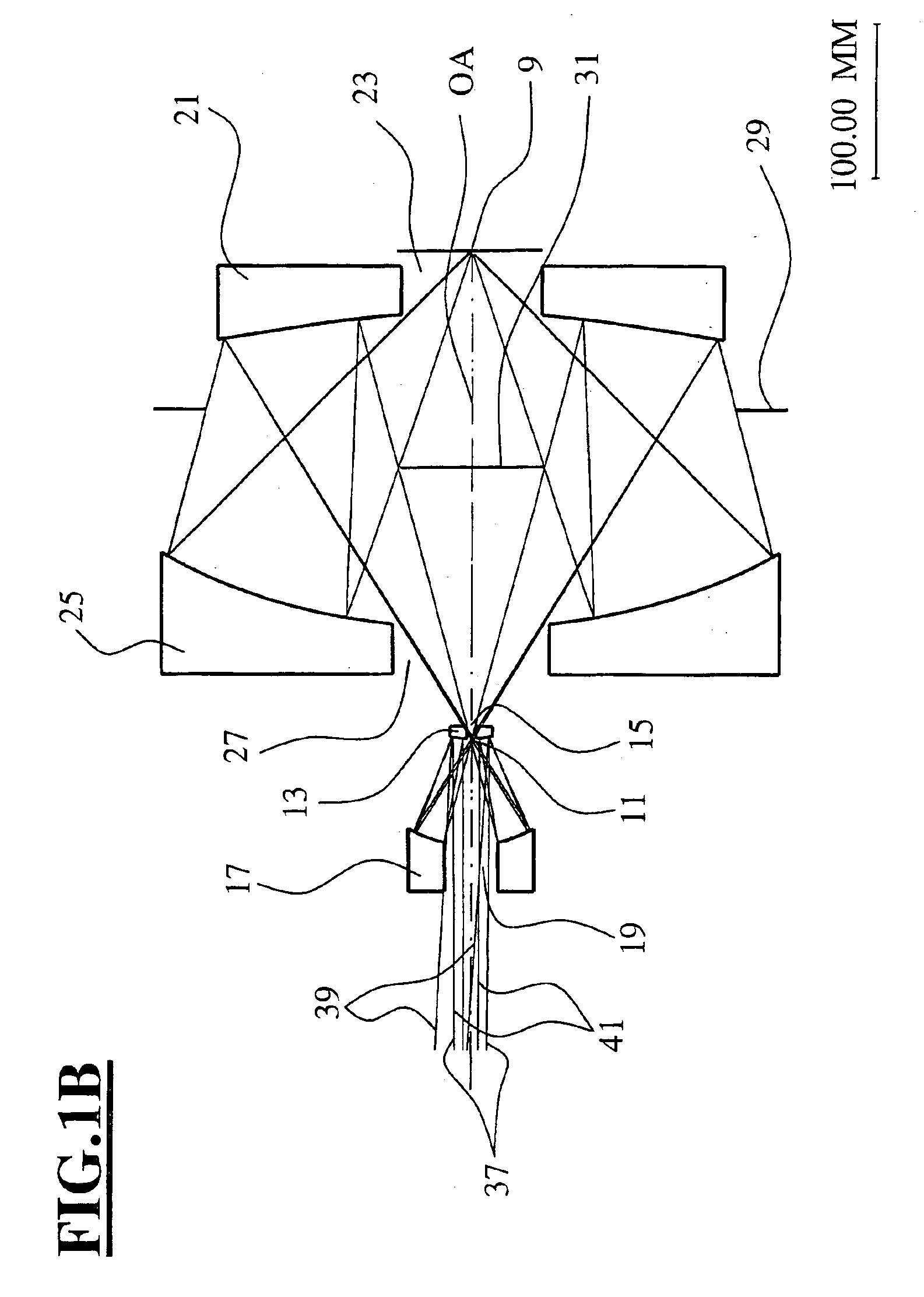
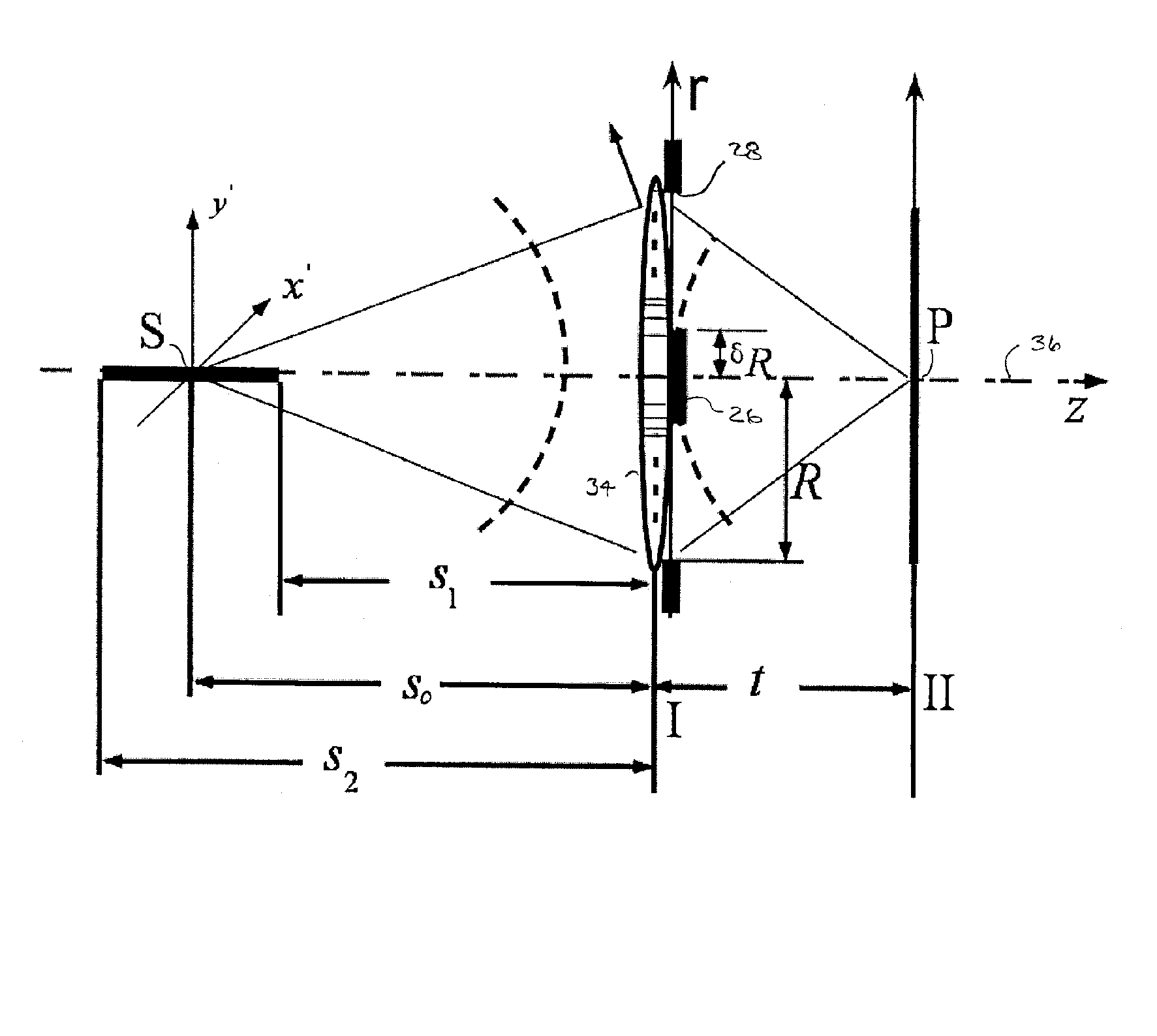
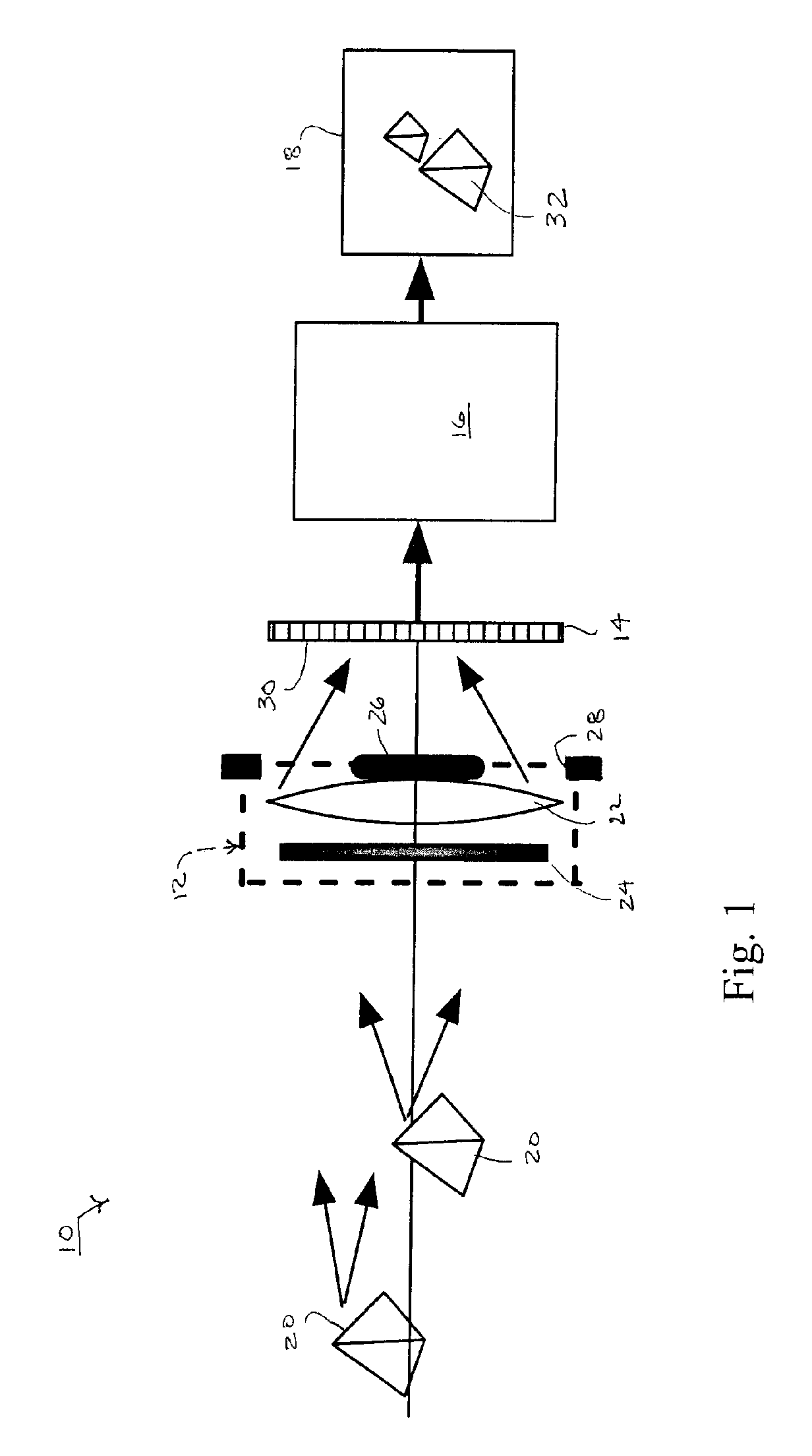
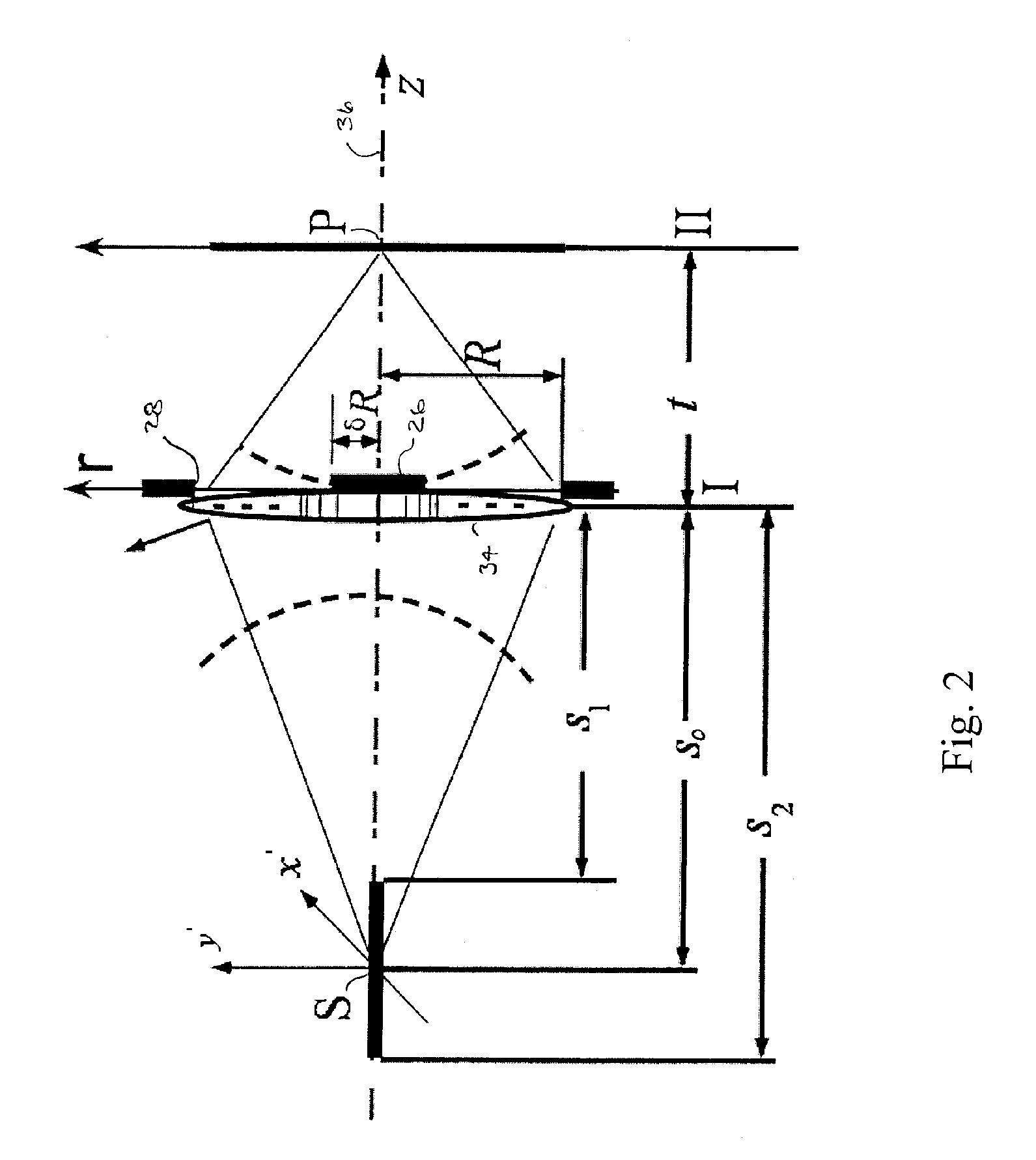
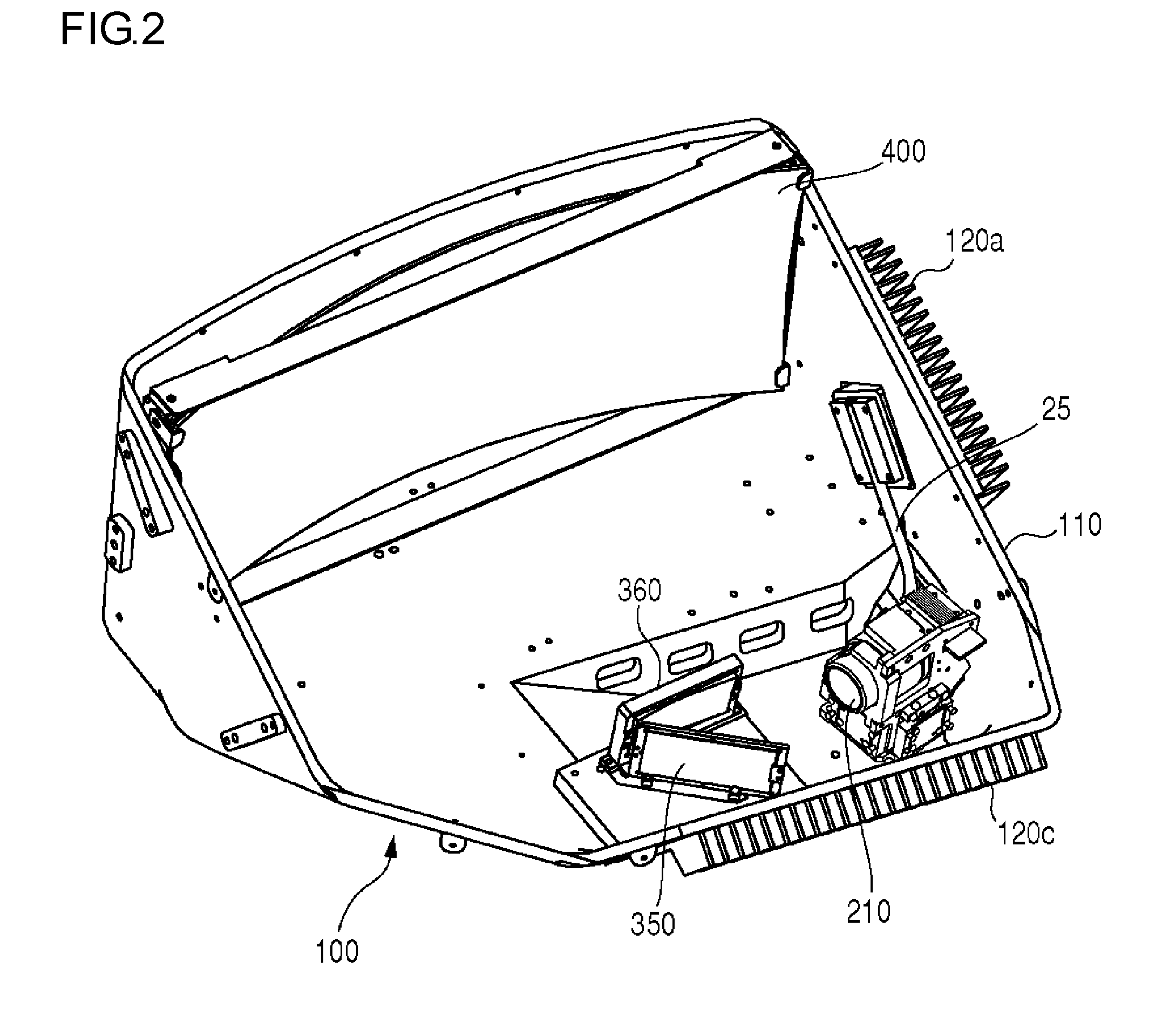
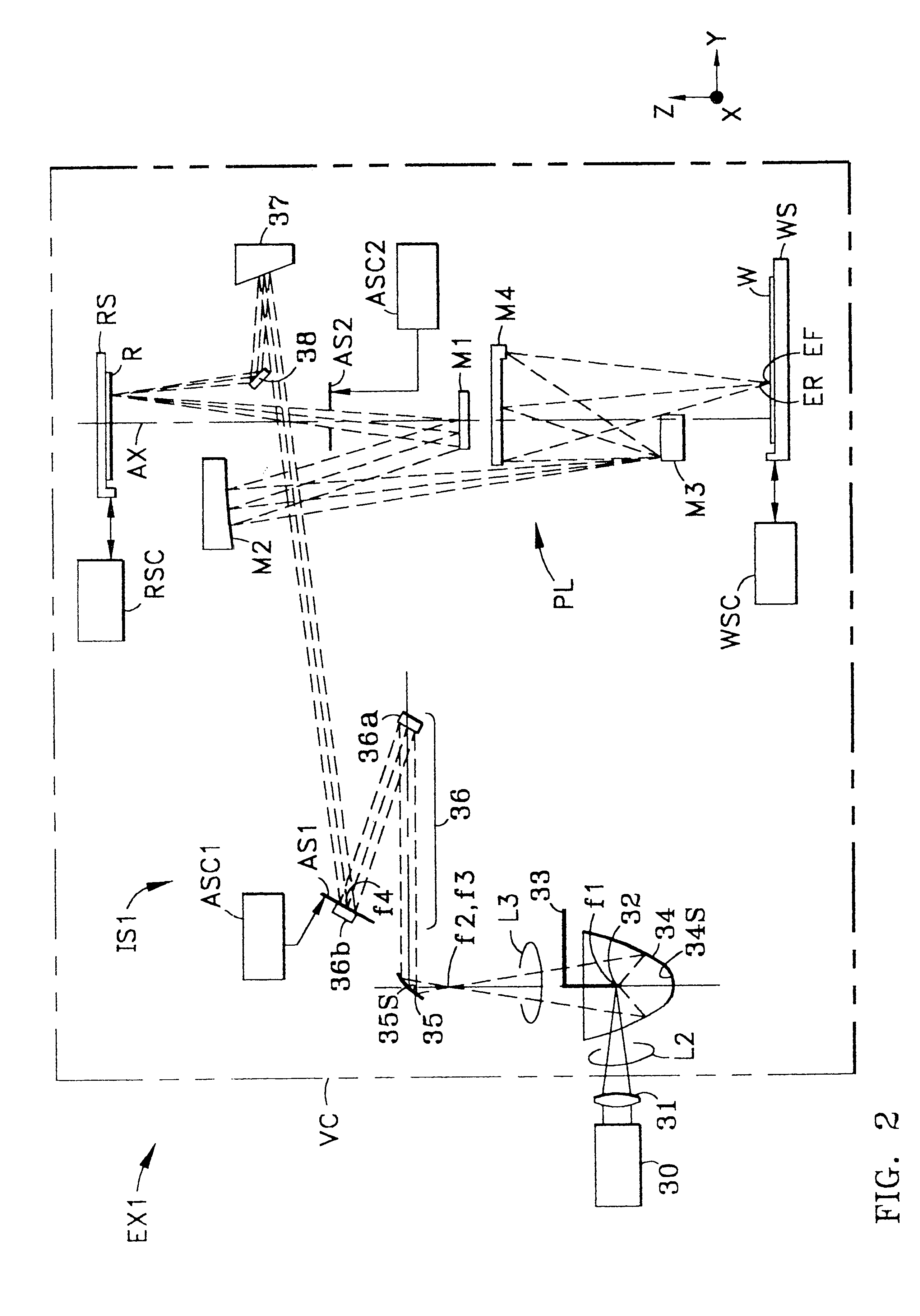
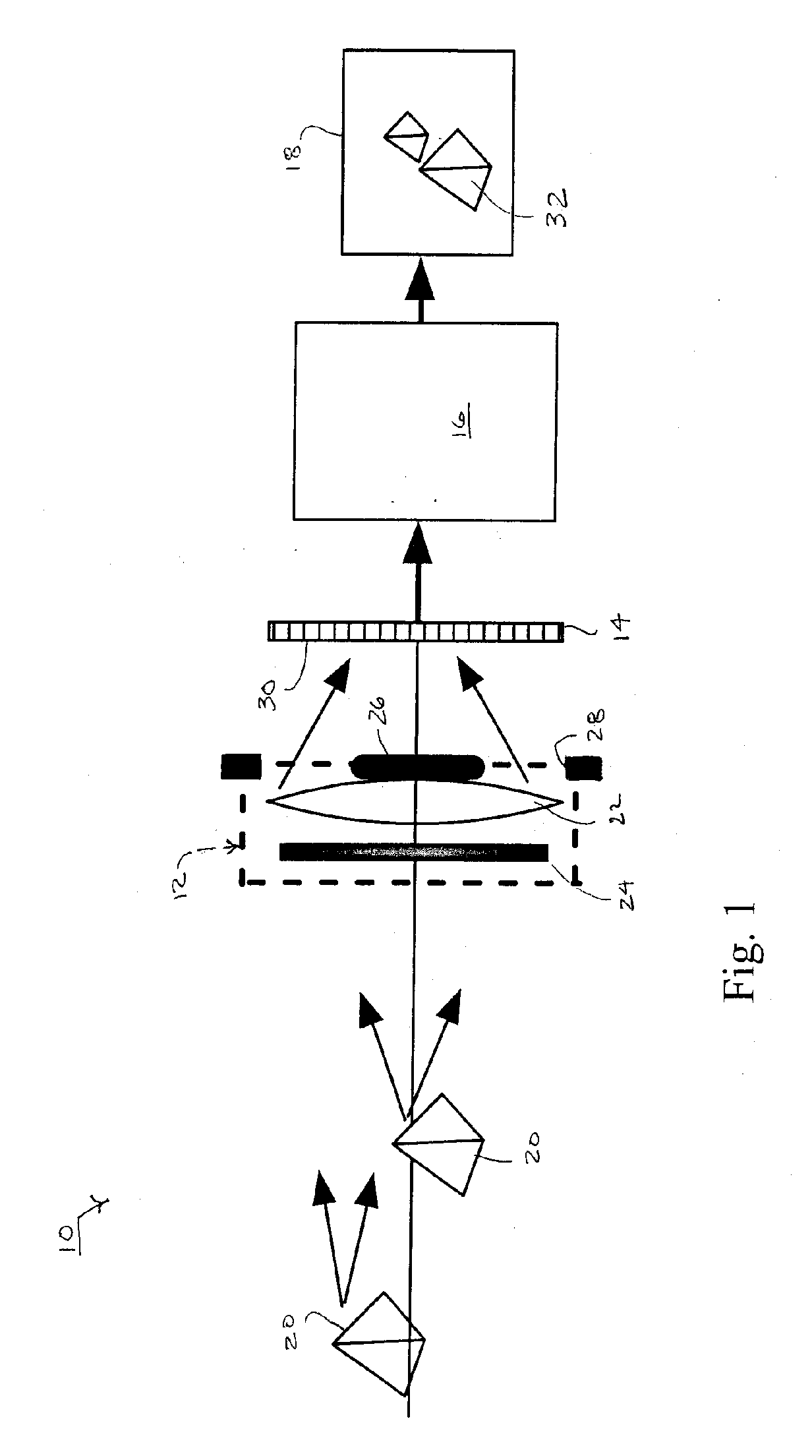
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050117224A1Good engineering qualityEasy to installMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
A catadioptric projection objective is used to project a pattern arranged in an object plane of the projection objective into an image plane of the projection objective with the formation of at least one real intermediate image and has an image-side numerical aperture NA>0.7. The projection objective comprises an optical axis and at least one catadioptric objective part that comprises a concave mirror and a first folding mirror. There are a first beam section running from the object plane to the concave mirror and a second beam section running from the concave mirror to the image plane. The first folding mirror is arranged with reference to the concave mirror in such a way that one of the beam sections is folded at the first folding mirror and the other beam section passes the first folding mirror without vignetting, the first beam section and the second beam section crossing one another in a cross-over region.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Catadioptric projection objective
ActiveUS20050190435A1High image side numerical apertureSmall amountSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesIntermediate imageHigh numerical aperture
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern provided in an object plane of the projection objective onto an image plane of the projection objective comprises: a first objective part for imaging the pattern provided in the object plane into a first intermediate image; a second objective part for imaging the first intermediate imaging into a second intermediate image; a third objective part for imaging the second intermediate imaging directly onto the image plane; wherein a first concave mirror having a first continuous mirror surface and at least one second concave mirror having a second continuous mirror surface are arranged upstream of the second intermediate image; pupil surfaces are formed between the object plane and the first intermediate image, between the first and the second intermediate image and between the second intermediate image and the image plane; and all concave mirrors are arranged optically remote from a pupil surface. The system has potential for very high numerical apertures at moderate lens material mass consumption.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050185269A1Easy to correctCorrect chromatic aberrationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageBeam splitting
A catadioptric projection objective for imaging a pattern arranged on the object plane of the projection objective, on the image plane of the projection objective, comprising: a first objective part for imaging an object field in a first real intermediate image; a second objective part for producing a second real intermediate image with the radiation coming from the first objective part; and a third objective part for imaging the second real intermediate image on the image plane; wherein at least one of the objective parts is a catadioptric objective part with a concave mirror, and at least one of the objective parts is a refractive objective part and a folding mirror is arranged within this refractive objective part in such a way that a field lens is arranged between the folding mirror and an intermediate image which is closest to the folding mirror.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
