Patents
Literature
601 results about "Level of detail" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
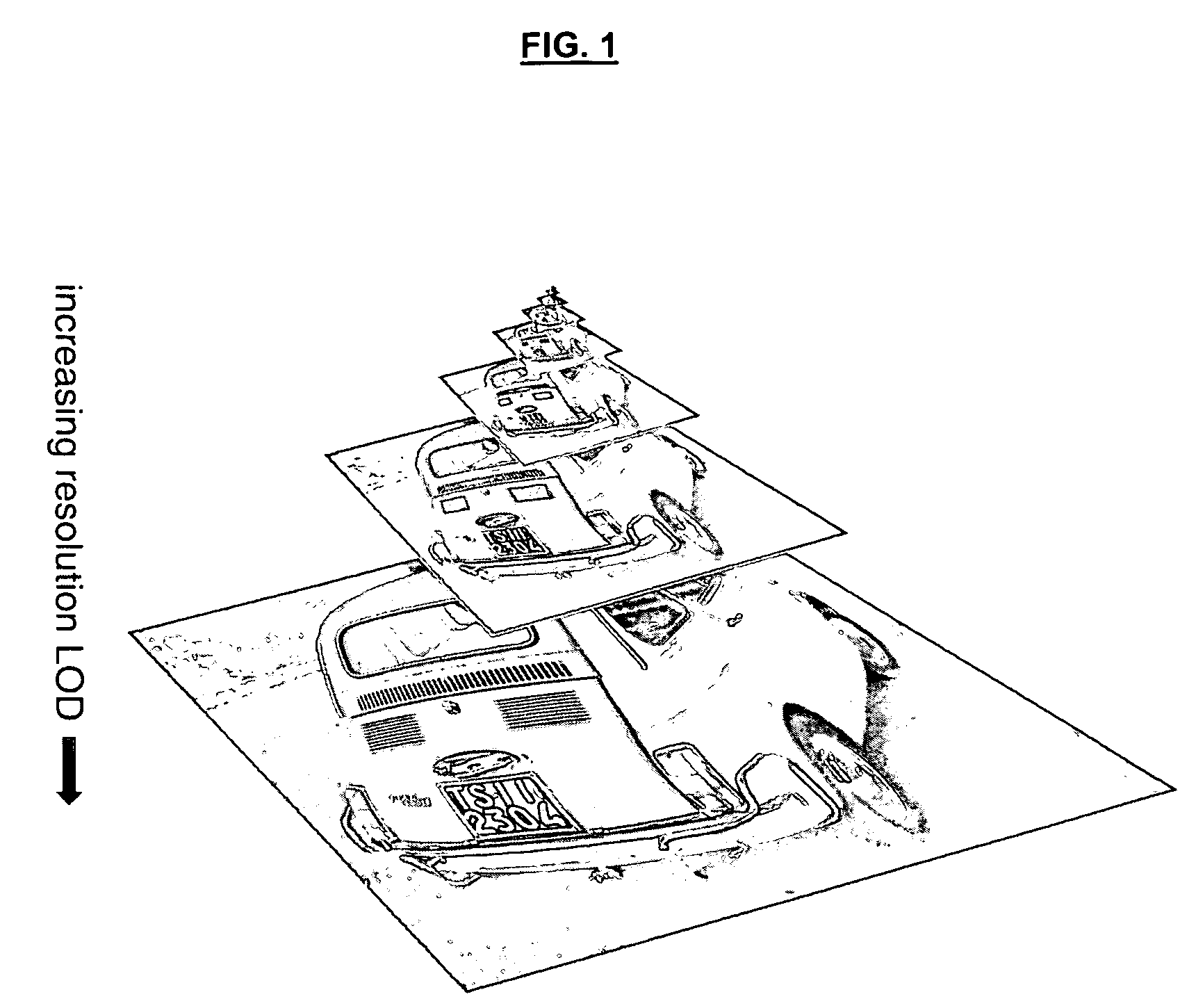
In computer graphics, accounting for Level of detail (LOD) involves decreasing the complexity of a 3D model representation as it moves away from the viewer or according to other metrics such as object importance, viewpoint-relative speed or position. Level of detail techniques increase the efficiency of rendering by decreasing the workload on graphics pipeline stages, usually vertex transformations. The reduced visual quality of the model is often unnoticed because of the small effect on object appearance when distant or moving fast.
Integrated routing/mapping information
InactiveUS6321158B1Enabling cooperationEnabling matingInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlImage resolutionLevel of detail
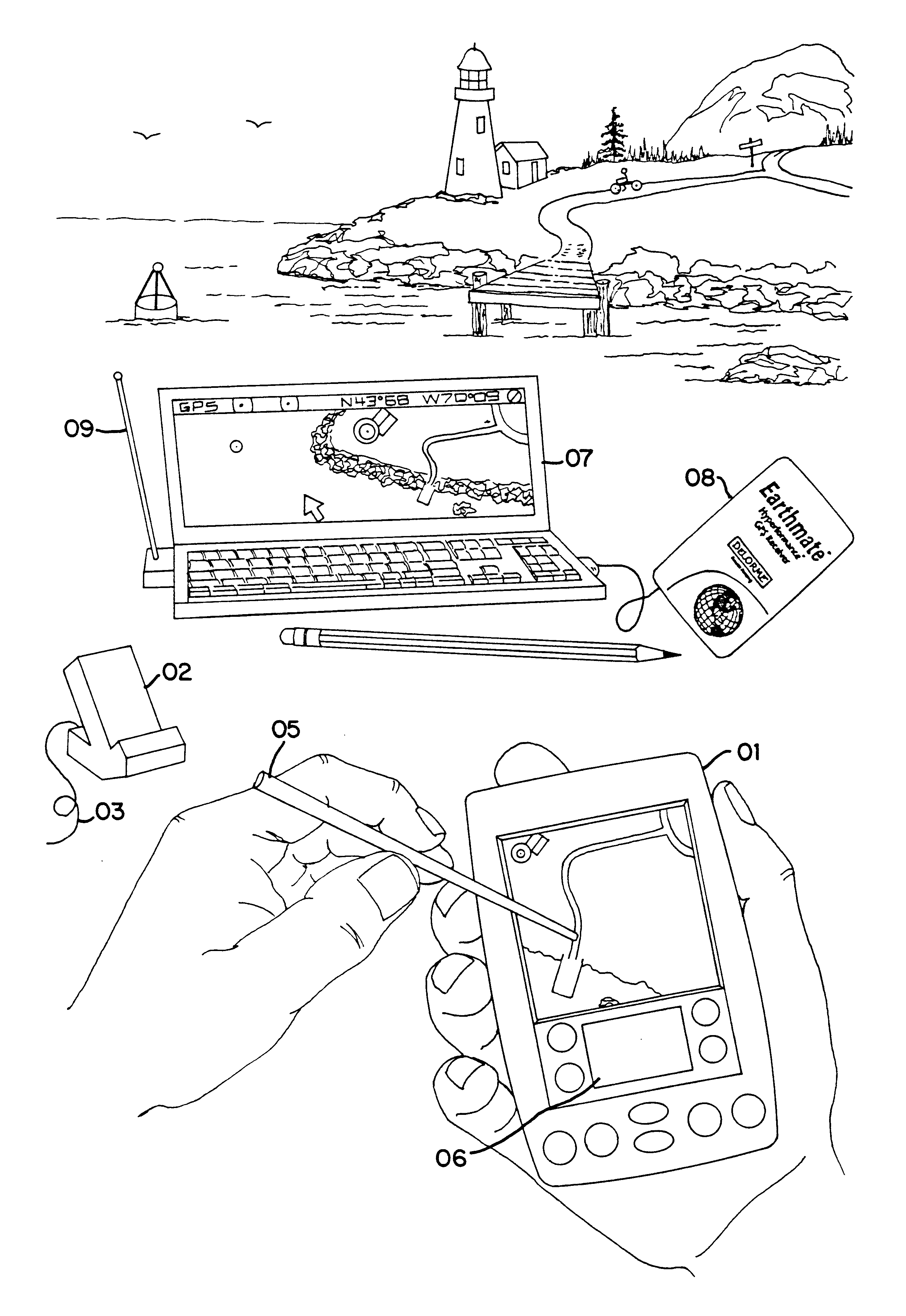
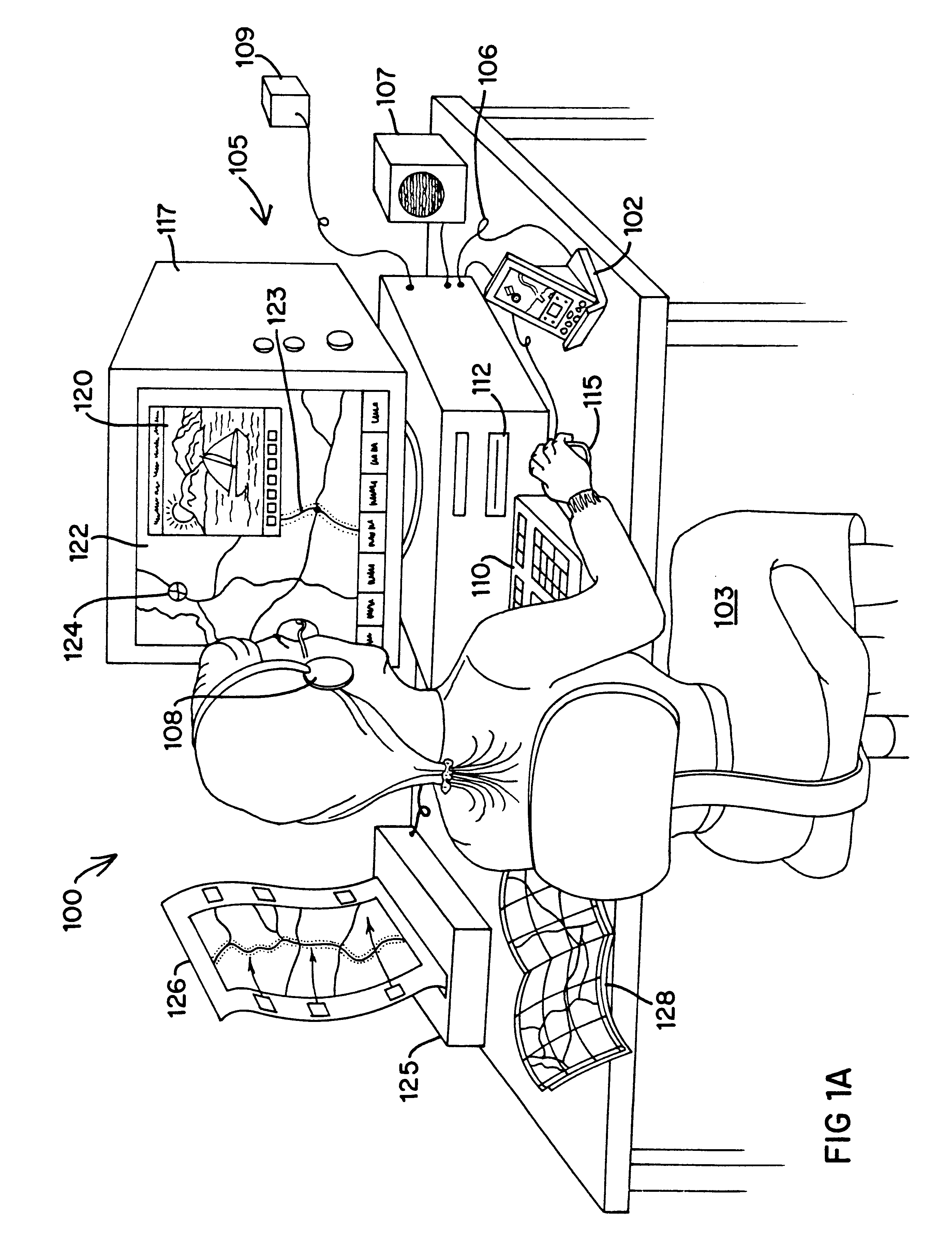
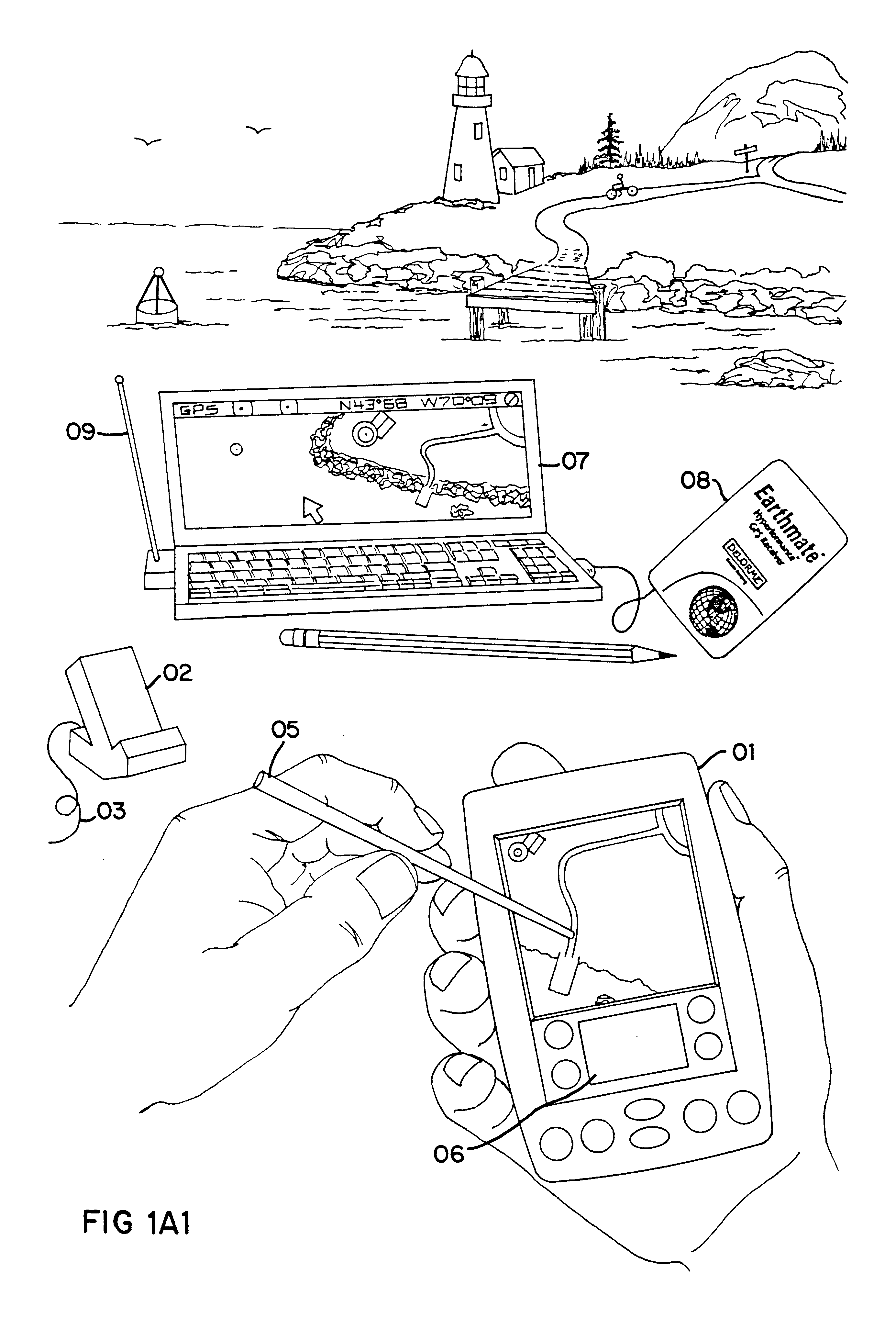
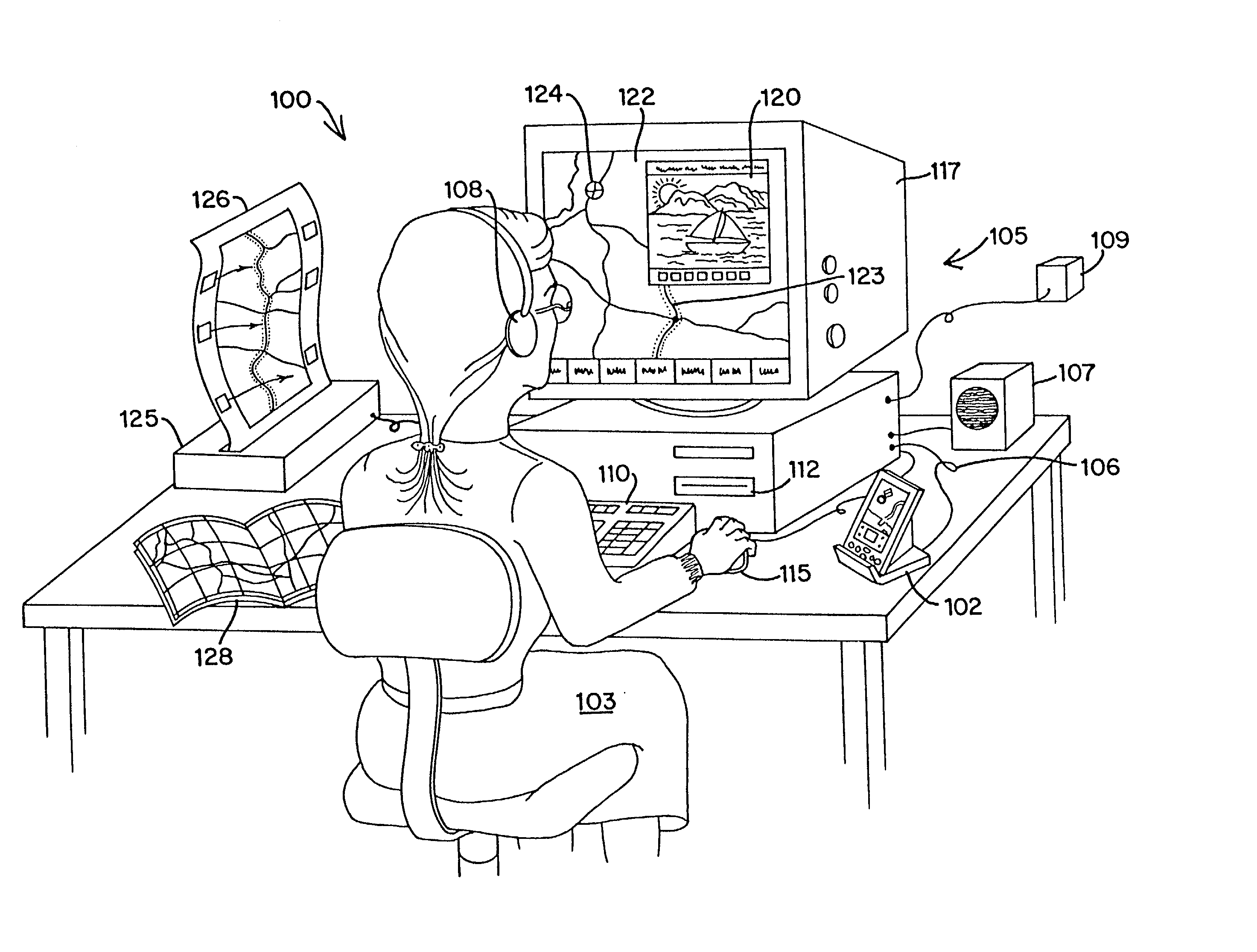
An Integrated Routing / Mapping Information System (IRMIS) links desktop personal computer cartographic applications to one or more handheld organizer, personal digital assistant (PDA) or "palmtop" devices. Such devices may be optionally equipped with, or connected to, portable Global Positioning System (GPS) or equivalent position sensing device. Desktop application facilitates user selection of areas, starts, stops, destinations, maps and / or point and / or route information. It optionally includes supplemental online information, preferably for transfer to the PDA or equivalent device. Users' options include route information, area, and route maps. Maps and related route information are configured with differential detail and levels of magnitude. Used in the field, in conjunction with GPS receiver, the PDA device is configured to display directions, text and map formats, the user's current position, heading, speed, elevation, and so forth. Audible signals identifying the next turn along the user's planned route are also provided. The user can pan across maps and zoom between two or more map scales, levels of detail, or magnitudes. The IRMIS also provides for "automatic zooming," e.g., to show greater detail or closer detail as the user approaches a destination, or to larger scale and lower resolution to show the user's overall planned route between points of interest. The IRMIS also enables the user to mark or record specific locations and / or log actual travel routes, using GPS position information. These annotated location marks and / or "breadcrumb" or GPS log data can be saved, uploaded, displayed, or otherwise processed on the user's desktop geographic information or cartographic system. The IRMIS application and data may be distributed online and / or in tangible media in limited and advanced manipulation formats.
Owner:GARMIN
Integrated routing/mapping information system
InactiveUS20030182052A1Enabling cooperationEnabling matingInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlImage resolutionLevel of detail
An Integrated Routing / Mapping Information System (IRMIS) links desktop personal computer cartographic applications to one or more handheld organizer, personal digital assistant (PDA) or "palmtop" devices. Such devices may be optionally equipped with, or connected to, portable Global Positioning System (GPS) or equivalent position sensing device. Desktop application facilitates user selection of areas, starts, stops, destinations, maps and / or point and / or route information. It optionally includes supplemental online information, preferably for transfer to the PDA or equivalent device. Users' options include route information, area, and route maps. Maps and related route information are configured with differential detail and levels of magnitude. Used in the field, in conjunction with GPS receiver, the PDA device is configured to display directions, text and map formats, the user's current position, heading, speed, elevation, and so forth. Audible signals identifying the next turn along the user's planned route are also provided. The user can pan across maps and zoom between two or more map scales, levels of detail, or magnitudes. The IRMIS also provides for "automatic zooming," e.g., to show greater detail or closer detail as the user approaches a destination, or to larger scale and lower resolution to show the user's overall planned route between points of interest. The IRMIS also enables the user to mark or record specific locations and / or log actual travel routes, using GPS position information. These annotated location marks and / or "breadcrumb" or GPS log data can be saved, uploaded, displayed, or otherwise processed on the user's desktop geographic information or cartographic system. The IRMIS application and data may be distributed online and / or in tangible media in limited and advanced manipulation formats.
