Patents
Literature
12089results about "Memory loss protection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
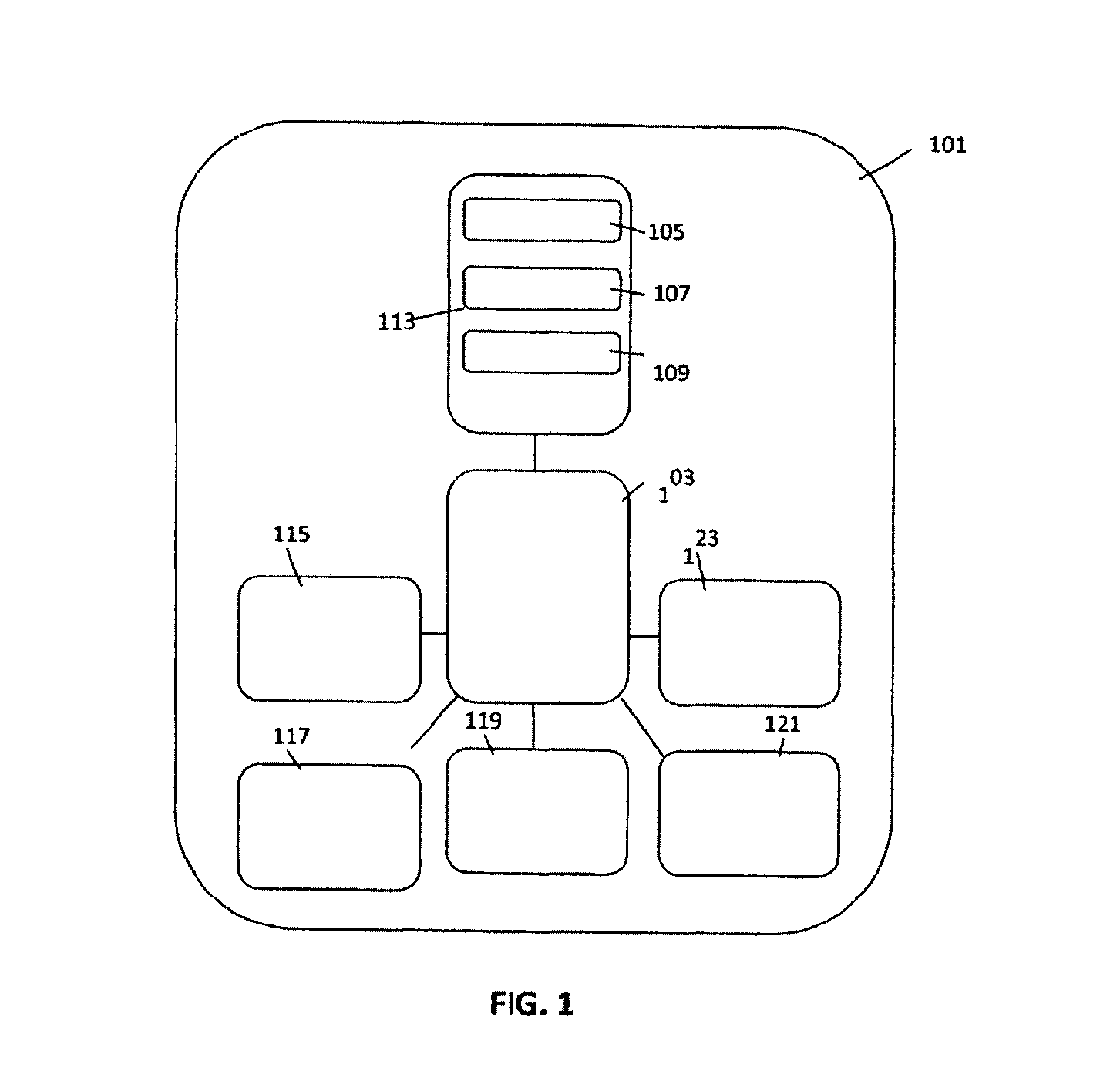
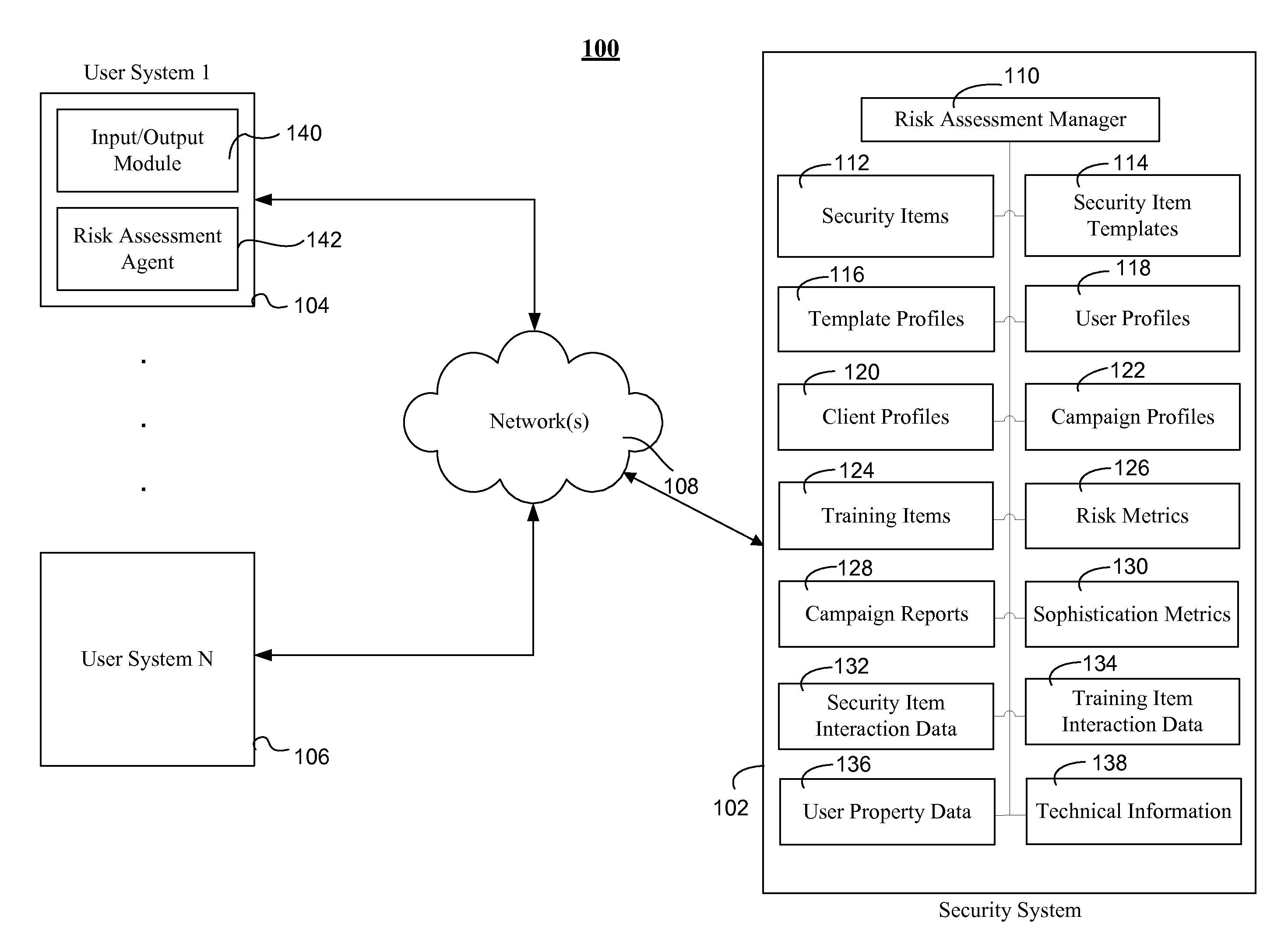
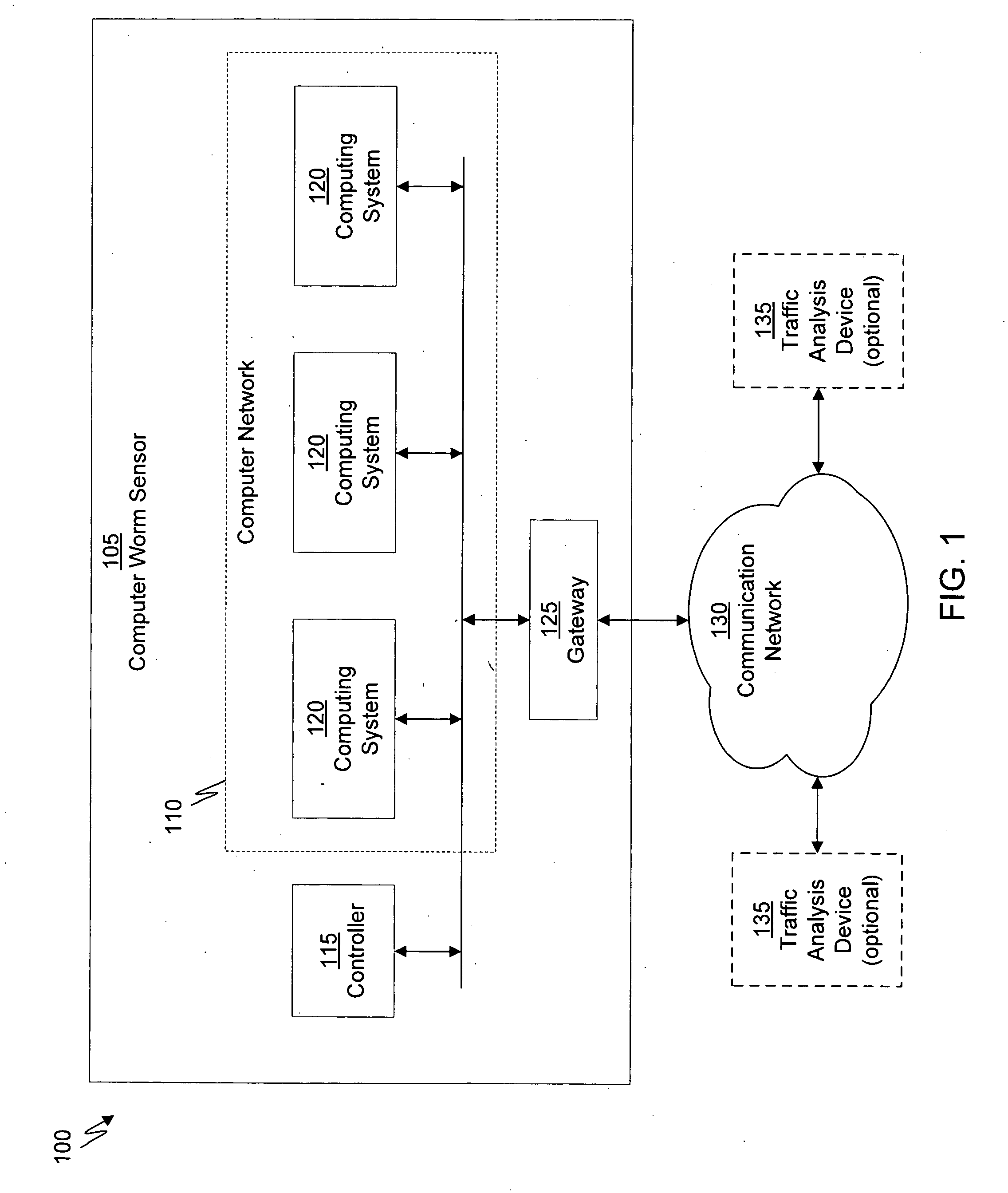
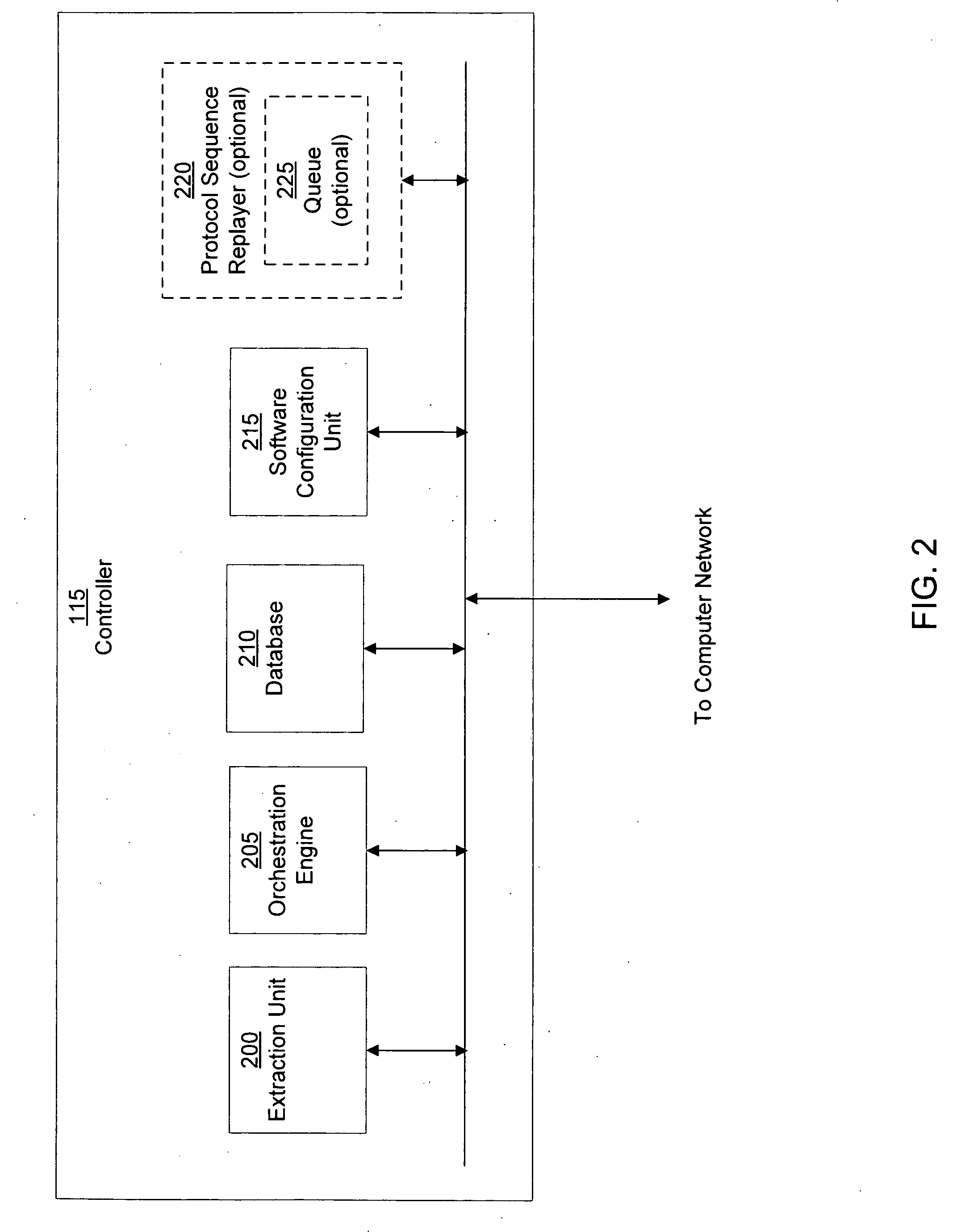
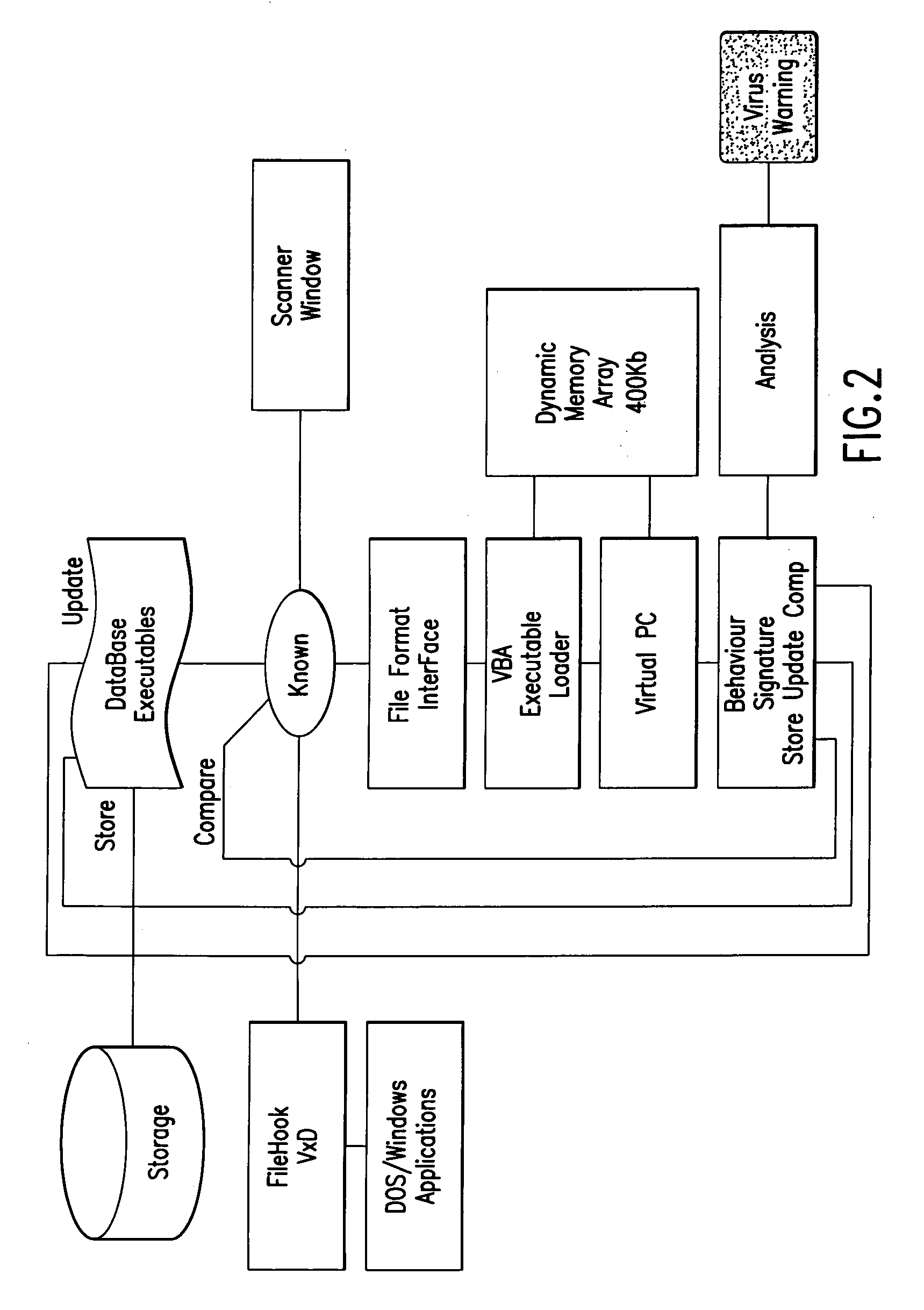
Data security system and method
ActiveUS7103915B2Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsPlaintextInformation processing
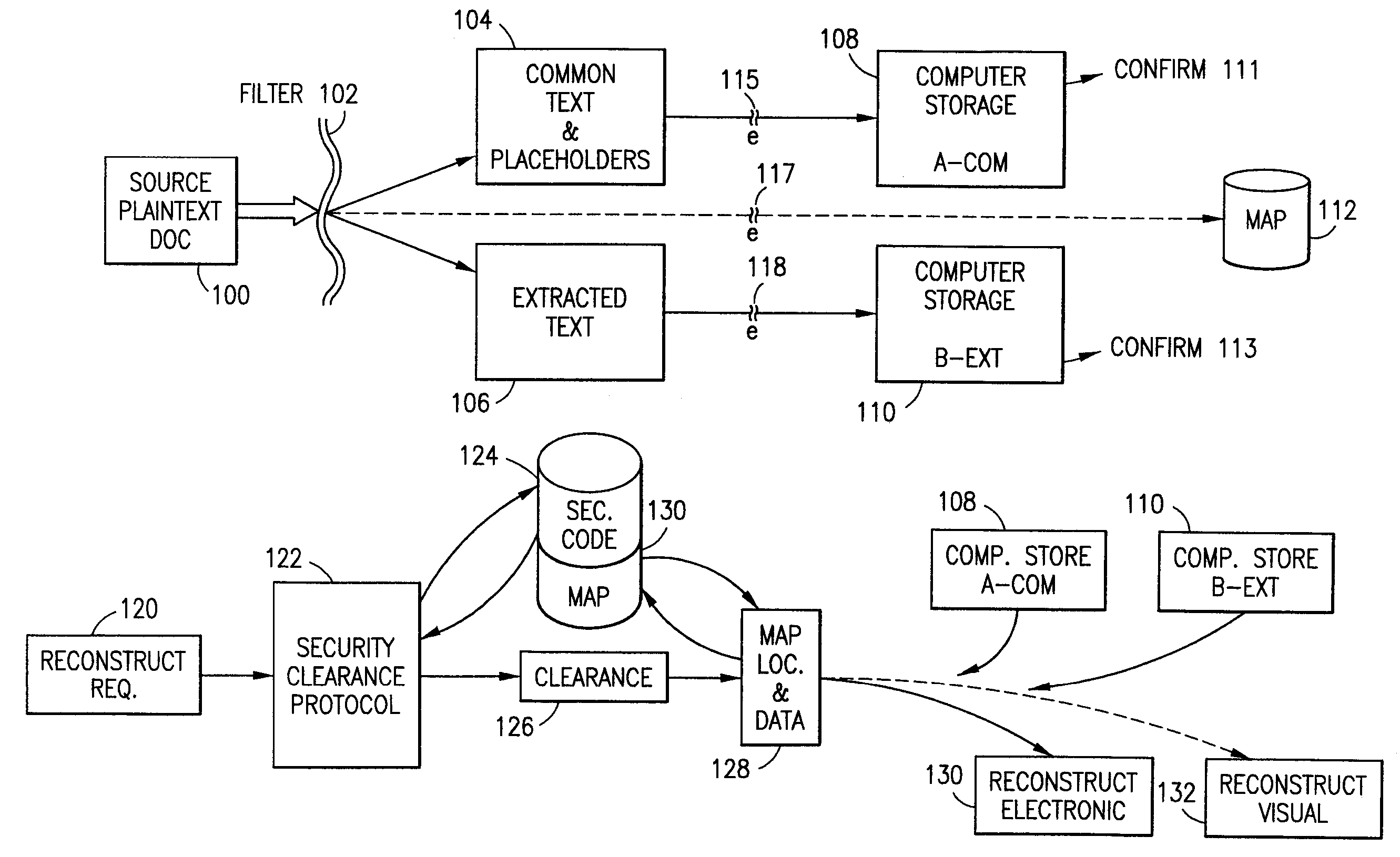
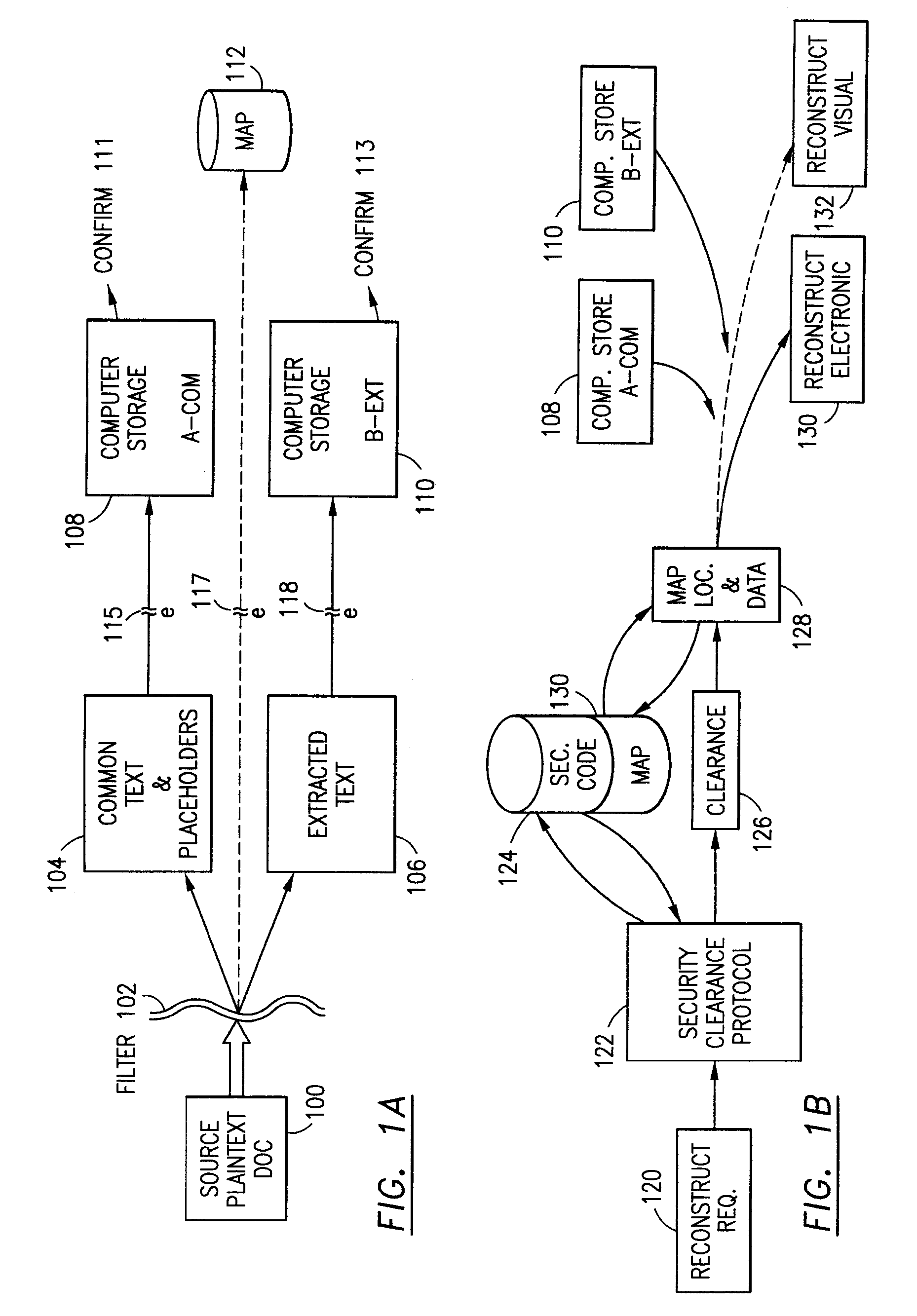
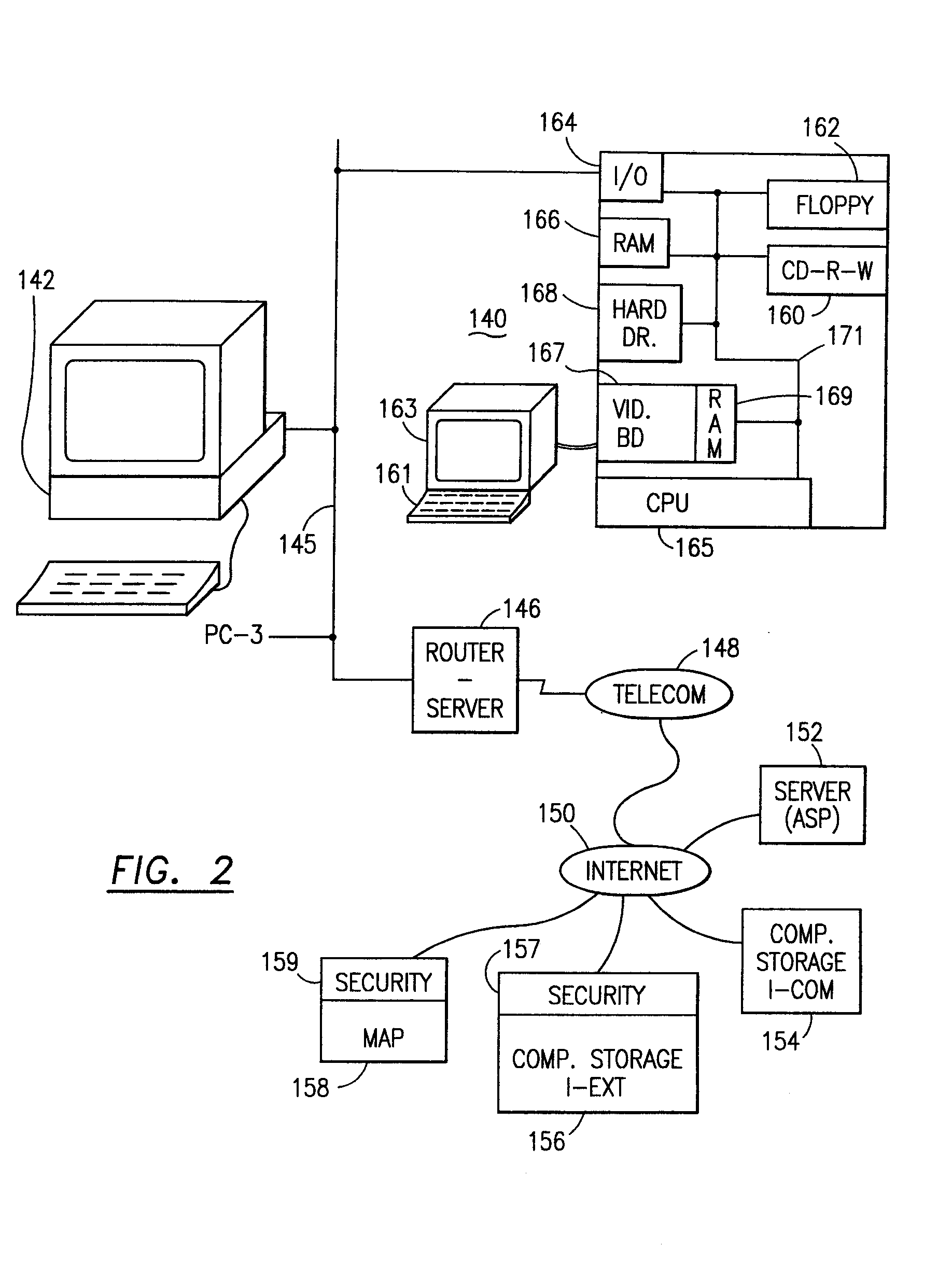
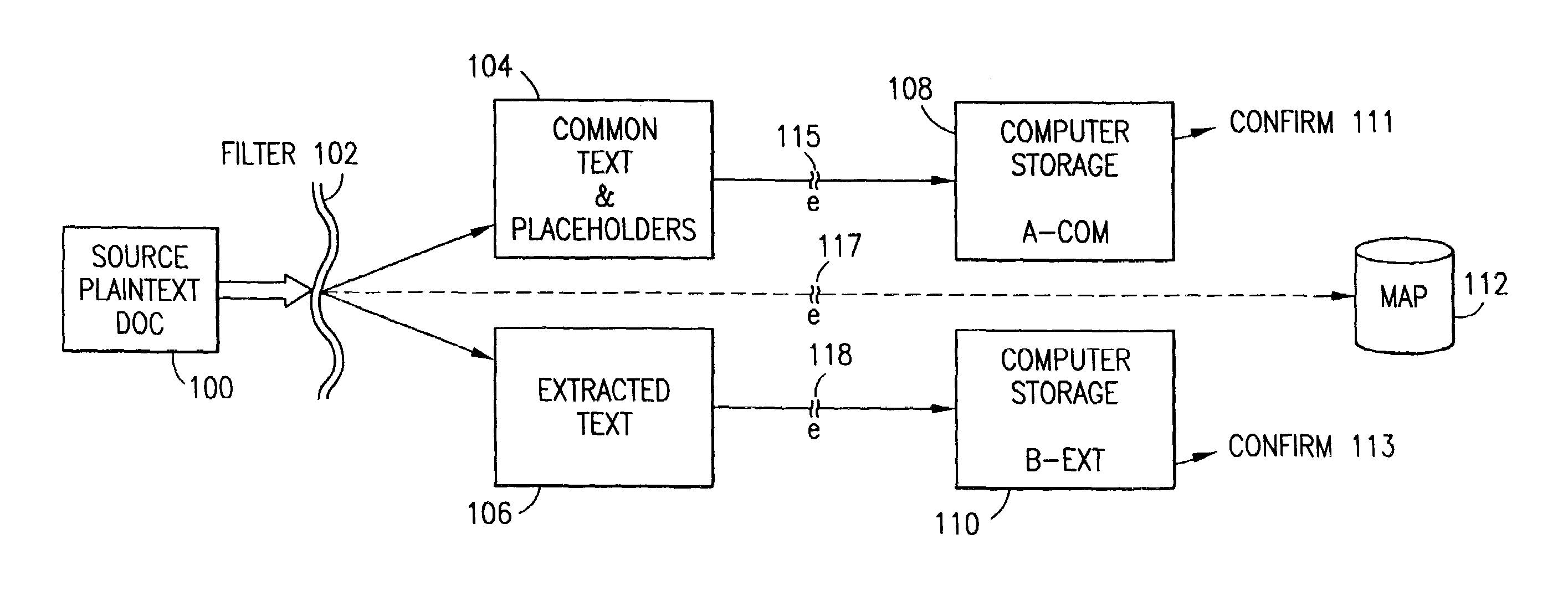
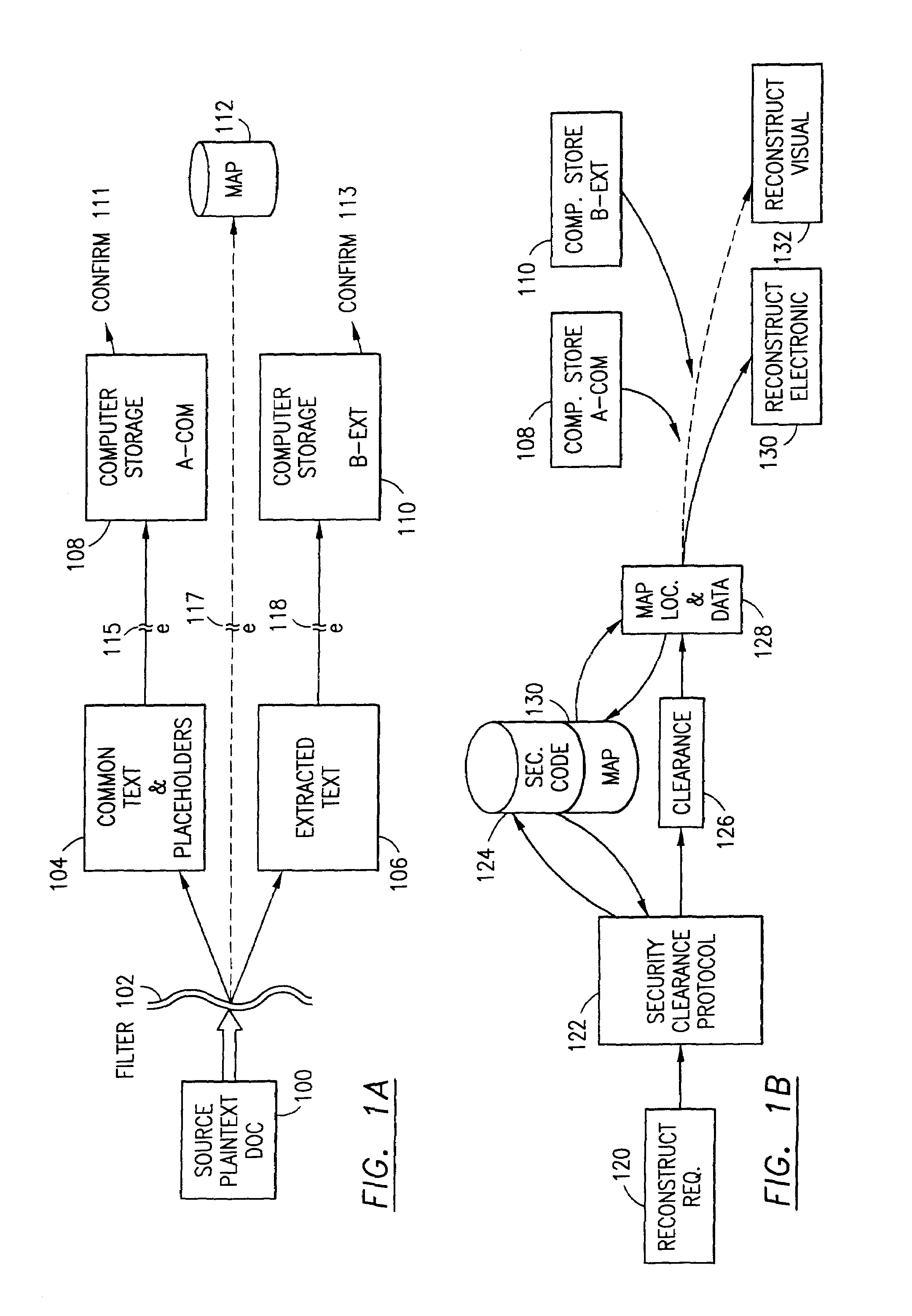
The method for securing data includes establishing a group of security sensitive items, filtering data and extracting and separating the security items from remainder data. The filtered data are separately stored (locally on a PC or on another computer in a LAN or WAN or on the Internet.) A map may be generated. The filter and / or map may be destroyed or stored. The data input, extracted data and remainder data may be deleted from the originating computer. Encryption may be utilized to enhance security (including transfers of data, filter and map). Reconstruction of the data is permitted only in the presence of a predetermined security clearance. A plurality of security clearances may be used to enable a corresponding plurality of partial, reconstructed views of the plaintext (omitting higher security words). A computer readable medium containing programming instructions and an information processing system is encompassed.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
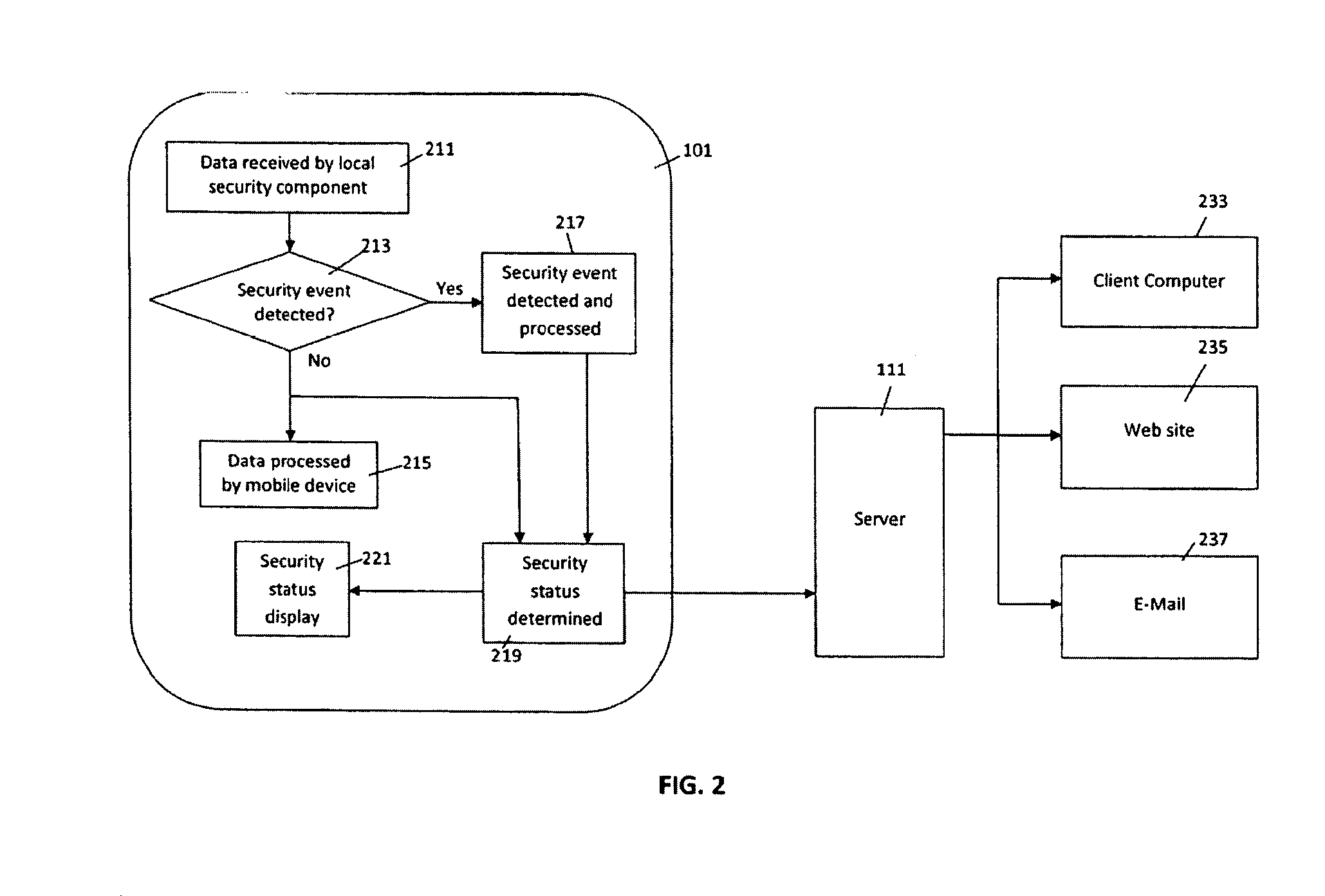
Data security system and method responsive to electronic attacks
ActiveUS7146644B2Ease overhead performanceHigh overhead performanceMemory loss protectionMultiple keys/algorithms usageInformation processingSelf adaptive
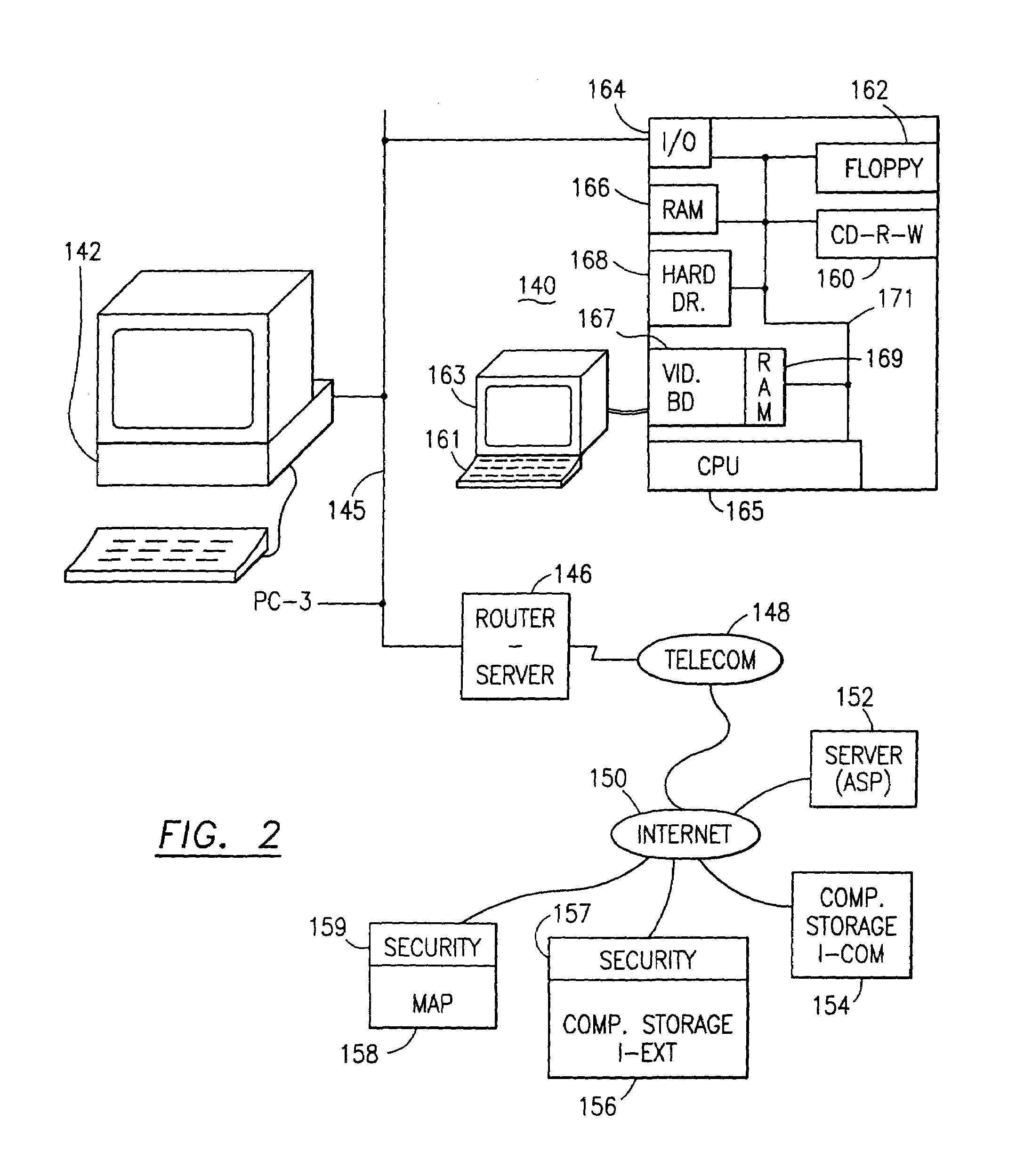
An adaptive method, system and program for securing data against a plurality of electronic and environmental events directed at computers utilizes a hacking monitor which generates attack warnings (such as a hacking warning) dependent upon the severity of the attack. Based upon these warnings, data is filtered to extract security sensitive words etc. and the extract and remainder data (if necessary) is stored in assigned memory. Full or partial reconstruction is permitted, manually or automatically, with a security clearance. Encryption is typically used dependent upon the warning. The information processing system includes a filter which is adjusted based upon the degree of attack warning to extract security sensitive words. A storage system stores extracted data and remainder data (if necessary) based upon the level of the warning and a compiler is used to reconstruct the data in the presence of the appropriate security clearance level.
