Patents
Literature
946 results about "Nonlinear distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nonlinear distortion is a term used (in fields such as electronics, audio and telecommunications) to describe the phenomenon of a non-linear relationship between the "input" and "output" signals of - for example - an electronic device.
System and methods for recognizing sound and music signals in high noise and distortion
ActiveUS6990453B2High of distortionHigh levelGearworksMusical toysNonlinear distortionLinear correlation
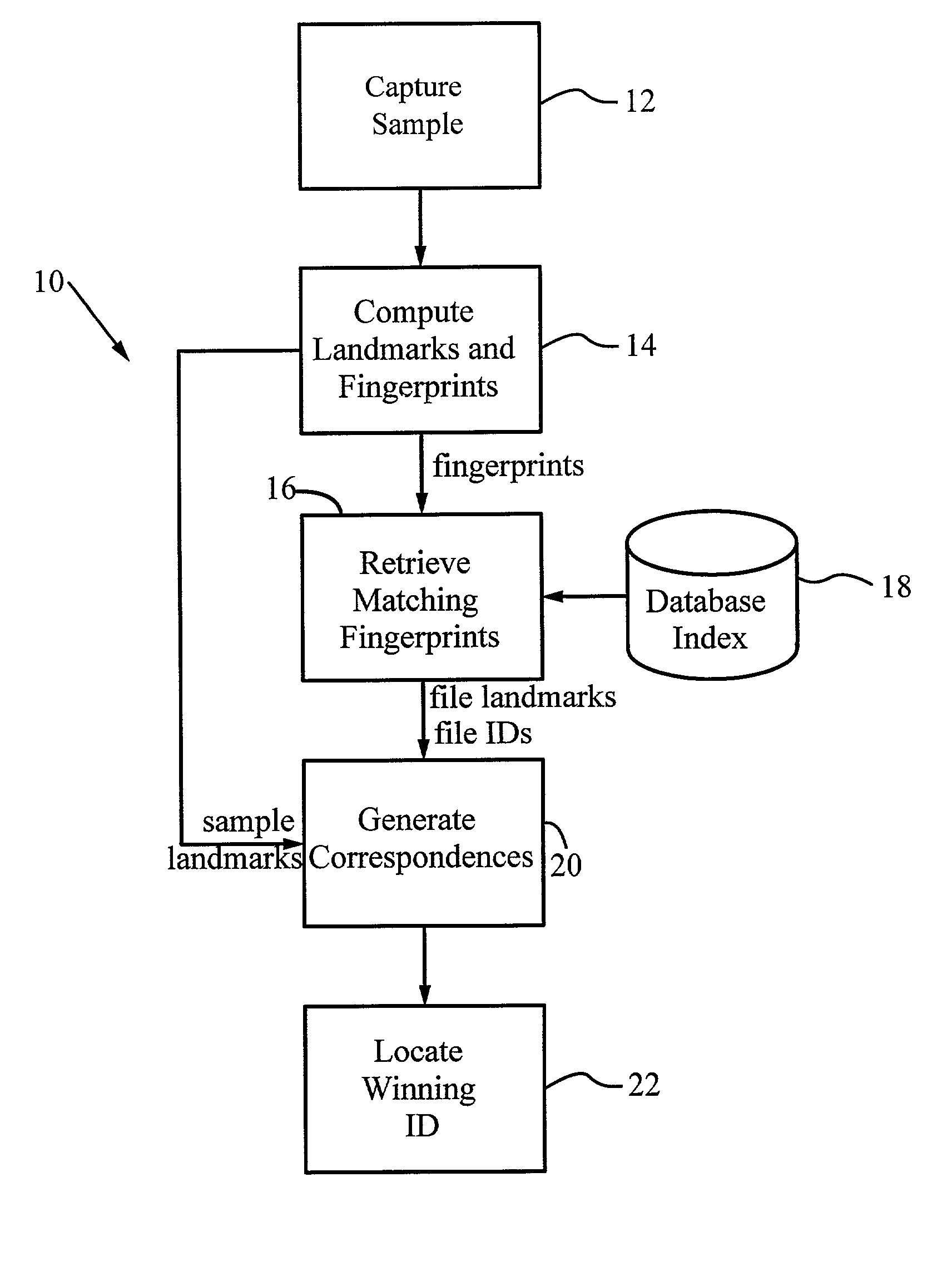
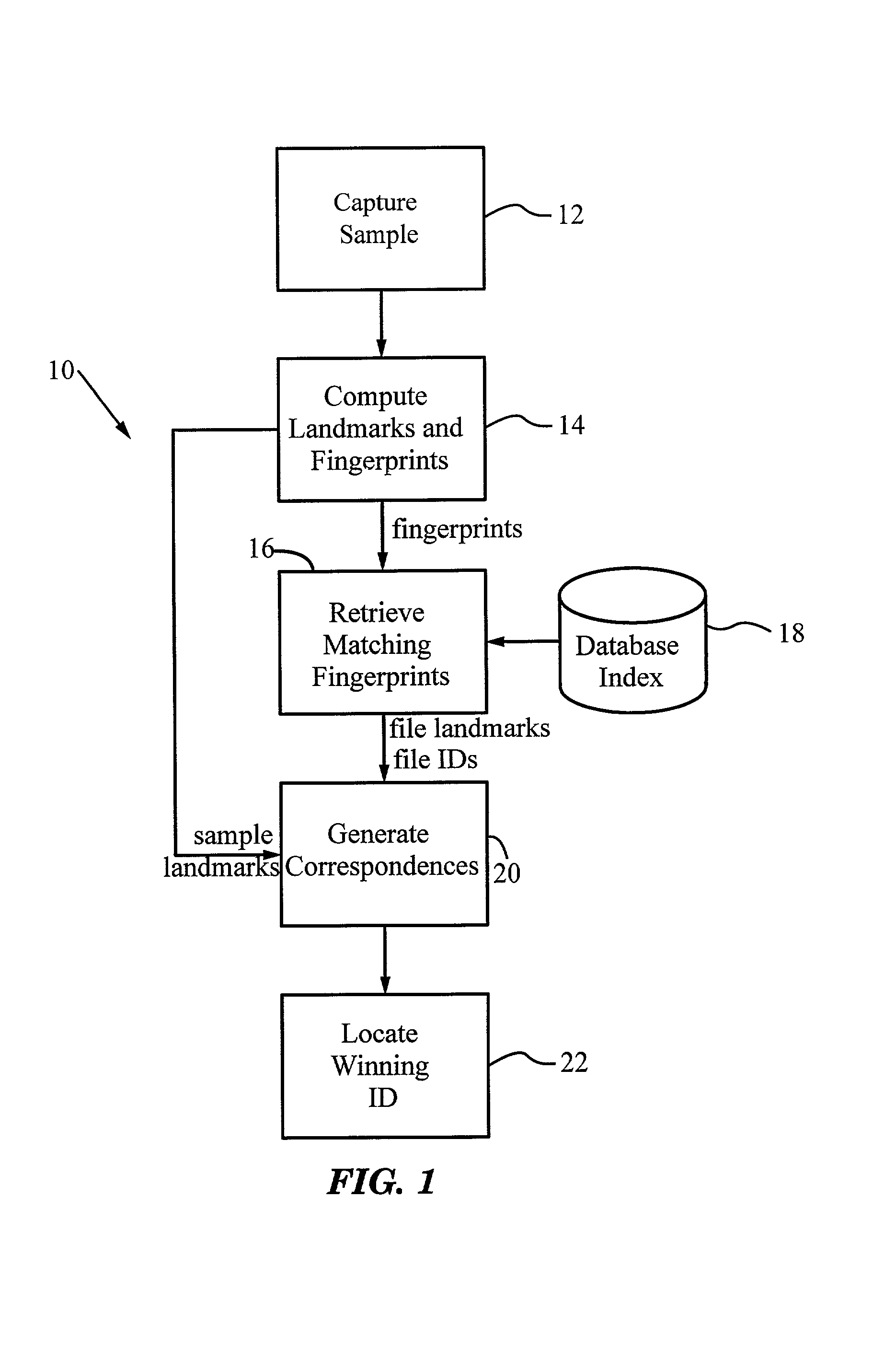
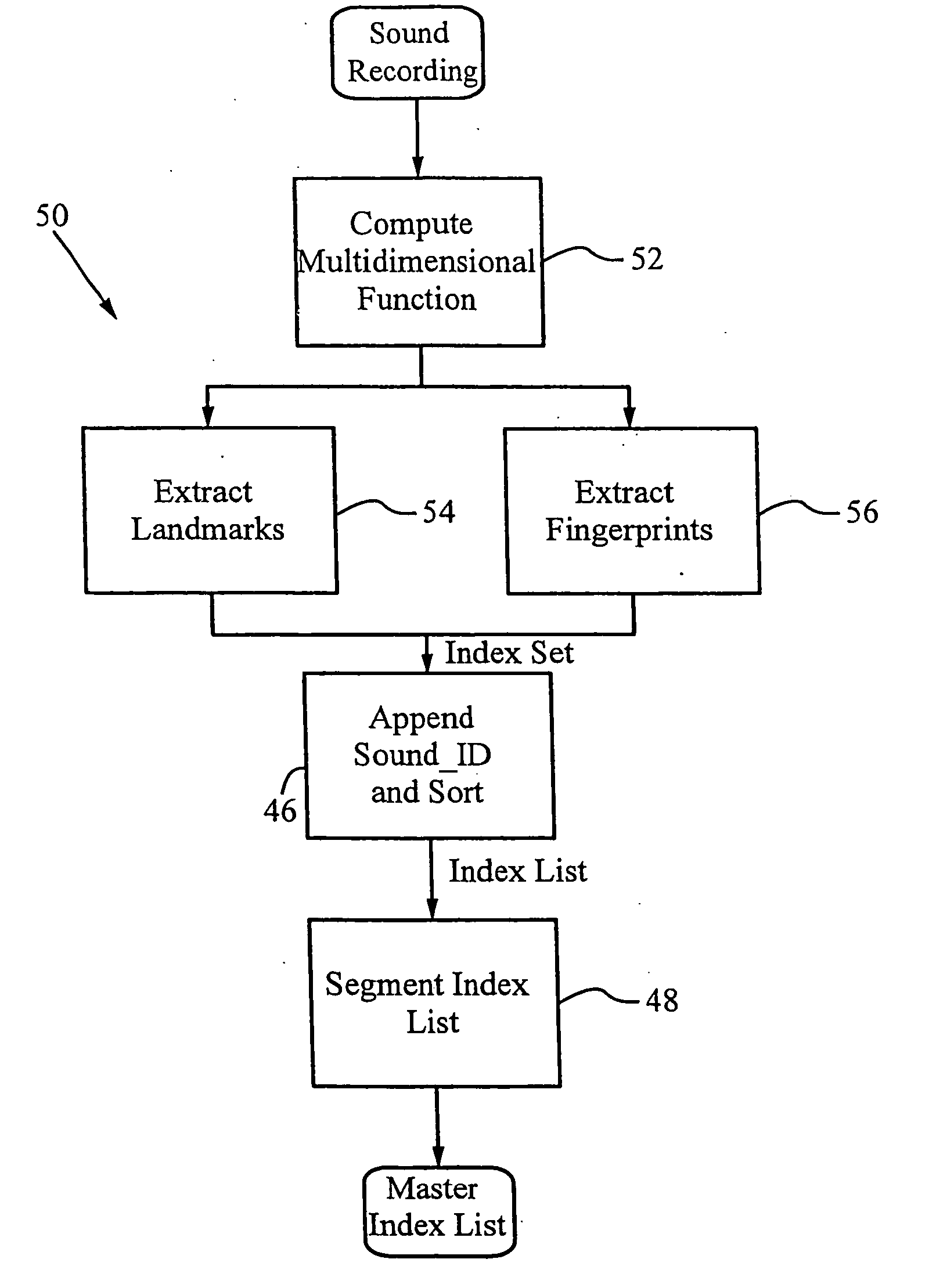
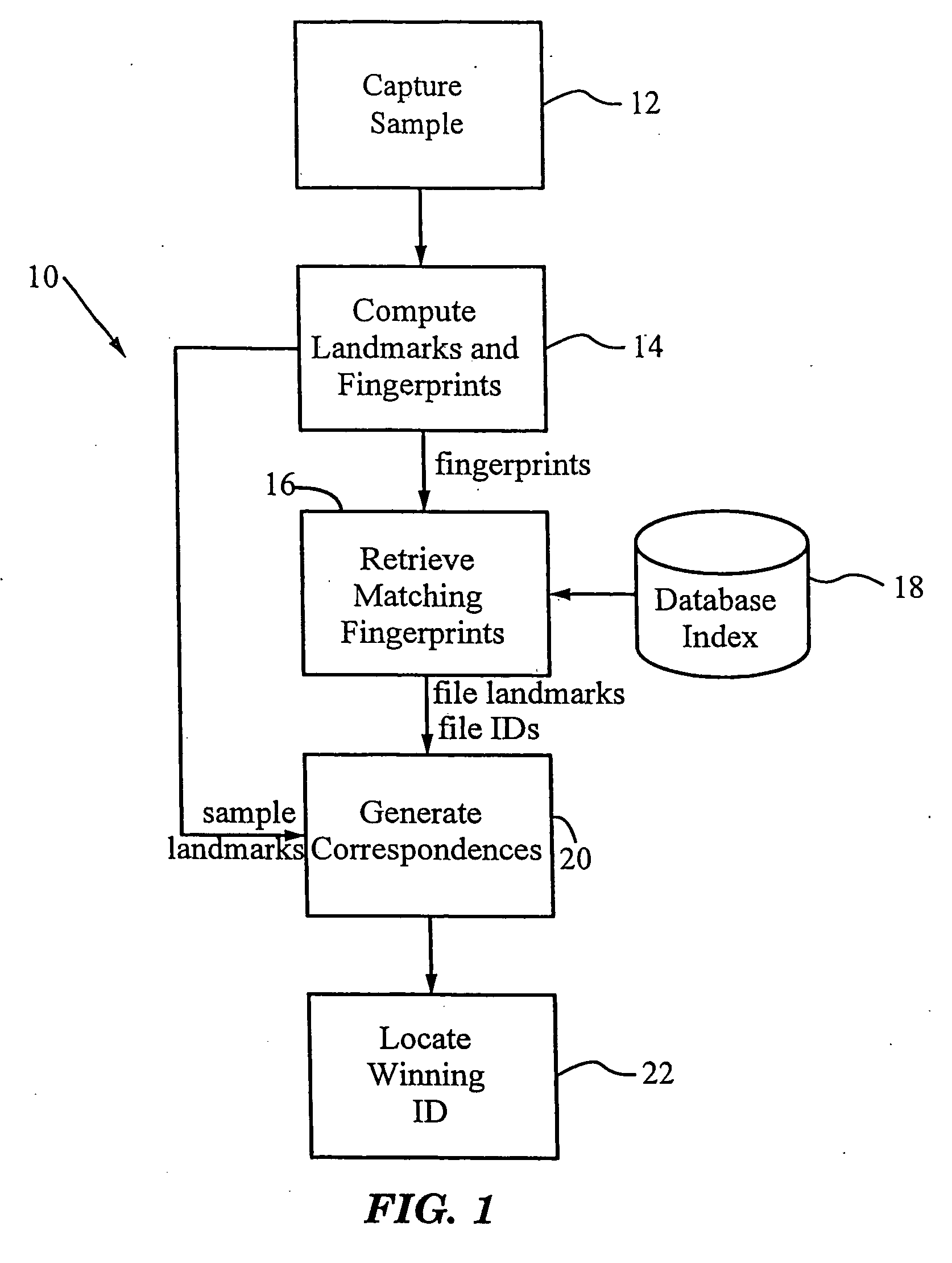
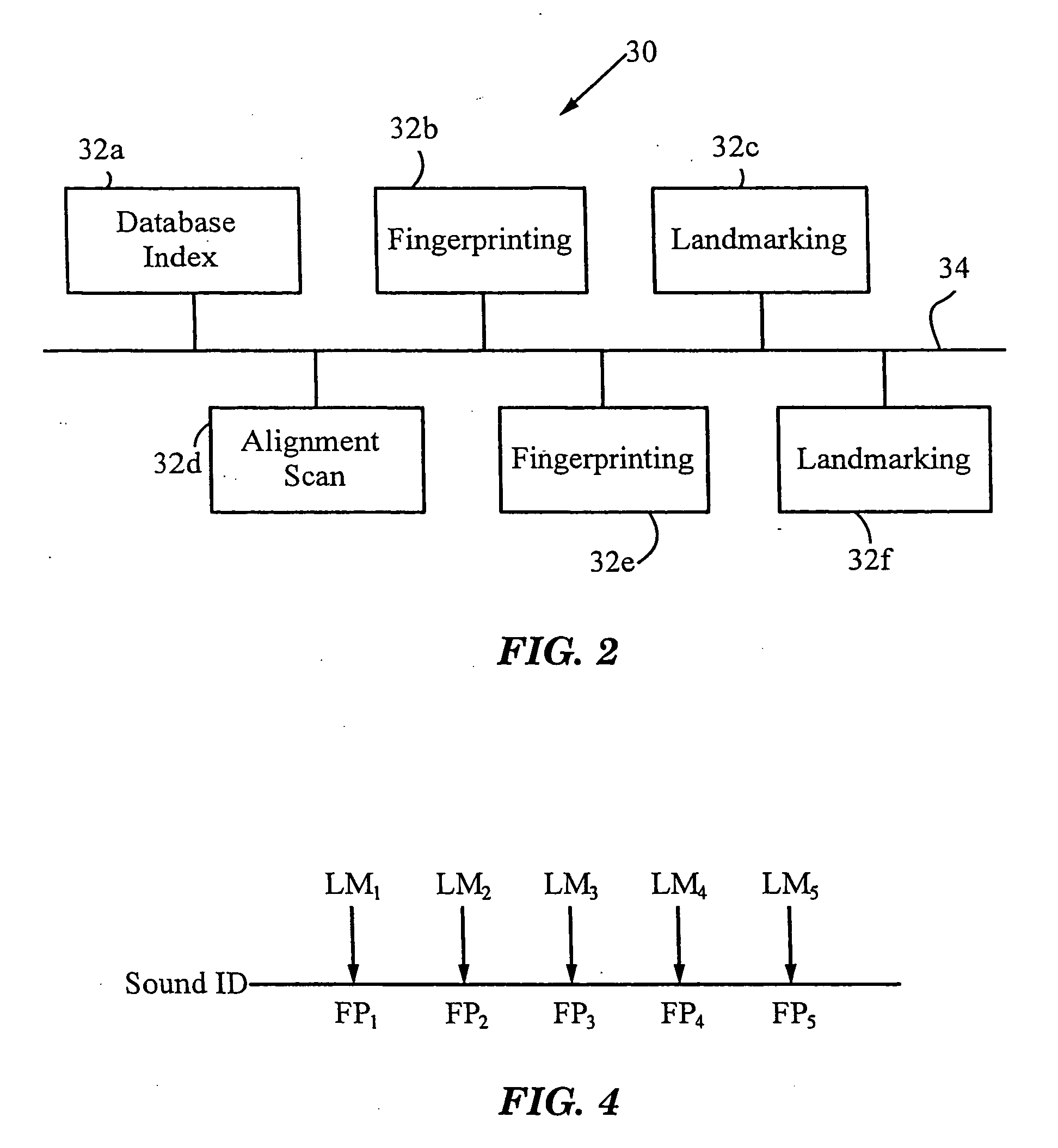
A method for recognizing an audio sample locates an audio file that most closely matches the audio sample from a database indexing a large set of original recordings. Each indexed audio file is represented in the database index by a set of landmark timepoints and associated fingerprints. Landmarks occur at reproducible locations within the file, while fingerprints represent features of the signal at or near the landmark timepoints. To perform recognition, landmarks and fingerprints are computed for the unknown sample and used to retrieve matching fingerprints from the database. For each file containing matching fingerprints, the landmarks are compared with landmarks of the sample at which the same fingerprints were computed. If a large number of corresponding landmarks are linearly related, i.e., if equivalent fingerprints of the sample and retrieved file have the same time evolution, then the file is identified with the sample. The method can be used for any type of sound or music, and is particularly effective for audio signals subject to linear and nonlinear distortion such as background noise, compression artifacts, or transmission dropouts. The sample can be identified in a time proportional to the logarithm of the number of entries in the database; given sufficient computational power, recognition can be performed in nearly real time as the sound is being sampled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Communication methods and systems for nonlinear multi-user environments
InactiveUS20150207527A1Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsNonlinear distortionMulti user environment
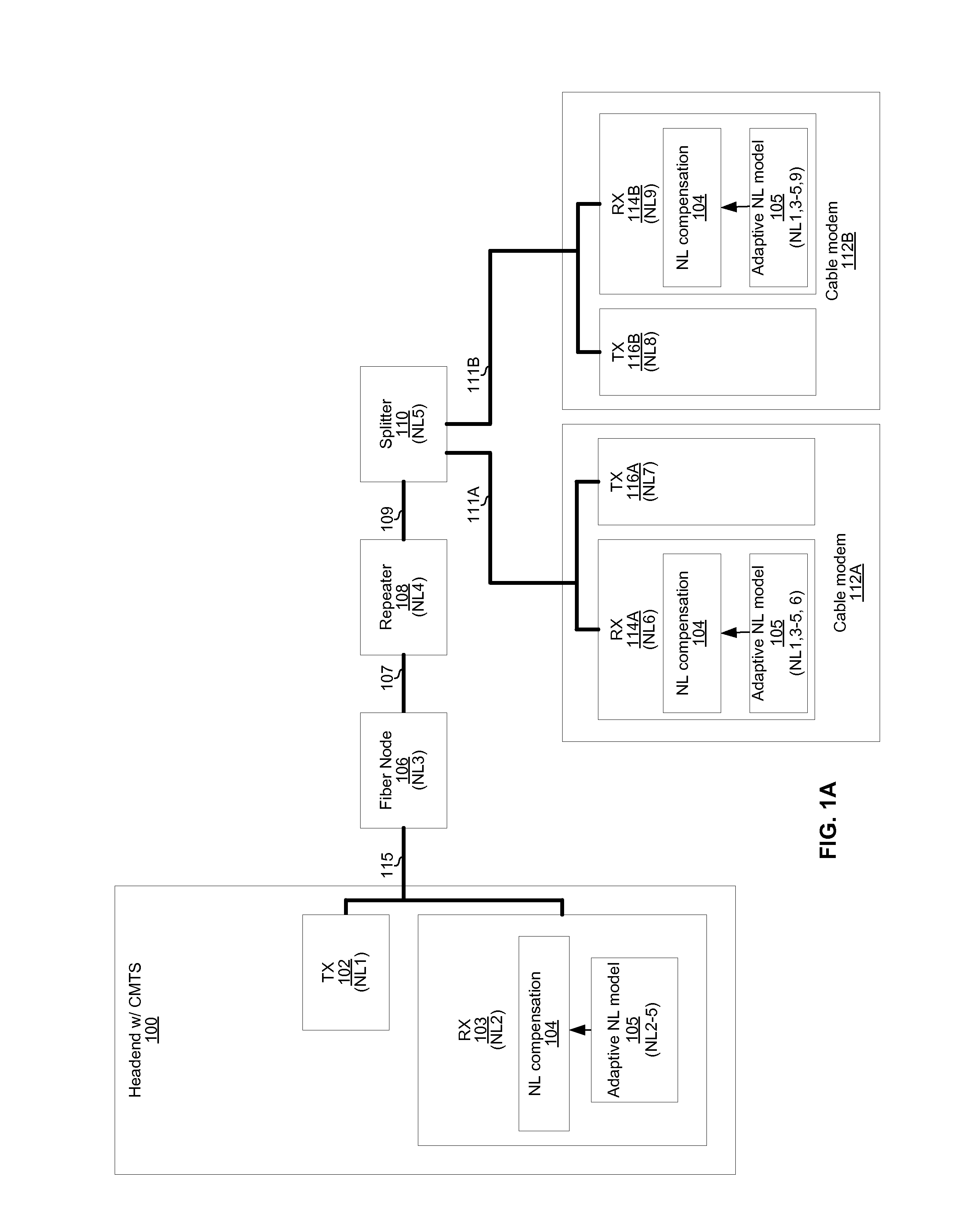
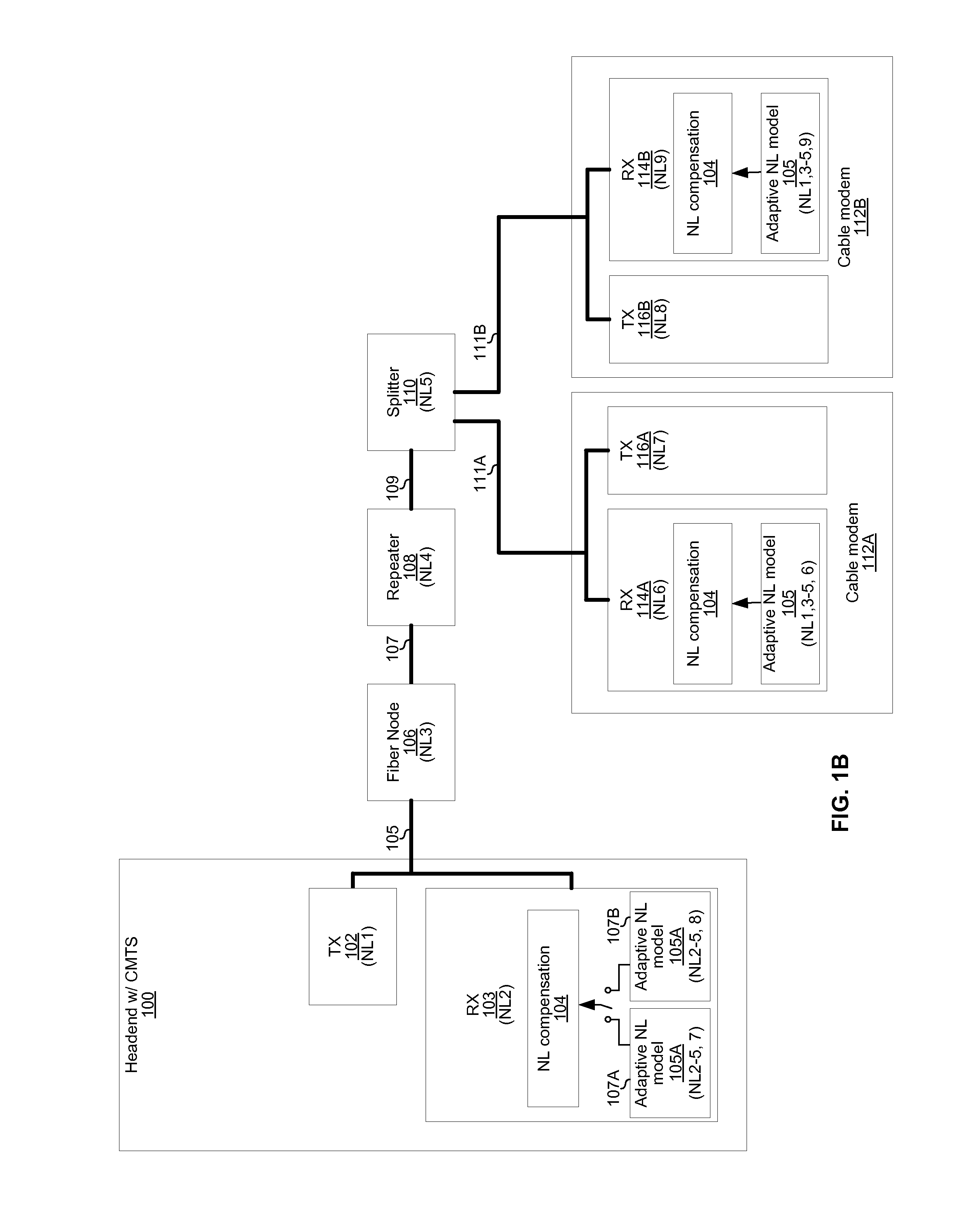
An electronic receiver comprises a nonlinear distortion modeling circuit and a nonlinear distortion compensation circuit. The nonlinear distortion modeling circuit is operable to determine a plurality of sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values, where each of the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values representing nonlinear distortion experienced by signals received by the electronic receiver from a respective one a plurality of communication partners. The nonlinear distortion compensation circuit is operable to use the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values for processing of signals from the plurality of communication partners. Each of the sets of nonlinear distortion model parameter values may comprises a plurality of values corresponding to a plurality of signal powers. The sets of nonlinear distortion model parameters may be stored in a lookup table indexed by a signal strength parameter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Estimation of non-linear distortion in memory devices
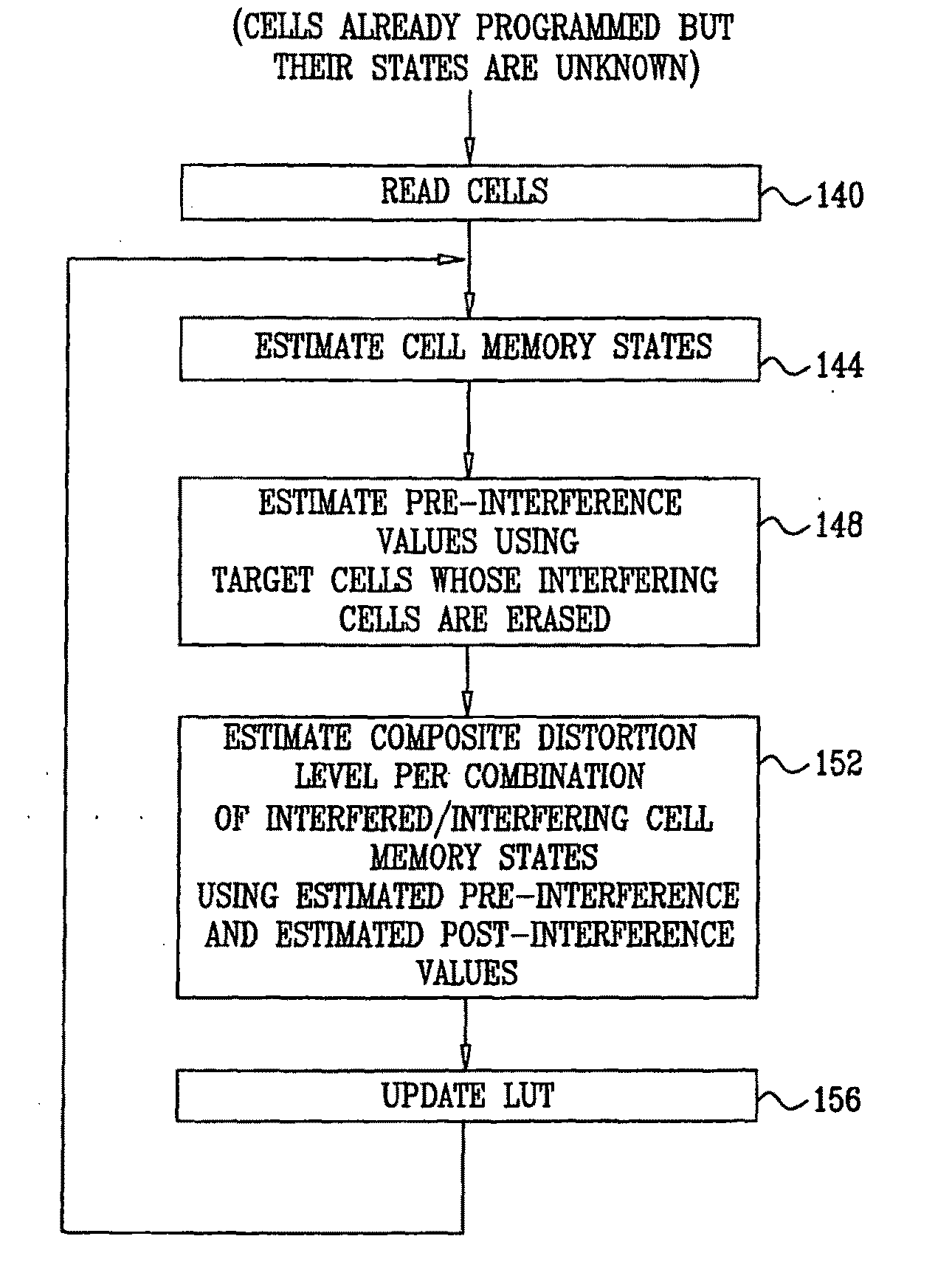
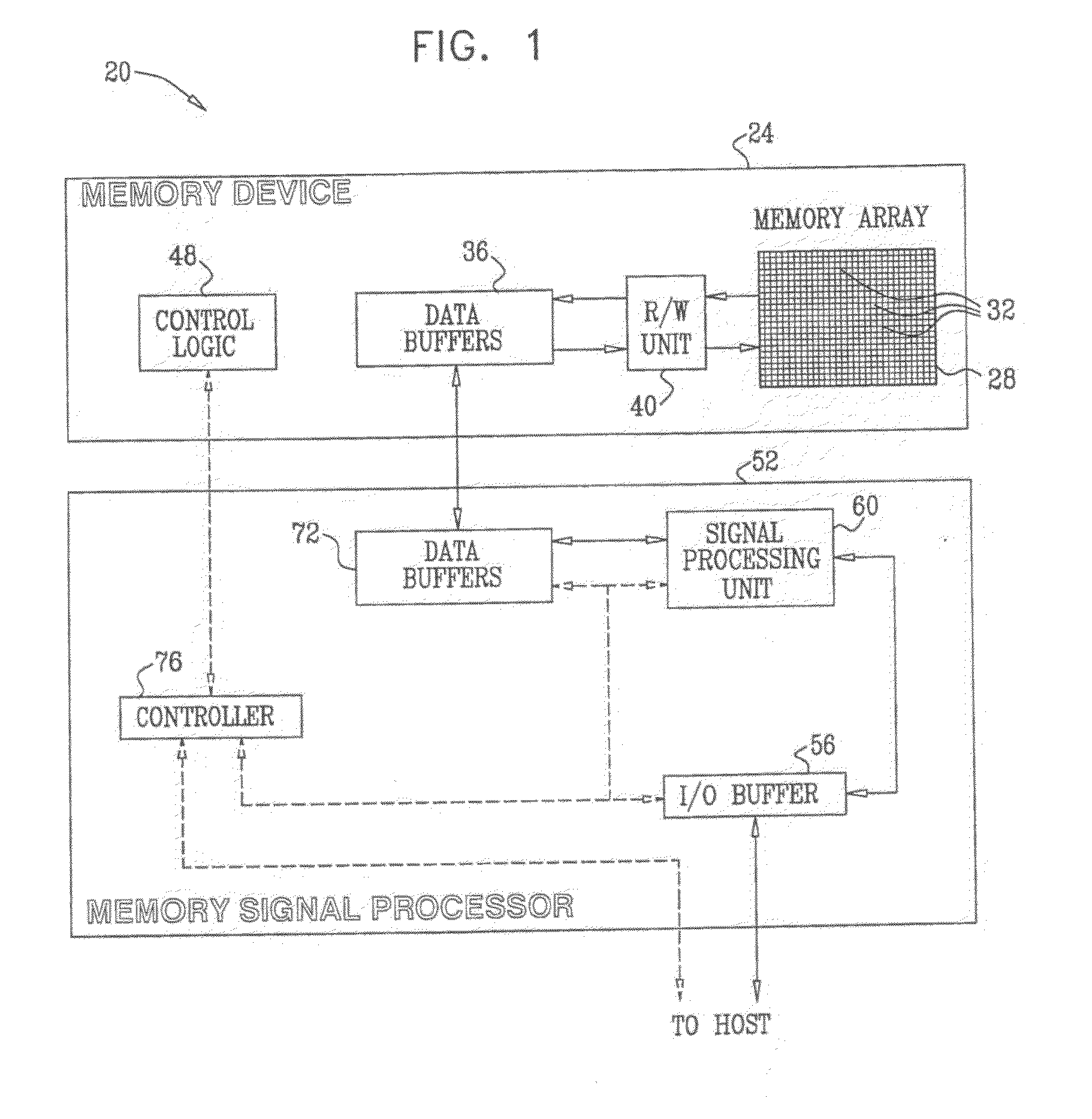
A method for operating a memory (24) includes storing data in analog memory cells (32) of the memory by writing respective analog values to the analog memory cells. A set of the analog memory cells is identified, including an interfered cell having a distortion that is statistically correlated with the respective analog values of the analog memory cells in the set. A mapping is determined between combinations of possible analog values of the analog memory cells in the set and statistical characteristics of composite distortion levels present in the interfered memory cell. The mapping is applied so as to compensate for the distortion in the interfered memory cell.