Owner:KHOURI ANTHONY
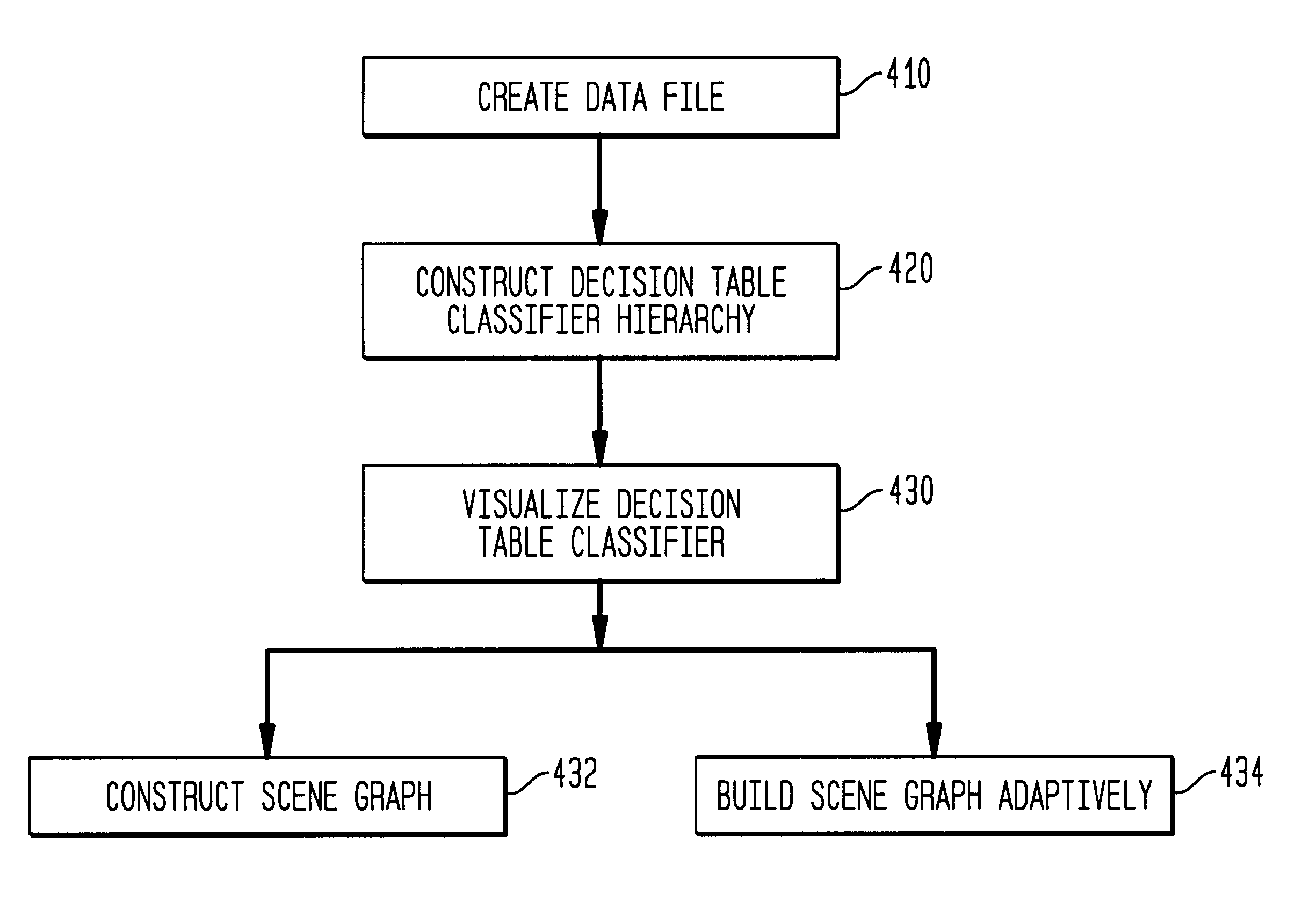
Method, system, and computer program product for visualizing a data structure
A data structure visualization tool visualizes a data structure such as a decision table classifier. A data file based on a data set of relational data is stored as a relational table, where each row represents an aggregate of all the records for each combination of values of the attributes used. Once loaded into memory, an inducer is used to construct a hierarchy of levels, called a decision table classifier, where each successive level in the hierarchy has two fewer attributes. Besides a column for each attribute, there is a column for the record count (or more generally, sum of record weights), and a column containing a vector of probabilities (each probability gives the proportion of records in each class). Finally, at the top-most level, a single row represents all the data. The decision table classifier is then passed to the visualization tool for display and the decision table classifier is visualized. By building a representative scene graph adaptively, the visualization application never loads the whole data set into memory. Interactive techniques, such as drill-down and drill-through are used view further levels of detail or to retrieve some subset of the original data. The decision table visualizer helps a user understand the importance of specific attribute values for classification.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Methods and systems for generating a zoomable graphical user interface
ActiveUS20050005241A1Easy and rapid selectionSmooth navigationTelevision system detailsMultimedia data browsing/visualisationGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:DRNC HLDG INC
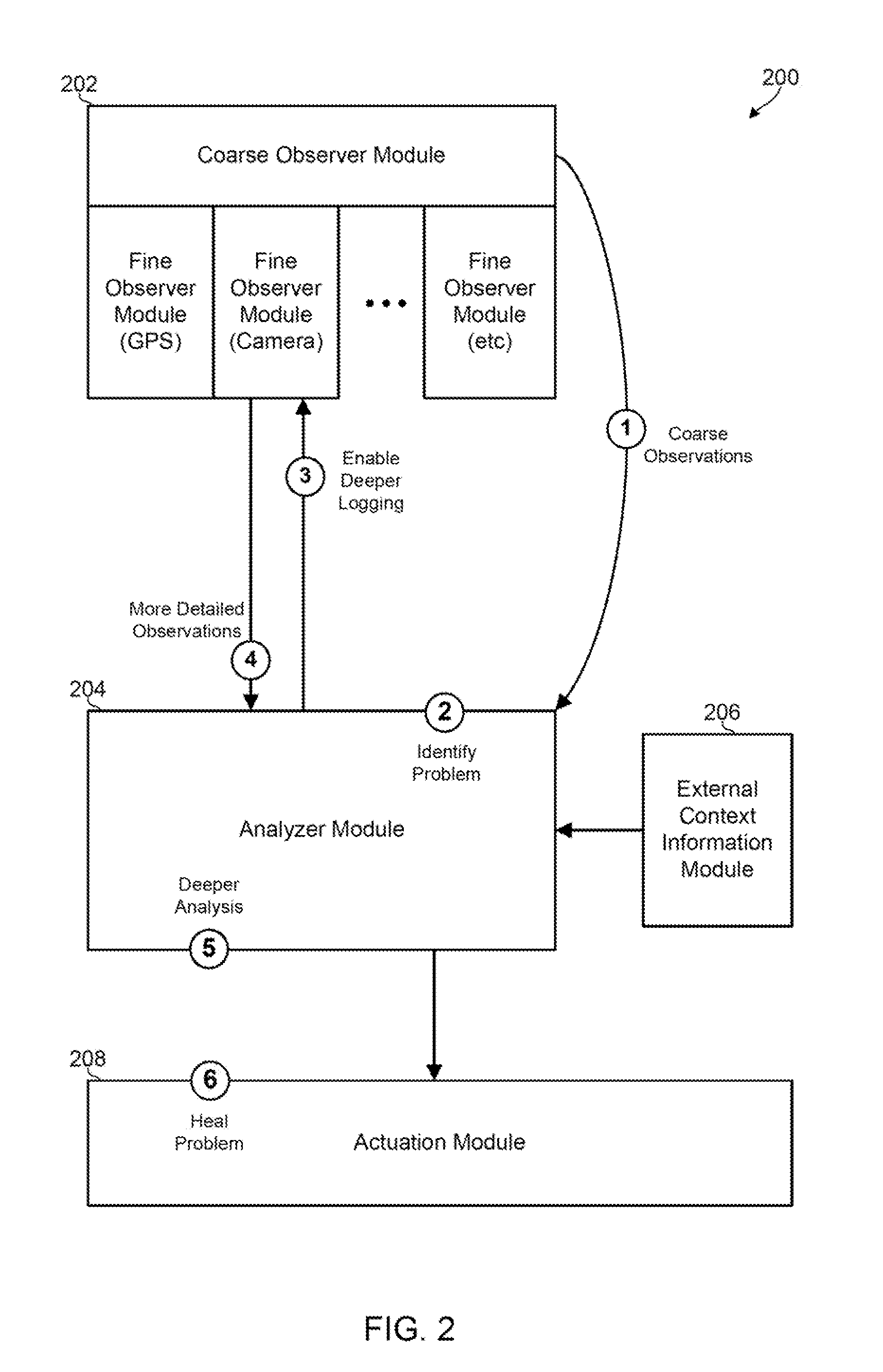
Adaptive Observation of Behavioral Features on a Mobile Device
Methods, devices and systems for detecting suspicious or performance-degrading mobile device behaviors intelligently, dynamically, and / or adaptively determine computing device behaviors that are to be observed, the number of behaviors that are to be observed, and the level of detail or granularity at which the mobile device behaviors are to be observed. The various aspects efficiently identify suspicious or performance-degrading mobile device behaviors without requiring an excessive amount of processing, memory, or energy resources.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
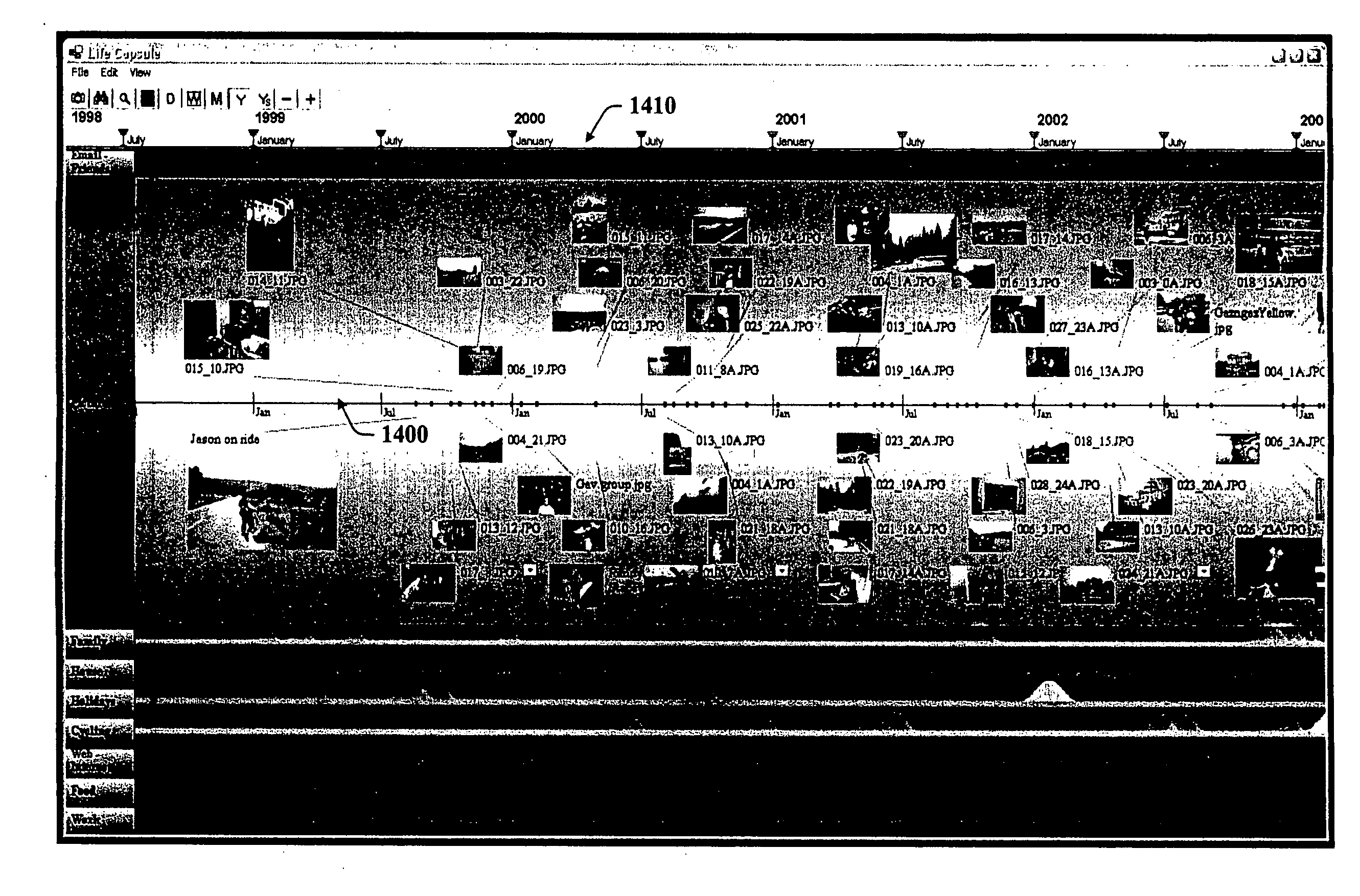
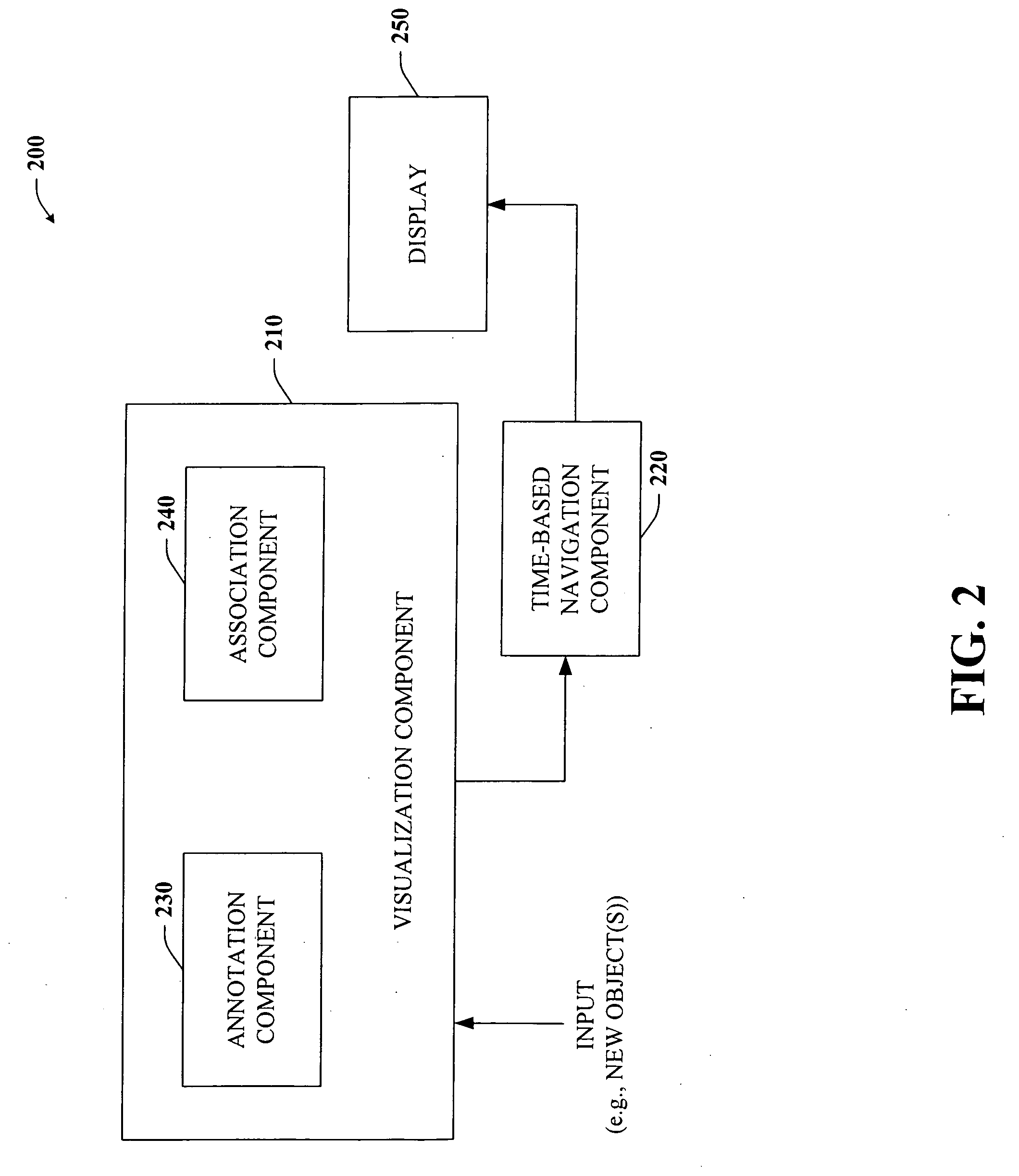