Owner:DIGITAL DOORS
Storage system and a storage management system
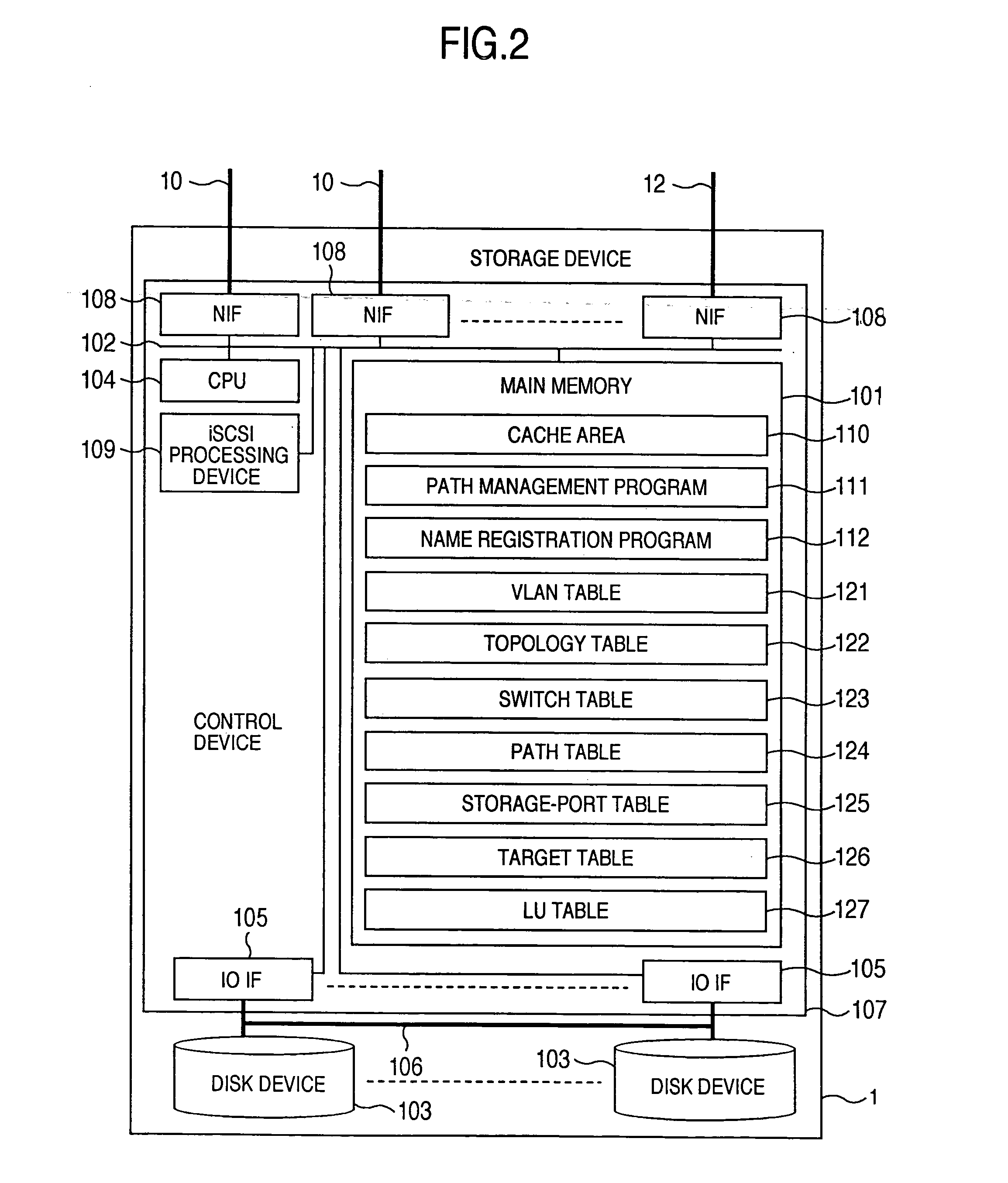
InactiveUS20060047907A1Improve matchMemory loss protectionMultiple digital computer combinationsData packStorage management
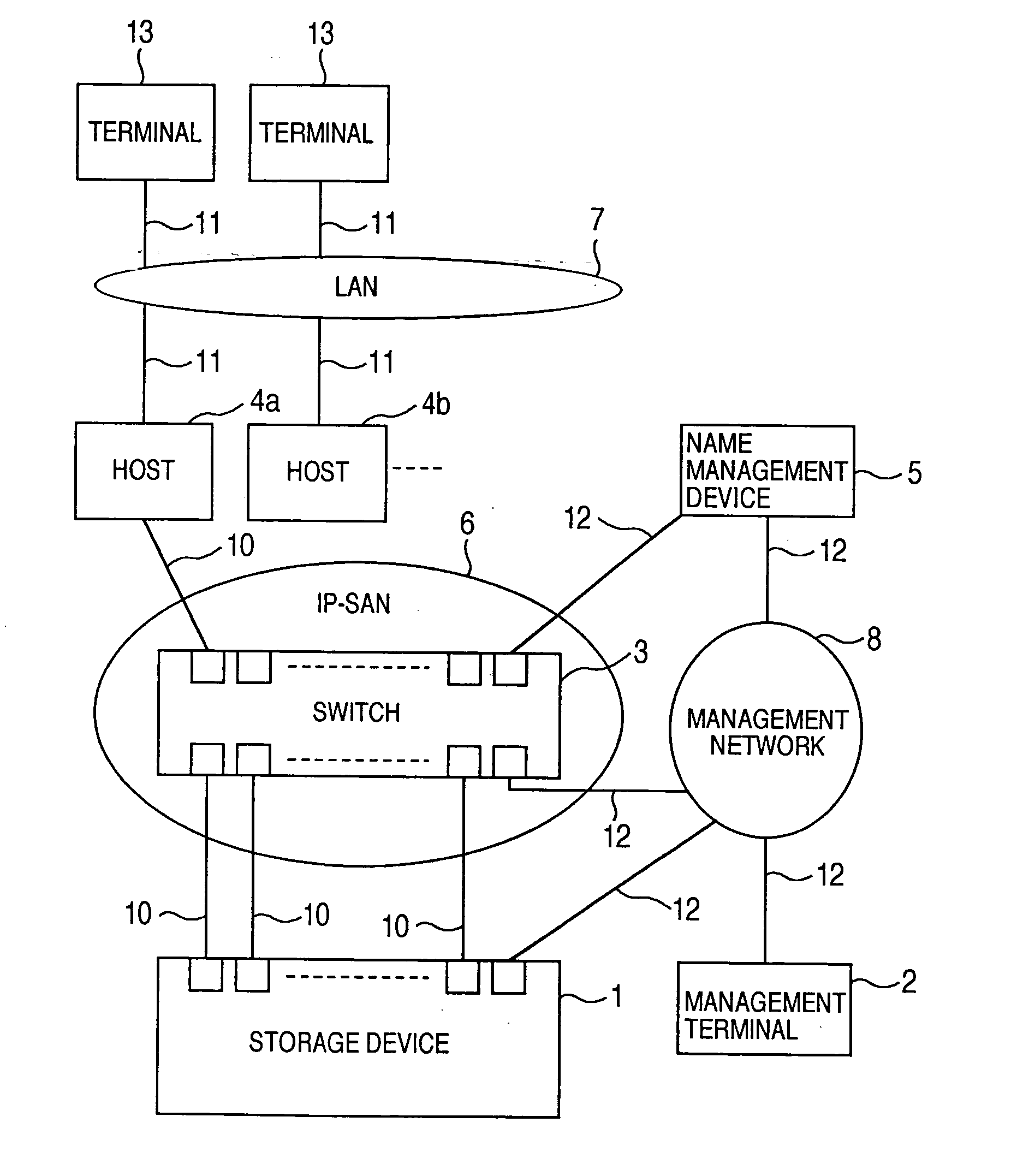
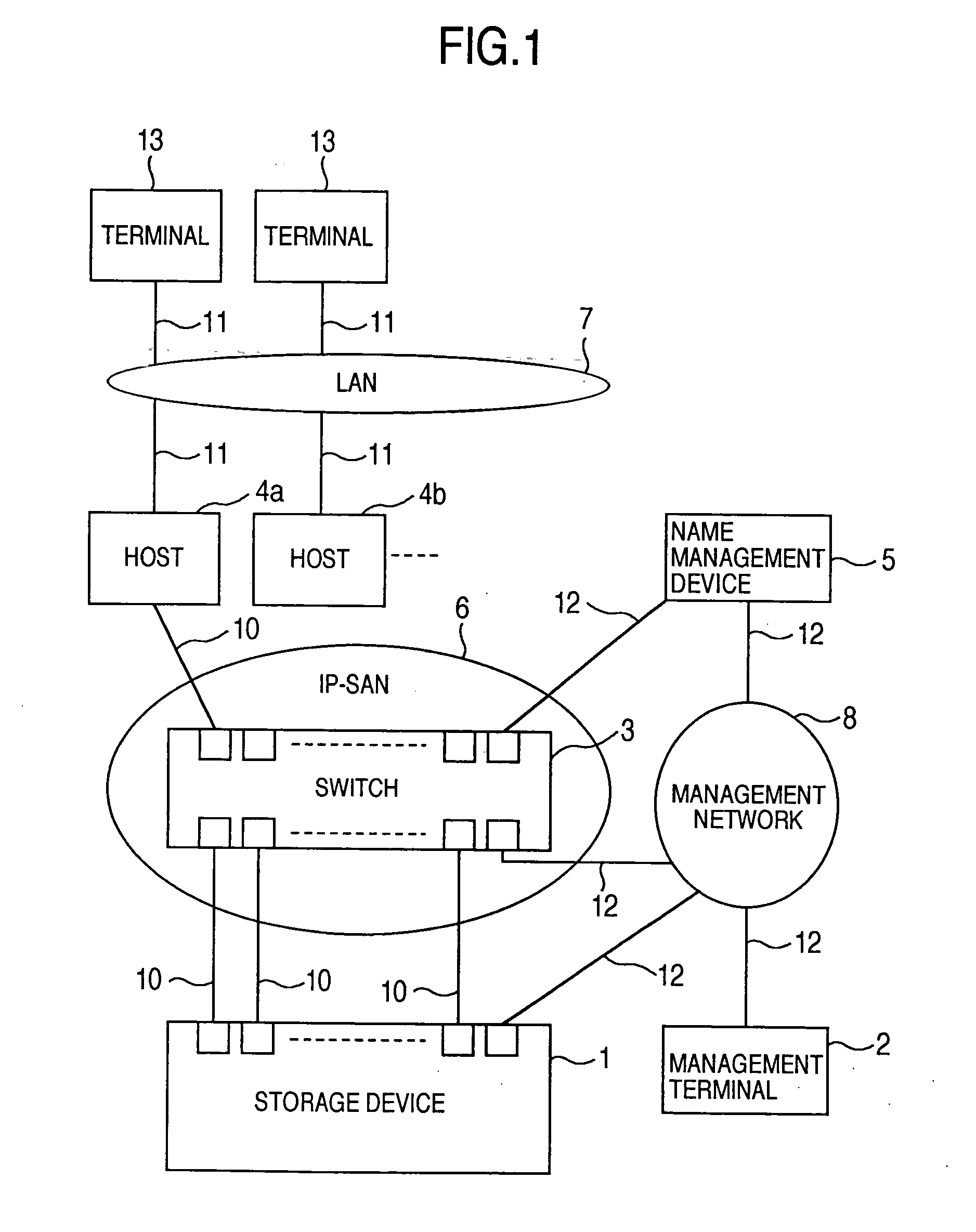
A storage device managing one or more logical volumes is connected with a name management device through an IP-SAN 6 composed of a switch. The storage device stores a topology table saving connecting relation among physical ports of host, physical ports of the storage device and physical ports of the switch, reads an identifier of the host and an identifier of the logical volume, selects a unused first physical port of the switch by referring to the topology table, selects a second physical port of the switch connected with the storage device, registers a group composed of the host and the logical volume with the name management device, and executes a configuration of allowing packets to be transferred between the first and the second physical ports with respect to the switch.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method, system, and program for managing data organization
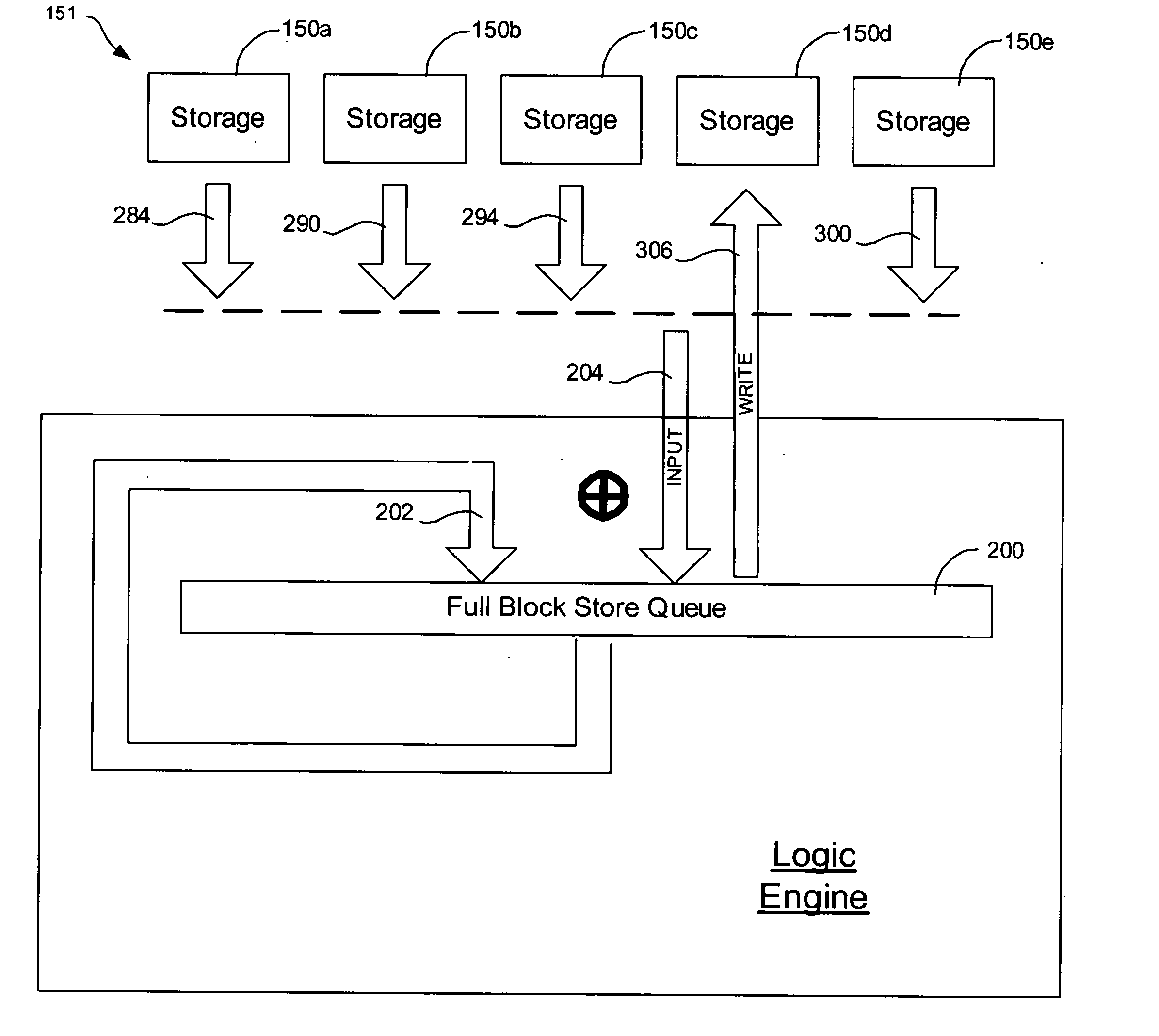
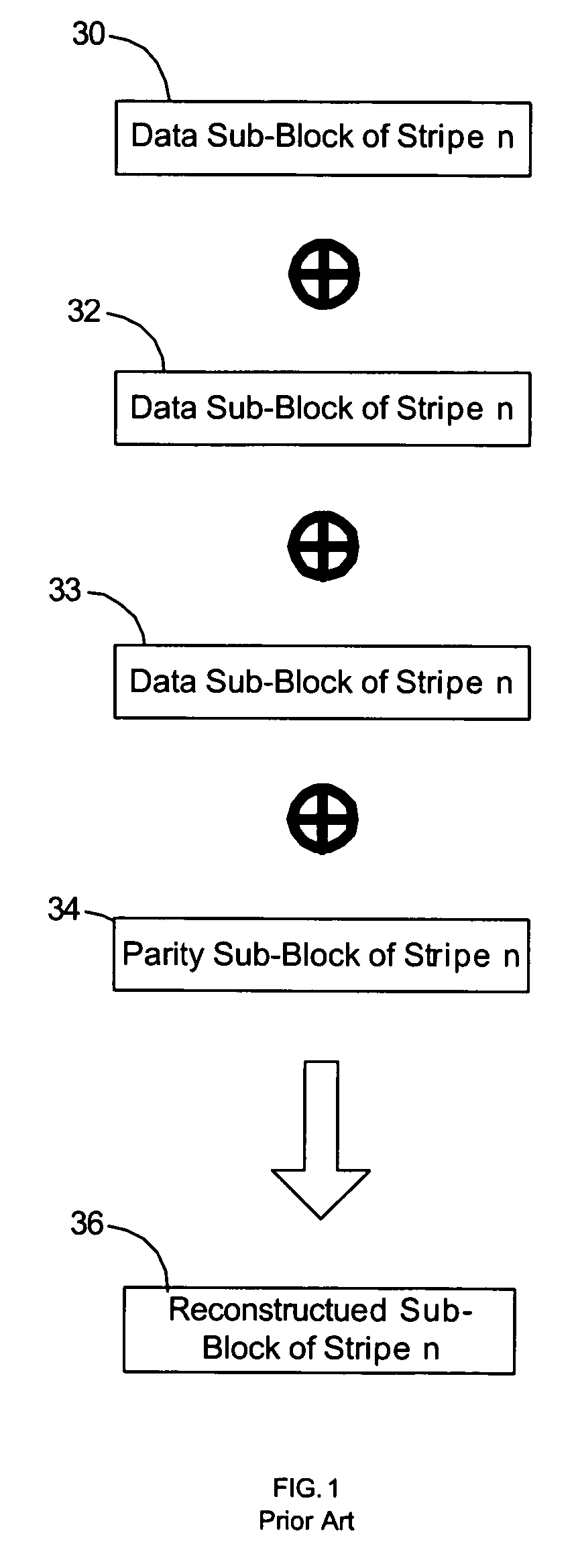
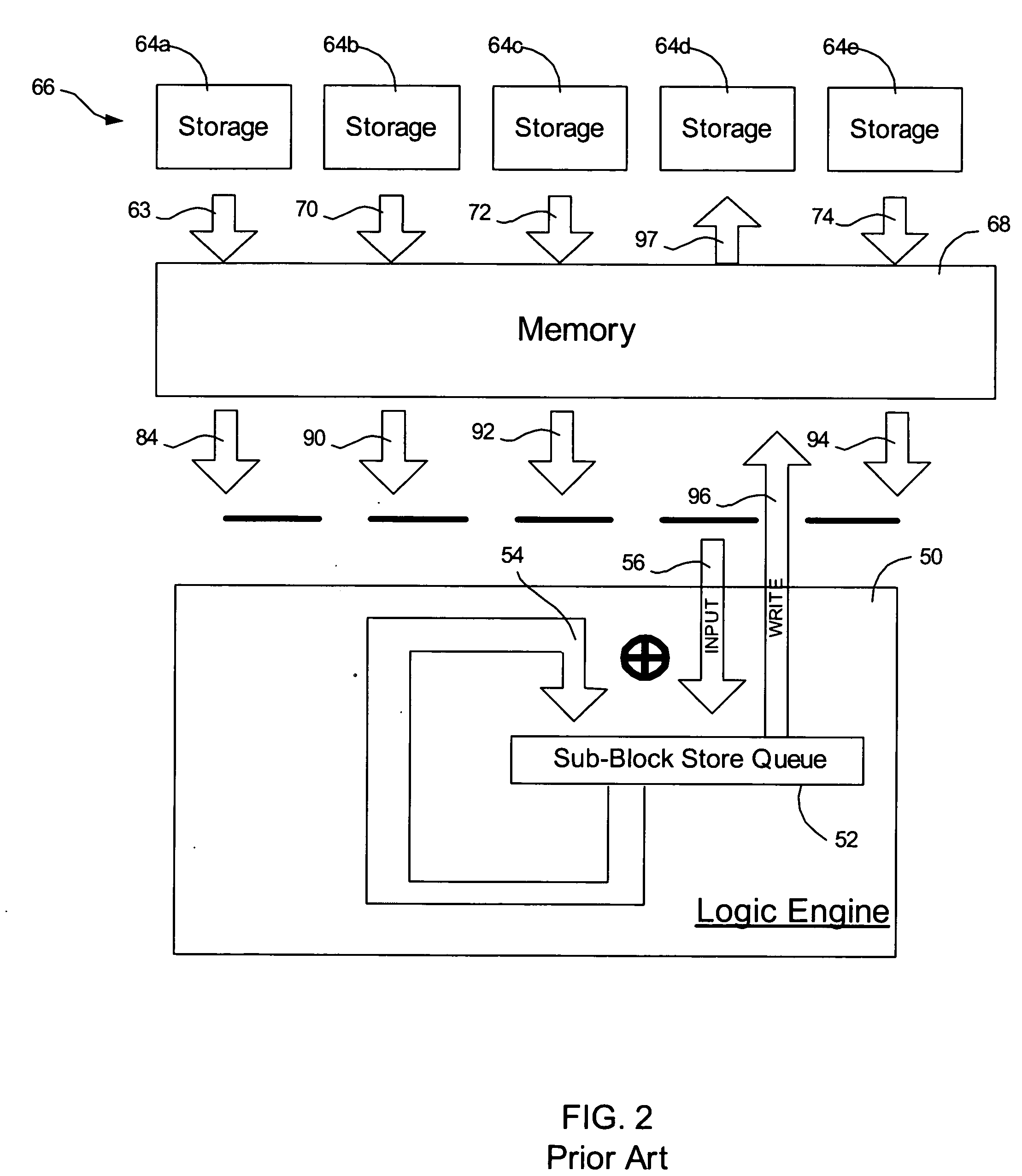
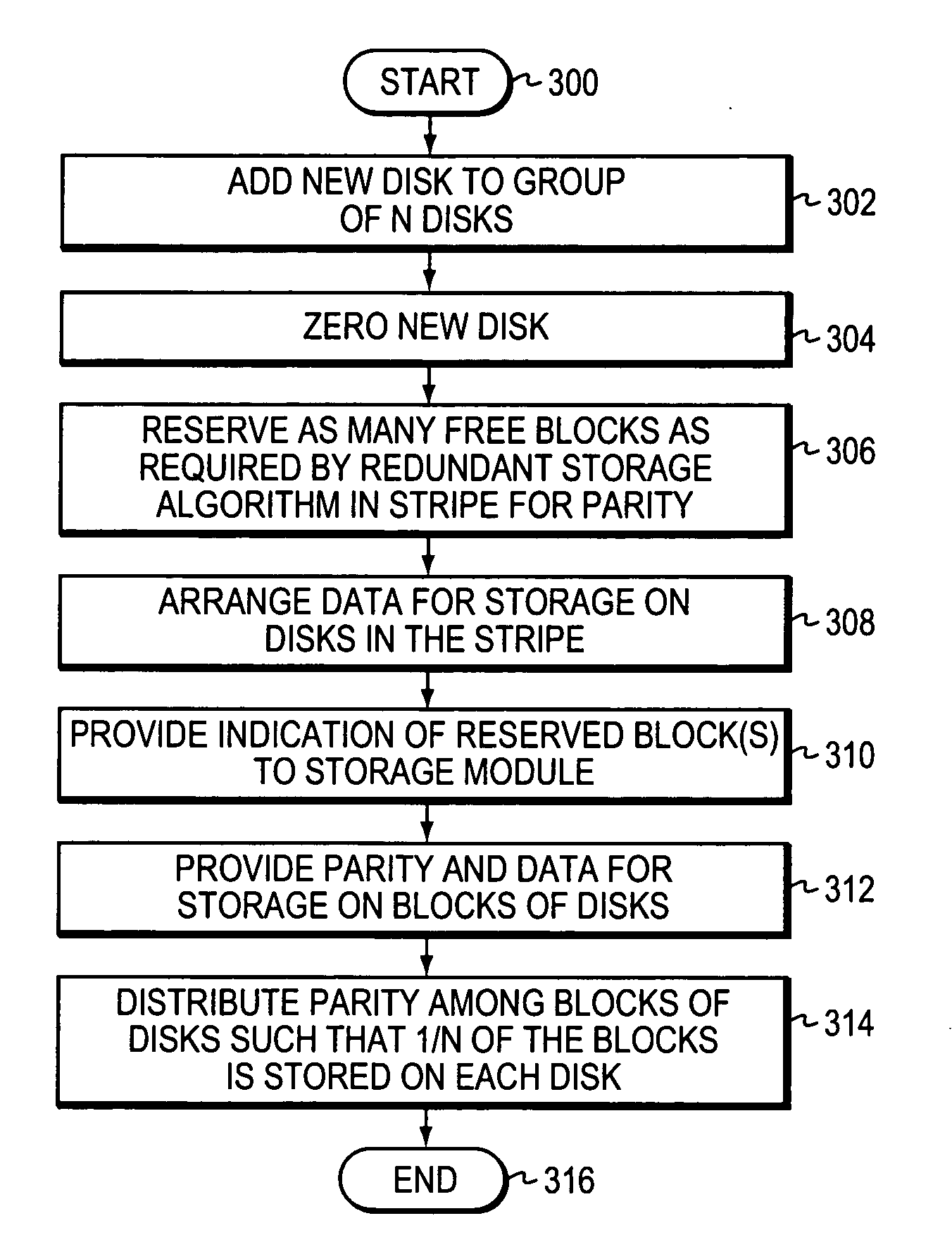
Provided are a method, system, and program for constructing data including reconstructing data organized in a data organization type, such as a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) organization, for example, which permits data reconstruction In one embodiment, blocks of data are transferred from a stripe of data stored across storage units, such as disk drives in a RAID array, to a logic engine of a storage processor, bypassing the cache memory of the storage processor. A store queue performs a logic function, such as Exclusive-OR, on each block of data as it is transferred from the disk drives, to reconstruct a block of data from the stripe. The constructed block of data may be subsequently transferred to a disk drive of the RAID array to replace a lost block of data in the stripe of data across the RAID array or to replace an old block of parity data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semi-static distribution technique
ActiveUS20050114594A1Improve performanceCase blockedMemory loss protectionRedundant data error correctionComputer sciencePre-existing
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
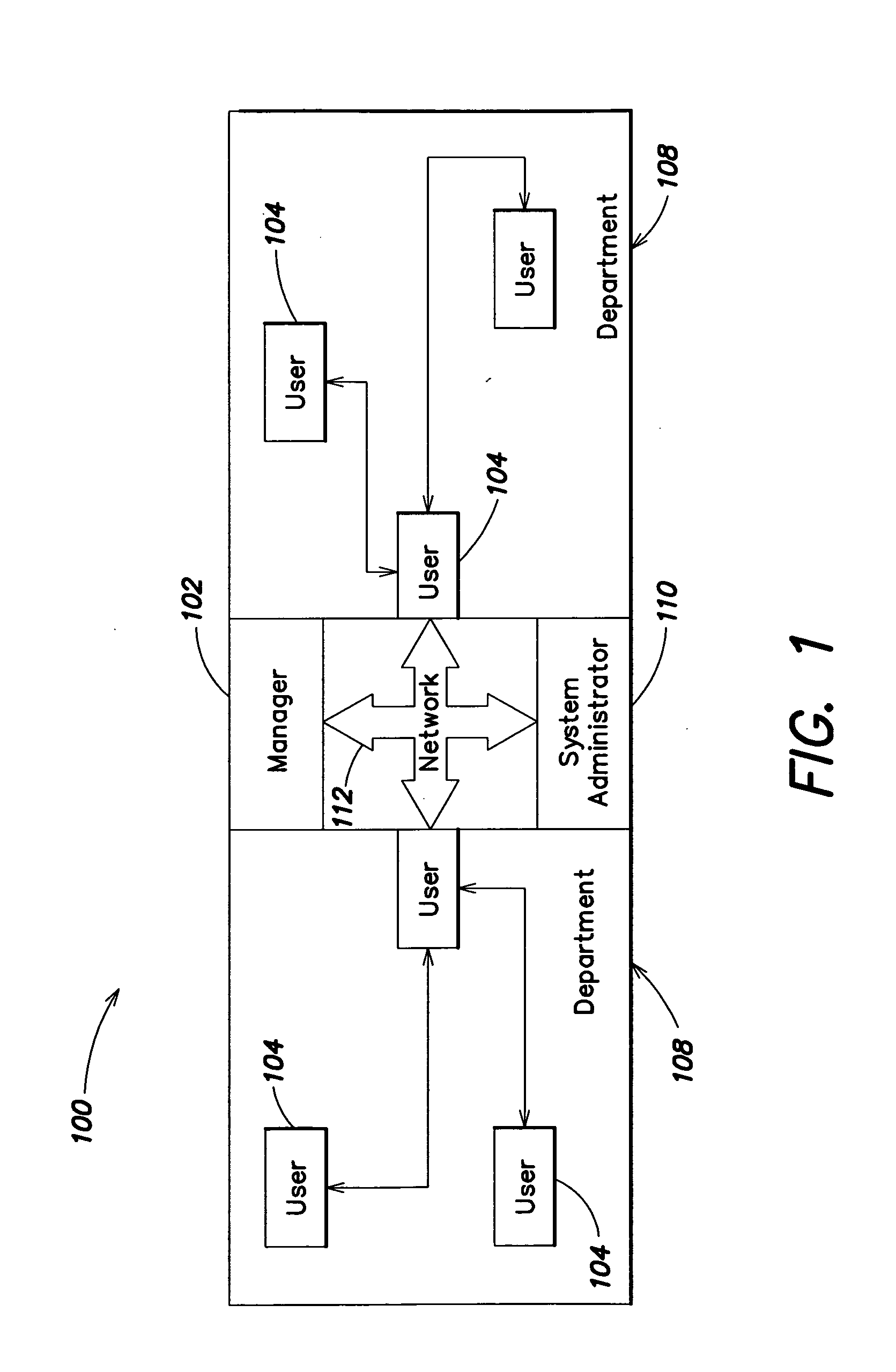
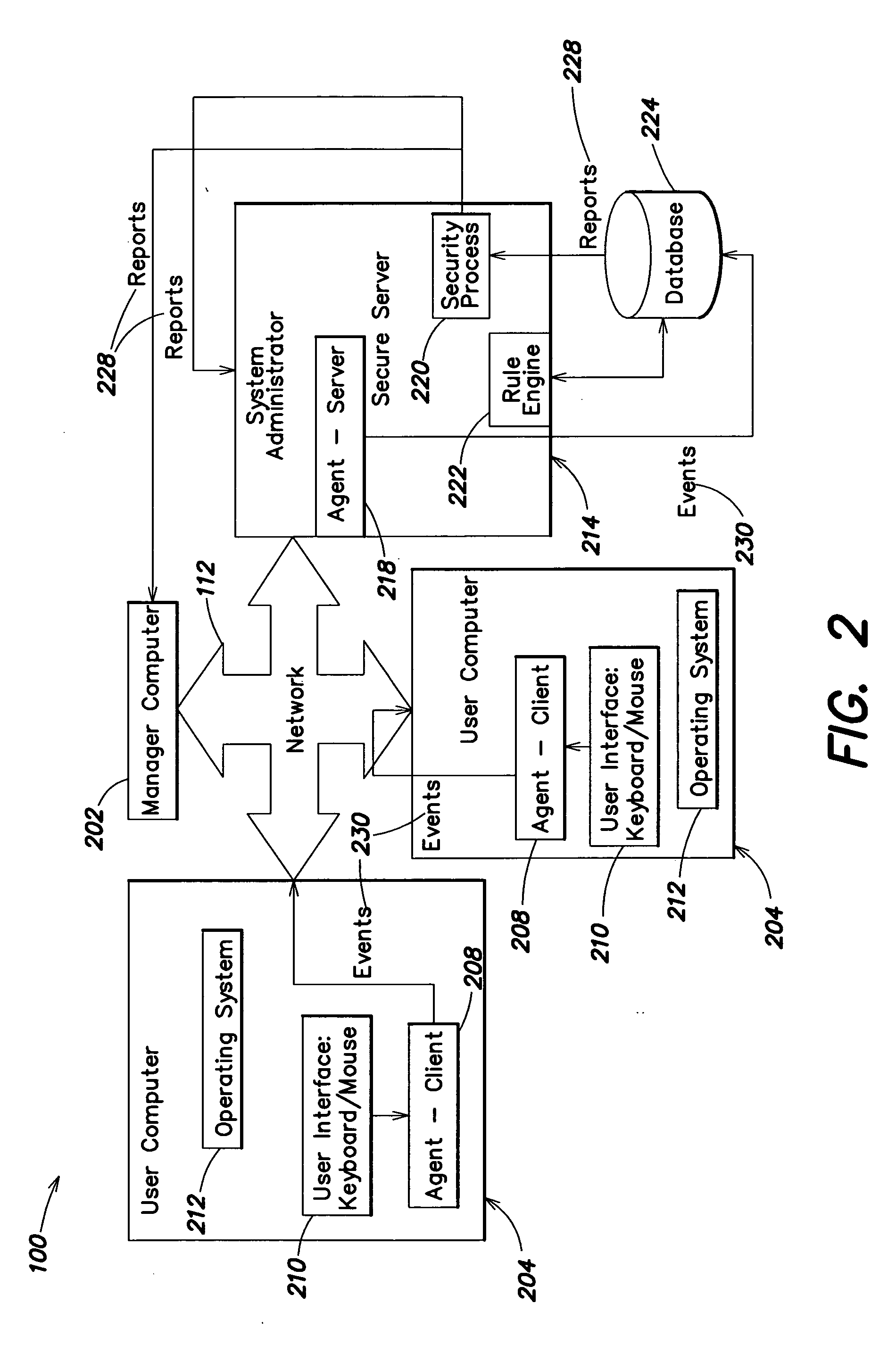
Methods and systems for monitoring user, application or device activity
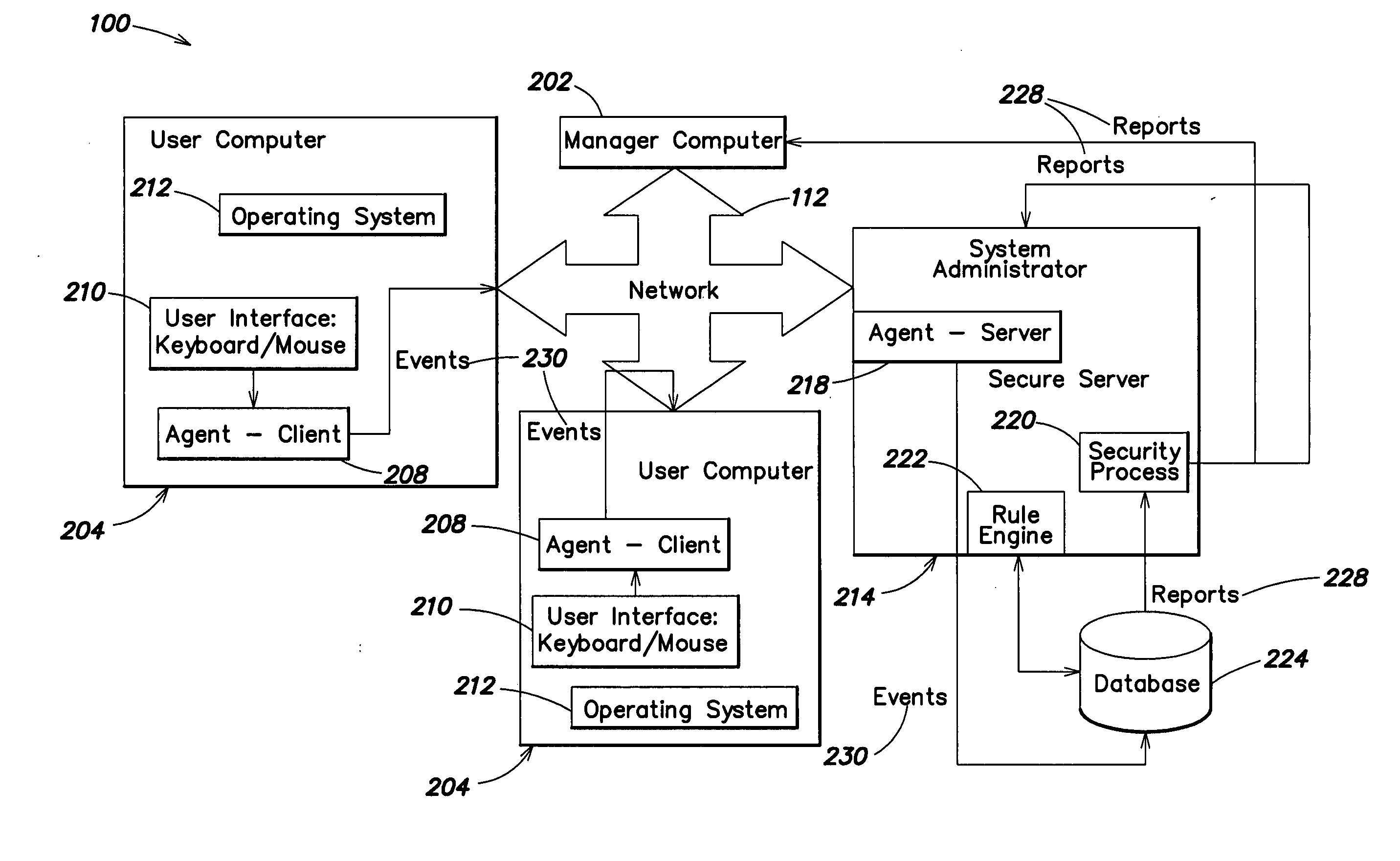
InactiveUS20050183143A1Improve securityMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionWorking environmentComputer usage
Methods and systems are provided for capturing usage data from a user computer, processing a subset of such data to form output, and offering access to selective views of such output, such as to assist a company's management in monitoring computer usage in a work environment. The output may be processed and viewed according to software application, device, or specified user. The output, or a report generated therefrom, may be accessible in differing degrees to individuals having appropriate levels of permission.
