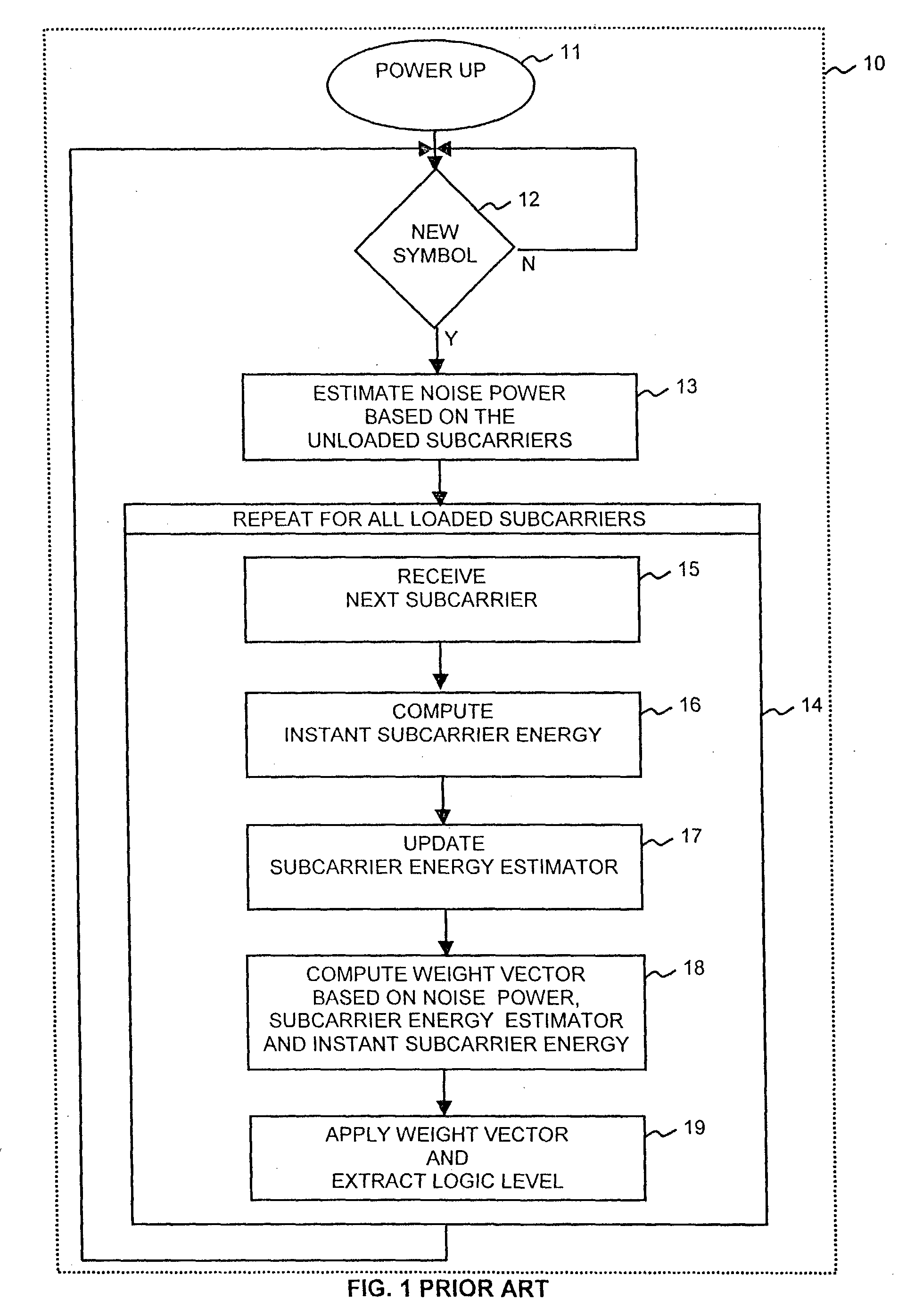
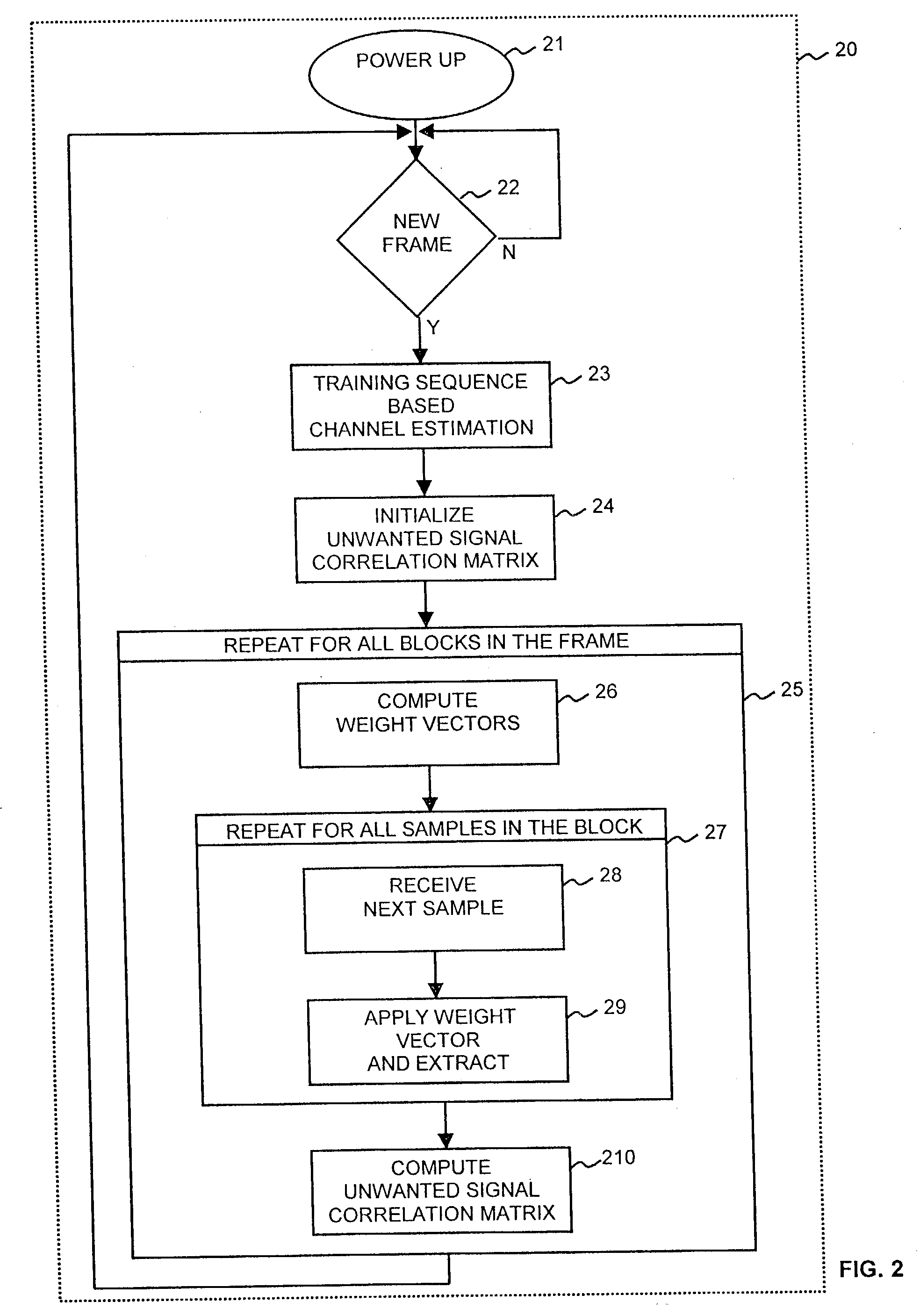
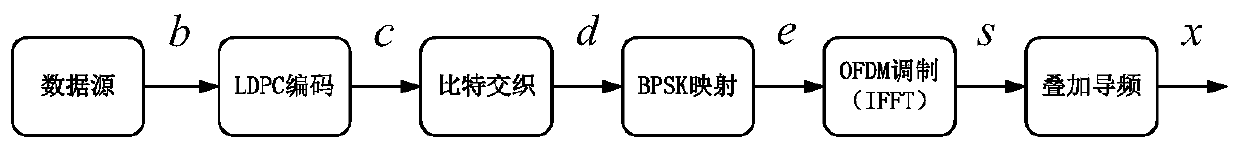
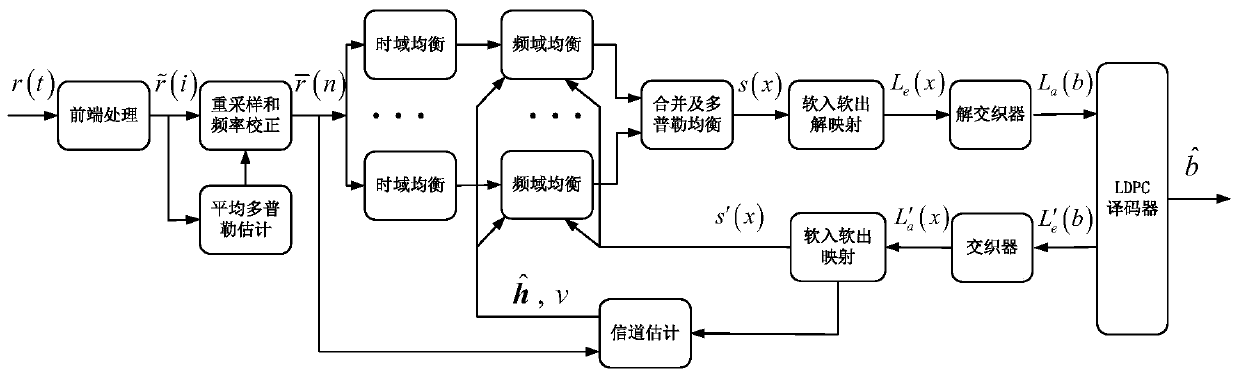
Patents
Literature
250 results about "Diversity combining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
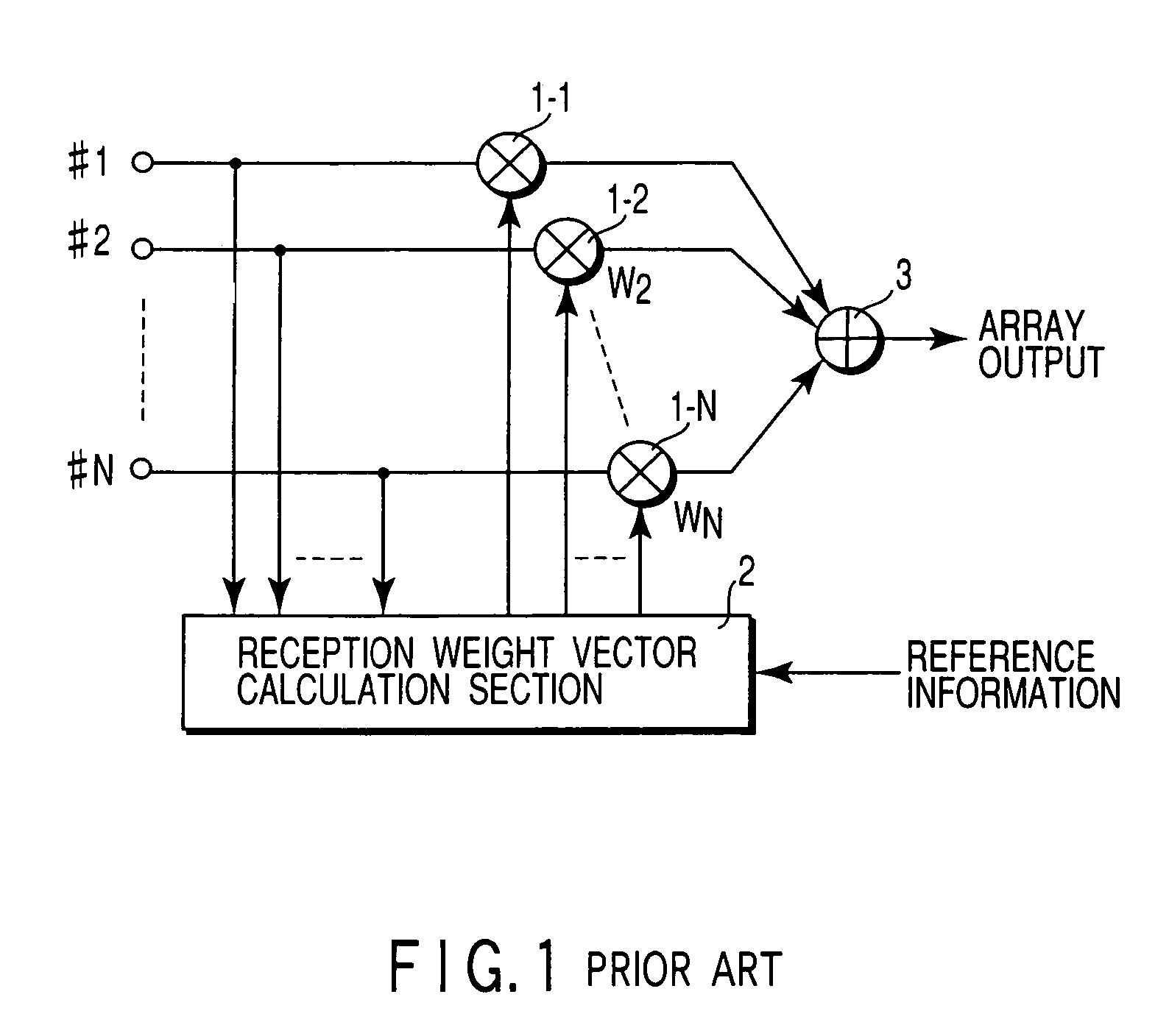
Diversity combining is the technique applied to combine the multiple received signals of a diversity reception device into a single improved signal.
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
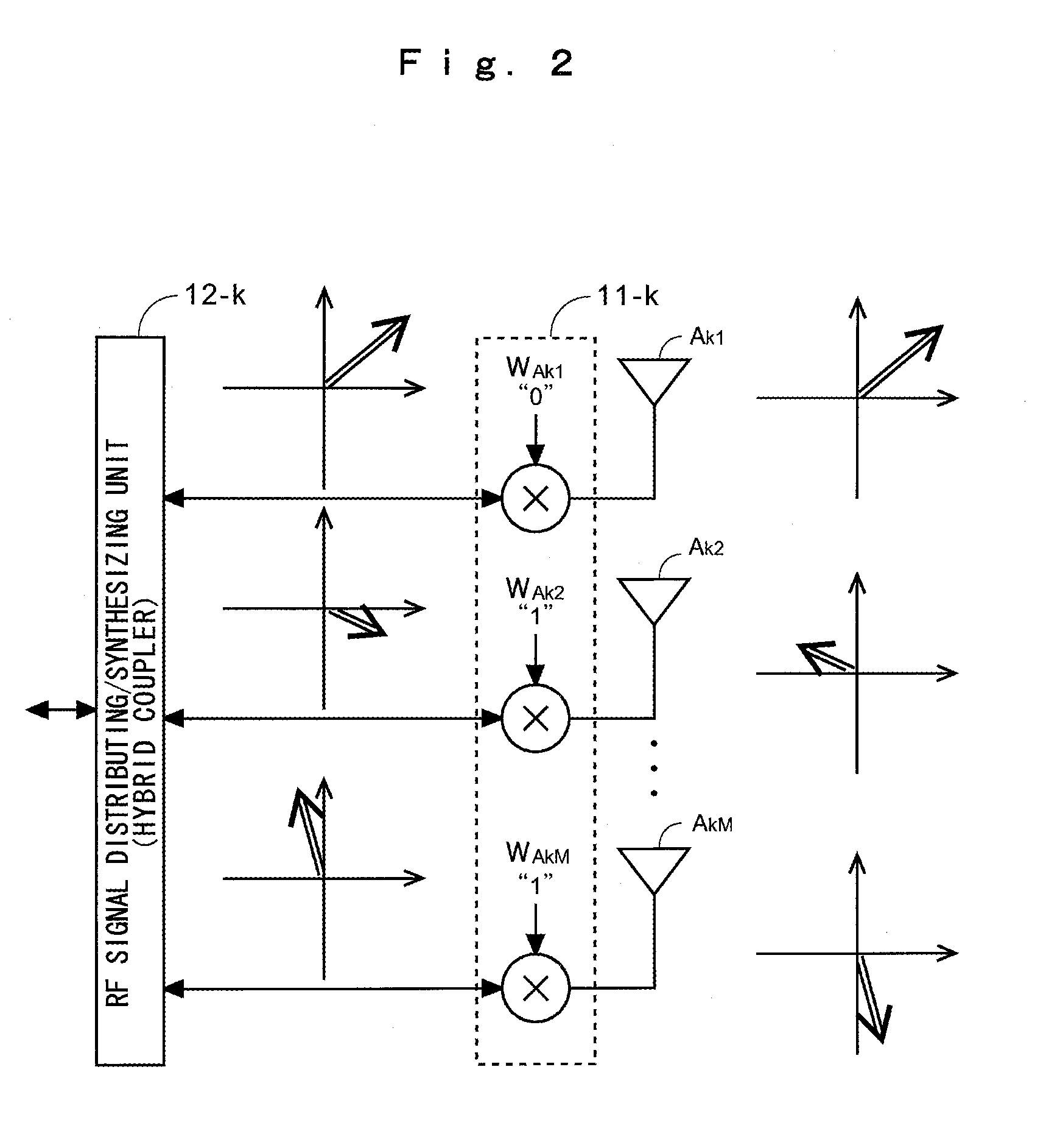
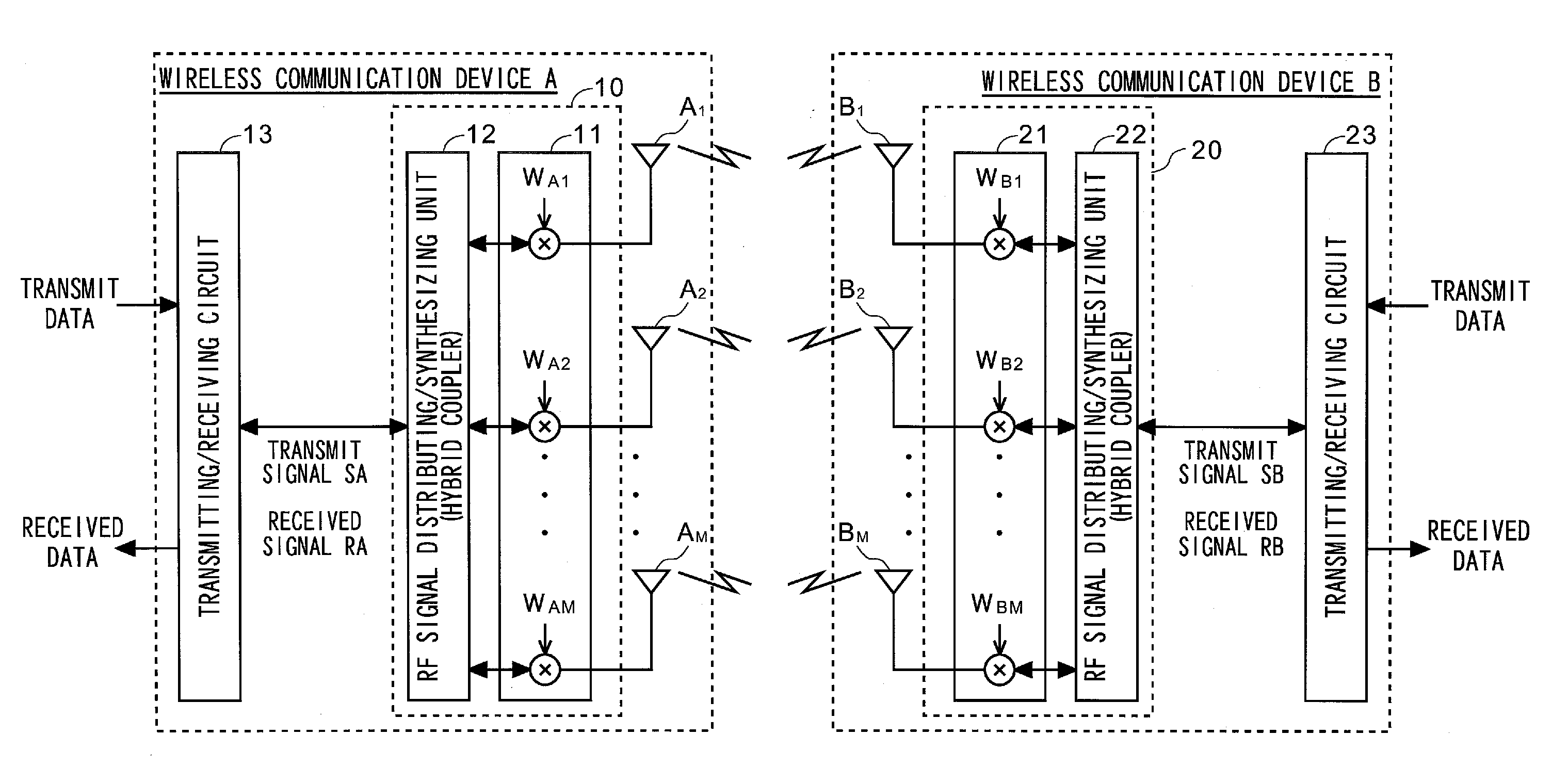
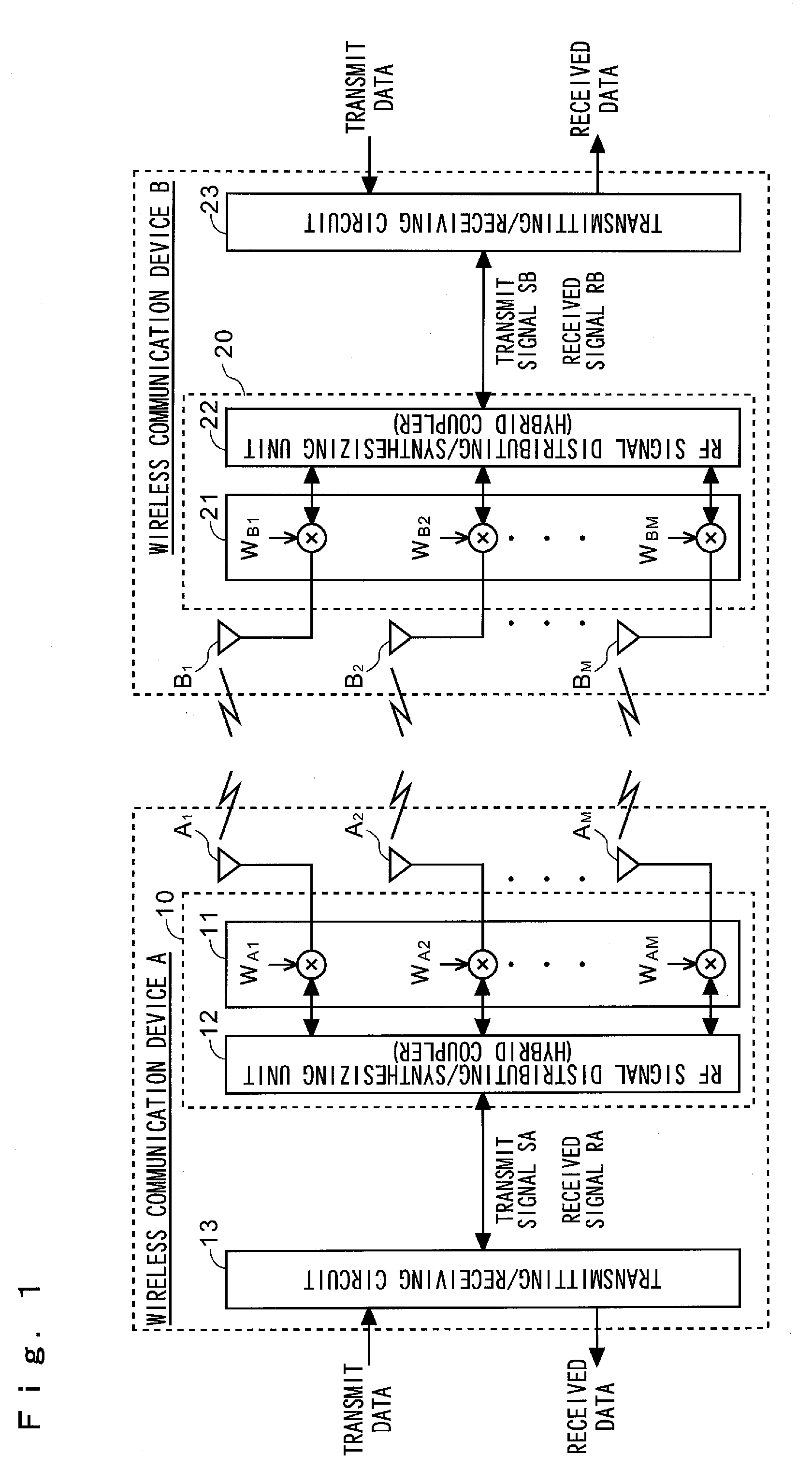
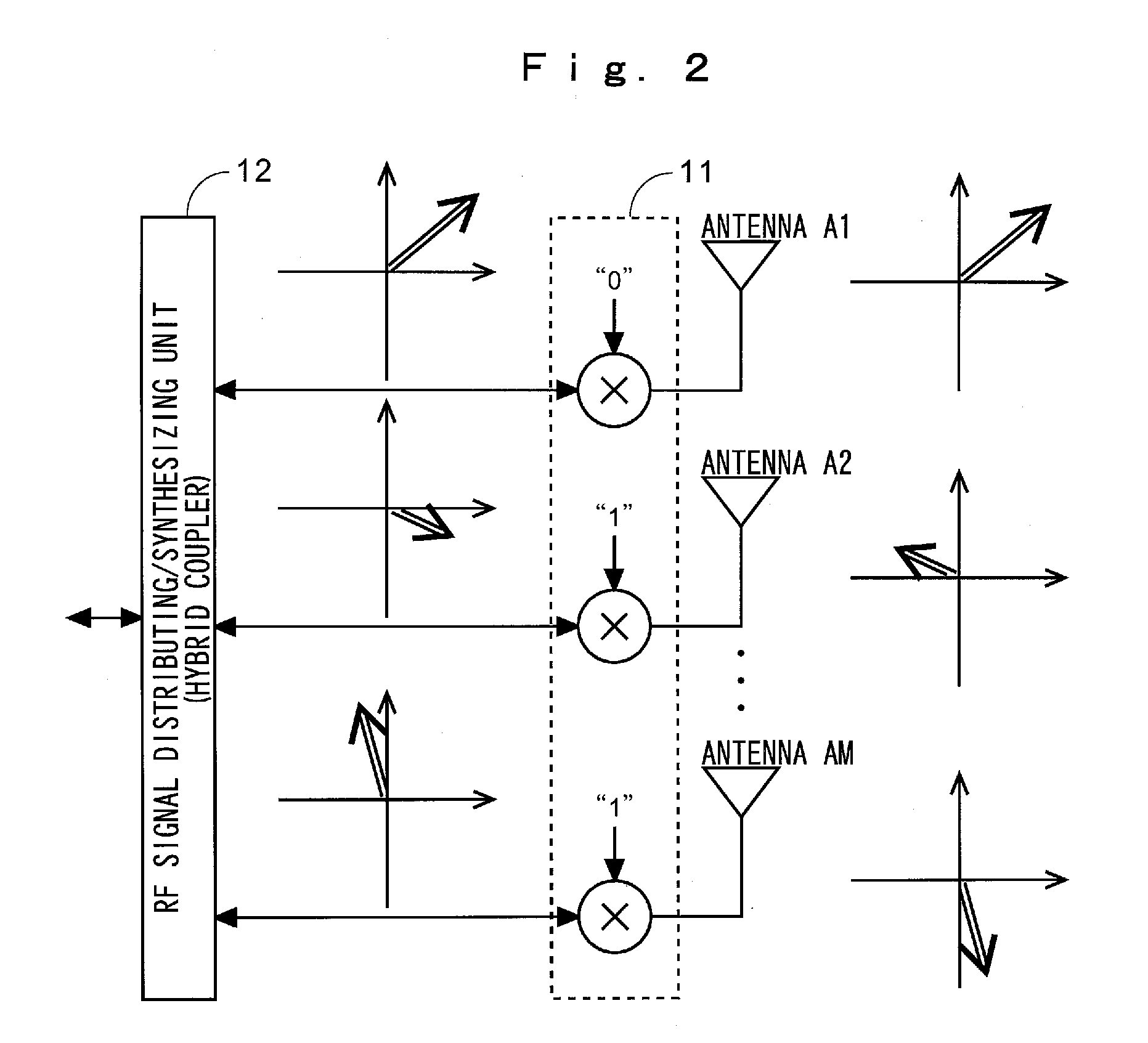
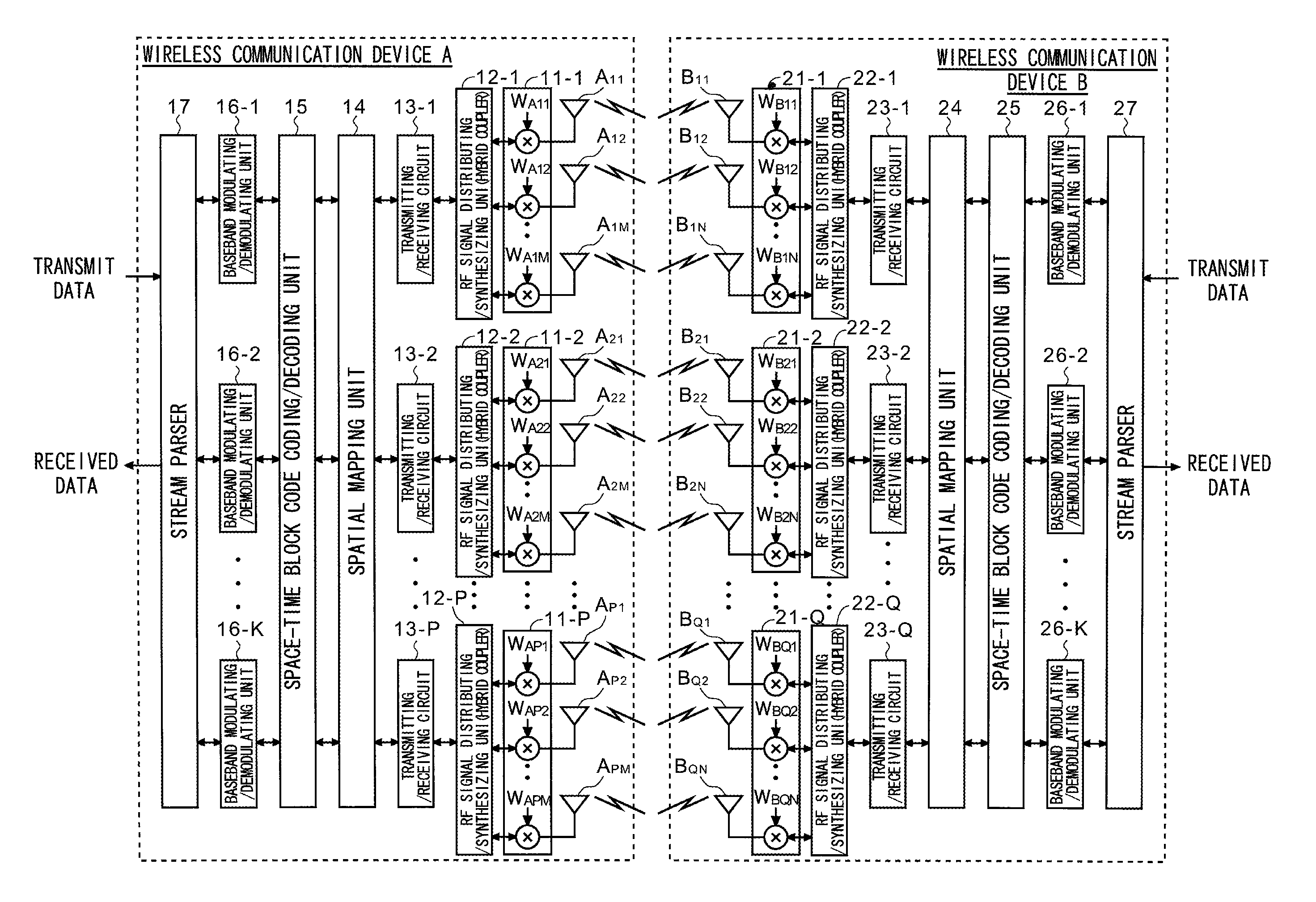
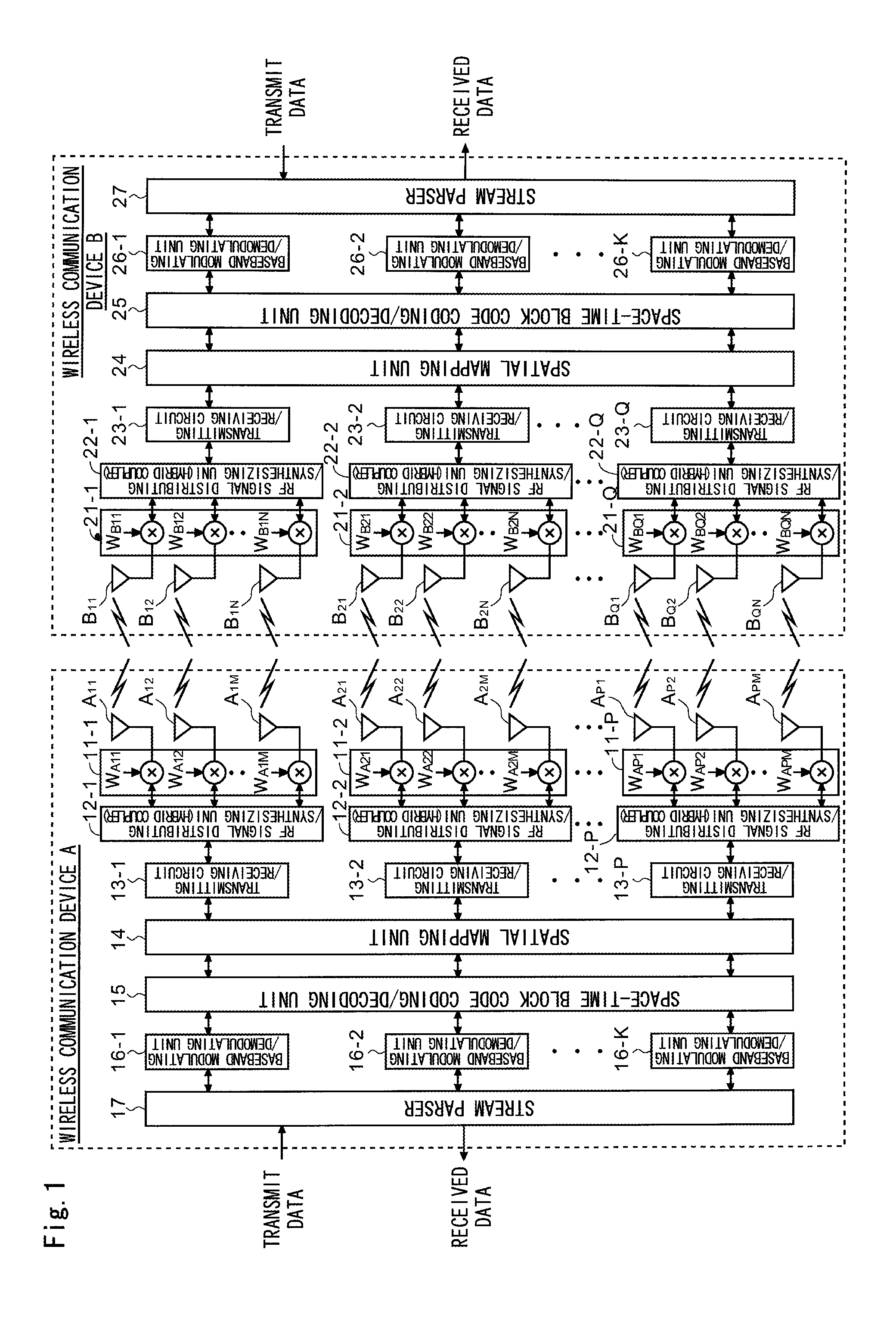
Multi-antenna wireless communication method and multi-antenna wireless communication device
InactiveUS20110268037A1Improve throughputEasy to calculateModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionCommunication unitSpatial mapping
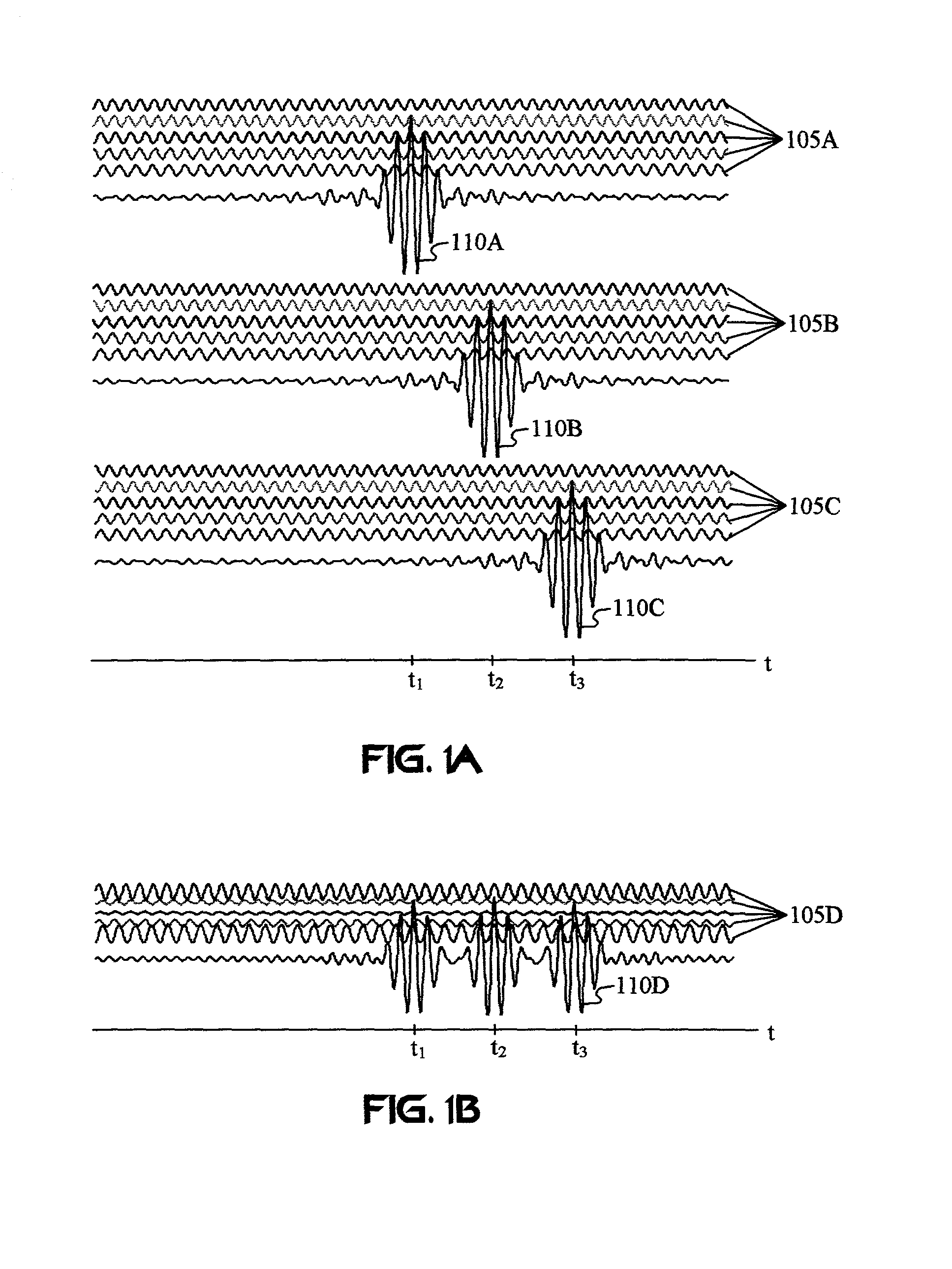
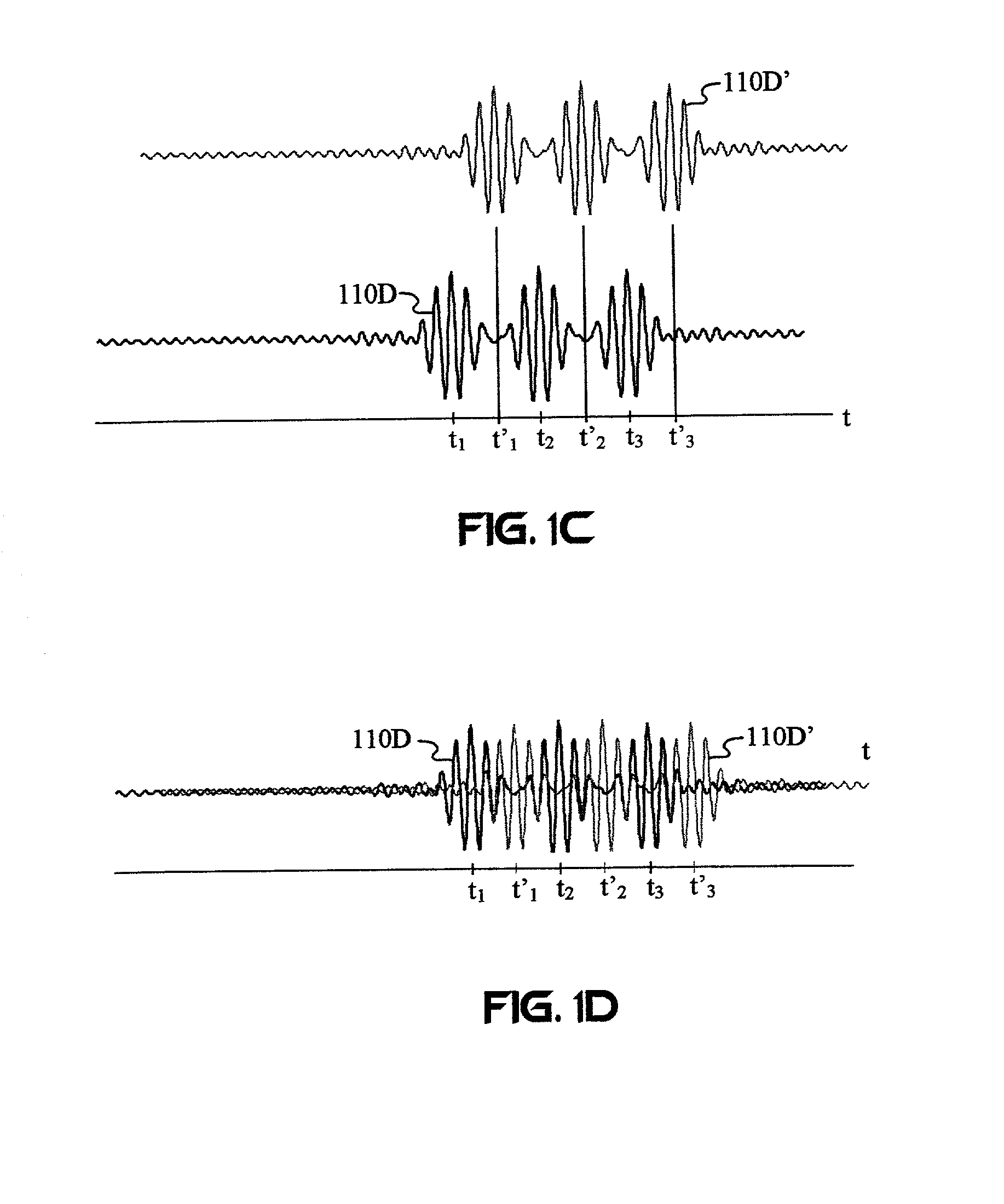
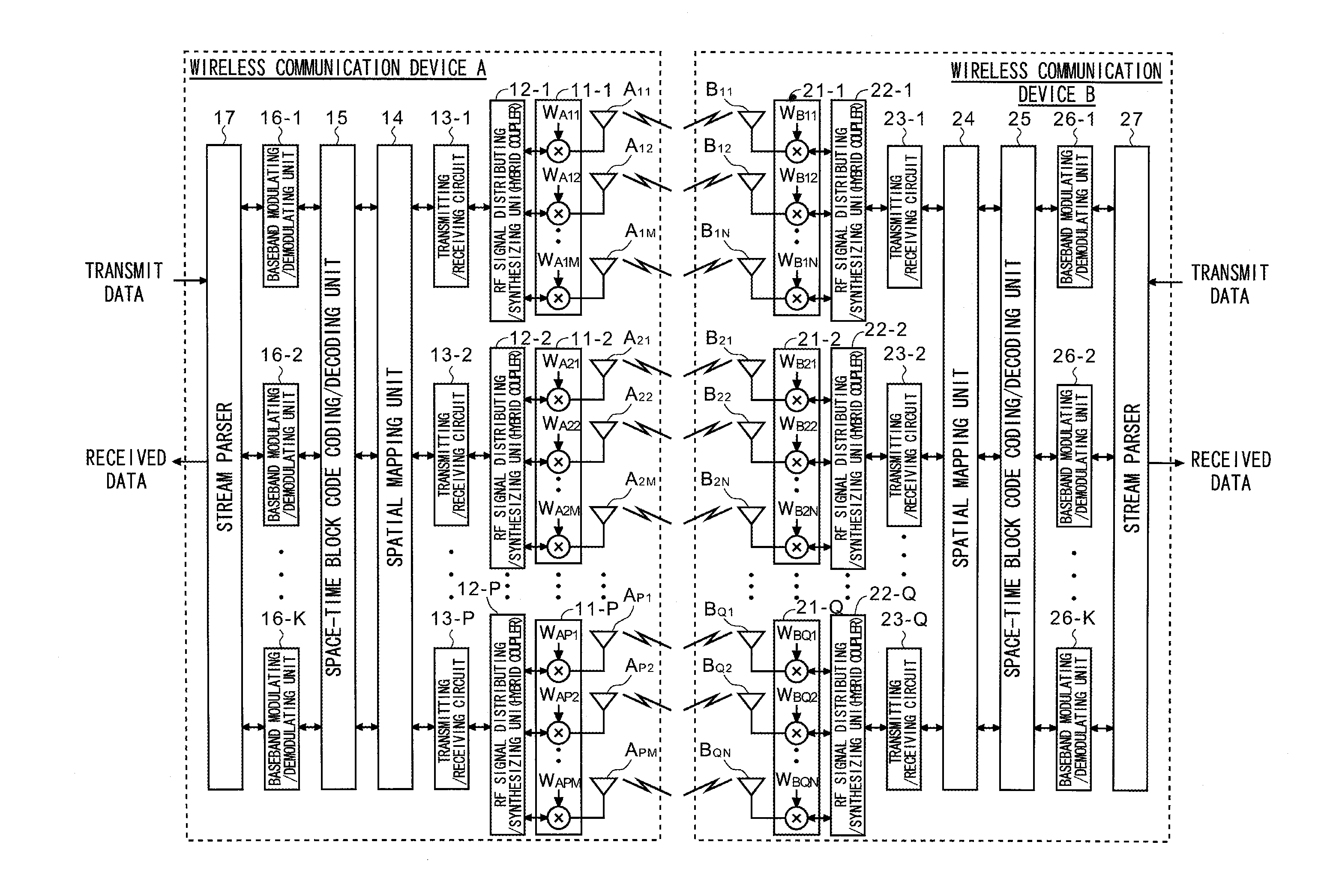
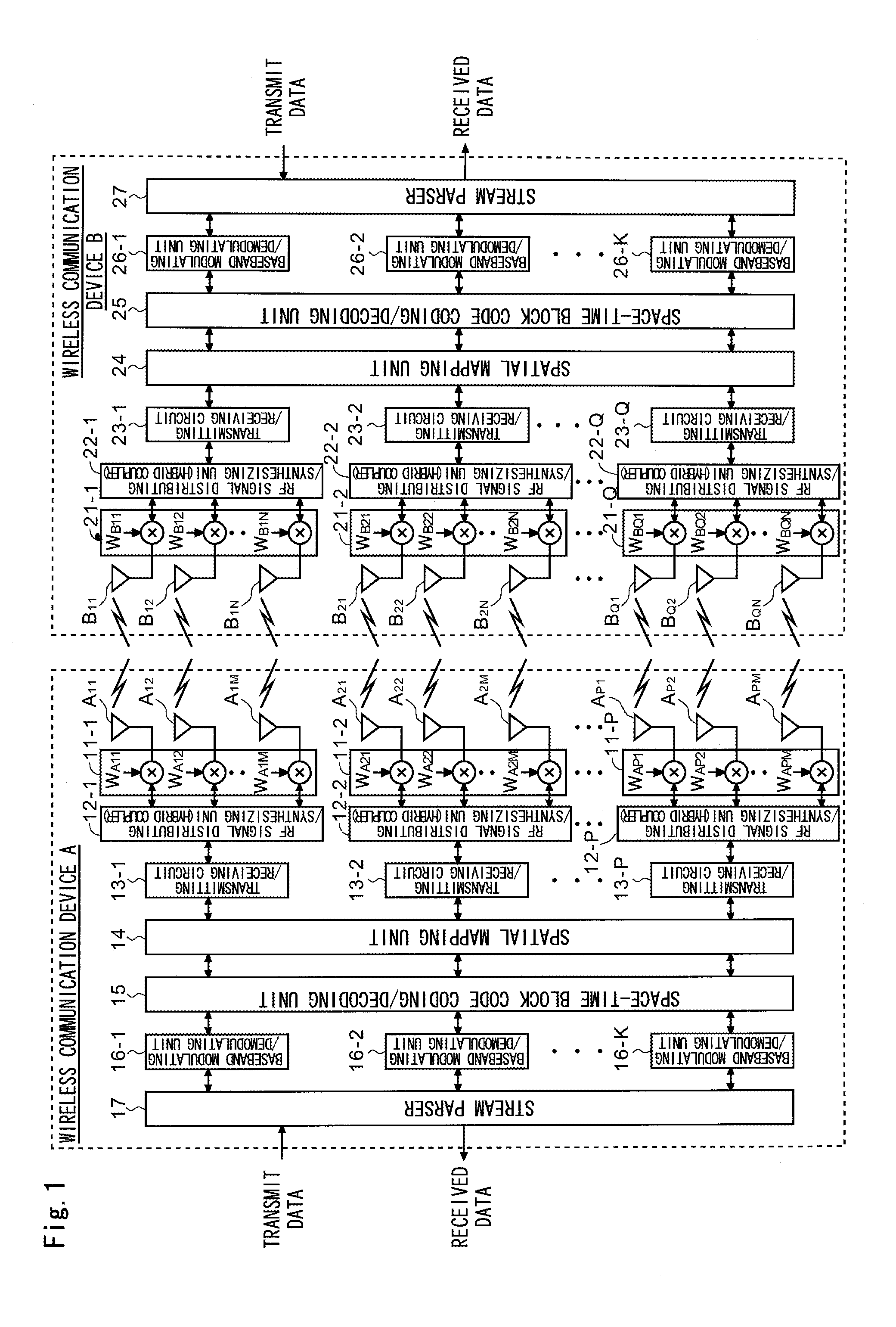
The wireless communication devices A and B determine the optimal diversity combining weight information that optimizes a diversity reception state at each antenna group A1, A2, . . . , AP through two-way training signal transfer between the wireless communication devices A and B. This optimal diversity combining weight information is set to each antenna of each antenna group A1, A2, . . . , AP. Wireless communication units A′, B′ perform spacial mapping of signals from antenna group A1, A2, . . . , AP using MIMO technology. Communication area can be enlarged by hierarchization MIMO using the optimal diversity combining weight information.
Owner:IWATSU ELECTRIC CO LTD
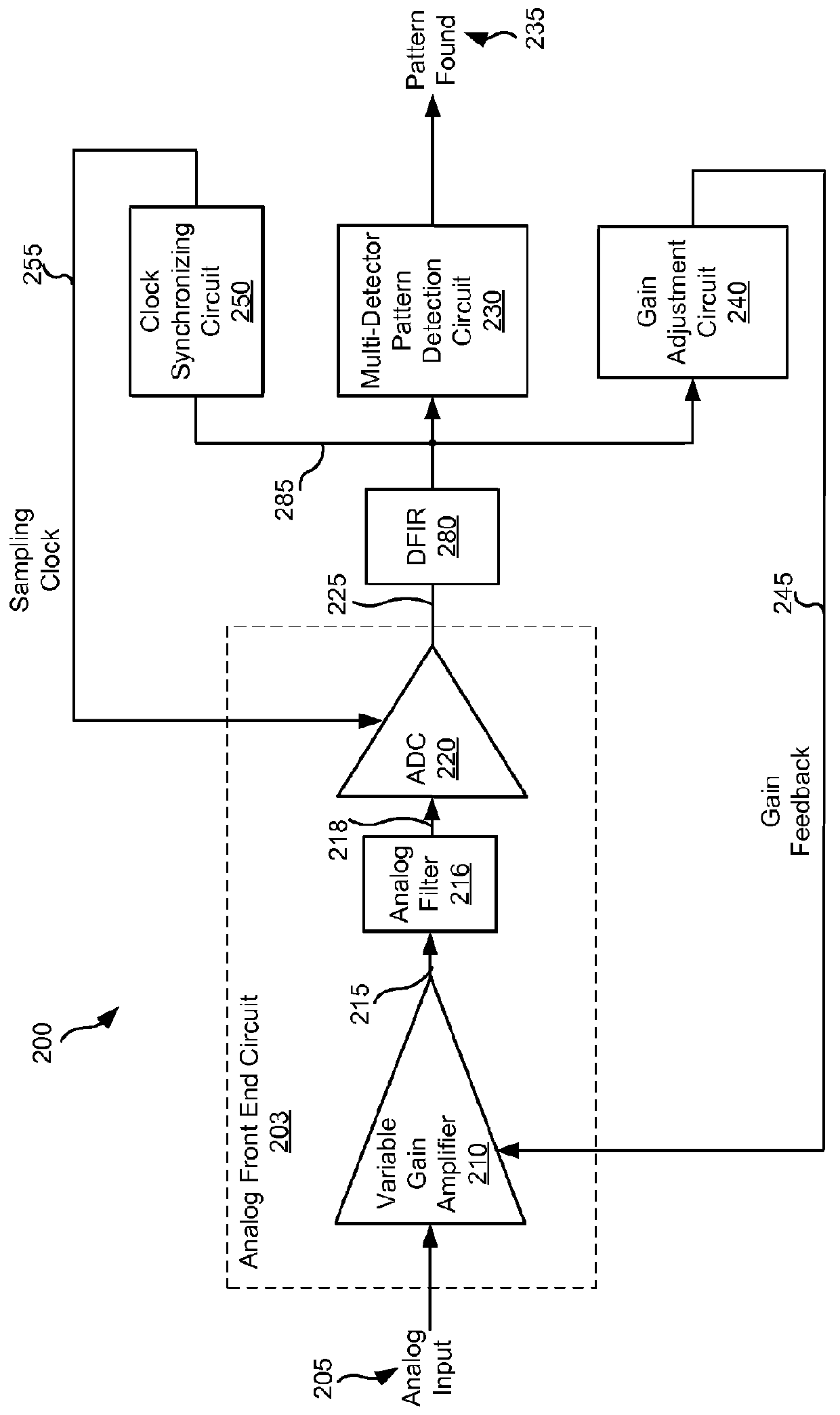
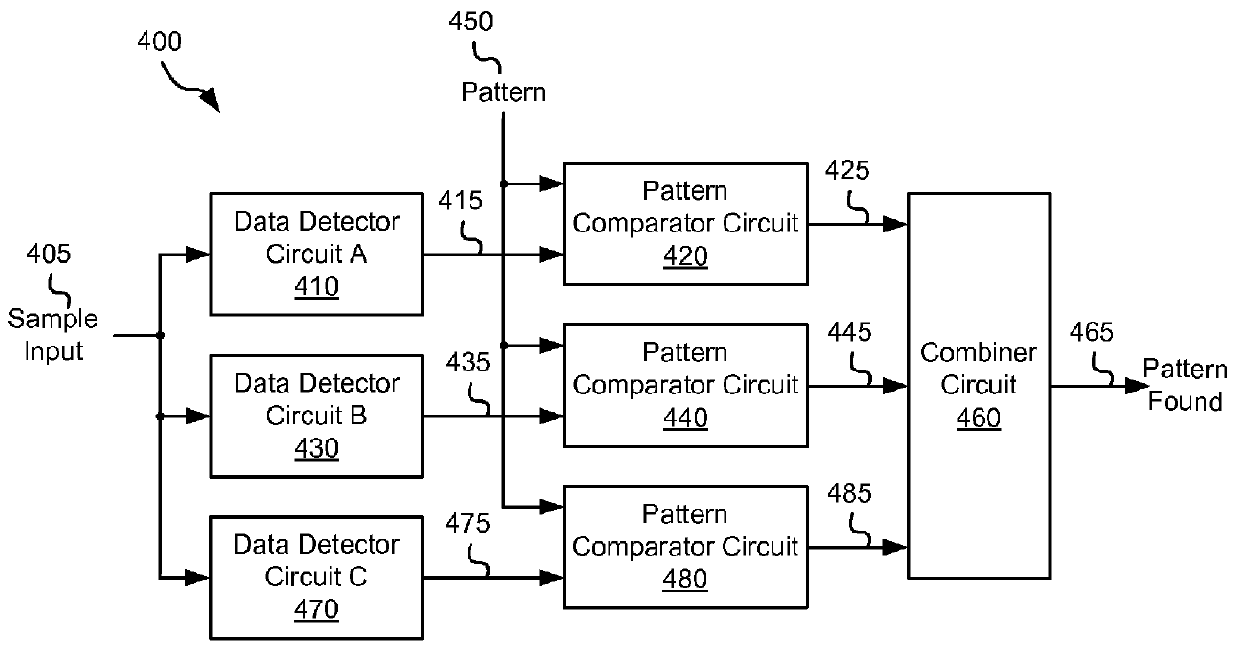
Systems and methods for diversity combined data detection
InactiveUS8261171B2Data representation error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsDetector circuitsPattern detection
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data processing. For example, some embodiments of the present invention provide data processing circuits including a pattern detection circuit having at least two data detector circuits each operable to receive the same series of data samples and to provide a first detected data output and a second detected data output, respectively. In addition, the data pattern detection circuit includes a result combining circuit that is operable to assert a pattern found output based at least in part on the first detected data output and the second detected data output.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Multi-antenna wireless communication method, multi-antenna wireless communication system, and multi-antenna wireless communication device
