Patents
Literature
10987 results about "Fourier transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Fourier transform (FT) decomposes a function of time (a signal) into its constituent frequencies. This is similar to the way a musical chord can be expressed in terms of the volumes and frequencies of its constituent notes. The term Fourier transform refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of time. The Fourier transform of a function of time is itself a complex-valued function of frequency, whose magnitude (modulus) represents the amount of that frequency present in the original function, and whose argument is the phase offset of the basic sinusoid in that frequency. The Fourier transform is not limited to functions of time, but the domain of the original function is commonly referred to as the time domain. There is also an inverse Fourier transform that mathematically synthesizes the original function from its frequency domain representation.
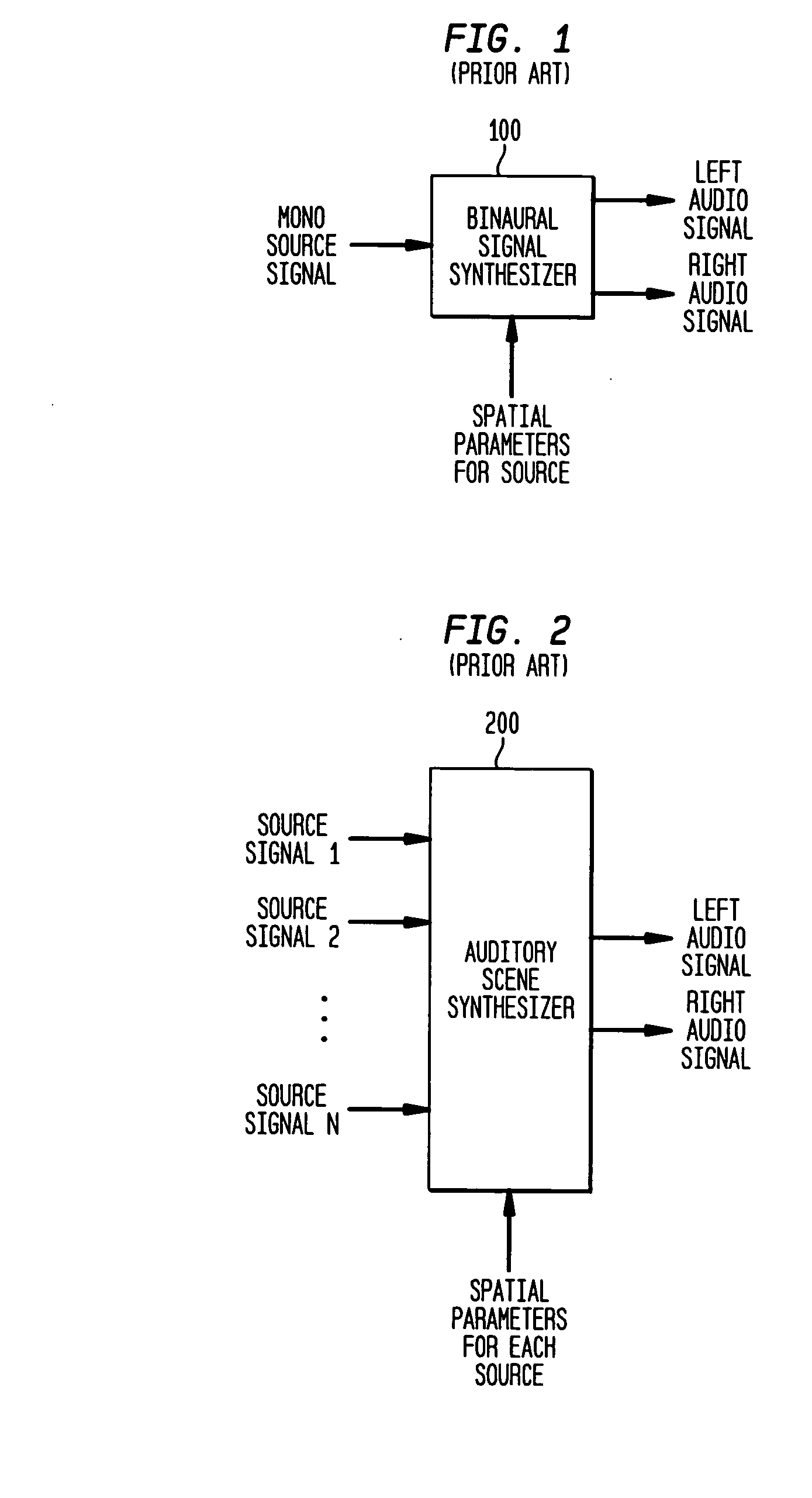
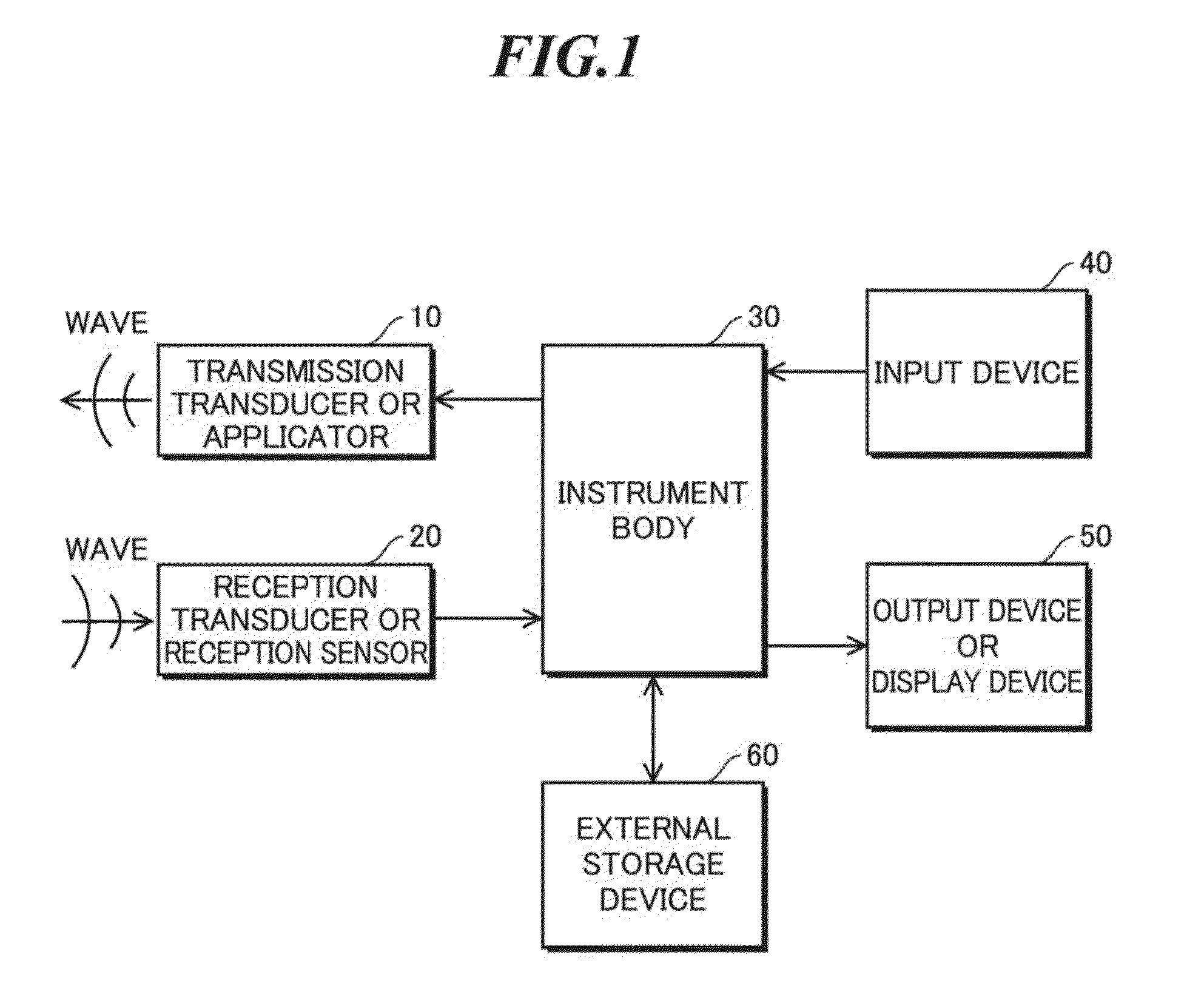
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUSRE38476E1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
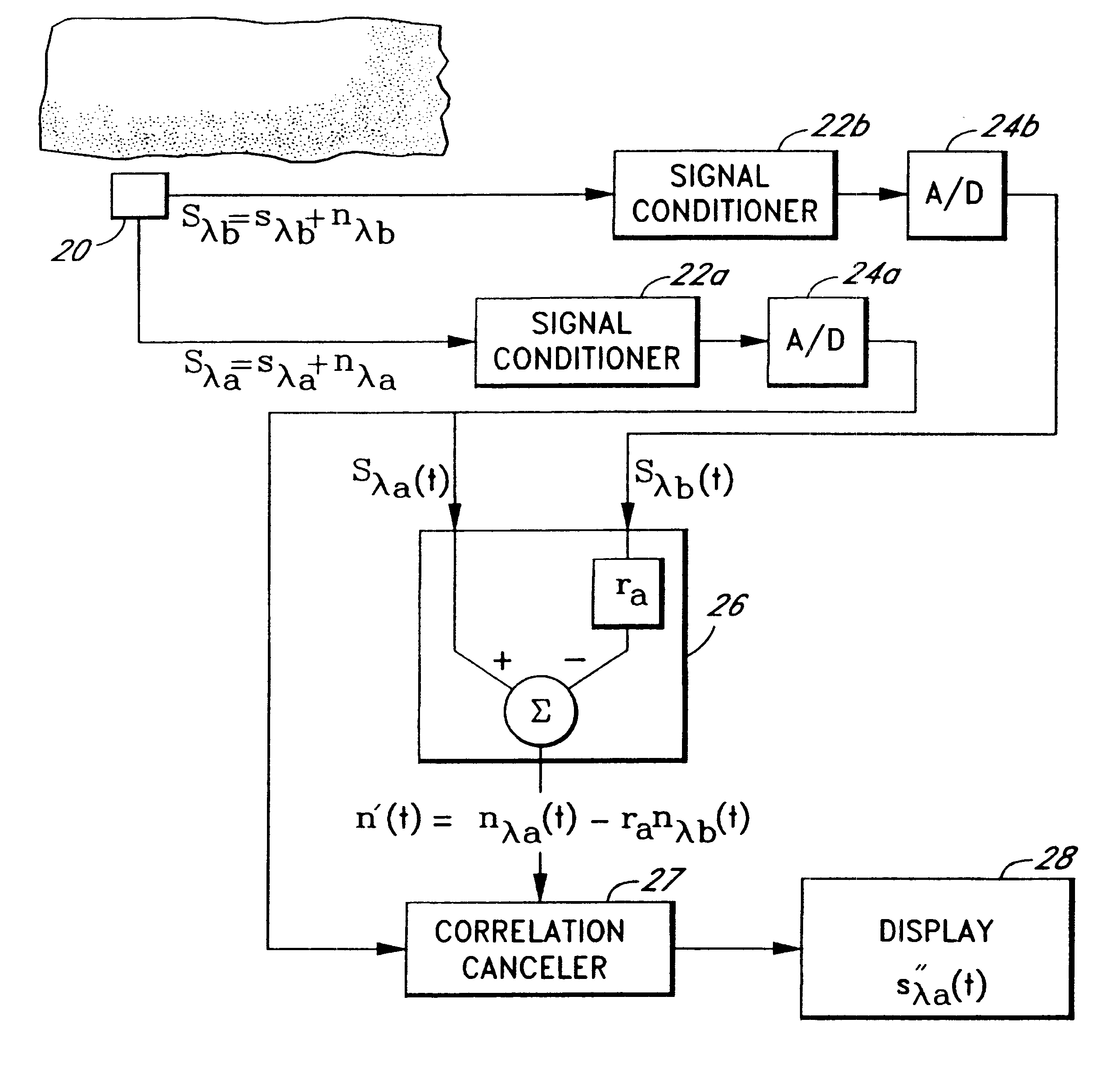
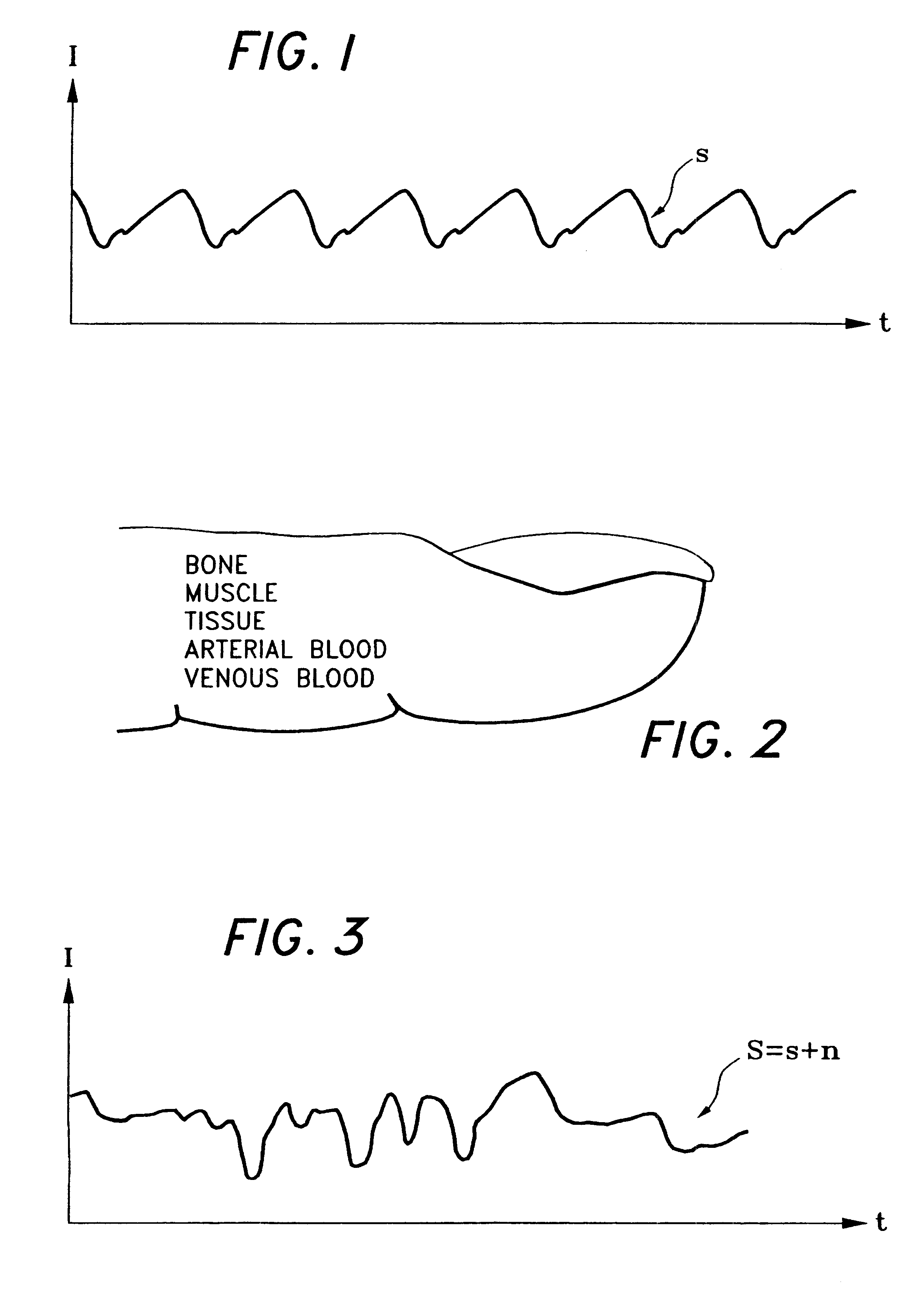
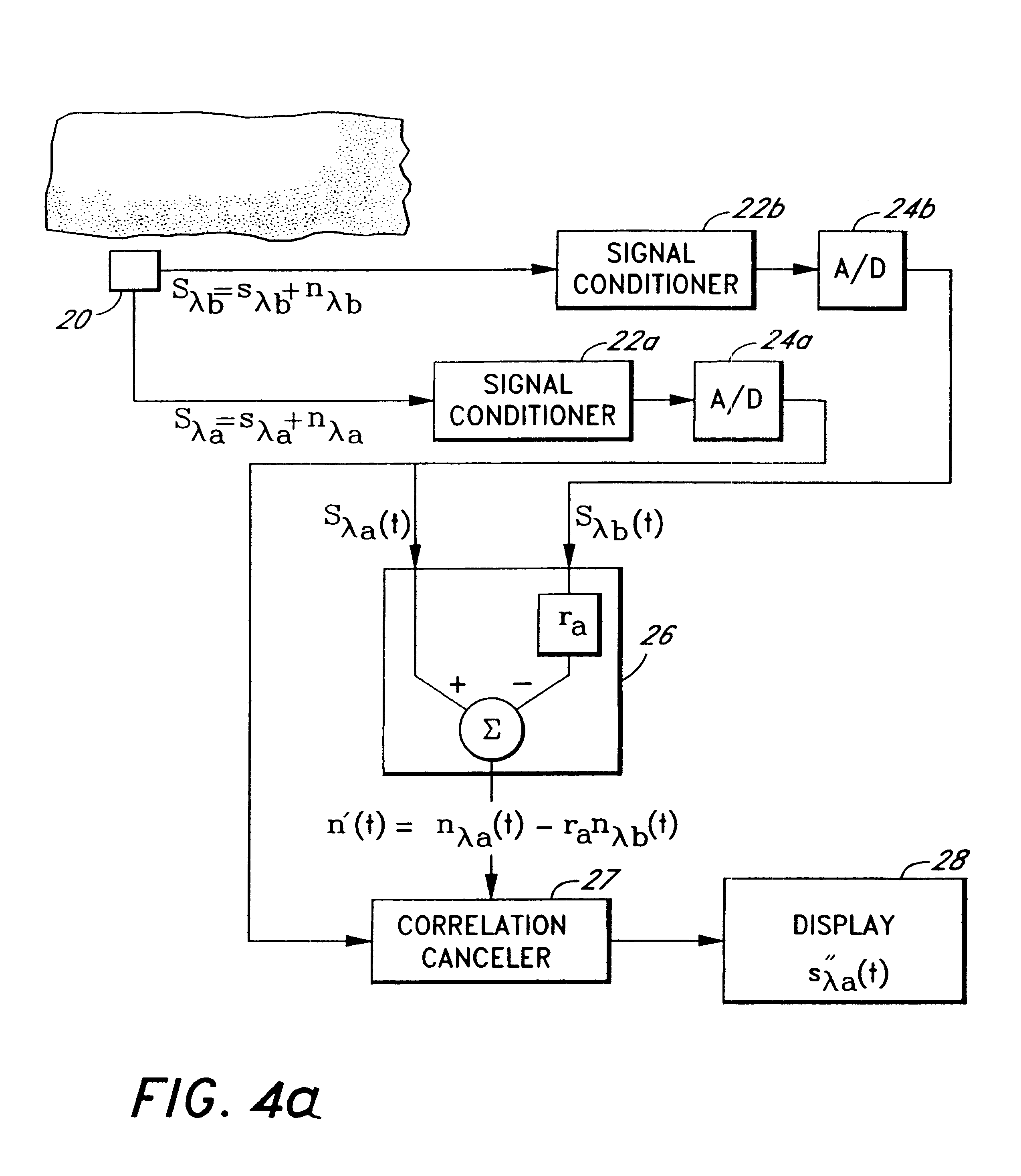
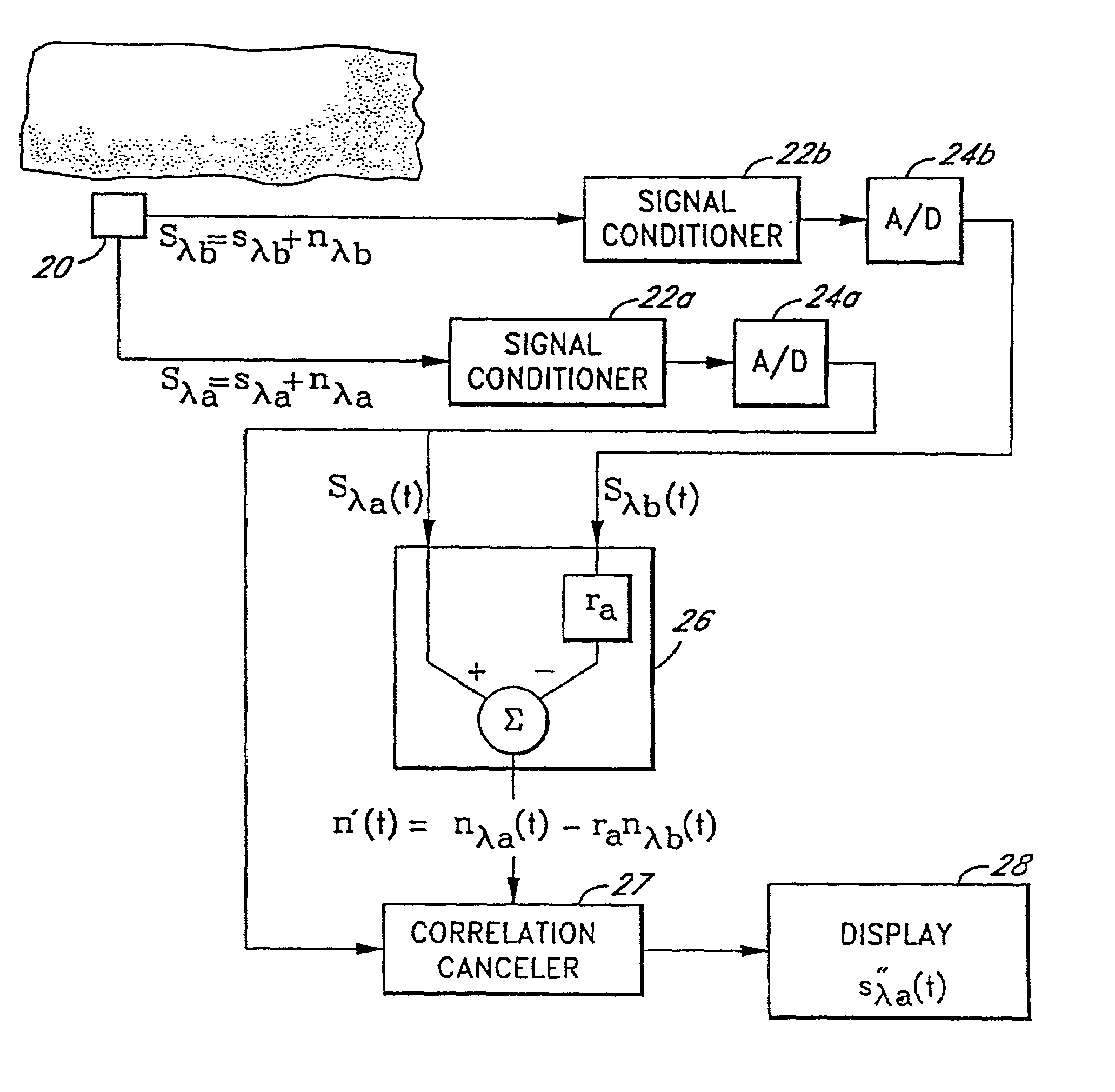
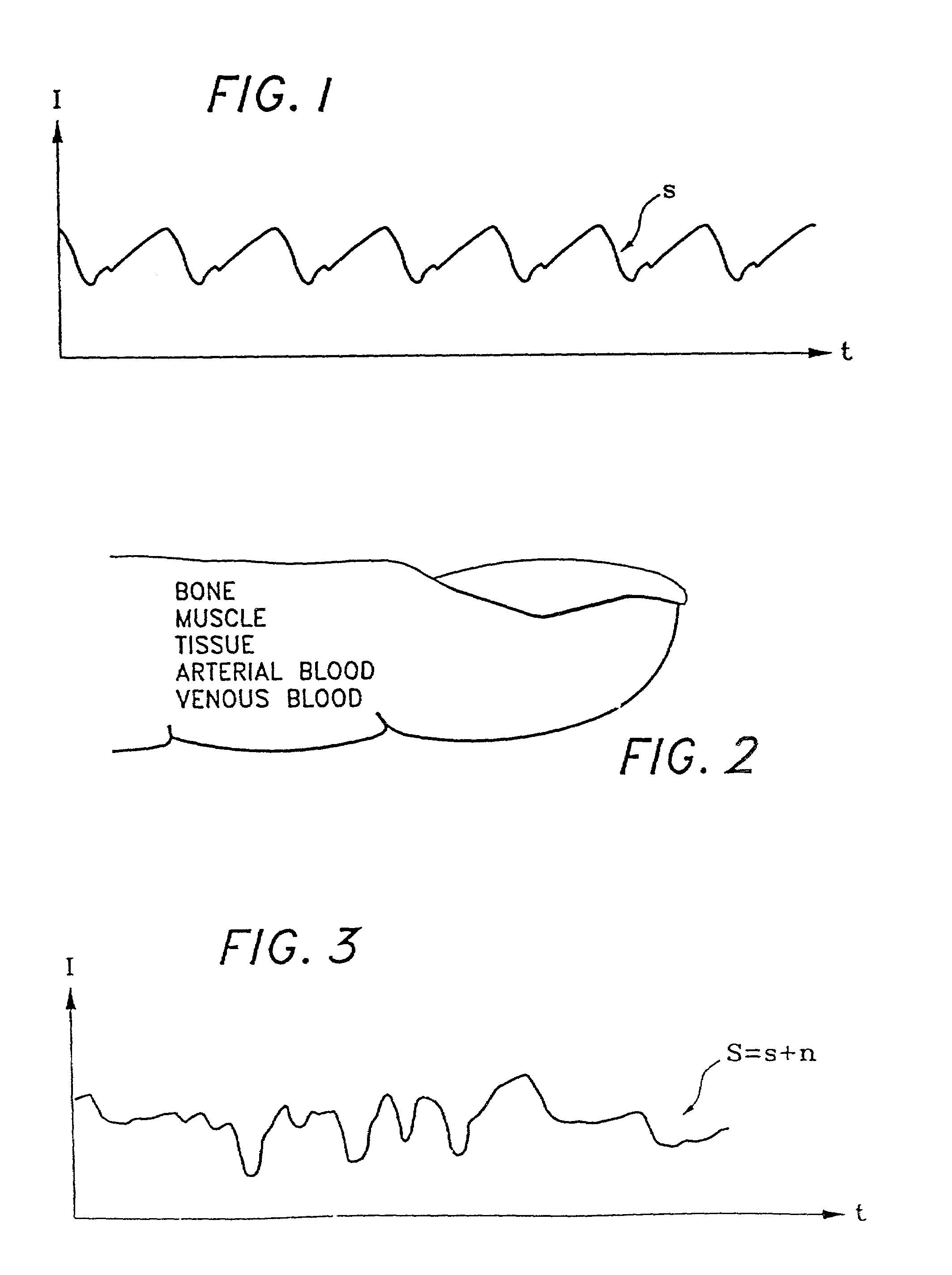
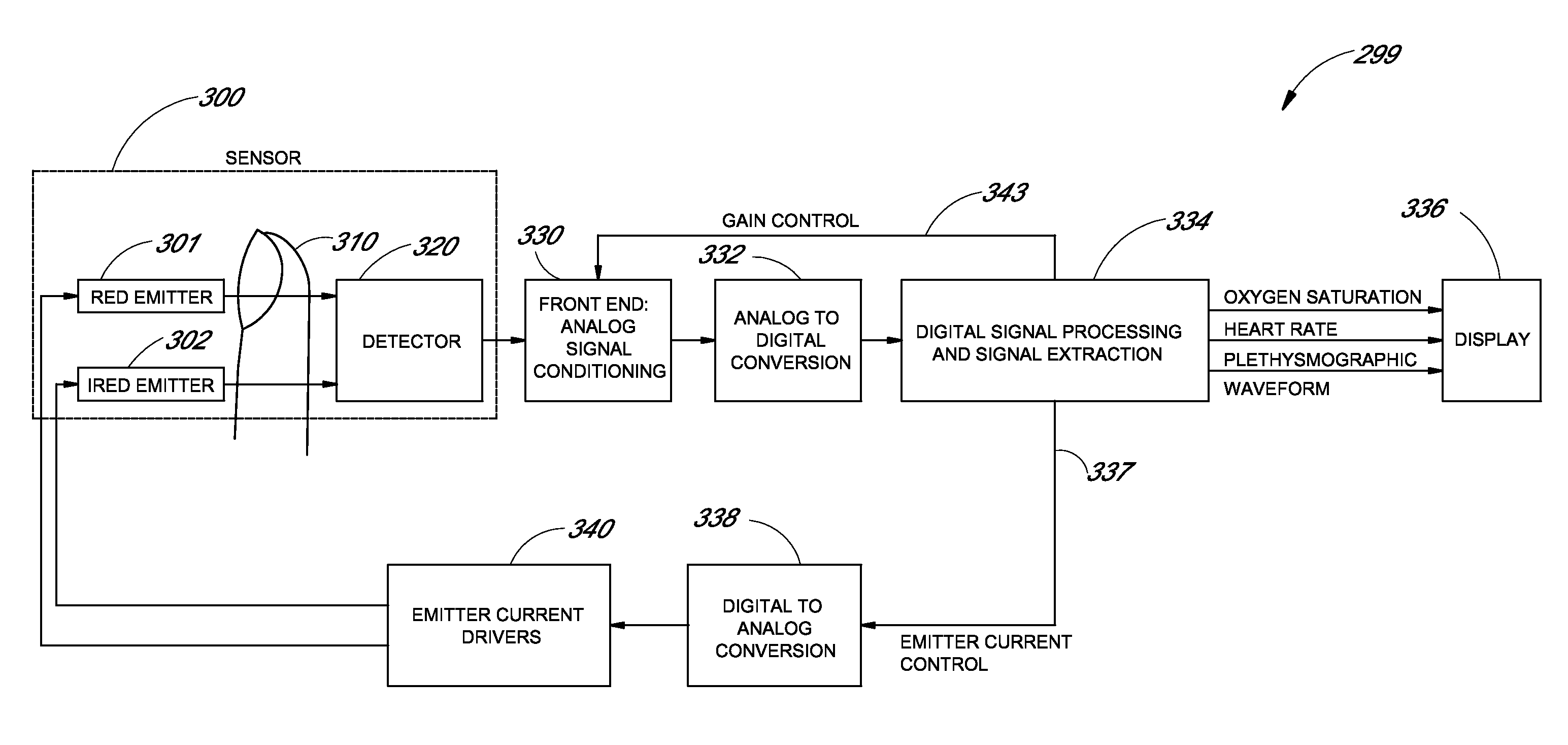
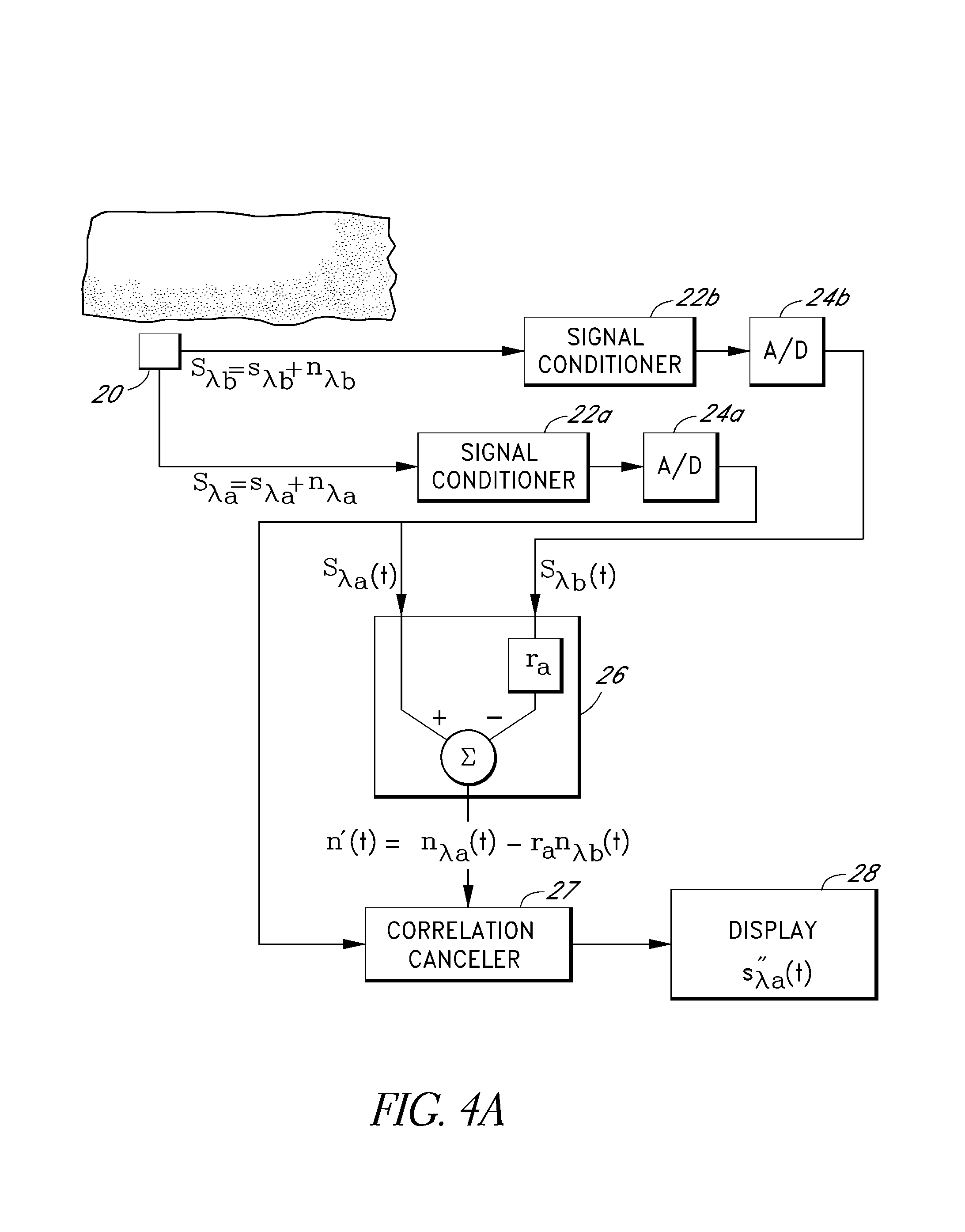
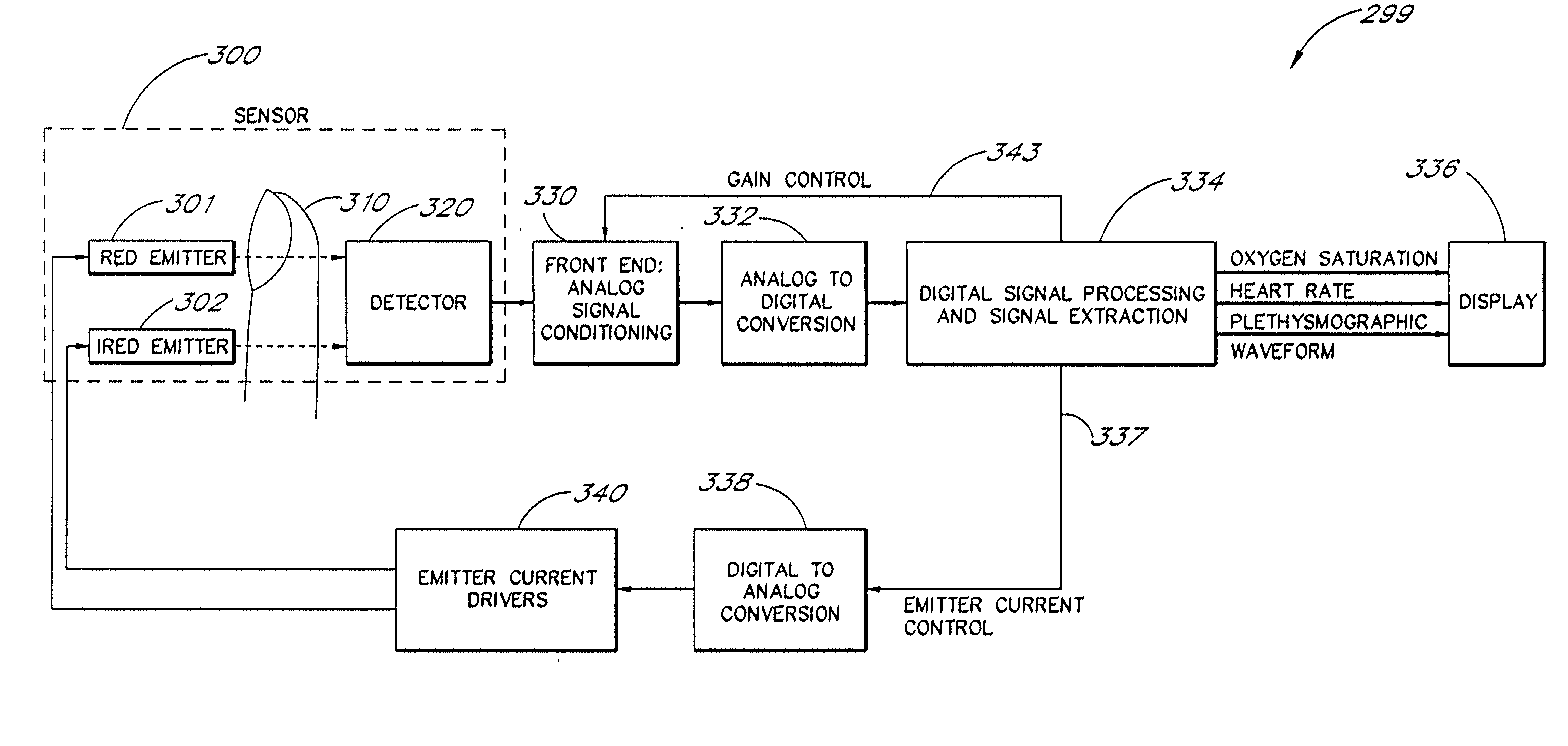
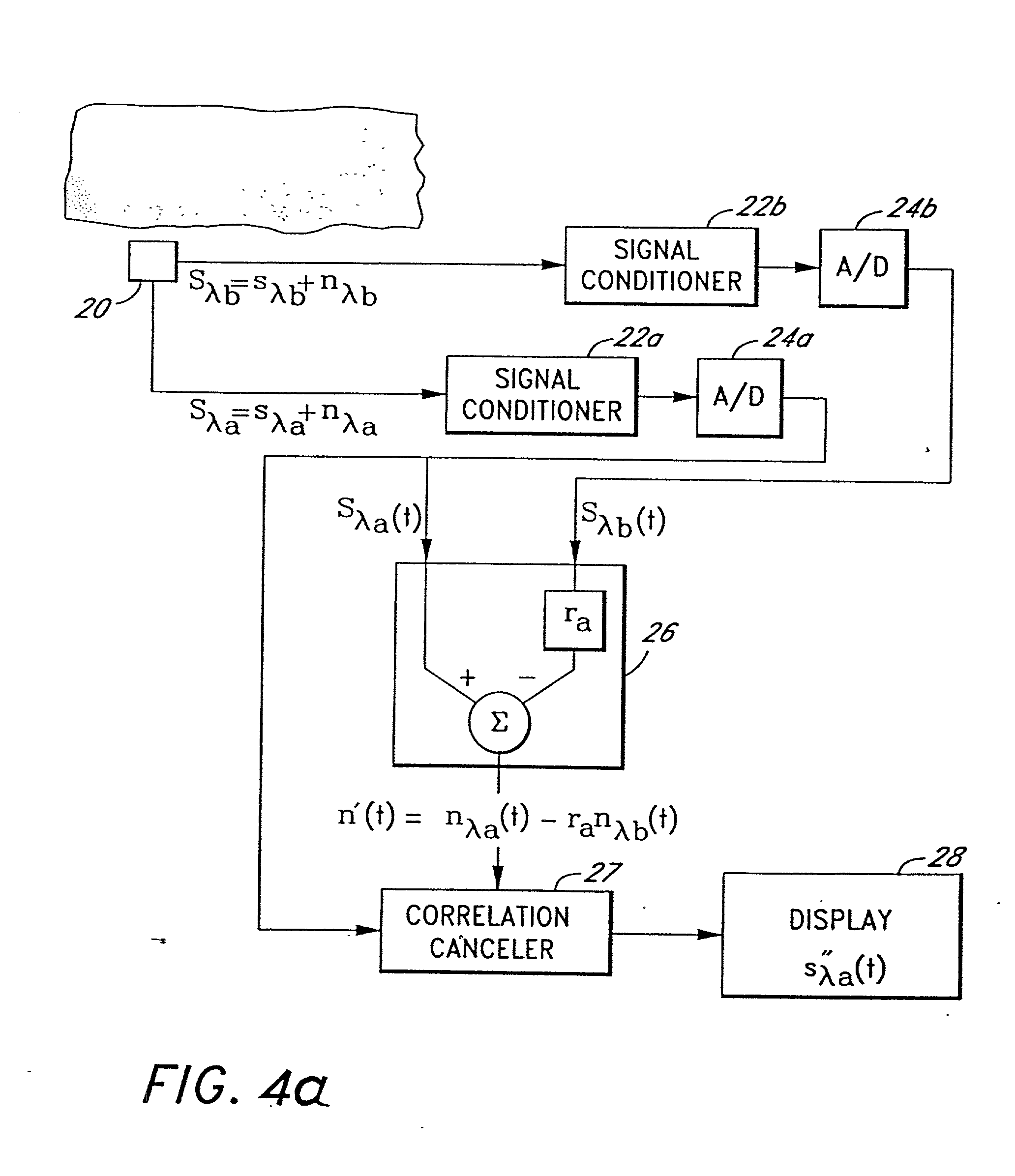
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients in order to find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS7376453B1Improve approximationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsStatistical functionFourier transform
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients in order to find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method, and device manufactured thereby
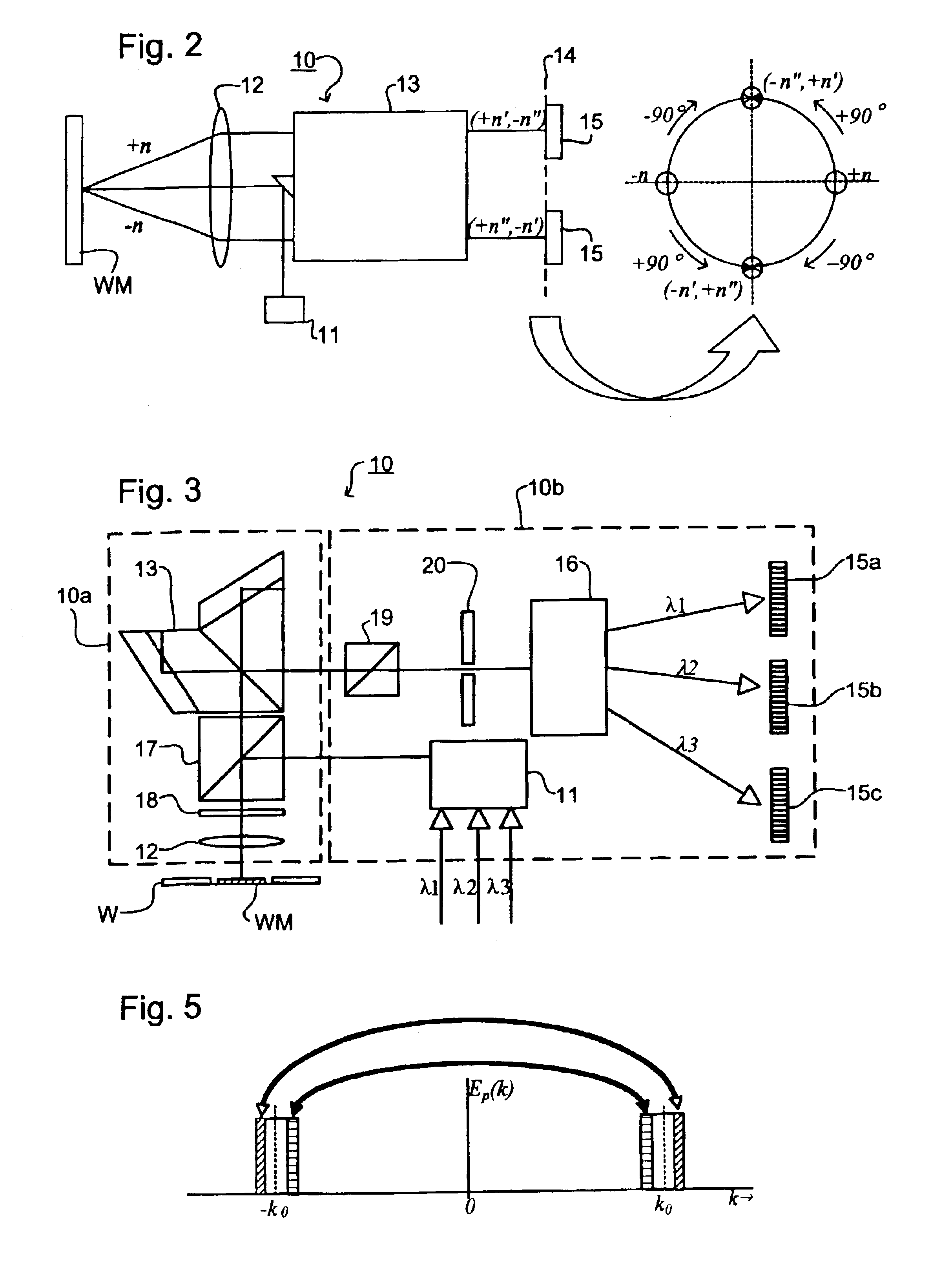
InactiveUS6961116B2Fine positioning informationLarge capture rangeDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsDiffraction orderPhase difference
An alignment system uses a self-referencing interferometer that produces two overlapping and relatively rotated images of an alignment markers. Detectors detect intensities in a pupil plane where Fourier transforms of the images are caused to interfere. The positional information is derived from the phase difference between diffraction orders of the two images which manifests as intensity variations in the interfered orders. Asymmetry can also be measured by measuring intensities at two positions either side of a diffraction order.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
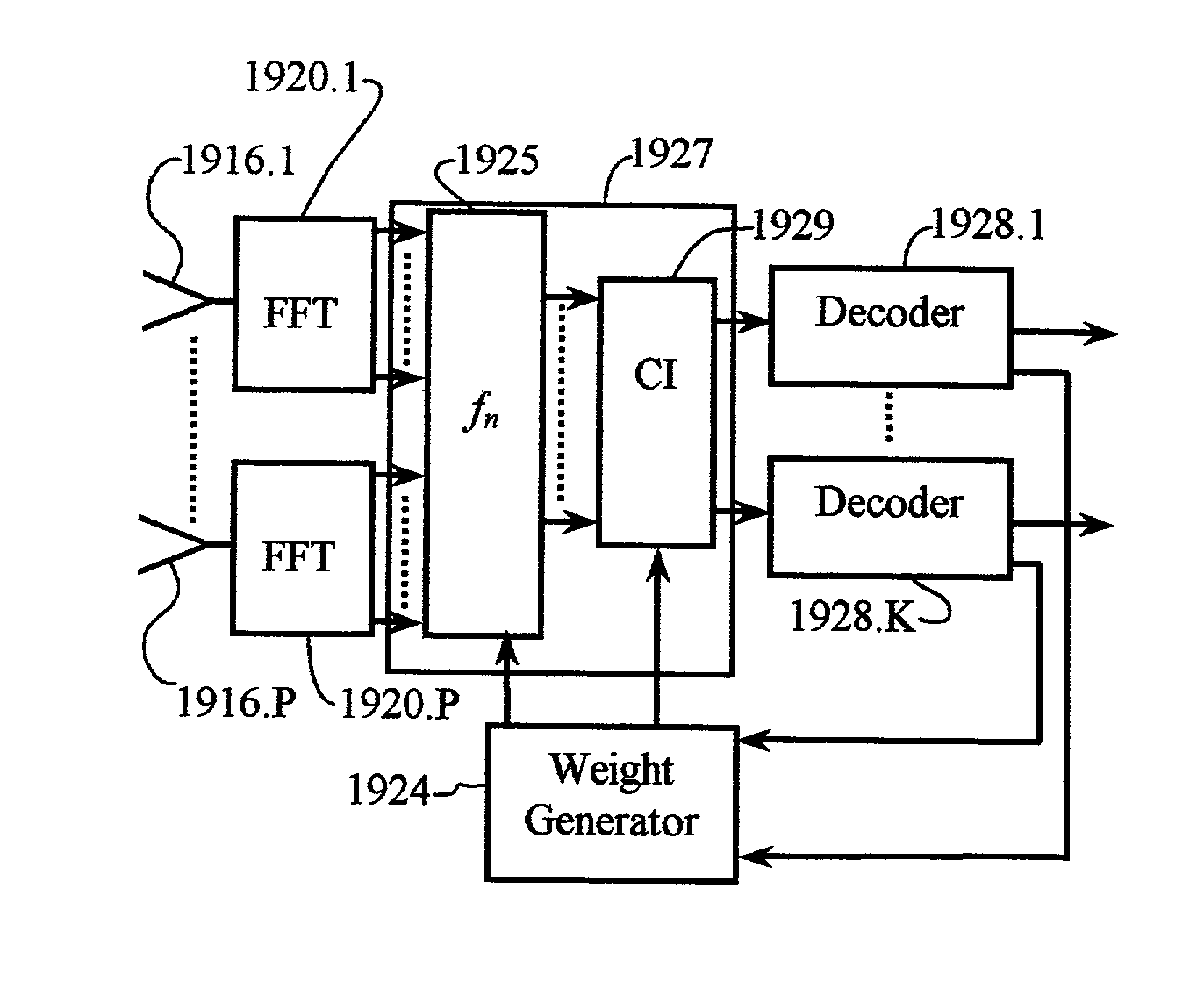
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
High efficiency high performance communications system employing multi-carrier modulation
InactiveUS20020154705A1Increase diversityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityData streamHigh performance communication
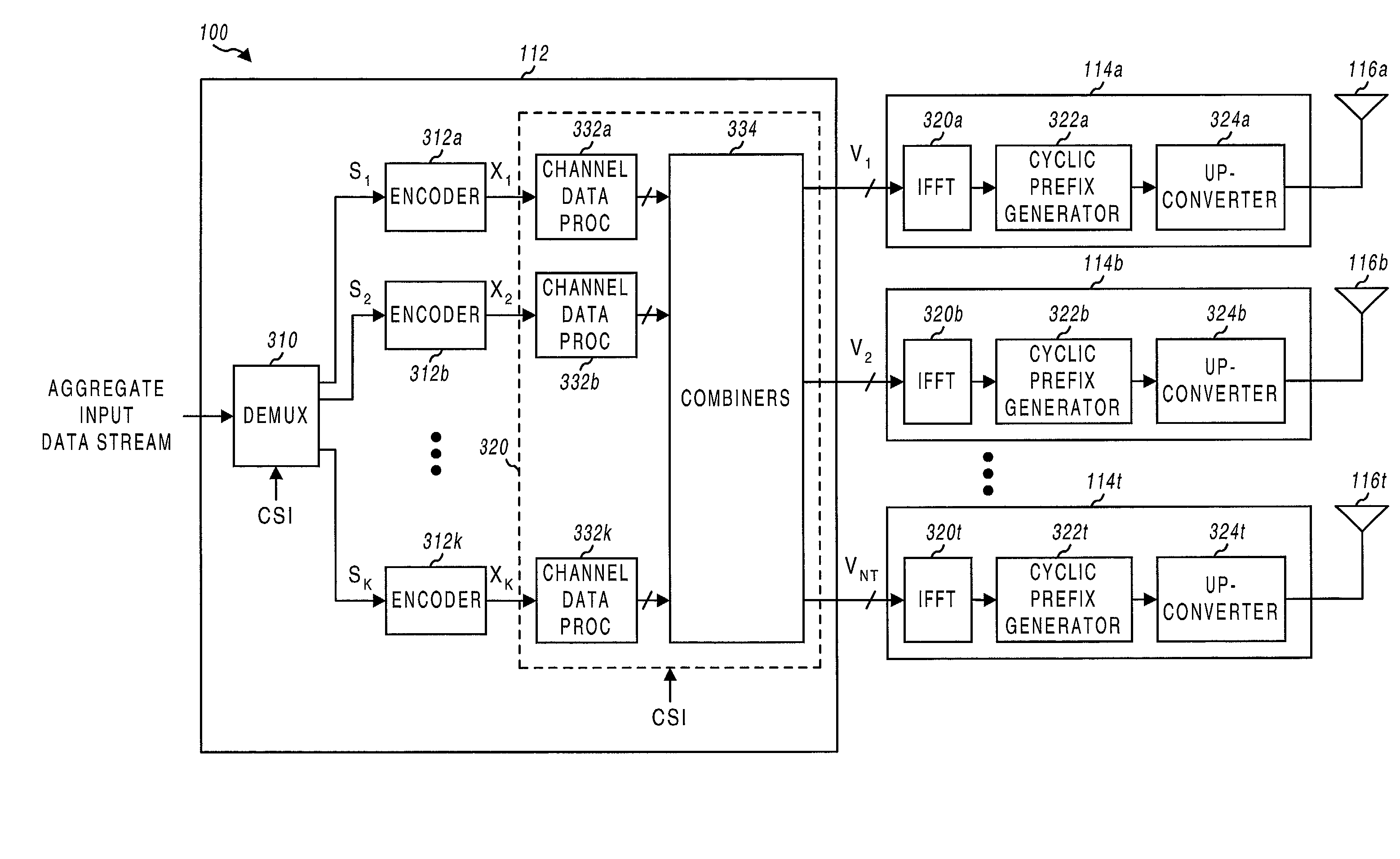
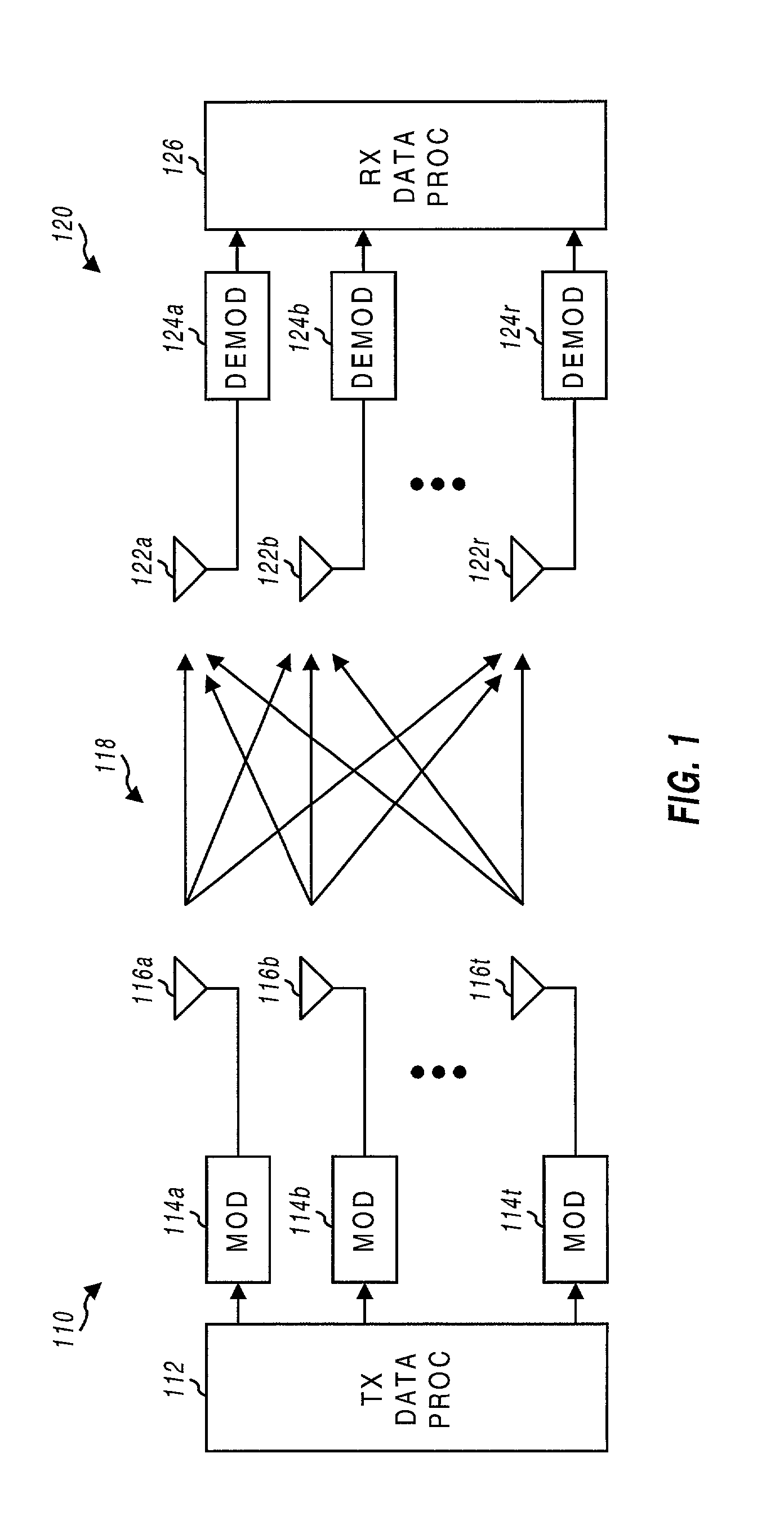