Owner:SERGEANT LAB
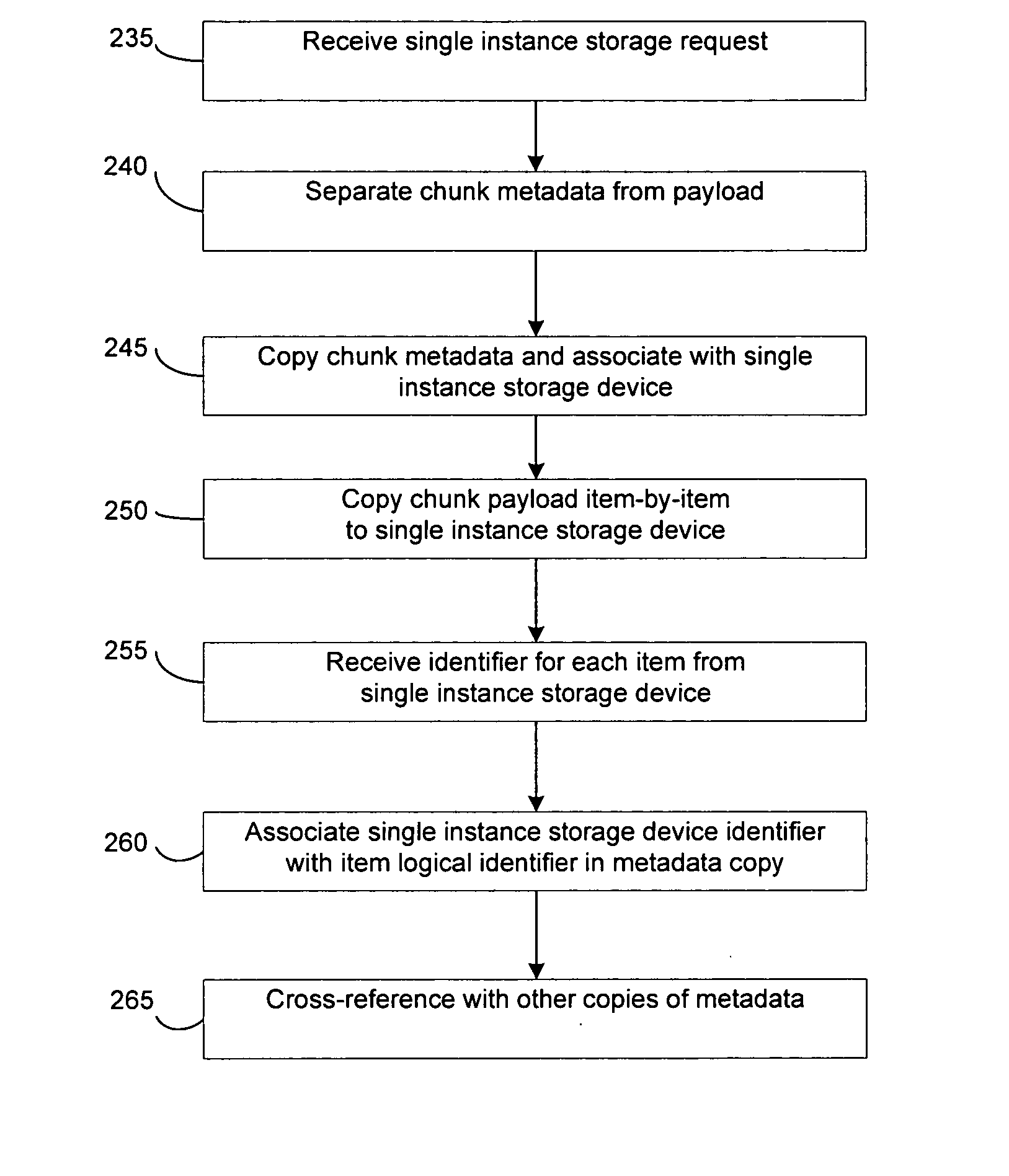
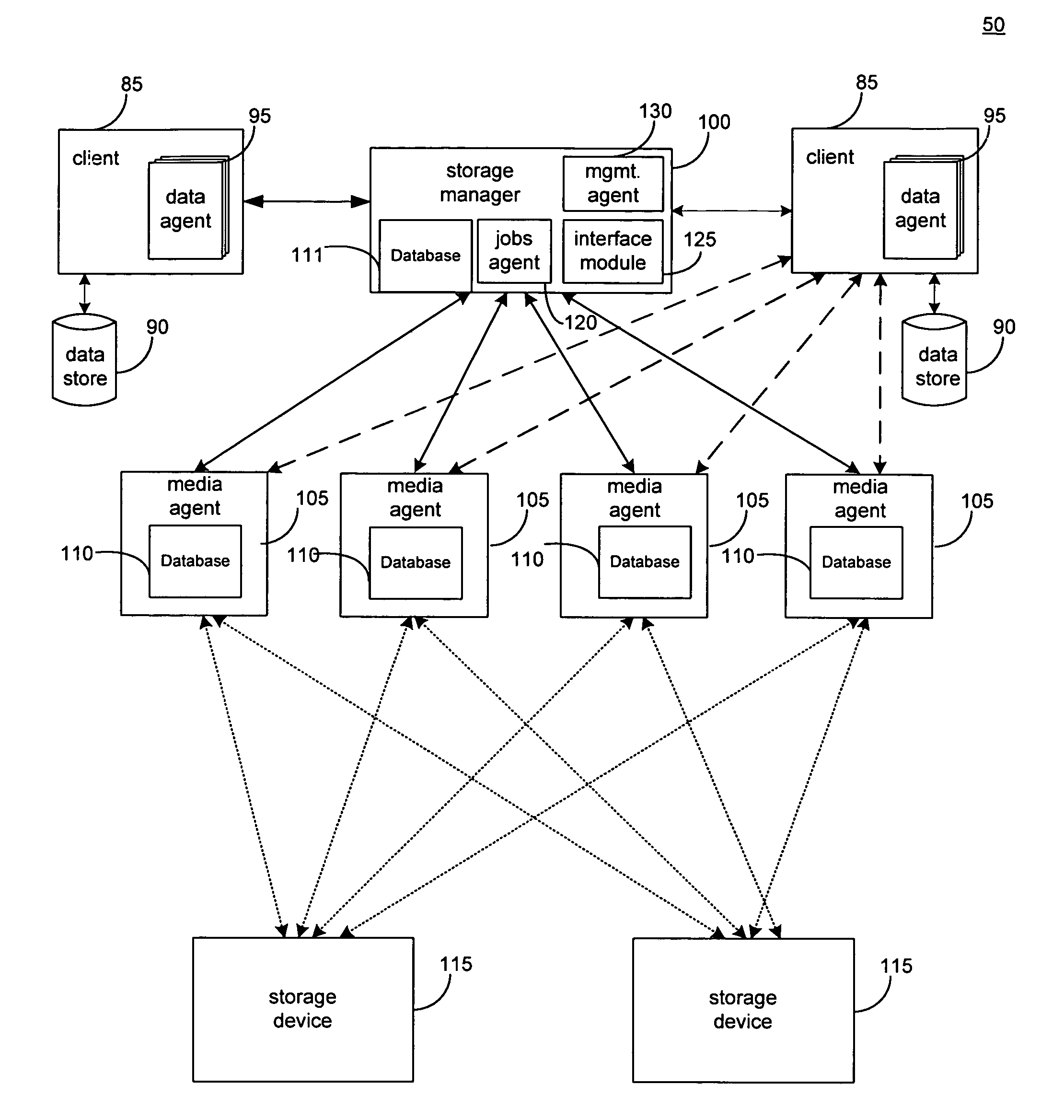
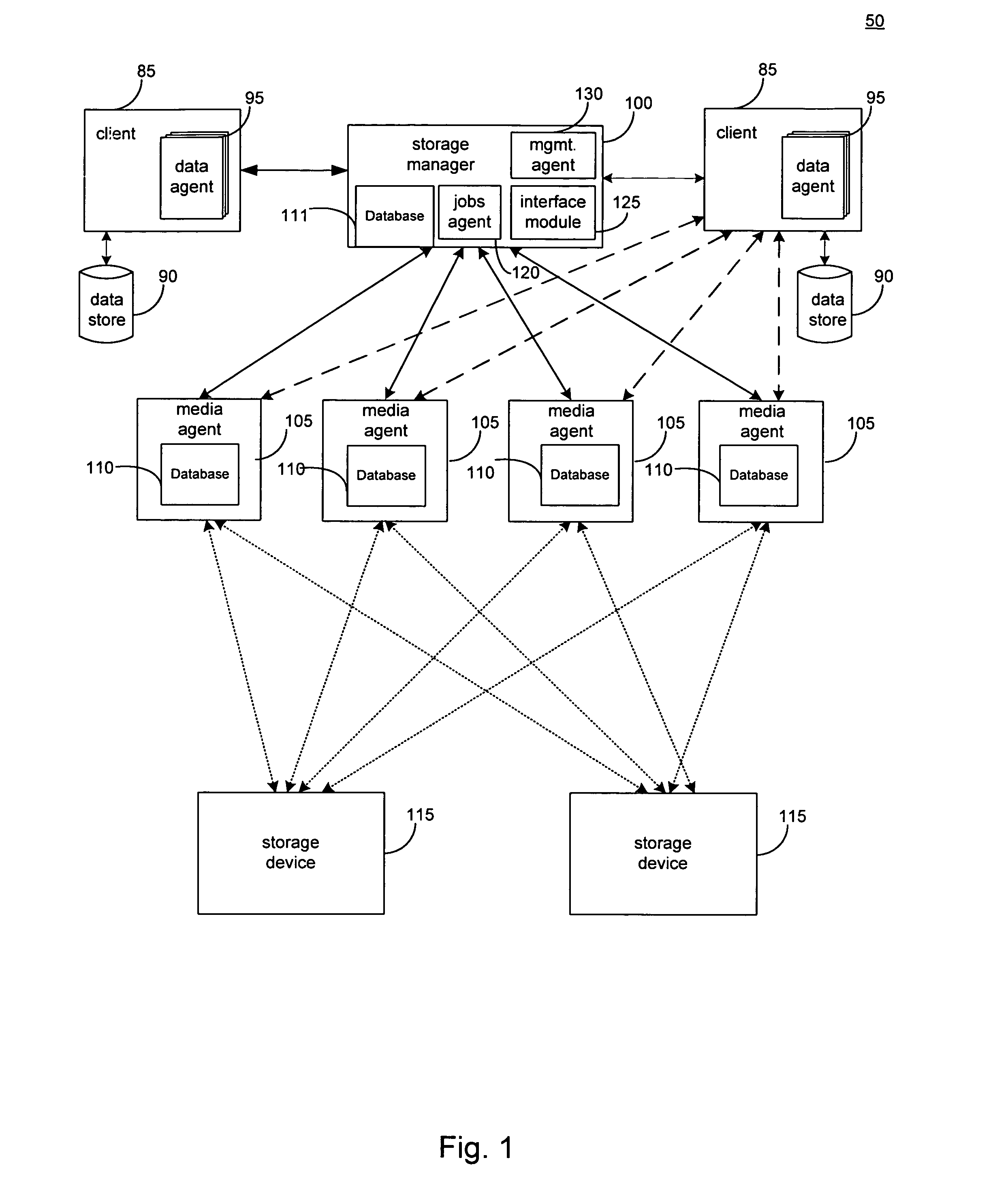
System and method to support single instance storage operations
Systems and methods for single instance storage operations are provided. Systems constructed in accordance with the principals of the present invention may process data containing a payload and associated metadata. Often, chunks of data are copied to traditional archive storage wherein some or all of the chunk, including the payload and associated metadata are copied to the physical archive storage medium. In some embodiments, chunks of data are designated for storage in single instance storage devices. The system may remove the encapsulation from the chunk and may copy the chunk payload to a single instance storage device. The single instance storage device may return a signature or other identifier for items copied from the chunk payload. The metadata associated with the chunk may be maintained in separate storage and may track the association between the logical identifiers and the signatures for the individual items of the chunk payload which may be generated by the single instance storage device.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
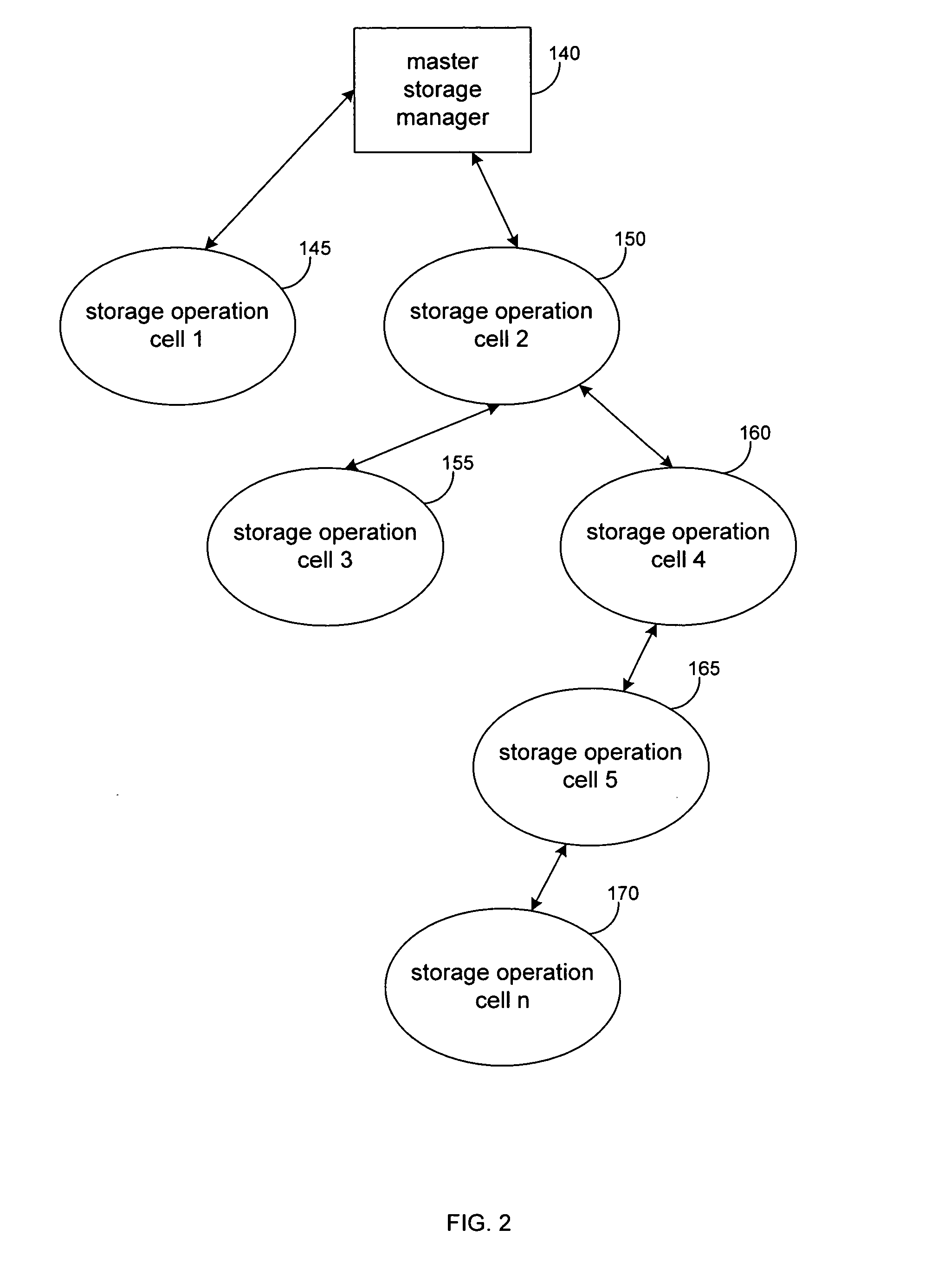
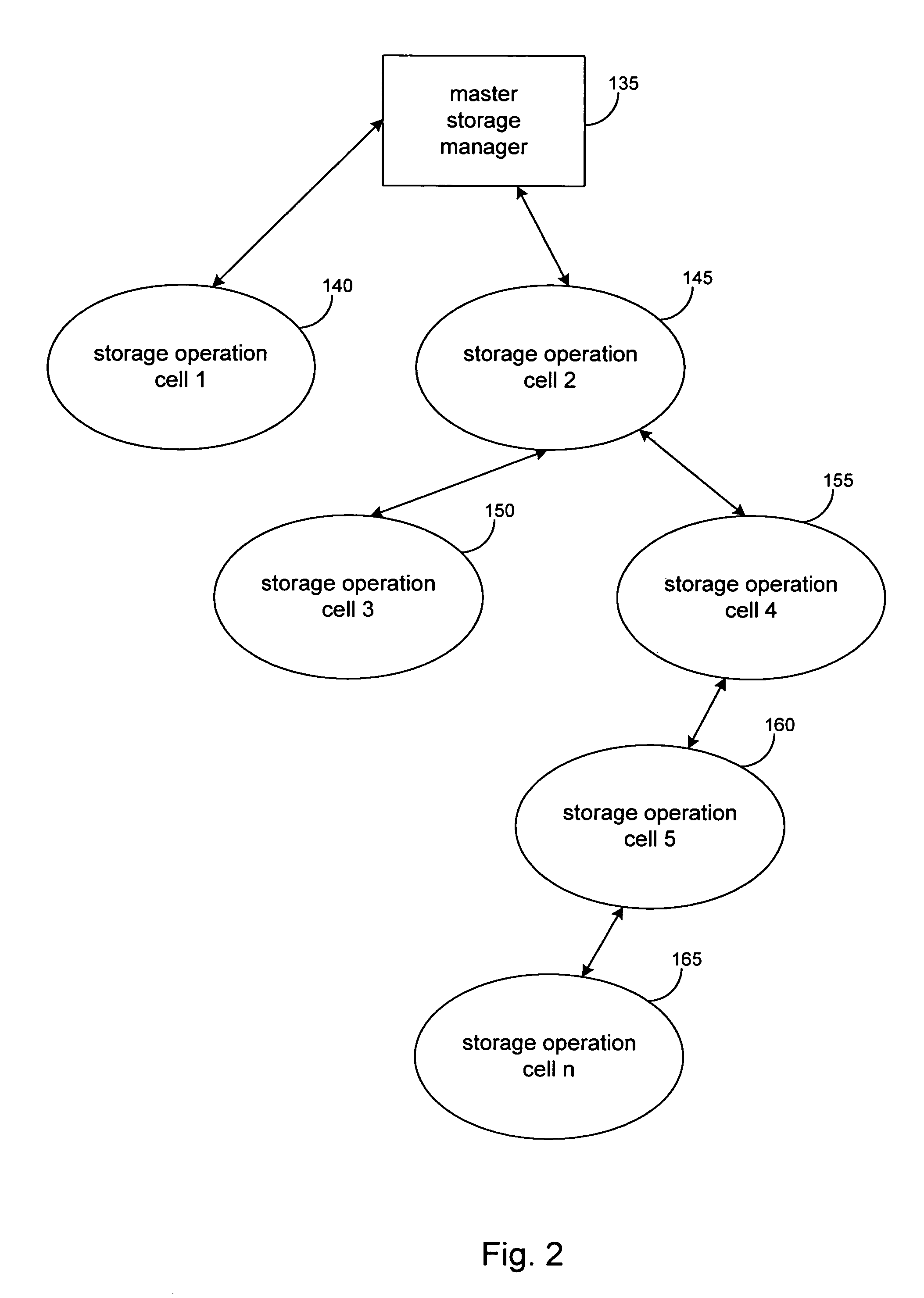
Hierarchical systems and methods for providing a unified view of storage information
The present invention provides systems and methods for data storage. A hierarchical storage management architecture is presented to facilitate data management. The disclosed system provides methods for evaluating the state of stored data relative to enterprise needs by using weighted parameters that may be user defined. Also disclosed are systems and methods evaluating costing and risk management associated with stored data.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
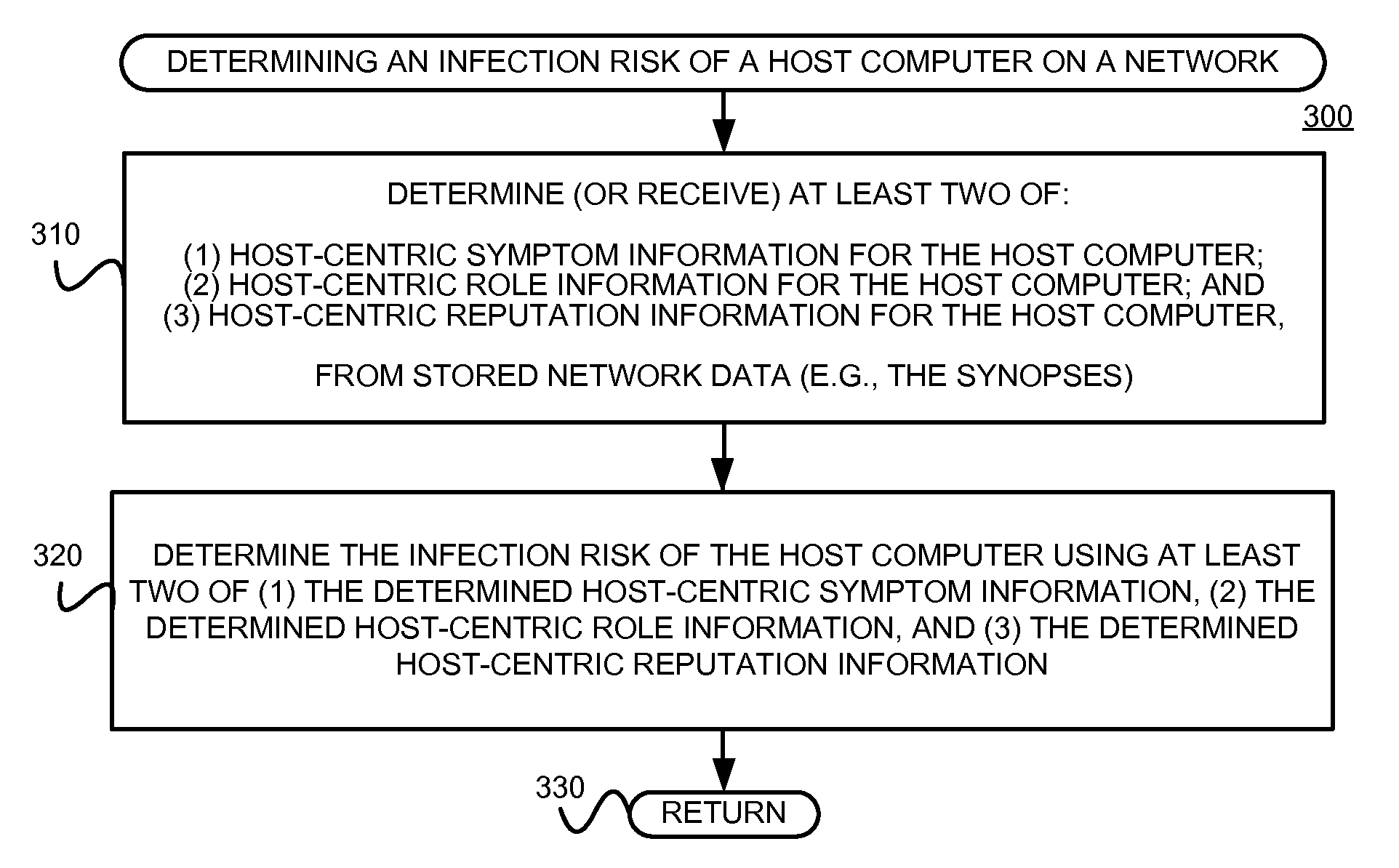
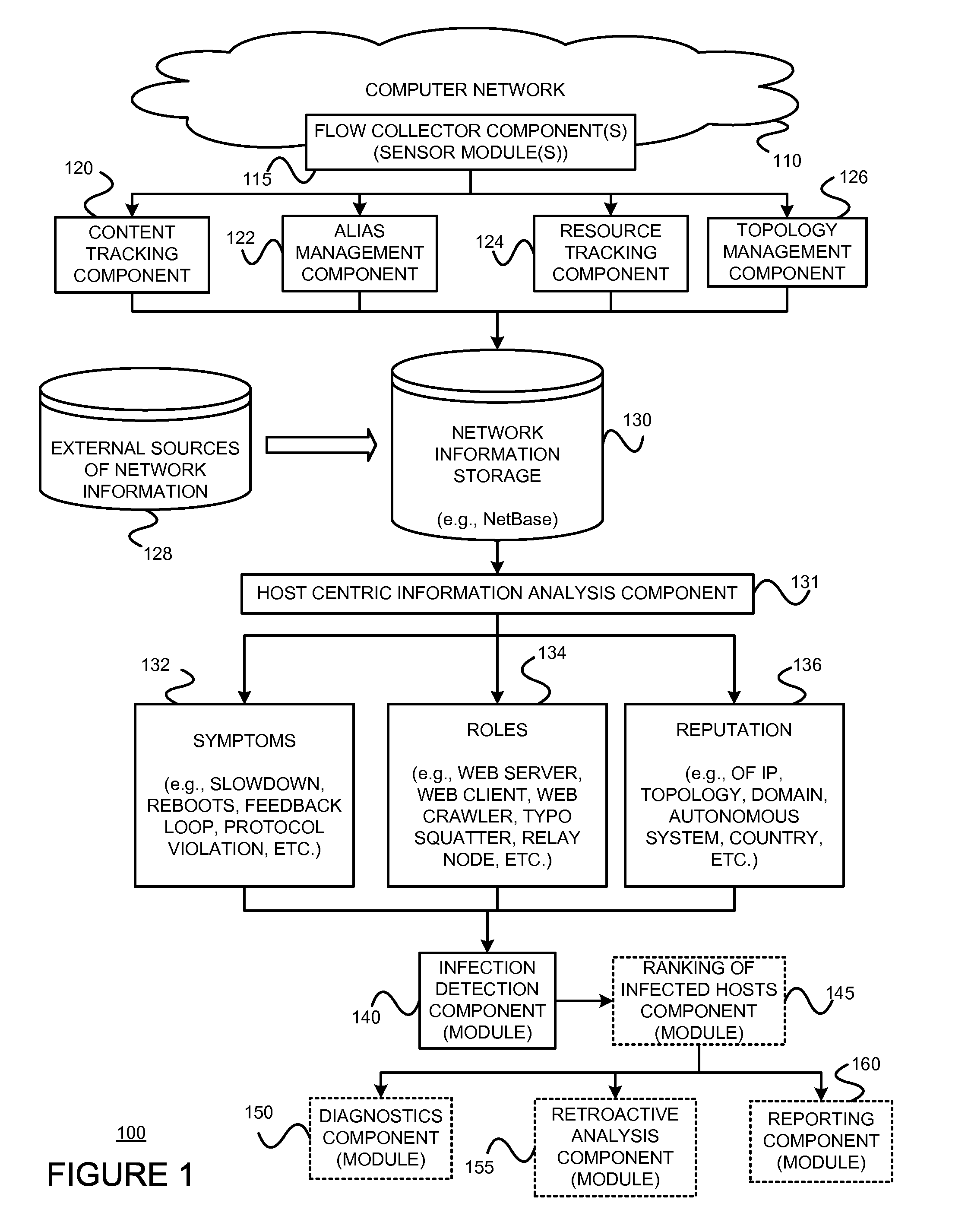
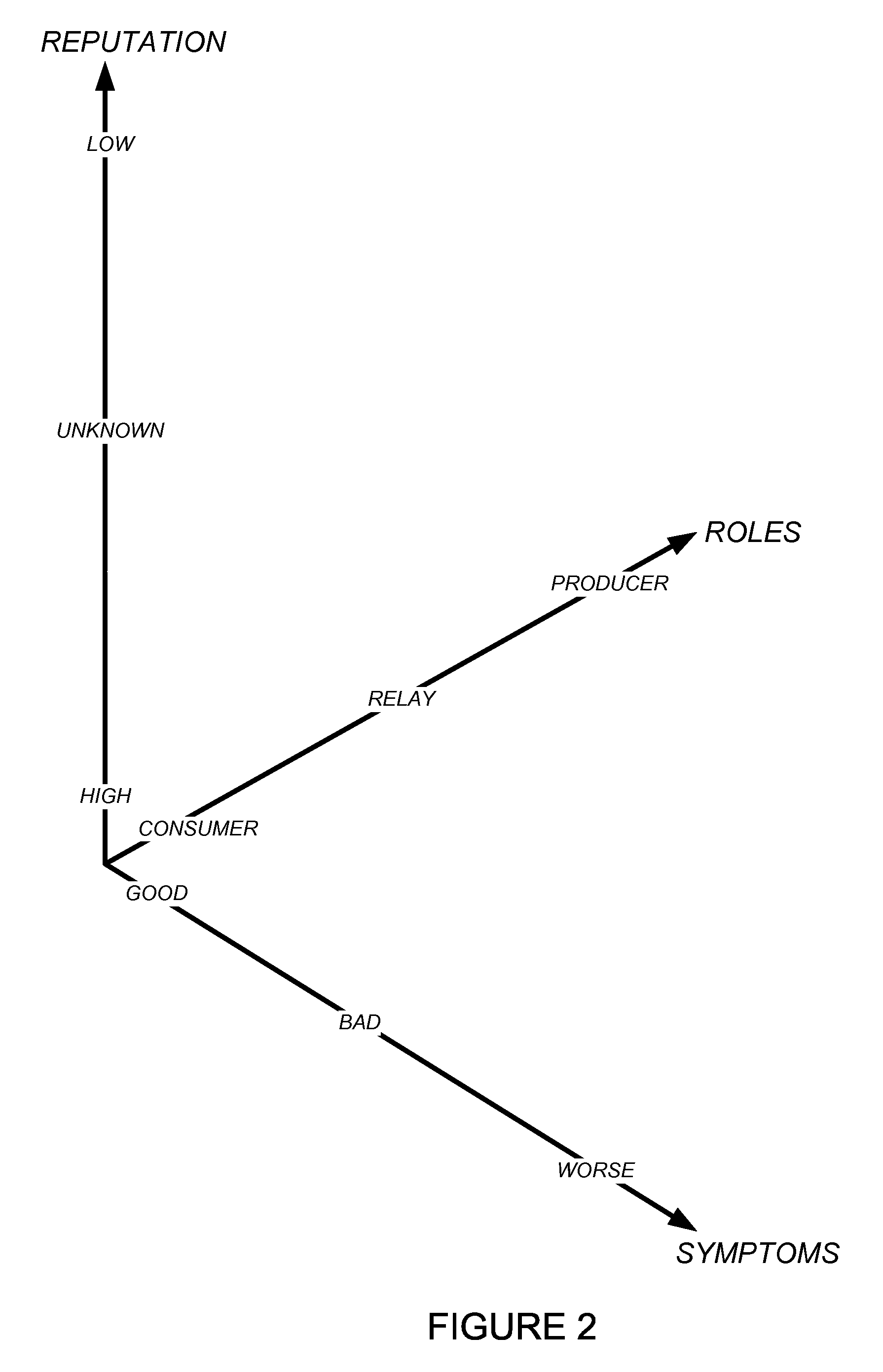
Using host symptoms, host roles, and/or host reputation for detection of host infection
InactiveUS20100235915A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionMalwareIntrusion prevention system
Detecting and mitigating threats to a computer network is important to the health of the network. Currently firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and intrusion prevention systems are used to detect and mitigate attacks. As the attackers get smarter and attack sophistication increases, it becomes difficult to detect attacks in real-time at the perimeter. Failure of perimeter defenses leaves networks with infected hosts. At least two of symptoms, roles, and reputations of hosts in (and even outside) a network are used to identify infected hosts. Virus or malware signatures are not required.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
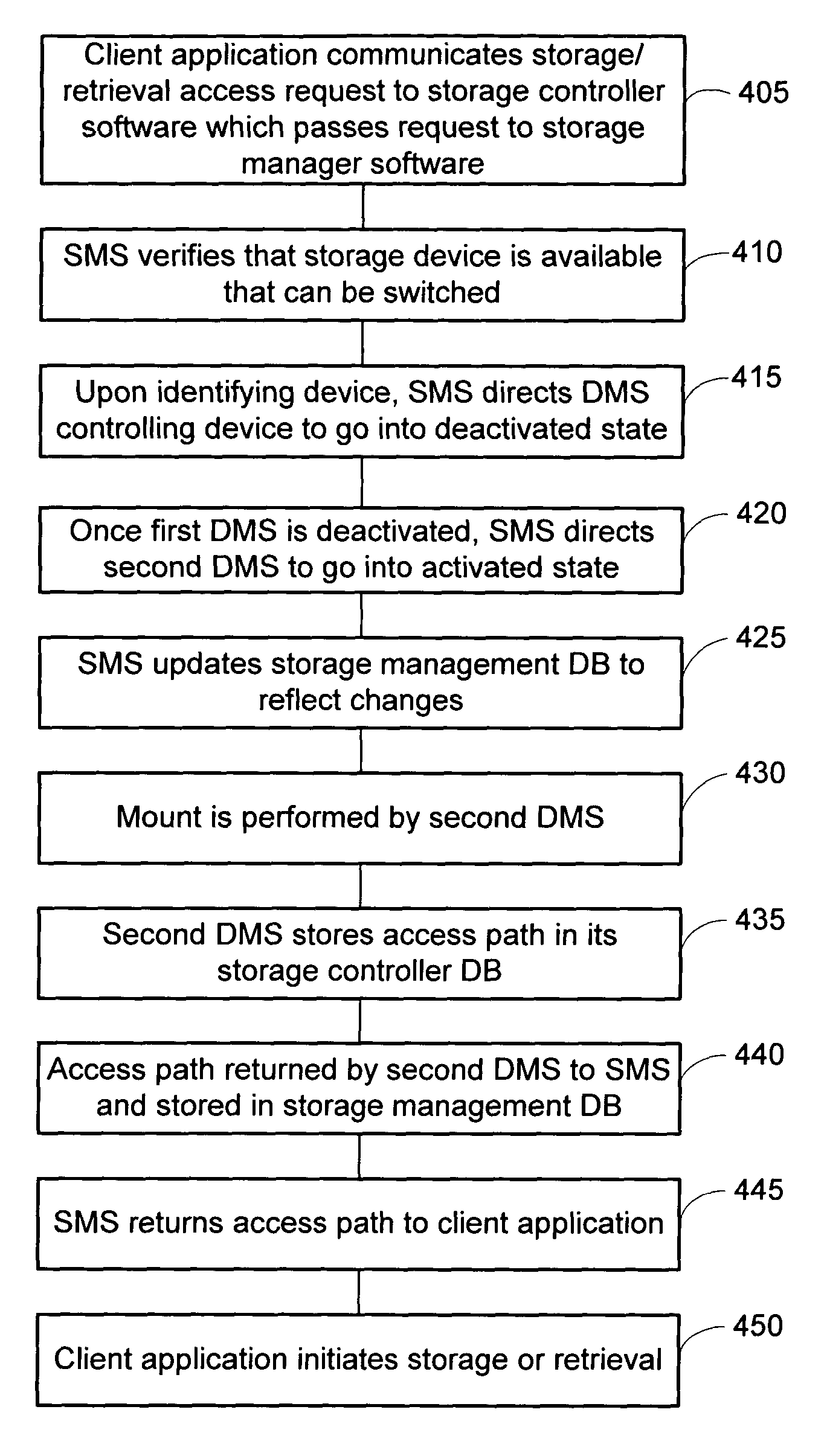
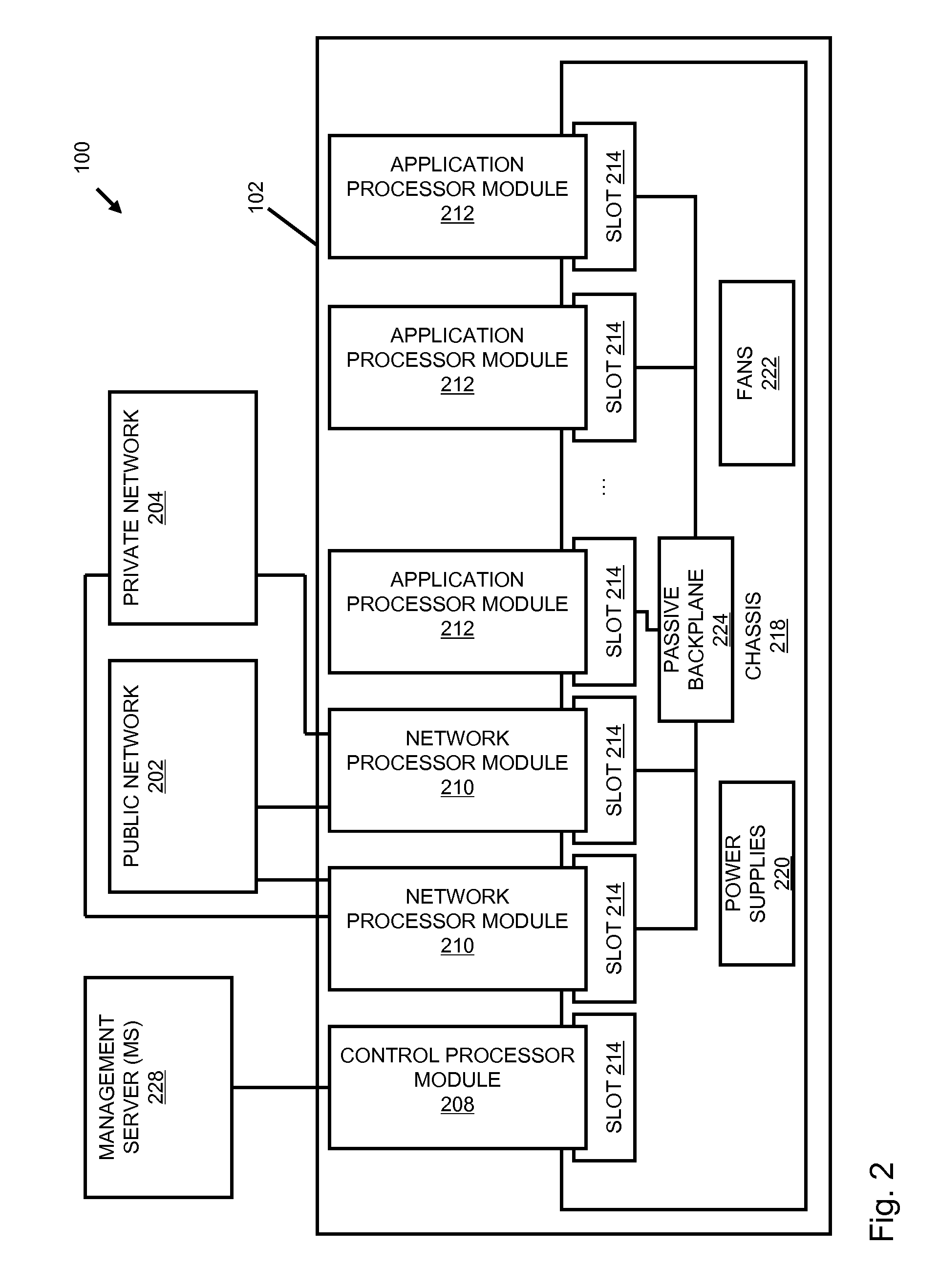
Dynamic storage device pooling in a computer system
ActiveUS7130970B2Not affectInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionDynamic storageComputerized system
A method for dynamically allocating control of a storage device, the method comprising receiving an access request from a first computer requesting access to a storage device; directing, based upon the access request, a first storage controller computer to assume an inactive state with respect to control of the storage device; and directing, based upon the access request, a second storage controller computer to assume an active state with respect to control of the storage device.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Systems and methods for processing data flows
InactiveUS20070192863A1Increased complexitySignificant expenseMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionData packData stream
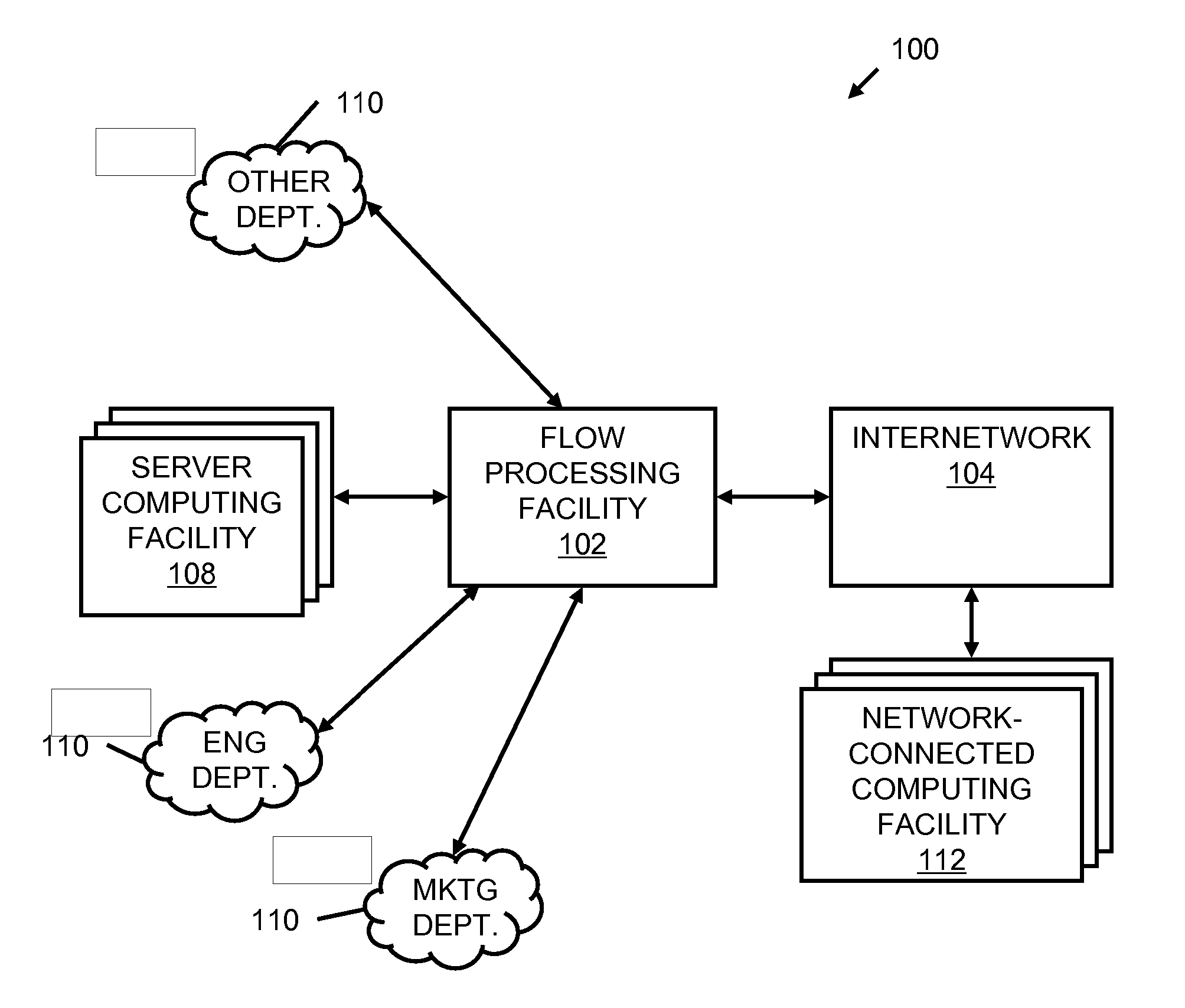
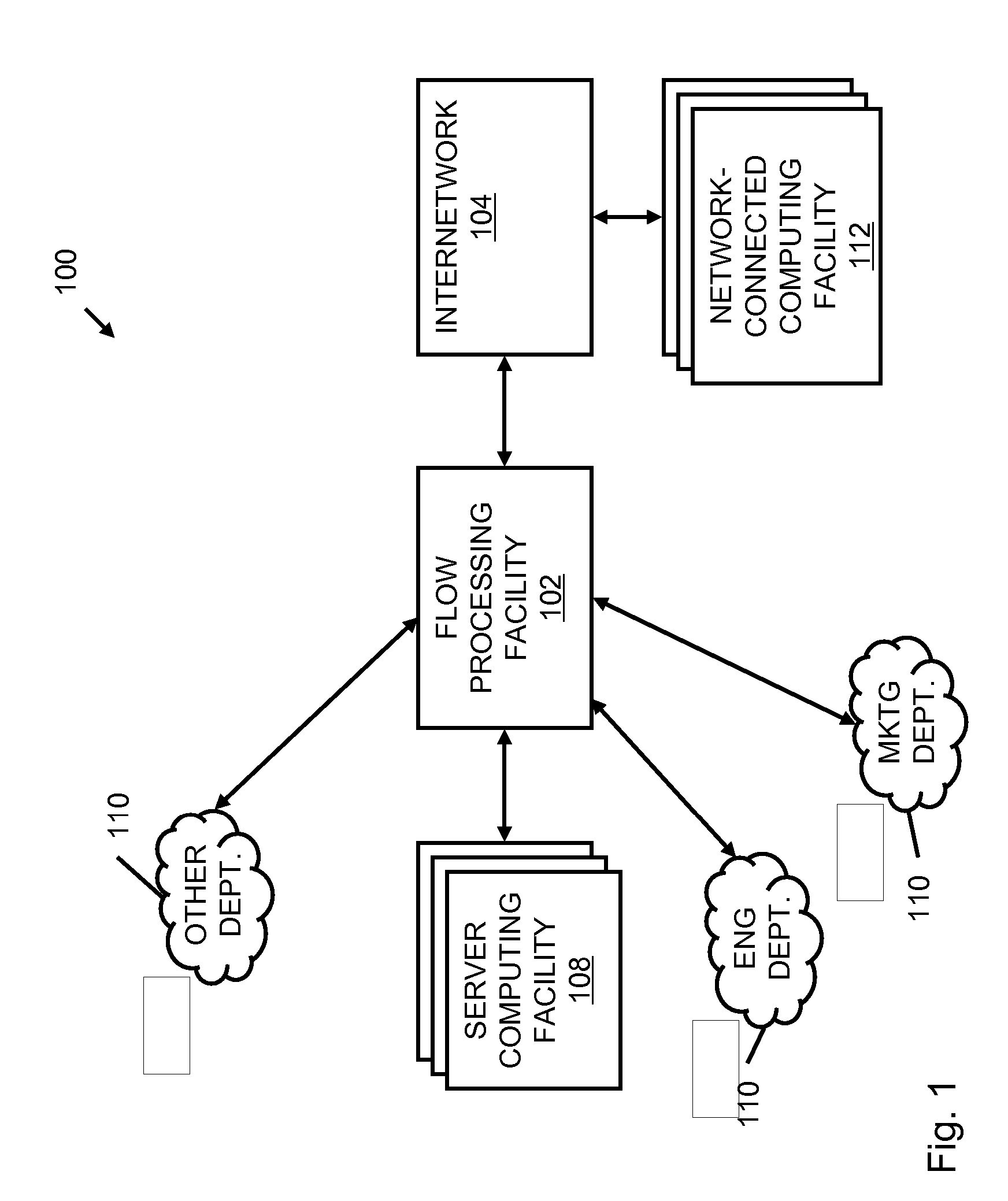