InactiveUS20110150066A1Easy to calculateReducing arithmetic amountDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemDiversity scheme
Wireless communication devices A and B perform wireless communication with the MIMO technology. The wireless communication devices A and B determine the optimal diversity combining information that optimizes a diversity reception state through a two-way training signal transfer. This determination can be made based on reception level information, baseband reception IQ information, correlation information between a diversity-combining received signal and a predetermined information sequence, or the like, which are obtained when the diversity combining information with respect to each antenna is sequentially changed. The optimal diversity combining information can be determined by receiving training frames or symbols (the number of antennas+1) times.
Owner:IWATSU ELECTRIC CO LTD
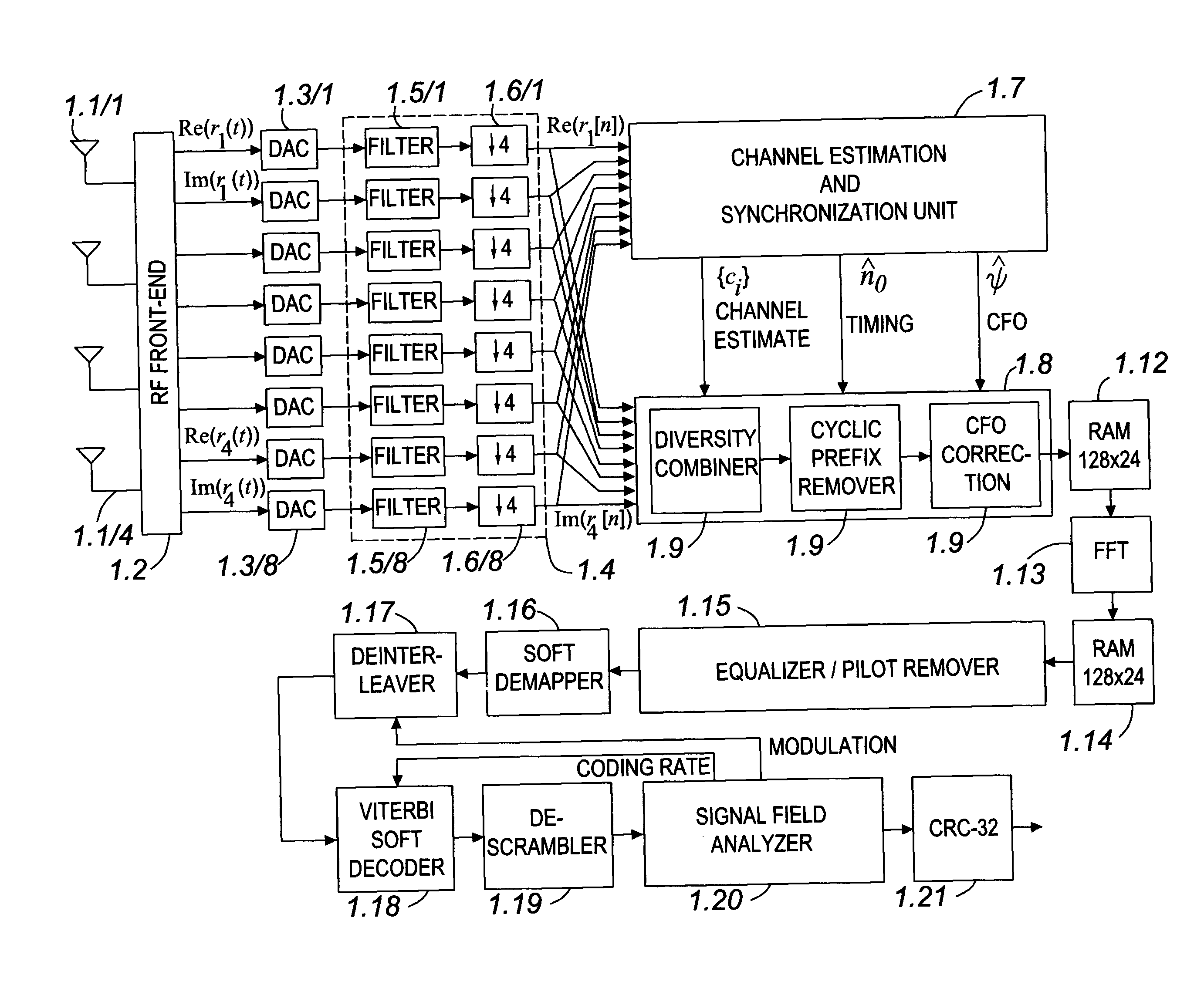
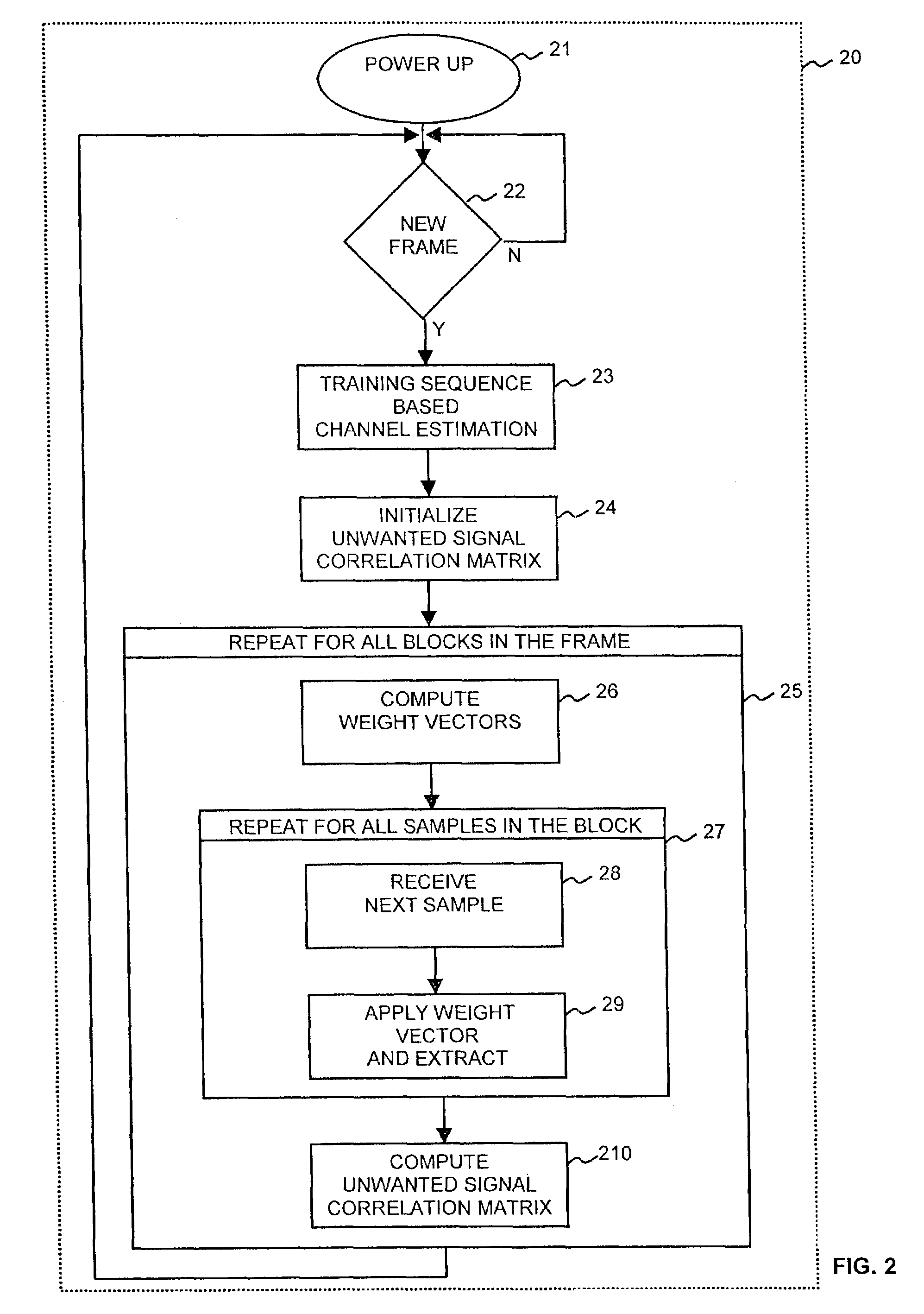
Method and apparatus for signal acquisition in OFDM receivers
InactiveUS20110293040A1Electric signal transmission systemsAdaptive networkCarrier frequency offsetEngineering
A method and apparatus for signal acquisition in an OFDM receiver relies on a preamble training sequence to synchronize the receiver in time (e.g. determining the start of a frame) and in frequency (carrier frequency offset compensation). The preamble training sequence has a periodic structure and the method and apparatus perform a cross-correlation technique using a matched filter to achieve time synchronization and / or frequency synchronization and / or channel estimation, the latter being especially useful in multi-antenna receivers for diversity combining purposes. Many advantages derive from performing at least two and preferably all three operations jointly, in terms of latency, hardware complexity, and length of training sequence required to achieve satisfactory convergence on all counts. The periodicity of the training sequence is exploited to reduce considerably the main filter complexity and optionally dynamically adjust carrier offset compensation throughout the filtering process, thus improving the quality of all final estimates (carrier frequency offset, time synchronization, and channel).
