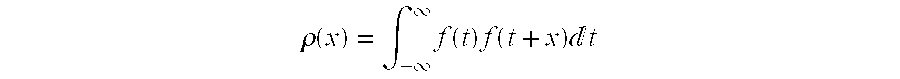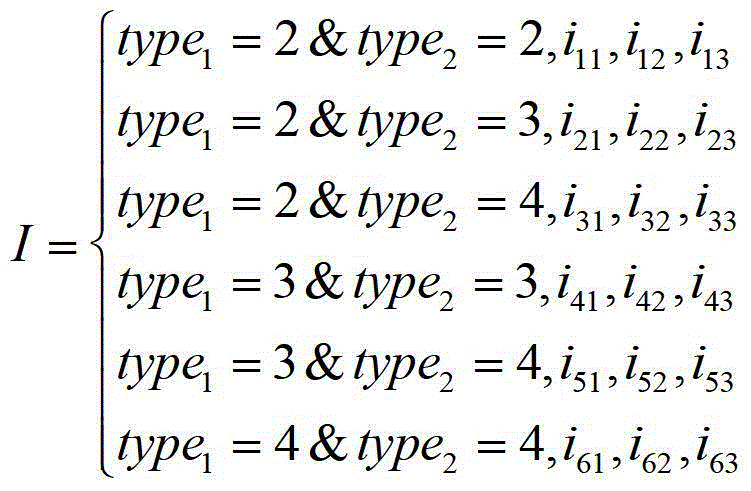Patents
Literature
543 results about "Logit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics, the logit (/ˈloʊdʒɪt/ LOH-jit) function or the log-odds is the logarithm of the odds p/(1 − p) where p is probability. It is a type of function that creates a map of probability values from [0,1] to (-∞,+∞). It is the inverse of the sigmoidal "logistic" function or logistic transform used in mathematics, especially in statistics. In deep learning, the term logits layer is popularly used for the last neuron layer of neural networks used for classification tasks, which produce raw prediction values as real numbers ranging from (-∞,+∞).
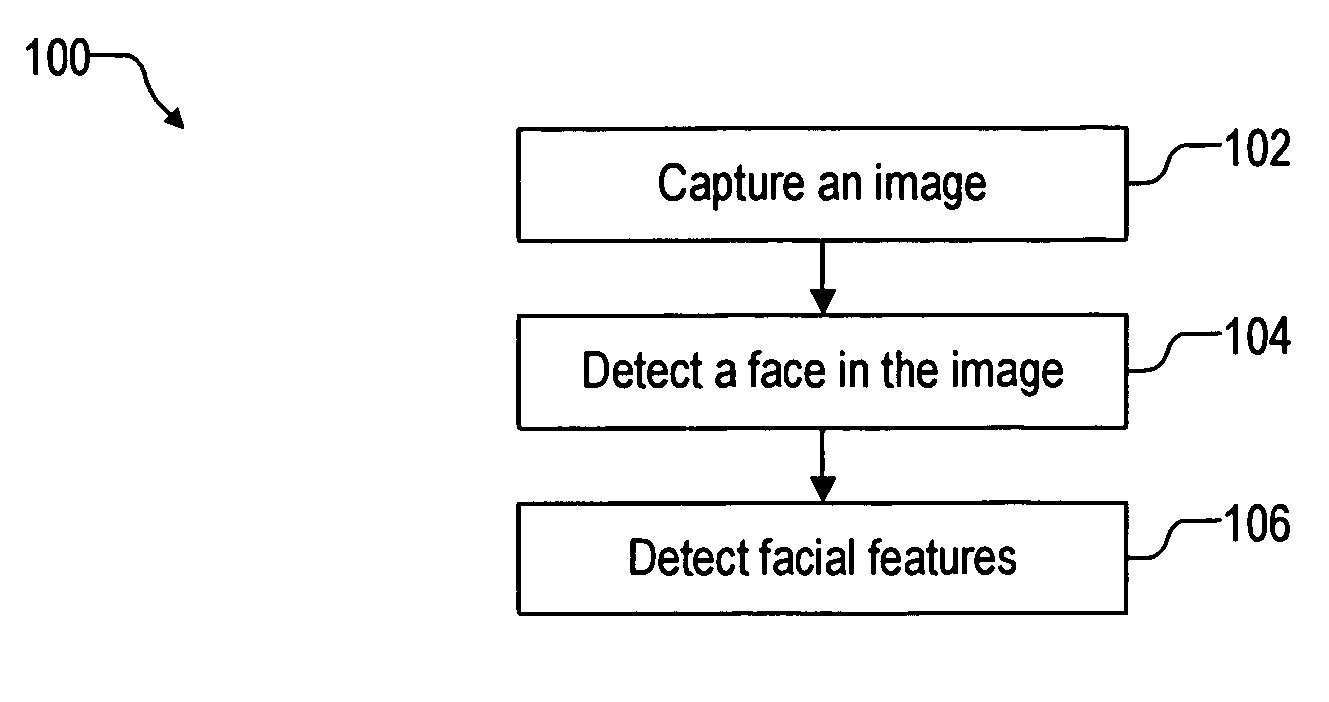
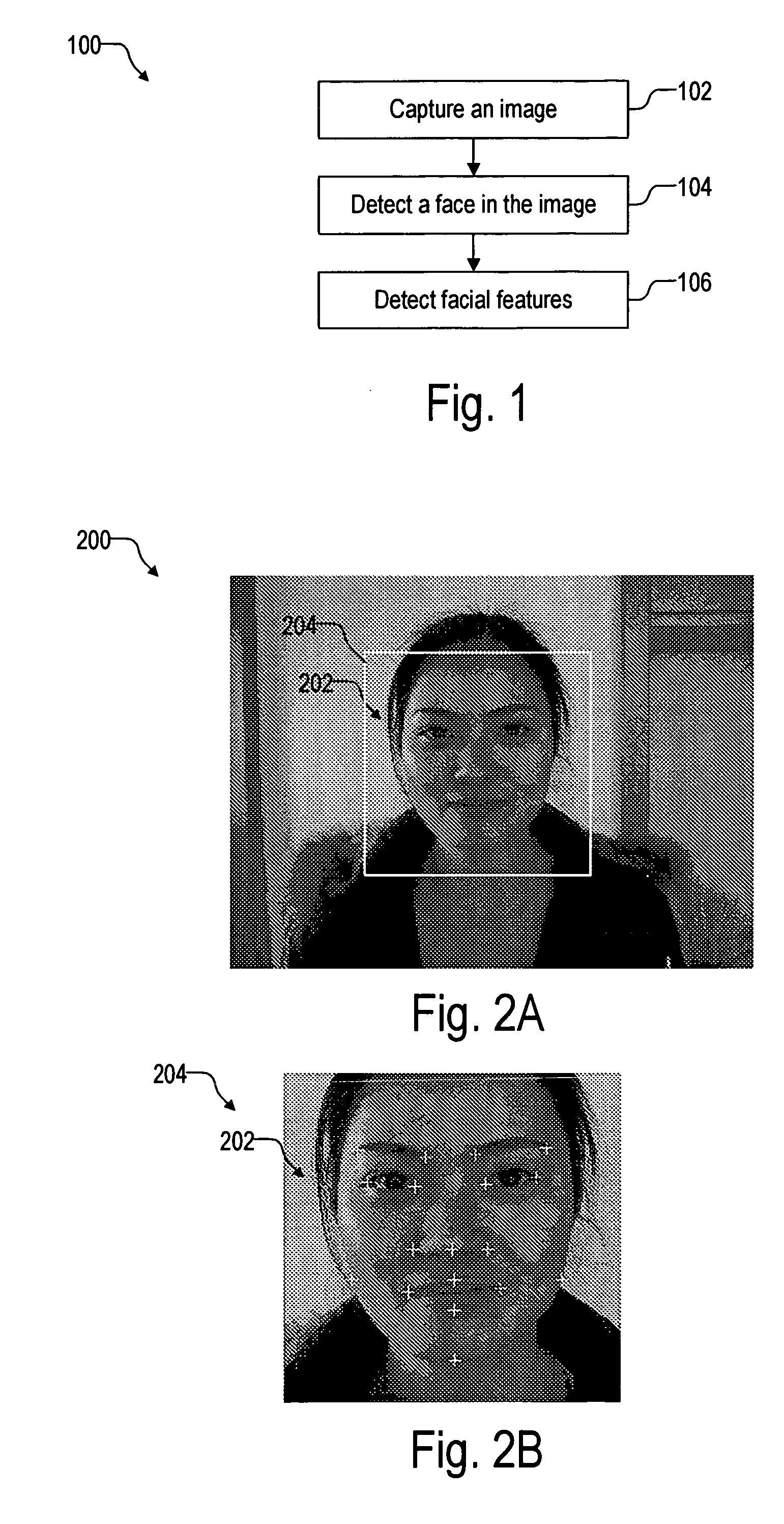
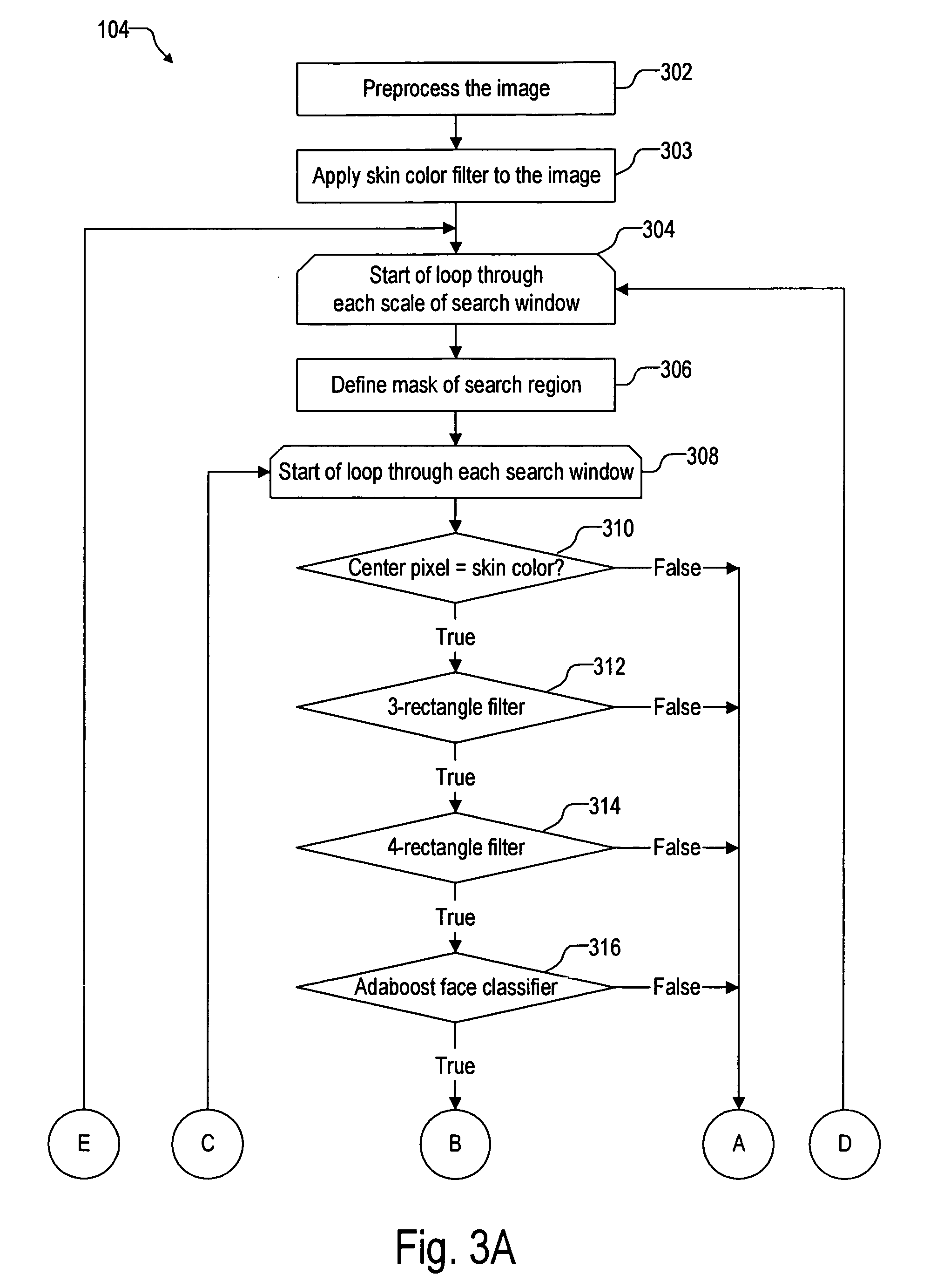
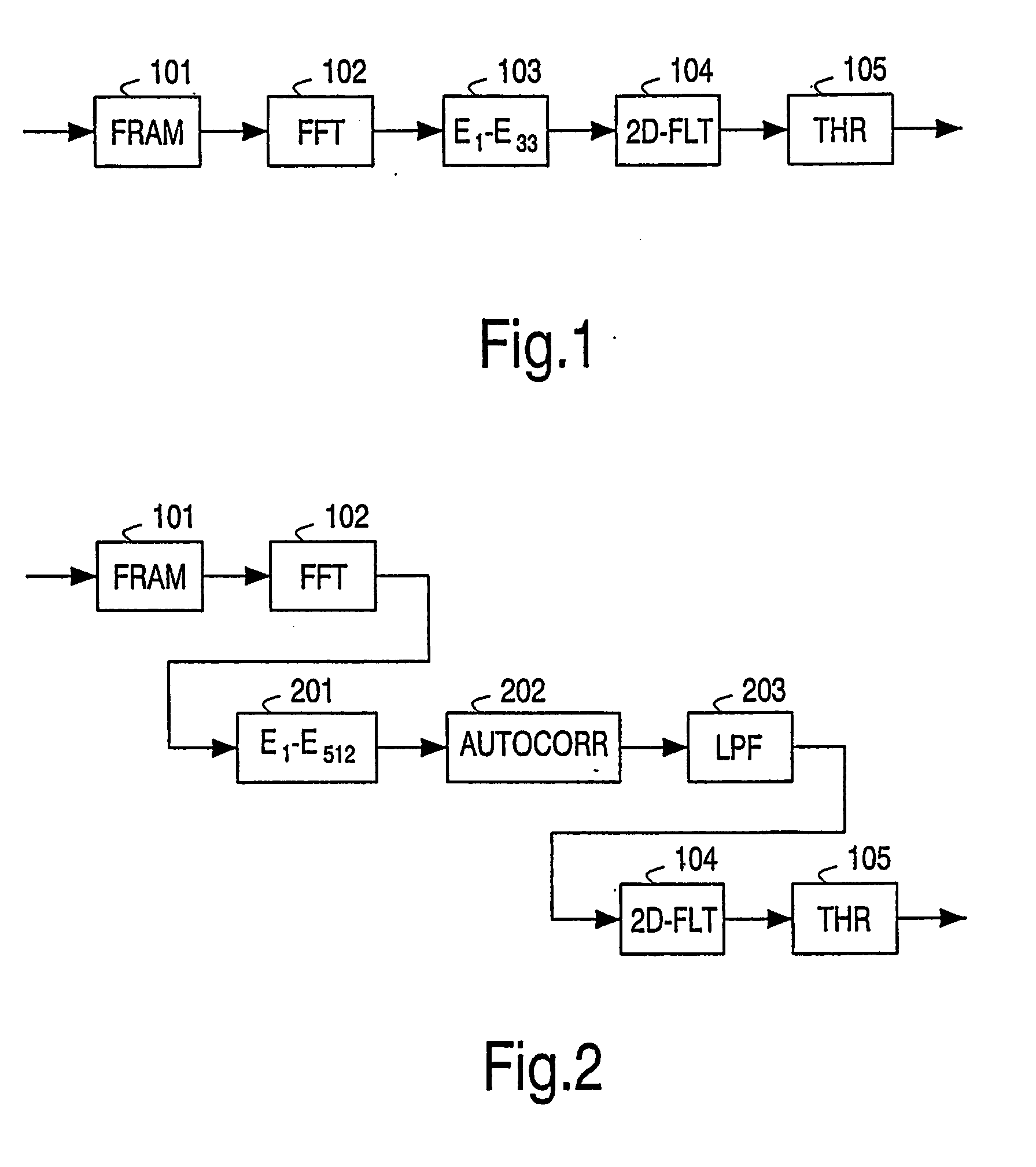
Facial feature detection on mobile devices
Locating an eye includes generating an intensity response map by applying a 3-rectangle filter and applying K-mean clustering to the map to determine the eye. Locating an eye corner includes applying logarithm transform and grayscale stretching to generate a grayscale eye patch, generating a binary map of the patch by using a threshold based on a histogram of the patch, and estimating the eye corner by averaging coordinates weighted by minimal eigenvalues of spatial gradient matrices in a search region based on the binary map. Locating a mouth corner includes generating another intensity response map and generating another binary map using another threshold based on another histogram of the intensity response map. Locating a chin or a cheek includes applying angle constrained gradient analysis to reject locations that cannot be the chin or cheek. Locating a cheek further includes removing falsely detected cheeks by parabola fitting curves through the cheeks.
Owner:ARCSOFT
Fingerprint extraction
InactiveUS20060041753A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsUser identity/authority verificationFrequency spectrumCorrelation function
Fingerprints are bit strings extracted from a media signal (e.g. an audio or video clip) to identify said media signal. Typically, they are derived from a perceptual property of the signal, for example, the spectral energy distribution of an audio fragment or the luminance distribution of a video image. A method and arrangement for extracting a fingerprint is here disclosed which is robust with respect to shifts of the perceptual property. Such shifts occur, inter alia, when the fingerprint is derived from a logarithmically mapped spectral energy distribution of an audio signal and said audio signal is subjected to speed changes. According to the invention, the fingerprint is not derived from the perceptual property as such, but from its auto-correlation function.
Owner:GRACENOTE
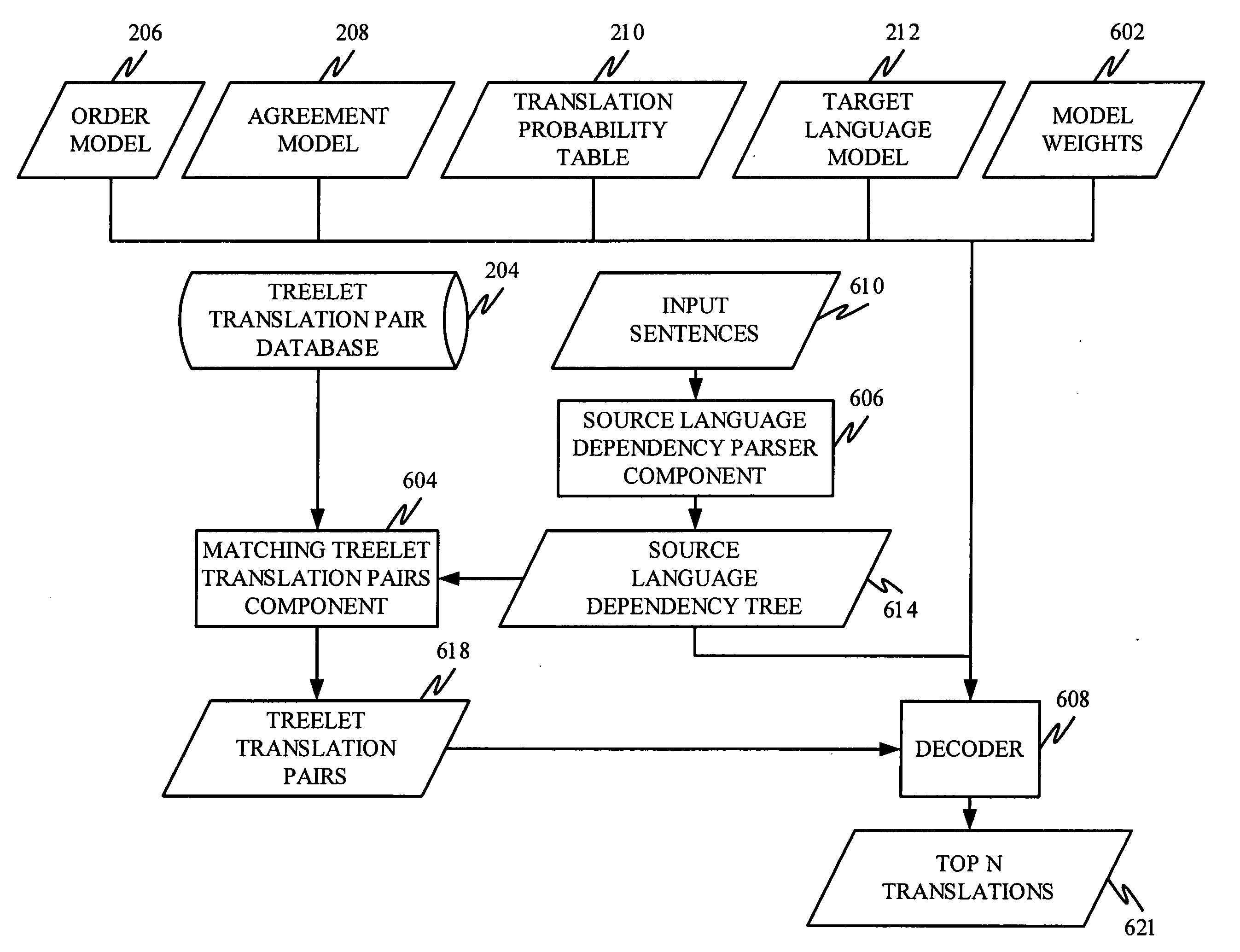
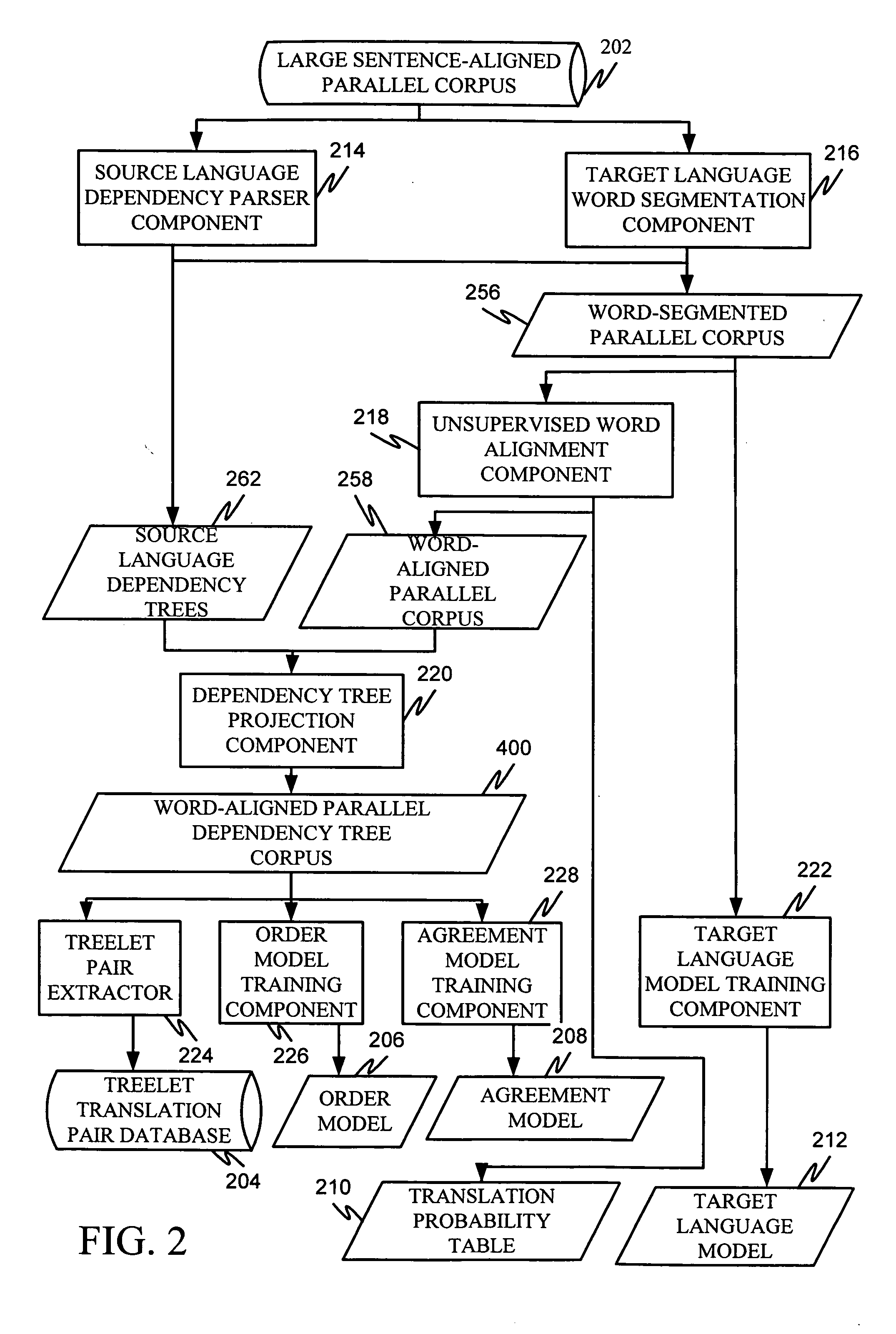
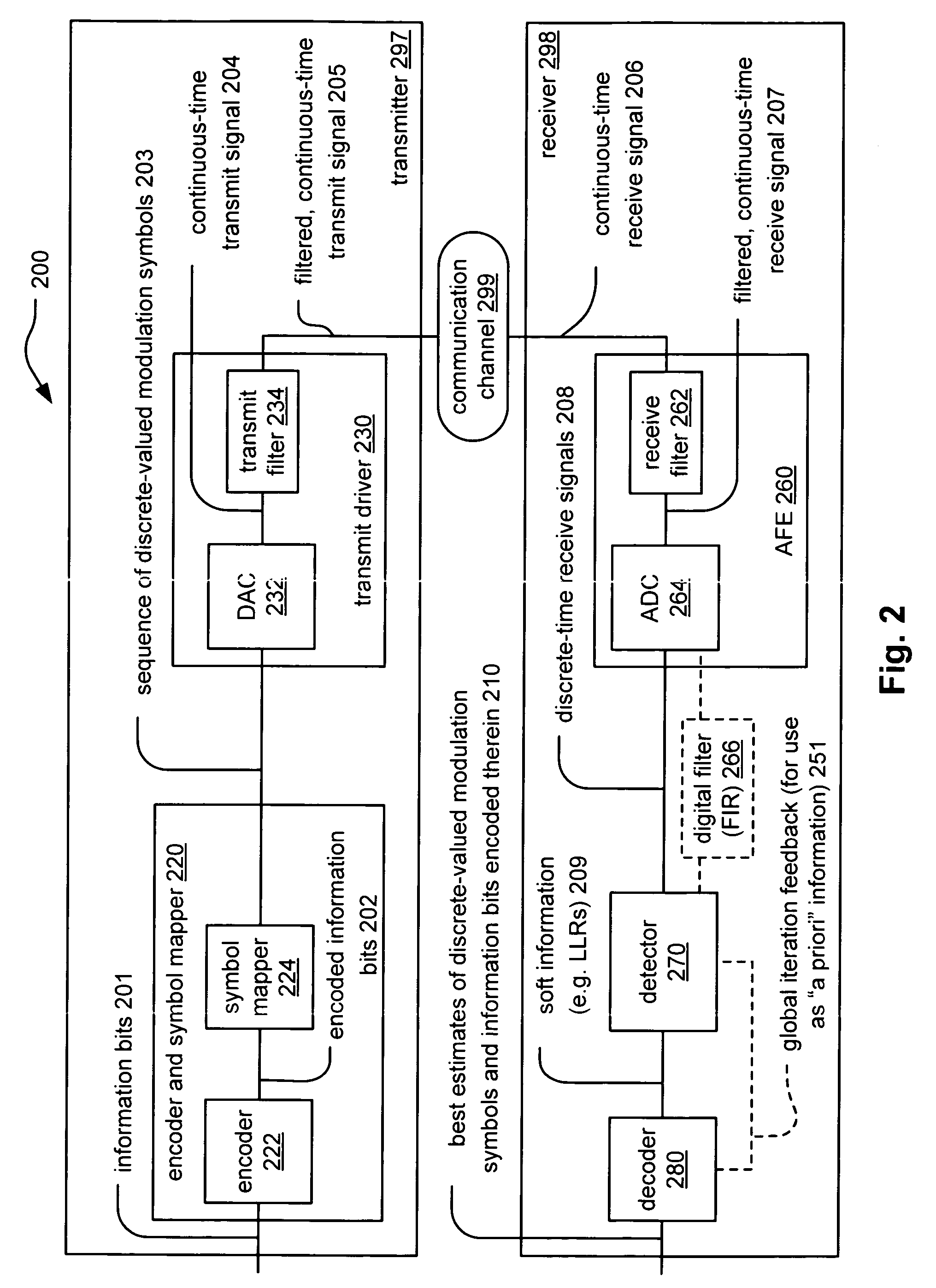
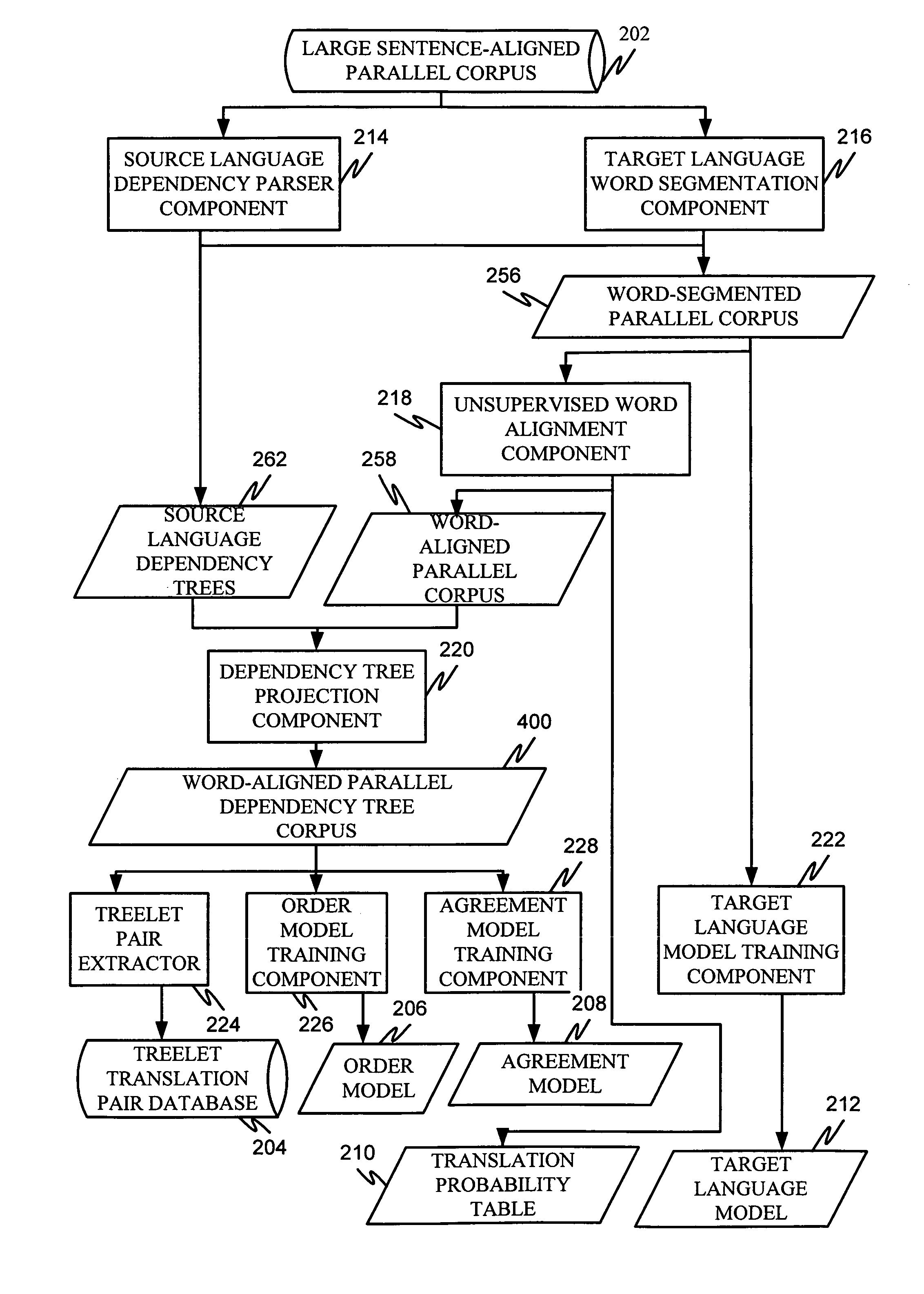
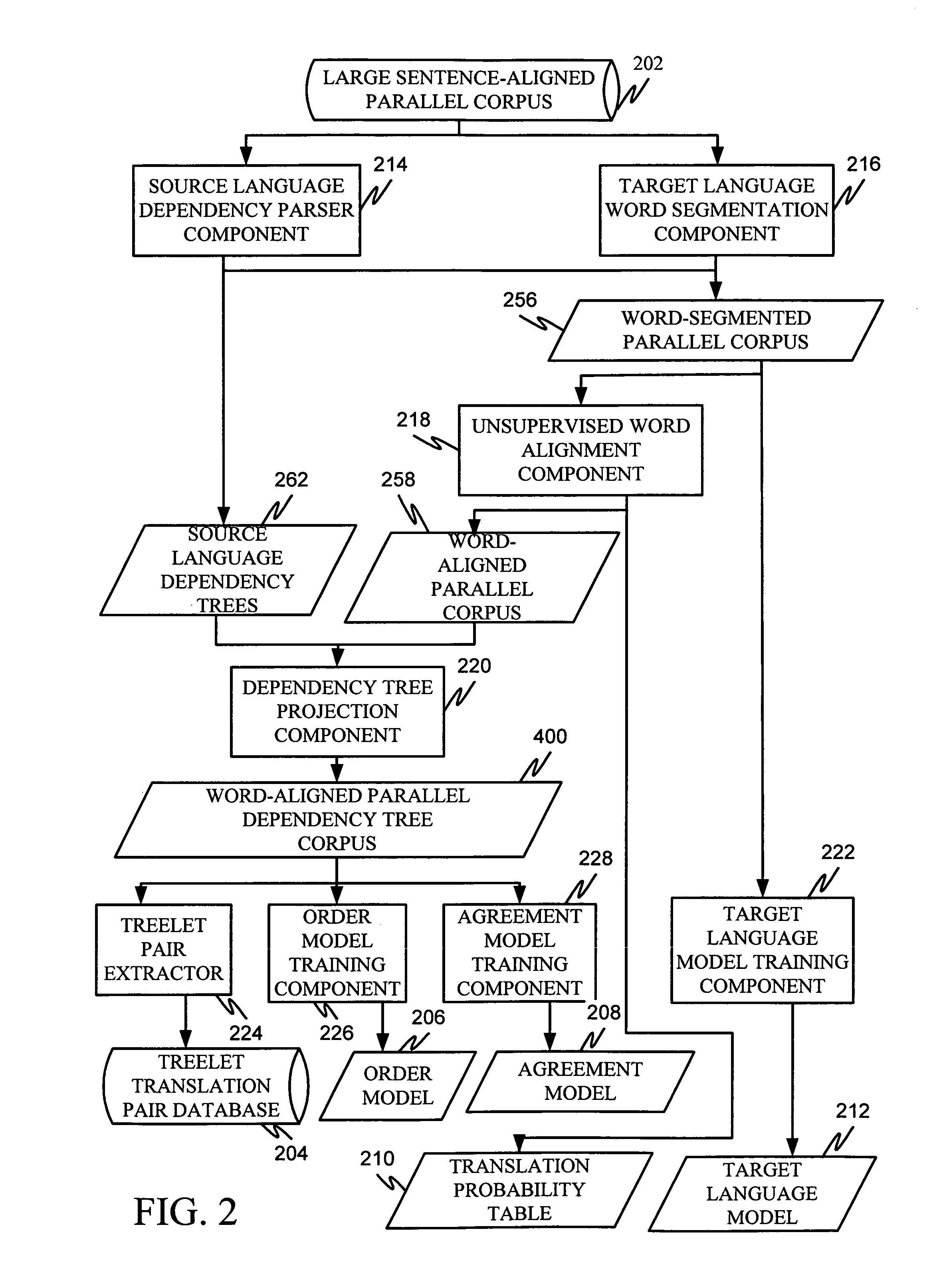
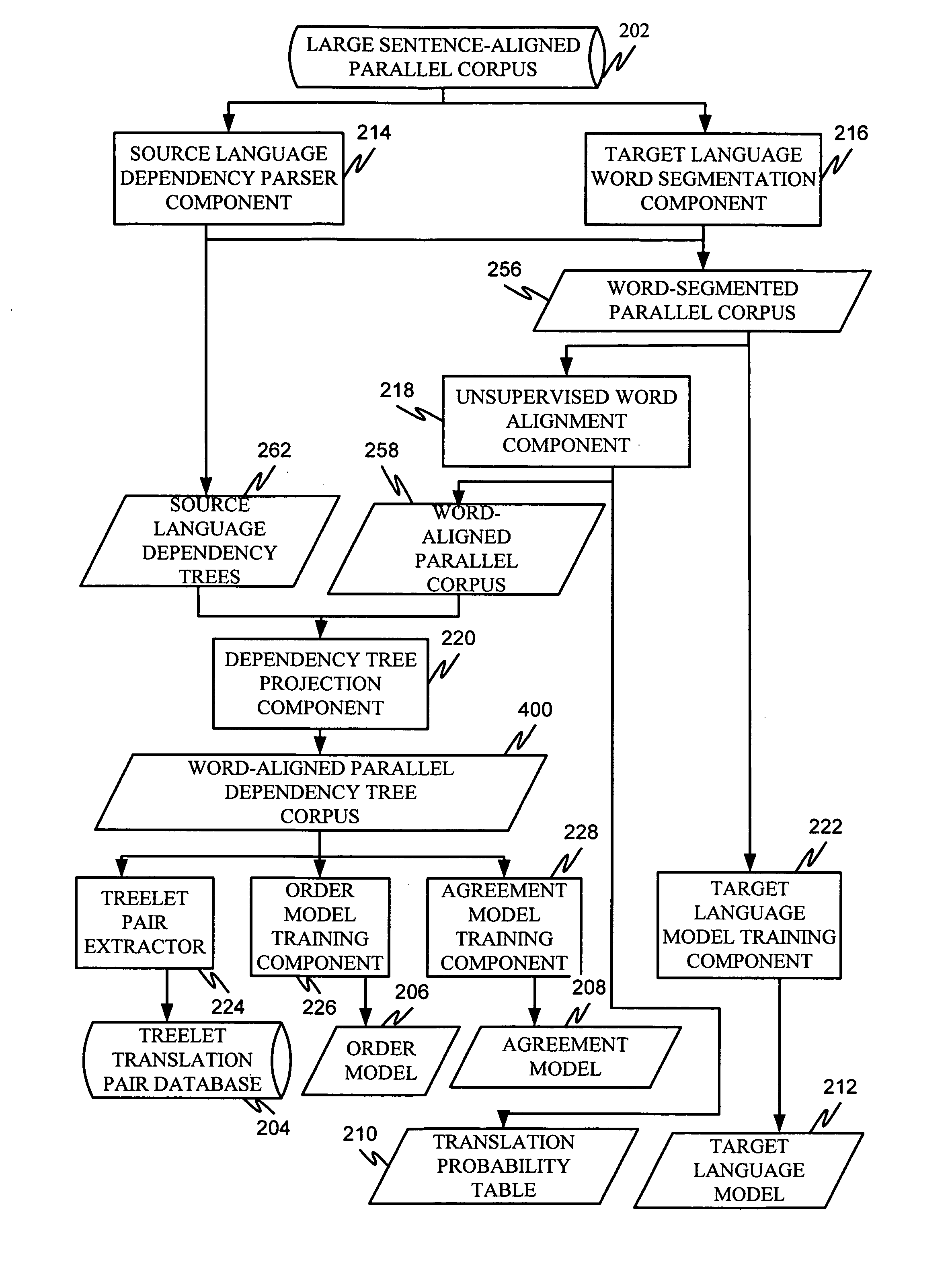
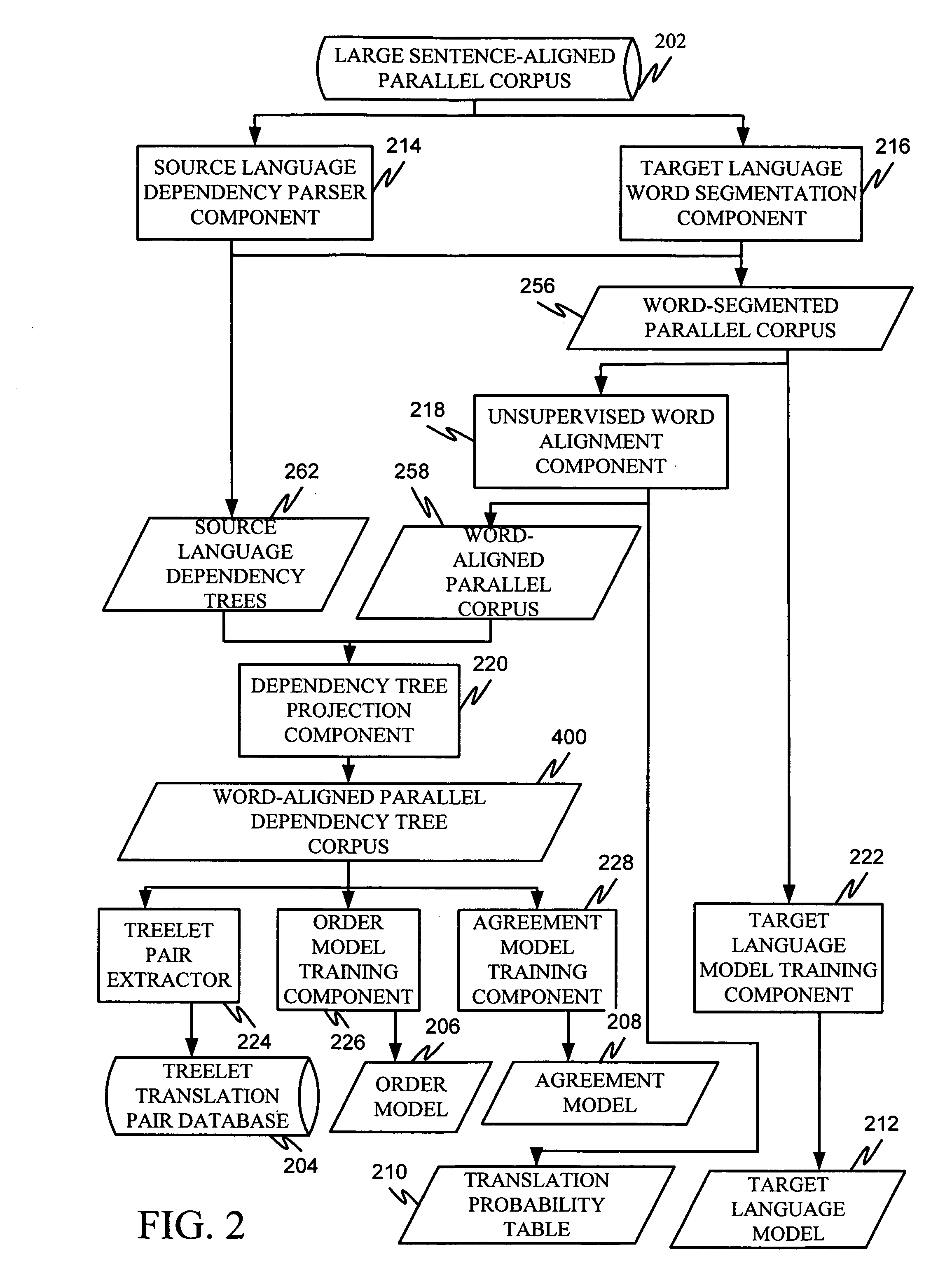
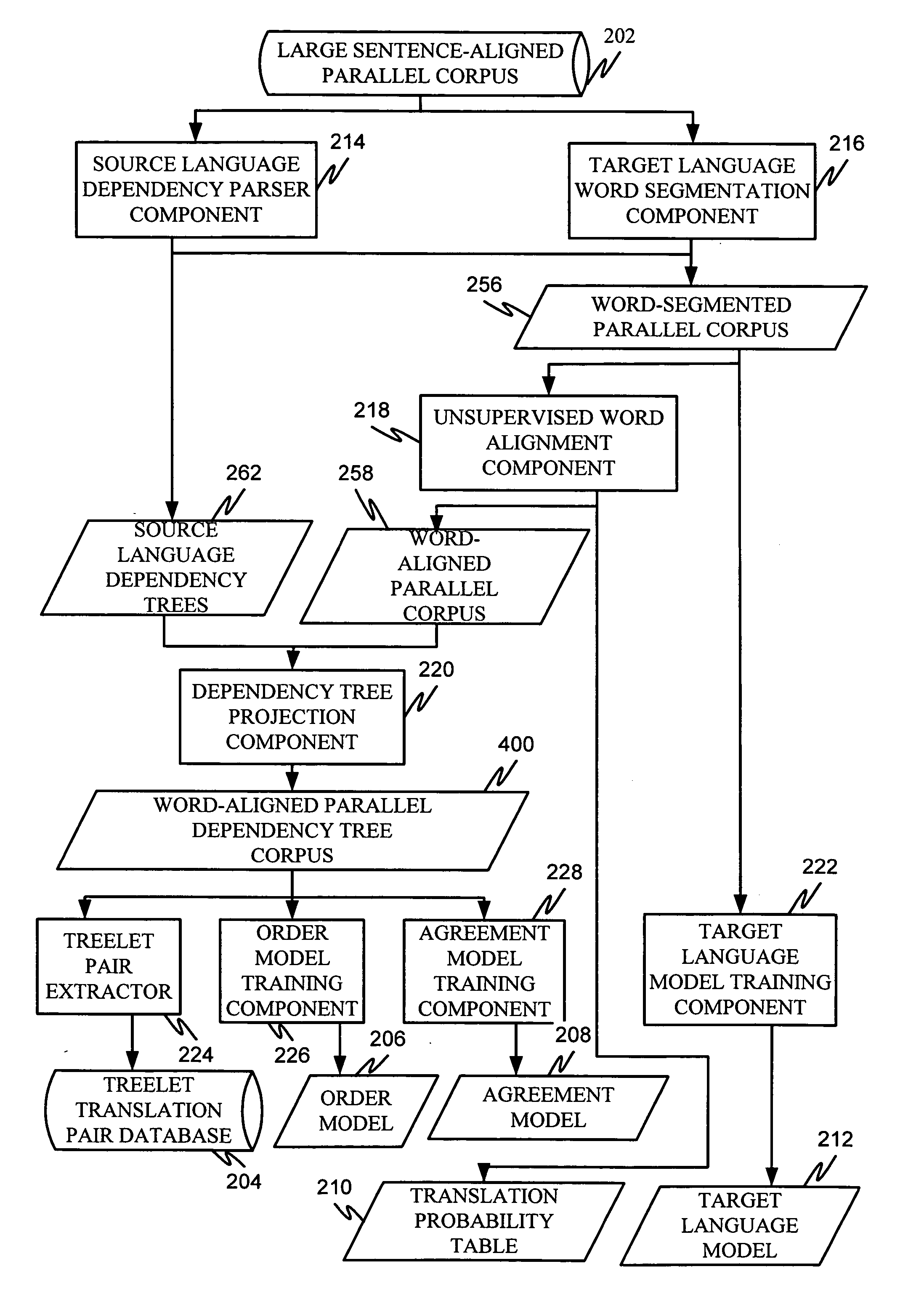
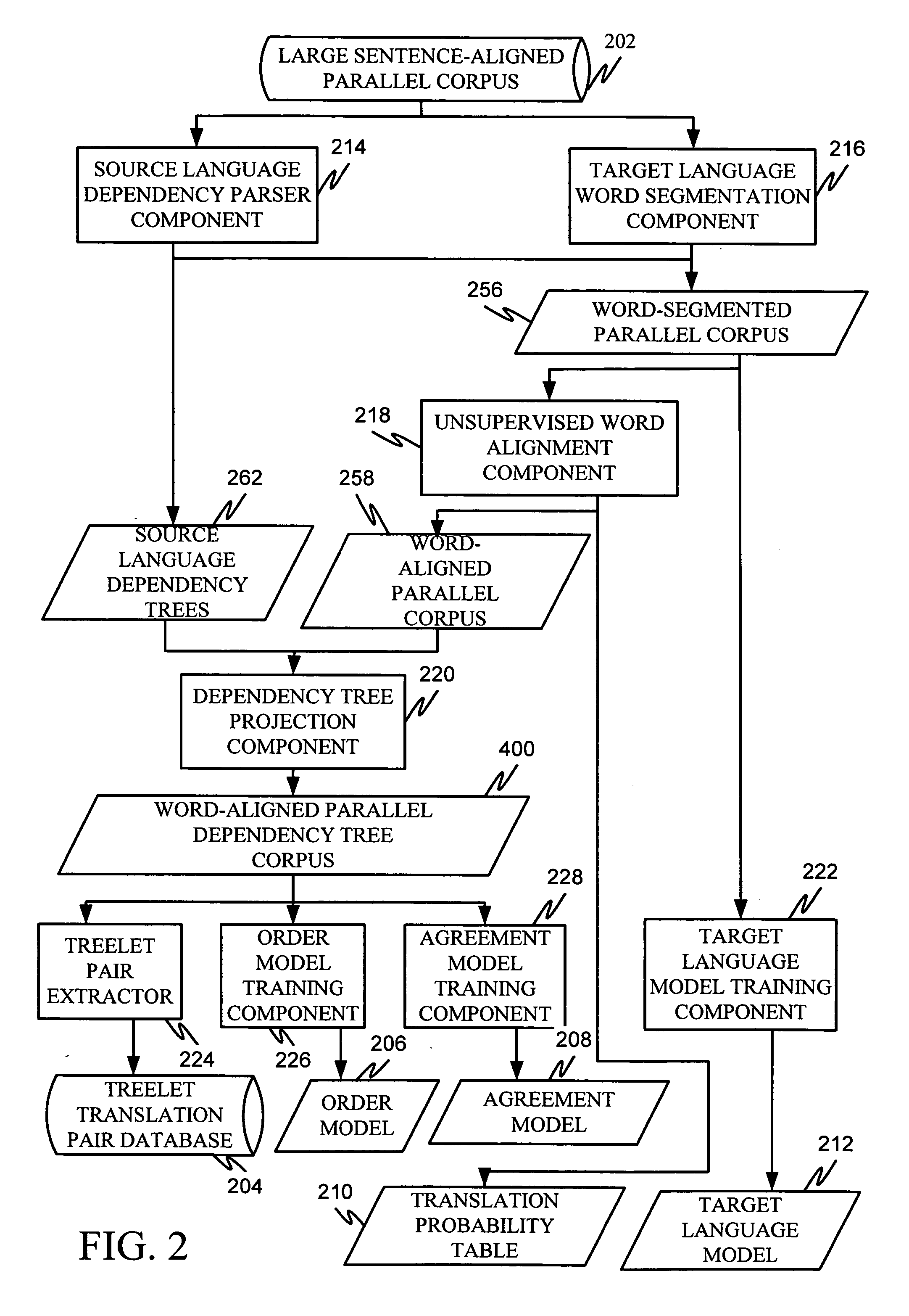
Machine translation system incorporating syntactic dependency treelets into a statistical framework
InactiveUS20060095248A1Efficiently translatedNatural language translationSpeech analysisTheoretical computer scienceMachine translation system
In one embodiment of the present invention, a decoder receives a dependency tree as a source language input and accesses a set of statistical models that produce outputs combined in a log linear framework. The decoder also accesses a table of treelet translation pairs and returns a target dependency tree based on the source dependency tree, based on access to the table of treelet translation pairs, and based on the application of the statistical models.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for evaluating performance of a read channel
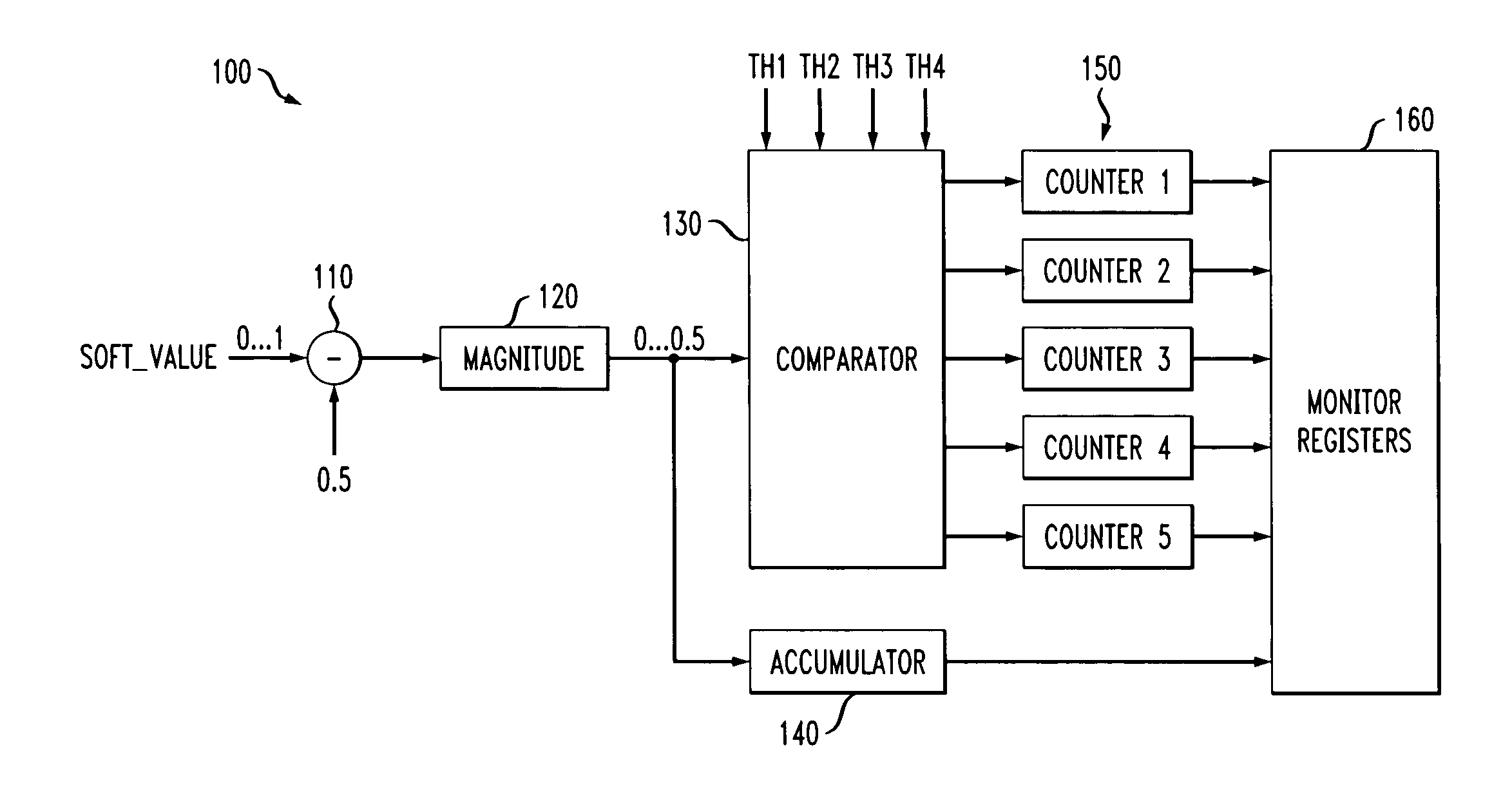
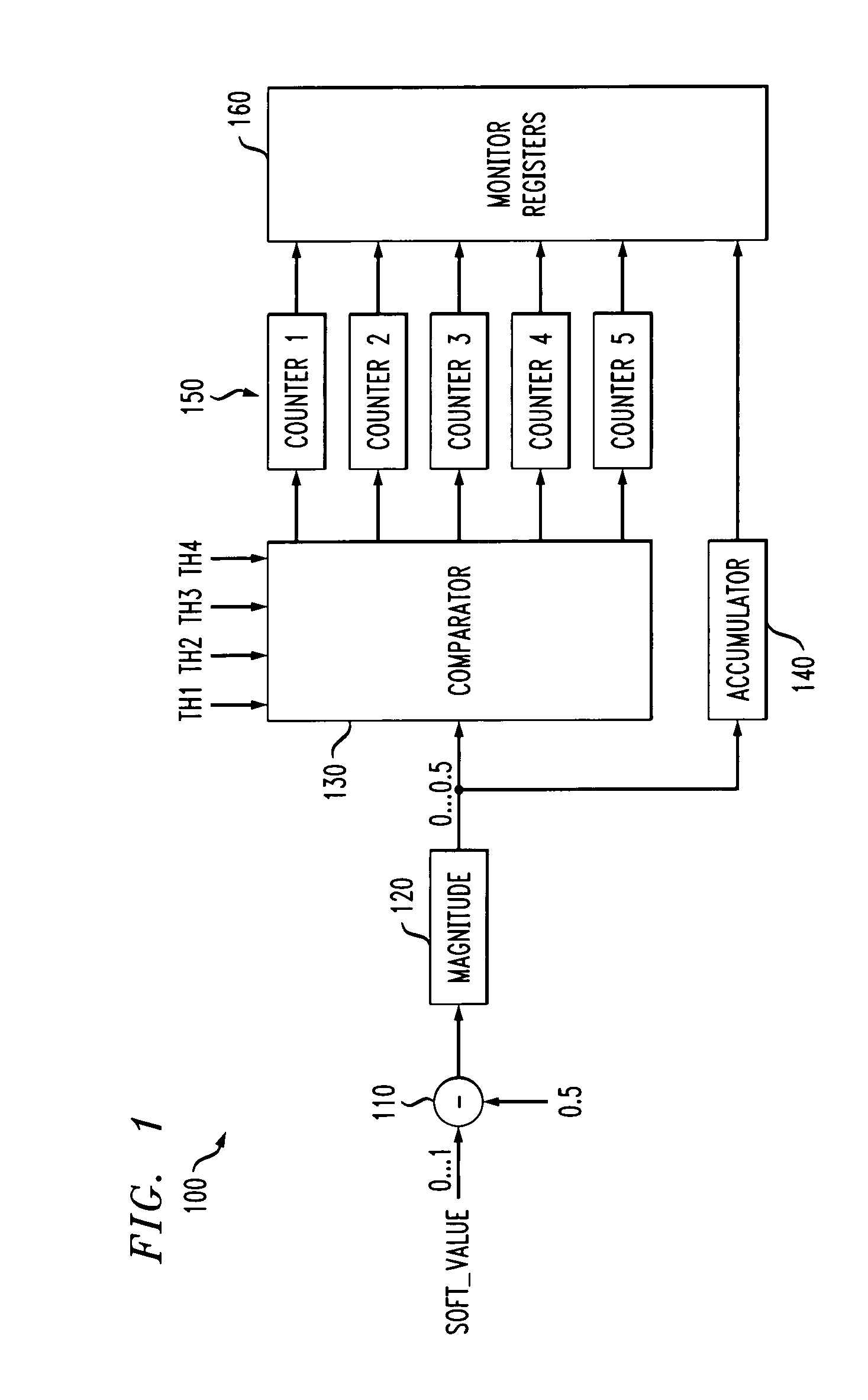
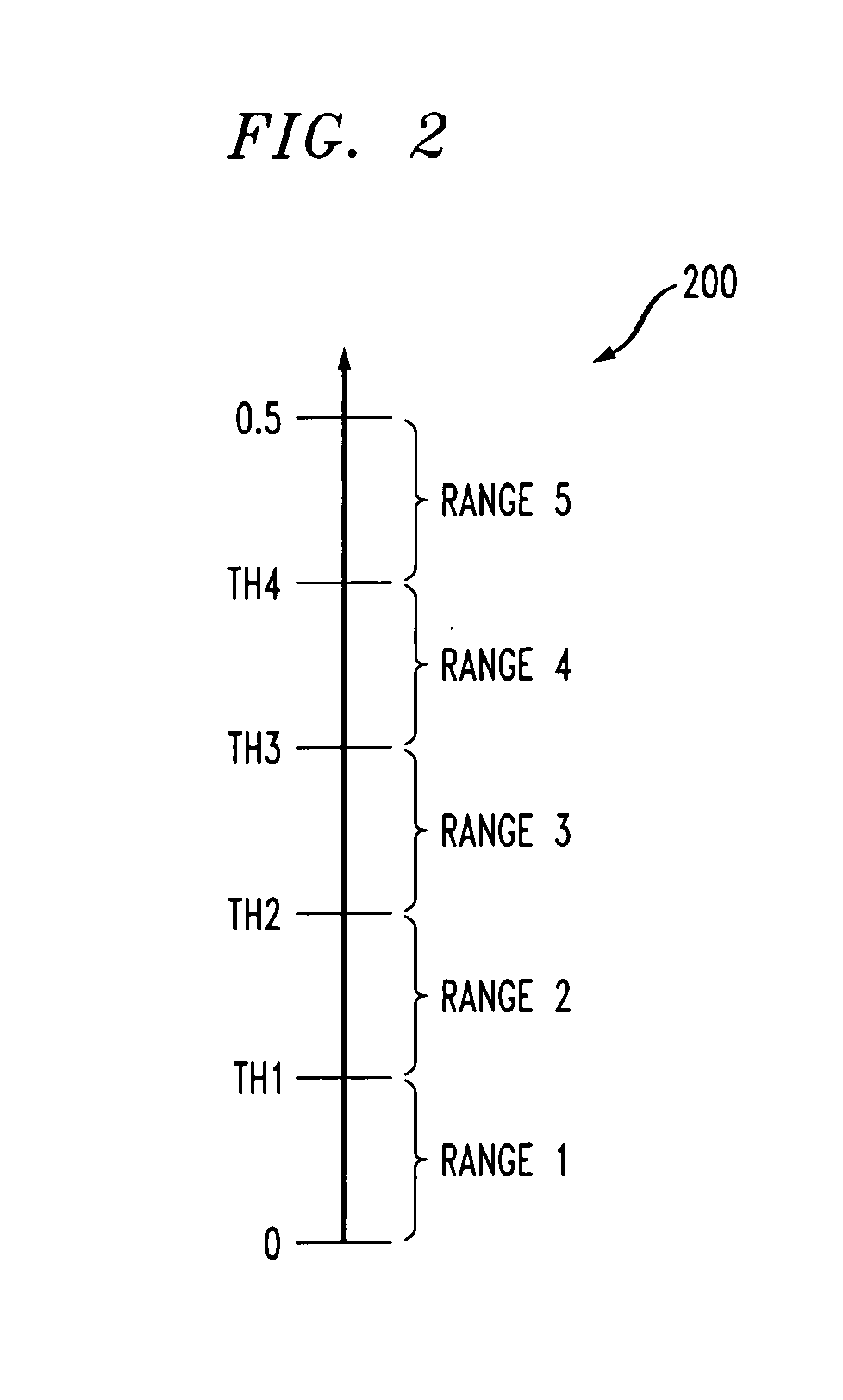