Transmitter and receiver units for use in a communications system and configurable to provide antenna, frequency, or temporal diversity, or a combination thereof, for transmitted signals. The transmitter unit includes a system data processor, one or more modulators, and one or more antennas. The system data processor receives and partitions an input data stream into a number of channel data streams and further processes the channel data streams to generate one or more modulation symbol vector streams. Each modulation symbol vector stream includes a sequence of modulation symbol vectors representative of data in one or more channel data streams. Each modulator receives and modulates a respective modulation symbol vector stream to provide an RF modulated signal, and each antenna receives and transmits a respective RF modulated signal. Each modulator may include an inverse (fast) Fourier transform (IFFT) and a cyclic prefix generator. The IFFT generates time-domain representations of the modulation symbol vectors, and the cyclic prefix generator repeats a portion of the time-domain representation of each modulation symbol vector. The channel data streams are modulated using multi-carrier modulation, e.g., OFDM modulation. Time division multiplexing (TDM) may also be used to increase flexibility.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS8560034B1Improve approximationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method for authenticating an individual by use of fingerprint data
InactiveUS7136514B1Simple methodElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisFast Fourier transformBiometrics
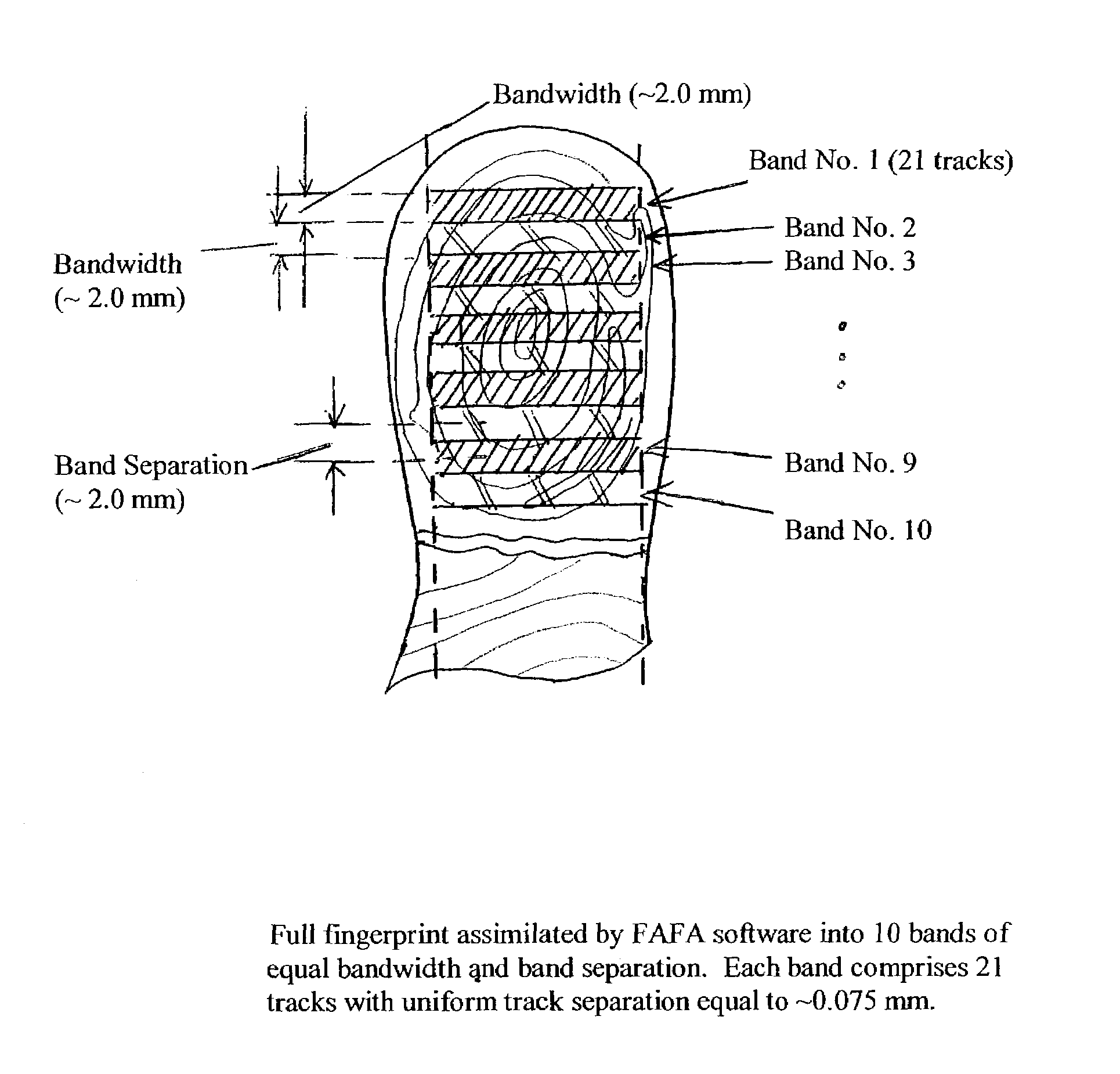
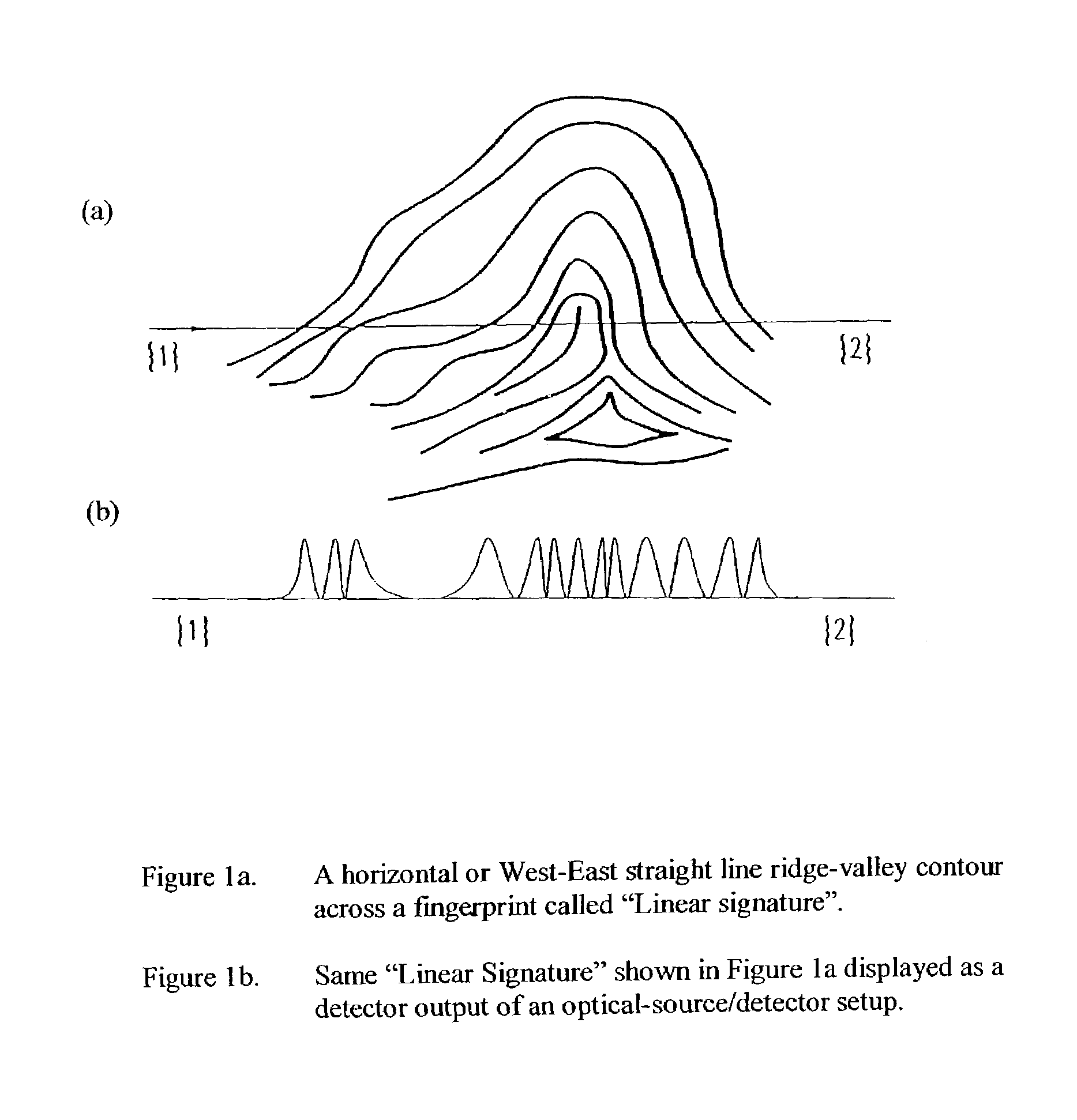
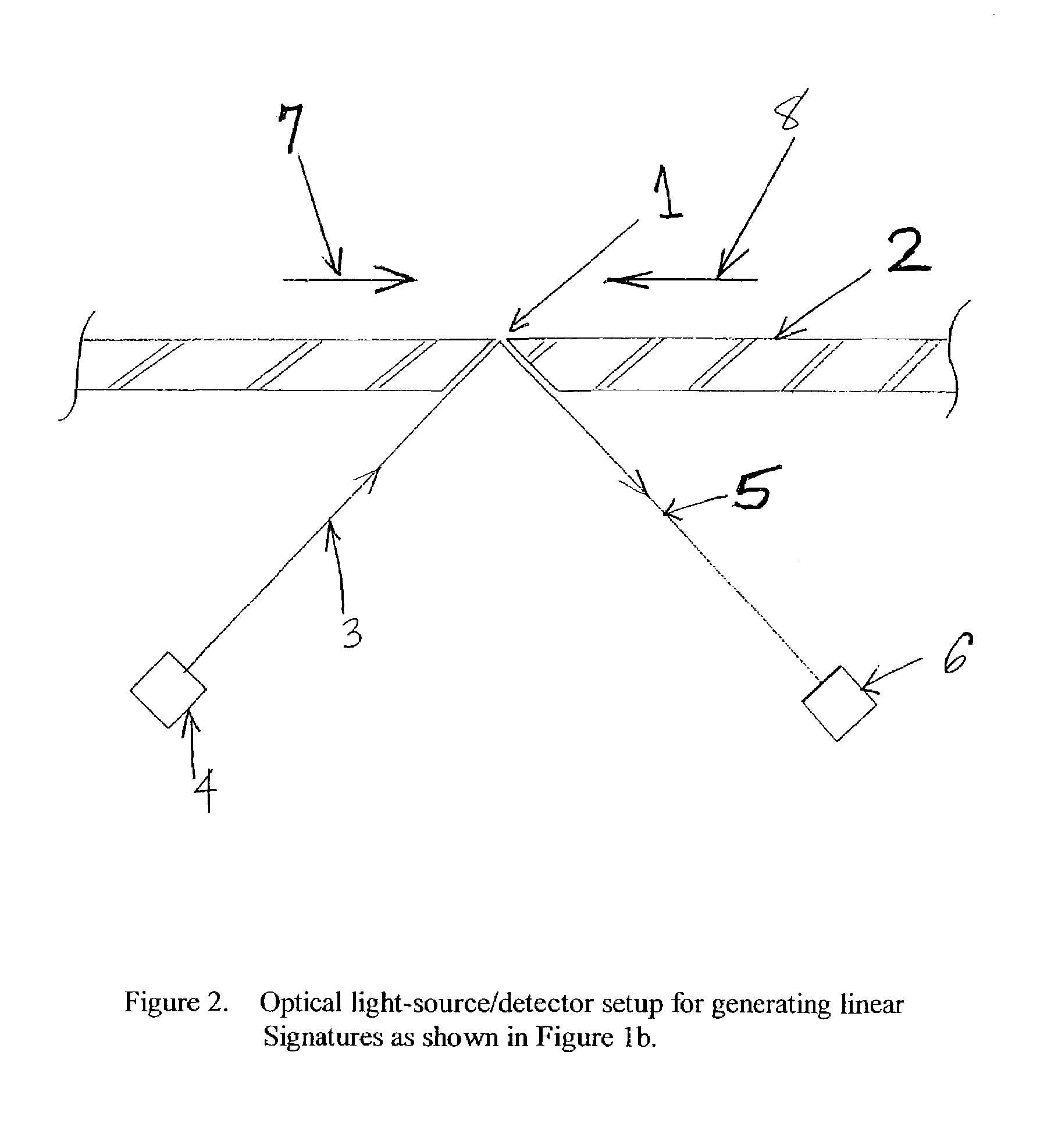
A method for authenticating an individual by use of fingerprint data that involves two different broad steps. The first step is to obtain a biometrics fingerprint signature template (“BFST”) for an individual in an enrollment process by selecting a plurality of bands for the BFST and obtaining a plurality of tracks corresponding to each of the plurality of bands by use of an enrollment frame of a selected finger of the individual, wherein the plurality of bands are spatially referenced to the enrollment frame and can be spatially referenced to a reference barrier. The second step is to authenticate (or not) a candidate finger against one or more BFST in an authentication process in which a swipe direction and an access code for the individual are selected, a plurality of candidate tracks are obtained from the candidate finger through use of the reference barrier in an authentication unit so that each of the plurality of candidate tracks is spatially referenced so as to be within a corresponding one of the plurality of bands, calculating a similarity index for each of the plurality of candidate tracks and each of the plurality of tracks for the band to which the candidate track corresponds by use of a Fast Fourier-transform fingerprint algorithm, and multiplying each maximum similarity index obtained for each of the plurality of candidate tracks to obtain a match index which indicates a match if it exceeds a preselected threshold.