Owner:APPLE INC
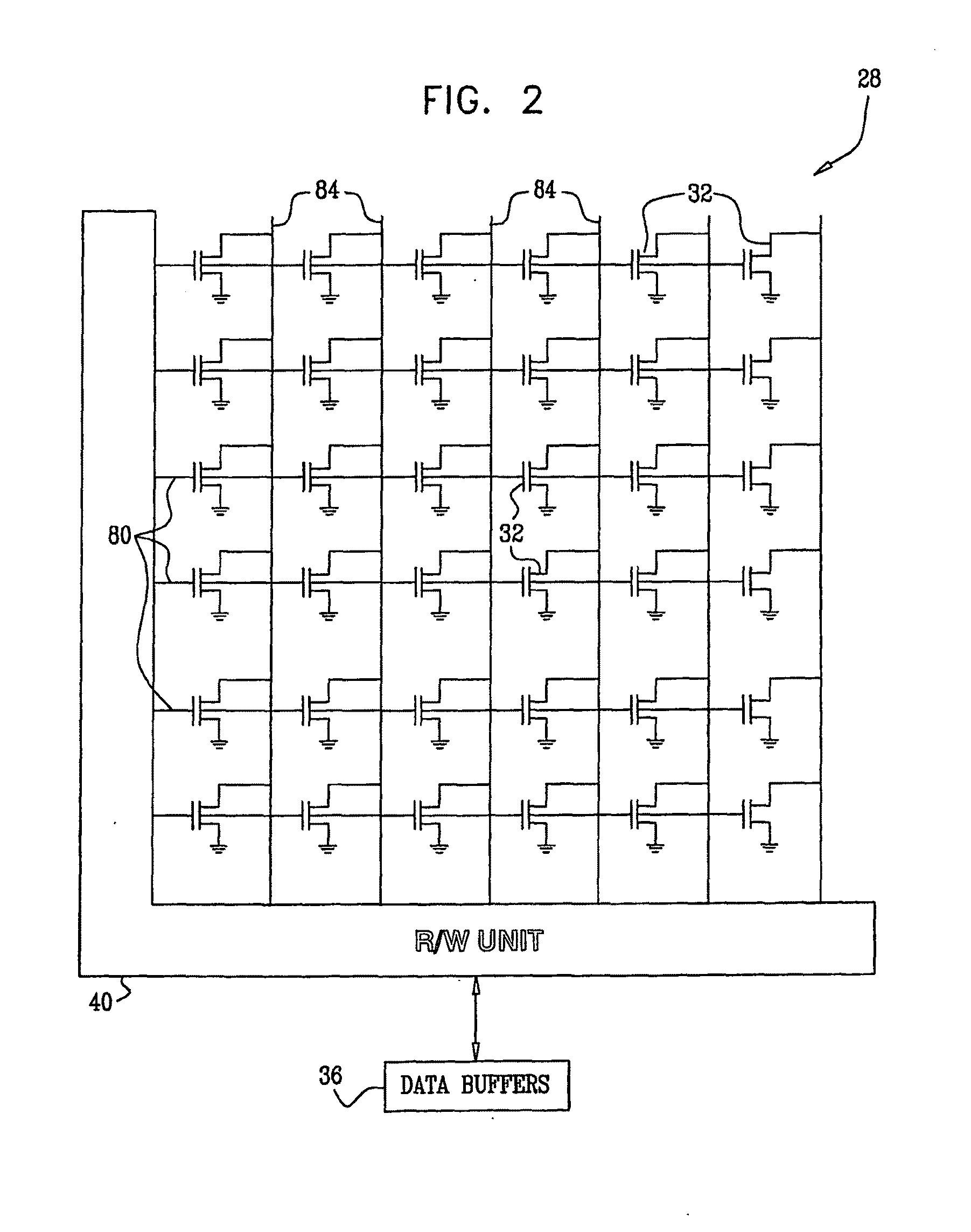
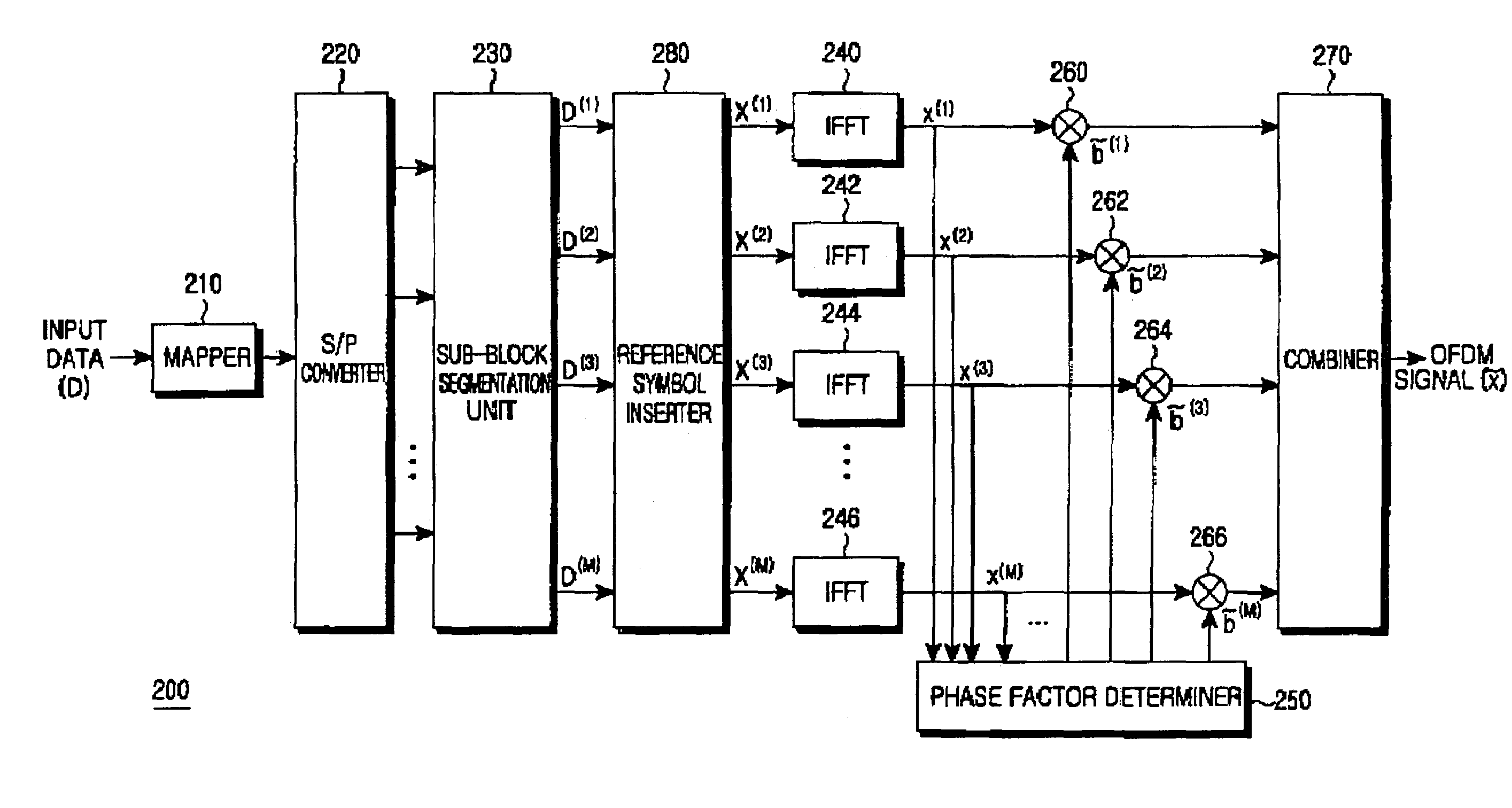
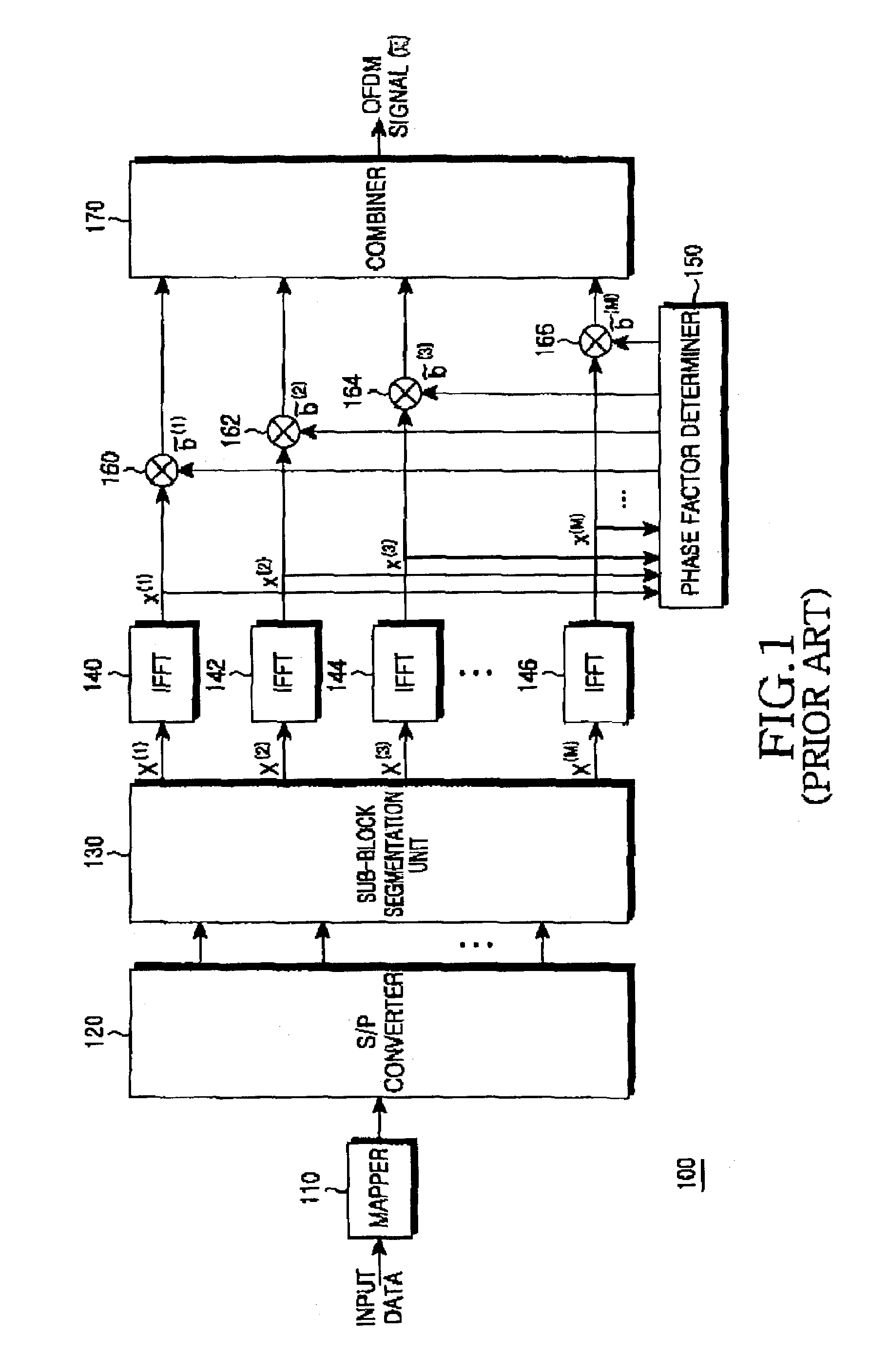
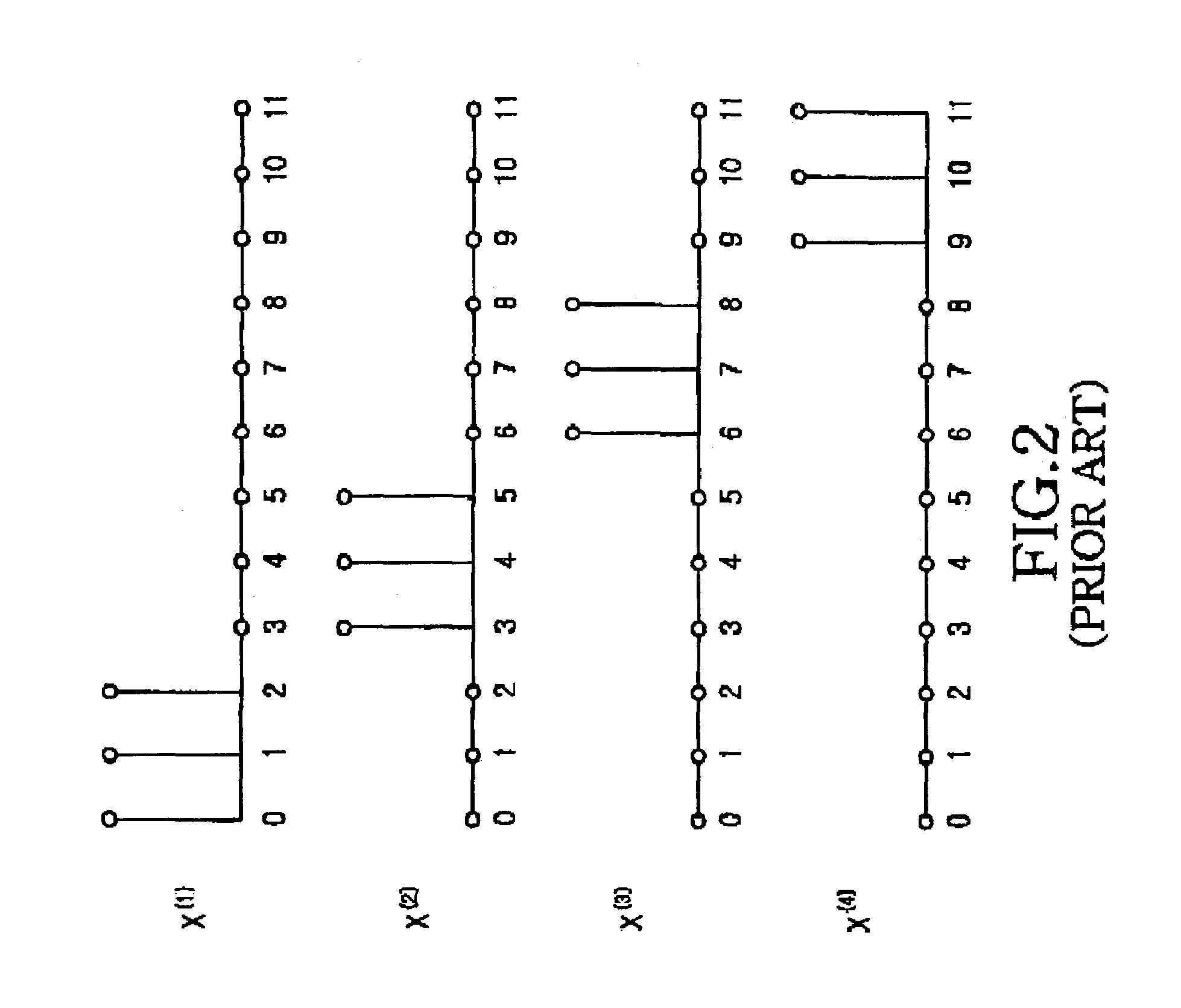
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving side information of a partial transmit sequence in an OFDM communication system
ActiveUS7376074B2Minimizing PAPRFrequency-division multiplexCode division multiplexNonlinear distortionData stream
An OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) communication system that multiplexes data with a plurality of orthogonal sub-carrier frequencies, which includes a transmitter for converting a serial data stream into parallel data, and segmenting the parallel data into a plurality of blocks having a plurality of data blocks; inserting reference data having information representing a phase value and a position into which the reference symbol is inserted, into each of the segmented blocks; IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform)-transforming the respective blocks into time-based signals where sub-carrier frequencies are separately assigned to the data blocks; and determining phase factors of the IFFT-transformed time-based signals to reduce a peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) where non-linear distortion occurs due to coincidence of phases of the data blocks IFFT-transformed with the sub-carrier frequencies, and phase-rotating the IFFT-transformed signals according to the determined phase factors before transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
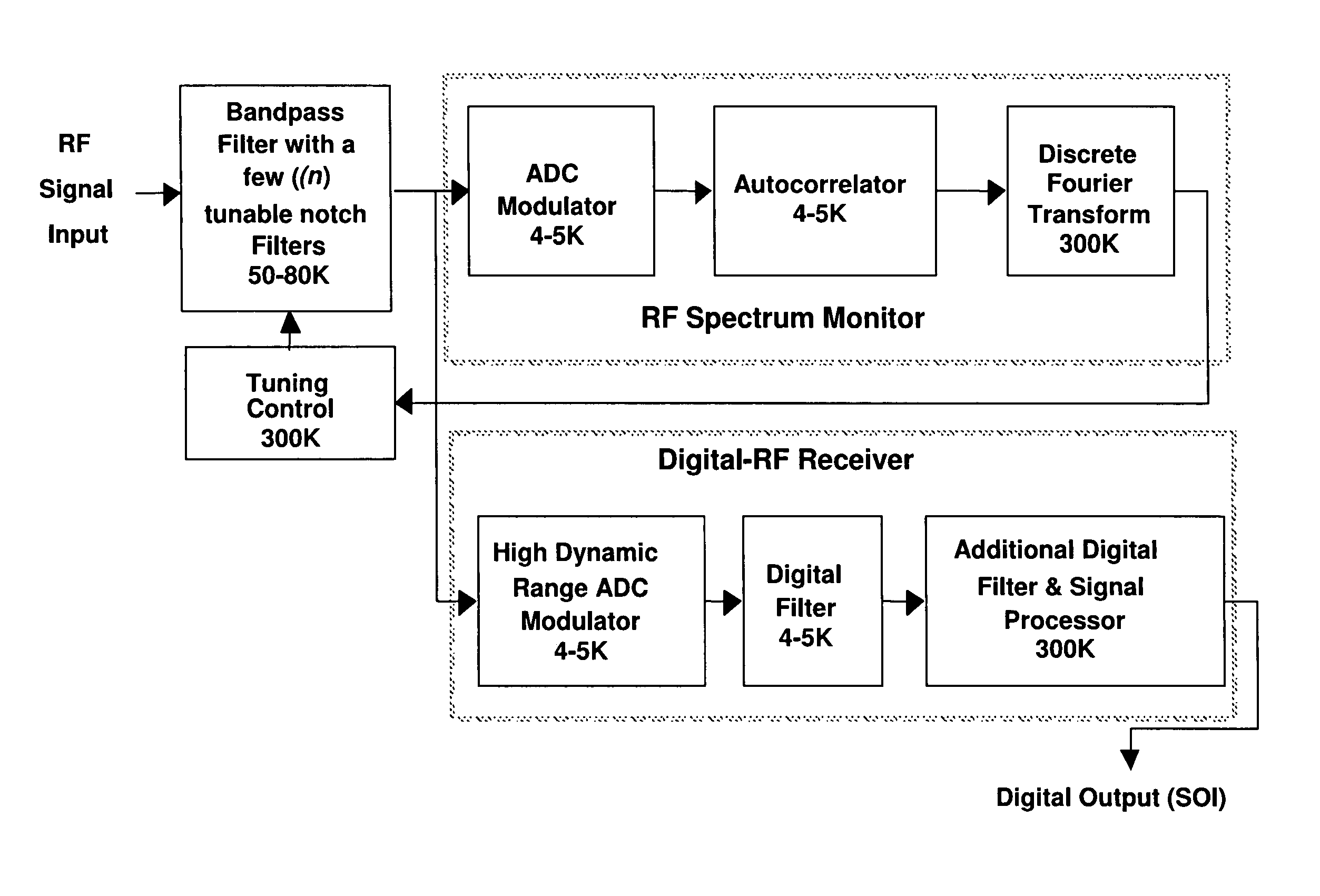
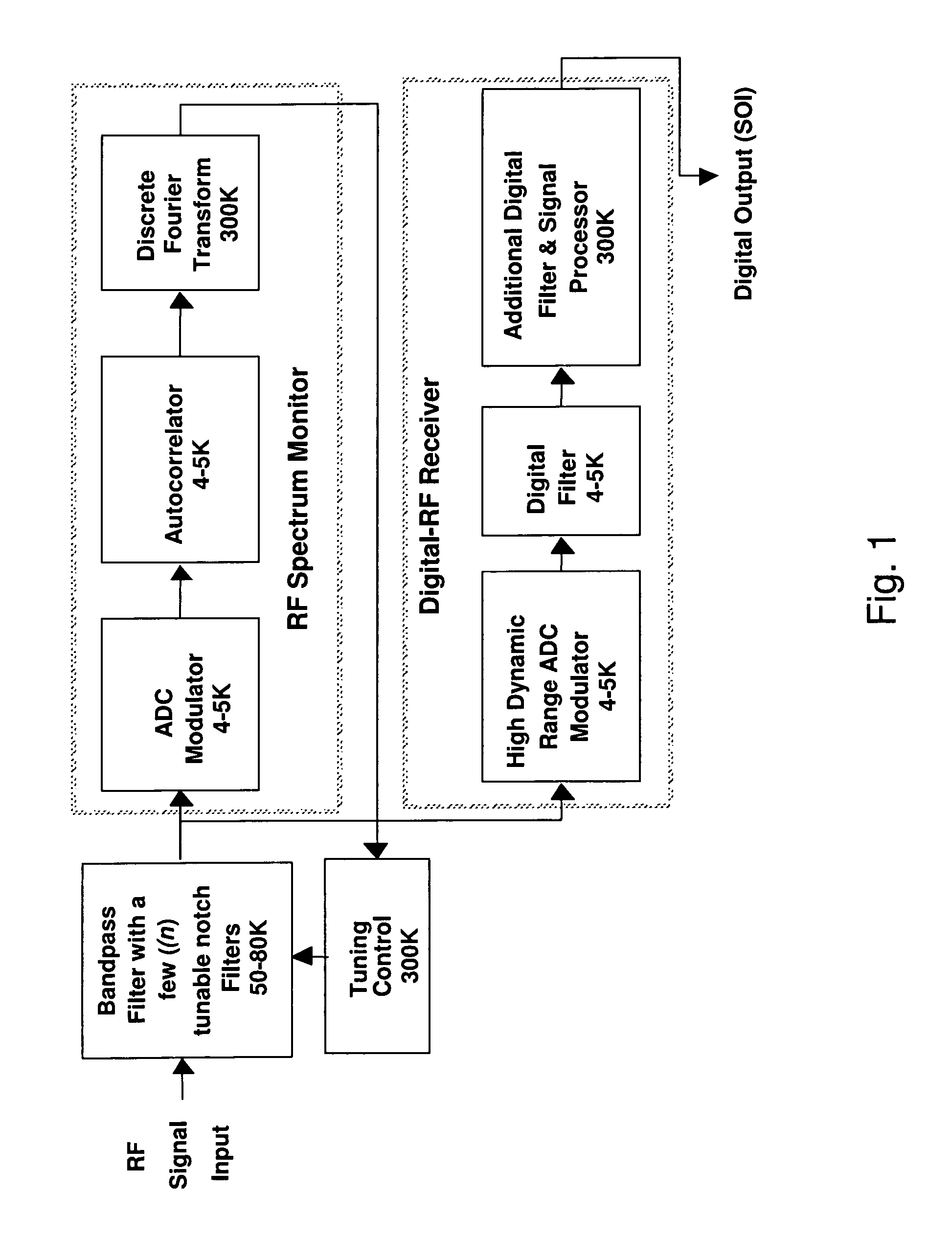
Wideband digital spectrometer
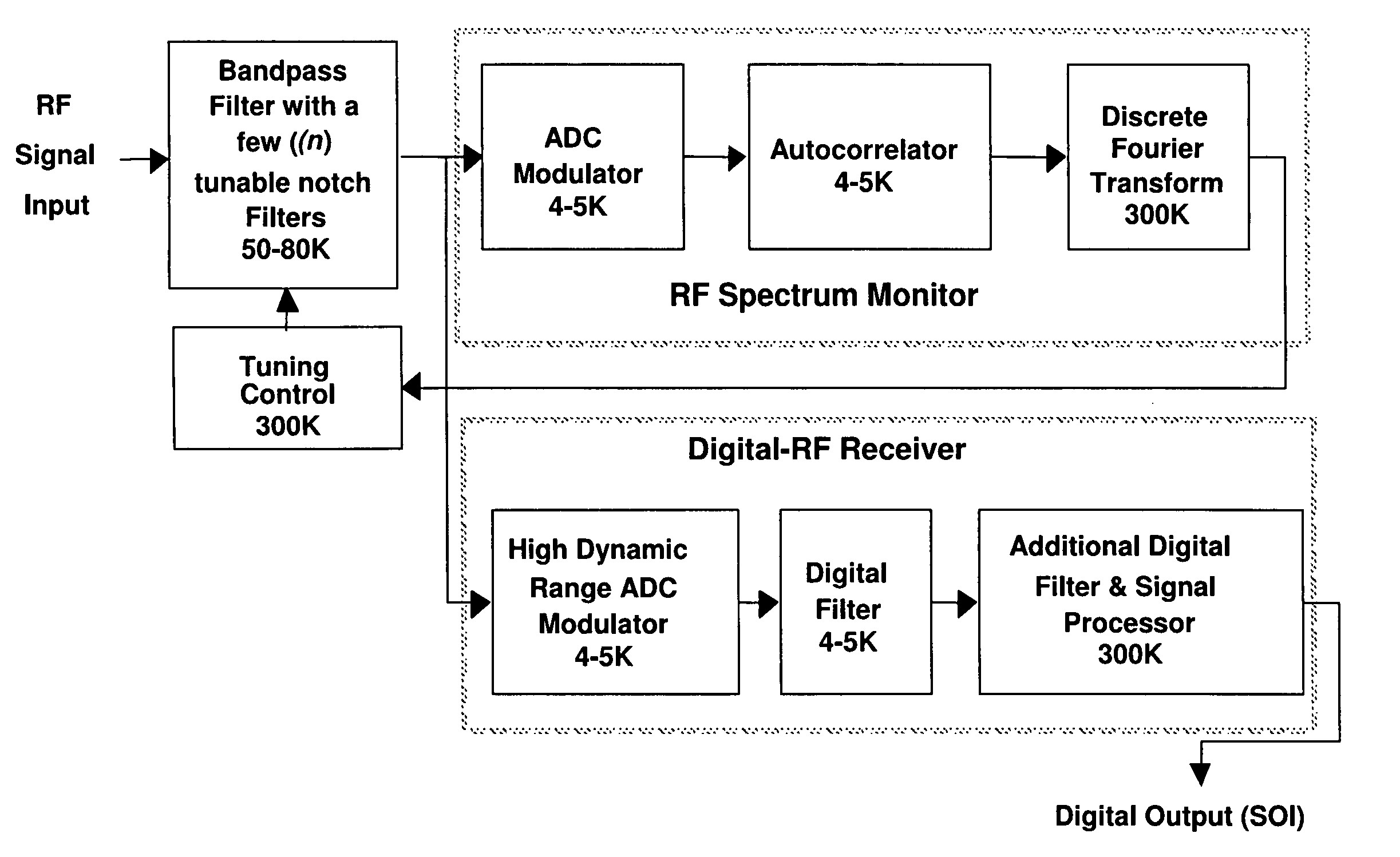
ActiveUS8045660B1Improve linearityIncrease speedTransmissionNonlinear distortionDigital signal processing
A method for reducing interference, comprising receiving a wideband signal, having at least one large amplitude component; adaptively modifying the wideband signal with respect to at least one high intensity component without substantial introduction of non-linear distortion, while reducing a residual dynamic range thereof; digitizing the modified wideband signal to capture information describing at least the high intensity signal at a sampling rate sufficient to extract modulated information present within the wideband signal at an upper limit of the band. The system analyzes a spectral characteristic of the wideband signal; and extracts adaptation parameters for the adaptive filtering. The system therefore provides both large net dynamic range and wideband operation. Preferably, the digitizer and filter, and part of the spectral characteristic analyzer is implemented in using superconducting circuit technology, with, for example low temperature superconducting digital signal processing components, and high temperature superconducting analog filtering components.
Owner:HYPRES
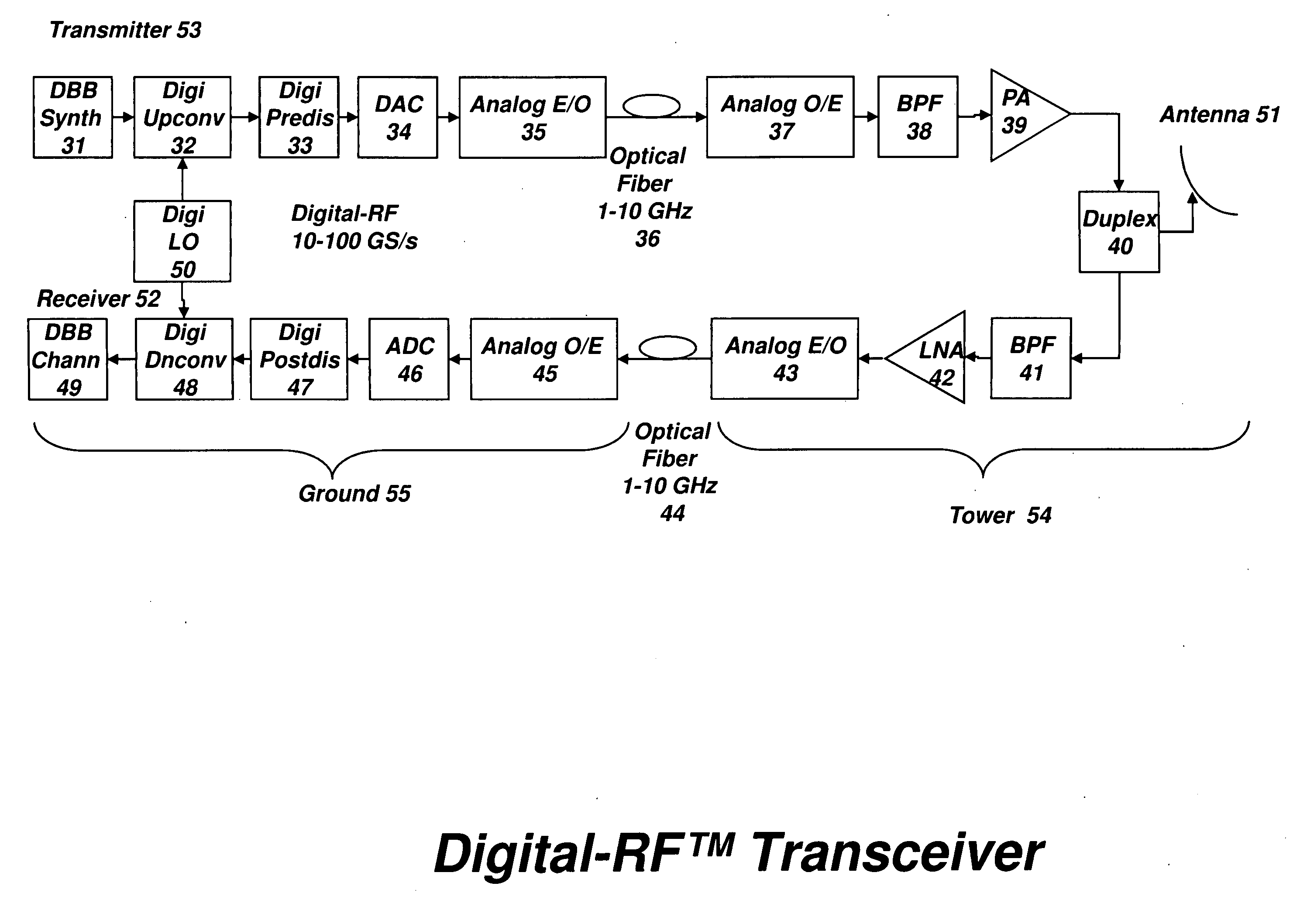
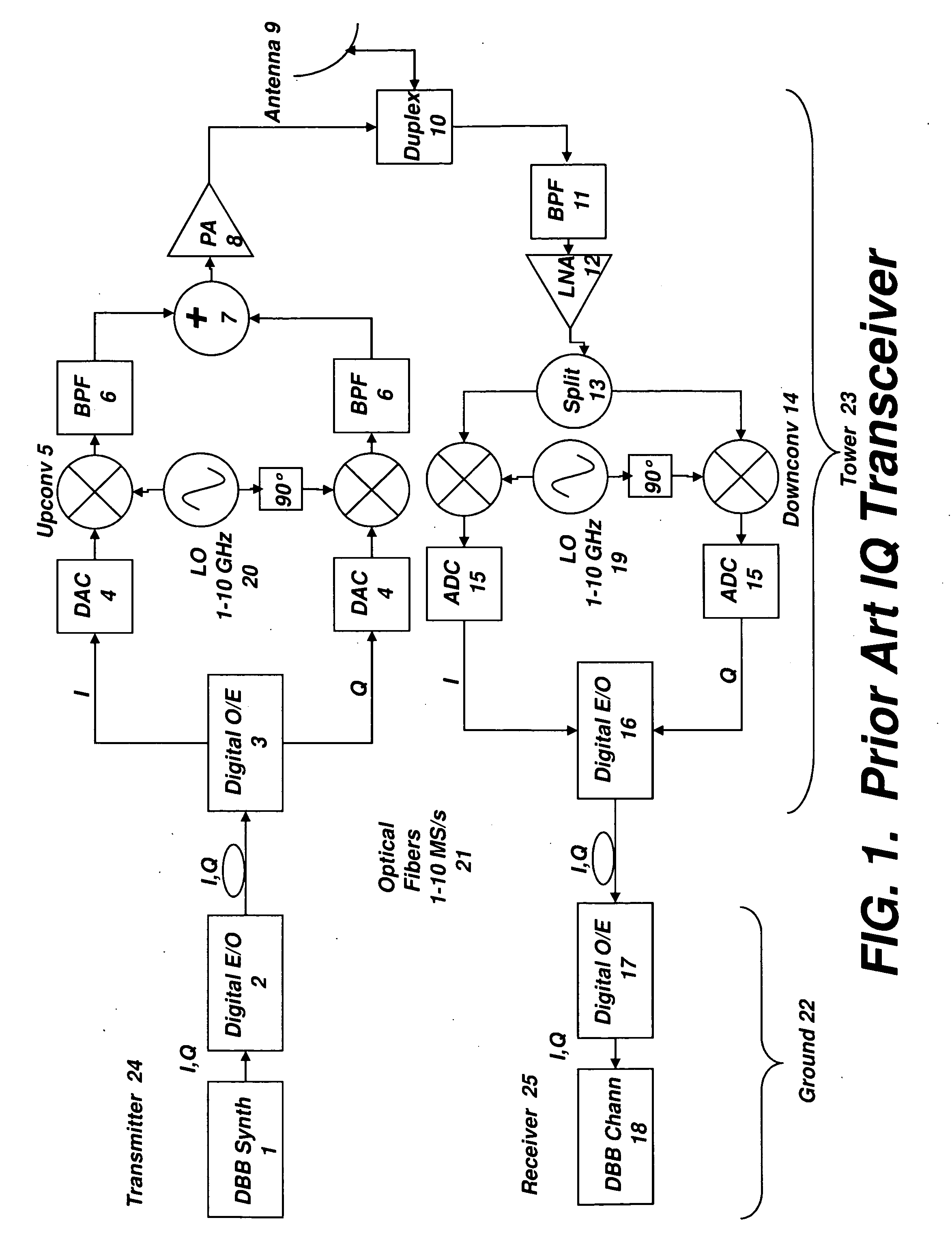
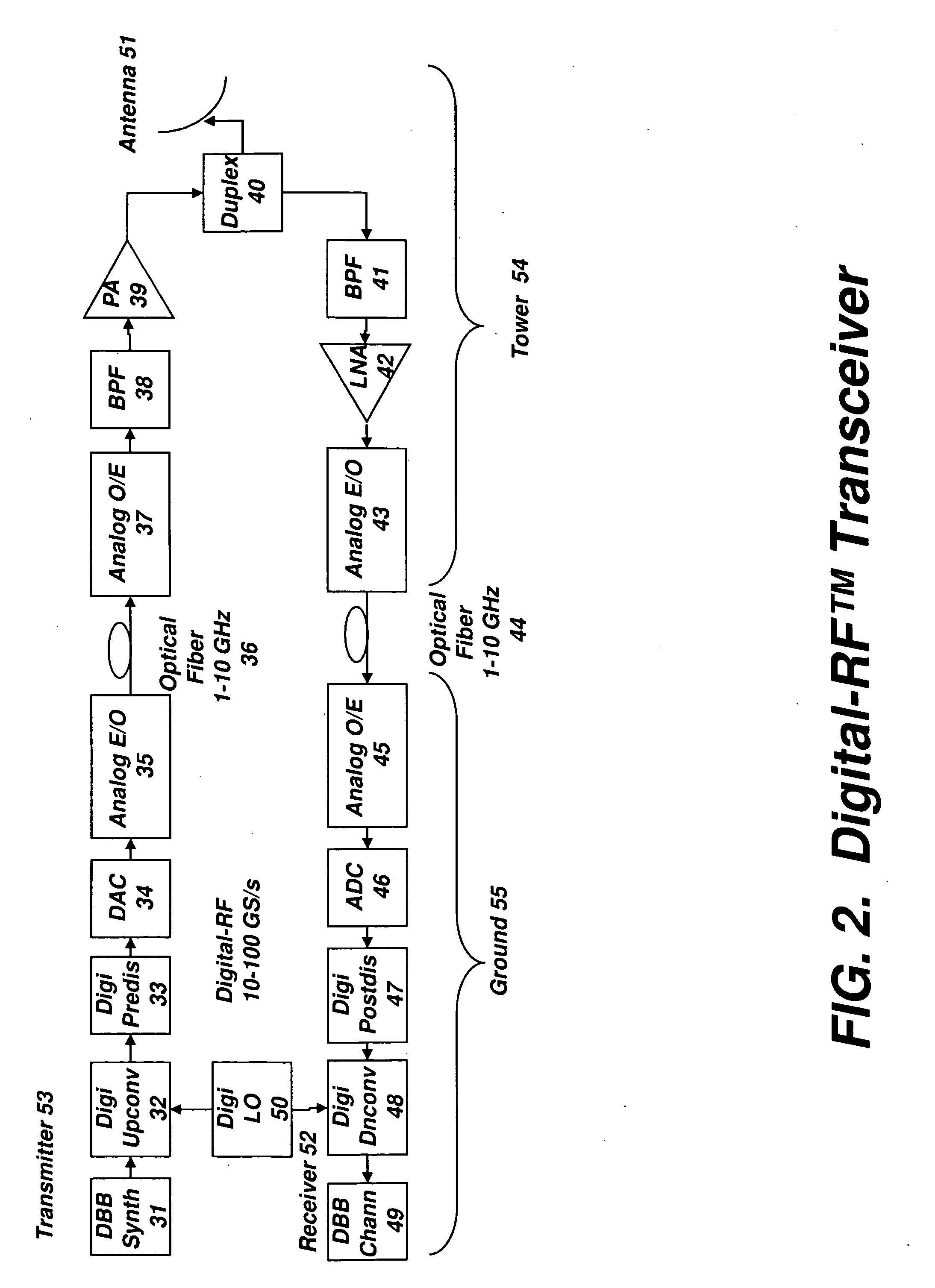
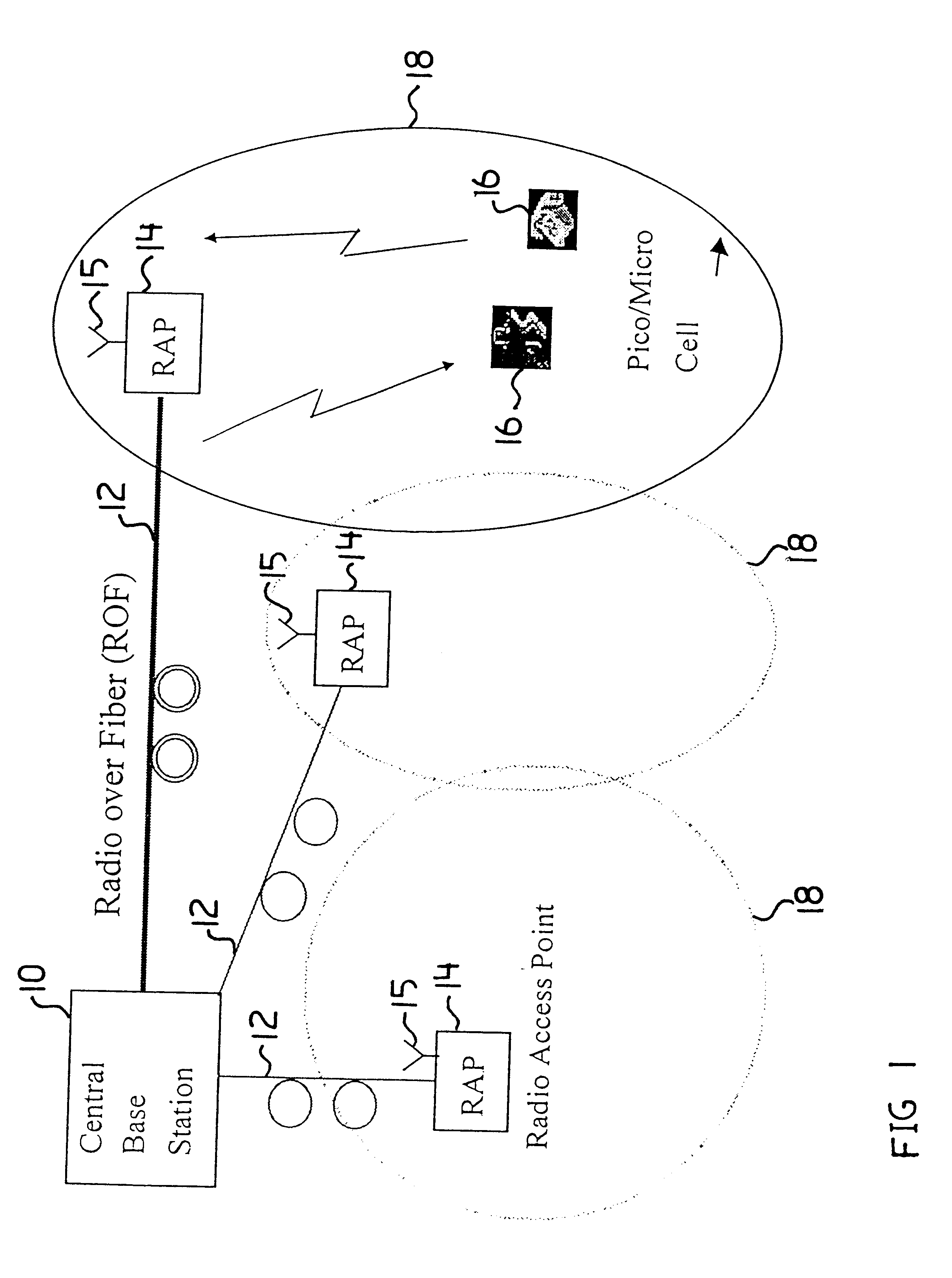
Digital radio frequency tranceiver system and method
ActiveUS20090232191A1Function increaseEfficient and effective communication of signalModulated-carrier systemsRadio-over-fibreDigital dataNonlinear distortion
A transceiver architecture for wireless base stations wherein a broadband radio frequency signal is carried between at least one tower-mounted unit and a ground-based unit via optical fibers, or other non-distortive media, in either digital or analog format. Each tower-mounted unit (for both reception and transmission) has an antenna, analog amplifier and an electro-optical converter. The ground unit has ultrafast data converters and digital frequency translators, as well as signal linearizers, to compensate for nonlinear distortion in the amplifiers and optical links in both directions. In one embodiment of the invention, at least one of the digital data converters, frequency translators, and linearizers includes superconducting elements mounted on a cryocooler.