A flow processing facility, which uses a set of artificial neurons for pattern recognition, such as a self-organizing map, in order to provide security and protection to a computer or computer system supports unified threat management based at least in part on patterns relevant to a variety of types of threats that relate to computer systems, including computer networks. Flow processing for switching, security, and other network applications, including a facility that processes a data flow to address patterns relevant to a variety of conditions are directed at internal network security, virtualization, and web connection security. A flow processing facility for inspecting payloads of network traffic packets detects security threats and intrusions across accessible layers of the IP-stack by applying content matching and behavioral anomaly detection techniques based on regular expression matching and self-organizing maps. Exposing threats and intrusions within packet payload at or near real-time rates enhances network security from both external and internal sources while ensuring security policy is rigorously applied to data and system resources. Intrusion Detection and Protection (IDP) is provided by a flow processing facility that processes a data flow to address patterns relevant to a variety of types of network and data integrity threats that relate to computer systems, including computer networks.
Owner:BLUE COAT SYSTEMS
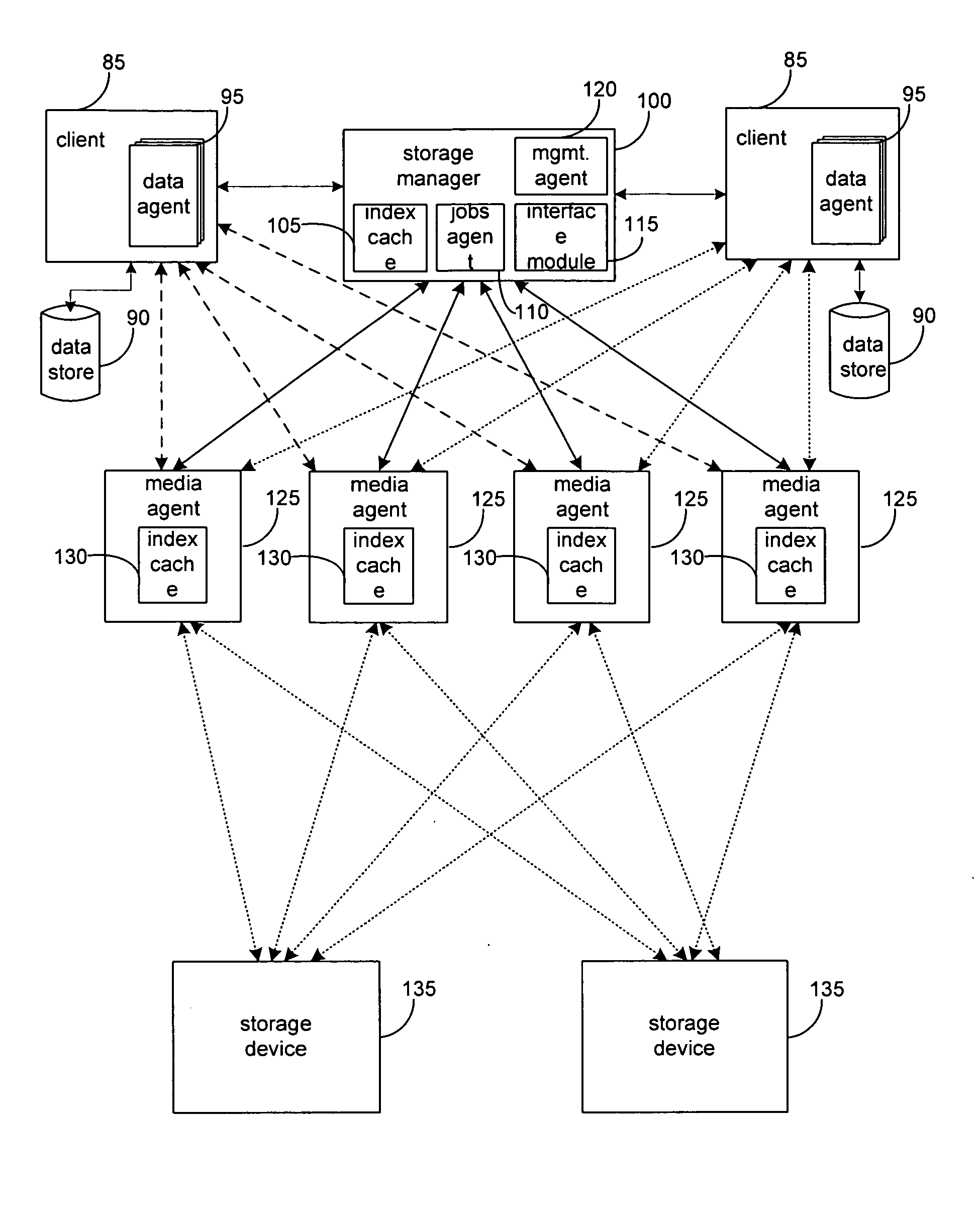
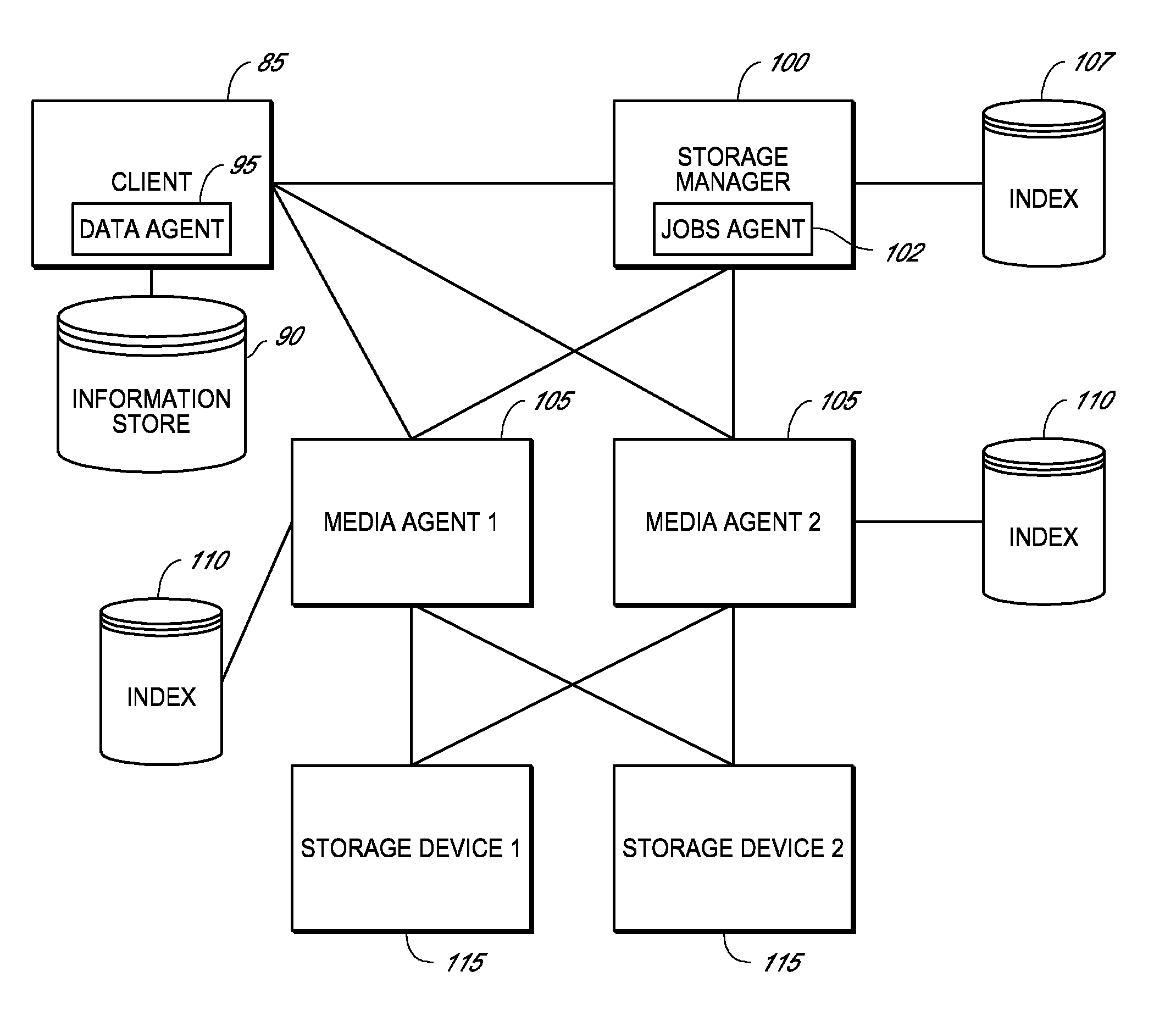
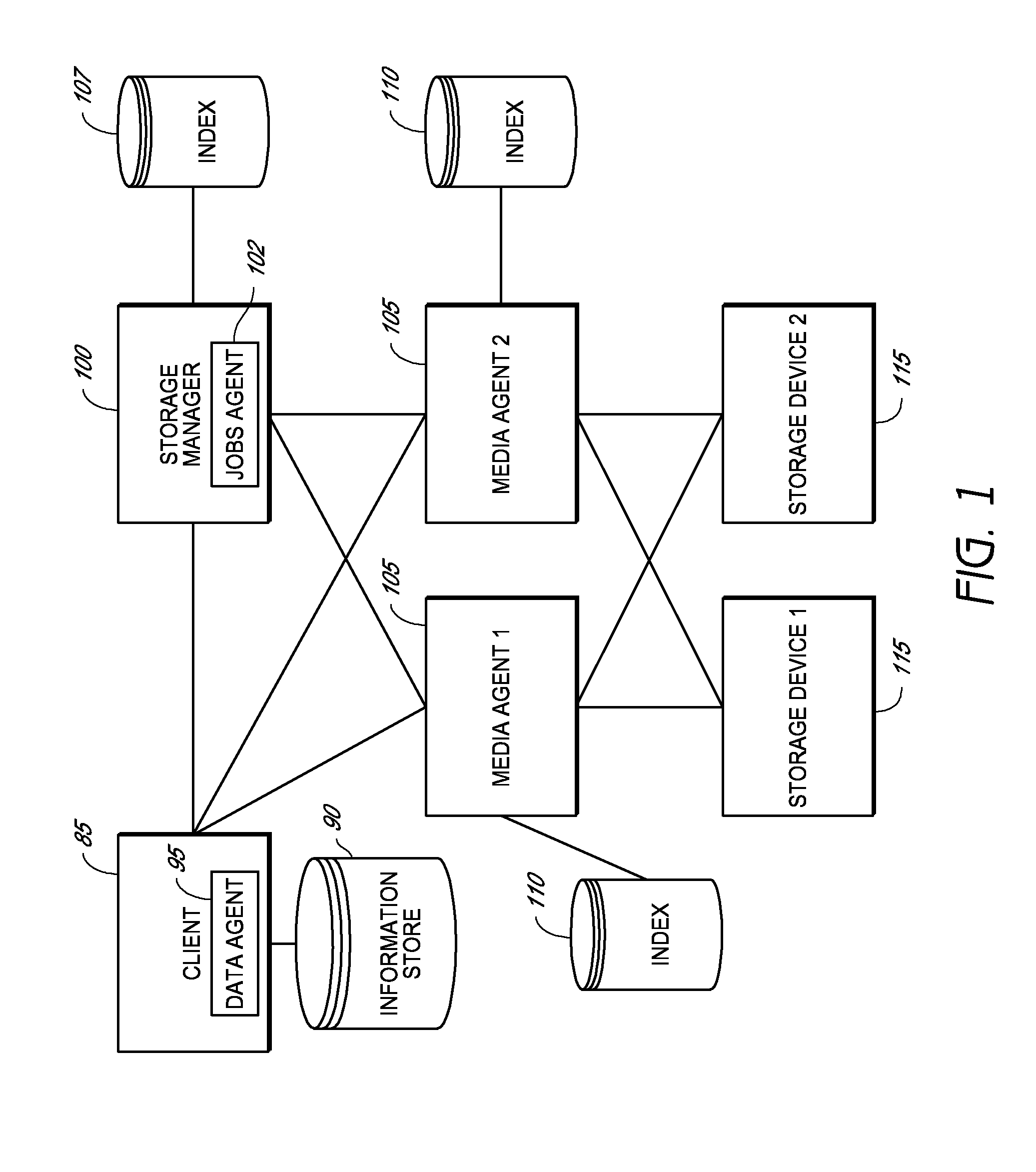
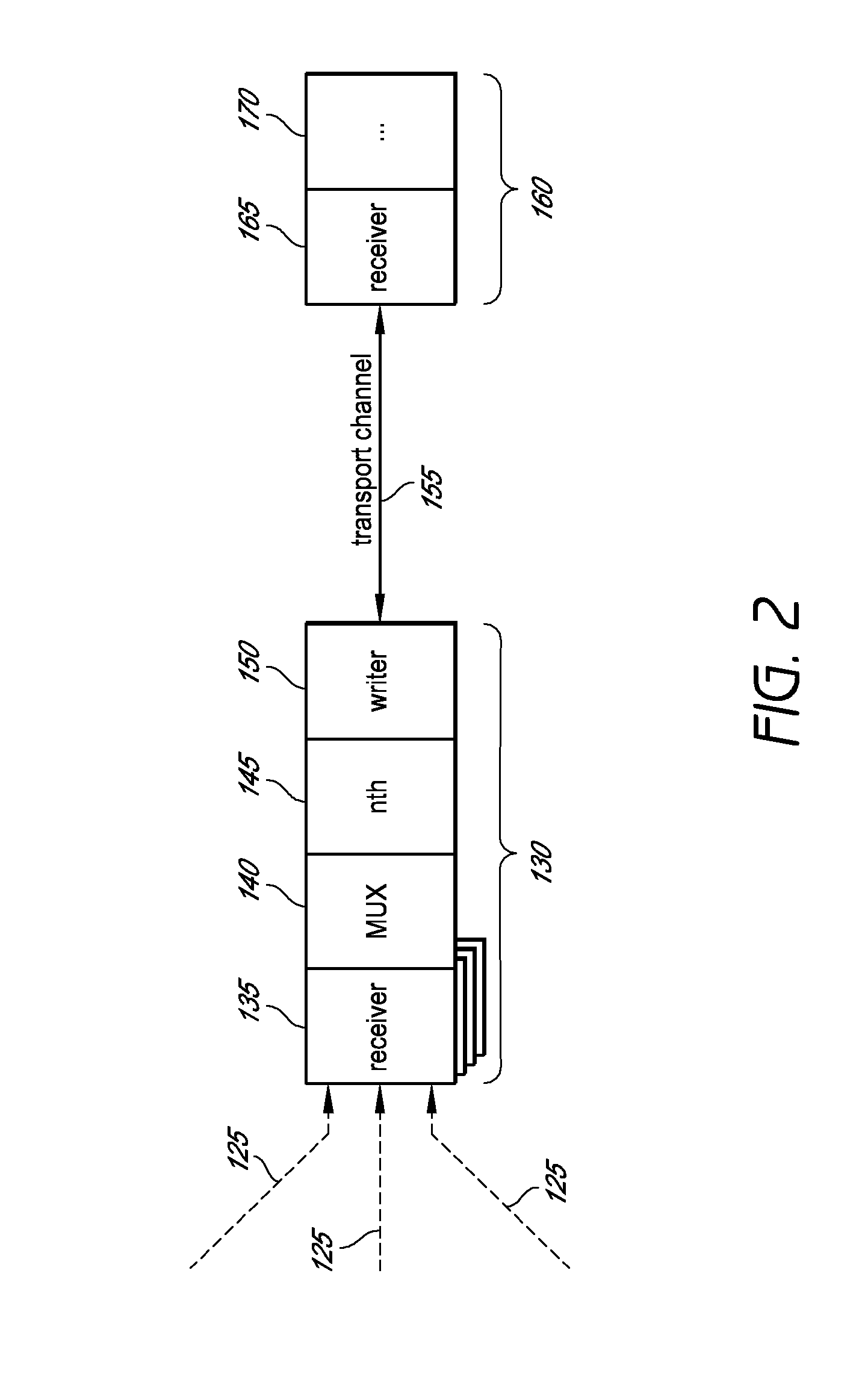
System and method for combining data streams in pipelined storage operations in a storage network
Described herein are systems and methods for multiplexing pipelined data for backup operations. Various data streams are combined such as by multiplexing by a multiplexing module. The multiplexing module combines the data from the various data streams received by receiver module(s) into a single stream of chunks. The multiplexing module may combine data from multiple archive files into a single chunk. Additional modules perform other operations on the chunks of data to be transported such as encryption, compression, etc. The data chunks are transmitted via a transport channel to a receive pipeline that includes a second receiver module and other modules. The data chunks are then stored in a backup medium. The chunks are later retrieved and separated such as by demultiplexing for restoring to a client or for further storage as auxiliary copies of the separated data streams or archive files.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
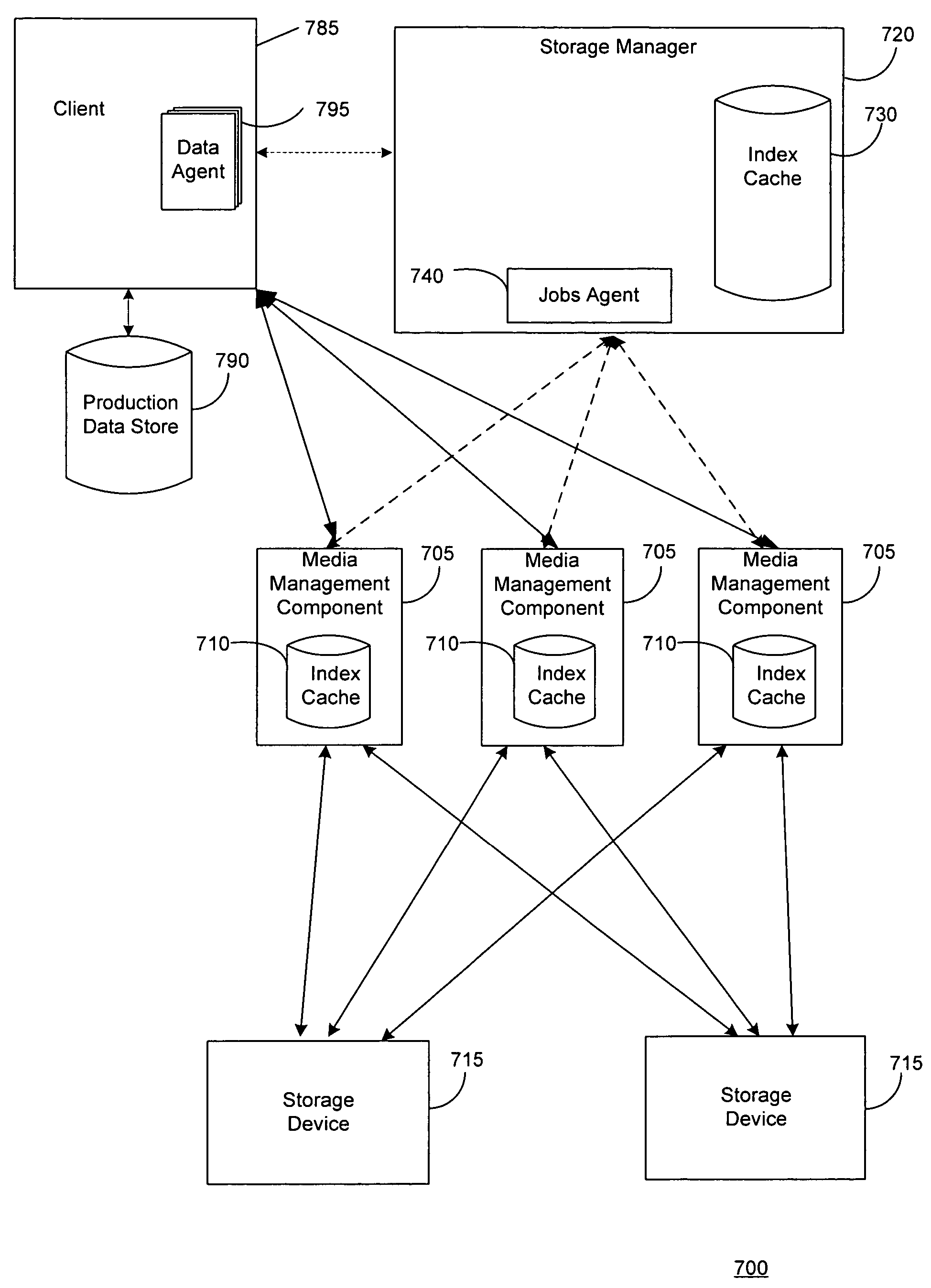
System and method for performing auxiliary storage operations
Systems and methods for protecting data in a tiered storage system are provided. The storage system comprises a management server, a media management component connected to the management server, a plurality of storage media connected to the media management component, and a data source connected to the media management component. Source data is copied from a source to a buffer to produce intermediate data. The intermediate data is copied to both a first and second medium to produce a primary and auxiliary copy, respectively. An auxiliary copy may be made from another auxiliary copy. An auxiliary copy may also be made from a primary copy right before the primary copy is pruned.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Methods and systems for sharing risk responses between collections of mobile communications devices
Methods are provided for determining an enterprise risk level, for sharing security risk information between enterprises by identifying a security response by a first enterprise and then sharing the security response to a second enterprise when a relationship database profile for the first collection indicates the security response may be shared. Methods are also provided for determining whether to allow a request from an originating device where the request may have been initiated by a remote device.
