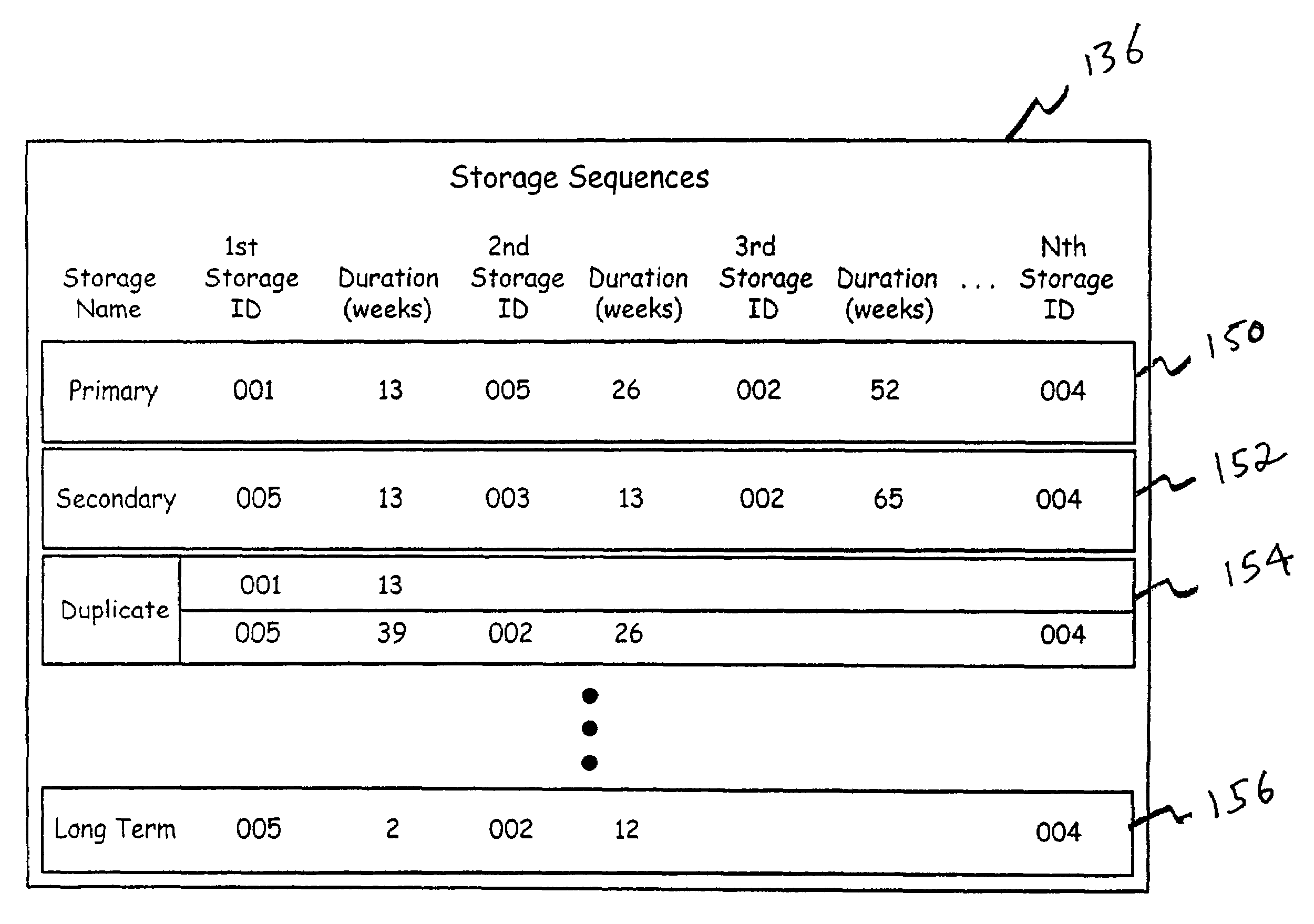
Patents
Literature
19497results about "Redundant operation error correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recovery from failures within data processing systems
InactiveUS20070088970A1Improve availabilityConsistent stateSpecial data processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionSuccessful completionData processing system
Provided are methods, data processing systems, recovery components and computer programs for recovering from storage failures affecting data repositories. At least a part of the recovery processing is performed while the data repositories are able to receive new data and to allow retrieval of such new data. Although new data items may be received into the repository and retrieved therefrom during recovery processing, updates to the data repository which were performed before the failure and which are then restored to the repository by the recovery processing are restored within a recovery unit of work and are inaccessible to processes other than the recovery process until successful completion of the recovery unit of work. The recovery processing ensures that the recovered repository is consistent with the state of the repository at the time of the failure, but is available for addition and retrieval of new data items before completion of the recovery processing.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
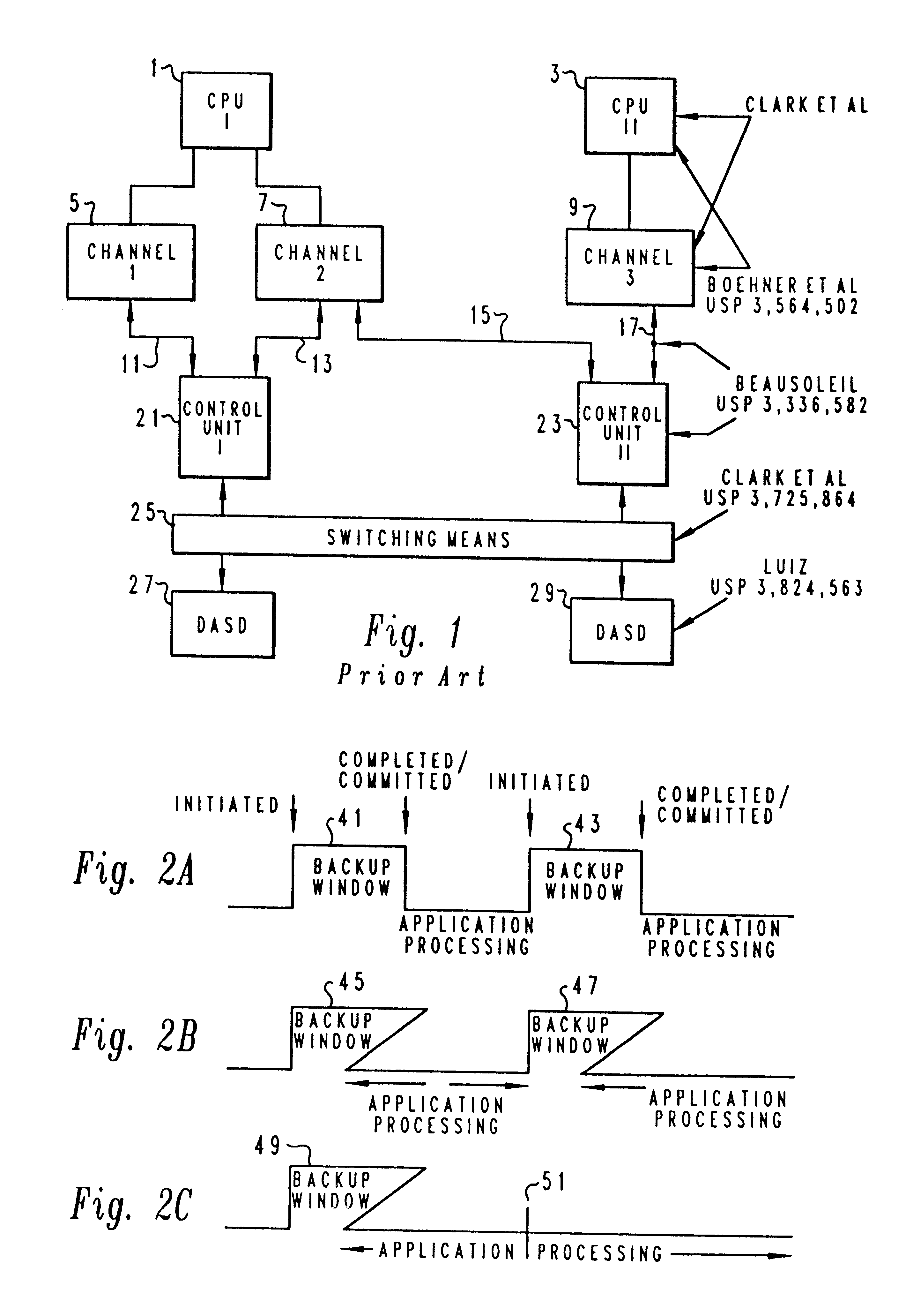
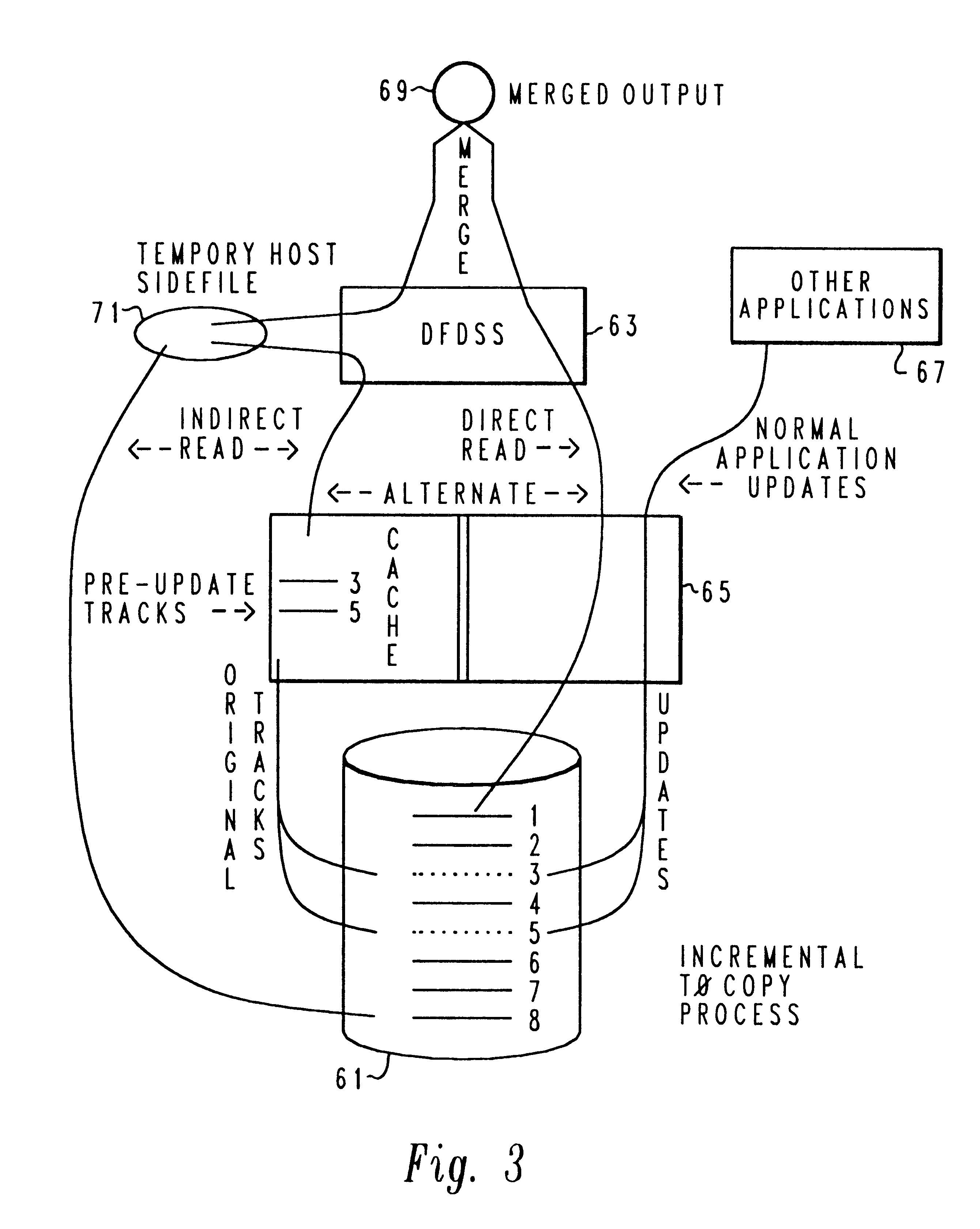
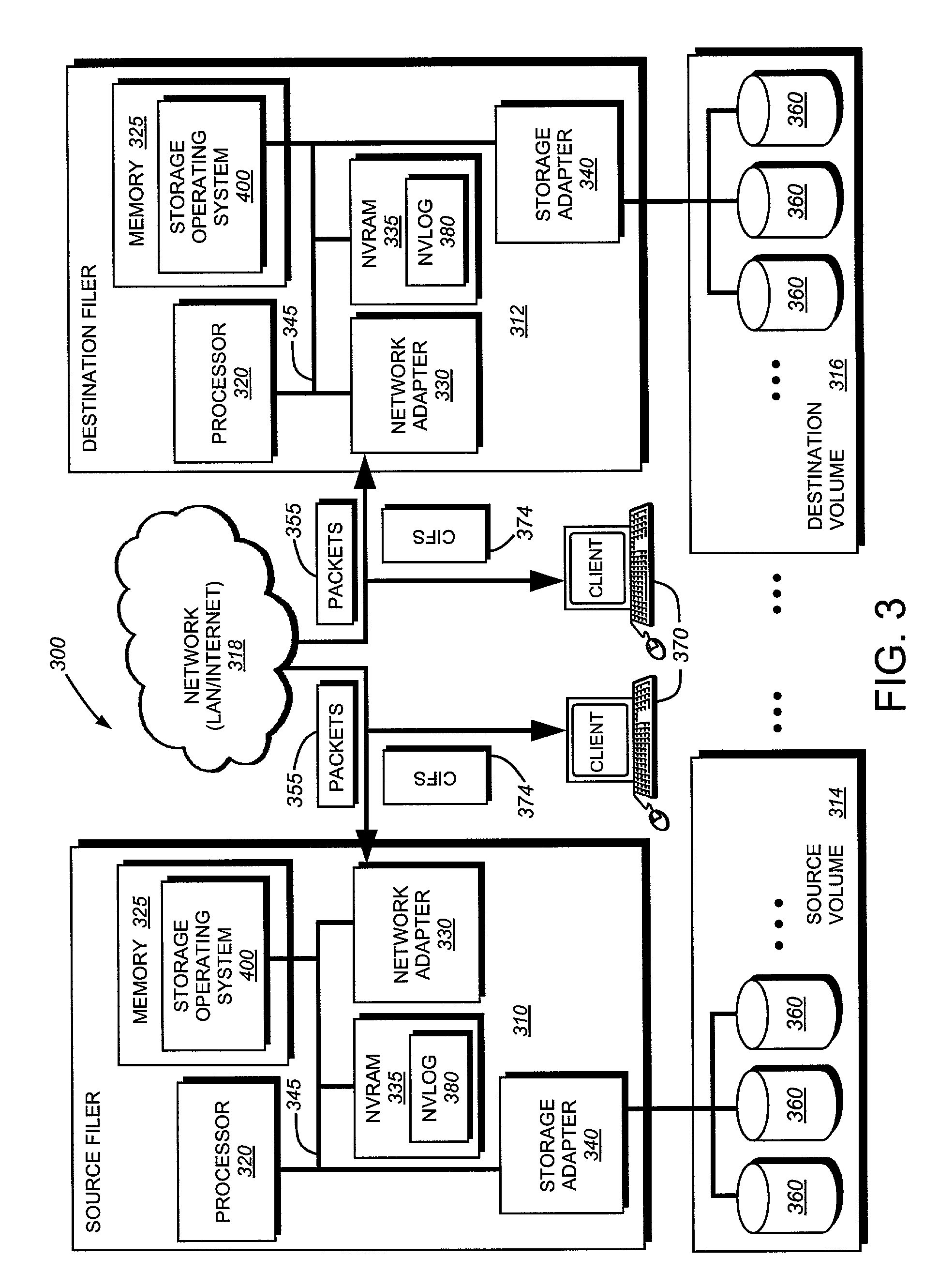
Method and system for incremental time zero backup copying of data
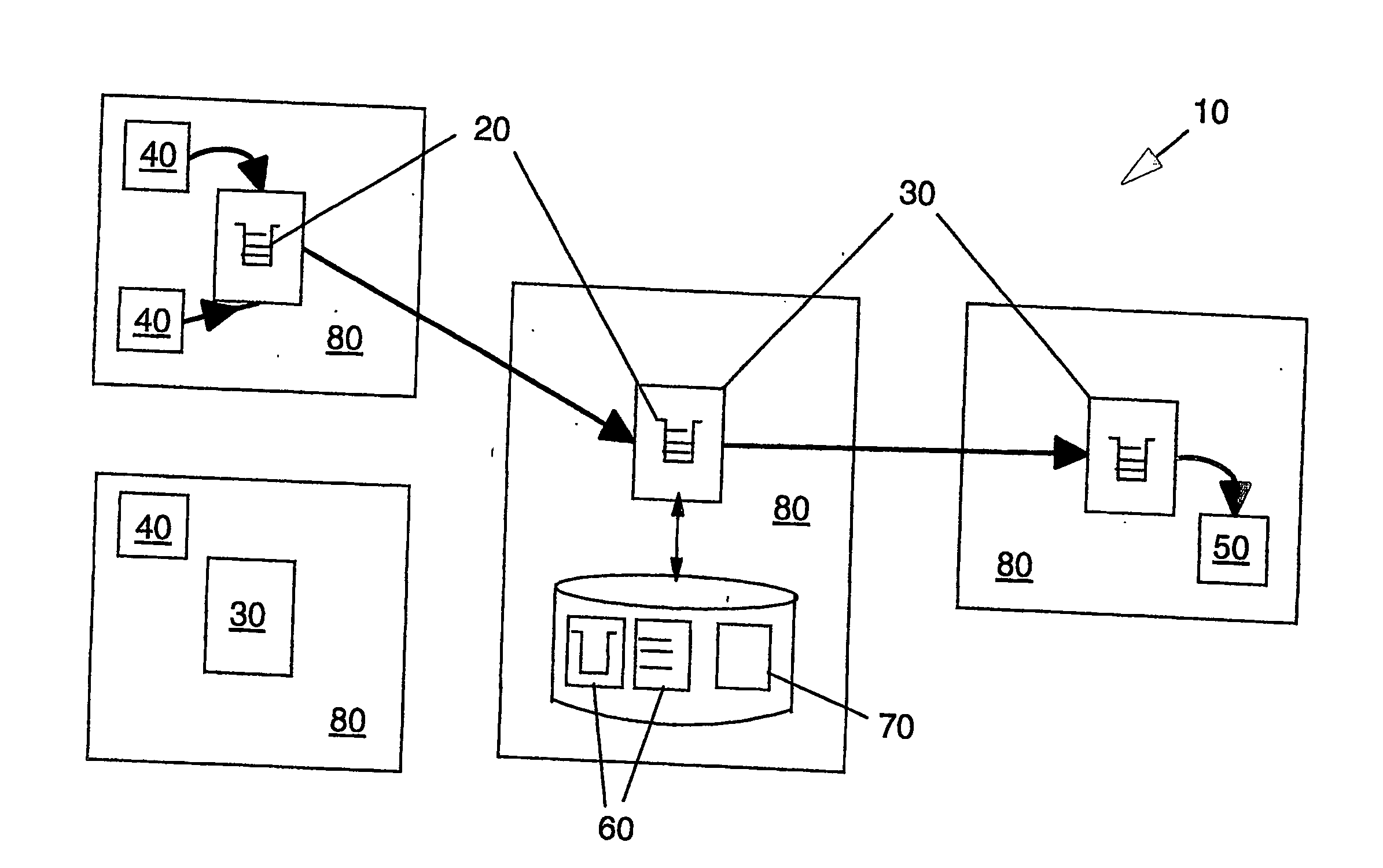
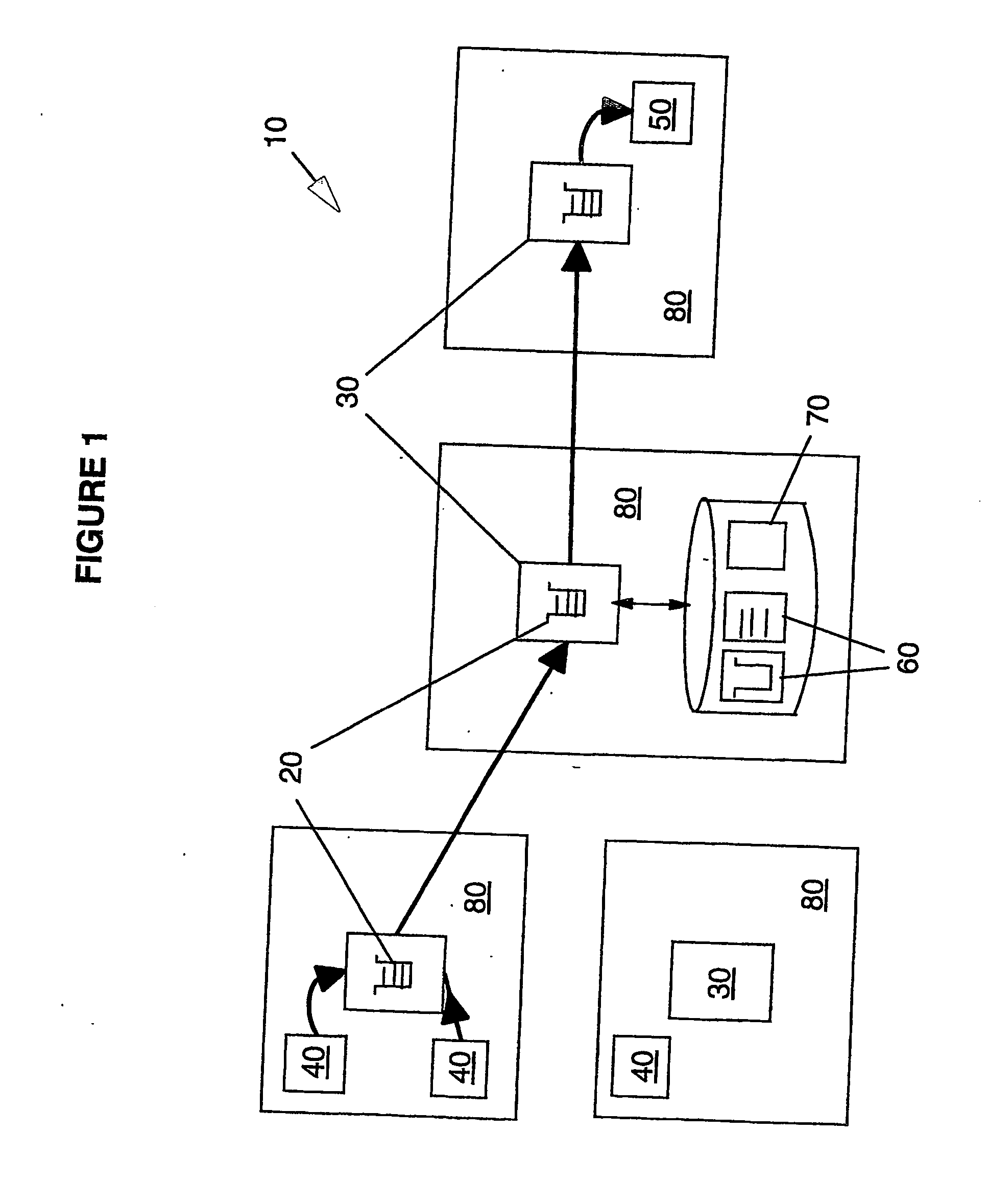
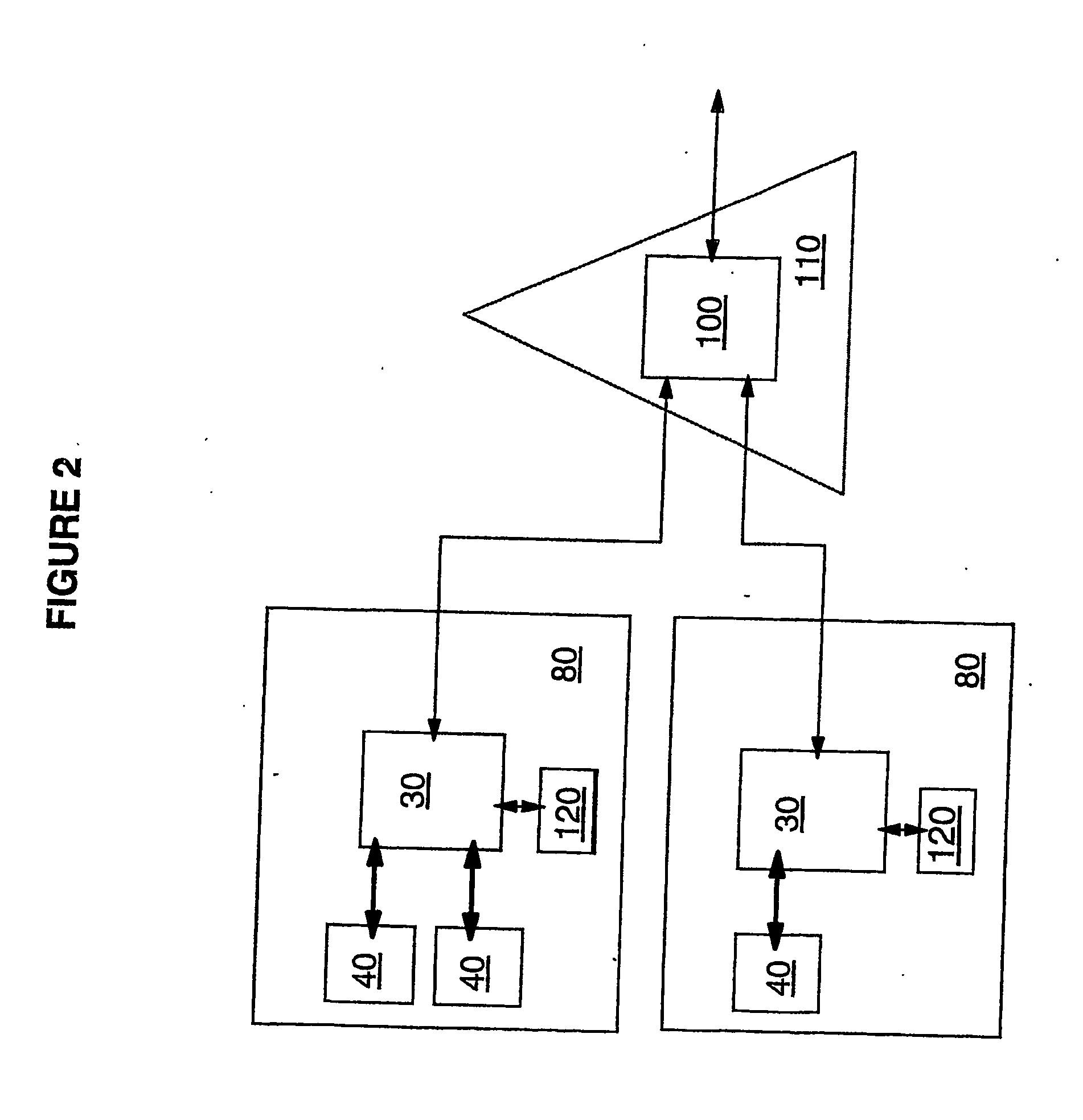
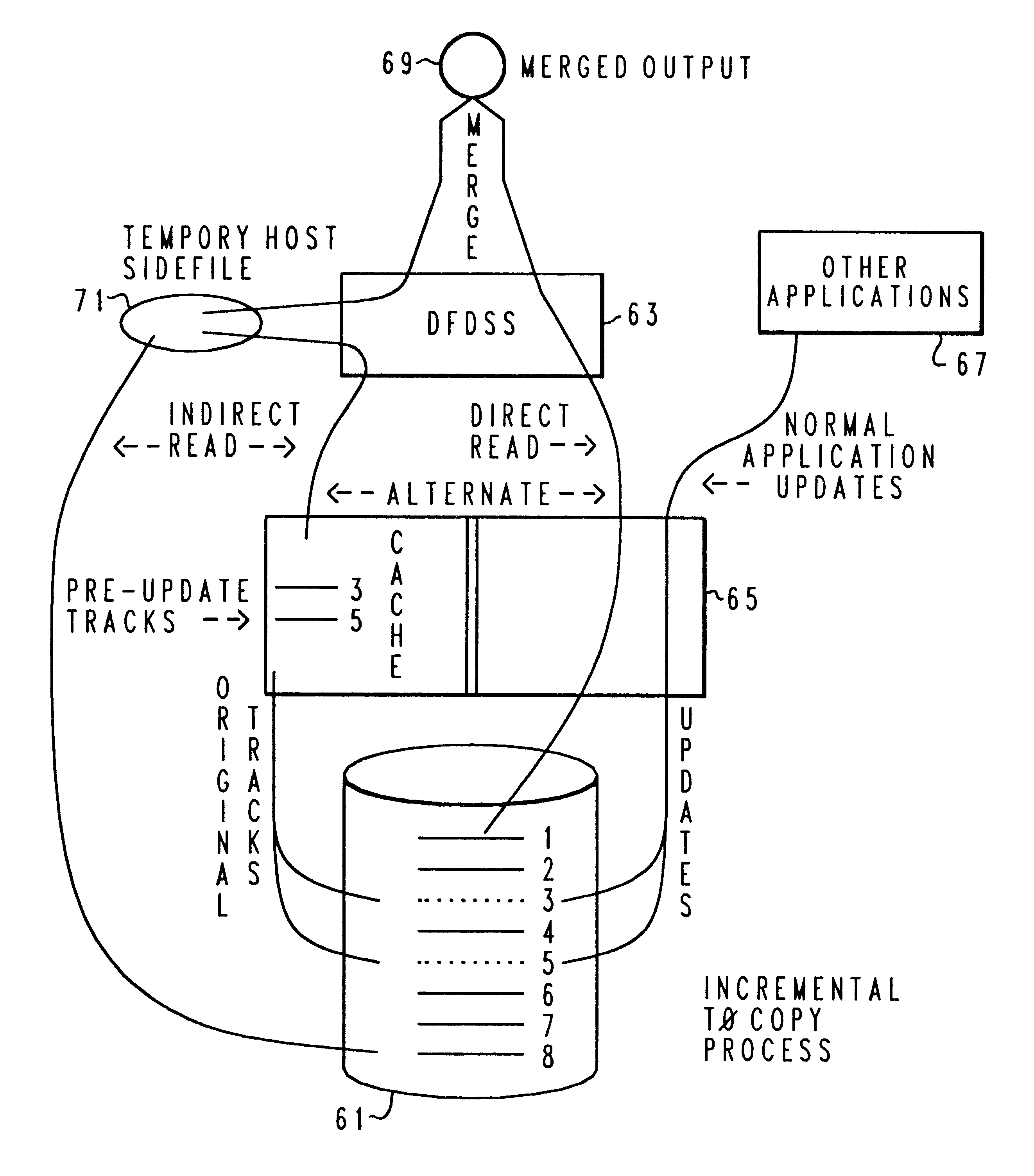
InactiveUSRE37601E1Maintaining continued availability of datasetsReduce suspensionRedundant operation error correctionMemory systemsData processing systemData set
Backup copying of designated datasets representing a first selected point in time consistency may be performed in a data processing system on an attached storage subsystem concurrent with data processing system application execution by first suspending application execution only long enough to form a logical-to-physical address concordance, and thereafter physically backing up the datasets on the storage subsystem on a scheduled or opportunistic basis. An indication of each update to a selected portion of the designated datasets which occurs after the first selected point in time is stored and application initiated updates to uncopied designated datasets are first buffered. Thereafter, sidefiles are made of the affected datasets, or portions thereof, the updates are then written through to the storage subsystem, and the sidefiles written to an alternate storage location in backup copy order, as controlled by the address concordance. At a subsequent point in time only those portions of the designated datasets which have been updated after the first selected period and time are copied, utilizing an identical technique.