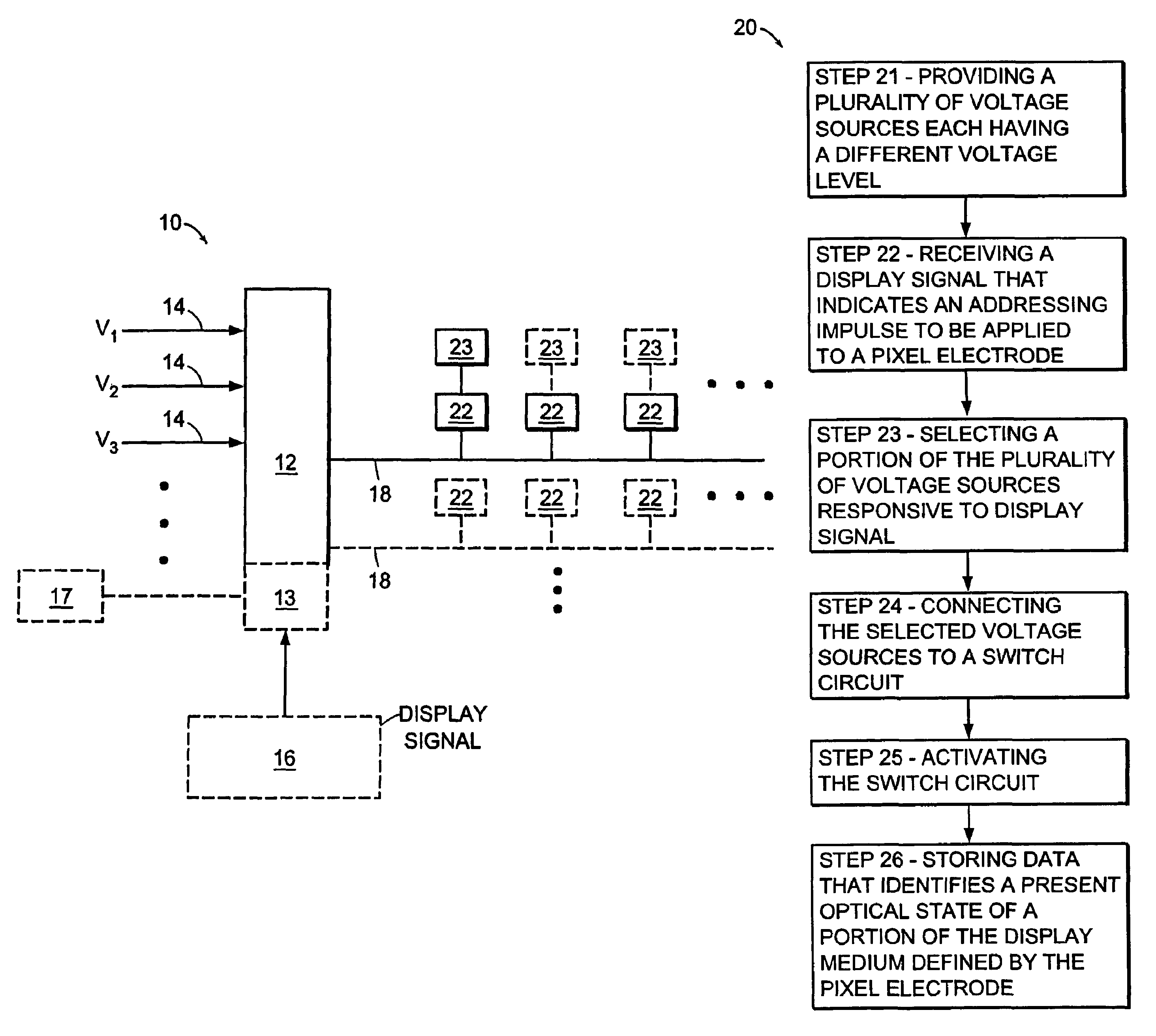
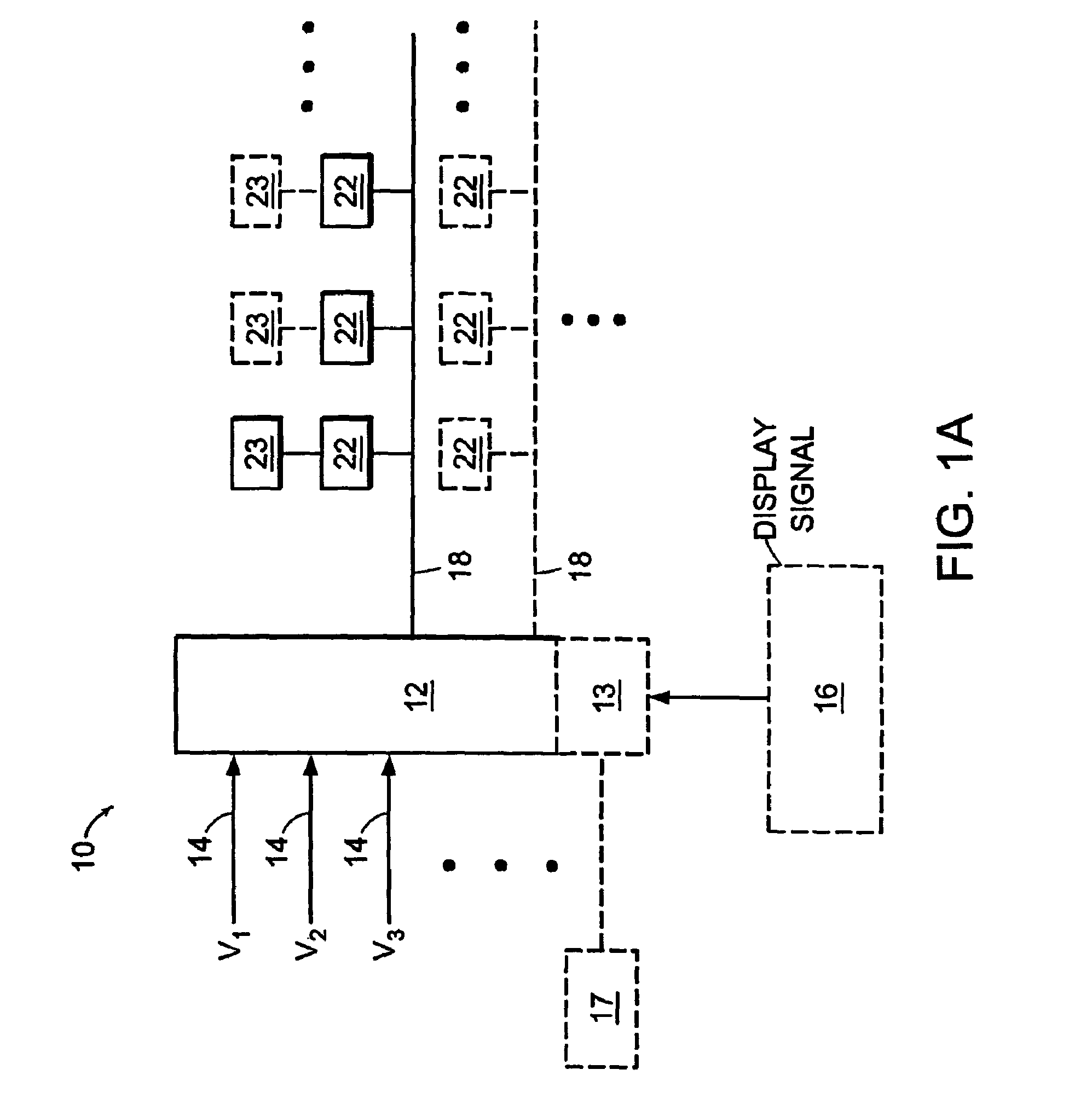
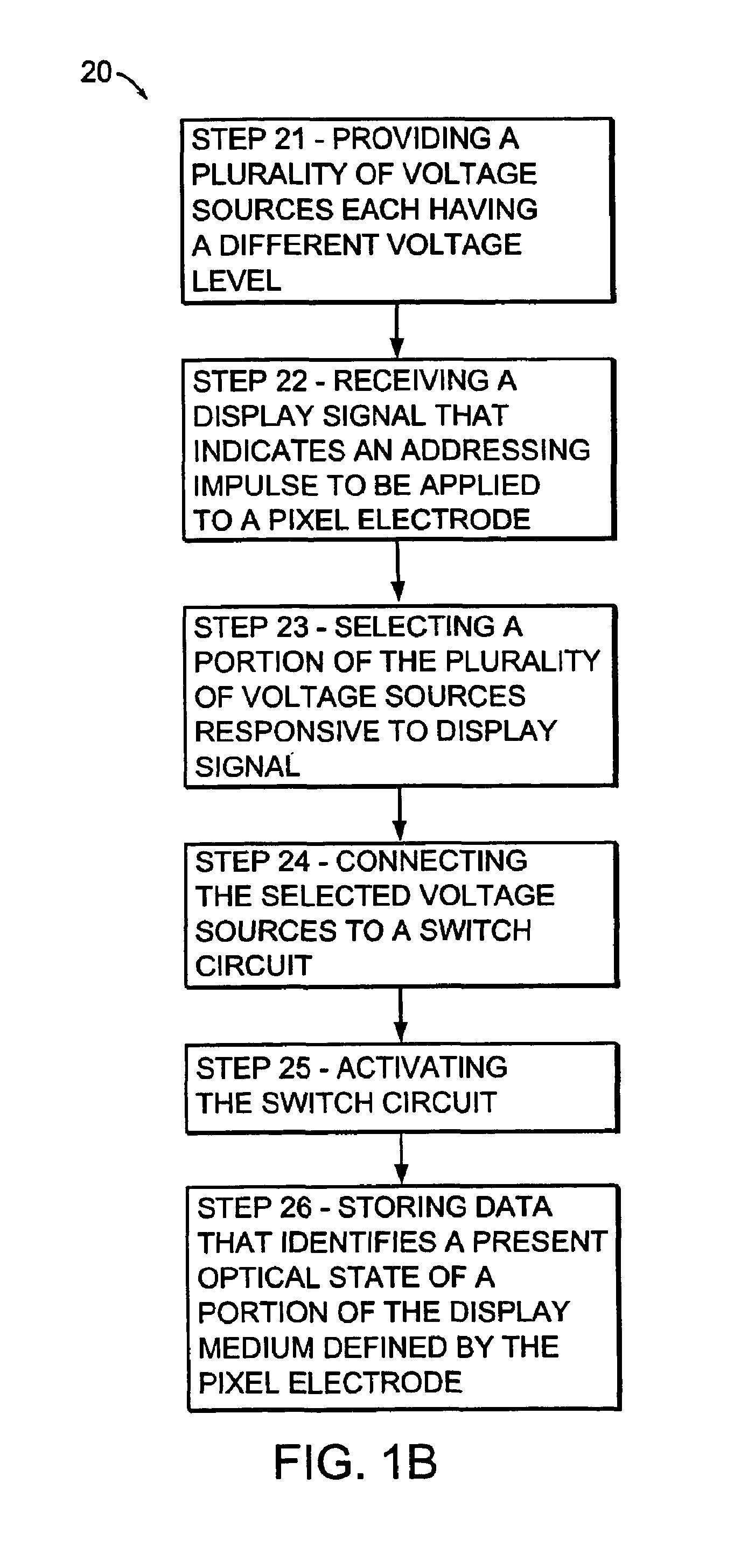
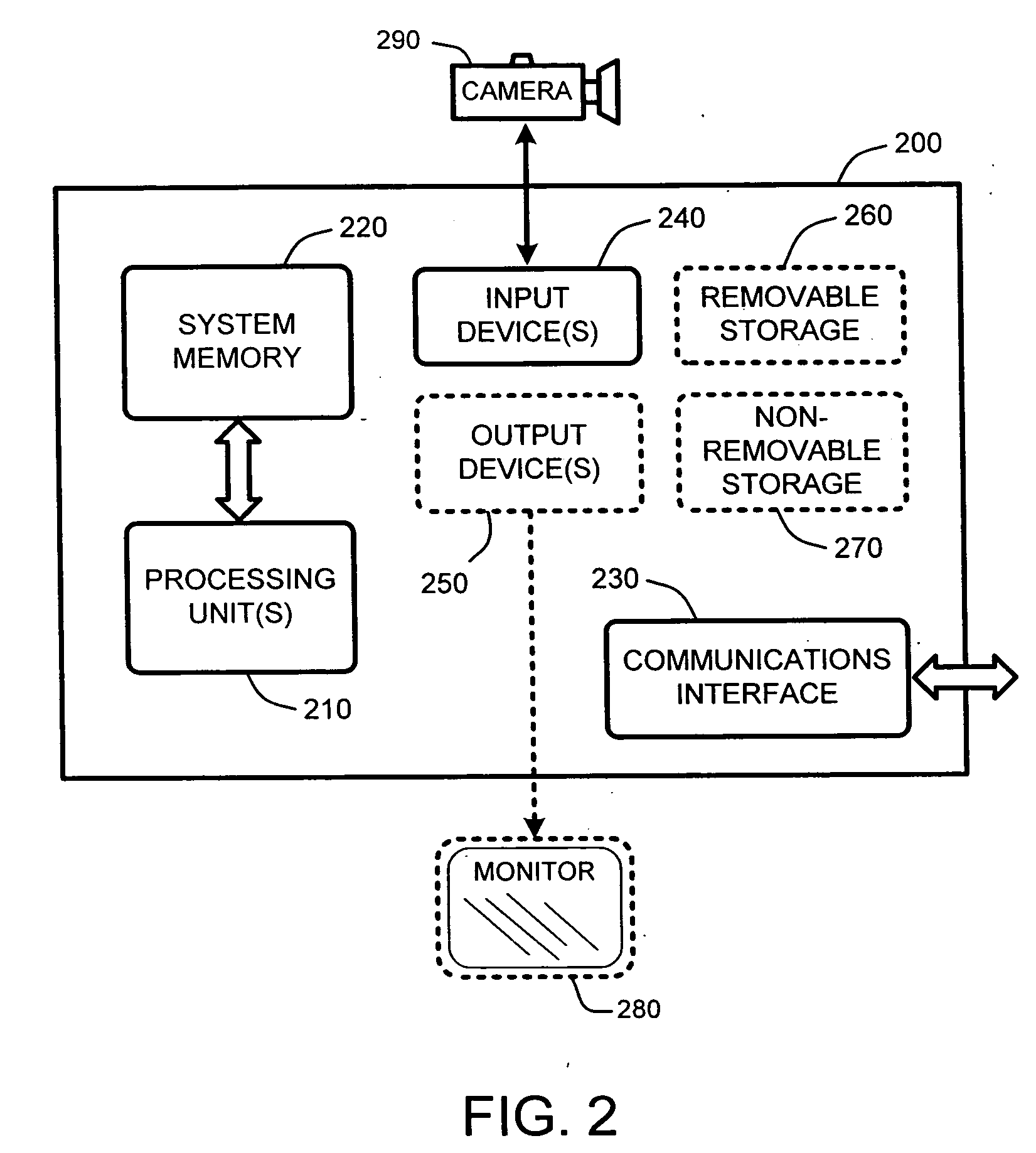
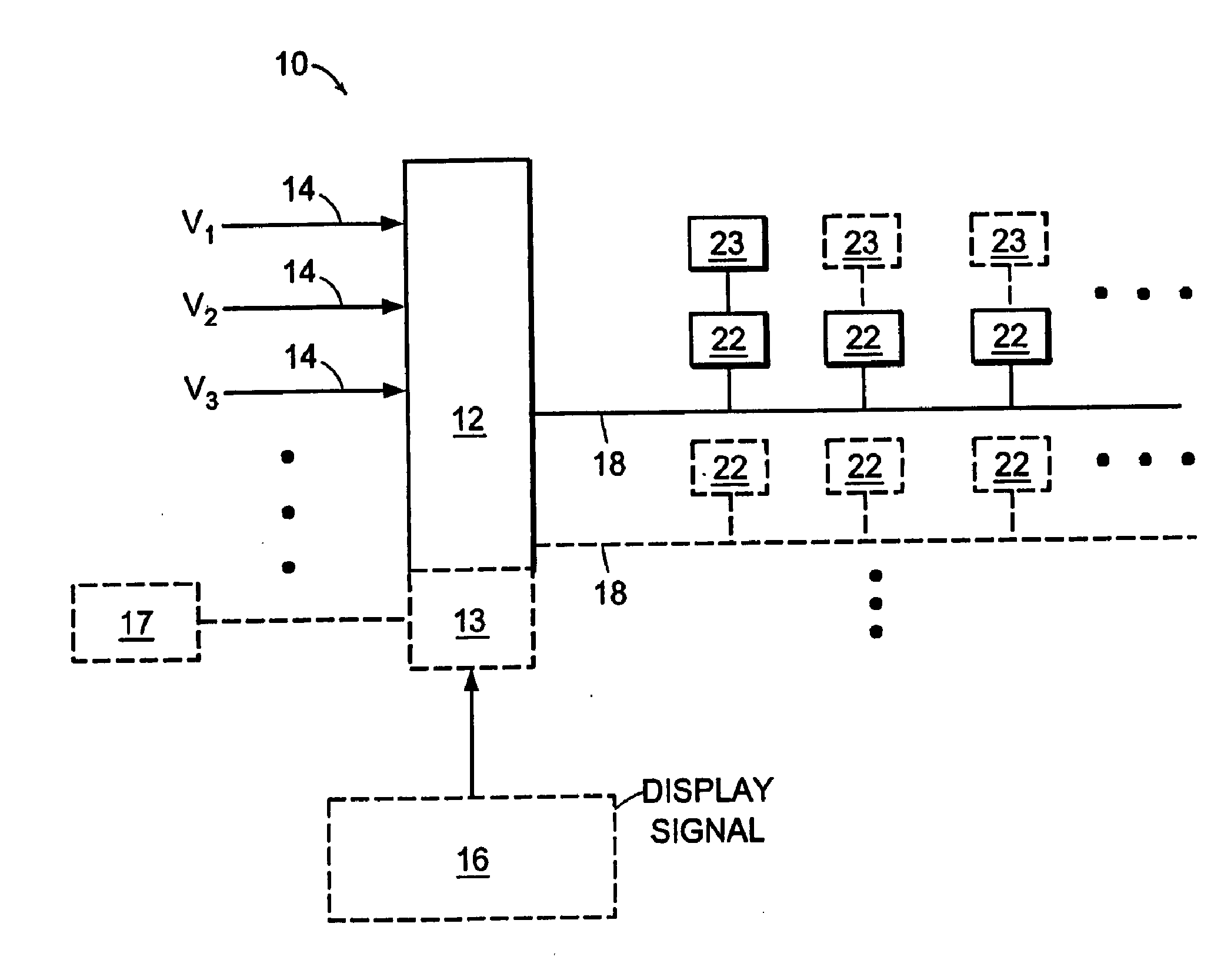
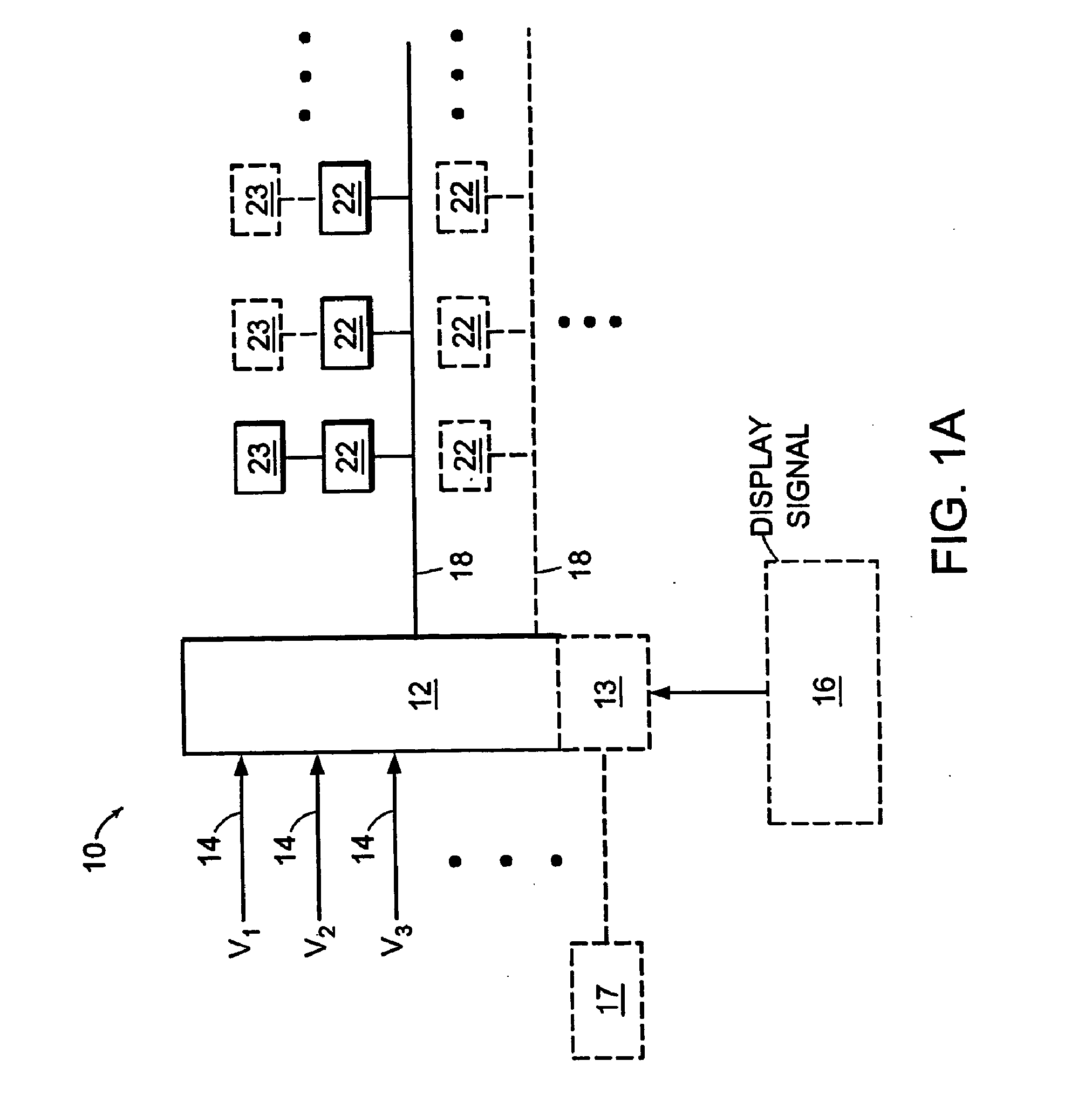
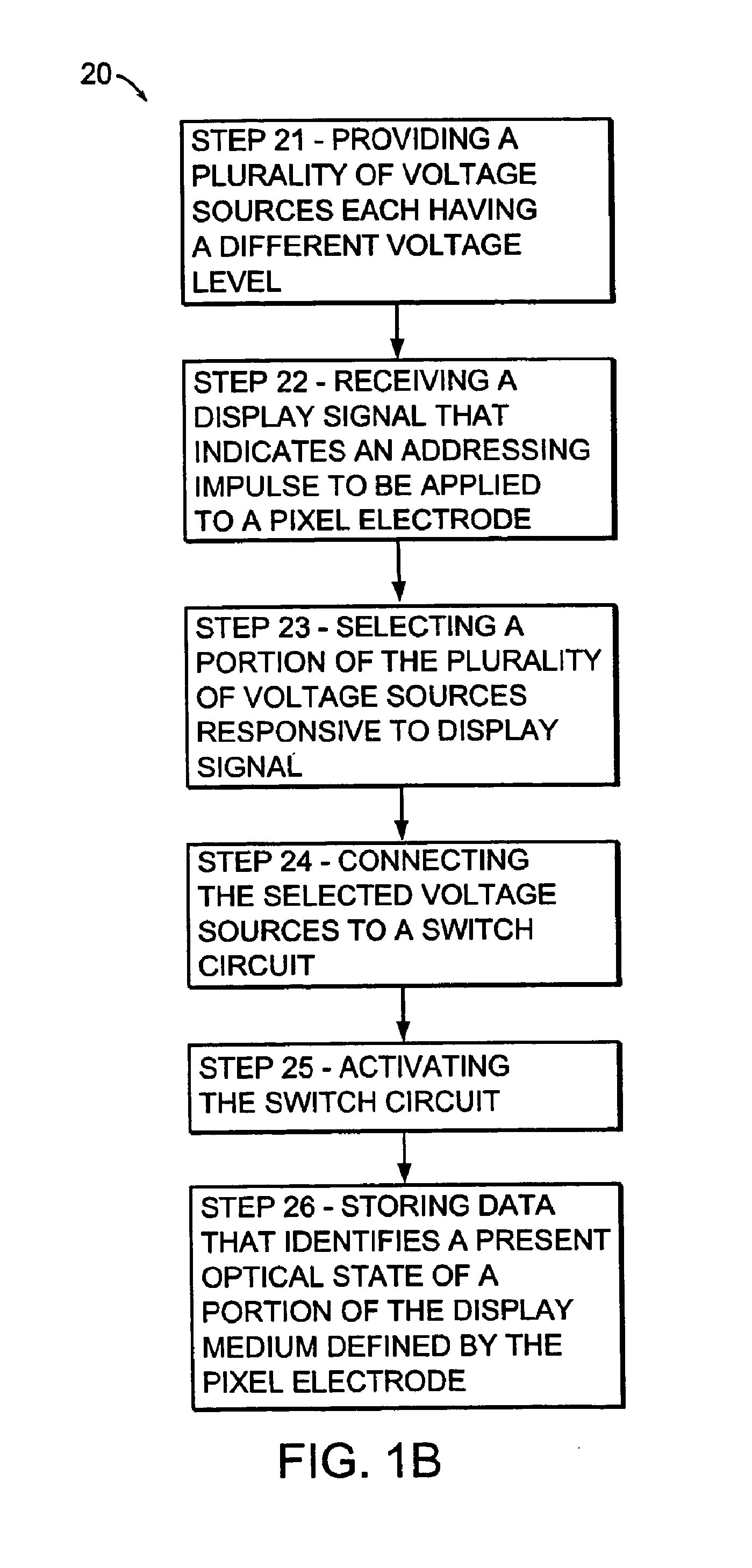
Voltage modulated driver circuits for electro-optic displays
ActiveUS8125501B2Low implementation costFaster design timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityDriver circuit
A method and system for applying addressing voltages to pixels of a display involves receiving input data. The input data includes an indication of an addressing voltage impulse to be applied to a pixel via an electrode. One or more voltage sources are selected, to provide the addressing voltage impulse. The one or more voltage sources each have a pre-selected voltage, The selected one or more voltage sources are electrically connected to an electrode to apply the addressing voltage impulse to the pixel. The invention also provides a method of driving an electro-optic display which uses an intermediate image of reduced bit depth, and a method of driving an electro-optic display which uses a limited number of differing drive voltages, with higher voltage pulses being used before lower voltage pulses.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
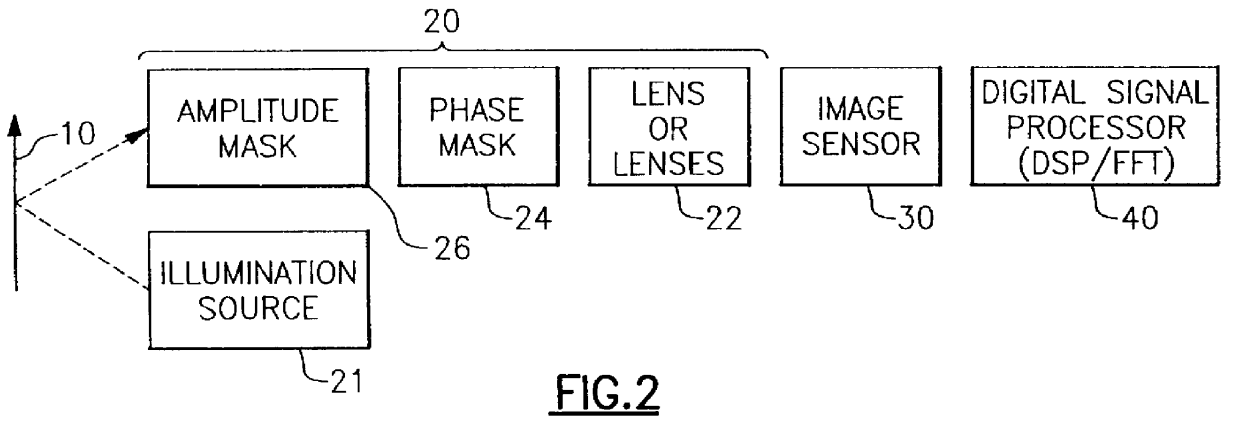
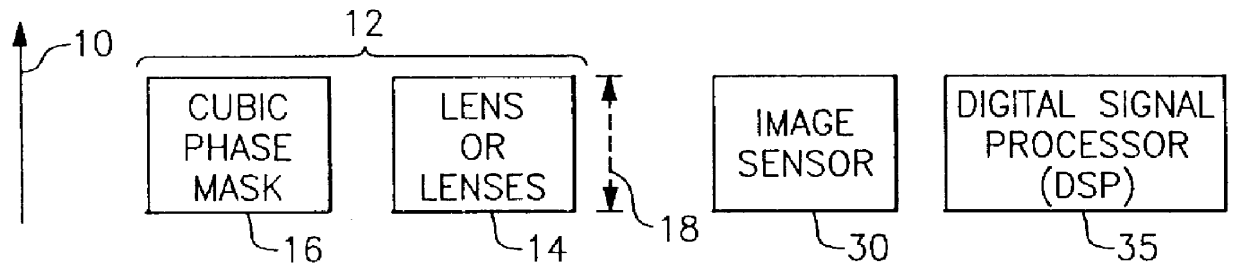
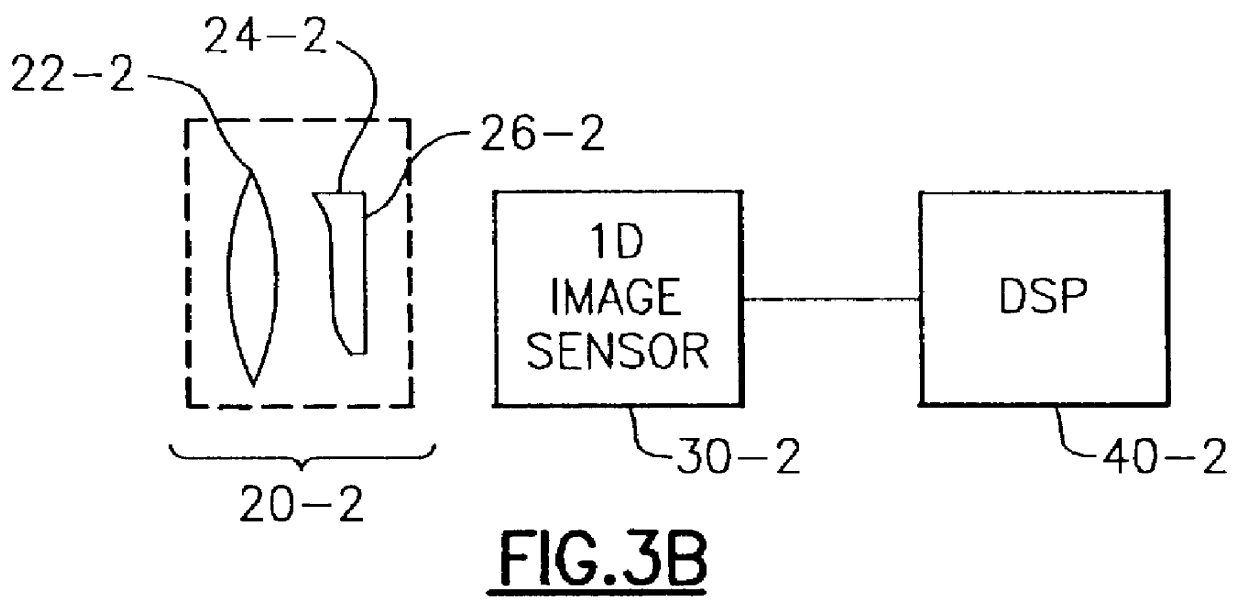
Apparatus and method for reducing imaging errors in imaging systems having an extended depth of field
An improved opto-electronic imaging system which is adapted for use with incoherently illuminated objects, and which produces final images having a reduced imaging error content. The imaging system includes an optical assembly for forming an intermediate image of the object to be imaged, an image sensor for receiving the intermediate image and producing an intermediate image signal, and processing means for processing the intermediate image signal to produce a final image signal having a reduced imaging error content. A reduction in imaging error content is achieved, in part, by including in the optical assembly a phase mask for causing the OTF of the optical assembly to be relatively invariant over a range of working distances, and an amplitude mask having a transmittance that decreases continuously as a function of distance from the center thereof. The reduction in imaging error content is also achieved, in part, by including in the processing means an improved generalized recovery function that varies in accordance with at least the non-ideal calculated IOTF of the optical assembly under a condition of approximately optimum focus.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Displaying optical system and image projection apparatus
InactiveUS20060033009A1Reduce light lossReduce speckle noiseTelevision system scanning detailsProjectorsIntermediate imageDivergence angle
A displaying optical system is disclosed, which is capable of reducing a speckle noise. The displaying optical system comprises a light source emitting coherent light, a scanning device scanning the light, a first optical system causing the light from the scanning device to form an intermediate image, a second optical system causing the light from the intermediate image to form an image on a real display surface, and an optical element arranged between the first and second optical systems. The optical element widens the divergence angle of the light emerged from the optical element toward the second optical system more than the incident angle of the light on the optical element from the first optical system.