Owner:HYPRES
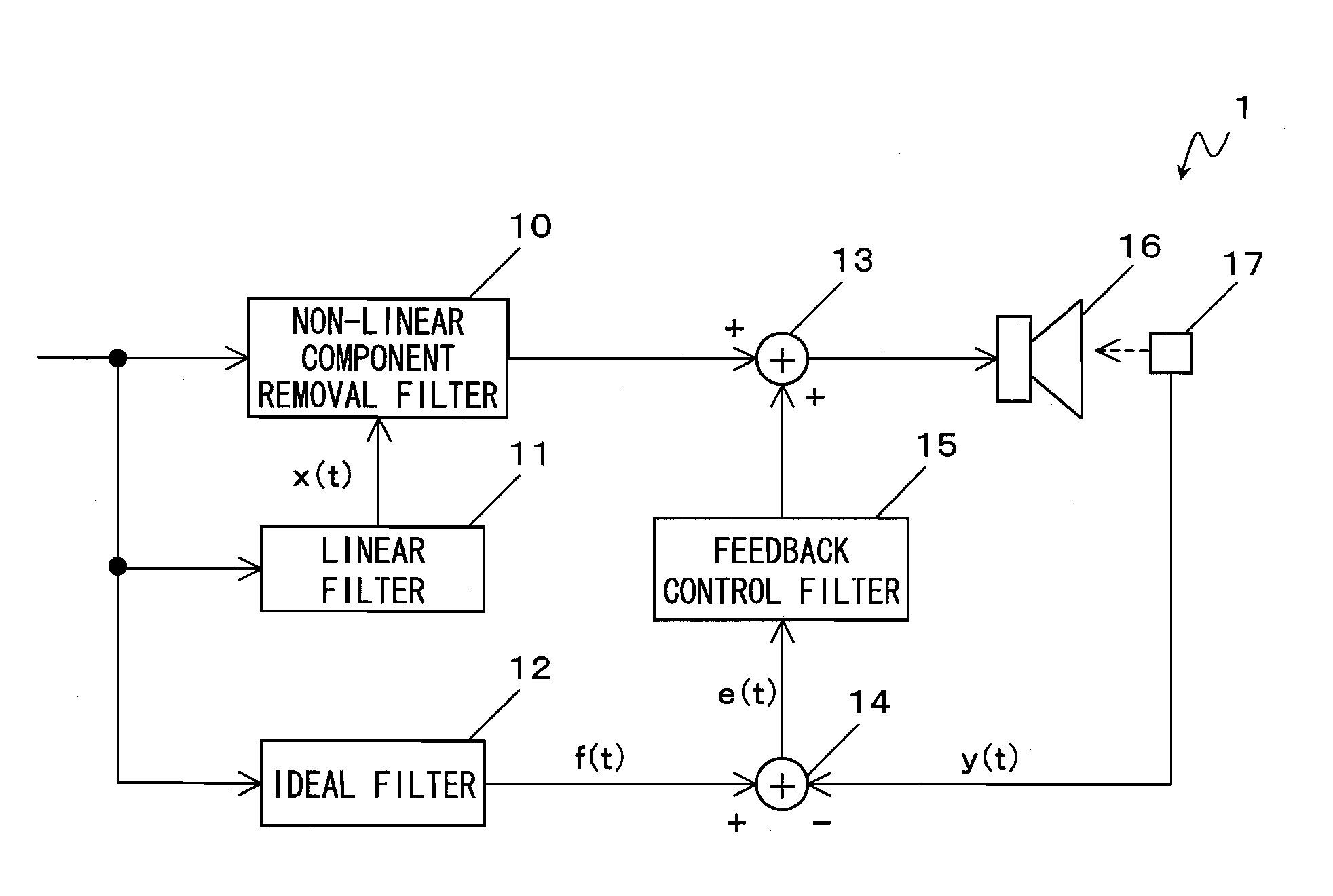
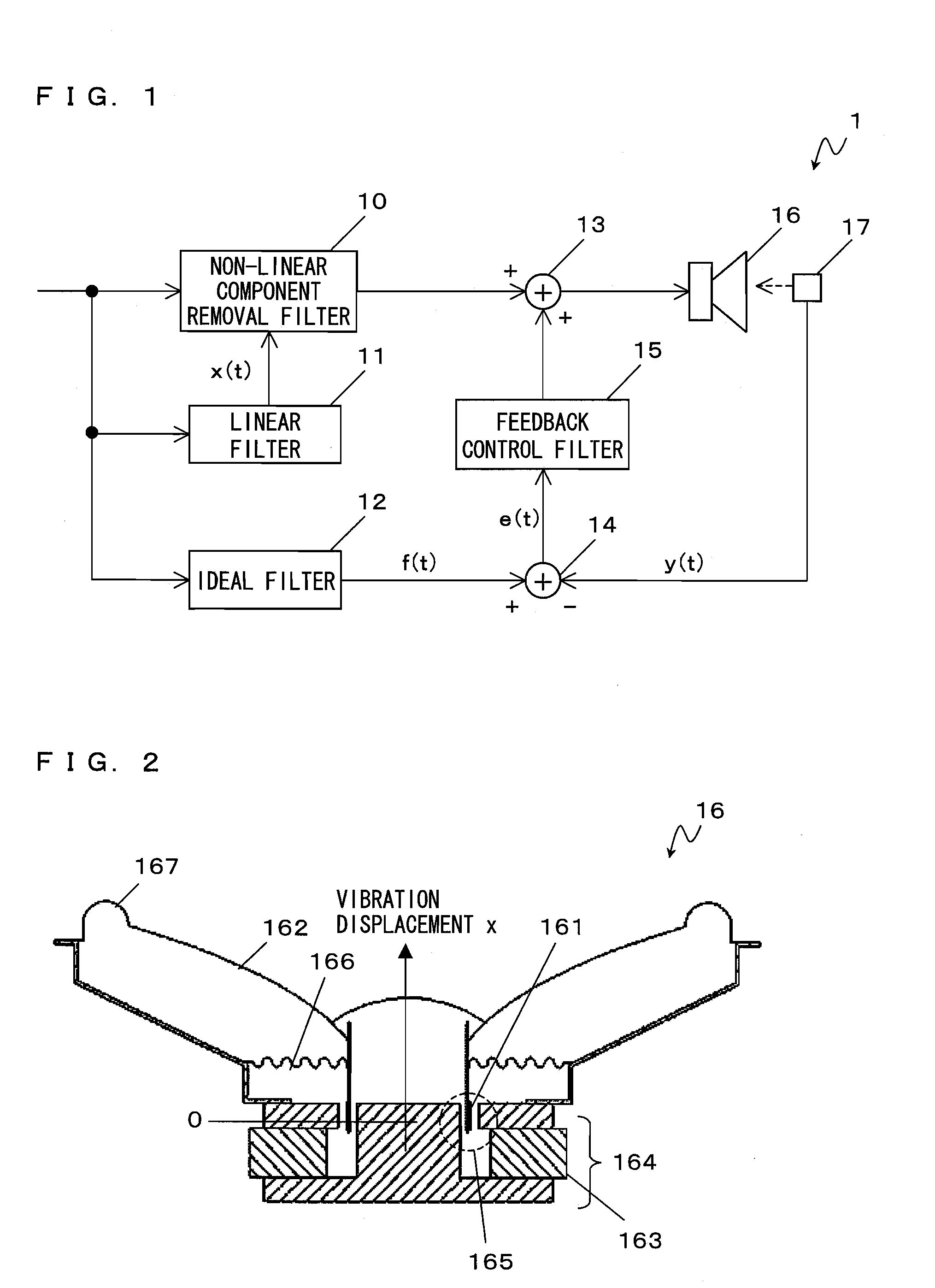
Loudspeaker device
ActiveUS20100092004A1Stable distortion removal processingHigh feasibilityEar treatmentNoise generationNonlinear distortionEngineering
The loudspeaker device according to the present invention comprises a loudspeaker; a feedforward processing section for performing feedforward processing on an electric signal to be inputted to the loudspeaker based on a preset filter coefficient so that non-linear distortion which occurs from the loudspeaker is removed; and a feedback processing section for detecting vibration of the loudspeaker, and performing feedback processing on an electric signal concerning the vibration with respect to the electric signal to be inputted to the loudspeaker. The feedback processing section performs feedback processing on the electric signal concerning the vibration so that the non-linear distortion which occurs from the loudspeaker is removed and so that a frequency characteristic concerning the vibration of the loudspeaker becomes a predetermined frequency characteristic.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Arrangement and method for identifying and compensating nonlinear vibration in an electro-mechanical transducer
ActiveUS20150296299A1Simple structural designImprove performanceFrequency response correctionDeaf-aid setsNonlinear distortionState variable
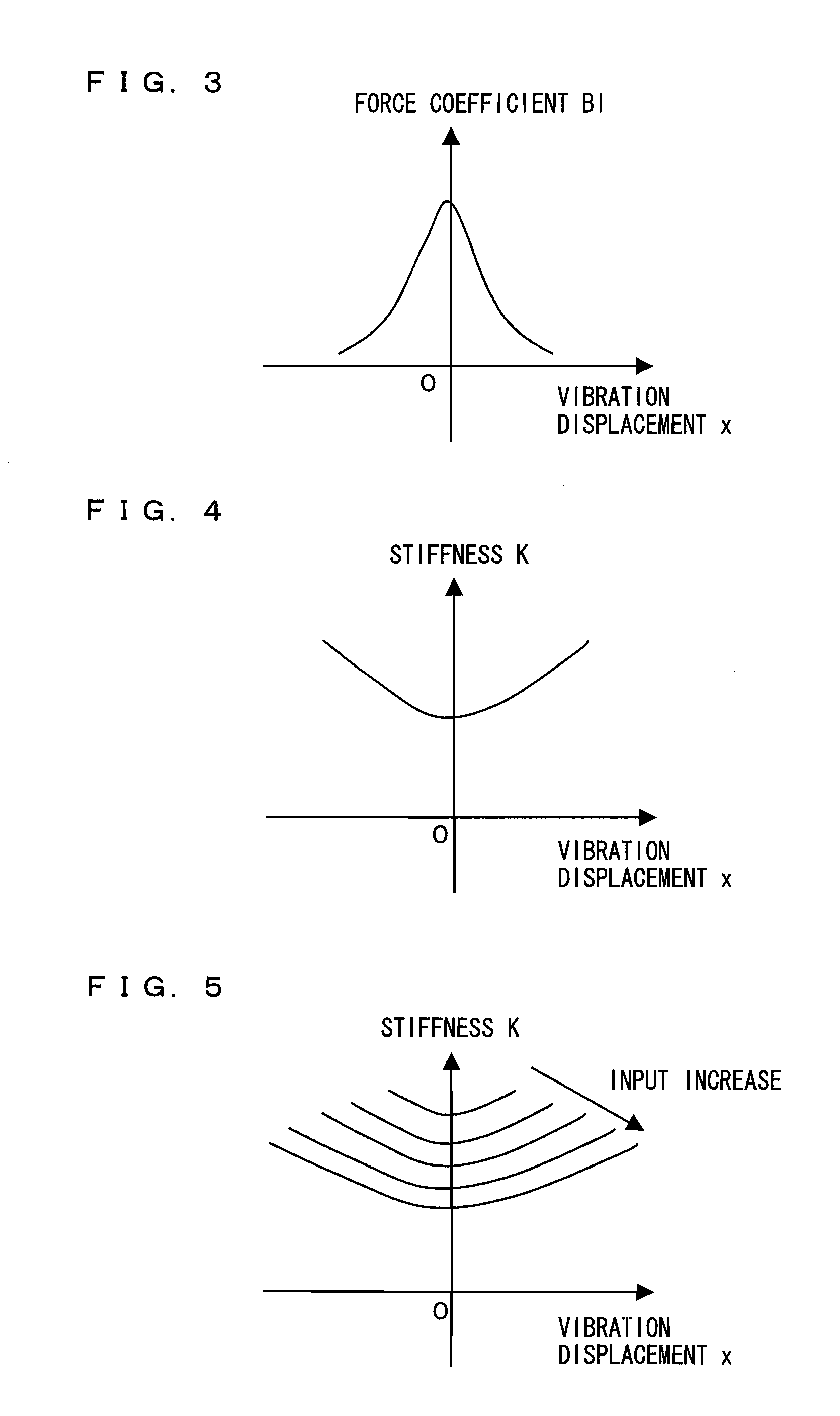
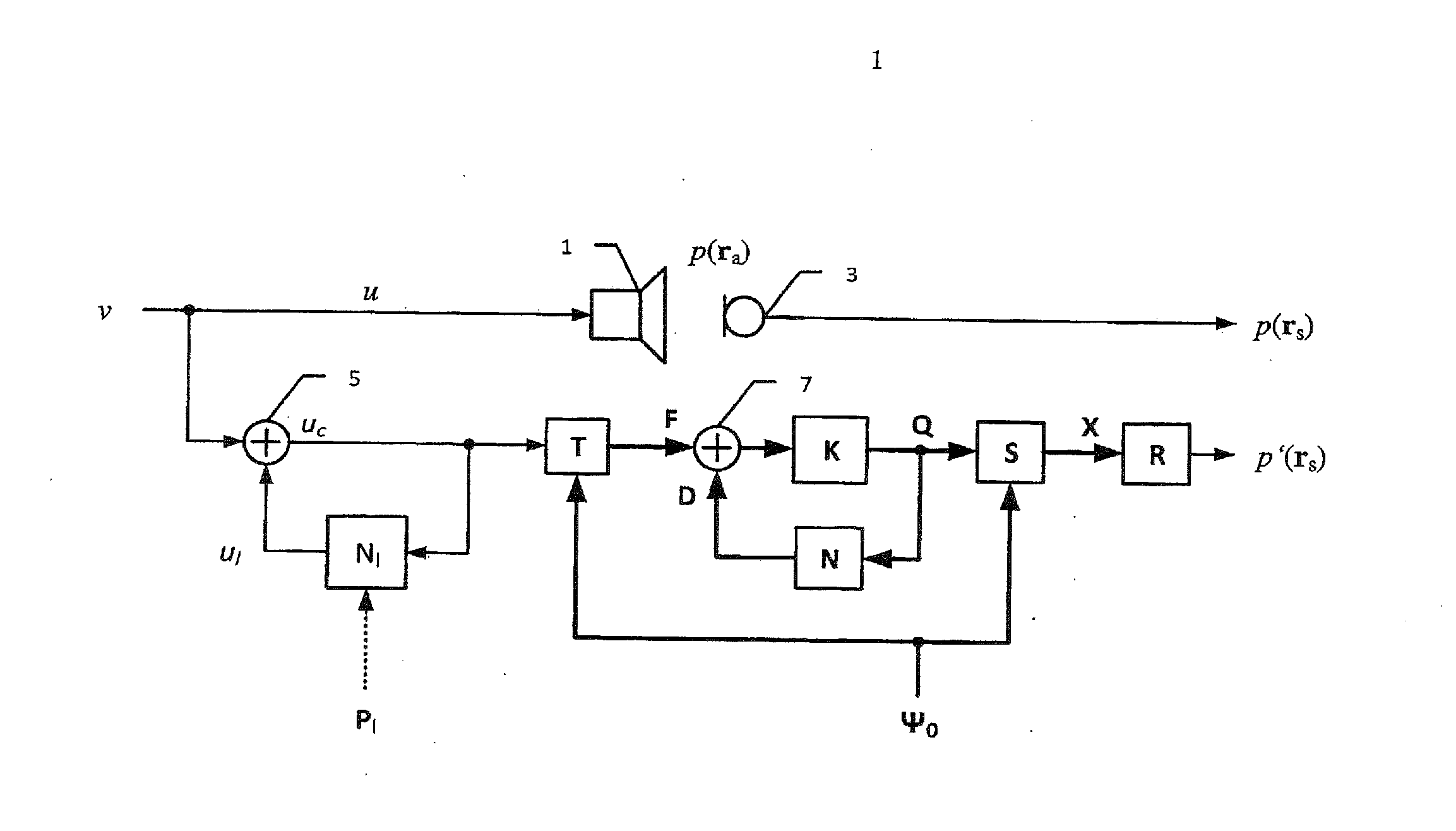
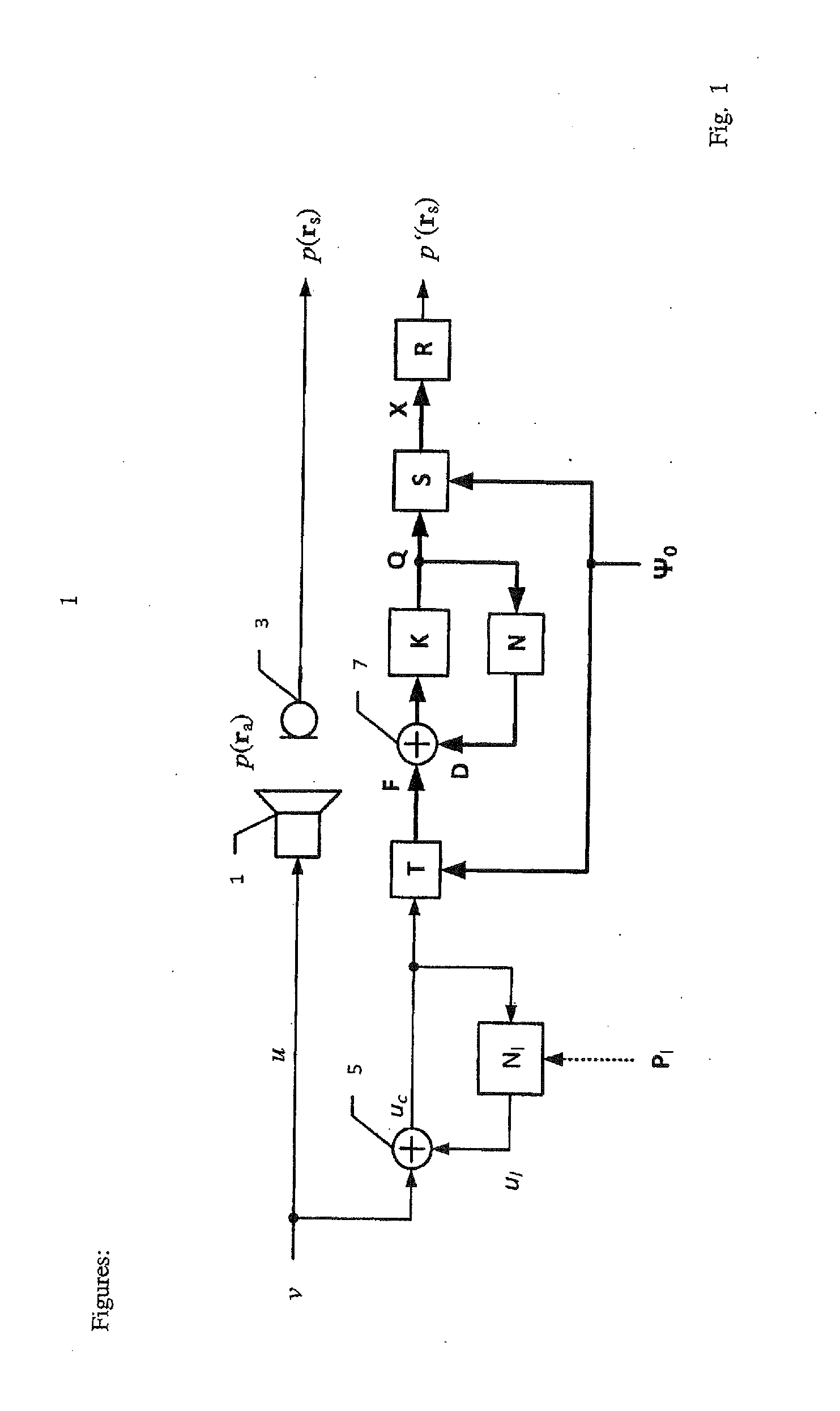
The invention relates to an arrangement and a method for converting an input signal v into an output signal p(ra) by using an electro-mechanical transducer and for reducing nonlinear total distortion pd in said output signal p(ra), whereas the nonlinear total distortion pd contains multi-modal distortion ud which are generated by nonlinear partial vibration of mechanical transducer components. An identification system generates distributed parameters Pd of a nonlinear wave model (Nd) and lumped parameters Pl of a network model (Nl) based on electrical, mechanical or acoustical state variables of transducer measured by a sensor. The nonlinear wave model distinguishes between activation modes and transfer modes, whereas the activation modes affect the transfer modes, which transfer the input signal u into the output signal p. A control system synthesizes based on the physical modeling and identified parameters Pd and Pl nonlinear distortion signals vd and vl which are supplied with the input signal v to the transducer and compensate for the distortion signals ul and ud generated by the transducer nonlinearities.
Owner:KLIPPEL WOLFGANG
Distortion compensating circuit for compensating distortion occurring in power amplifier
ActiveUS6928272B2Good effectReduce distortion componentAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
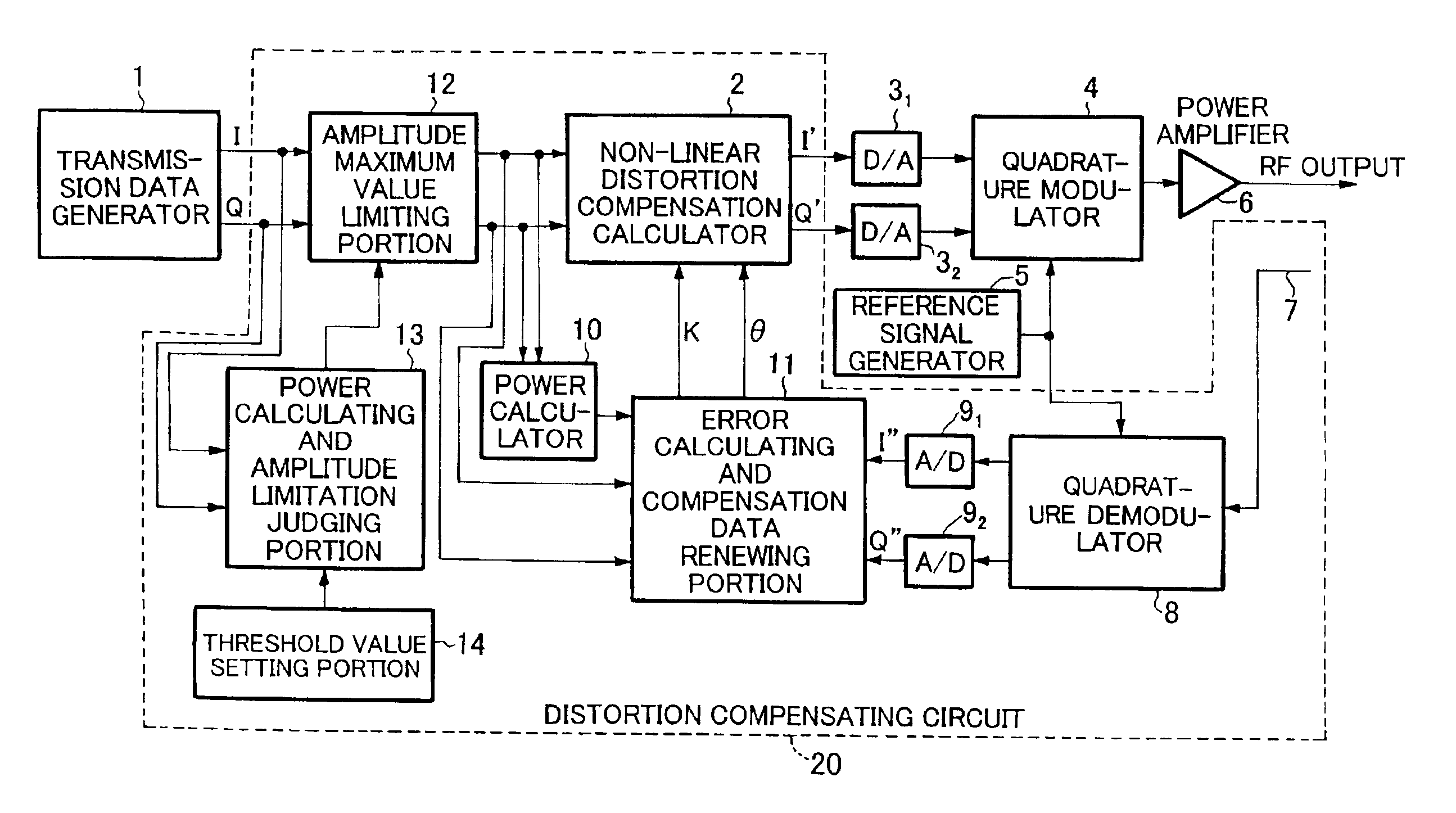
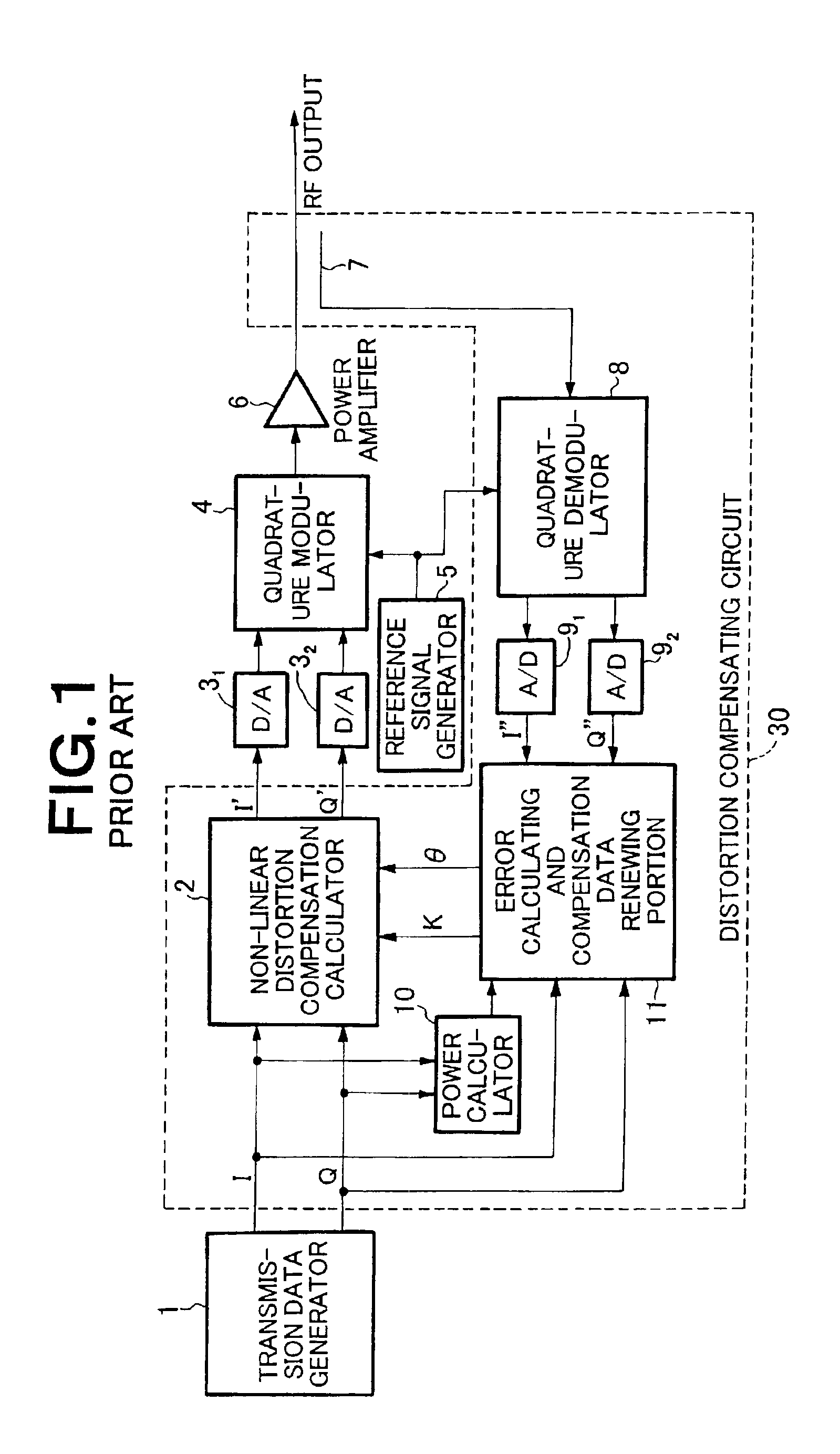
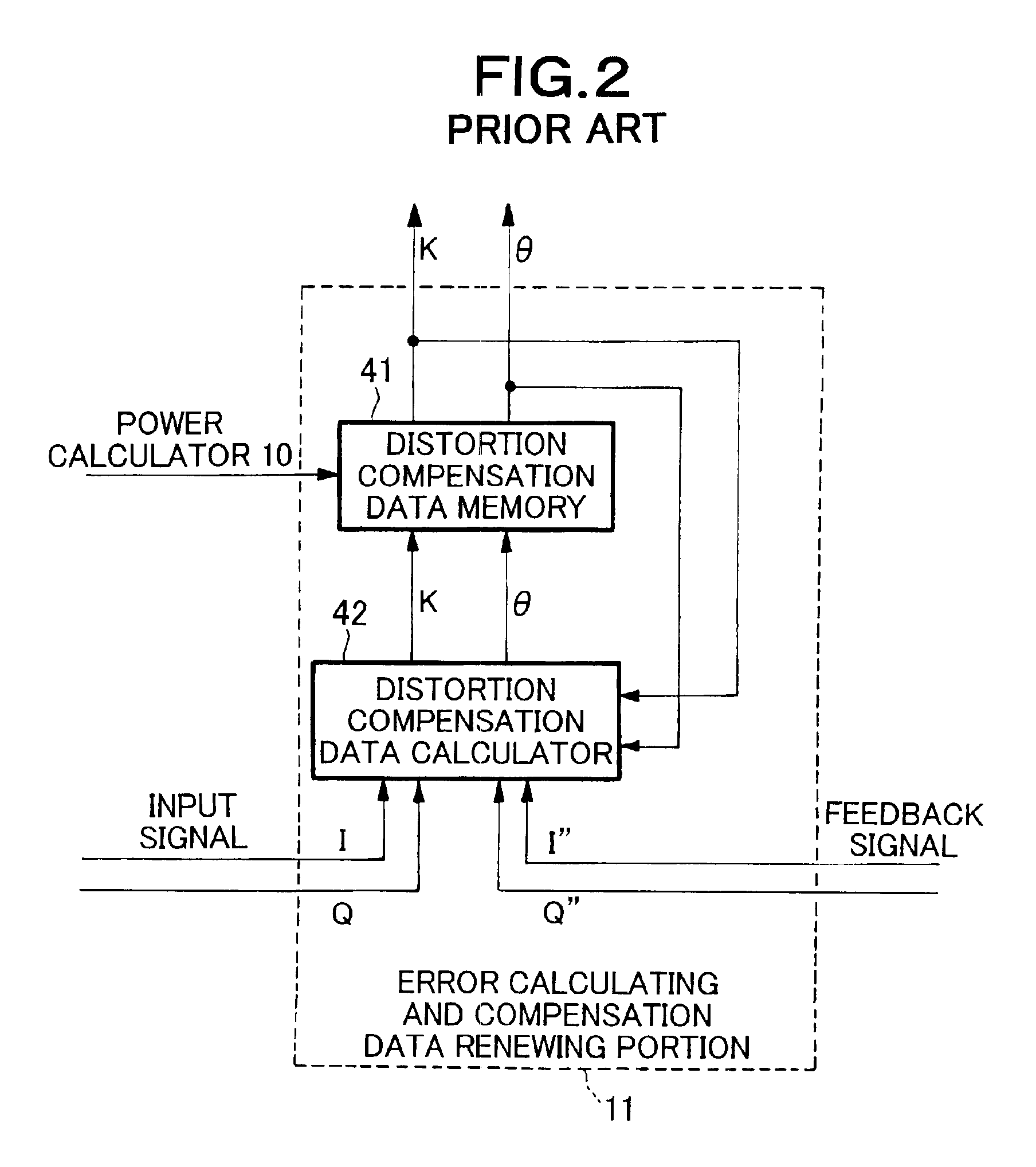
A power calculating and amplitude limitation judging portion 13 calculates the power value x of the digital quadrature baseband signal I, Q from a transmission data generator 1, and compares the power value x with a power threshold value y set by a threshold value setting portion 14 to judge whether amplitude limitation is needed or not. An amplitude maximum limiting portion 12 subjects the quadrature baseband signal from the transmission data generator 1 to the amplitude maximum value limitation based on the judgment result in the power calculating and amplitude limitation judging portion 13. Thereafter, the digital quadrature baseband signal which has been subjected to the amplitude maximum value limitation by the amplitude maximum value limiting portion 12 is subjected to the distortion compensation using complex multiplication based on the distortion compensation data by a non-linear distortion compensation calculator 2.
