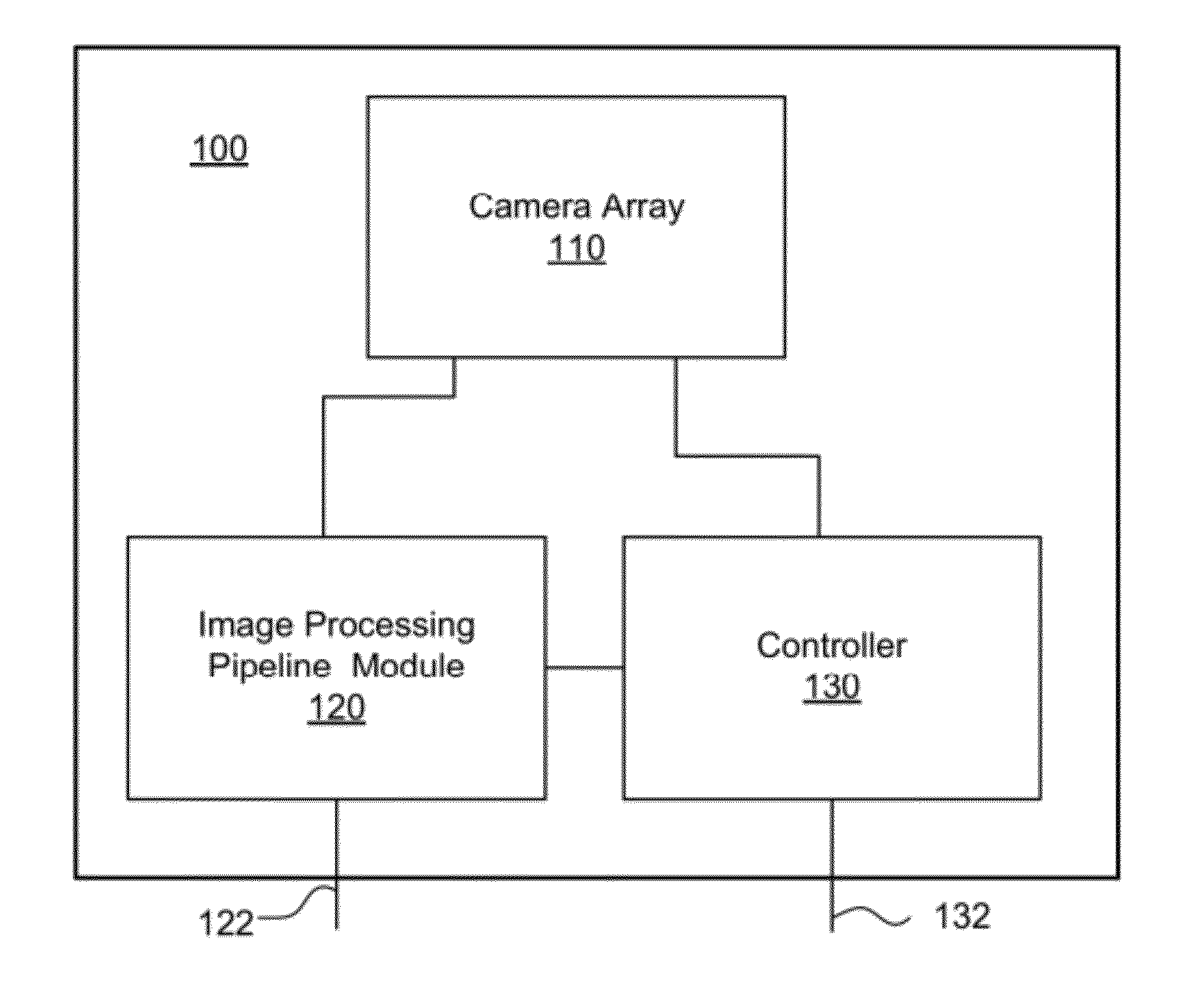
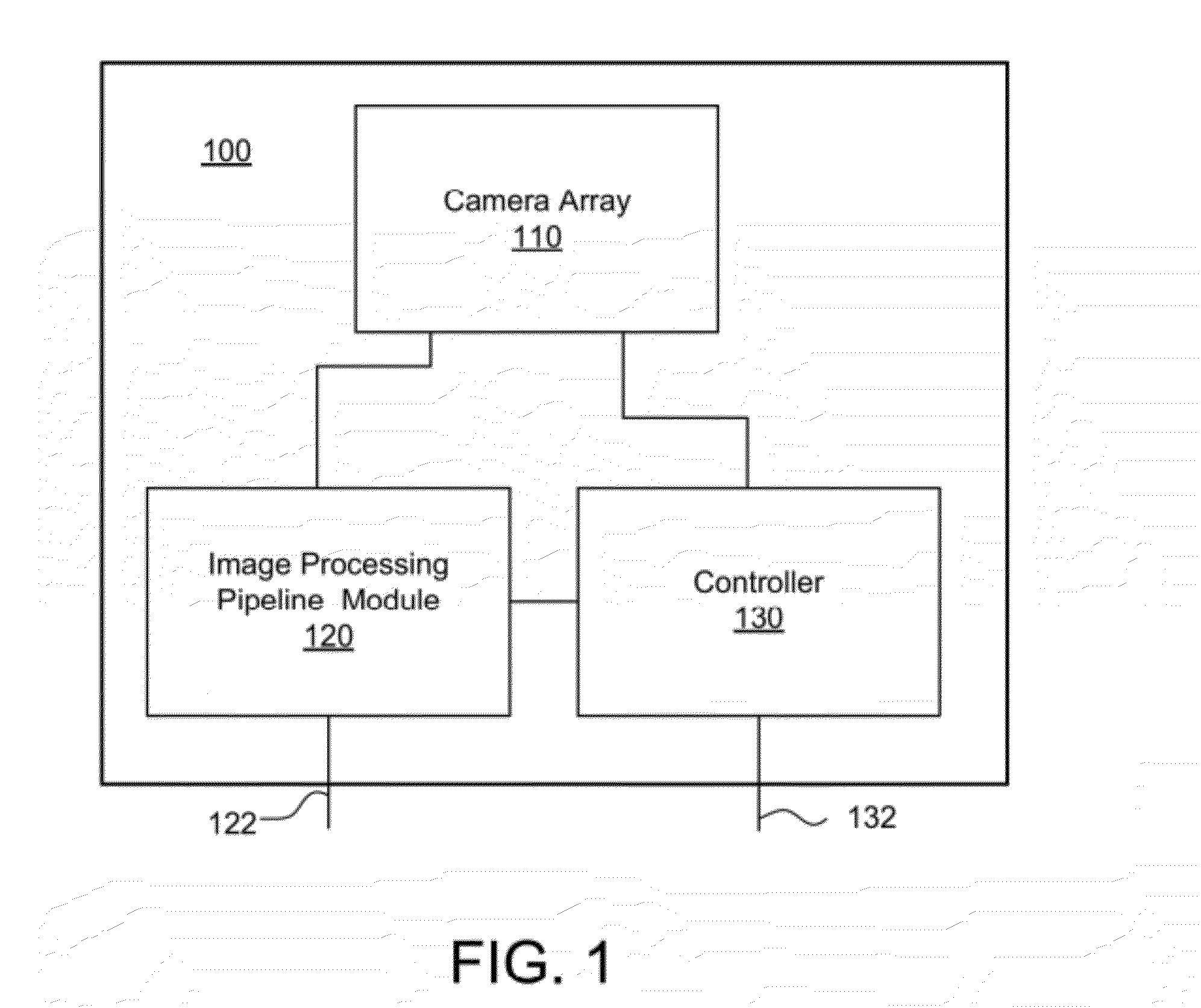
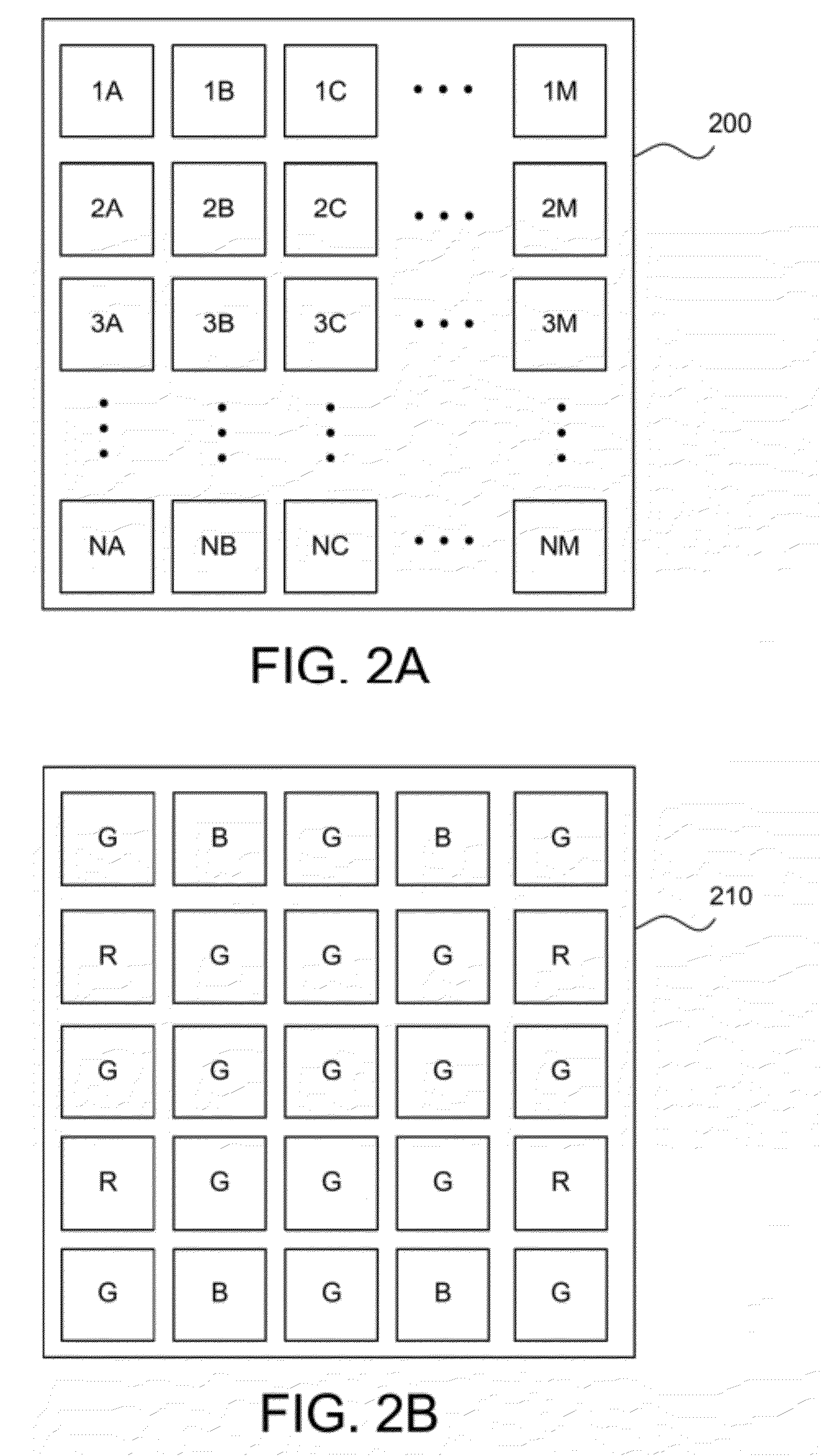
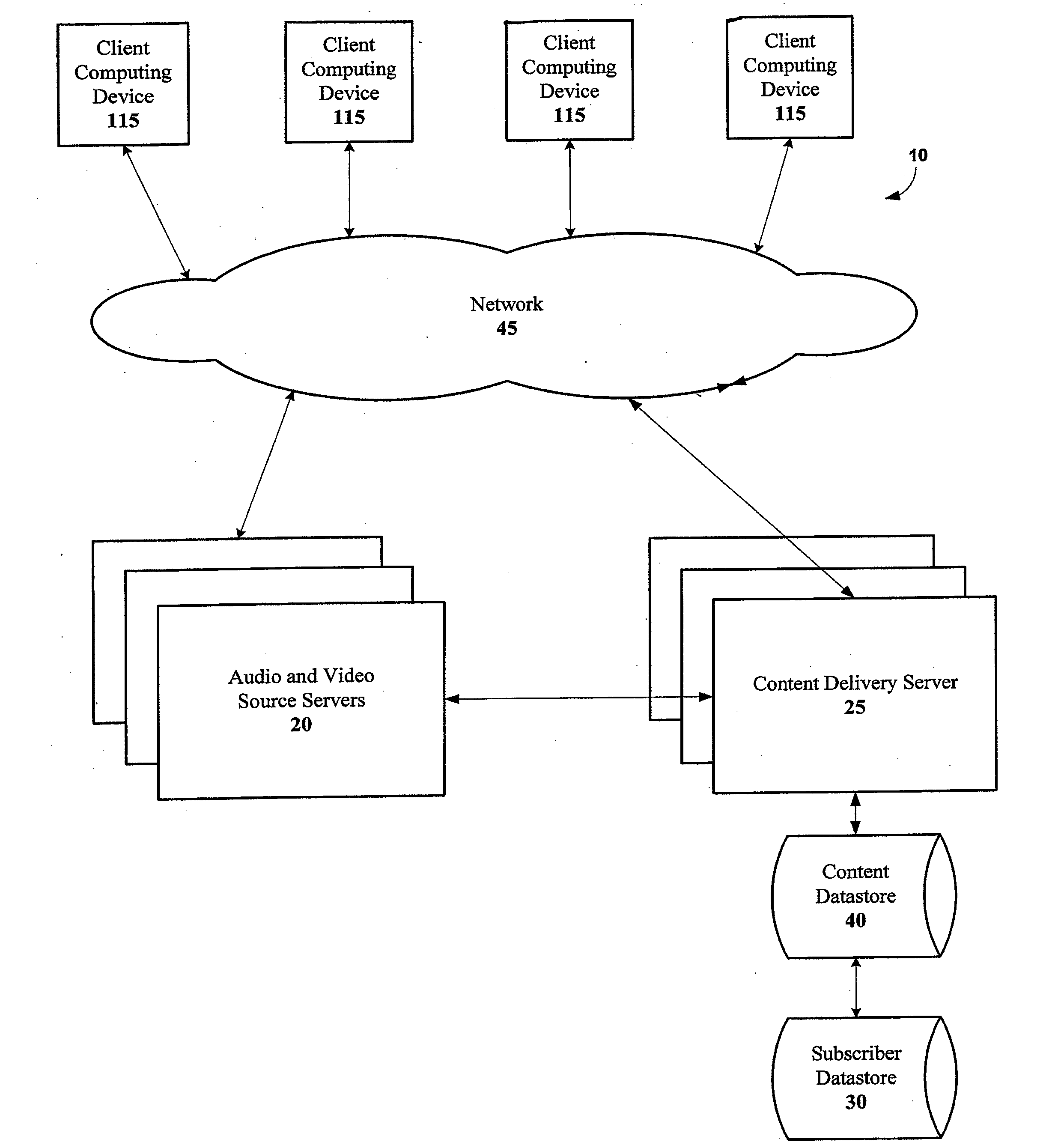
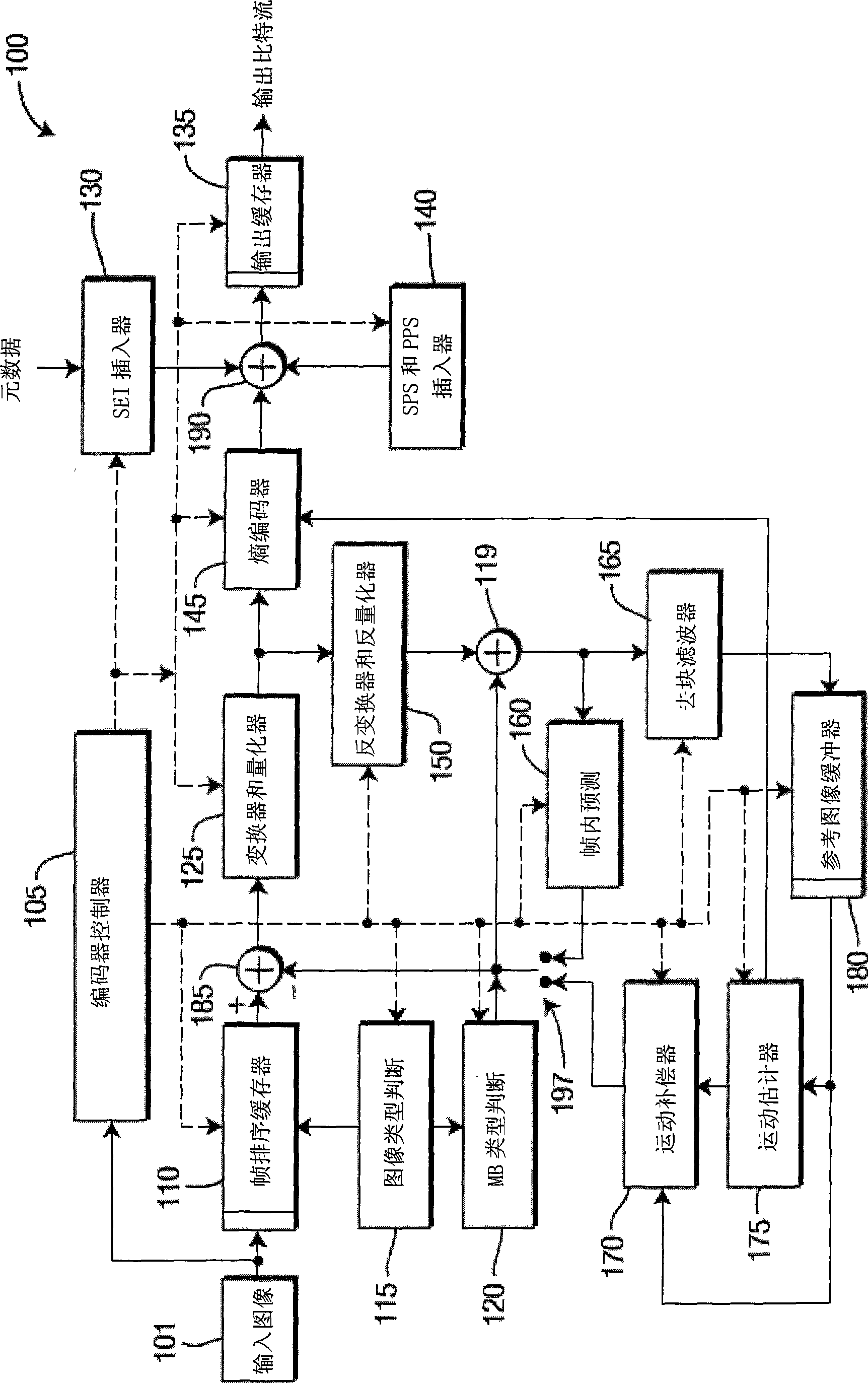
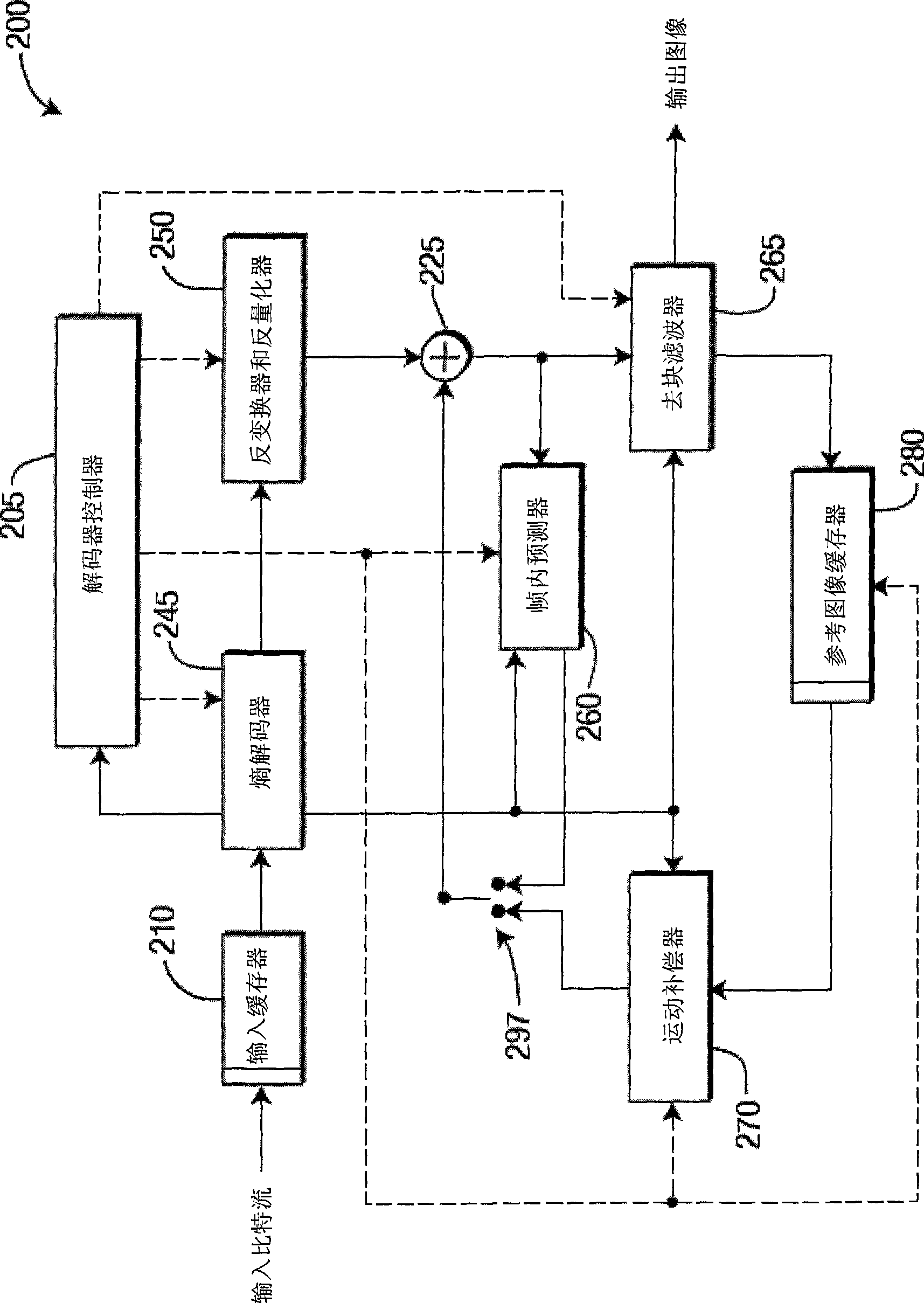
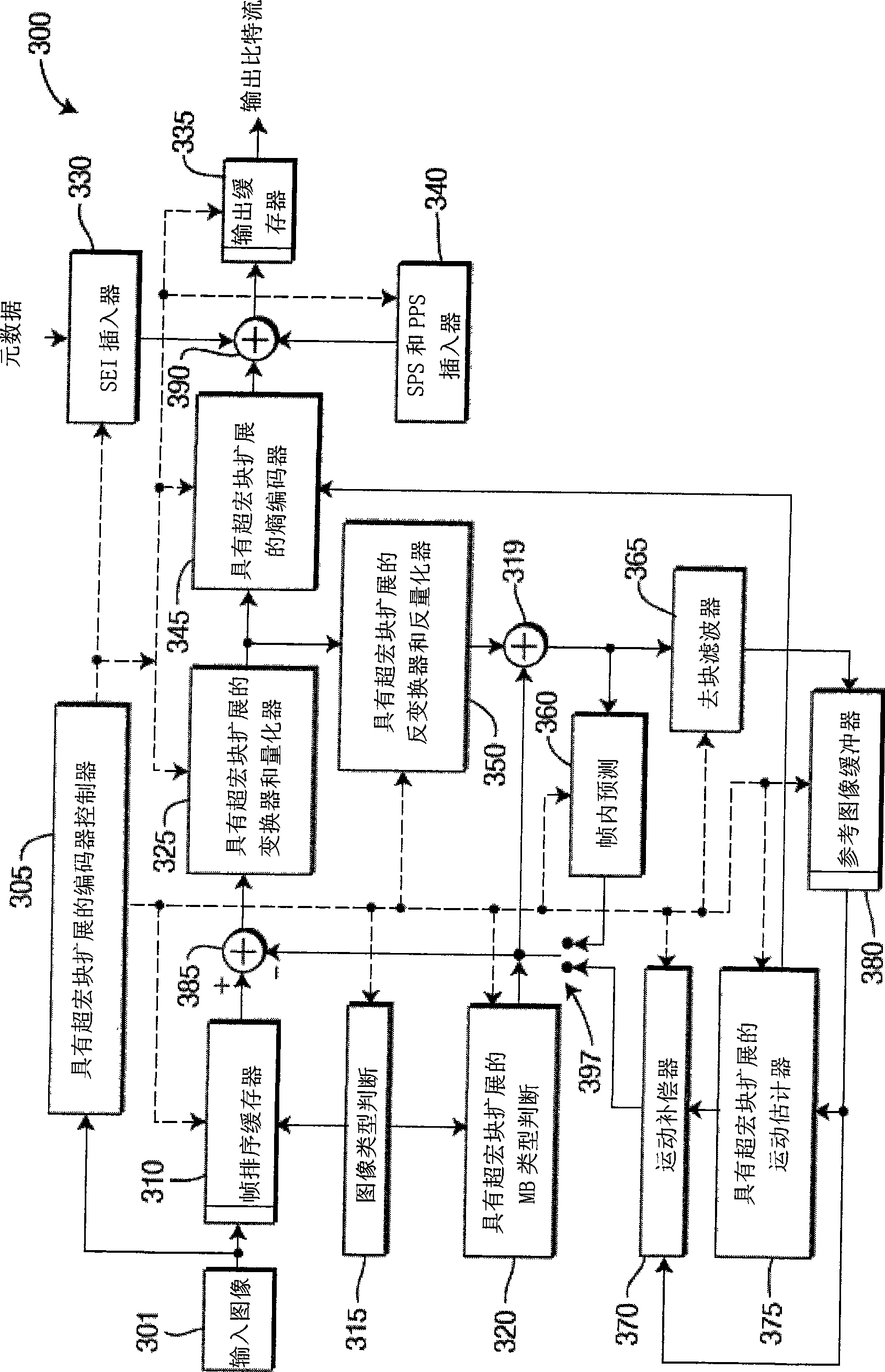
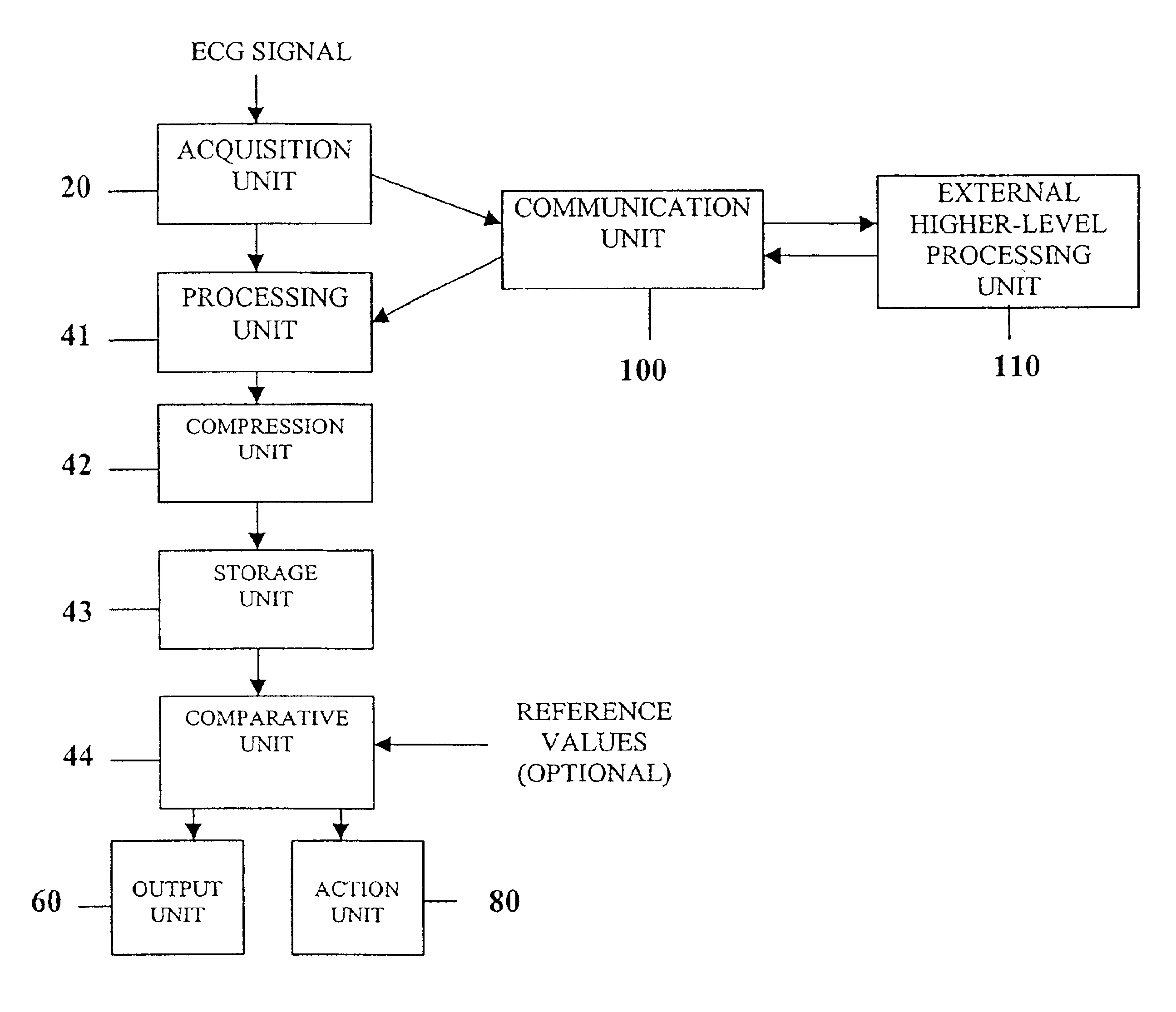
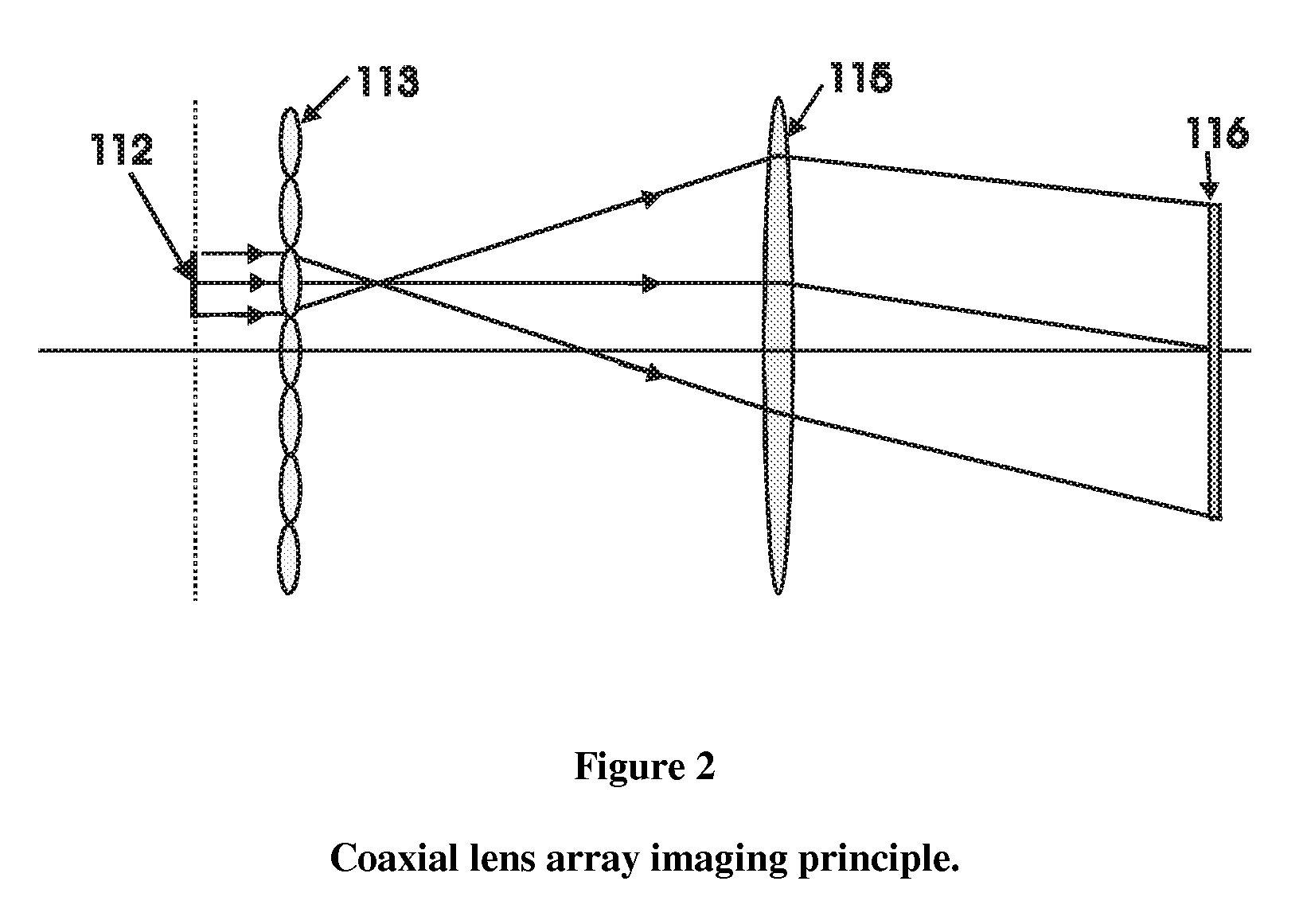
Patents
Literature
5709 results about "Low resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low resolution. Sometimes abbreviated as lo-res or lowres, low resolution is a term that describes an image or video, such as on a computer screen or printout, displayed with a low DPI (dots per inch).