Owner:WONG JACOB Y
Frequency encoding of resonant mass sensors
InactiveUS20050016276A1Sufficient ring timeImprove stabilityVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayFrequency spectrum
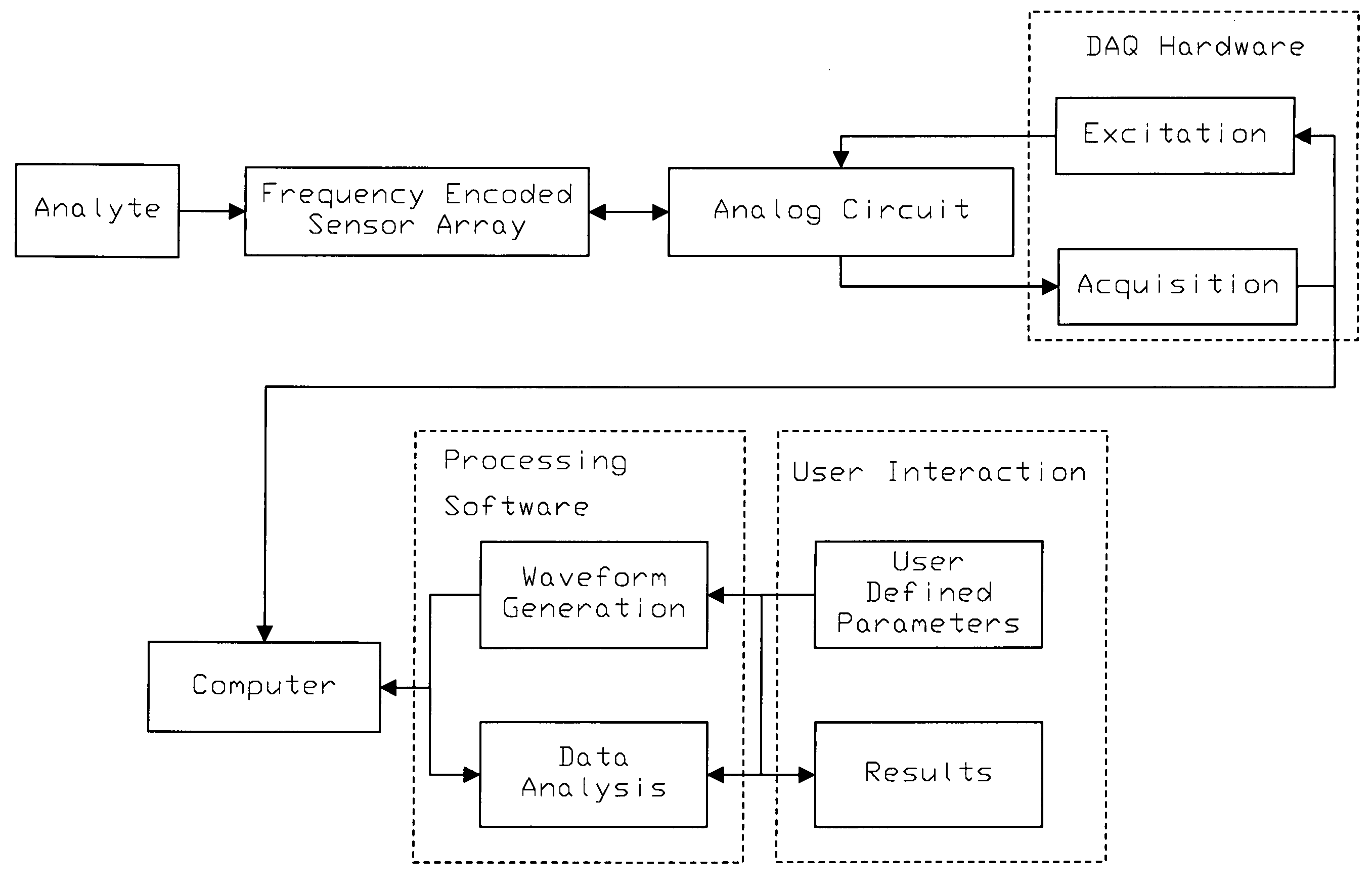
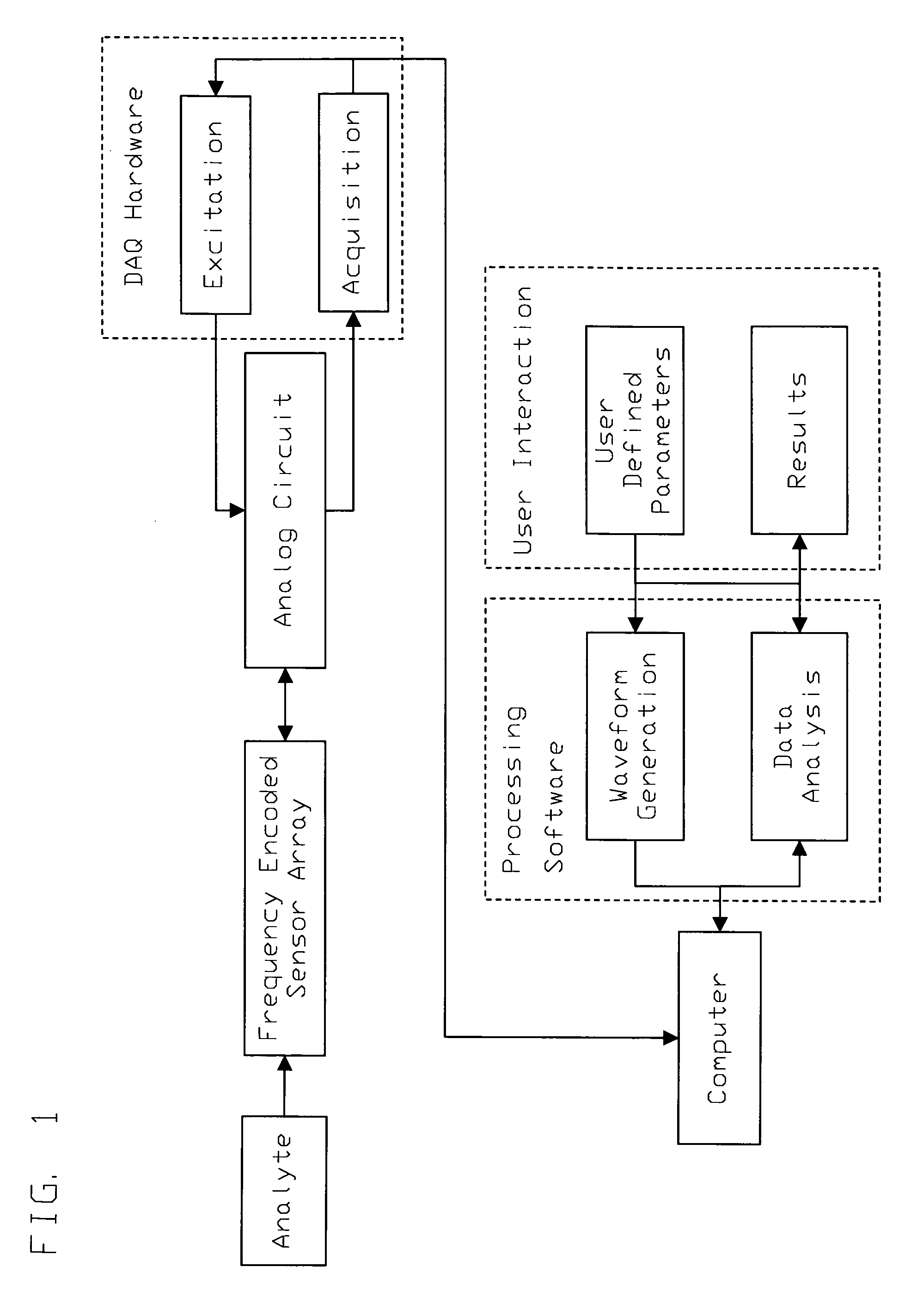
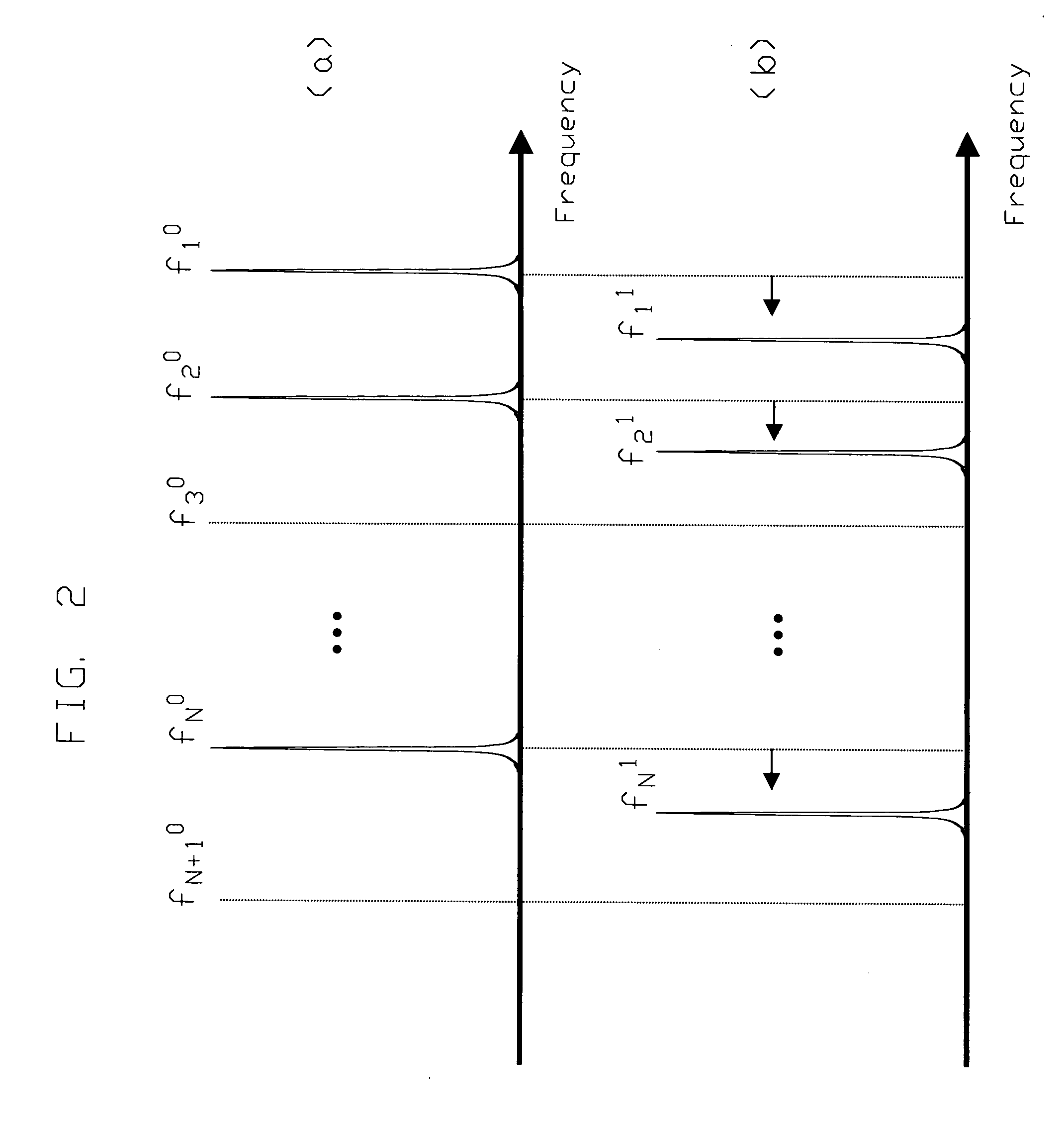
A method for the detection of analytes using resonant mass sensors or sensor arrays comprises frequency encoding each sensor element, acquiring a time-domain resonance signal from the sensor or sensor array as it is exposed to analyte, detecting change in the frequency or resonant properties of each sensor element using a Fourier transform or other spectral analysis method, and classifying, identifying, and / or quantifying analyte using an appropriate data analysis procedure. Frequency encoded sensors or sensor arrays comprise sensor elements with frequency domain resonance signals that can be uniquely identified under a defined range of operating conditions. Frequency encoding can be realized either by fabricating individual sensor elements with unique resonant frequencies or by tuning or modifying identical resonant devices to unique frequencies by adding or removing mass from individual sensor elements. The array of sensor elements comprises multiple resonant structures that may have identical or unique sensing layers. The sensing layers influence the sensor elements' response to analyte. Time-domain signal is acquired, typically in a single data acquisition channel, and typically using either (1) a pulsed excitation followed by acquisition of the free oscillatory decay of the entire array or (2) a rapid scan acquisition of signal from the entire array in a direct or heterodyne configuration. Spectrum analysis of the time domain data is typically accomplished with Fourier transform analysis. The methods and sensor arrays of the invention enable rapid and sensitive analyte detection, classification and / or identification of complex mixtures and unknown compounds, and quantification of known analytes, using sensor element design and signal detection hardware that are robust, simple and low cost.
Owner:PALO ALTO SENSOR TECH INNOVATION
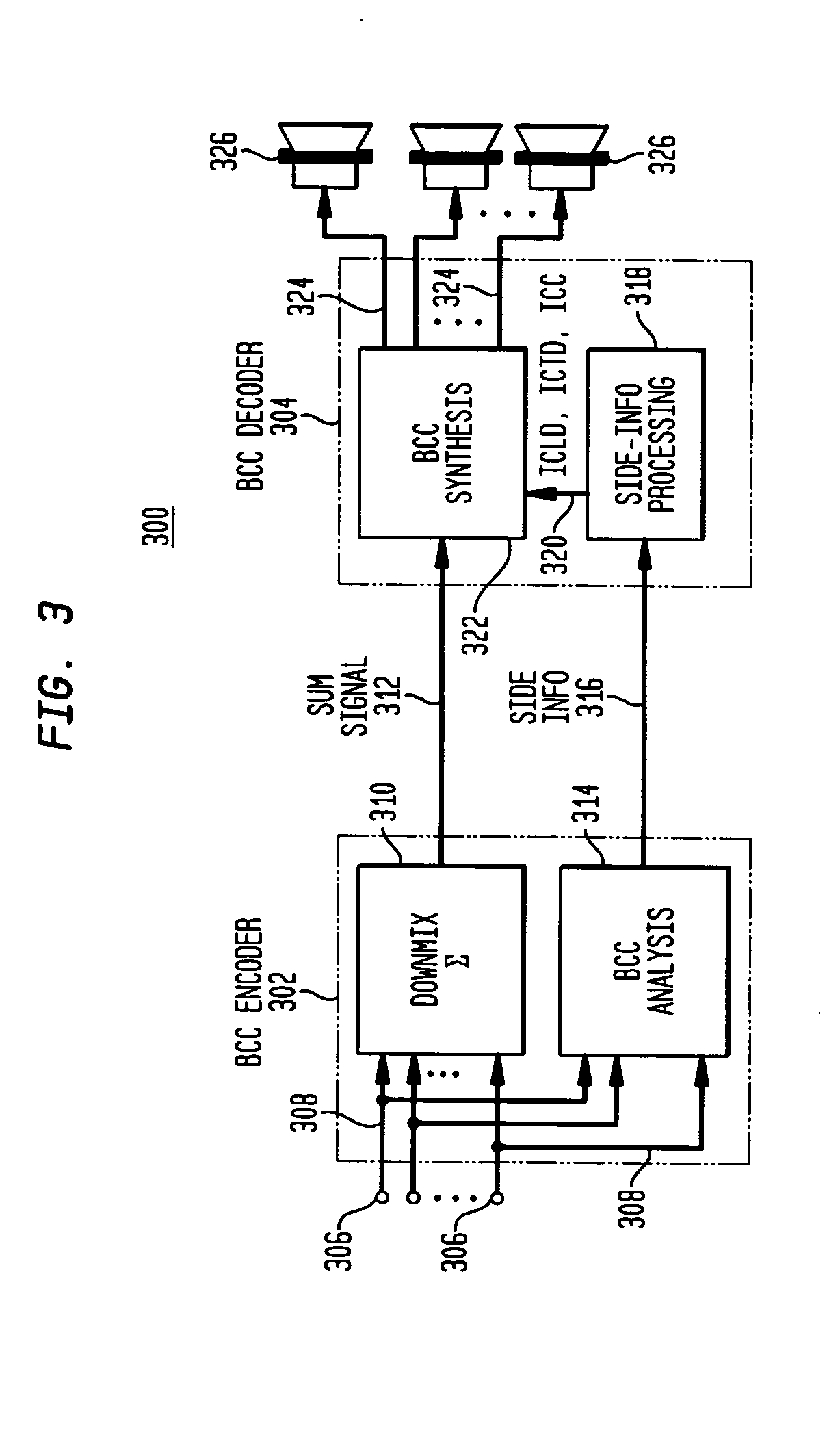
Late reverberation-based synthesis of auditory scenes
ActiveUS20050180579A1Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsGain controlSpeech analysisComputation complexityChannel correlation
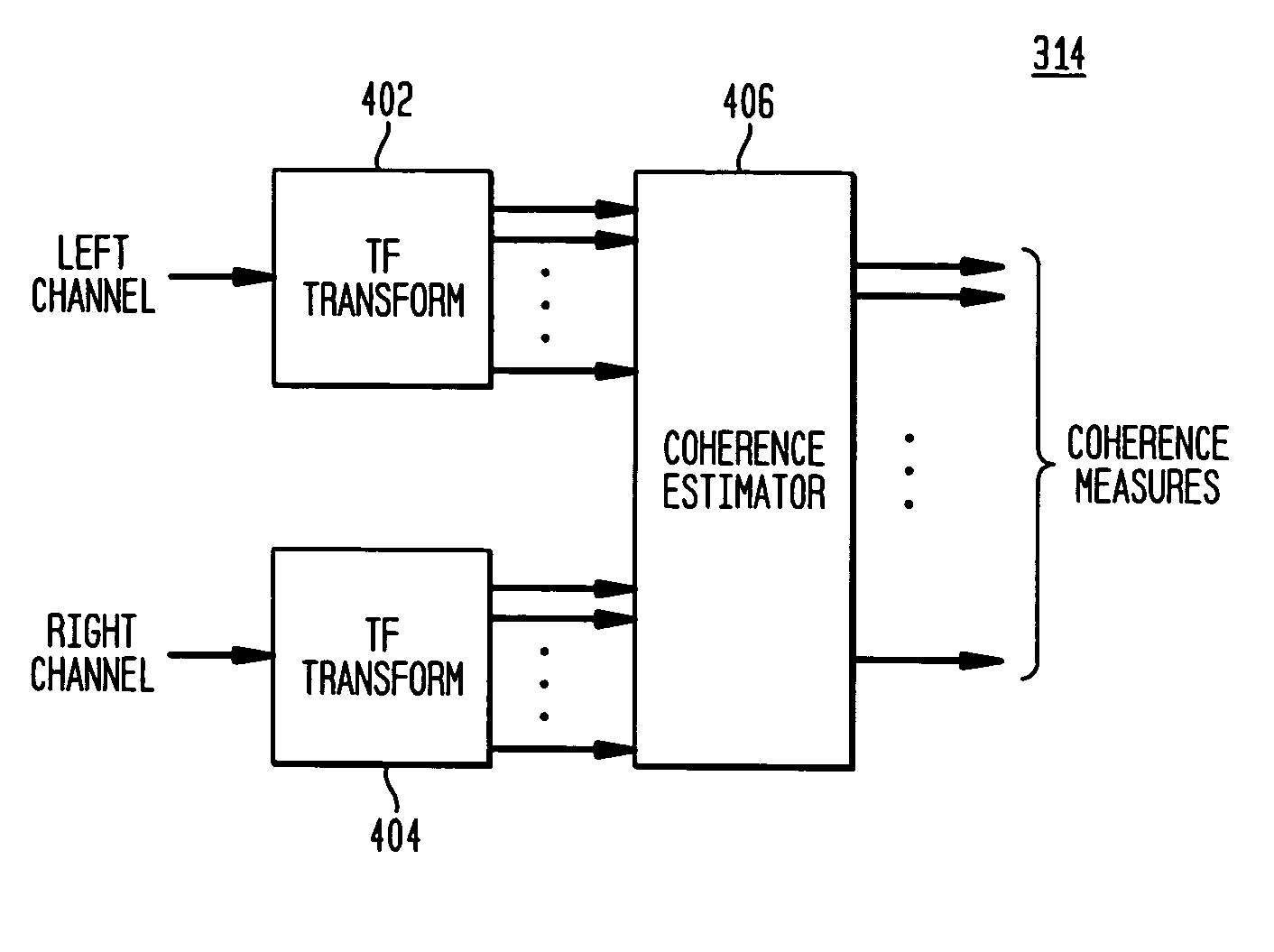
A scheme for stereo and multi-channel synthesis of inter-channel correlation (ICC) (normalized cross-correlation) cues for parametric stereo and multi-channel coding. The scheme synthesizes ICC cues such that they approximate those of the original. For that purpose, diffuse audio channels are generated and mixed with the transmitted combined (e.g., sum) signal(s). The diffuse audio channels are preferably generated using relatively long filters with exponentially decaying Gaussian impulse responses. Such impulse responses generate diffuse sound similar to late reverberation. An alternative implementation for reduced computational complexity is proposed, where inter-channel level difference (ICLD), inter-channel time difference (ICTD), and ICC synthesis are all carried out in the domain of a single short-time Fourier transform (STFT), including the filtering for diffuse sound generation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Passive physiological monitoring (P2M) system
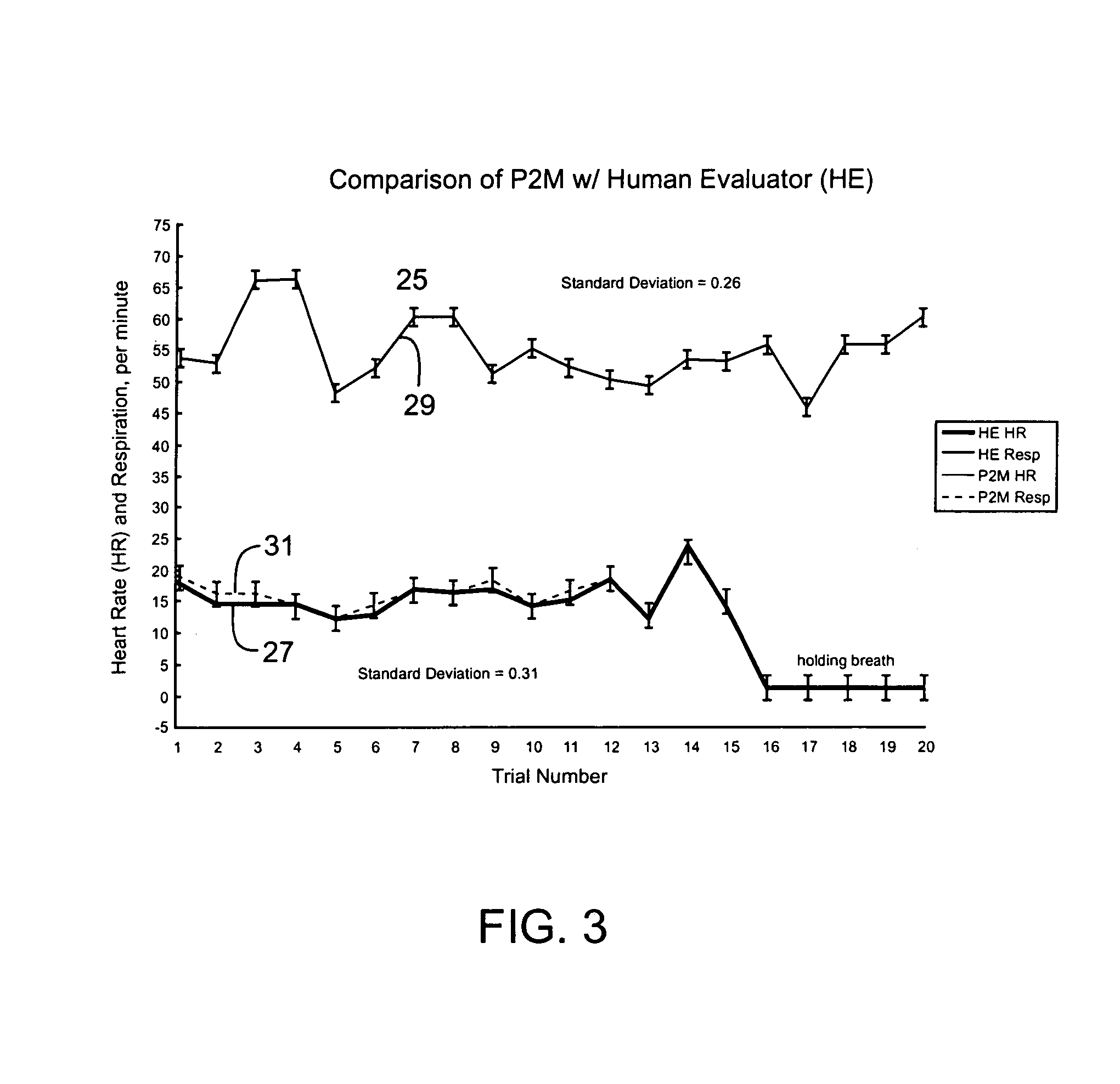
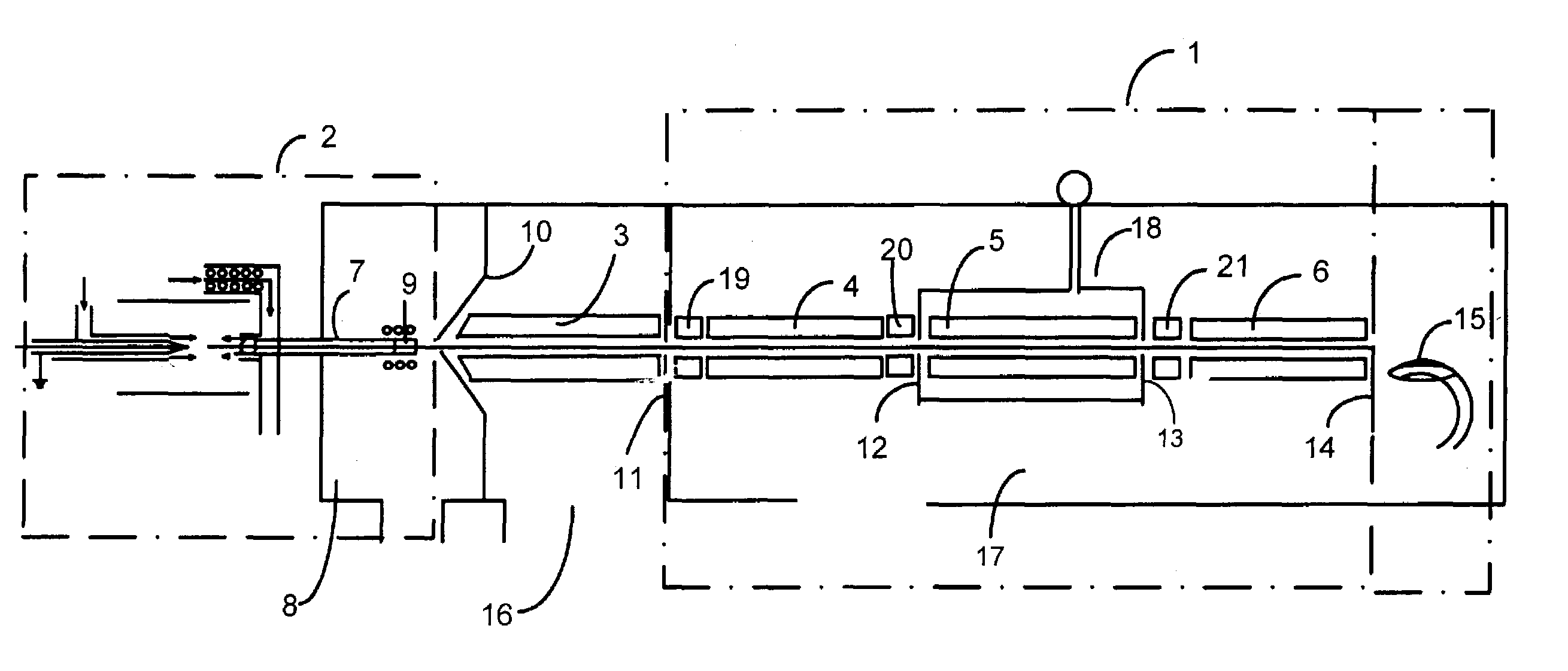
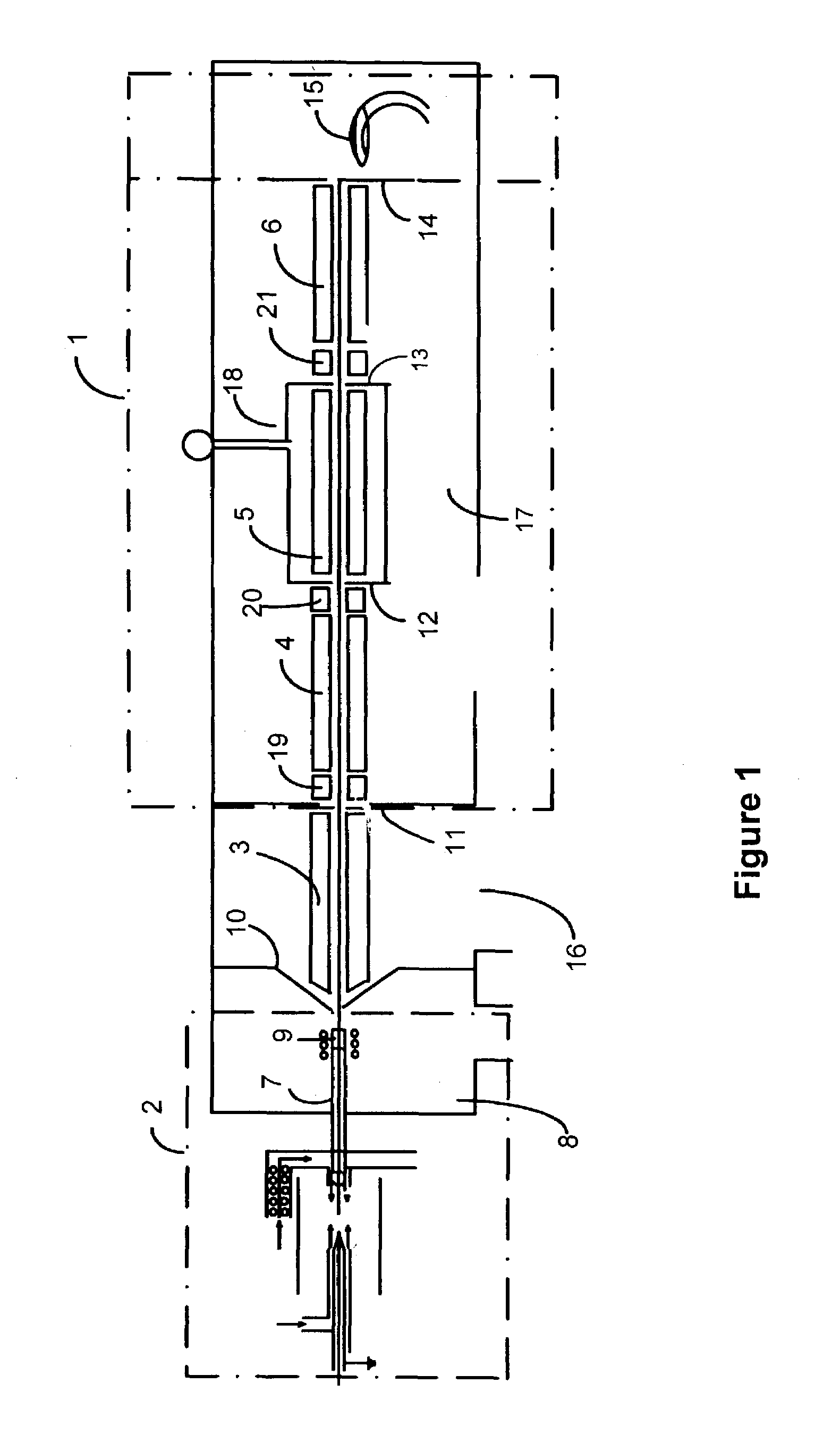
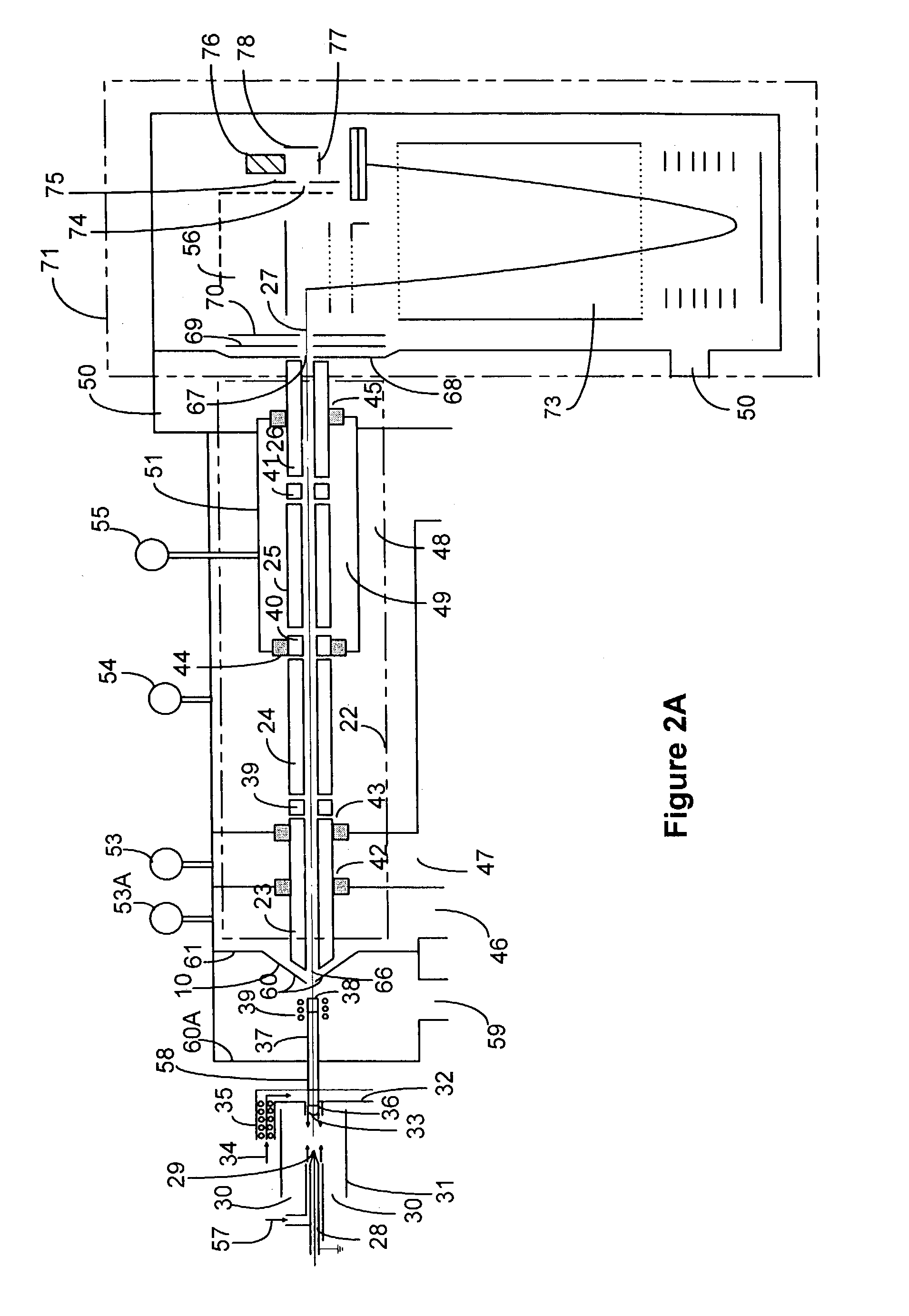
InactiveUS6984207B1Easy to deployEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterInternal bleedingBand-pass filter
Passive Physiological monitoring apparatus and method have a sensor for sensing physiological phenomenon. A converter converts sensed data into electrical signals and a computer receives and computes the signals, and outputs computed data for real-time interactive display. The sensor is a piezoelectric film of polyvinylidene fluoride. A band-pass filter filters out noise and isolates the signals to reflect data from the body. A pre-amplifier amplifies signals. Signals detected include mechanical, thermal and acoustic signatures reflecting cardiac output, cardiac function, internal bleeding, respiratory, pulse, apnea, and temperature. A pad may incorporate the PVDF film and may be fluid-filled. The film converts mechanical energy into analog voltage signals. Analog signals are fed through the band-pass filter and the amplifier. A converter converts the analog signals to digital signals. A Fourier transform routine is used to transform into the frequency domain. A microcomputer is used for recording, analyzing and displaying data for on-line assessment and for providing realtime response. A radio-frequency filter may be connected to a cable and the film for transferring signals from the film through the cable. The sensor may be an array provided in a MEDEVAC litter or other device for measuring acoustic and hydraulic signals from the body of a patient for field monitoring, hospital monitoring, transport monitoring, home, remote monitoring.