Owner:NEC CORP
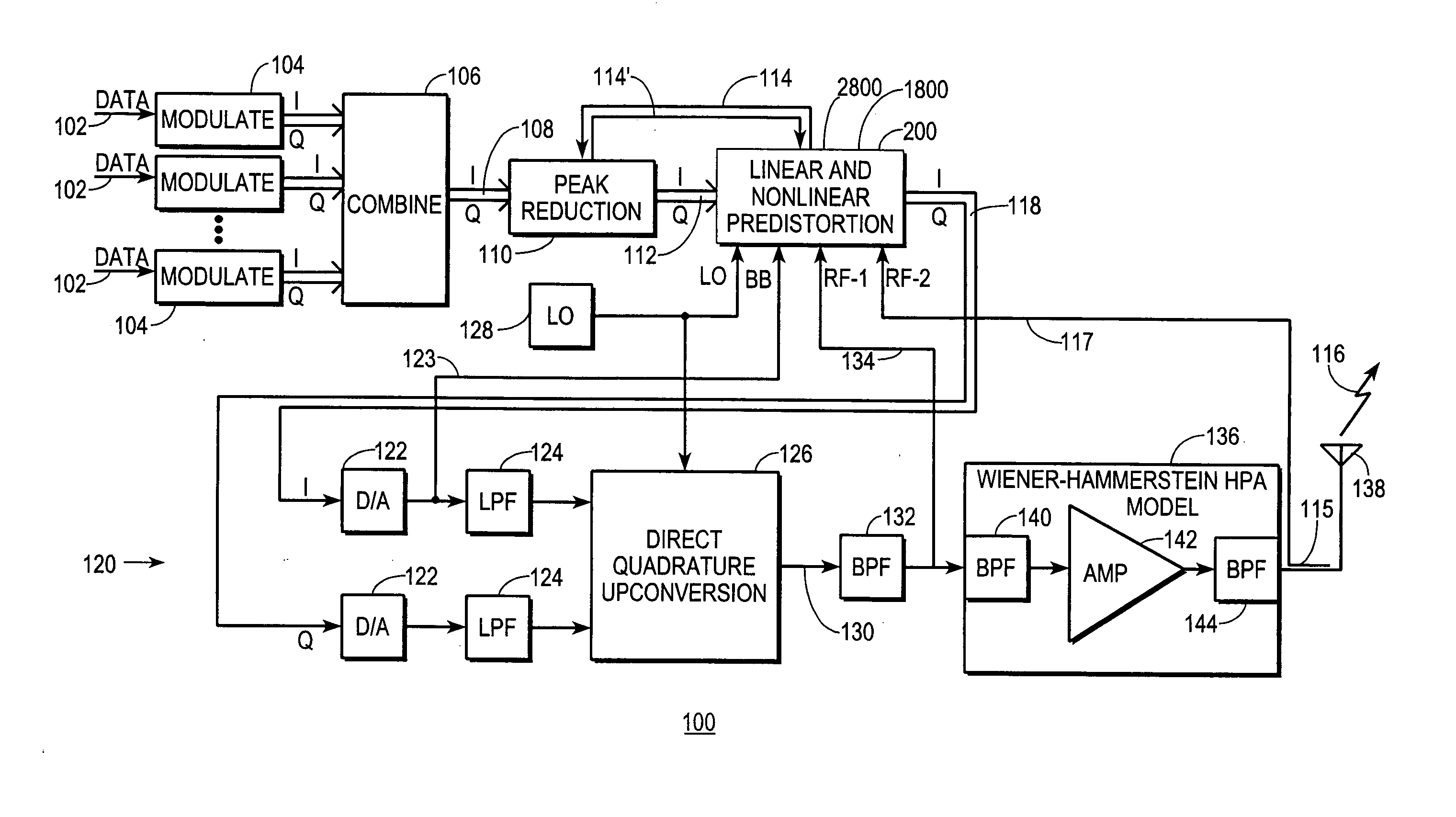
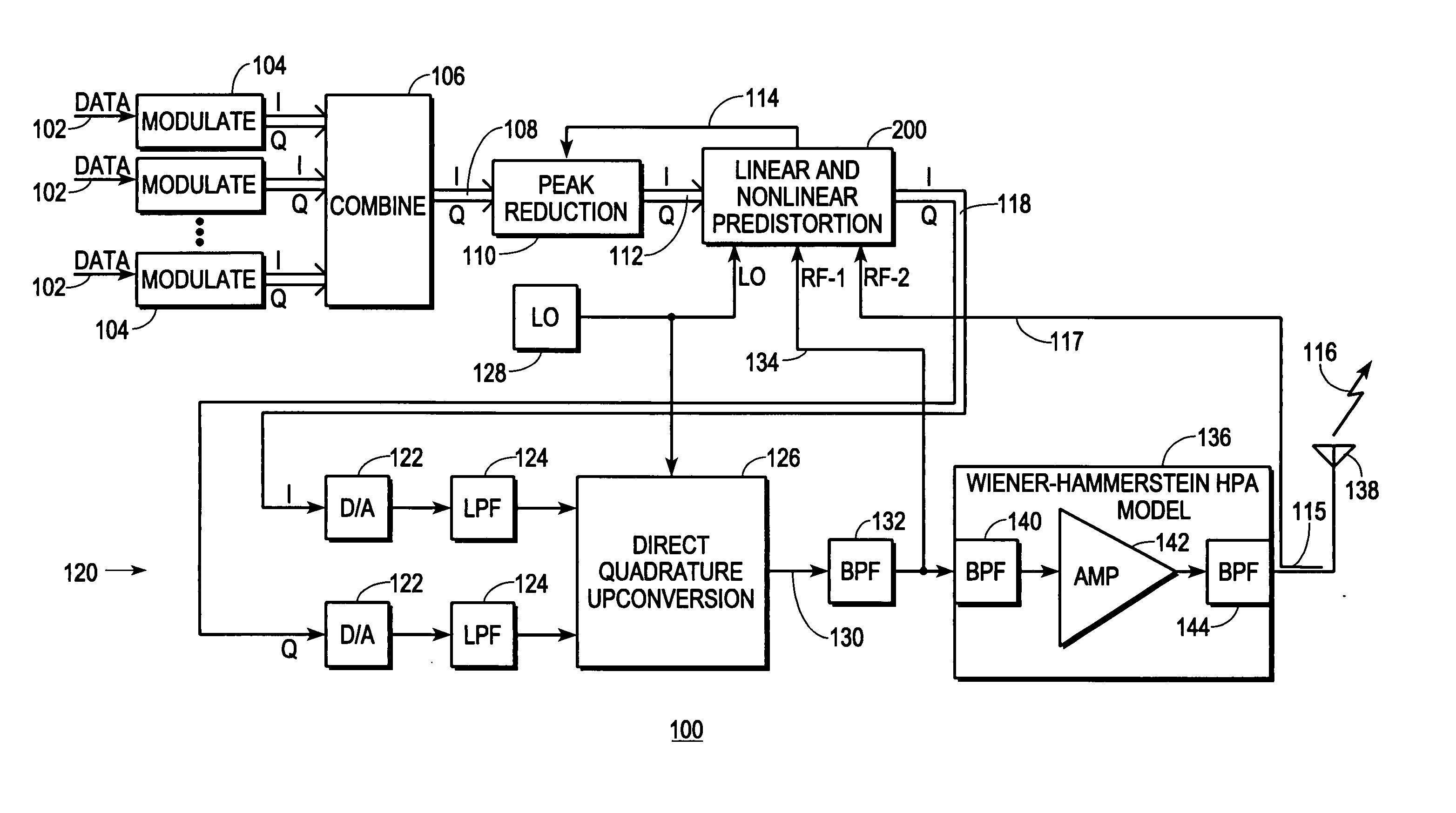
Transmitter predistortion circuit and method therefor
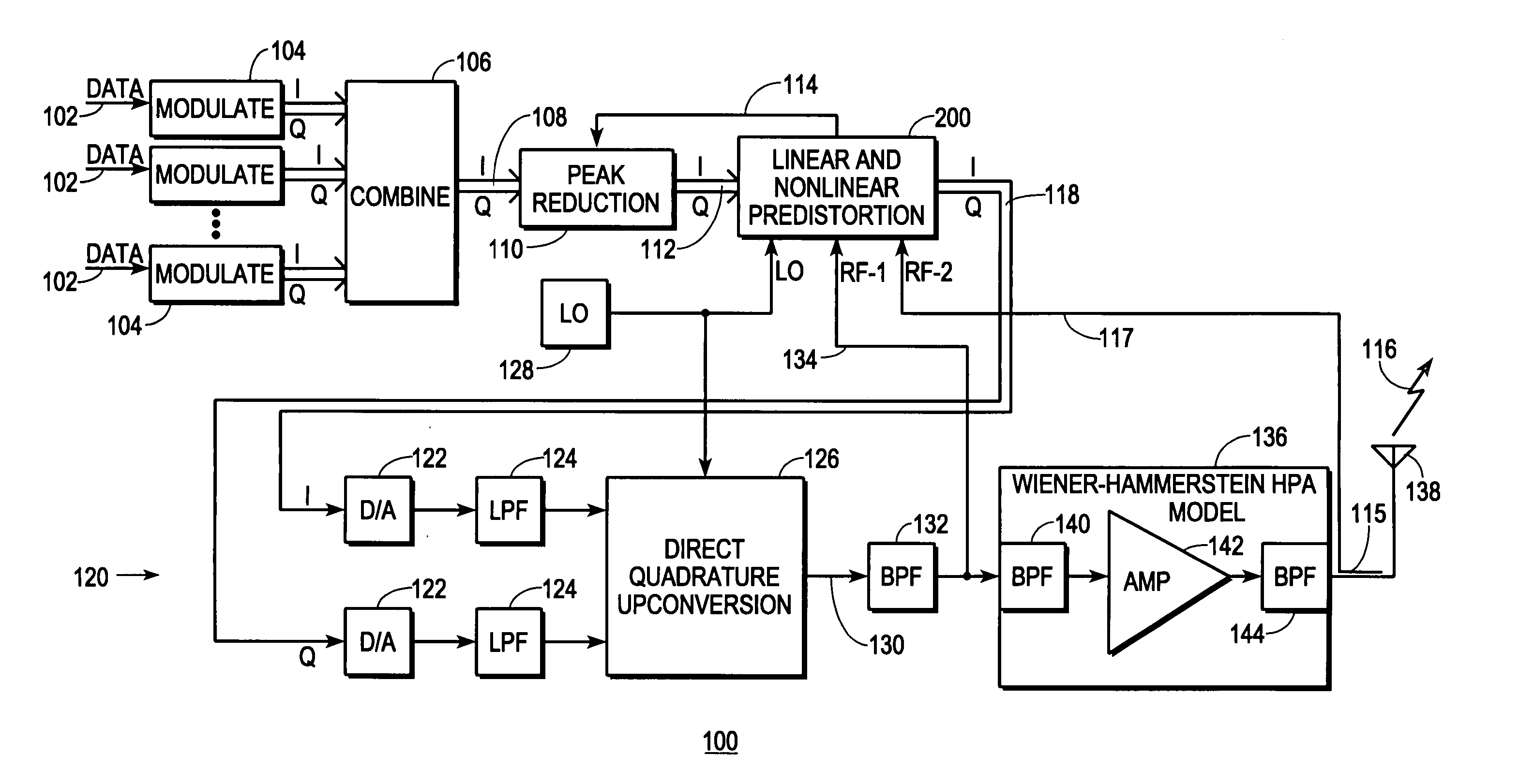
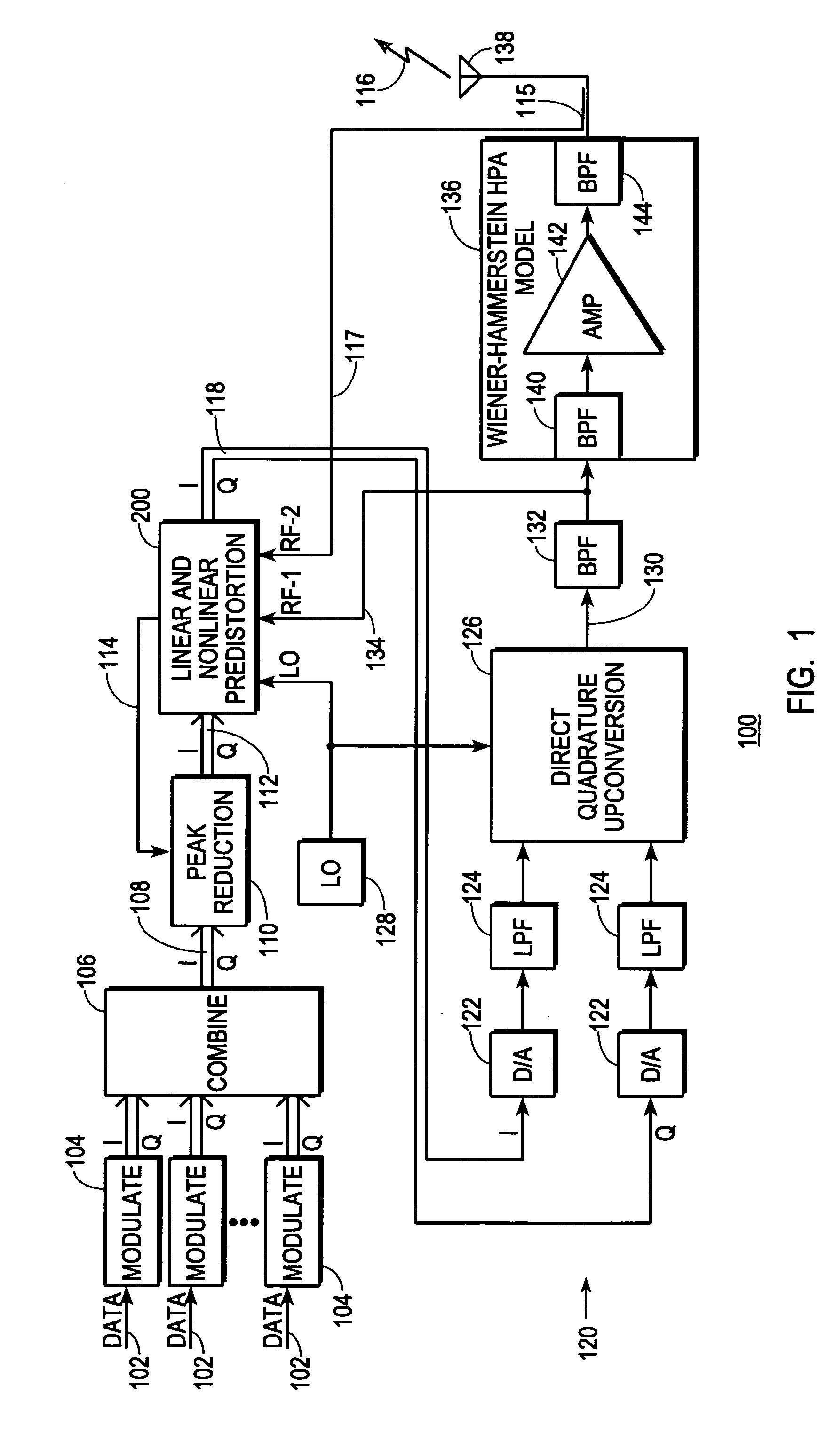
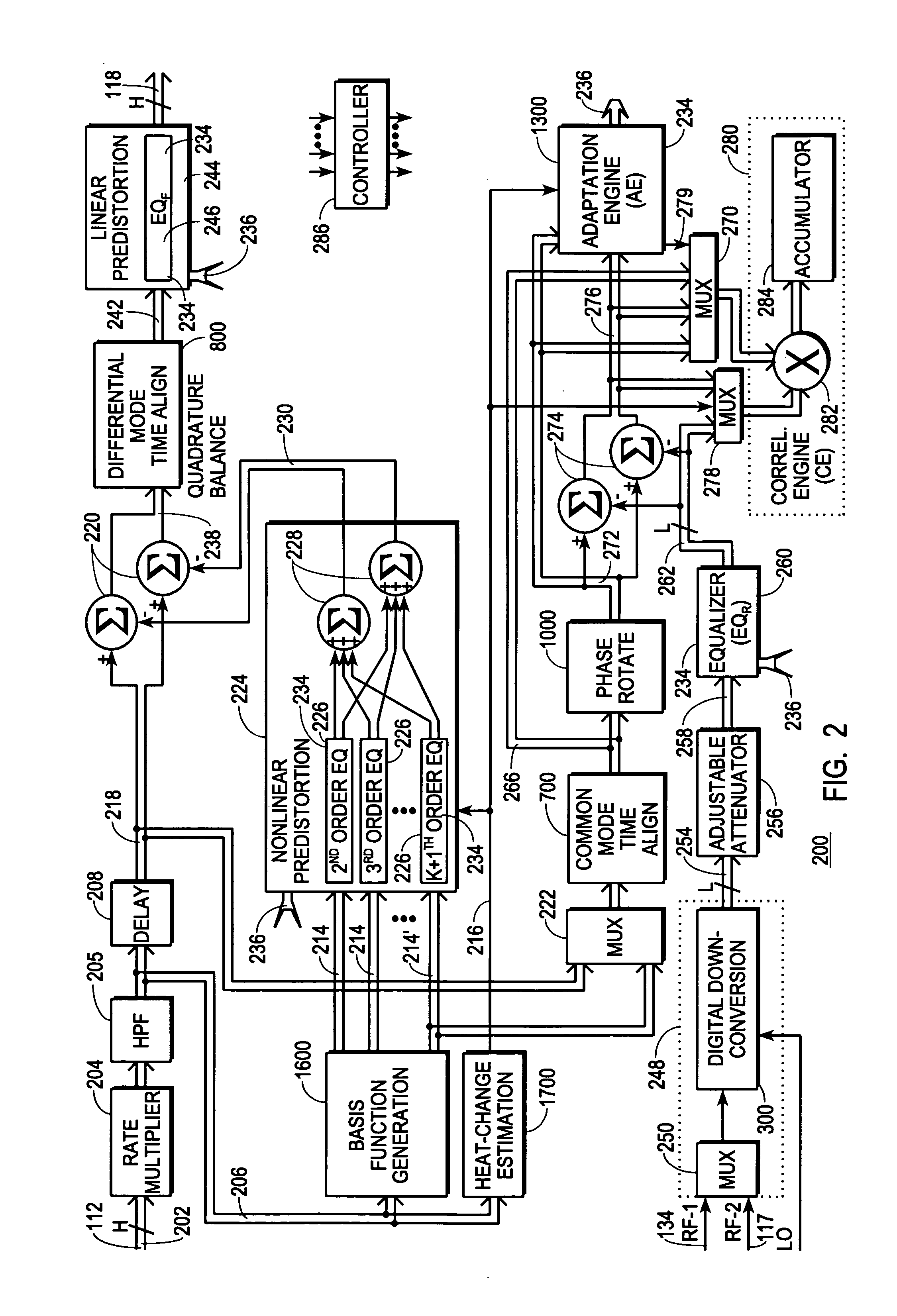
InactiveUS7469491B2Compensation DistortionMultiple-port networksPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionData stream
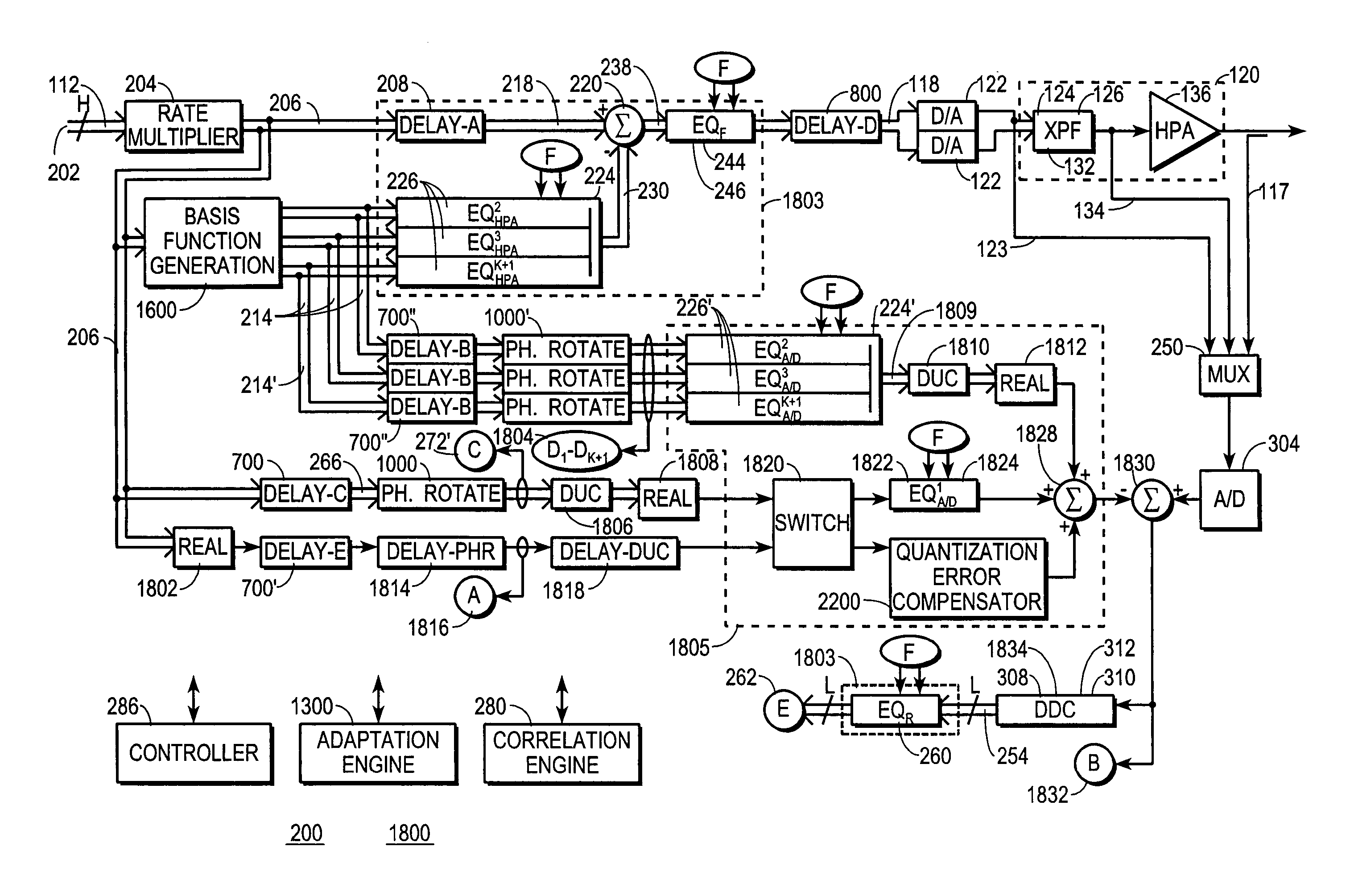
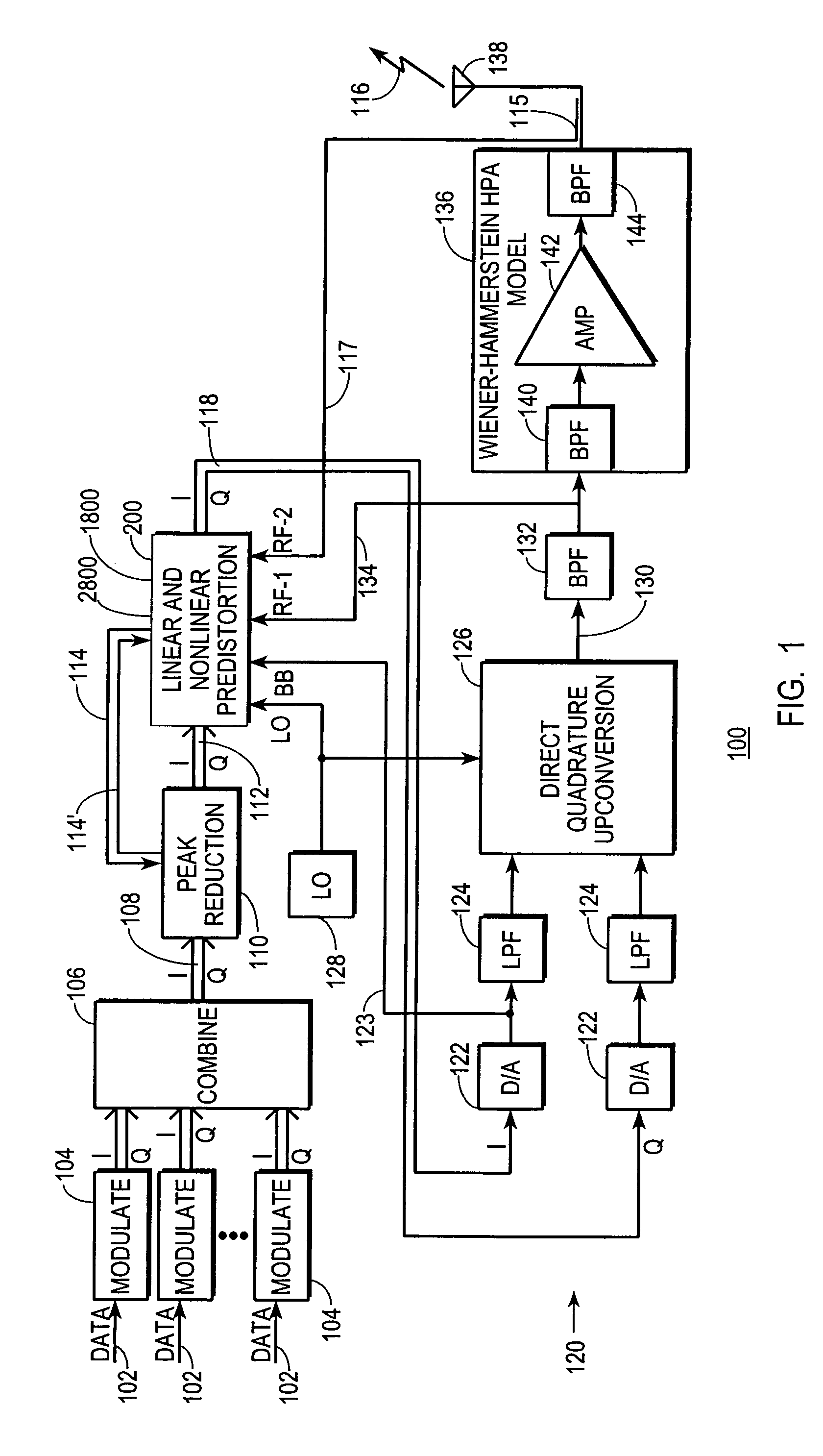
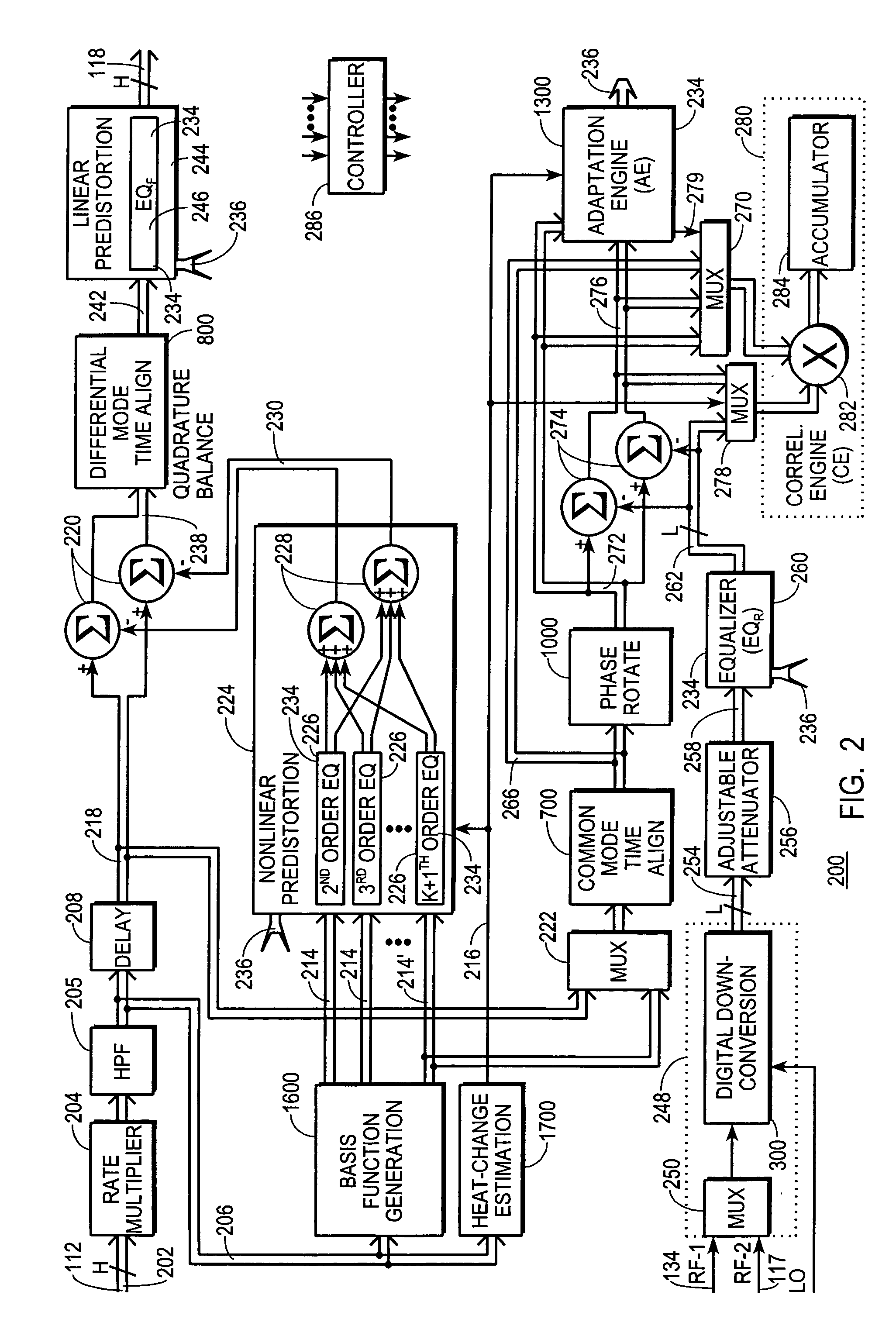
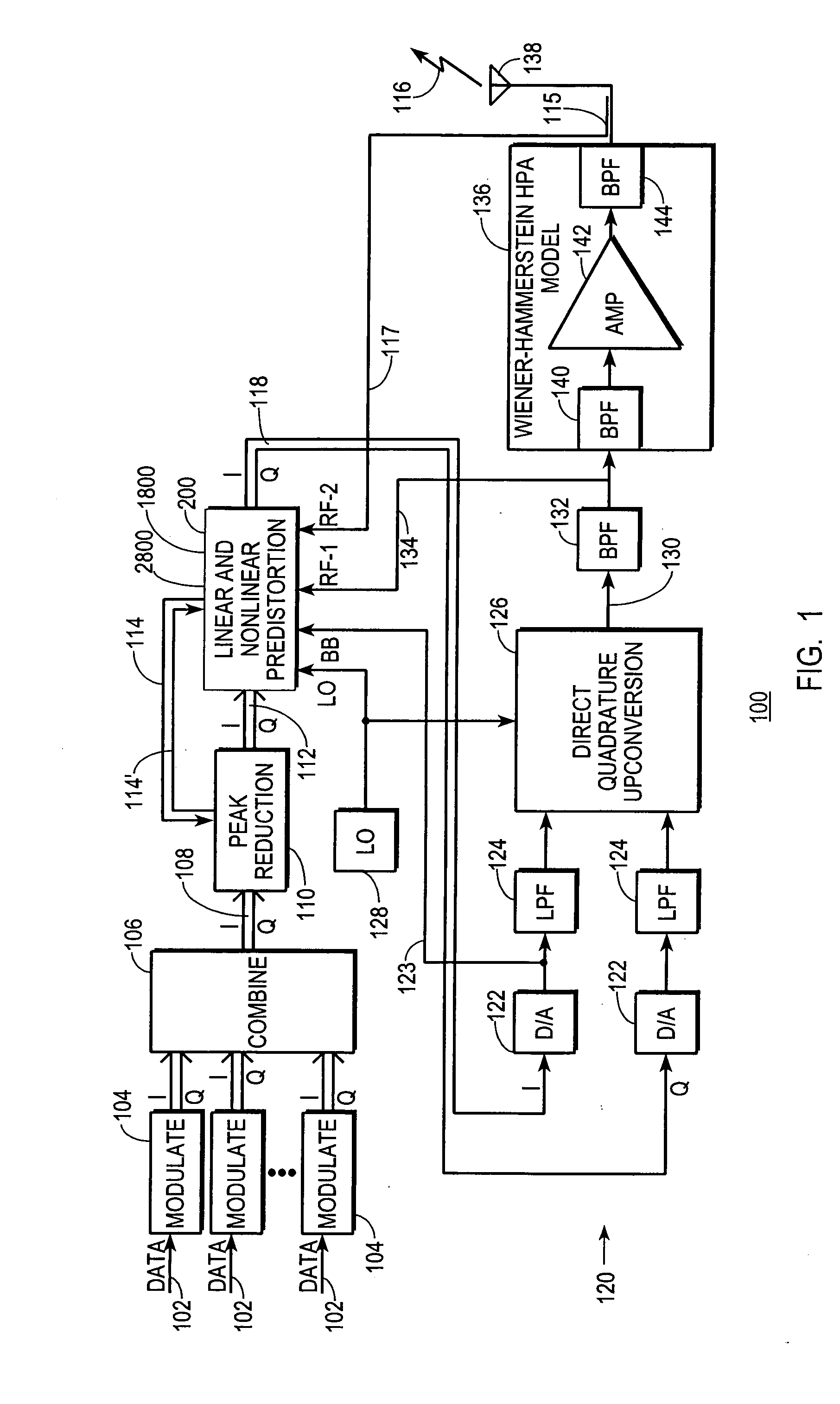
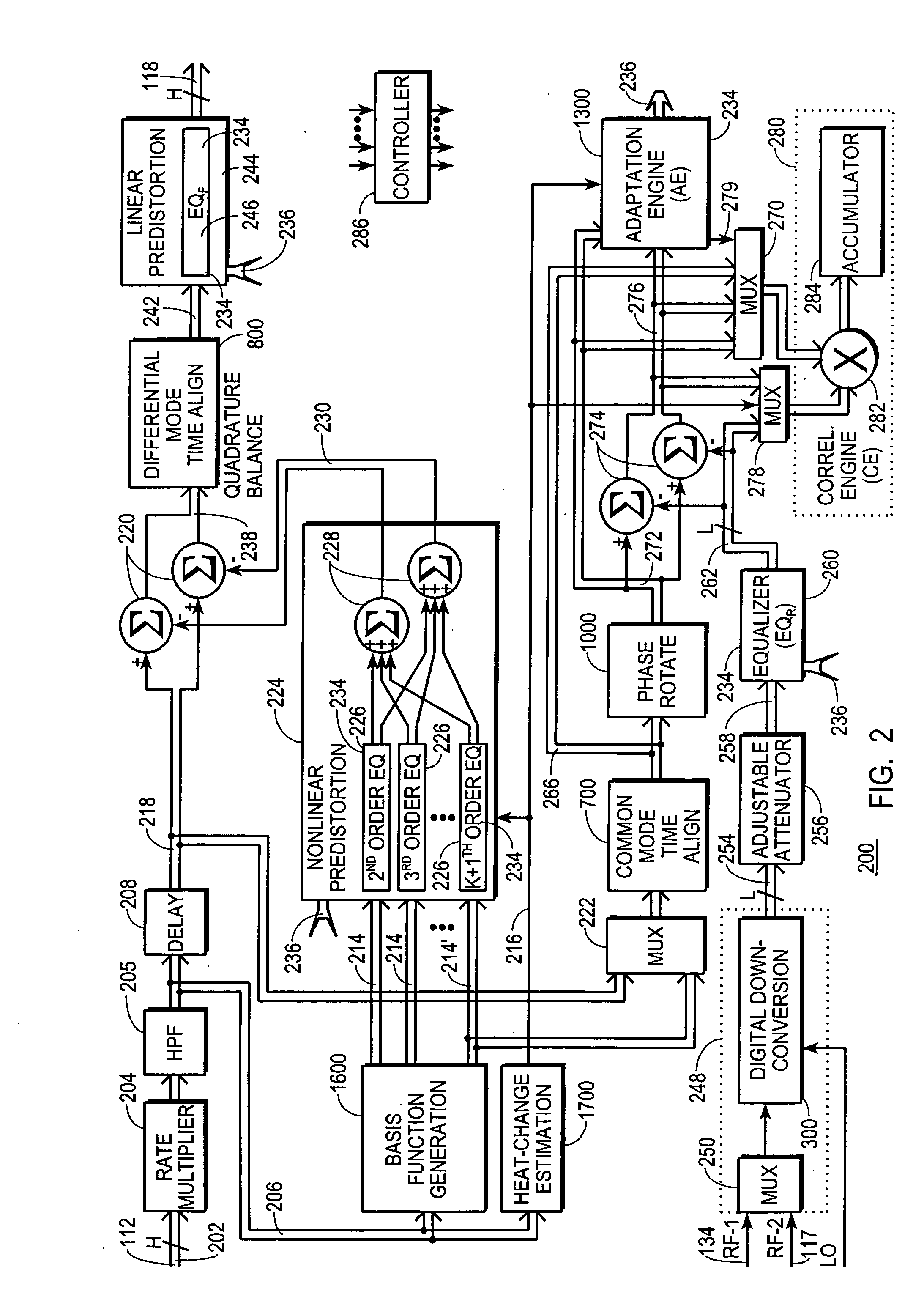
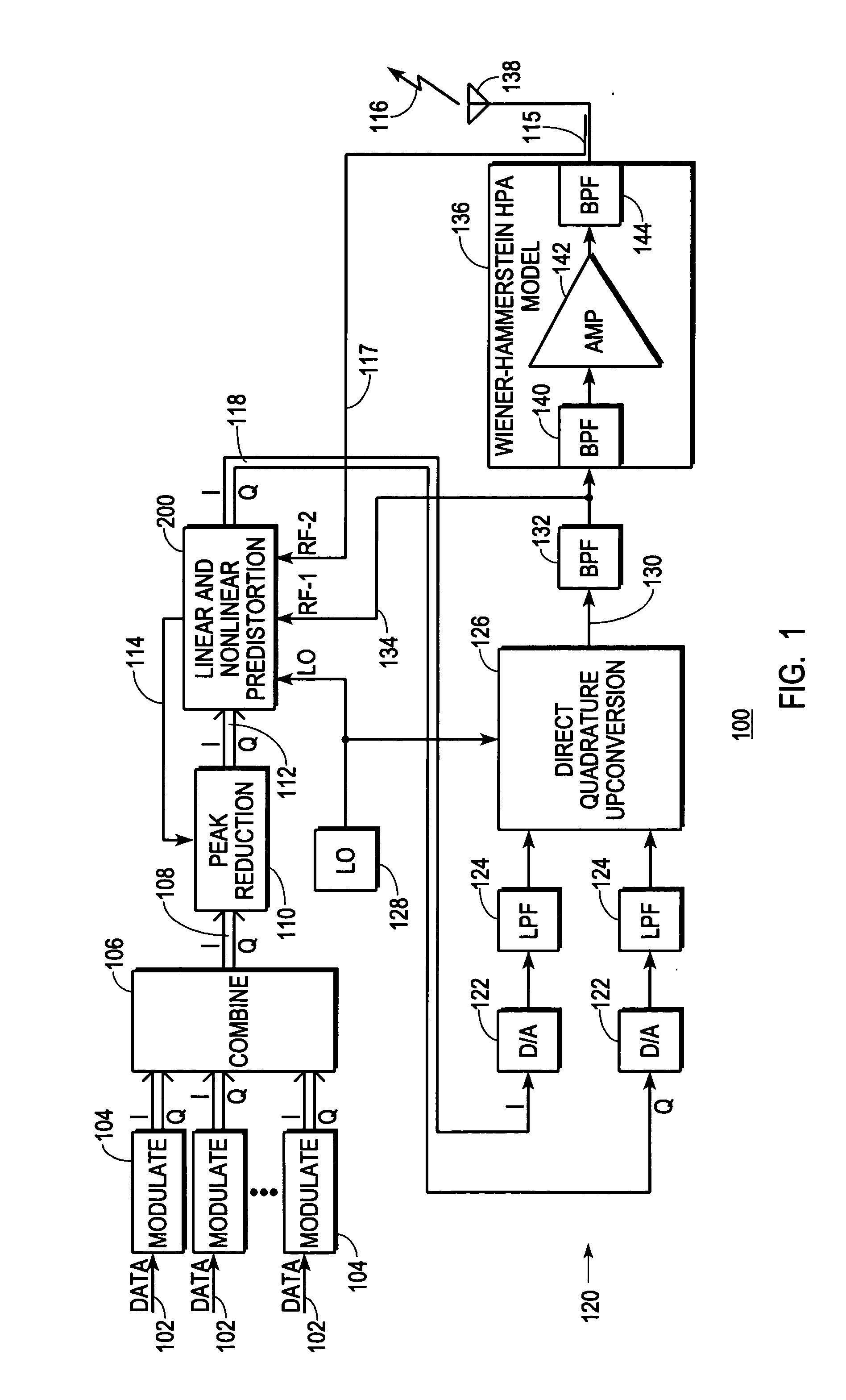
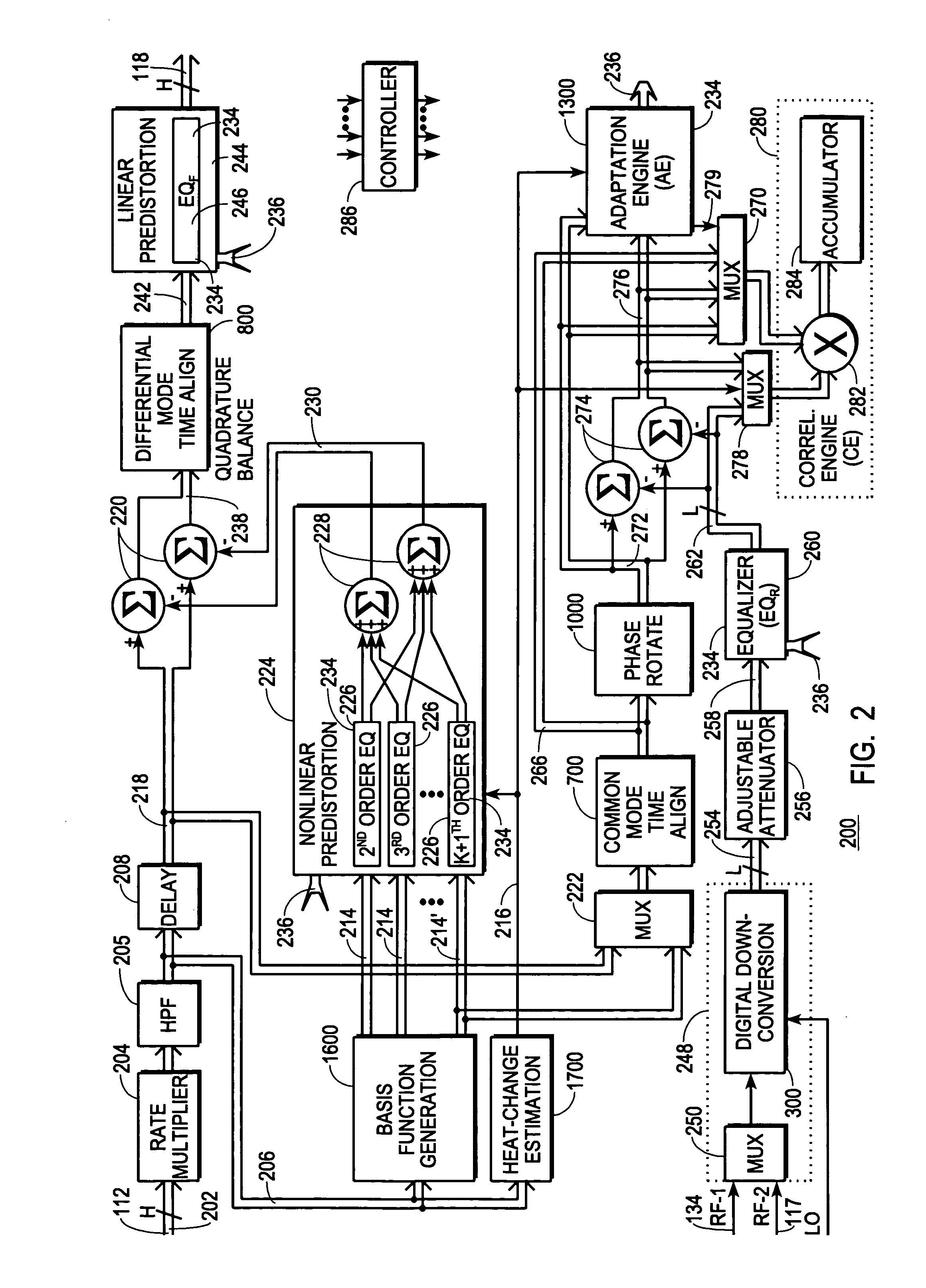
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200, 1800, 2800) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Distortion introduced by an analog-to-digital converter (304) may be compensated using a variety of adaptive techniques. Linear distortion is compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
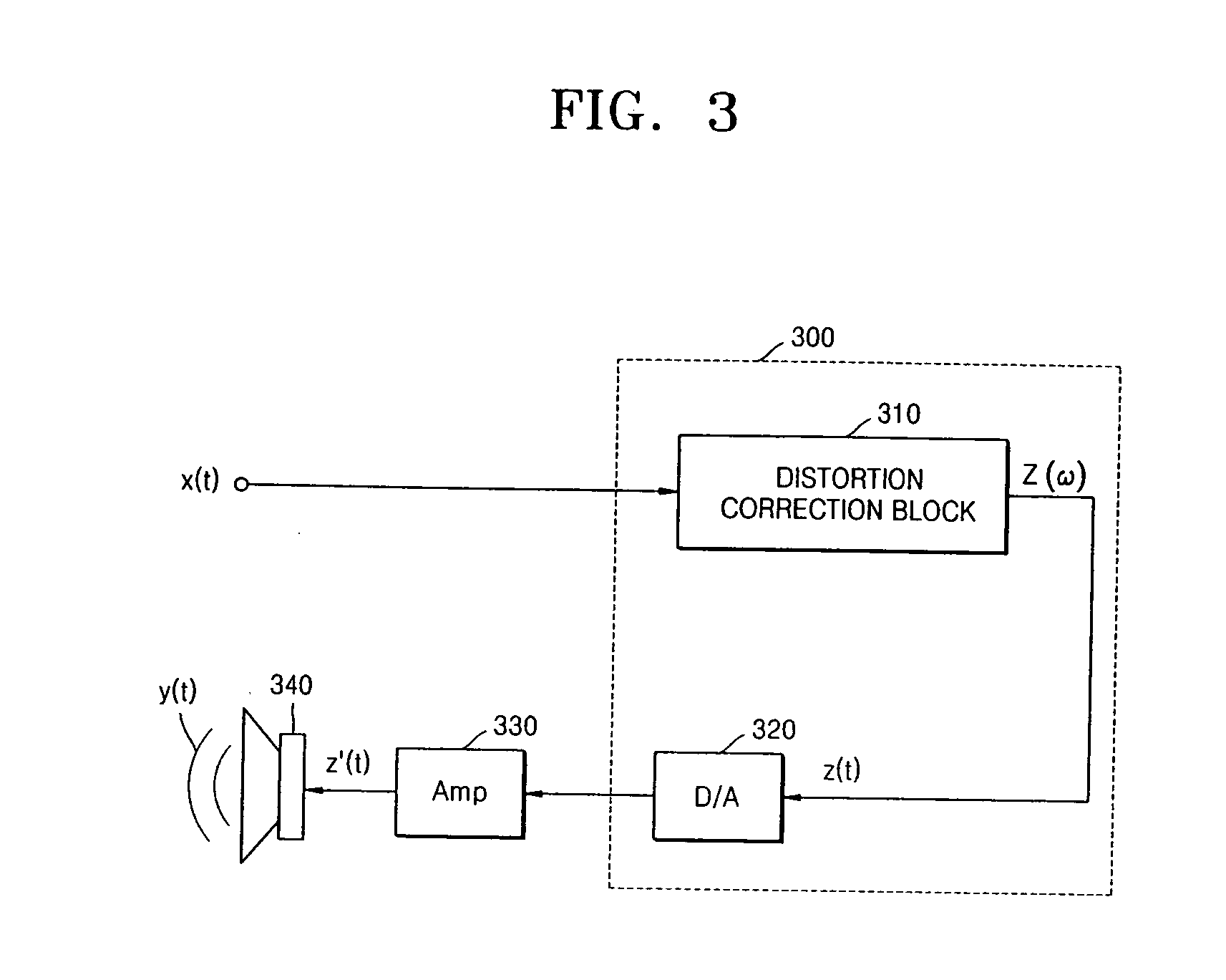
Method and apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion of speaker system
InactiveUS20050047606A1Improve output signal qualityEasy to implementTransducer circuit dampingFrequency response correctionTime domainViscous damping
A method and an apparatus for compensating for nonlinear distortion are provided to divide audio signals reproduced in a nonlinear speaker system into linear and nonlinear components in a time domain and a frequency domain, and then generate inversely-corrected signals by means of an inverse filtering scheme, so that it is possible to further consider a variety of nonlinear distortion characteristics such as viscous damping and structural damping which have not been reflected in the conventional lumped parameter method, and thus to obtain better sound quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical fiber based on wireless scheme for wideband multimedia access
InactiveUS6889060B2Good compensationLess complexMultiple-port networksError preventionNonlinear distortionRadio over fiber
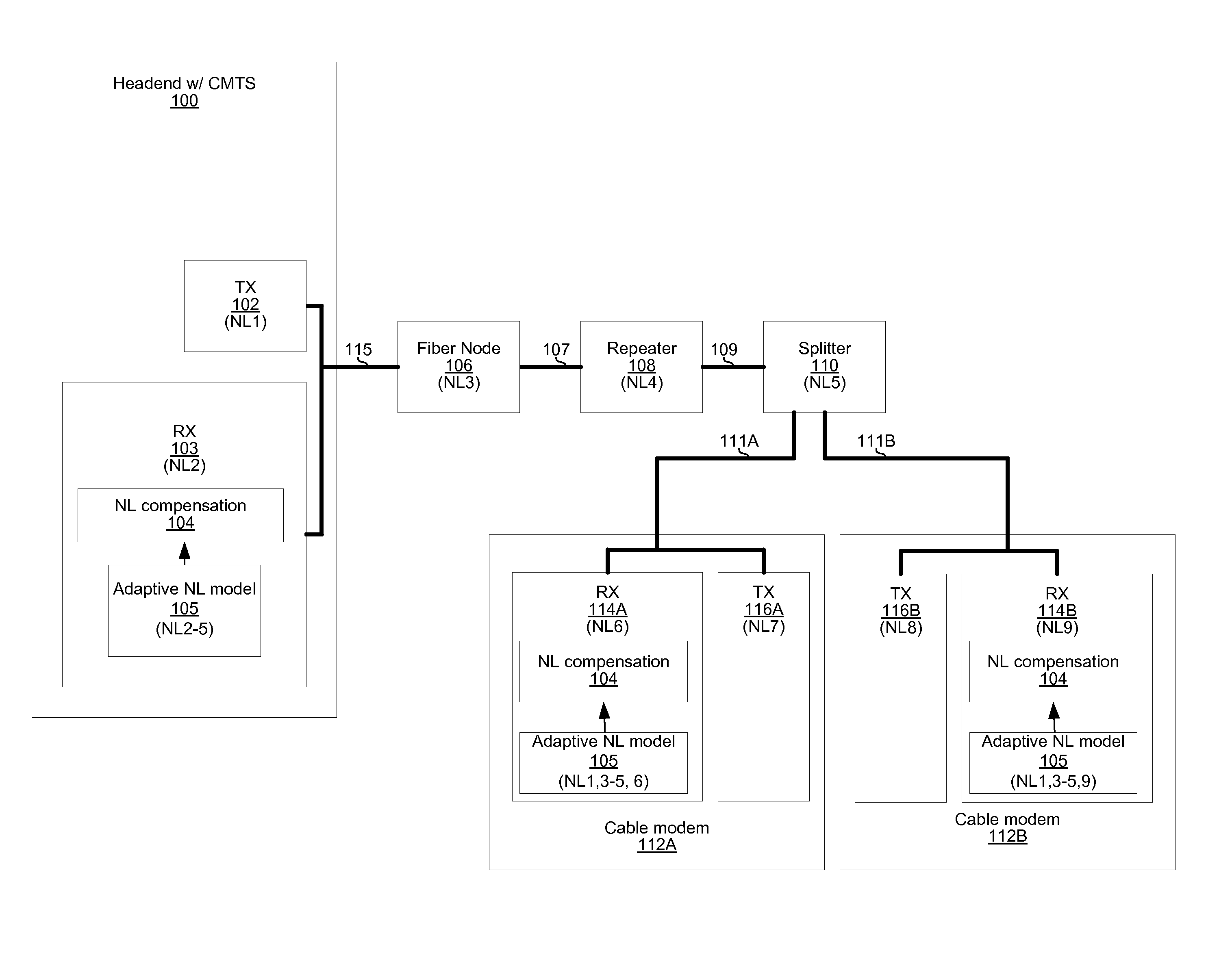
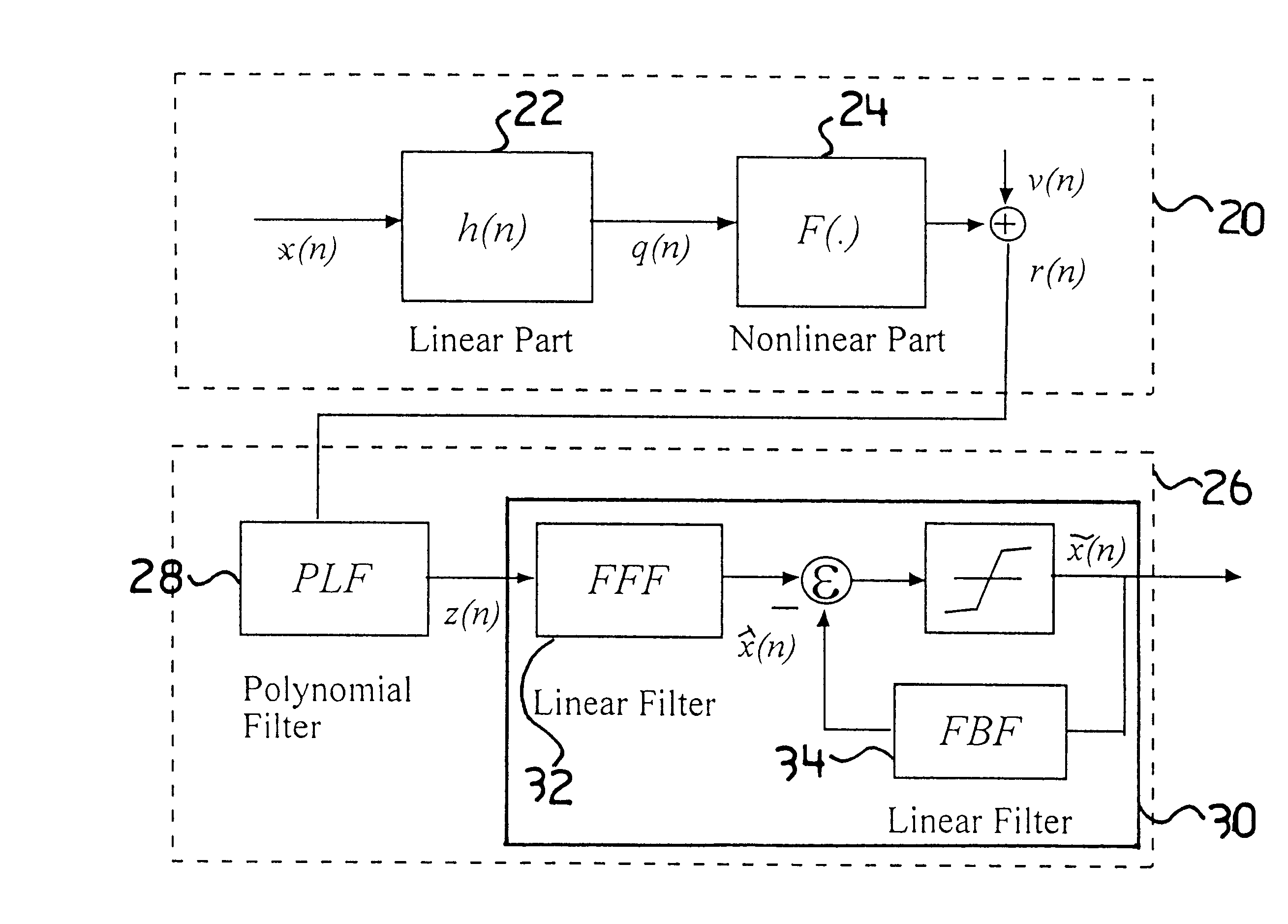
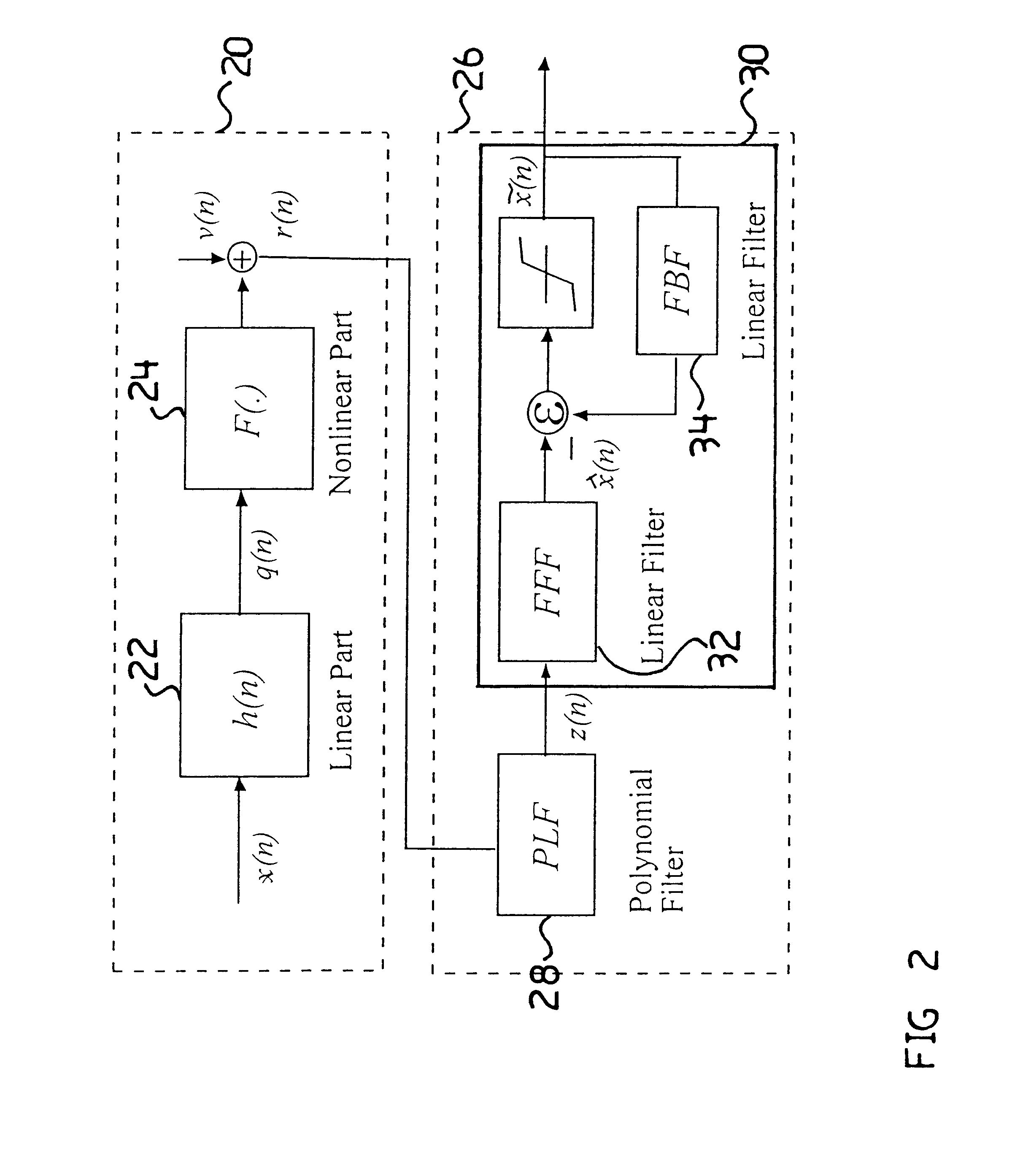
A Fiber-wireless uplink consists of a wireless channel followed by a radio-over-fiber (ROF) link. Typically, nonlinear distortion of the ROF link is the major concern when the radio frequency is only a few GHz. This especially severe in the uplink, because of the multipath fading of the wireless channel. A Hammerstein type decision feedback equalizer is described for the fiber wireless uplink, that compensates for nonlinear distortion of the ROF link as well as linear dispersion of the wireless channel. Since the linear and nonlinear parts of the receiver are separated, tracking the fast changing wireless channel is virtually independent of compensating for the relatively static nonlinearity. Analytical results show that the receiver provides excellent compensation with notably less complexity.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
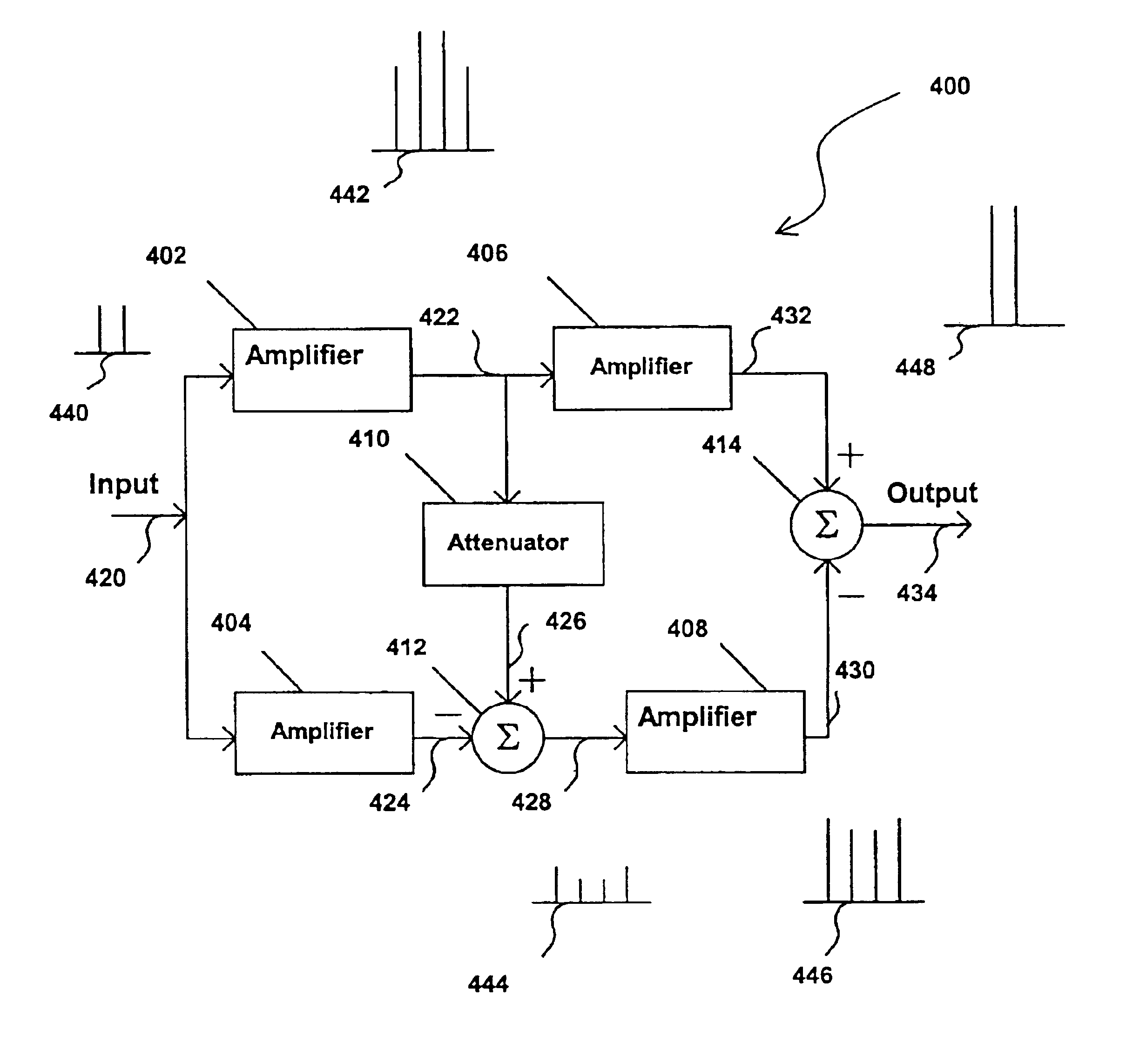
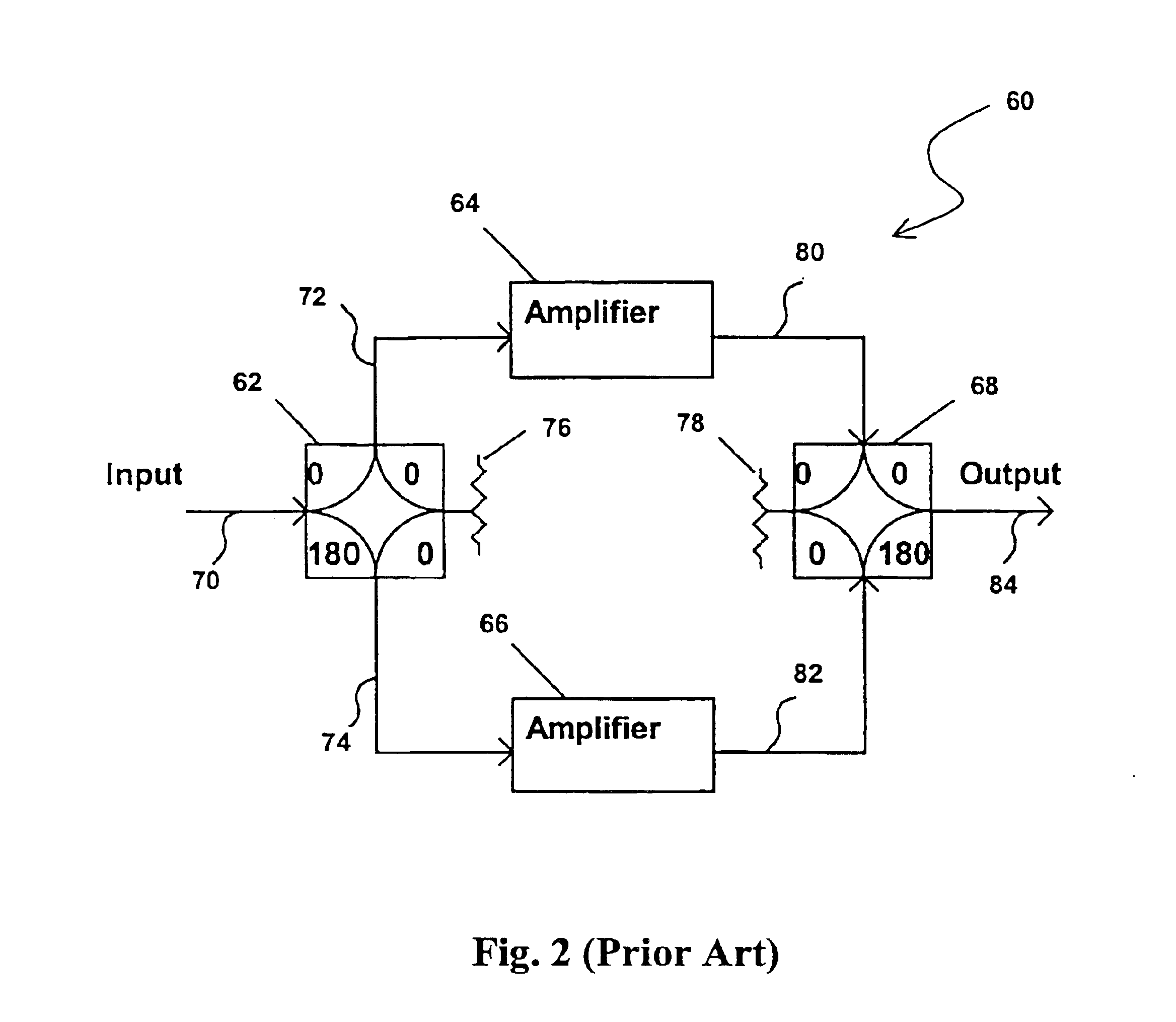
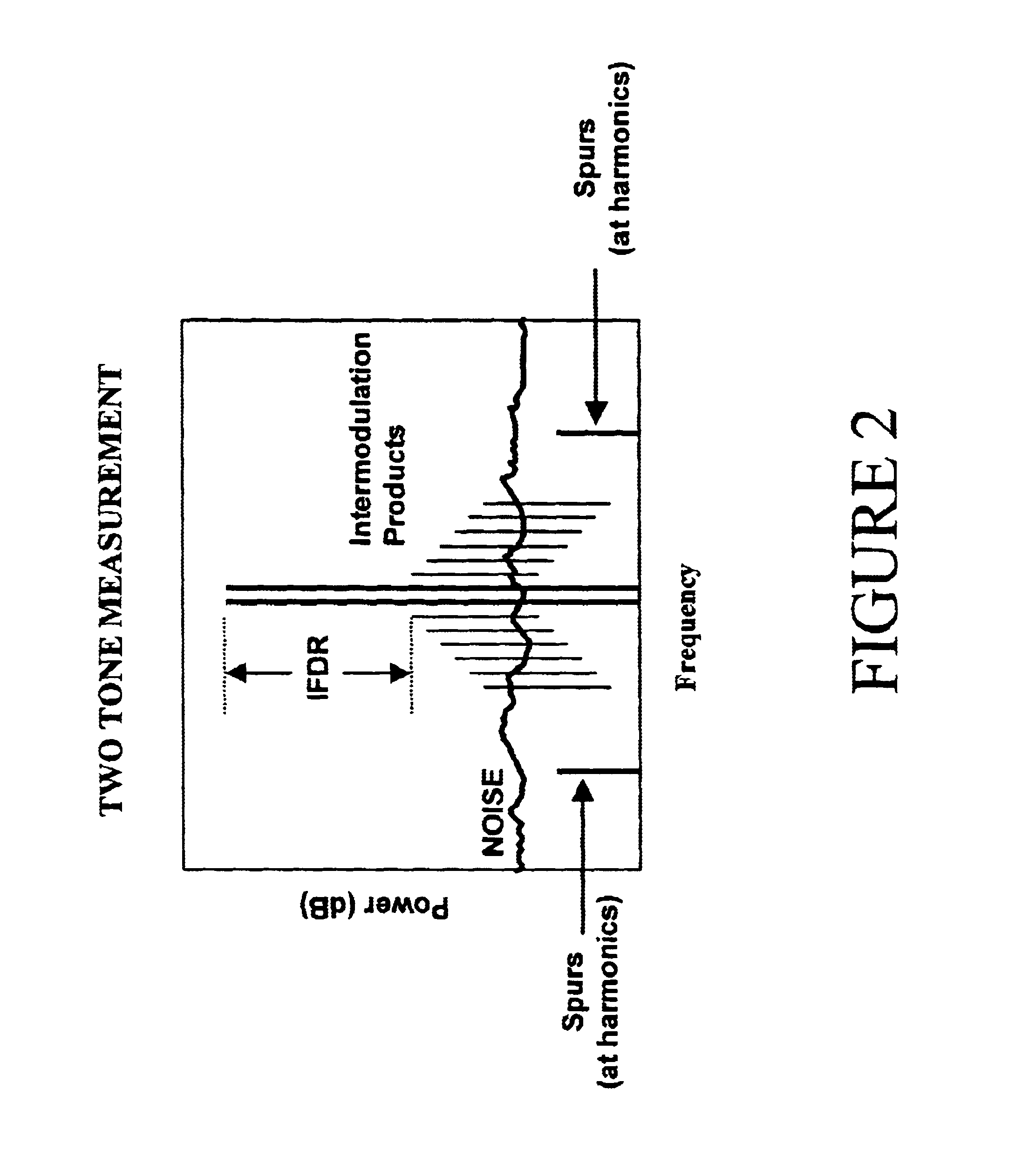
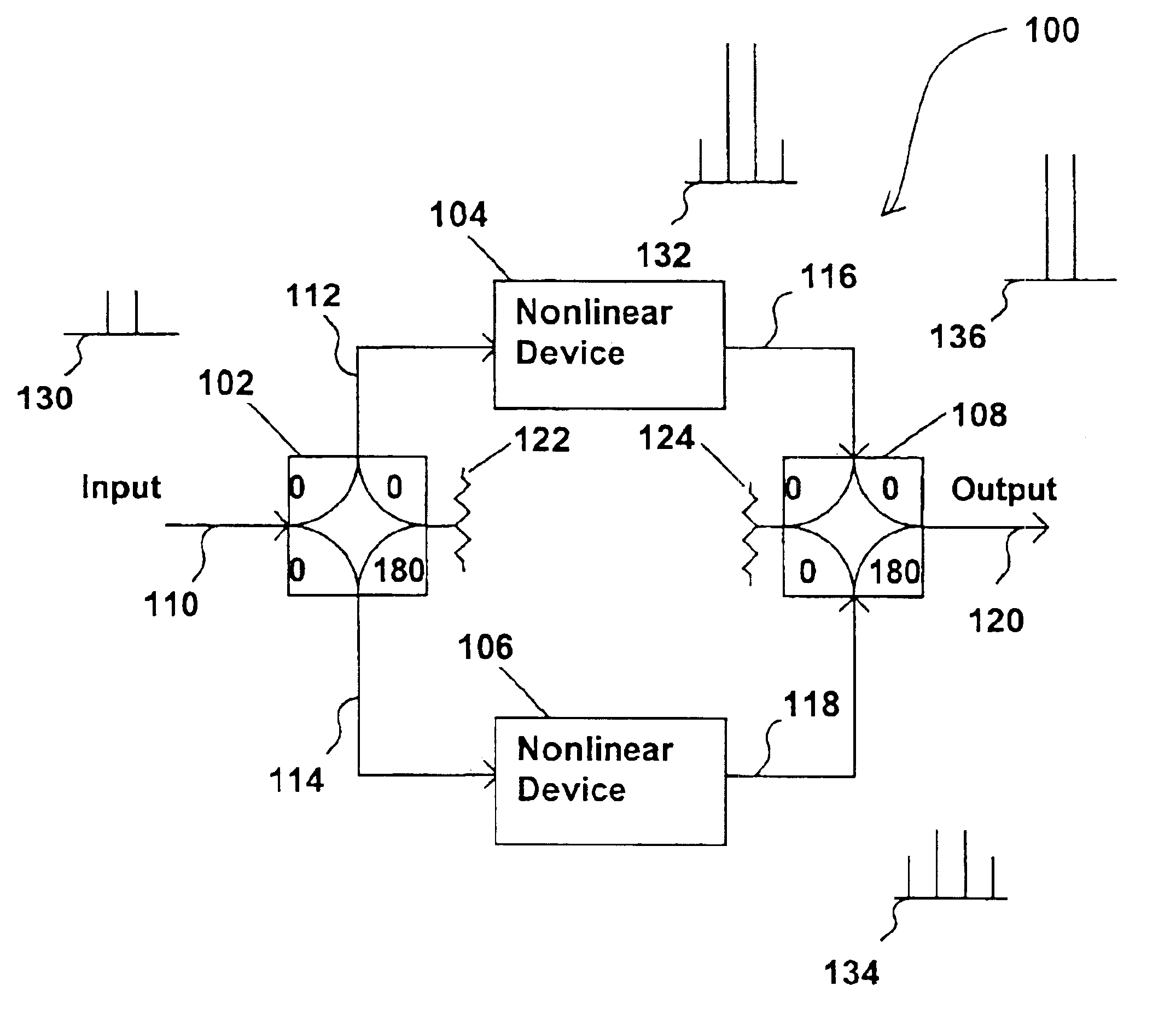
Methods and apparatus for substantially reducing nonlinear distortion using multiple nonlinear devices
InactiveUS6853248B2Reducing canceling nonlinearitiesReducing and canceling third order nonlinearitiesAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
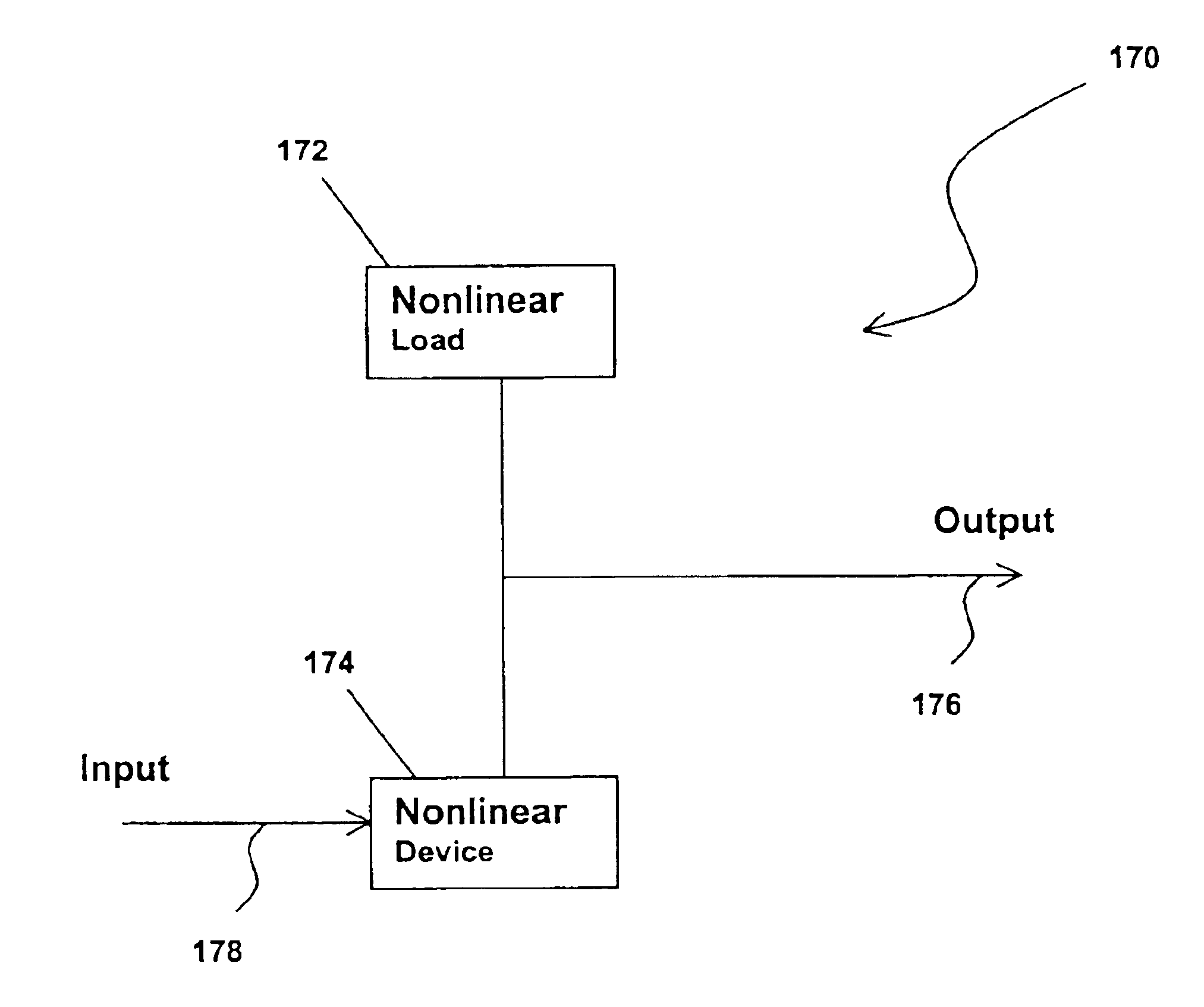