Owner:IBM CORP
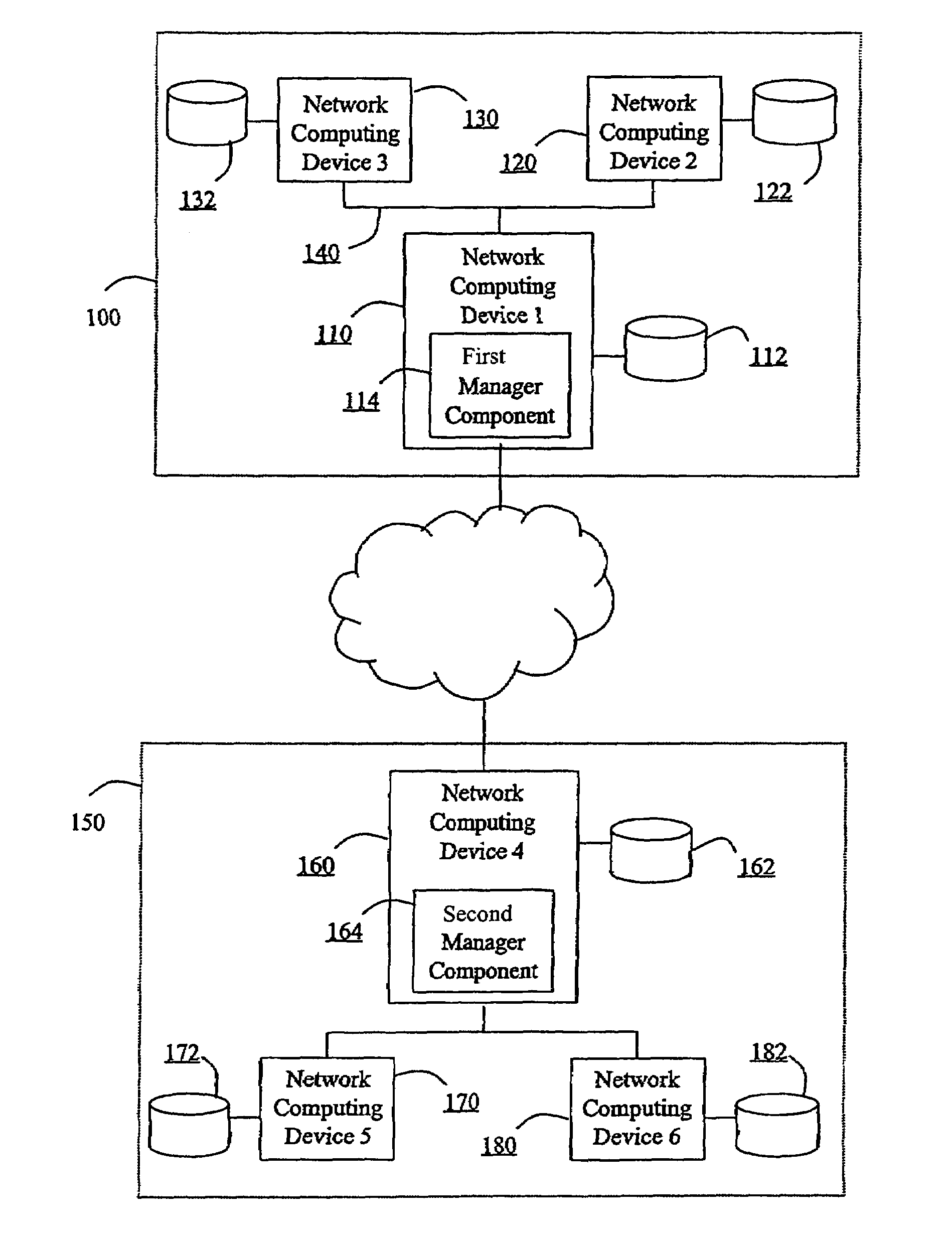
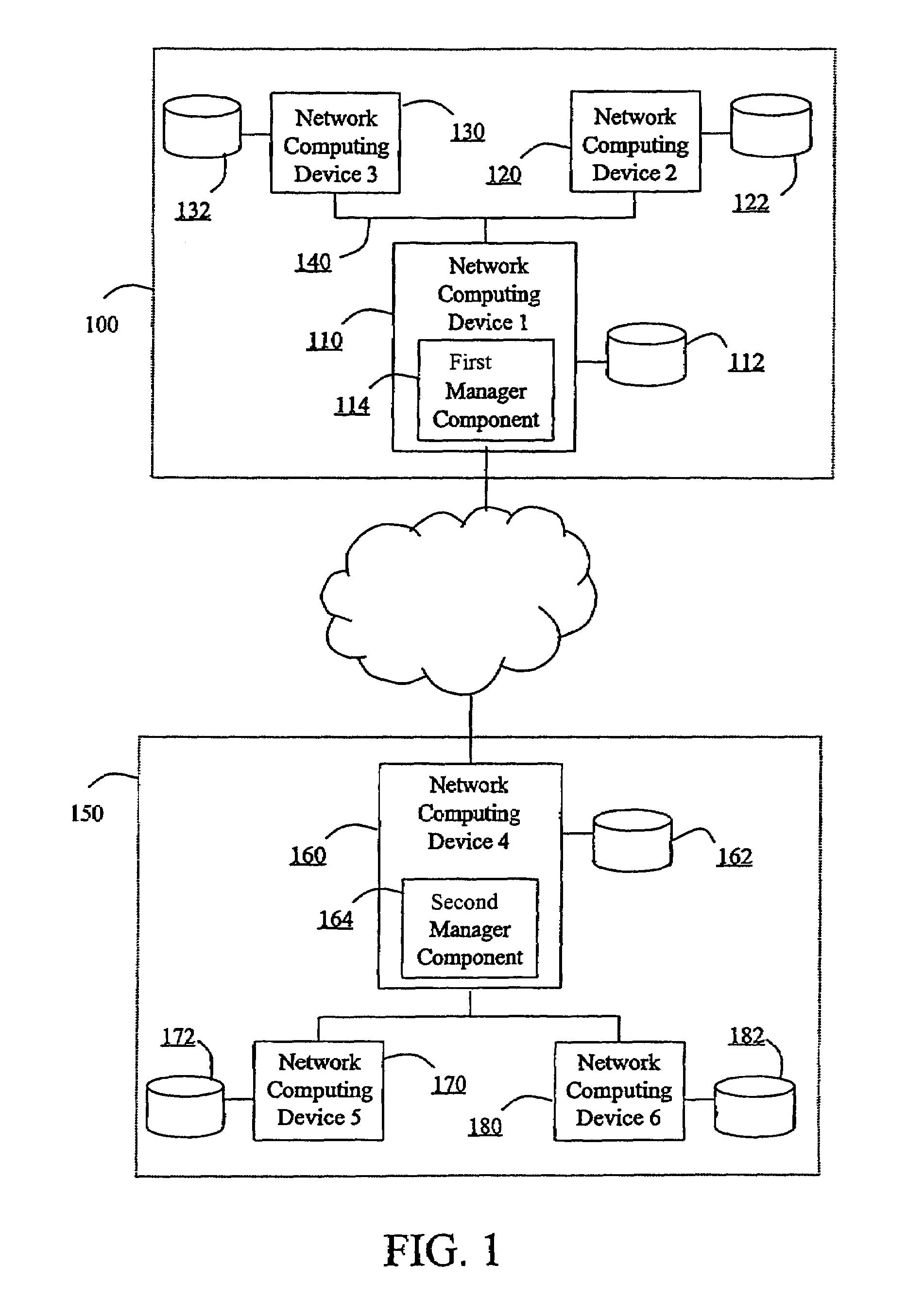
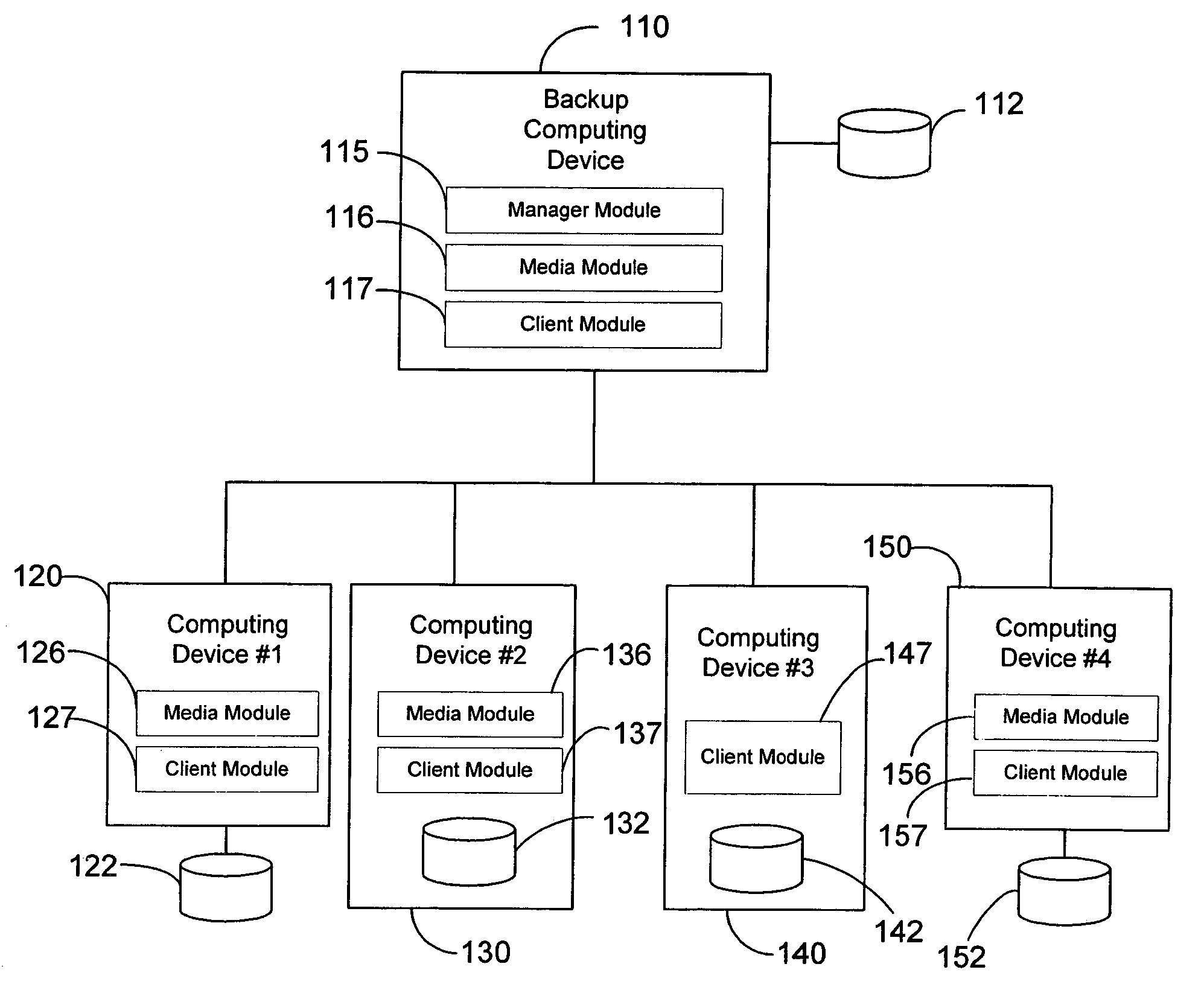
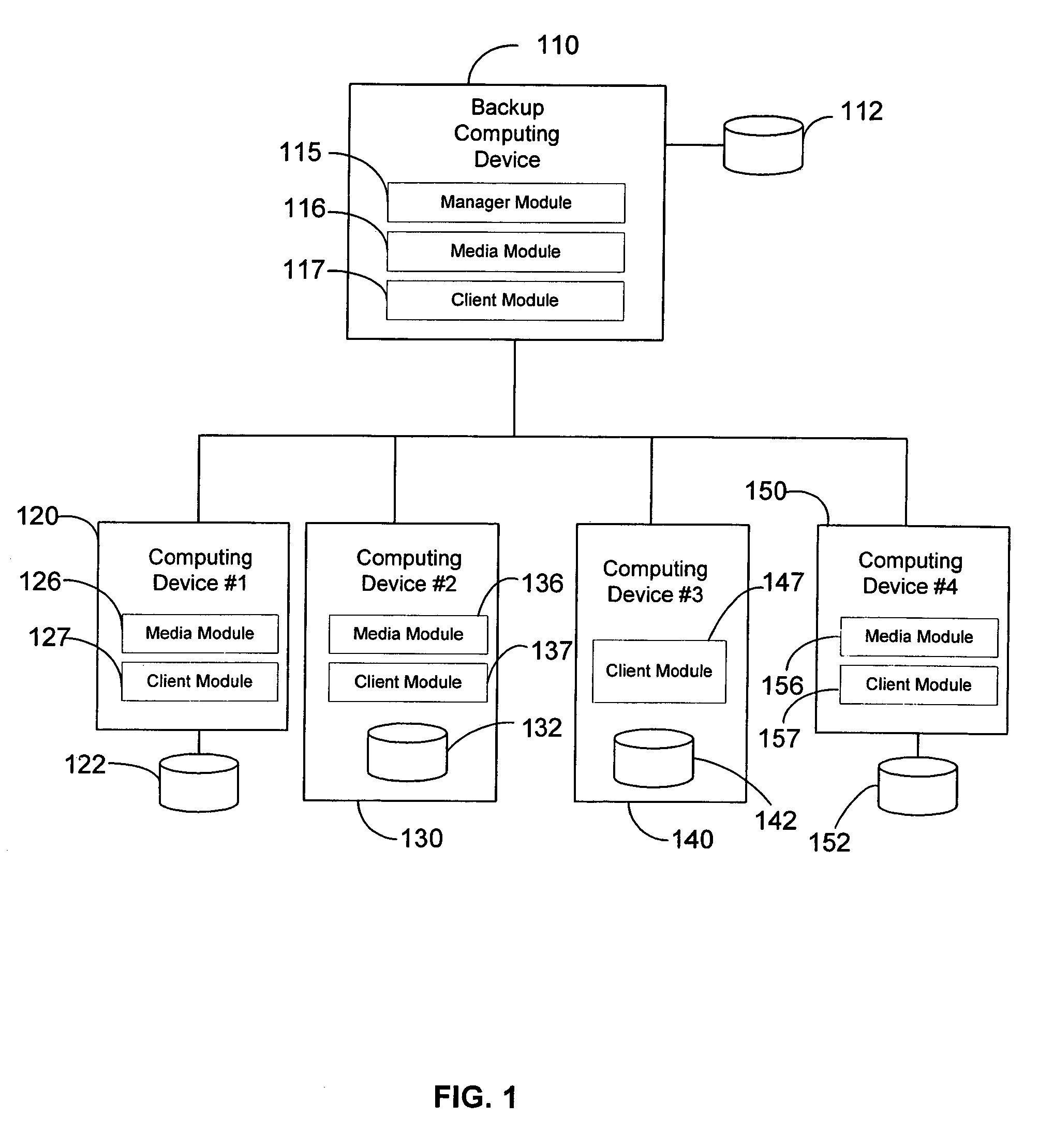
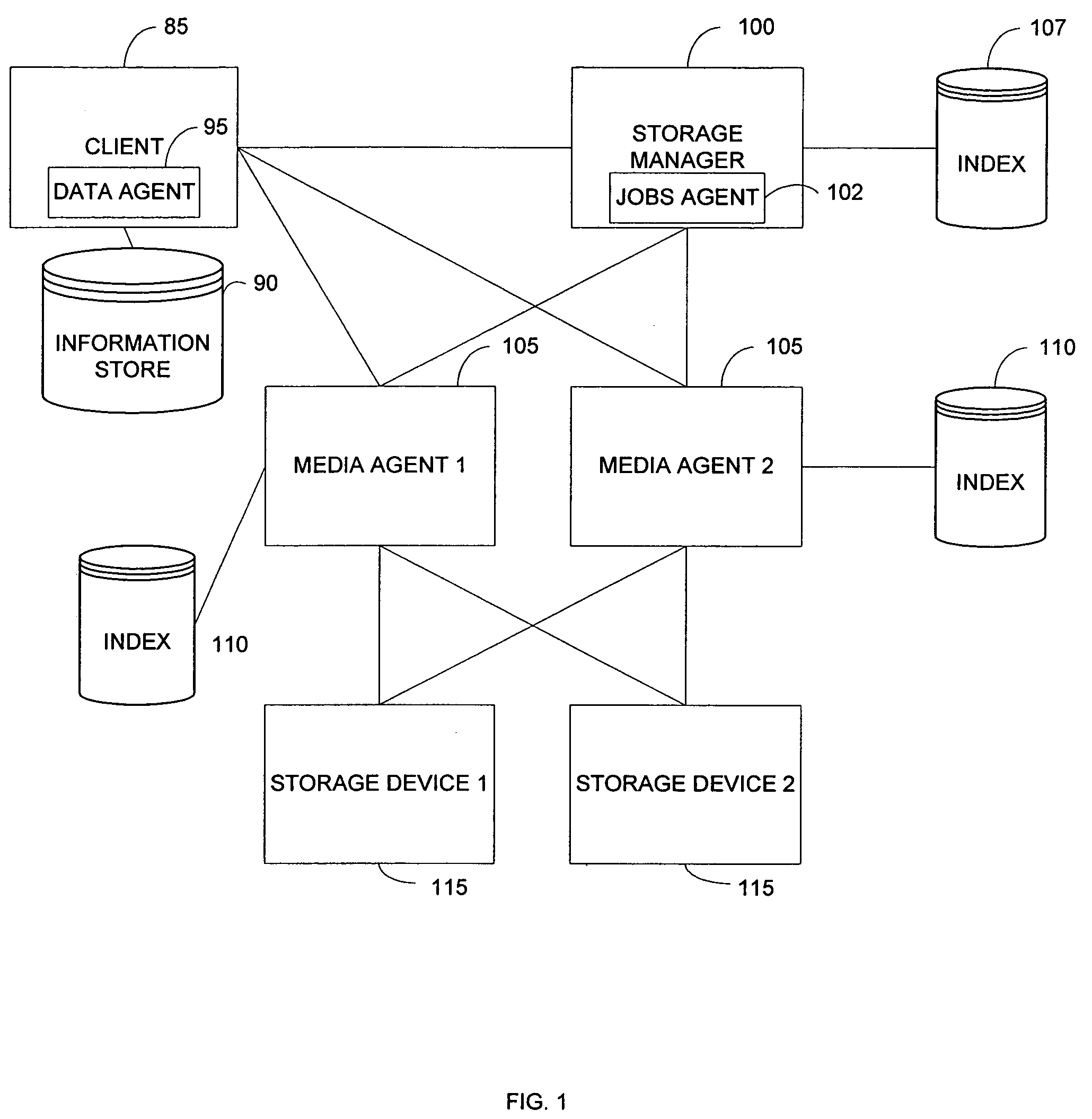
Hierarchical backup and retrieval system
InactiveUS7395282B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSoftware agentAdministrative controls
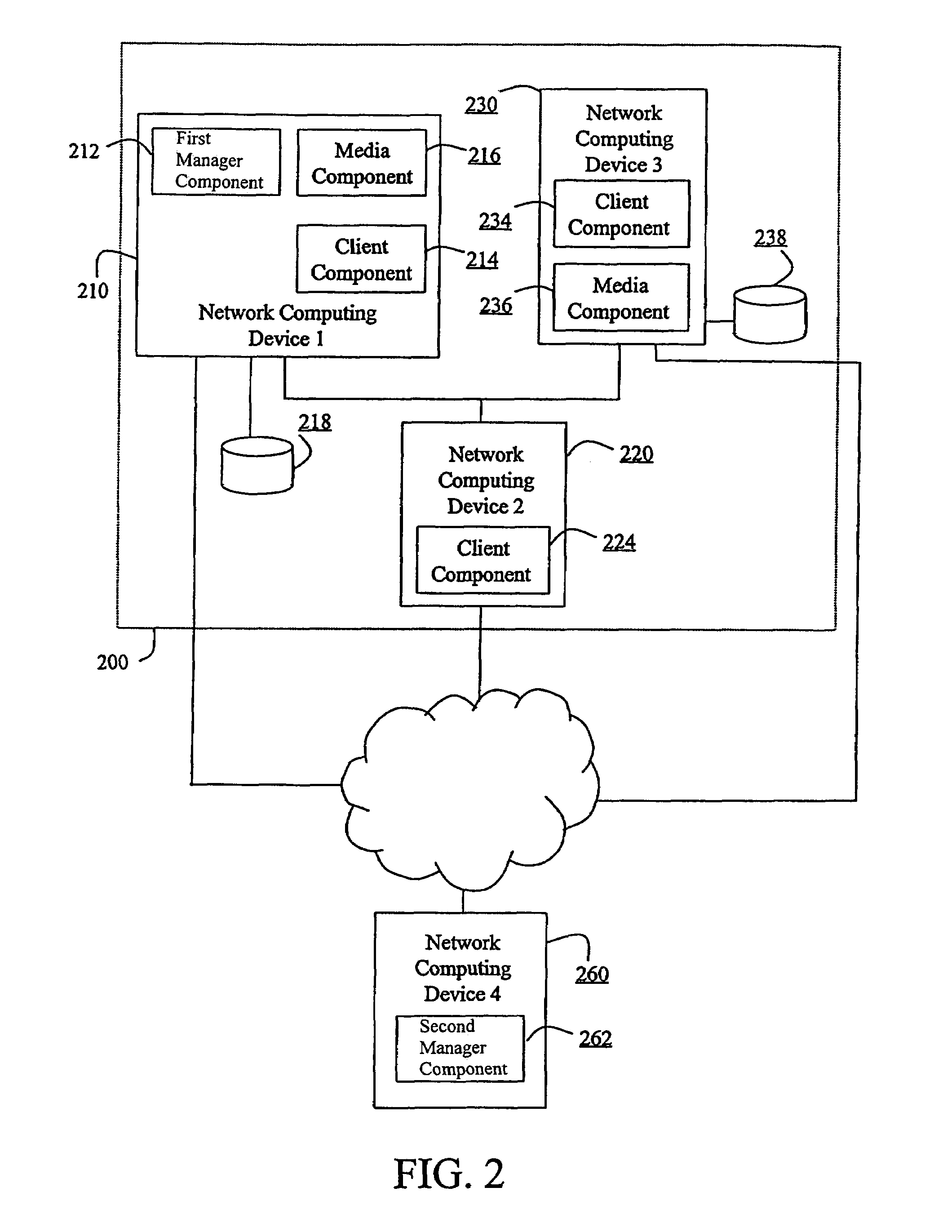
The invention is a hierarchical backup system. The interconnected network computing devices are put into groups of backup cells. A backup cell has a manager software agent responsible maintaining and initiating a backup regime for the network computing devices in the backup cell. The backups are directed to backup devices within the backup cell. Several backup cells can be defined. A manager software agent for a particular cell may be placed into contact with the manager software agent of another cell, by which information about the cells may be passed back and forth. Additionally, one of the software agents may be given administrative control over another software agent with which it is in communication.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
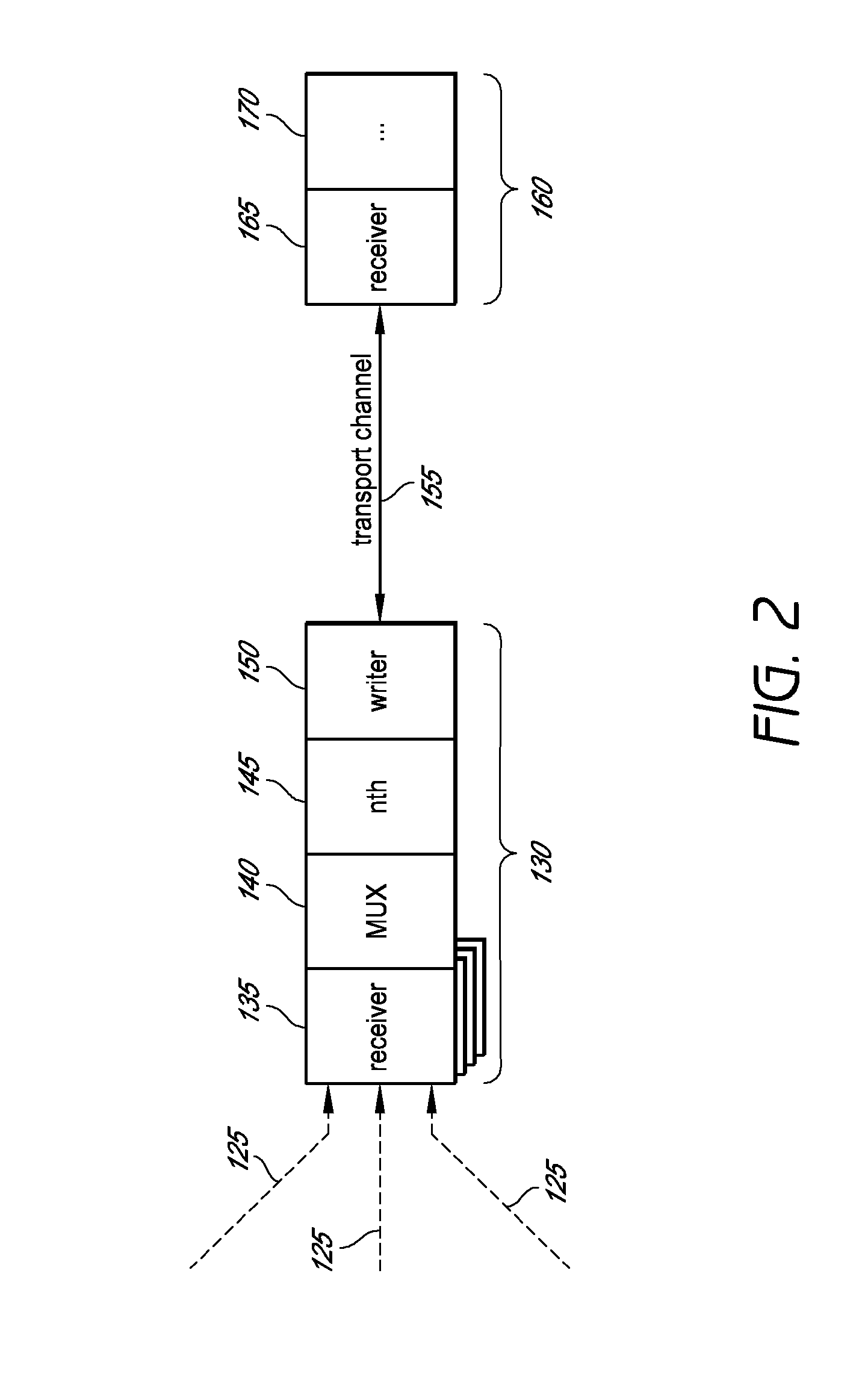
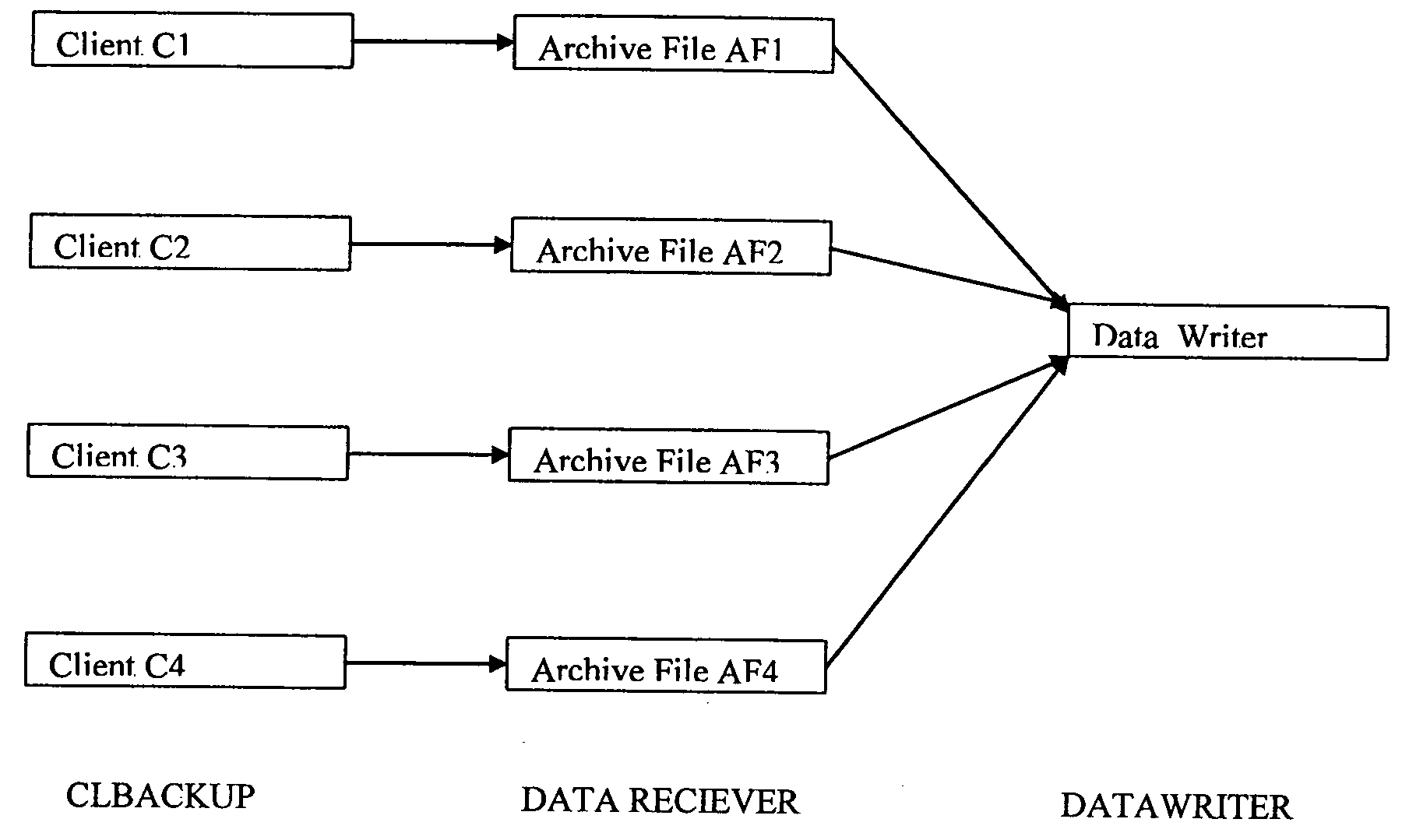
System and method for combining data streams in pipelined storage operations in a storage network
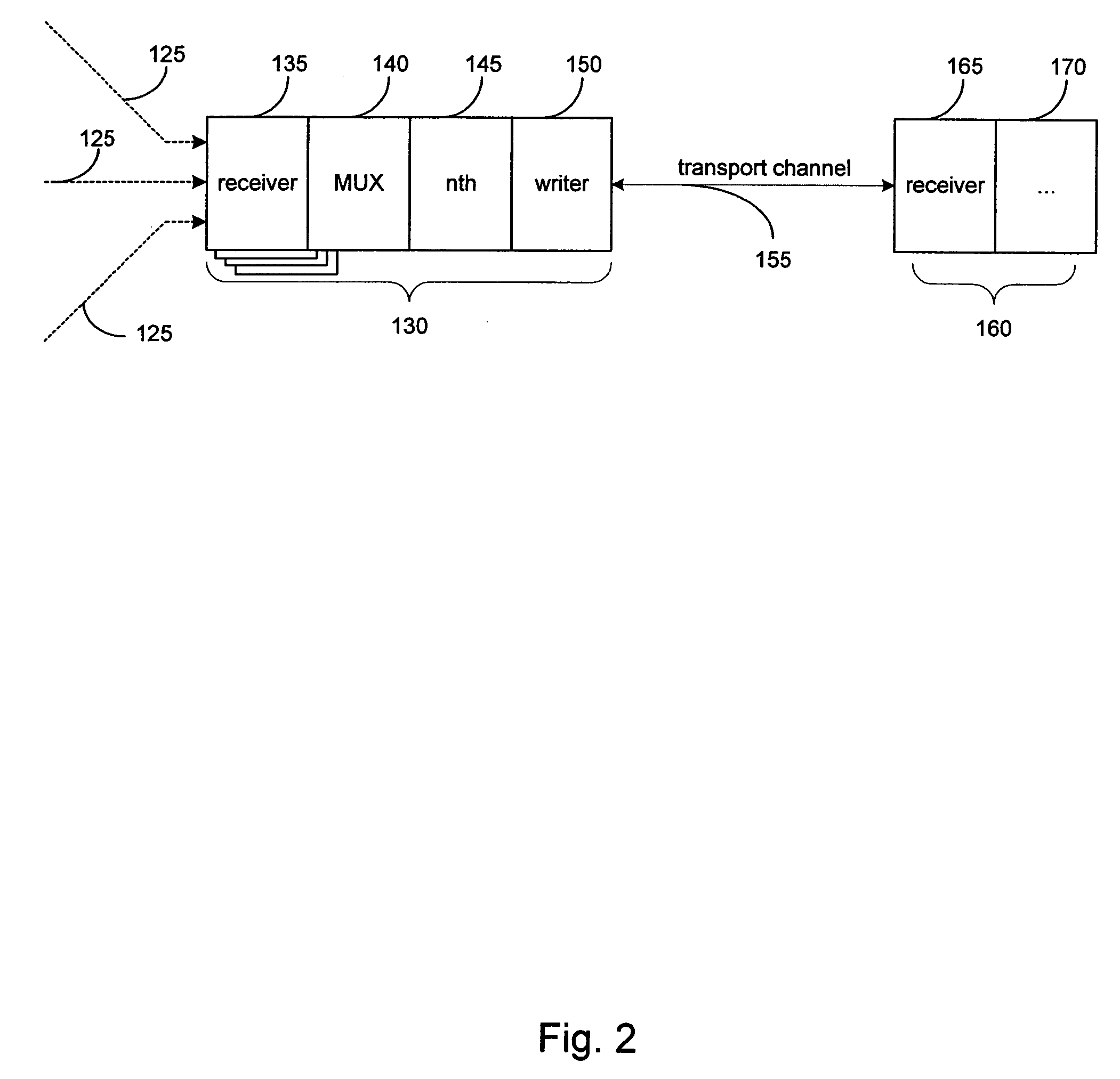
Described herein are systems and methods for multiplexing pipelined data for backup operations. Various data streams are combined such as by multiplexing by a multiplexing module. The multiplexing module combines the data from the various data streams received by receiver module(s) into a single stream of chunks. The multiplexing module may combine data from multiple archive files into a single chunk. Additional modules perform other operations on the chunks of data to be transported such as encryption, compression, etc. The data chunks are transmitted via a transport channel to a receive pipeline that includes a second receiver module and other modules. The data chunks are then stored in a backup medium. The chunks are later retrieved and separated such as by demultiplexing for restoring to a client or for further storage as auxiliary copies of the separated data streams or archive files.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
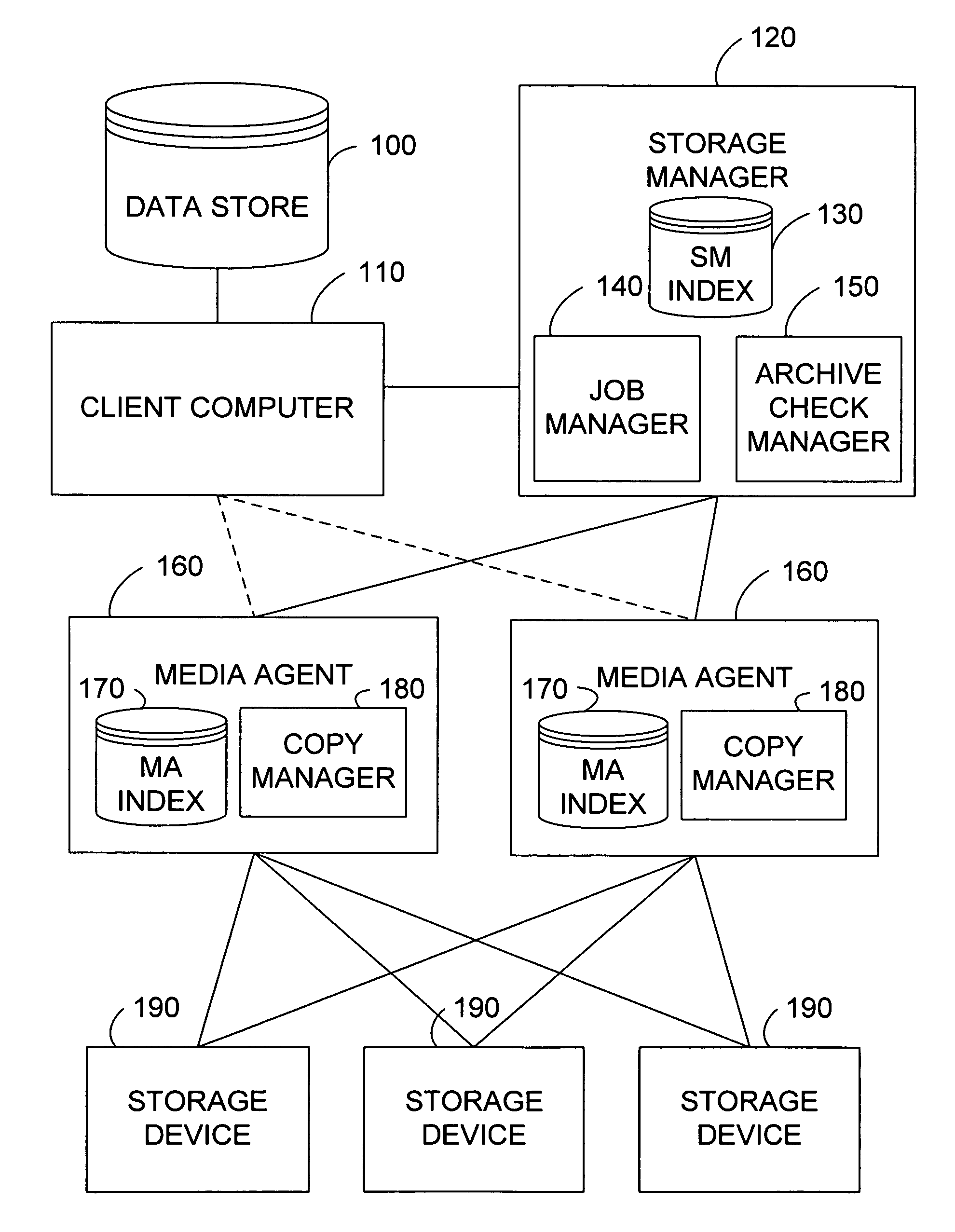
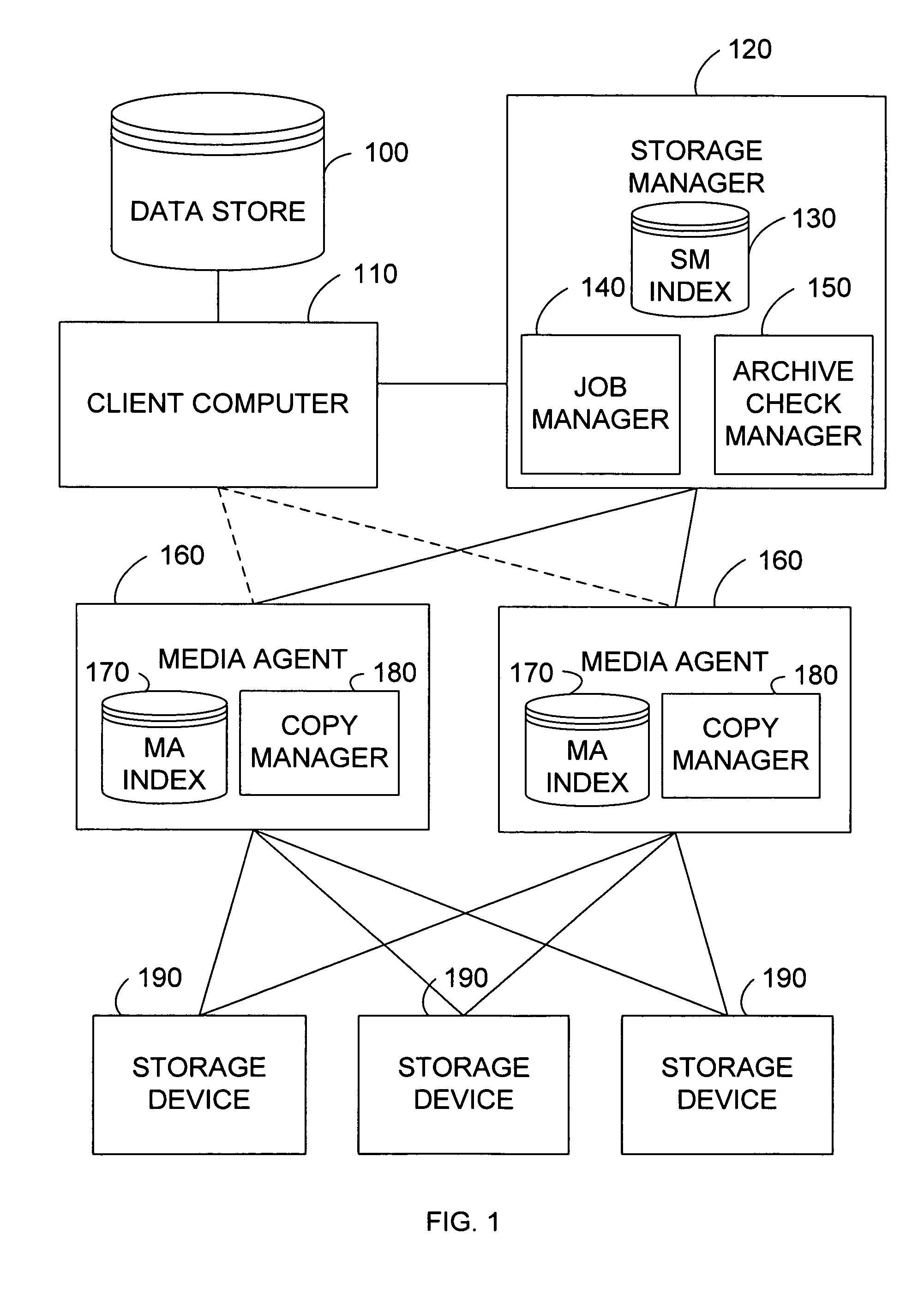
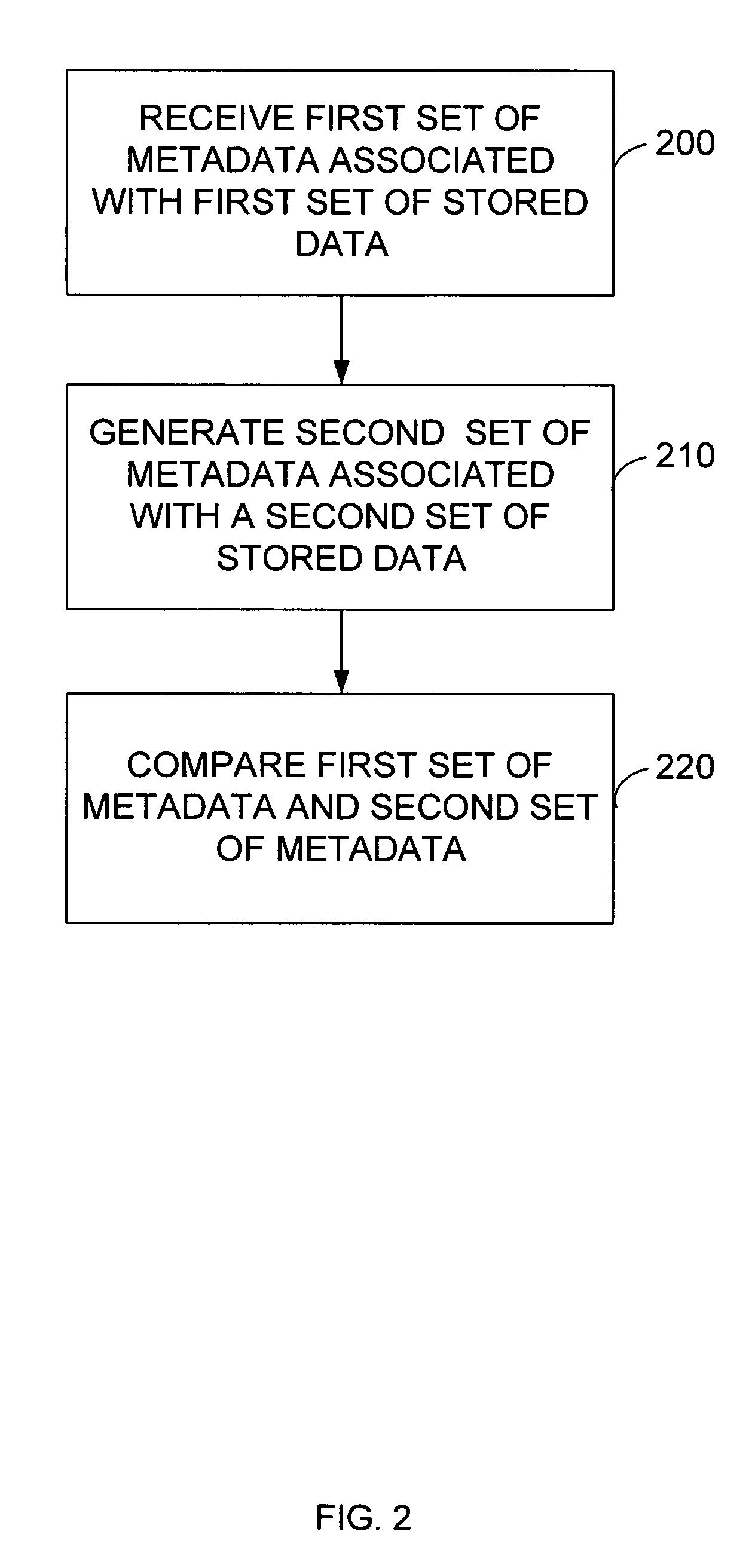
System and method for stored data archive verification
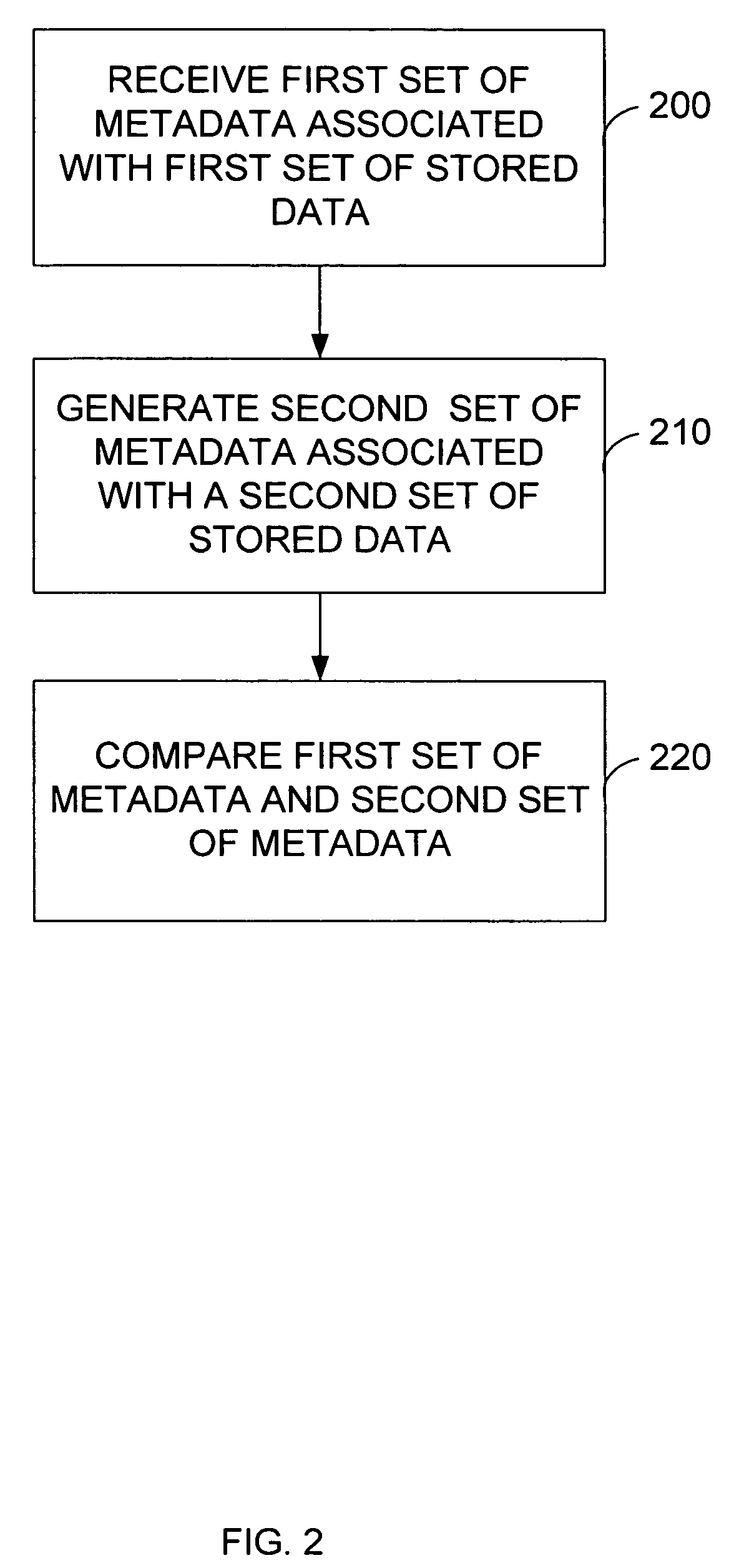
Methods and systems are described for verifying stored data by receiving a first set of metadata associated with a first set of stored data, generating a second set of metadata associated with a second set of stored data which is associated with the first set of stored data, and comparing the first set of metadata and second set of metadata. Alternatively, the storage system can also generate a first set of metadata associated with a first set of stored data, generate a second set of stored data which is a copy of the first set of stored data, generate a second set of metadata associated with the second set of stored data, and compare the first set of metadata and the second set of metadata.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