ActiveUS20060195772A1Less timeData representation error detection/correctionOther error detection/correction/protectionLogitLog likelihood
Methods and apparatus are provided for measuring the performance of a read channel. A number of detection techniques, such as SOVA and maximum-a-posteriori (MAP) detectors, produce a bit decision and a corresponding reliability value associated with the bit decision. The reliability value associated with the bit decision may be expressed, for example, in the form of log likelihood ratios (LLRs). The reliability value can be monitored and used as a performance measure. The present invention provides a channel performance measure that generally correlates directly to the BER but can be collected in less time.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and methods for recognizing sound and music signals in high noise and distortion
InactiveUS20060122839A1High of distortionHigh levelDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionNonlinear distortionLinear correlation
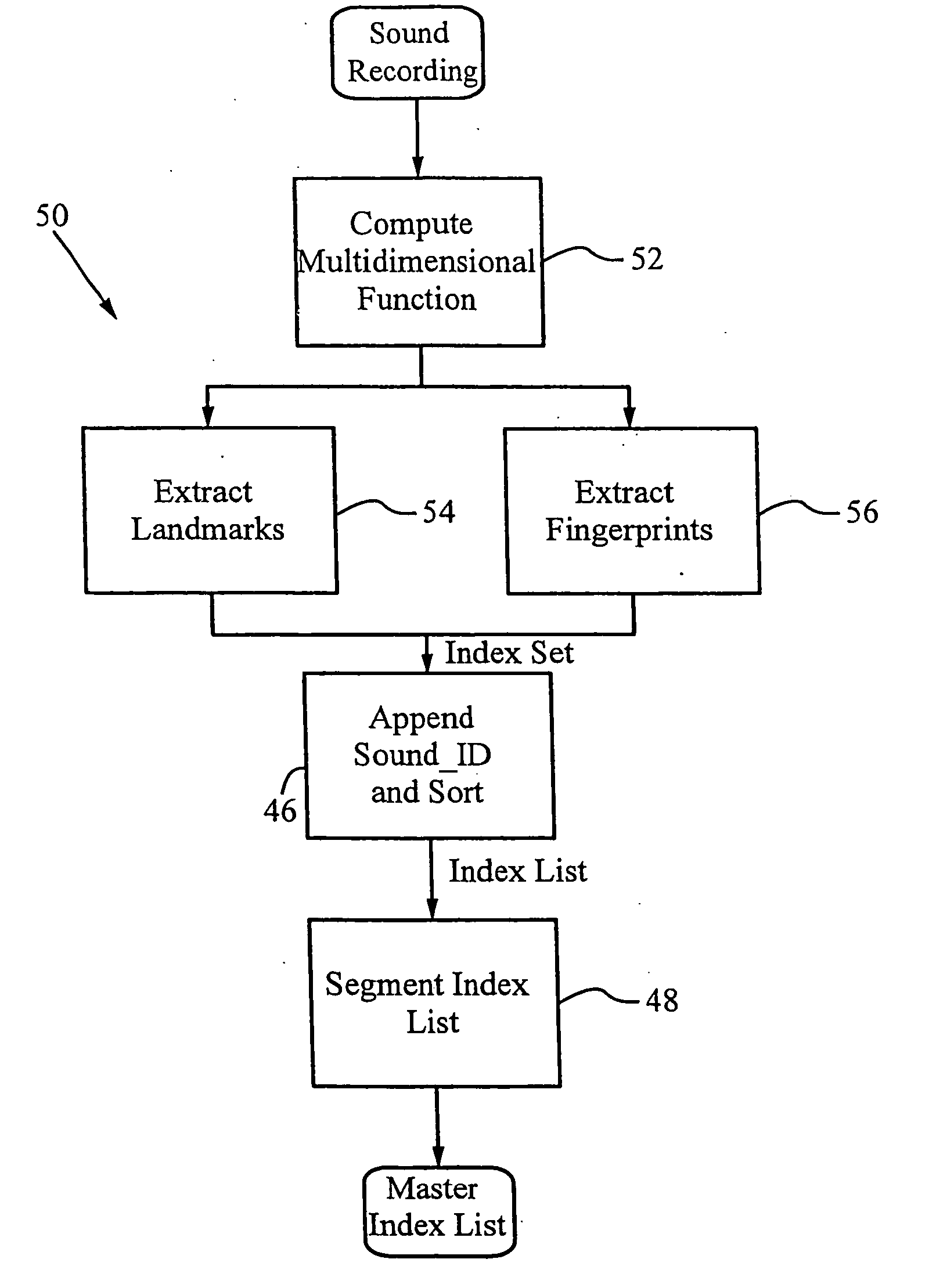
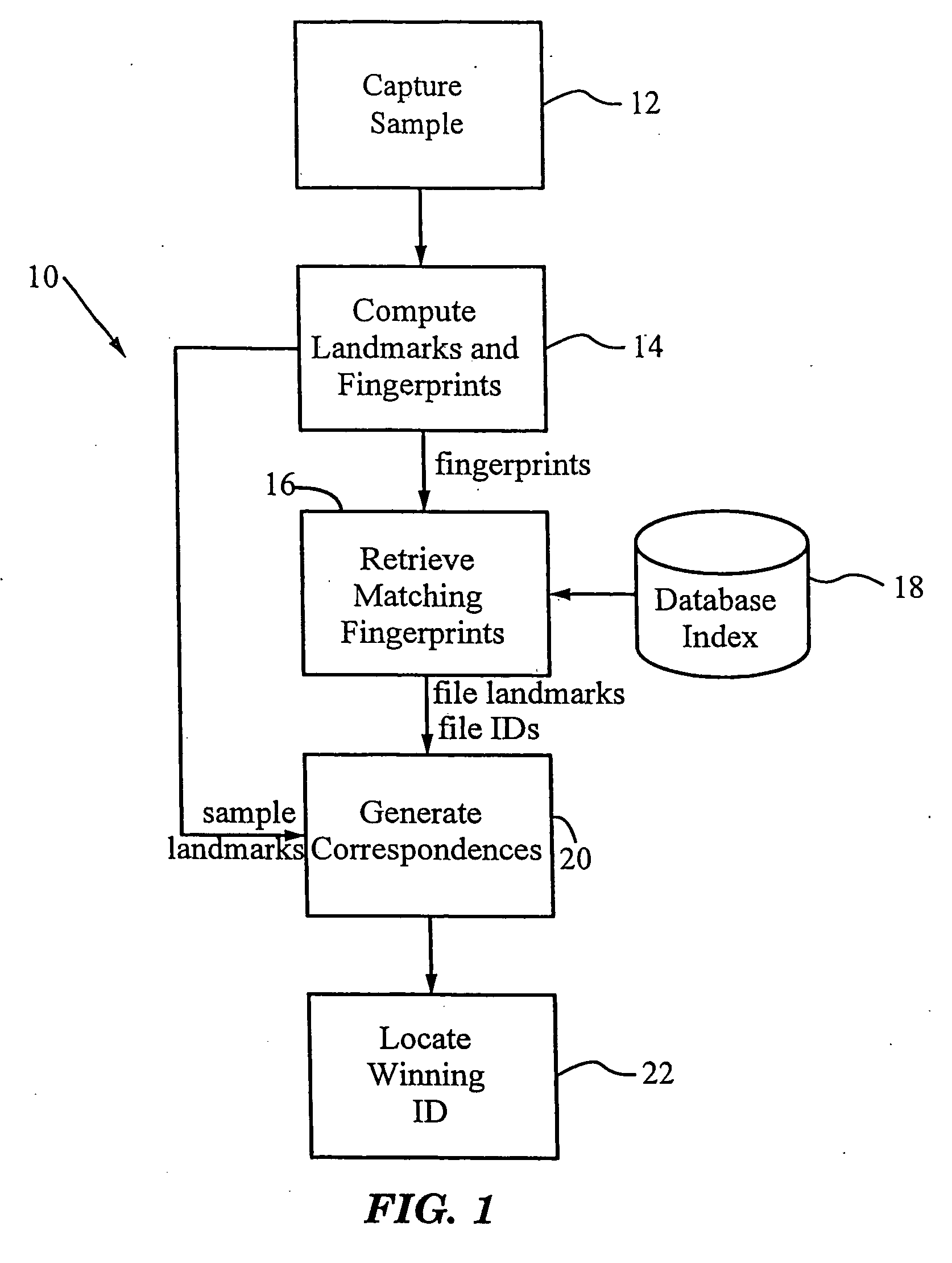
A method for recognizing an audio sample locates an audio file that most closely matches the audio sample from a database indexing a large set of original recordings. Each indexed audio file is represented in the database index by a set of landmark timepoints and associated fingerprints. Landmarks occur at reproducible locations within the file, while fingerprints represent features of the signal at or near the landmark timepoints. To perform recognition, landmarks and fingerprints are computed for the unknown sample and used to retrieve matching fingerprints from the database. For each file containing matching fingerprints, the landmarks are compared with landmarks of the sample at which the same fingerprints were computed. If a large number of corresponding landmarks are linearly related, i.e., if equivalent fingerprints of the sample and retrieved file have the same time evolution, then the file is identified with the sample. The method can be used for any type of sound or music, and is particularly effective for audio signals subject to linear and nonlinear distortion such as background noise, compression artifacts, or transmission dropouts. The sample can be identified in a time proportional to the logarithm of the number of entries in the database; given sufficient computational power, recognition can be performed in nearly real time as the sound is being sampled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Integrated maximum a posteriori (MAP) and turbo product coding for optical communications systems
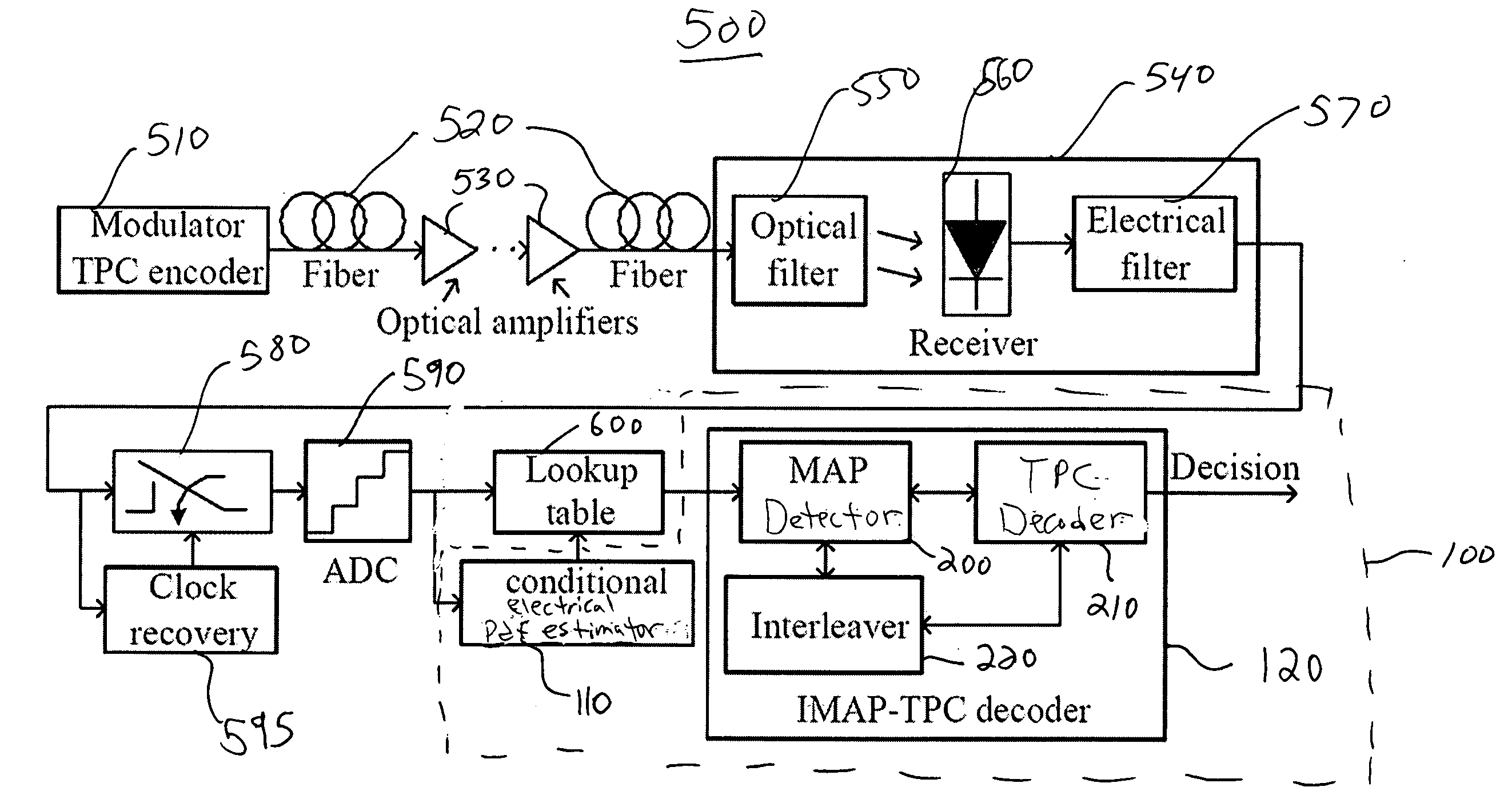
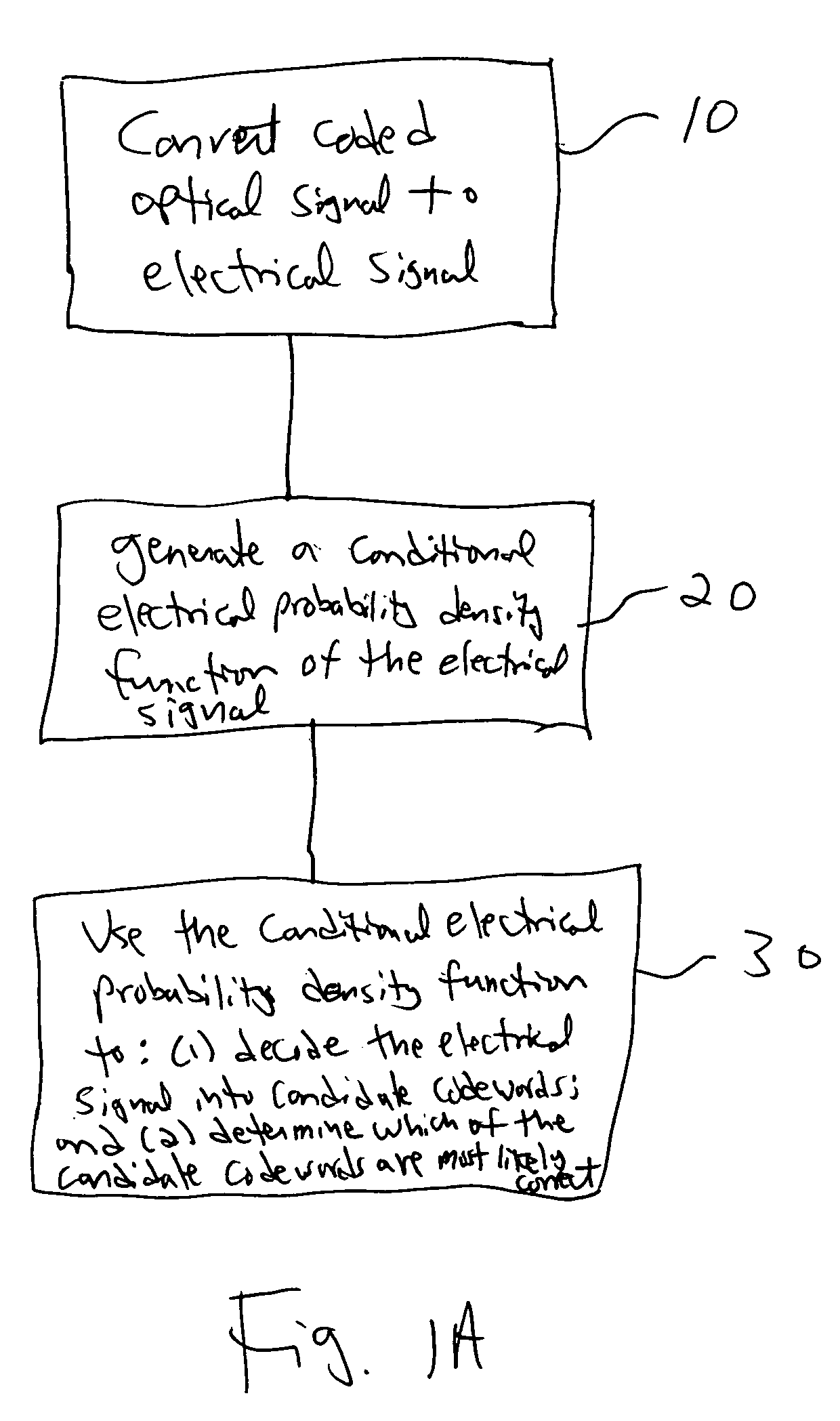
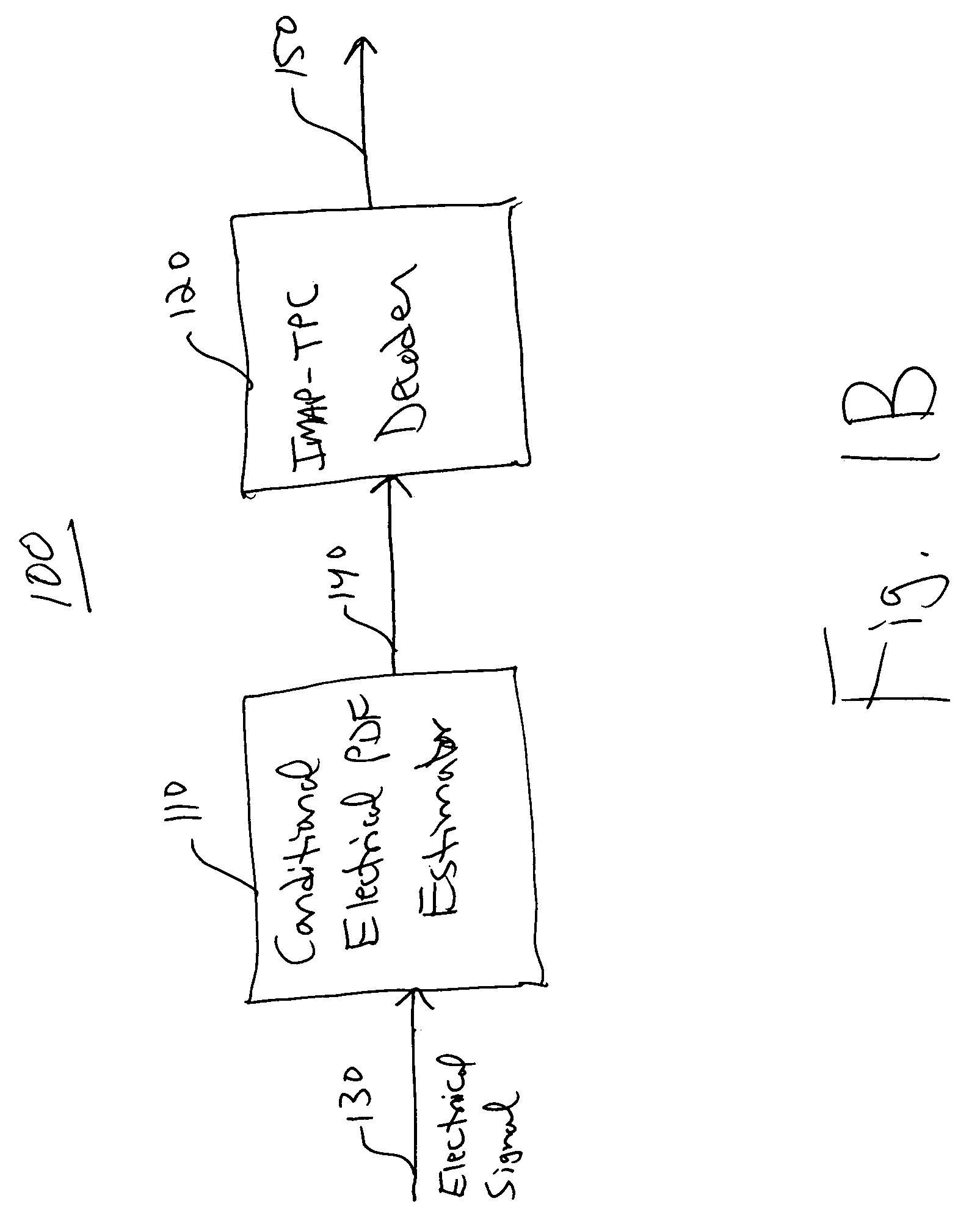
InactiveUS20060285852A1Improve fiber performanceImprove bit error rateElectromagnetic transmissionBaseband systemsLogitEqualization
An integrated maximum a posteriori equalization and turbo product coding (IMAP-TPC) system for optical fiber communications systems (OFCS) is provided that uses probabilistic characterization of the electrical current in the presence of inter-symbol interference (ISI) and noise to compensate their effects and improve the bit error rate. In the IMAP-TPC system, turbo product code (TPC) decoding is integrated with a symbol-by-symbol maximum a posteriori (MAP) detector. The MAP detector calculates the log-likelihood ratio of a received symbol using the conditional electrical probability density information, and hence obtains a much more accurate reliability measure than the traditional measure used in the TPC decoder.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Symbol by symbol map detection for signals corrupted by colored and/or signal dependent noise
ActiveUS20070226599A1Data representation error detection/correctionModification of read/write signalsHard disc driveCommunications system