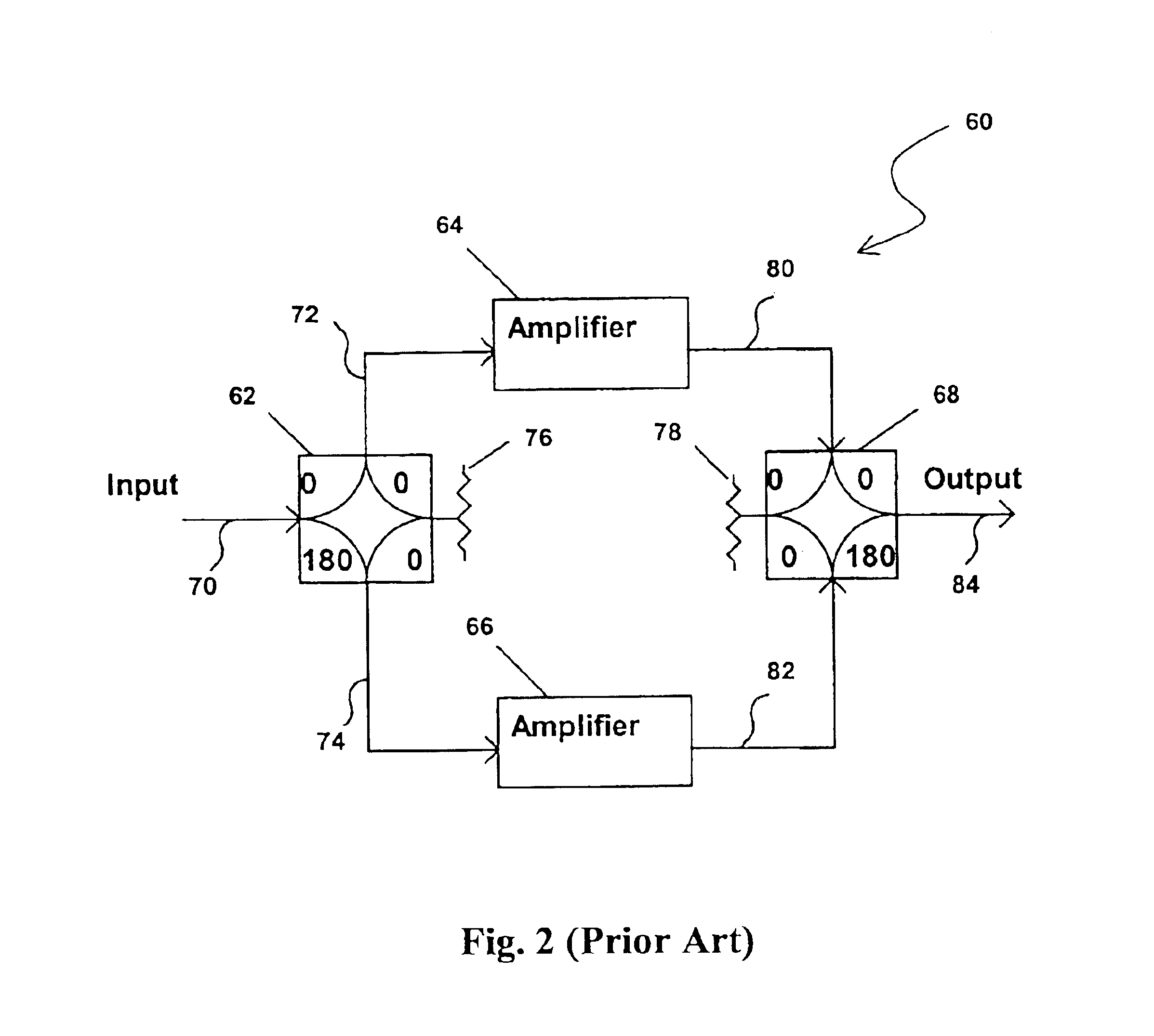
Methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling nonlinearities of any order in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. In particular, methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling third order nonlinearities in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. A first coupler is used to split an input signal into two equal-amplitude in-phase components, each component is processed by two nonlinear devices with different nonlinearities, and a final combiner, such as a 180-degree hybrid, recombines the processed signals 180 degrees out of phase and substantially reduces and / or cancels the undesired nonlinear distortion components arising due to nonlinearities in the nonlinear devices.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Transmitter predistortion circuit and method therefor
InactiveUS20050163252A1Easy to optimizeCompensation DistortionMultiple-port networksPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionData stream
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200, 1800, 2800) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Distortion introduced by an analog-to-digital converter (304) may be compensated using a variety of adaptive techniques. Linear distortion is compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
System and methods for recognizing sound and music signals in high noise and distortion
InactiveUS20060122839A1High of distortionHigh levelDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionNonlinear distortionLinear correlation
A method for recognizing an audio sample locates an audio file that most closely matches the audio sample from a database indexing a large set of original recordings. Each indexed audio file is represented in the database index by a set of landmark timepoints and associated fingerprints. Landmarks occur at reproducible locations within the file, while fingerprints represent features of the signal at or near the landmark timepoints. To perform recognition, landmarks and fingerprints are computed for the unknown sample and used to retrieve matching fingerprints from the database. For each file containing matching fingerprints, the landmarks are compared with landmarks of the sample at which the same fingerprints were computed. If a large number of corresponding landmarks are linearly related, i.e., if equivalent fingerprints of the sample and retrieved file have the same time evolution, then the file is identified with the sample. The method can be used for any type of sound or music, and is particularly effective for audio signals subject to linear and nonlinear distortion such as background noise, compression artifacts, or transmission dropouts. The sample can be identified in a time proportional to the logarithm of the number of entries in the database; given sufficient computational power, recognition can be performed in nearly real time as the sound is being sampled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and apparatus for using Taylor series expansion concepts to substantially reduce nonlinear distortion
InactiveUS6853247B2Reducing canceling nonlinearitiesReduce and cancel nonlinearitiesAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
Methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling nonlinearities of any order in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. In particular, methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling third order nonlinearities in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. A first coupler is used to split an input signal into two equal-amplitude in-phase components, each component is processed by two nonlinear devices with different nonlinearities, and a final combiner, such as a 180-degree hybrid, recombines the processed signals 180 degrees out of phase and substantially reduces and / or cancels the undesired nonlinear distortion components arising due to nonlinearities in the nonlinear devices.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Sampled amplitude read channel employing an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in a read signal
InactiveUS7012772B1Minimize complexityLow costMultiple-port networksModification of read/write signalsNonlinear distortionAsymmetric head
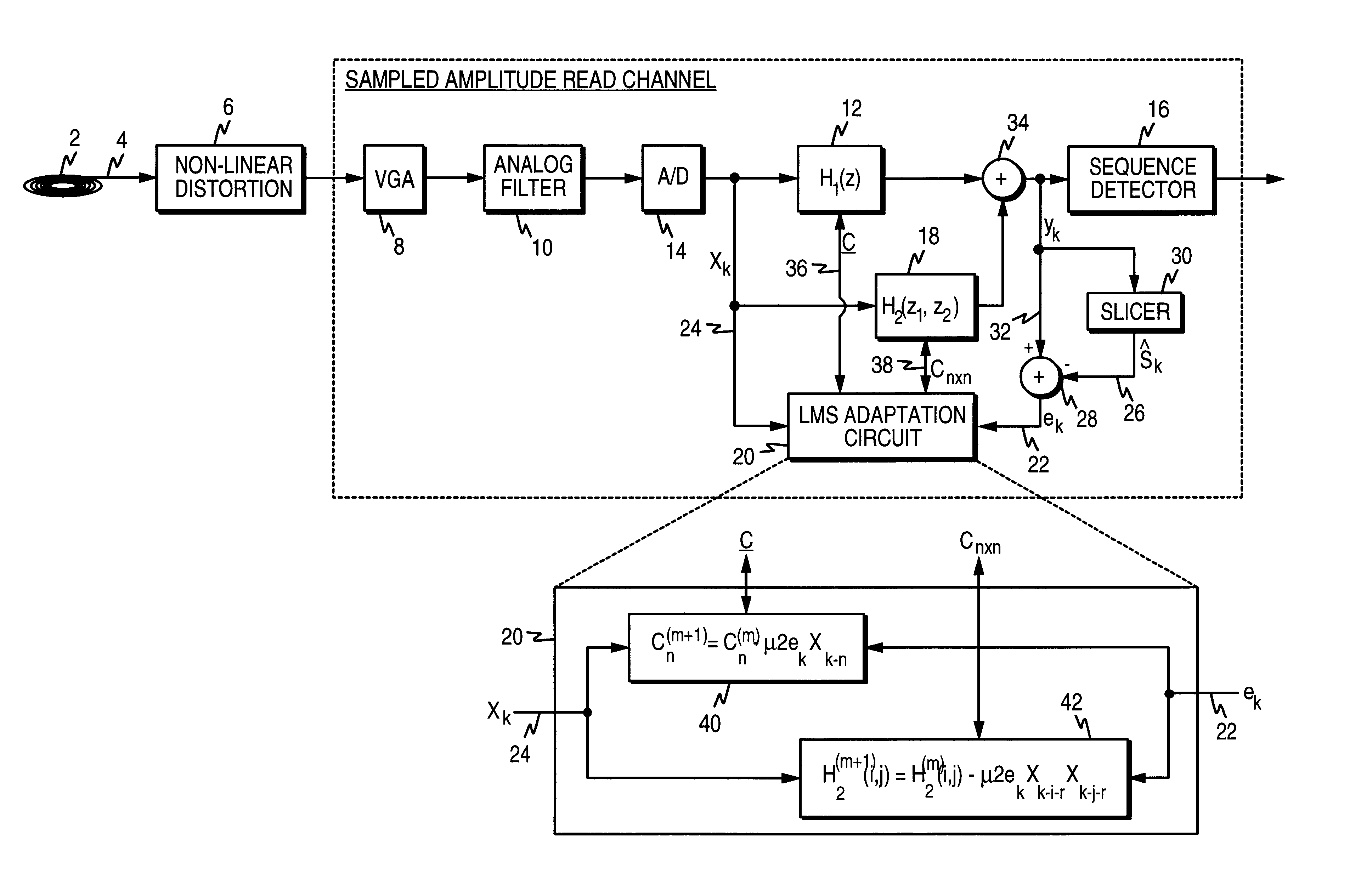
A sampled amplitude read channel is disclosed for magnetic disk storage systems comprising an adaptive non-linear correction circuit for correcting non-linear distortions in the read signal, such as asymmetry caused by the non-linear response of a magneto-resistive (MR) read head. The analog read signal is sampled and the discrete time sample values equalized into a desired partial response prior to sequence detection. The non-linear correction circuit is inserted into the read path prior to the sequence detector and adaptively tuned by a least-mean-square (LMS) adaptation circuit. In one embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit is a discrete-time Volterra filter comprising a linear response for implementing an equalizing filter, and a non-linear response for attenuating non-linear distortions in the read signal. The filter coefficients of both the linear and non-linear sections of the Volterra filter are adaptively adjusted by the LMS adaptation circuit. In an alternative embodiment, the non-linear correction circuit operates in the analog domain, prior to the sampling device, where the cost and complexity can be minimized. The analog correction circuit implements an inverse response to that of the non-linearity in the read signal, and the response is adaptively tuned using an LMS update value computed in discrete-time for a Volterra filter, without actually implementing a Volterra filter. Further, the LMS update value for the analog correction circuit can be implemented using a simple squaring circuit.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
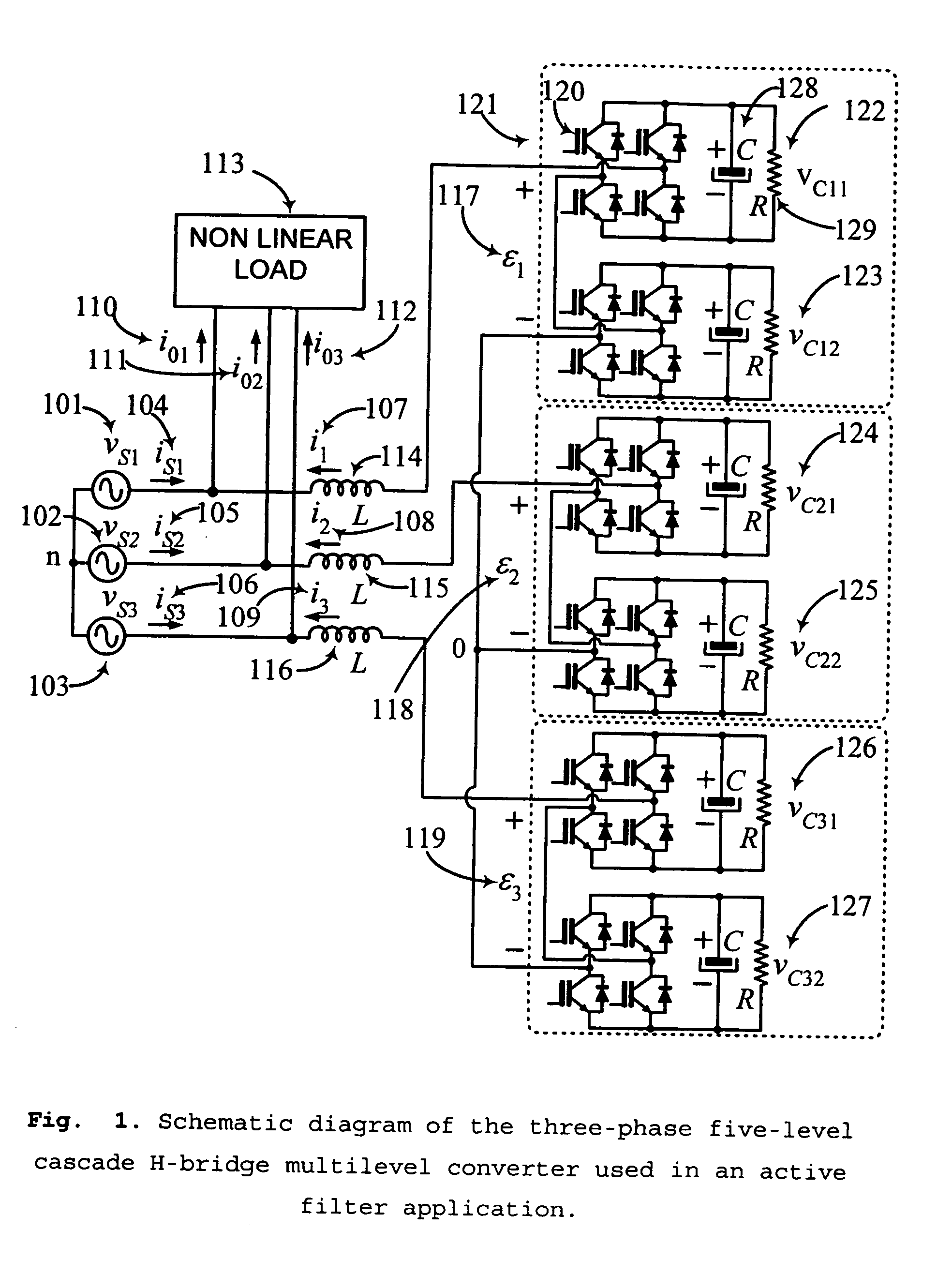
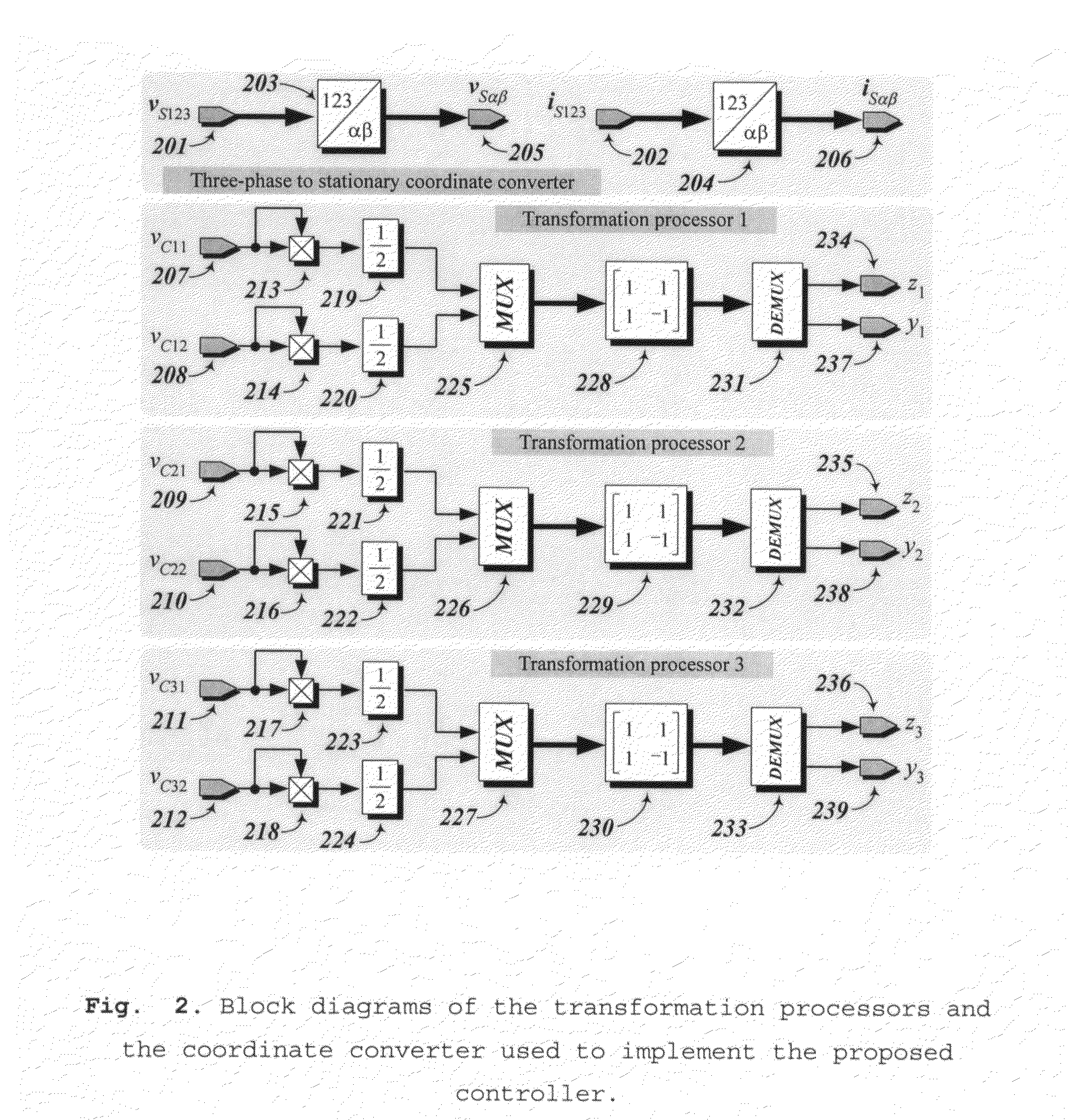
Controller for the three-phase cascade multilevel converter used as shunt active filter in unbalanced operation with guaranteed capacitors voltages balance
InactiveUS20090102436A1Increase the switching frequencyDesigning can be facilitatedActive power filteringElectric variable regulationNonlinear distortionCapacitor voltage
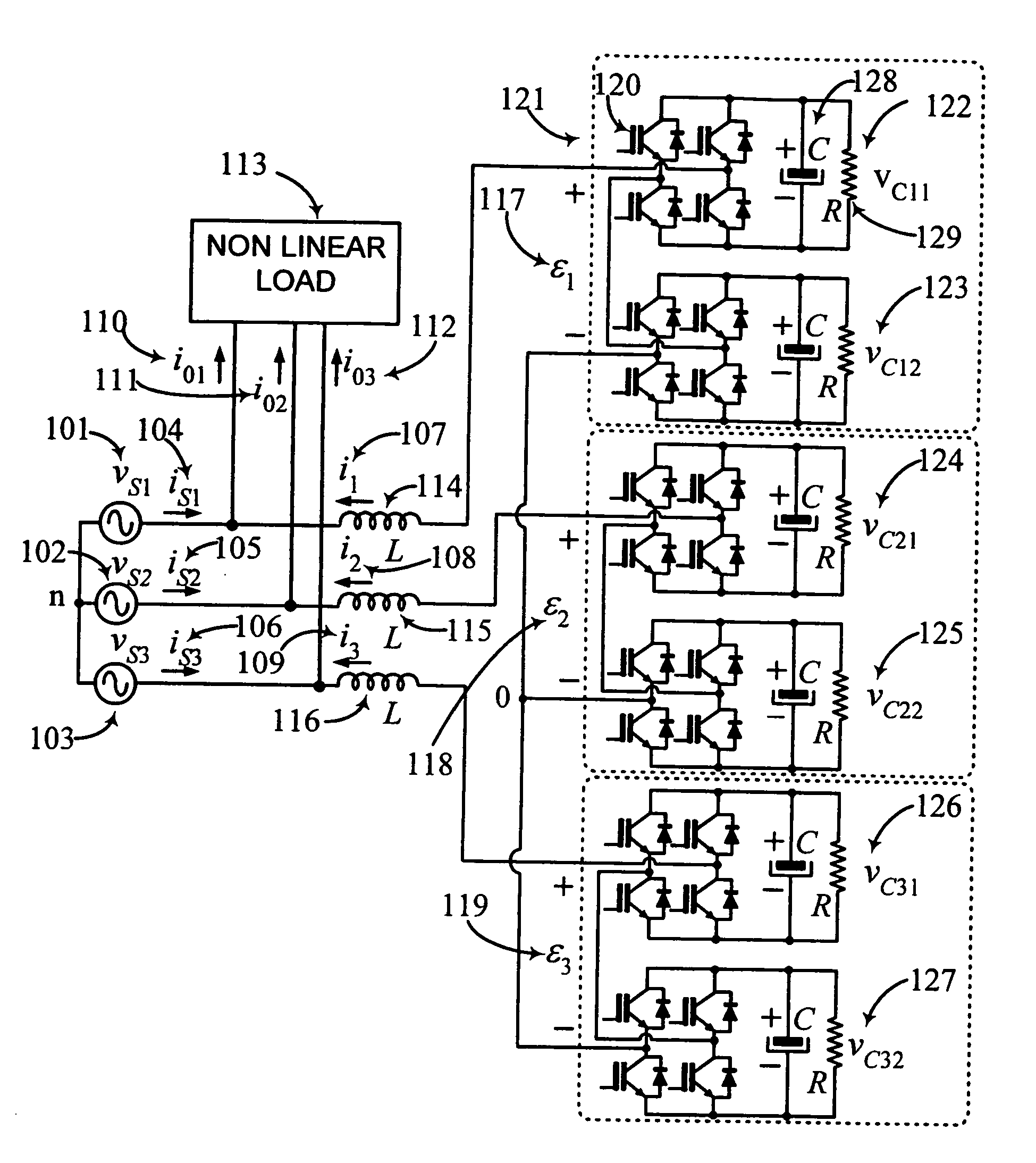
The present invention comprises a controller for the cascade H-bridge three-phase multilevel converter used as a shunt active filter. Based on the proposed mathematical model, the controller is designed to compensate harmonic distortion and reactive power due to a nonlinear distorting load. Simultaneously, the controller guarantees regulation and balance of all capacitor voltages. The idea behind the controller is to allow distortion of the current reference during the transients to guarantee regulation and balance of the capacitors voltages. The controller provides the duty ratios for each H-bridge of the cascade multilevel converter.