Owner:DUPONT LOUIS +1
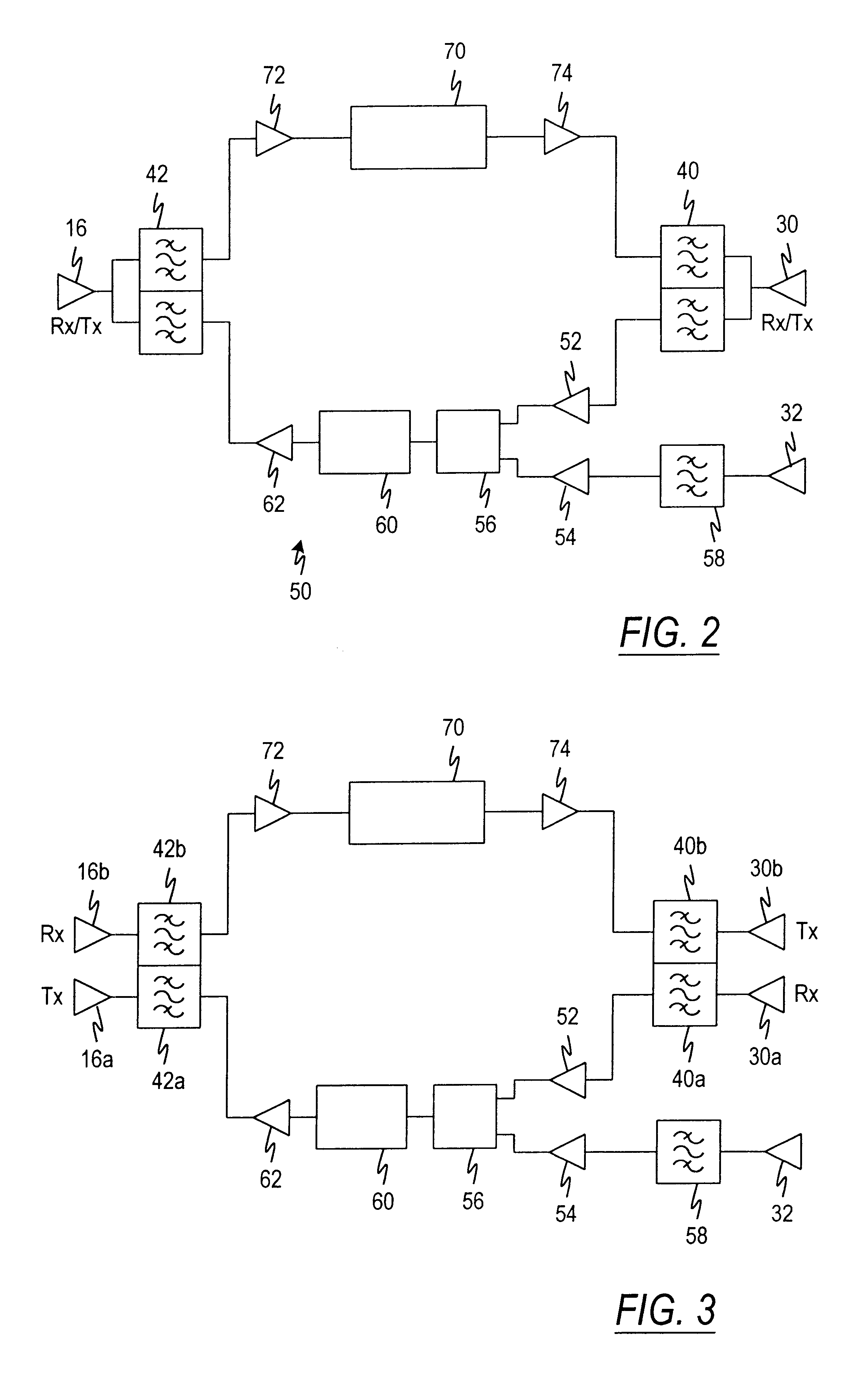
Repeater diversity system
InactiveUS6445904B1Improve reception performanceActive radio relay systemsRepeater circuitsEngineeringDiversity scheme
A repeater diversity system includes a null antenna having a given phase center and polarization for receiving a communications signal from a remote signal source, a donor antenna for transmitting a signal to a base station, and a diversity null antenna having the same phase center as the receive null antenna and a polarization orthogonal to the polarization of the main null antenna. A combining network is coupled to the main null antenna and the diversity null antenna for combining the signals therefrom and an uplink channel module is coupled with the combining network for delivering diversity combined receive signals to the donor antenna.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
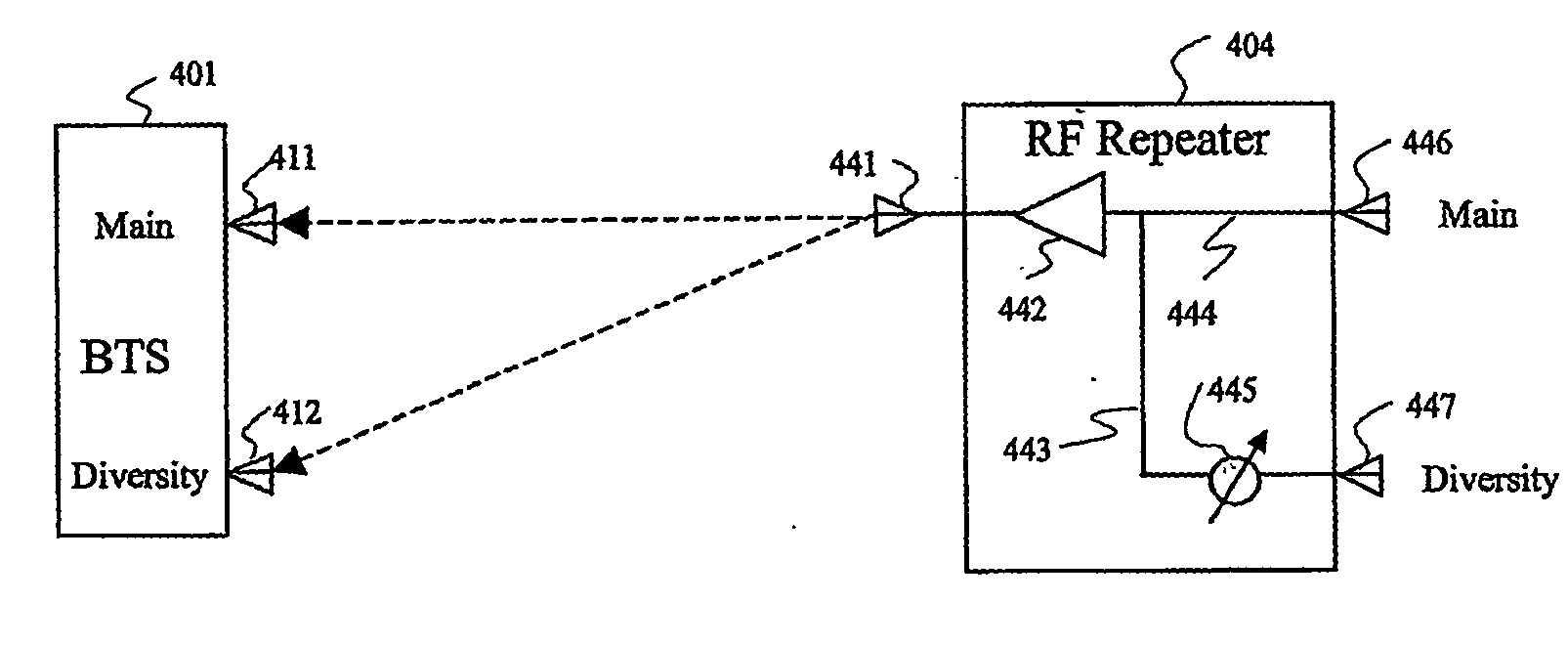
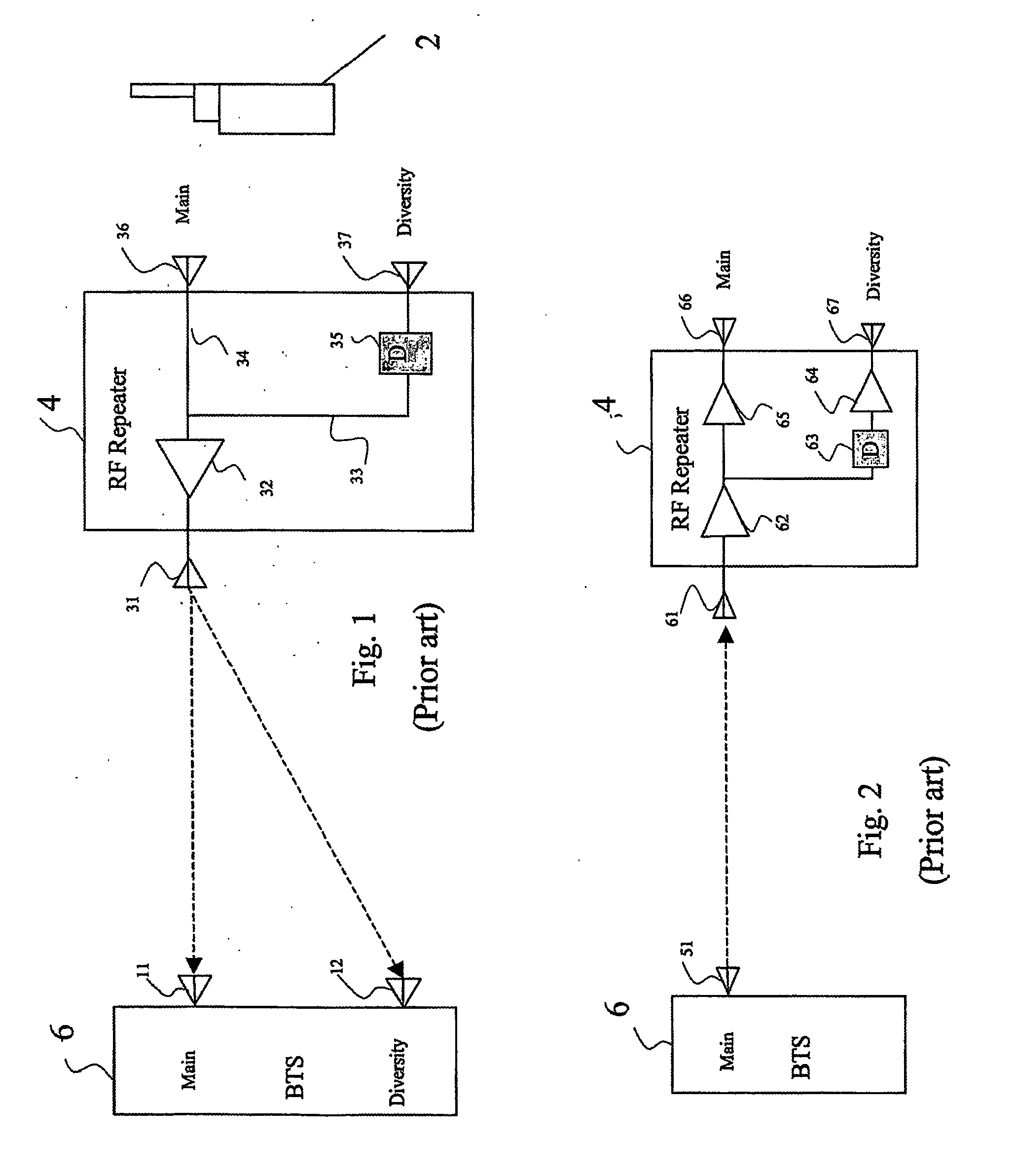
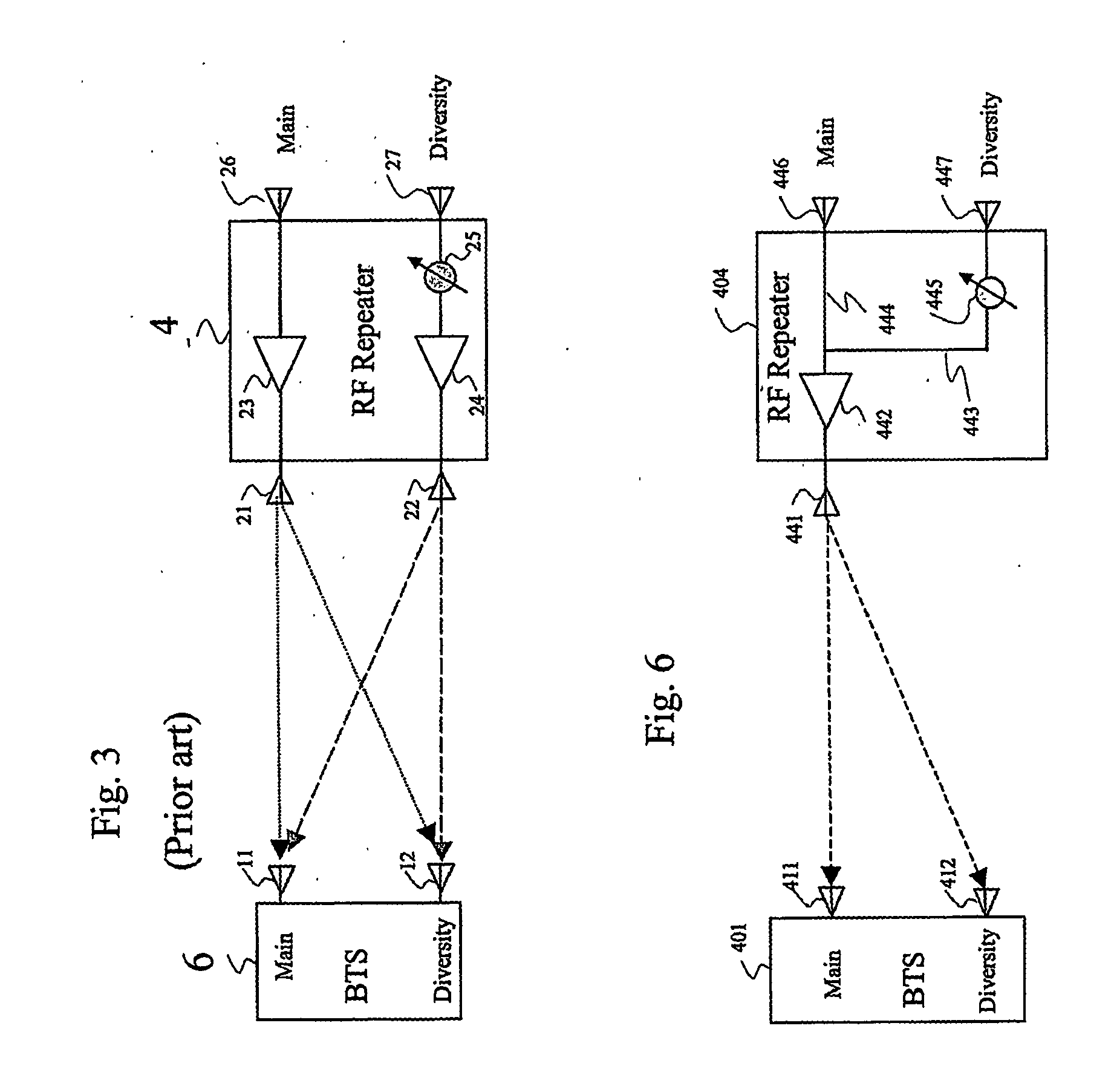
Phase sweeping methods for transmit diversity and diversity combining in bts sector extension and in wireless repeaters
InactiveUS20060172710A1Spatial transmit diversityElectromagnetic wave modulationEngineeringWireless repeater
Apparatus for inserting transmit diversity into an RF signal for transmission, comprises: an RF splitter for splitting the RF signal to be transmitted into two signal parts, and a non-linear phase modulator which applies a non-linear phase modulation to one of the two signal parts, thereby to provide transmit diversity between the first signal part and the second signal part. One of the ways of inserting a non-linear phase modulation into the RF signal is to use a spinning disc with tracks of different dielectric strength. The apparatus is useful in cellular telephony for supplying repeaters and base station extensions with diversity capability.
Owner:CELLETRA
Efficient diversity combining for wideband downlink
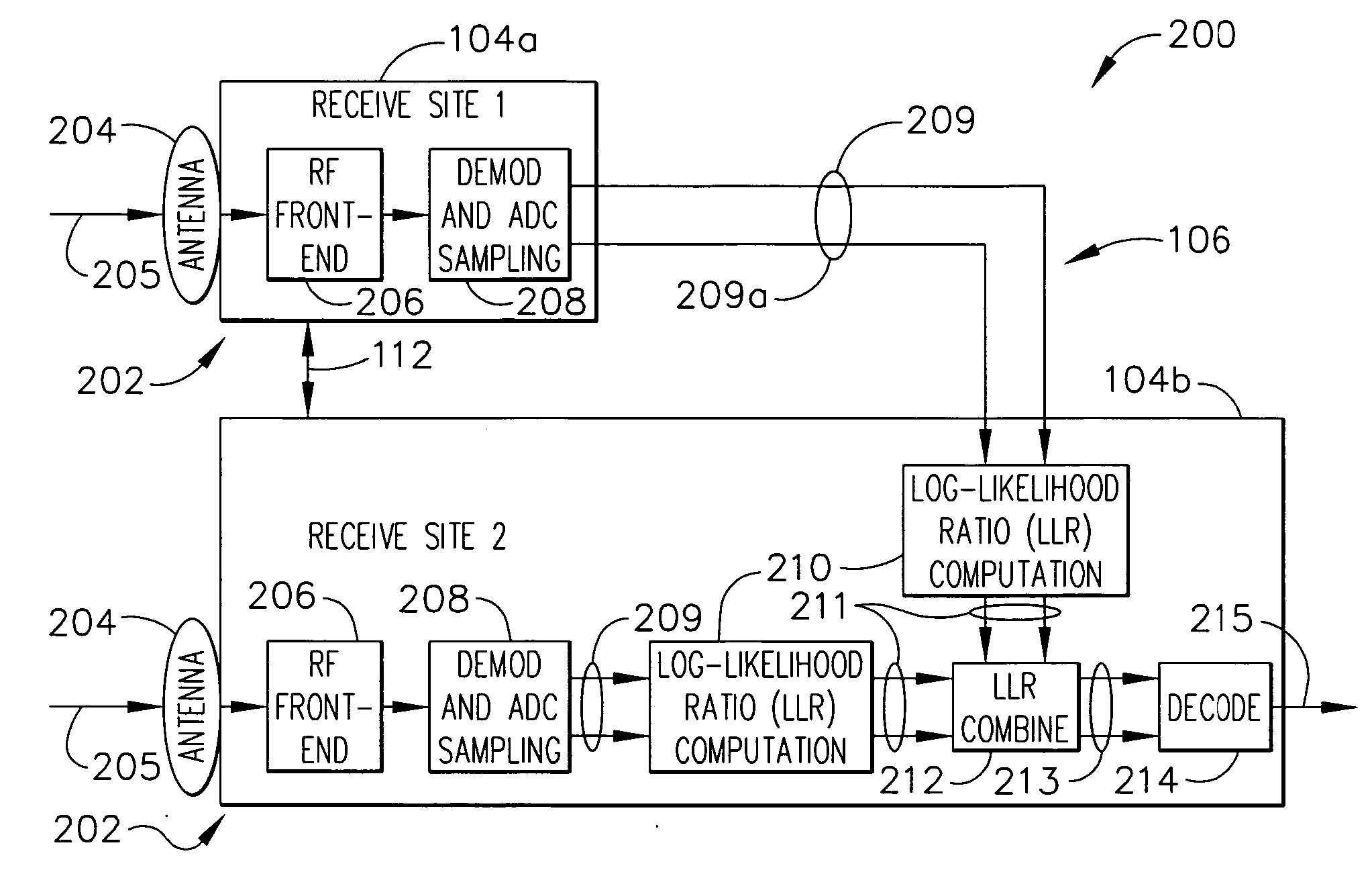
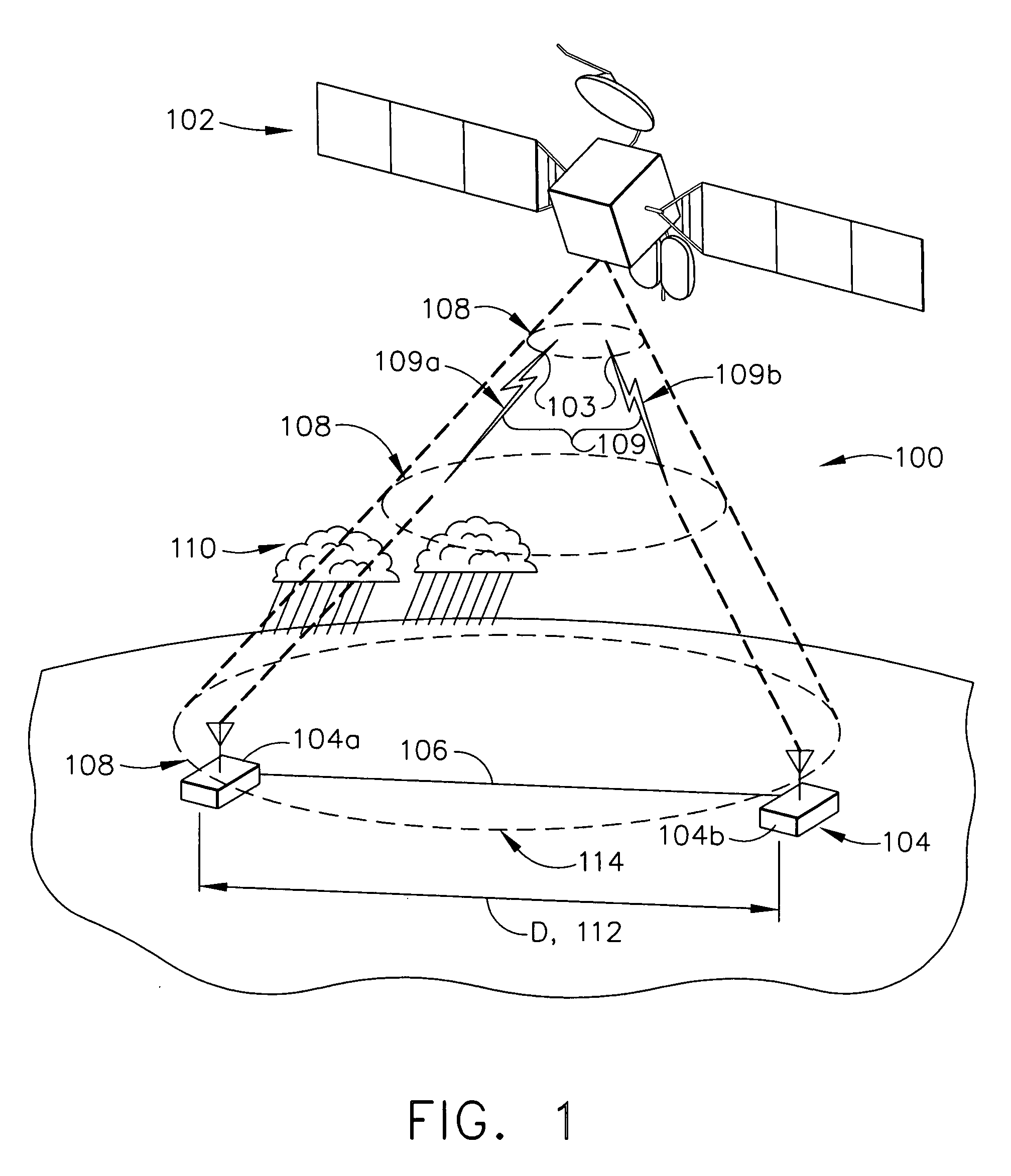
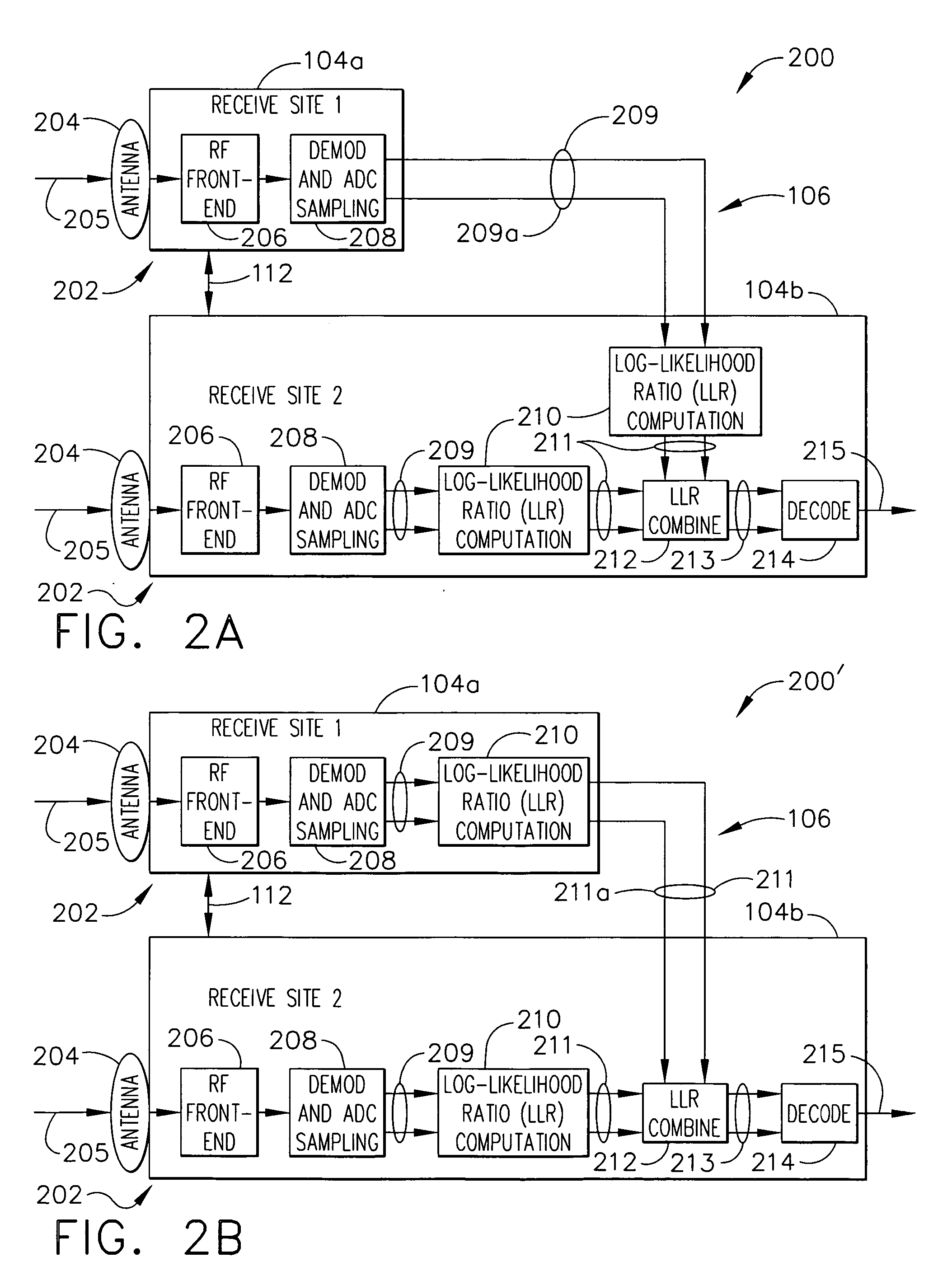
A communication system employing site diversity combing to increase link availability includes at least two receivers at receive sites within a single downlink beam separated by enough distance to provide decorrelation of weather phenomena—such as rain fade outages. A signal transmits digital symbols to all the receivers and may use bandwidth efficient modulation with forward error correction coding. Sampled symbol values for each codeword are produced at each receiver, which are connected by one or more ground links so that all data can be collected at one site. At least two different soft-decision computation modules translate the sampled symbol values from the different receivers into different sets of soft-decision values—which may be log-likelihood-ratio (LLR) values reflecting the probability value for each bit of the codeword—that are digitally synchronized and combined for use by a decoder. The technique thus avoids disadvantages of either coherent waveform combining or BER-based digital switching.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
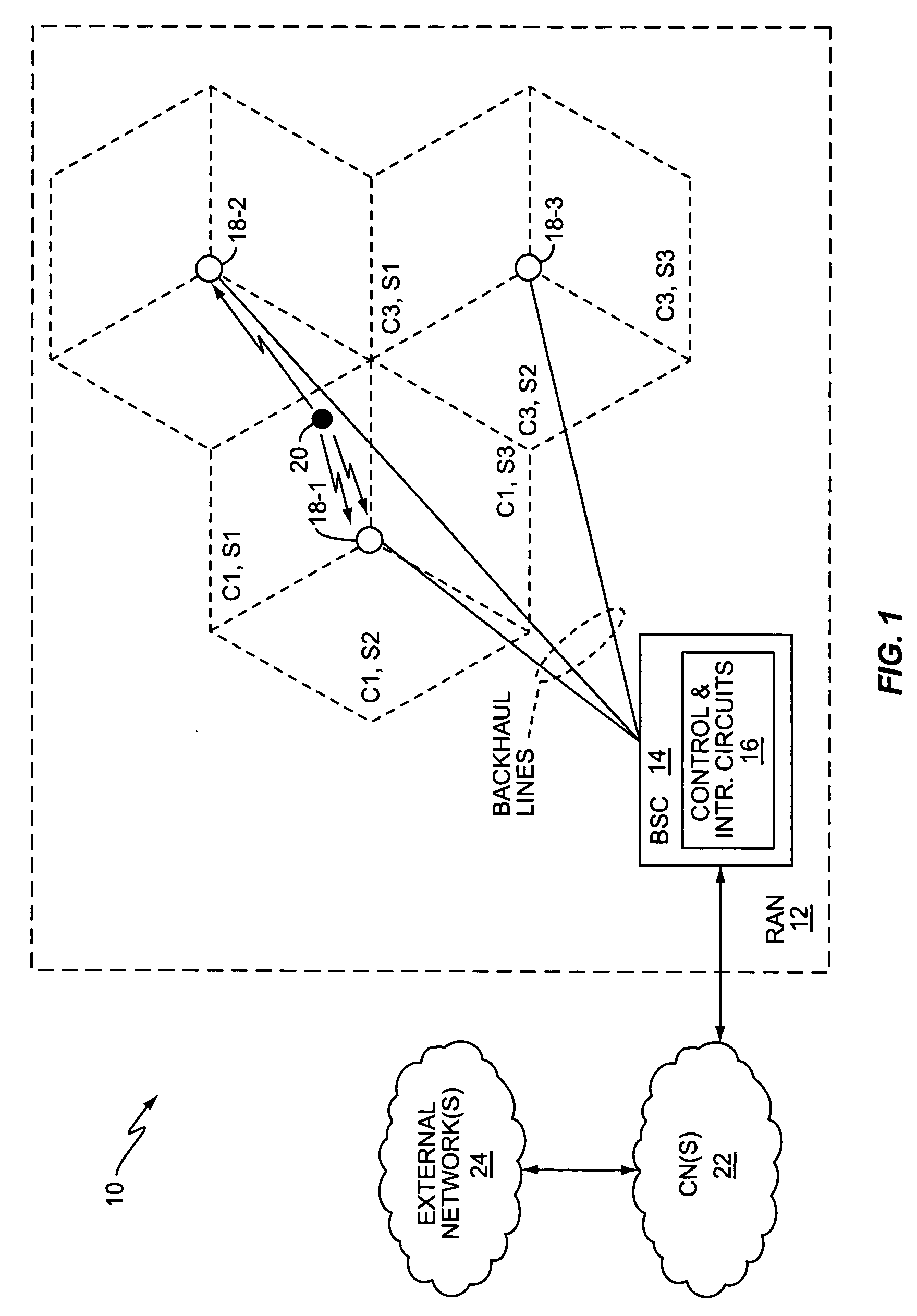
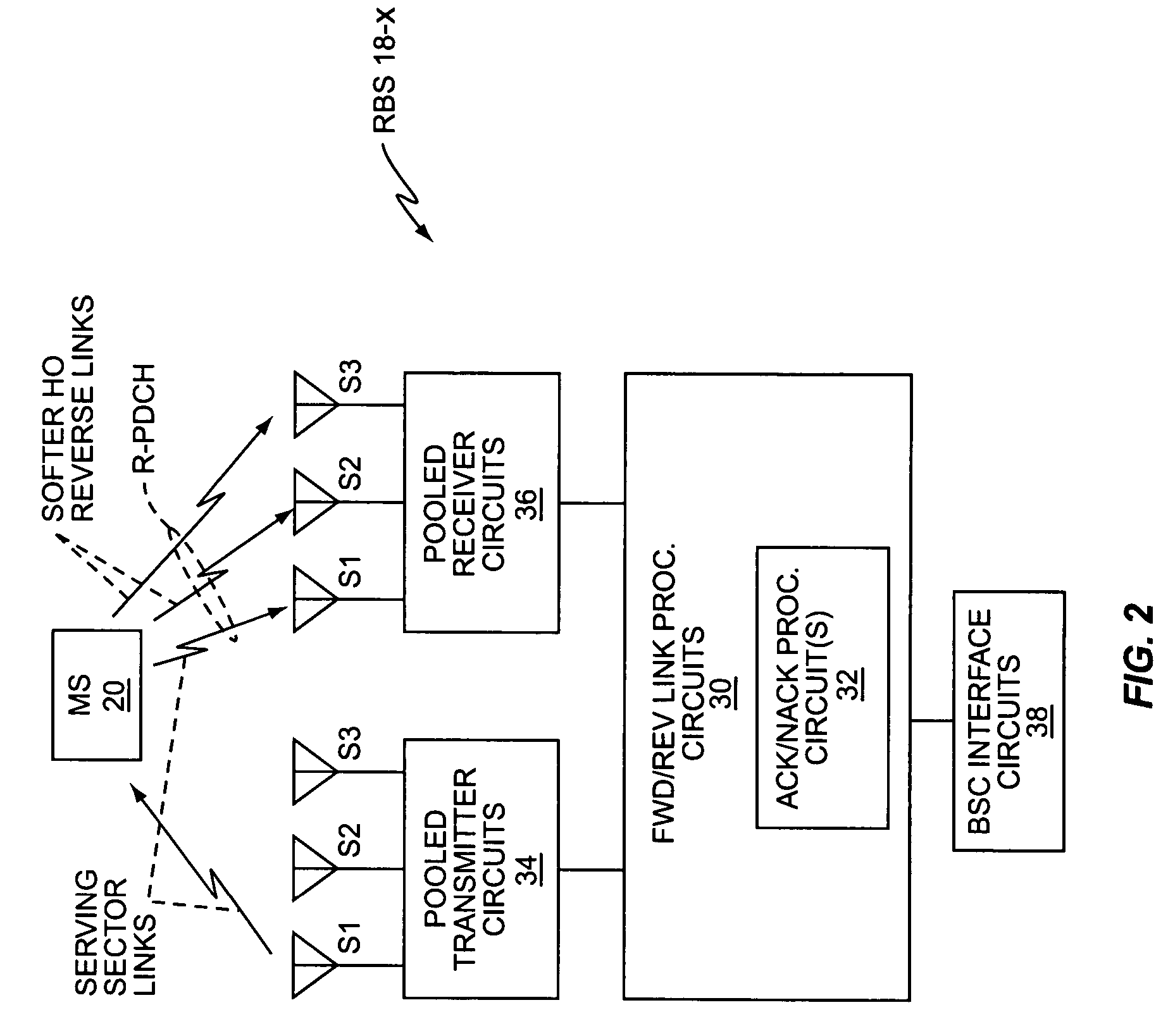
Method and apparatus for cell-site ARQ generation under softer handoff conditions
InactiveUS20050181834A1Improve reliabilityReduce power levelError prevention/detection by using return channelSubstation equipmentCell siteMobile station