Owner:LOOKOUT MOBILE SECURITY
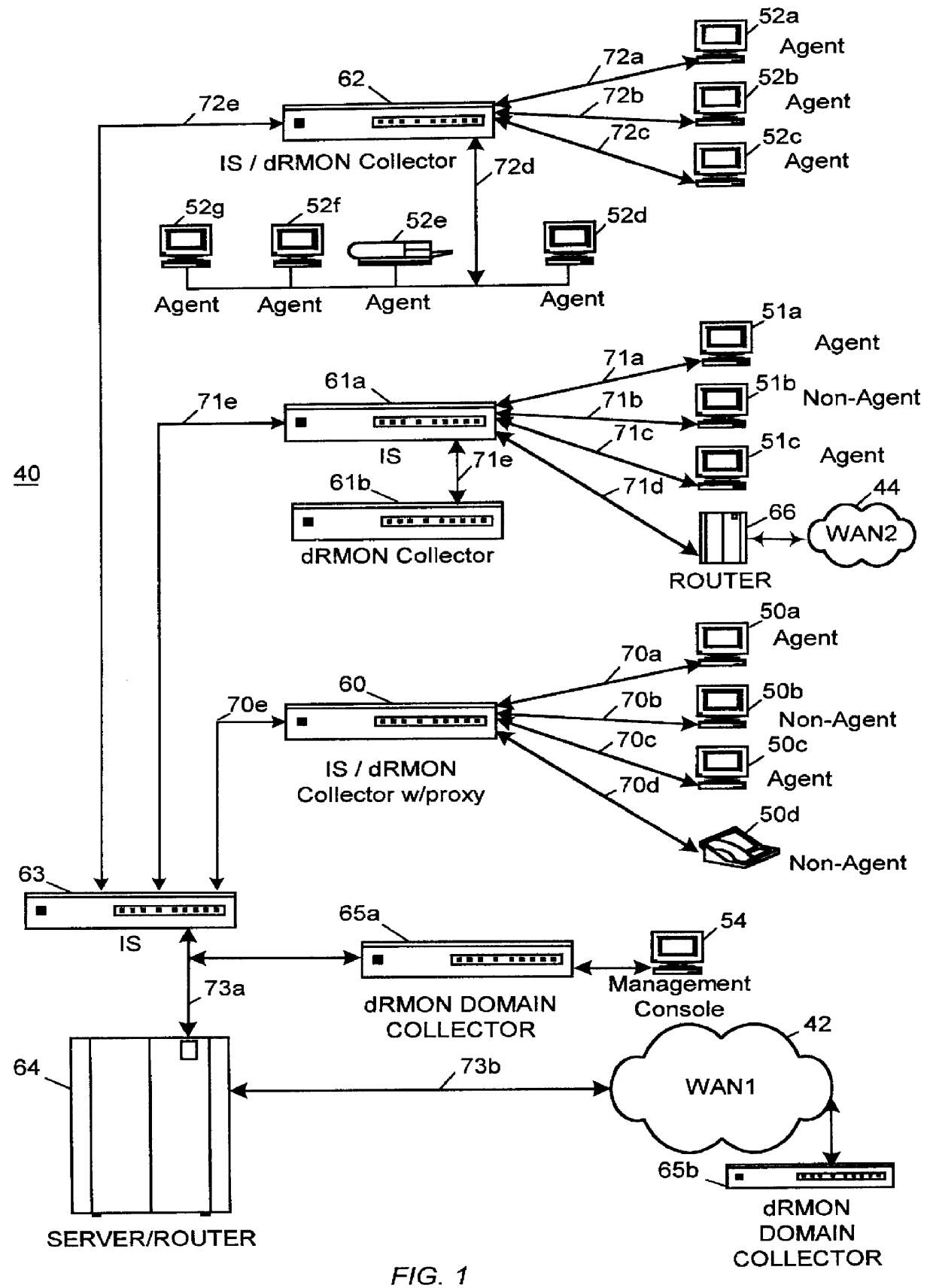
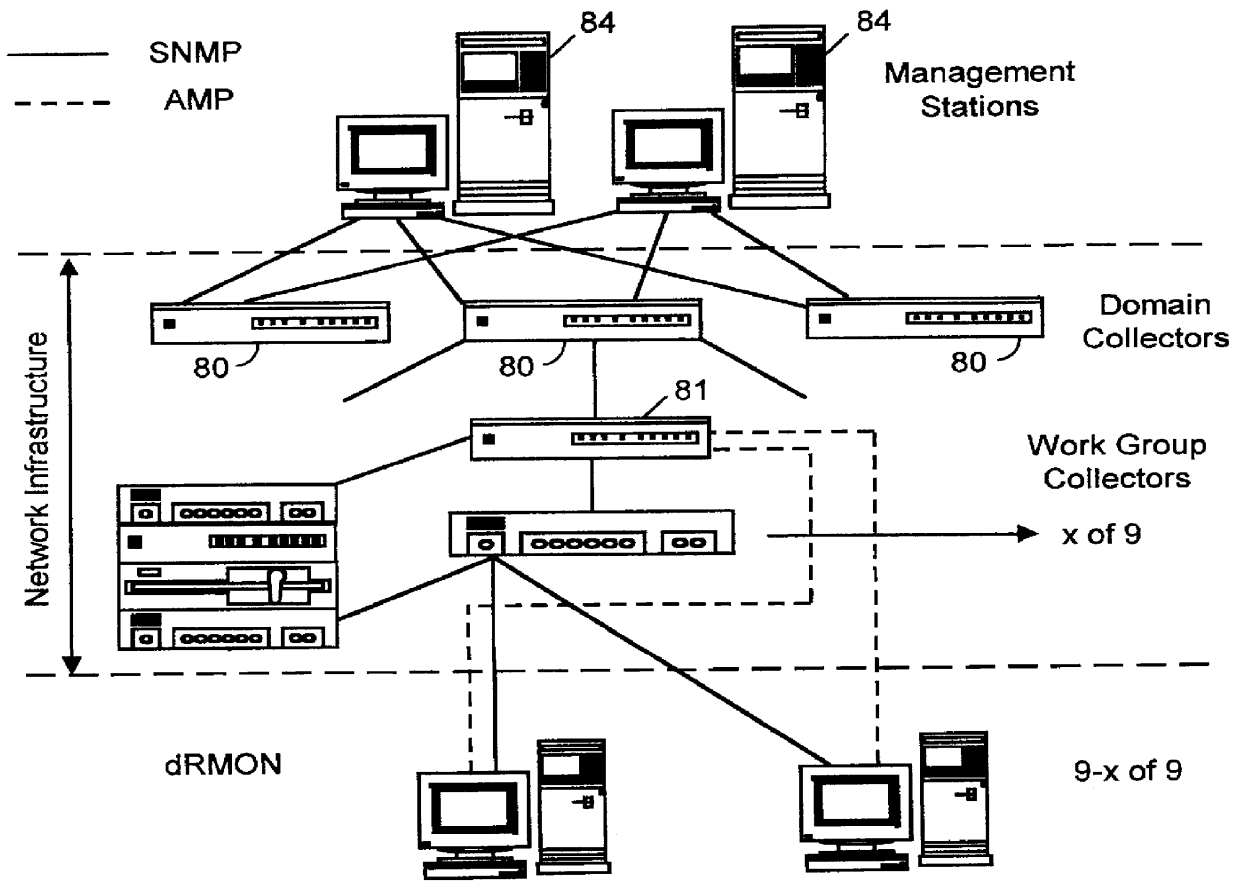
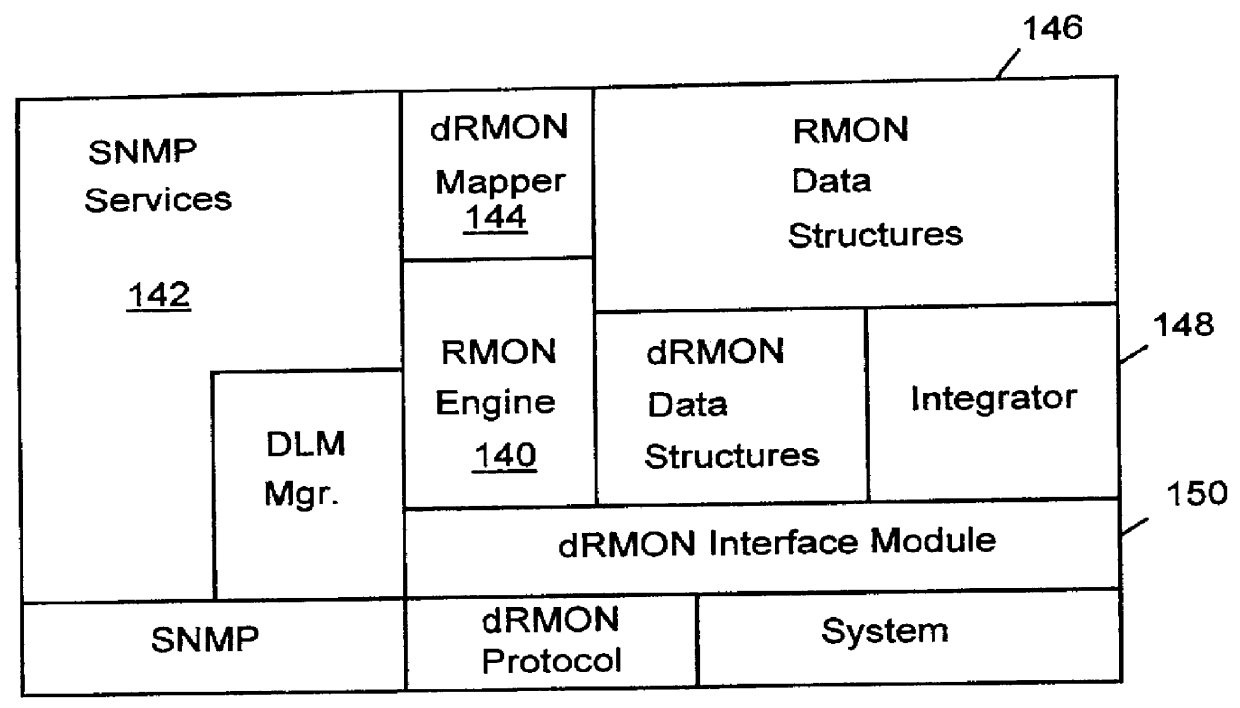
Distributed remote monitoring (dRMON) for networks
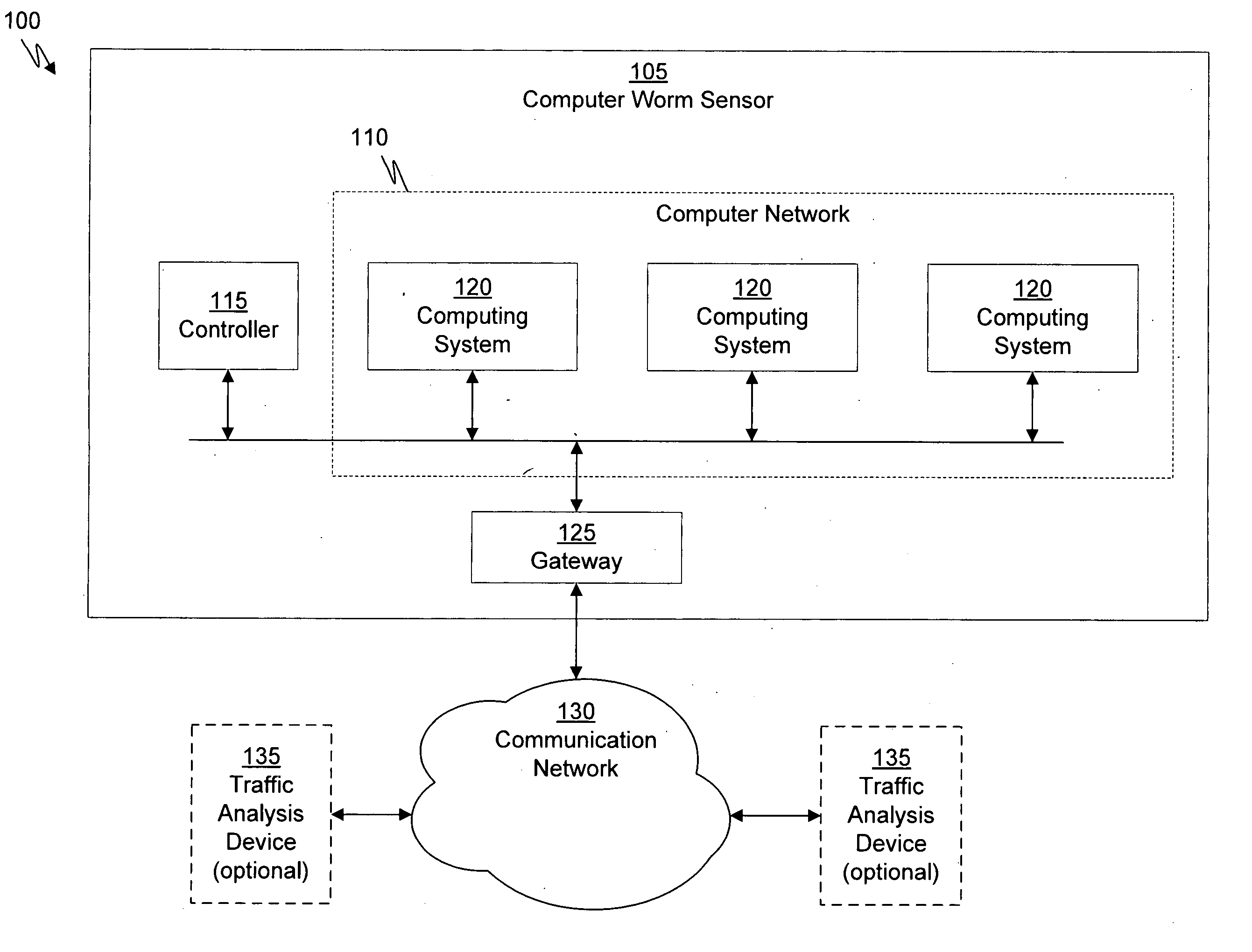
InactiveUS6108782AError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork operating systemOperational system
Distributed remote monitoring (dRMON) of network traffic and performance uses distributed nodes to collect traffic statistics at distributed points in the network. These statistics are forwarded to collectors which compile the statistics to create combined views of network performance. A collector may mimic a prior art, non-distributed, network probe and may interact with network management software as though it were a stand alone network probe thereby simplifying a user's interaction with the distributed system. The invention is designed to work in accordance with a variety of standard network management protocols including SNMP, RMON, and RMON2 but is not limited to those environments. The invention has applications in a variety of communication system environments including local area networks, cable television distribution systems, ATM systems, and advanced telephony systems. A specific embodiment of the invention solves is particularly optimized to work in LAN environments with end systems running under Windows-compatible network operating systems.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
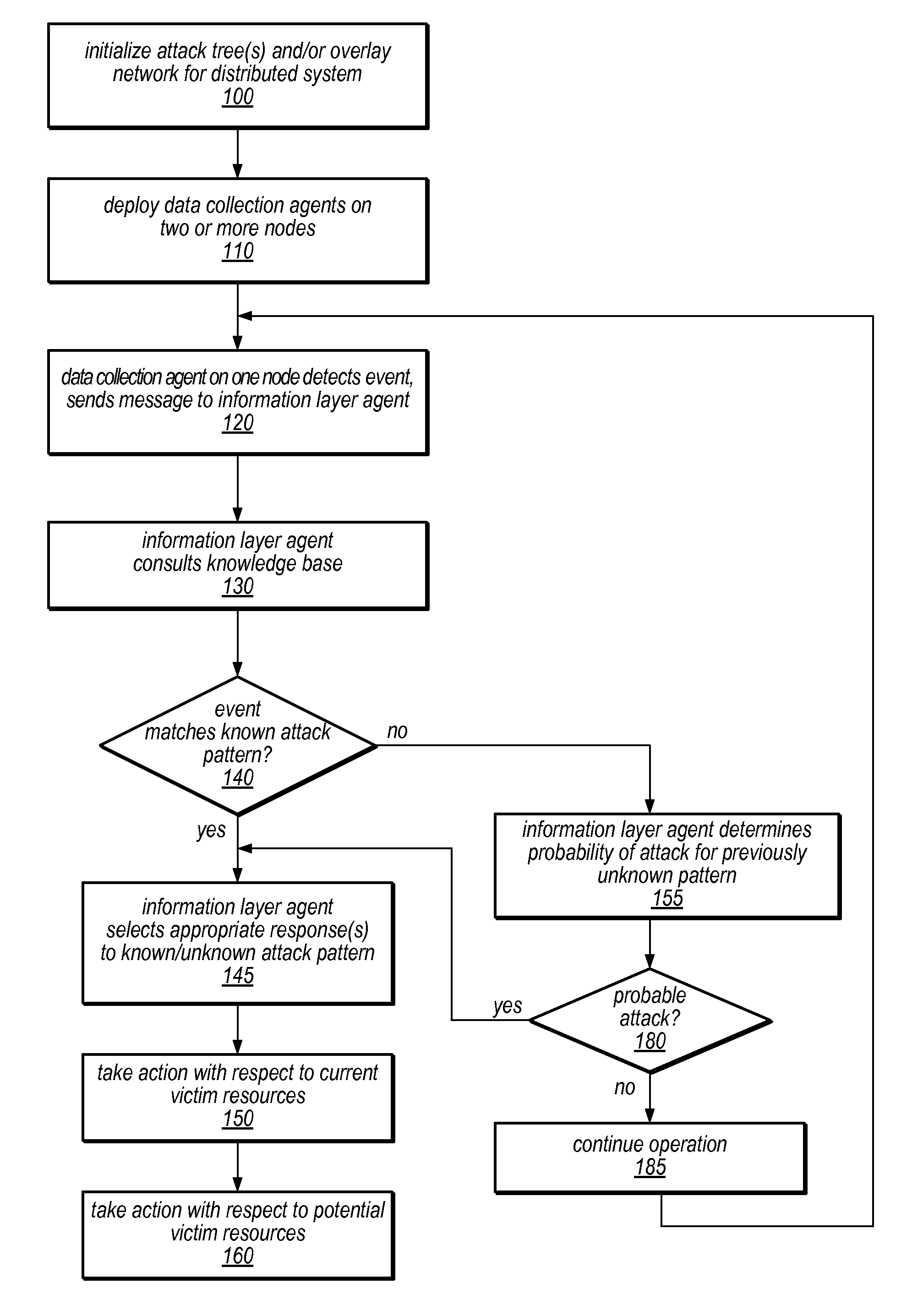
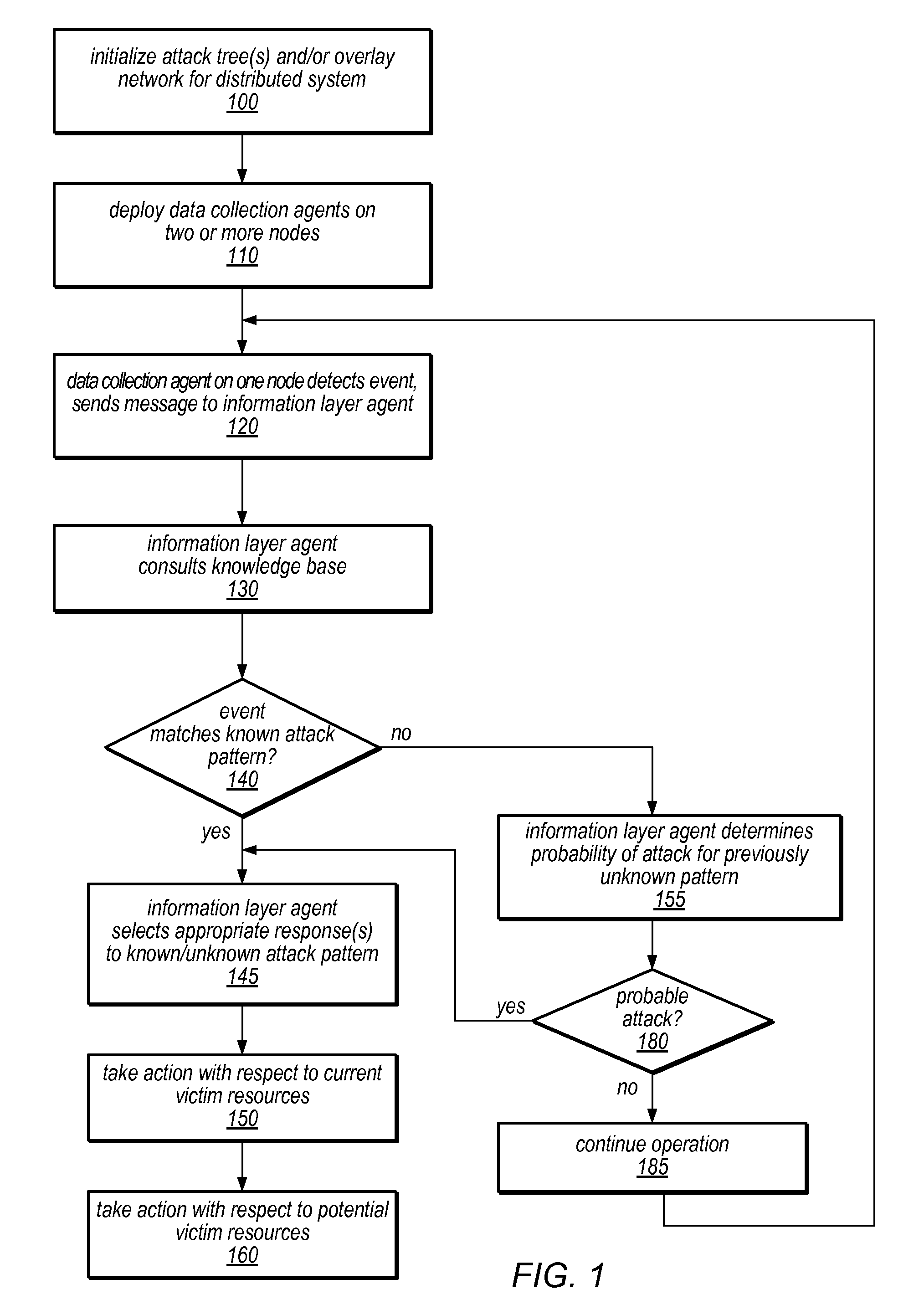
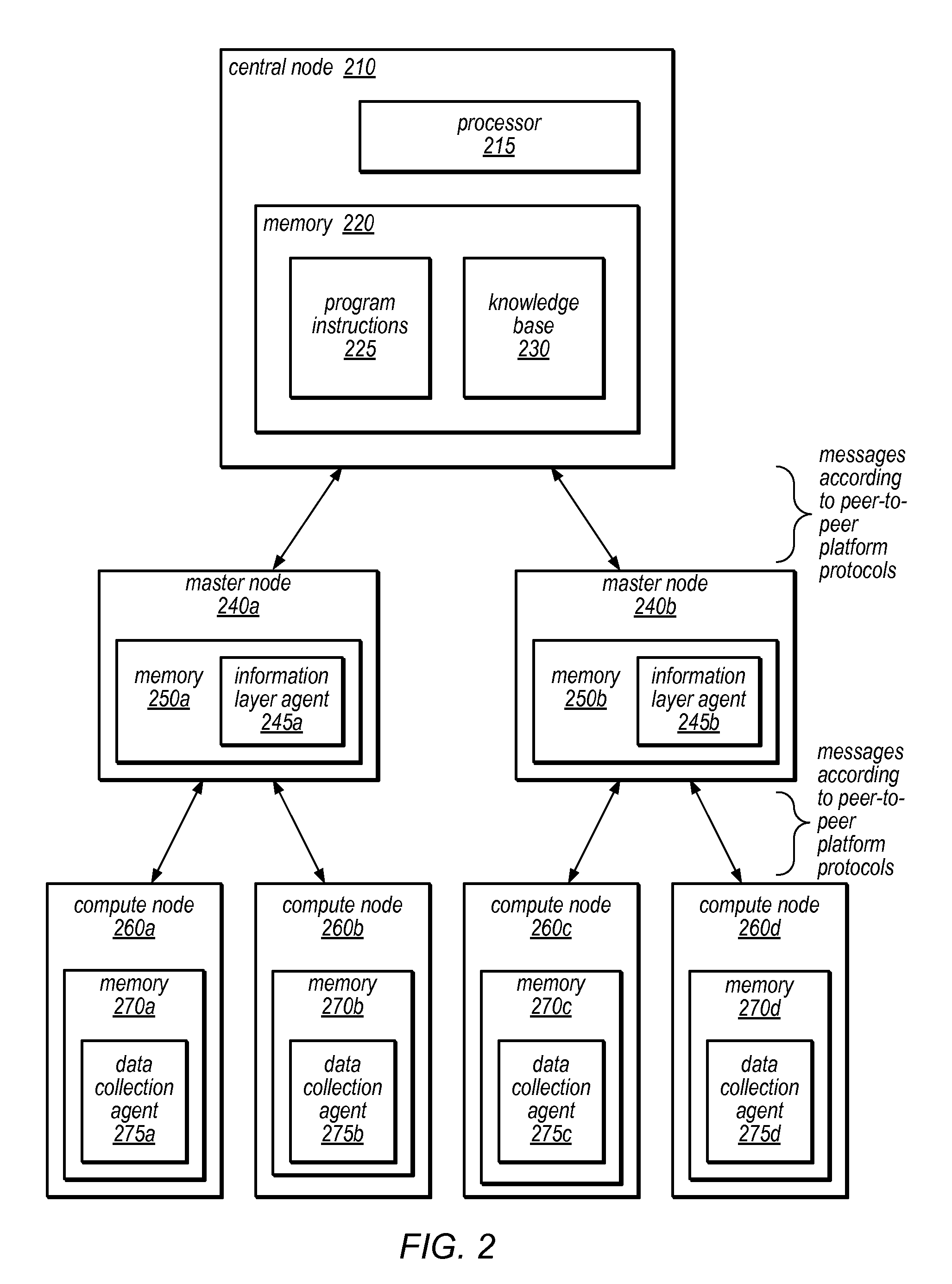
System and Method for Distributed Denial of Service Identification and Prevention
Systems and methods for discovery and classification of denial of service attacks in a distributed computing system may employ local agents on nodes thereof to detect resource-related events. An information later agent may determine if events indicate attacks, perform clustering analysis to determine if they represent known or unknown attack patterns, classify the attacks, and initiate appropriate responses to prevent and / or mitigate the attack, including sending warnings and / or modifying resource pool(s). The information layer agent may consult a knowledge base comprising information associated with known attack patterns, including state-action mappings. An attack tree model and an overlay network (over which detection and / or response messages may be sent) may be constructed for the distributed system. They may be dynamically modified in response to changes in system configuration, state, and / or workload. Reinforcement learning may be applied to the tuning of attack detection and classification techniques and to the identification of appropriate responses.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
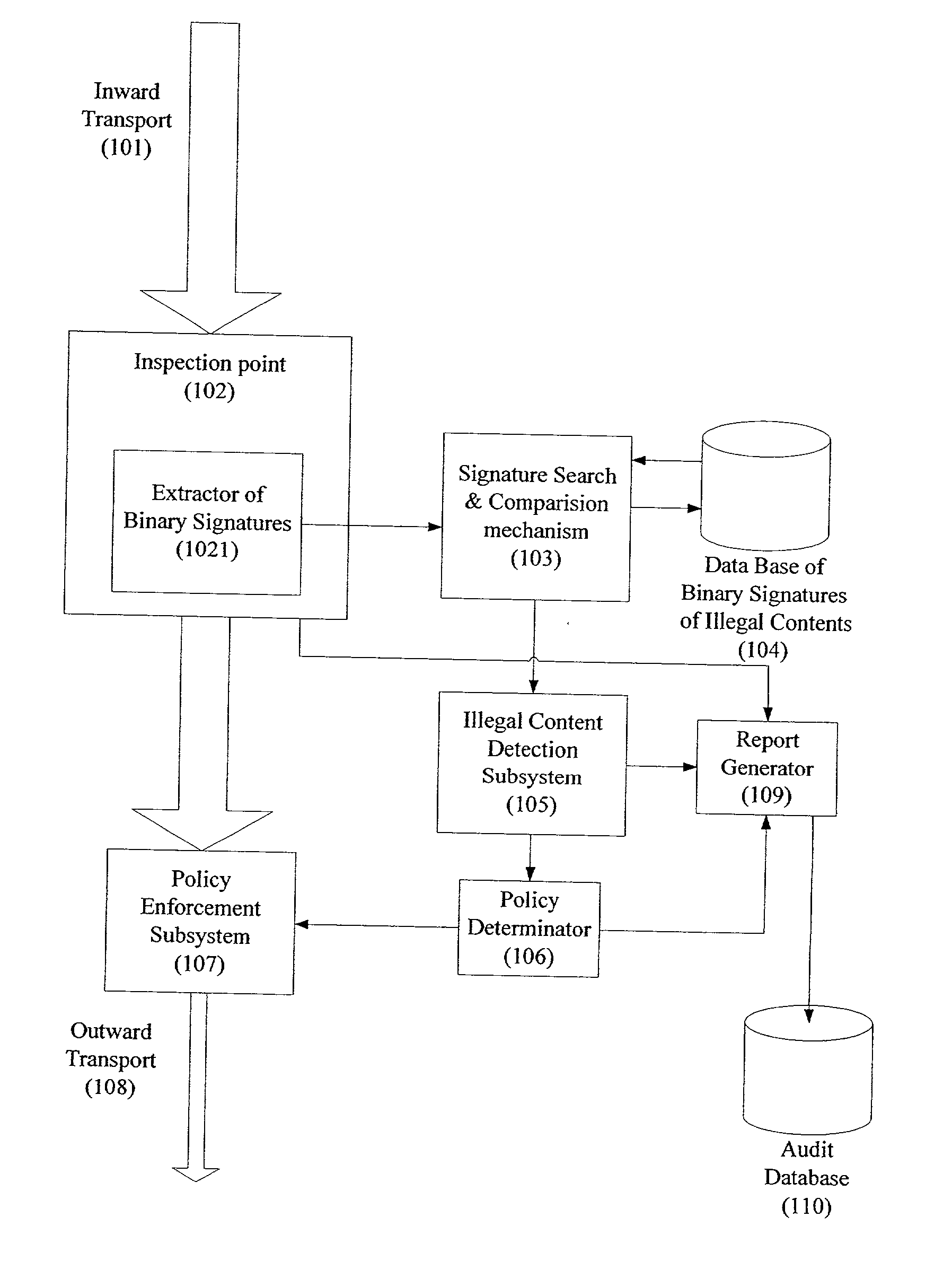
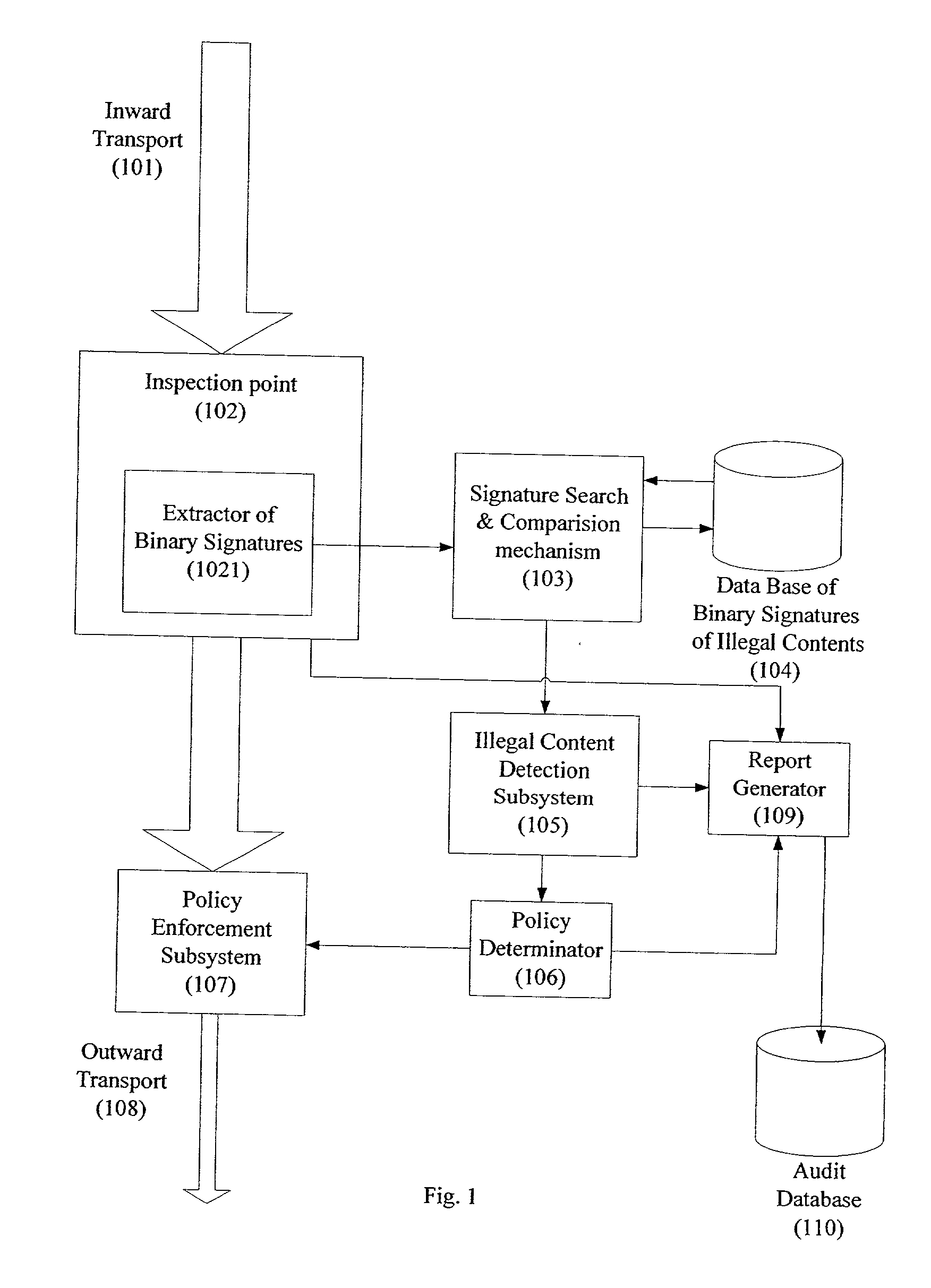
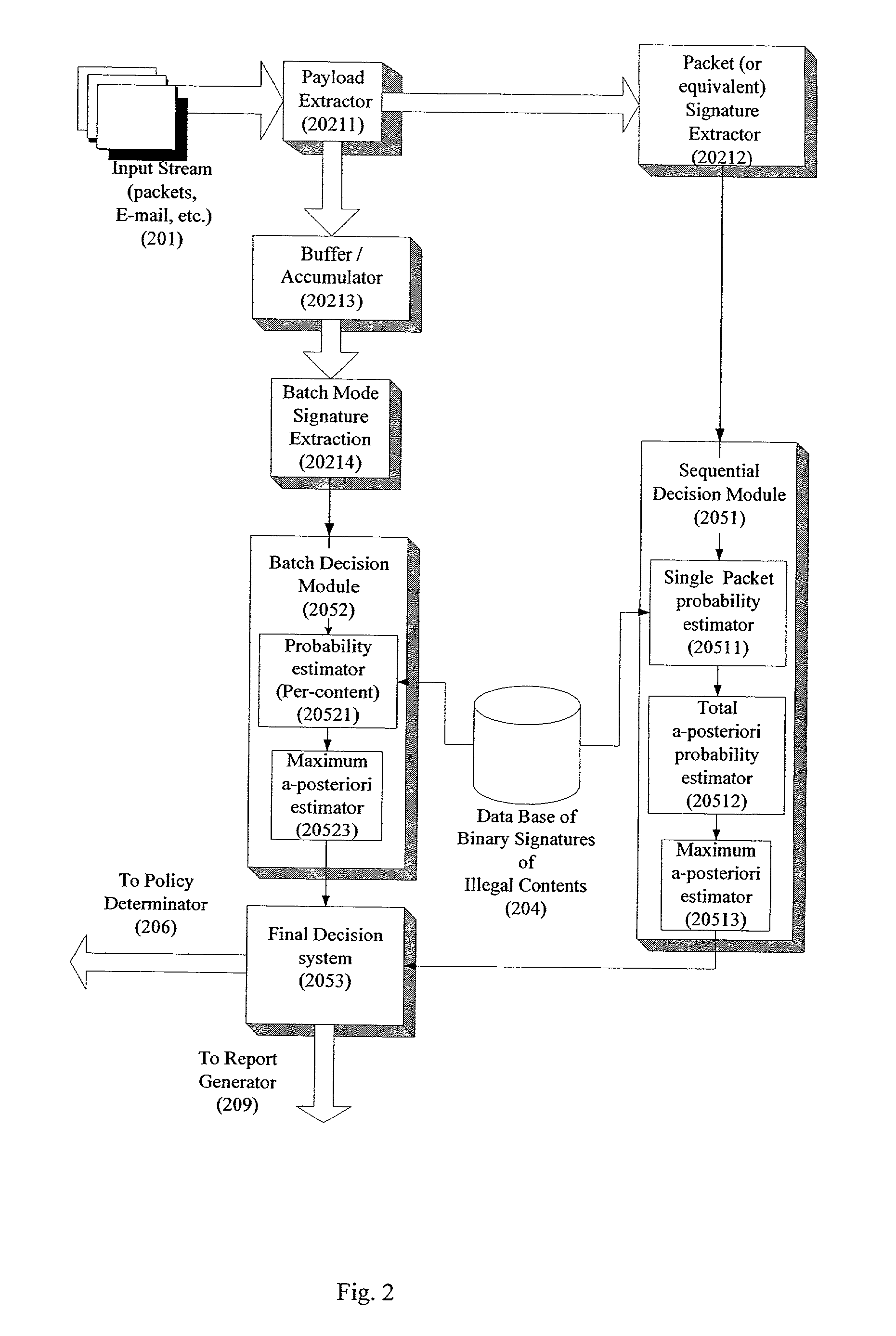
System and method for monitoring unauthorized transport of digital content
ActiveUS20020129140A1Reduce decreaseAttenuation bandwidthMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionDigital contentNumber content
A system for network content monitoring and control, comprising: a transport data monitor, connectable to a point in a network, for monitoring data being transported past said point, a signature extractor, associated with said transport data monitor, for extracting a derivation of said data, said derivation being indicative of content of said payload, a database of preobtained signatures of content whose movements it is desired to monitor, and a comparator for comparing said derivation with said preobtained signatures, thereby to determine whether said payload comprises any of said content whose movements it is desired to monitor. The monitoring result may be used in bandwidth control on the network to restrict transport of the content it is desired to control.