Owner:INST POTOSINO DE INVESTIGACION CIENTIFICA Y TECHCA A C
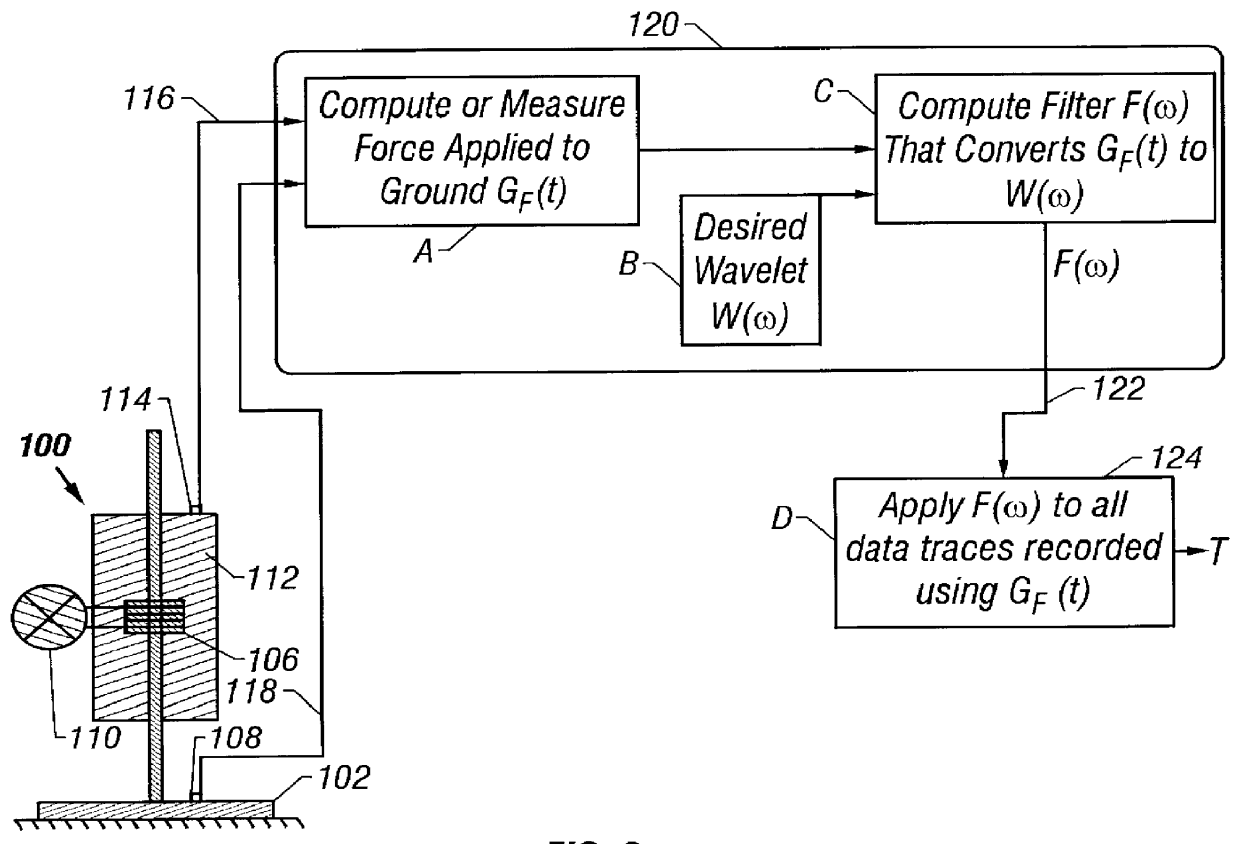
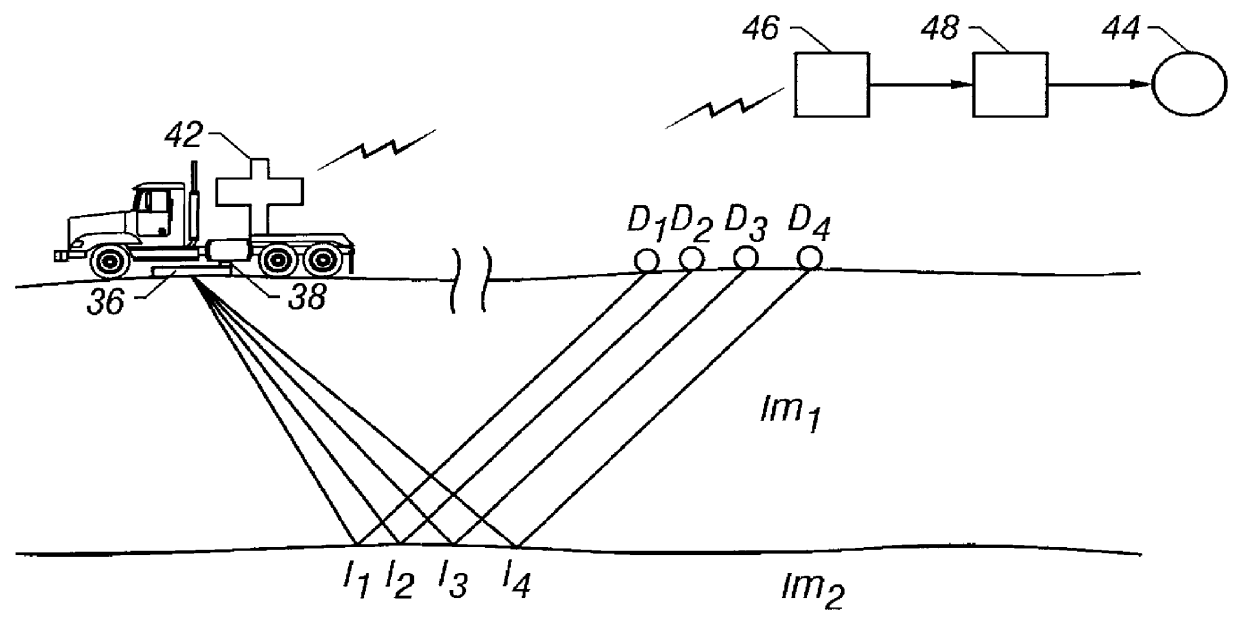
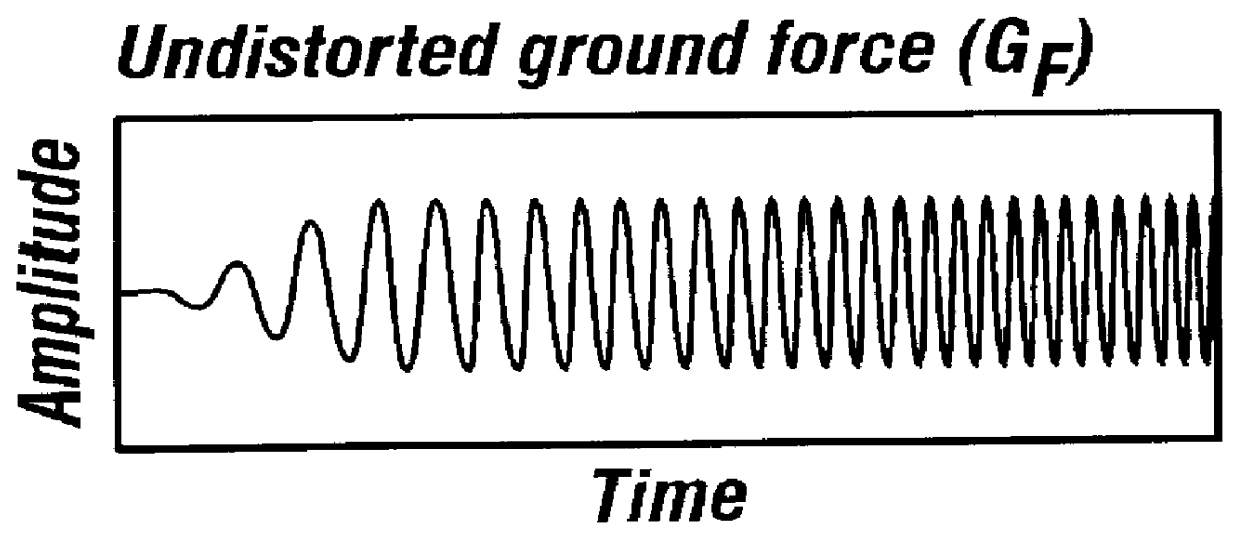
Seismic data acquisition and processing using non-linear distortion in a vibratory output signal
InactiveUS6161076AImprove stabilityCancel noiseBeacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSeismic signal processingNonlinear distortionRelative phase
A method for improving vibratory source seismic data uses a filter which converts a recorded seismic groundforce signal (including harmonic distortion therein) into a desired short-duration wavelet. A plurality of surveys may be carried out using a plurality of sweeps from plurality of vibrators that have their relative phases encoded, the groundforce signal of each vibrator being measured. The recorded seismic reflection signals are then processed to separate out the signals from each vibrator. In another aspect, harmonics of upto any desired order may be canceled while carrying out multiple surveys with a plurality of vibrators. In a marine environment, the recorded signal from a vibrator towed by a moving vessel is used to derive a Doppler shift correction filter that is applied to reflection seismic data.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC +1
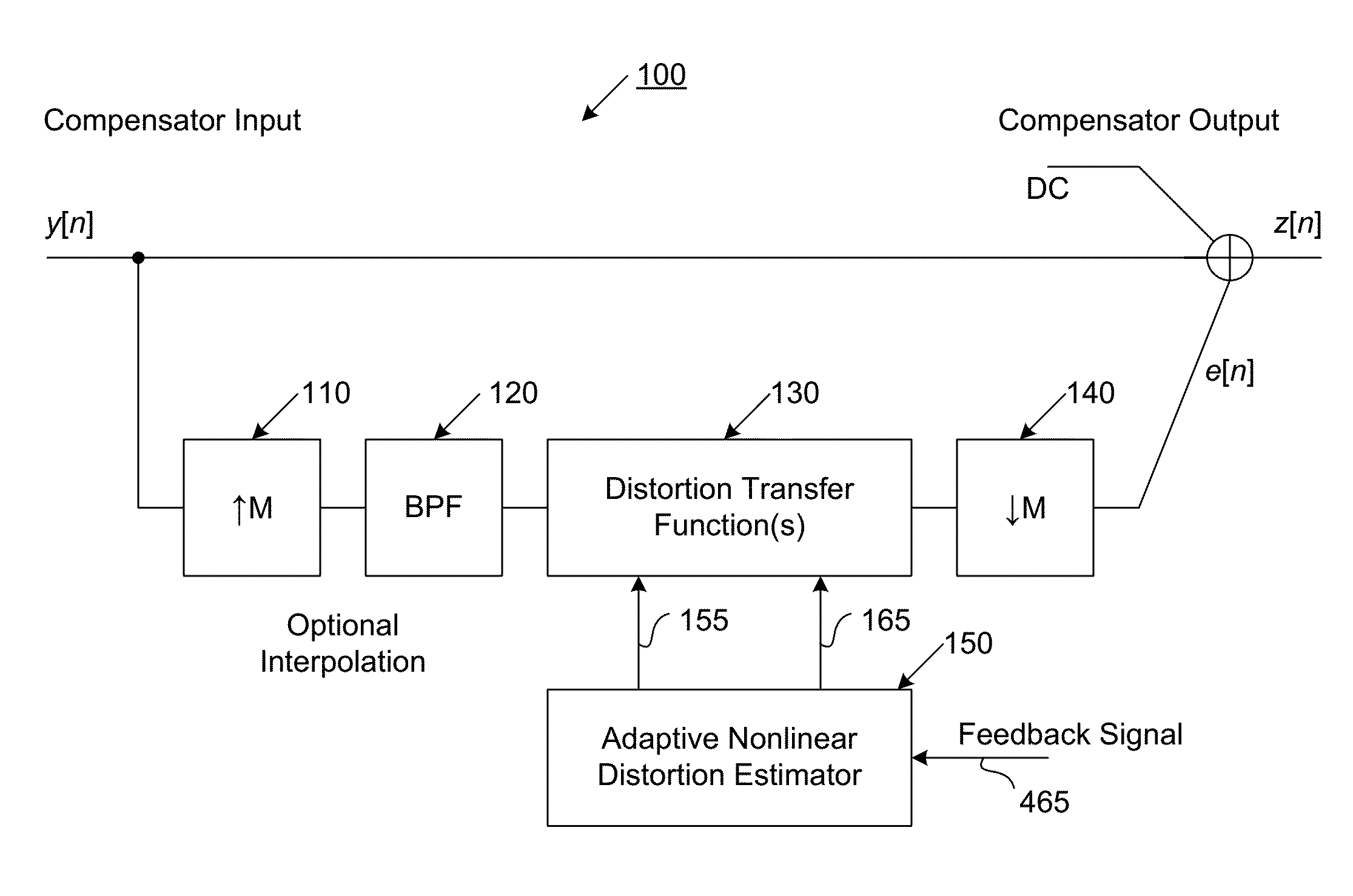
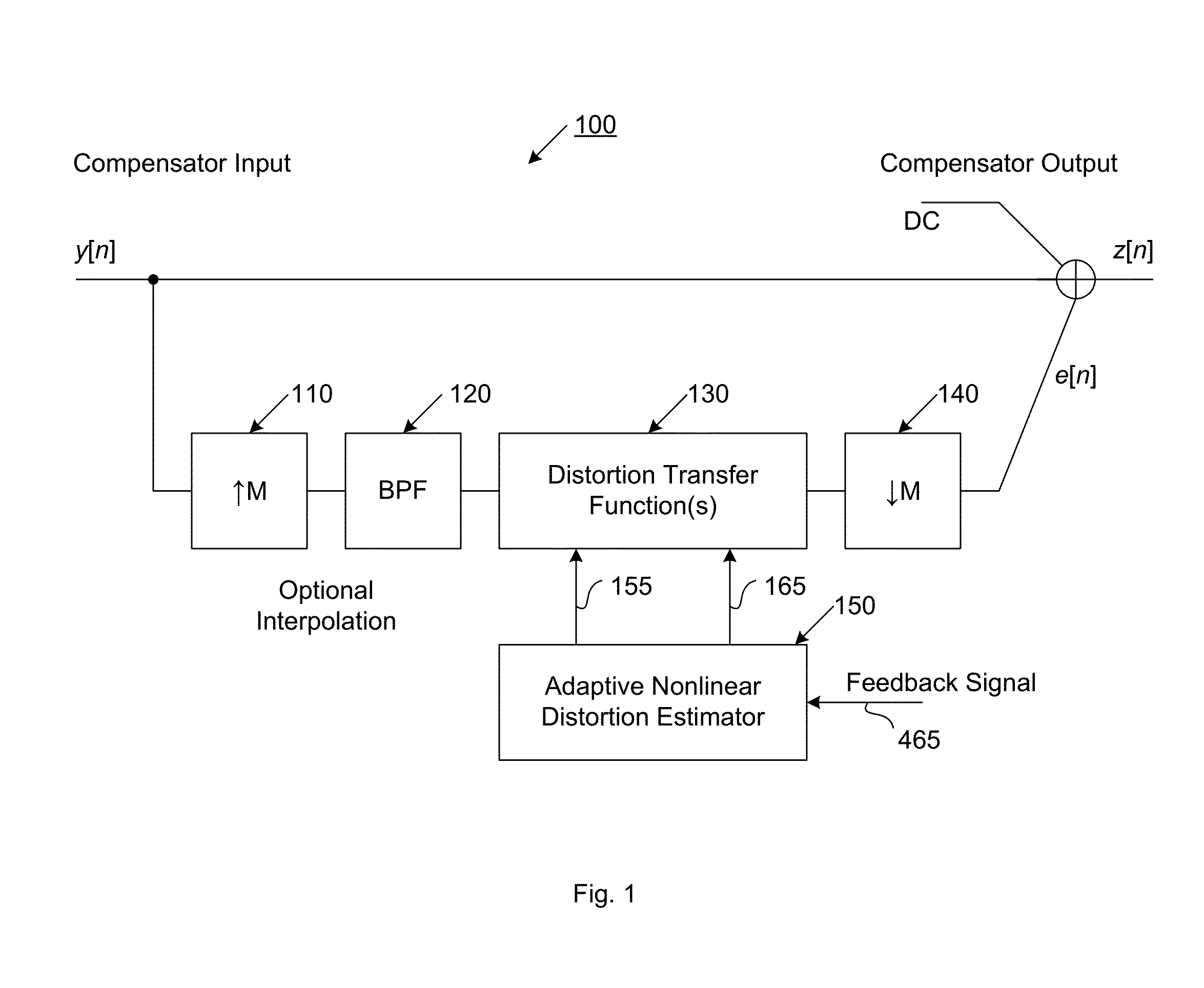
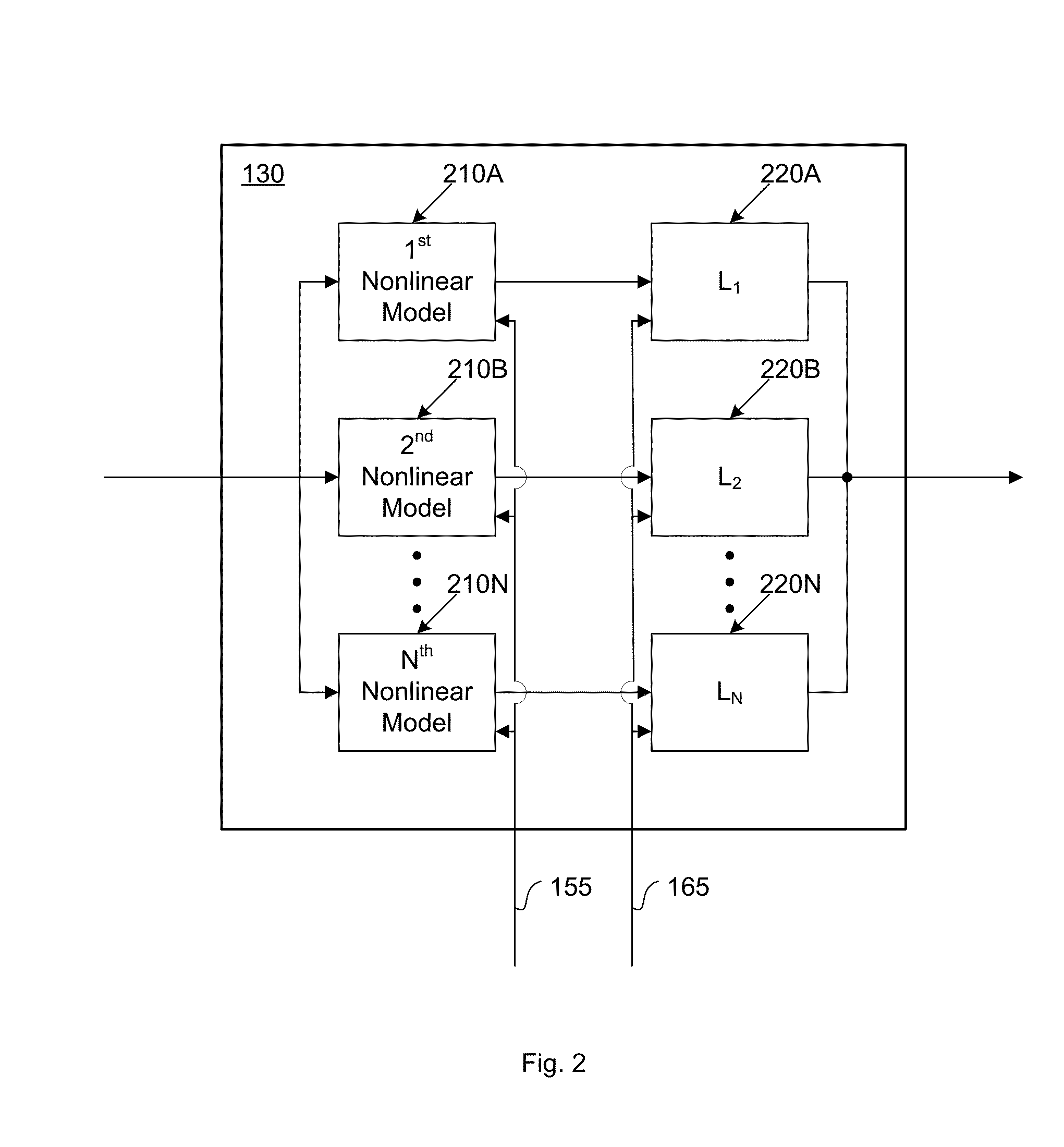
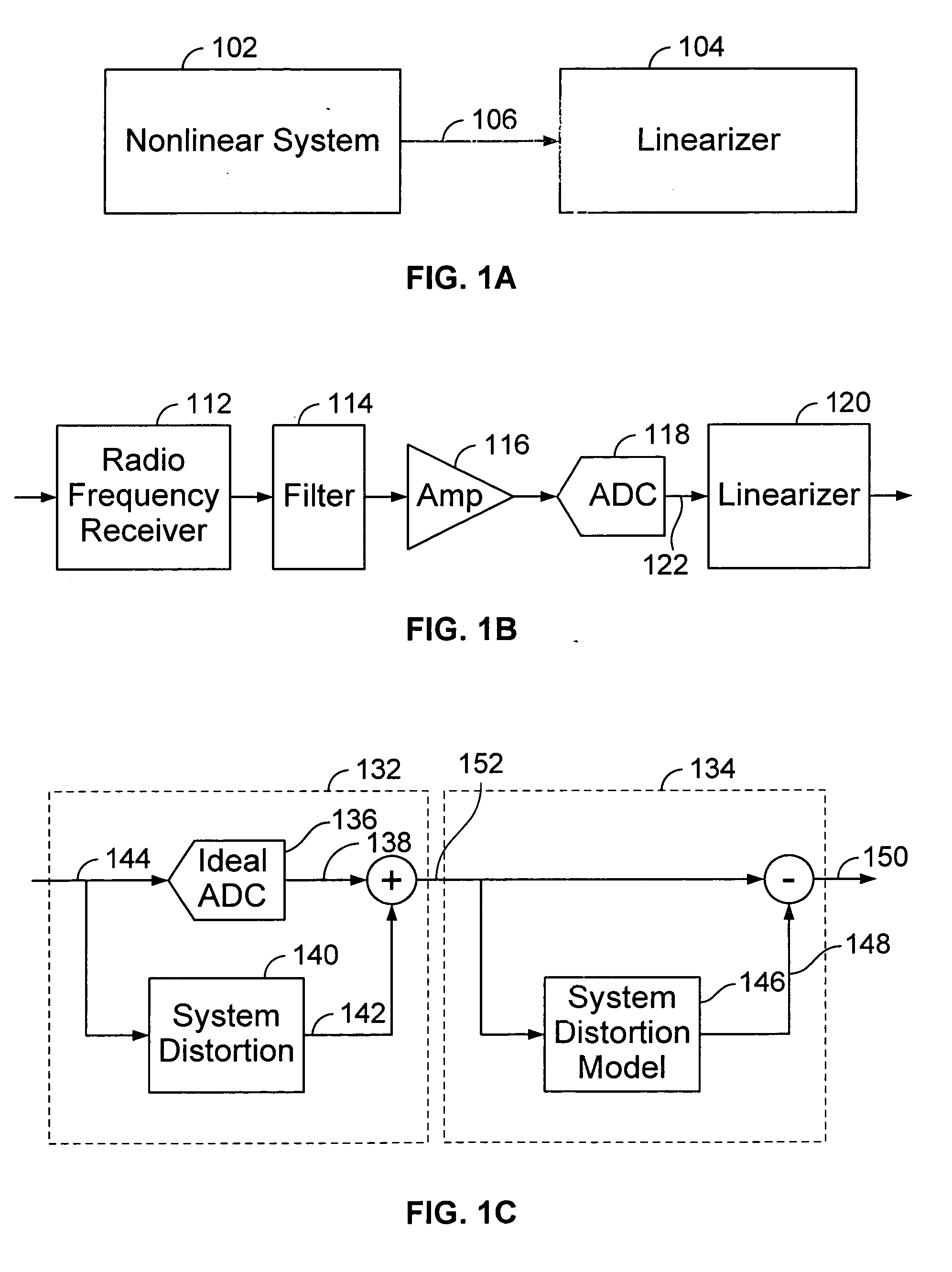
Compensator for removing nonlinear distortion
ActiveUS20160191020A1Easy to processReduce complexityChannel dividing arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionComputation complexity
The present invention is a computationally-efficient compensator for removing nonlinear distortion. The compensator operates in a digital post-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as analog-to-digital converters and RF receiver electronics. The compensator also operates in a digital pre-compensation configuration for linearization of devices or systems such as digital-to-analog converters, RF power amplifiers, and RF transmitter electronics. The compensator effectively removes nonlinear distortion in these systems in a computationally efficient hardware or software implementation by using one or more factored multi-rate Volterra filters. Volterra filters are efficiently factored into parallel FIR filters and only the filters with energy above a prescribed threshold are actually implemented, which significantly reduces the complexity while still providing accurate results. For extremely wideband applications, the multi-rate Volterra filters are implemented in a demultiplexed polyphase configuration which performs the filtering in parallel at a significantly reduced data rate. The compensator is calibrated with an algorithm that iteratively subtracts an error signal to converge to an effective compensation signal. The algorithm is repeated for a multiplicity of calibration signals, and the results are used with harmonic probing to accurately estimate the Volterra filter kernels. The compensator improves linearization processing performance while significantly reducing the computational complexity compared to a traditional nonlinear compensator.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
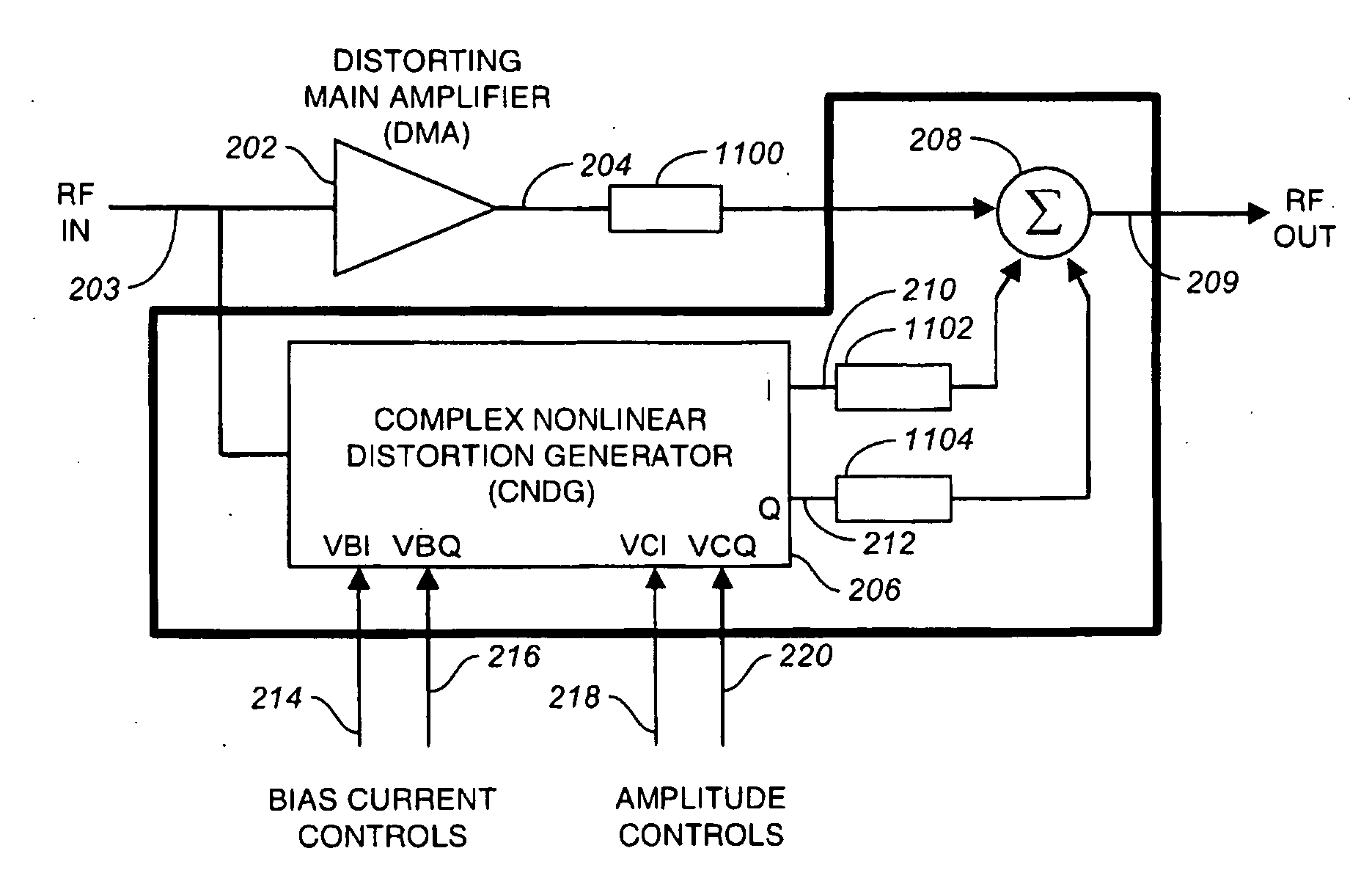
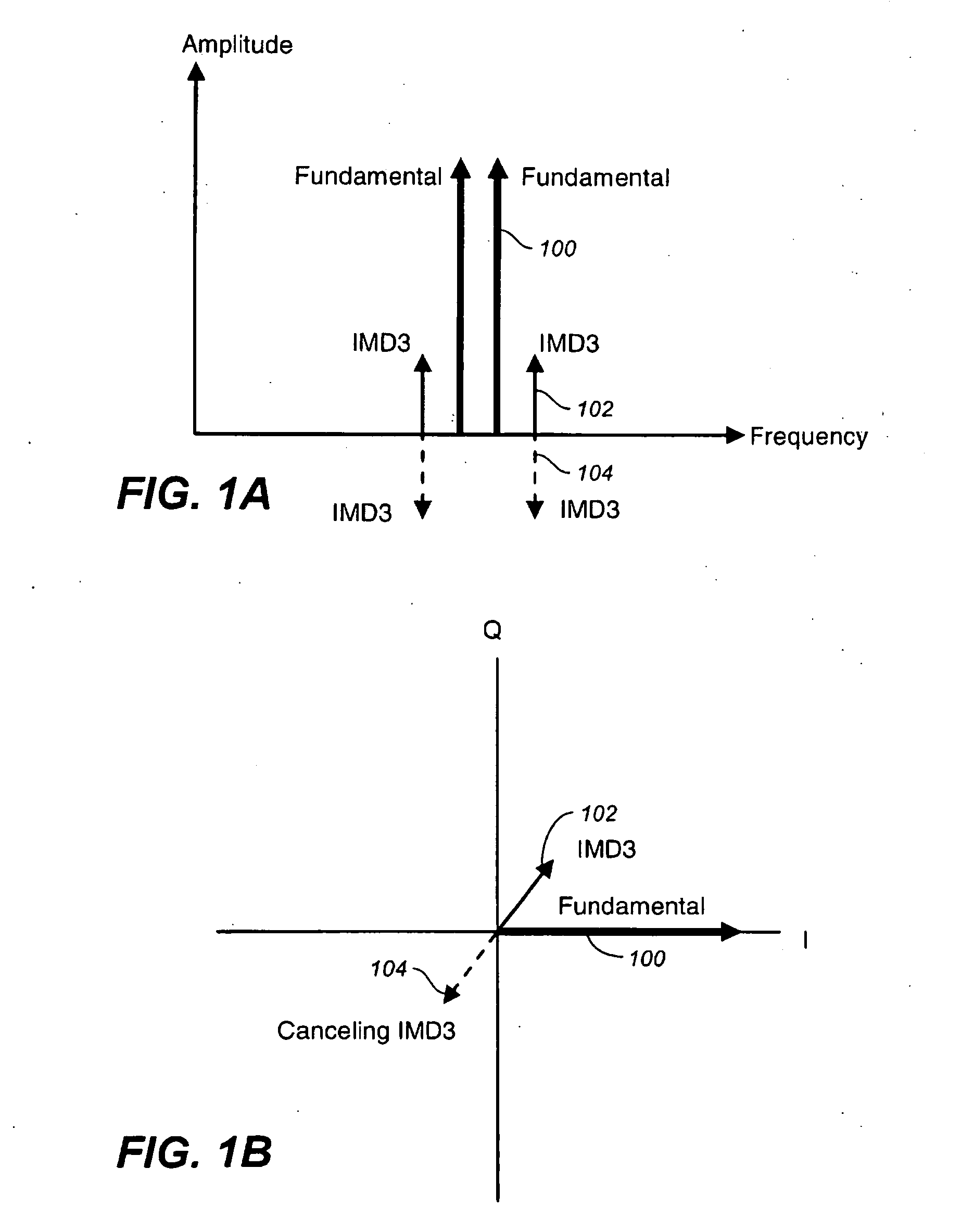
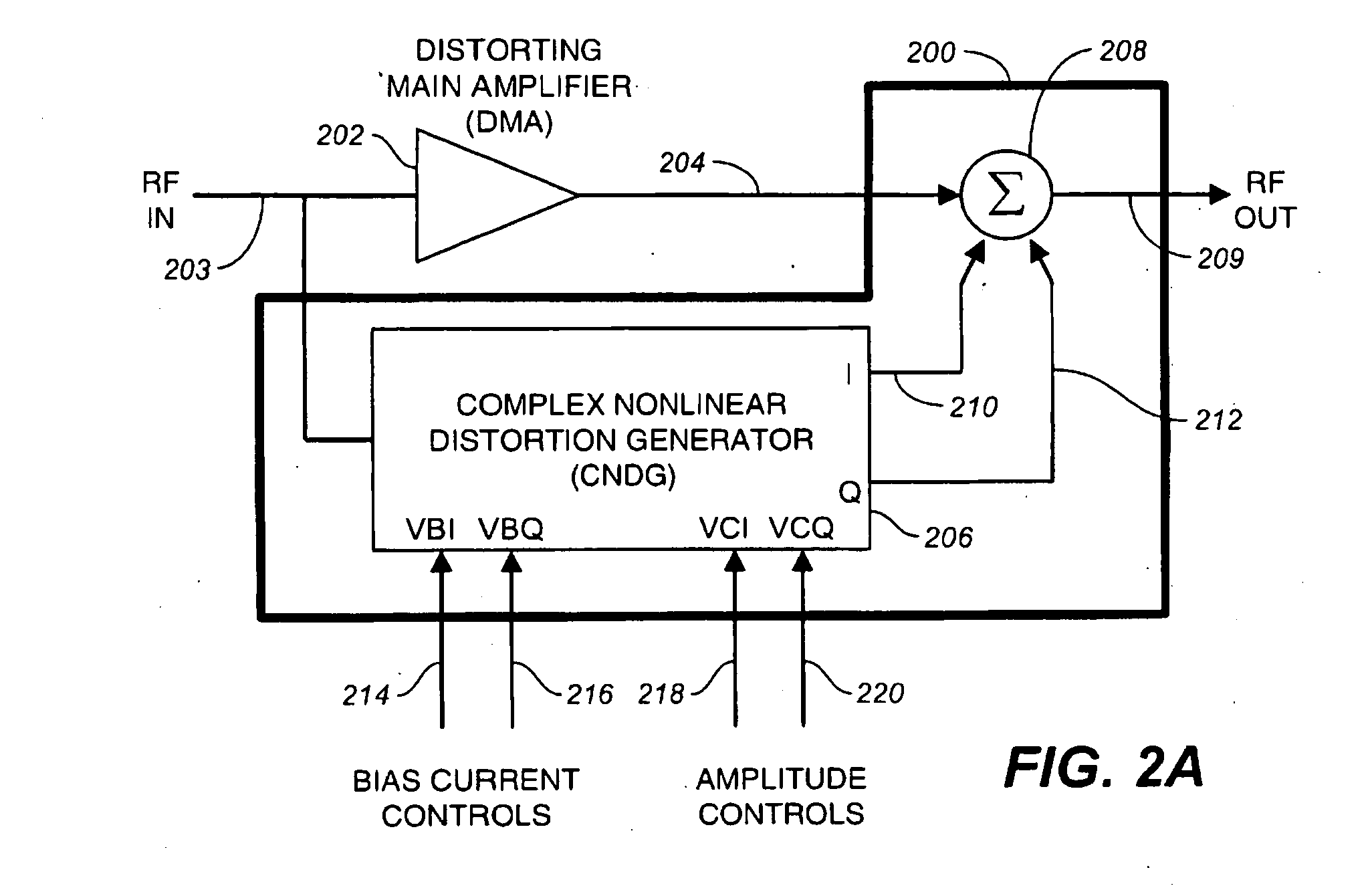
High efficiency RF system linearizer using controlled complex nonlinear distortion generators
InactiveUS20100225389A1Reduces nonlinear intermodulation distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationNonlinear distortionFour quadrants
A linearizer reduces nonlinear intermodulation distortion in radio frequency and microwave systems by first directly generating in-phase and quadrature nonlinear intermodulation products of the system input. Controllable amounts of each phase are then added back into the system such that the vector sum of nonlinear intermodulation products at the output is reduced or eliminated by destructive interference, while the fundamentals are substantially unaffected. The quadrature distorted signals are generated with two lightly-biased and thus overdriven differential pairs having gain-determining degeneration impedances that are in quadrature with each other. The amount of each quadrature phase summed to the output is controlled with electronically tunable four-quadrant variable attenuators. The quadrature phasing enables rapidly convergent tuning to minimize distortion using conventional scalar spectral analysis. The advantages of a linearizer using rectangular vector coordinate system are significant.