Owner:CANON KK
Video registration and image sequence stitching
ActiveUS20070031062A1Reduce computational complexityEasy constructionTelevision system detailsDigital data information retrievalIntermediate imageImage pair
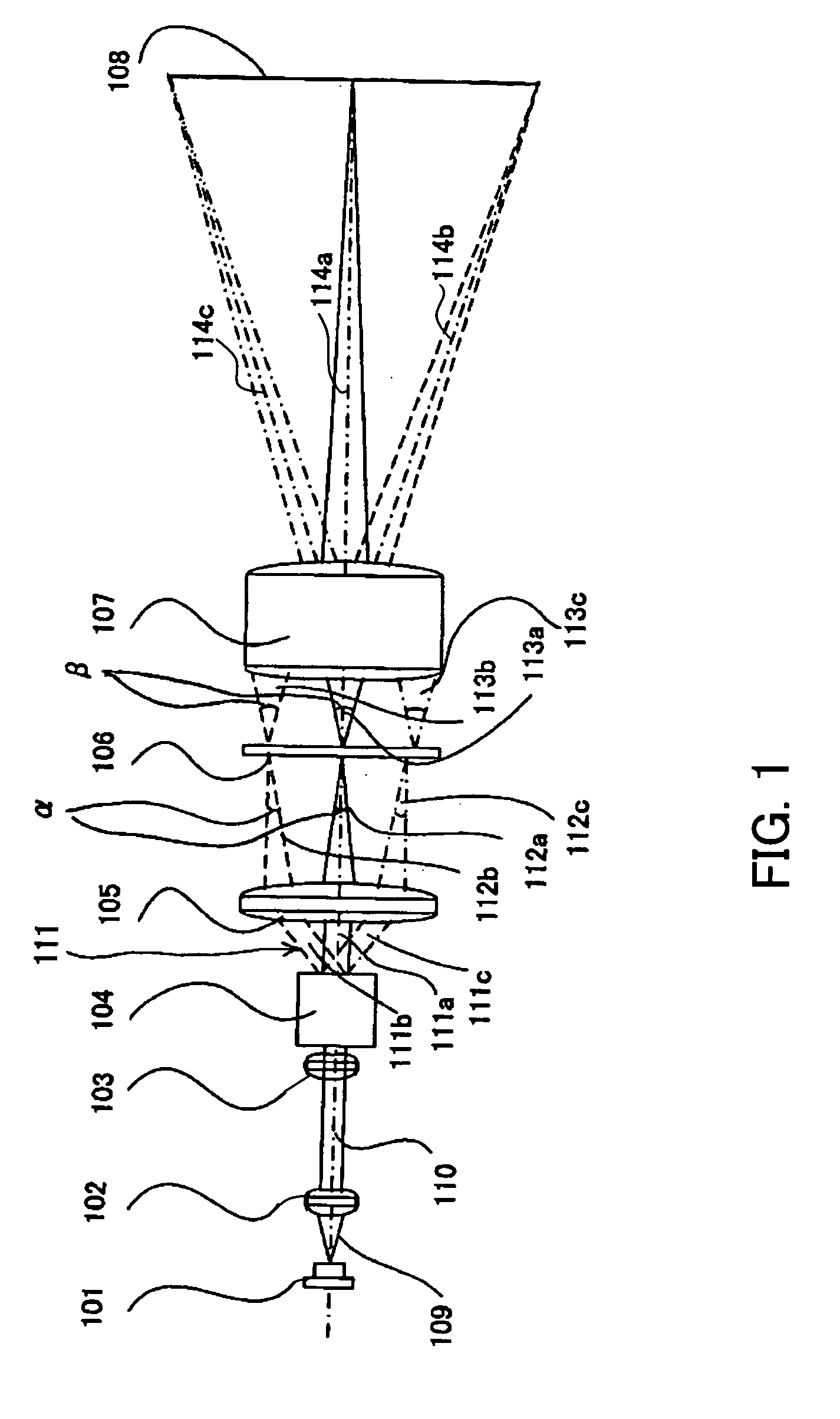
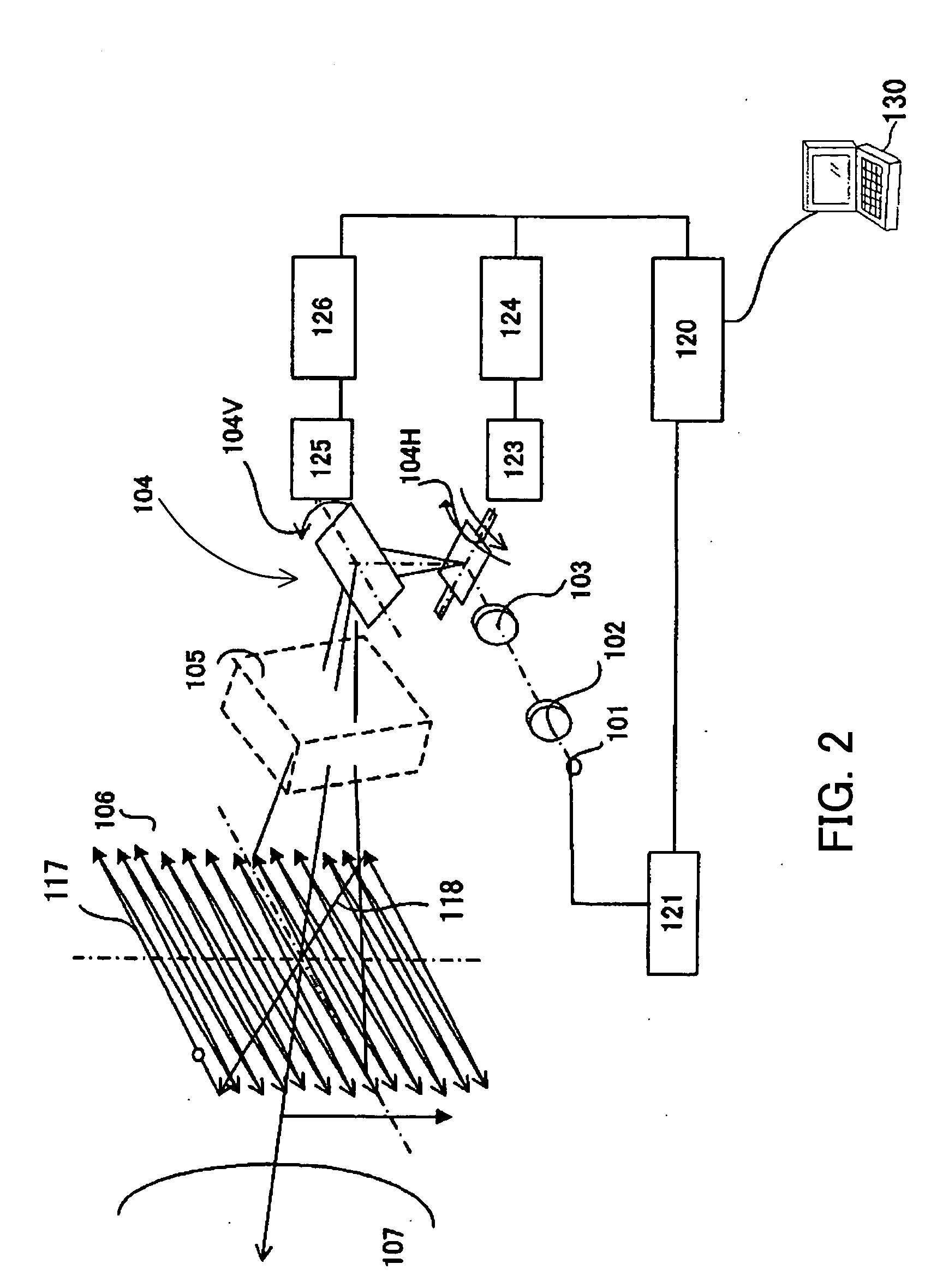
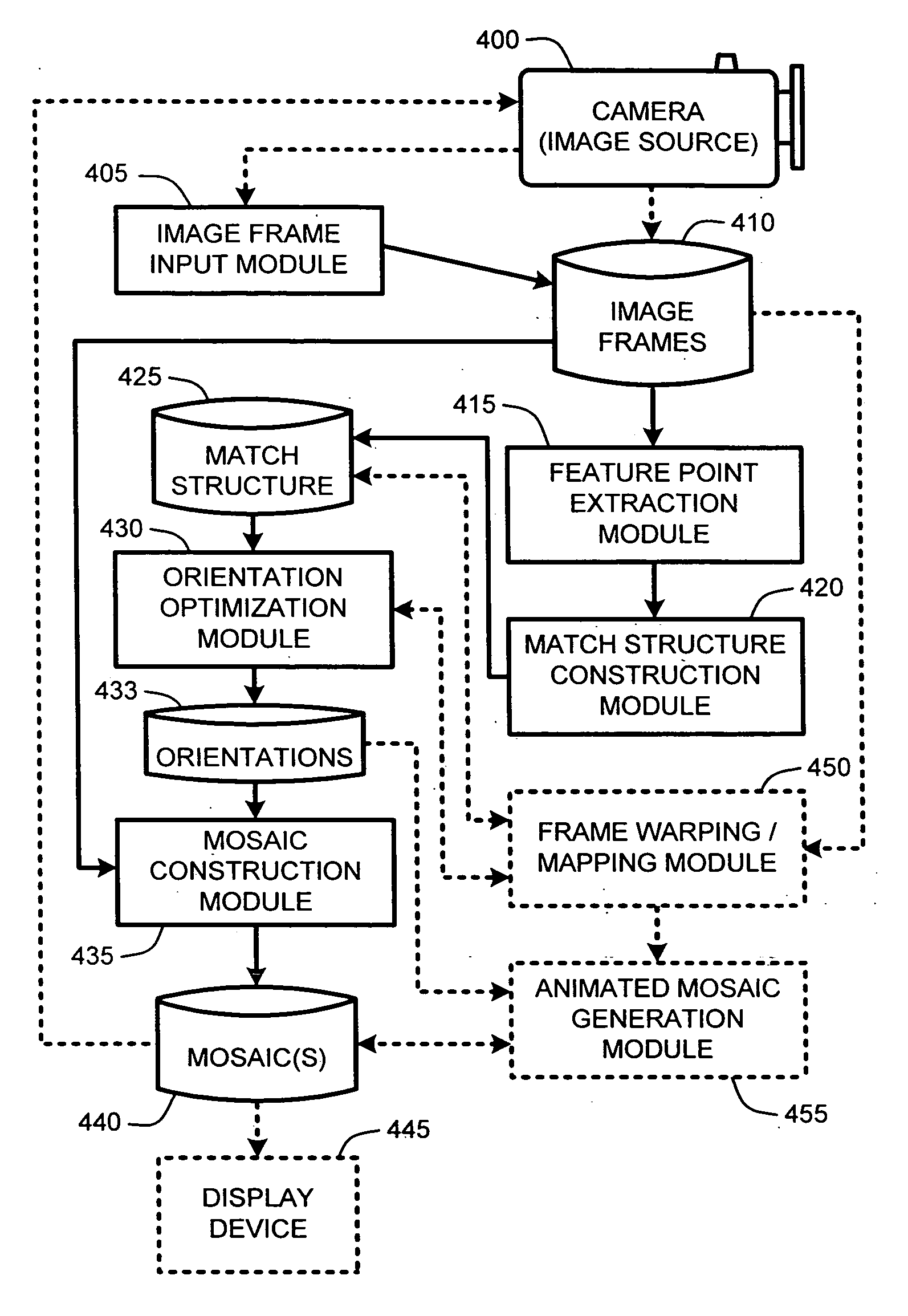
A “Keyframe Stitcher” provides an efficient technique for building mosaic panoramic images by registering or aligning video frames to construct a mosaic panoramic representation. Matching of image pairs is performed by extracting feature points from every image frame and matching those points between image pairs. Further, the Keyframe Stitcher preserves accuracy of image stitching when matching image pairs by utilizing ordering information inherent in the video. The cost of searching for matches between image frames is reduced by identifying “keyframes” based on computed image-to-image overlap. Keyframes are then matched to all other keyframes, but intermediate image frames are only matched to temporally neighboring keyframes and neighboring intermediate frames to construct a “match structure.” Image orientations are then estimated from this match structure and used to construct the mosaic. Matches between image pairs may be compressed to reduce computational overhead by replacing groups of feature points with representative measurements.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
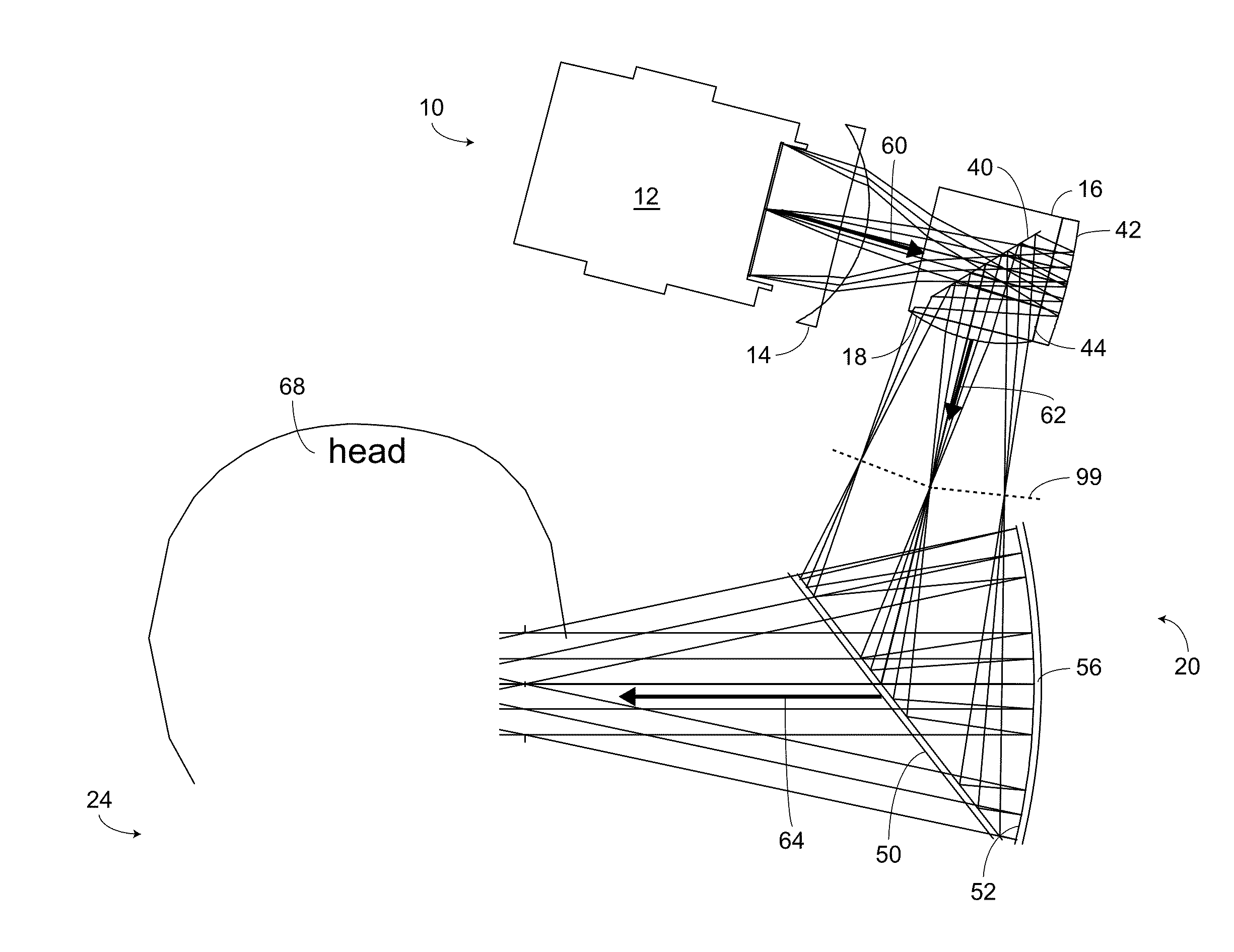
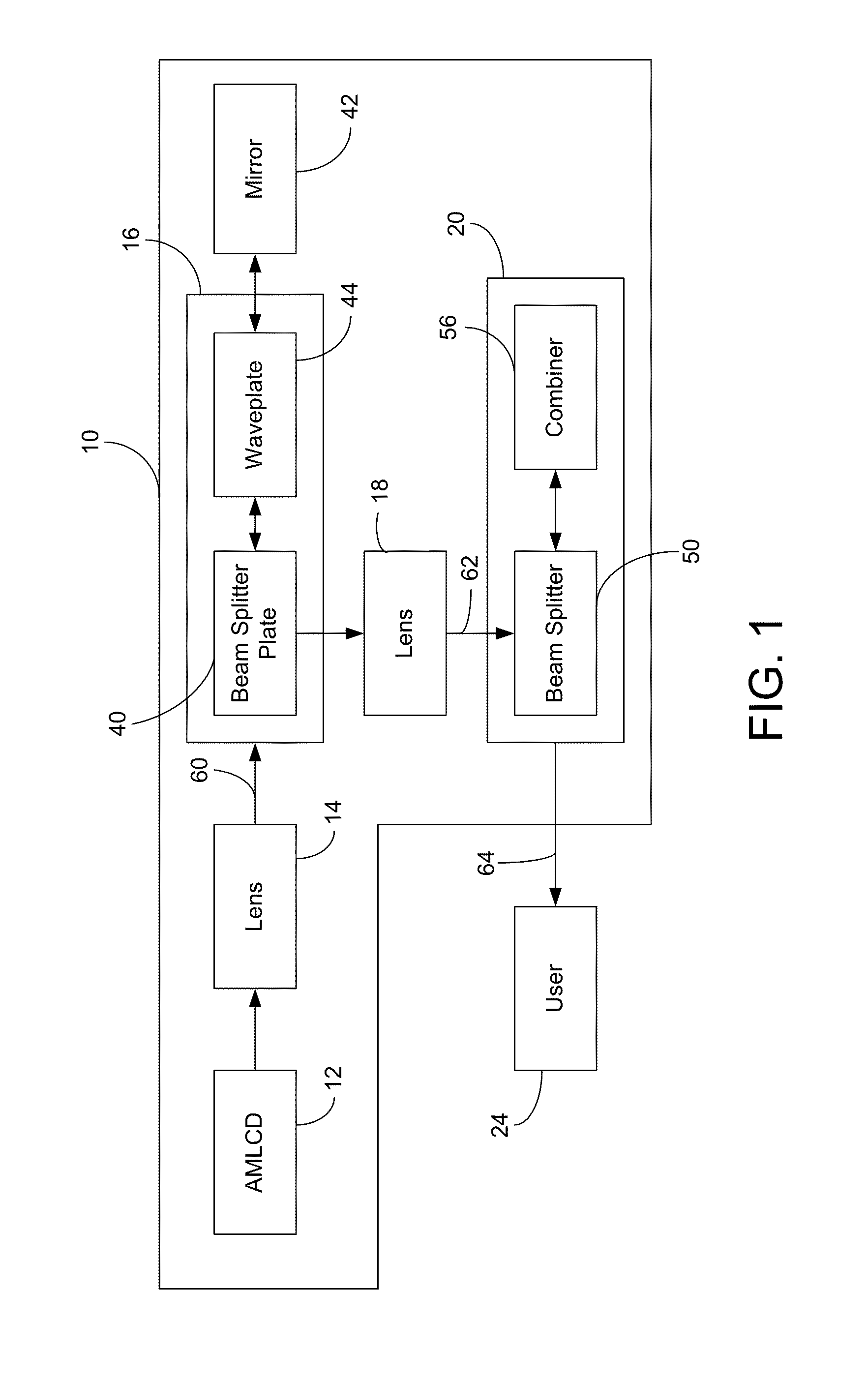
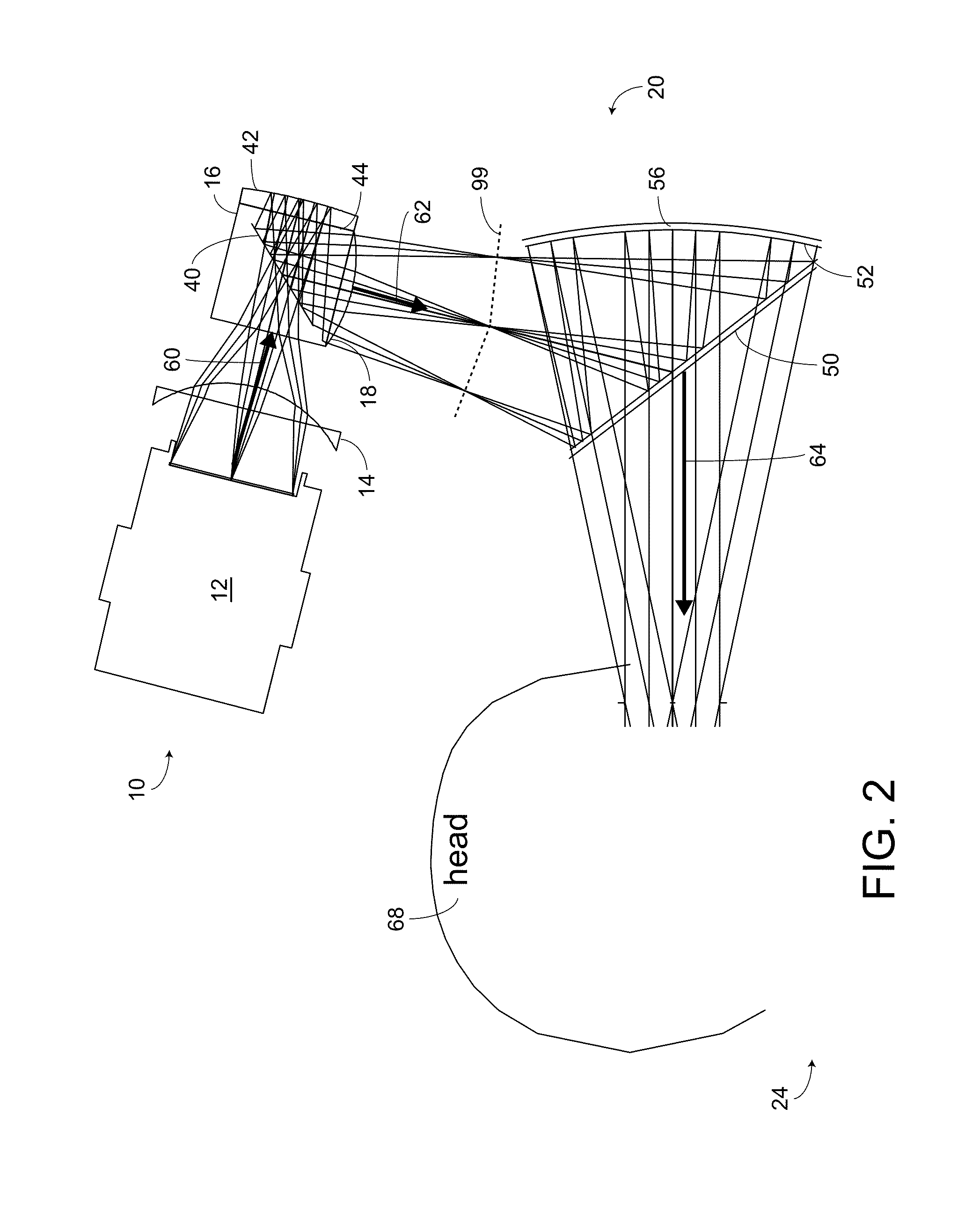
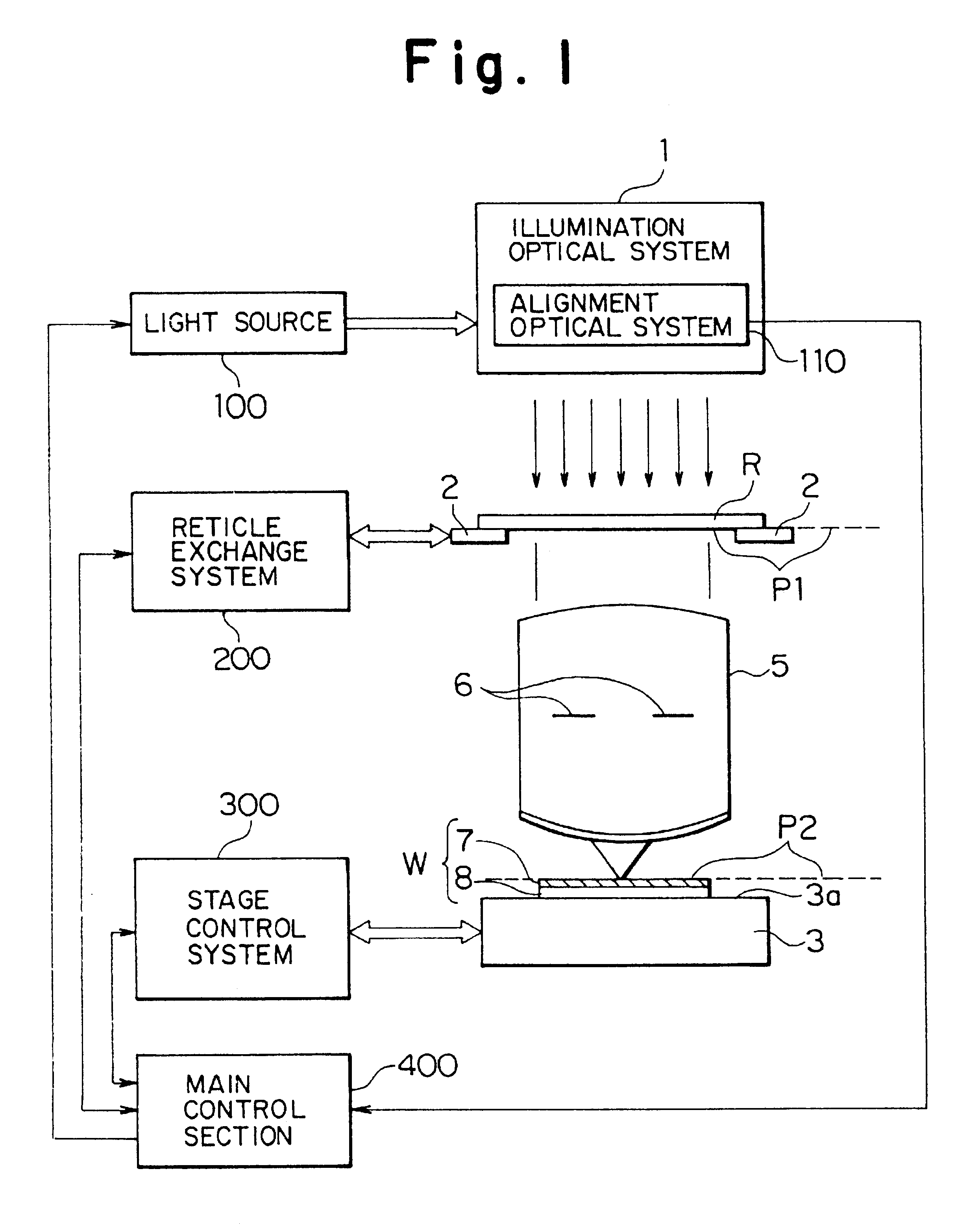
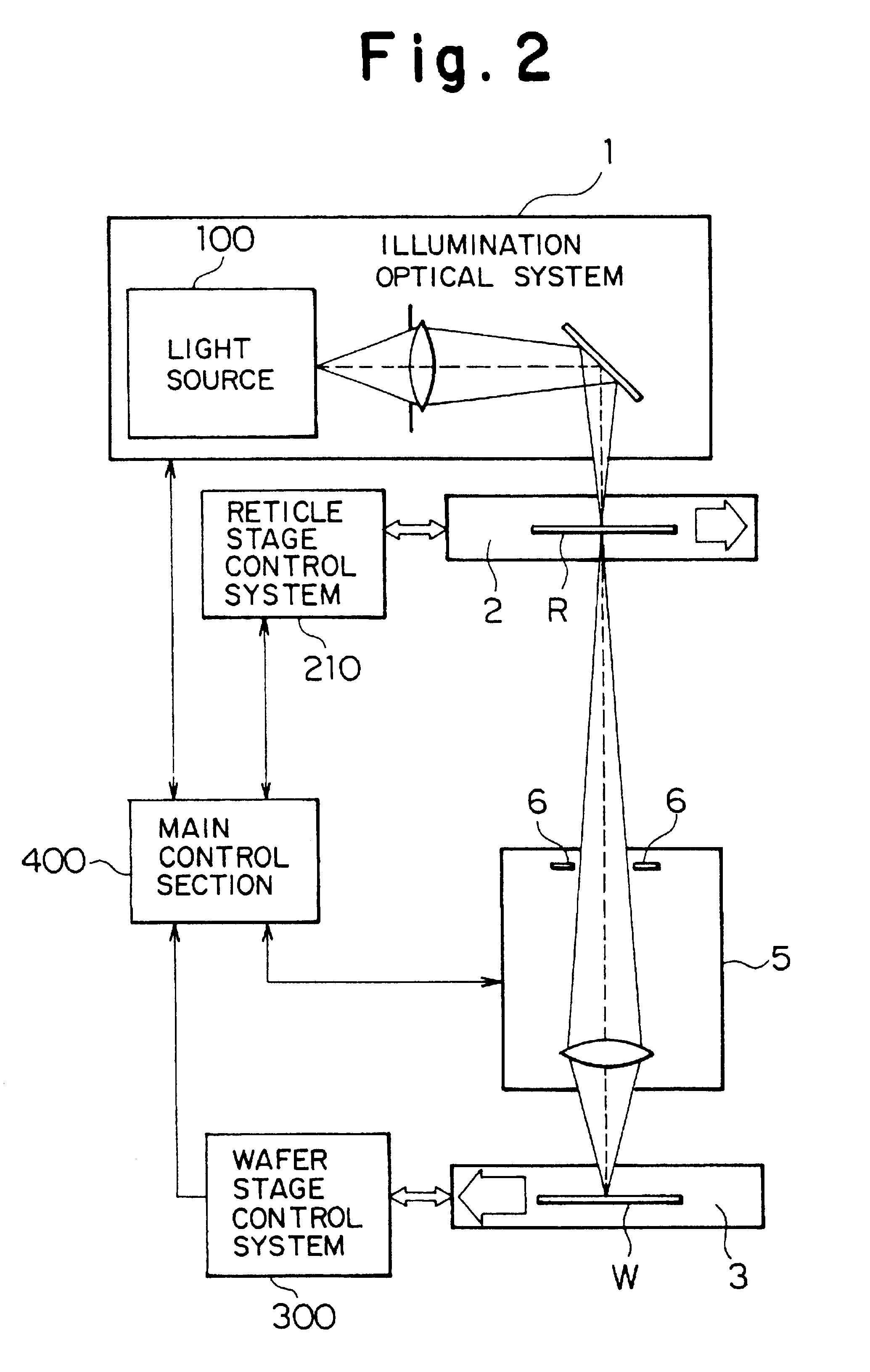
Method of and system for providing a head up display (HUD)
A head up display (HUD) includes an image source, a first lens, a second lens, a focusing mirror, a polarizing beam splitter, a second beam splitter and a combiner. The first lens is disposed between the image source and polarizing beam splitter. The second lens is disposed between the polarizing beam splitter and the second beam splitter. The polarizing beam splitter is disposed between the first lens, the mirror, and the second lens. The optical system for the HUD forms an intermediate image between the second lens and the second beam splitter. The intermediate image is located at the focal point of the curved combiner, and therefore the curved combiner collimates the display light upon reflection. The HUD can be compact and have a wide field of view.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Virtual image display apparatus
ActiveUS20130222919A1Wide viewing angleImprove performanceOptical elementsIntermediate imageDisplay device
An intermediate image is formed inside a first prism, and an image light, which is reflected on the order of a third surface, a first surface and a second surface, is transmitted through the first surface and reaches the eyes of the observer, therefore it is possible to make the entire optical system small and light in weight by making the first prism thin, and realize a high performance display device with a wide angle of view. Further, when an external light is passed through, for example, the first surface and the third surface and observed, a diopter scale is set to approximately zero, and thereby reducing the defocus or distortion of the external light when observed in a see-through manner. And, it is possible such that the shape of the first prism conforms to the face of the observer, the center is also close to the face.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Display management method and system of mobile terminal
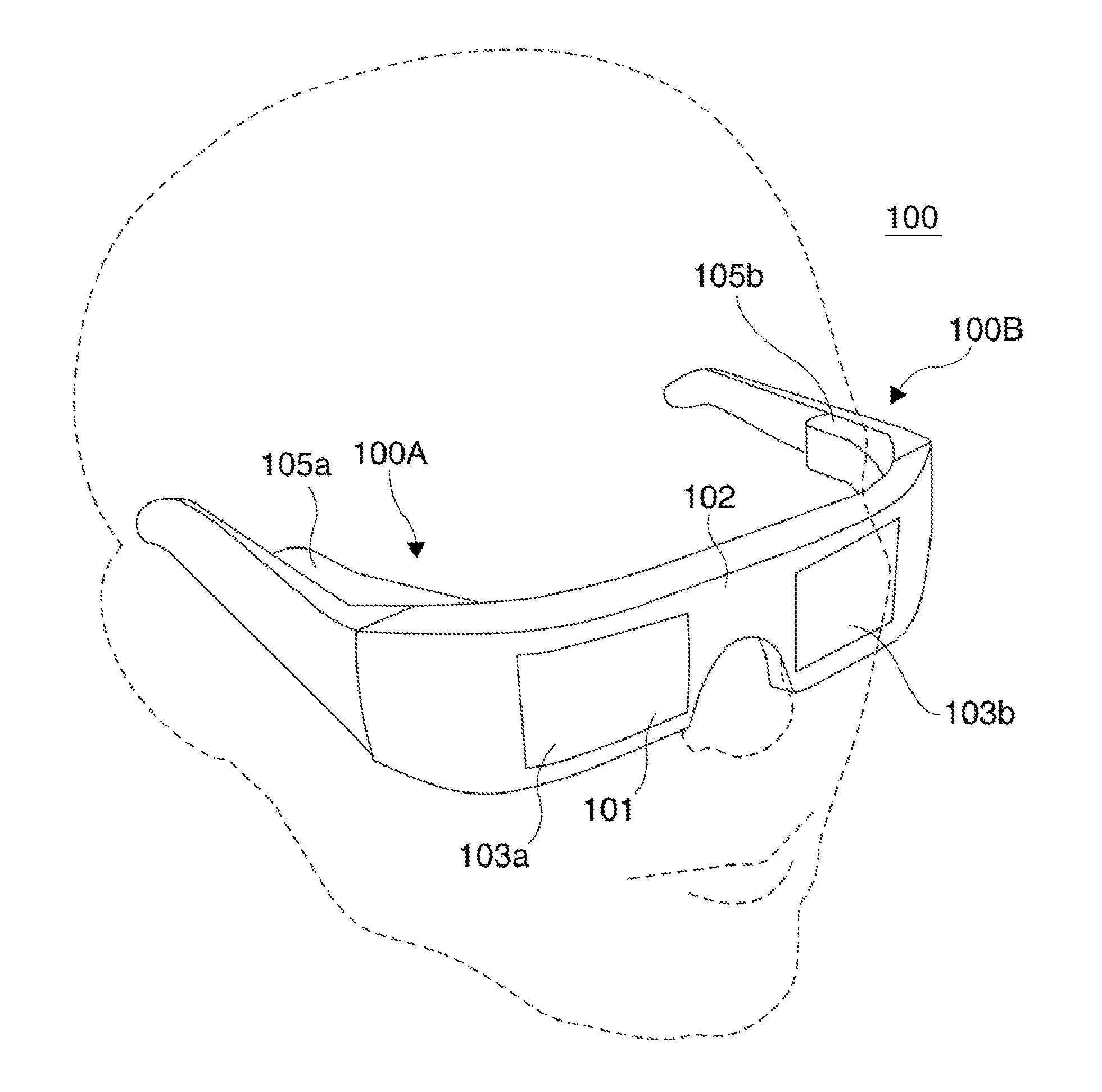
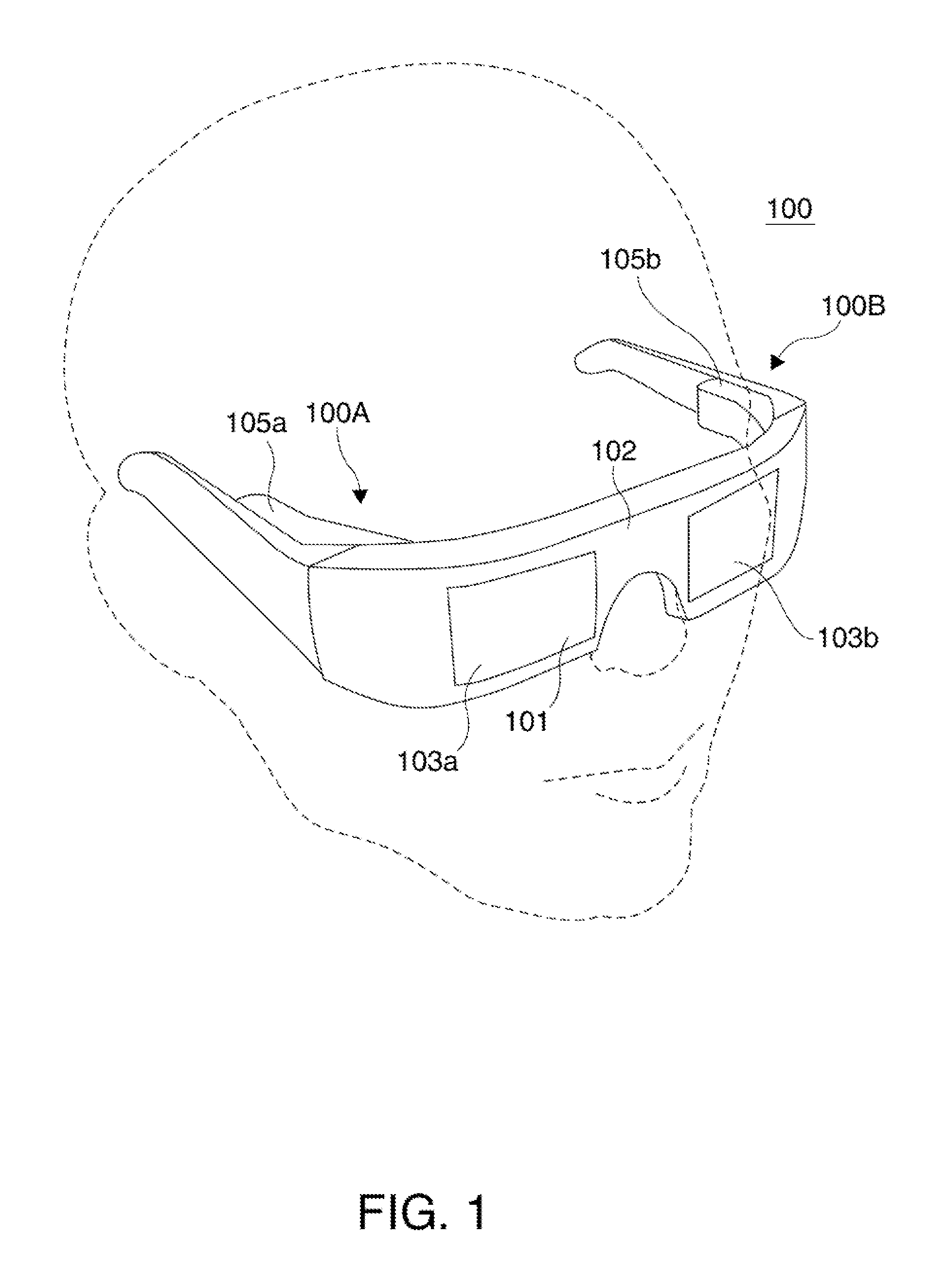
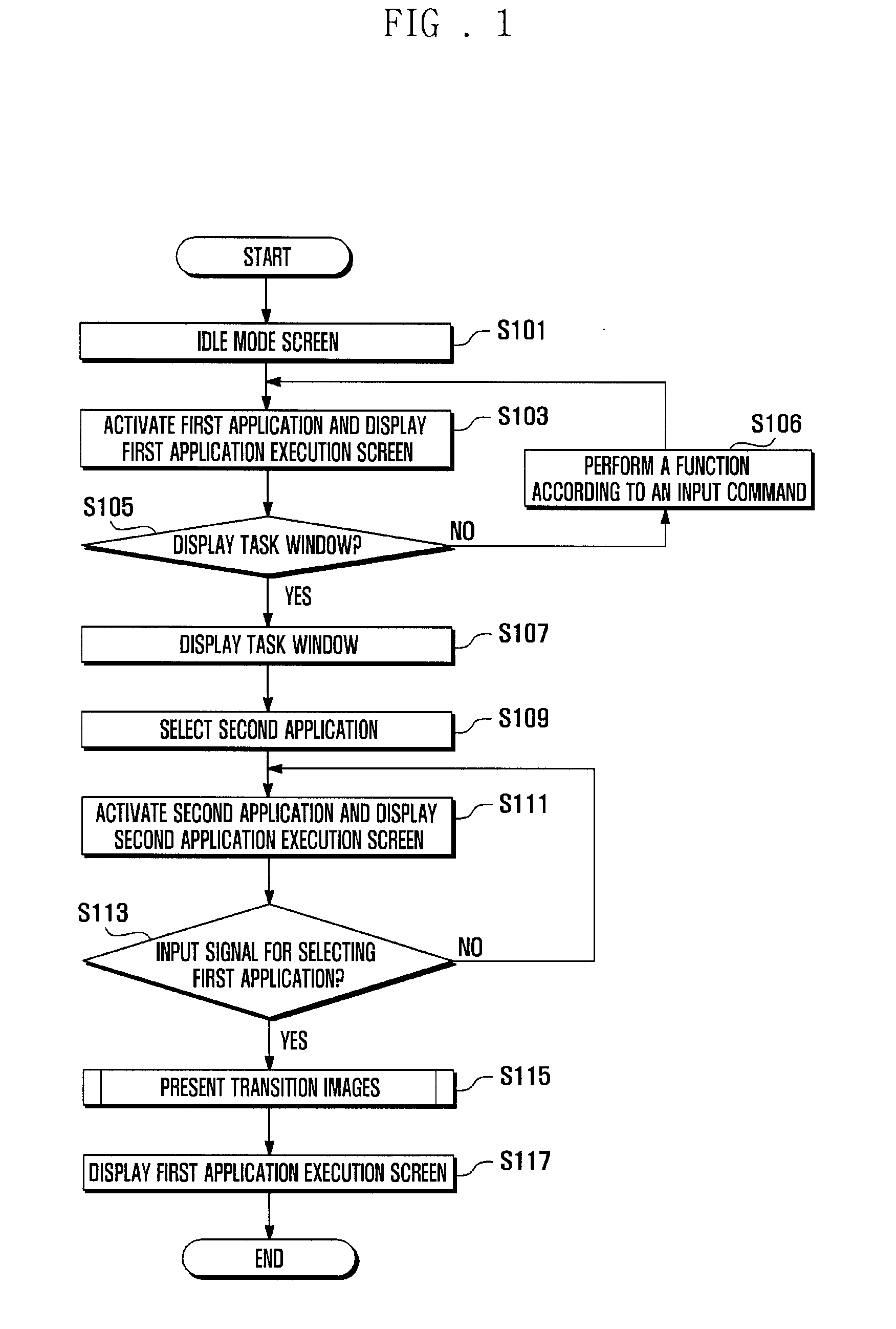
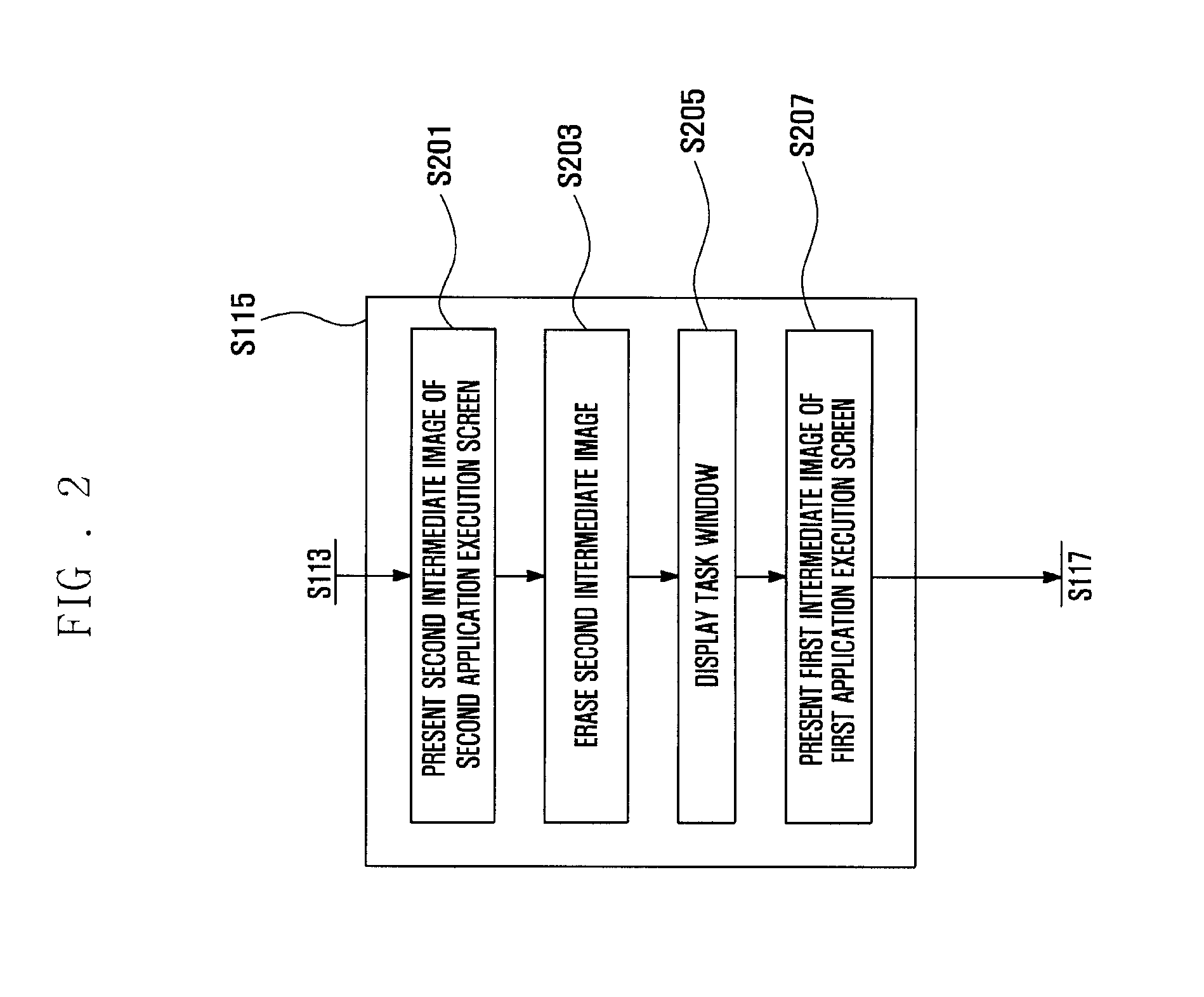
ActiveUS20100299597A1Input/output for user-computer interactionMowersIntermediate imageDisplay device
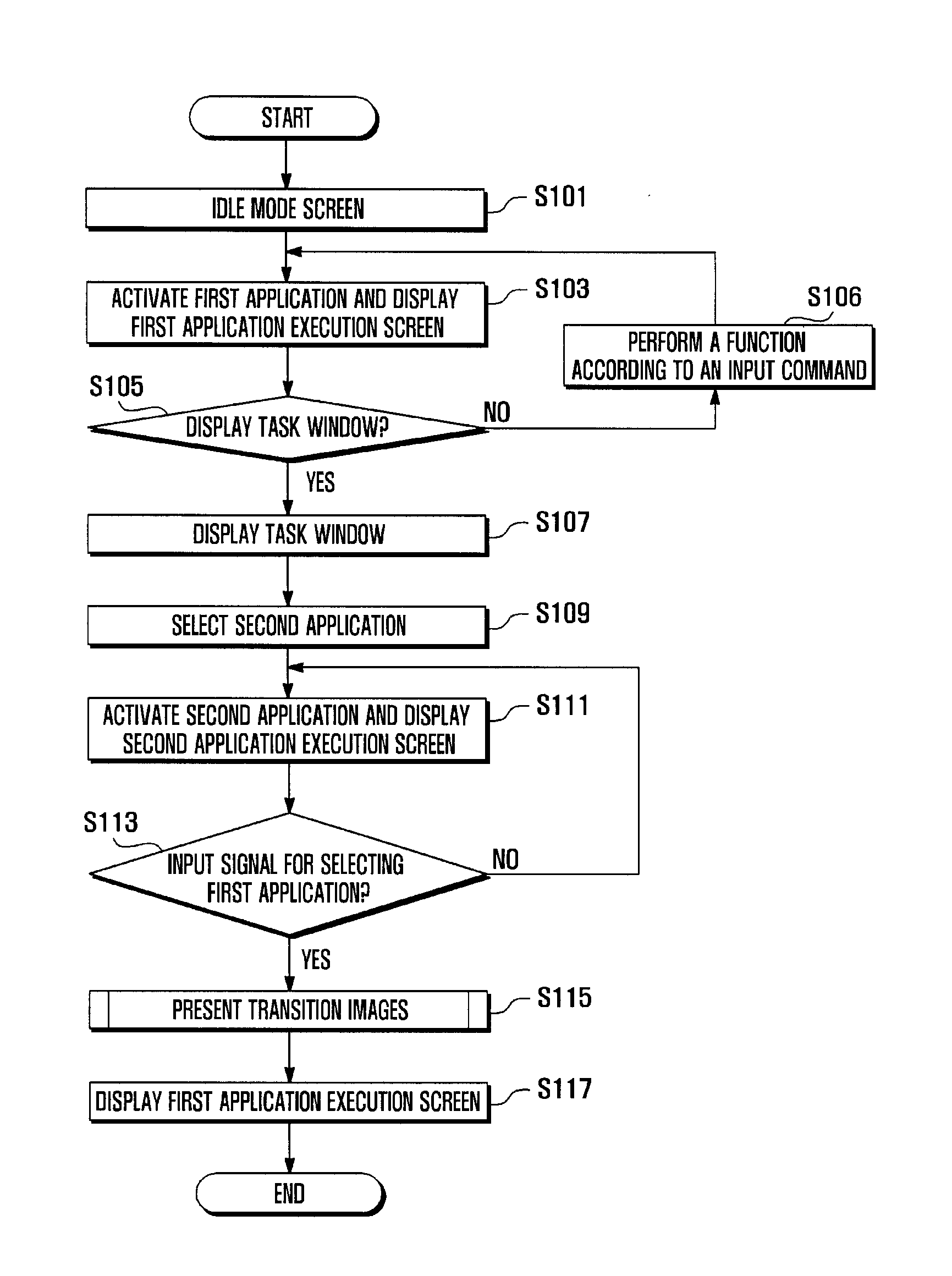
A display management method and system of a mobile terminal for switching between user interfaces of applications is disclosed. A display management method of a mobile terminal according to the present invention includes displaying a first execution screen of a first application on a display; detecting an input signal for activating a second application; and displaying a second execution screen corresponding to the second application in response to the input signal, wherein displaying the second execution screen comprising presenting at least one of a first intermediate image obtained by downsizing an image contained within the first execution screen, a second intermediate image obtained by downsizing an image contained within the second execution screen, and a task window containing at least the downsized first and second intermediate images in a sequential order.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