Owner:HOANA MEDICAL
Mass spectrometry with segmented RF multiple ion guides in various pressure regions
InactiveUS7034292B1Reduce lossesEliminate and reduce numberIsotope separationSpectrometer combinationsFourier transform on finite groupsMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer is configured with individual multipole ion guides, configured in an assembly in alignment along a common centerline wherein at least a portion of at least one multipole ion guide mounted in the assembly resides in a vacuum region with higher background pressure, and the other portion resides in a vacuum region with lower background pressure. Said multipole ion guides are operated in mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation modes, in either a high or low pressure region, said region being selected according to the optimum pressure or pressure gradient for the function performed. The diameter, lengths and applied frequencies and phases on these contiguous ion guides may be the same or may differ. A variety of MS and MS / MSn analysis functions can be achieved using a series of contiguous multipole ion guides operating in either higher background vacuum pressures, or along pressure gradients in the region where the pressure drops from high to low pressure, or in low pressure regions. Individual sets of RF, + / −DC and resonant frequency waveform voltage supplies provide potentials to the rods of each multipole ion guide allowing the operation of ion transmission, ion trapping, mass to charge selection and ion fragmentation functions independently in each ion guide. The presence of background pressure maintained sufficiently high to cause ion to neutral gas collisions along a portion of each multiple ion guide linear assembly allows the conducting of Collisional Induced Dissociation (CID) fragmentation of ions by axially accelerating ions from one multipole ion guide into an adjacent ion guide. Alternatively ions can be fragmented in one or more multipole ion guides using resonant frequency excitation CID. A multiple multipole ion guide assembly can be configured as the primary mass analyzer in single or triple quadrupole mass analyzers with or without mass selective axial ejection. Alternatively, the multiple multipole ion guide linear assembly can be configured as part of a hybrid Time-Of-Flight, Magnetic Sector, Ion Trap or Fourier Transform mass analyzer.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20020128544A1Improve approximationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients in order to find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:DIAB MOHAMED K +5
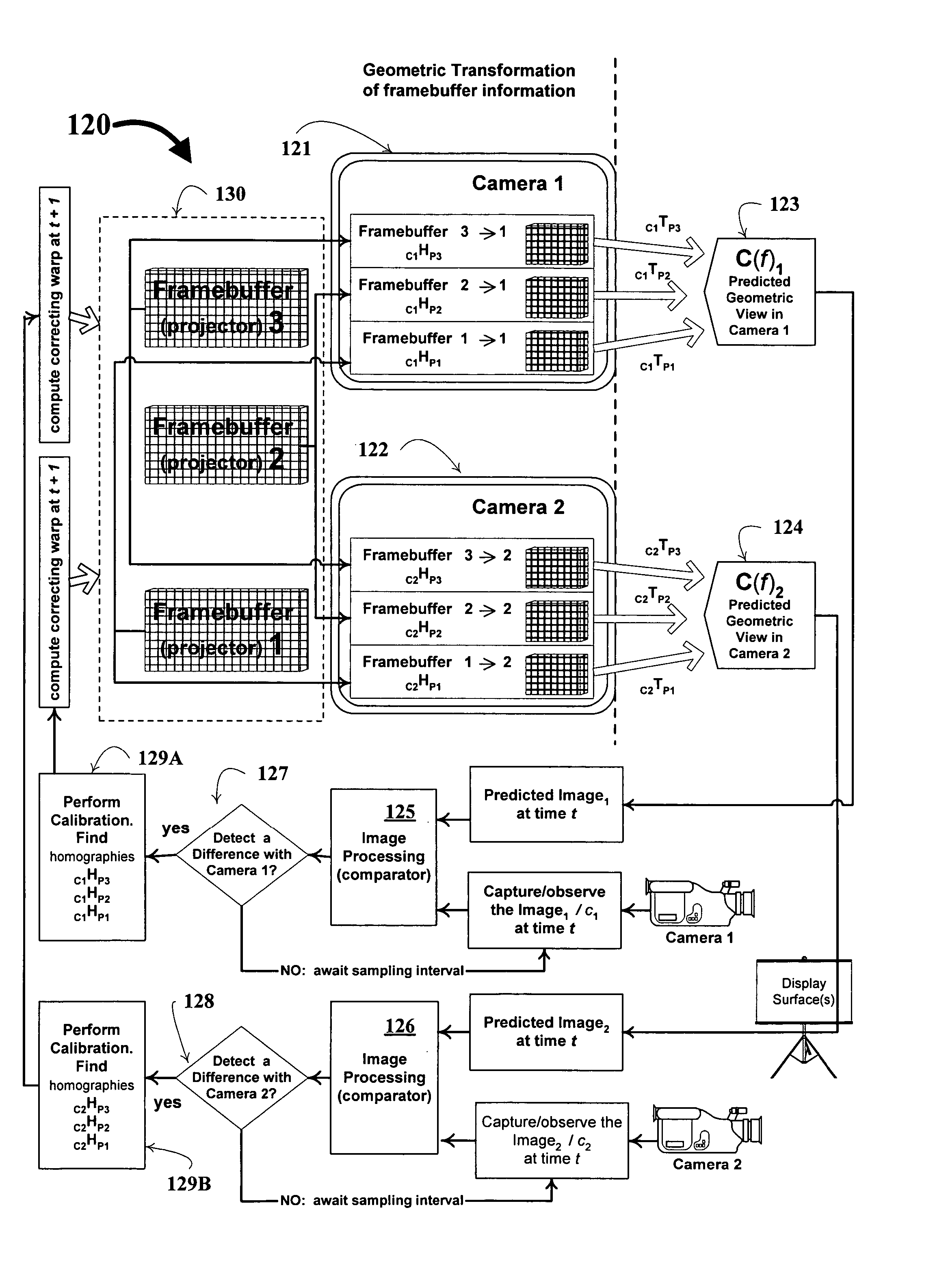
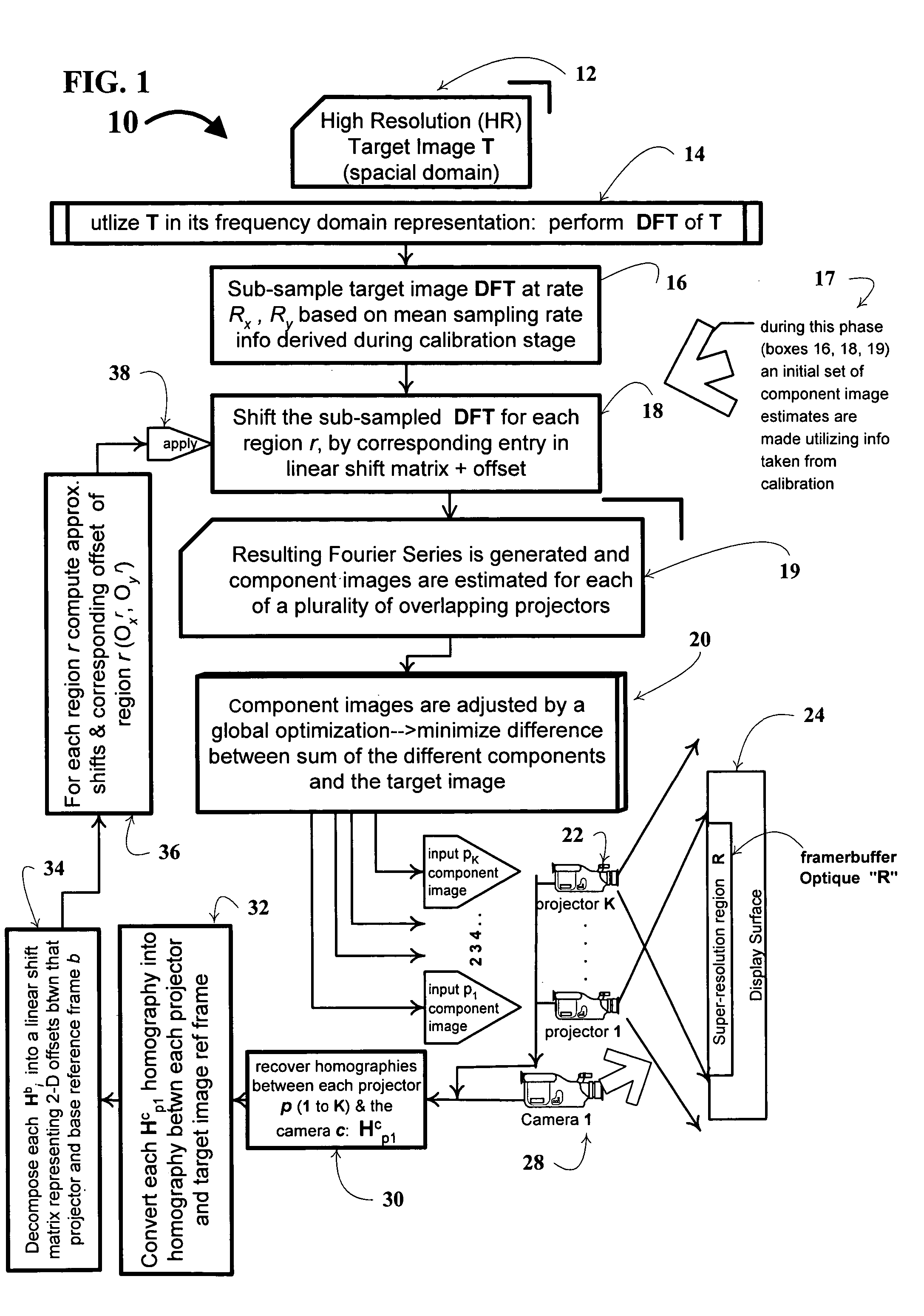
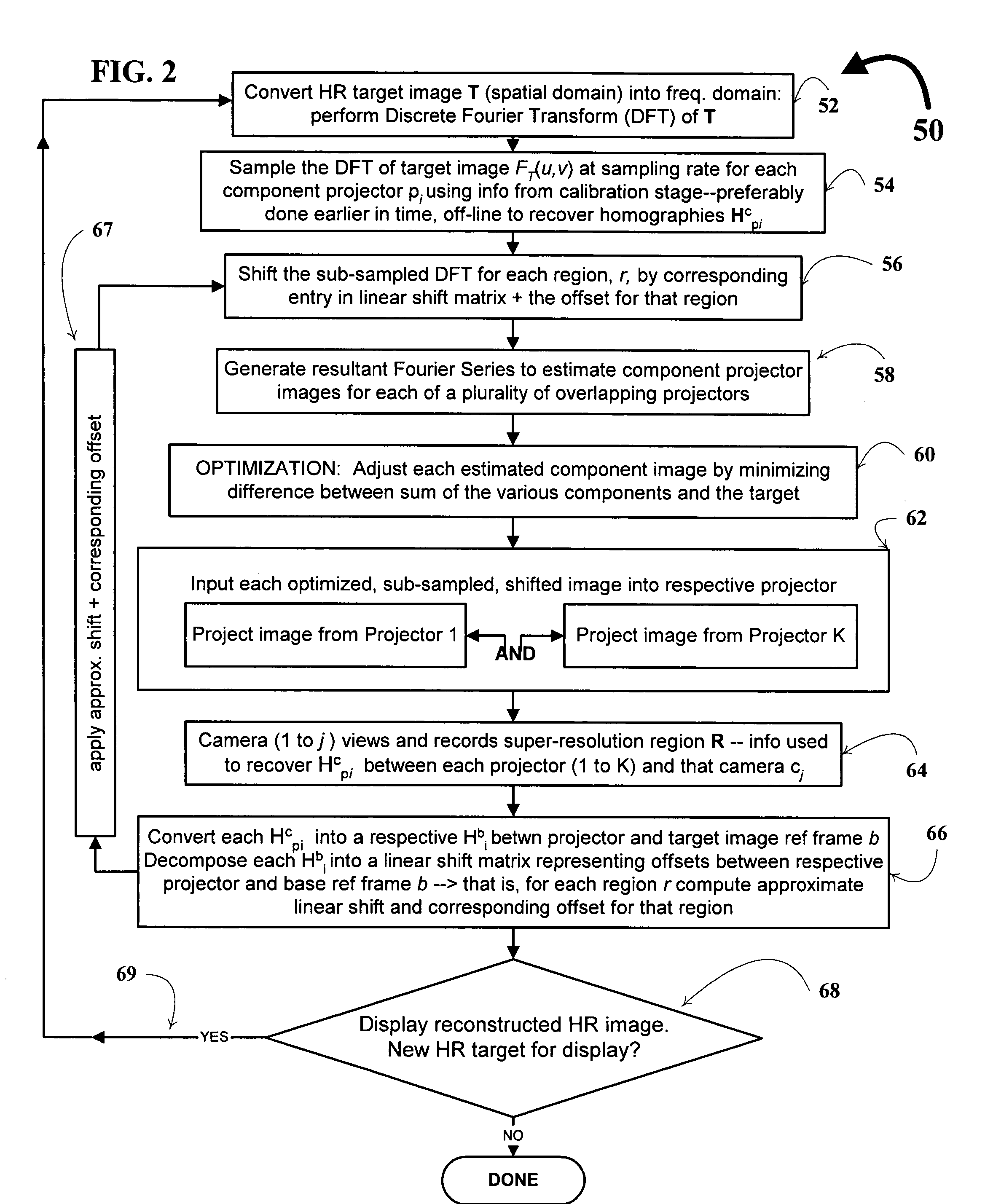
Super-resolution overlay in multi-projector displays
InactiveUS20040239885A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProgram codeFourier transform
A technique, associated system and computer executable program code, for projecting a superimposed image onto a target display surface under observation of one or more cameras. A projective relationship between each projector being used and the target display surface is determined using a suitable calibration technique. A component image for each projector is then estimated using the information from the calibration, and represented in the frequency domain. Each component image is estimated by: Using the projective relationship, determine a set of sub-sampled, regionally shifted images, represented in the frequency domain; each component image is then composed of a respective set of the sub-sampled, regionally shifted images. In an optimization step, the difference between a sum of the component images and a frequency domain representation of a target image is minimized to produce a second, or subsequent, component image for each projector. Here, a second set of frequency domain coefficients for use in producing a frequency domain representation of the second component image for each projector is identified. Taking the inverse Fourier transform of the frequency domain representation of the second component image, converts the information into a spatial signal that is placed into the framebuffer of each component projector and projected therefrom to produce the superimposed image.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
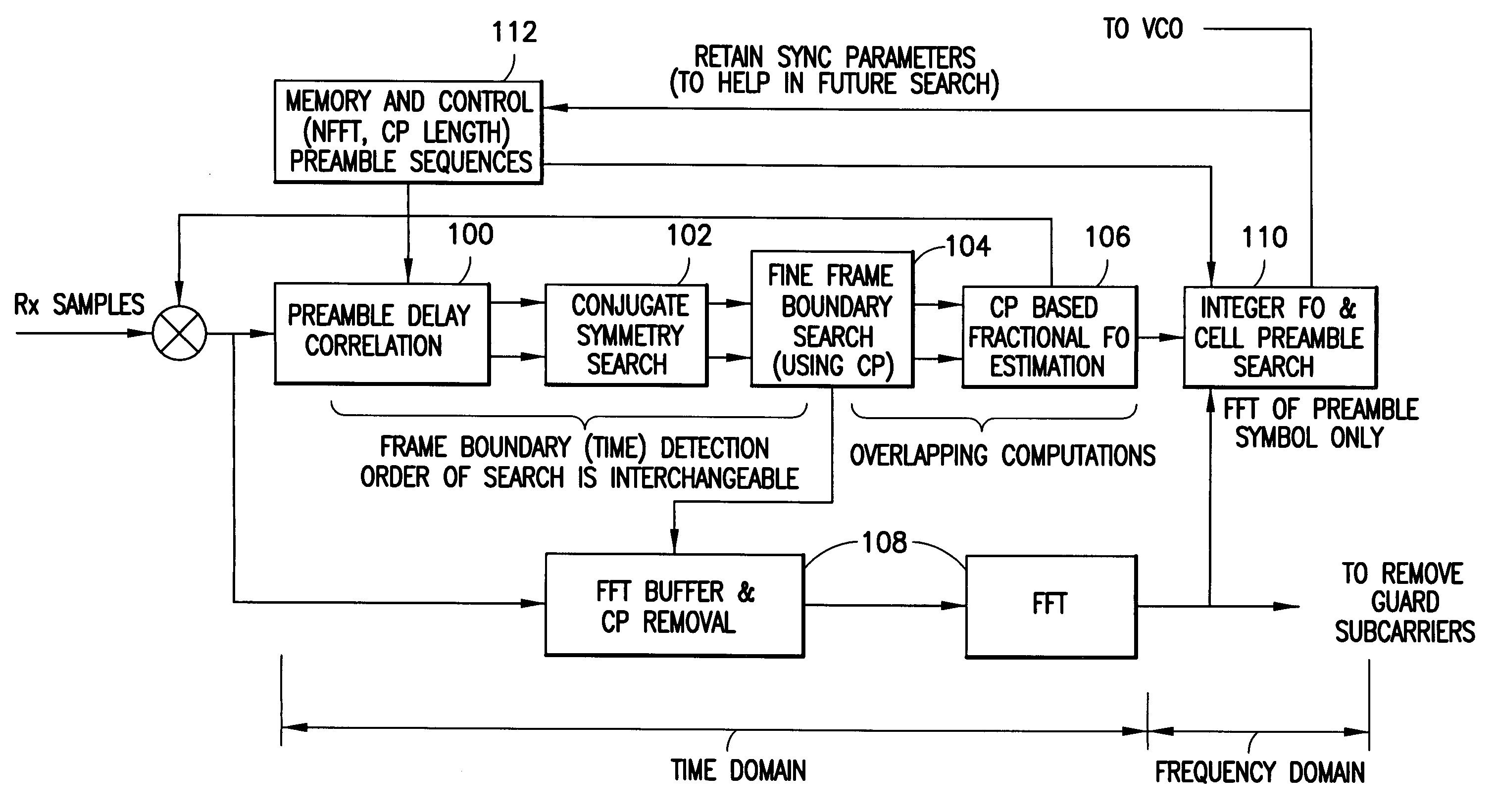
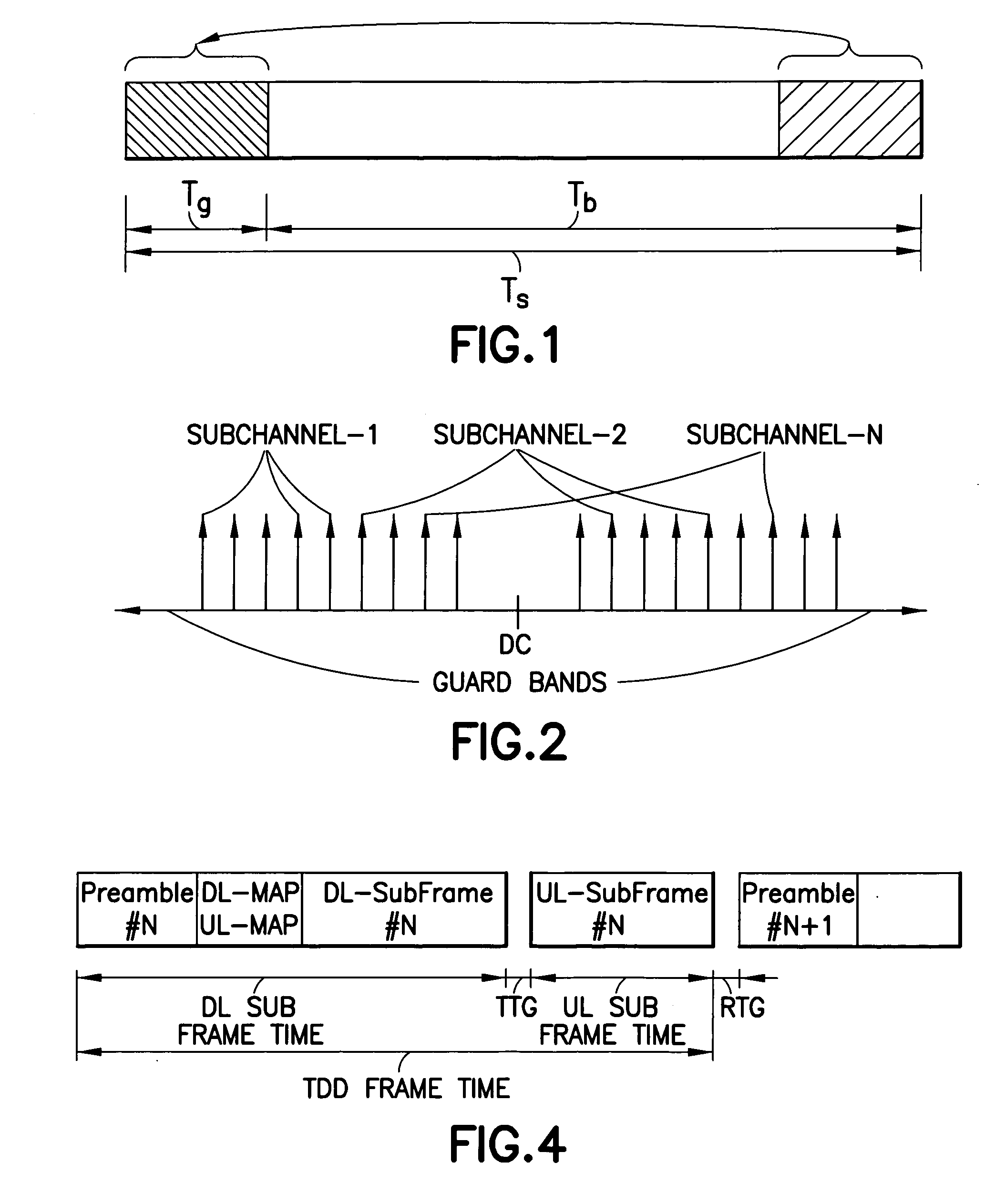
Method, apparatus and computer program product providing synchronization for OFDMA downlink signal
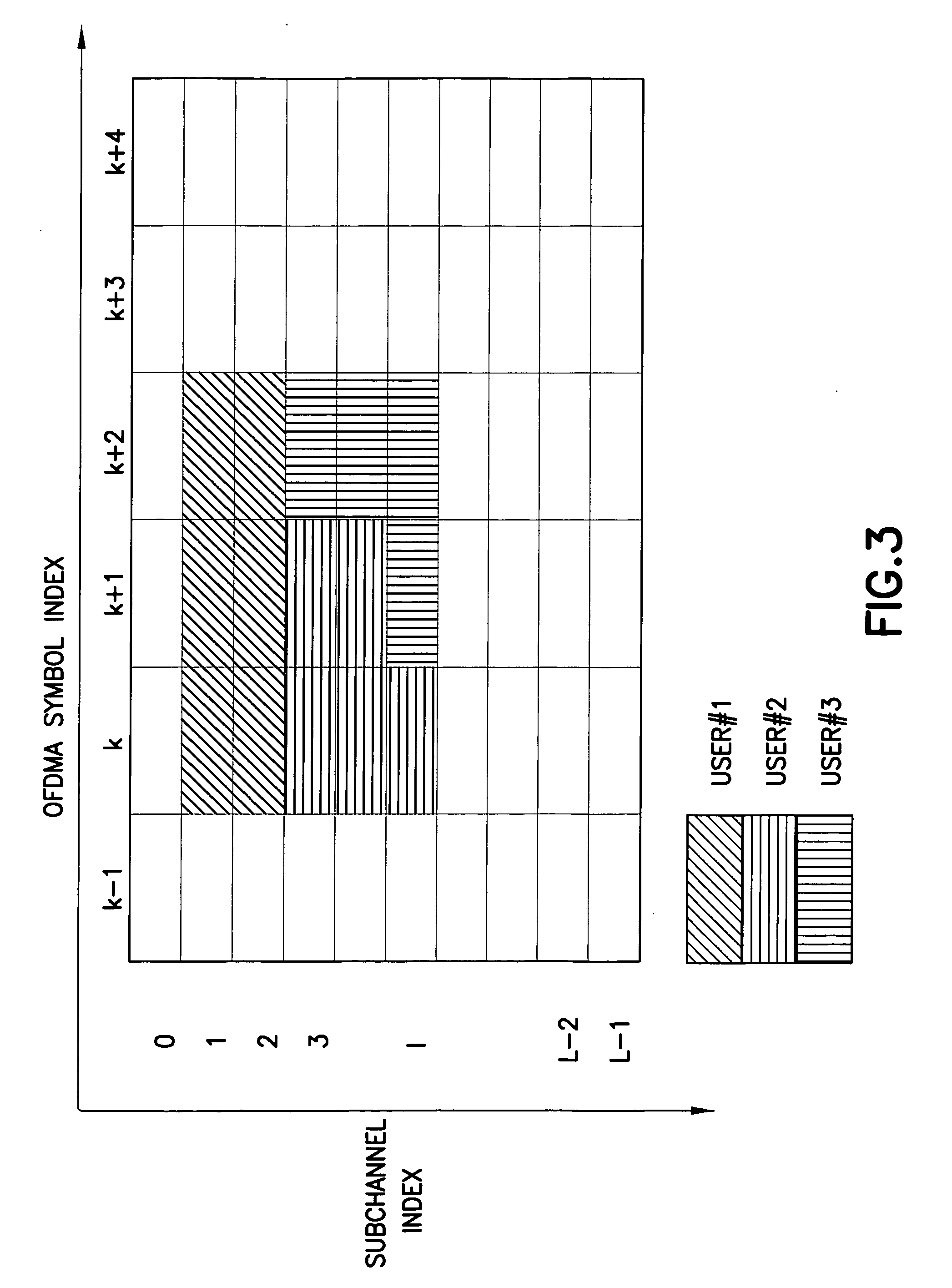
InactiveUS20070280098A1Good precisionModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCell specificCarrier frequency offset
Disclosed is a method, a computer program product and a device that includes a receiver for receiving a downlink signal transmitted into a cell. The receiver is operable to obtain time, carrier frequency and cell-specific preamble synchronization to the received signal and includes a plurality of synchronization units that include a first detector to detect a frame boundary using preamble delay correlation; a second detector to detect the frame boundary with greater precision using a conjugate symmetry property over a region identified by the first detector; a cyclic prefix correlator to resolve symbol boundary repetition; an estimator, using the cyclic prefix, to estimate and correct a fractional carrier frequency offset; an operator to perform a Fast Fourier Transform of an identified preamble symbol and a frequency domain cross-correlator to identify cell-specific preamble sequences and an integer frequency offset in sub-carrier spacing. The transmitted signal may be a downlink signal transmitted into the cell from a base station that is compatible with IEEE 802.16e (WiMAX).
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
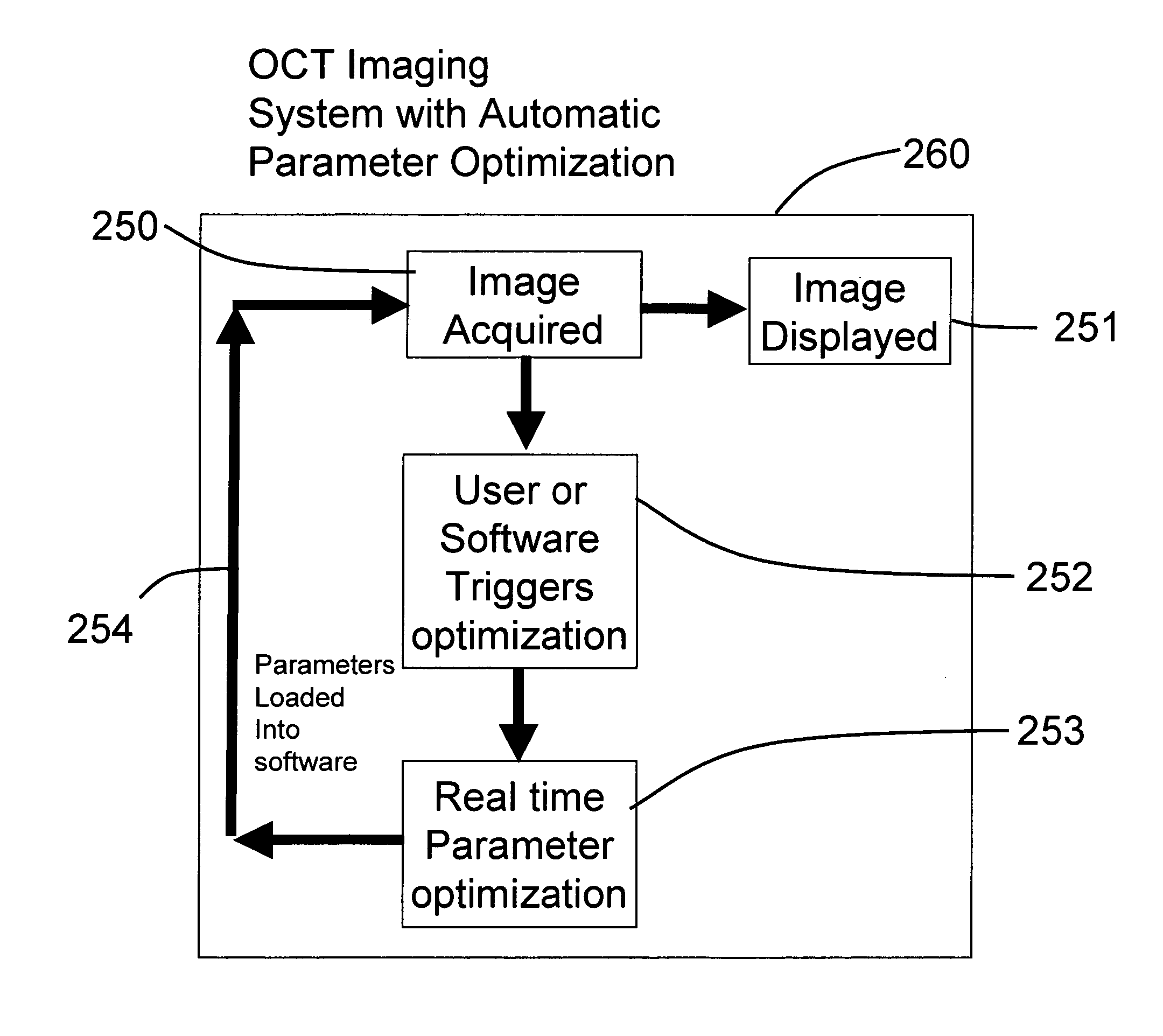
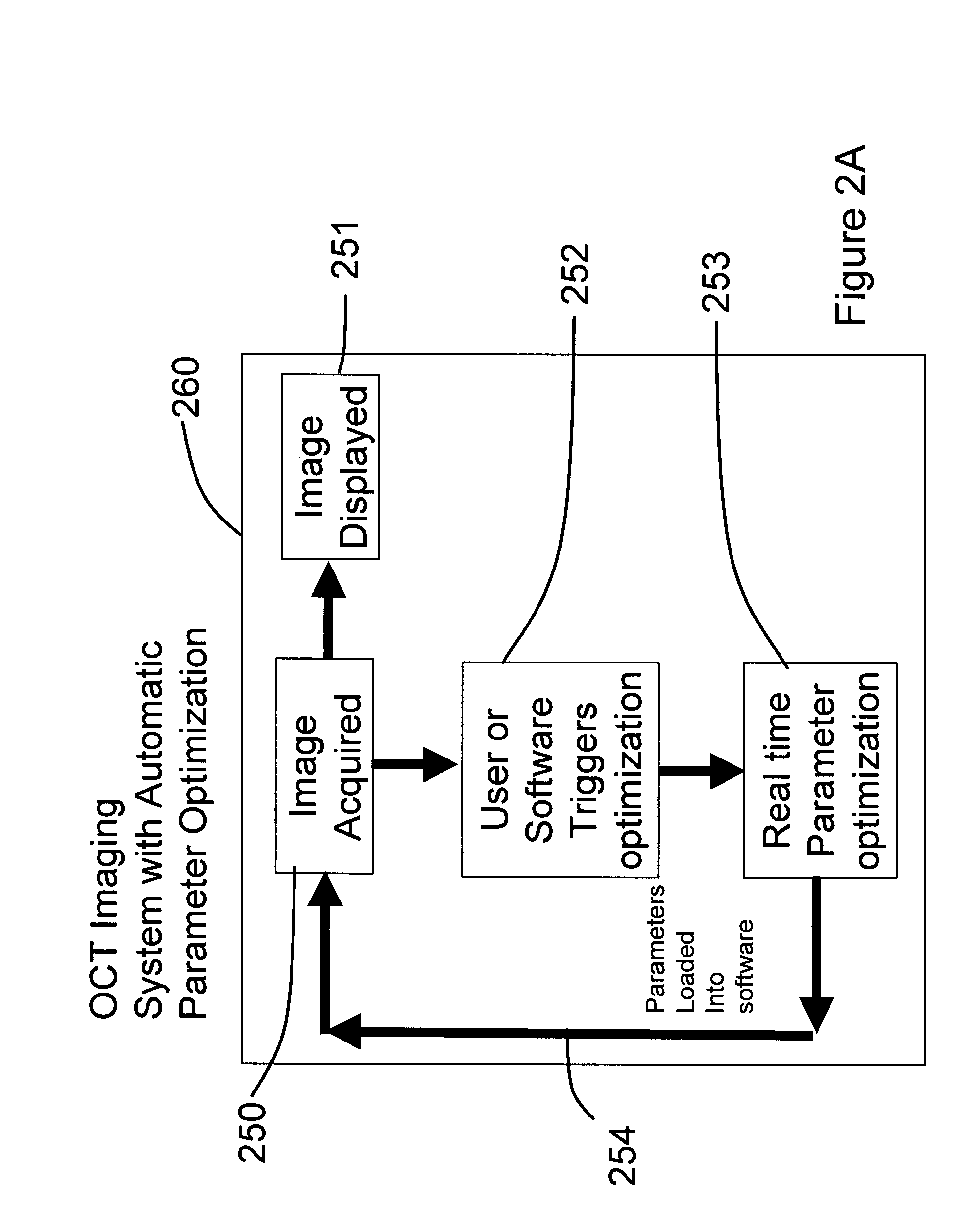
Methods, systems and computer program products for optical coherence tomography (OCT) using automatic dispersion compensation
ActiveUS20070258094A1Extended processing timeRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryComputer scienceDispersion compensation
Methods, systems and computer program products for generating parameters for software dispersion compensation in optical coherence tomography (OCT) systems are provided. Raw spectral interferogram data is acquired for a given lateral position on a sample and a given reference reflection. A trial spectral phase corresponding to each wavenumber sample of the acquired spectral interferogram data is postulated. The acquired raw spectral data and the postulated trial spectral phase data are assembled into trial complex spectrum data. Trial A-scan data is computed by performing an inverse Fourier transform on the trial complex spectrum data and determining the magnitude of a result.