Symbol by symbol MAP detection for signals corrupted by colored and / or signal dependent noise. A novel means is presented for recursive calculation of forward metrics (α), backward metrics (β), and corresponding soft information (e.g., which can be provided as LLRs (log likelihood ratios)) within communication systems in which a trellis can be employed to perform demodulation of a received signal sequence. For signals that have been corrupted by colored and / or signal dependent noise, this means provides for the ability to perform novel soft information calculation for subsequent use in iterative decoding processing. Many types of communication channels can benefit from this novel means of detection including communication channels within hard disk drives (HDDs).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Order model for dependency structure
InactiveUS20060111891A1Natural language translationSpeech analysisDependency structureTheoretical computer science
In one embodiment of the present invention, a decoder receives a dependency tree as a source language input and accesses a set of statistical models that produce outputs combined in a log linear framework. The decoder also accesses a table of treelet translation pairs and returns a target dependency tree based on the source dependency tree, based on access to the table of treelet translation pairs, and based on the application of the statistical models.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
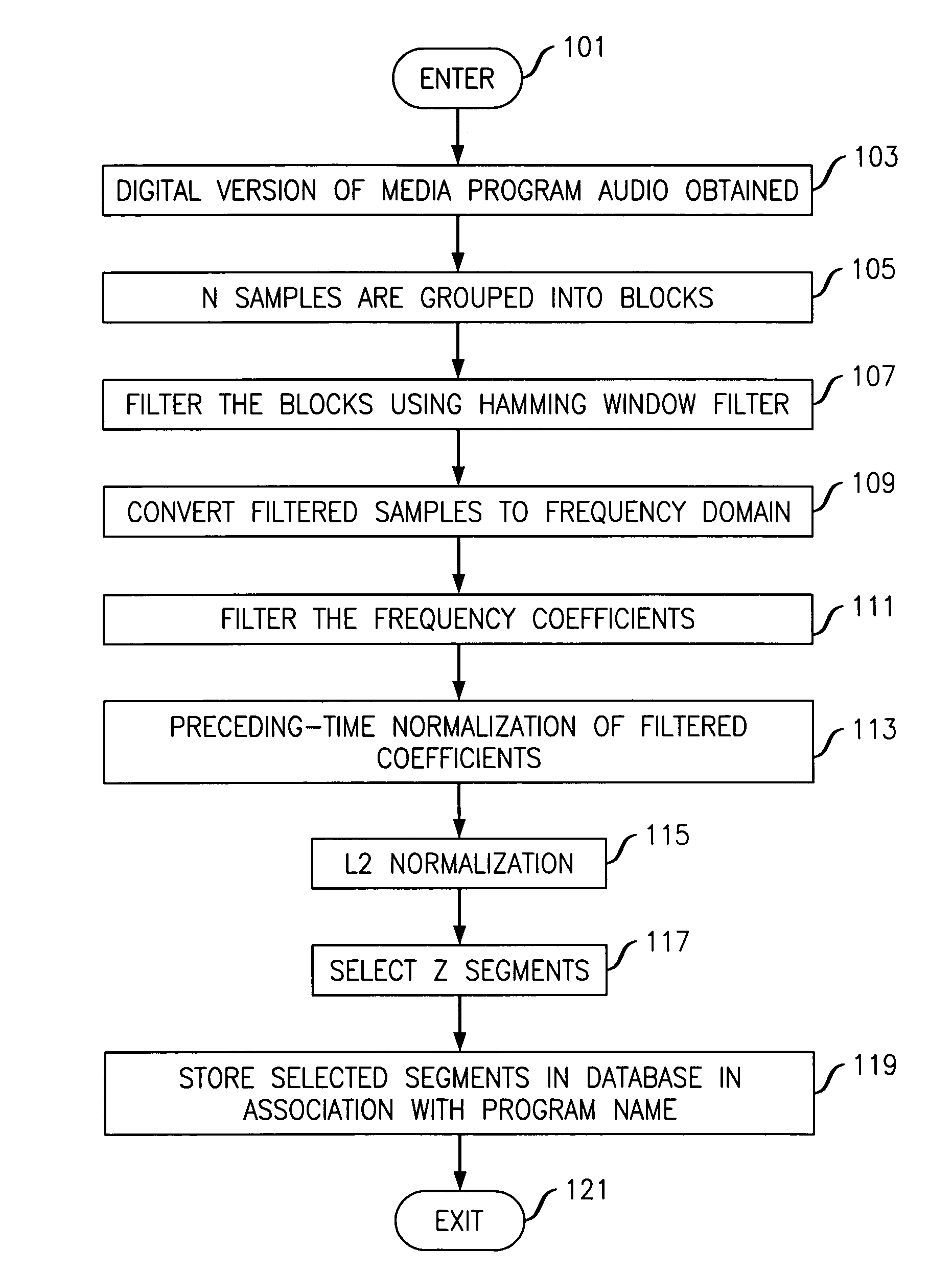
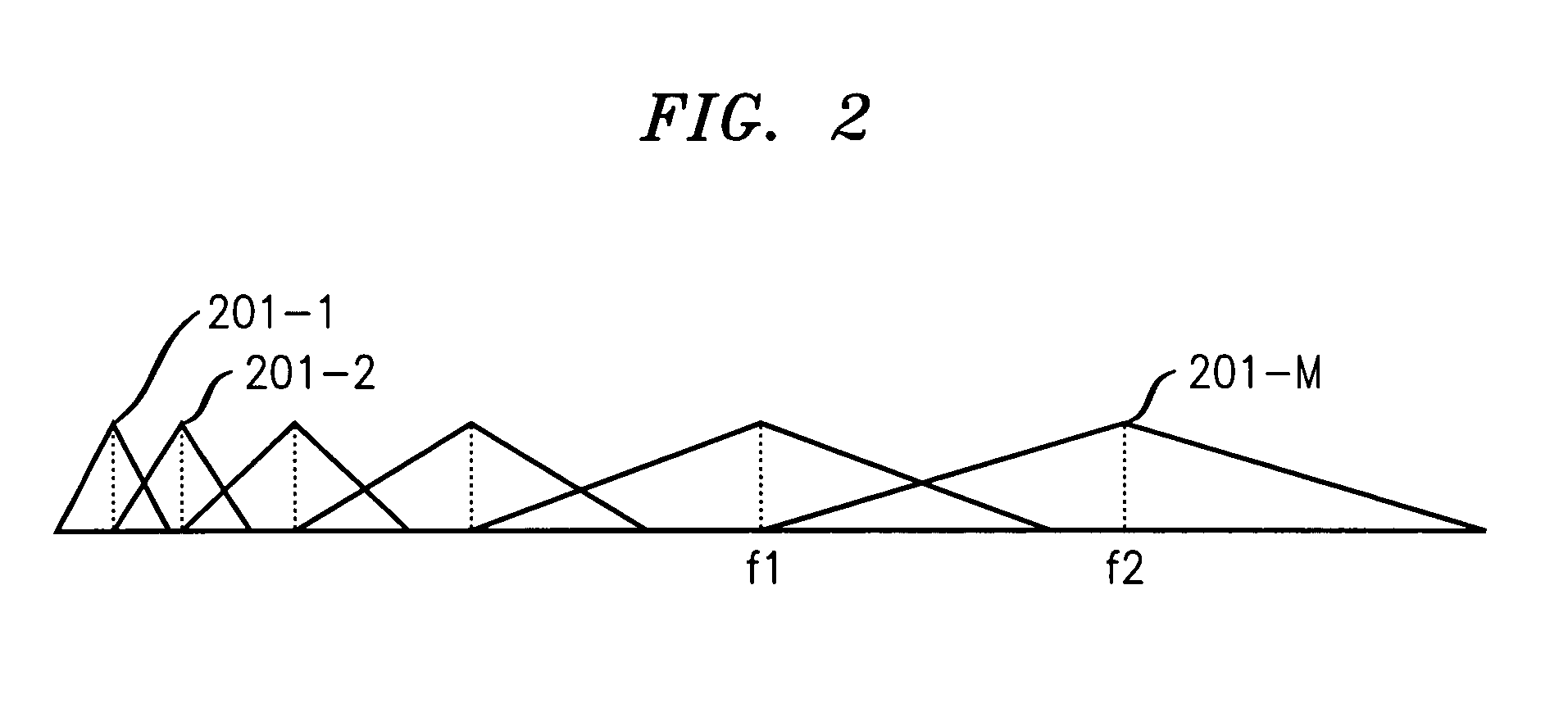
Content identification system
ActiveUS20050027766A1Improve performanceSpeed up searchUsing non-detectable carrier informationUsing detectable carrier informationLogitIdentification system
The content of a media program is recognized by analyzing its audio content to extract therefrom prescribed features, which are compared to a database of features associated with identified content. The identity of the content within the database that has features that most closely match the features of the media program being played is supplied as the identity of the program being played. The features are extracted from a frequency domain version of the media program by a) filtering the coefficients to reduce their number, e.g., using triangular filters; b) grouping a number of consecutive outputs of triangular filters into segments; and c) selecting those segments that meet prescribed criteria, such as those segments that have the largest minimum segment energy with prescribed constraints that prevent the segments from being too close to each other. The triangular filters may be log-spaced and their output may be normalized.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Projecting dependencies to generate target language dependency structure
ActiveUS20060111896A1Natural language translationSpeech analysisDependency structureTheoretical computer science
In one embodiment of the present invention, a decoder receives a dependency tree as a source language input and accesses a set of statistical models that produce outputs combined in a log linear framework. The decoder also accesses a table of treelet translation pairs and returns a target dependency tree based on the source dependency tree, based on access to the table of treelet translation pairs, and based on the application of the statistical models.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) detector incorporating efficient signal point search
InactiveUS20080279298A1Improve soft informationEnhanced informationSignal channelsLocal circuitsCommunications systemSingle stage
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of multiple input multiple output (MIMO) detection for use in MIMO based communication systems. The mechanism of the invention performs a simplified tree search utilizing a single stage expansion of the most likely first symbol candidates, in the case of a 2×2 MIMO system. The invention also provides a refinement mechanism that is operative to significantly improve the log likelihood (LLR) of the list of candidates. To improve the LLR, the mechanism applies refinements rounds to generate additional candidates for both first and second detected symbols.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
Method for estimation of interval seismic quality factor
ActiveUS20060265132A1Enhanced reflection seismic dataSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsUltrasound attenuationEstimation methods