Integrated routing/mapping information
InactiveUS6321158B1Enabling cooperationEnabling matingInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlImage resolutionLevel of detail
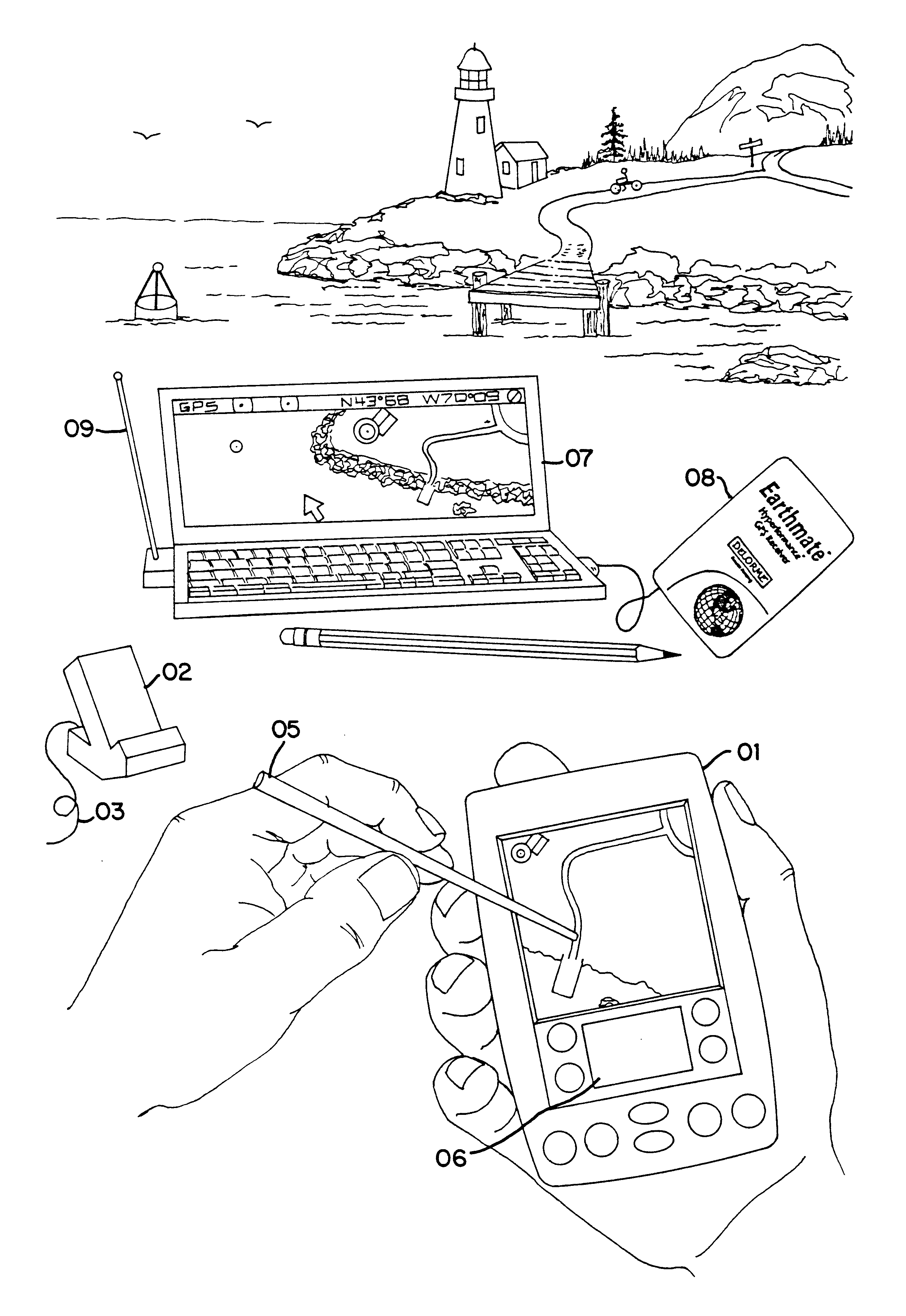
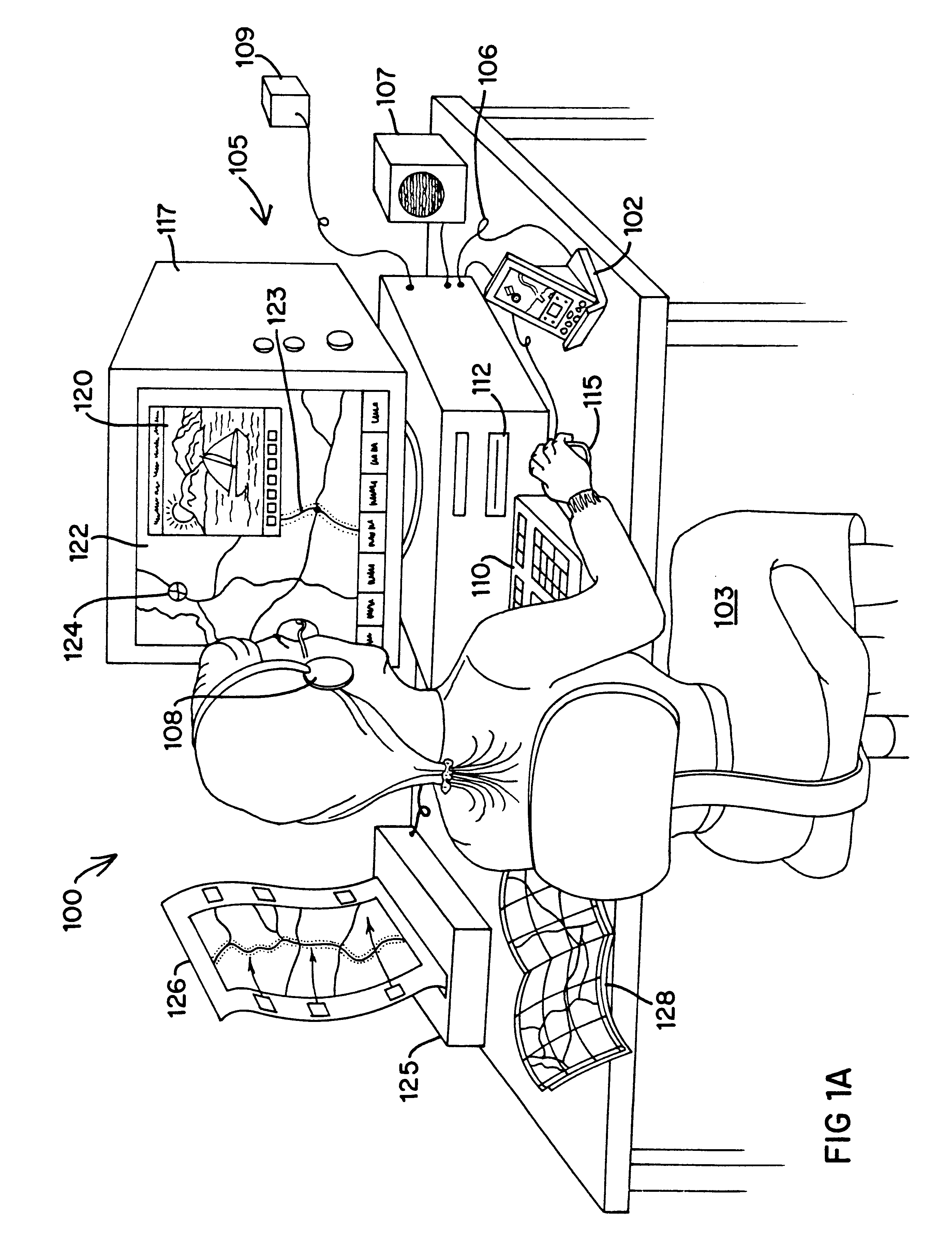
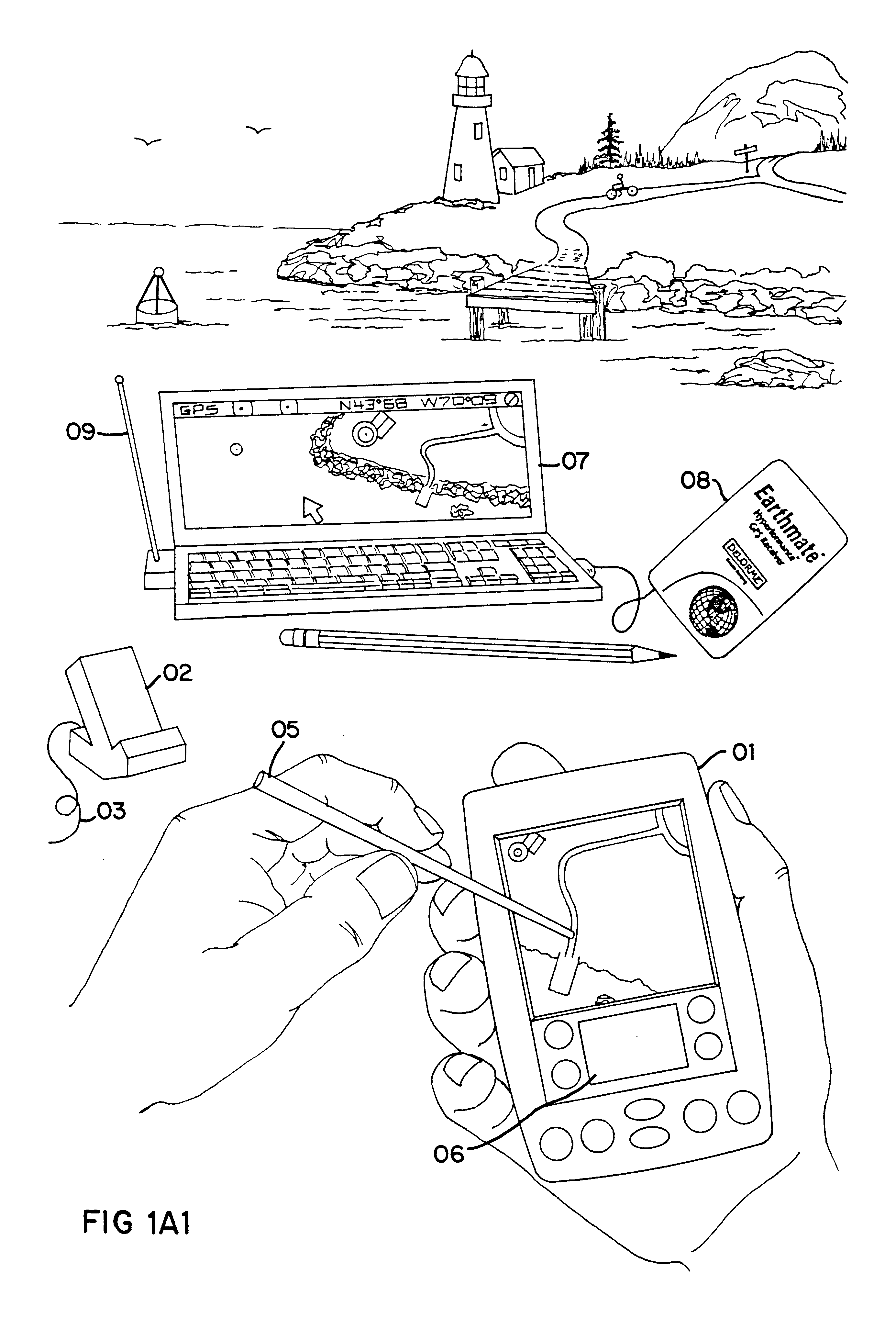
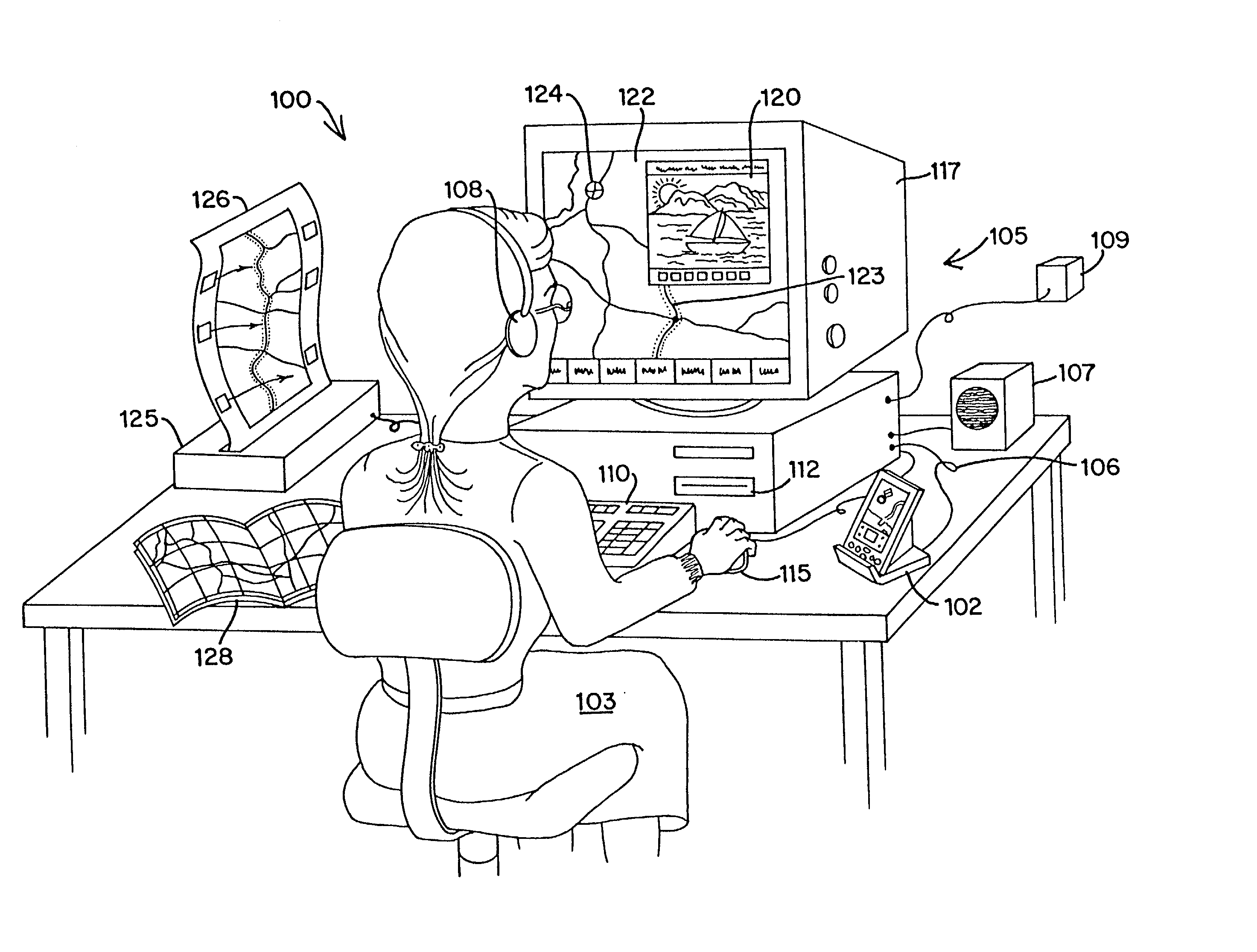
An Integrated Routing / Mapping Information System (IRMIS) links desktop personal computer cartographic applications to one or more handheld organizer, personal digital assistant (PDA) or "palmtop" devices. Such devices may be optionally equipped with, or connected to, portable Global Positioning System (GPS) or equivalent position sensing device. Desktop application facilitates user selection of areas, starts, stops, destinations, maps and / or point and / or route information. It optionally includes supplemental online information, preferably for transfer to the PDA or equivalent device. Users' options include route information, area, and route maps. Maps and related route information are configured with differential detail and levels of magnitude. Used in the field, in conjunction with GPS receiver, the PDA device is configured to display directions, text and map formats, the user's current position, heading, speed, elevation, and so forth. Audible signals identifying the next turn along the user's planned route are also provided. The user can pan across maps and zoom between two or more map scales, levels of detail, or magnitudes. The IRMIS also provides for "automatic zooming," e.g., to show greater detail or closer detail as the user approaches a destination, or to larger scale and lower resolution to show the user's overall planned route between points of interest. The IRMIS also enables the user to mark or record specific locations and / or log actual travel routes, using GPS position information. These annotated location marks and / or "breadcrumb" or GPS log data can be saved, uploaded, displayed, or otherwise processed on the user's desktop geographic information or cartographic system. The IRMIS application and data may be distributed online and / or in tangible media in limited and advanced manipulation formats.
Owner:GARMIN
Integrated routing/mapping information system
InactiveUS20030182052A1Enabling cooperationEnabling matingInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlImage resolutionLevel of detail
An Integrated Routing / Mapping Information System (IRMIS) links desktop personal computer cartographic applications to one or more handheld organizer, personal digital assistant (PDA) or "palmtop" devices. Such devices may be optionally equipped with, or connected to, portable Global Positioning System (GPS) or equivalent position sensing device. Desktop application facilitates user selection of areas, starts, stops, destinations, maps and / or point and / or route information. It optionally includes supplemental online information, preferably for transfer to the PDA or equivalent device. Users' options include route information, area, and route maps. Maps and related route information are configured with differential detail and levels of magnitude. Used in the field, in conjunction with GPS receiver, the PDA device is configured to display directions, text and map formats, the user's current position, heading, speed, elevation, and so forth. Audible signals identifying the next turn along the user's planned route are also provided. The user can pan across maps and zoom between two or more map scales, levels of detail, or magnitudes. The IRMIS also provides for "automatic zooming," e.g., to show greater detail or closer detail as the user approaches a destination, or to larger scale and lower resolution to show the user's overall planned route between points of interest. The IRMIS also enables the user to mark or record specific locations and / or log actual travel routes, using GPS position information. These annotated location marks and / or "breadcrumb" or GPS log data can be saved, uploaded, displayed, or otherwise processed on the user's desktop geographic information or cartographic system. The IRMIS application and data may be distributed online and / or in tangible media in limited and advanced manipulation formats.
Owner:KHOURI ANTHONY
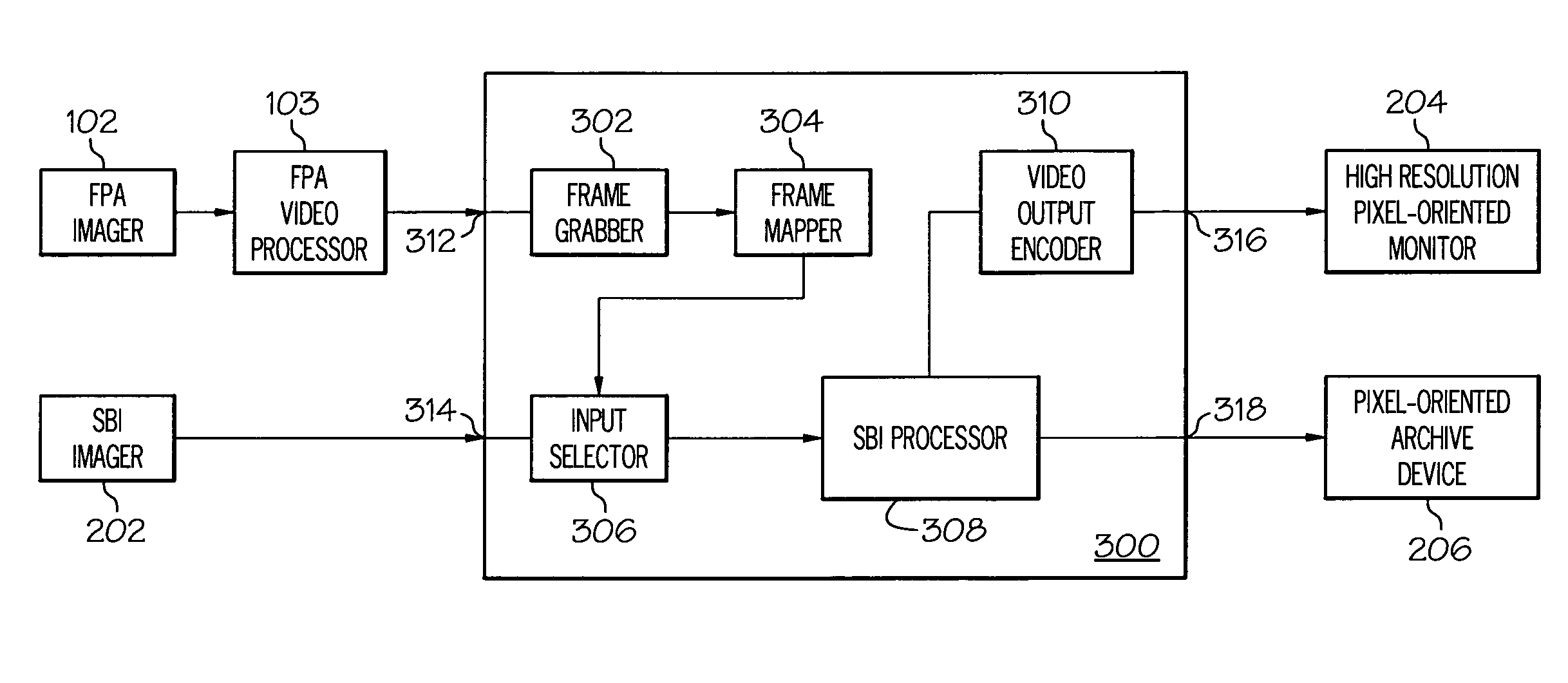
Combined SBI and conventional image processor
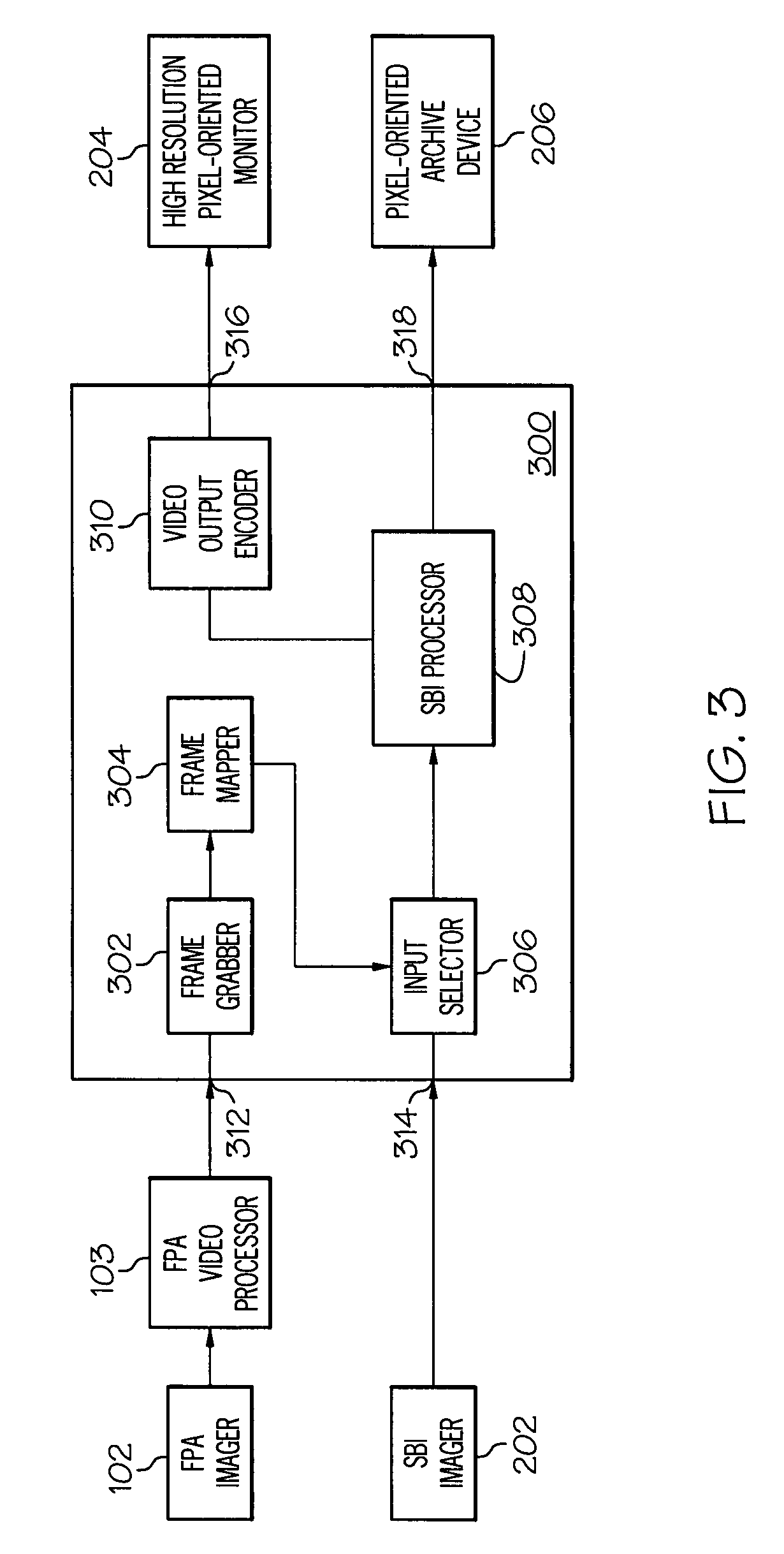
InactiveUS7995045B2Increasing and significantly changing footprintTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsData streamComputer graphics (images)
An apparatus and method for allowing multiple high and low resolution SBI and conventional FPA imaging devices to use a common high resolution monitor and archive device without increasing or significantly changing the footprint of existing devices. This system and method uses a frame grabber for digitizing video from the legacy FPA devices, a frame mapper for rendering or mapping the FPA video into the SBI digital format, a converter for rasterizing SBI data streams into pixel-oriented FPA video frames, an input selector for selecting which FPA or SBI imaging device to display on a high resolution monitor, an processor for storing and manipulating frames of video, a video output encoder for converting the SBI frames into a video signal appropriate for display on the high resolution monitor, and an output means for connecting to a storage device for archiving video and images.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Producing digital image with different resolution portions
InactiveUS20080030592A1Improve image qualityReduce complexityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDigital zoomImage resolution
A method of producing a digital image with improved resolution during digital zooming, including simultaneously capturing a first low resolution digital image of a scene and a second higher resolution digital image of a portion of substantially the same scene. A composite image is then formed by combining the first low-resolution digital image and a corresponding portion of the high resolution digital image. Digital zooming of the composite image produces a zoomed image with high resolution throughout the zoom range and improved image quality.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
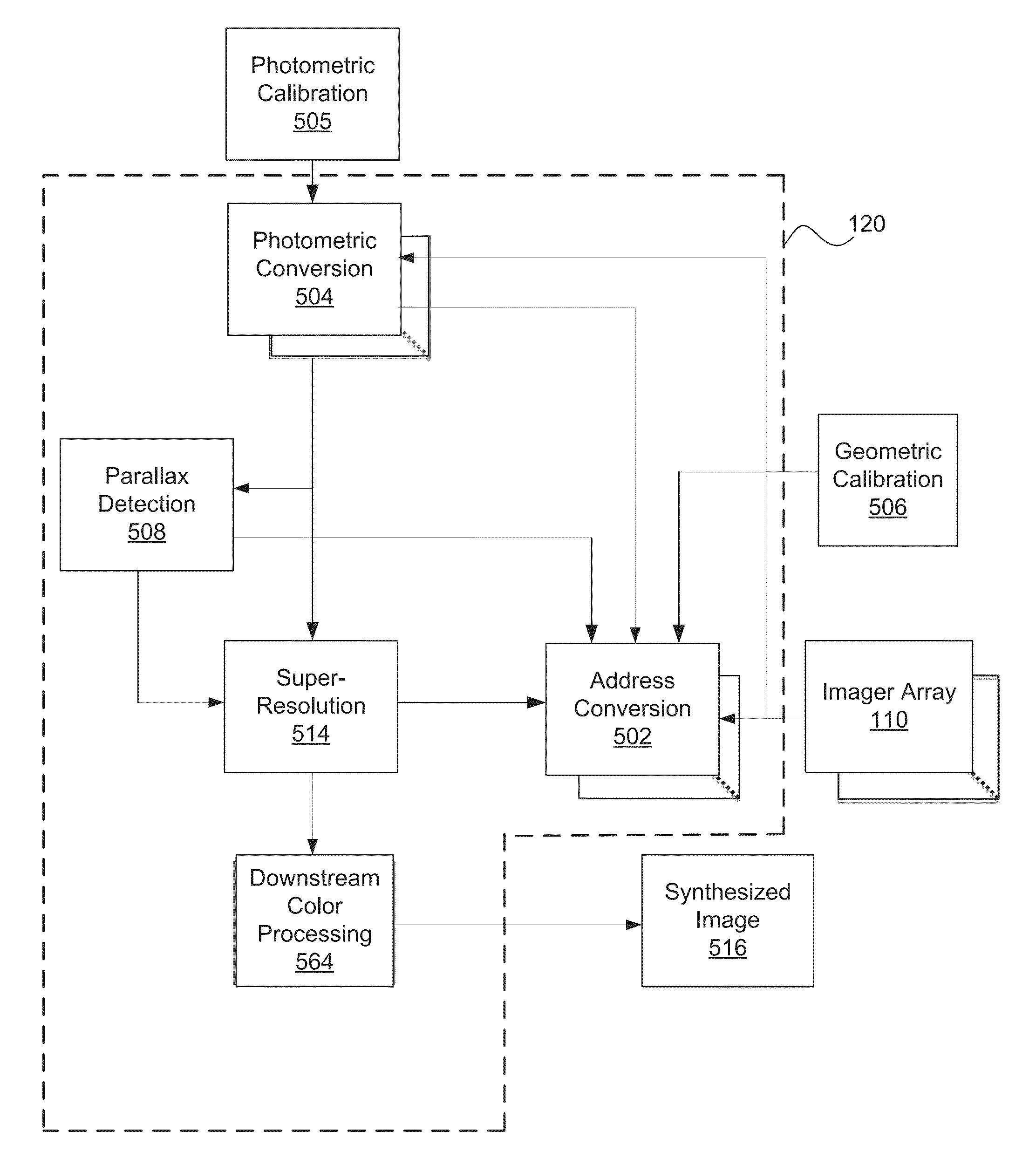
Systems and methods for synthesizing high resolution images using super-resolution processes
ActiveUS20120147205A1Promote recoveryHigh resolutionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsProcess systemsImage resolution
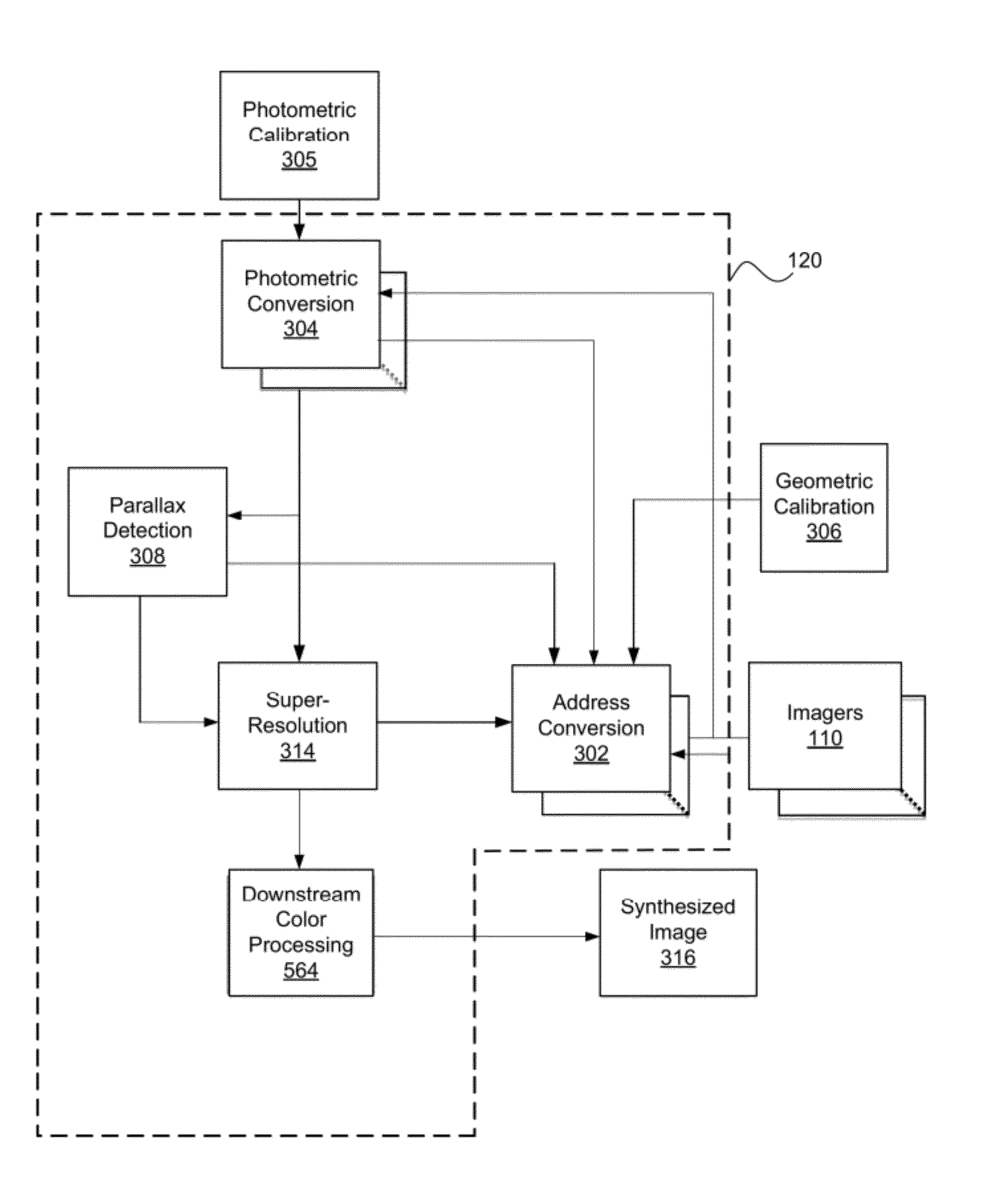
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed that use super-resolution (SR) processes to use information from a plurality of low resolution (LR) images captured by an array camera to produce a synthesized higher resolution image. One embodiment includes obtaining input images using the plurality of imagers, using a microprocessor to determine an initial estimate of at least a portion of a high resolution image using a plurality of pixels from the input images, and using a microprocessor to determine a high resolution image that when mapped through the forward imaging transformation matches the input images to within at least one predetermined criterion using the initial estimate of at least a portion of the high resolution image. In addition, each forward imaging transformation corresponds to the manner in which each imager in the imaging array generate the input images, and the high resolution image synthesized by the microprocessor has a resolution that is greater than any of the input images.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
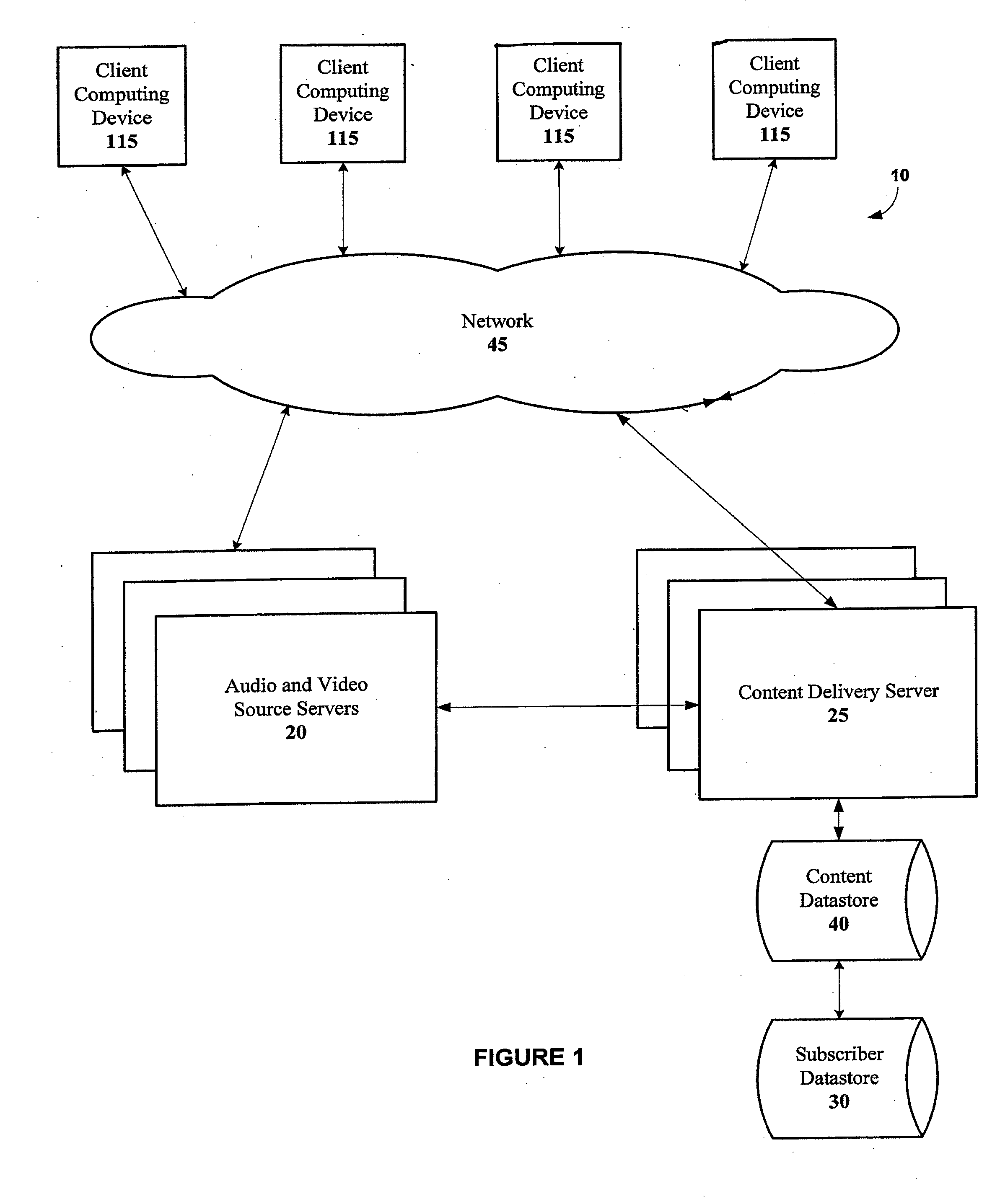
System and method for delivering video and audio content over a network
ActiveUS20070143493A1Decrease the decibel levelLower Level RequirementsMultimedia data retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsImage resolutionLive video
A content delivery system according to various embodiments of the invention substantially concurrently streams a plurality of live videos to a client computing device over a network, allowing the user to view two or more live videos at the same time. In a particular embodiment, the system is configured to display a high resolution version of a live video feed in a “primary” pane of a main display dialog window and one or more additional live video feeds in low resolution in “preview” panes of the main display dialog window substantially concurrently, wherein the additional live video feeds are different from the first video feed and each other. In this particular embodiment, the system allows the user to preview the additional videos while the first video is playing. In addition, according to one embodiment, the live video feeds may be from independent sources.