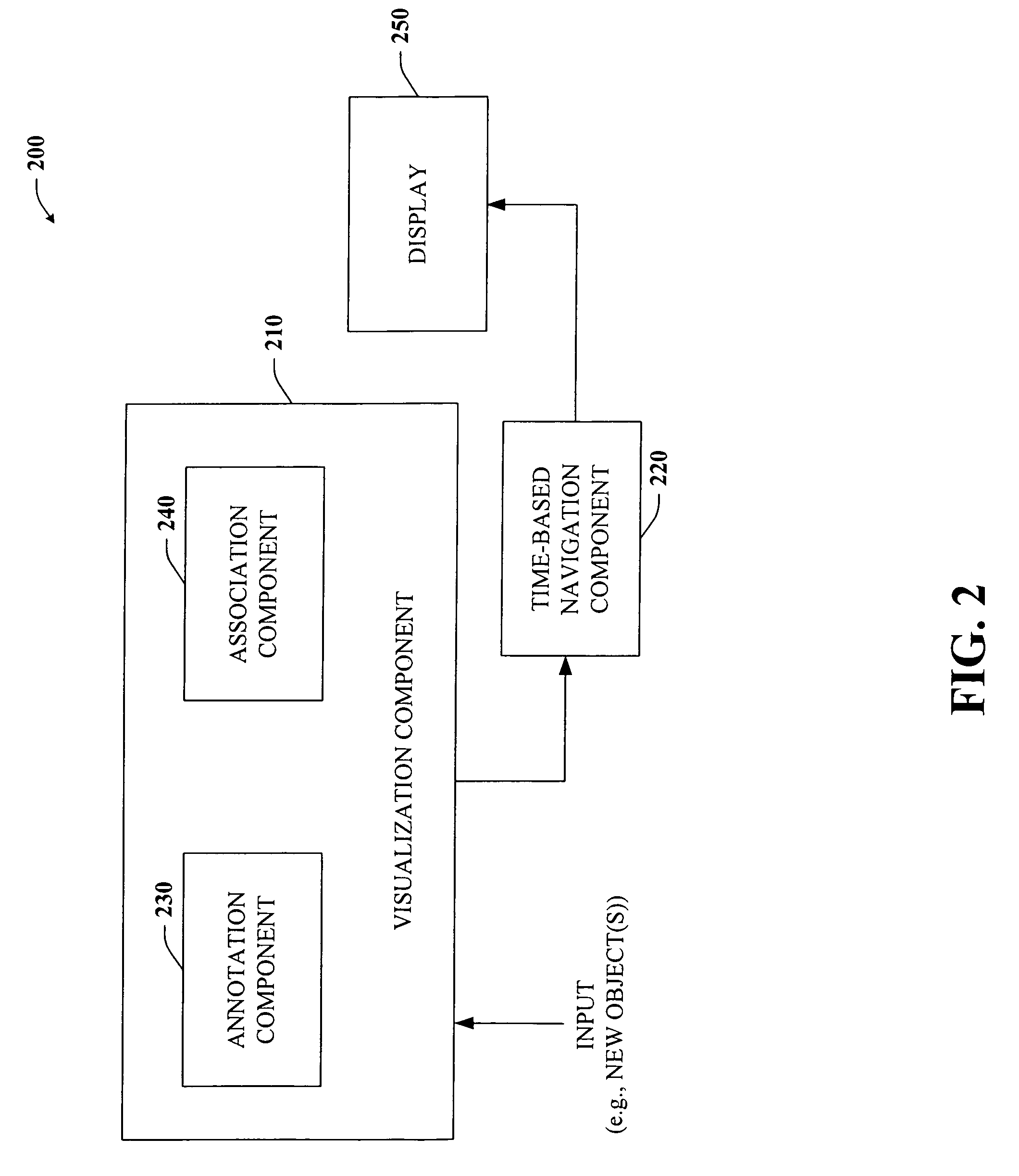
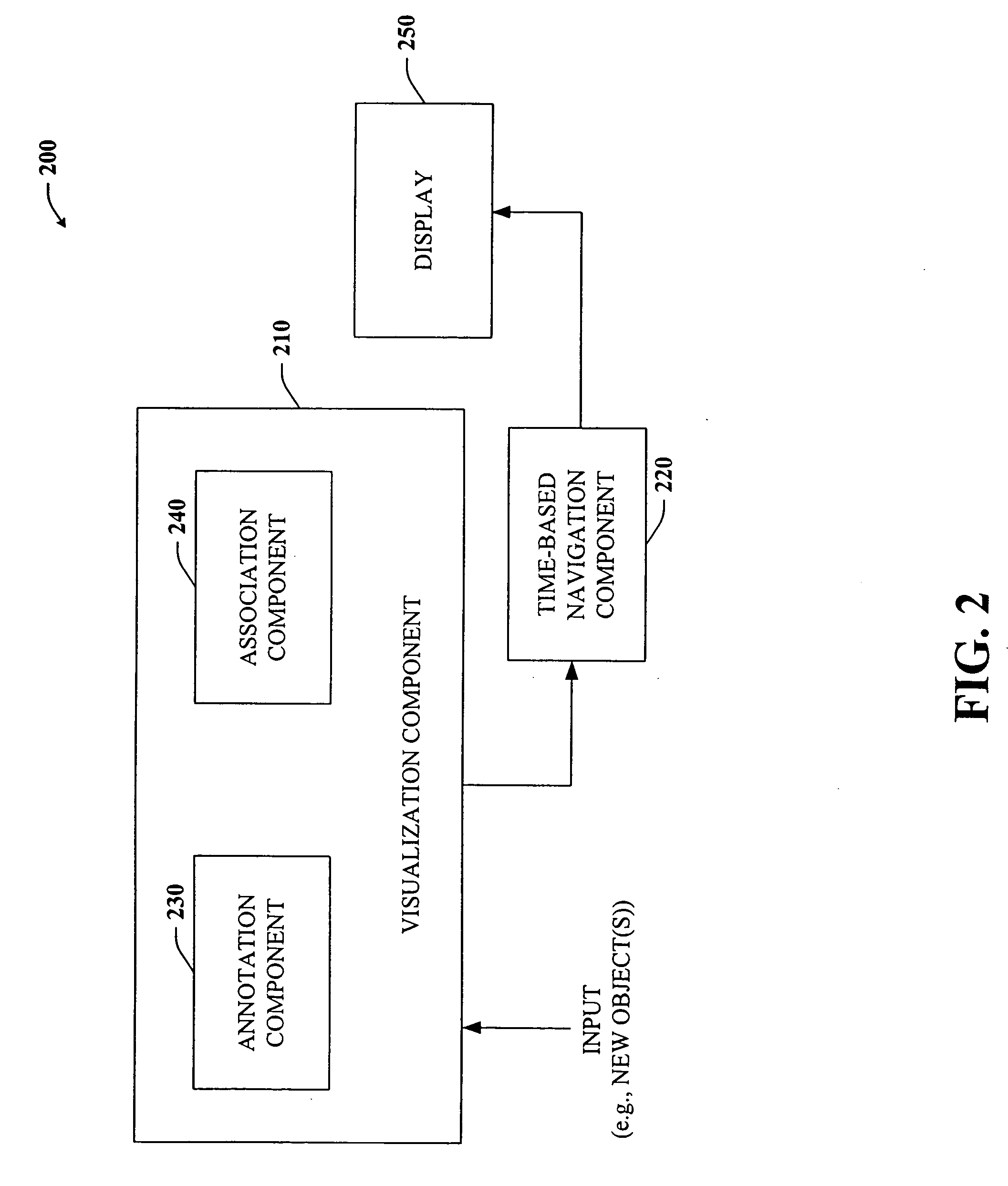
Architecture and engine for time line based visualization of data
InactiveUS20060156246A1Easy to watchFacilitate navigating and managingData processing applicationsVisual data miningLevel of detailThumbnail
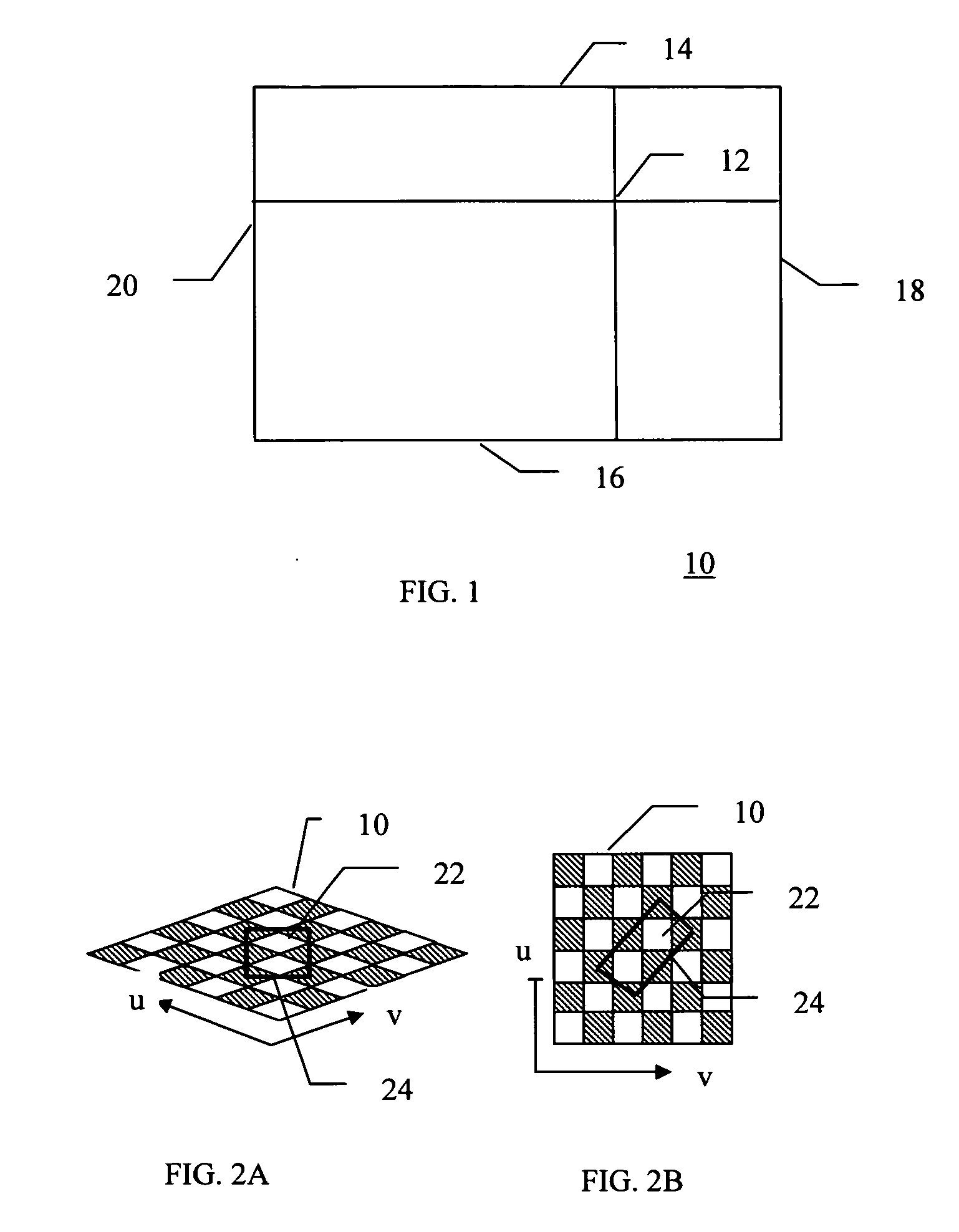
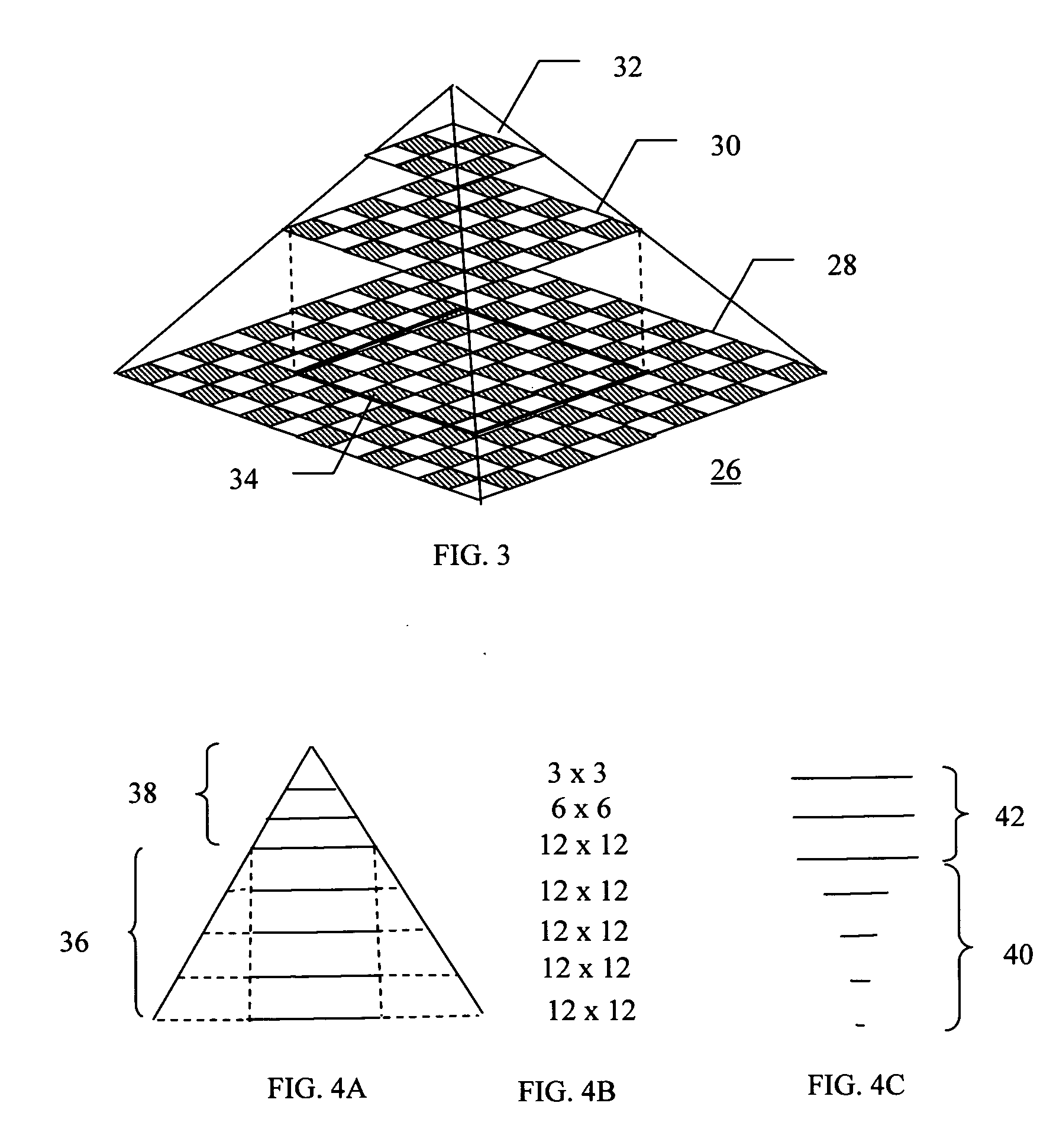
The subject invention provides a unique system and method that facilitates management and navigation of various data objects by making use of a unique time-line based navigation tool. In particular, objects can organized into a plurality of bands based on their respective subject matter. Each band can be created to designate a particular topic. Objects are organized within the appropriate bands based in part on a time parameter such as a time or date that the object was created, for example. The navigation tool allows a user to navigate or browse through the bands and objects according to a desired time parameter or range of time. Zooming and other browsing options are available to the user to view objects of interest at varying levels of detail. The objects are represented as ASCII thumbnails that are operational. Thus, the content of any object can be modified directly via the thumbnail.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
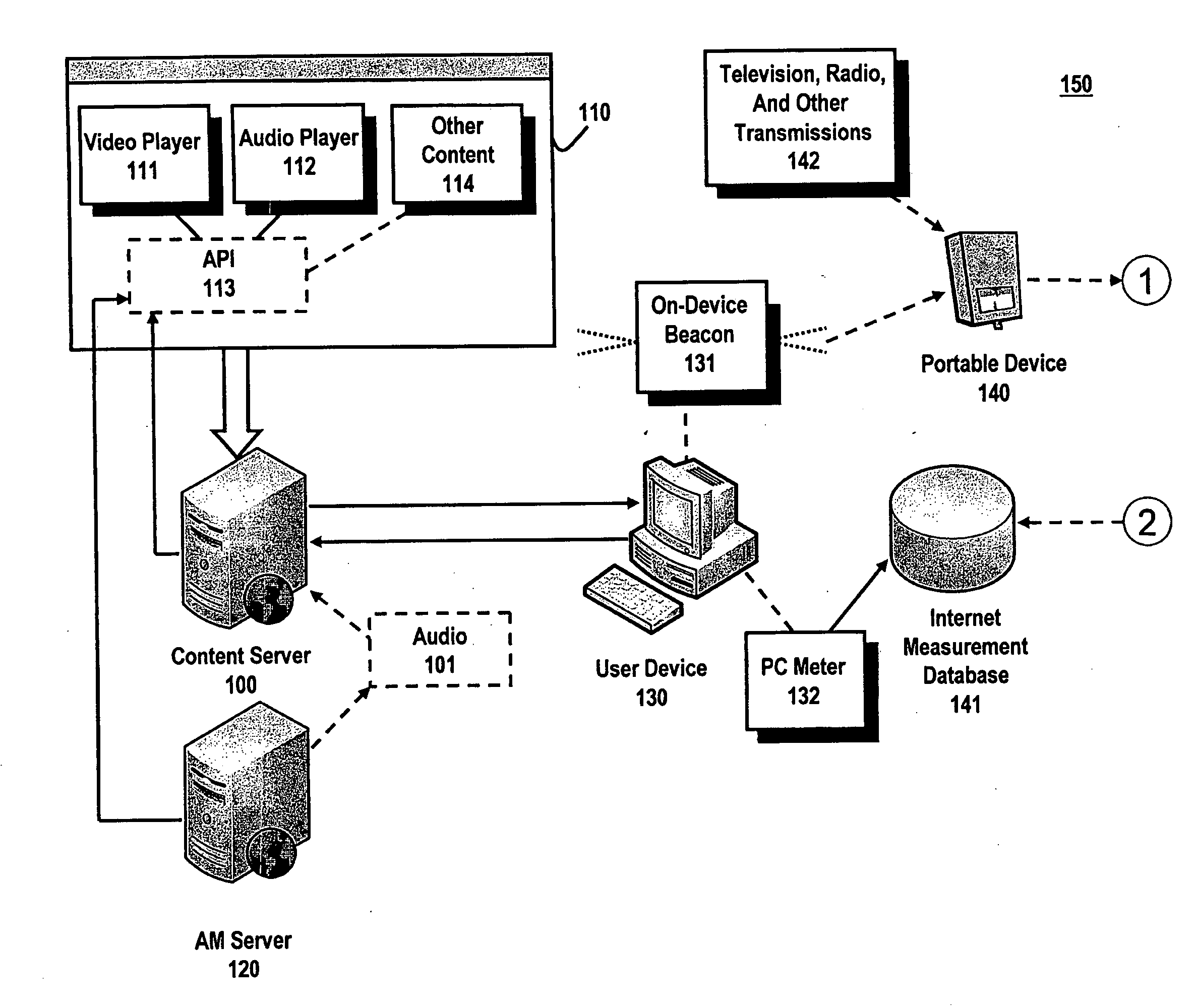
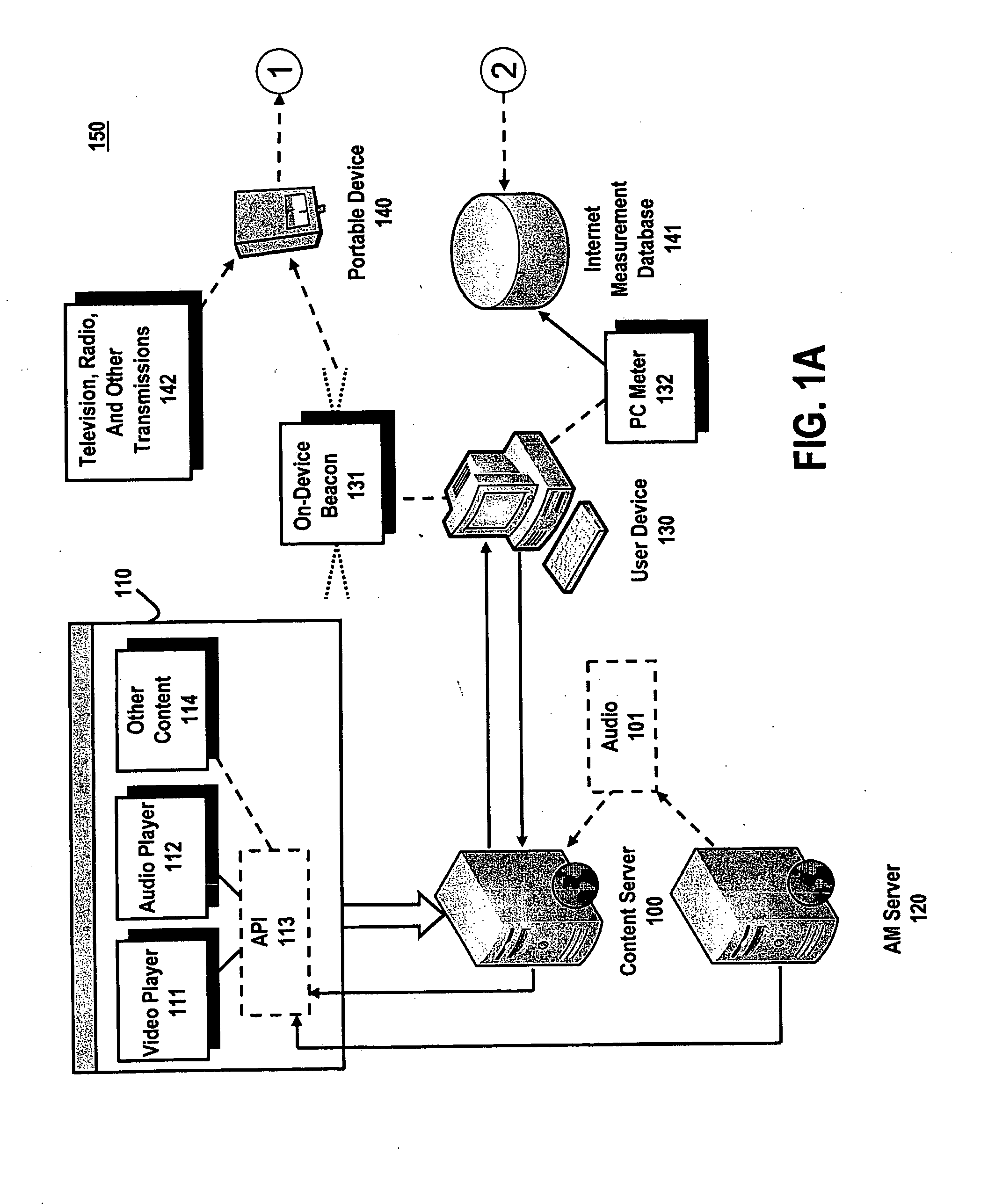
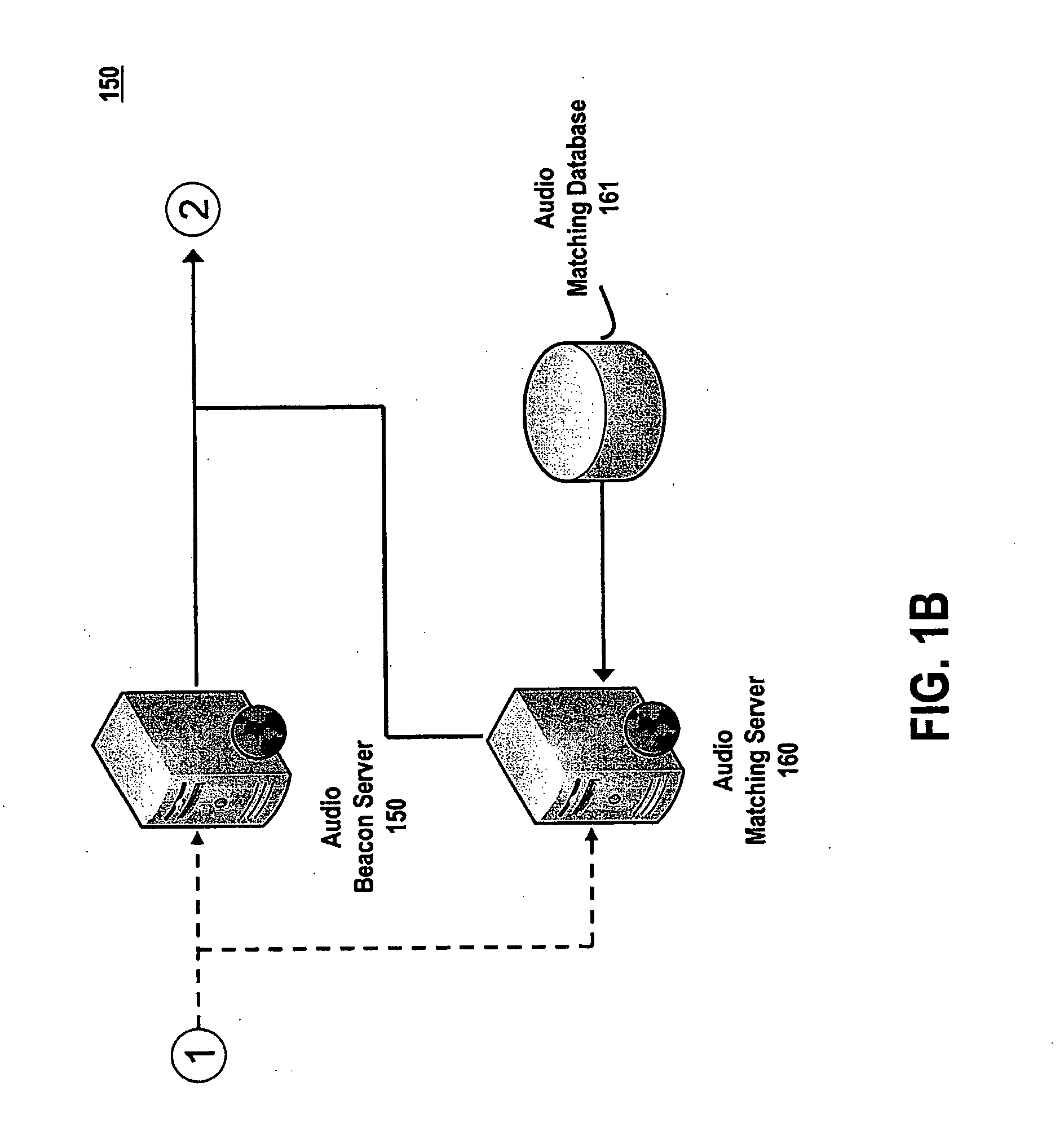
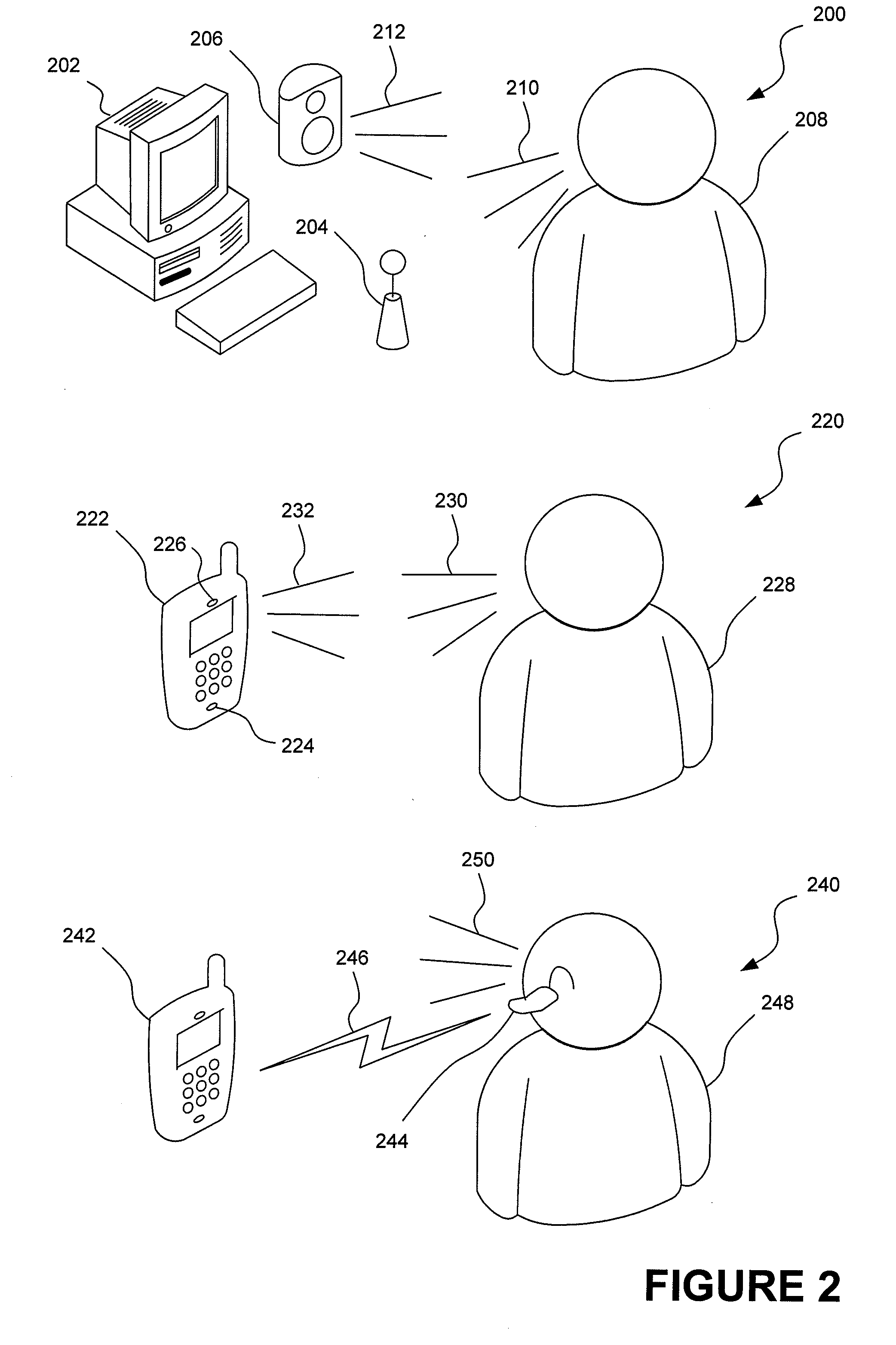
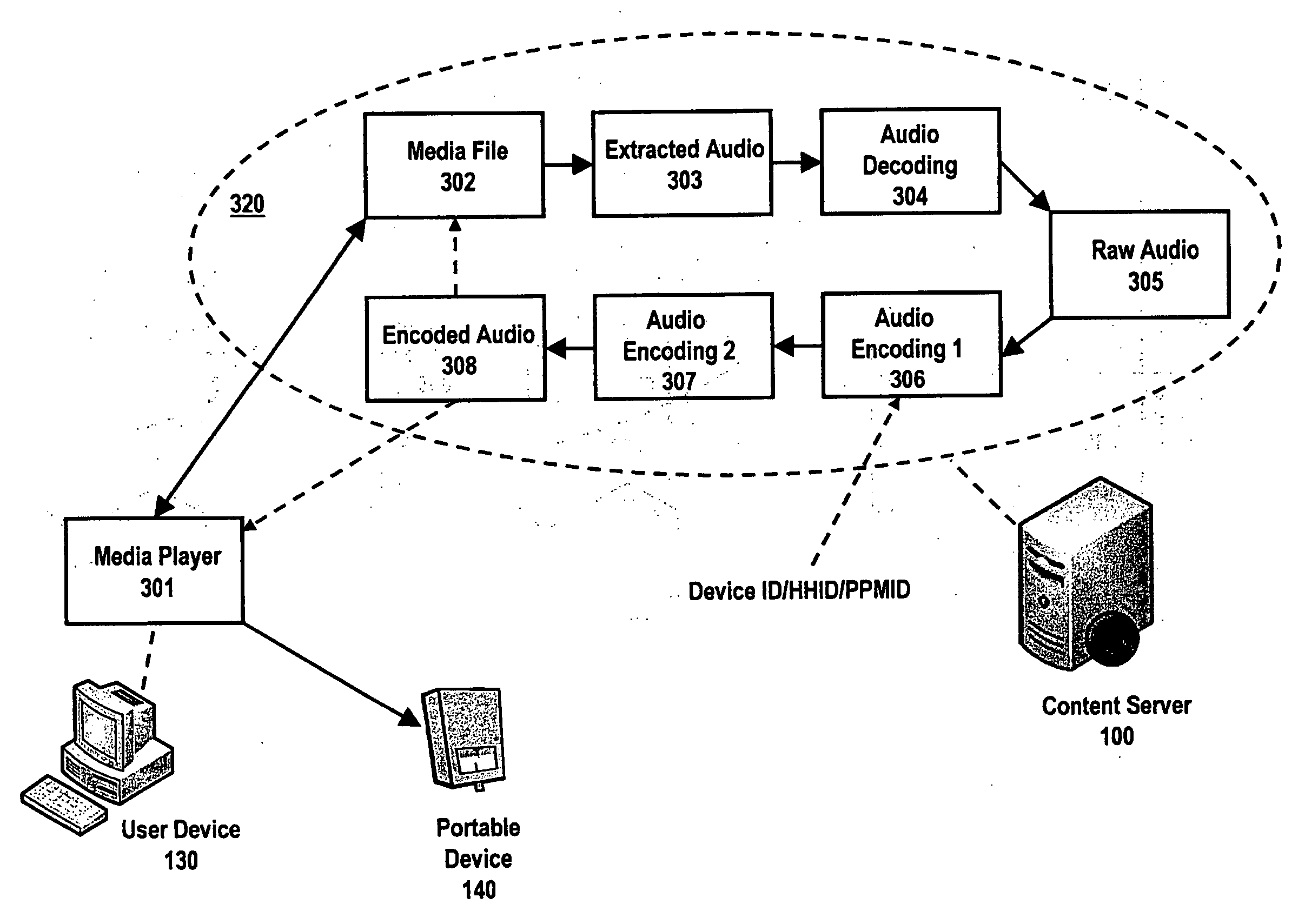
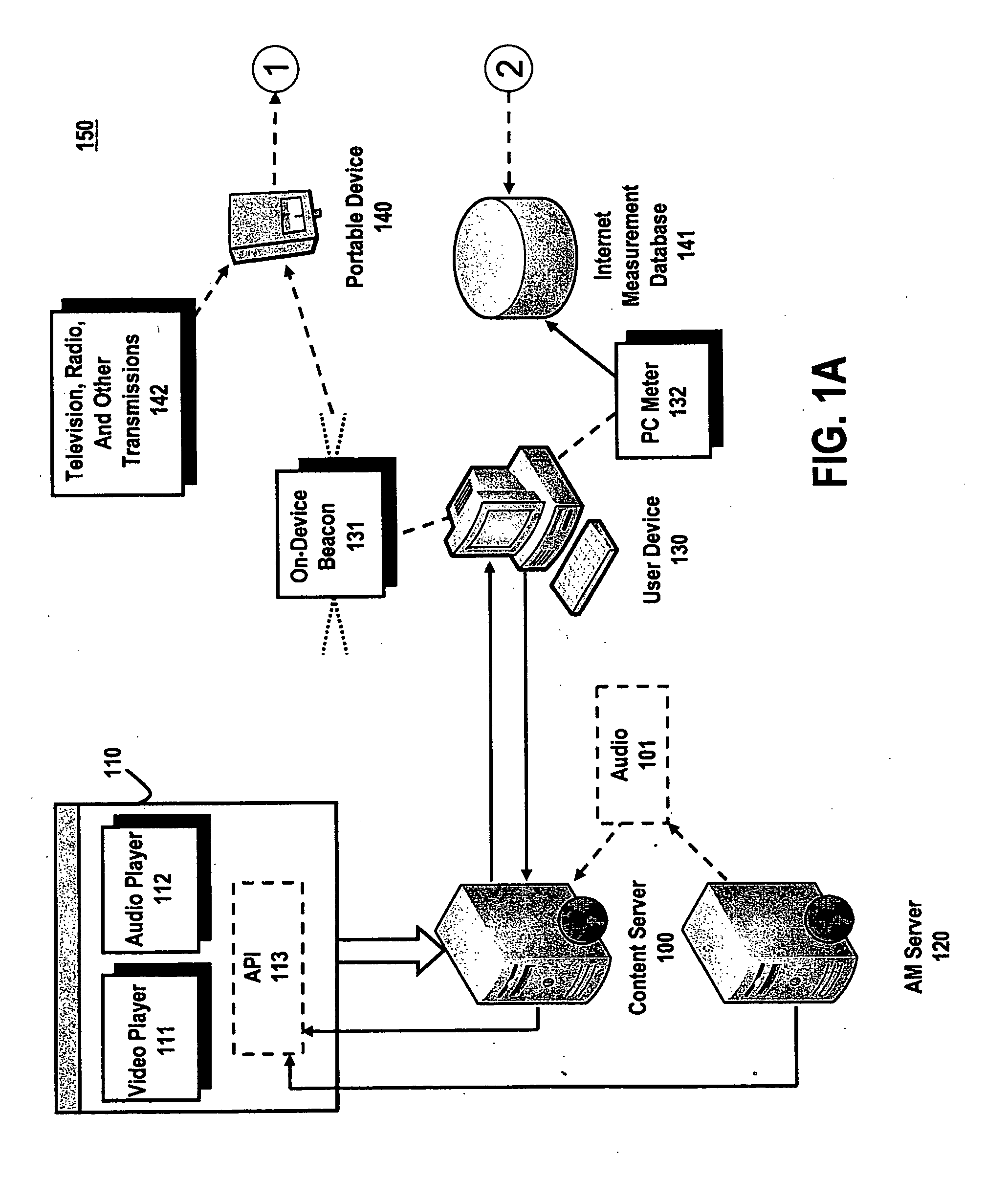
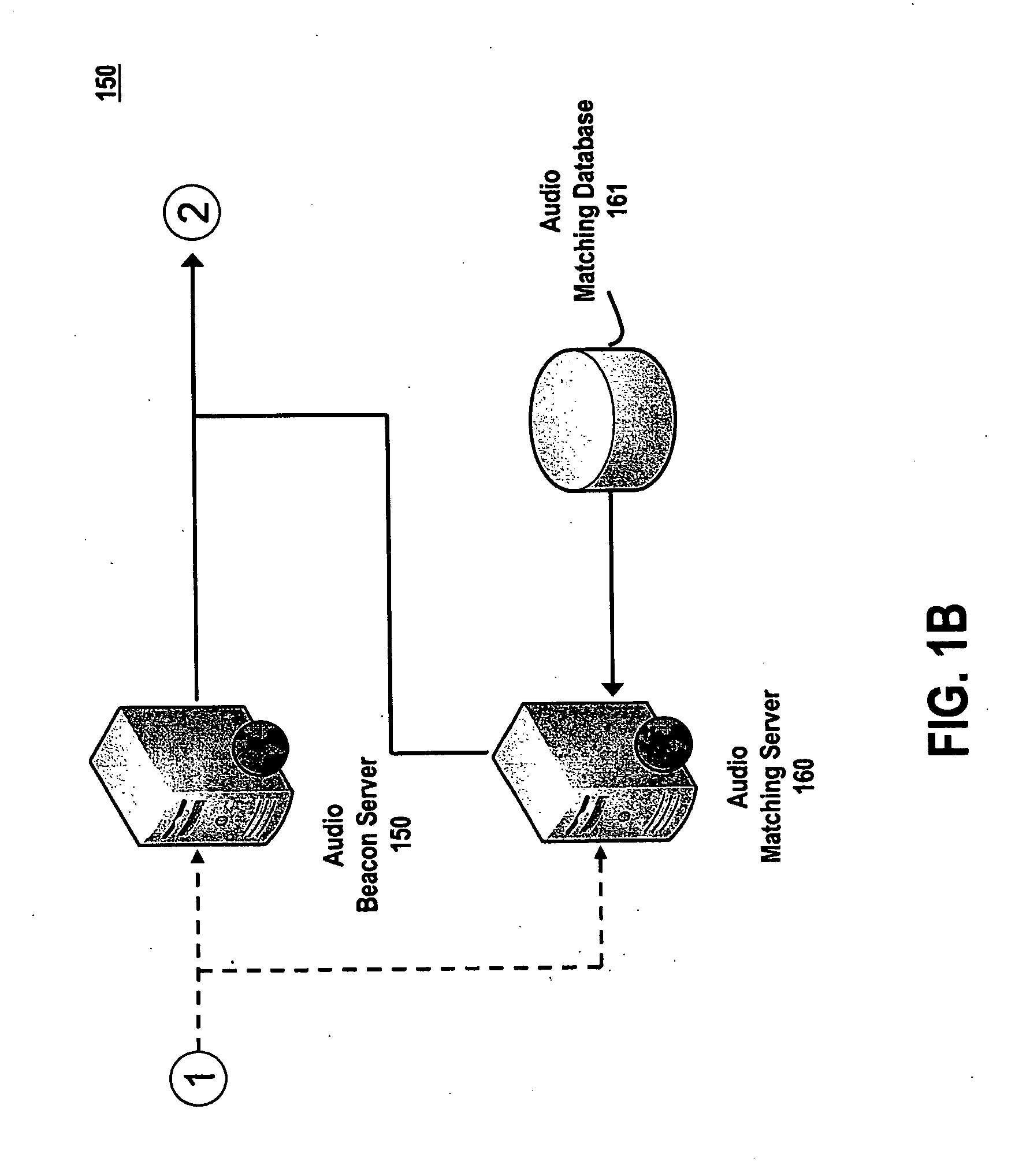
System and method for utilizing supplemental audio beaconing in audience measurement
InactiveUS20100268573A1High level of detailGood associationMarket predictionsBroadcast systems characterised by watermarksMeasurement deviceLevel of detail
An audio beacon system, apparatus and method for collecting information on a panelist's exposure to media. An audio beacon is configured as on-device encoding technology that is operative in a panelist's processing device (e.g., cell phone, PDA, PC) to enable the device to encode an acoustic tone and transmit it for a predetermined period of time. The acoustically transmitted data is received and processed by a portable audience measurement device, such as Arbitron's Personal People Meter™ (“PPM”), or other specially equipped portable device to enable audience measurement systems to achieve higher levels of detail on panel member activity and greater association of measurement devices to their respective panelists.