A base station generates per-cell ACK / NACK responses rather than per-sector ACK / NACK responses. For a given mobile station signal received in softer handoff at two of the base station's sectors, the base station generates an ACK response if at least one of the soft handoff sectors correctly receives the signal, and otherwise generates a NACK response. Alternatively, the base station can combine the softer handoff signals and generate ACK / NACK responses based on whether the combined signal is correctly received. Since only one set of ACK / NACK responses are generated for all of the softer handoff sectors, the base station can use the forward link in just one softer handoff sector to send the ACK / NACK responses to the mobile station, consuming fewer forward link transmit resources at the base station. Or, the base station can send the same ACK / NACK responses from two or more softer handoff sectors, thus allowing diversity combining of the ACK / NACK responses at the mobile station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
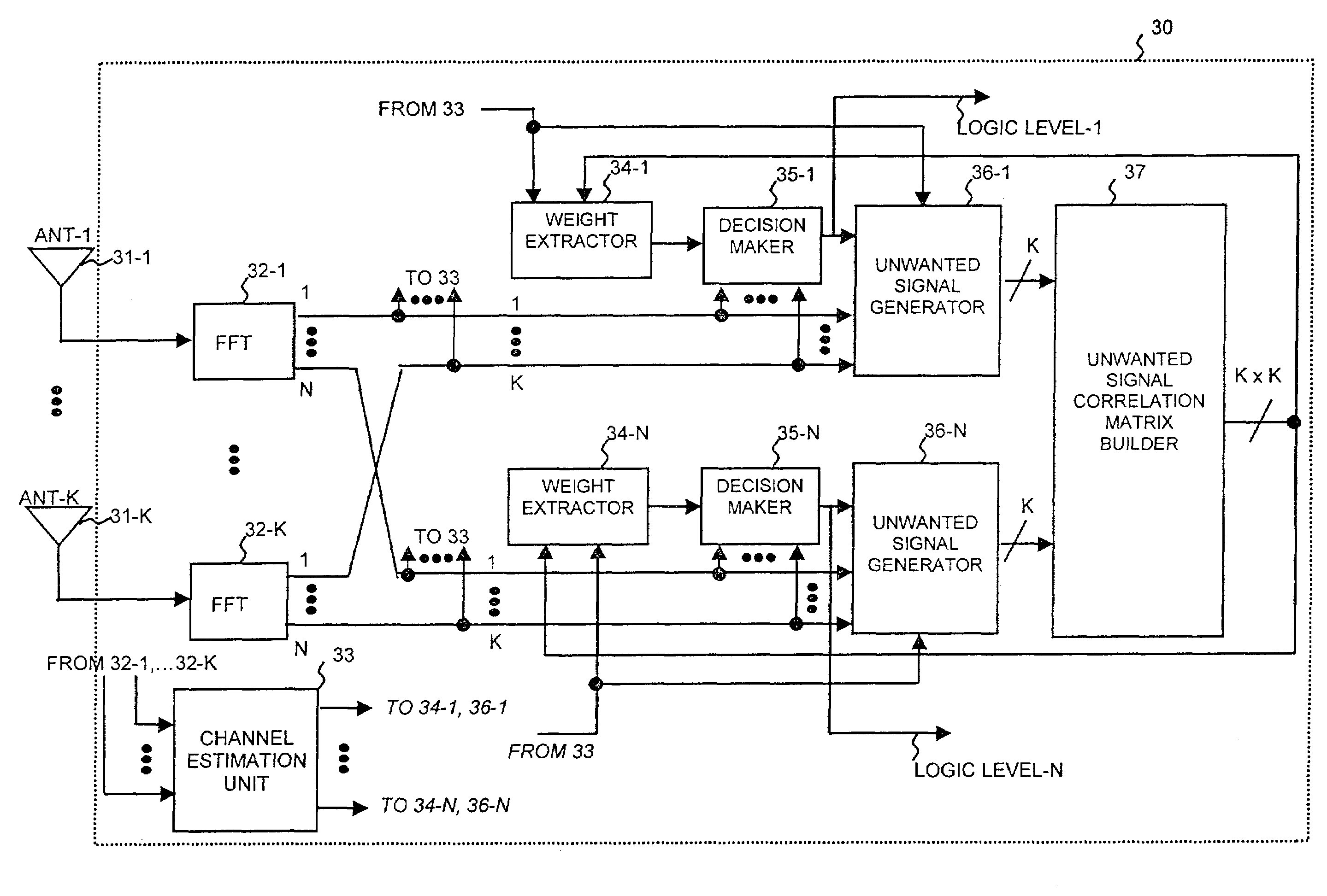
Method and apparatus for diversity combining and co-channel interference suppression
InactiveUS7295637B2Polarisation/directional diversityChannel estimationCommunications systemCombined use
A method and apparatus for controlling an antenna array for wireless communication are described. The method uses the statistical characteristics of the received signal noise in controlling the antenna array in order to achieve directional reception in a wireless communication system and suppress co-channel interference. Furthermore, the method can be used to power space-division multiple access and can be used in conjunction with multi-carrier modulation signaling.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
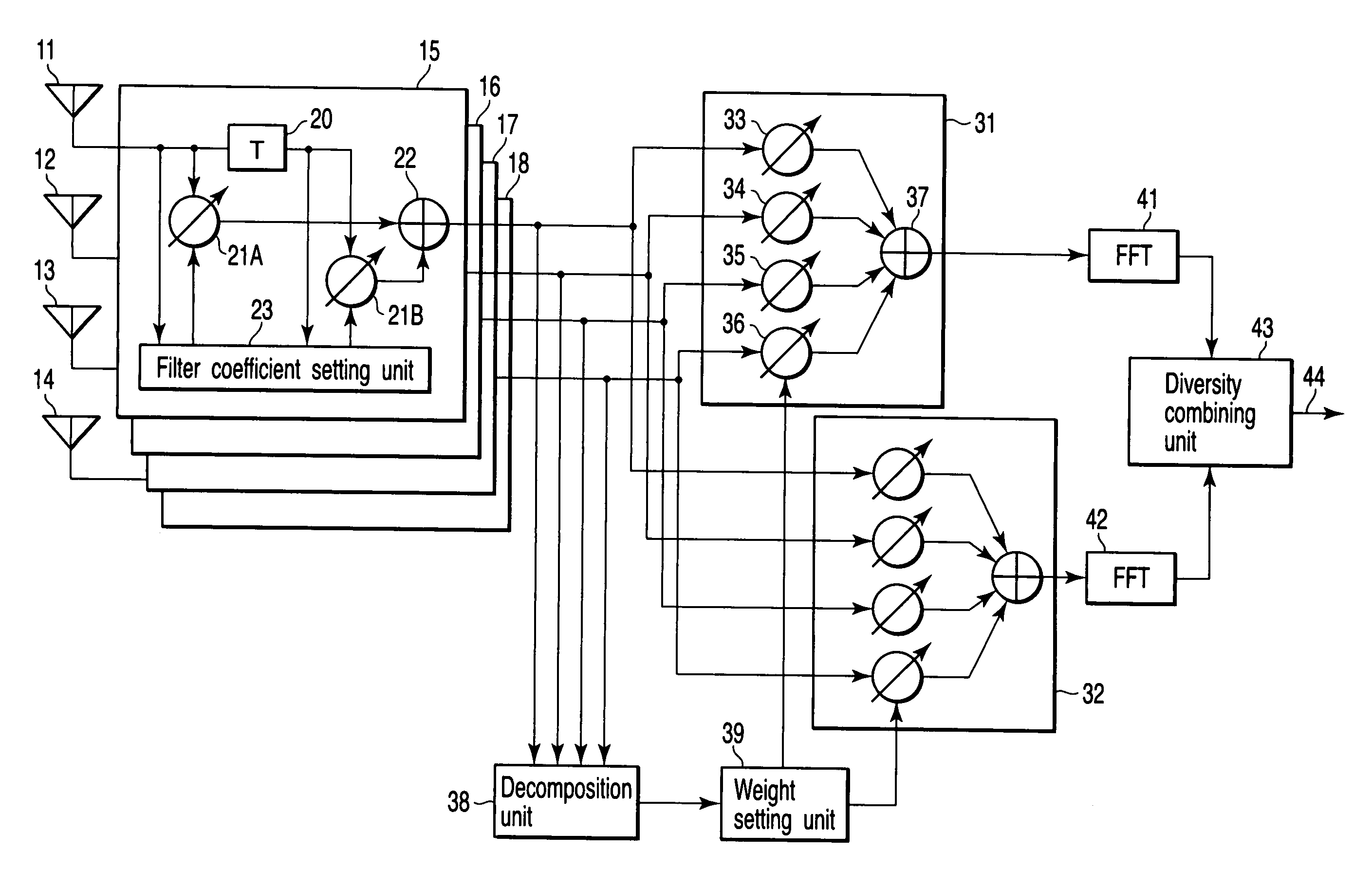
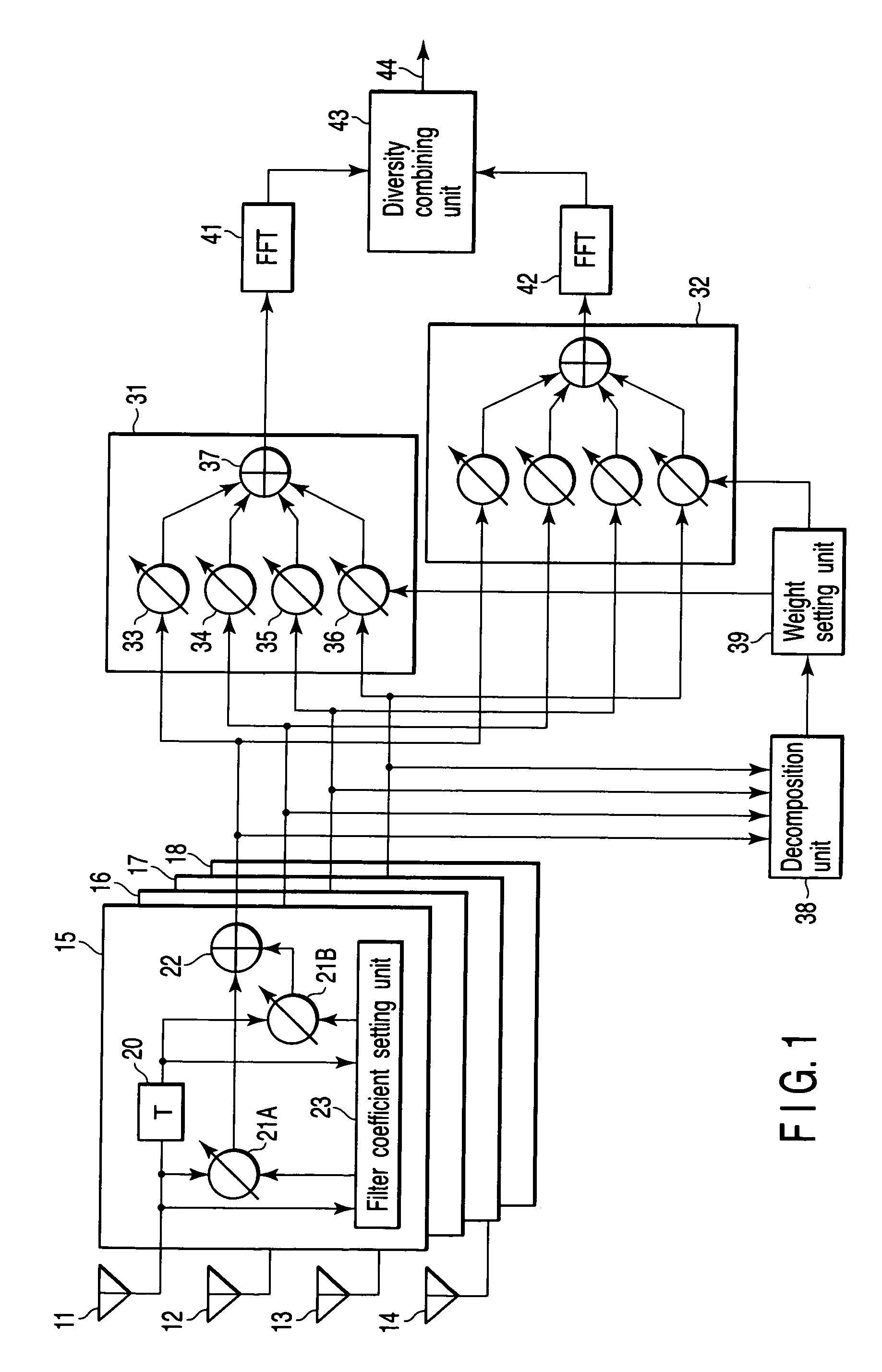
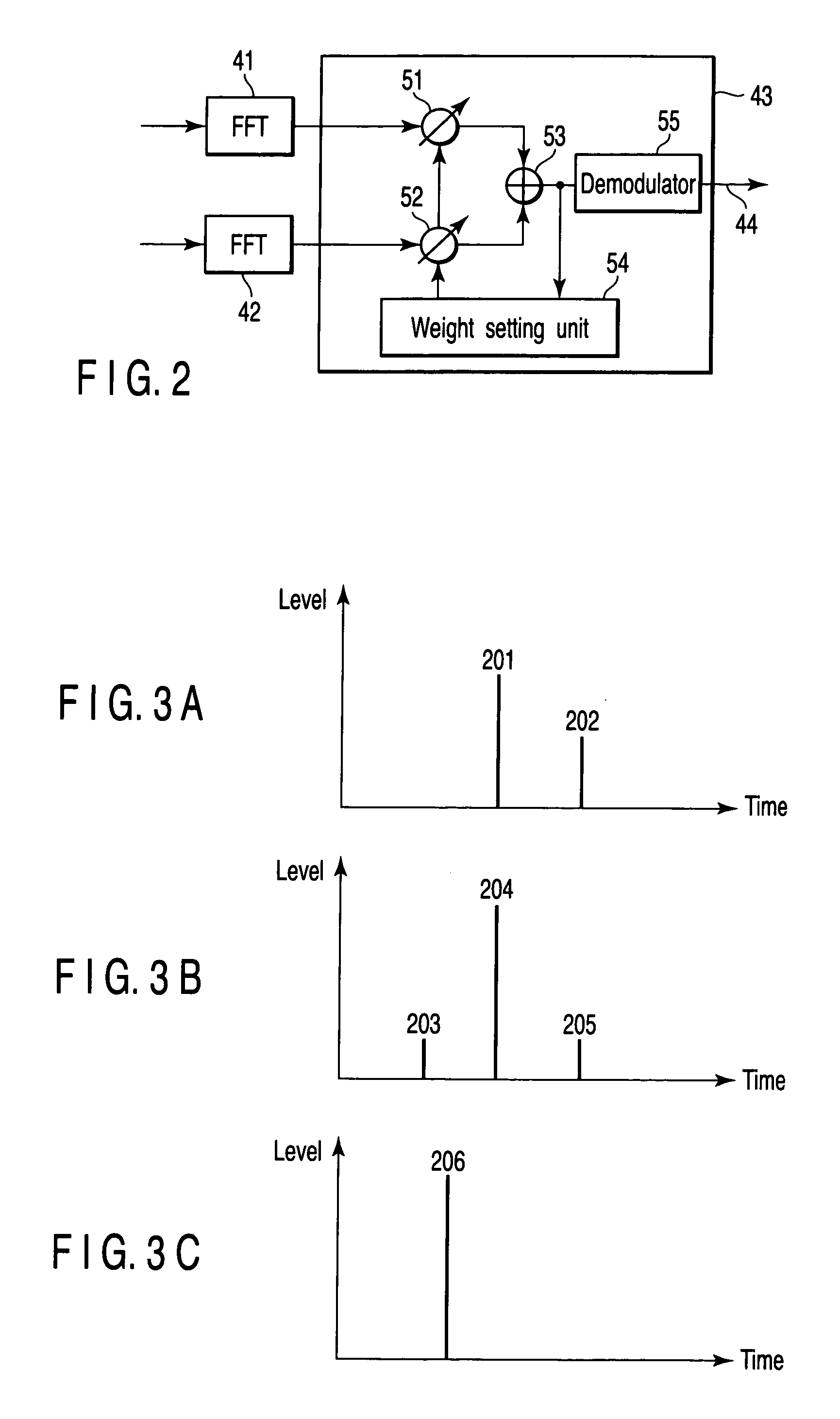
Diversity receiver device
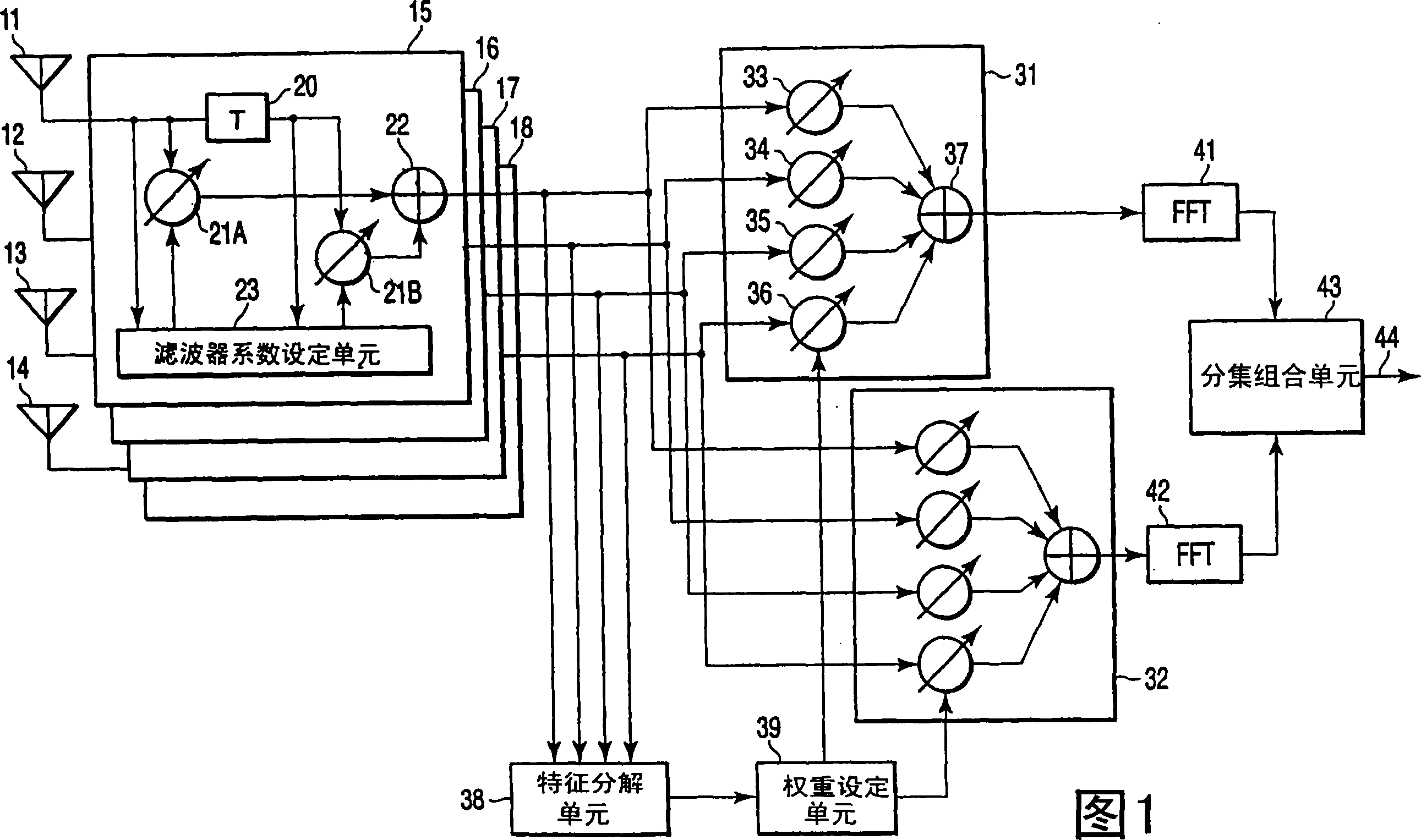
InactiveUS20060294170A1Reduce delay spreadReduce spreadModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionDelay spreadFeature vector
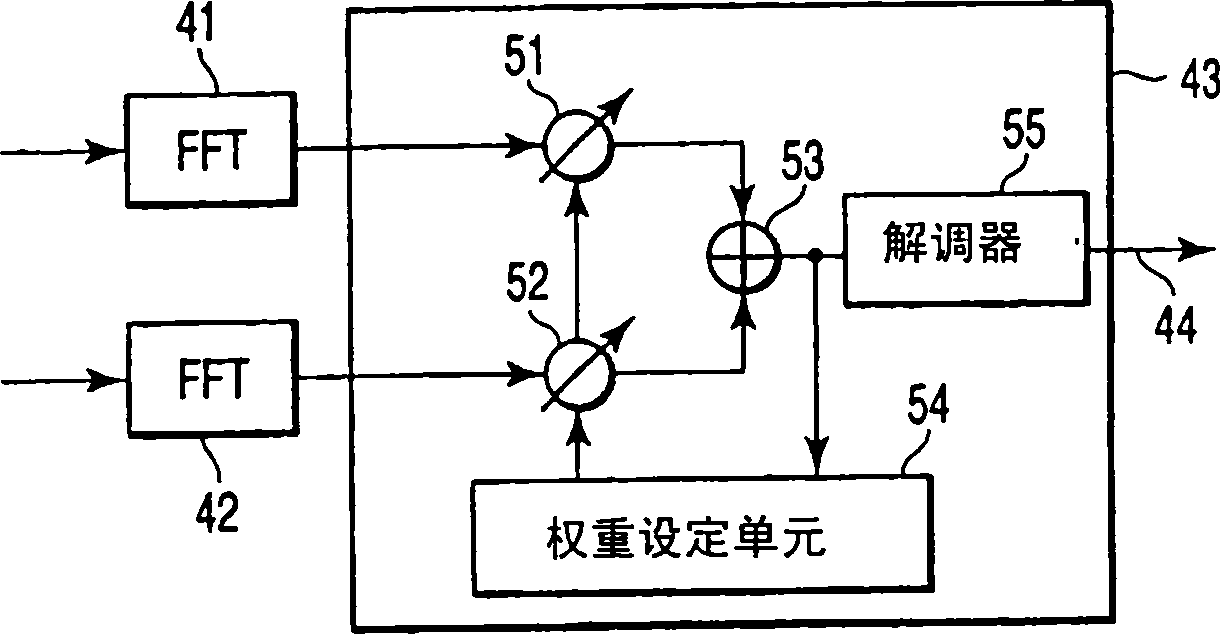
A diversity receiver device includes N antennas to receive OFDM signals, N digital filters to filter the signals received by the N antennas in order to reduce delay spread, K (K≦N) beamforming units configured to subject the filtered signals to a beamforming process by using combining weights, an eigen-decomposition unit configured to subject the filtered signals to eigen-decomposition to generate N eigenvalues, a weight setting unit configured to select K eigenvalues in descending order from the generated N eigenvalues in order to set eigenvectors corresponding to the K eigenvalues to the beamforming units as the combing weight, respectively, K FFT units configured to subject the output signals of the beamforming units to fast Fourier transformation to output FFT signals, and a diversity combining unit configured to combine the FFT signals.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Polarization-diverse antenna array and associated methods
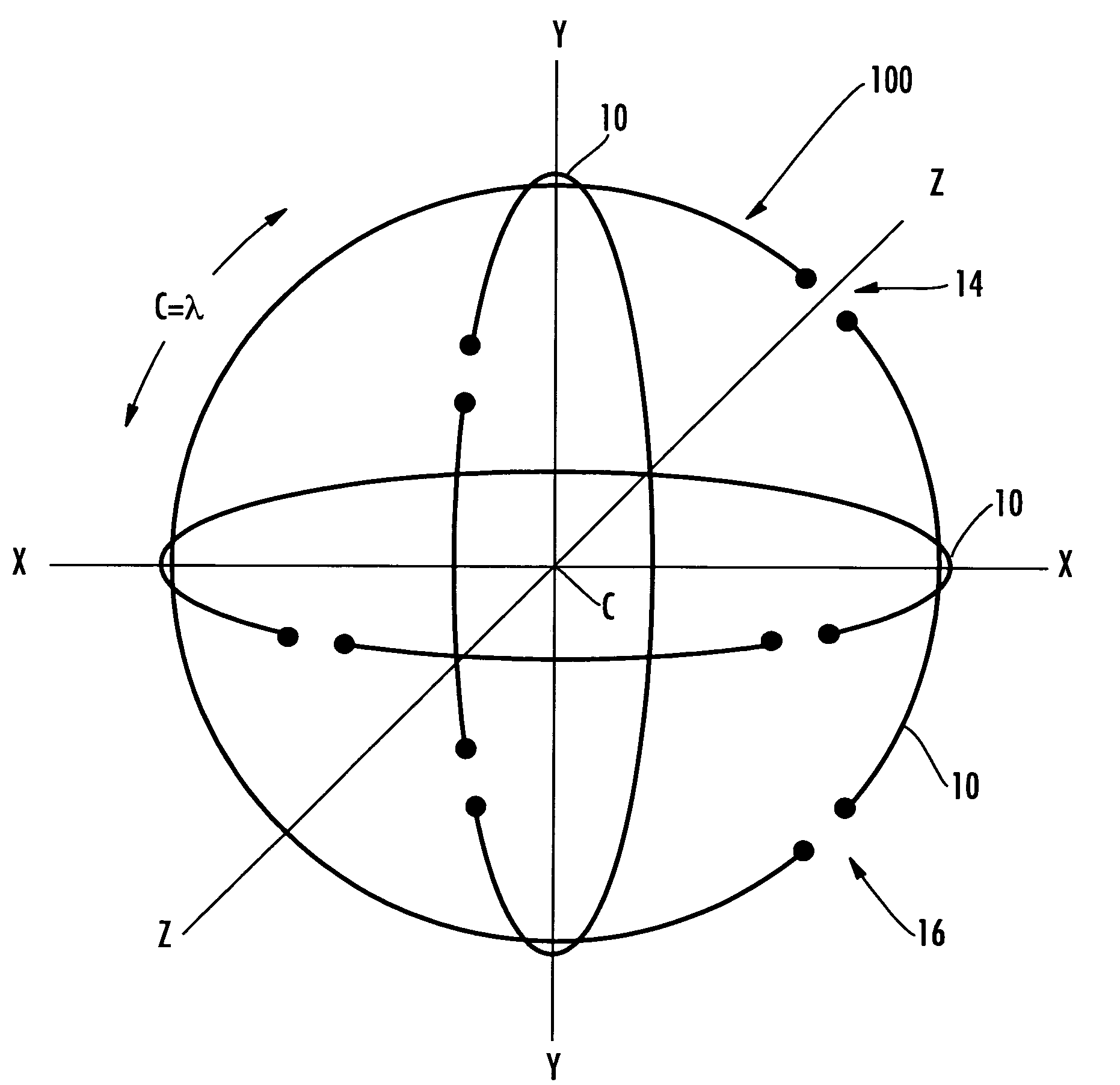
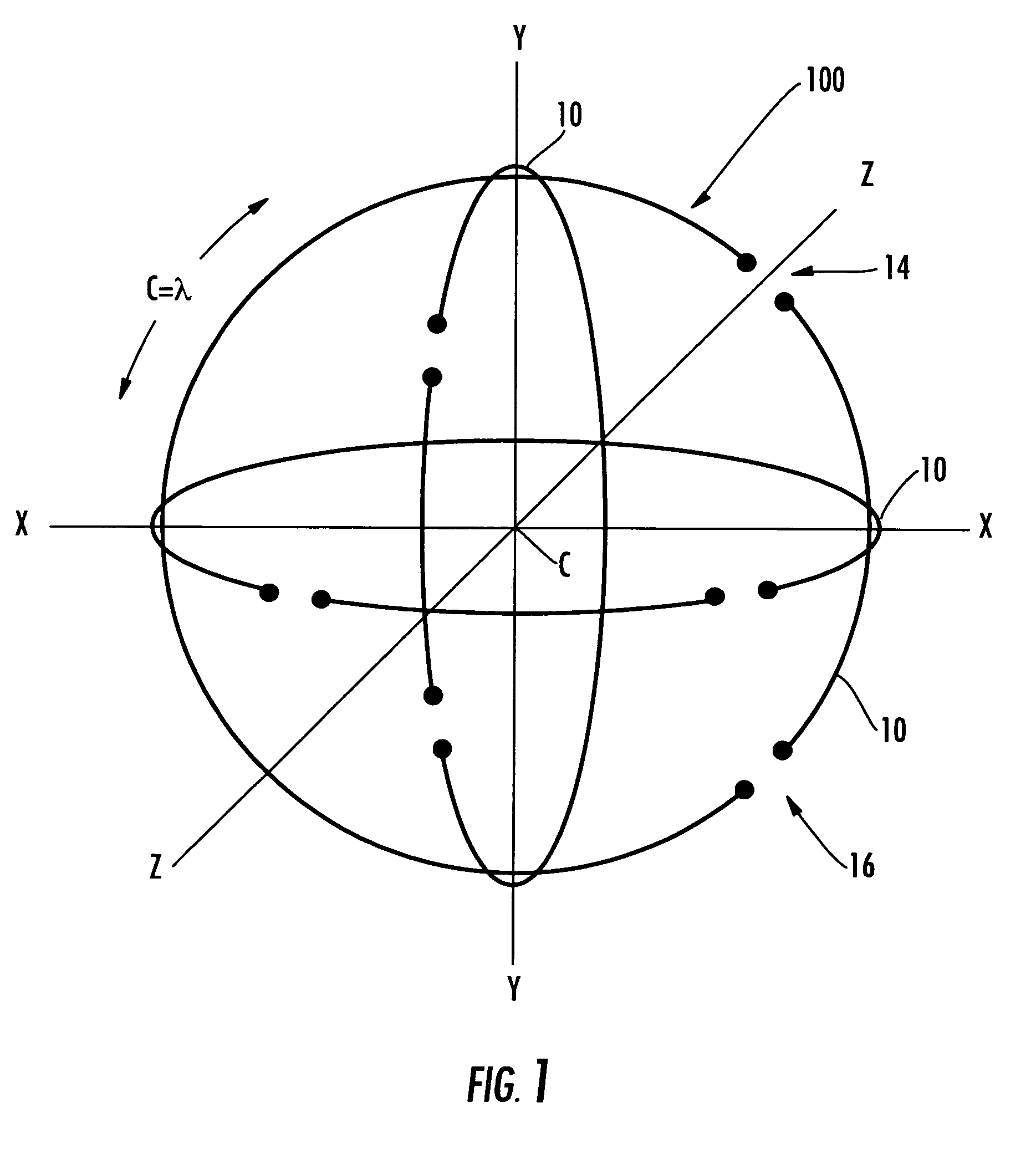
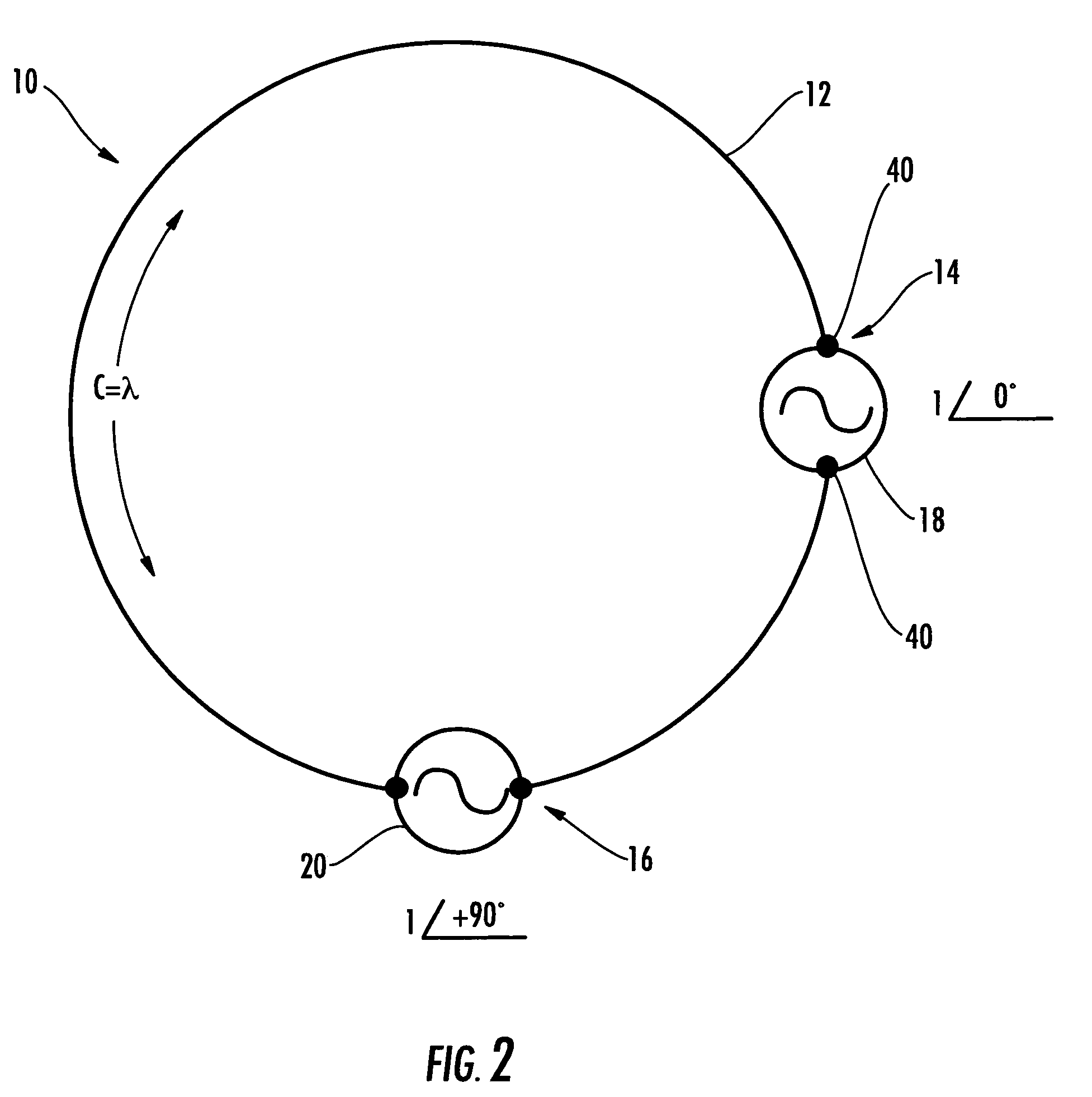
InactiveUS7505009B2Rapidly deployableResonant long antennasIndividually energised antenna arraysPolarization diversityElectrical conductor
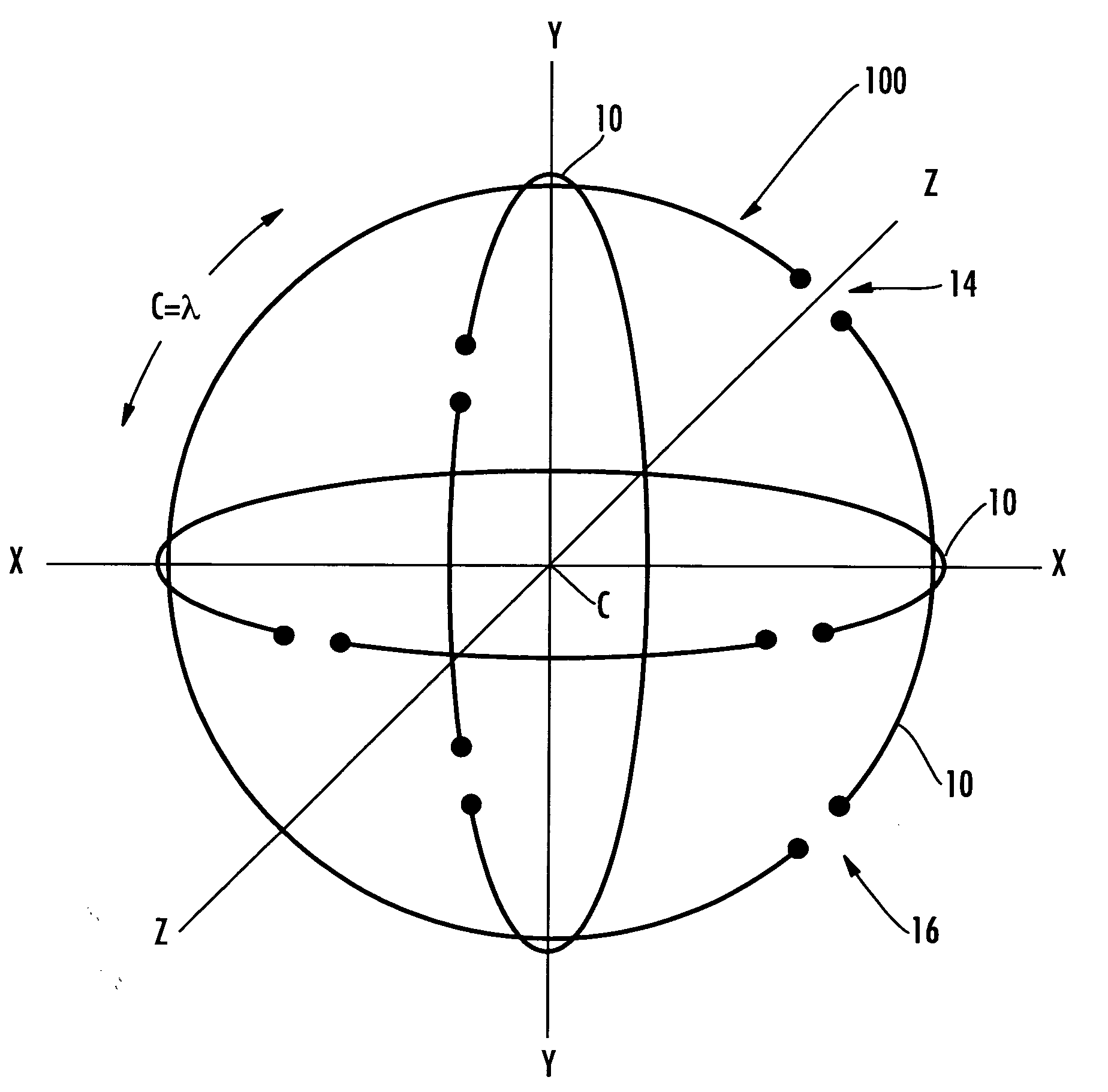
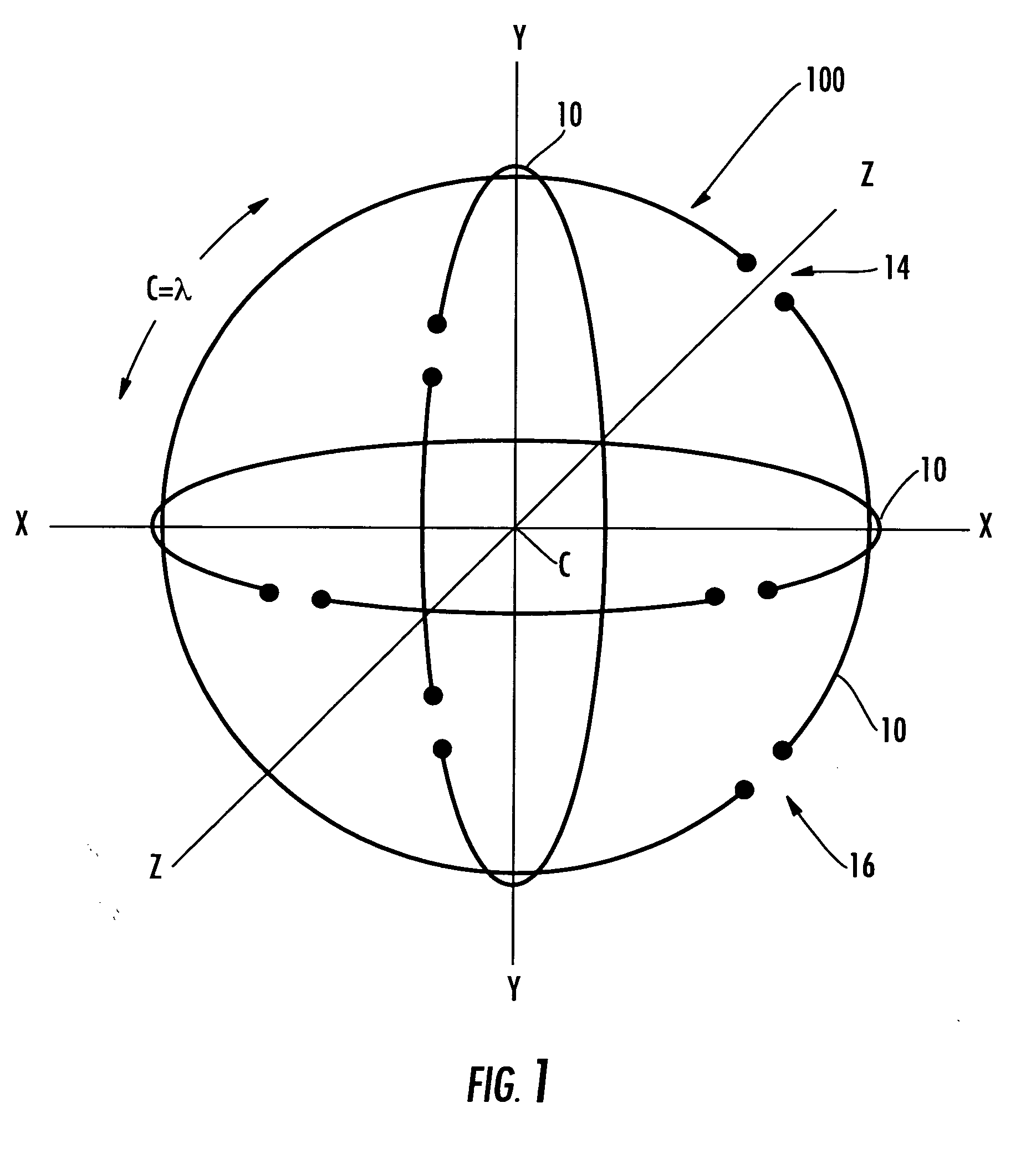
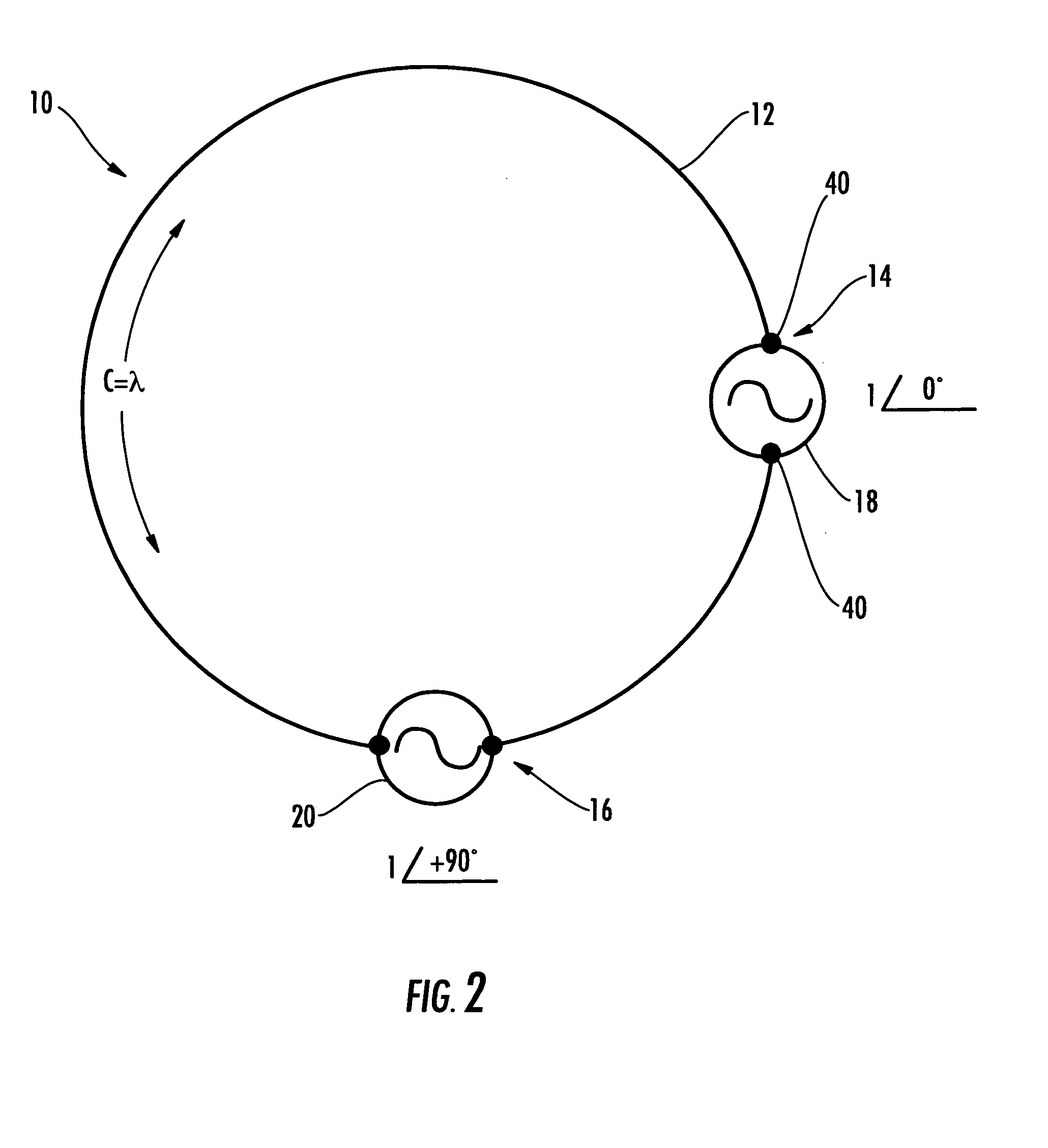