Owner:FORCEPOINT LLC
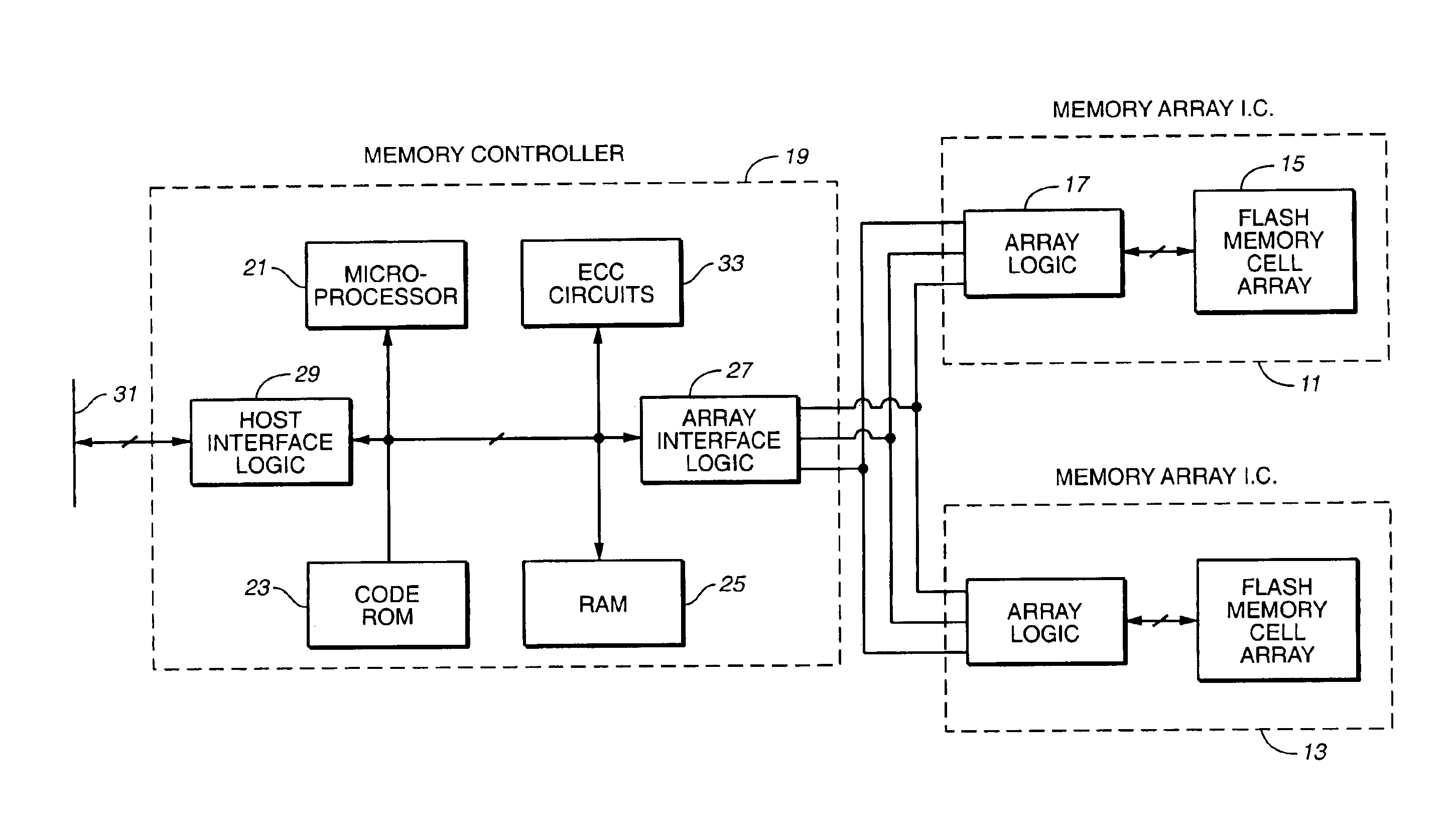
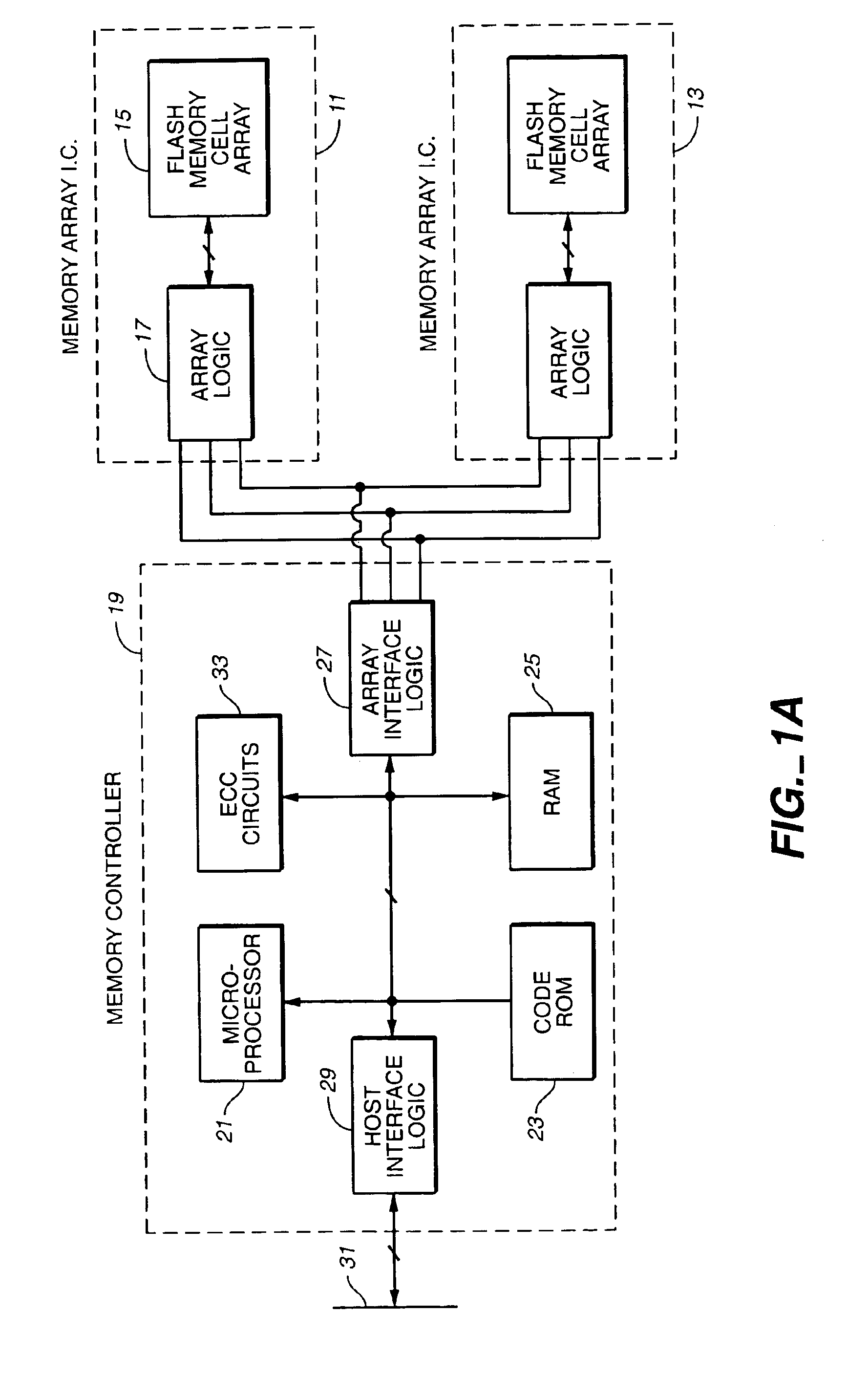
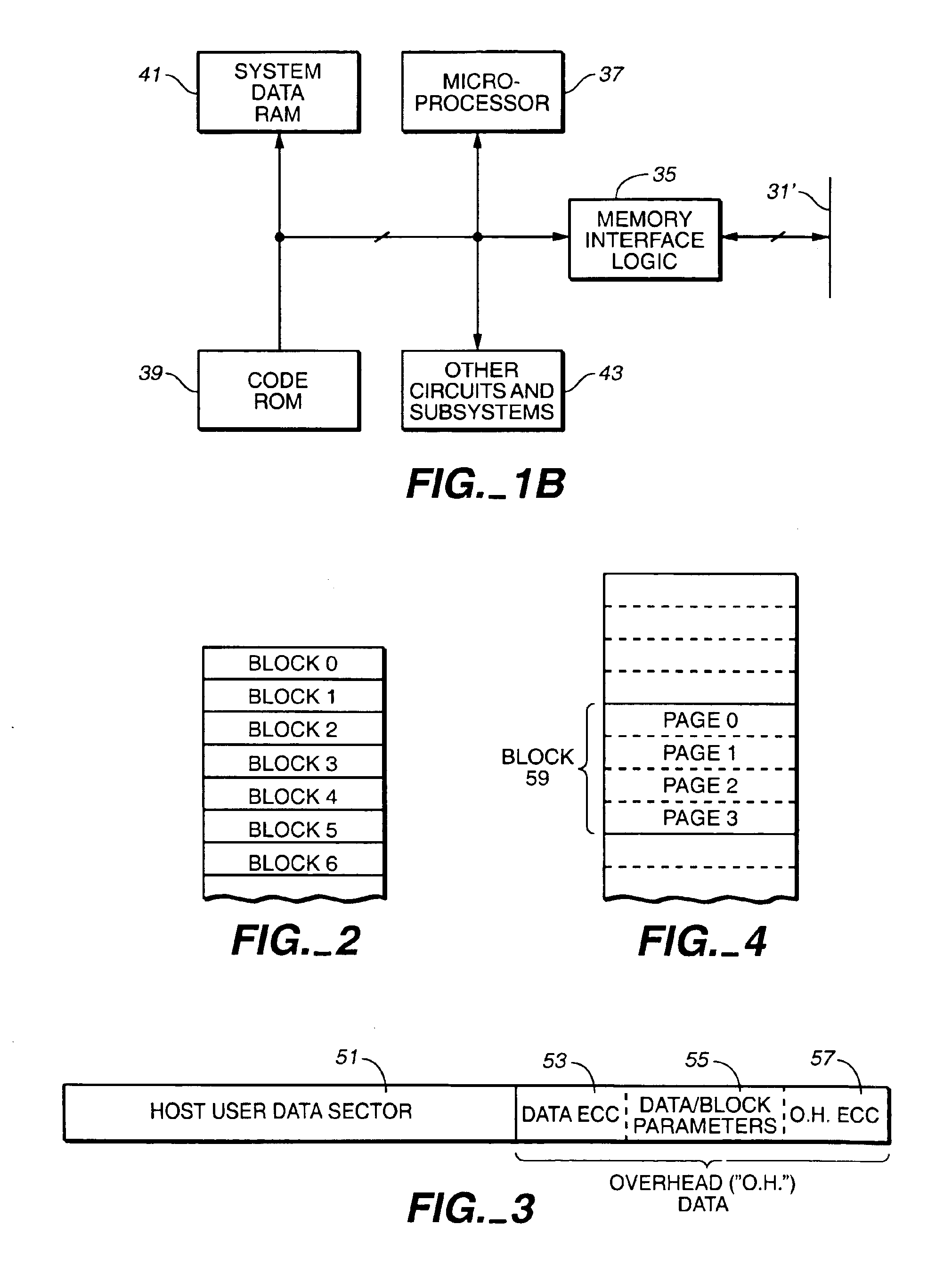
Flash memory data correction and scrub techniques
ActiveUS7012835B2Data disturbanceReduce storage dataMemory loss protectionRead-only memoriesData integrityData storing
In order to maintain the integrity of data stored in a flash memory that are susceptible to being disturbed by operations in adjacent regions of the memory, disturb events cause the data to be read, corrected and re-written before becoming so corrupted that valid data cannot be recovered. The sometimes conflicting needs to maintain data integrity and system performance are balanced by deferring execution of some of the corrective action when the memory system has other high priority operations to perform. In a memory system utilizing very large units of erase, the corrective process is executed in a manner that is consistent with efficiently rewriting an amount of data much less than the capacity of a unit of erase.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
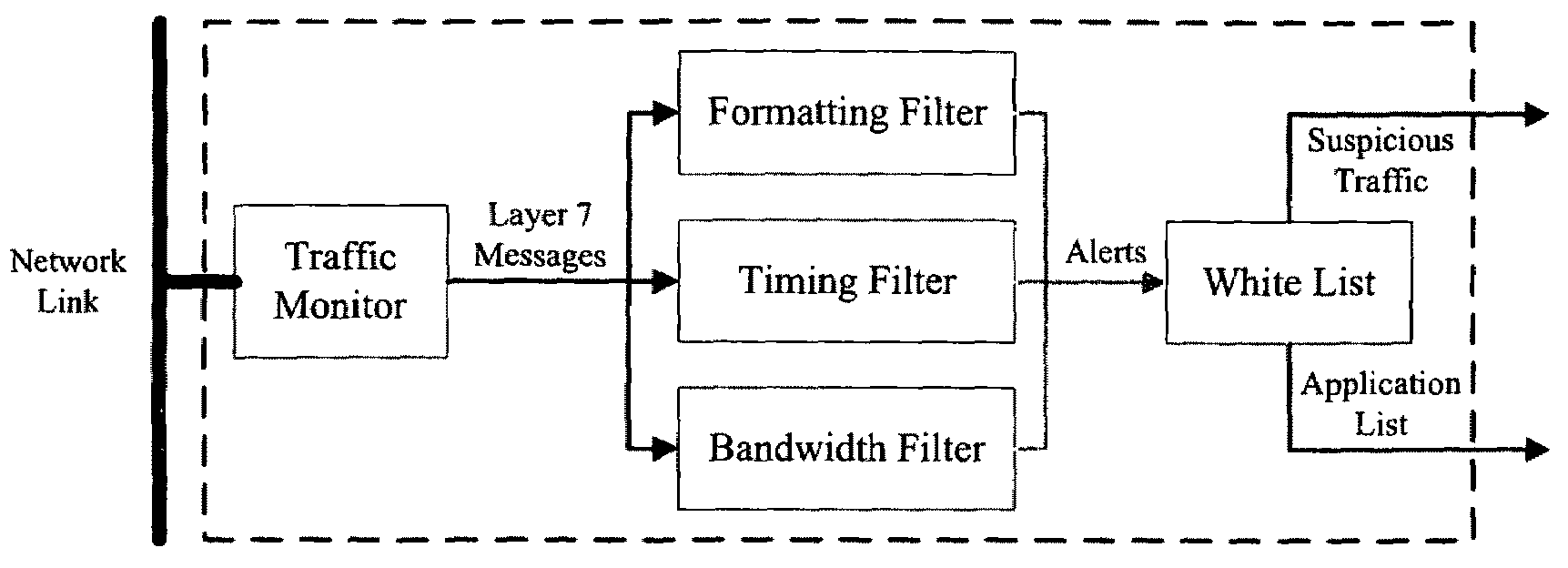
Method, system and computer program product for detecting at least one of security threats and undesirable computer files
Method, system and computer program product for detecting at least one of security threats and undesirable computer files are provided. A first method includes receiving a data stream which represents outbound, application layer messages from a first computer process to at least one second computer process. The computer processes are implemented on one or more computers. The method further includes monitoring the data stream to detect a security threat based on a whitelist having entries which contain metadata. The whitelist describes legitimate application layer messages based on a set of heuristics. The method still further includes generating a signal if a security threat is detected. A second method includes comparing a set of computer files with a whitelist which characterizes all legitimate computer files. The whitelist contains one or more entries. Each of the entries describe a plurality of legitimate computer files.
Owner:SYROWIK DAVID R
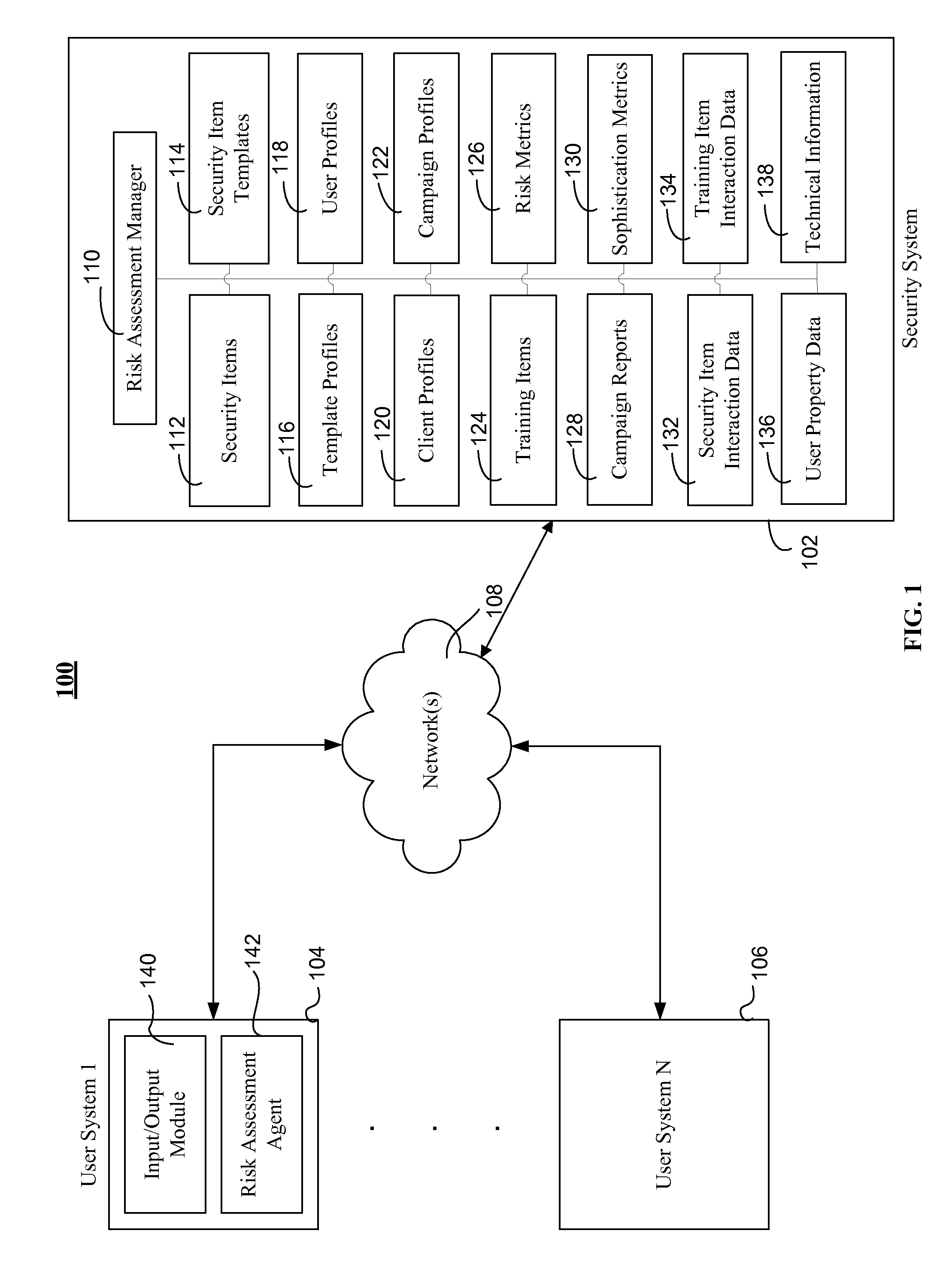
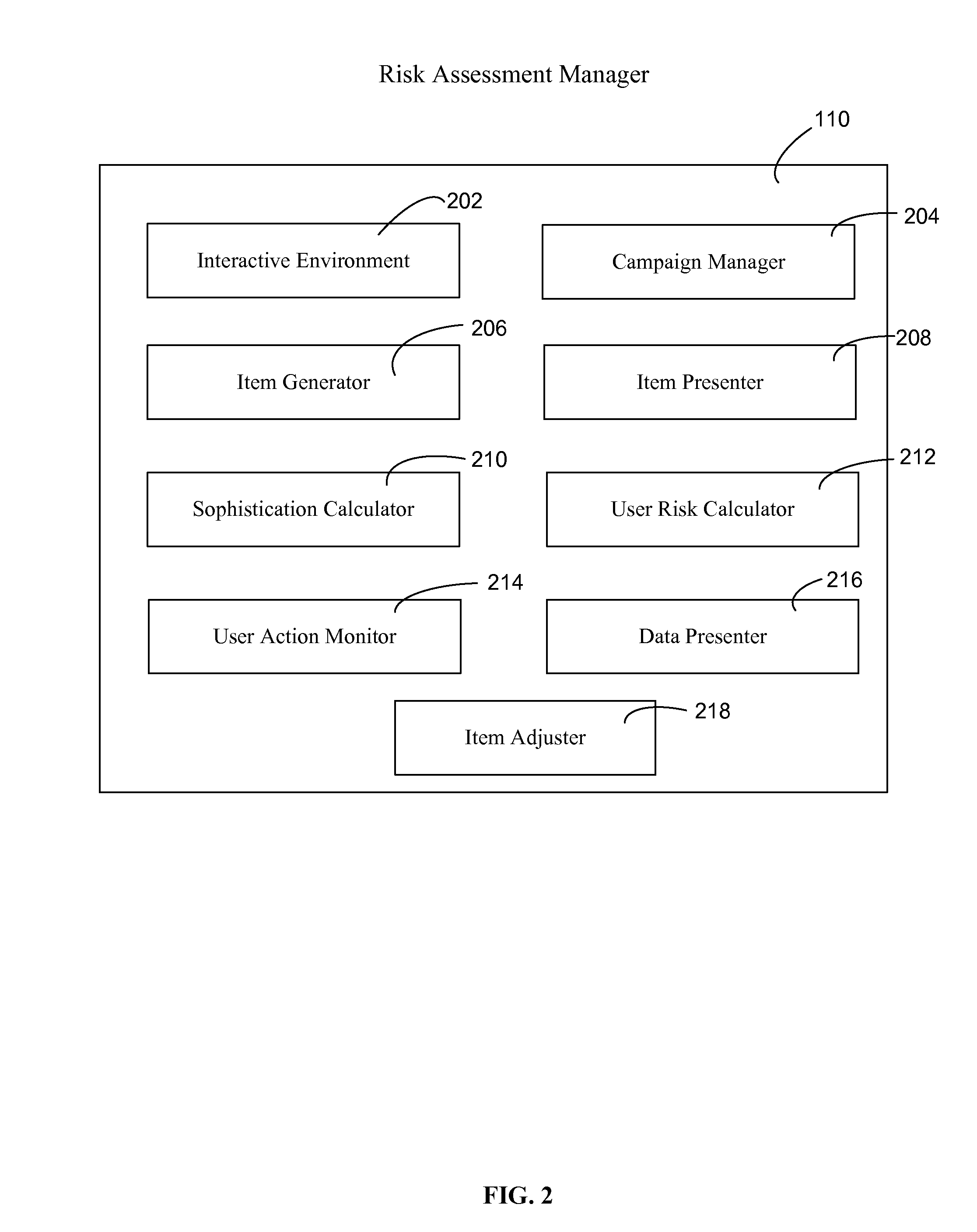
Assessing security risks of users in a computing network
InactiveUS20150229664A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionTechnical informationComputer security
Various embodiments assess security risks of users in computing networks. In one embodiment, a set of input data is obtained. The set of input data comprises at least one of security item interaction data, training interaction data, and technical information for each of a set of users in a plurality of users associated with an entity. The security item interaction data comprises at least one action performed by each of the set of users with respect to at least one computing network-based security item presented to each of the set of users. The set of input data to is compared to a plurality of security risk scoring metrics. Based on this comparison, a security risk score for each of the set of users with respect to a computing network is calculated.