Owner:NIELSEN HLDG NV +1
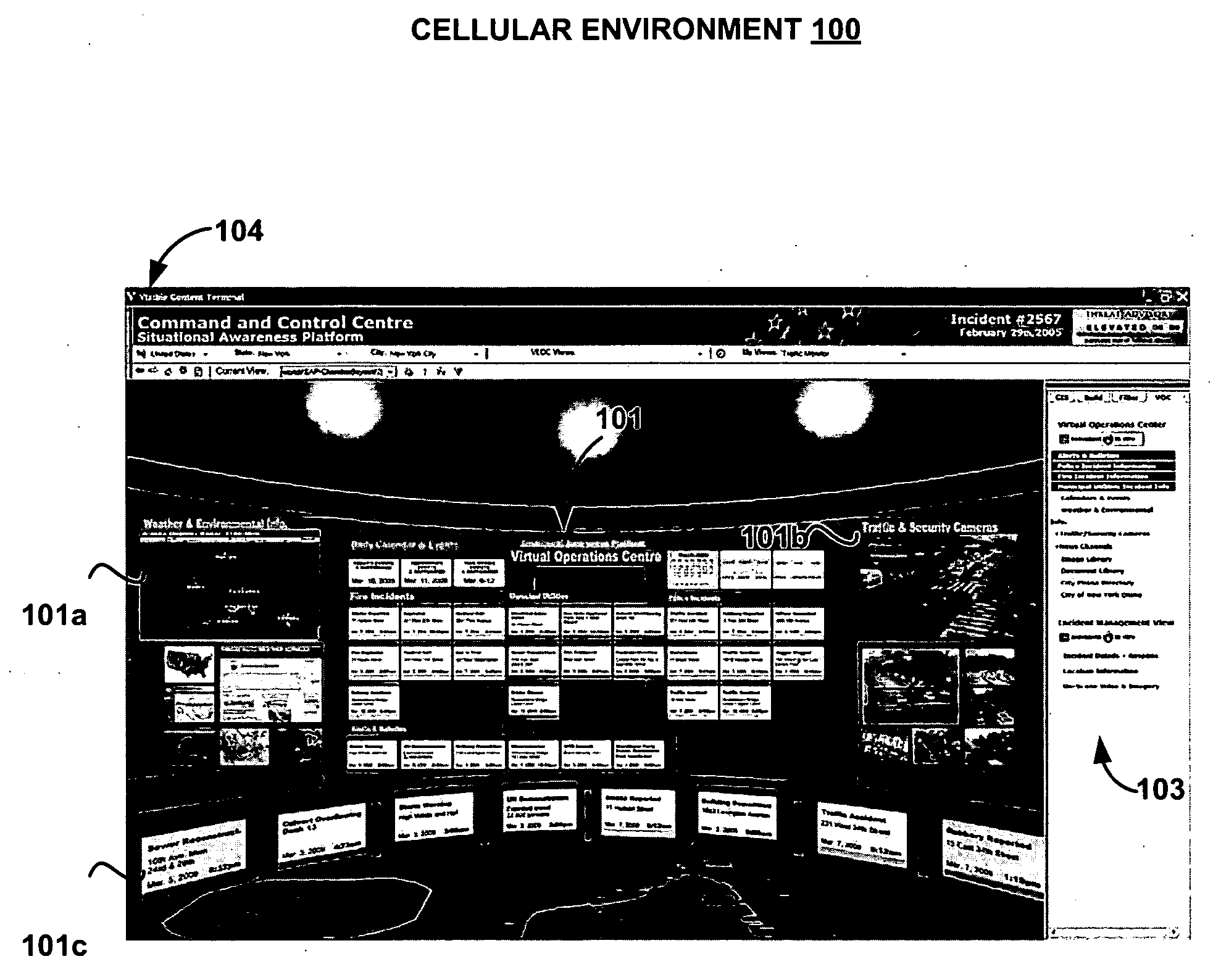
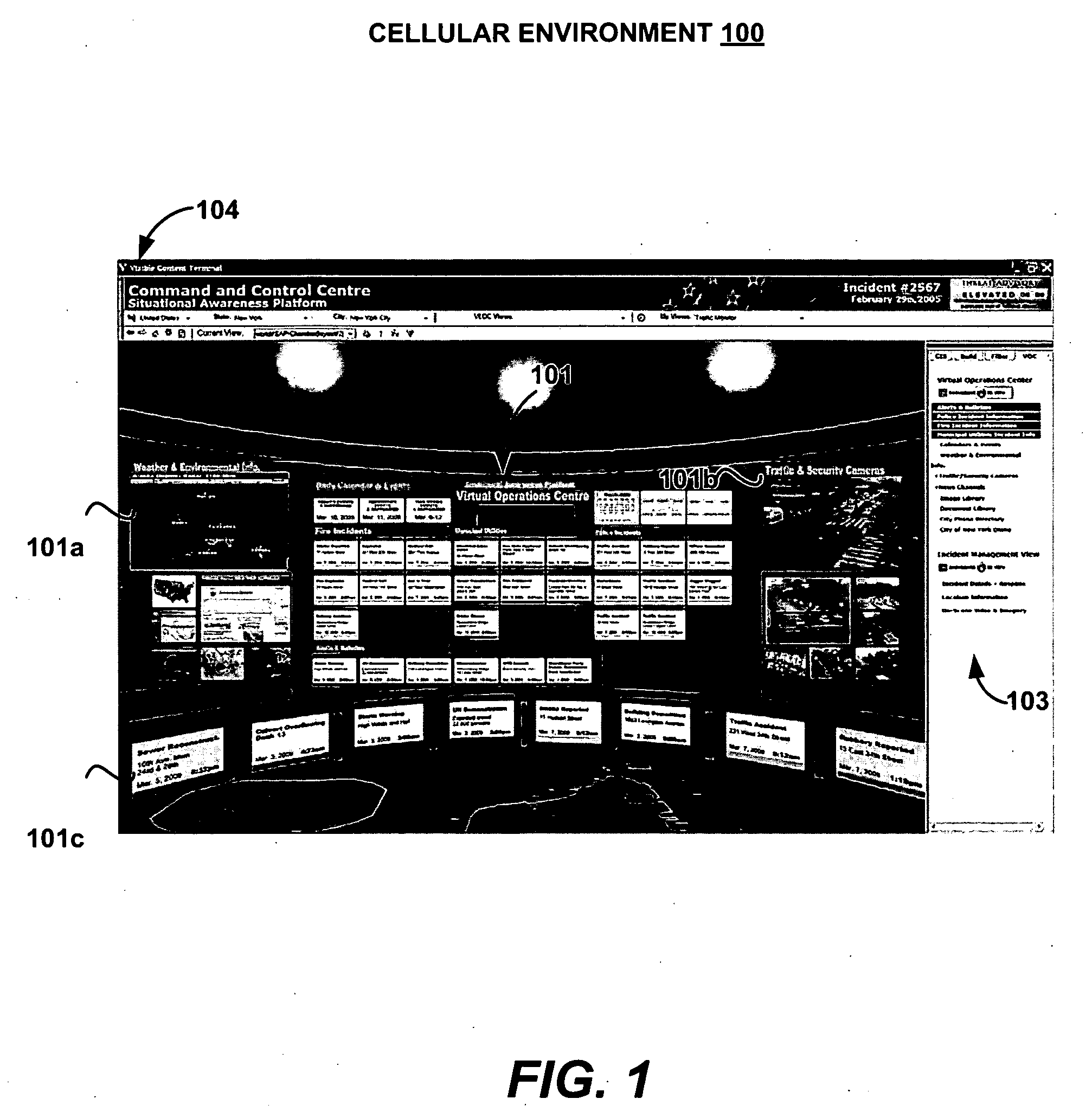
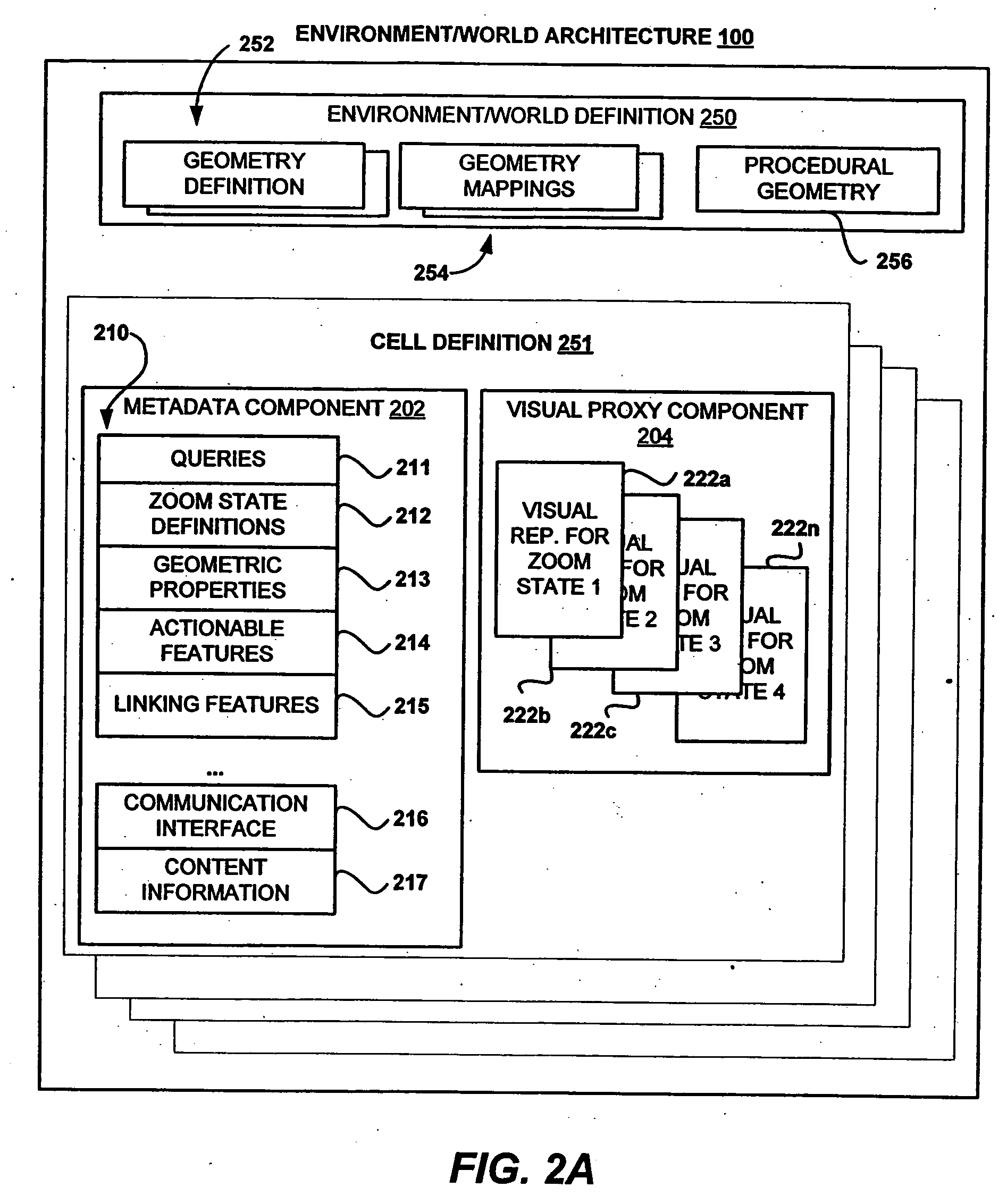
Cellular user interface
InactiveUS20060161863A1Increase flexibilityExecution for user interfacesSpecial data processing applicationsLevel of detailData source
Configurations for a cellular user interface are provided. In one embodiment, a client configuration includes a viewer and a content development kit. A content server distributes cellularized content among several client viewers. Connectors in a scheduled configuration regularly acquire updated content from data sources. An integration server interfaces between the connectors and the content server for distributing content. A monitoring agent assists with content updating upon detecting source changes. A registration server enables cell content update in client viewers through the content server. Cells in the cellularized environment include a visual proxy component and a metadata component. The visual proxy component can be configured for displaying different content at various levels of detail. The metadata component enables intelligent organization and display of content through queries, channels, and data updates. In addition, procedural geometry in the cellularized environment automates the content presentation and provides a flexible arrangement of the cells.
Owner:OPEN TEXT SA ULC
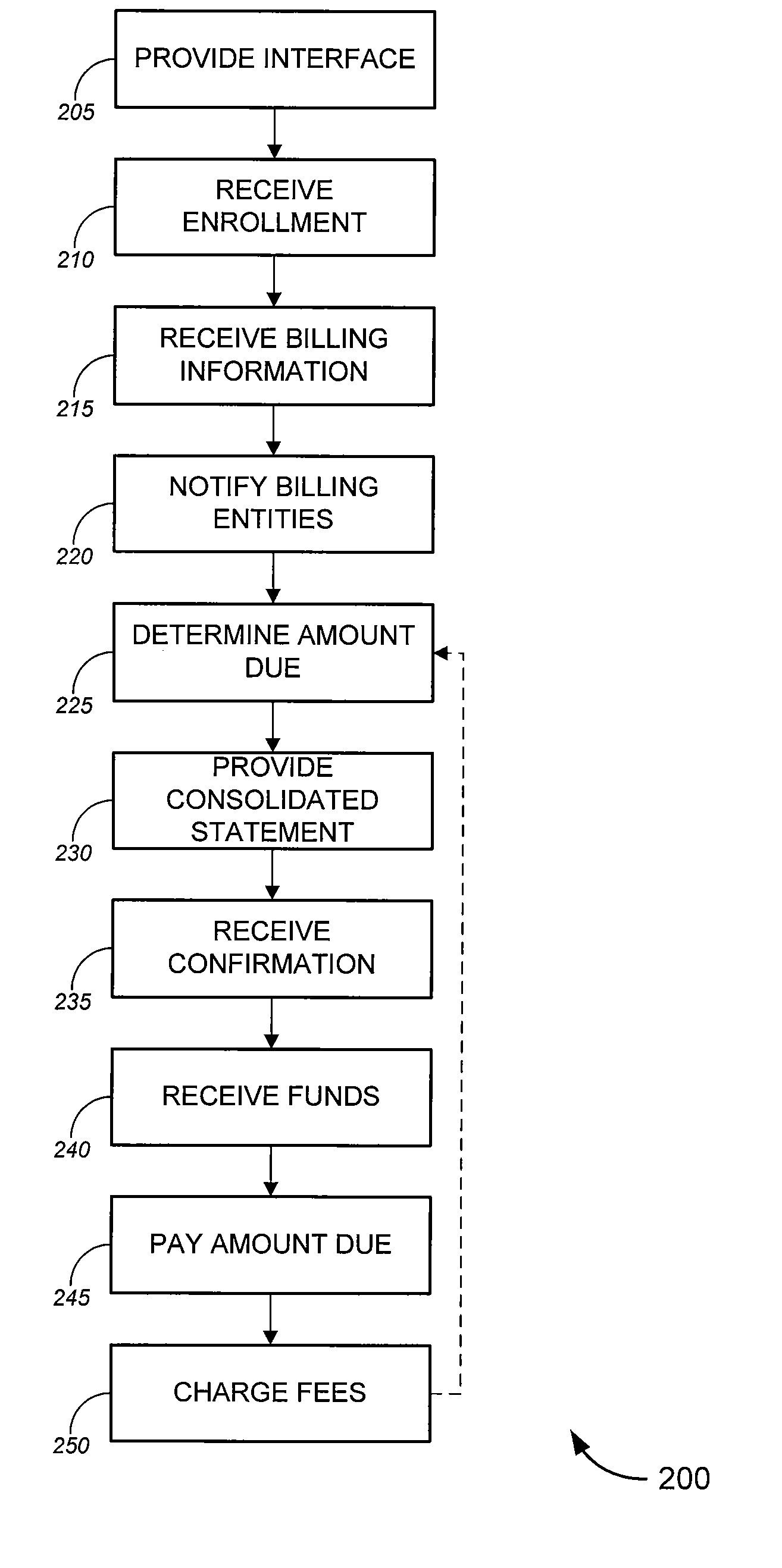
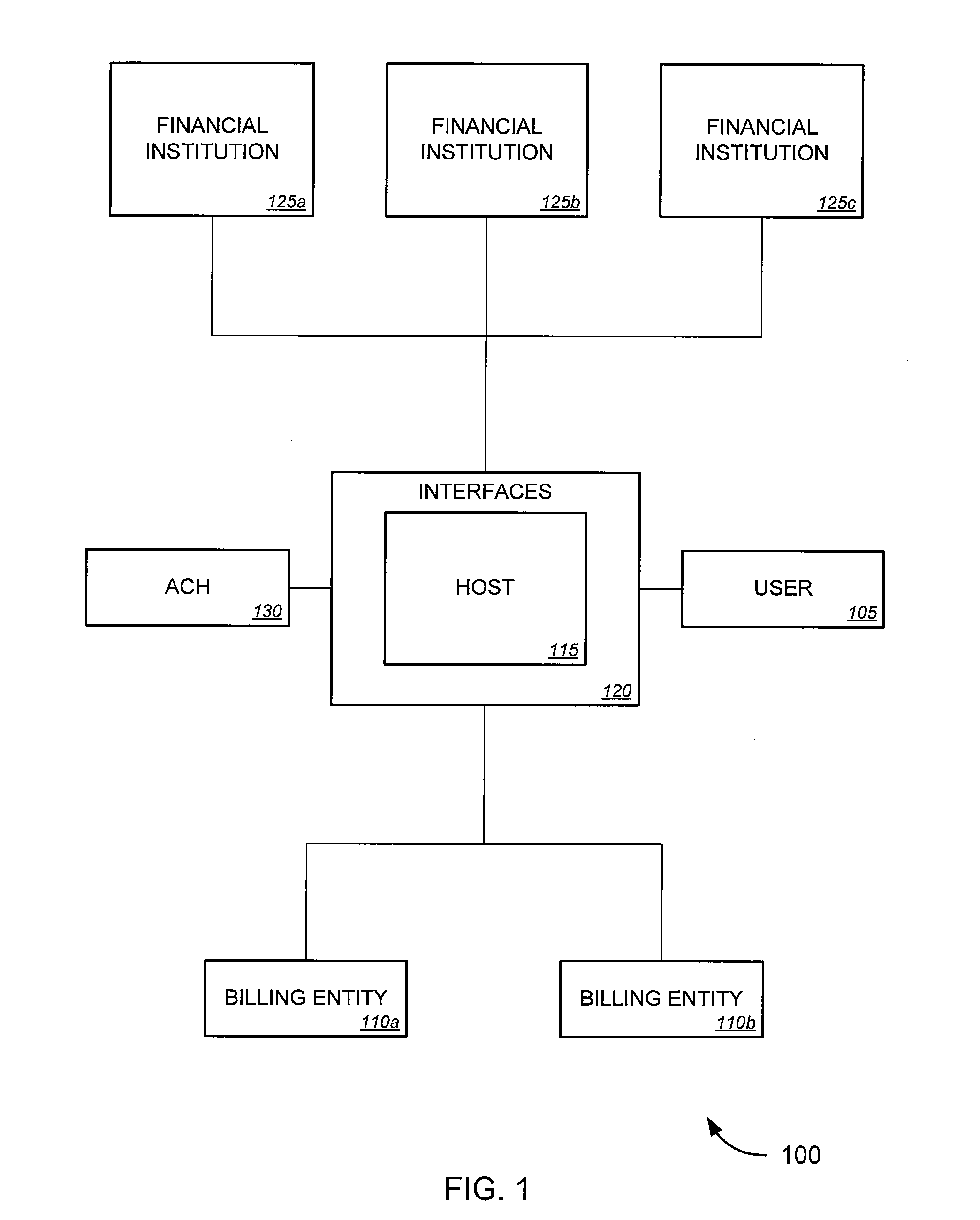
Bill payment aggregation service
ActiveUS20090089193A1Avoid traditional hassleRelieve stressComplete banking machinesFinancePaymentLevel of detail
Tools for providing bill aggregation and / or payment services. In an aspect, such tools aggregate all payments over a given period of time, allowing a user to make a single payment to ensure that all appropriate bills are paid in timely fashion. In another aspect, the tools determine, without requiring user input, an amount due on each bill, as well, in some cases, of a due date for each payment. Optionally, the tools can provide a consolidated statement to inform the user of payments to be made over a given period. Such statements can provide a varying level of detail, depending on the implementation and / or on user preferences. In some cases, a consolidated statement might provide line items and / or detailed support for each payment to be made. In other cases, the consolidated statement might simply provide a single consolidated payment amount.
Owner:THE WESTERN UNION CO
Layered prompting: self-calibrating instructional prompting for verbal interfaces
ActiveUS20090210232A1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpeech recognitionLevel of detailHuman–computer interaction
A plurality of prompting layers configured to provide varying levels of detailed assistance in prompting a user are maintained. A prompt from a current prompting layer is presented to a user. Input is received from the user. A level of detail in prompting the user is adaptively changed based on user behavior. Upon the user making a hesitant verbal gesture that reaches a threshold duration, a transition is made from the current prompting layer to a more detailed prompting layer. Upon the user interrupting the prompt with a valid input, a transition is made from the current prompting layer to a less detailed prompting layer.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for utilizing audio beaconing in audience measurement
InactiveUS20100268540A1High level of detailGood associationSpeech analysisMarketingMeasurement deviceLevel of detail
An audio beacon system, apparatus and method for collecting information on a panelist's exposure to media. An audio beacon is configured as on-device encoding technology that is operative in a panelist's processing device (e.g., cell phone, PDA, PC) to enable the device to encode and / or process media data and acoustically transmit it for a predetermined period of time. The acoustically transmitted data is received and processed by a portable audience measurement device, such as Arbitron's Personal People Meter™ (“PPM”), or other specially equipped portable device to enable audience measurement systems to achieve higher levels of detail on panel member activity and greater association of measurement devices to their respective panelists.