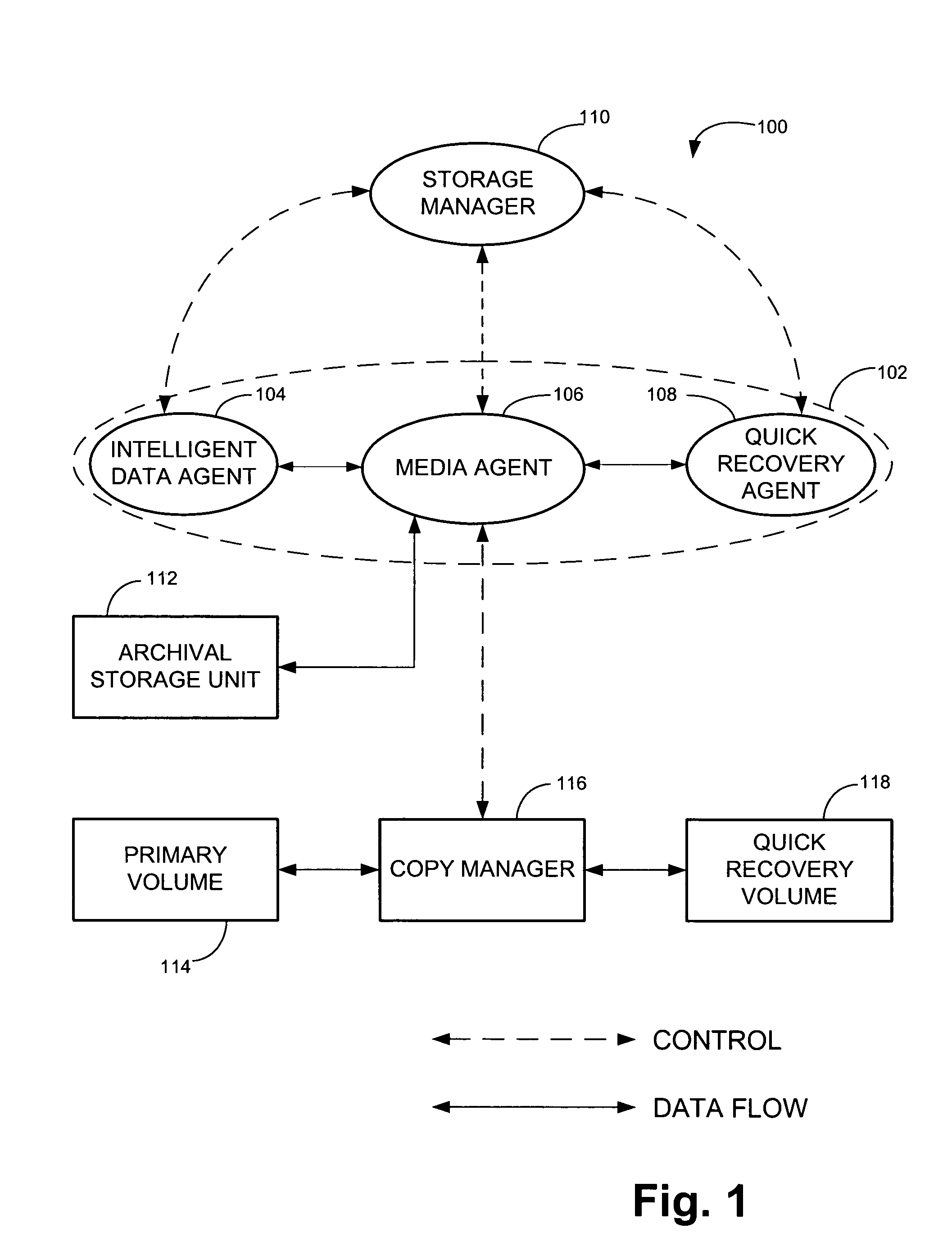
System and method for generating and managing quick recovery volumes
InactiveUS7346623B2Efficient creation and management and recoveryInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsData setApplication software
The invention relates to computer readable medium storing program code which when executed on a computer causes the computer to perform a method for creating a quick recovery volume of a primary data set used by a first computer in a backup storage system, which includes identifying a snapshot image of the primary data set generated by a snapshot application, creating the quick recovery volume of the primary data set from the snapshot image of the primary data set and controlling transfer of data from the first computer to an archival storage unit. In one embodiment, the invention provides a method for creating a quick recovery volume of a primary data set that includes creating a snapshot image of the primary data set and creating a quick recovery volume of the primary data set from the snapshot image of the primary data set. In another embodiment, the invention provides a user interface screen enabling browser style browsing and recovery of quick recovery volumes and snapshot images.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Modular backup and retrieval system
InactiveUS7389311B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSystems managementModularity
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
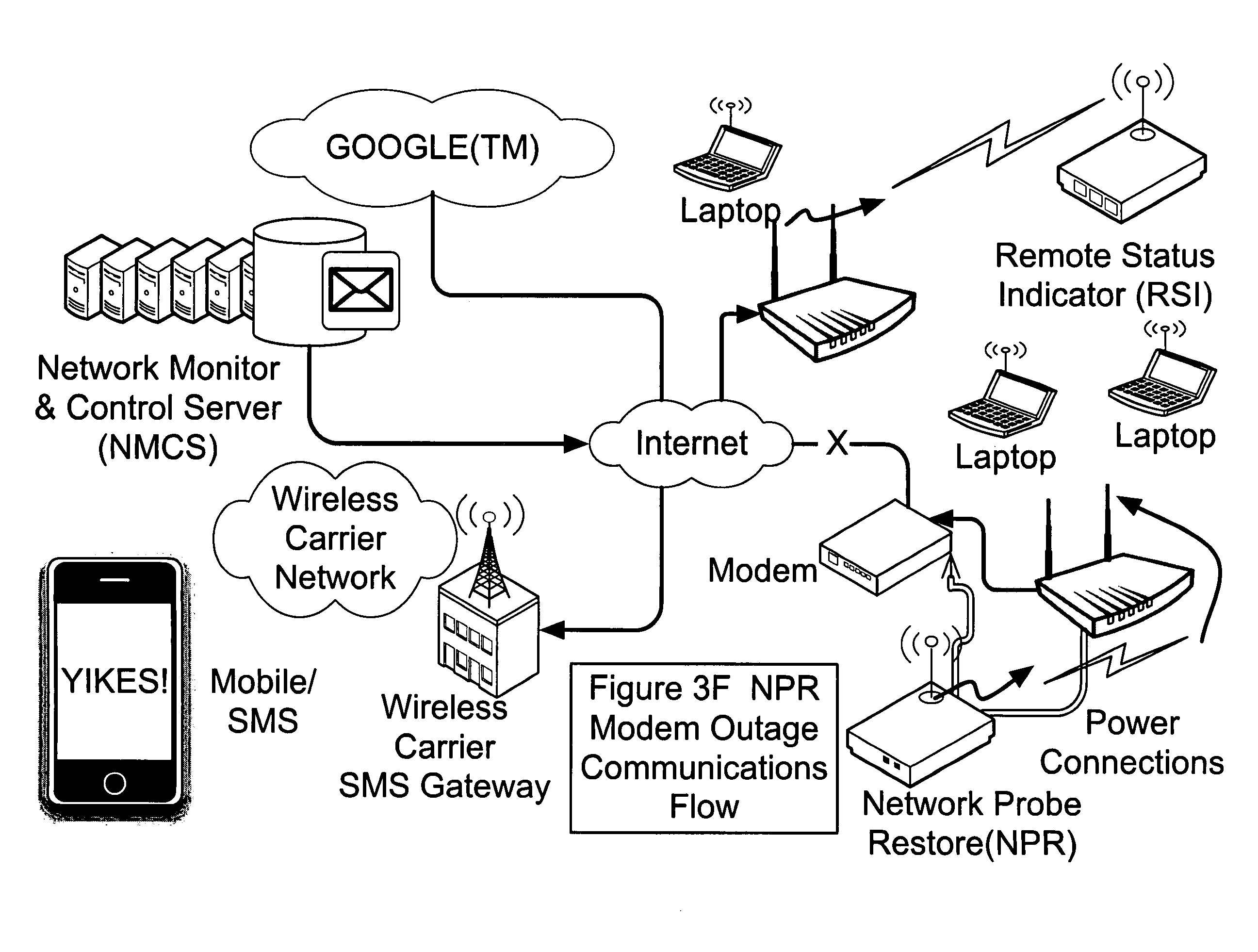
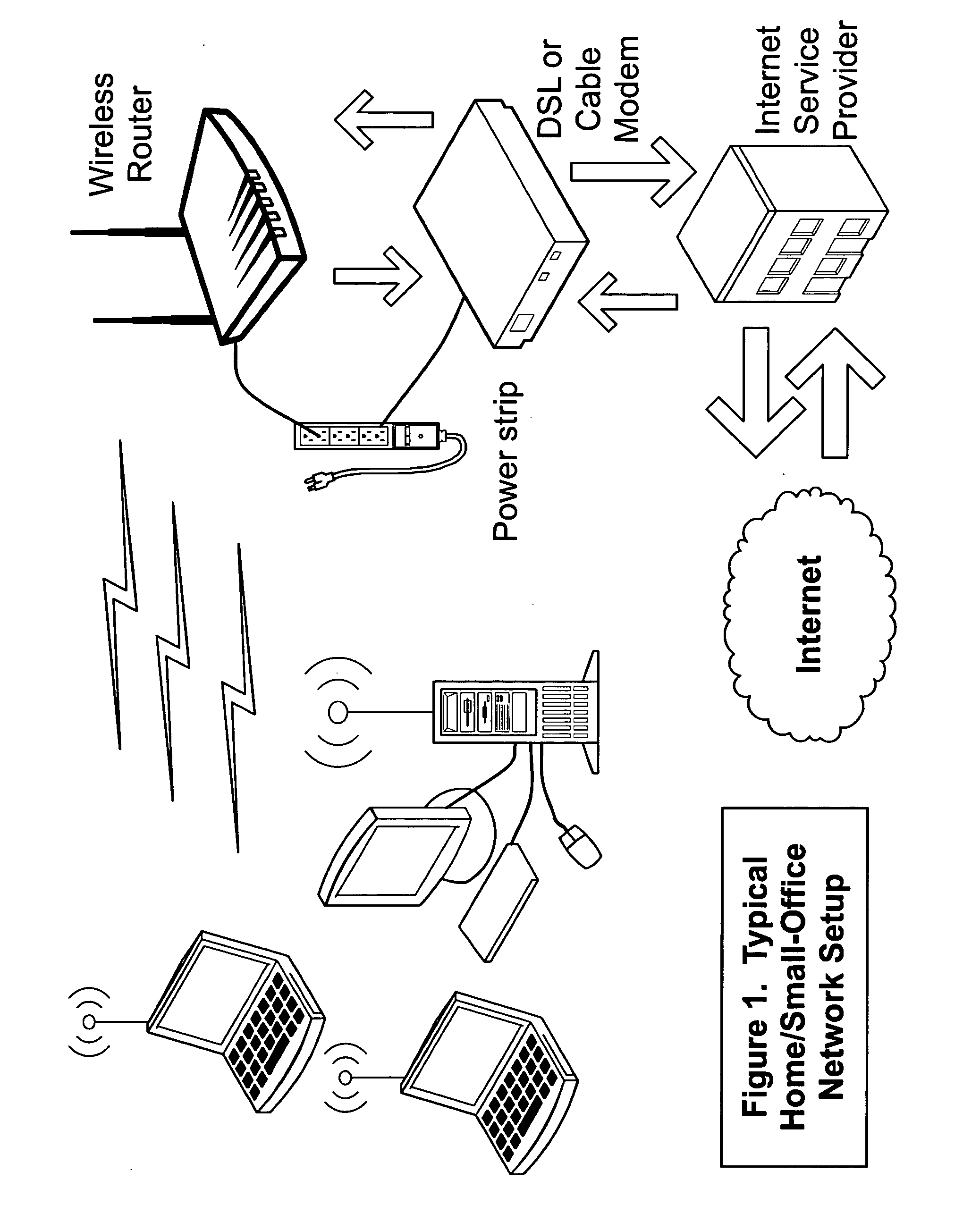
Systems, devices, agents and methods for monitoring and automatic reboot and restoration of computers, local area networks, wireless access points, modems and other hardware
ActiveUS20090013210A1Data switching networksRedundant operation error correctionDomain nameFully qualified domain name
An embodiment of the invention is a client on a local area network that periodically and automatically evaluates its physical connectivity with the local area network, exercises local-network services such as DHCP, and verifies Internet connectivity and function by pinging one or more numerically specified IP addresses and by pinging one or more IP addresses specified by an FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) known to the assigned DNS servers. An embodiment of the invention may include a plurality of client elements monitoring one or more networks. Functionality according to embodiments of the invention can send notices, automatically initiate action, and otherwise assist in, among other things, remote monitoring and administration of networks, and particularly wireless networks.
Owner:SAND HLDG LLC
Software update method, apparatus and system
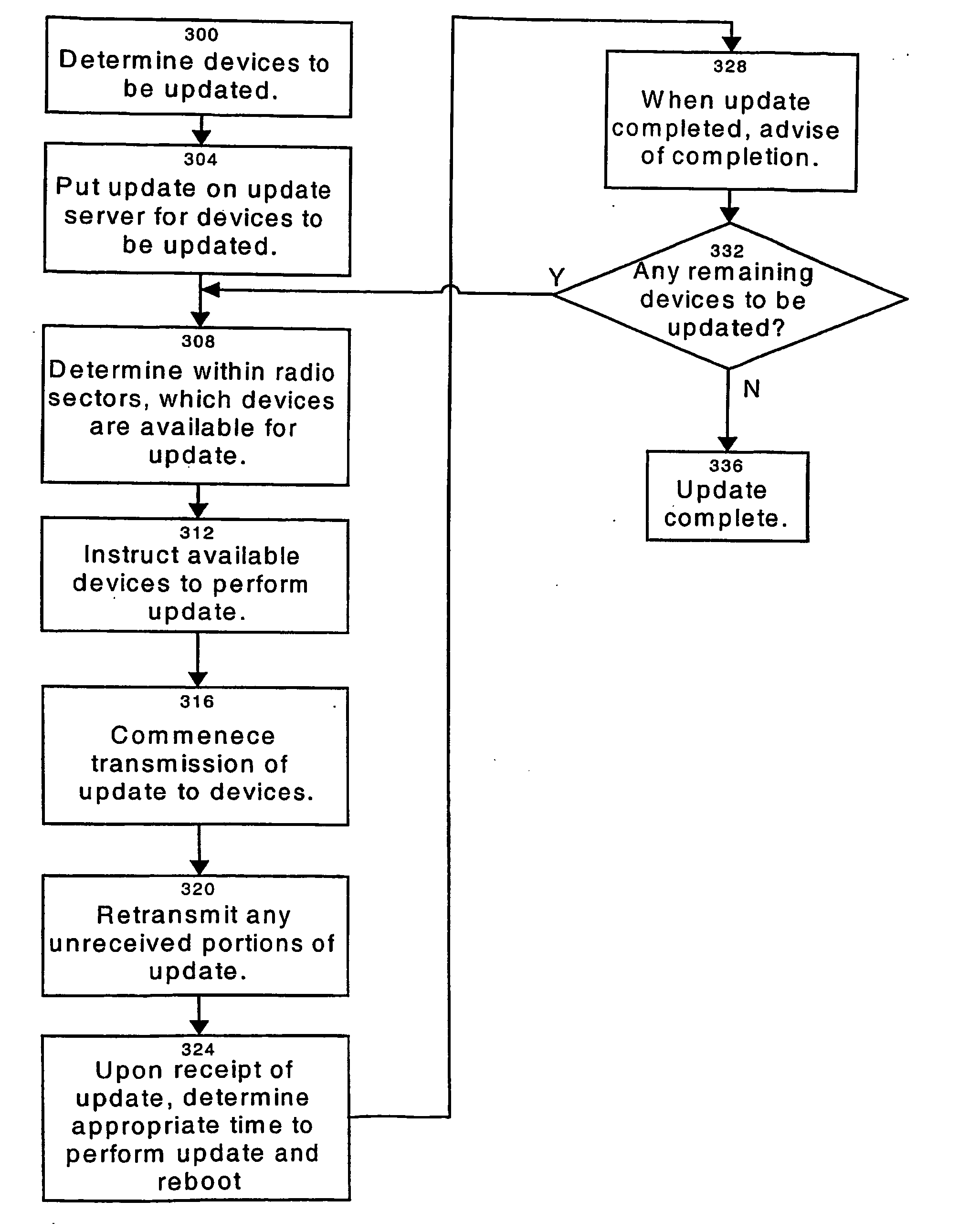