Owner:BIOPTIGEN
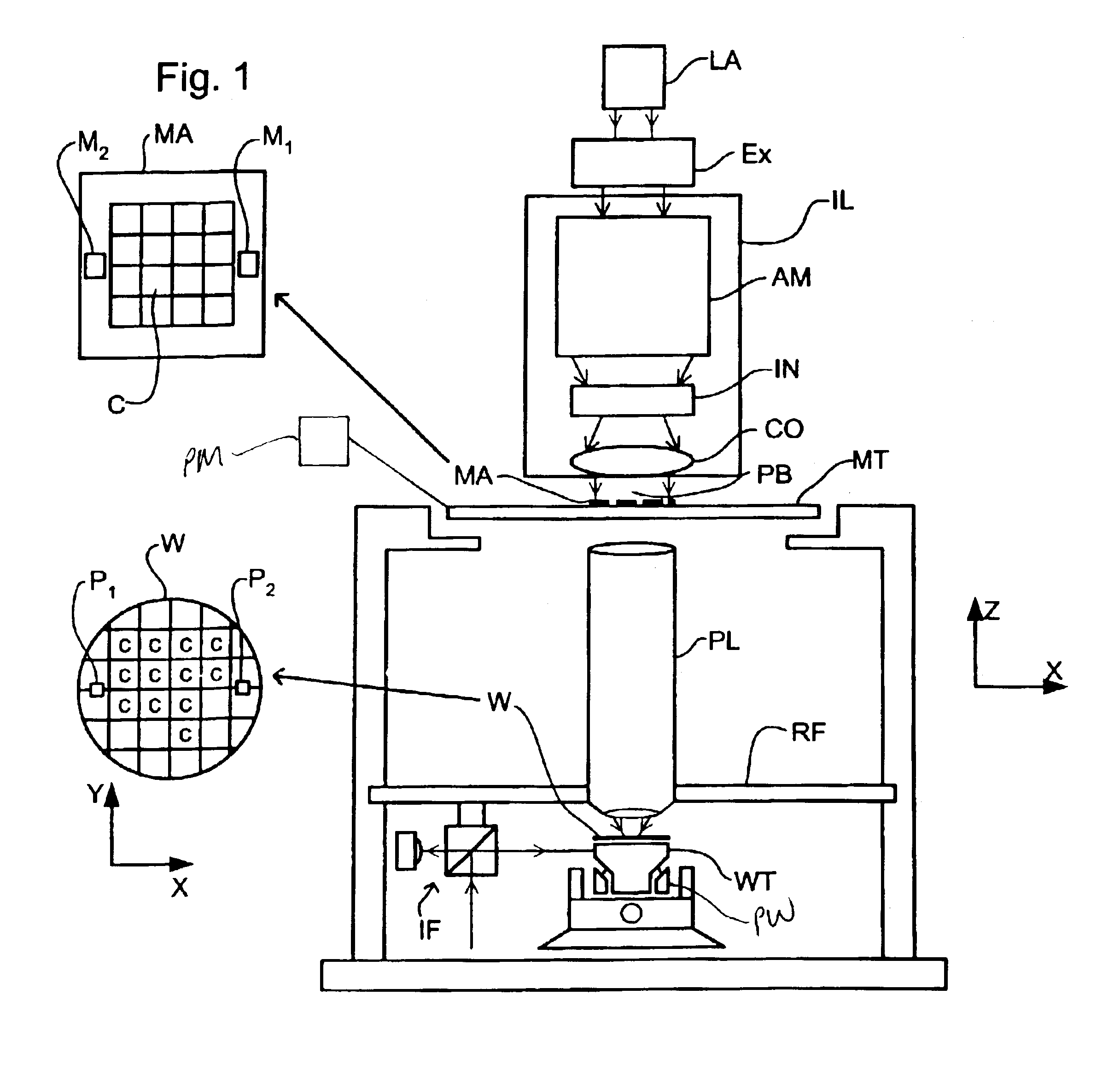
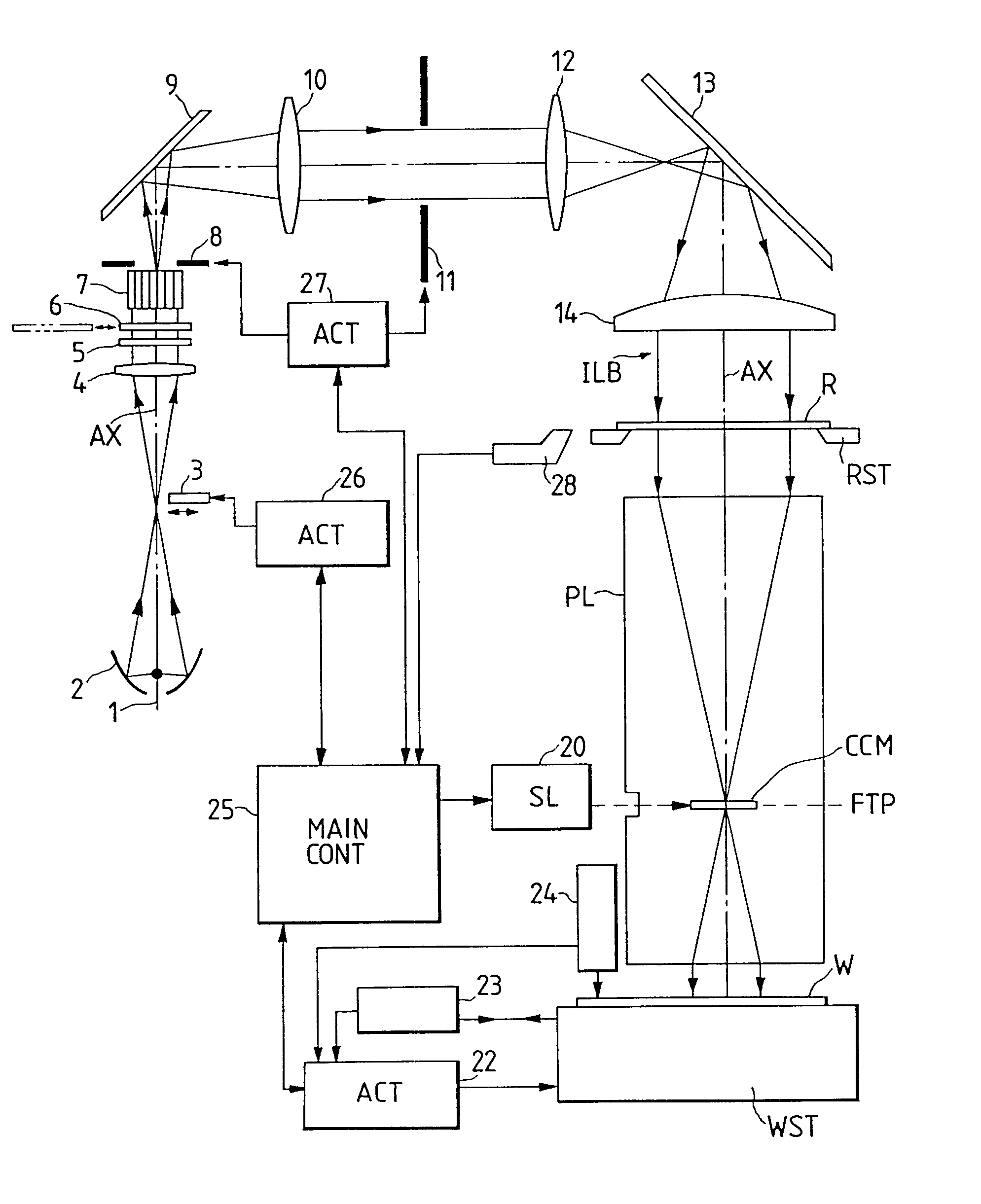
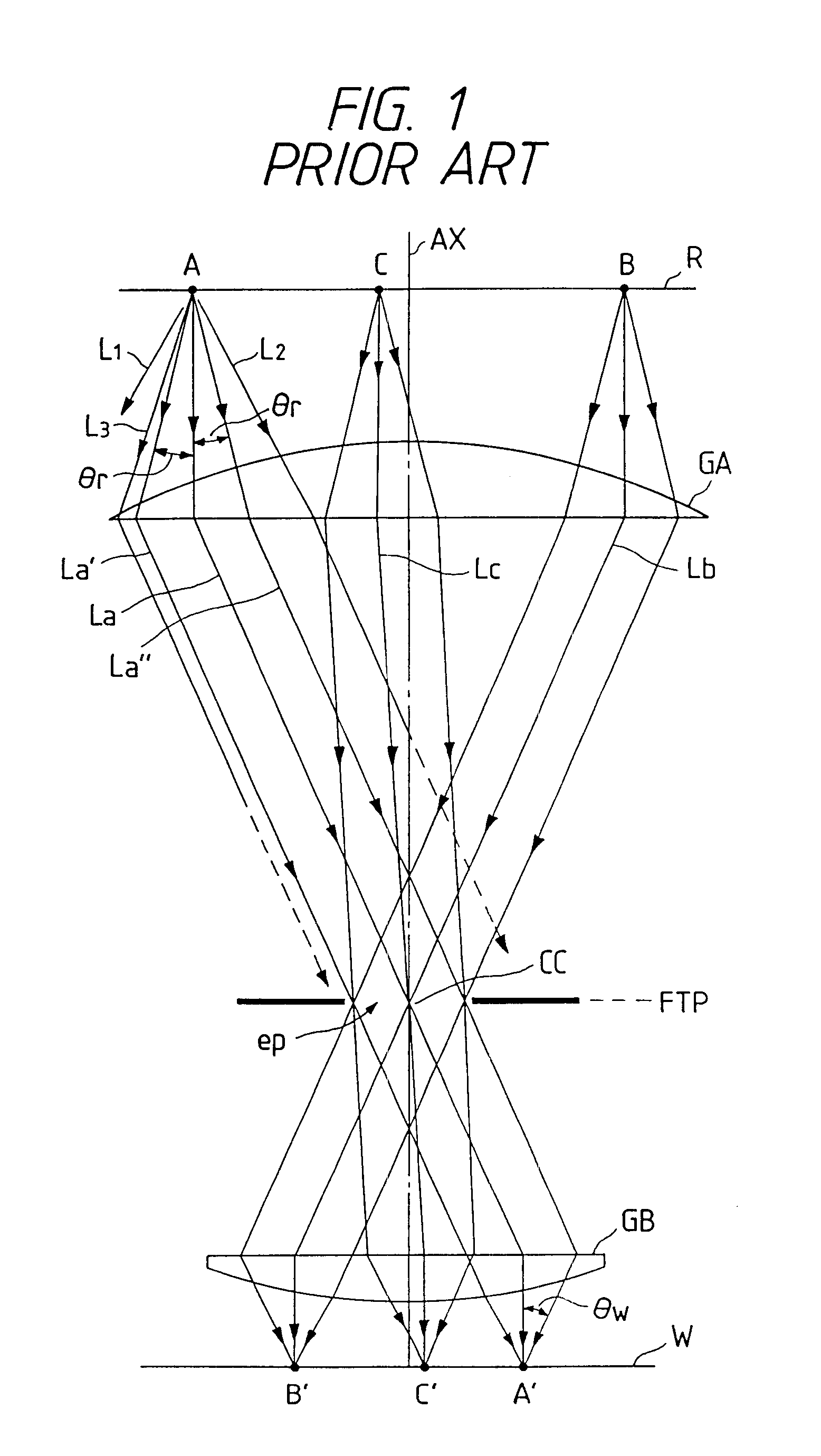
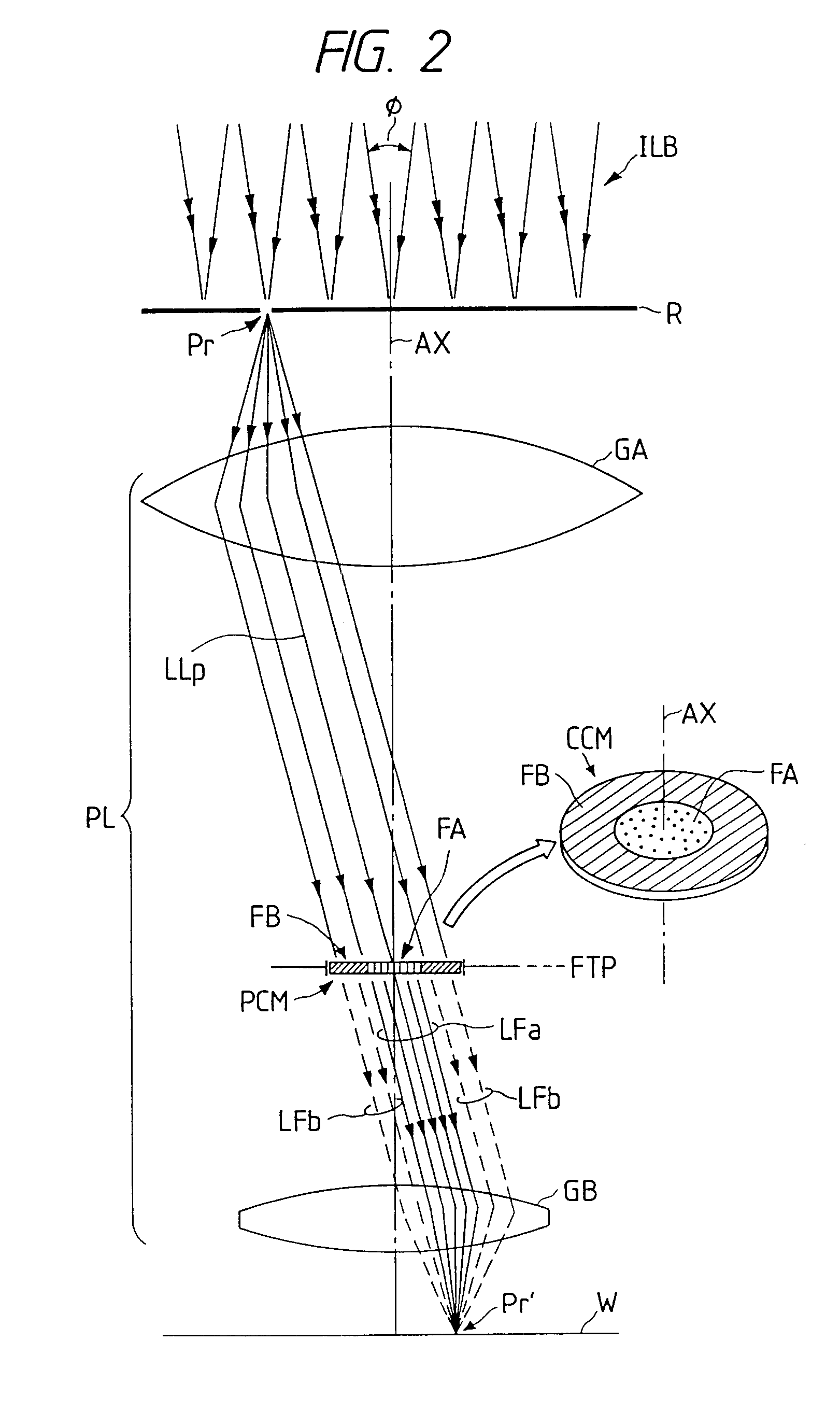
Projection exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS6404482B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisFourier transform on finite groups
In projection exposure of isolated pattern such as a contact hole, in order to increase the depth of focus a coherence reducing member is disposed on a Fourier transform plane in an image-forming optical path between a mask and a sensitized base, so that coherence is reduced between image-forming beams respectively passing through a plurality of different, concentric regions around the optical axis of the projection optical system on the Fourier transform plane. The coherence reducing member may be a polarization state control member for making a difference in polarization state, a member for making a difference in optical path length, or space filters with different shapes.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Beamforming method, measurement and imaging instruments, and communication instruments
ActiveUS20160157828A1Increase speedImprove accuracyProcessing detected response signalCatheterEngineeringWavenumber
Beamforming method that allows a high speed and high accuracy beamforming with no approximate interpolations. This beamforming method includes step (a) that generates reception signals by receiving waves arrival from a measurement object; and step (b) that performs a beamforming with respect to the reception signals generated by step (a); and step (b) including without performing wavenumber matching including approximate interpolation processings with respect to the reception signals, and the reception signals are Fourier's transformed in the axial direction and the calculated Fourier's transform is multiplied to a complex exponential function expressed using a wavenumber of the wave and a carrier frequency to perform wavenumber matching in the lateral direction and further, the product is Fourier's transformed in the lateral direction and the calculated result is multiplied to a complex exponential function, from which an effect of the lateral wavenumber matching is removed, to perform wavenumber matching in the axial direction, by which an image signal is generated.
Owner:CHIKAYOSHI SUMI
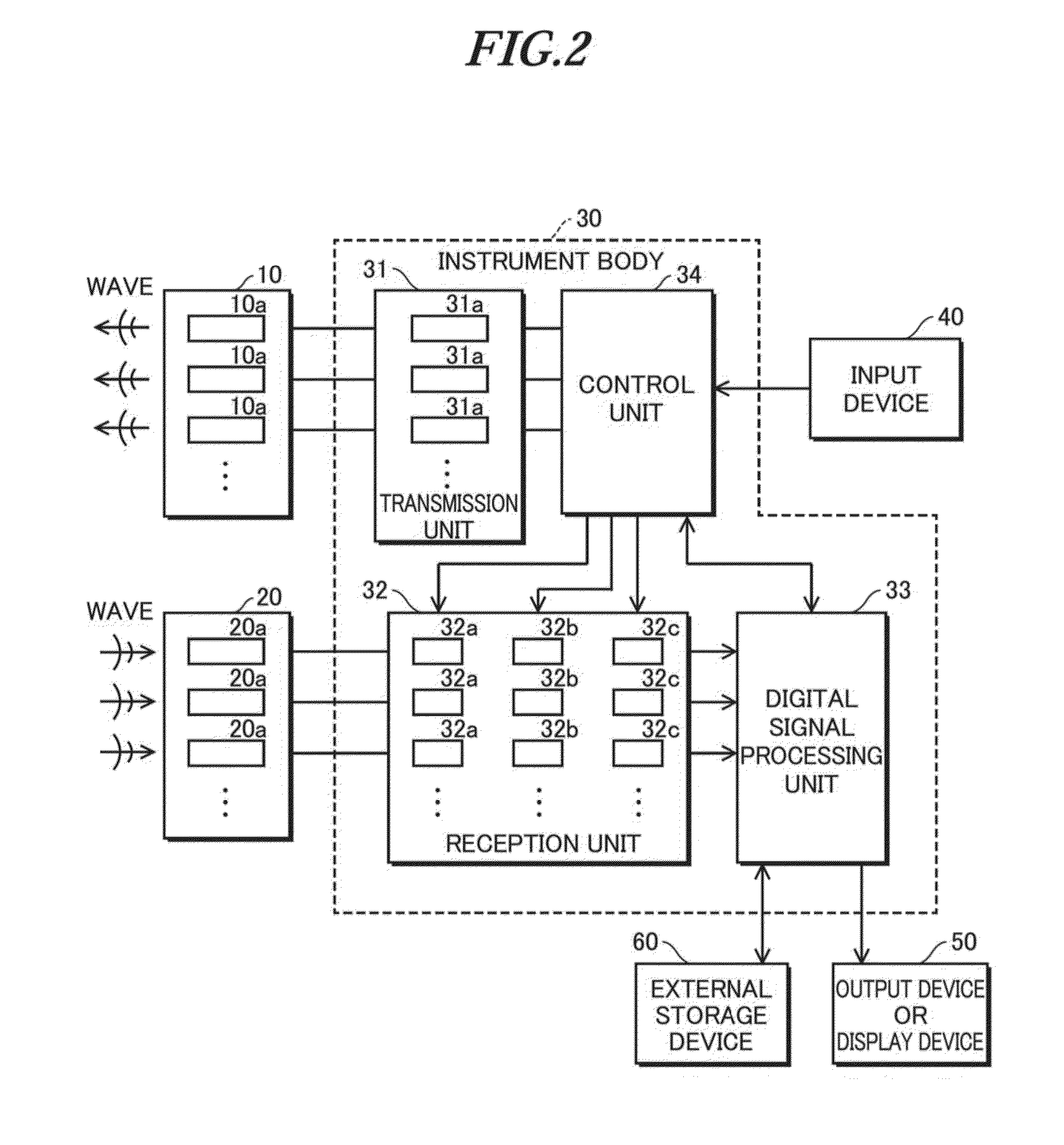
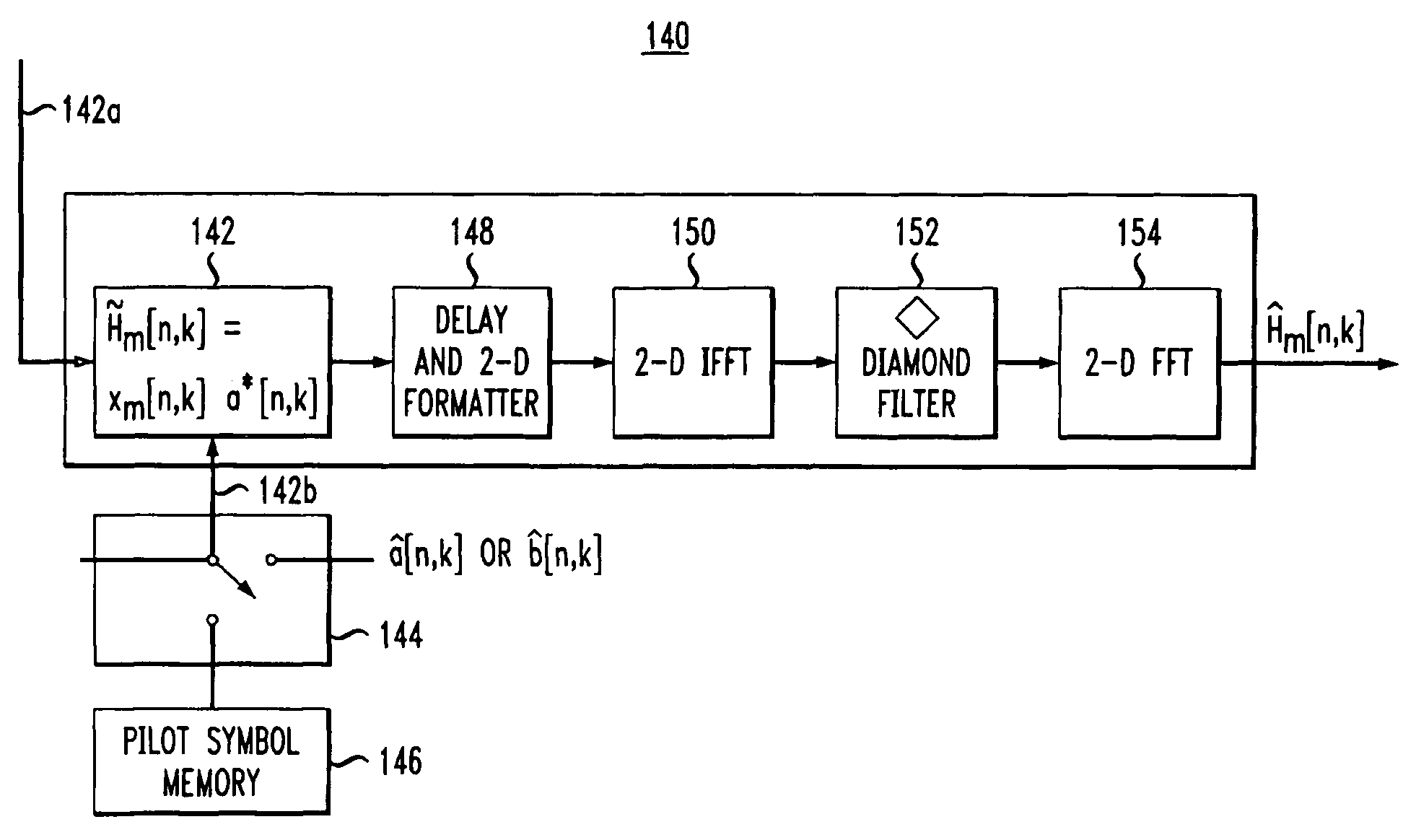
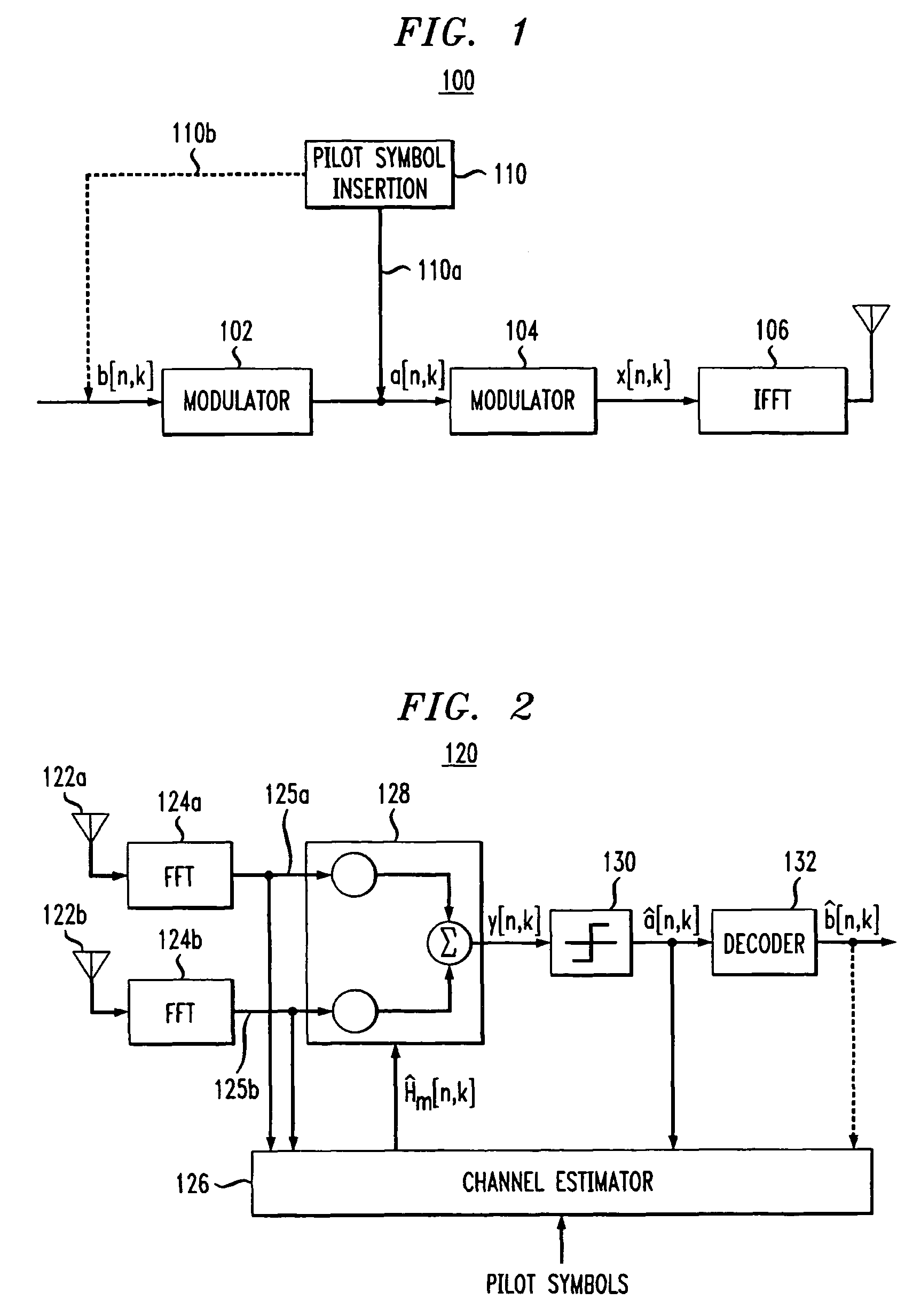
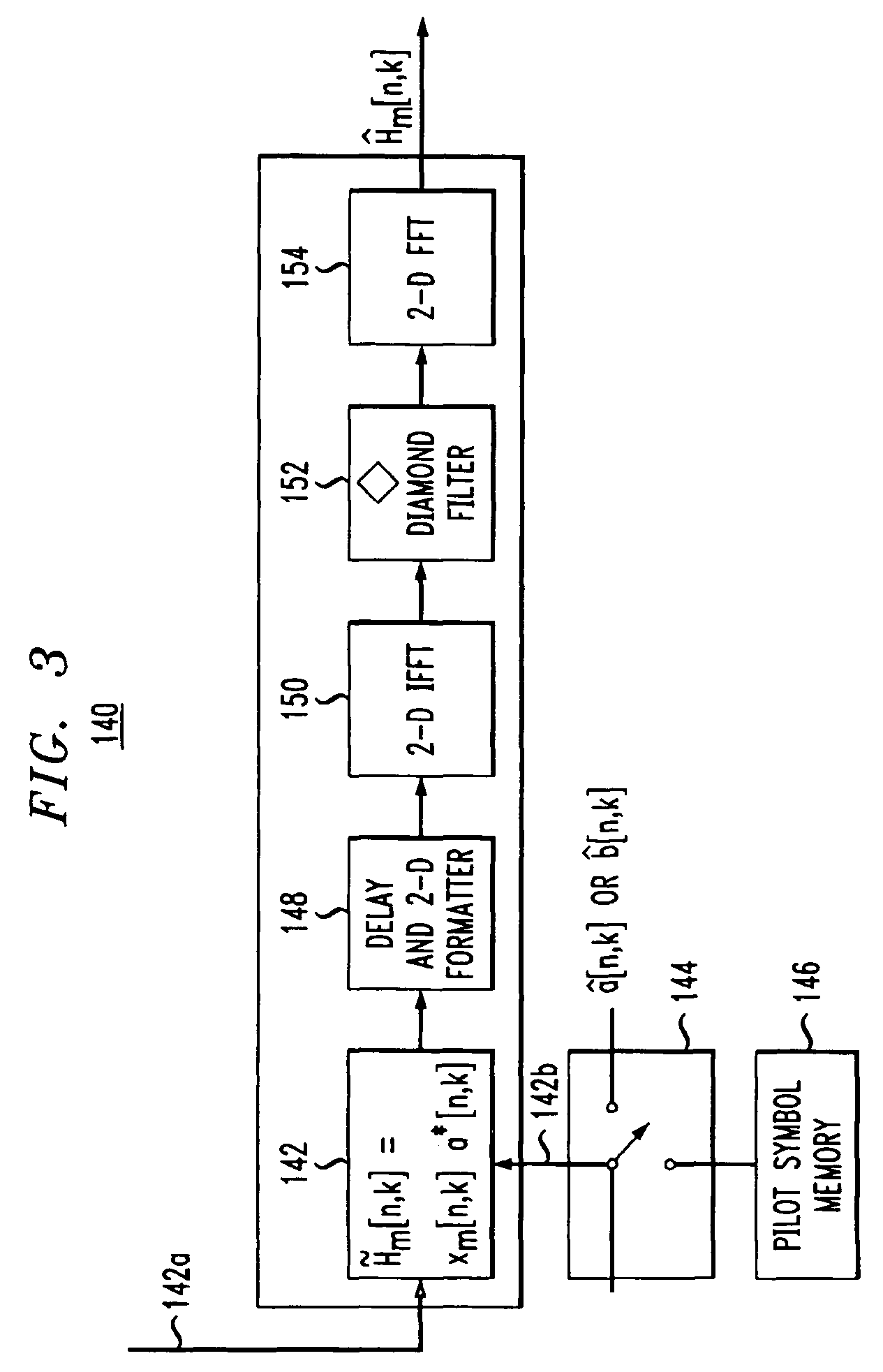
Pilot-aided channel estimation for OFDM in wireless systems
InactiveUS7292651B2Robust parameter estimationNoise-reduced channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsSecret communicationCommunications systemFourier transform on finite groups
A method and apparatus for pilot-symbol aided channel estimation in a wireless digital communication system which transmits packets of N OFDM data blocks, each data block comprising a set of K orthogonal carrier frequencies. At the transmitter, pilot symbols are inserted into each data packet at known positions so as to occupy predetermined positions in the time-frequency space. At the receiver, the received signal is subject to a two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform, two-dimensional filtering and a two-dimensional Fourier transform to recover the pilot symbols so as to estimate the channel response.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
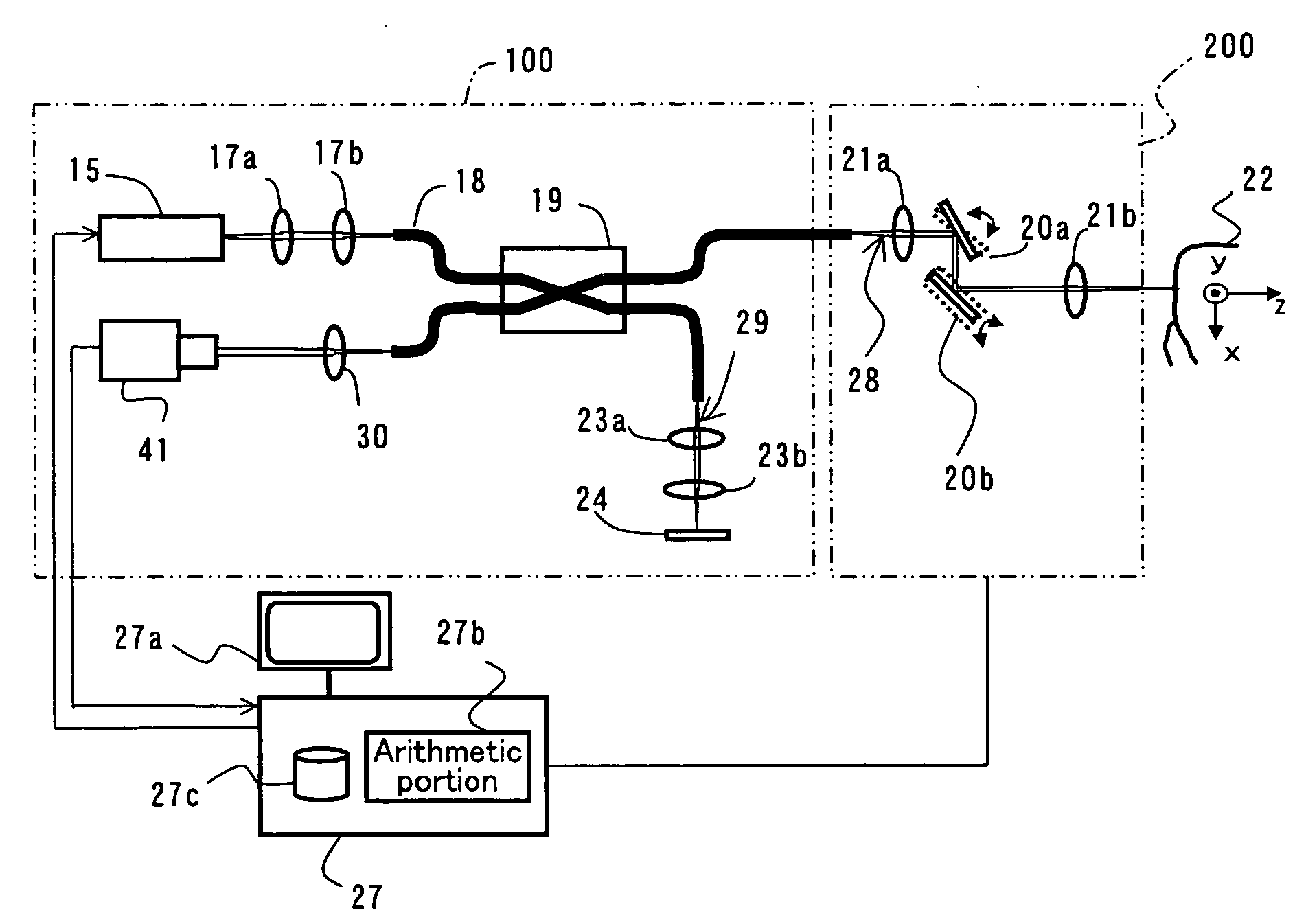
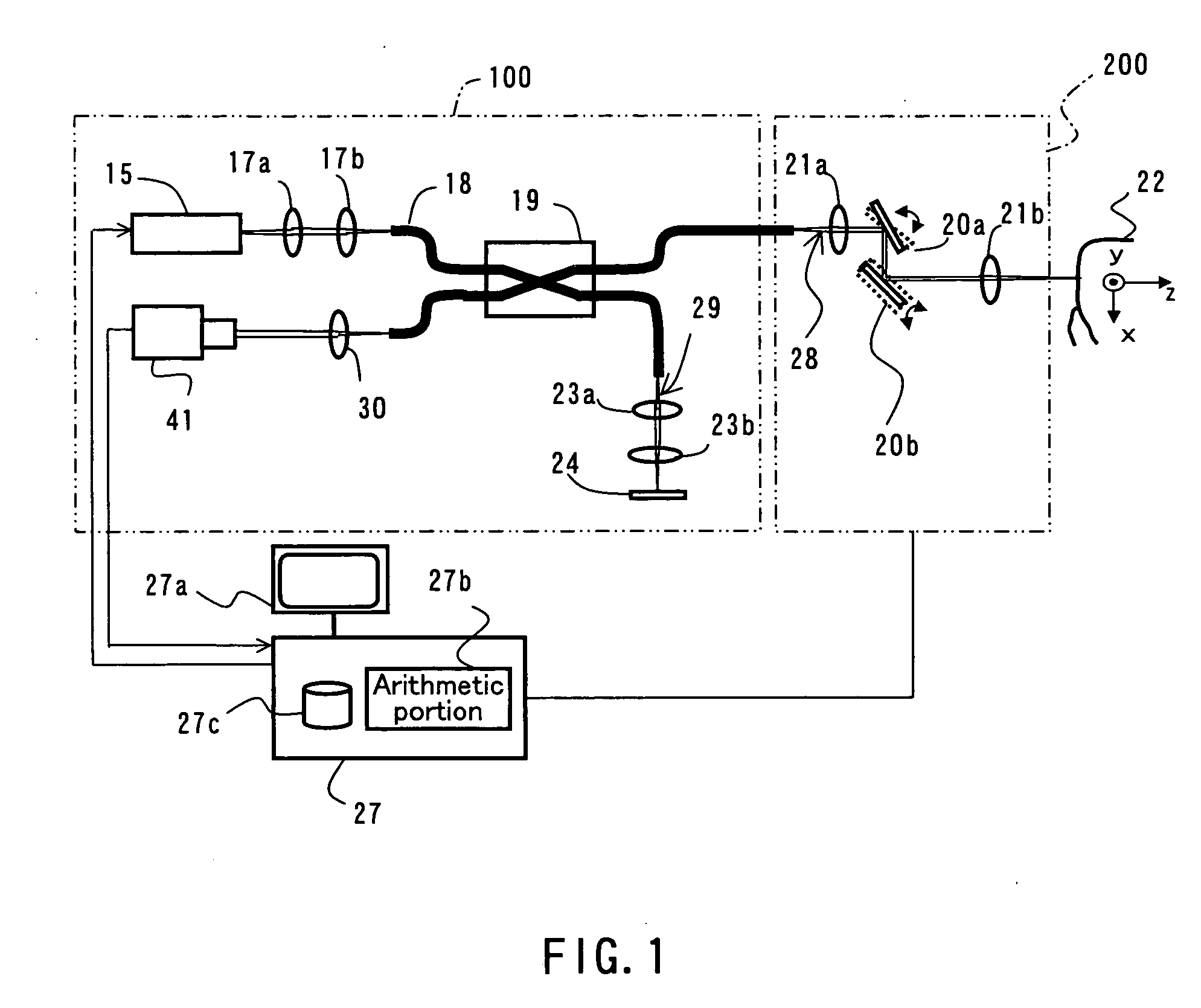
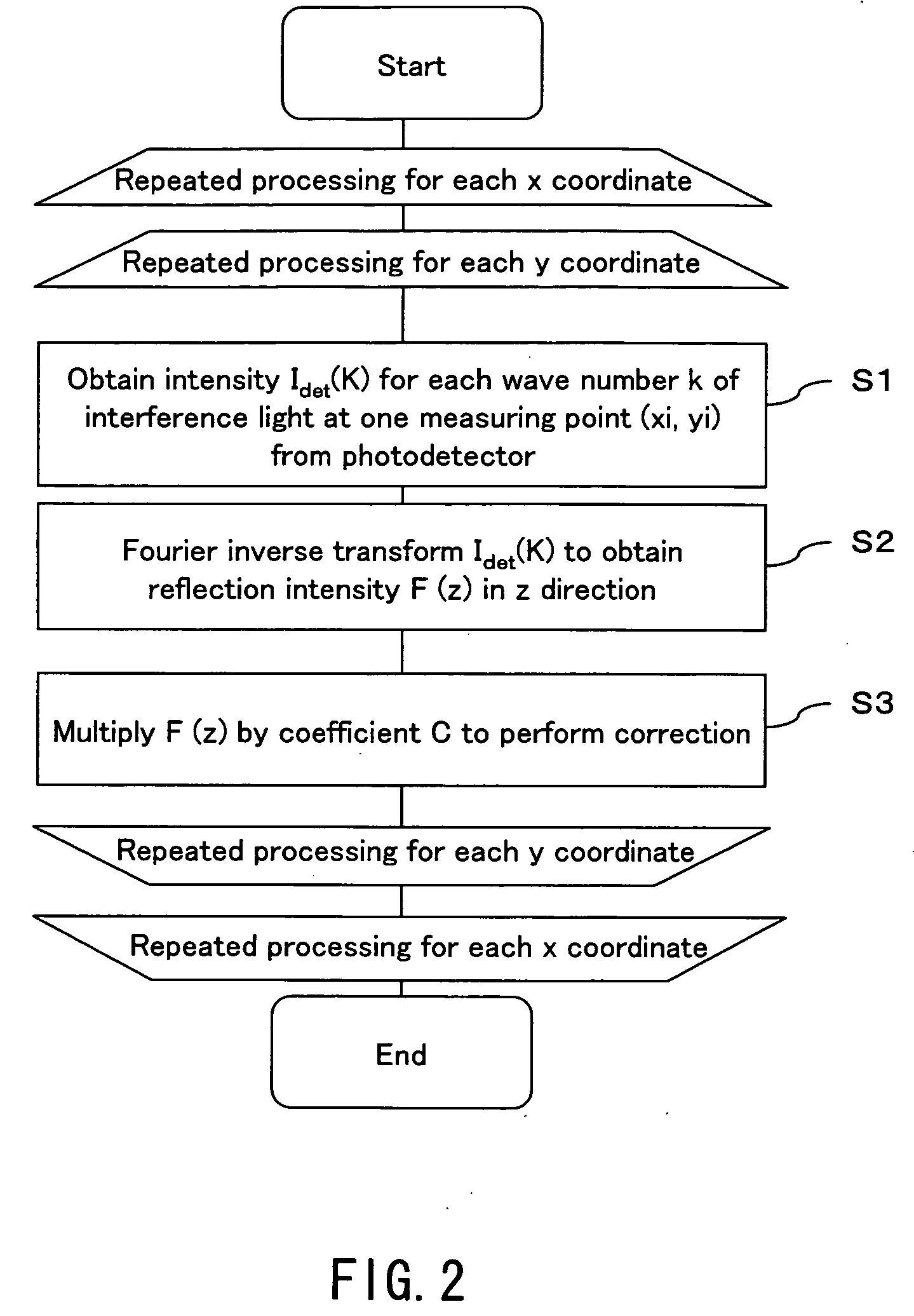
Dental Optical Coherence Tomograph
InactiveUS20090079993A1Simple structureHigh imagingInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological bodyFourier transform on finite groups