Owner:TEETZEL ANDREW M
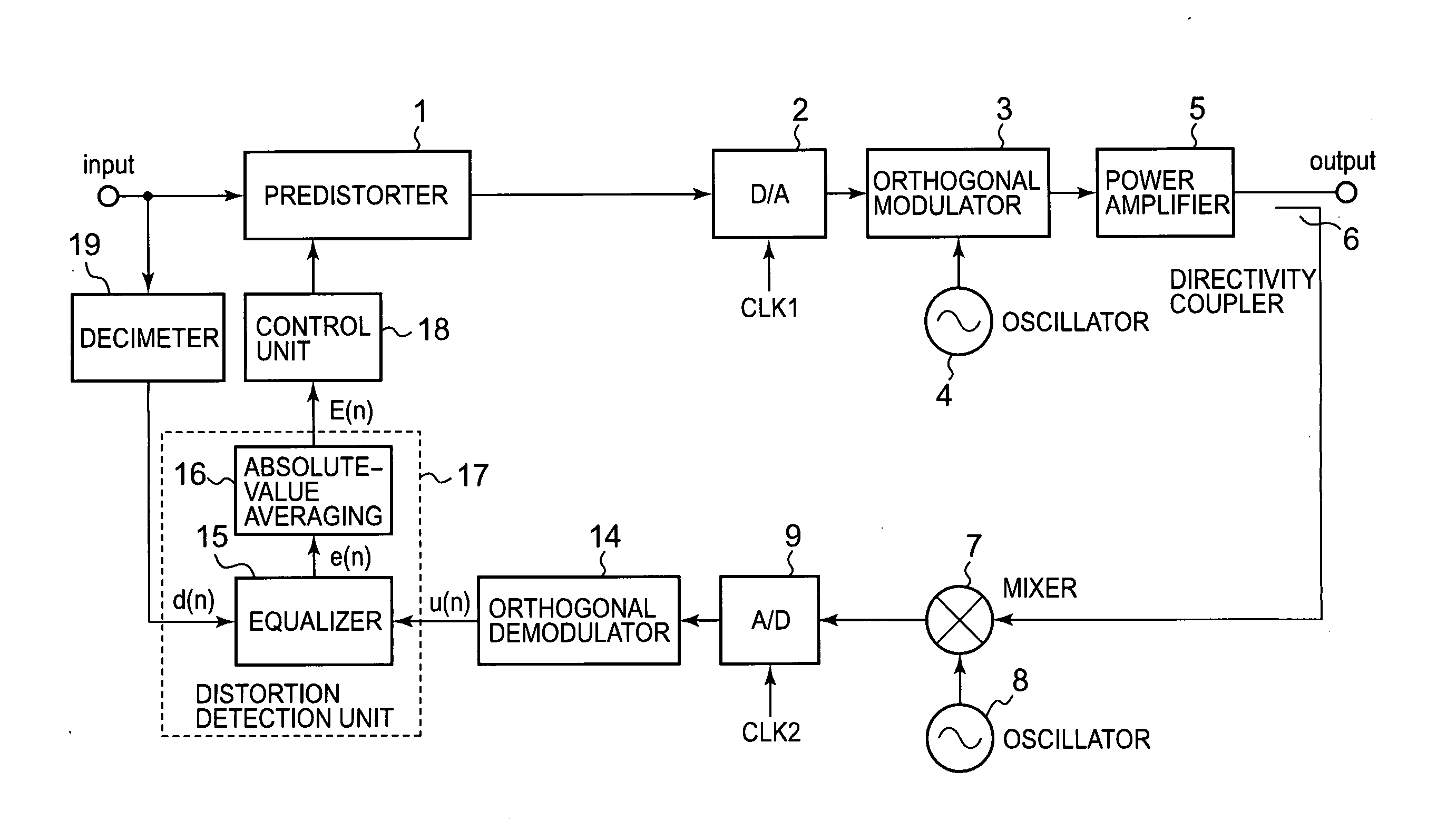
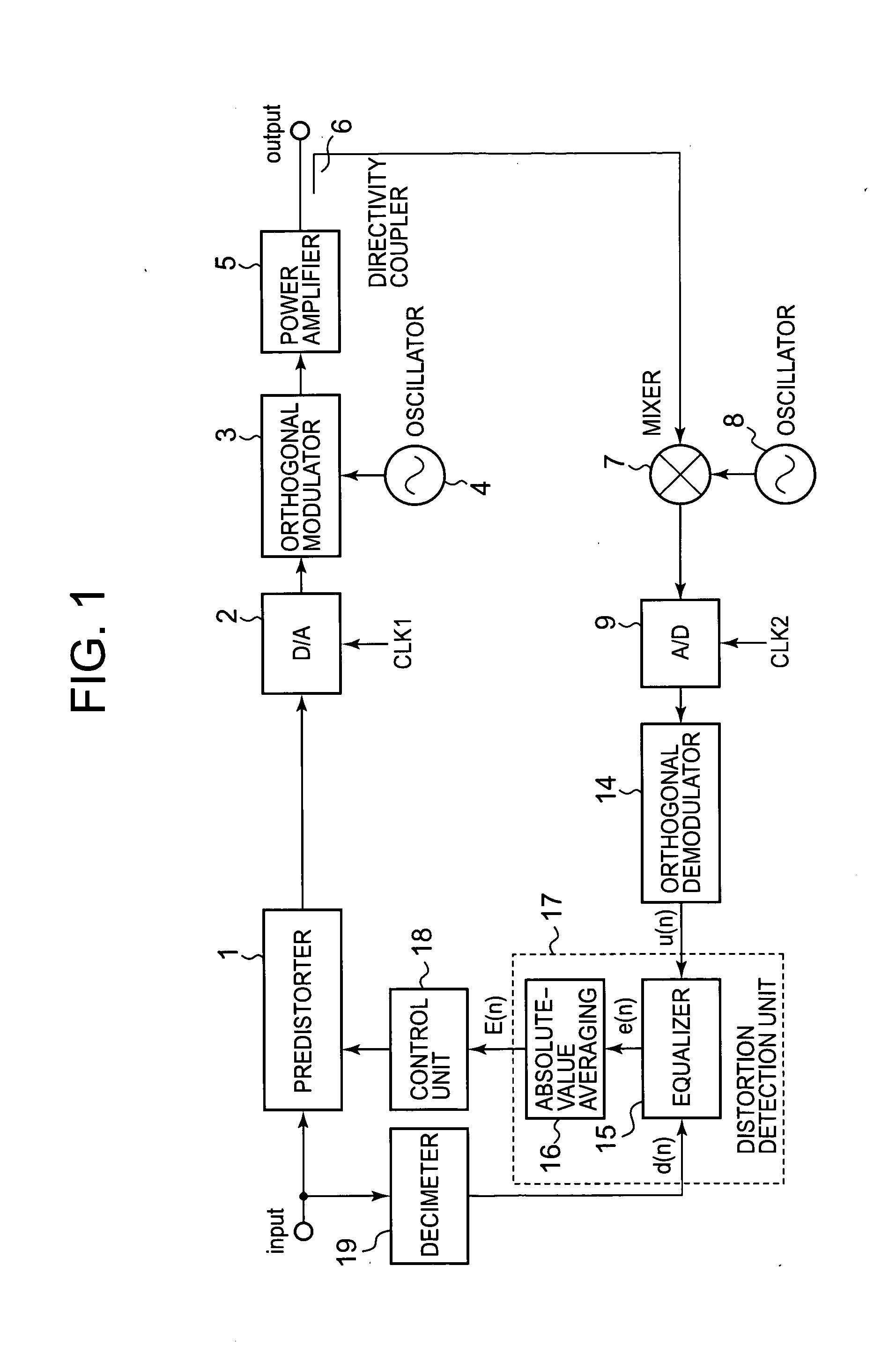
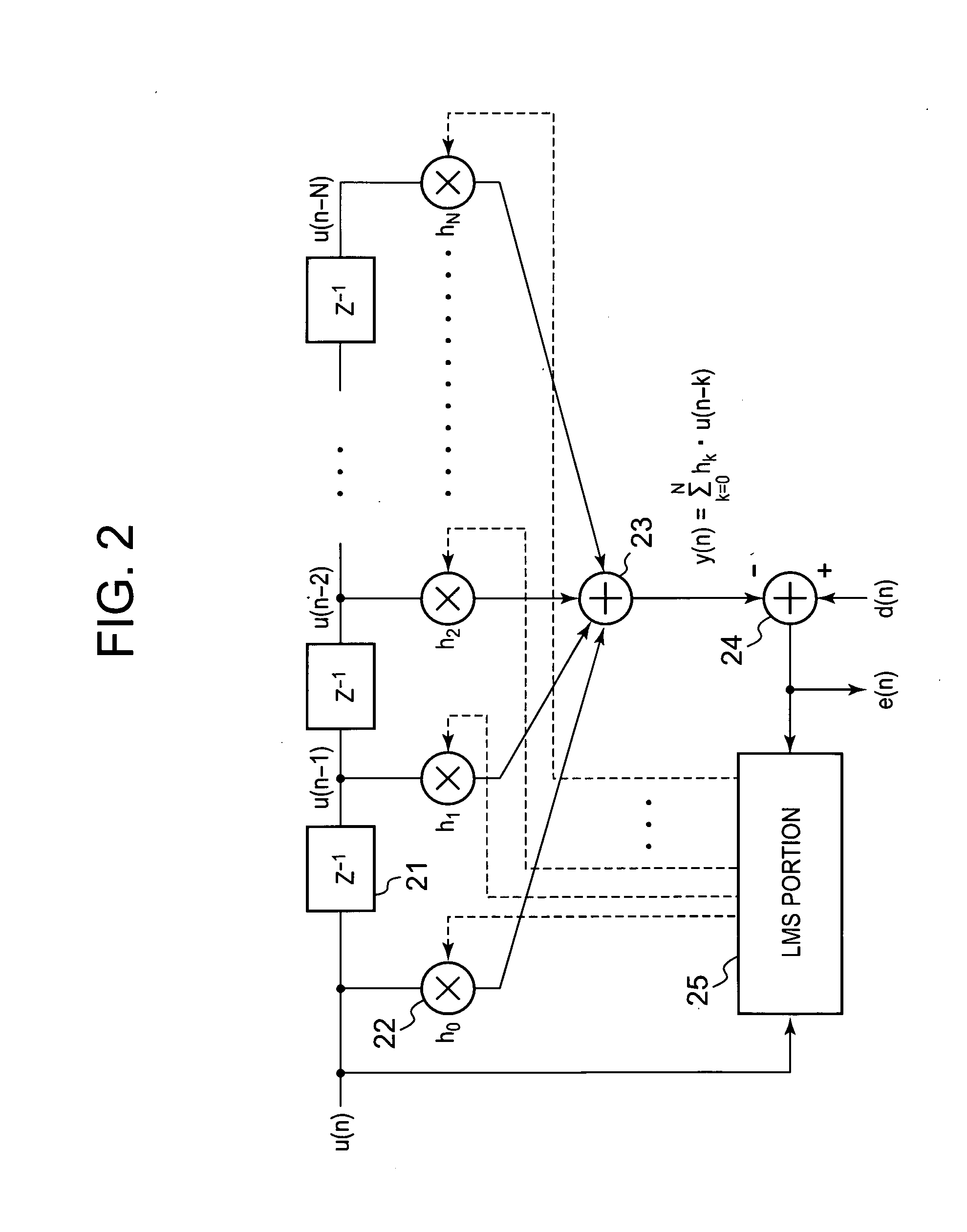
Non-linear distortion detection method and distortion compensation amplifying device
InactiveUS20080187035A1Improve accuracyImprove convergence stabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionMultiple-port networksNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
A conventional power amplifying device has a problem that when a signal band is widened, sampling frequency for distortion detection is increased and an FFT calculation amount of a distortion compensation unit is increased, which increase a circuit size and power consumption. The present invention provides a non-linear distortion detection method and a distortion compensation amplifying device capable of suppressing increase of the circuit size and the power consumption even if the signal band is widened. A signal obtained by feeding back an output of a power amplifier is sampled by an A / D converter. An equalizer of a distortion detection unit uses an input signal d(n) of a predistorter as a reference symbol to detect an equalization error e(n) of the orthogonal demodulation signal u(n). An absolute value averaging unit outputs an absolute value of the equalization error e(n) which has been temporally averaged to E(n) as a distortion value to a control unit. According to the distortion value, the control unit adaptively controls the predistorter to perform distortion compensation.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
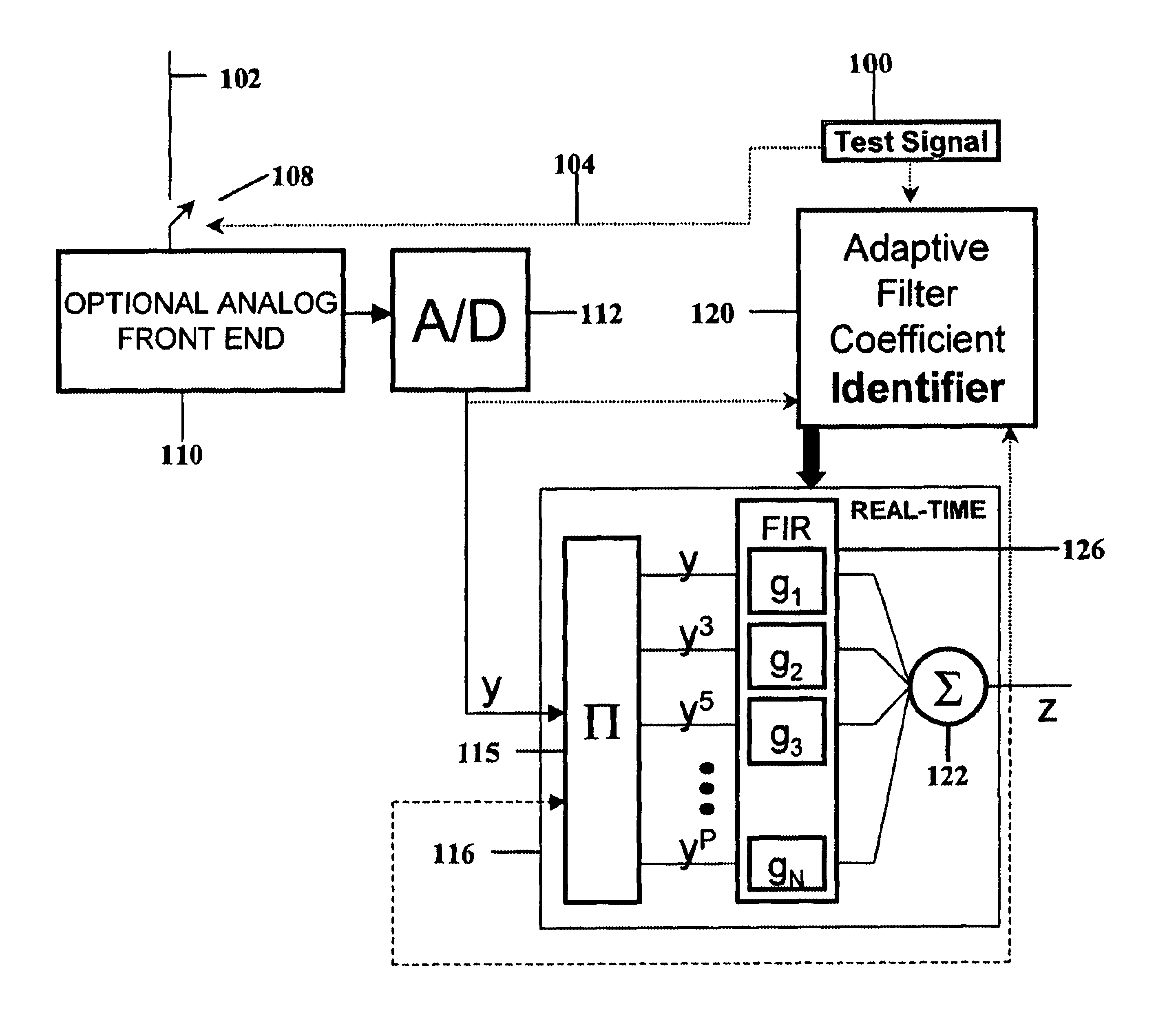
Highly linear analog-to-digital conversion system and method thereof
InactiveUS6639537B1Reduce nonlinear distortionMinimizes non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFinite impulse responseNonlinear distortion
A highly linear analog-to-digital (ADC) conversion system has an analog front-end device in cascade with a standard ADC converter, and a tunable digital non-linear equalizer. The equalizer corrects the quantization distortion, deviations from ideal response, and additive noises generated by the analog front-end device and ADC converter. The equalizer is formed by three main parts: Generate Function Streams Unit, Finite Impulse Response FIR filters and a summer. The equalizer receives the unequalized output from the ADC converter and generates a plurality of monomial streams in a systolic fashion. Each of the monomial streams is passed through a corresponding linear finite impulse response FIR filter. A convolution sum of all outputs from the FIR filters produces a unique equalized output with the non-linear distortion reduced to a satisfactory level. The FIR filter coefficients are determined by an Identity Equalizer Coefficient Unit, and a Test Signal Generator with different types of test signals. The FIR filter coefficients are set to minimize an error function.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
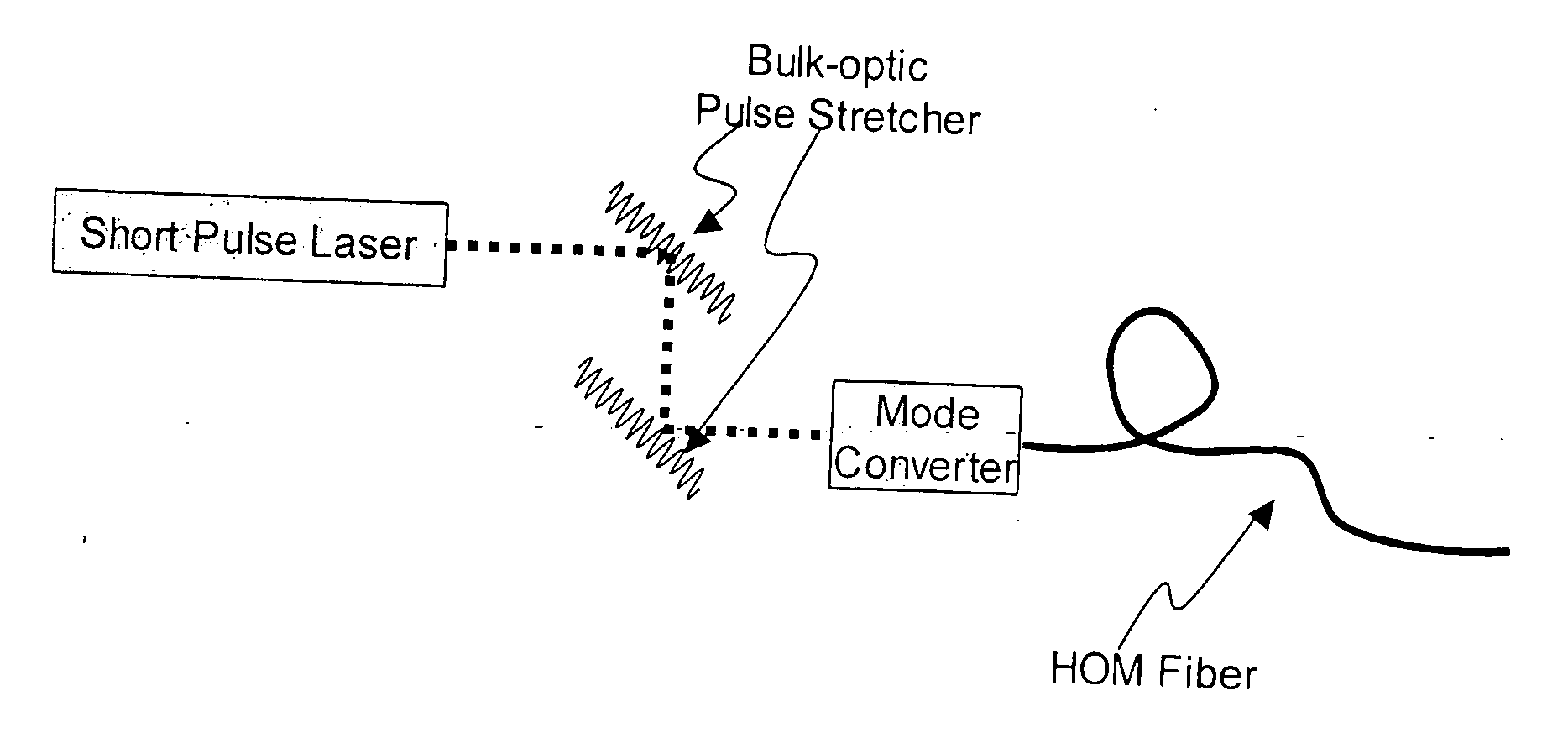
Optical fiber systems for delivering short high power pulses
InactiveUS20060233554A1Minimal distortionMinimum non-linear impairmentDistortion/dispersion eliminationOptical light guidesNonlinear distortionFew mode fiber
Described is an optical fiber system for delivering ultrashort pulses with minimal distortions due to nonlinearity. The system is based on delivering the optical pulses in a higher order mode (HOM) of a few-moded fiber. The fiber is designed so that the dispersion for the HOM is very large. This results in a dispersion length LD for the delivery fiber that is exceptionally small, preferably less than the non-linear length LNL. Under these conditions the system may be designed so the optical pulses experience minimum non-linear impairment, and short pulse / high peak power levels are reproduced at the output of the delivery fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Methods and apparatus for substantially reducing third order intermodulation distortion and other nonlinear distortions
InactiveUS6906585B2Reducing canceling nonlinearitiesReducing and canceling third order nonlinearitiesAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
Methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling nonlinearities of any order in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. In particular, methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling third order nonlinearities in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. A first coupler is used to split an input signal into two equal-amplitude in-phase components, each component is processed by two nonlinear devices with different nonlinearities, and a final combiner, such as a 180-degree hybrid, recombines the processed signals 180 degrees out of phase and substantially reduces and / or cancels the undesired nonlinear distortion components arising due to nonlinearities in the nonlinear devices.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Predistortion circuit and method for compensating nonlinear distortion in a digital RF communications transmitter
InactiveUS20050163268A1Improve accuracyMinimize processing complexityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionError preventionNonlinear distortionData stream
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Linear distortion is first compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Closed-loop receiver feedback pre-distortion
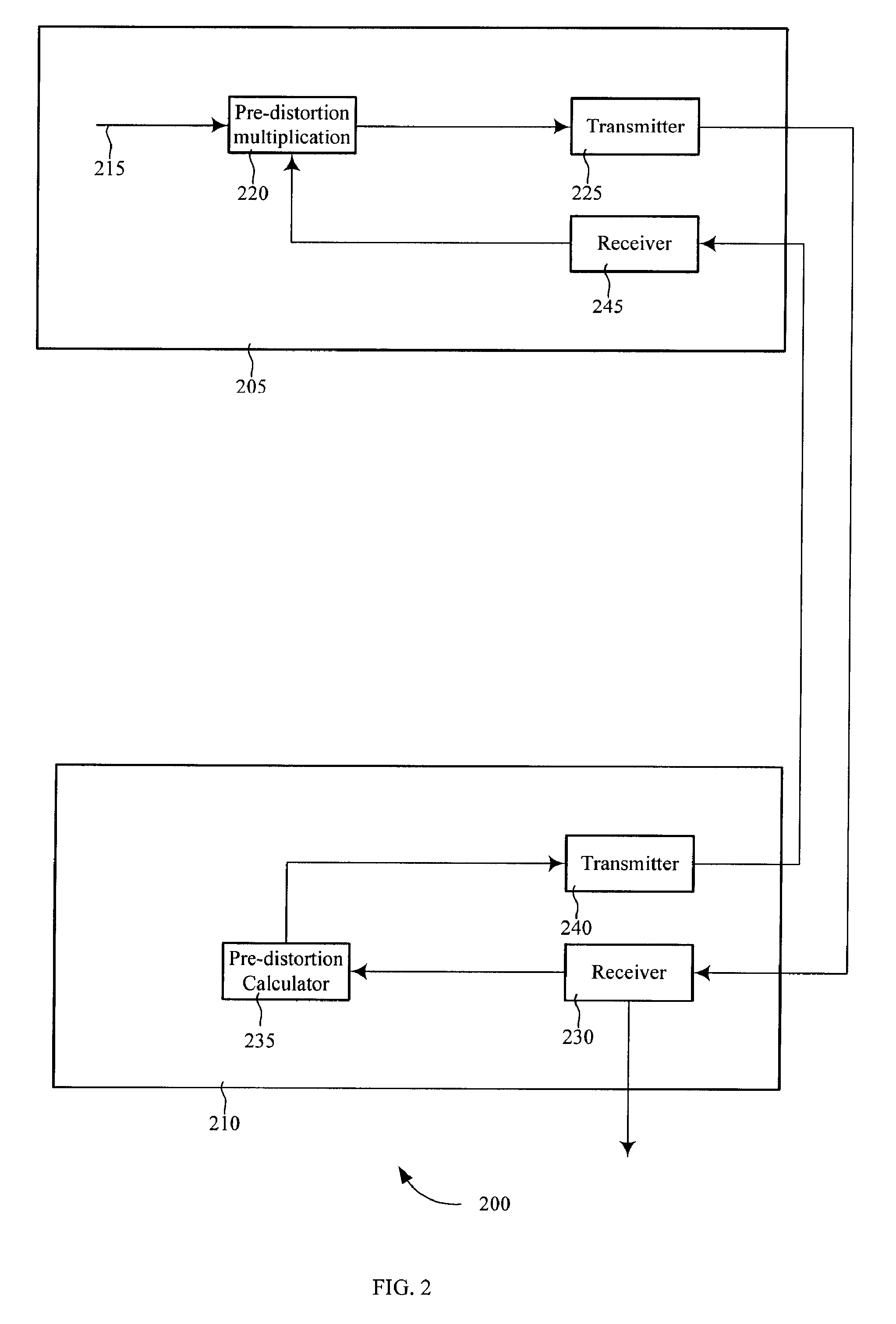
ActiveUS20070153884A1Power managementModulated-carrier systemsNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
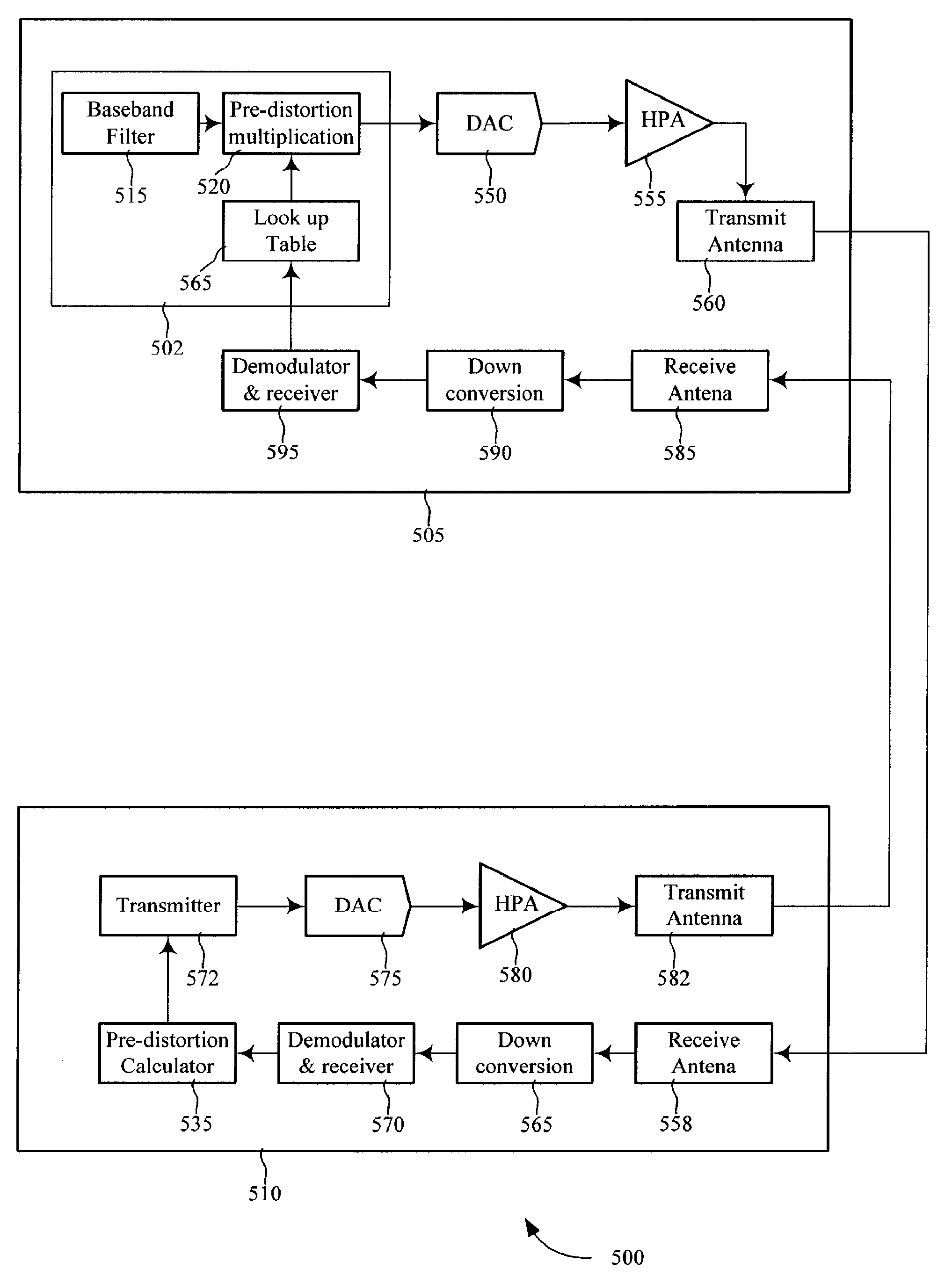
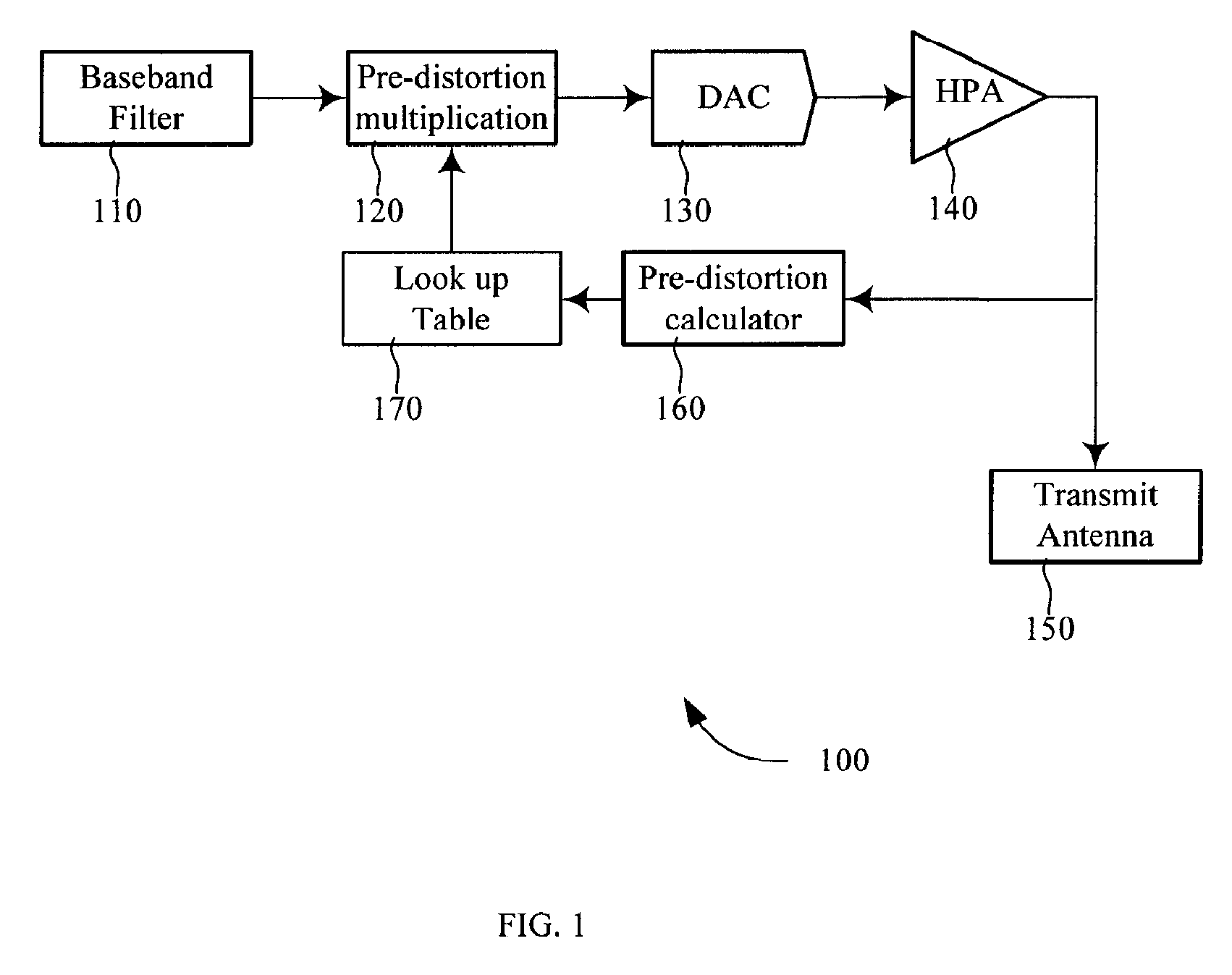
Methods and systems for calculating pre-distortion coefficients in a closed-loop communication system are presented. Transmission terminals that include high power amplifiers are difficult to operate at or near the saturation point without transmitting signals with nonlinear distortions. By pre-distorting the signal prior to amplification the transmitted nonlinear distortions may be decreased. A closed-looped pre-distortion system may include a receiver that calculates the pre-distortion coefficients and transmits these coefficients back to the transmitter. These coefficients may be stored in a pre-distortion coefficient lookup table and may be updated by the receiver terminal.
Owner:VIASAT INC
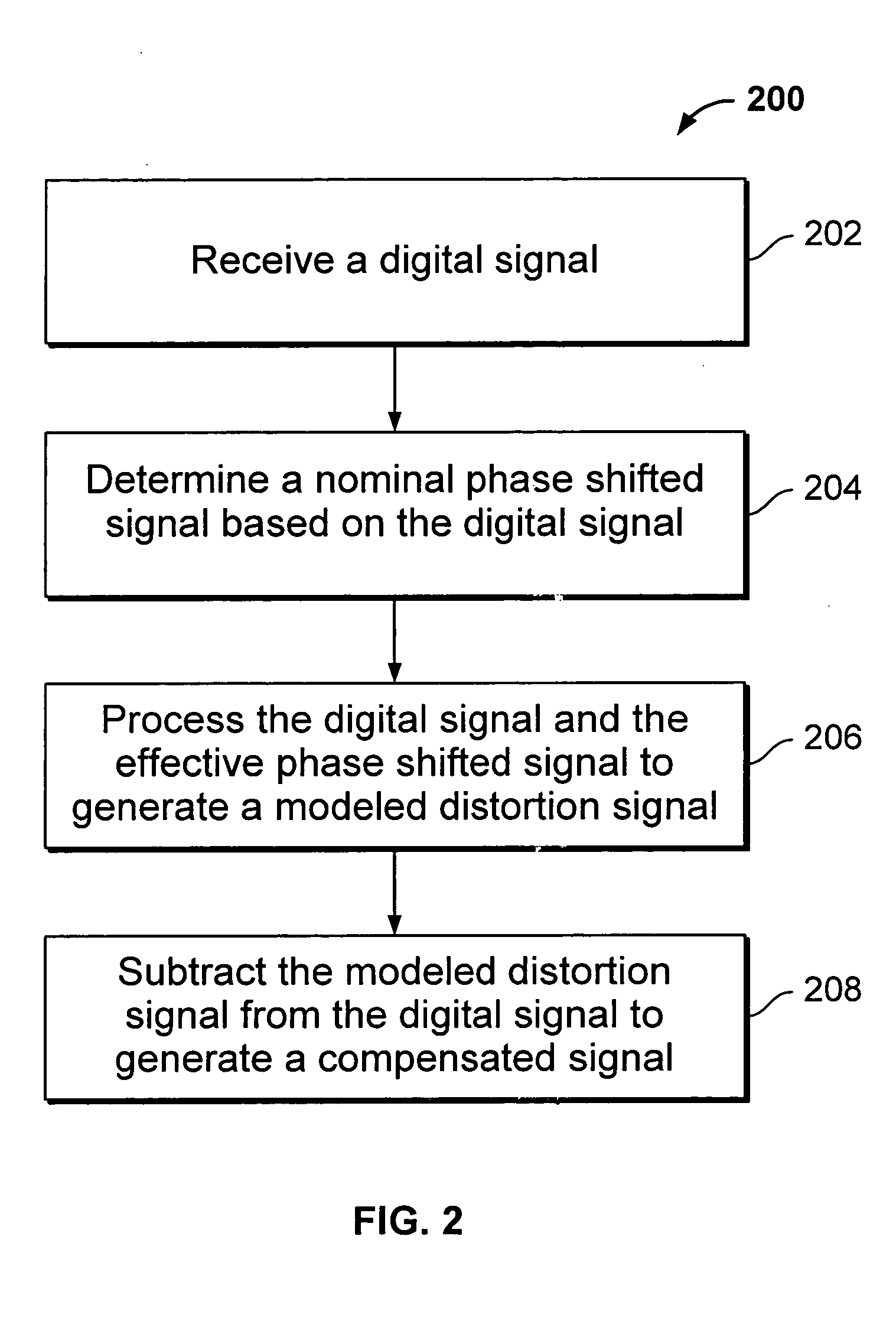
Digital linearizing system
InactiveUS20050219089A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionPhase shifted
A method of compensating for nonlinear distortions in a digital signal comprises receiving the digital signal, generating a nominal phase shifted signal based on the digital signal, generating a modeled distortion signal based on the digital signal and the nominal phase shifted signal, subtracting the modeled distortion signal from the digital signal, and generating a compensated signal. A compensating system comprises an input interface configured to receive a digital signal having nonlinear distortion, and a distortion model coupled to the interface, configured to generate a nominal phase shifted signal based on the digital signal, generate a modeled distortion signal based on the digital signal and the nominal phase shifted signal, subtract the modeled distortion signal from the digital signal, and generate a compensated signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Wideband digital spectrometer
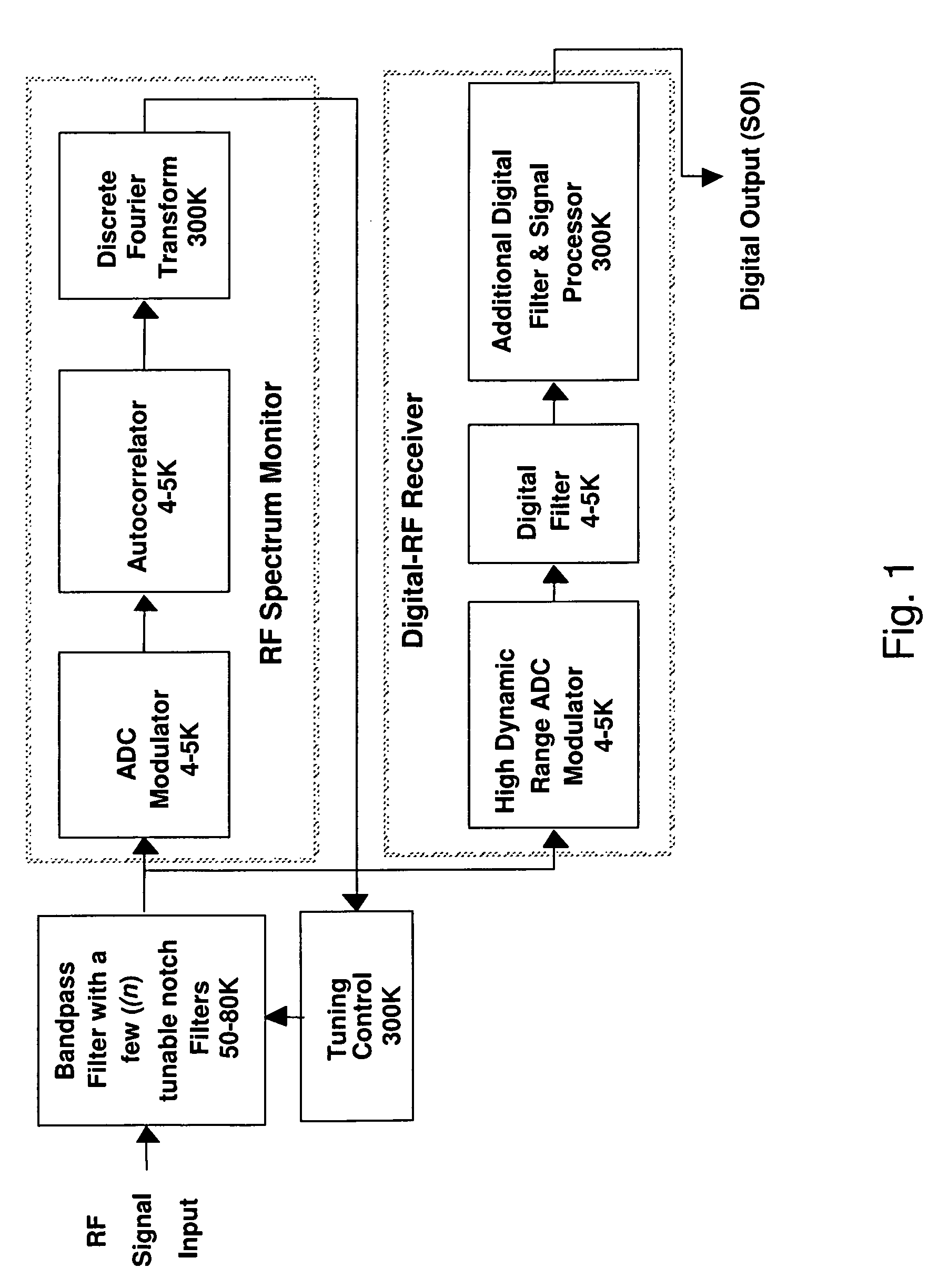
InactiveUS7876869B1Efficient processingAvoid attenuationTransmissionNonlinear distortionDigital signal processing
A method for reducing interference, comprising receiving a wideband signal, having at least one large amplitude component; adaptively modifying the wideband signal with respect to at least one high intensity component without substantial introduction of non-linear distortion, while reducing a residual dynamic range thereof; digitizing the modified wideband signal to capture information describing at least the high intensity signal at a sampling rate sufficient to extract modulated information present within the wideband signal at an upper limit of the band. The system analyzes a spectral characteristic of the wideband signal; and extracts adaptation parameters for the adaptive filtering. The system therefore provides both large net dynamic range and wideband operation. Preferably, the digitizer and filter, and part of the spectral characteristic analyzer is implemented in using superconducting circuit technology, with, for example low temperature superconducting digital signal processing components, and high temperature superconducting analog filtering components.
Owner:HYPRES
Distortion-managed digital RF communications transmitter and method therefor
ActiveUS20050163250A1Improved distortion-managedImprove accuracySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNonlinear distortionData stream
A digital communications transmitter (100) includes a digital linear-and-nonlinear predistortion section (200) to compensate for linear and nonlinear distortion introduced by transmitter-analog components (120). A direct-digital-downconversion section (300) generates a complex digital return-data stream (254) from the analog components (120) without introducing quadrature imbalance. A relatively low resolution exhibited by the return-data stream (254) is effectively increased through arithmetic processing. Linear distortion is first compensated using adaptive techniques with an equalizer (246) positioned in the forward-data stream (112). Nonlinear distortion is then compensated using adaptive techniques with a plurality of equalizers (226) that filter a plurality of orthogonal, higher-ordered-basis functions (214) generated from the forward-data stream (112). The filtered-basis functions are combined together and subtracted from the forward-data stream (112).
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com