A system for remotely updating software on at least one electronic device connected to a network. The electronic devices have a non-volatile rewritable storage unit divided into at least two partitions, one of which will contain core firmware and the other of which will contain auxiliary software. When an update is received at the device, the updated core firmware is written to overwrite the partition in the rewritable storage unit that contained the auxiliary software. When this is completed and verified, the previous version of the core firmware stored in the storage unit is disabled from execution by the device. Next, the updated auxiliary software is written to overwrite the old version of the core firmware. When this write is complete, the device determines a suitable time for it to be rebooted to execute the updated software. In another embodiment, the present core firmware in the device is copied from the partition it is in to the other partition, overwriting the auxiliary software stored there. The new core firmware received to update the device is overwritten into the first partition, the old copied core firmware being present in case of an upgrade failure, and upon a successful update of the first partition, the auxiliary software is written to the second partition, overwriting the copied old core firmware. In this manner, the position of the core firmware and auxiliary software within the partitions is preserved during normal operation of the device.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Method and apparatus for storing information in a data processing system
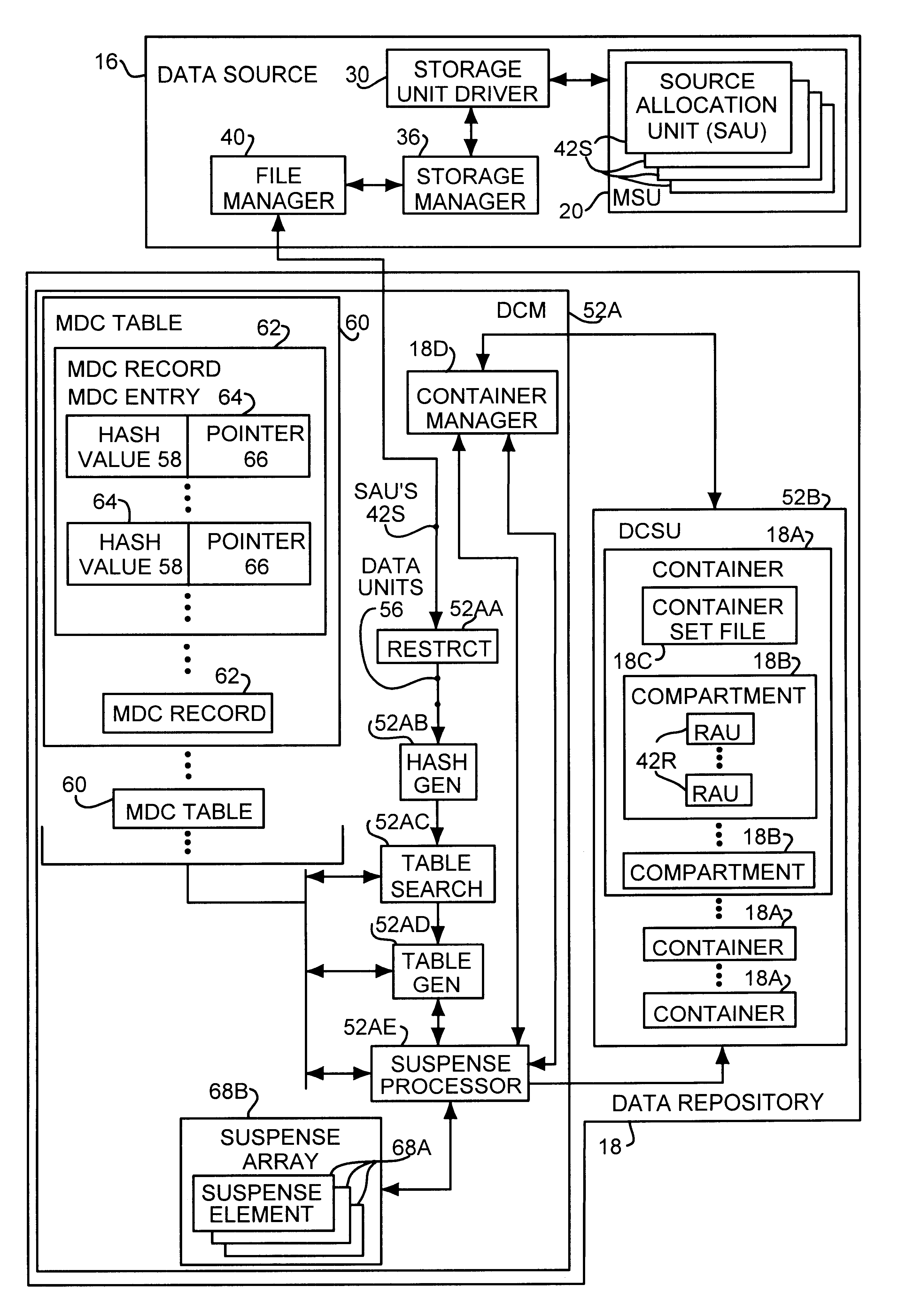
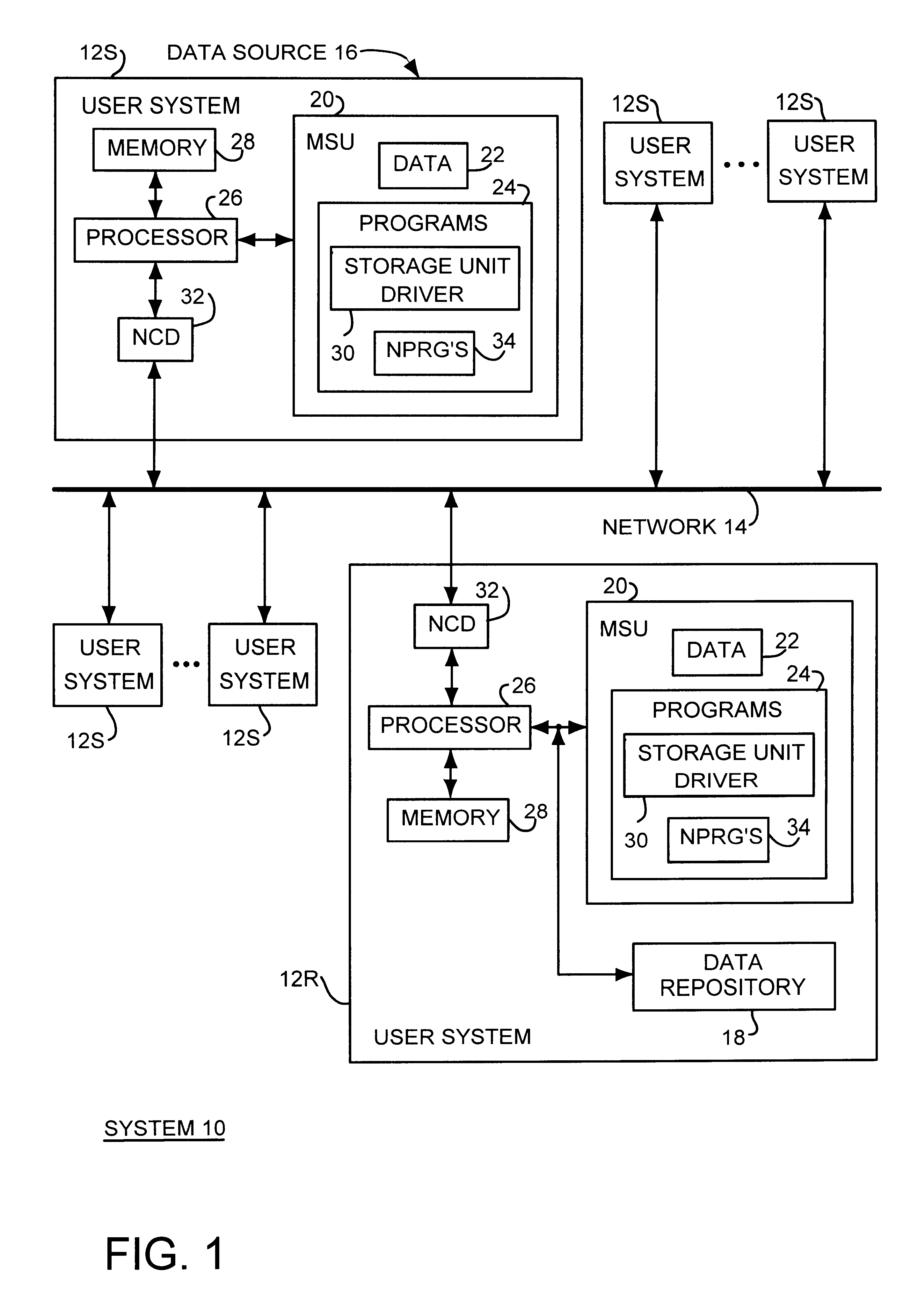
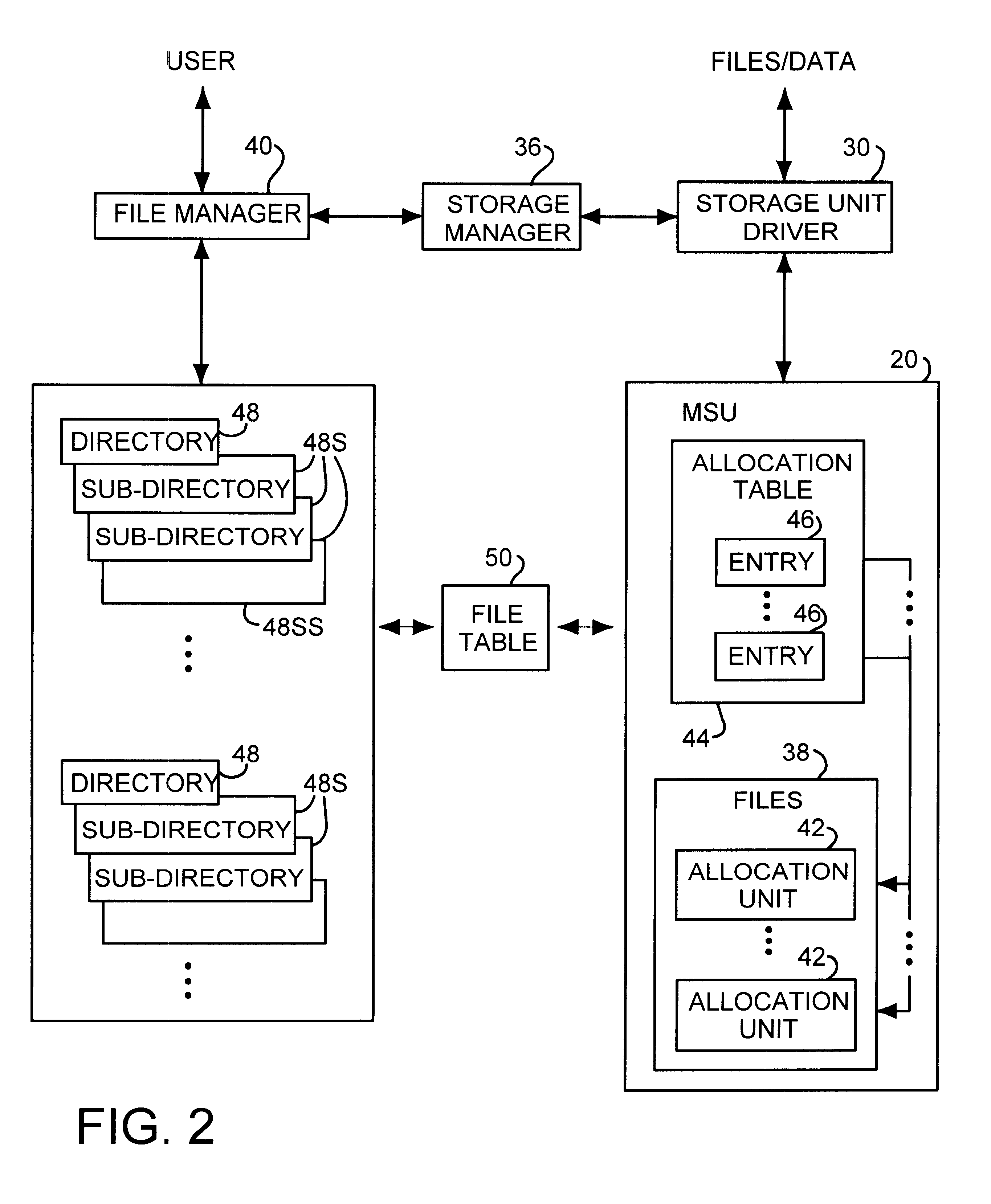
InactiveUS6374266B1Erroneous identificationAvoid problemsData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData processing systemData source
A method for storing data from a data source in a storage device of a data repository by reading all source allocation units, restructuring the data into data units having a size corresponding to the repository allocation units, and generating a hash value for the data of each data unit read from the data source. For each data unit, a data table is searched for a table entry having a matching hash value wherein each table entry contains the hash value of a data unit stored in a repository allocation unit and a repository allocation unit pointer to the corresponding repository allocation unit. When the hash value of a data unit does not match any hash value of any table entry in the data table, the data of the data unit is written into a newly allocated repository allocation unit a new table entry is written to the data table. When the hash value of a data unit matches the hash value of a data entry in the data table, the data of the corresponding repository allocation unit and is compared with the data of the data unit. If the data of the data unit matches the repository allocation unit, the data unit is discarded. If the data of the data unit does not match the corresponding repository allocation unit, the data unit is written into a newly allocated repository allocation unit and a new table entry is inserted into the data table.