Owner:THE NIELSEN CO (US) LLC +1
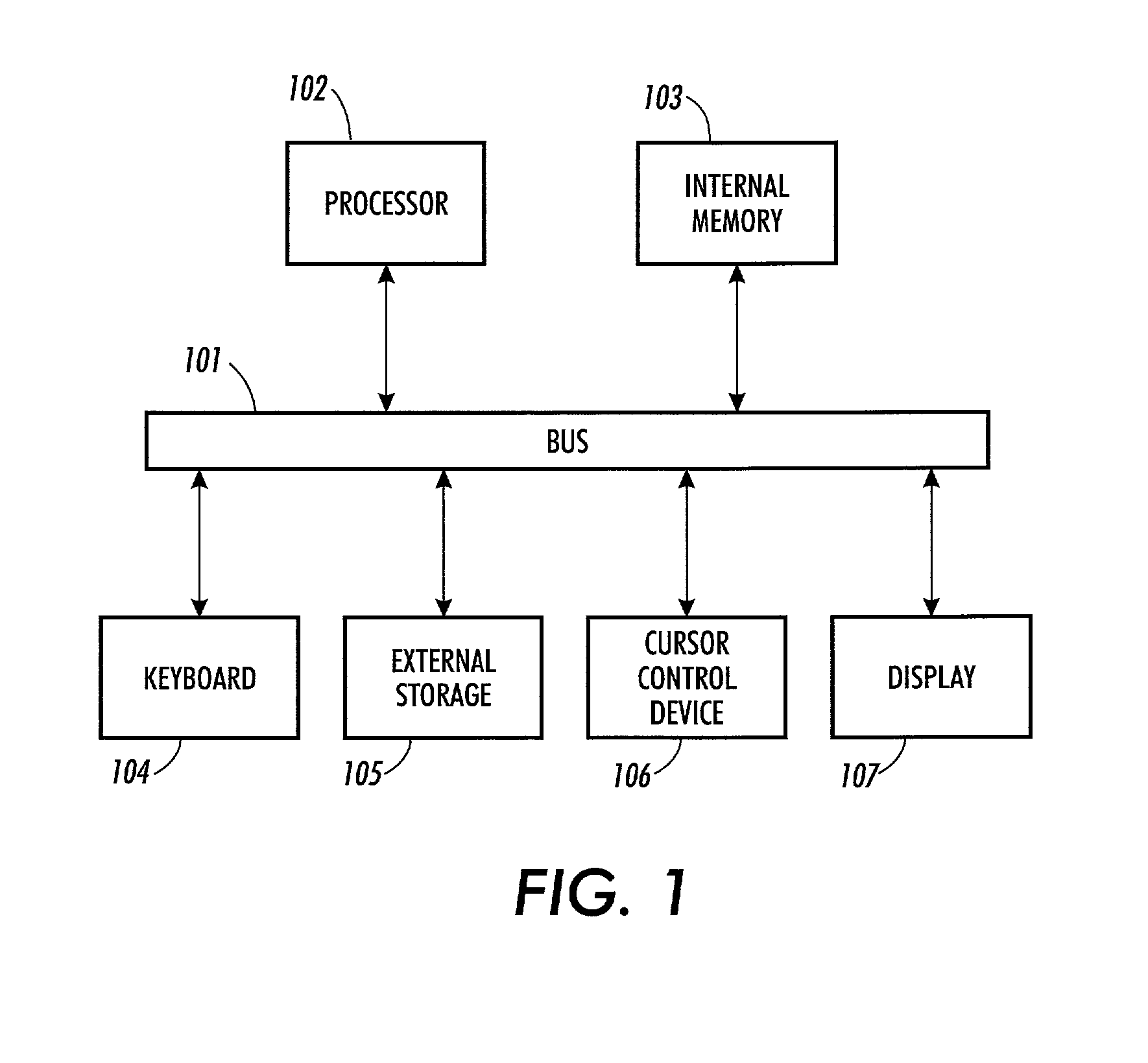
System and device for multi-scale analysis and representation of physiological data
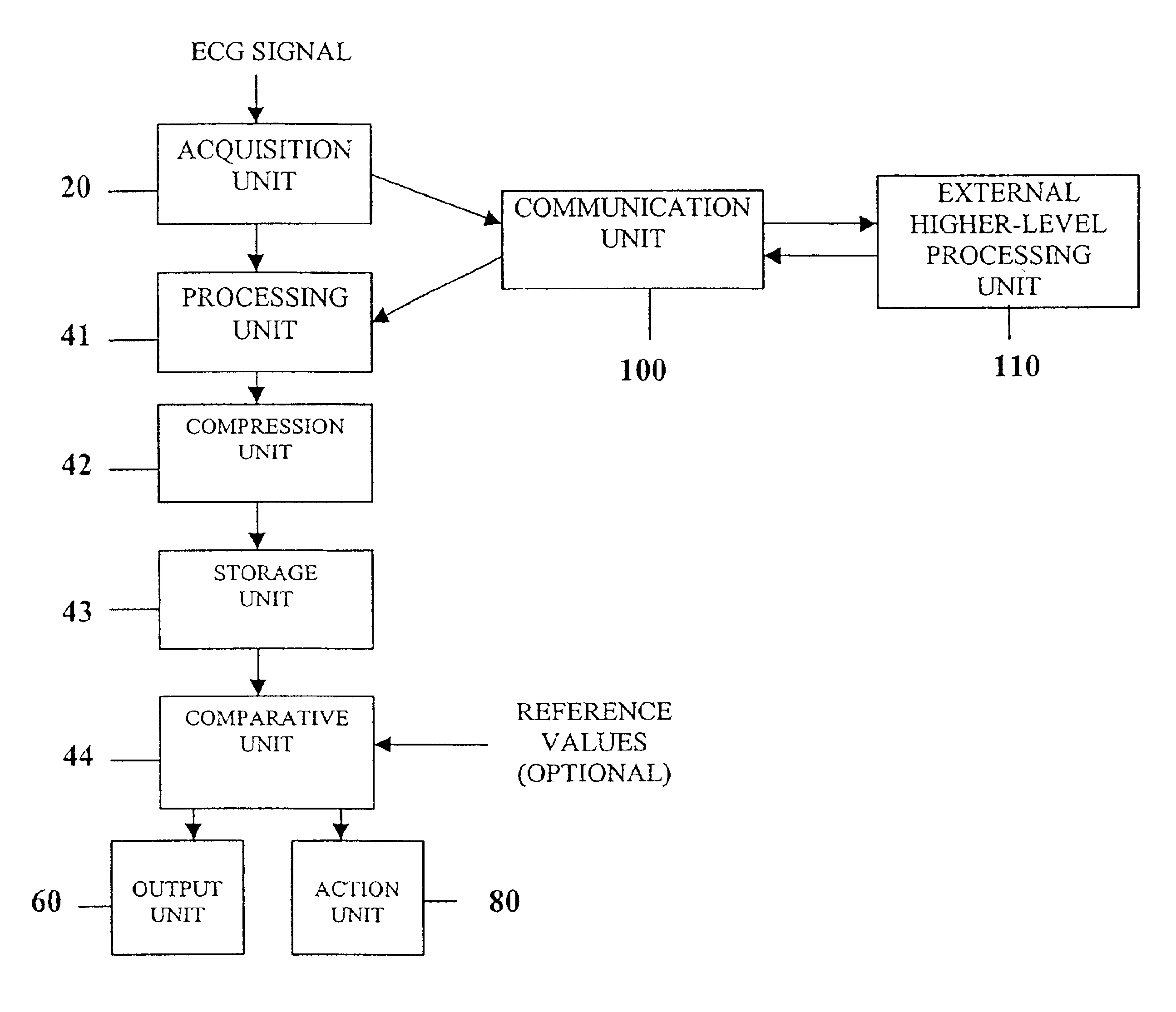
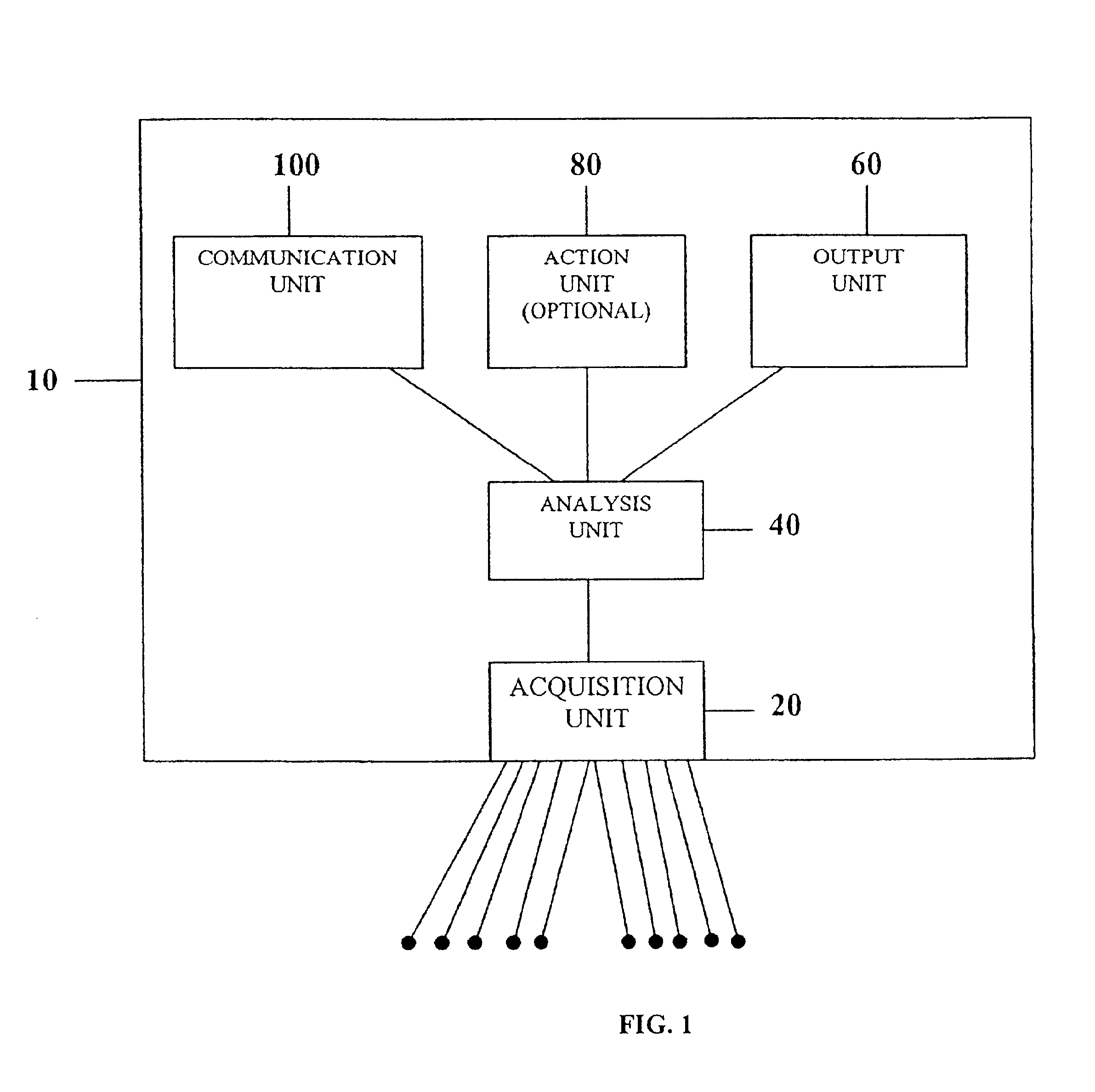
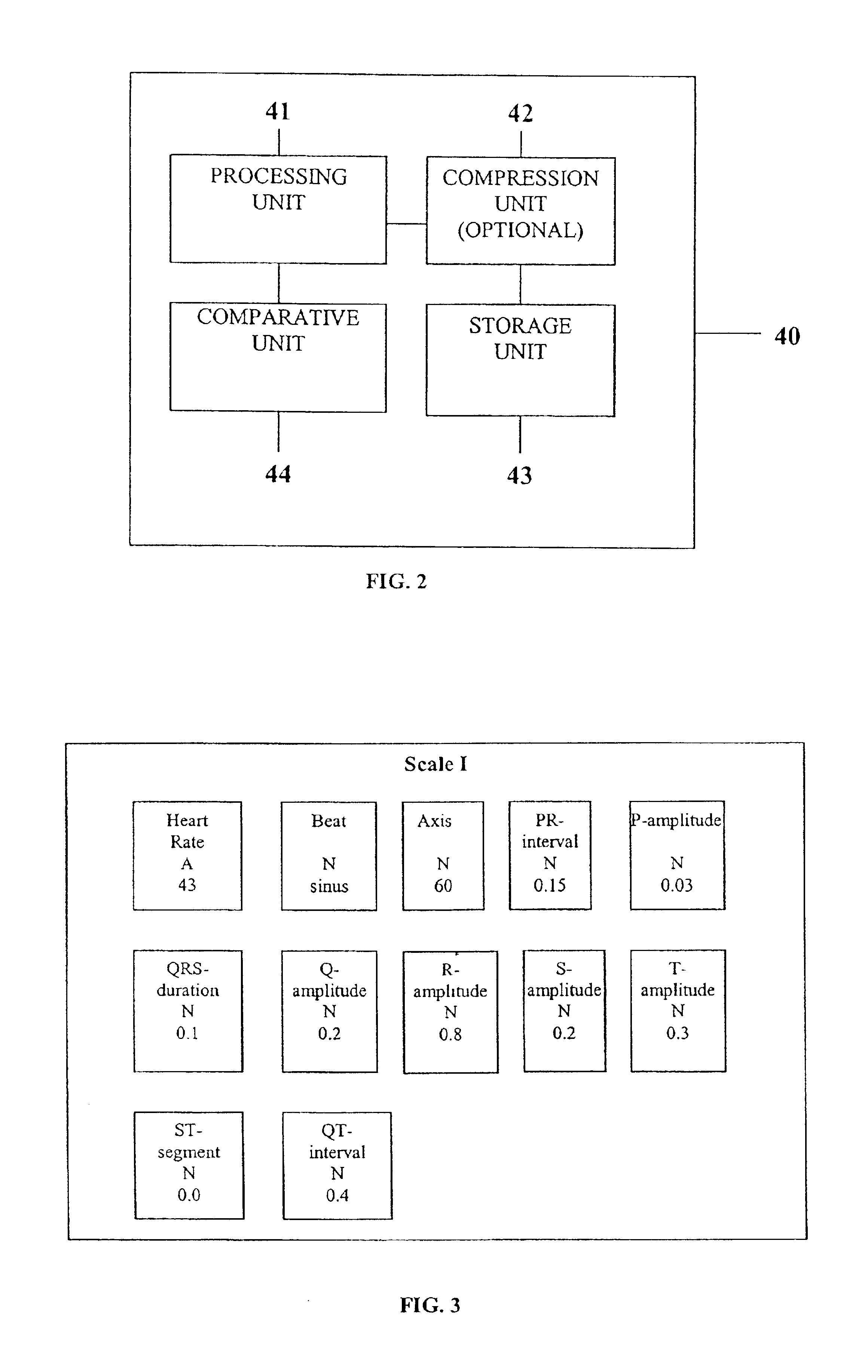
InactiveUS6925324B2Easy to analyzeIncrease computing resourcesElectrocardiographySensorsReal time analysisT wave
System comprised of a medical device and method for analyzing physiological and health data and representing the most significant parameters at different levels of detail which are understandable to a lay person and a medical professional. Low, intermediate and high-resolution scales can exchange information between each other for improving the analyses; the scales can be defined according to the corresponding software and hardware resources. A low-resolution Scale I represents a small number of primary elements such as intervals between the heart beats, duration of electrocardiographic PQ, QRS, and QT-intervals, amplitudes of P-, Q-, R-, S-, and T-waves. This real-time analysis is implemented in a portable device that requires minimum computational resources. The set of primary elements and their search criteria can be adjusted using intermediate or high-resolution levels. At the intermediate-resolution Scale II, serial changes in each of the said elements can be determined using a mathematical decomposition into series of basis functions and their coefficients. This scale can be implemented using a specialized processor or a computer organizer. At the high-resolution Scale III, combined serial changes in all primary elements can be determined to provide complete information about the dynamics of the signal. This scale can be implemented using a powerful processor, a network of computers or the Internet. The system can be used for personal or group self-evaluation, emergency or routine ECG analysis, or continuous event, stress-test or bed-side monitoring.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
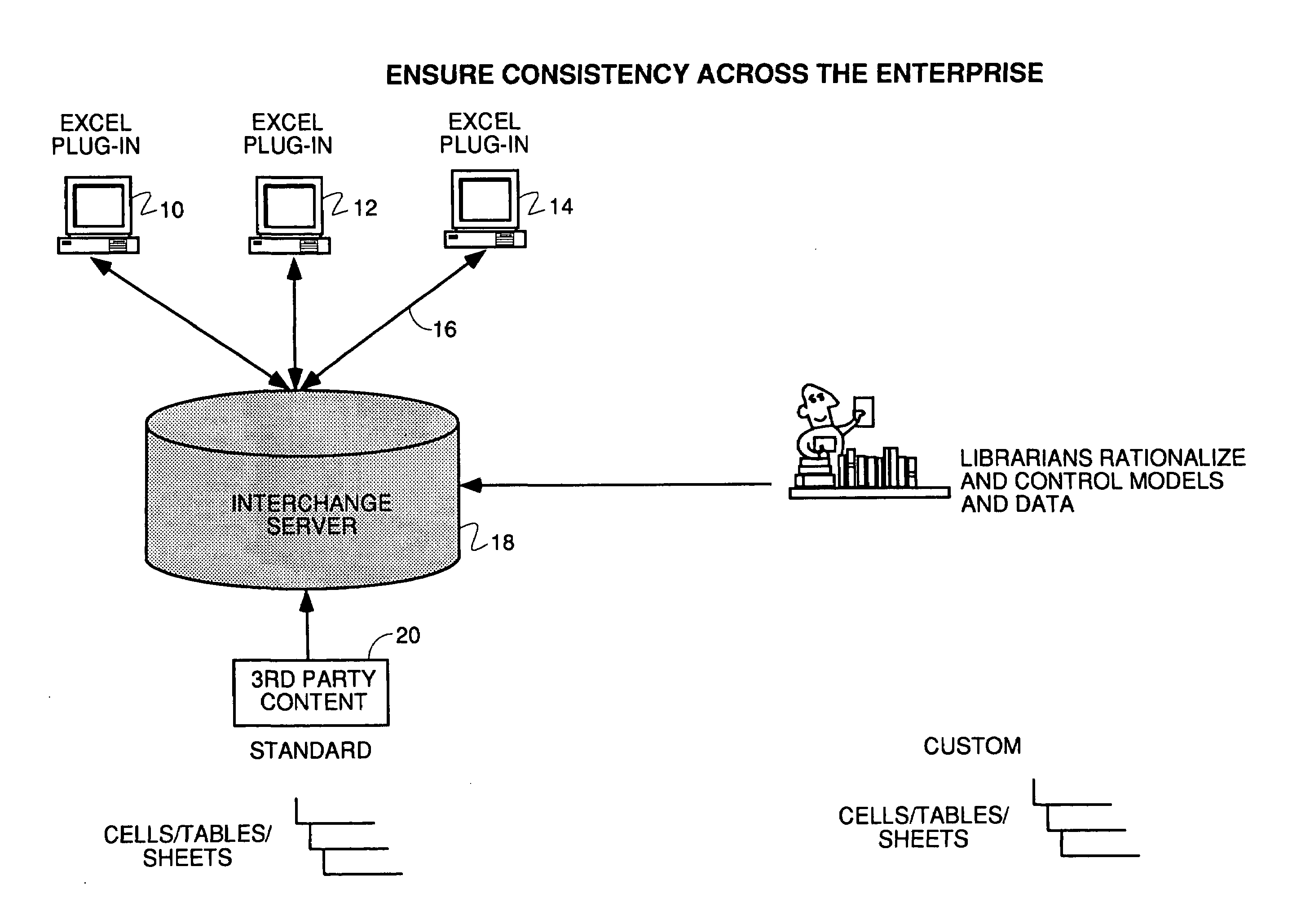
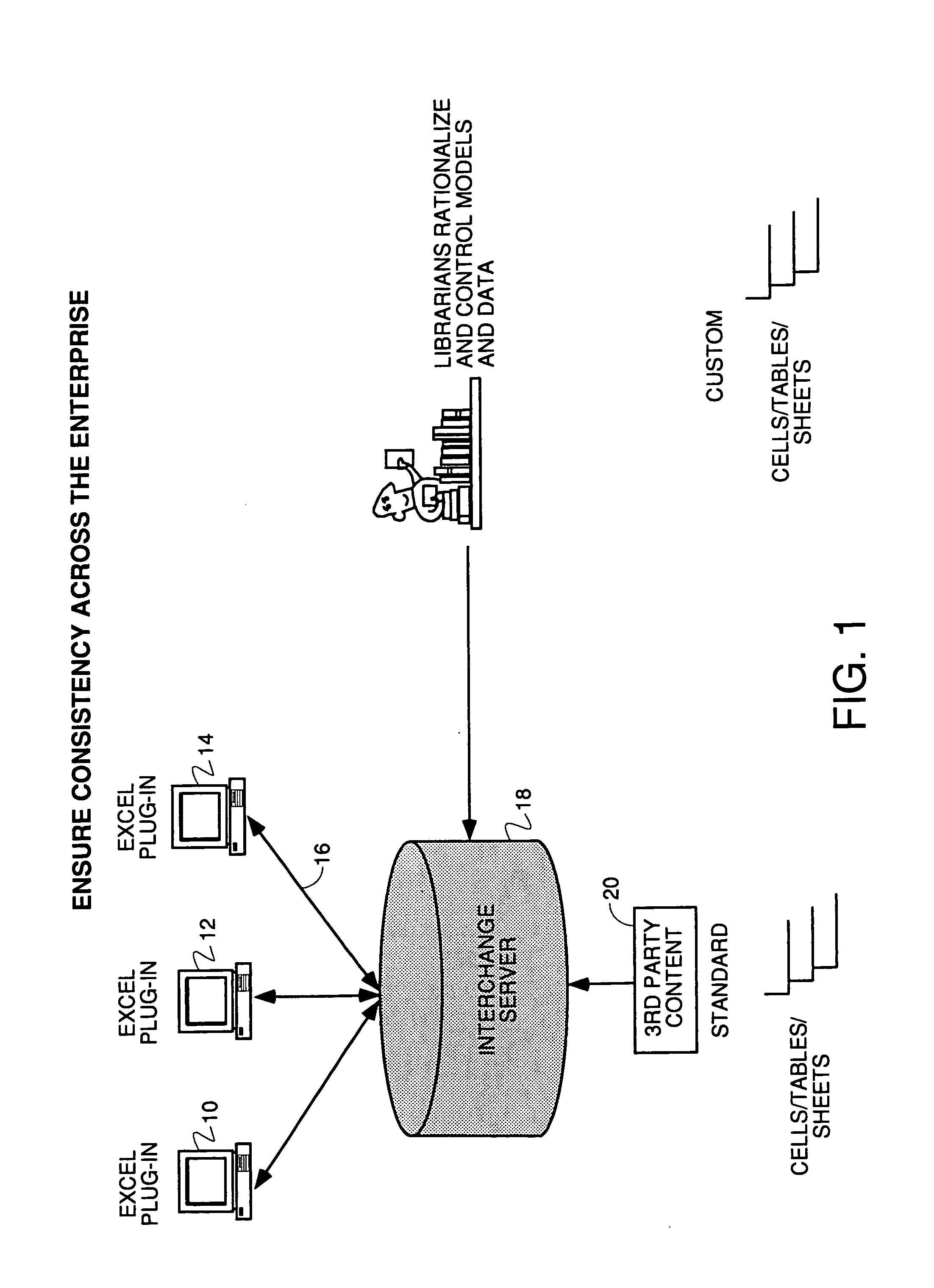
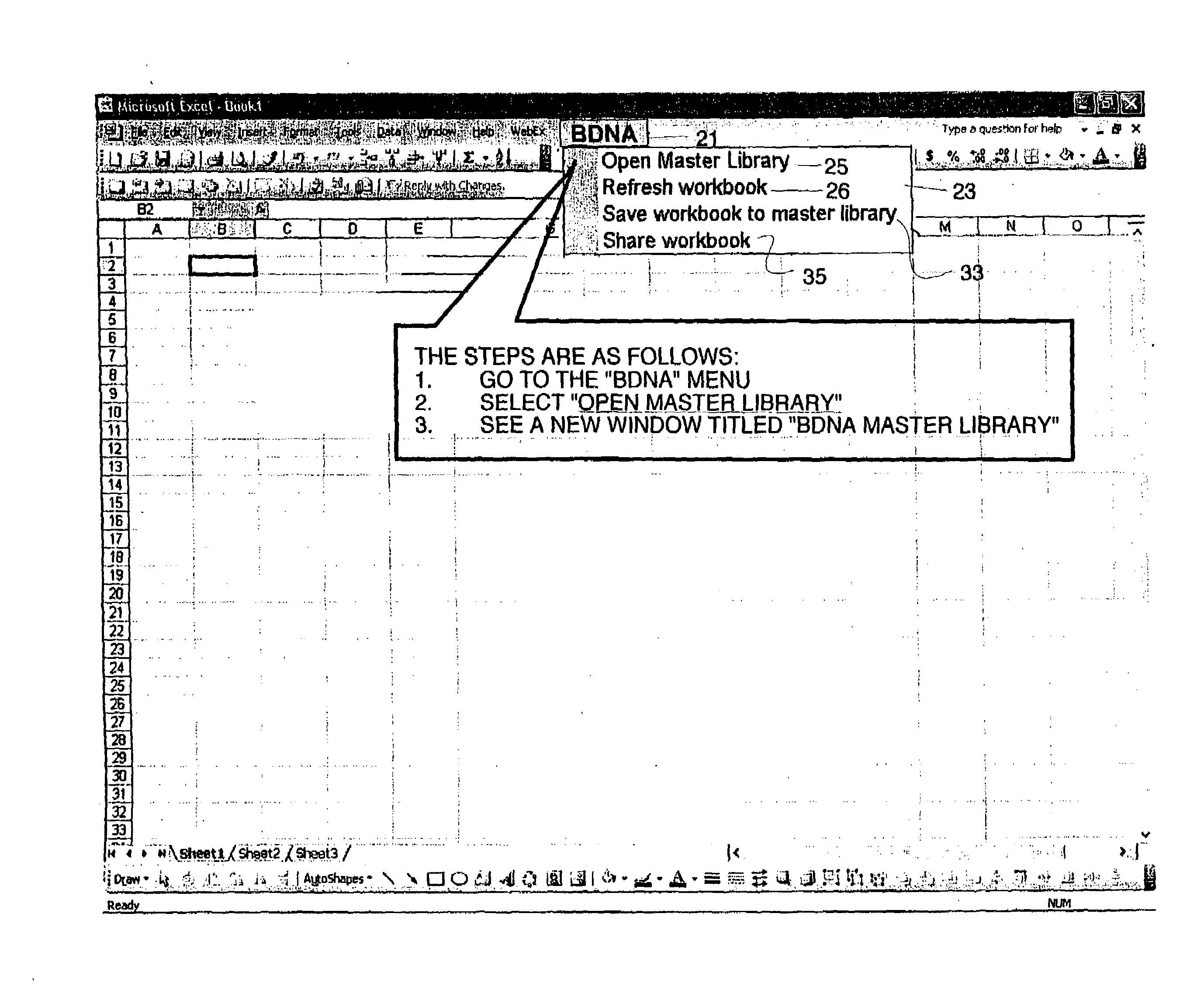
Excel spreadsheet parsing to share cells, formulas, tables, etc.
InactiveUS20070219956A1Improve abilitiesDigital data processing detailsText processingLevel of detailClient-side
Discloses a method and apparatus and user interface for parsing individual objects of a spreadsheet created on a client computer and sending the entire workbook, its binary and the objects for storage on a server computer in a master library. The master library can be opened, searched and objects downloaded. The downloaded object can have their metadata displayed, and the level of detail about each object that is downloaded can be controlled by the user. The user can designate objects for sharing in the master library with other spreadsheet users. Downloaded objects can be modified with the native tools of the spreadsheet application, typically Excel, and re-stored in the master library under a different name and with the person who changed the object listed in the metadata as the owner. Searches can controlled by user interface tools to designate object type to search, and search type can be by owner or functional area of the company. Users can enter their own metadata. Automatic naming of objects decouples objects from their original locations in the workbooks upon which they were created.