The polarization-diverse antenna array includes three orthogonal loop antennas having a common center, e.g. together defining a sphere. Each loop antenna includes a loop electrical conductor. Two signal feedpoints are along the loop electrical conductor and separated by a fraction of a length of the loop electrical conductor. Each of the signal feedpoints includes a series signal feedpoint so that a polarization diversity controller coupled thereto may selectively provide vertical, horizontal, lefthand circular and righthand circular polarization for a single loop electrical conductor, including simultaneous (dual) polarizations. These signal feedpoints may supply signals with vertical, horizontal, lefthand circular and righthand circular polarization from each of the three orthogonal look-angles provided by the three loop electrical conductors. Thus the antenna array may provide a compact facility for using Diversity Combining to improve communications performance and / or Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MIMO) schemes that furthermore also increase capacity. The polarization-diverse antenna array provides a rigorous polarization and look angle approach for communications diversity.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
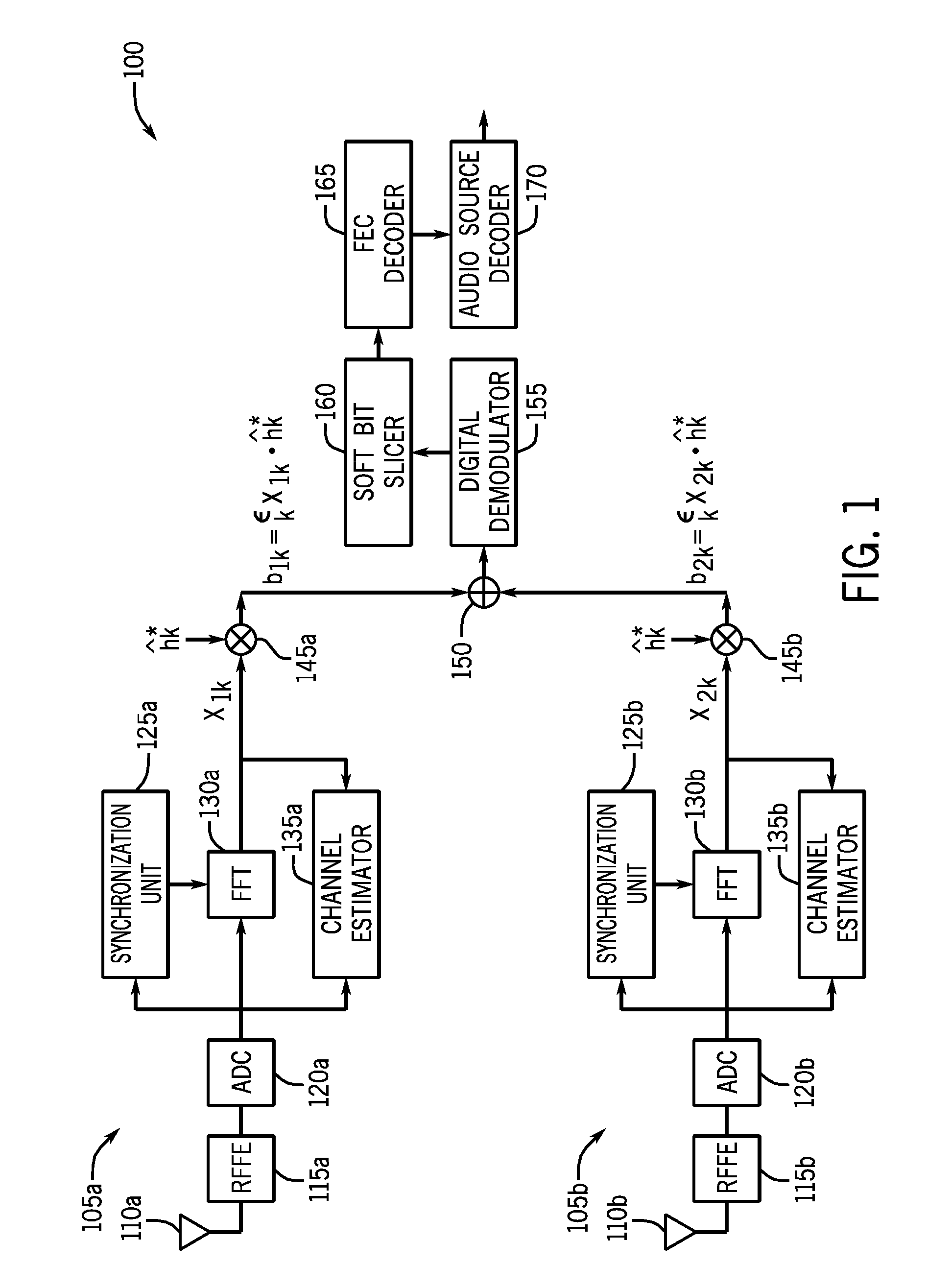
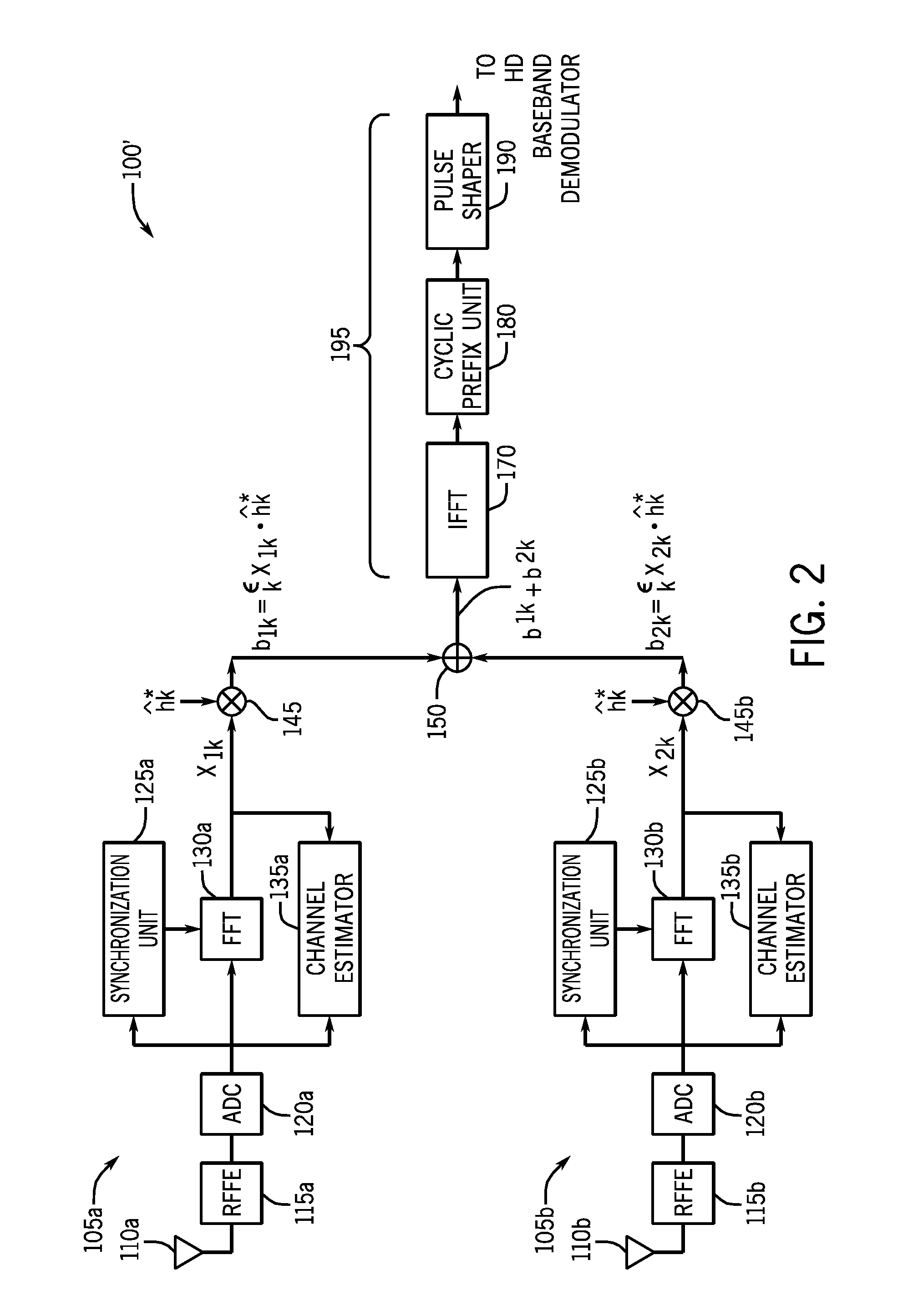
Providing Phase Diversity Combining Of Digital Radio Broadcast Signals
ActiveUS20120321012A1Weight optimizationGreat weightError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTime domainSignal quality
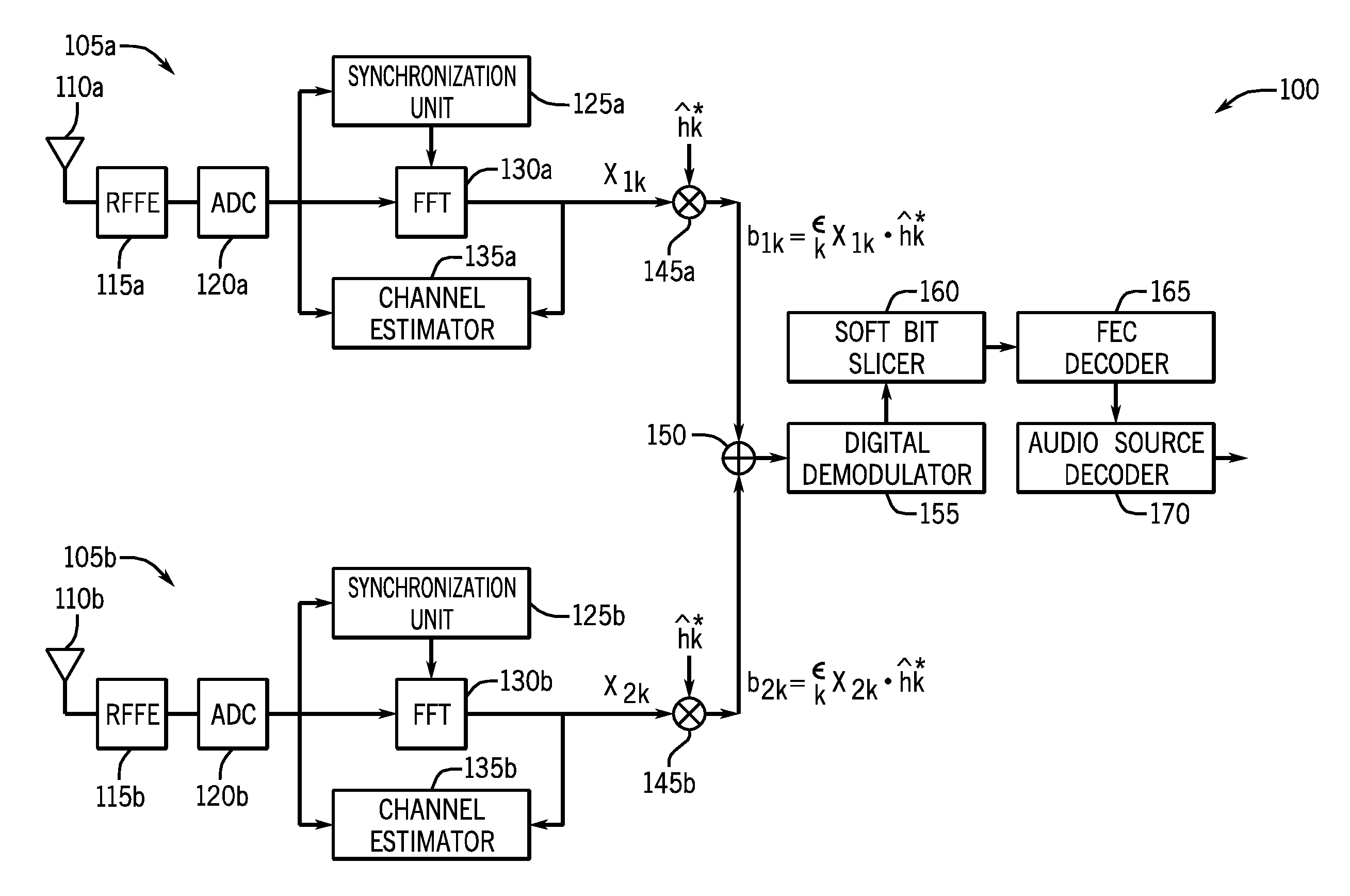
In one embodiment, a method for performing antenna diversity combining for digitally broadcast radio signals includes generating a first signal quality metric for a first signal obtained from an incoming digitally broadcast radio signal received in a first signal path, and similarly generating a second signal quality metric for a second signal obtained from the radio signal received in a second signal path. Then the first and second signals from these paths can be coherently combined based on the signal quality metrics to obtain a combined frequency domain symbol. In some embodiments, this combined frequency domain symbol may be remodulated to a time domain symbol. Also in some embodiments N tuners can be daisy chained to generate a final output that is either a frequency domain symbol of combined sub-carriers, soft bits to a forward error correction (FEC) decoder, or a remodulated time domain symbol. As a further possibility, each of the N tuners can use a different local oscillator (LO) frequency.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Multi-antenna wireless communication method and multi-antenna wireless communication device
InactiveUS8605658B2Improve throughputLarge MIMO gainDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission monitoringCommunication unitSpatial mapping
Owner:IWATSU ELECTRIC CO LTD
Radio communication apparatus using adaptive antenna
InactiveUS7043275B2Spatial transmit diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementDirectional antennaEngineering
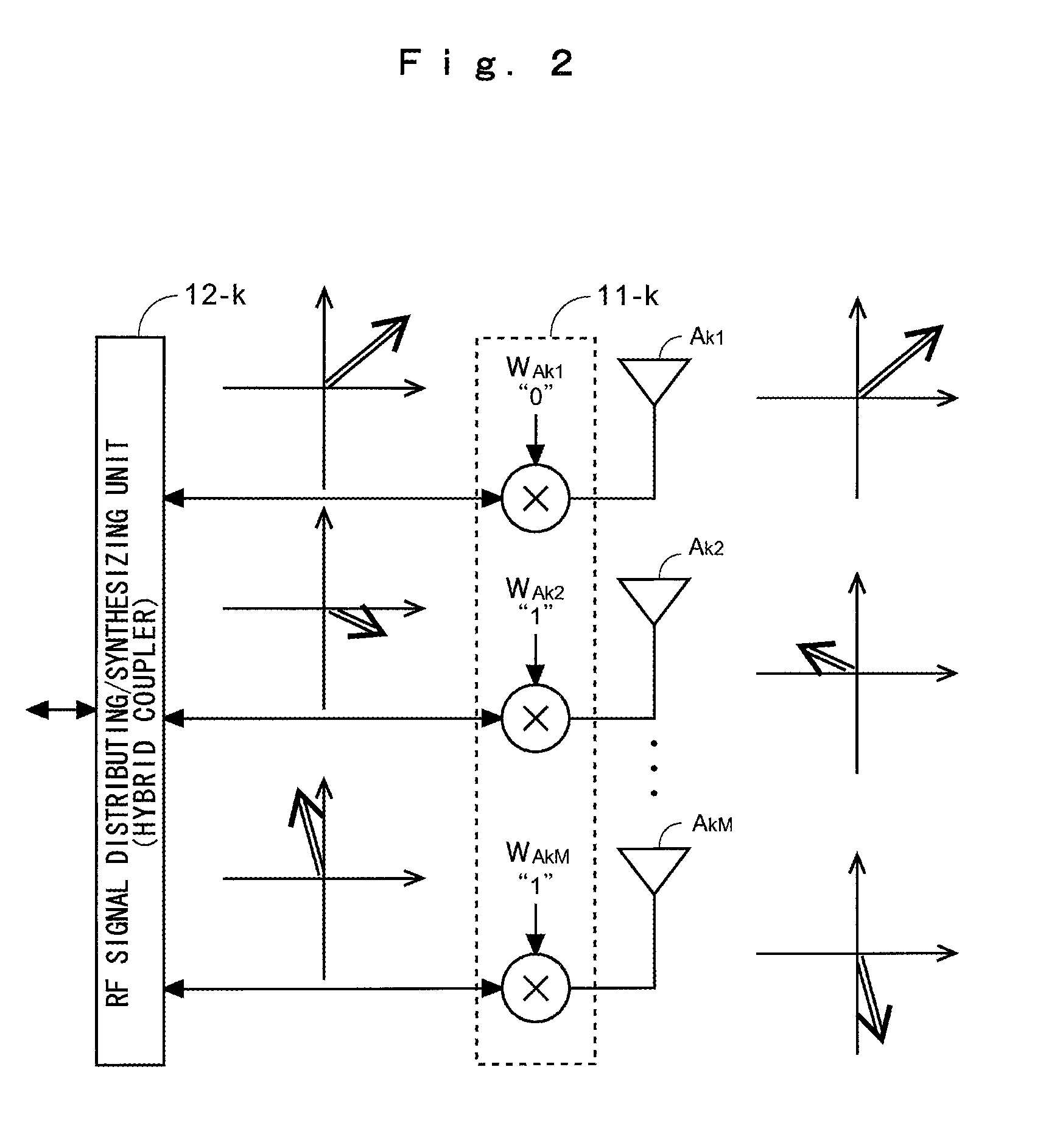
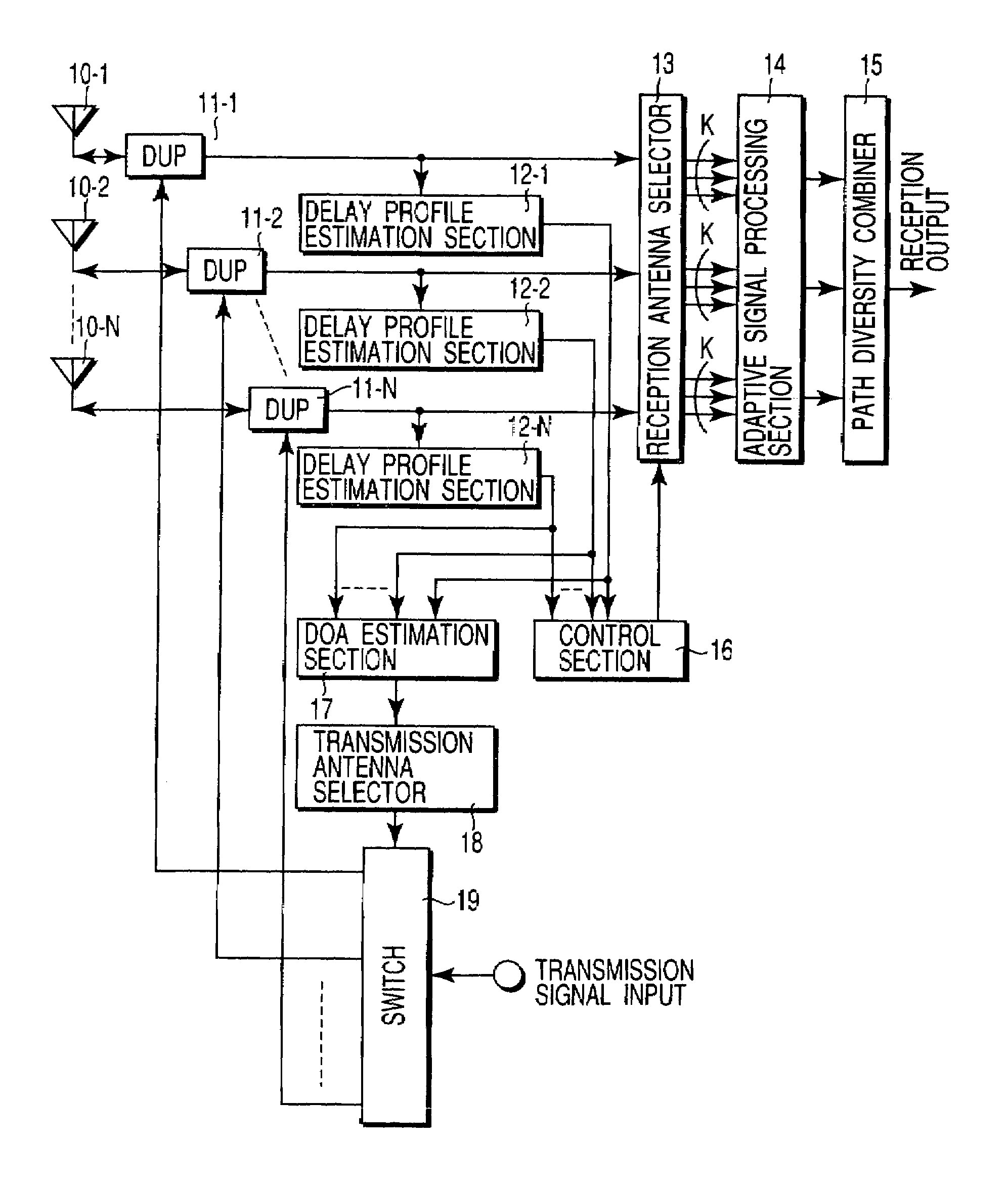
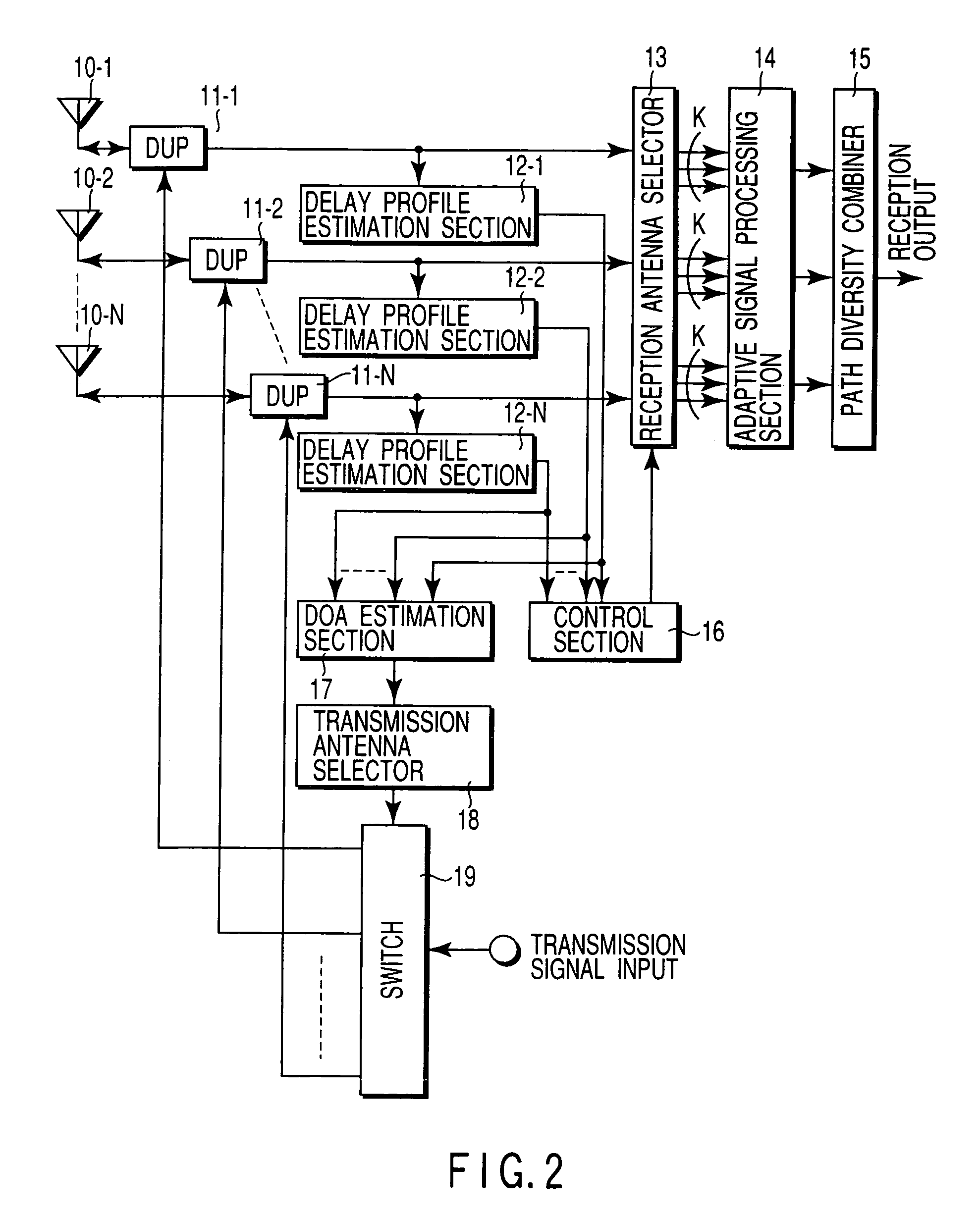
In a radio communication apparatus, delay profiles of a desired wave and delay waves thereof are estimated by plural delay profile estimation sections for each of received signals from directional antennas constituting an array antenna. Received signals from the antennas selected by a reception antenna selector on the basis of the delay profile are subjected to a temporal / spatial equalization processing by an adaptive signal processing section and a path diversity combining section, thereby obtaining a reception output. An arrival angle range of the desired wave is estimated by a DOA estimation section from the delay profile estimated by the delay profile estimation section. Based on the arrival angle range, the antenna for transmission is selected by a transmission antenna selection section, and transmission signals are sent out.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Radio transmission method for multiple self adaption antenna array