Owner:TURNER BROADCASTING SYST INC
Systems and methods for determining depth from multiple views of a scene that include aliasing using hypothesized fusion
InactiveUS20130070060A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionHigh resolution image
Array cameras in accordance with embodiments of the invention perform super resolution processing using images of a scene that contain aliasing. In several embodiments, the depth of pixels is determined by fusing portions of a higher resolution image at a number of hypothesized depths and determining the depth at which the portion of the higher resolution image best matches the scene captured in the lower resolution images used to fuse the higher resolution image.
Owner:FOTONATION CAYMAN LTD
Techniques for automatically providing a high-resolution rendering of a low resolution digital image in a distributed network
InactiveUS6577311B1Easy accessImprove the display effectDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionLow resolution
In one embodiment, a method of providing a recipient of a low-resolution digital image a way to automatically obtain a high-resolution rendering of the digital image is disclosed. In one embodiment, in a distributed system having a first node coupled to a second node, a method of outputting at the first node a composited digital image at a selected resolution is disclosed. At the second node, the composited digital image at a first resolution is generated and the composited digital image is then converted to a second resolution. The converted composited digital image is then transferred to the first node where the selected resolution is determined. If the selected resolution is the first resolution then the composited digital image is fetched and the composited digital image is then output at the first resolution. If, however, it is determined that the selected resolution is the second resolution, then the composited digital image is output at the at the second resolution.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
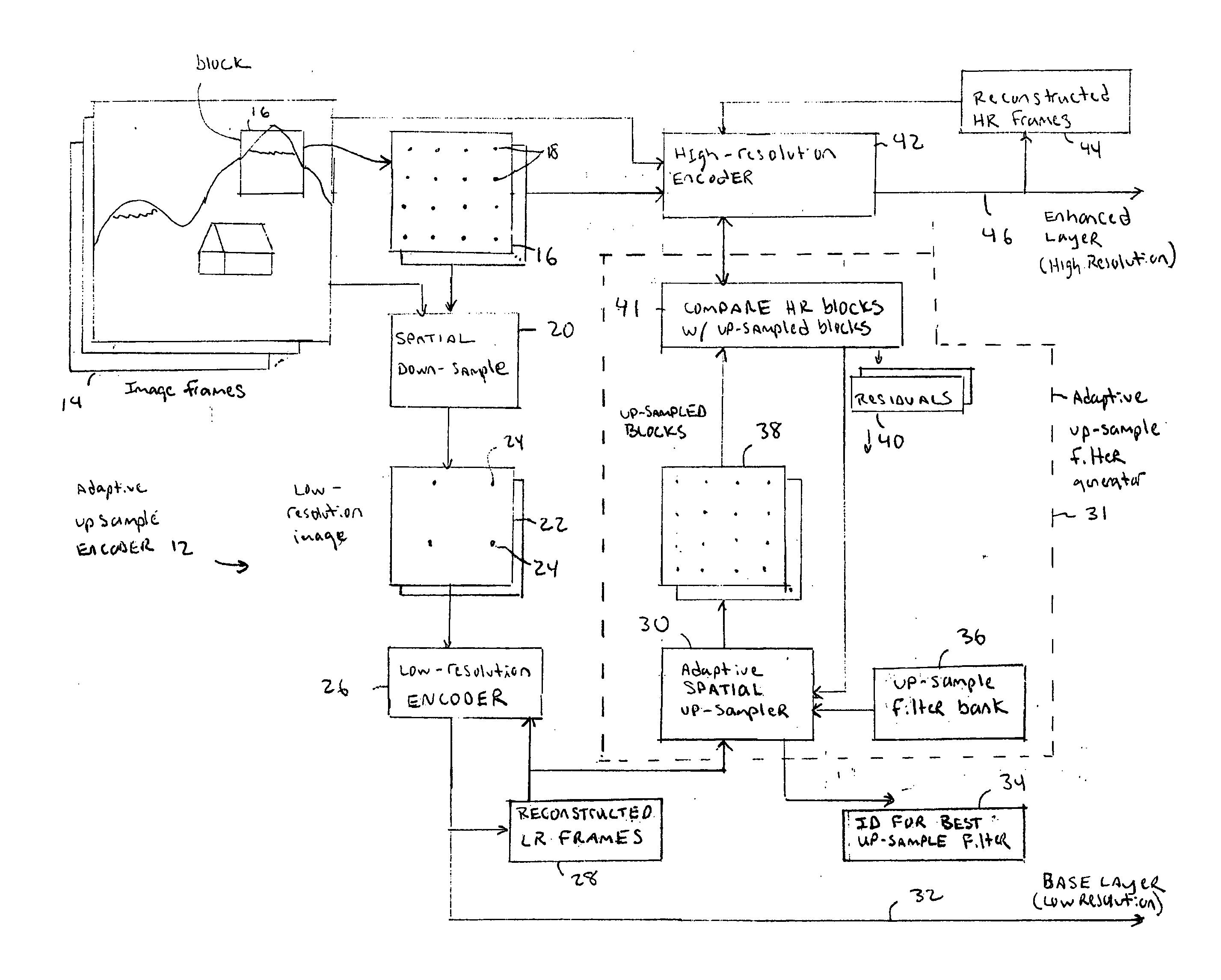
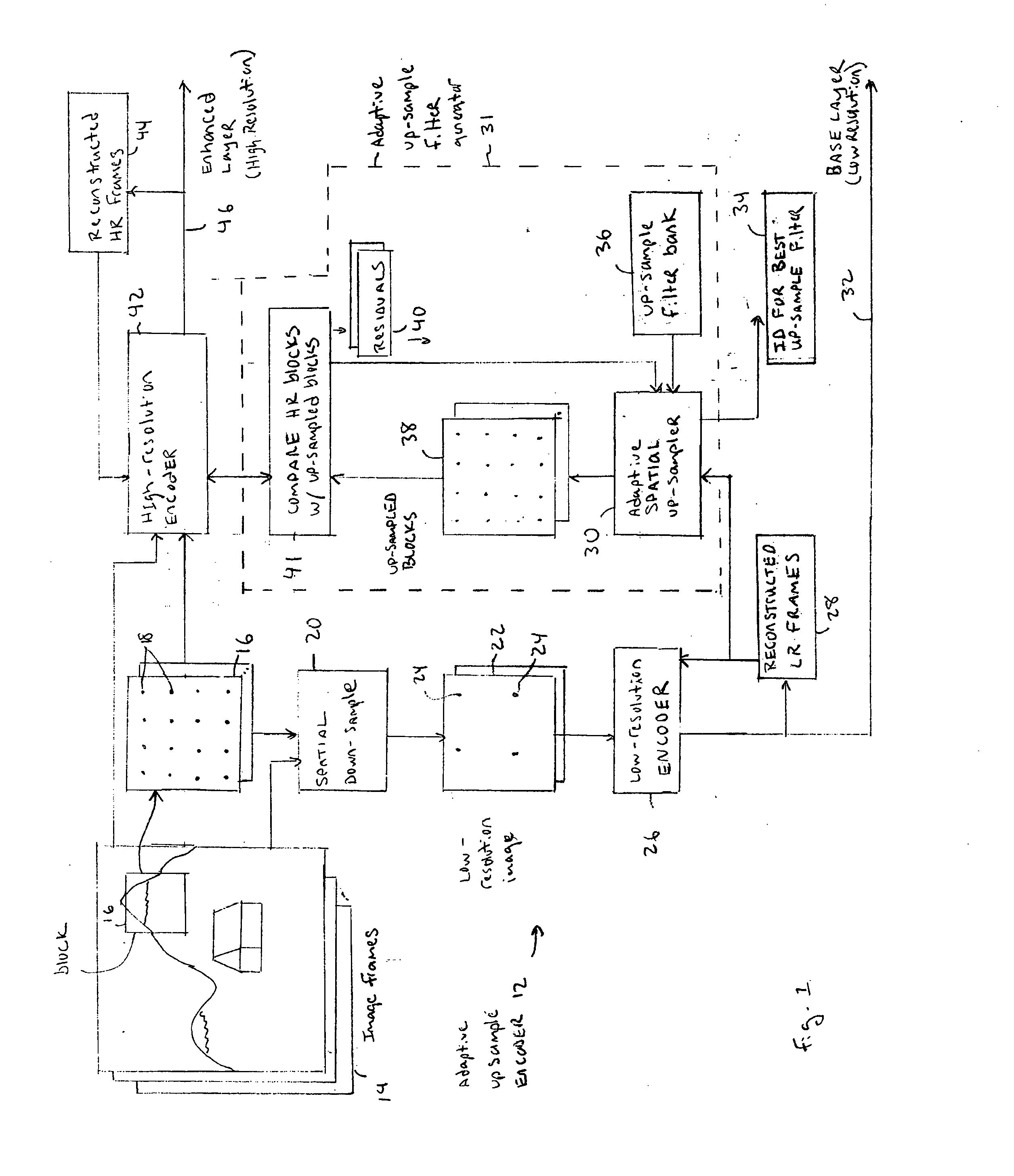
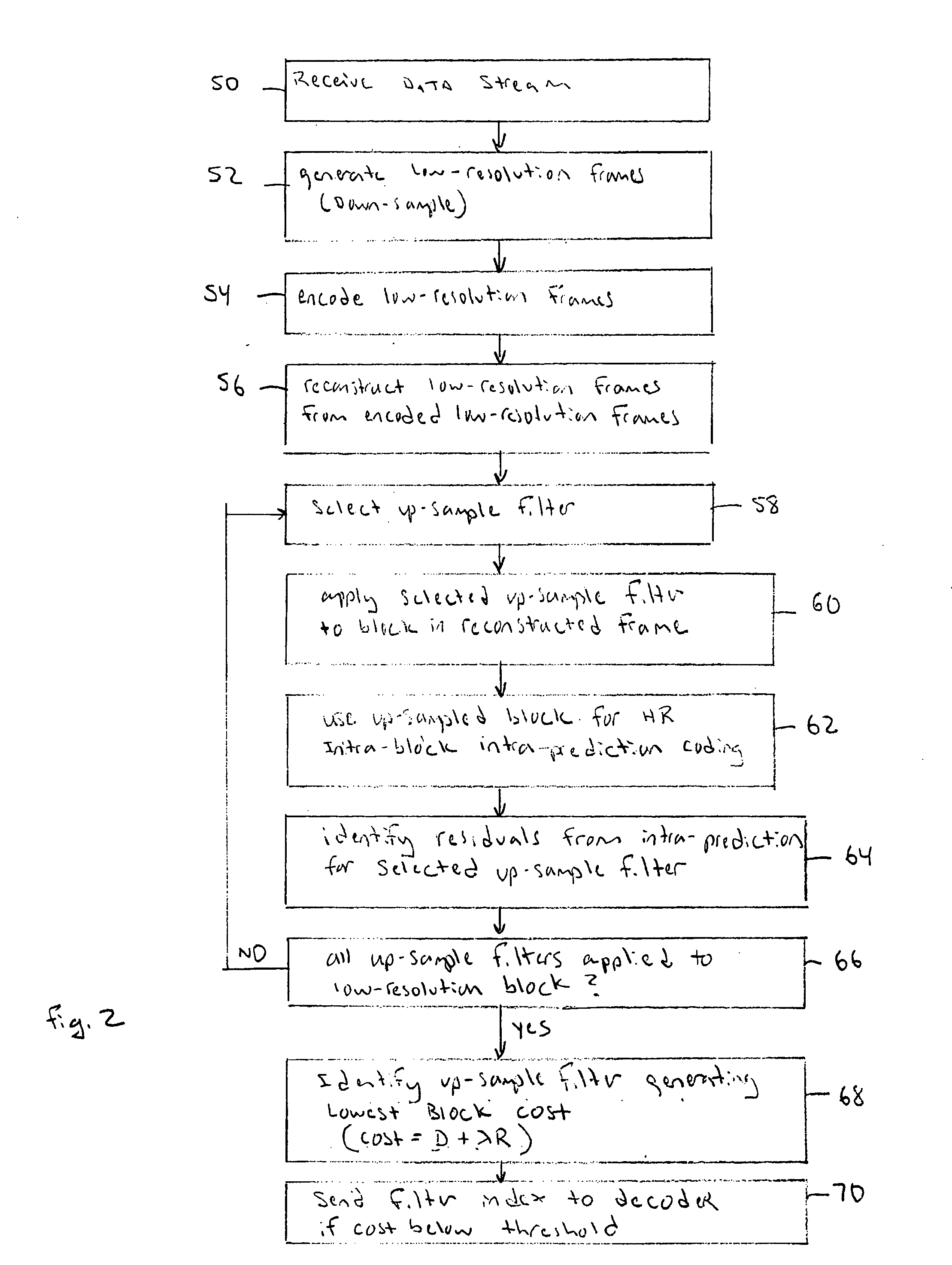
Method and apparatus for adaptive up-scaling for spatially scalable coding
InactiveUS20060268991A1Improve compression efficiencyImageColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionSelf adaptive
Adaptive up-sample filtering is used to improve compression efficiency of spatially scalable coding systems by more effectively predicting the high-resolution (enhanced-layer) video (or image) from the low-resolution lower-layer video (or image). Different up-sample filters adaptive to local image properties are selectively used for different portions of a low resolution frame to generate a better up-sampled image. Selection between different up-sample filters is determined by a variety of different information available to both the encoder and decoder. In one embodiment, the up-sample filters are selected by the encoder and then explicitly identified to the decoder. Other techniques are then used to minimize the cost of transmitting the up-sample filter identifiers. In alternative embodiments, the encoder and decoder independently make up-sample filters selections.
Owner:SHARP KK
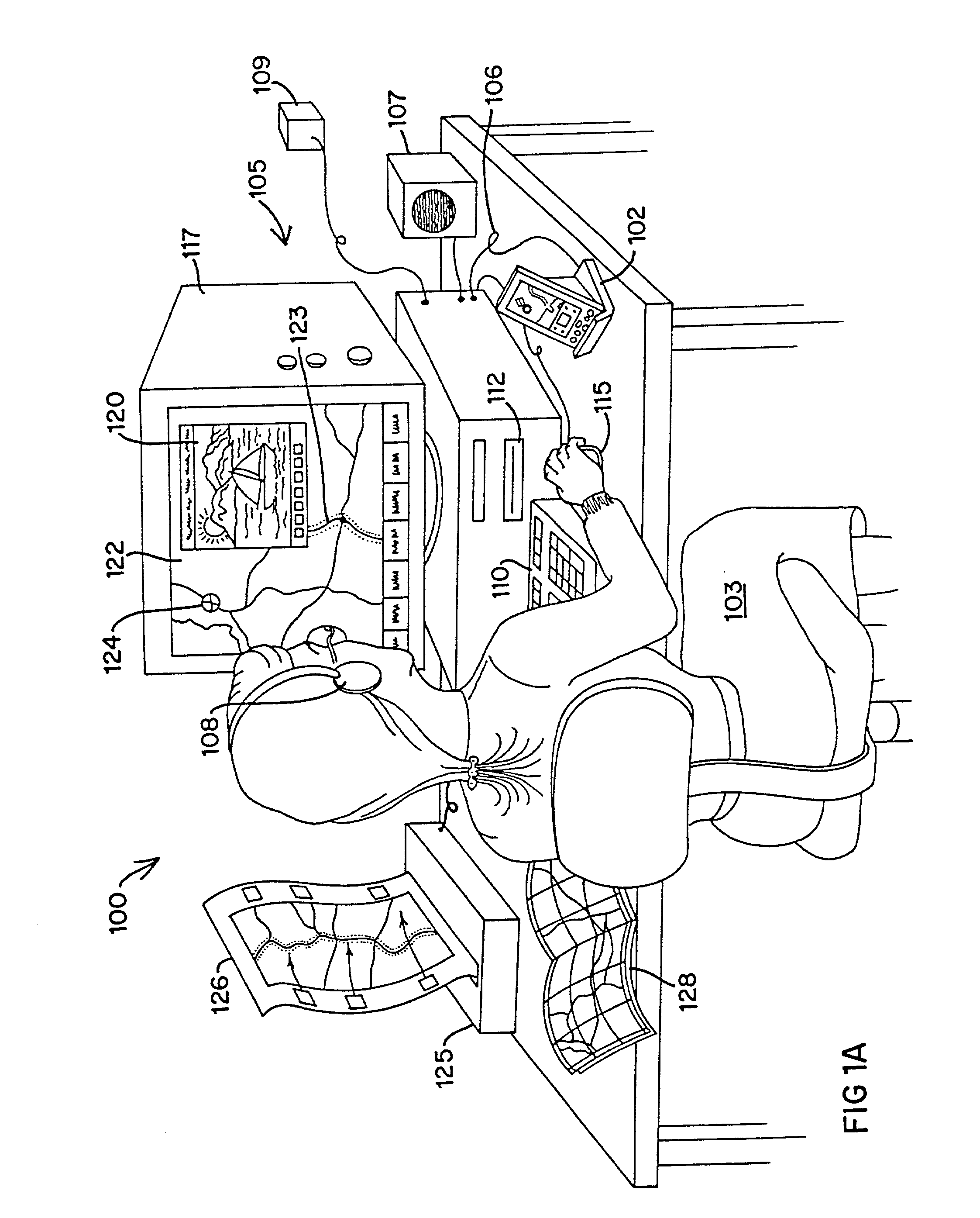
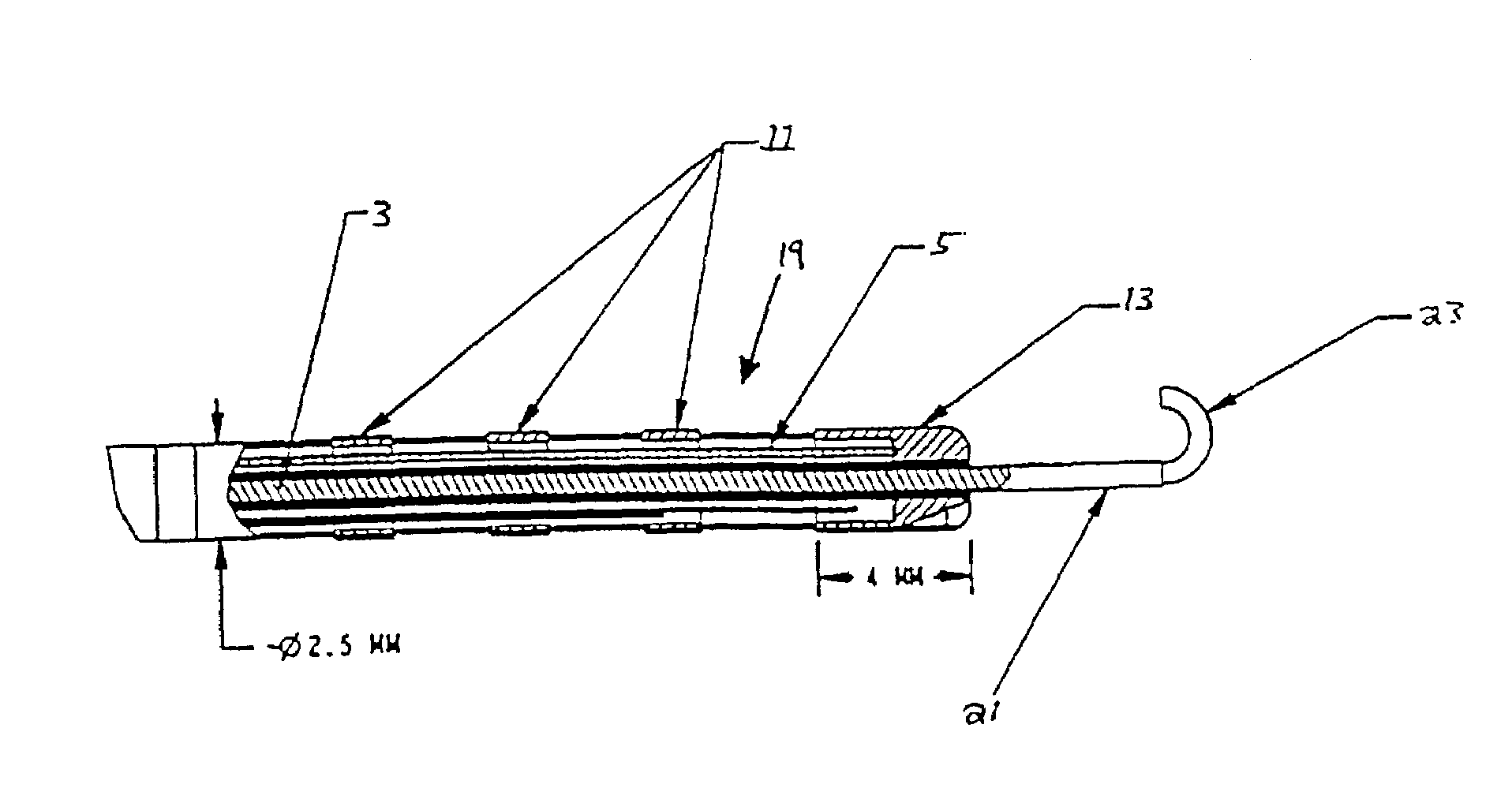
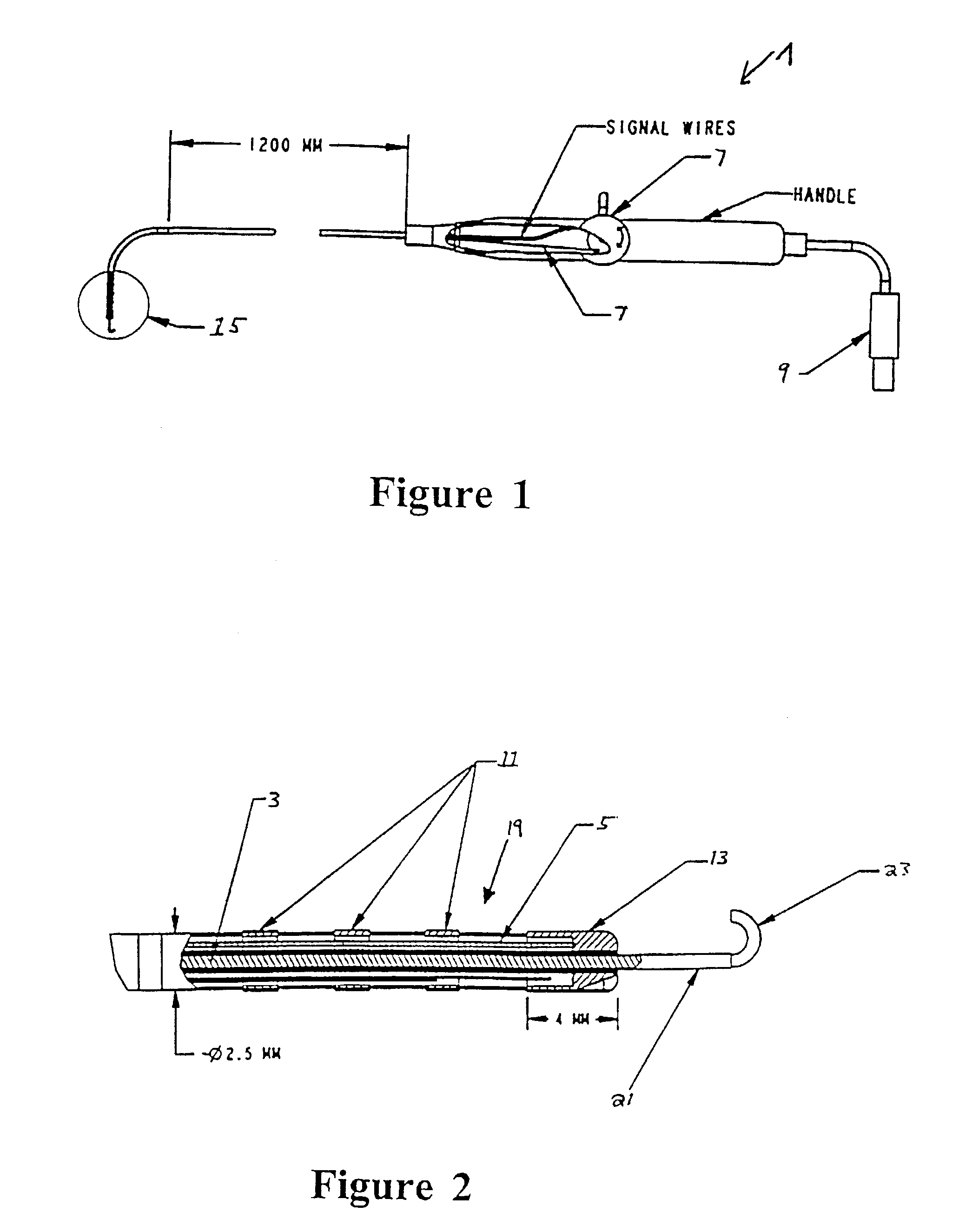
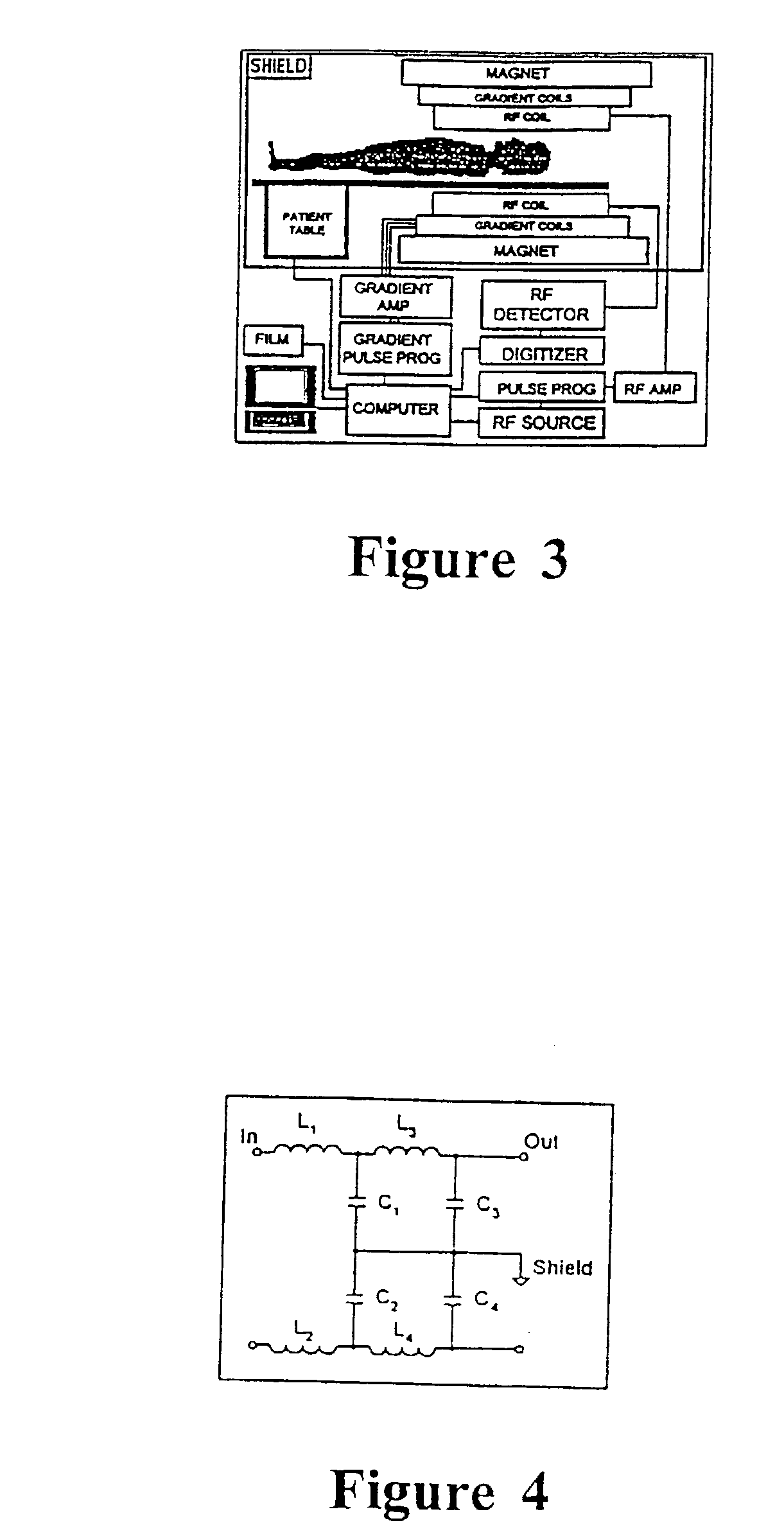
System and method for magnetic-resonance-guided electrophysiologic and ablation procedures
InactiveUS7155271B2Increased resolution and reliabilityImprove accuracySurgical instrument detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringMr guidanceMr contrast agent
A system and method for using magnetic resonance imaging to increase the accuracy of electrophysiologic procedures is disclosed. The system in its preferred embodiment provides an invasive combined electrophysiology and imaging antenna catheter which includes an RF antenna for receiving magnetic resonance signals and diagnostic electrodes for receiving electrical potentials. The combined electrophysiology and imaging antenna catheter is used in combination with a magnetic resonance imaging scanner to guide and provide visualization during electrophysiologic diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. The invention is particularly applicable to catheter ablation, e.g., ablation of atrial fibrillation. In embodiments which are useful for catheter ablation, the combined electrophysiology and imaging antenna catheter may further include an ablation tip, and such embodiment may be used as an intracardiac device to both deliver energy to selected areas of tissue and visualize the resulting ablation lesions, thereby greatly simplifying production of continuous linear lesions. The invention further includes embodiments useful for guiding electrophysiologic diagnostic and therapeutic procedures other than ablation. Imaging of ablation lesions may be further enhanced by use of MR contrast agents. The antenna utilized in the combined electrophysiology and imaging catheter for receiving MR signals is preferably of the coaxial or “loopless” type. High-resolution images from the antenna may be combined with low-resolution images from surface coils of the MR scanner to produce a composite image. The invention further provides a system for eliminating the pickup of RF energy in which intracardiac wires are detuned by filtering so that they become very inefficient antennas. An RF filtering system is provided for suppressing the MR imaging signal while not attenuating the RF ablative current. Steering means may be provided for steering the invasive catheter under MR guidance. Other ablative methods can be used such as laser, ultrasound, and low temperatures.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
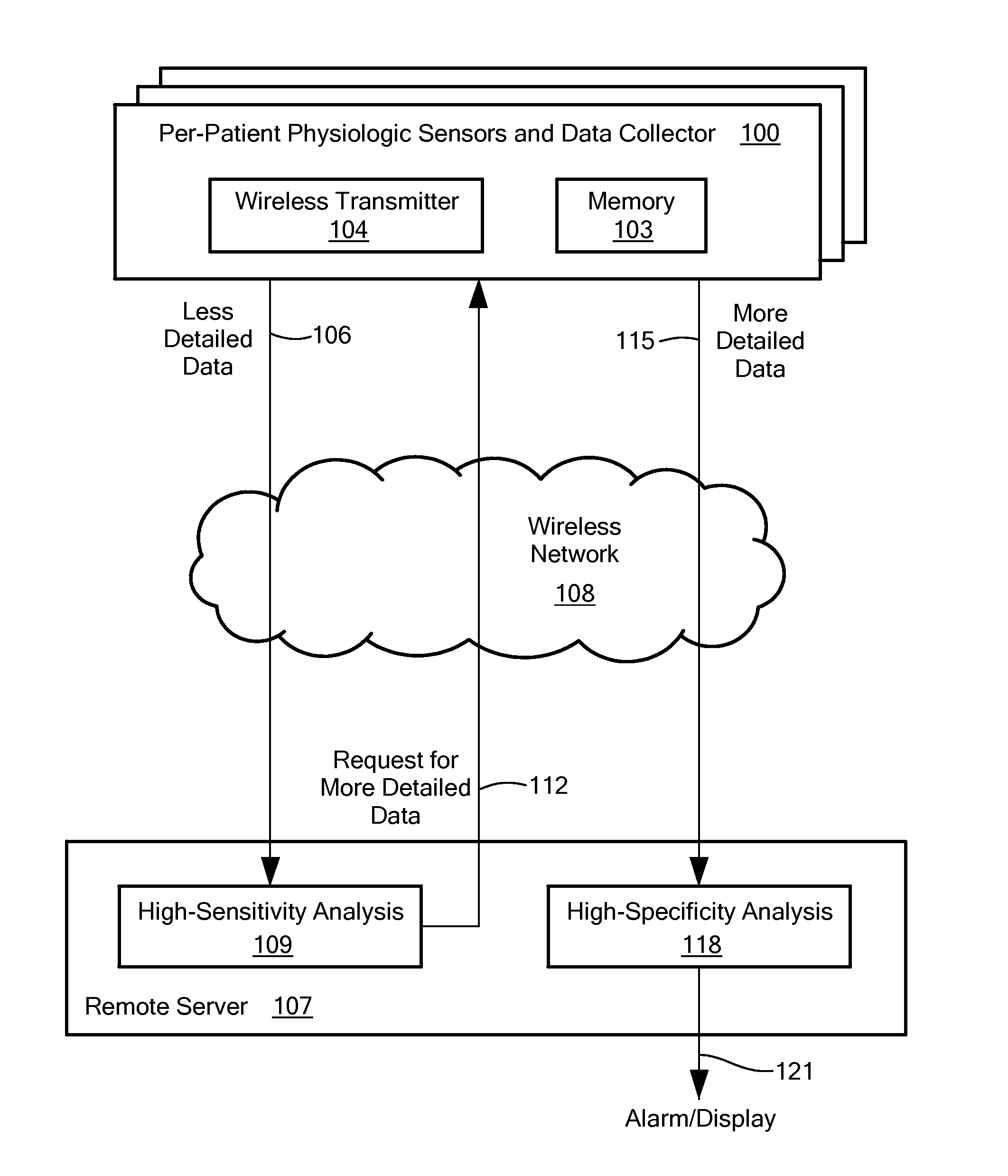
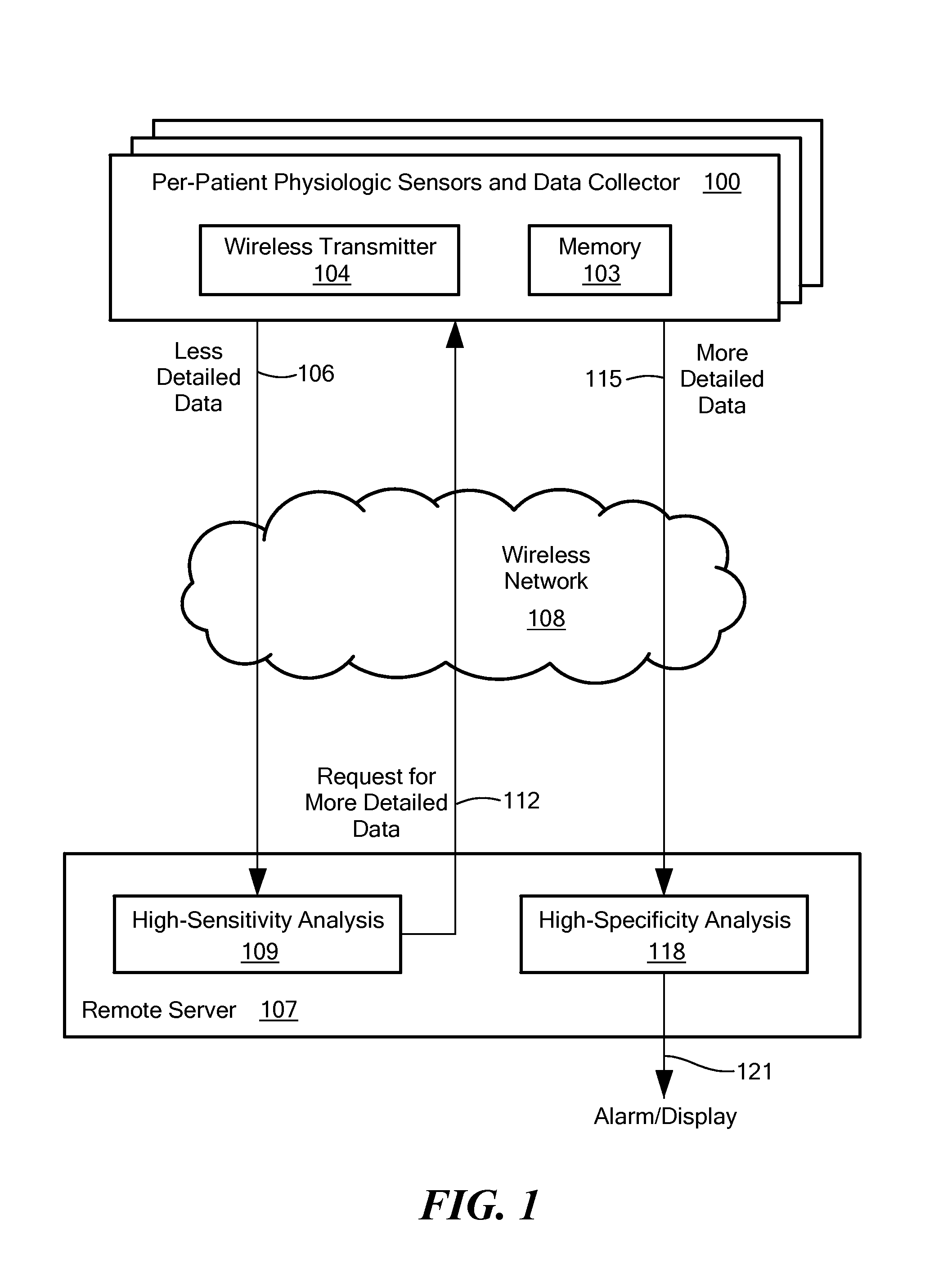
Remote health monitoring system
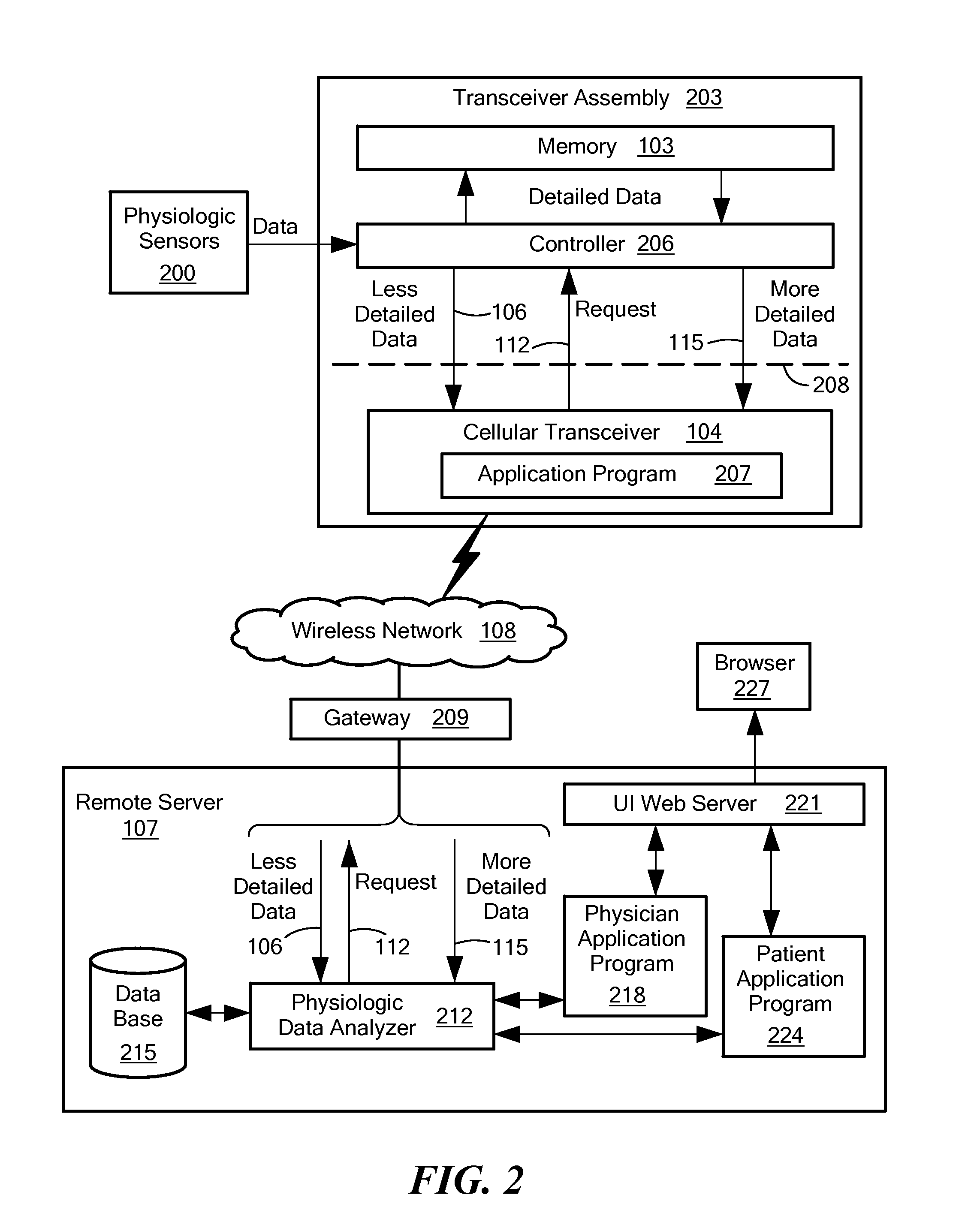
A data collection system collects and stores physiological data from an ambulatory patient at a high resolution and / or a high data rate (“more detailed data”) and sends a low-resolution and / or downsampled version of the data (“less detailed data”) to a remote server via a wireless network. The server automatically analyzes the less detailed data to detect an anomaly. A two-tiered analysis is used, where the first tier is less specific than the second tier. If the less specific analysis detects or suspects the anomaly, the server signals the data collector to send more detailed data that corresponds to a time period associated with the anomaly. The more specific second tier analysis the more detailed data to verify the anomaly. The server may also store the received data and make it available to a user.