Owner:BONA AB
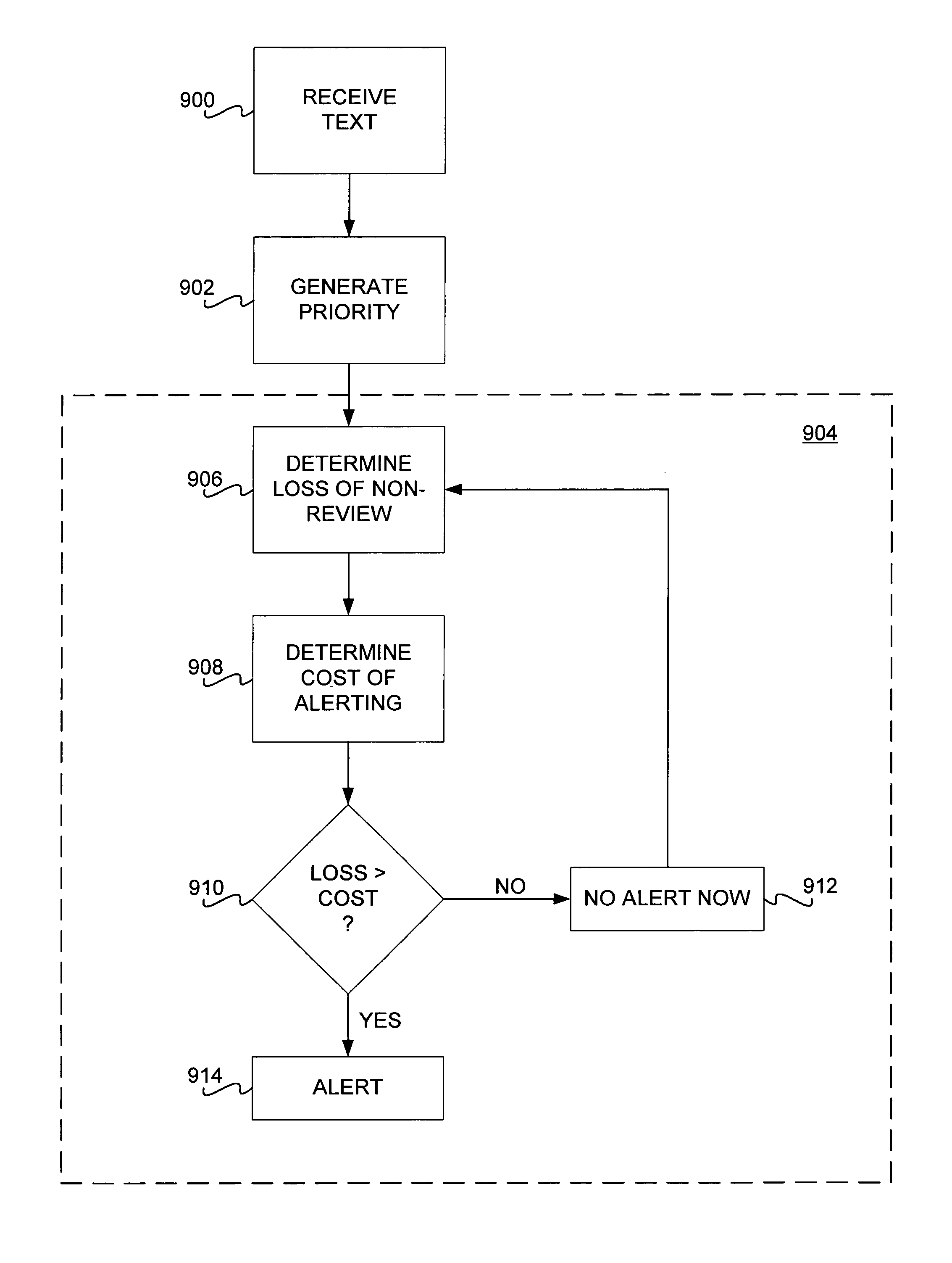
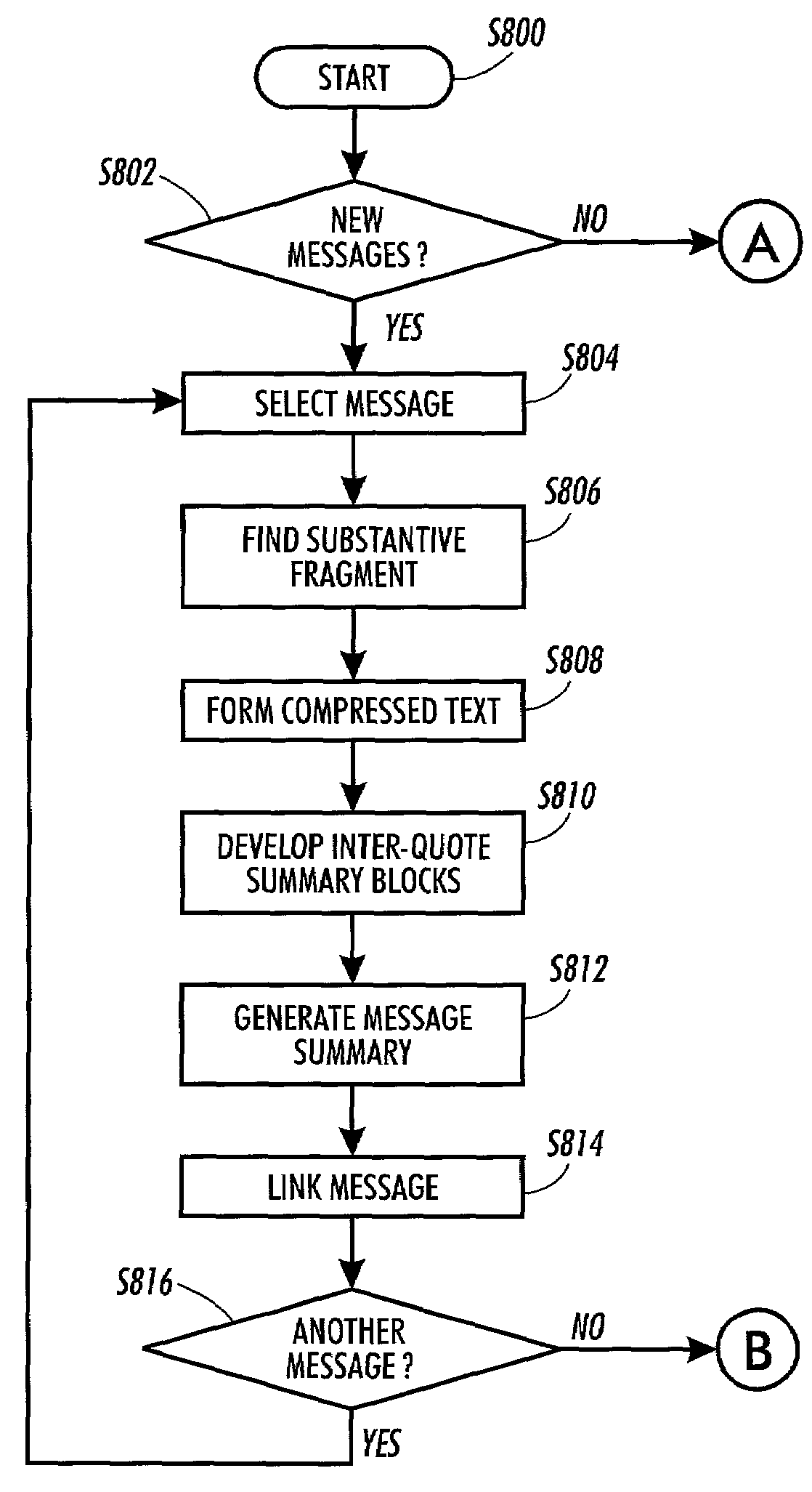
Methods for display, notification, and interaction with prioritized messages
InactiveUS7120865B1Digital computer detailsTransmissionLevel of detailSupport vector machine classifier
Prioritization of document, such as email messages, is disclosed. In one embodiment, a computer-implemented method first receives a document. The method generates a priority of the document, based on a document classifier such as a Bayesian classifier or a support-vector machine classifier. The method then outputs the priority. In one embodiment, the method includes alerting the user based on an expected loss of now-review of the document as compared to an expected cost of alerting the user of the document, at a current time. Several methods are reviewed for display and interaction that leverage the assignment of priorities to documents, including a means for guiding visual and auditory actions by priority of incoming messages. Other aspects of the machinery include a special viewer that allows users to scope a list of email sorted by priority so that it can include varying histories of time, to annotate a list of messages with color or icons based on the automatically assigned priority, to harness the priority to control the level of detail provided in a summarization of a document, and to use a priority threshold to invoke an interaction context that lasts for some period of time that can be dictated by the priority of the incoming message.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Telecommunication-based time-management system and method
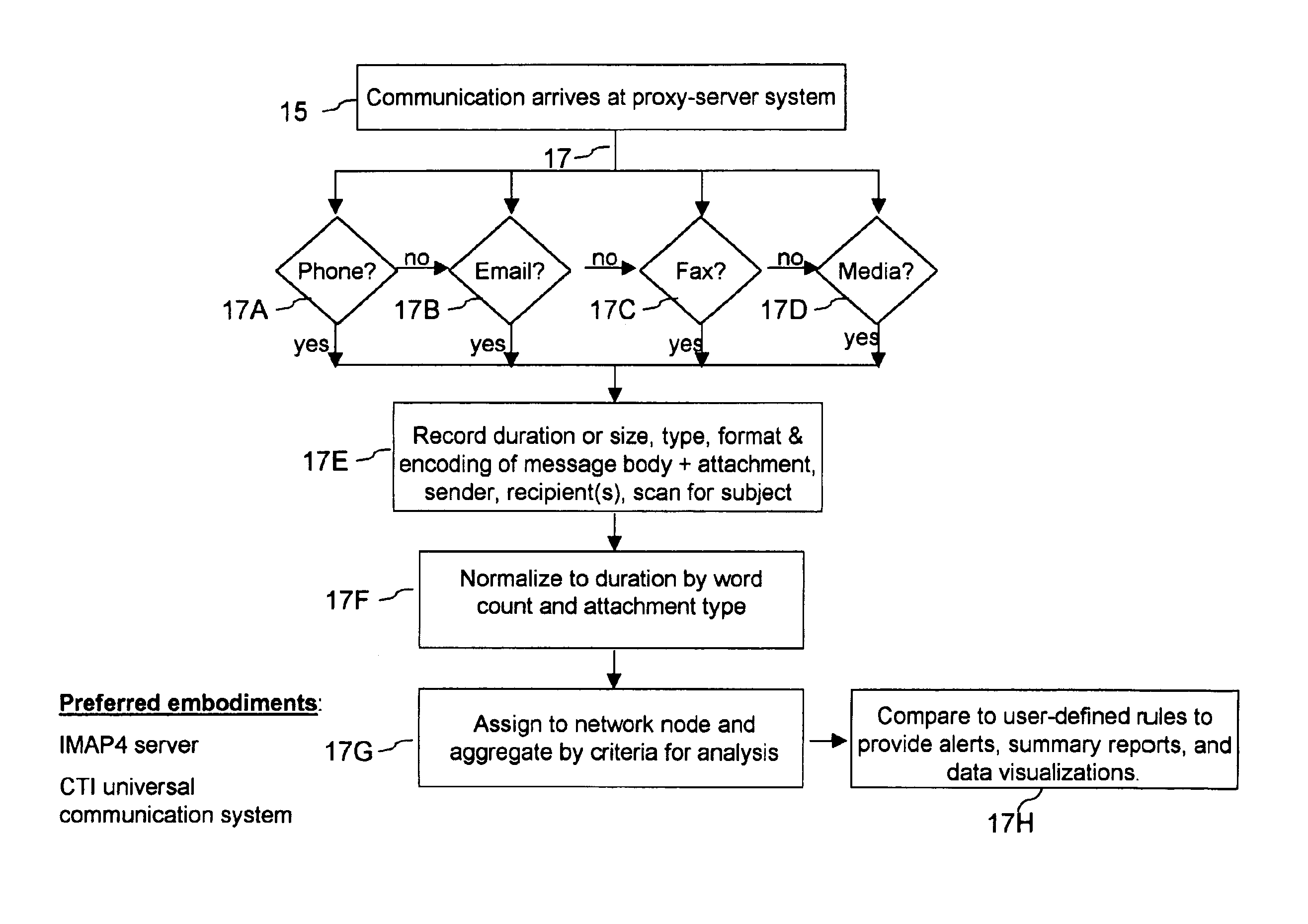
InactiveUS6895438B1Improve business processImprove organizational strategySpeech analysisTime-division multiplexNon real timeRelational database
A proxy-server system (15) connected preferably to a computer-telephone system (10) intercepts, processes, and analyzes as traffic-analysis results (68A-C) all forms of real- and non-real-time electronic communication passing over the network in the form of raw traffic data (61). The proxy-server system normalizes each communication into the measure of time needed by recipient(s) of the communication to understand the information contained therein. Once normalized, the data may be aggregated into summary reports (69A-C). As part of the analysis, the aggregated communication records are compared with user-defined rules to provide alerts if the individual or aggregated durations exceed boundaries set by the rules. In one embodiment, the summary reports may be integrated with general-ledger data (94) and other raw business data (74) via a relational database (72) to derive more accurate records of activity-based-costing information (76). Additionally, the data of the summary reports may be visualized in two- or three-dimensional representations of communication-flow patterns to illustrate in an intuitive and semantically scalable manner the desired level of detail for time and time-based expense consumed by the electronic interactions of an individual or organization.
Owner:PAUL ULRICH
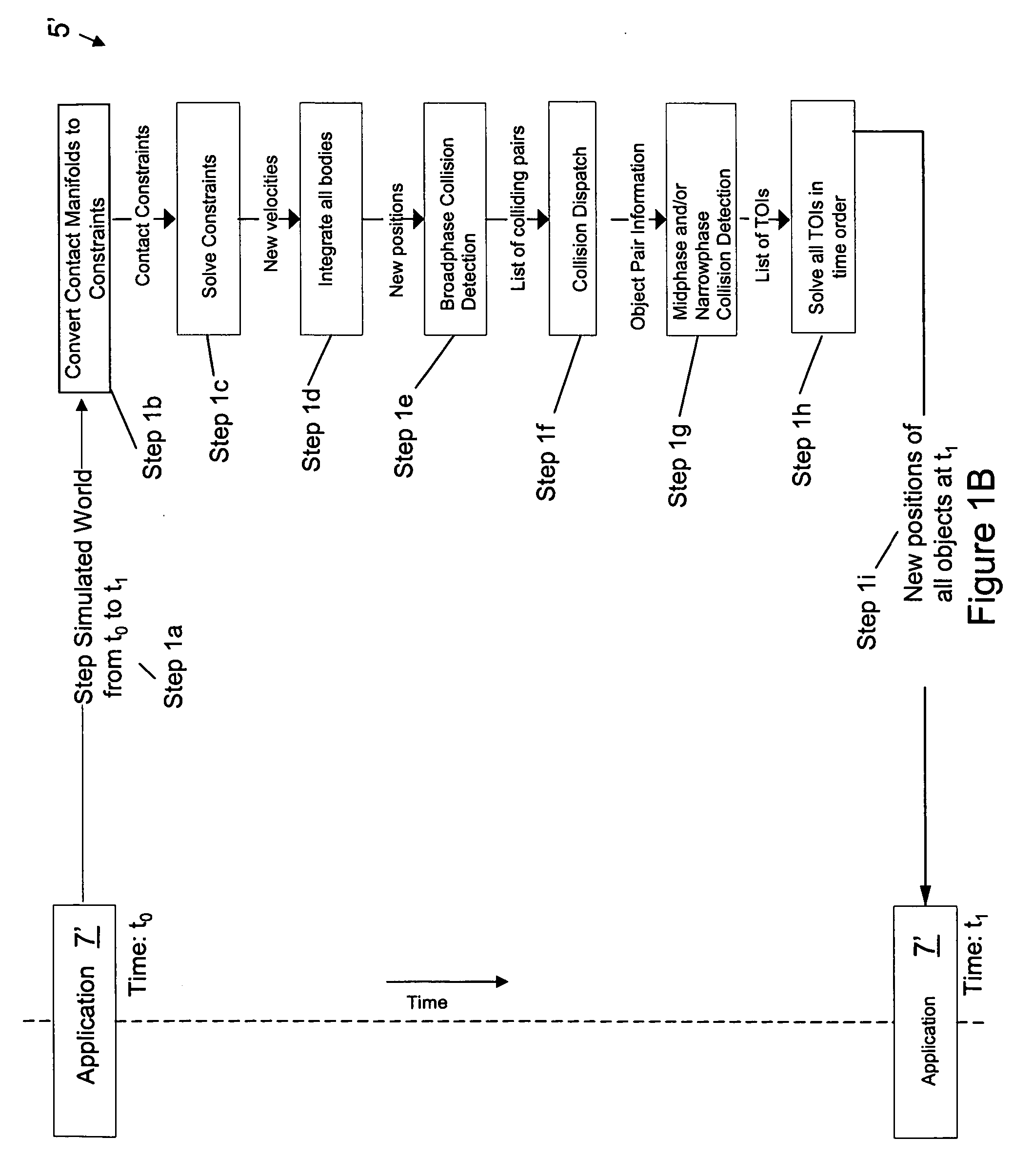
Physics simulation apparatus and method
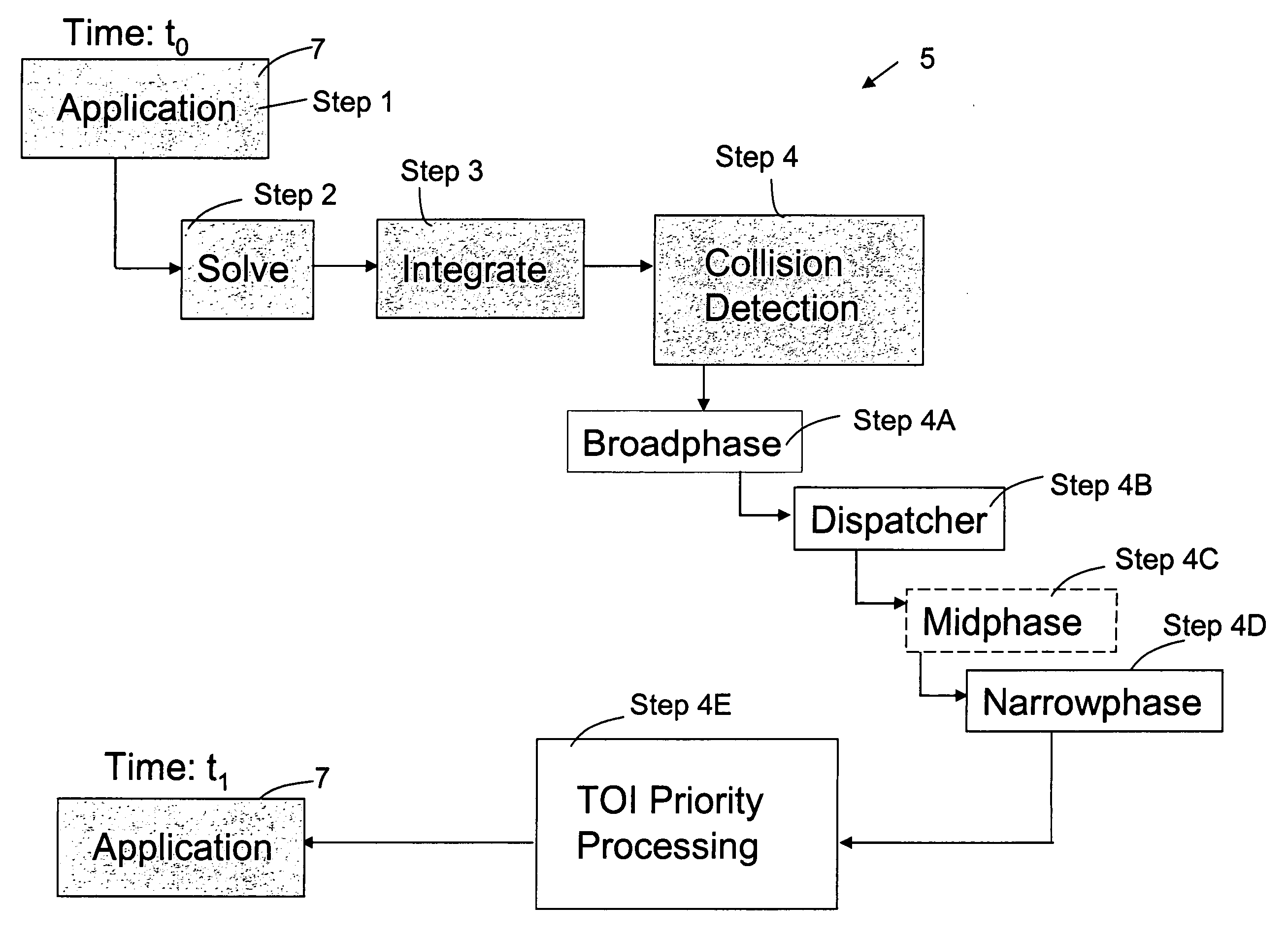
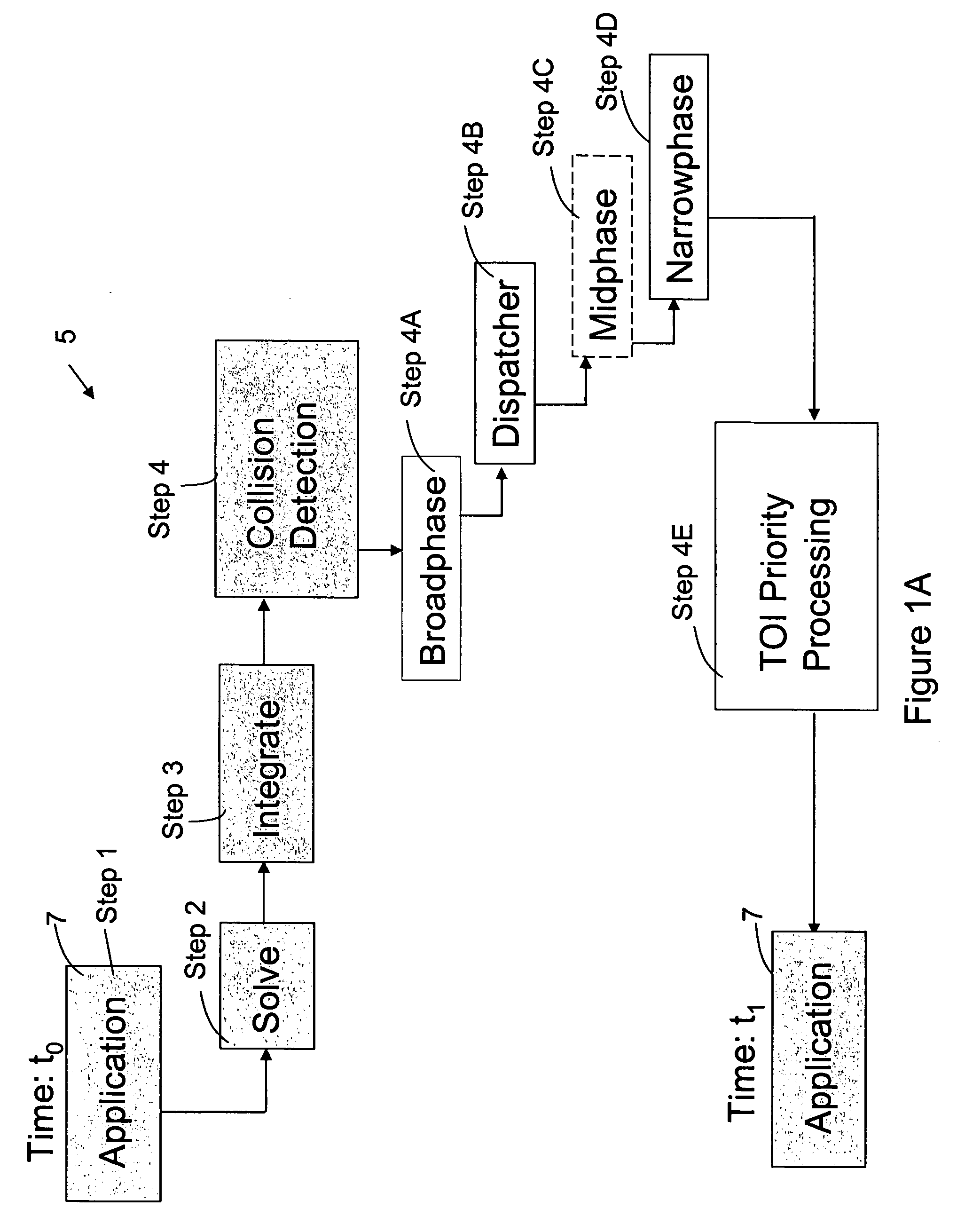
InactiveUS20060149516A1Improve the level ofImprove stabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationLevel of detailCollision response
A method and apparatus wherein complex physical interactions and collisions are modeled at a high level of detail while reducing the computational demands placed on the processing system. In one embodiment the method comprising the steps of defining a first object and a second object, each object adapted for colliding with the other object; assigning an interaction type for at least one of the first and second object in response to an object parameter; and selecting between a continuous simulation of a collision and a discrete simulation of the collision in response to the interaction type.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
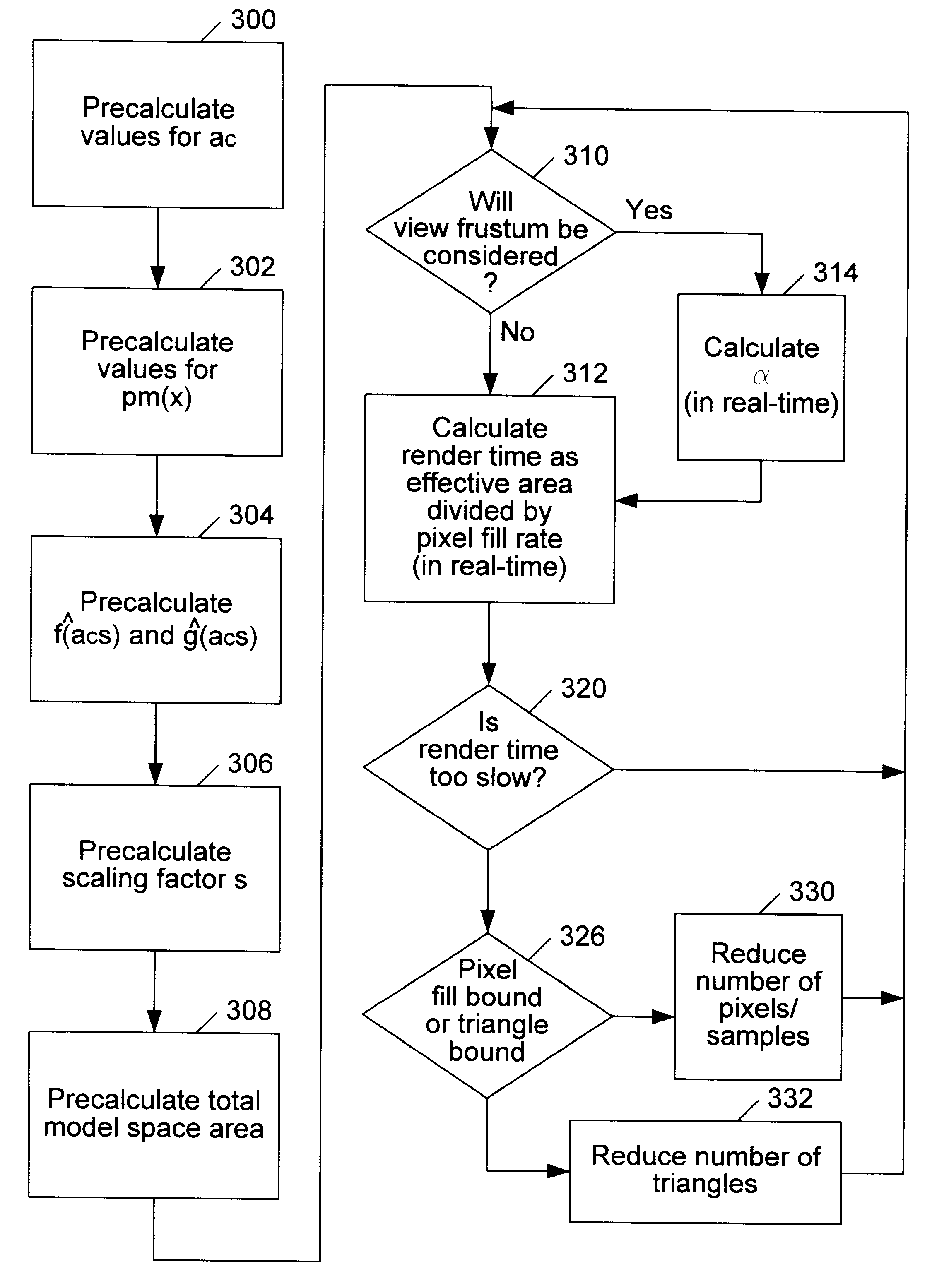
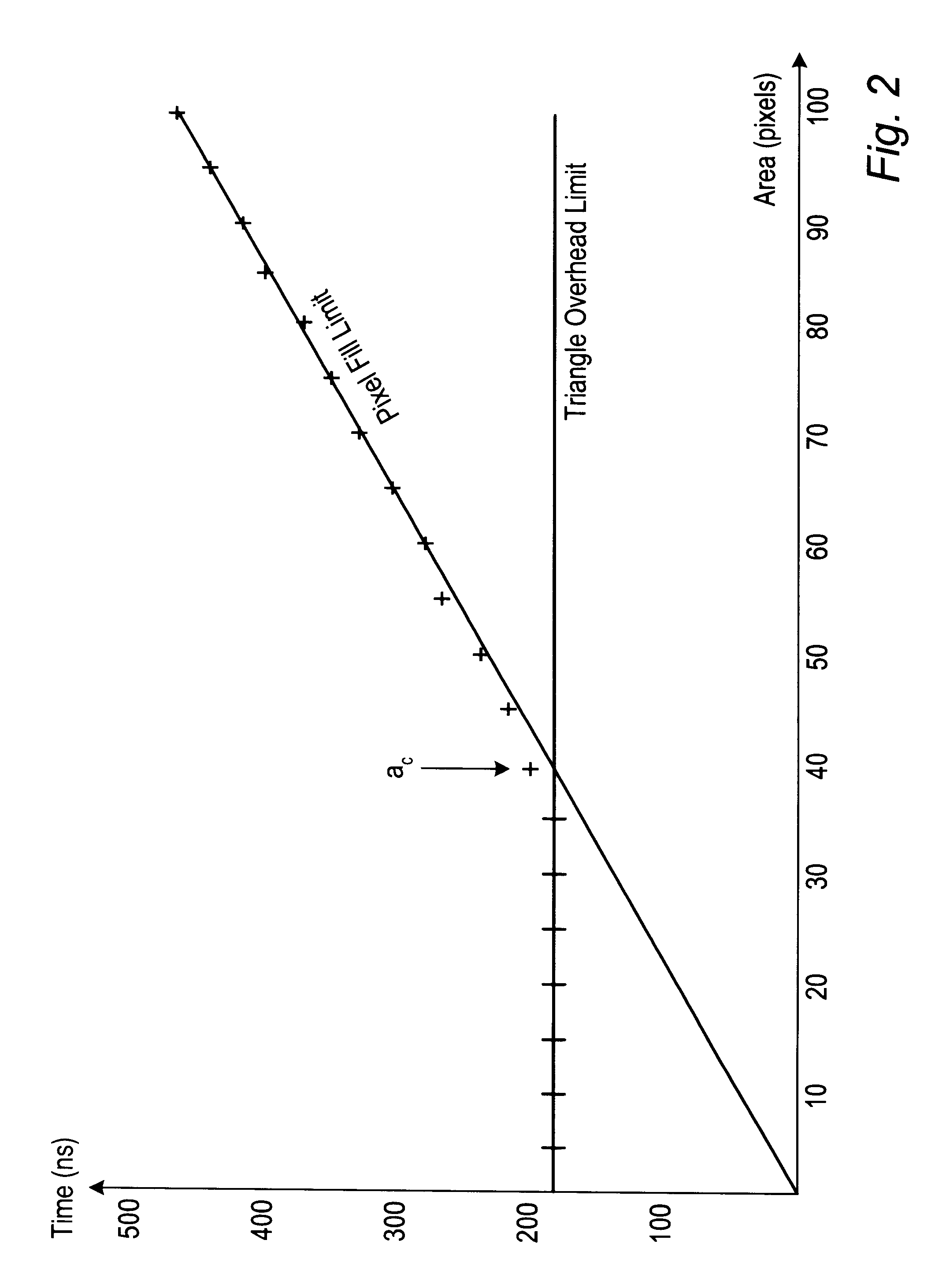
Estimating graphics system performance for polygons
InactiveUS6313838B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsComputational scienceGraphic system
A method for estimating rendering times for three-dimensional graphics objects and scenes is disclosed. The rendering times may be estimated in real-time, thus allowing a graphics system to alter rendering parameters (such as level of detail and number of samples per pixel) to maintain a predetermined minimum frame rate. Part of the estimation may be performed offline to reduce the time required to perform the final estimation. The method may also detect whether the objects being rendered are pixel fill limited or polygon overhead limited. This information may allow the graphics system to make more intelligent choices as to which rendering parameters should be changed to achieve the desired minimum frame rate. A software program configured to efficiently estimate rendering times is also disclosed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