Owner:CHRYSALIS STORAGE
Method and apparatus for independent and simultaneous access to a common data set
InactiveUS6101497AData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersData processing systemData set
A data network with data storage facilities for providing redundant data storage and for enabling concurrent access to the data for multiple purposes. A first data processing system with a first data facility stores a data base and processes transactions or other priority applications. A second data storage facility, that may be physically separated from the first data storage facility, mirrors the data in the first data storage facility. In a concurrent access operating mode, the second data storage facility makes the data available to an application concurrently with, but independently of, the operation of the other application. On completion of the concurrent operation, the second data storage facility can reconnect with and synchronizes with the first data storage facility thereby to reestablish the mirroring operation.
Owner:EMC CORP
Method, software and apparatus for saving, using and recovering data
InactiveUS6016553ADigital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersOperational systemOriginal data
A method and apparatus for reverting a disk drive to an earlier point in time is disclosed. Changes made to the drive are saved in a circular history buffer which includes the old data, the time it was replaced by new data, and the original location of the data. The circular history buffer may also be implemented by saving new data elements into new locations and leaving the old data elements in their original locations. References to the new data elements are mapped to the new location. The disk drive is reverted to an earlier point in time by replacing the new data elements with the original data elements retrieved from the history buffer, or in the case of the other embodiment, reads to the disk are mapped to the old data elements stilled stored in their original locations. The method and apparatus may be implemented as part of an operating system, or as a separate program, or in the controller for the disk drive. The method and apparatus are applicable to other forms of data storage as well. Also disclosed are method and apparatus for providing firewall protection to data in a data storage medium of a computer system.
Owner:POWER MANAGEMENT ENTERPRISES
Stored data reverification management system and method
ActiveUS7613748B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalManagement systemDatabase
A system and method are provided for verifying data copies and reverifying the copies over the life span of media according to a verification policy. Characteristics of media and use of media are tracked to provide metrics which may be used to dynamically reevaluate and reassign verification policies to optimize media usage. Copies that fail verification operations may be repaired by repeating a storage operation for recent copies or by substituting a close temporal copy of the failed copy.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
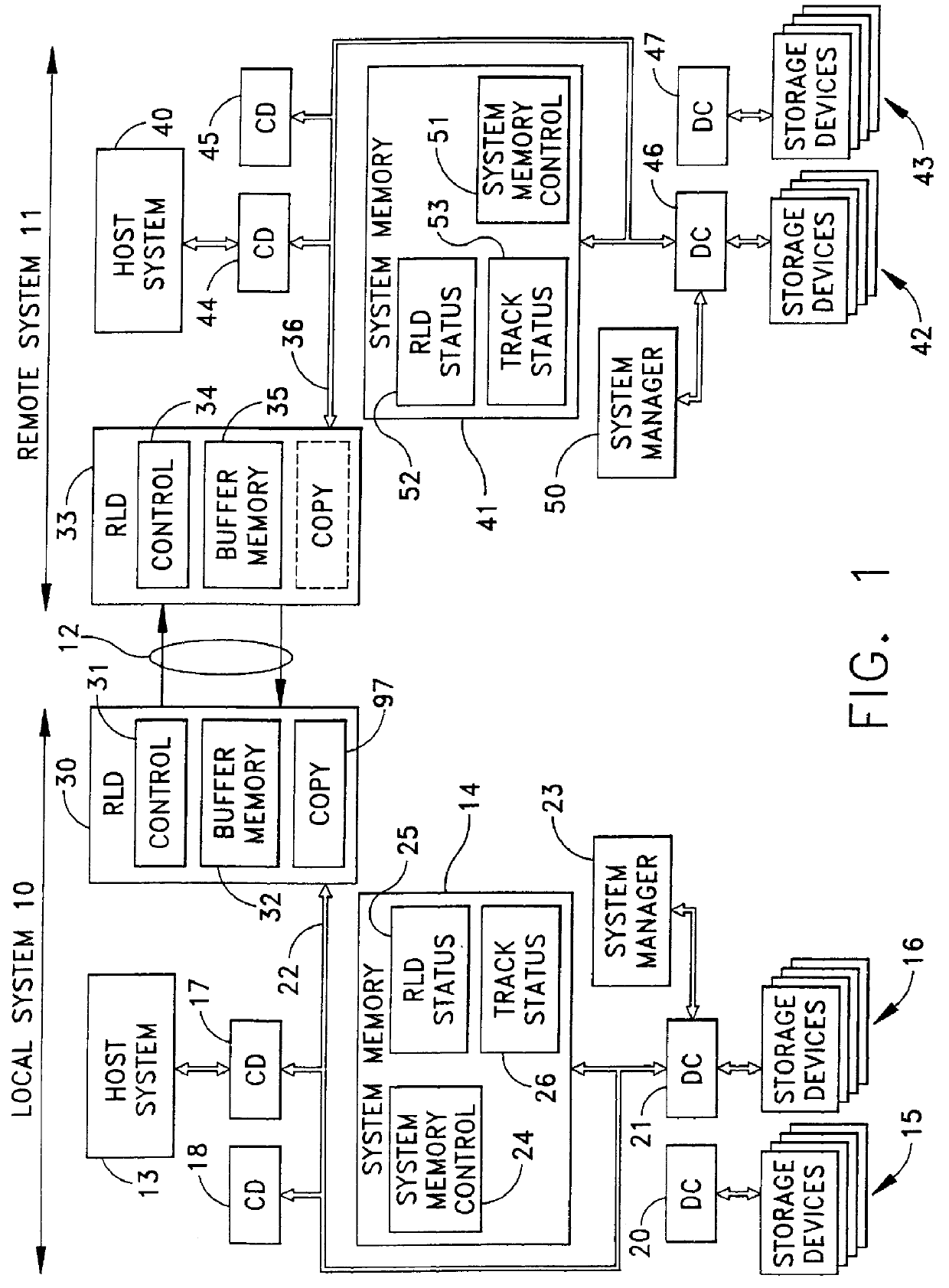
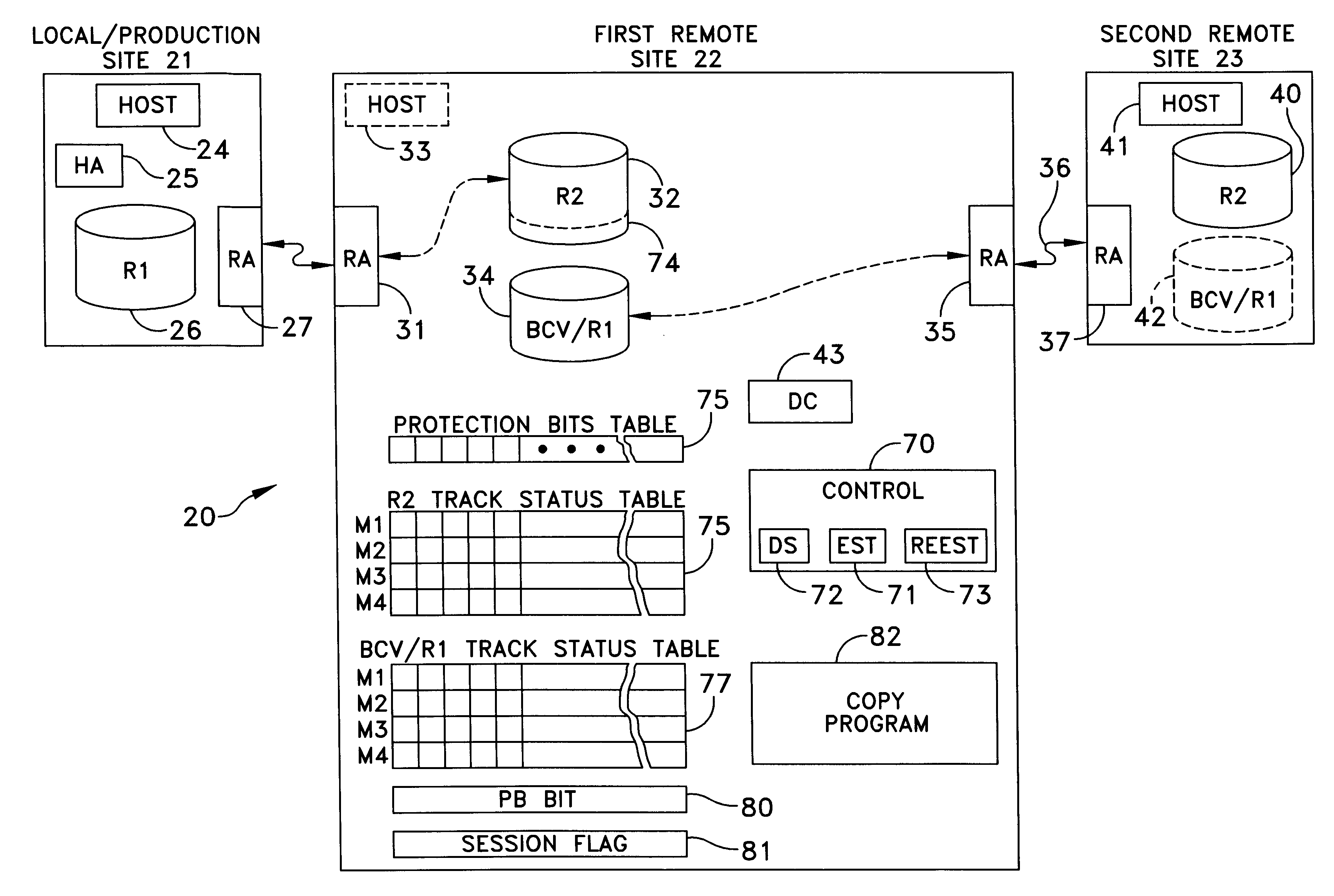
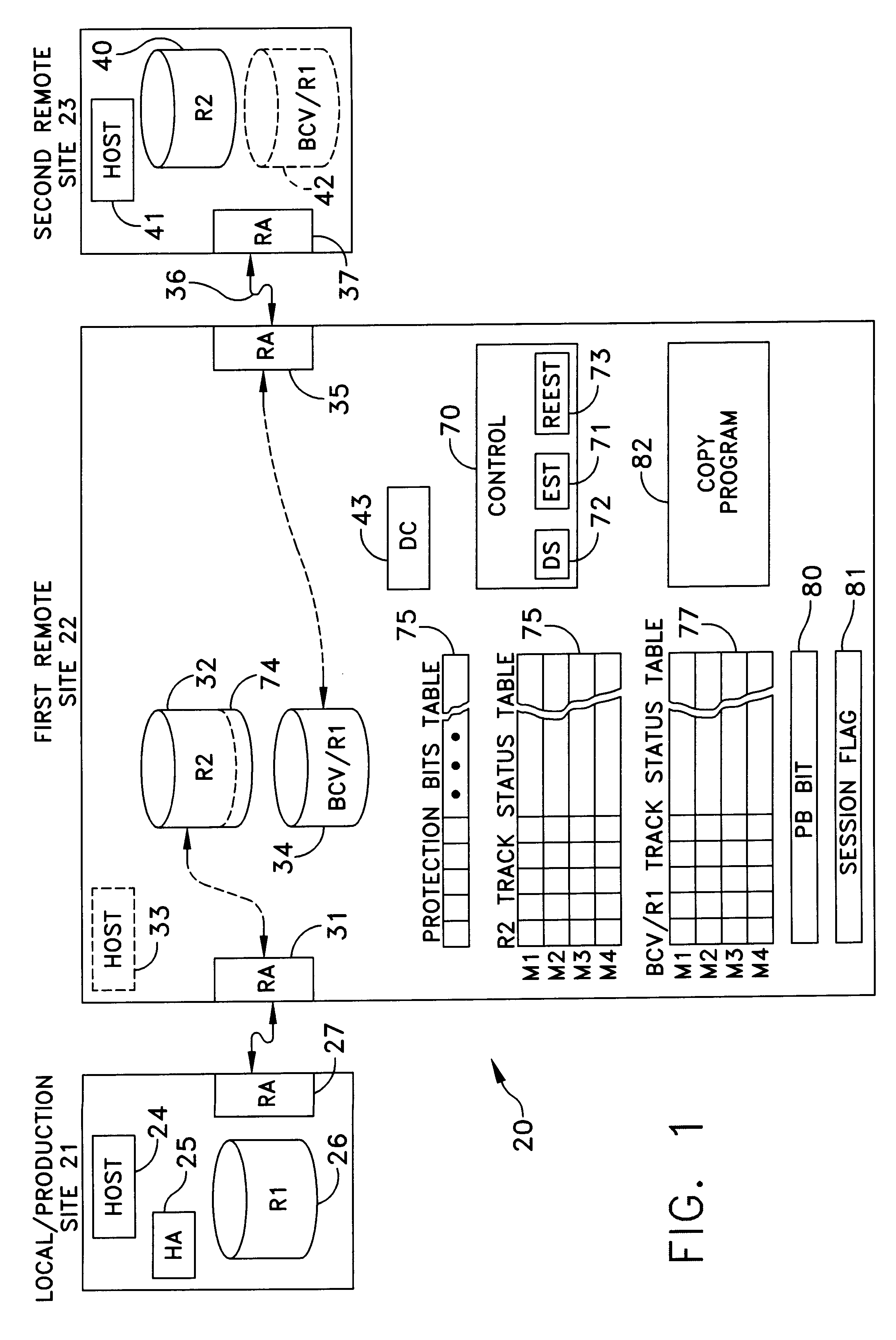
Method and apparatus for cascading data through redundant data storage units
A data storage facility for transferring data from a data altering apparatus, such as a production data processing site to a remote data receiving site. The data storage facility includes a first data store for recording each change in the data generated by the data altering apparatus. A register set records each change on a track-by-track basis. A second data store has first and second operating modes. During a first operating mode the second data store becomes a mirror of the first data store. During a second operating mode the second data store ceases to act as a mirror and becomes a source for a transfer of data to the data receiving site. Only information that has been altered, i.e., specific tracks that have been altered, are transferred during successive operations in the second operating mode. Commands from the local production site initiate the transfers between the first and second operating modes.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for combining data streams in pipelined storage operations in a storage network
ActiveUS20050246510A1Memory loss protectionRedundant operation error correctionMultiplexingData stream
Described herein are systems and methods for multiplexing pipelined data for backup operations. Various data streams are combined such as by multiplexing by a multiplexing module. The multiplexing module combines the data from the various data streams received by receiver module(s) into a single stream of chunks. The multiplexing module may combine data from multiple archive files into a single chunk. Additional modules perform other operations on the chunks of data to be transported such as encryption, compression, etc. The data chunks are transmitted via a transport channel to a receive pipeline that includes a second receiver module and other modules. The data chunks are then stored in a backup medium. The chunks are later retrieved and separated such as by demultiplexing for restoring to a client or for further storage as auxiliary copies of the separated data streams or archive files.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Non-volatile memory data storage system with reliability management
InactiveUS20100017650A1Improve reliabilityReliable managementMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDData recovery
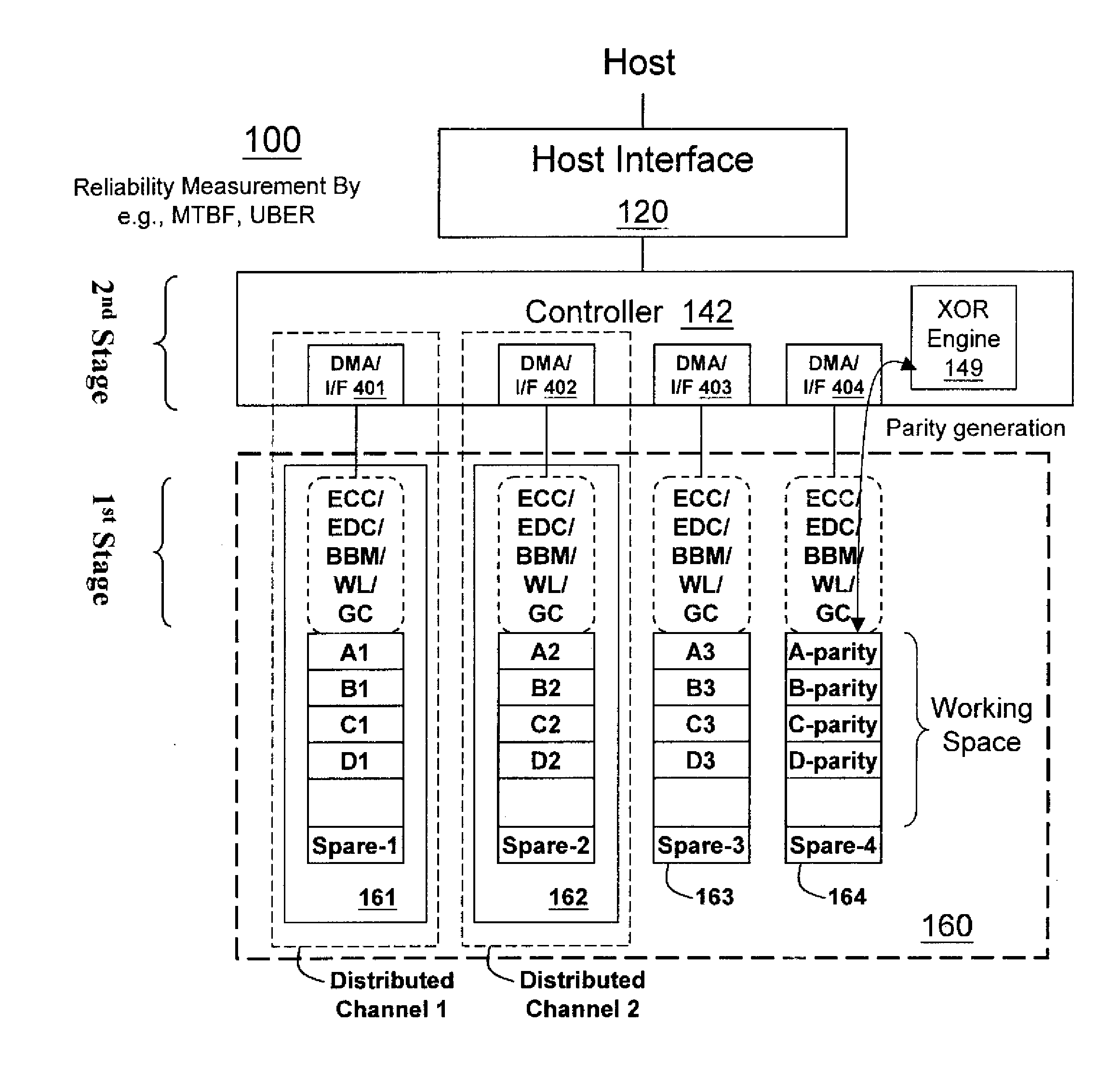
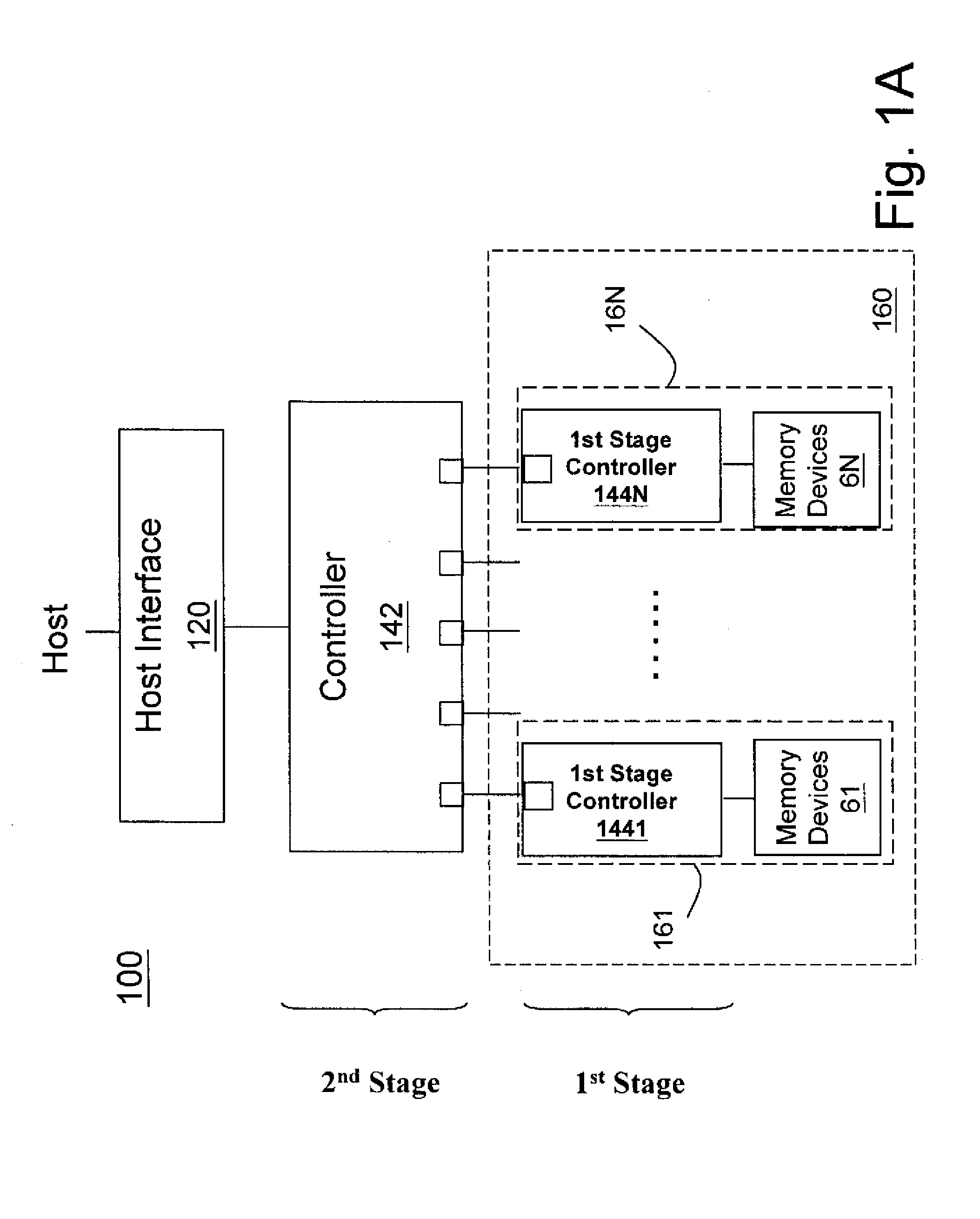
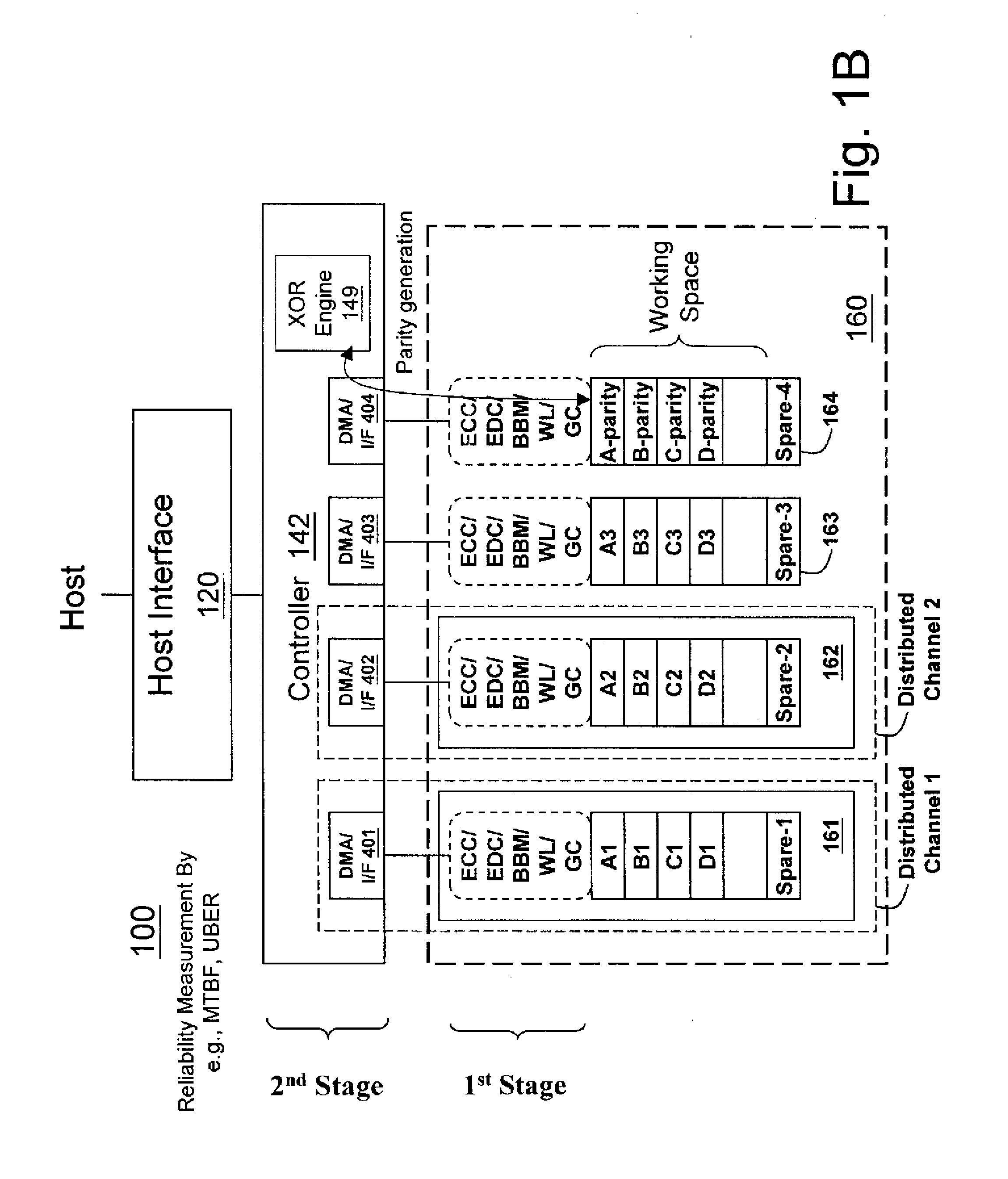
A non-volatile memory data storage system, comprising: a host interface for communicating with an external host; a main storage including a first plurality of flash memory devices, wherein each memory device includes a second plurality of memory blocks, and a third plurality of first stage controllers coupled to the first plurality of flash memory devices; and a second stage controller coupled to the host interface and the third plurality of first stage controller through an internal interface, the second stage controller being configured to perform RAID operation for data recovery according to at least one parity.