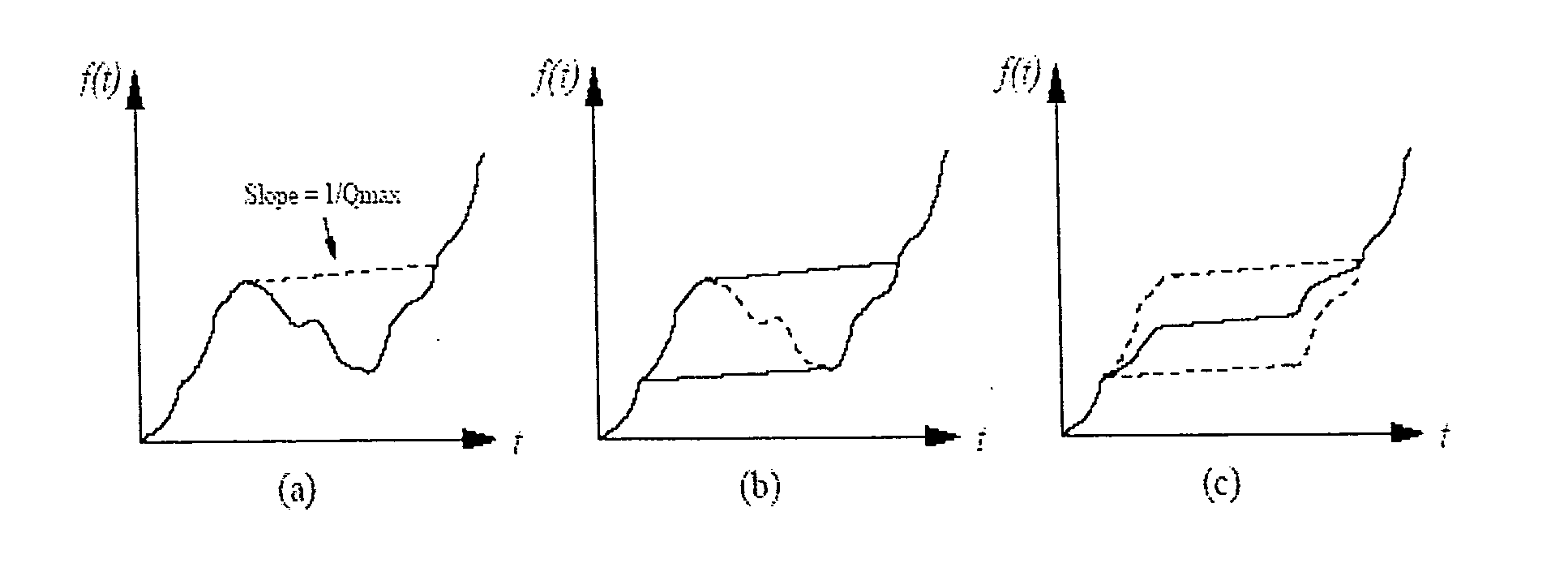
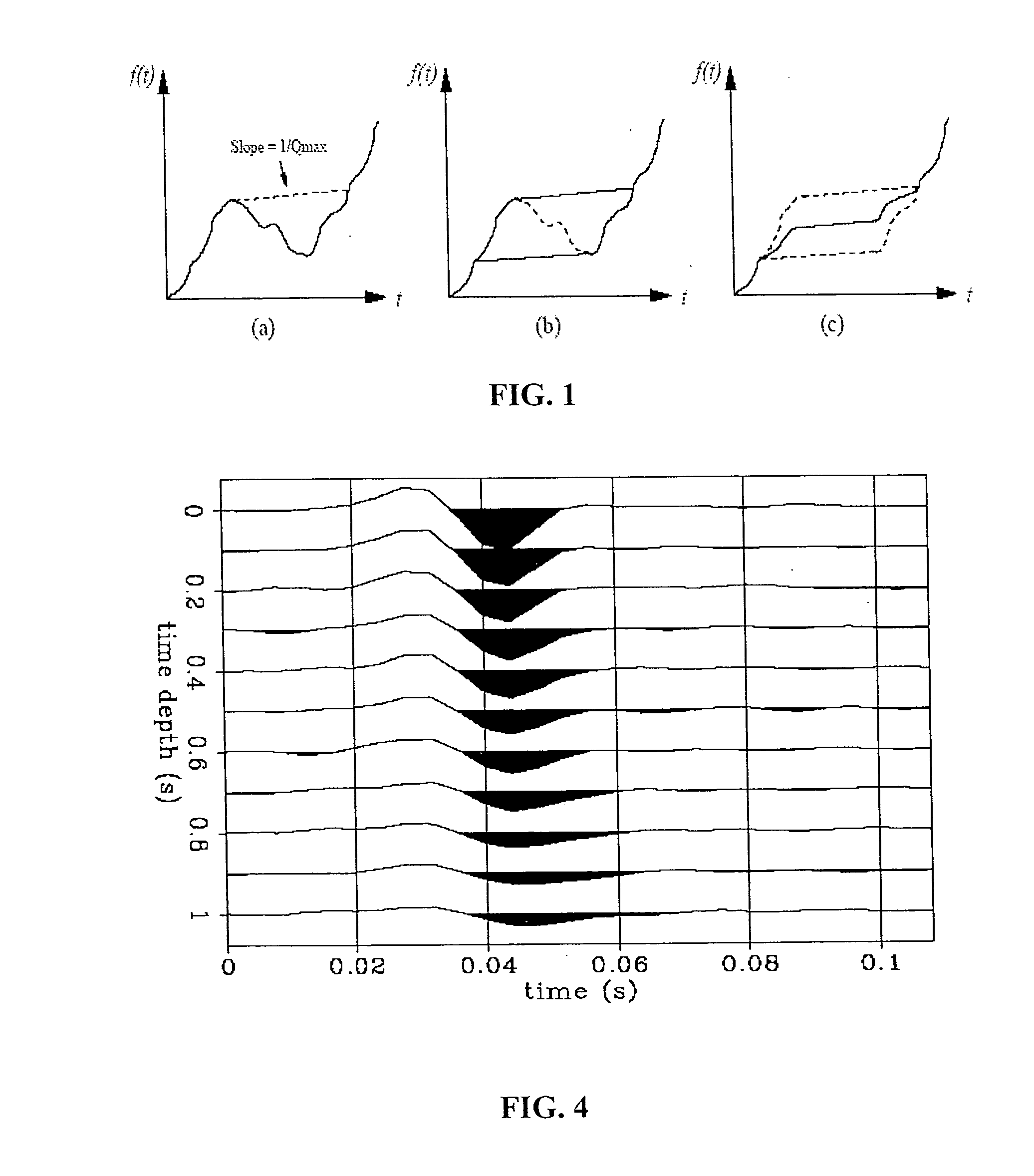
The present invention includes a method for determining interval values of seismic quality factor, Q, from seismic data. Seismic data is recorded and preprocessed as necessary. Estimates of amplitude spectra are determined from the seismic data. Logarithms are taken of the amplitude spectra and weights derived from the amplitude spectra. Interval values of seismic quality factor, Q, are determined by performing a weighted fit to the log-amplitude spectra with a function that is parameterized by an initial wavelet, an attenuation profile (1 / Q) and an absolute-scaling profile.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
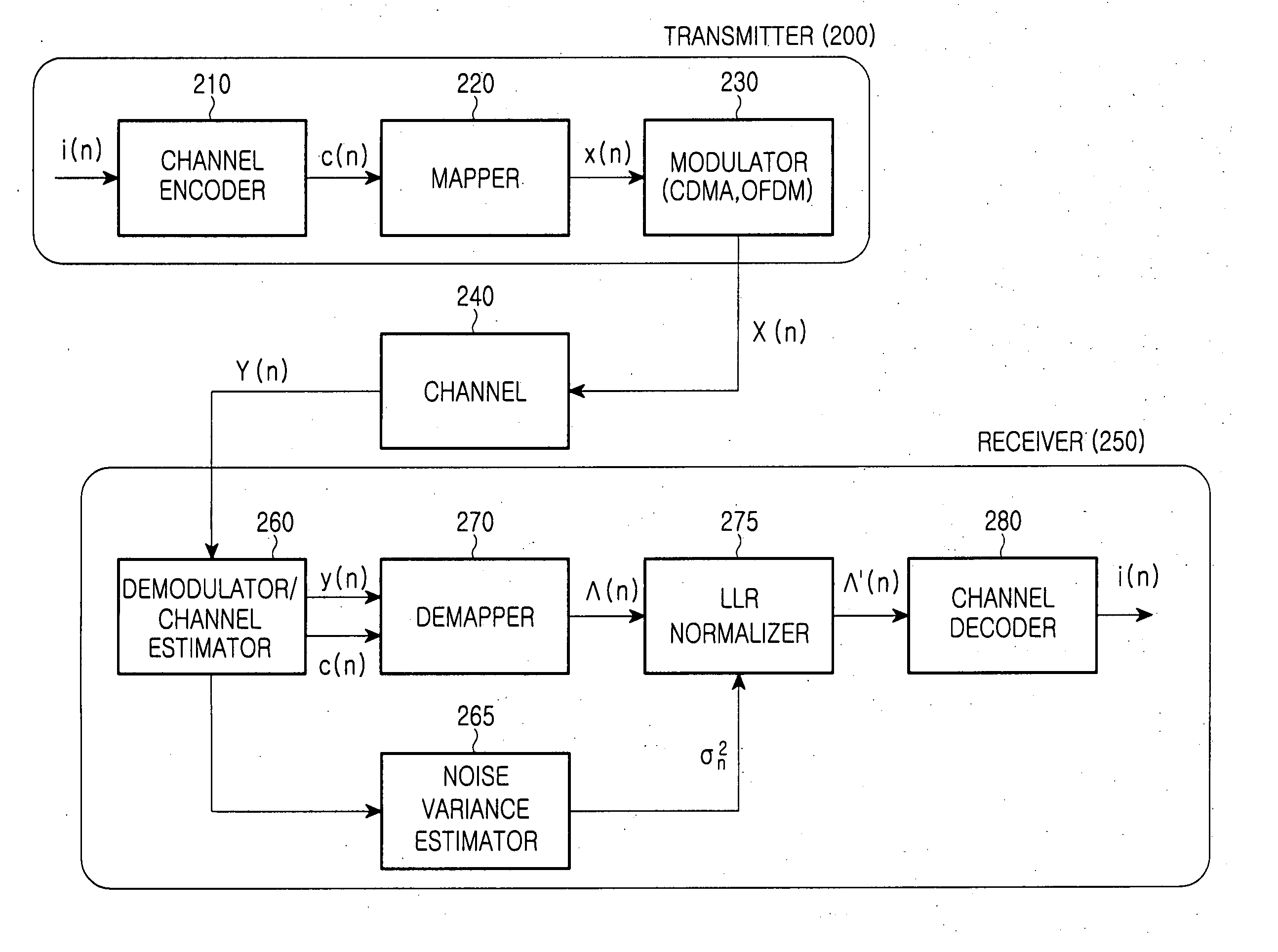
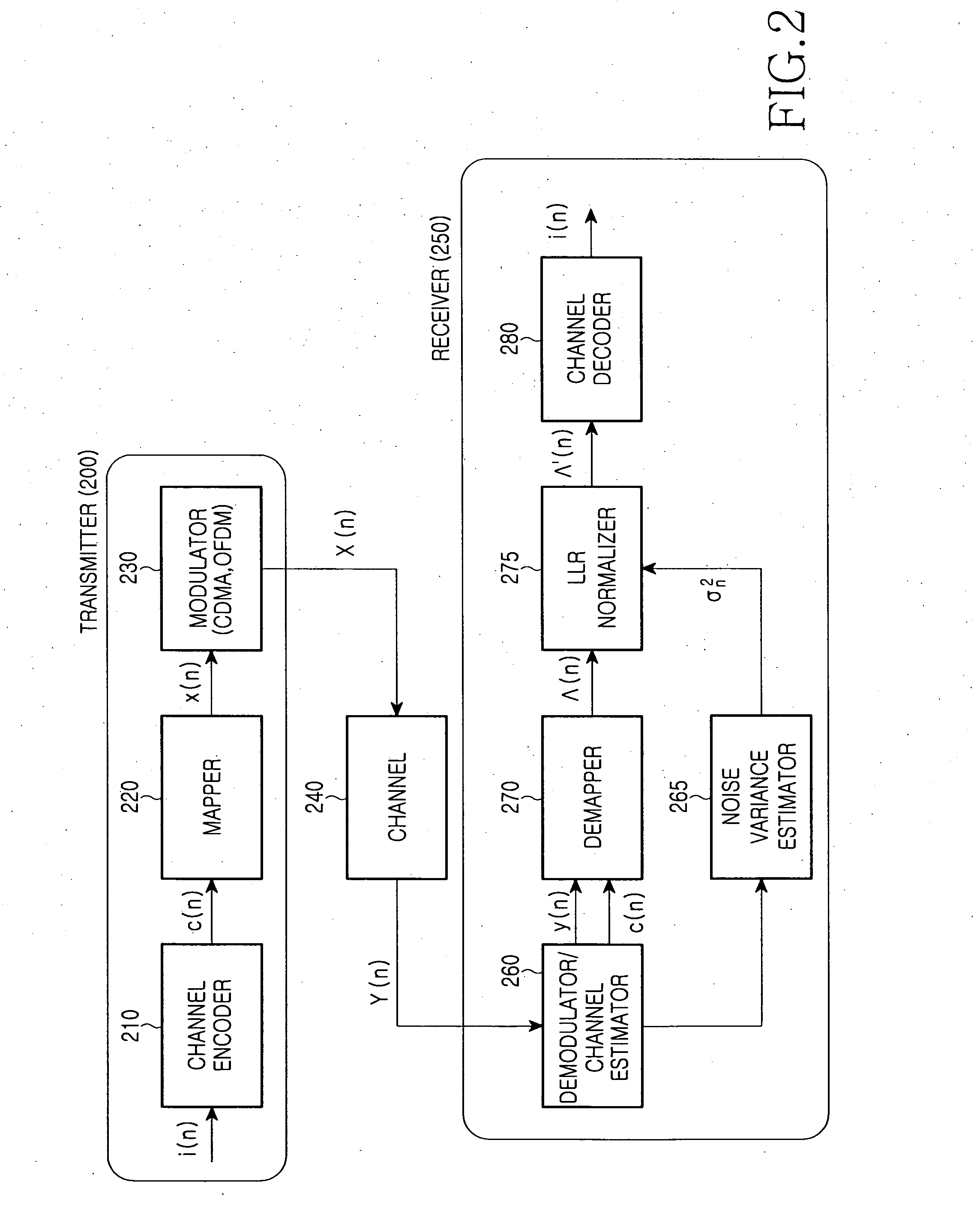
Method and apparatus for normalizing input metric to a channel decoder in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20070110191A1Improve decoding performanceData representation error detection/correctionMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsCommunications systemLogit
An apparatus and method are provided for normalizing input soft metric to a channel decoder in a wireless communication system. A demapper generates soft metric using an in-phase component (Xk) and a quadrature component (Yk) of a received modulated symbol (Rk), a channel fading coefficient (gk) and a constant value (c) defined by a modulation order of the received modulated symbol. A normalizer receives the soft metric, computes a normalized log likelihood ratio (LLR) by multiplying the soft metric by a ratio of the constant value to a noise variance value, transforms the normalized LLR into a desired range and a desired number of bits, and outputs an input LLR of the channel decoder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Extracting treelet translation pairs
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
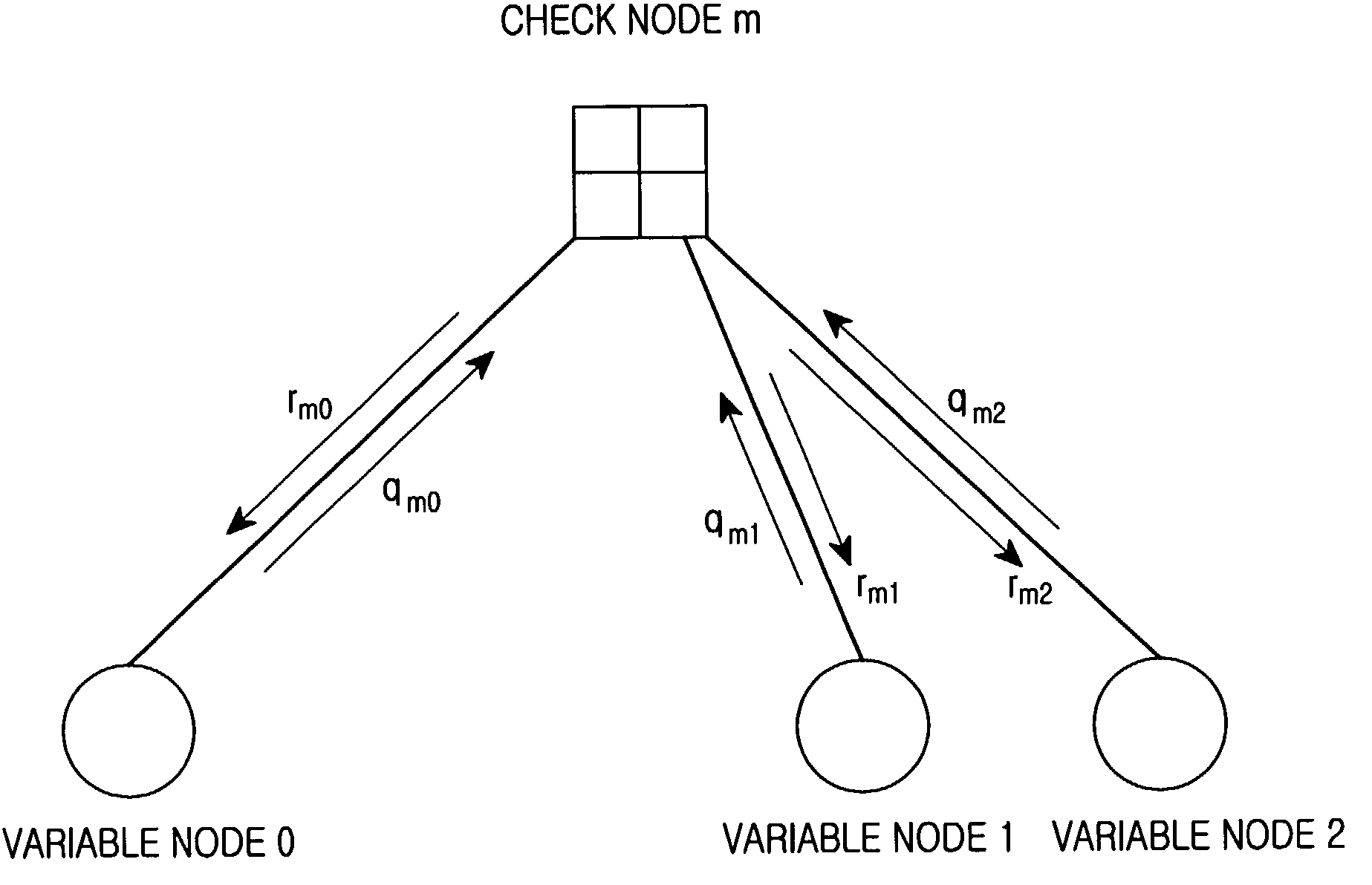
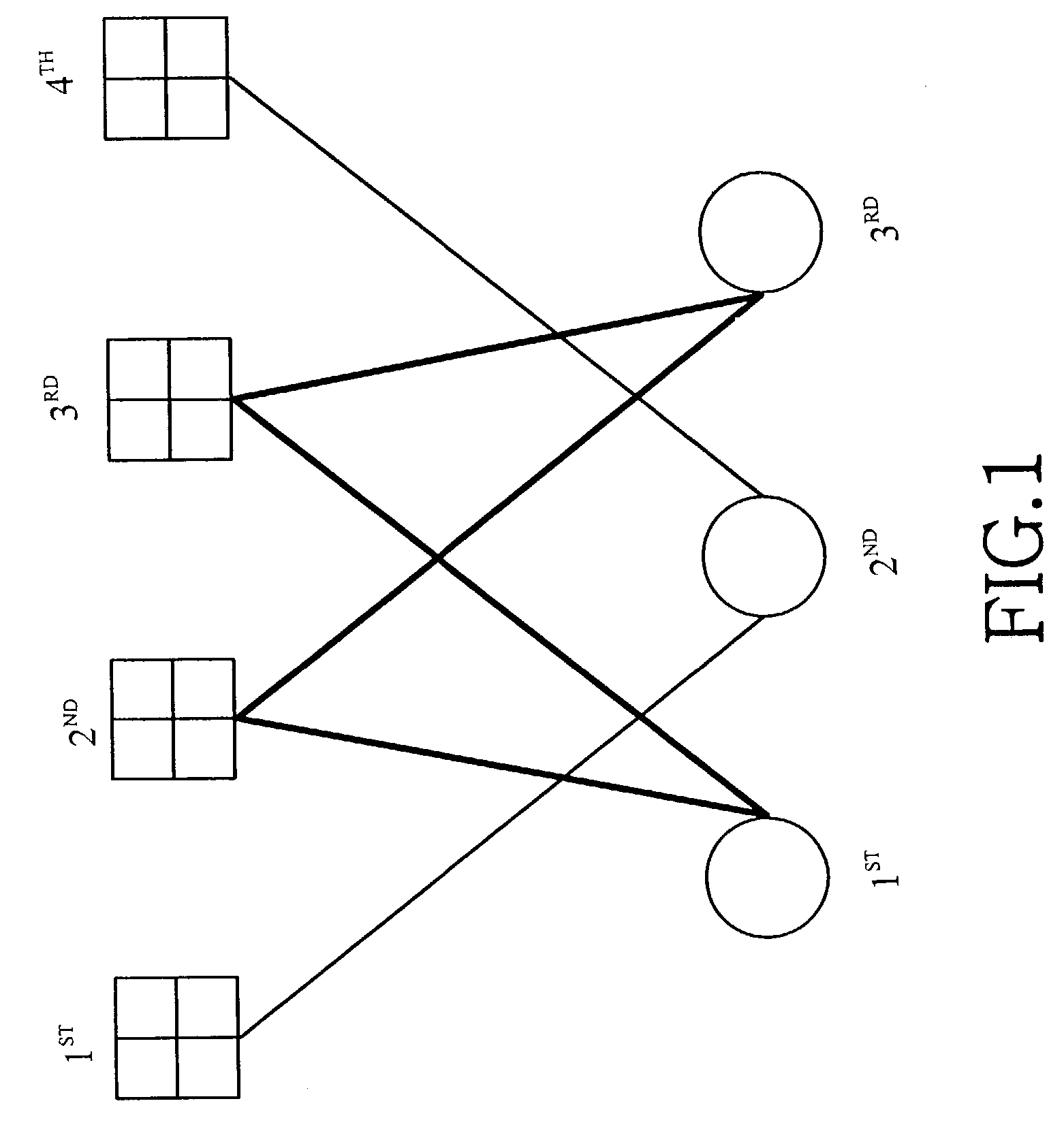
Forward error correction apparatus and method in a high-speed data transmission system
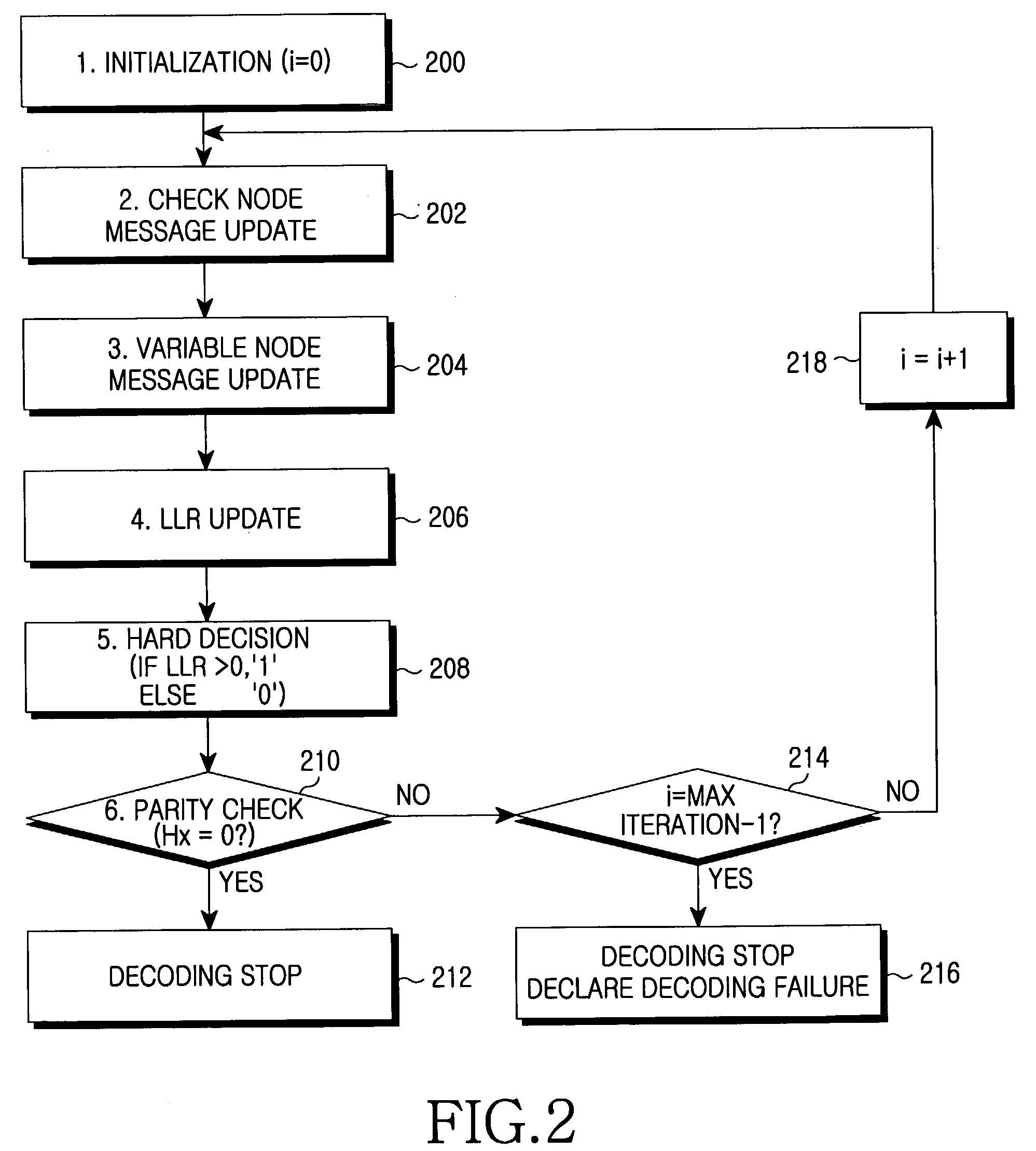
ActiveUS7137060B2Simple methodReduce the amount of calculationTransmission control/equalisingError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer hardwareTransport system
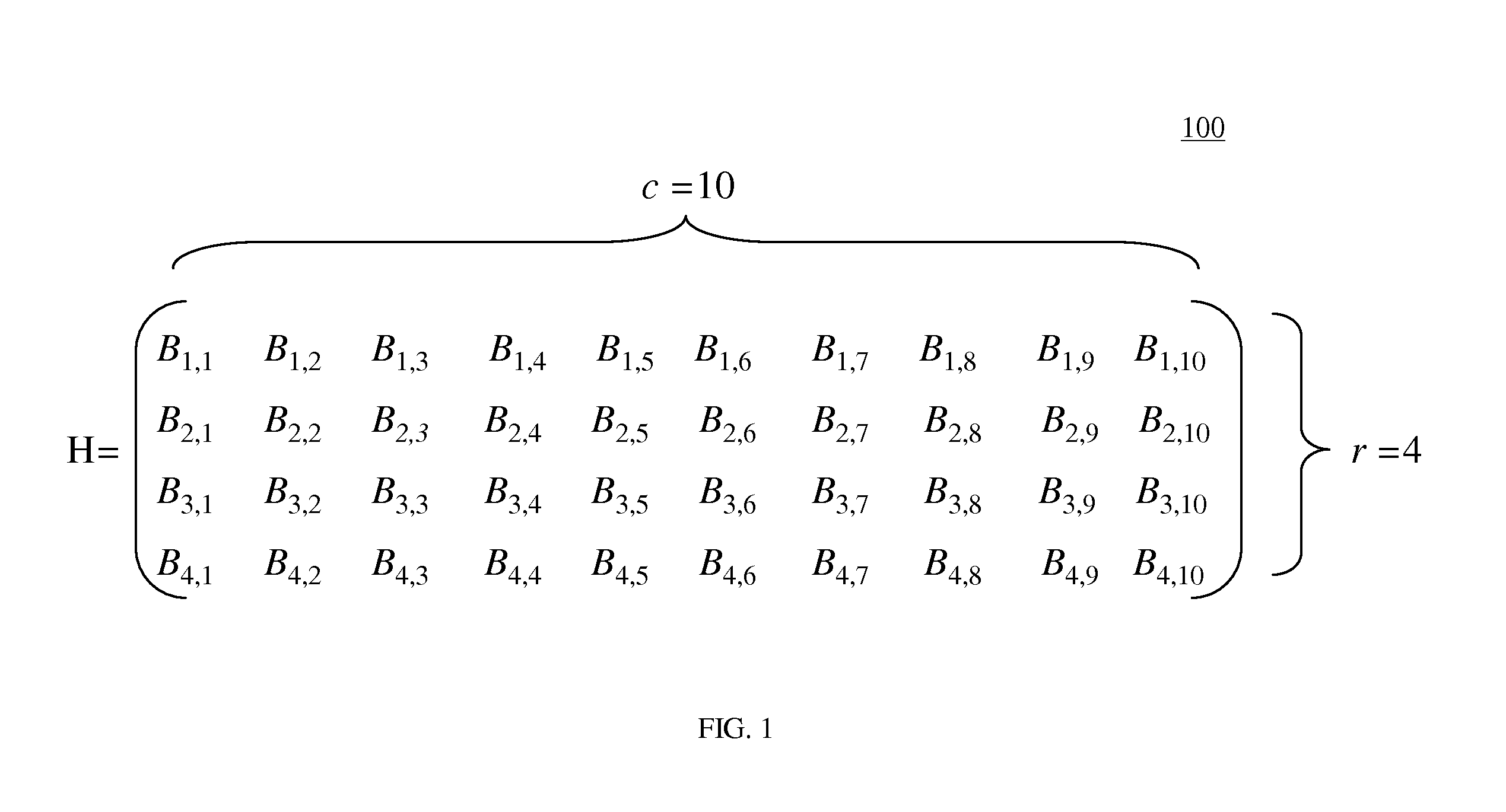
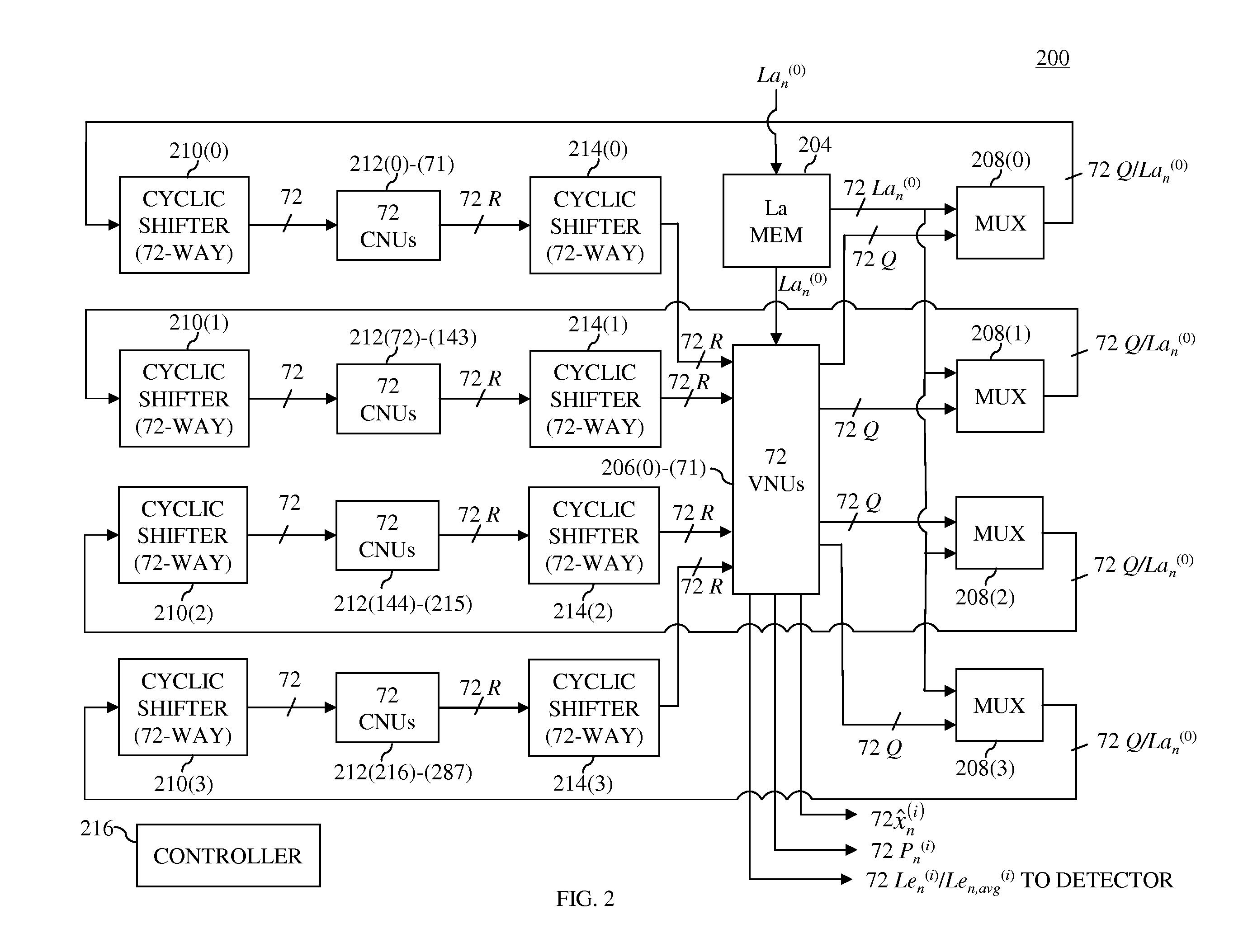
A forward error correction method for decoding coded bits generated by low density parity check matrixes. The method comprises converting each of the coded bits into a log likelihood ratio (LLR) value, and applying the converted values to variable nodes; delivering messages applied to the variable nodes to check nodes; checking a message having a minimum value among the messages, and determining a sign of the message having the minimum value; receiving messages updated in the check nodes, adding up signs of the received messages and a sign of an initial message, applying a weighting factor of 1 when all signs are identical, and when all signs are not identical, updating a message of a variable node by applying a weighting factor; determining LLR of an initial input value; and hard-deciding values of the variable nodes, performing parity check on the hard decision values, and stopping the decoding when no error occurs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus to detect a timeout condition for a data item within a process
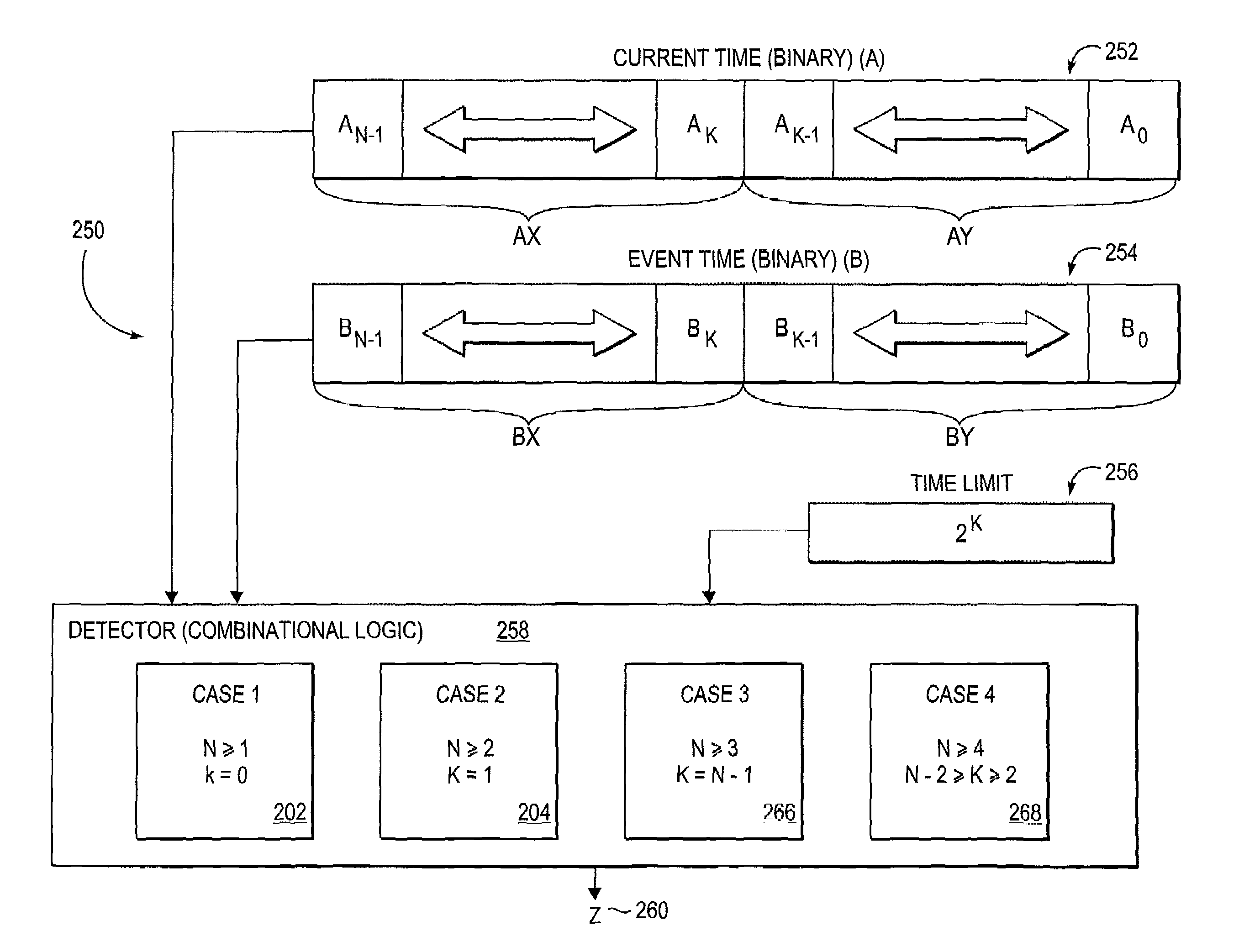
InactiveUS7016996B1Minimize impactMinimize timeMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsSingle stageTime limit
A method for detecting a timeout condition for a data item (e.g., a request) within the process (e.g., within an arbitration process) includes maintaining a current time as a first N-bit binary number (A). An event time of an occurrence of an event pertaining to the data item within the process is recorded and stored as a second N-bit binary number (B). A predetermined time limit, expressed as a non-negative integer K, is configured. K is less than N and K is a logarithm base 2 of the predetermined time limit. A timeout condition pertaining to the data item is detected when a difference between the current time and the event time exceeds the predetermined time limit. The detection of the timeout condition is performed utilizing a single-stage operation. This single stage operation may include computing A (current time)−B (event time) modulo 2n≧2k.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOLUTIONS (US) INC