Owner:INFOBIONIC
Image input device
InactiveUS20060072029A1Quality improvementHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionComplementary colors
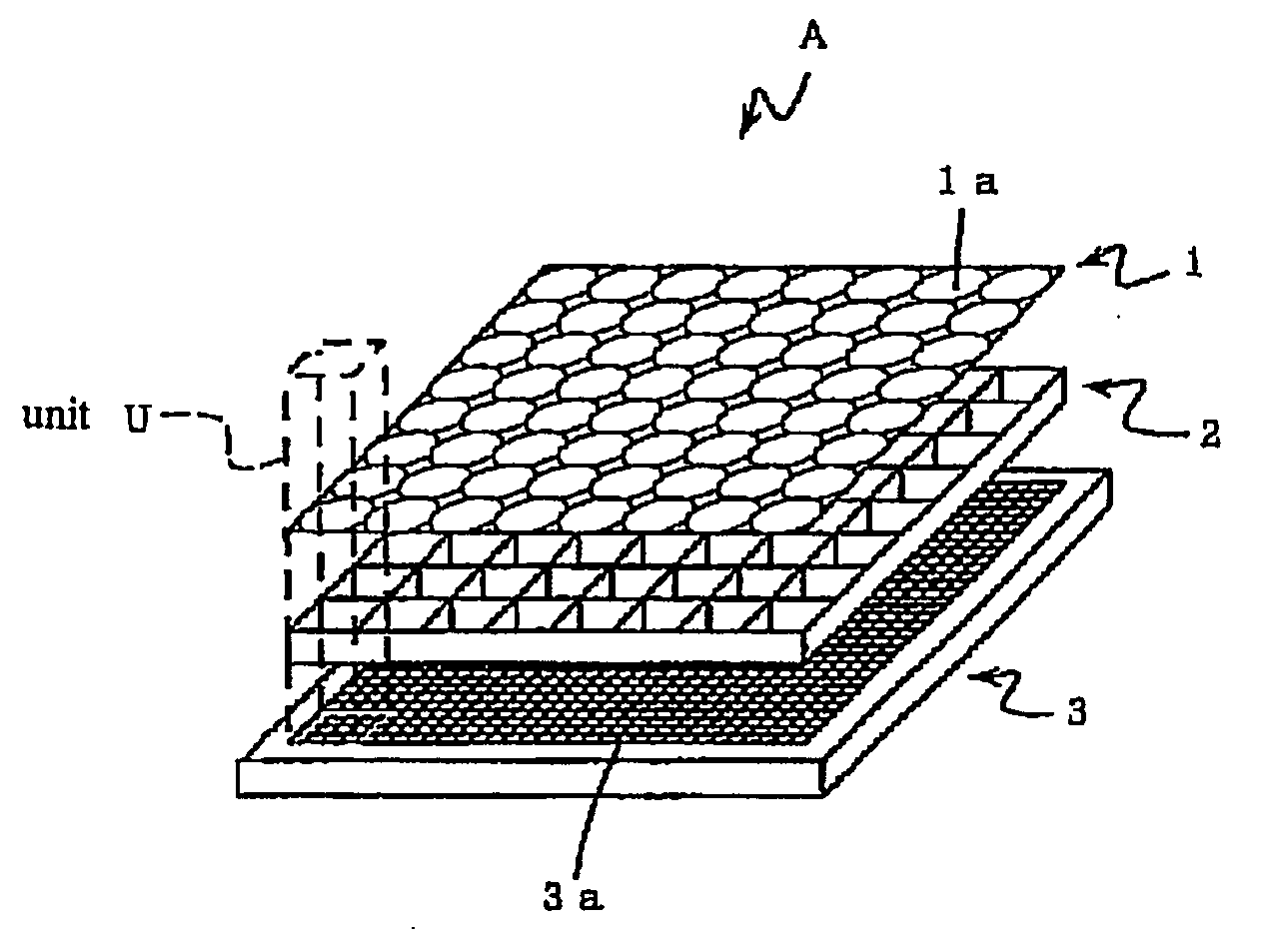
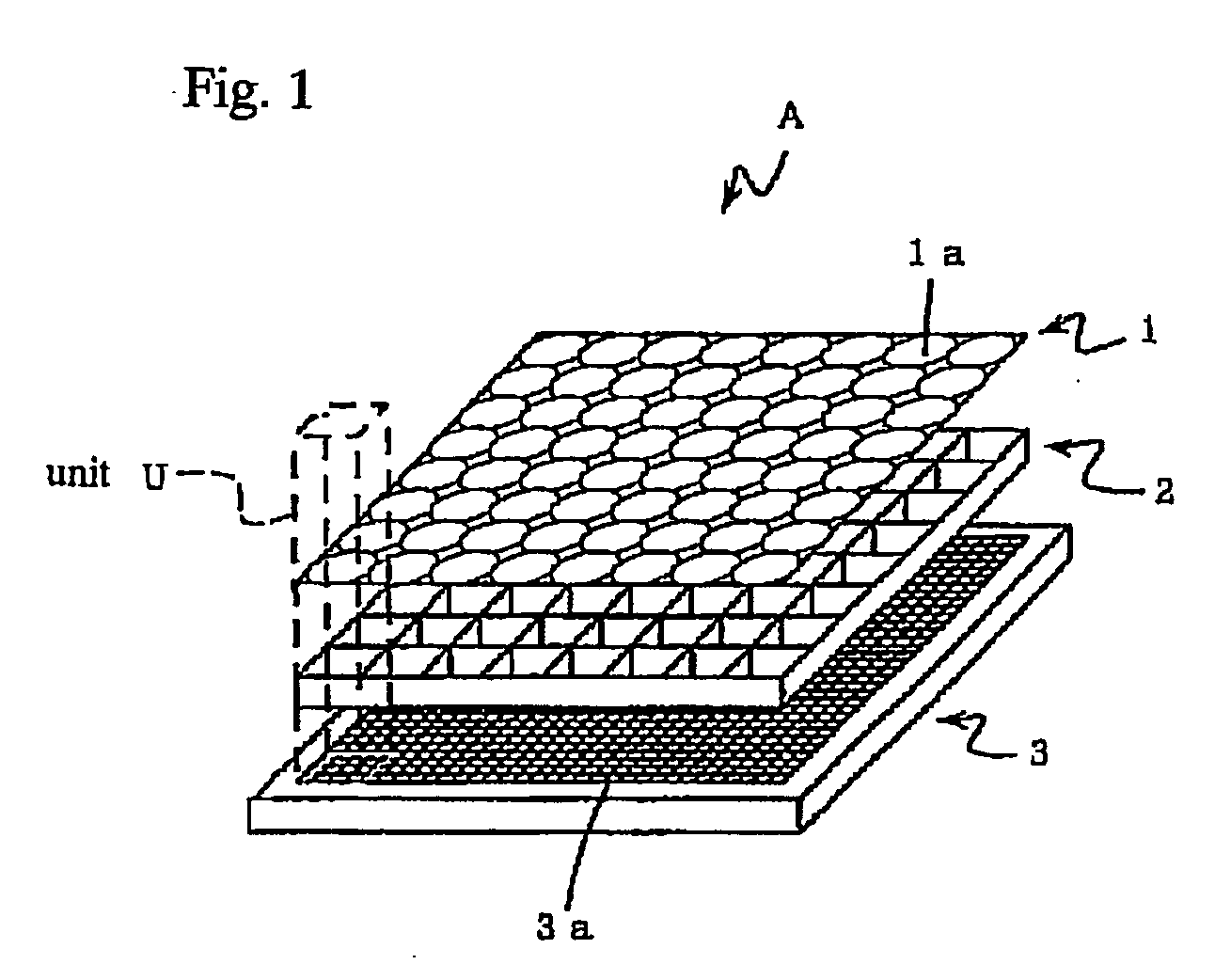
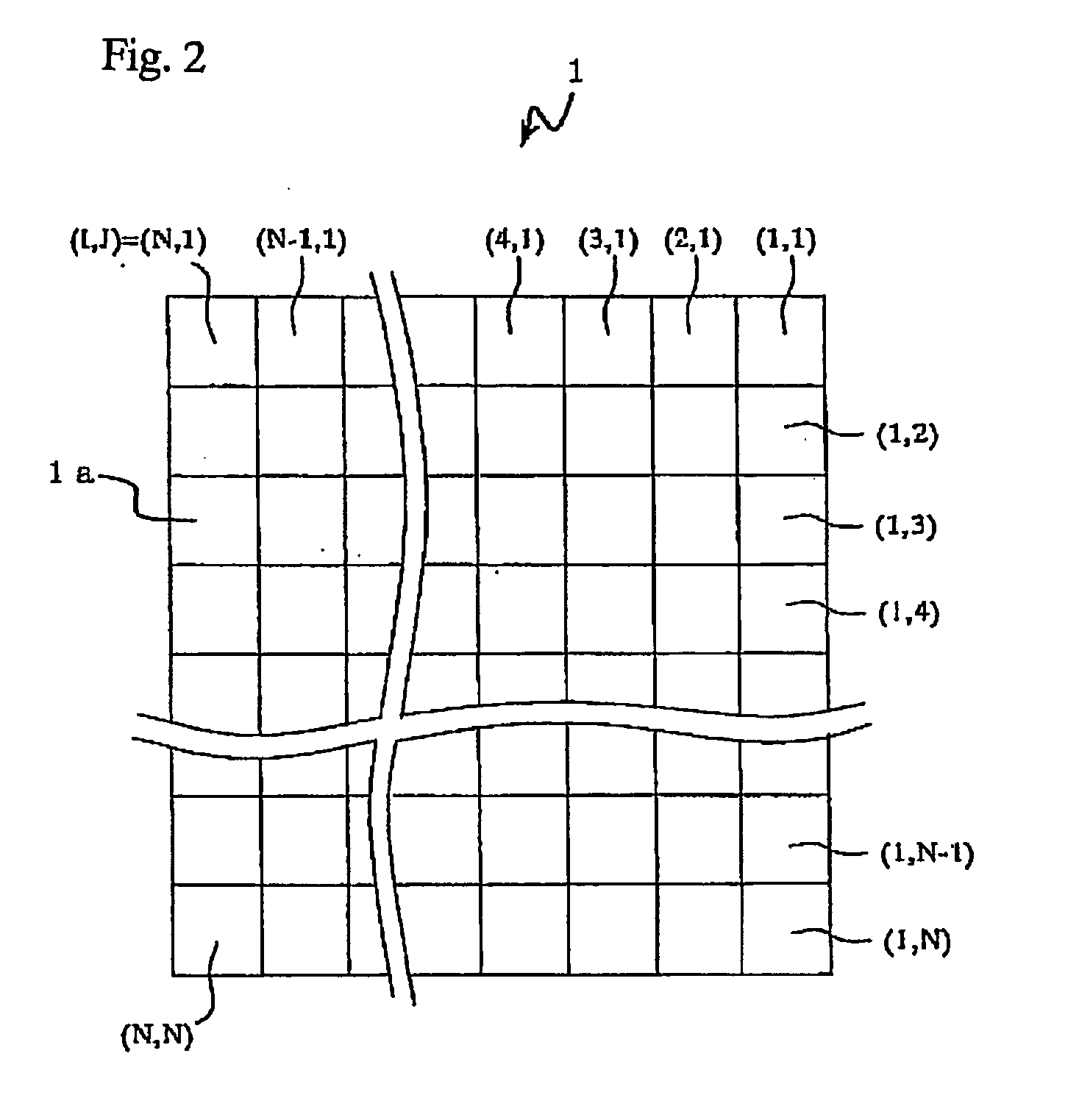
An image input apparatus which reconfigures a single reconfigured image from a plurality of low-resolution, object reduced images formed in a specified region on the light detecting element by the micro-lens array, wherein a high-resolution, single reconfigured image can be obtained even if the distance between the subject and the micro-lens array is long (infinitely long, for example), and further a reconfigured image can be realized in colors. The image input apparatus is characterized in that the relative distance between a micro-lens (1a) and light detecting cells (3a) in a specified region, where object reduced images corresponding to the micro-lens (1a) are formed, is different in each micro-lenses (1a). In addition, the light detecting cells (3a) are divided into a plurality of regions, and color filters (primary color filter, or complementary color filter, for example) are disposed in each of the divided regions.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Human face super-resolution reconstruction method based on generative adversarial network and sub-pixel convolution
ActiveCN107154023AImprove recognition accuracyClear outline of the faceGeometric image transformationNeural architecturesData setImage resolution
The invention discloses a human face super-resolution reconstruction method based on a generative adversarial network and sub-pixel convolution, and the method comprises the steps: A, carrying out the preprocessing through a normally used public human face data set, and making a low-resolution human face image and a corresponding high-resolution human face image training set; B, constructing the generative adversarial network for training, adding a sub-pixel convolution to the generative adversarial network to achieve the generation of a super-resolution image and introduce a weighted type loss function comprising feature loss; C, sequentially inputting a training set obtained at step A into a generative adversarial network model for modeling training, adjusting the parameters, and achieving the convergence; D, carrying out the preprocessing of a to-be-processed low-resolution human face image, inputting the image into the generative adversarial network model, and obtaining a high-resolution image after super-resolution reconstruction. The method can achieve the generation of a corresponding high-resolution image which is clearer in human face contour, is more specific in detail and is invariable in features. The method improves the human face recognition accuracy, and is better in human face super-resolution reconstruction effect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
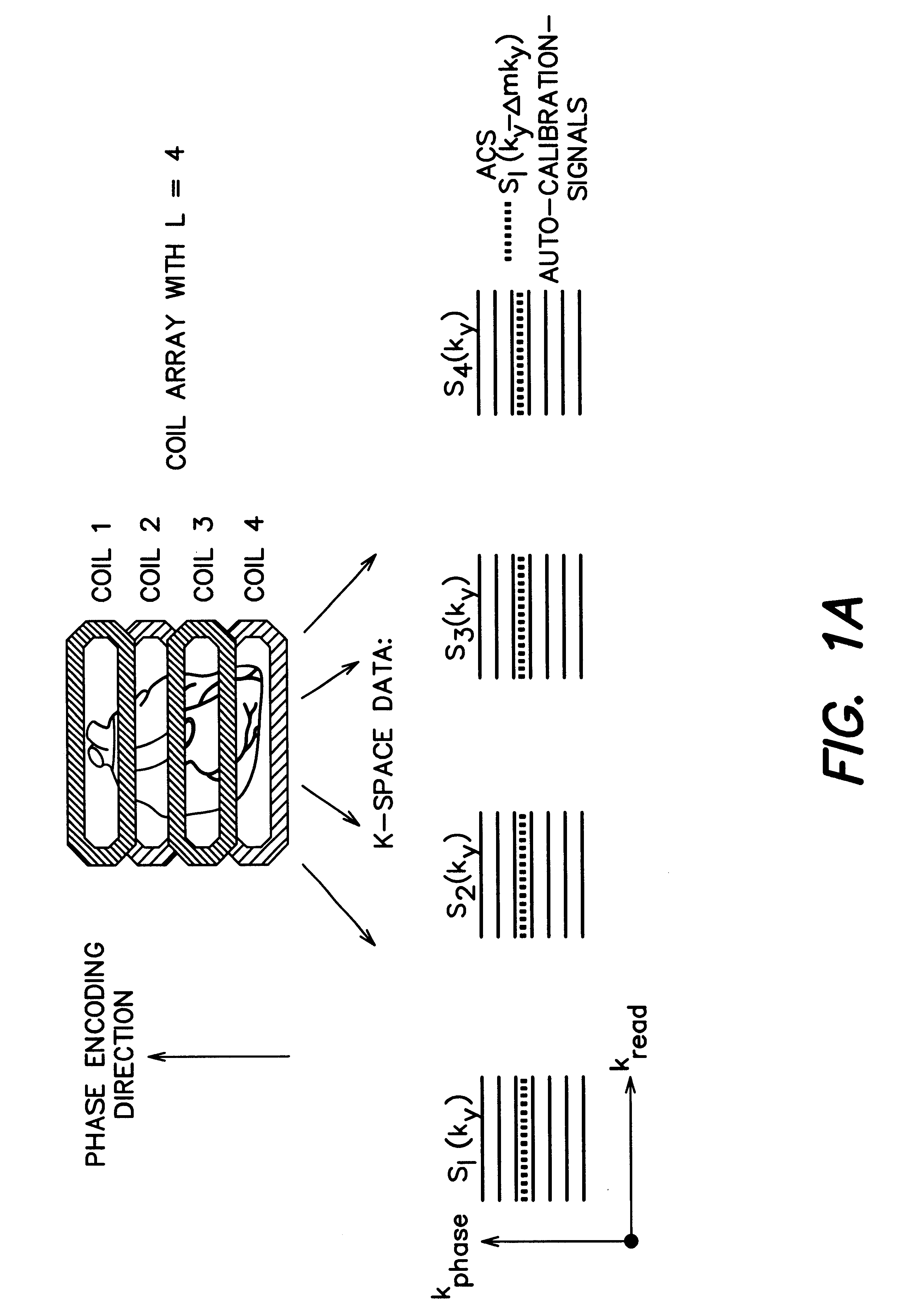
Coil array autocalibration MR imaging
InactiveUS6289232B1Shorten the timeEasy accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData spaceIn vivo
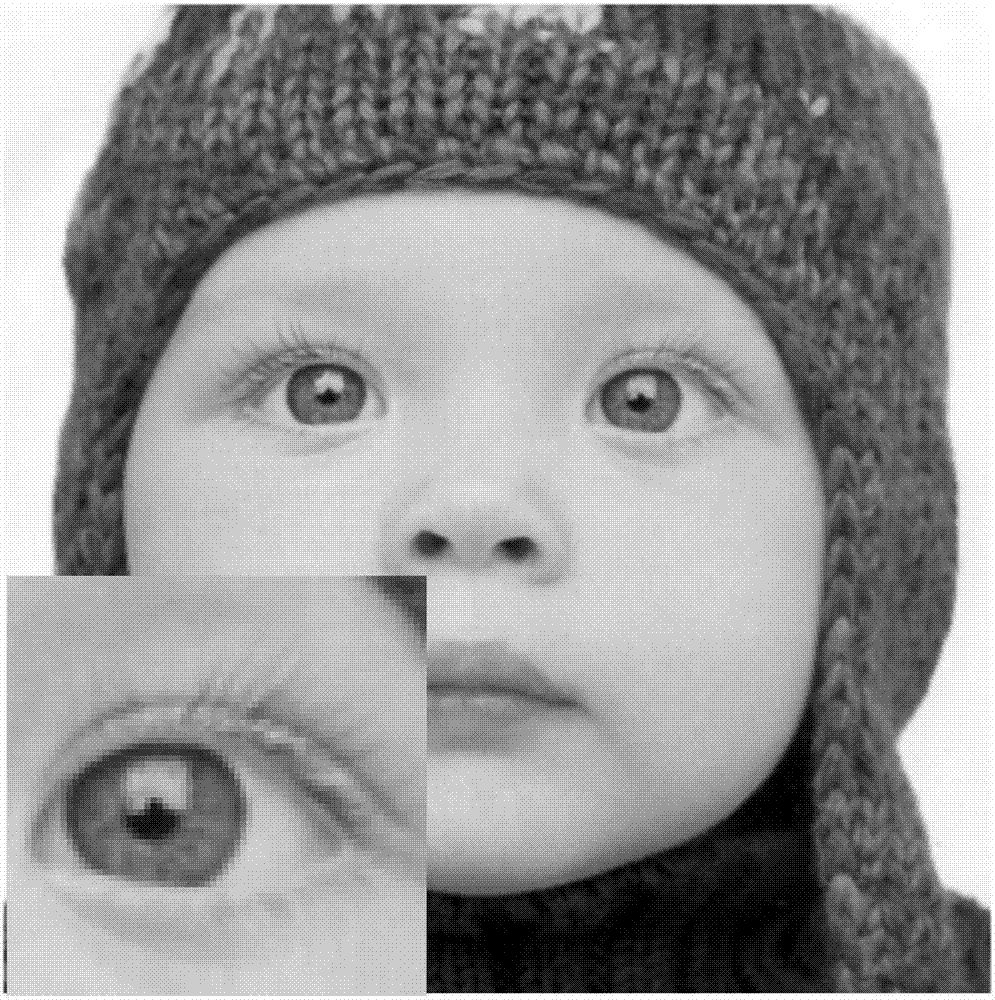
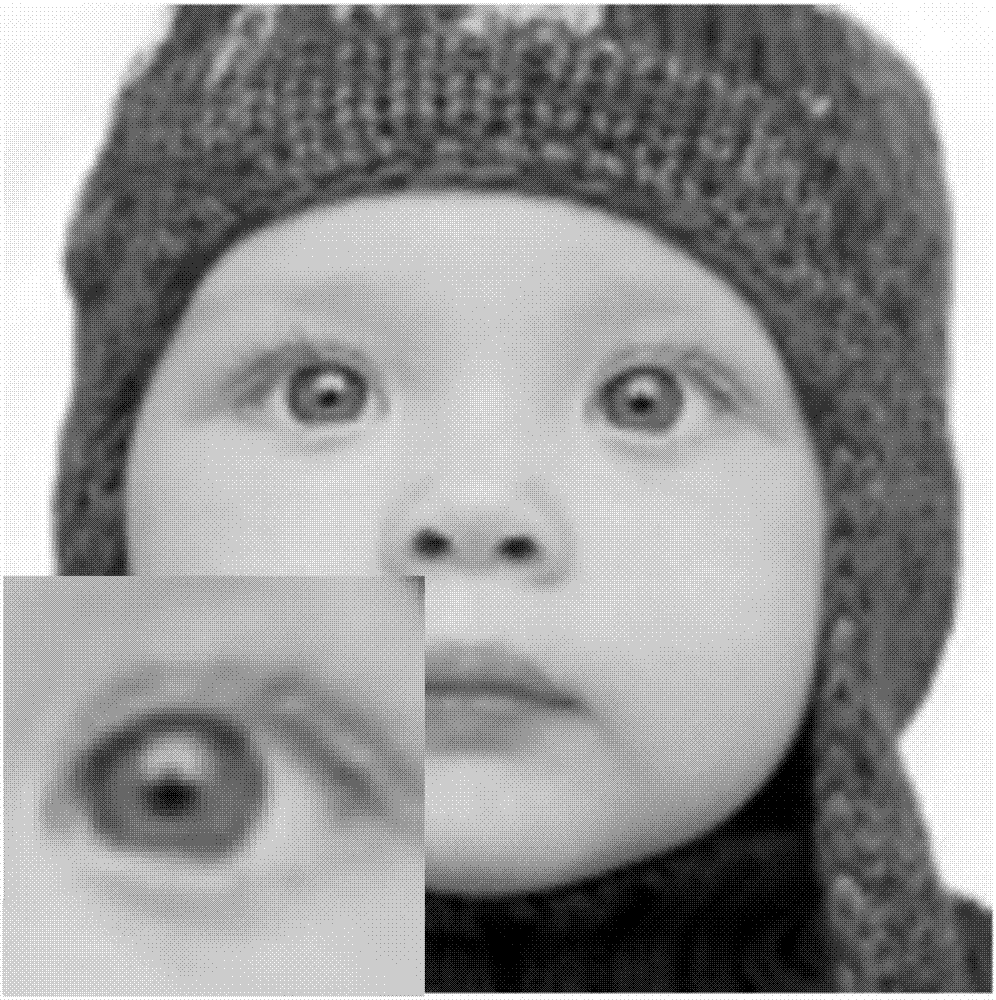
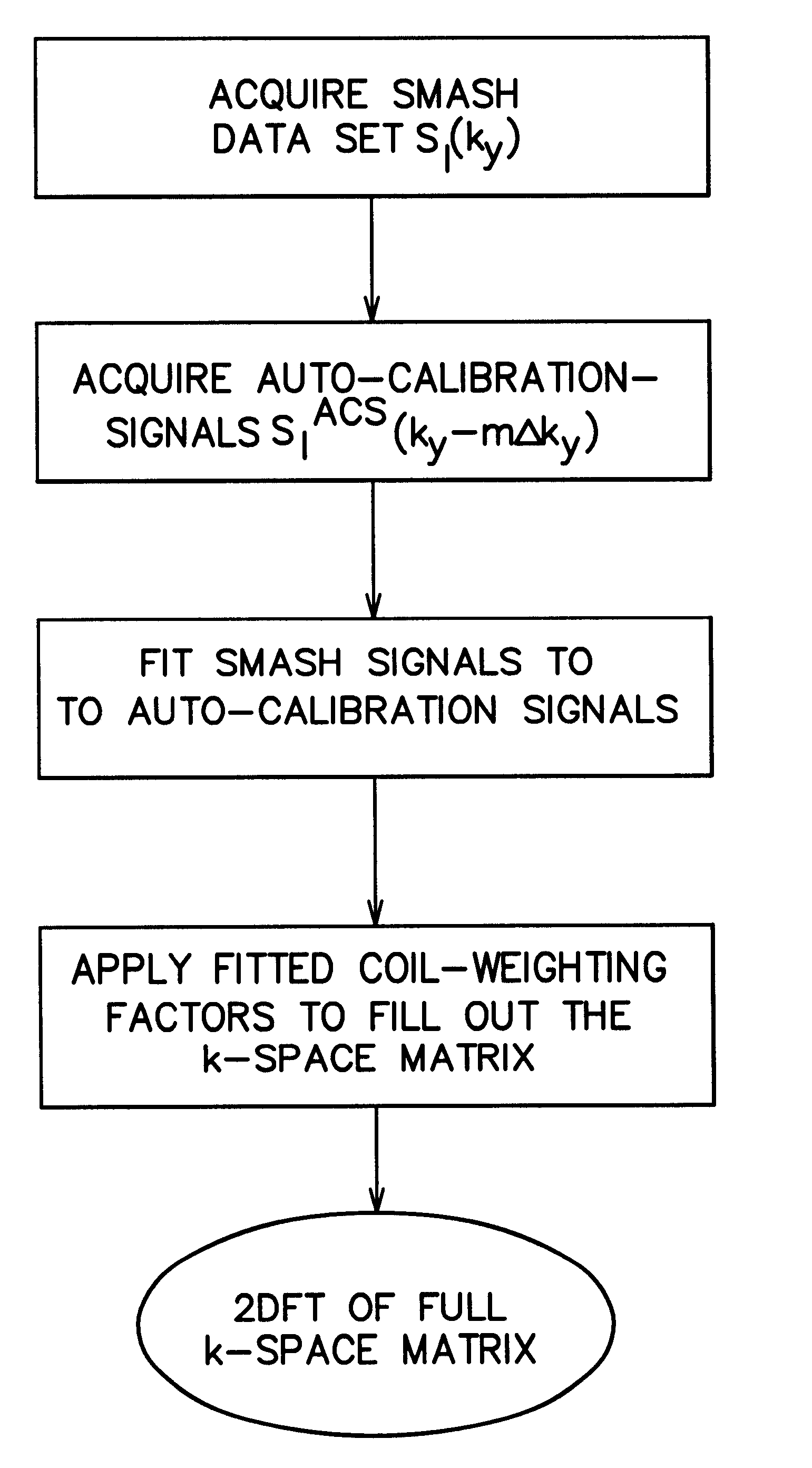
A magnetic resonance (MR) imaging apparatus and technique exploits spatial information inherent in a surface coil array to increase MR image acquisition speed, resolution and / or field of view. Magnetic resonance response signals are acquired simultaneously in the component coils of the array and, using an autocalibration procedure, are formed into two or more signals to fill a corresponding number of lines in the signal measurement data matrix. In a Fourier embodiment, lines of the k-space matrix required for image production are formed using a set of separate, preferably linear combinations of the component coil signals to substitute for spatial modulations normally produced by phase encoding gradients. One or a few additional gradients are applied to acquire autocalibration (ACS) signals extending elsewhere in the data space, and the measured signals are fitted to the ACS signals to develop weights or coefficients for filling additional lines of the matrix from each measurement set. The ACS lines may be taken offset from or in a different orientation than the measured signals, for example, between or across the measured lines. Furthermore, they may be acquired at different positions in k-space, may be performed at times before, during or after the principal imaging sequence, and may be selectively acquired to optimized the fitting for a particular tissue region or feature size. The in vivo fitting procedure is readily automated or implemented in hardware, and produces an enhancement of image speed and / or quality even in highly heterogeneous tissue. A dedicated coil assembly automatically performs the calibration procedure and applies it to measured lines to produce multiple correctly spaced output signals. One application of the internal calibration technique to a subencoding imaging process applies the ACS in the central region of a sparse set of measured signals to quickly form a full FOV low resolution image. The full FOV image is then used to determine coil sensitivity related information and dealias folded images produced from the sparse set.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