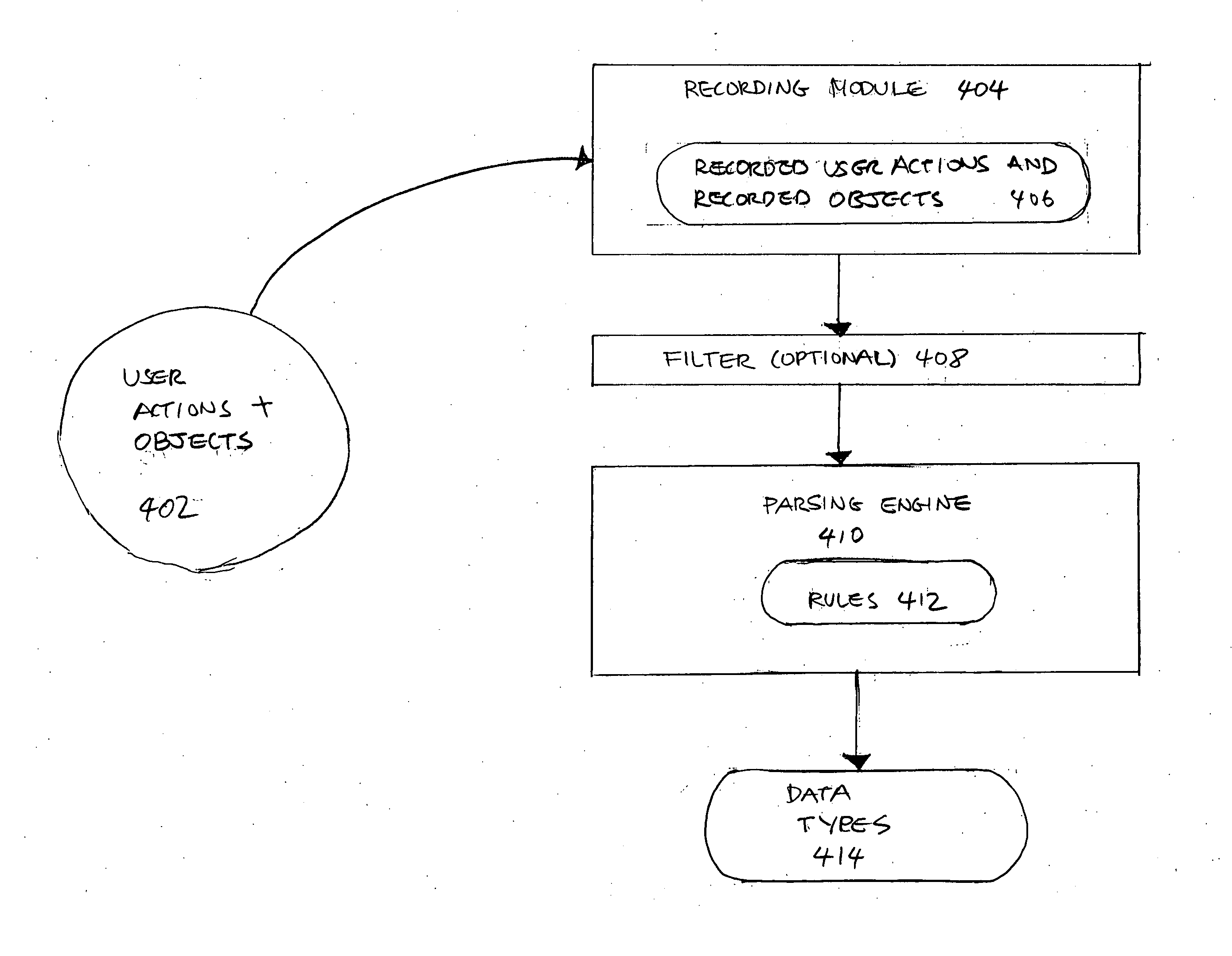
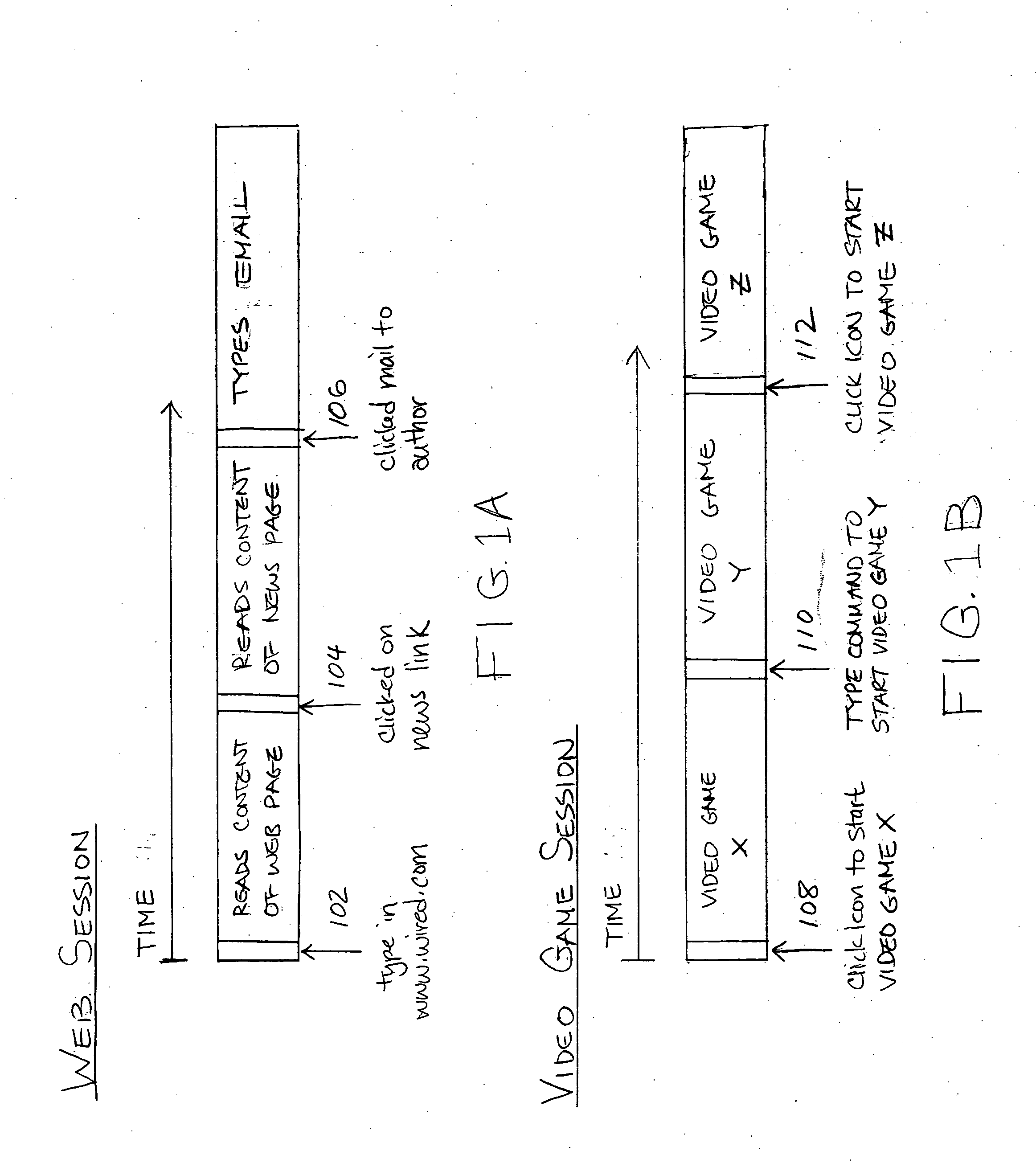
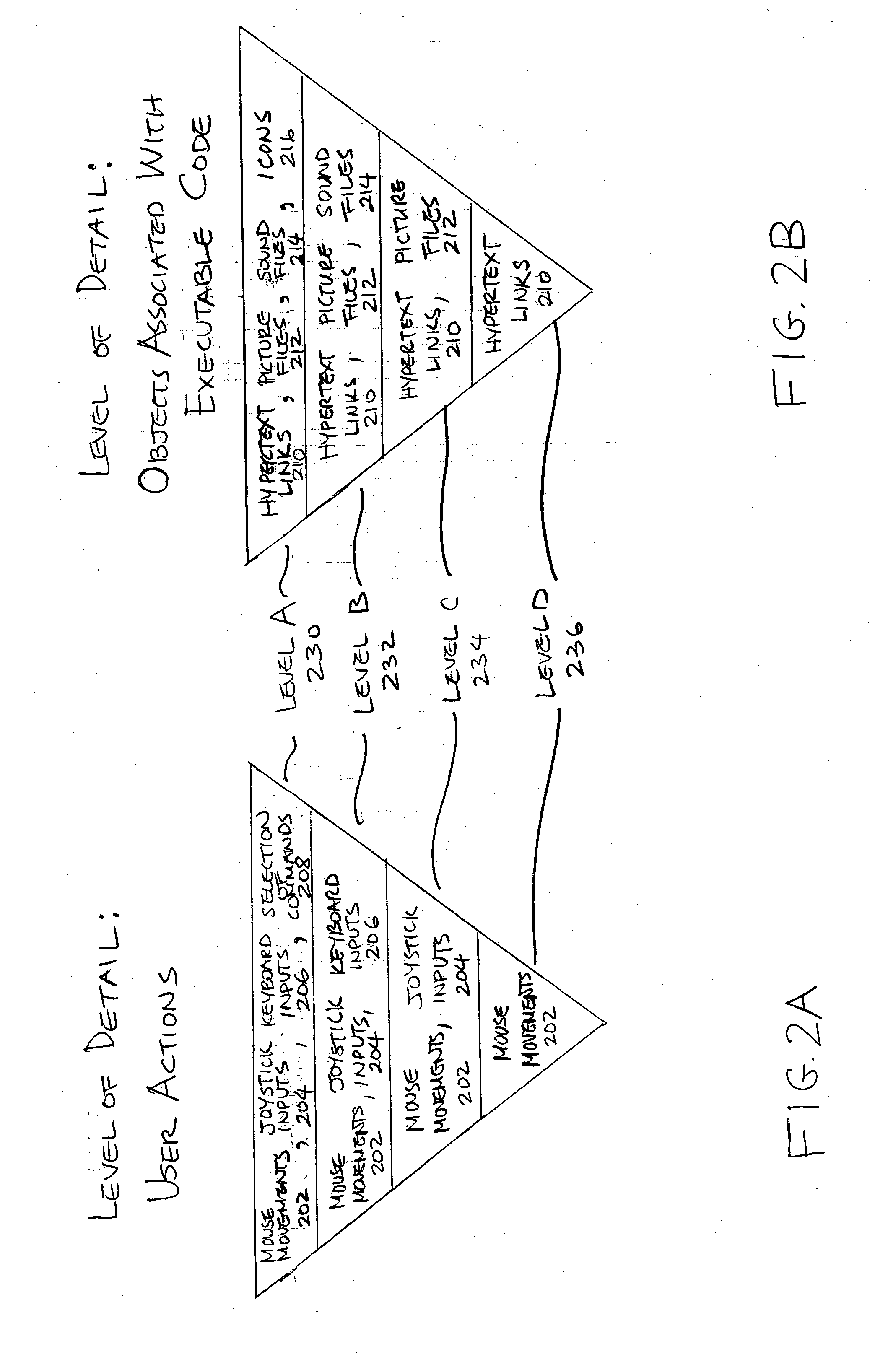
Methods and systems for recording user actions in computer programs
A method for recording a sequence of user actions made when interfacing with objects associated with an executable code is provided. In this method, a selection of a level of detail to record when user actions enable interfacing with the objects associated with the executable code is enabled. Subsequently, the sequence of user actions is recorded. The recorded sequence of user actions is defined by the selected level of detail. Thereafter, the recorded sequence of user actions is parsed by applying rules that enable the generation of a defined number of data types. The data types are capable of being utilized by an application that is designed to generate information that is related to one or more of the data types.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Architecture and engine for time line based visualization of data
InactiveUS7788592B2Facilitate navigating and managingUser may experienceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsLevel of detailThumbnail
The subject invention provides a unique system and method that facilitates management and navigation of various data objects by making use of a unique time-line based navigation tool. In particular, objects can organized into a plurality of bands based on their respective subject matter. Each band can be created to designate a particular topic. Objects are organized within the appropriate bands based in part on a time parameter such as a time or date that the object was created, for example. The navigation tool allows a user to navigate or browse through the bands and objects according to a desired time parameter or range of time. Zooming and other browsing options are available to the user to view objects of interest at varying levels of detail. The objects are represented as ASCII thumbnails that are operational. Thus, the content of any object can be modified directly via the thumbnail.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for identifying network devices on a storage network
InactiveUS6845395B1Unauthorized memory use protectionDigital data protectionGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method and system for display of electronic mail
InactiveUS7003724B2Maintaining awarenessDigital computer detailsData switching networksLevel of detailMinutiae
The invention provides a sequence of increasingly detailed presentation levels to assist a user in deciding whether a thread is of interest. If so, the text of the threaded messages is presented at a level of detail corresponding to the user's level of indicated interest. In particular, the invention provides a method comprising creating a message collection viewing cascade including a plurality of viewing levels for presenting one or more message threads and abbreviated forms of one or more messages, abbreviating at least one of the messages using one of a plurality of abbreviation techniques, and formatting each abbreviated message to be displayed at one of the plurality of viewing levels in the message collection viewing cascade. Each abbreviation technique specifies a manner in which the messages can be abbreviated, and each viewing level in the collection viewing cascade offers a different degree of detail for presenting the abbreviated forms of the messages.
Owner:XEROX CORP
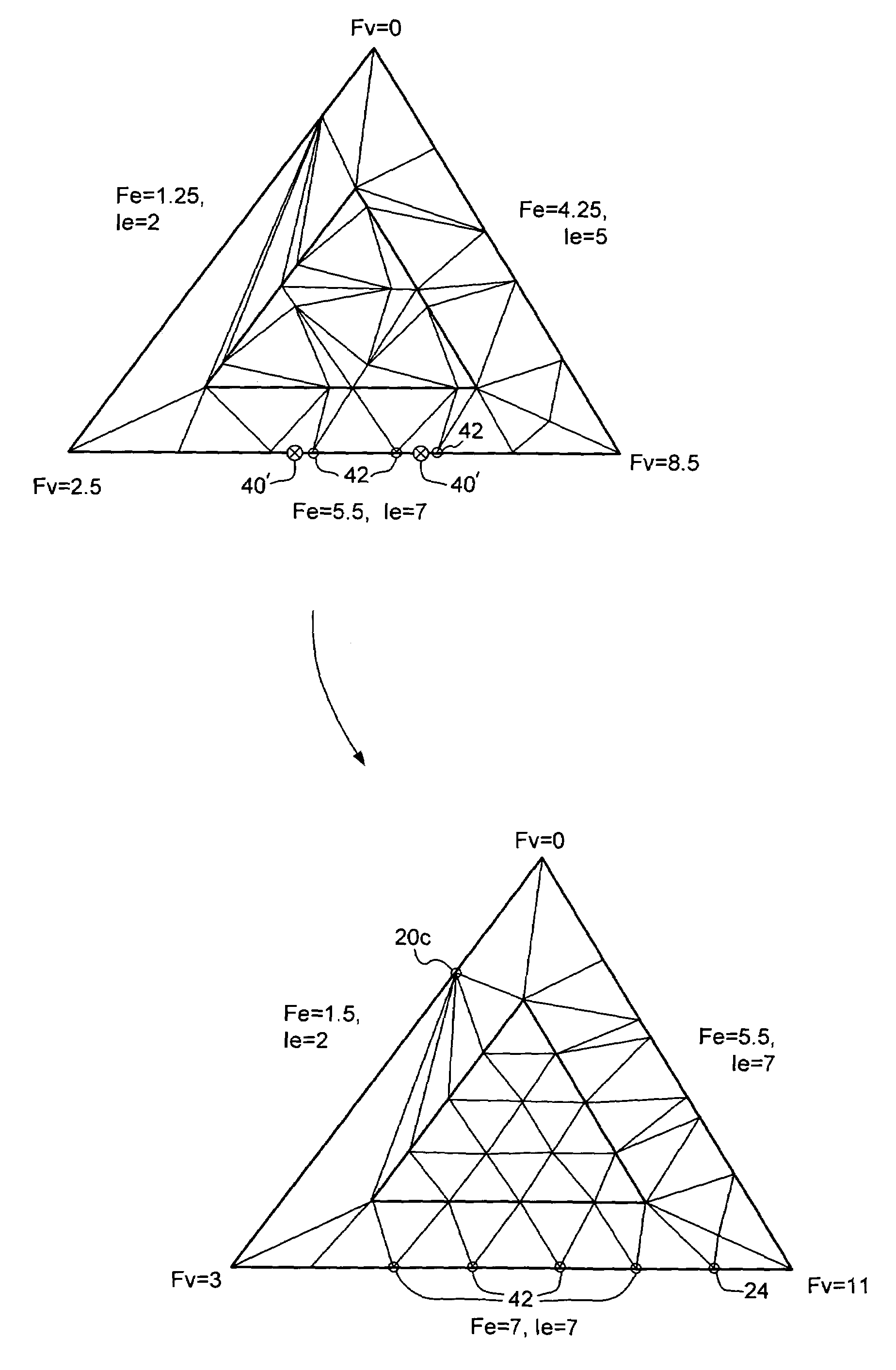
Dynamic tessellation of a base mesh
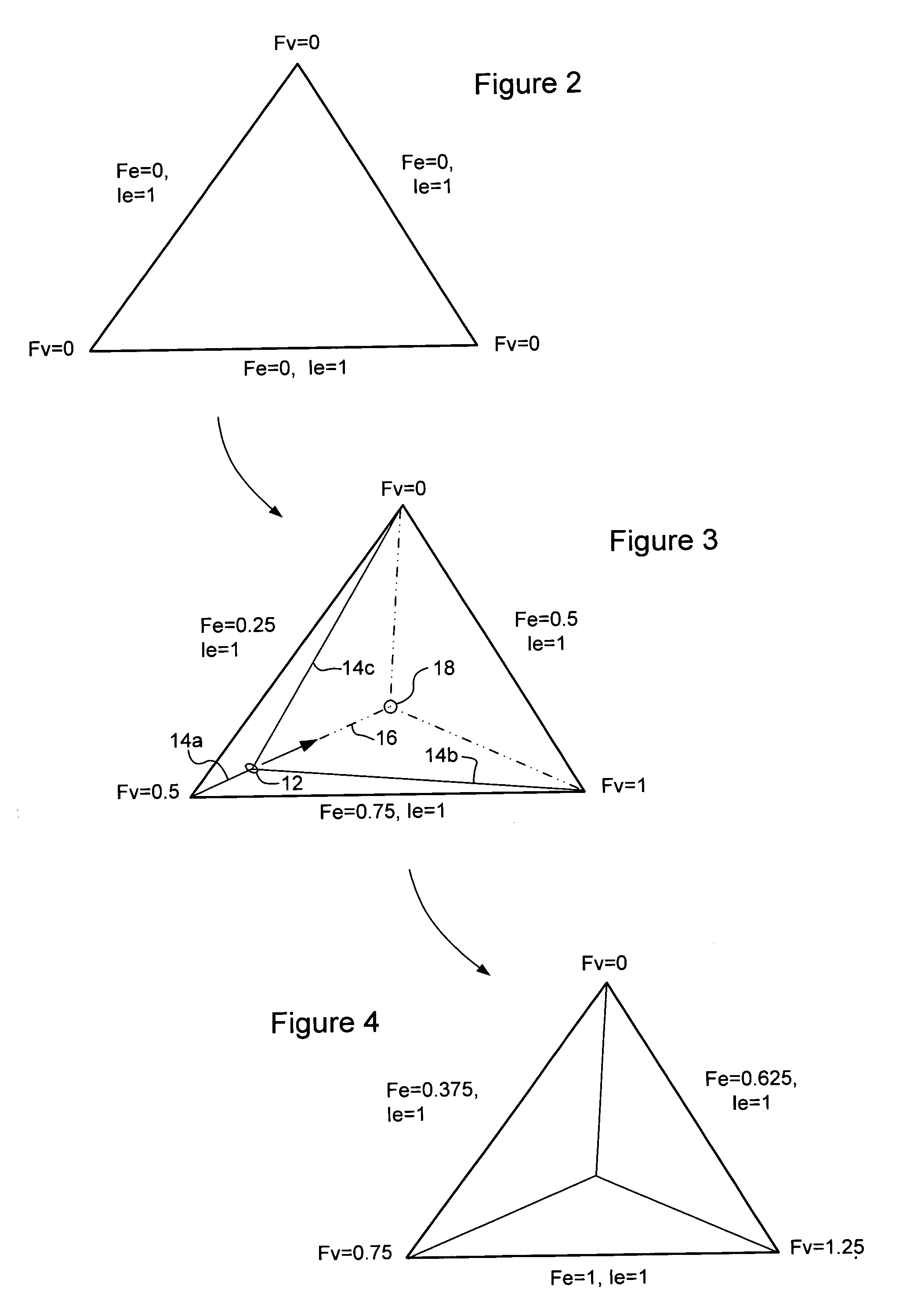
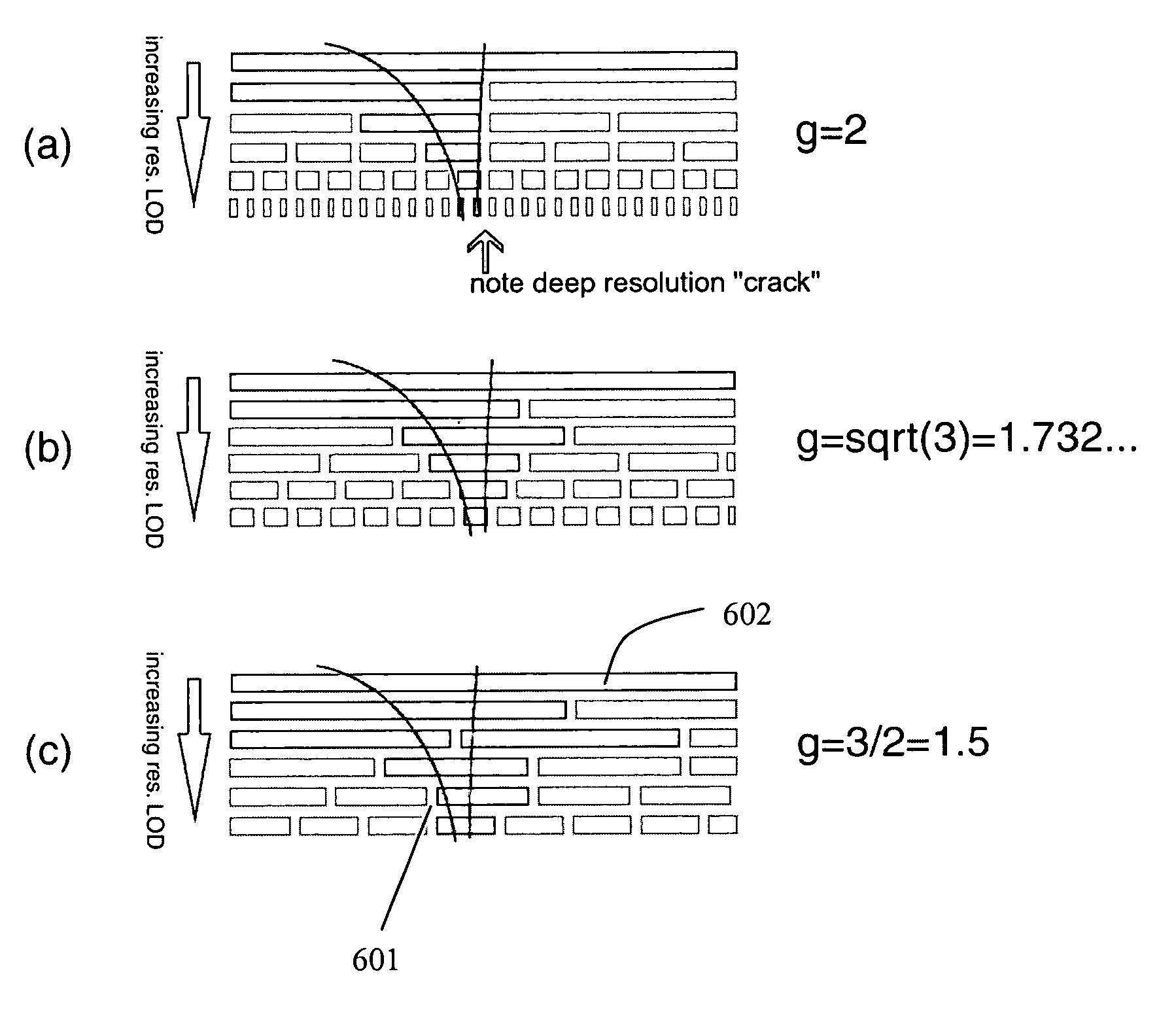
InactiveUS6940505B1Avoid crackingEfficient of processing resourceDrawing from basic elements3D-image renderingComputational scienceLevel of detail
A primitive of a base mesh having at least three base vertices is dynamically tessellated to enable smooth changes in detail of an image rendered on a screen. A respective floating point vertex tessellation value (Fv) is assigned to each base vertex of the base mesh, based on a desired level of detail in the rendered image. For each edge of the primitive: a respective floating point edge tessellation rate (Fe) of the edge is calculated using the respective vertex tessellation values (Fv) of the base vertices terminating the edge. A position of at least one child vertex of the primitive is then calculated using the respective calculated edge tessellation rate (Fe). By this means, child vertices of the primitive can be generated coincident with a parent vertex, and smoothly migrate in response to changing vertex tessellation values of the base vertices of the primitive.