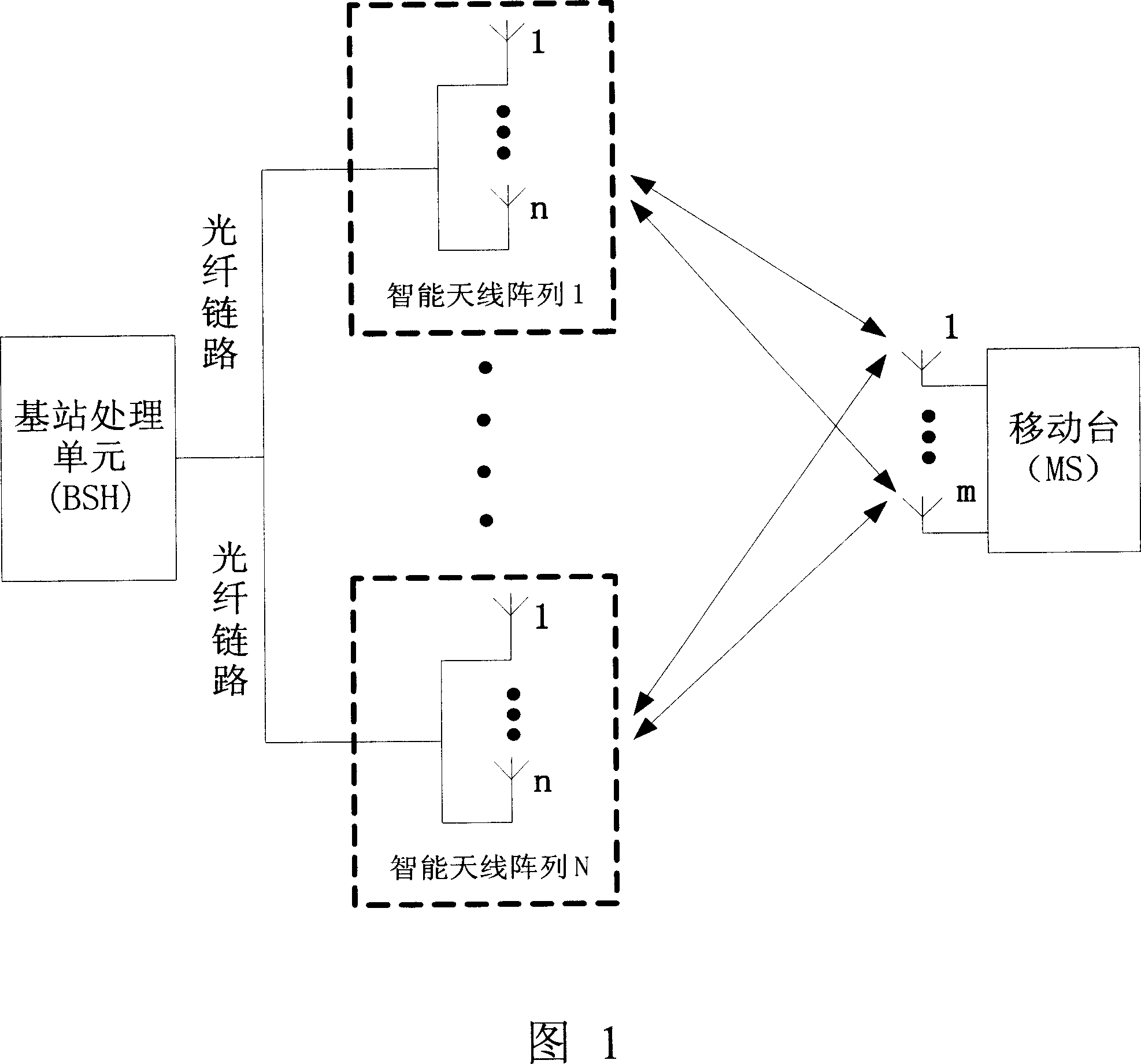
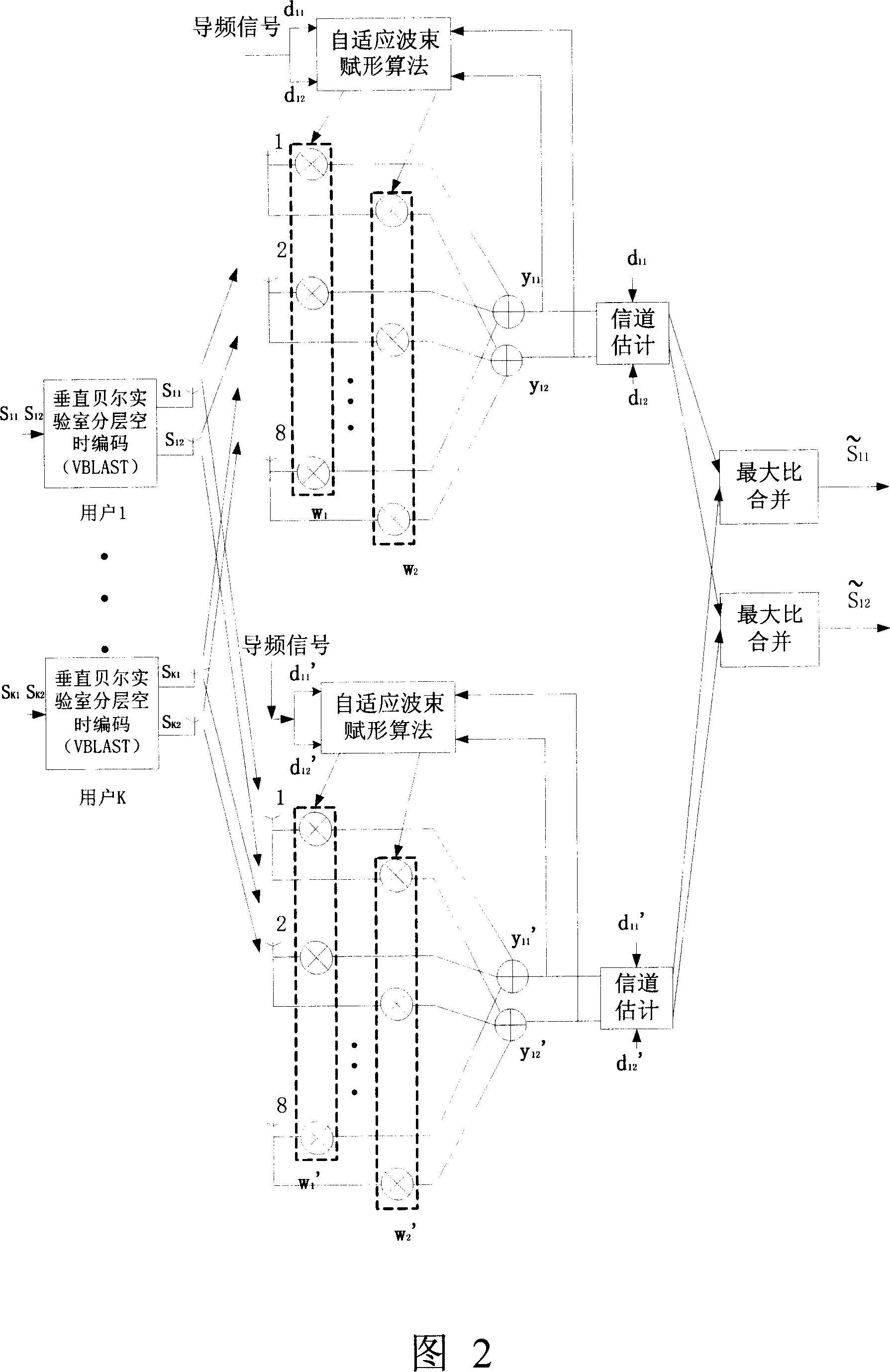
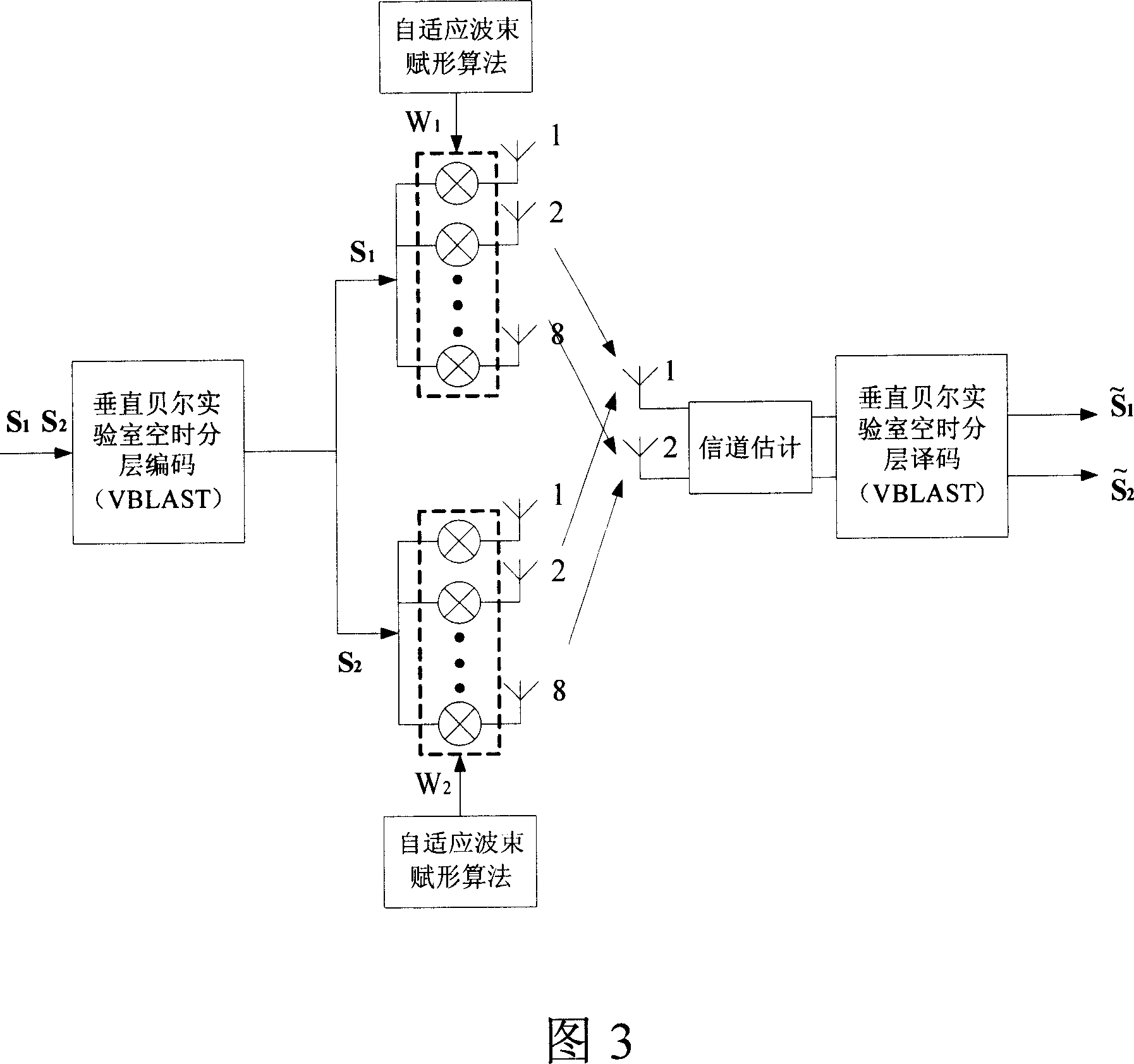
InactiveCN1988410AImprove communication performanceSpatial transmit diversityFiberWireless transmission
This invention relates to a radio transmission method for multiple adaptive antenna arrays, in which, a mobile station utilizes MIMO empty time process technology to send signals from multiple antennas simultaneously when the mobile station transmits signals and the base station receives them, multiple intelligent antenna arrays receive signals simultaneously and transmit them to a base station process unit (BSH) via fiber links, which first of all carries out adaptive wave beam shaping process to the received signals of each intelligent antenna array then utilizes the MIMO technology to diversify and merge signals of the array, when the base station transmits signals and the mobile station receives them, the BSH divides the signals into multiple signals by MIMO empty time process then carries out adaptive wavebeam shaping to the multiple signals to be transmitted by multiple intelligent antennas at the same time, and the mobile station gets signals by related empty time process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Diversity receiver device
A diversity receiver device includes N antennas to receive OFDM signals, N digital filters to filter the signals received by the N antennas in order to reduce delay spread, K (K<=N) beamforming units configured to subject the filtered signals to a beamforming process by using combining weights, an eigen-decomposition unit configured to subject the filtered signals to eigen-decomposition to generate N eigenvalues, a weight setting unit configured to select K eigenvalues in descending order from the generated N eigenvalues in order to set eigenvectors corresponding to the K eigenvalues to the beamforming units as the combing weight, respectively, K FFT units configured to subject the output signals of the beamforming units to fast Fourier transformation to output FFT signals, and a diversity combining unit configured to combine the FFT signals.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and system for restraining interference and combining diversity
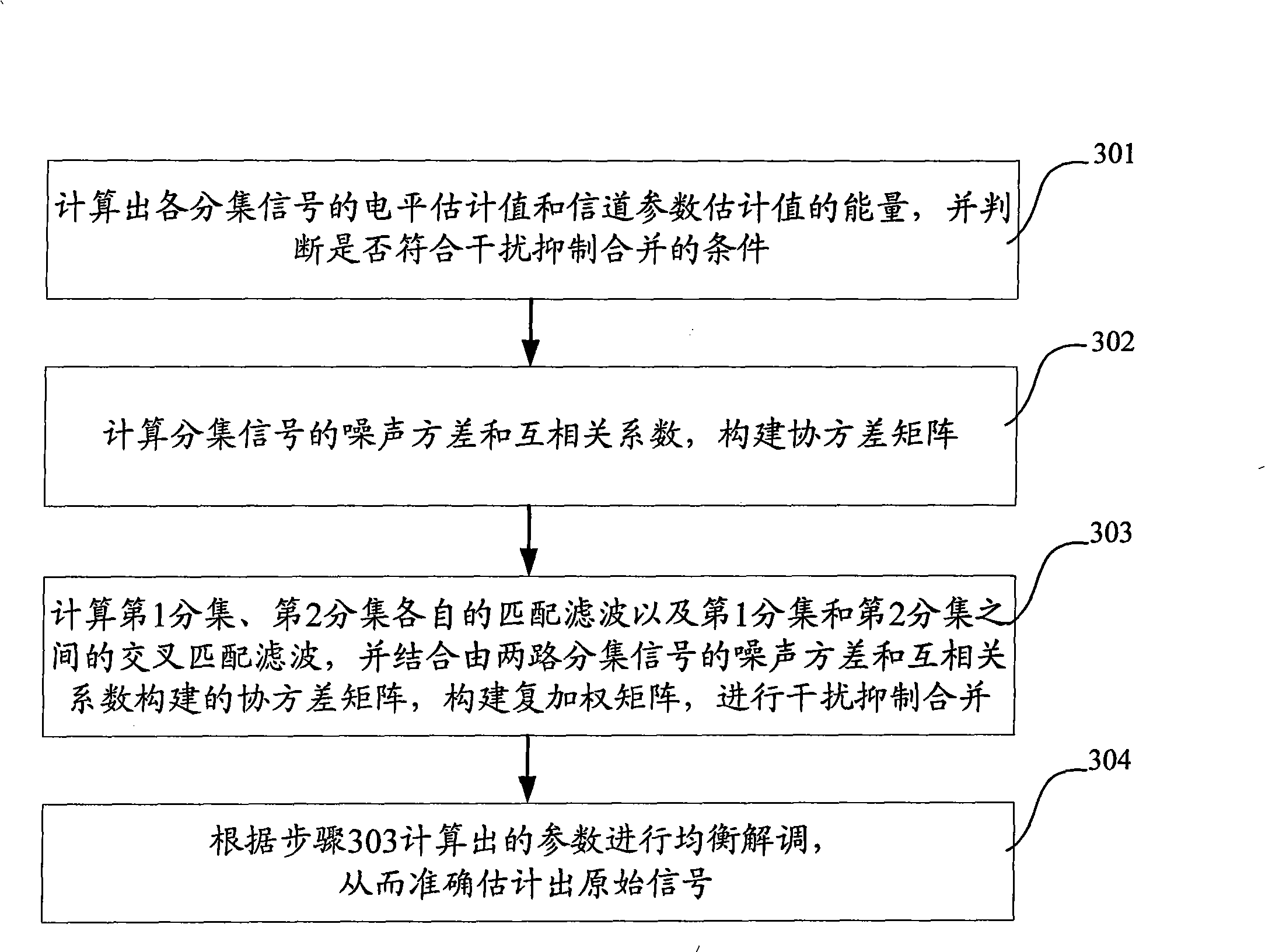
ActiveCN101330358AImprove receiver sensitivityExpand coverageTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionConducted InterferenceEngineering
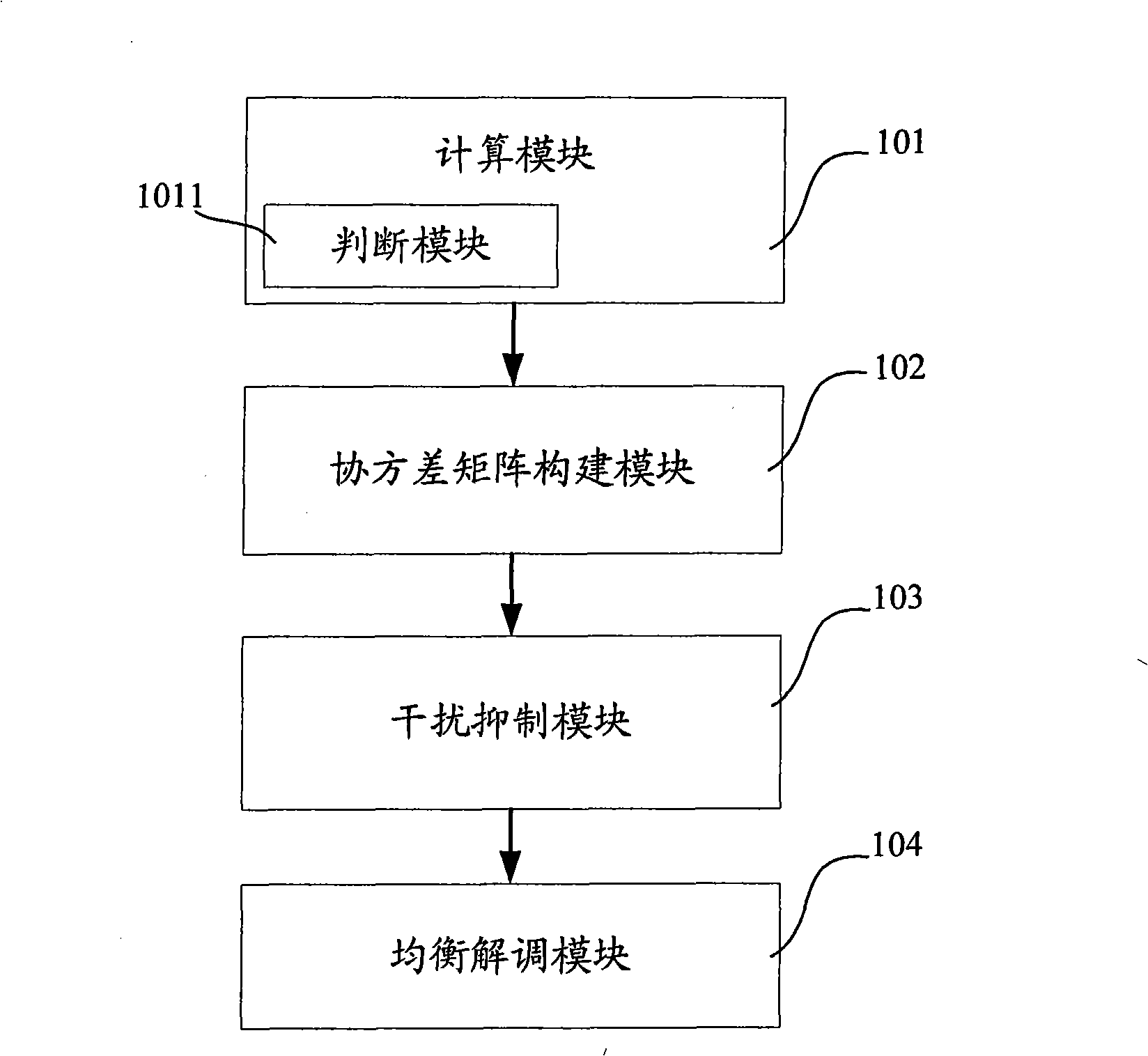
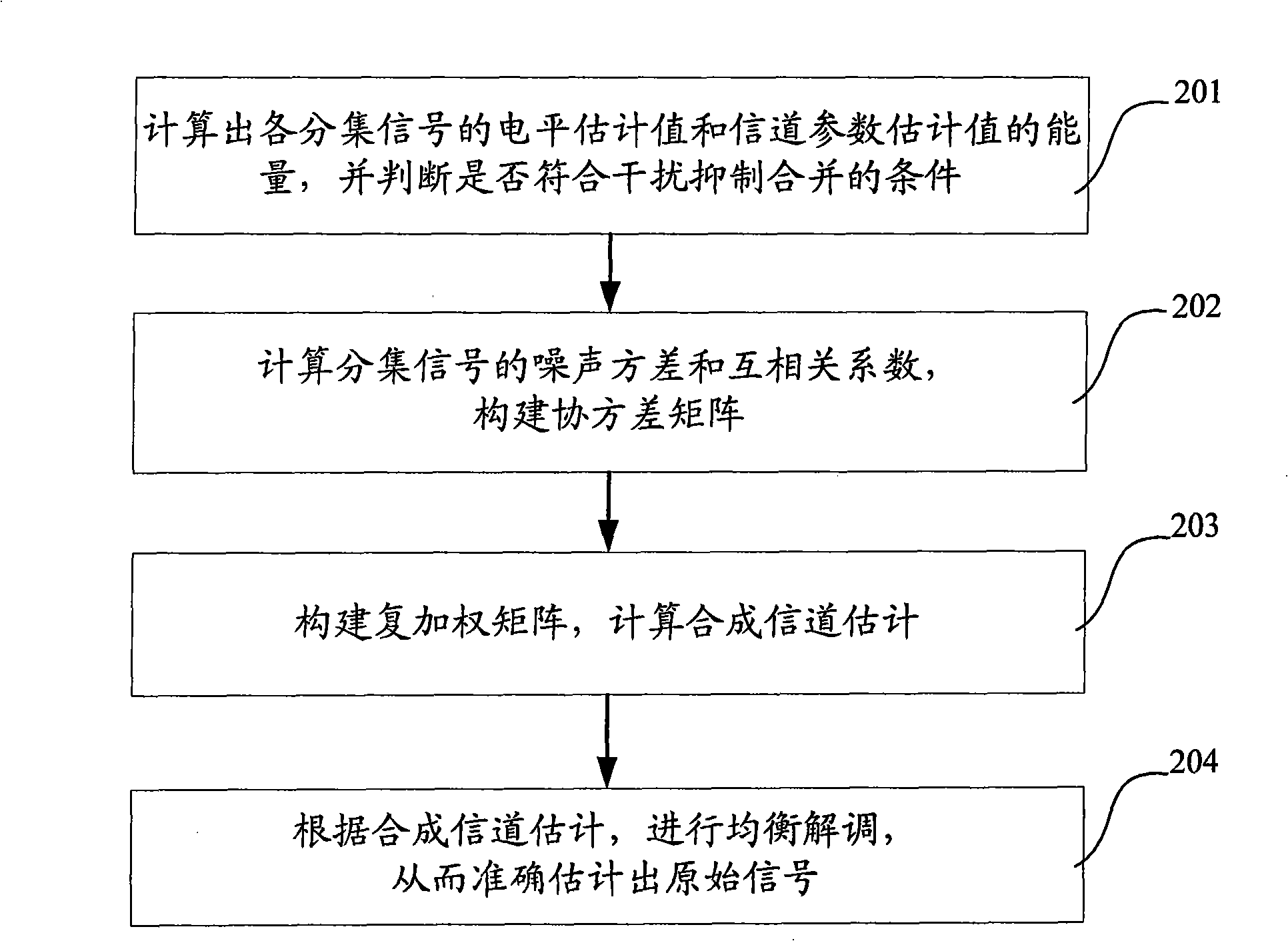
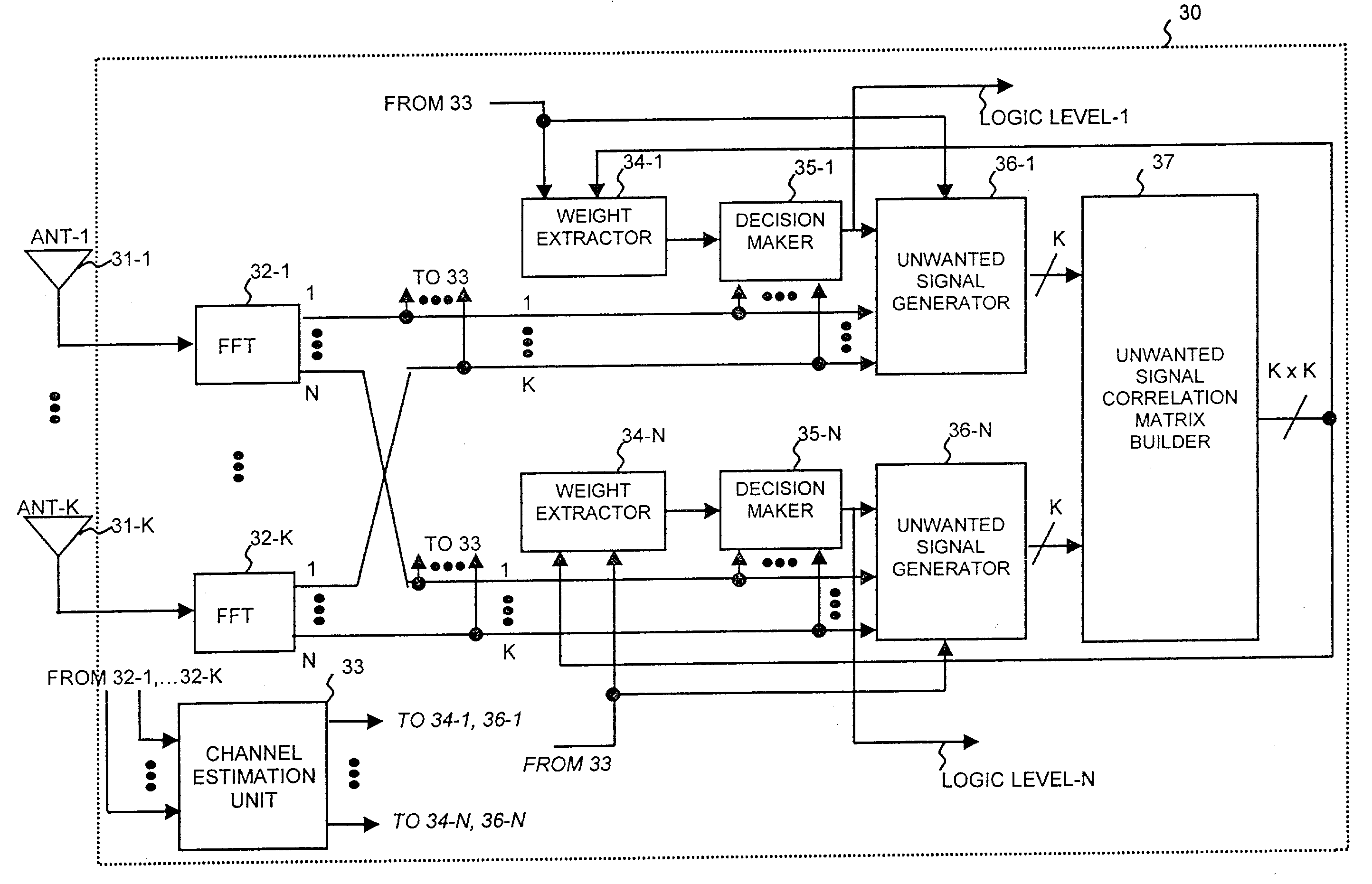
The invention discloses an interference suppression diversity and combination method which comprises the steps of calculating the capacities of a level estimation value of a diversity signal and a channel parameter estimation value; calculating the noise variance and cross correlation coefficient of the diversity signal to construct a covariance matrix; constructing a weighted matrix according to the covariance matrix to conduct interference, suppression and combination; and conducting equal demodulation according to a result of the interference, suppression and combination. The invention also discloses an interference suppression diversity and combination system which comprises a calculation module, a covariance matrix construction module, an interference suppression module and an equal demodulation module. The method greatly reduces the complexity of a system, improves the receiving sensitivity of a receiver, and enlarges the coverage of a base station, thereby providing an interference suppression diversity and combination technical proposal which has the advantages of low complexity, high estimation accuracy and easy realized engineering.