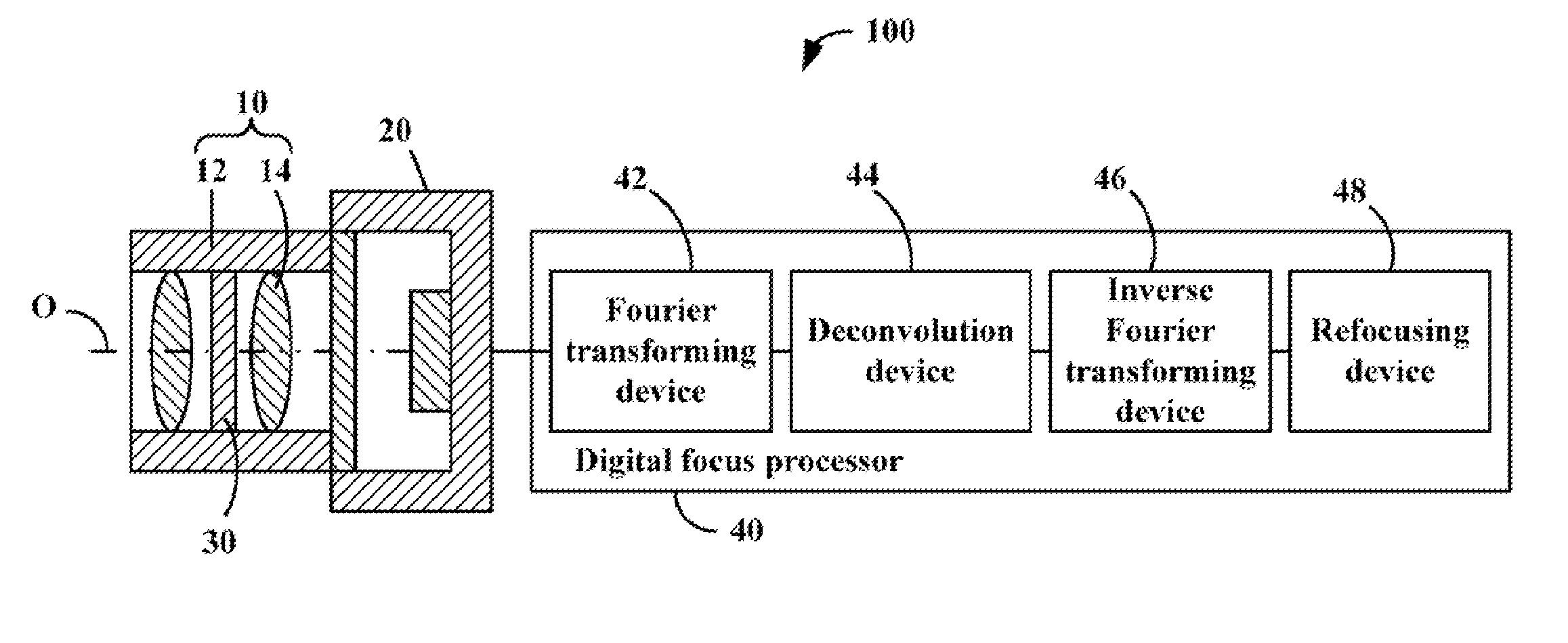
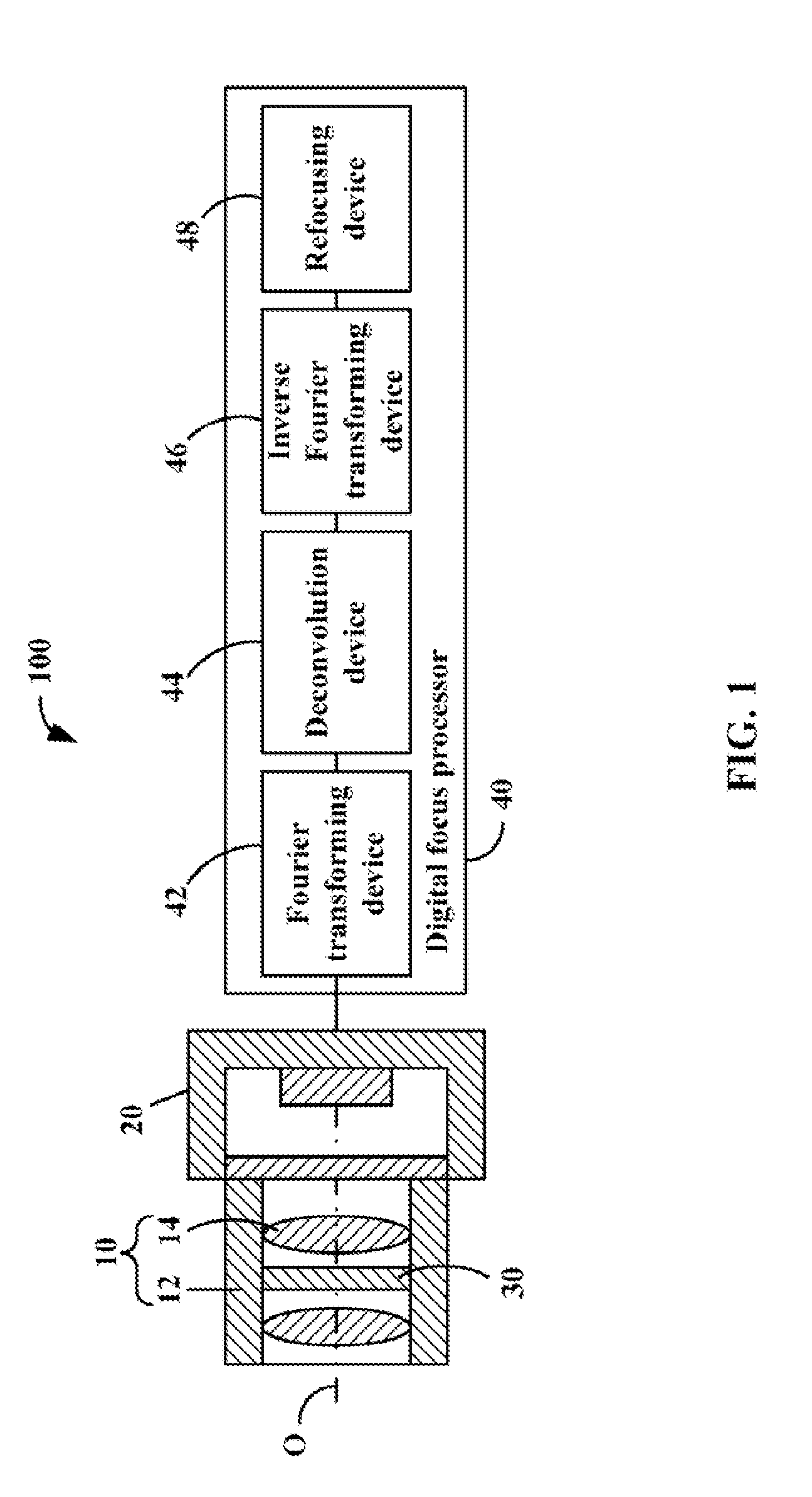
Computational imaging system
InactiveUS8212914B2Television system detailsSolid-state devicesModulation functionIntermediate image
An imaging sub-system, a liquid crystal (LC) element, and a digital focus processor are provided. The LC element is placed in the light path of the imaging sub-system, functioning as the aperture of the imaging sub-system, and includes a periodically patterned electrode which is patterned according to a periodical modulation function and configured to blur an intermediate image captured by the imaging sub-system by applying a controllable voltage thereto. The digital focus processor is configured to deconvolute the periodical modulation function to remove the blur away from the intermediate image and determine an all-in-focus real image.
Owner:GOLD CHARM LTD
Projection optical system, magnification projection optical system, magnification projection apparatus, and image projection apparatus
ActiveUS7048388B2Increase in sizeReduce spacingProjectorsNon-linear opticsProjection opticsIntermediate image
A projection optical system guiding and projecting a light beam from a projected object surface onto a projection surface in an upstream-downstream direction through a transmission dioptric system and a reflection dioptric system. An intermediate image surface of the projected object surface is positioned closer to the reflection dioptric system than to the transmission dioptric system, and an intermediate image on the intermediate image surface is formed as the final image on the projection surface via the reflecting mirrors, which include at least one anamorphic polynomial free-formed surface having different vertical and lateral powers. A light beam from the reflection dioptric system to the projection surface is guided at an angle to a normal of the projection surface and the transmission dioptric system is decentered with respect to a normal of the projected object surface, the transmission refractive elements prevented from being decentered with respect to each other.
Owner:RICOH KK
Voltage modulated driver circuits for electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20070200874A1Low implementation costFaster design timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDriver circuitElectricity
A method and system for applying addressing voltages to pixels of a display involves receiving input data. The input data includes an indication of an addressing voltage impulse to be applied to a pixel via an electrode. One or more voltage sources are selected, to provide the addressing voltage impulse. The one or more voltage sources each have a pre-selected voltage, The selected one or more voltage sources are electrically connected to an electrode to apply the addressing voltage impulse to the pixel. The invention also provides a method of driving an electro-optic display which uses an intermediate image of reduced bit depth, and a method of driving an electro-optic display which uses a limited number of differing drive voltages, with higher voltage pulses being used before lower voltage pulses.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
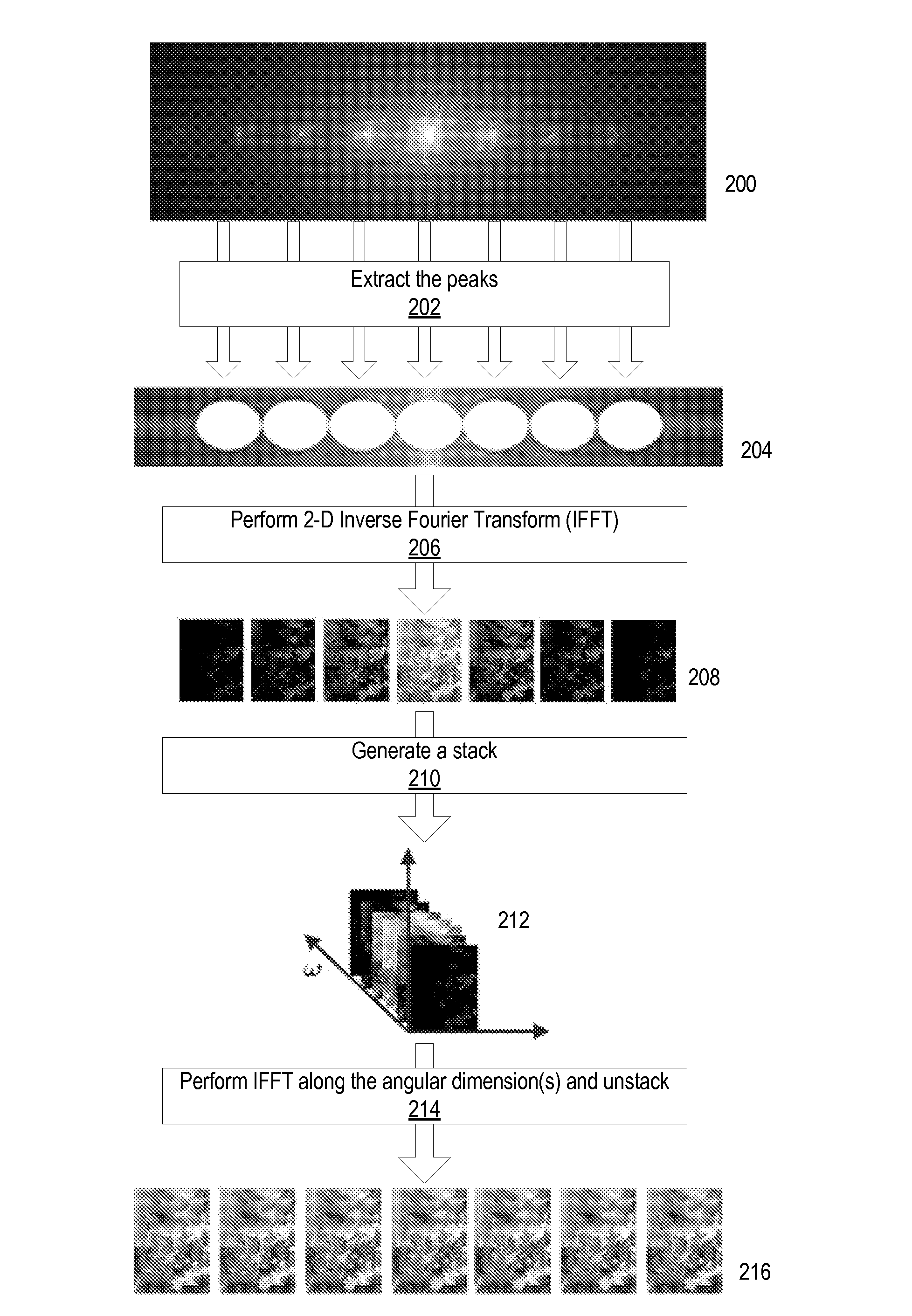
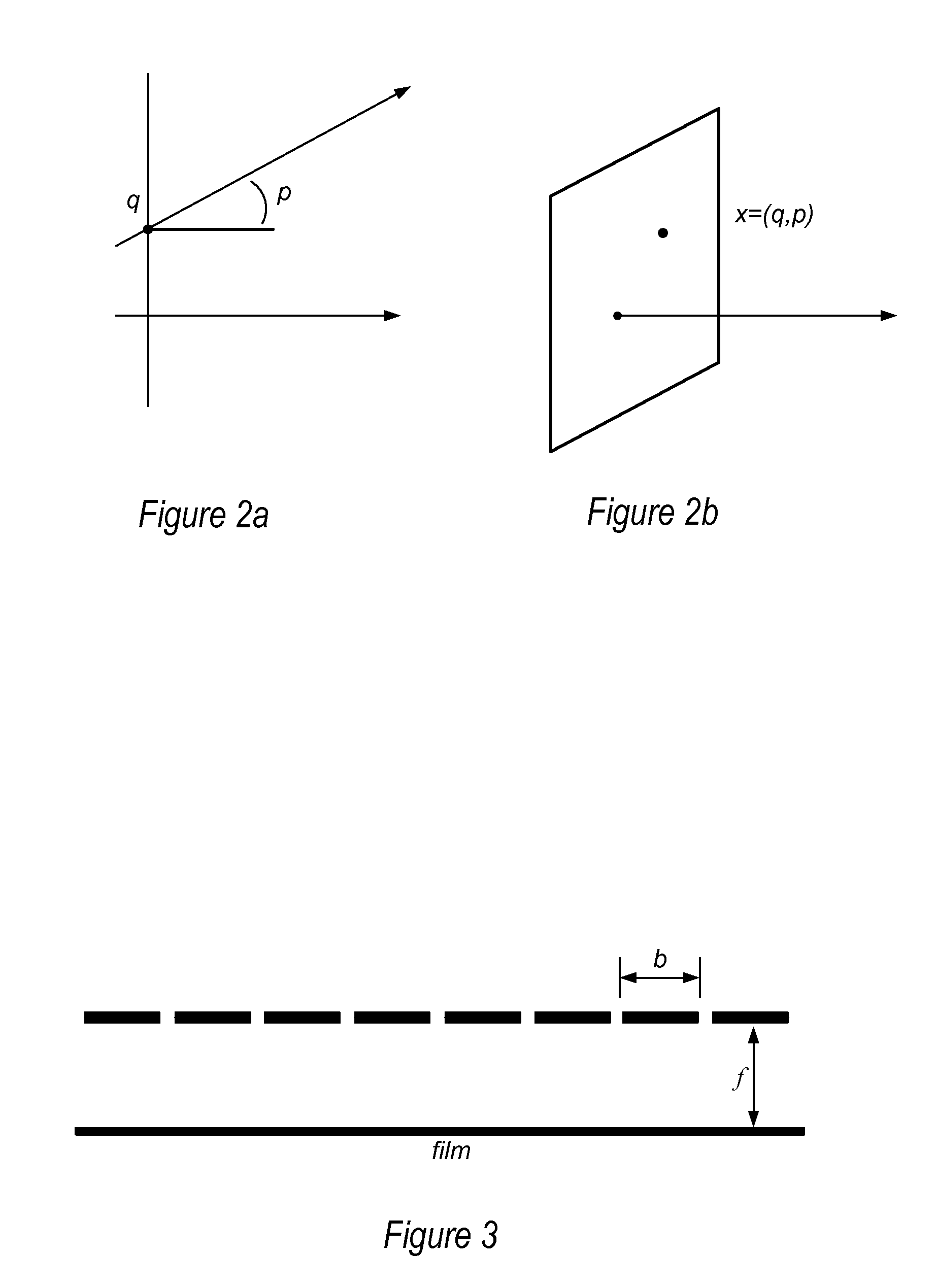
Method and Apparatus for Radiance Processing by Demultiplexing in the Frequency Domain
ActiveUS20090041381A1Guaranteed corrective effectPromote resultsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxPhase correction
Method and apparatus for radiance processing by demultiplexing in the frequency domain. A frequency domain demultiplexing module obtains a radiance image captured with a lens-based radiance camera. The image includes optically mixed spatial and angular frequency components of light from a scene. The module performs frequency domain demultiplexing on the radiance image to generate multiple parallax views of the scene. The method may extract multiple slices at different angular frequencies from a Fourier transform of the radiance image, apply a Fourier transform to each of the multiple slices to generate intermediate images, stack the intermediate images to form a 3- or 4-dimensional image, apply an inverse Fourier transform along angular dimension(s) of the 3- or 4-dimensional image, and unstack the transformed 3- or 4-dimensional image to obtain the multiple parallax views. During the method, phase correction may be performed to determine the centers of the intermediate images.