Owner:NANOSTAR CORP
Locking technique for control and synchronization
InactiveUS6973549B1Digital data information retrievalMultiprogramming arrangementsFast pathLocking mechanism
Described are techniques used in a computer system for handling data operations to storage devices. A switching fabric includes one or more fast paths for handling lightweight, common data operations and at least one control path for handling other data operations. A control path manages one or more fast paths. The fast path and the control path are utilized in mapping virtual to physical addresses using mapping tables. The mapping tables include an extent table of one or more entries corresponding to varying address ranges. The size of an extent may be changed dynamically in accordance with a corresponding state change of physical storage. The fast path may cache only portions of the extent table as needed in accordance with a caching technique. The fast path may cache a subset of the extent table stored within the control path. A set of primitives may be used in performing data operations. A locking mechanism is described for controlling access to data shared by the control paths.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for transferring data in a storage operation
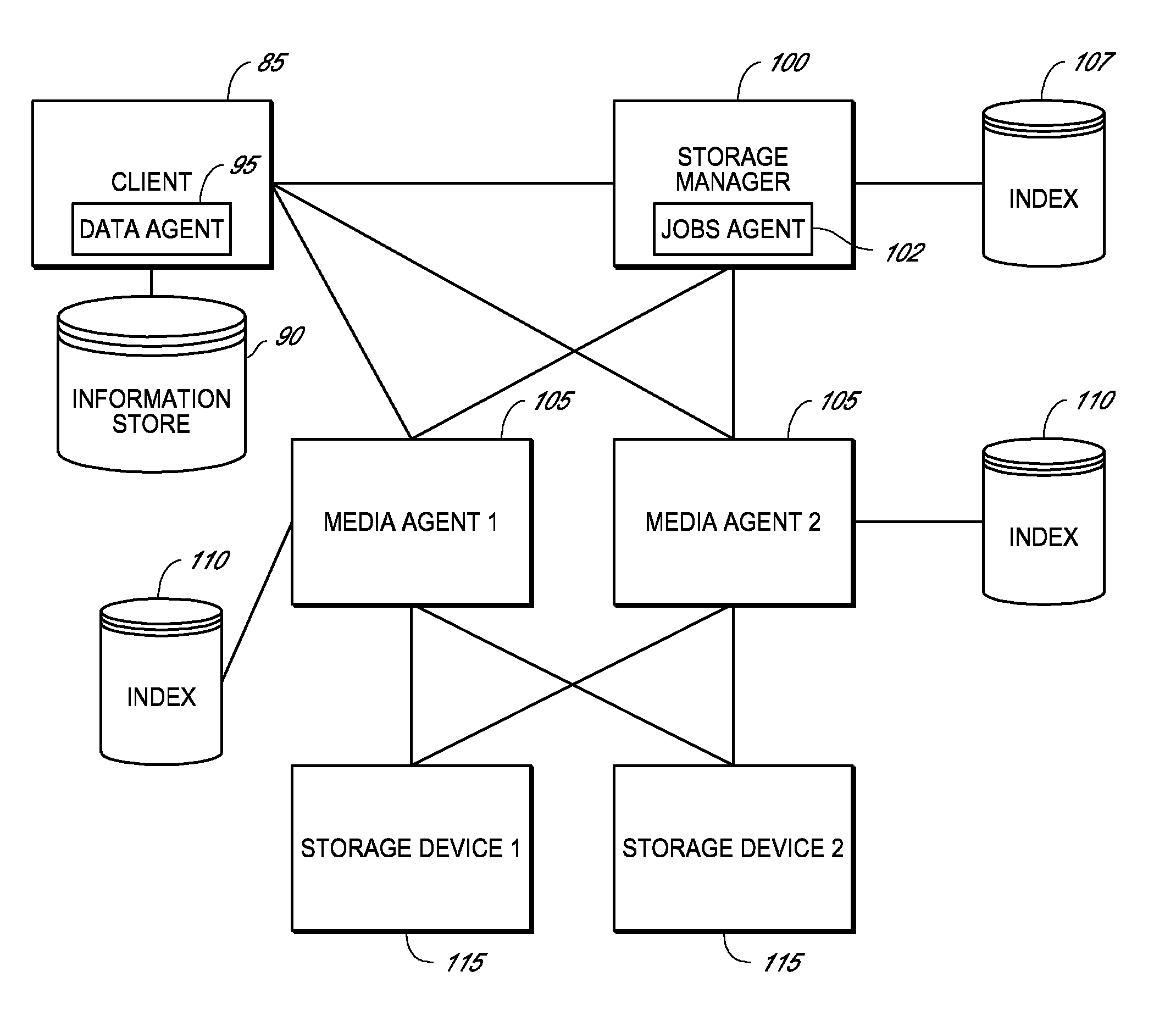
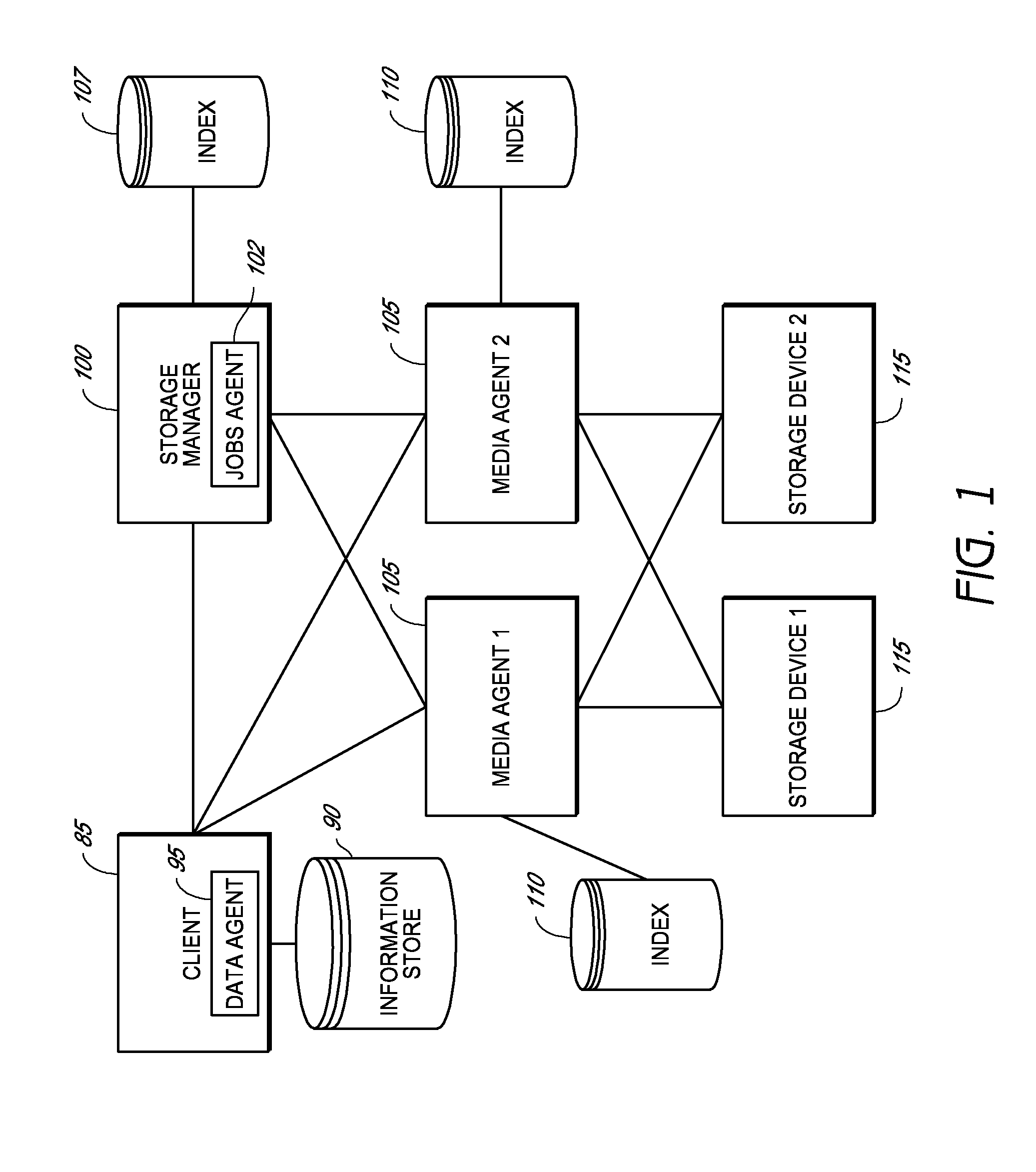
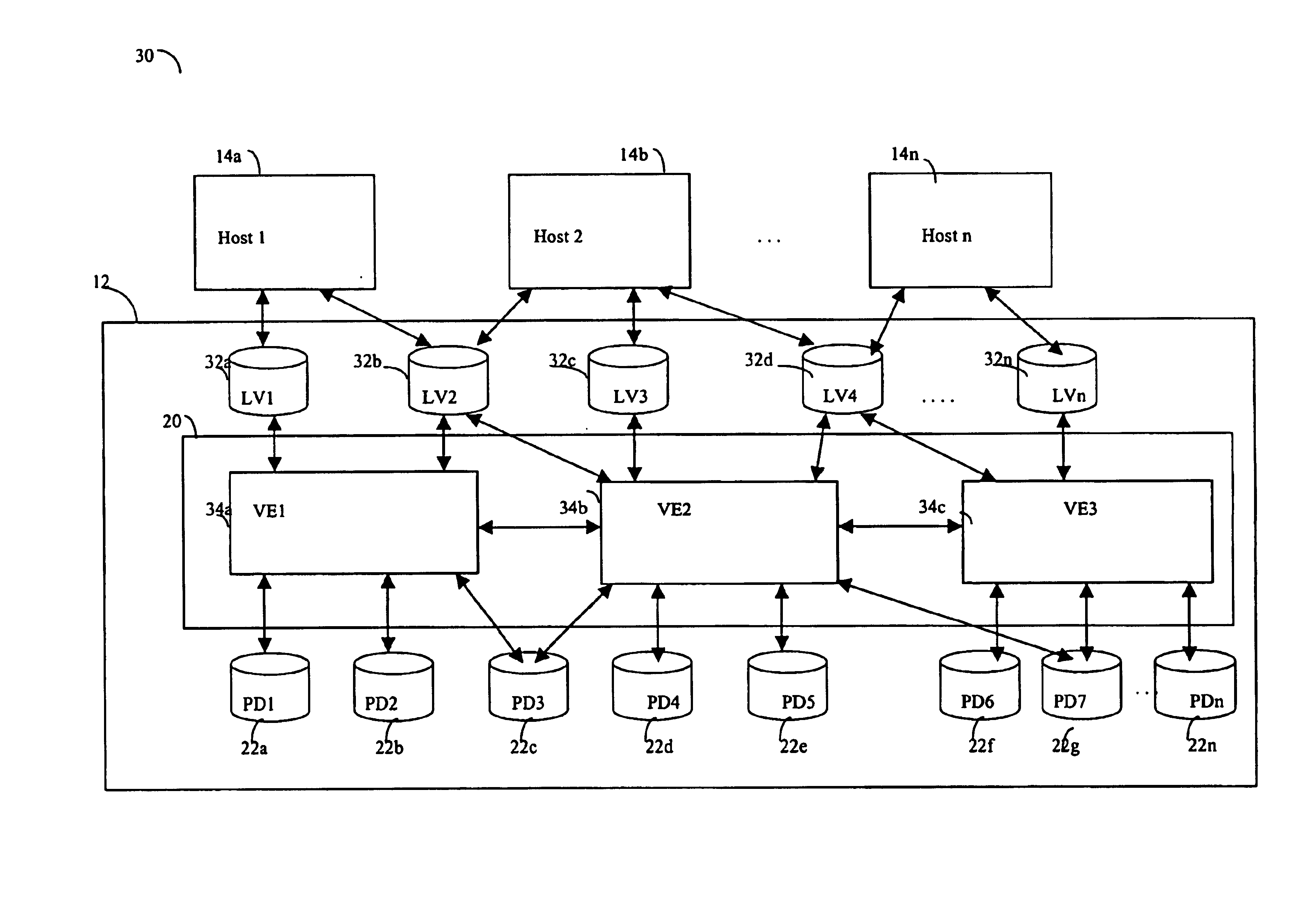
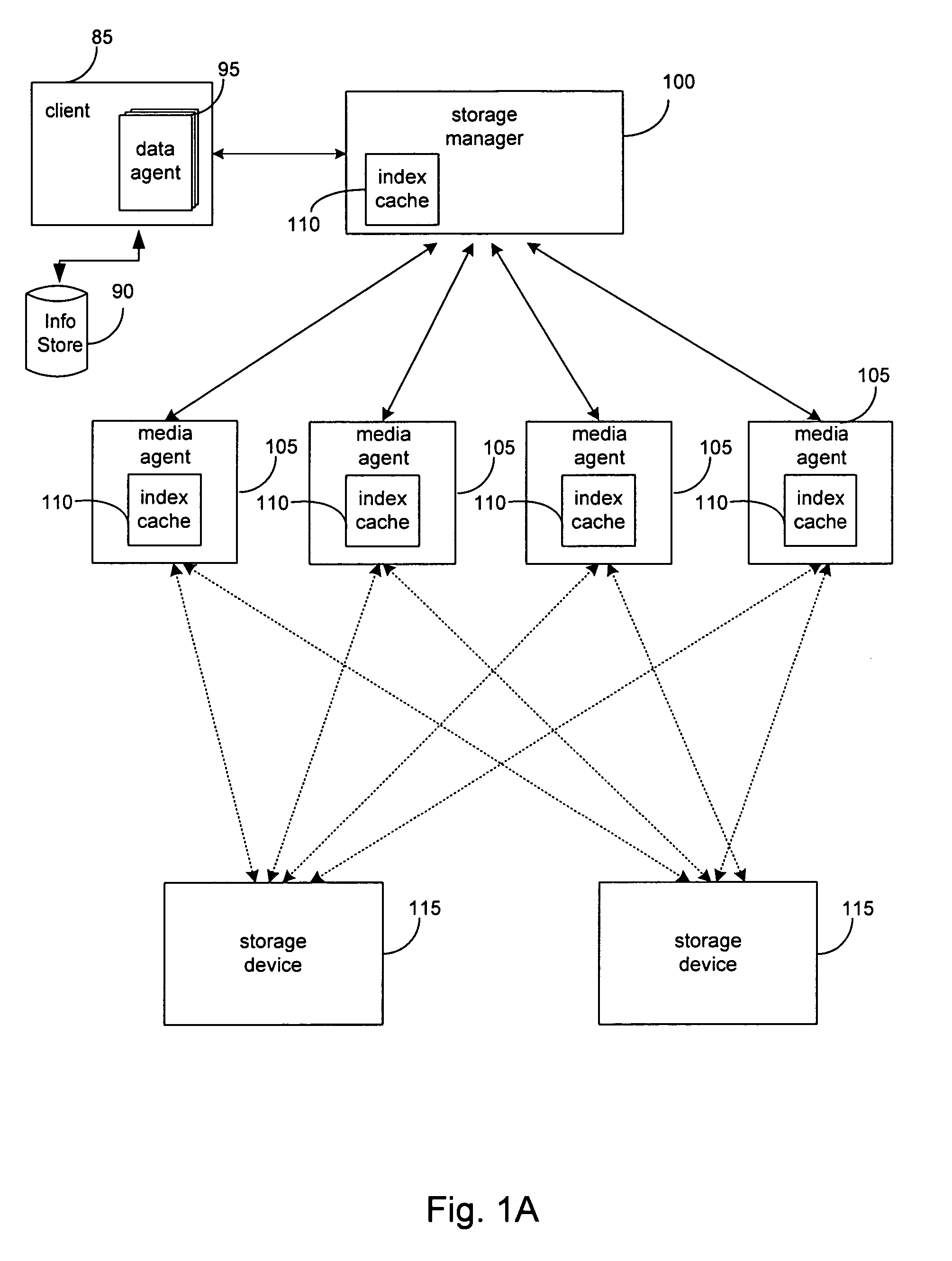
InactiveUS7581077B2Input/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionData storingData store
The invention provides a system and method for storing a copy of data stored in an information store. In one embodiment, a data agent reads one or more blocks containing the data from the information store. The data agent maps the one or more blocks to provide a mapping of the blocks, and transmits the one or more blocks and mapping to a media agent for a storage device. The media agent stores the one or more blocks in the storage device according to the mapping.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Computer with switchable components
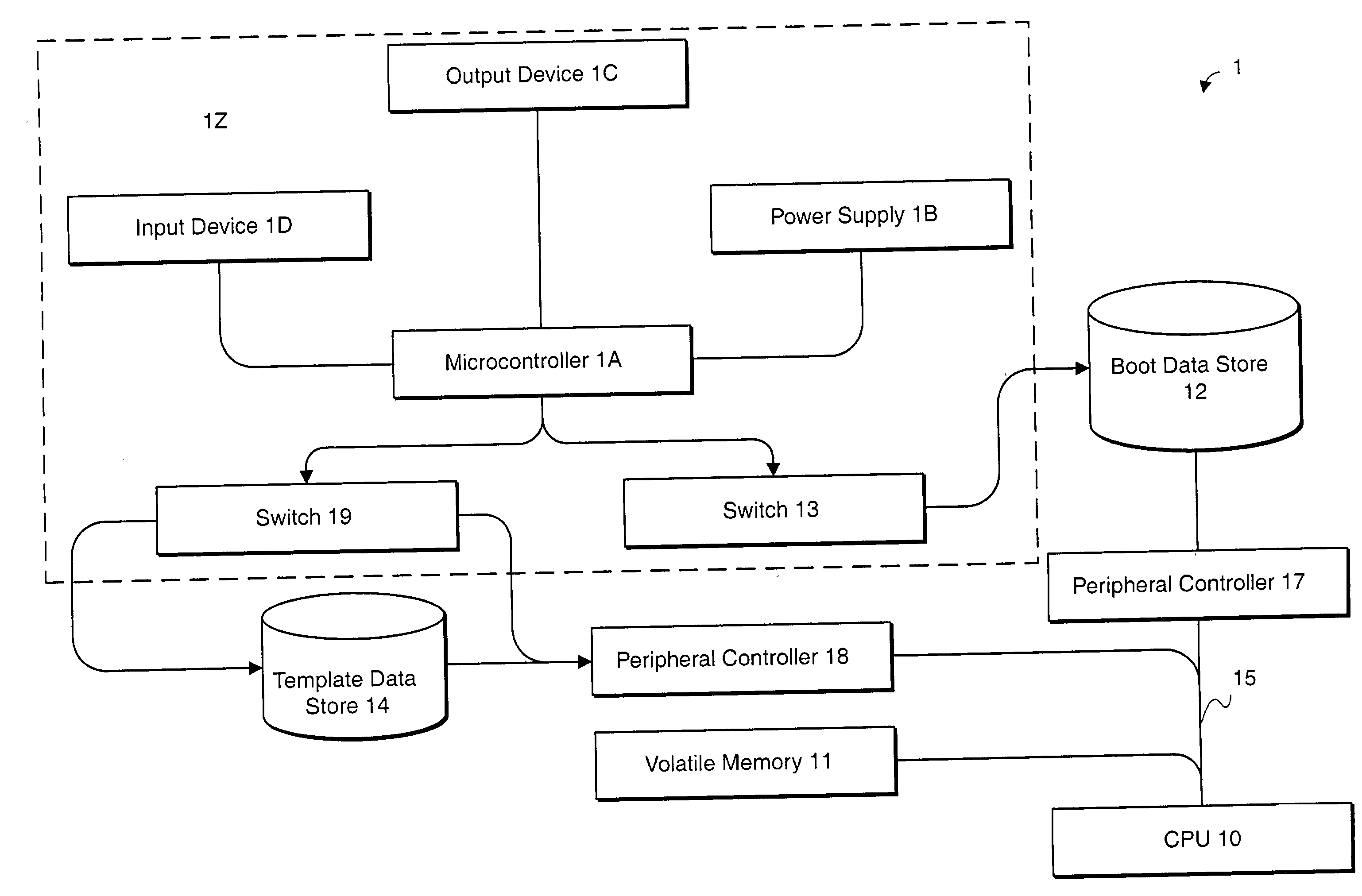
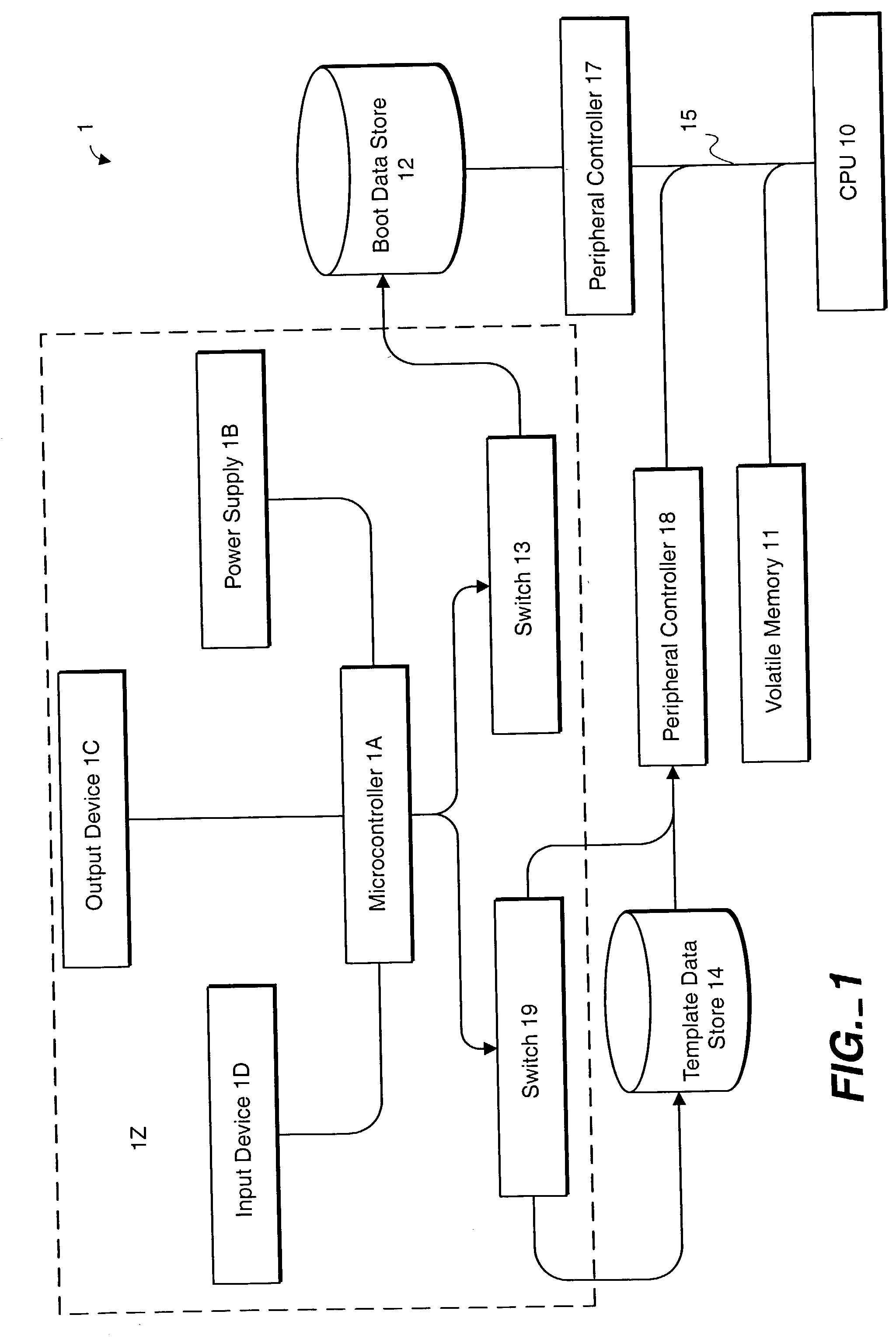
InactiveUS20020188887A1Redundant operation error correctionRedundant hardware error correctionComputerized systemBIOS
A method or system for supporting a computer systems self repair, including the computer executed steps for booting from a first boot device, and booting from a second boot device in response to a signal indicating a need for repair. While booted from the second boot device the computer system is capable of repairing software on the first boot device. The signal may effect a logical or physical switch. Repairing software may be performed in part by copying BIOS, template, backup or archive software from a device other than the first boot device. Repairing software may be performed automatically without direction by a user or according to preset preferences.