Owner:ZTE CORP
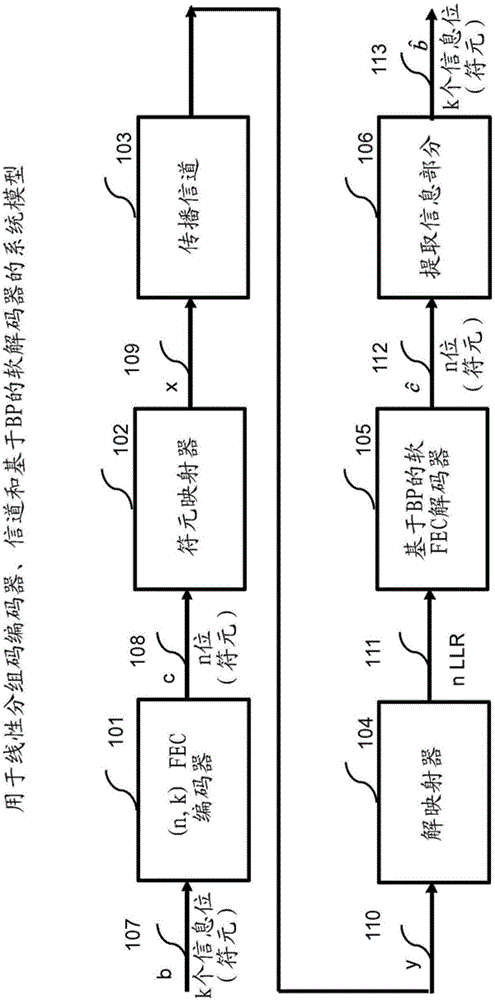
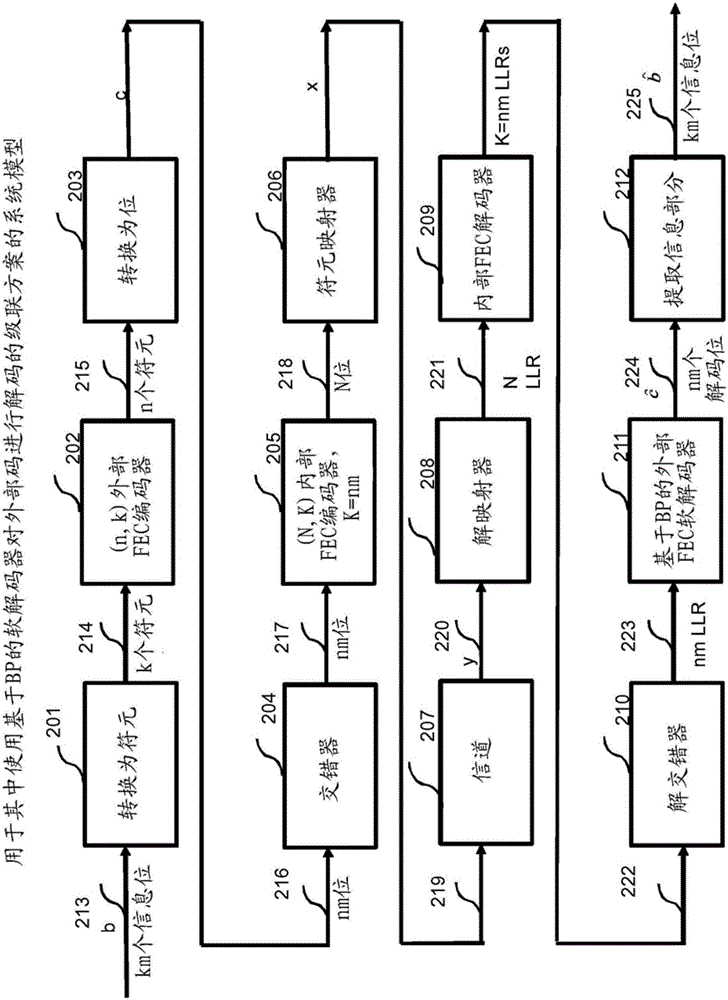
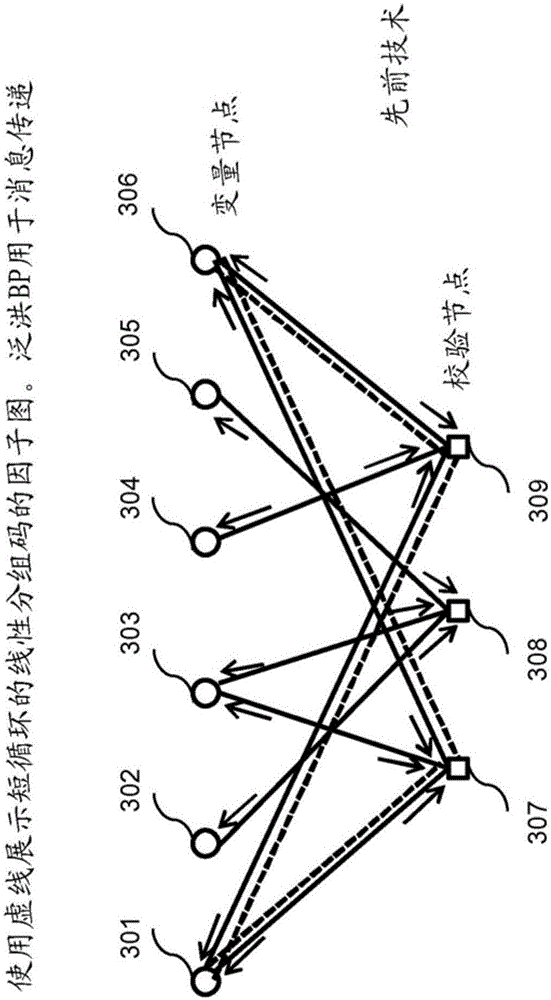
Systems and methods for advanced iterative decoding and channel estimation of concatenated coding systems
InactiveCN105144598AError correction/detection using convolutional codesModulated-carrier systemsHD RadioAlgorithm
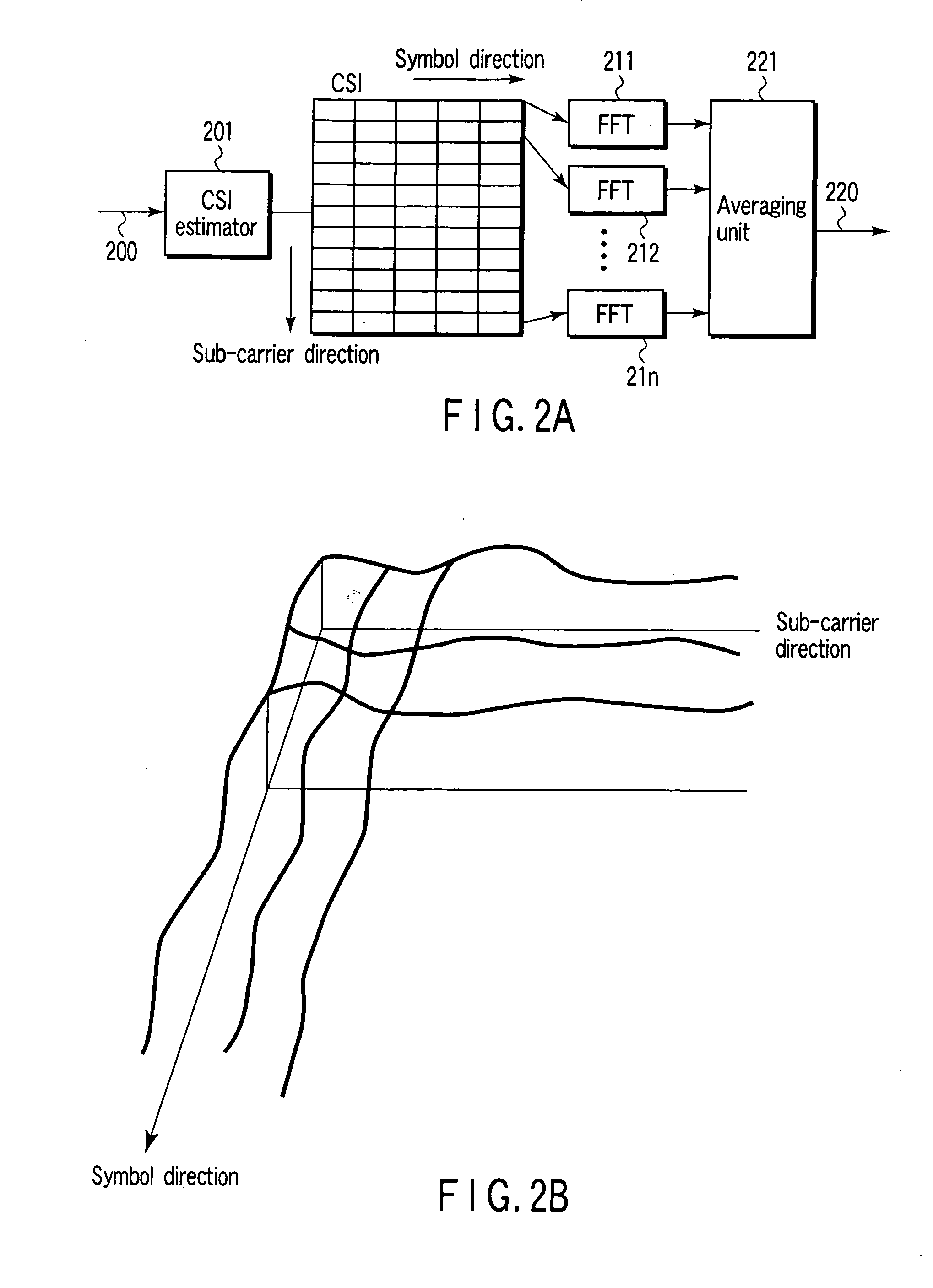
Systems and methods for decoding block and concatenated codes are provided. These include advanced iterative decoding techniques based on belief propagation algorithms, with particular advantages when applied to codes having higher density parity check matrices. Improvements are also provided for performing channel state information estimation including the use of optimum filter lengths based on channel selectivity and adaptive decision-directed channel estimation. These improvements enhance the performance of various communication systems and consumer electronics. Particular improvements are also provided for decoding HD Radio signals, including enhanced decoding of reference subcarriers based on soft-diversity combining, joint enhanced channel state information estimation, as well as iterative soft-input soft-output and list decoding of convolutional codes and Reed-Solomon codes. These and other improvements enhance the decoding of different logical channels in HD Radio systems.
Owner:LN2 DB LLC
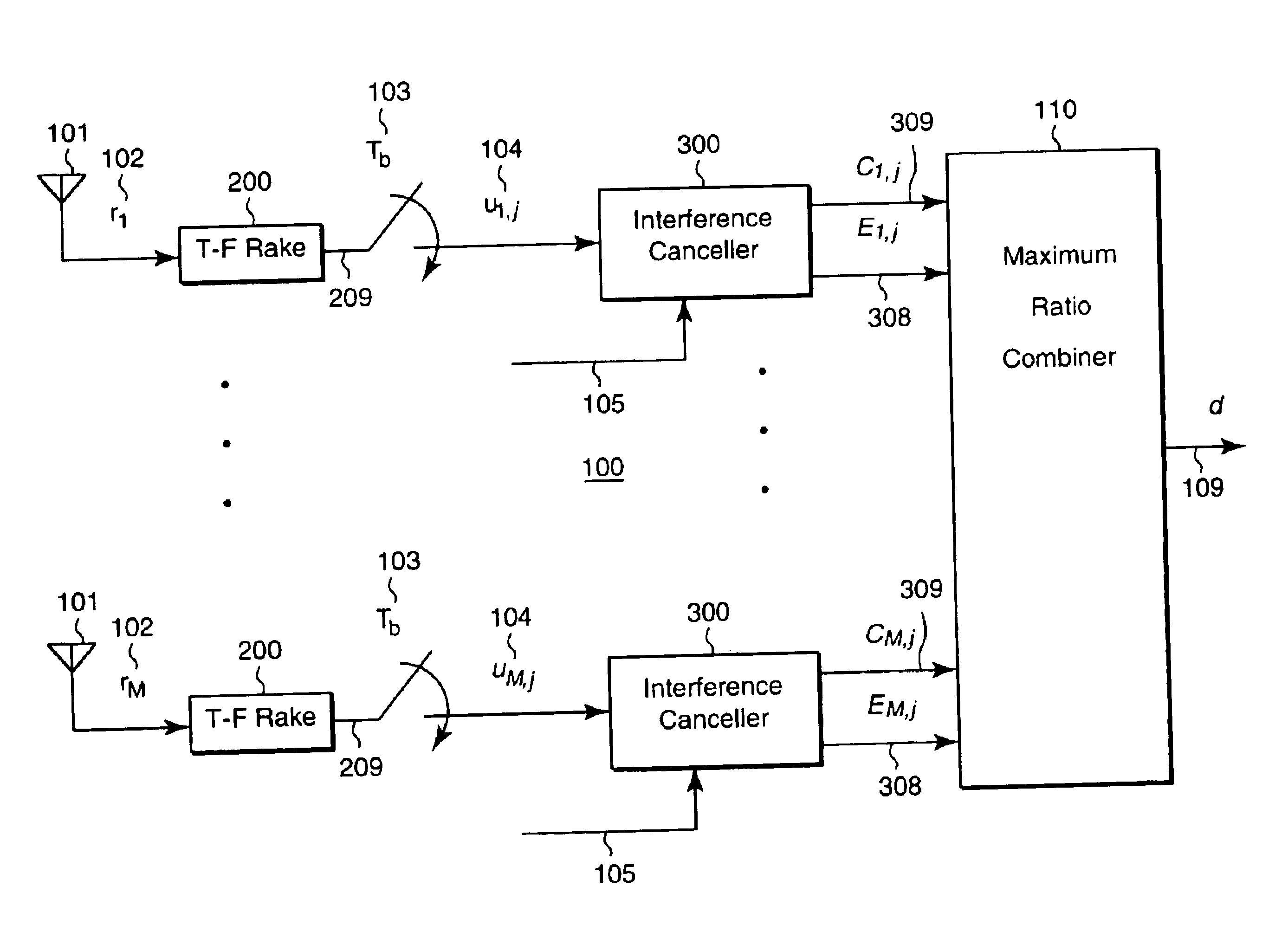
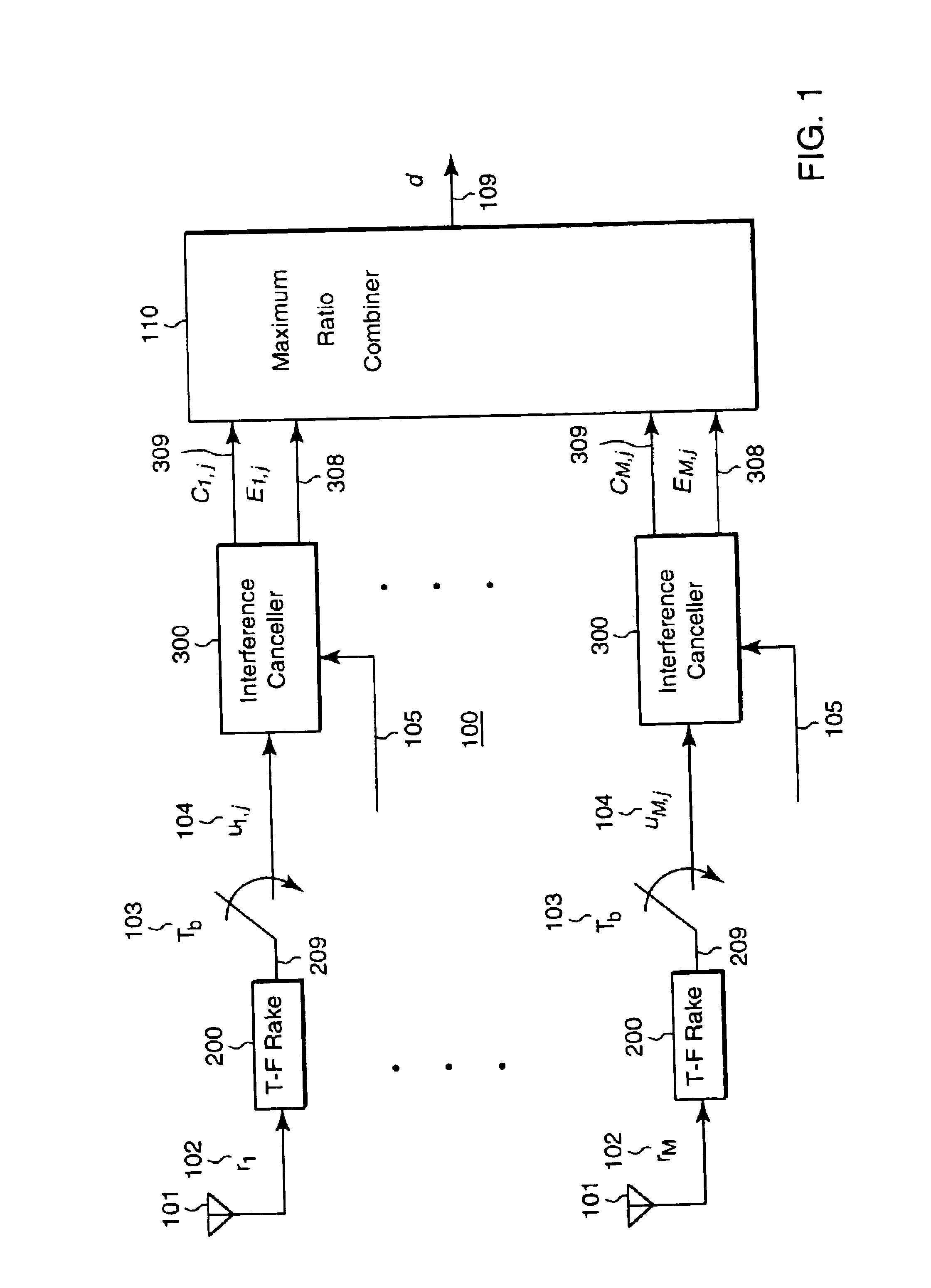
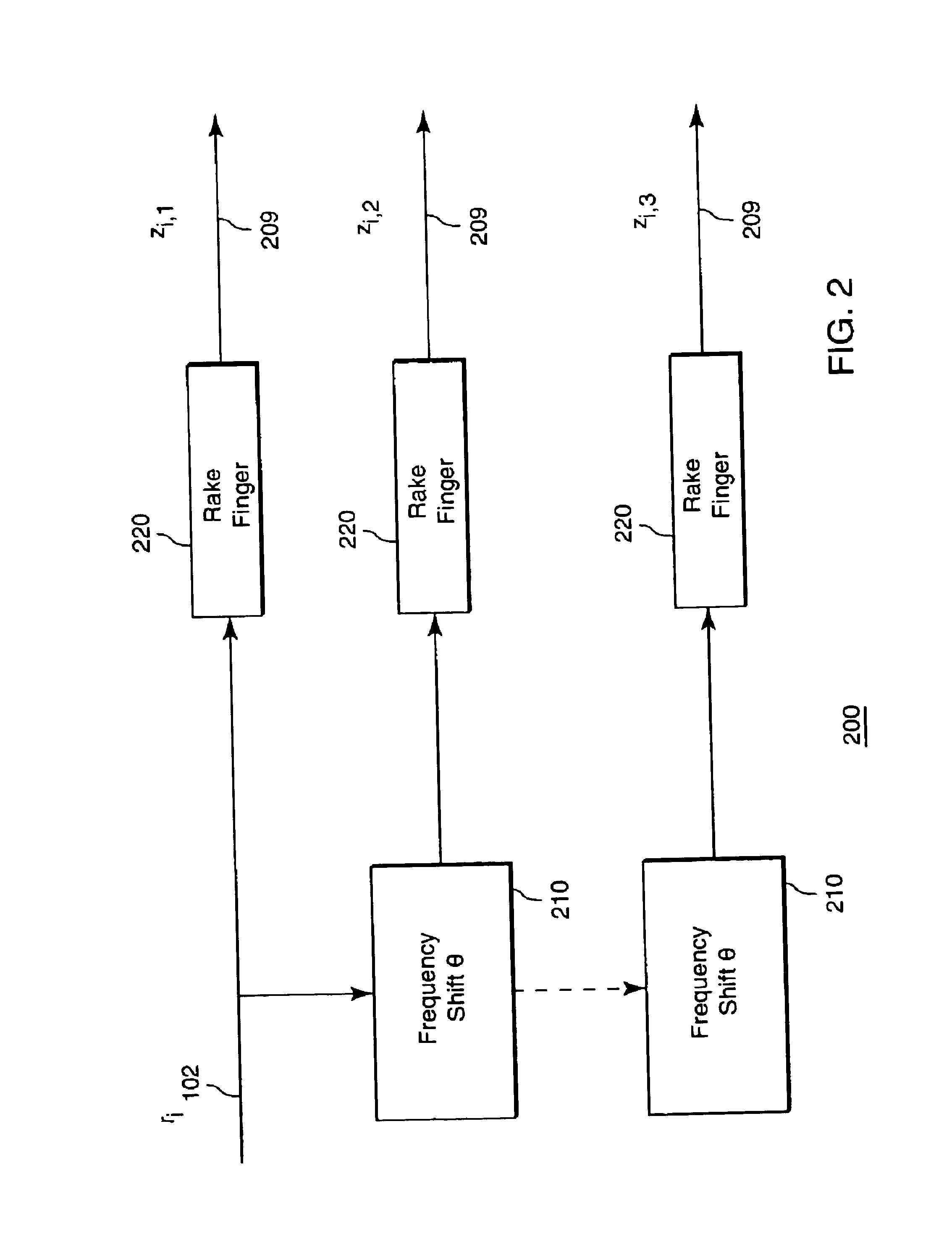
Adaptive DS-CDMA multi-user receiver with diversity combining for interference cancellation
InactiveUS6839379B1Spatial transmit diversityMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsInterference cancellerRake receiver
A digital receiver detects symbols in a baseband signal in a DS-CDMA network. The receiver includes multiple spaced apart antennas. A time-frequency rake receiver is connected to each of the antennas. An interference canceller is connected to each output of each of the rake receiver. Each interference canceller produces a contributing symbol in parallel. A diversity combiner determines a decision symbol corresponding to the baseband signal from the contributing symbols.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Information carrying synchronization code and method for frame timing synchronization
ActiveUS20090116470A1Reduce complexitySimple procedureSynchronisation arrangementError coding/decoding sychronisationComputer hardwareRound complexity
An improved method for conveying data and synchronization information in a telecommunication system is disclosed. The method uses a cyclically permutable code, to which a repetitive structure has been imposed, for carrying the data and synchronization information. The decoding procedure at the receiver then uses this repetitive structure of the code to reduce complexity by first evaluating, by use of hypotheses Hx, the repetitive codeword structure of received codewords and choosing a hypothesis corresponding to the repetitive codeword structure. Then the decoding procedure performs diversity combining of codeword elements of the codewords in accordance with the chosen hypothesis. The received codewords are further detected by comparing the diversity combined codeword elements to all possible codewords fulfilling the hypothesis.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
receiver
ActiveUS20110200089A1Increase delayMultiple-port networksPolarisation/directional diversityWeight coefficientEngineering
A receiver receives a reception signal subjected to orthogonal frequency division multiplexing modulation or orthogonal frequency division multiple access modulation. The receiver has: an array antenna for receiving the reception signal; adaptive equalizers provided in each of the plurality of antennas, and reducing advanced or delayed waves having a delay time to a main wave in the reception signal; a spatial diversity combining portion which multiplies output signals of the adaptive equalizers by a weighting coefficient and adds the multiplied signals; a weight control portion generating the weighting coefficient; and an equalizer setting unit which estimates an arrival angle and a delay time for each path of the reception signal, and based on the estimation, decides an interference wave to be eliminated by the adaptive equalizers among interference waves, and sets in the adaptive equalizers the delay time of the decided interference wave.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) receiver
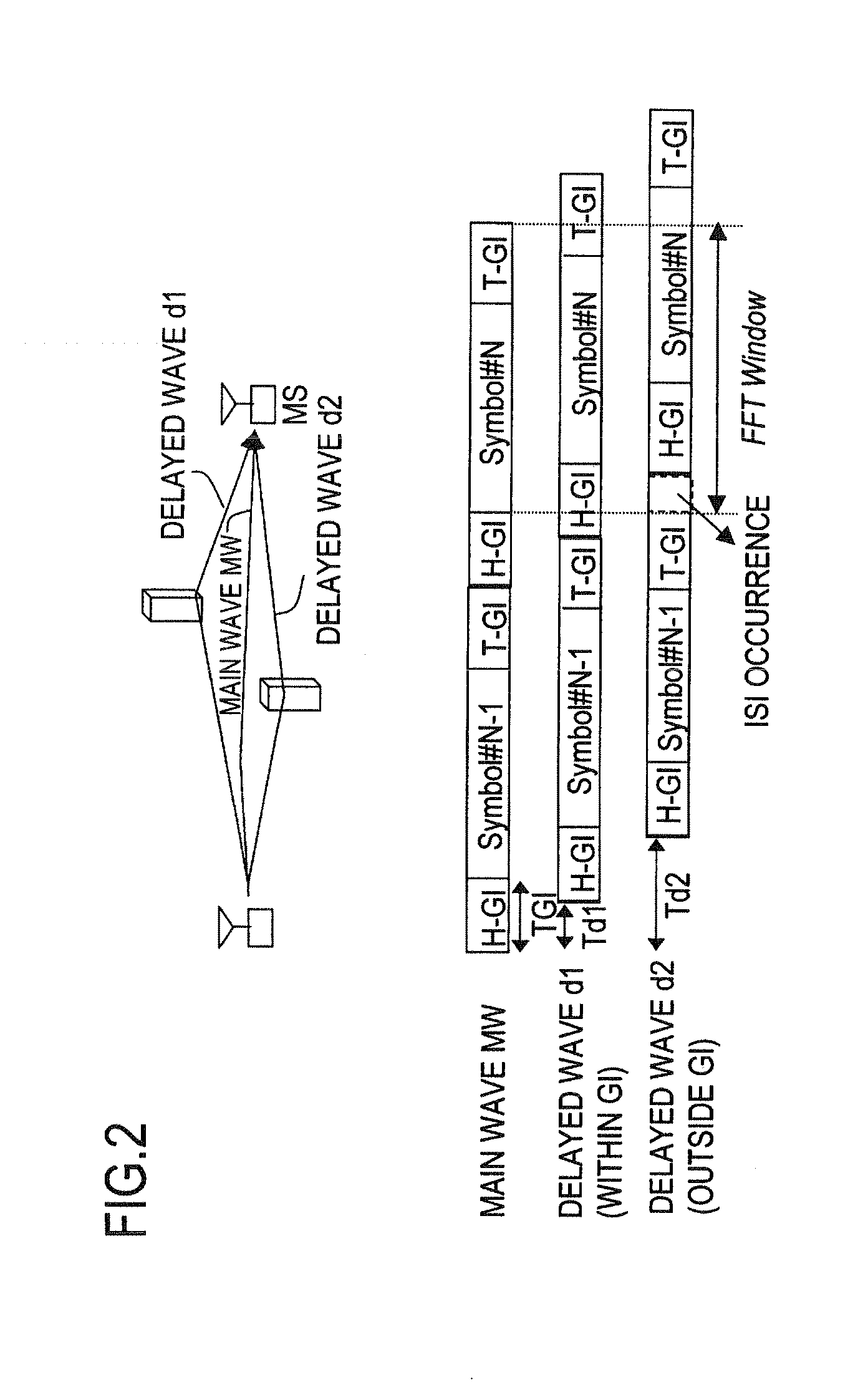
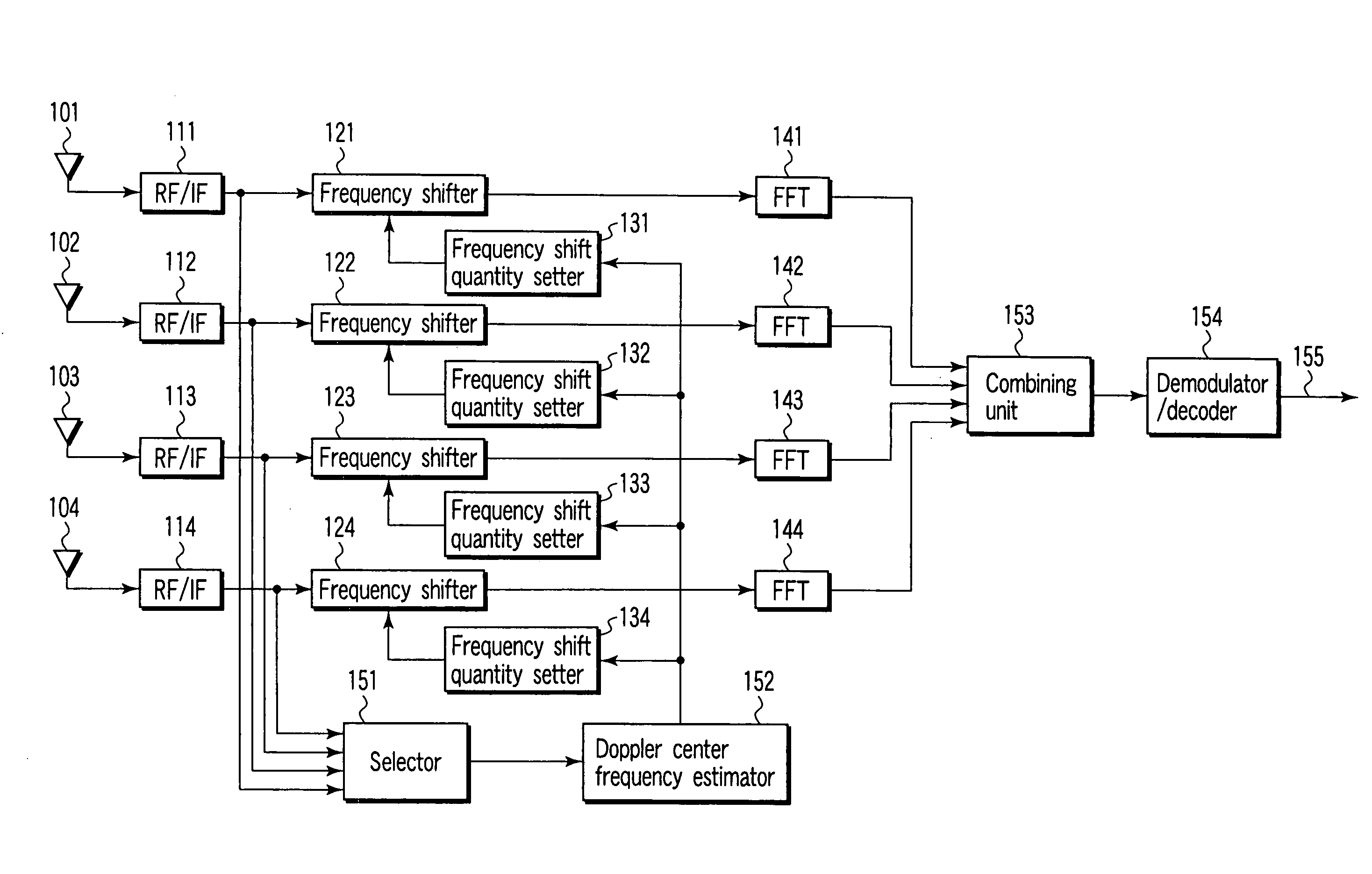
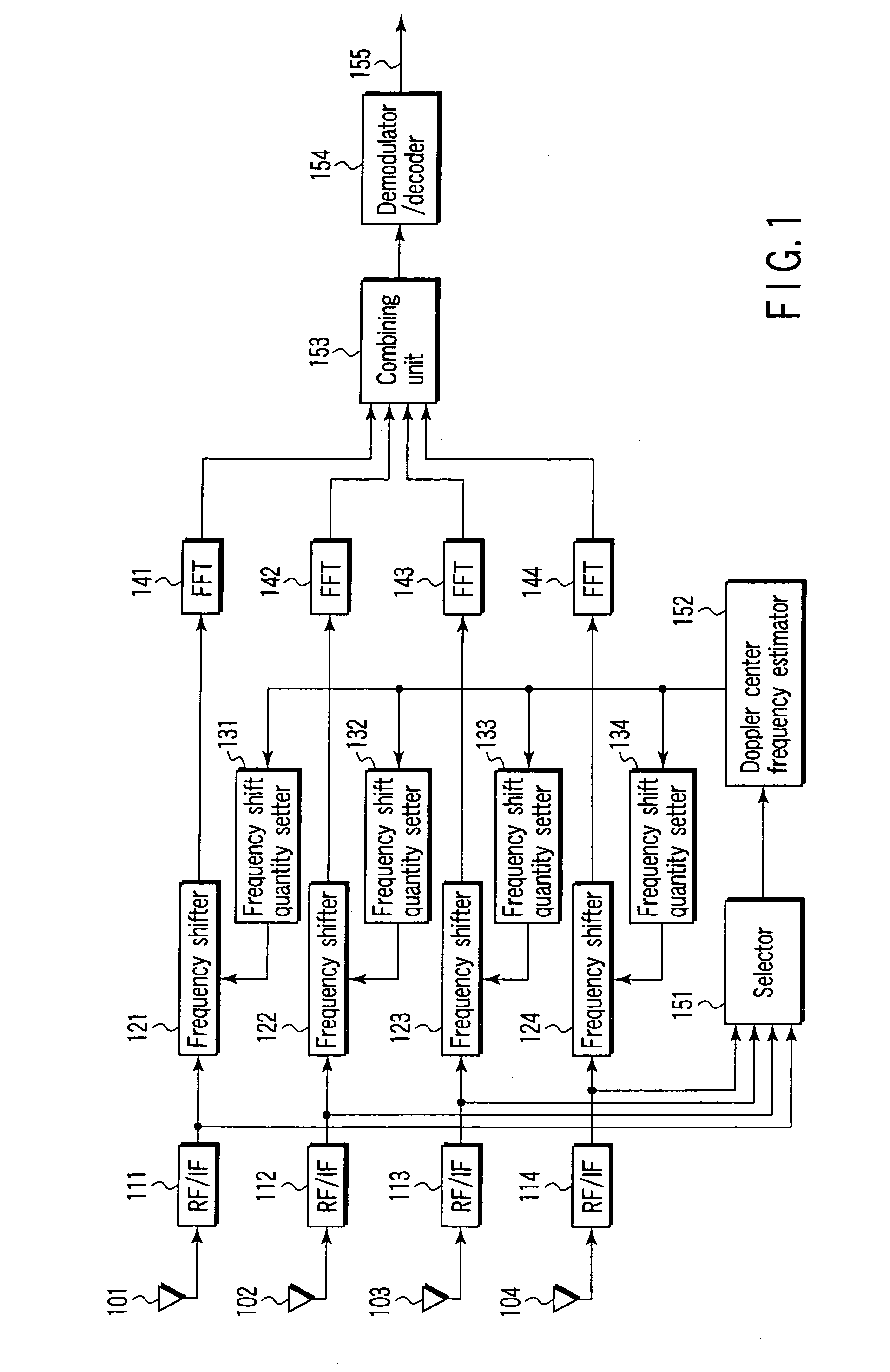
InactiveUS20060115011A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsMultiplexingFrequency spectrum
An OFDM receiver apparatus mounted on a movable object for receiving an OFDM signal, includes a plurality of directional antennas which receive an OFDM signal, an estimator to estimate a center frequency of a spectrum of a Doppler component from one of the received signals or a multiplexed signal obtained by multiplexing the received signals, a shift quantity calculator to calculate a shift quantity from the estimated center frequency of the estimator and directivity information representing directivity directions of the directional antennas, a plurality of frequency shifters to subject the received signals to frequency shift according to the shift quantity to compensate for Doppler shift, a combining unit to diversity-combine frequency shifted signals of the frequency shifters, and a demodulator / decoder to demodulate and decode combining diversity signals of the combining unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Polarization-diverse antenna array and associated methods
InactiveUS20080136721A1Rapidly deployableResonant long antennasIndividually energised antenna arraysPolarization diversityElectrical conductor