Owner:ADOBE INC
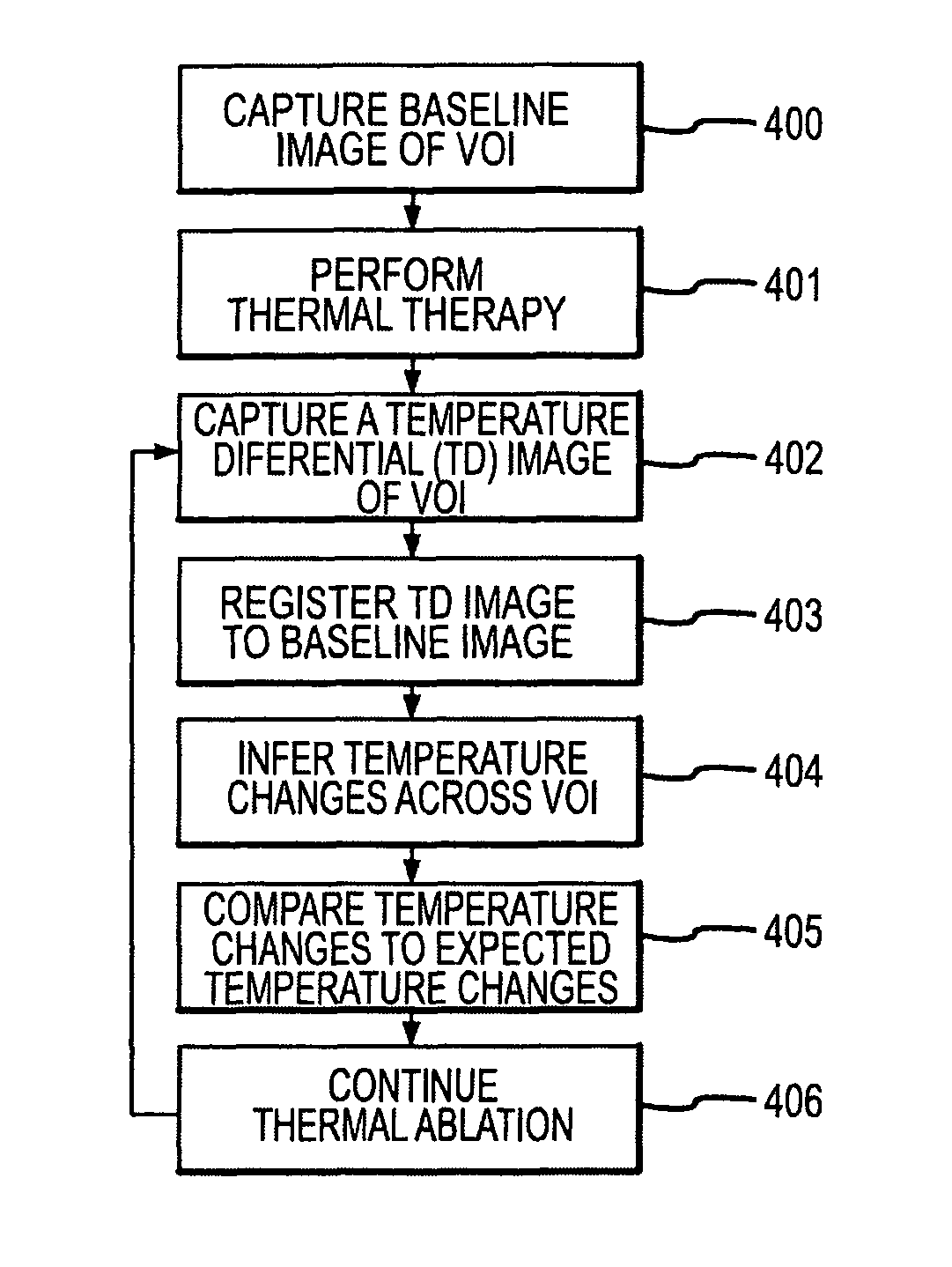
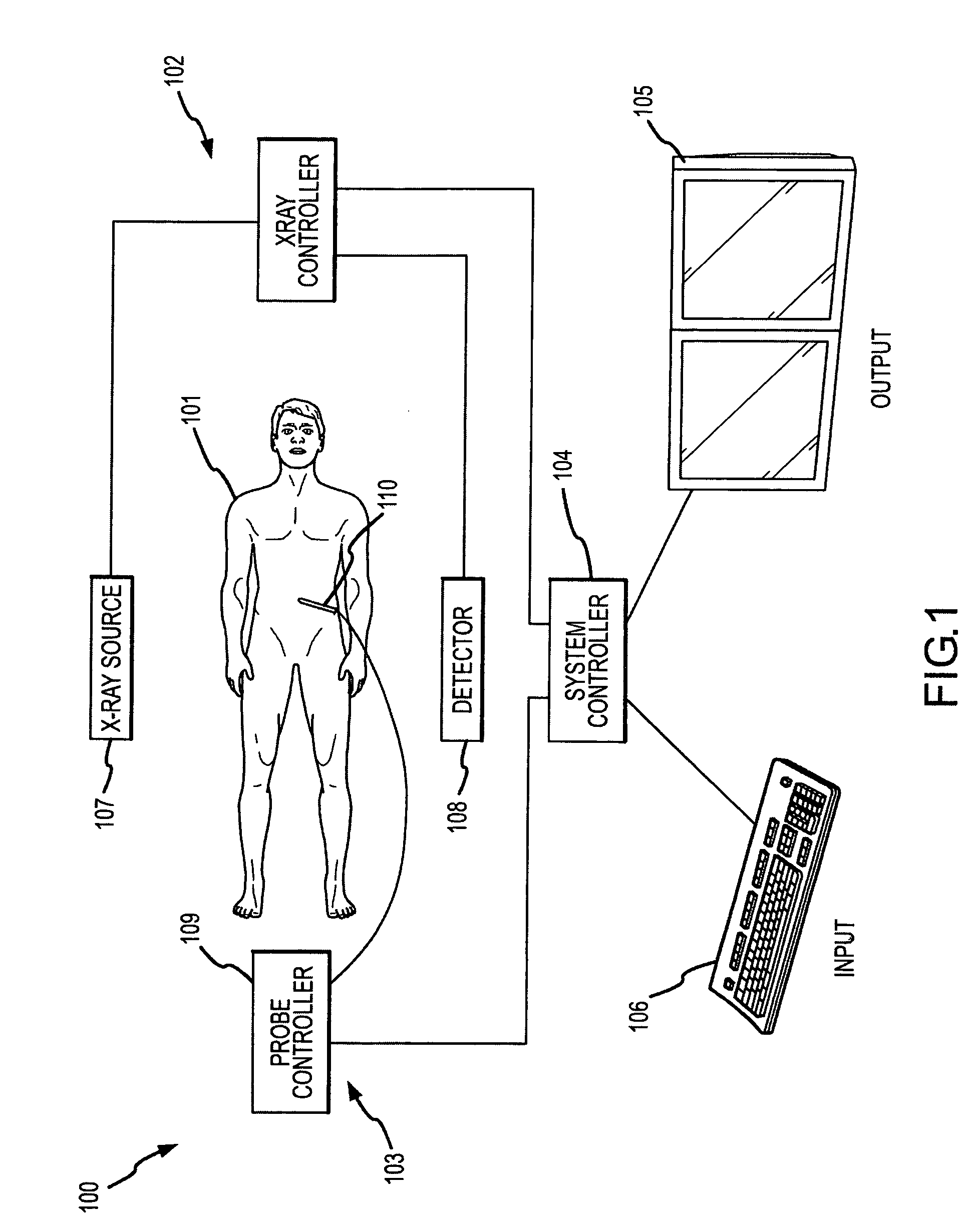
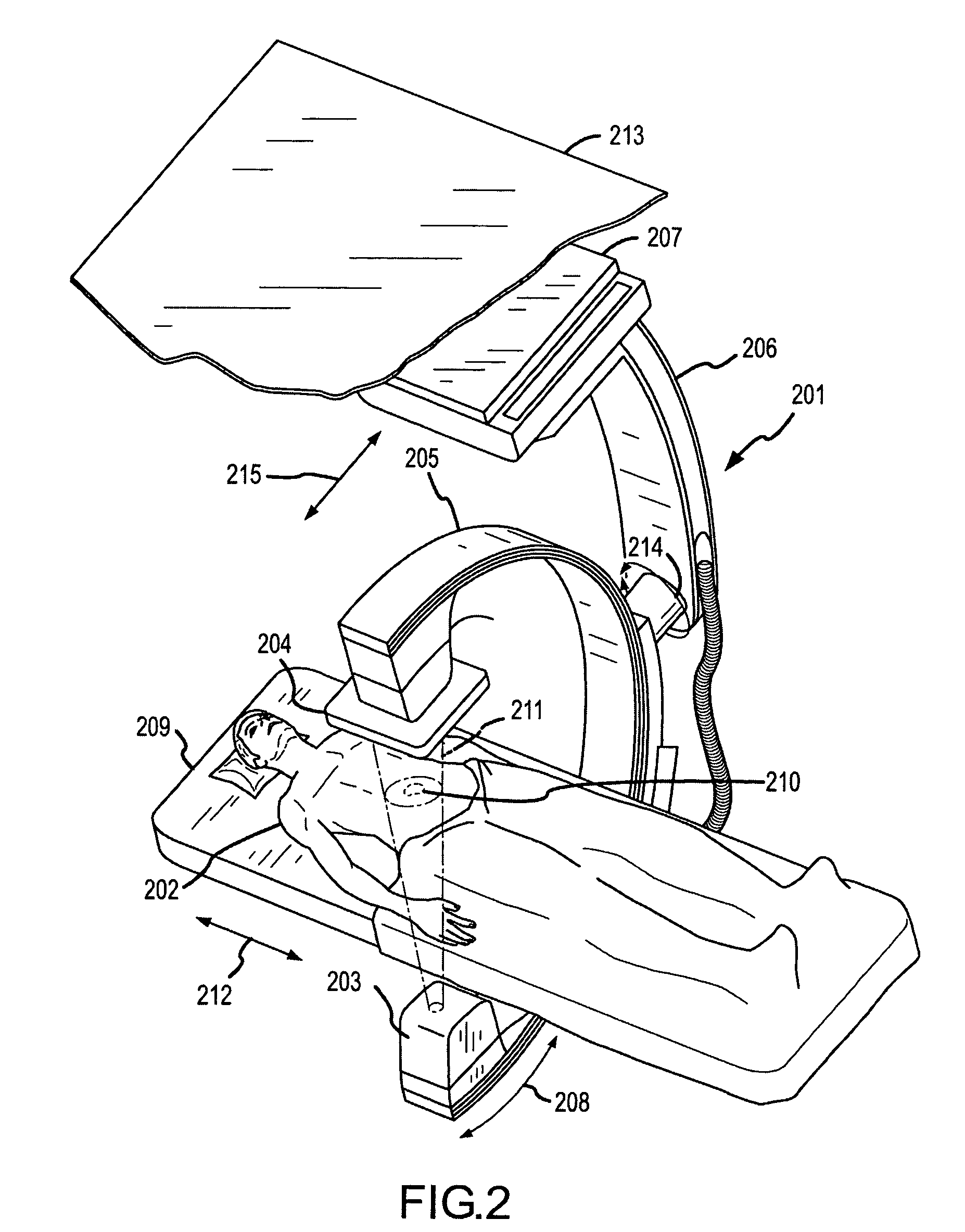
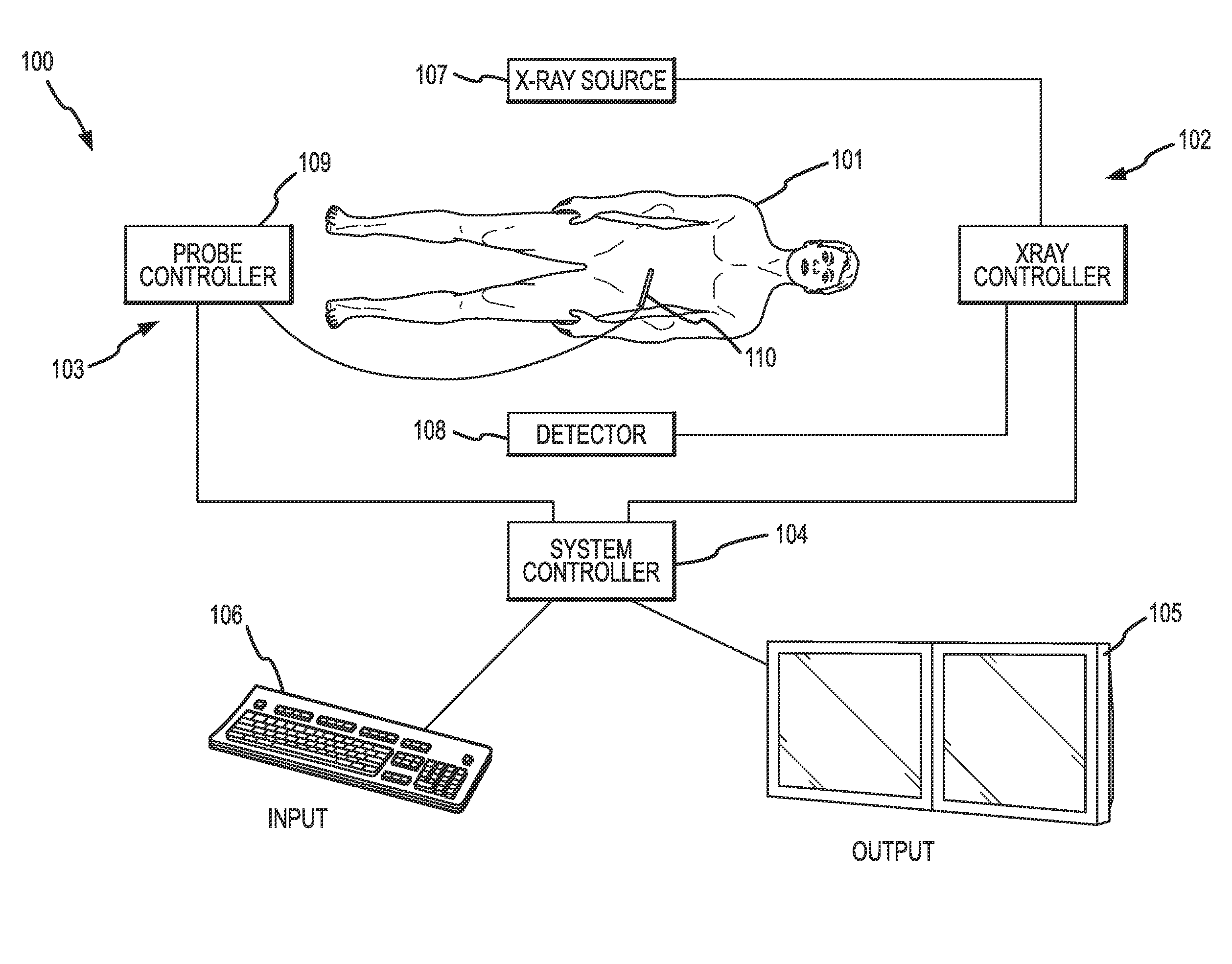
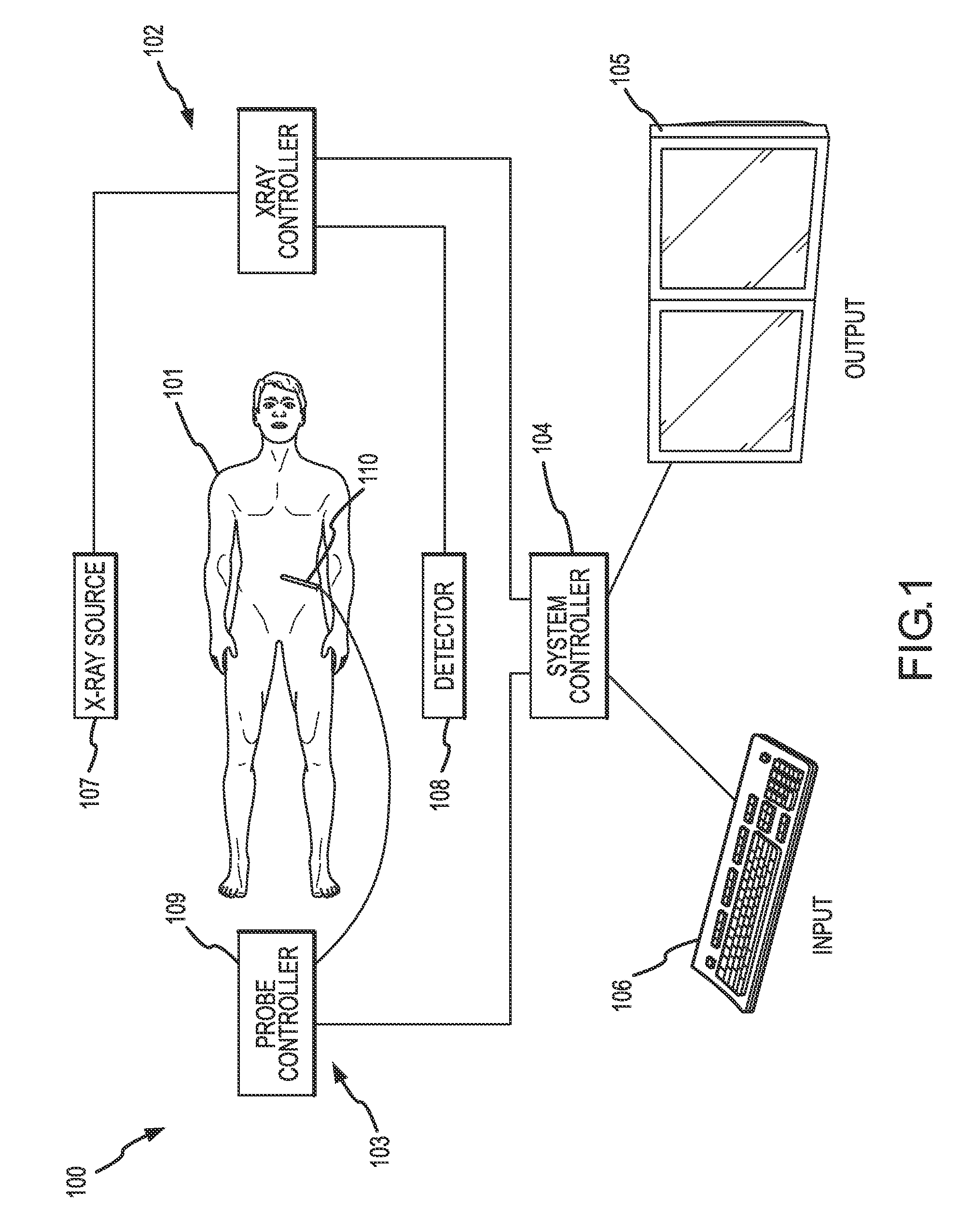
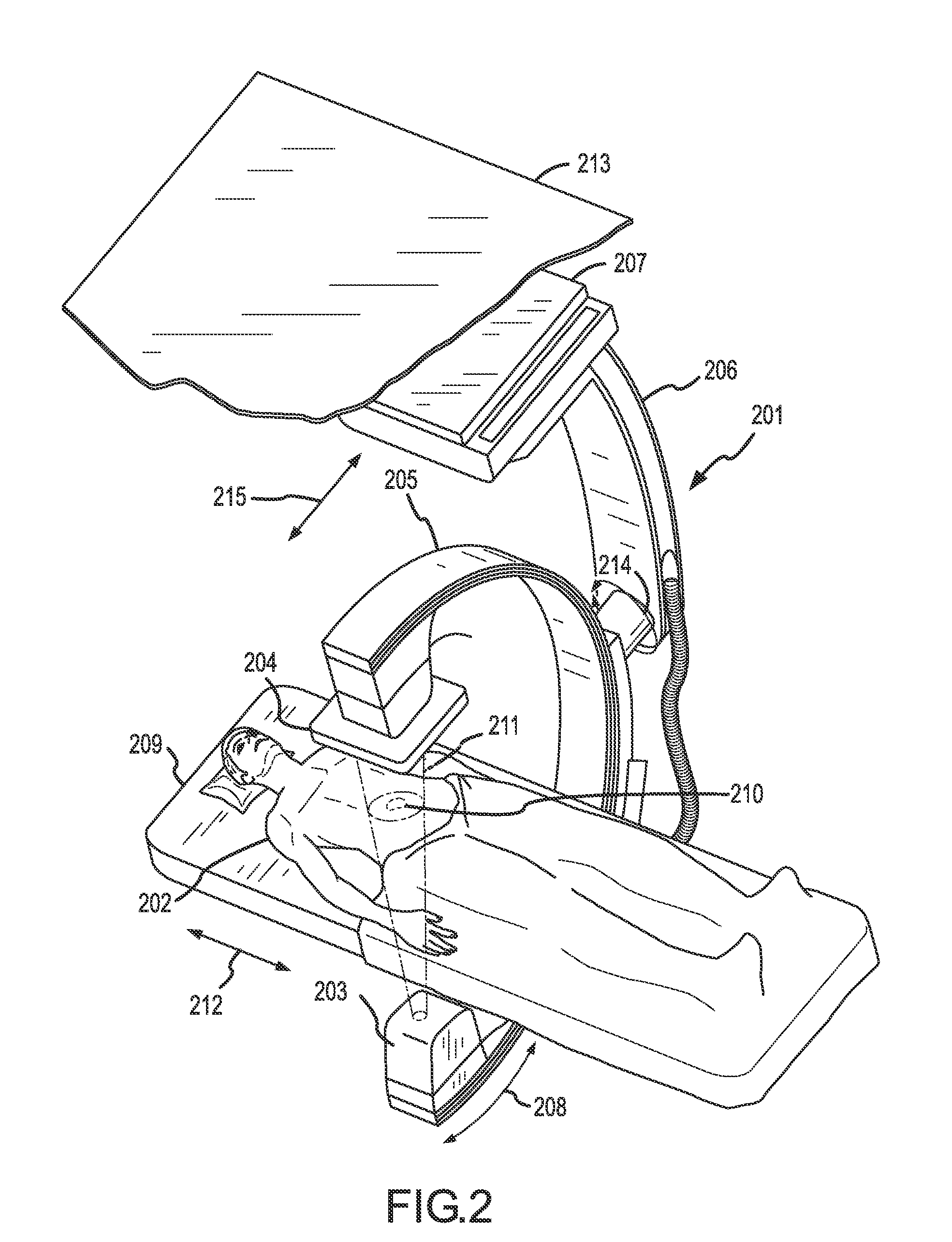
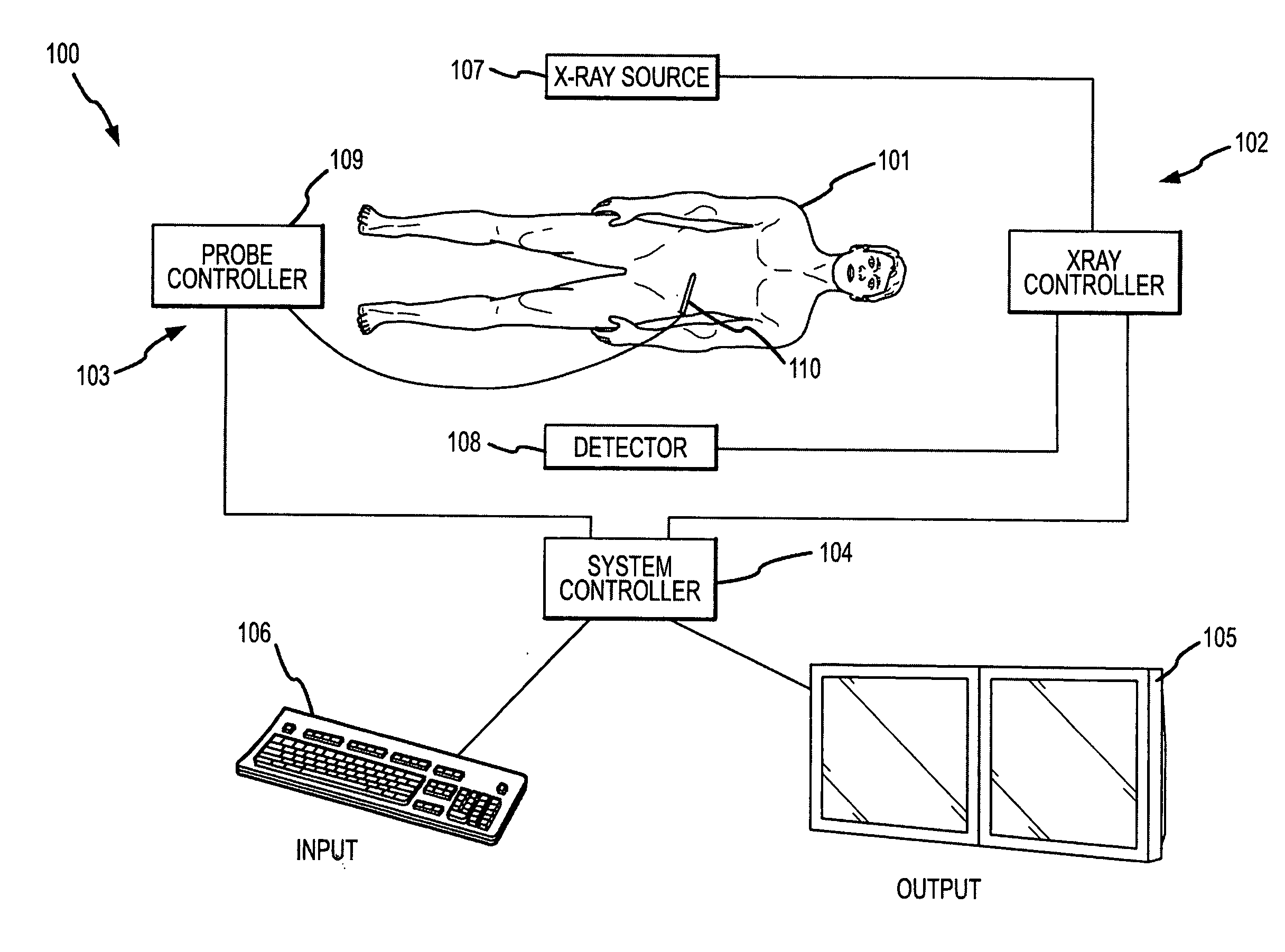
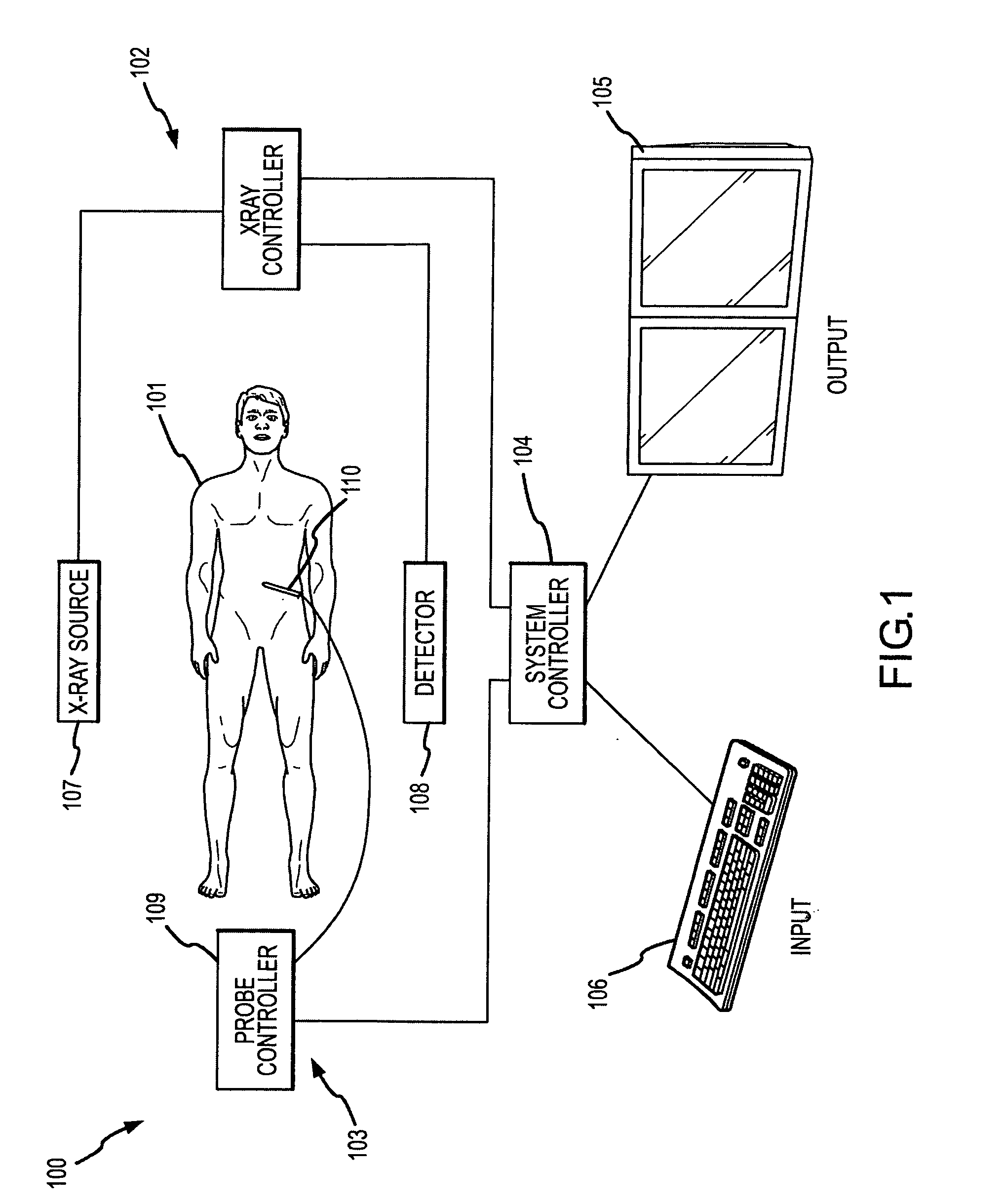
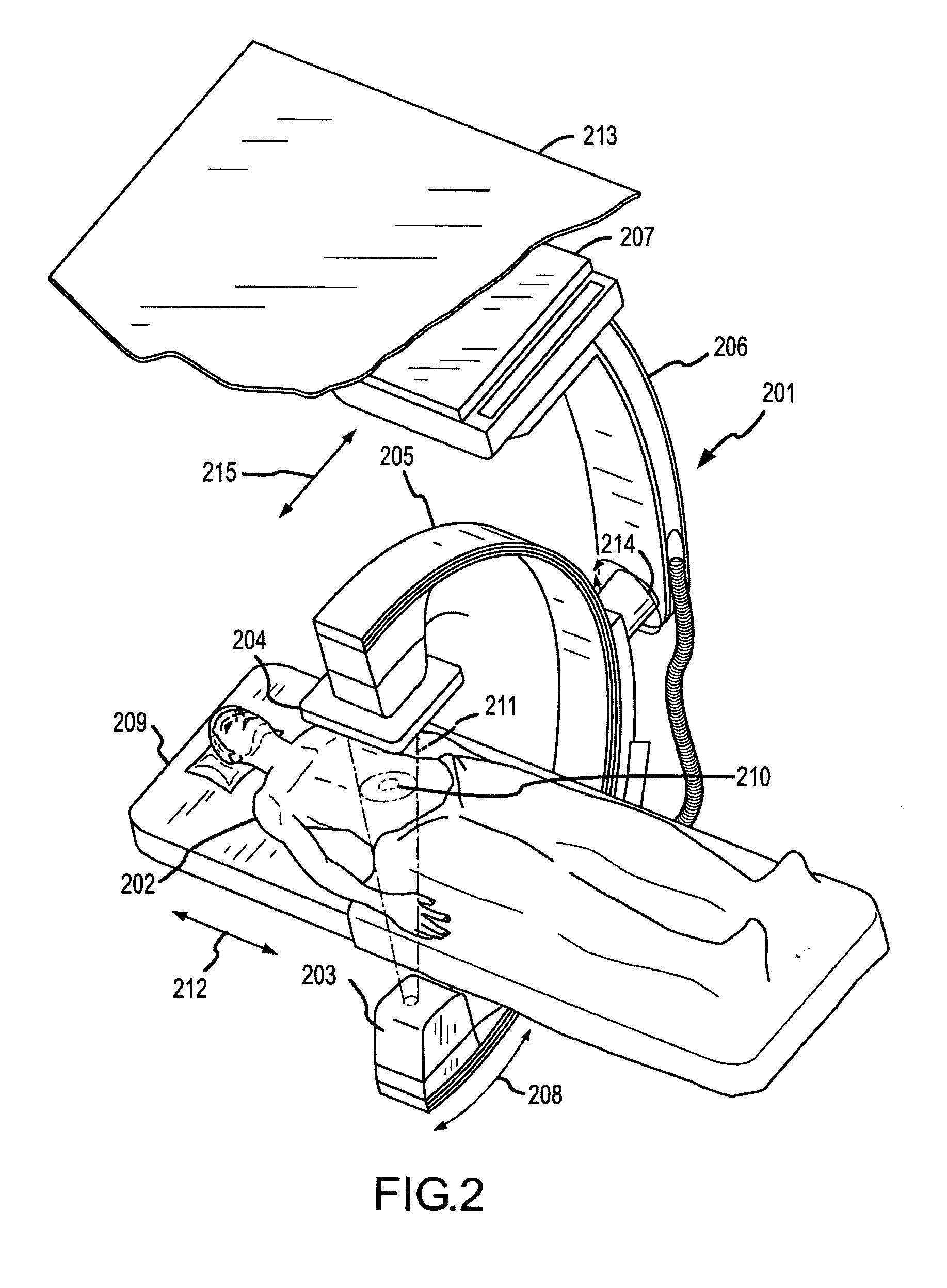
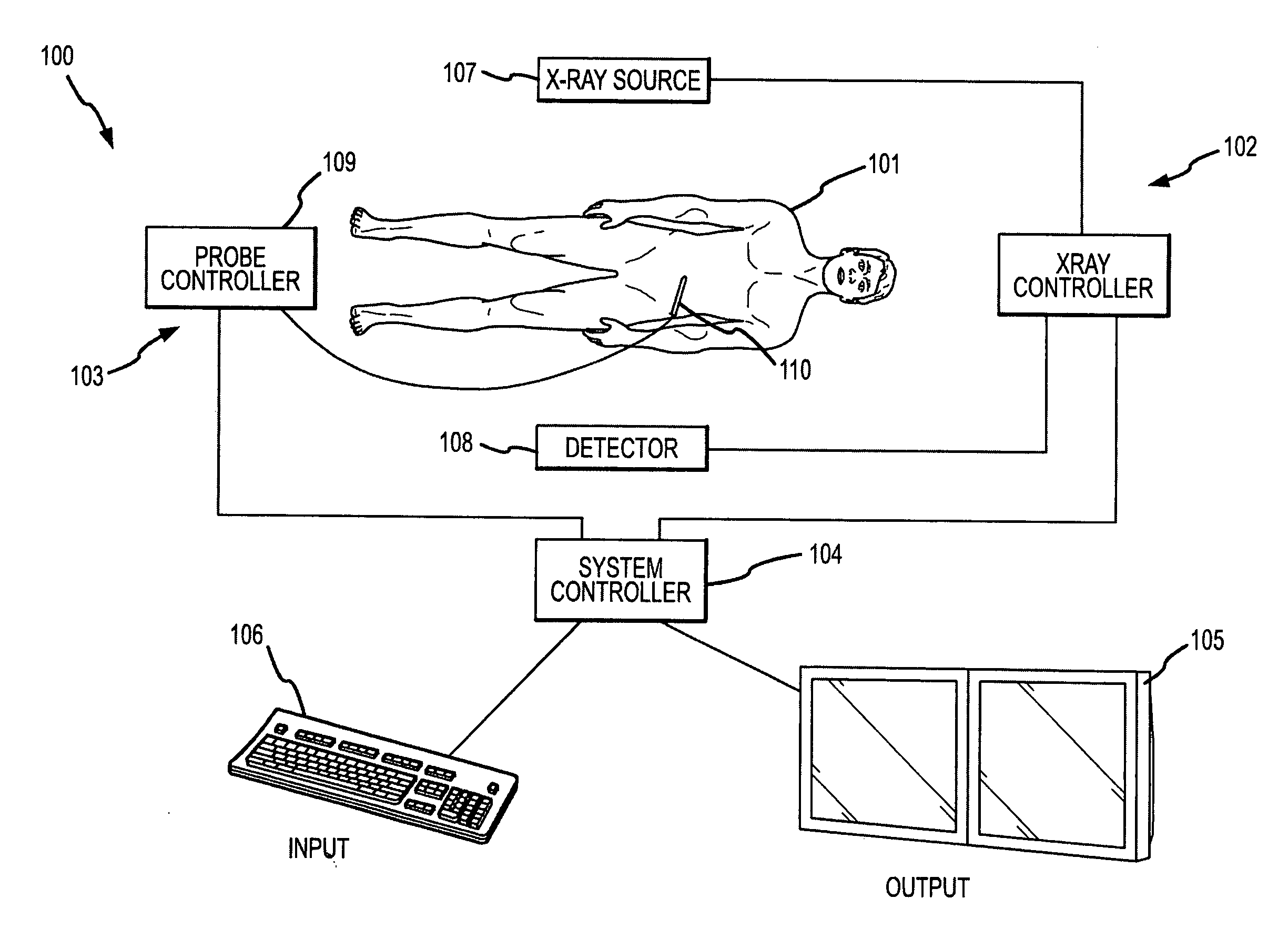
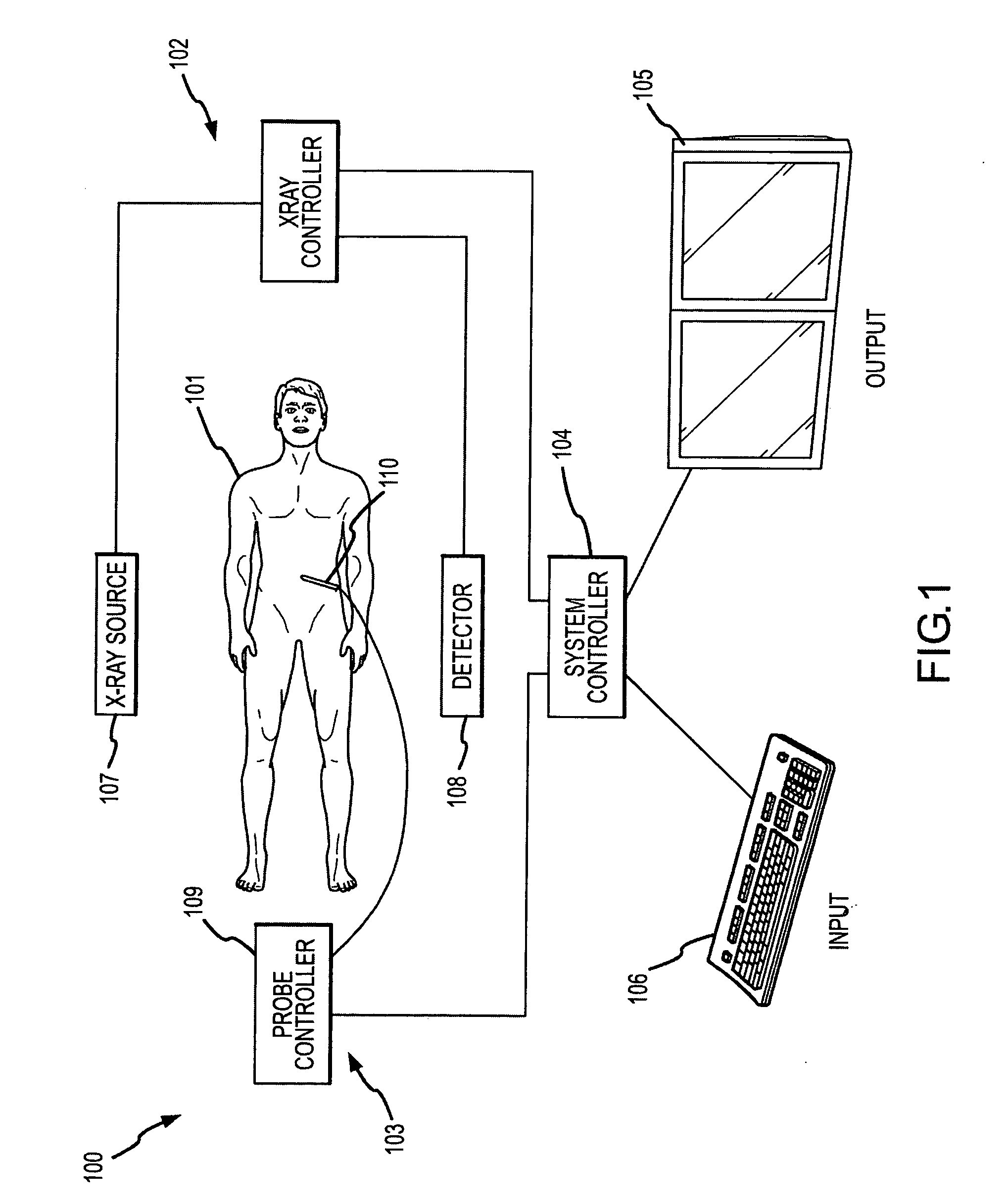
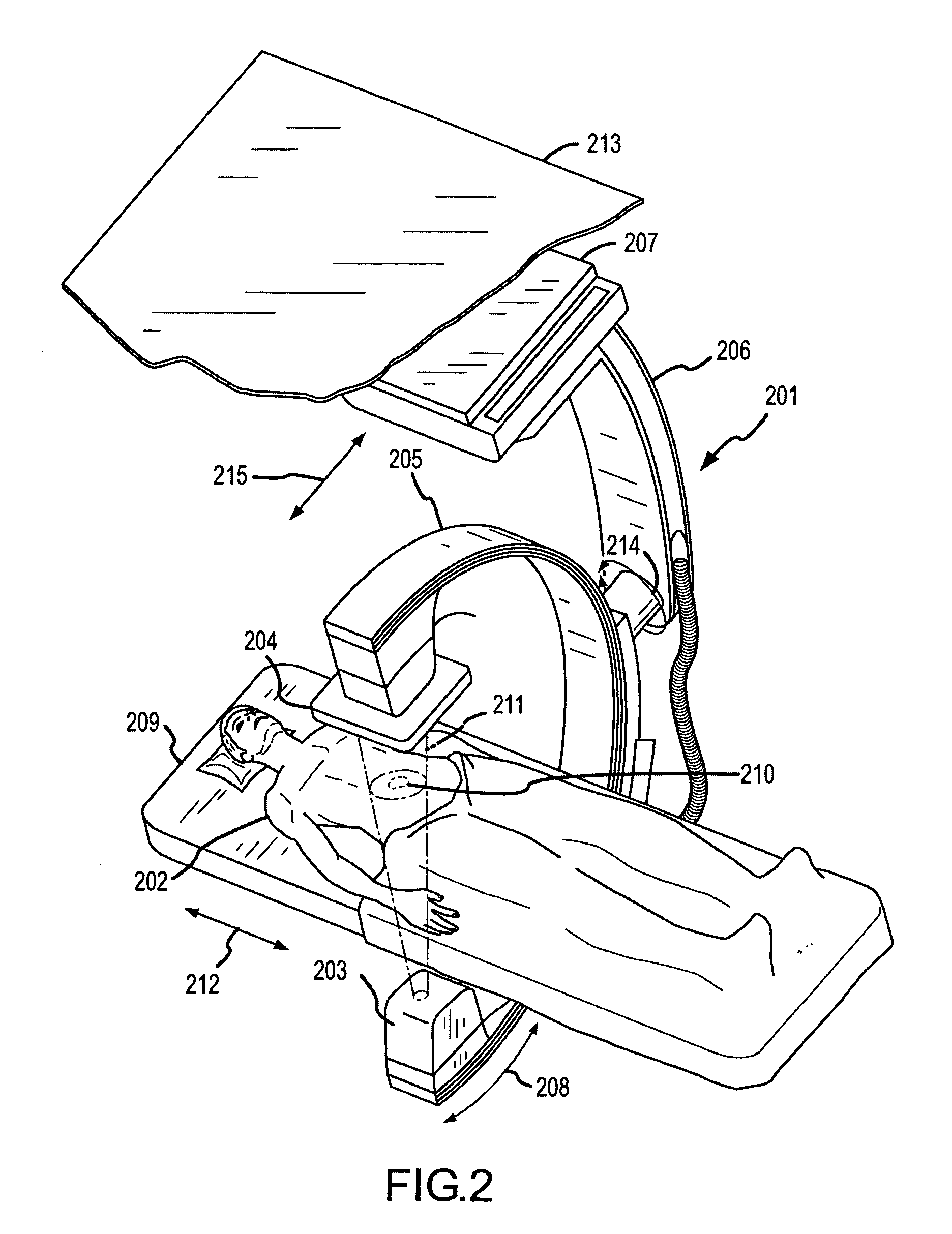
Methods for planning and performing thermal ablation
ActiveUS7871406B2Shorten the timeMovement is minimized and eliminatedUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingIntermediate imageRadiofrequency ablation
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC
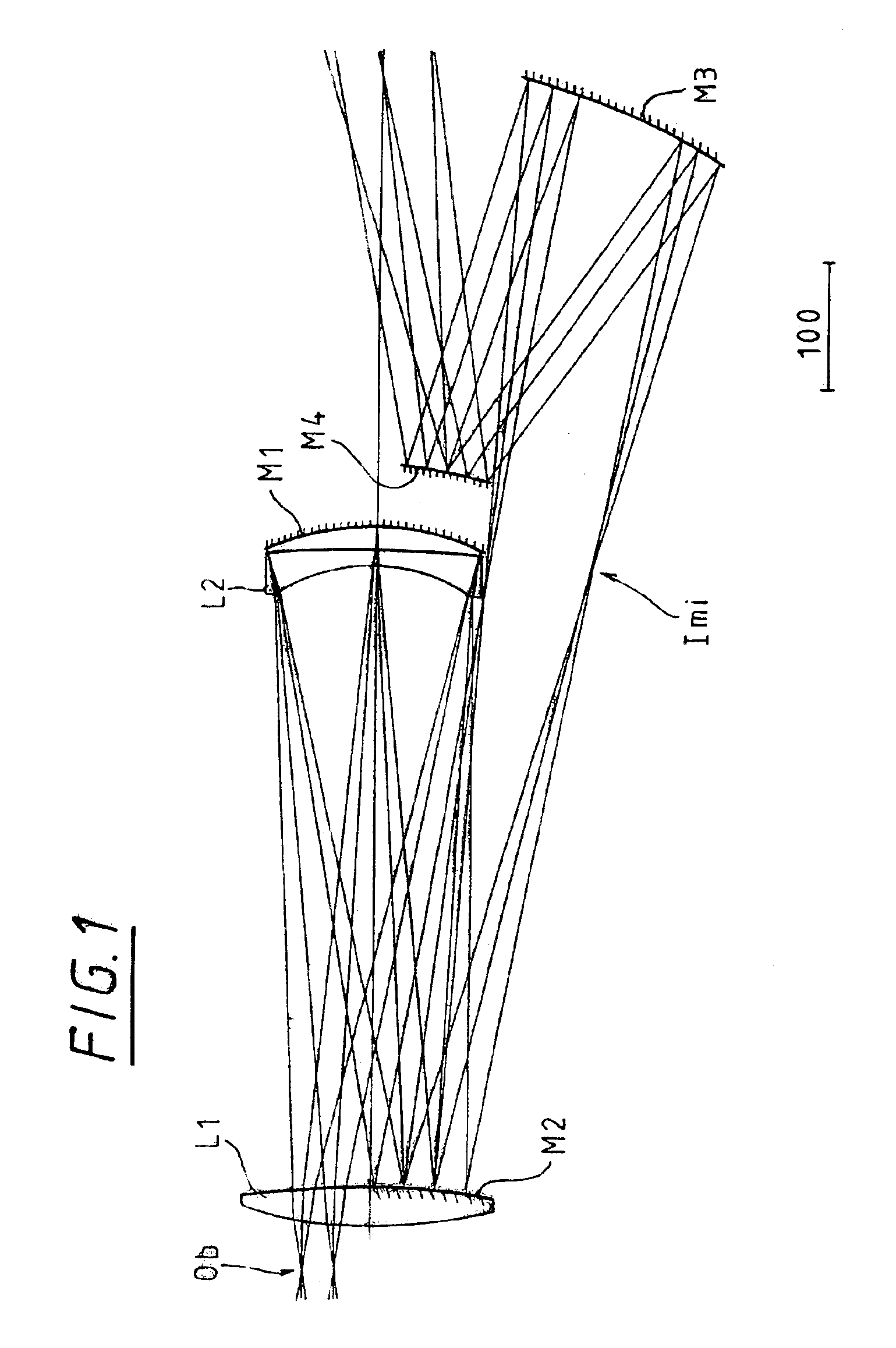
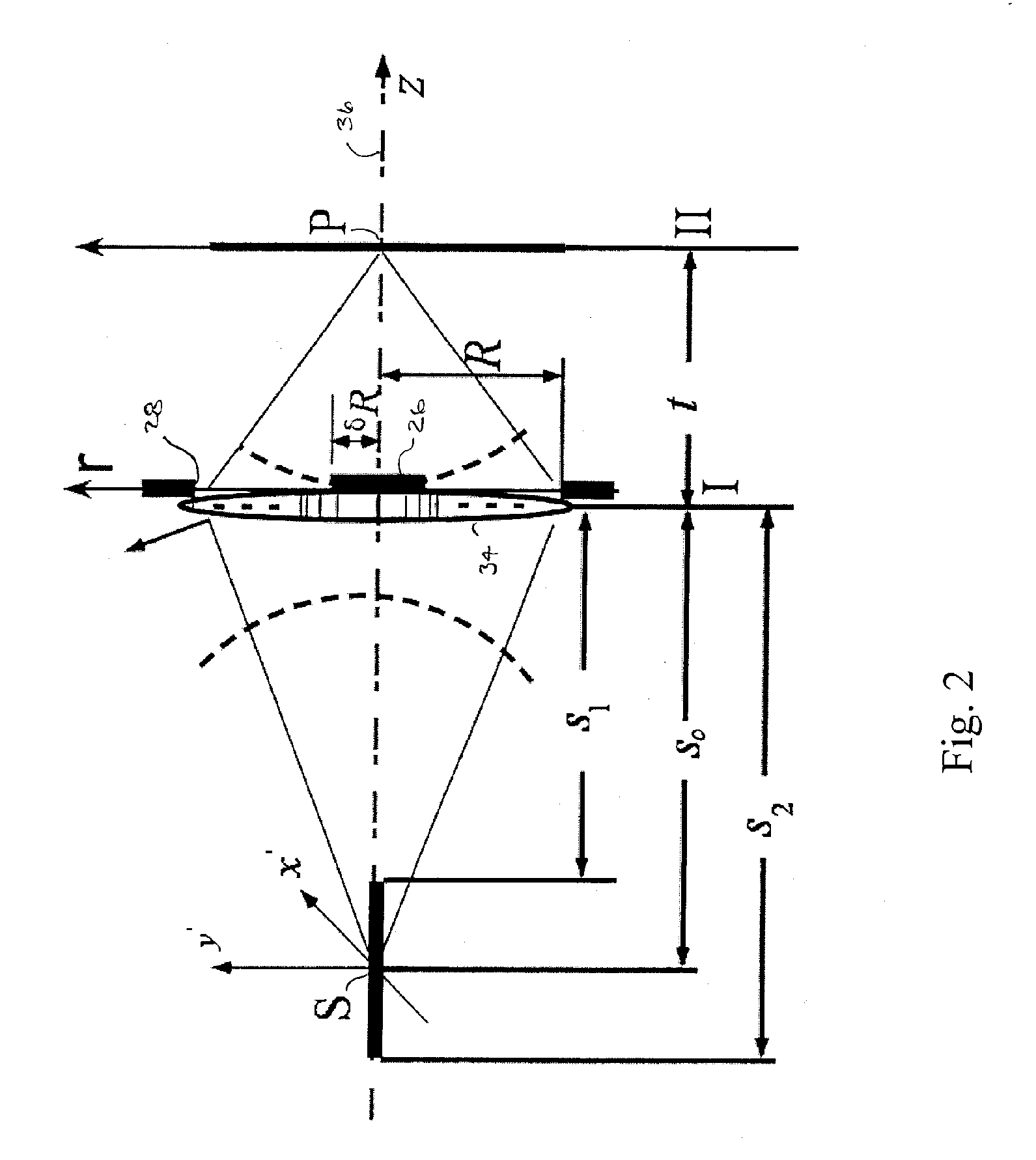
Objective with pupil obscuration
InactiveUS6894834B2Reduce occlusionAvoid excessive diameterMirrorsOptical filtersIntermediate imagePupil
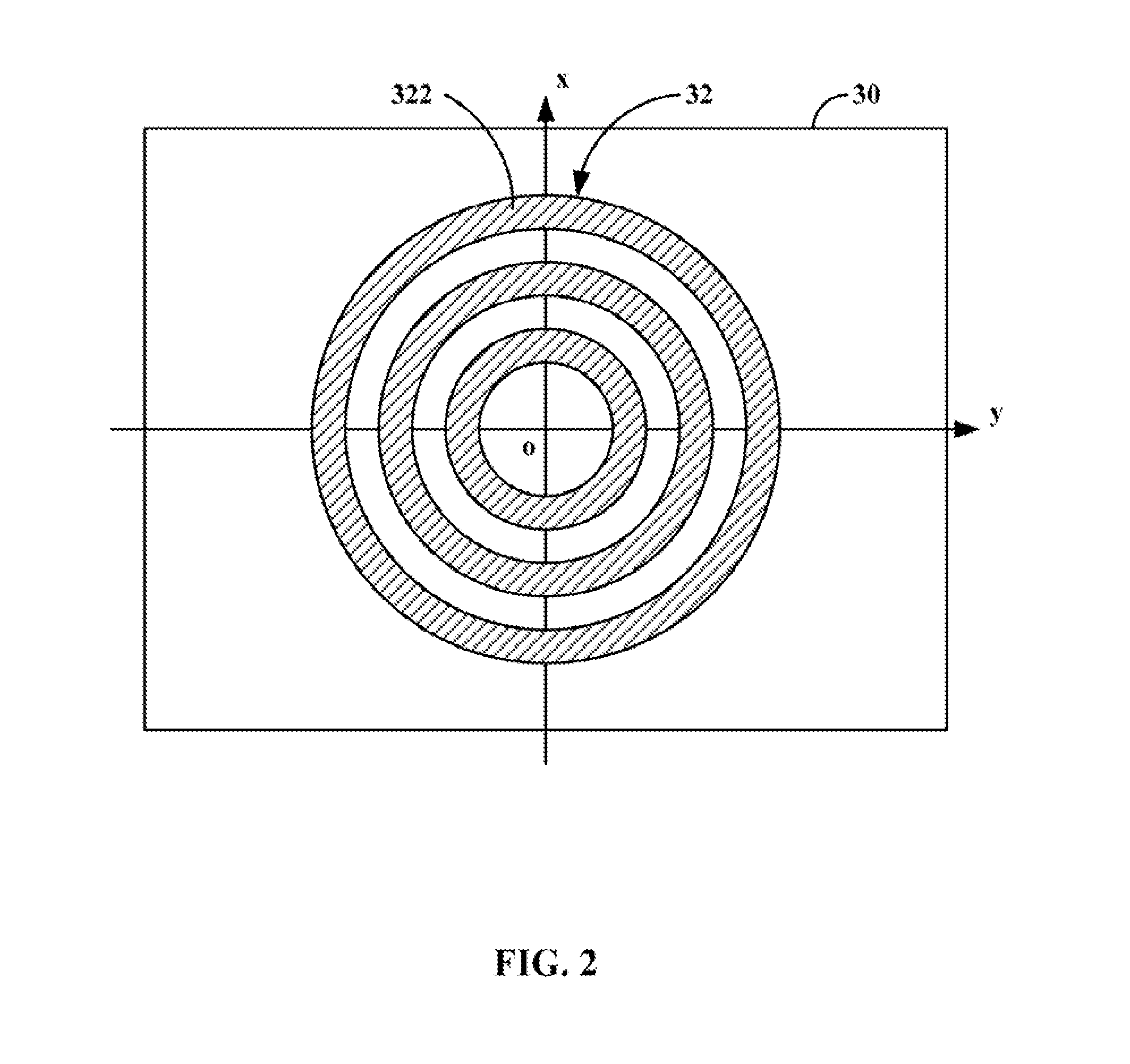
An objective is configured with a first partial objective and a second partial objective. The first partial objective, which projects a first field plane onto an intermediate image, has a first, convex mirror and a second, concave mirror. The second partial objective, which projects the intermediate image onto a second field plane, has a third and a fourth mirror, both concave. All of the four mirrors have central mirror apertures. The axial distance between the first and second mirrors is in a ratio between 0.95 and 1.05 relative to the distance between the second mirror and the intermediate image. The axial distance ZM3-IM between the third mirror and the second field plane conforms to the relationship 0.03·DuM3+5.0 mm<ZM3-IM<0.25·DuM3tan(arcsin(NA)).NA represents the numerical aperture NA in the second field plane, and DuM3 represents the diameter of the third mirror. The objective furthermore has a Petzval radius with an absolute value larger than the distance between the first and second field planes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS7336430B2Easy to manufactureUniform responseImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIntermediate imageImaging quality
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Virtual image display apparatus
ActiveUS20130222896A1Wide viewing angleImprove performanceMicroscopesTelescopesIntermediate imageDisplay device
An intermediate image is formed inside a prism by a projection lens and the like. Image light, totally reflected, in the order of a third surface, a first surface and a second surface, on two or more surfaces thereof, reaches an eye of an observer after passing through the first surface. Thus, it is possible to decrease the thickness of the prism and to reduce the size and weight of the entire optical system. Further, it is possible to realize a bright high-performance display with a wide viewing angle. With respect to external light, it is possible to pass the external light through the first surface and the third surface, for example, for observation. Further, by setting diopter at this time to about 0, it is possible to reduce defocusing or warp of the external light when the external light is observed in a see-through manner.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
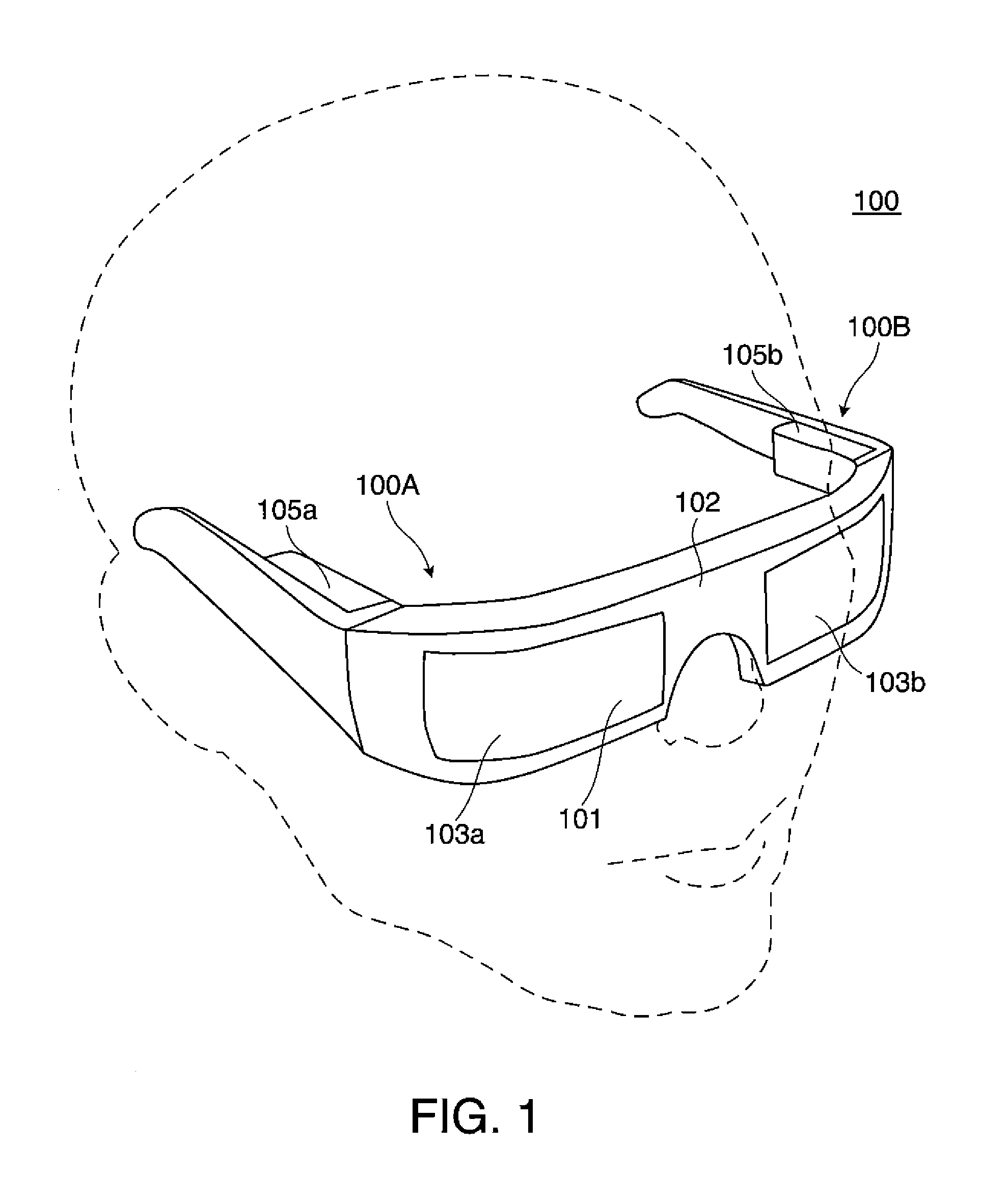
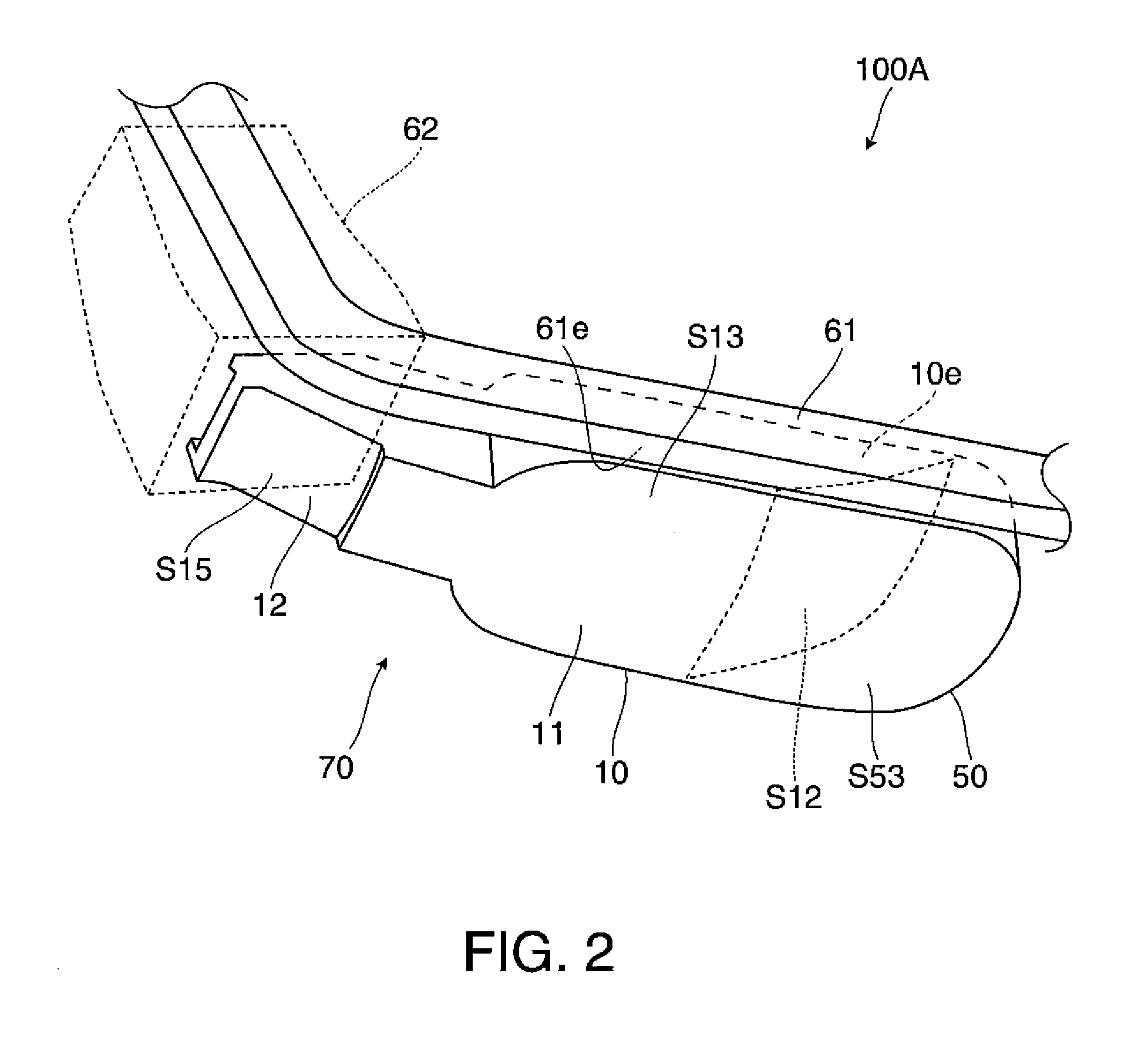
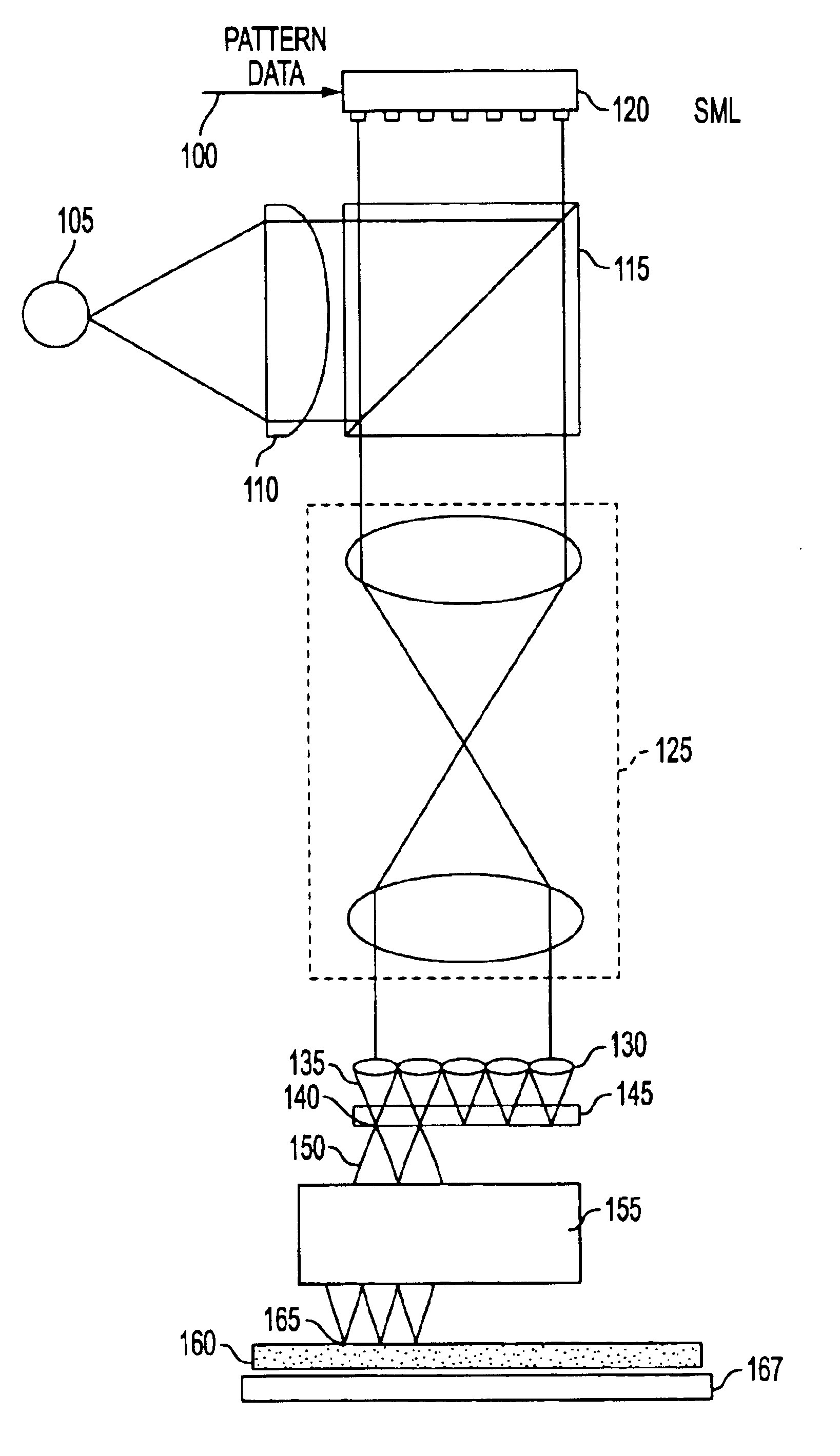
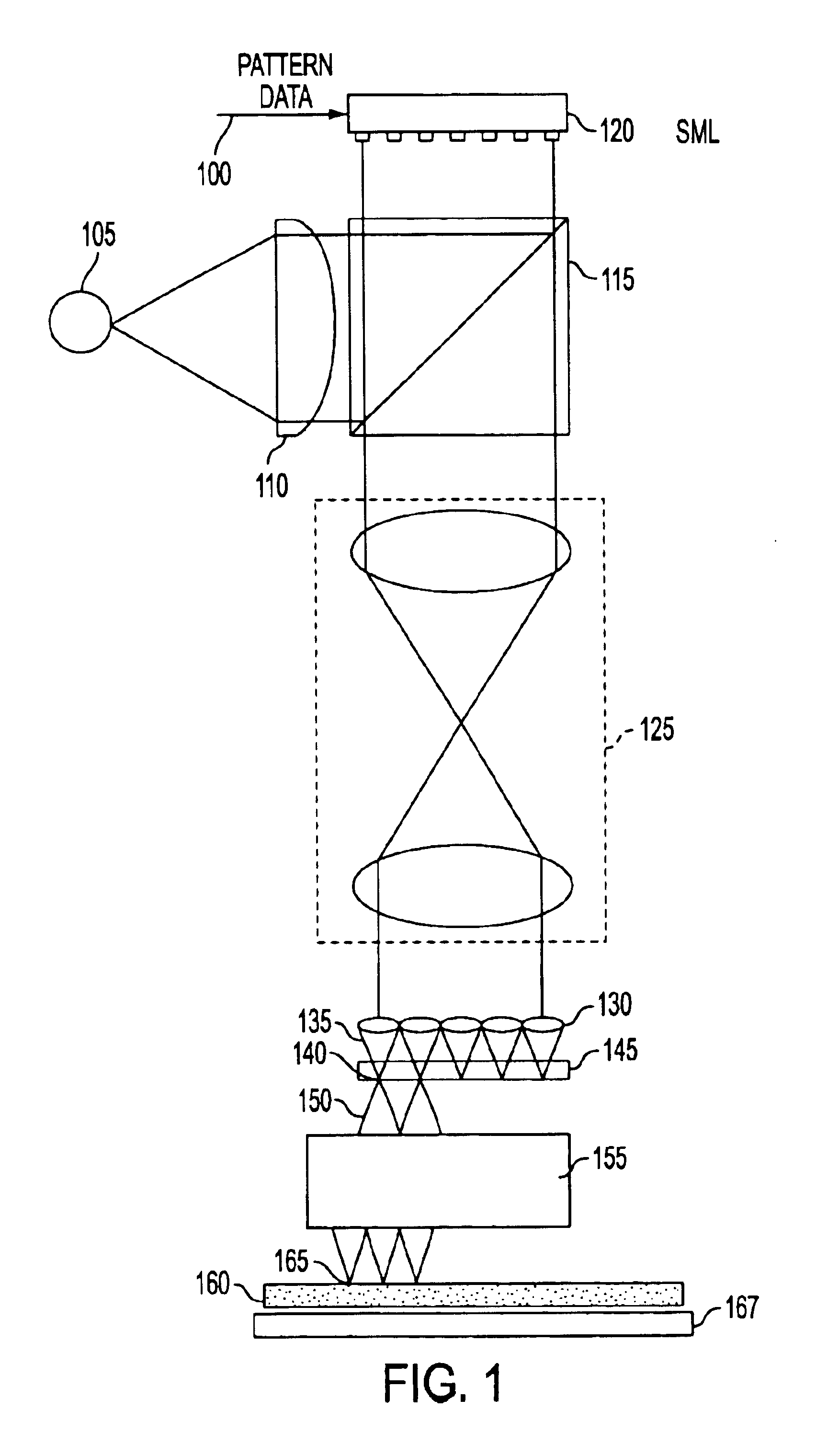
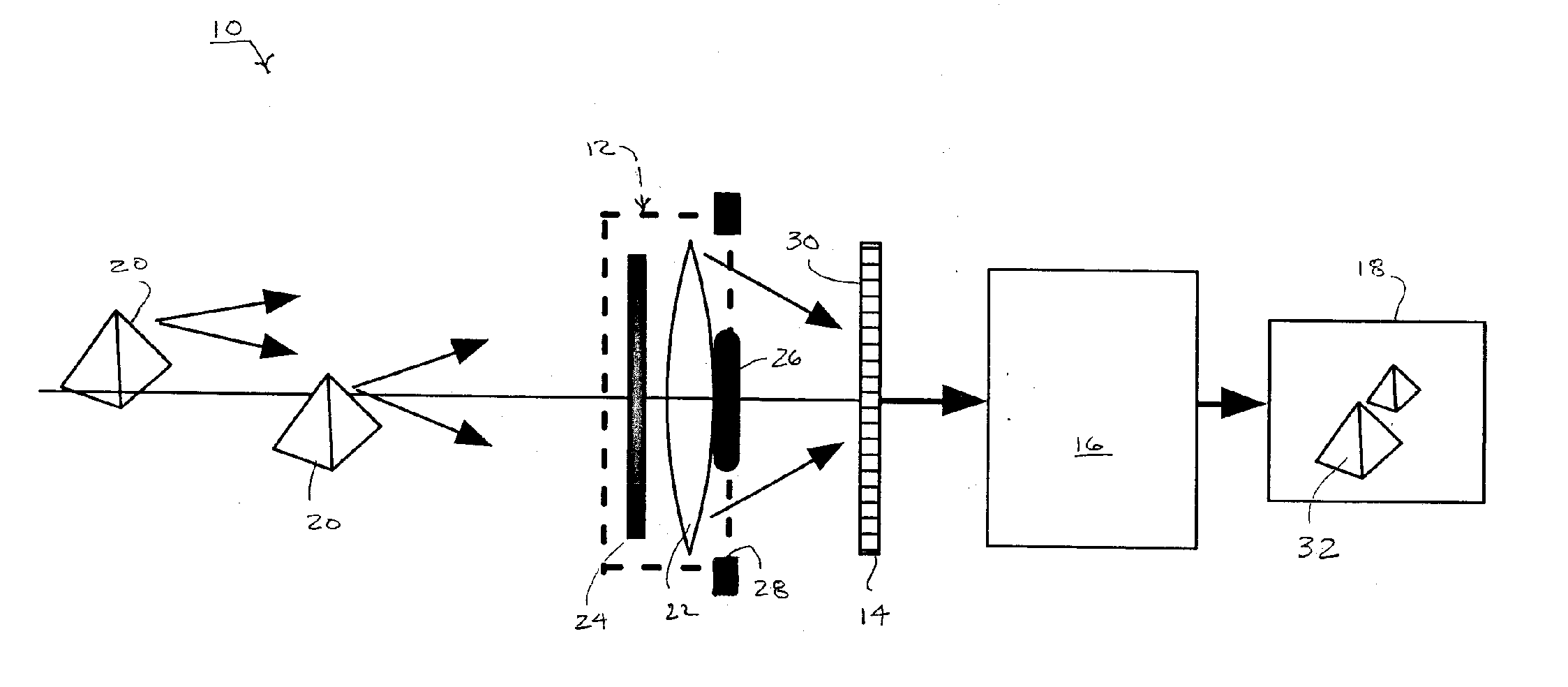
Maskless photon-electron spot-grid array printer
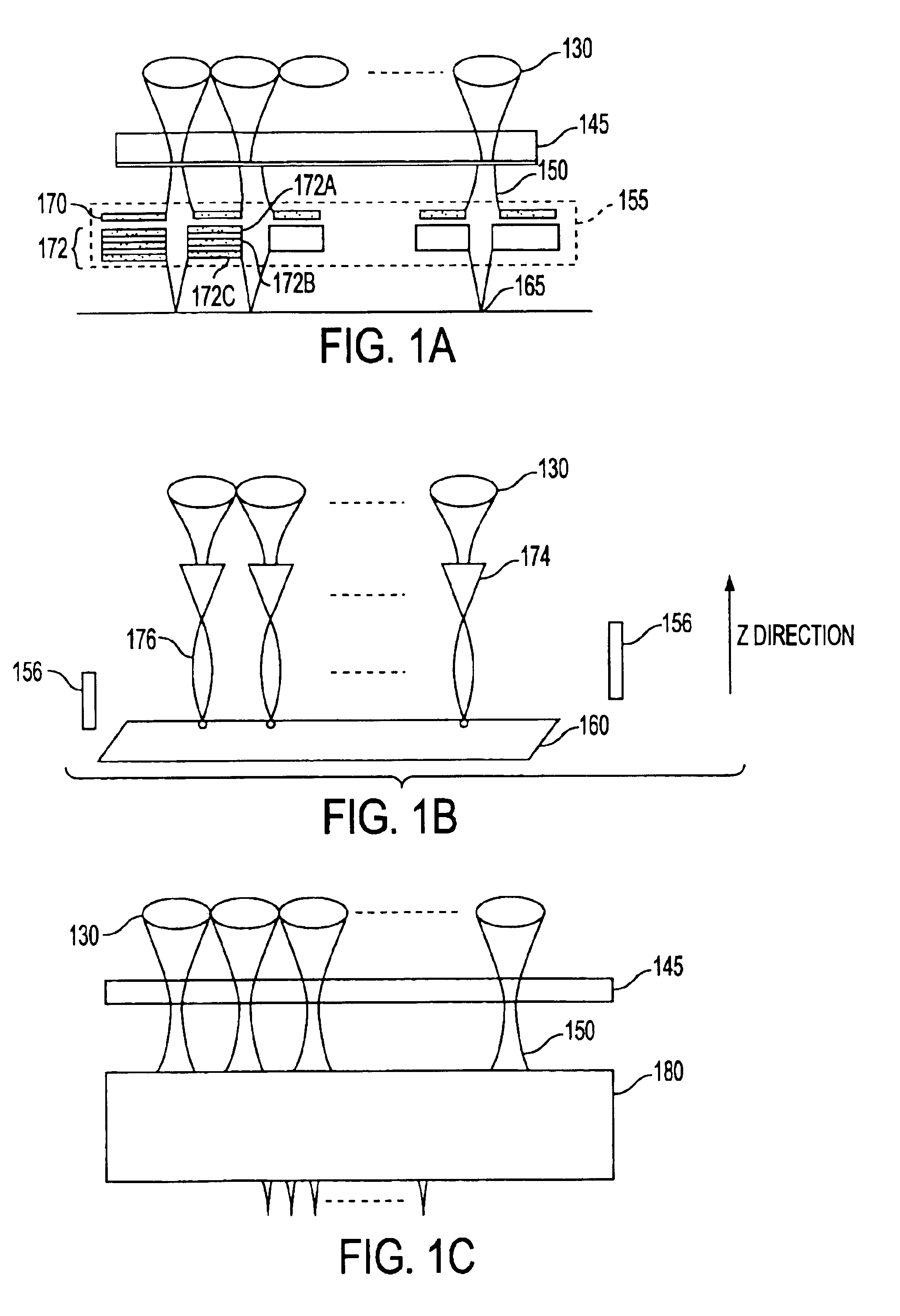
InactiveUS6841787B2Readily apparentElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsOptical radiationIntermediate image