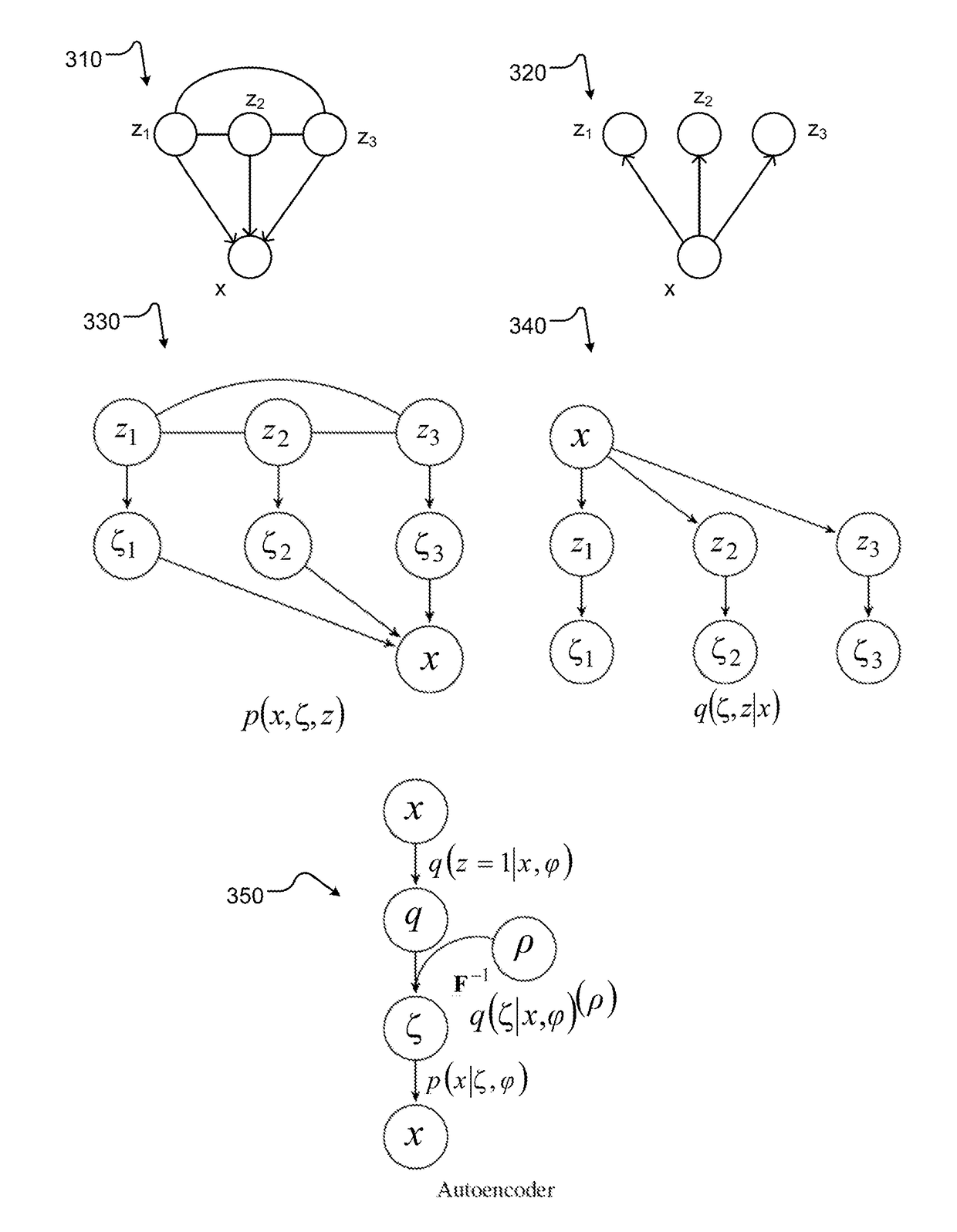
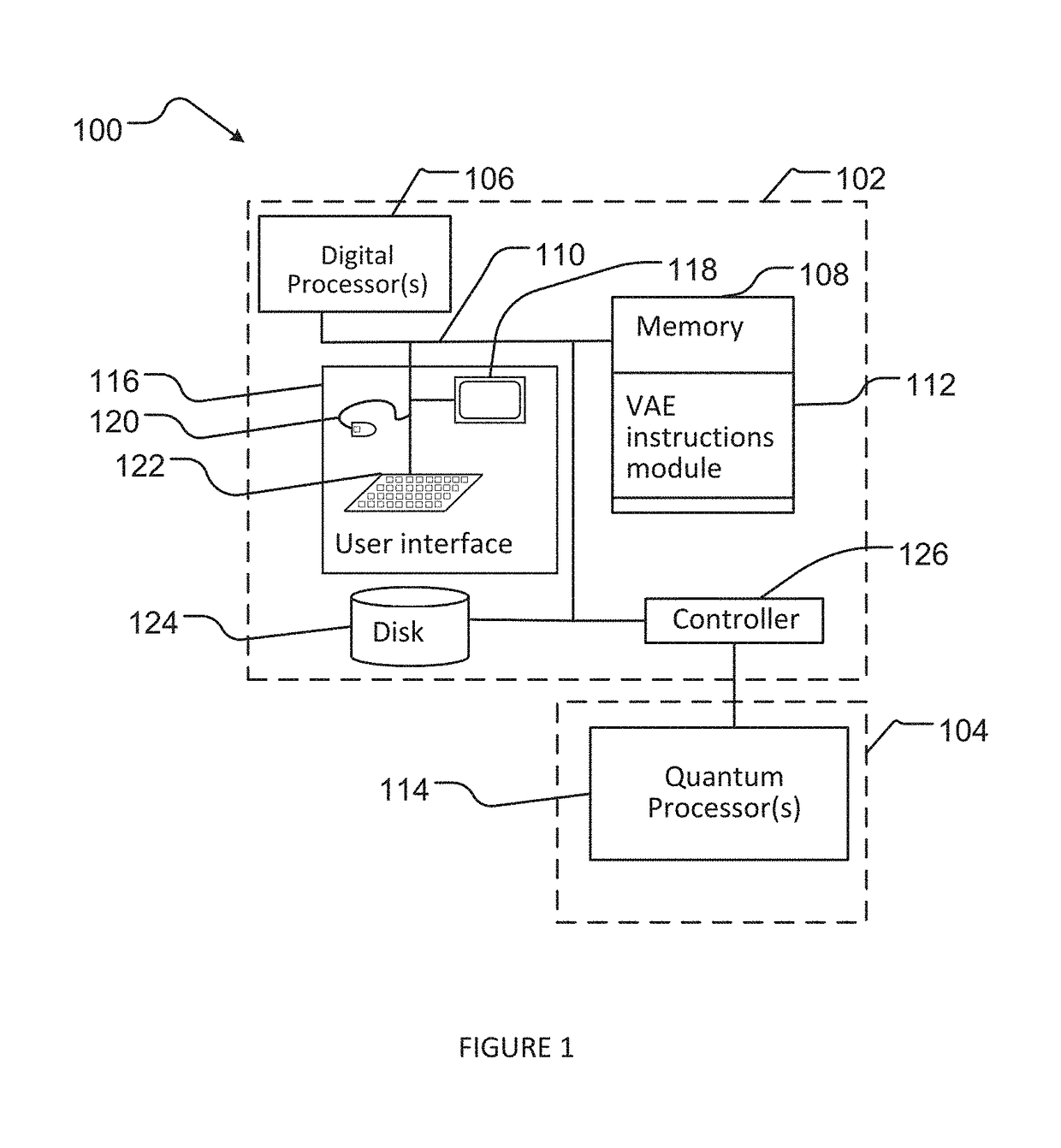
Discrete variational auto-encoder systems and methods for machine learning using adiabatic quantum computers
A computational system can include digital circuitry and analog circuitry, for instance a digital processor and a quantum processor. The quantum processor can operate as a sample generator providing samples. Samples can be employed by the digital processing in implementing various machine learning techniques. For example, the computational system can perform unsupervised learning over an input space, for example via a discrete variational auto-encoder, and attempting to maximize the log-likelihood of an observed dataset. Maximizing the log-likelihood of the observed dataset can include generating a hierarchical approximating posterior. Unsupervised learning can include generating samples of a prior distribution using the quantum processor. Generating samples using the quantum processor can include forming chains of qubits and representing discrete variables by chains.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
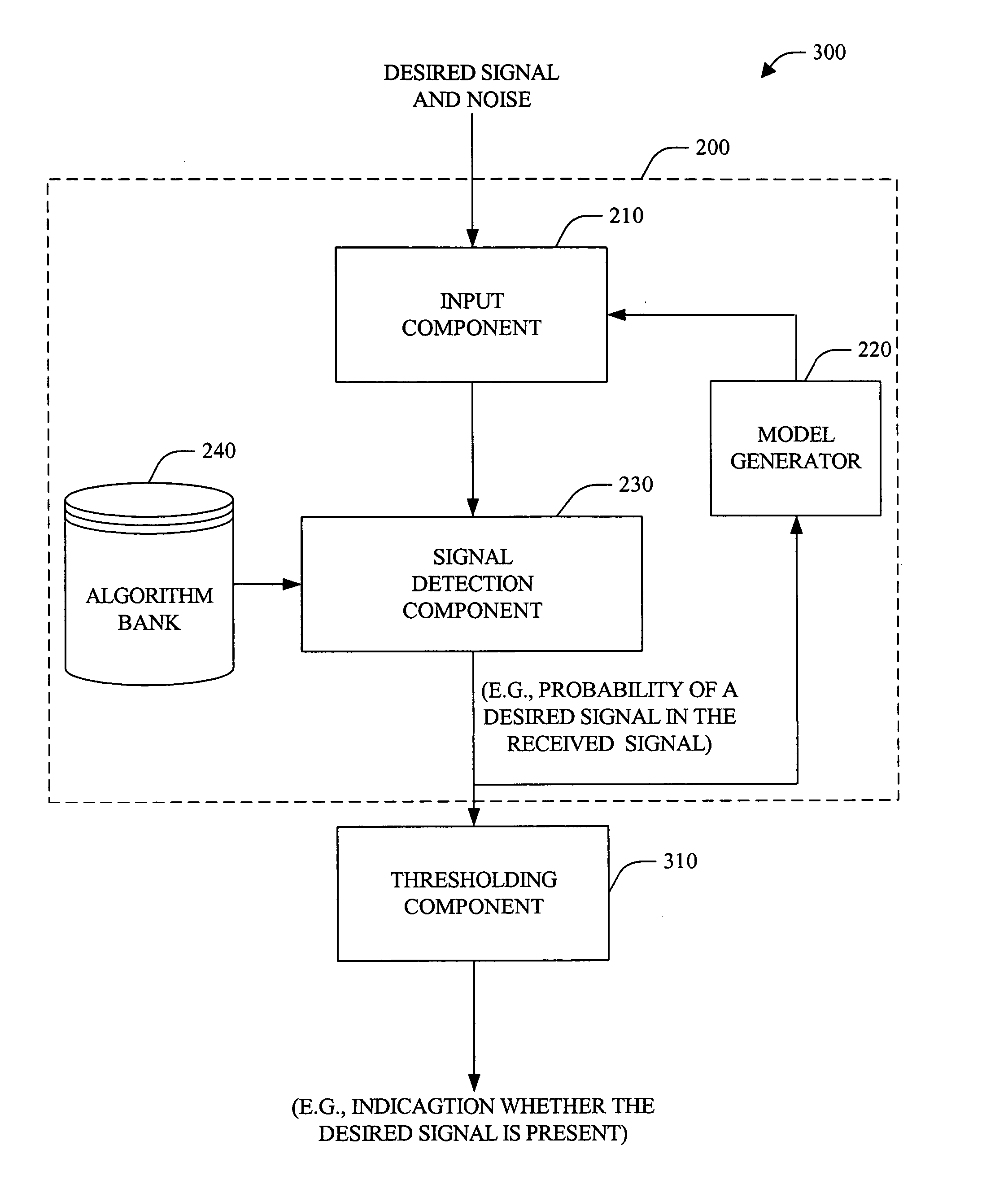
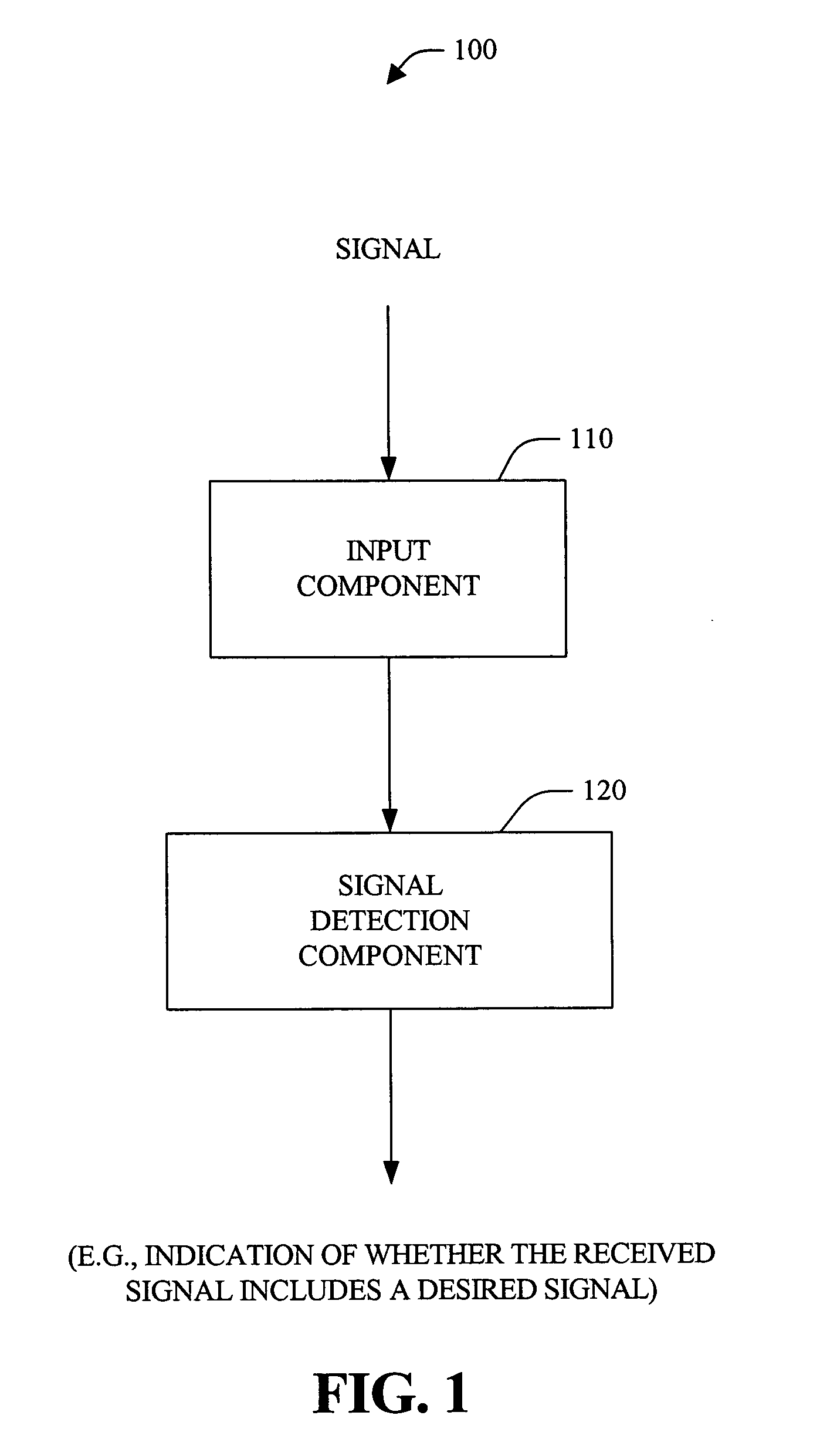
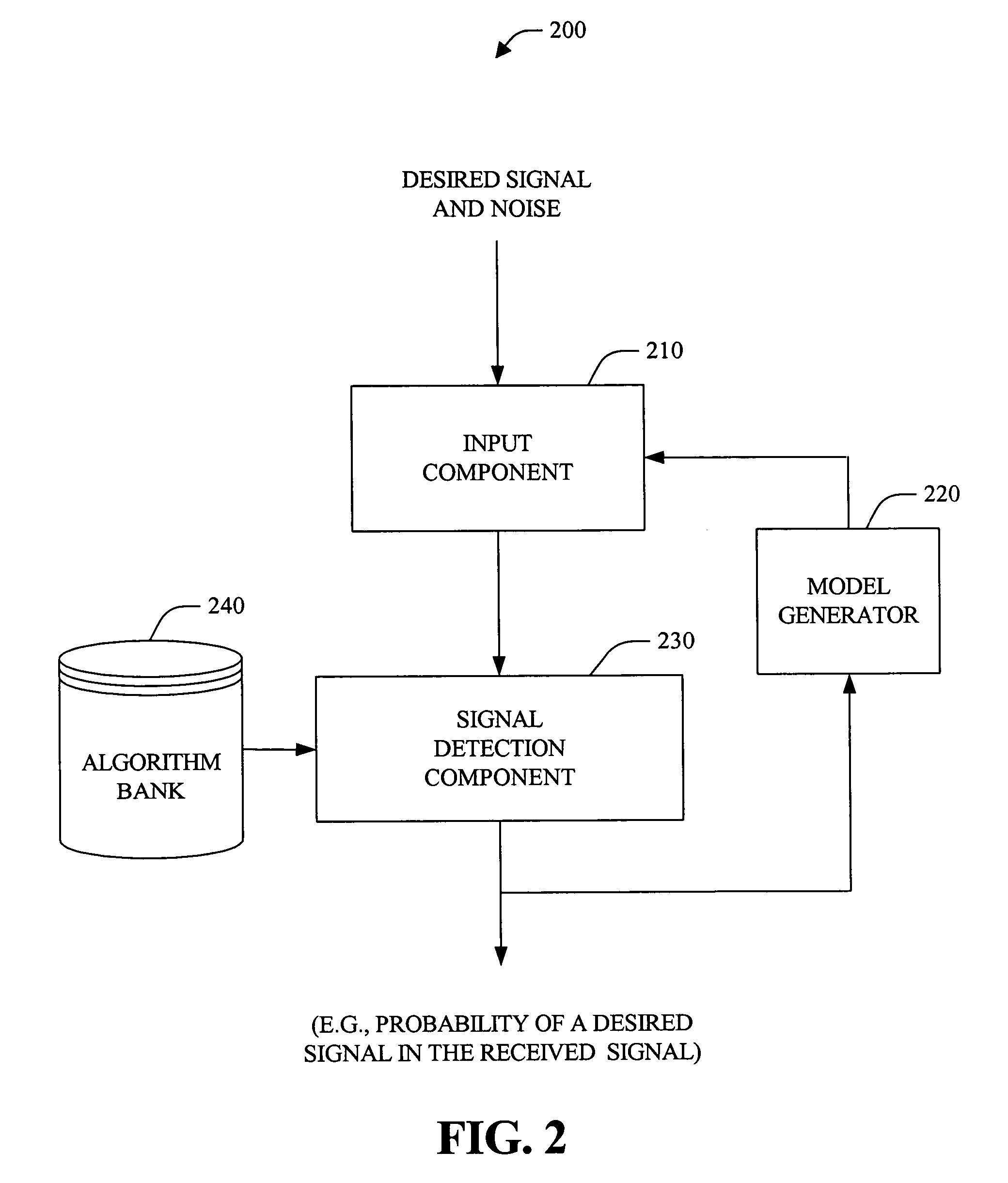
Systems and methods that detect a desired signal via a linear discriminative classifier that utilizes an estimated posterior signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
The present invention provides systems and methods for signal detection and enhancement. The systems and methods utilize one or more discriminative classifiers (e.g., a logistic regression model and a convolutional neural network) to estimate a posterior probability that indicates whether a desired signal is present in a received signal. The discriminative estimators generate the estimated probability based on one or more signal-to-noise ratio (SNRs) (e.g., a normalized logarithmic posterior SNR (nlpSNR) and a mel-transformed nlpSNR (mel-nlpSNR)) and an estimated noise model. Depending on the resolution desired, the estimated SNR can be generated at a frame level or at an atom level, wherein the atom level estimates are utilized to generate the frame level estimate. The novel systems and methods can be utilized to facilitate speech detection, speech recognition, speech coding, noise adaptation, speech enhancement, microphone arrays and echo-cancellation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
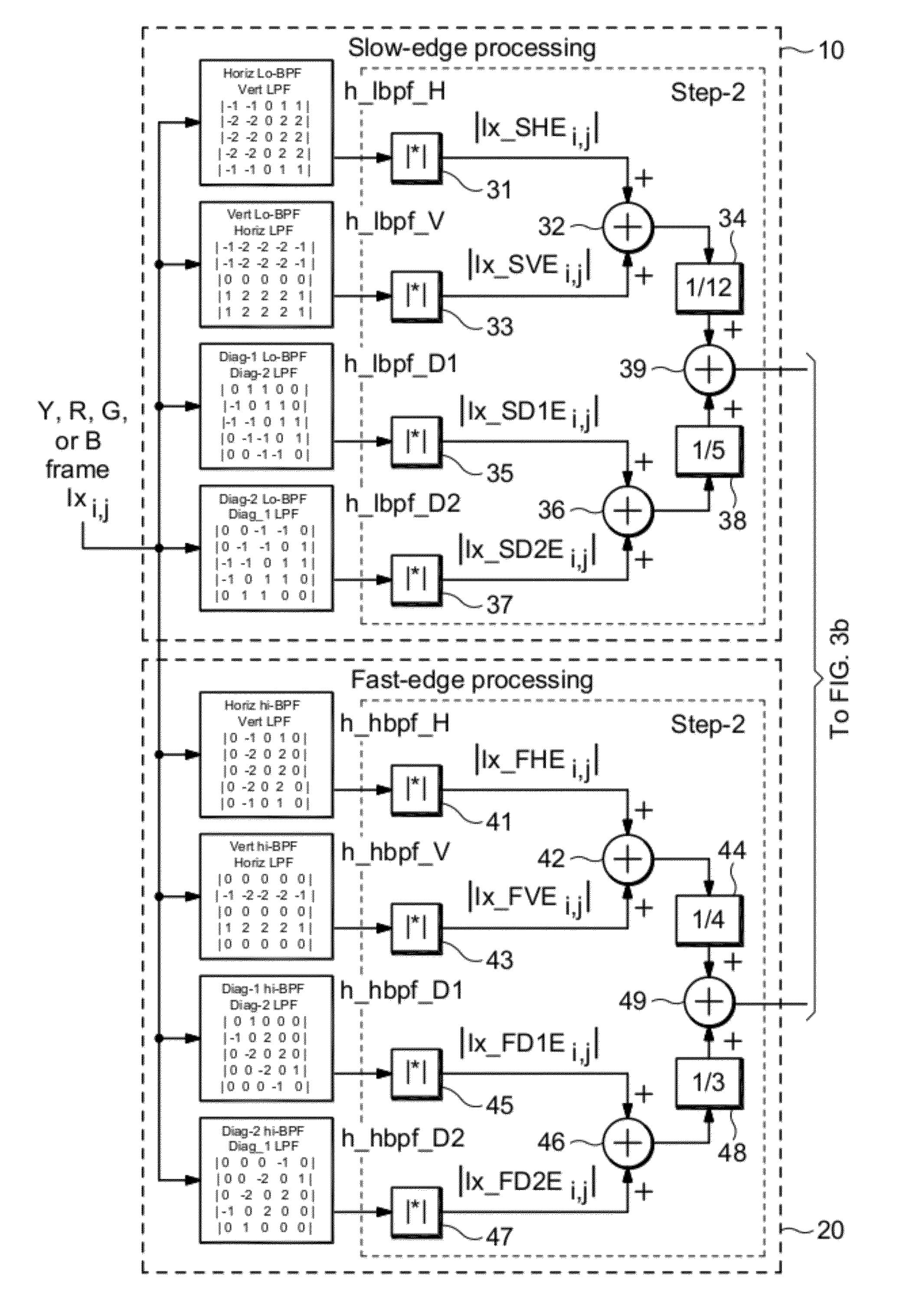
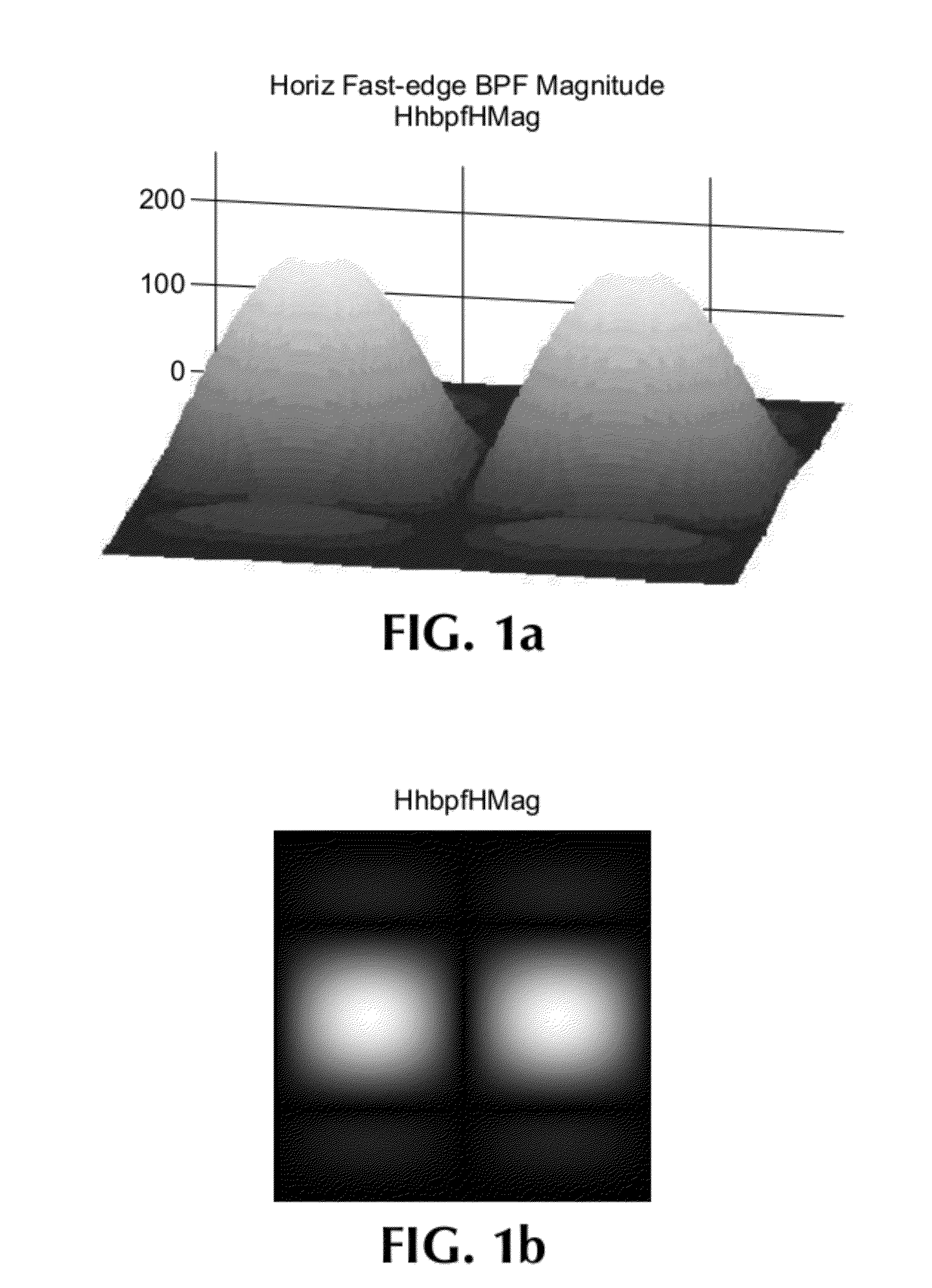
Blur detection with local sharpness map
ActiveUS20120162527A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionBandpass filtering
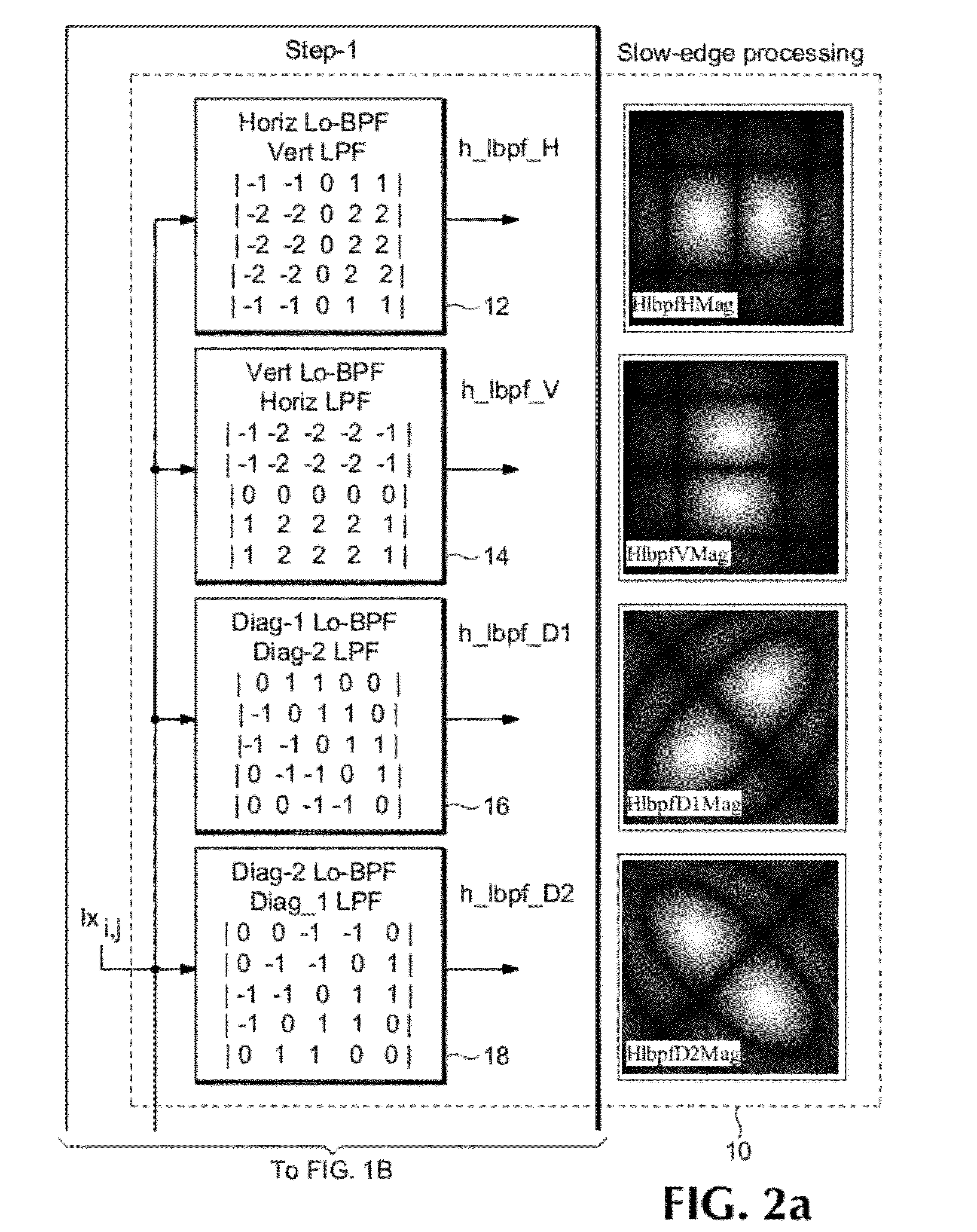
A single-ended blur detection probe and method with a local sharpness map for analyzing a video image sequence uses two sets of edge filters, one for “fast edges” and the other for “slow edges.” Each set of edge filters includes a horizontal bandpass filter, a vertical bandpass filter and a pair of orthogonal diagonal filters where the frequency response of the fast edge filters overlap the frequency response of the slow edge filters. The video image sequence is input to each filter of each set, and the output absolute values are combined with weighting factors to produce a slow edge weighted sum array and a fast edge weighted sum arra. The respective weighted sum arrays are then decimated to produce a slow edge decimated array and a fast edge decimated array. The ratio of the maximum difference value between the decimated arrays and the maximum value from the fast edge decimated array, weighted by an appropriate factor, produces a localized maximum sharpness value, the log of which produces a dimensionless blur value.