The polarization-diverse antenna array includes three orthogonal loop antennas having a common center, e.g. together defining a sphere. Each loop antenna includes a loop electrical conductor. Two signal feedpoints are along the loop electrical conductor and separated by a fraction of a length of the loop electrical conductor. Each of the signal feedpoints includes a series signal feedpoint so that a polarization diversity controller coupled thereto may selectively provide vertical, horizontal, lefthand circular and righthand circular polarization for a single loop electrical conductor, including simultaneous (dual) polarizations. These signal feedpoints may supply signals with vertical, horizontal, lefthand circular and righthand circular polarization from each of the three orthogonal look-angles provided by the three loop electrical conductors. Thus the antenna array may provide a compact facility for using Diversity Combining to improve communications performance and / or Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MIMO) schemes that furthermore also increase capacity. The polarization-diverse antenna array provides a rigorous polarization and look angle approach for communications diversity
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Method and apparatus for diversity combining and co-channel interference suppression
InactiveUS20050074071A1Polarisation/directional diversityChannel estimationCommunications systemCombined use
A method and apparatus for controlling an antenna array for wireless communication are described. The method uses the statistical characteristics of the received signal noise in controlling the antenna array in order to achieve directional reception in a wireless communication system and suppress co-channel interference. Furthermore, the method can be used to power space-division multiple access and can be used in conjunction with multi-carrier modulation signaling.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
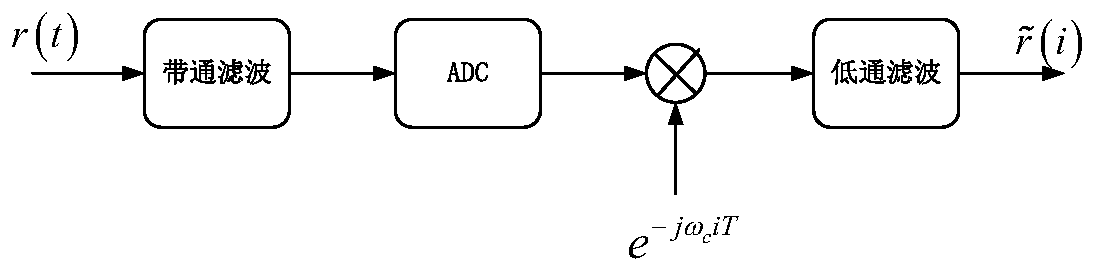
An OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication method with high spectral efficiency under a time-varying double-spread channel condition
ActiveCN109743118AImprove reliabilityReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) underwater acoustic communication method with high spectral efficiency under a time-varying double-spread channel condition, and belongs to the technical field of underwater acoustic communication. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out band-pass filtering on a received signal r (k), carrying out front-endprocessing such as ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) conversion into a digital signal, carrying out down-conversion and low-pass filtering, estimating average Doppler by utilizing a fuzzy function method, carrying out resampling and frequency correction, multiplexing the signal, carrying out time domain equalization and frequency domain equalization, carrying out diversity combination, and then adopting the OMP-DCD algorithm to perform residual Doppler compensation. an iterative signal processing technology is adopted, an LDPC decoder and an equalizer are cascaded through soft-in soft-out mapping / demapping and an interleaver / deinterleaver, close information interaction is achieved in the two modules, soft information transmitted in a reciprocating mode is fully utilized, and interferenceof a time-varying double-spread channel is effectively resisted. According to the method, the complexity and the performance can be well compromised, and serious inter-symbol interference, inter-carrier interference and pilot frequency-pilot frequency interference in the transmission process are efficiently solved. And the method is low in complexity and can be realized on the DSP in real time.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
Constellation rearrangement for transmit diversity schemes
InactiveUS7164727B2Improve decoding performanceReduce the differenceError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemDiversity scheme
A method of transmitting data in a wireless communication system from a transmitter to a receiver, comprising the steps of modulating data at the transmitter using a first signal constellation pattern to obtain a first data symbol. The first data symbol is transmitteds to the receiver using a first diversity branch. Further, the data is modulated at the transmitter using a second signal constellation pattern to obtain a second data symbol. Then, the second data symbol is transmitted to the receiver over a second diversity path. Finally, the received first and second data symbol are diversity combined at the receiver. The invention further relates to a transmitter and a receiver embodies to carry out the method of invention.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Fast self-optimization self-adaptive signal processing method and device of coherent communication technology
ActiveCN101272188AReduce overheadGood signal processing performanceModulated-carrier systemsSynchronising arrangementSelf adaptiveComputer science
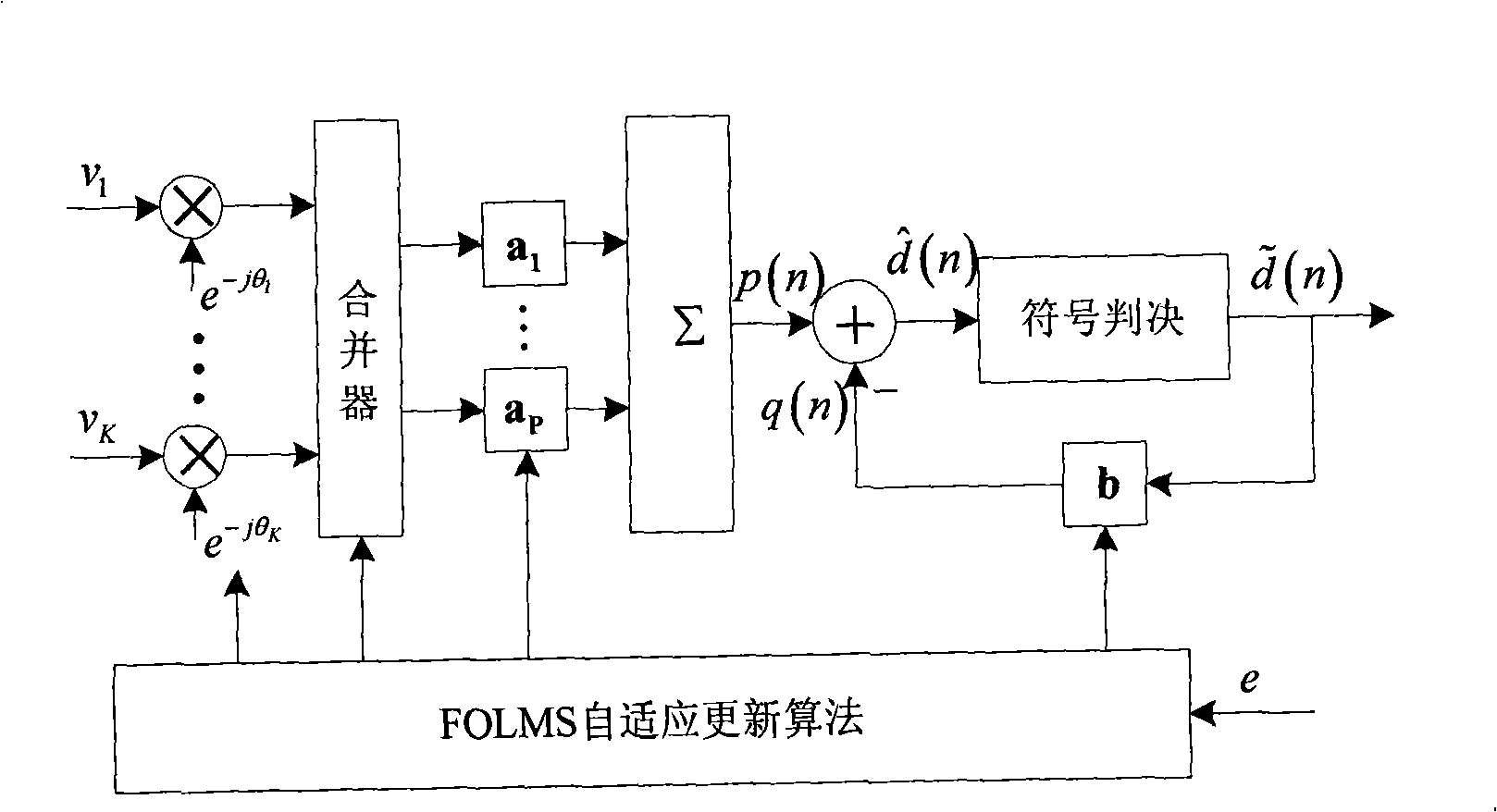
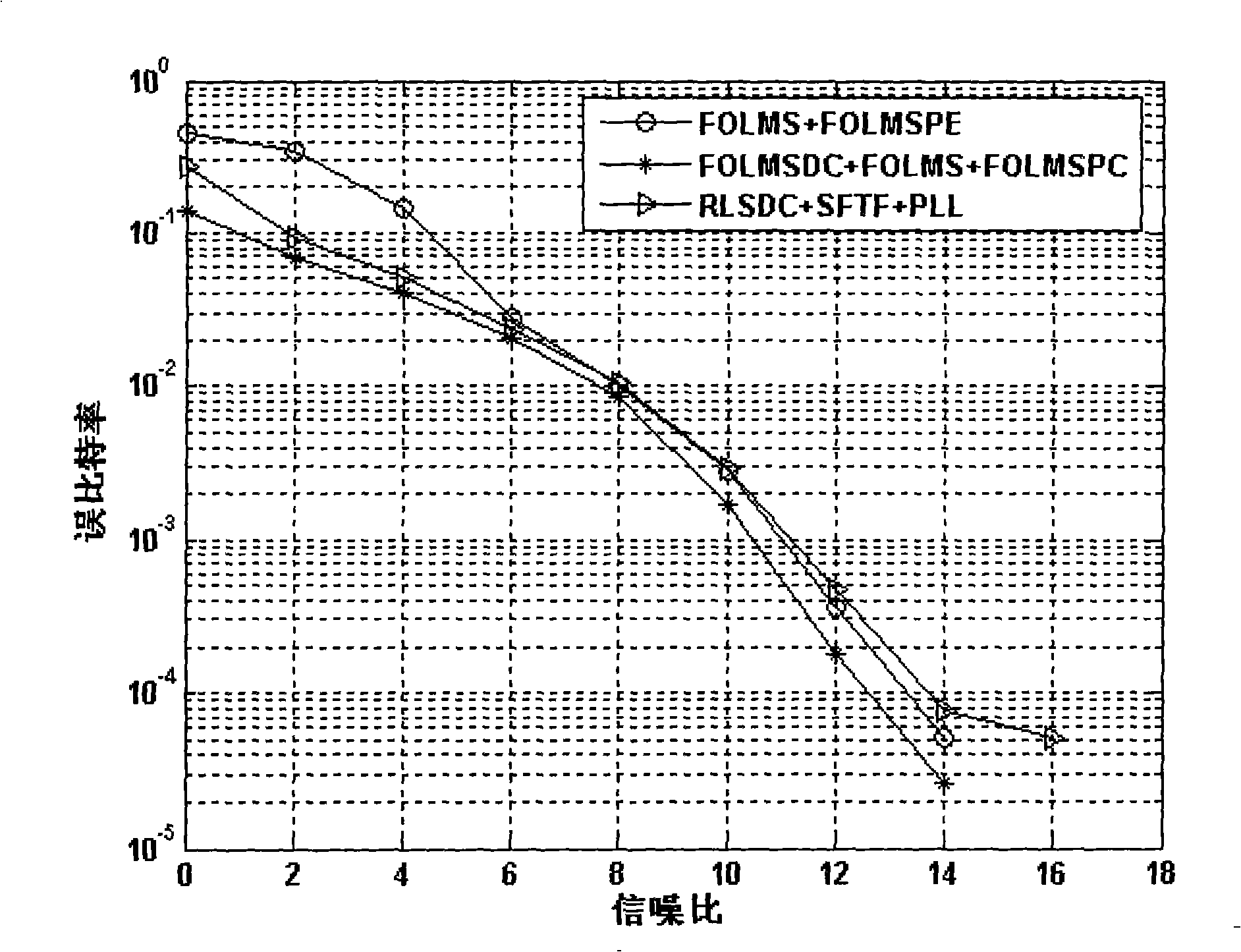
The invention discloses a fast self-optimizing self-adaptive signal processing method and processing device of a coherent communication technology as well as a coherent communication machine which comprises the processing device. The method comprises the steps: a signal is received; phase compensation is carried out on the signal; the signal is simplified and outputted through a diversity combiner; the signal that is simplified and outputted is processed through an equalizer; the signal outputted by the equalizer is carried out symbol judgment, the signal is outputted and simultaneously feeding back to the equalizer to generate an error signal. The device comprises a phase compensation unit, a diversity combiner unit, a self-adaptive judgment feedback equalizer unit, an error signal unit and a self-adaptive updating control unit that are sequentially connected in order. The self-adaptive updating control unit adopts a fast self-optimizing LMS algorithm to update the phase, the diversity combiner parameters and the equalizer parameters. The invention has a better signal processing performance, a lower bit error rate as well as a less calculation amount and saves the hardware cost.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for receiving spread spectrum signal
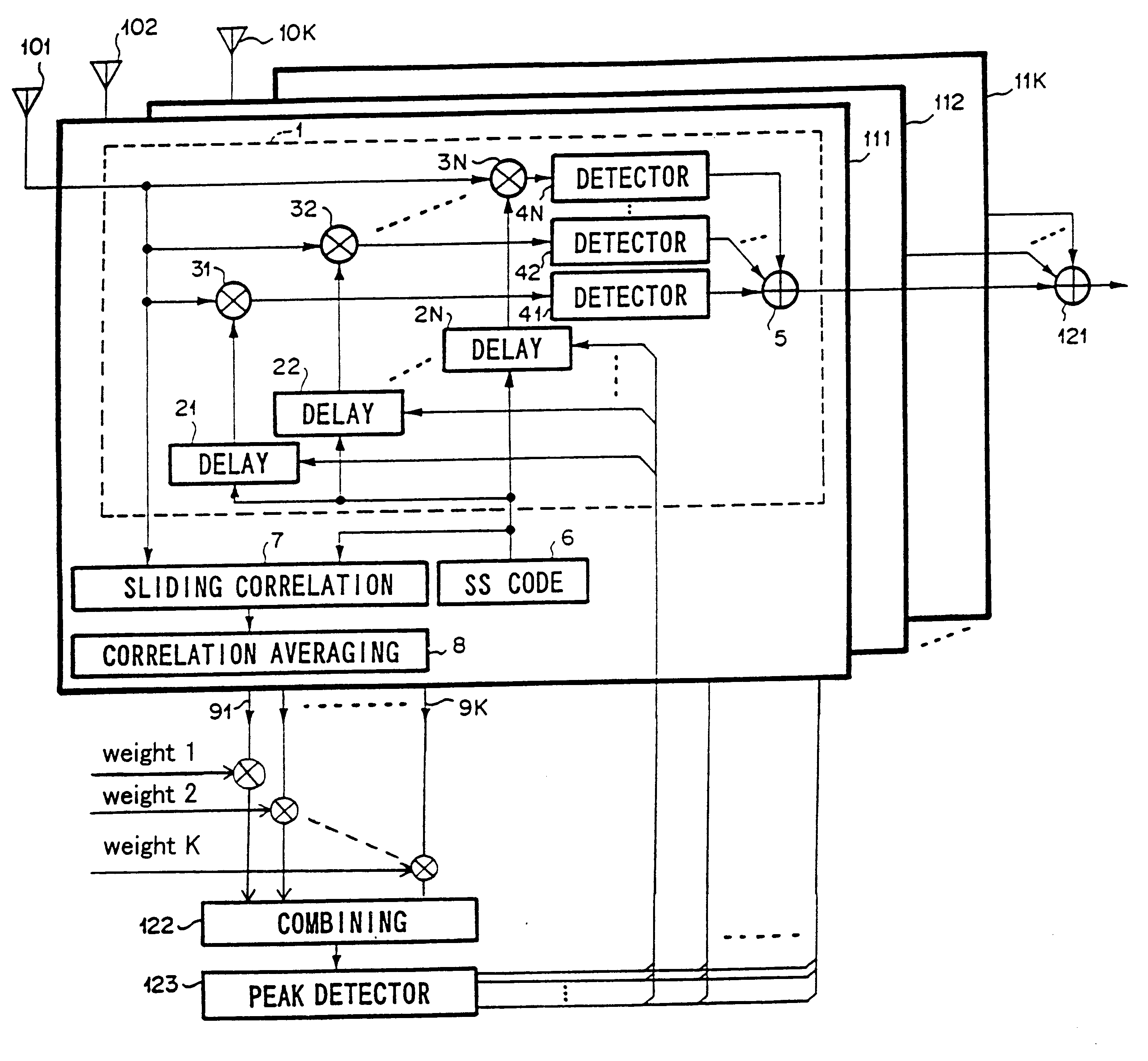
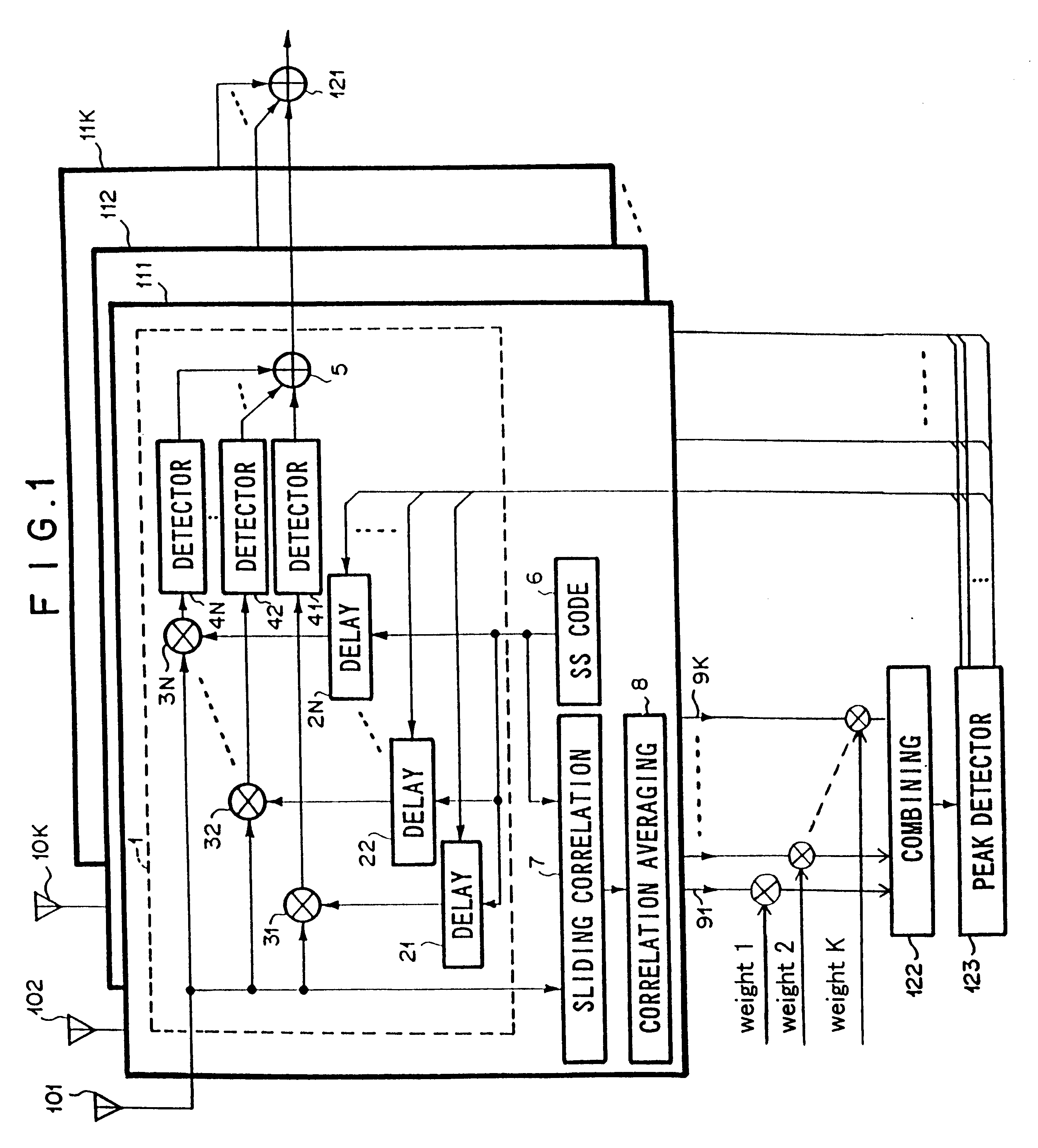
To synchronize spread spectrum (SS) signal with PN sequence, even when a Doppler frequency of fading is low. Delay profile combining means outputs a combined delay profile from delay profiles which are outputted from receiving units. Further, the synch chip timing which is obtained from the combined delay profile is fed commonly to receiving units for path diversity combining.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com