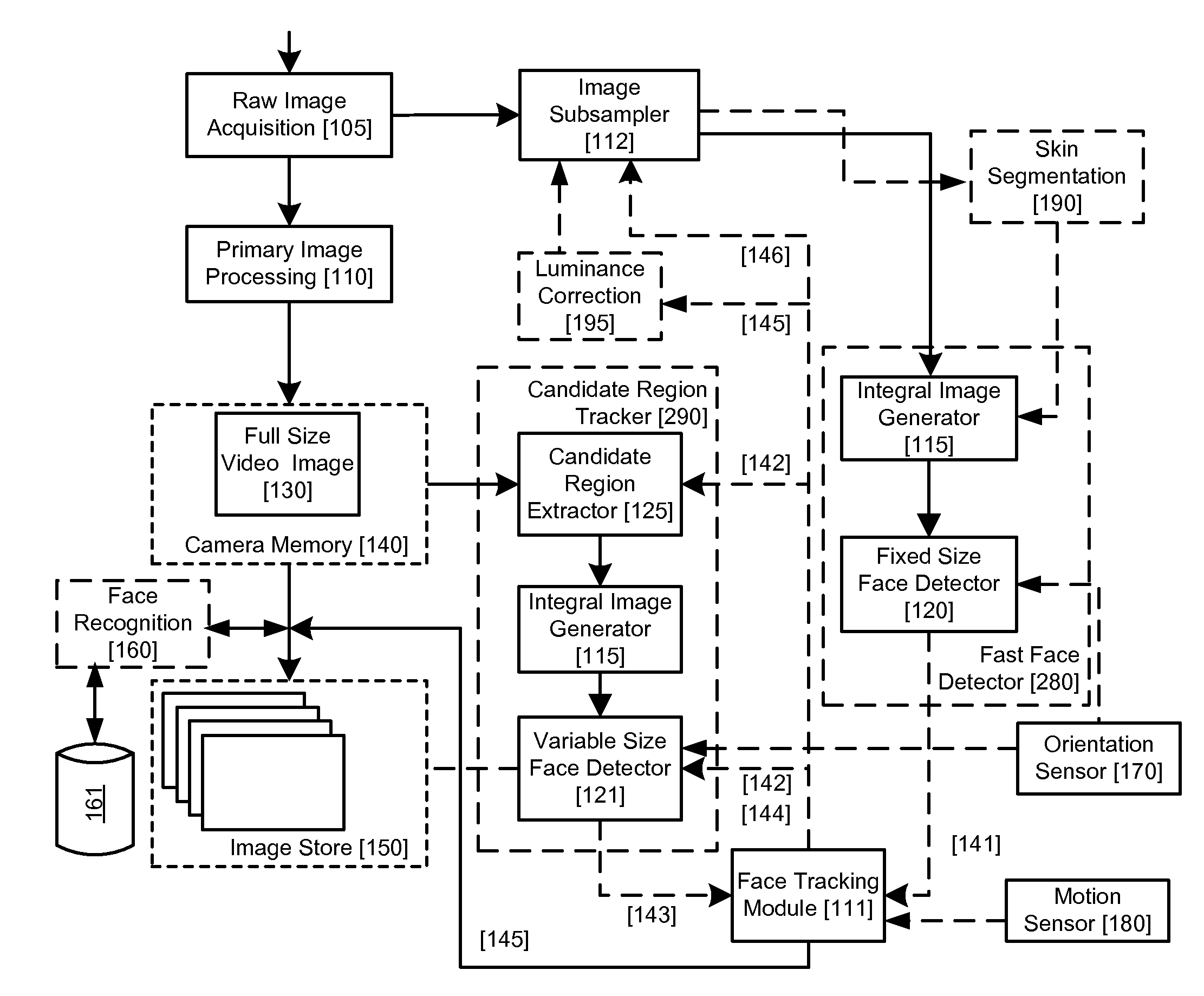
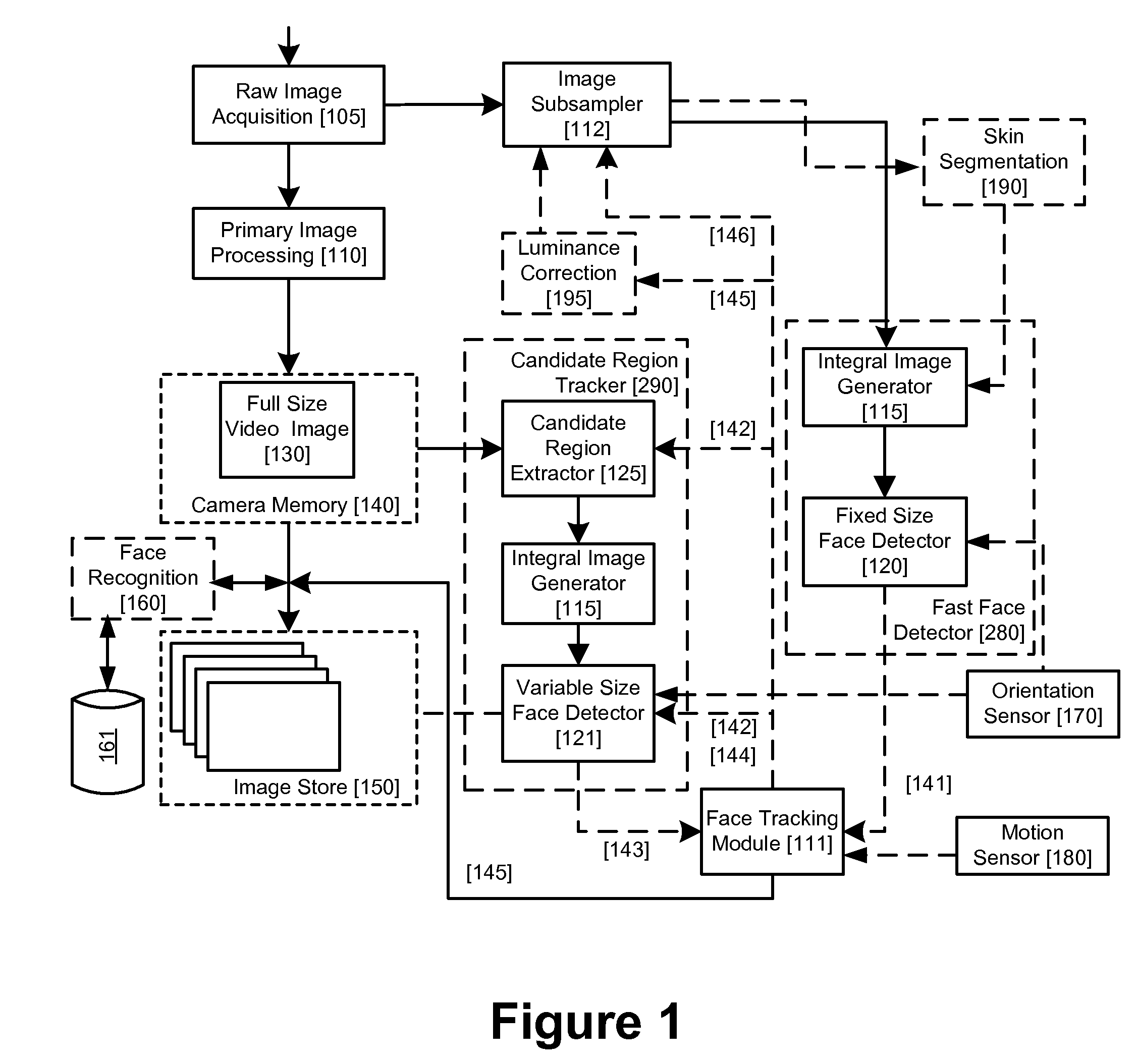
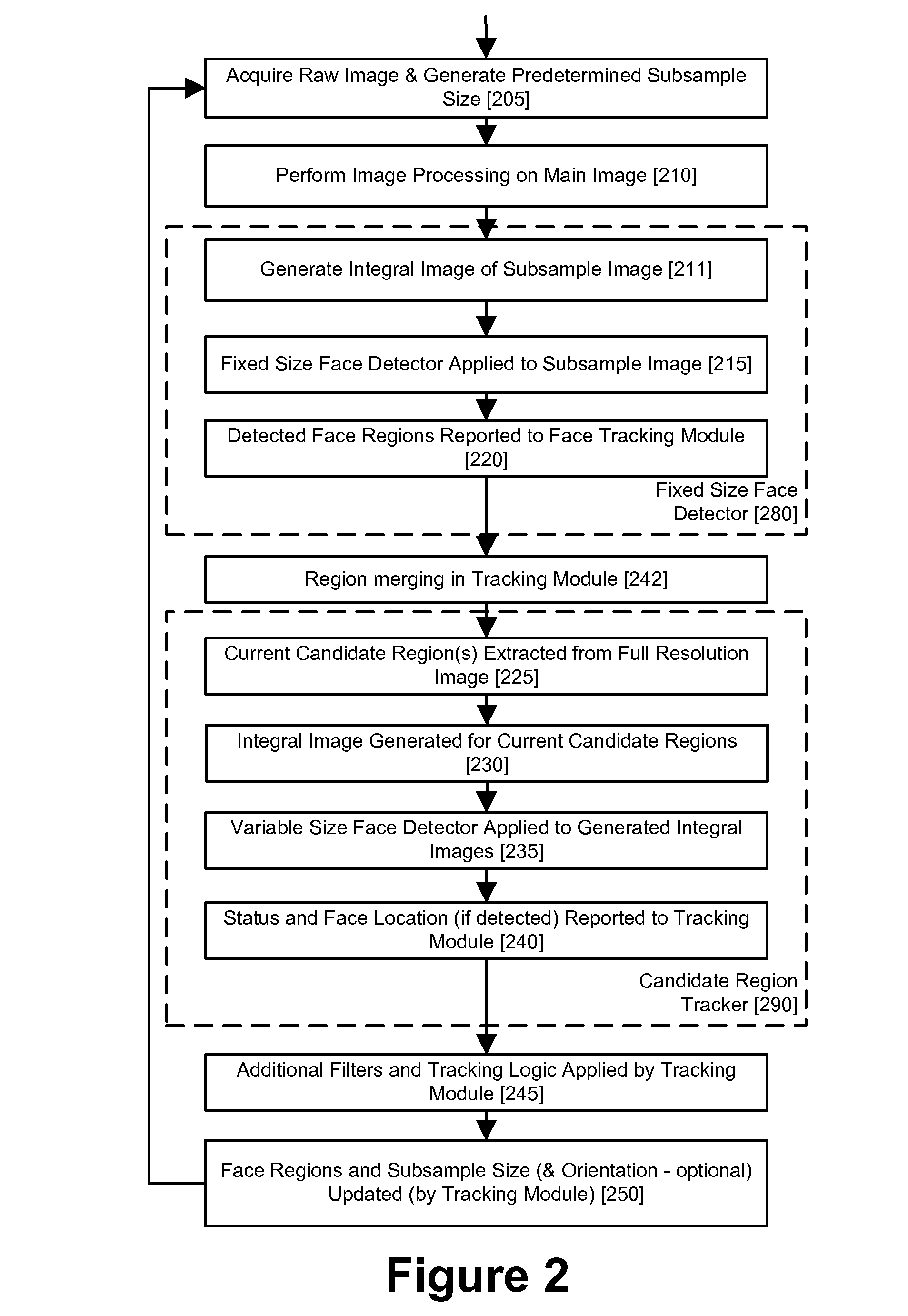
Real-time face tracking with reference images
A method of tracking a face in a reference image stream using a digital image acquisition device includes acquiring a full resolution main image and an image stream of relatively low resolution reference images each including one or more face regions. One or more face regions are identified within two or more of the reference images. A relative movement is determined between the two or more reference images. A size and location are determined of the one or more face regions within each of the two or more reference images. Concentrated face detection is applied to at least a portion of the full resolution main image in a predicted location for candidate face regions having a predicted size as a function of the determined relative movement and the size and location of the one or more face regions within the reference images, to provide a set of candidate face regions for the main image.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Methods and apparatus for reduced resolution partitioning
ActiveCN101507280APulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationImage resolutionTheoretical computer science
There are provided methods and apparatus for reduced resolution partitioning. An apparatus includes an encoder (300) for encoding video data using adaptive tree-based frame partitioning, wherein partitions are obtained from a combination of top-down tree partitioning and bottom-up tree joining.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
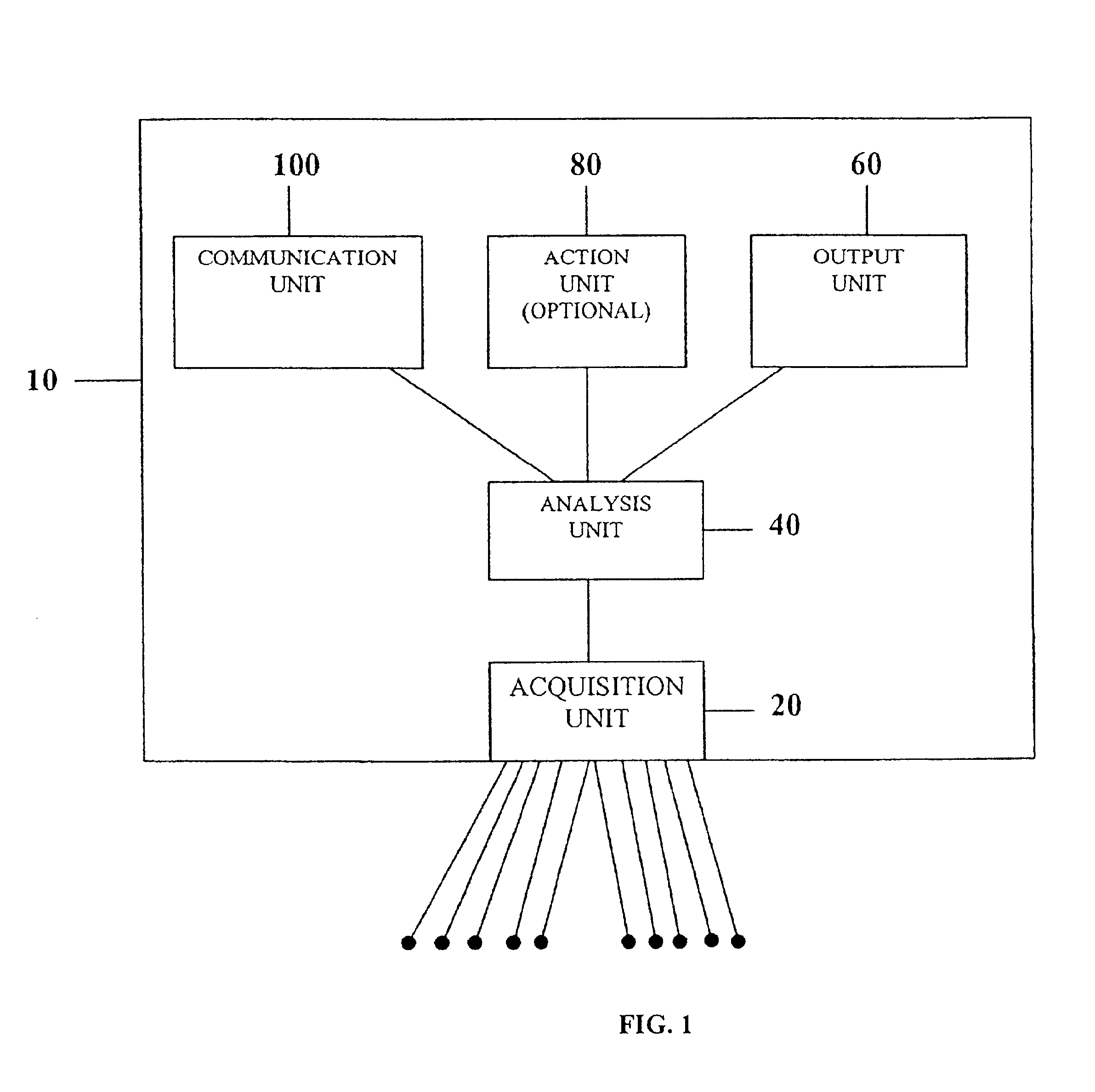
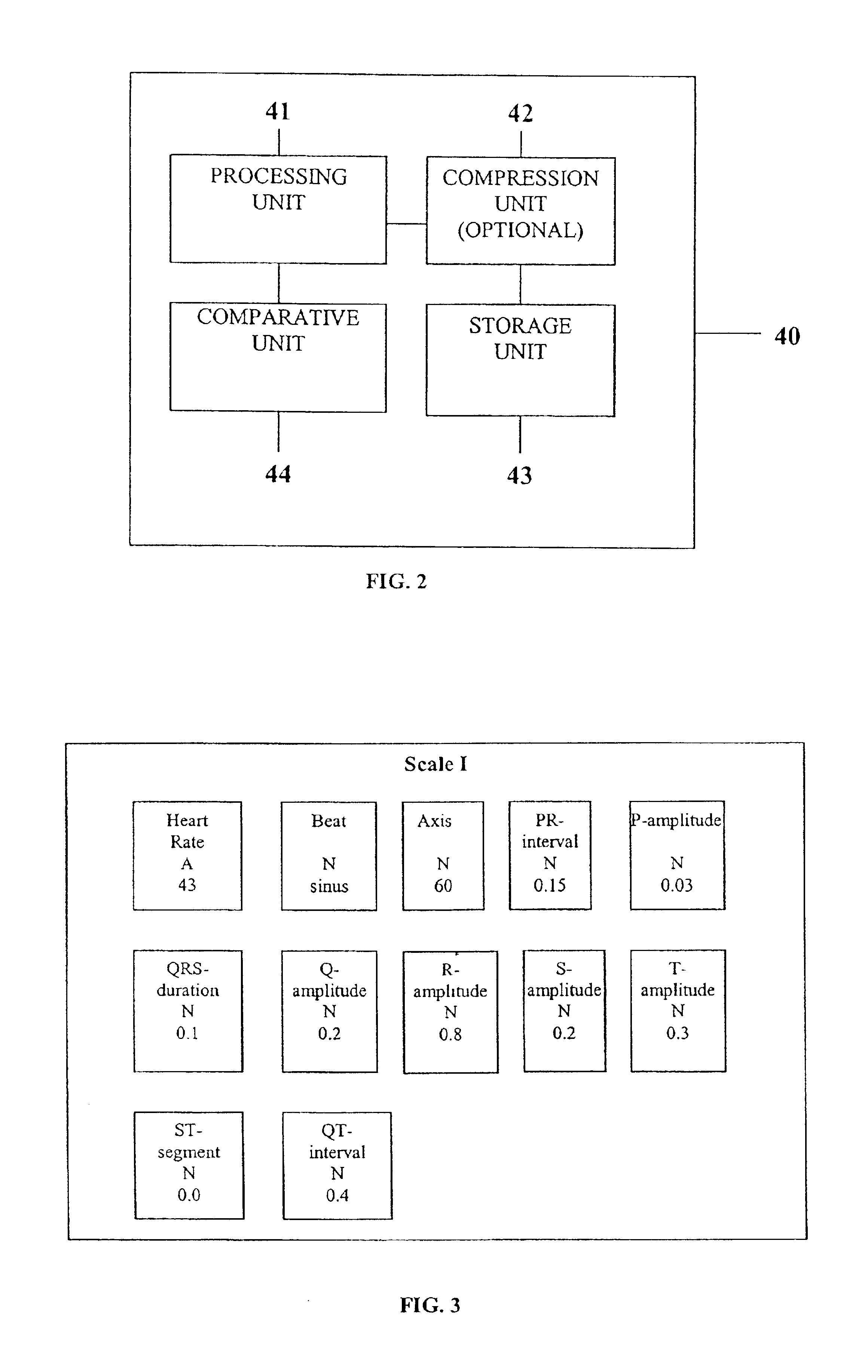
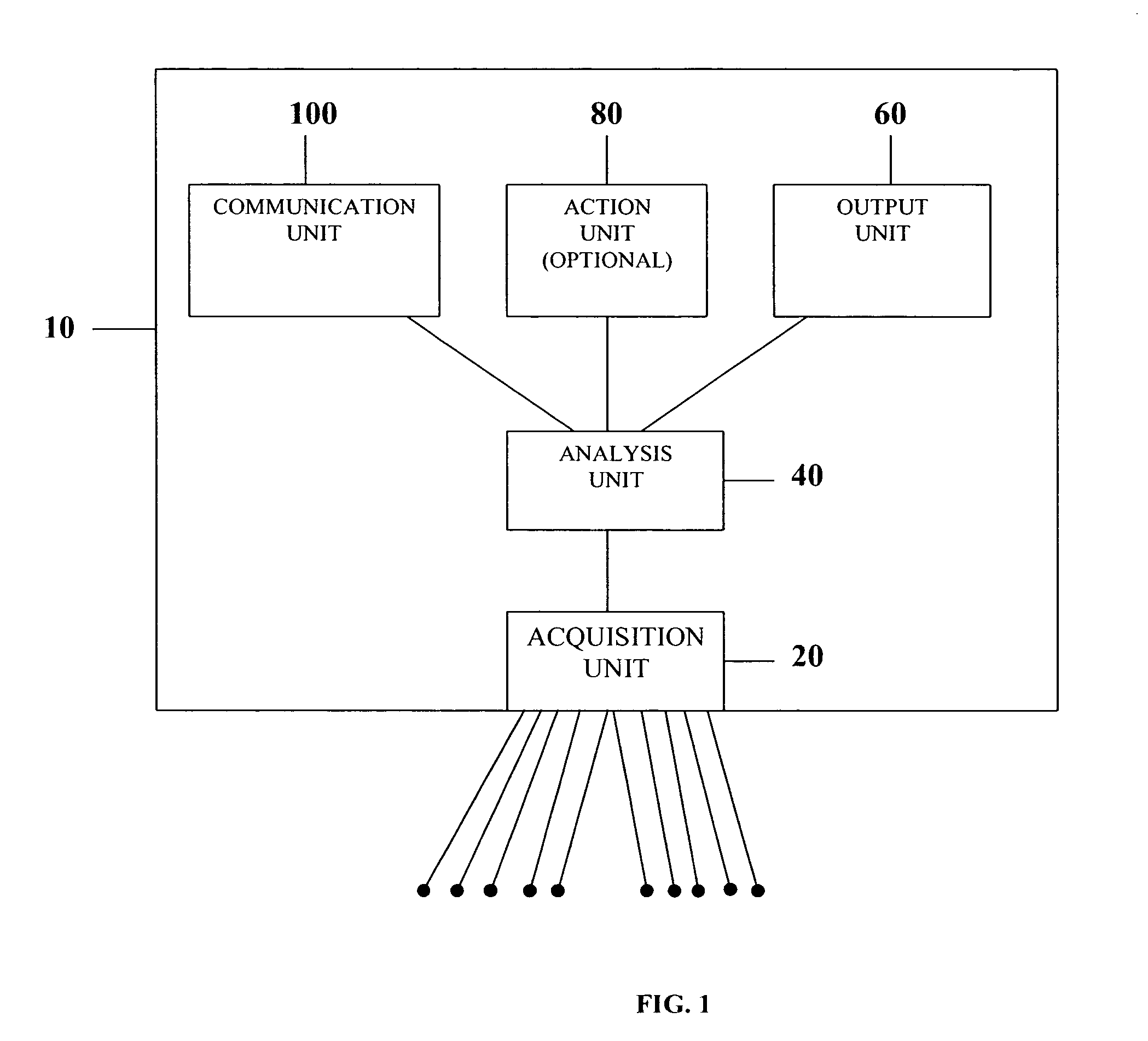
System and device for multi-scale analysis and representation of physiological data
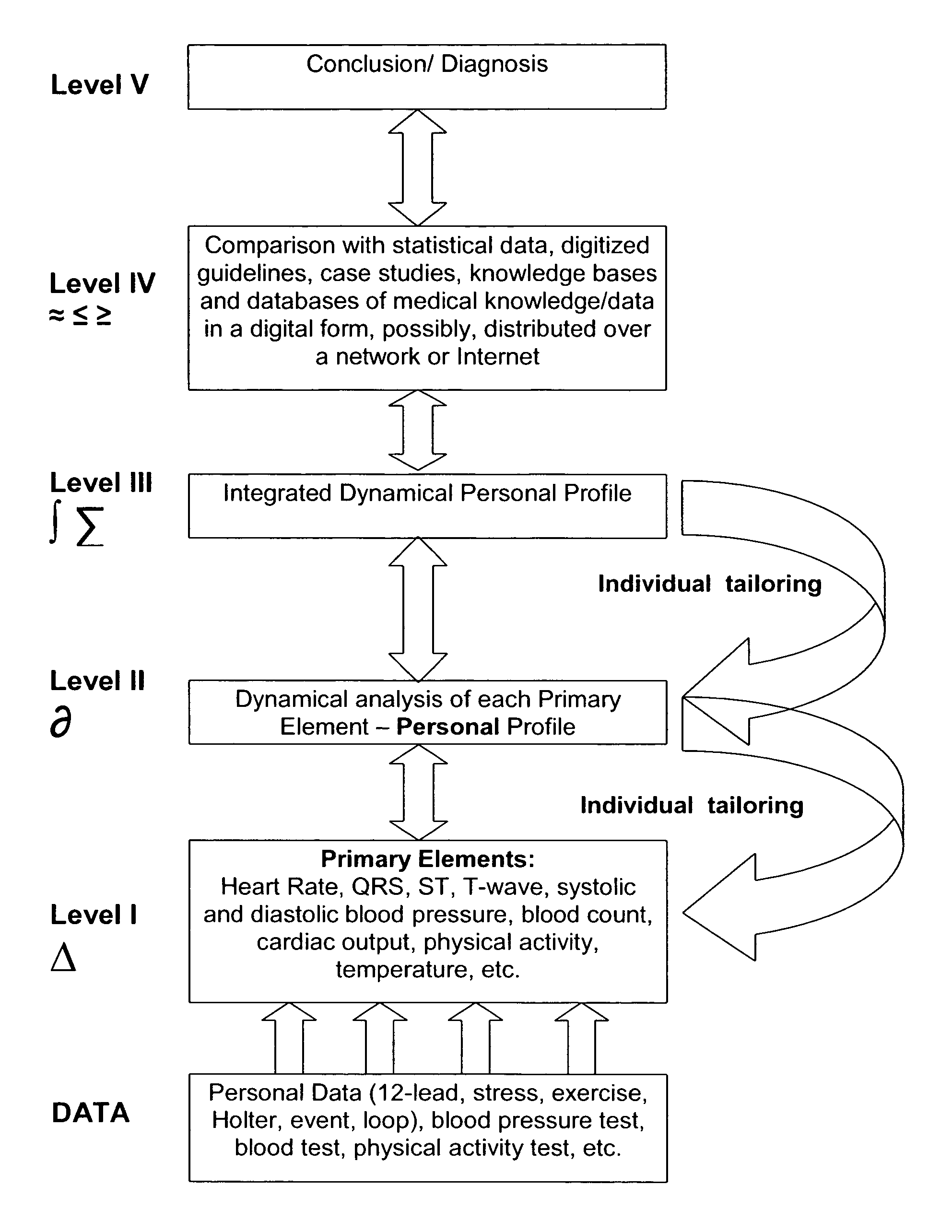
InactiveUS6925324B2Easy to analyzeIncrease computing resourcesElectrocardiographySensorsReal time analysisT wave
System comprised of a medical device and method for analyzing physiological and health data and representing the most significant parameters at different levels of detail which are understandable to a lay person and a medical professional. Low, intermediate and high-resolution scales can exchange information between each other for improving the analyses; the scales can be defined according to the corresponding software and hardware resources. A low-resolution Scale I represents a small number of primary elements such as intervals between the heart beats, duration of electrocardiographic PQ, QRS, and QT-intervals, amplitudes of P-, Q-, R-, S-, and T-waves. This real-time analysis is implemented in a portable device that requires minimum computational resources. The set of primary elements and their search criteria can be adjusted using intermediate or high-resolution levels. At the intermediate-resolution Scale II, serial changes in each of the said elements can be determined using a mathematical decomposition into series of basis functions and their coefficients. This scale can be implemented using a specialized processor or a computer organizer. At the high-resolution Scale III, combined serial changes in all primary elements can be determined to provide complete information about the dynamics of the signal. This scale can be implemented using a powerful processor, a network of computers or the Internet. The system can be used for personal or group self-evaluation, emergency or routine ECG analysis, or continuous event, stress-test or bed-side monitoring.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
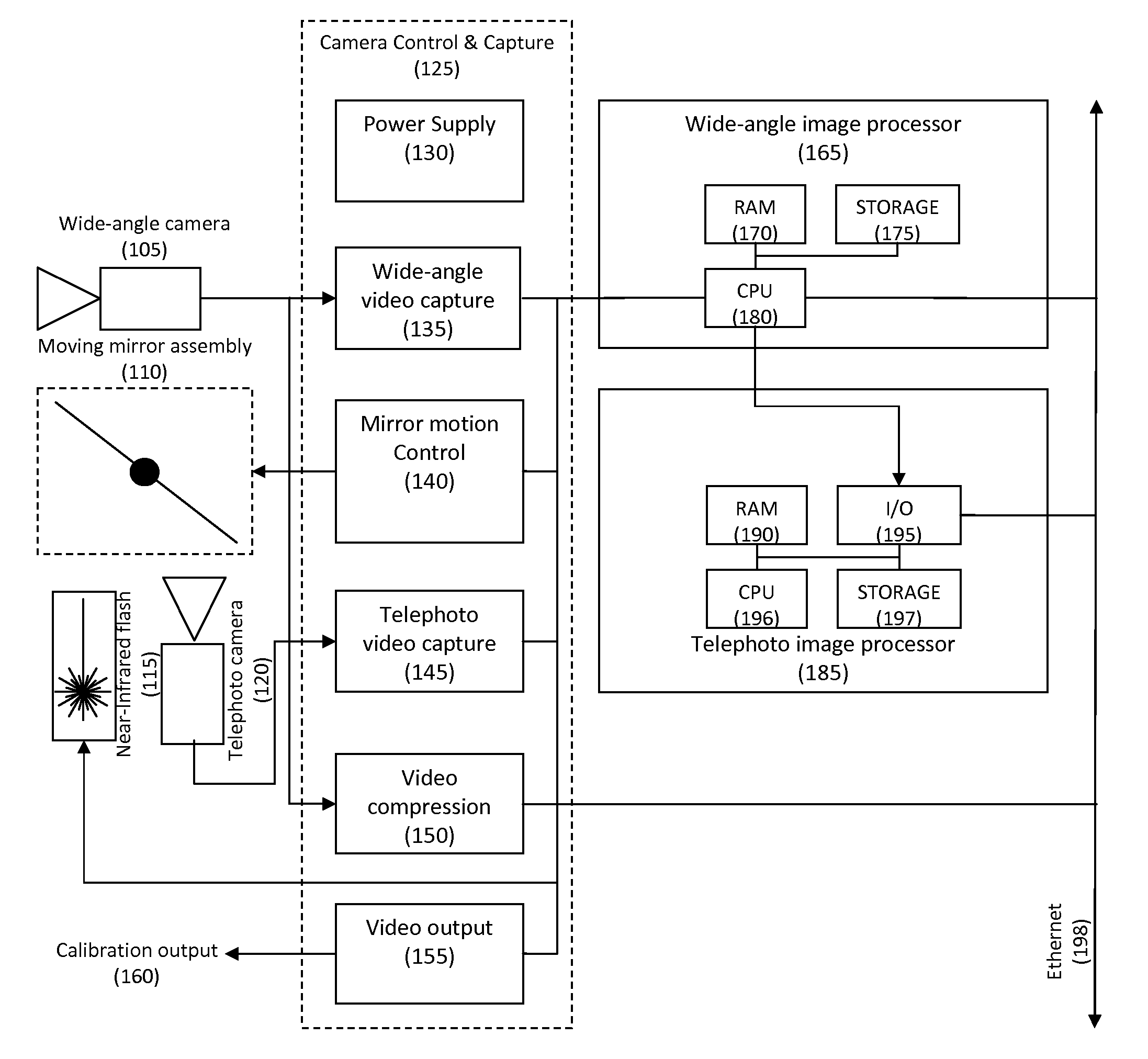
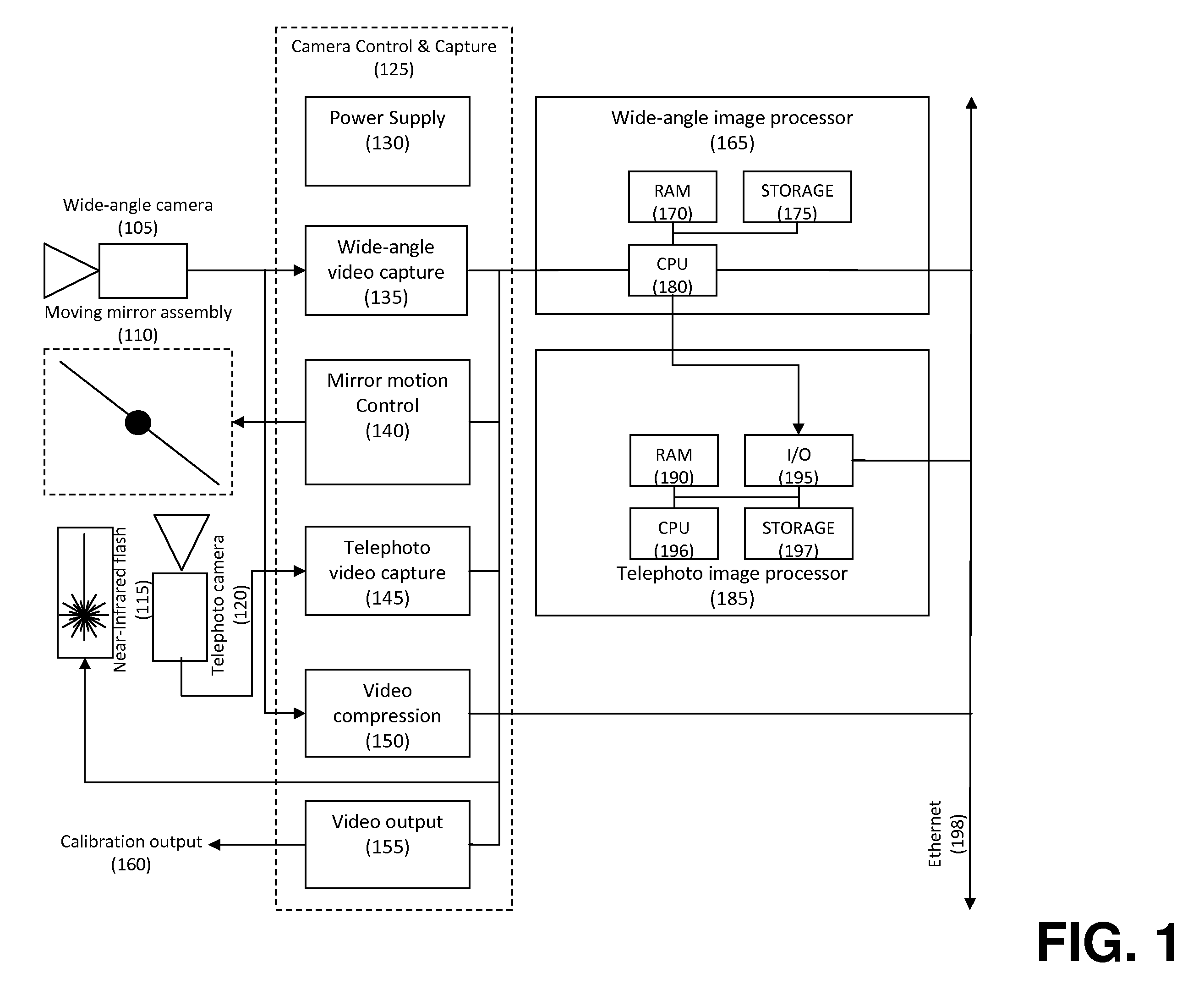
Saccadic dual-resolution video analytics camera
InactiveUS20110063446A1Improve performanceAugment ambient illuminationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage resolution
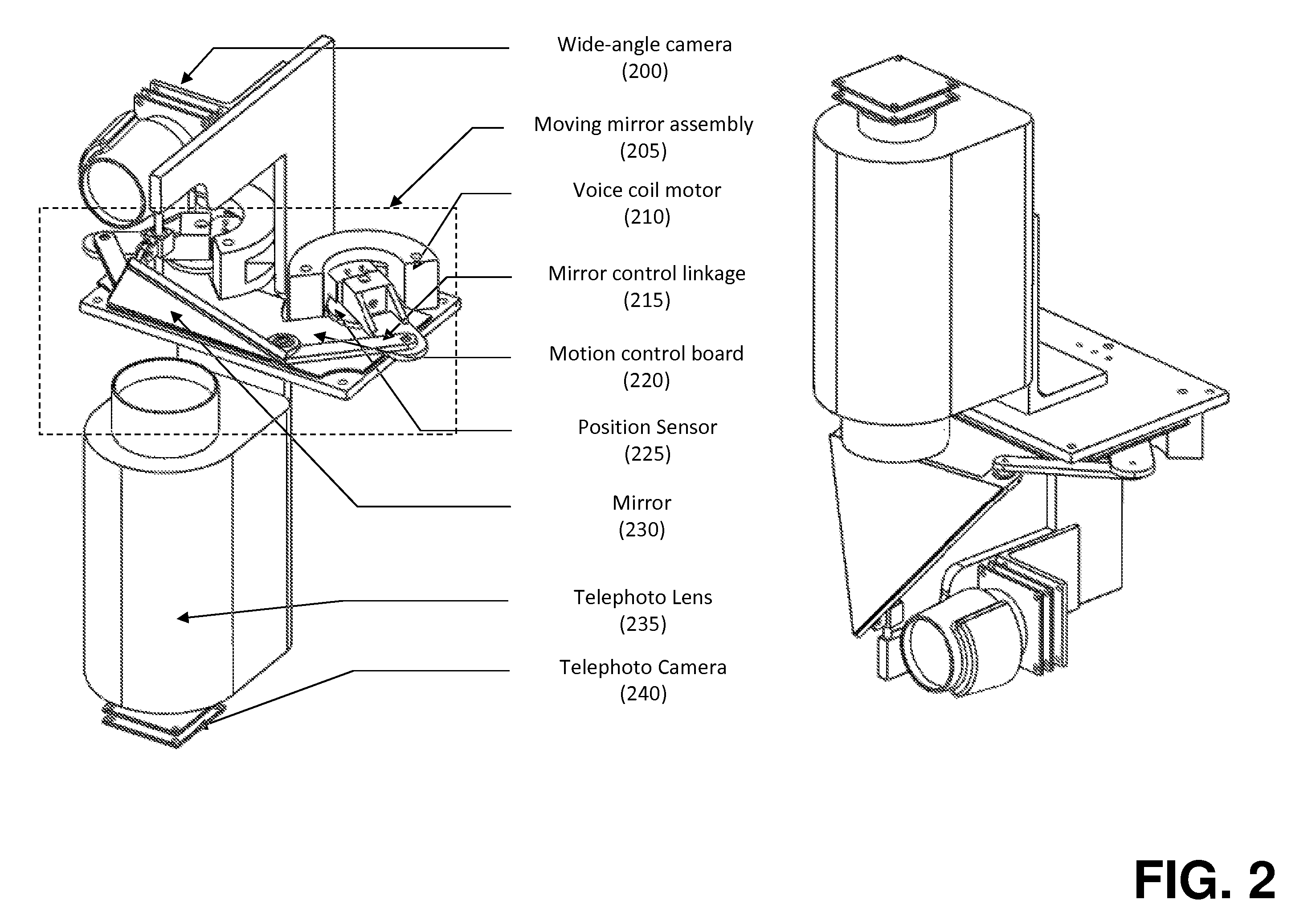
Objects of interest are detected and identified using multiple cameras having varying resolution and imaging parameters. An object is first located using a low resolution camera. A second camera (or lens) is then directed at the object's location using a steerable mirror assembly to capture a high-resolution image at a location where the object is thought to be based on image acquired by the wide-angle camera. Various image processing algorithms may be applied to confirm the presence of the object in the telephoto image. If an object is detected and the image is of sufficiently high quality, detailed facial, alpha-numeric, or other pattern recognition techniques may be applied to the image.