Owner:PROJECT GIANTS LLC
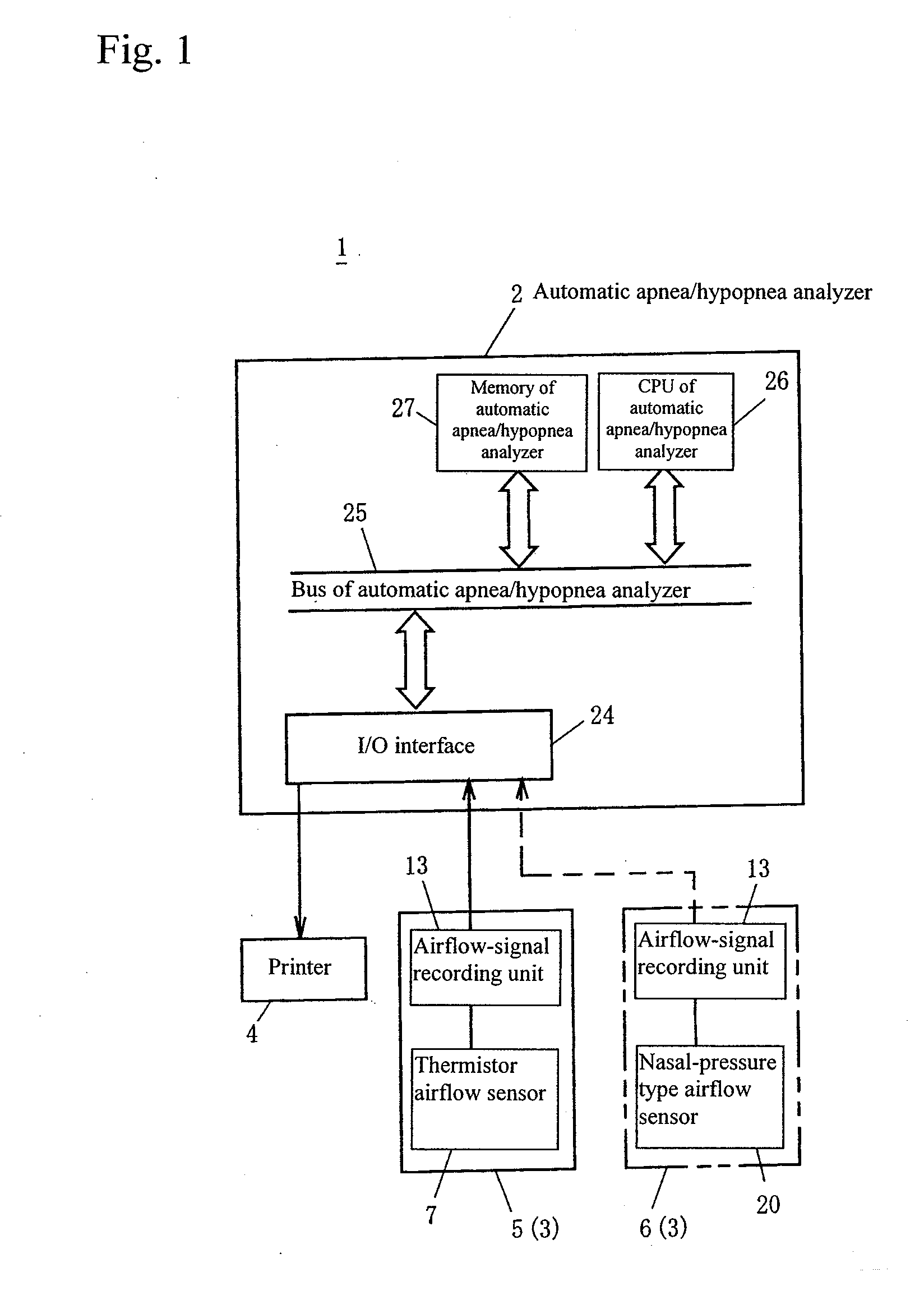
Automatic apnea/hypopnea detection device, detection method, program and recording medium
InactiveUS20070093724A1Improve reliabilityRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory flowDigital data
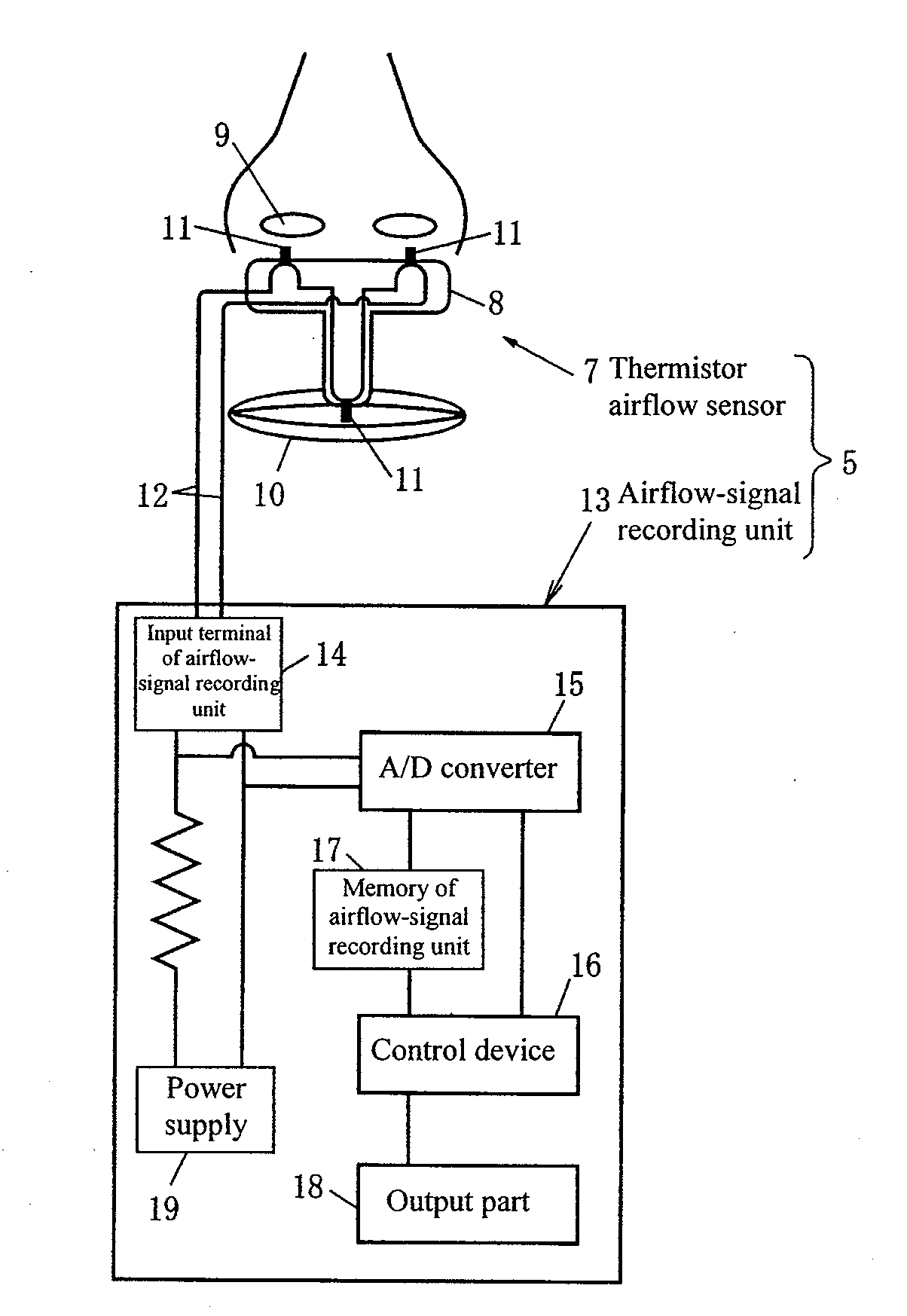
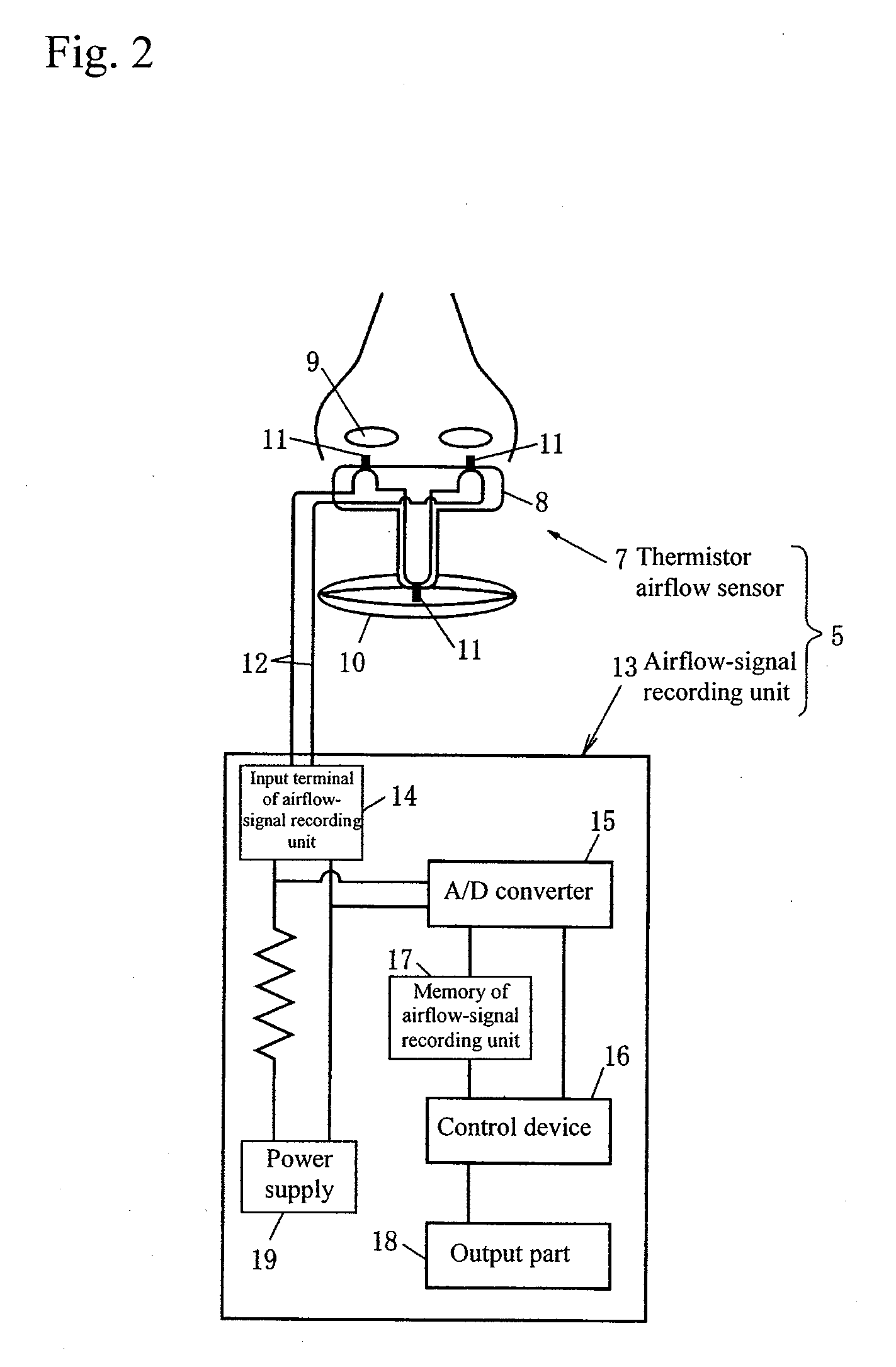
A device includes a respirometer 3 and an automatic apnea / hypopnea analyzer 2. The respirometer 3 includes an airflow-signal recording unit 13 that is connected to a thermistor respiratory flow meter 5 or a nasal-pressure type flow meter 6 detecting the airflow waveform signals, converts to digital data the airflow waveform signals obtained by the thermistor respiratory flow meter 5 or the nasal-pressure type flow meter 6, and stores the converted data as measured respiratory flow values. The automatic apnea / hypopnea analyzer 2 obtains power spectra in the breathing frequency band from the measured respiratory flow values, calculates logarithmic time-series data from the power spectra, smoothes the data, and then detects transitory drops (flow power dips) in the smoothed data, to automatically detect apnea / hypopnea.
Owner:TANIGAWA TAKESHI +1
Decoder for Low-Density Parity-Check Convolutional Codes
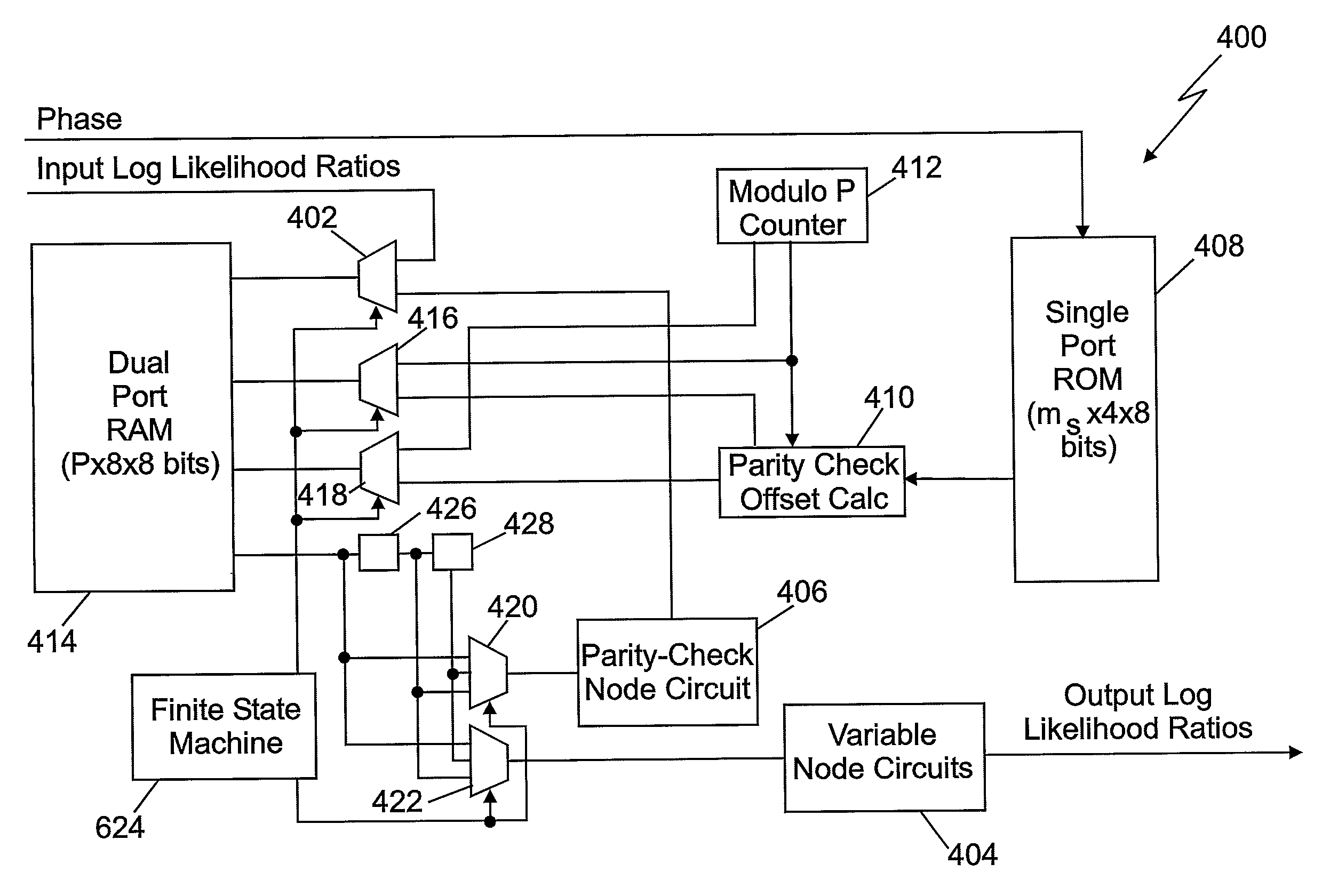
InactiveUS20080195913A1Accurately decisionedImprove accuracyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionRandom access memoryParallel computing
Decoder for low-density parity check convolutional codes. In at least some embodiments, a decoder (200) for arbitrary length blocks of low-density, parity-check codes includes a plurality of interconnected processors (202), which further include a plurality of interconnected nodes. A memory can be interconnected with the nodes to store intermediate log likelihood ratio (LLR) values based on channel LLR values. Thus, LLR values having successively improved accuracy relative to the channel LLR values can be output from each processor, and eventually used to decision information bits. In some embodiments, the memory is a random access memory (RAM) device that is adapted to store the intermediate LLR values in a circular buffer. Additionally, a storage device such as a read-only memory (ROM) device can be used to generate a predetermined plurality of addresses for reading and writing LLR values.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
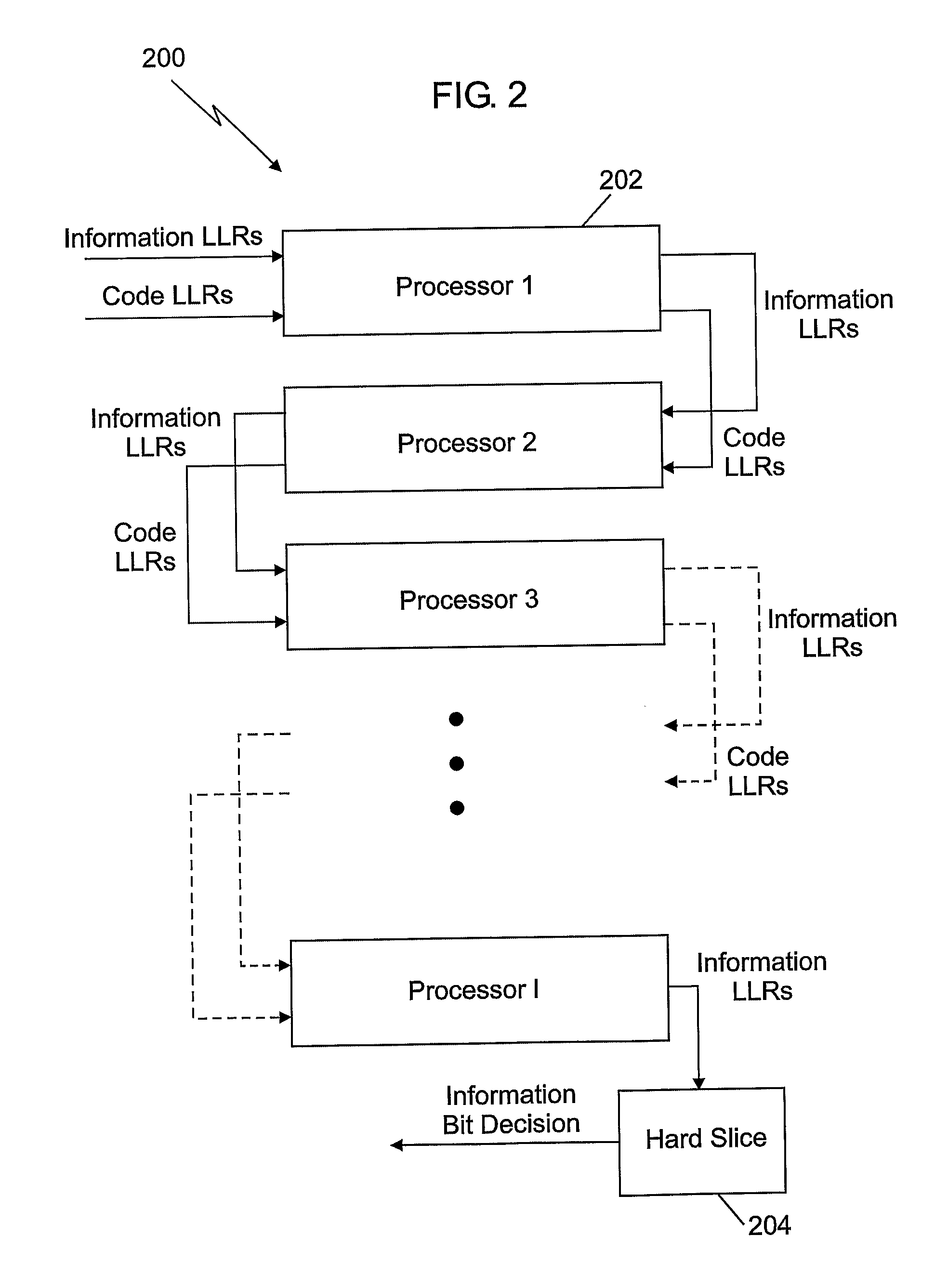
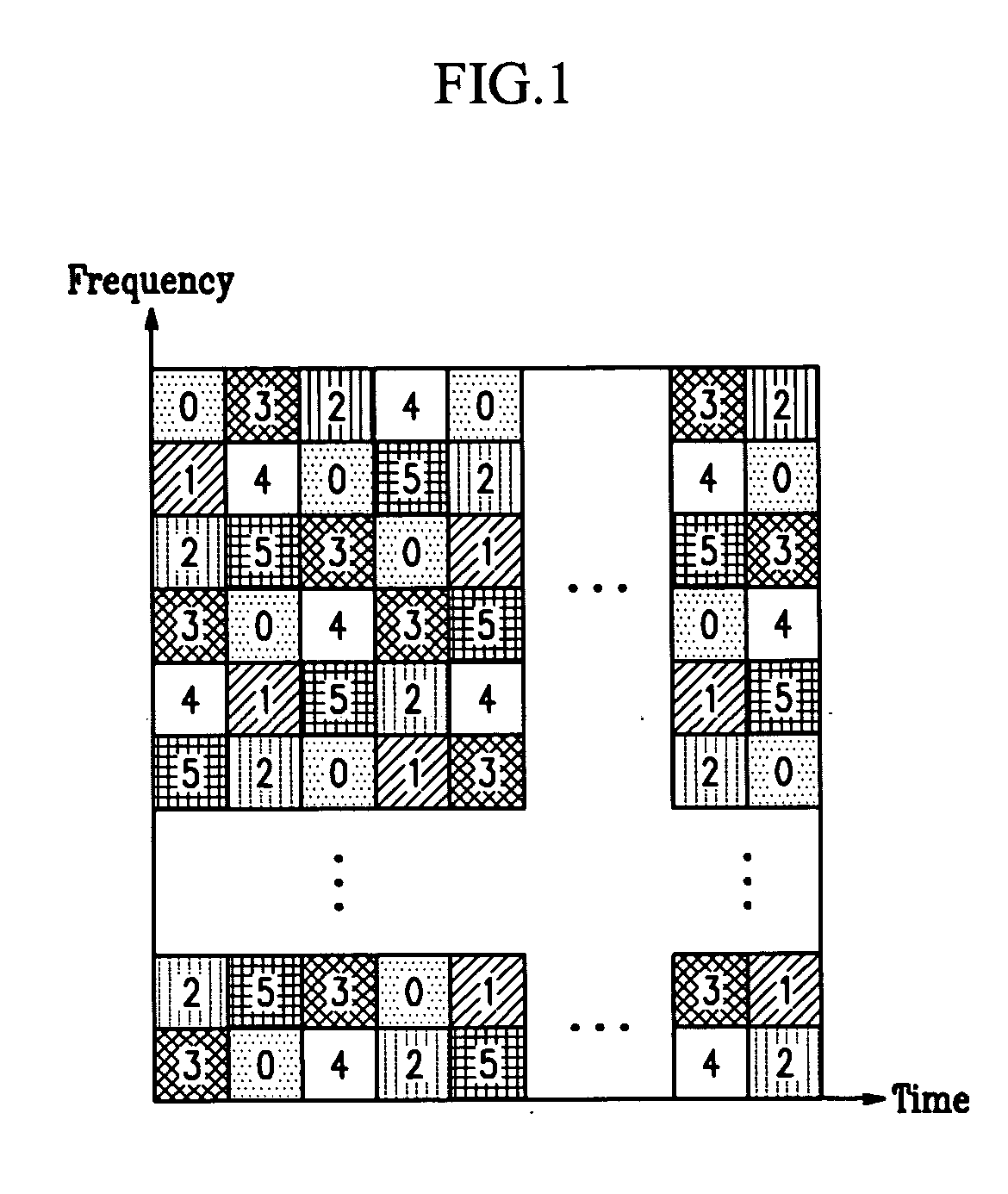
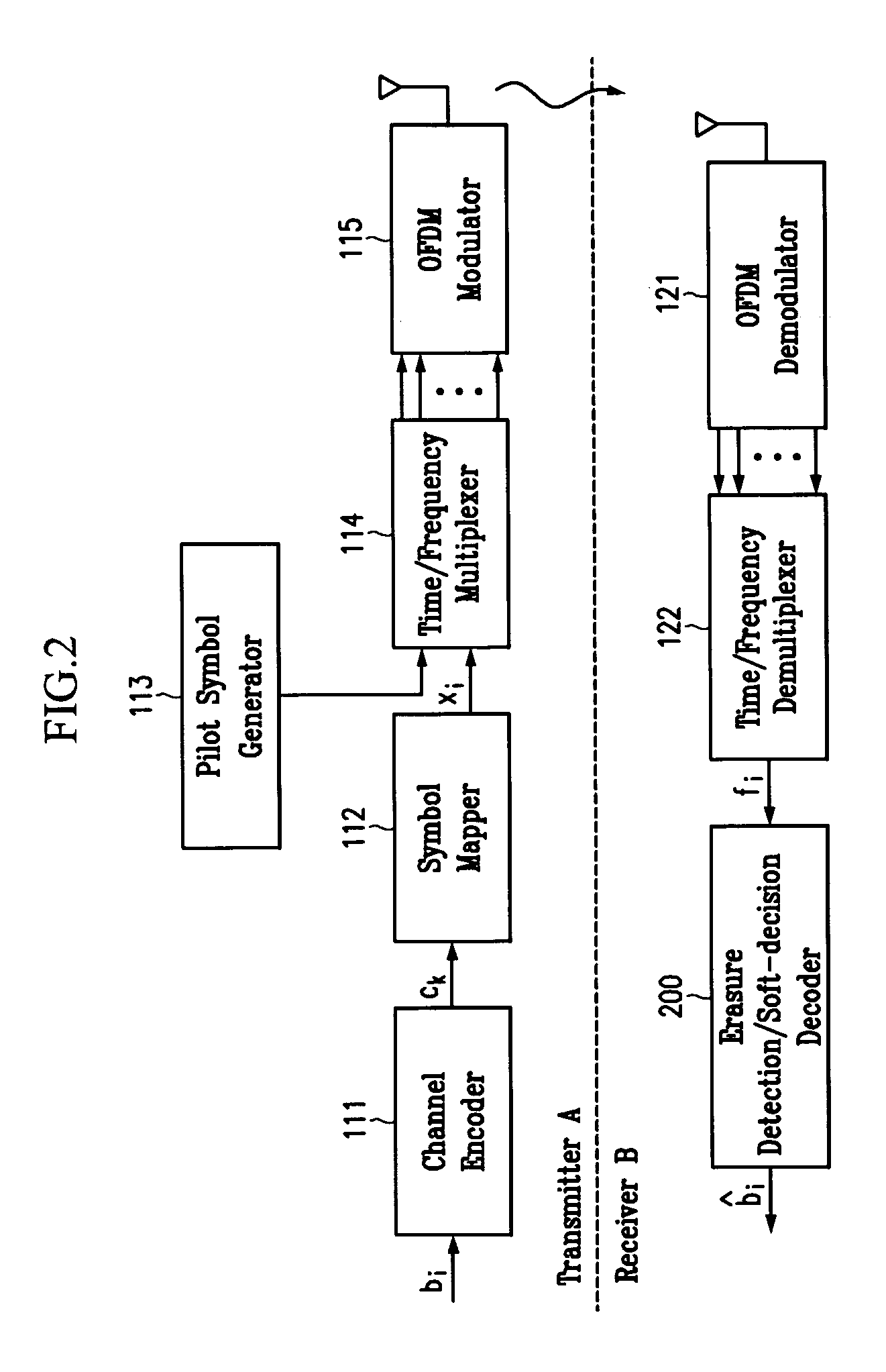
Apparatus and method for erasure detection and soft-decision decoding in cellular system receiver
InactiveUS20050278609A1High power interferenceReduce the impactError preventionOther decoding techniquesLogitLog likelihood