Owner:WOMBAT SECURITY TECH
Virtual machine with dynamic data flow analysis
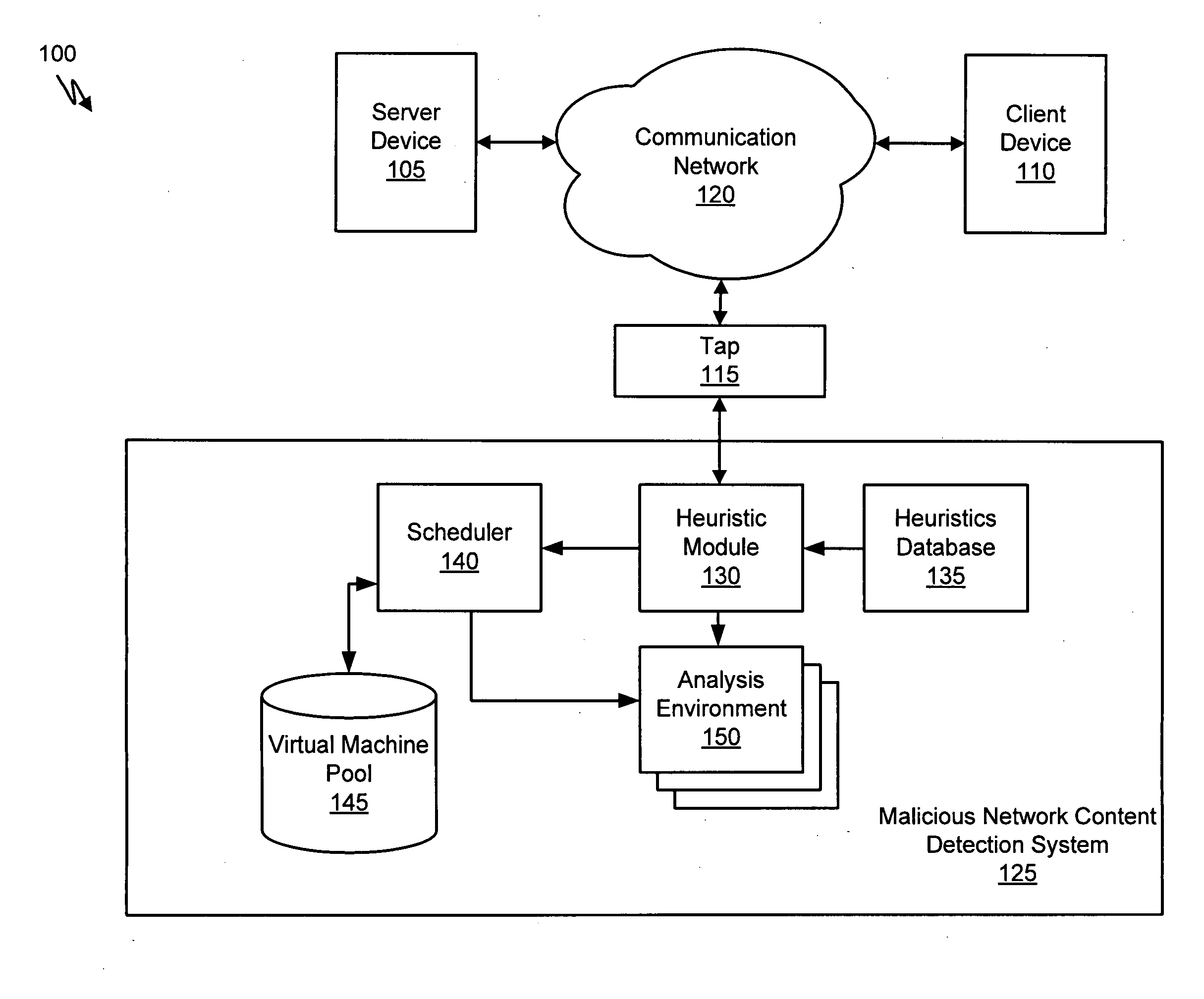
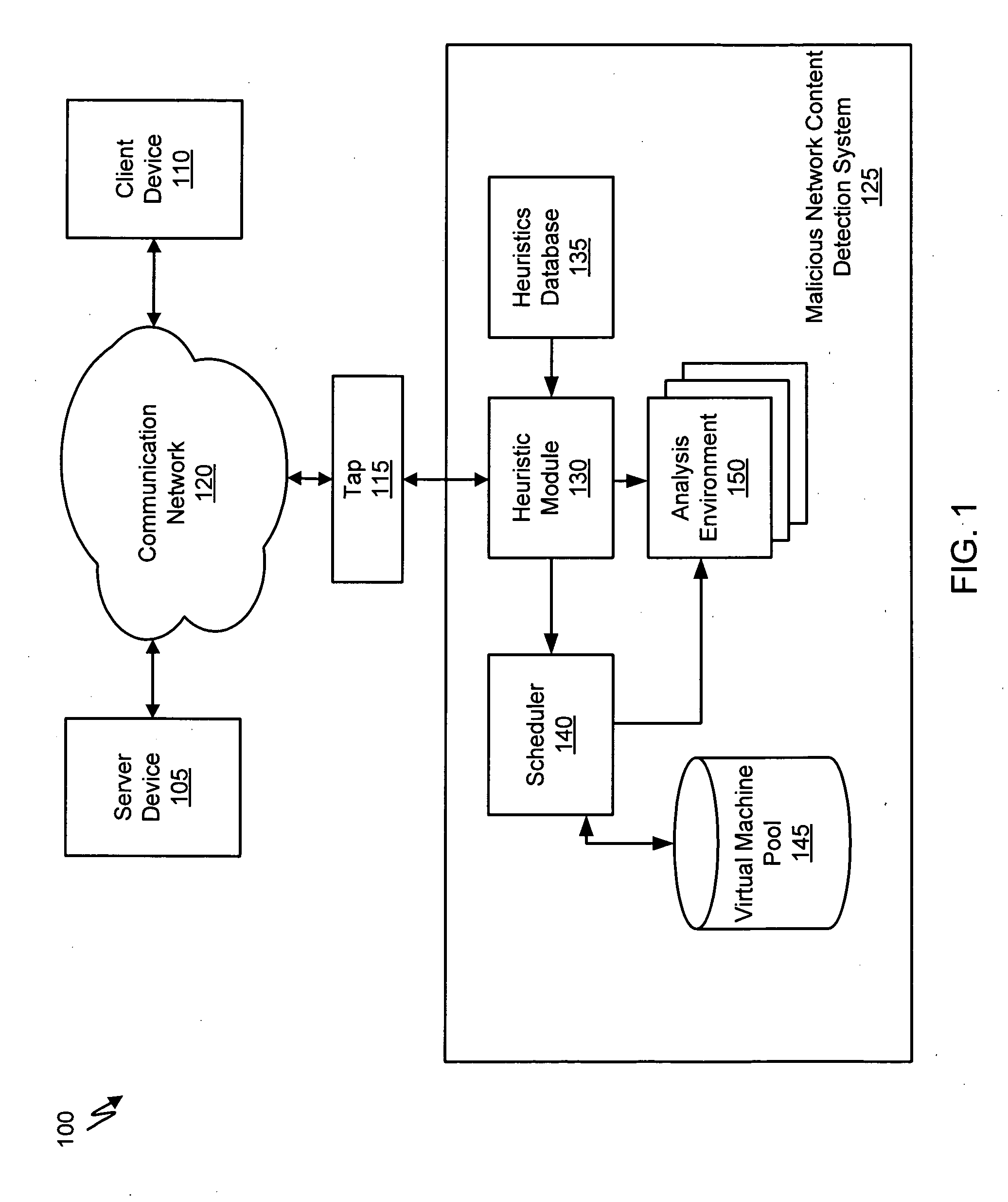
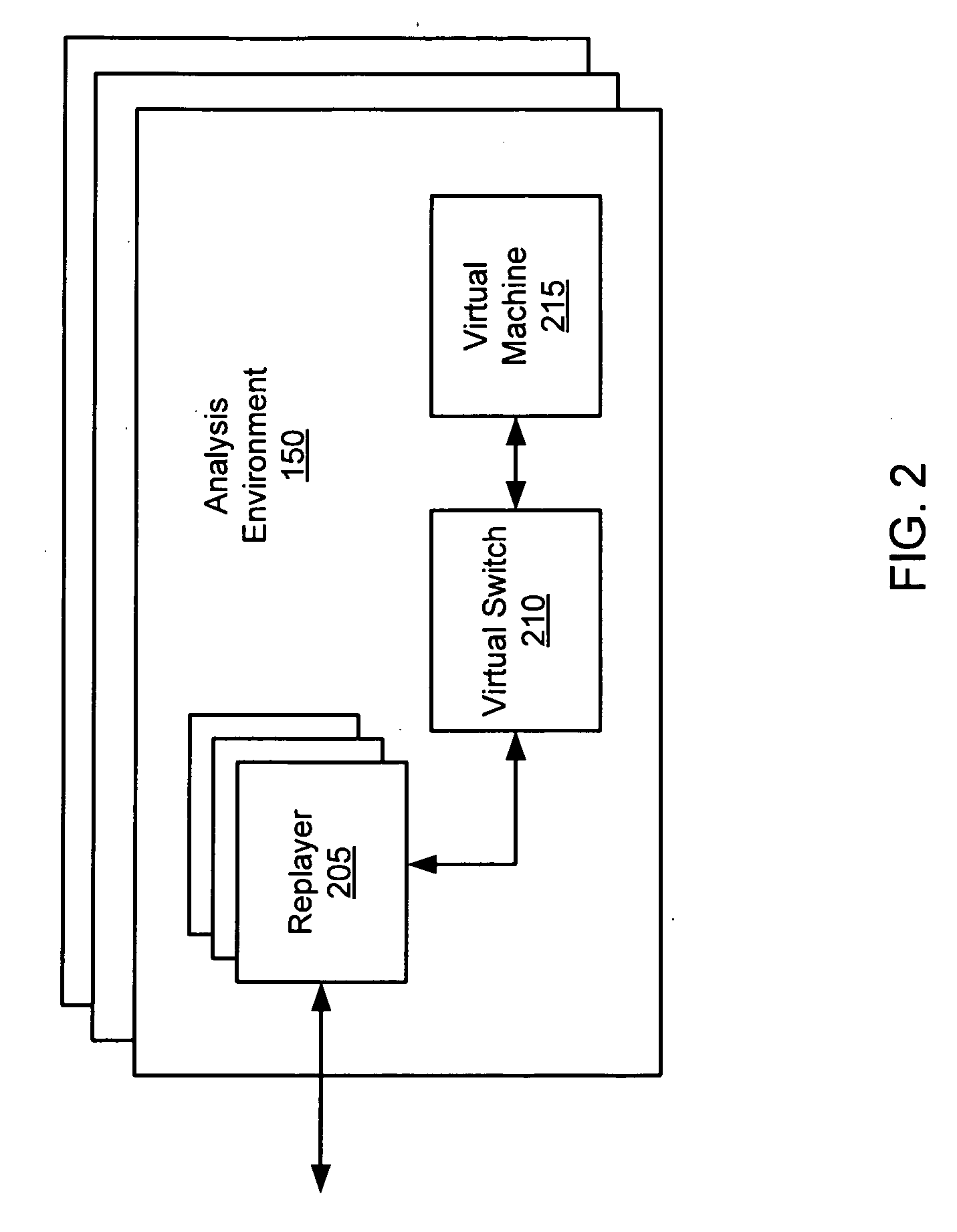
ActiveUS20070250930A1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionDynamic data flow analysisNetwork data
A suspicious activity capture system can comprise a tap configured to copy network data from a communication network, and a controller coupled to the tap. The controller is configured to receive the copy of the network data from the tap, analyze the copy of the network data with a heuristic to determine if the network data is suspicious, flag the network data as suspicious based on the heuristic determination, and concurrently simulate transmission of the network data to a plurality of destination devices.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
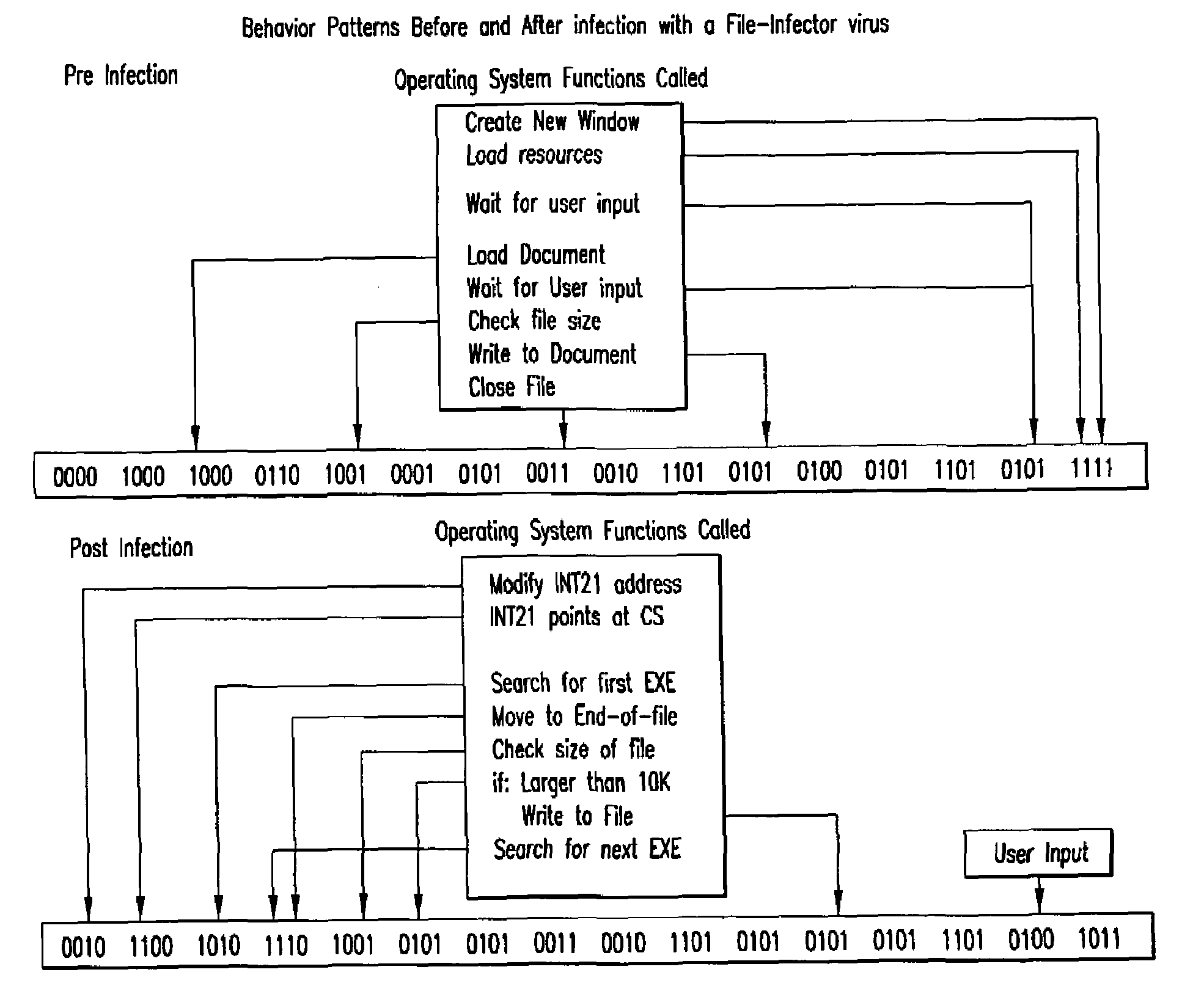
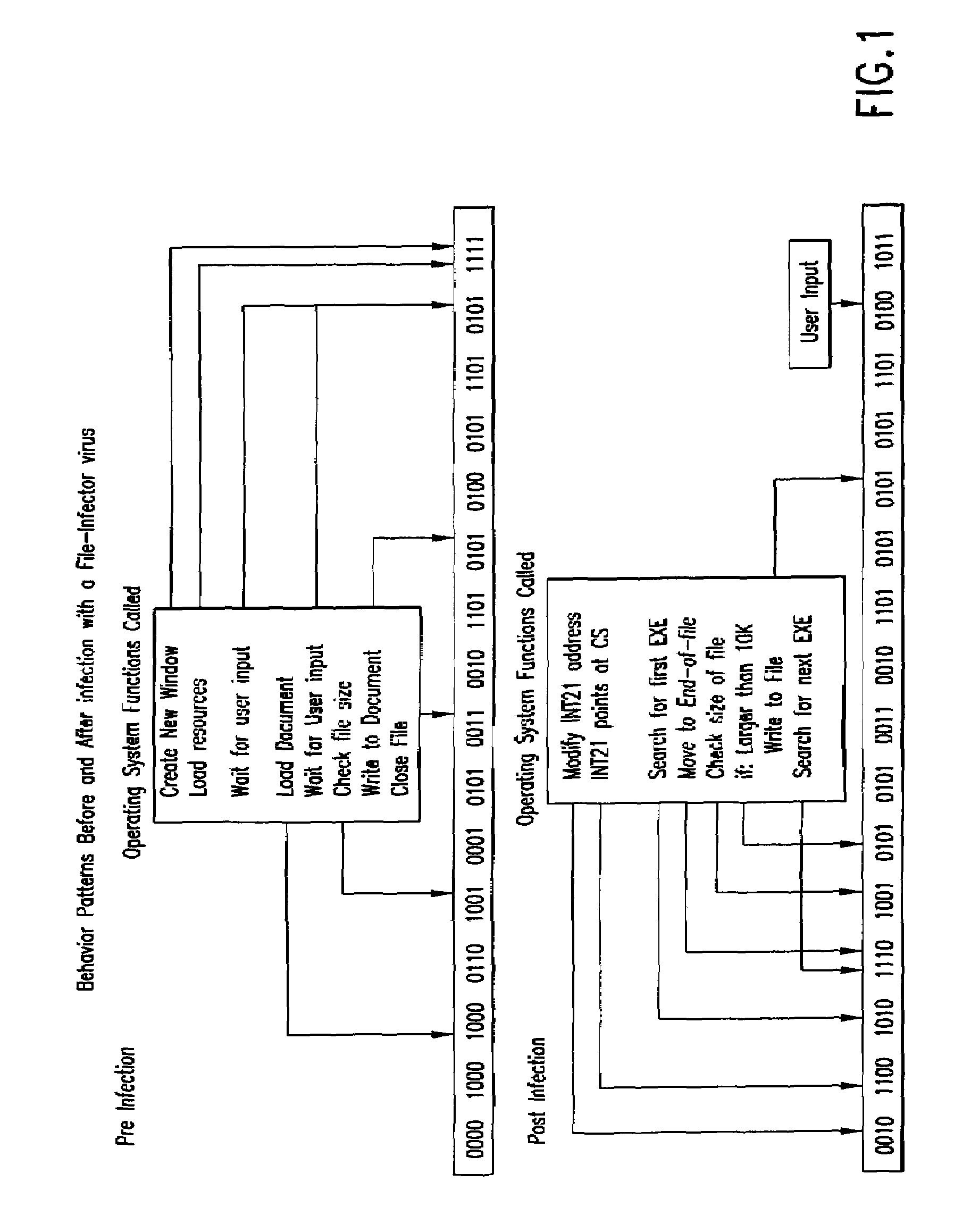
Computer immune system and method for detecting unwanted code in a computer system
InactiveUS7093239B1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceComputerized system
An automated analysis system detects malicious code within a computer system by generating and subsequently analyzing a behavior pattern for each computer program introduced to the computer system. Generation of the behavior pattern is accomplished by a virtual machine invoked within the computer system. An initial analysis may be performed on the behavior pattern to identify infected programs on initial presentation of the program to the computer system. The analysis system also stores behavior patterns and sequences with their corresponding analysis results in a database. Newly infected programs can be detected by analyzing a newly generated behavior pattern for the program with reference to a stored behavior pattern to identify presence of an infection or payload pattern.
Owner:PALO ALTO NETWORKS INC
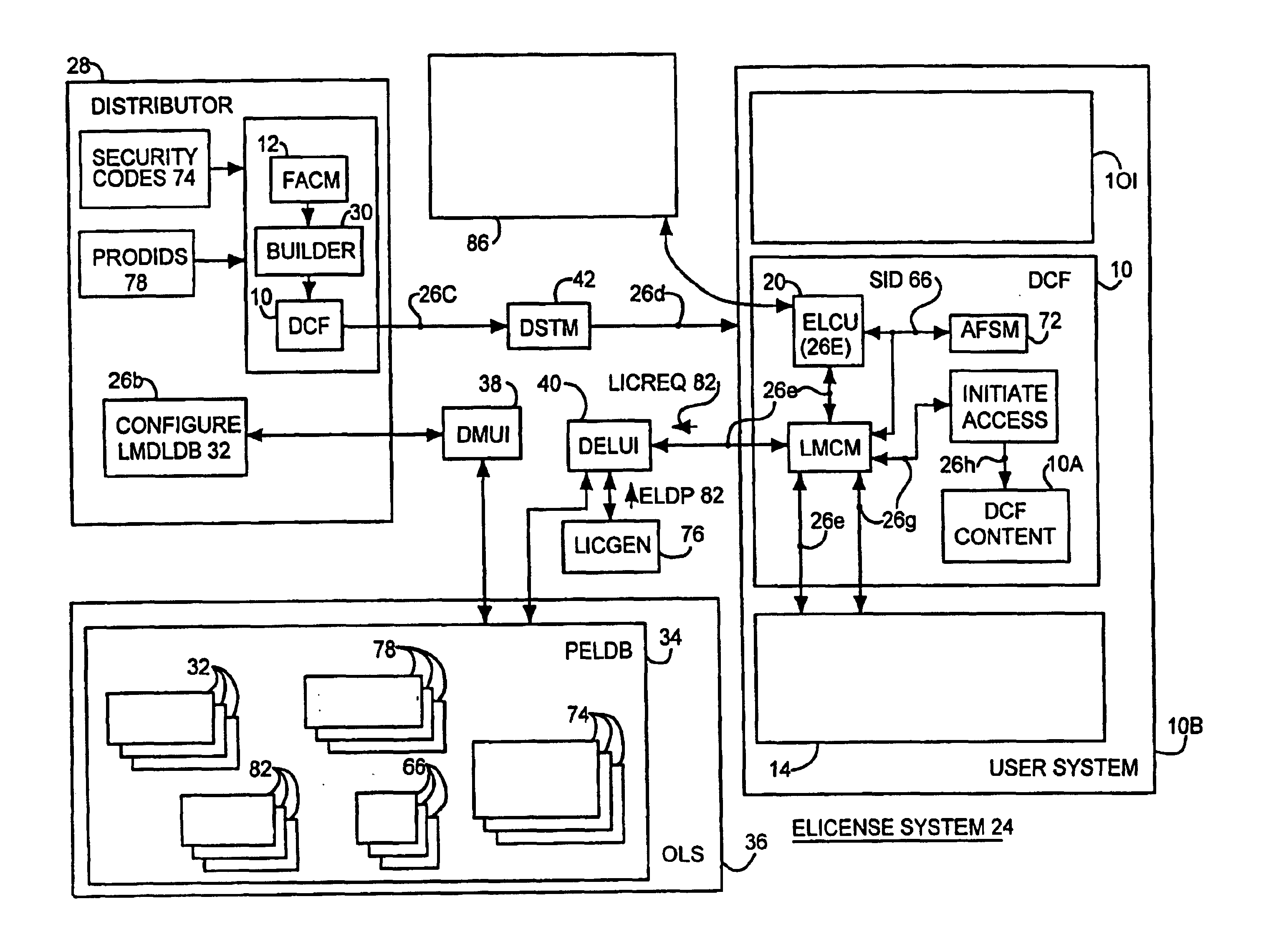
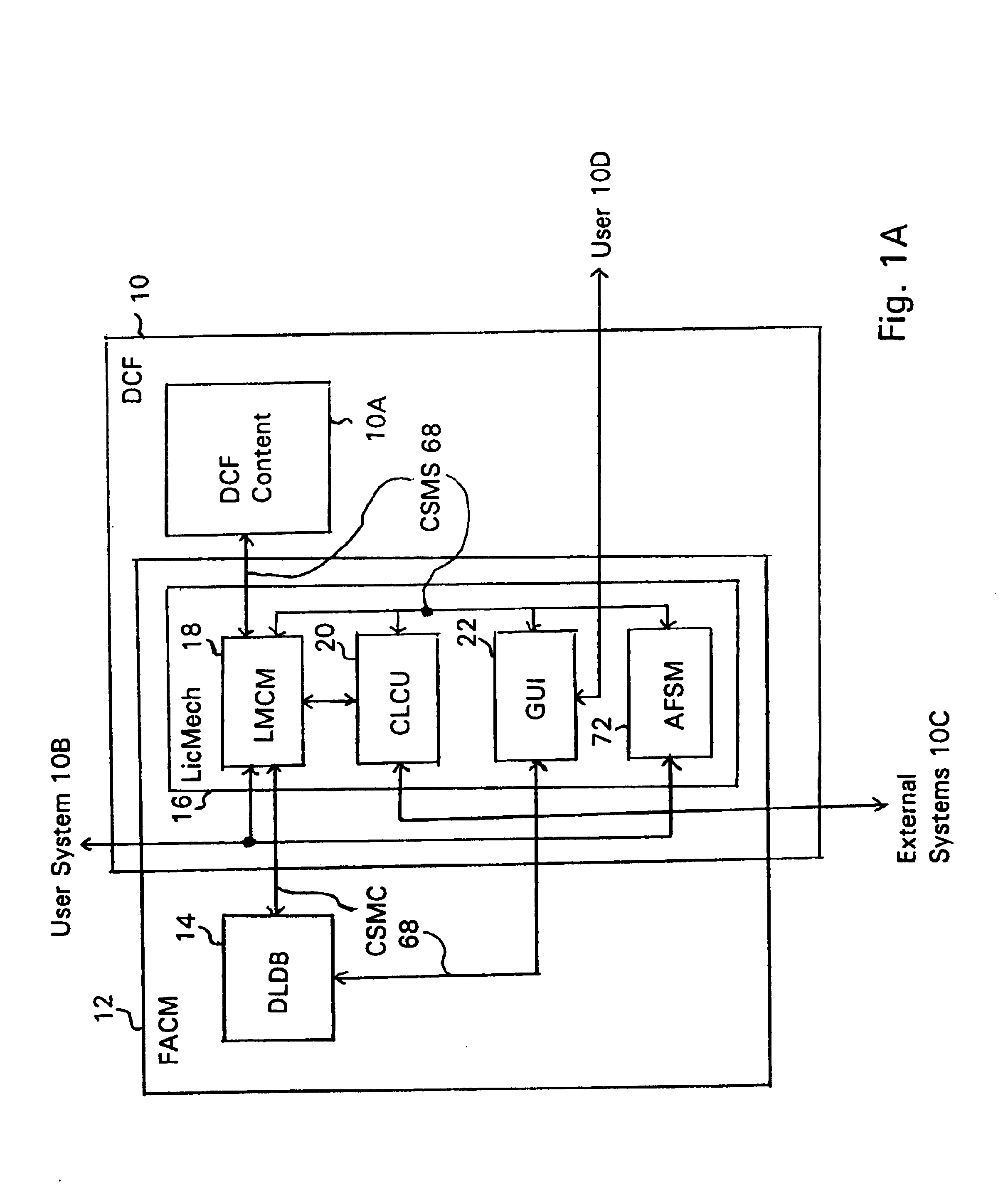
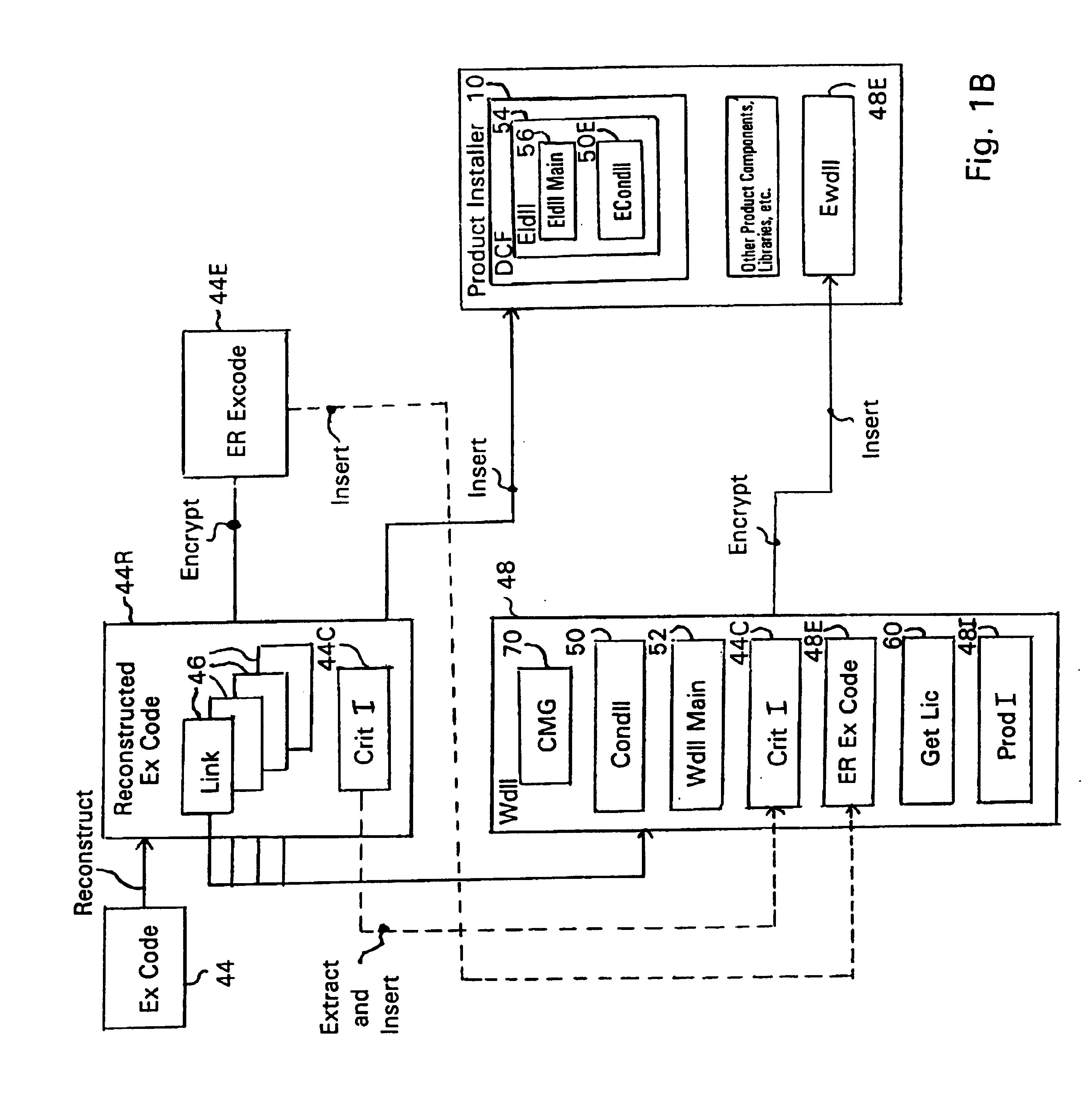
System and embedded license control mechanism for the creation and distribution of digital content files and enforcement of licensed use of the digital content files
A digital content file including a license control mechanism controlling the licensed use of digital content and a system and method for distributing licensable digital content files and licenses. A digital content file includes a digital content, which may be executable code or data, an embedded file access control mechanism and a dynamic license database associated with the file access mechanism for storing license information used by the file access control mechanism in controlling use of the digital content. The file access control mechanism includes a license monitor and control mechanism communicating with the dynamic license database and controlling use of the digital content and a license control utility providing communications between a user system and an external system to communicate license definition information and includes a graphical user interface. License information may be stored initially in the dynamic license database or provided from an external system. The system allows the distribution of digital content files and the acquisition of licenses with seamless transaction processing through an order processing system generating an order identification and authorization for a license and a product configuration and order database containing license management databases associated with the digital content files and containing license information to be transmitted to a user system upon receipt of an order identifier. The product configuration and order database also generates a license record for each transaction.
Owner:VIATECH TECH
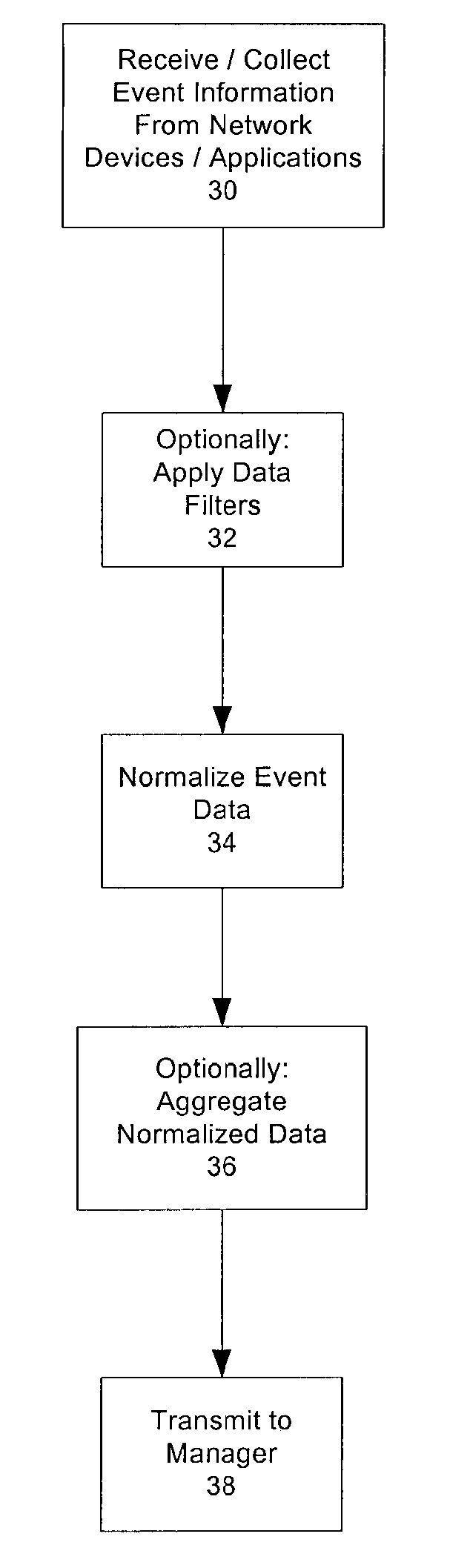
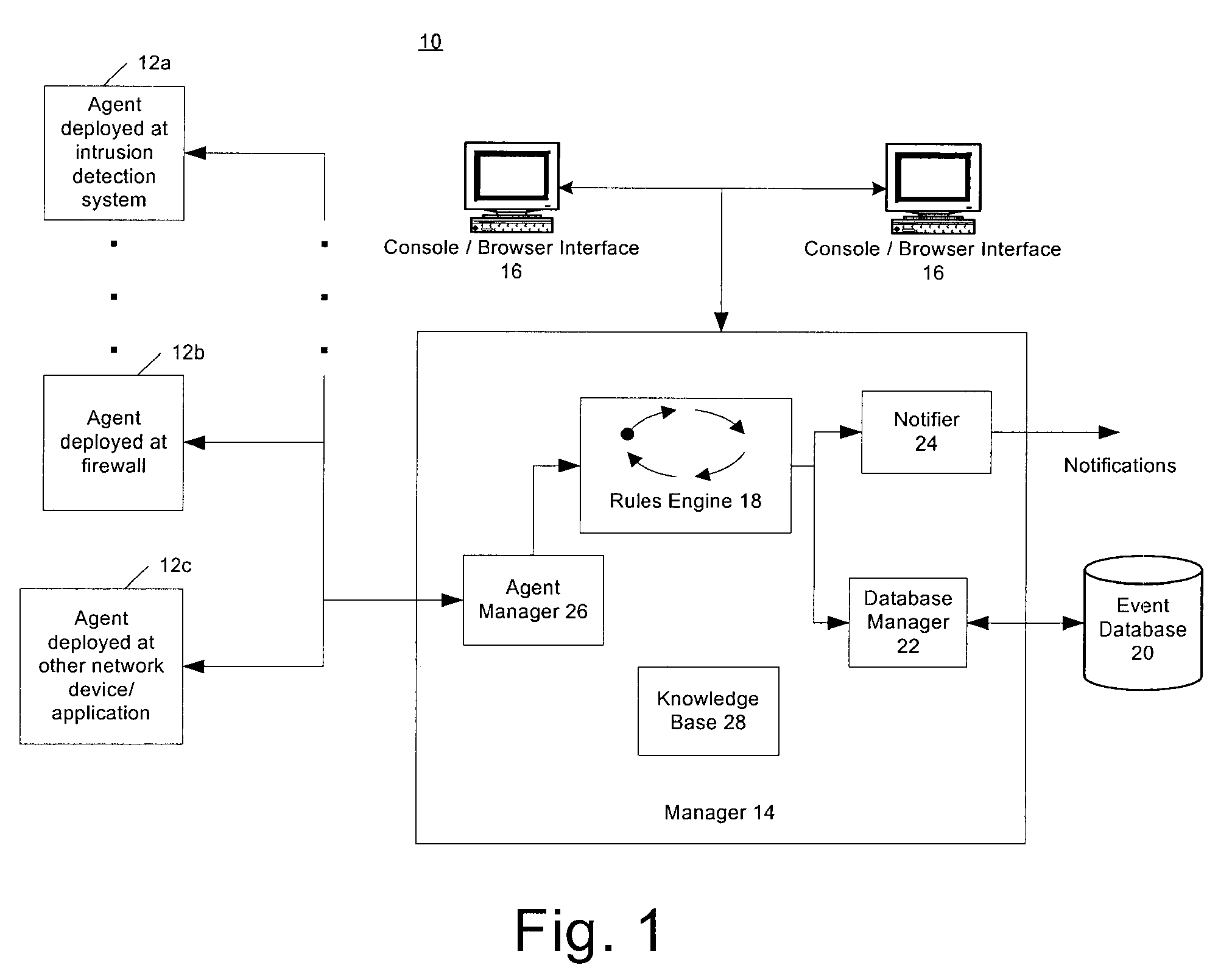
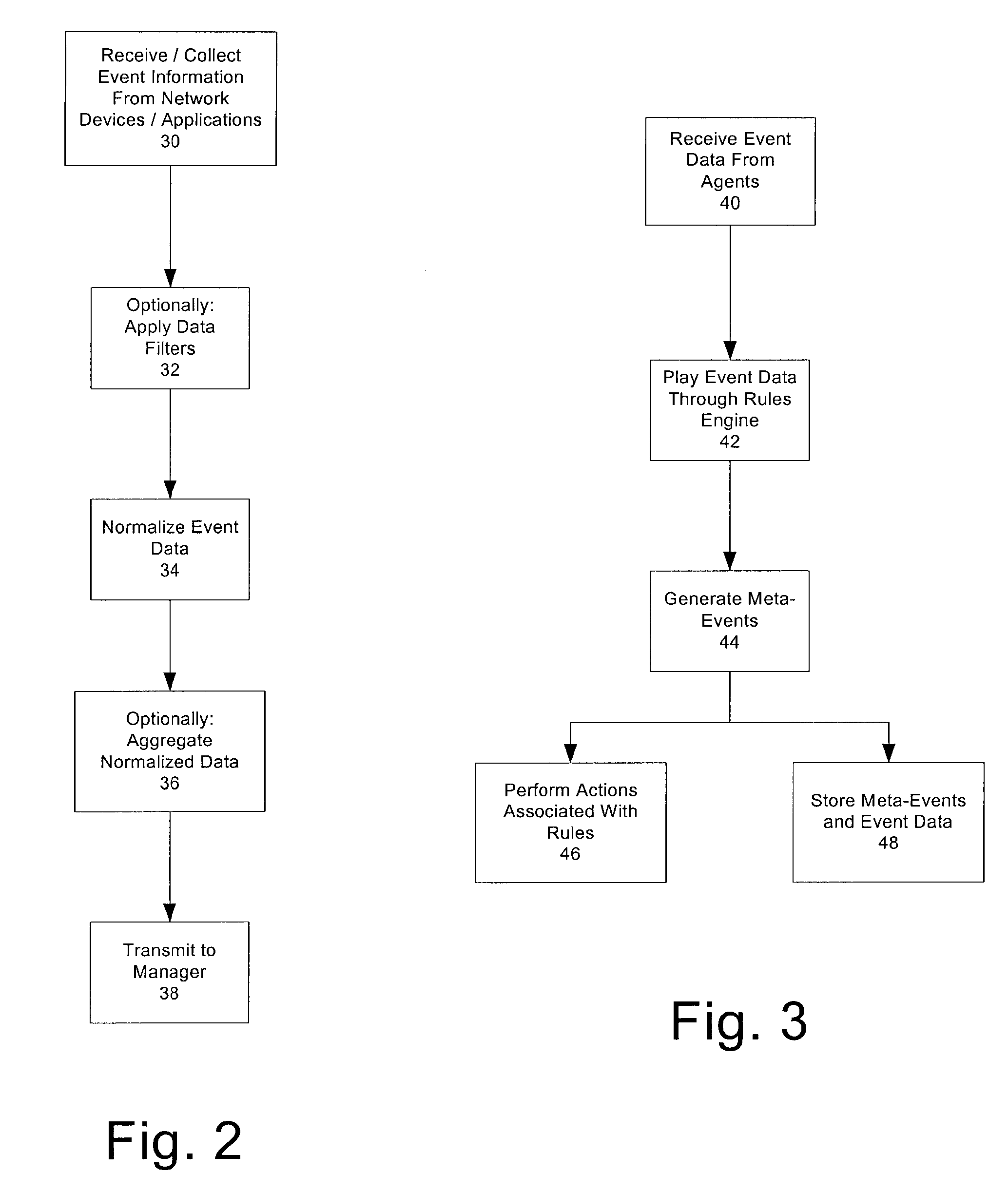
Real time monitoring and analysis of events from multiple network security devices
Security events generated by a number of network devices are gathered and normalized to produce normalized security events in a common schema. The normalized security events are cross-correlated according to rules to generate meta-events. The security events may be gathered remotely from a system at which the cross-correlating is performed. Any meta-events that are generated may be reported by generating alerts for display at one or more computer consoles, or by sending an e-mail message, a pager message, a telephone message, and / or a facsimile message to an operator or other individual. In addition to reporting the meta-events, the present system allows for taking other actions specified by the rules, for example executing scripts or other programs to reconfigure one or more of the network devices, and or to modify or update access lists, etc.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
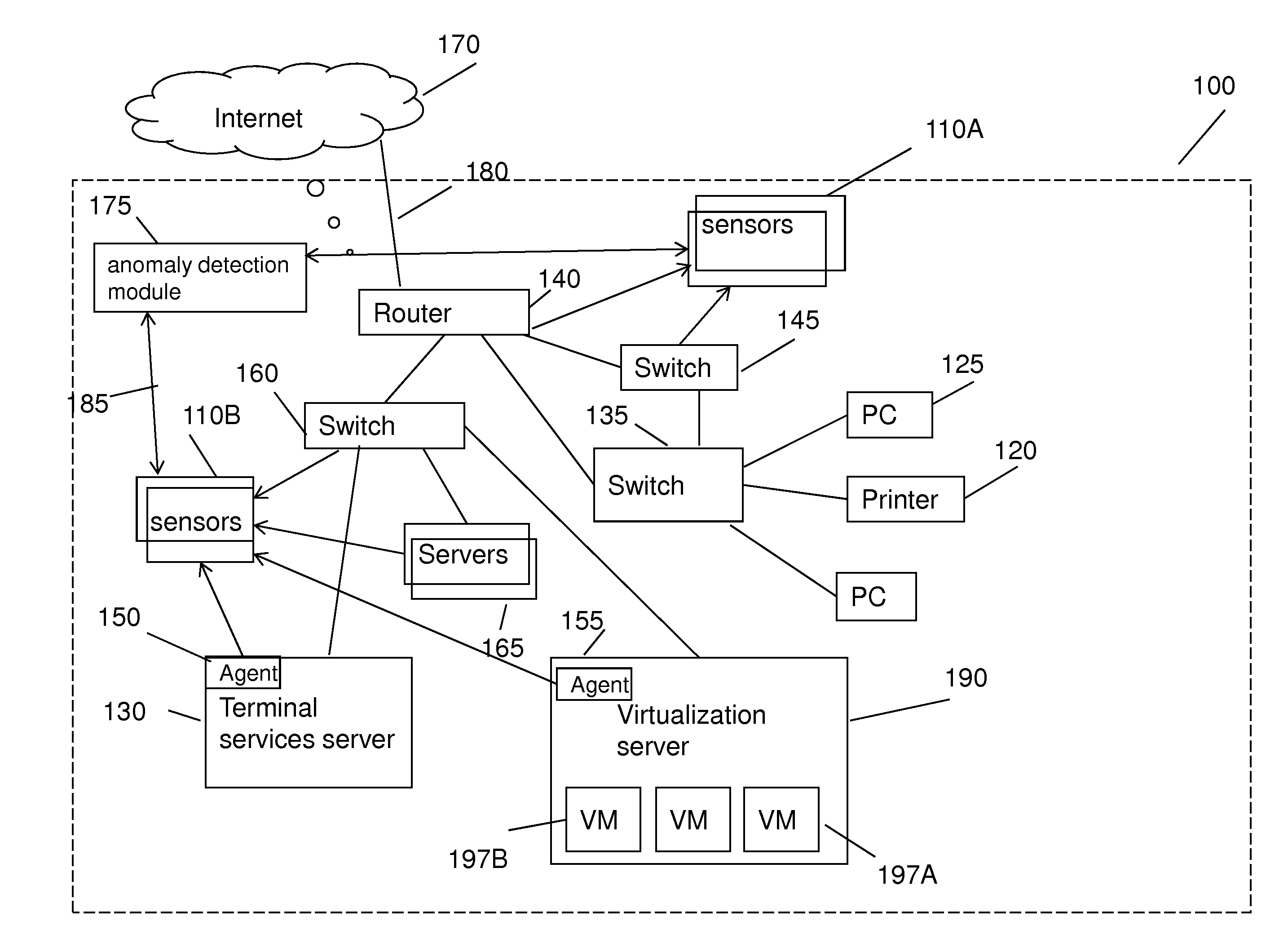
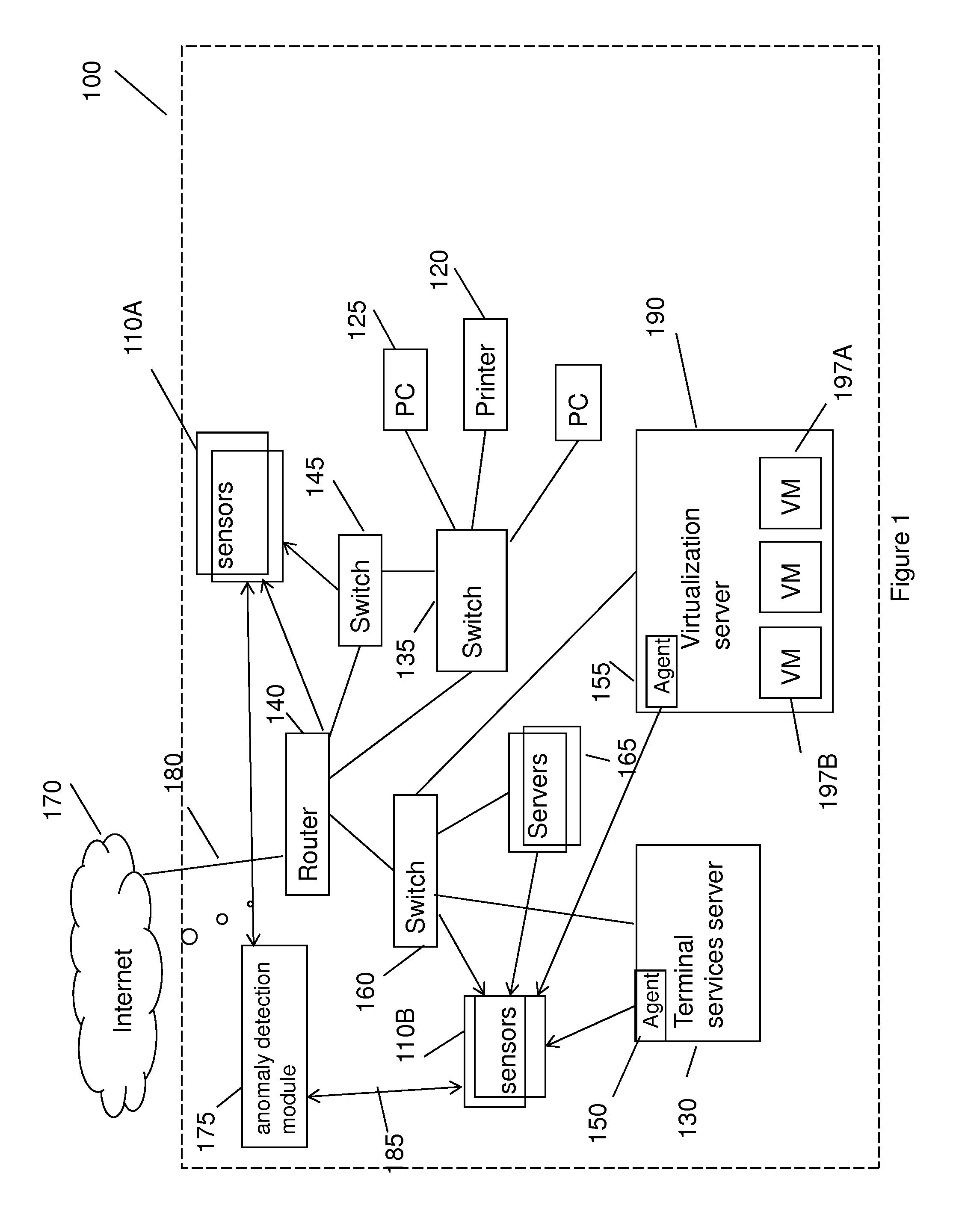
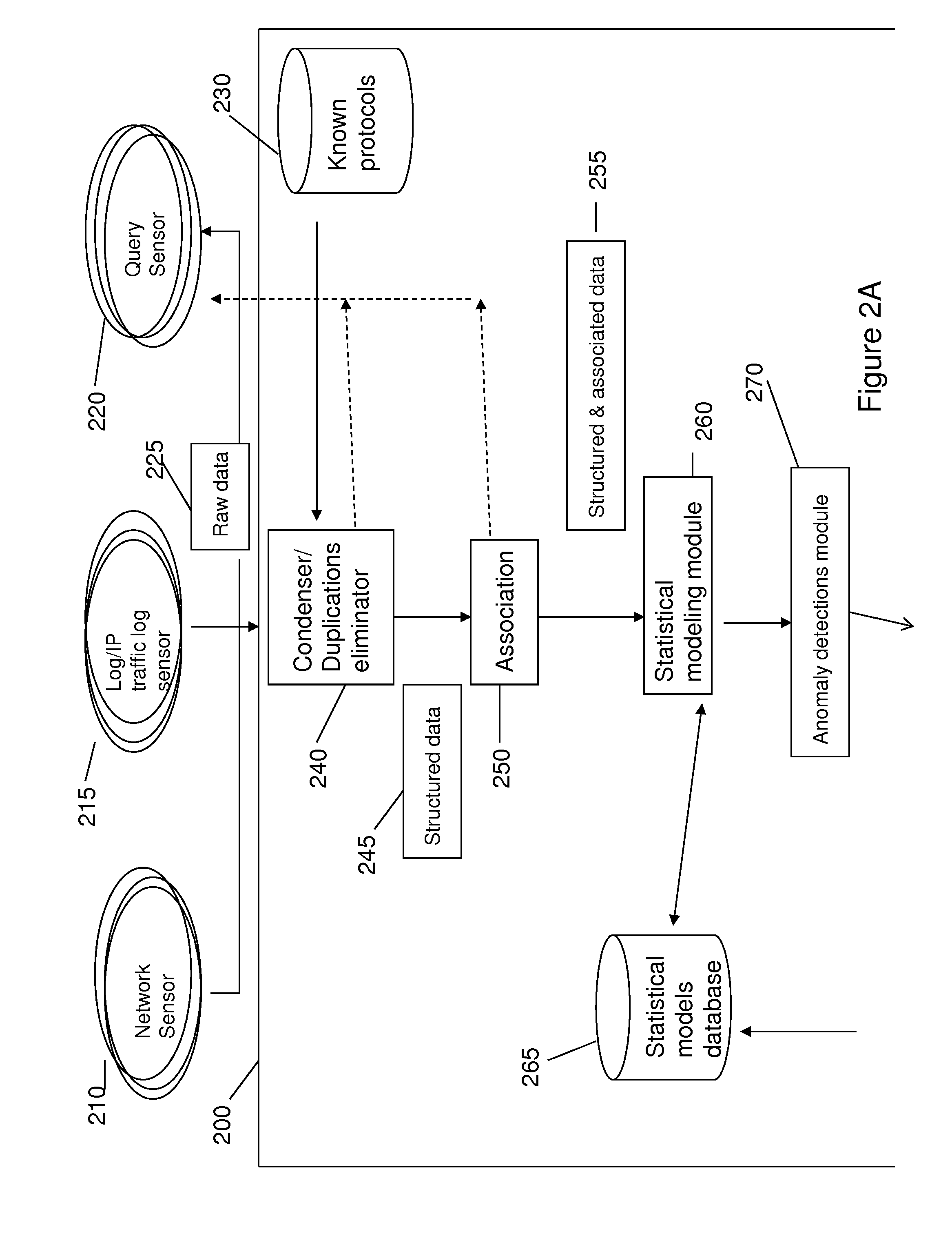
Method for detecting anomaly action within a computer network
InactiveUS20140165207A1Eliminating duplication and processing dataMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionOriginal dataDistributed computing
A method and system for detecting anomalous action within a computer network is provided herein. The method starts with collecting raw data from at least one probe sensor that is associated with at least one router, switch or at least one server which are part of the computer network. Next, the raw data is being parsed and analyzed and meta-data is created from the raw data. Computer network actions are being identified based on existing knowledge about network protocols. The meta-data is associated with entities by analyzing the identified network actions and correlating between different computer network actions. Finally, creating at least one statistical model of the respective computer network said model including network actions' behavior pattern and online or batch detection of anomalous network actions associated with entities based on the statistical models.