Owner:VIION SYST
Systems and methods for synthesizing high resolution images using super-resolution processes
ActiveUS8878950B2Promote recoveryHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementProcess systemsImage resolution
Systems and methods in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed that use super-resolution (SR) processes to use information from a plurality of low resolution (LR) images captured by an array camera to produce a synthesized higher resolution image. One embodiment includes obtaining input images using the plurality of imagers, using a microprocessor to determine an initial estimate of at least a portion of a high resolution image using a plurality of pixels from the input images, and using a microprocessor to determine a high resolution image that when mapped through the forward imaging transformation matches the input images to within at least one predetermined criterion using the initial estimate of at least a portion of the high resolution image. In addition, each forward imaging transformation corresponds to the manner in which each imager in the imaging array generate the input images, and the high resolution image synthesized by the microprocessor has a resolution that is greater than any of the input images.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Methods and systems for laser based real-time structured light depth extraction
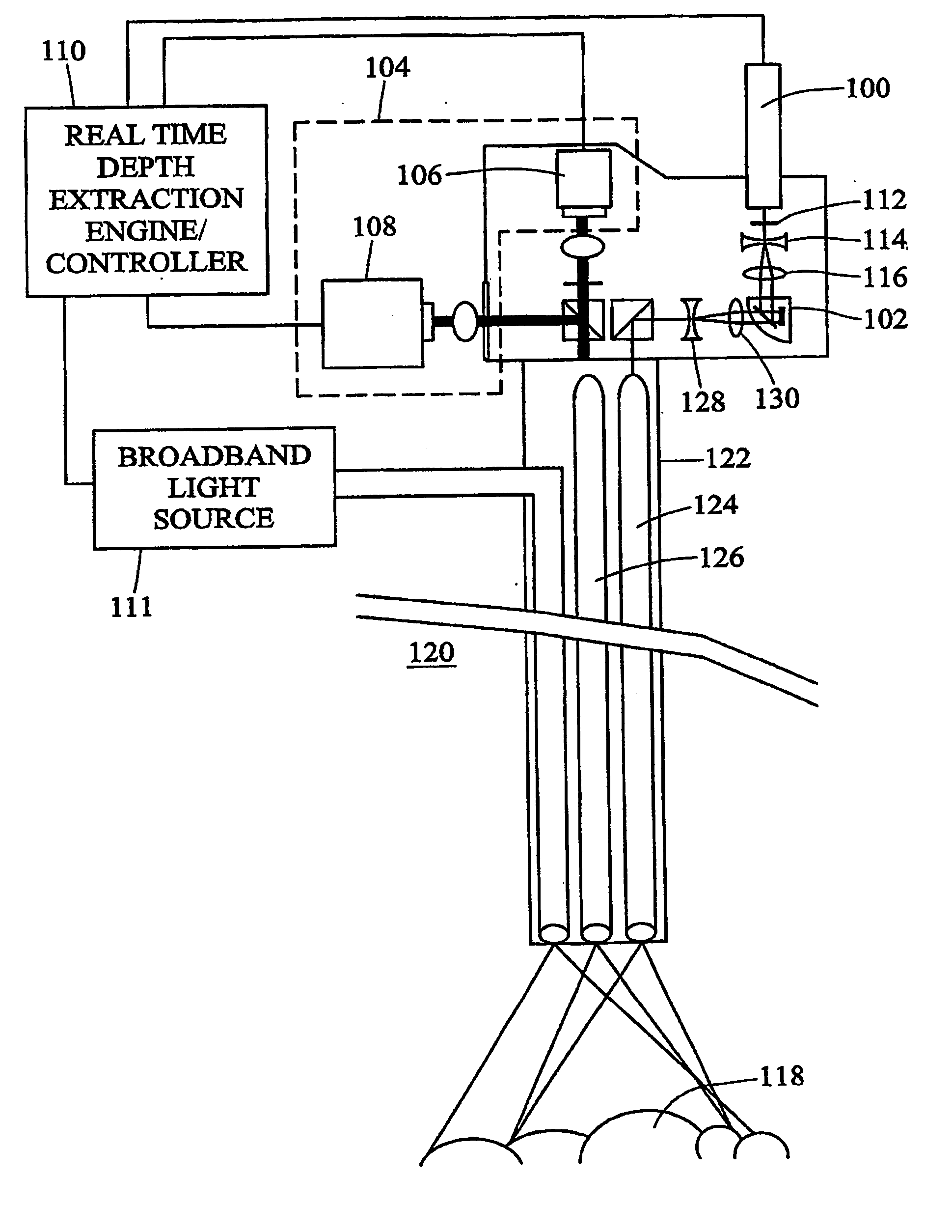
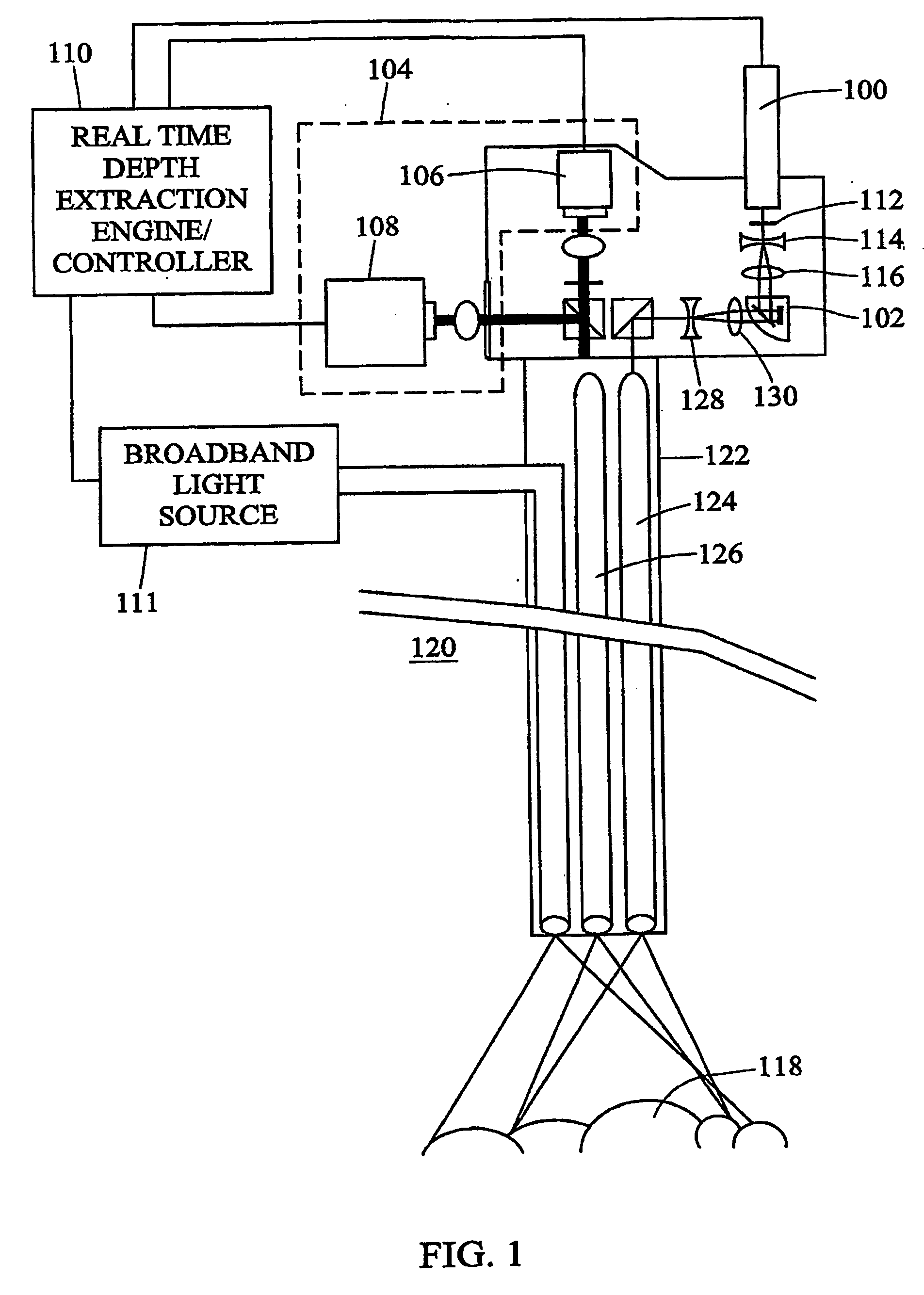
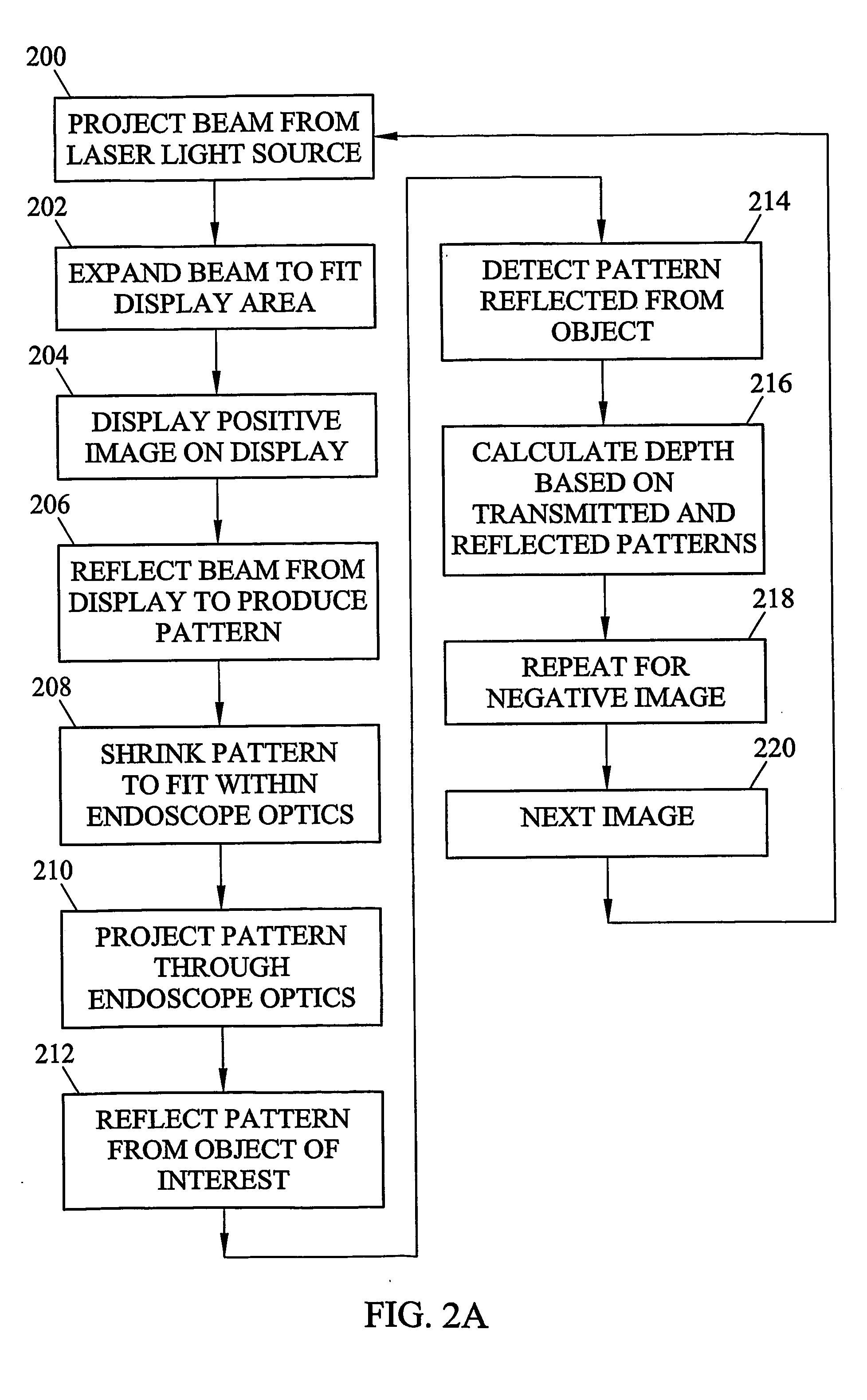
InactiveUS20050219552A1Photonic efficiencyImprove efficiencyImage analysisSurgeryLow speedImage resolution
Laser-based methods and systems for real-time structured light depth extraction are disclosed. A laser light source (100) produces a collimated beam of laser light. A pattern generator (102) generates structured light patterns including a plurality of pixels. The beam of laser light emanating from the laser light source (100) interacts with the patterns to project the patterns onto the object of (118). The patterns are reflected from the object of interest (118) and detected using a high-speed, low-resolution detector (106). A broadband light source (111) illuminates the object with broadband / light, and a separate high-resolution, low-speed detector (108) detects broadband light reflected from the object (118). A real-time structured light depth extraction engine / controller (110) based on the transmitted and reflected patterns and the reflected broadband light.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Method and apparatus for implementing a class D driver and speaker system
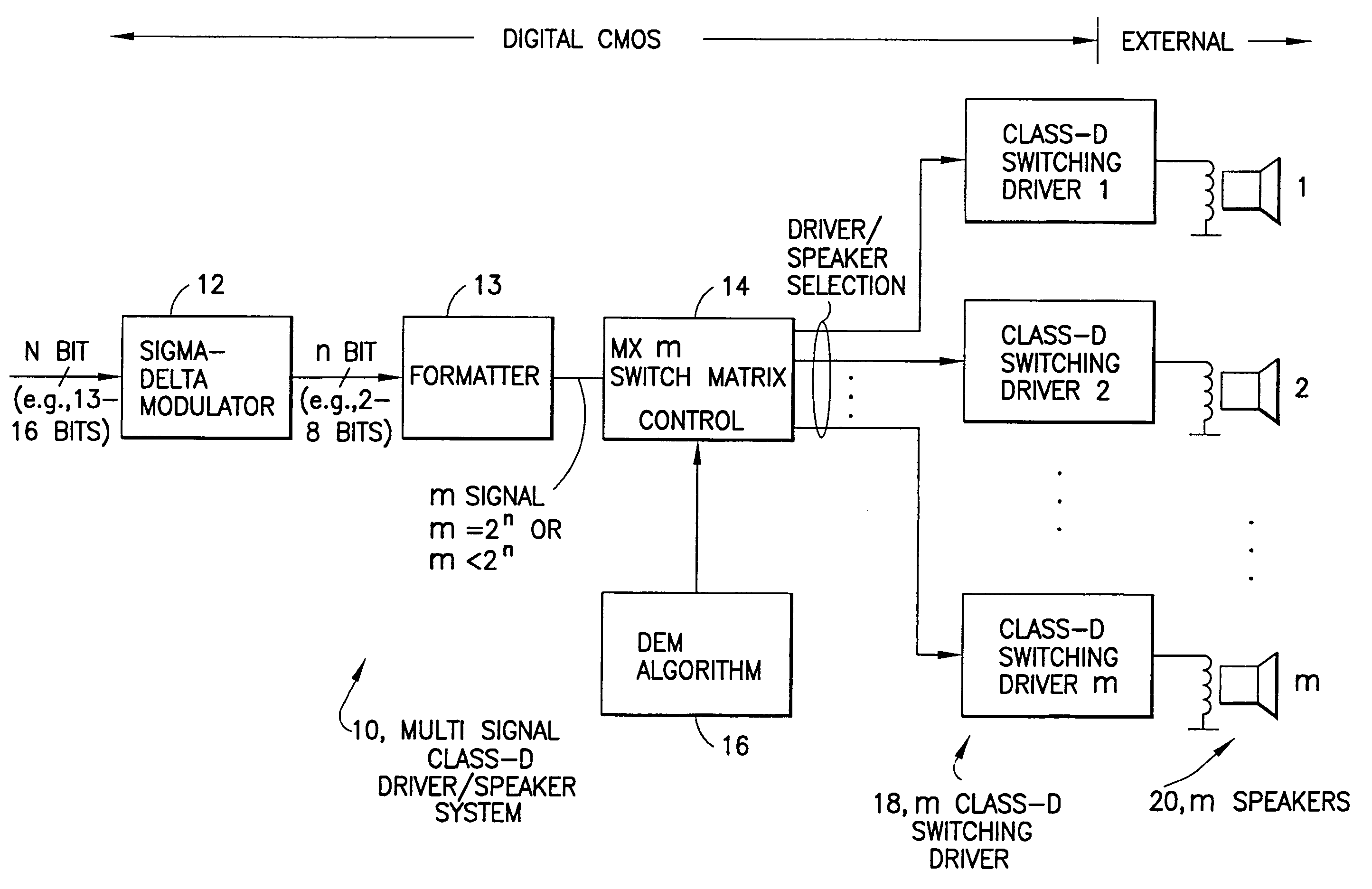
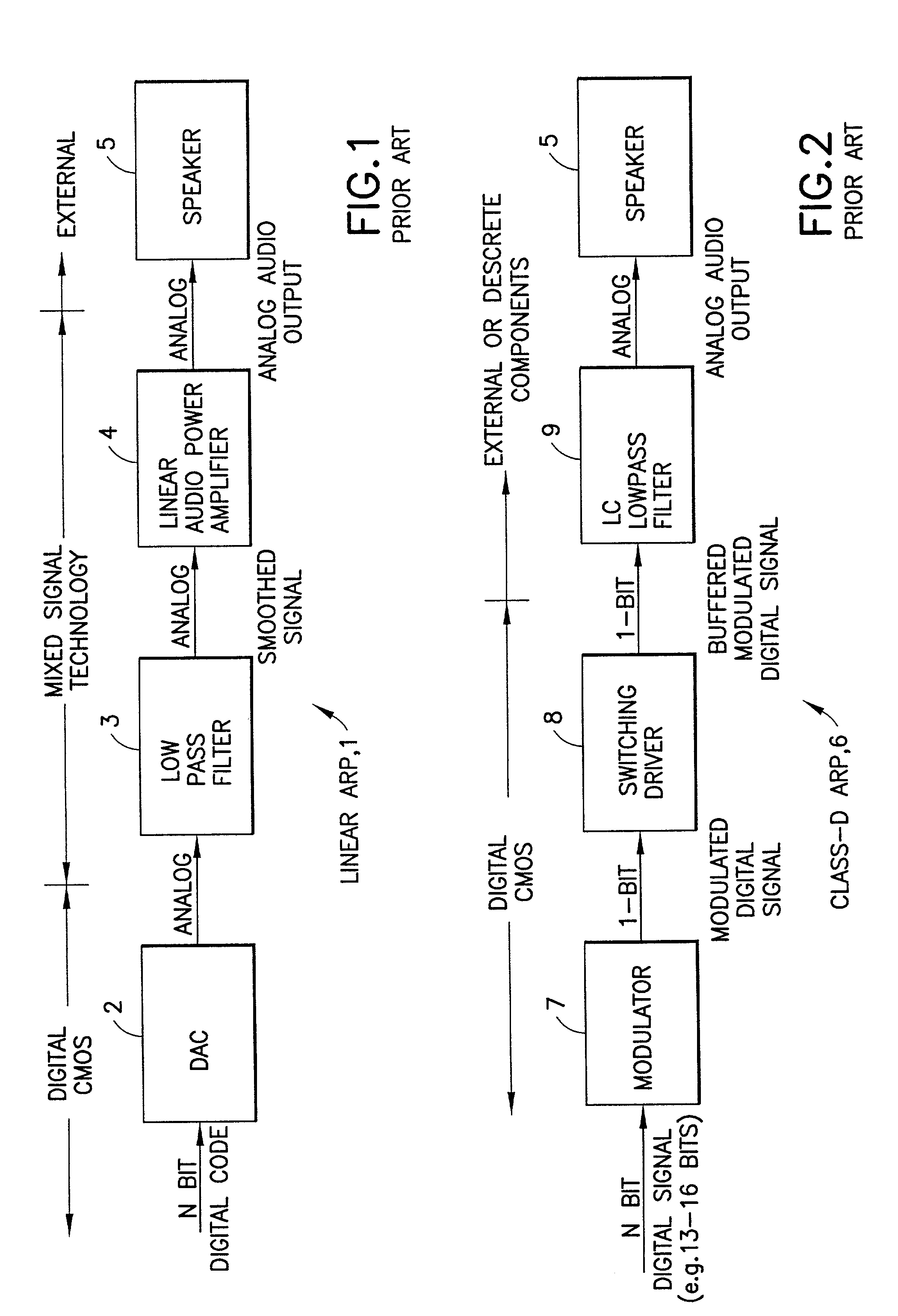
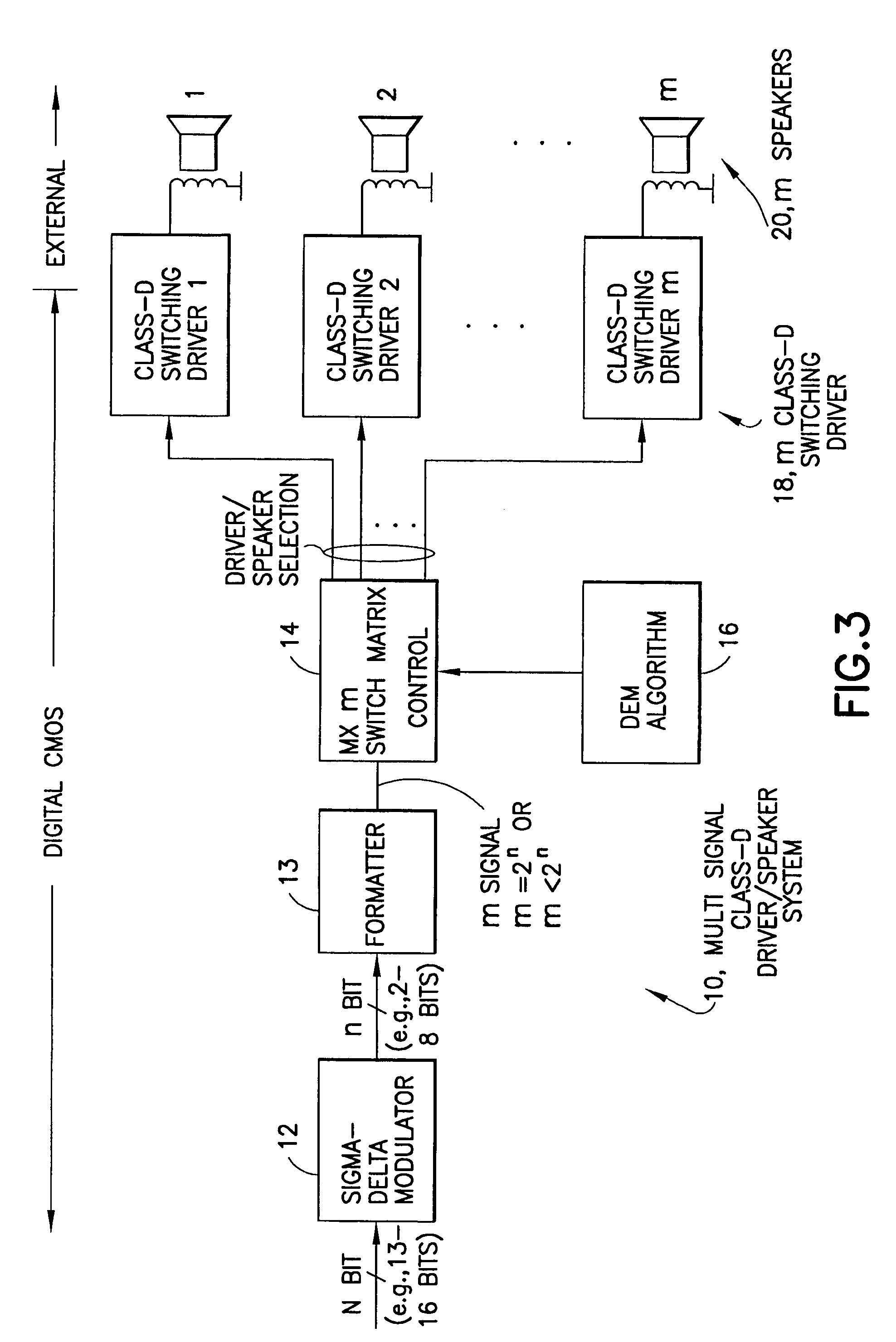
InactiveUS7058463B1Spread distortionDigitally weighted transducing elementsAnalogue conversionImage resolutionWide band
An audio path is constructed to include a multi-bit sigma-delta converter for converting an N-bit digital input to an n-bit output representing an over-sampled, lower resolution n-bit version of the N-bit digital input; a formatter for converting the n-bit output to an m signal output (e.g., as a thermometer code, a SDM format or a PWM format); an m-by-m switching matric for receiving the m output signals and for reordering the m output signals, m class-D drivers individual ones of which are driven by one of the reordered m output signals for driving one of m speakers; and a dynamic element matching (DEM) block coupled to the switching matric for controlling the reordering of the m output signals driving the m class-D drivers for spreading the distortion due at least to driver-speaker pair mismatch to wide band noise. The DEM may operate to generate white noise, or it may generate shaped (colored) noise.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Digital healthcare information management
InactiveUS7801591B1Easy to analyzeImproves and optimizes flowMedical data miningElectrocardiographyPersonal information managementMedical treatment
System for diagnosis, medical decision support, and healthcare information management that performs analysis of serial health data, adapts to the individual data, and represents dynamics of the most significant parameters (indicators), using at least two scales. The system uses the first-scale (low-resolution) analysis of a snapshot measurement of at least one indicator (primary element) such as heart rate or blood pressure and uses a second-scale (higher-resolution) analysis to determine serial changes in each of the said primary elements. The system optimizes information flow, usage of medical knowledge, and improves accuracy of analysis of serial changes, and adaptability to each individual's data. The information can be distributed in parallel to separate databases at different locations.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
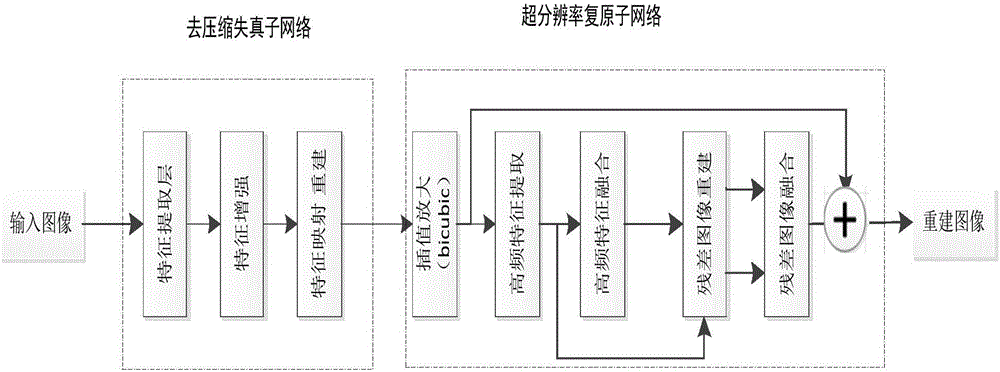
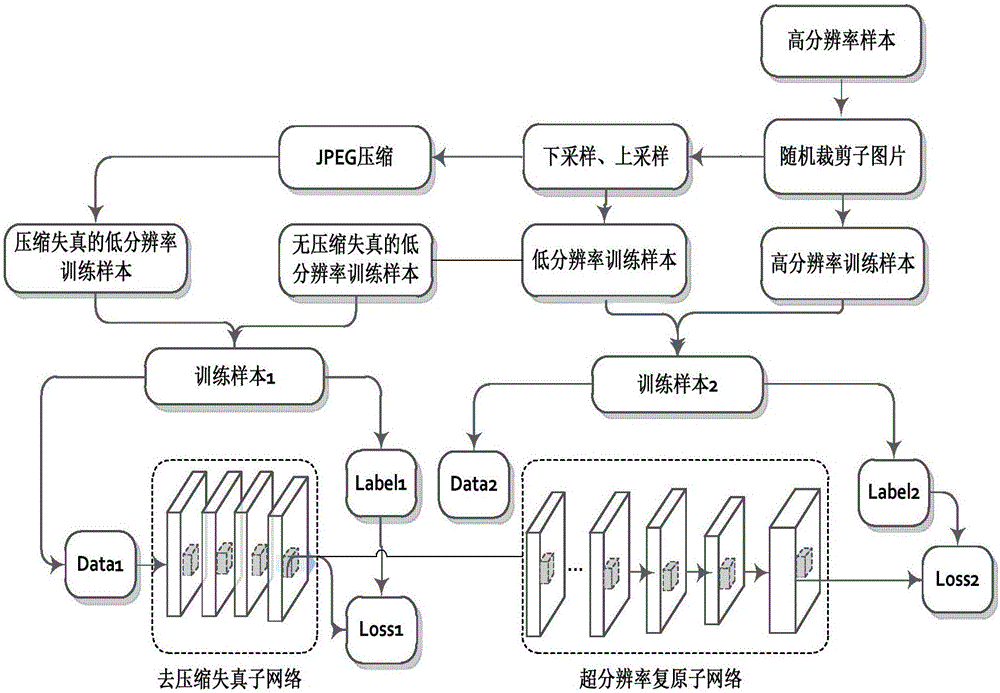
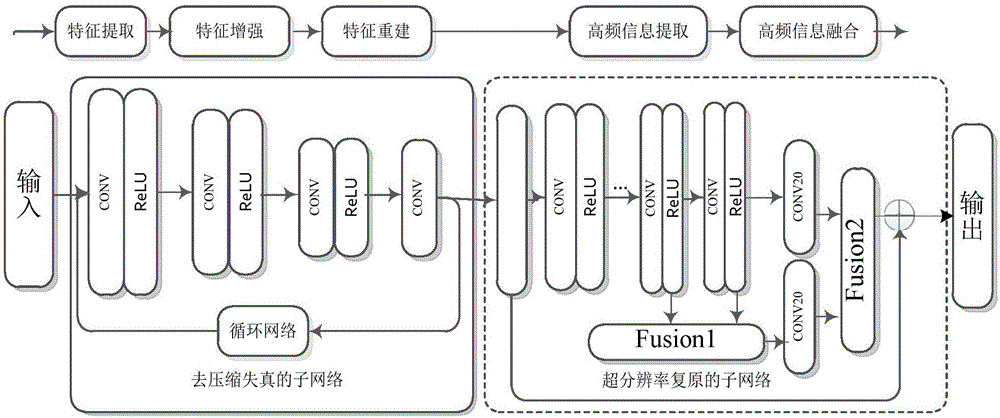
Compressed low-resolution image restoration method based on combined deep network
The present invention provides a compressed low-resolution image restoration method based on a combined deep network, belonging to the digital image / video signal processing field. The compressed low-resolution image restoration method based on the combined deep network starts from the aspect of the coprocessing of the compression artifact and downsampling factors to complete the restoration of a degraded image with the random combination of the compression artifact and the low resolution; the network provided by the invention comprises 28 convolution layers to establish a leptosomatic network structure, according to the idea of transfer learning, a model trained in advance employs a fine tuning mode to complete the training convergence of a greatly deep network so as to solve the problems of vanishing gradients and gradient explosion; the compressed low-resolution image restoration method completes the setting of the network model parameters through feature visualization, and the relation of the end-to-end learning degeneration feature and the ideal features omits the preprocessing and postprocessing; and finally, three important fusions are completed, namely the fusion of the feature figures with the same size, the fusion of residual images and the fusion of the high-frequency information and the high-frequency initial estimation figure, and the compressed low-resolution image restoration method can solve the super-resolution restoration problem of the low-resolution image with the compression artifact.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