A high resolution and high data rate spot grid array printer system is provided, wherein an image representative of patterns to be recorded on a reticle or on a layer of a semiconductor die is formed by scanning a substrate with electron beams. Embodiments include a printer comprising an optical radiation source for irradiating a photon-electron converter with a plurality of substantially parallel optical beams, the optical beams being individually modulated to correspond to an image to be recorded on the substrate. The photon-electron converter produces an intermediate image composed of an array of electron beams corresponding to the modulated optical beams. A de-magnifier is interposed between the photon-electron converter and the substrate, for reducing the size of the intermediate image. A movable stage introduces a relative movement between the substrate and the photon-electron converter, such that the substrate is scanned by the electron beams.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
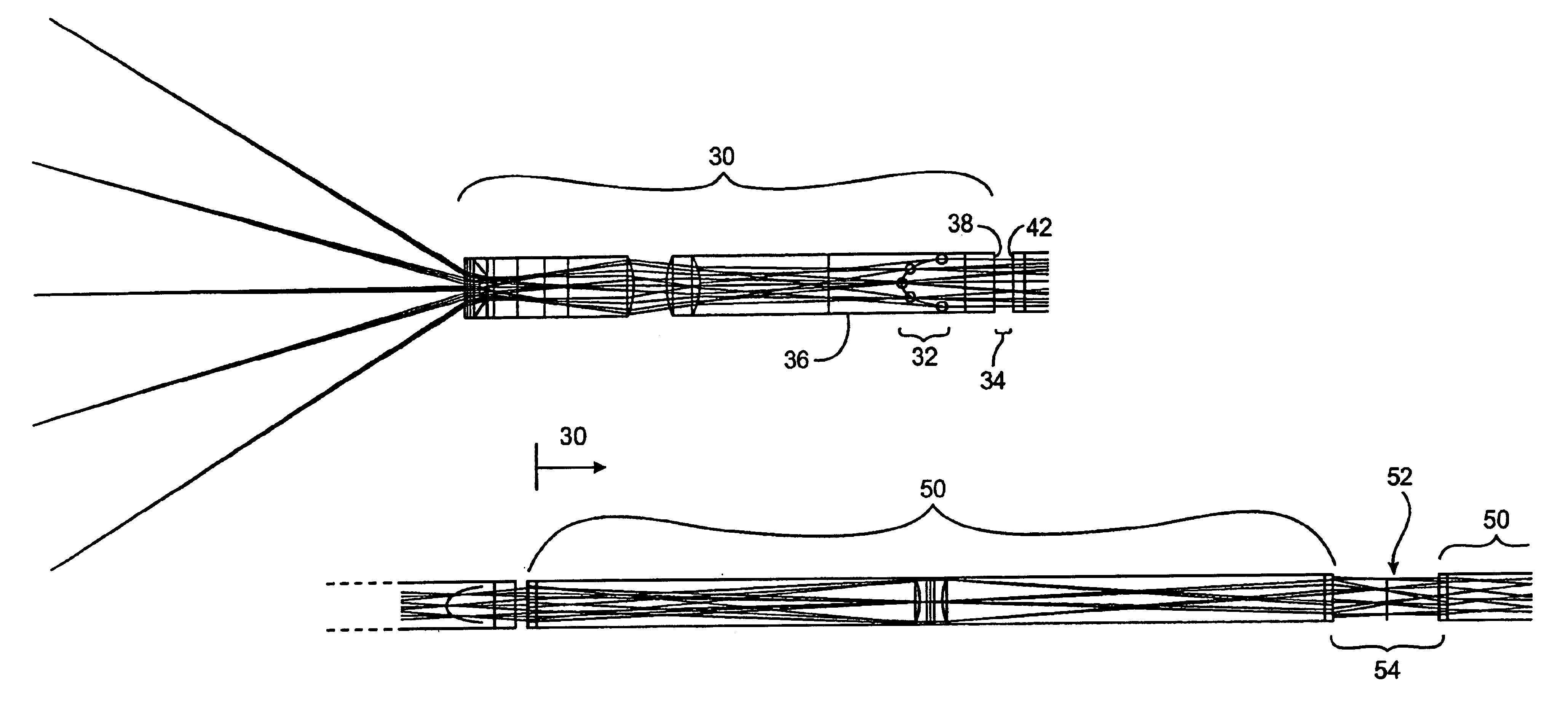
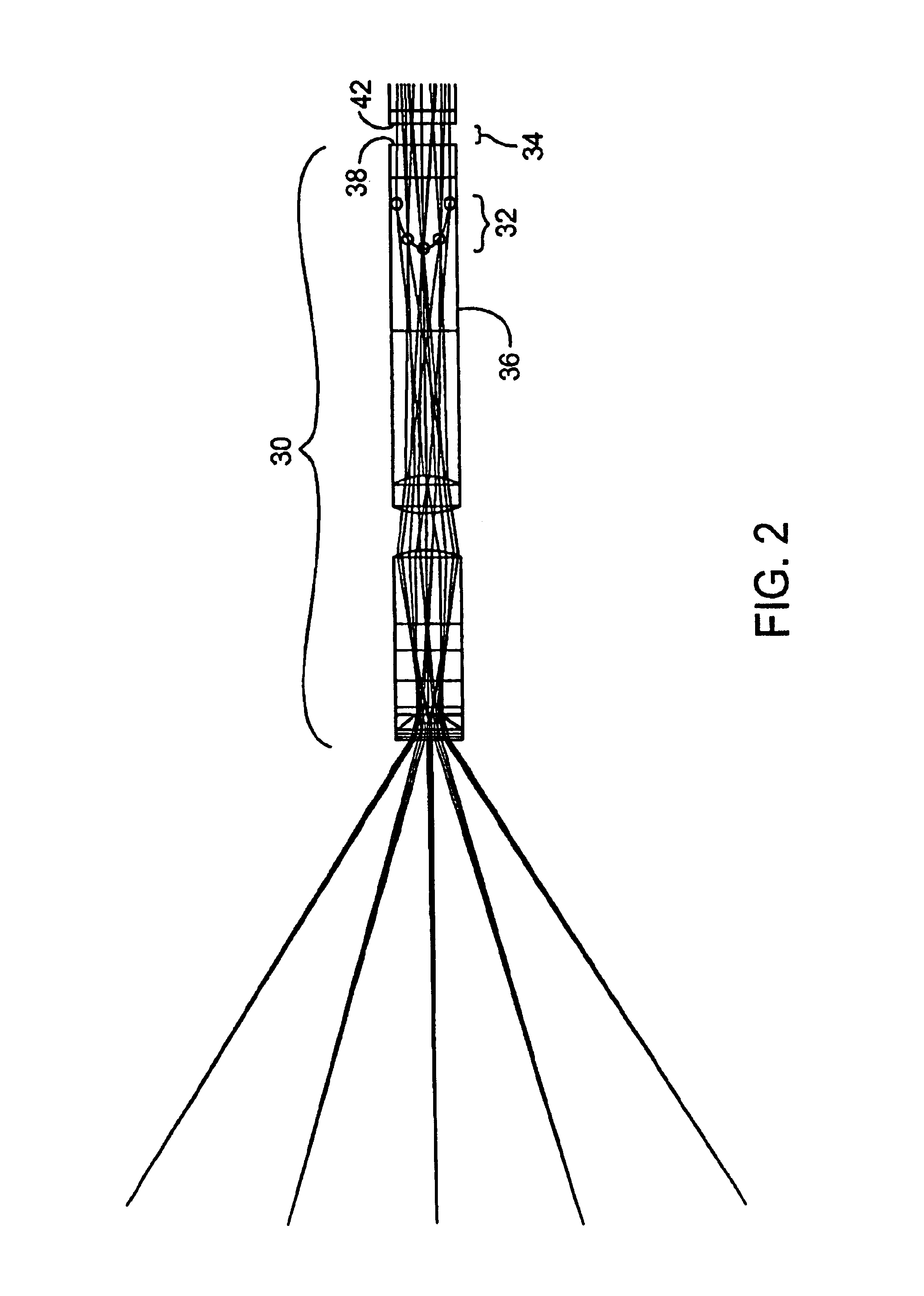
Endoscope
InactiveUS6817975B1Highly aberration correctedReduce sensitivitySurgeryEndoscopesIntermediate imageMagnification
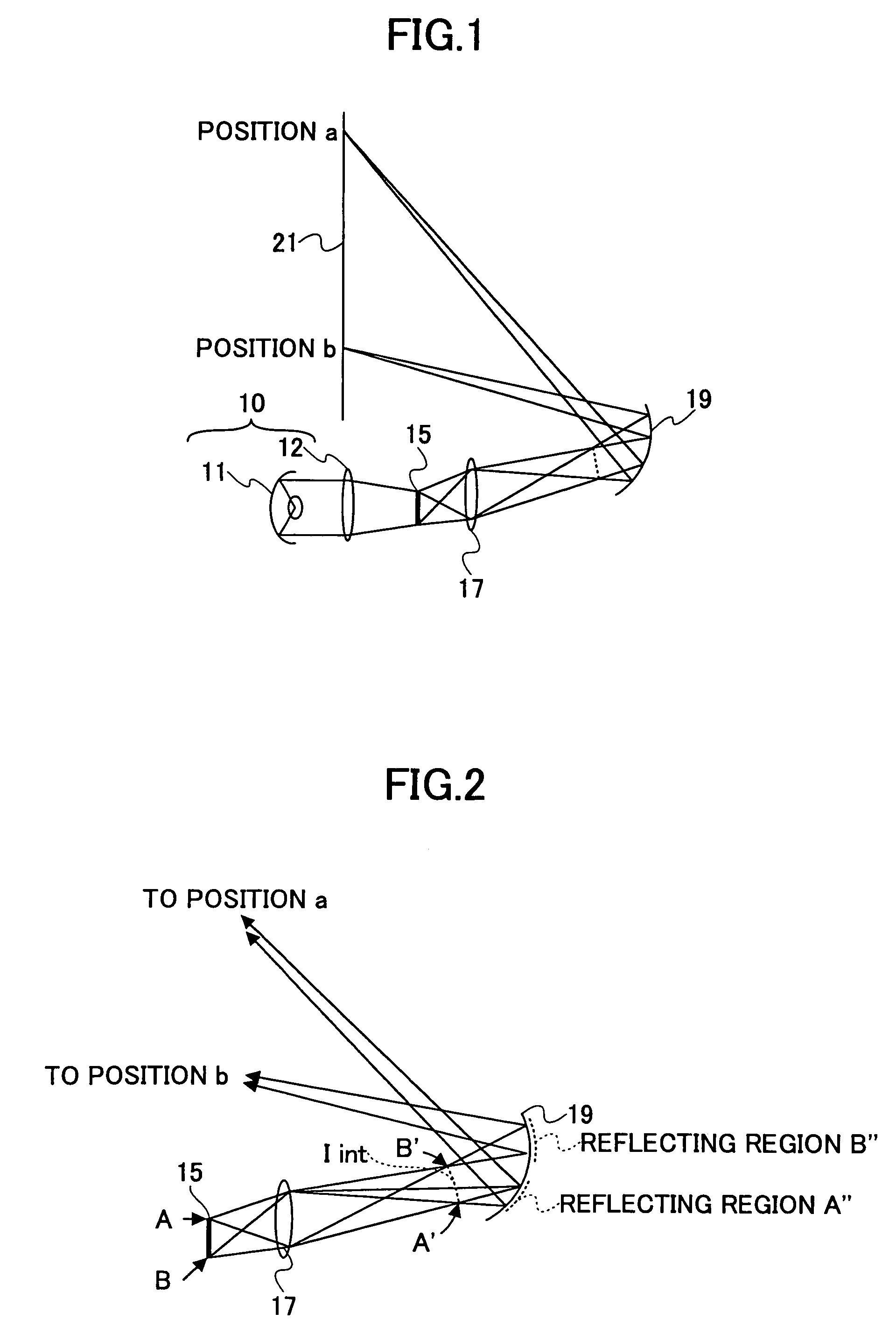
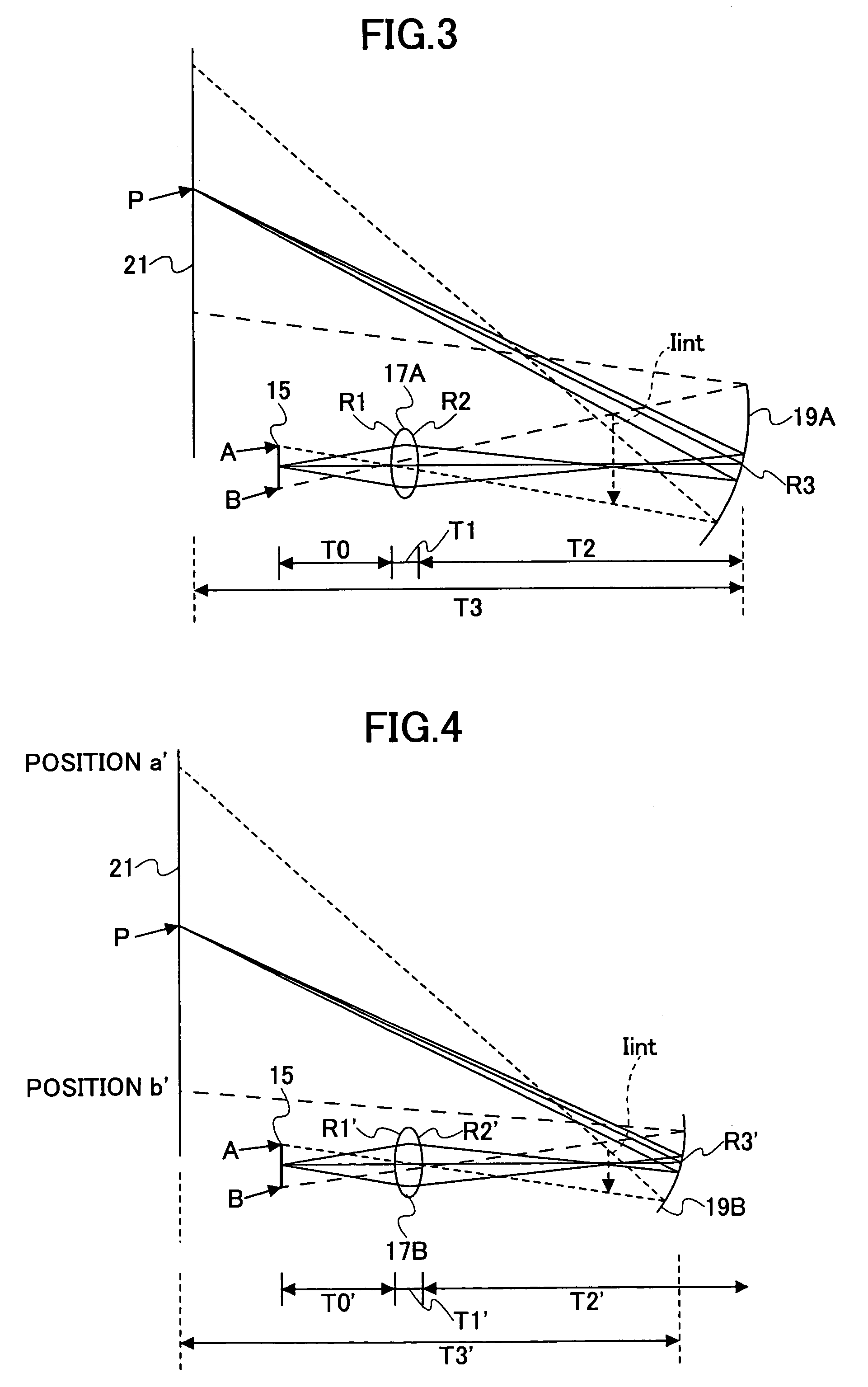
Improved optical devices and methods transmit optical images along elongate optical paths with relatively limited cross-sectional dimensions using an improved objective, relay, and ocular systems. In a first aspect, at least one intermediate image formed within an optical component, rather than being formed in a gap between optical components. In a preferred embodiment, a first intermediate image is formed within glass of the most proximal objective lens, with the first intermediate image extending axially along a curved image location within the glass. The last intermediate image may similarly be disposed within a distal lens of the ocular system. By making use of a first and / or last intermediate image disposed in this manner within a lens, endoscopes can exhibit a significantly larger Numerical Aperture than known endoscopes having similar cross-sectional dimensions. In a second aspect, the ocular system allows independent adjustment of diopters, magnification, X-Y positioning, and rotation orientation of the captured image while introducing minimal aberrations.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Methods and apparatuses for performing and monitoring thermal ablation
ActiveUS20100185087A1Maintain positionShorten the timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyHigh-intensity focused ultrasoundIntermediate image
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided. Methods of assessing the post-ablation status of the patient and performance of the system are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC
Apparatus for planning and performing thermal ablation
InactiveUS20080033417A1Maintain positionShorten the timeUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsData setRadiofrequency ablation
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:ABLA TX +1
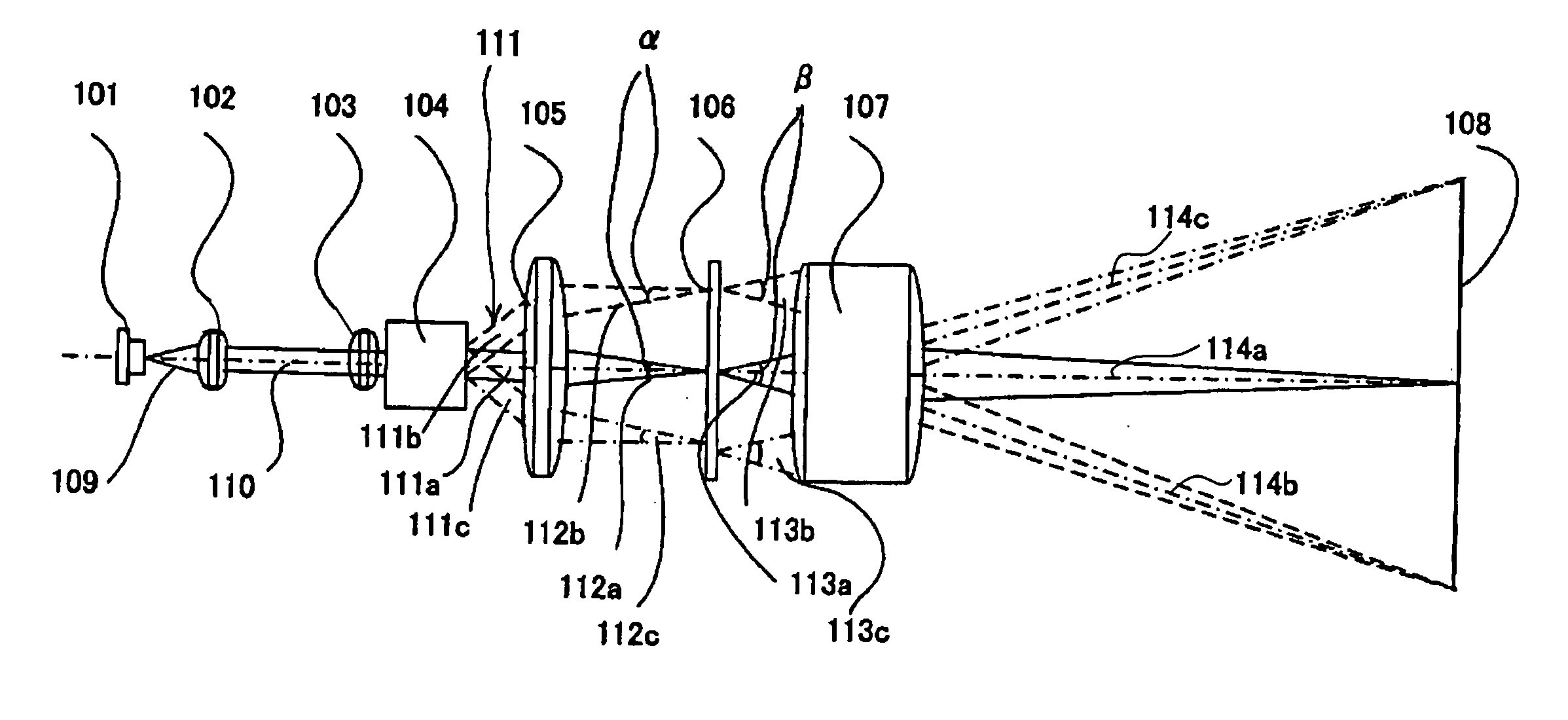
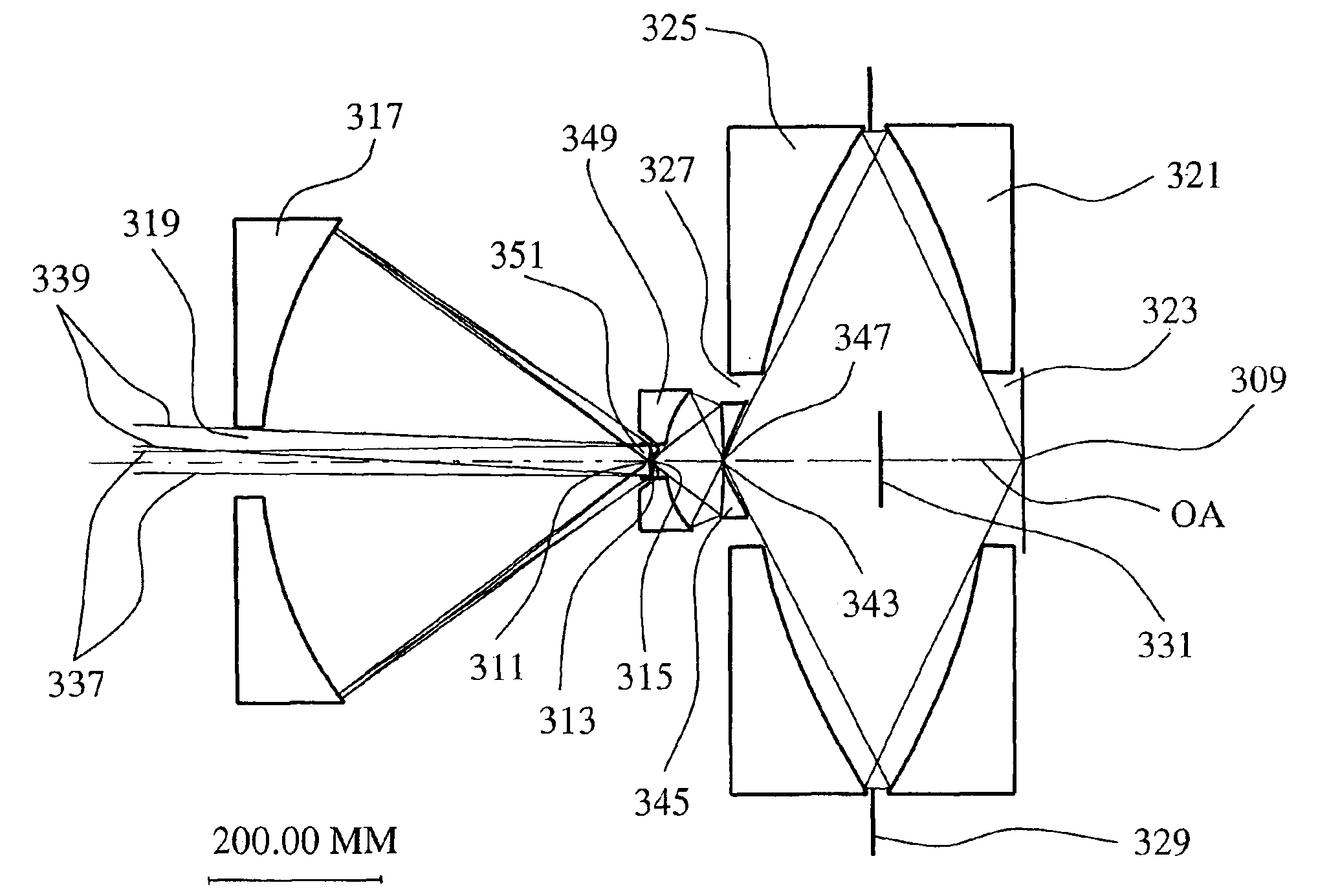
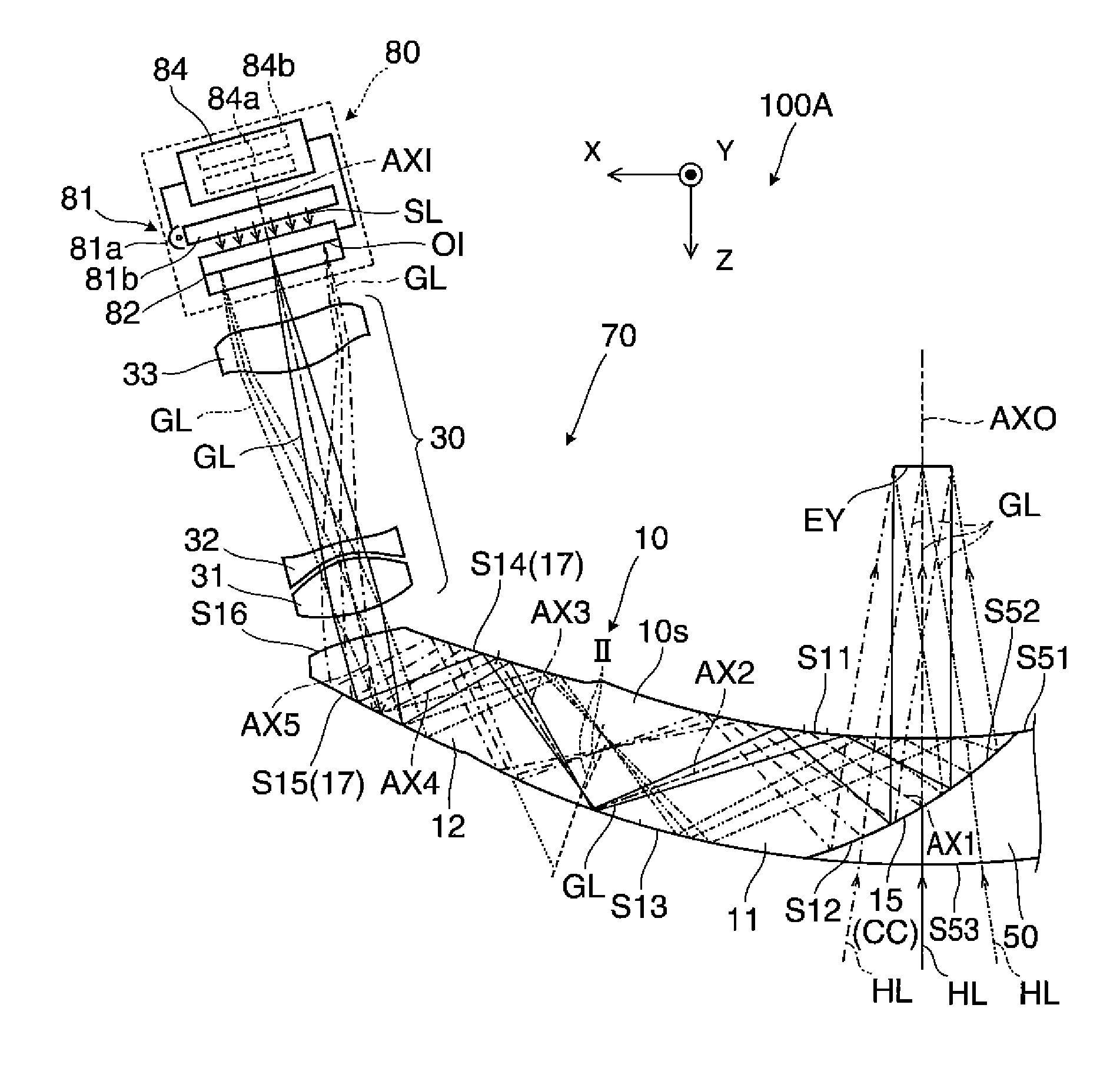
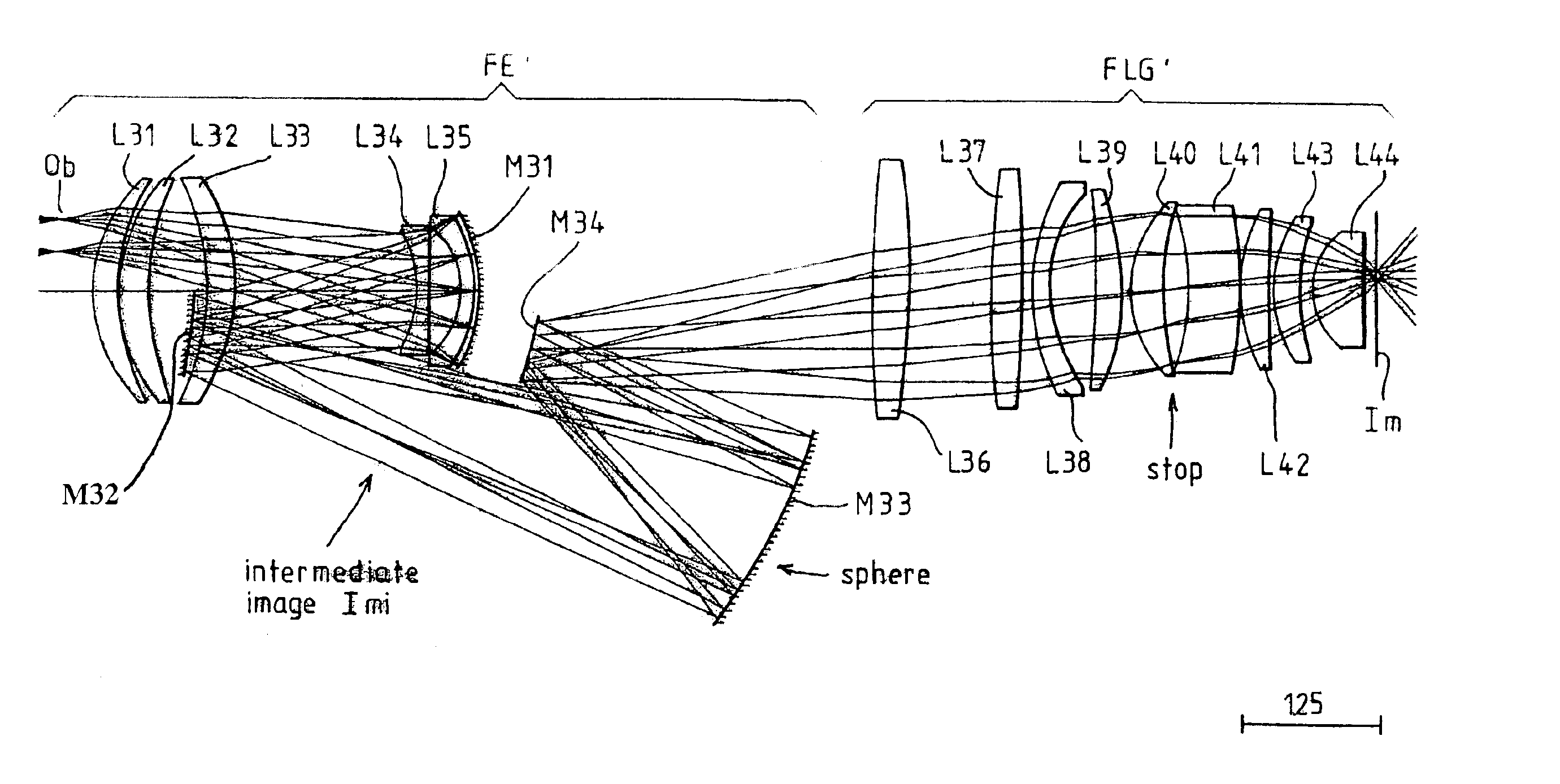
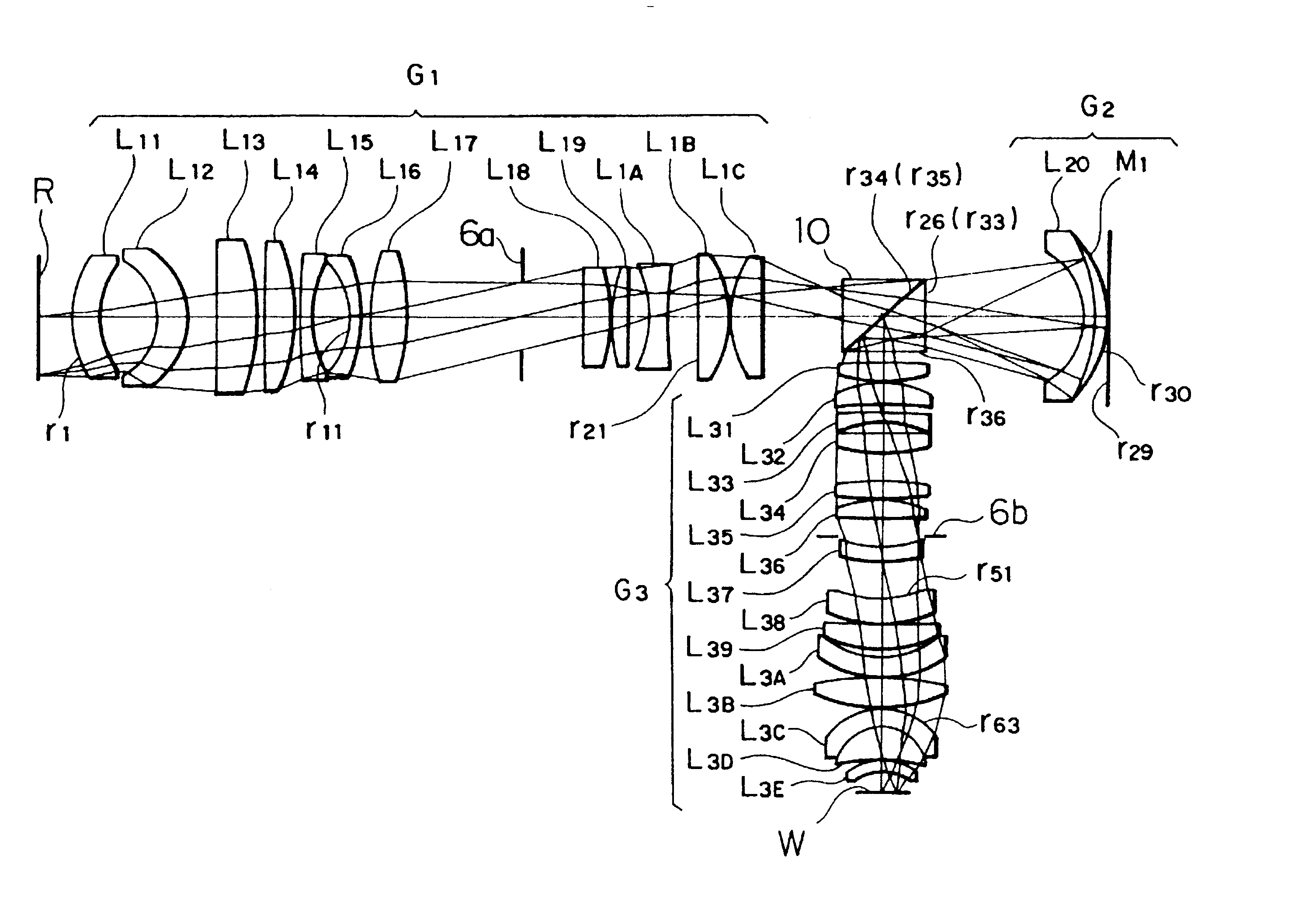
Microlithographic reduction projection catadioptric objective
InactiveUS6873476B2Reduce complexityIncrease the number ofProjectorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntermediate imageVirtual image