A dental optical coherence tomography apparatus for measuring tissue in a stomatognathic region of a living body or an artificial composition in the stomatognathic region as a measured object includes: a variable wavelength light source (15); a light splitting portion (19) that splits light-source light emitted from the variable wavelength light source (15) into reference light (29) and measuring light (28); an interference portion (19) that causes the measuring light (28) and the reference light (29) to interfere with each other, thereby generating interference light; a photodetection portion (41) that measures the interference light; and an arithmetic portion (27b) that generates an image of a measured object (22) by Fourier transforming or inverse Fourier transforming the intensity of the interference light, whose wavelength changes with time, that has been detected by the photodetection portion for each of the wavelengths. Accordingly, an optical coherence tomography apparatus applicable to dental measurement can be provided.
Owner:SHOFU INC
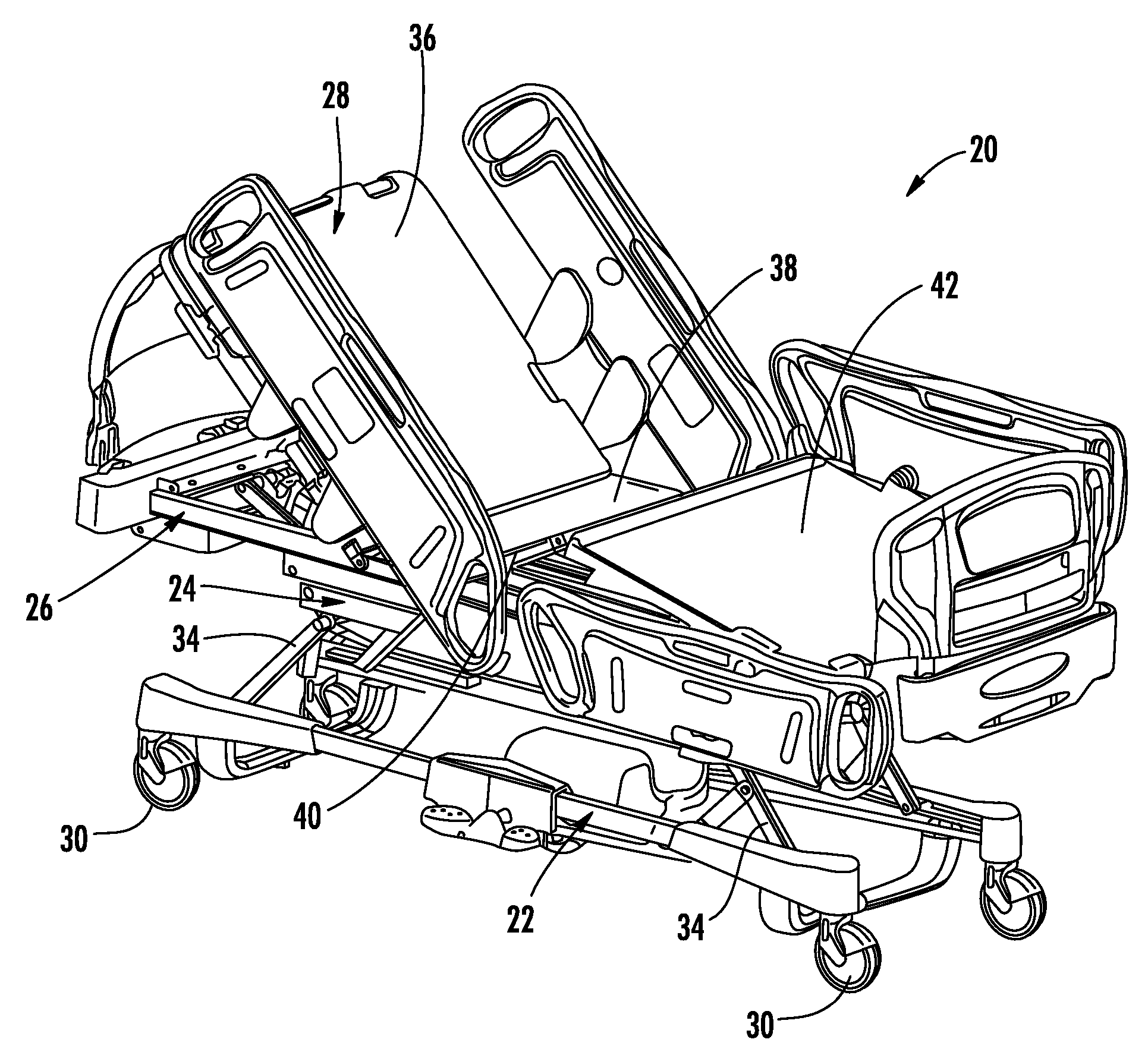
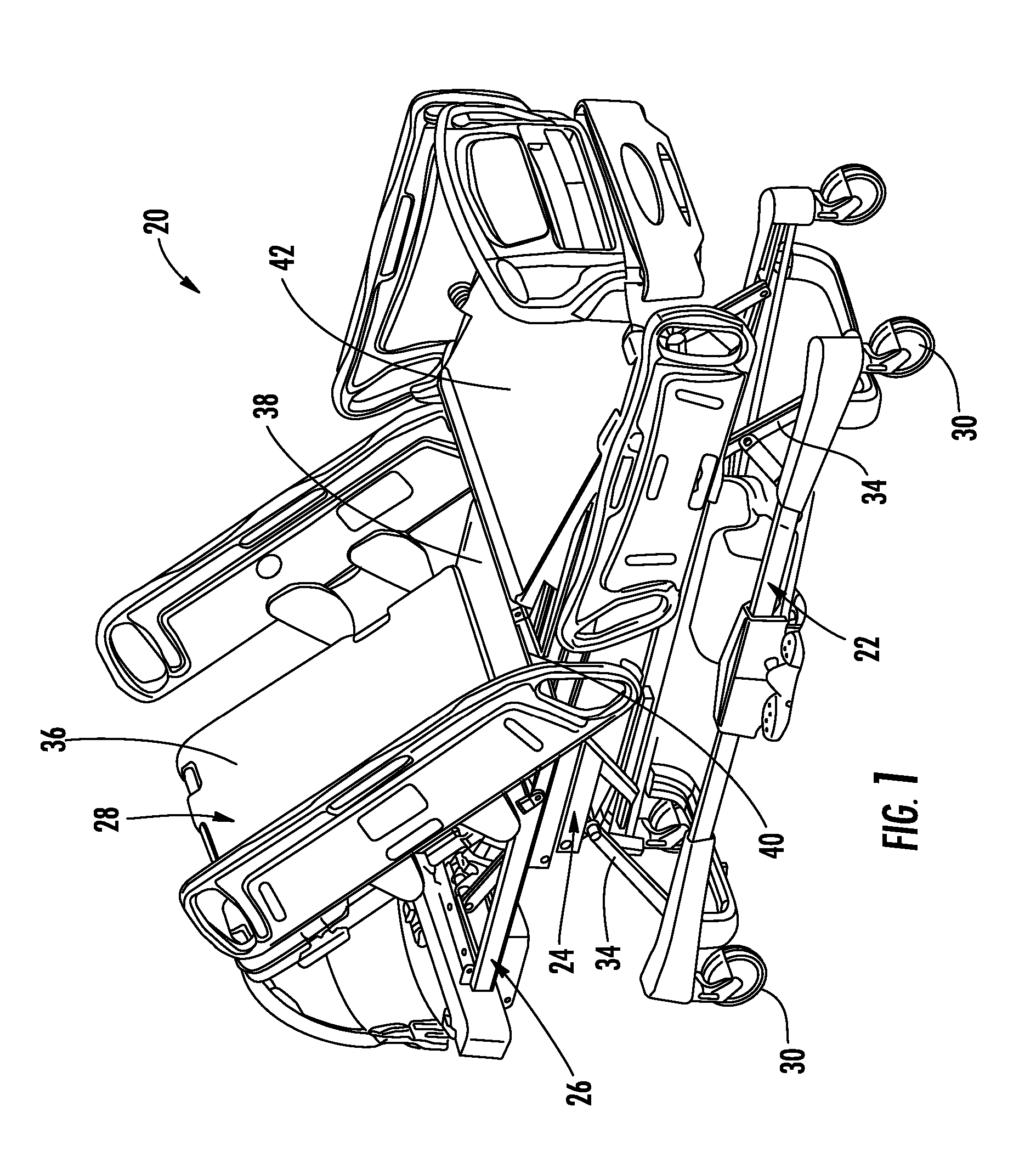
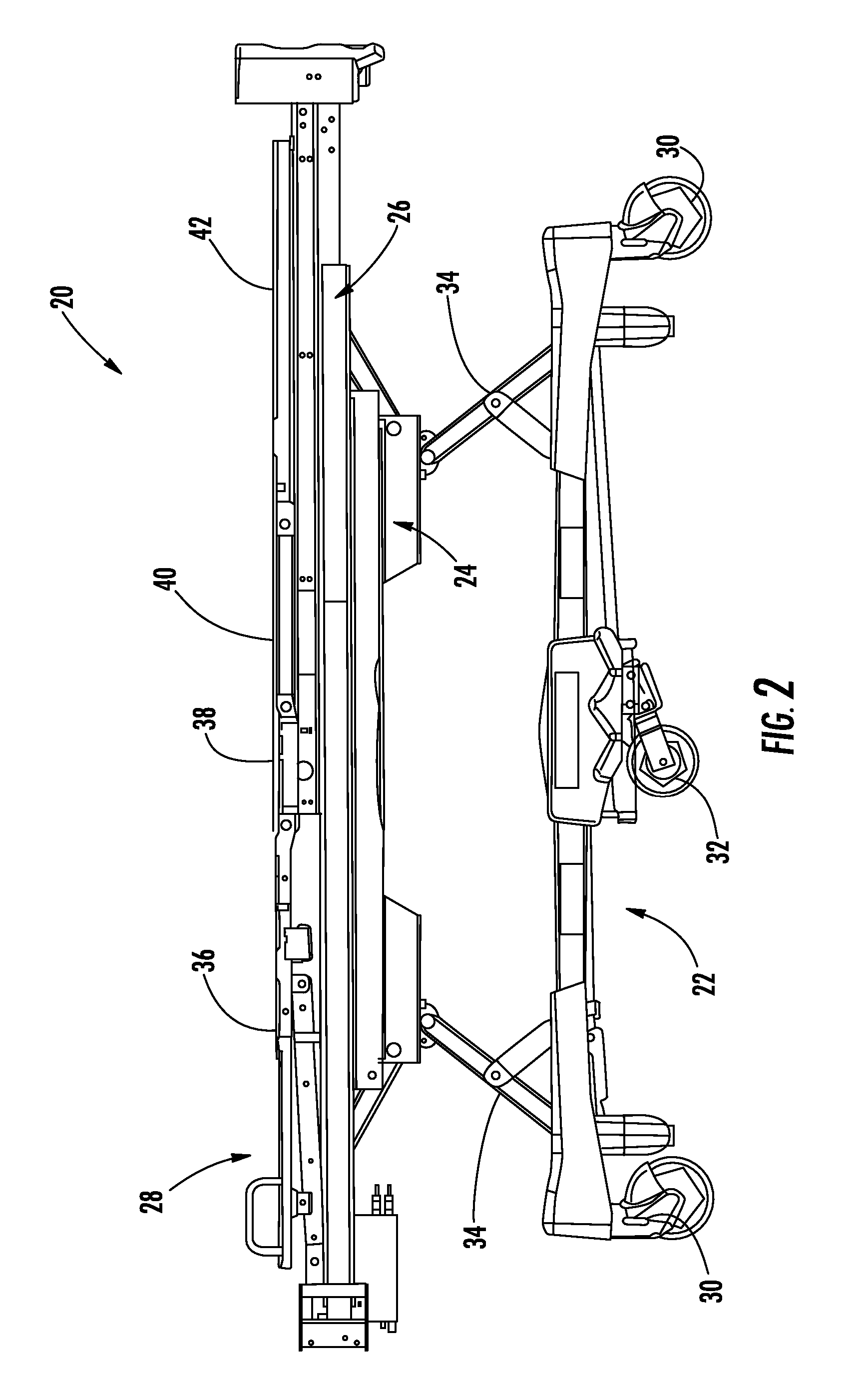
System for detecting and monitoring vital signs
ActiveUS20080005838A1Simple systemCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationFast Fourier transformPhysical therapy
A system and method for determining and monitoring various characteristics of a patient positioned on a patient support apparatus, such as a bed, stretcher, or cot, is disclosed. The system and method involve monitoring the forces exerted by the patient on one or more force sensors, which may be load cells on the support apparatus. These force sensors will detect vibrations that correspond to various conditions of the patient, including the patient's heart rate, breathing rate, and / or the seizure status of a patient. These vibrations may be analyzed, such as by Fast Fourier Transforms, in order to determine the various conditions of the patient.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
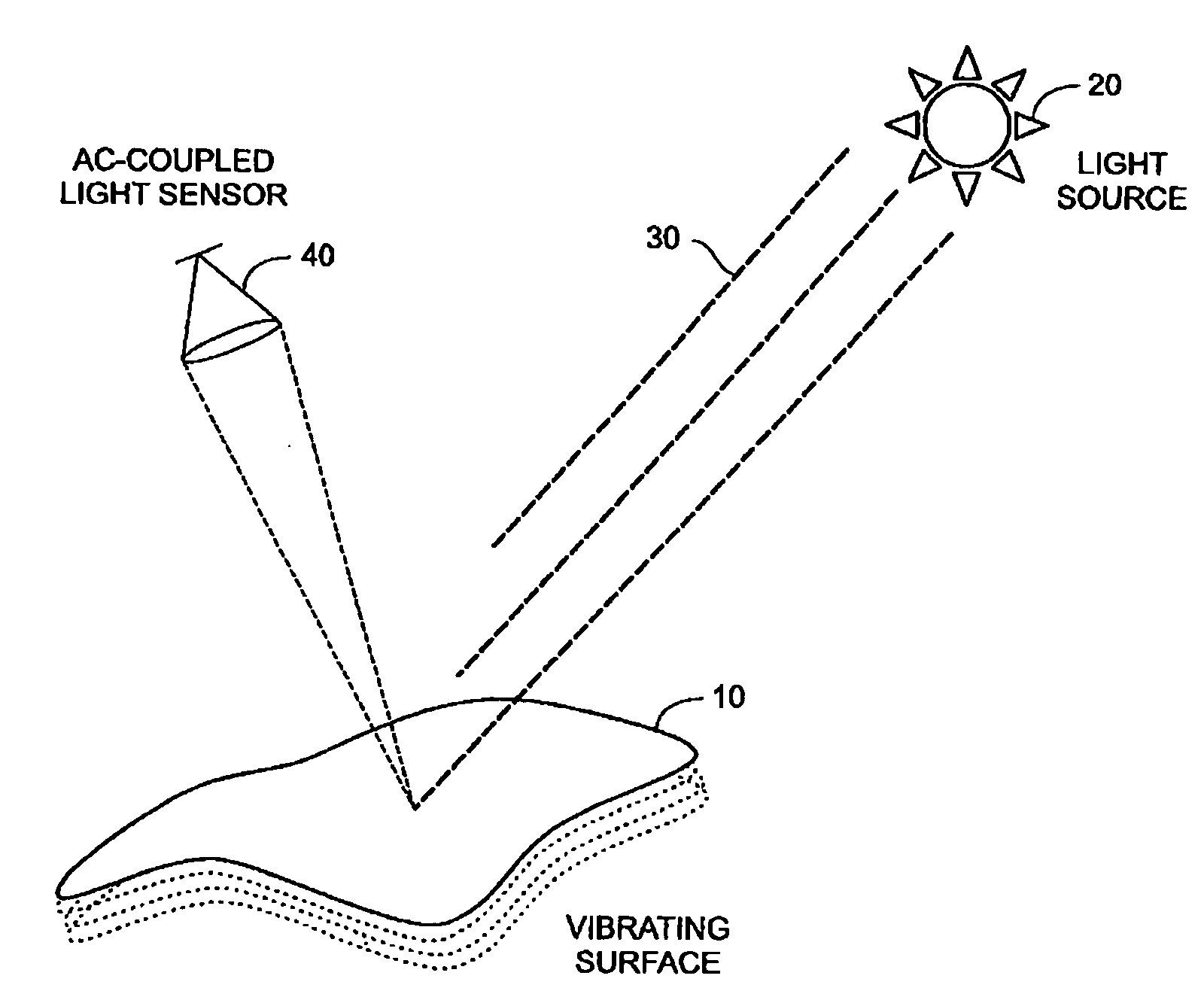
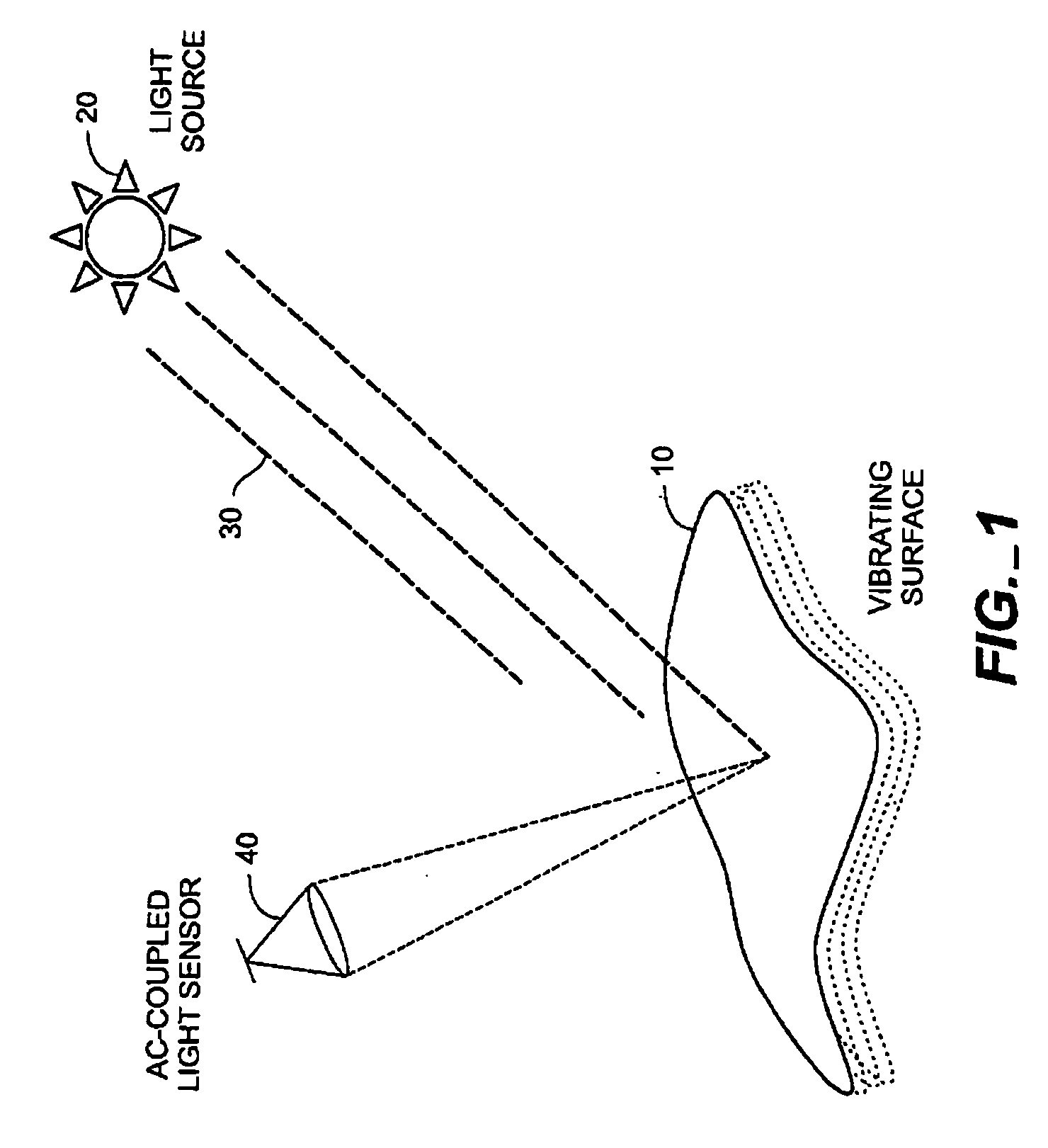
Method for detecting vibrations in a biological organism using real-time vibration imaging
InactiveUS20060209631A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis by observing immersed bodiesUltravioletDetector array
The present invention provides a method for detecting vibration information by receiving electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from a biological organism at a light amplitude modulation detector array to provide real-time imaging of the target object. The detected radiation may be visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, and / or of other desired frequency ranges. The detected radiation is preferably AC-coupled to isolate components relating to oscillations of the biological organism from components relating to ambient radiation, e.g. background sunlight. The isolated oscillations may then be digitized, stored, and subjected to processing such as a Fourier transform to generate outputs representative of frequencies of oscillation. This output can then be used for analysis of the target object.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
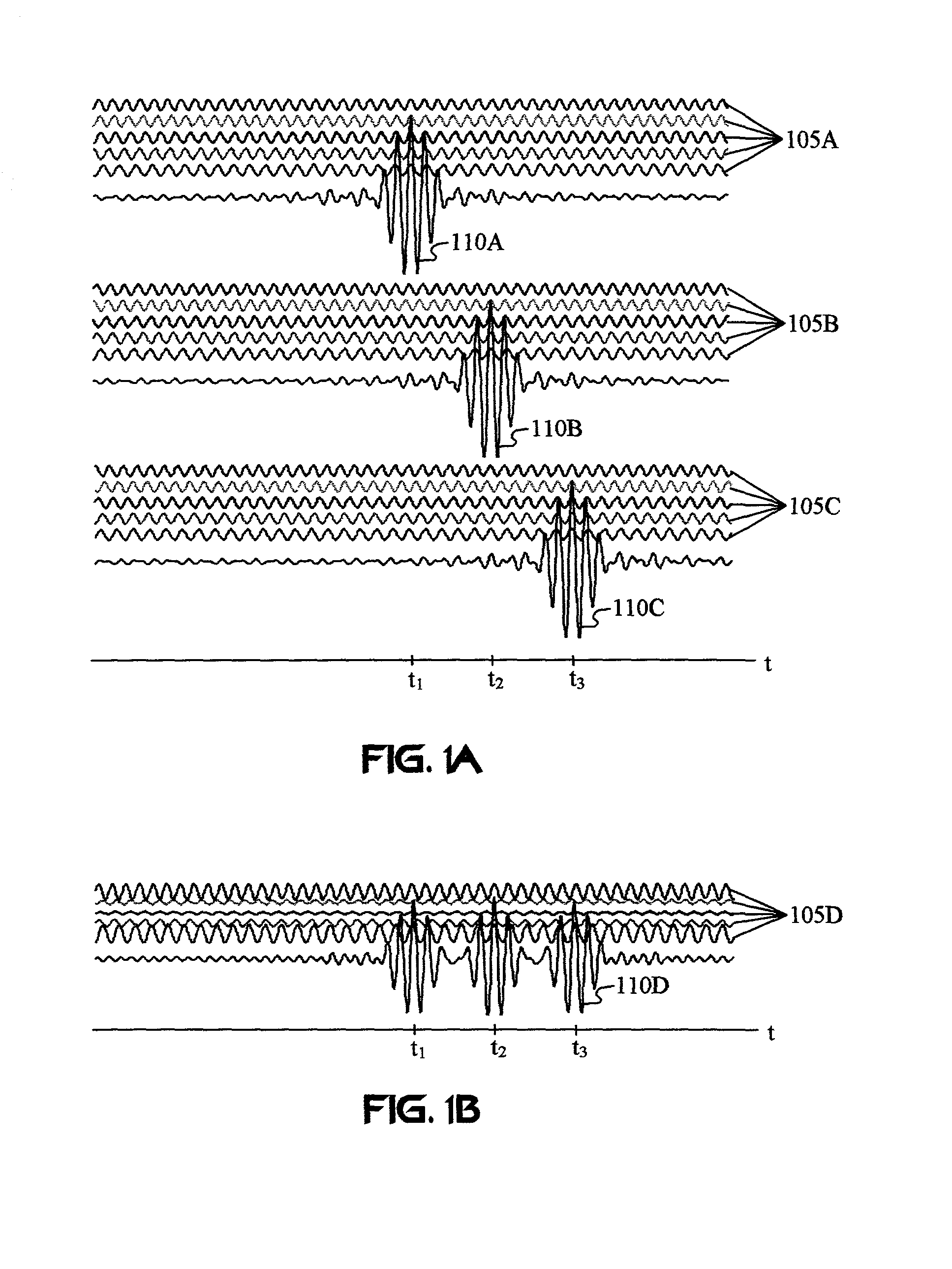
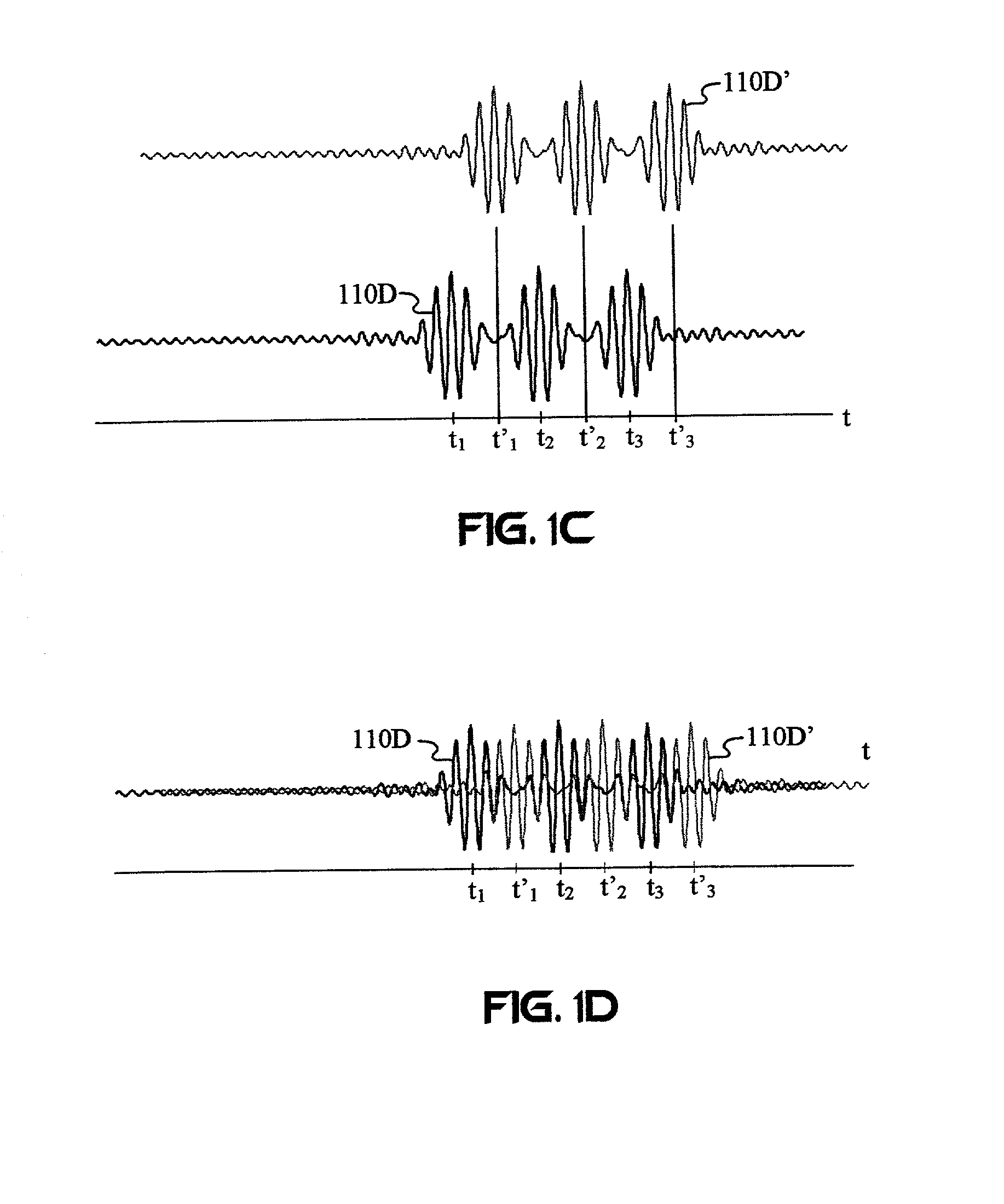
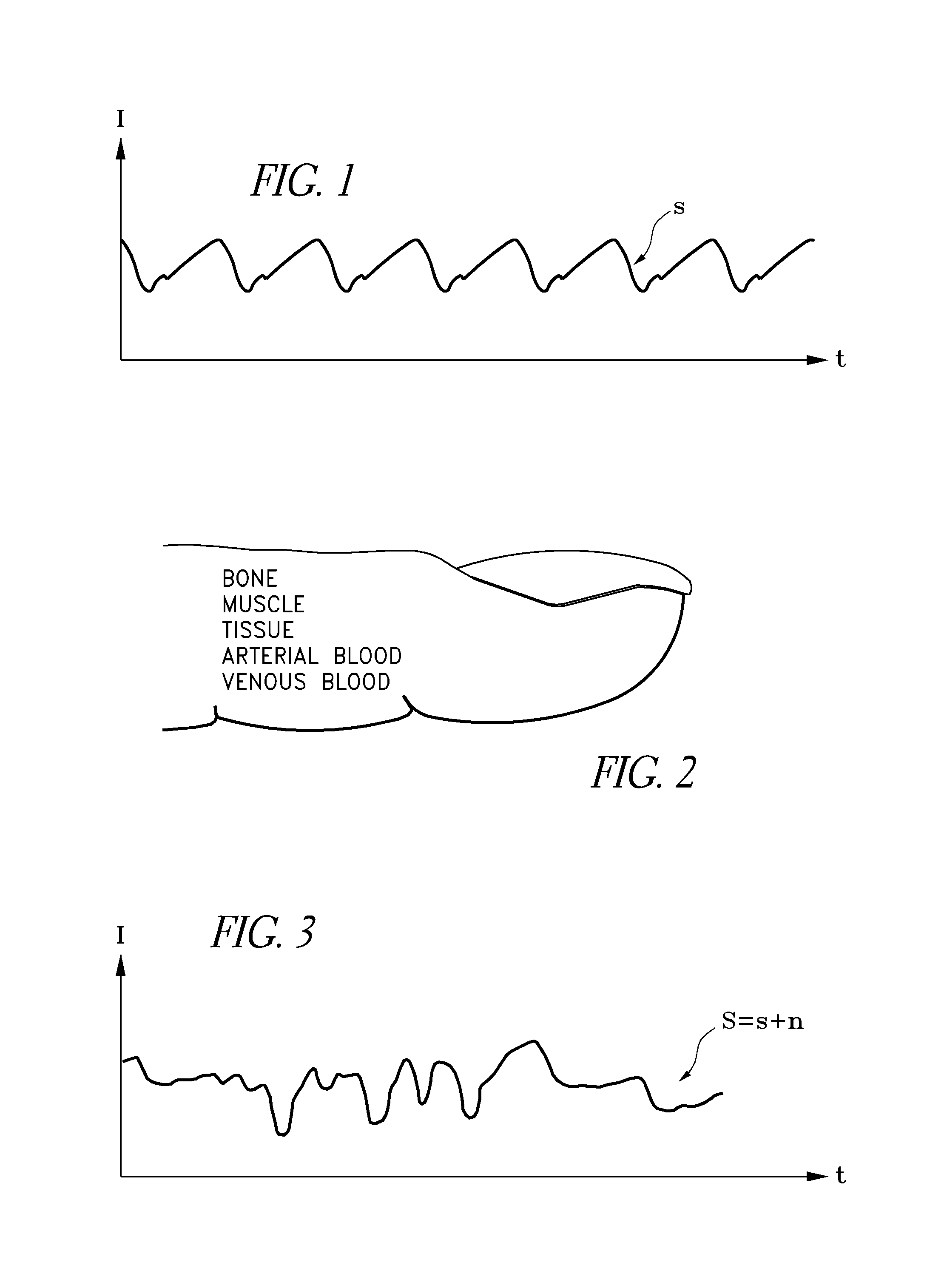
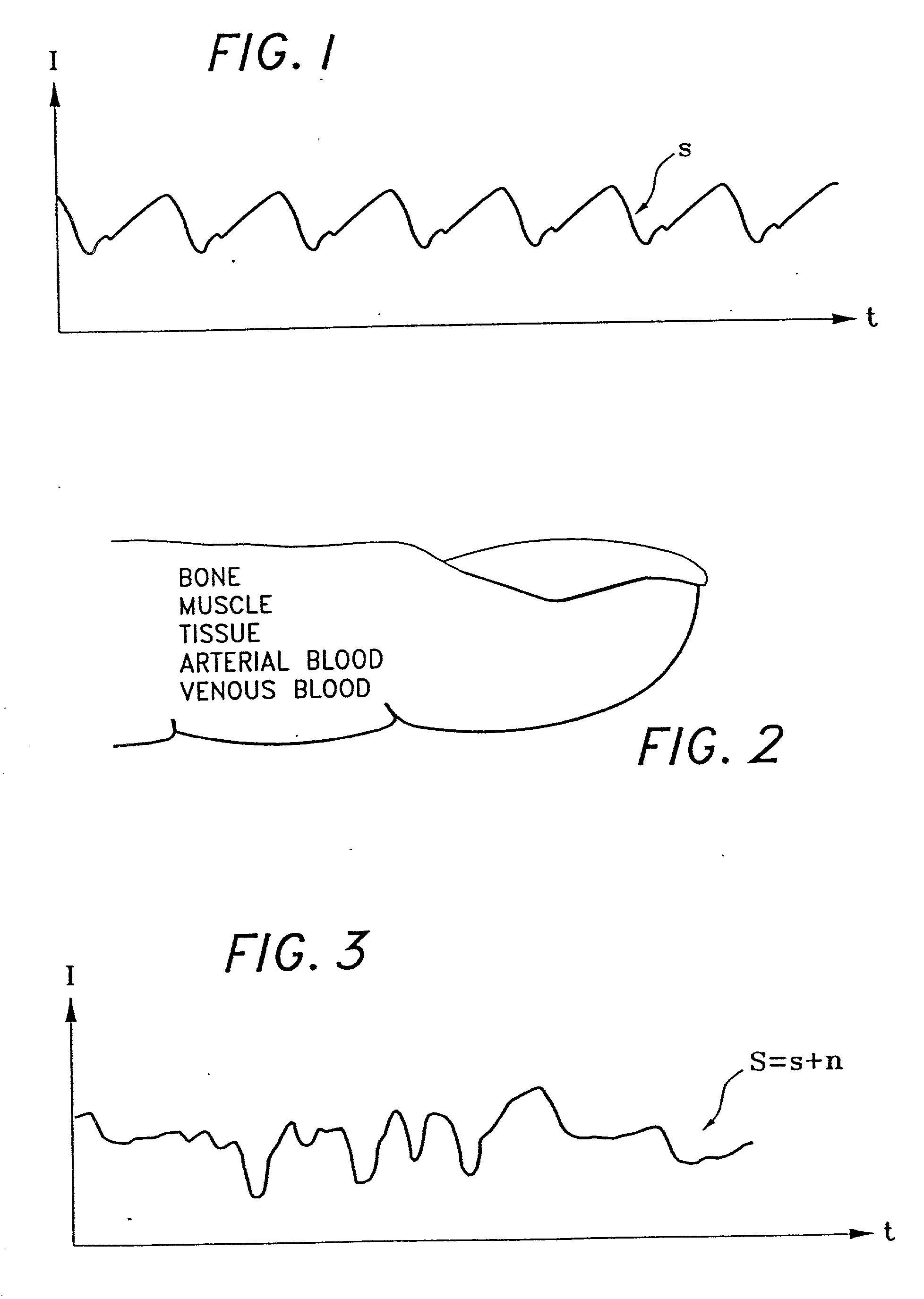
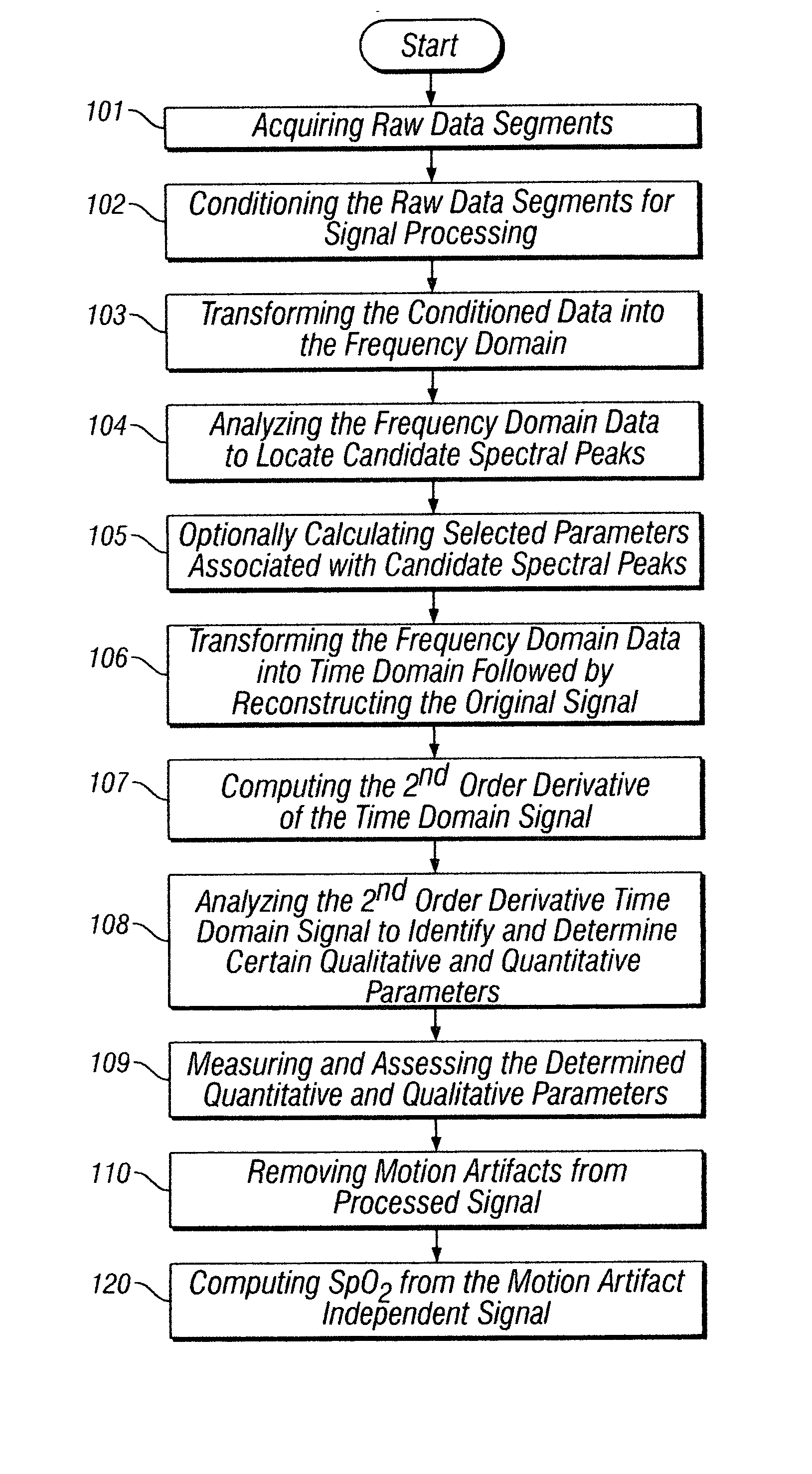
Separating motion from cardiac signals using second order derivative of the photo-plethysmogram and fast fourier transforms
The present invention is directed toward a pulse oximetry system for the determination of a physiological parameter capable of removing motion artifacts from physiological signals comprises a hardware subsystem and a software subsystem. The software subsystem is used in conjunction with the hardware subsystem to perform a method for removing a plurality of motion artifacts from the photo-plethysmographic data and for obtaining a measure of at least one physiological parameter from the data. The method comprises acquiring the raw photo-plethysmographic data, transforming the data into the frequency domain, analyzing the transformed data to locate a series of candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), reconstructing a photo-plethysmographic signal in the time domain