High resolution image reconstruction
ActiveUS20050013509A1Image enhancementGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh resolution image
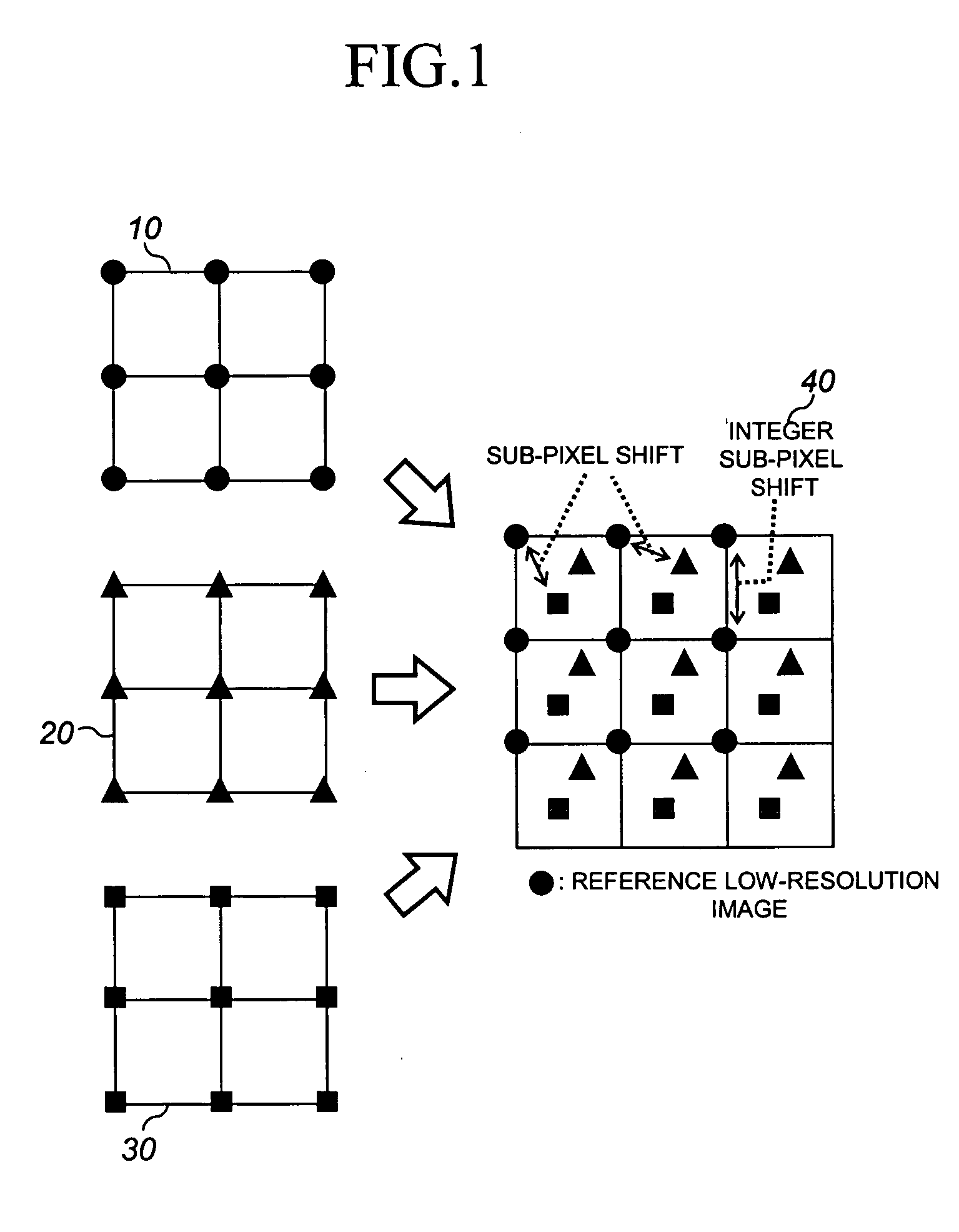
A technique of reconstructing a high resolution image from at least one image sequence of temporally related high and low resolution image frames wherein each of said high resolution image frames includes a low spatial frequency component and a high spatial frequency component is described. The high-resolution image reconstruction technique uses spatial interpolation to generate a low spatial frequency component from a low-resolution image frame of the image sequence. The technique is adapted to generate a high spatial frequency component from at least one high resolution image frame of the image sequence which is closely related to the low resolution image frame, and to remap the high spatial frequency component to a motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate of the low resolution image frame. The motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate is added to the generated low spatial frequency component to form a reconstructed high-resolution image of the low-resolution image frame.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
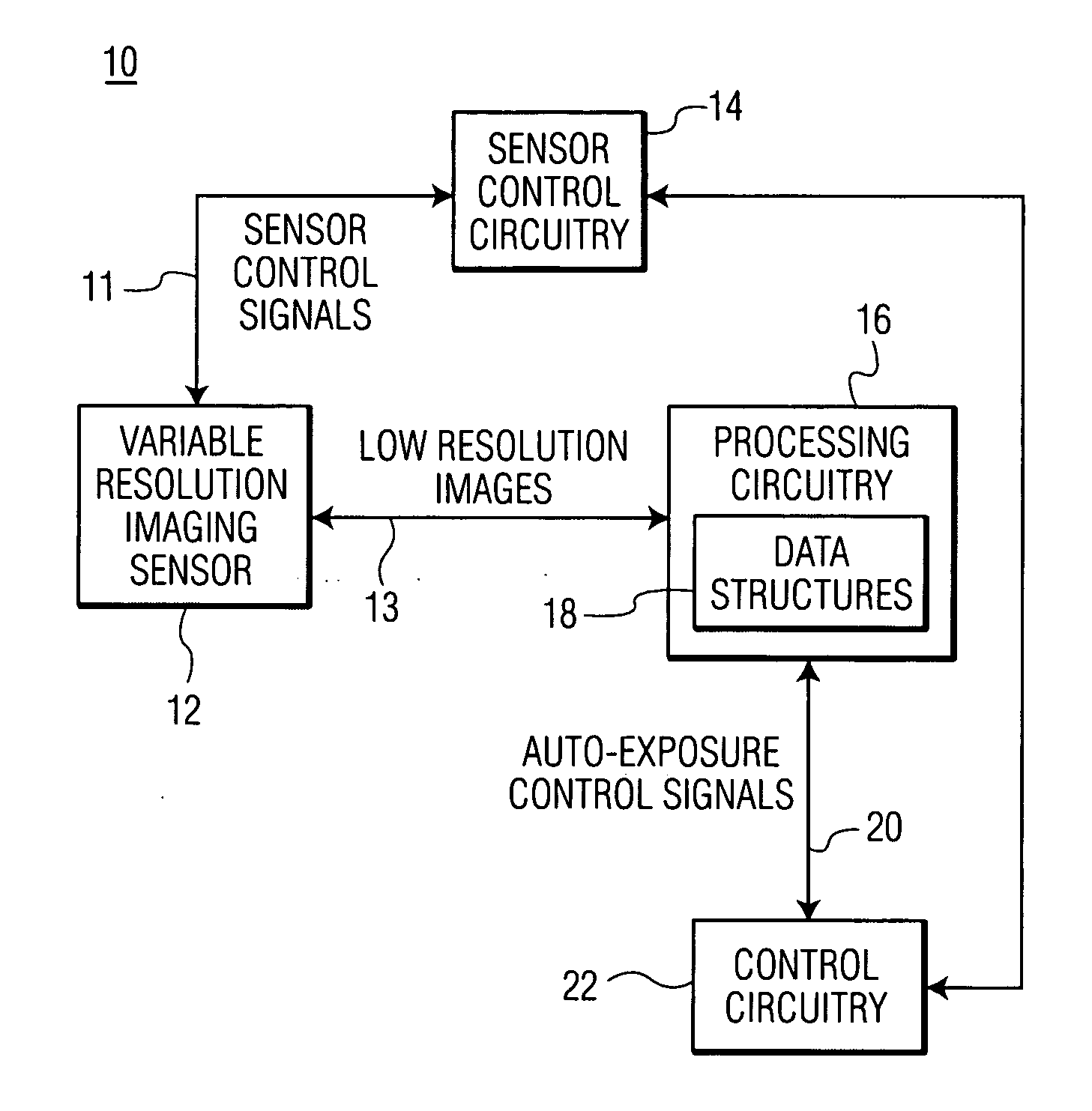
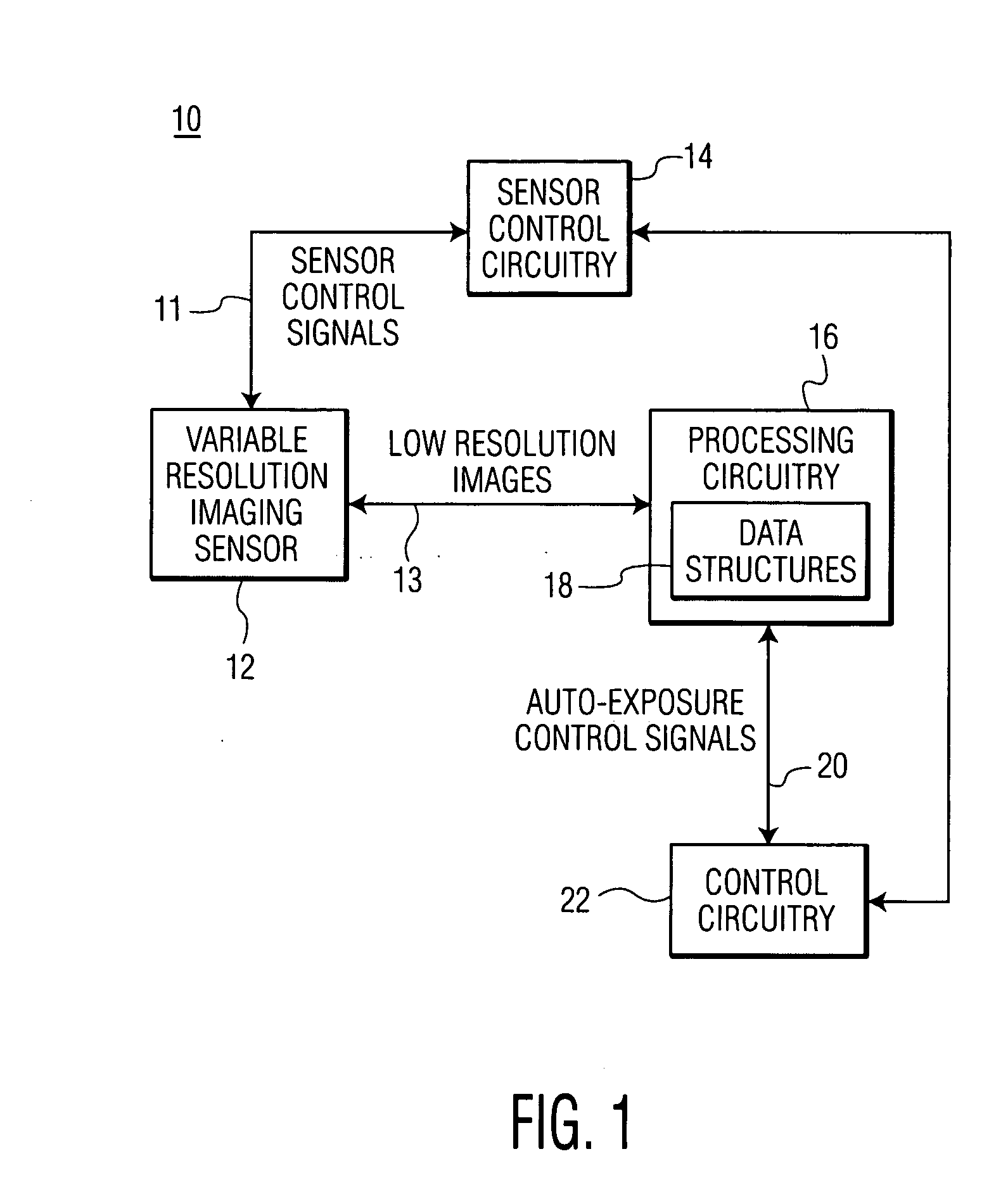
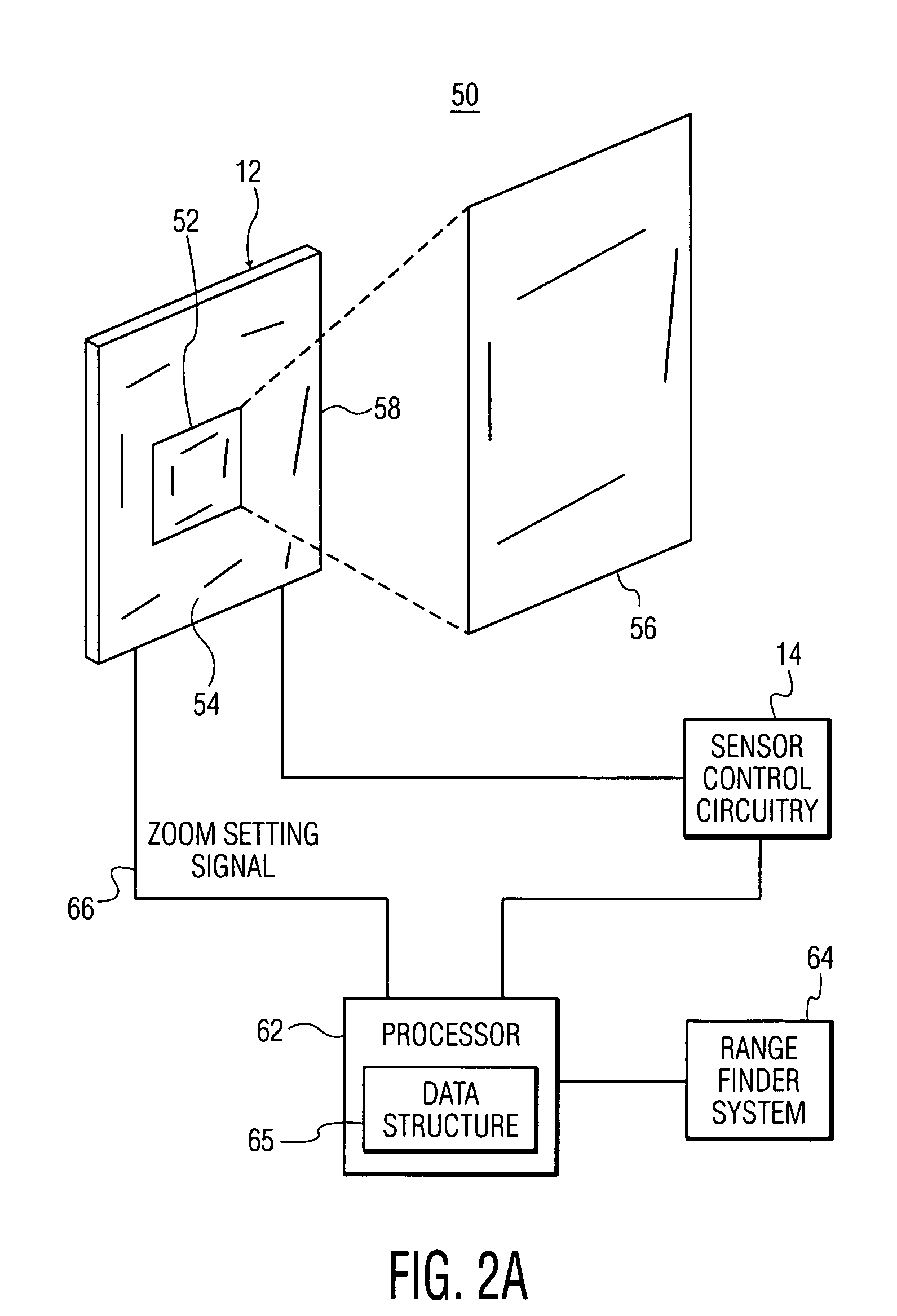
Optical code reading system and method using a variable resolution imaging sensor
InactiveUS20060011724A1Improve performanceLess timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionVariable resolution
An optical code reading system having an auto-exposure system for use with a variable resolution imaging sensor in which very low resolution images are used to determine exposure parameters is presented. The very low resolution images can be transferred much faster than high resolution images which results in a very fast auto-exposure system. The optical code reading system further includes an optical zoom system for zooming in and out of a target without the use of any moveable components. The optical zoom system makes use of a binning and / or subsampling feature of the imaging sensor for zooming in and out of the target. High-speed decoding methodologies are also presented for the optical code reading system. One decoding methodology utilizes low resolution images for performing high-speed decoding. Other methodologies utilize low resolution images and higher resolution images, if the optical code imaged by the low resolution images is not decoded successfully.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
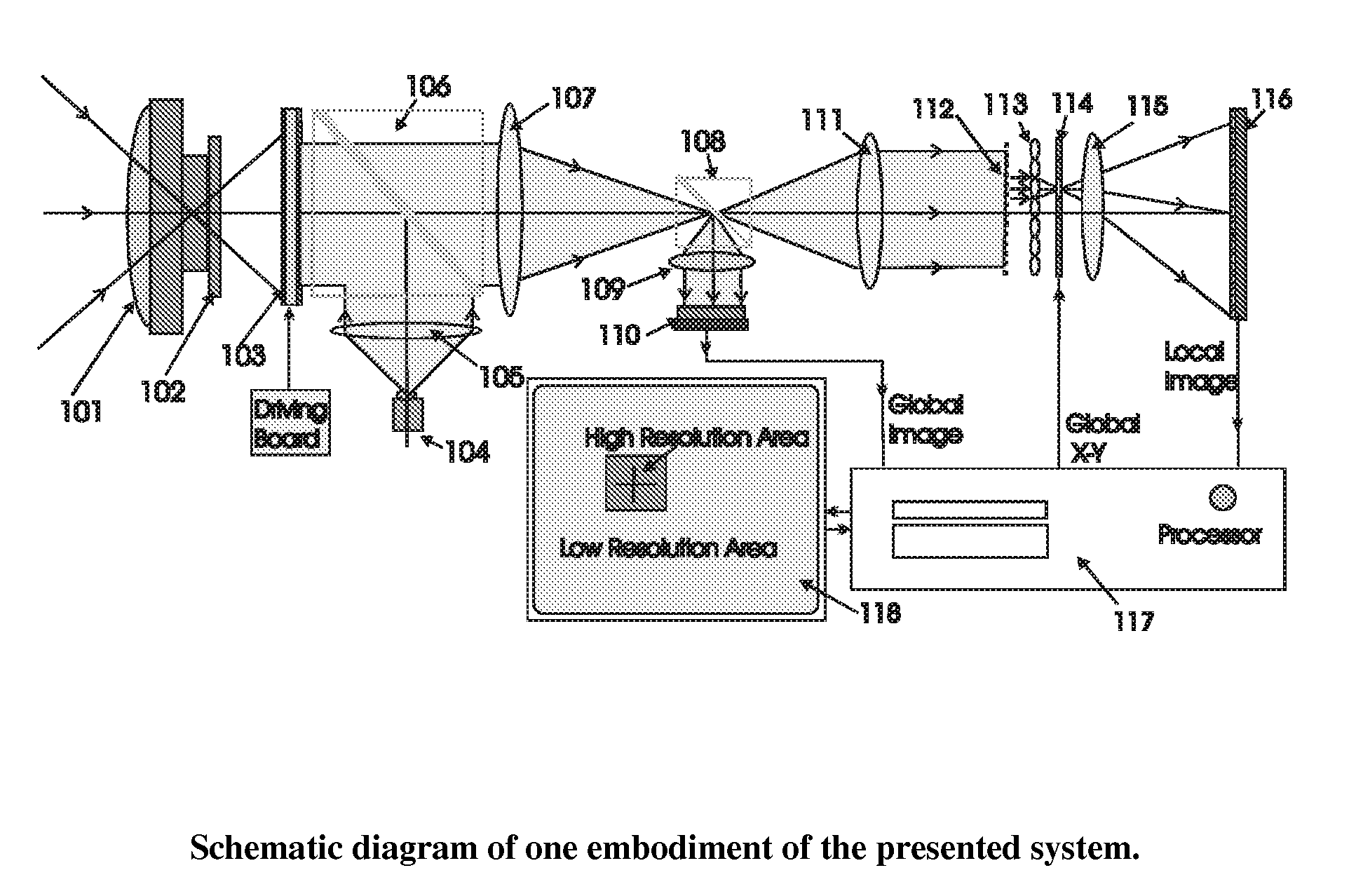
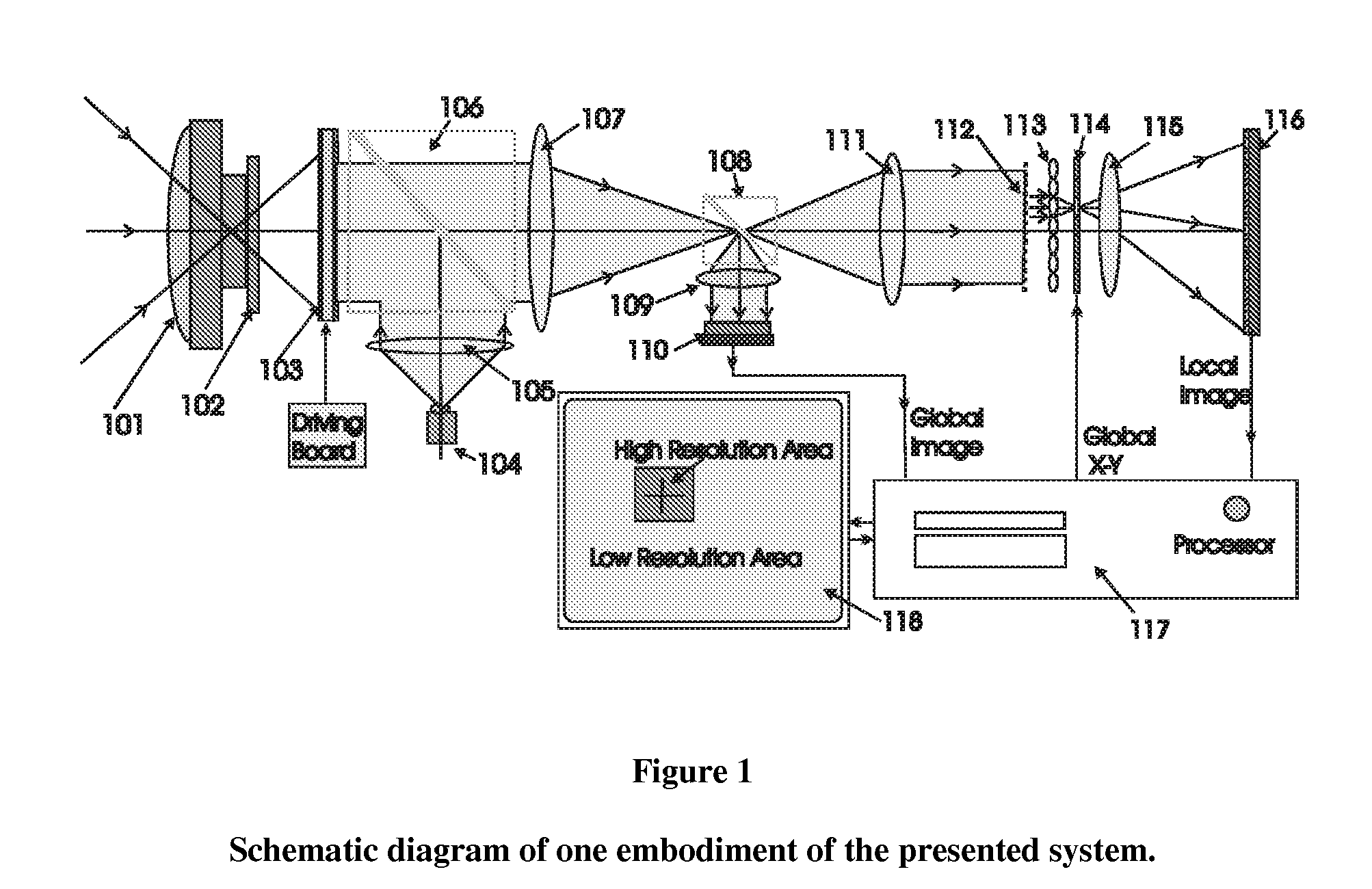
Electro-optical foveated imaging and tracking system
InactiveUS7973834B2Improve spatial resolutionWide field-of-viewTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayHigh resolution image
Conventional electro-optical imaging systems can not achieve wide field of view (FOV) and high spatial resolution imaging simultaneously due to format size limitations of image sensor arrays. To implement wide field of regard imaging with high resolution, mechanical scanning mechanisms are typically used. Still, sensor data processing and communication speed is constrained due to large amount of data if large format image sensor arrays are used. This invention describes an electro-optical imaging system that achieves wide FOV global imaging for suspect object detection and local high resolution for object recognition and tracking. It mimics foveated imaging property of human eyes. There is no mechanical scanning for changing the region of interest (ROI). Two relatively small format image sensor arrays are used to respectively acquire global low resolution image and local high resolution image. The ROI is detected and located by analysis of the global image. A lens array along with an electronically addressed switch array and a magnification lens is used to pick out and magnify the local image. The global image and local image are processed by the processor, and can be fused for display. Three embodiments of the invention are described.
Owner:NEW SPAN OPTO TECH
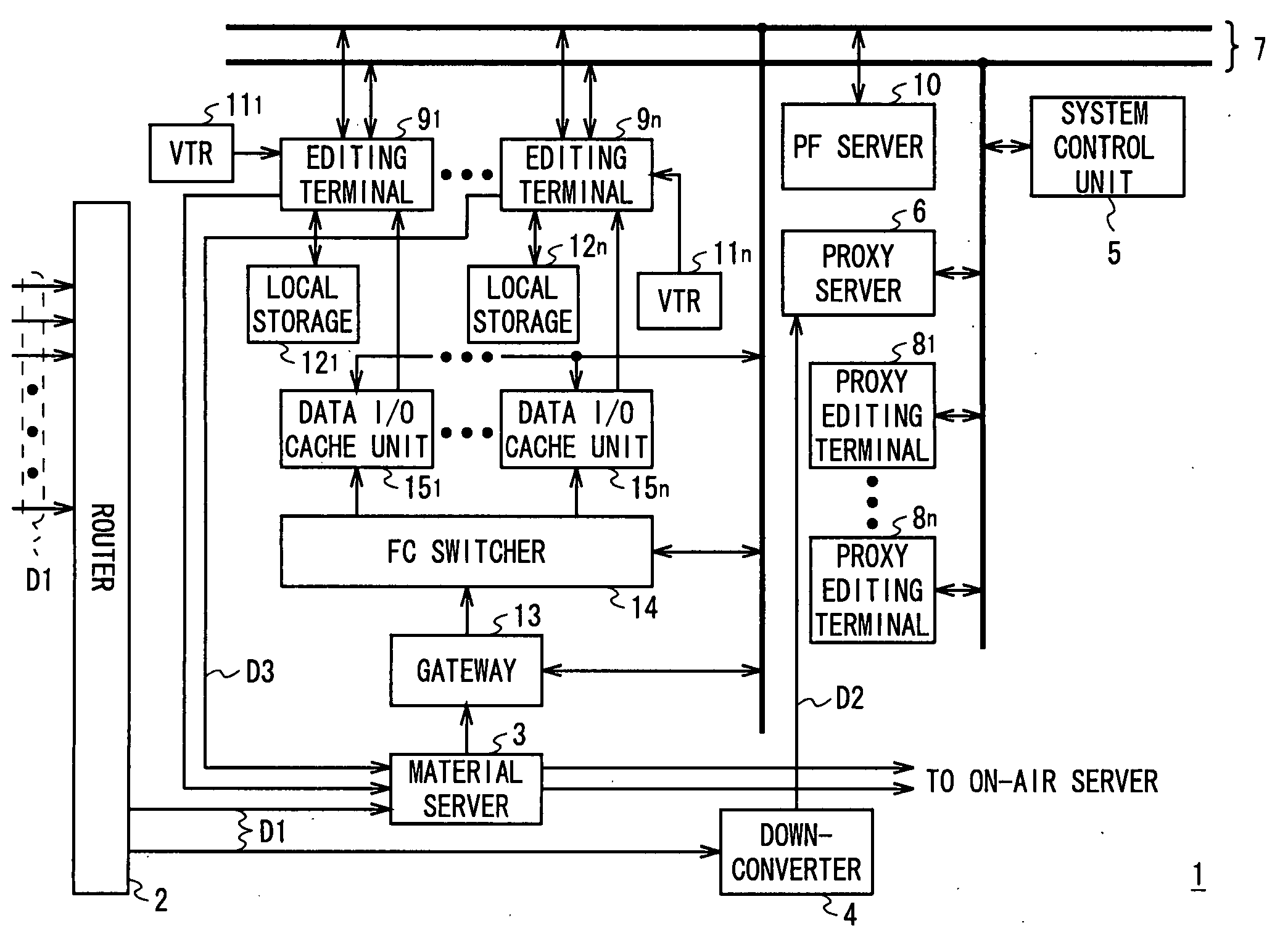
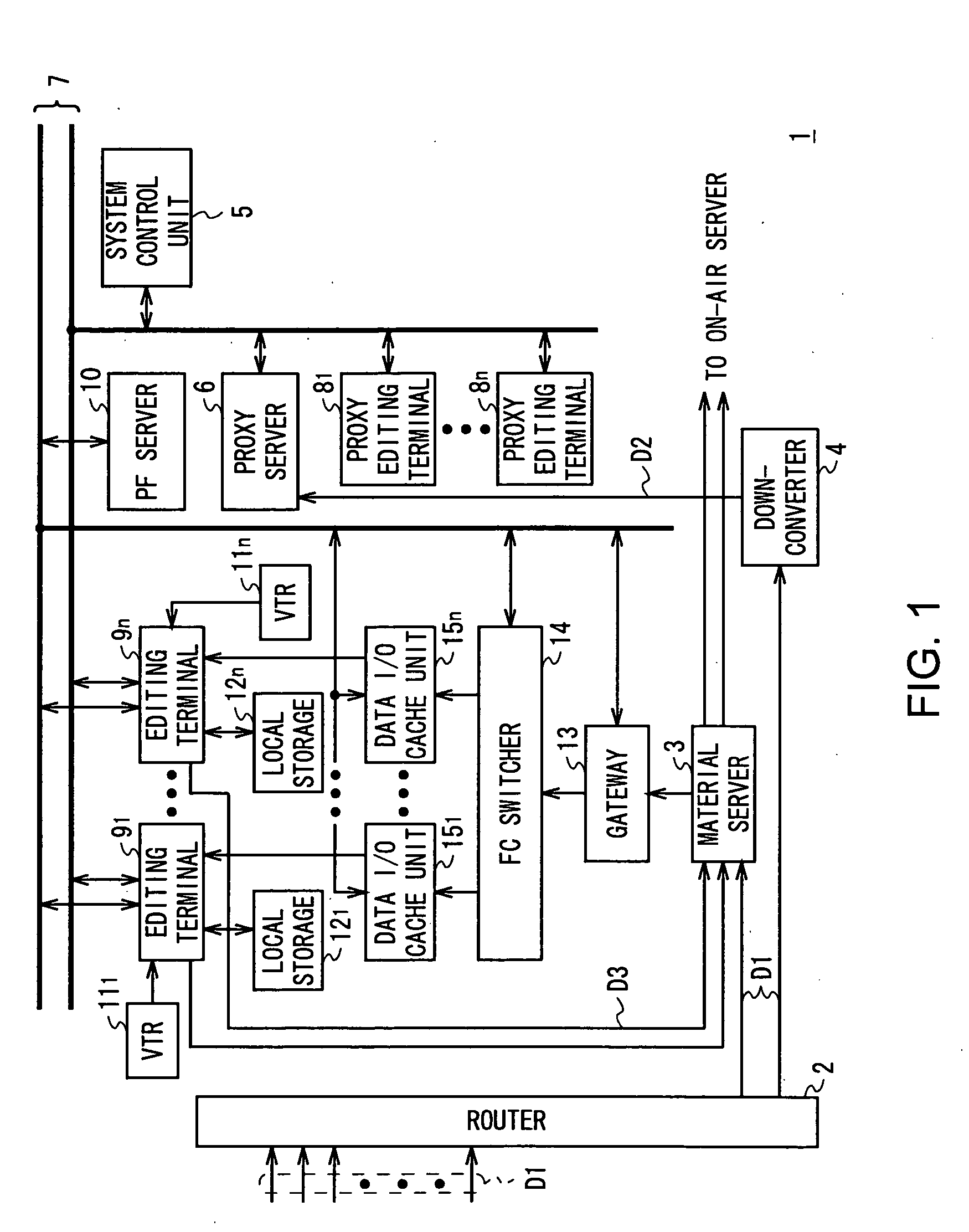
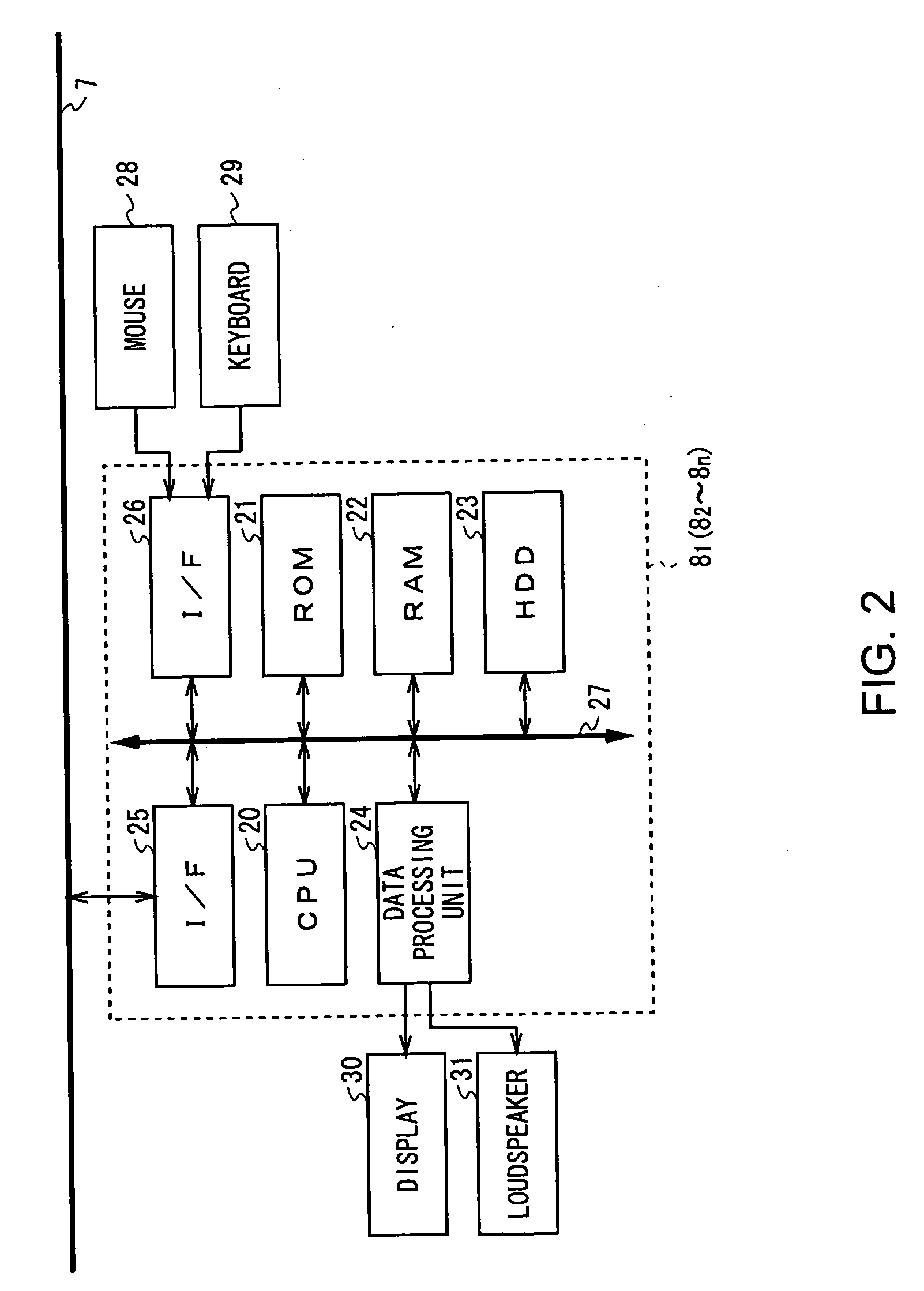
Editing system and control method thereof
ActiveUS20050025454A1Improve work efficiencyShorten the timeTelevision system detailsRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
This invention realizes an editing system and control method thereof capable of significantly improving working efficiency of editing work. A proxy editing terminal device creates an EDL with low-resolution video / audio data, resulting in reducing time to create the EDL. Further, the low-resolution video / audio data and high-resolution video / audio data having the same contents and different resolutions are previously stored, so that the creation of a final edit list with the high-resolution video / audio data based on the EDL can be started in a short time after the EDL is created with the low-resolution video / audio data. Thus working efficiency of the editing work can be significantly reduced with reducing time to create the EDL and the final edit list.