Dislosed is an apparatus and method for erasure detection and soft-decision decoding in a cellular system receiver. In the present invention, a complex channel gain and a noise variance of a received symbol from a cellular system transmitter are estimated, and an erasure symbol (a symbol with high power interference) is detected by comparing a threshold value according to the estimated complex channel gain or noise variance with power of the received symbol. Log-likelihood ratios corresponding to constituent bits of the detected erasure symbols are allowed to be 0, and the log-likelihood ratios of the constituent bits of the other received symbols are calculated. A soft-decision decoding operation of received bits is performed with the calculated log-likelihood ratios.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
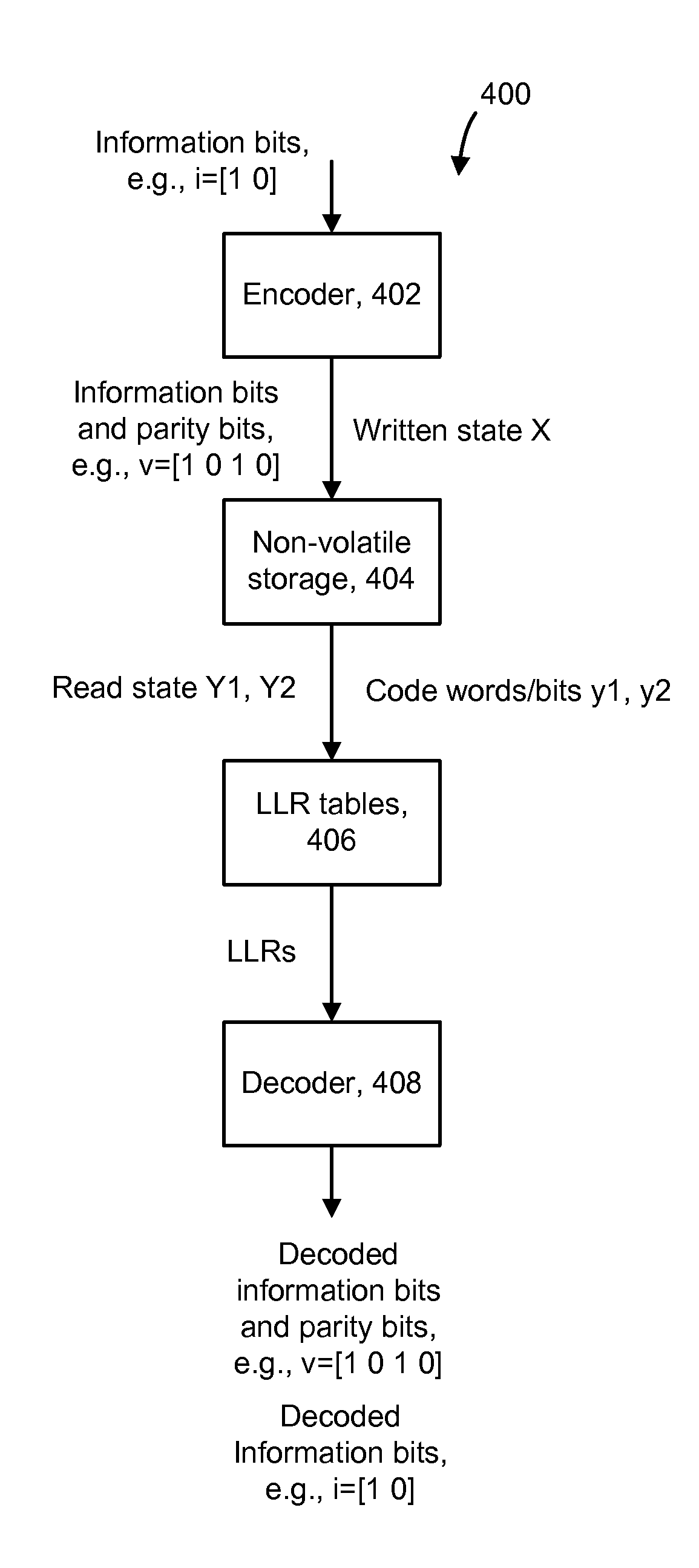
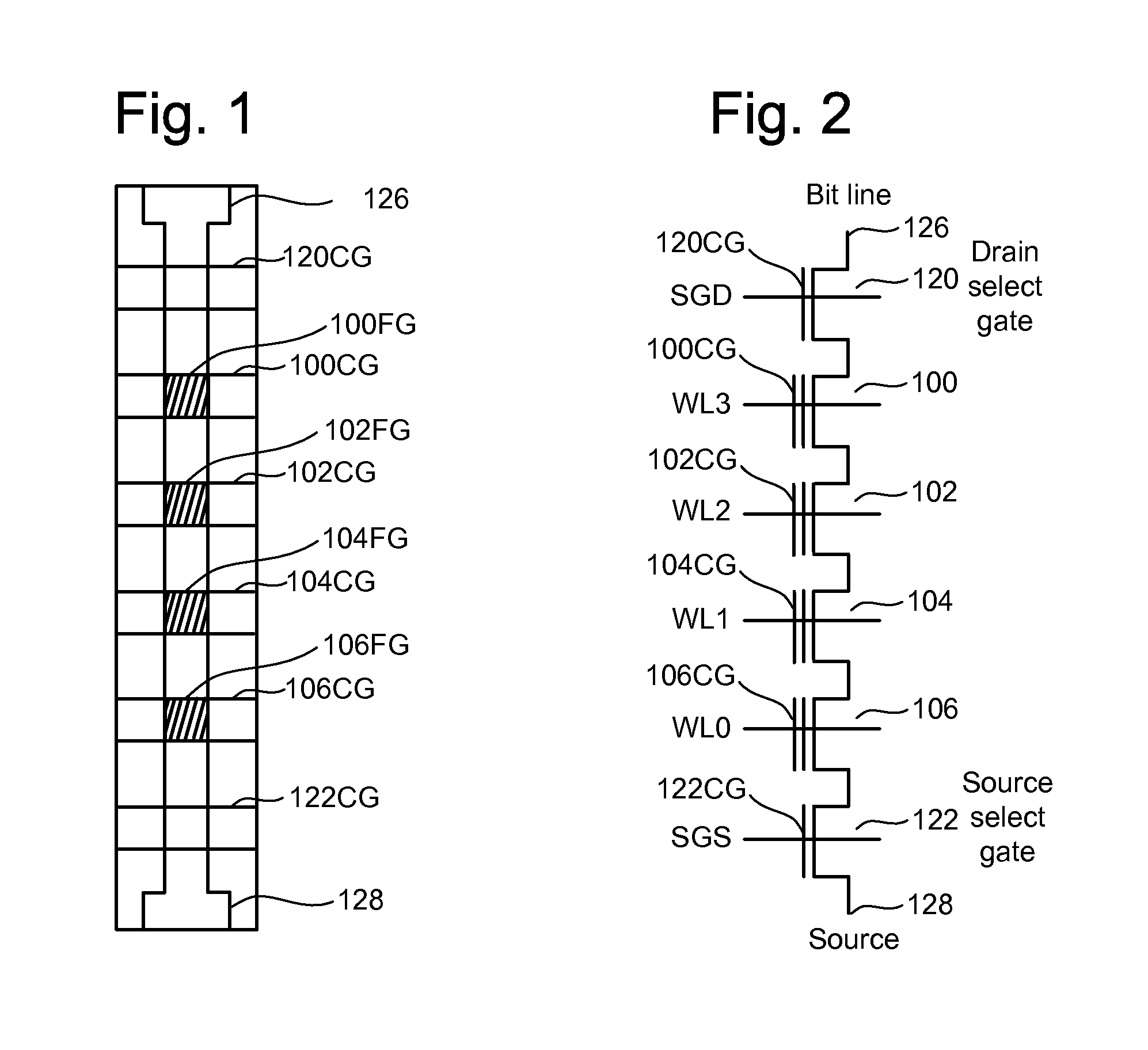
Method For Decoding Data In Non-Volatile Storage Using Reliability Metrics Based On Multiple Reads
ActiveUS20110131473A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesLow-density parity-check codeLogit
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding and multiple read operations to achieve greater reliability. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding read data of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. If convergence does not occur, e.g., within a set time period, the state of the non-volatile storage element is sensed again, current values of the reliability metrics in the decoder are adjusted, and the decoding again attempts to converge.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
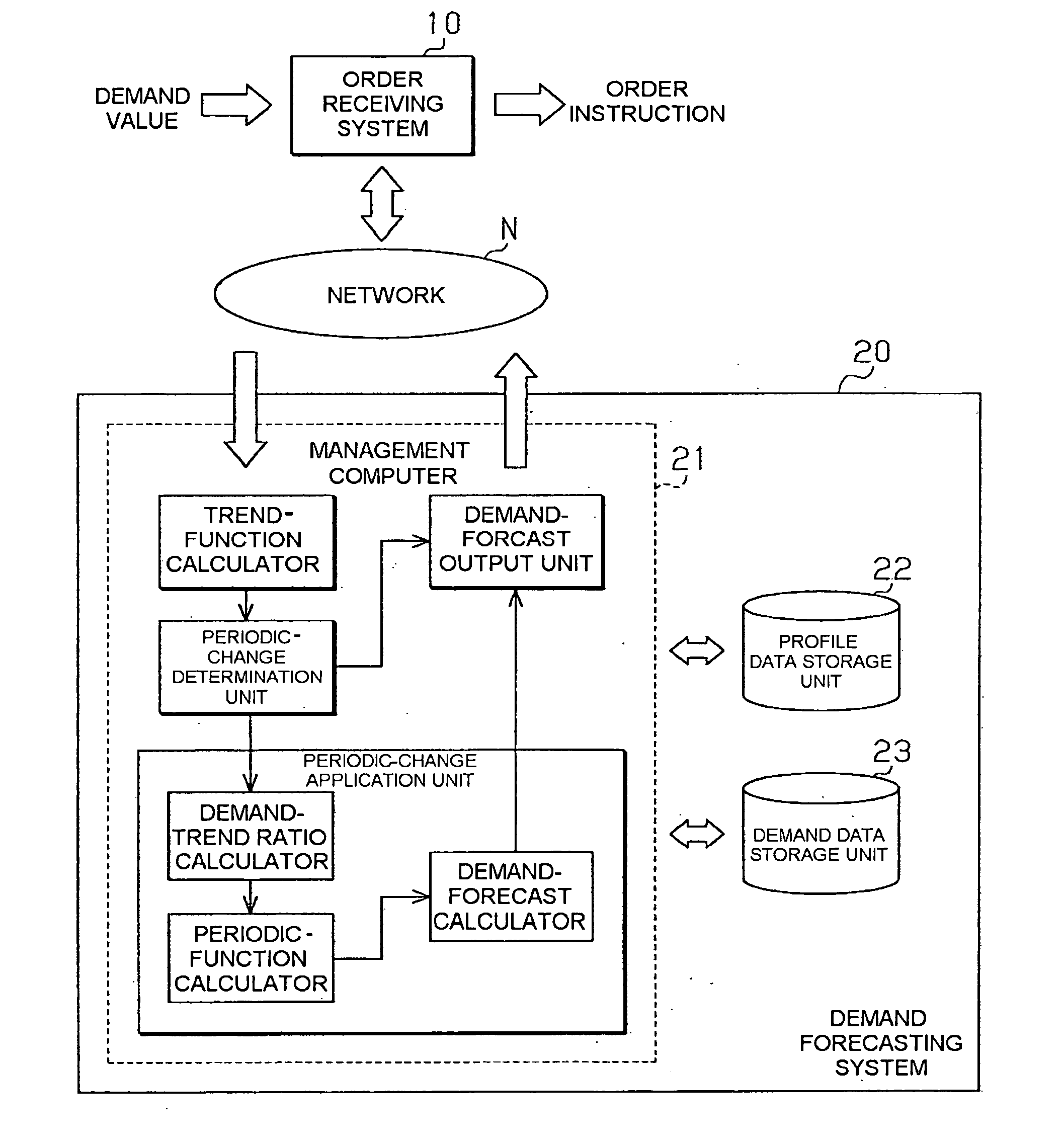
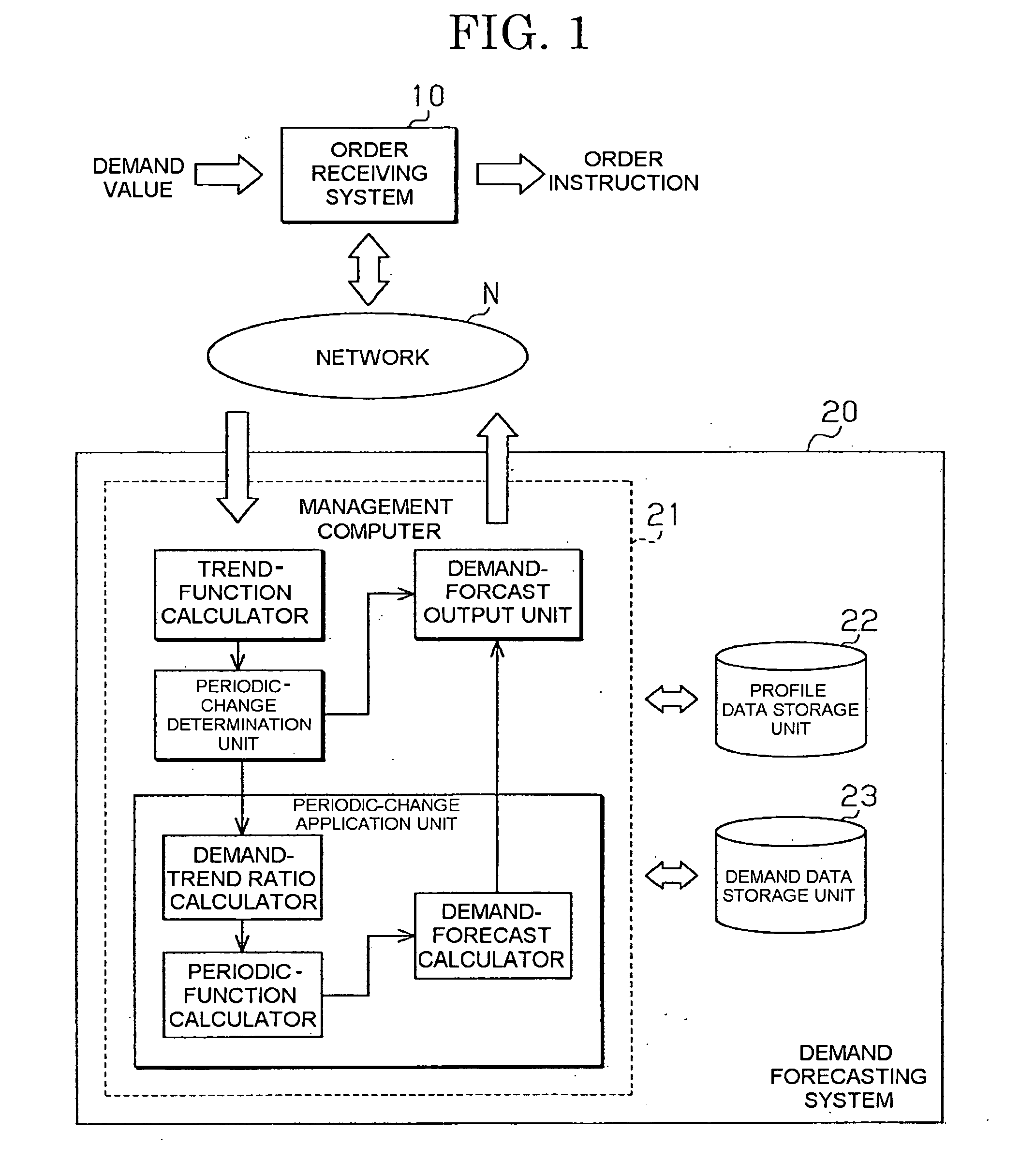
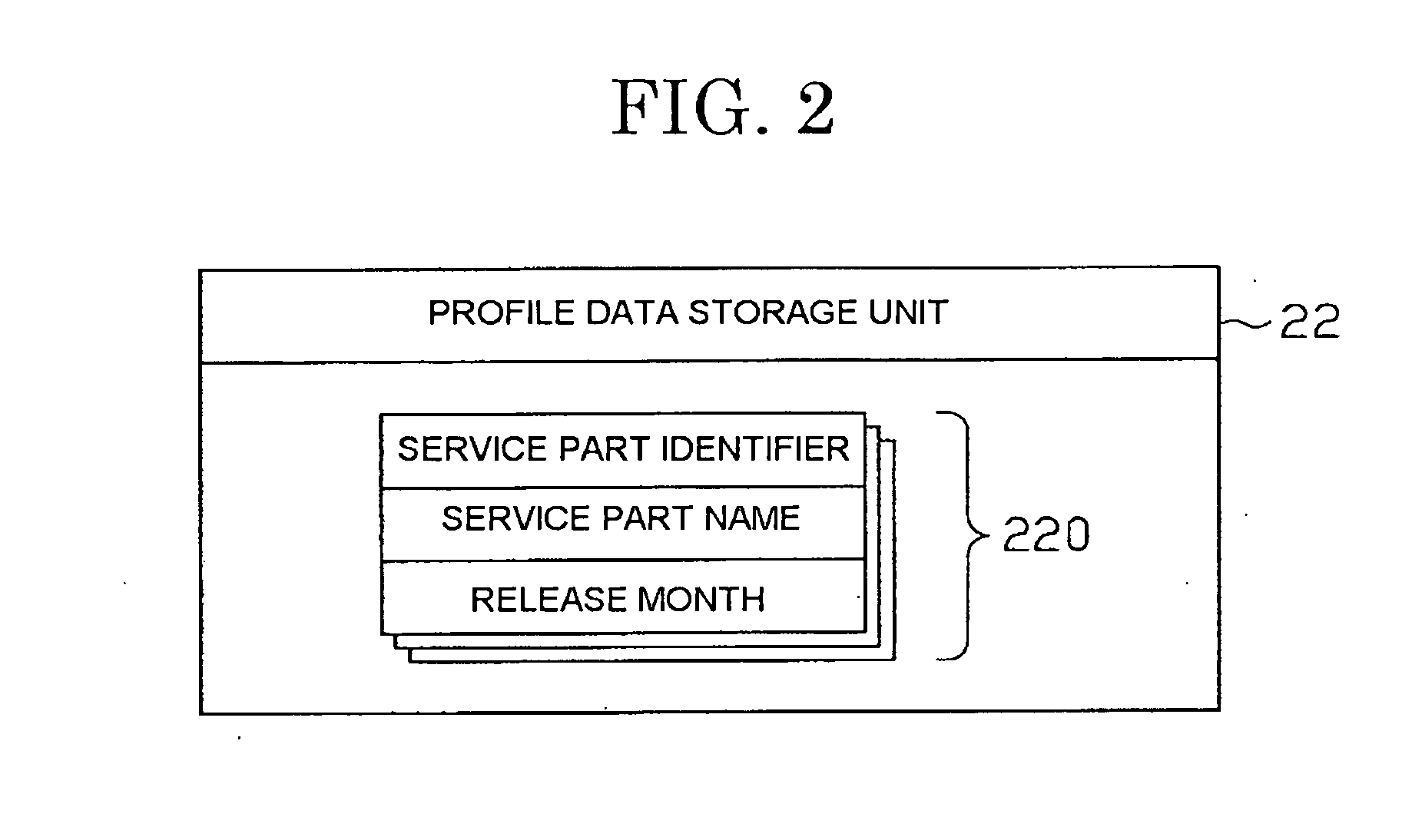
Demand forecasting method, system and computer readable storage medium
InactiveUS20070118421A1Amplitude of the periodicity tendsImprove approximationForecastingCommerceLogitData mining
Disclosed are a demand forecasting method, a demand forecasting program, and a demand forecasting system that can adequately forecast a demand for a commodity. A management computer calculates a trend function with respect to demand values. The management computer then calculates the ratio of the demand values to a trend curve, and calculates a logarithm of the ratio. Then, the management computer approximates the calculated natural logarithm curve with a periodic model, and converts the logarithmic scale of the acquired periodic model to a normal scale. Demand forecasting is performed using a demand forecasting model acquired by combining a periodic change model of the normal scale with a trend curve (trend function).