with only the candidate cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics), computing the second order derivative of the reconstructed photo-plethysmographic signal, analyzing the candidate second order derivative photo-plethysmographic signal to determine the absence or presence of cardiac physiologic signal characteristics, and finally selecting the best physiologic candidate from the series of potential cardiac spectral peaks (primary plus harmonics) based upon a second derivative scoring system. This scoring system is preferentially based upon second derivative processing analysis, but can be equally applied using the first, third, fourth or other similar derivative processing analysis.
Owner:SPACELABS HEALTHCARE LLC
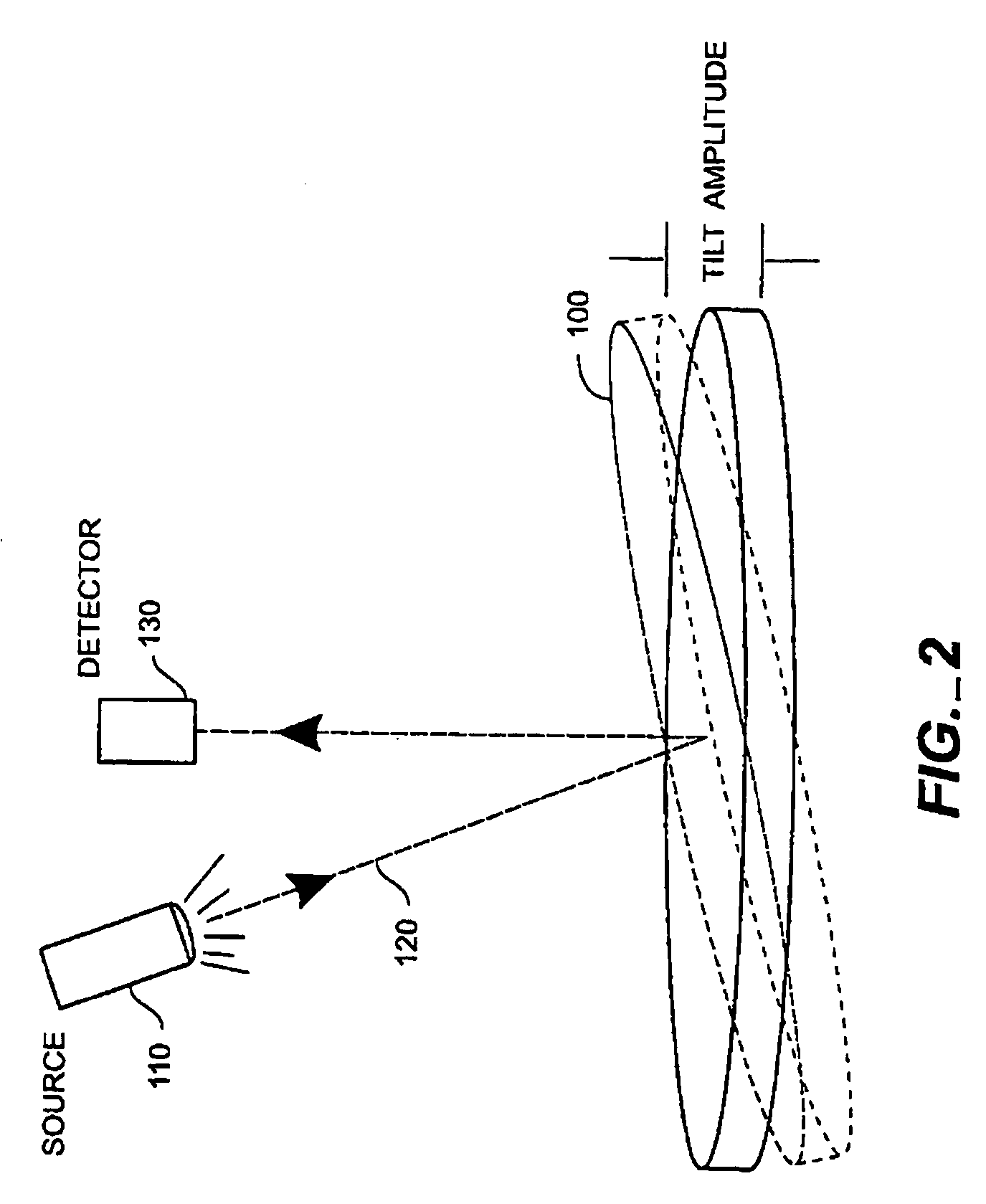
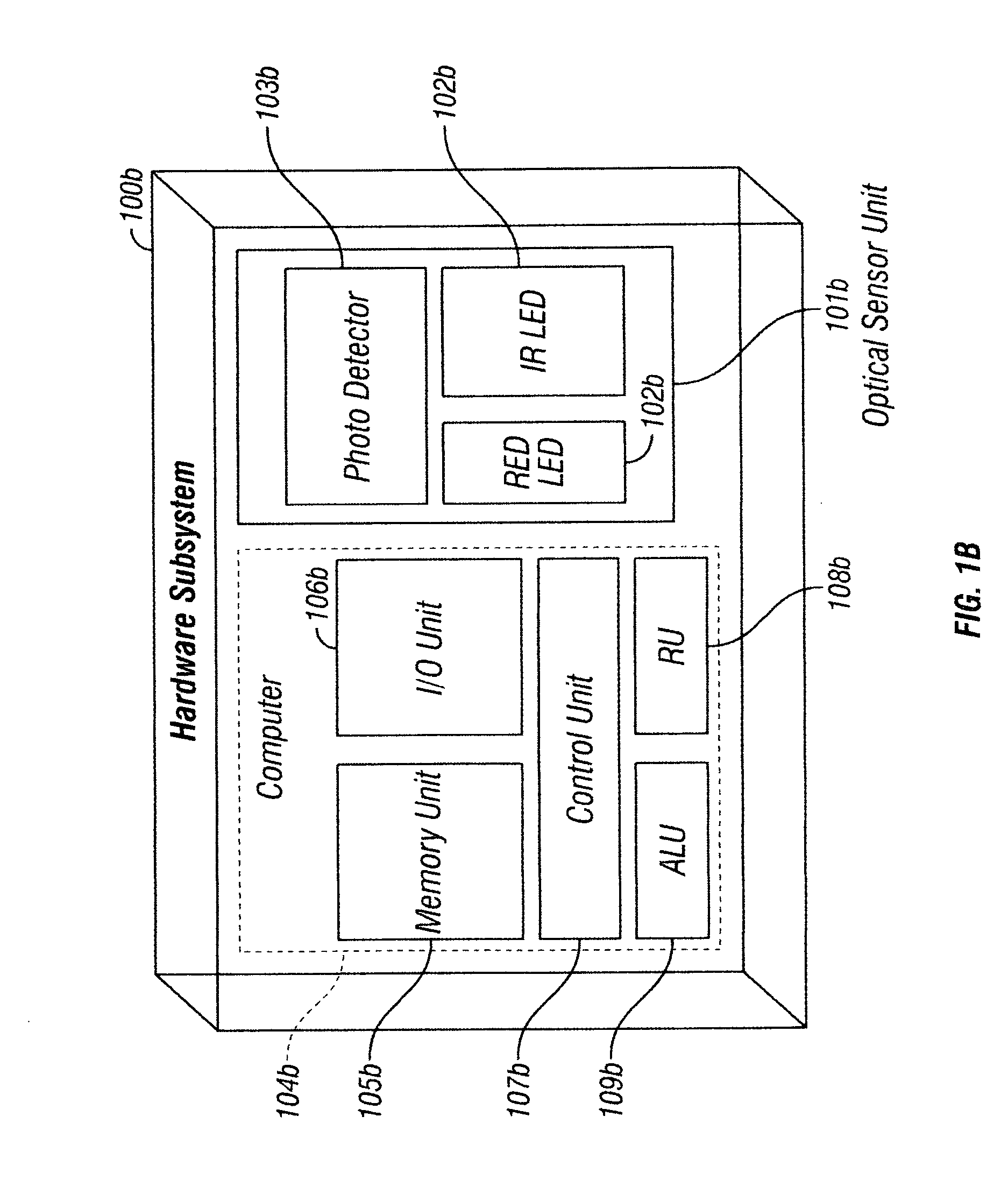
Magnetoelastic sensing apparatus and method for remote pressure query of an environment
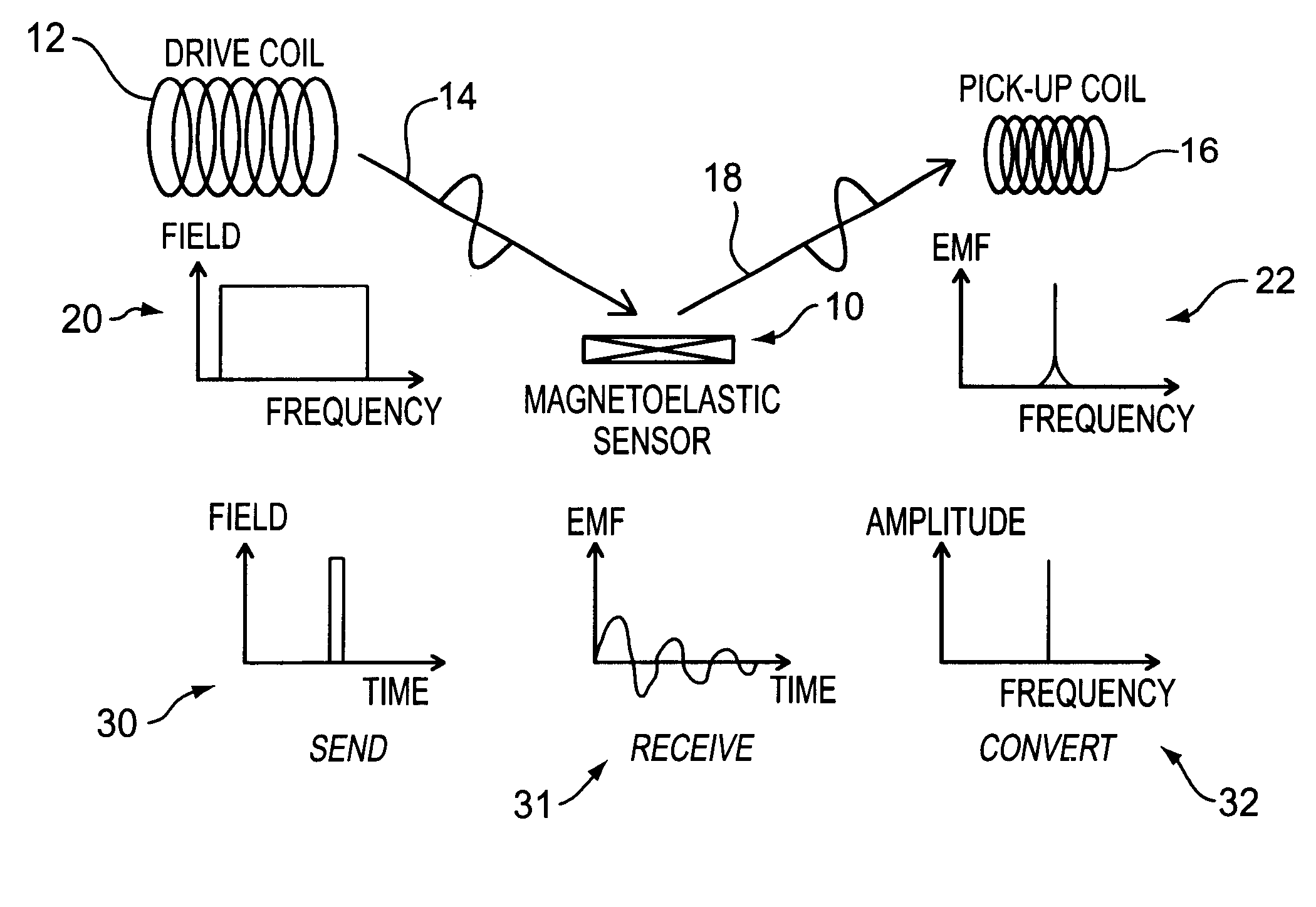
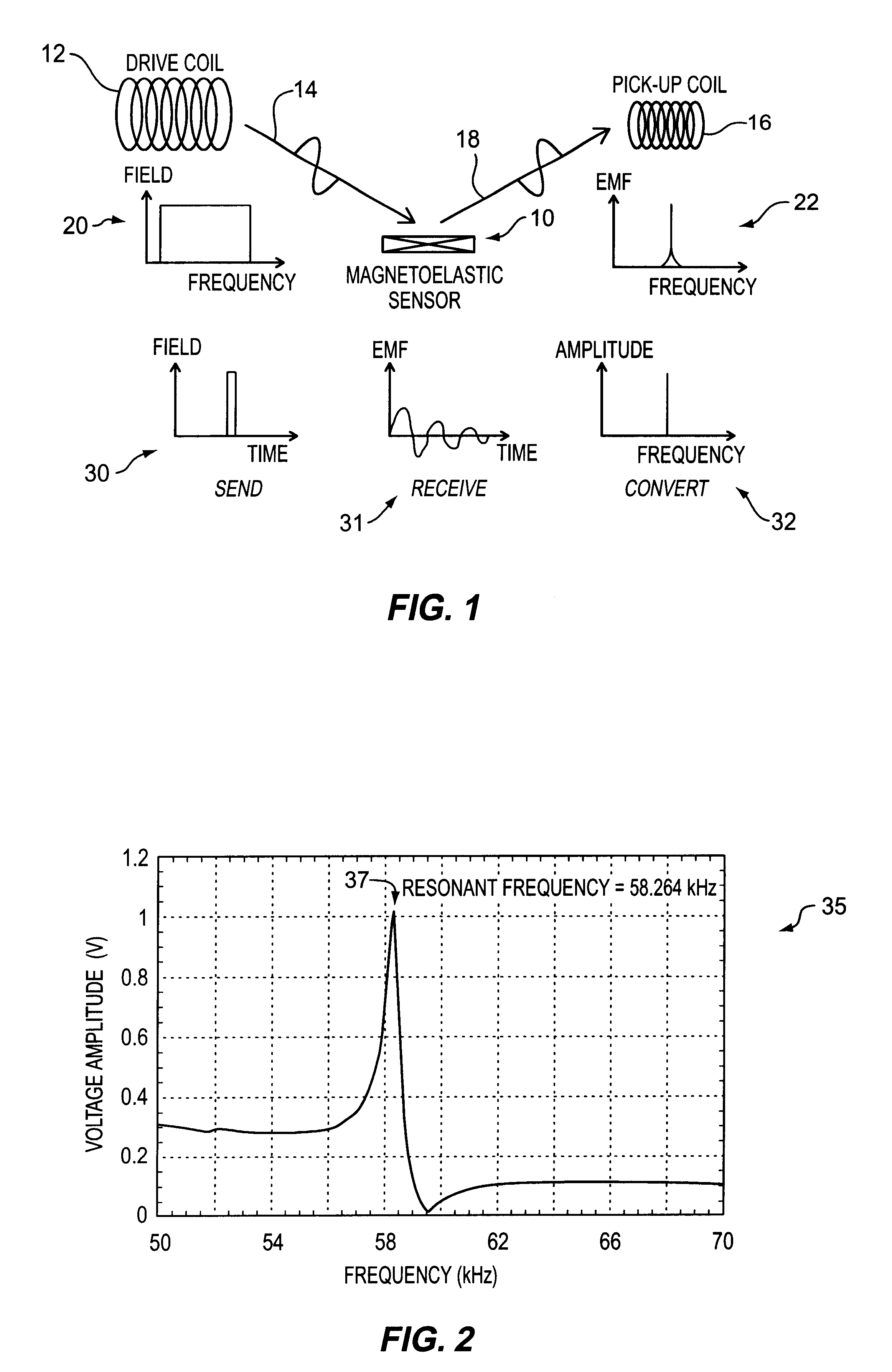
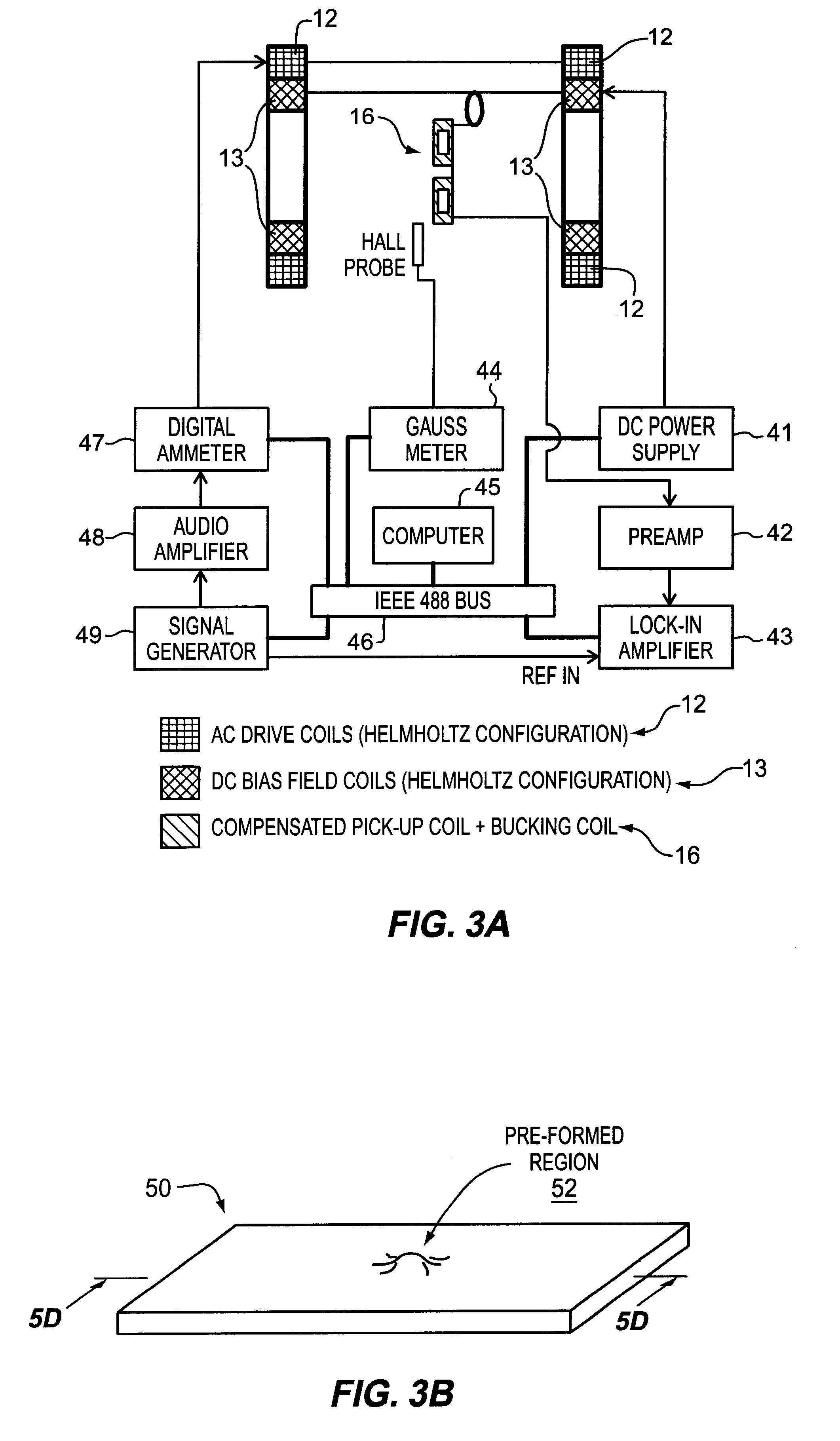
InactiveUS6393921B1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementMagneto elasticPressure sense
A pressure sensing apparatus for operative arrangement within an environment, having: a sensor comprising a hermetically-sealed receptacle, at least one side of which has an flexible membrane to which a magnetically hard element is attached. Enclosed within the receptacle is a magnetostrictive element that vibrates in response to a time-varying magnetic field. Also included is a receiver to measure a plurality of successive values for magneto-elastic emission intensity of the sensor taken over an operating range of successive interrogation frequencies to identify a resonant frequency value for the sensor. Additional features include: (a) the magnetically hard element may be adhered to an inner or outer side of, or embedded within, the membrane; (b) the magnetostrictive element can include one or more of a variety of different pre-formed, hardened regions; (c) the magneto-elastic emission may be a primarily acoustic or electromagnetic emission; and (d) in the event the time-varying magnetic field is emitted as a single pulse or series of pulses, the receiver unit can detect a transitory time-response of the emission intensity of each pulse (detected after a threshold amplitude value for the transitory time-response is observed). A Fourier transform of the time-response can yield results in the frequency domain. Also, an associated method of sensing pressure of an environment is included that uses a sensor having a magnetostrictive element to identify a magneto-elastic resonant frequency value therefore. Using the magneto-elastic resonant frequency value identified, a value for the pressure of the environment can be identified.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Frequency hopping spread spectrum system with high sensitivity tracking and synchronization for frequency unstable signals
InactiveUS6934316B2Improve dynamic rangeReduce sensitivityData switching by path configurationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlFrequency-hopping spread spectrumFast Fourier transform
A wireless spread spectrum communication system for transmitting data includes a plurality of end point transmitters and at least one receiver. The end point transmitters transmit data via a frequency hopped spread spectrum signal where the transmitting signal is sent without the benefit of frequency stabilization. The receiver is responsive to the frequency hopping spread spectrum signals and includes a correlator and a signal processor. The correlator samples at least a first portion of a preamble of the signal and correlates the portion of the preamble with a known preamble pattern to determine a probability of correlation. The signal processor applies a Fast Fourier Transform algorithm to the signal in response to the probability of correlation to track a narrowband frequency of the signal based on at least a second portion of the preamble and to decode data encoded within the signal subsequent to the preamble.