Owner:SONY CORP
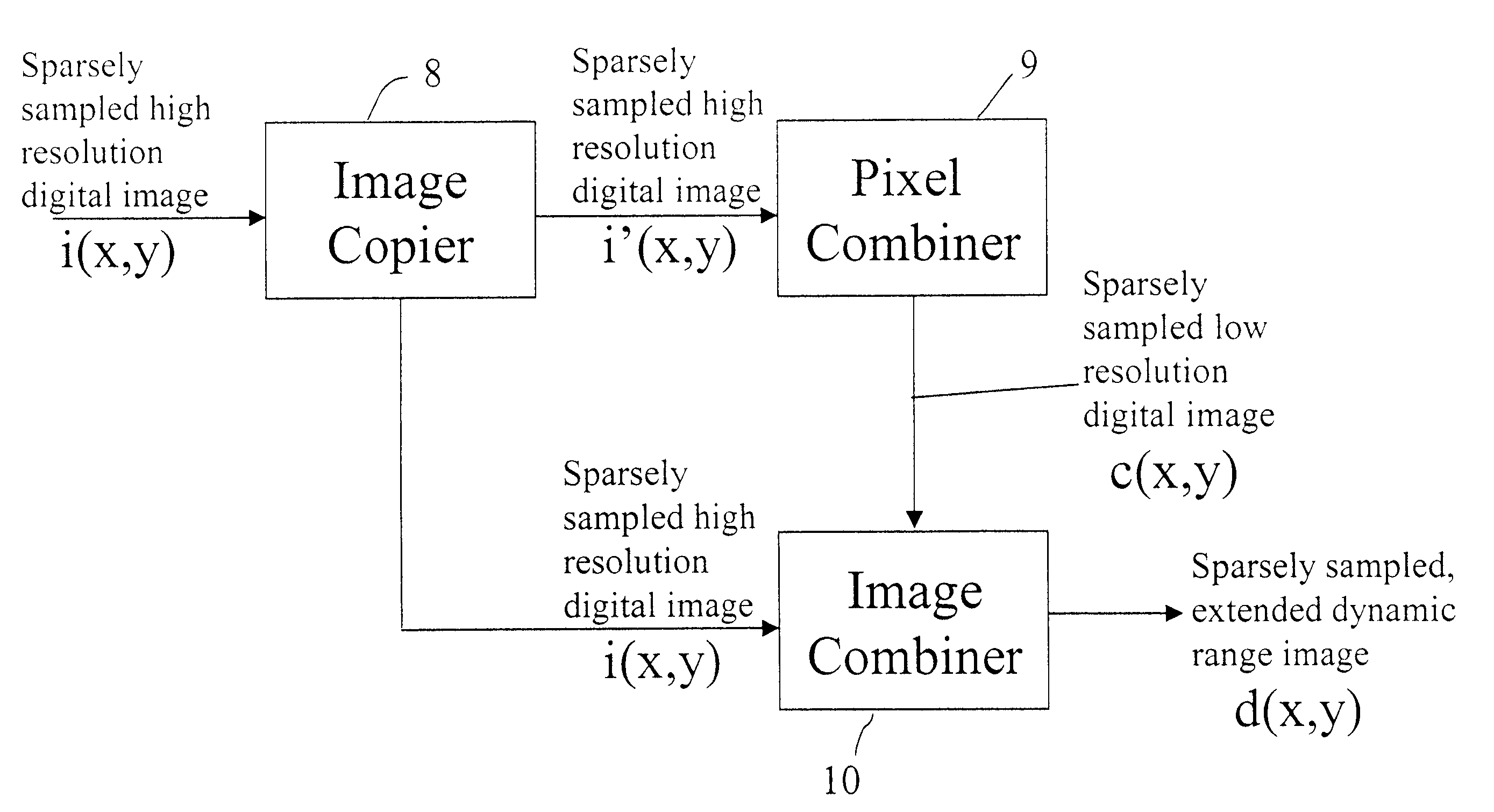
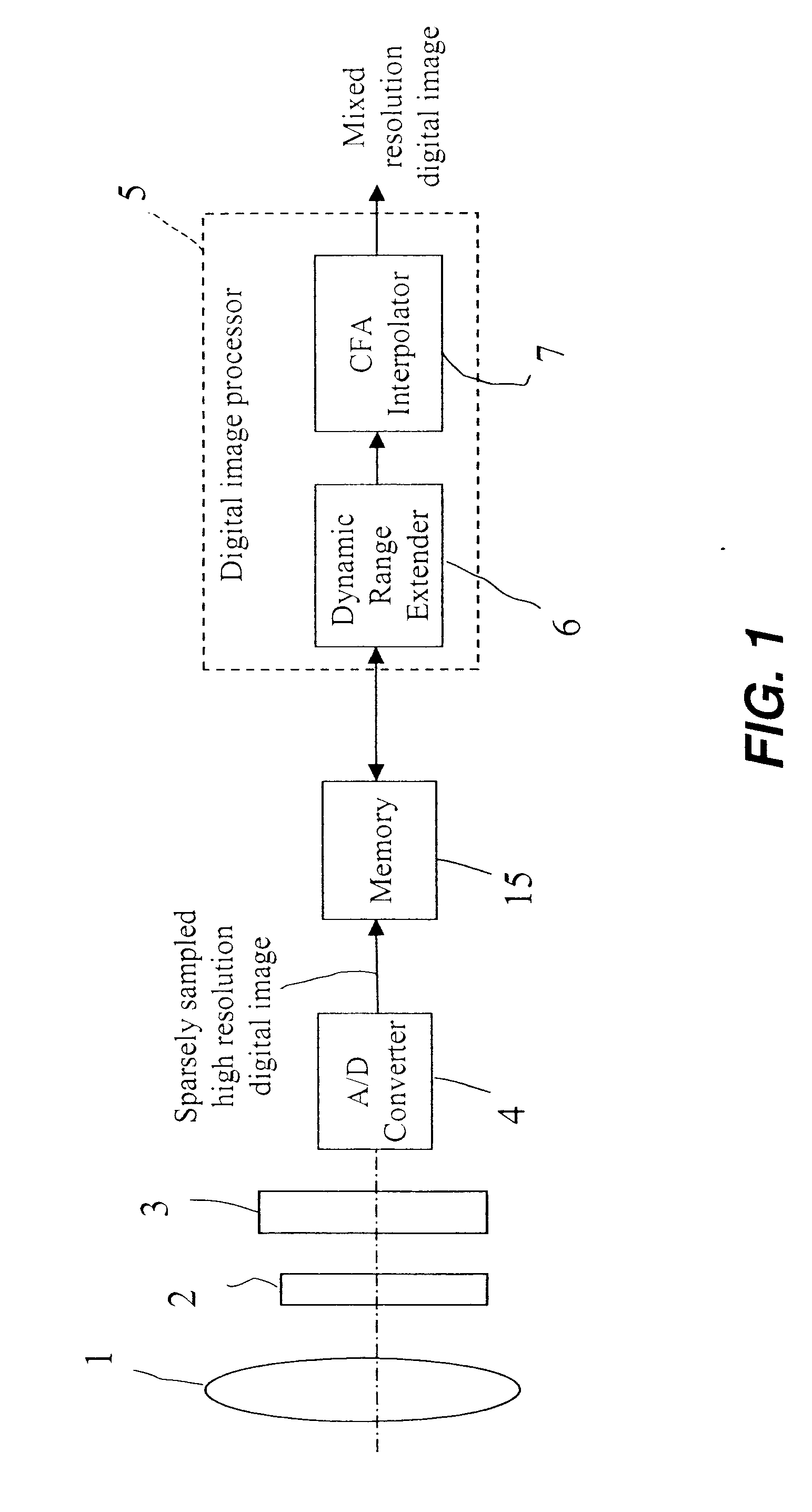
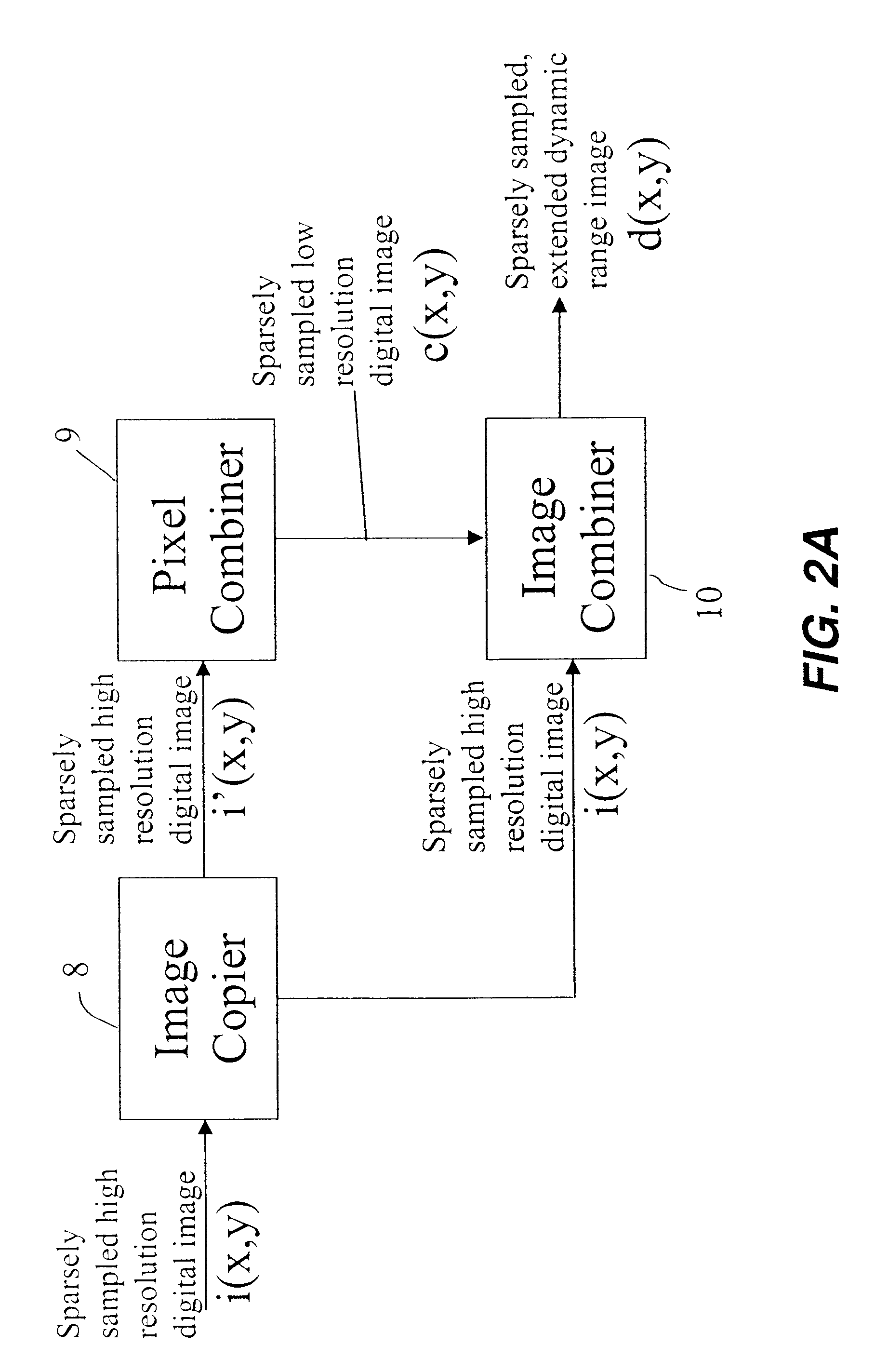
Producing an extended dynamic range digital image
InactiveUS20080025634A1Improve dynamic rangeEnhance the imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage resolutionDigital image
A method of producing a digital image with extended dynamic range, includes capturing at least a first full resolution digital image of a scene; combining pixels of a first full resolution digital image to produce a lower resolution digital image identifying dark regions in a first full resolution digital image and replacing the dark regions in the full resolution image with corresponding regions from the brighter, lower resolution image to thereby provide a digital image with extended dynamic range.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Cellular telephone based document scanner
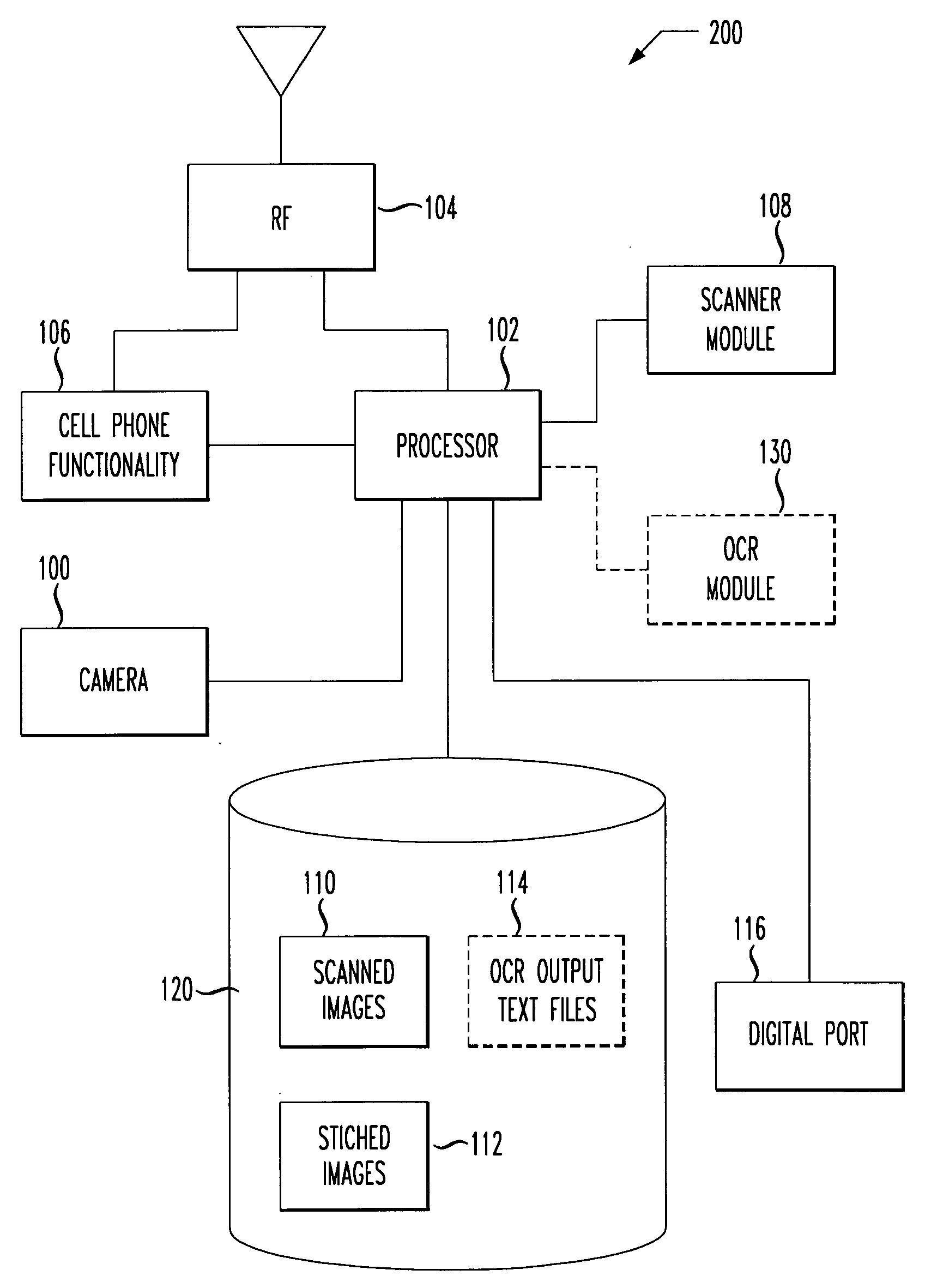
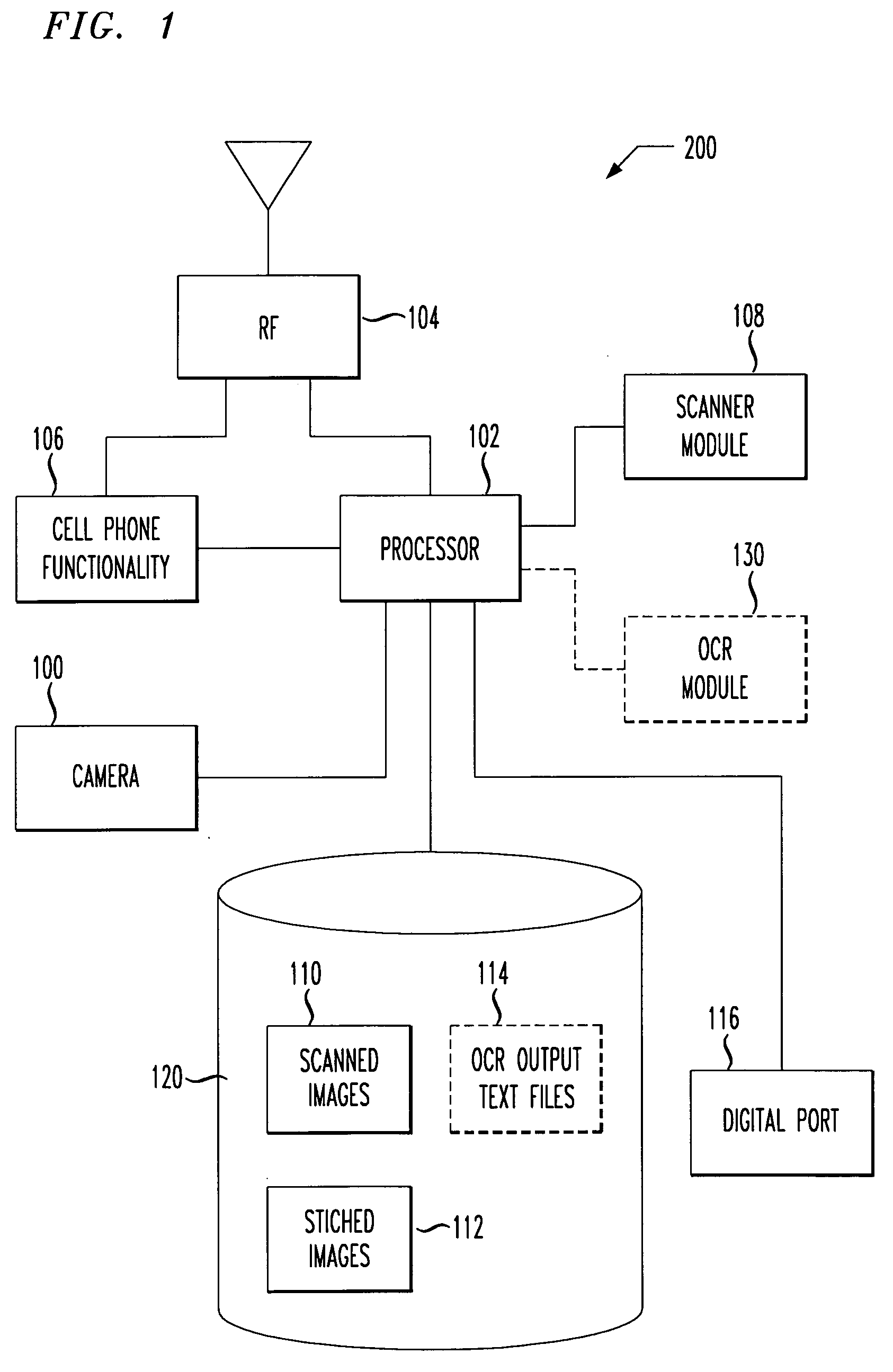
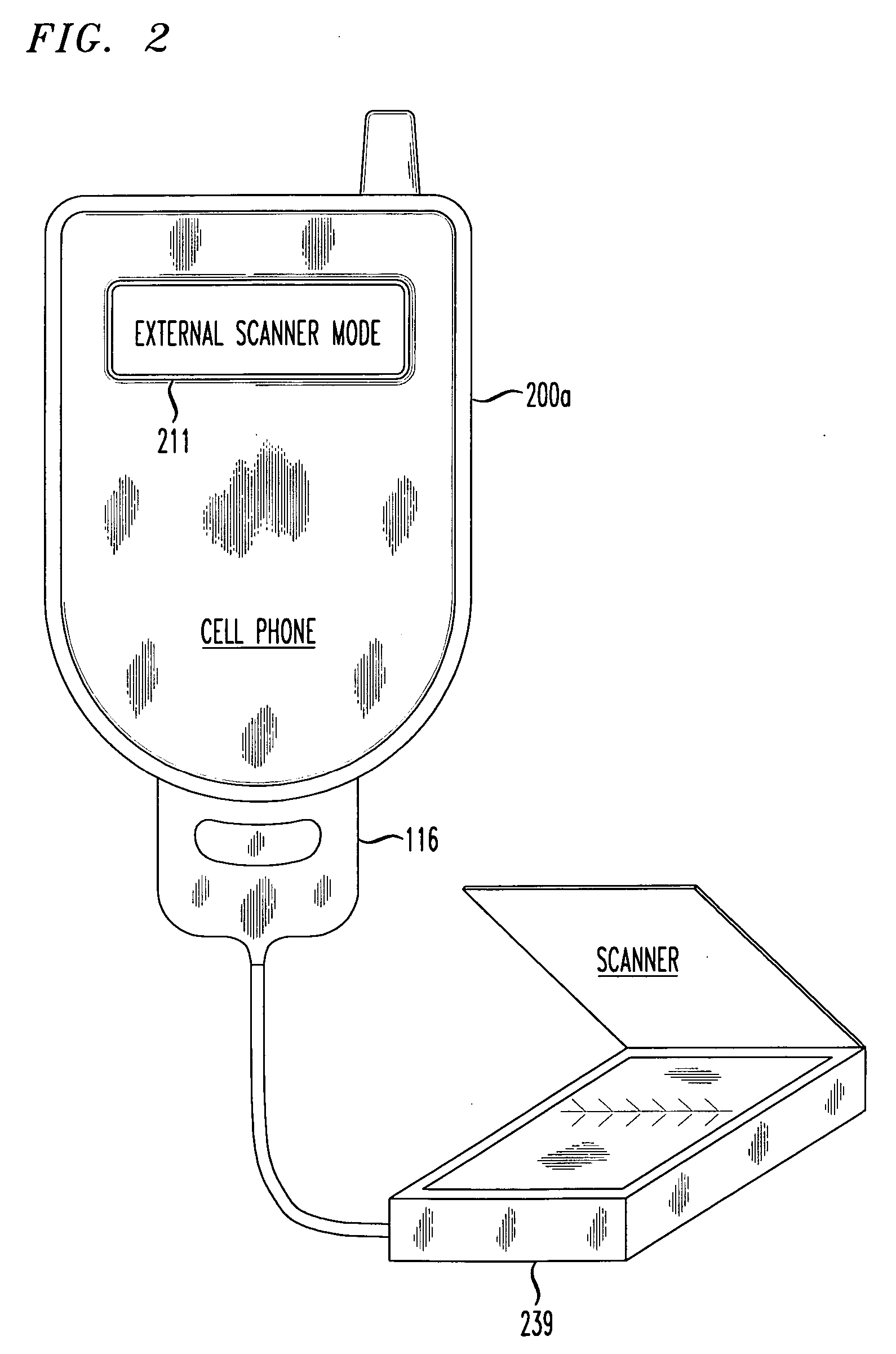
A cellular phone contains a scanner feature for scanning documents directly into a cell phone. The cell phone may scan a small document (e.g., a business card) or a much larger: document (e.g., multiple pages of standard 8½″×11″ paper.). Business card scanning can include a feature to automatically enter data into a contact list, which is then synchronized with a host PC. The particular scanning and stitching methods disclosed in a cell phone are capable of scanning objects that are virtually limitless in size and / or shape, making use of even a low resolution camera integrated into many currently available cell phones. In first embodiments, the disclosed scanner makes use of an external scanner interfaced directly to a digital port of a cell phone, and in second embodiments, the scanner uses a low resolution internal camera to capture images of matrixed portions of a larger object or document.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
Method of restoring and reconstructing super-resolution image from low-resolution compressed image
InactiveUS20050019000A1Preserving contourRemove image blurImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDigital videoImage compression
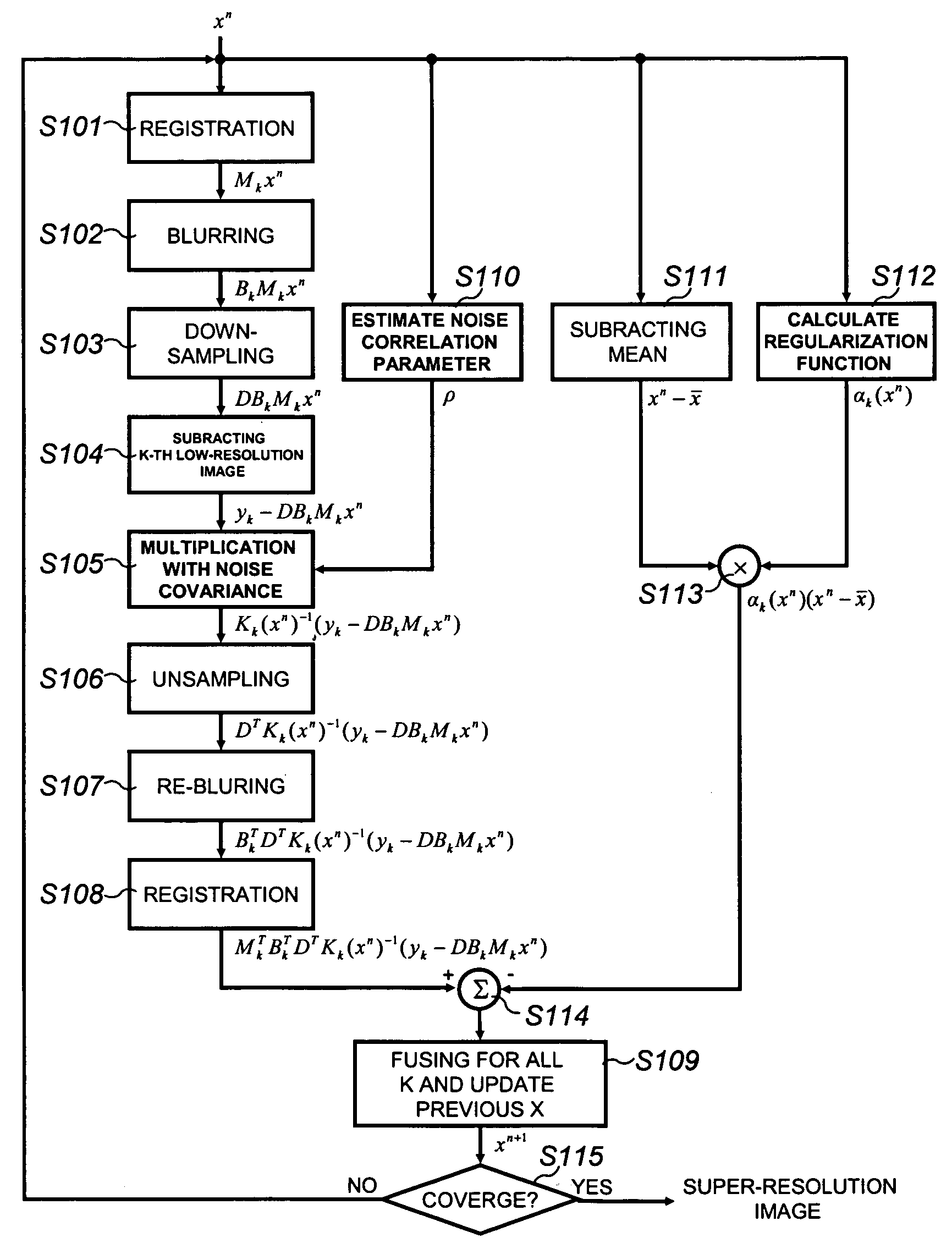
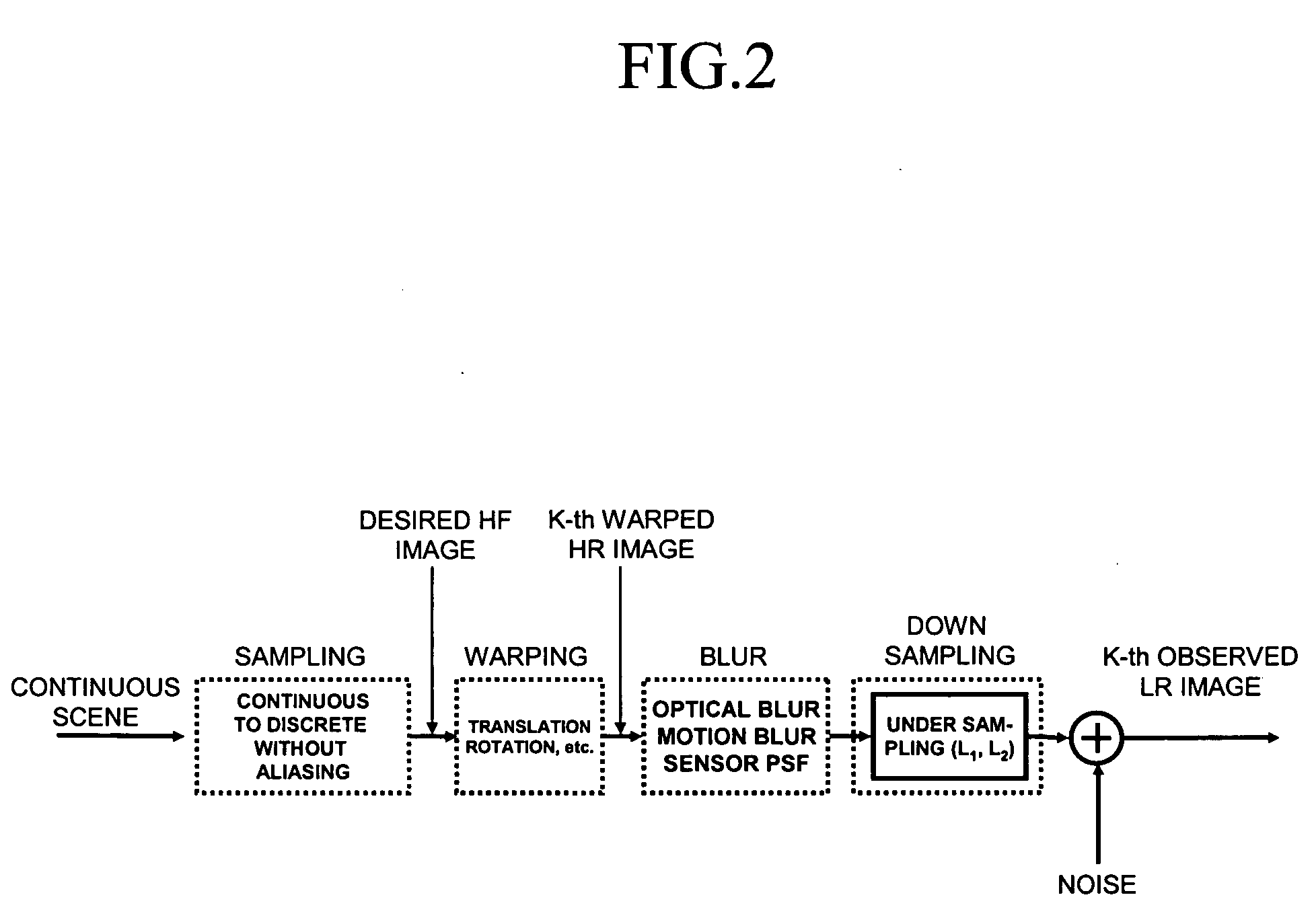
Provided is a method of restoring and / or reconstructing a super-resolution image from low-resolution images compressed in a digital video recorder (DVR) environment. The present invention can remove a blur of a video sequence, caused by optical limitations due to a miniaturized camera of a digital video recorder monitoring system, a limitation of spatial resolution due to an insufficient number of pixels of a CCD / CMOS image sensor, and noises generated during image compression, transmission and storing processes, to restore high-frequency components of low-resolution images (for example, the face and appearance of a suspect or numbers of a number plate) to reconstruct a super-resolution image. Consequently, an interest part of a low-resolution image stored in the digital video recorder can be magnified to a high-resolution image later, and the effect of an expensive high-performance camera can be obtained from an inexpensive low-performance camera.
Owner:YONSEI UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com