The invention concerns a microlithographic reduction projection catadioptric objective having an even number greater than two of curved mirrors, being devoid of planar folding mirrors and featuring an unobscured aperture. The objective has a plurality of optical elements, and no more than two optical elements deviate substantially from disk form. The objective has an object side and an image side, and has in sequence from the object side to the image side a catadioptric group providing a real intermediate image, a catoptric or catadioptric group providing a virtual image, and a dioptric group providing a real image.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH +1
Holographic image display systems
InactiveUS20110002019A1Speckle reductionTelevision system detailsDiffusing elementsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
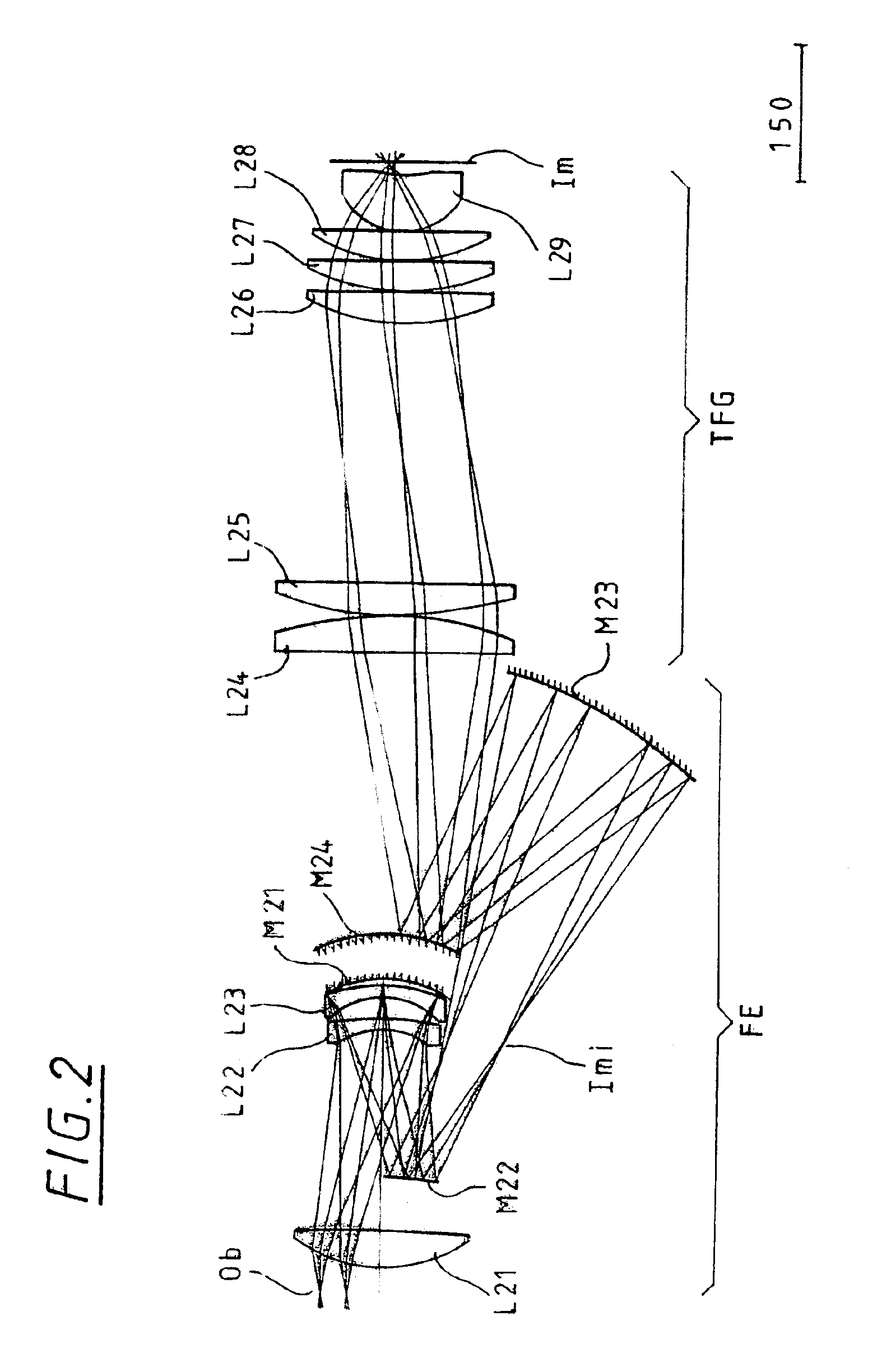
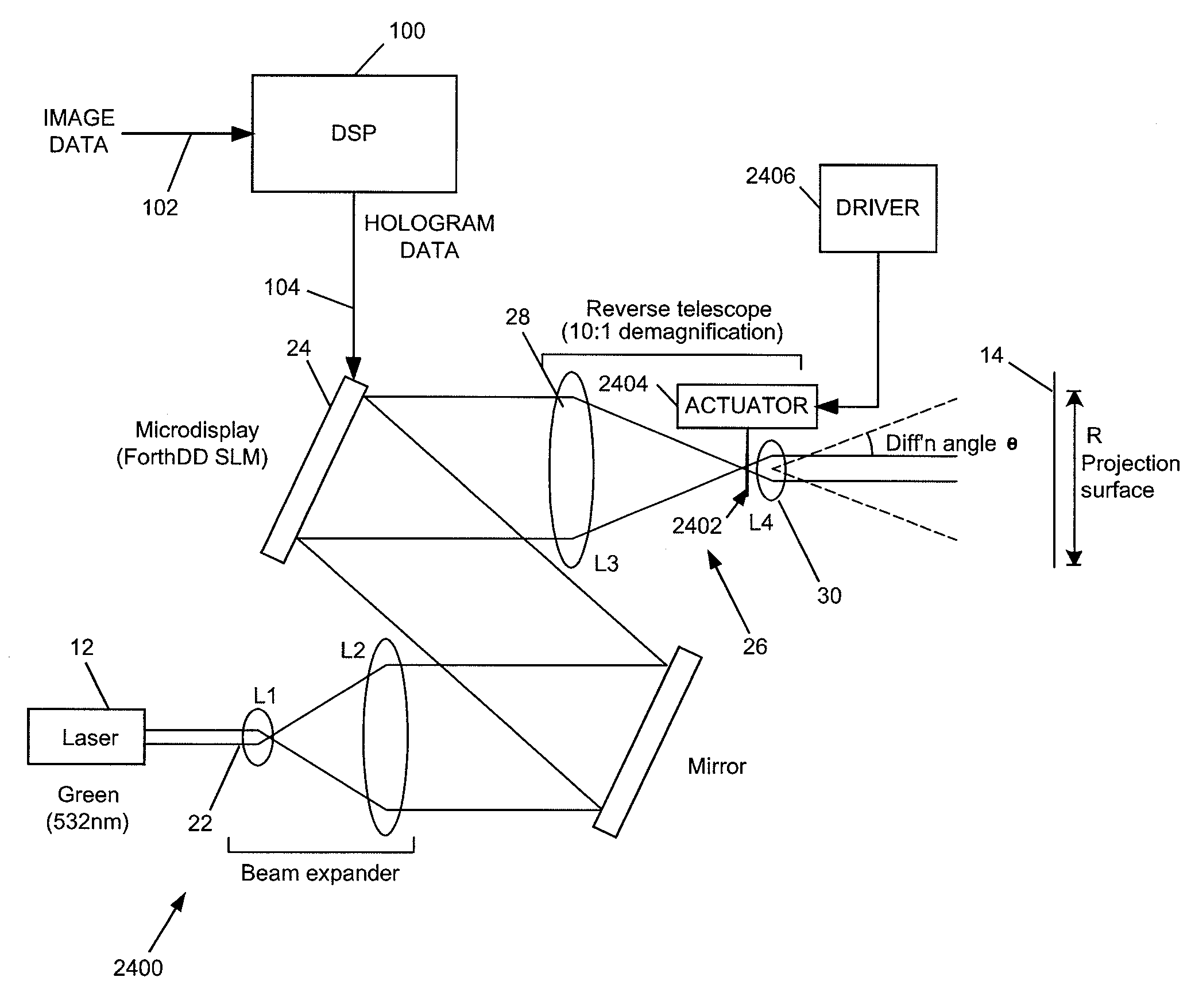
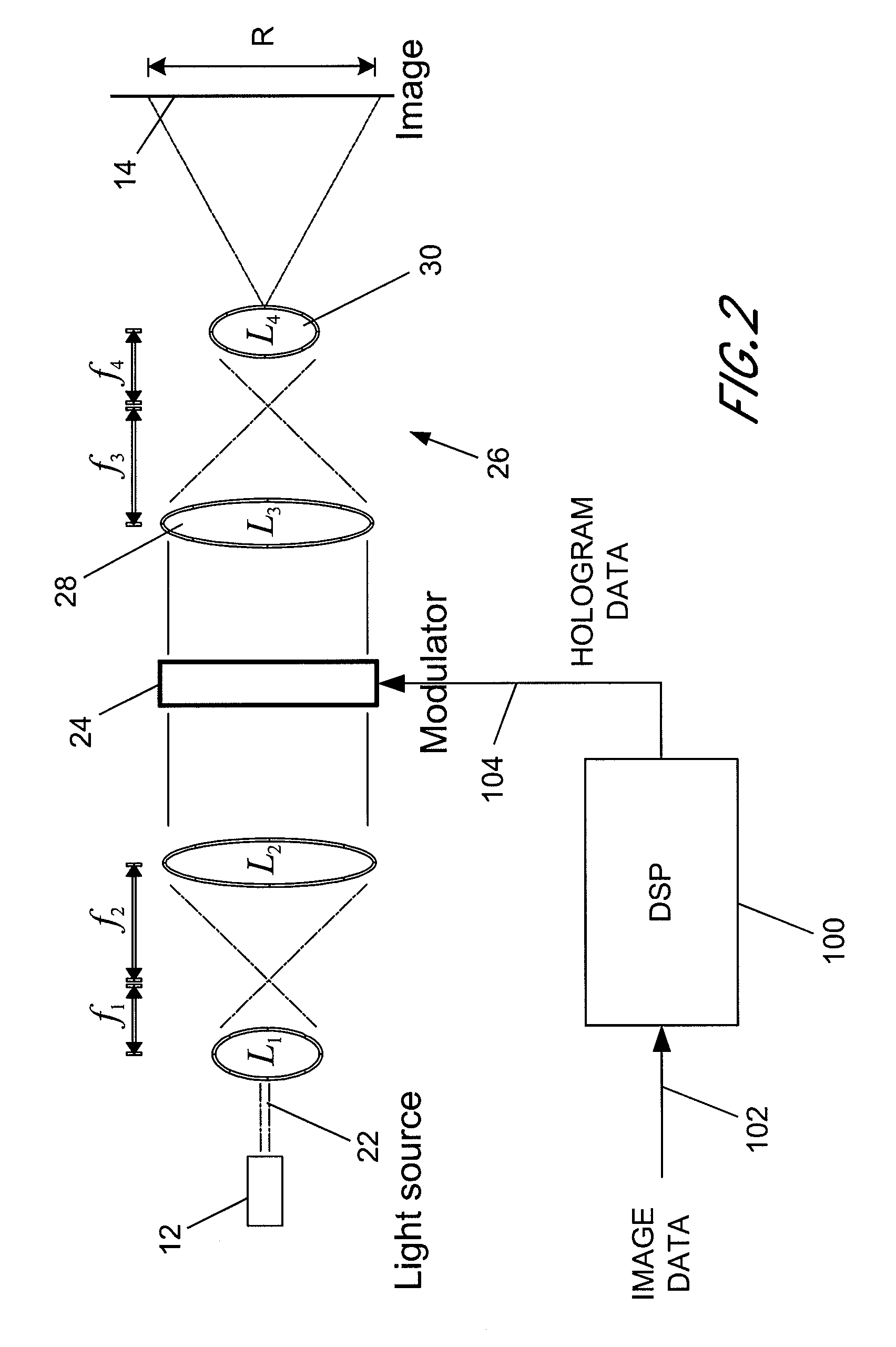
The invention relates to techniques for speckle reduction in holographic optical systems, in particular holographic image display systems. We describe a holographic image display system for displaying an image holographically on a display surface, the system including: a spatial light modulator (SLM) to display a hologram; a light source to illuminate said displayed hologram; projection optics to project light from said illuminated displayed hologram onto said display surface to form a holographically generated two-dimensional image, said projection optics being configured to form, at an intermediate image surface, an intermediate two-dimensional image corresponding to said holographically generated image; a diffuser located at said intermediate image surface; and an actuator mechanically coupled to said diffuser to, in operation, move said diffuser to randomise phases over pixels of said intermediate image to reduce speckle in an image displayed by the system.
Owner:LIGHT BLUE OPTICS
Method for planning, performing and monitoring thermal ablation
InactiveUS20080033419A1Shorten the timeMovement is minimized and eliminatedUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsRadiofrequency ablationData set
A thermal ablation system is operable to perform thermal ablation using an x-ray system to measure temperature changes throughout a volume of interest in a patient. Image data sets captured by the x-ray system during a thermal ablation procedure provide temperature change information for the volume being subjected to the thermal ablation. Intermediate image data sets captured during the thermal ablation procedure may be fed into a system controller, which may modify or update a thermal ablation plan to achieve volume coagulation necrosis targets. The thermal ablation may be delivered by a variety of ablation modes including radiofrequency ablation, microwave therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, laser ablation, and other interstitial heat delivery methods. Methods of performing thermal ablation using x-ray system temperature measurements as a feedback source are also provided.
Owner:FISCHER ACQUISITION LLC +1
Image Processing Apparatus, Image Apparatus, Image Processing Method, and Computer Program
ActiveUS20080219585A1High quality imagingGuaranteed high-quality imagingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingIntermediate image
An image processing apparatus includes the following elements. An image input unit receives a long-time exposure image and a short-time exposure image. An image analysis unit detects a brightness-change pixel in which a brightness change has occurred during a photographic period on the basis of analysis of pixel values in the long-time exposure image and the short-time exposure image. A pixel value correction unit corrects a pixel value of the detected brightness-change pixel. In the pixel value correction unit, a combined image generator selectively combines pixel values in the long-time exposure image and pixel values in the short-time exposure image to generate a combined image; an intermediate image generator generates a blurred image of the combined image; and an output image generator determines a pixel value of the detected brightness-change pixel using a pixel value of a corresponding pixel in each of the combined image and the blurred image.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Image display apparatus