Owner:LIGHT CYBER
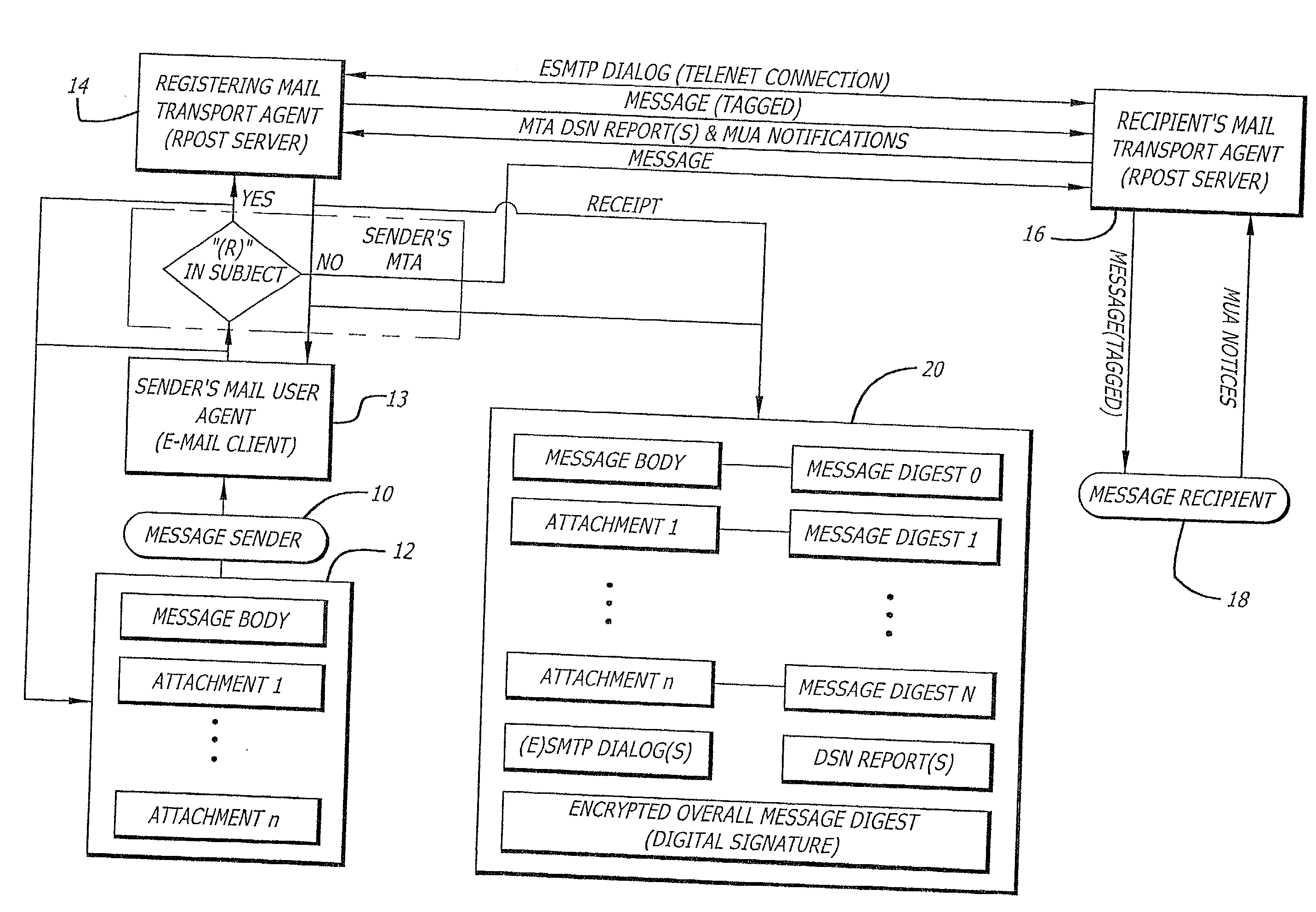
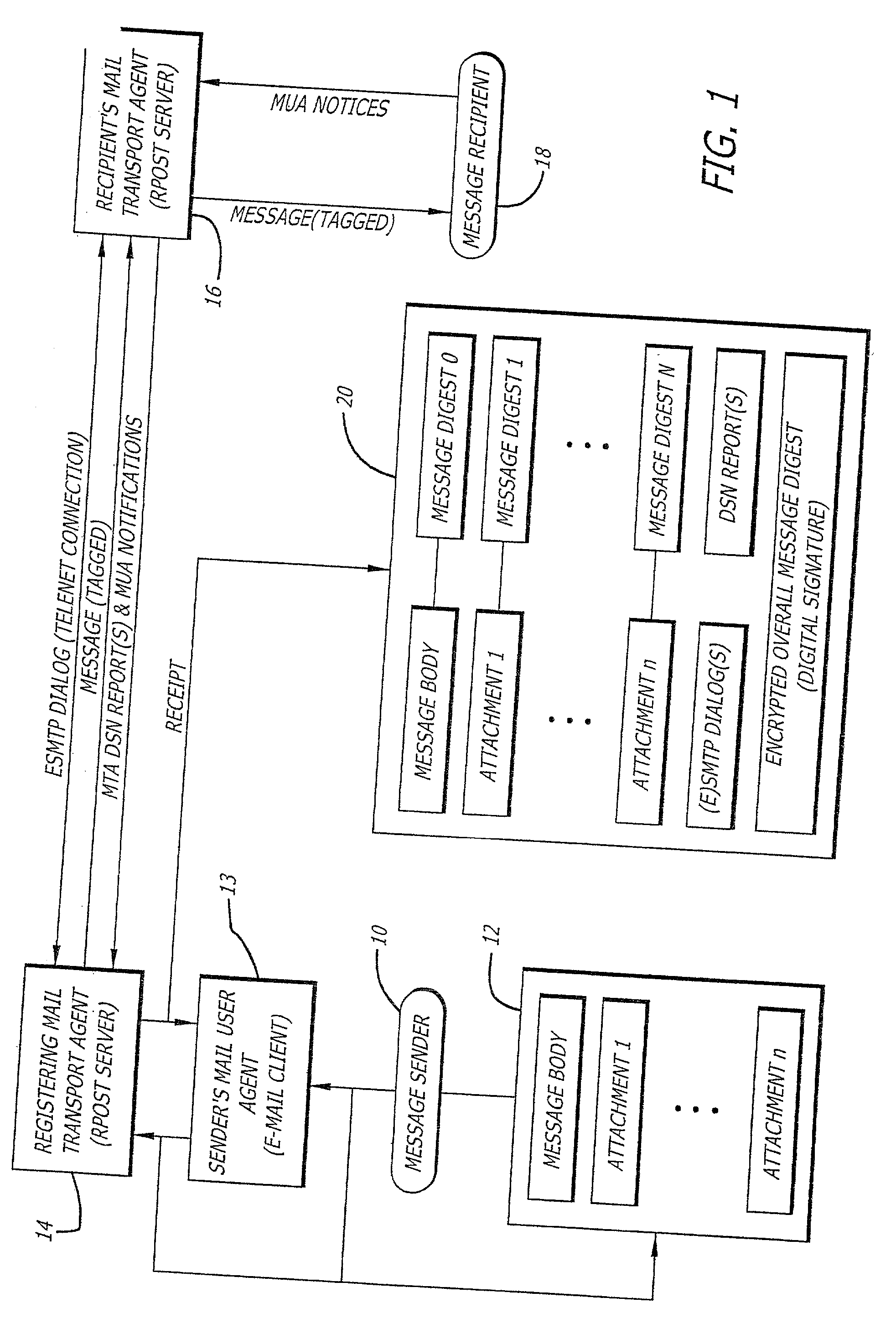
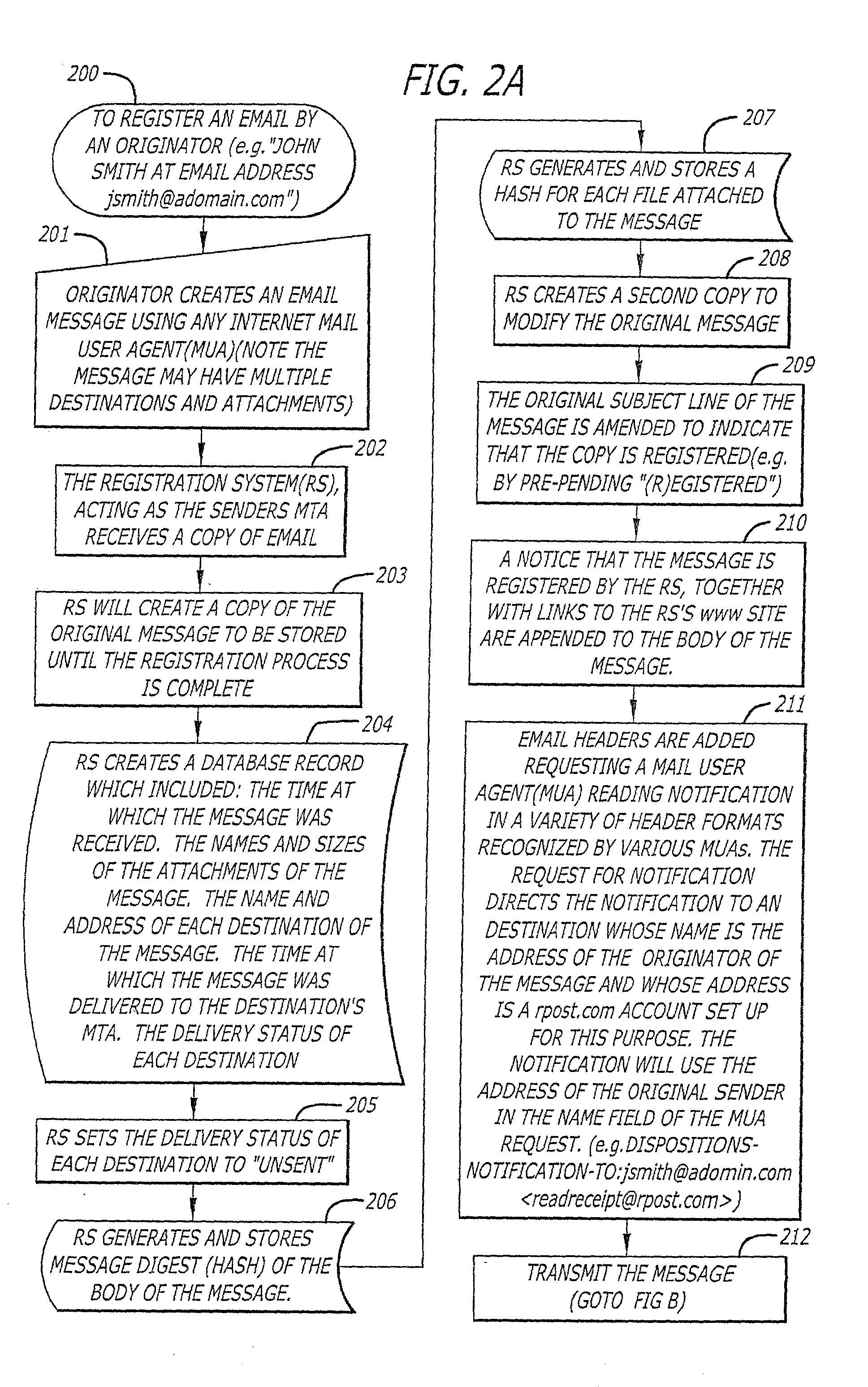
System and method for verifying delivery and integrity of electronic messages
InactiveUS20020144154A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsDigital signatureThe Internet
A server receives a message from a sender and transmits the message through the Internet to a recipient. The server normally transmits the message in a first path through the Internet to the recipient. When the sender indicates at a particular position in the message that the message is registered, the server transmits the message in a second path through the Internet to the recipient. The sender can also provide additional indications in the message to have the server handle the message in other special ways not normally provided by the server. After learning from the receipt or the recipient's agent through the Internet that the message was successfully received, the server creates, and forwards to the sender, an electronic receipt. The receipt includes at least one, and preferably all: the message and any attachments, a delivery success / failure table listing the receipts, and the receipt times, of the message by the recipient's specific agents, and the failure of other agents of the recipient to receive the message and a digital signature of the message and attachments subsequently. By verifying that the digital signature on the sender's receipt matches the digital receipt at the server, the server can verify, without retaining the message, that the receipt is genuine and that the message is accurate.
Owner:RPOST COMM
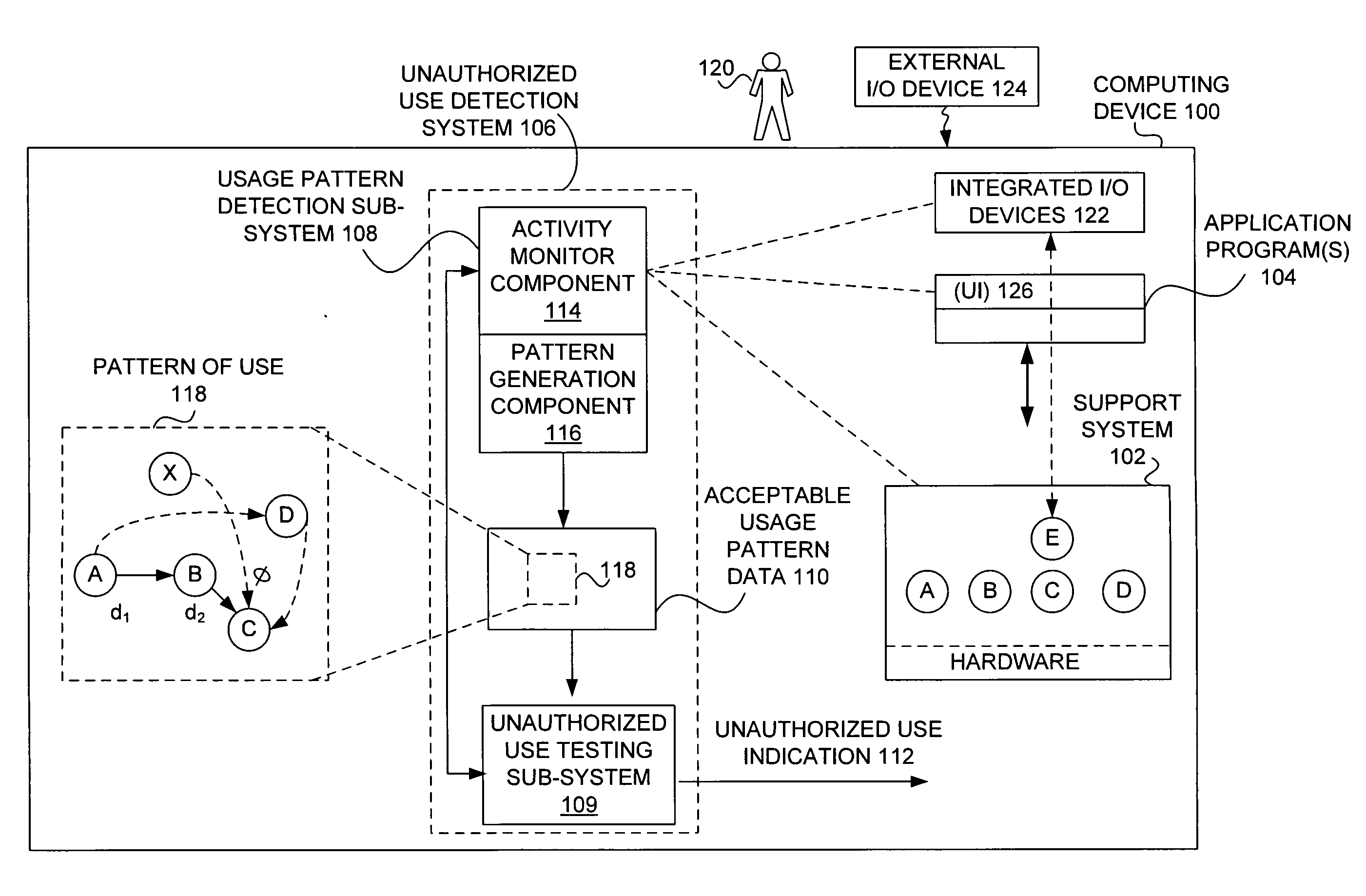
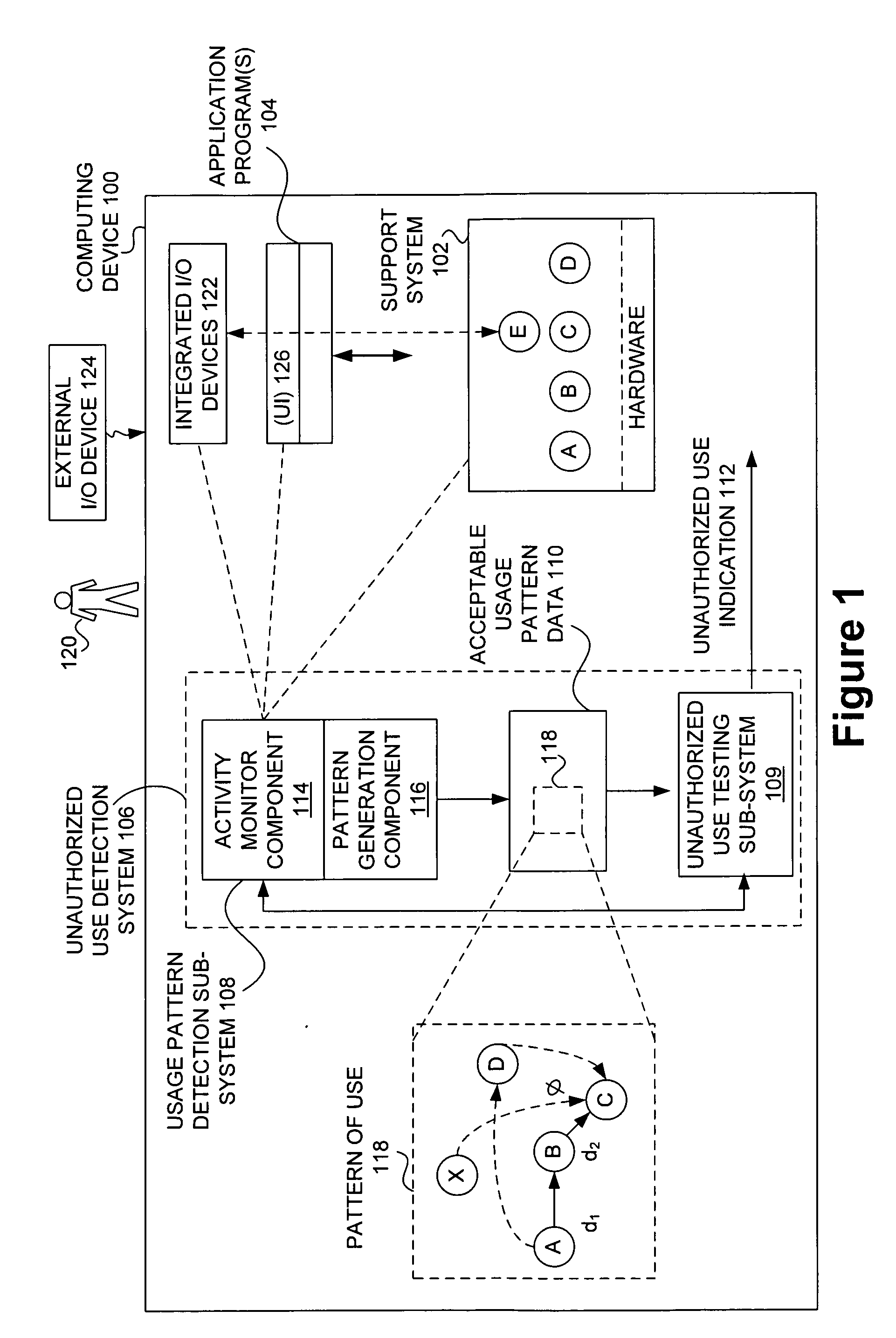
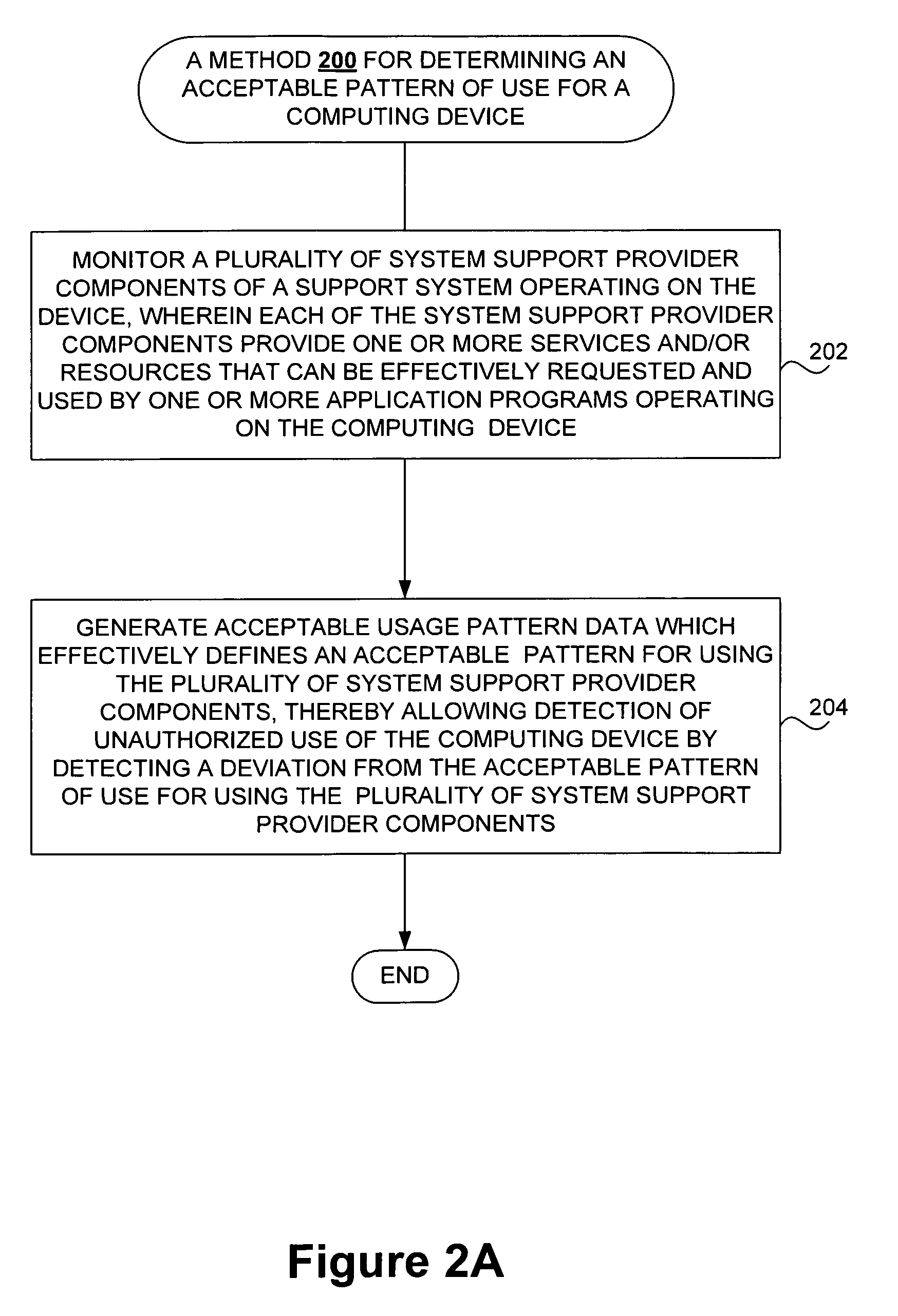
Detecting unauthorized use of computing devices based on behavioral patterns
InactiveUS20090199296A1Efficiently definedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionSupporting systemOperational system
Techniques for detecting unauthorized use (e.g., malicious attacks) of the computing systems (e.g., computing devices) are disclosed. Unauthorized use can be detected based on patterns of use (e.g., behavioral patterns of use typically associated with a human being) of the computing systems. Acceptable behavioral pattern data can be generated for a computing system by monitoring the use of a support system (e.g., an operating system, a virtual environment) operating on the computing system. For example, a plurality of system support provider components of a support system (e.g., system calls, device drivers) can be monitored in order to generate the acceptable behavioral pattern data in a form which effectively defines an acceptable pattern of use (usage pattern) for the monitored system support provider components, thereby allowing detection of unauthorized use of a computing system by detecting any deviation from the acceptable pattern of use of the monitored system support provider components.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and Methods for Detecting Malicious Network Content
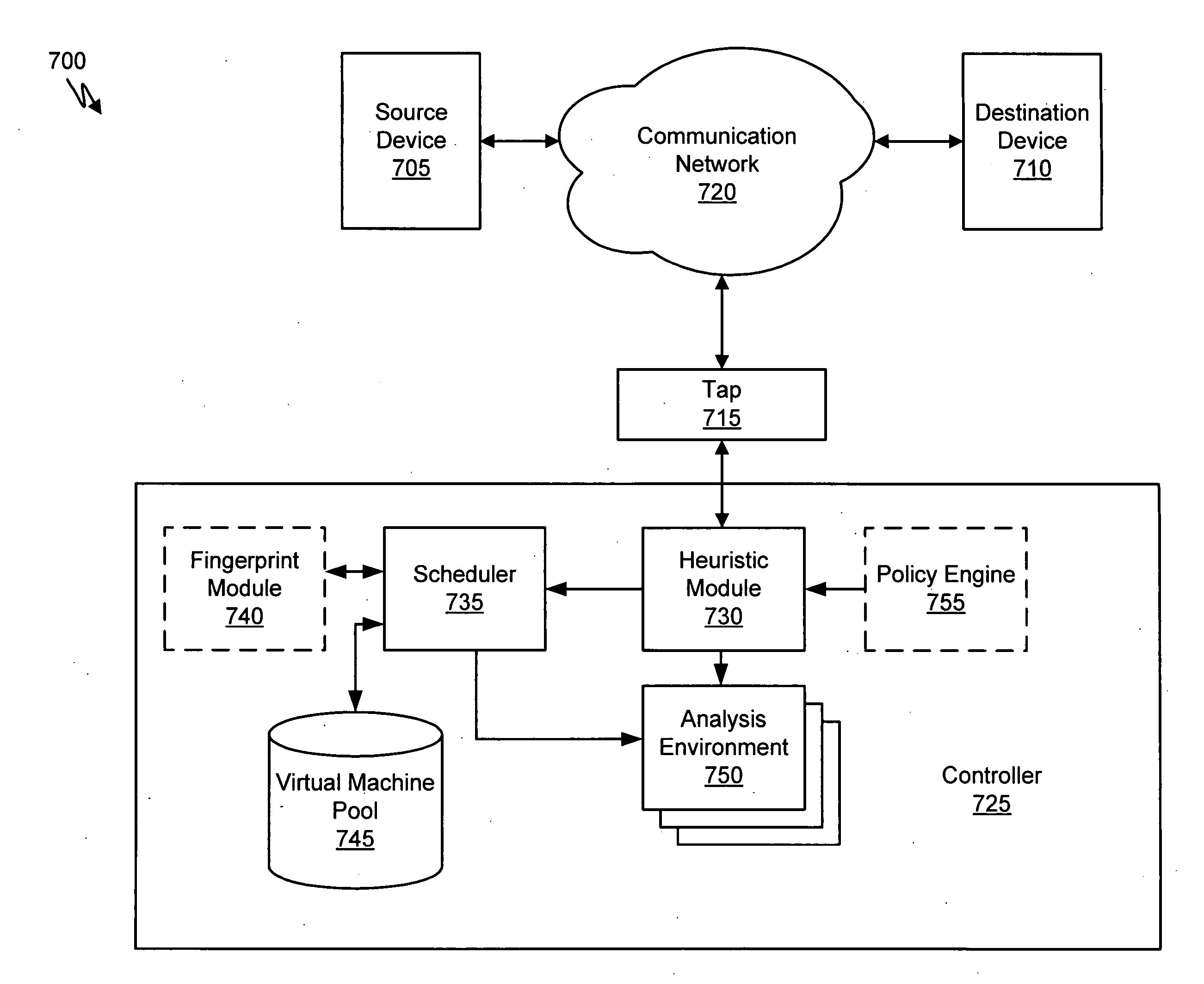
A method for detecting malicious network content comprises inspecting one or more packets of network content, identifying a suspicious characteristic of the network content, determining a score related to a probability that the network content includes malicious network content based on at least the suspicious characteristic, identifying the network content as suspicious if the score satisfies a threshold value, executing a virtual machine to process the suspicious network content, and analyzing a response of the virtual machine to detect malicious network content.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Heuristic based capture with replay to virtual machine
A suspicious activity capture system can comprise a tap configured to copy network data from a communication network, and a controller coupled to the tap. The controller is coupled to the tap and is configured to receive the copy of the network data from the tap, analyze the copy of the network data with a heuristic to flag the network data as suspicious, and simulate transmission of the network data to a destination device.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com