Owner:SELF REPAIRING COMP
Method and apparatus for synchronizing device information
InactiveUS6874037B1Enabling of informationMultiple digital computer combinationsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPositioning technologyComputer science
Two electronic devices automatically perform a synchronization session when one of the electronic devices is brought in proximity to the other electronic device. The synchronization session is initiated without user intervention based simply on the fact that the two devices have recently been brought within a predetermined distance of each other. The two electronic devices communicate in a wireless manner. The two devices may determine that they are within a predetermined distance of each other using global positioning technology, via which one of the devices determines its own position and compares it to a known position of the other electronic device. Alternatively, one of the electronic devices may output a low level signal that can be received by the other electronic device when within a certain range. Once the low level signal is received, the recipient of the low level signal outputs a stronger signal to ensure that it is received by the other electronic device requesting a synchronization session, which once established enables synchronization of information between the two devices.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC +2
Selective data replication system and method
InactiveUS7287047B2Input/output to record carriersData processing applicationsData setSelection criterion
The invention relates generally to copying electronic data. More particularly, the invention provides a computerized method for identifying, in a first backup data set, a data item satisfying a selection criterion, and copying to a second backup data set at least a portion of the data item.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
System and method for determining changes in two snapshots and for transmitting changes to destination snapshot
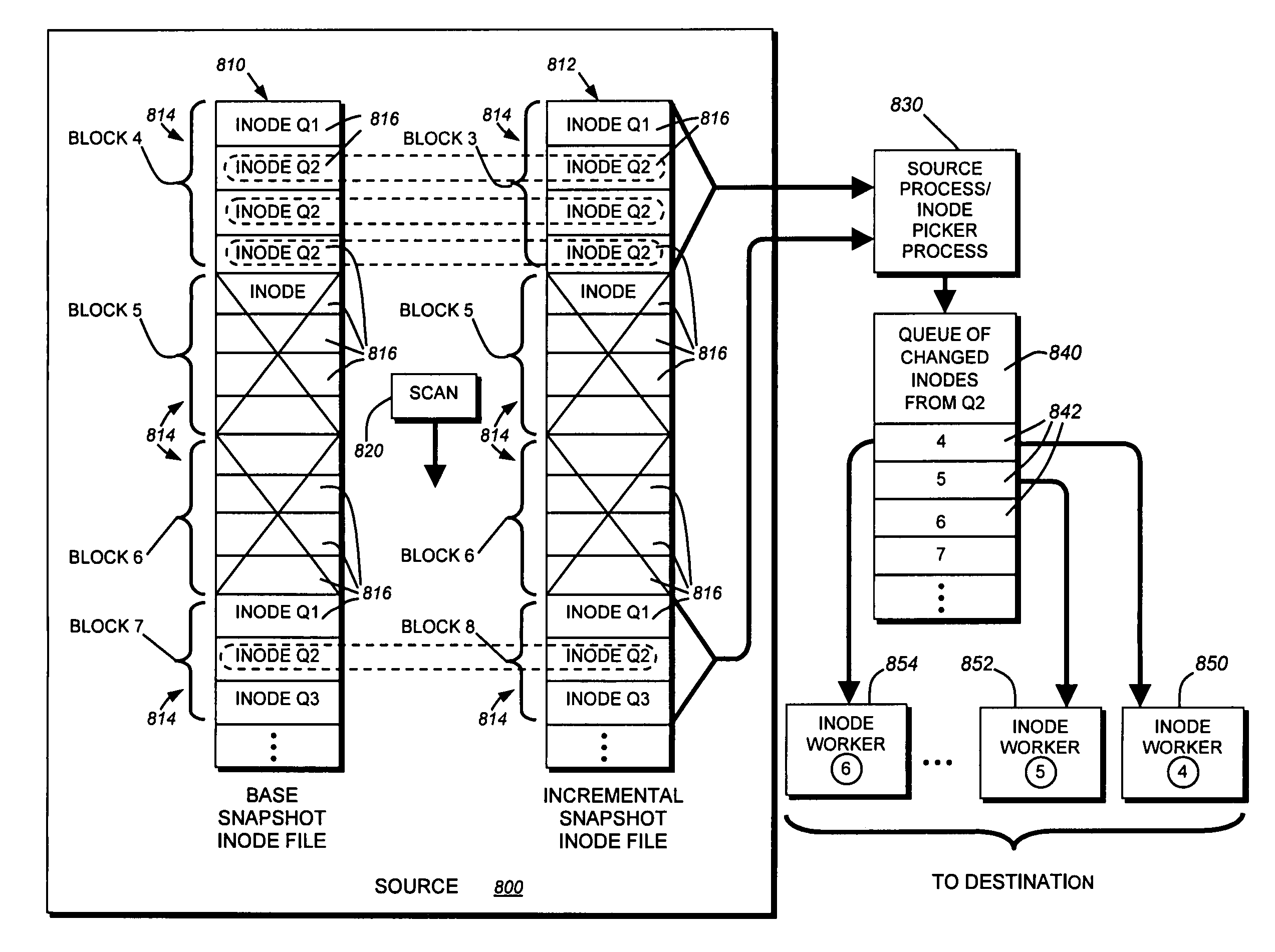
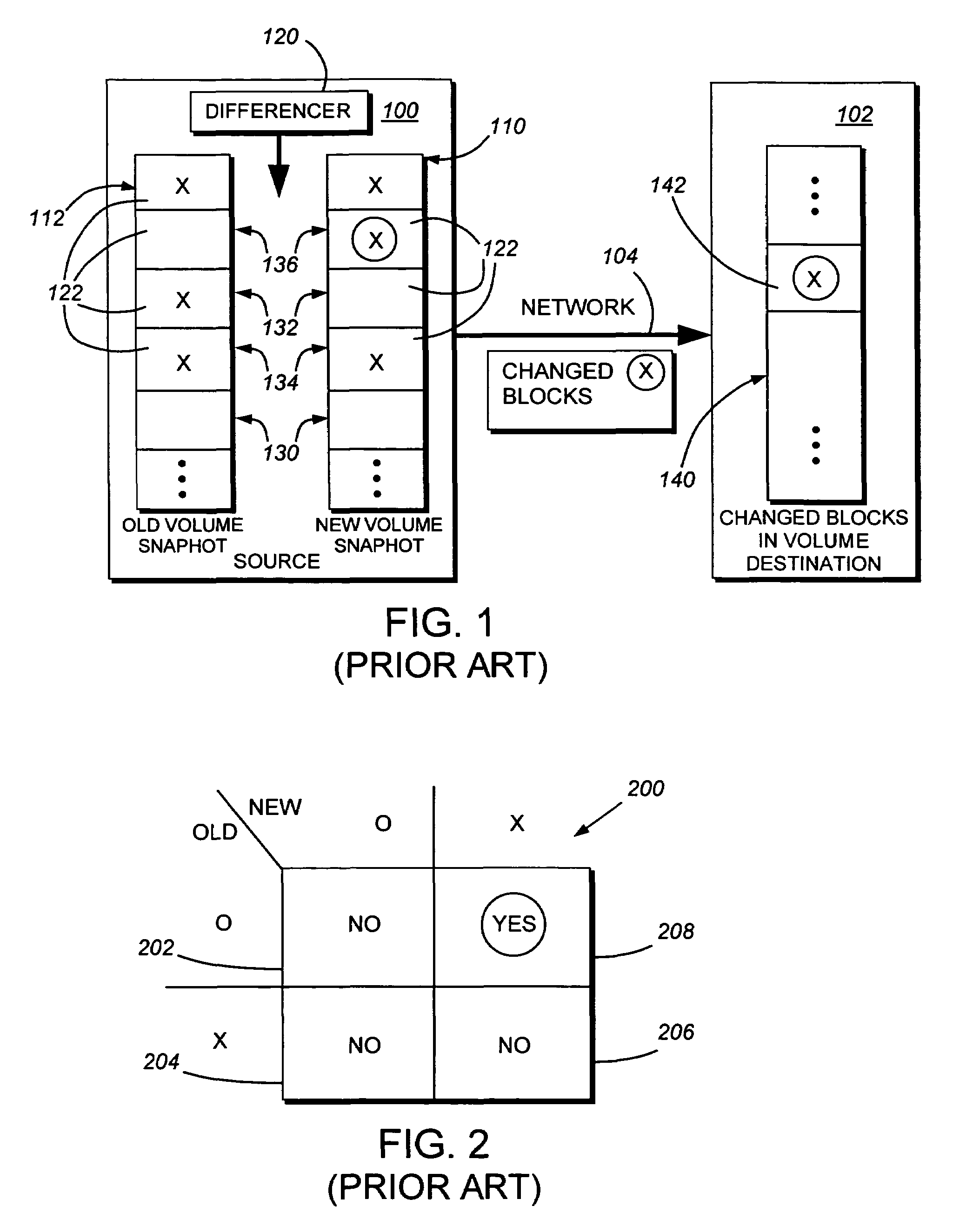
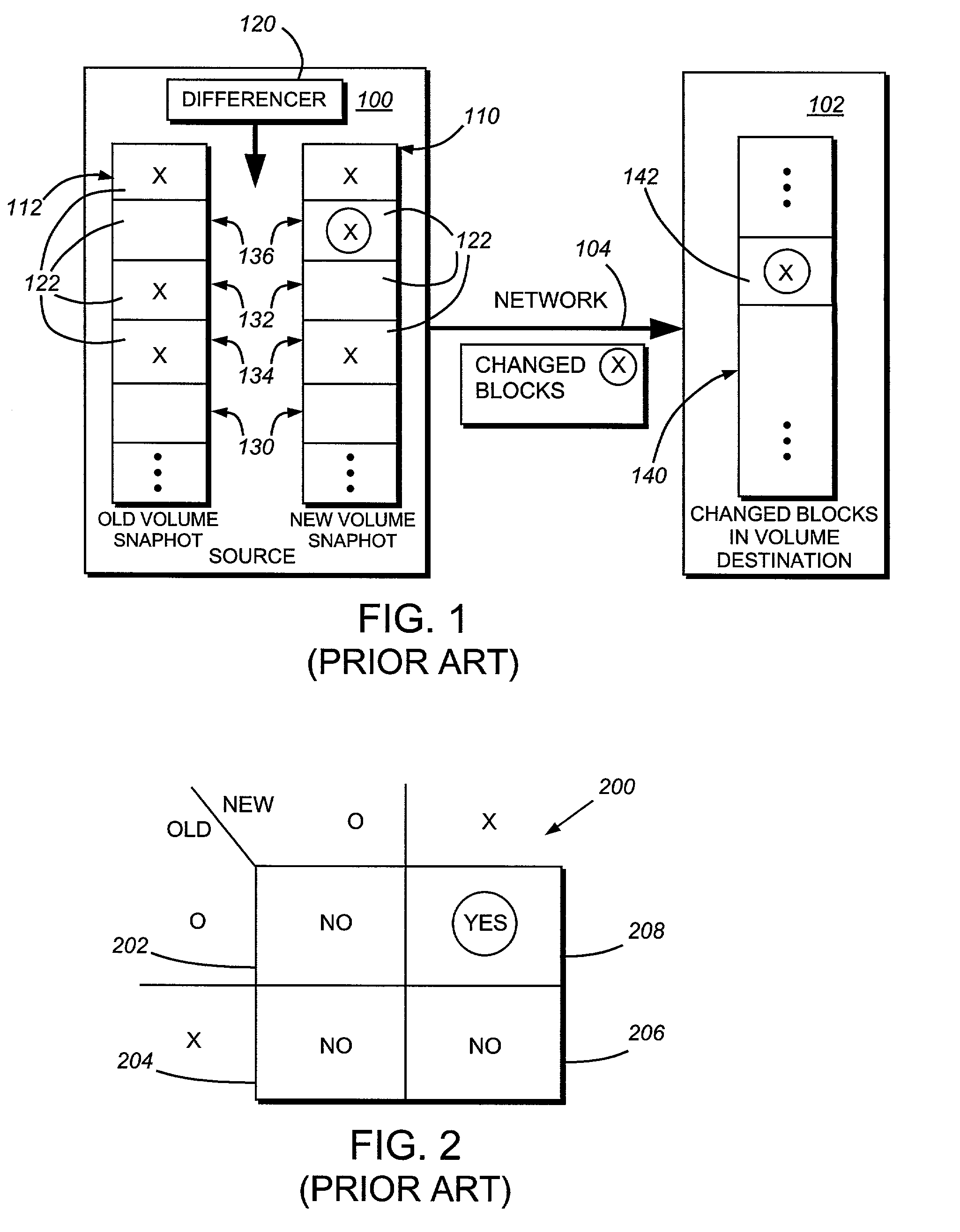
InactiveUS6993539B2Efficient scanningOvercome disadvantagesData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData streamInode
A system and method for remote asynchronous replication or mirroring of changes in a source file system snapshot in a destination replica file system using a scan (via a scanner) of the blocks that make up two versions of a snapshot of the source file system, which identifies changed blocks in the respective snapshot files based upon differences in volume block numbers identified in a scan of the logical file block index of each snapshot. Trees of blocks associated with the files are traversed, bypassing unchanged pointers between versions and walking down to identify the changes in the hierarchy of the tree. These changes are transmitted to the destination mirror or replicated snapshot. This technique allows regular files, directories, inodes and any other hierarchical structure to be efficiently scanned to determine differences between versions thereof. The changes in the files and directories are transmitted over the network for update of the replicated destination snapshot in an asynchronous (lazy write) manner. The changes are described in an extensible, system-independent data stream format layered under a network transport protocol. At the destination, source changes are used to update the destination snapshot. Any deleted or modified inodes already on the destination are moved to a temporary or “purgatory” directory and, if reused, are relinked to the rebuilt replicated snapshot directory. The source file system snapshots can be representative of a volume sub-organization, such as a qtree.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
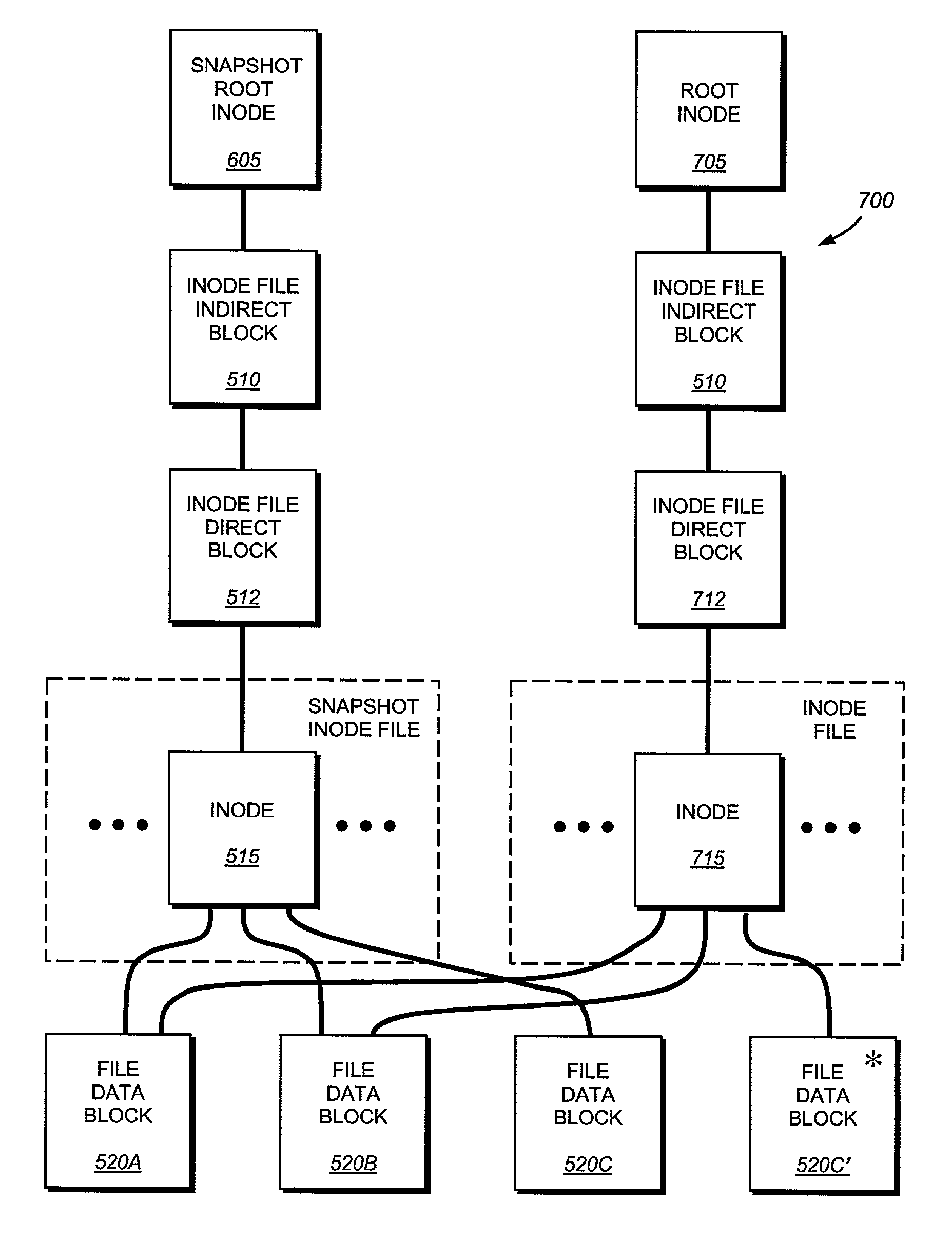
System and method for asynchronous mirroring of snapshots at a destination using a purgatory directory and inode mapping
ActiveUS7225204B2Improve versatilityImprove utilizationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInodeComputer science
A system and method for updating a replicated destination file system snapshot with changes in a source file system snapshot, facilitates construction of a new directory tree on the destination from source update information using a temporary or “purgatory” directory that allows any modified and deleted files on the destination active file system to be associated with (e.g. moved to) the purgatory directory if and until they are reused. In addition, an inode map is established on the destination that maps source inode numbers to destination inode numbers so as to facilitate building of the destination tree using inode / generation number tuples. The inode map allows resynchronization of the source file system to the destination. The inode map also allows association of two or more destination snapshots to each other based upon their respective maps with the source.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
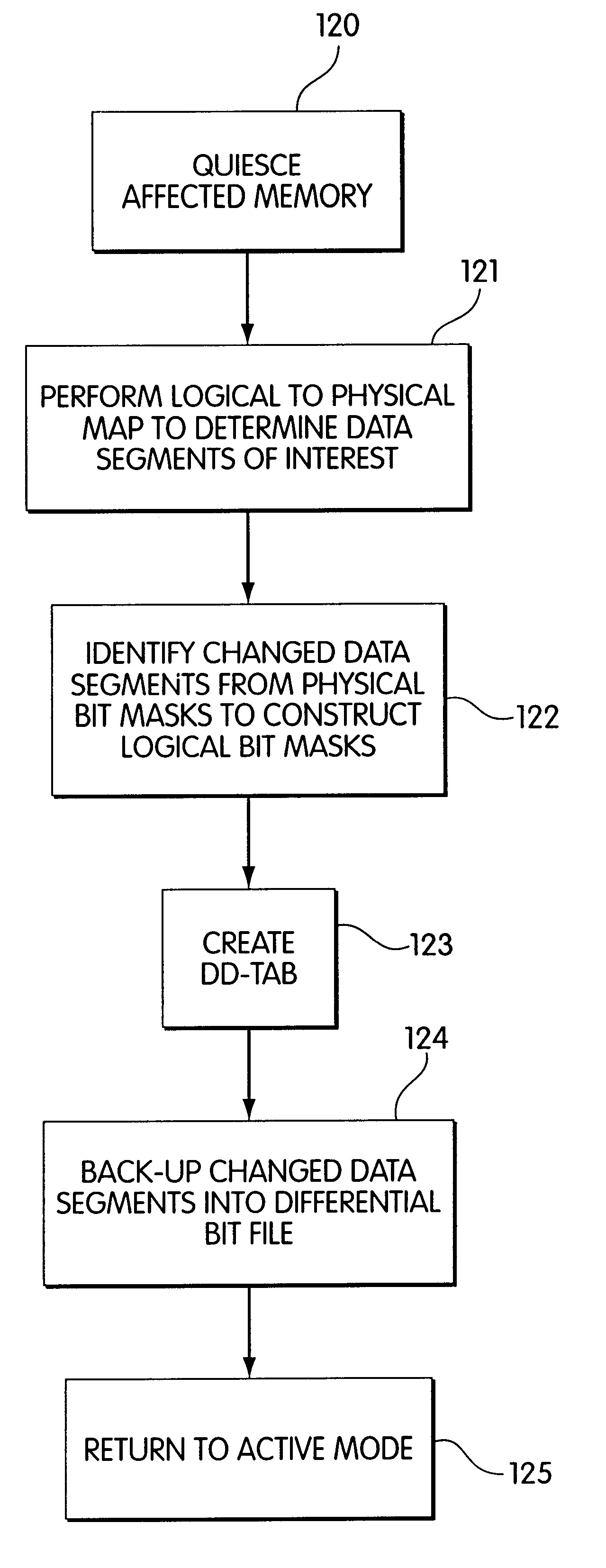
Method and apparatus for differential backup in a computer storage system
InactiveUS6366986B1Memory loss protectionRedundant operation error correctionComputer hardwareComputerized system
Method and apparatus for backup in restoring data on a computer system are disclosed. Backups may include a differential backup. In a differential backup, only some (but not all) segments of data in a primary copy are backed up. The segments may correspond to physical segments of storage in a storage system, rather than logical level segments of storage. The method and apparatus may include constructing a complete copy of a backed up element from an earlier fill backup and a subsequent differential backup.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
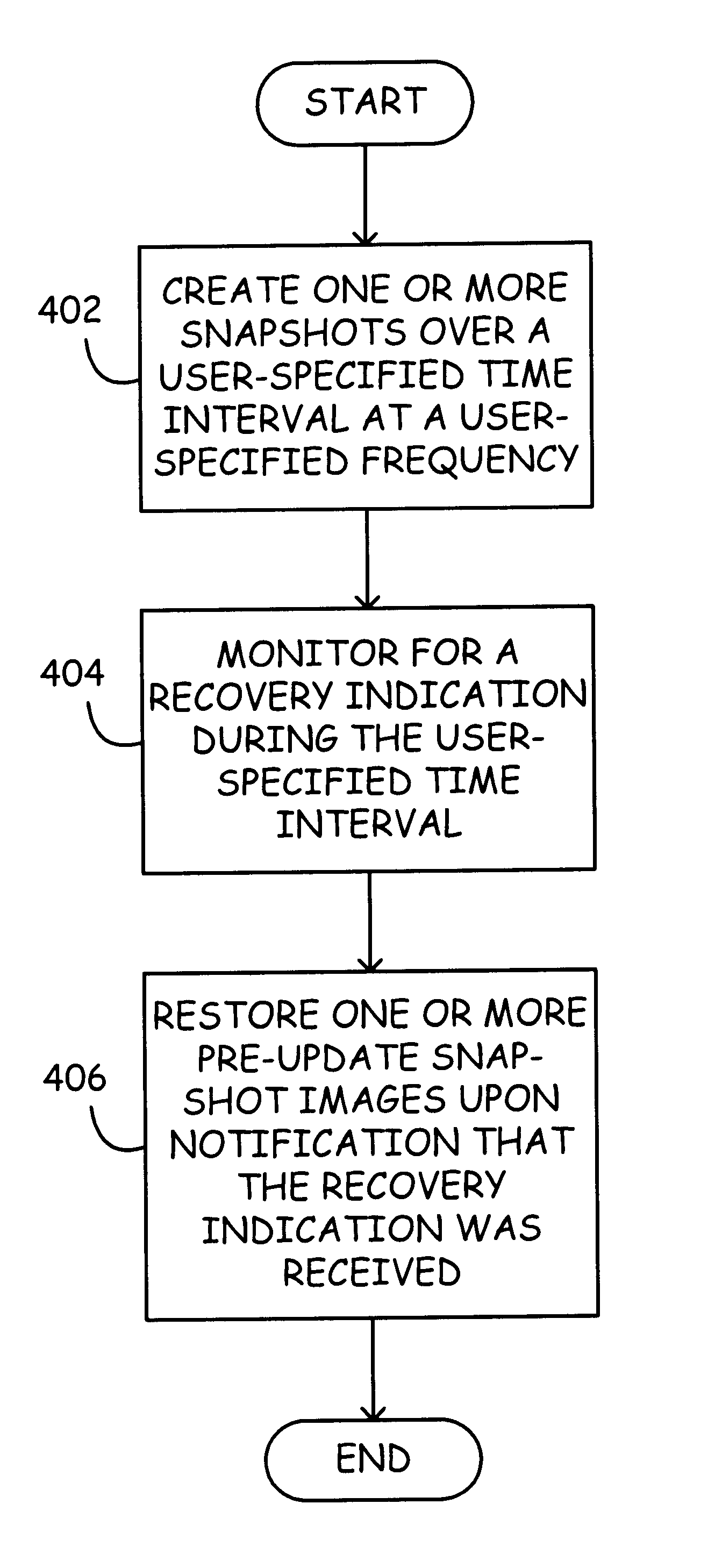
System and method for creating a series of online snapshots for recovery purposes
InactiveUS6799189B2Data processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDatabase fileData mining
A method and system for creating a series of online snapshots for recovery purposes. A series of concurrent, overlapping snapshots (e.g., file snapshots or database file snapshots) may be created over a user-specified time interval at a user-specified frequency. Monitoring for a recovery indication may occur during the user-specified time interval. Once it is established that a "recovery" is necessary, a snapback procedure may be implemented to iteratively restore one or more pre-update snapshot images. Between restore iterations, testing to determine if the problem still exists may occur. When the testing of the data results in a determination that the problem is resolved, no further restores are necessary.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
System and method of implementing an object storage infrastructure for cloud-based services
ActiveUS20140149794A1Easy retrievalWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsUniversally unique identifierNetwork connection
A method for storing objects in an object storage system includes the steps of establishing a network connection with a client over an inter-network, receiving an upload request indicating an object to be uploaded by the client, selecting at least two storage nodes on which the object will be stored, receiving the object from the client via the network connection, and streaming the object to each of the selected storage nodes such that the object is stored on each of the selected storage nodes. The method can also include writing an object record associating the object and the selected storage nodes to a shard of an object database and generating a Universally Unique Identifier (UUID). The UUID indicates the shard and the object ID of the object record, such that the object record can be quickly retrieved. Object storage infrastructures are also disclosed.