InactiveUS20160147074A1Improve visibilitySmall sizeDiffusing elementsBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsIntermediate imageProjection image
An image display apparatus includes an image projection unit that projects image display light, an intermediate image forming unit that forms a real image based on the image display light projected from the image projection unit, and a projection mirror that reflects the image display light, which has passed through the intermediate image forming unit, toward the surface for presenting a virtual image. The intermediate image forming unit has a first means that controls the direction of a chief ray of the image display light, which has passed through the intermediate image forming unit, and a second means that controls the light distribution angle of the chief ray.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Catadioptric reduction projection optical system and exposure apparatus having the same
InactiveUSRE38438E1Easy to adjustImprove imaging effectPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusProjection opticsBeam splitter
A catadioptric projection optical system is provided, which can use a beam splitting optical system smaller in size than a conventional polarizing beam splitter, can set a long optical path from a concave reflecting mirror to an image plane, allows easy adjustment of the optical system, and has excellent imaging performance. A light beam from an object surface forms a first intermediate image through a refracting lens group. A light beam from the first intermediate image passes through a polarizing beam splitter and is reflected by a concave reflecting mirror to form a second intermediate image in the polarizing beam splitter. A light beam from the second intermediate image is reflected by the polarizing beam splitter means to form a final image on the image plane via a refracting lens group. The polarizing beam splitter means is arranged near the positions at which the intermediate images are formed.
Owner:NIKON CORP
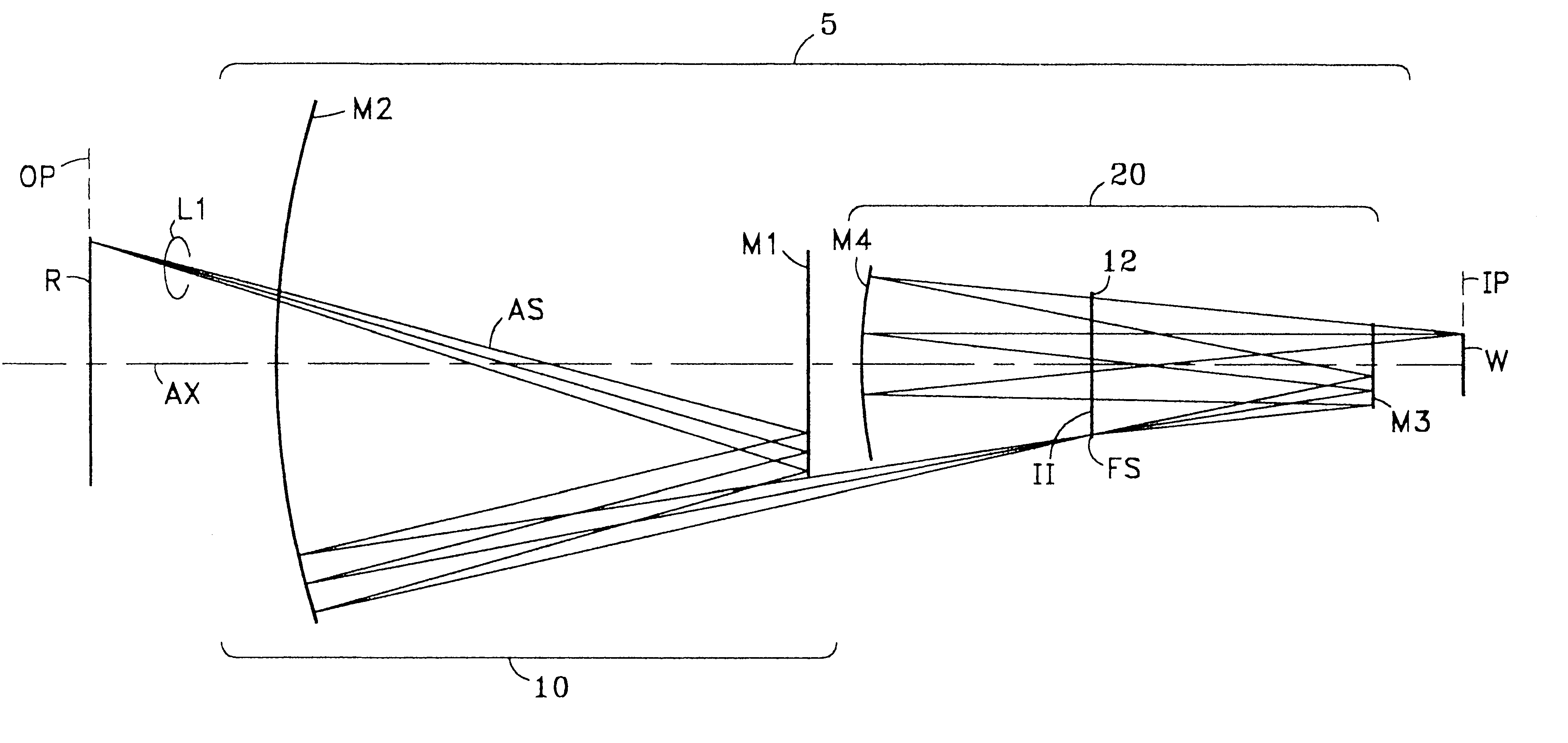
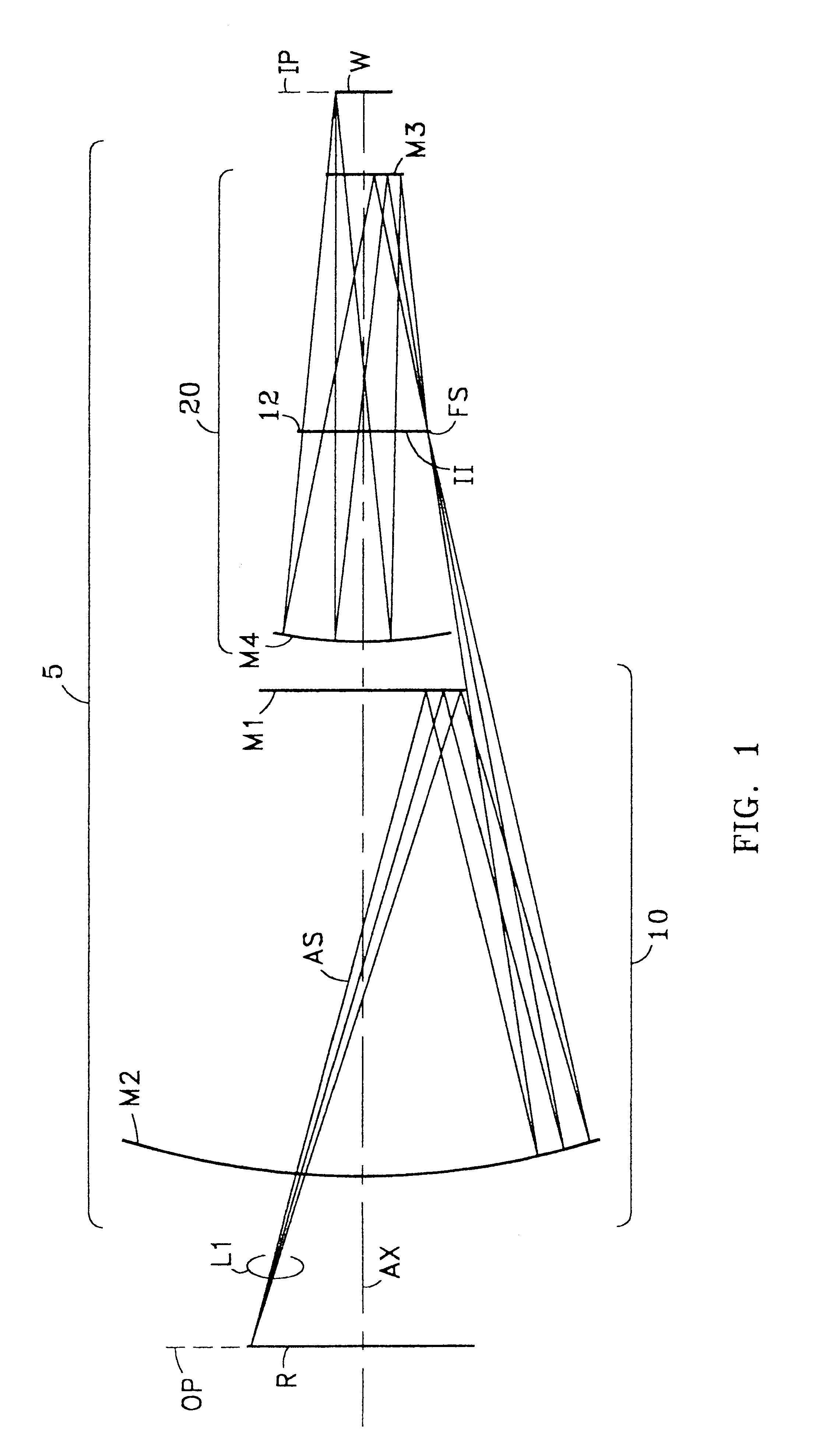
Catoptric reduction projection optical system and exposure apparatus and method using same
A catoptric reduction projection optical system (5) is provided with a first catoptric optical system (10) that images an object (R) in first (object) plane (OP) into a second plane (12) and forming an intermediate image (II) therein, and a second catoptric optical system (20) that images the intermediate image in the second plane onto a third (image) plane (IP), thereby forming a reduced image of the object in the first (object) plane onto the third (image) plane. The first catoptric optical system comprises a first mirror pair comprising two reflective mirrors (M1, M2). The second catoptric optical system comprises a second mirror pair comprising a convex mirror (M3) and a concave mirror (M4). The system also preferably satisfied a number of design conditions.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS20060050409A1Increase contrastReduce image contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spreadIntermediate image
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com