Owner:ITRON
Pump potential cavitation fault detecting method based on quick spectrum kurtosis analysis
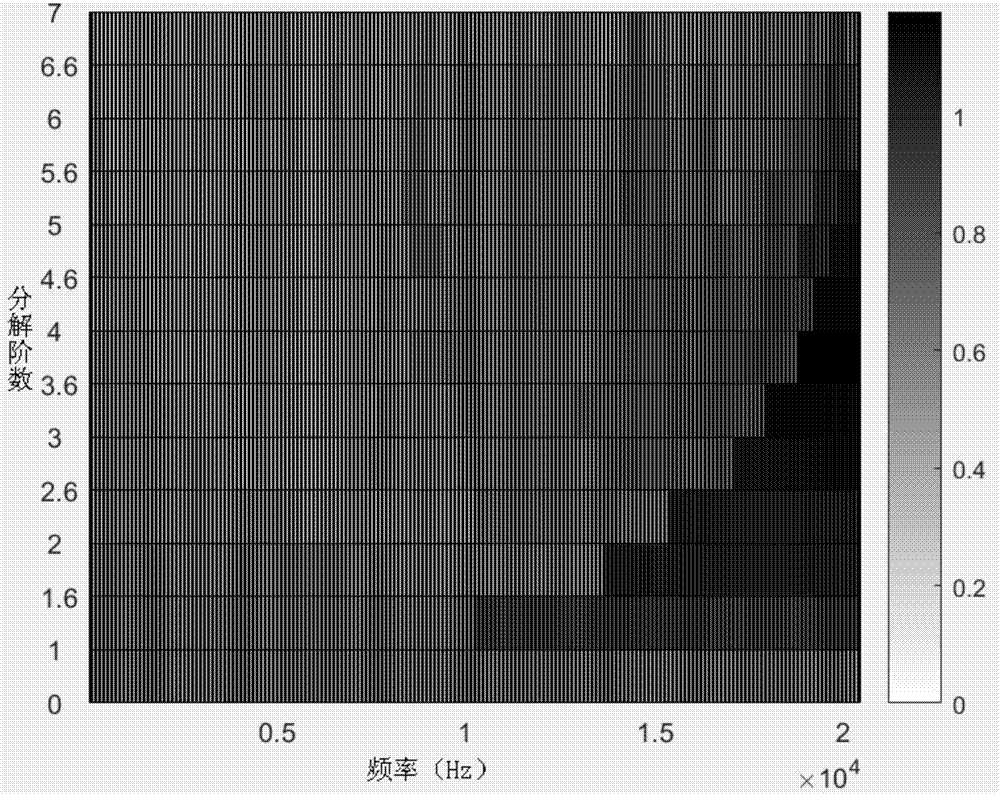
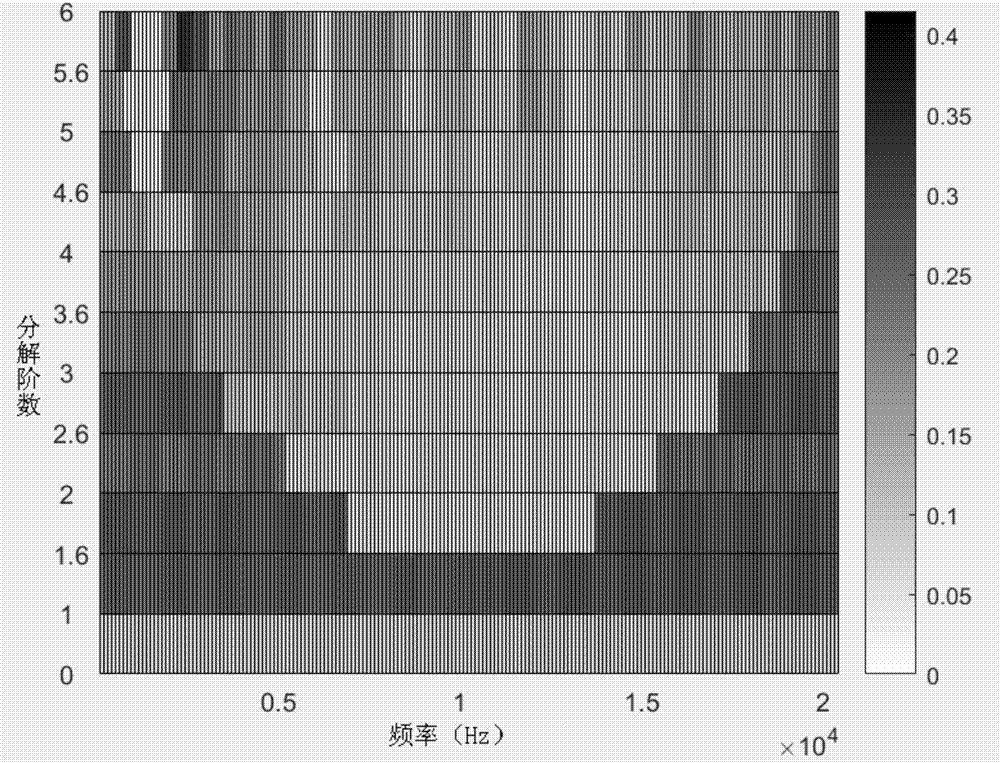
ActiveCN107956708AImprove acceleration performanceClear resolutionPump controlNon-positive displacement fluid enginesVibration accelerationCavitation
The invention discloses a pump potential cavitation fault detecting method based on quick spectrum kurtosis analysis. The pump potential cavitation fault detecting method comprises the steps that 1, vibration acceleration signals are collected to be subject to noise reduction to serve as to-be-processed signals; 2, according to the data size of the signals, the resolving order of signal processingis determined; 3, according to the quick spectrum kurtosis algorithm computation result, the optimal carrier frequency and bandwidth are selected; 4, the selected signals within the carrier frequencyand bandwidth are subject to Fourier transformation, and a frequency spectrum envelope diagram is obtained; and 5, an original signal time domain figure, a signal time domain figure treated through quick spectrum kurtosis filtering processing and the frequency spectrum envelope diagram obtained after selected zone Fourier transformation are compared, and cavitation trouble signal time and frequency characteristics are analyzed. By means of the method, more cavitation instant signals can be detected, information in the aspects of time domain and frequency domain is seen more clearly, and the normal state and the cavitation state of a pump can be distinguished obviously.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
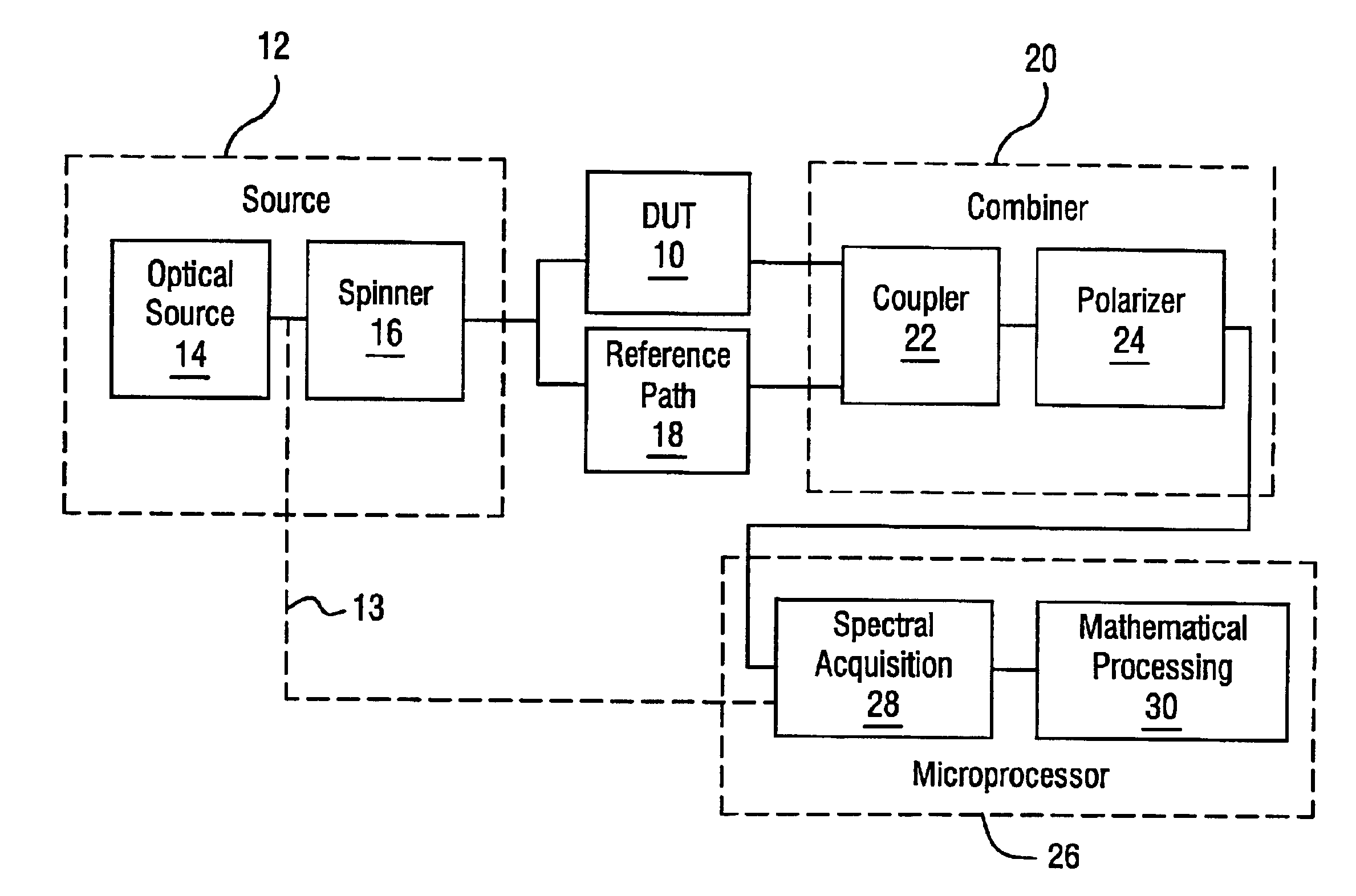
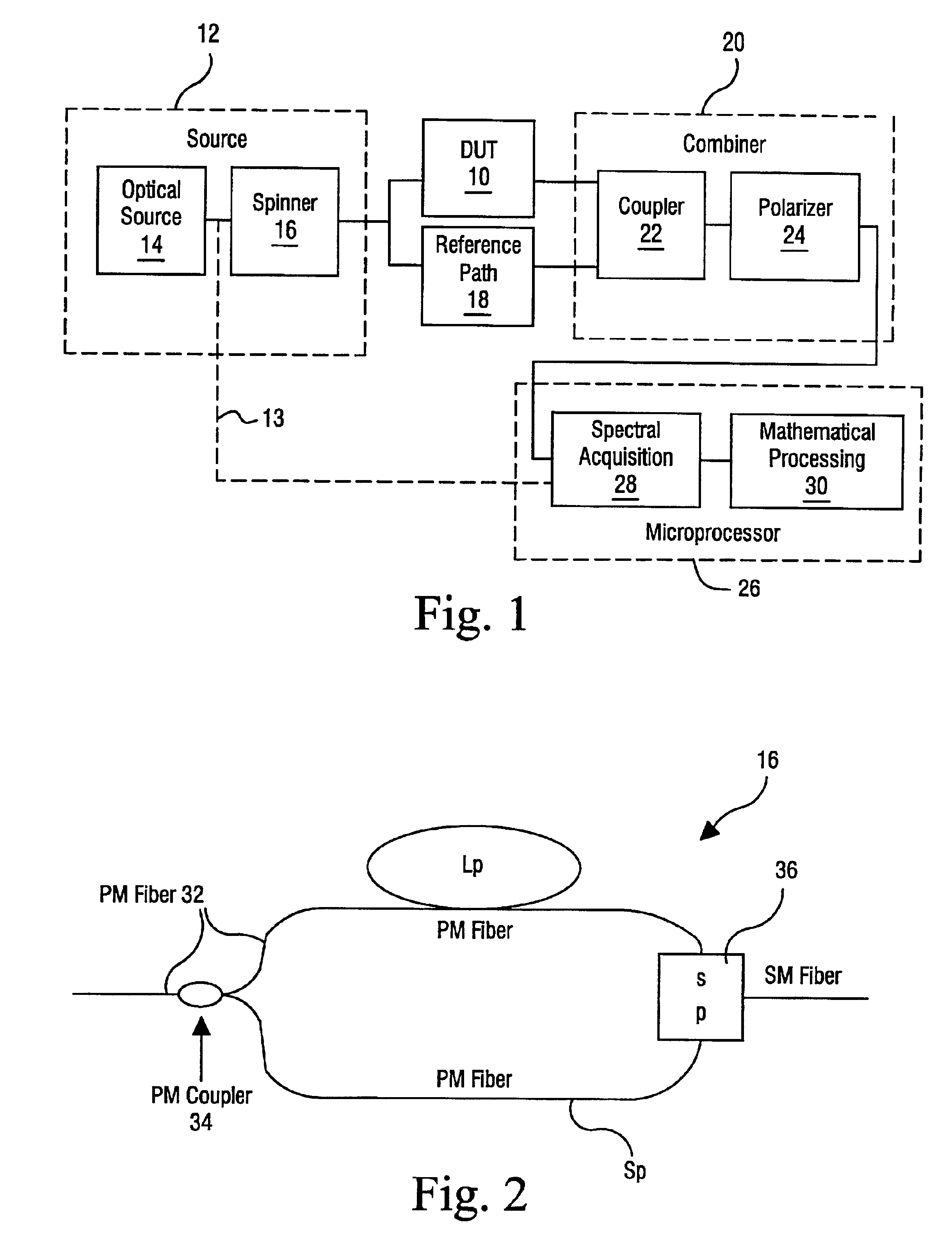
Apparatus and method for the complete characterization of optical devices including loss, birefringence and dispersion effects
InactiveUS6856400B1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical frequenciesCurve fitting
In order to characterize the optical characteristics of a device, a source of light having a variable frequency with a polarization state which varies linearly with frequency is provided as an input to the device under test. The input light is also passed through a known reference path and is added to the light output from the device under test in a beam combiner. The combined light for the frequencies of interest is split into two orthogonal polarizations which are then detected in a spectral acquisition apparatus and supplied to a microprocessor. The spectral measurements are digitized and curve-fitted to provide optical power versus optical frequency curves. Fourier transforms of each of the curves are calculated by the microprocessor. From the Fourier transforms, the four arrays of constants are calculated for the Jones matrix characterizing the device under test.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method and Apparatus for Radiance Processing by Demultiplexing in the Frequency Domain
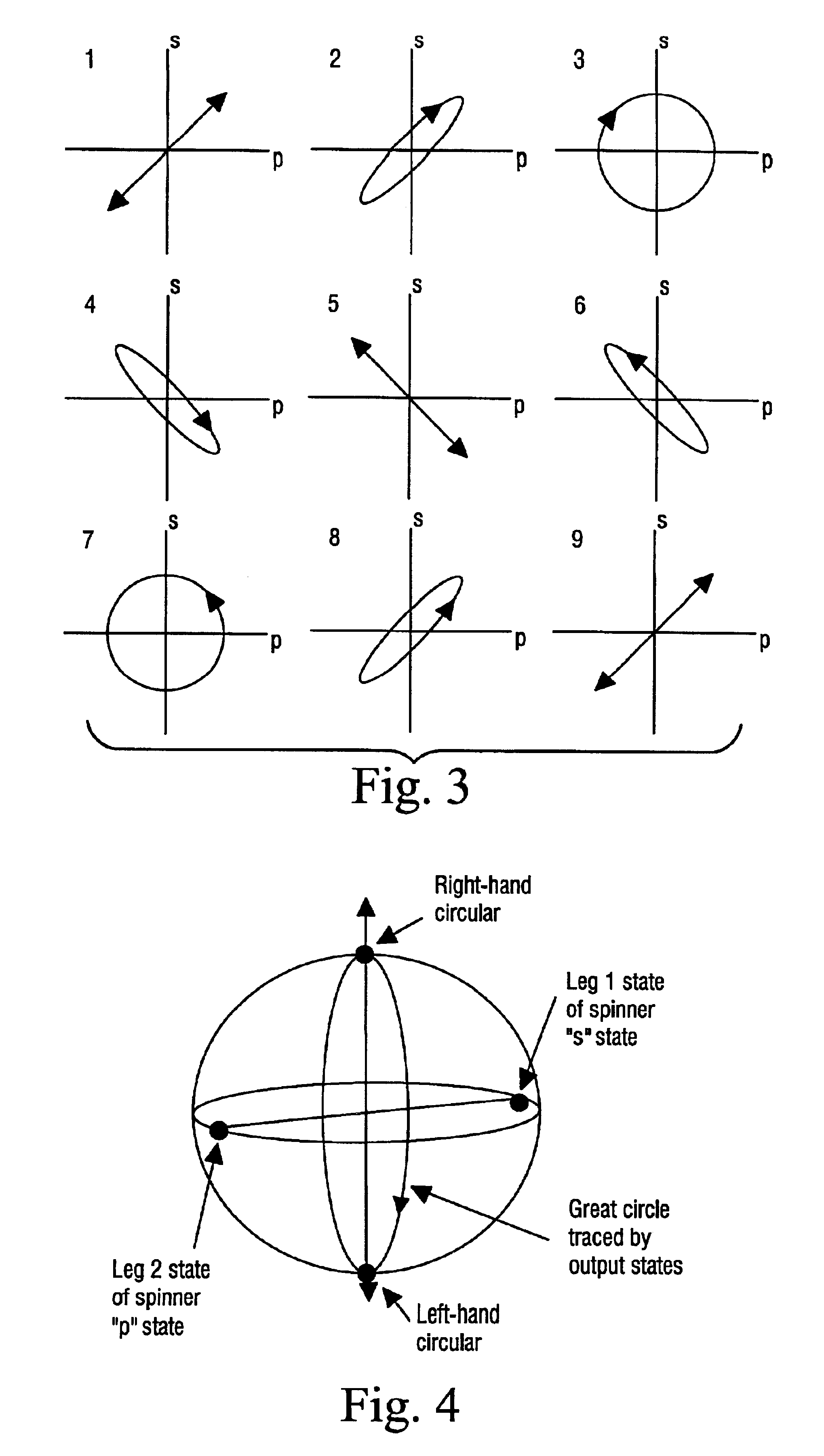
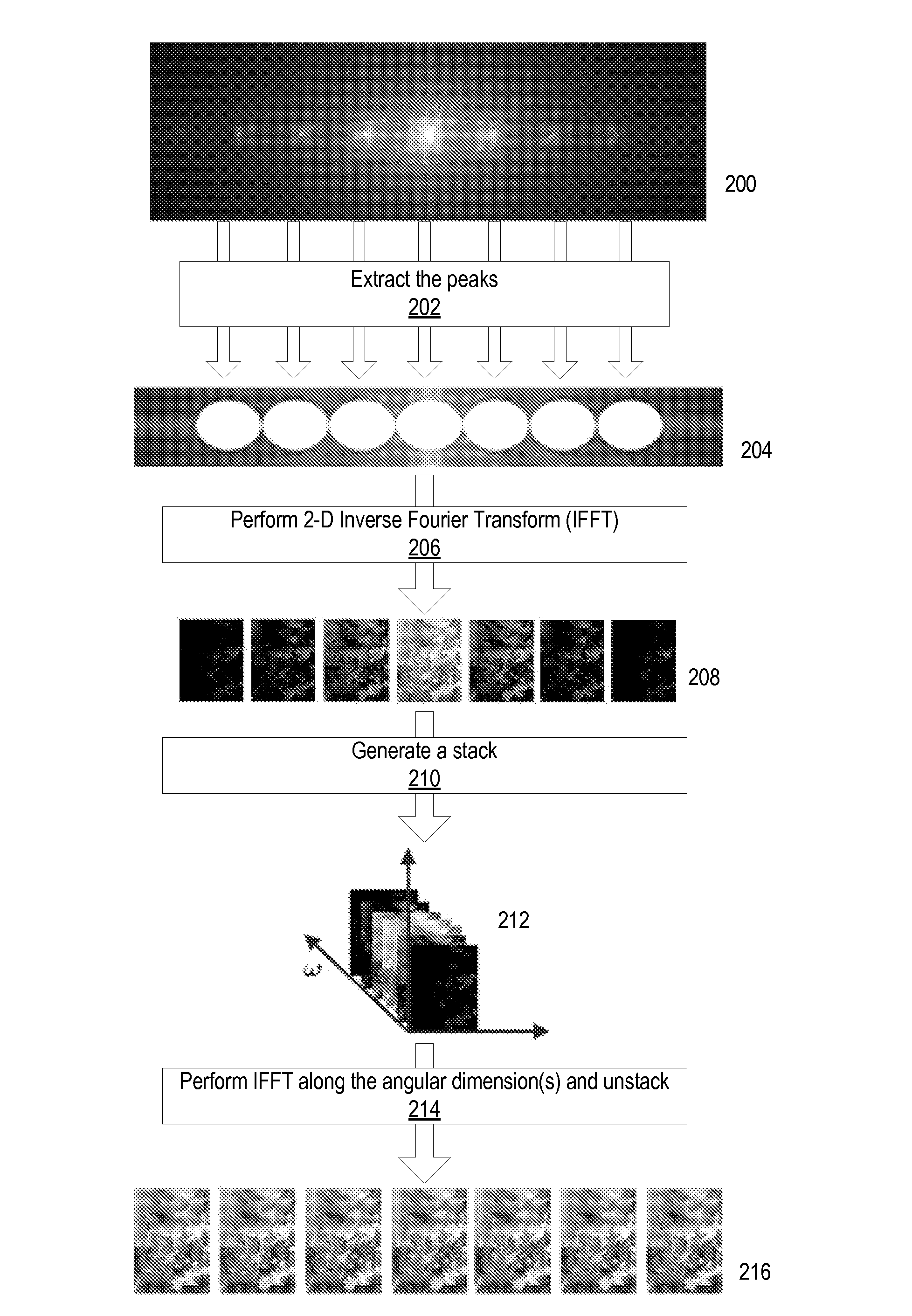
ActiveUS20090041381A1Guaranteed corrective effectPromote resultsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxPhase correction
Method and apparatus for radiance processing by demultiplexing in the frequency domain. A frequency domain demultiplexing module obtains a radiance image captured with a lens-based radiance camera. The image includes optically mixed spatial and angular frequency components of light from a scene. The module performs frequency domain demultiplexing on the radiance image to generate multiple parallax views of the scene. The method may extract multiple slices at different angular frequencies from a Fourier transform of the radiance image, apply a Fourier transform to each of the multiple slices to generate intermediate images, stack the intermediate images to form a 3- or 4-dimensional image, apply an inverse Fourier transform along angular dimension(s) of the 3- or 4-dimensional image, and unstack the transformed 3- or 4-dimensional image to obtain the multiple parallax views. During the method, phase correction may be performed to determine the centers of the intermediate images.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Method and apparatus for multicarrier channel estimation and synchronization using pilot sequences
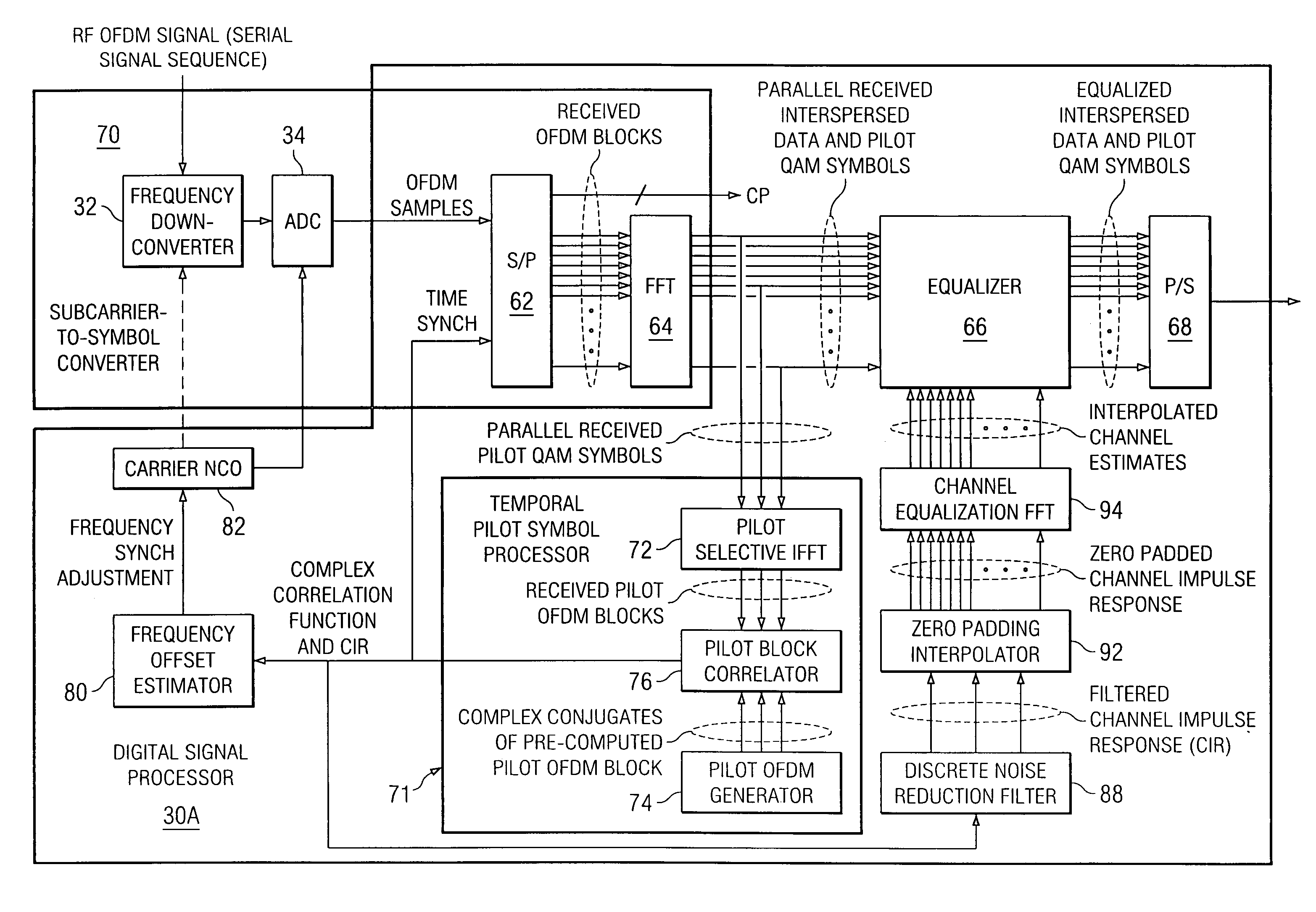
ActiveUS7139320B1Extension of timeTransmission path divisionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPilot systemChannel impulse response
Method and apparatus for OFDM synchronization and channel estimation. In a temporal embodiment, received embedded system pilot symbols are inverse Fourier transformed at expected index locations and correlated with computed complex conjugates of inverse Fourier transforms of pilot symbols for providing a correlation function for the channel impulse response. In a frequency domain embodiment, embedded system pilot symbols are augmented with pilot-spaced inferred guard band symbols, multiplied by scaled complex conjugates of computed pilot systems, and inverse Fourier transformed into the channel impulse response. Time and frequency are synchronized in feedback loops from information in the channel impulse response. The channel impulse response is filtered, interpolated, and then Fourier transformed for determining channel estimates for equalization.
Owner:RADIA COMM
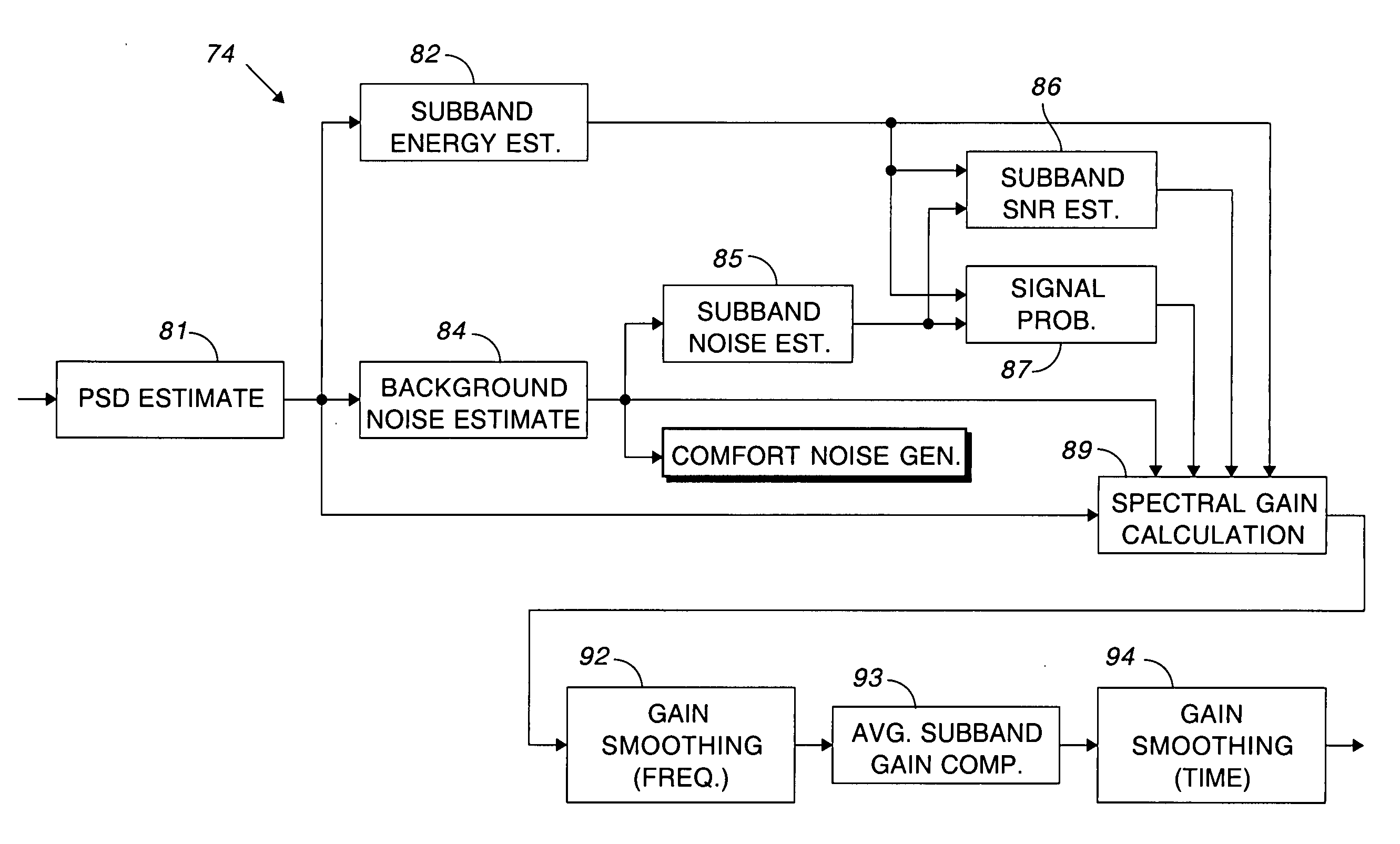
Comfort noise generator using modified doblinger noise estimate
ActiveUS20050278171A1Generate efficientlyEliminates noise pumpingSpeech analysisTime domainComfort noise
A background noise estimate based upon a modified Doblinger noise estimate is used for modulating the output of a pseudo-random phase spectrum generator to produce the comfort noise. The circuit for estimating noise includes a smoothing filter having a slower time constant for updating the noise estimate during noise than during speech. Comfort noise is smoothly inserted by basing the amount of comfort noise on the amount of noise suppression. A discrete inverse Fourier transform converts the comfort noise back to the time domain and overlapping windows eliminate artifacts that may have been produced during processing.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com