Owner:MATROX
Method for requesting and viewing a zoomed area of detail from an image attachment on a mobile communication device
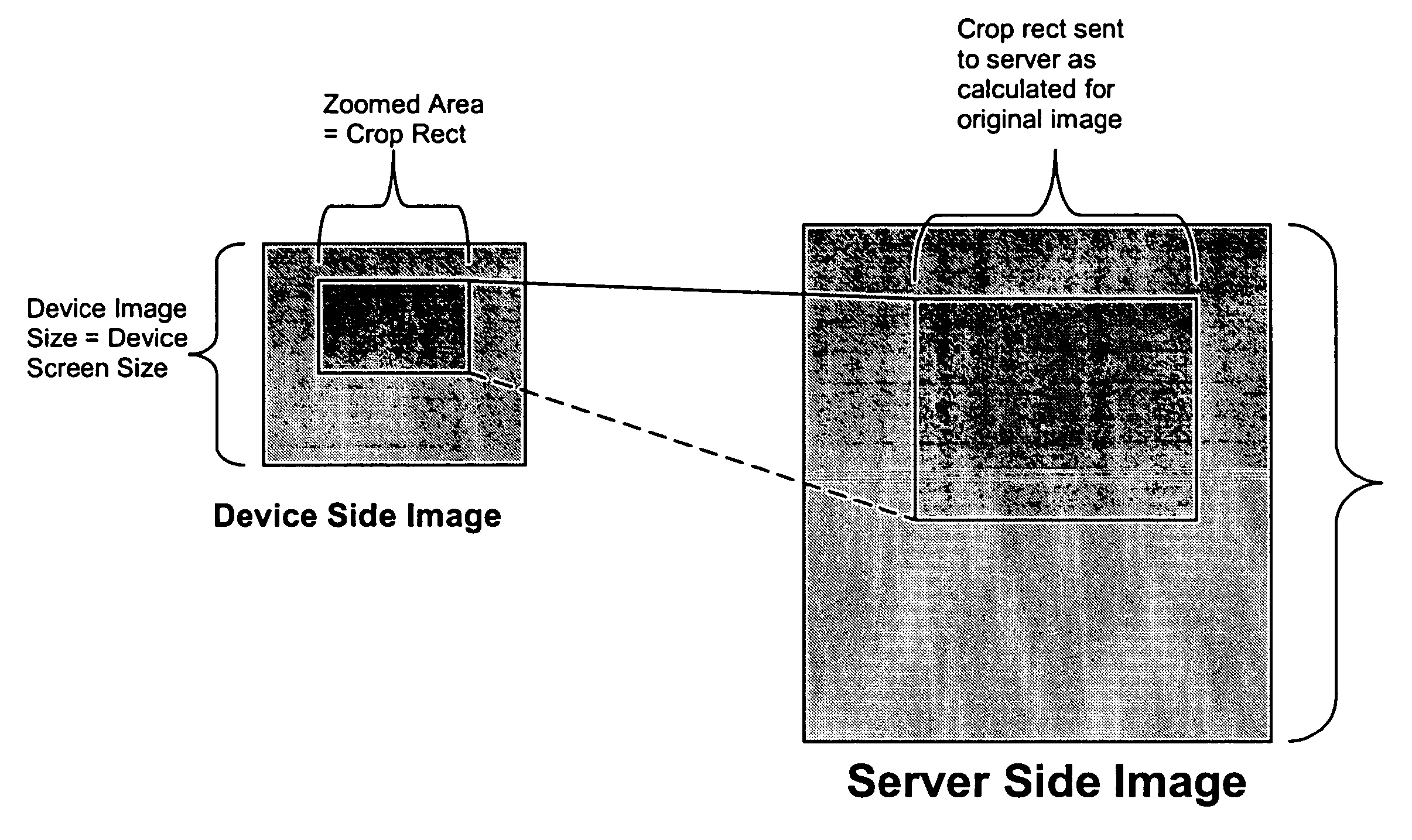
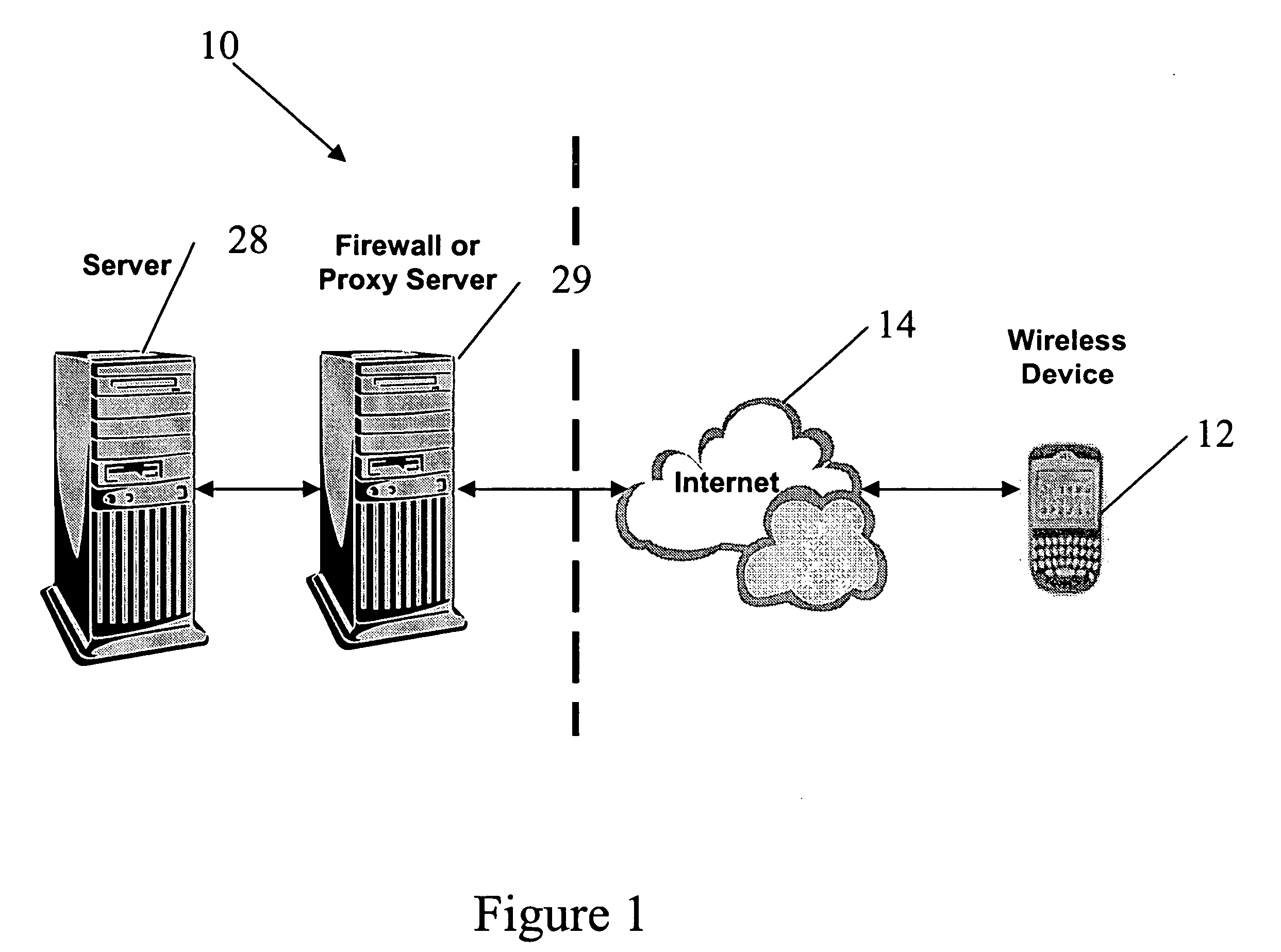
ActiveUS20060055693A1Reduce data volumeReduce resolutionGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsLevel of detailResponse delay
A process is set forth for viewing an enlarged area of an image. The image is stored on a server and re-sized for viewing on a mobile communication device based on screen size and colour display capabilities of the device. The image is enlarged within the server by modifying binary raw data of the original image based on crop rectangle coordinates entered at the mobile communication device. The process allows users to quickly retrieve any relevant part of a large image attachment that has been resized by the server. This minimizes bandwidth usage, device memory / CPU consumption, and request / response latency while still allowing the user to view an image area in its original level of detail.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Excel spreadsheet parsing to share cells, formulas, tables or entire spreadsheets across an enterprise with other users
InactiveUS20070220415A1Improve abilitiesLarge spreadsheetText processingDigital computer detailsElectronic formLevel of detail
Discloses a method and apparatus and user interface for parsing individual objects of a spreadsheet created on a client computer and sending the entire workbook, its binary and the objects for storage on a server computer in a master library. The master library can be opened, searched and objects downloaded. The downloaded object can have their metadata displayed, and the level of detail about each object that is downloaded can be controlled by the user. The user can designate objects for sharing in the master library with other spreadsheet users. Downloaded objects can be modified with the native tools of the spreadsheet application, typically Excel, and re-stored in the master library under a different name and with the person who changed the object listed in the metadata as the owner. Searches can controlled by user interface tools to designate object type to search, and search type can be by owner or functional area of the company. Users can enter their own metadata. Automatic naming of objects decouples objects from their original locations in the workbooks upon which they were created.
Owner:BNDENA
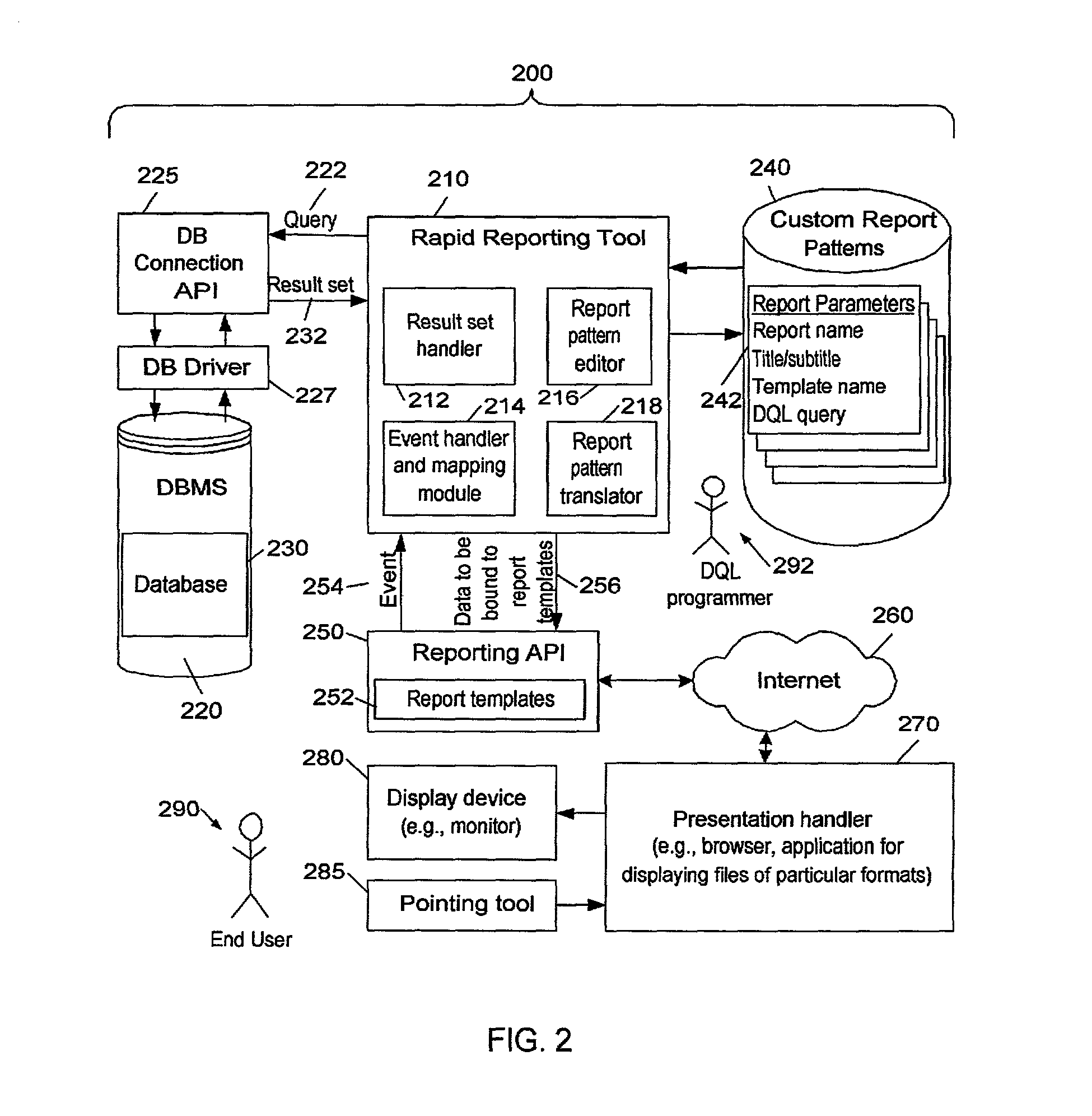
Relational database drill-down convention and reporting tool
InactiveUS6993533B1Avoid viewingEfficient implementationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPie chartDrill down
A system generates linked sets of drill-down-enabled reports of increasing levels of detail from one or more databases. Linking relationships between reports are defined using the query language of the databases. Result sets are obtained that includes (1) the sought-after data, and (2) metadata that identifies drill-down reports to be generated if related report elements are selected. When the query is executed, the system passes the sought-after data to a reporting application programming interface, which generates a report (e.g., a pie chart, 3-D bar chart, cross-tabbed table). If an end-user selects one of the report elements (e.g., a bar on the chart), the system maps the reported event to the associated data of the result set. If the associated data has corresponding meta-data containing a drill-down directive, the system then generates the report identified by the drill-down directive.
Owner:BIF TECH CORP
System and method for exact rendering in a zooming user interface
InactiveUS7075535B2Avoid excessive computationMinimize imperfectionGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsLevel of detailZoom
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for optimizing keyframe and blob retrieval and storage
A method and apparatus for forming a visual index of scenes in a video image which has been or is being recorded in a computer readable memory. A selected number of keyframes are derived from the recorded image, each being representative of a respective scene therein. The keyframes are then ordered into a selected number of levels of detail of the scenes represented thereby, each level including a predetermined number of keyframes, each subsequent level including keyframes of greater detail than those in a preceding level. A header file is then formed which is descriptive of the ordered set of keyframes, and the header file is stored together with the ordered set of keyframes in the computer readable memory. A user can thereby identify and obtain optimized retrieval in accordance with his preferences of particular segments of the video image from a relatively slow memory device. The method and apparatus are equally applicable to formation of an indexed order of binary large objects ("blobs") in a set of multimedia documents in accordance with a user's preferences.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
System and method for asynchronous continuous-level-of-detail texture mapping for large-scale terrain rendering
InactiveUS20070171234A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsLevel of detailMulti resolution
A multi-resolution texture mapping system suitable for large scale terrain rendering using commodity graphics processing units (GPU). The GPU vertex and fragment shaders are used to implement the clip-mapping functionality. The terrain texture is represented by a combination of a mip-map and a multi-level clip-map having independent origins and off-set values. The independent clip-map levels may be independently updated. The offset values allow the origins to be associated with a reference point in a scene to be rendered. The desired clip-map level to be used to render a particular fragment may be determined using the base 2 logarithm of the maximum screen-space derivative of the source texture required by the terrain geometry to be drawn. If the desired clip-map level is non-integer and lies between two clip-map levels, appropriate texel data is created by interpolating between the bounding clip-map levels. This interpolation allows a multi-resolution texture mapping to be displayed.
Owner:D& S CONSULTANTS
File management system employing time line based representation of data
ActiveUS20060155757A1Easy to watchFacilitate navigating and managingData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalLevel of detailThumbnail
The subject invention provides a unique system and method that facilitates management and navigation of various data objects by making use of a unique time-line based navigation tool. In particular, objects can organized into a plurality of bands based on their respective subject matter. Each band can be created to designate a particular topic. Objects are organized within the appropriate bands based in part on a time parameter such as a time or date that the object was created, for example. The navigation tool allows a user to navigate or browse through the bands and objects according to a desired time parameter or range of time. Zooming and other browsing options are available to the user to view objects of interest at varying levels of detail. The objects are represented as ASCII thumbnails that are operational. Thus, the content of any object can be modified directly via the thumbnail.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
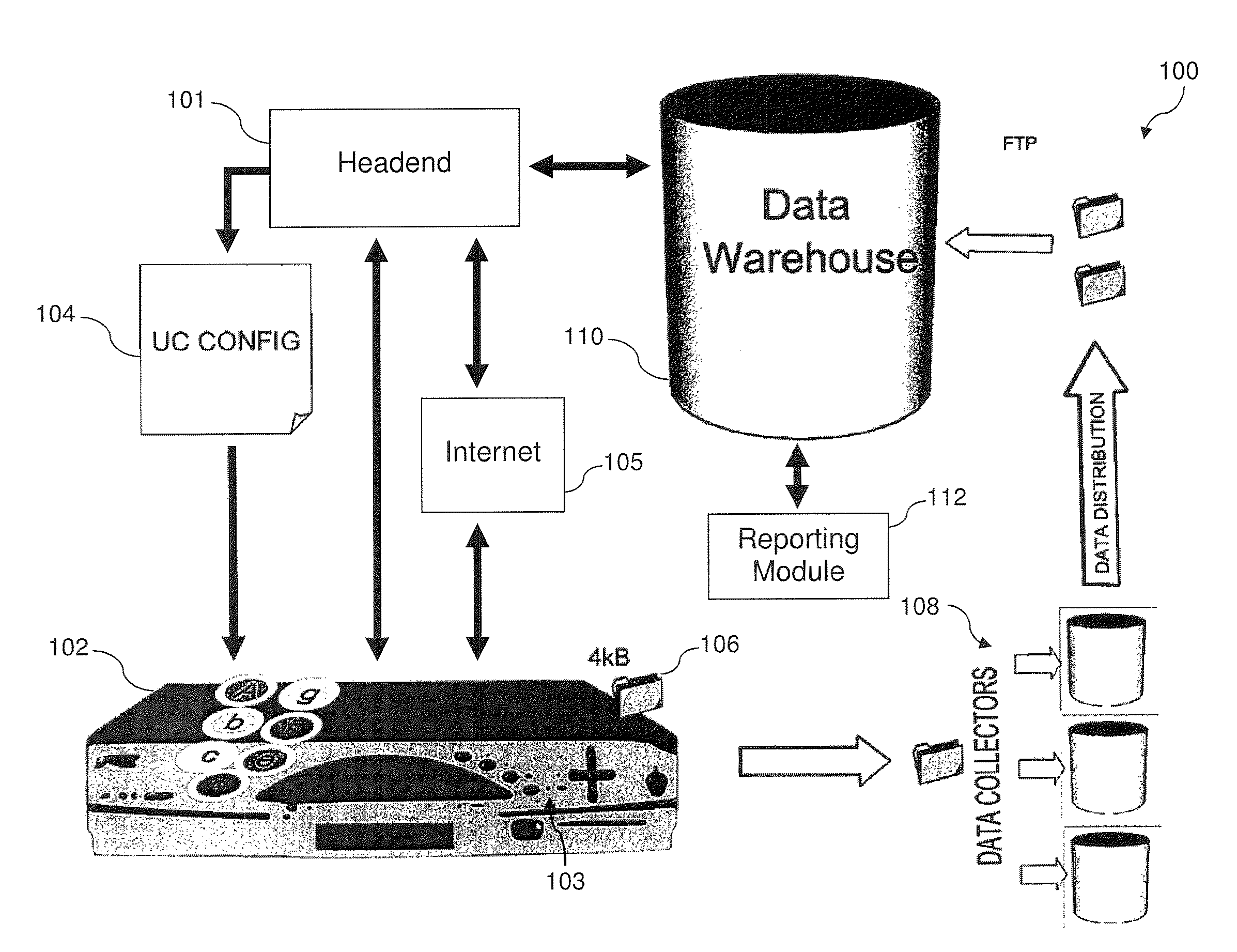
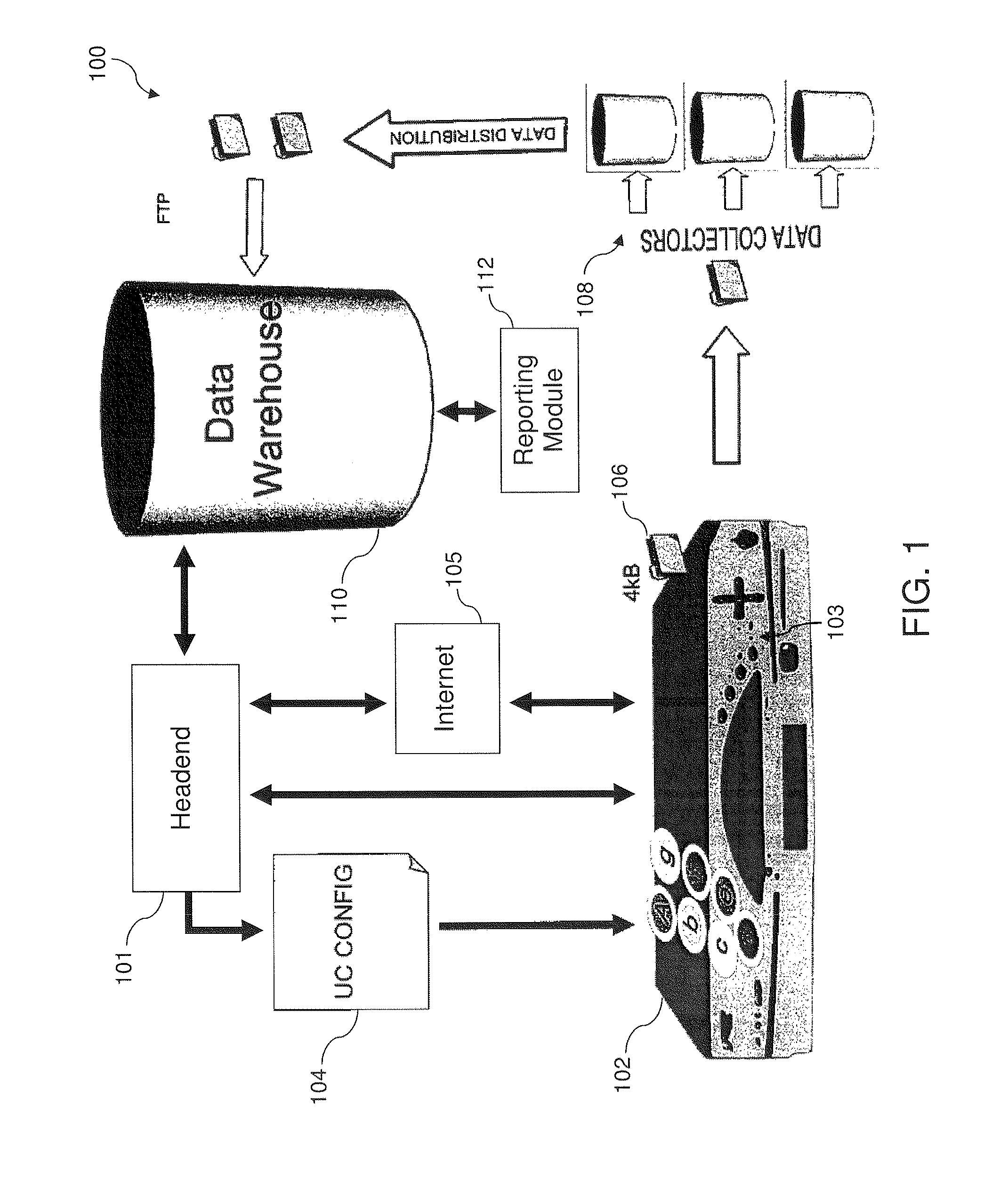
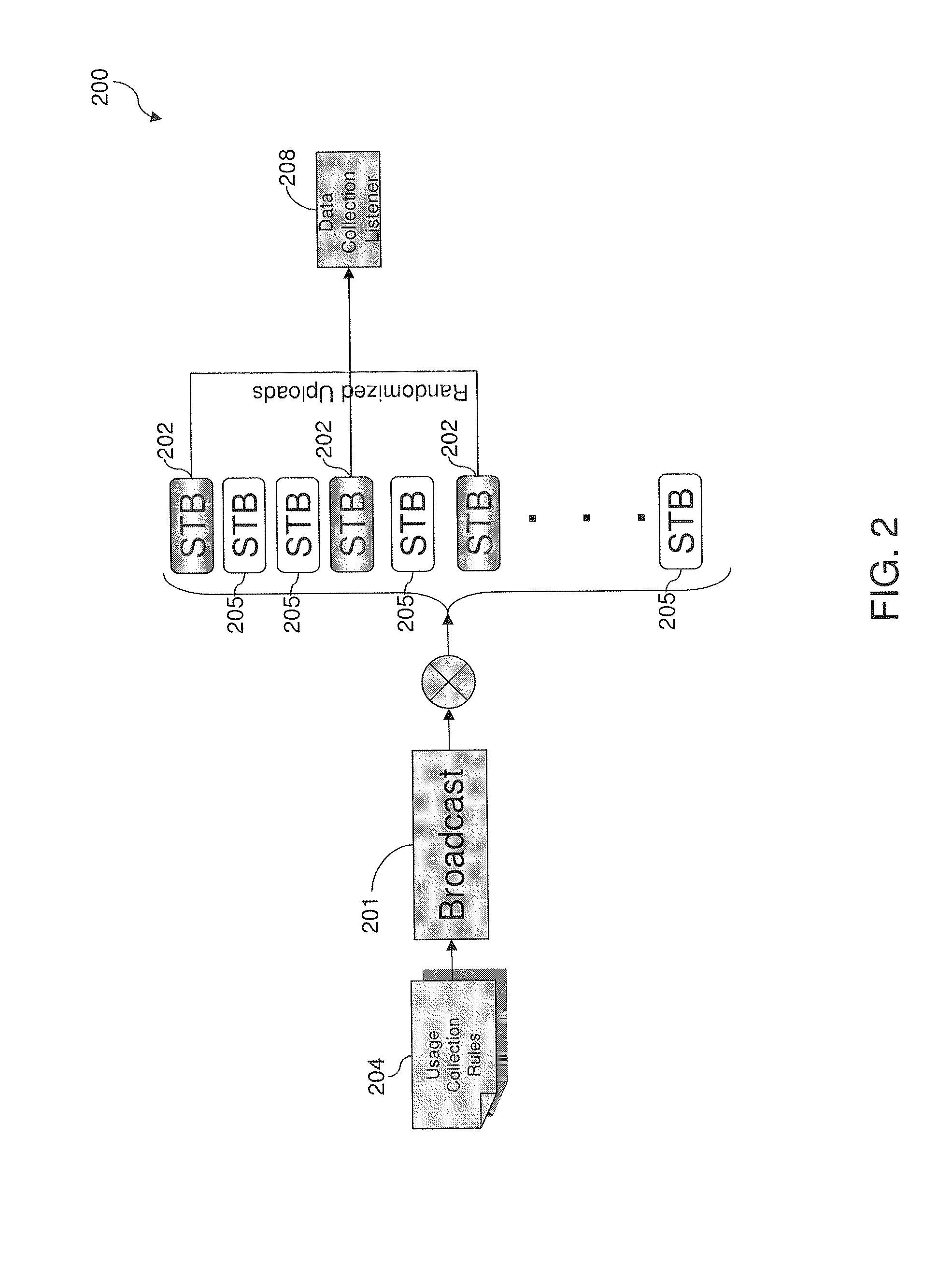
System and Method for Set Top Viewing Data
ActiveUS20110289524A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast services for monitoring/identification/recognitionData warehouseControl manner
In a video delivery context, collection and analysis of viewing data can provide insight into viewer interaction with video and the Internet. The viewing data can be transmitted in a controlled manner to a data repository. The system can selectively target specific viewers / households to obtain viewing data, which can be combined with demographics, anonymized, and encrypted. Embodiments enable precision selection of media opportunities, by determining detailed characteristics associated with broadcasts including movement of audiences and specific viewer behavior, such as visits to websites on the Internet. The effective yield of broadcasts, including promotional spots and advertisements, can be determined and predicted based on concrete data at a level of detail down to individual viewers. Accordingly, embodiments enable improvement of the effectiveness and return on investment for programming, promotional spots, and advertisements.
Owner:CSC HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com