Owner:RICOH KK
Separating multiple audio signals recorded as a single mixed signal
InactiveUS20060056647A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpeech analysisSlide windowLogit
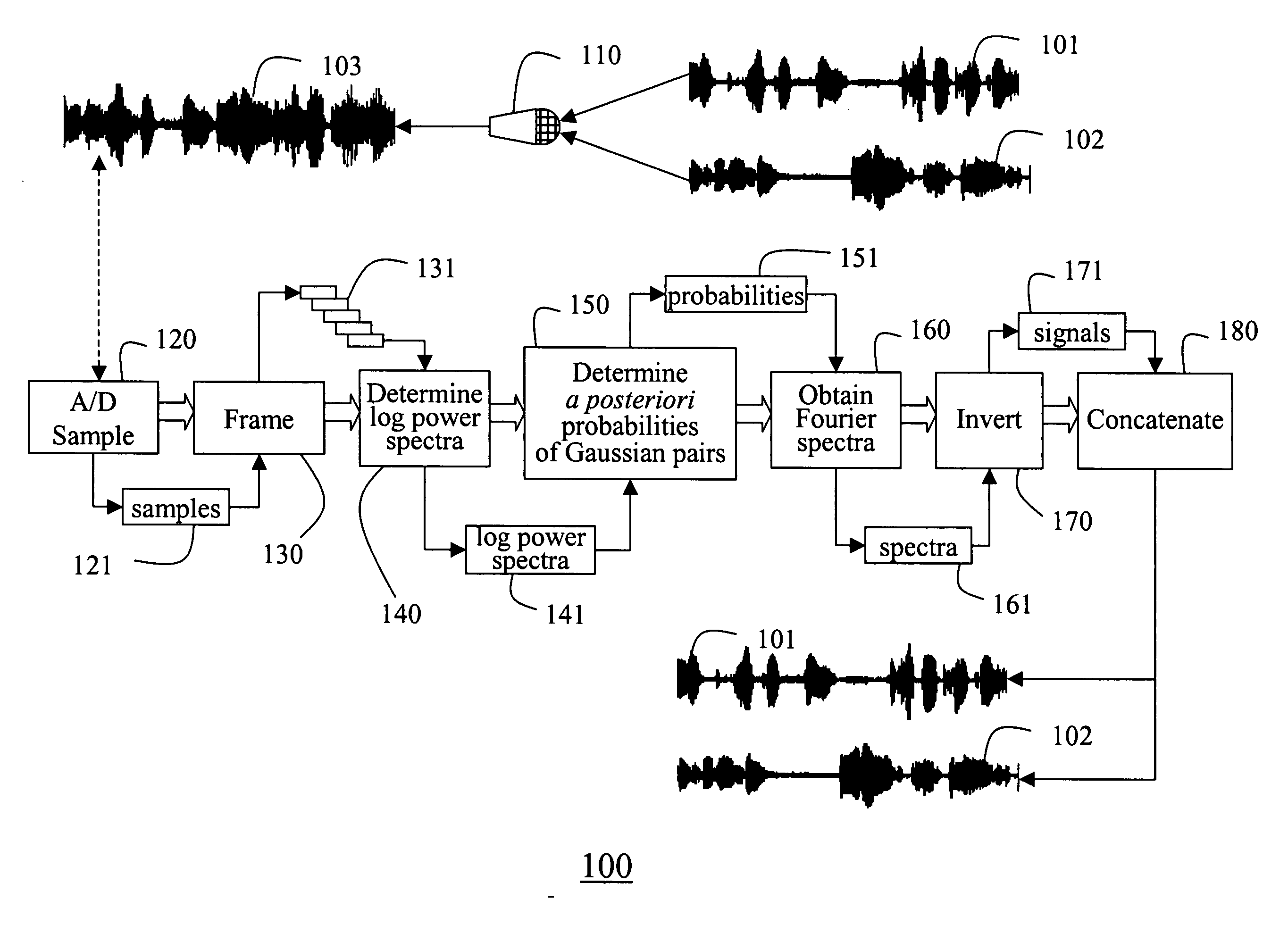
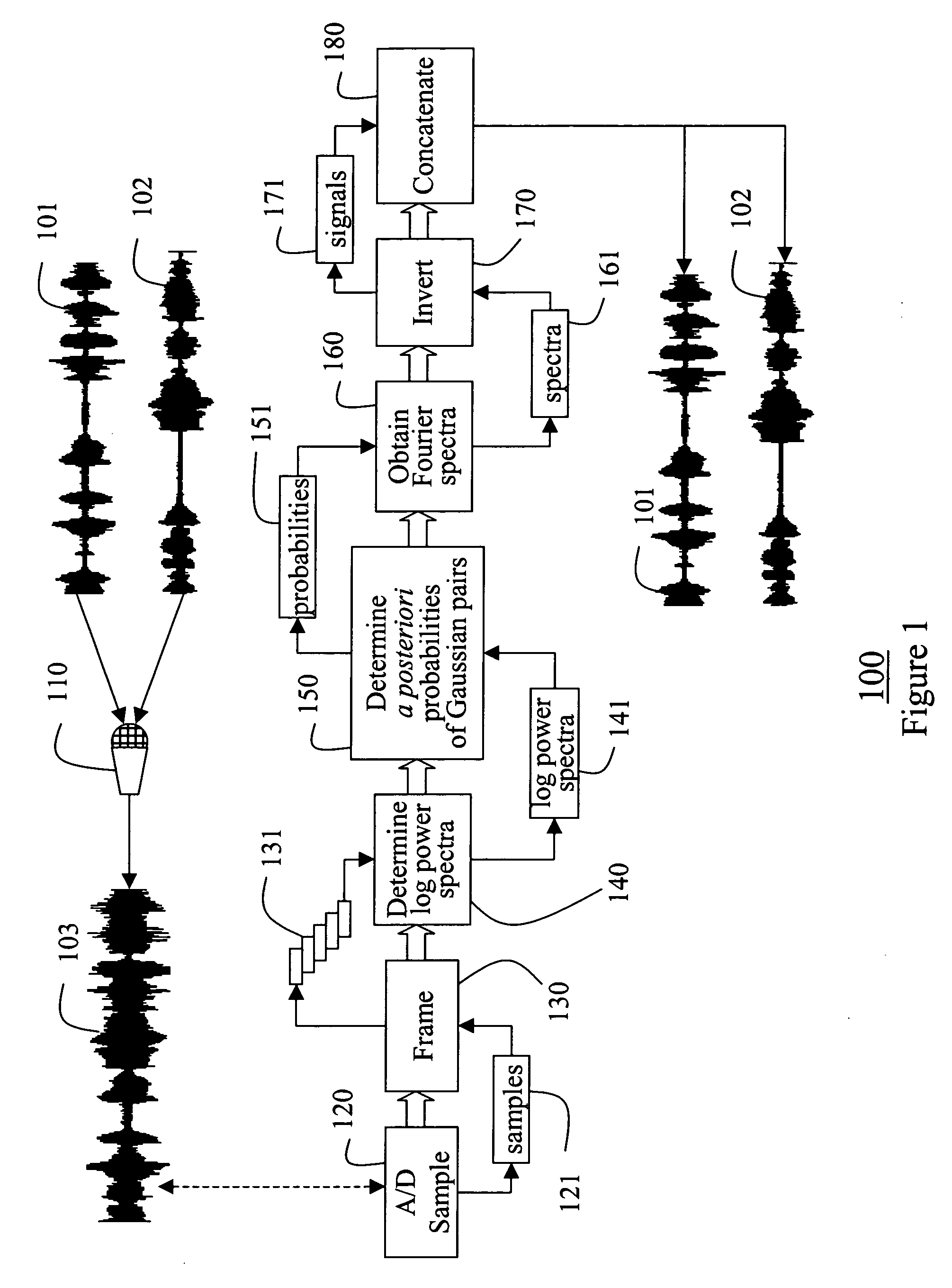
A method according to the invention separates multiple audio signals recorded as a mixed signal via a single channel. The mixed signal is A / D converted and sampled. A sliding window is applied to the samples to obtain frames. The logarithms of the power spectra of the frames are determined. From the spectra, the a posteriori probabilities of pairs of spectra are determined. The probabilities are used to obtain Fourier spectra for each individual signal in each frame. The invention provides a minimum-mean-squared error metho or a soft mask method for making this determination. The Fourier spectra are inverted to obtain corresponding signals, which are concatenated to recover the individual signals.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
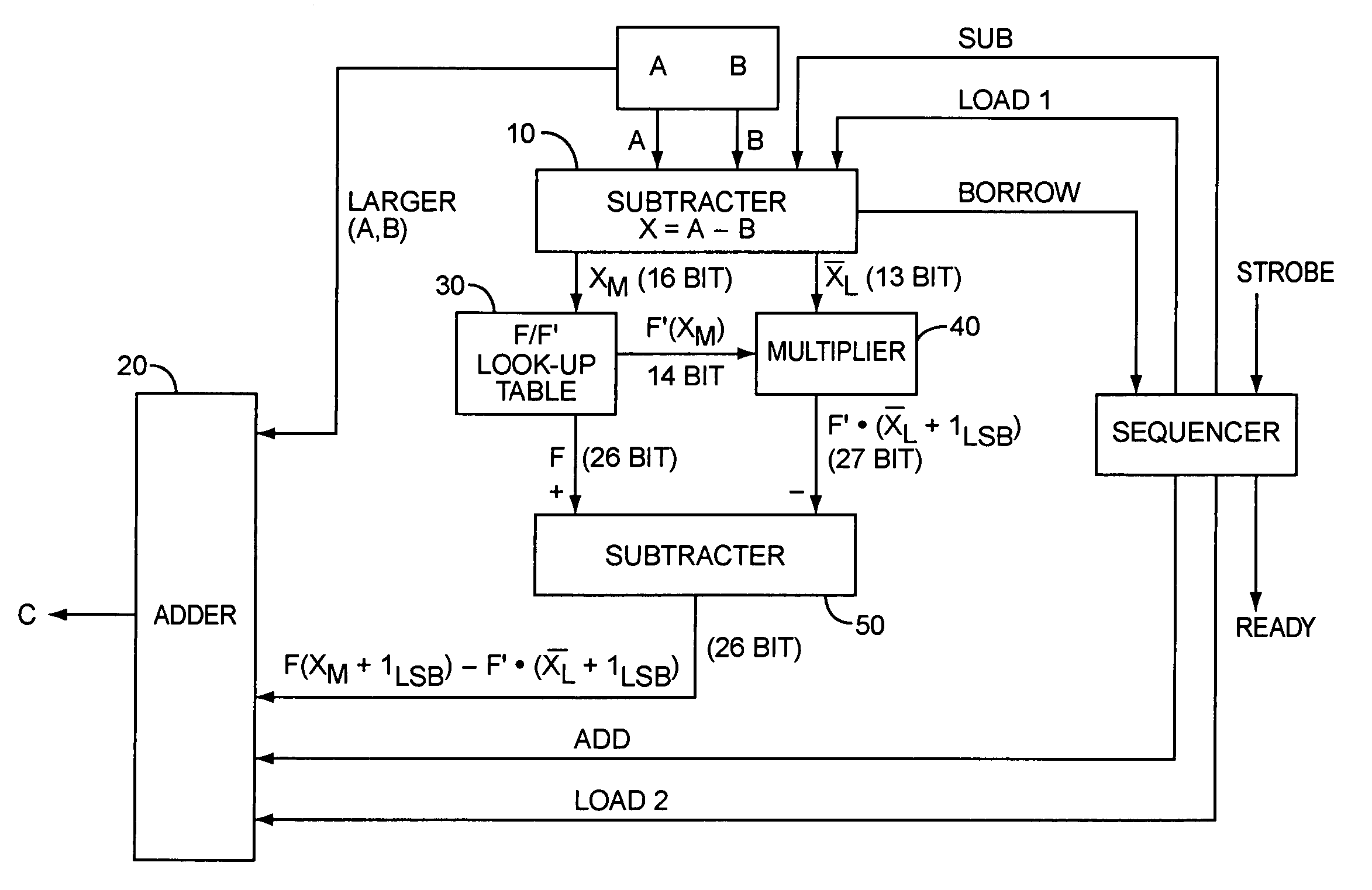
Complex logarithmic ALU
InactiveUS20050273483A1Simplifies divisionSimplifies multiplicationComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsReal arithmeticLogit
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
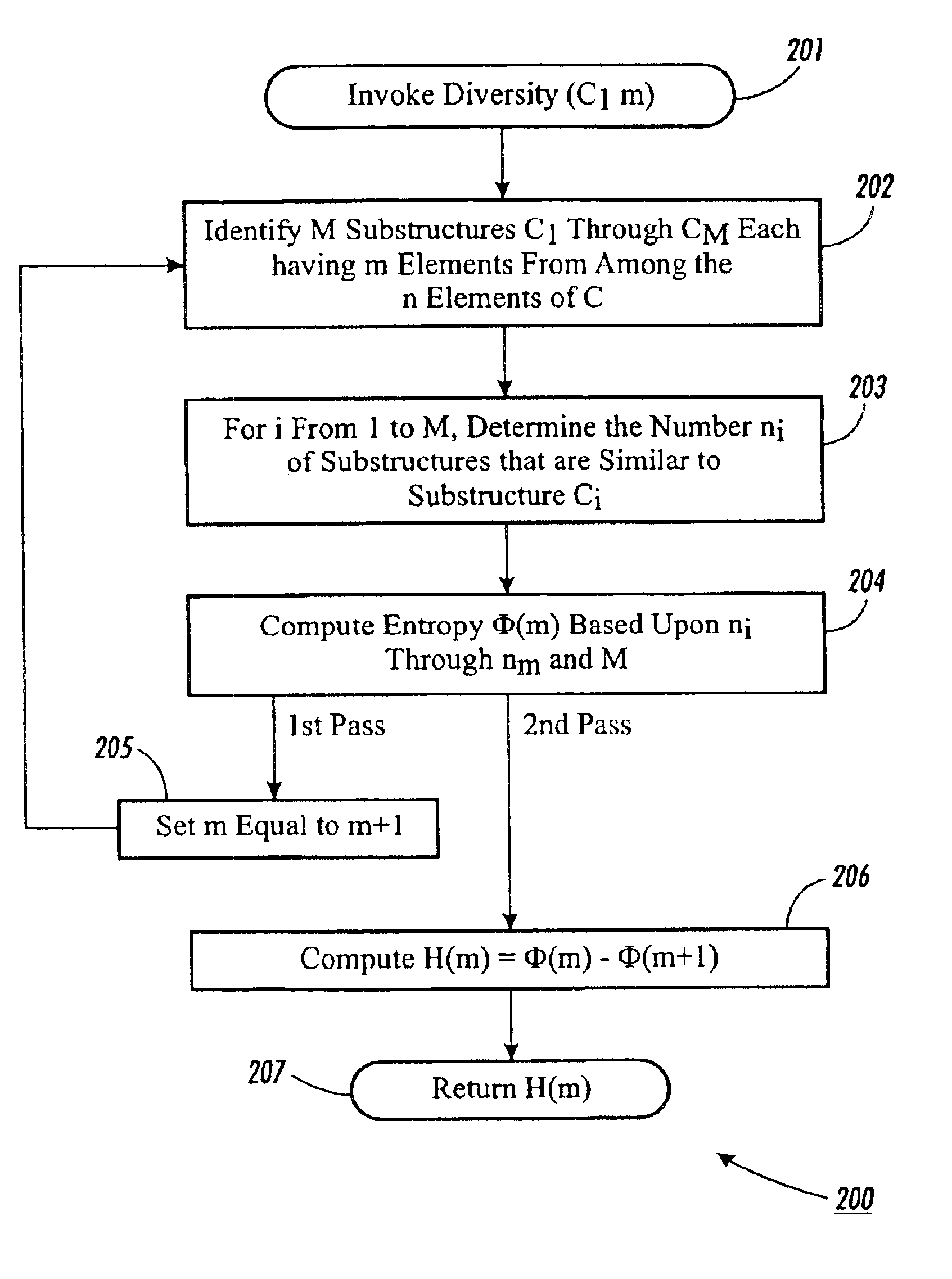
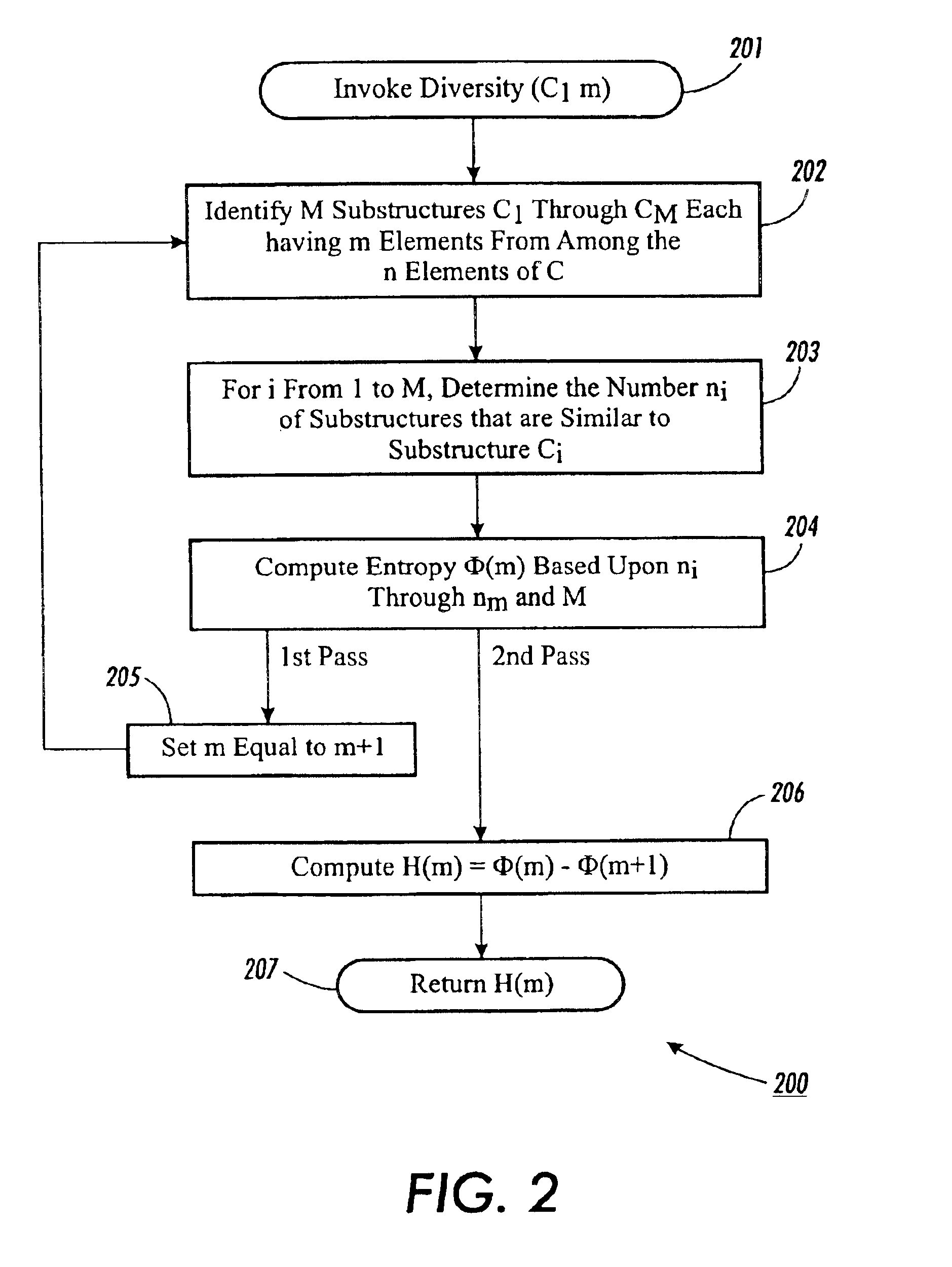
Methods and apparatuses for measuring diversity in combinatorial structures
InactiveUS6862559B1Data processing applicationsWeb data indexingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
A method for computing a diversity measure H(m) for combinatorial structures involves identifying all M possible substructures having m elements from among the n elements of the combinatorial structure. The number of the substructures that are similar to each such substructure is determined, and the frequency of each distinct substructure is calculated using the number of similar substructures and the total number of substructures M. The method uses the frequency of each distinct substructure to compute an entropy corresponding to m. By the same process described above, and entropy corresponding to m+1 is computed. The entropy corresponding to m+1 is subtracted from the entropy corresponding to m to produce the diversity measure H(m). In the preferred embodiment, similar substructures are determined by being identical or isomorphic. In an alternative embodiment, a distance function is used to compute a distance between two substructures, and only if the distance is less than a predetermined threshold are the two substructures determined to be similar. In the preferred embodiment, the entropy is computed by summing the frequency of each distinct substructure multiplied by the logarithm of the frequency of each distinct substructure. In an alternative embodiment, the entropy is computed by summing the frequency of each distinct substructure by the logarithm of the quotient of the frequency divided by an expected frequency of the distinct substructure. Generalized graphs such as can be used to model the Web are combinatorial structures suitable for use with the methods according to the present invention.
Owner:XEROX CORP
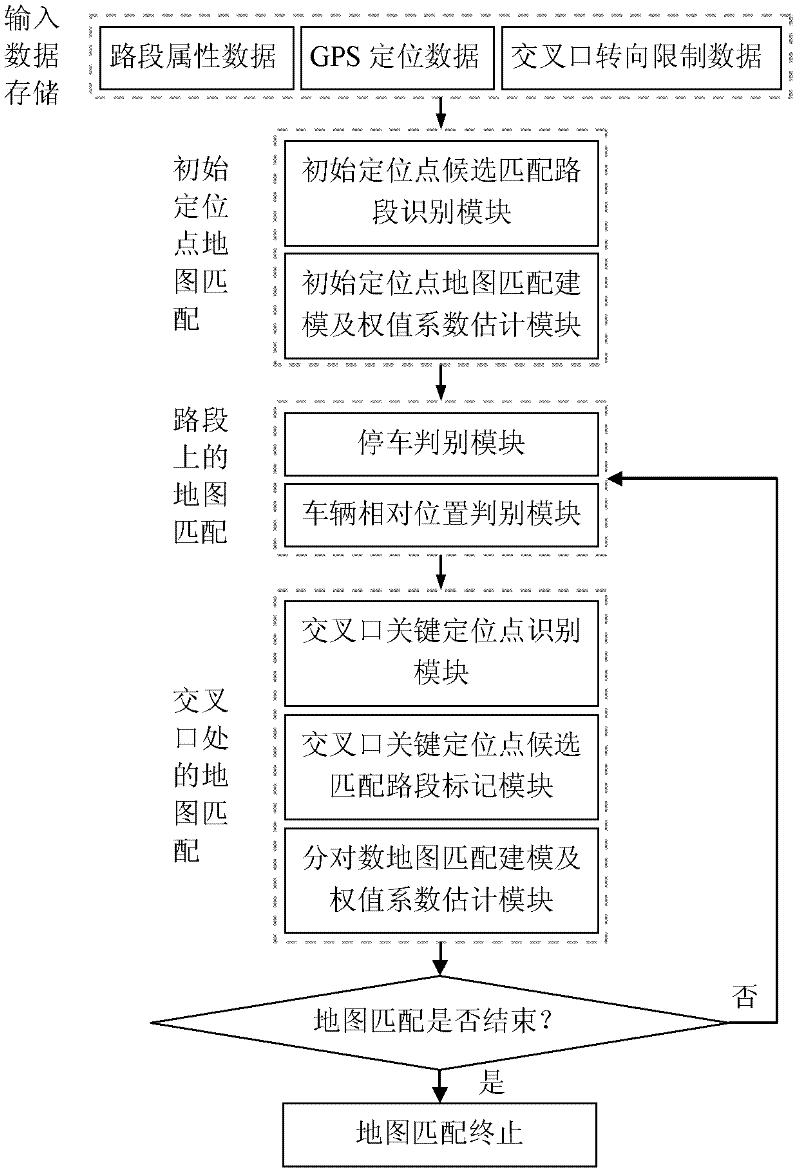
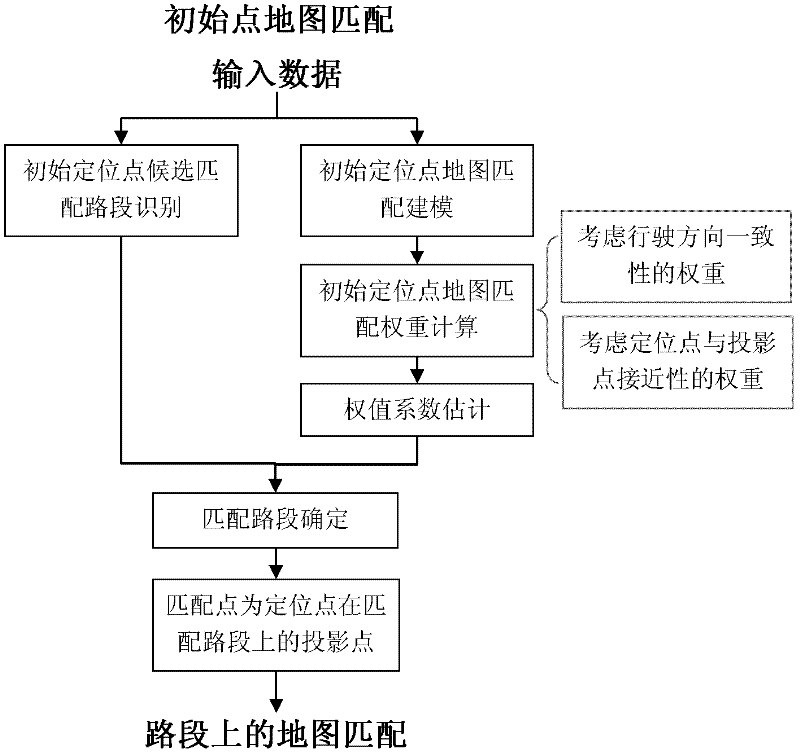
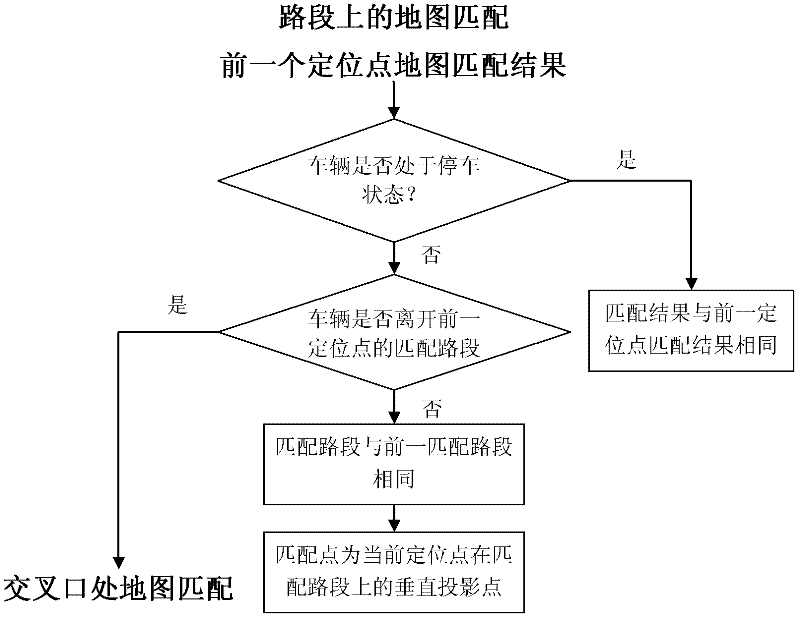
Intersection map matching method based on driver behavior characteristics and logit model
InactiveCN102589557AHigh precisionMatch in real timeInstruments for road network navigationLogitVehicle driving
The invention provides an intersection map matching method based on driver behavior characteristics and a logit model, relating to the field of vehicle positioning and map matching. The method comprises four phases of storing input data, mapping an initial site map, matching a map on a road section and matching an intersection map, so as to finish high-precision and real-time positioning of a vehicle driving track. The intersection map matching method disclosed by the invention solves the problem that the matching precision of the intersection map is low and overcomes the defect of the traditional intersection map matching method, so that the high-precision and real-time positioning of an intersection is realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Modeling method of traffic prediction
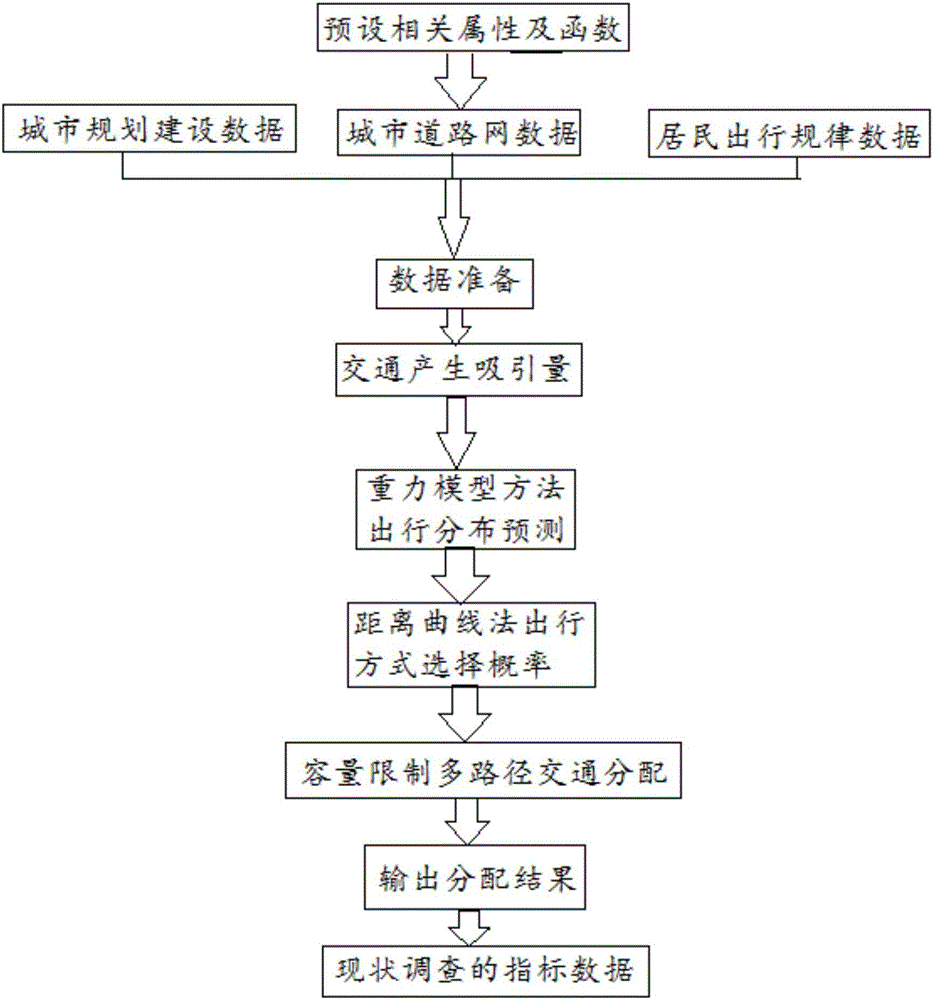
ActiveCN105070042AEasy to operateSimple calculationRoad vehicles traffic controlSpecial data processing applicationsTravel modeTraffic prediction
The invention discloses a model method of a traffic prediction. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing a road traffic basic facility geographical information database, storing and updating traffic planning schemes, and establishing intersection delay determination; (2) establishing an urban planning construction geographical information database, storing regulatory detailed plans of each area, and utilizing an original unit method to construct traffic generation cases; (3) calling data of the road traffic basic facility geographical information database and the urban planning construction geographical information database, and utilizing a gravity model method to predict parallel distributed matrixes; (4) constructing a multi-element logit model, and determining the probability distribution for a single person selecting a travelling mode in specific travelling information; and (5) utilizing a capacity-limited multi-path distribution method to carry out traffic distribution. The modeling purpose, method to realization are overall planed, modeling parameter selection, basic data sources and calculation program design are coordinated, and the convenient application and operation of a traffic prediction model system are ensured.
Owner:JINAN MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INSITITUTE GRP
Error-correction decoder employing extrinsic message averaging
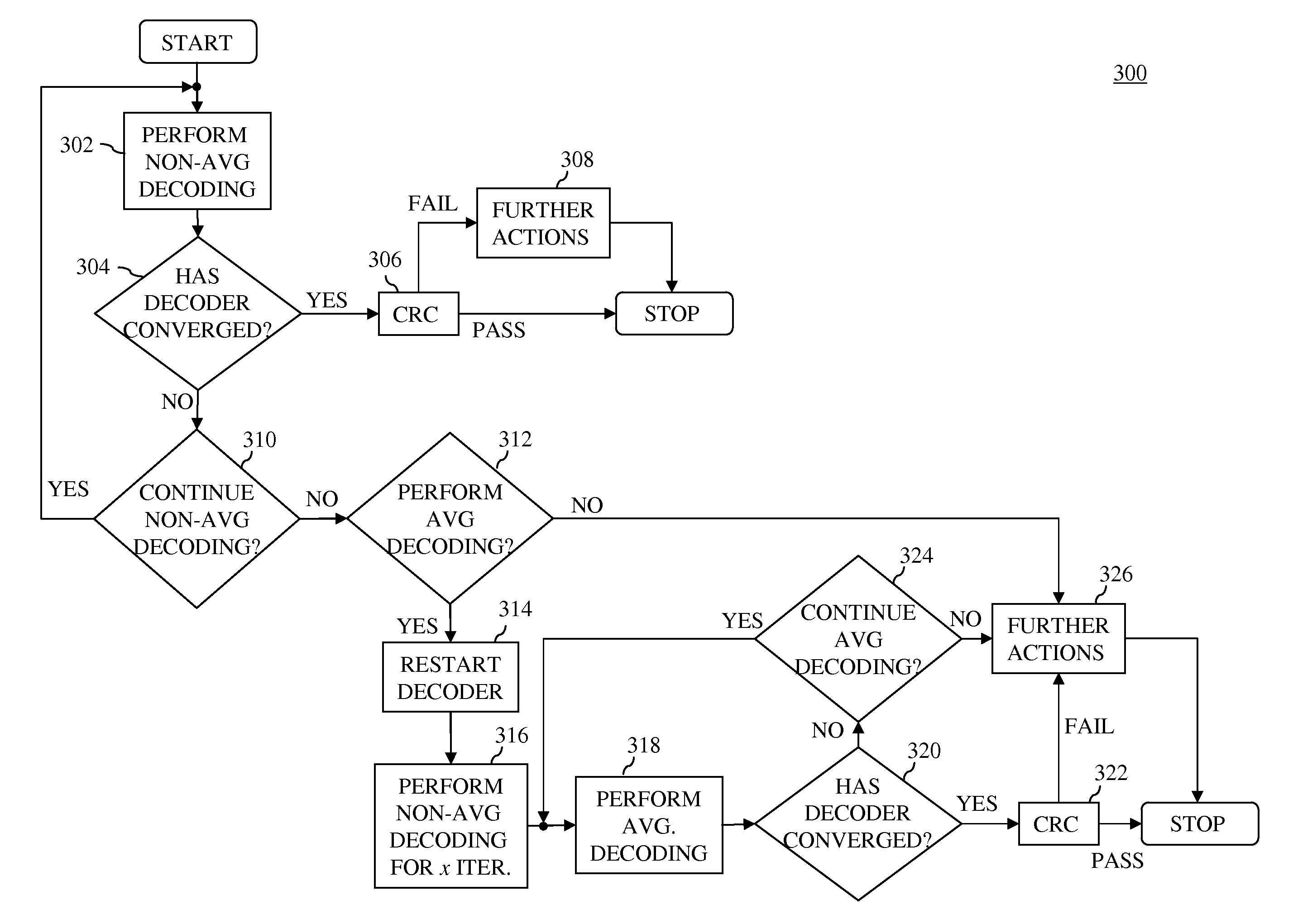
In one embodiment, an LDPC decoder has a controller and an extrinsic log-likelihood (LLR) value generator. The extrinsic LLR value generator is selectively configurable to operate in either (i) a non-averaging mode that updates extrinsic LLR values without averaging or (ii) an averaging mode that updates extrinsic LLR values using averaging. Initially, the extrinsic LLR value generator is configured to generate non-averaged extrinsic LLR values, and the decoder attempts to recover an LDPC-encoded codeword using the non-averaged extrinsic LLR values. If the decoder is unable to recover the correct codeword, then (i) the controller selects the averaging mode, (ii) the extrinsic LLR value generator is configured to generate average extrinsic LLR values, and (iii) the decoder attempts to recover the correct codeword using the average extrinsic LLR values. Averaging the extrinsic LLR values may slow down the propagation of erroneous messages that lead the decoder to convergence on trapping sets.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com