Owner:EGNYTE
High speed data transfer mechanism
InactiveUS7209972B1Input/output to record carriersData switching by path configurationMedia typeOperational system
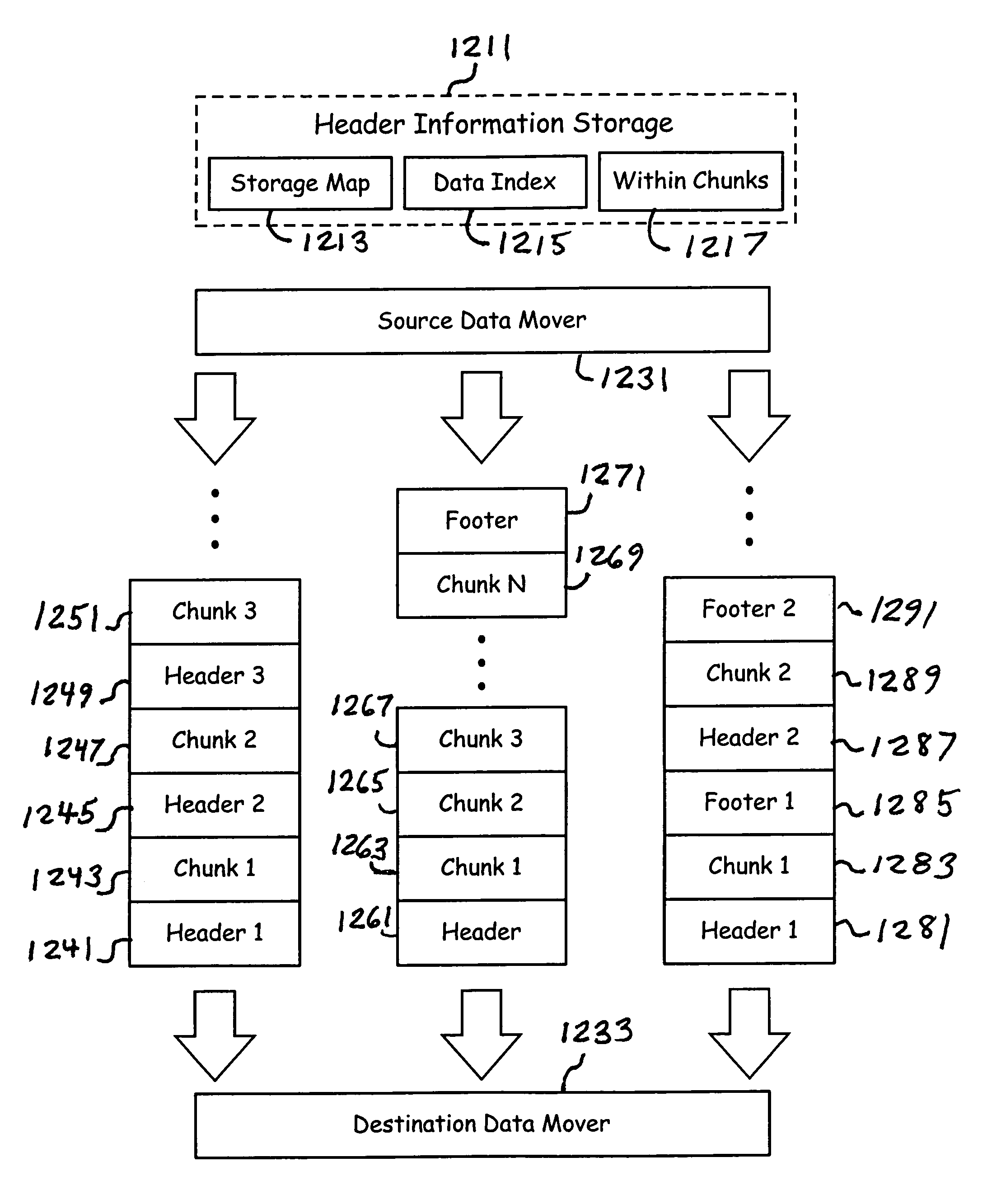
A storage and data management system establishes a data transfer pipeline between an application and a storage media using a source data mover and a destination data mover. The data movers are modular software entities which compartmentalize the differences between operating systems and media types. In addition, they independently interact to perform encryption, compression, etc., based on the content of a file as it is being communicated through the pipeline. Headers and chunking of data occurs when beneficial without the application ever having to be aware. Faster access times and storage mapping offer enhanced user interaction.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Multimedia synchronization method and device
ActiveUS7136934B2Direct accessTelevision system detailsData processing applicationsComputer hardwareContent management
A system and method for synchronizing a multiplicity of devices in a multimedia environment is described. The system has at least one central storage and interface device, wherein audio, video, and photographic information including content information and content management information, relating to at least one user, are stored in digital form. The system further has a plurality of zones each having a zone specific storage and interface device being capable of storing or interfacing with information stored in the central storage and interface device, wherein audio, video, or photographic information, relating to at least one user, contained within each one of the plurality of zone specific storage and interface devices and the central storage and interface device, are updated in relation with other zone specific storage and interface devices and the central storage and interface device. This results in the at least one user can be situated at anyone of the zones and access substantially identical audio, video, and photographic information related to the at least one user. The method includes providing the plurality of devices, providing the plurality of zones, determining whether a current synchronization point exists, if a previous synchronization point exists, receiving information from a server, if a previous synchronization point does not exists, sending information to a at least one client by a host, wherein the at least one user is disposed to have control, determining what information is needed by the at least one client, and establishing the resultant state as a synchronization point.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
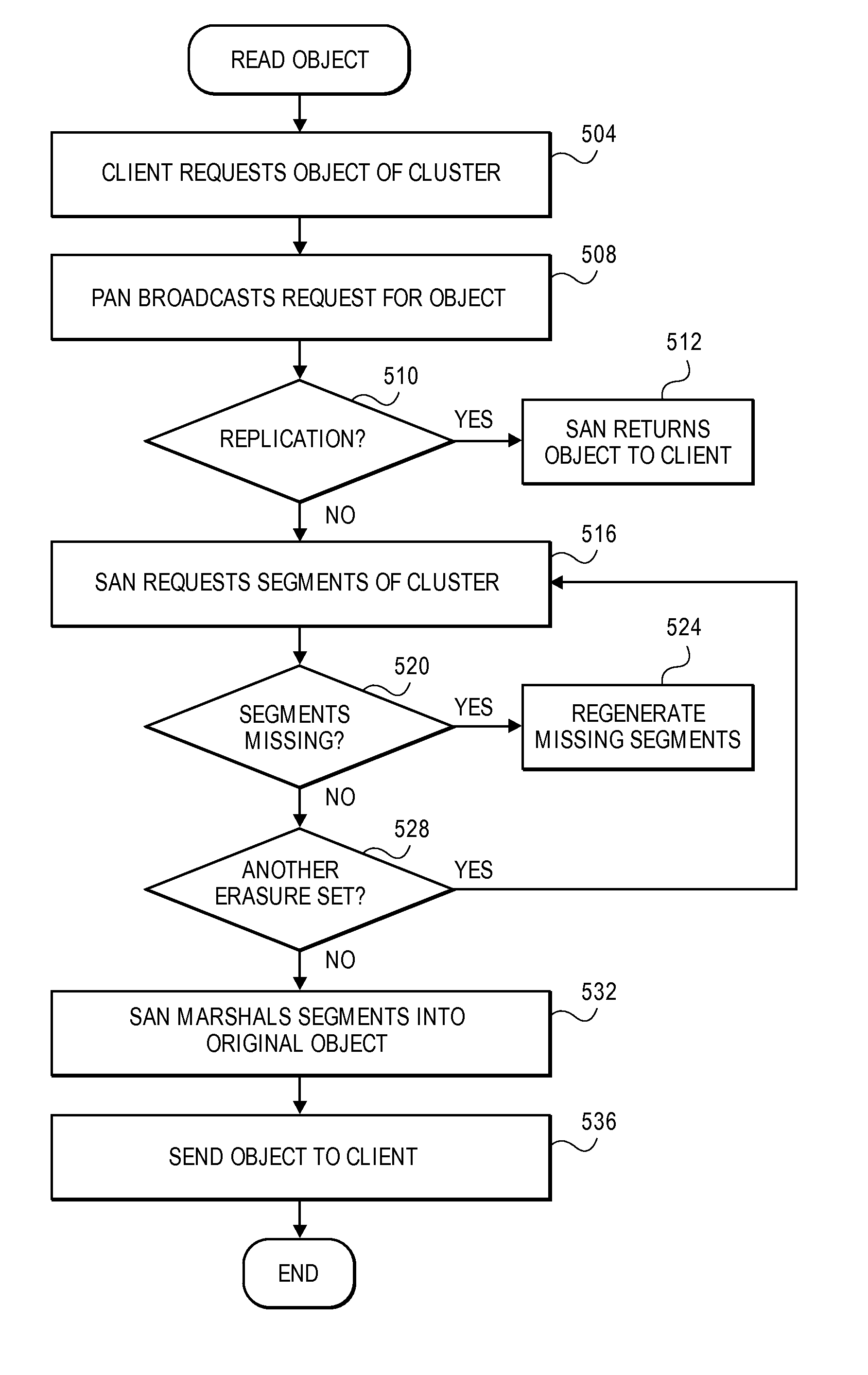
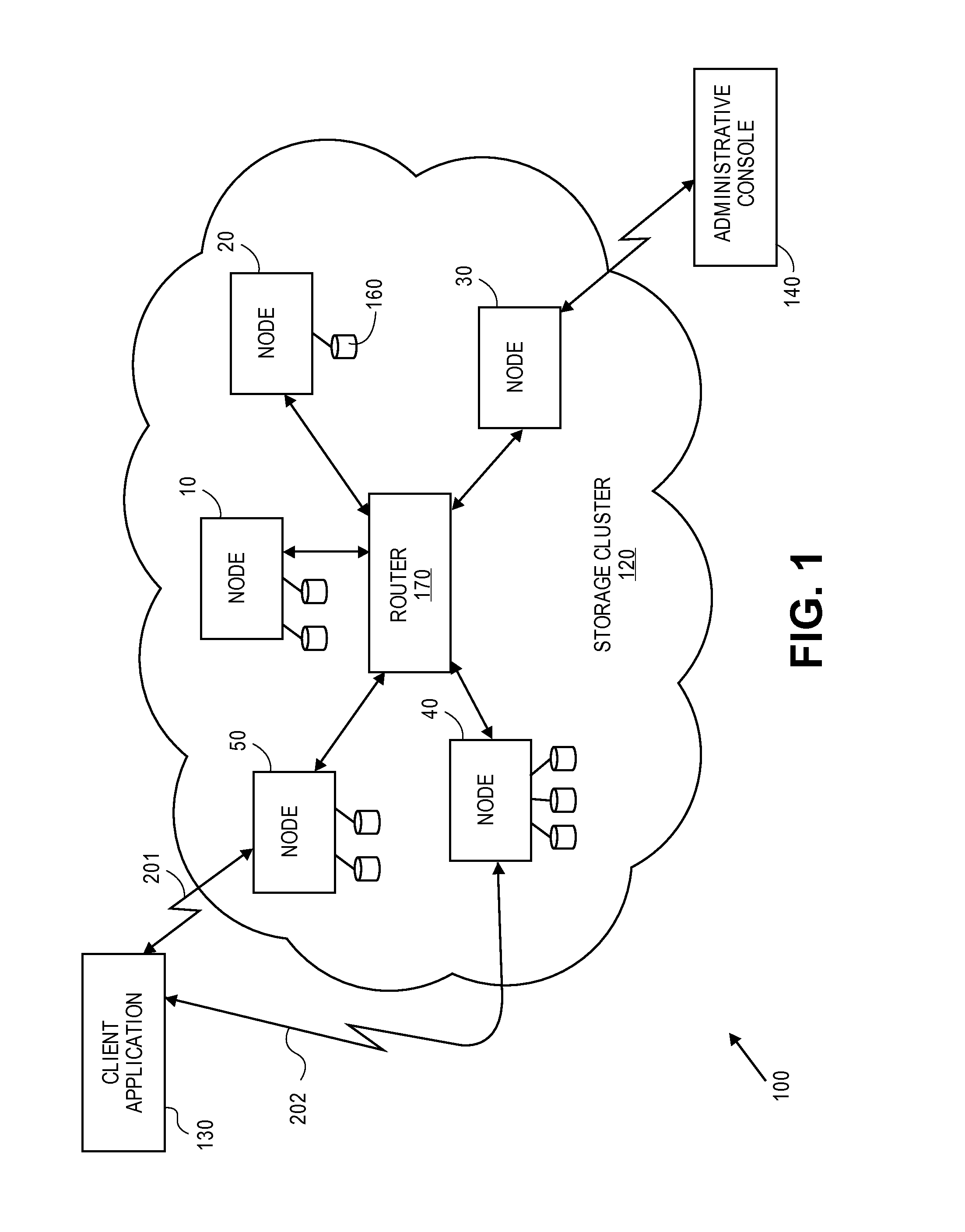
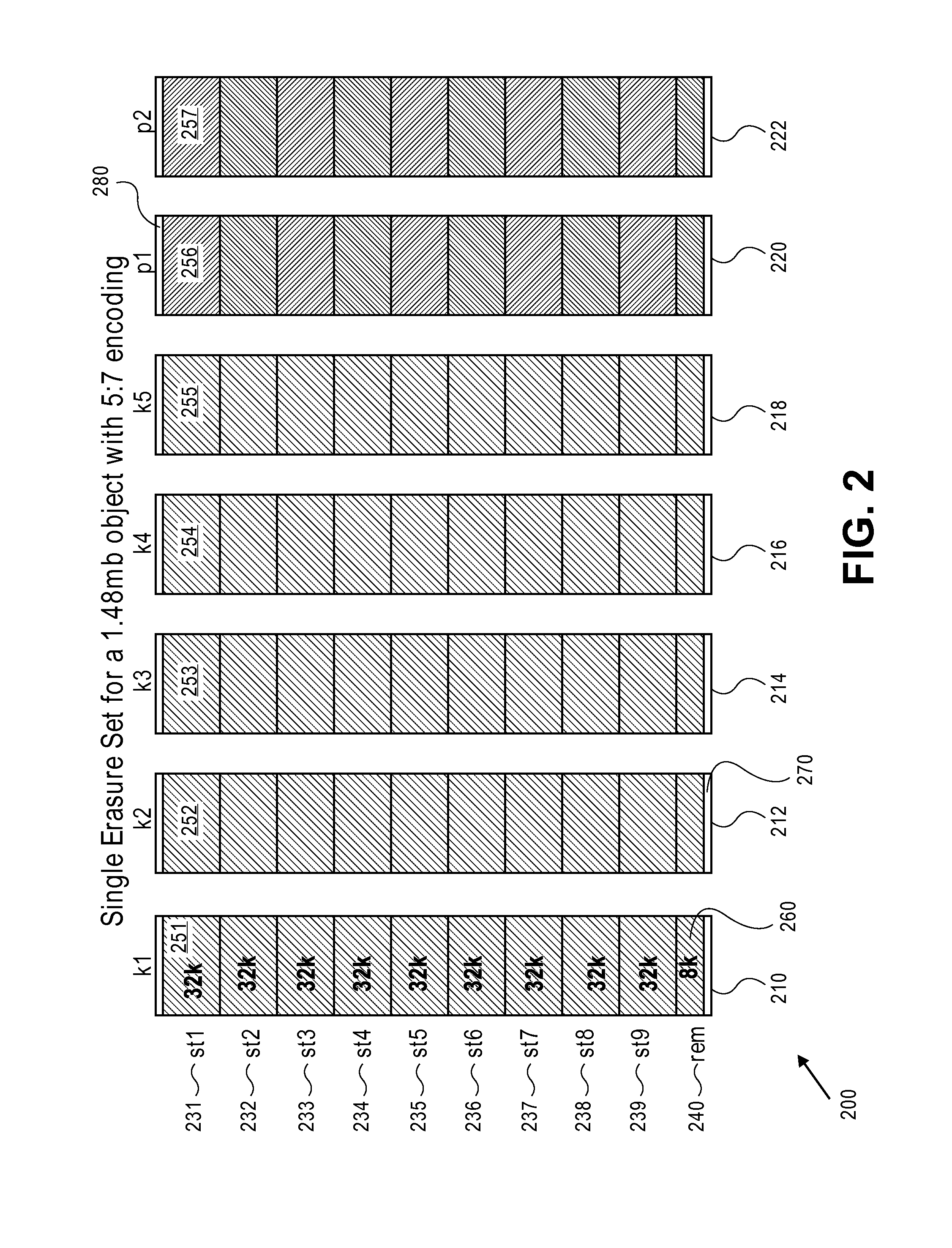
Erasure coding and replication in storage clusters
ActiveUS20130339818A1Error correction/detection using block single space codingCode conversionUnique identifierOperating system
A cluster receives a request to store an object using replication or erasure coding. The cluster writes the object using erasure coding. A manifest is written that includes an indication of erasure coding and a unique identifier for each segment. The cluster returns a unique identifier of the manifest. The cluster receives a request from a client that includes a unique identifier. The cluster determines whether the object has been stored using replication or erasure coding. If using erasure coding, the method reads a manifest. The method identifies segments within the cluster using unique segment identifiers of the manifest. Using these unique segment identifiers, the method reconstructs the object. A persistent storage area of another disk is scanned to find a unique identifier of a failed disk. If using erasure coding, a missing segment previously stored on the disk is identified. The method locates other segments. Missing segments are regenerated.
Owner:DATACORE SOFTWARE
Method and apparatus of transmitting information in wireless communication system
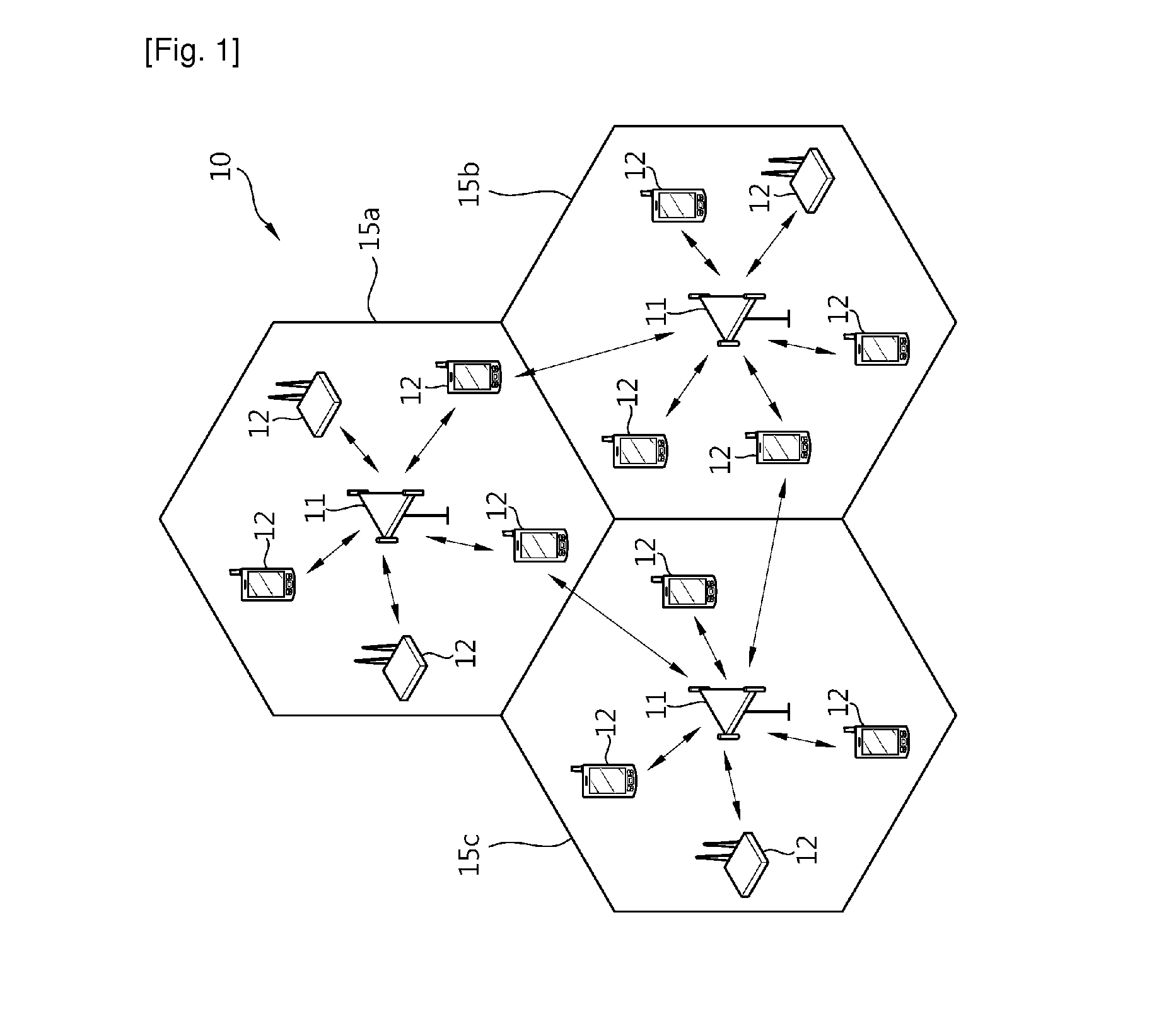
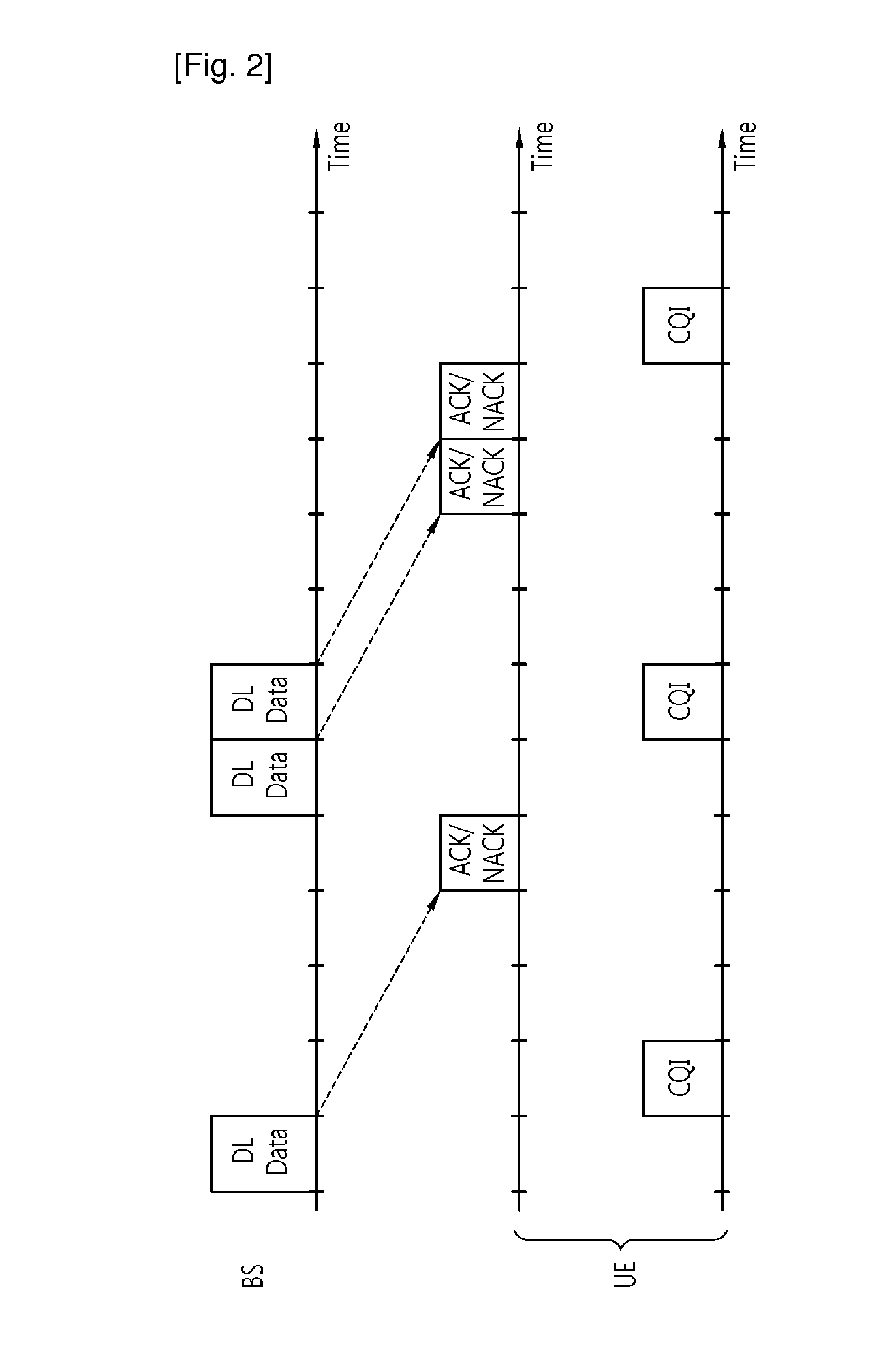
InactiveUS20110126071A1Efficiently transmitting informationImprove system performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationCommunications system
A method and an apparatus of transmitting information in a wireless communication system are provided. The method includes transmitting first information based on a first resource index through a first antenna and transmitting second information based on a second resource index through a second antenna.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Popular searches
Database distribution/replication Transmission Input/output processes for data processing File systems Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnection Digital computer details Program loading/initiating Generating/distributing signals Transmission path multiple use Synchronising arrangement
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com